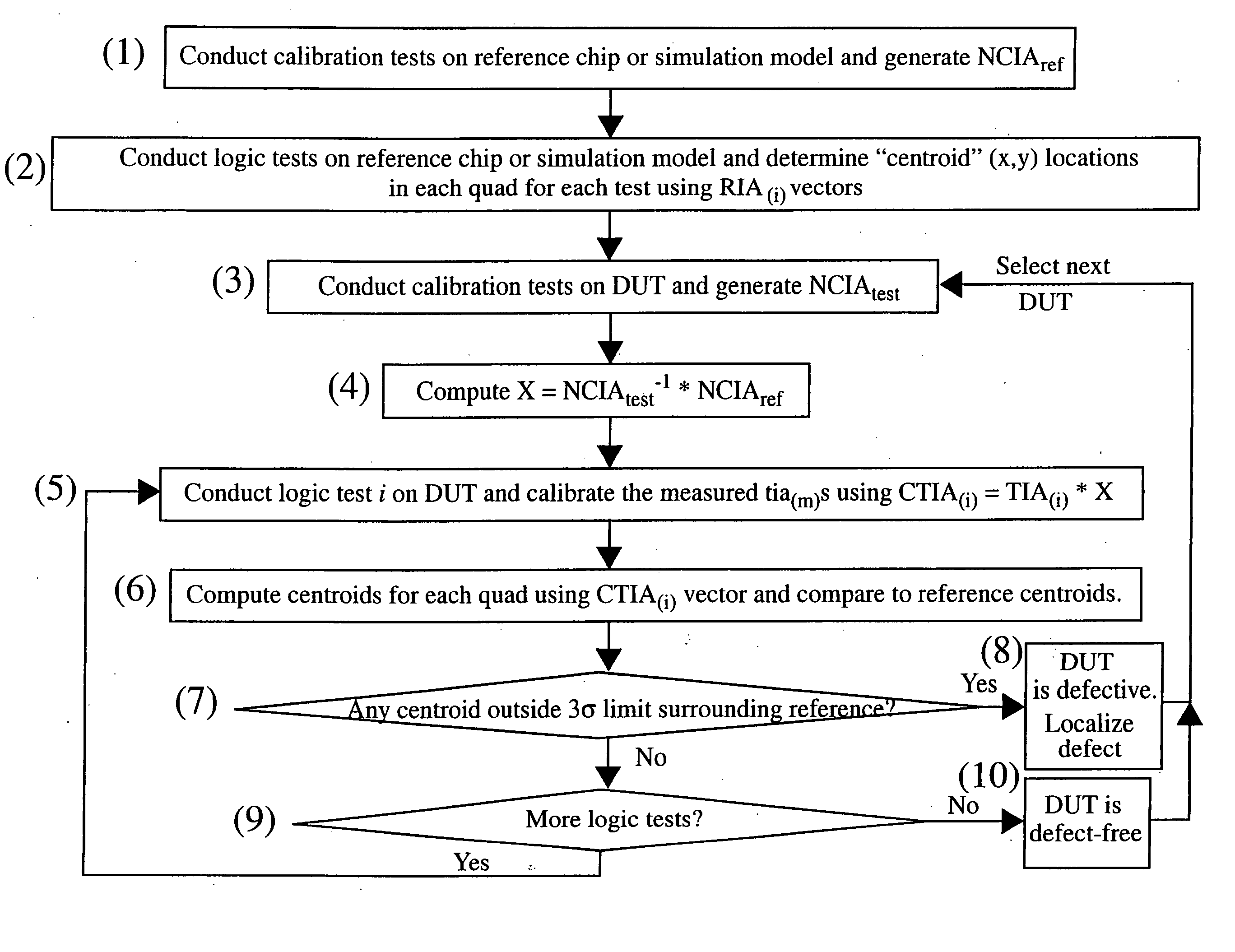
Patents
Literature
640results about "Marginal circuit testing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
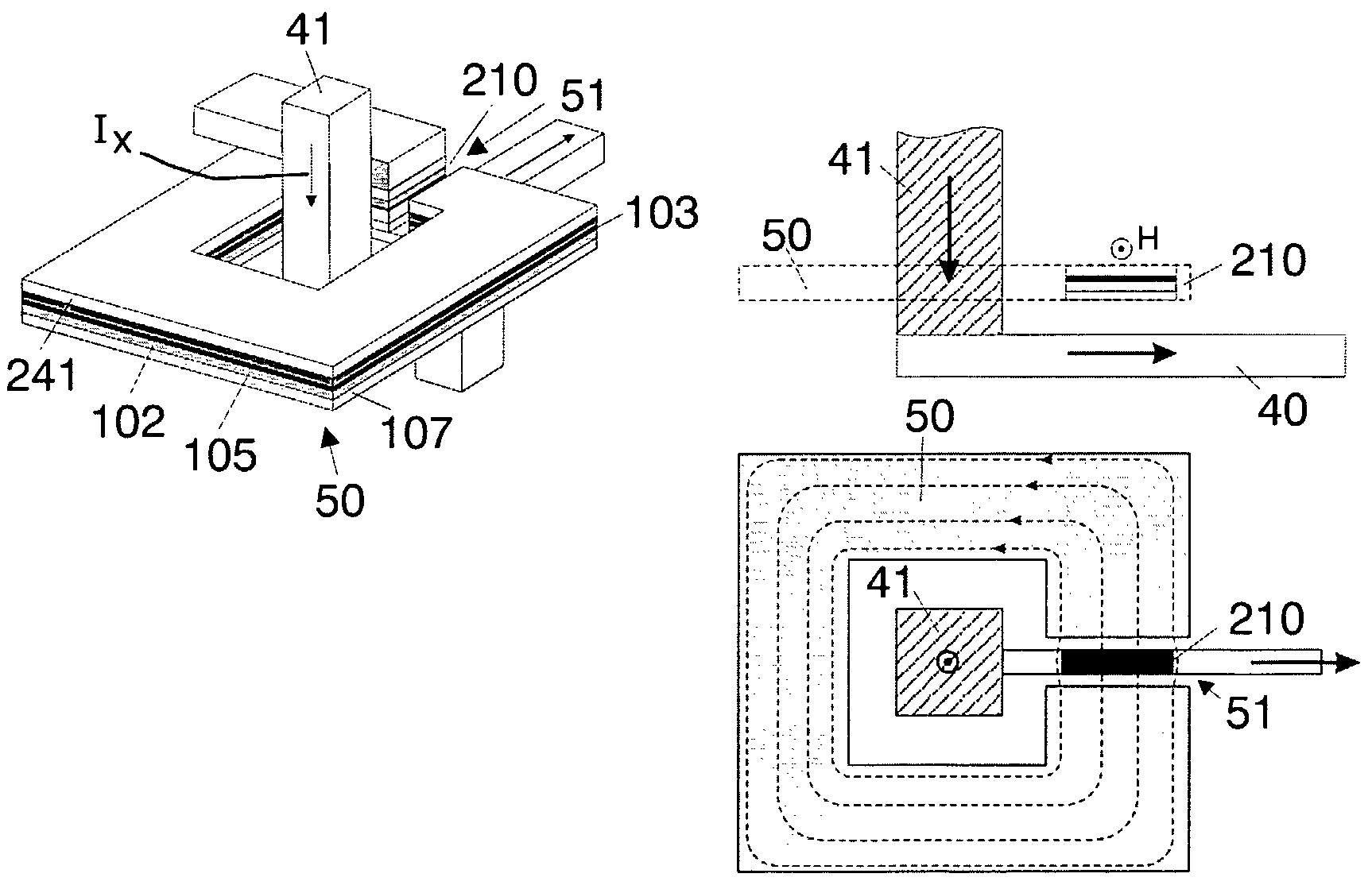
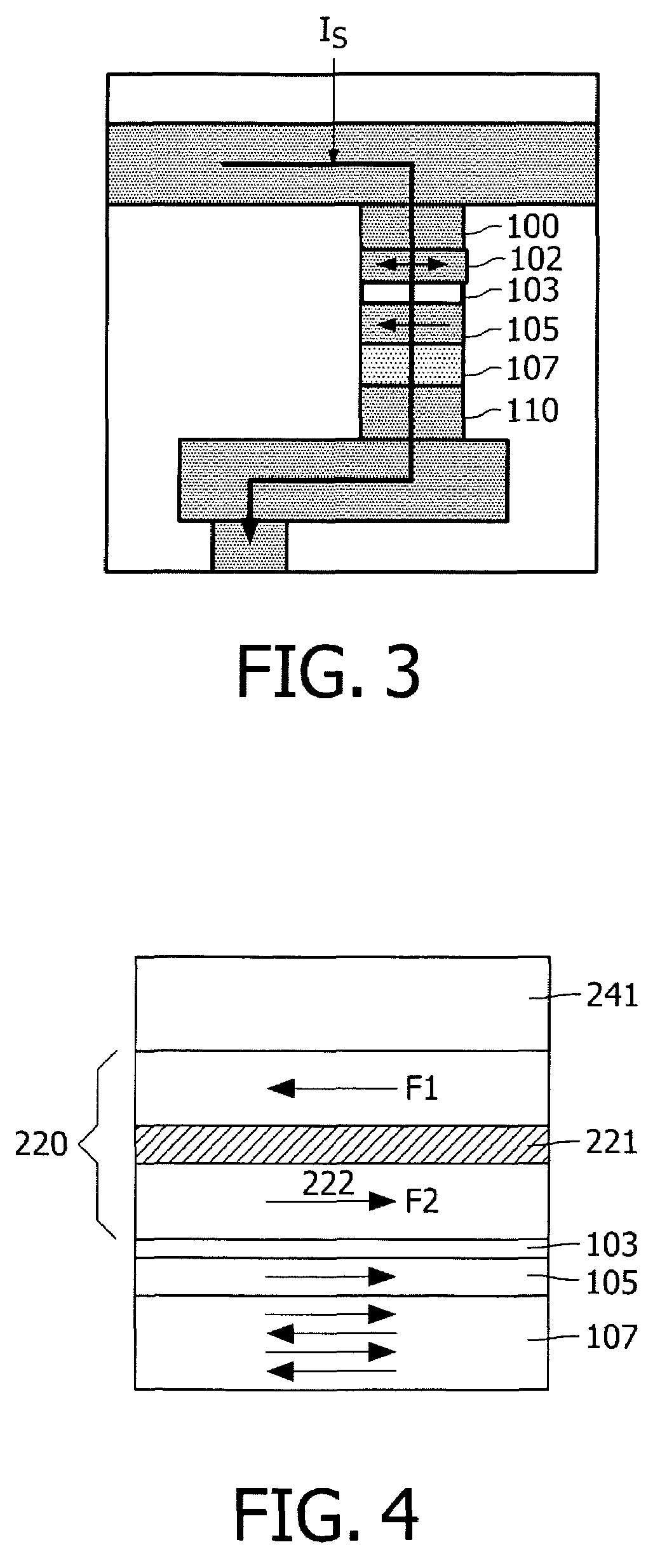
High sensitivity magnetic built-in current sensor
InactiveUS7619431B2Improve sensor sensitivityHigh sensitivityMagnetic measurementsDigital storageElectrical conductorEngineering
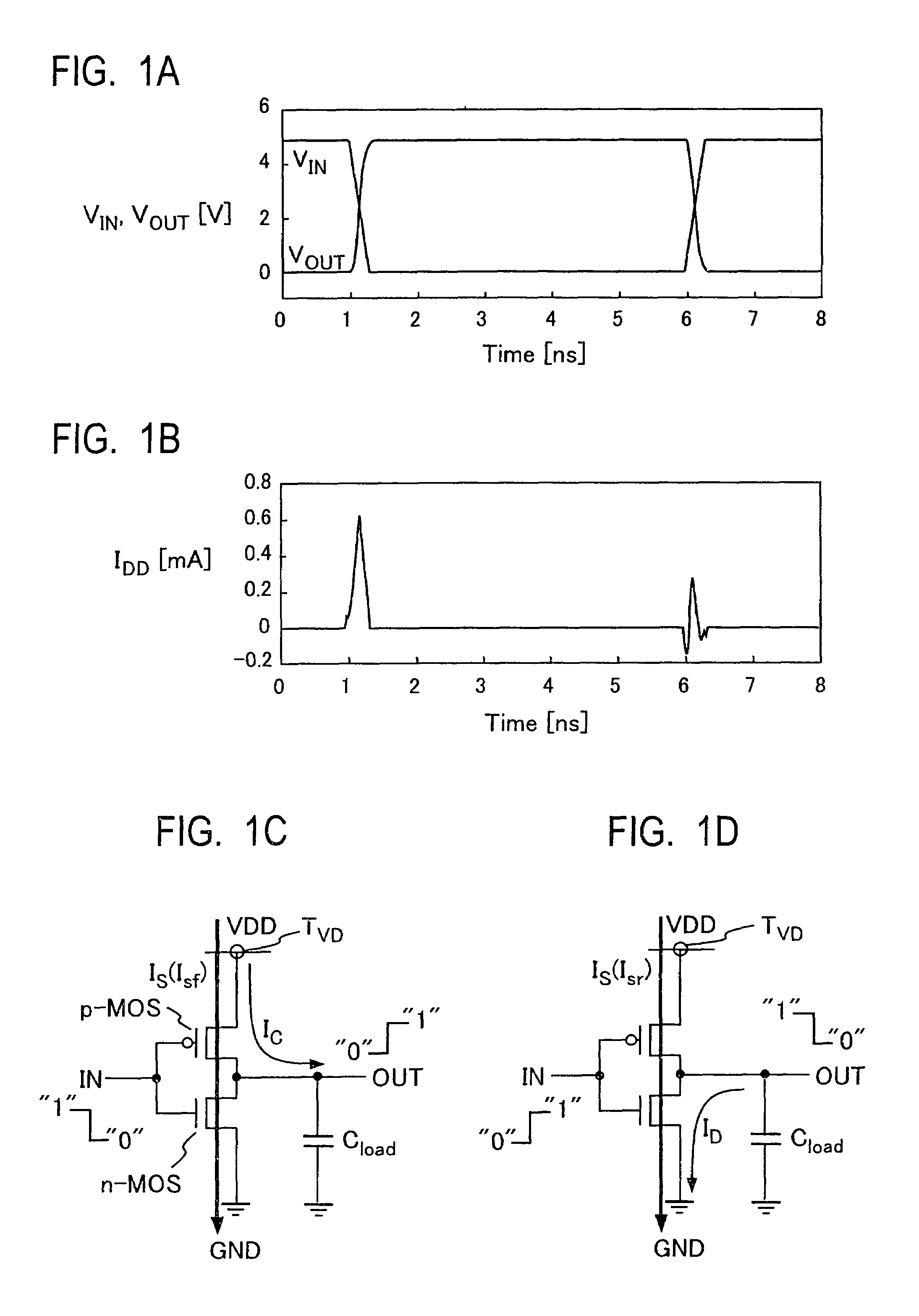
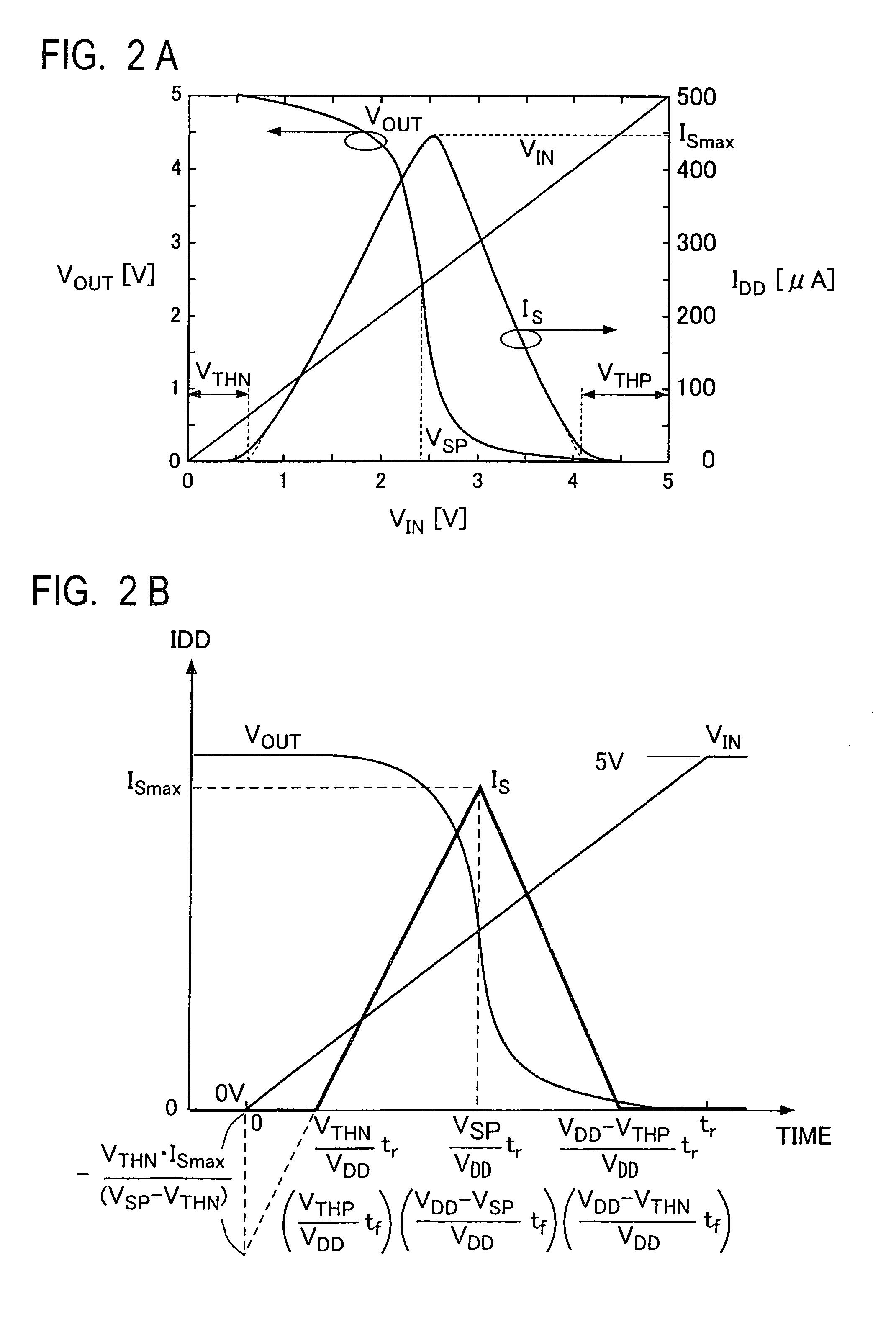
A sensor for contactlessly detecting currents, has a sensor element having a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ), and detection circuitry, the sensor element having a resistance which varies with the magnetic field, and the detection circuitry is arranged to detect a tunnel current flowing through the tunnel junction. The sensor element may share an MTJ stack with memory elements. Also it can provide easy integration with next generation CMOS processes, including MRAM technology, be more compact, and use less power. Solutions for increasing sensitivity of the sensor, such as providing a flux concentrator, and for generating higher magnetic fields with a same current, such as forming L-shaped conductor elements, are given. The greater sensitivity enables less post processing to be used, to save power for applications such as mobile devices. Applications include current sensors, built-in current sensors, and IDDQ and IDDT testing, even for next generation CMOS processes.
