Patents
Literature
288 results about "Cardiac chamber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
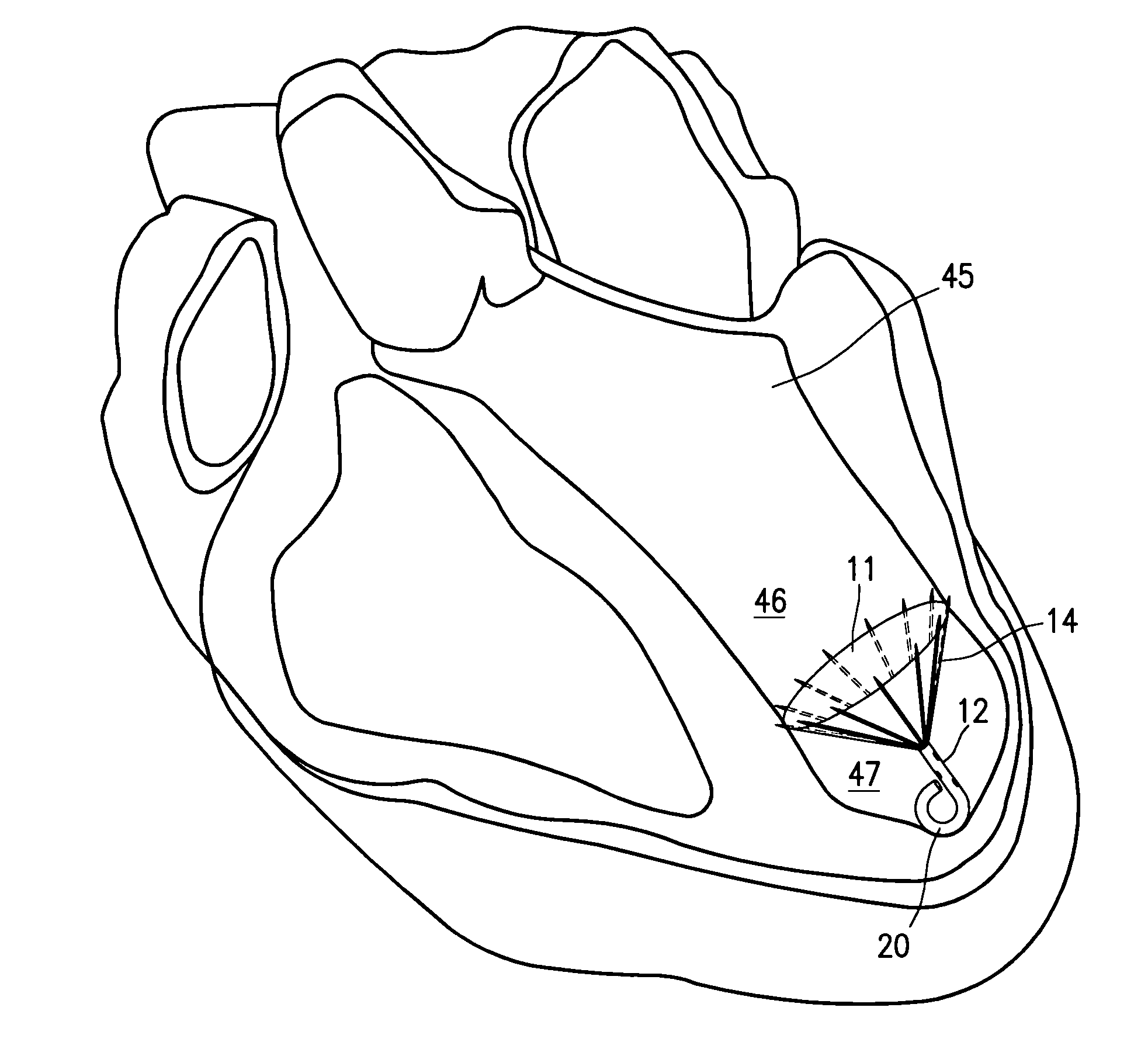
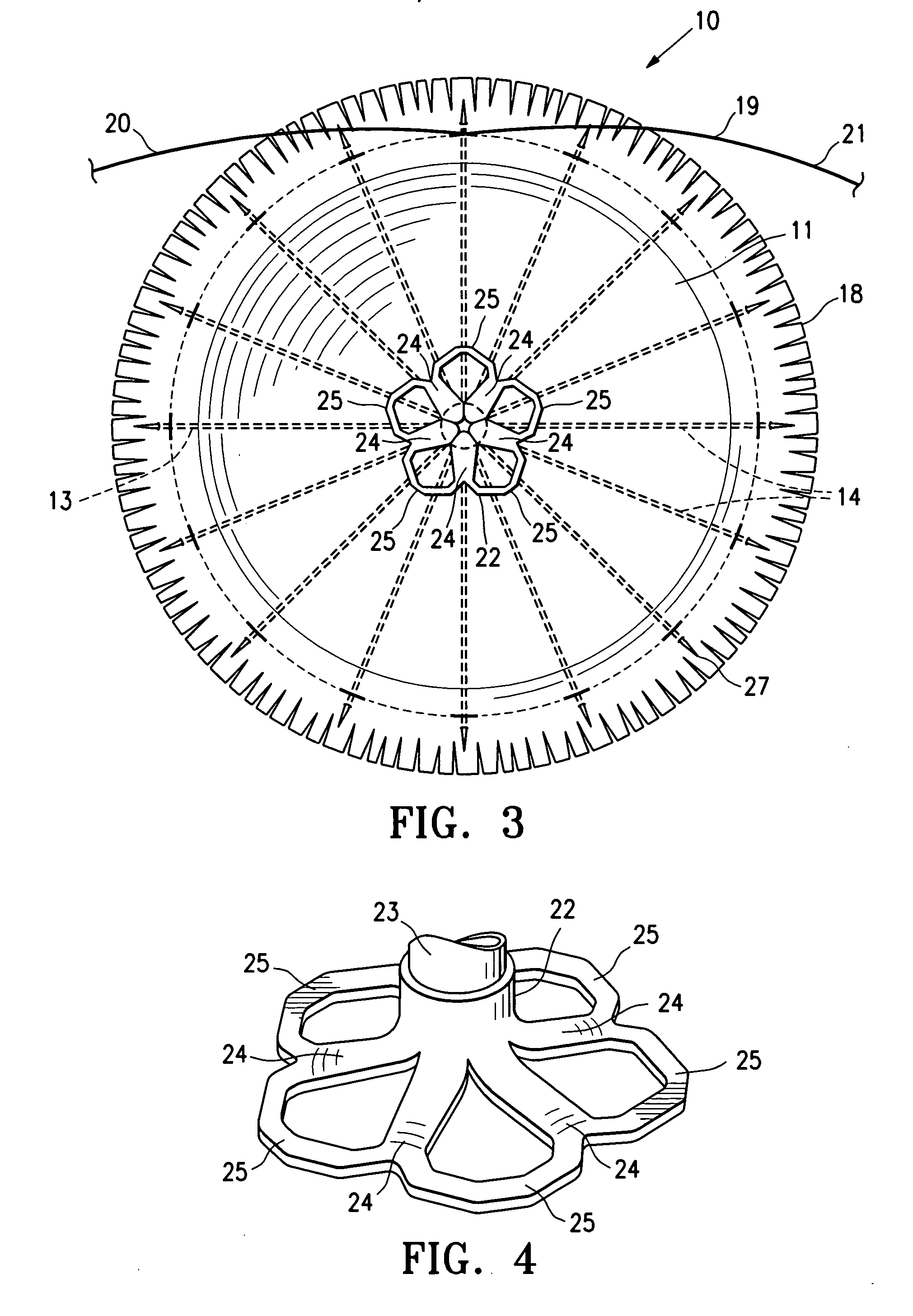
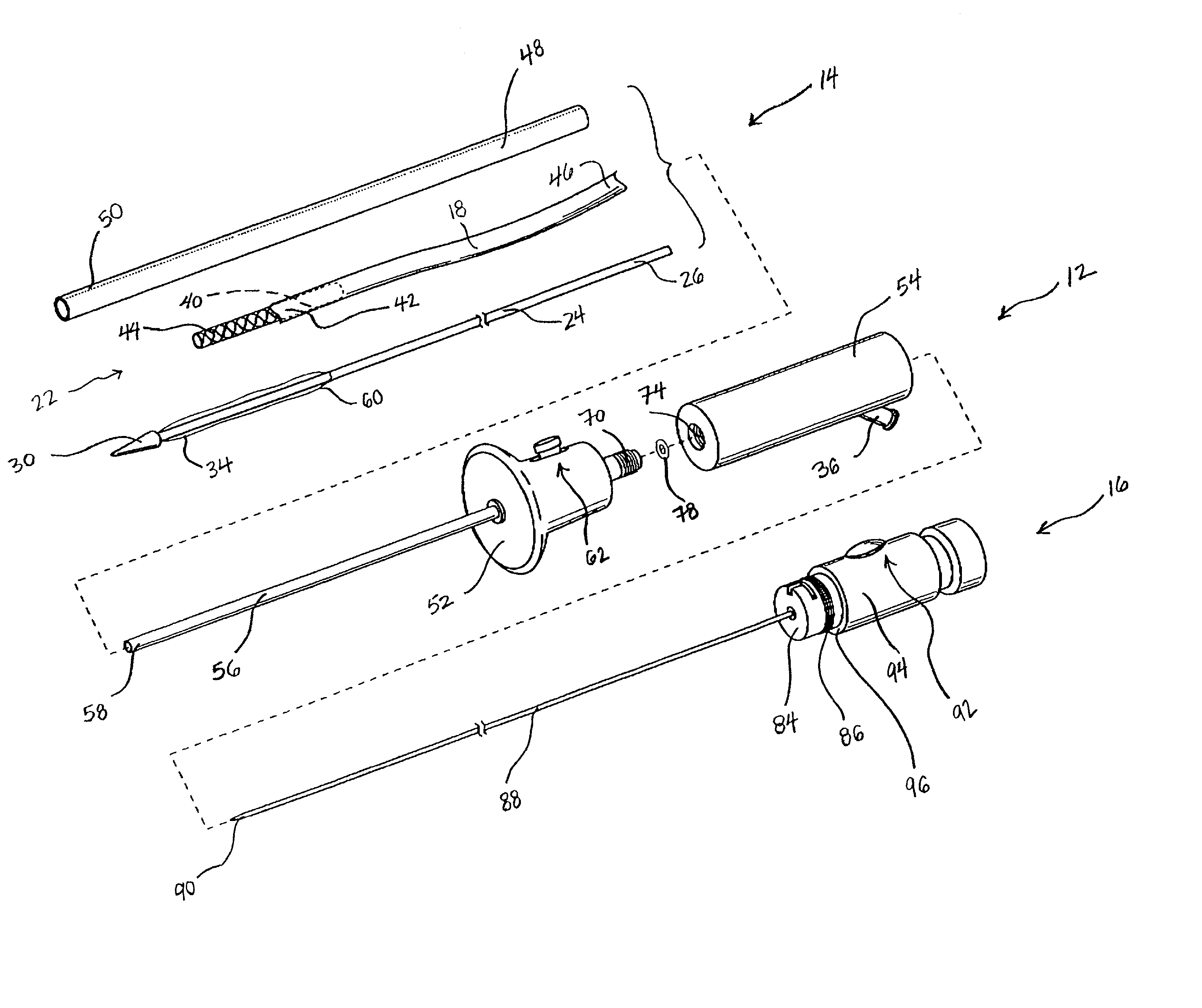
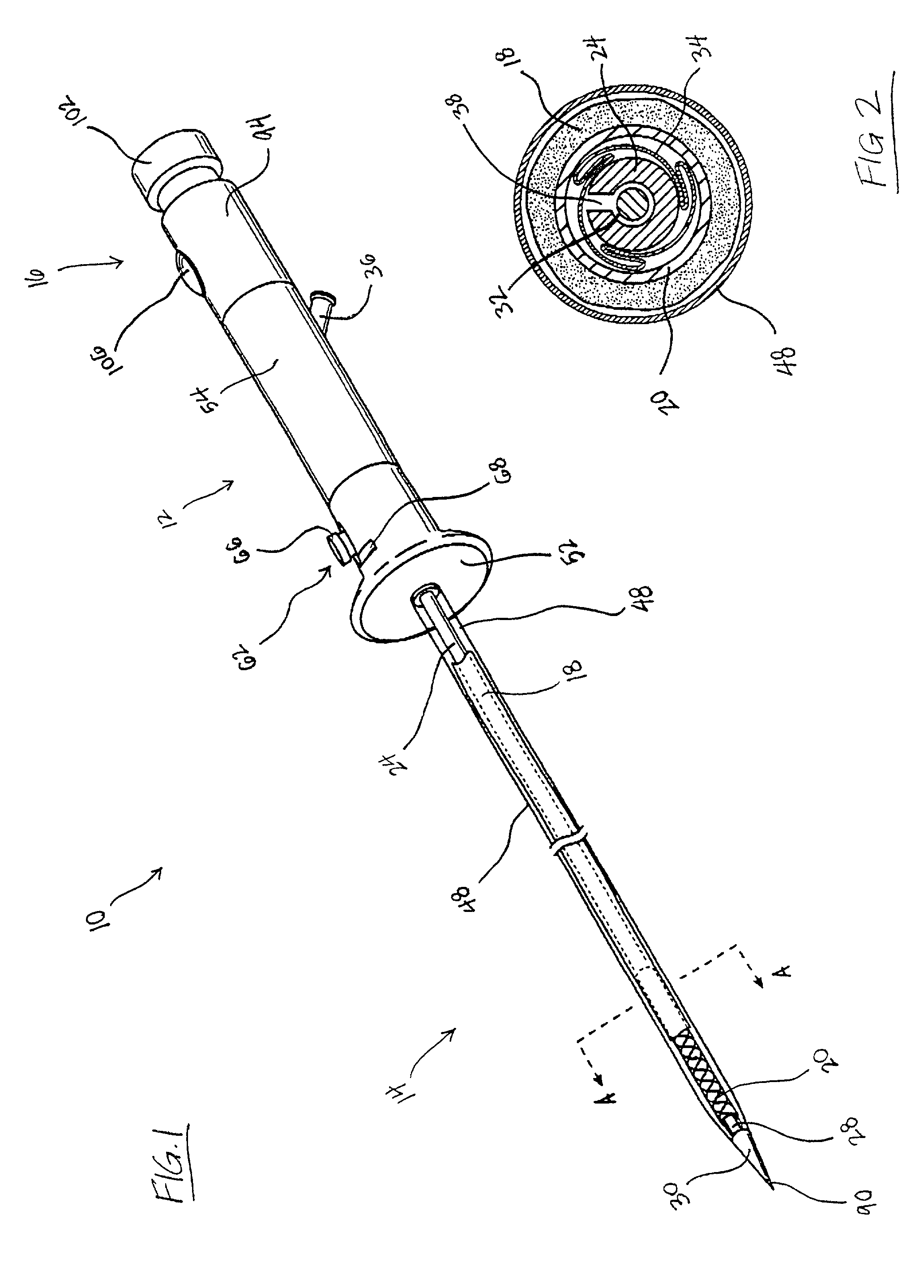
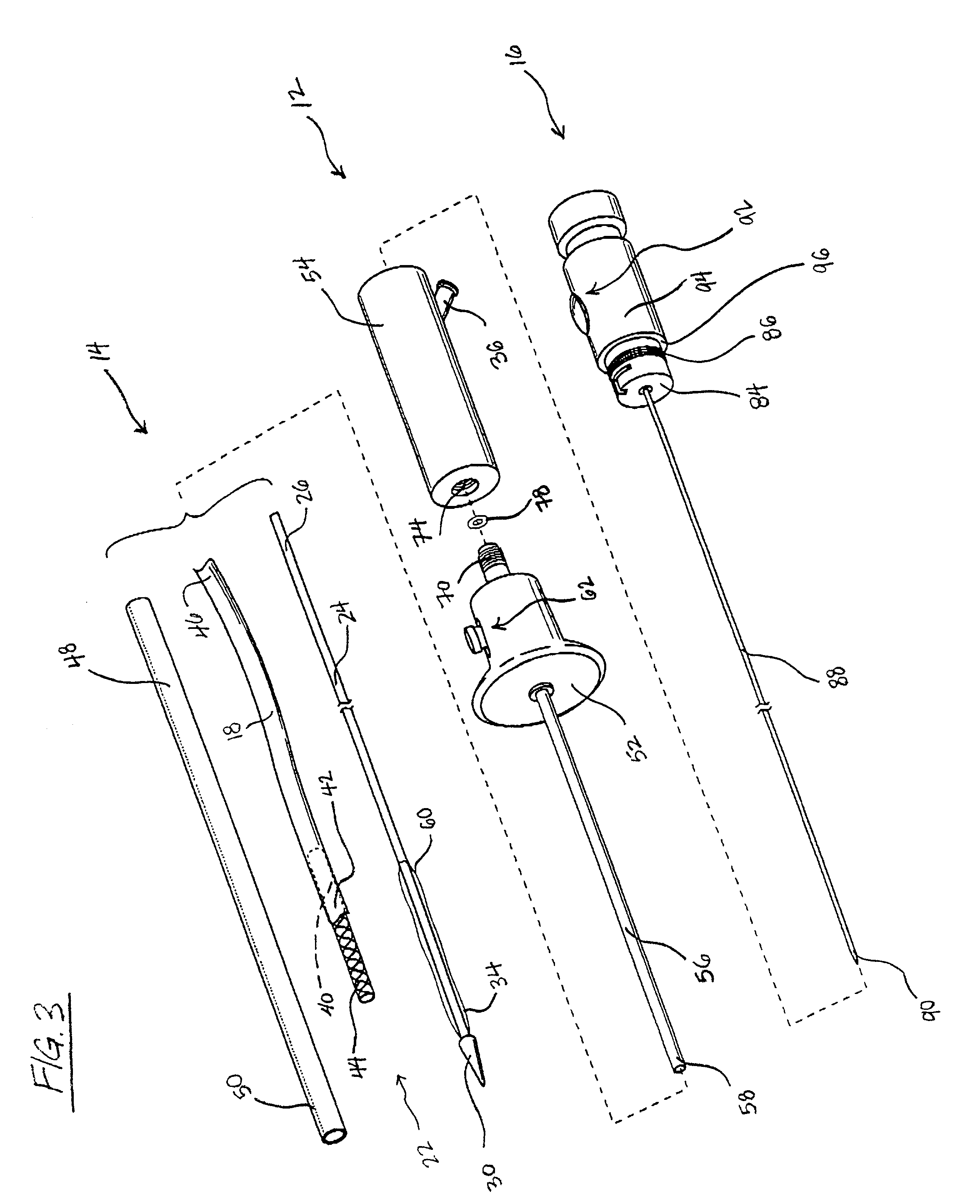
Organ chamber which consists of a wall that surrounds the cavity of a cardiac atrium or ventricle.
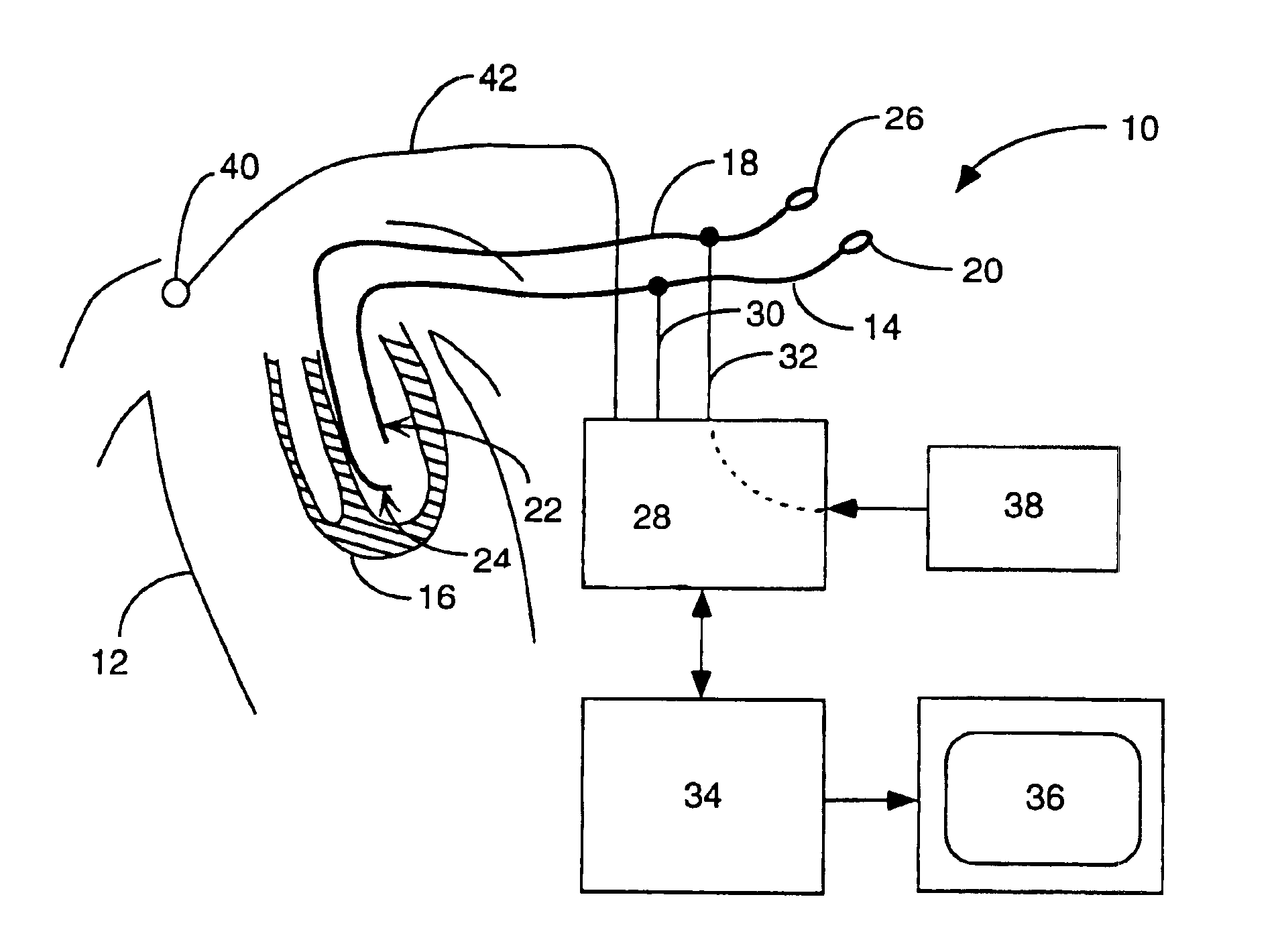
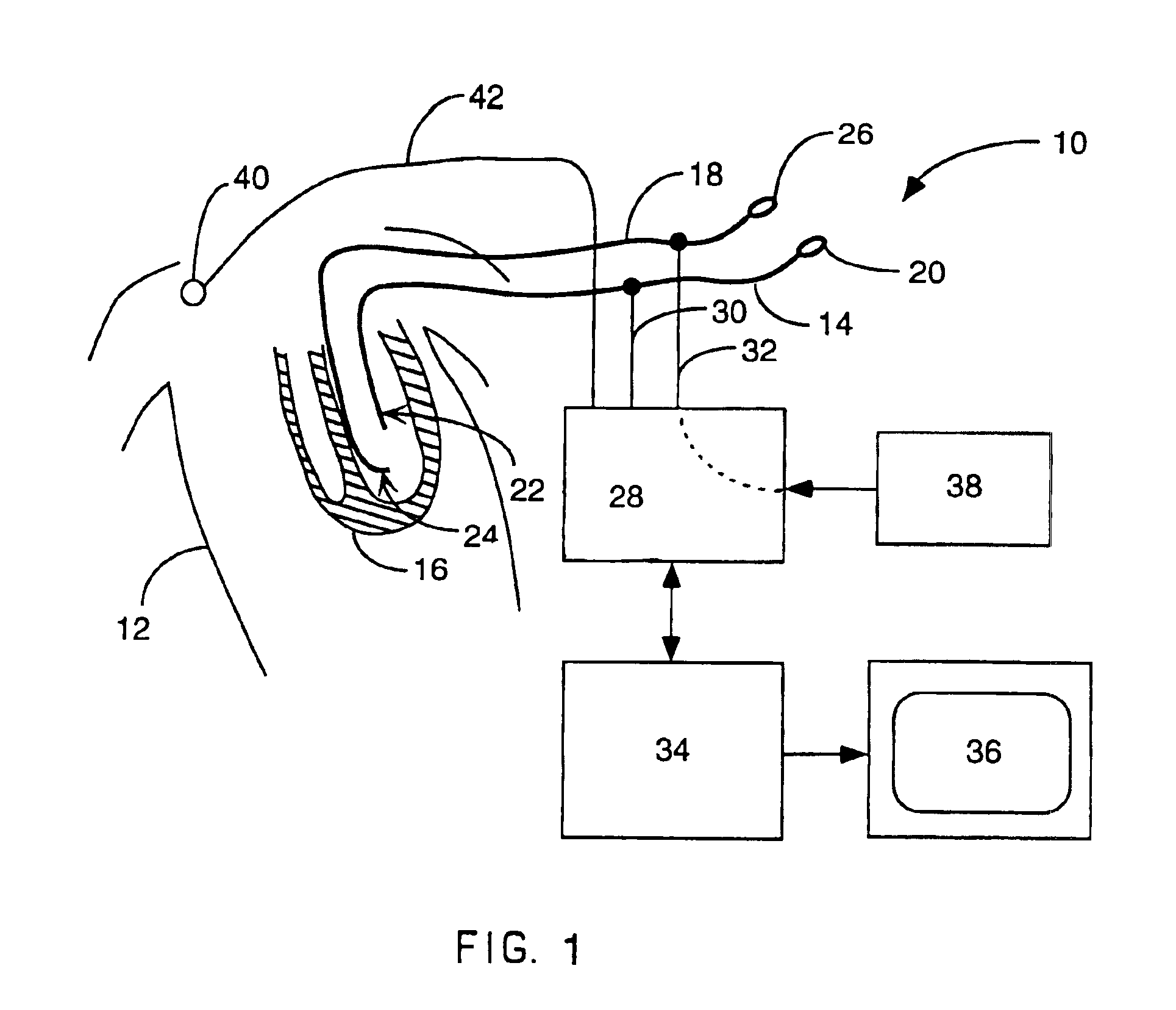
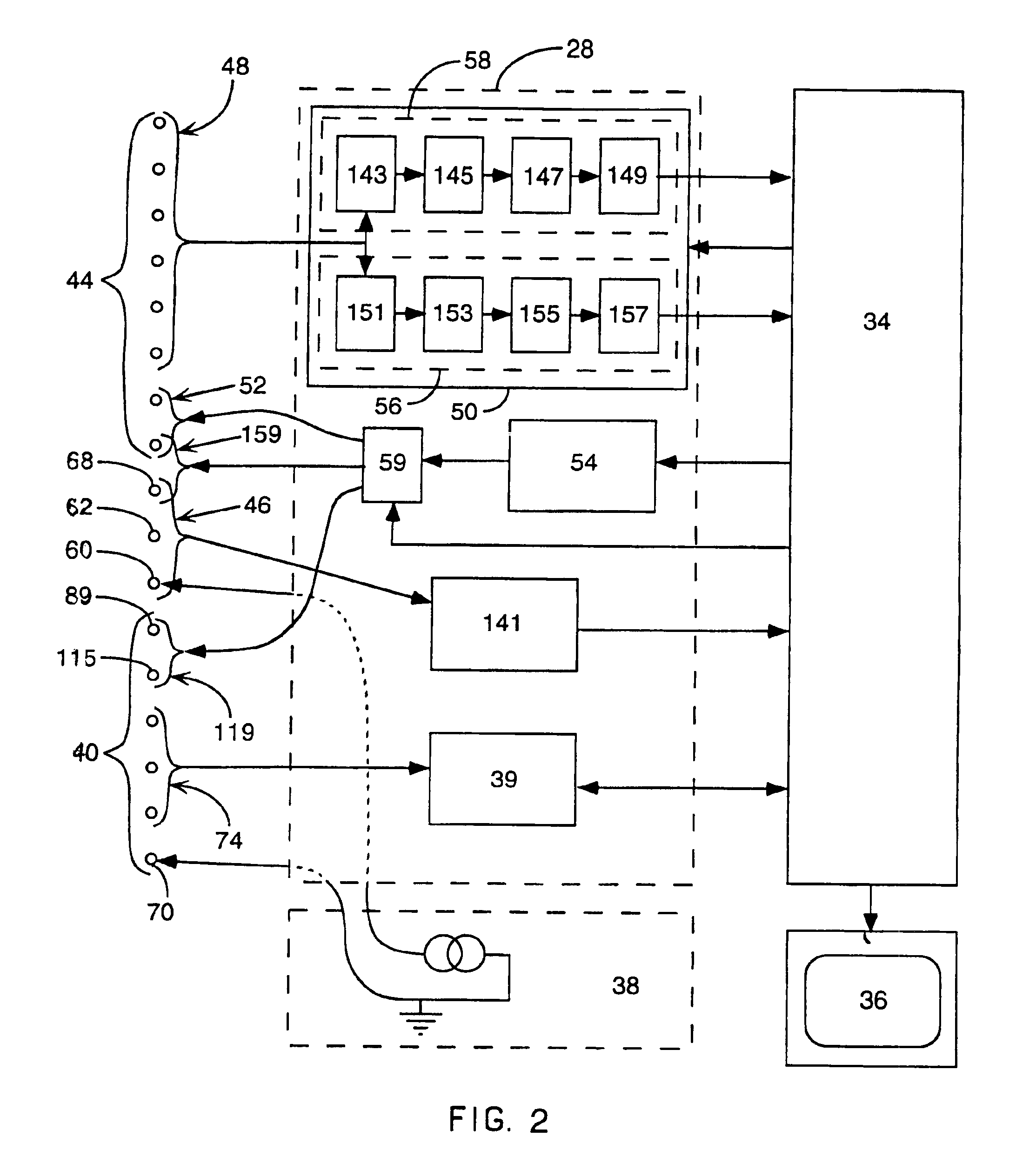
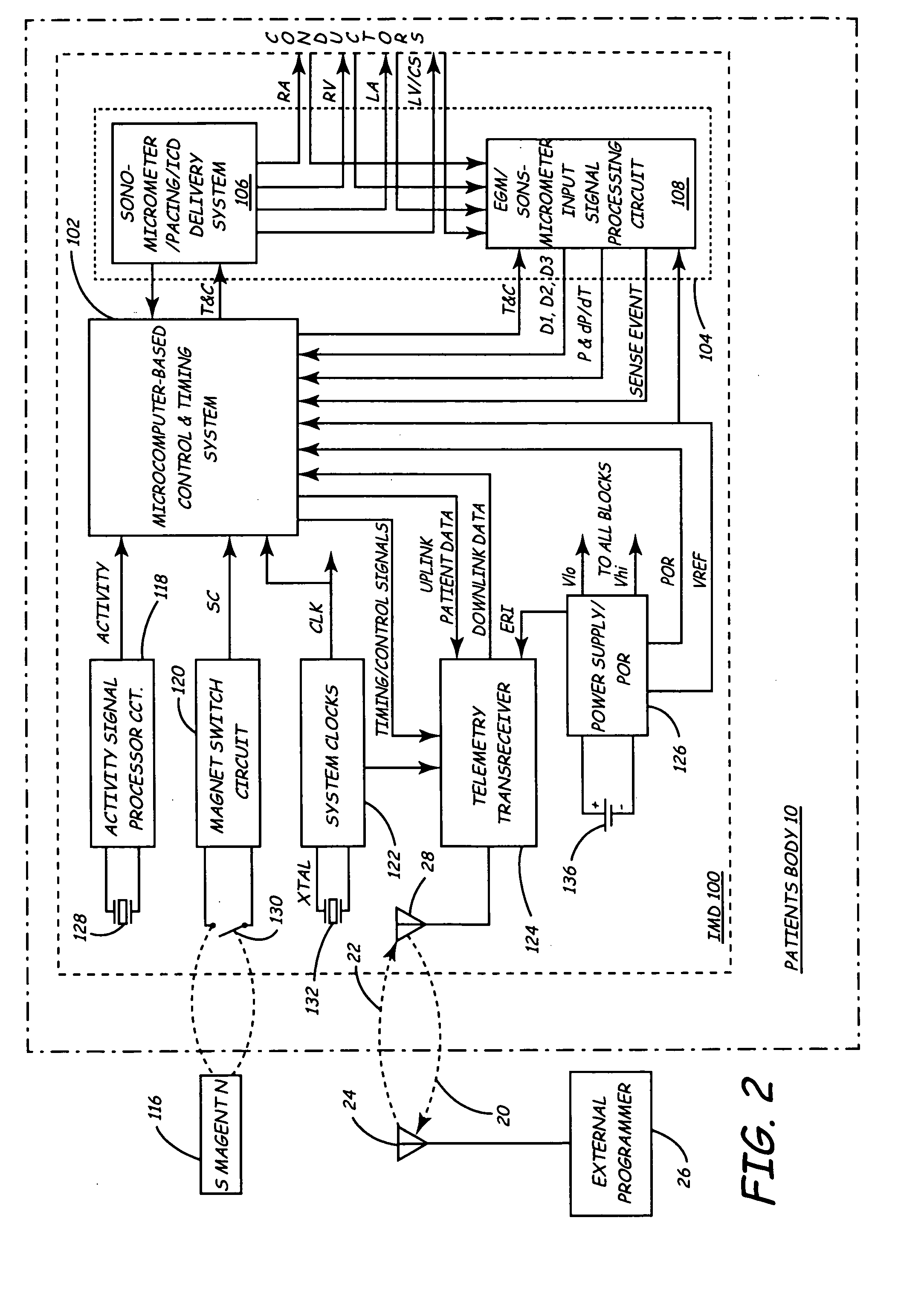
Implantable monitor
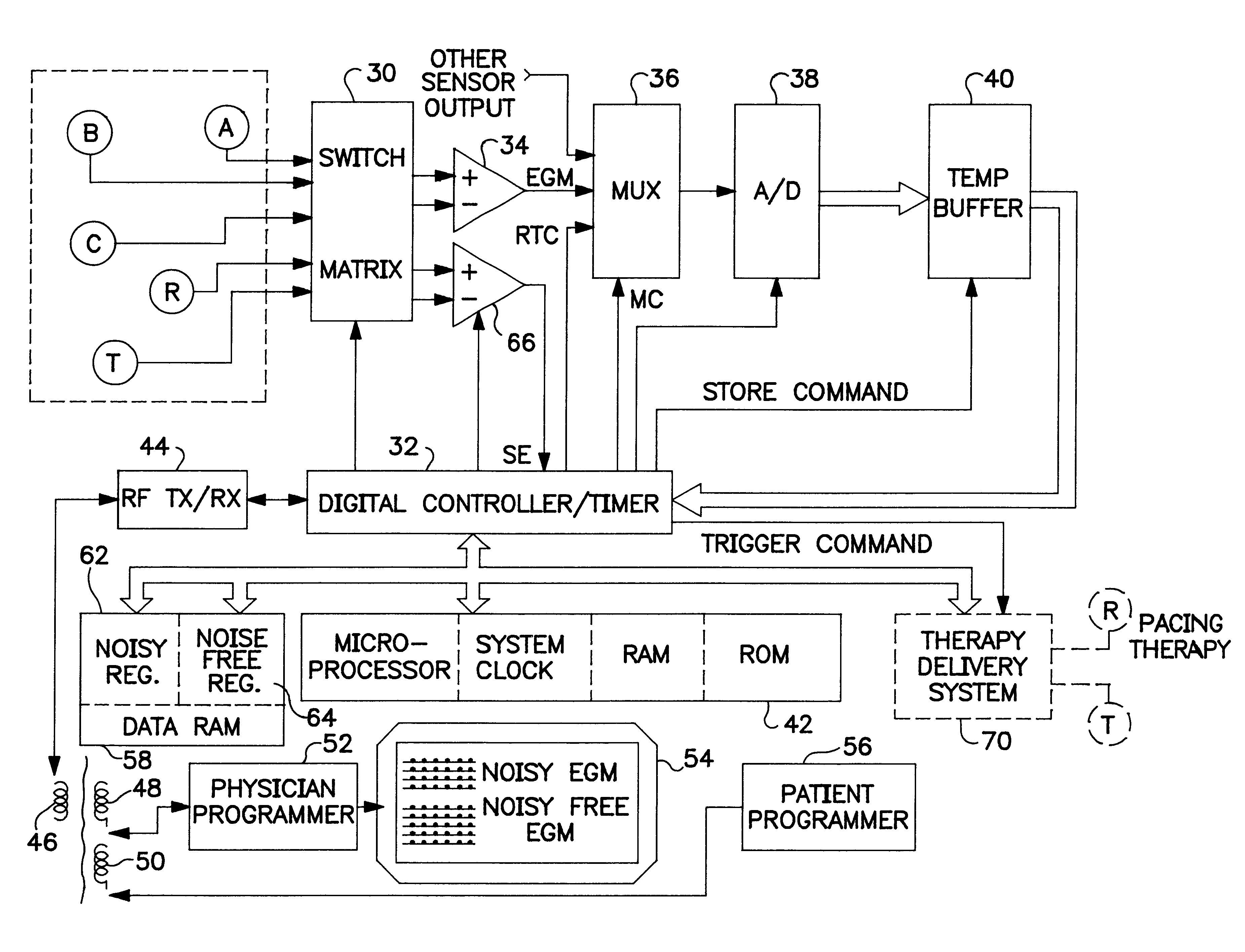
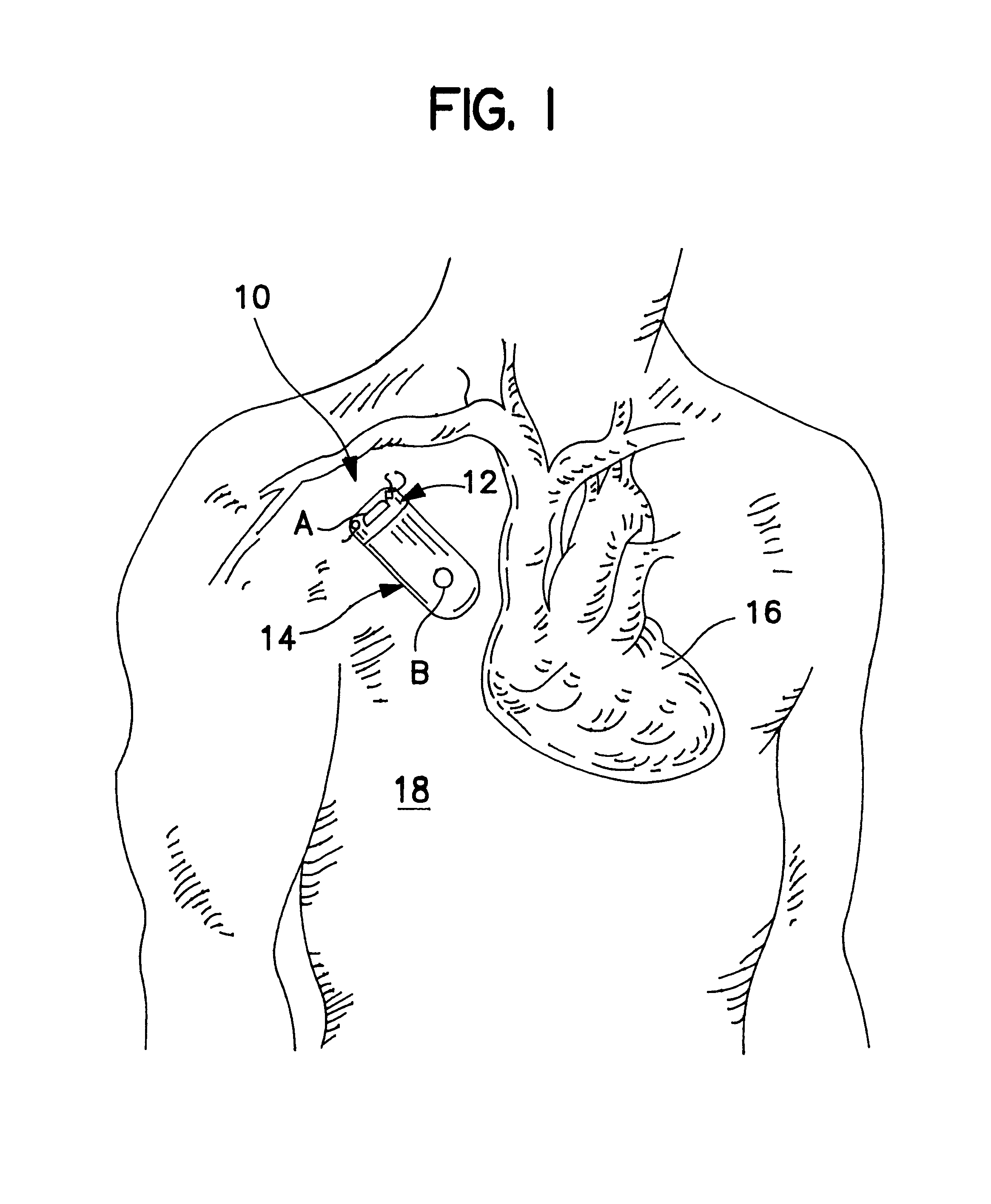
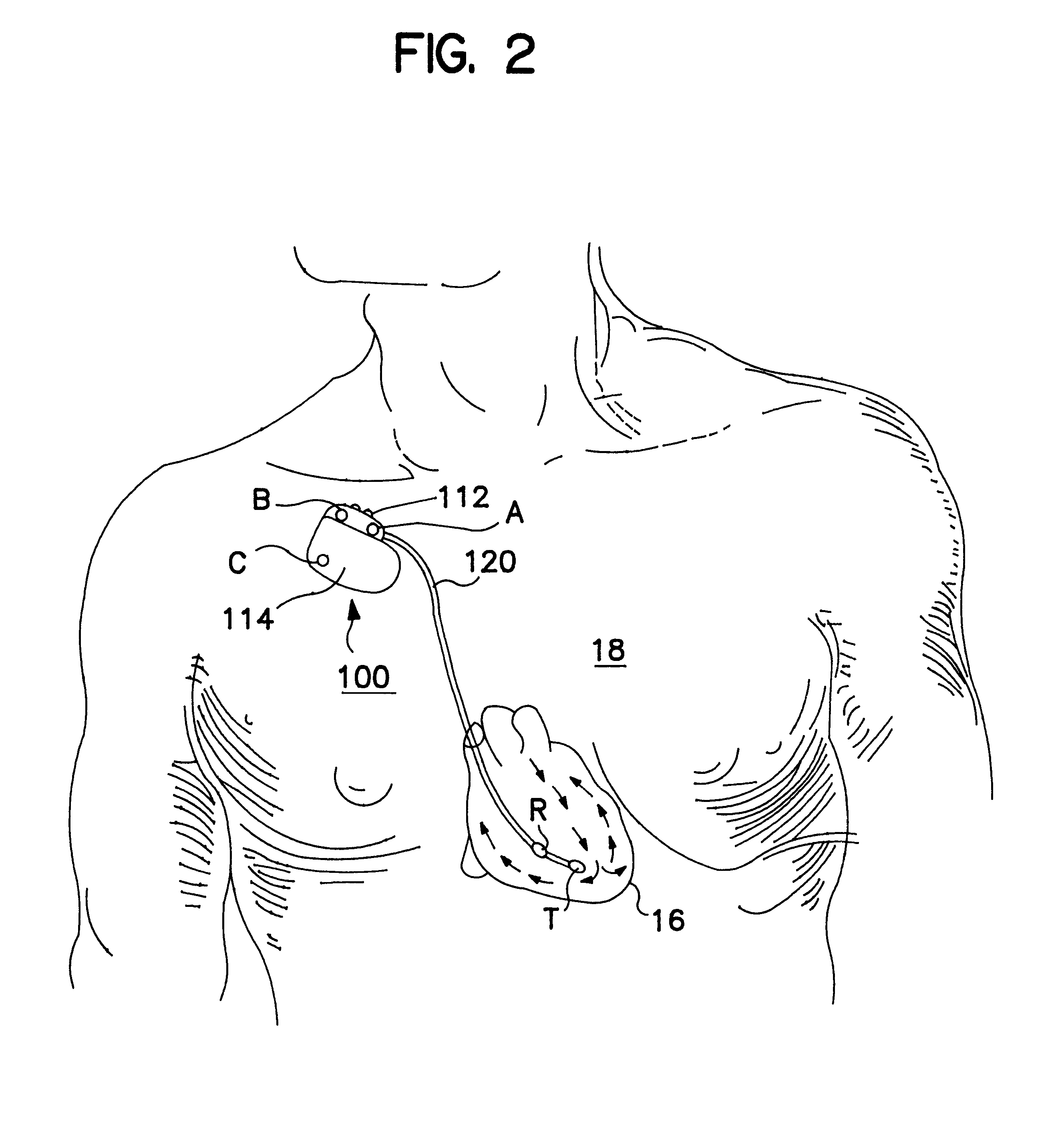
An implantable medical device (IMD) capable of monitoring physiologic data, distinguishing relatively noisy and noise free physiologic data, and recording noisy and relatively noise free segments of physiologic data in separate memory registers of a limited memory for retrieval and analysis at a later time. Preferably the physiologic data comprises the sampled EGM of the heart detected from sense electrode pairs that are implanted in the patient at sites where extraneous electrical noise, e.g., electromyographic signals, are also capable of being detected. The sense electrode pairs can constitute one or both sense electrodes located on or adjacent to the atrial and / or ventricular heart chambers and coupled to the IMD by a lead body or sense electrode pairs that are located remotely from the heart, e.g. at a subcutaneous implantation site of the IMD. A plurality of noisy EGM episode data registers store a corresponding plurality of noisy EGM episode data sets on a FIFO basis and another plurality of noise free EGM episode data registers to store a corresponding plurality of relatively noise free EGM episode data sets on a FIFO basis. Any form of discrimination of noisy data from relatively noise free data can be employed at the time of recording, but because the stored EGM episode data sets are subsequently viewed and analyzed by a physician, discrimination with absolute certainty is not required, and the physician can alter the detection criteria to fine tune it.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Microwave ablation catheter with loop configuration
A catheter which may be configured as a loop during an ablation procedure, and a method of use for such a catheter, are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, an ablation catheter includes a flexible distal member arranged to inserted into a first vessel in the body of a patient, and an elongated flexible tubular member with a distal portion which is coupled to a proximal portion of the flexible distal member. The elongated flexible tubular member has a flexibility that is greater than or equal to the flexibility of the flexible distal member. The catheter also includes a transmission line which is at least partially disposed within the elongated flexible tubular member. A proximal end of the transmission line is suitable for connection to an electromagnetic energy source. The catheter further includes a transducer that is coupled to the transmission line, and is arranged to generate an electric field sufficiently strong to cause tissue ablation. In one embodiment, a distal portion of the flexible distal member is arranged to protrude from a second vessel of the body of the patient while at least part of the elongated flexible tubular member is located in a cardiac chamber of the heart of the patient.
