Patents
Literature
457 results about "Relative permittivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
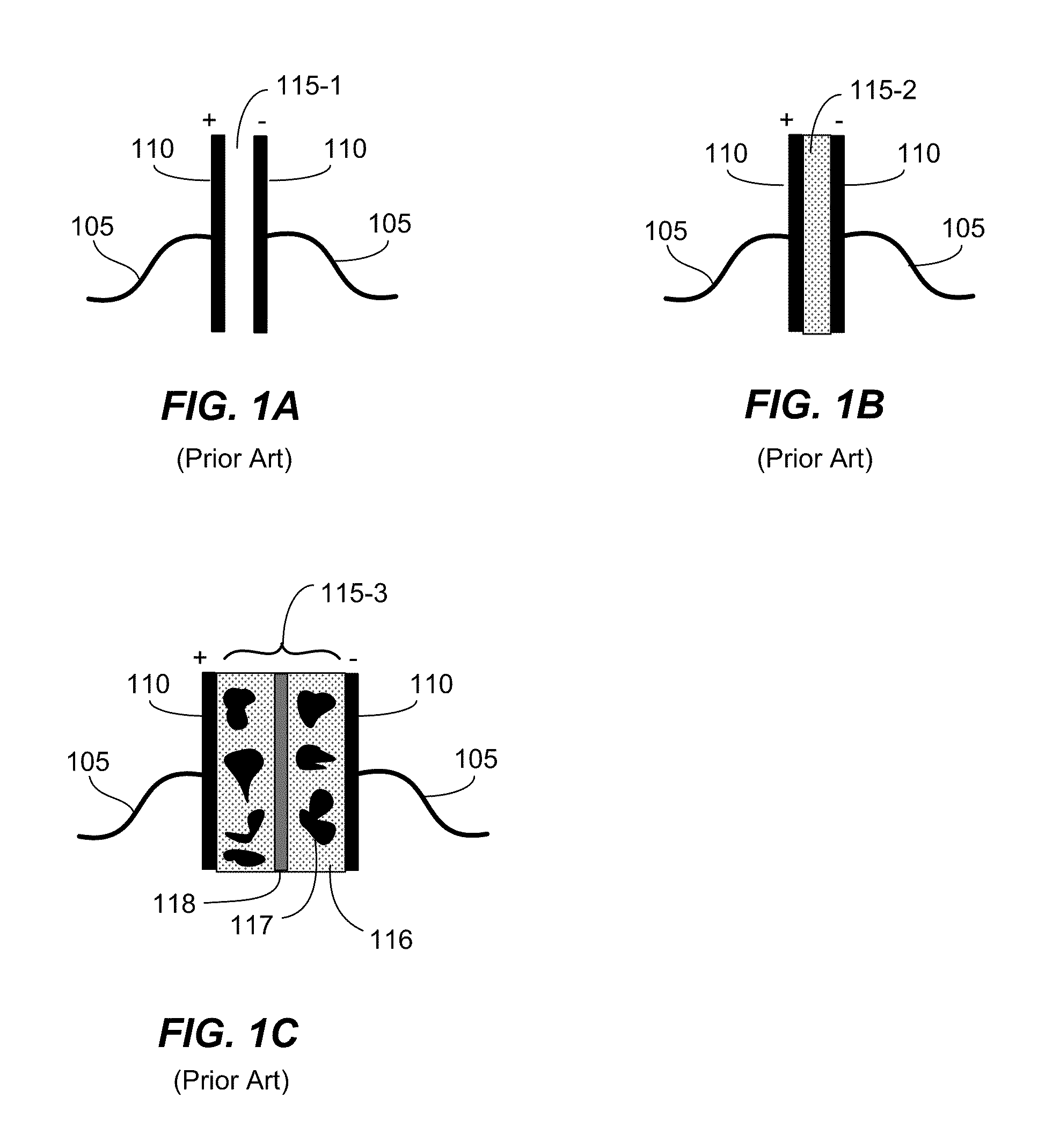
The relative permittivity of a material is its (absolute) permittivity expressed as a ratio relative to the vacuum permittivity. Permittivity is a material property that affects the Coulomb force between two point charges in the material. Relative permittivity is the factor by which the electric field between the charges is decreased relative to vacuum.
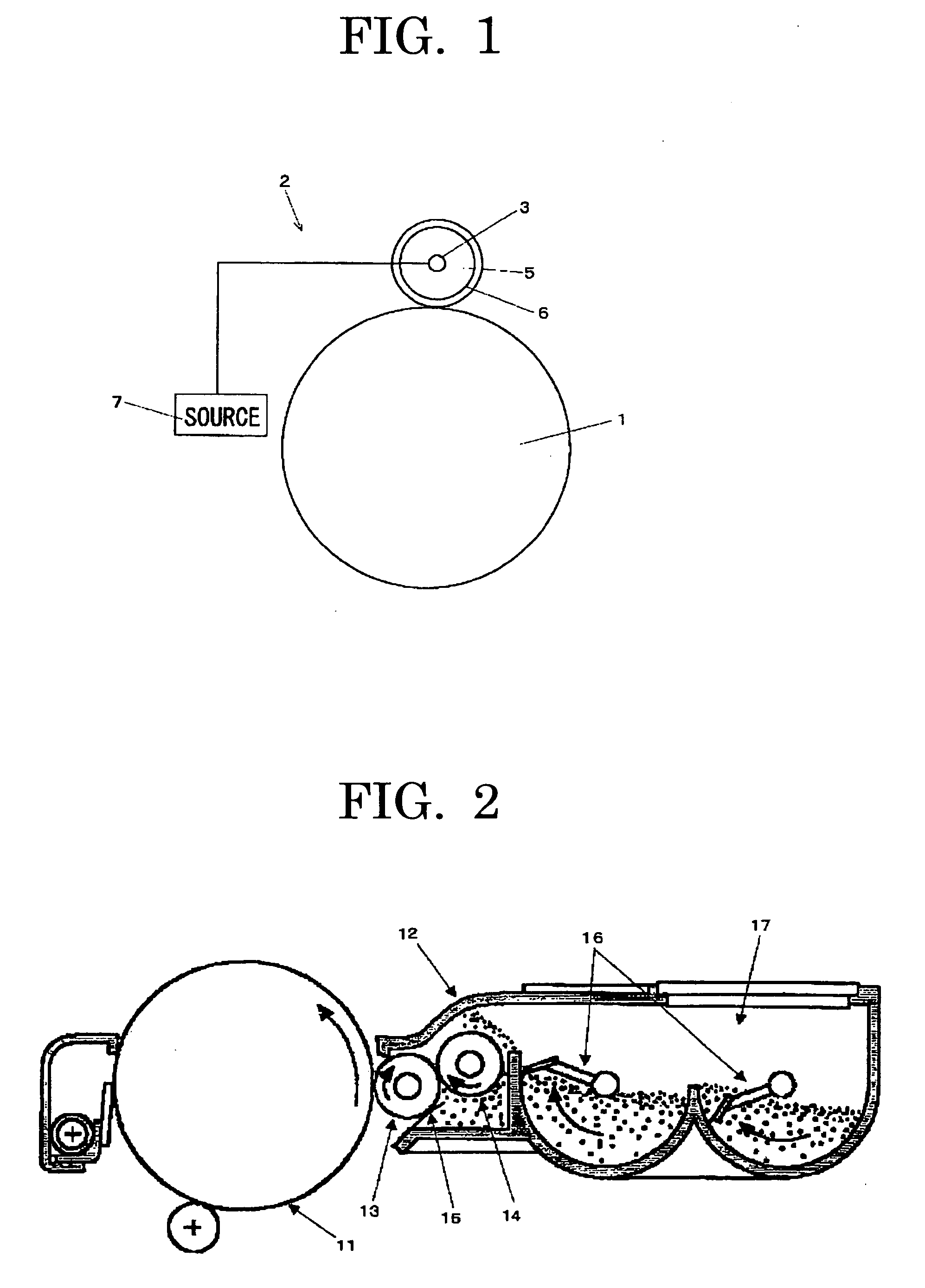
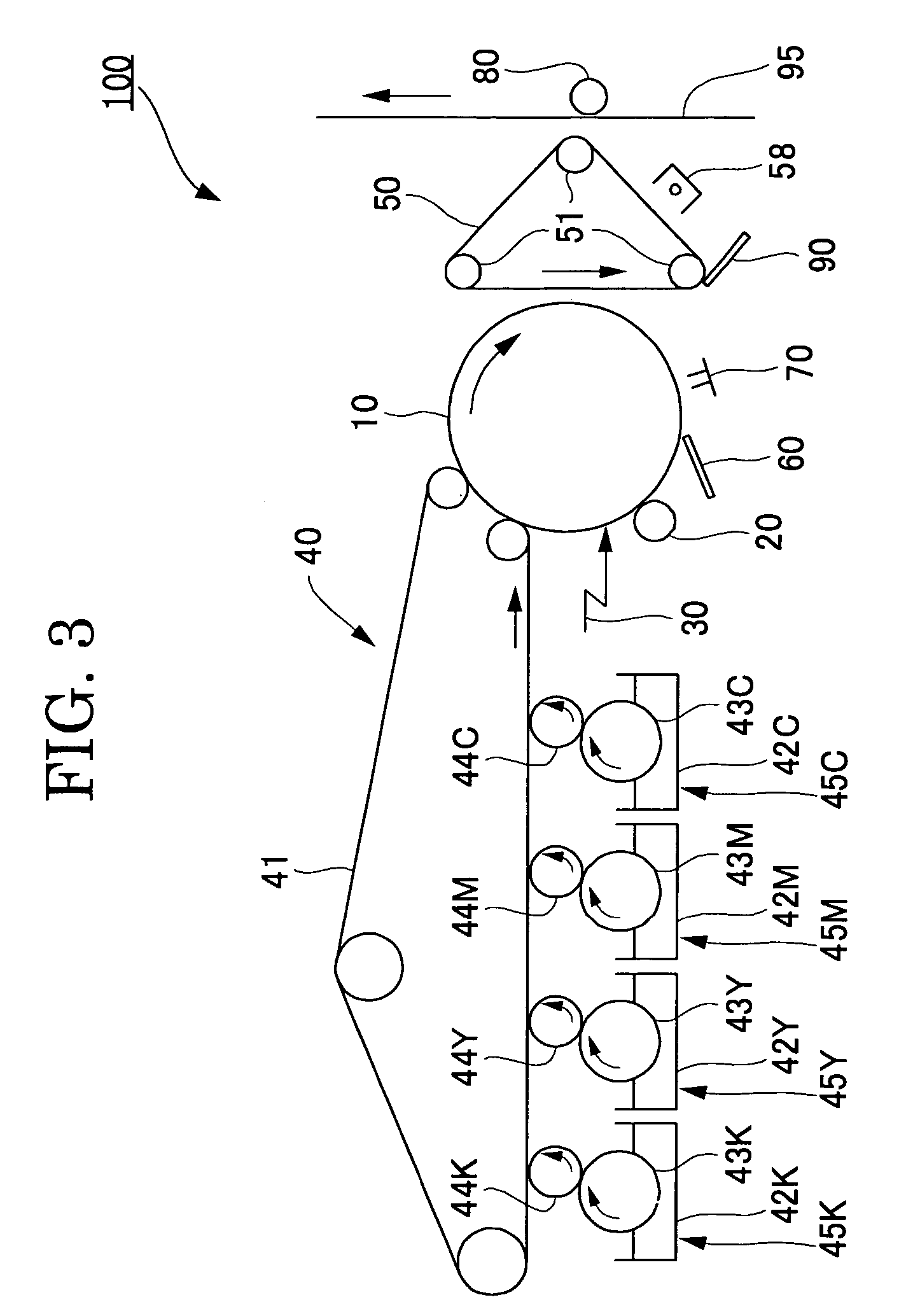
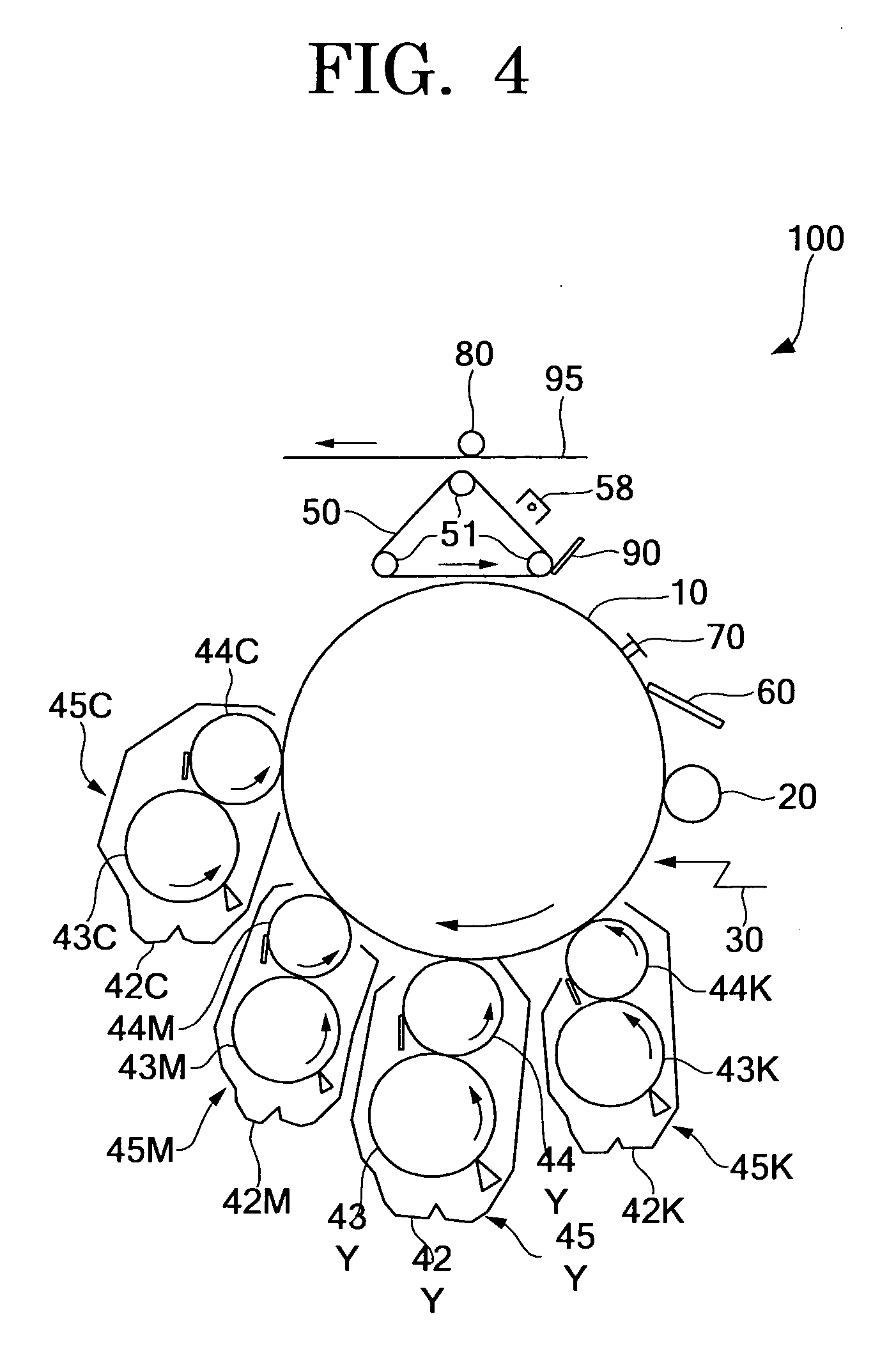
Toner for electrostatic development, developer, image forming method, image-forming apparatus and process for cartridge using the same
InactiveUS20060275686A1Improve stabilityEffectively and uniformlyDevelopersElectrographic processes using charge patternImage formationEngineering
It is an object of the present invention to provide a toner containing toner particles and inorganic fine particles wherein the inorganic fine particles are externally added to the toner particles which contain a binder resin and a colorant and at least one type of the inorganic fine particles is a compound oxide having a relative permittivity measured at 1 MHz of 2 to 10 and a volume resistivity of 1011 Ω*cm or more and an image forming method using the toner.