Owner:ELIPOSKI REMOTE
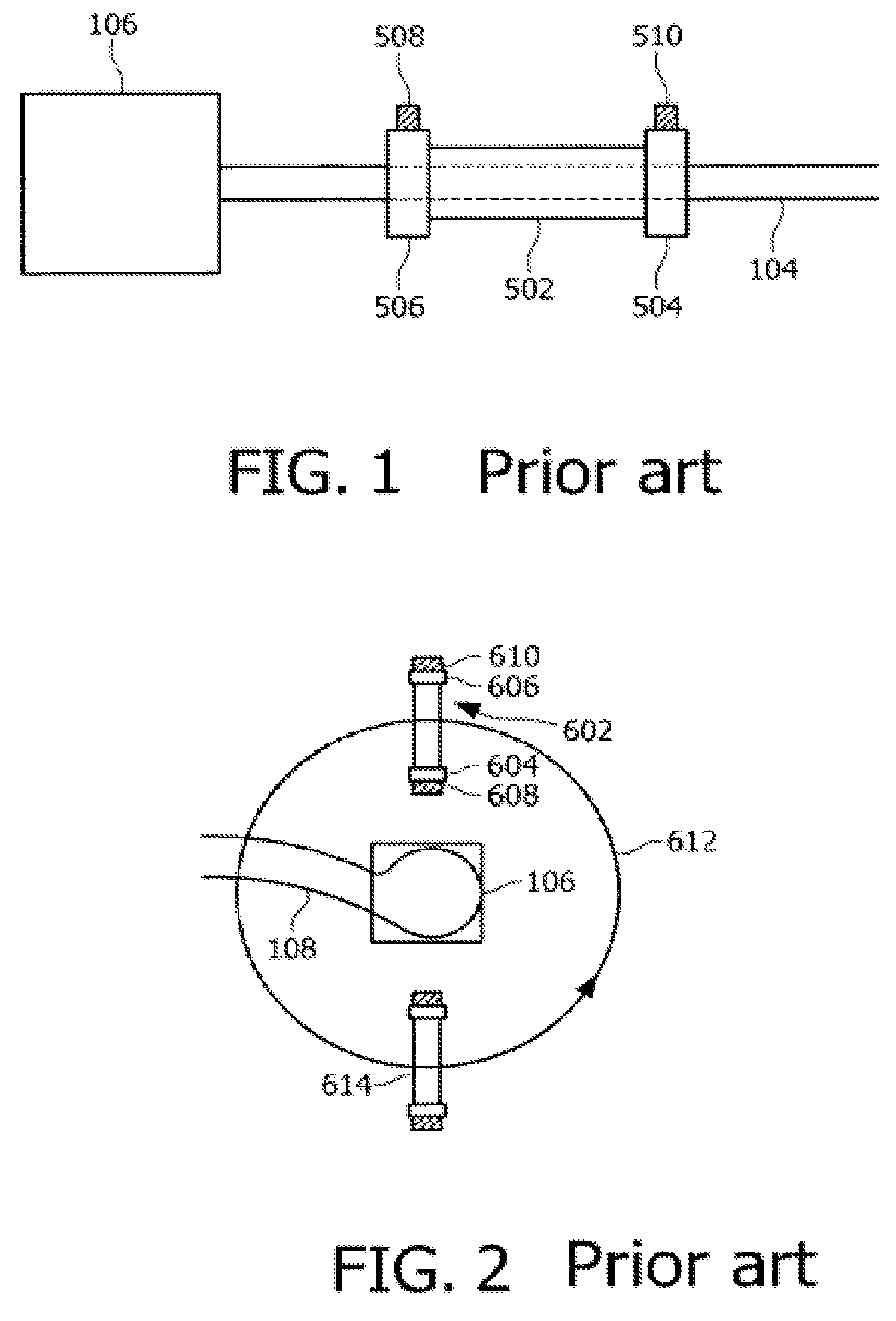
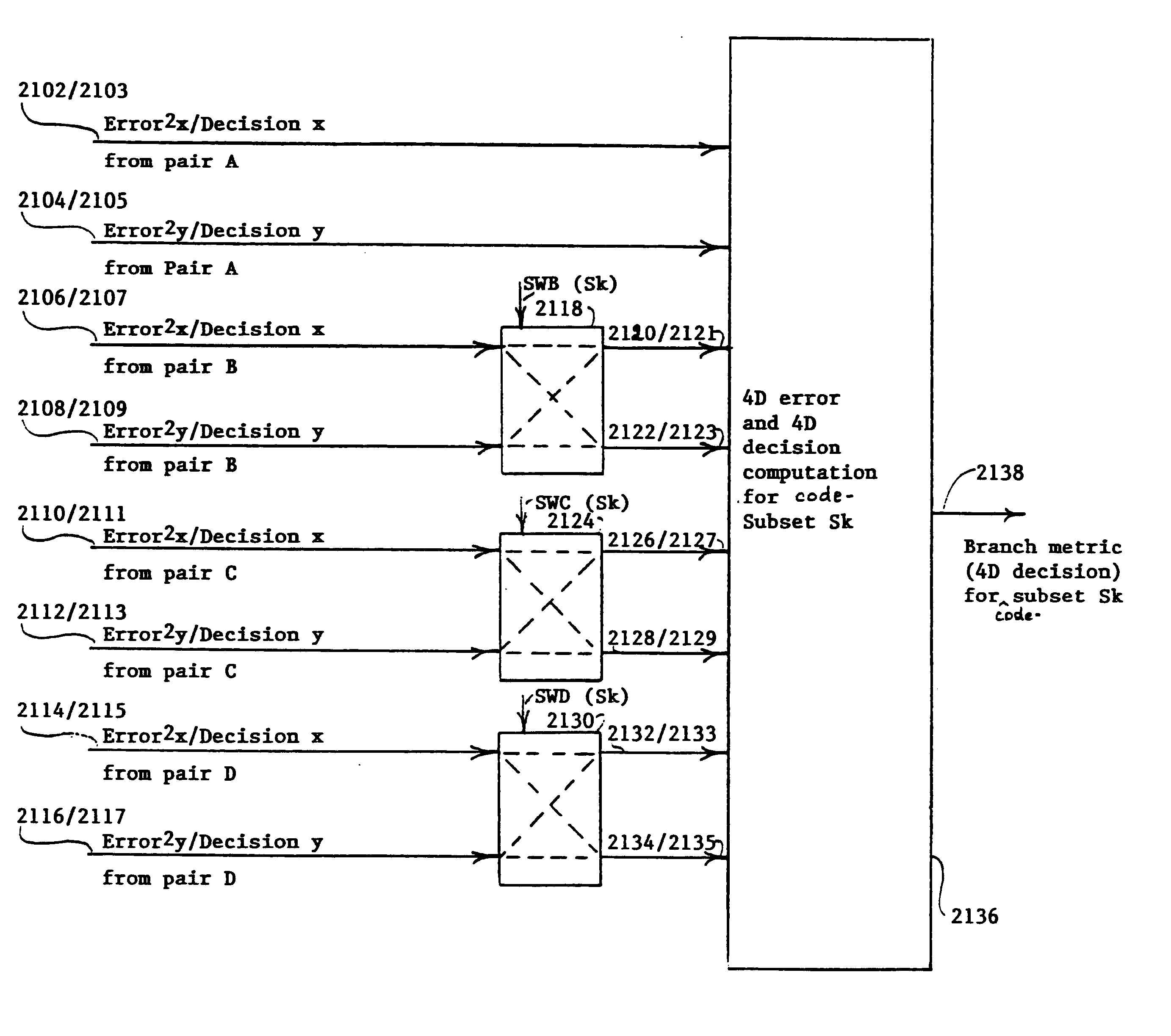
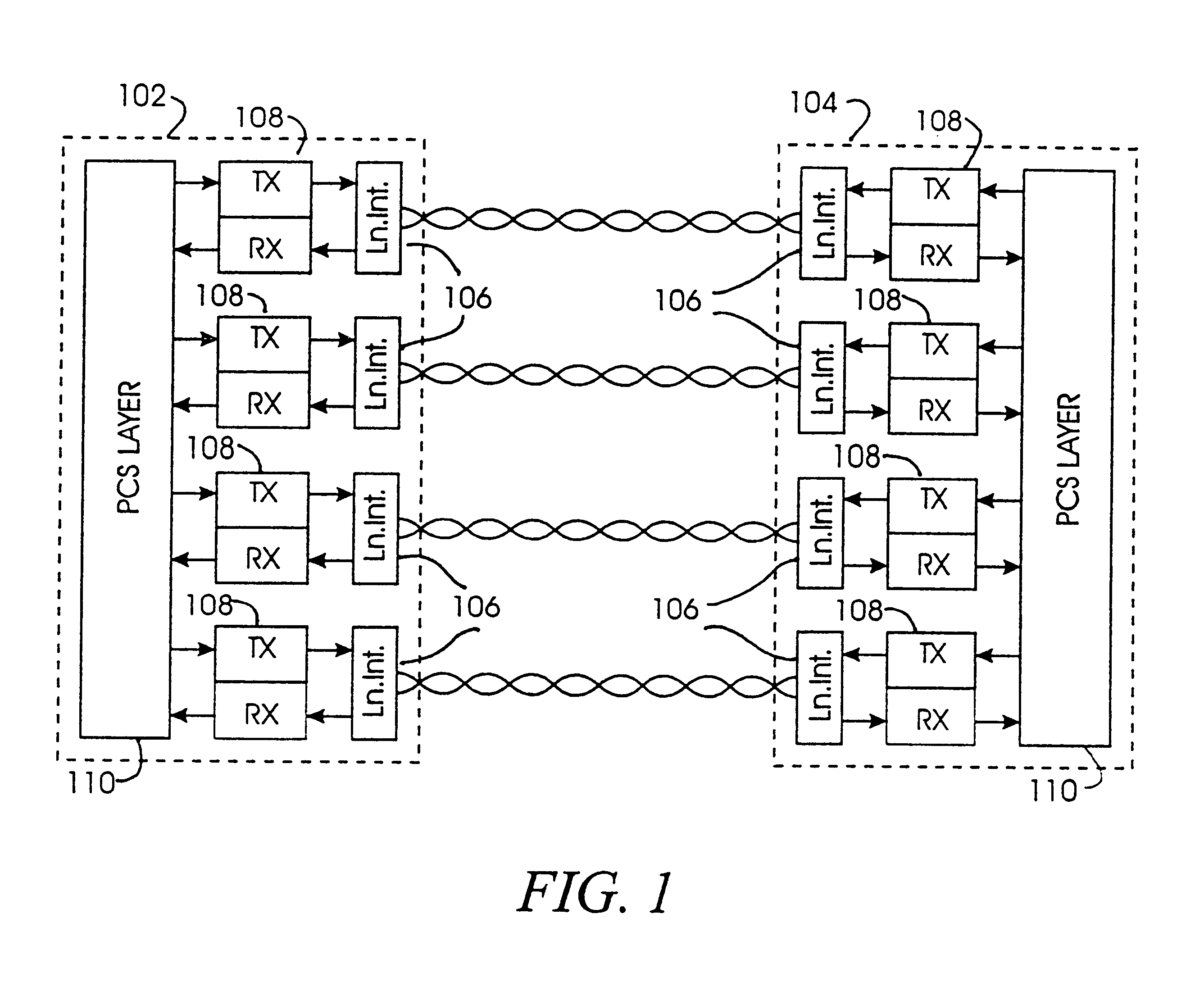
Pair-swap independent trellis decoder for a multi-pair gigabit transceiver
InactiveUS6865234B1Channel dividing arrangementsDigital circuit testingGigabitMulti-gigabit transceiver
A method and a system for compensating for a permutation of L pairs of cable such that the compensation is localized in a trellis decoder of a receiver. The L pairs of cable correspond to L dimensions of a trellis code associated with the trellis decoder. The trellis code includes a plurality of code-subsets. The permutation of the L pairs of cable is determined. A plurality of sets of swap indicators based on the permutation of the L pairs of cable is generated. Each of the sets of swap indicators corresponds to one of the code-subsets. The code-subsets are remapped based on the corresponding sets of swap indicators.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
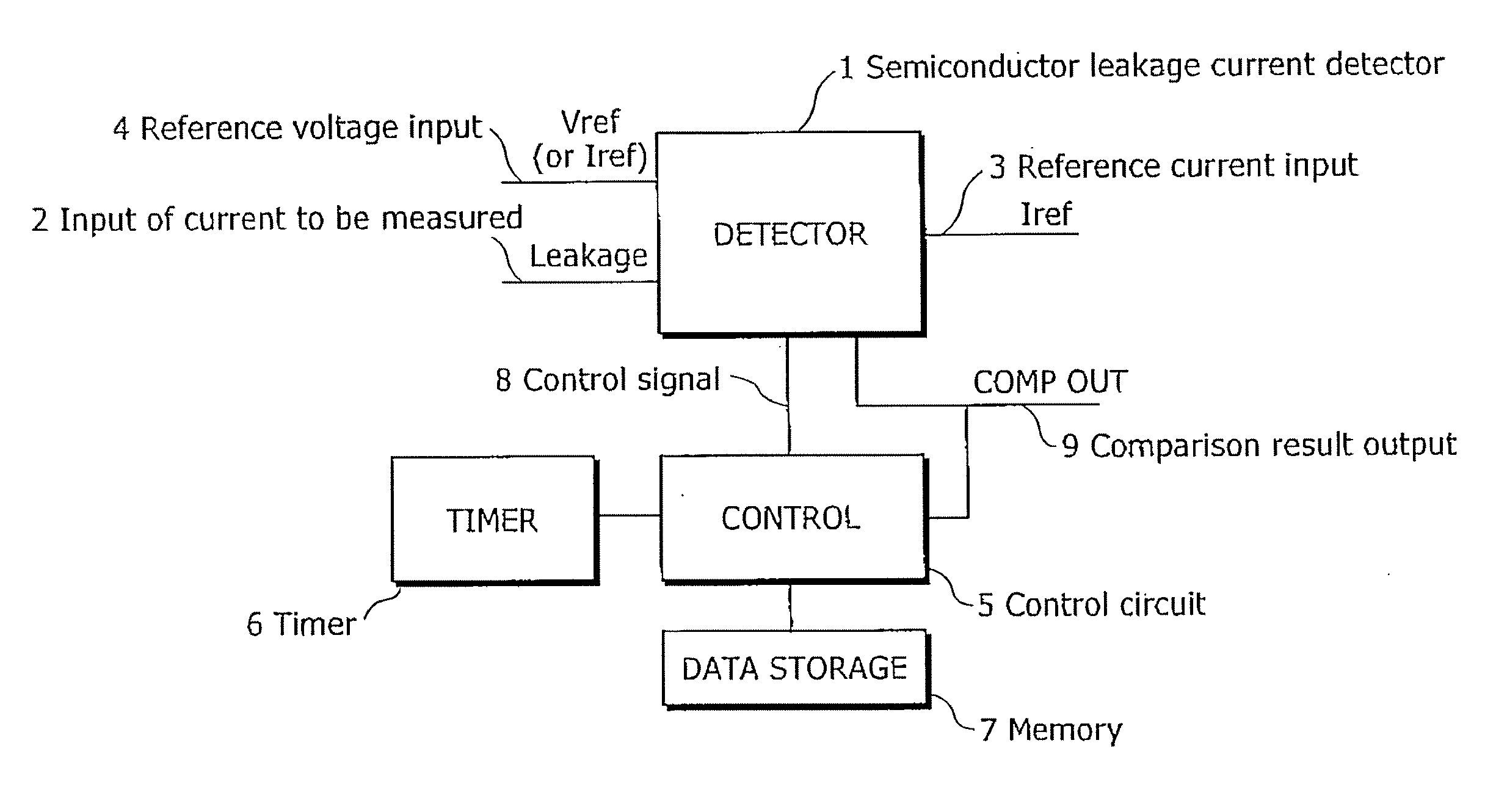
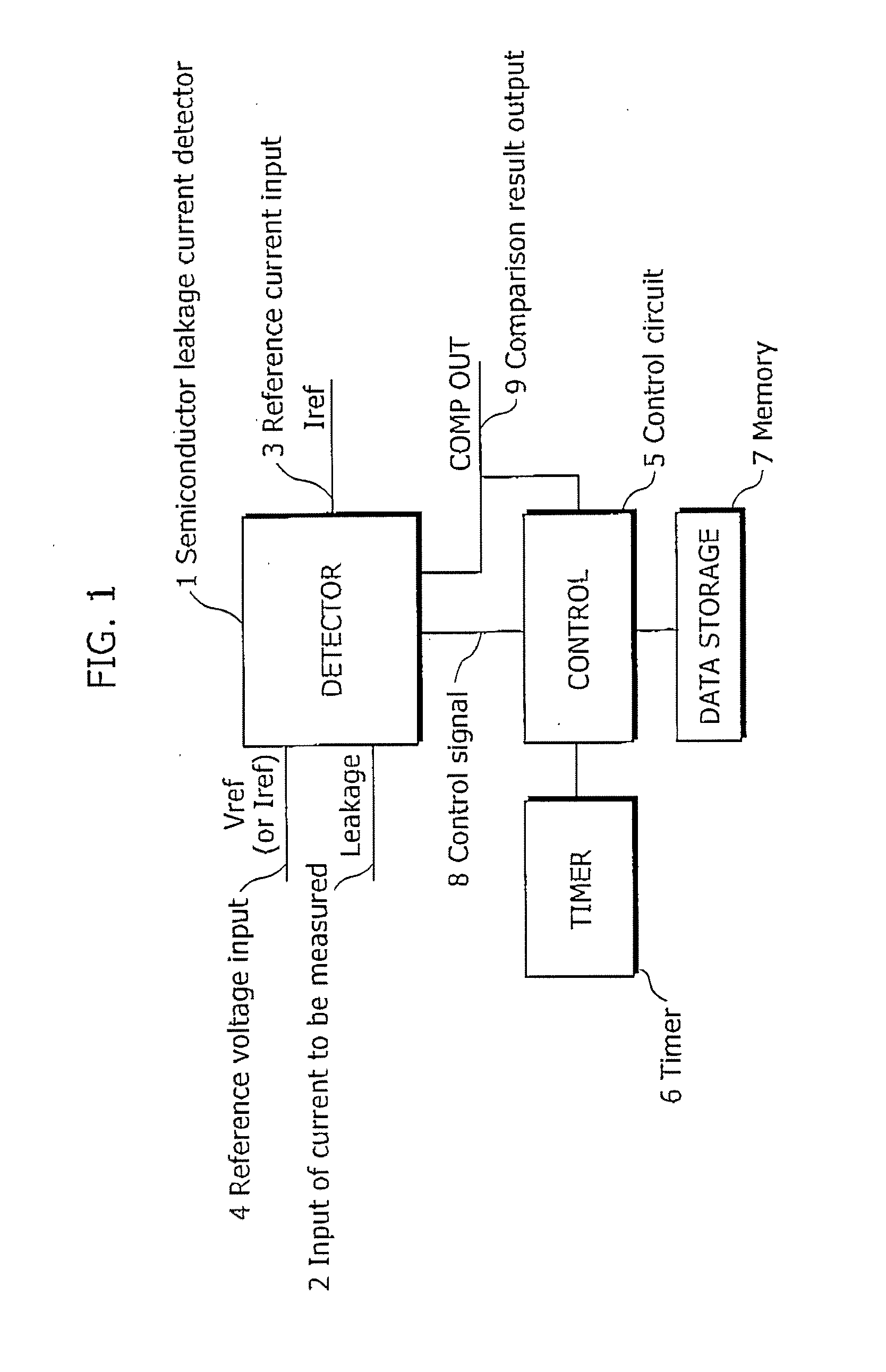
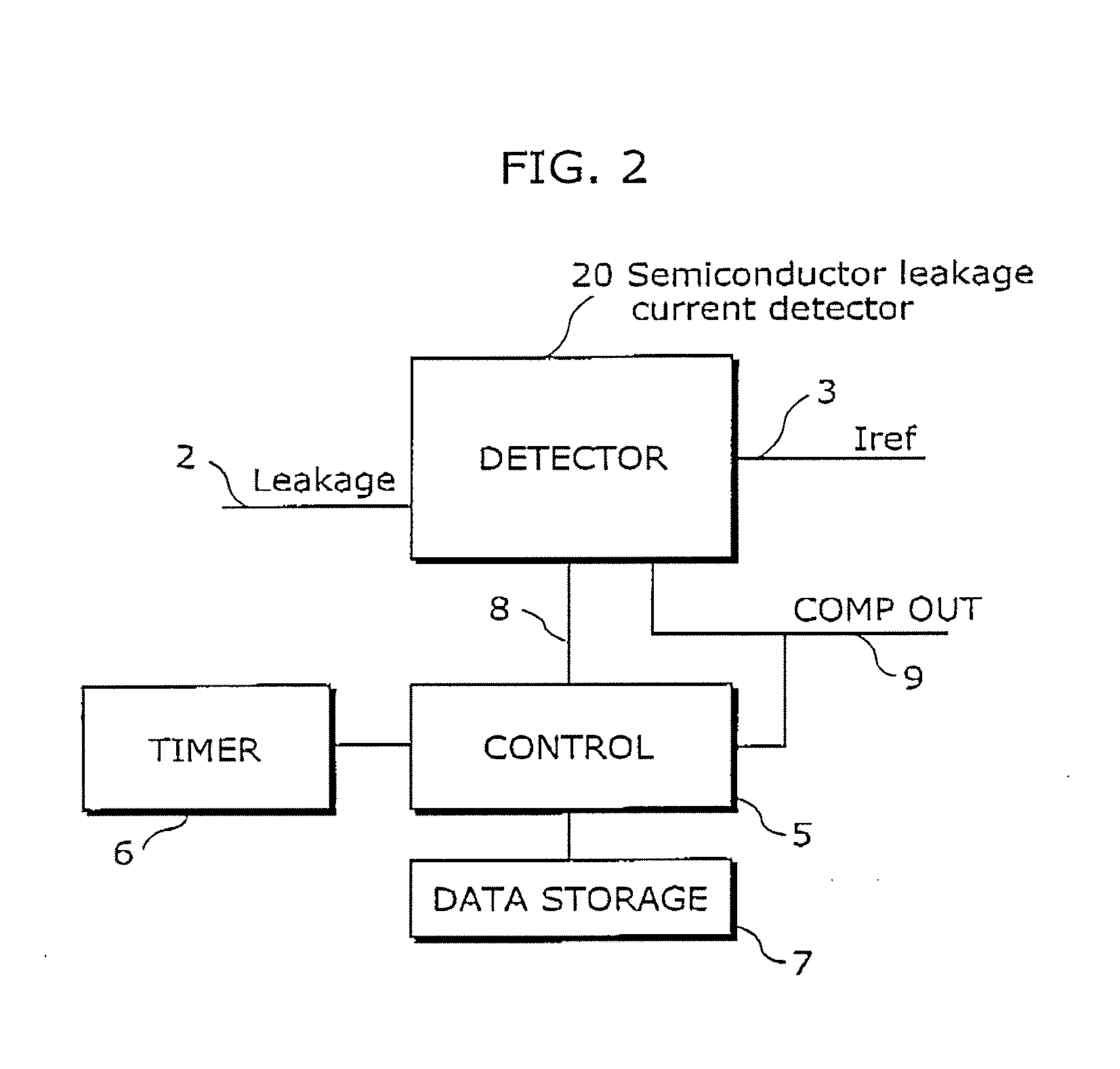
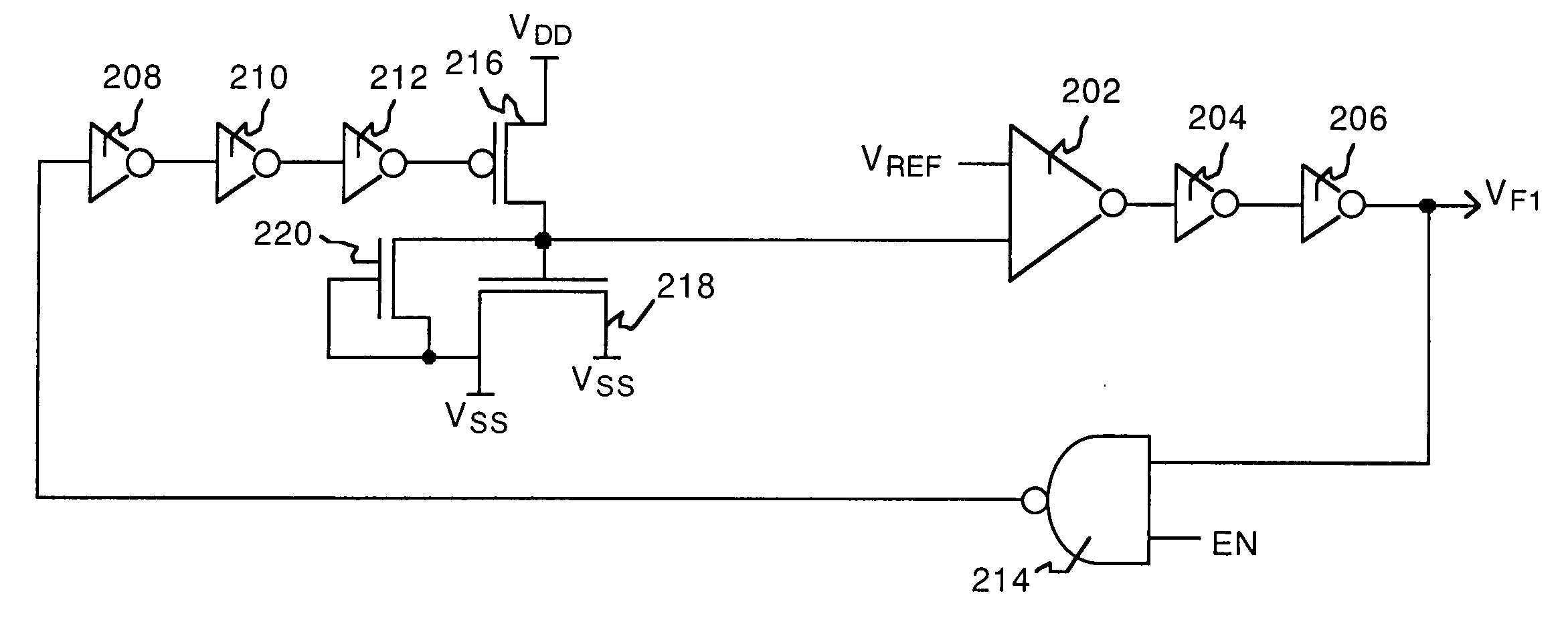
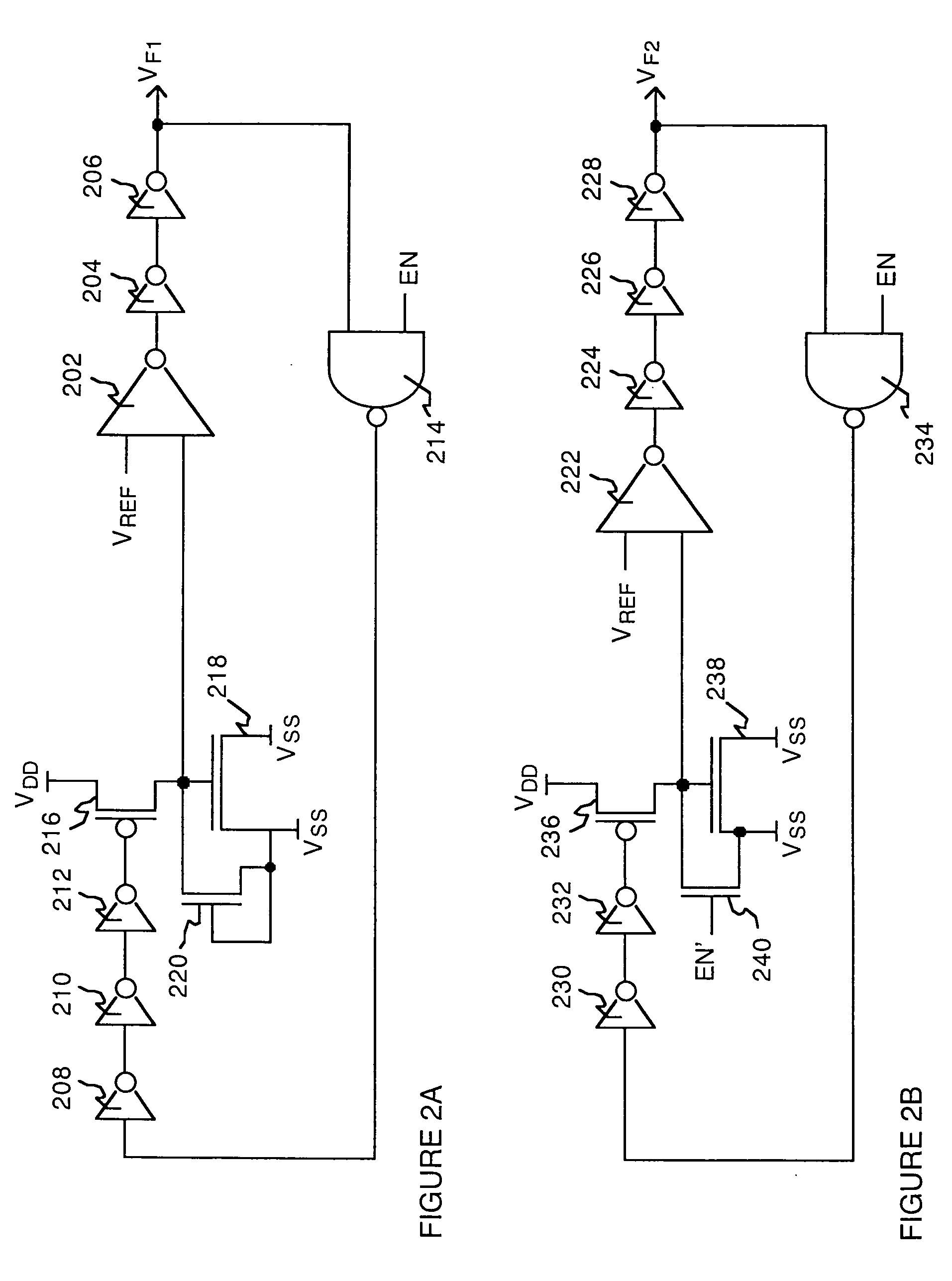
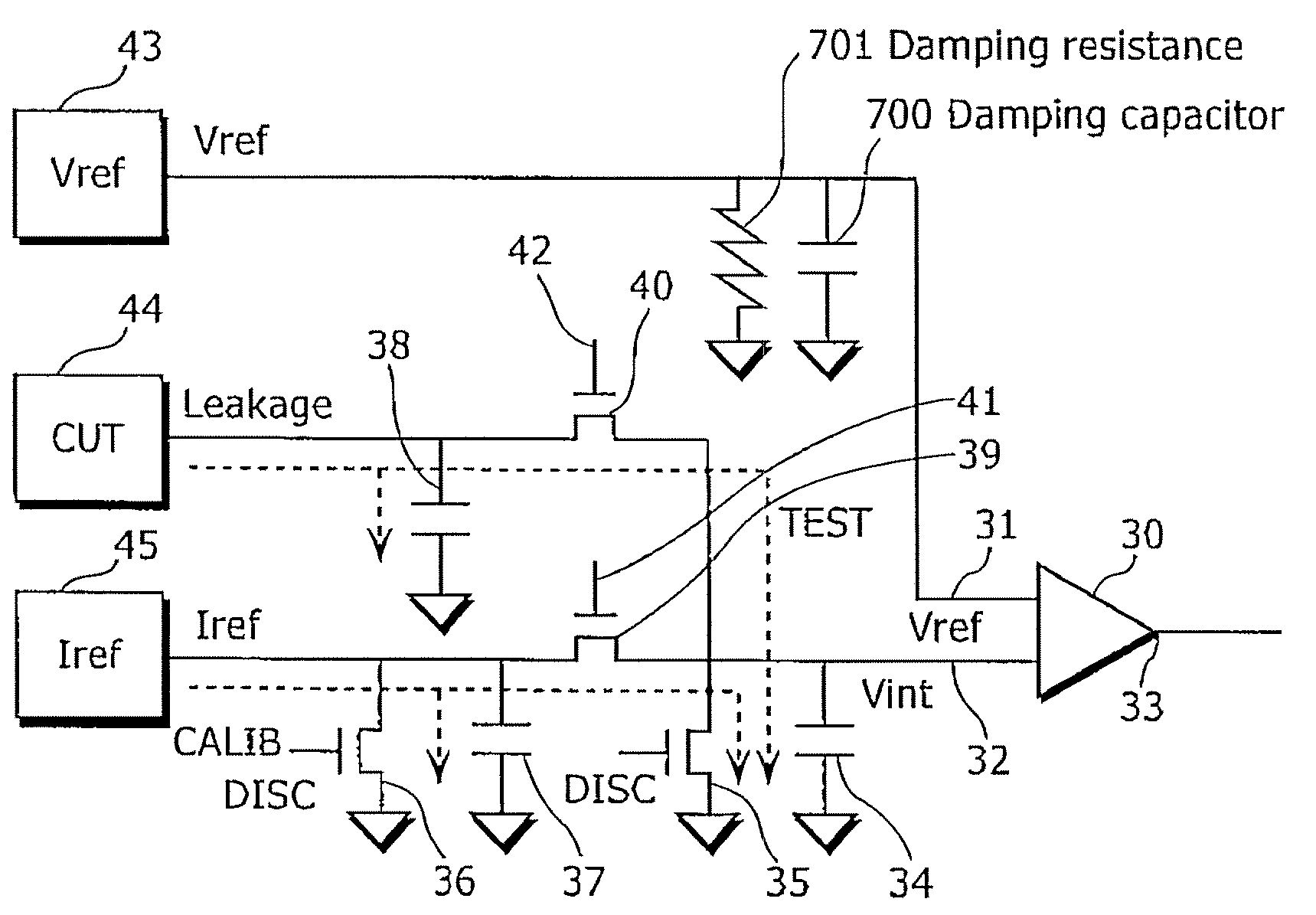
