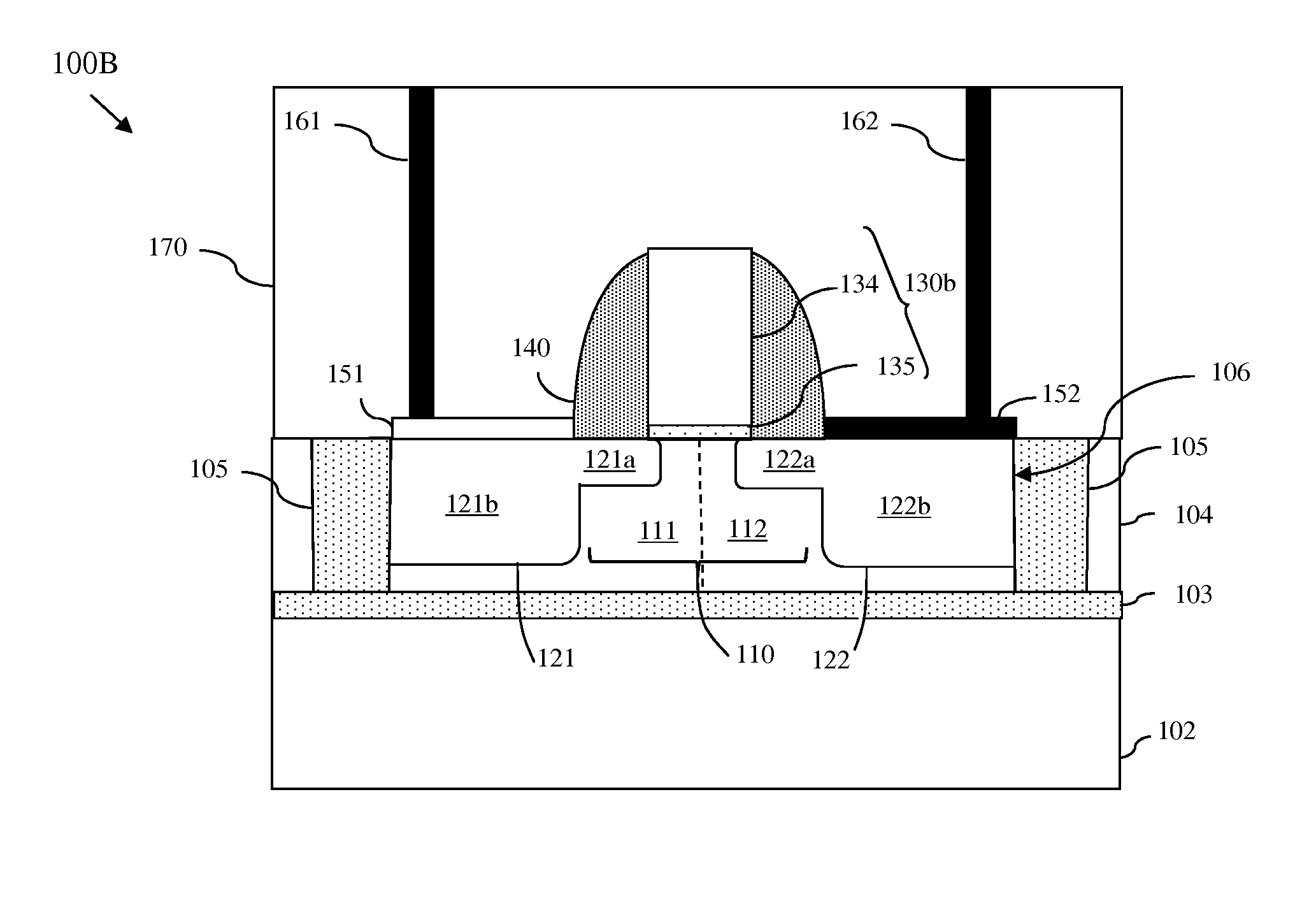
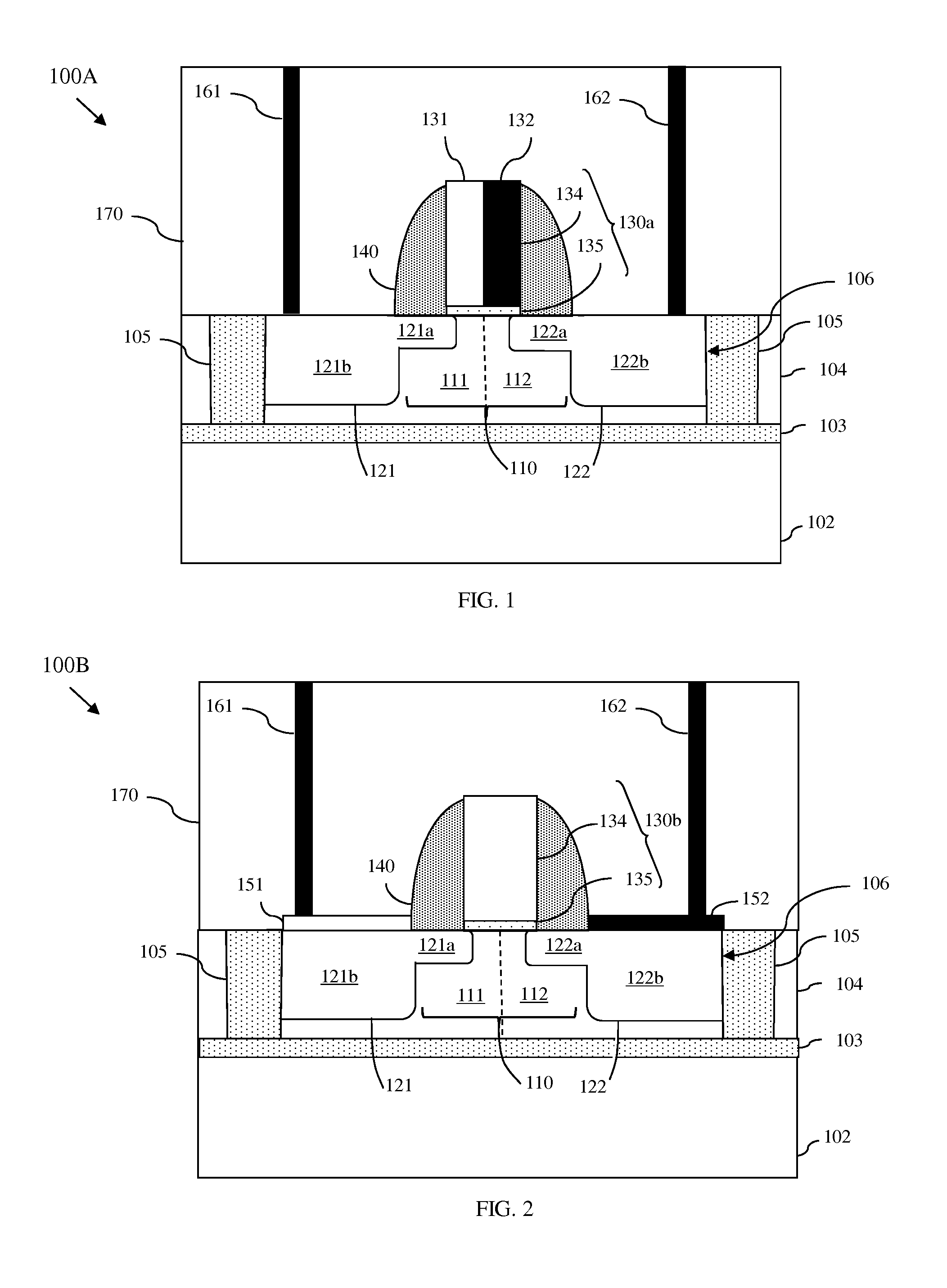
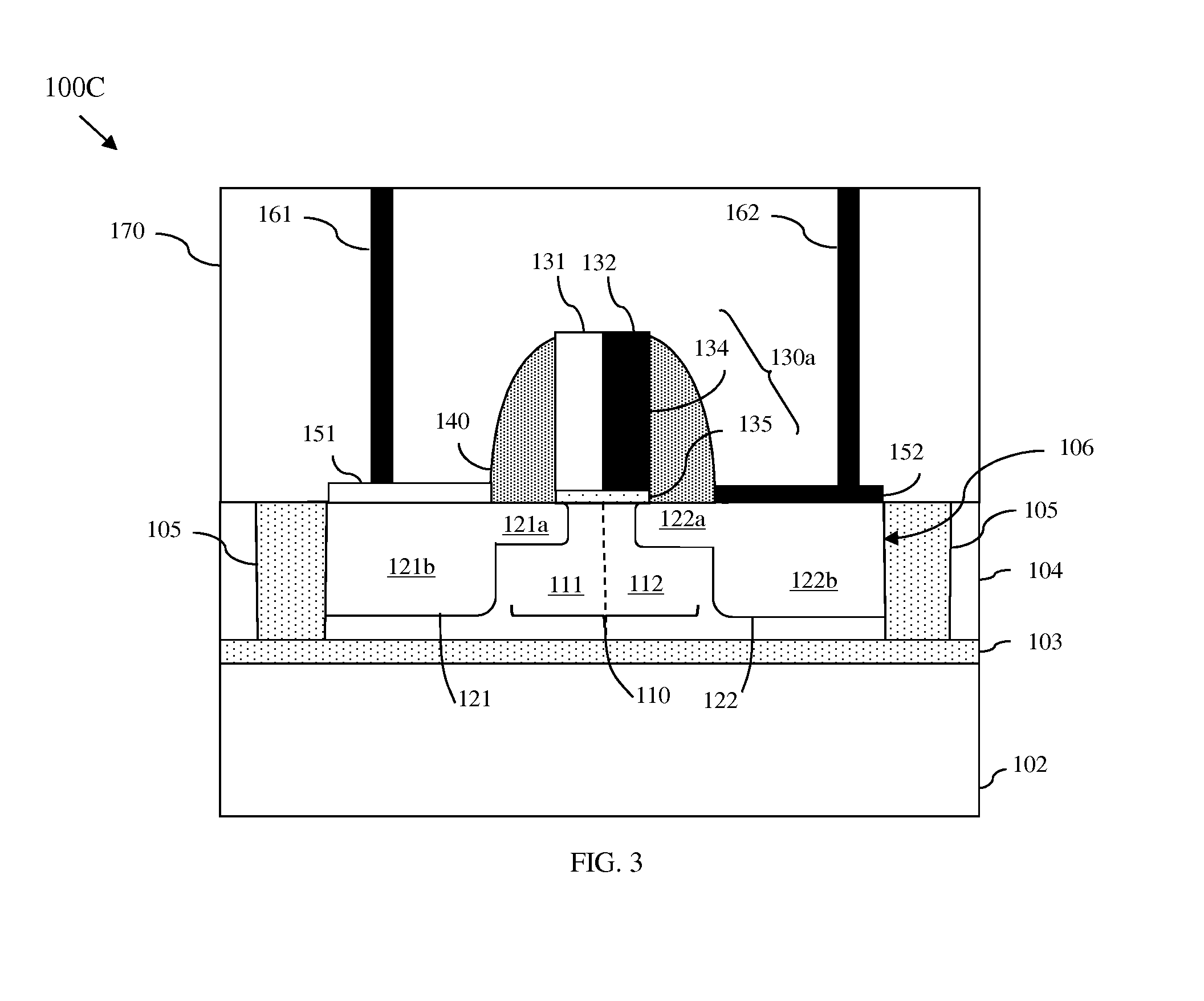
Patents
Literature
380 results about "Gate leakage current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
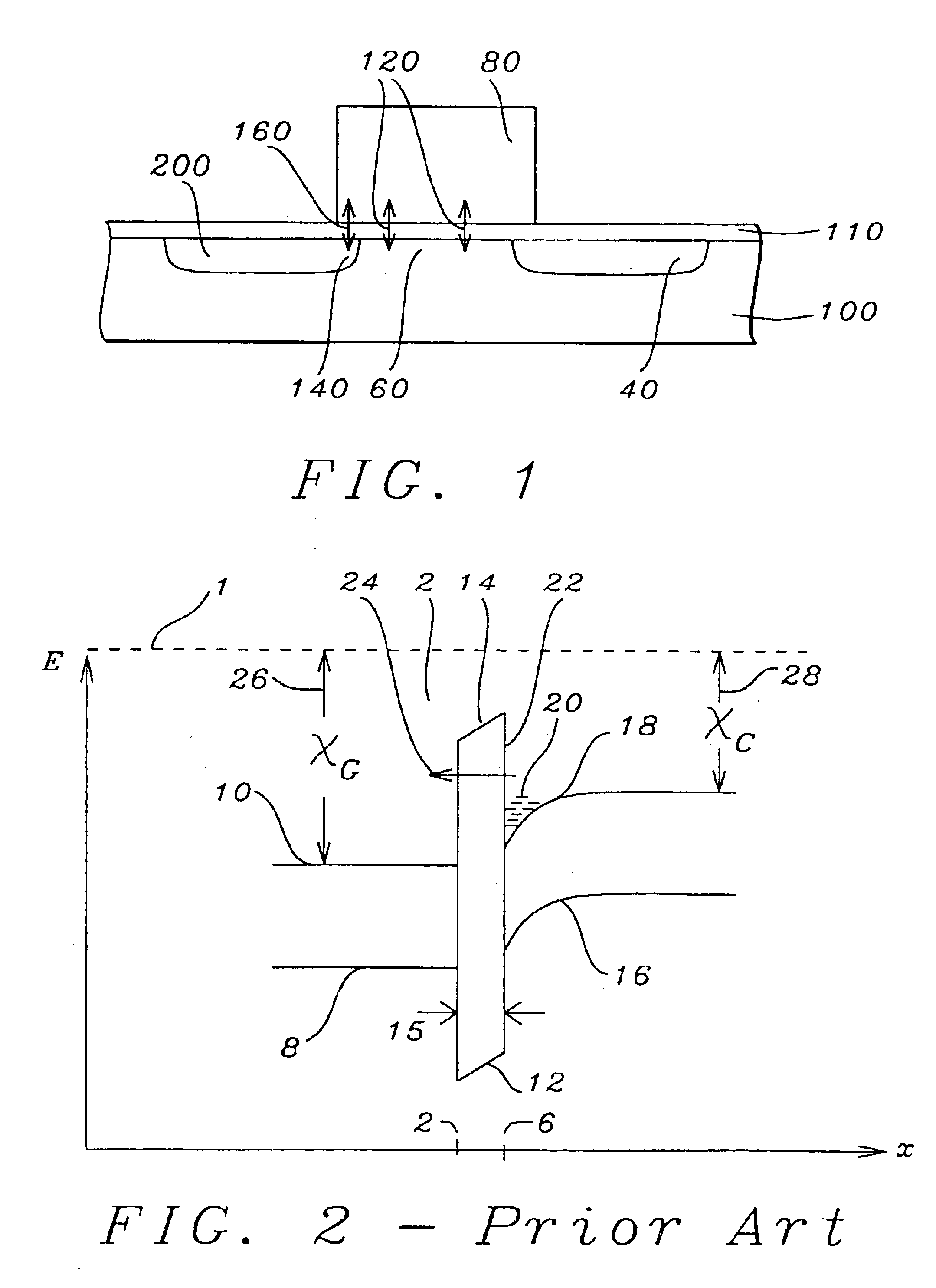
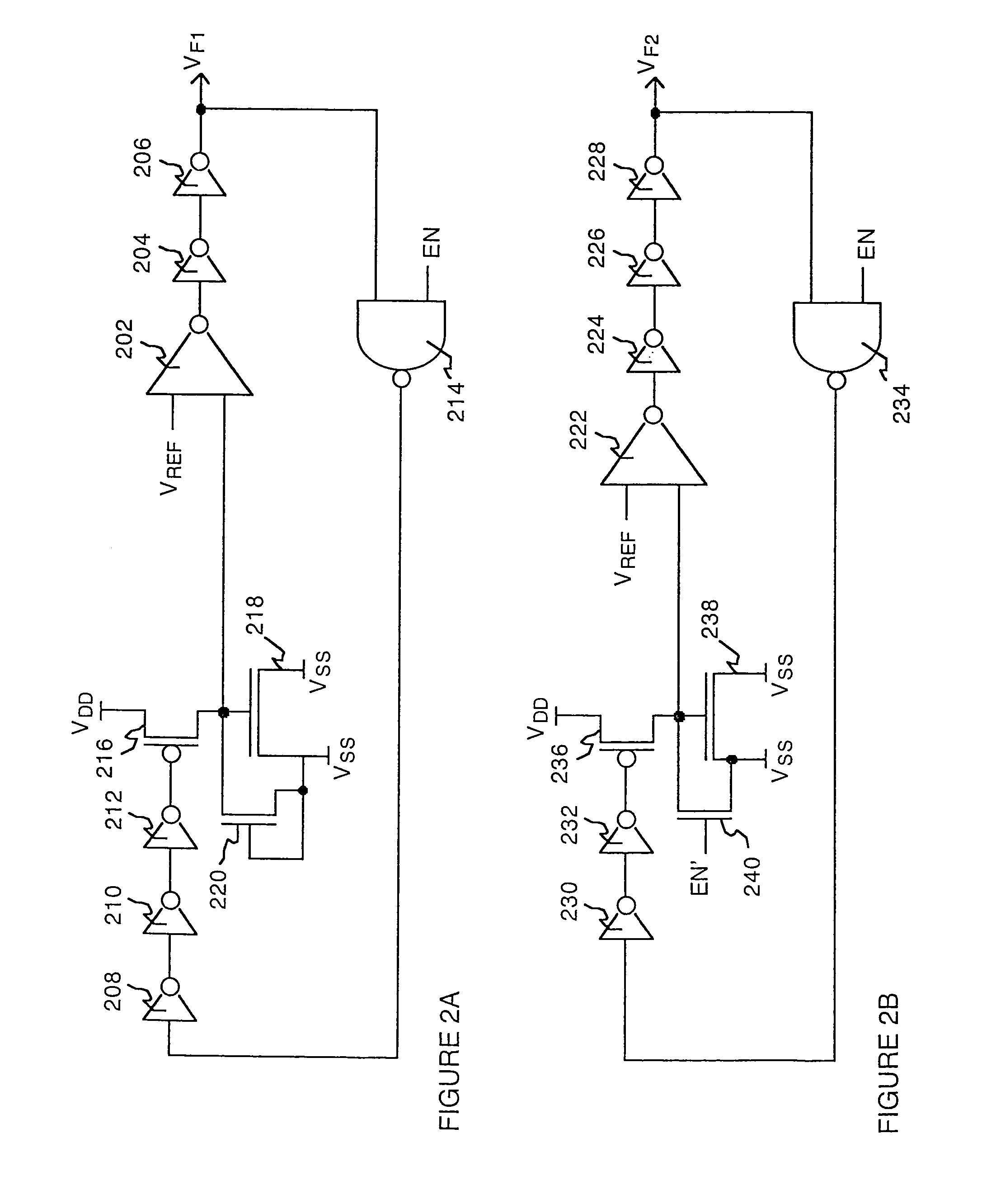
The gate leakage current due to tunnelling effects is represented in circuit form as a generator connected between the gate and drain terminals of the device. The electric field at the edge of the gate terminal is reduced by the electrostatic feedback. This reduces the electron tunnel leakage current.
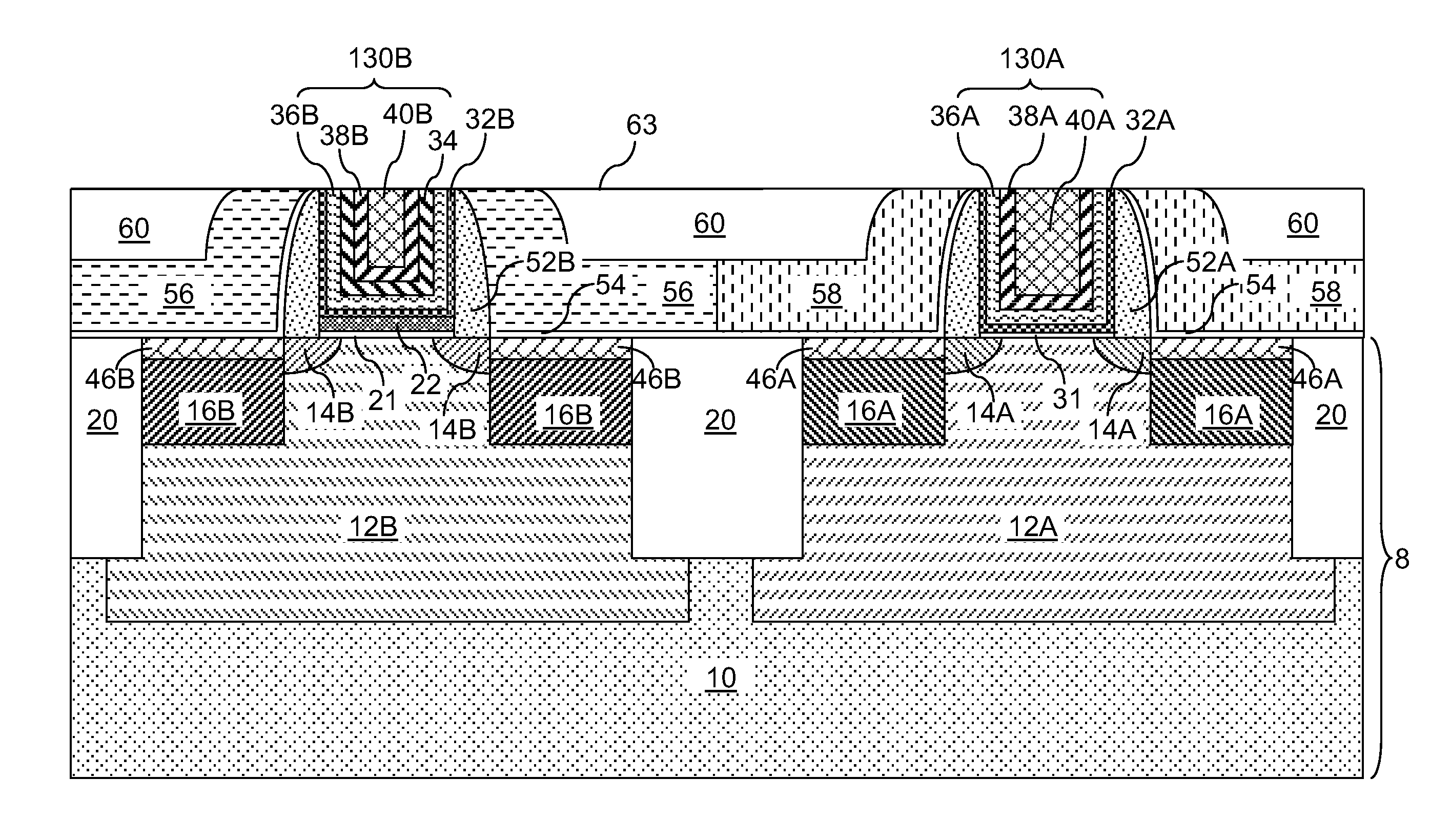
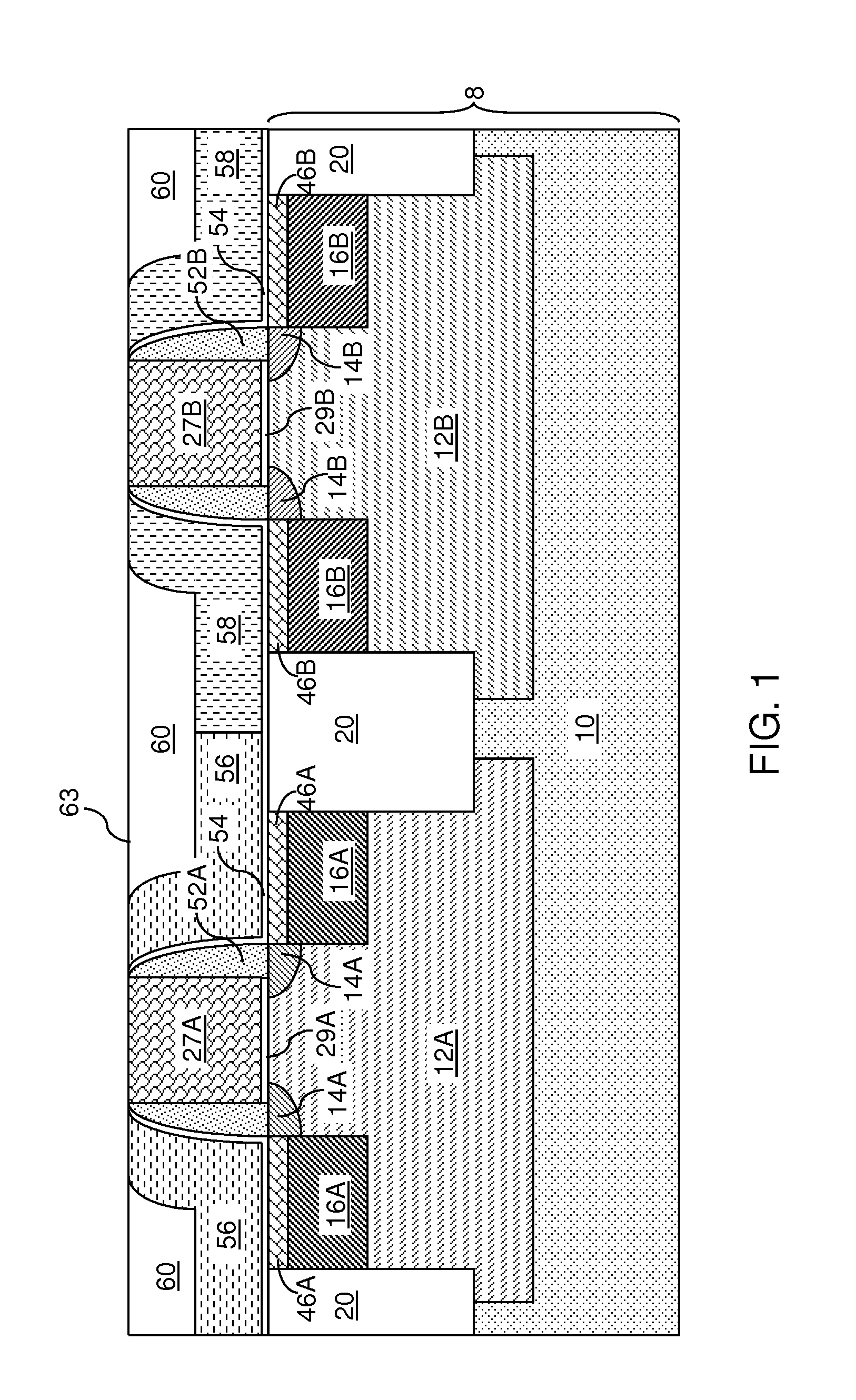
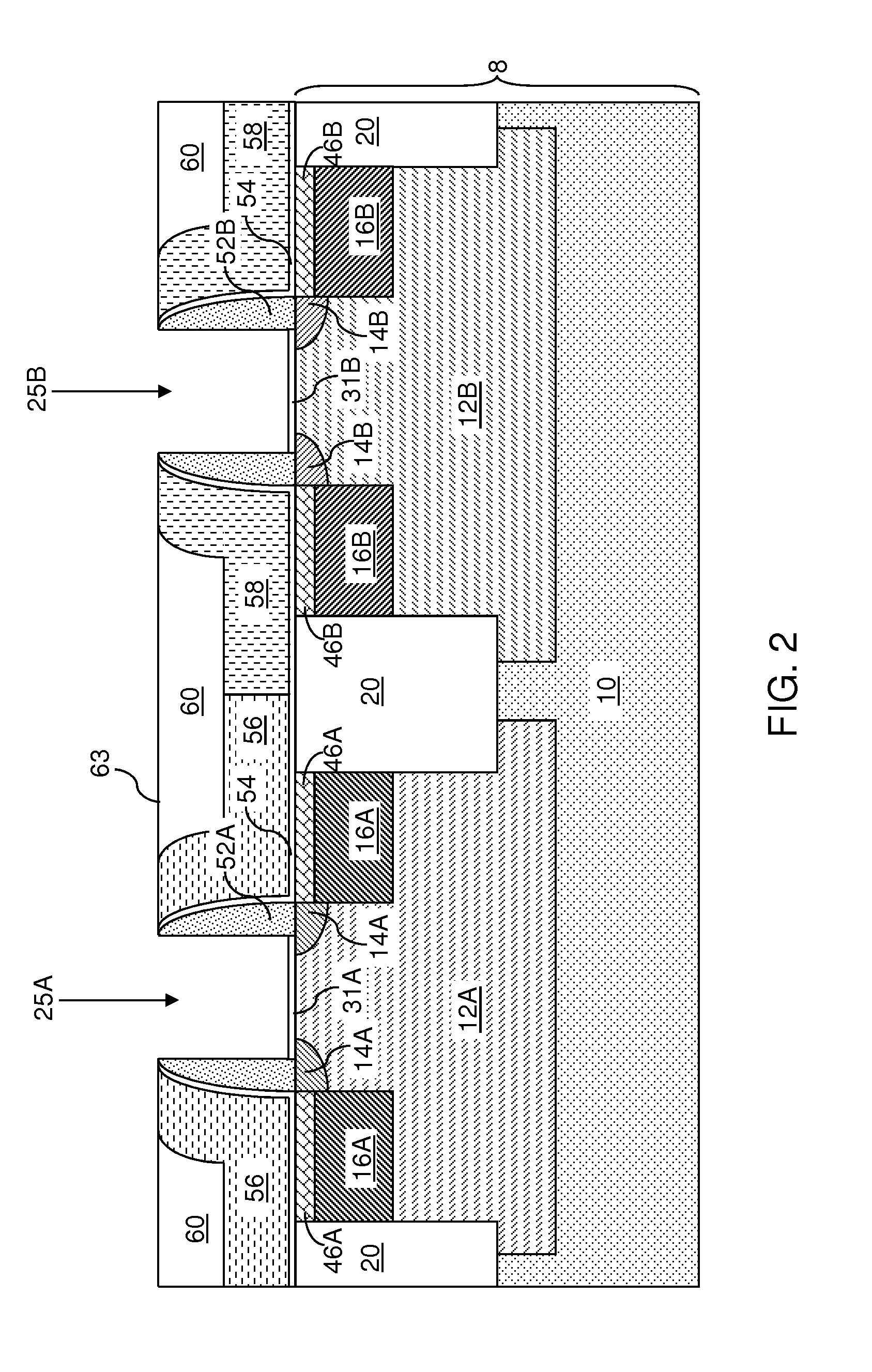
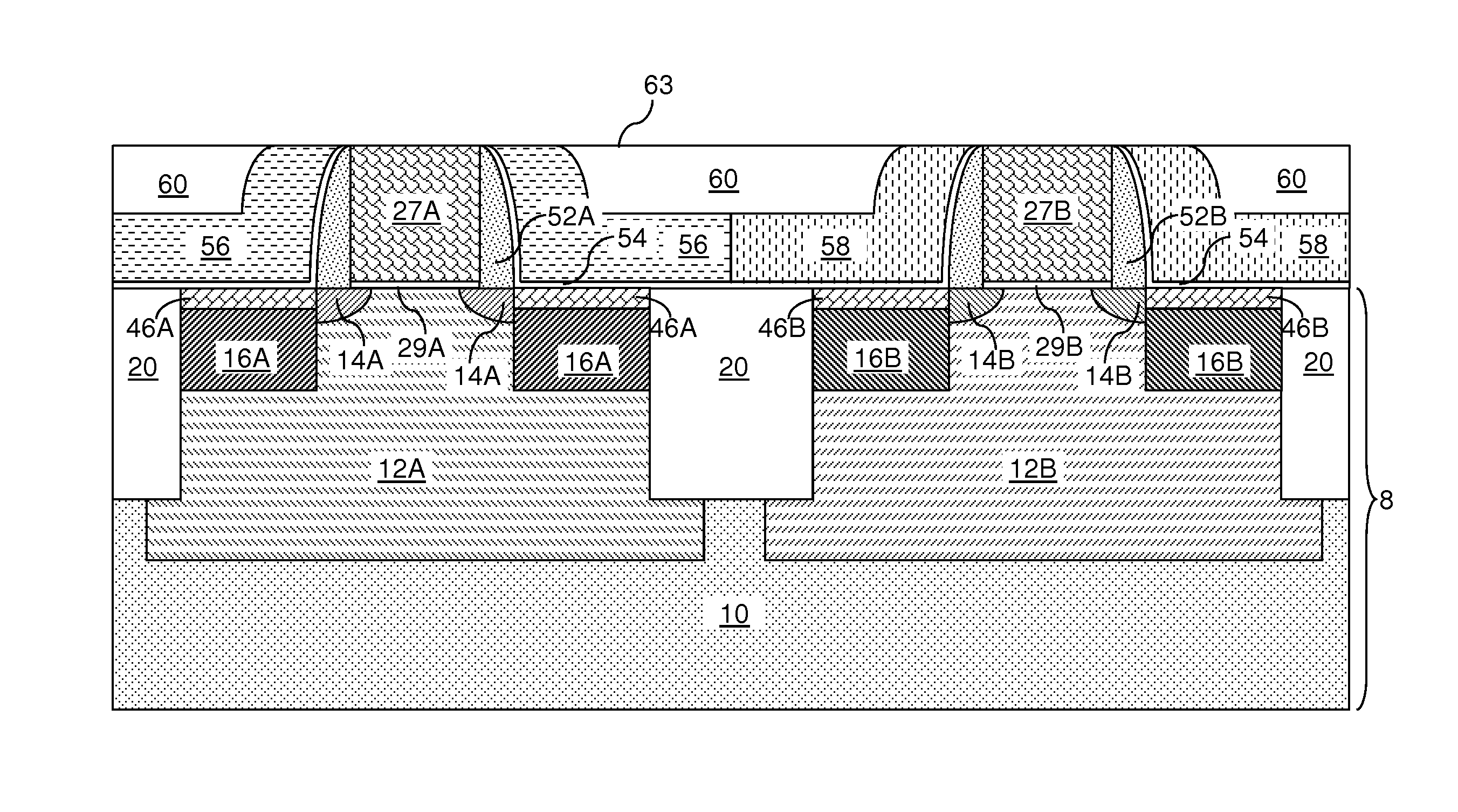
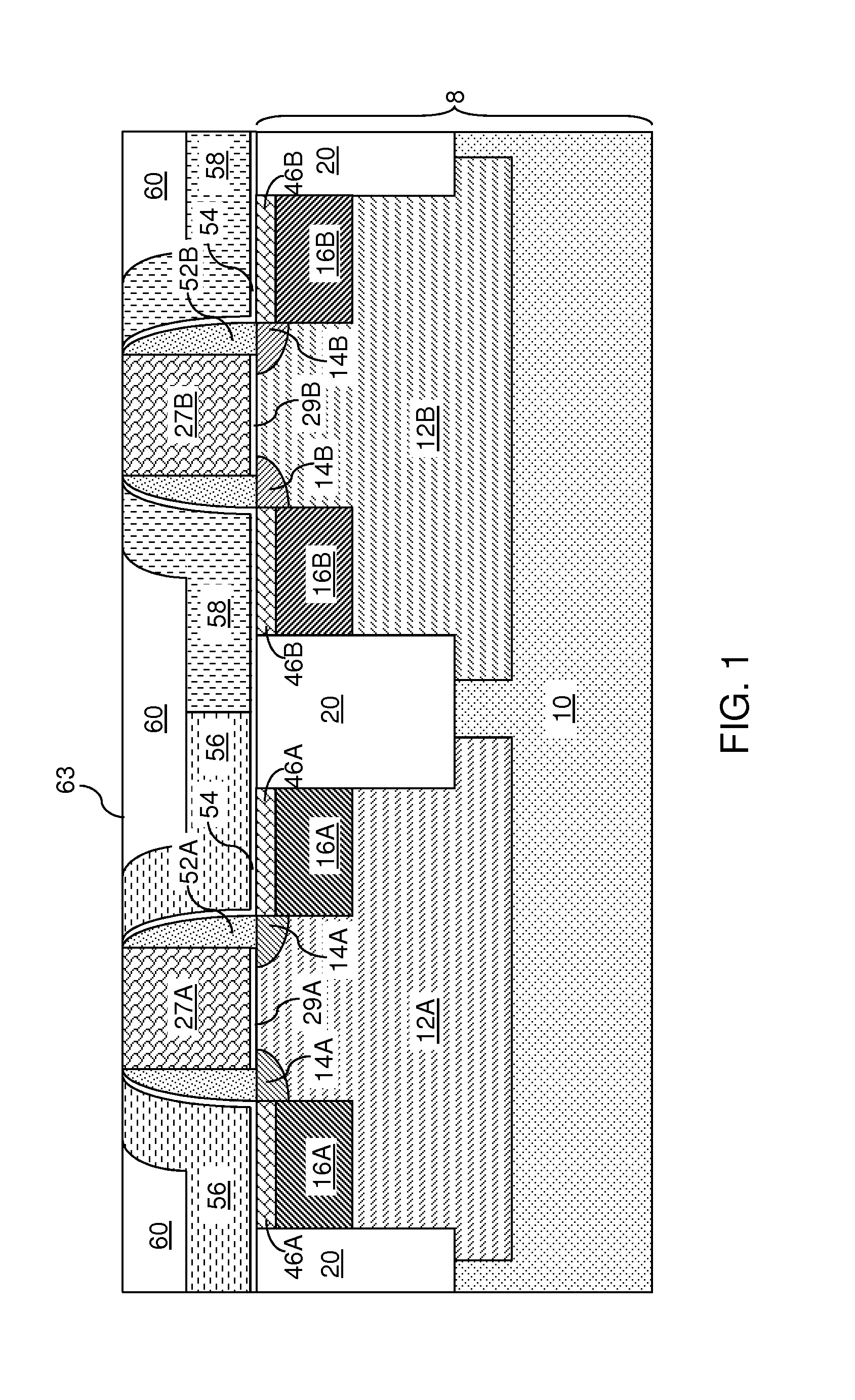
Replacement Metal Gate Structures Providing Independent Control On Work Function and Gate Leakage Current
The thickness and composition of a gate dielectric can be selected for different types of field effect transistors through a planar high dielectric constant material portion, which can be provided only for selected types of field effect transistors. Further, the work function of field effect transistors can be tuned independent of selection of the material stack for the gate dielectric. A stack of a barrier metal layer and a first-type work function metal layer is deposited on a gate dielectric layer within recessed gate cavities after removal of disposable gate material portions. After patterning the first-type work function metal layer, a second-type work function metal layer is deposited directly on the barrier metal layer in the regions of the second type field effect transistor. A conductive material fills the gate cavities, and a subsequent planarization process forms dual work function metal gate structures.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