Owner:RICOH KK
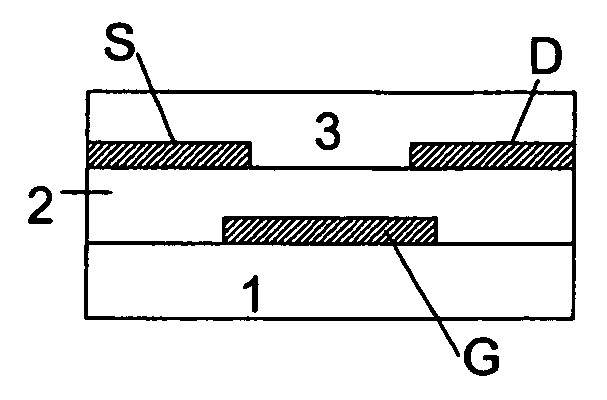
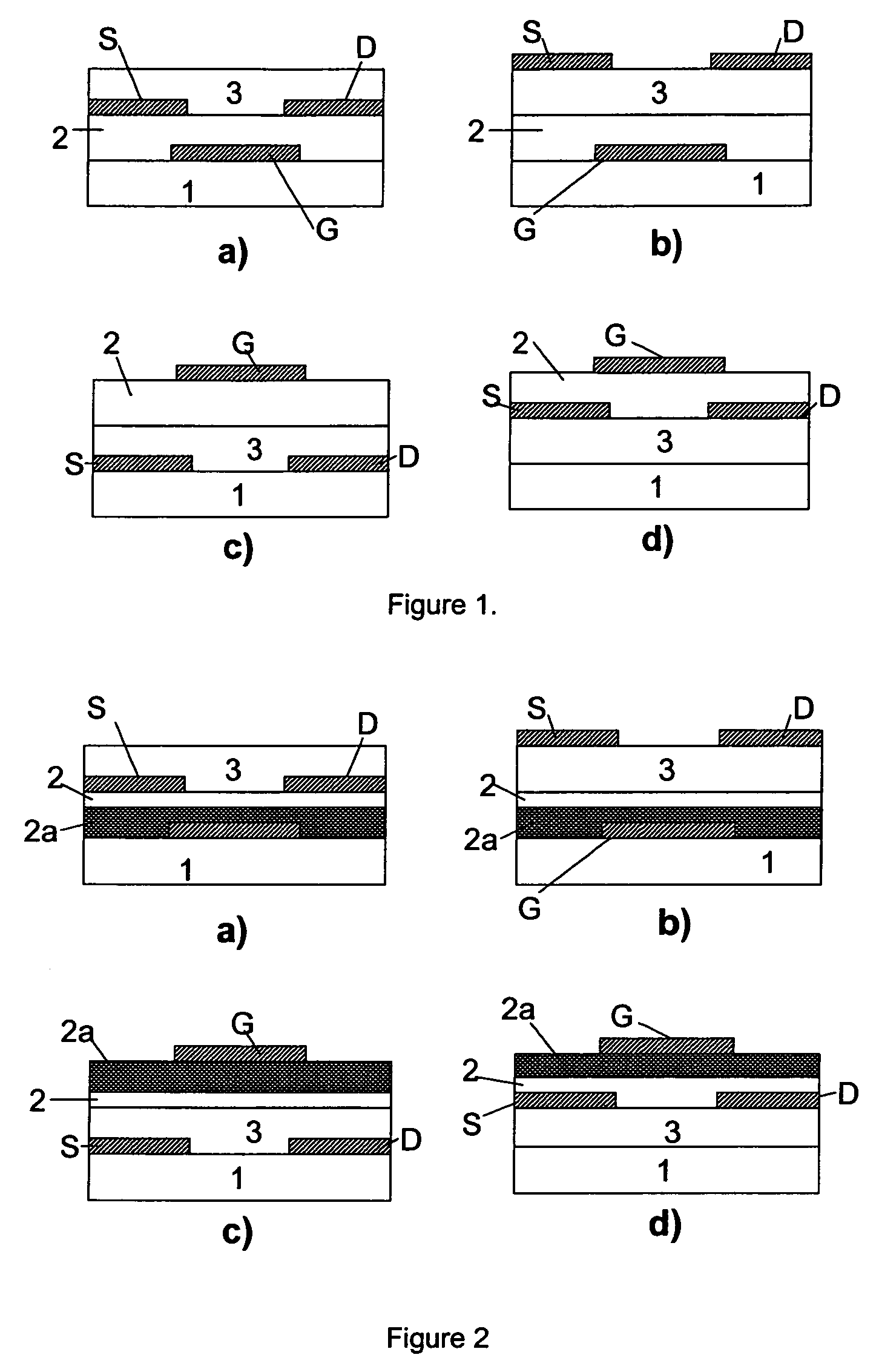
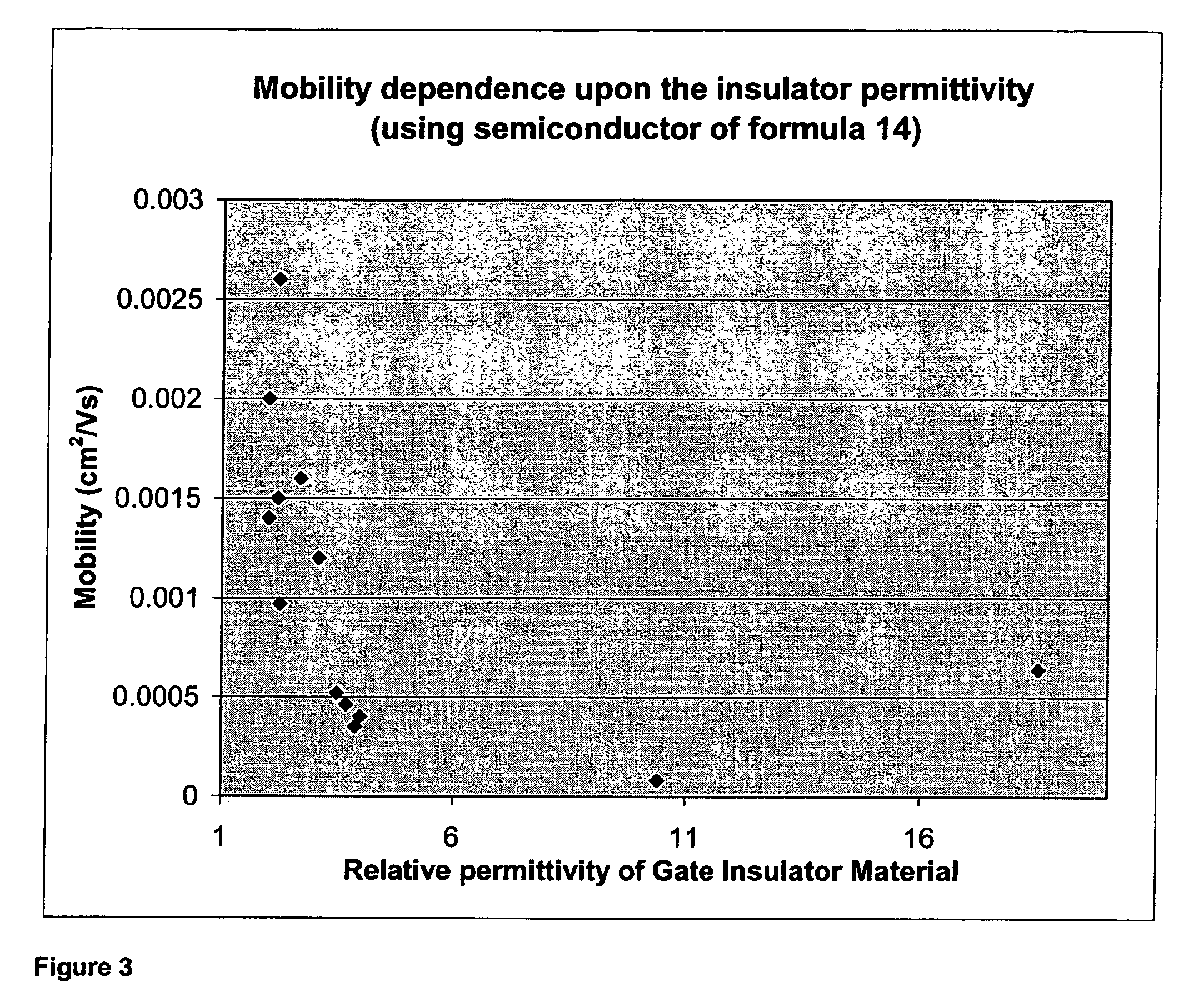
Organic field effect transistor with an organic dielectric
InactiveUS7029945B2Improve performancePreventing modulationTransistorSolid-state devicesOrganic field-effect transistorGate insulator
A process of manufacturing an organic field effect device is provided comprising the steps of (a) depositing from a solution an organic semiconductor layer; and (b) depositing from a solution a layer of low permittivity insulating material forming at least a part of a gate insulator, such that the low permittivity insulating material is in contact with the organic semiconductor layer, wherein the low permittivity insulating material is of relative permittivity from 1.1 to below 3.0. In addition, an organic field effect device manufactured by the process is provided.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
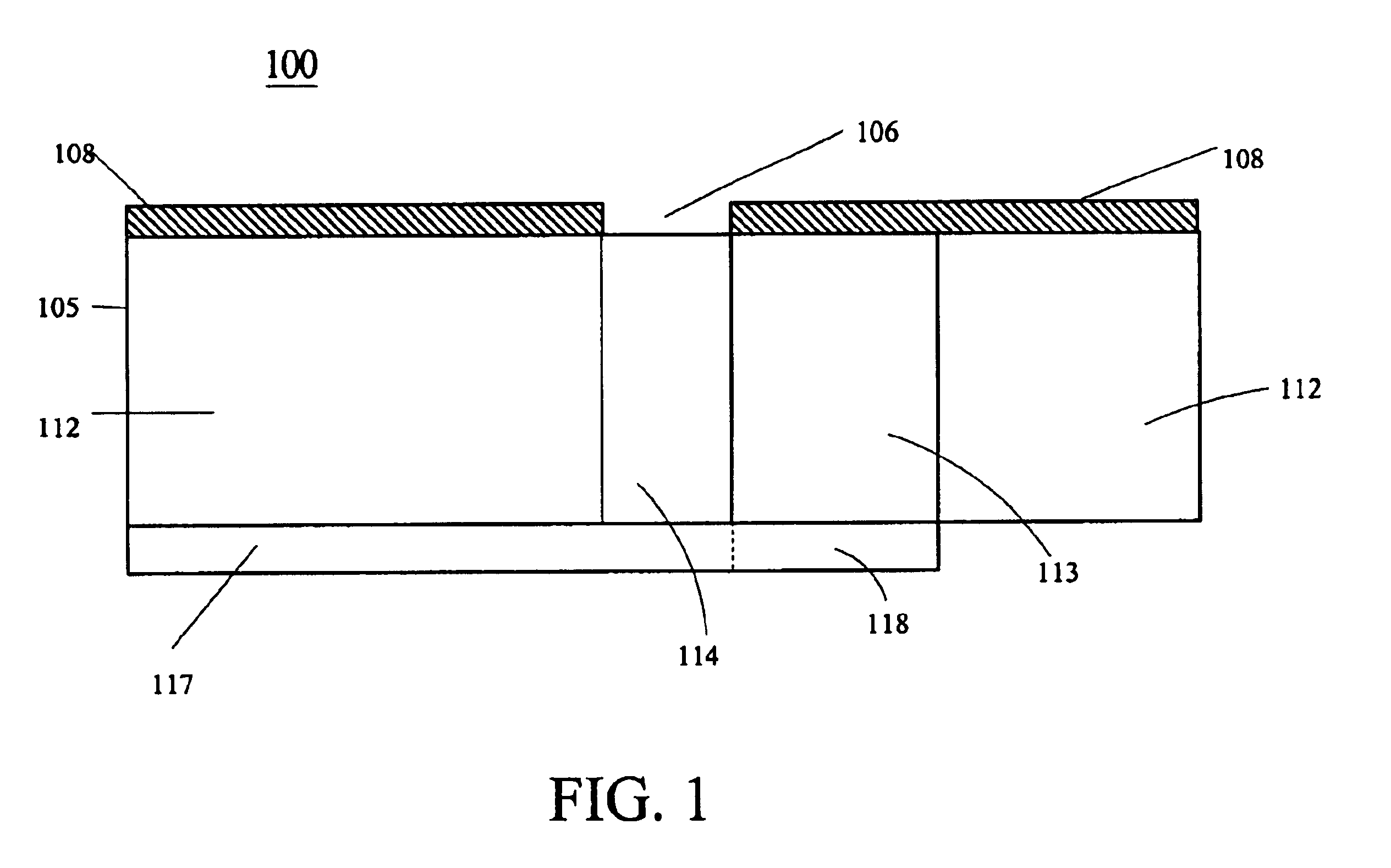
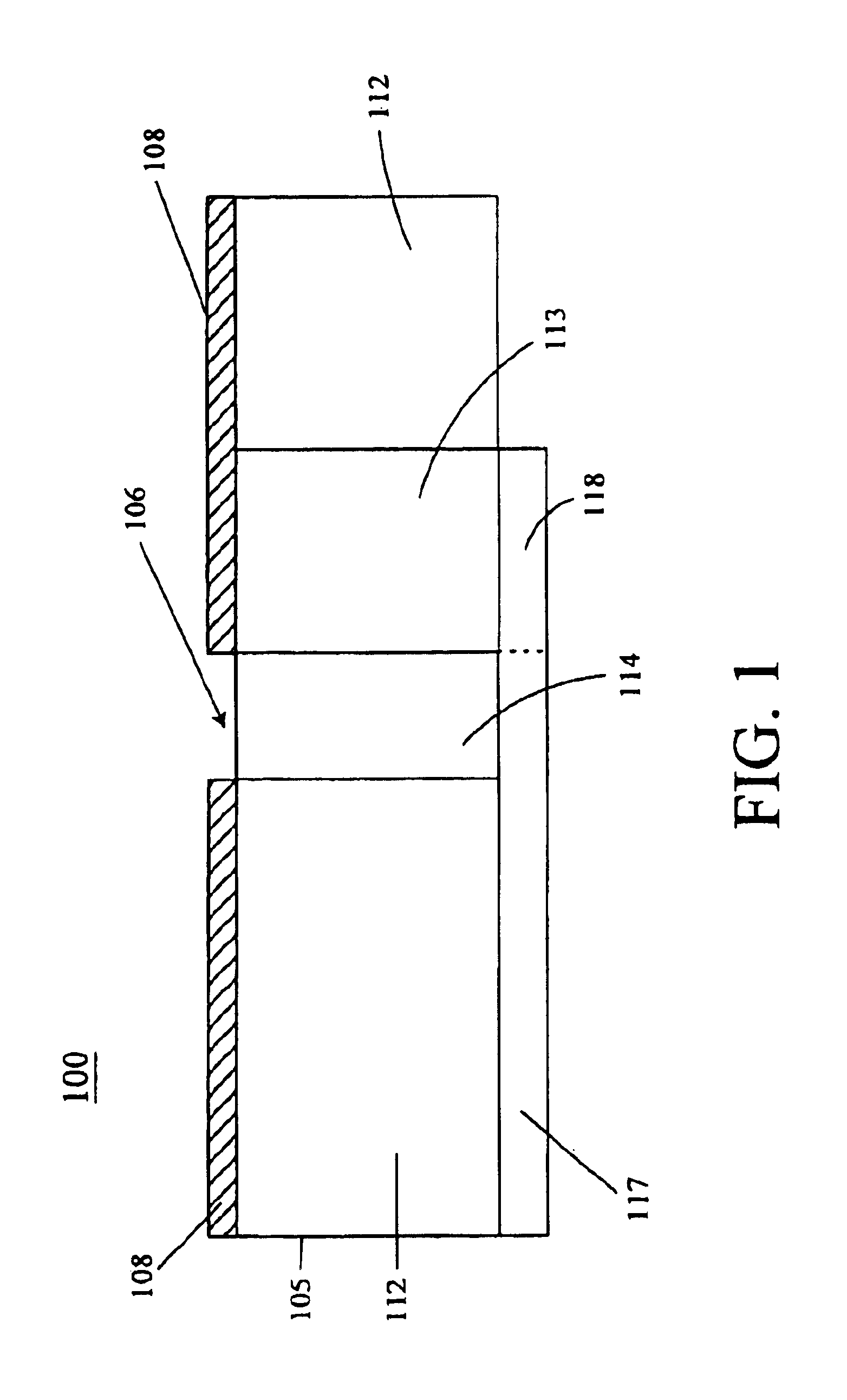
High efficiency slot fed microstrip antenna having an improved stub
InactiveUS6791496B1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsCouplingGround plane
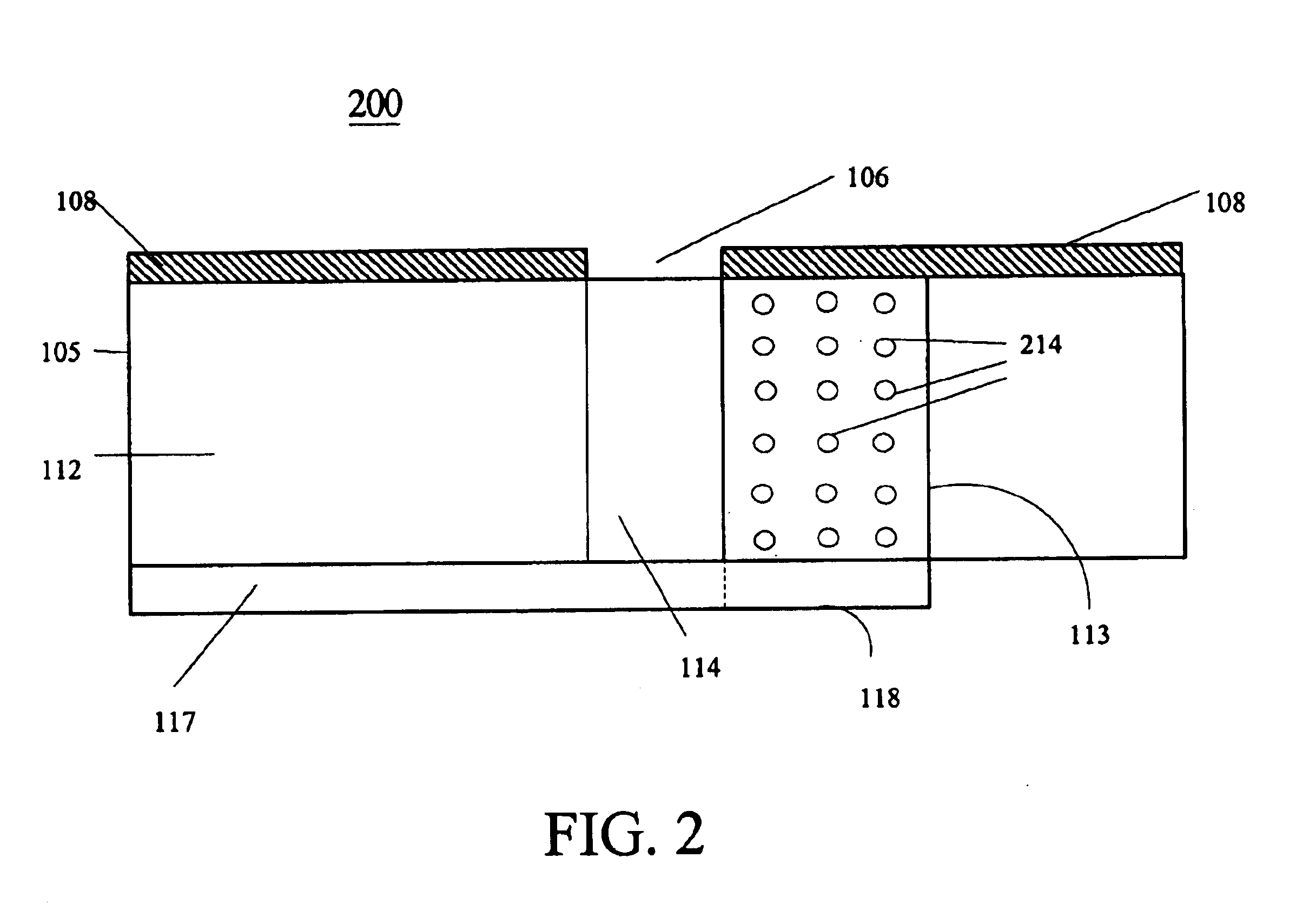
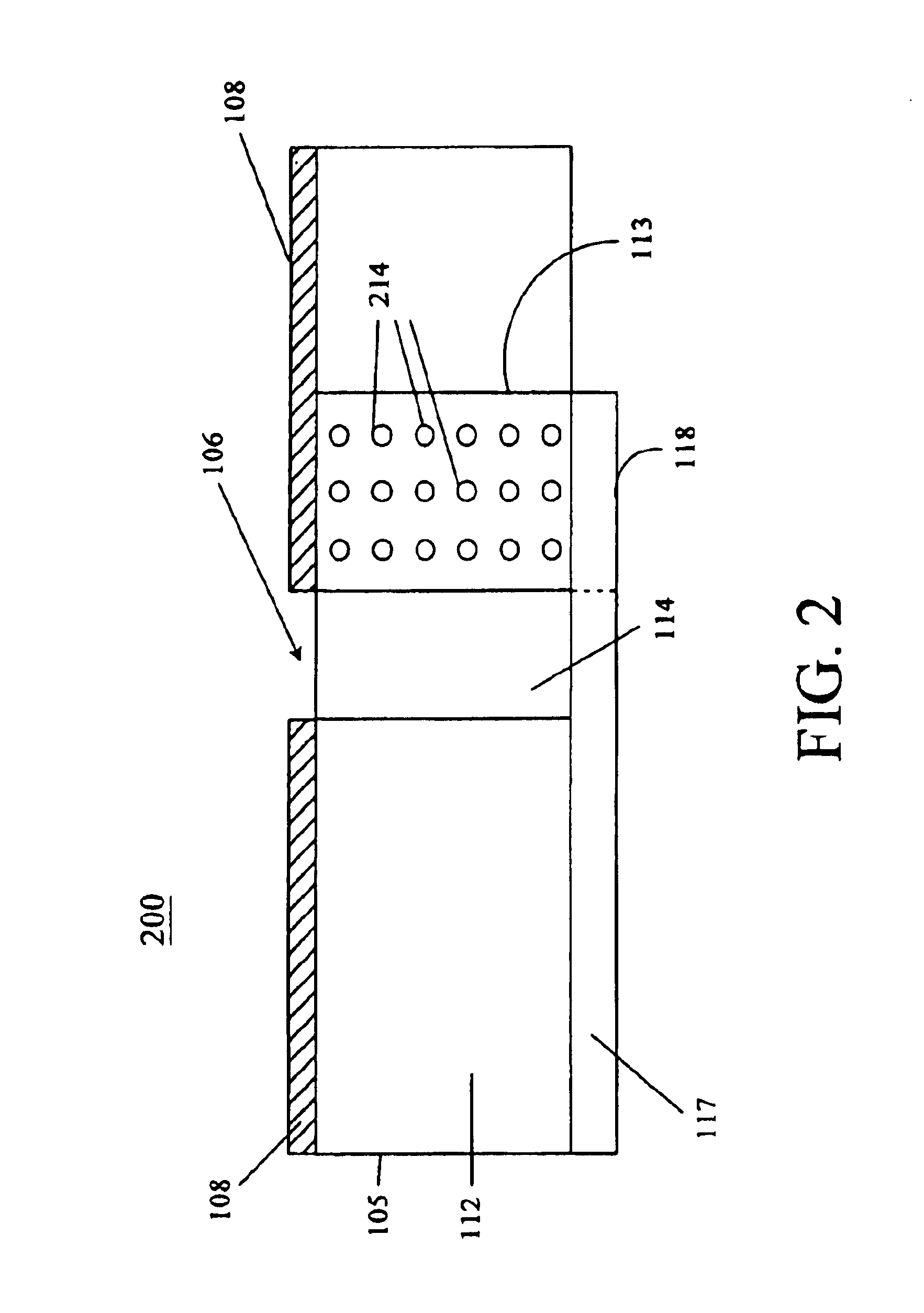
A slot fed microstrip antenna (100) having an improved stub (118) provides enhanced efficiency through more efficient coupling of electromagnetic energy between the feed line (117) and the slot (106). A dielectric layer (105) disposed between the feed line (117) and the ground plane (108) provides a first region (112) having a first relative permittivity and at least a second region (113) having a second relative permittivity. The second relative permittivity is higher as compared to the first relative permittivity. The stub (118) is disposed on the high permittivity region (113). The dielectric layer can include magnetic particles, which are preferably disposed underlying the stub.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Broad band antenna
InactiveUS20080055178A1Big decrease in gainRadiating elements structural formsElongated active element feedPolymer resinBroadband
A broad band antenna including: a body formed of a material having a relative permittivity of 2 to 20, a relative permeability of 1 to 10, and a magnetic loss tangent of 0.001 to 0.2, at a usable frequency; and at least one radiator disposed on the body. The material forming the body may be a composite material formed of a polymer resin mixed with a magnetic powder. The composite material may contain the magnetic powder by 90 wt % with respect to a total weight.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
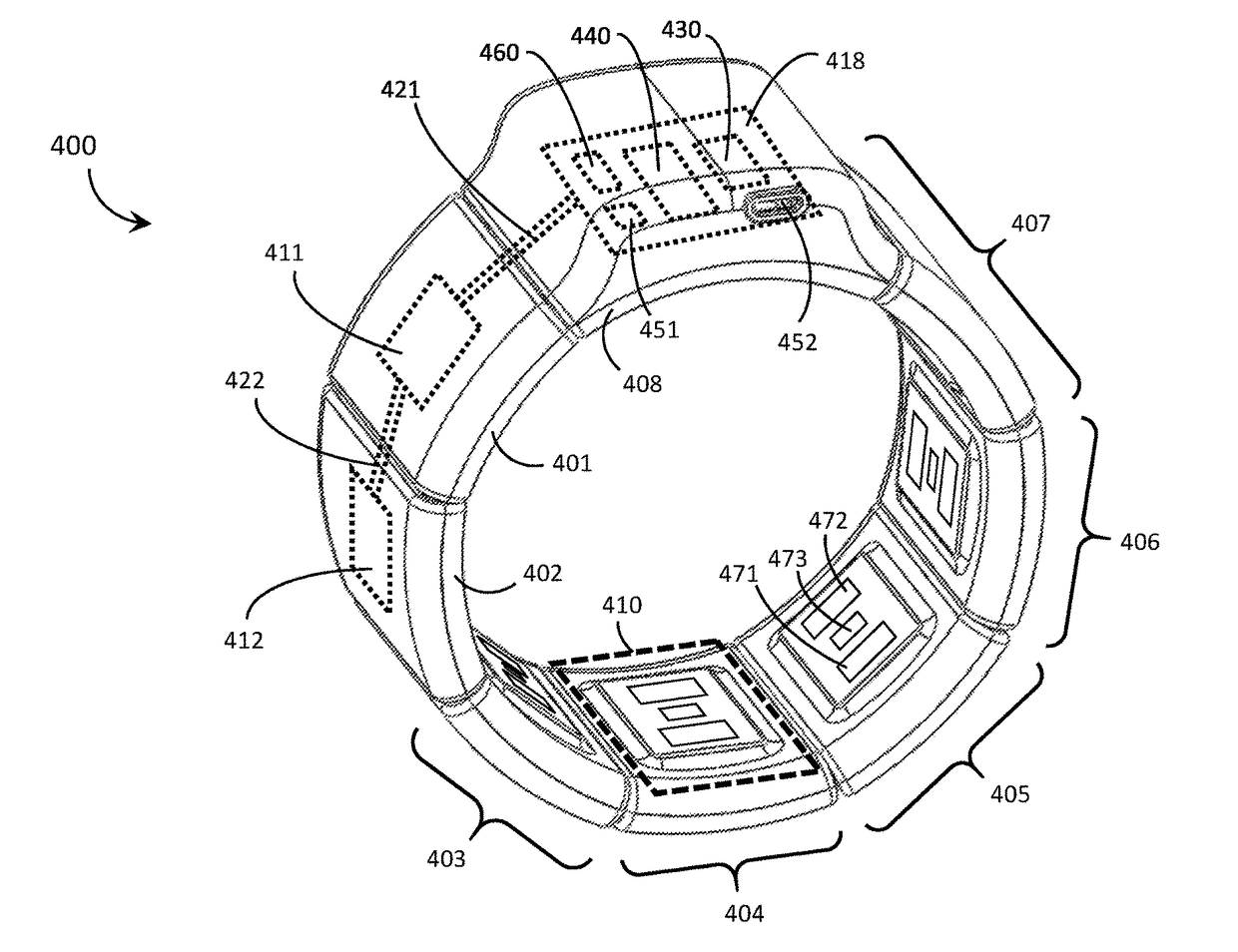
Systems, articles, and methods for capacitive electromyography sensors
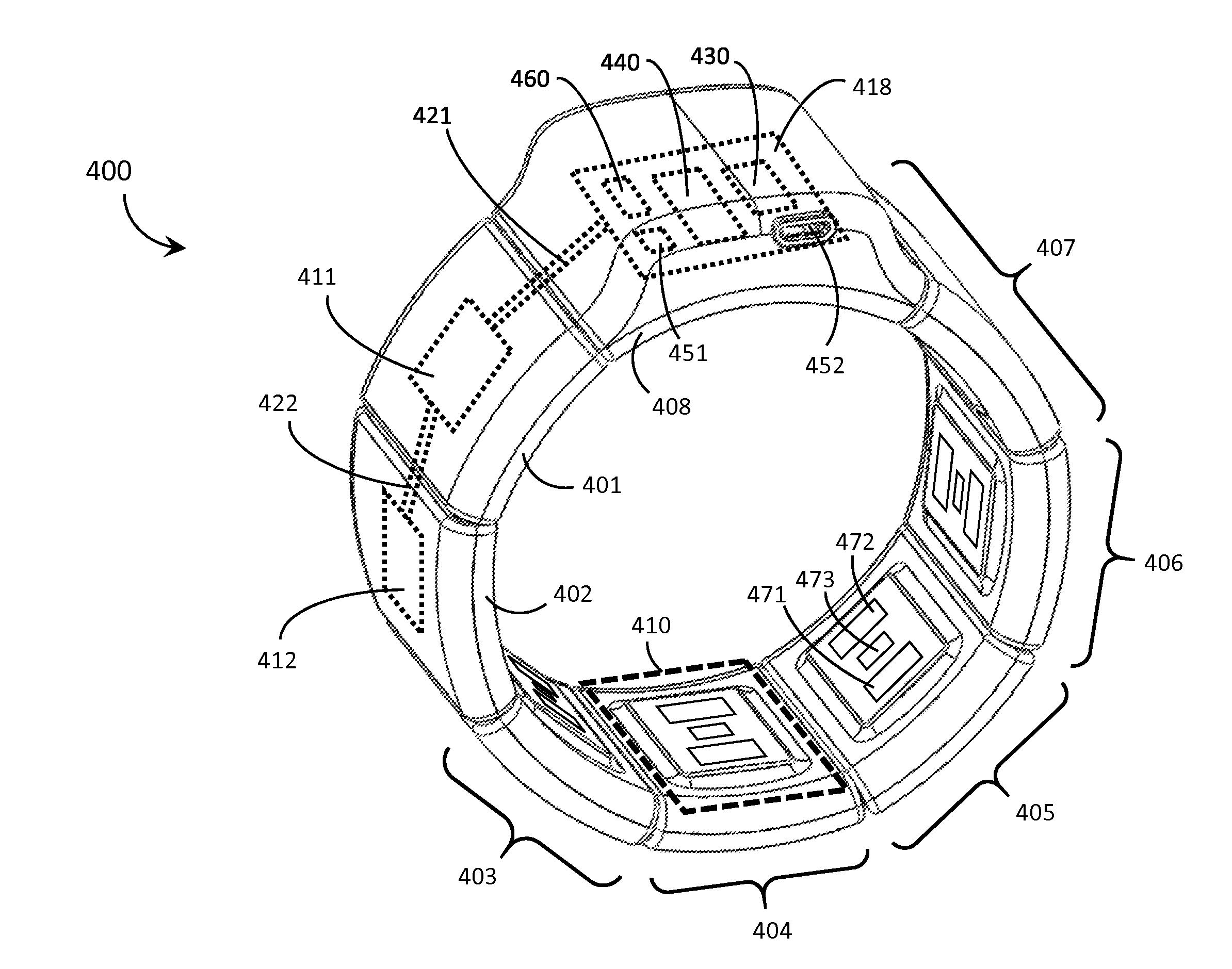
ActiveUS20150141784A1Input/output for user-computer interactionElectromyographyHuman–machine interfaceEngineering
Systems, articles, and methods for improved capacitive electromyography (“EMG”) sensors are described. The improved capacitive EMG sensors include one or more sensor electrode(s) that is / are coated with a protective barrier formed of a material that has a relative permittivity ∈r of about 10 or more. The protective barrier shields the sensor electrode(s) from moisture, sweat, skin oils, etc. while advantageously contributing to a large capacitance between the sensor electrode(s) and the user's body. In this way, the improved capacitive EMG sensors provide enhanced robustness against variations in skin and / or environmental conditions. Such improved capacitive EMG sensors are particularly well-suited for use in wearable EMG devices that may be worn by a user for an extended period of time and / or under a variety of skin and / or environmental conditions. A wearable EMG device that provides a component of a human-electronics interface and incorporates such improved capacitive EMG sensors is described.