Owner:AFX
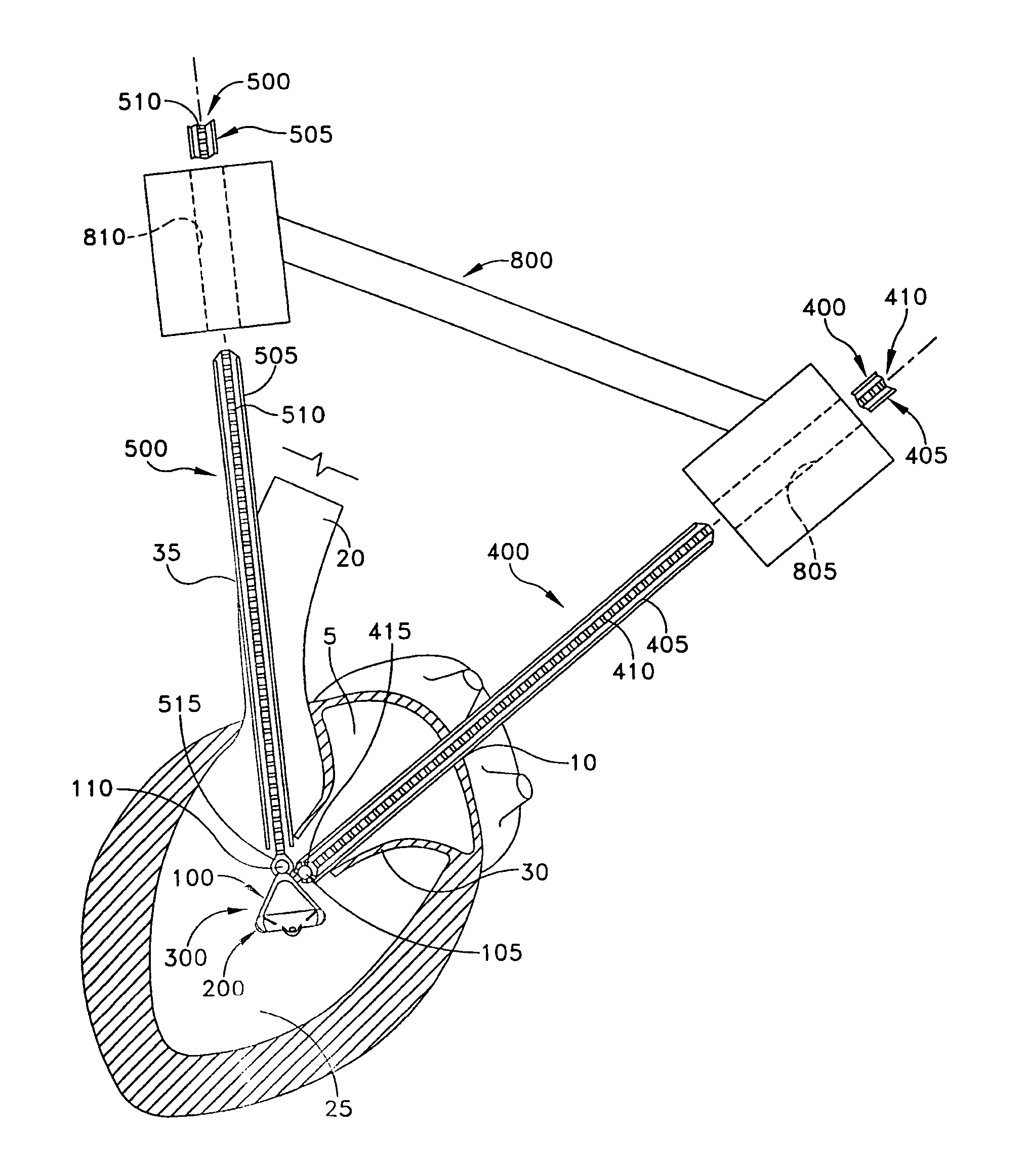
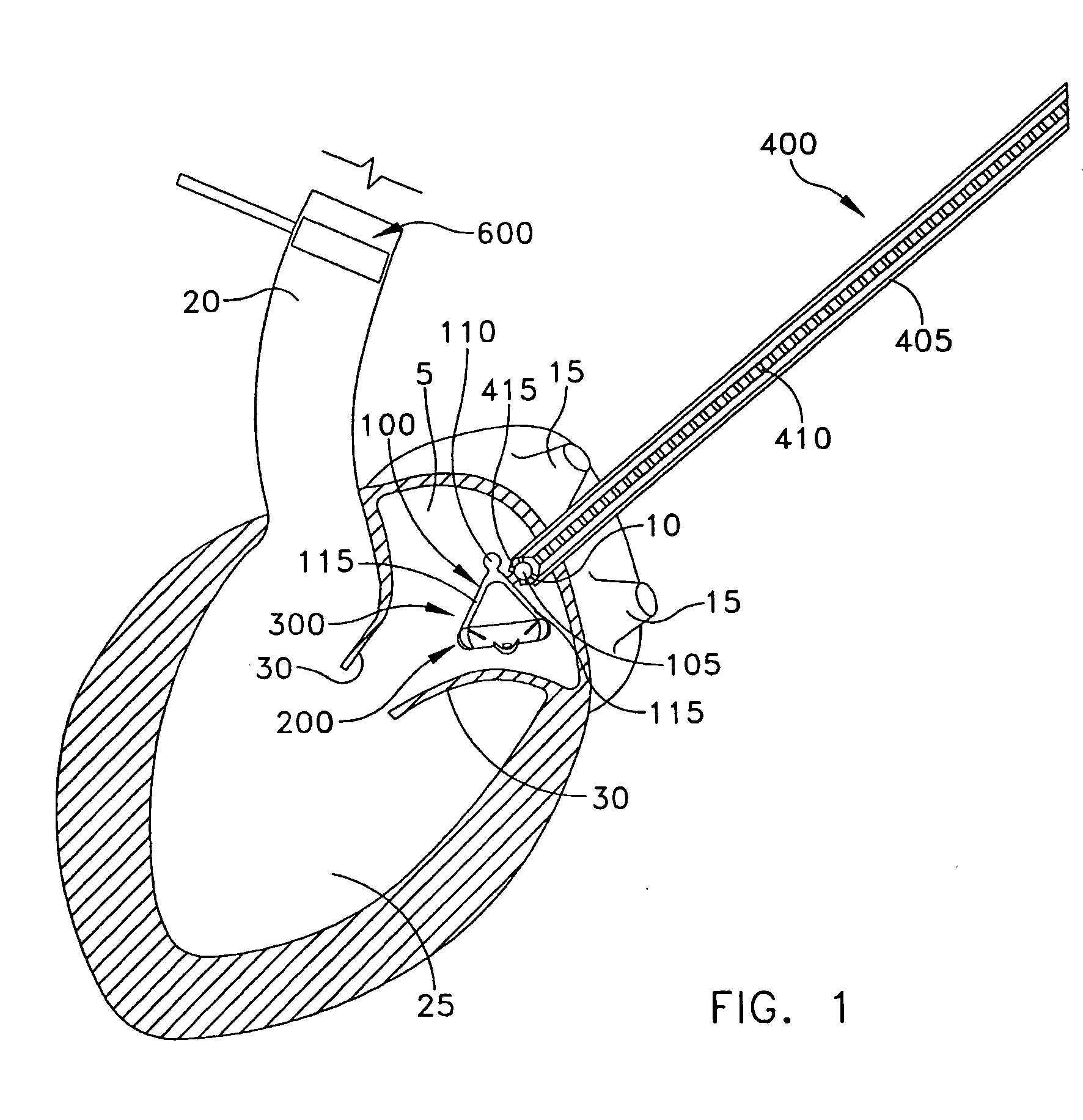
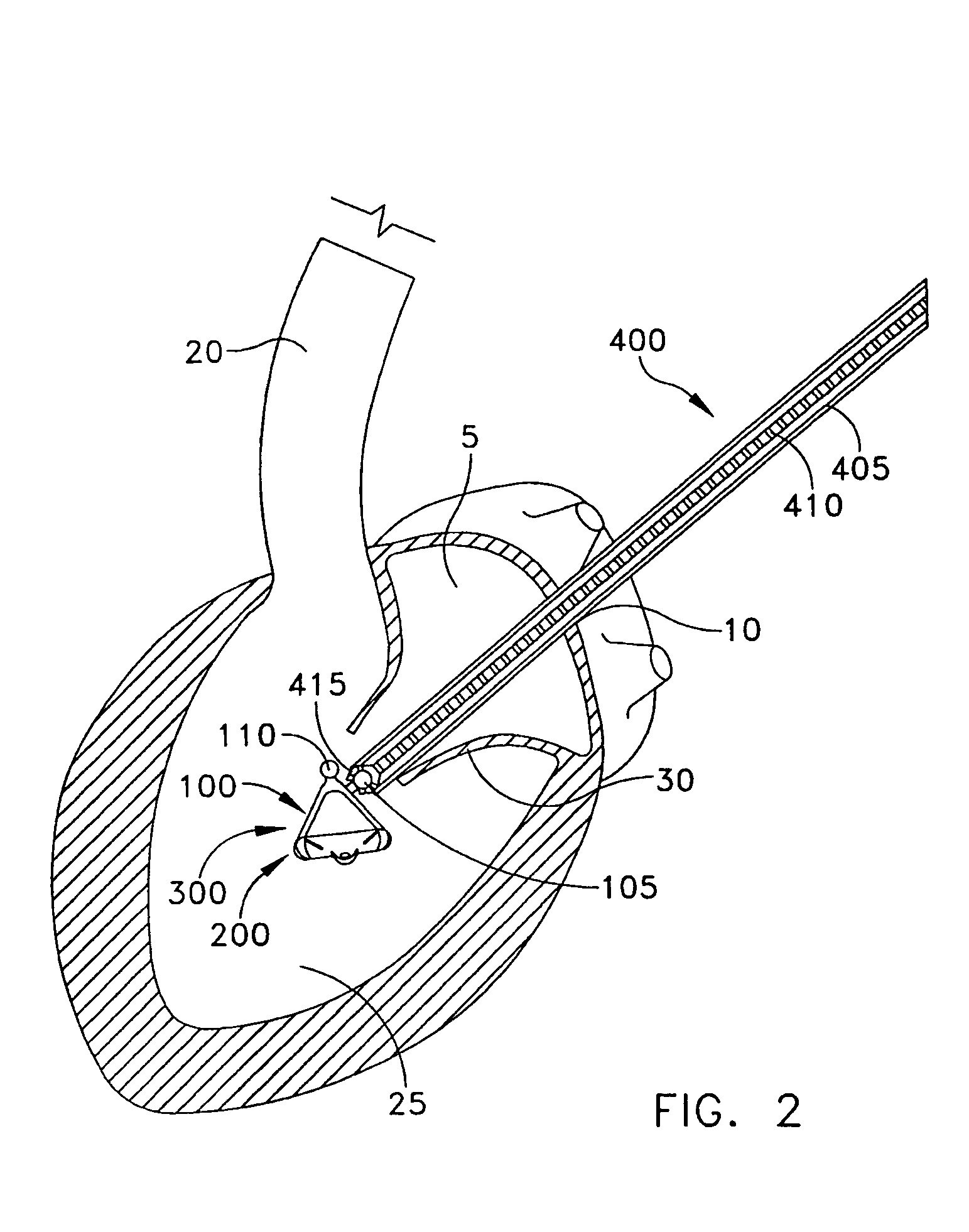
Methods and devices for improving mitral valve function
InactiveUS20050075723A1Less riskMinimally invasiveSuture equipmentsHeart valvesMitral valve functionCardiac wall
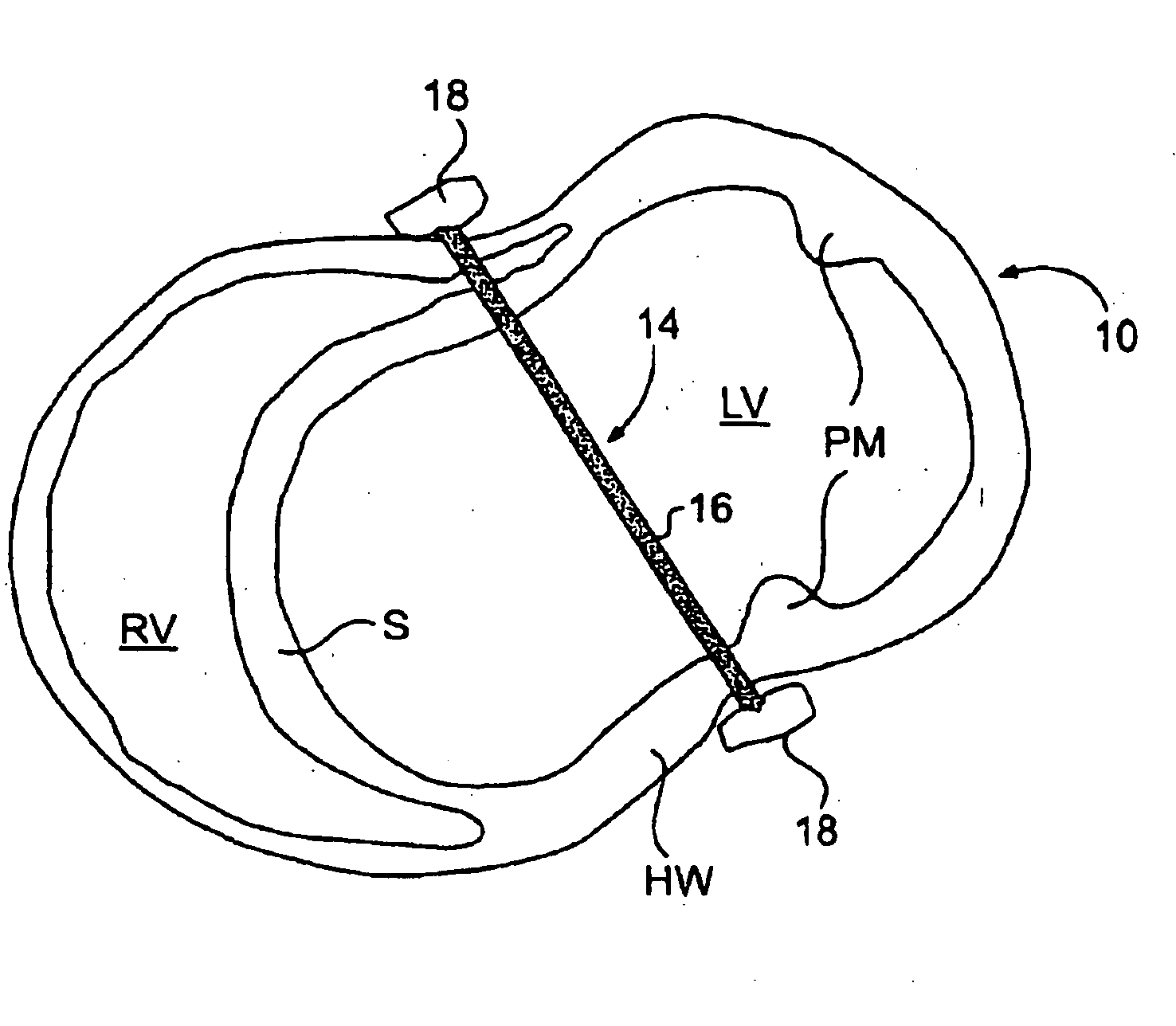
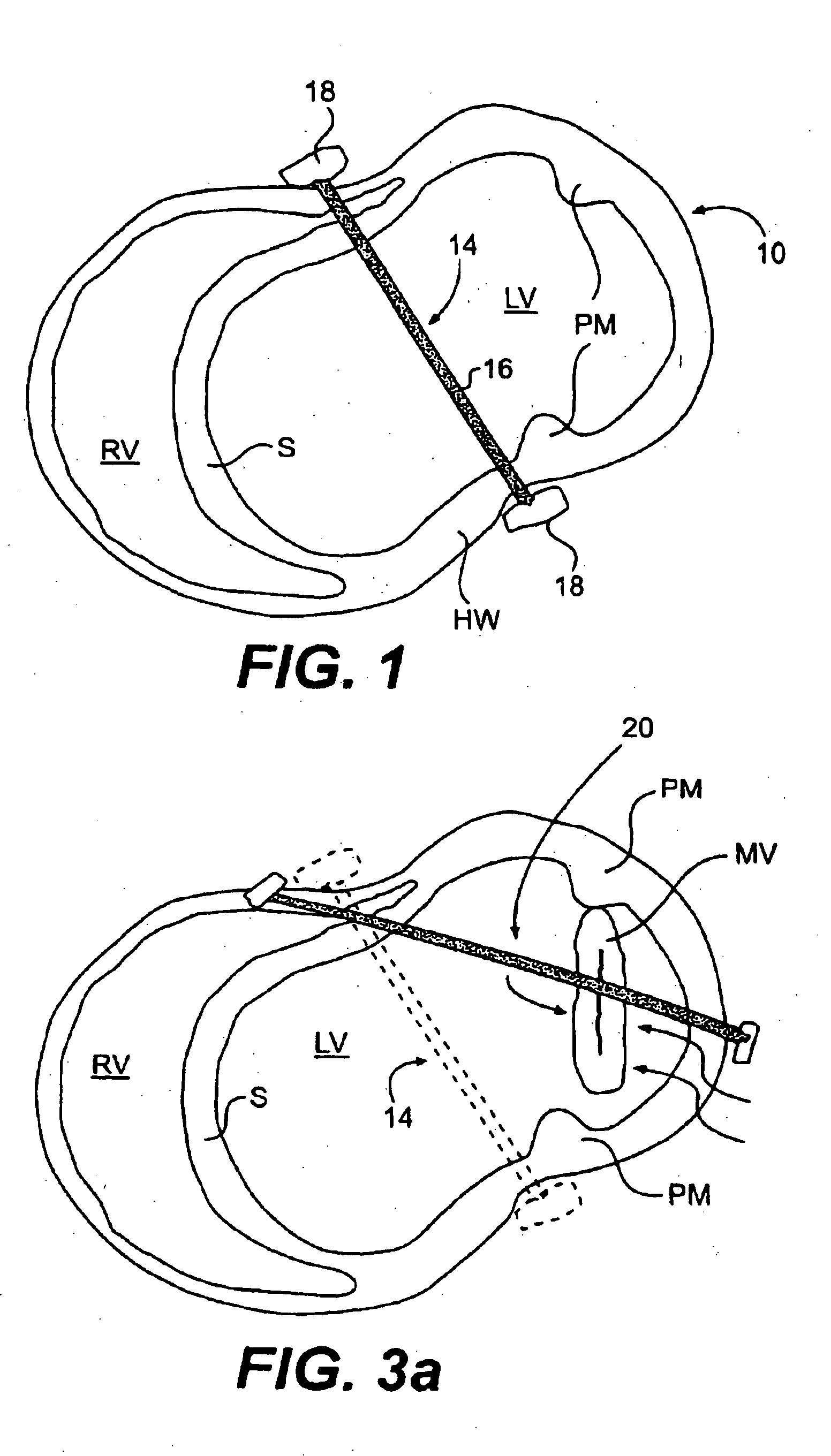
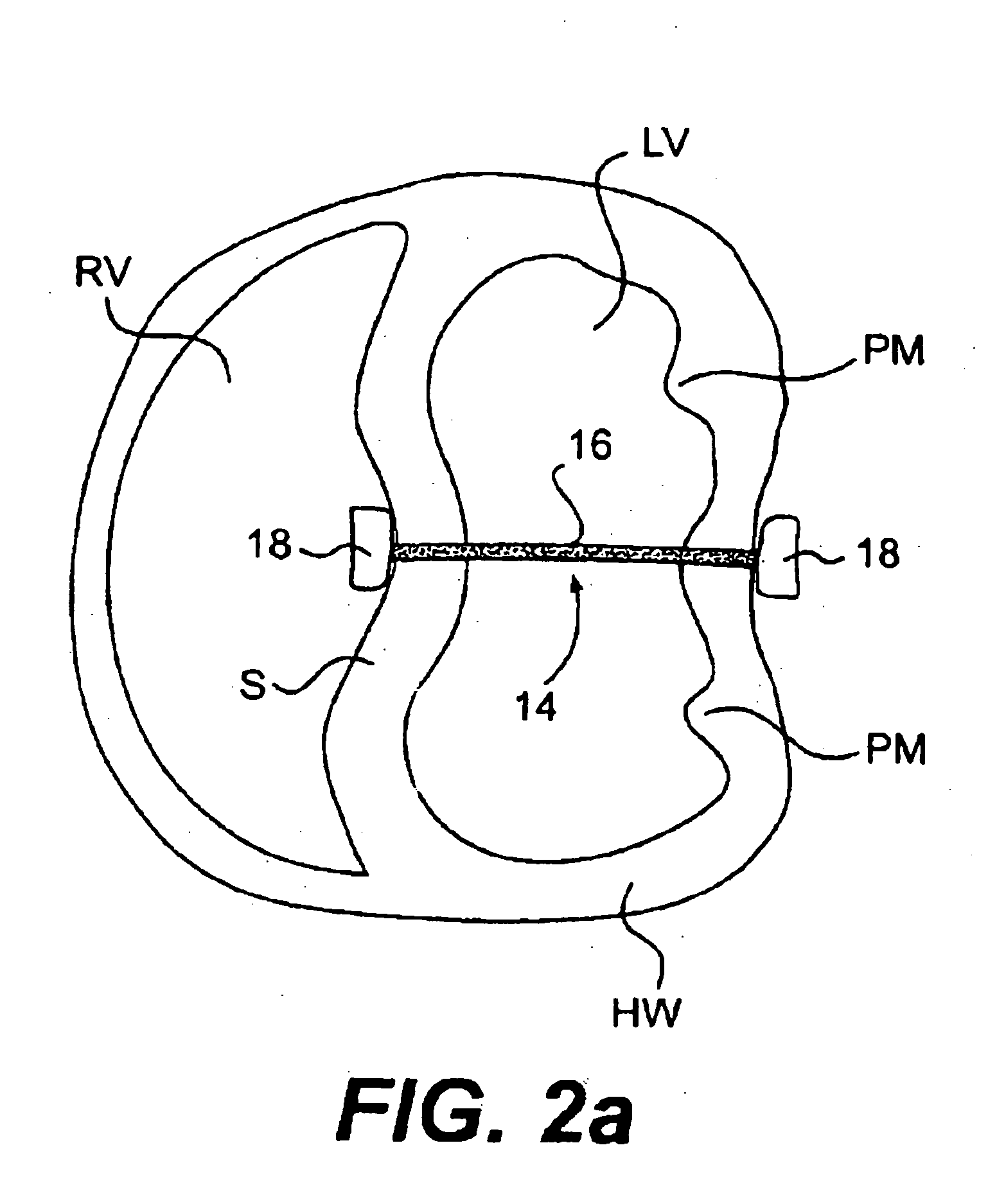
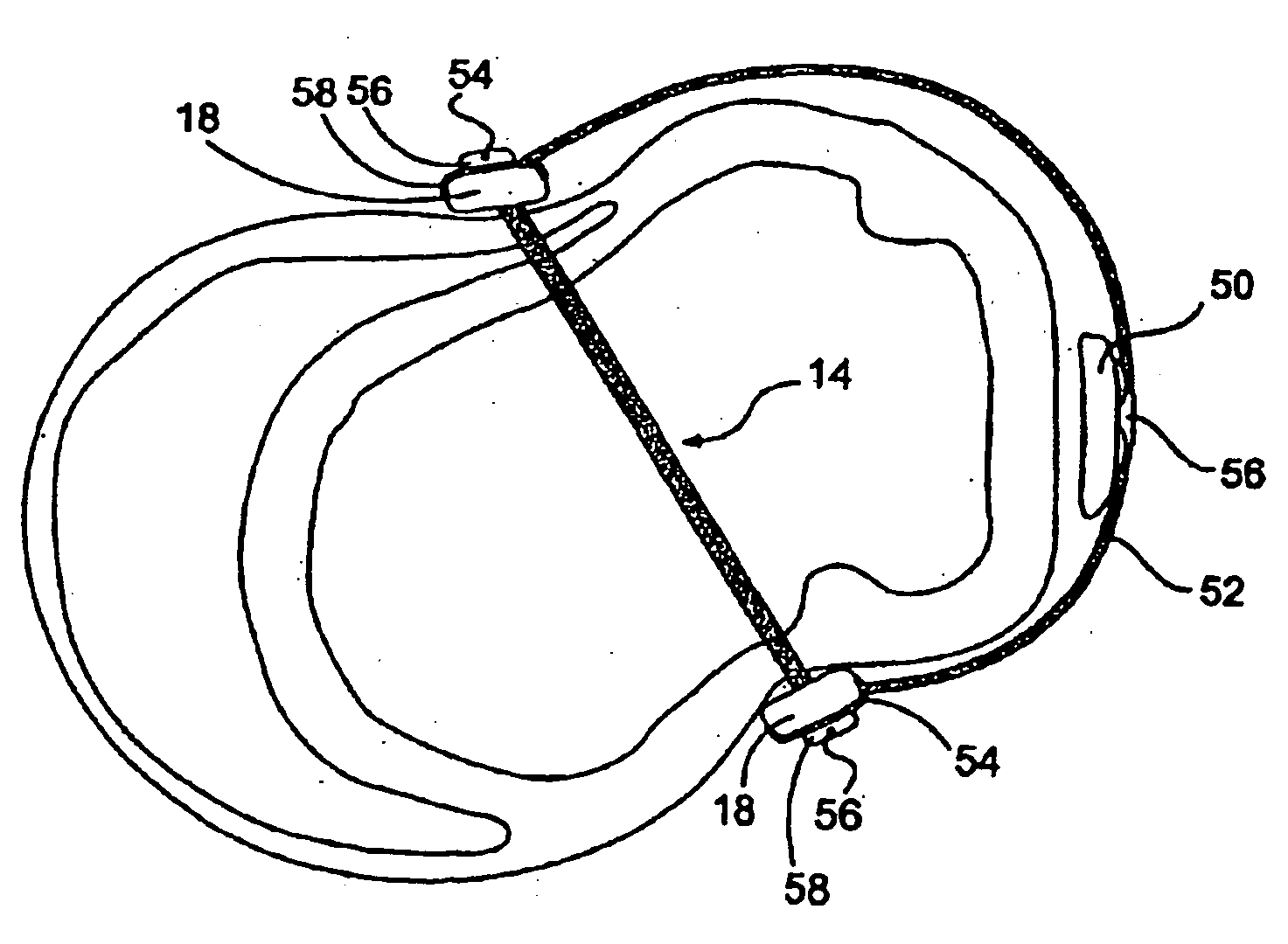
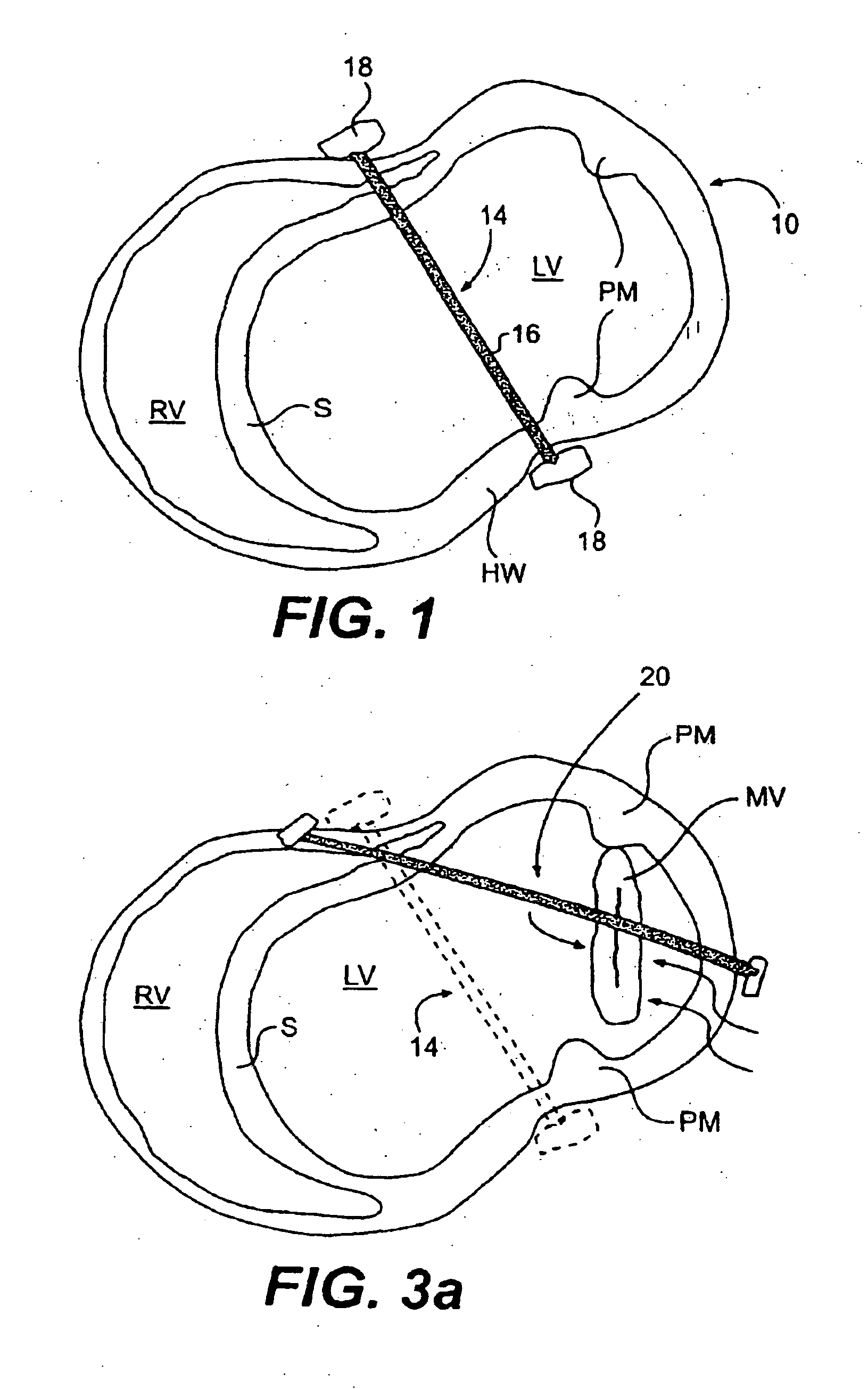
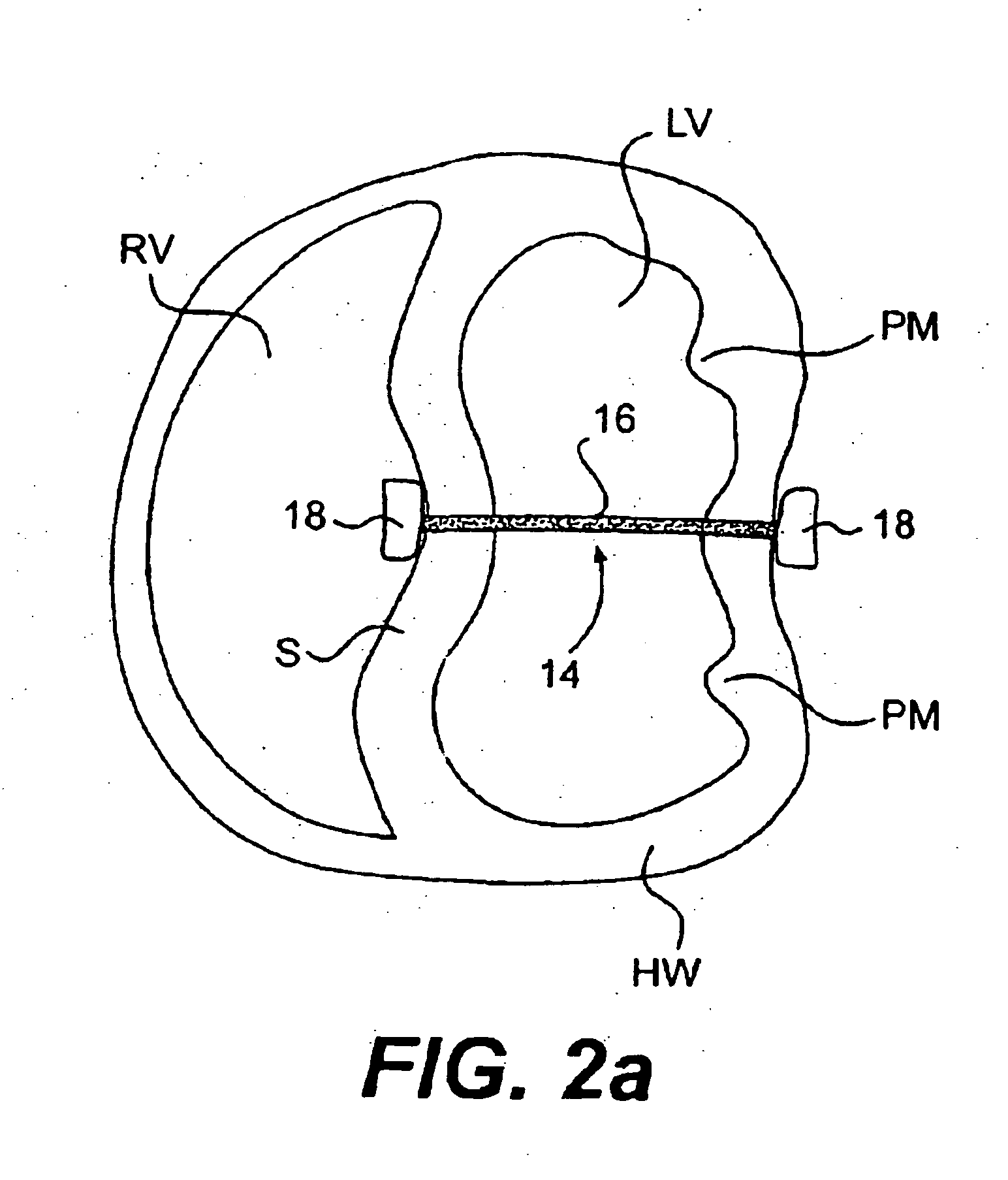
The various aspects of the invention pertain to devices and related methods for treating heart conditions, including, for example, dilatation, valve incompetencies, including mitral valve leakage, and other similar heart failure conditions. The devices and related methods of the present invention operate to assist in the apposition of heart valve leaflets to improve valve function. According to one aspect of the invention, a method improves the function of a valve of a heart by placing an elongate member transverse a heart chamber so that each end of the elongate member extends through a wall of the heart, and placing first and second anchoring members external the chamber. The first and second anchoring members are attached to first and second ends of the elongate member to fix the elongate member in a position across the chamber so as to reposition papillary muscles within the chamber. Also described herein is a method for placing a splint assembly transverse a heart chamber by advancing an elongate member through vasculature structure and into the heart chamber.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Apparatuses and methods for performing minimally invasive diagnostic and surgical procedures inside of a beating heart
InactiveUS6840246B2Reduce needRisk minimizationSuture equipmentsStapling toolsFluid transportHeart chamber
Diagnostic and surgical procedures may be performed on a beating heart using an assembly which includes a port and a fluid transport device. The port has a housing for insertion through a wall of the heart chamber and may include one valve disposed in the housing and an inlet connected to the housing. Methods for repair and diagnosis of the heart are also described. A specific method for repairing a mitral valve uses staples which may be banded together with a strip of material.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Method and apparatus for performing a procedure on a cardiac valve
InactiveUS20050055088A1Risk minimizationWithout riskHeart valvesBlood vesselsLeft atriumValvular prosthesis