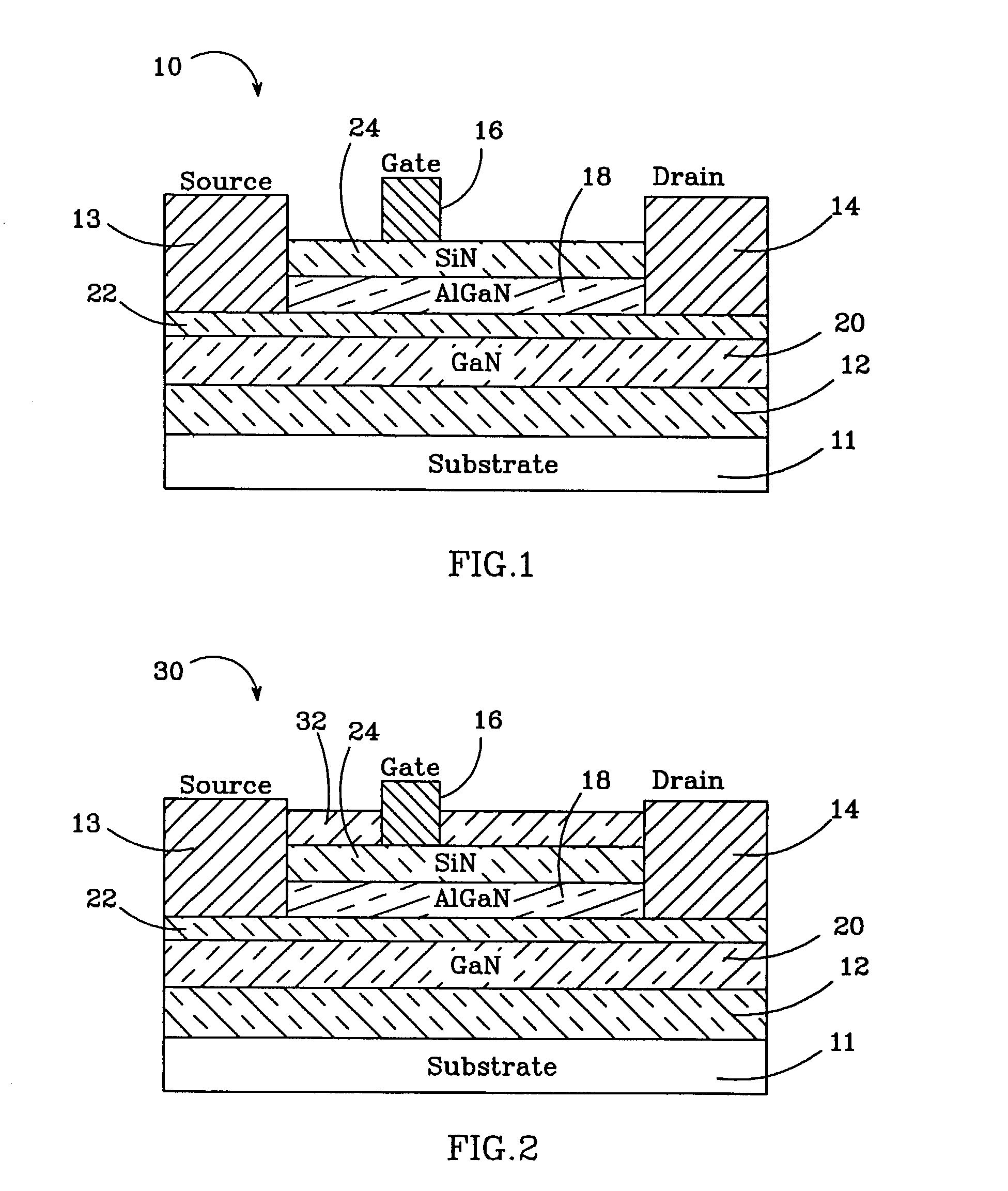
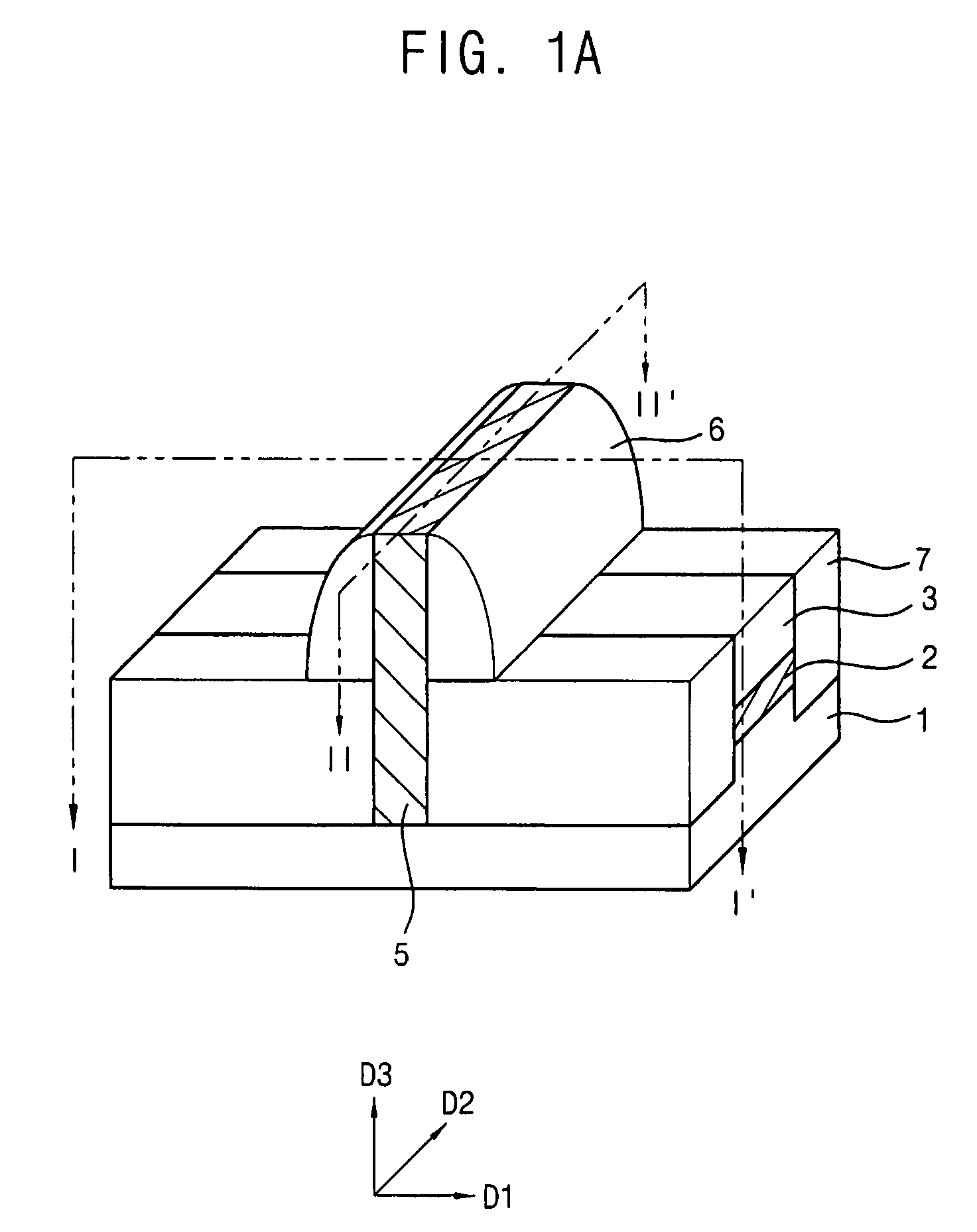
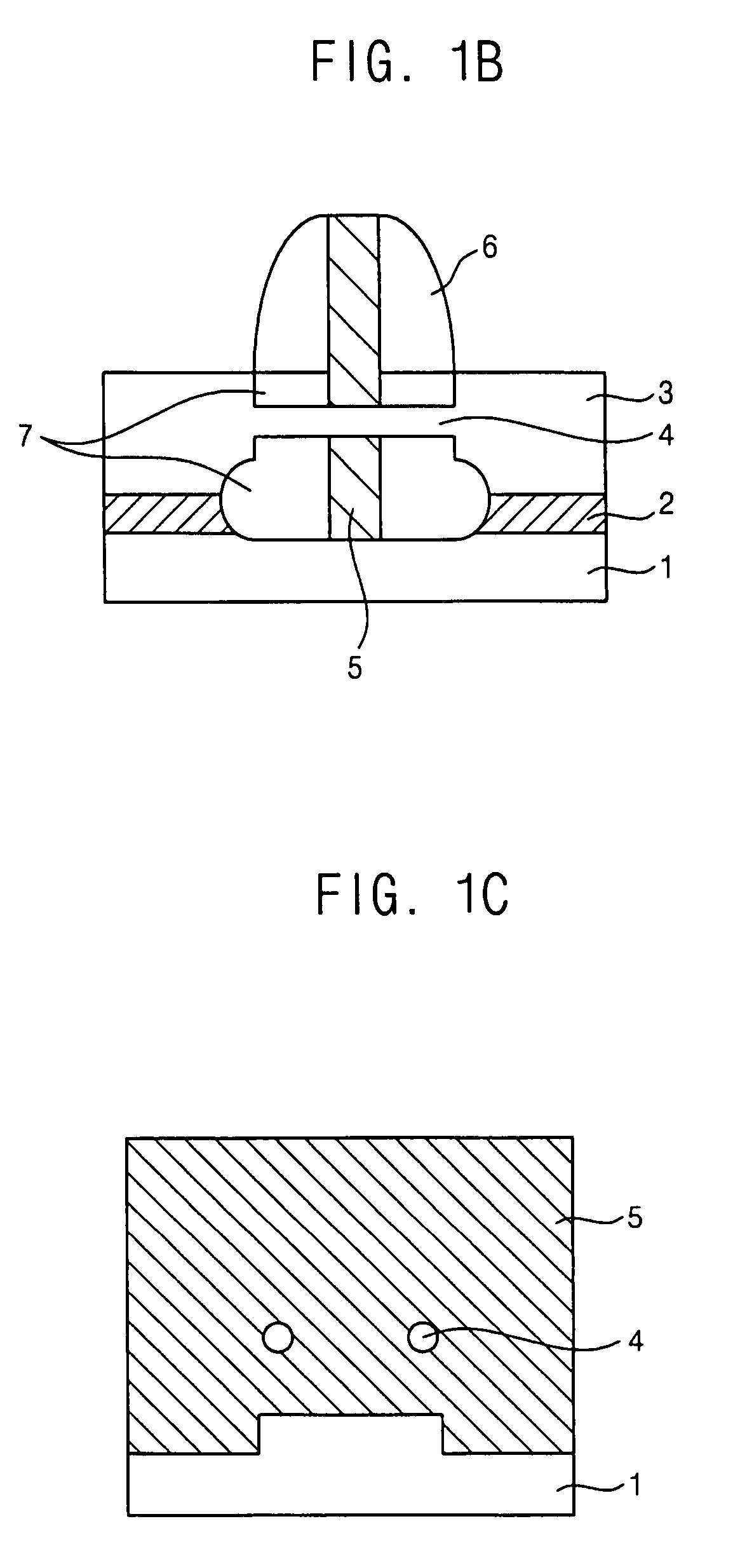
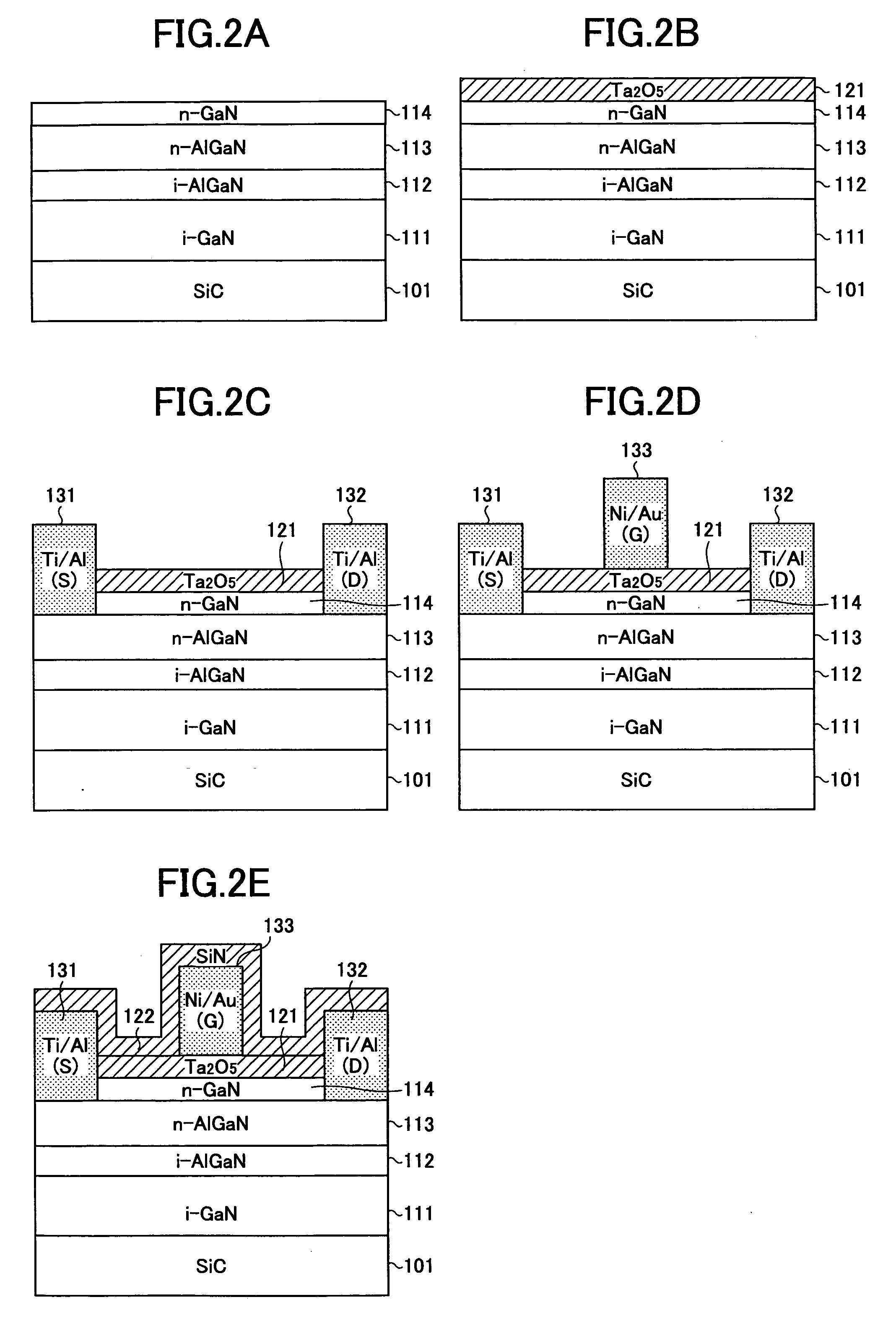
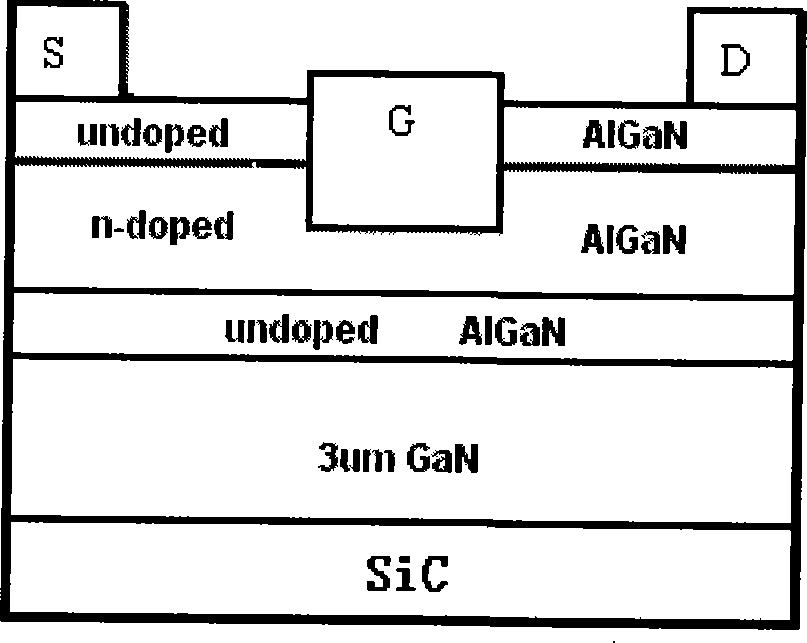
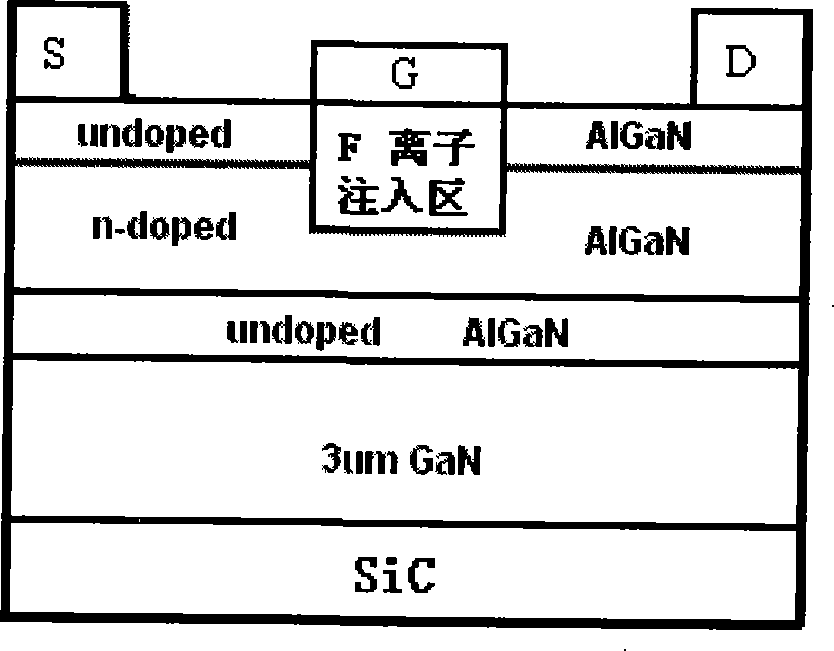
Insulating gate AlGaN/GaN HEMT
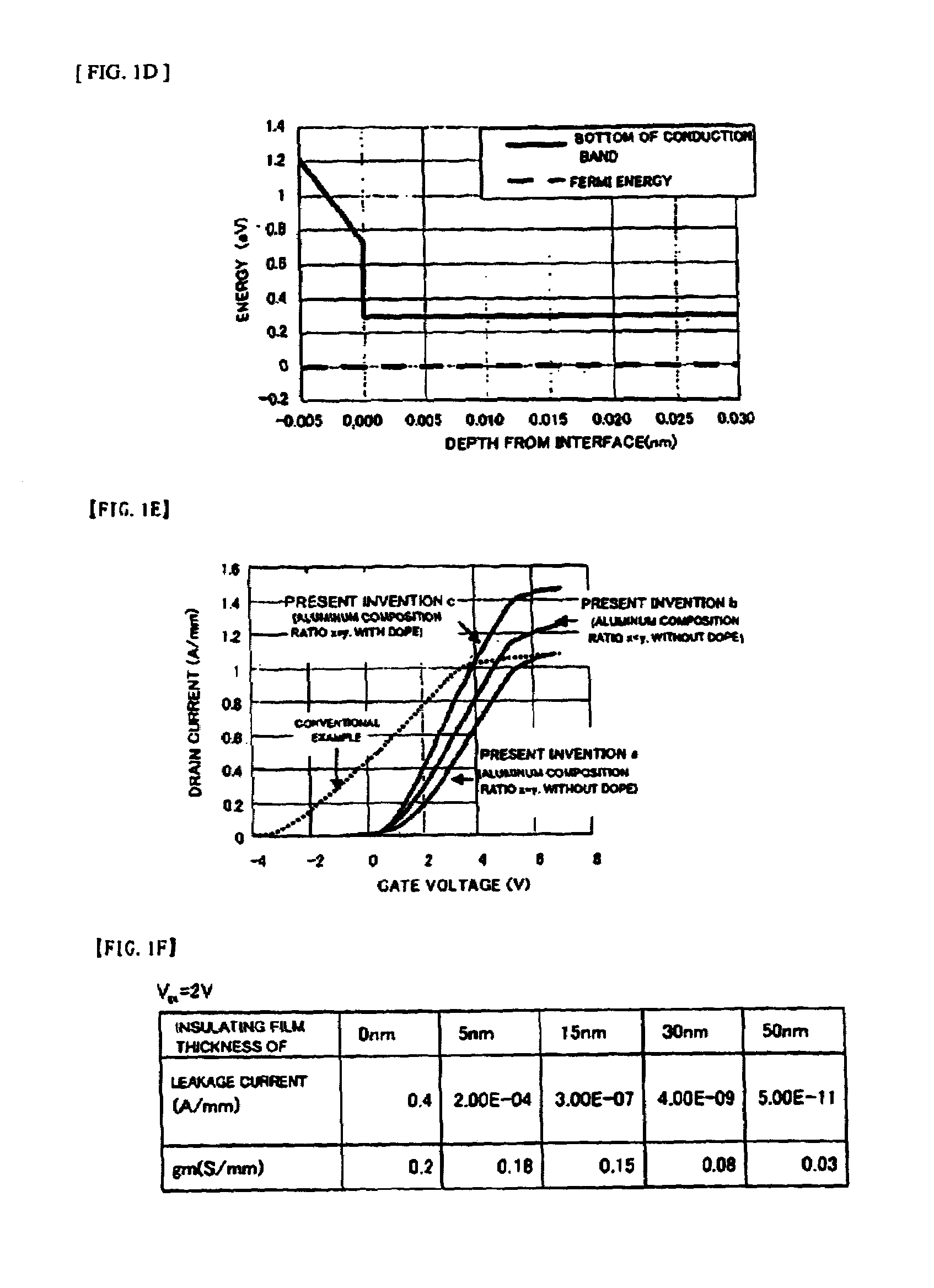
InactiveUS7230284B2Reduce trappingReduce gate leakageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGate leakage currentDriving current
AlGaN / GaN HEMTs are disclosed having a thin AlGaN layer to reduce trapping and also having additional layers to reduce gate leakage and increase the maximum drive current. One HEMT according to the present invention comprises a high resistivity semiconductor layer with a barrier semiconductor layer on it. The barrier layer has a wider bandgap than the high resistivity layer and a 2DEG forms between the layers. Source and drain contacts contact the barrier layer, with part of the surface of the barrier layer uncovered by the contacts. An insulating layer is included on the uncovered surface of the barrier layer and a gate contact is included on the insulating layer. The insulating layer forms a barrier to gate leakage current and also helps to increase the HEMT's maximum current drive. The invention also includes methods for fabricating HEMTs according to the present invention. In one method, the HEMT and its insulating layer are fabricated using metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD). In another method the insulating layer is sputtered onto the top surface of the HEMT in a sputtering chamber.
