Patents
Literature
609 results about "Electromyography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
<ul><li>Electrical activity in resting state may infer to conditions like muscle disorder, nerve disorder, inflammation or other disorders.</li><li>Abnormal electrical activity on muscle contraction suggests nerve disorders like ALS or herniated disc.</li></ul>
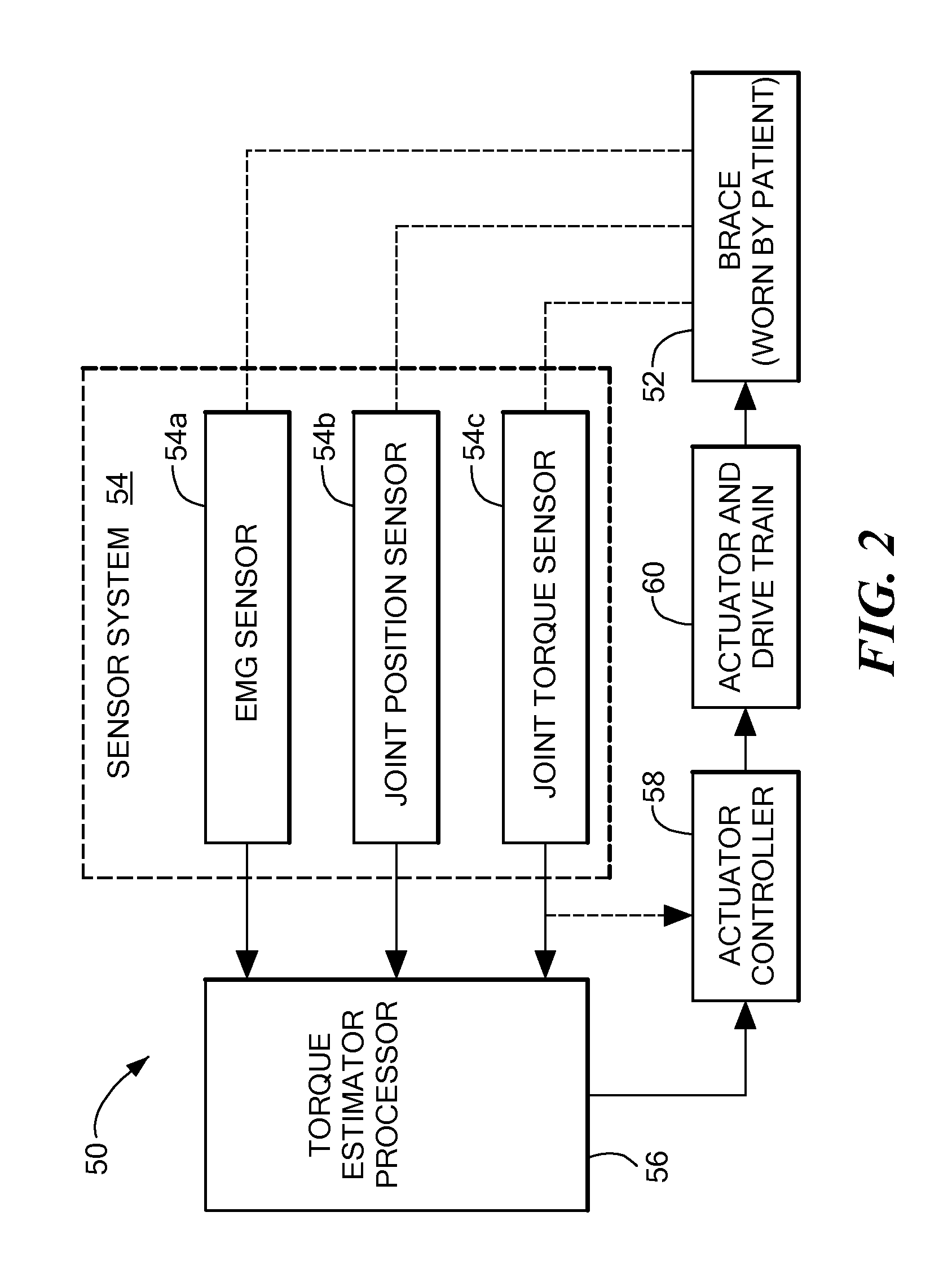
Implantable monitor
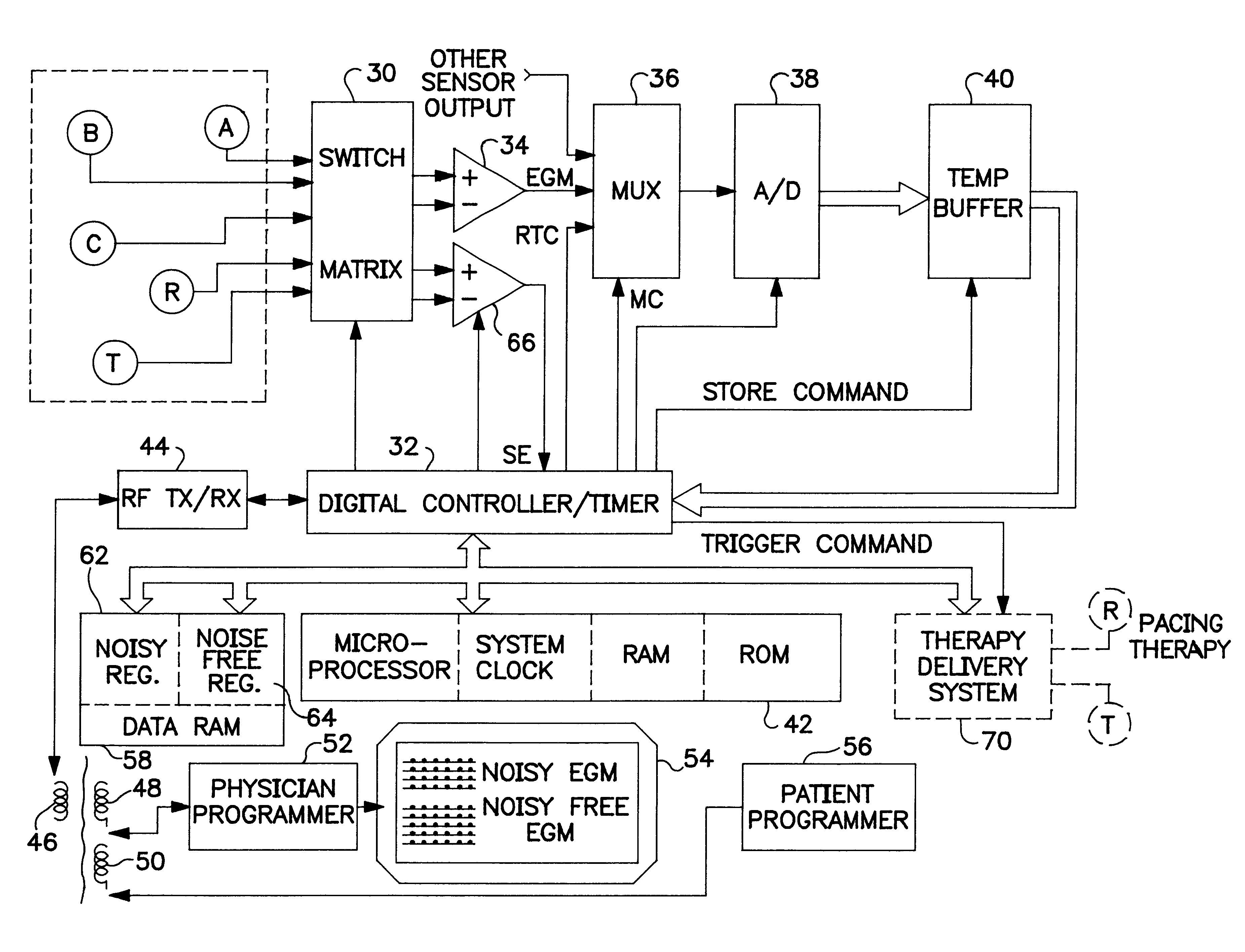
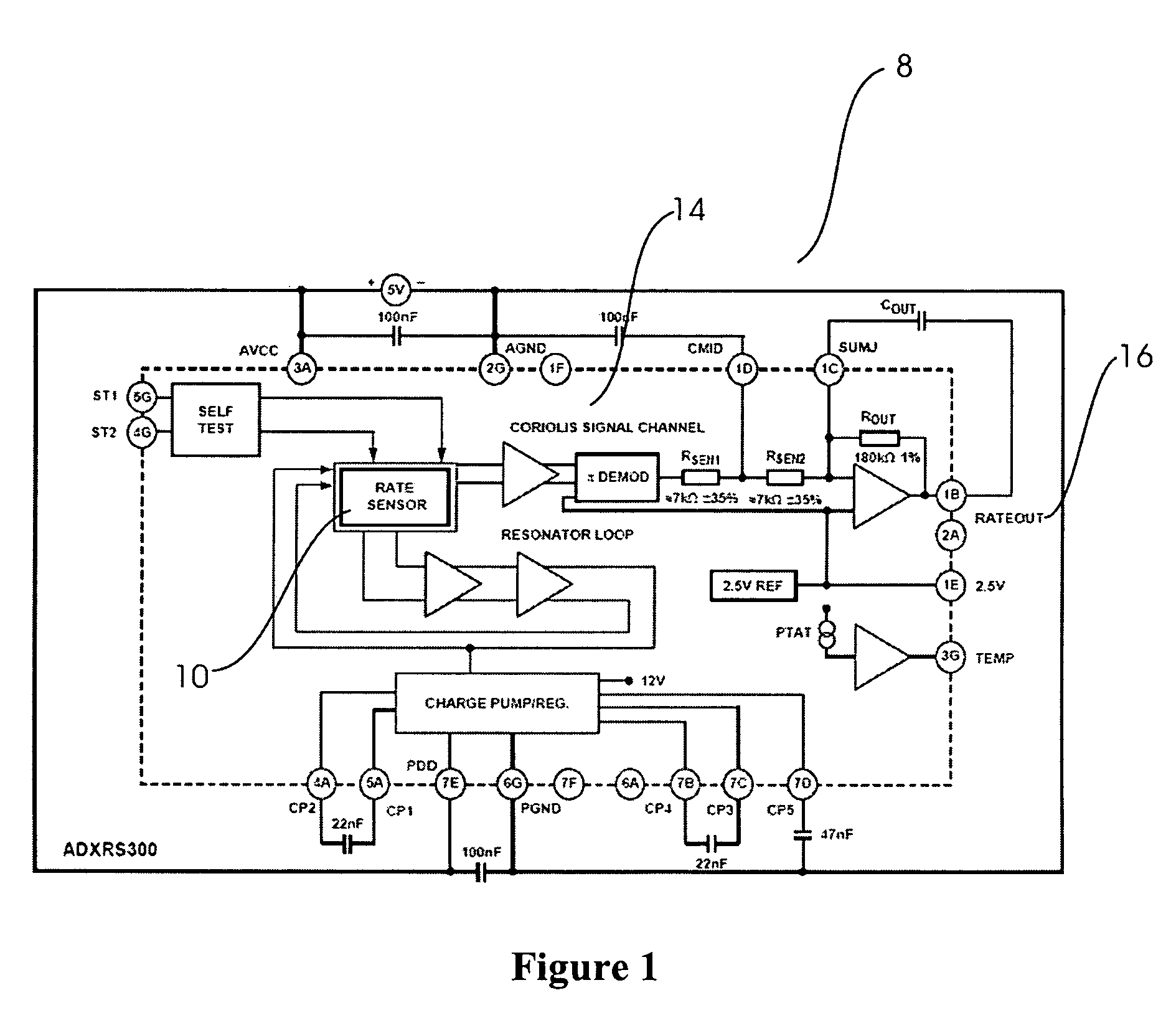
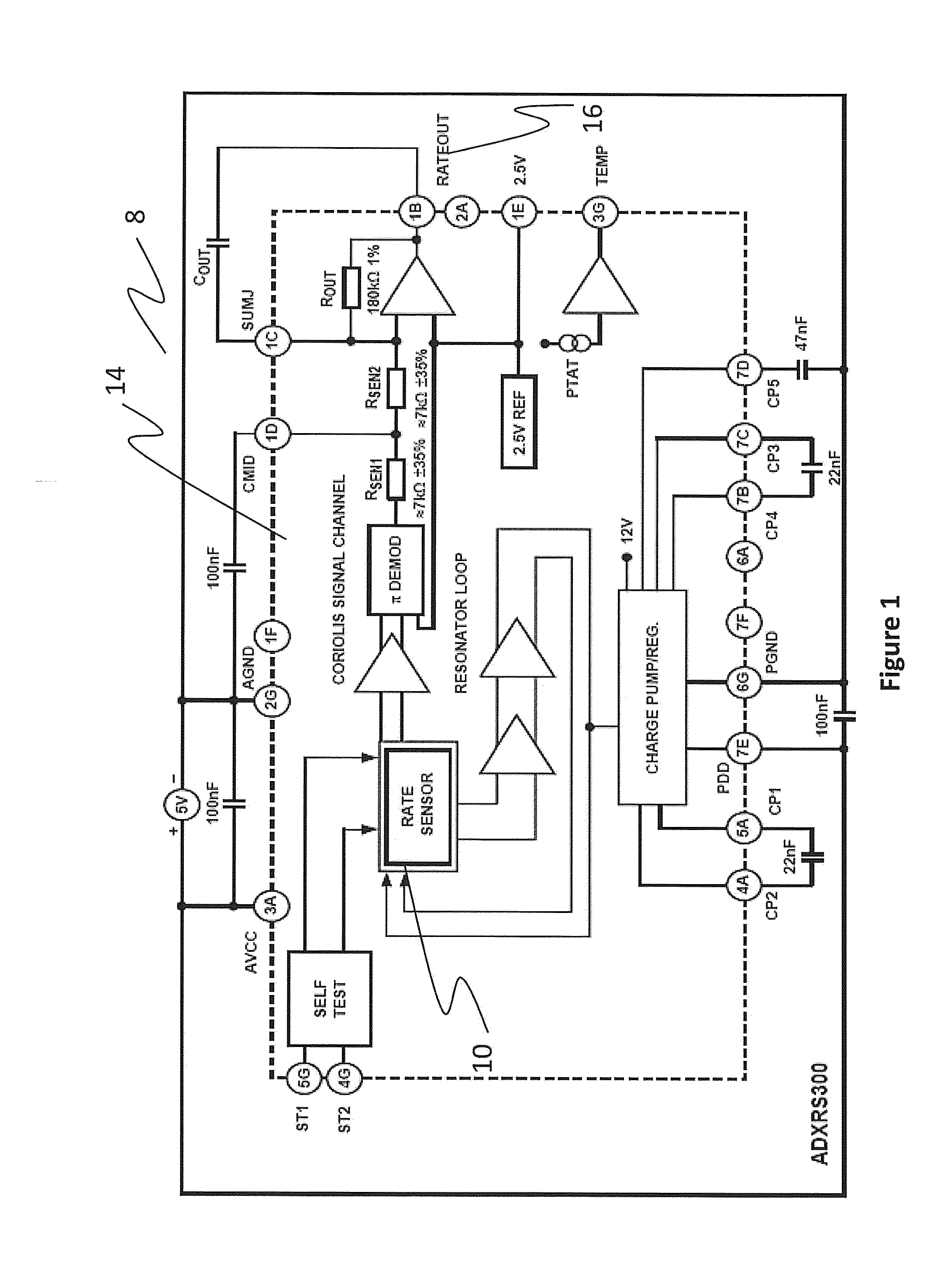
An implantable medical device (IMD) capable of monitoring physiologic data, distinguishing relatively noisy and noise free physiologic data, and recording noisy and relatively noise free segments of physiologic data in separate memory registers of a limited memory for retrieval and analysis at a later time. Preferably the physiologic data comprises the sampled EGM of the heart detected from sense electrode pairs that are implanted in the patient at sites where extraneous electrical noise, e.g., electromyographic signals, are also capable of being detected. The sense electrode pairs can constitute one or both sense electrodes located on or adjacent to the atrial and / or ventricular heart chambers and coupled to the IMD by a lead body or sense electrode pairs that are located remotely from the heart, e.g. at a subcutaneous implantation site of the IMD. A plurality of noisy EGM episode data registers store a corresponding plurality of noisy EGM episode data sets on a FIFO basis and another plurality of noise free EGM episode data registers to store a corresponding plurality of relatively noise free EGM episode data sets on a FIFO basis. Any form of discrimination of noisy data from relatively noise free data can be employed at the time of recording, but because the stored EGM episode data sets are subsequently viewed and analyzed by a physician, discrimination with absolute certainty is not required, and the physician can alter the detection criteria to fine tune it.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
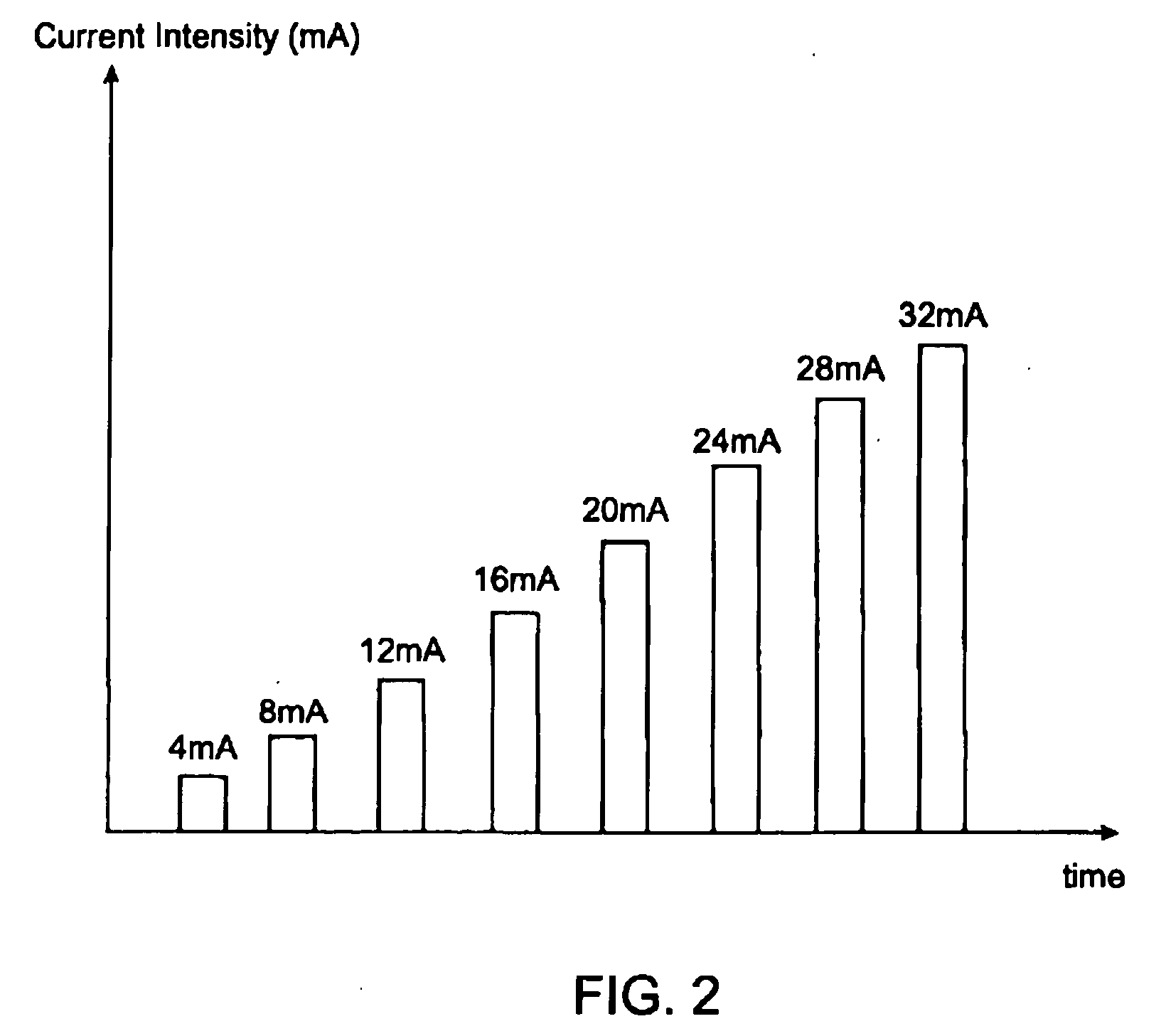
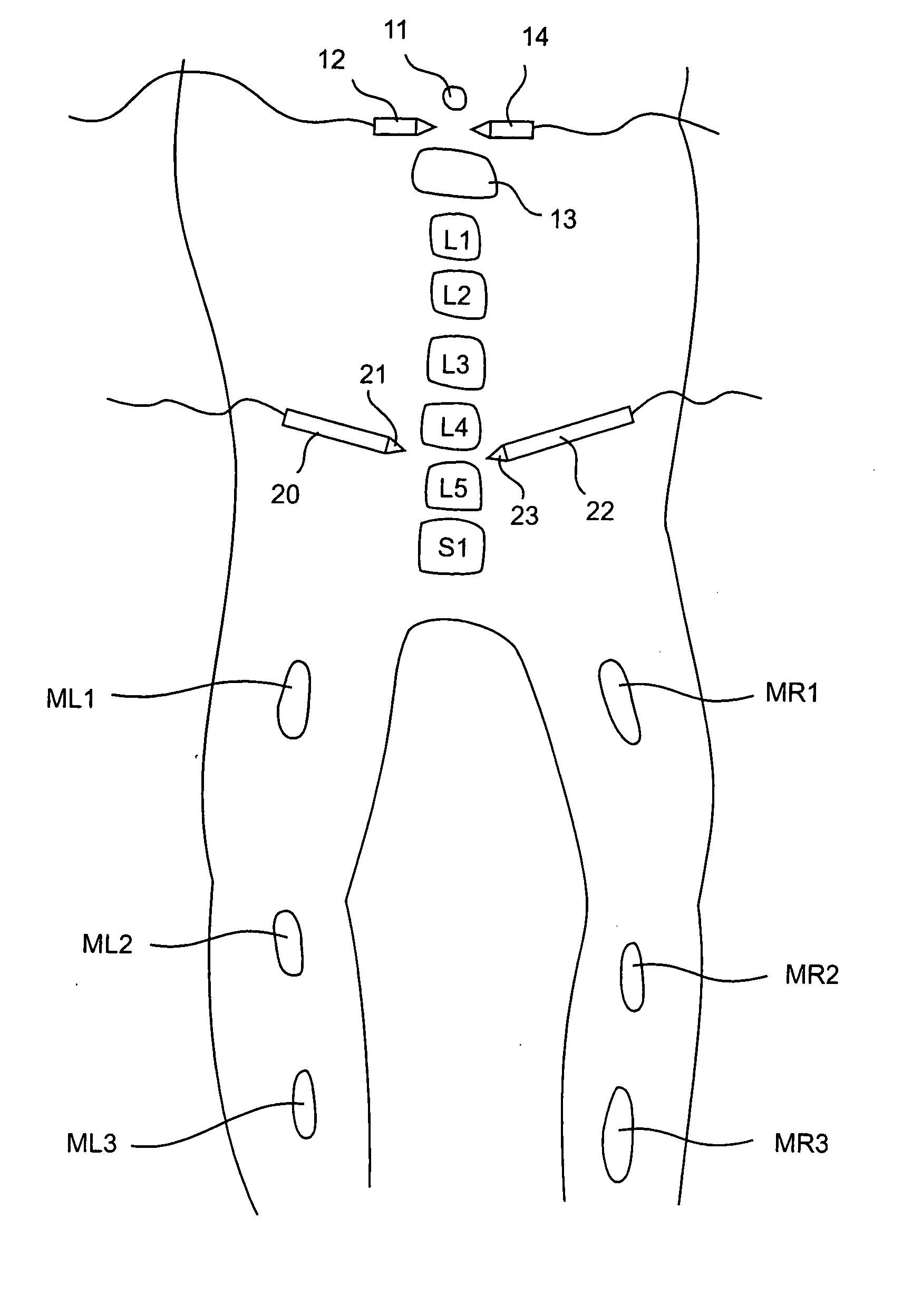
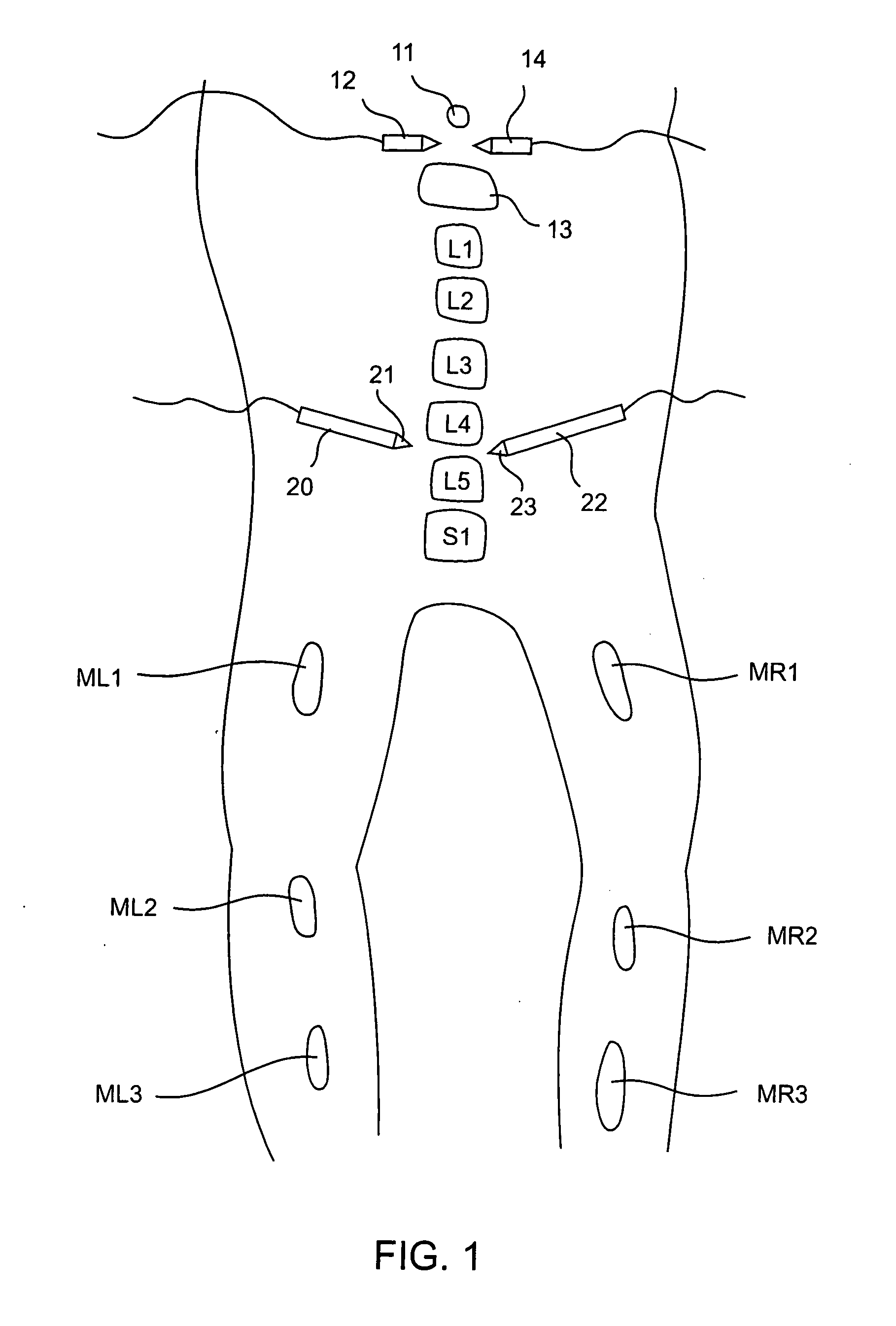
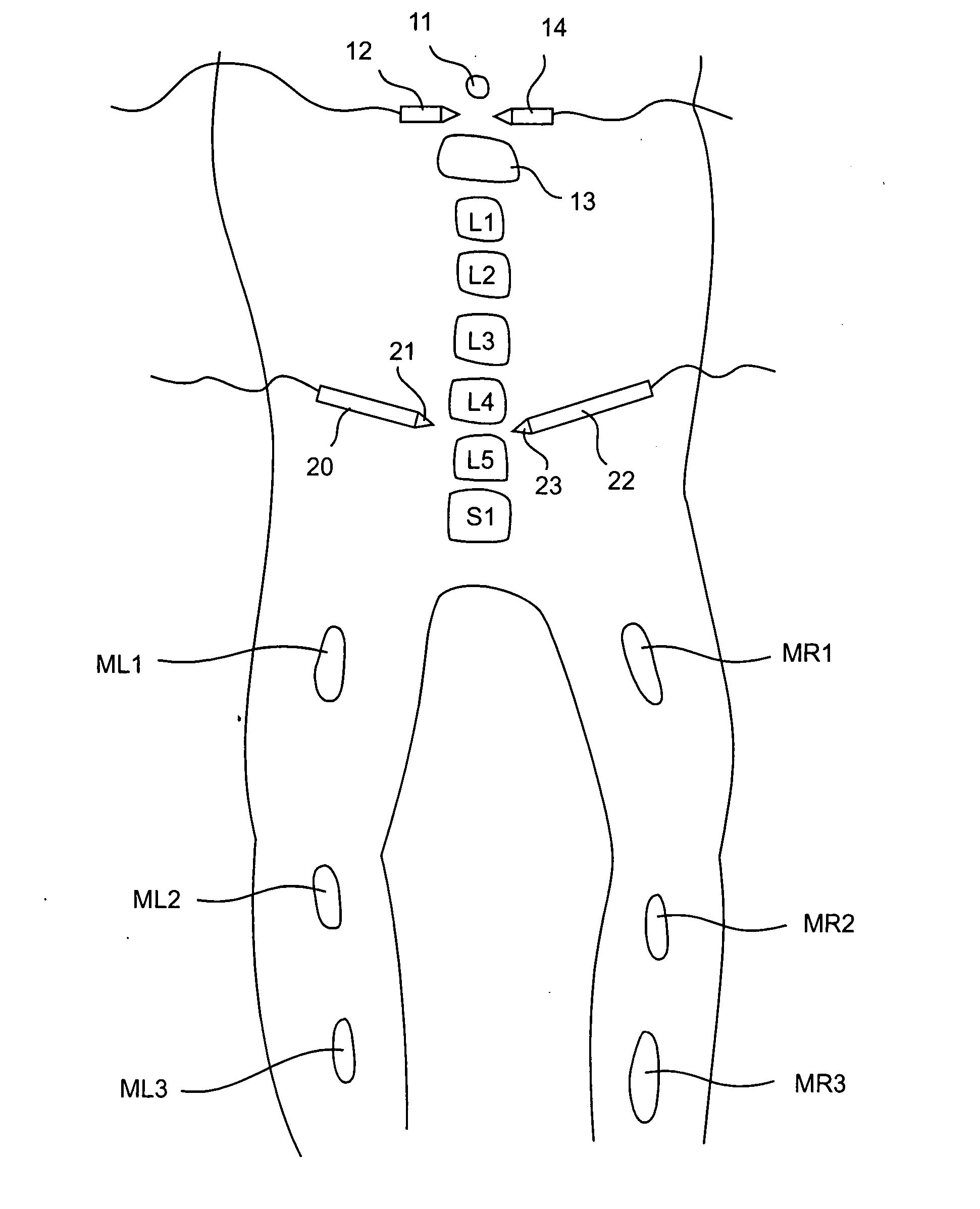
Electromyography system
InactiveUS20070293782A1Interpret accuracyLess sensitiveElectrotherapyElectromyographyPower flowMedicine
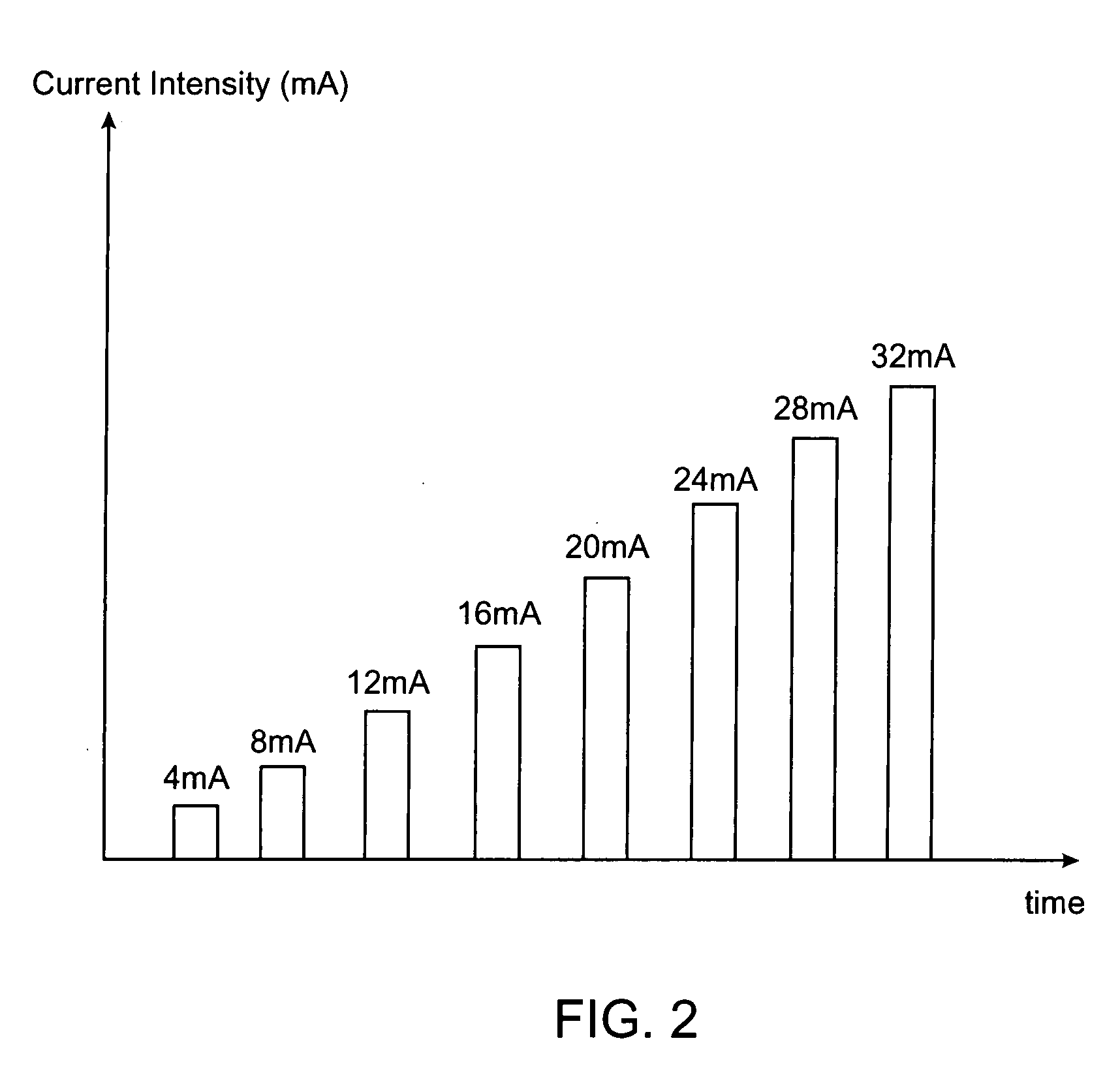
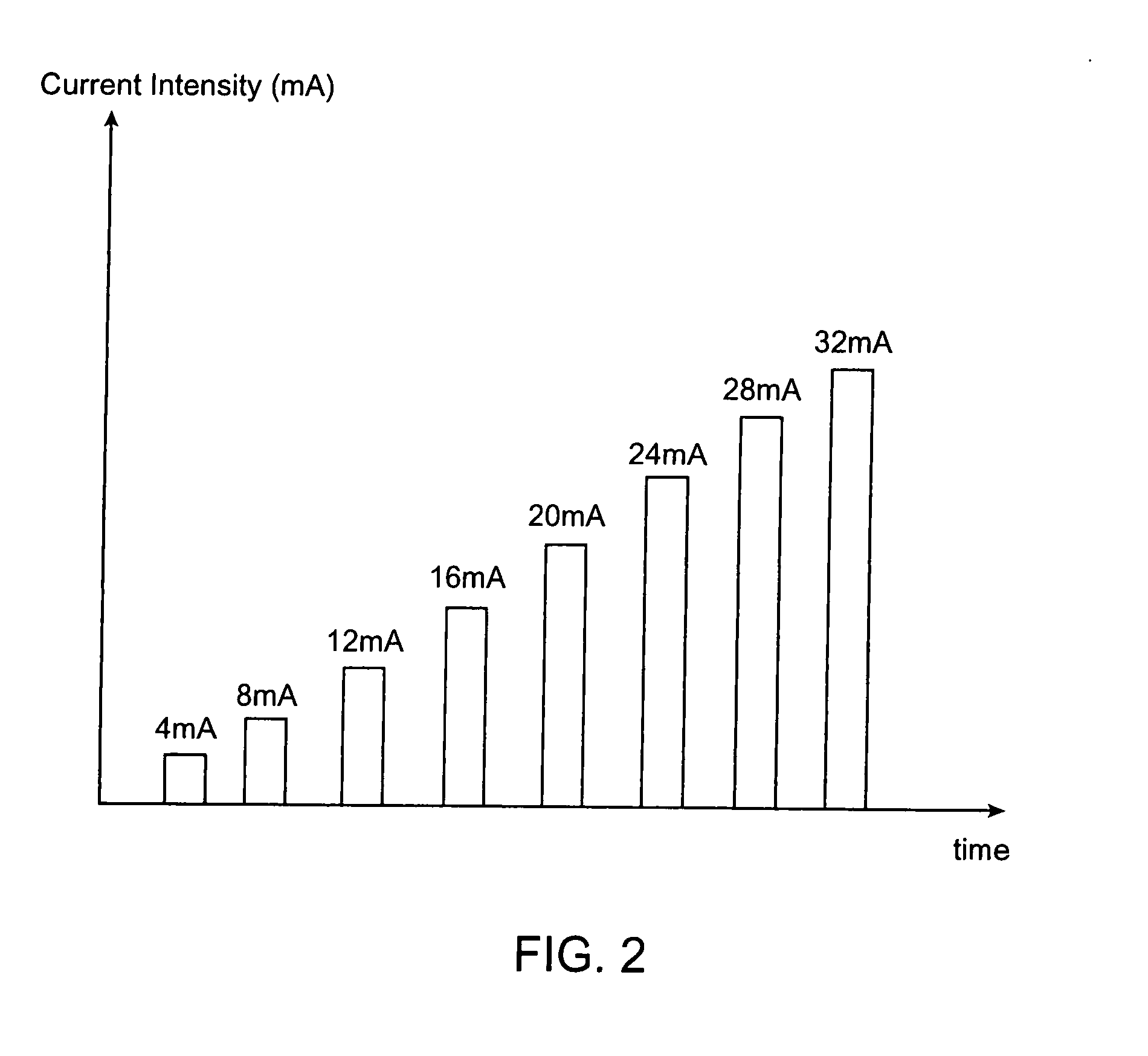
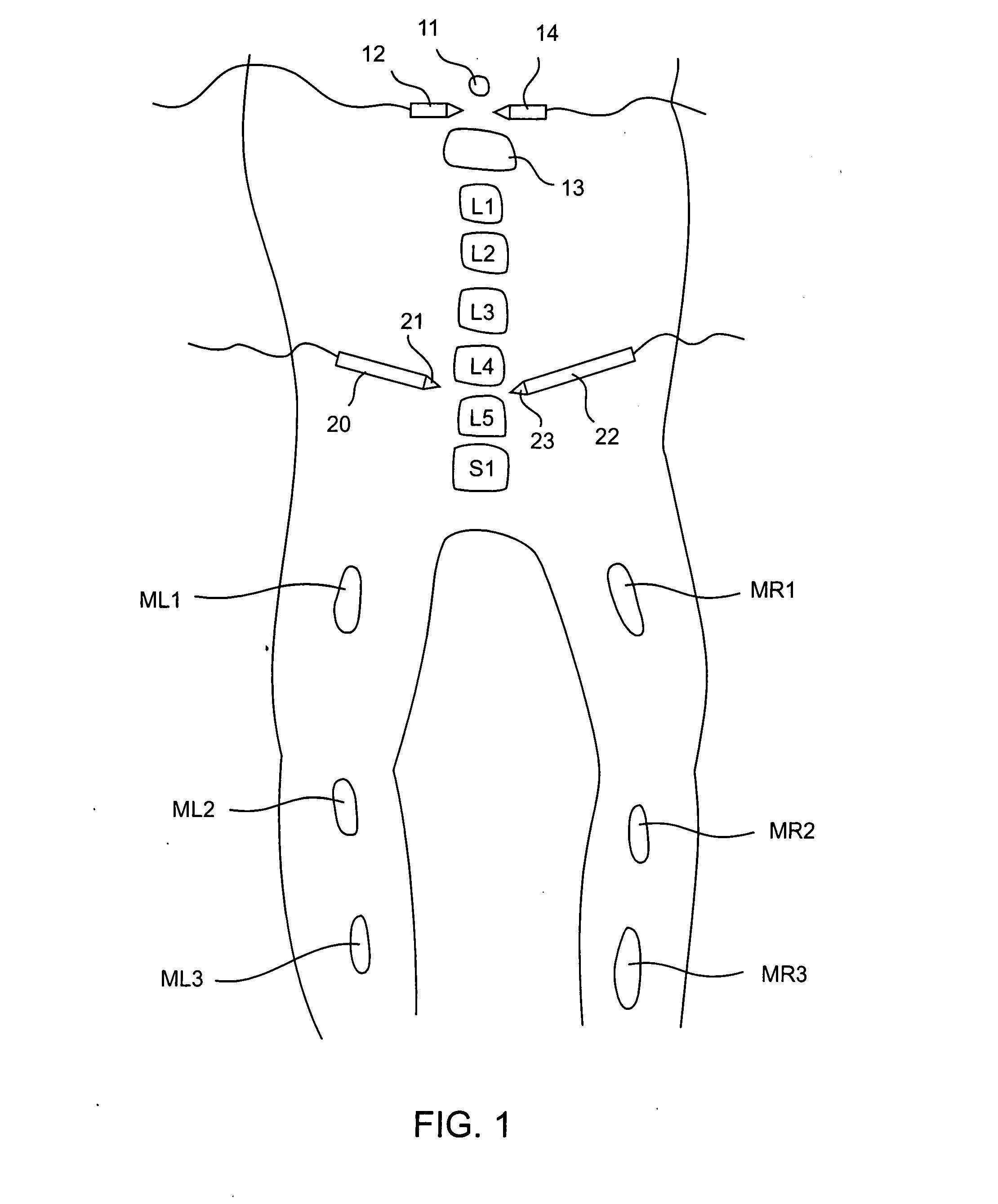
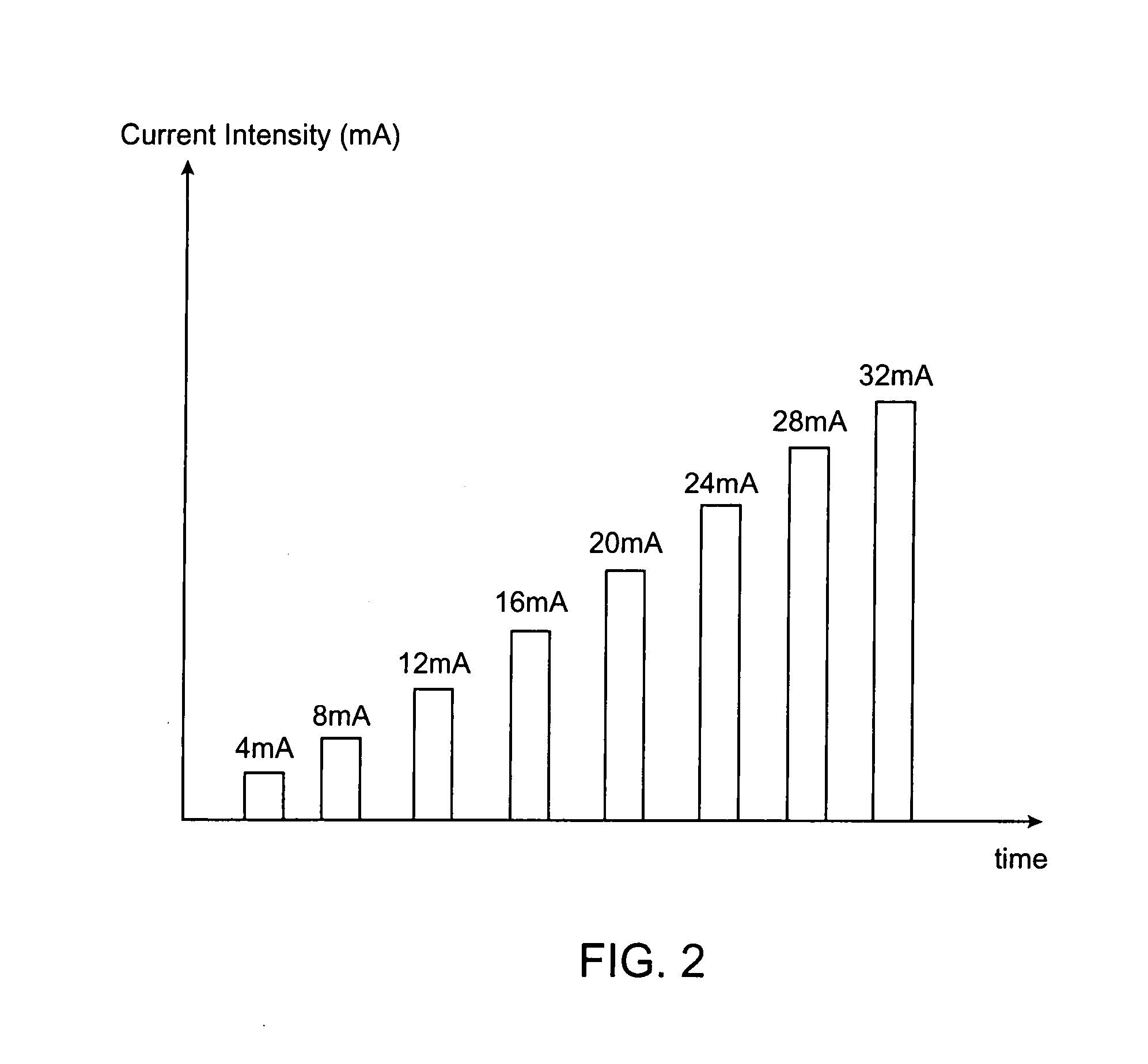
A method of determining relative neuro-muscular response onset value thresholds for a plurality of spinal nerves, comprising: depolarizing a portion of the patient's cauda equina; and measuring the current intensity level at which a neuro-muscular response to the depolarization of the cauda equina is detected in each of the plurality of spinal nerves. A method for detecting the presence of a nerve adjacent the distal end of at least one probe, comprising: determining relative neuro-muscular response onset values for a plurality of spinal nerves; emitting a stimulus pulse from a probe or surgical tool; detecting neuro-muscular responses to the stimulus pulse in each of the plurality of spinal nerves; and concluding that the electrode disposed on the distal end of the at least one probe is positioned adjacent to a first spinal nerve when the neuro-muscular response detected in the first spinal nerve is detected as a current intensity level less than or equal to a corresponding neuro-muscular response onset value of the first spinal nerve.