The present invention comprises a method for deploying an aortic valve prosthesis. This valve prosthesis may include any of the known aortic valves including, but not limited to, stented and unstented bioprosthetic valves, stented mechanical valves, and expandable or self-expanding valves, whether biological or artificial. The method involves the steps of: making a first opening leading to the left atrium; passing a valve prosthesis through the opening and into a cardiac chamber of the left side of the heart using a first manipulation instrument; making a second opening in the arterial system and advancing one end of a second manipulation instrument through the arterial opening and into the aforementioned cardiac chamber; securing the second manipulation instrument to the valve prosthesis; and using the second manipulation instrument to retract at least some portion of the valve prosthesis out of the aforementioned cardiac chamber.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Interface system for endocardial mapping catheter
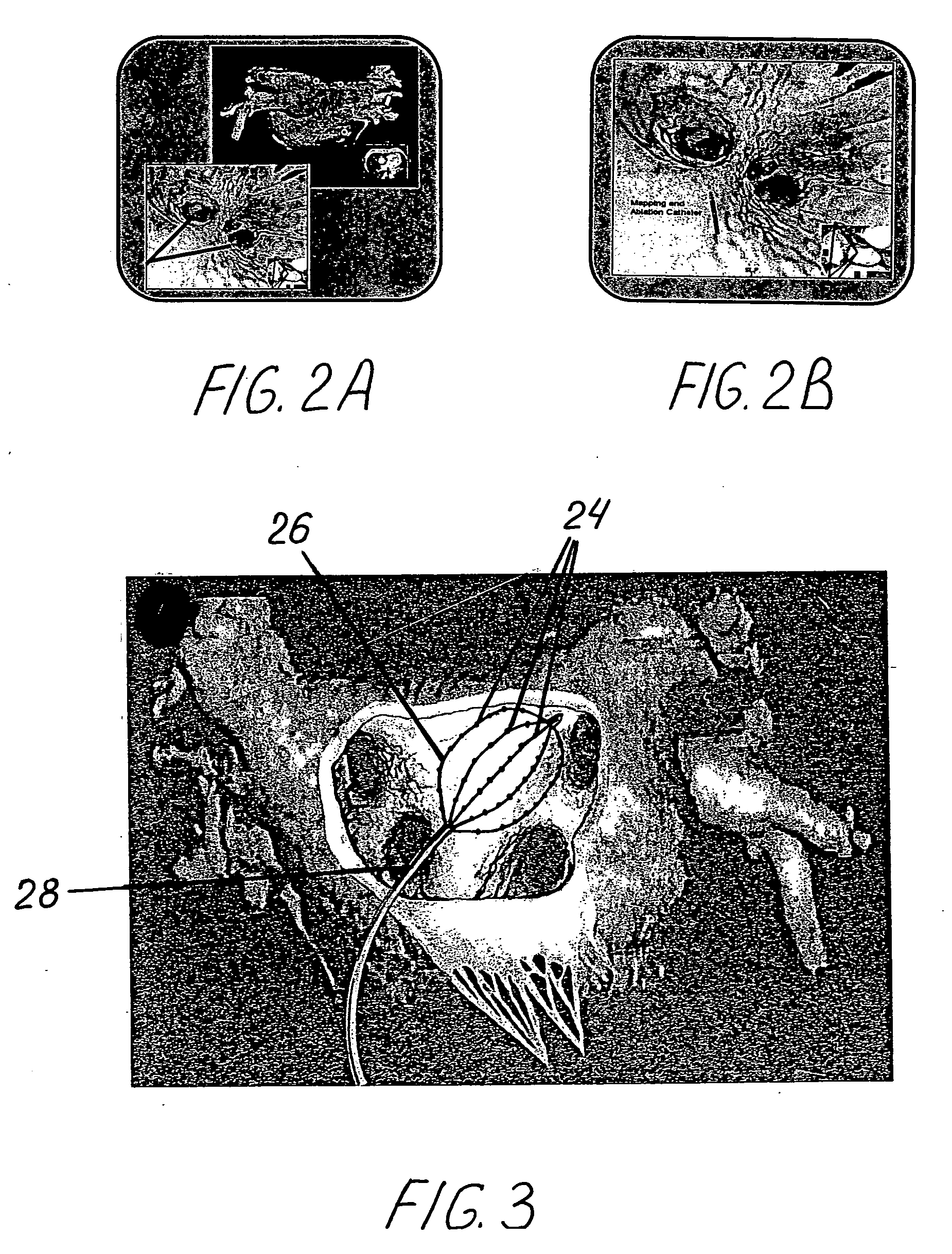
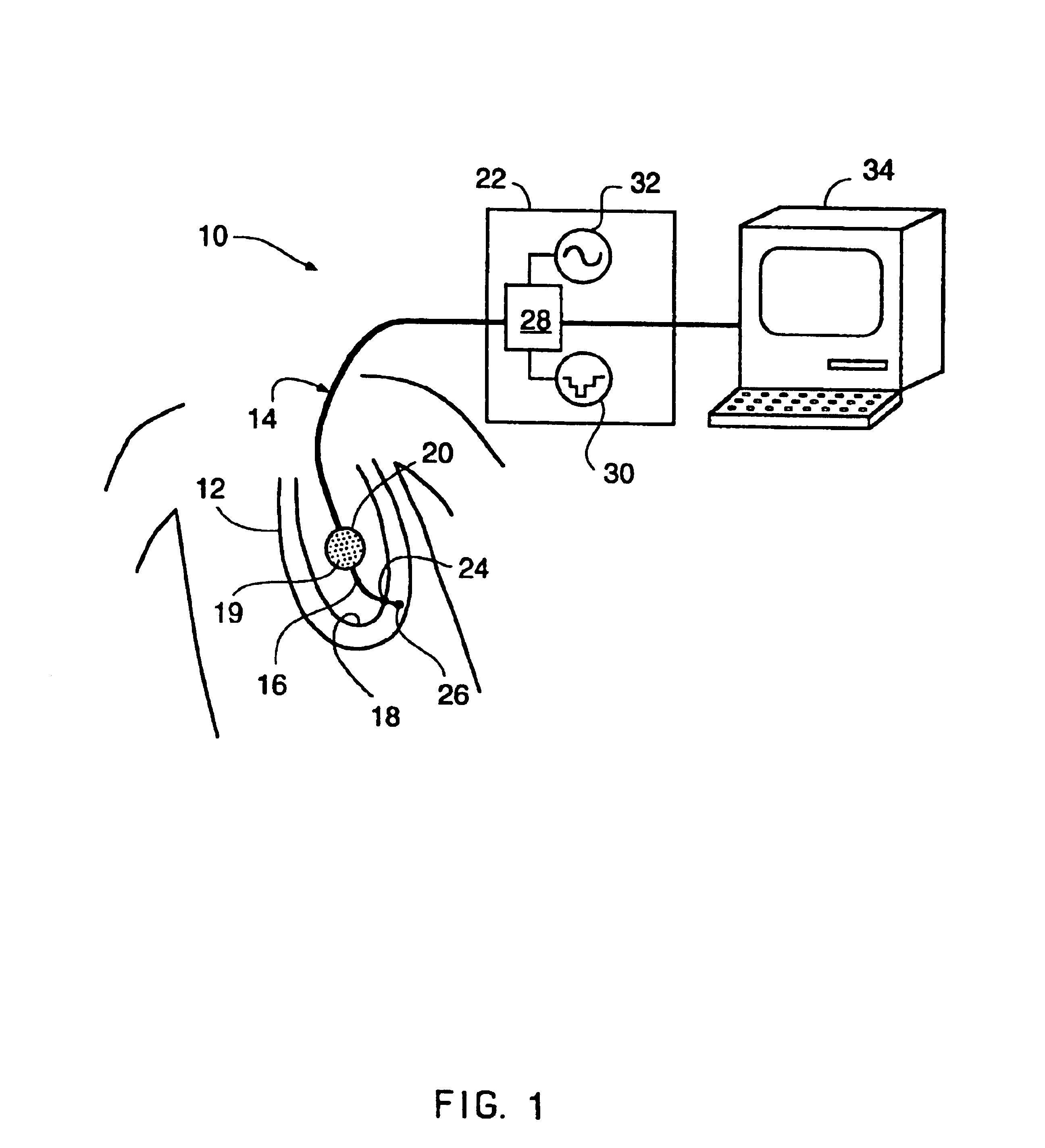
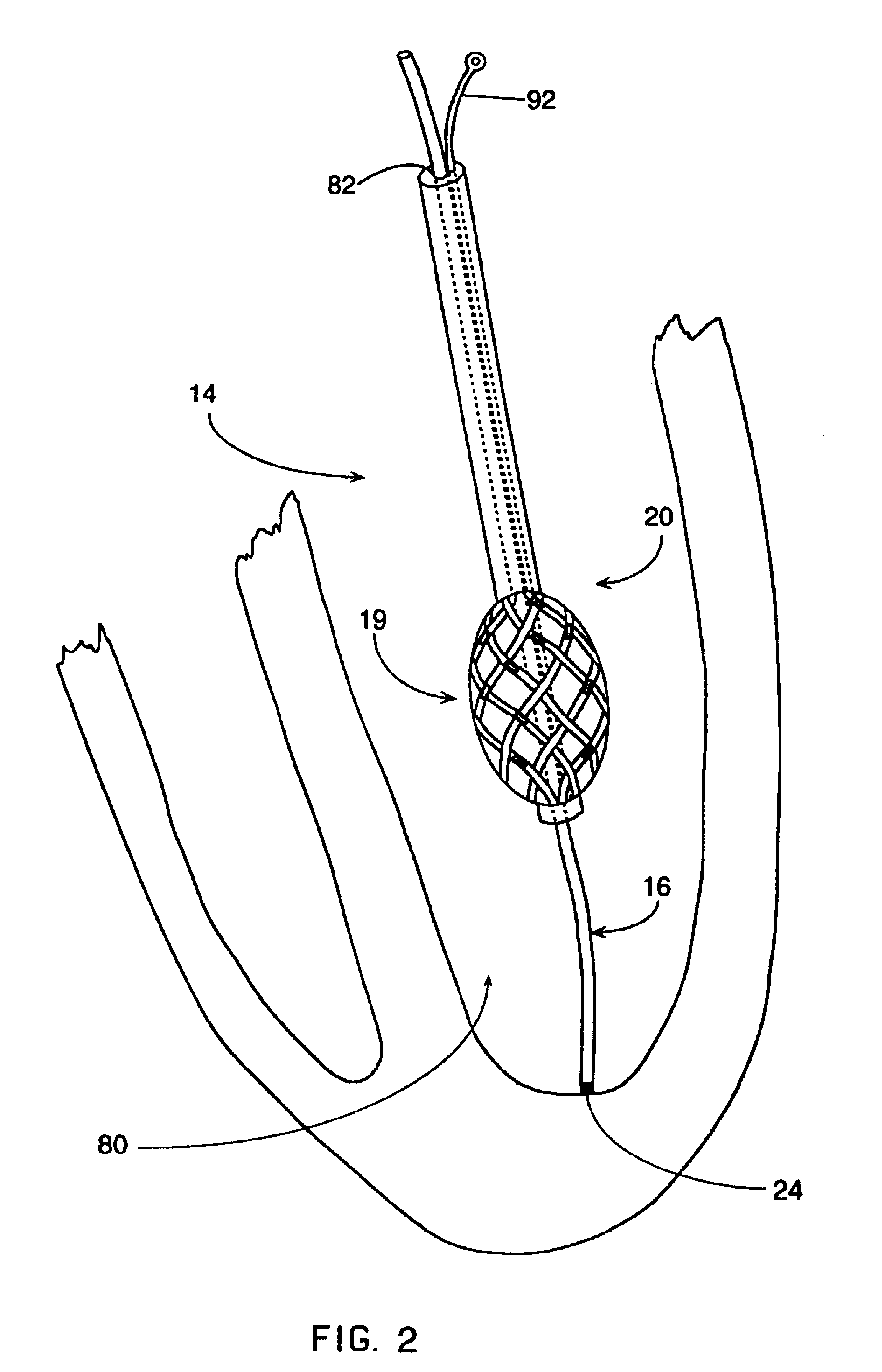
A mapping catheter is positioned in a heart chamber, and active electrode sites are activated to impose an electric field within the chamber. The blood volume and wall motion modulates the electric field, which is detected by passive electrode sites on the preferred catheter. Electrophysiology measurements, as well as geometry measurements, are taken from the passive electrodes and used to display a map of intrinsic heart activity.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Leadless intra-cardiac medical device with dual chamber sensing through electrical and/or mechanical sensing
ActiveUS20130325081A1Small sizeConvenient to accommodateHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac activityCardiac chamber
A leadless intra-cardiac medical device senses cardiac activity from multiple chambers and applies cardiac stimulation to at least one cardiac chamber and / or generates a cardiac diagnostic indication. The leadless device may be implanted in a local cardiac chamber (e.g., the right ventricle) and detect near-field signals from that chamber as well as far-field signals from an adjacent chamber (e.g., the right atrium).
Owner:PACESETTER INC
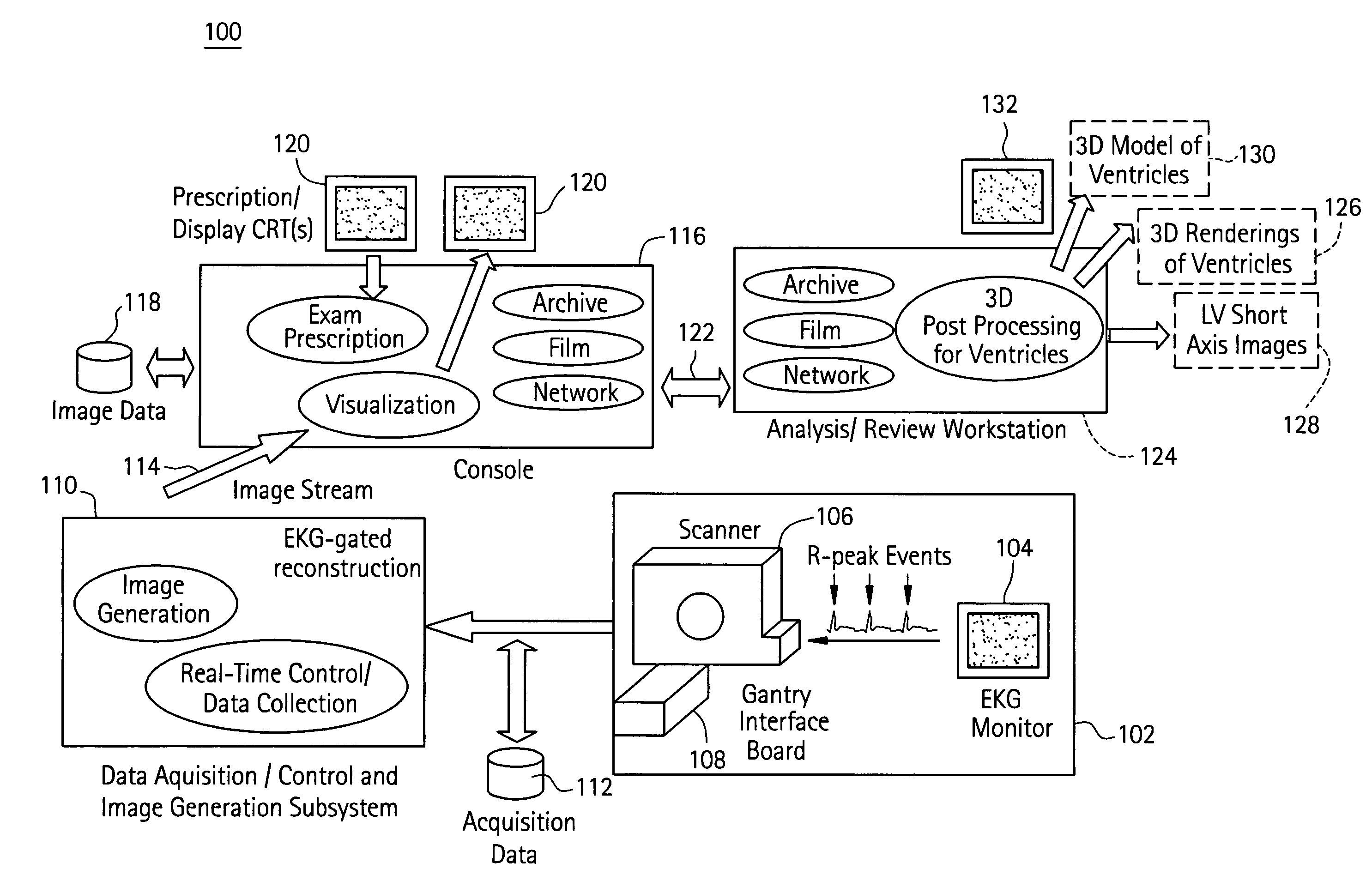
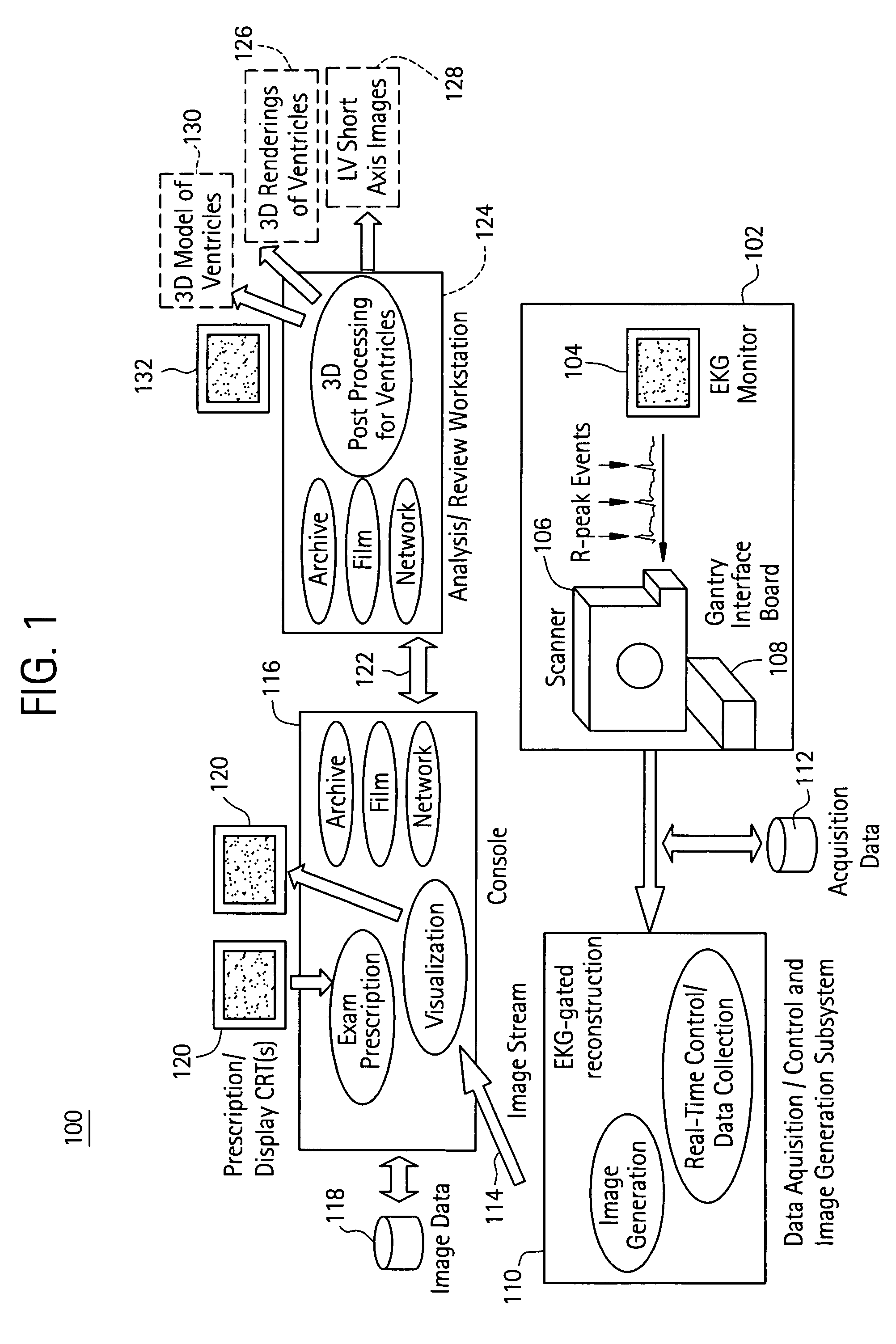
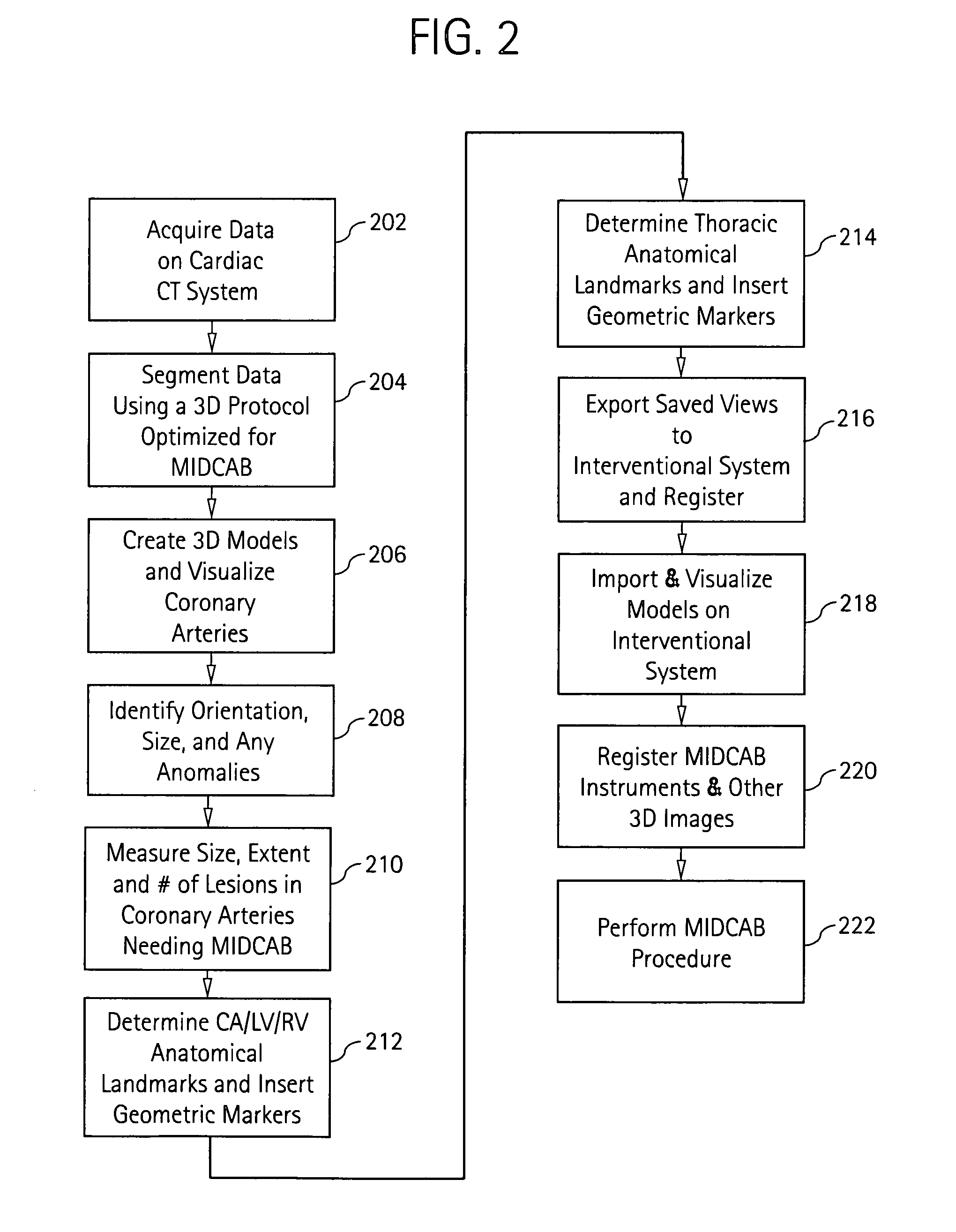
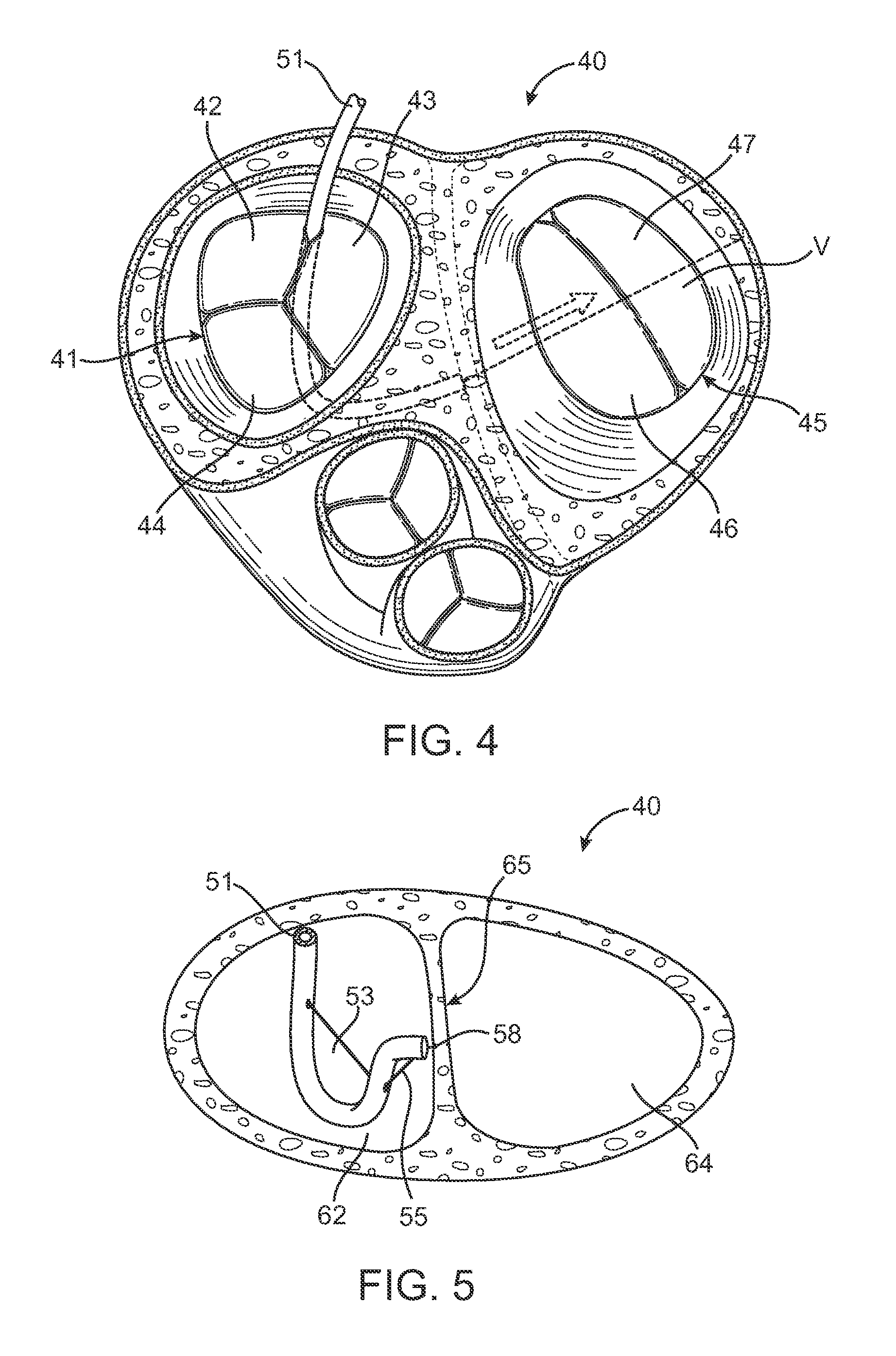
Cardiac imaging system and method for planning minimally invasive direct coronary artery bypass surgery
ActiveUS7813785B2High precisionShorten the construction periodUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical simulationAnatomical landmarkCoronary arteries
A method for planning minimally invasive direct coronary artery bypass (MIDCAB) for a patient includes obtaining acquisition data from a medical imaging system, and generating a 3D model of the coronary arteries and one or more cardiac chambers of interest. One or more anatomical landmarks are identified on the 3D model, and saved views of the 3D model are registered on an interventional system. One or more of the registered saved views are visualized with the interventional system.