Owner:CREE INC
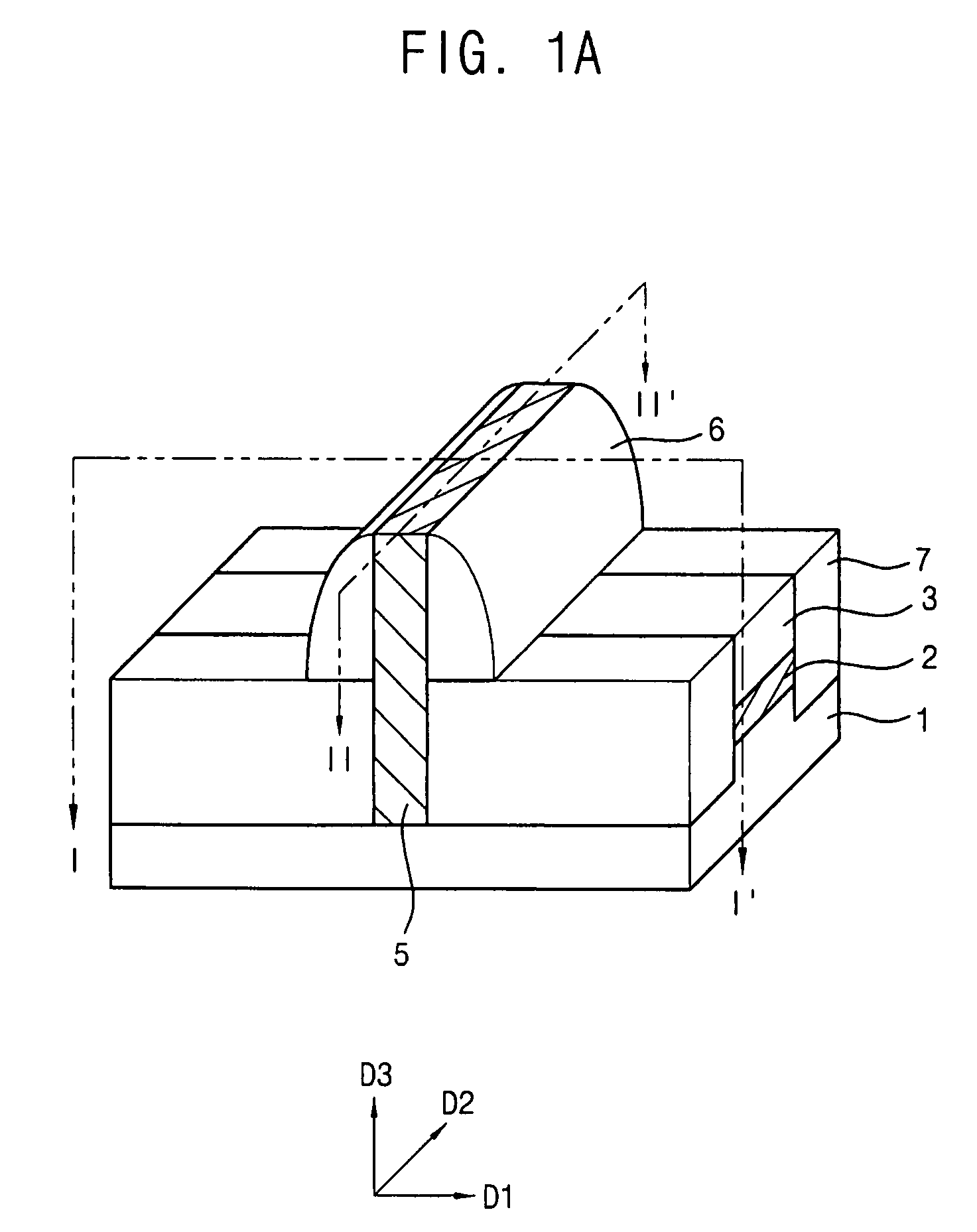
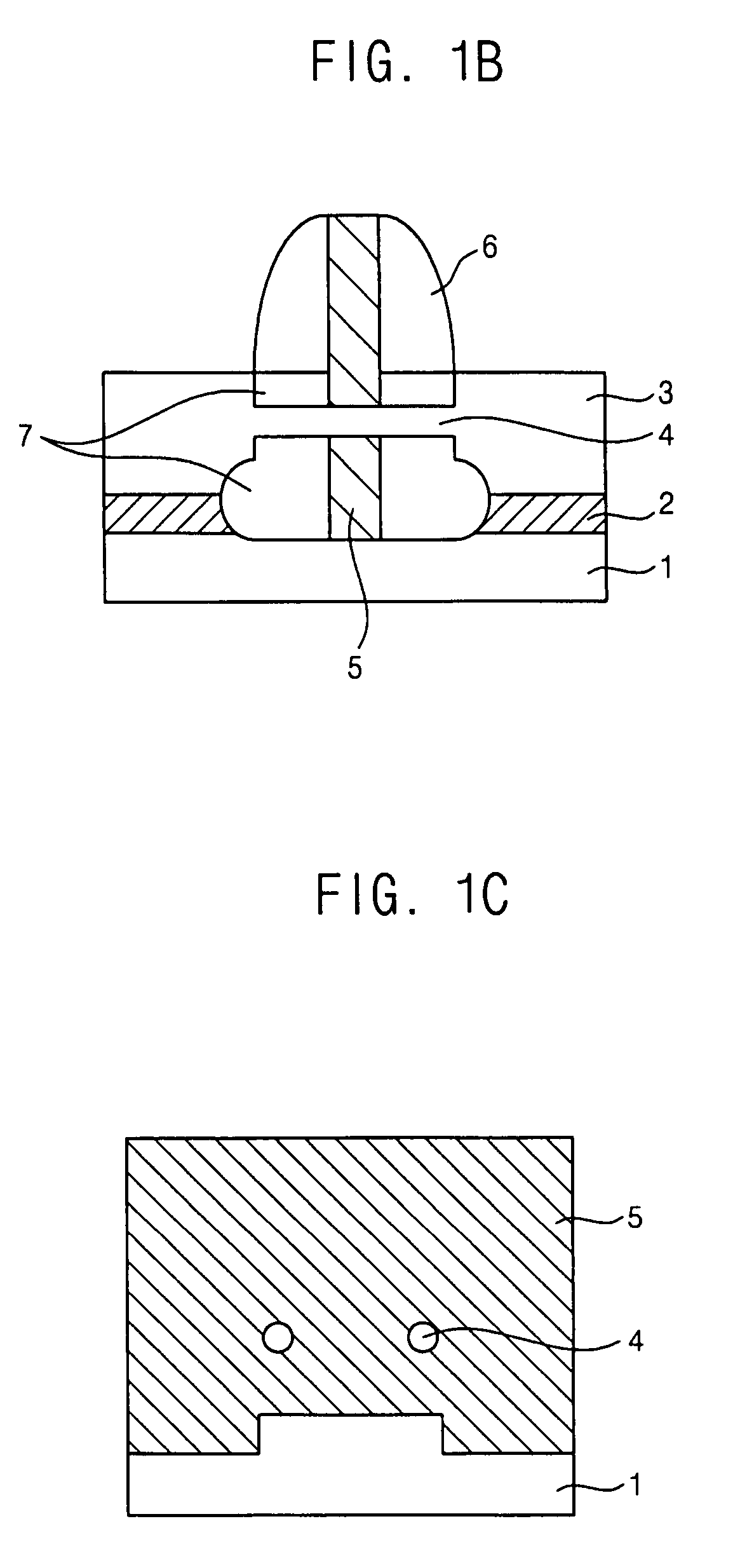
Vertical semiconductor device with tunnel insulator in current path controlled by gate electrode
InactiveUS6873009B2Suppress lowering of driving forceLower average currentTransistorSolid-state devicesGate leakage currentJunction leakage
It is an object of the present invention to provides a field effect transistor with extremely low leakage current. It is another object of the invention to provide a semiconductor memory device having an excellent information holding characteristic. It is a further object of the invention to provide a method for manufacturing in a simple manner a novel field effect transistor or semiconductor memory device with extremely low leakage current. According to a typical basic configuration of the present invention, a thin insulating film is inserted in a vertically disposed Schottky junction to form source and drain electrodes and a tunnel of the insulating film in the junction is controlled by a gate electrode. The gate electrode is disposed on each of both sides of a vertical channel, permitting a field effect to be exerted effectively on the junction, whereby a junction leakage in an OFF state can be made extremely low.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
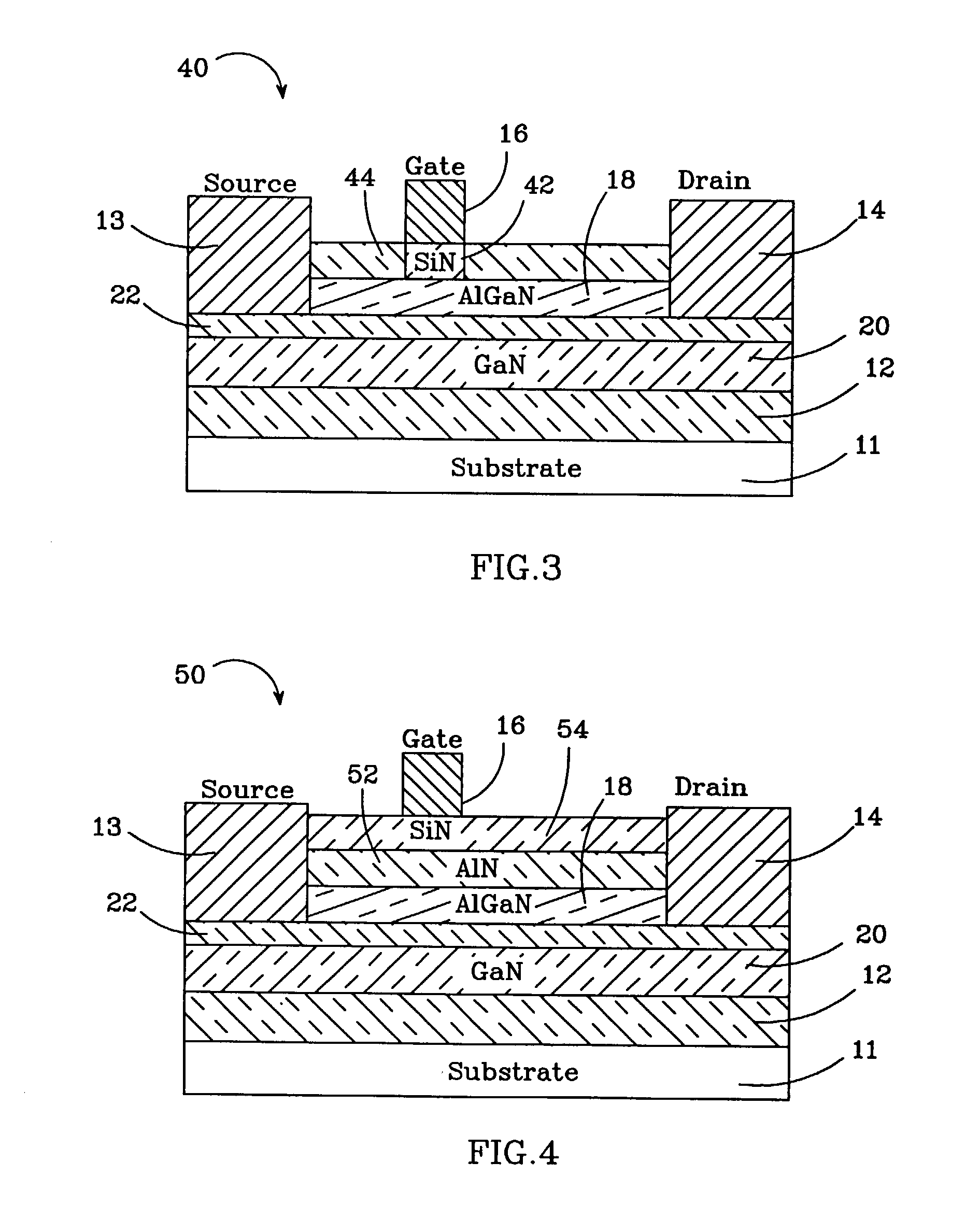
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20060157729A1Total current dropReduce leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate leakage currentDevice material
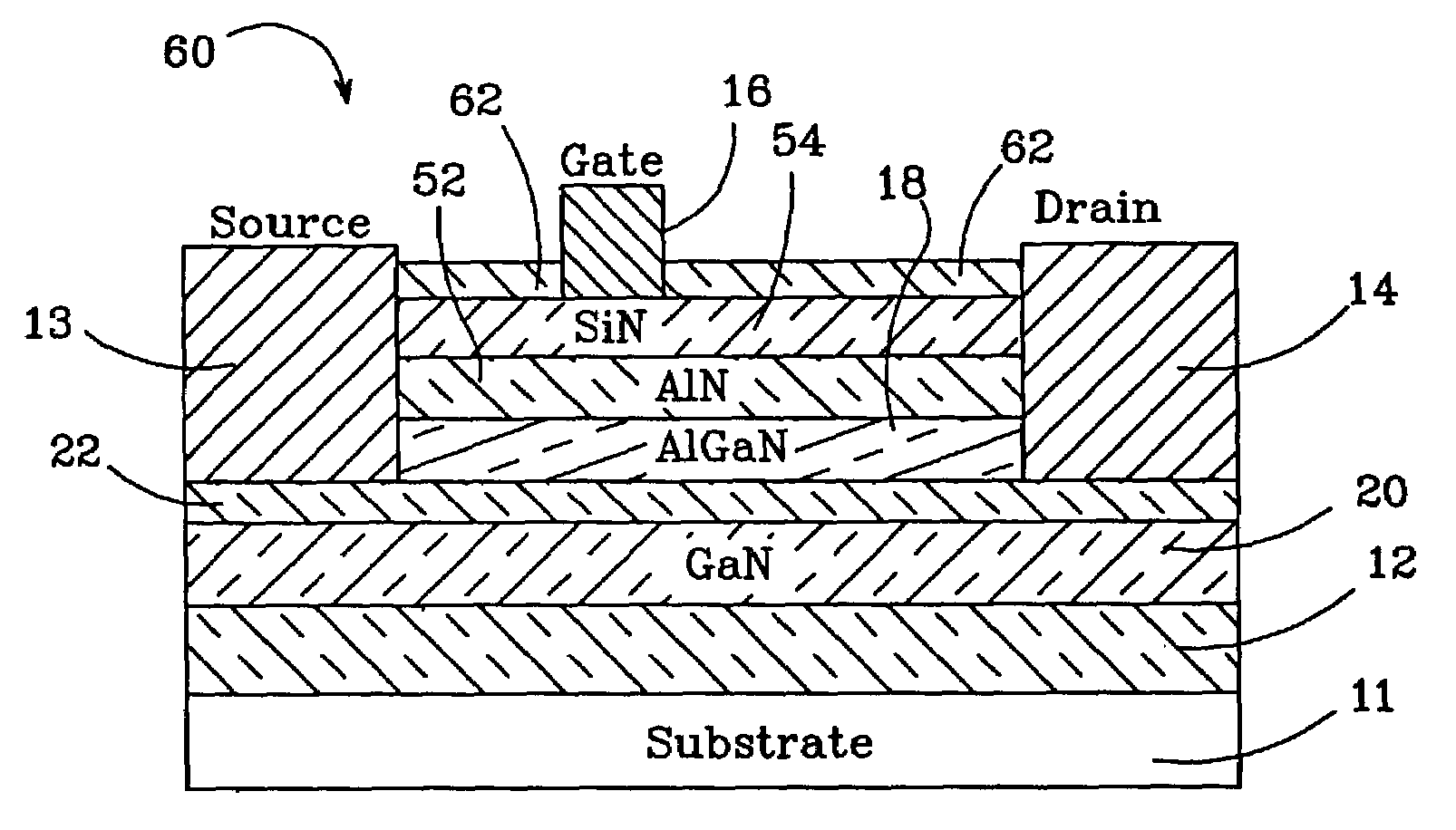
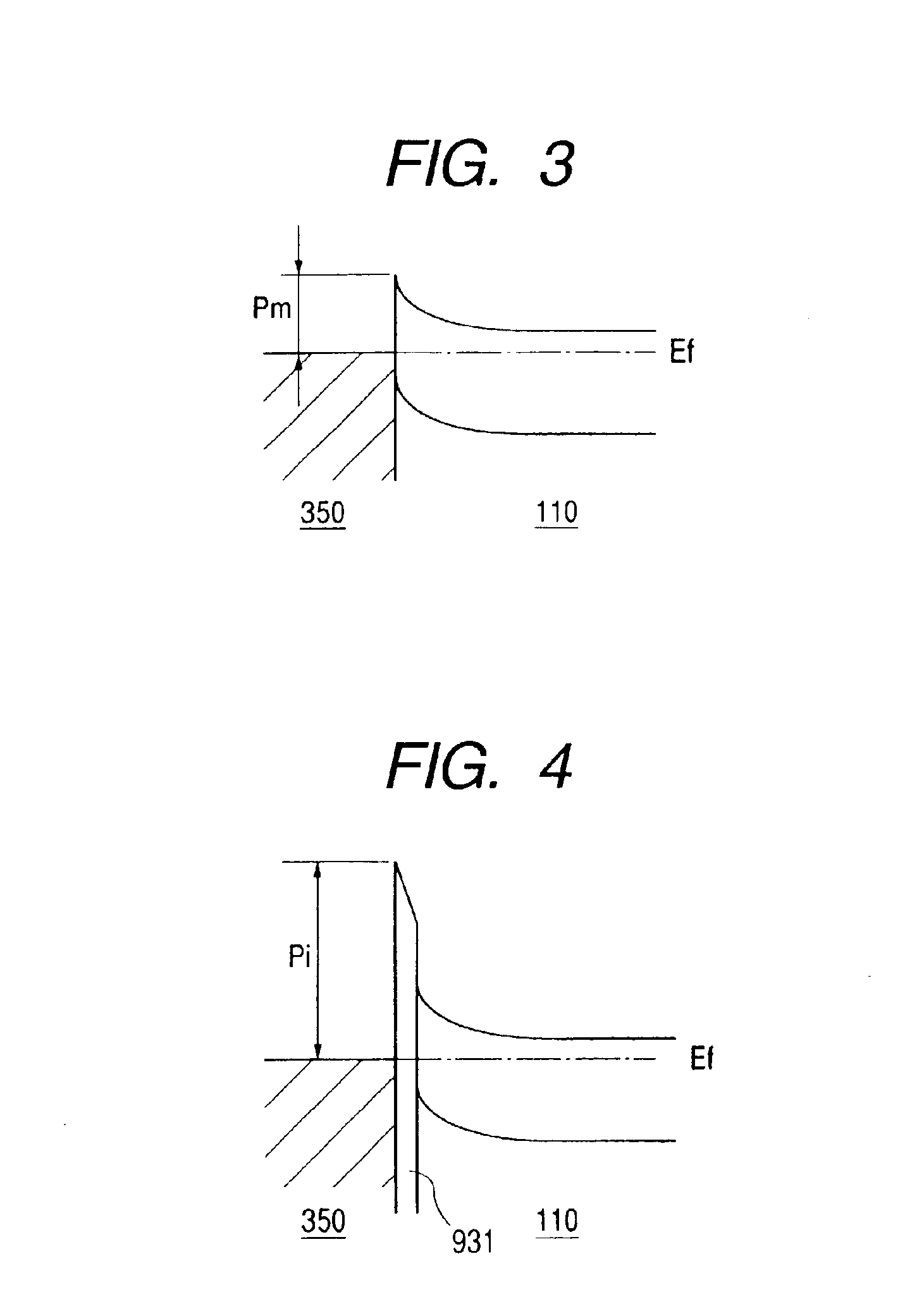
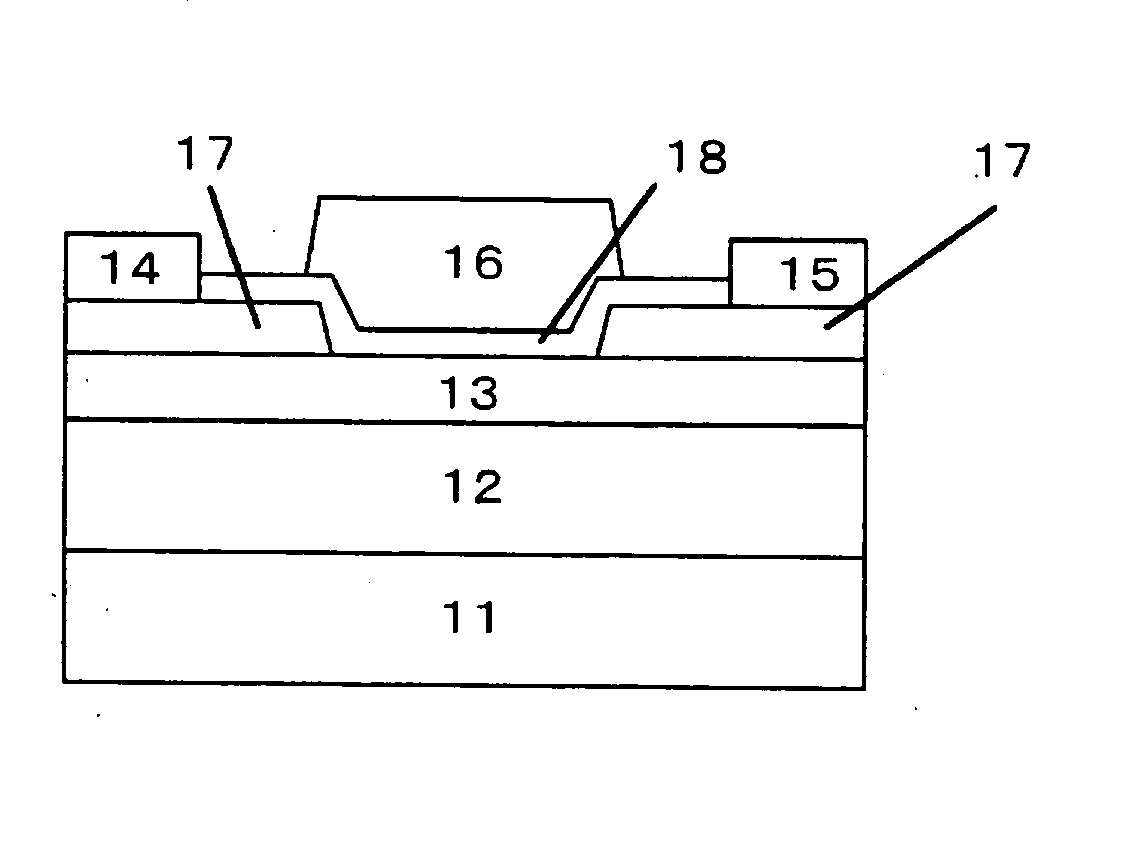
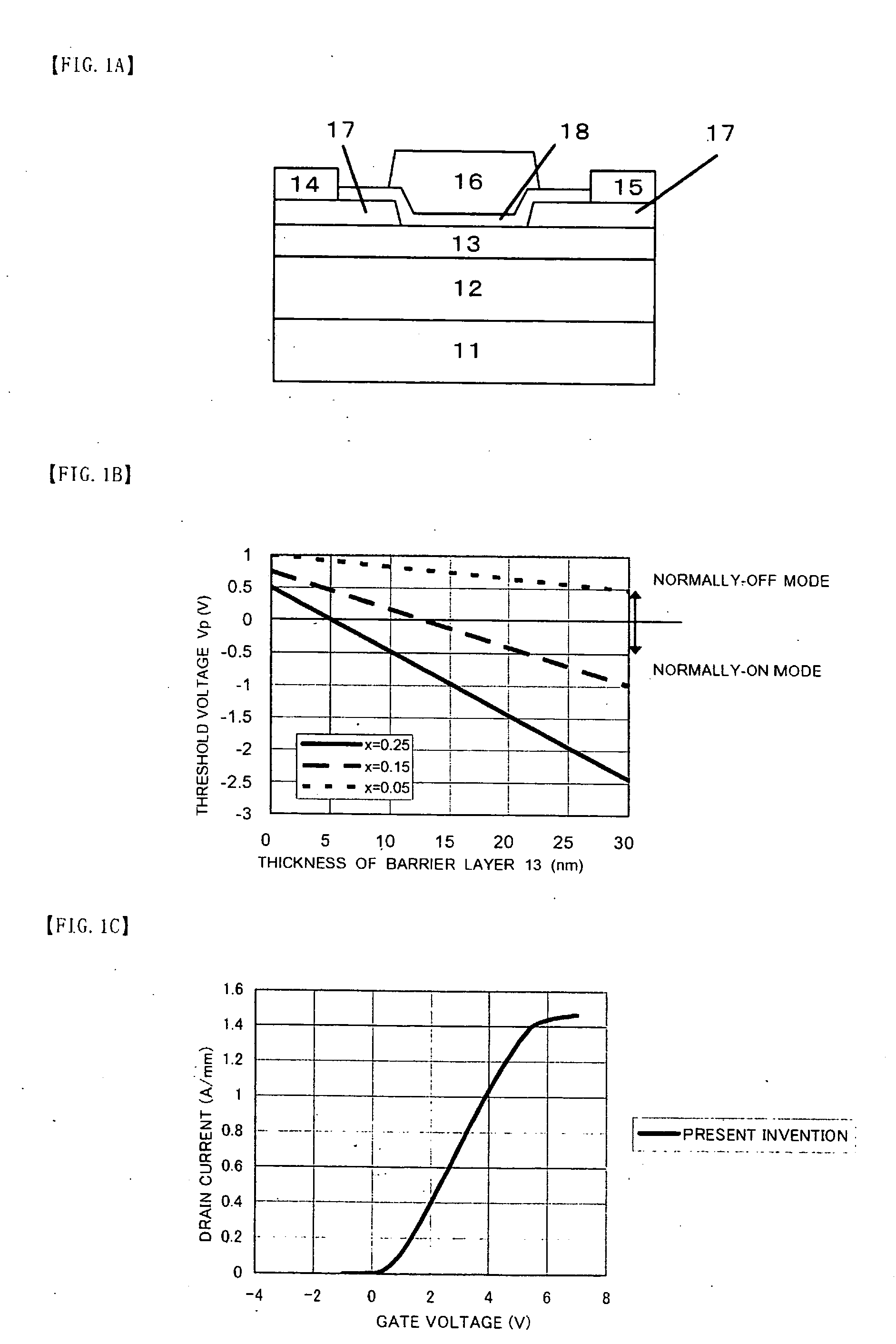
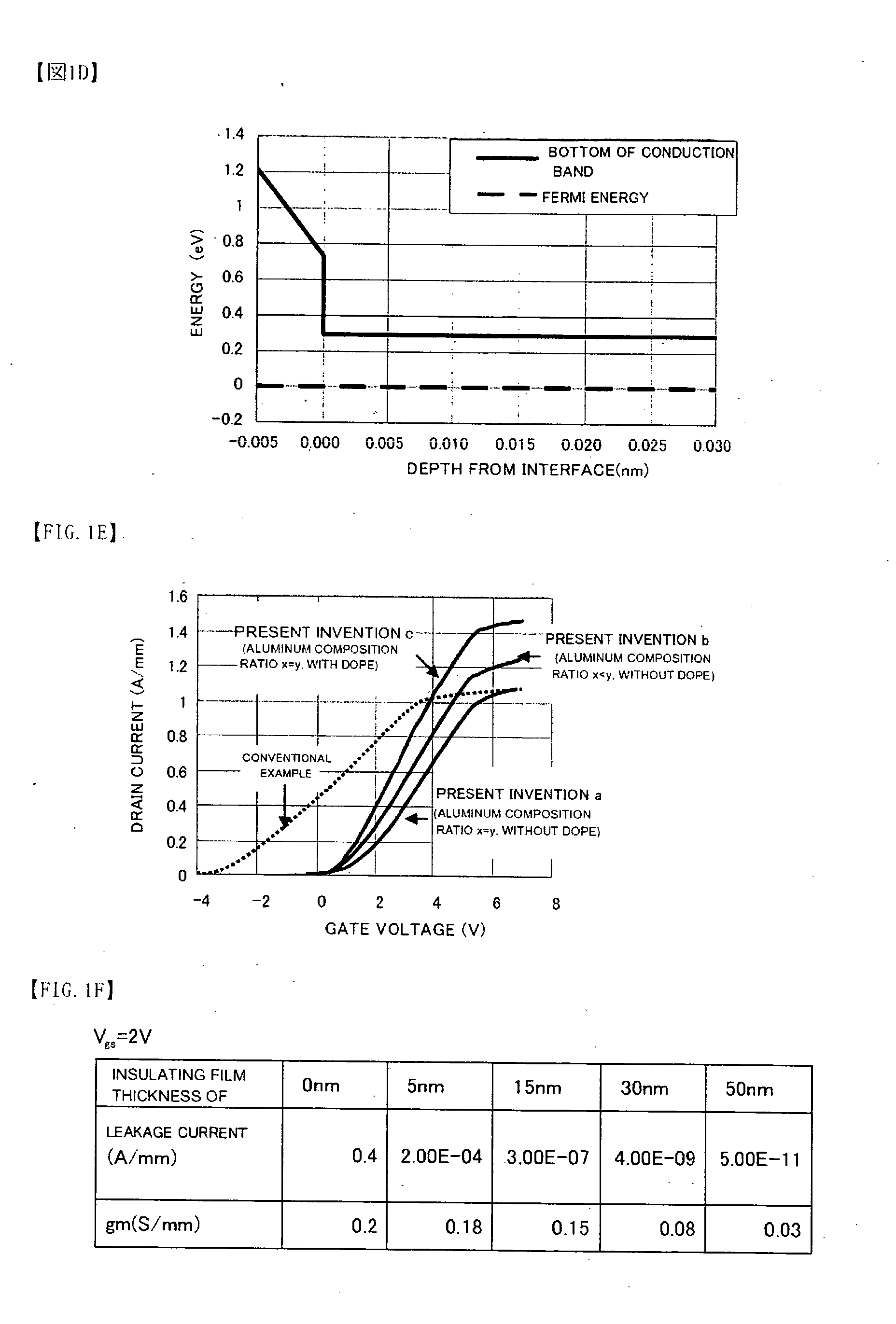
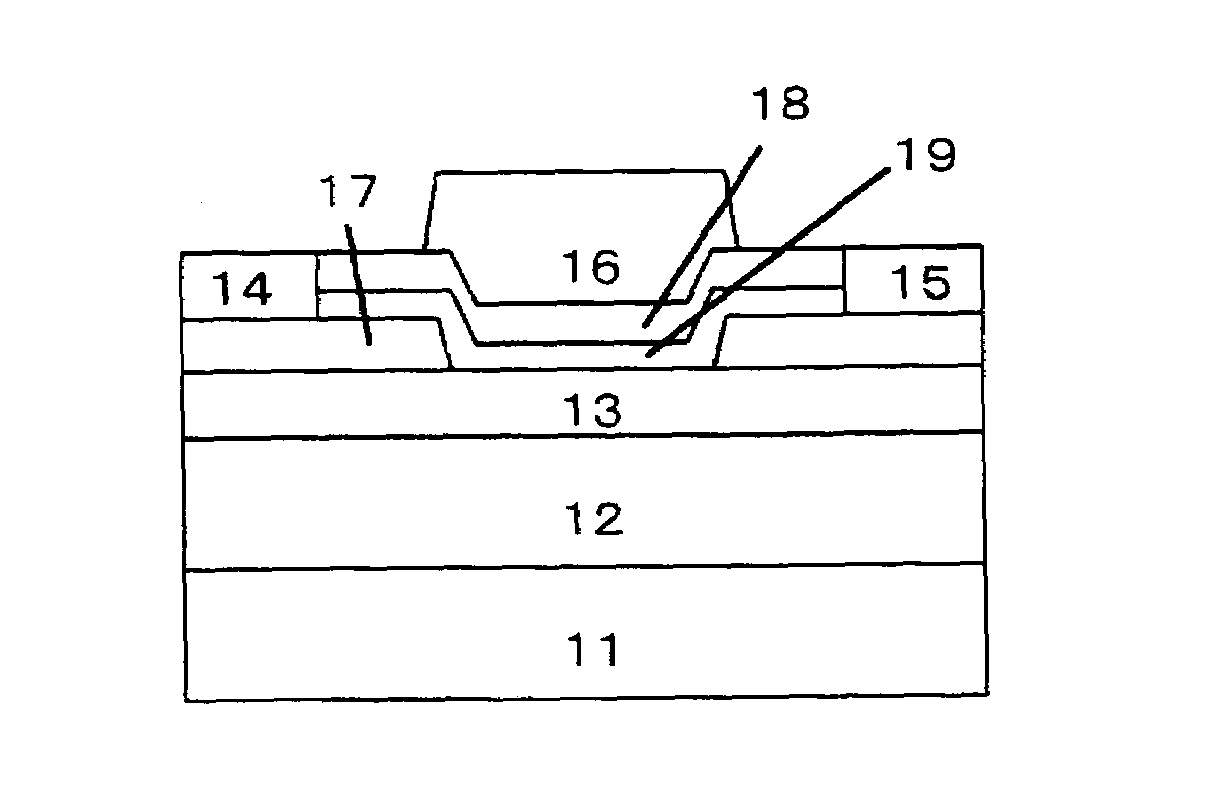
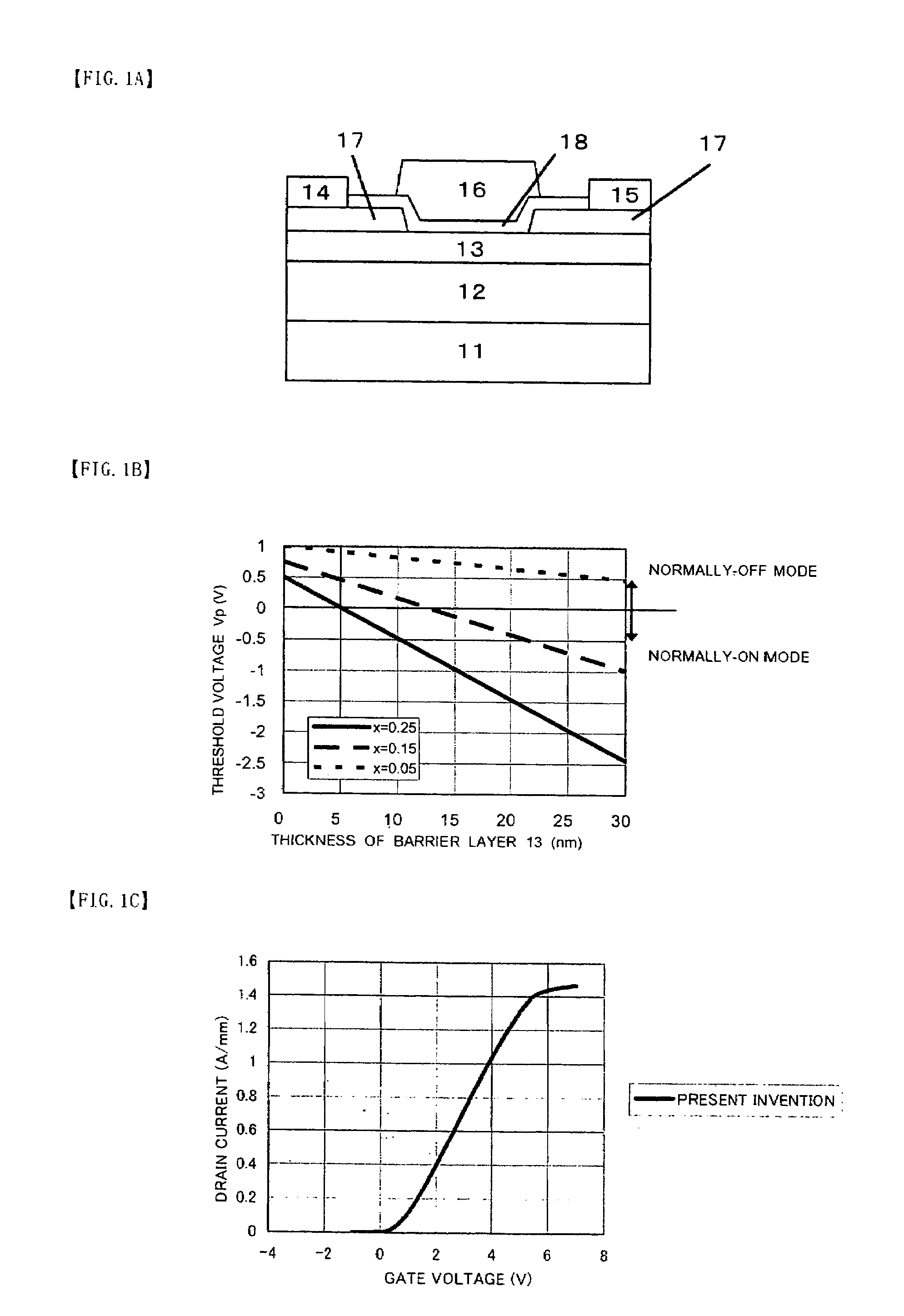
It is an object of the present invention to provide a semiconductor device, which can simultaneously achieve a normally-off mode of HFET and an improvement in Imax, and further achieve an improvement in gm and a reduction in gate leakage current. In order to keep a thin barrier layer 13 on an operation layer 12 of a substrate 11 directly under a gate electrode for mostly contributing to achieve the normally-off mode and also implement the high Imax, it is configured in such a way that a thickness of the barrier layer 13 can be increased by the semiconductor layer 17 between gate and source regions and between gate and drain regions. It is therefore possible to achieve the normally-off mode and an improvement in Imax as compared with an FET in which a thickness of the barrier layer is designed so as to be uniform. An insulating film 18 with a dielectric constant higher than that of the barrier layer is further inserted between a gate electrode 16 and the barrier layers 13, so that an improvement in gm and a reduction in gate leakage current can be achieved.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Semiconductor memory device capable of controlling potential level of power supply line and/or ground line
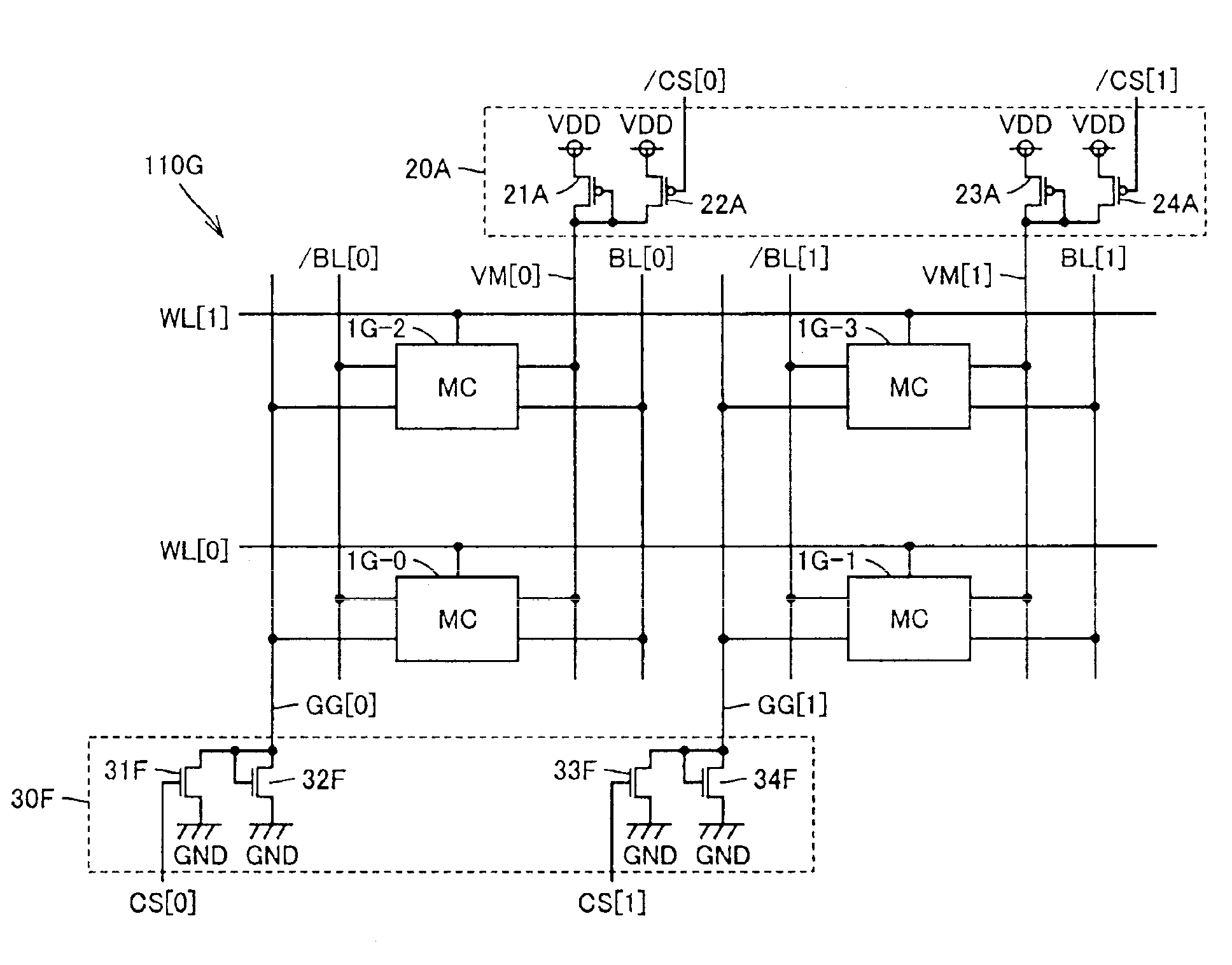
InactiveUS6903962B2Reduce power consumptionAverage power consumptionDigital storageGate leakage currentControl signal
Level control signals are both set to H level, and potentials of power supply lines are both set to be lower than a power supply potential. In this manner, a gate leakage current during waiting and writing operation of a memory cell array can significantly be reduced. The level control signals are set to L level and H level respectively, and solely the potential of one of the power supply lines is set to be lower than the power supply potential. In this manner, power consumption during a reading operation of the memory cell array can be reduced.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Suppression of MOSFET gate leakage current
InactiveUS6949769B2Reduce leakage currentReduce and eliminate leakage currentTransistorGate leakage currentMOSFET
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Fin field effect transistor having low leakage current and method of manufacturing the finfet
ActiveUS20100270619A1Reduce leakage currentHigh densityTransistorSolid-state devicesGate leakage currentEngineering
Provided is a fin field effect transistor (FinFET) having low leakage current and a method of manufacturing the same. The FinFET includes: a bulk silicon substrate; a fence-shaped body formed by patterning the substrate; an insulating layer formed on a surface of the substrate to a first height of the fence-shaped body; a gate insulating layer formed at side walls and an upper surface of the fence-shaped body at which the insulating layer is not formed; a gate electrode formed on the gate insulating layer; source / drain formed at regions of the fence-shaped body where the gate electrode is not formed. The gate electrode includes first and second gate electrodes which are in contact with each other and have different work functions. Particularly, the second gate electrode having a low work function is disposed to be close to the drain. As a result, the FinFET according to the present invention increases a threshold voltage by using a material having the high work function for the gate electrode and lowers the work function of the gate electrode overlapping with the drain, so that gate induced drain leakage (GIDL) can be reduced.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Pillar-type field effect transistor having low leakage current
InactiveUS20080251825A1Reduced cell device areaGood miniaturization characteristicTransistorSolid-state devicesGate leakage currentWork function