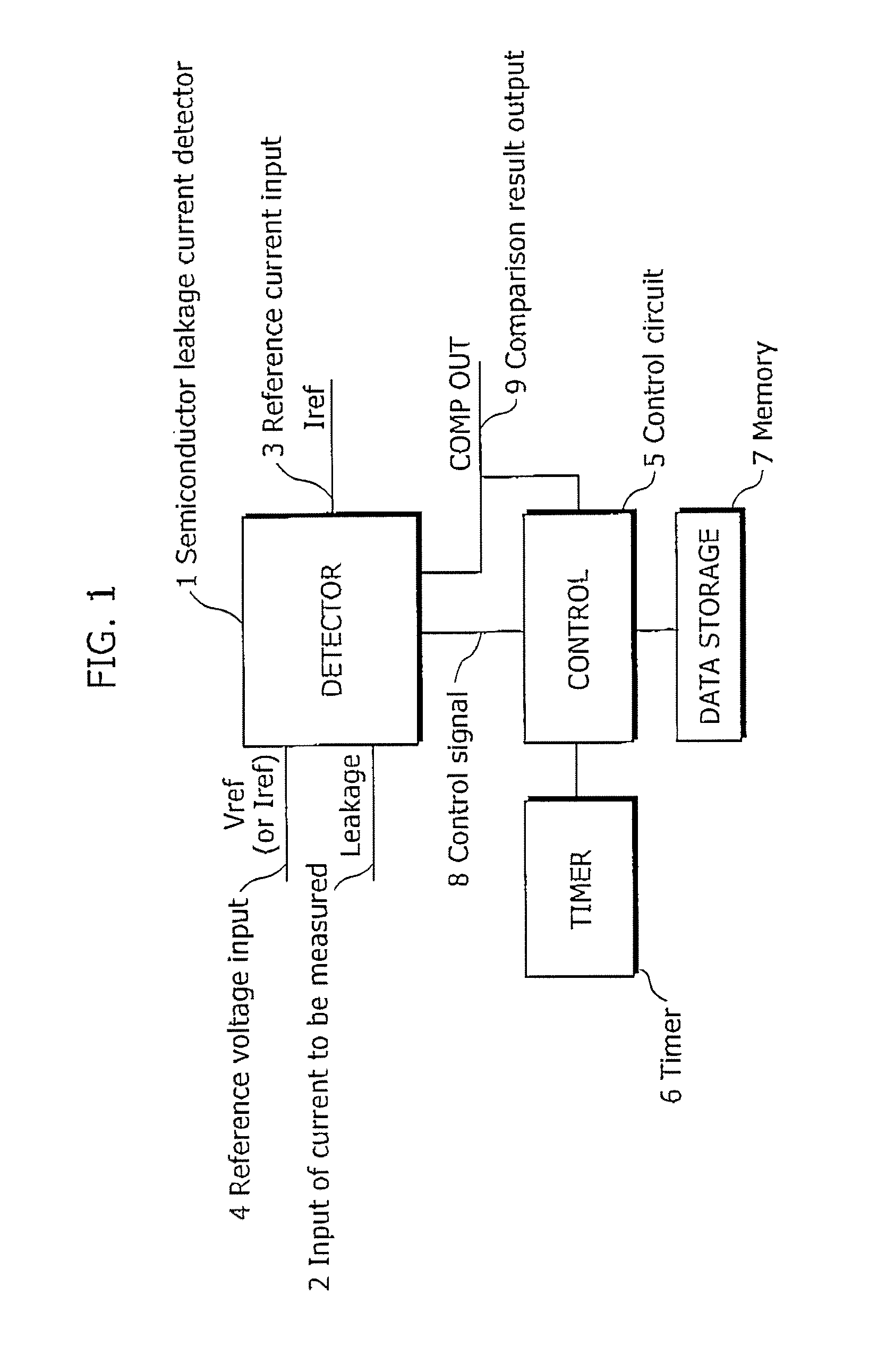
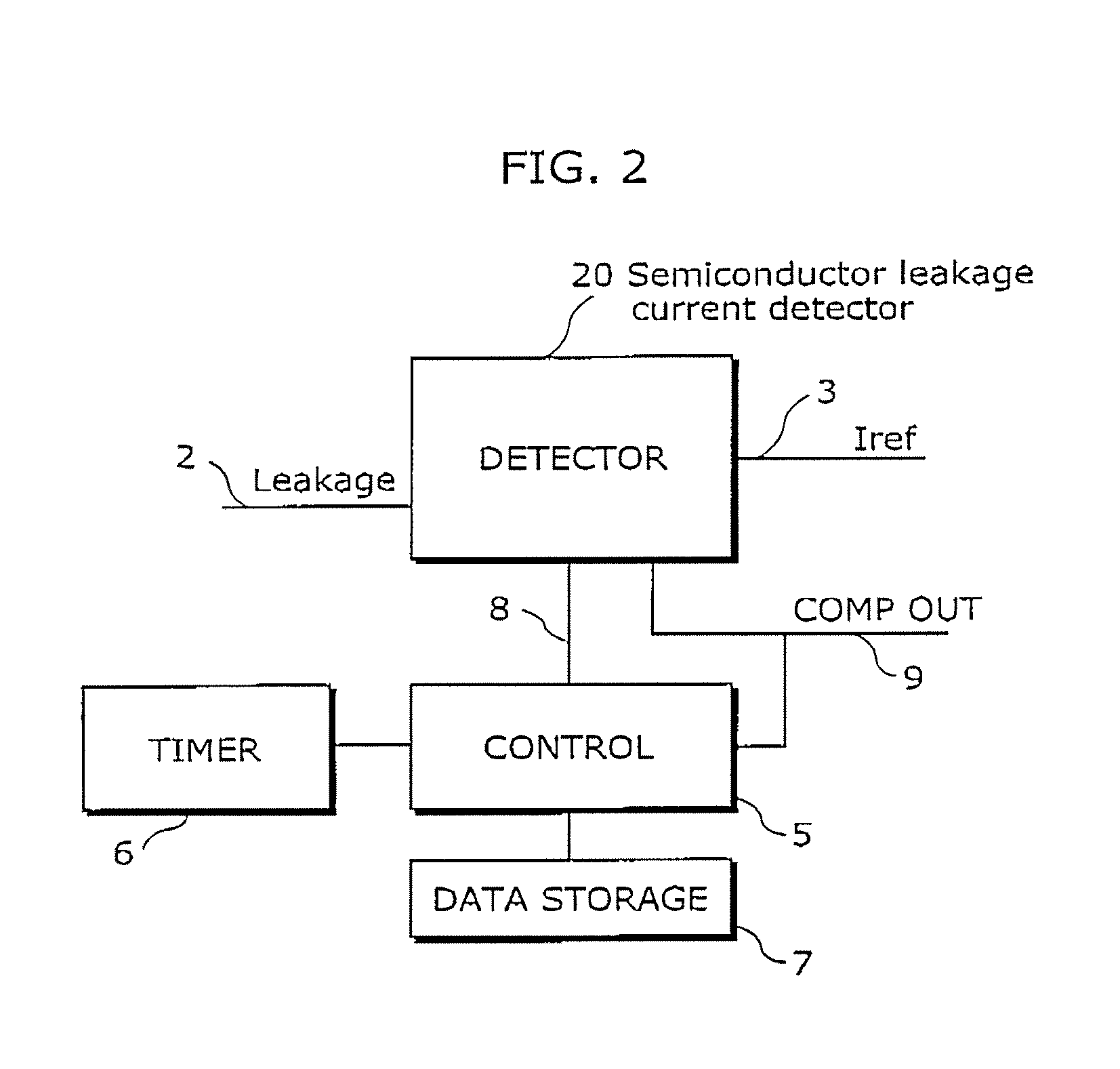
Semiconductor leakage current detector and leakage current measurement method, semiconductor leakage current detector with voltage trimming function and reference voltage trimming method, and semiconductor intergrated circuit thereof
ActiveUS20070145981A1Improve search speedReduce trimming timeMultiple input and output pulse circuitsDirection of current indicationCapacitanceReference current
A semiconductor leakage current detector of the present invention includes a first analog switch which causes a current to be measured to flow or to be cut off, a second analog switch which causes a reference current to flow or to be cut off, an integral capacitance element which is connected by the first analog switch and the second analog switch and is charged with the current to be measured or the reference current, a discharge unit which discharges the integral capacitor, and a comparison unit which compares the reference voltage with each of an integral voltage generated in the integral capacitor by a reference current after the discharge of the integral capacitor and an integral voltage generated in the integral capacitance element by the current to be measured after the discharge of the integral capacitor