Owner:NUVASIVE
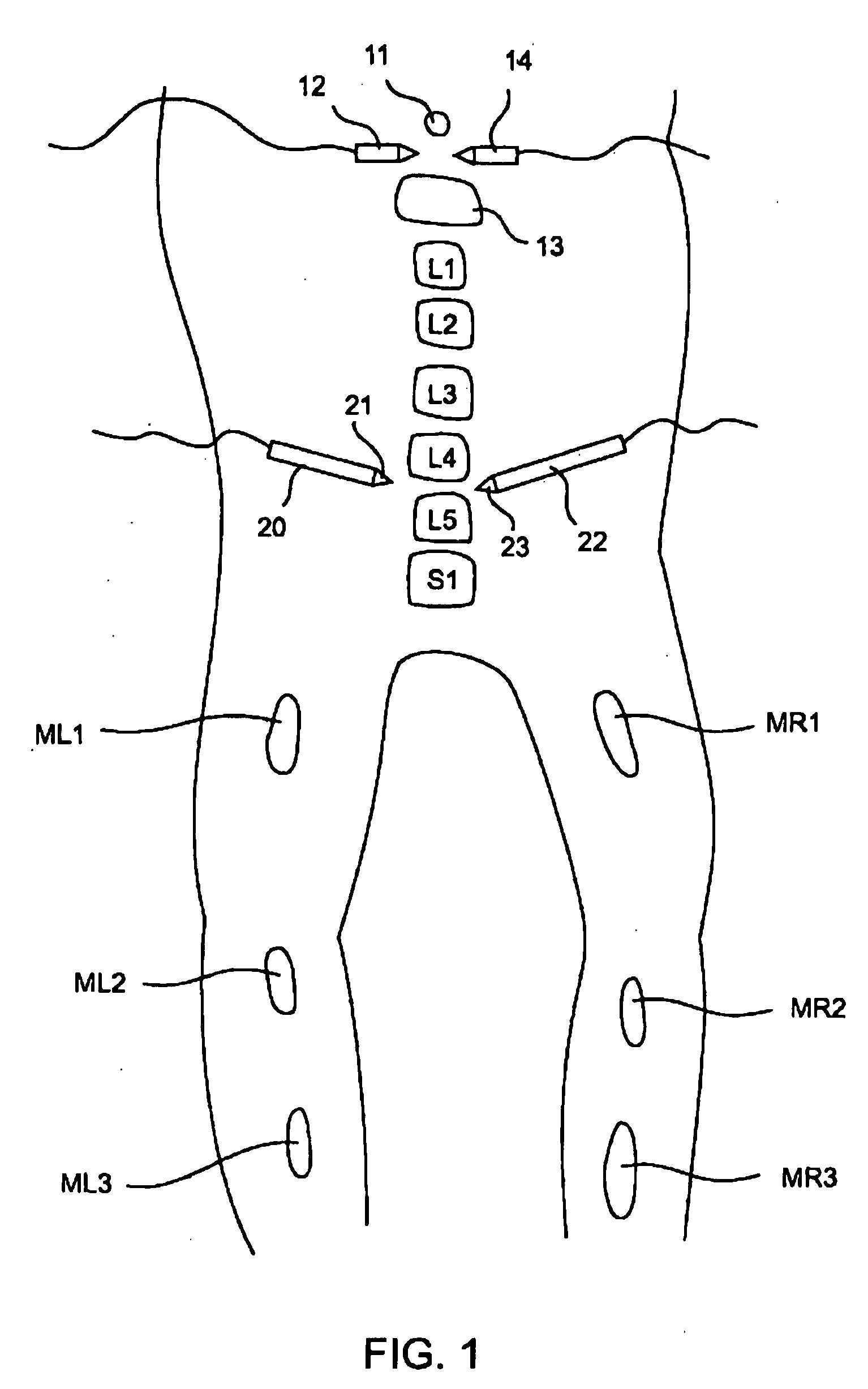
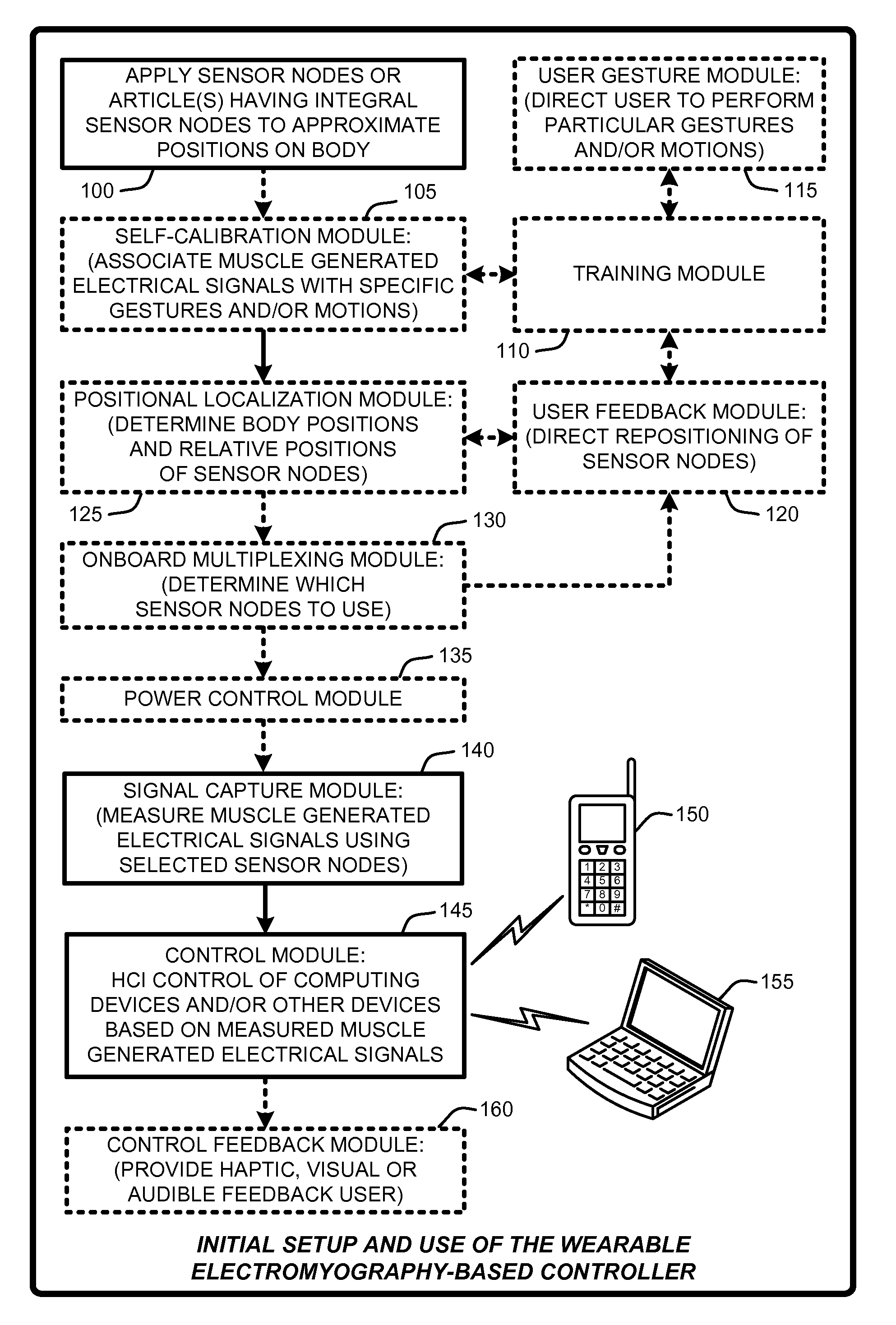
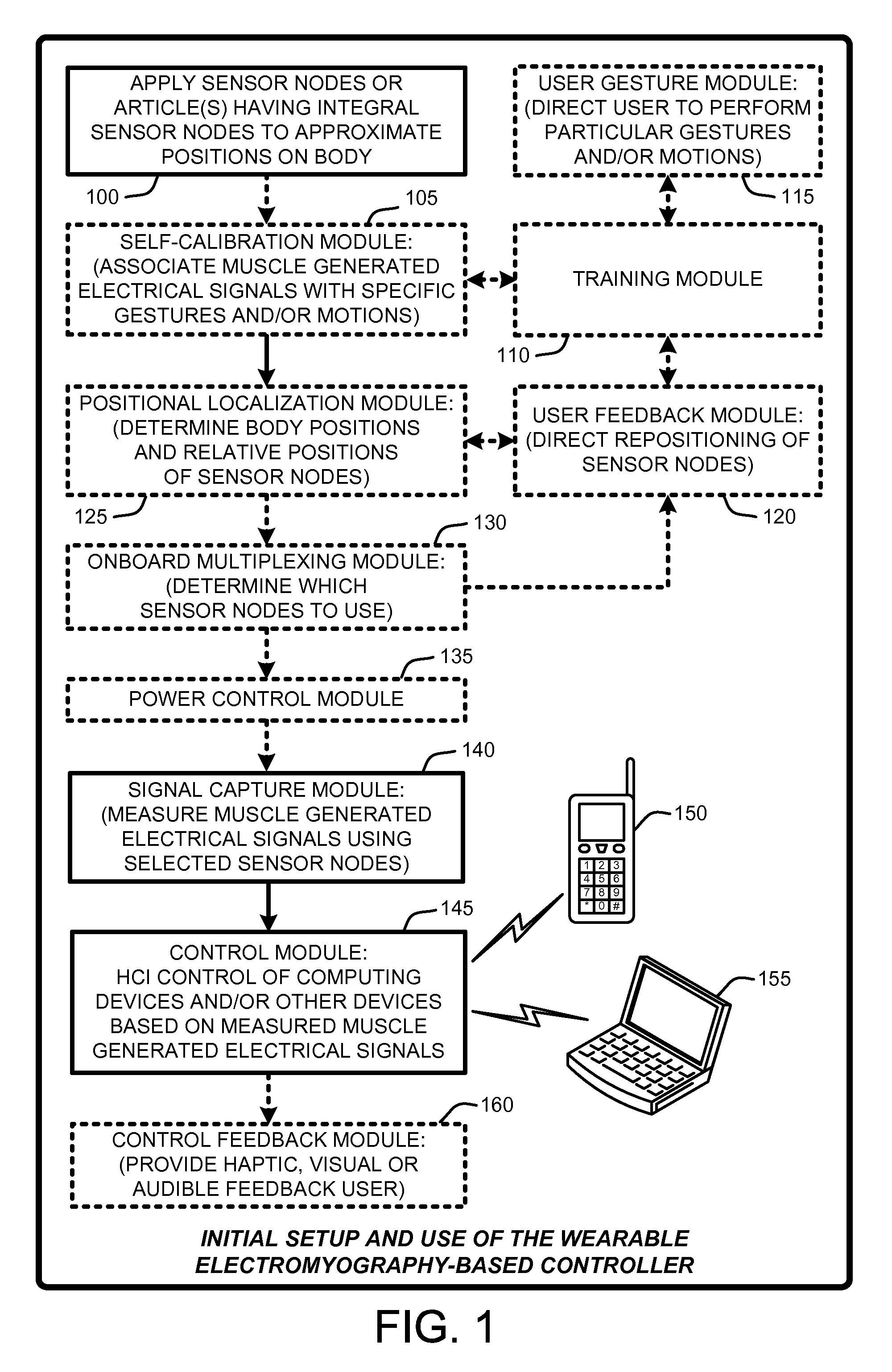
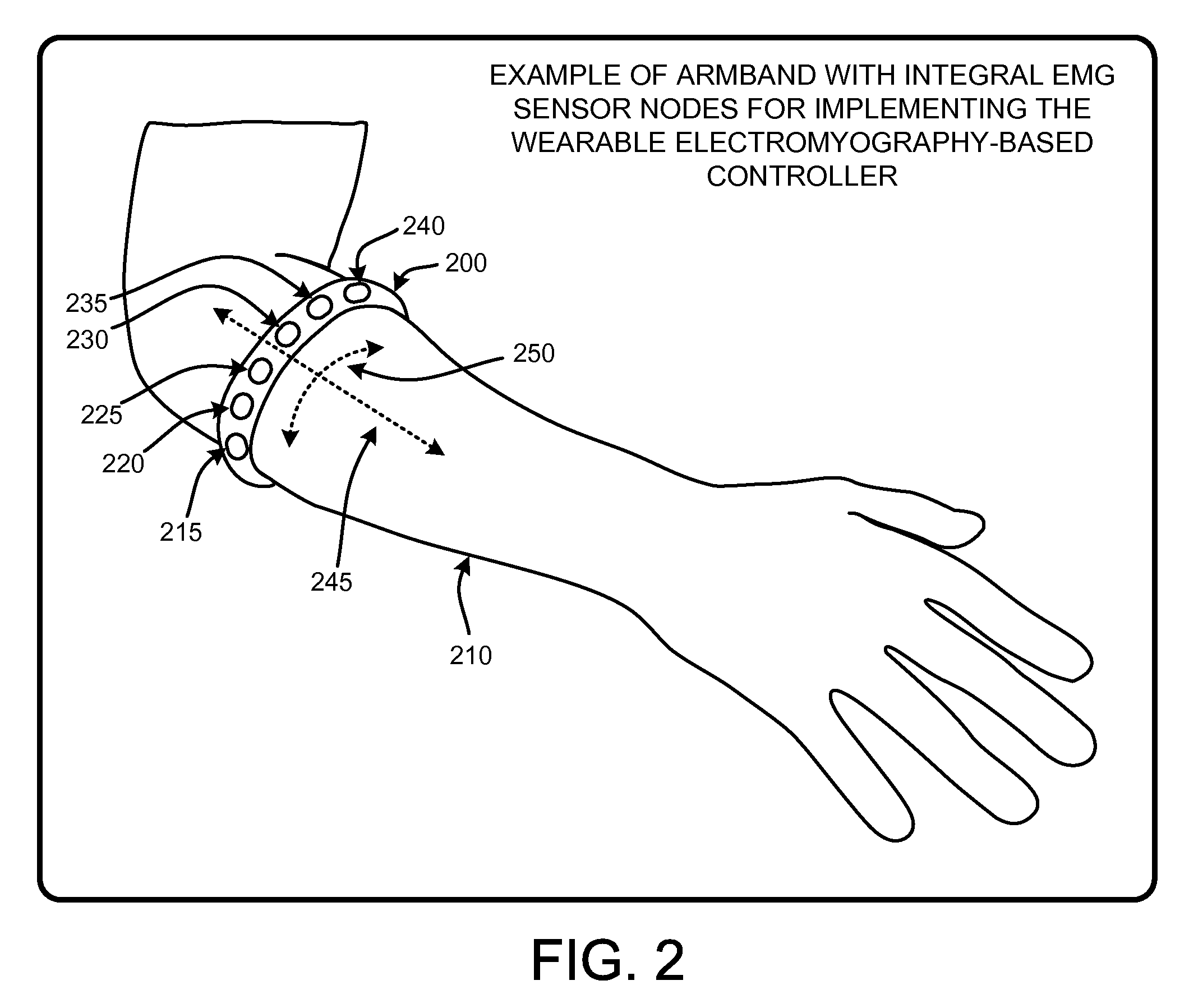
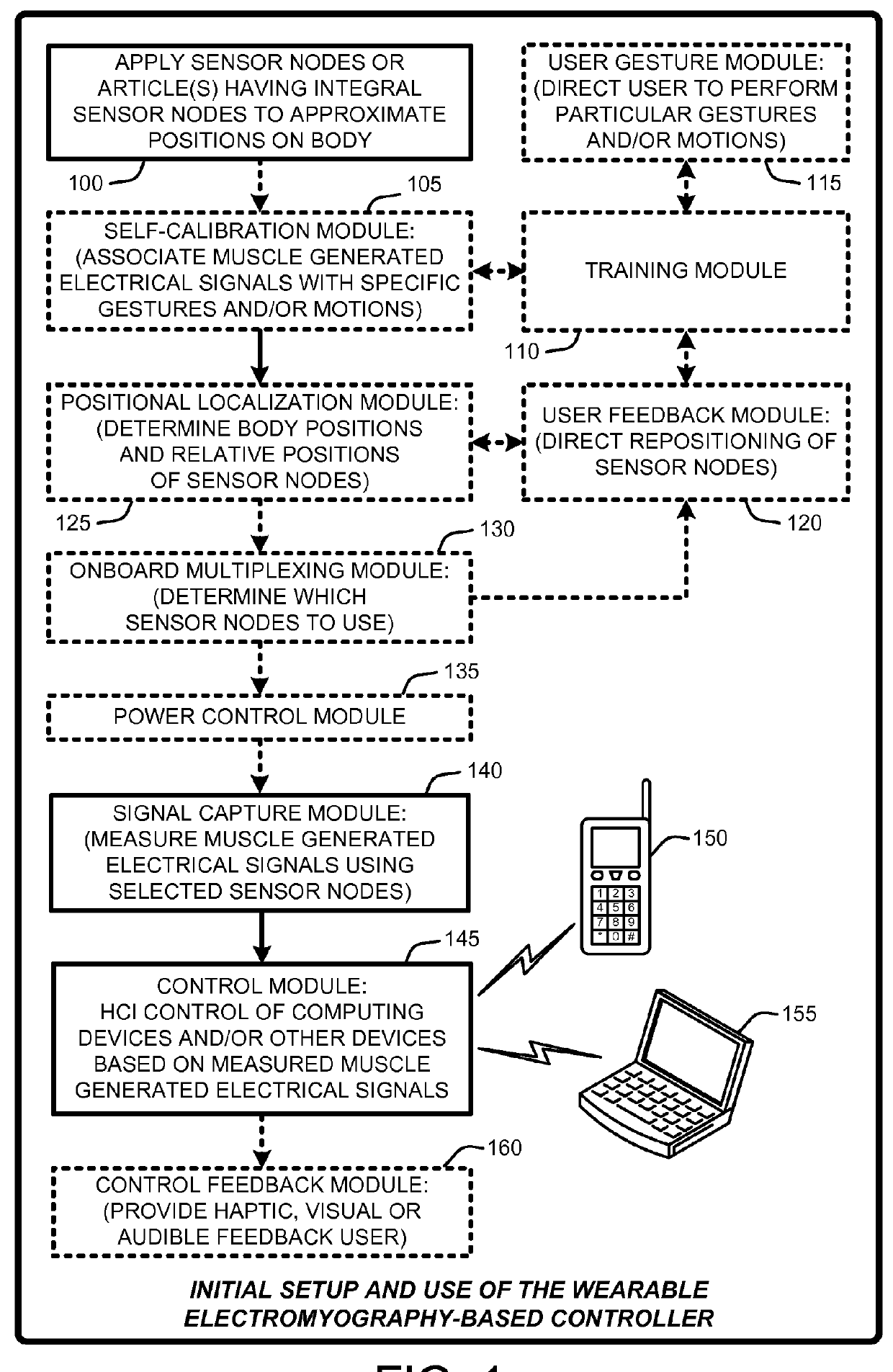
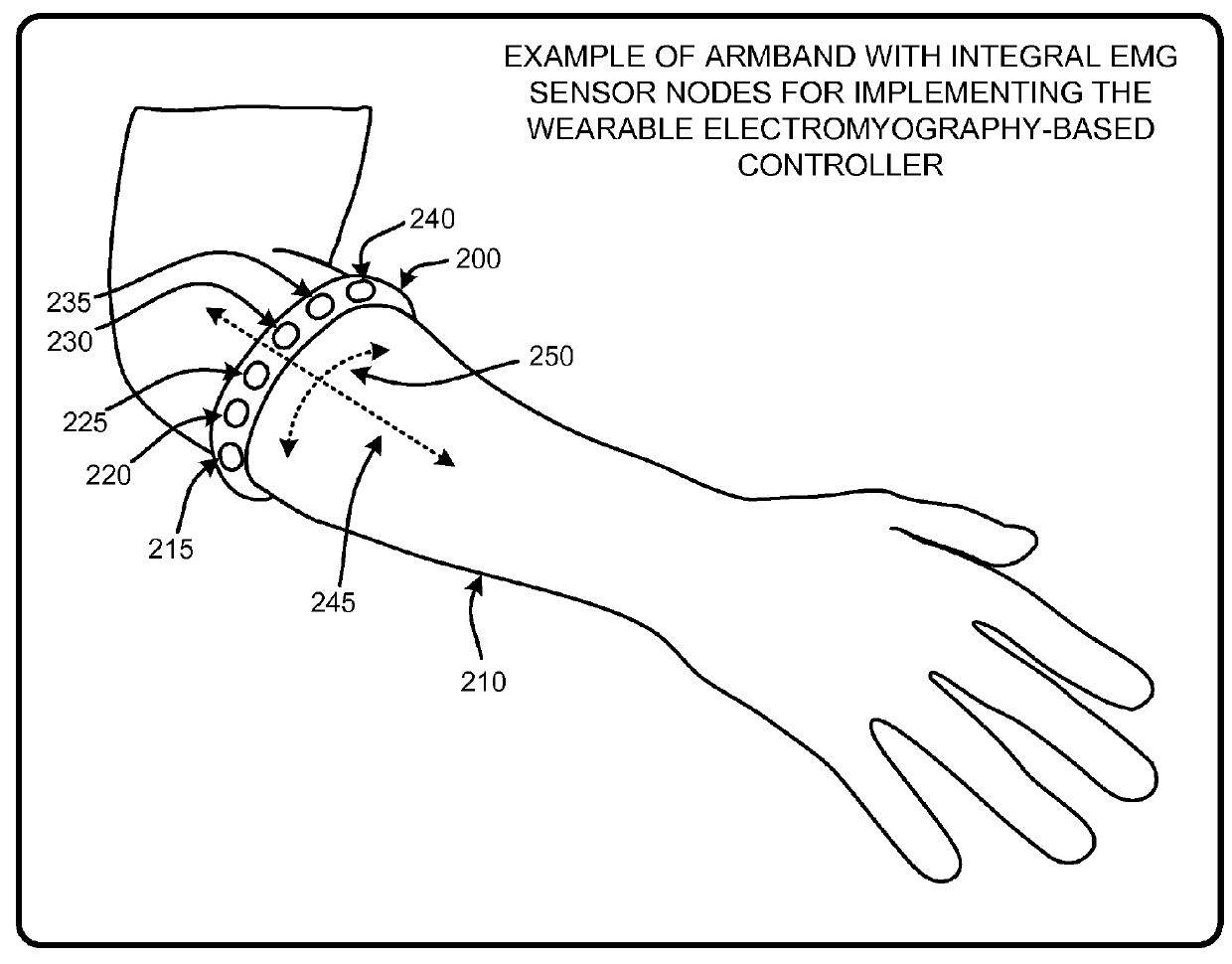
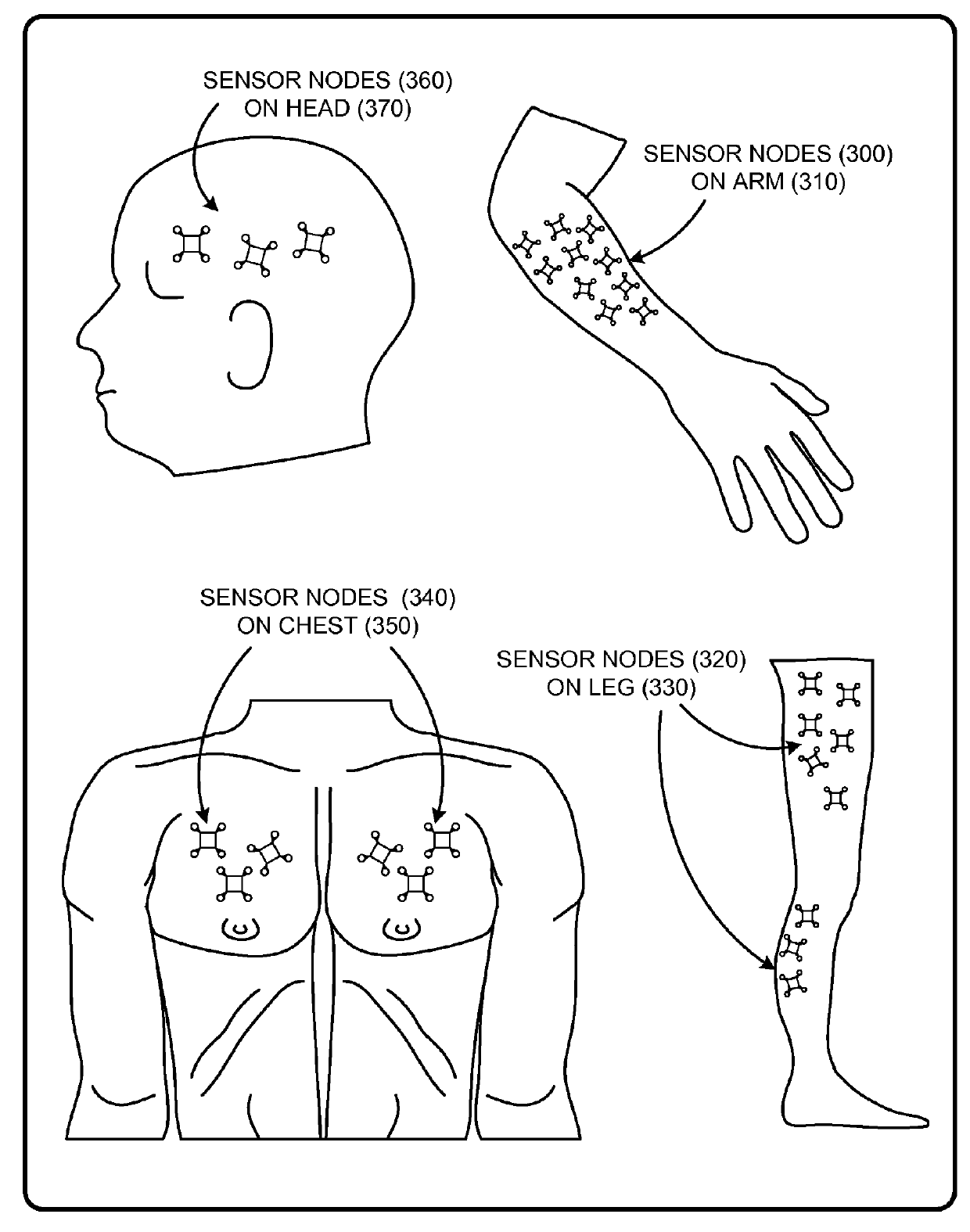
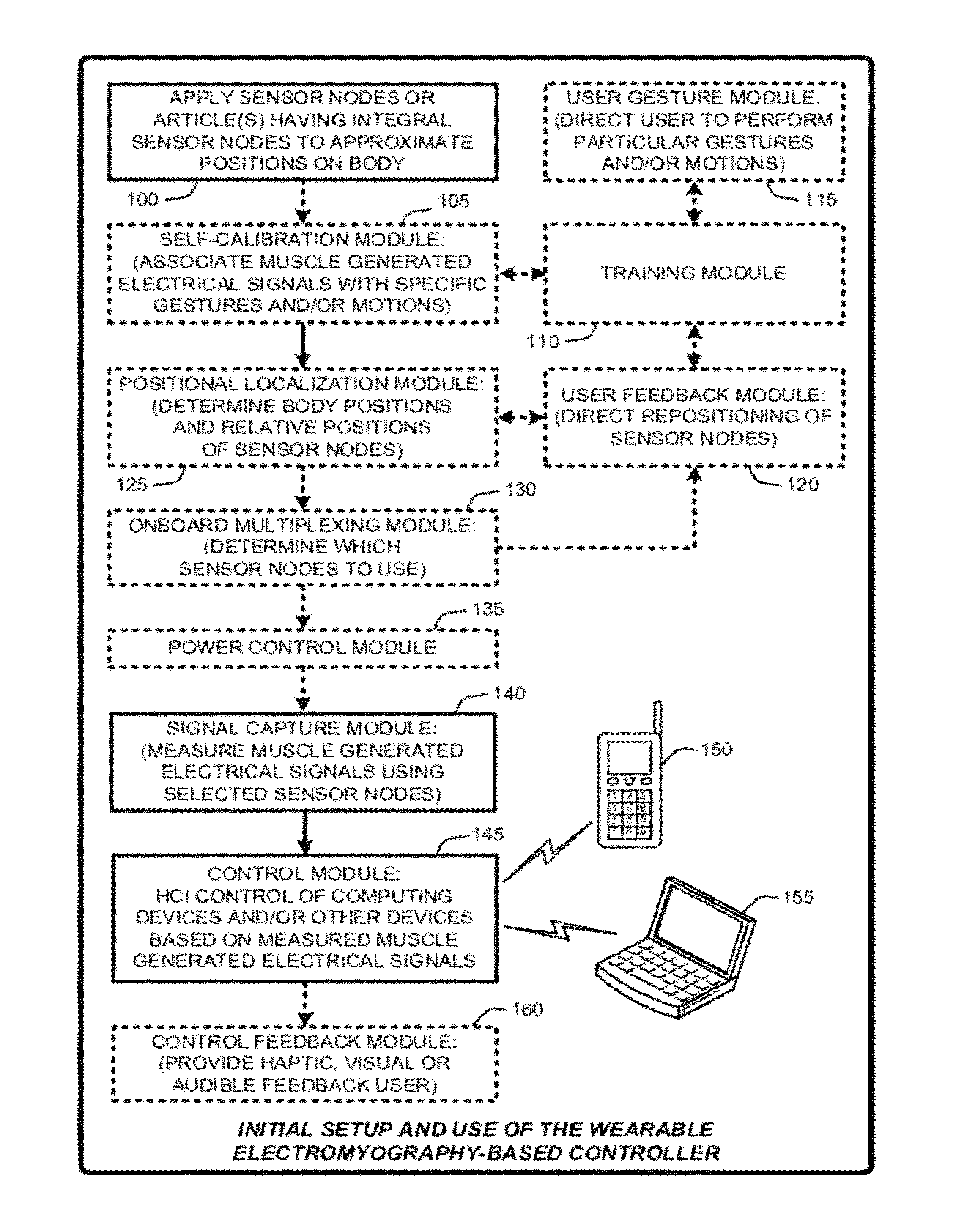
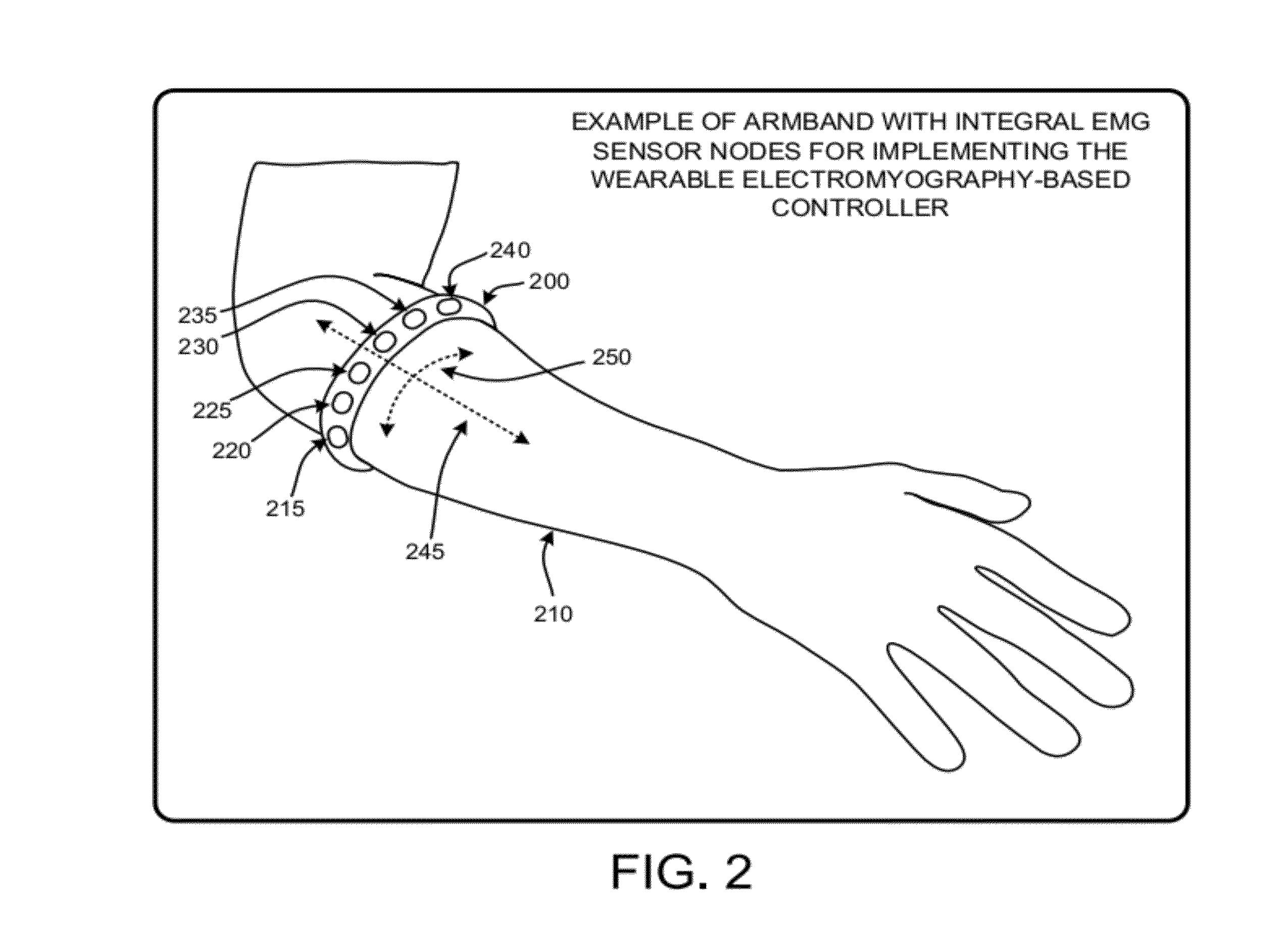
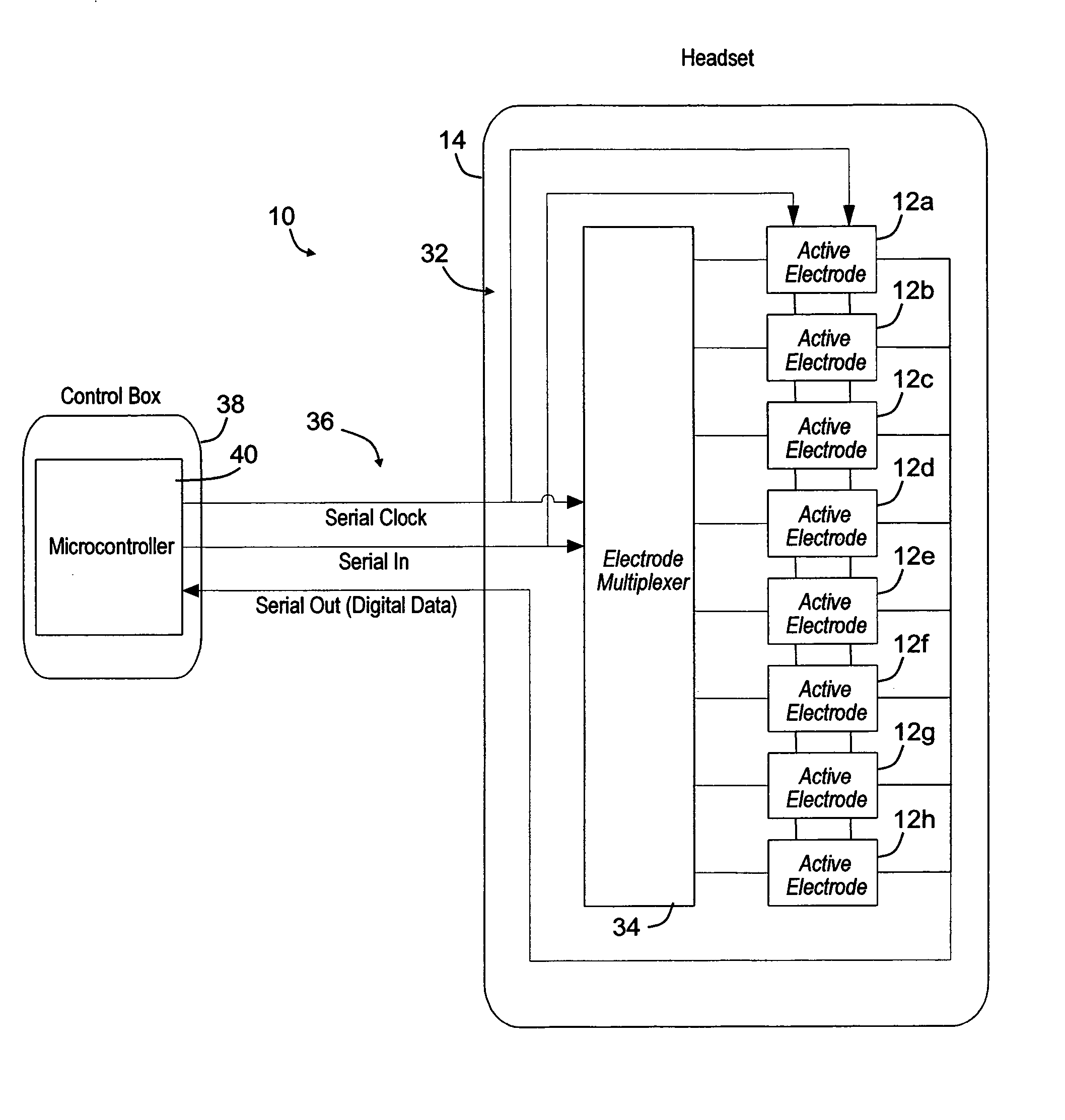
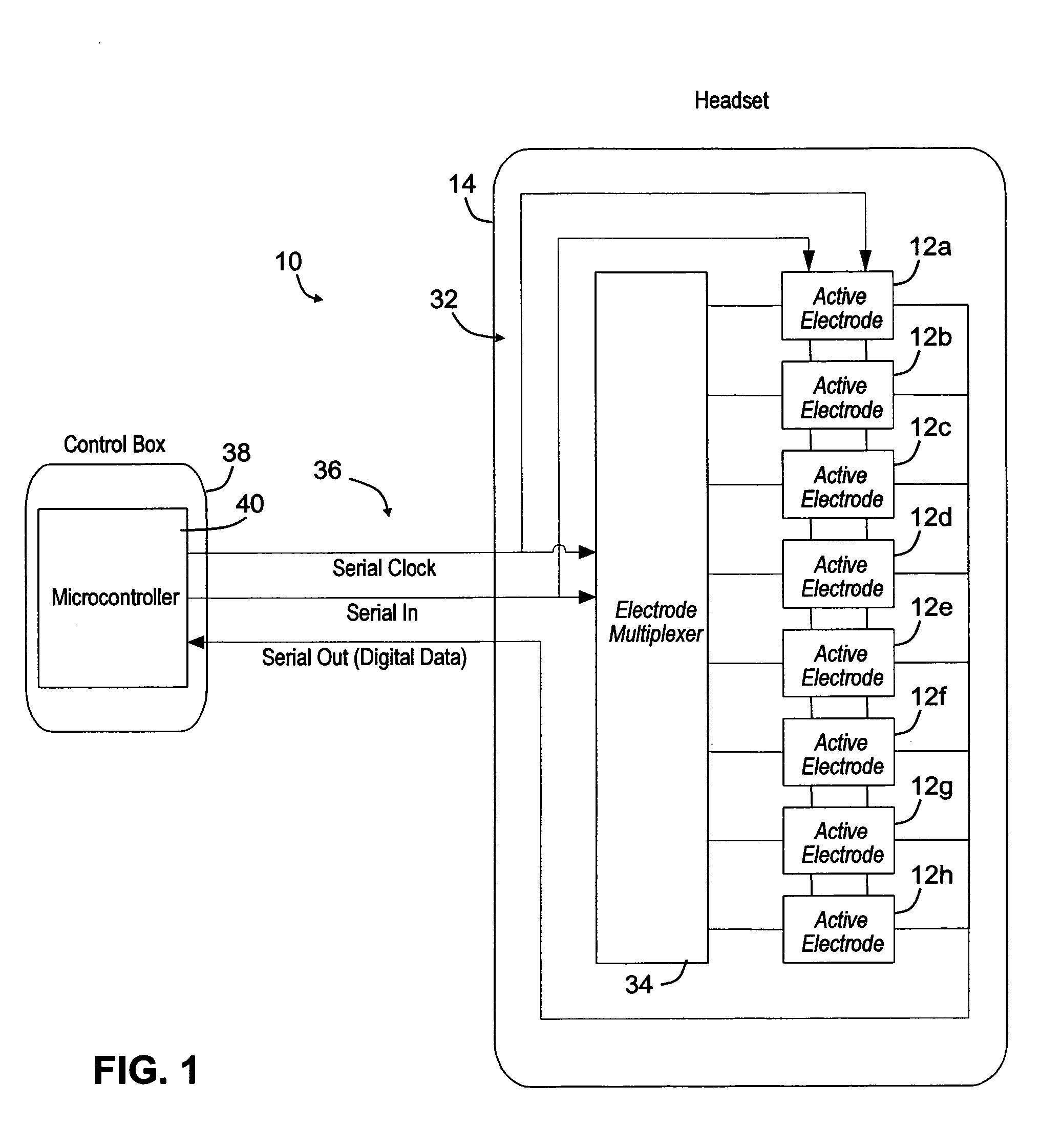
Wearable electromyography-based controllers for human-computer interface
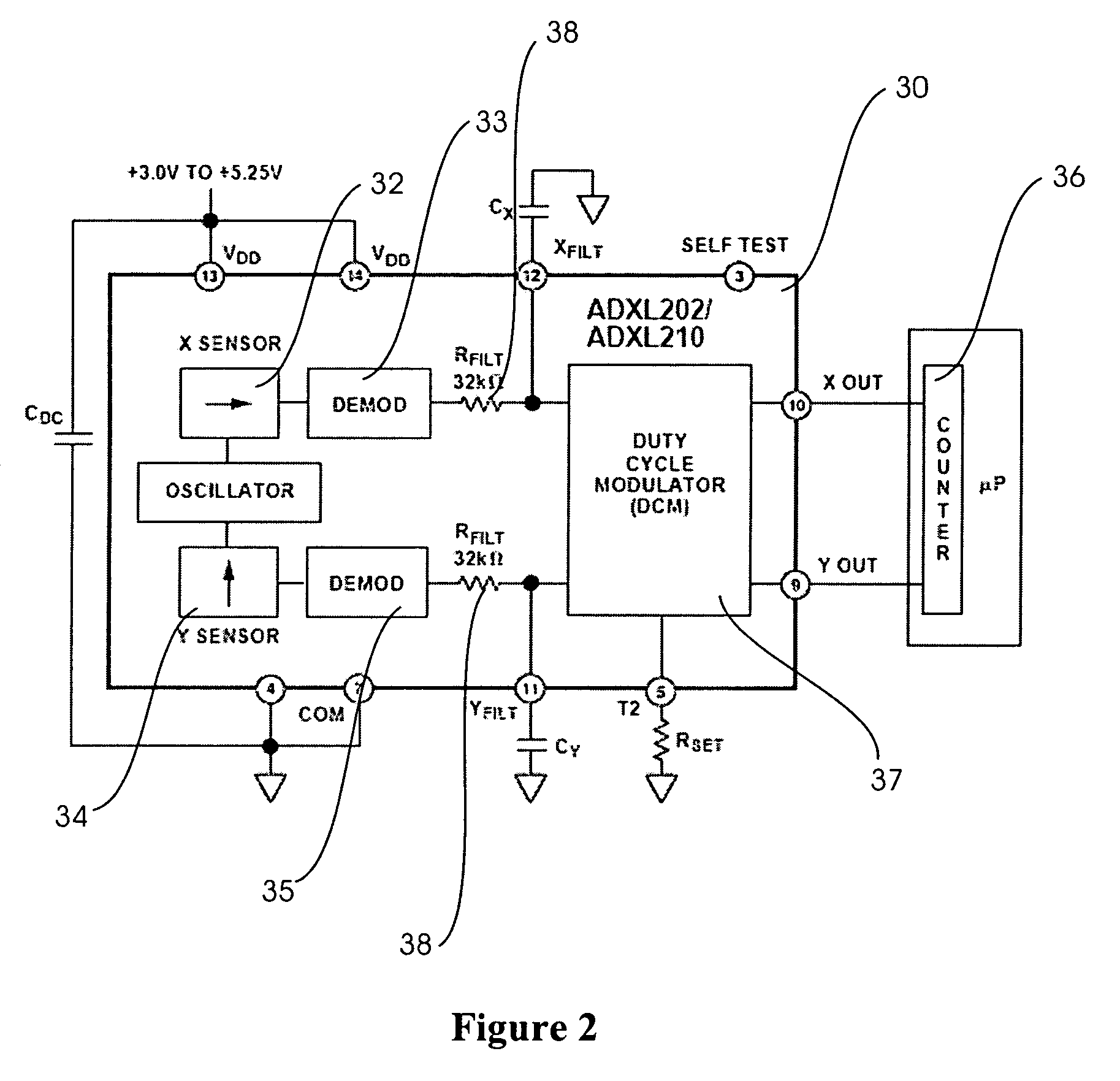
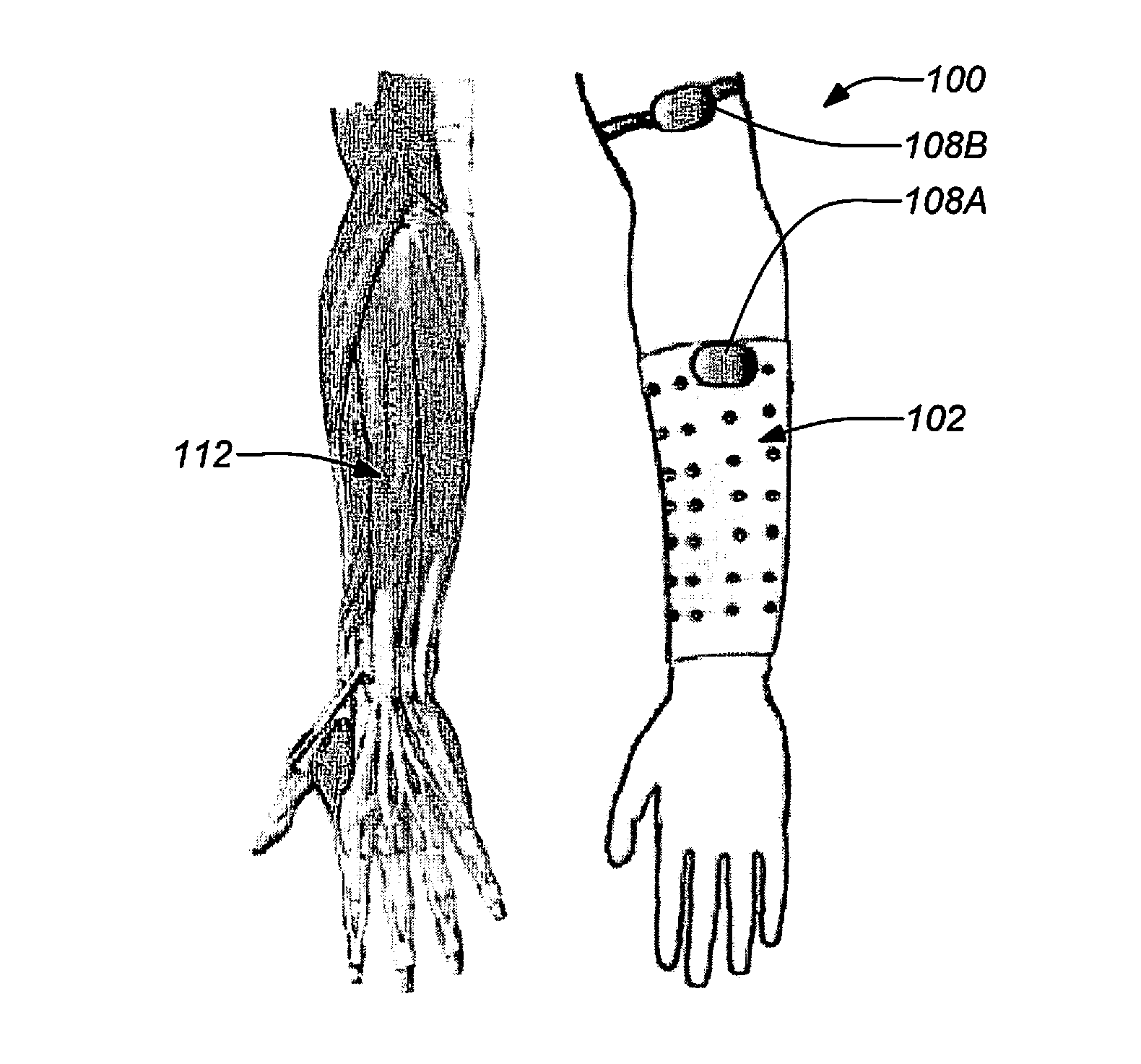
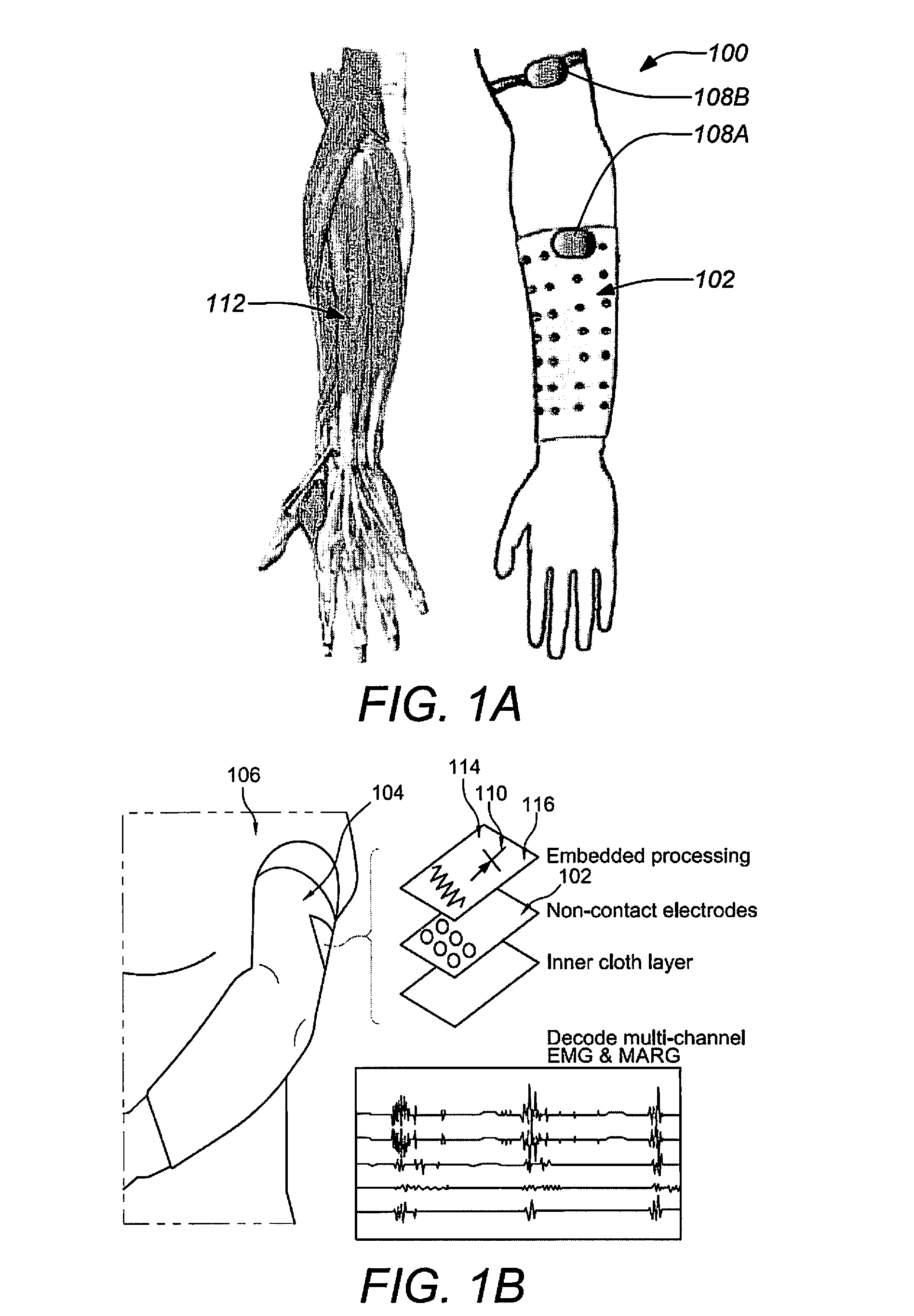
A “Wearable Electromyography-Based Controller” includes a plurality of Electromyography (EMG) sensors and provides a wired or wireless human-computer interface (HCl) for interacting with computing systems and attached devices via electrical signals generated by specific movement of the user's muscles. Following initial automated self-calibration and positional localization processes, measurement and interpretation of muscle generated electrical signals is accomplished by sampling signals from the EMG sensors of the Wearable Electromyography-Based Controller. In operation, the Wearable Electromyography-Based Controller is donned by the user and placed into a coarsely approximate position on the surface of the user's skin. Automated cues or instructions are then provided to the user for fine-tuning placement of the Wearable Electromyography-Based Controller. Examples of Wearable Electromyography-Based Controllers include articles of manufacture, such as an armband, wristwatch, or article of clothing having a plurality of integrated EMG-based sensor nodes and associated electronics.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Electromyography system
InactiveUS20080064977A1Reduce pressureInterpret accuracyElectrotherapyElectromyographyMedicineSpinal nerve
Systems for determining structural integrity of a bone within the spine of a patient, the bone having a first aspect and a second aspect, wherein the second aspect separated from the first aspect by a width and located adjacent to a spinal nerve. A stimulator is configured to generate an electrical stimulus to be applied to the first aspect of the bone. A monitor is configured to electrically monitor a muscle myotome associated with the spinal nerve to detect if an onset neuro-muscular response occurs in response to the application of the electrical stimulus to the first aspect of the bone. An adjuster is configured to automatically increase the magnitude of the electrical stimulus to until the onset neuro-muscular response is detected. Lastly, a communicator is configured to communicate to a user via at least one of visual and audible means information representing the magnitude of the electrical stimulus which caused the onset neuro-muscular response.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Electromyography system
InactiveUS20080065178A1Reduce pressureInterpret accuracyElectromyographyInternal electrodesPower flowMedicine