A pillar-type field effect transistor having low leakage current is provided. The pillar-type field effect transistor includes a semiconductor pillar, a gate insulating layer formed on a portion of a surface of the semiconductor pillar, a gate electrode formed on the gate insulating layer, and source / drain regions formed on portions of the semiconductor pillar where the gate electrode is not formed, in which the gate electrode includes a first gate electrode, a second gate electrode, and an inter-gate insulating layer, in which the first gate electrode has a work function higher than that of the second gate electrode, in which the inter-gate insulating layer is formed between the first gate electrode and the second gate electrode, and in which the first gate electrode and the second gate electrode are electrically connected by a contact or a metal interconnection line. A portion of the second gate electrode having the work function lower than that of the first gate electrode is overlapped by the drain region. Accordingly, the gate electrode of the pillar-type FET is formed using a material having a high work function, so that the threshold voltage can be increased and the work function of the portion of the gate electrode overlapped by the drain region can be decreased. Therefore, gate induced drain leakage is reduced, so that off-state leakage current can likewise be greatly reduced.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
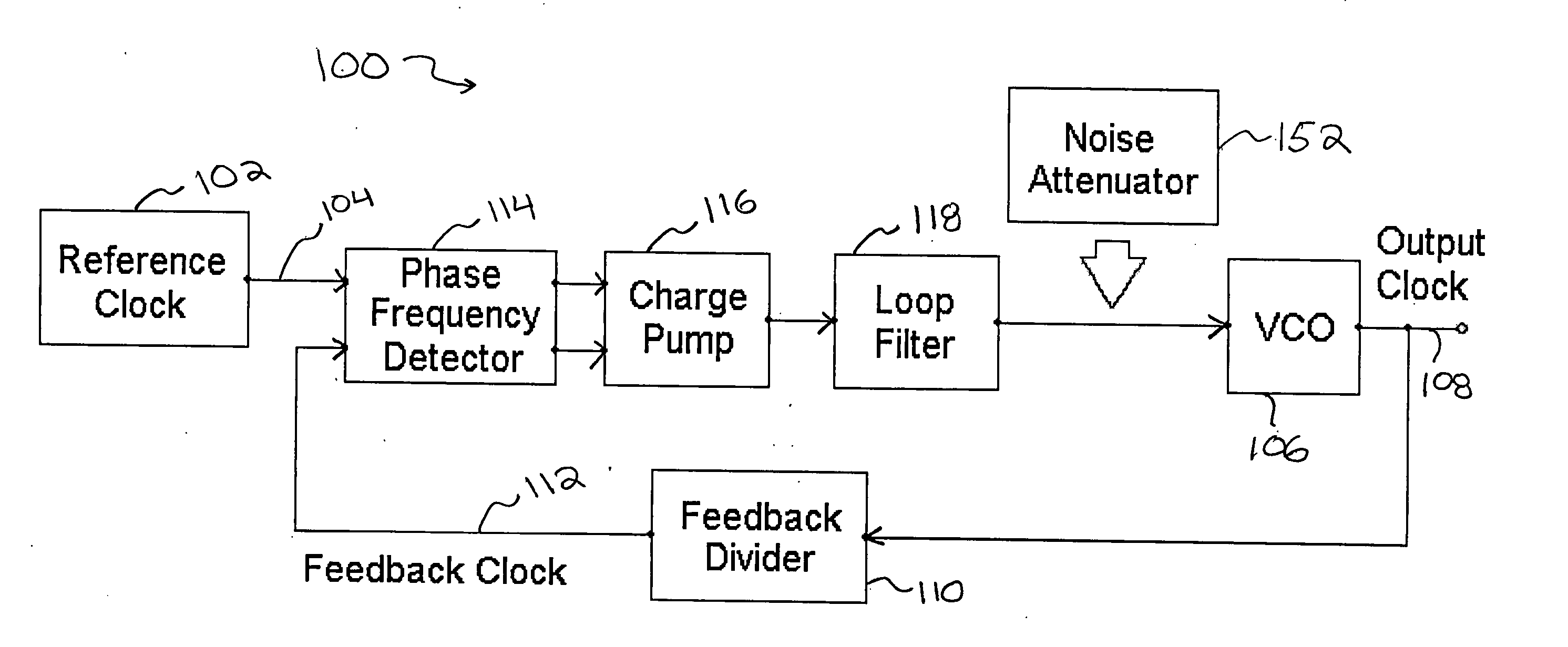
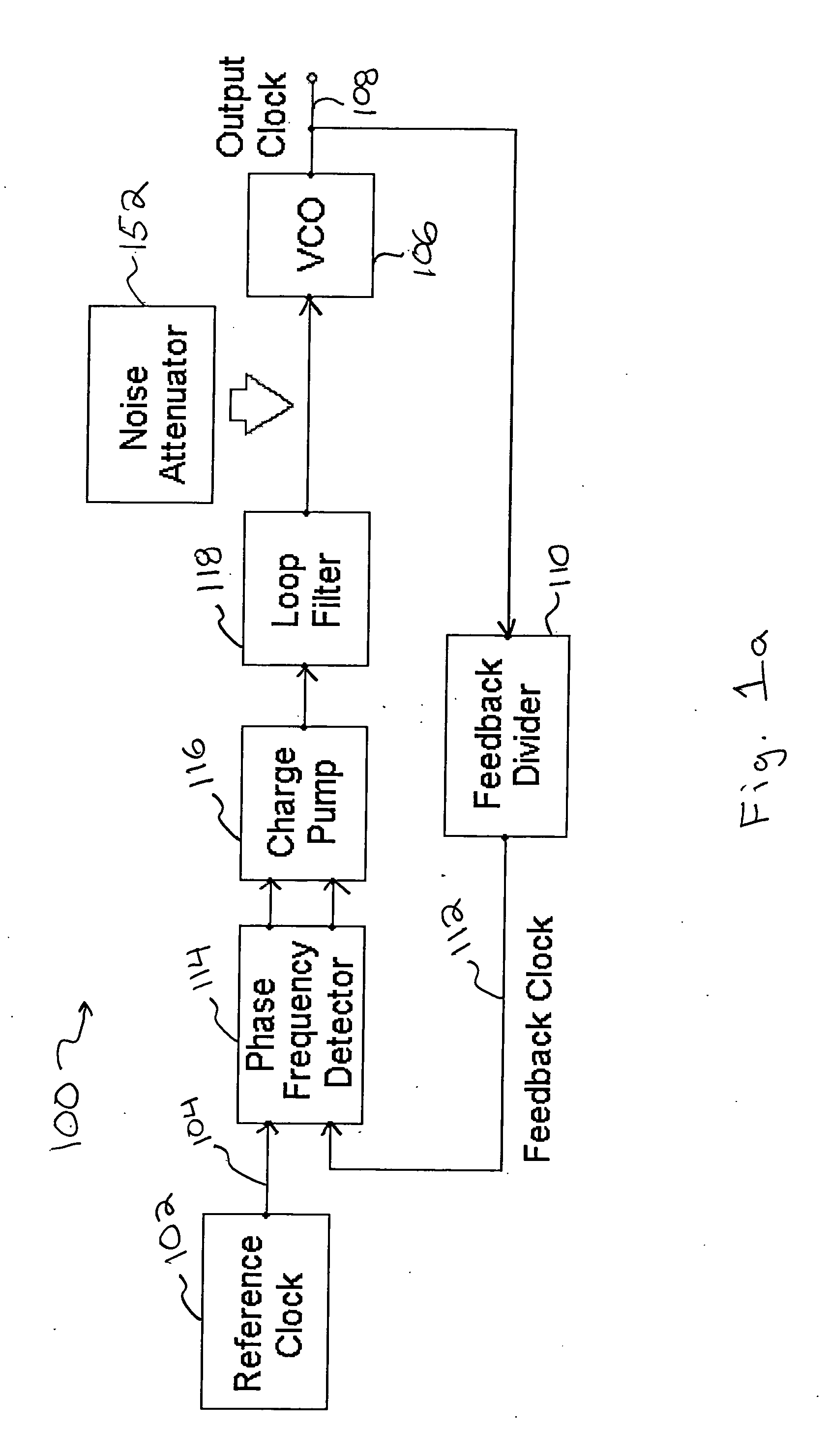
Method and apparatus to reduce the jitter in wideband PLL frequency synthesizers using noise attenuation
InactiveUS20060141963A1Reduce noise contributionReduce phase noisePulse automatic controlTransmissionMOSFETCapacitance
A noise attenuator loop filter for PLL applications that allows a full on-chip integration of the loop filter capacitors, while ensuring a low output clock phase noise (jitter) is disclosed. A voltage attenuator (A) is inserted between the loop filter (passive or active) and the controlled oscillator. The attenuator attenuates the noise coming from the loop filter. In case of a passive RC filter, the series resistor noise power is attenuated by A2 times, allowing the usage of a resistor that is A2 times larger and therefore the loop filter capacitors result A2 times smaller (easy to integrate on-chip). The relatively low value capacitor allows the usage of thick-oxide accumulation-mode MOSFET capacitors that take a reasonable low area, have a good linearity, are isolated from the substrate by the grounded N-well, and have negligible gate leakage current. Several embodiments of the noise attenuator are proposed for different practical applications: clock generation for digital circuits, frequency translation, low or high supply voltage, narrow or wide frequency range, processes with or without isolated well devices, processes with or without polysilicon resistors, and medium or high reference spurs rejection.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Gate-all-around type semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080079041A1Reduce leakage currentDistanceNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate leakage currentNanowire
The gate-all-around (GAA) type semiconductor device may include source / drain layers, a nanowire channel, a gate electrode and an insulation layer pattern. The source / drain layers may be disposed at a distance in a first direction on a semiconductor substrate. The nanowire channel may connect the source / drain layers. The gate electrode may extend in a second direction substantially perpendicular to the first direction. The gate electrode may have a height in a third direction substantially perpendicular to the first and second directions and may partially surround the nanowire channel. The insulation layer pattern may be formed between and around the source / drain layers on the semiconductor substrate and may cover the nanowire channel and a portion of the gate electrode. Thus, a size of the gate electrode may be reduced, and / or a gate induced drain leakage (GIDL) and / or a gate leakage current may be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
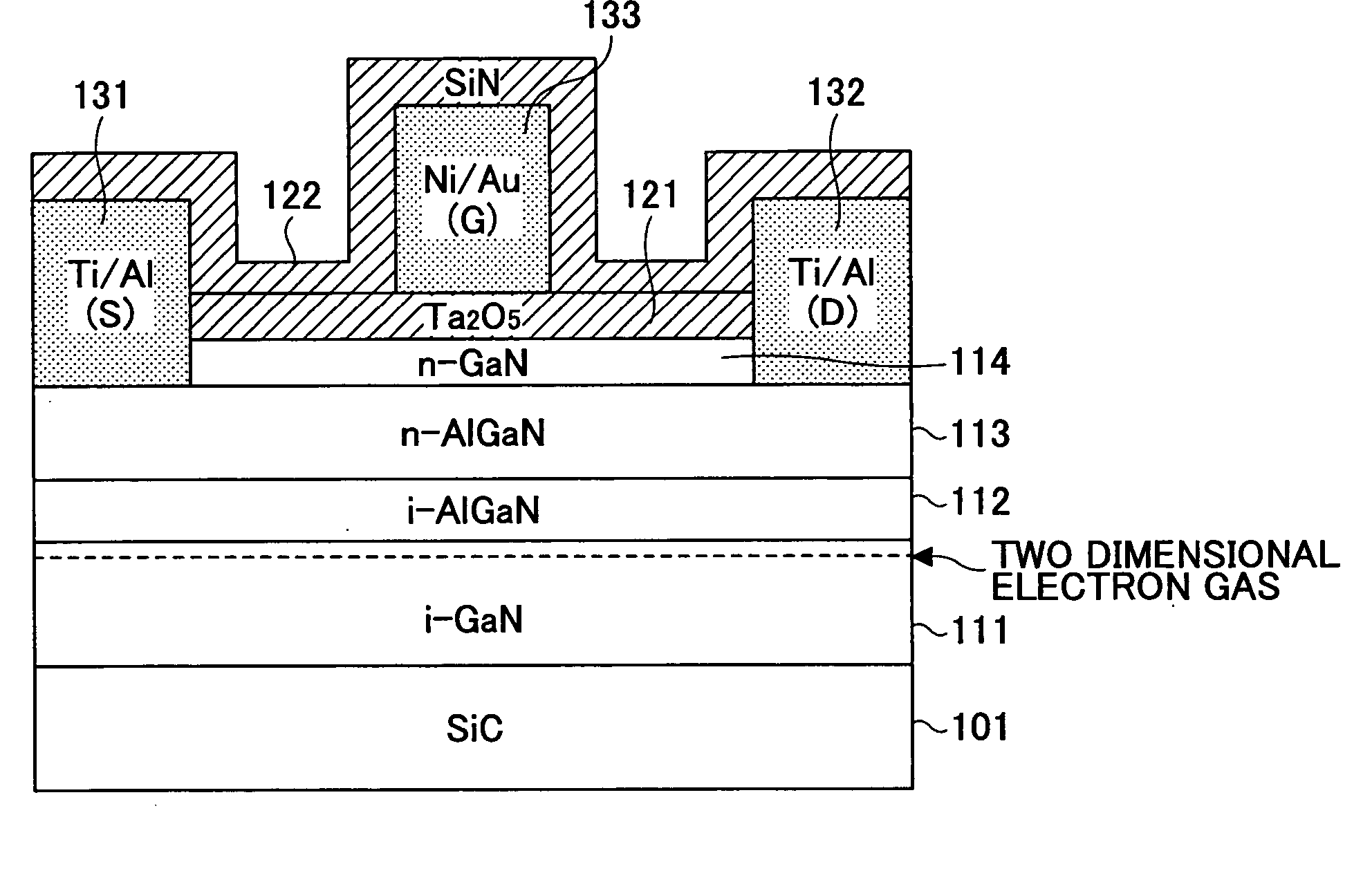
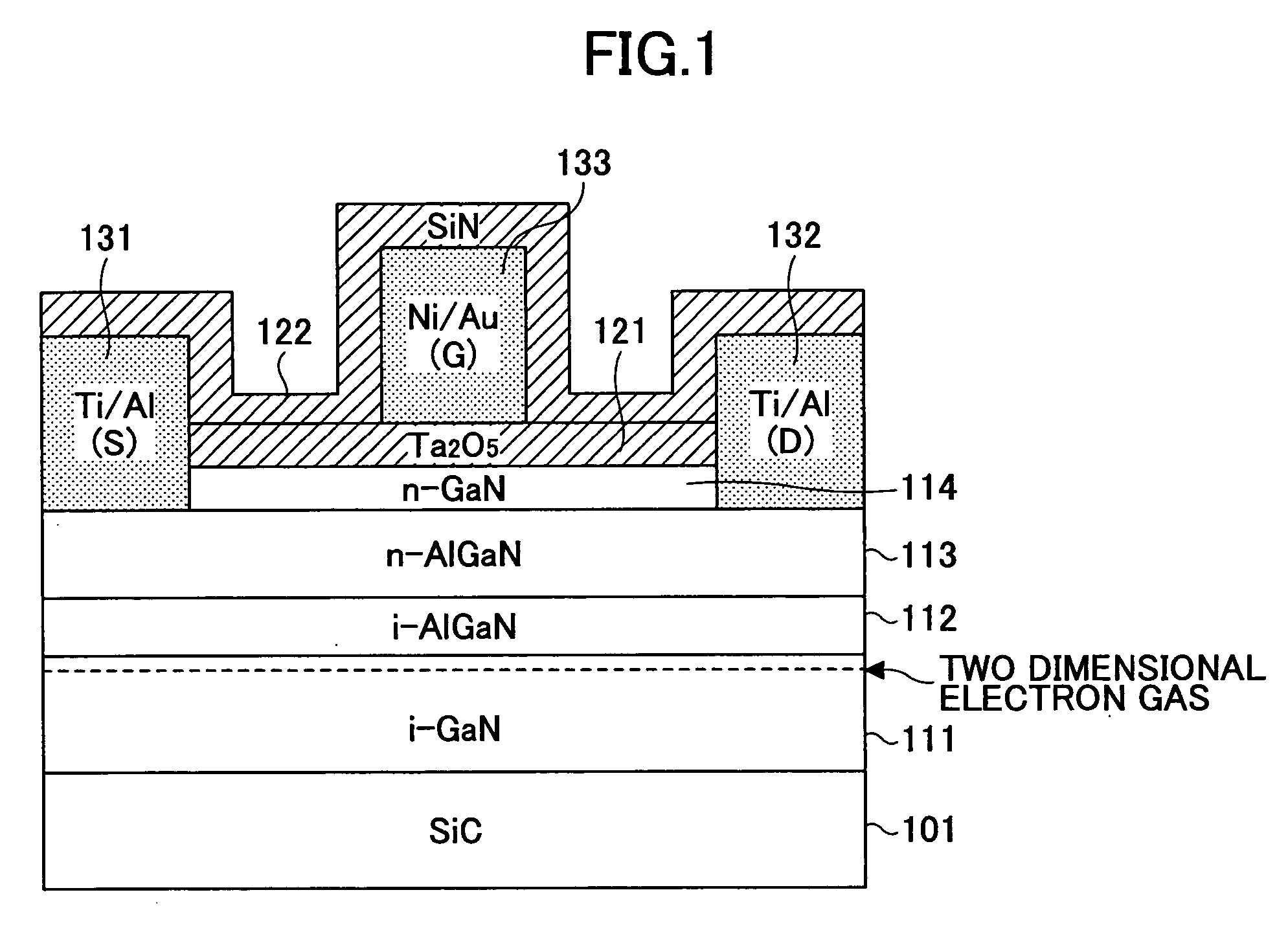
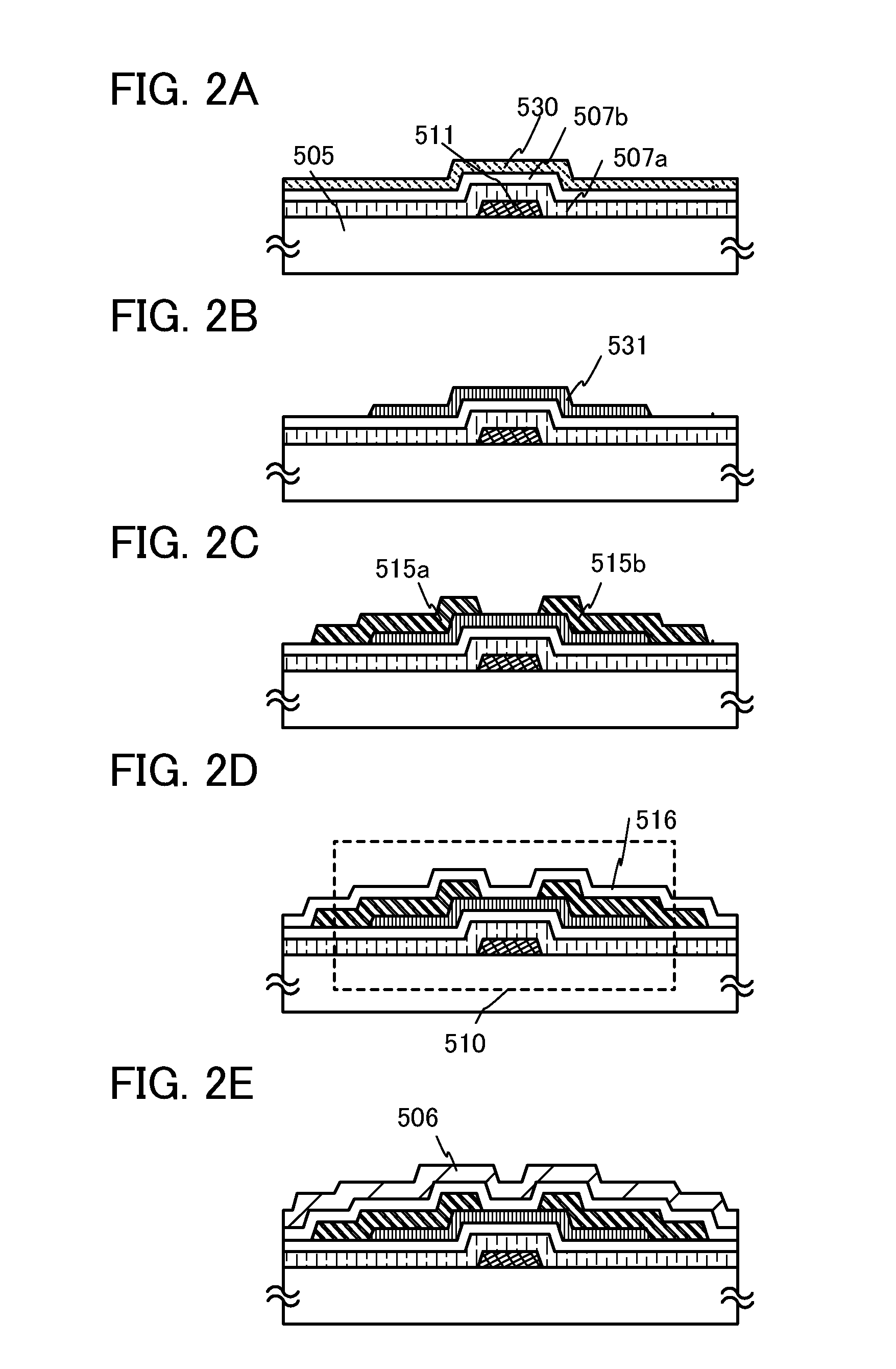
Semiconductor device and production method thereof
InactiveUS20060197107A1Reduce gate leakage currentSimple interfaceSemiconductor devicesGate leakage currentDevice material
A semiconductor device formed from a III-V nitride family semiconductor is disclosed that has a reduced gate leakage current and good interface characteristics between the III-V nitride family semiconductor and a gate insulating film. The semiconductor device includes a semiconductor layer formed from the III-V nitride family semiconductor, a gate insulating film on the semiconductor layer, and a gate electrode on the gate insulating film. The gate insulating film is formed from one of a tantalum oxide, a hafnium oxide, a hafnium aluminum oxide, a lanthanum oxide, and a yttrium oxide.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Vertical semiconductor device with tunnel insulator in current path controlled by gate electrode