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
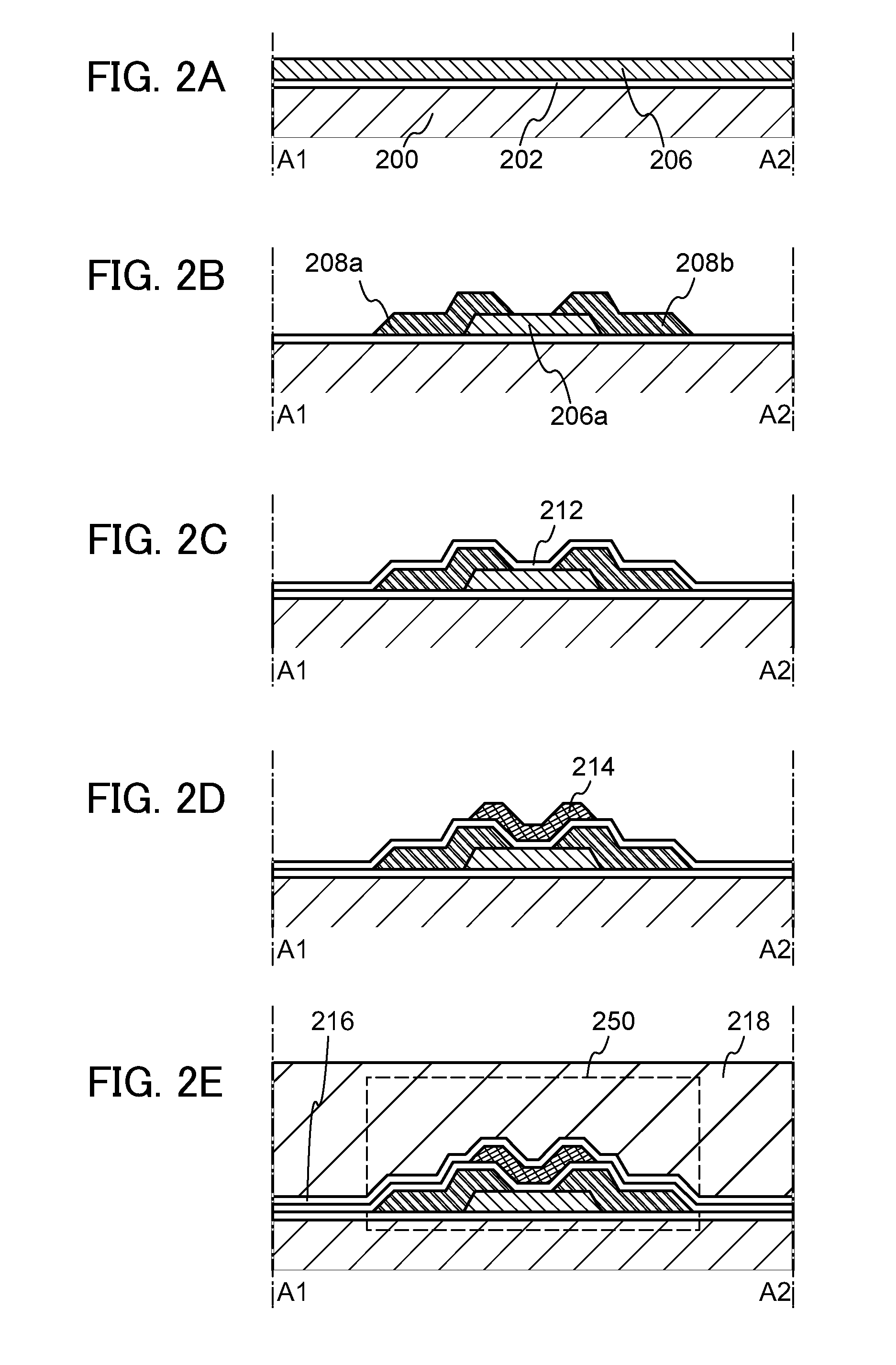
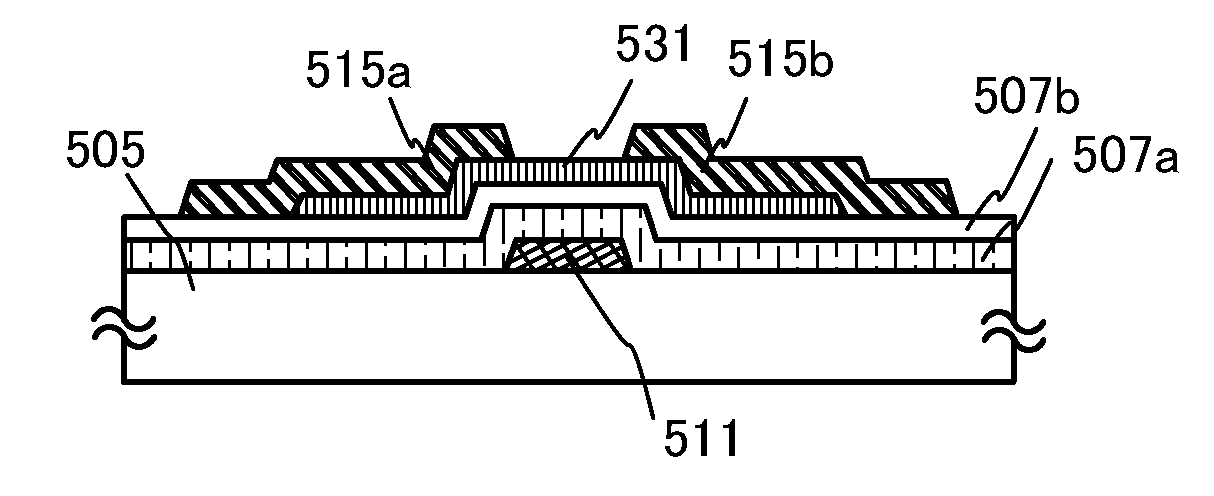
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
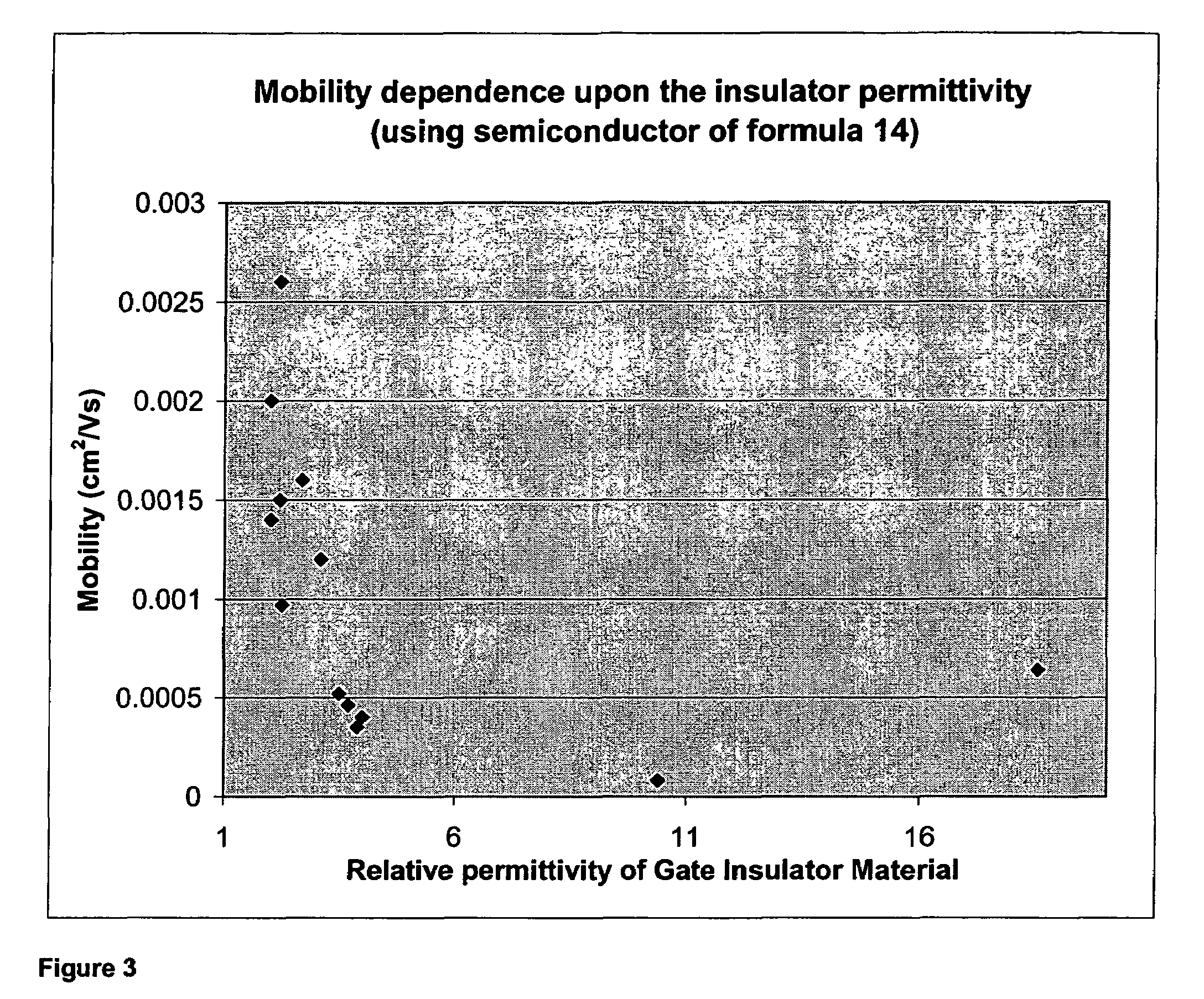
InactiveUS20110156022A1Run at high speedReduce power consumptionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesRelative permittivitySemiconductor
A semiconductor device which includes an oxide semiconductor layer, a source electrode and a drain electrode electrically connected to the oxide semiconductor layer, a gate insulating layer covering the oxide semiconductor layer, the source electrode, and the drain electrode, and a gate electrode over the gate insulating layer is provided. The thickness of the oxide semiconductor layer is greater than or equal to 1 nm and less than or equal to 10 nm. The gate insulating layer satisfies a relation where εr / d is greater than or equal to 0.08 (nm−1) and less than or equal to 7.9 (nm−1) when the relative permittivity of a material used for the gate insulating layer is εr and the thickness of the gate insulating layer is d. The distance between the source electrode and the drain electrode is greater than or equal to 10 nm and less than or equal to 1 μm.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Organic field effect transistor with an organic dielectric
A process of manufacturing an organic field effect device is provided comprising the steps of (a) depositing from a solution an organic semiconductor layer; and (b) depositing from a solution a layer of low permittivity insulating material forming at least a part of a gate insulator, such that the low permittivity insulating material is in contact with the organic semiconductor layer, wherein the low permittivity insulating material is of relative permittivity from 1.1 to below 3.0. In addition, an organic field effect device manufactured by the process is provided.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Method for imaging multiphase flow using electrical capacitance tomography
InactiveUS7496450B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGenetic algorithmGlobal optimization
The invention relates to an image-reconstruction technique which is used to view multiphase flows using electrical capacitance tomography (ECT), which is based on non-linear heuristic global optimization methods involving simulated annealing and genetic algorithms. The inventive method consists in obtaining electrical capacitance data which are measured between electrodes positioned on the outer surface of pipeline, well or tank (electrically-insulating) containing fluids. The aforementioned data are dependent on the distribution of the fluids inside the pipeline, well or tank. Moreover, the data are processed in order to reconstruct an image of the spatial distribution of the relative electrical permittivity (also known as the dielectric constant) inside the tube, well or tank, which reflects the distribution of the different phases present in the flow.