A method of determining relative neuro-muscular response onset value thresholds for a plurality of spinal nerves, comprising: depolarizing a portion of the patient's cauda equina; and measuring the current intensity level at which a neuro-muscular response to the depolarization of the cauda equina is detected in each of the plurality of spinal nerves. A method for detecting the presence of a nerve adjacent the distal end of at least one probe, comprising: determining relative neuro-muscular response onset values for a plurality of spinal nerves; emitting a stimulus pulse from a probe or surgical tool; detecting neuro-muscular responses to the stimulus pulse in each of the plurality of spinal nerves; and concluding that the electrode disposed on the distal end of the at least one probe is positioned adjacent to a first spinal nerve when the neuro-muscular response detected in the first spinal nerve is detected as a current intensity level less than or equal to a corresponding neuro-muscular response onset value of the first spinal nerve.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Electromyography system
InactiveUS20080064976A1Reduce pressureInterpret accuracyElectromyographySurgerySpinal nervePhysical therapy
Methods for determining structural integrity of a bone within the spine of a patient, the bone having a first aspect and a second aspect, wherein the second aspect separated from the first aspect by a width and located adjacent to a spinal nerve. The methods involve (a) applying an electrical stimulus to the first aspect of the bone; (b) electrically monitoring a muscle myotome associated with the spinal nerve to detect if an onset neuro-muscular response occurs in response to the application of the electrical stimulus to the first aspect of the bone; (c) automatically increasing the magnitude of the electrical stimulus to until the onset neuro-muscular response is detected; and (d) communicating to a user via at least one of visual and audible means information representing the magnitude of the electrical stimulus which caused the onset neuro-muscular response.
Owner:NUVASIVE
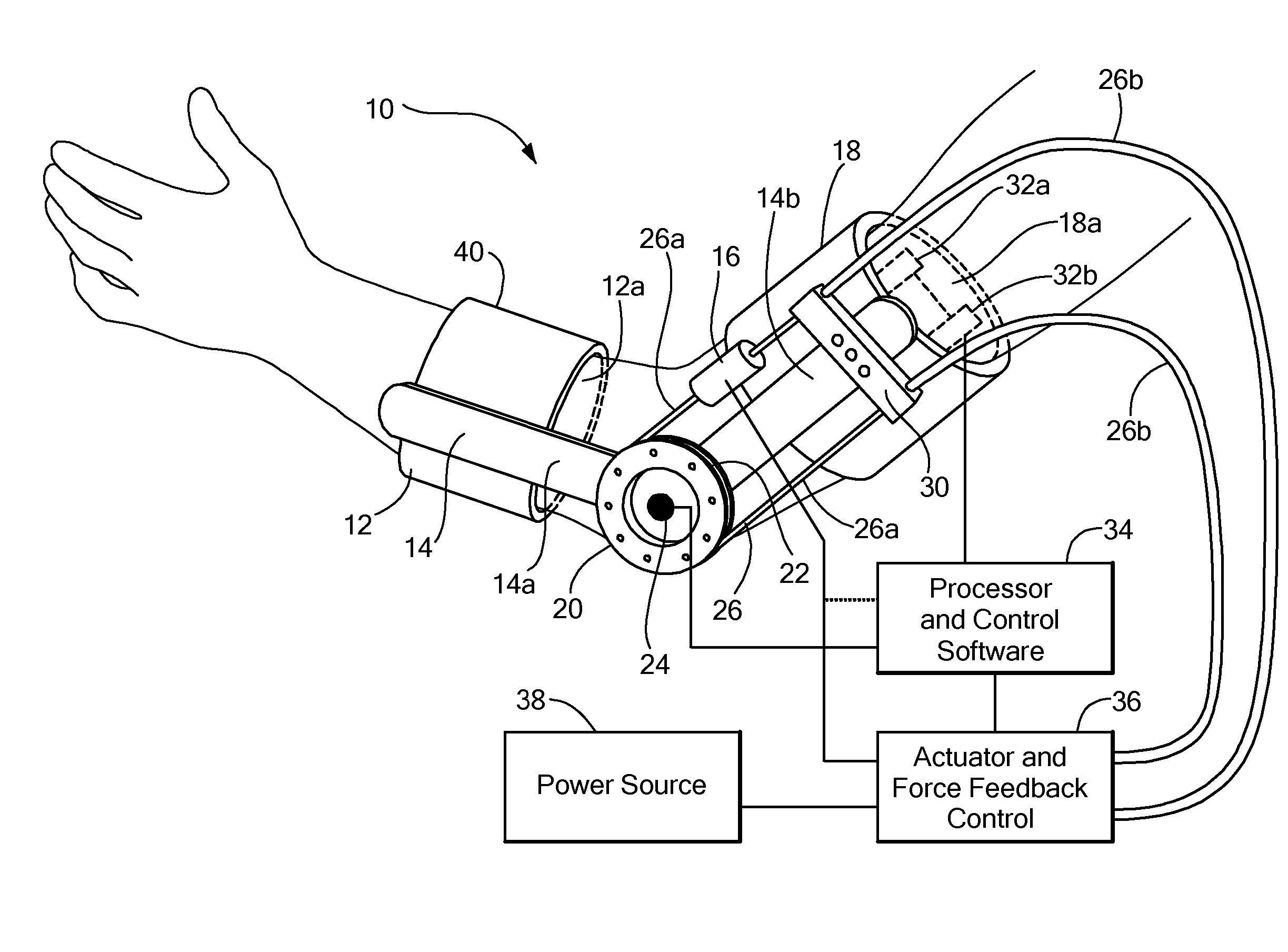
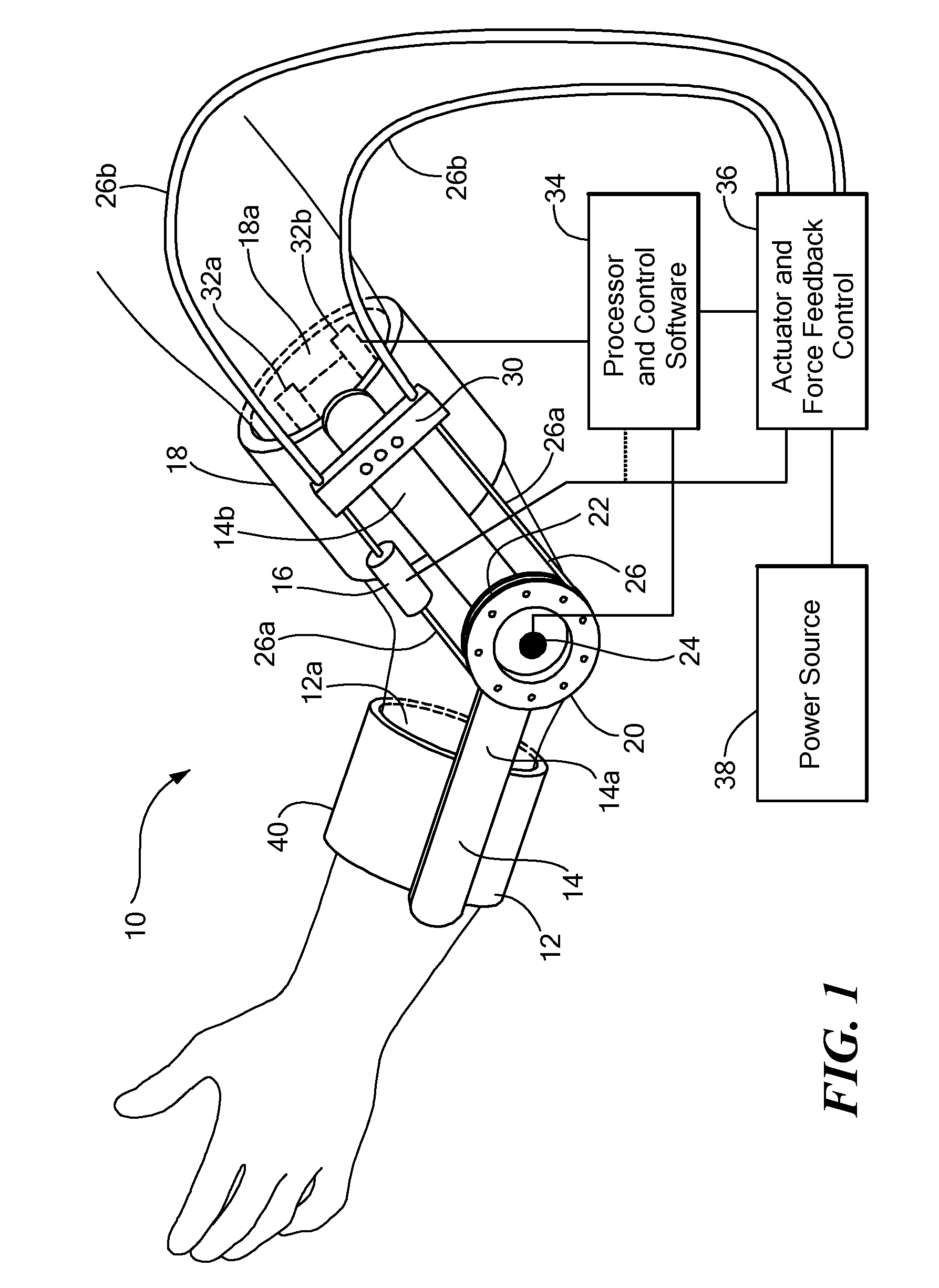
Methods and Apparatus for Rehabilitation and Training
ActiveUS20070282228A1Significant motionAvoid structural overloadingPhysical therapies and activitiesChiropractic devicesElectrical stimulationsBody Regions
Apparatus for rehabilitating a patient who has a paretic body part, the apparatus comprising: a) at least one electromyography (EMG) sensor adapted to being applied to a voluntary muscle of a healthy body part of the same type as the paretic body part which at least one sensor produces at least one EMG signal; b) a neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) device adapted to stimulating at least one voluntary muscle of the paretic body part; and c) a controller which controls the NMES device, making the amplitude of stimulation of the paretic body part at least partly dependent on the EMG signal from the healthy body part.