It is an object of the present invention to provides a field effect transistor with extremely low leakage current. It is another object of the invention to provide a semiconductor memory device having an excellent information holding characteristic. It is a further object of the invention to provide a method for manufacturing in a simple manner a novel field effect transistor or semiconductor memory device with extremely low leakage current. According to a typical basic configuration of the present invention, a thin insulating film is inserted in a vertically disposed Schottky junction to form source and drain electrodes and a tunnel of the insulating film in the junction is controlled by a gate electrode. The gate electrode is disposed on each of both sides of a vertical channel, permitting a field effect to be exerted effectively on the junction, whereby a junction leakage in an OFF state can be made extremely low.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
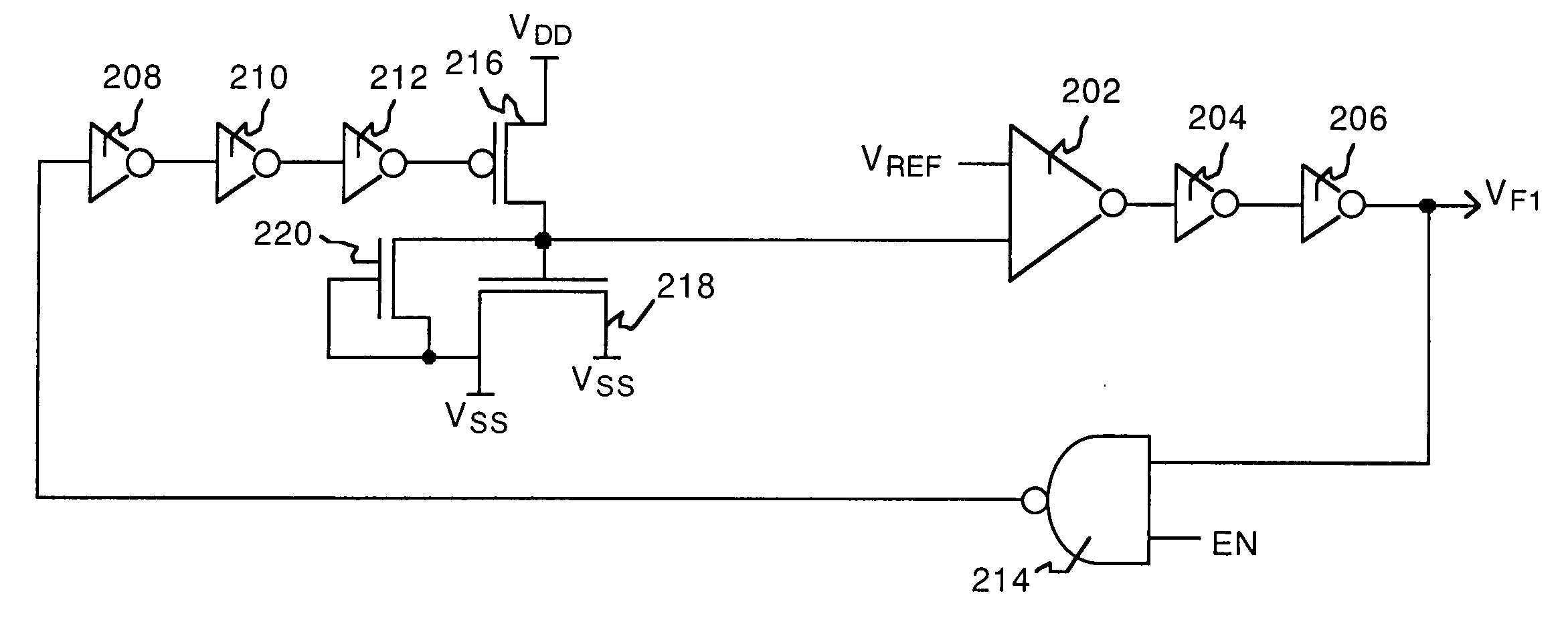
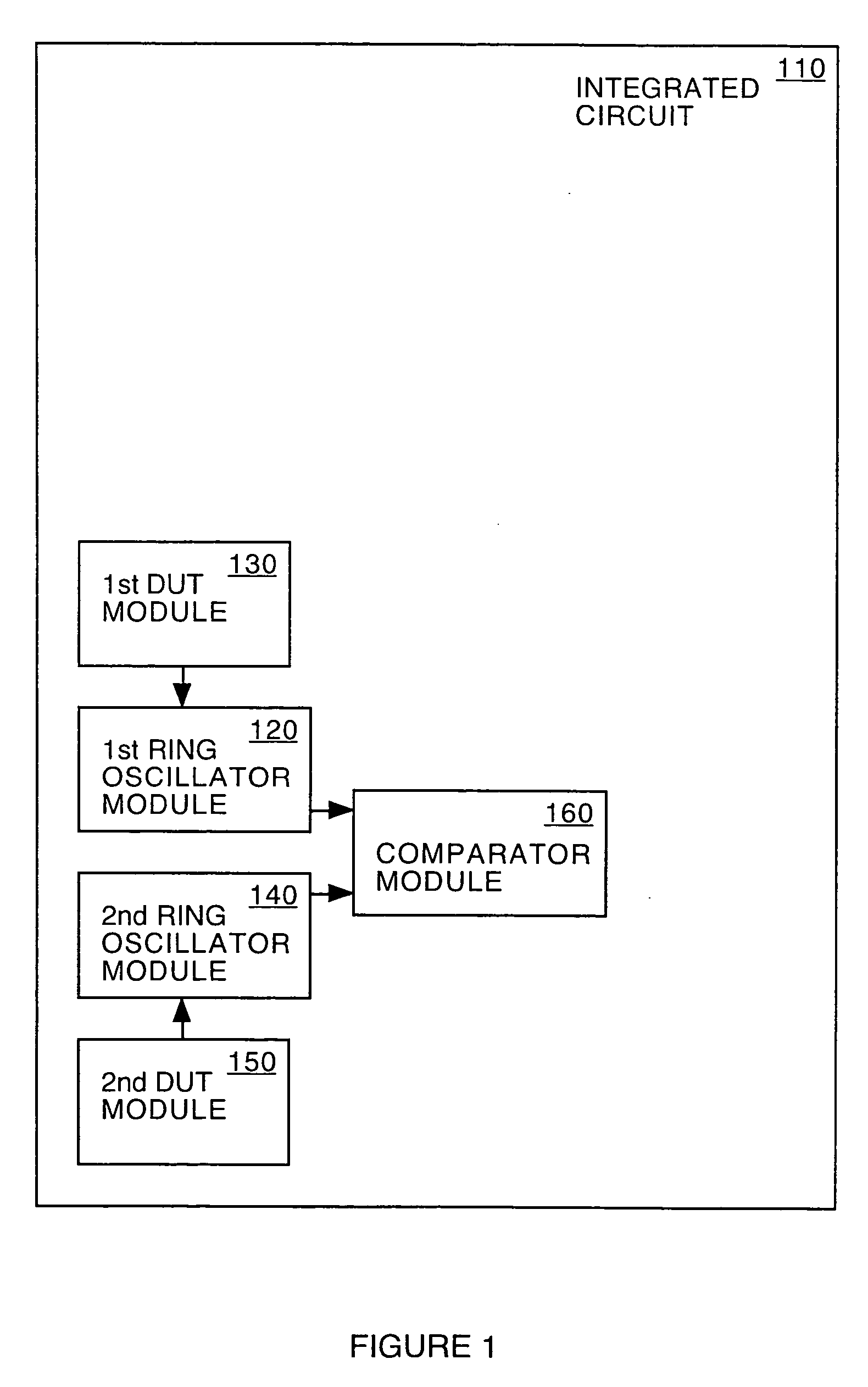
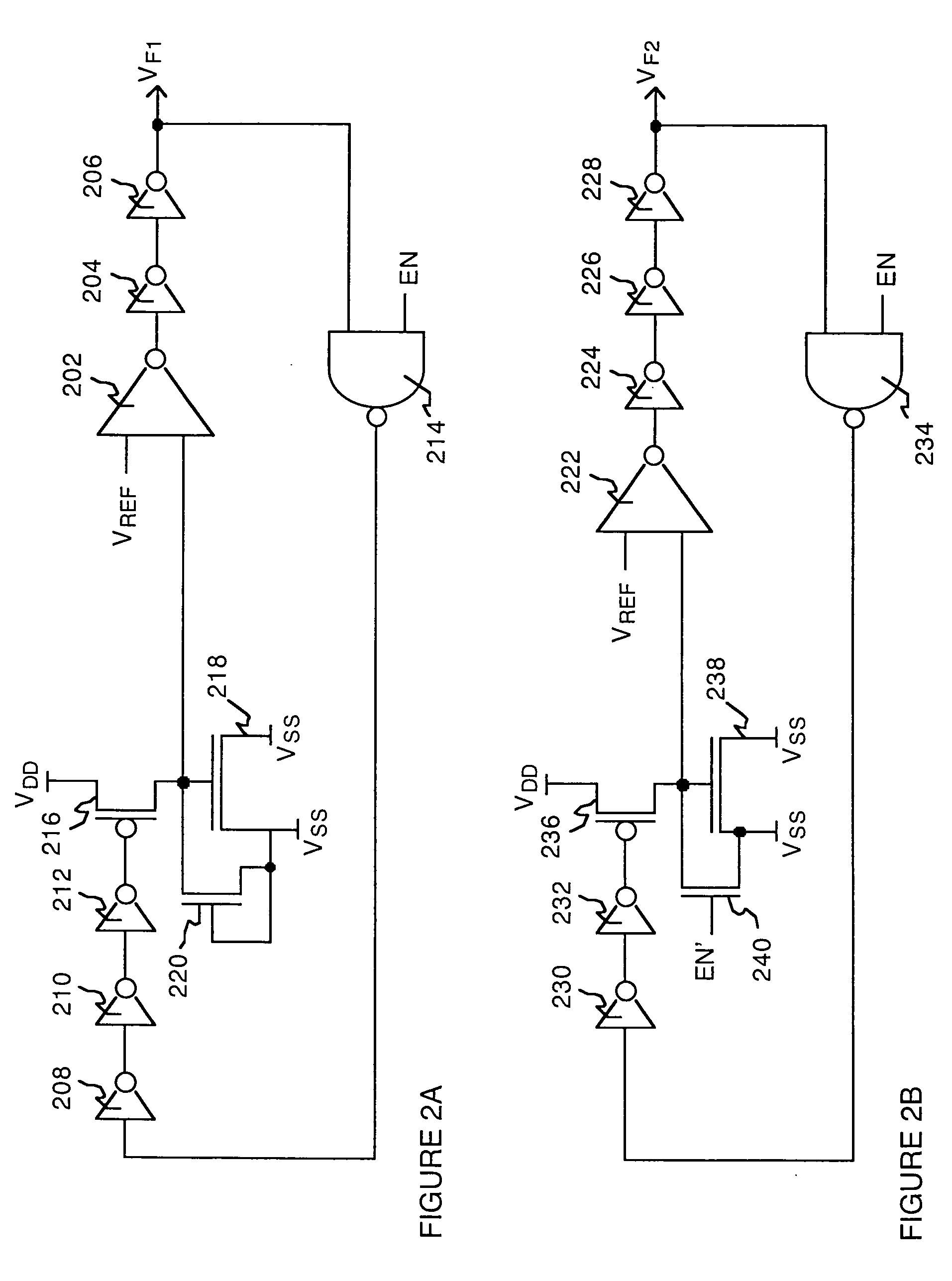
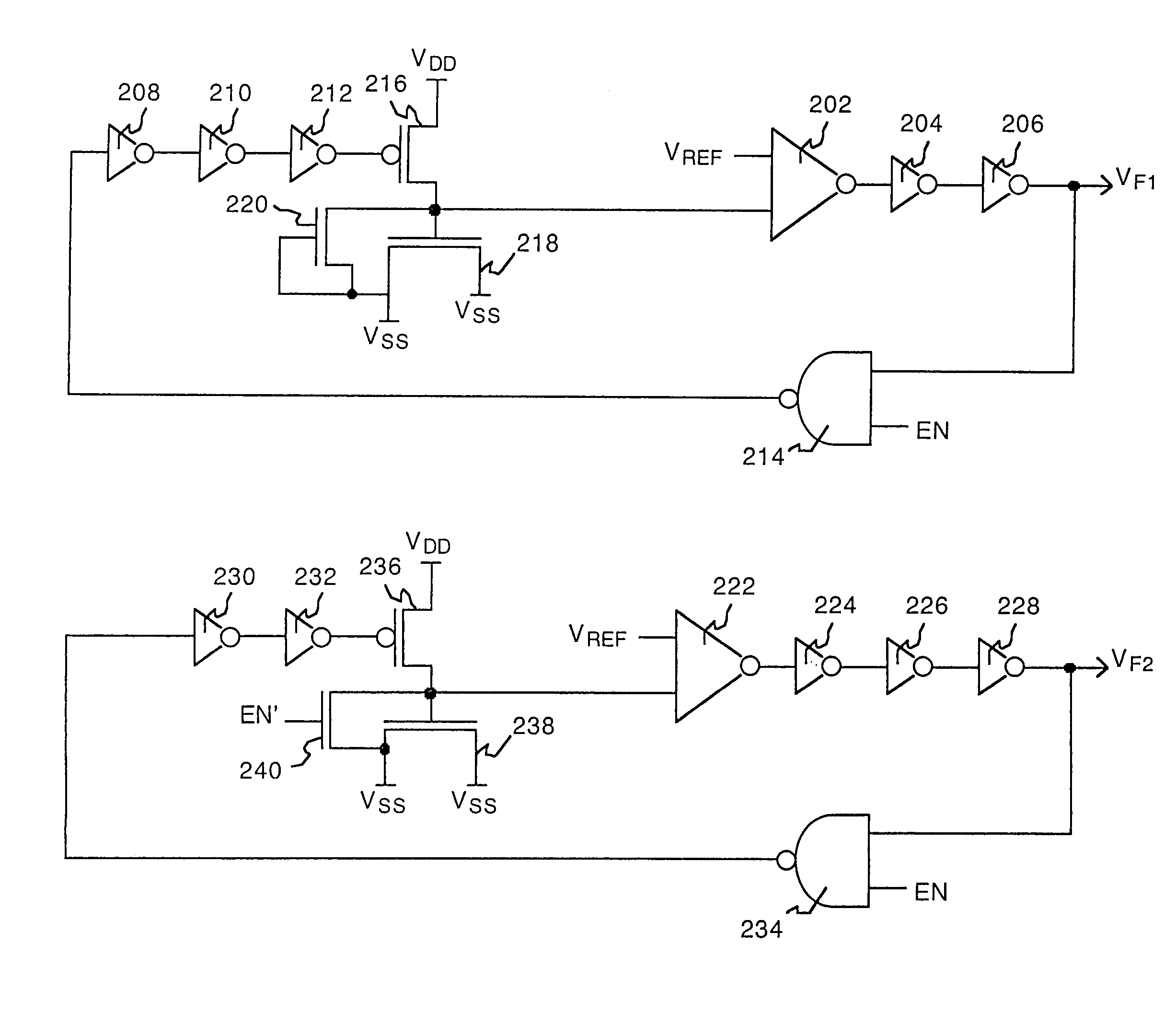
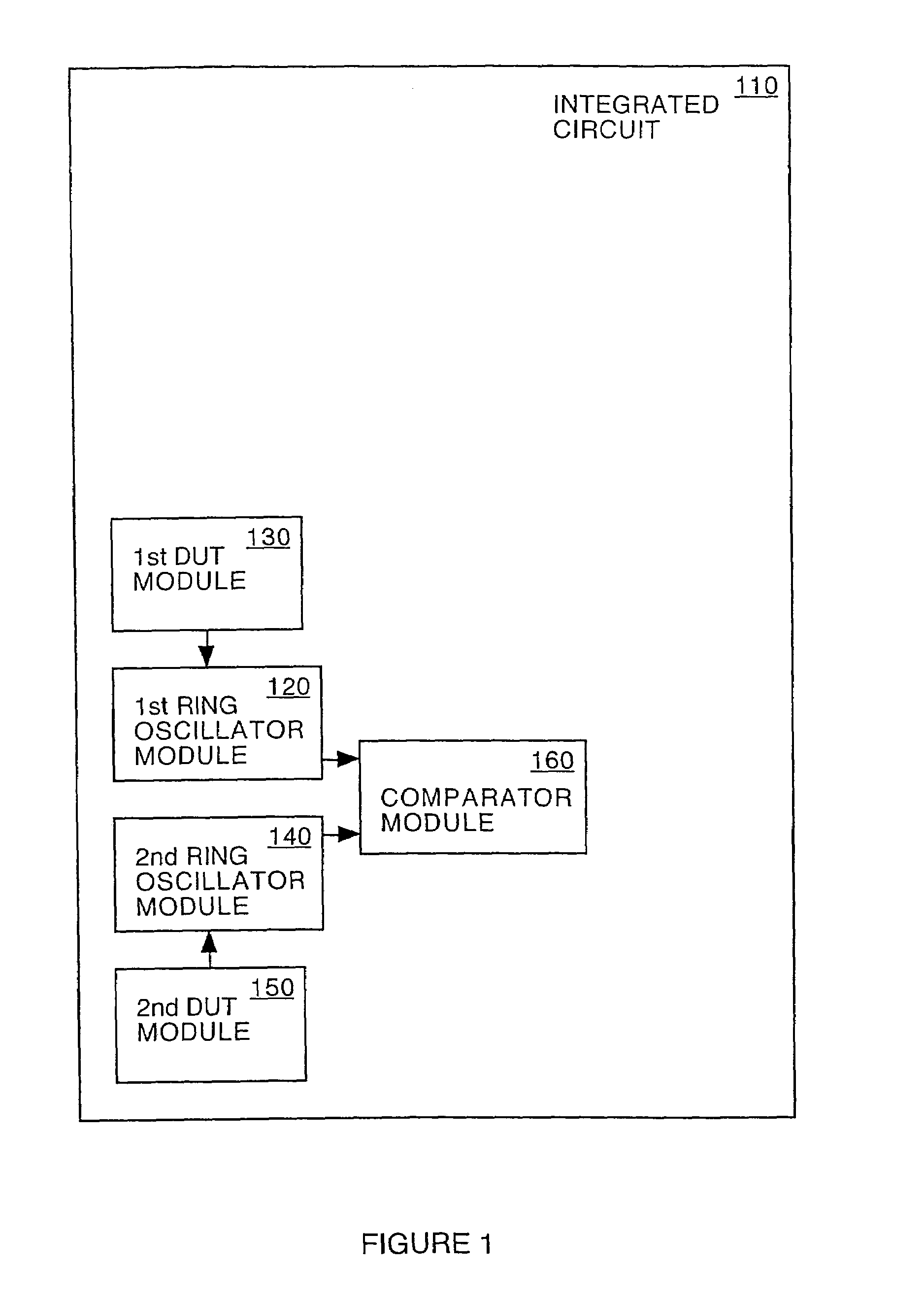
System and method for measuring time dependent dielectric breakdown with a ring oscillator
InactiveUS20050212547A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectricityGate leakage current
An integrated circuit, in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, includes a first device under test (DUT) module coupled to a first ring oscillator module and a second DUT module coupled to a second ring oscillator module. A dielectric layer of the first DUT is stressed during a first mode, thereby causing time dependent dielectric breakdown in the first dielectric layer. A dielectric layer of the second DUT is maintained as a reference. The operating frequency of the first ring oscillator module, during a second mode, is a function of a gate leakage current of the stressed dielectric layer. The operating frequency of the second ring oscillator module, during the second mode, is a function of a gate leakage current the reference dielectric layer. The integrated circuit may also include a comparator module for generating an output signal as a function of a difference between the operating frequency of the first and second ring oscillator modules.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
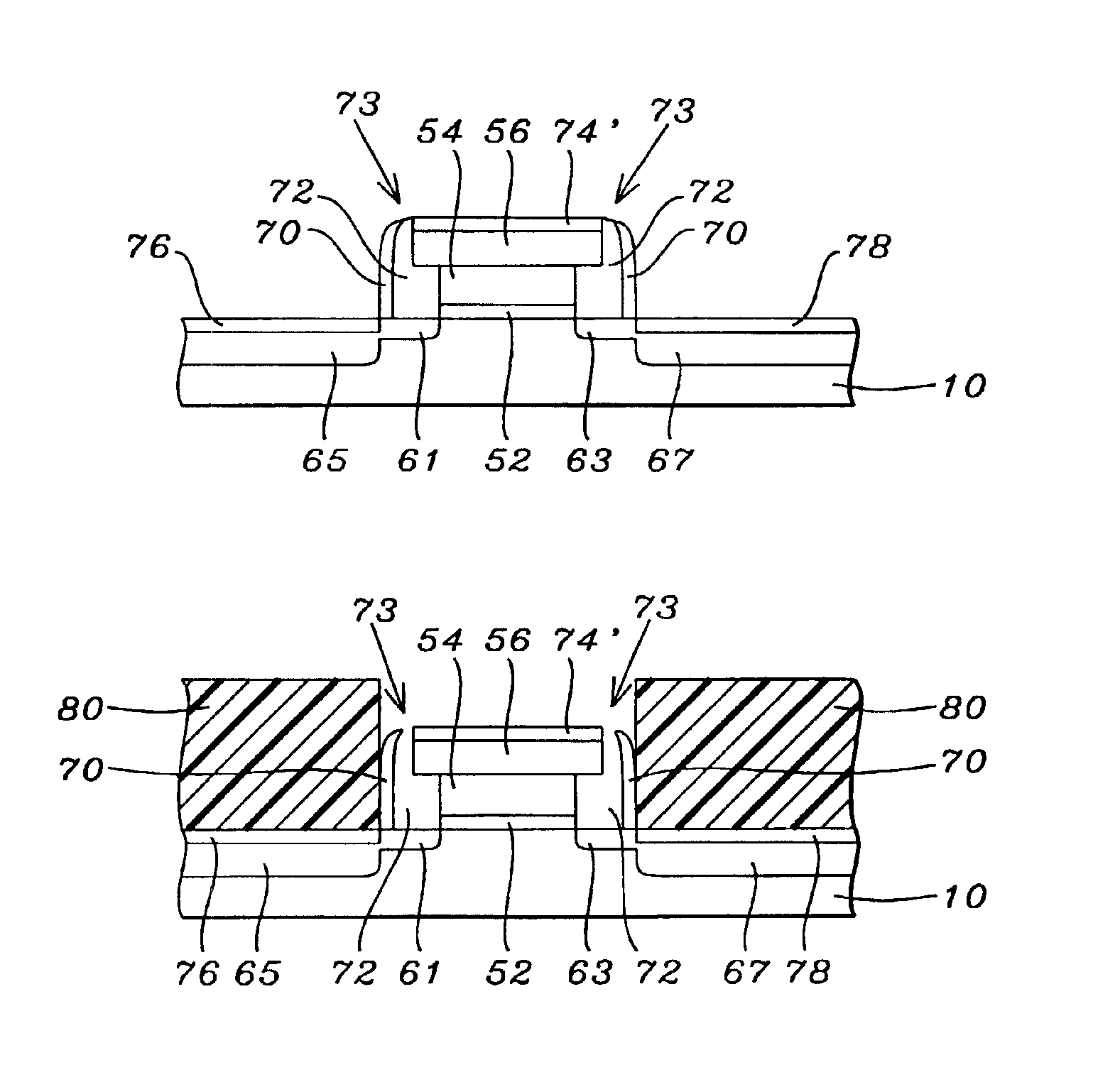
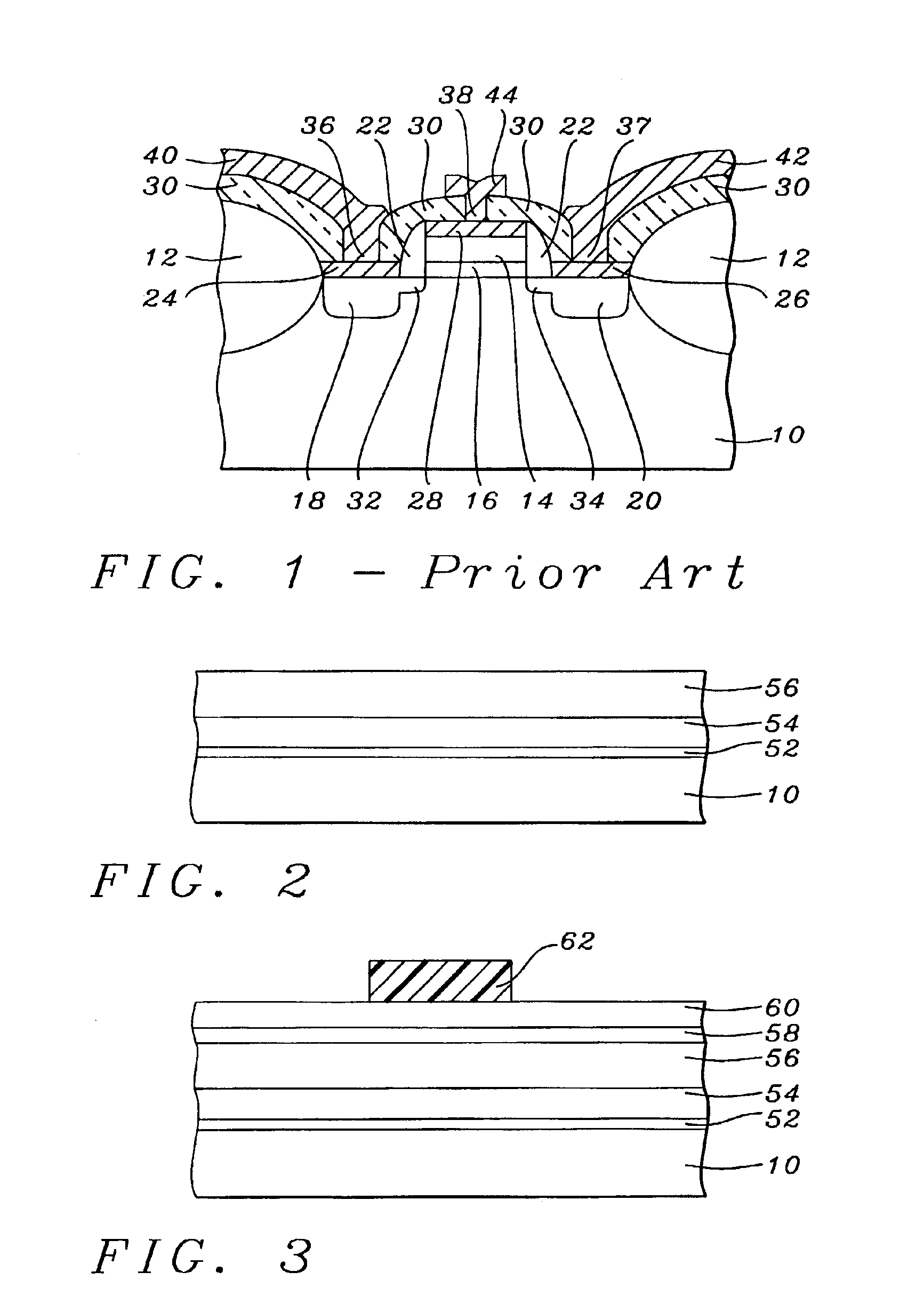
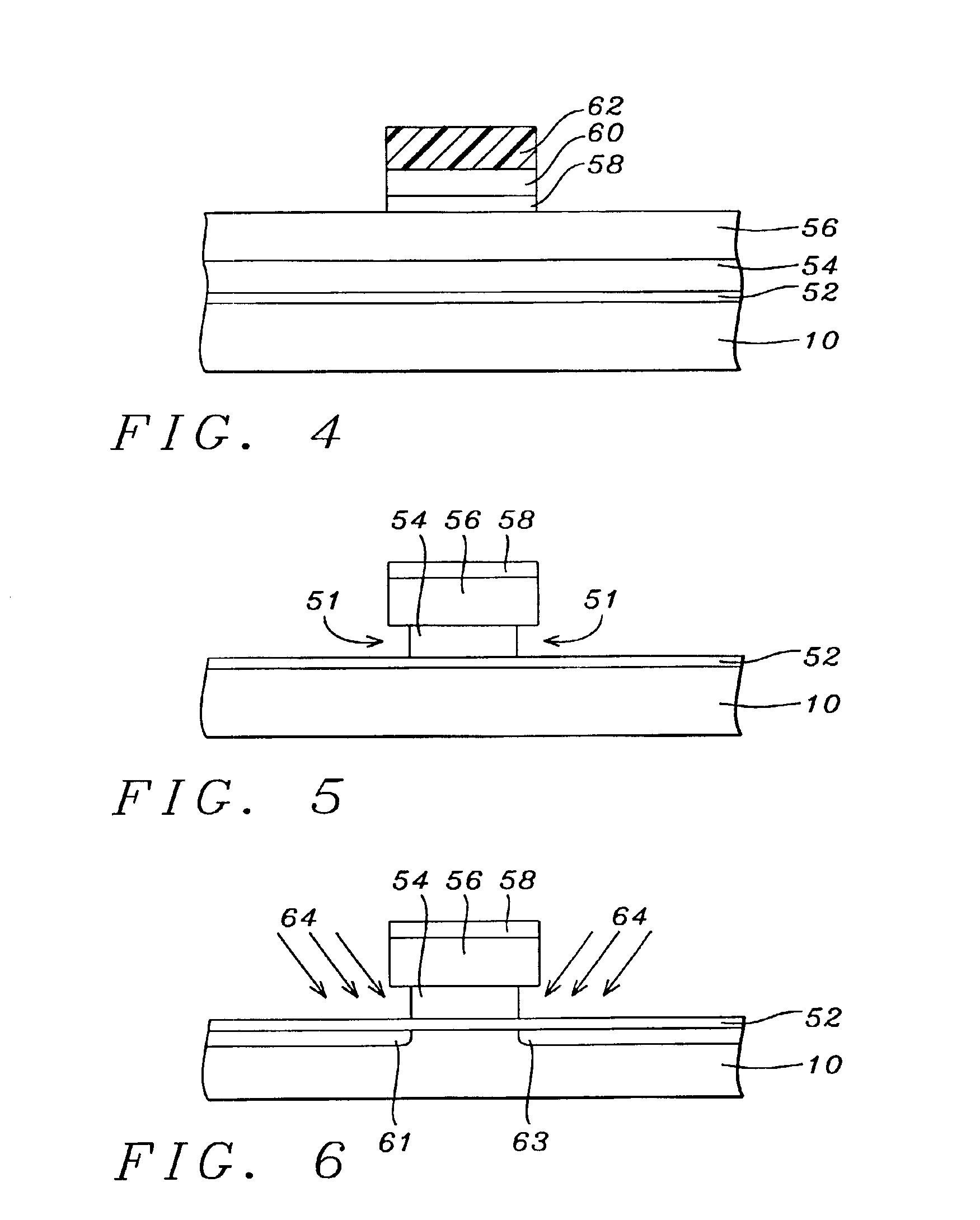
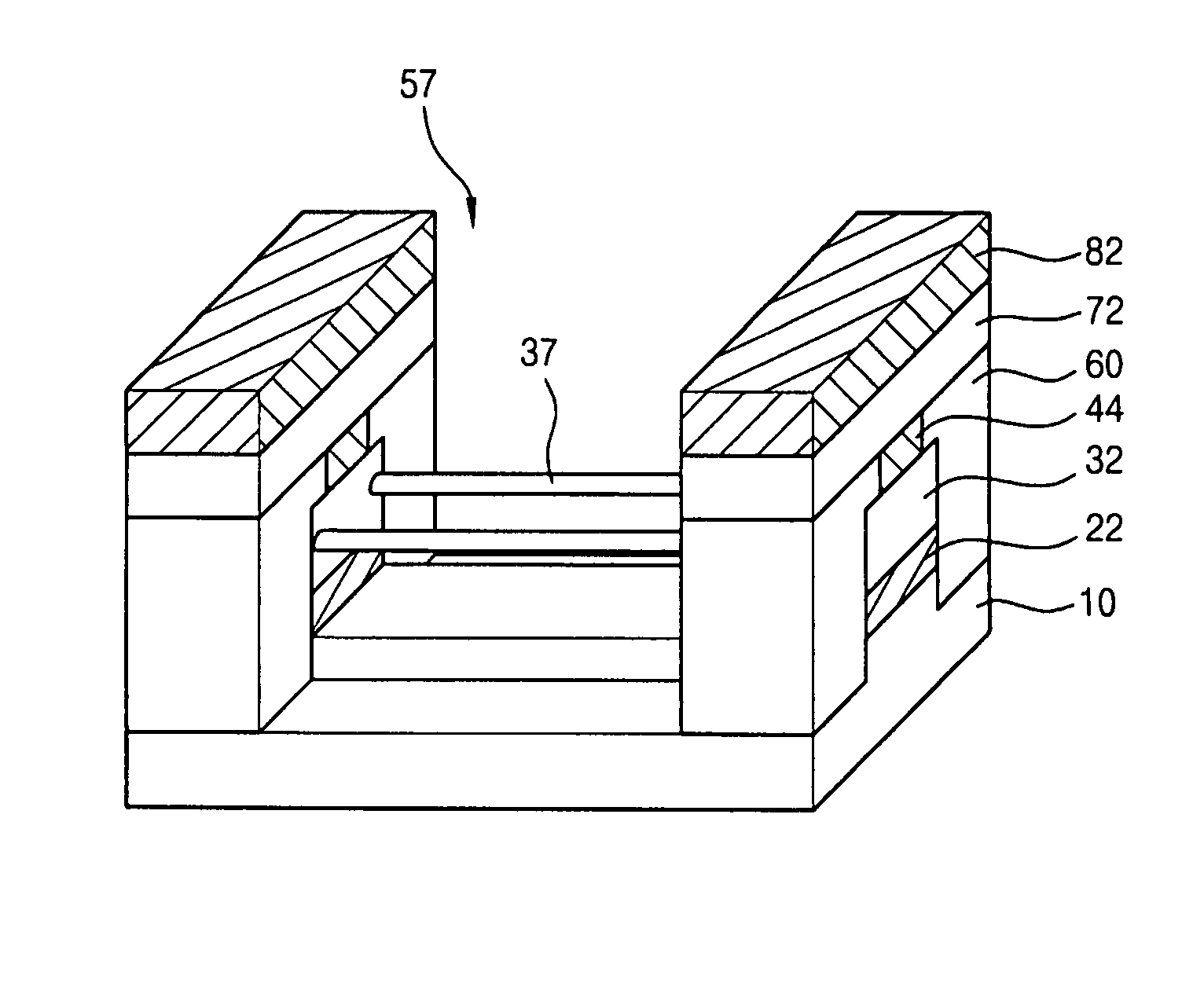
Replacement gate with reduced gate leakage current
InactiveUS20130260549A1Improve performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricSilicon alloy
Replacement gate work function material stacks are provided, which provides a work function about the energy level of the conduction band of silicon. After removal of a disposable gate stack, a gate dielectric layer is formed in a gate cavity. A metallic compound layer including a metal and a non-metal element is deposited directly on the gate dielectric layer. At least one barrier layer and a conductive material layer is deposited and planarized to fill the gate cavity. The metallic compound layer includes a material, which provides, in combination with other layer, a work function about 4.4 eV or less, and can include a material selected from tantalum carbide, metallic nitrides, and a hafnium-silicon alloy. Thus, the metallic compound layer can provide a work function that enhances the performance of an n-type field effect transistor employing a silicon channel. Optionally, carbon doping can be introduced in the channel.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Replacement Gate With Reduced Gate Leakage Current
InactiveUS20130256802A1Improve performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricSilicon alloy
Replacement gate work function material stacks are provided, which provides a work function about the energy level of the conduction band of silicon. After removal of a disposable gate stack, a gate dielectric layer is formed in a gate cavity. A metallic compound layer including a metal and a non-metal element is deposited directly on the gate dielectric layer. At least one barrier layer and a conductive material layer is deposited and planarized to fill the gate cavity. The metallic compound layer includes a material, which provides, in combination with other layer, a work function about 4.4 eV or less, and can include a material selected from tantalum carbide, metallic nitrides, and a hafnium-silicon alloy. Thus, the metallic compound layer can provide a work function that enhances the performance of an n-type field effect transistor employing a silicon channel. Optionally, carbon doping can be introduced in the channel.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
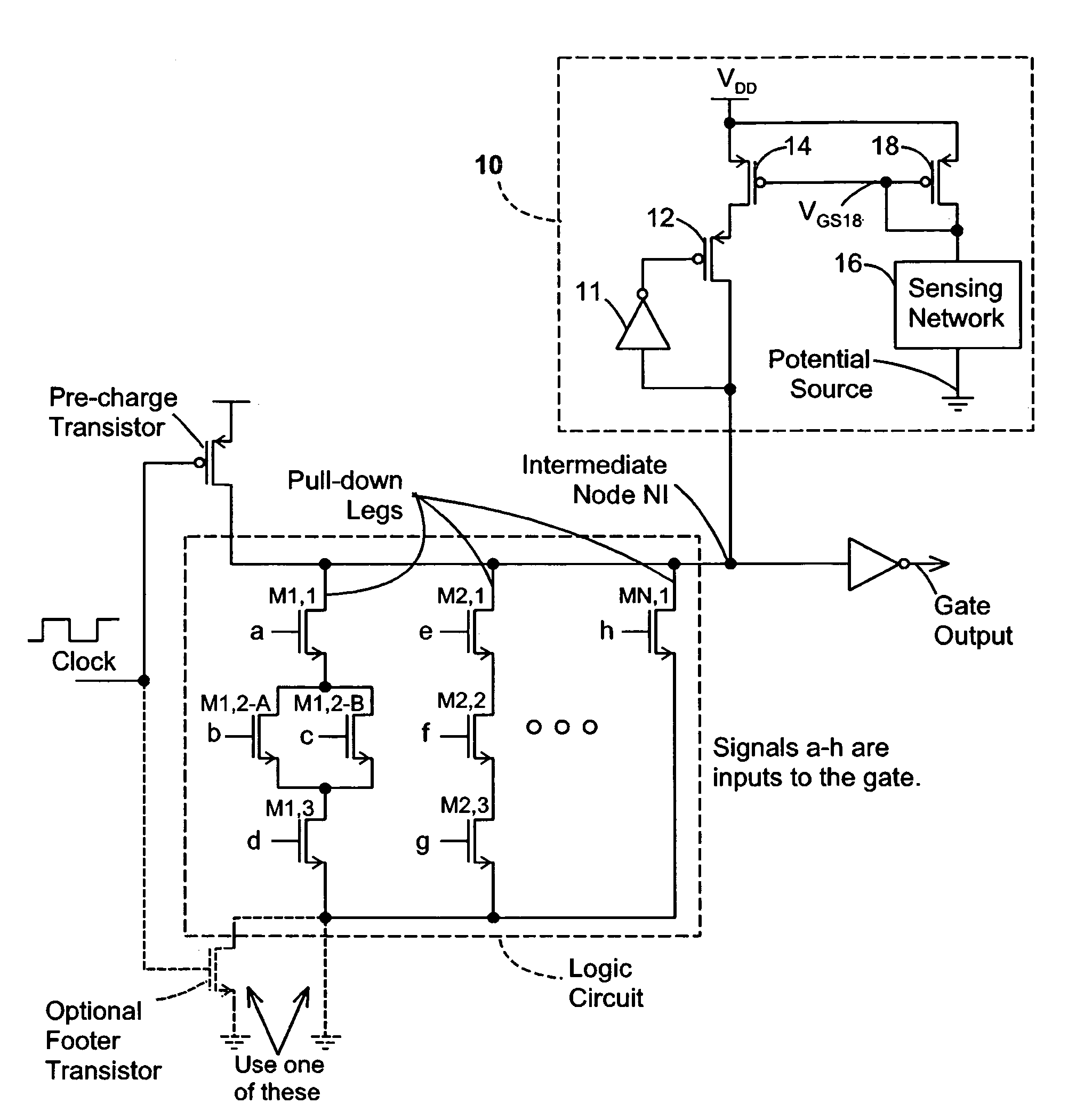
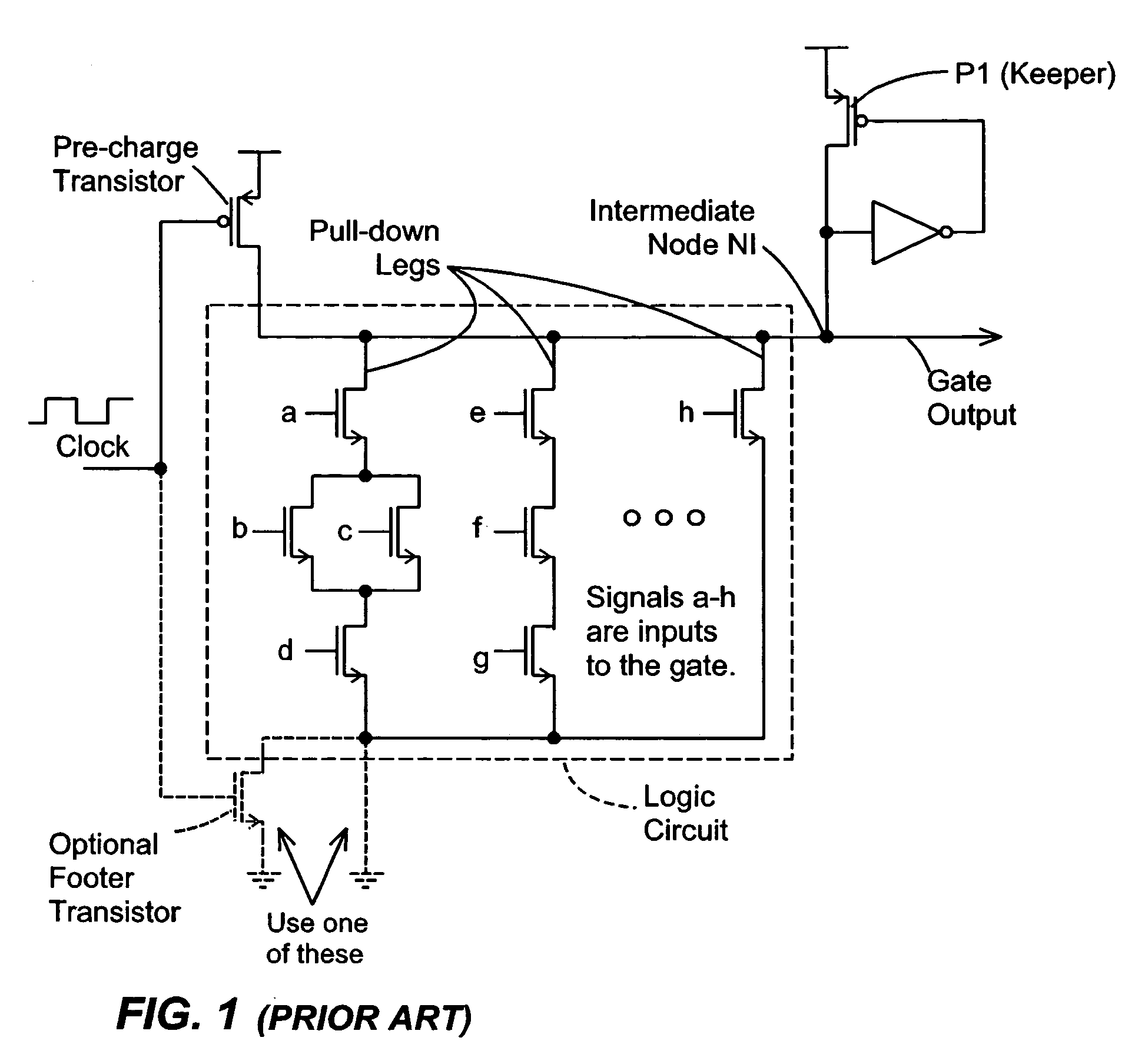
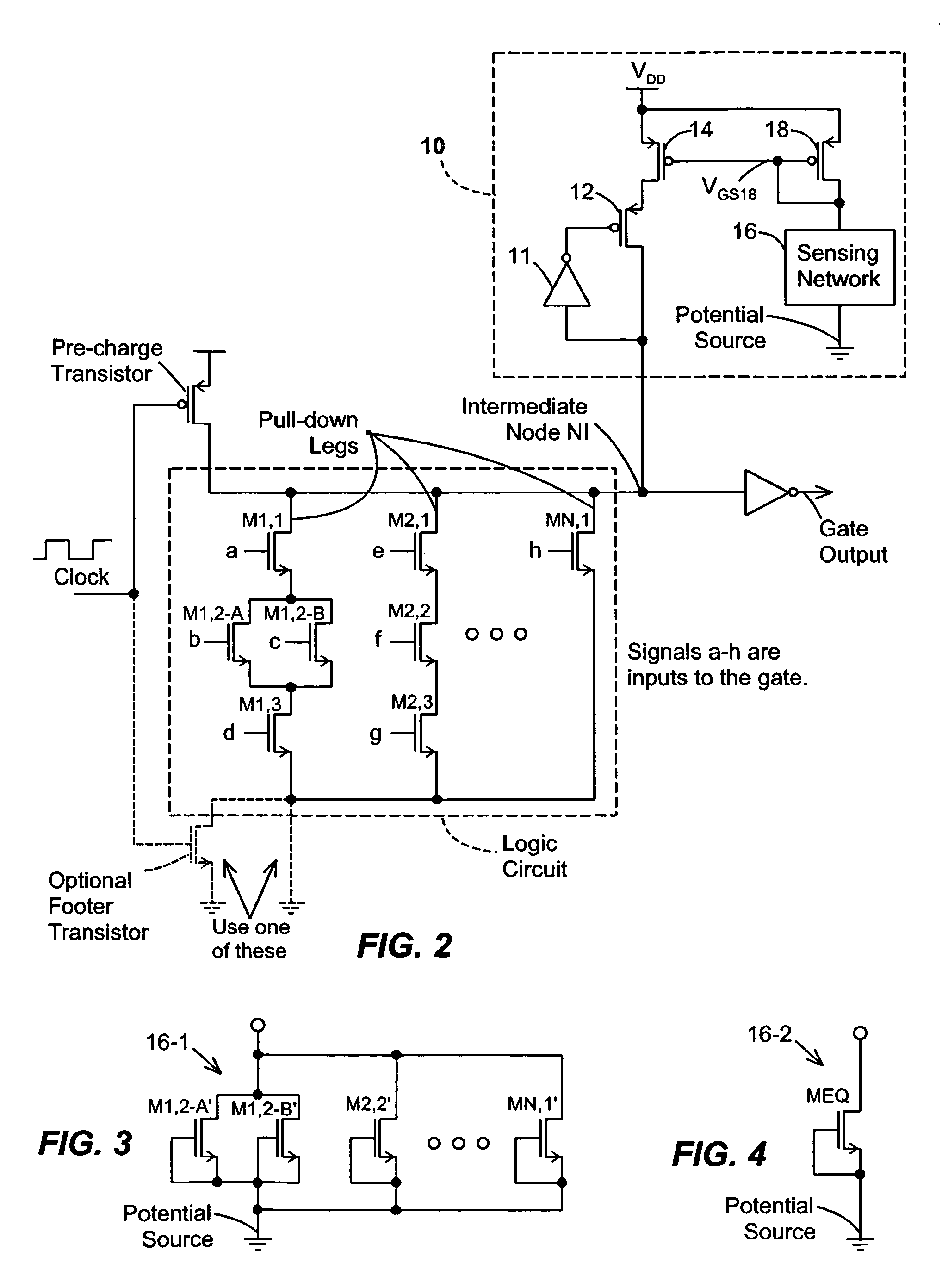
Keeper circuits having dynamic leakage compensation
ActiveUS7256621B2High conductanceMinimize impactPower reduction in field effect transistorsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionGate leakage currentDrain current
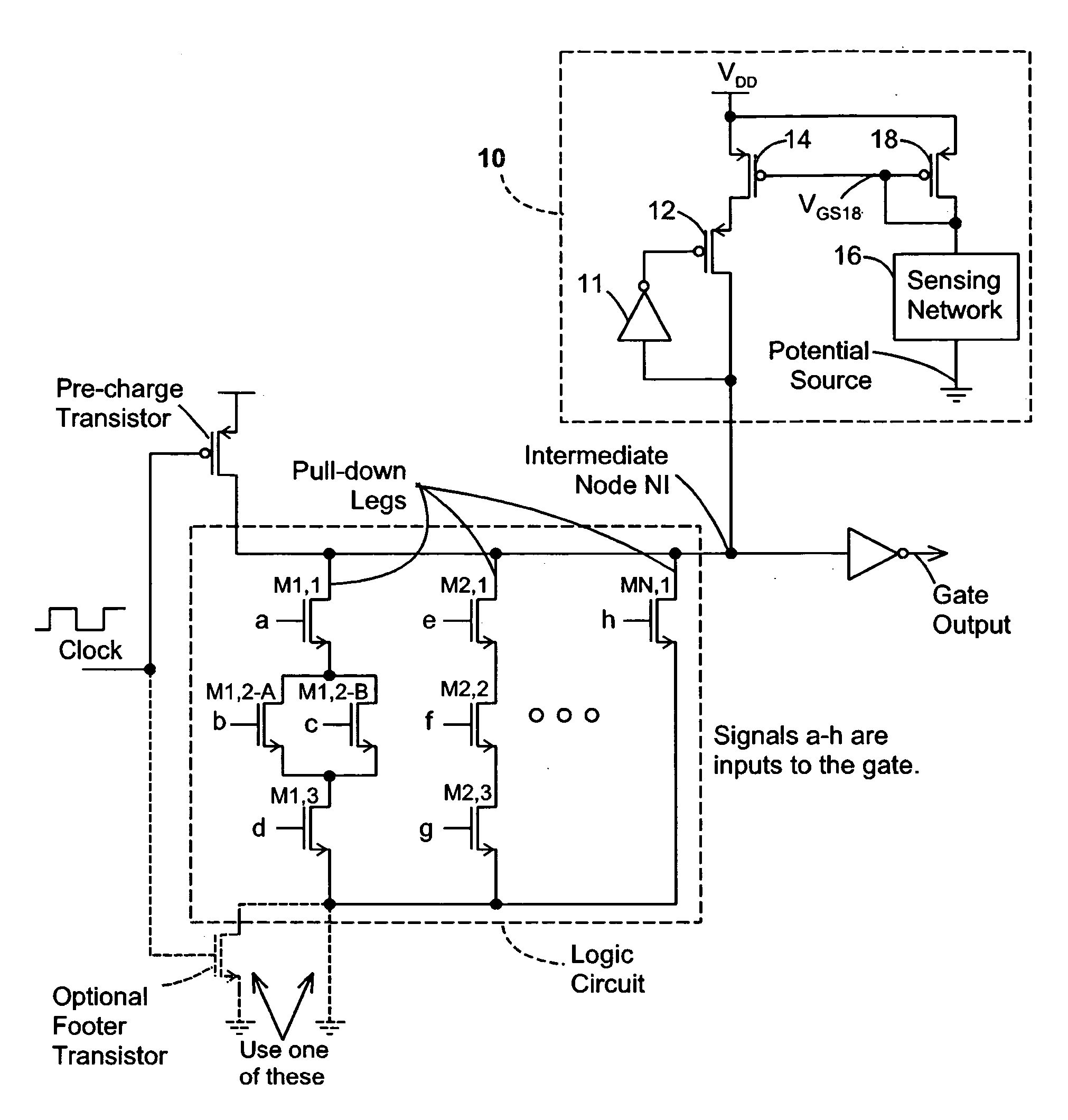
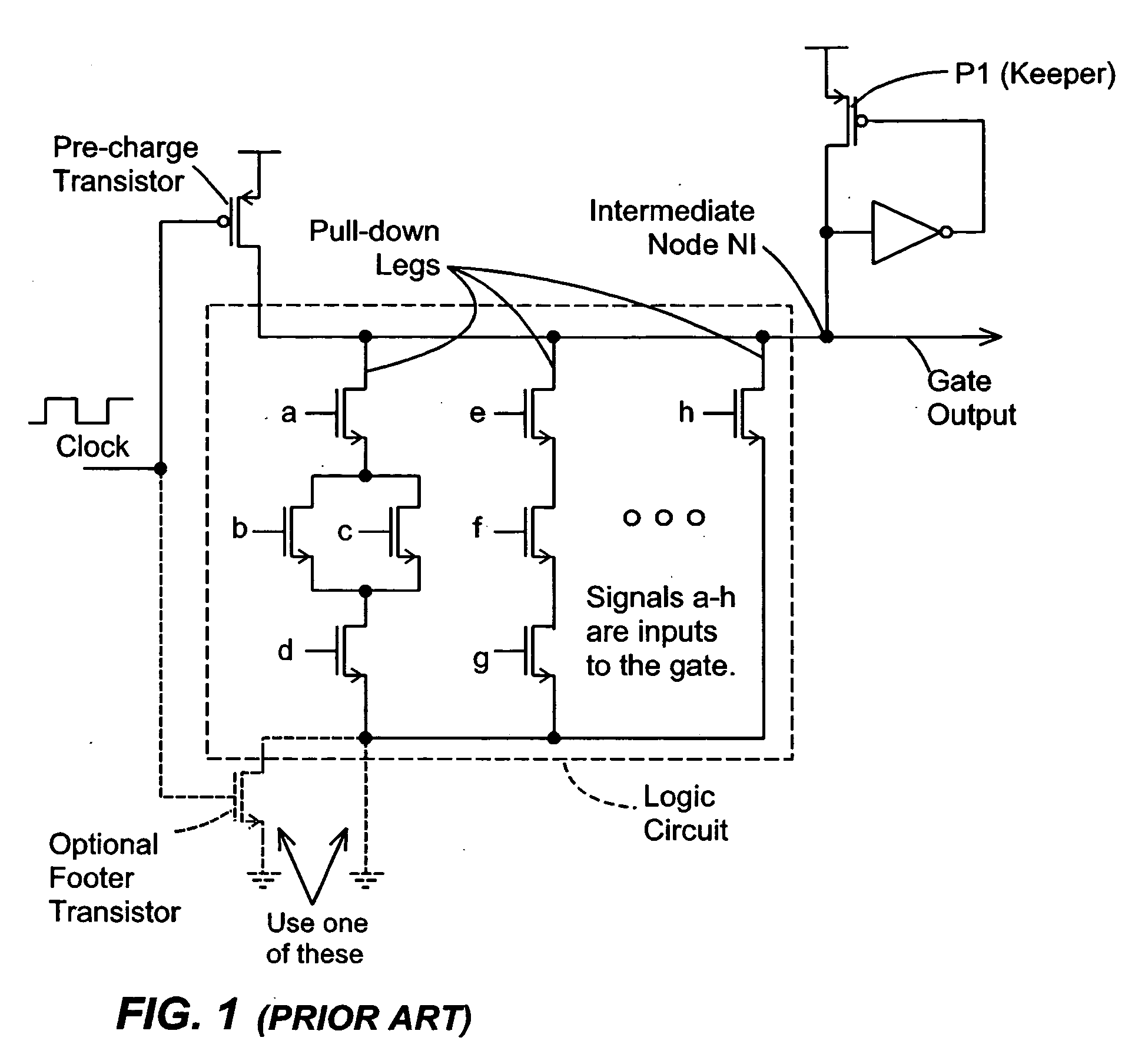
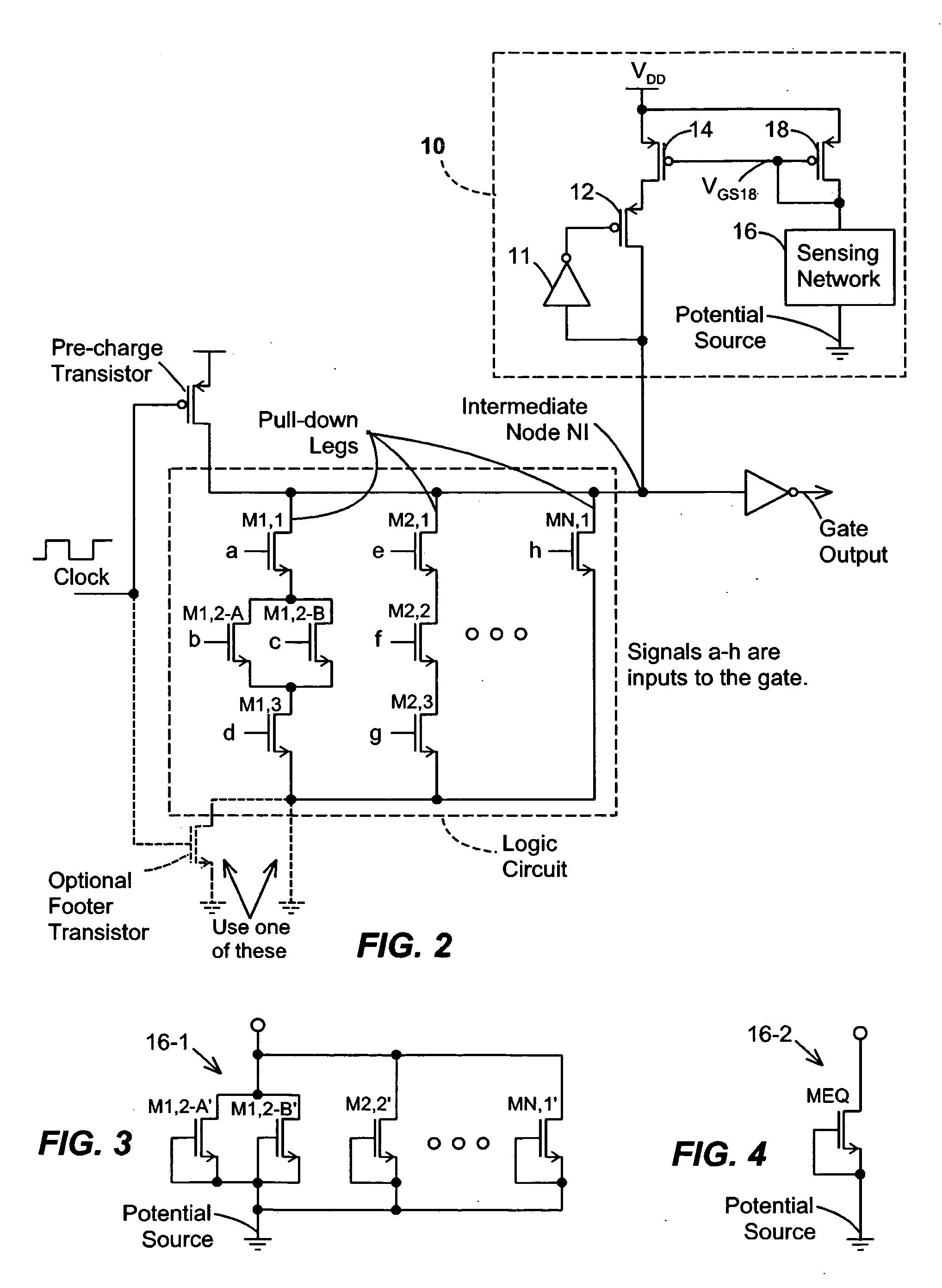
Disclosed are keeper circuits for electronic circuits that selectively maintain the voltage level of an intermediate circuit node at a desired level. In one exemplary embodiment, a keeper transistor either provides current or drains current from the intermediate node to maintain the desired voltage level in response to a signal to do so. The keeper circuit works against a leakage current that either drains current from the node or supplies current to the node. A current-setting transistor is coupled in series with the keeper transistor to set the maximum current through the keeper circuit to a value that is related to this leakage current, preferably tracking the leakage current. With this construction, the current-setting transistor is able to track variations in the leakage current caused by variations in the manufacturing process, and thereby provide dynamic leakage compensation.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Bias circuit linearization and dynamic power control