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
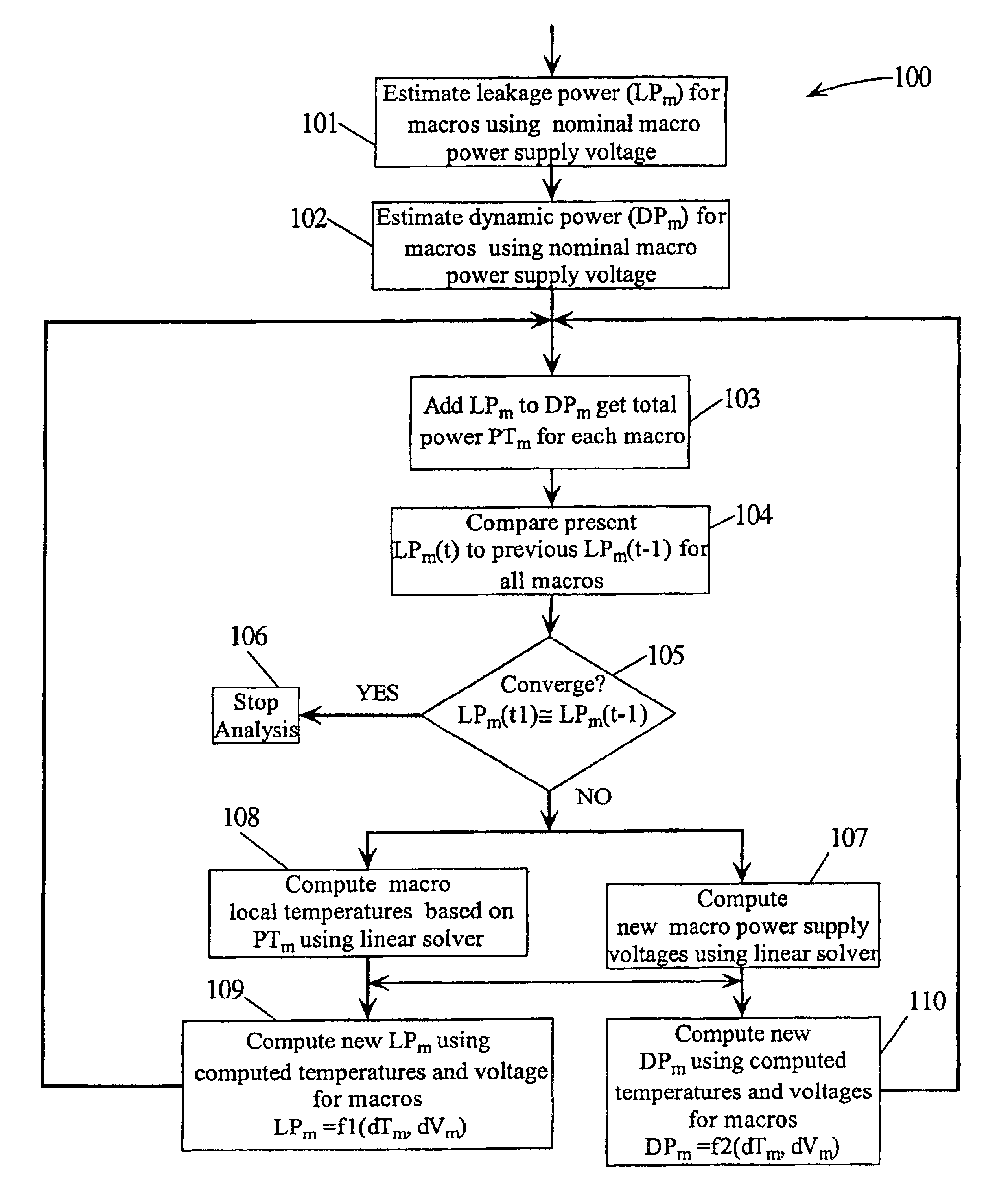
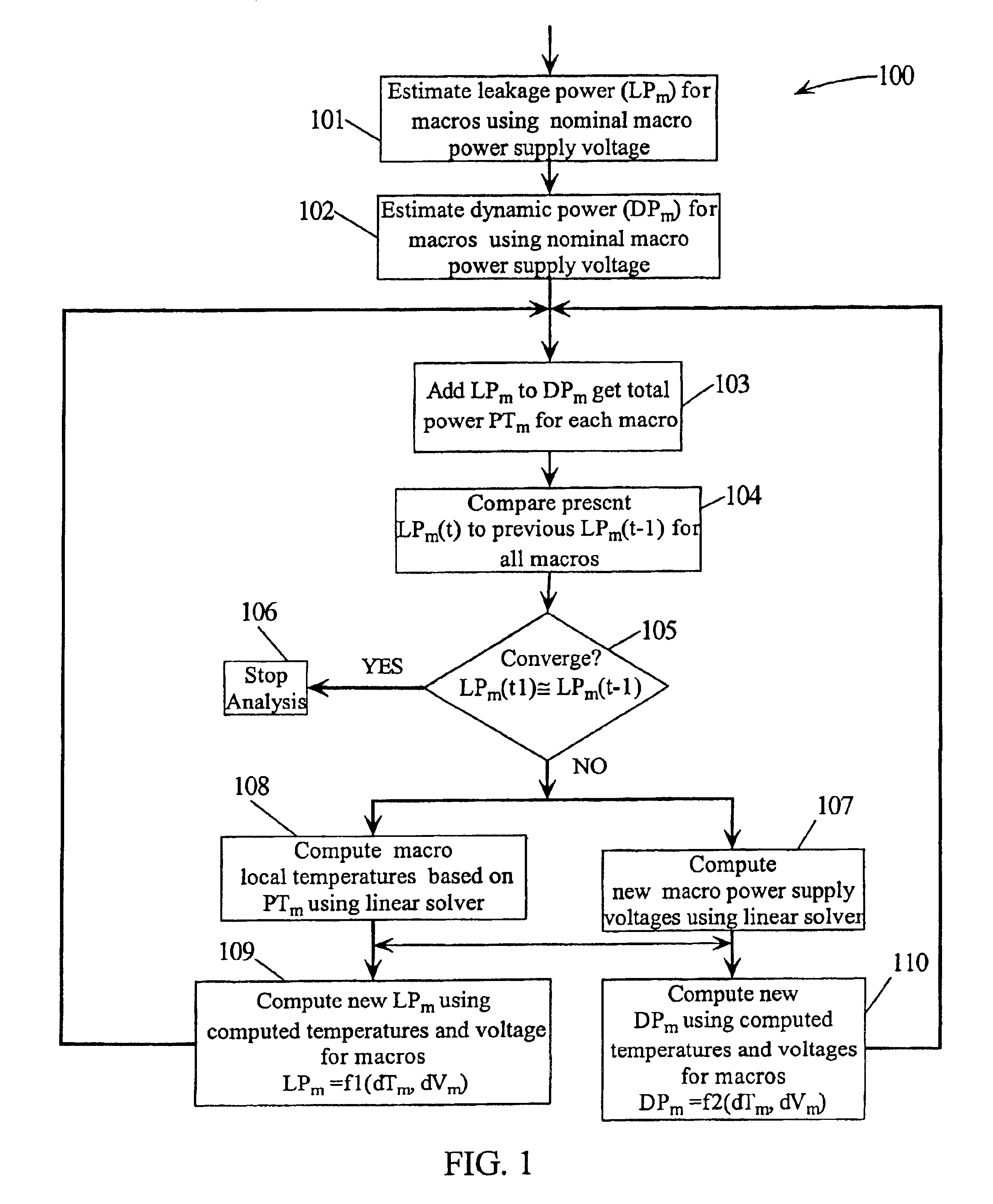
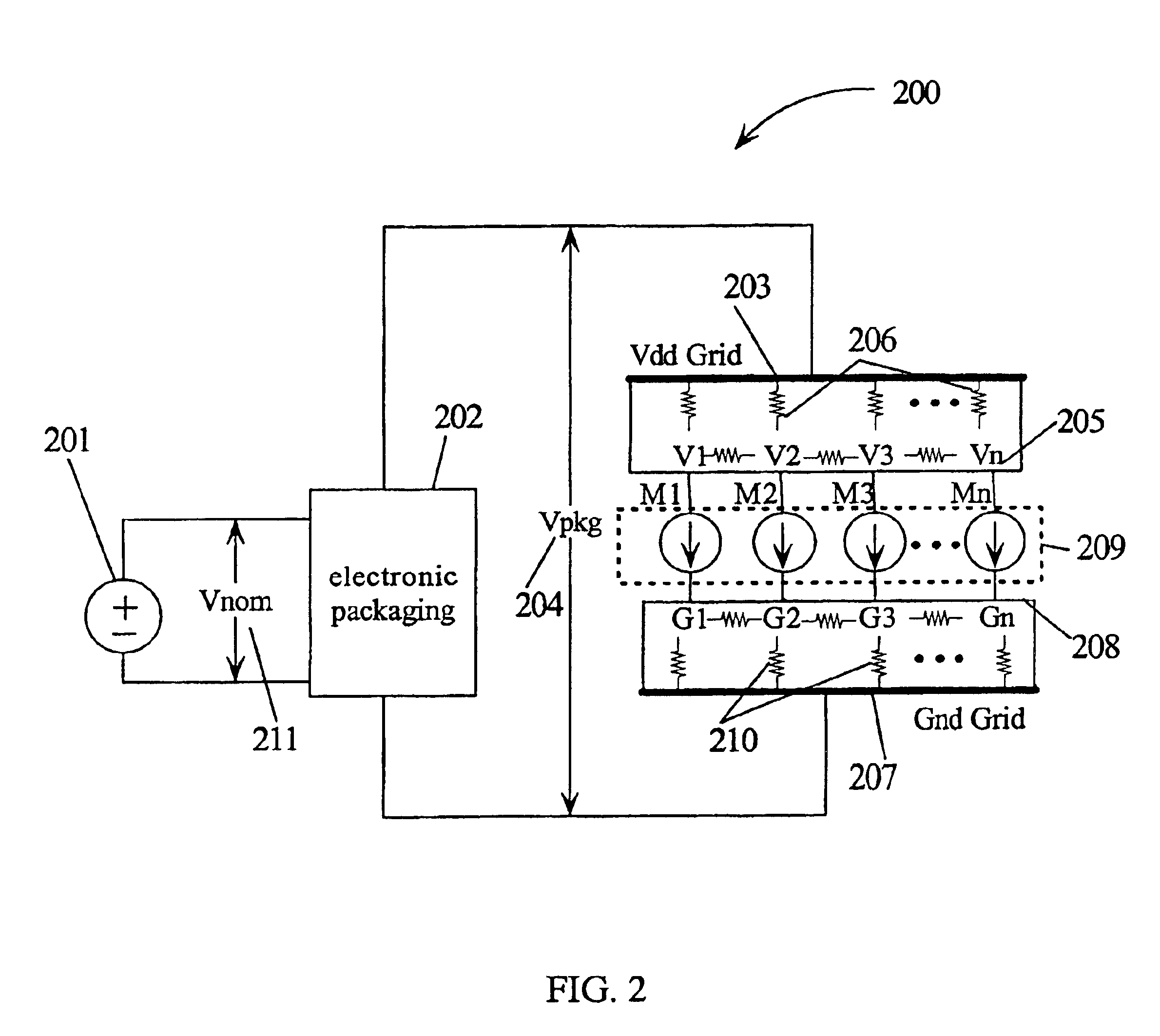
Method for determining the leakage power for an integrated circuit
InactiveUS6842714B1Electric devicesCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical resistance and conductanceElectric distribution network
A method for determining full chip leakage power first estimates leakage power and dynamic power for each circuit macro. The power supply voltage to each macro is first assumed to be nominal. The power dissipation for each macro is modeled as a current source whose value is the estimated power divided by the nominal power supply voltage. The power distribution network is modeled as a resistive grids. The thermal environment of the IC and its electronic package are modeled as multi dimensional grids of thermal elements. Algebraic multi-grid (AMG) methods are used to calculate updated circuit macro voltages and temperatures. The macro voltages and temperatures are updated and updated leakage and dynamic power dissipation are calculated. Iterations are continued until leakage power converges to a final value.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for IDDQ measurement in system on a chip (SOC) design