Owner:MOTORIKA
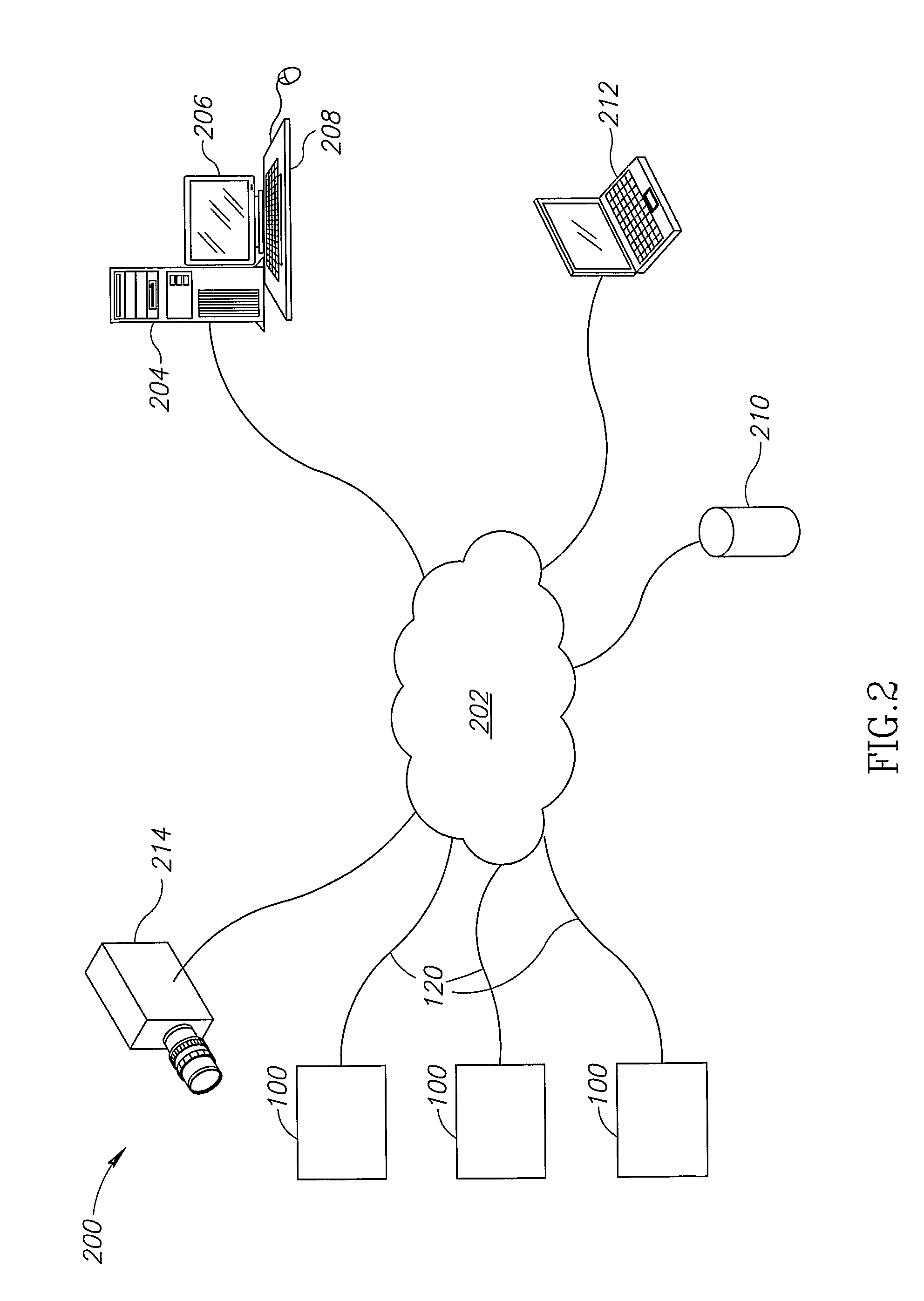
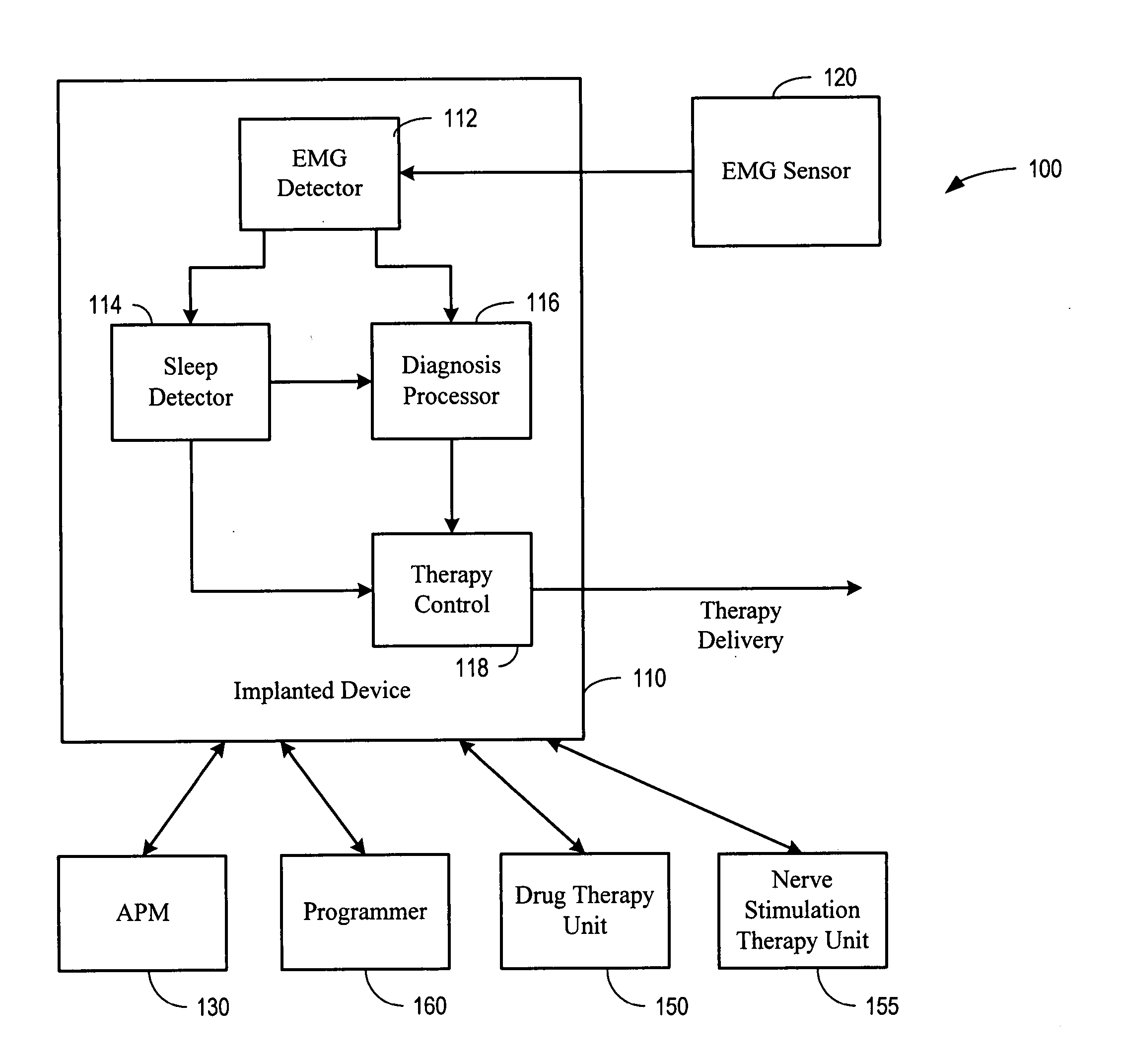
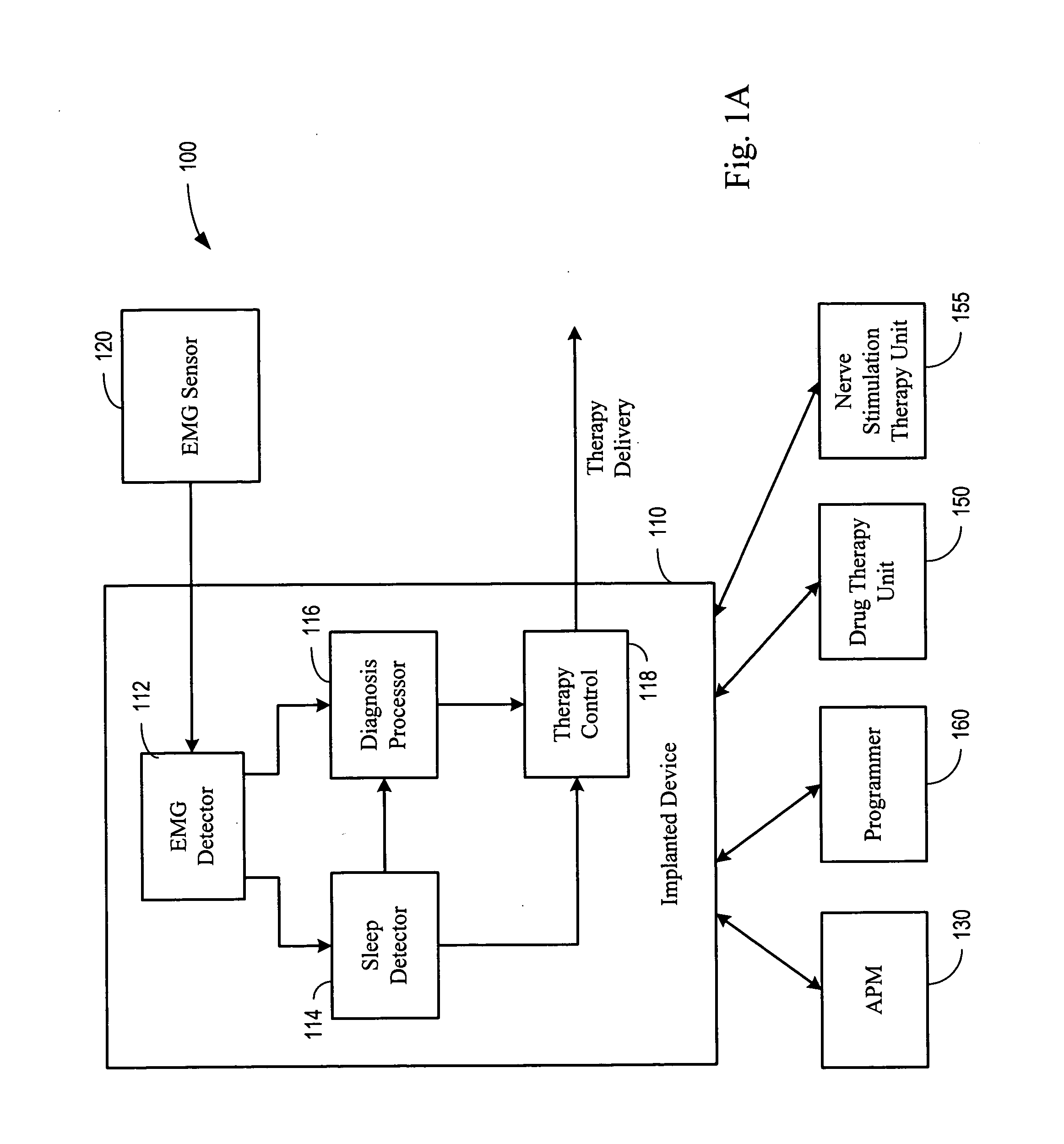
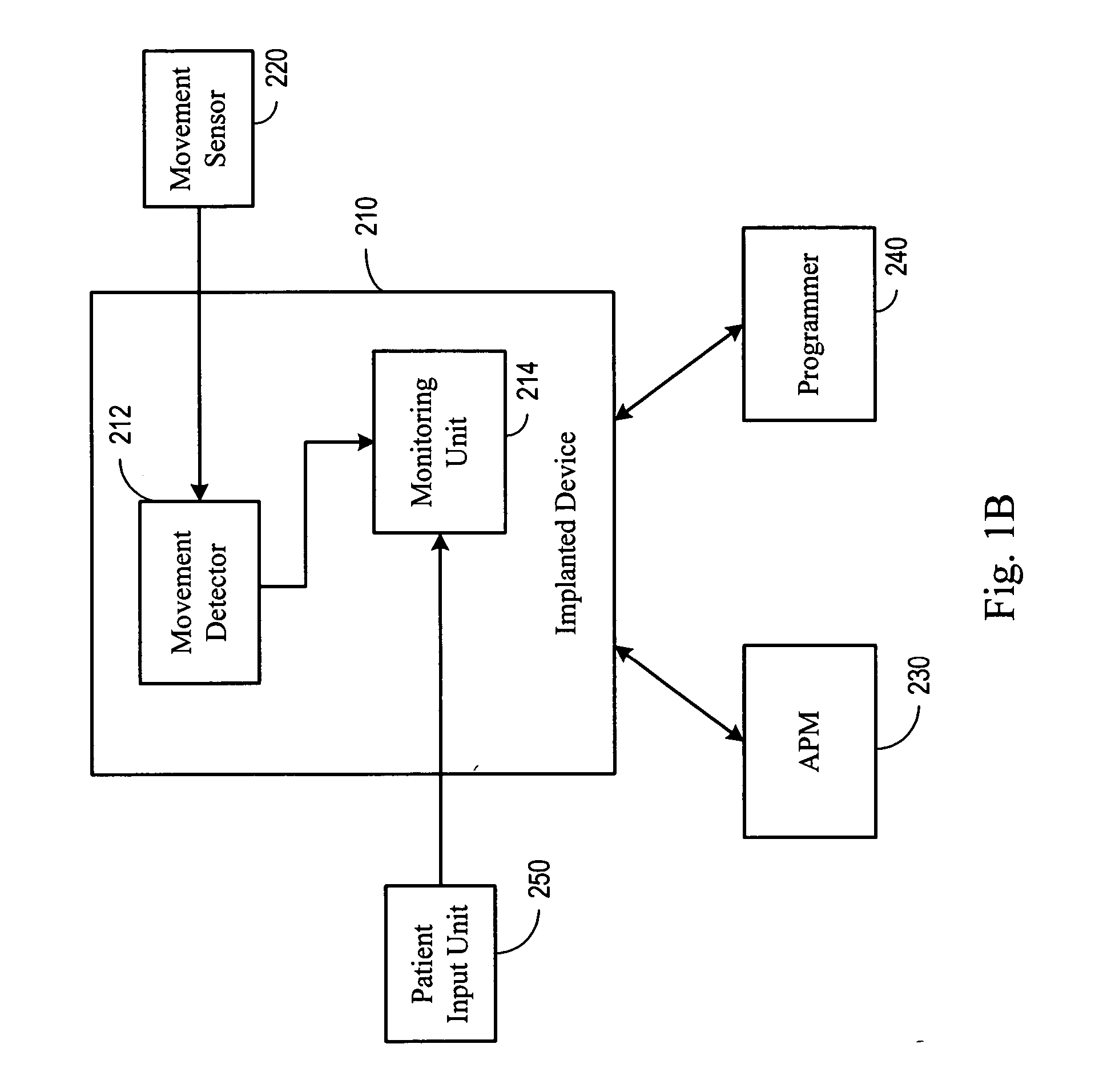
System and method for detecting an involuntary muscle movement disorder
Methods and systems are directed to evaluating a pathological condition and involve acquiring muscle movement signals, such as electromyogram (EMG) or accelerometer signals, and detecting the presence of the pathological condition. Methods and systems also provide for detecting sleep-related involuntary muscle disorders and non sleep-related involuntary muscle disorders using muscle movement signals. Drug therapy, transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation therapy, or other therapy may be delivered to treat a detected or diagnosed involuntary muscle disorder.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Wearable electromyography-based controllers for human-computer interface
A “Wearable Electromyography-Based Controller” includes a plurality of Electromyography (EMG) sensors and provides a wired or wireless human-computer interface (HCl) for interacting with computing systems and attached devices via electrical signals generated by specific movement of the user's muscles. Following initial automated self-calibration and positional localization processes, measurement and interpretation of muscle generated electrical signals is accomplished by sampling signals from the EMG sensors of the Wearable Electromyography-Based Controller. In operation, the Wearable Electromyography-Based Controller is donned by the user and placed into a coarsely approximate position on the surface of the user's skin. Automated cues or instructions are then provided to the user for fine-tuning placement of the Wearable Electromyography-Based Controller. Examples of Wearable Electromyography-Based Controllers include articles of manufacture, such as an armband, wristwatch, or article of clothing having a plurality of integrated EMG-based sensor nodes and associated electronics.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
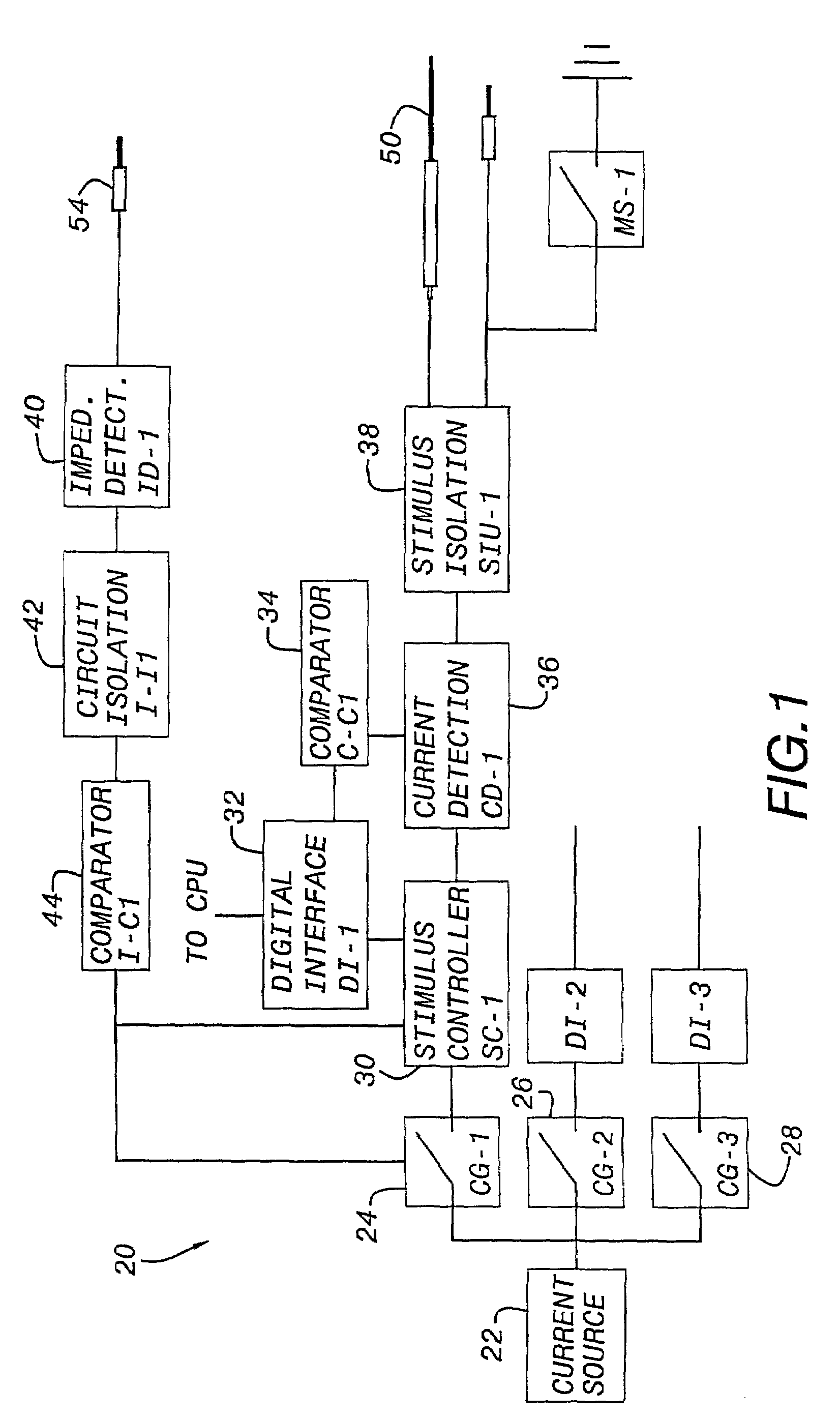
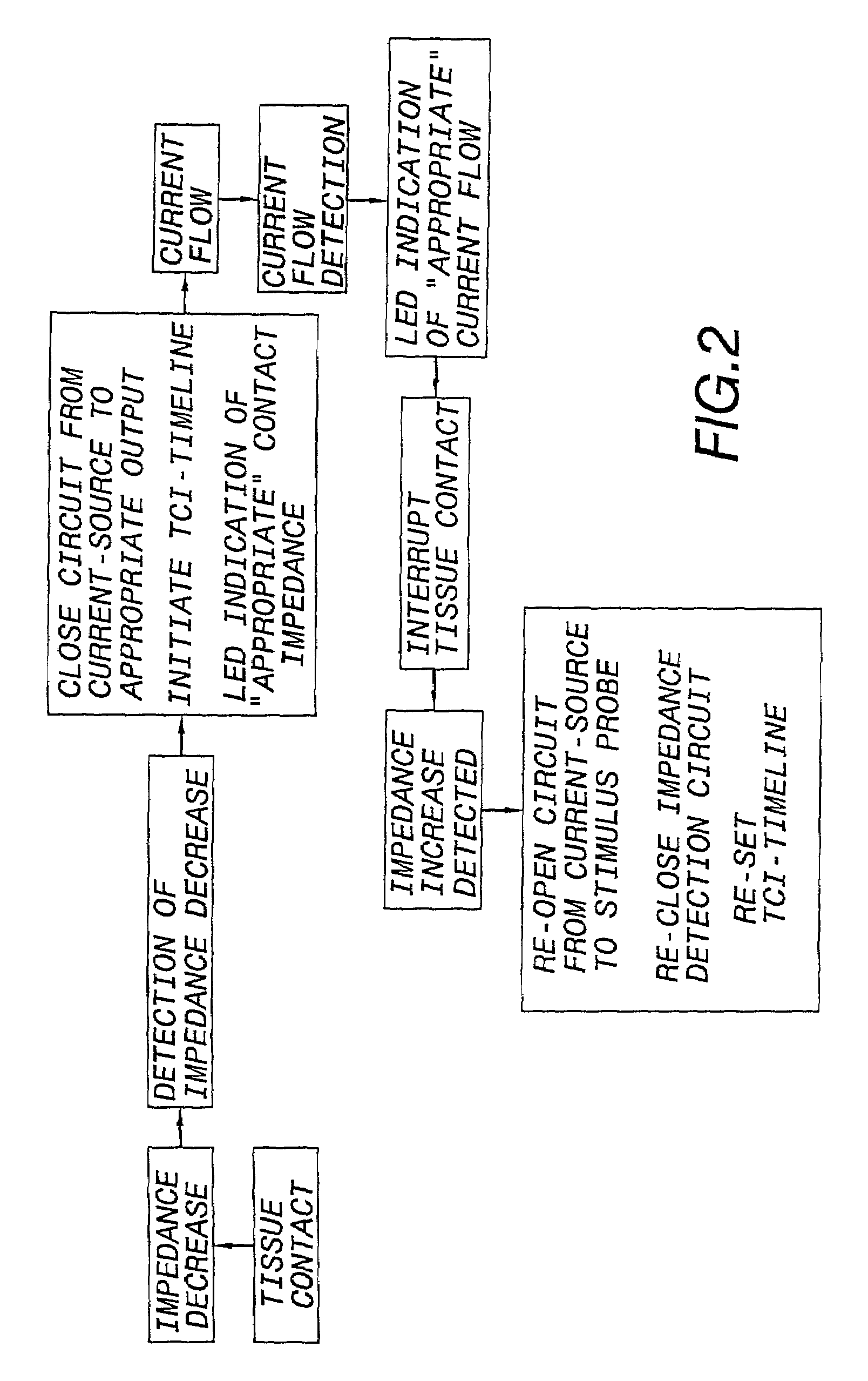
Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring system
ActiveUS7214197B2High sensitivityNovel featuresElectromyographyInternal electrodesIntraoperative neurophysiological monitoringMonitoring system
An intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring system includes an adaptive threshold detection circuit adapted for use in monitoring with a plurality of electrodes placed in muscles which are enervated by a selected nerve and muscles not enervated by the nerve. Nerve monitoring controller algorithms permit the rapid and reliable discrimination between non-repetitive electromyographic (EMG) events repetitive EMG events, thus allowing the surgeon to evaluate whether nerve fatigue is rendering the monitoring results less reliable and whether anesthesia is wearing off. The intraoperative monitoring system is designed as a “surgeon's monitor,” and does not require a neurophysiologist or technician to be in attendance during surgery. The advanced features of the intraoperative monitoring system will greatly assist neurophysiological research toward the general advancement of the field intraoperative EMG monitoring through post-surgical analysis. The intraoperative monitoring system is preferably modular, in order to allow for differential system pricing and upgrading as well as to allow for advances in computer technology; modularity can also aid in execution of the design.