Owner:APN HEALTH +1
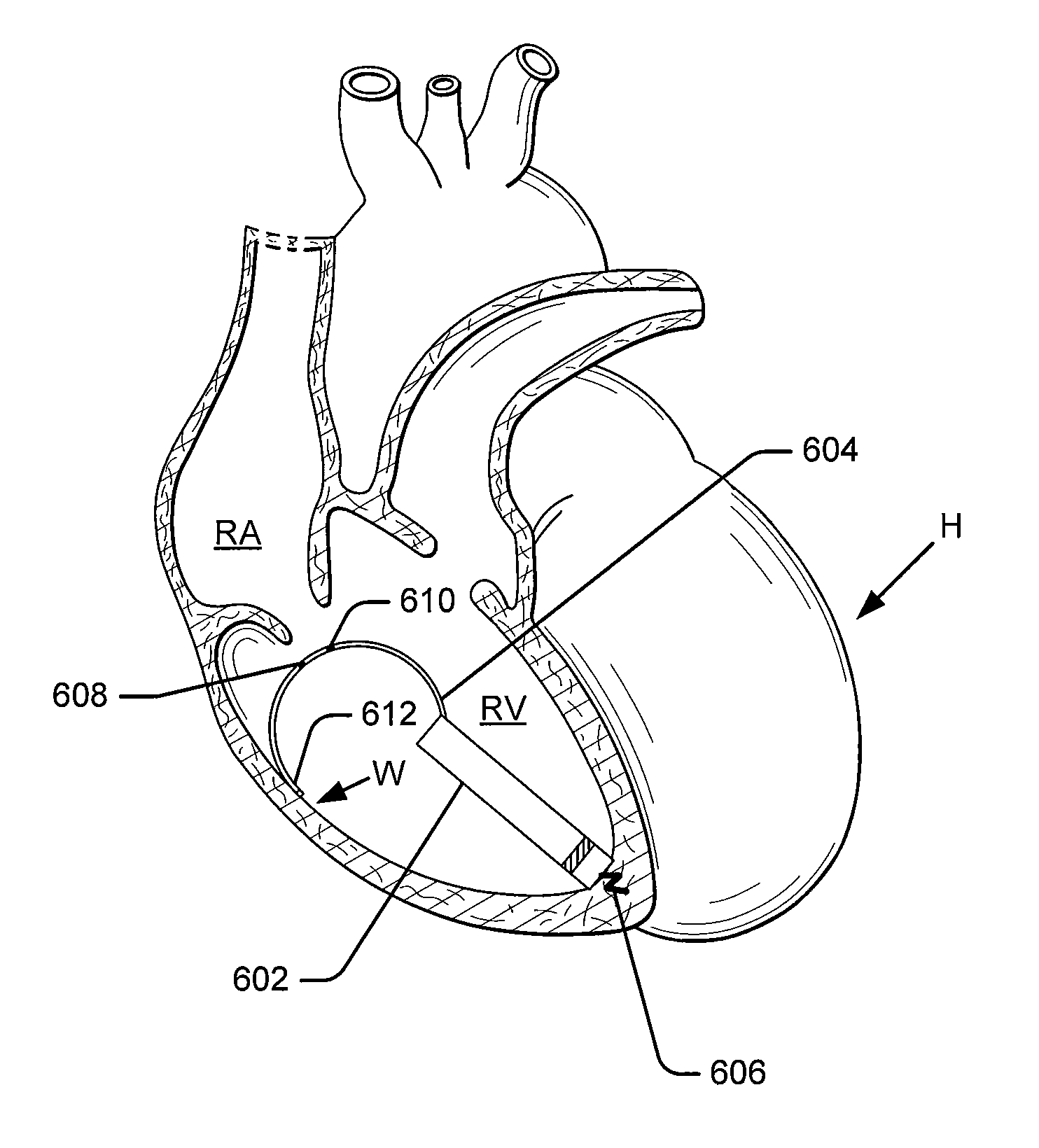
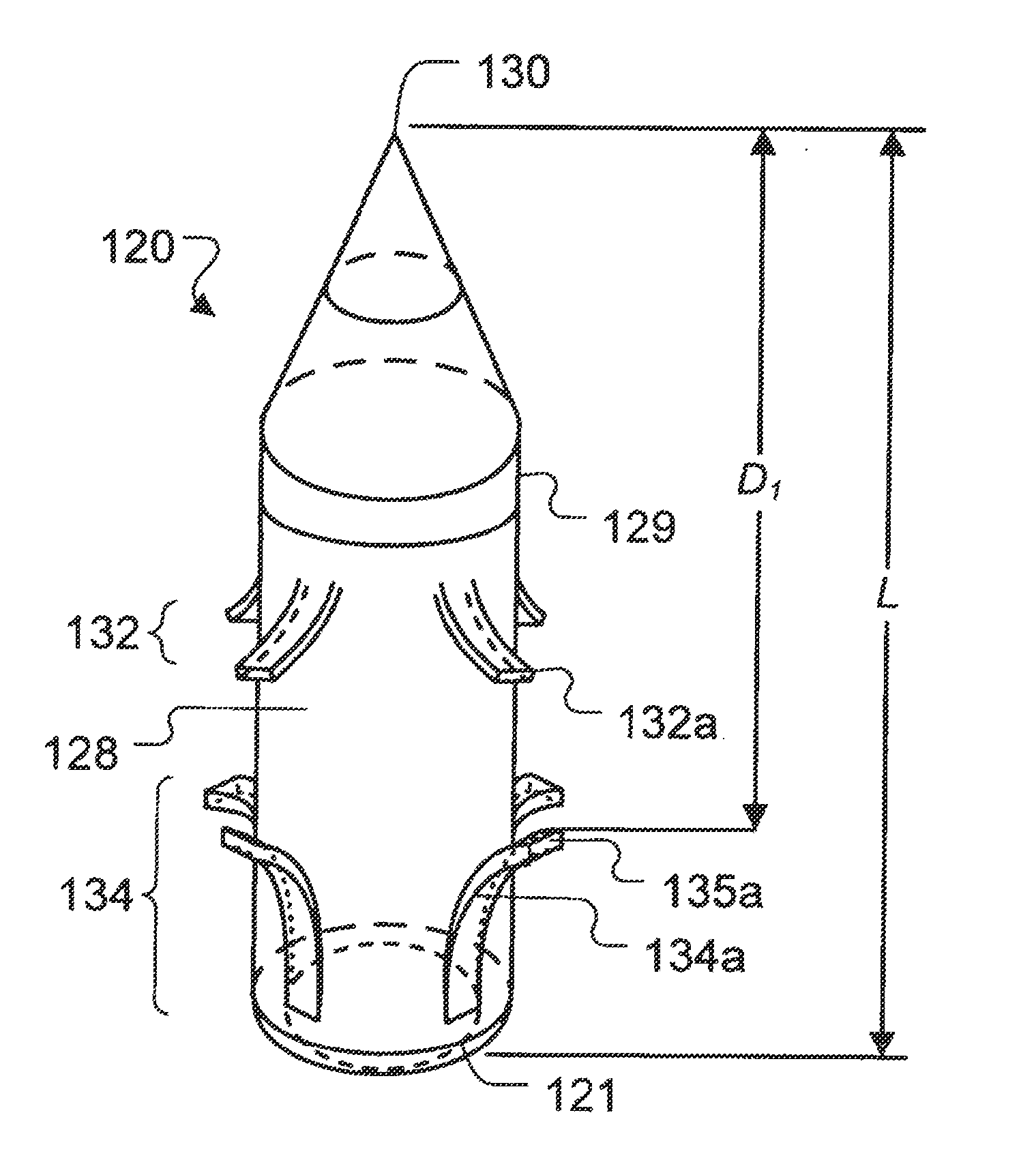
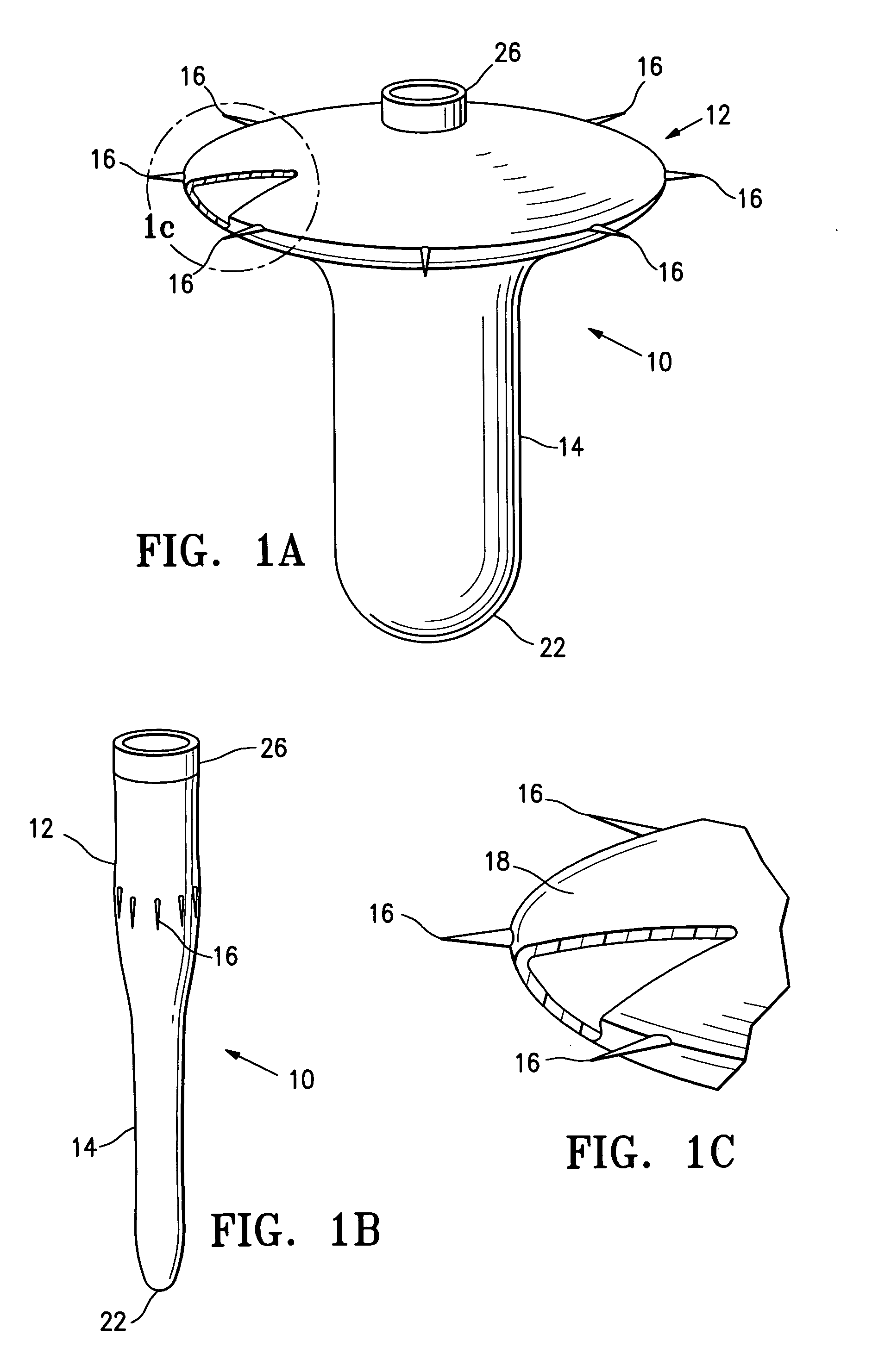
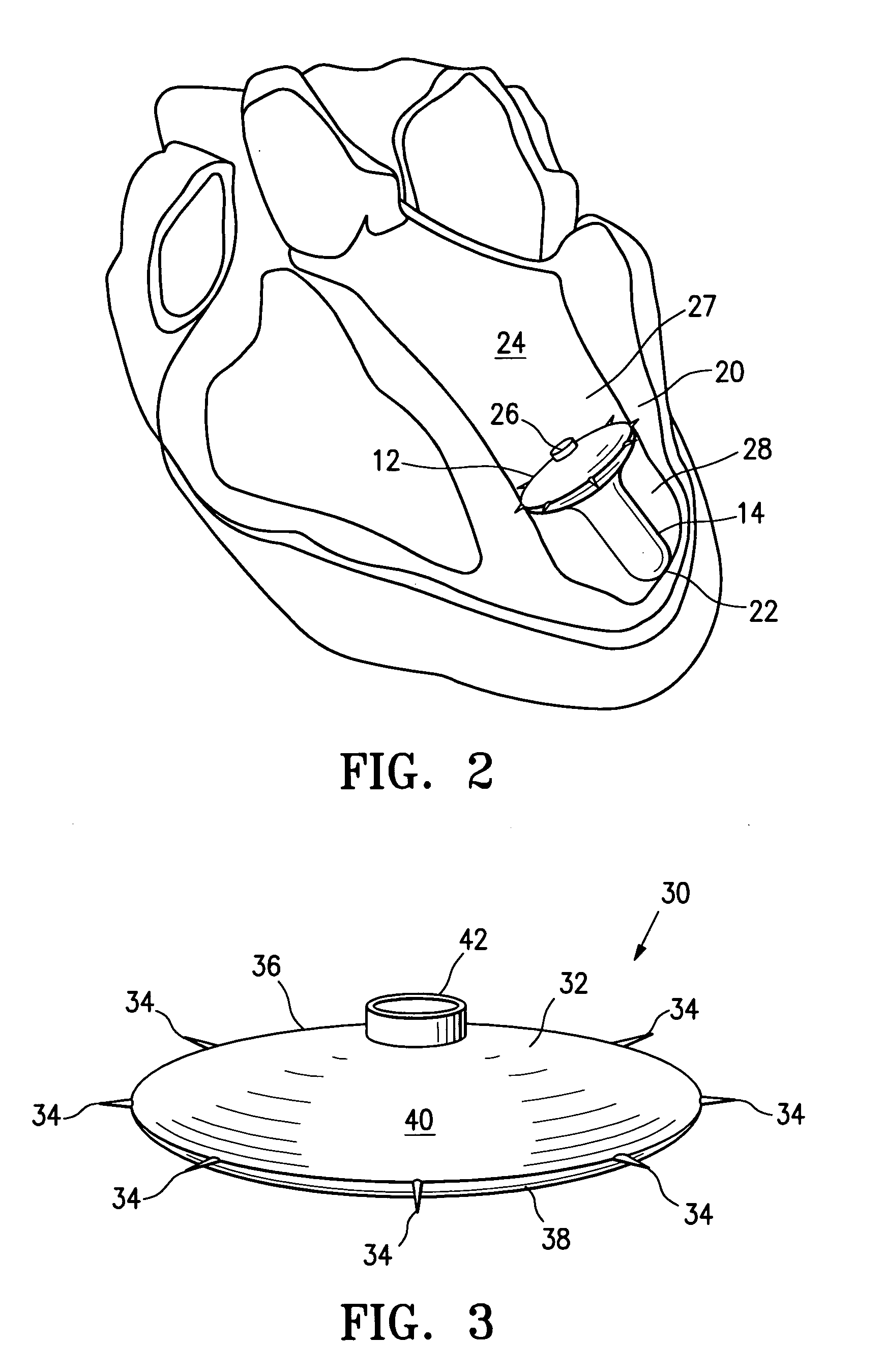
Ventricular partitioning device
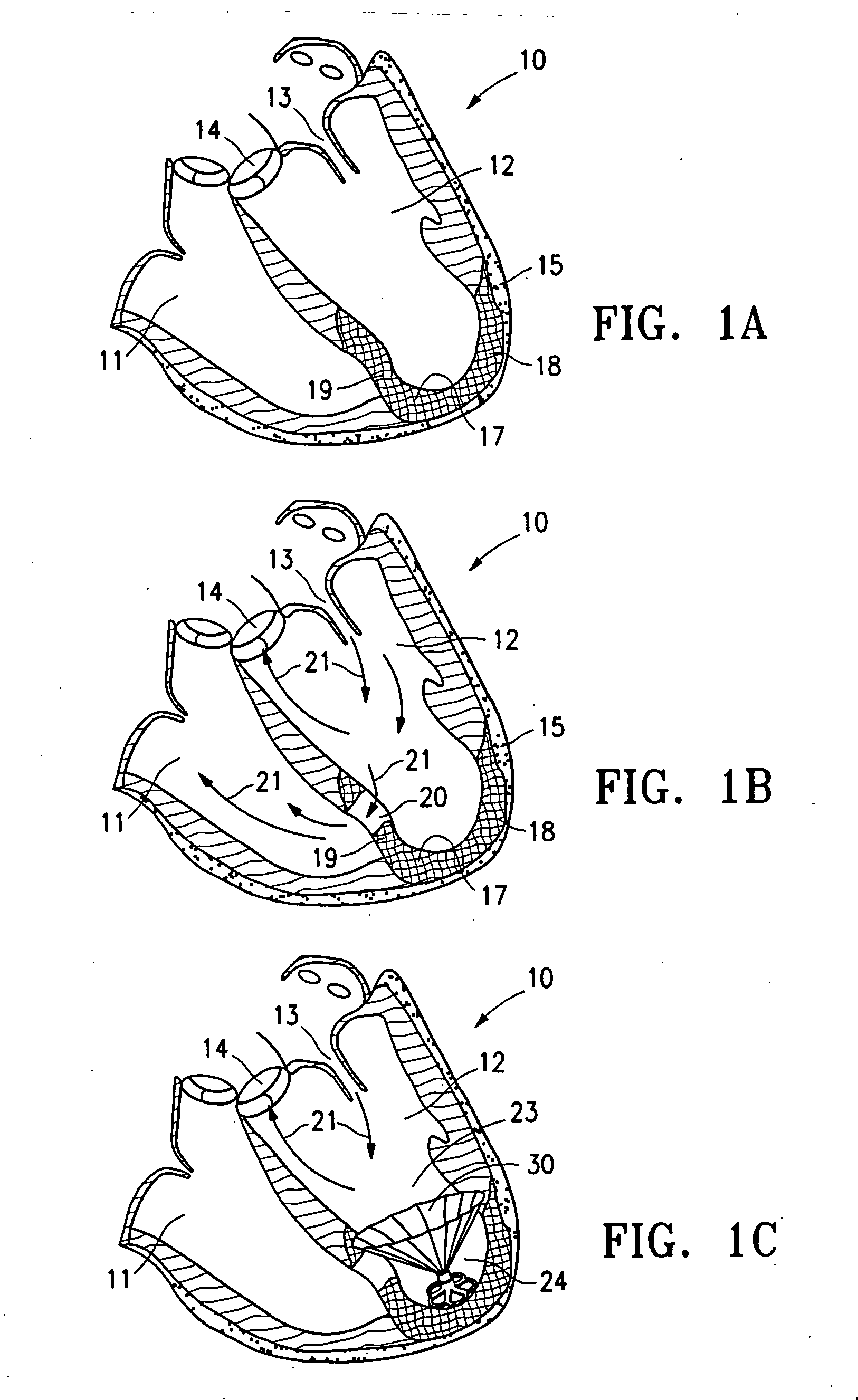
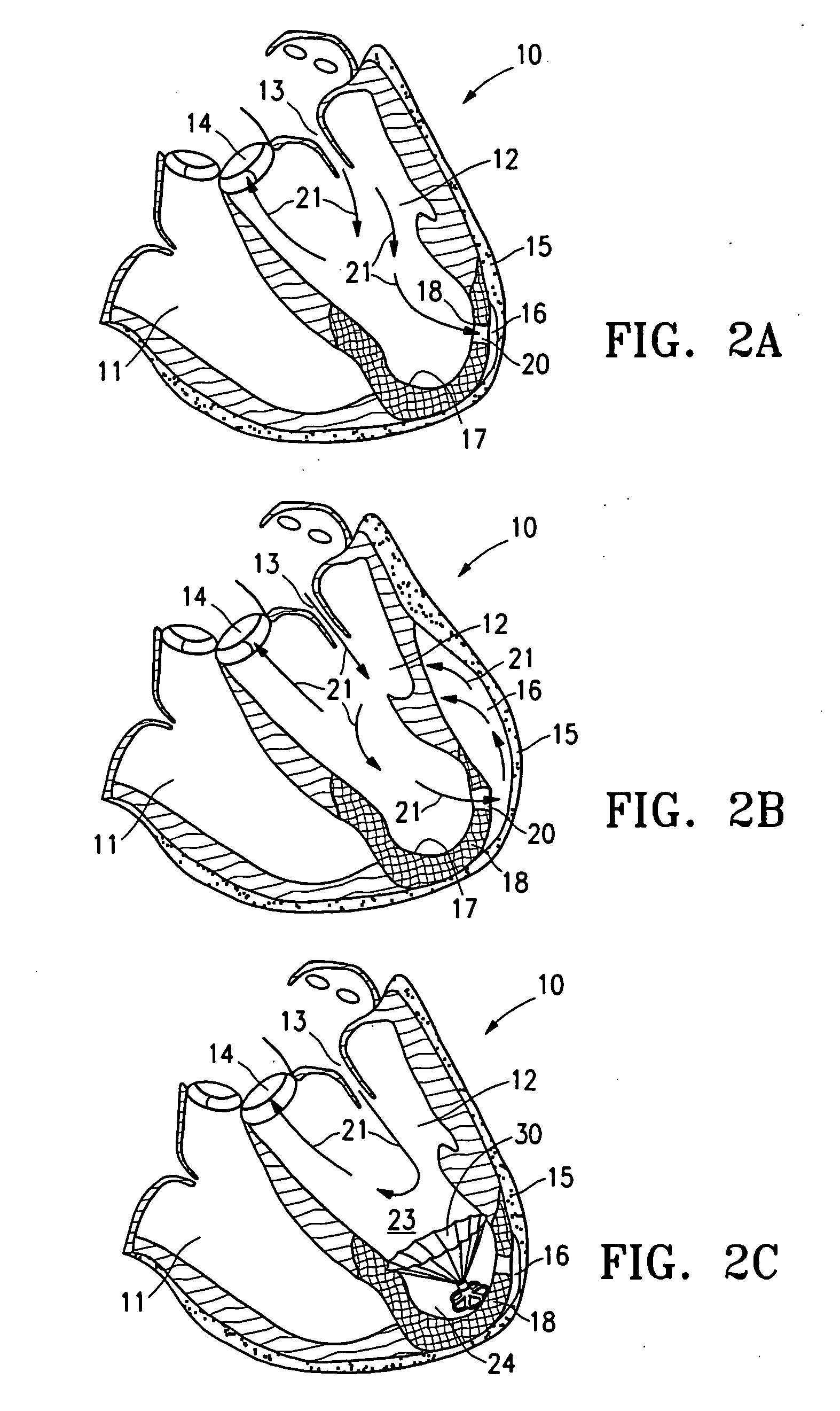
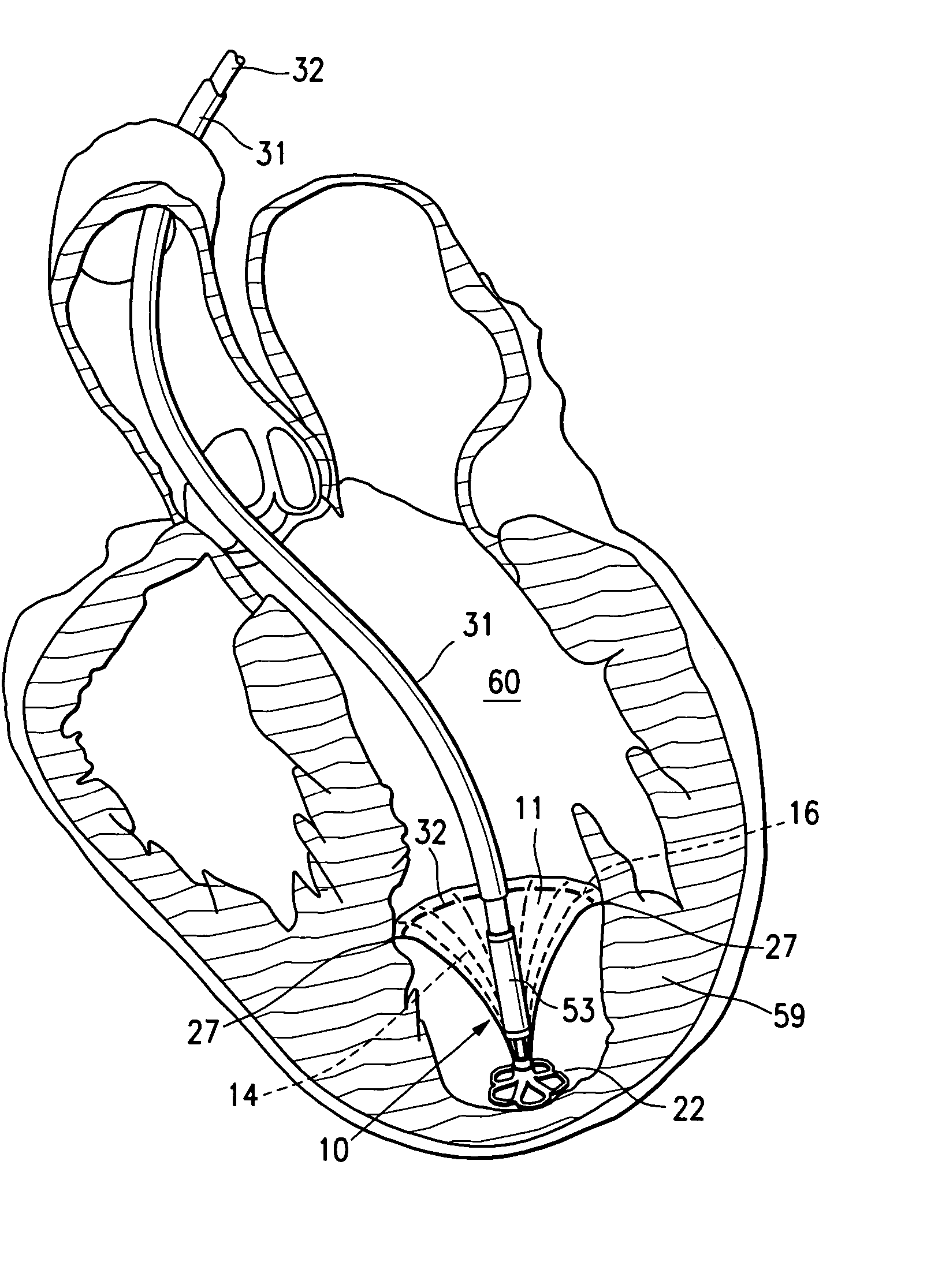
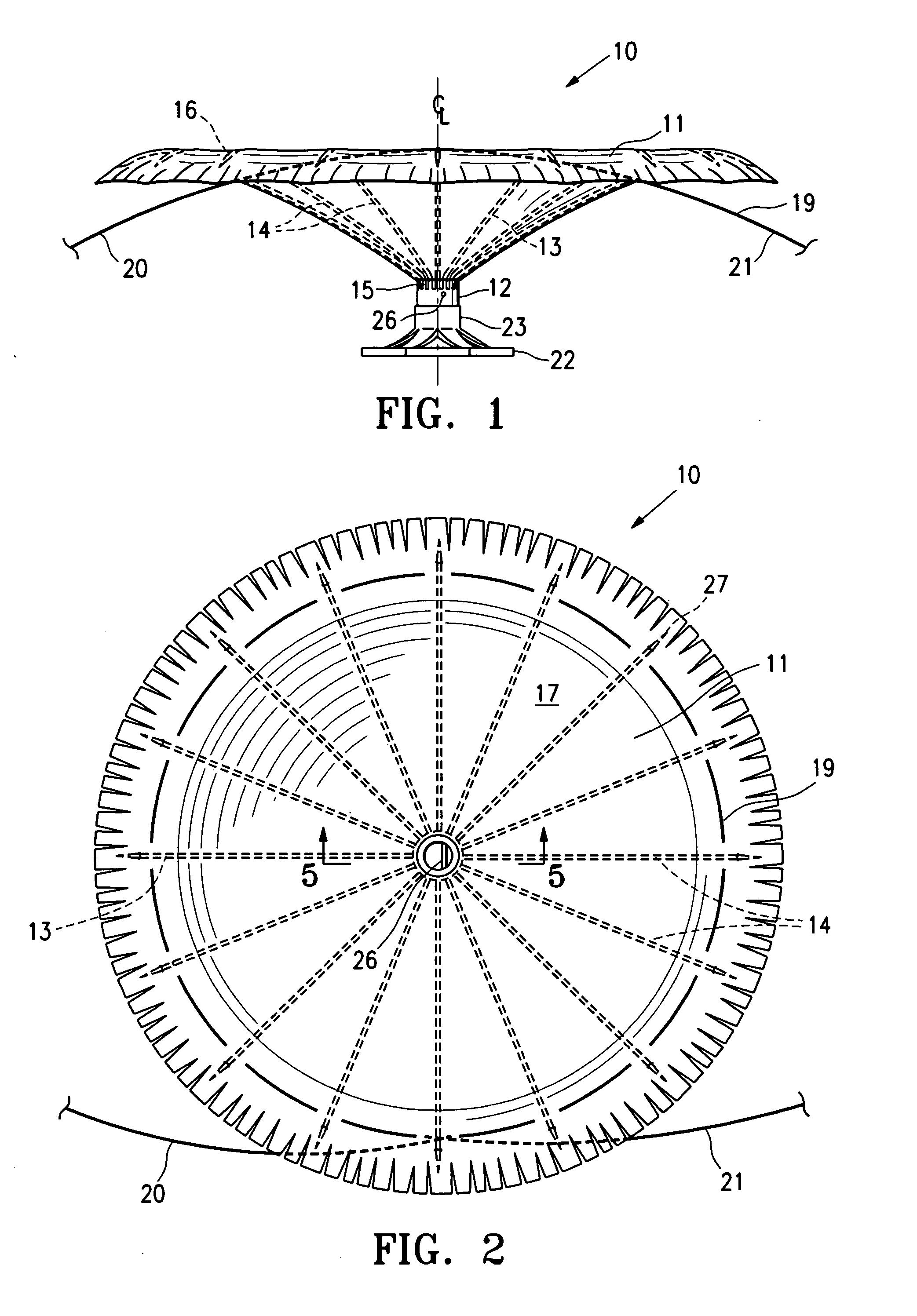
ActiveUS20050154252A1Lower the volumeImprove ejection fractionHeart valvesHeart stimulatorsHeart chamberNon traumatic
This invention is directed to a partitioning device for separating a patient's heart chamber into a productive portion and a non-productive portion. The device is particularly suitable for treating patients with congestive heart failure. The partitioning device has a reinforced, expandable membrane which separates the productive and non-productive portions of the heart chamber and a support or spacing member extending between the reinforced membrane and the wall of the patient's heart chamber. The support or spacing member has a non-traumatic distal end to engage the ventricular wall.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
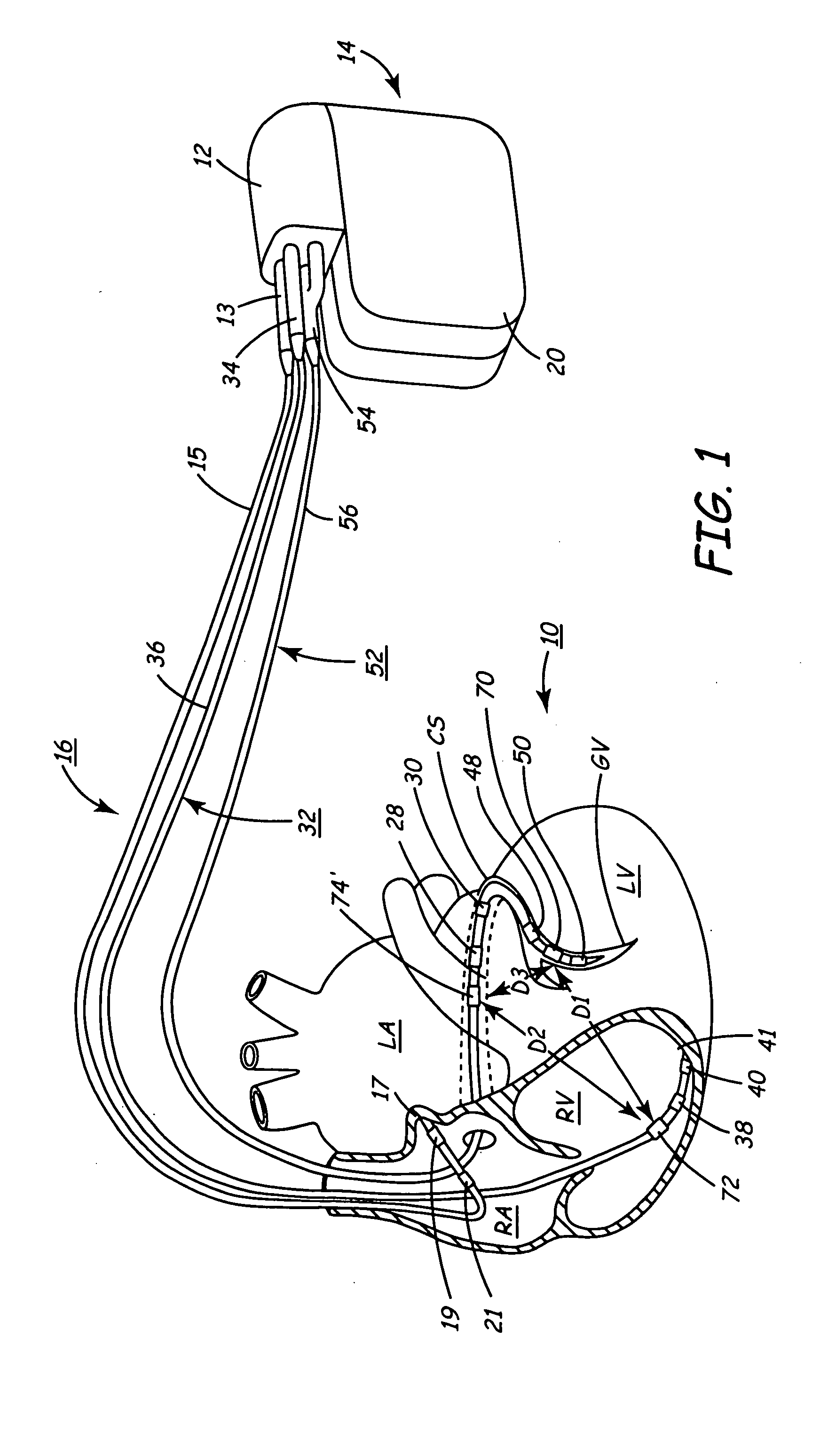
Implantable medical device for monitoring cardiac blood pressure and chamber dimension
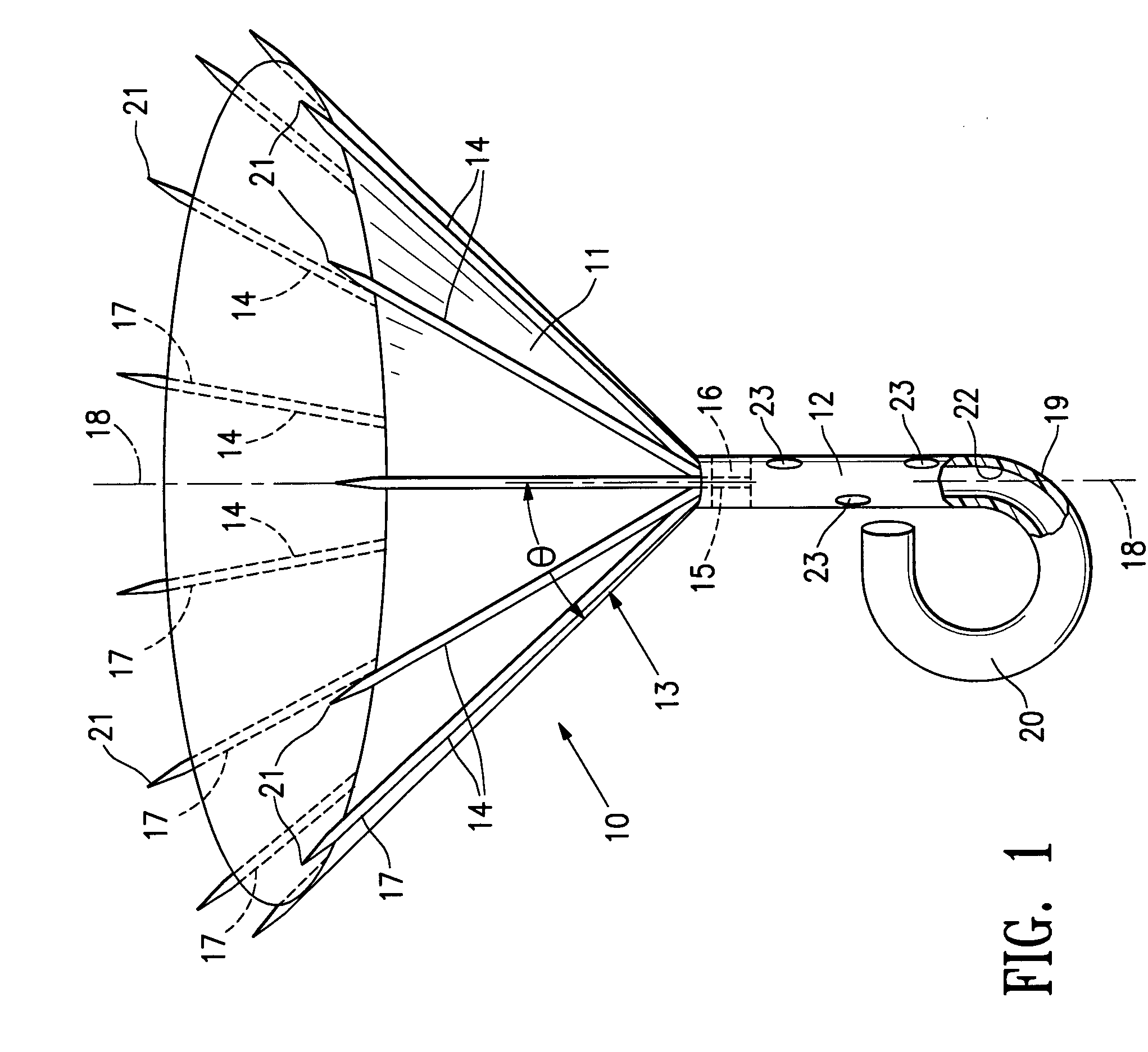
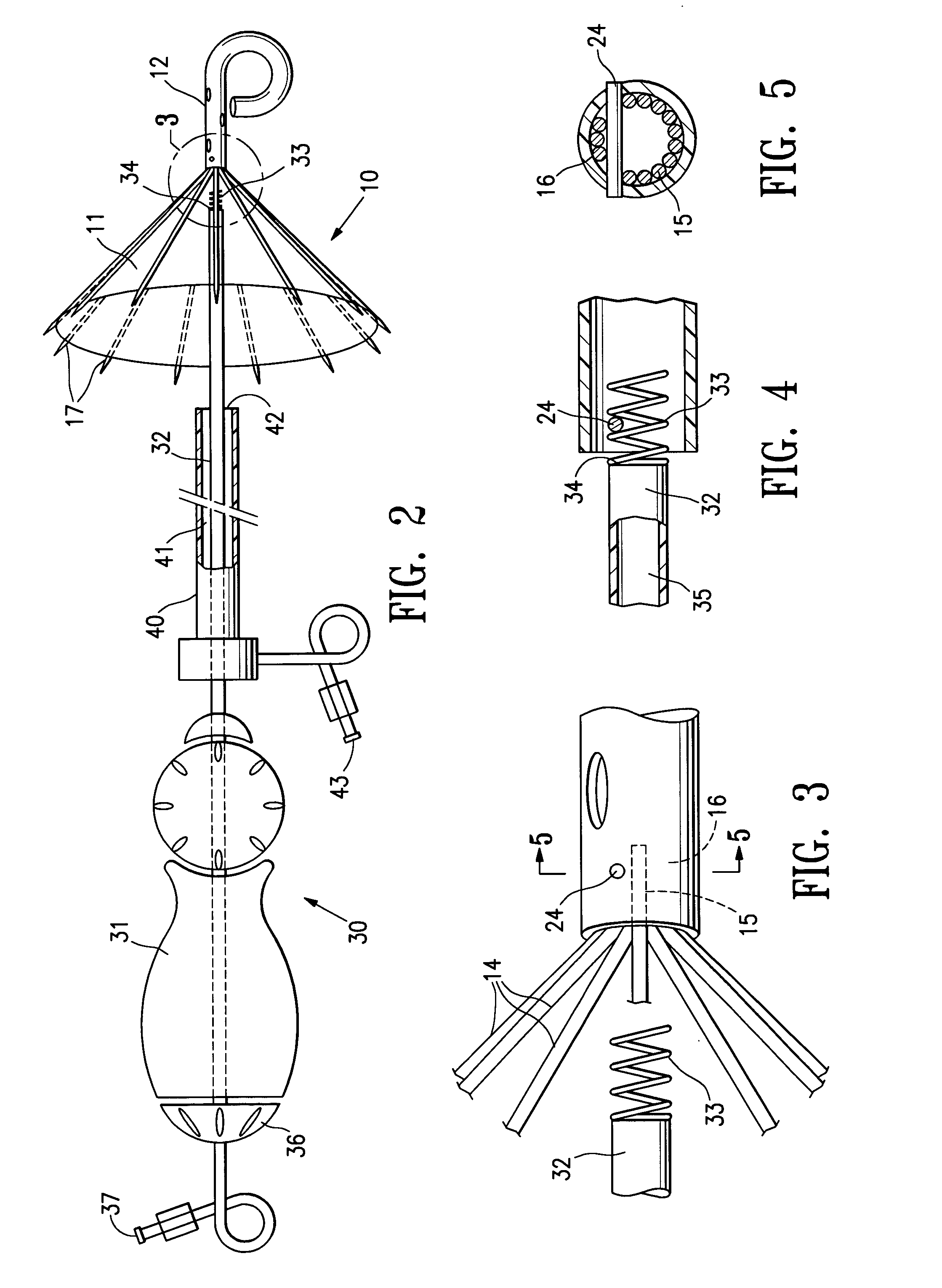
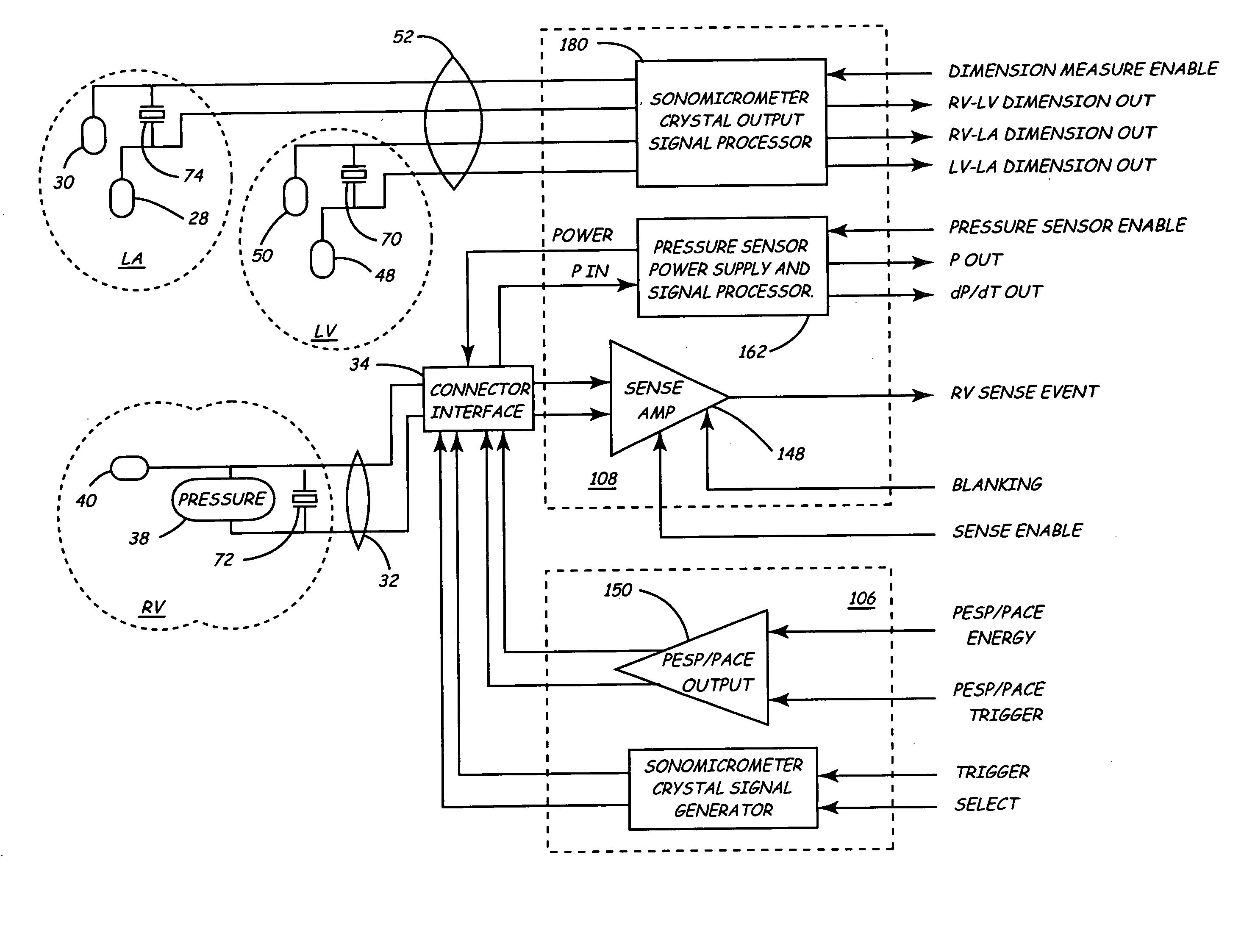
InactiveUS20050027323A1Maximize cardiac outputConvenient timeCatheterHeart stimulatorsSonificationHeart chamber
Implantable medical devices (IMDs) for monitoring signs of acute or chronic cardiac heart failure by measuring cardiac blood pressure and mechanical dimensions of the heart and providing multi-chamber pacing optimized as a function of measured blood pressure and dimensions are disclosed. The dimension sensor or sensors comprise at least a first sonomicrometer piezoelectric crystal mounted to a first lead body implanted into or in relation to one heart chamber that operates as an ultrasound transmitter when a drive signal is applied to it and at least one second sonomicrometer crystal mounted to a second lead body implanted into or in relation to a second heart chamber that operates as an ultrasound receiver. The ultrasound receiver converts impinging ultrasound energy transmitted from the ultrasound transmitter through blood and heart tissue into an electrical signal. The time delay between the generation of the transmitted ultrasound signal and the reception of the ultrasound wave varies as a function of distance between the ultrasound transmitter and receiver which in turn varies with contraction and expansion of a heart chamber between the first and second sonomicrometer crystals. One or more additional sonomicrometer piezoelectric crystal can be mounted to additional lead bodies such that the distances between the three or more sonomicrometer crystals can be determined. In each case, the sonomicrometer crystals are distributed about a heart chamber such that the distance between the separated ultrasound transmitter and receiver crystal pairs changes with contraction and relaxation of the heart chamber walls.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
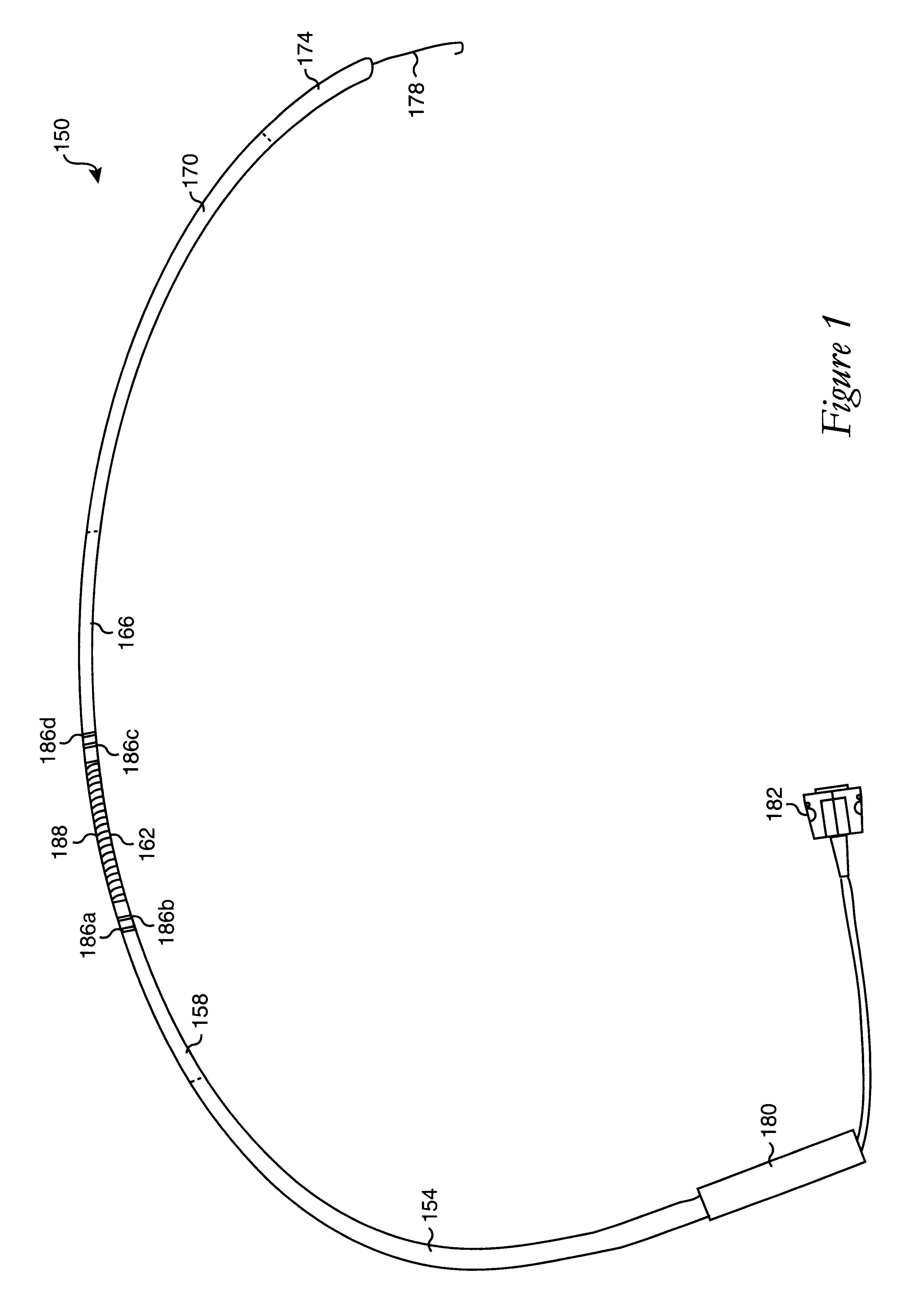
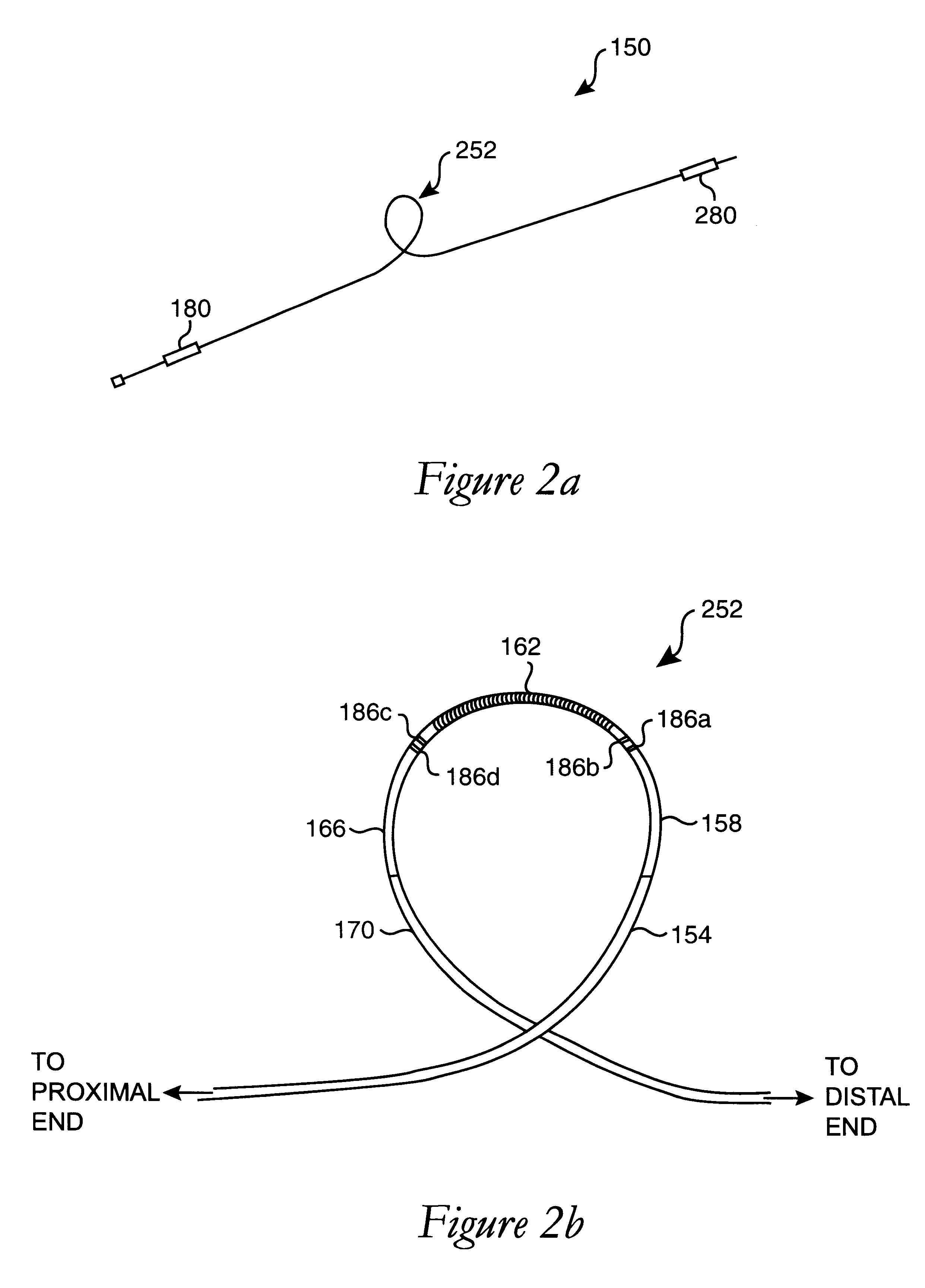
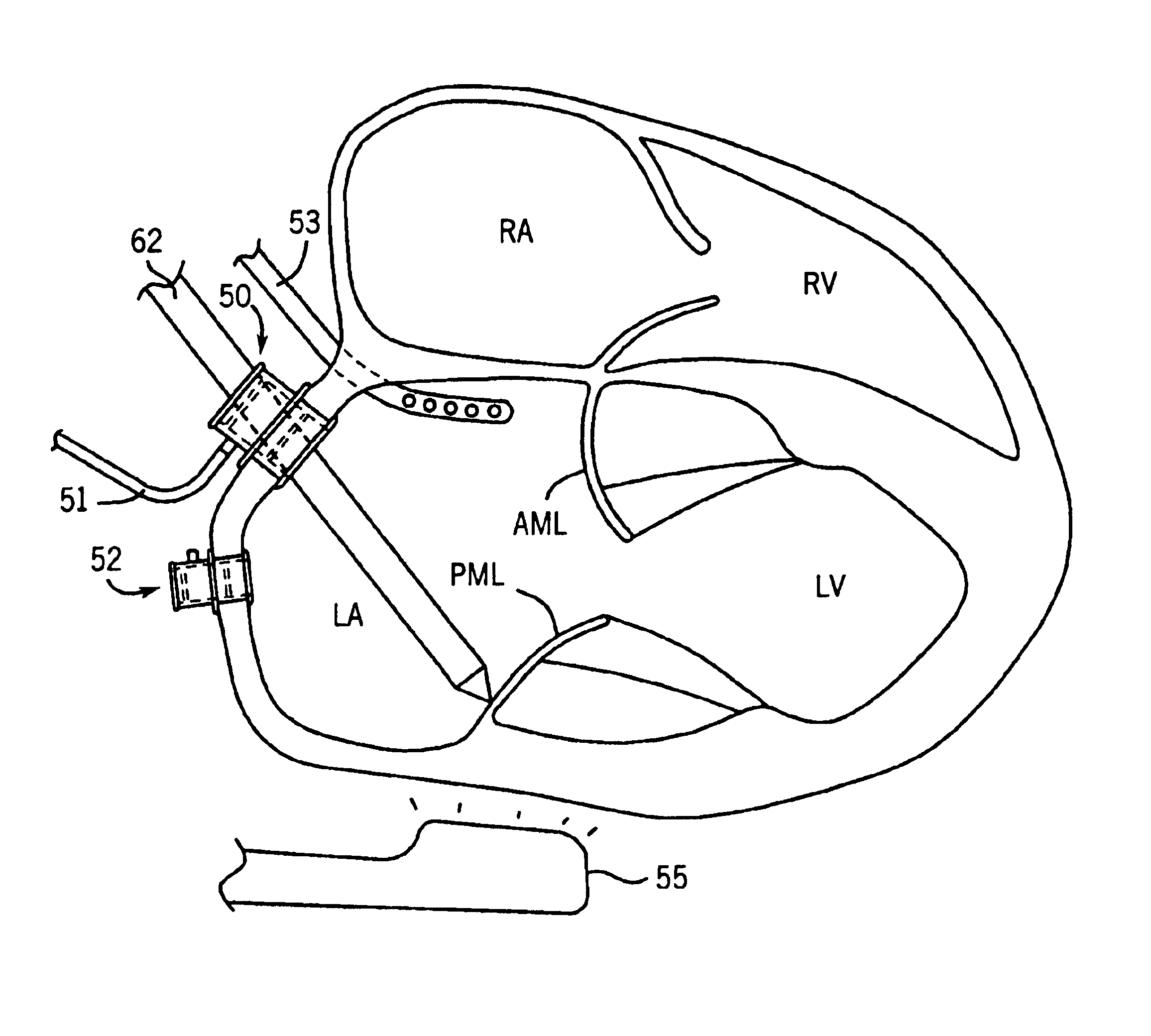
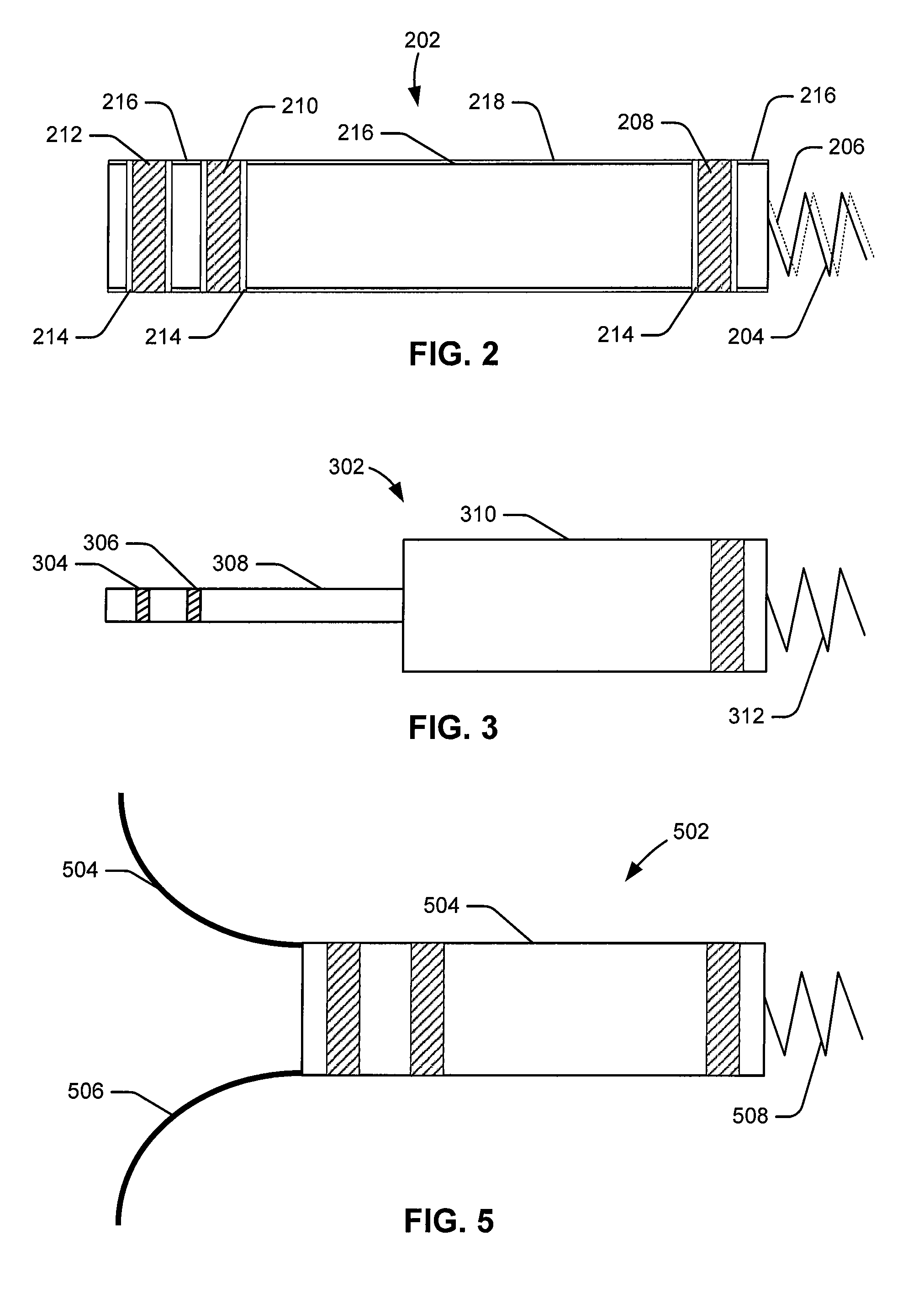
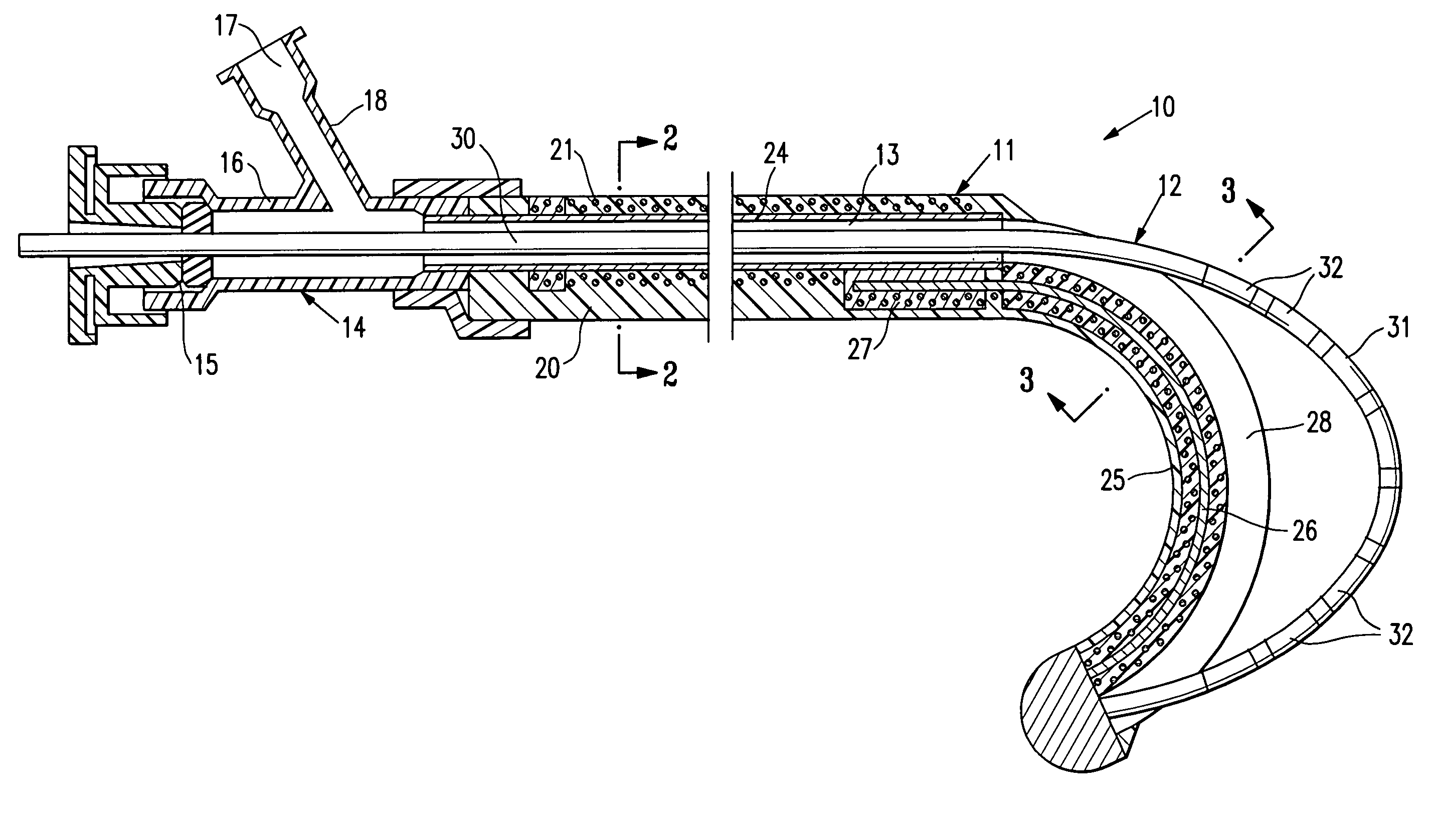
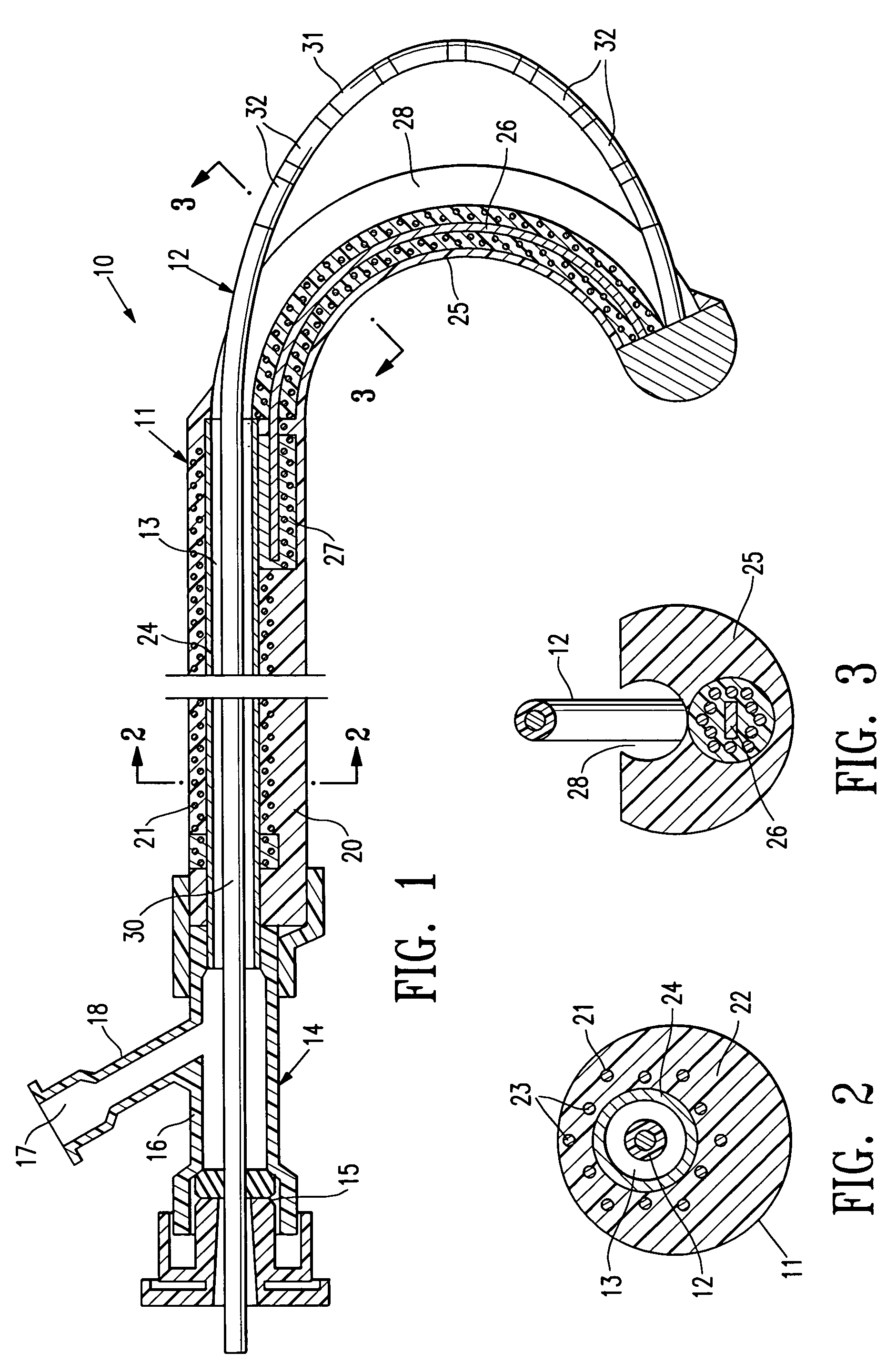
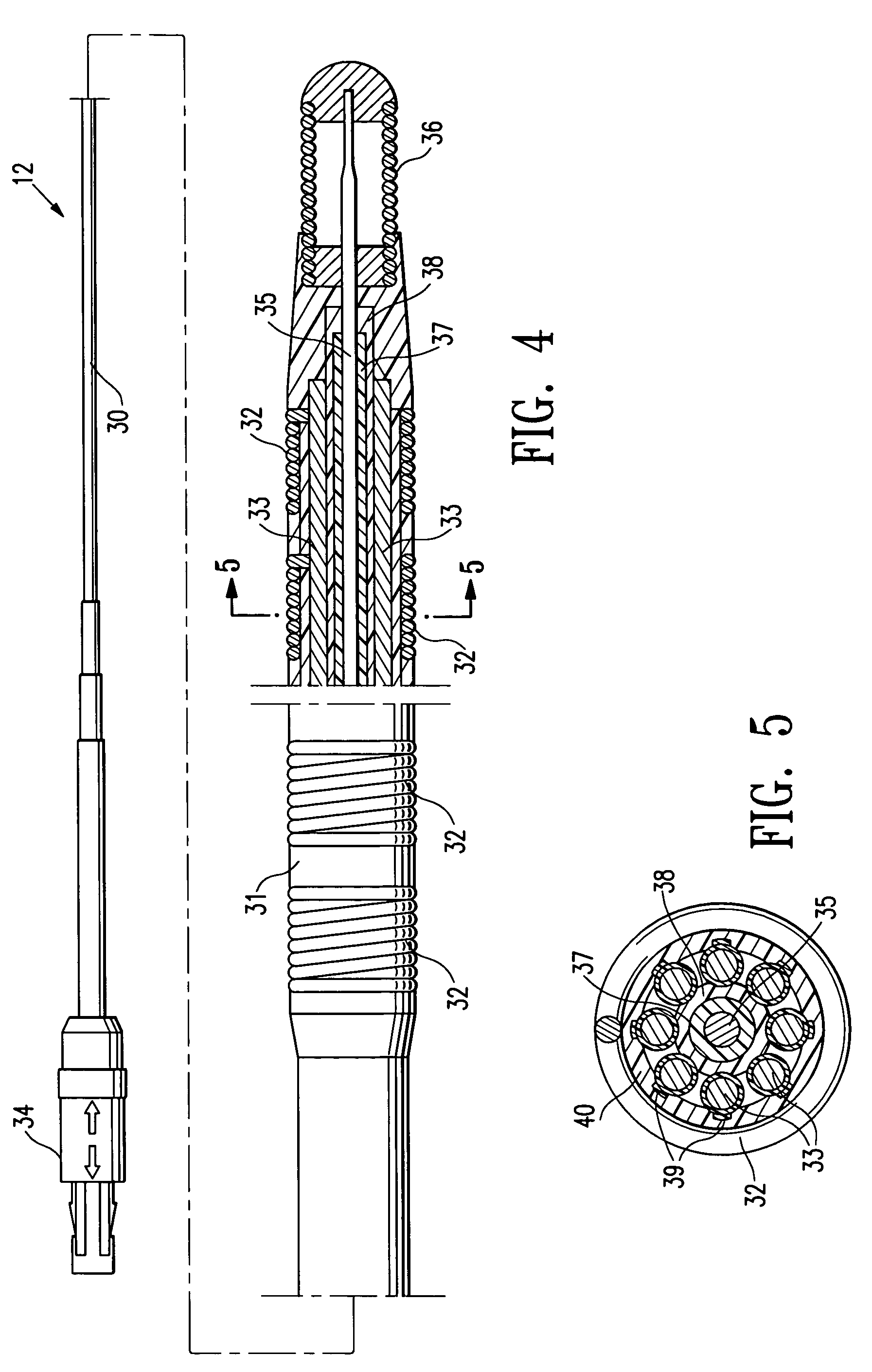
Catheter Having a Selectively Formable Distal Section
The current invention discloses a delivery catheter with a selectively formable distal section. The catheter comprises a central lumen that is configured to receive a puncture catheter that is used for puncturing the septum of a heart and to emplace devices used for treating mitral regurgitation. The delivery catheter includes control members disposed in a control lumen, and a plurality curved areas can be selectively formed in the distal section of the delivery catheter by applying tension to the control members. A first curve is shaped to conform to the interior of a heart chamber and a combination of the first curve and a second curve allows a clinician to manipulate the distal end of the catheter for selection of the proper vector for deploying a treatment device, or for guiding a treatment device around obstacles in a heart chamber.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
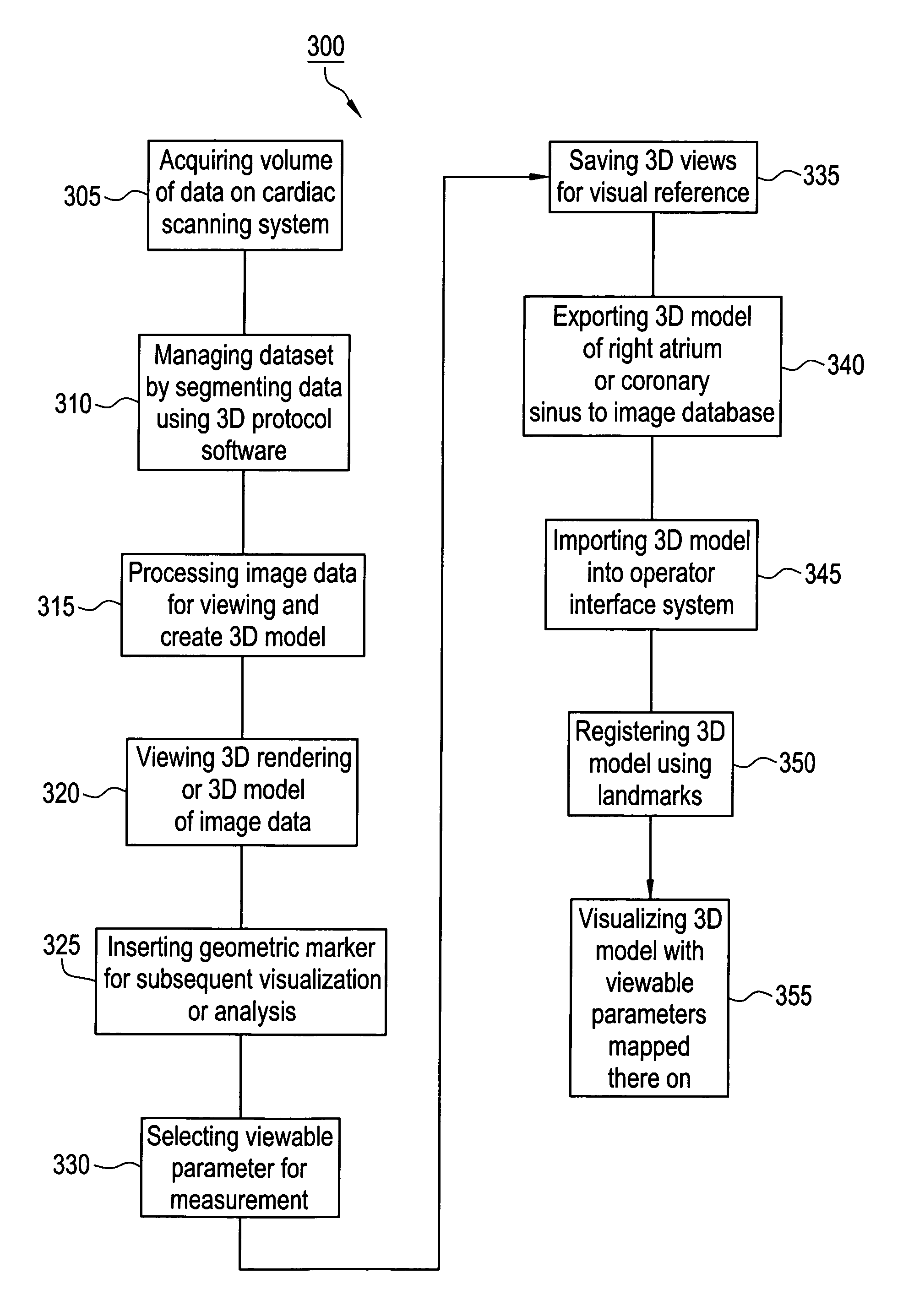
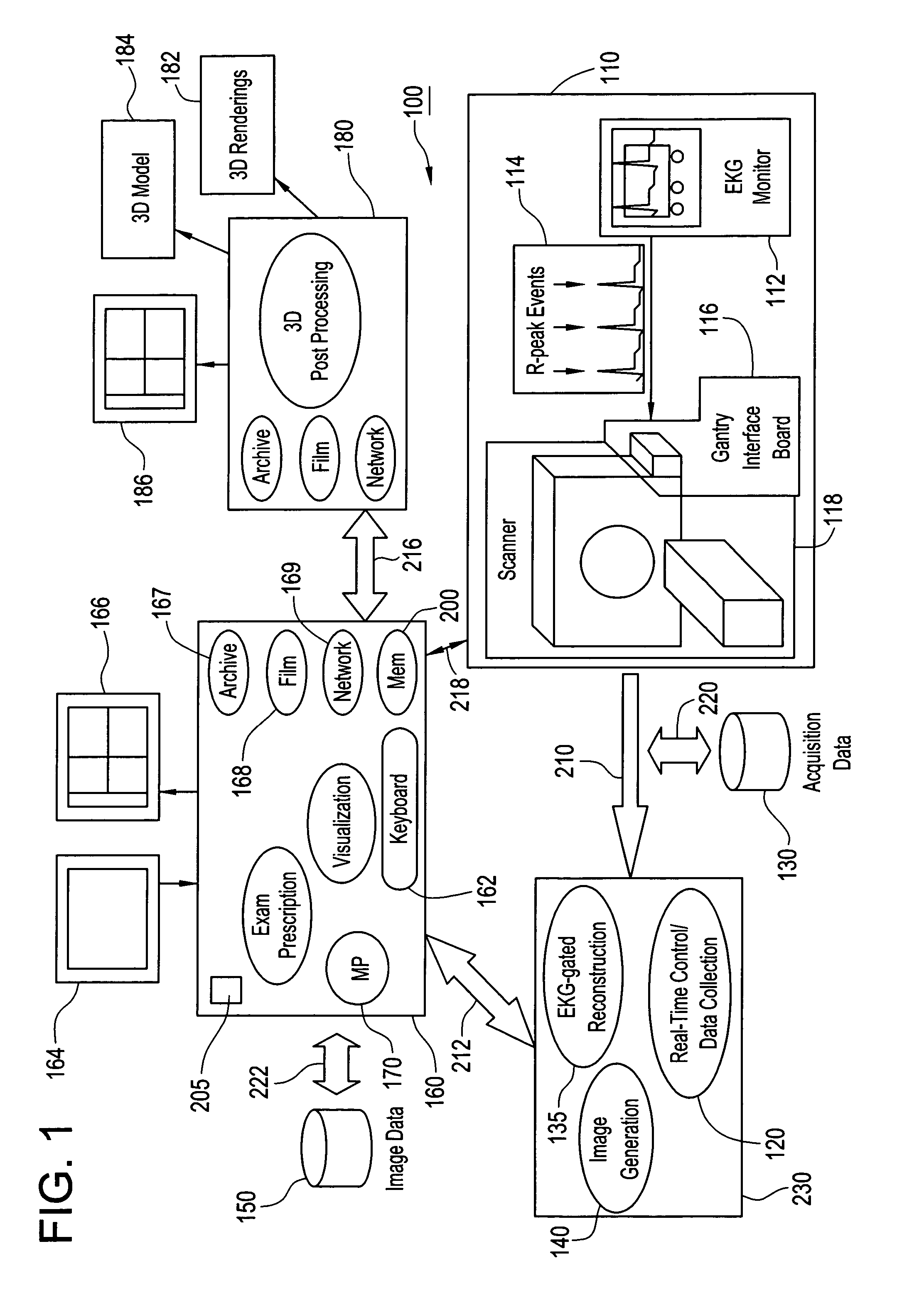
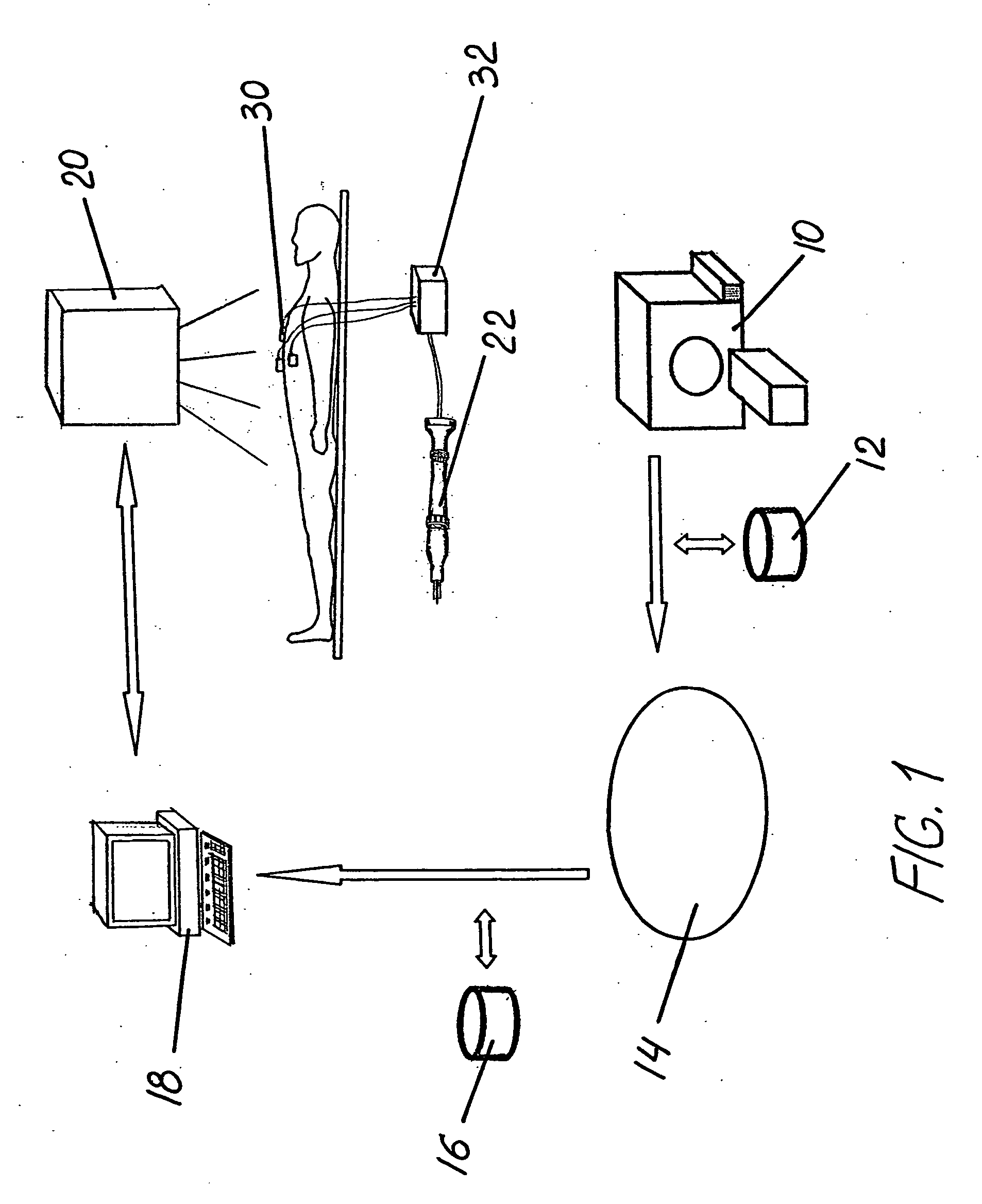
Method and apparatus for medical intervention procedure planning and location and navigation of an intervention tool
A system and method for a medical intervention procedure within a cardiac chamber having an imaging system to obtain image data of the cardiac chamber and to create a 3D model from that image data, an interventional system to register the 3D model with a real-time image of the cardiac chamber and to display the 3D model, and an interventional tool positioned in the cardiac chamber to be displayed upon the interventional system and to be navigated in real-time over the registered 3D model. Preferably, the method and system also includes a storage medium to store the 3D model and wherein the interventional system receives the stored 3D model to register with the real-time image of the cardiac chamber.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