Owner:INST MEXICANO DEL GASOLINEEO
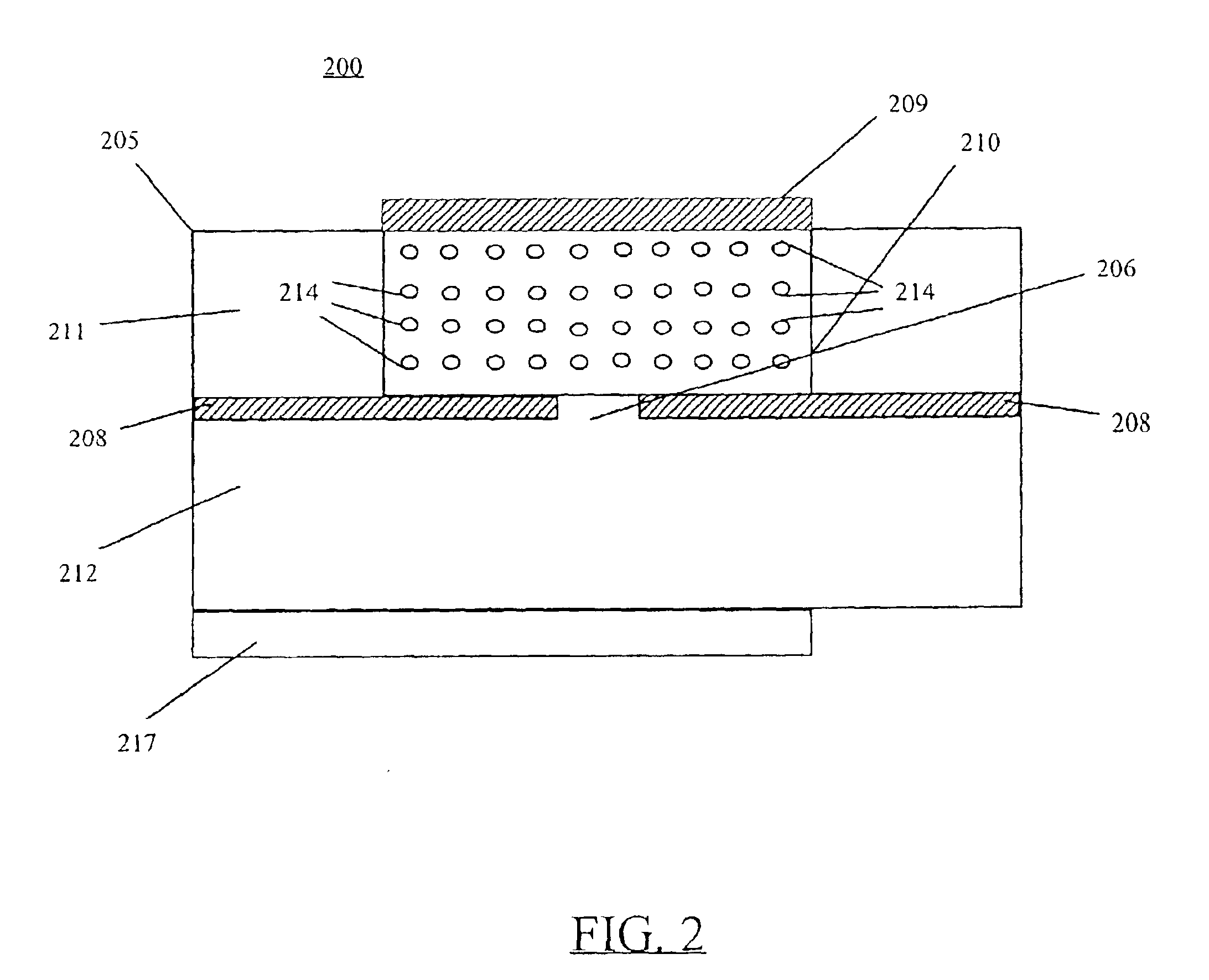
High efficiency slot fed microstrip patch antenna
InactiveUS6842140B2Small sizeLack of efficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip patch antennaReduced size
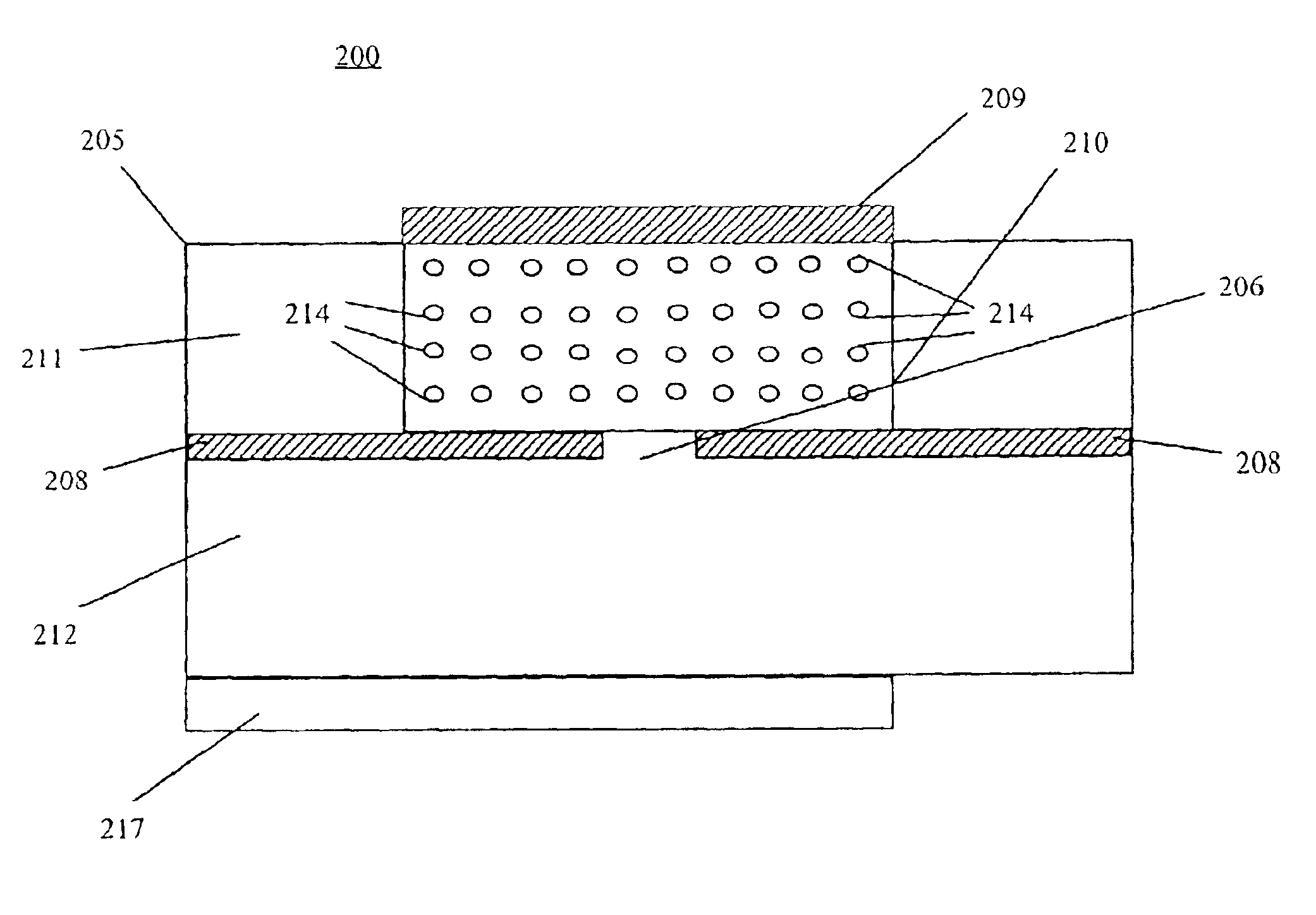
A slot fed microstrip patch antenna (200) includes an electrically conducting ground plane (208), the ground plane (208) having at least one coupling slot (206) and at least a first patch radiator (209). An antenna dielectric substrate material (205) is disposed between the ground plane (208) and the first patch radiator (209), wherein at least a portion of the antenna dielectric (210) includes magnetic particles (214). A feed dielectric substrate (212) is disposed between a feed line (217) and the ground plane (208). Magnetic particles can also be used in the feed line (217) dielectric. Patch antennas according to the invention can be of a reduced size through use of high relative permittivity dielectric substrate portions, yet still be efficient through use of dielectrics including magnetic particles which permit impedance matching of dielectric medium interfaces, such as the feed line (217) into the slot (206).
Owner:HARRIS CORP
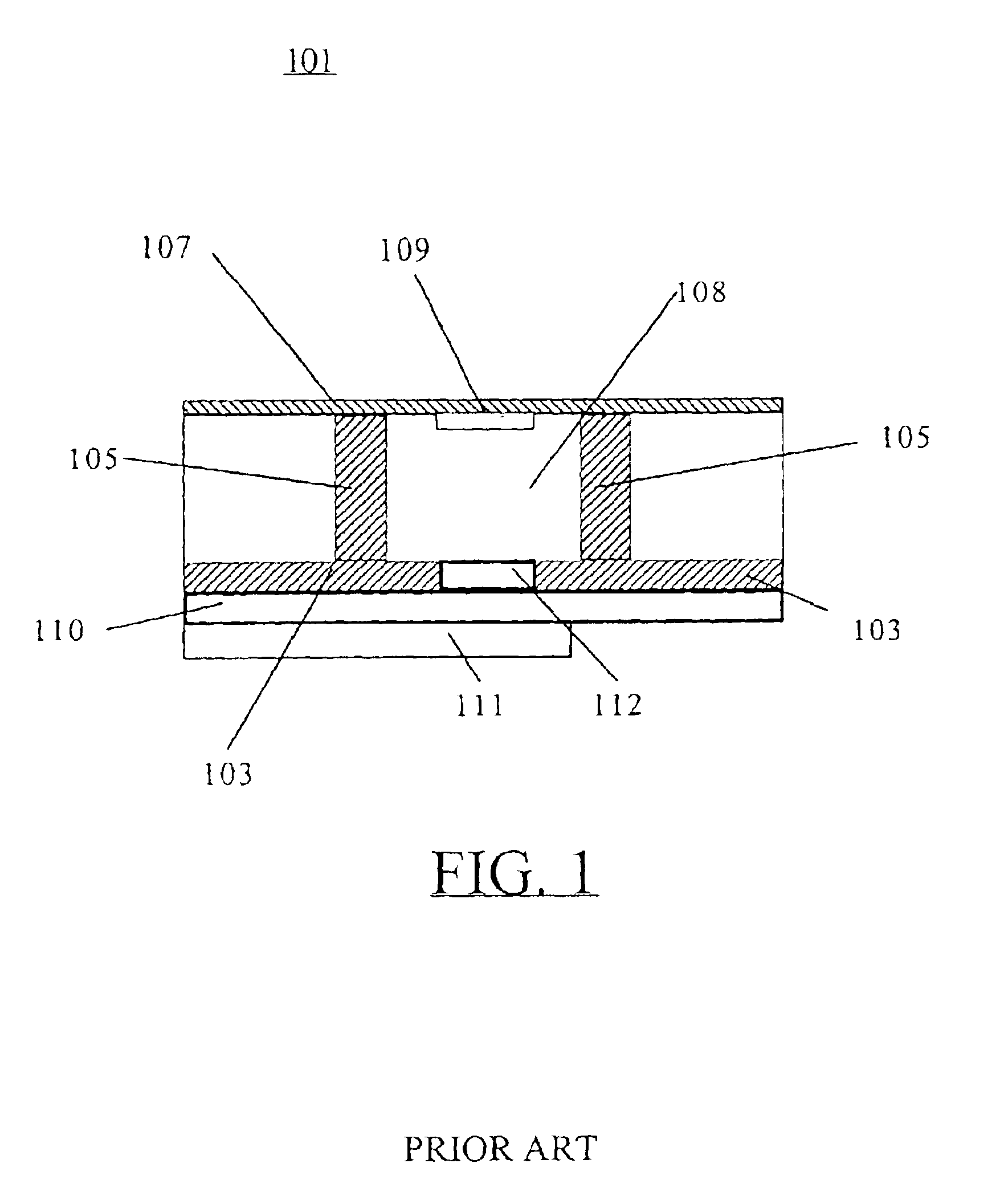
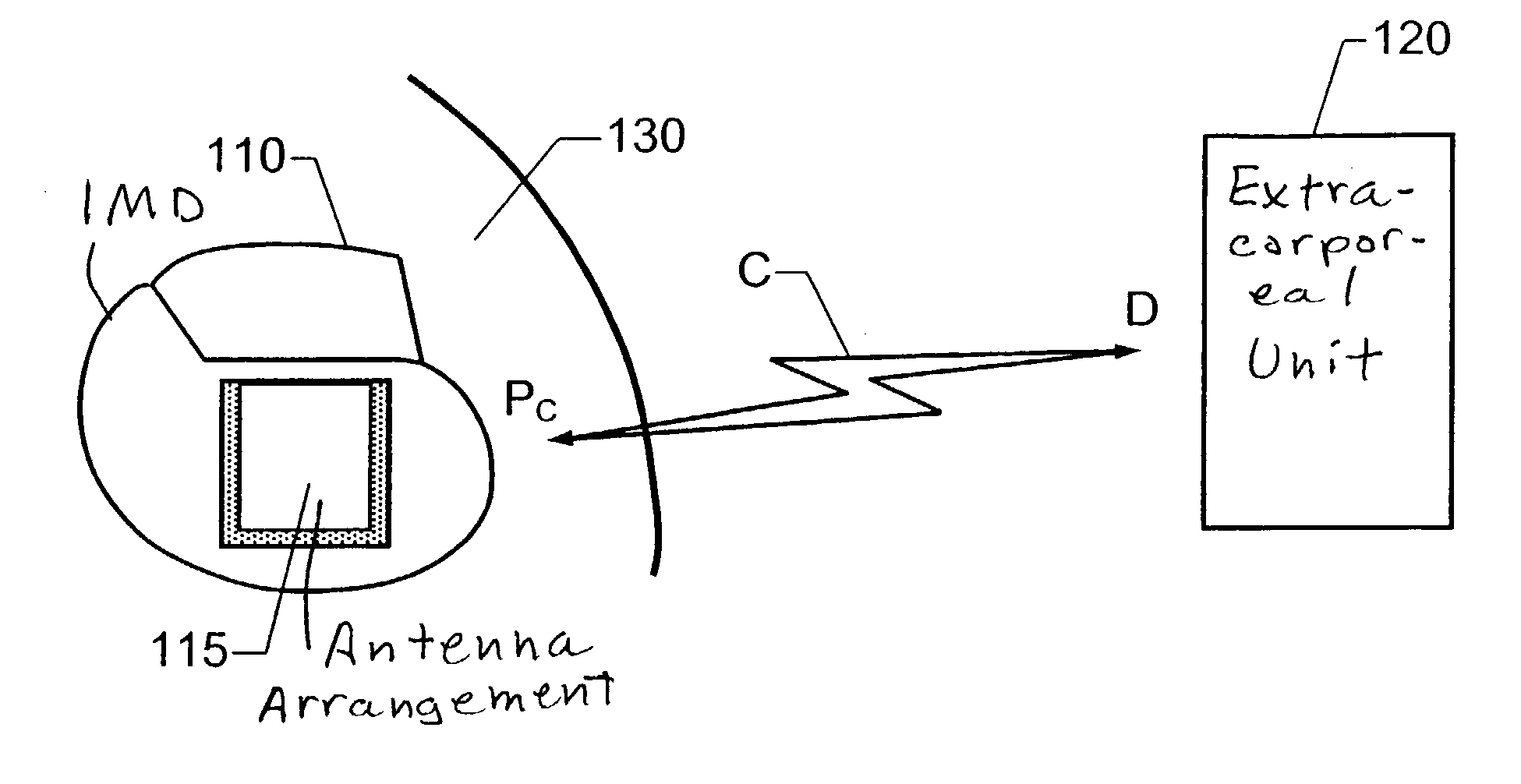
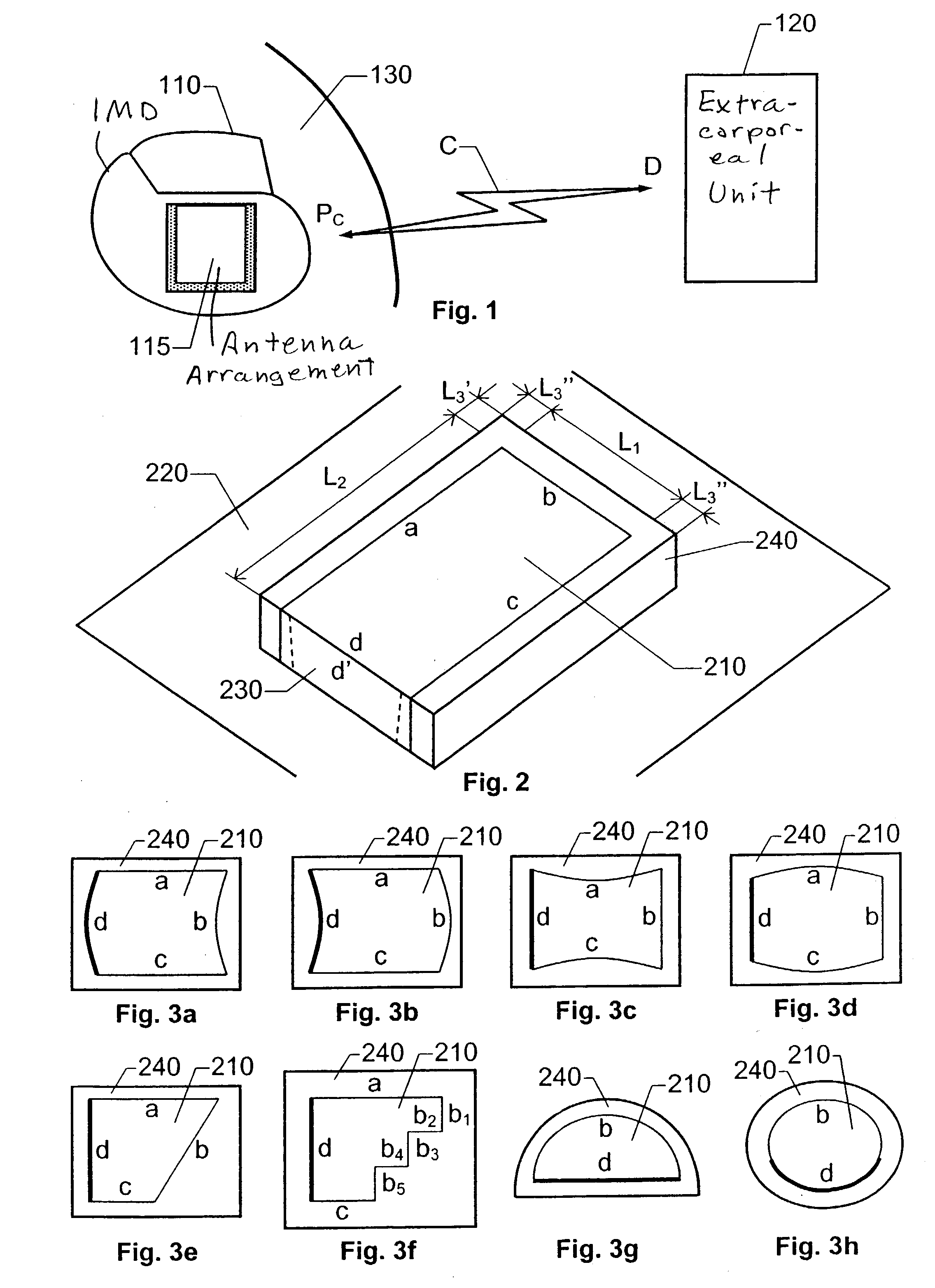
Implantable antenna for use with an implantable medical device
InactiveUS20030216793A1Reduce lossesReduce designElectrotherapyResonant antennasDielectric substrateWireless data
For wireless data exchange between an implantable medical device and an extracorporal unit by means of an antenna arrangement for communicating radio frequent signals, the antenna arrangement includes a patch plane having a perimeter, a ground plane of an electrically conducting material and a dielectric substrate filling a volume between the patch plane and the ground plane. The ground plane has an area which is larger than the patch plane and is located in relation to the patch plane such that a perpendicular projection of the patch plane onto the ground plane falls entirely within the ground plane. A grounding member connects the patch plane electrically to the ground plane at a first segment of the perimeter. The substrate has a comparatively high relative permittivity and extends a well-defined distance outside the volume between the patch plane and the ground plane with respect to at least one second segment of the perimeter. A non-conducting region thus is created outside the patch plane and therefore only a relatively small amount of electromagnetic losses will occur in this region.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Capacitor that includes high permittivity capacitor dielectric
A decoupling capacitor is formed on a semiconductor substrate that includes a silicon surface layer. A substantially flat bottom electrode is formed in a portion of the semiconductor surface layer. A capacitor dielectric overlies the bottom electrode. The capacitor dielectric is formed from a high permittivity dielectric with a relative permittivity, preferably greater than about 5. The capacitor also includes a substantially flat top electrode that overlies the capacitor dielectric. In the preferred application, the top electrode is connected to a first reference voltage line and the bottom electrode is connected to a second reference voltage line.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
High permittivity fluid
The present invention provides for an electrically insulating fluid or material of high relative permittivity or dielectric constant. The fluid has a low conductivity and high relative strength and is applicable to pulsed power drilling applications.