Owner:PRASS RICHARD L
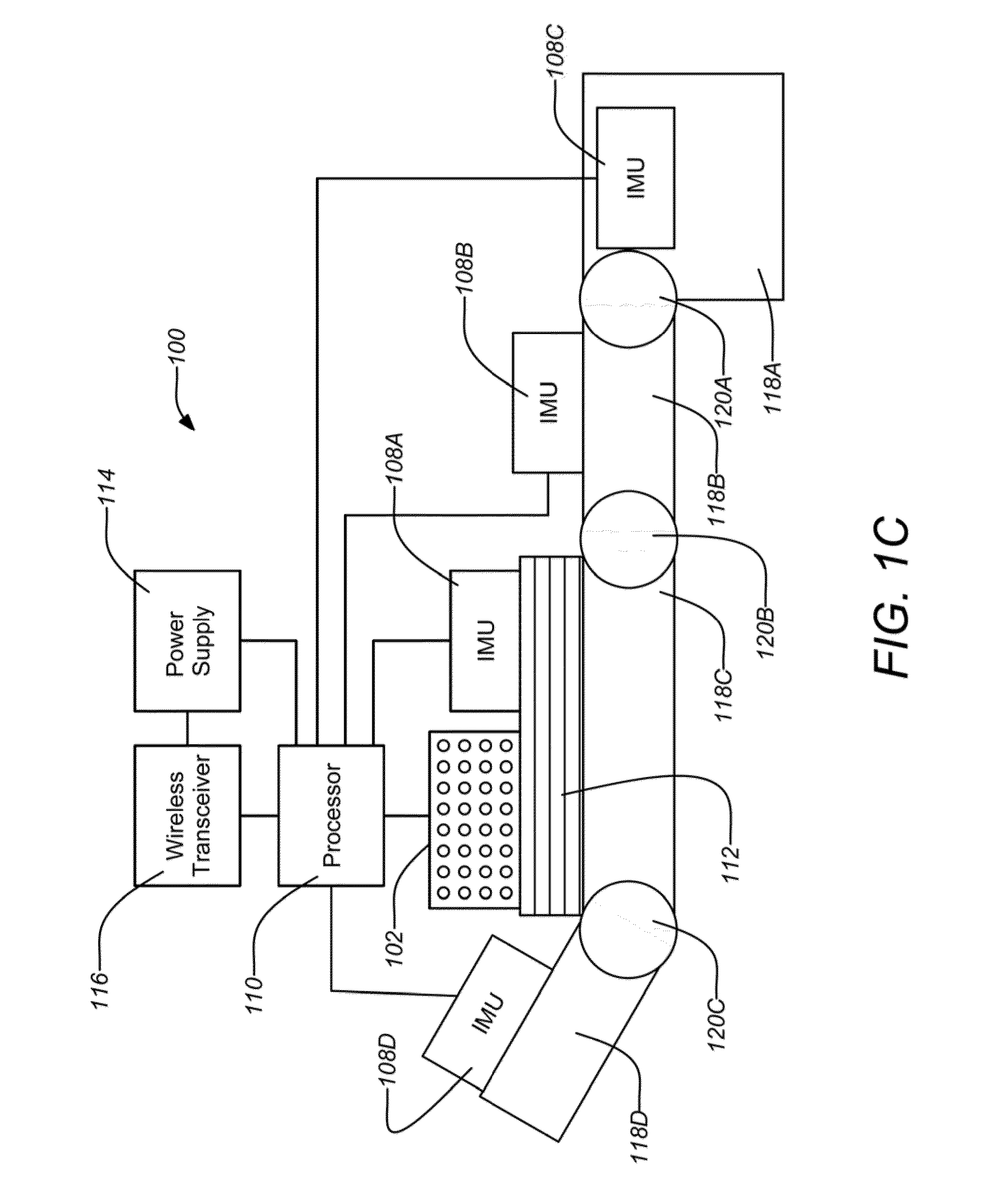
Biosleeve human-machine interface
ActiveUS20130317648A1Programme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorHuman–machine interfaceControl data
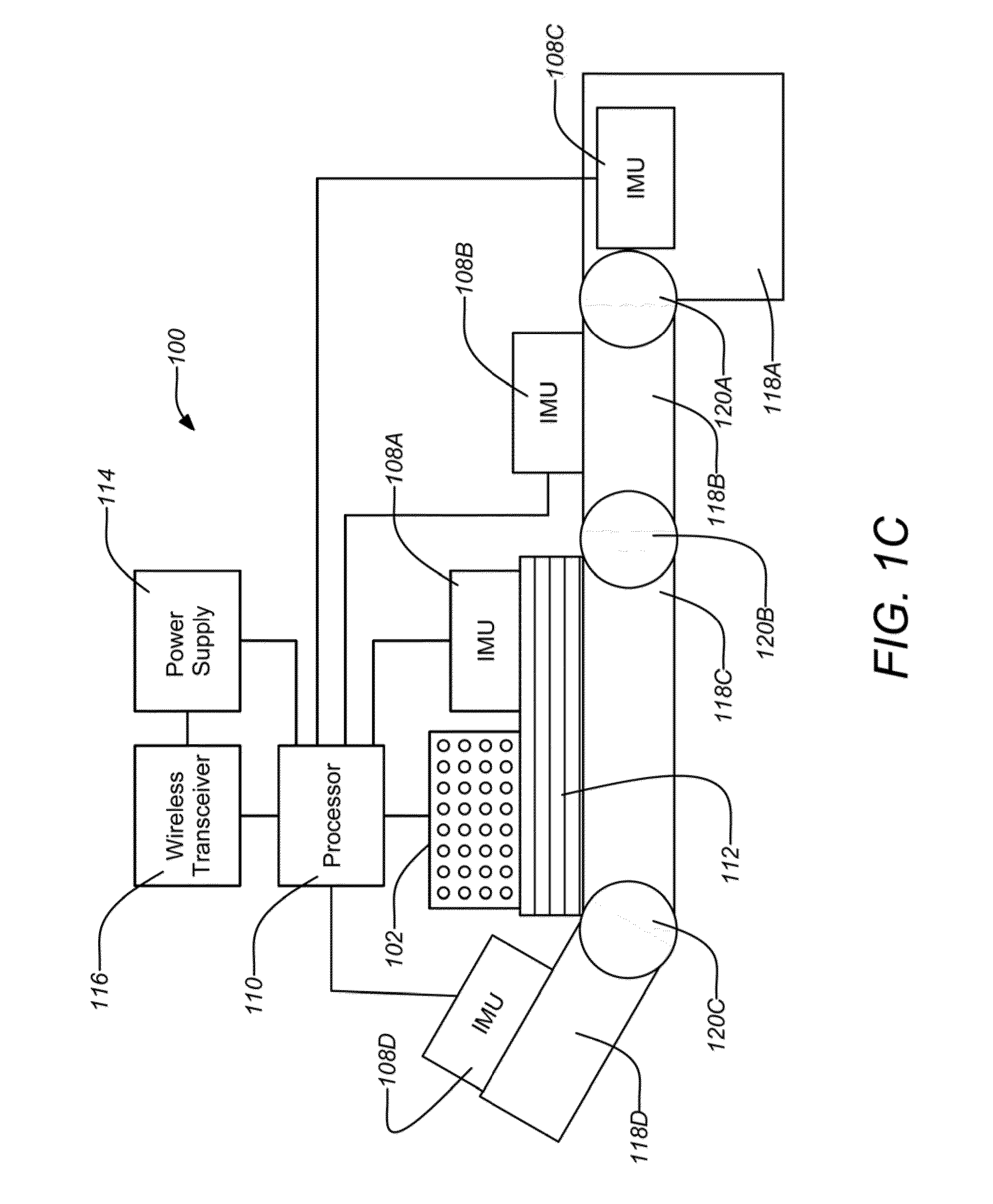
Systems and methods for sensing human muscle action and gestures in order to control machines or robotic devices are disclosed. One exemplary system employs a tight fitting sleeve worn on a user arm and including a plurality of electromyography (EMG) sensors and at least one inertial measurement unit (IMU). Power, signal processing, and communications electronics may be built into the sleeve and control data may be transmitted wirelessly to the controlled machine or robotic device.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
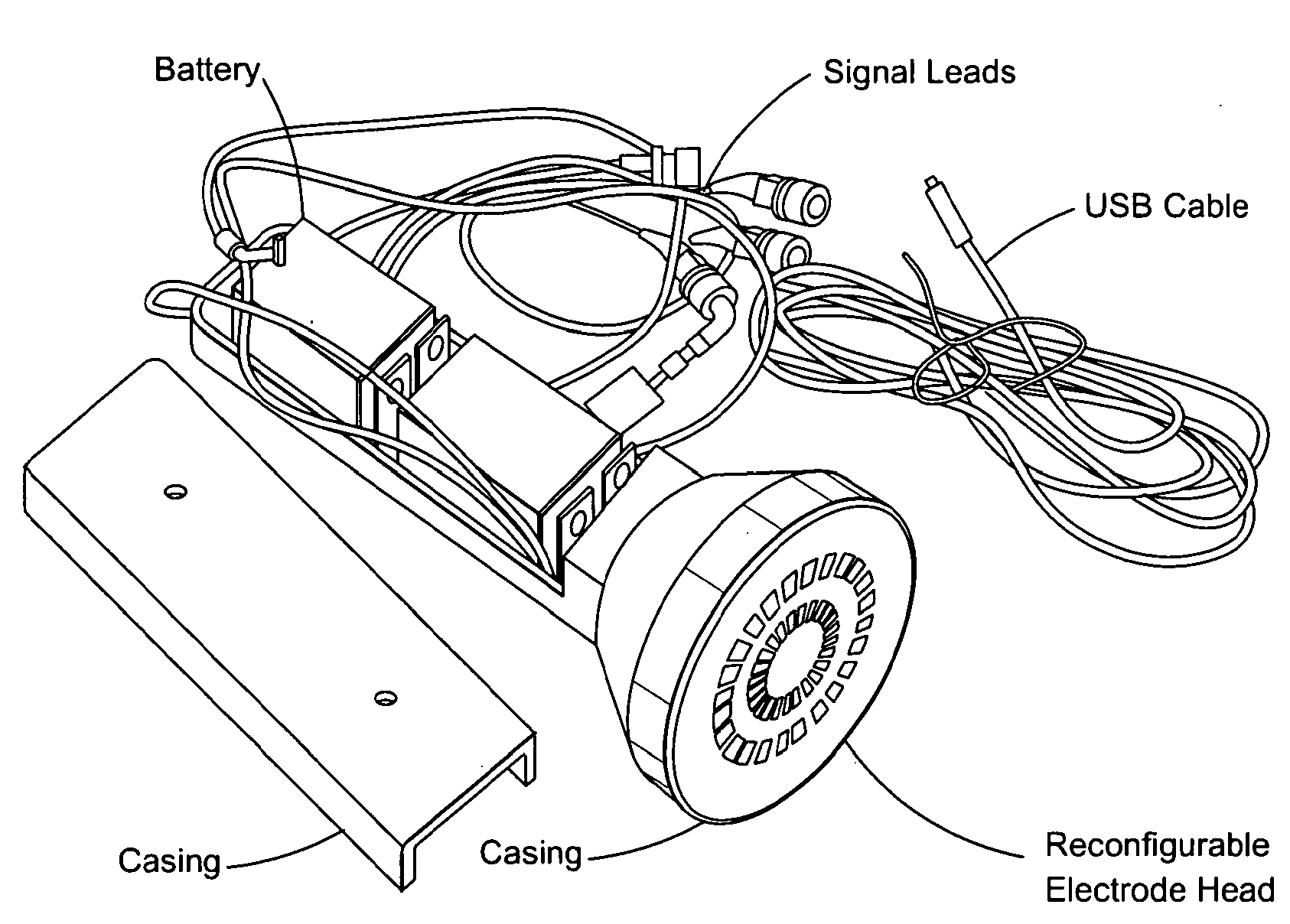
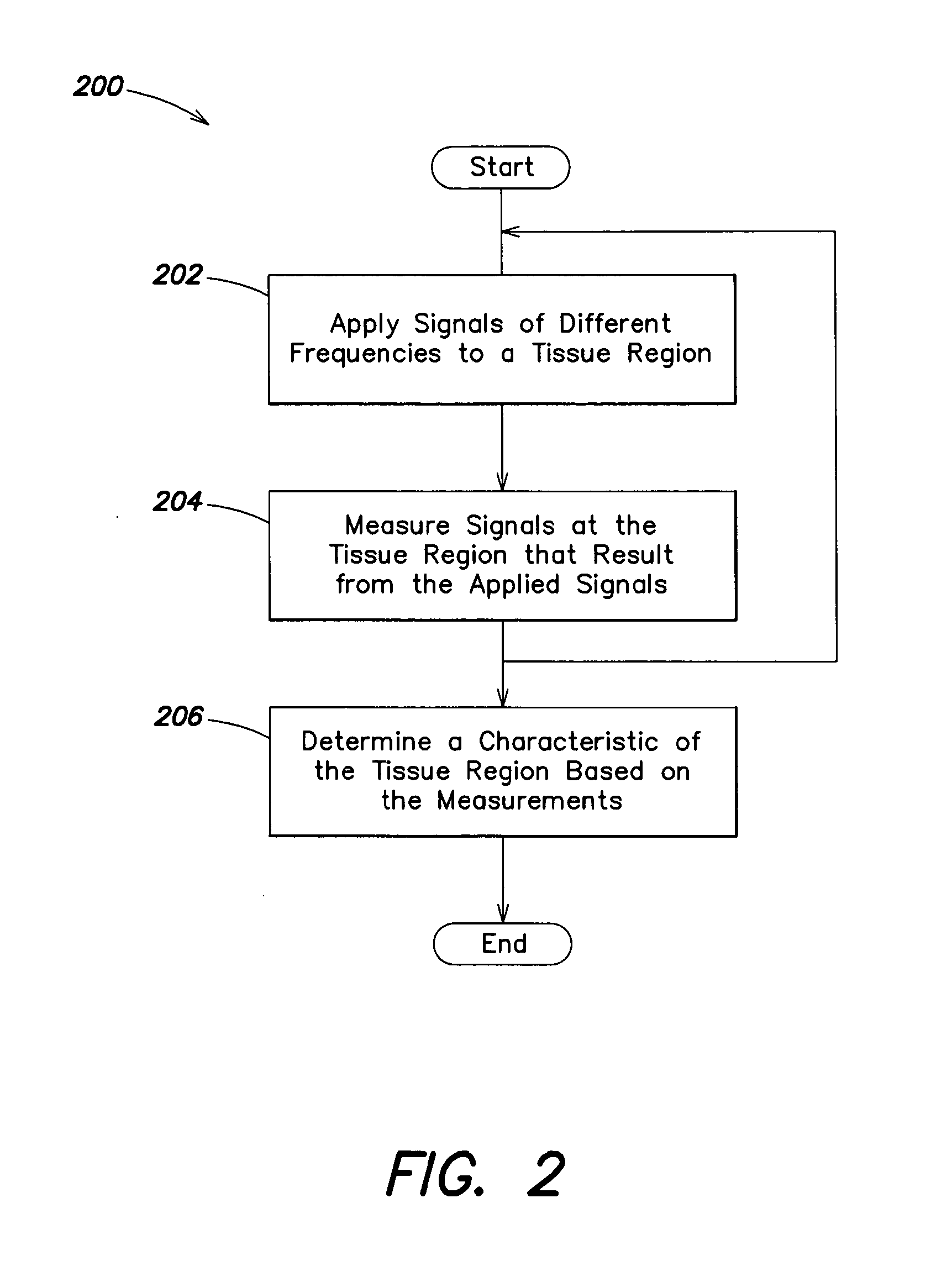
Hand-held device for electrical impedance myography
ActiveUS20120245436A1Improve assessmentEasy diagnosisUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringFiberElectrical resistance and conductance
A device for determining muscle condition of a region of tissue. The device comprises an electrical impedance myography (EIM) portable probe bearing an electrode array. The electrode array comprises excitation electrodes used to apply multi-frequency electrical signals to the region of tissue and pickup electrodes that are used to collect electrical signals resulting from the application of the multi-frequency electrical signals to the region of tissue. To improve accuracy and reproducibility of EIM measurements, the electrode array is reconfigurable to select different subsets of excitation and pickup electrodes so that the electrodes are oriented differently with respect to muscle fibers. Additional devices may be associated with the EIM probe to measure such parameters as temperature, moisture content of the region, quality of contact of electrodes of the electrode array with a surface of the region and pressure with which the EEM probe is applied to the region. The EIM measurements may be adjusted based on these parameters. Also, ultrasound and electrical impedance tomography measurements may supplement the ELM measurements for more complete analysis of the muscle condition.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Wearable electromyography-based human-computer interface
ActiveUS9037530B2Input/output for user-computer interactionElectromyographyHuman–machine interfaceSkin surface
A “Wearable Electromyography-Based Controller” includes a plurality of Electromyography (EMG) sensors and provides a wired or wireless human-computer interface (HCI) for interacting with computing systems and attached devices via electrical signals generated by specific movement of the user's muscles. Following initial automated self-calibration and positional localization processes, measurement and interpretation of muscle generated electrical signals is accomplished by sampling signals from the EMG sensors of the Wearable Electromyography-Based Controller. In operation, the Wearable Electromyography-Based Controller is donned by the user and placed into a coarsely approximate position on the surface of the user's skin. Automated cues or instructions are then provided to the user for fine-tuning placement of the Wearable Electromyography-Based Controller. Examples of Wearable Electromyography-Based Controllers include articles of manufacture, such as an armband, wristwatch, or article of clothing having a plurality of integrated EMG-based sensor nodes and associated electronics.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
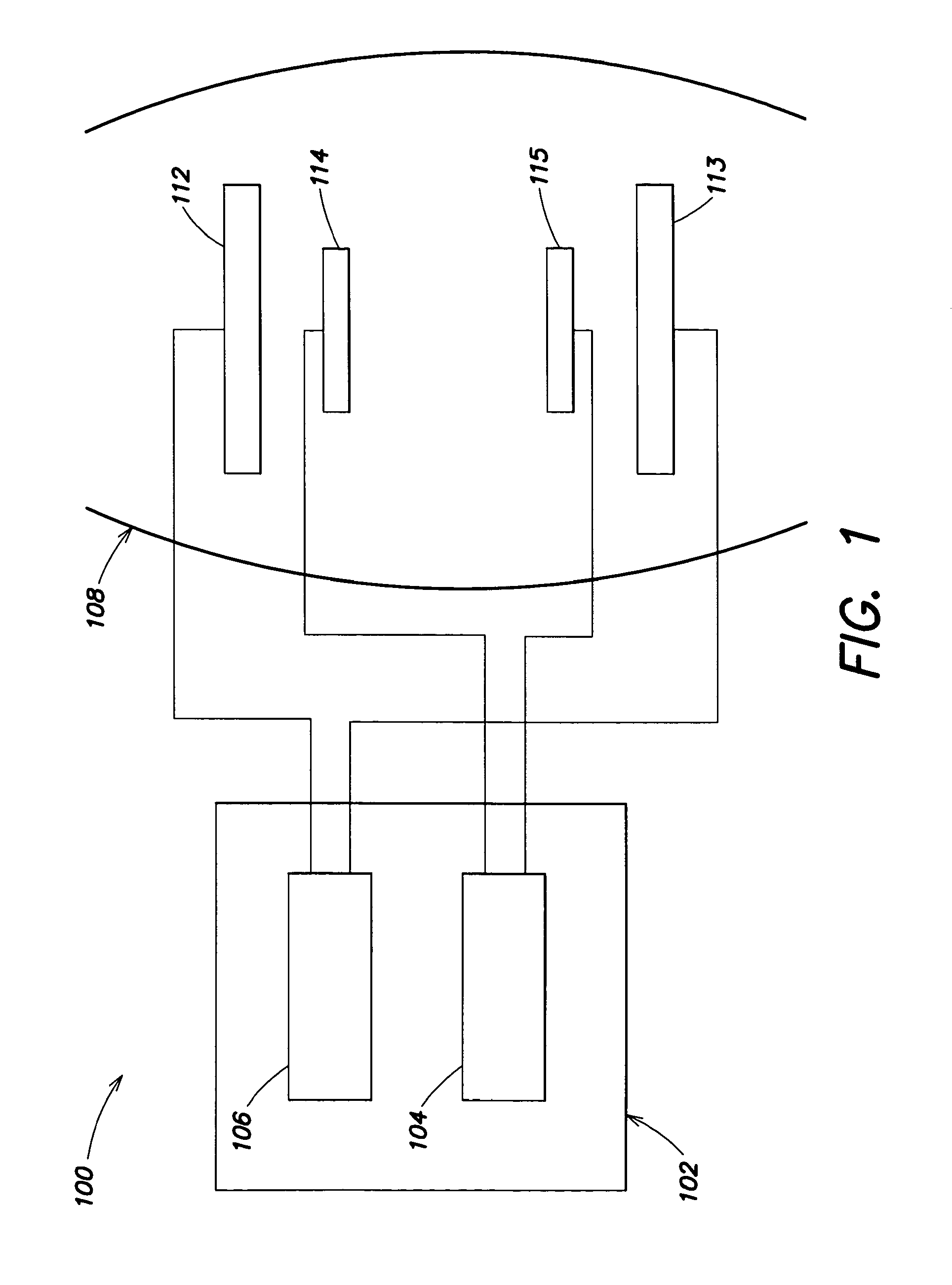
EMG electrode
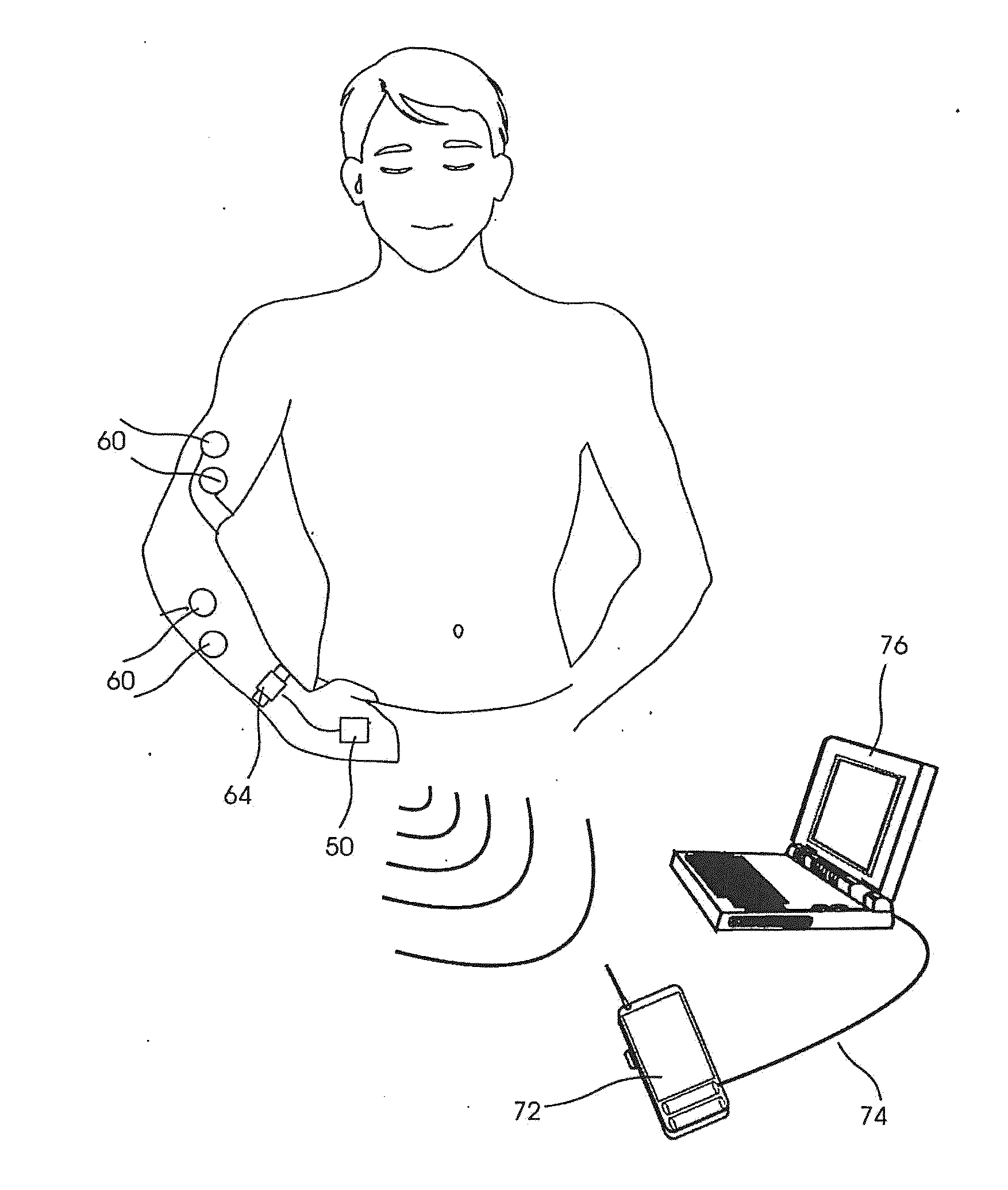
An electrode for collecting surface electromyographic (EMG) signals consists of a generally bolt-shaped structure having a circular signal-gathering head and an integral shaft for support purposes and for transmission of electrical signals. The head of the electrode is configured as a disc having a plurality of pyramids distributed substantially evenly over the signal gathering surface with the tips of the pyramids projecting outwardly of the head for contact with the skin of a patient. Preferably, the electrode consists entirely of 316L stainless steel, the pyramids are formed by grinding or electromachining and the shaft is threaded for receipt of a clamp nut. The electrode is adapted for mounting in a hole in a thin, flexible support member by means of the shaft to maintain spacing among adjacent electrodes and to assure proper contact with the patient.
Owner:SPINEMATRIX
Method of using powered orthotic device
InactiveUS7367958B2Smooth movementHigh strengthElectromyographyChiropractic devicesDiseaseNeuromuscular disease
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Designation of a Characteristic of a Physical Capability by Motion Analysis, Systems and Methods
ActiveUS20110052005A1Physical therapies and activitiesMedical automated diagnosisData dredgingOriginal data
Motion Analysis is used to classify or rate human capability in a physical domain via a minimized movement and data collection protocol producing a discreet, overall figure of merit of the selected physical capability. The minimal protocol is determined by data mining of a more extensive movement and data collection. Protocols are relevant in medical, sports and occupational applications. Kinematic, kinetic, body type, Electromyography (EMG), Ground Reactive Force (GRF), demographic, and psychological data are encompassed. Resulting protocols are capable of transforming raw data representing specific human motions into an objective rating of a skill or capability related to those motions.
Owner:SELNER ALLEN JOSEPH
Method, apparatus and system for characterizing sleep
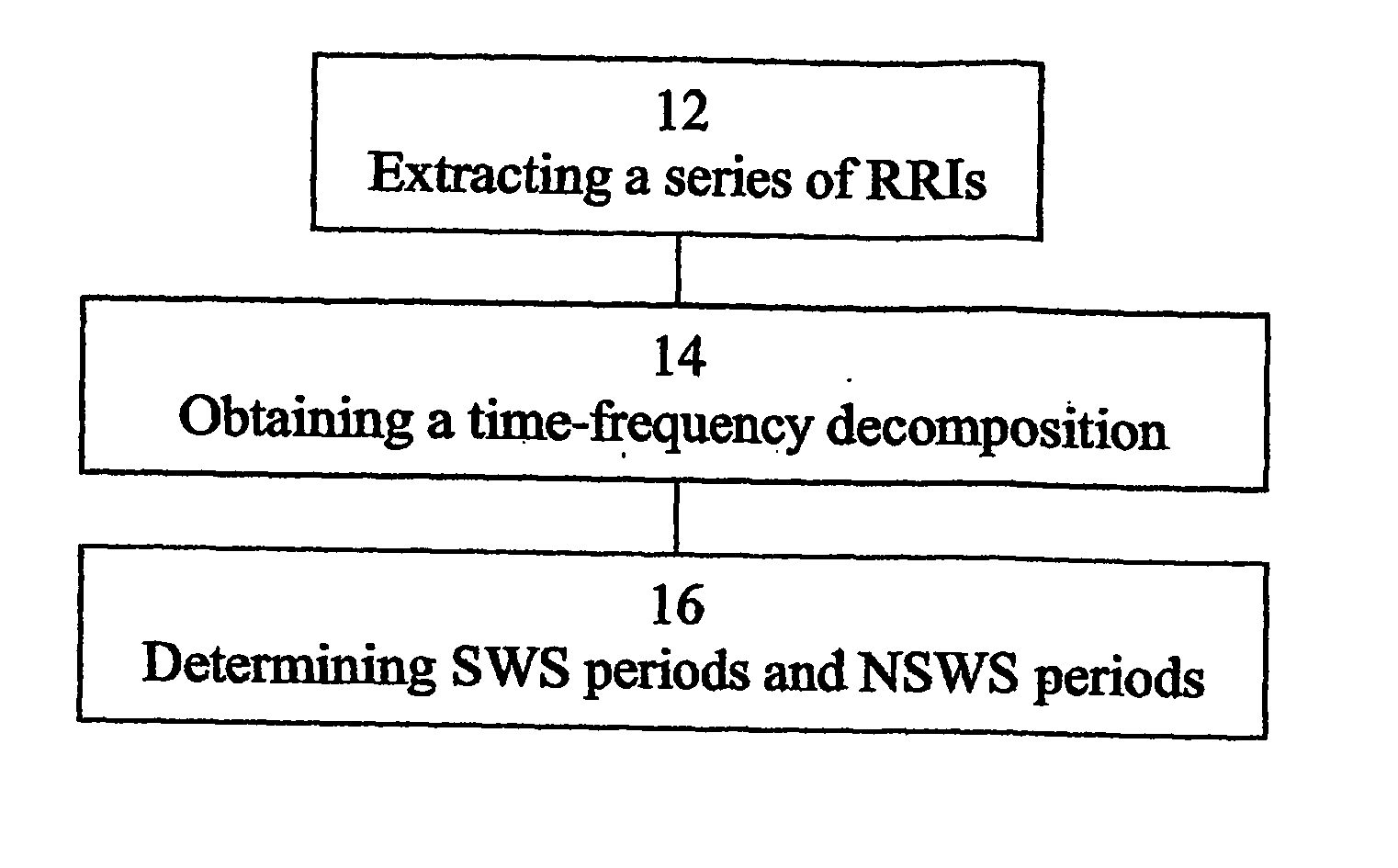
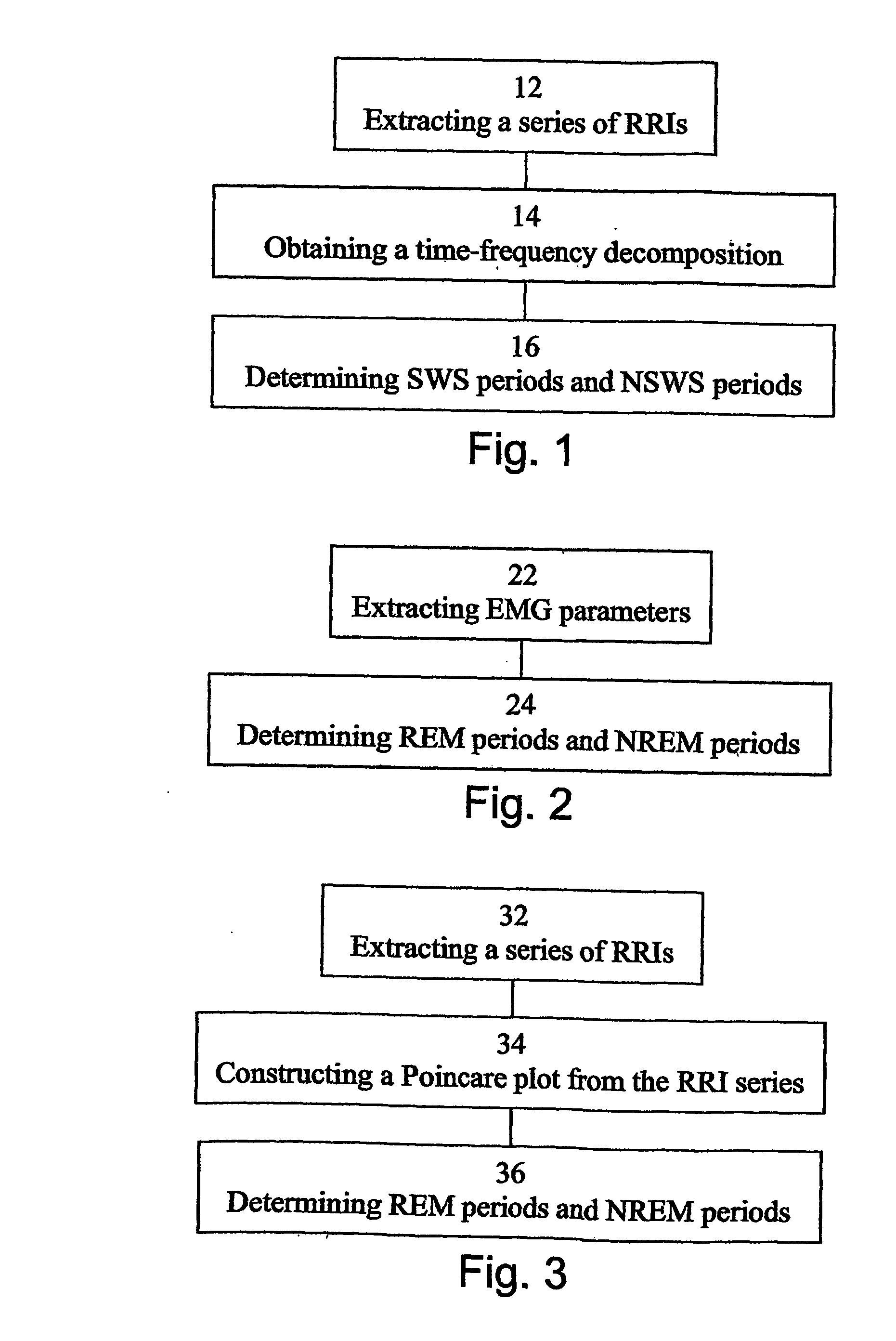
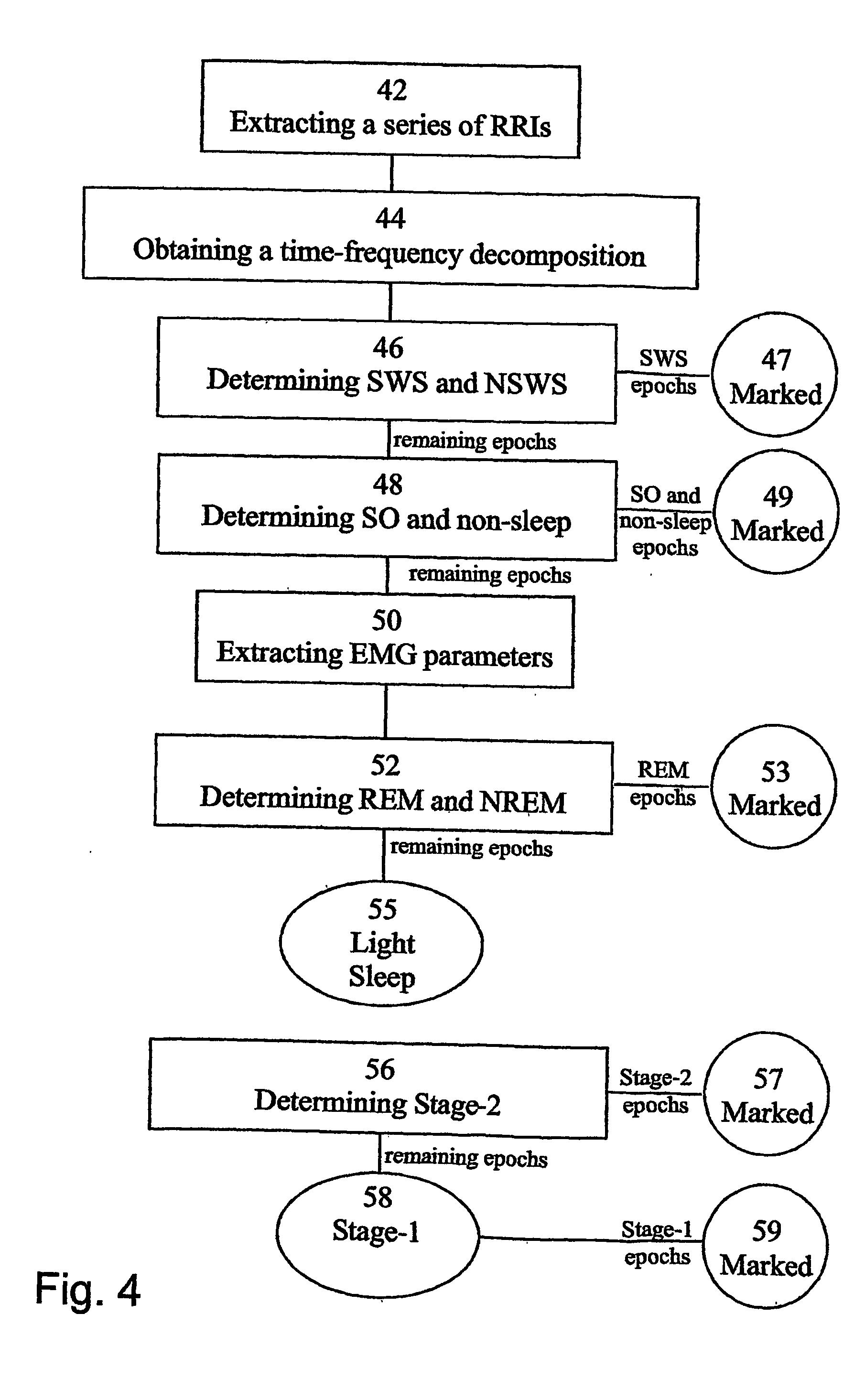
A method of determining sleep stages from signals of electrical activity recorded of a chest of a sleeping subject, the signals being measured over a plurality of epochs. The method comprising: (a) extracting a series of cardiac R-R intervals from the signals and obtaining a time-frequency decomposition from the series of cardiac R-R intervals; (b) using the time-frequency decomposition to determine at least one Slow-Wave-Sleep (SWS) period and at least one Non-SWS (NSWS) period; (c) from the at least one NSWS period, determining at least one sleep-onset (SO) period and a plurality of non-sleep periods; (d) extracting a plurality of electromyogram (EMG) parameters from a portion of the signals, the portion corresponds to a NSWS period other than the at least one SO period and other than the plurality of non-sleep period; (e) using the plurality of EMG parameters to determine at least one REM period thereby also to obtain also at least one light-sleep (LS) period defined as a NSWS period other than the SO periods, other than the non-sleep periods and other than the REM periods; thereby determining the sleep stages of the sleeping subject.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Movement disorder monitoring system and method
ActiveUS8187209B1Correct symptomsMaximize safetyElectromyographyPerson identificationKinetic informationDisease
The present invention relates to a movement disorder monitor, and a method of measuring the severity of a subject's movement disorder. The present invention additionally relates to a drug delivery system for dosing a subject in response to the increased severity of a subject's symptoms. The present invention provides for a system and method, which can accurately quantify symptoms of movements disorders, accurately quantifies symptoms utilizing both kinetic information and electromyography (EMG) data, that can be worn continuously to provide continuous information to be analyzed as needed by the clinician, that can provide analysis in real-time, that allows for home monitoring of symptoms in subject's with these movement disorders to capture the complex fluctuation patterns of the disease over the course of days, weeks or months, that maximizes subject safety, and that provides remote access to the clinician or physician.
Owner:GREAT LAKES NEUROTECH
Movement disorder monitoring and symptom quantification system and method
InactiveUS20140257141A1Correct symptomsMaximizes subject safetyPerson identificationSensorsDiseaseKinetic information
The present invention relates to a movement disorder monitor with high sensitivity, and a method of measuring the severity of a subject's movement disorder. The present invention additionally relates to a drug delivery system for dosing a subject in response to the increased severity of a subject's symptoms. The present invention provides for a system and method, which can accurately and repeatably quantify symptoms of movements disorders, accurately quantifies symptoms utilizing both kinetic information and / or electromyography (EMU) data, that can be worn continuously to provide continuous information to be analyzed as needed by the clinician, that can provide analysis in real-time, that allows for home monitoring of symptoms in subject's with these movement disorders to capture the complex fluctuation patterns of the disease over the course of days, weeks or months, that maximizes subject safety, and that provides substantially real-time remote access to data by the clinician or physician.
Owner:GREAT LAKES NEUROTECH
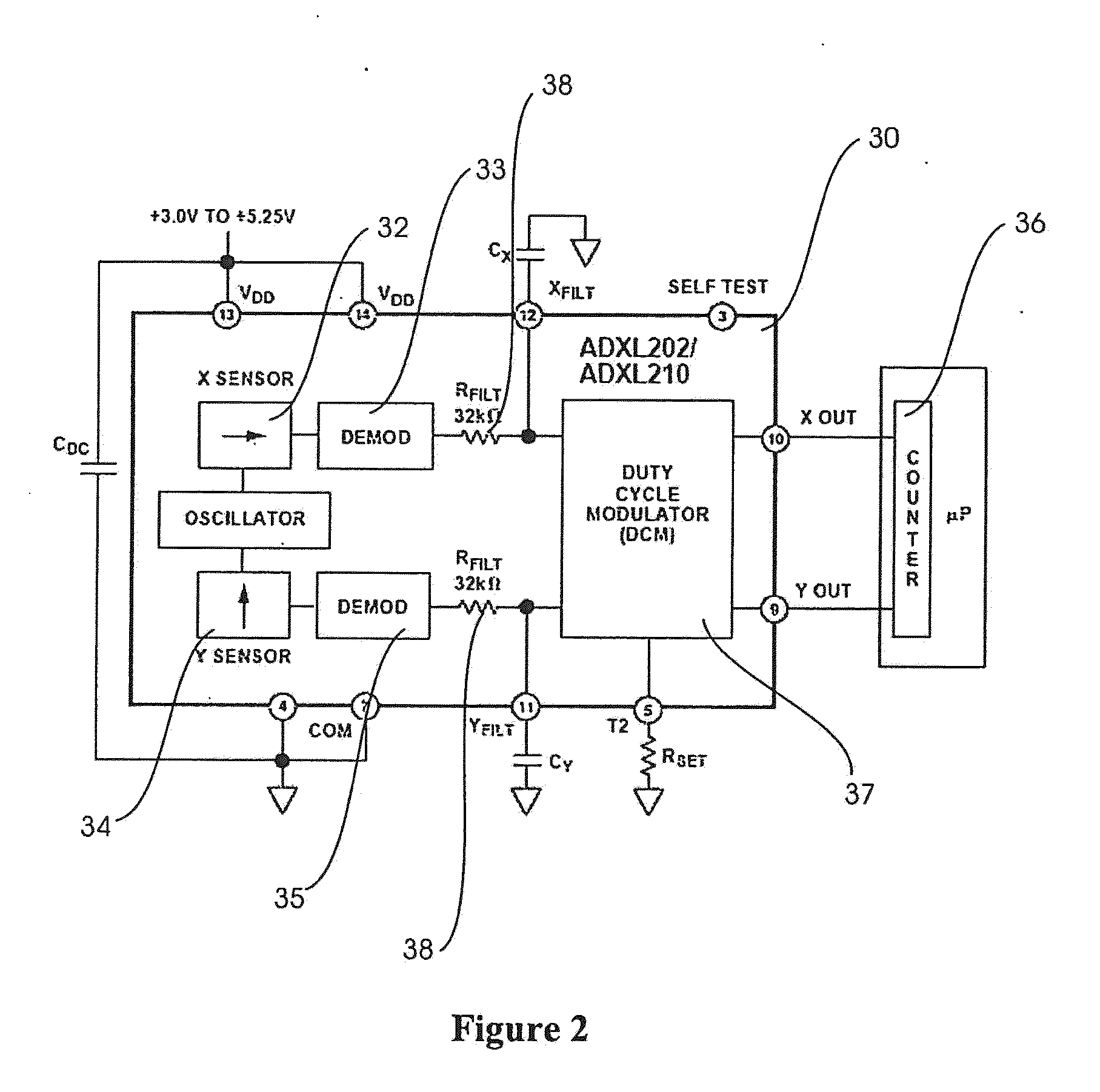
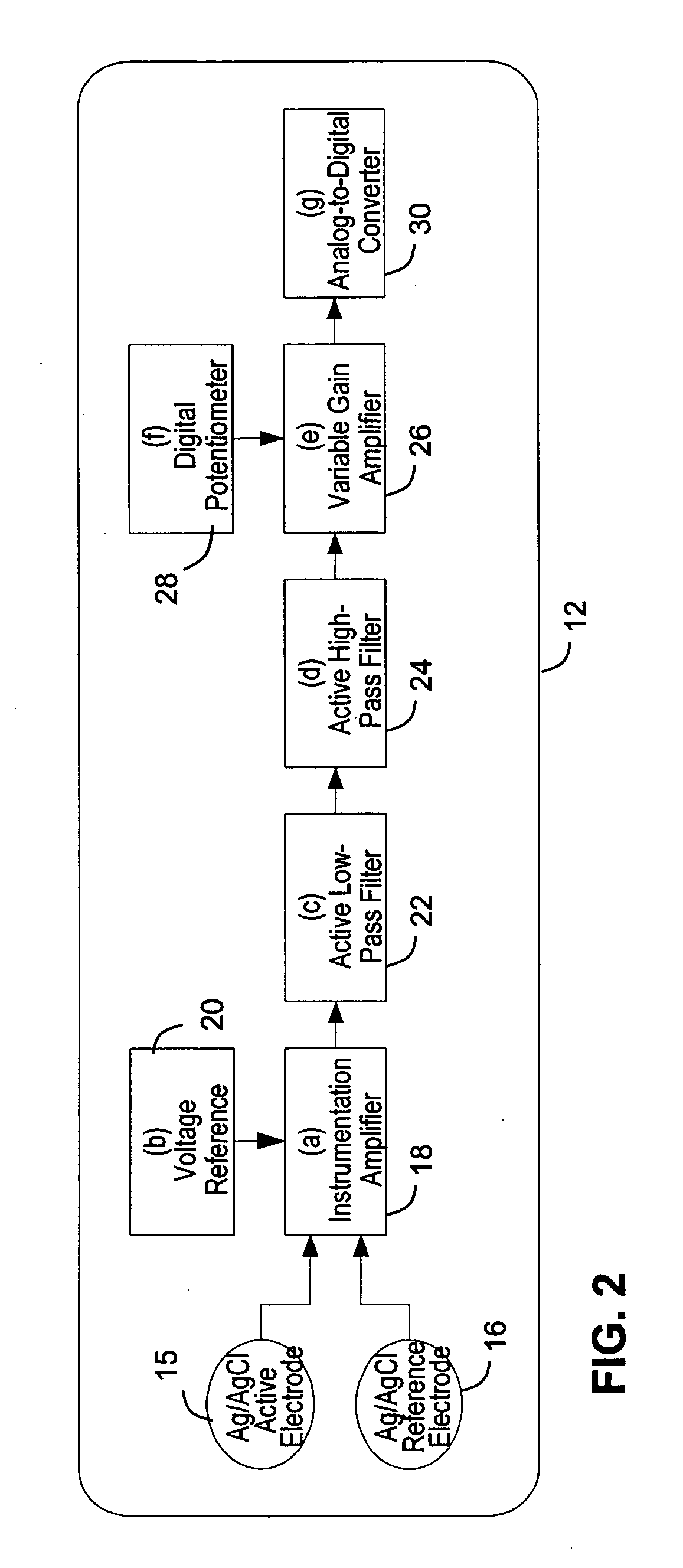
Active, multiplexed digital electrodes for EEG, ECG and EMG applications
InactiveUS20050215916A1Conveniently providedImprove signal-to-noise ratioElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyMultiplexingElectroencephalography
A biopotential measurement system incorporates a revolutionary approach to the acquisition of signals such as Electroencephalograms (EEG), Electrocardiograms (ECG), and Electromyograms (EMG) by incorporating active, digital electrodes that amplify and digitally convert biopotential signals at the source, thereby eliminating noise and signal degradation issues. This is to date the most integrated and advanced electrode designed for any biopotential measurement eliminating the poor Signal-to-Noise (SNR) problems seen in biopotential recordings.