Multiple partitioning devices for heart treatment
ActiveUS20060014998A1Lower the volumeReduce stressHeart valvesHeart stimulatorsHeart chamberCongestive heart failure chf
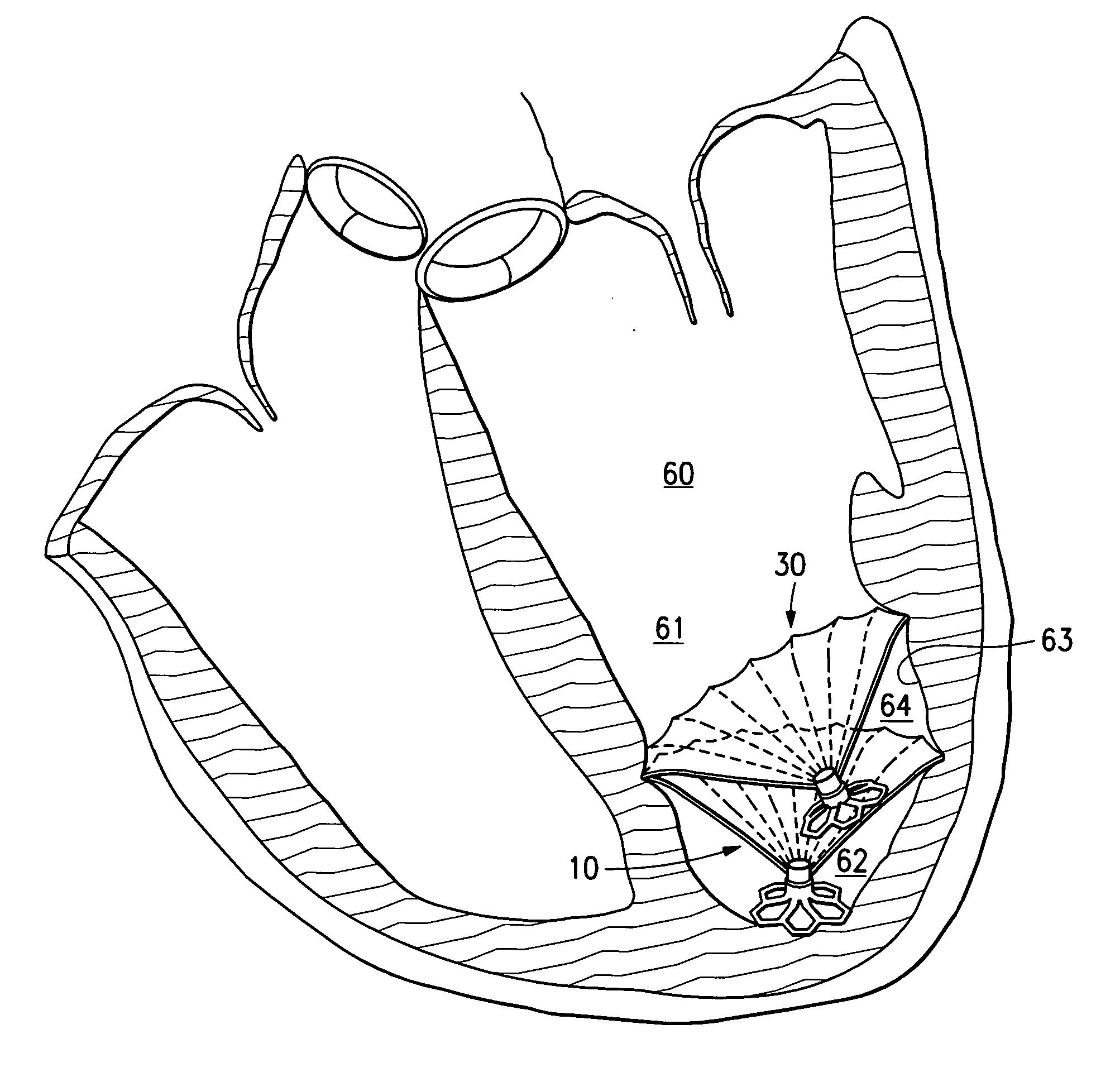
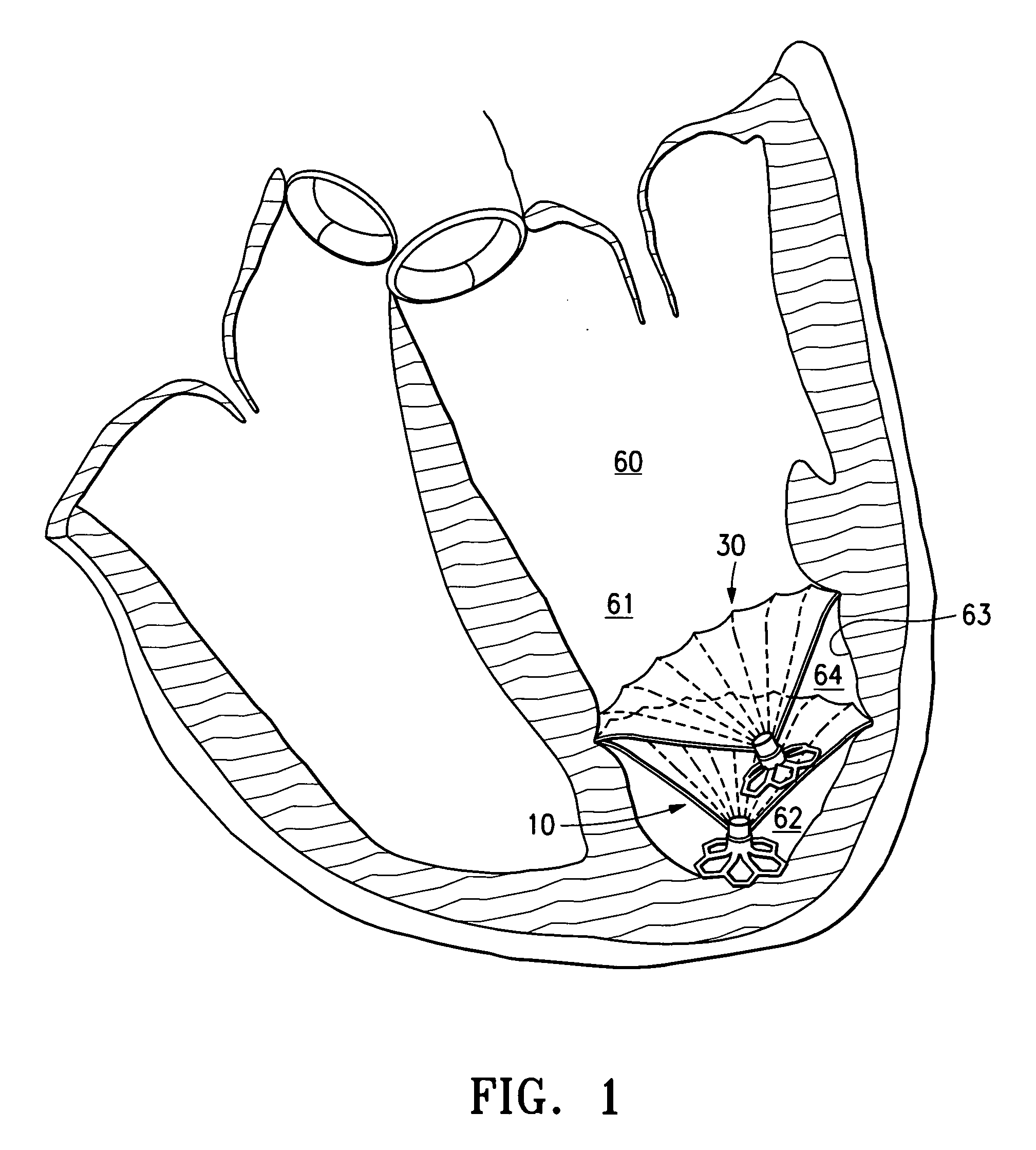
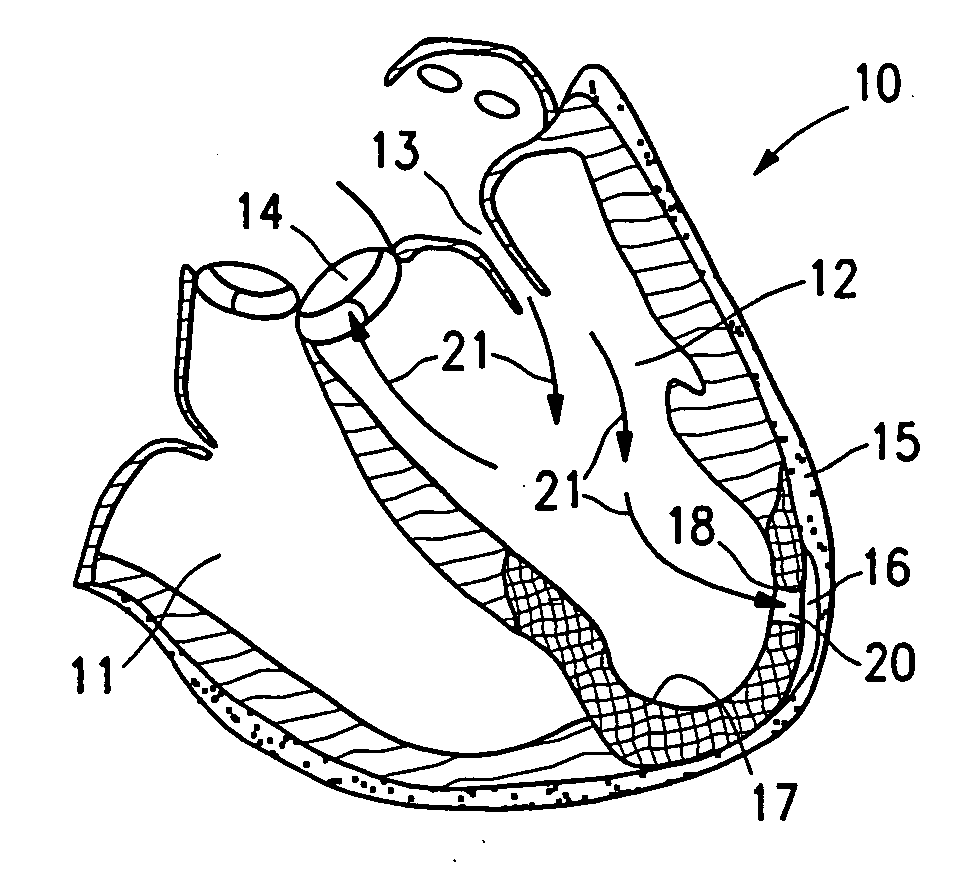
This invention is directed to a system and method for partitioning a patient's heart chamber into a productive portion and a non-productive portion which are particularly suitable for treating patients with congestive heart failure. The partitioning system has a plurality of partitioning devices with reinforced, expandable membranes which separate the productive and non-productive portions of the heart chamber. When deployed within the patient's heart chamber, the second partitioning device is off-set from the deployed first partitioning device to cover a region of the wall defining the patient's heart chamber which is not covered by the first partitioning device. The multiple partitioning devices may be independent from each other or may be interconnected, e.g. a tether or strand.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Method for treating myocardial rupture
InactiveUS20060229491A1Avoid Insufficient SealingImprove sealingOcculdersSuction devicesHeart chamberCardiac muscle
A method and device for the treatment of a patient with heart disease and particularly a heart chamber having a myocardial rupture or characteristics of an incipient myocardial rupture. The heart chamber is partitioned so as to isolate a non-productive portion having a rupture or a region of an incipient rupture from a productive portion. The heart chamber is preferably partitioned with a reinforced membrane which has a pressure receiving surface that defines part of the productive portion of the heart chamber. The peripheral base of the reinforced membrane may have an eccentric configuration.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Peripheral seal for a ventricular partitioning device
ActiveUS20060281965A1Lower the volumeImprove ejection fractionHeart stimulatorsOcculdersHeart chamberCongestive heart failure chf
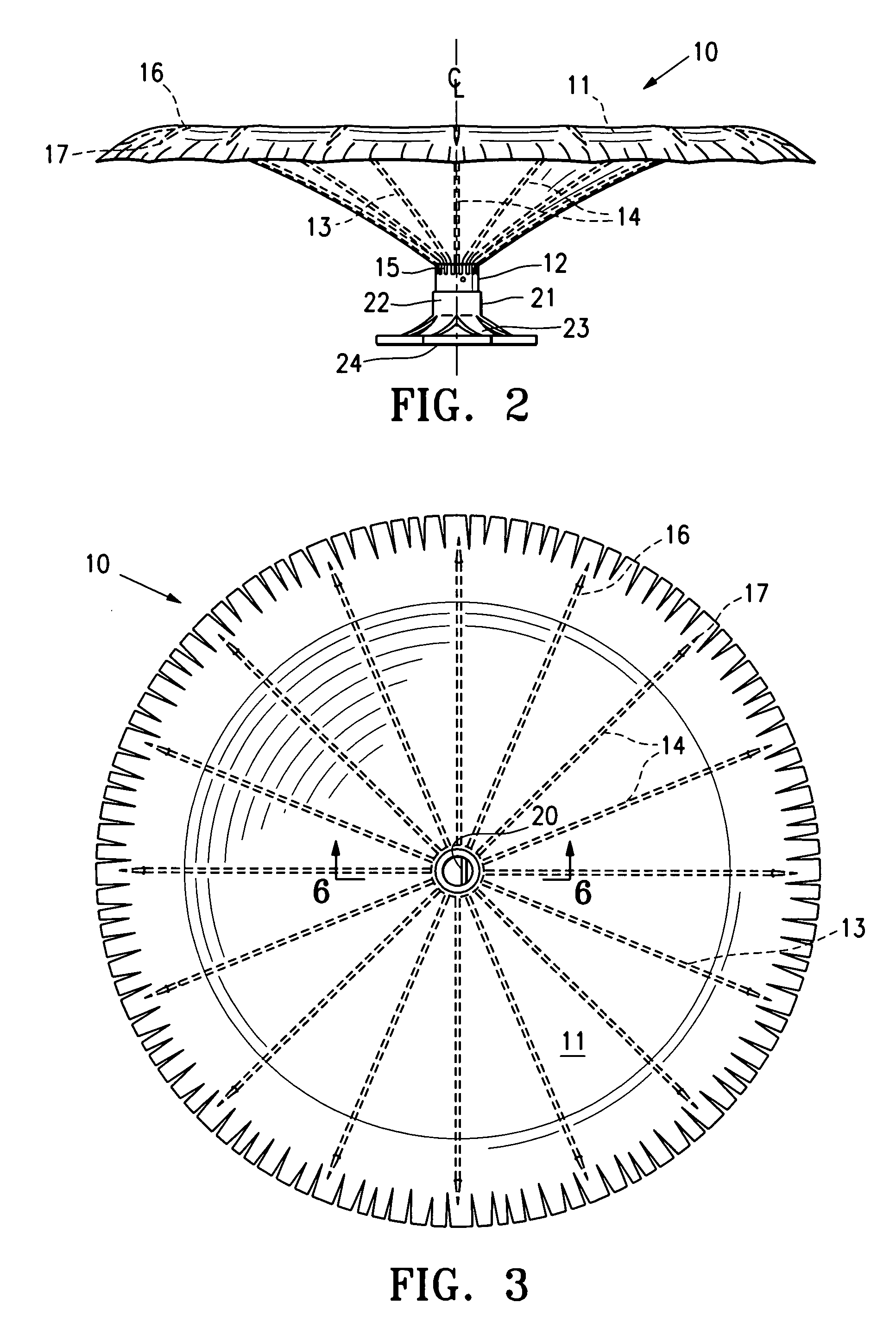
This invention is directed to a partitioning device for separating a patient's heart chamber into a productive portion and a non-productive portion which is suitable for treating patients with heart disease, particularly congestive heart failure. The partitioning device has a reinforced membrane with outwardly biased members to help seal the periphery of the membrane against the wall of the patient's heart chamber. In one embodiment, the outwardly biased member is an expansive strand that extends between adjacent ribs of an expandable frame which reinforces the membrane. In another embodiment, the outwardly biased member is a hydrophilic body such as foam which swells upon contact with body fluid such as blood in the heart chamber. The reinforced membrane has a central hub with a distally extending support stem with a plurality of feet which extend radially from a centerline axis and preferably have ends that are aligned in a common plane. The ends of the pods which extend radially away from the centerline axis may be interconnected by flexible struts and / or webs.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Methods and devices for bypassing an obstructed target vessel by placing the vessel in communication with a heart chamber containing blood
Methods and devices for forming an anastomosis during a bypass procedure utilize a graft vessel secured to a vessel coupling adapted to be fixed to a target vessel without using suture. The graft vessel is placed in fluid communication with a heart chamber containing blood. The vessel coupling may be collapsed for introduction into the target vessel and then expanded to fix the coupling thereto. The vessel coupling may be a stent with the graft vessel secured thereto to form a stent-graft assembly. The anastomosis is carried out to place the graft and target vessels in fluid communication while preserving native proximal flow through the target vessel, which may be a coronary artery. As a result, blood flowing from the aorta and past an obstruction in the coronary artery is not blocked by formation of the anastomosis; rather, such proximal blood flow is free to move past the vessel coupling and the anastomosis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and system for ablation of atrial fibrillation and other cardiac arrhythmias
InactiveUS20060009755A1TomographySurgical instruments for heatingRadio frequency energyDigital imaging
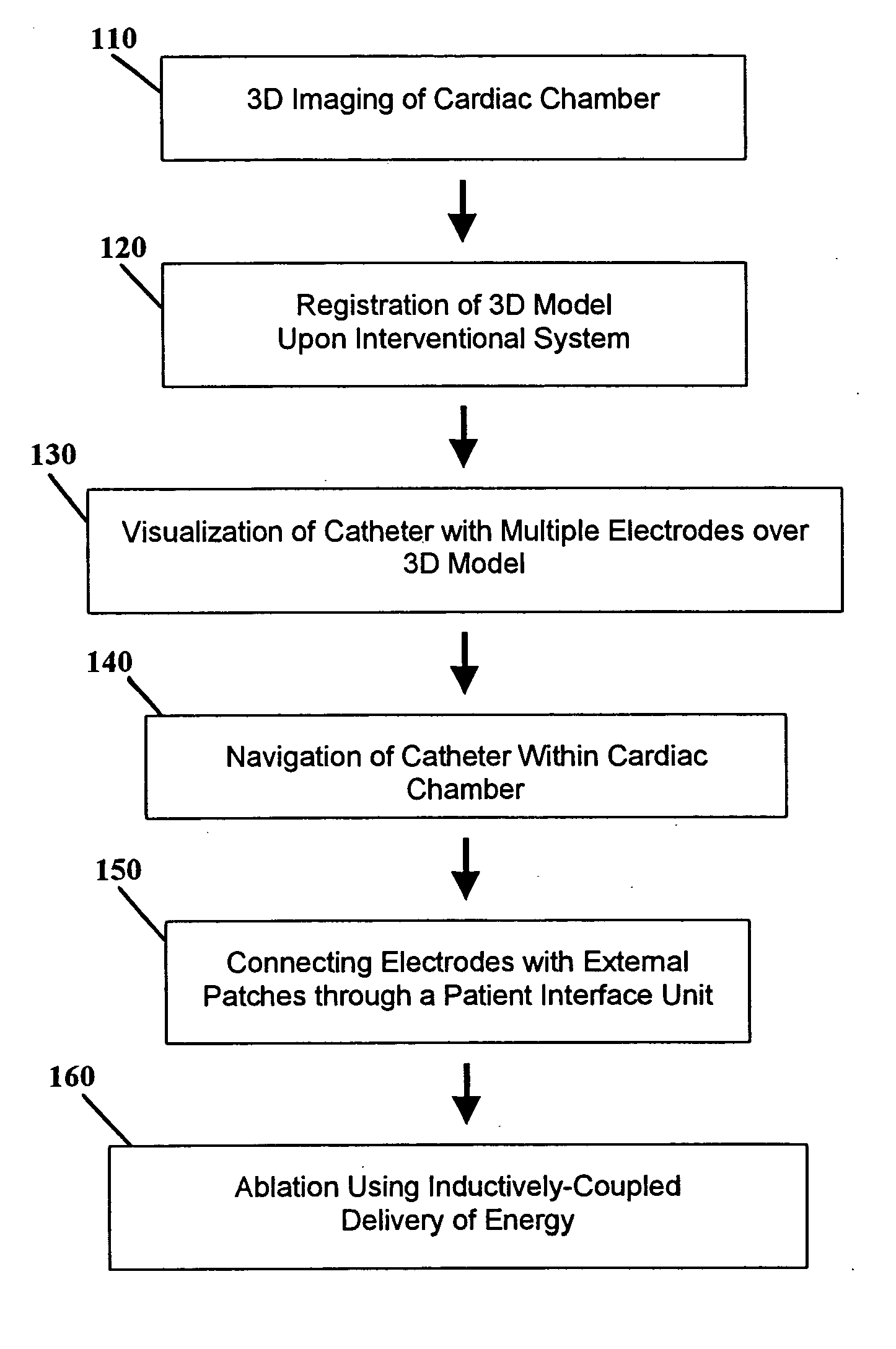