Owner:TETRA
Capacitors using preformed dielectric
Devices for storing energy at a high density are described. The devices include a solid dielectric that is preformed to present a high exposed area onto which an electrode is formed. The dielectric material has a high dielectric constant (high relative permittivity) and a high breakdown voltage, allowing a high voltage difference between paired electrodes to effect a high stored energy density.
Owner:SPACE CHARGE
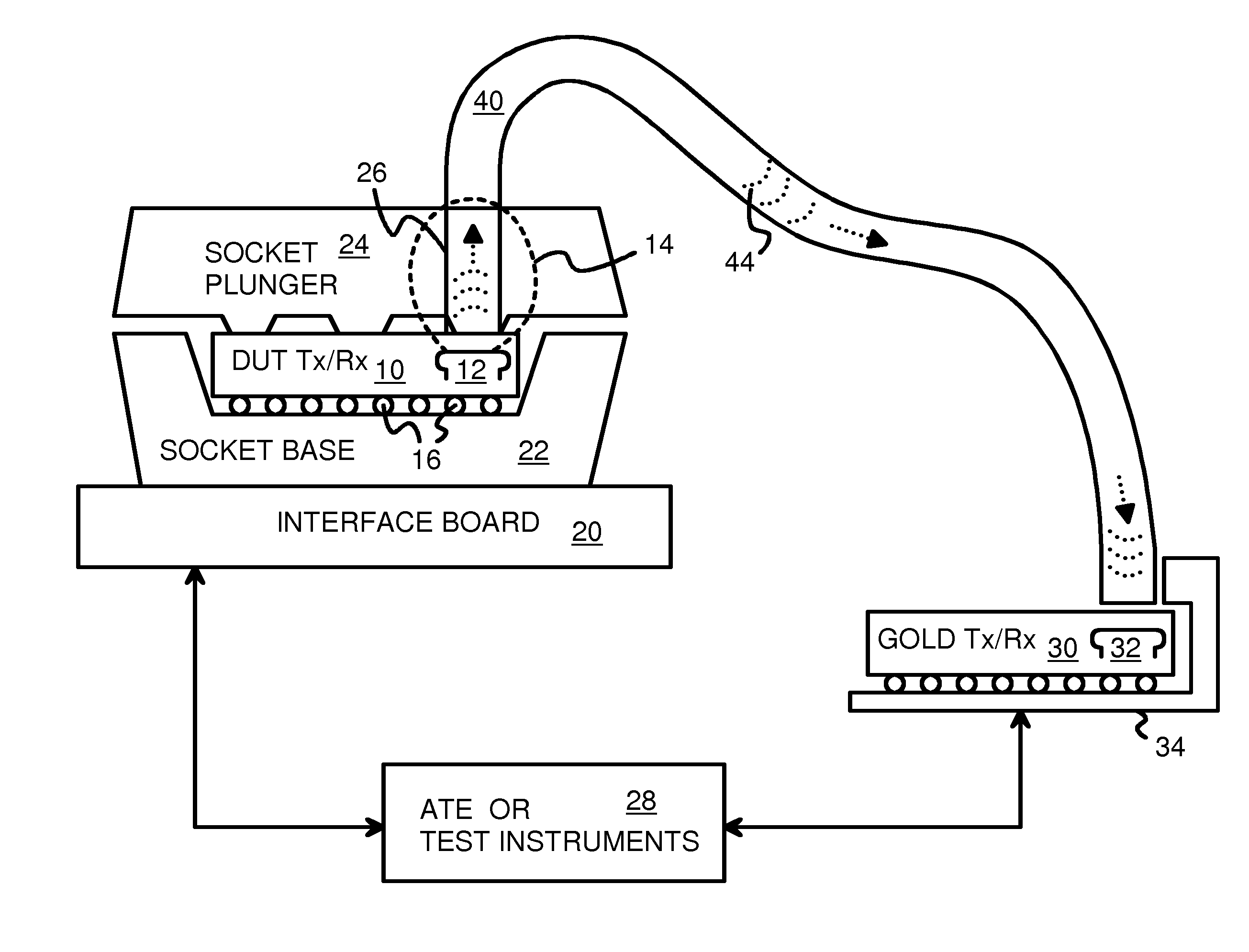
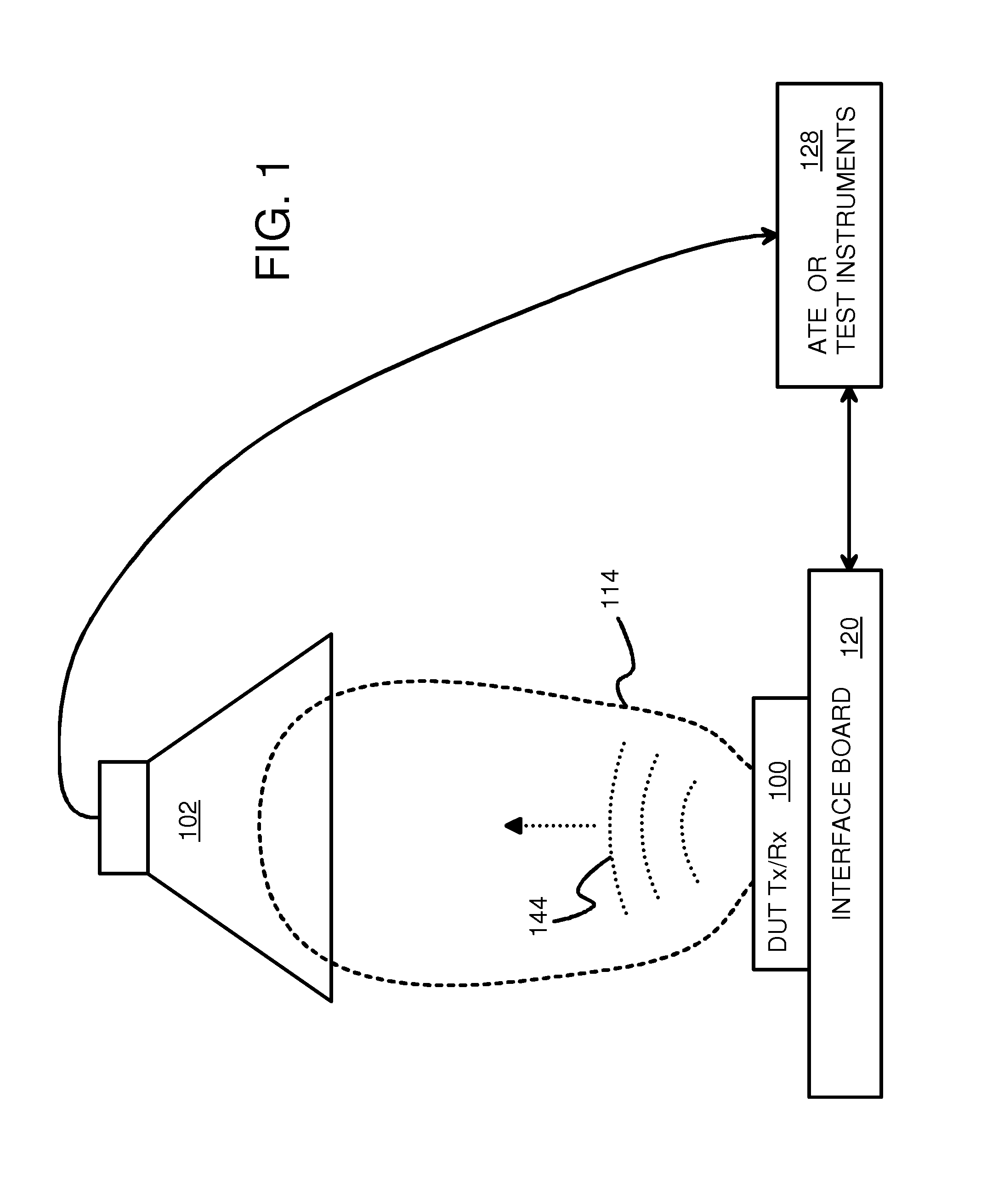
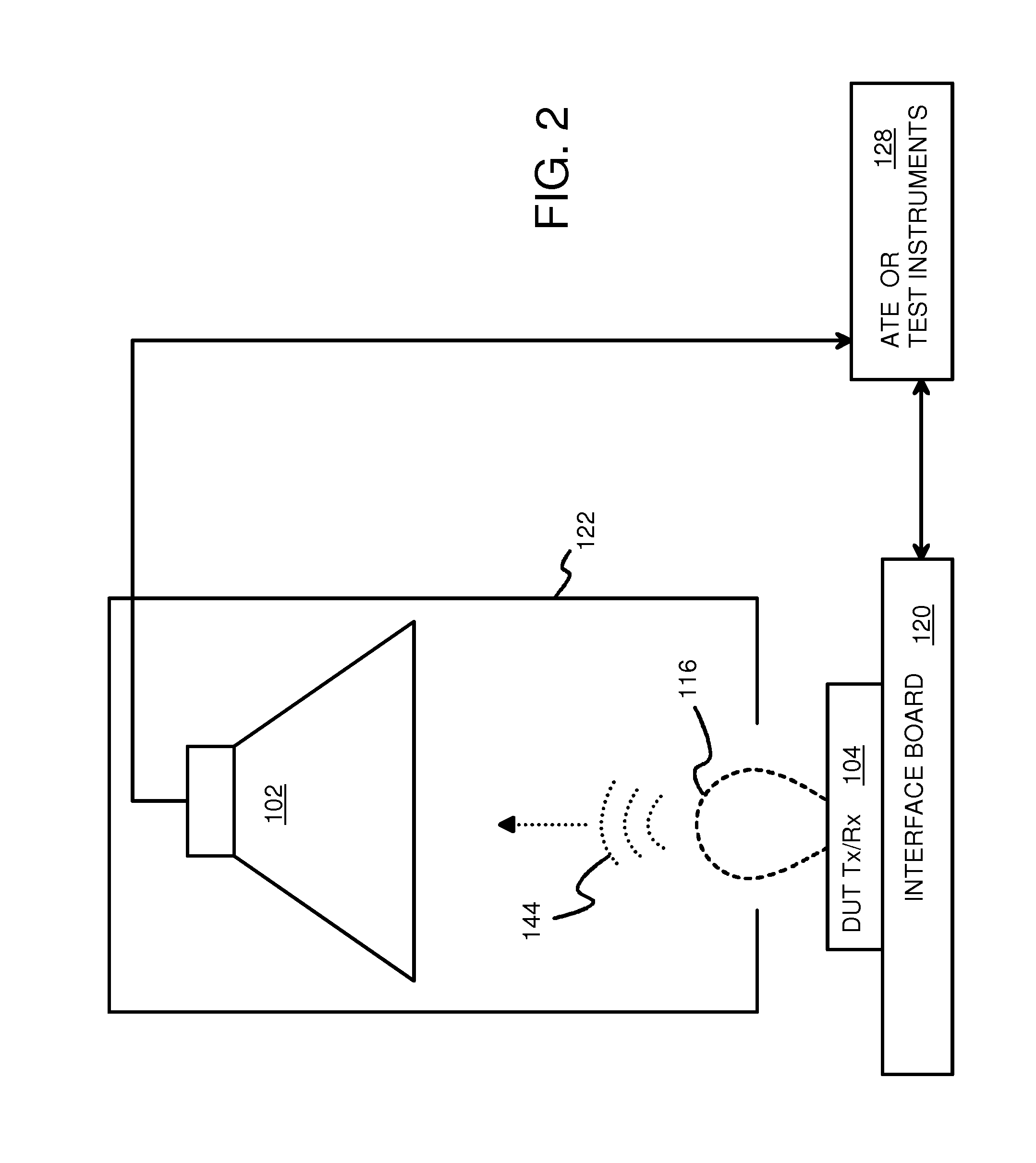
Waveguides for Capturing Close-Proximity Electromagnetic Radiation Transmitted by Wireless Chips During Testing on Automated Test Equipment (ATE)
A test fixture has a flexible plastic cable that acts as a waveguide. The Device-Under-Test (DUT) is a small transceiver and antenna that operate in the Extremely High-Frequency (EHF) band of 30-300 GHz. The size of the DUT transceiver is very small, limiting the power of emitted electromagnetic radiation so that close-proximity communication is used. The envelope for reception may only extend for about a centimeter from the DUT transceiver, about the same size as the test socket. A slot is formed in the test socket very near to the antenna. The slot receives one end of the plastic waveguide. The slot extends into the envelope by the DUT transceiver so that close-proximity radiation is captured by the plastic waveguide. The waveguide has a high relative permittivity and reflective metalized walls so that the radiation may be carried to a receiver that is outside the envelope.