InactiveUS6882227B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPulse automatic controlEngineeringRadio frequency
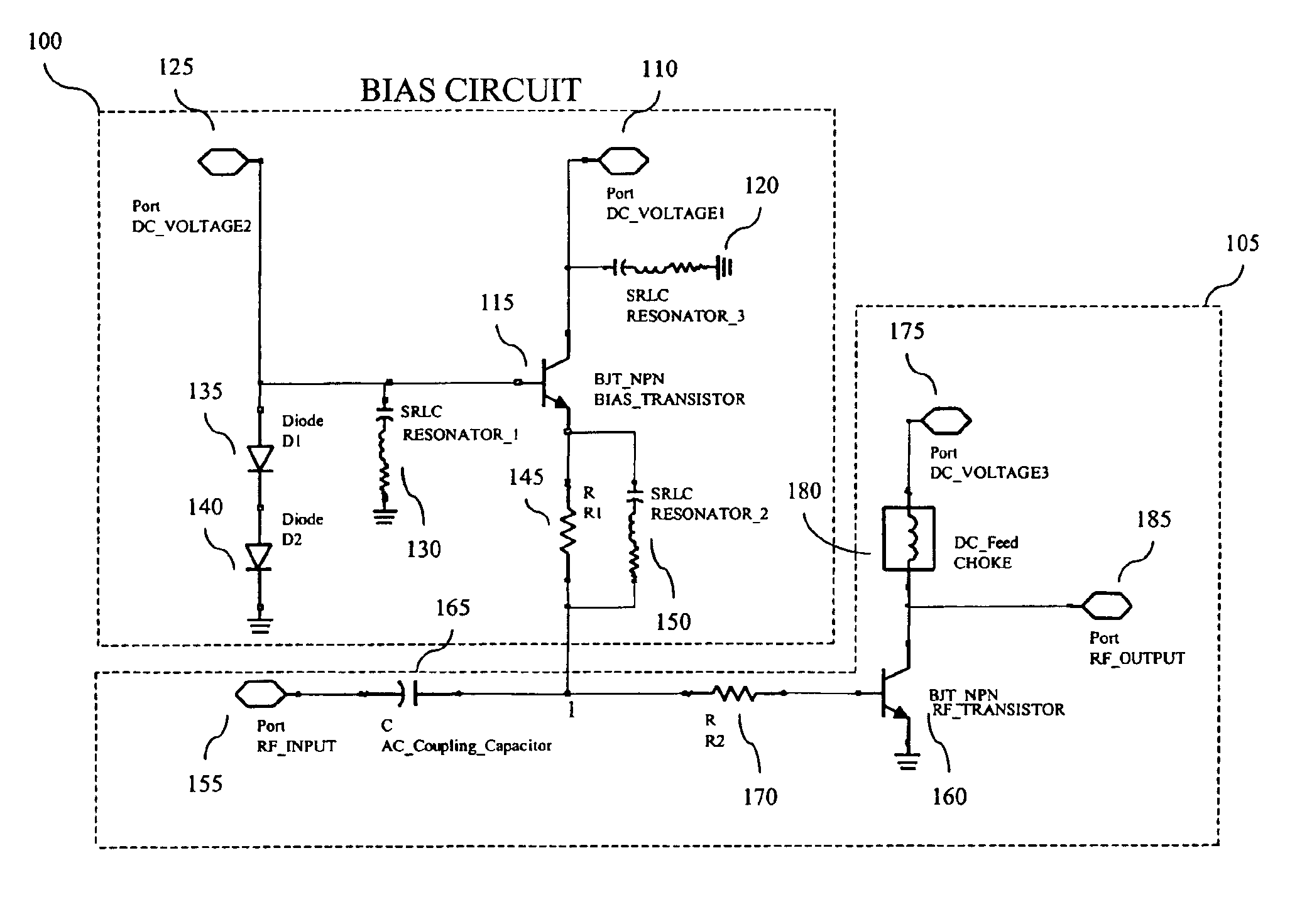
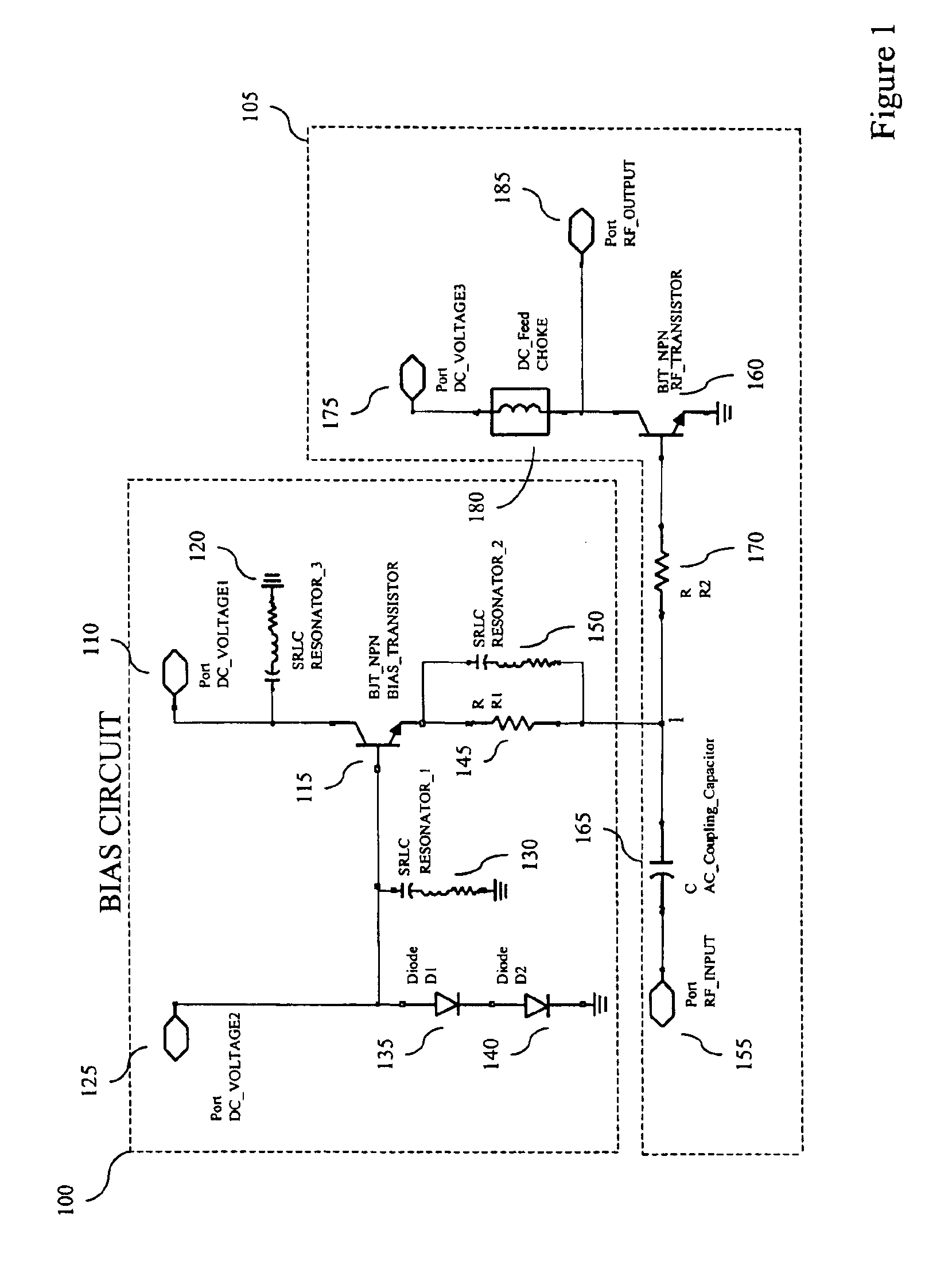
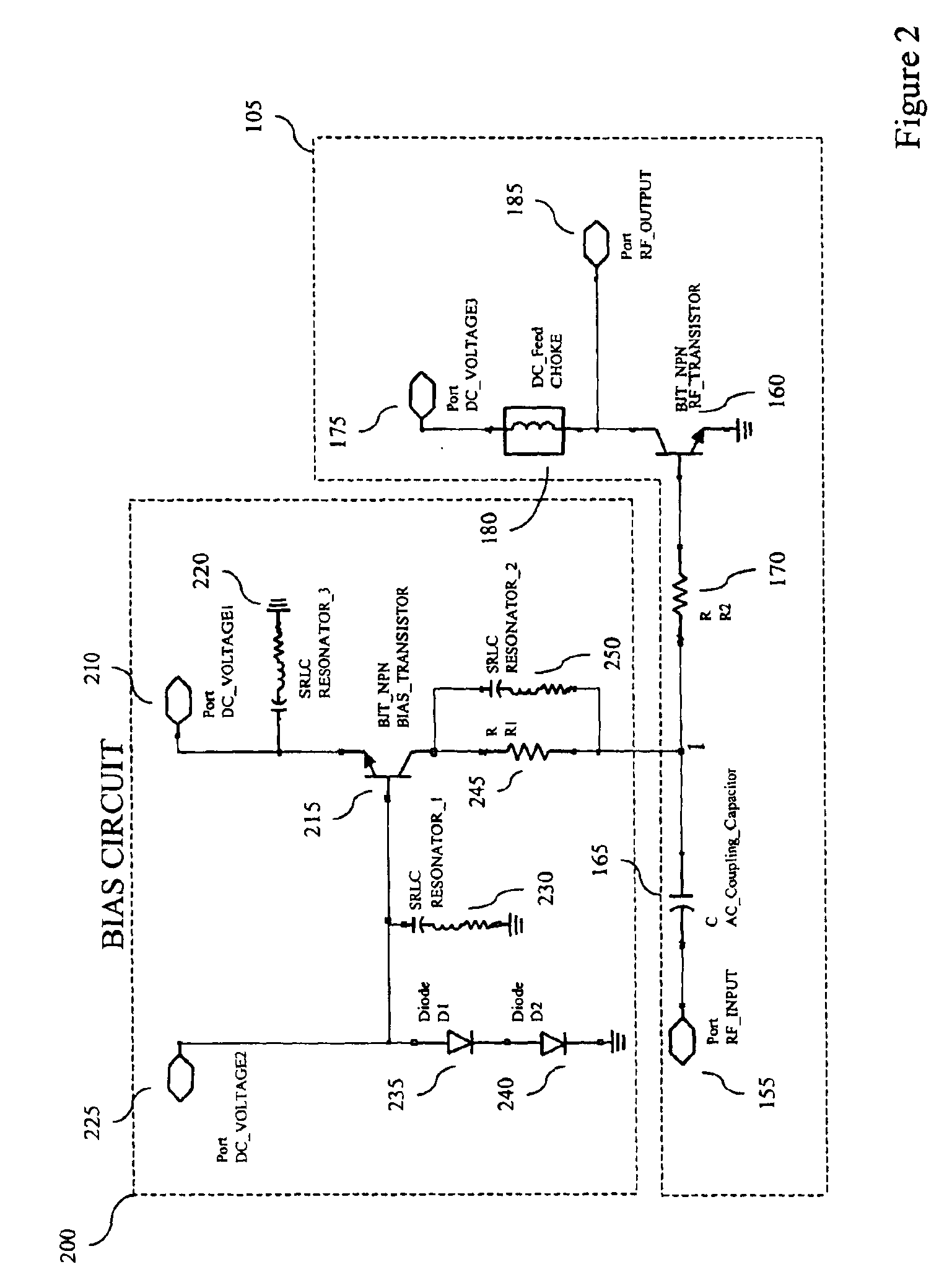
A transistor bias circuit is provided that is capable of biasing an amplifier transistor having a control terminal, a current-sink terminal, and a current-source terminal in order to control inter-modulation and linearize the output corresponding to radio frequency and microwave frequency ranges. Additionally, an embodiment of the present circuit is capable of dynamic power control. The transistor bias circuit according to the present invention utilizes a leakage current to alter the electrical characteristics of the amplifier transistor. The bias circuit comprises a bias transistor having a control terminal, a current-sink terminal, and a current-source terminal. Additionally, at least one DC input port, at least one resonator element, a diode element, and a resistive element is provided.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Semiconductor device with reduced current consumption in standby state
InactiveUS6992946B2Total current dropCurrent consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate leakage currentPower semiconductor device
In order to reduce a gate-source leakage current in a standby state, the gate insulating film of one of transistors in each of inverters IV1–IV5 is made thick. In a standby state, an input signal IN has L level and accordingly one of the transistors in inverters IV1–IV5 each that is connected to a main power supply line or a main ground line is turned on. The turned-on transistors have the gate insulating film which is made thicker than that of normal transistors to reduce the gate leakage current thereby reduce current consumption in the standby state.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110193079A1Reduce manufacturing costReduce hydrogen concentrationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceGate leakage current
In a miniaturized transistor, a gate insulating layer is required to reduce its thickness; however, in the case where the gate insulating layer is a single layer of a silicon oxide film, a physical limit on thinning of the gate insulating layer might occur due to an increase in tunneling current, i.e. gate leakage current. With the use of a high-k film whose relative permittivity is higher than or equal to 10 is used for the gate insulating layer, gate leakage current of the miniaturized transistor is reduced. With the use of the high-k film as a first insulating layer whose relative permittivity is higher than that of a second insulating layer in contact with an oxide semiconductor layer, the thickness of the gate insulating layer can be thinner than a thickness of a gate insulating layer considered in terms of a silicon oxide film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Gate stack for high performance sub-micron CMOS devices
InactiveUS6894357B2Increased drive current capabilityMinimize the effect of parasitic capacitanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceDielectric
A new method is provided for the creation of sub-micron gate electrode structures. A high-k dielectric is used for the gate dielectric, providing increased inversion carrier density without having to resort to aggressive scaling of the thickness of the gate dielectric while at the same time preventing excessive gate leakage current from occurring. Further, air-gap spacers are formed over a stacked gate structure. The gate structure consists of pre-doped polysilicon of polysilicon-germanium, thus maintaining superior control over channel inversion carriers. The vertical field between the gate structure and the channel region of the gate is maximized by the high-k gate dielectric, capacitive coupling between the source / drain regions of the structure and the gate electrode is minimized by the gate spacers that contain an air gap.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Preparation method of graphene MOS transistor
InactiveCN101783366AWide band gapReduce gate leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate leakage currentCMOS
The invention belongs to the technical field of semiconductor devices and particularly discloses a preparation method of a graphene MOS transistor, which is as follows: firstly intrinsic grapheme is processed through hydrogen plasma to obtain hydrogenated graphene, and then the large pi bonds of the graphene are destructed through the method of atomic layer metallic oxide deposition. In this way, the forbidden gap of the graphene can be effectively expanded and the gate leakage current in the graphene MOS transistor can be reduced. Meanwhile, the graphene with no metallic oxide deposition can maintain the semimetal property to be used as the source electrode and the drain electrode of the graphene MOS transistor, thus reducing the contact resistance between the source electrode and the channel. The preparation method is compatible with the existing CMOS technique and makes large grapheme-based integrated circuits possible.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