ActiveUS7282905B2Short test timeReduce chip areaMarginal circuit testingIndividual semiconductor device testingElectricityEngineering
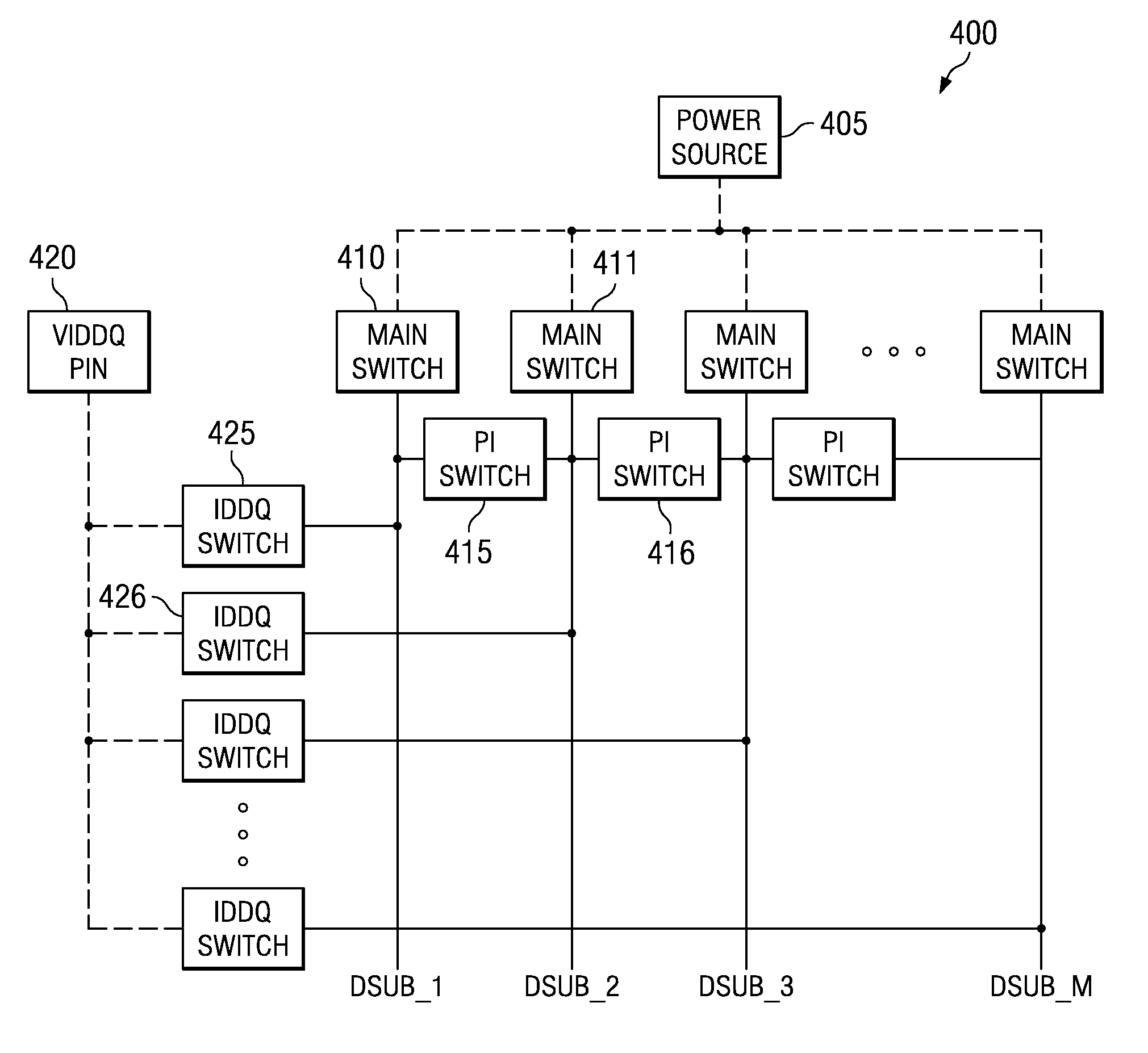
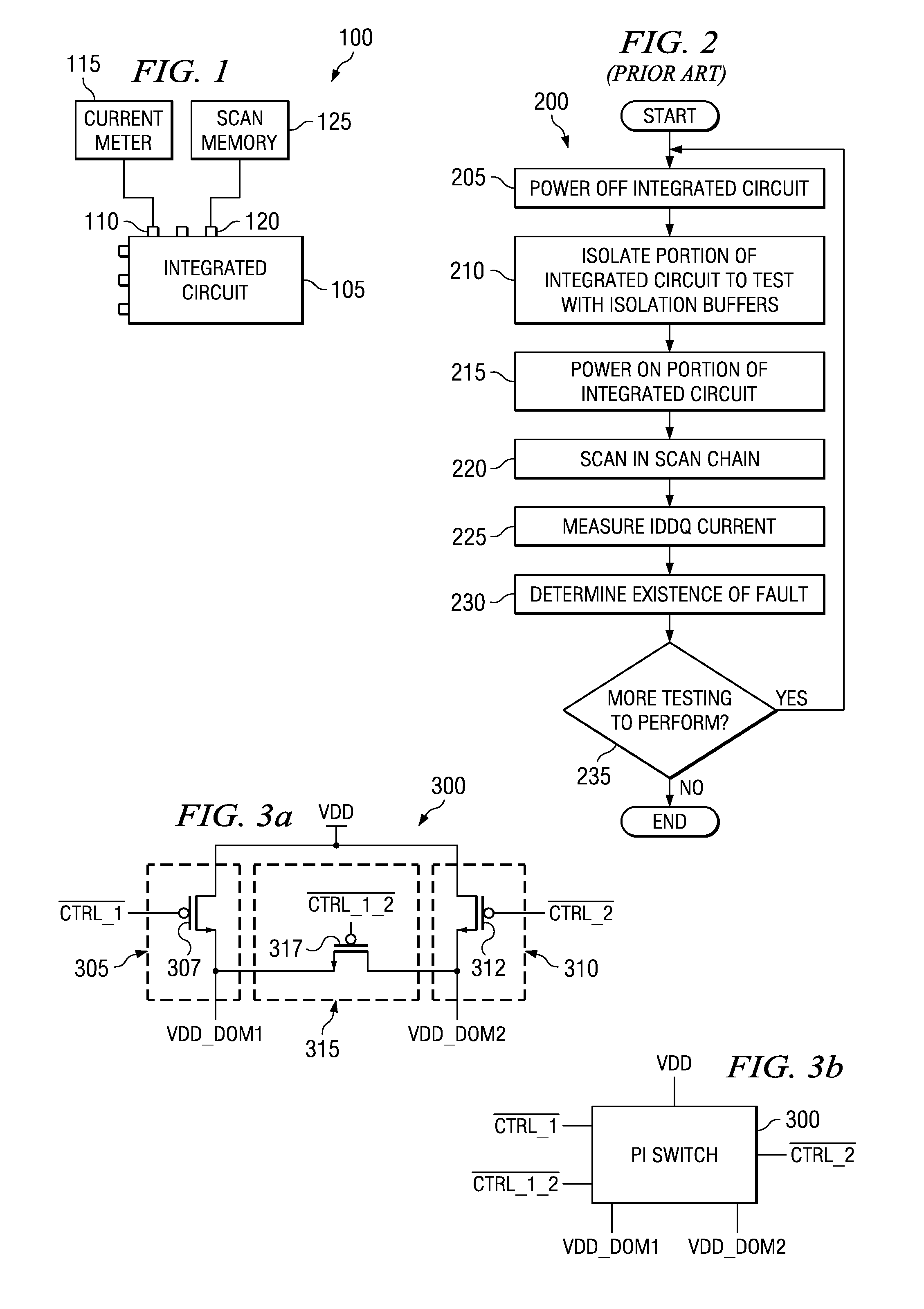
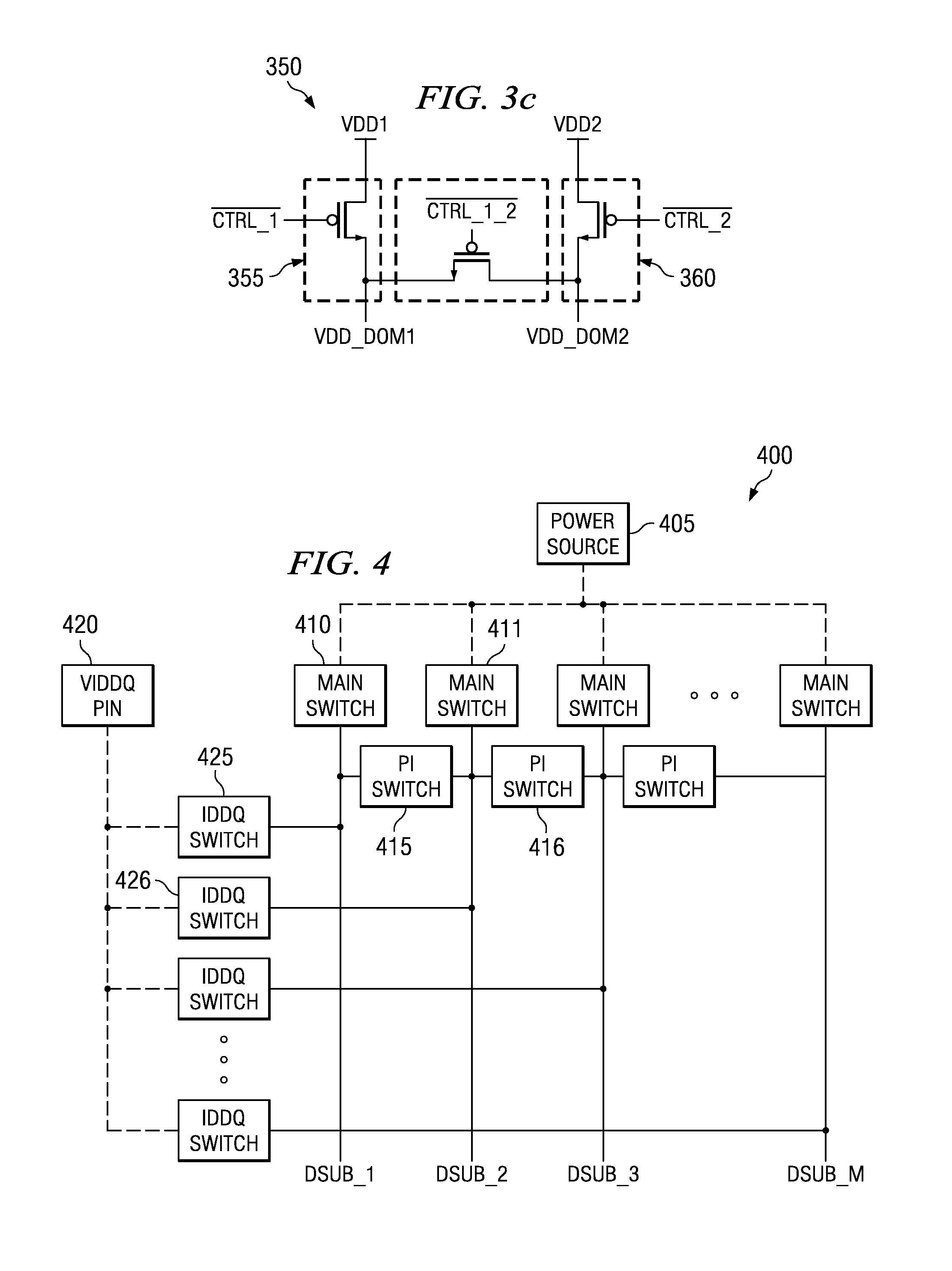
System and method for detecting transistor failure in large-scale integrated circuits by measuring IDDQ. A preferred embodiment comprises a switch structure for an integrated circuit made up of a plurality of main switches (such as main switch 410) selectively coupling a power sub-domain to a power source pin, a plurality of pi-switches (such as pi-switch 415) selectively coupling pairs of power sub-domains, and a plurality of IDDQ switches (such as IDDQ switch 425) selectively coupling the power sub-domains to a VIDDQ pin. The pi-switches can decouple the power sub-domains while the IDDQ switches can enable the measurement of the quiescent current in the power sub-domains. The use of pi-switches and IDDQ switches can permit the measurement of the quiescent current in the power sub-domains without requiring the use of isolation buffers and needed to powering on and off the integrated circuit between current measurements in the different power sub-domains.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