Owner:MOLEX INC
Group III nitride semiconductor device of field effect transistor type having reduced parasitic capacitances
InactiveUS6765241B2Increase heatIncrease productivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProduction rateParasitic capacitance
Owner:NEC CORP
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7521324B2Quality improvementHigh dielectric constantSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesRelative permittivityNitride
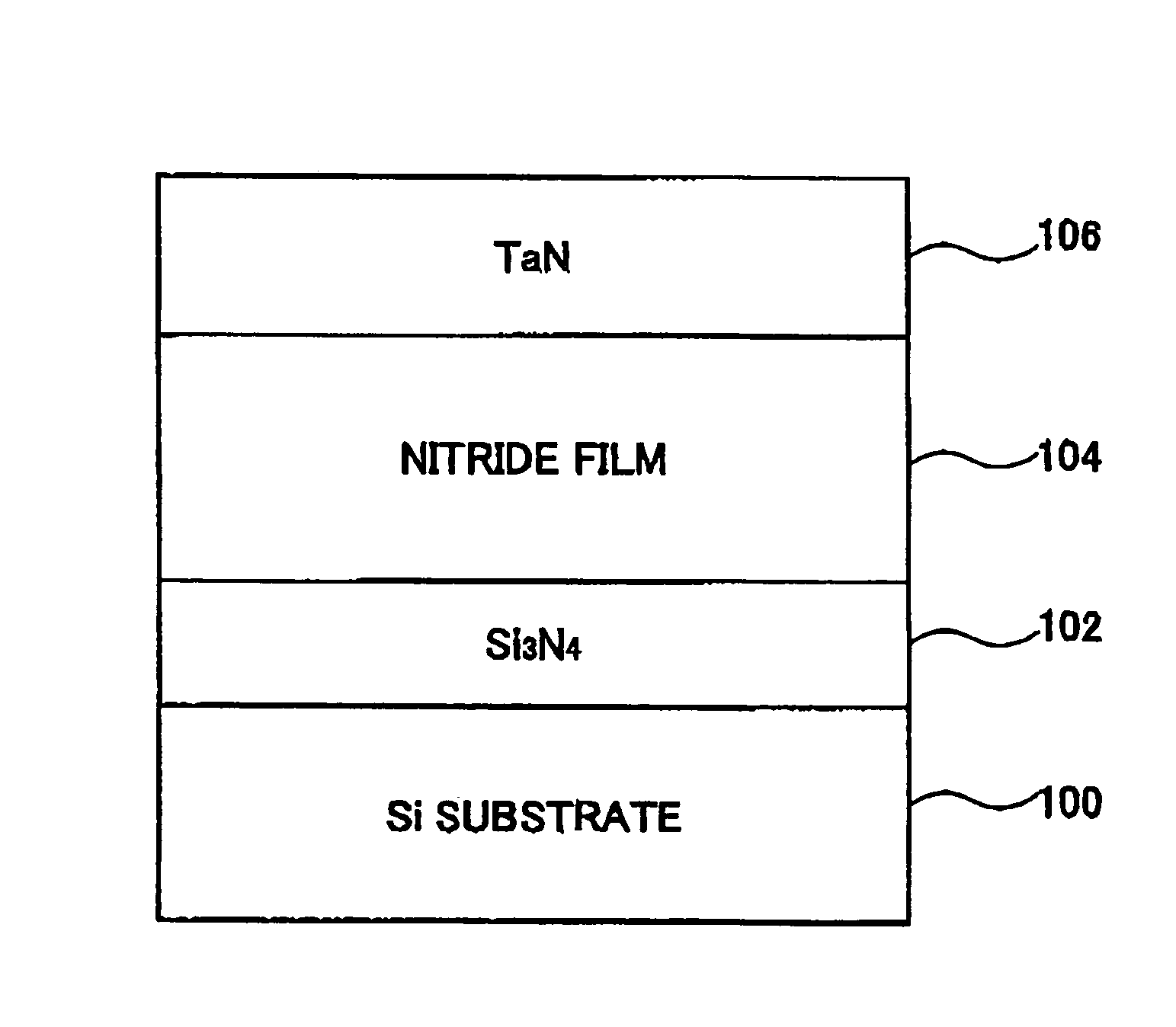
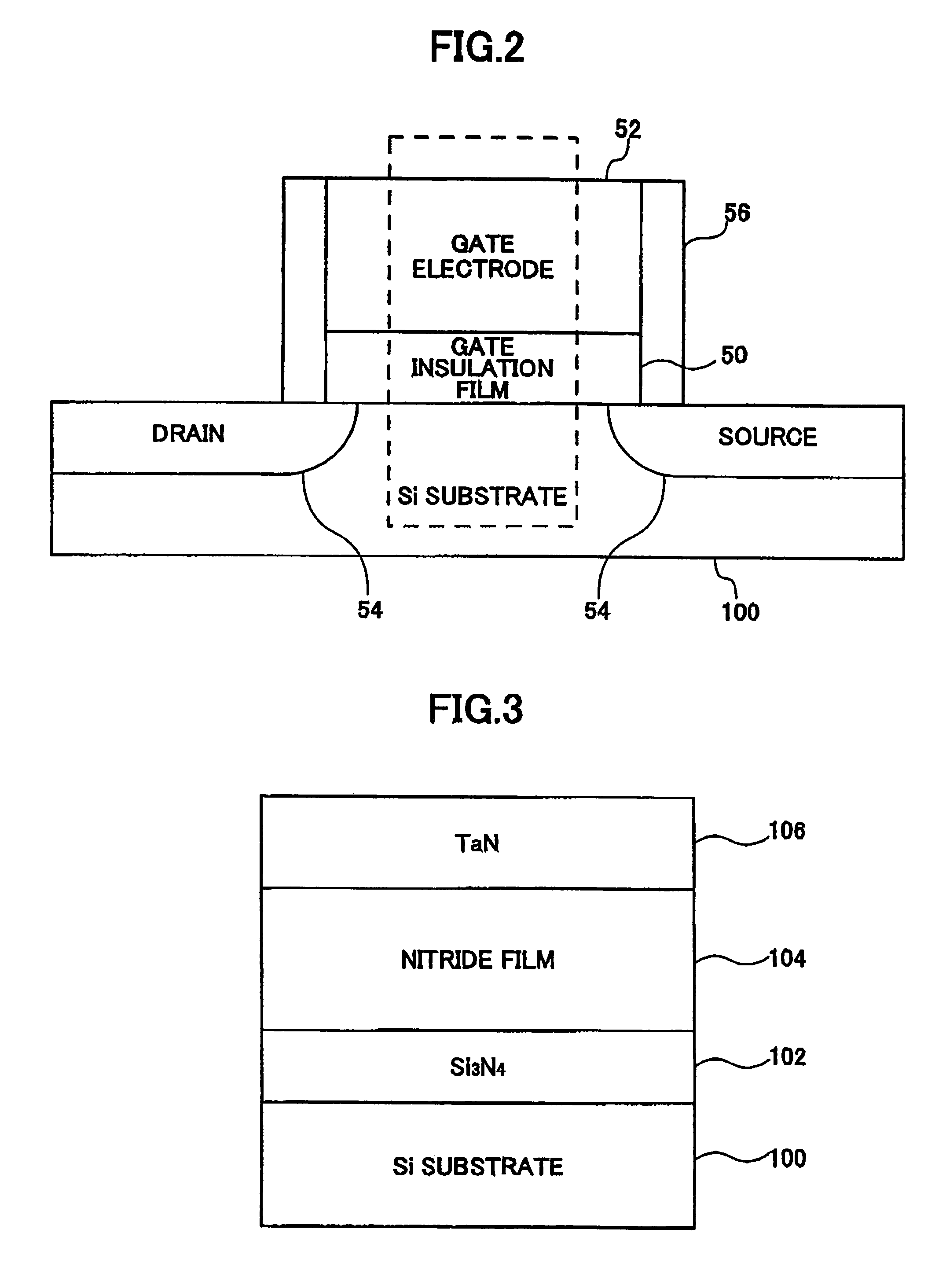
In order to provide a semiconductor device having good quality by keeping the relative permittivity of a High-K insulation film in a high state, or to provide a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device in which the relative permittivity of the High-K insulation film can be kept in a high state, a semiconductor device is disclosed that includes a silicon substrate, a gate electrode layer, and a gate insulation film between the silicon substrate and the gate electrode layer. The gate insulation film is a high relative permittivity (high-k) film being formed by performing a nitriding treatment on a mixture of a metal and silicon. The High-K film itself becomes a nitride so as to prevent SiO2 from being formed.
Owner:OHMI +1
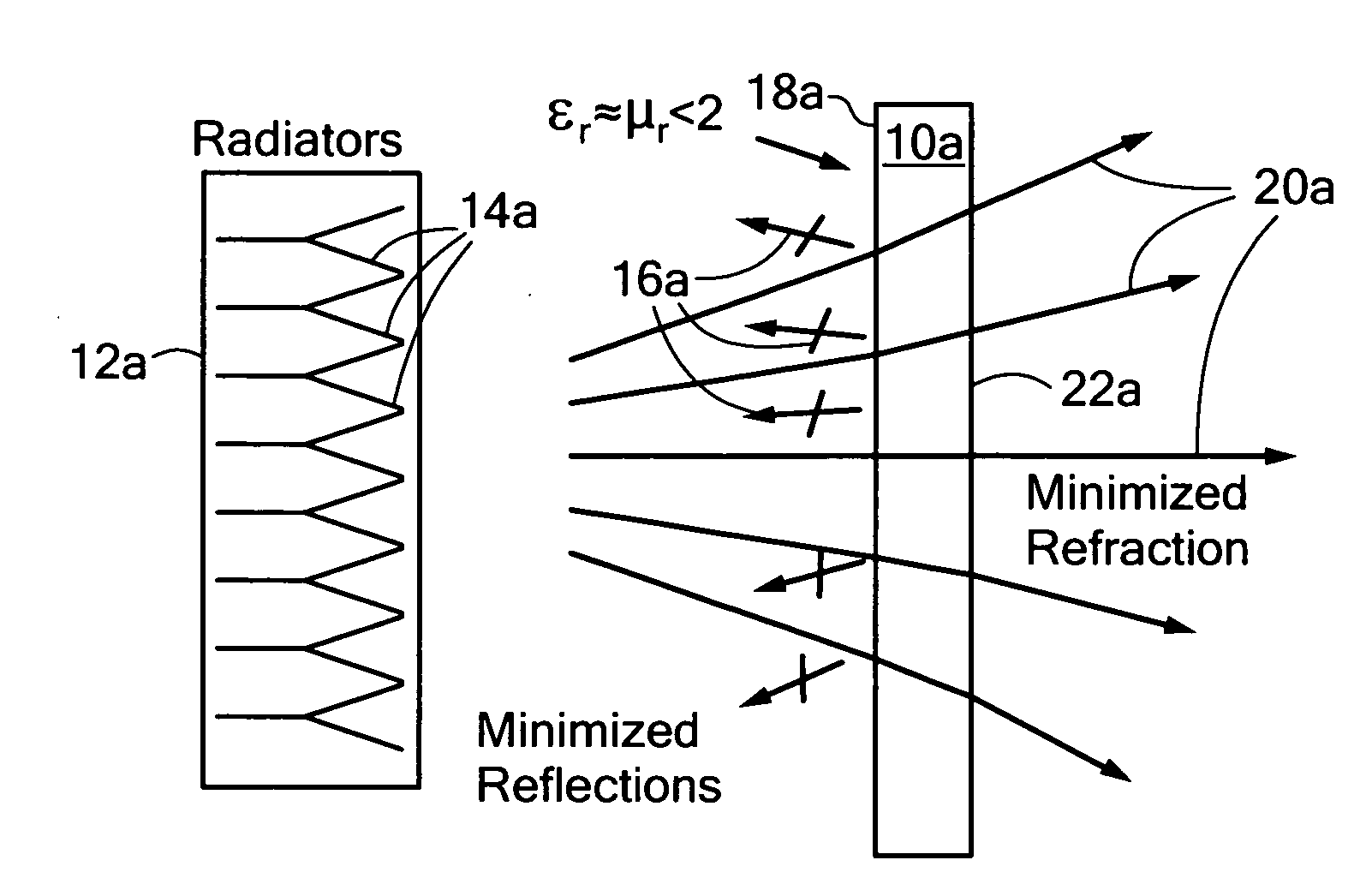
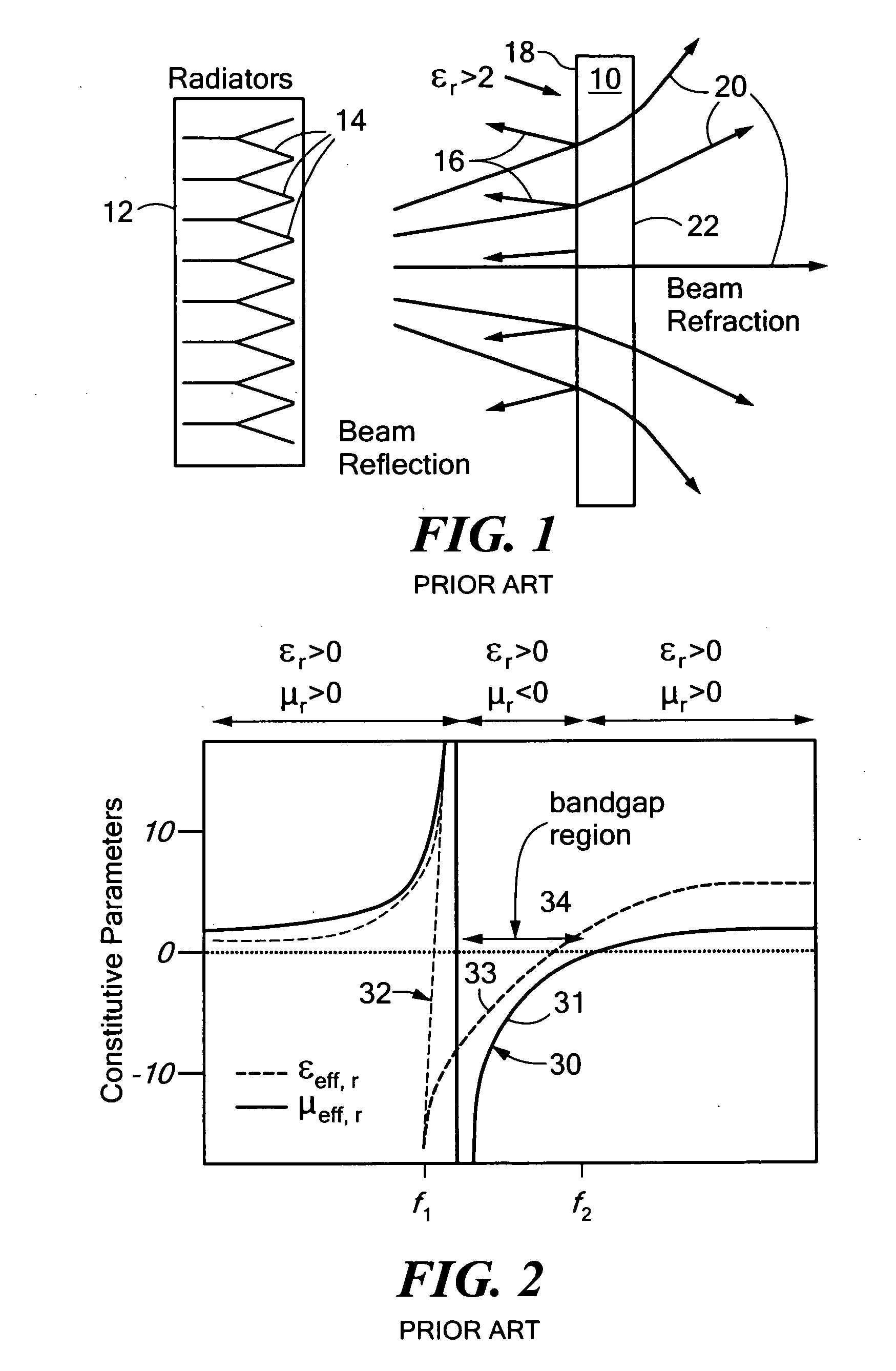
Metamaterial radome/isolator
ActiveUS20110199281A1Reduce reflectionLess acute diffractionRadiating element housingsRadomeRelative permittivity
A metamaterial radome / isolator system includes a radiation source for providing a radiation beam through the radome / isolator having a frequency beyond the bandgap region where the metamaterial permittivity and permeability are both positive and the metamaterial medium has a low, matched relative permittivity and relative permeability.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Diaper structure capable of wirelessly detecting a soaking wet condition thereof and diaper detection system of the same
InactiveUS20150080819A1Uncomfortable to wearerUncomfortable for wearerBaby linensTamponsEngineeringAbsorbent material
The present invention is to provide a diaper structure, which includes a diaper main body formed by a fabric layer, an anti-leak layer and an absorbent material layer sequentially from the inner side to outer side thereof, and a communication chip and a metal antenna attached to the outer surface of the anti-leak layer and connected with each other to form an RFID tag. Thus, when the absorbent material layer absorbs the urine passing through the fabric layer and the inner surface of the anti-leak layer is in contact with the urine on the surface of the absorbent material layer, the change in the relative permittivity of the anti-leak layer causes a change in the impedance value of the metal antenna and consequently a change in the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave signal transmitted by the RFID tag, thereby enabling rapid detection of a soaking wet condition of the diaper.
Owner:SINGLI TECH
Small low profile antennas using high impedance surfaces and high permeability, high permittivity materials
InactiveUS6967621B1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric substrateGround plane
A low profile antenna includes an antenna and a ground plane structure operatively associated with the antenna. The ground plane structure has a generally planar surface, at least one protrusion extending from the planar surface and a dielectric substrate supported by the planar surface. The dielectric substrate includes a relative permeability (μ) of greater than or equal to about one and a relative permittivity (ε) of greater than or equal to about one.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE THE
Electrical cables
InactiveUS7288721B2Power cables with screens/conductive layersInsulated cablesElectrical conductorEngineering
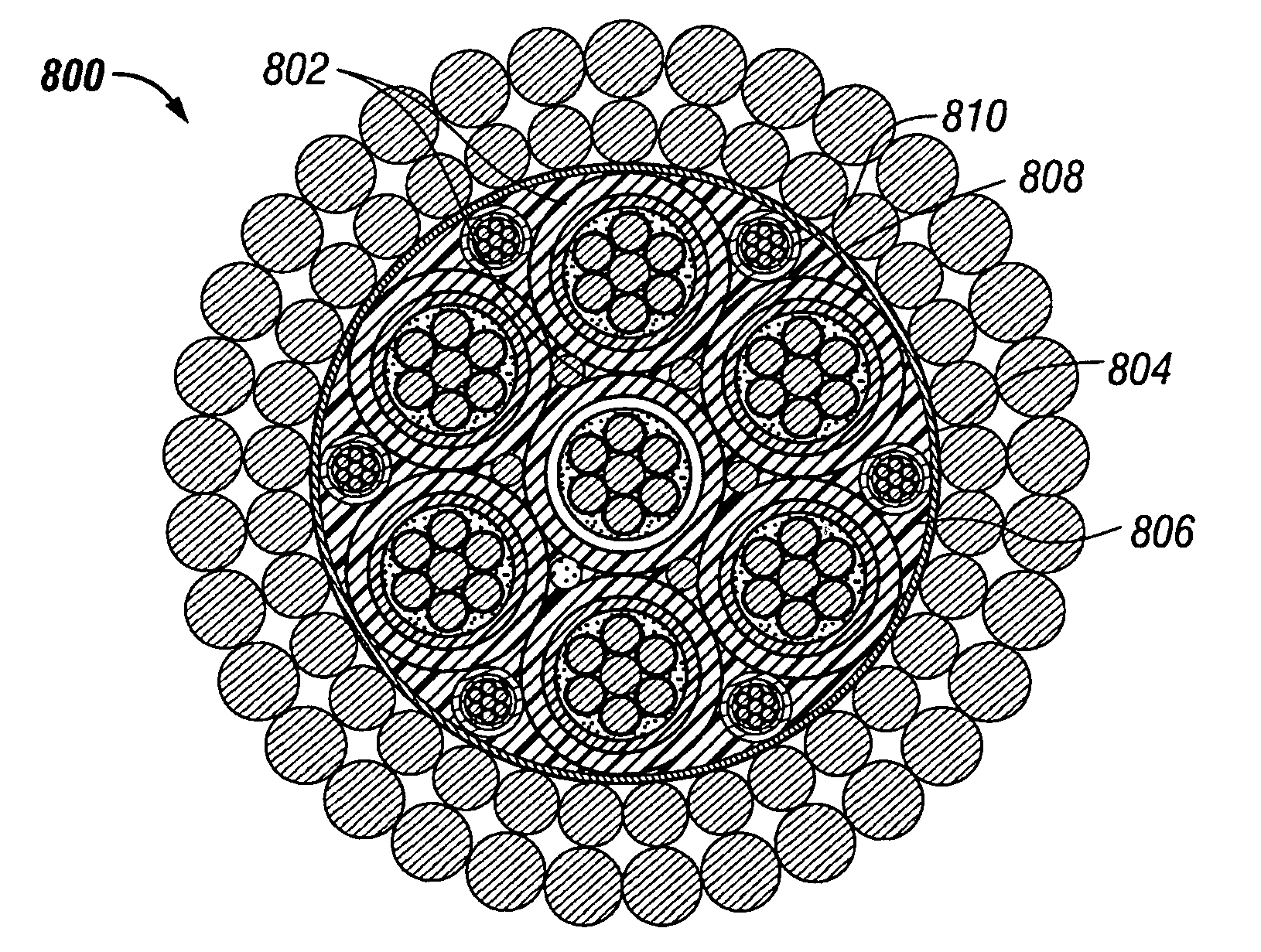
Disclosed are durable corrosion resistant wellbore electrical cables including a coated electrical conductor, a polymeric protective layer for trapping coating flakes, a first insulating jacket disposed adjacent to the polymeric protective layer and having a first relative permittivity. A second insulating jacket is disposed adjacent to the first insulating jacket and has a second relative permittivity that is less than the first relative permittivity. Another aspect of the invention is a method for manufacturing a cable that includes providing a coated electrical conductor, extruding a polymeric protective layer over the coated electrical conductor, extruding a first insulating jacket over the protective polymeric layer, and extruding a second insulating jacket thereon. Cables of the invention may further include armor wire layers or even current return conductors.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER CONVEYANCE & DELIVERY
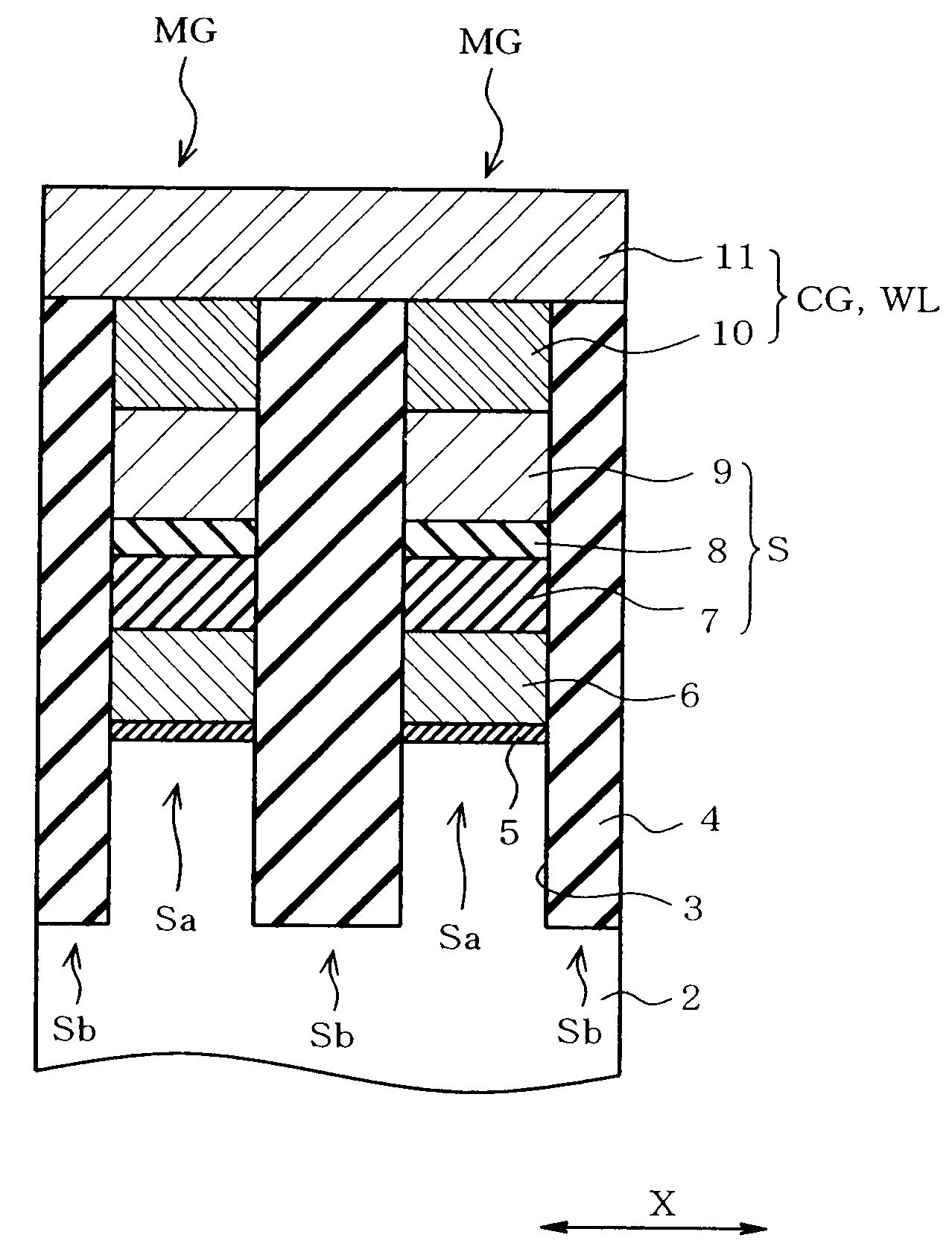
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20090152618A1High dielectric constantSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerOptoelectronics