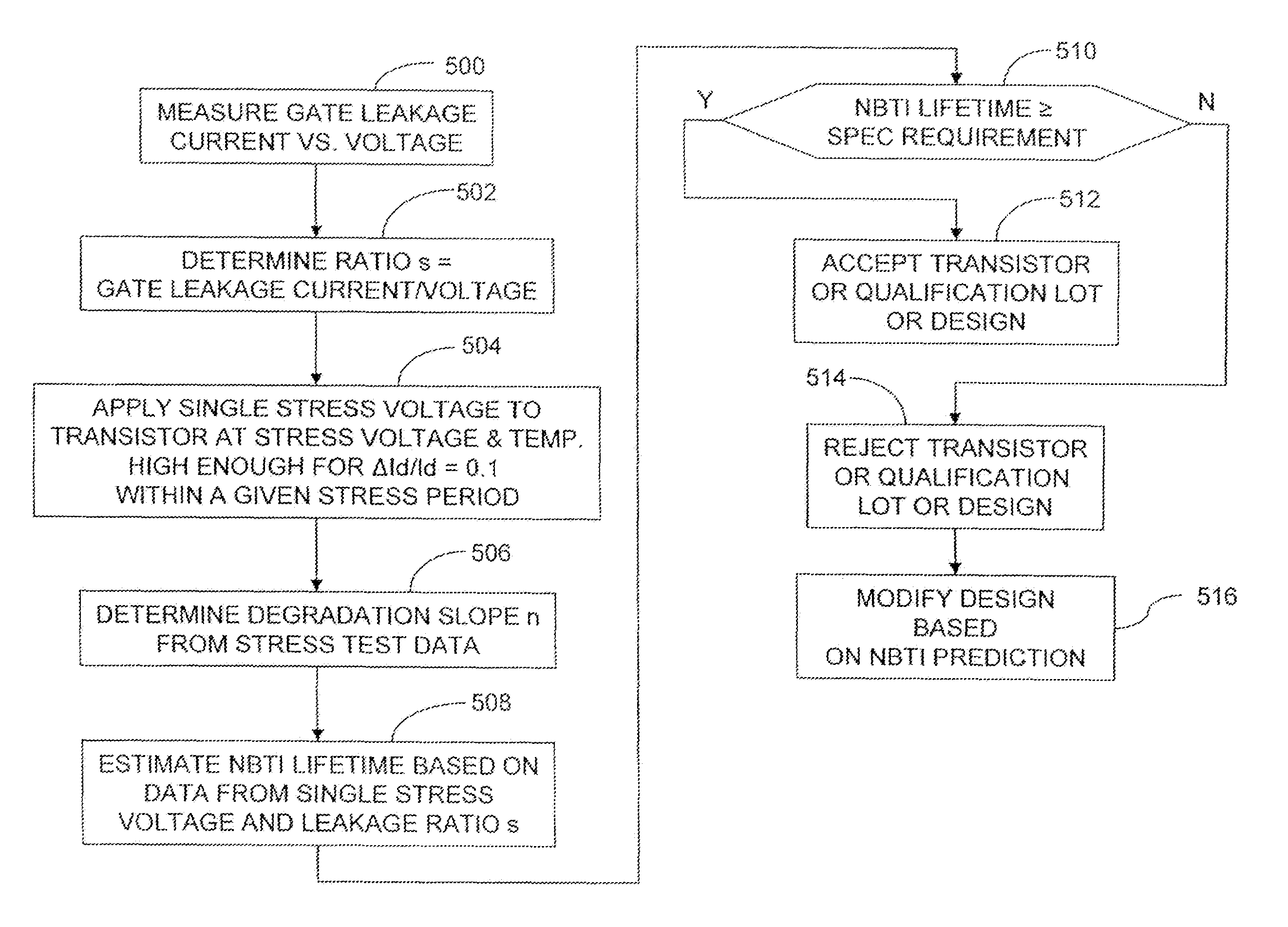
Method of NBTI prediction
InactiveUS7268575B1Semiconductor operation lifetime testingMarginal circuit testingGate leakage currentDriving current
A method includes measuring a gate leakage current of at least one transistor. A single stress bias voltage is applied to the at least one transistor at a given temperature for a stress period t. The stress bias voltage causes a 10% degradation in a drive current of the transistor at the given temperature within the stress period t. A negative bias temperature instability (NBTI) lifetime τ of the transistor is estimated based on the measured gate leakage current and a relationship between drive current degradation and time observed during the applying step.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS7217960B2Total current dropReduce leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate leakage currentDevice material
It is an object of the present invention to provide a semiconductor device, which can simultaneously achieve a normally-off mode of HFET and an improvement in Imax, and further achieve an improvement in gm and a reduction in gate leakage current. In order to keep a thin barrier layer 13 on an operation layer 12 of a substrate 11 directly under a gate electrode for mostly contributing to achieve the normally-off mode and also implement the high Imax, it is configured in such a way that a thickness of the barrier layer 13 can be increased by the semiconductor layer 17 between gate and source regions and between gate and drain regions. It is therefore possible to achieve the normally-off mode and an improvement in Imax as compared with an FET in which a thickness of the barrier layer is designed so as to be uniform. An insulating film 18 with a dielectric constant higher than that of the barrier layer is further inserted between a gate electrode 16 and the barrier layers 13, so that an improvement in gm and a reduction in gate leakage current can be achieved.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Keeper circuits having dynamic leakage compensation
ActiveUS20060214695A1High conductanceMinimize impactPower reduction in field effect transistorsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionGate leakage currentDrain current
Disclosed are keeper circuits for electronic circuits that selectively maintain the voltage level of an intermediate circuit node at a desired level. In one exemplary embodiment, a keeper transistor either provides current or drains current from the intermediate node to maintain the desired voltage level in response to a signal to do so. The keeper circuit works against a leakage current that either drains current from the node or supplies current to the node. A current-setting transistor is coupled in series with the keeper transistor to set the maximum current through the keeper circuit to a value that is related to this leakage current, preferably tracking the leakage current. With this construction, the current-setting transistor is able to track variations in the leakage current caused by variations in the manufacturing process, and thereby provide dynamic leakage compensation.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Field effect transistor having phase transition material incorporated into one or more components for reduced leakage current
ActiveUS20140110765A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesVanadium dioxideMOSFET
Disclosed is a metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) having phase transition material incorporated into one or more components and an associated method. The MOSFET can comprise an asymmetric gate electrode having a phase transition material section (e.g., a chromium or titanium-doped vanadium dioxide (VO2) section) above the drain-side of the channel region. Additionally or alternatively, the MOSFET can comprise source and drain contact landing pads comprising different phase transition materials (e.g., un-doped VO2 and chromium or titanium-doped VO2, respectively). In any case, the phase transition material(s) are pre-selected so as to be insulative when the MOSFET is in the OFF state and the voltage difference between the drain region and the source region (VDS) is high in order to minimize leakage current and so as to be conductive when the MOSFET is in the ON state and VDS is high in order to maintain drive current.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
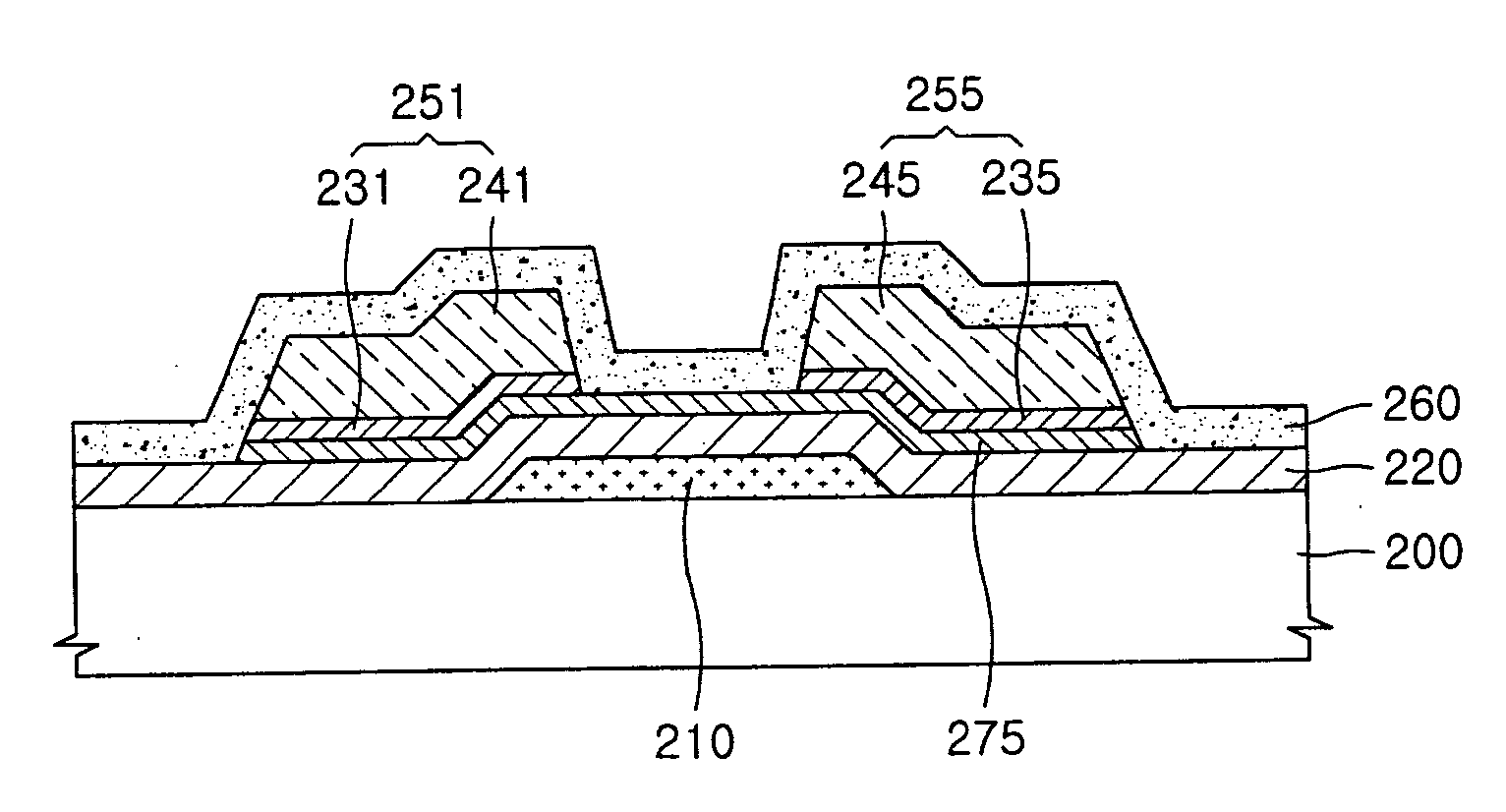
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
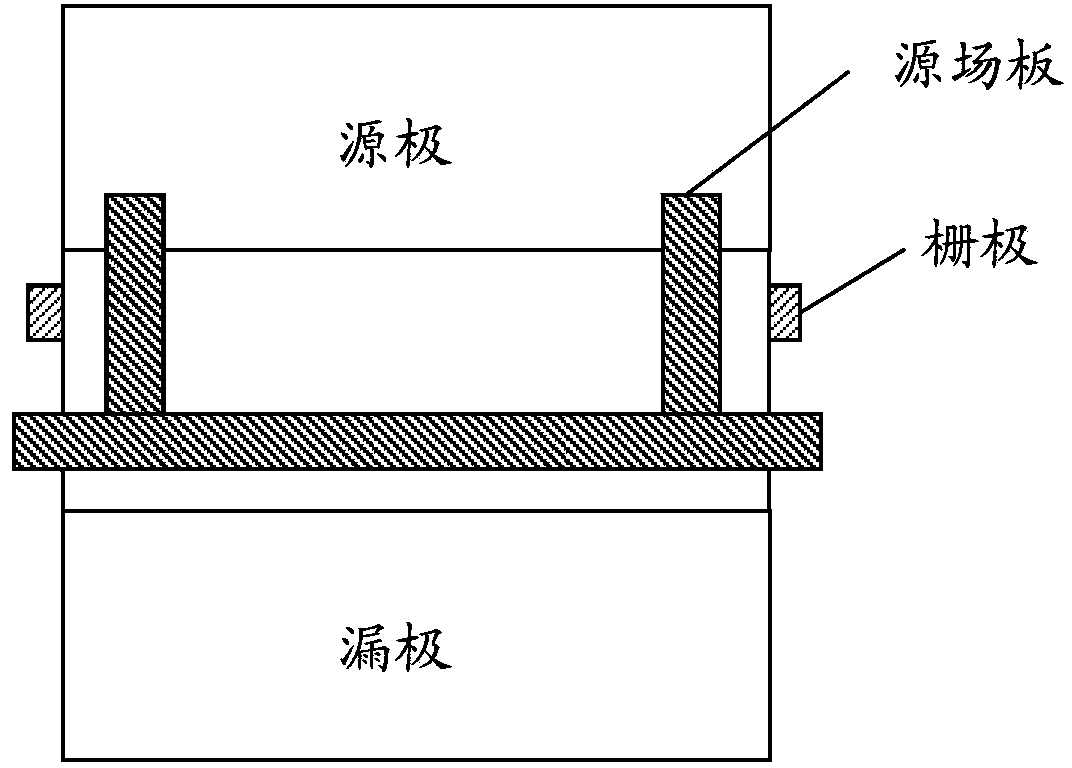
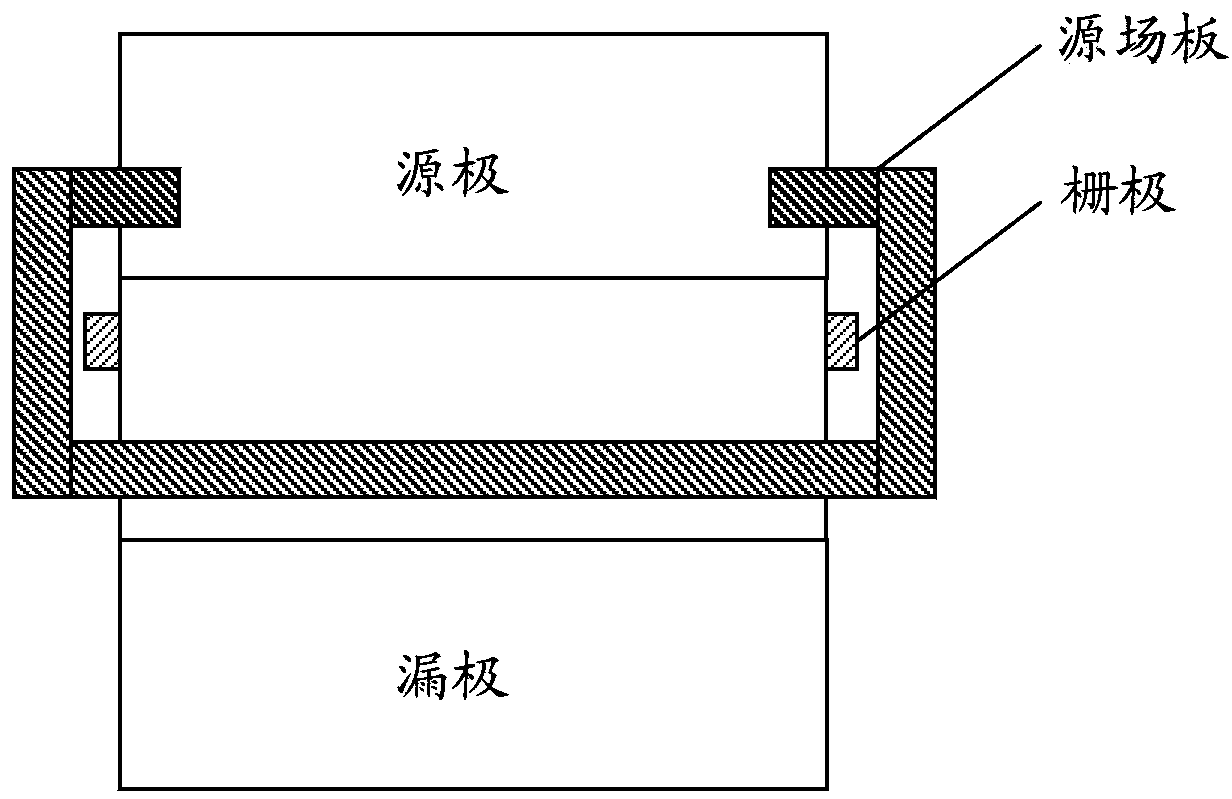
ActiveCN103367403AIncreasing the thicknessReduces the effect of modulating the electric field distributionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceSource field
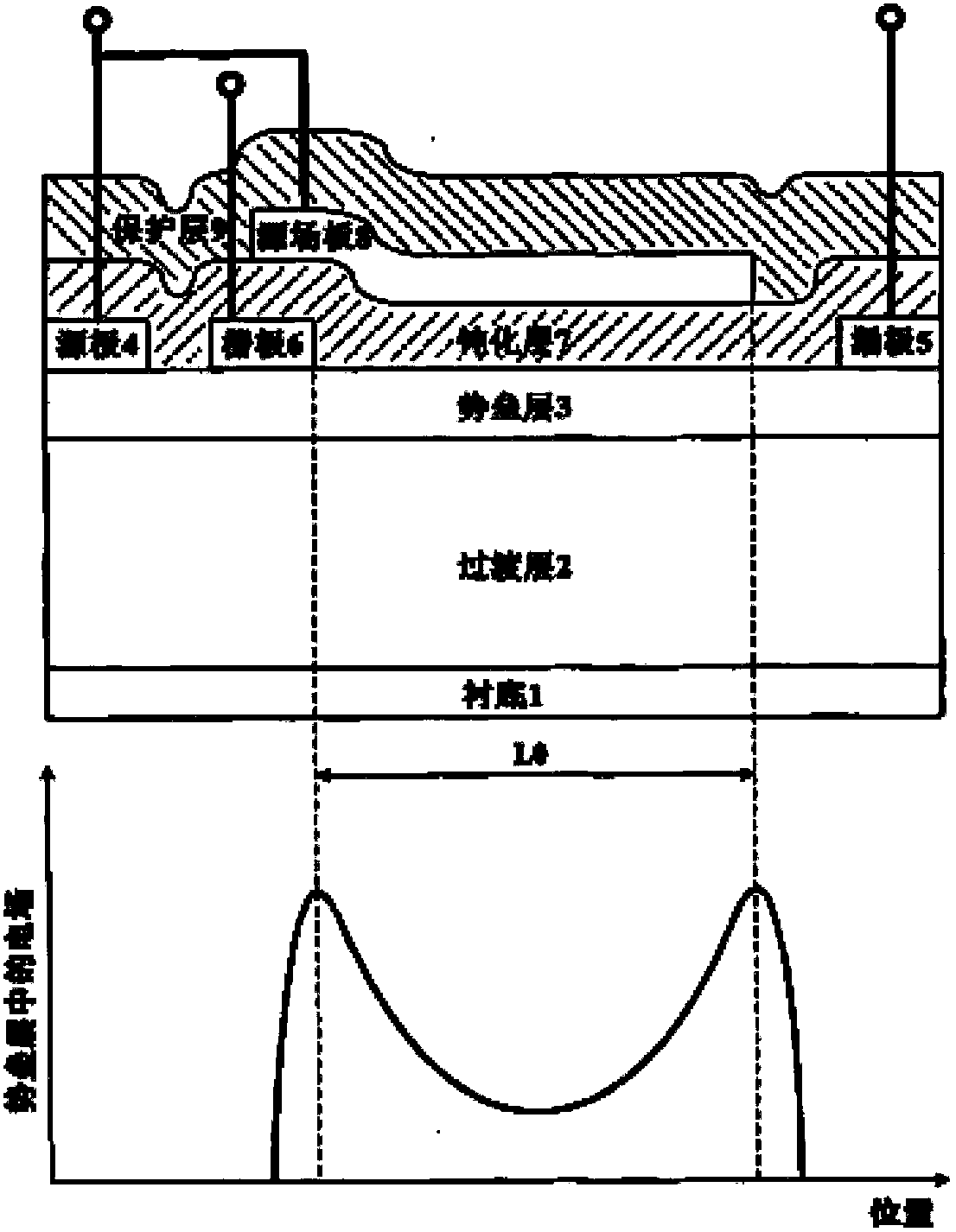