Owner:FADEM KALFORD C +1
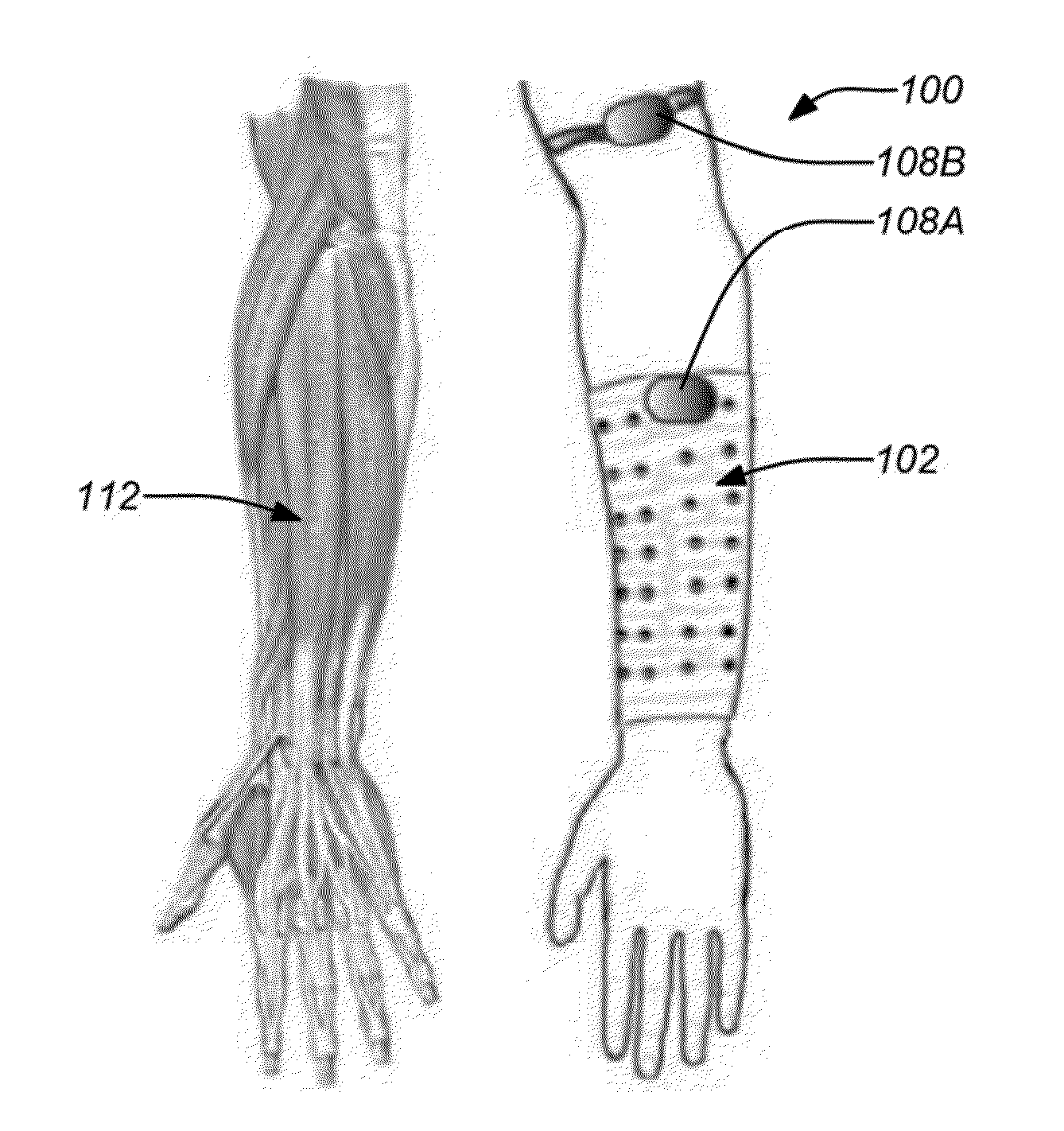
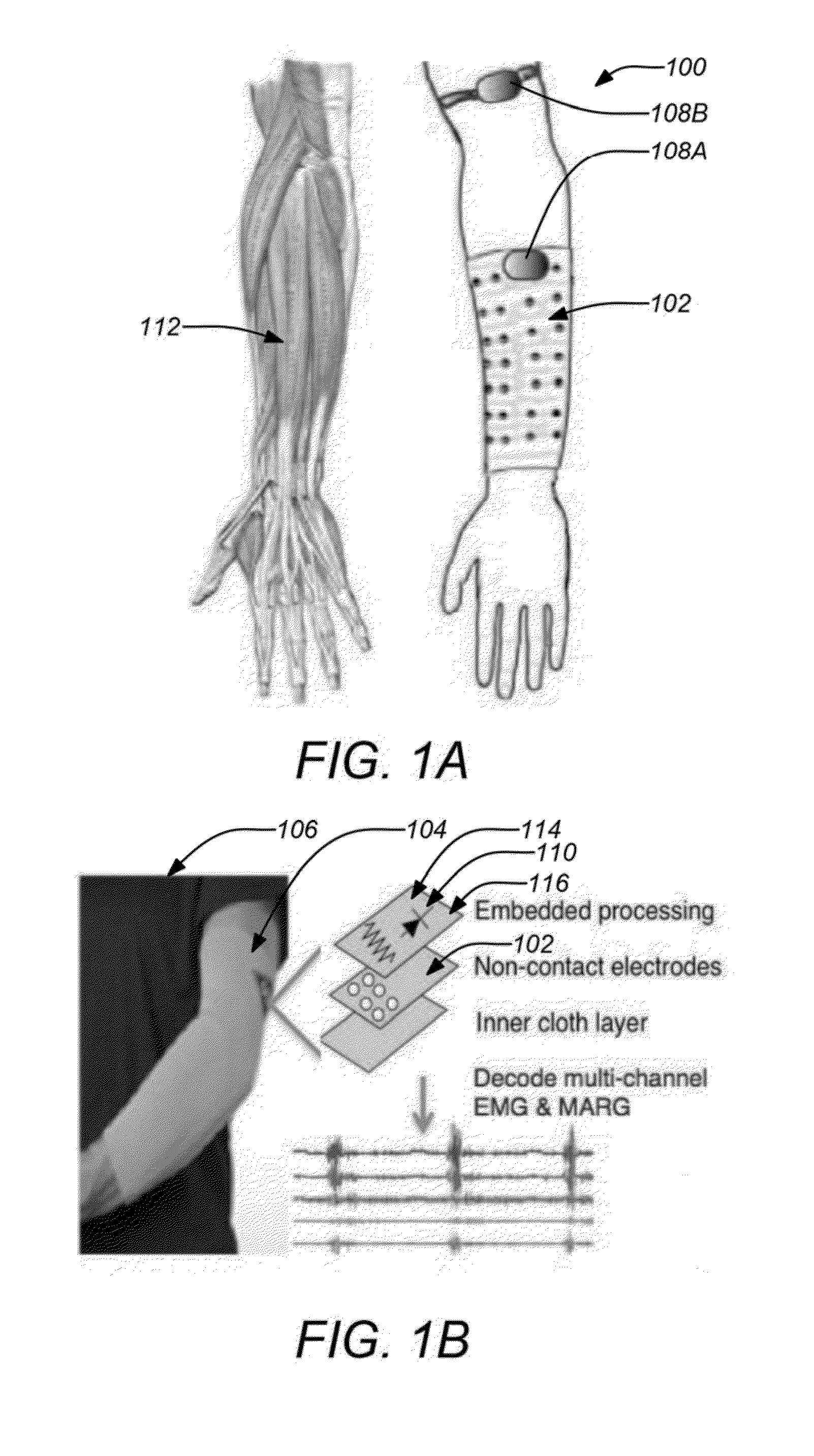
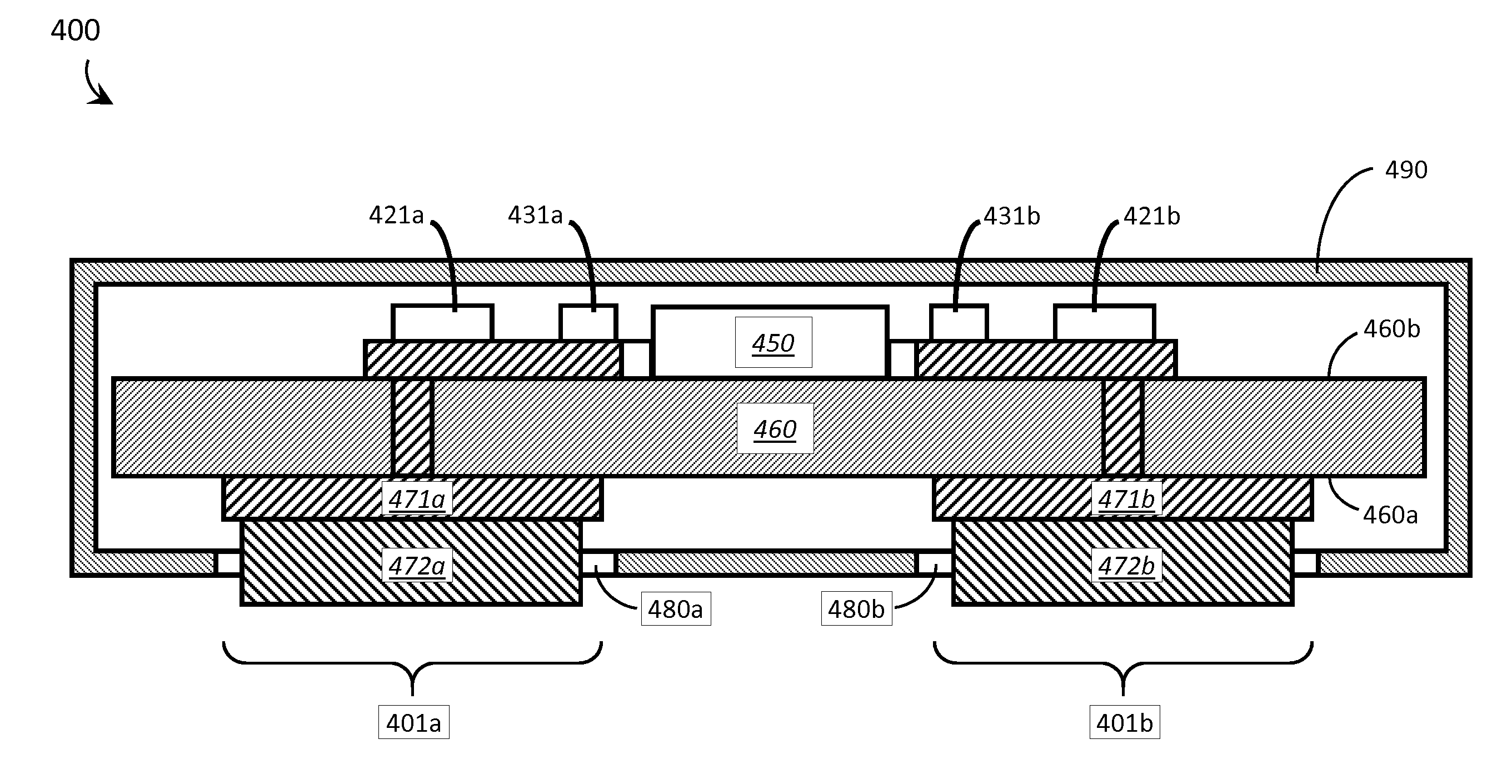
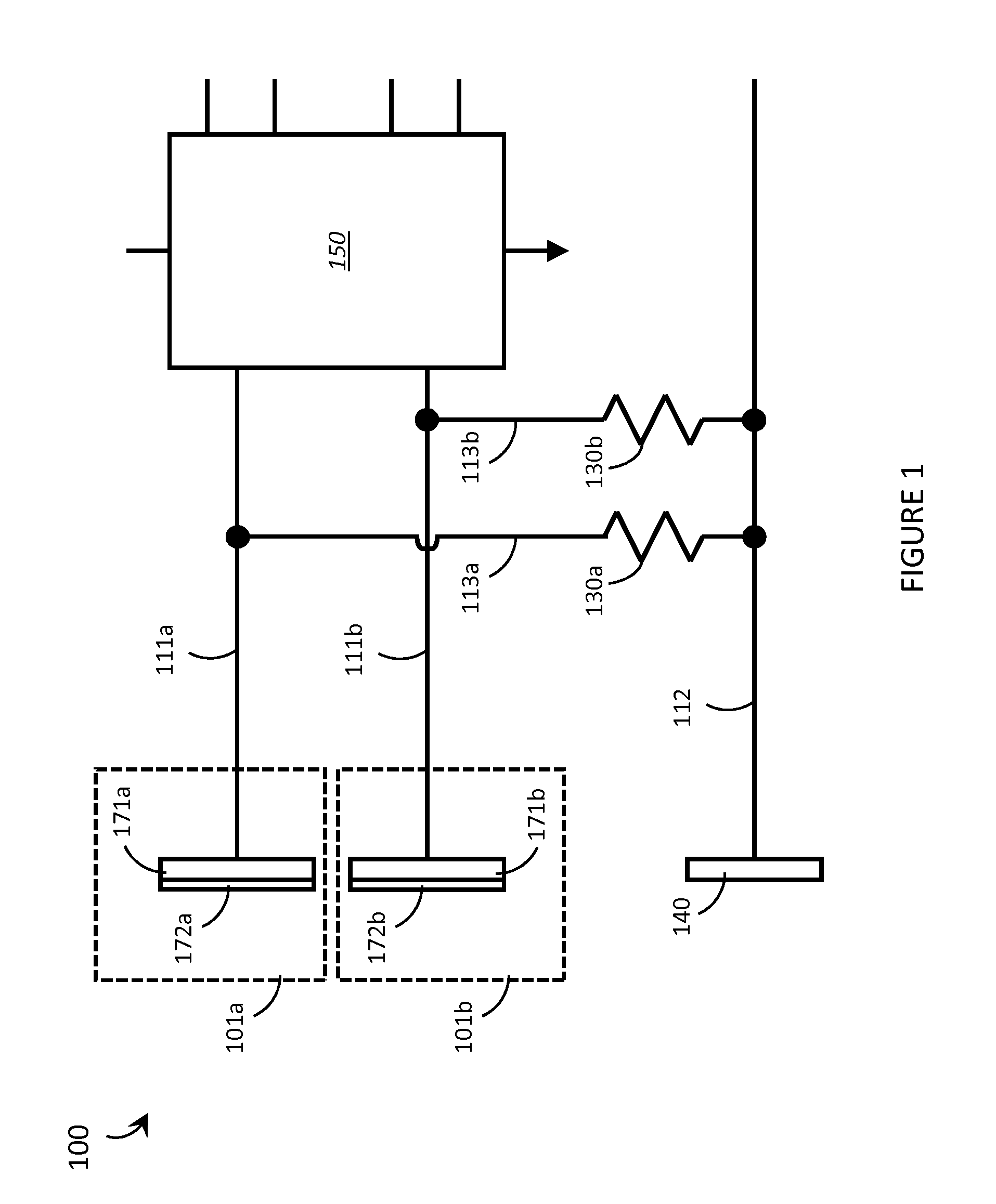
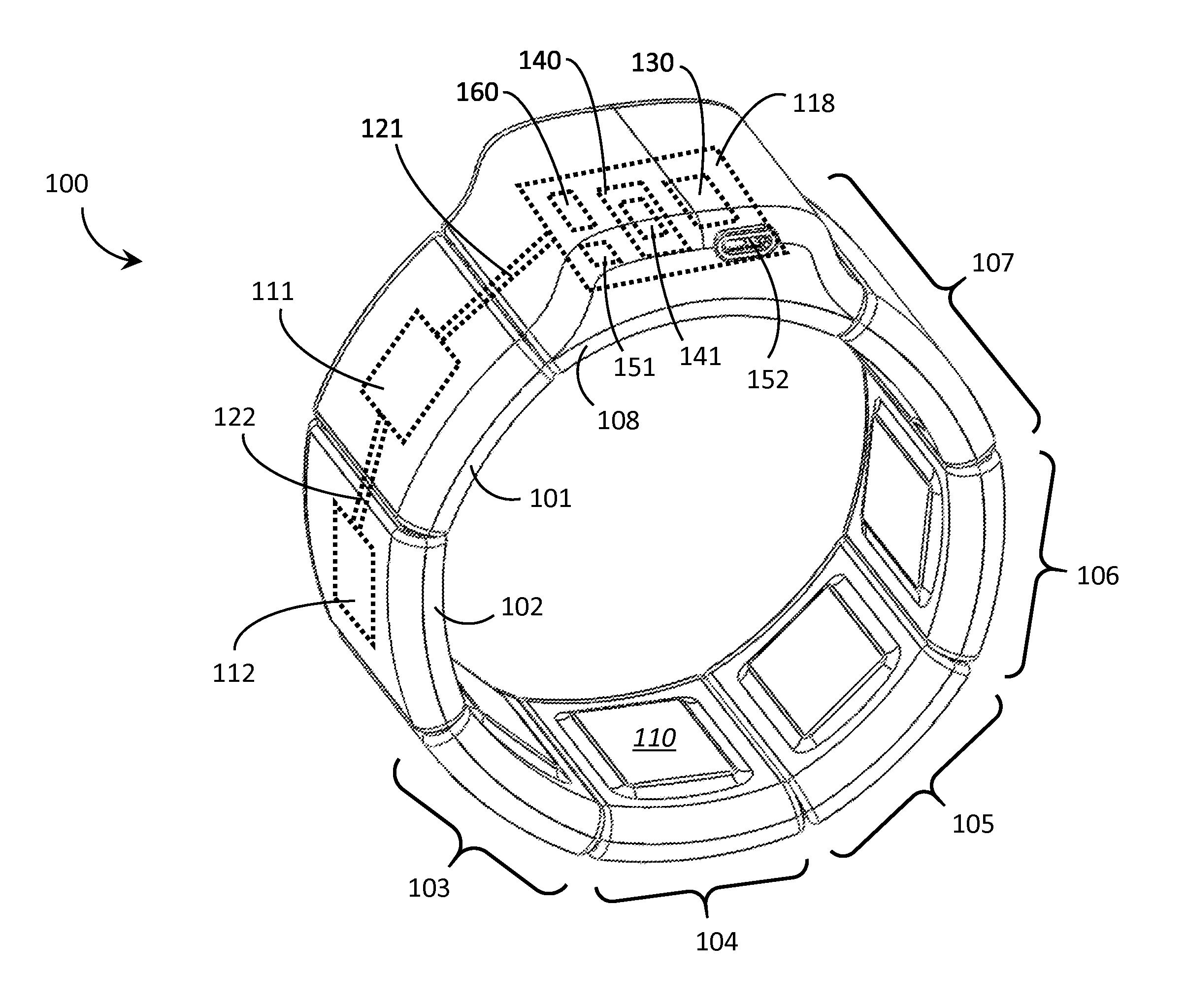
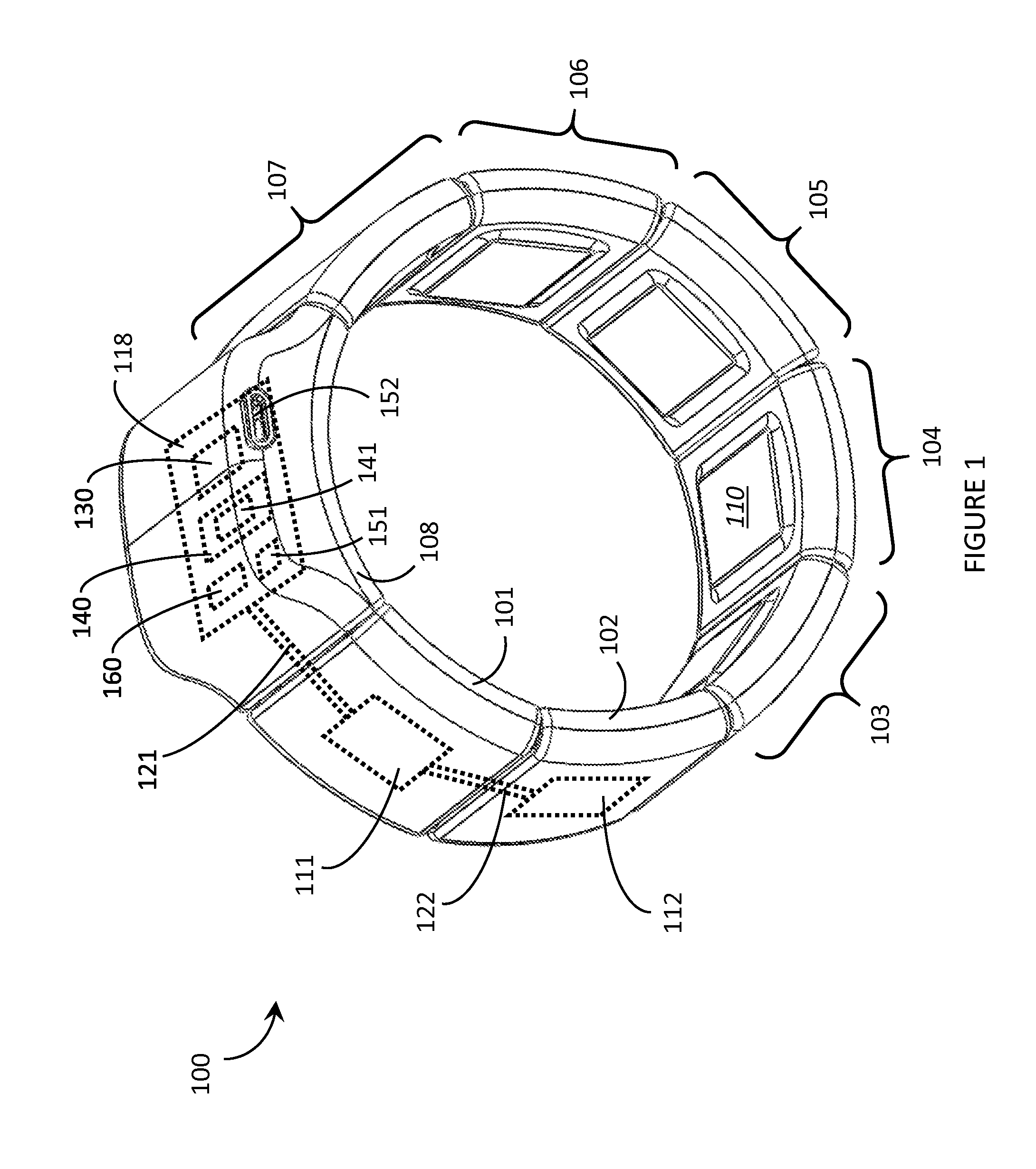
Systems, articles, and methods for capacitive electromyography sensors
ActiveUS20150141784A1Input/output for user-computer interactionElectromyographyHuman–machine interfaceEngineering
Systems, articles, and methods for improved capacitive electromyography (“EMG”) sensors are described. The improved capacitive EMG sensors include one or more sensor electrode(s) that is / are coated with a protective barrier formed of a material that has a relative permittivity ∈r of about 10 or more. The protective barrier shields the sensor electrode(s) from moisture, sweat, skin oils, etc. while advantageously contributing to a large capacitance between the sensor electrode(s) and the user's body. In this way, the improved capacitive EMG sensors provide enhanced robustness against variations in skin and / or environmental conditions. Such improved capacitive EMG sensors are particularly well-suited for use in wearable EMG devices that may be worn by a user for an extended period of time and / or under a variety of skin and / or environmental conditions. A wearable EMG device that provides a component of a human-electronics interface and incorporates such improved capacitive EMG sensors is described.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
Wearable electromyogram sensor system
ActiveUS20140364703A1Efficient use ofAccurate identificationElectromyographySensorsEngineeringSensor system
A wearable electromyogram sensor system is provided. The wearable electromyogram sensor system includes: an elastic band having a plurality of electrodes; an electromyogram sensor including an electrode connected to an electrode of the band so as to receive a bio-signal related to contraction of a muscle, and configured to sense a change of motion information through the bio-signal or previously sense the change of the motion information before the motion information is changed; and a fixing unit fixing the electromyogram sensor to the band. The electrode of the electromyogram sensor is connected to an electrode at an arbitrary position of the band.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
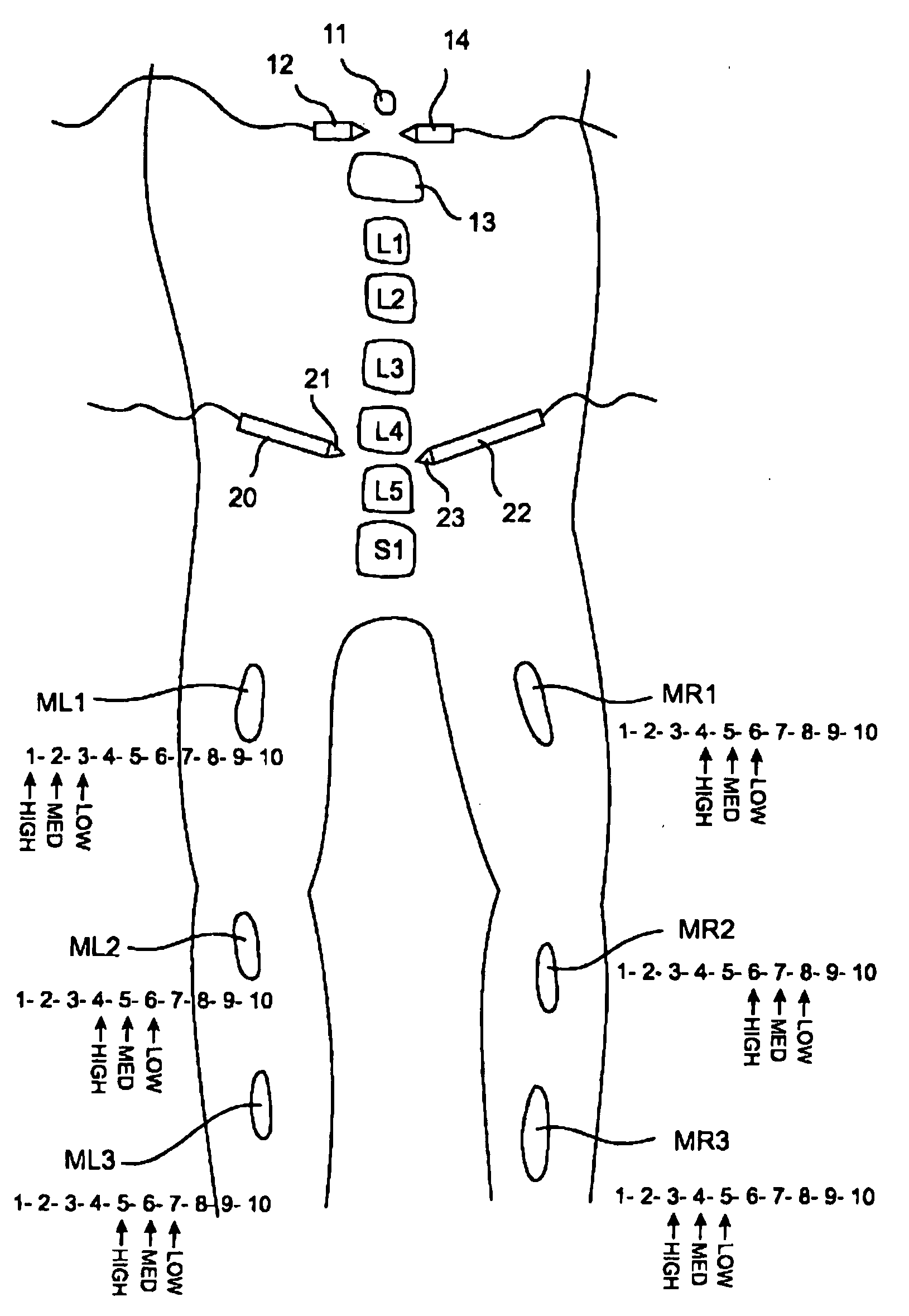