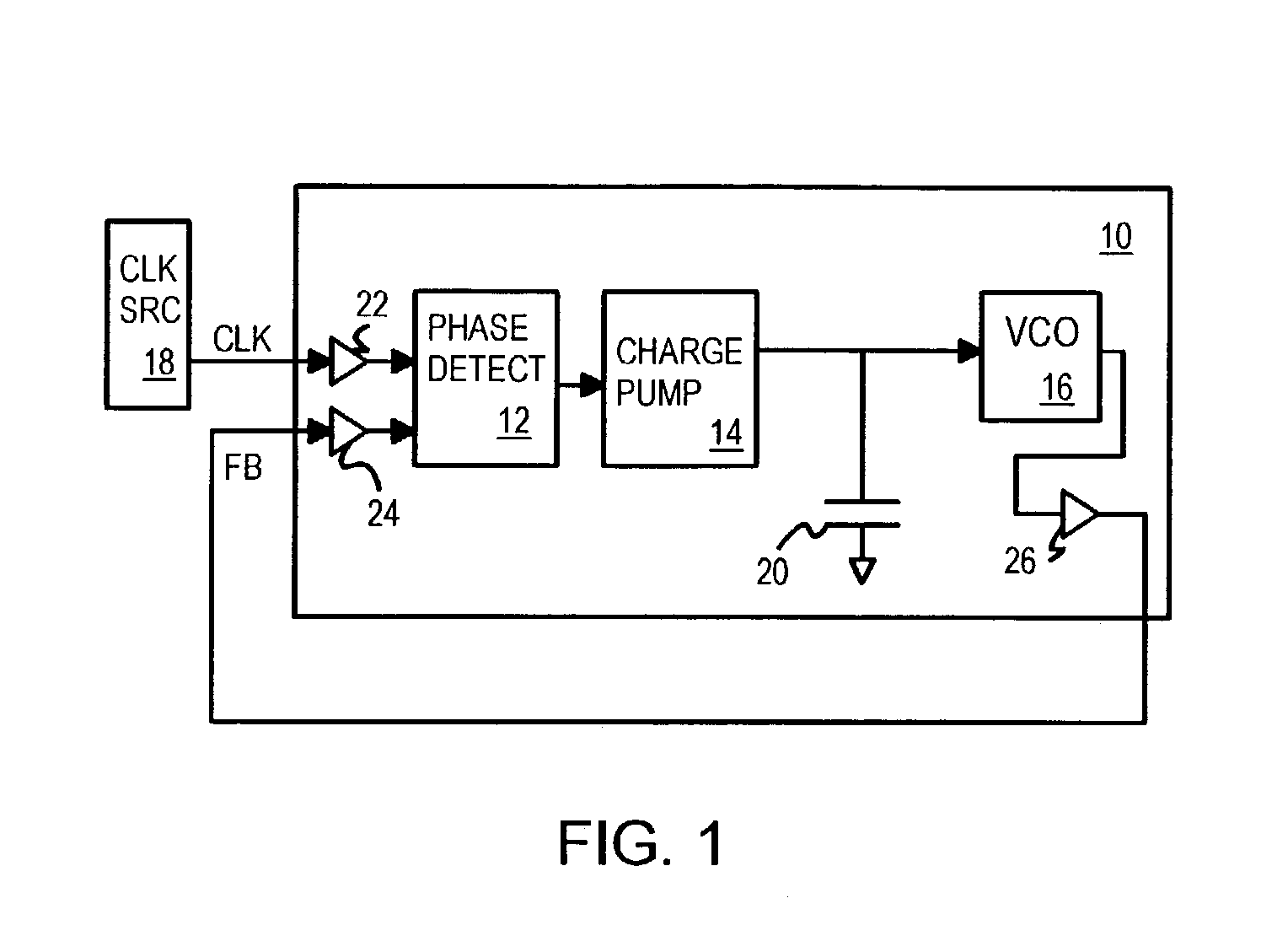
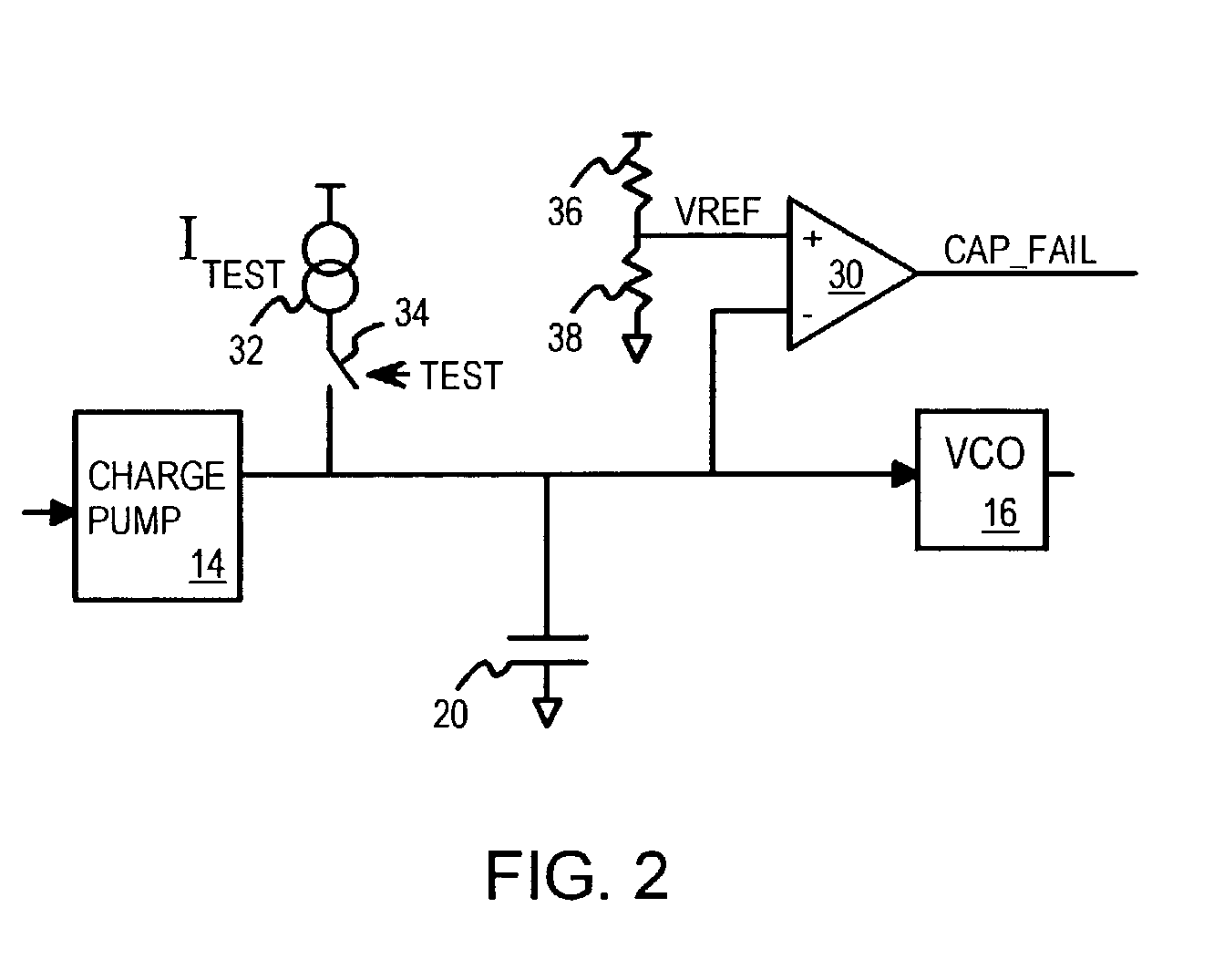
PLL with built-in filter-capacitor leakage-tester with current pump and comparator
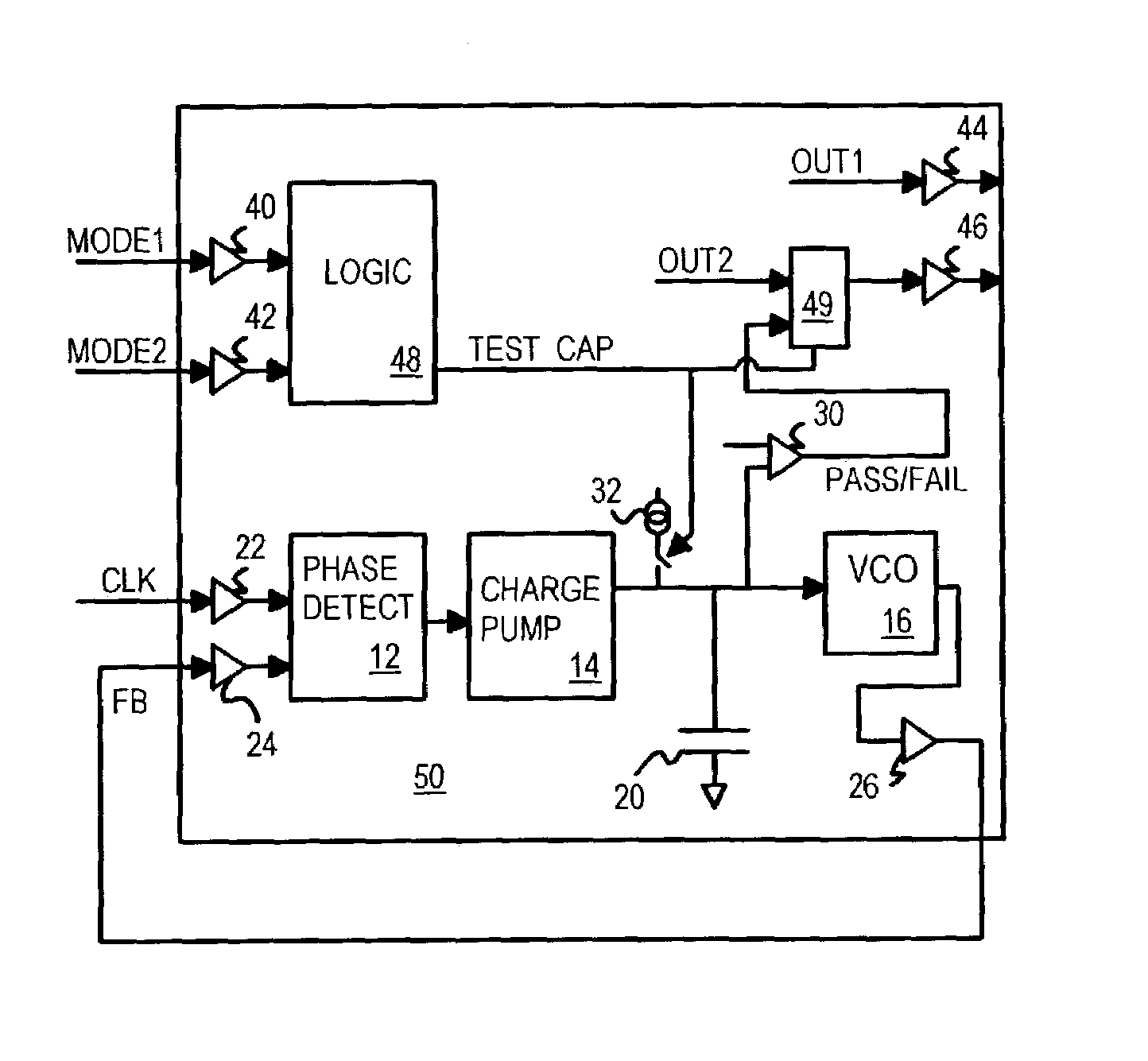
A filter capacitor within a phase-locked loop (PLL) can be tested using a built-in test circuit. The PLL's charge pump is deactivated while a test-current source is activated to supply a test current to the PLL filter capacitor. When the test current is larger than any leakage currents through the capacitor, the capacitor's voltage rises above a reference voltage. A test comparator compares the capacitor's voltage to the reference voltage and signals a good test result when the capacitor's voltage rises above the reference voltage. When leakage current is larger than the test current, the capacitor's voltage cannot rise above the reference voltage and the test comparator signal a leakage failure. The test current source can share a bias voltage with the charge pump and can drive the capacitor to a voltage higher than the charge pump does to increase leakage and stress during testing.