The invention discloses a semiconductor device and a manufacturing method thereof. The device comprises a substrate, a multi-layer semiconductor layer positioned on the substrate, a source electrode and a drain electrode positioned on the multi-layer semiconductor layer, a grid electrode positioned between the source electrode and the drain electrode, as well as a dielectric layer positioned on at least one part of the surface of the multi-layer semiconductor layer arranged between the grid electrode and the drain electrode and a source field plate positioned on the dielectric layer, wherein a groove is formed in the dielectric layer, the source field plate is electrically connected to the source electrode through at least one conductive path, and the source field plate completely or partially covers the groove in the dielectric layer. The semiconductor device and the manufacturing method thereof provided by the invention have the advantages that the source field plate is given a full play, grid source capacitance Cgs is reduced, a peak value electric field at the edge of the grid electrode is reduced, the breakdown voltage of the device is improved, the grid leakage current of the device is reduced, the frequency characteristic of the device is improved, and the advantage of the high output power of the device is fully played.
Owner:DYNAX SEMICON
System and method for measuring time dependent dielectric breakdown with a ring oscillator
An integrated circuit, in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, includes a first device under test (DUT) module coupled to a first ring oscillator module and a second DUT module coupled to a second ring oscillator module. A dielectric layer of the first DUT is stressed during a first mode, thereby causing time dependent dielectric breakdown in the first dielectric layer. A dielectric layer of the second DUT is maintained as a reference. The operating frequency of the first ring oscillator module, during a second mode, is a function of a gate leakage current of the stressed dielectric layer. The operating frequency of the second ring oscillator module, during the second mode, is a function of a gate leakage current the reference dielectric layer. The integrated circuit may also include a comparator module for generating an output signal as a function of a difference between the operating frequency of the first and second ring oscillator modules.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
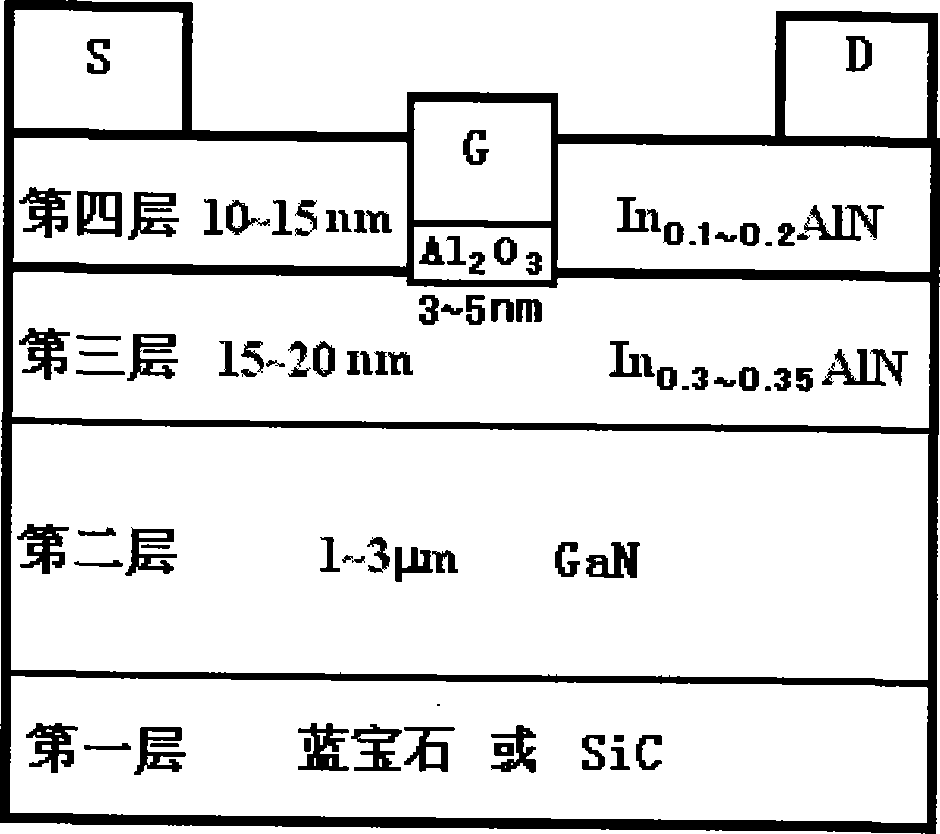
InA1N/GaN heterojunction enhancement type high electron mobility transistor structure and production method thereof
InactiveCN101246902AWide operating voltage rangeReduce gate leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionGate leakage current
The present invention discloses an InAIN / GaN heterojunction enhanced high electron mobility transistor structure and fabricating method thereof. The steps of manufacture are: 1) epitaxial growth of 1-3 mum GaN on sapphire or SiC substrate; 2) epitaxial growth of 15-20 nm first InAlN layer on GaN, In components is 30-35%, the temperature of epitaxial growth is 800 degree C; 3) epitaxial growth of 10-15 nm second InAlN layer on first InAlN layer, In components is 10-20%, the temperature of epitaxial growth is 800 degree C; 4) active region insulation and ohm touching manufacture processed on second InAlN layer; 5) gate lithographic mask on the second InAlN layer, the second InAlN layer below the gate is removed and grooved-gate structure is formed; 6) deposition of 3-5 nm Al2O3 medium layer in grating groove; 7) gate touching is produced on Al2O3 medium layer and electrodes are introduced of source-drain and gate. The present invention has merits of high positive threshold, large working range of positive gate voltage and small gate leakage current, can use for enhanced high electron mobility transistor.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Gate-all-around type semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7803675B2Reduce leakage currentDistanceNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate leakage currentInsulation layer
The gate-all-around (GAA) type semiconductor device may include source / drain layers, a nanowire channel, a gate electrode and an insulation layer pattern. The source / drain layers may be disposed at a distance in a first direction on a semiconductor substrate. The nanowire channel may connect the source / drain layers. The gate electrode may extend in a second direction substantially perpendicular to the first direction. The gate electrode may have a height in a third direction substantially perpendicular to the first and second directions and may partially surround the nanowire channel. The insulation layer pattern may be formed between and around the source / drain layers on the semiconductor substrate and may cover the nanowire channel and a portion of the gate electrode. Thus, a size of the gate electrode may be reduced, and / or a gate induced drain leakage (GIDL) and / or a gate leakage current may be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
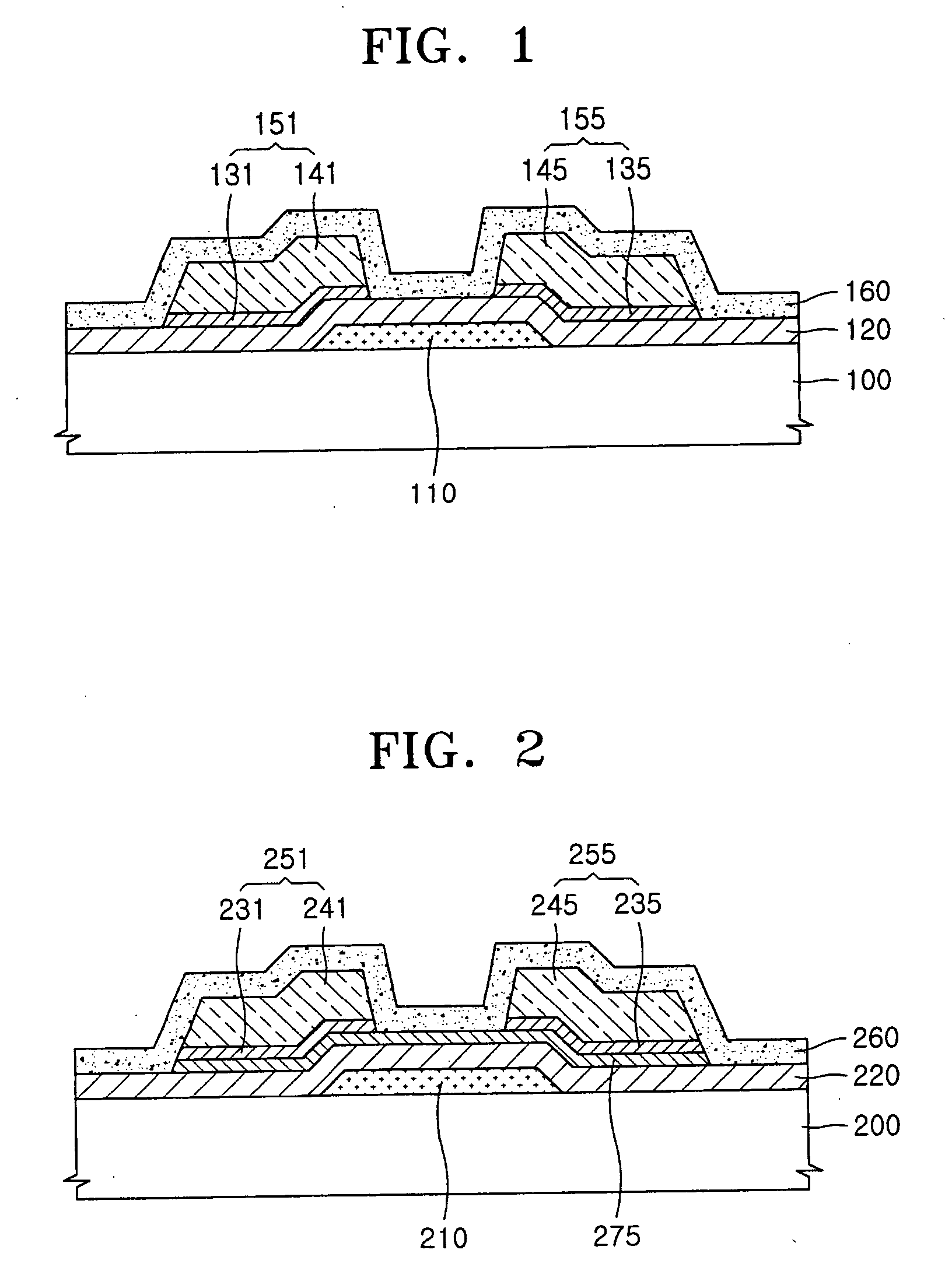
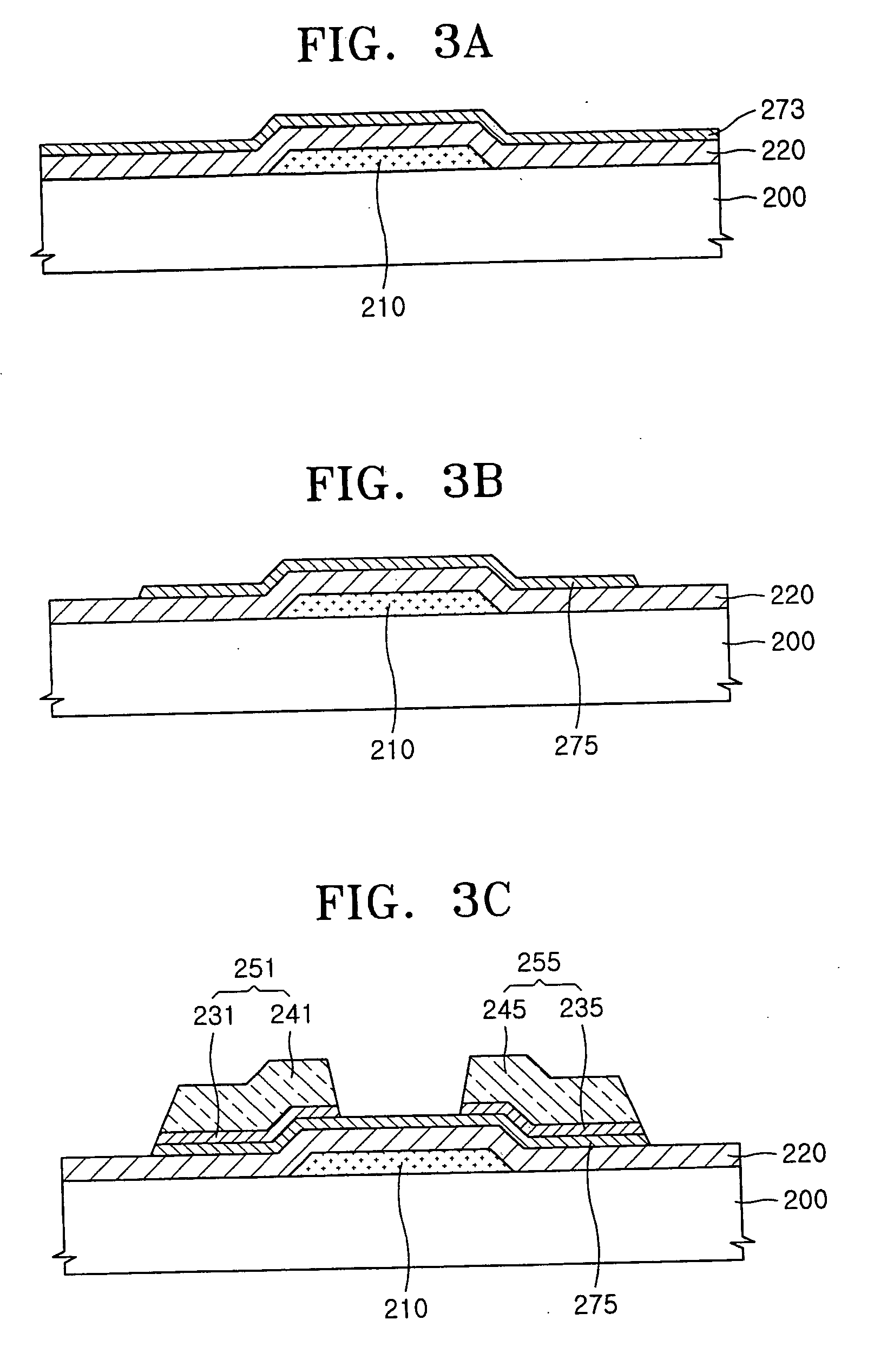
Thin film transistor and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20060027805A1Simple designSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate leakage currentDrain current
An organic thin film transistor (OTFT) having an adhesive layer and a method of fabricating the same. The OTFT includes a gate electrode formed on a substrate, a gate insulating layer formed on the gate electrode and on remaining exposed portions of the substrate, an adhesive layer formed on the gate insulating layer, source / drain electrodes formed on the adhesive layer, and a semiconductor layer formed on the source / drain electrodes and on the adhesive layer. The gate insulating layer and the semiconductor layer are organic, the adhesive layer providing adhesion between the source / drain electrodes and the gate insulating film while preventing gate leakage current while also improving contact resistance.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com