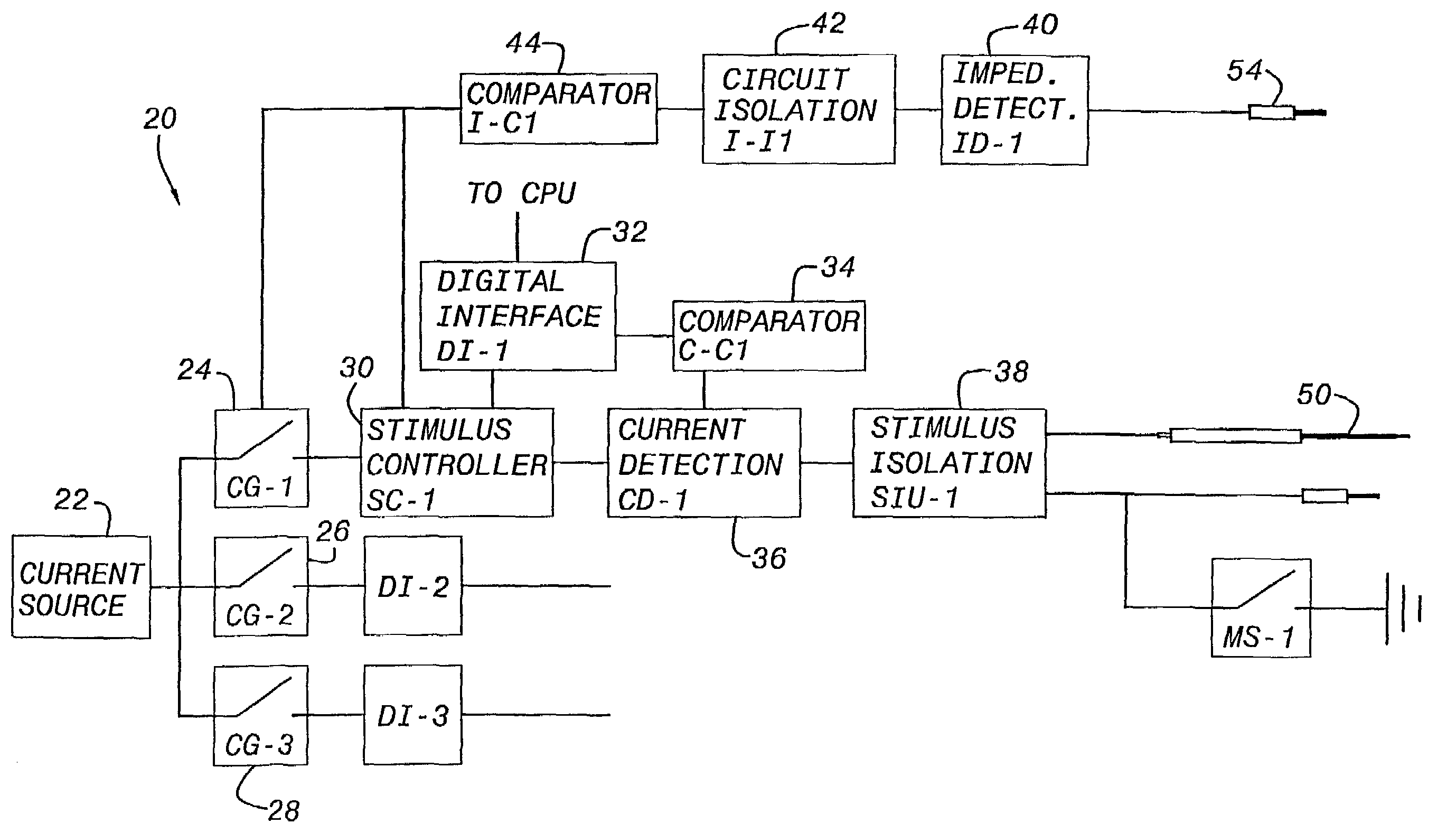
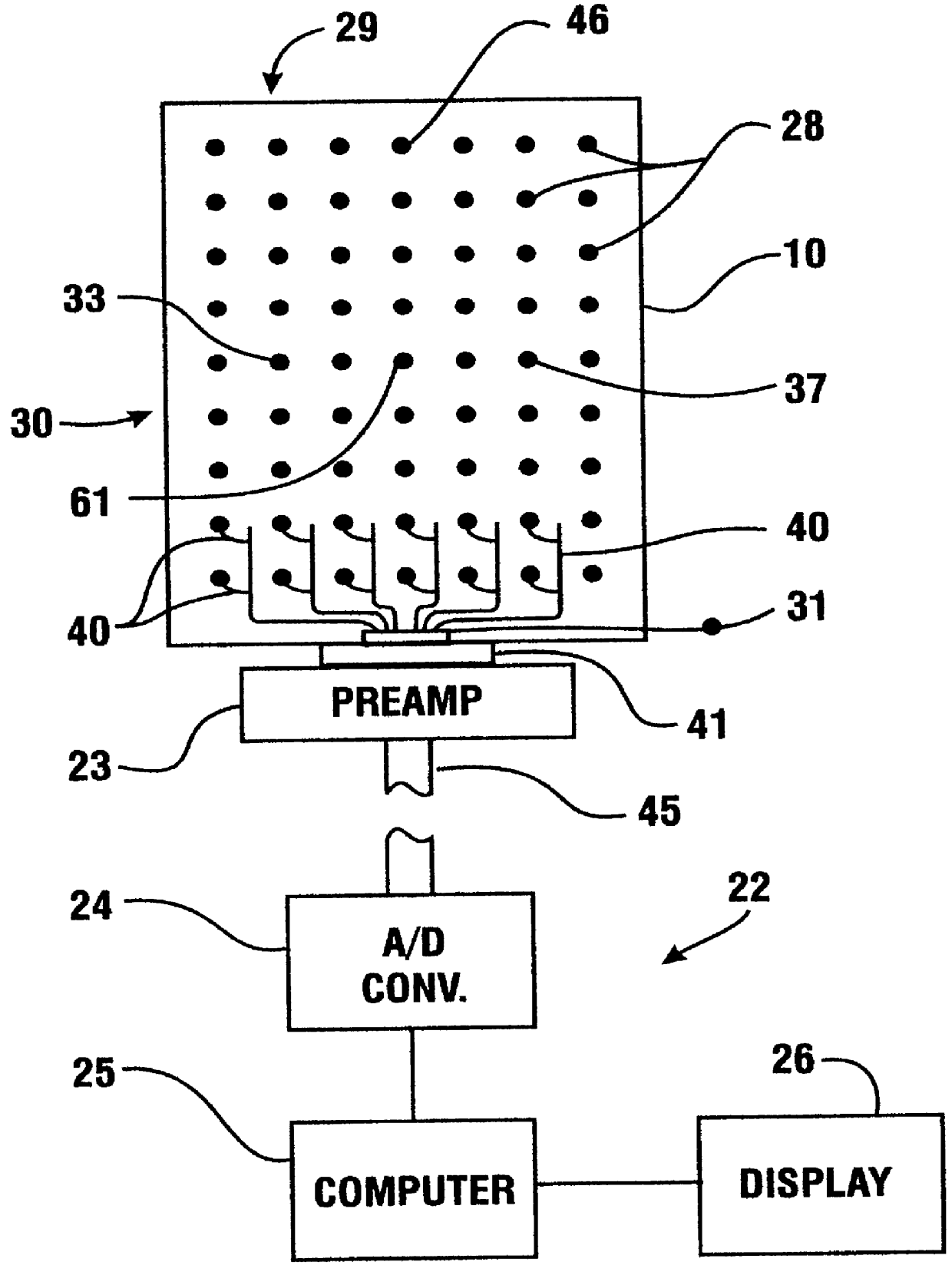
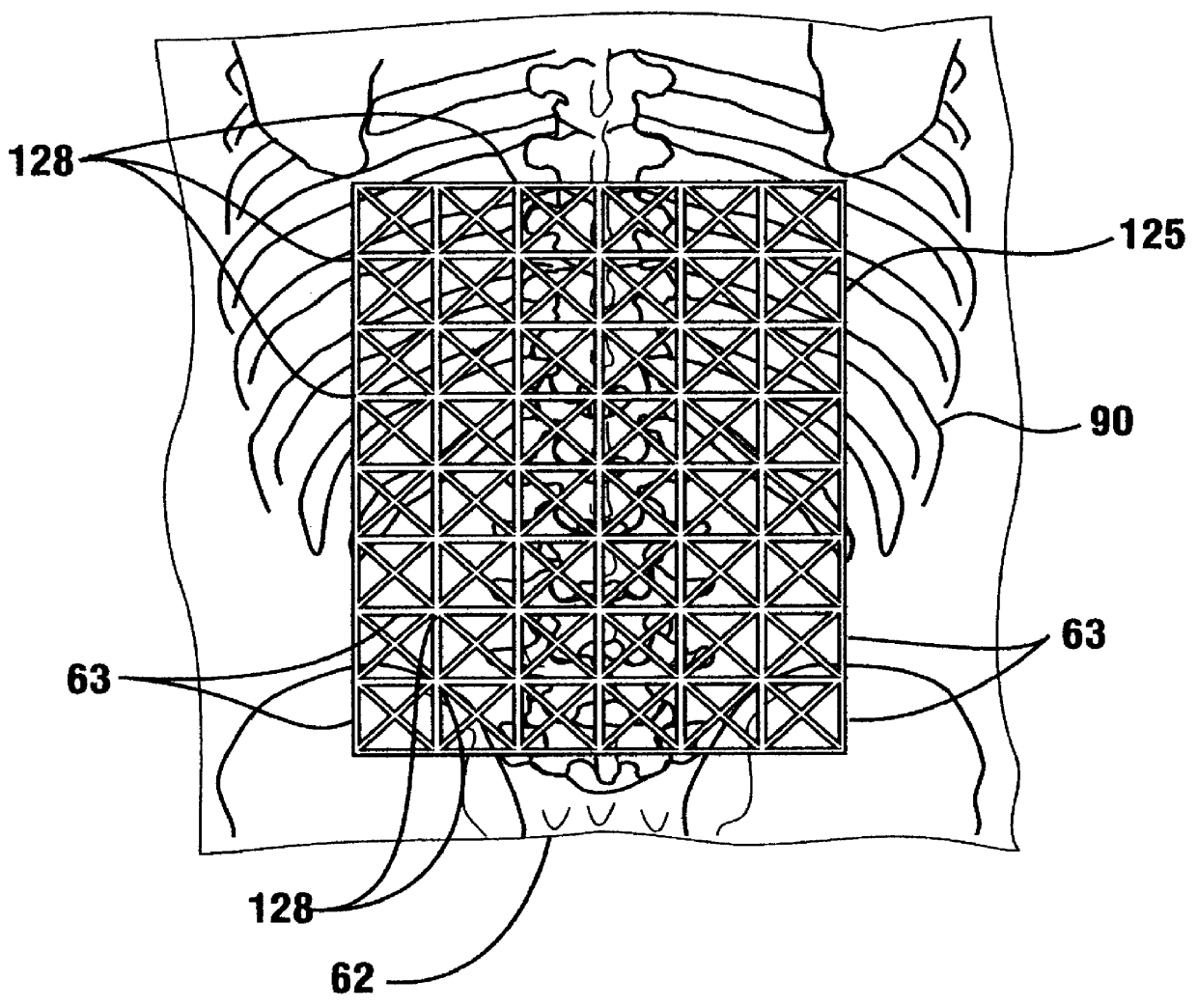
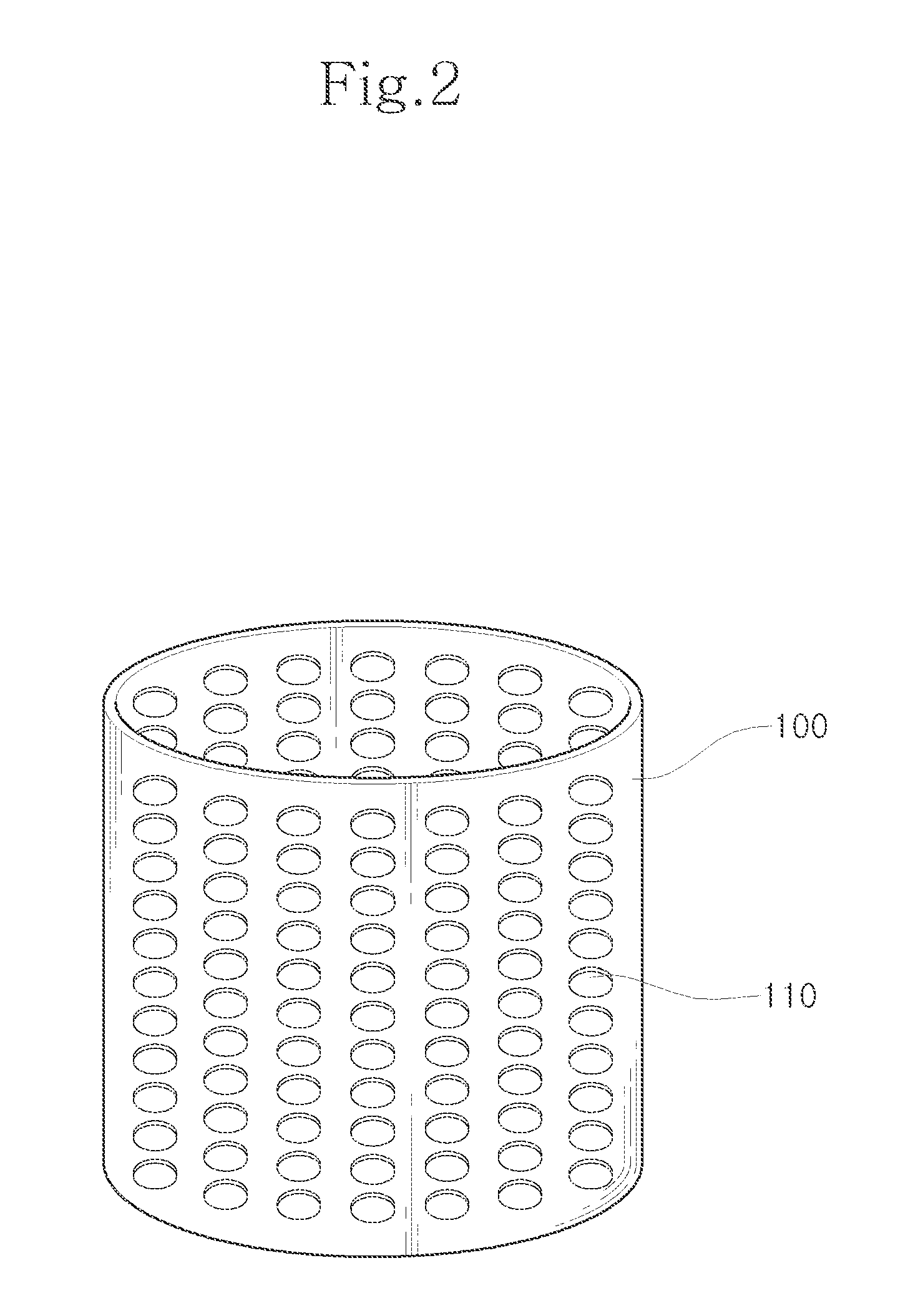
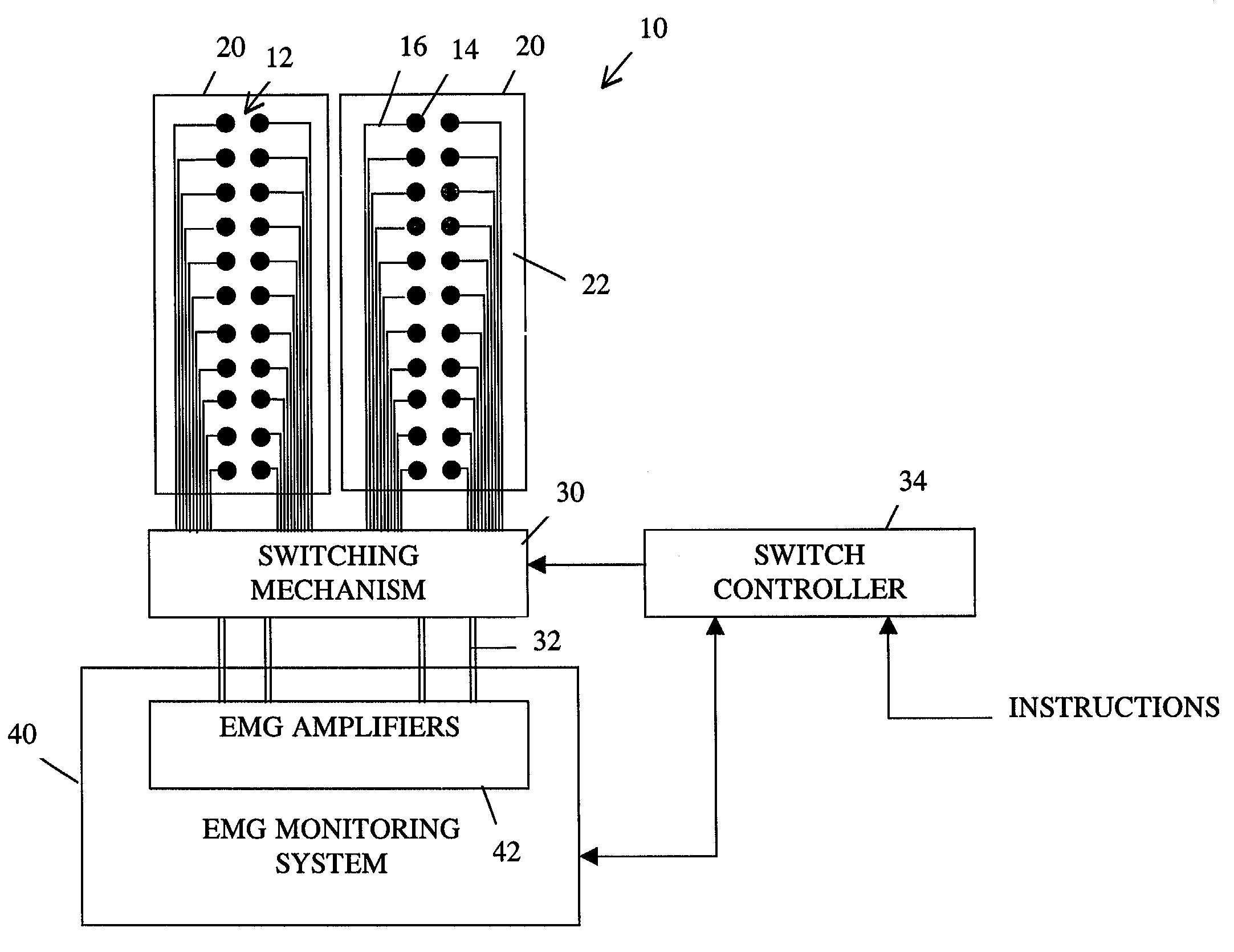
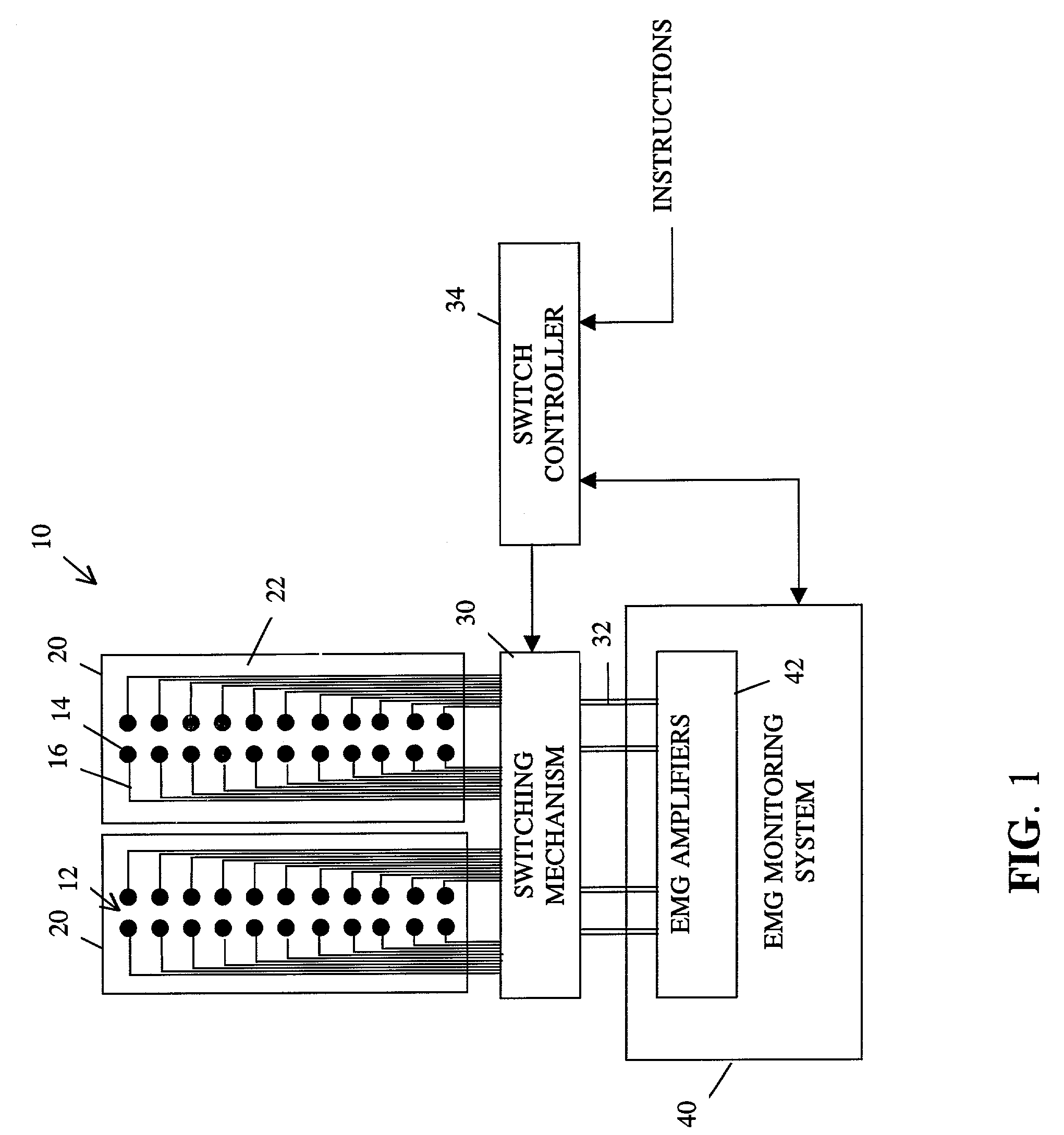
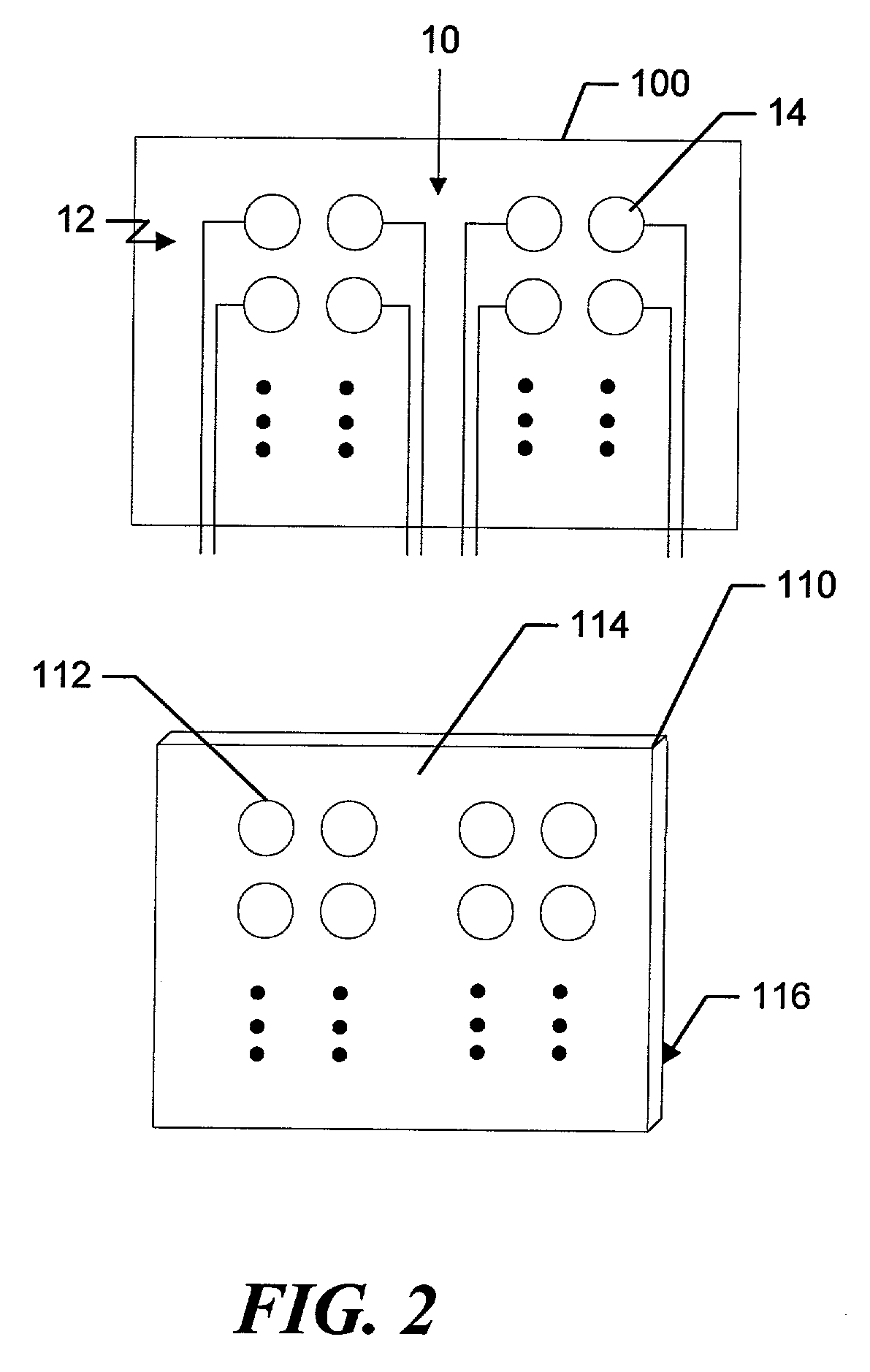
Apparatus for routing electromyography signals
An EMG monitoring system includes a matrix of detection electrode arrays that is positioned on the patient along his or her spine. The arrays are electrically connected through a switching mechanism to EMG amplifiers that are included in conventional monitoring instrumentation. A switch controller operates the switches to provide signals to the EMG amplifiers from selected sets of detection electrode arrays. The controller controls the switches to provide signals simultaneously to each EMG amplifier. If the monitoring instrumentation includes four EMG amplifiers, the matrix of electrode arrays and the switching mechanism may be used to take simultaneous measurements at two different spinal levels. If additional EMG amplifiers are included, simultaneous measurements at additional spinal levels may also be made. The matrix may also include redundant arrays and / or electrodes, such that the clinician can select the sets of electrodes that conform to the size of the patient.
Owner:FASSTECH
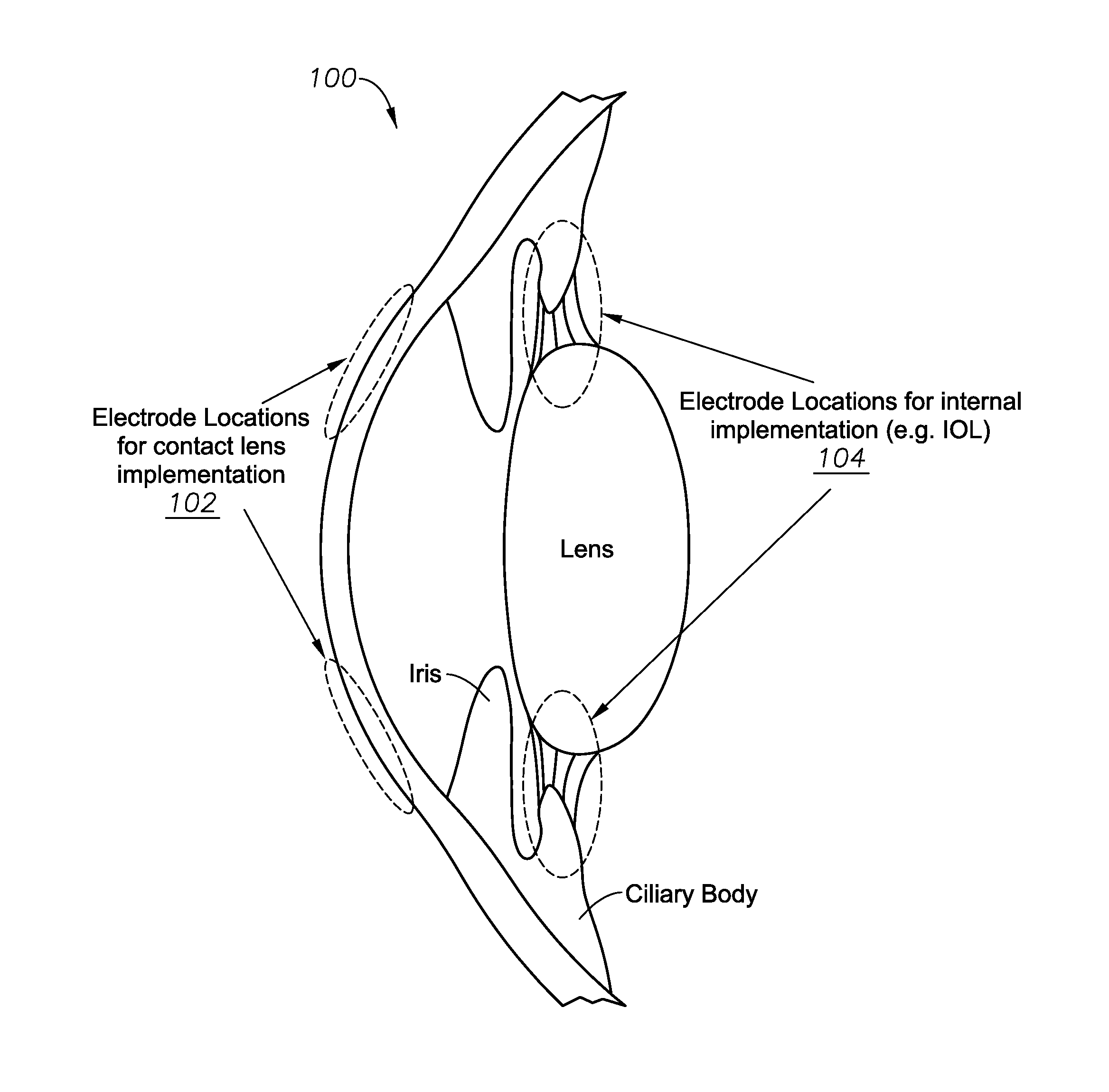
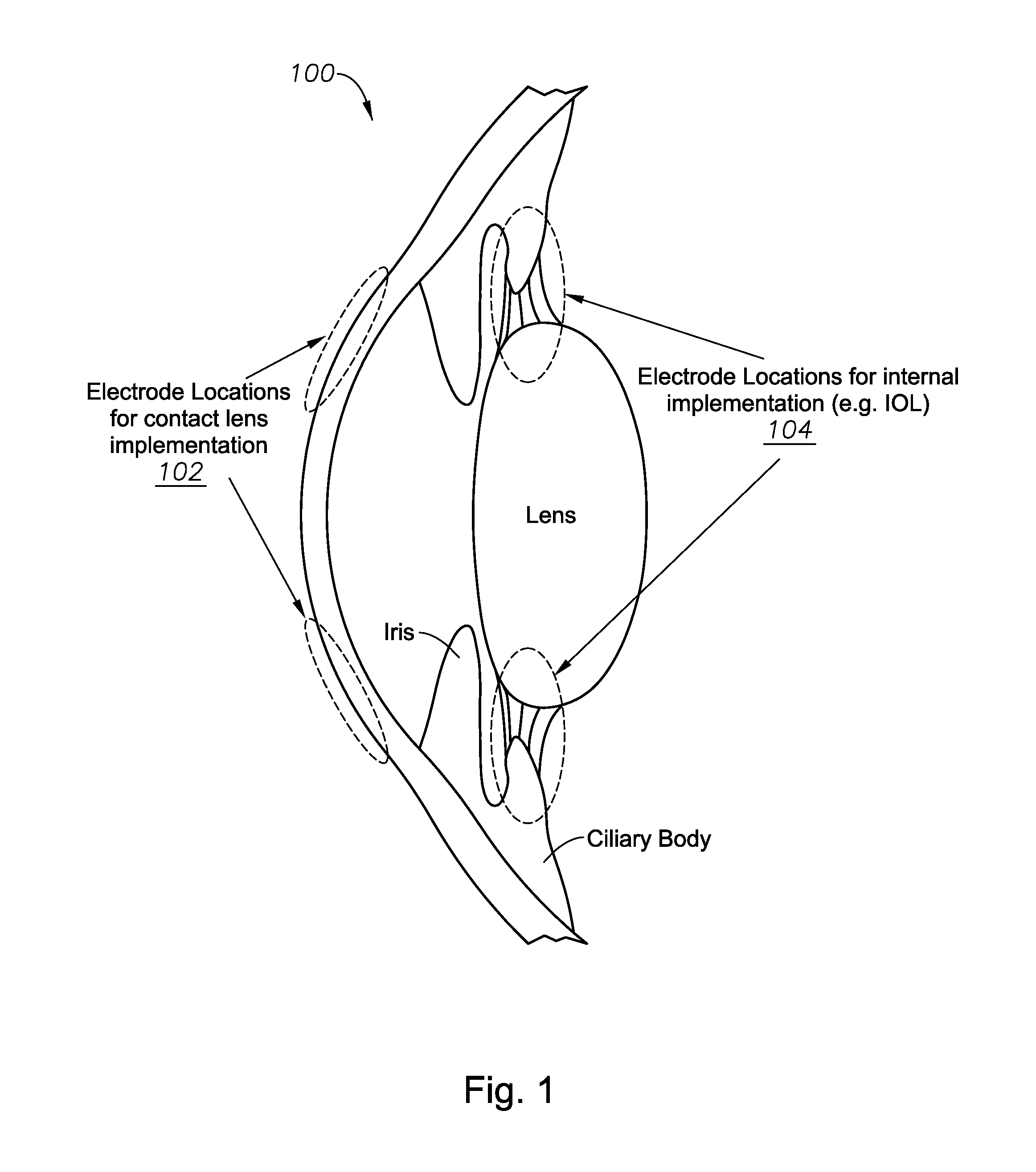
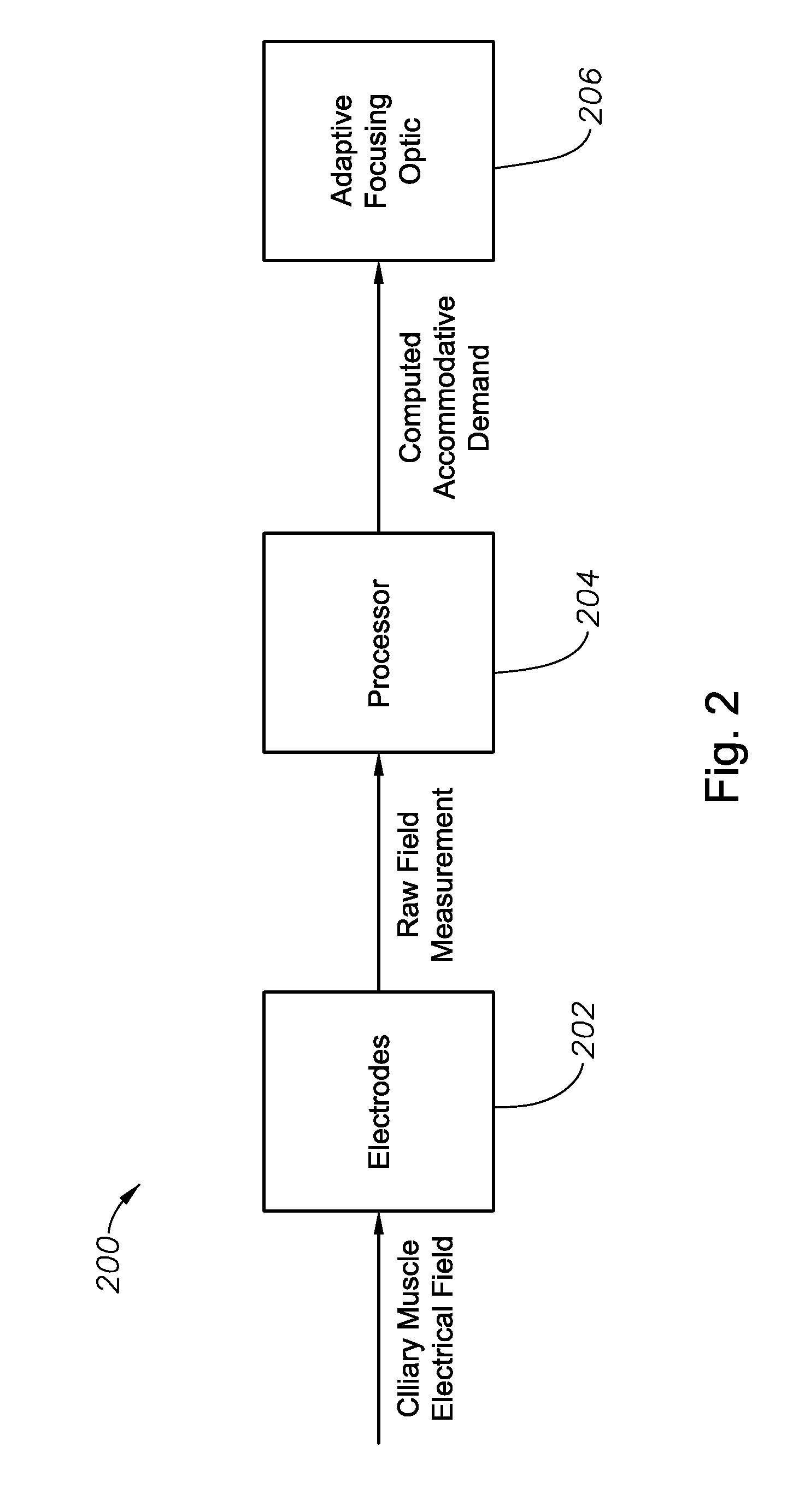
Sensors for triggering electro-active ophthalmic lenses
ActiveUS20140156000A1Diagnostic recording/measuringEye diagnosticsOphthalmology departmentControl signal
An electro-active ophthalmic lens includes an electromyography sensor, a processor, and an electro-active optical element. The electromyography sensor is configured to detect an electric field in a ciliary muscle of the eye that is proportional to a force exerted by the ciliary muscle and to generate a sensor signal indicative of the electric field. The processor is operable to receive the signal from the electromyography sensor and to determine, based on the sensor signal, an adjustment to optical power for an electro-active optical element and to generate a control signal for the electro-active optical element. The electro-active optical element is operable to receive the control signal and to change an optical power of the electro-active optical element in response to the control signal.