A method is provided for ablation in treatment of heart arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation that includes positioning a catheter apparatus with multiple electrodes within a cardiac chamber, visualizing the catheter apparatus with an interventional system, navigating the catheter apparatus within the cardiac chamber, and delivering energy to selected electrodes of the catheter apparatus from an external source to ablate heart tissue at select locations. Preferably, the external source is an external patch placed on the patient for the delivery of radio-frequency energy. The electrodes of the catheter apparatus are connected to the patch through a patient interface unit where the interface unit selects the electrodes to which radio-frequency energy is to be delivered. In another aspect of the invention, a system for ablation of heart arrhythmias is provided that has a catheter apparatus with multiple electrodes, an interventional system for visualizing the catheter apparatus within a cardiac chamber, and an external source for delivering energy to selected electrodes of the catheter apparatus within the cardiac chamber to ablate heart tissue. Preferably, the system further includes a digital imaging system for obtaining cardiac image data, an image generation system for generating a 3D model of the cardiac chamber from the cardiac image data, and a workstation for registering the 3D model with the interventional system and for visualizing the catheter apparatus over this registered 3D model upon the interventional system.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
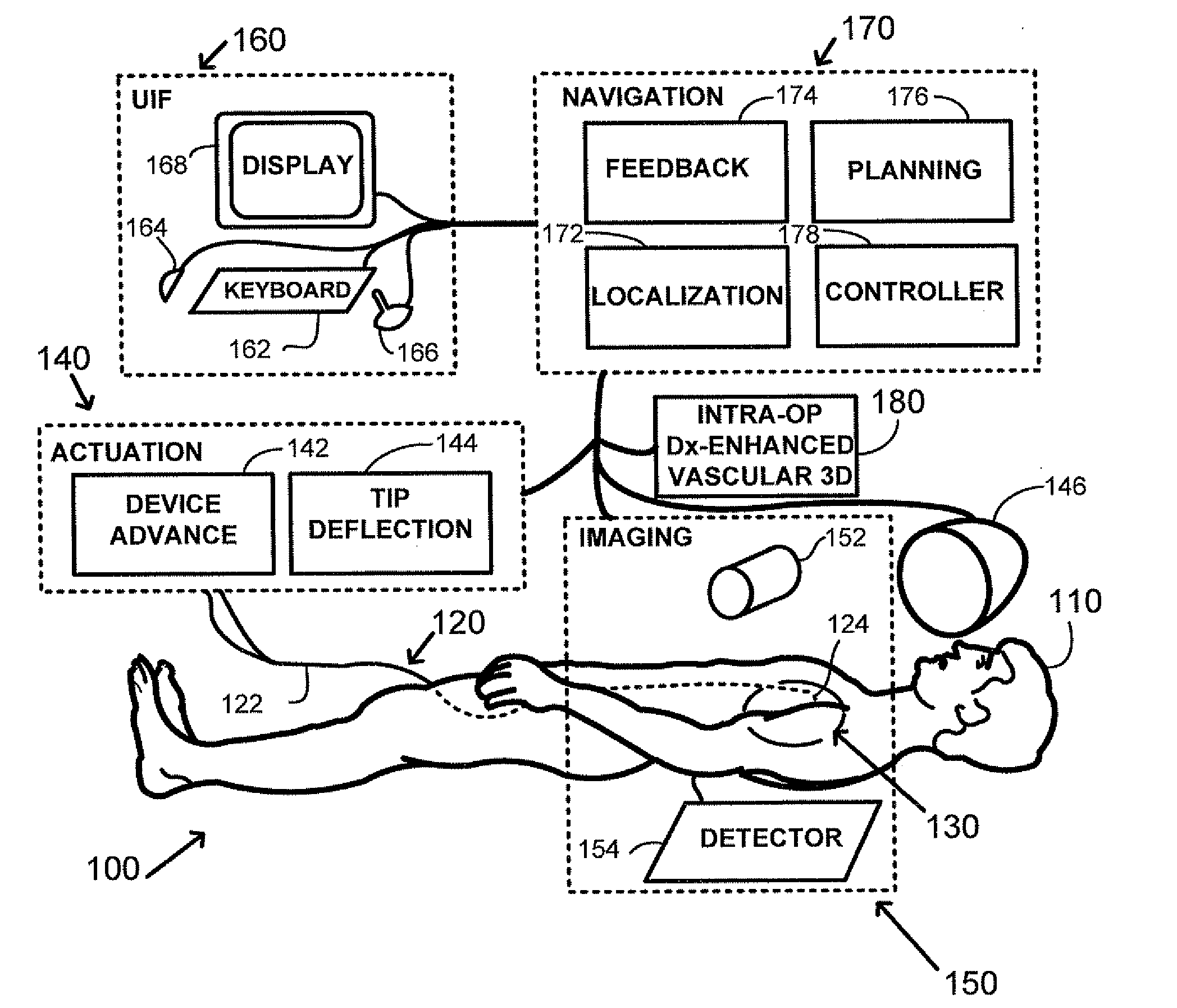
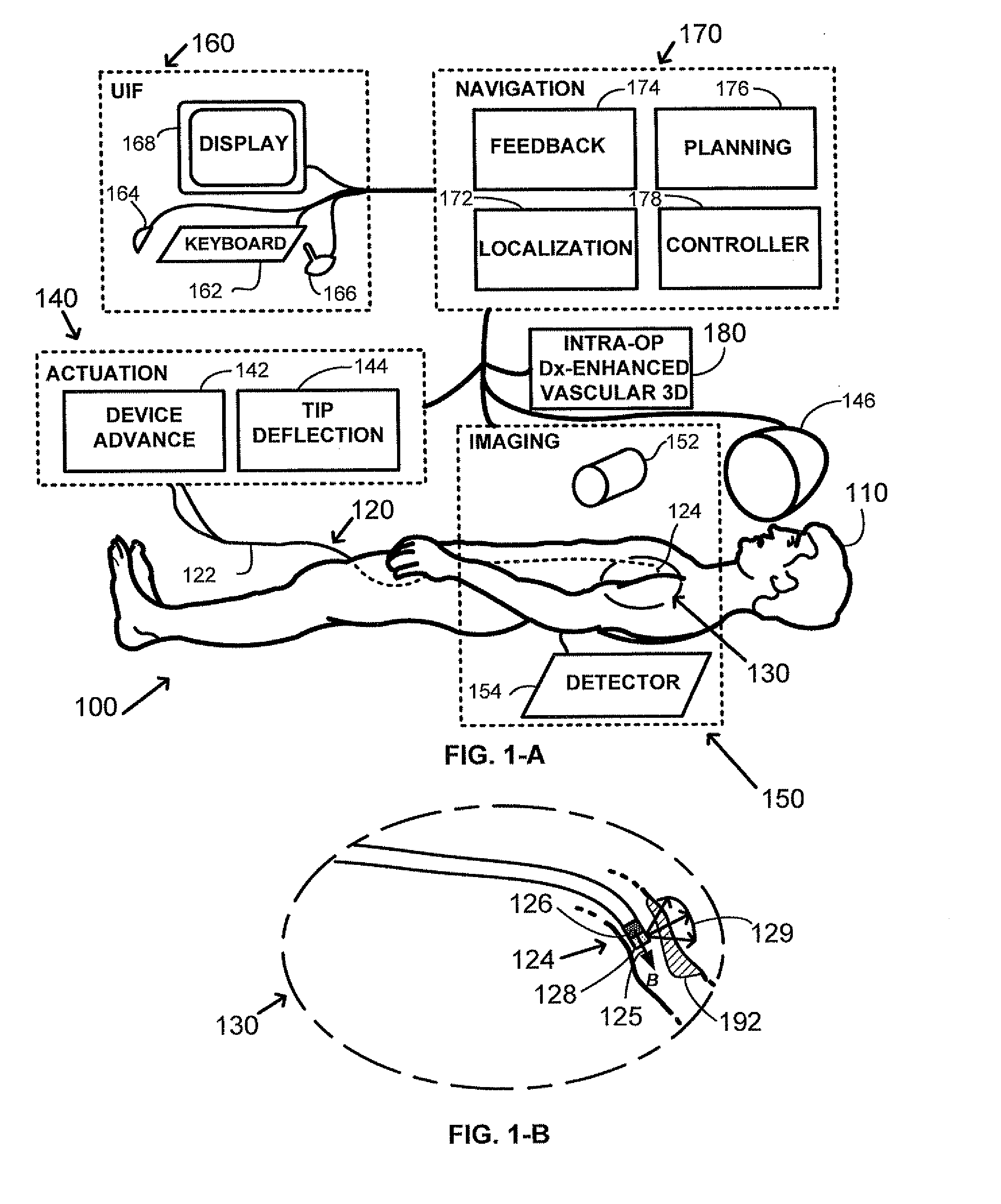
Method and apparatus for remotely controlled navigation using diagnostically enhanced intra-operative three-dimensional image data
InactiveUS20090105579A1Effective diagnosisUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementVascular diseaseRadiology
A method of performing intra-operative three-dimensional imaging and registering diagnostic functional information to the three-dimensional anatomical data is introduced. The availability of co-registered diagnostic information to intra-operative data enables fast and efficient navigation to pre-selected target areas, and allows automatic or semi-automatic treatment of cardiac cavity or vascular disease.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
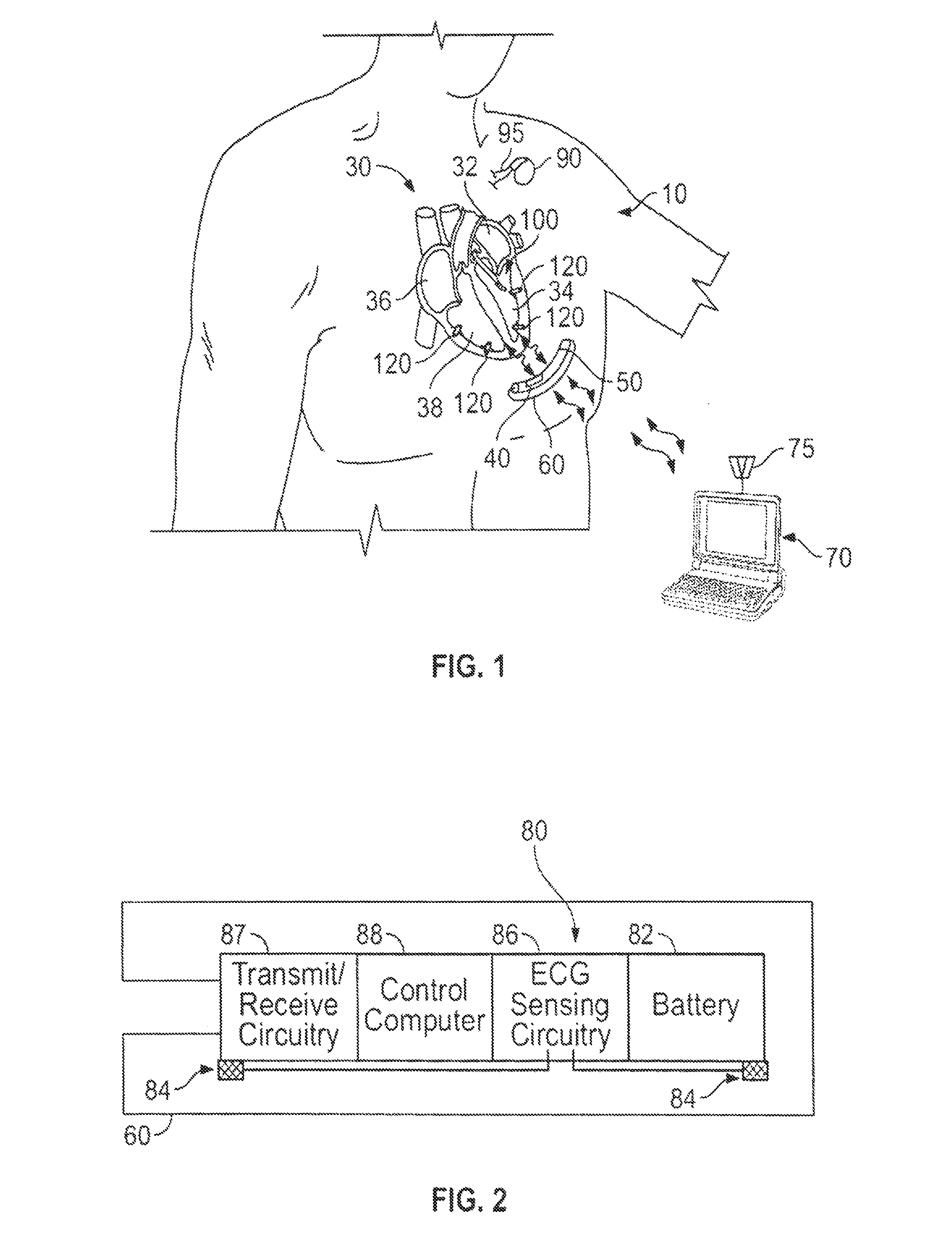
Leadless intra-cardiac medical device with dual chamber sensing through electrical and/or mechanical sensing
ActiveUS8996109B2Small sizeConvenient to accommodateElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsCardiac activityRight atrium
A leadless intra-cardiac medical device senses cardiac activity from multiple chambers and applies cardiac stimulation to at least one cardiac chamber and / or generates a cardiac diagnostic indication. The leadless device may be implanted in a local cardiac chamber (e.g., the right ventricle) and detect near-field signals from that chamber as well as far-field signals from an adjacent chamber (e.g., the right atrium).
Owner:PACESETTER INC
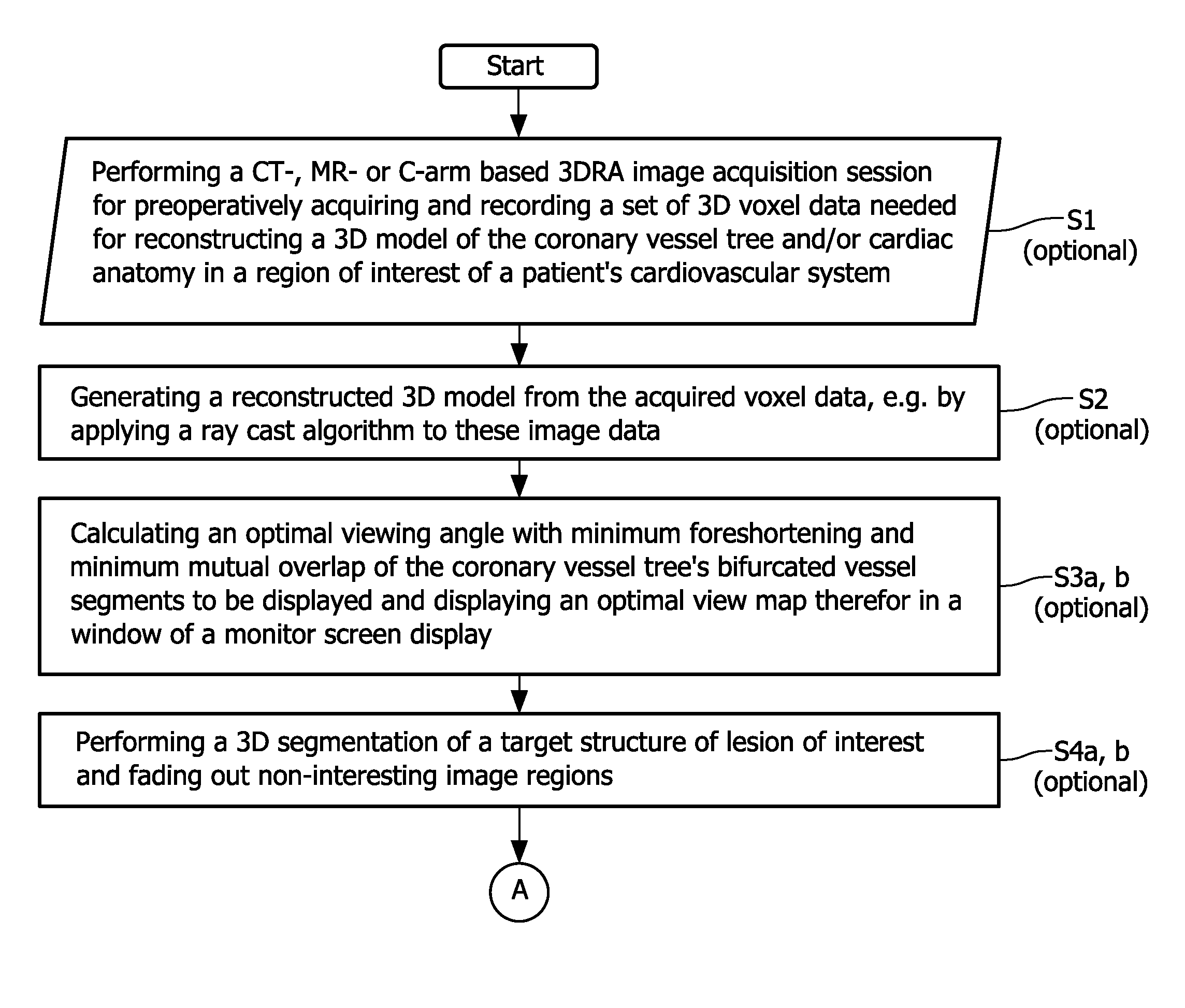
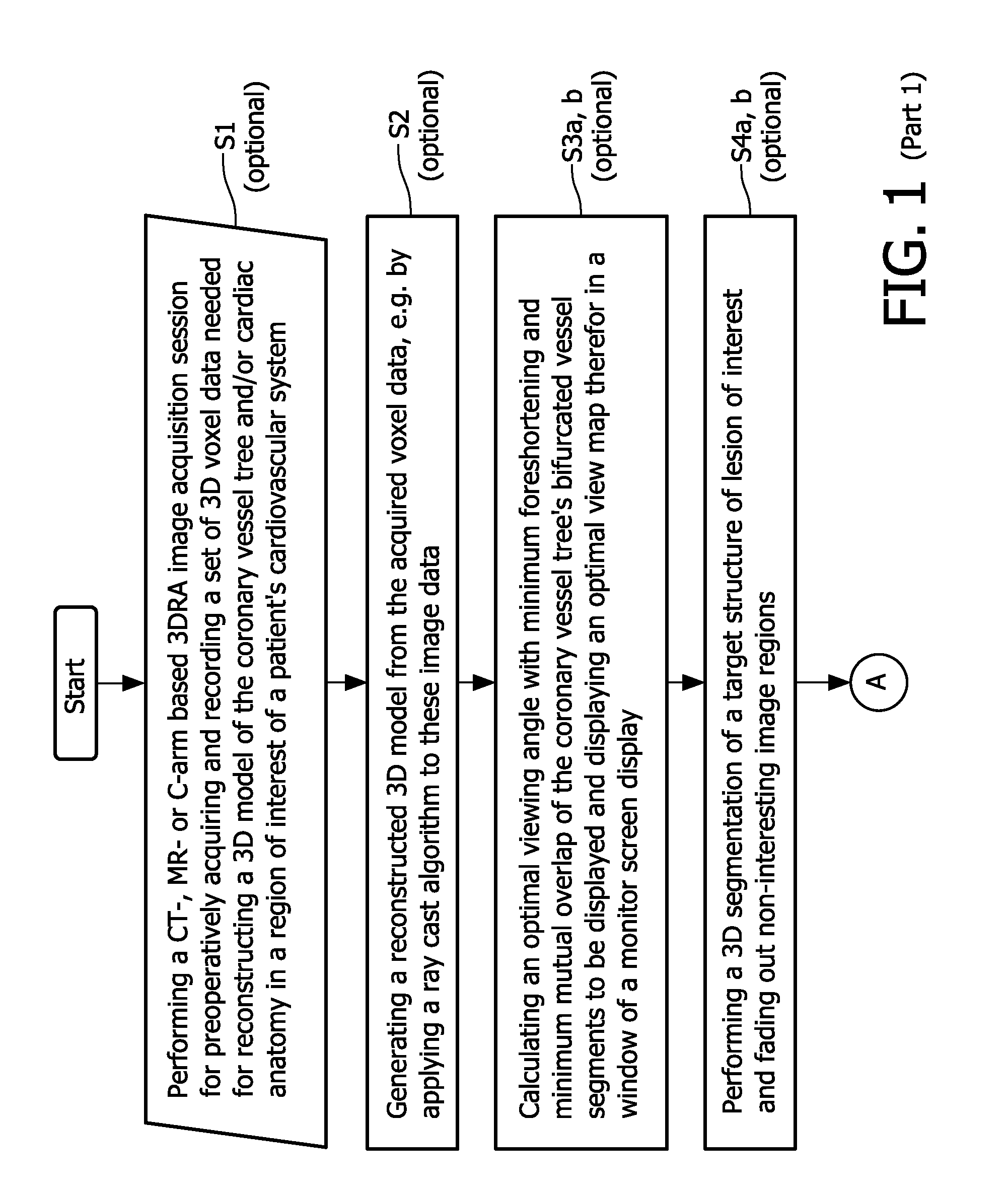
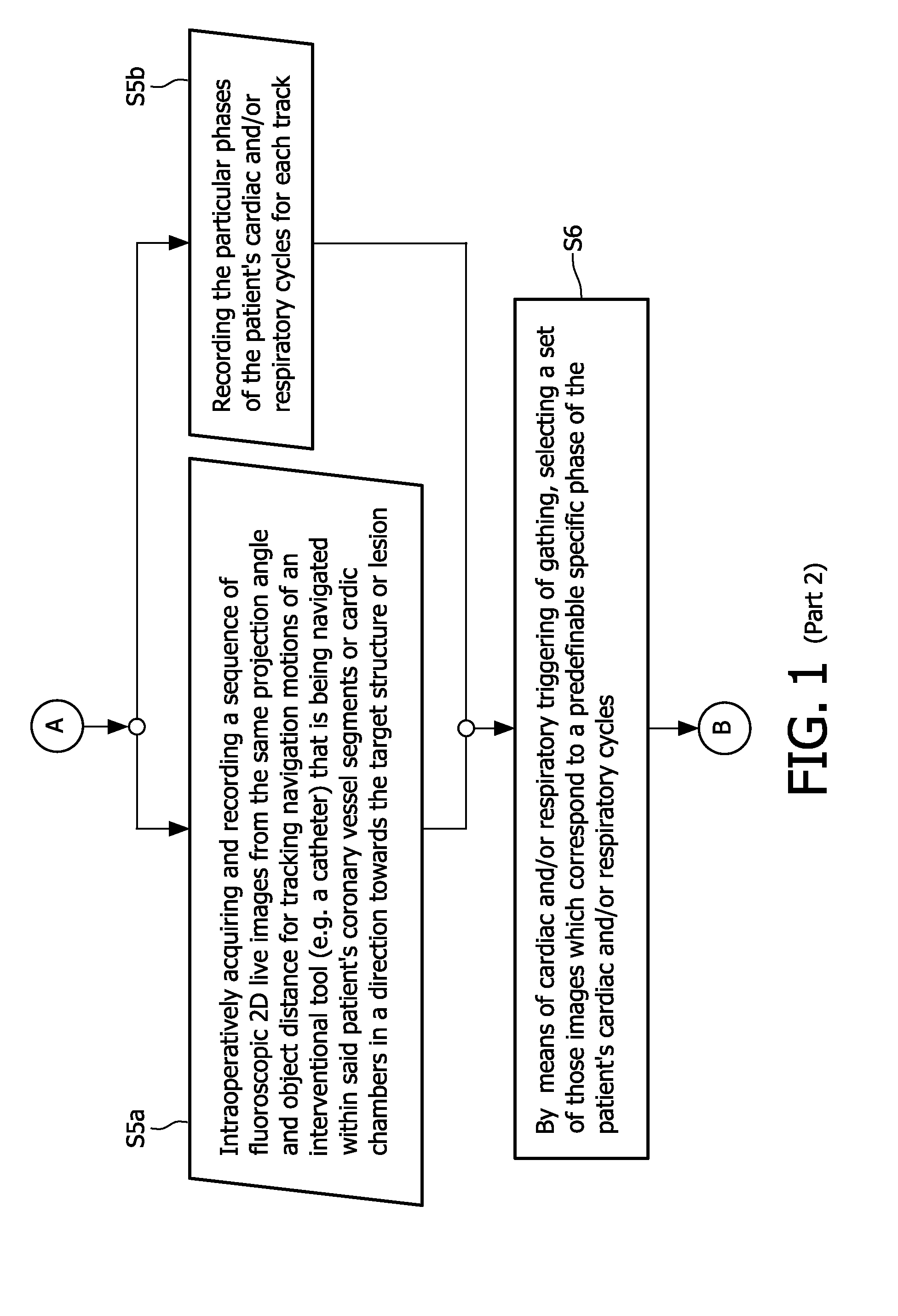
Cardiac and or respiratory gated image acquisition system and method for virtual anatomy enriched real time 2d imaging in interventional radiofrequency ablation or pace maker replacement procecure
ActiveUS20110201915A1Improve accuracyReduce inaccuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyCardiac pacemaker electrodePacemaker Placement
The present invention refers to the field of cardiac electrophysiology (EP) and, more specifically, to image-guided radio frequency ablation and pacemaker placement procedures. For those procedures, it is proposed to display the overlaid 2D navigation motions of an interventional tool intraoperatively obtained from the same projection angle for tracking navigation motions of an interventional tool during an image-guided intervention procedure while being navigated through a patient's bifurcated coronary vessel or cardiac chambers anatomy in order to guide e.g. a cardiovascular catheter to a target structure or lesion in a cardiac vessel segment of the patient's coronary venous tree or to a region of interest within the myocard. In such a way, a dynamically enriched 2D reconstruction of the patient's anatomy is obtained while moving the interventional instrument. By applying a cardiac and / or respiratory gating technique, it can be provided that the 2D live images are acquired during the same phases of the patient's cardiac and / or respiratory cycles. Compared to prior-art solutions which are based on a registration and fusion of image data independently acquired by two distinct imaging modalities, the accuracy of the two-dimensionally reconstructed anatomy is significantly enhanced.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Methods and devices for improving mitral valve function
InactiveUS20060241340A1Function increaseSuture equipmentsHeart valvesMitral valve functionHeart chamber
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Endocardial mapping catheter