Owner:DIODES INC
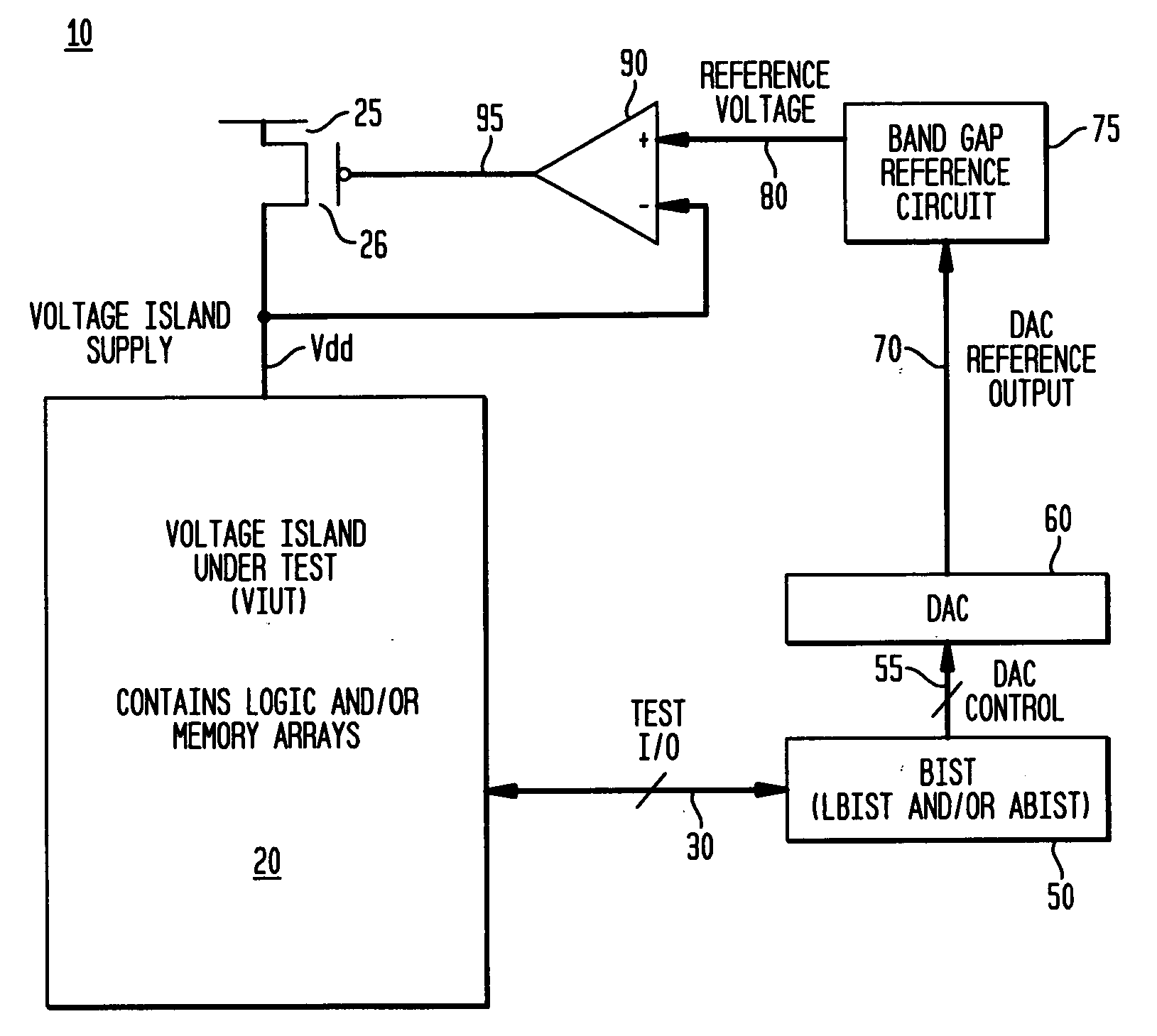
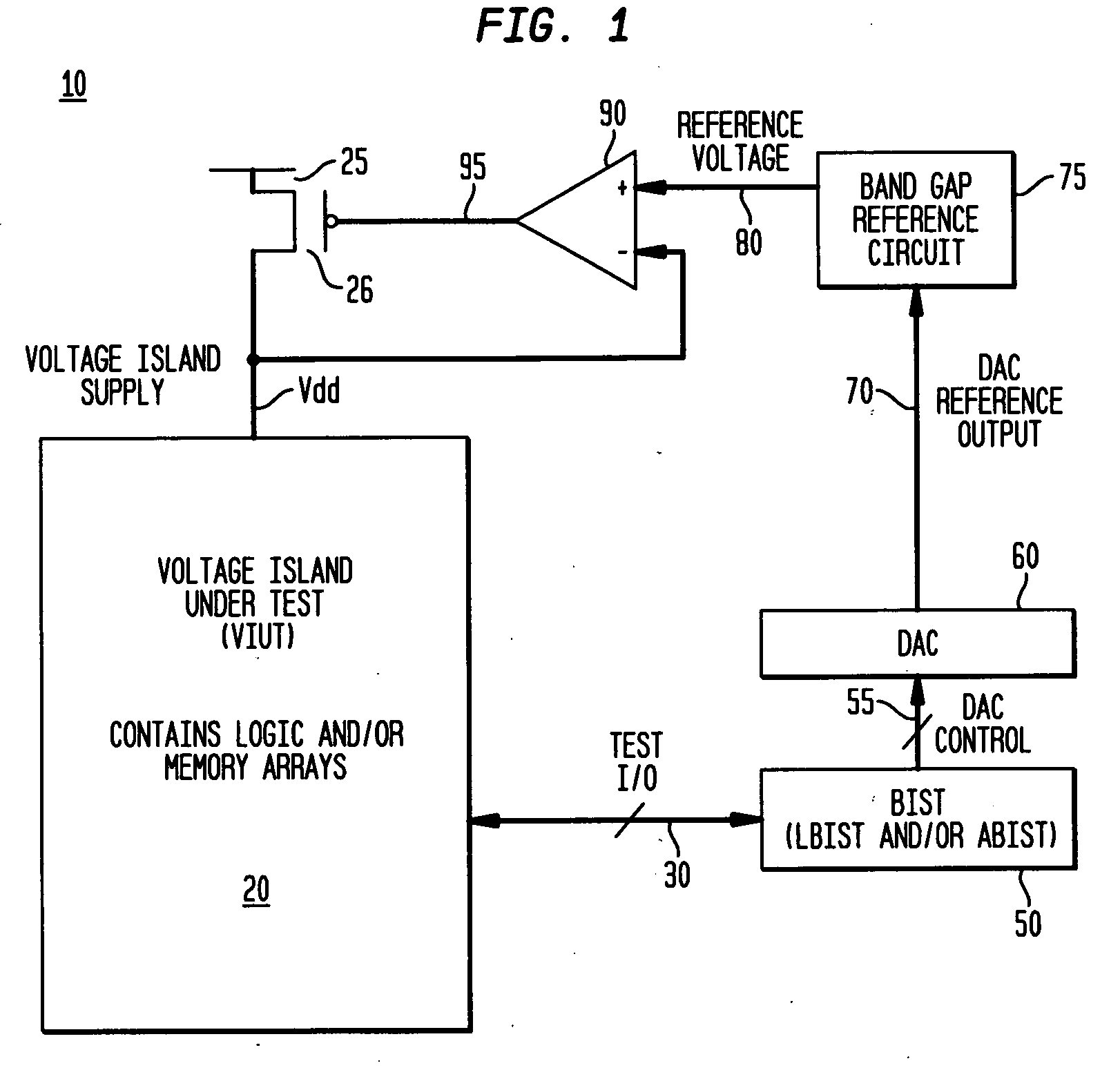
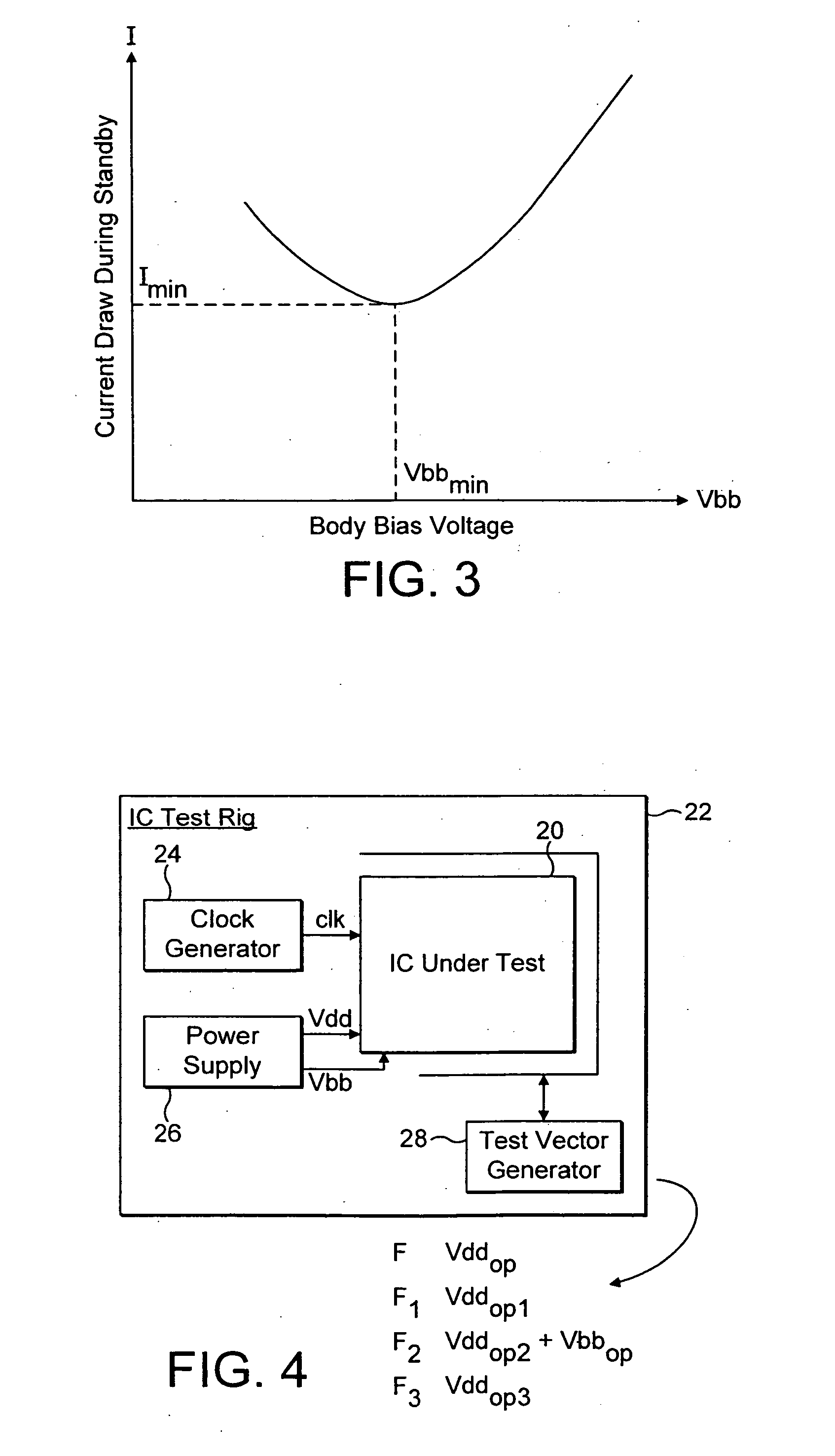
Self-test circuitry to determine minimum operating voltage
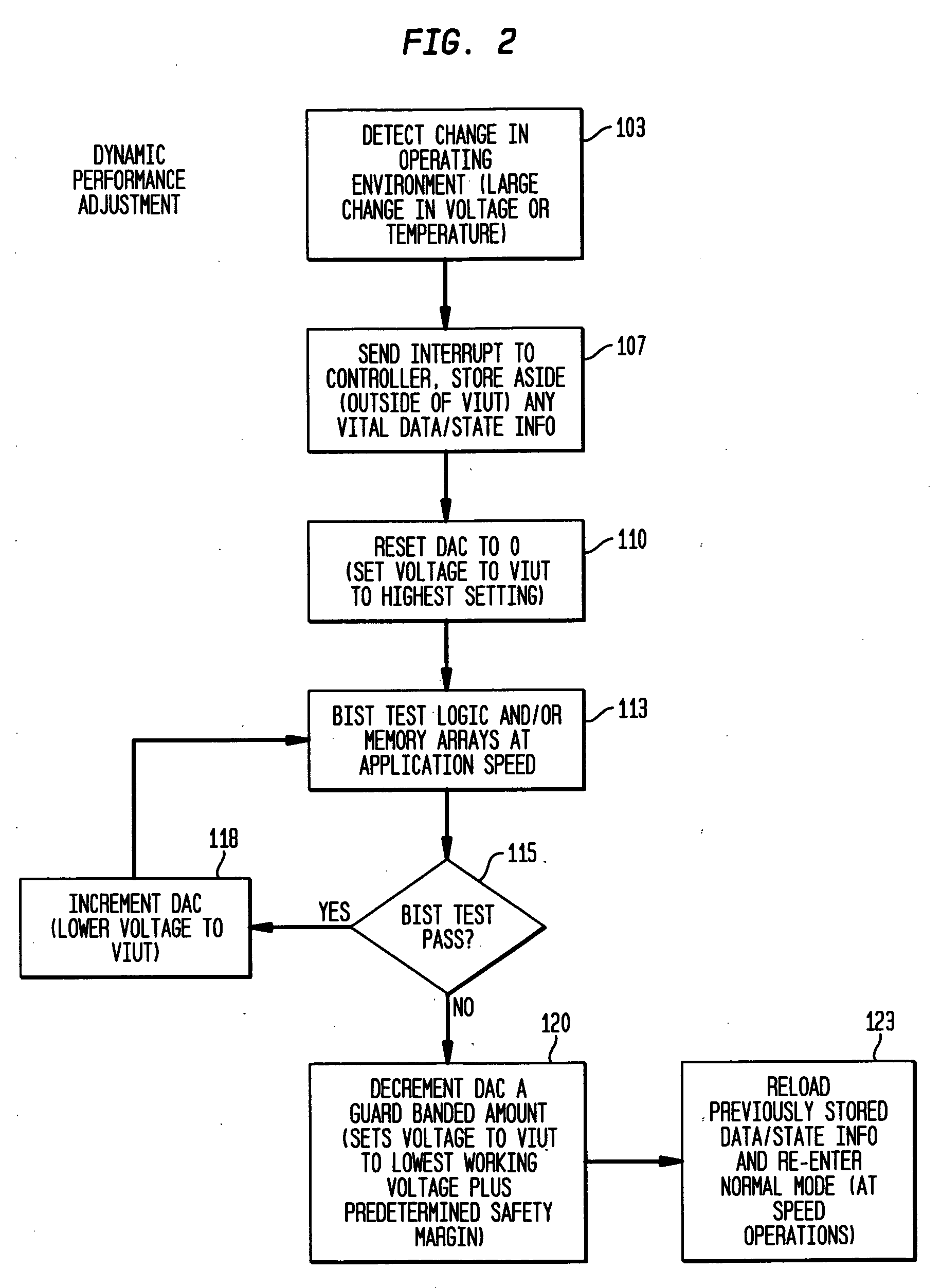
InactiveUS20060259840A1Reduce power consumptionMaintaining at-application speed performanceMarginal circuit testingTest flowVoltage source
A solution for determining minimum operating voltages due to performance / power requirements would be valid for a wide range of actual uses. The solution includes a test flow methodology for dynamically reducing power consumption under applied conditions while maintaining application performance via a BIST circuit. There is additionally provided a test flow method for dynamically reducing power consumption to the lowest possible stand-by / very low power level under applied conditions that will still be sufficient to maintain data / state information. One possible application would be for controlling the voltage supply to a group of particular circuits on an ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit). These circuits are grouped together in a voltage island where they would receive a voltage supply that can be different from the voltage supply other circuits on the same chip are receiving. The same solution could be applied to a portion of a microprocessor (the cache logic control, for example).