Owner:ALCON INC
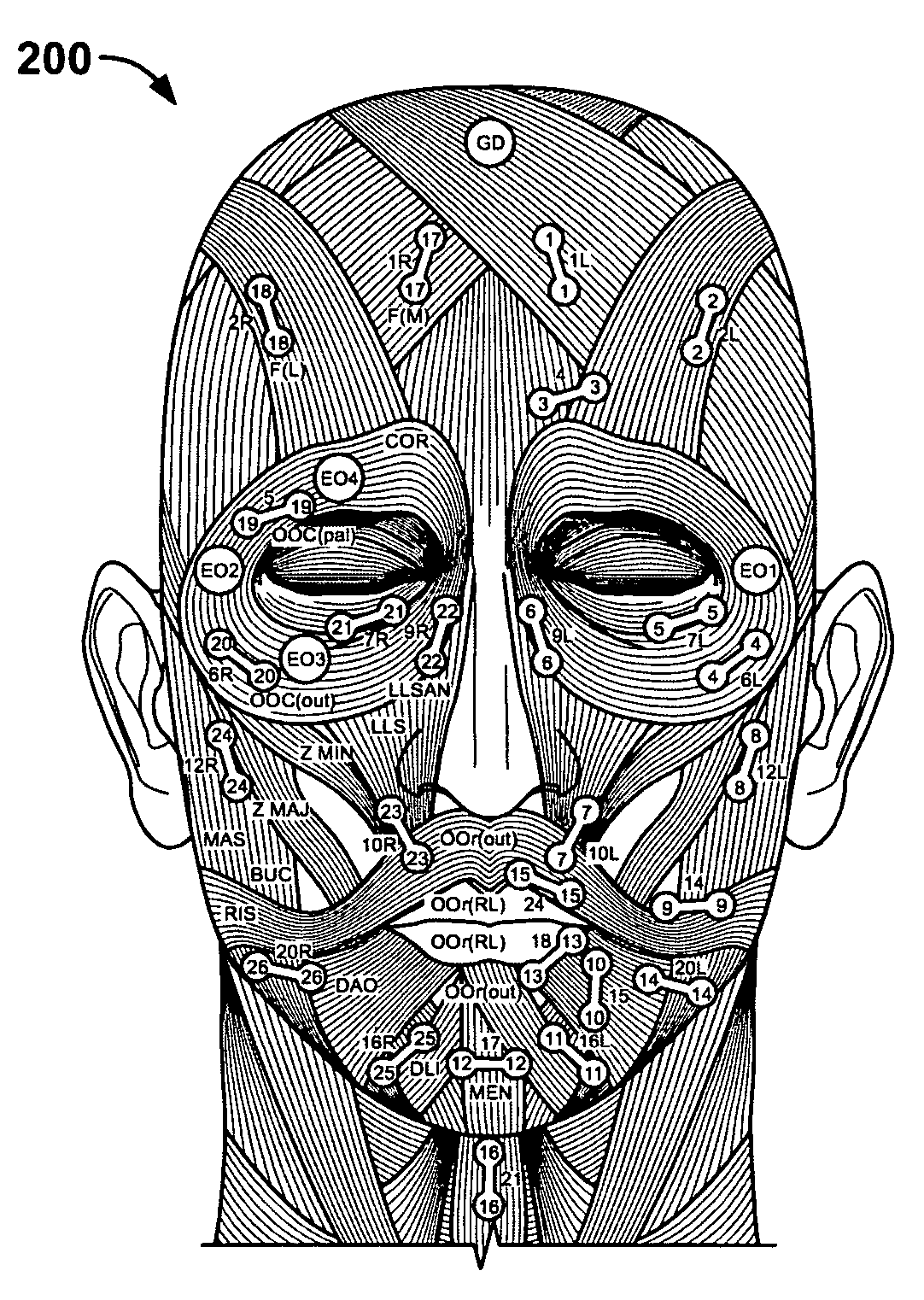
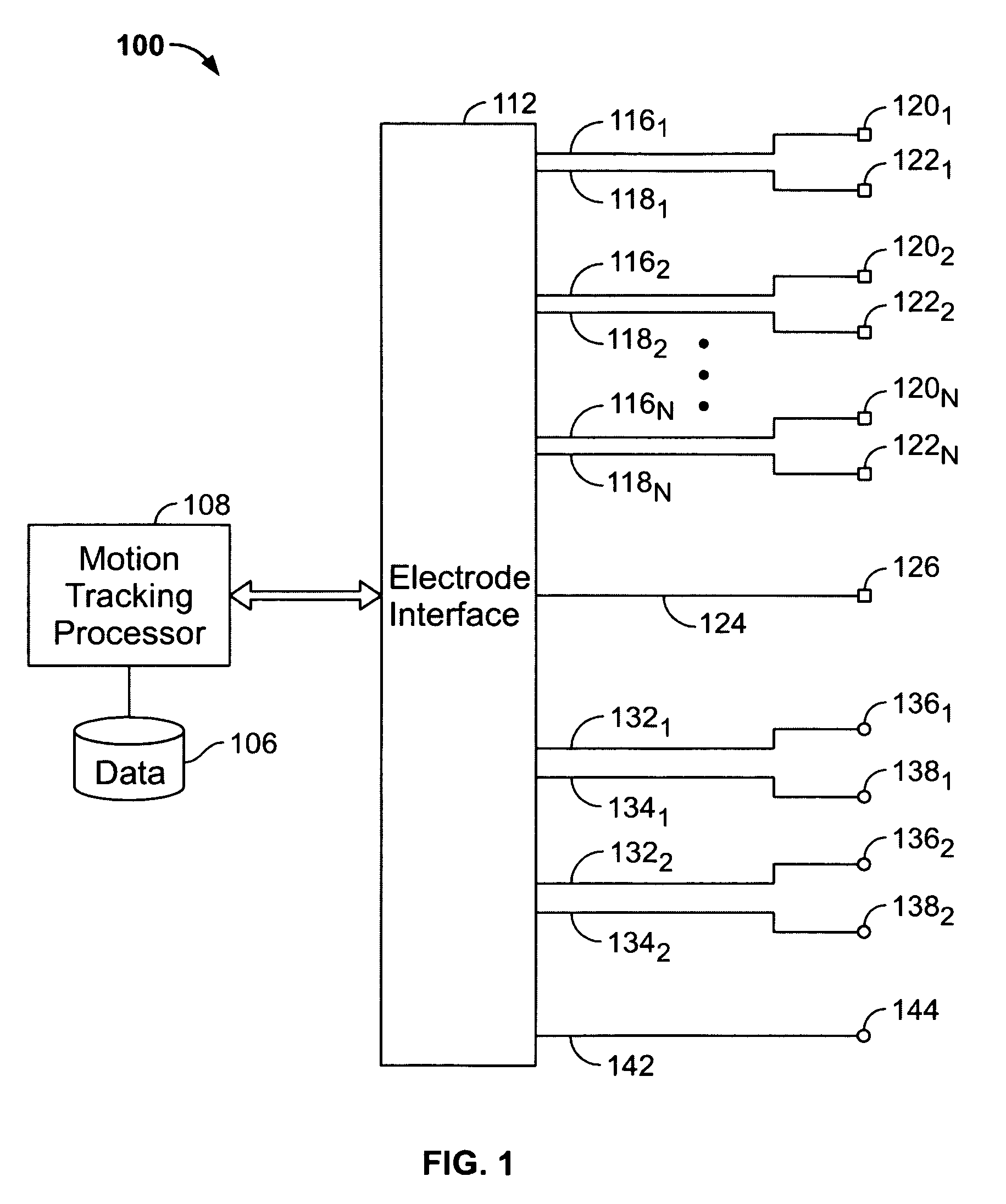
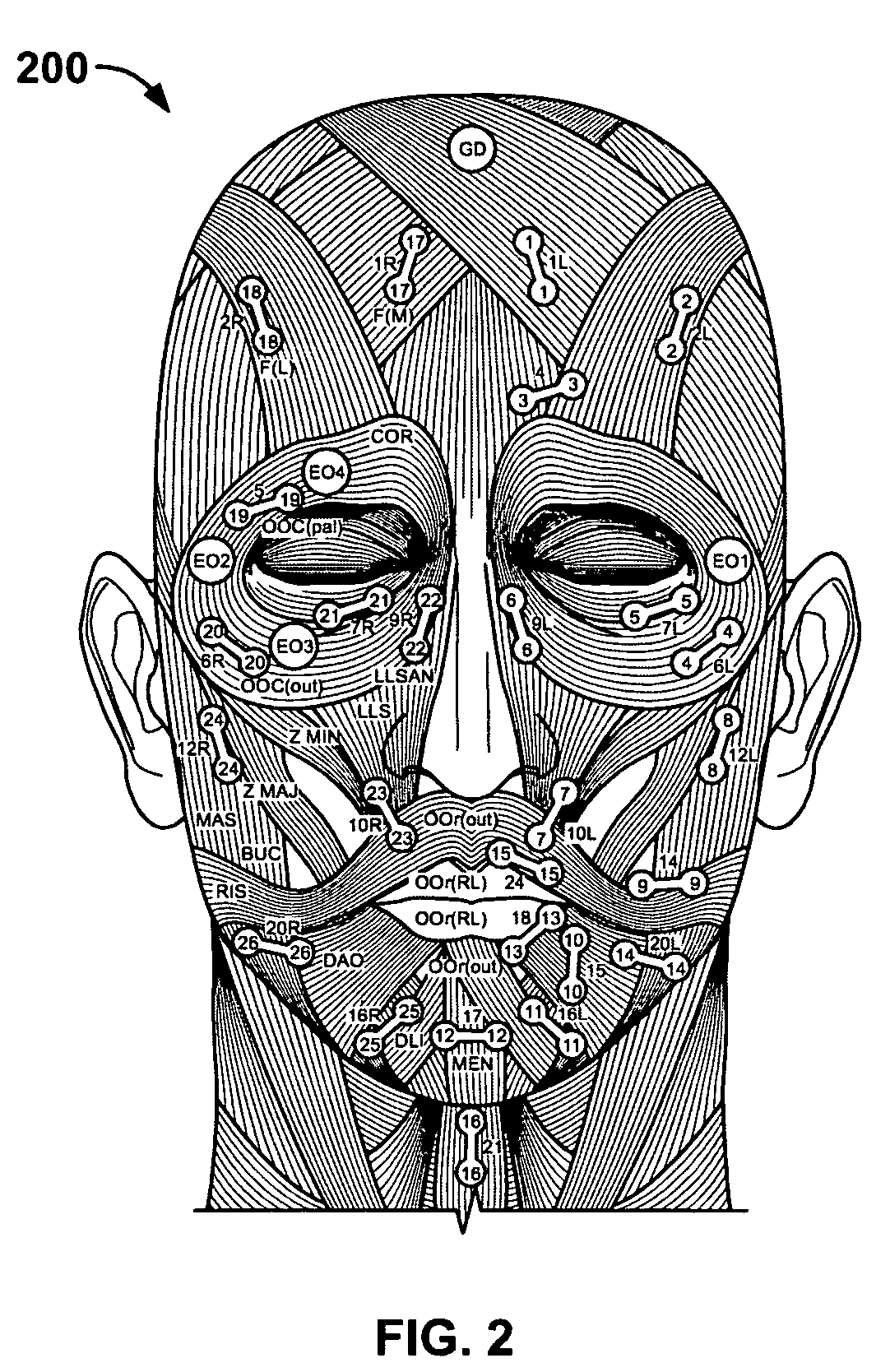
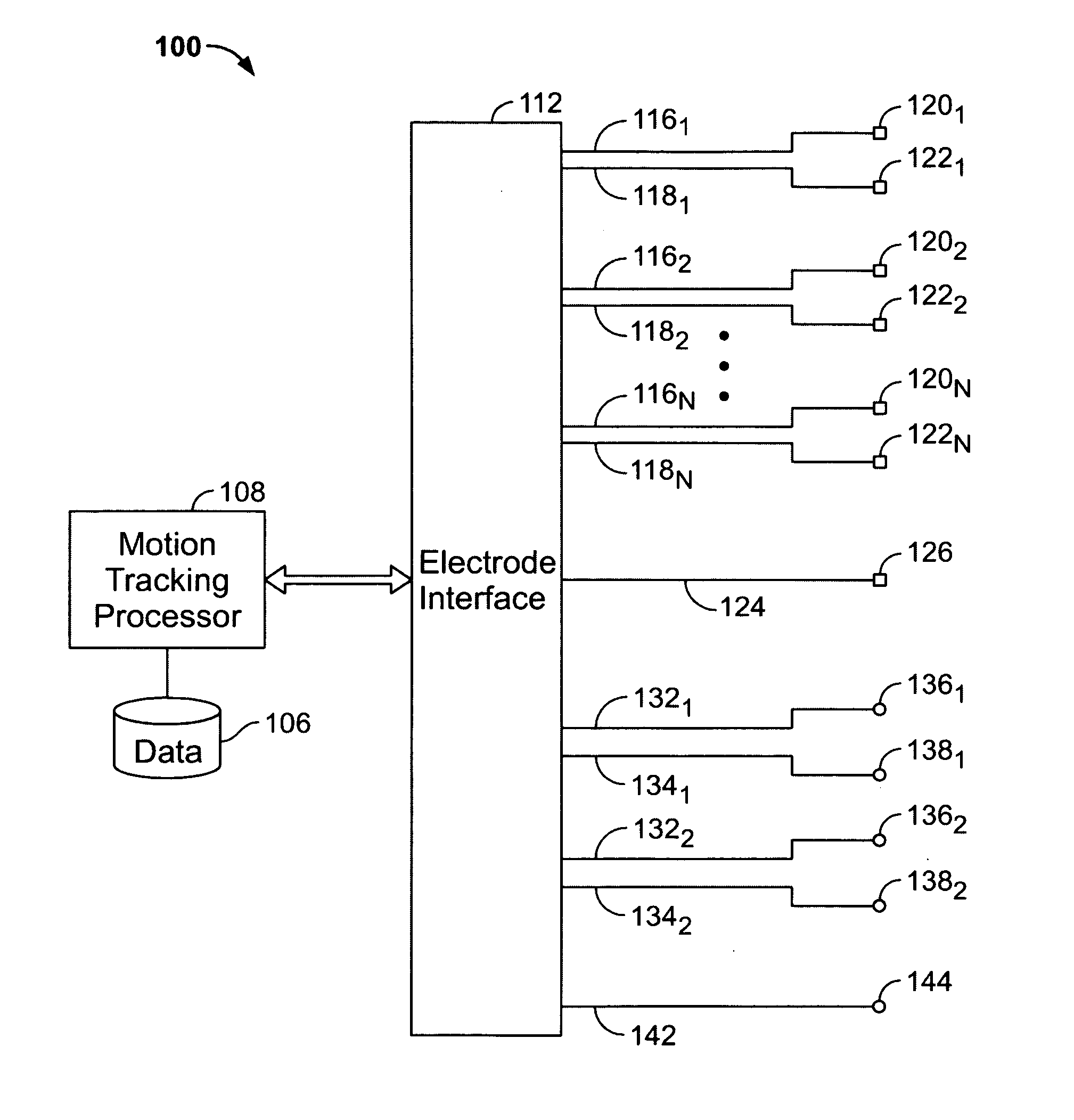
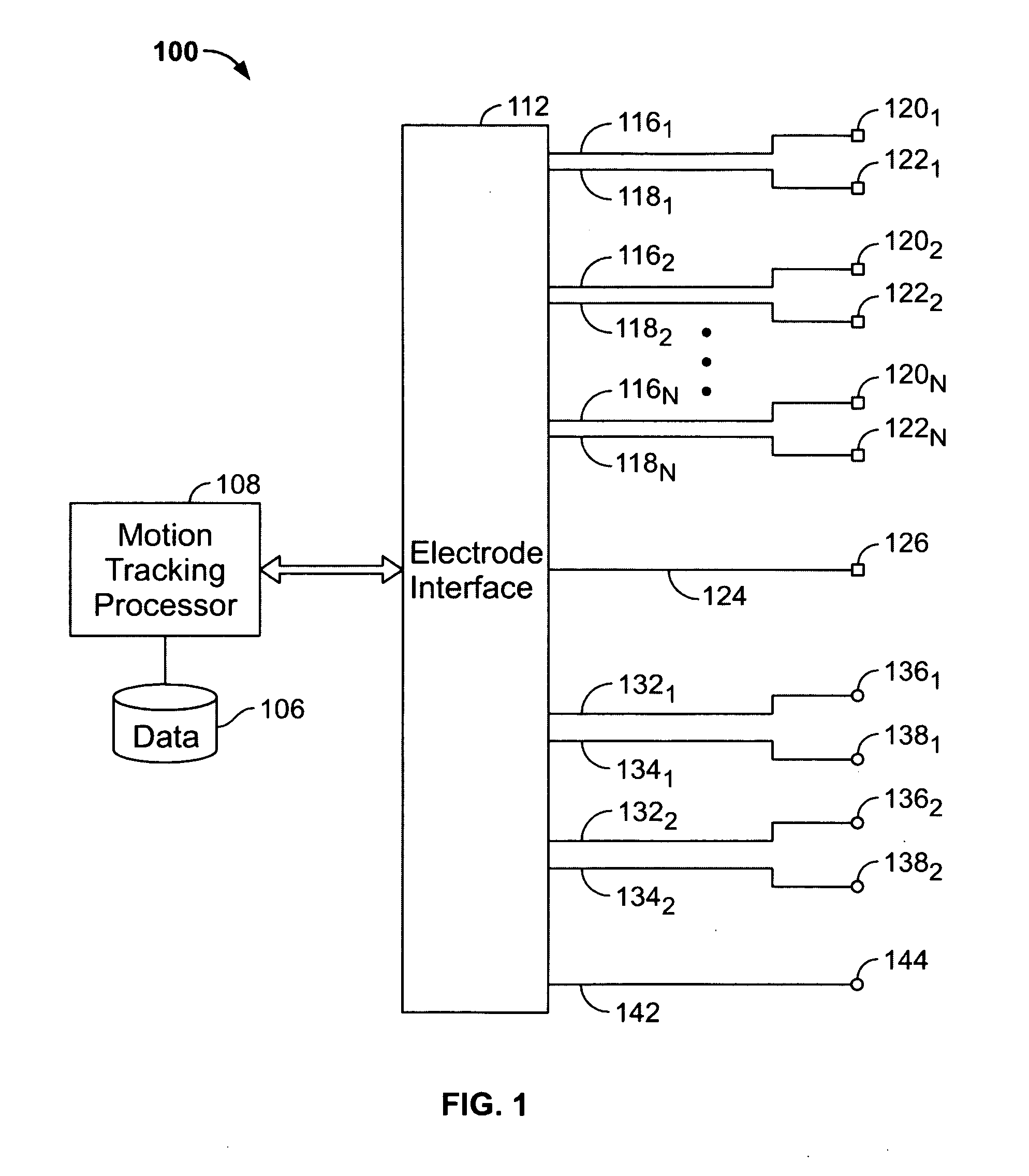
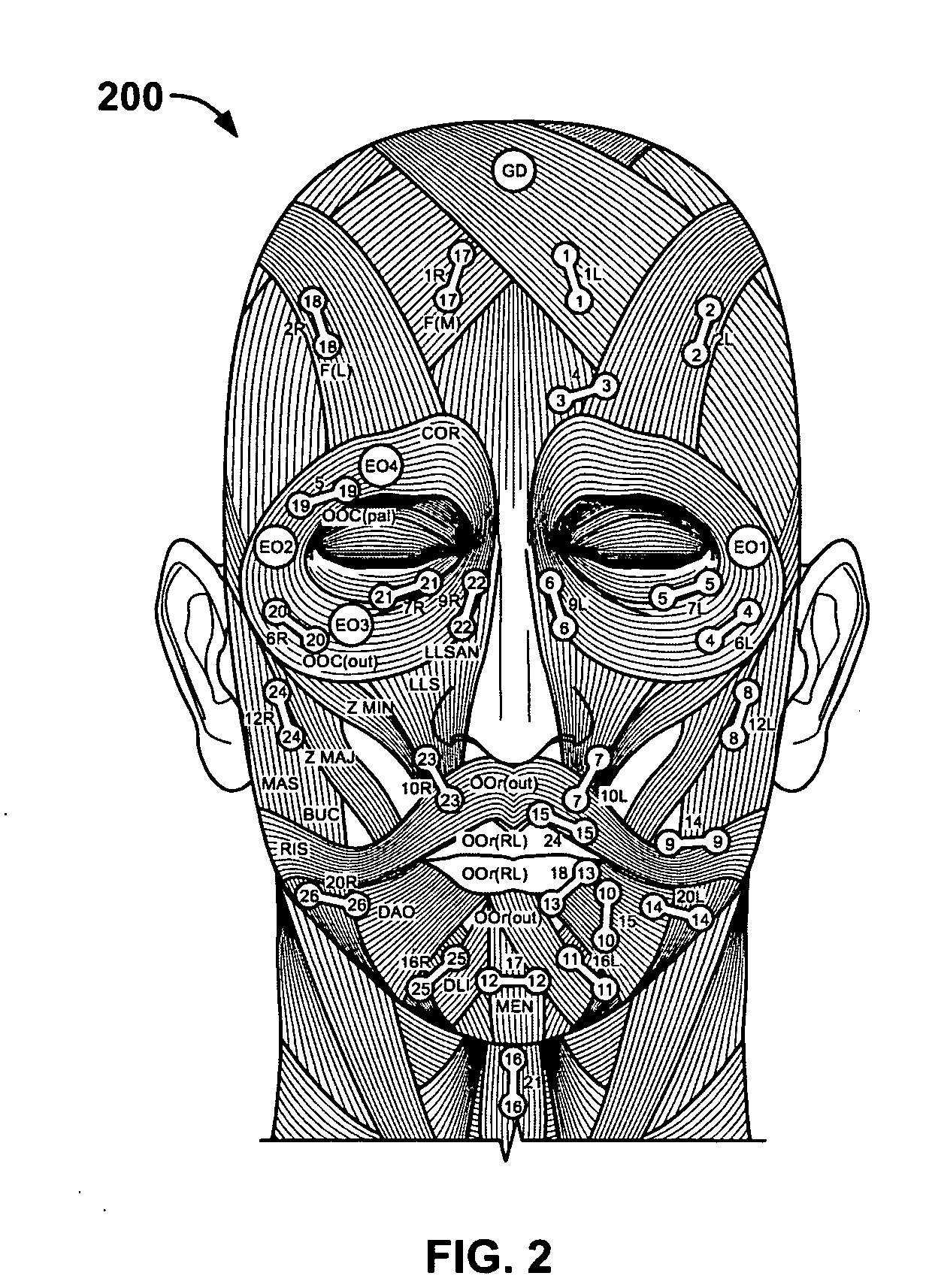
System and method for tracking facial muscle and eye motion for computer graphics animation
A motion tracking system enables faithful capture of subtle facial and eye motion using a surface electromyography (EMG) detection method to detect muscle movements and an electrooculogram (EOG) detection method to detect eye movements. An embodiment of the motion tracking animation system comprises a plurality of pairs of EOG electrodes adapted to be affixed to the skin surface of the performer at locations adjacent to the performer's eyes. The EOG data comprises electrical signals corresponding to eye movements of a performer during a performance. Programming instructions further provide processing of the EOG data and mapping of processed EOG data onto an animated character. As a result, the animated character will exhibit he same muscle and eye movements as the performer.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Systems, articles, and methods for electromyography sensors
ActiveUS20150148641A1Printed circuit assemblingElectromyographyElectromyographyCapacitive transducer
Systems, articles, and methods for surface electromyography (“EMG”) sensors that combine elements from traditional capacitive and resistive EMG sensors are described. For example, capacitive EMG sensors that are adapted to resistively couple to a user's skin are described. Resistive coupling between a sensor electrode and the user's skin is galvanically isolated from the sensor circuitry by a discrete component capacitor included downstream from the sensor electrode. The combination of a resistively coupled electrode and a discrete component capacitor provides the respective benefits of traditional resistive and capacitive (respectively) EMG sensor designs while mitigating respective drawbacks of each approach. A wearable EMG device that provides a component of a human-electronics interface and incorporates such capacitive EMG sensors is also described.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
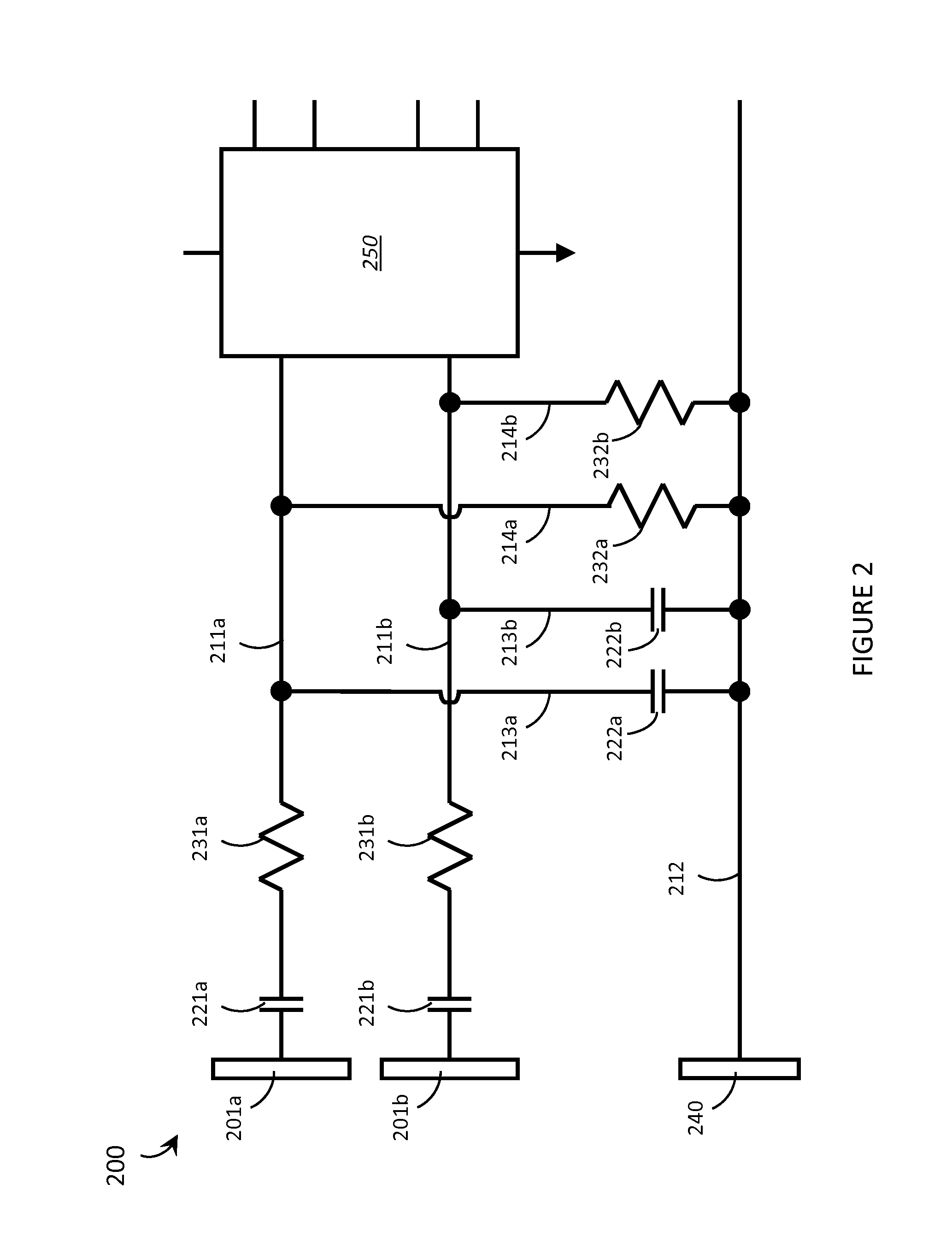
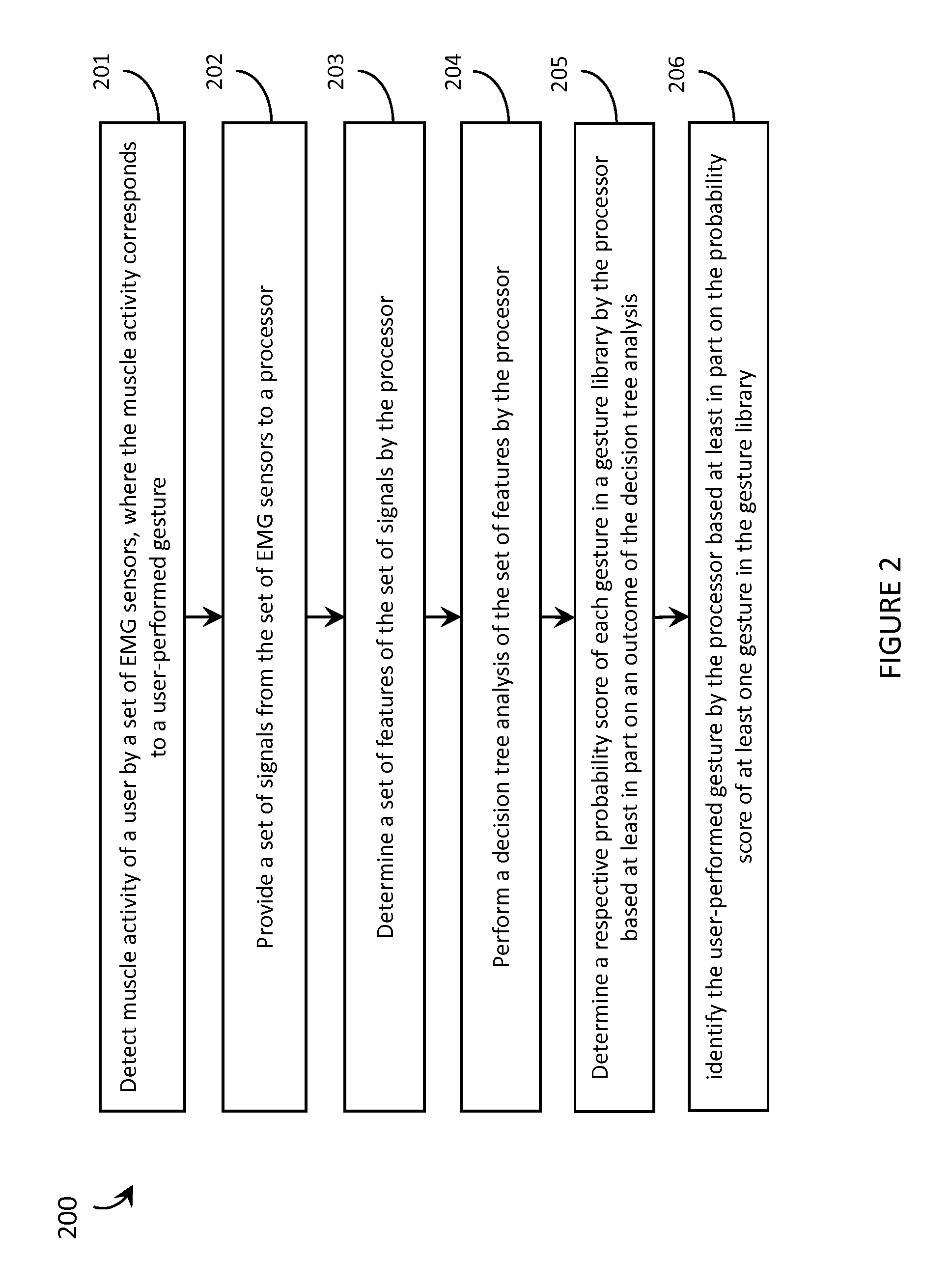
Systems, articles, and methods for gesture identification in wearable electromyography devices
ActiveUS9389694B2Input/output for user-computer interactionMedical data miningAlgorithmProbability vector
Systems, articles, and methods perform gesture identification with limited computational resources. A wearable electromyography (“EMG”) device includes multiple EMG sensors, an on-board processor, and a non-transitory processor-readable memory that stores data and / or processor-executable instructions for performing gesture identification. The wearable EMG device detects and determines features of signals when a user performs a physical gesture, and processes the features by performing a decision tree analysis. The decision tree analysis invokes a decision tree stored in the memory, where storing and executing the decision tree may be managed by limited computational resources. The outcome of the decision tree analysis is a probability vector that assigns a respective probability score to each gesture in a gesture library. The accuracy of the gesture identification may be enhanced by performing multiple iterations of the decision tree analysis across multiple time windows of the EMG signal data and combining the resulting probability vectors.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
System and method for tracking facial muscle and eye motion for computer graphics animation
A motion tracking system enables faithful capture of subtle facial and eye motion using a surface electromyography (EMG) detection method to detect muscle movements and an electrooculogram (EOG) detection method to detect eye movements. Signals corresponding to the detected muscle and eye movements are used to control an animated character to exhibit the same movements performed by a performer. An embodiment of the motion tracking animation system comprises a plurality of pairs of EMG electrodes adapted to be affixed to a skin surface of a performer at plural locations corresponding to respective muscles, and a processor operatively coupled to the plurality of pairs of EMG electrodes. The processor includes programming instructions to perform the functions of acquiring EMG data from the plurality of pairs of EMG electrodes. The EMG data comprises electrical signals corresponding to muscle movements of the performer during a performance. The programming instructions further include processing the EMG data to provide a digital model of the muscle movements, and mapping the digital model onto an animated character. In another embodiment of the invention, a plurality of pairs of EOG electrodes are adapted to be affixed to the skin surface of the performer at locations adjacent to the performer's eyes. The processor is operatively coupled to the plurality of pairs of EOG electrodes and further includes programming instructions to perform the functions of acquiring EOG data from the plurality of pairs of EOG electrodes. The EOG data comprises electrical signals corresponding to eye movements of the performer during a performance. The programming instructions further provide processing of the EOG data and mapping of the processed EOG data onto the animated character. As a result, the animated character will exhibit the same muscle and eye movements as the performer.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Systems, articles, and methods for gesture identification in wearable electromyography devices
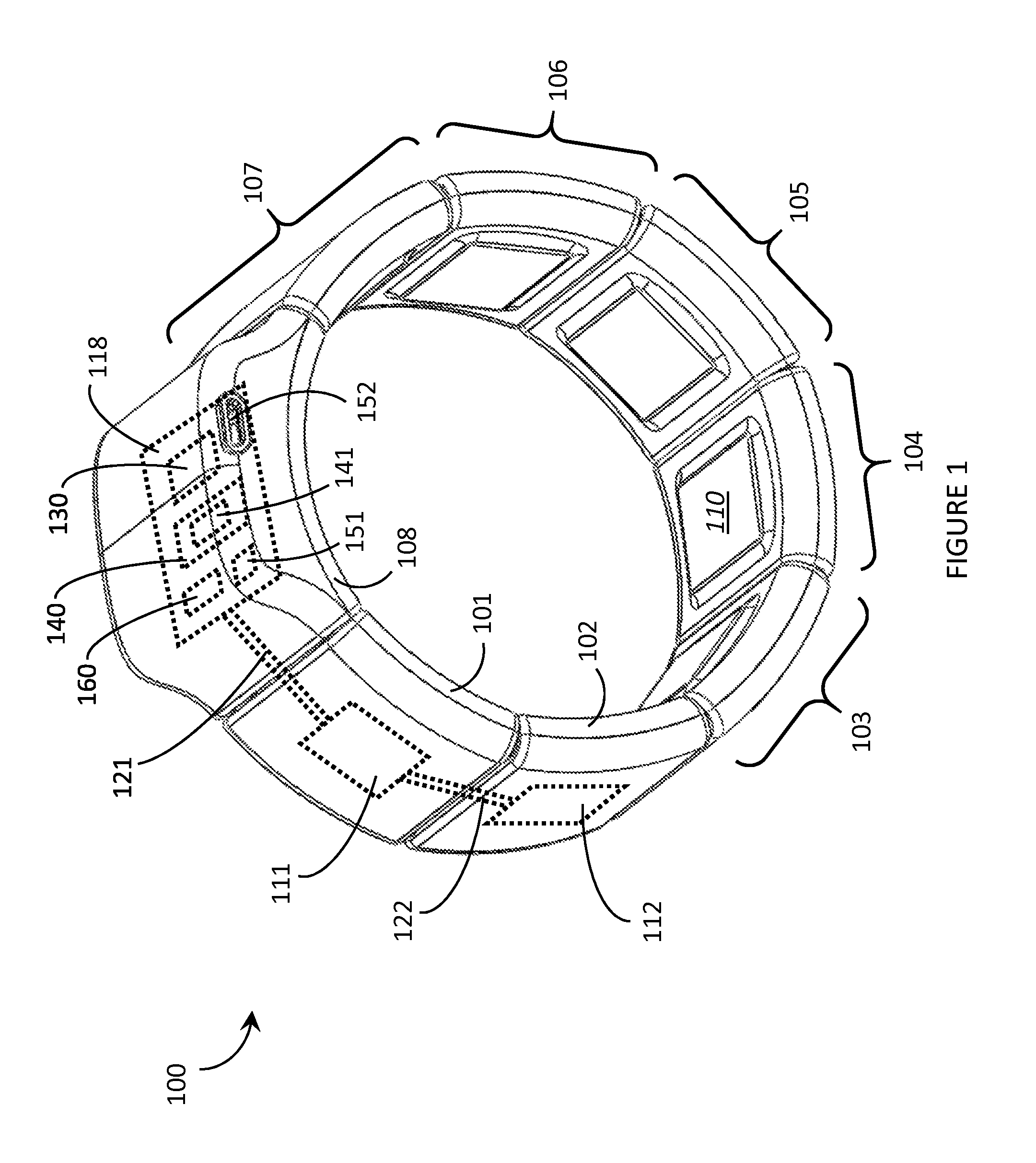
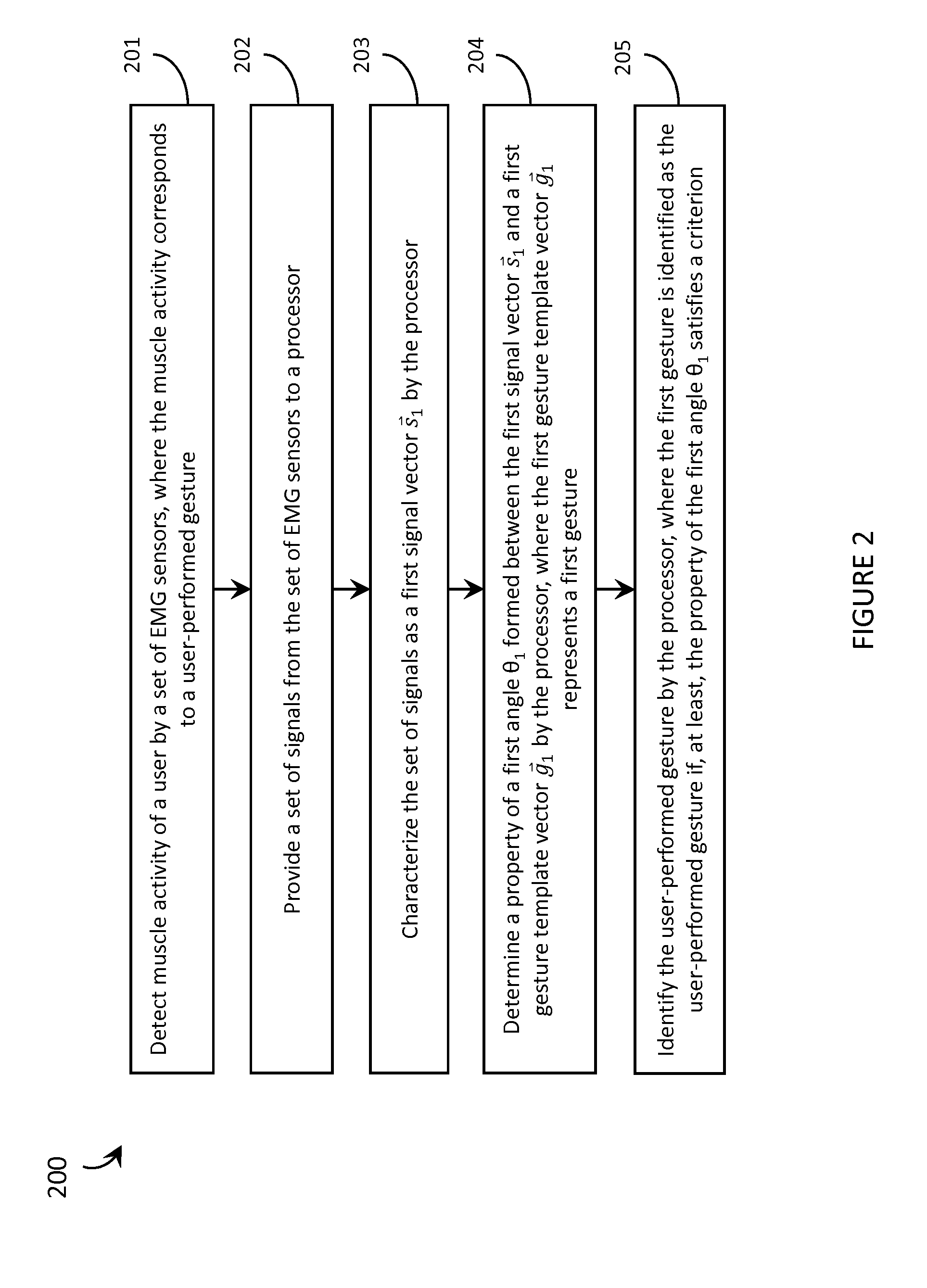
ActiveUS9367139B2Input/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingOn boardHuman–computer interaction
Systems, articles, and methods perform gesture identification with limited computational resources. A wearable electromyography (“EMG”) device includes multiple EMG sensors, an on-board processor, and a non-transitory processor-readable memory storing data and / or instructions for performing gesture identification. The wearable EMG device detects signals when a user performs a physical gesture and characterizes a signal vector {right arrow over (s)} based on features of the detected signals. A library of gesture template vectors G is stored in the memory of the wearable EMG device and a respective property of each respective angle θi formed between the signal vector {right arrow over (s)} and respective ones of the gesture template vectors {right arrow over (g)}i is analyzed to match the direction of the signal vector {right arrow over (s)} to the direction of a particular gesture template vector {right arrow over (g)}*. The accuracy of the gesture identification may be enhanced by performing multiple iterations across multiple time-synchronized portions of the EMG signal data.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
Biosleeve human-machine interface
ActiveUS9278453B2Input/output for user-computer interactionProgramme controlHuman–machine interfaceEngineering
Systems and methods for sensing human muscle action and gestures in order to control machines or robotic devices are disclosed. One exemplary system employs a tight fitting sleeve worn on a user arm and including a plurality of electromyography (EMG) sensors and at least one inertial measurement unit (IMU). Power, signal processing, and communications electronics may be built into the sleeve and control data may be transmitted wirelessly to the controlled machine or robotic device.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com