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device includes a semiconductor substrate, a first insulation layer formed on the semiconductor substrate, a charge storage layer formed on the first insulation layer, a second insulation layer formed on the charge storage layer, a control electrode formed on the second insulation layer. The second insulation layer includes a first silicon oxide film, an intermediate insulating film formed on the first silicon oxide film and having a relative permittivity of not less than 7, and a second silicon oxide film formed on the intermediate insulating film. A charge trap layer is formed at least in either first or second silicon oxide film or a boundary between the first silicon oxide film and the intermediate insulating film or a boundary between the second silicon oxide film and the intermediate insulating film.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
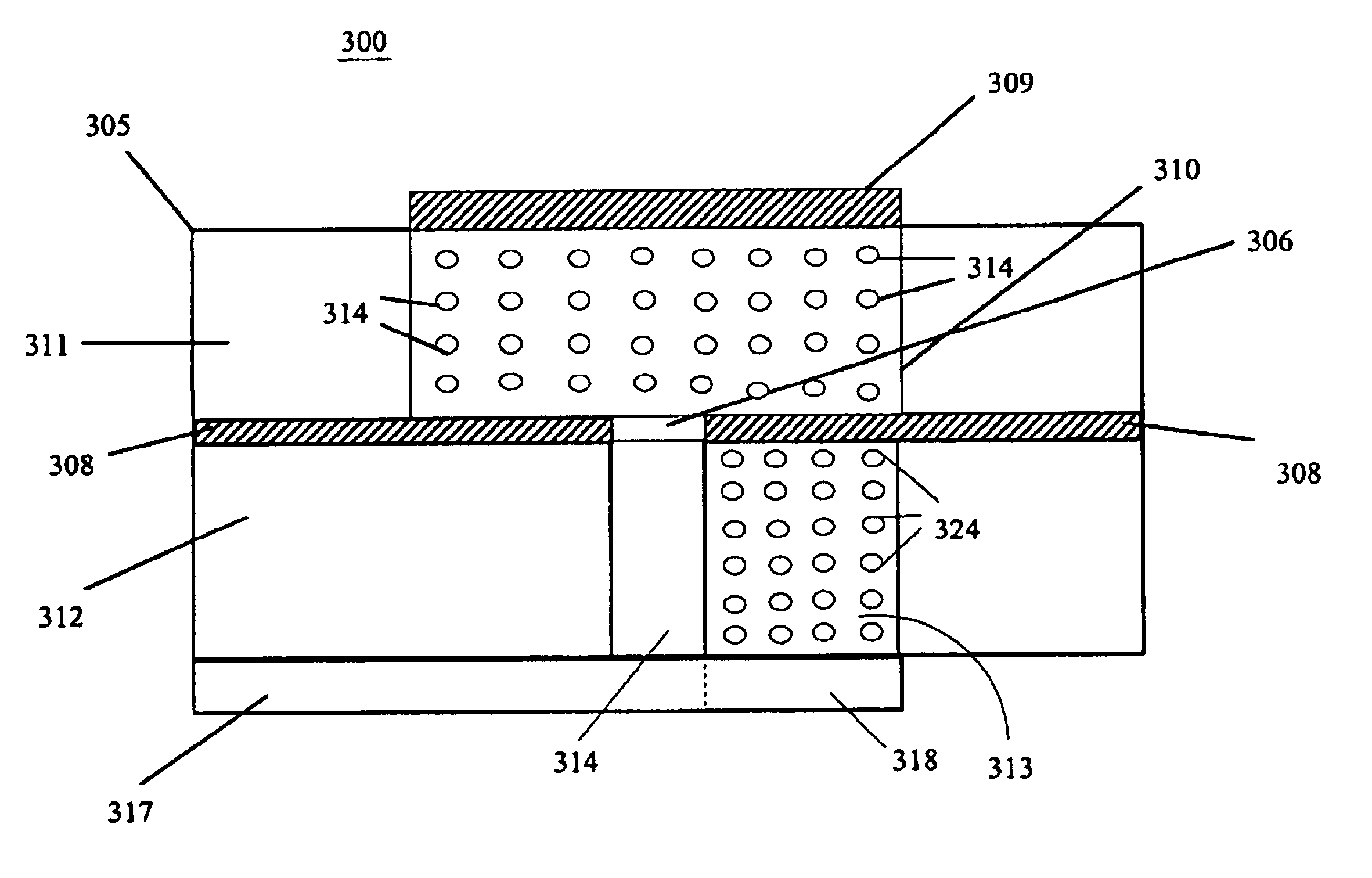
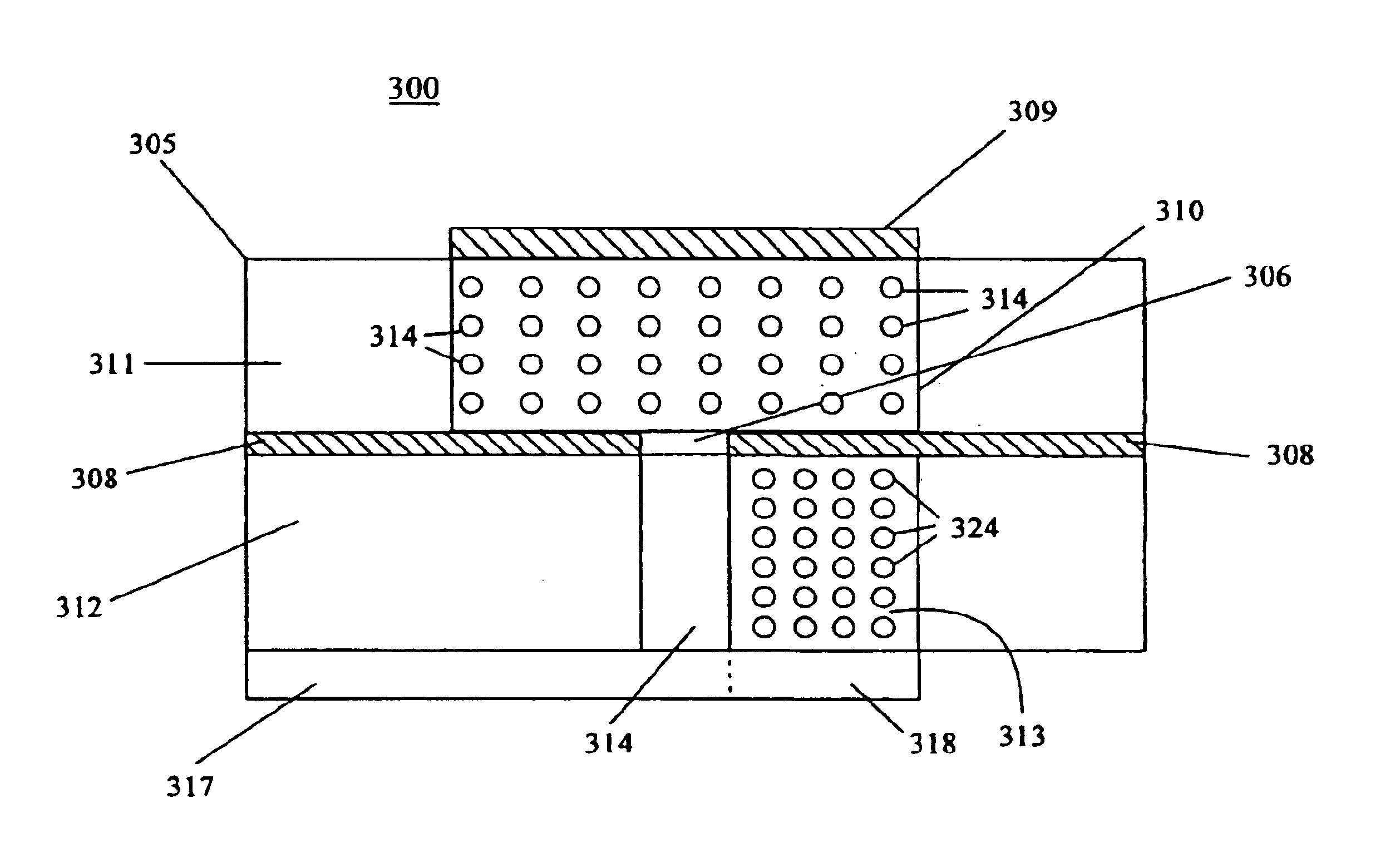
Arangements of microstrip antennas having dielectric substrates including meta-materials
InactiveUS6943731B2High dielectric constantSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip patch antennaDielectric substrate
A slot fed microstrip patch antenna (300) includes a conducting ground plane (308), the conducting ground plane (308) including at least one slot (306). A dielectric material is disposed between the ground plane (308) and at least one feed line (317), wherein at least a portion of the dielectric layer (313) includes magnetic particles (324). The dielectric layer between the feed line (317) and the ground plane (308) provides regions having high relative permittivity (313) and low relative permittivity (312). At least a portion of the stub (318) is disposed on the high relative permittivity region (313).
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Mis gate structure type HEMT device and method of fabricating mis gate structure type HEMT device
InactiveUS20090050938A1Lower access resistanceLower on-resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionElectrical resistance and conductance
A normally-off operation type HEMT device excellent in characteristics can be realized. A two-dimensional electron gas region is formed in a periphery of a hetero-junction interface of a base layer and a barrier layer, so that access resistance in an access portion, that is, between a drain and a gate and between a gate and a source is sufficiently lowered, and at the same time, a P-type region is formed immediately under the gate. This realizes a normally-off type HEMT device having a low on-resistance. Further, when a film thickness of an insulating layer is defined as t (nm) and a relative permittivity of a substance forming the insulating layer is defined as k, a threshold voltage as high as +3 V or more can be attained by satisfying k / t≦0.85 (nm−1).
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Systems, articles, and methods for capacitive electromyography sensors
ActiveUS20180067553A1Input/output for user-computer interactionElectromyographyCapacitanceEngineering
Systems, articles, and methods for improved capacitive electromyography (“EMG”) sensors are described. The improved capacitive EMG sensors include one or more sensor electrode(s) that is / are coated with a protective barrier formed of a material that has a relative permittivity εr of about 10 or more. The protective barrier shields the sensor electrode(s) from moisture, sweat, skin oils, etc. while advantageously contributing to a large capacitance between the sensor electrode(s) and the user's body. In this way, the improved capacitive EMG sensors provide enhanced robustness against variations in skin and / or environmental conditions. Such improved capacitive EMG sensors are particularly well-suited for use in wearable EMG devices that may be worn by a user for an extended period of time and / or under a variety of skin and / or environmental conditions. A wearable EMG device that provides a component of a human-electronics interface and incorporates such improved capacitive EMG sensors is described.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
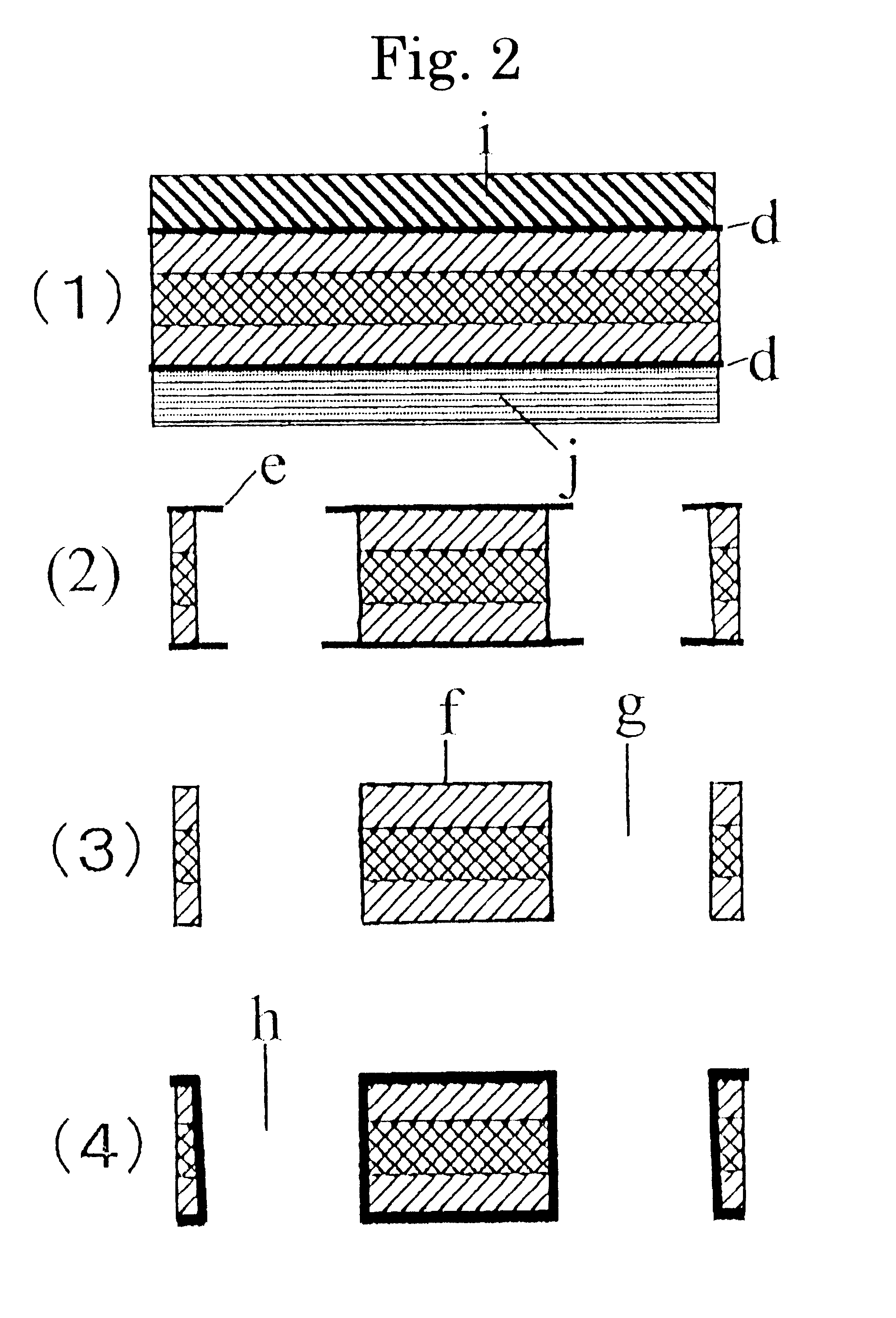
High relative-permittivity B-staged sheet, high relative-permittivity prepreg, its production process, and printed wiring board comprising any one of these
InactiveUS6562179B1High relative permittivityImprove heat resistanceLight absorption dielectricsAdhesive processes with surface pretreatmentPolymer scienceRoom temperature
A high relative-permittivity B-staged sheet obtained by incorporating an insulating inorganic filler having a relative permittivity of at least 500 at room temperature into a solvent-less resin component so as to have an insultaing inorganic filler content of 80 to 99% by weight, a high relative-permittivity prepreg obtained from the above high relative-permittivity B-staged sheet, a process for the production of the high relative-permittivity prepreg, and a printed wiring board obtained from any one of the above high relative-permittivity B-staged sheet and the high relative-permittivity prepreg.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
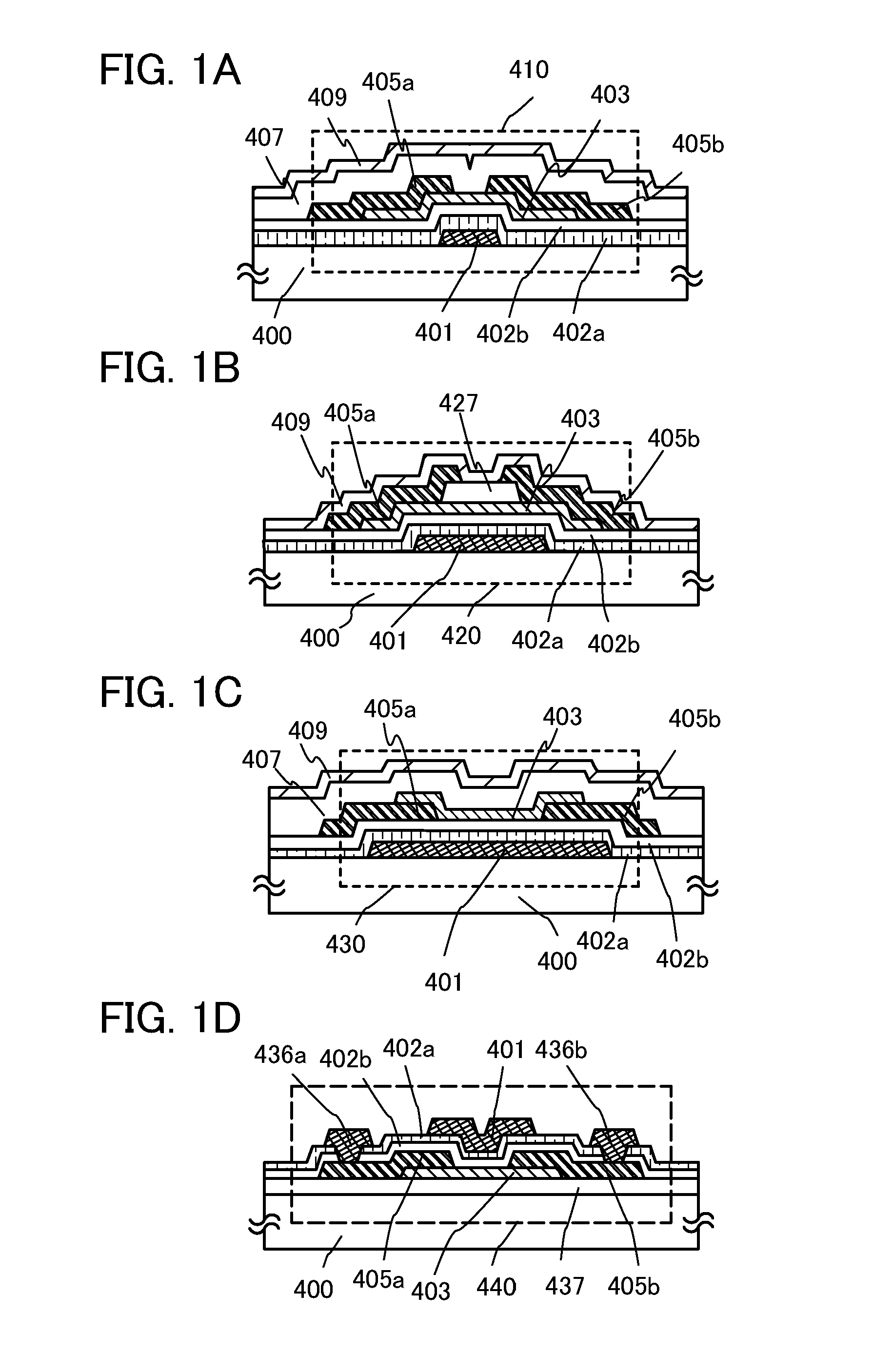
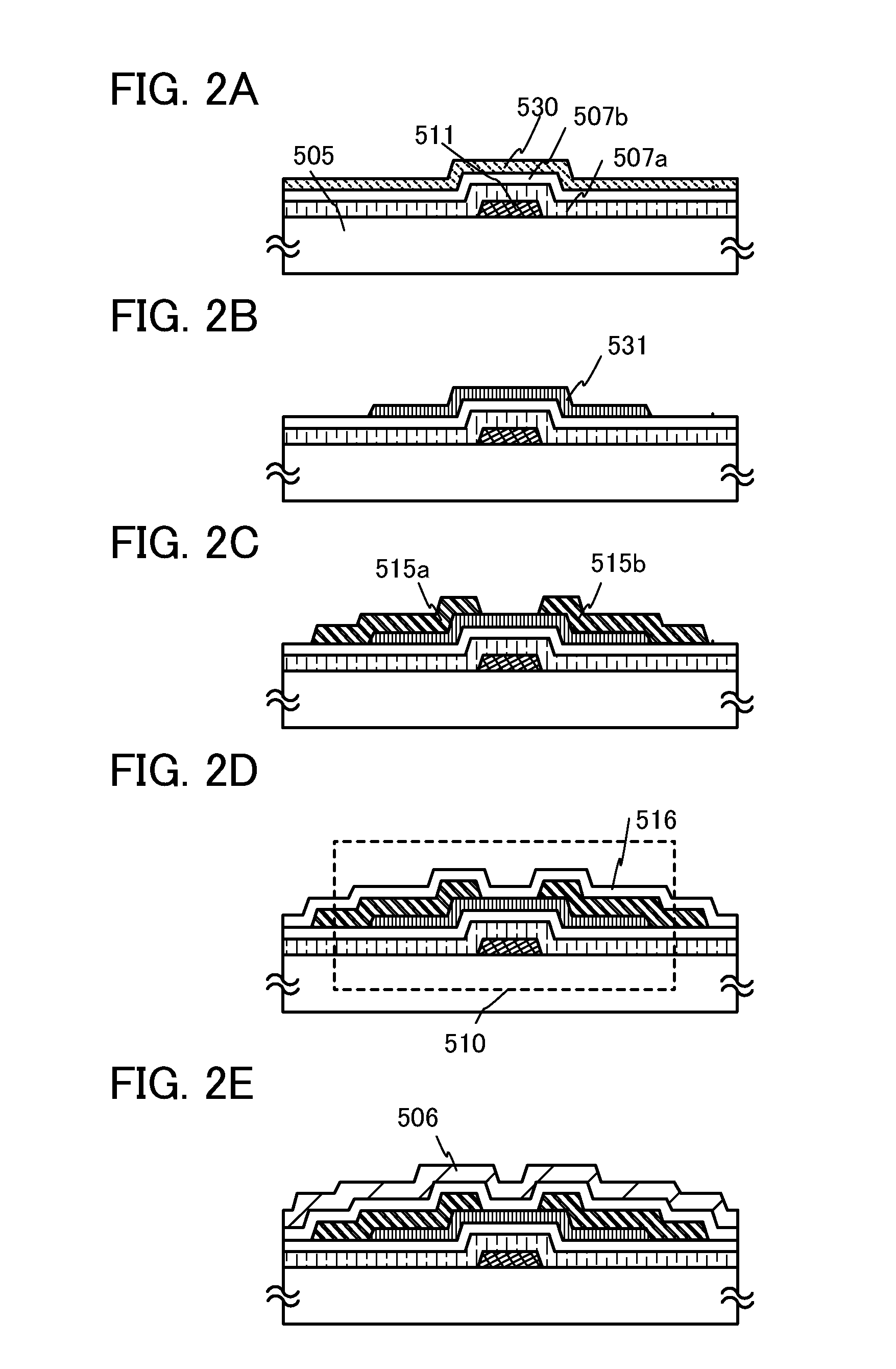