A mapping catheter is described to map electric field activity in a heart chamber. The catheter has a first grouping of electrodes positioned so that they are not in contact with the patient's heart. The catheter also having a second set of electrodes positioned in contact with the patient's heart.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
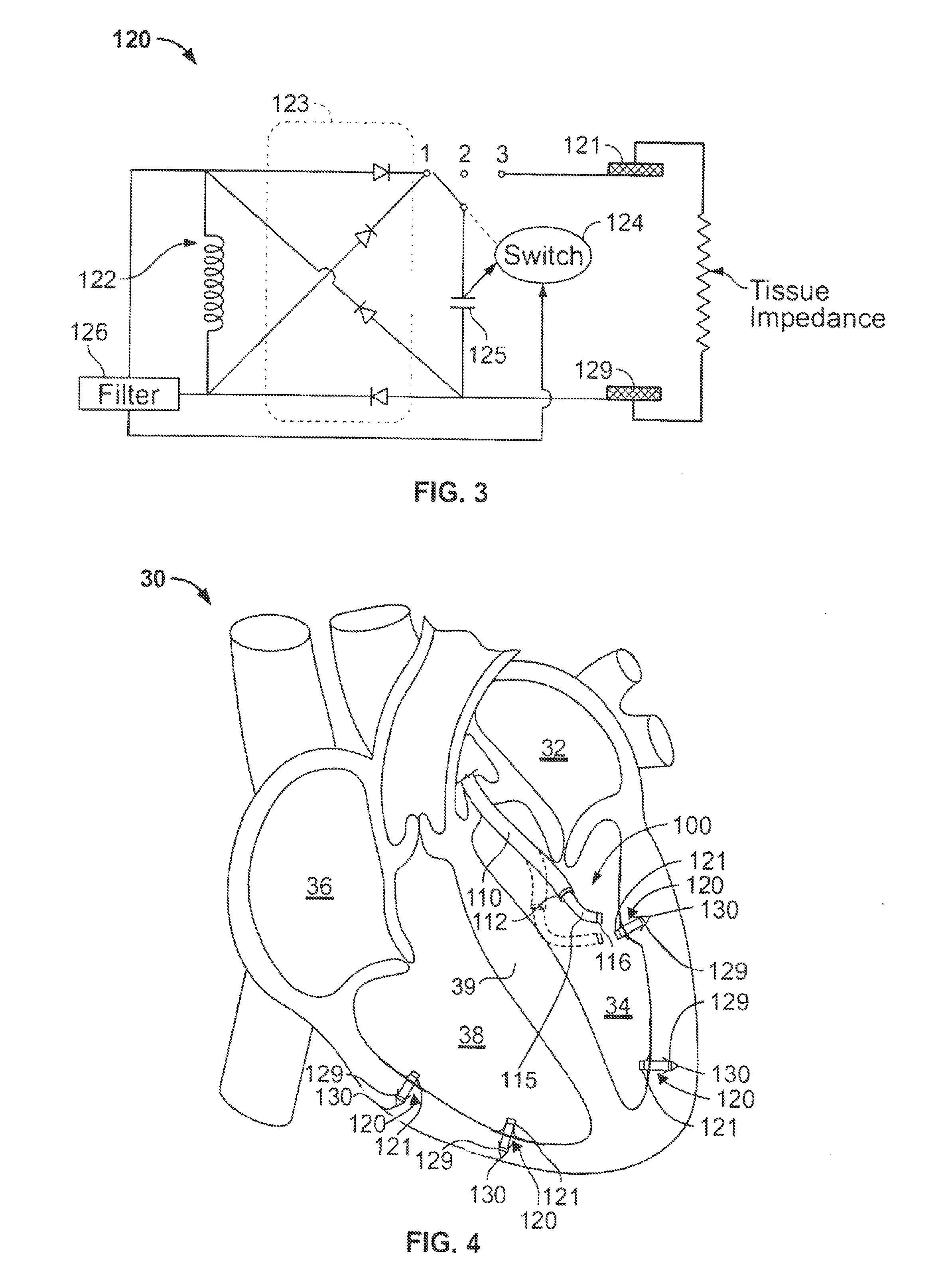
Cardiac stimulation system
ActiveUS20140039591A1Reduced effectivenessReduce injuriesEpicardial electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringHeart chamberEngineering
Some embodiments of pacing systems employ wireless electrode assemblies to provide pacing therapy. The wireless electrode assemblies may wirelessly receive energy via an inductive coupling so as to provide electrical stimulation to the surrounding heart tissue. In certain embodiments, the wireless electrode assembly may include one or more biased tines that shift from a first position to a second position to secure the wireless electrode assembly into the inner wall of the heart chamber.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
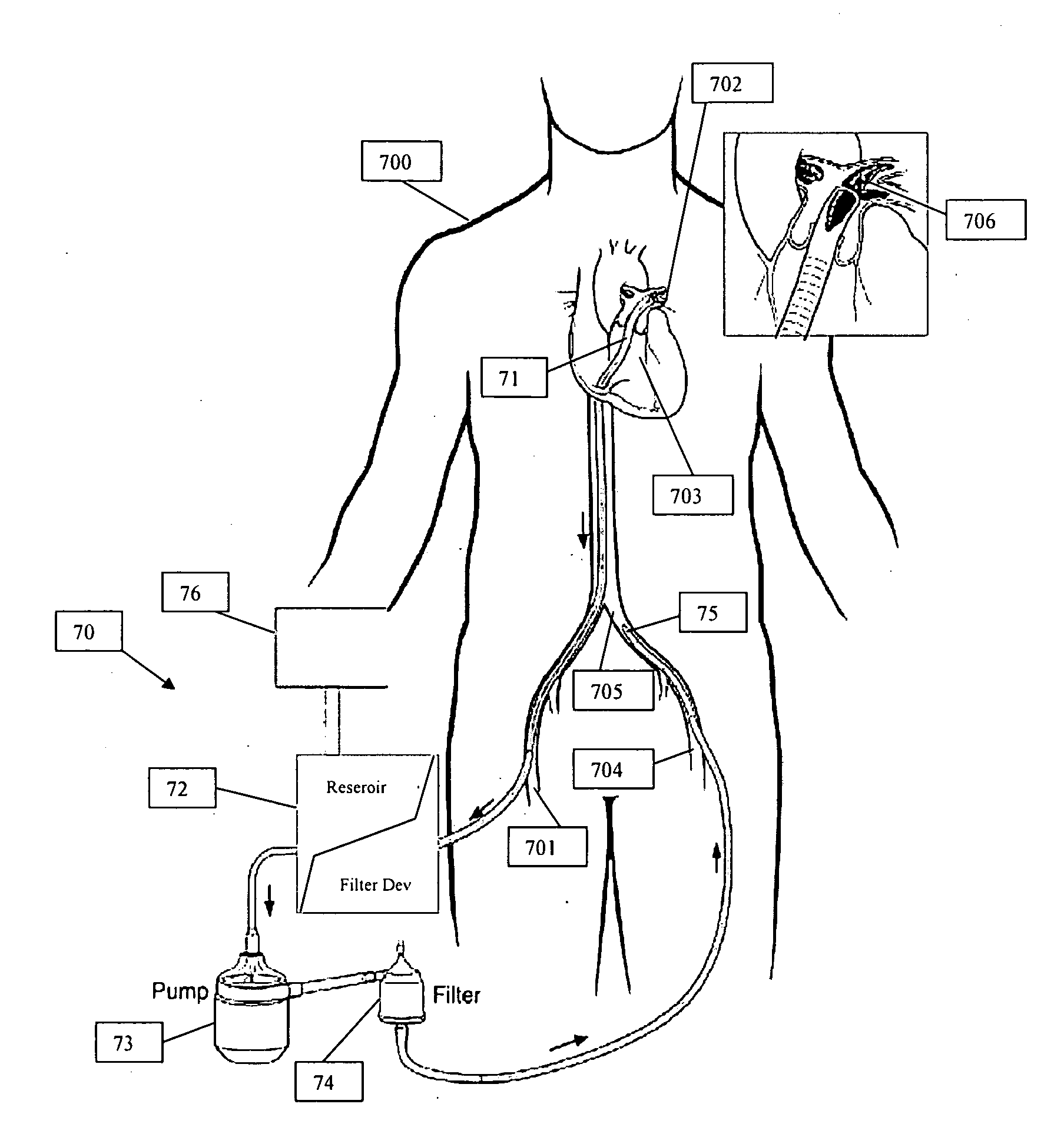
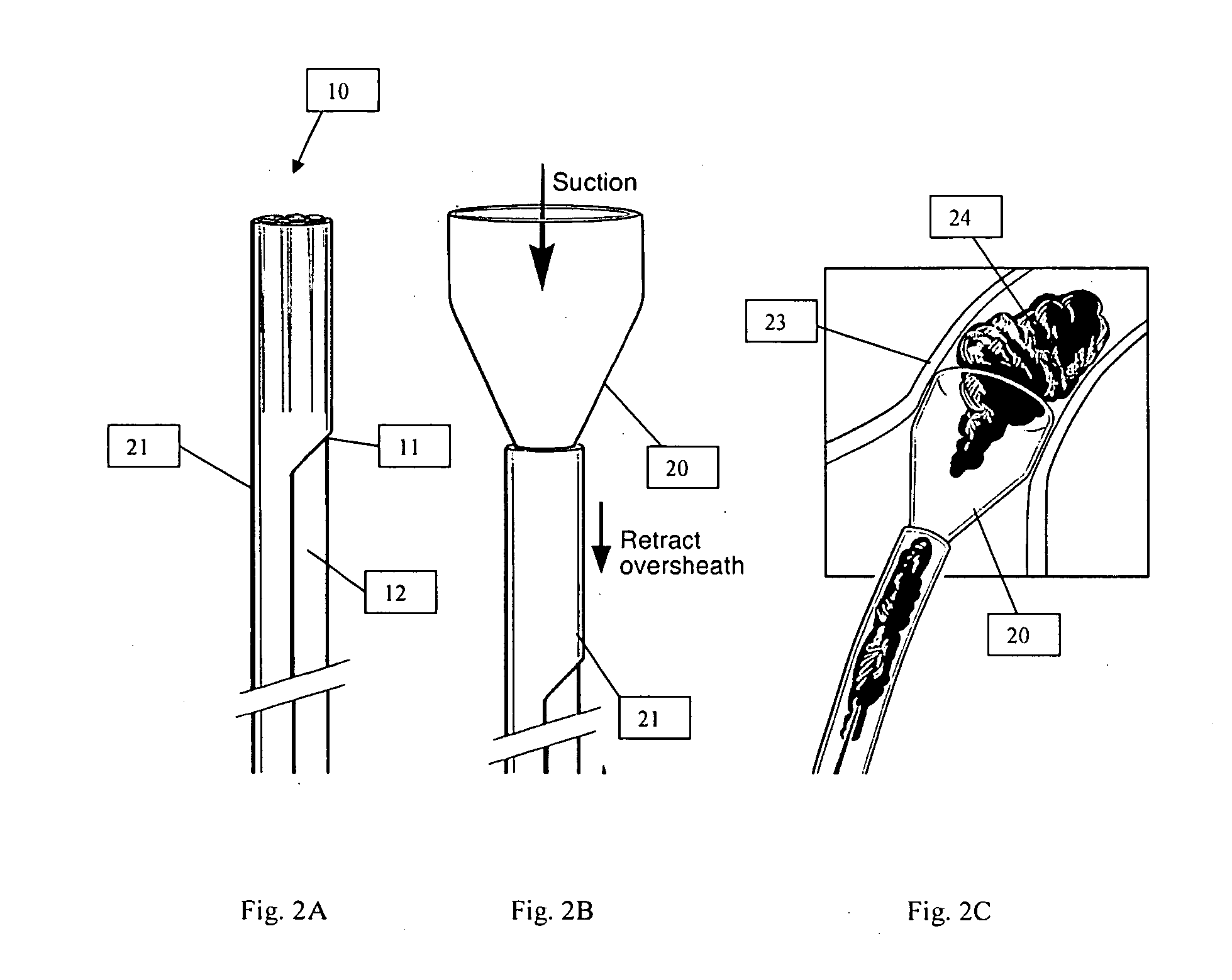
Systems and methods for removing undesirable material within a circulatory system
ActiveUS20090163846A1Without excessive fluid lossOccurrence of loss and shockHaemofiltrationDilatorsSuction forceHeart chamber
A system for removing undesirable material from vessels and from chambers within the heart is provided. The system includes a suction cannula for removing the undesirable material from a site of interest within a patient. A filter device may be provided for capturing the undesirable material and removing it from the fluid flow. The system also includes pump for generating the necessary suction force through the suction cannula to dislodge the undesirable material from the site of interest and for generating a sufficient driving force to direct the fluid flow downstream within the system. The system further includes a reinfusion cannula for introducing fluid removed from the site of interest back into a patient. A method for removing undesirable material from vessels and from heart chambers is also provided.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
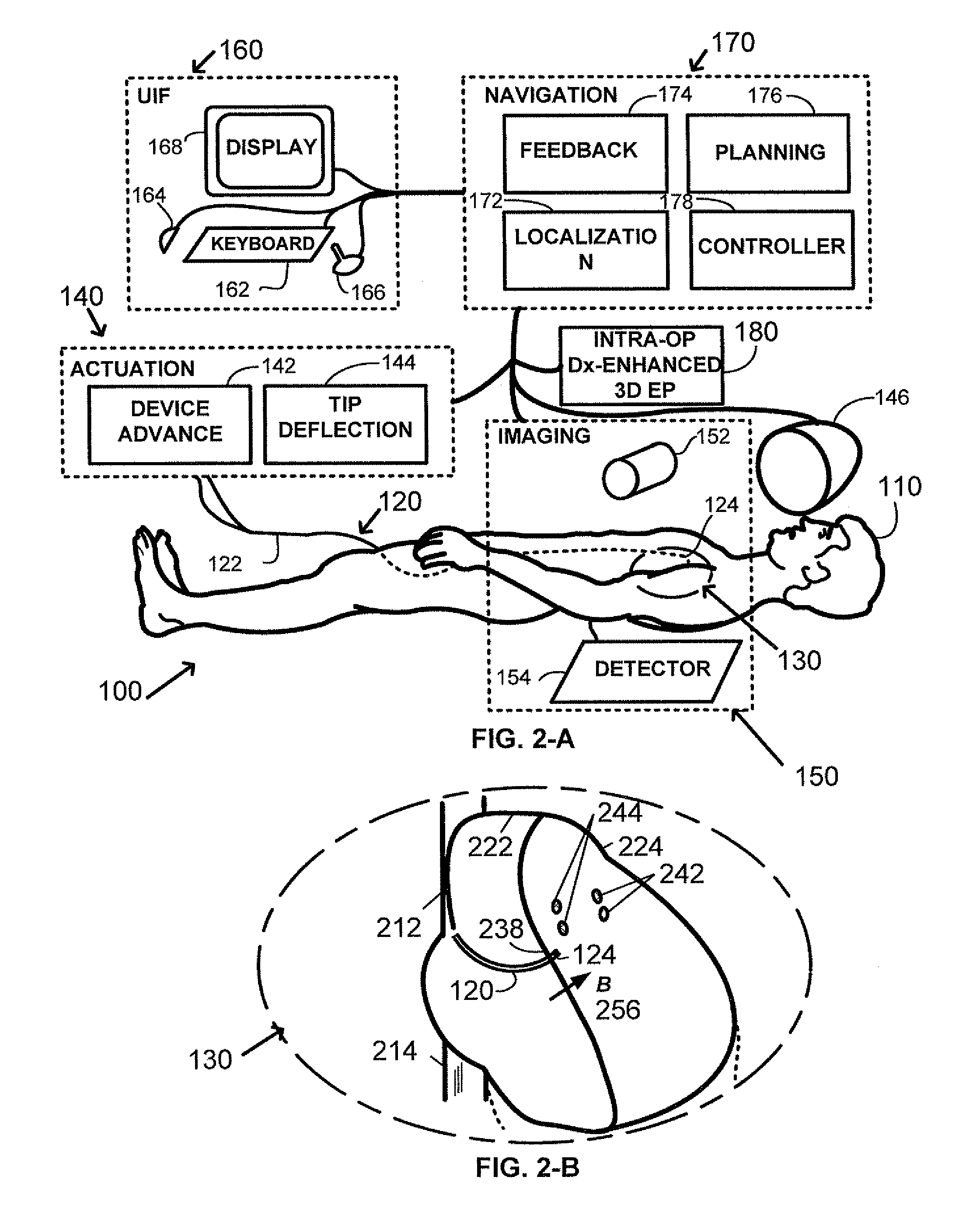
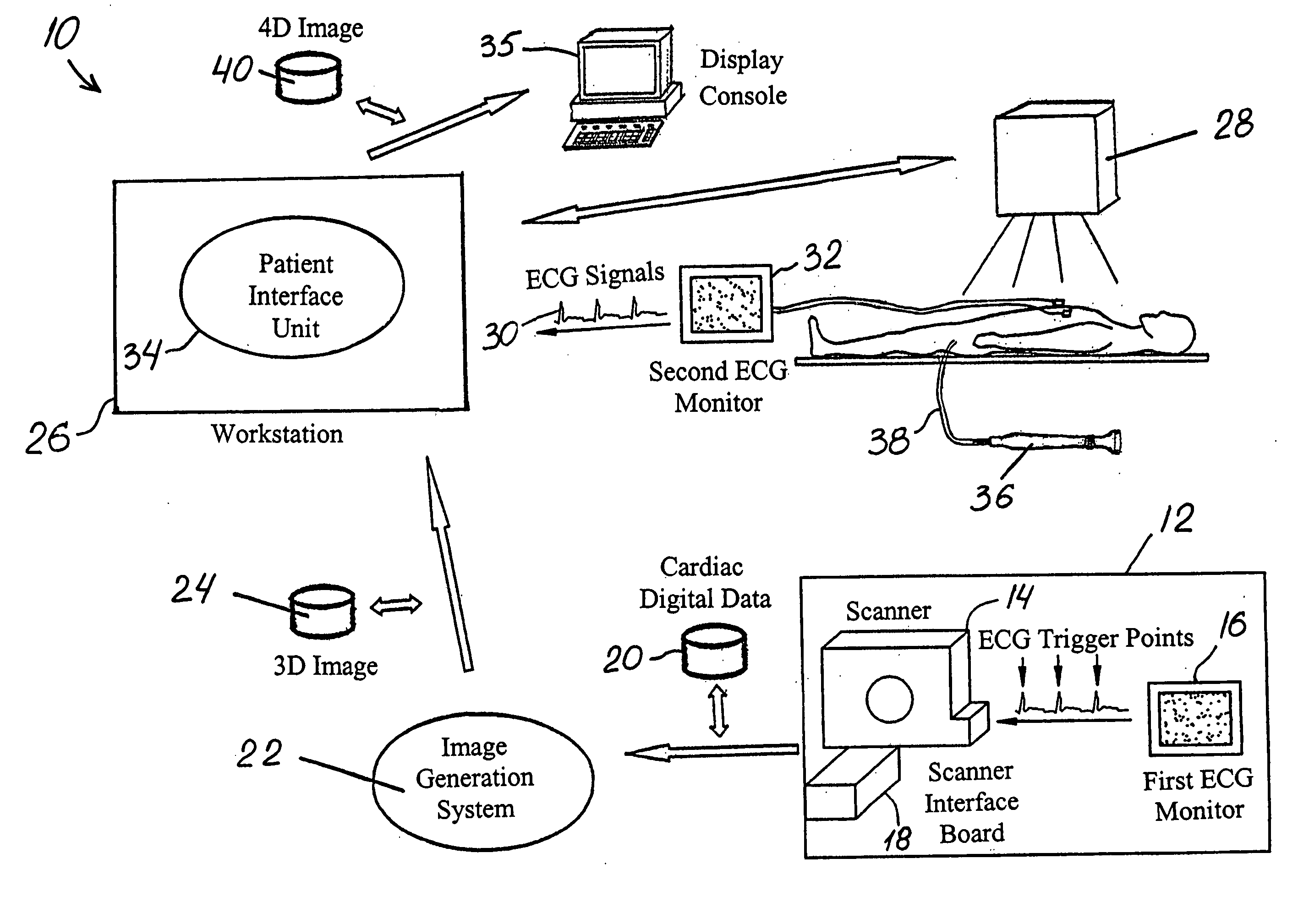
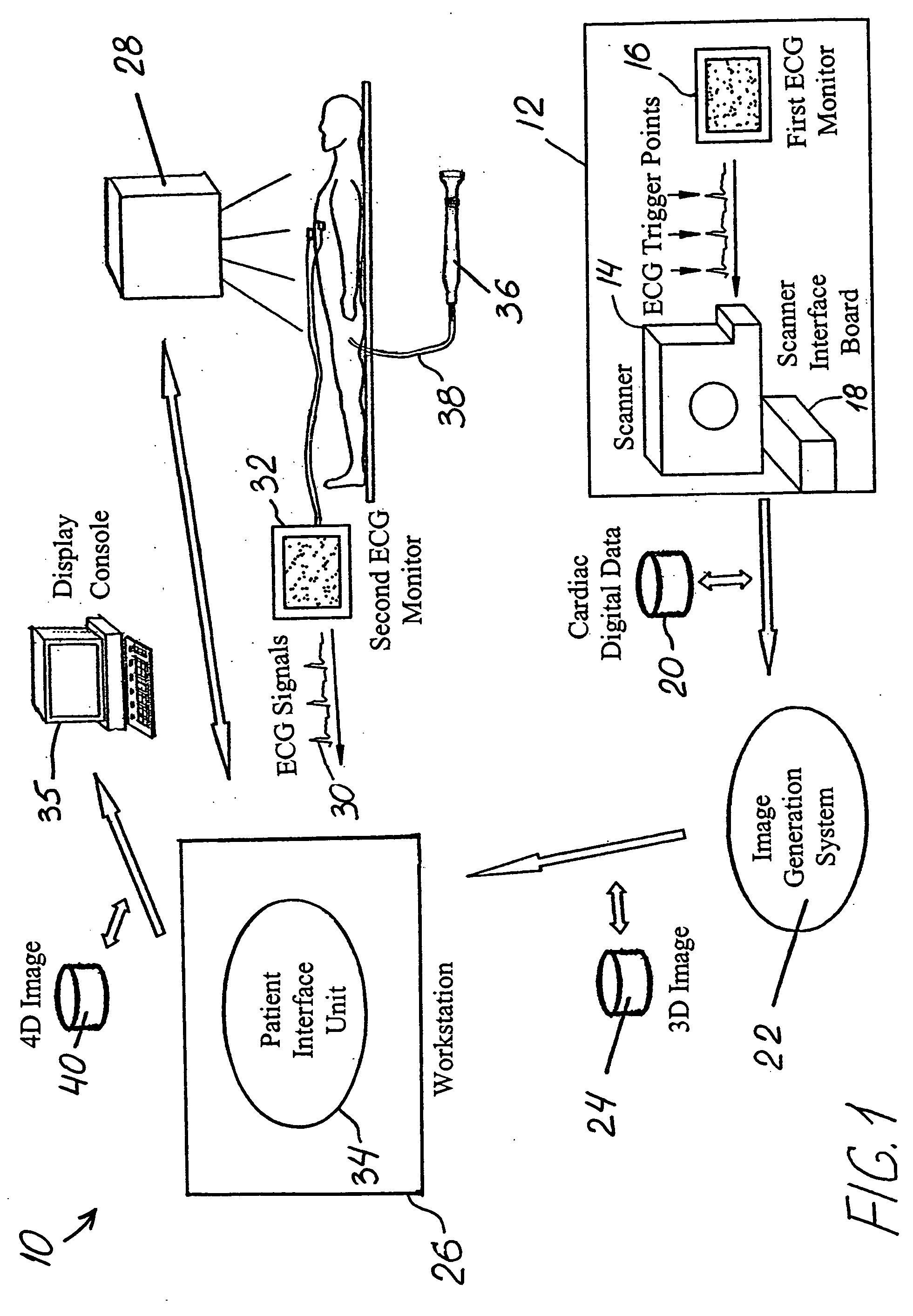
Method and system of treatment of cardiac arrhythmias using 4D imaging
InactiveUS20050137661A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyDigital dataEcg signal
A method is provided for treating a heart arrhythmia having the steps of obtaining cardiac digital data from a medical imaging system utilizing an ECG gated protocol; generating a series of 3D images of a cardiac chamber and its surrounding structures, preferably the left atrium and pulmonary veins, from this cardiac digital data at select ECG trigger points that correspond to different phases of the cardiac cycle; registering these 3D images with an interventional system; acquiring ECG signals from the patient in real-time; transmitting these ECG signals to the interventional system; synchronizing the registered 3D images with trigger points on the transmitted ECG signals to generate a 4D image; visualizing this 4D image upon the interventional system in real-time; visualizing a catheter over the 4D image upon the interventional system; navigating the catheter within the cardiac chamber utilizing the 4D image; and using the catheter to treat the cardiac chamber, preferably with ablation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus, system, and method for treating a regurgitant heart valve
An apparatus for treating regurgitation of blood through a diseased heart valve having at least two leaflets includes a lollipop-shaped body member having a proximal end portion, a distal end portion, and an intermediate portion extending between the end portions. The intermediate portion includes an expandable occluding member having an adjustable diameter so that, during at least a portion of the cardiac cycle, at least one of the heart leaflet coapts with a portion of the occluding member to mitigate or prevent regurgitation of blood through the diseased heart valve. The proximal end portion is physically connected to the occluding member and includes a connecting mechanism for operably mating with an adjustment member for adjusting the position and diameter of the occluding member within the diseased heart valve. The distal end portion includes an anchoring member for securing the apparatus in a heart chamber containing the diseased heart valve.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
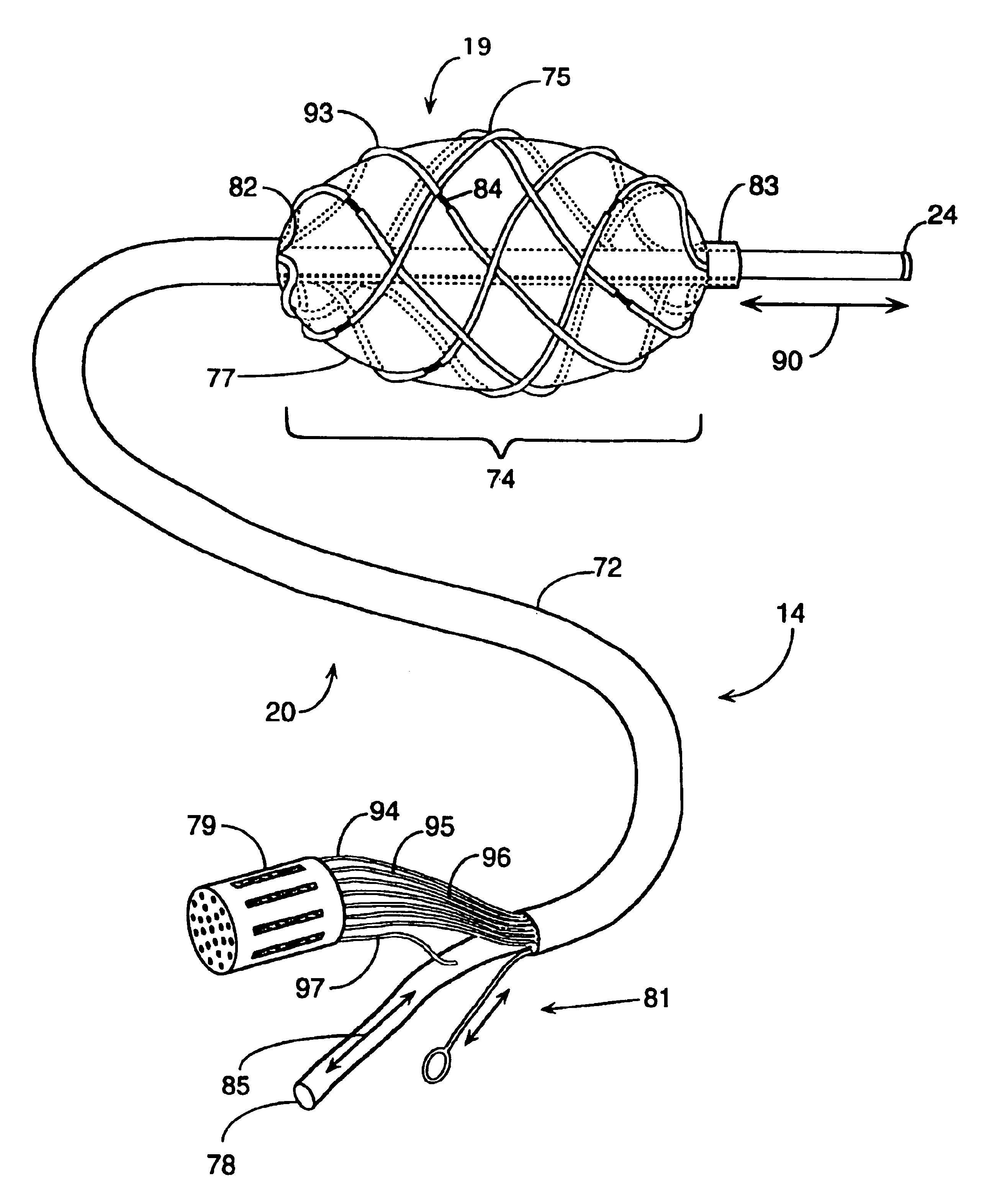
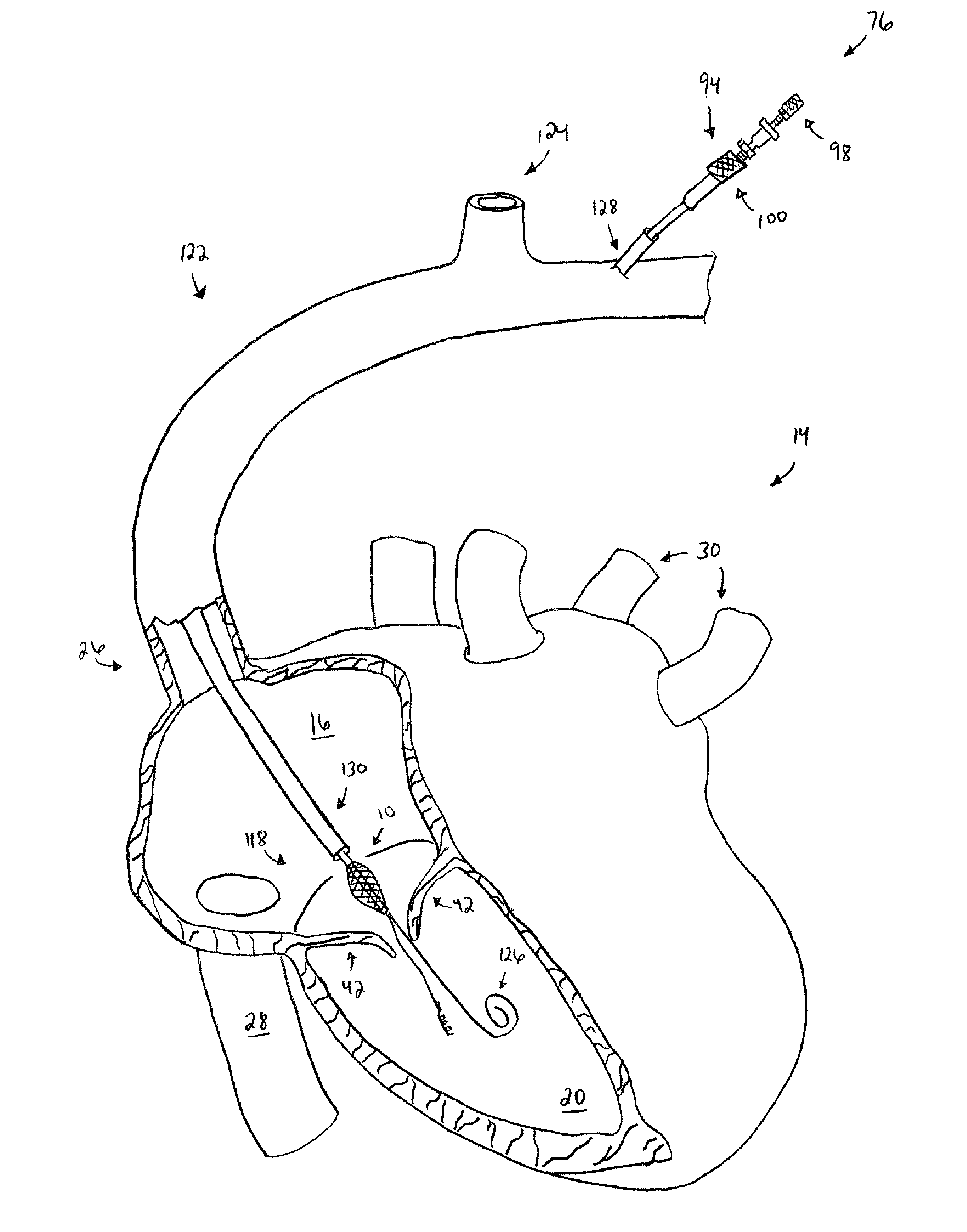
Splint assembly for improving cardiac function in hearts, and method for implanting the splint assembly
InactiveUS20060149123A1Reduce tensionReduce consumptionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesHeart chamberCardiac wall
A splint assembly for placement transverse a heart chamber to reduce the heart chamber radius and improve cardiac function has a tension member formed of a braided cable with a covering. A fixed anchor assembly is attached to one end of the tension member and a leader for penetrating a heart wall and guiding the tension member through the heart is attached to the other end. An adjustable anchor assembly can be secured onto the tension member opposite to the side on which the fixed pad assembly is attached. The adjustable anchor assembly can be positioned along the tension member so as to adjust the length of the tension member extending between the fixed and adjustable anchor assemblies. The pad assemblies engage with the outside of the heart wall to hold the tension member in place transverse the heart chamber. A probe and marker delivery device is used to identify locations on the heart wall to place the splint assembly such that it will not interfere with internal heart structures. The device delivers a marker to these locations on the heart wall for both visual and tactile identification during implantation of the splint assembly in the heart.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Method and system for treatment of atrial fibrillation and other cardiac arrhythmias
A method is provided for treatment of a heart arrhythmia such as atrial fibrillation that includes obtaining cardiac image data using a digital imaging system, generating a 3D model of a cardiac chamber and surrounding structures from such cardiac image data, registering the 3D model with an interventional system, visualizing this registered 3D model on the interventional system, positioning a catheter apparatus within the cardiac chamber, visualizing the catheter apparatus over the registered 3D model of the cardiac chamber upon the interventional system, navigating the catheter apparatus within the cardiac chamber utilizing this registered 3D model, and delivering biological material through the catheter apparatus to heart tissue at select locations within the cardiac chamber. Preferably, the biological material are transplanted cells or antibodies. In another aspect of the invention, a system for treatment of heart arrhythmias is provided that has a digital imaging system to obtain cardiac image data, an image generation system to generate a 3D model of a cardiac chamber and its surrounding structures from this cardiac image data, a workstation to register the 3D model onto an interventional system so that the registered 3D model can be visualized upon the interventional system, and a catheter apparatus to deliver biological material such as transplanted cells or antibodies to heart tissue within this cardiac chamber at certain select locations, the catheter apparatus being visualized upon the interventional system over the registered 3D model.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Linear ablation assembly
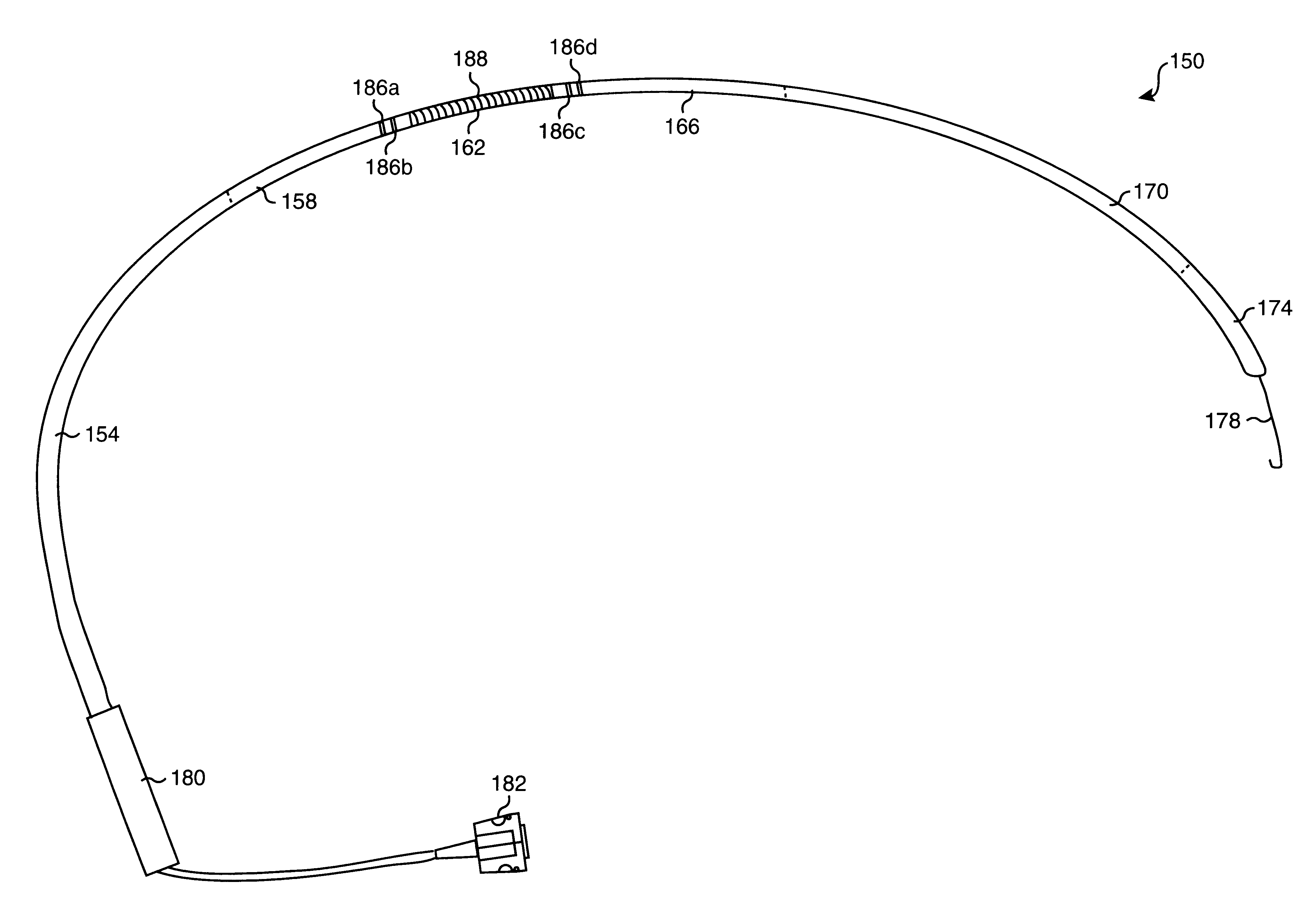
InactiveUS7331960B2Facilitate entryEffective length of elongatedInternal electrodesCatheterHeart chamberAxial force
An intravascular device for the formation of linear lesions which has particular utility in the treatment of atrial fibrillation and flutter. The intravascular device has an outer delivery member with a distal section which has an elongated opening and a support element coextending with the opening. An EP device having a plurality of electrodes on its distal section is slidably disposed within the inner lumen of the delivery member but it is secured by its distal end within the distal extremity of the delivery member at least while in operation. In this manner an axial force in the proximal direction on the proximal extremity of the EP device, which extends out of the patient during the procedure, will cause the distal shaft section of the EP device to arch outwardly out of and away from the distal section of the delivery shaft along an inner side of the curved distal section and engage the surface of the patient's heart chamber. RF electrical energy delivered to the electrodes on the distal shaft section of the EP device will form a linear lesion which terminates the fibrillation or flutter.
Owner:SICHUAN JINJIANG ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH CO LTD
Inflatable ventricular partitioning device
ActiveUS20050197716A1Lower the volumeImprove ejection fractionHeart valvesSurgeryCardiac wallHeart chamber
This invention is directed to a device and method of using the device for partitioning a patient's heart chamber into a productive portion and a non-productive portion. The device is particularly suitable for treating patients with congestive heart failure. The device has an inflatable partitioning element which separates the productive and non-productive portions of the heart chamber and in some embodiments also has a supporting element, which may also be inflatable, extending between the inflatable partitioning element and the wall of the non-productive portion of the patient's heart chamber. The supporting element may have a non-traumatic distal end to engage the ventricular wall or a tissue penetrating anchoring element to secure the device to the patient's heart wall.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com