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110193079A1Reduce manufacturing costReduce hydrogen concentrationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceGate leakage current
In a miniaturized transistor, a gate insulating layer is required to reduce its thickness; however, in the case where the gate insulating layer is a single layer of a silicon oxide film, a physical limit on thinning of the gate insulating layer might occur due to an increase in tunneling current, i.e. gate leakage current. With the use of a high-k film whose relative permittivity is higher than or equal to 10 is used for the gate insulating layer, gate leakage current of the miniaturized transistor is reduced. With the use of the high-k film as a first insulating layer whose relative permittivity is higher than that of a second insulating layer in contact with an oxide semiconductor layer, the thickness of the gate insulating layer can be thinner than a thickness of a gate insulating layer considered in terms of a silicon oxide film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Insulating film and electronic device
An insulating film comprising: a first barrier layer;a well layer provided; and a second barrier layer is proposed. The first barrier layer consists of a material having a first bandgap and a first relative permittivity. The well layer is provided on the first barrier layer, and consists of a material having a second bandgap smaller than the first bandgap and having a second relative permittivity larger than first relative permittivity. Discrete energy levels are formed in the well layer by a quantum effect. The second barrier layer is provided on the well layer, and consists of a material having a third bandgap larger than the second bandgap and having a third relative permittivity smaller than second relative permittivity. Alternatively, an insulating film comprising: n (n being an integer larger than 2) layers of barrier layer consisting of a material having a bandgap larger than a first bandgap and having a relative permittivity smaller than a first relative permittivity; and (n−1) layers of well layers consisting of a material having a bandgap smaller than the first bandgap and having a relative permittivity larger than the first relative permittivity, discrete energy levels being formed in the well layer by a quantum effect, each of the barrier layers and each of the well layers being stacked by turns, and discrete energy levels being formed in each of the well layers by a quantum effect, is provided. Alternatively, an insulating film having a lattice mismatch within a range of plus-or-minus 1.5% to the substrate, and further having a high barrier and a large permittivity is provided.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Radio Frequency (RF) Microwave Components and Subsystems Using Loaded Ridge Waveguide
InactiveUS20120092091A1Small component sizeImprove power performanceWaveguidesMicrowaveConductive materials
A waveguide having a non-conductive material with a high permeability (μ, μr for relative permeability) and / or a high permittivity (∈, ∈r for relative permittivity) positioned within a housing. When compared to a hollow waveguide, the waveguide of this invention, reduces waveguide dimensions by∝1μr*ɛr.The waveguide of this invention further includes ridges which further reduce the size and increases the usable frequency bandwidth.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
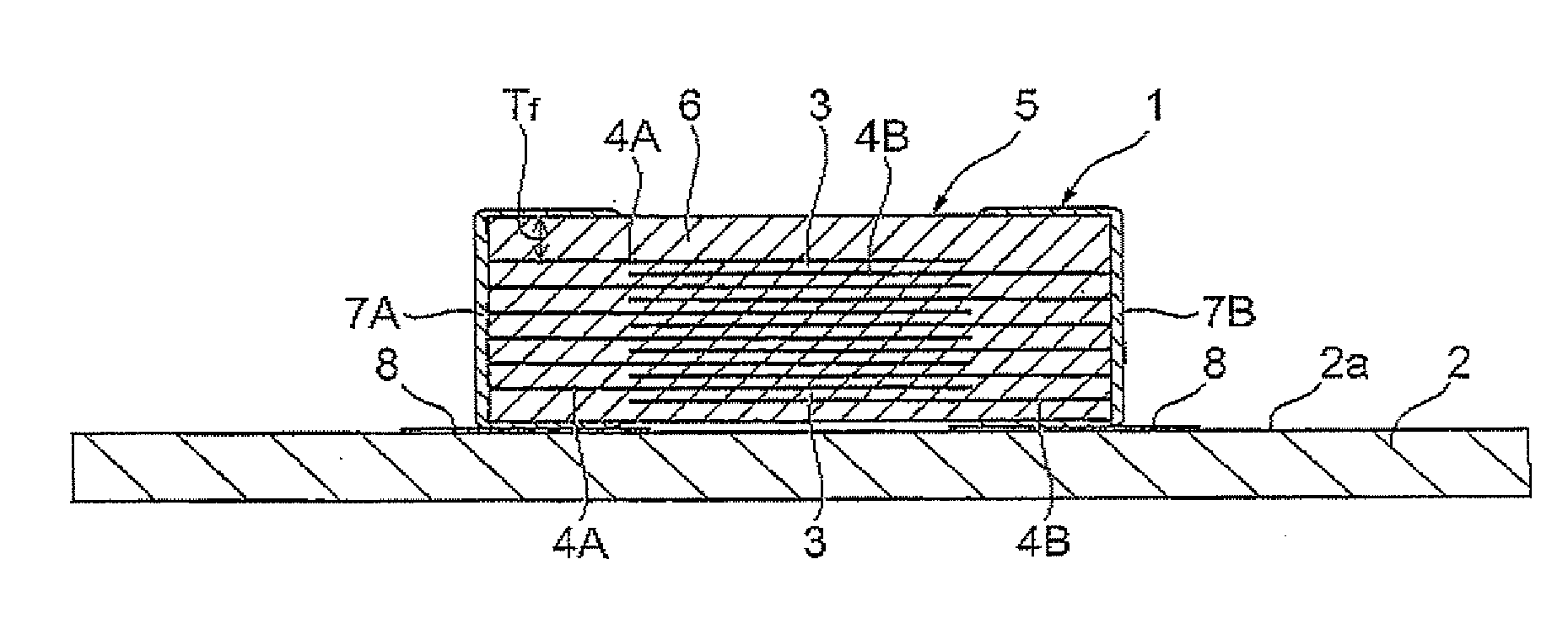
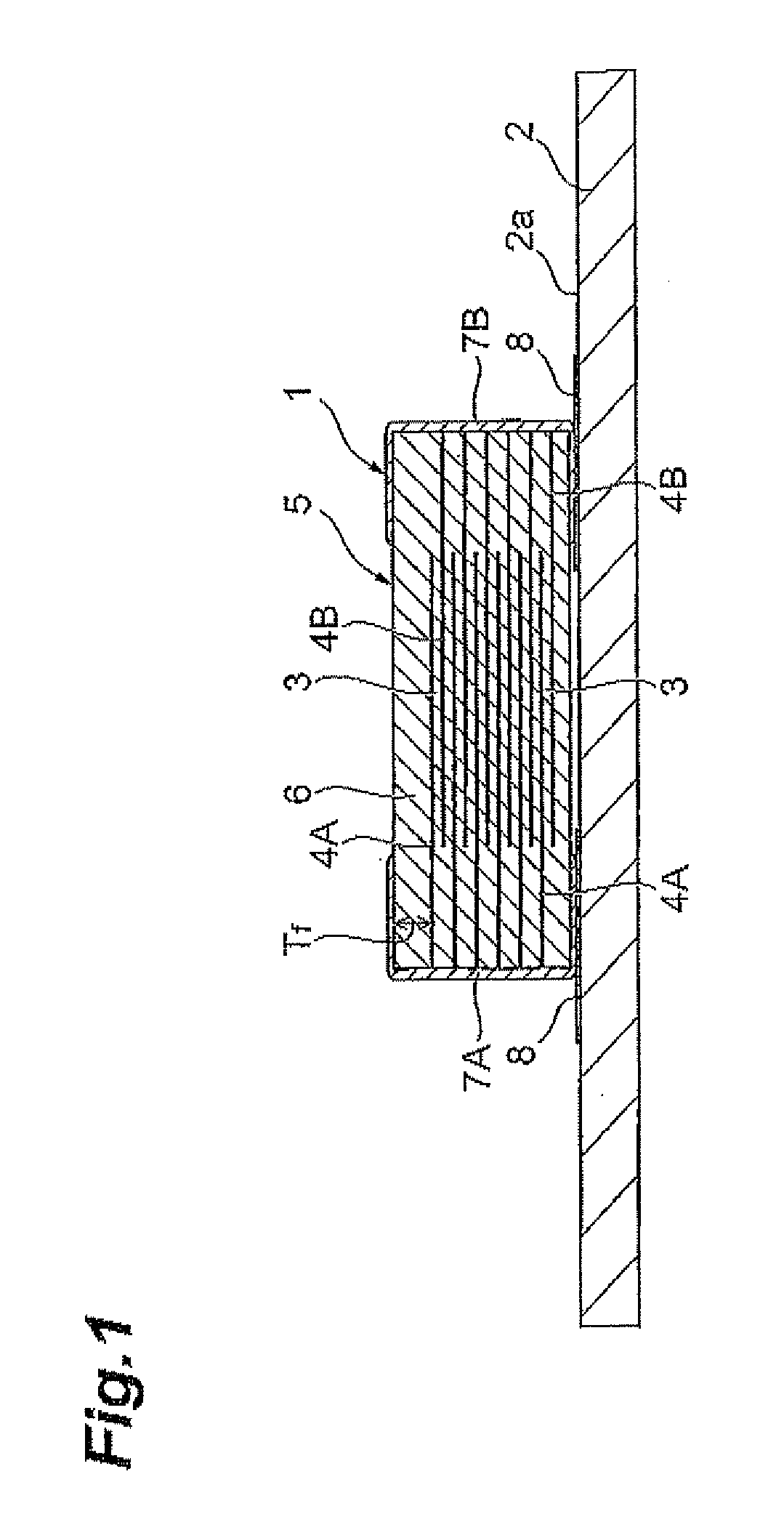
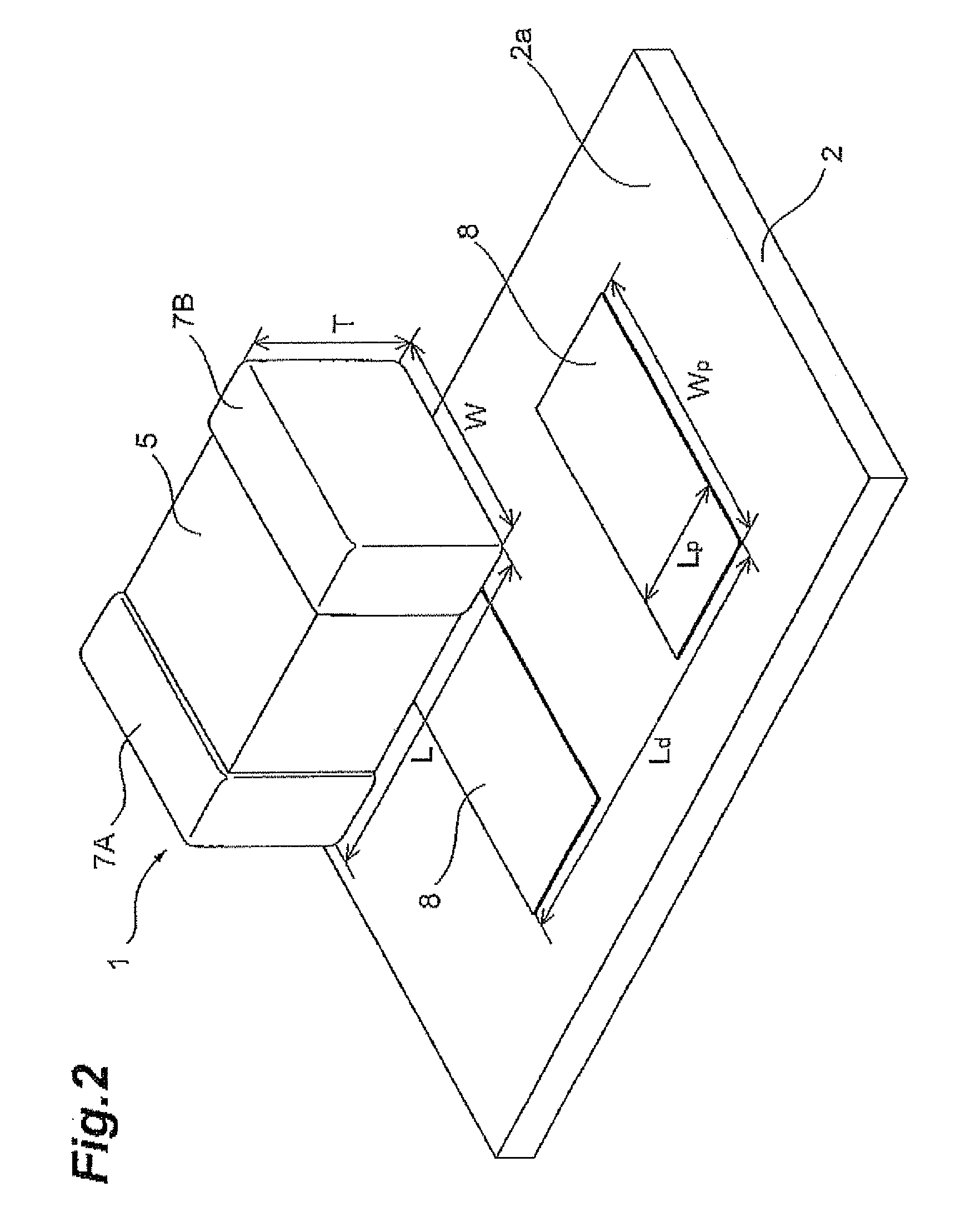
Multilayer ceramic capacitor mounting structure and multilayer ceramic capacitor
ActiveUS20110114378A1Increasing capacitor mounting area of substrateReduce vibration soundFinal product manufactureFixed capacitor dielectricMetallurgyCeramic capacitor
A multilayer ceramic capacitor has an element body formed by alternately laminating a plurality of dielectric layers and a plurality of inner electrodes. On a substrate having a mounting surface provided with at least two lands, the multilayer ceramic capacitor is mounted such that the inner electrodes are parallel to the mounting surface. A multilayer ceramic capacitor mounting structure satisfies Tf / T>0.1 and 300≦∈r≦2800, where T is the height of the multilayer ceramic capacitor, Tf is the outer covering thickness of the element body, and ∈r is the relative permittivity of the dielectric layers, and 0.6≦Wp / W≦1.0, where W is the width of the multilayer ceramic capacitor, and Wp is the size of the land in a direction corresponding to the width of the multilayer ceramic capacitor.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Capacitors using preformed dielectric
InactiveUS20100195261A1High dielectric constantImprove breakdown voltageFixed capacitor electrodesElectrolytic capacitorsDielectricVolumetric Mass Density
Devices for storing energy at a high density are described. The devices include an electrode preformed to present a high exposed area onto which a dielectric is formed. The dielectric material has a high dielectric constant (high relative permittivity) and a high breakdown voltage, allowing a high voltage difference between paired electrodes to effect a high stored energy density.
Owner:SPACE CHARGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com