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for fault simulation of semiconductor integrated circuit
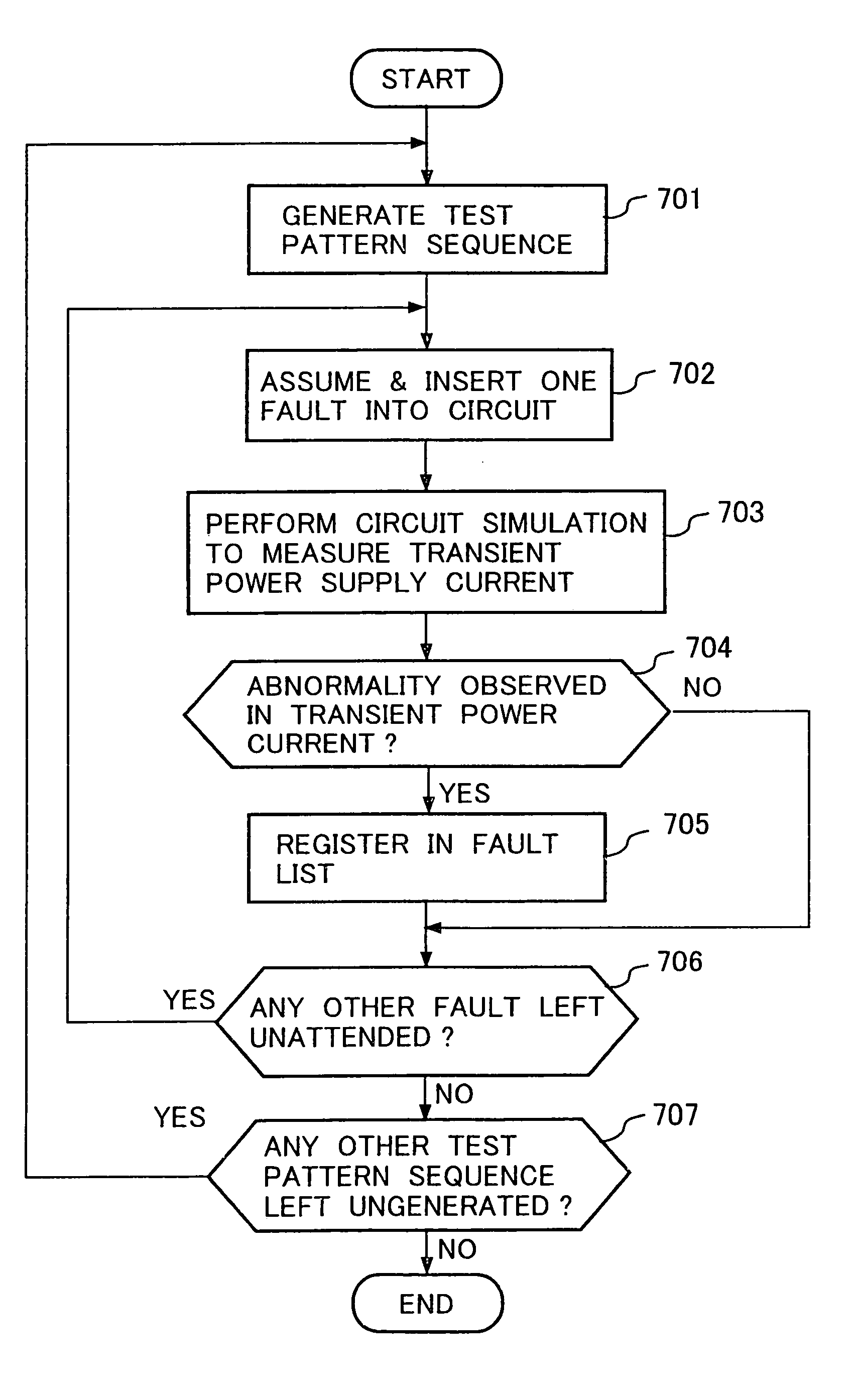
InactiveUS6975978B1Improve test efficiencyImpossible to detectSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDetecting faulty computer hardwarePattern sequenceEngineering
A test pattern sequence is generated (101), then a logic simulation of the operation of an IC under test in the case of applying each test pattern of the test pattern sequence, and a logic signal value sequence occurring in each signal line of the IC under test (102). The logic signal value sequence in each signal line is used to register in a fault list parts (a logic gate, signal line or signal propagation path) in which a fault (a delay fault or an open fault) detectable by a transient power supply current testing using the test pattern sequence is likely to occur (103).
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
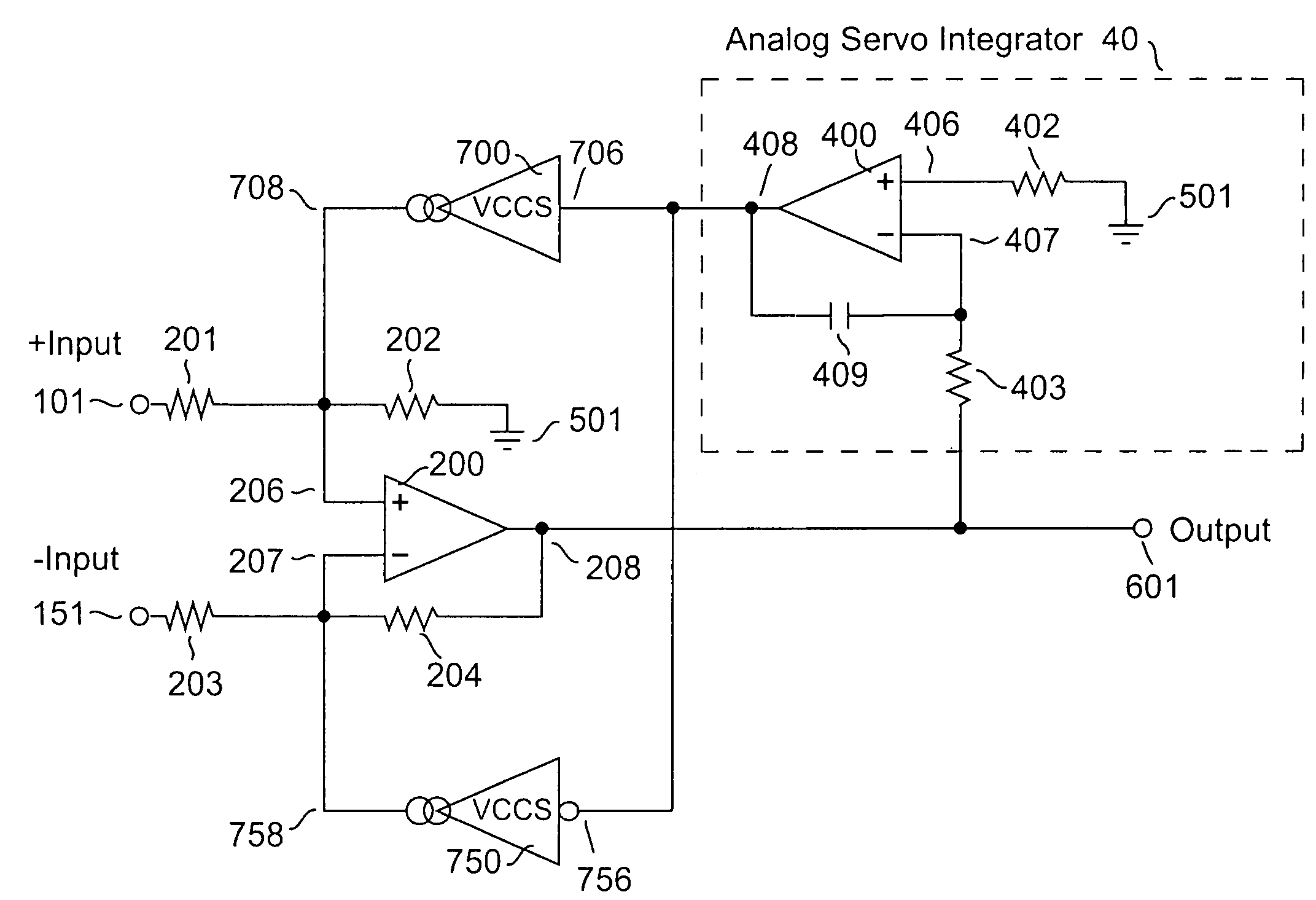
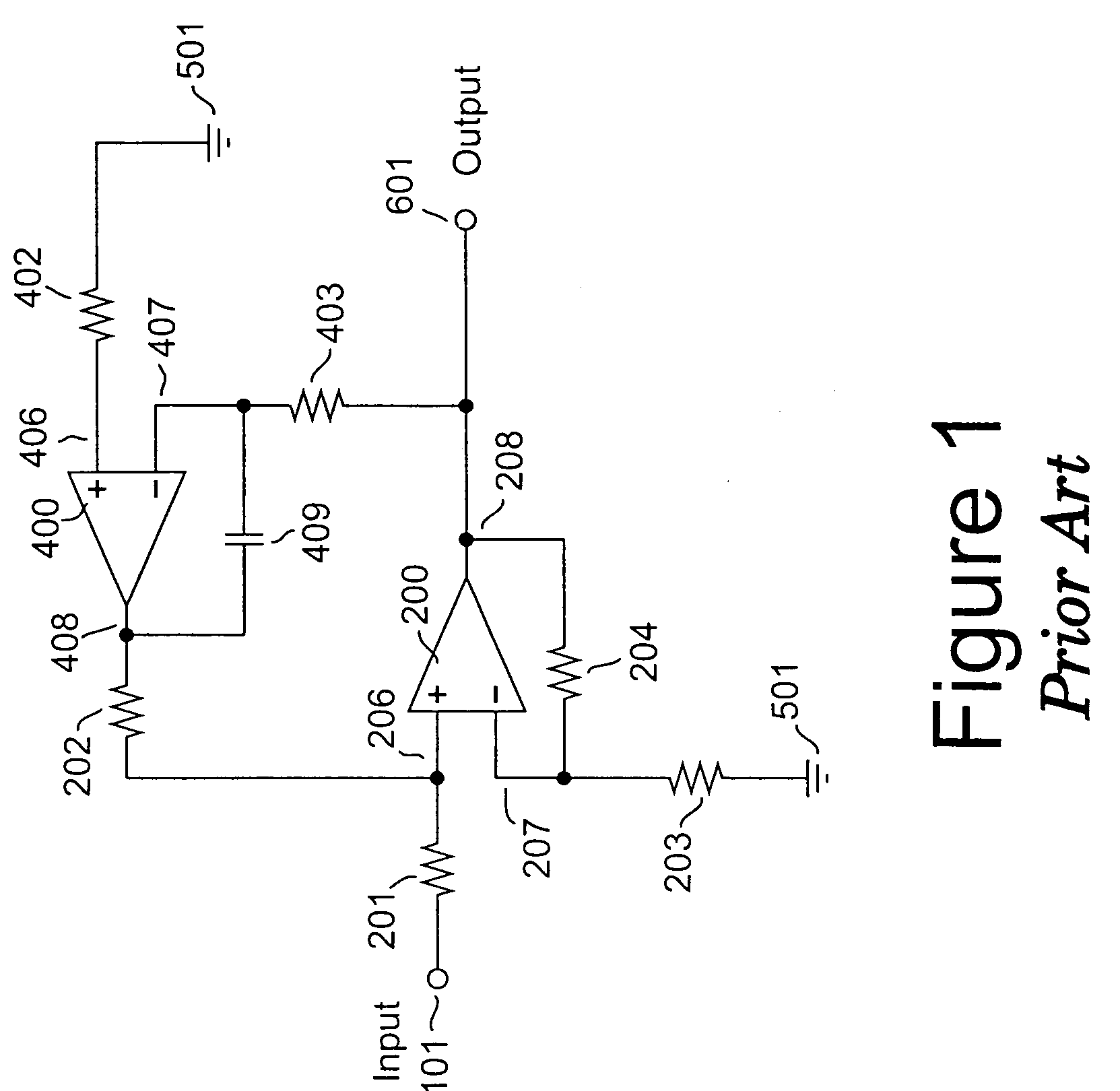
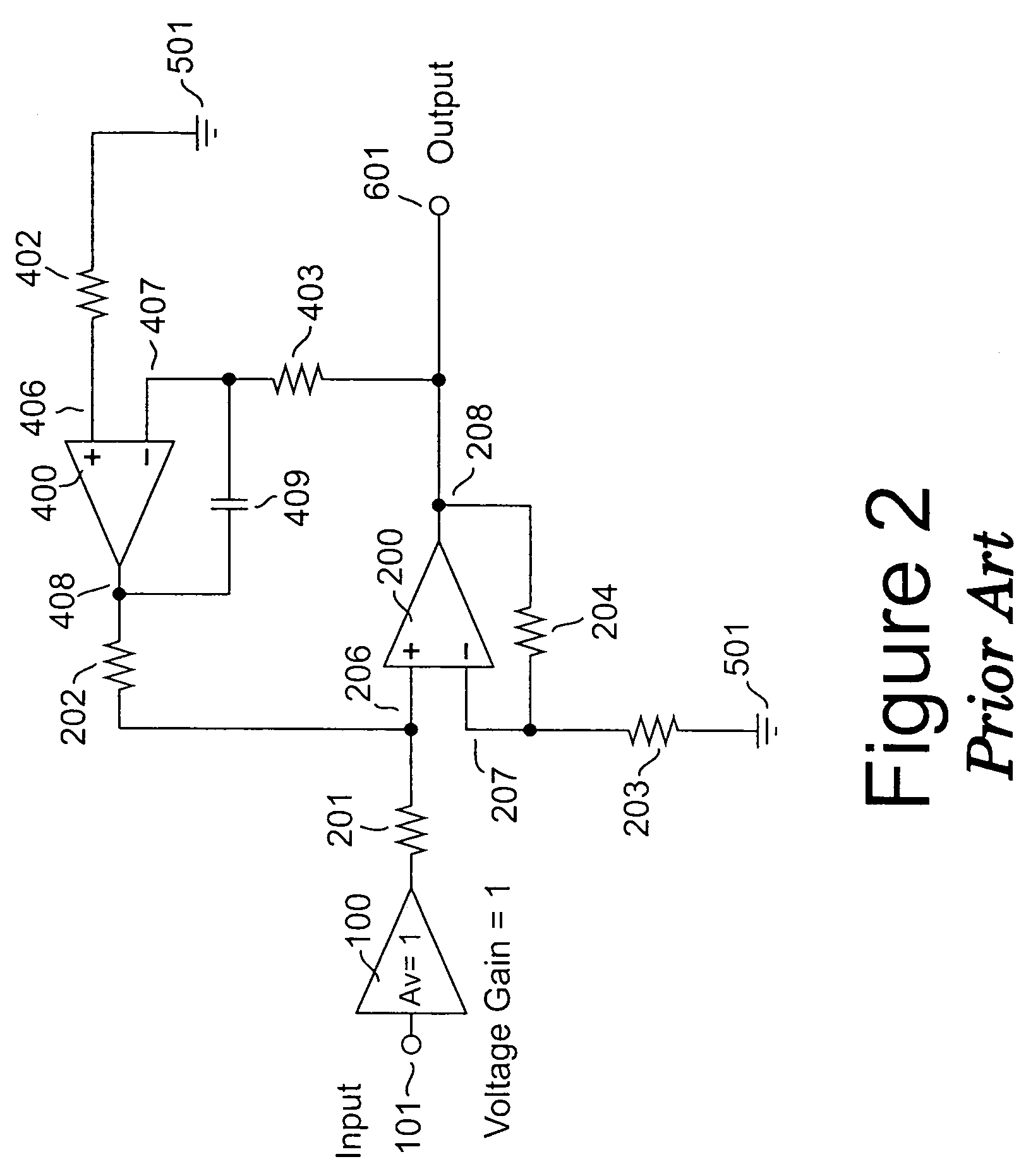
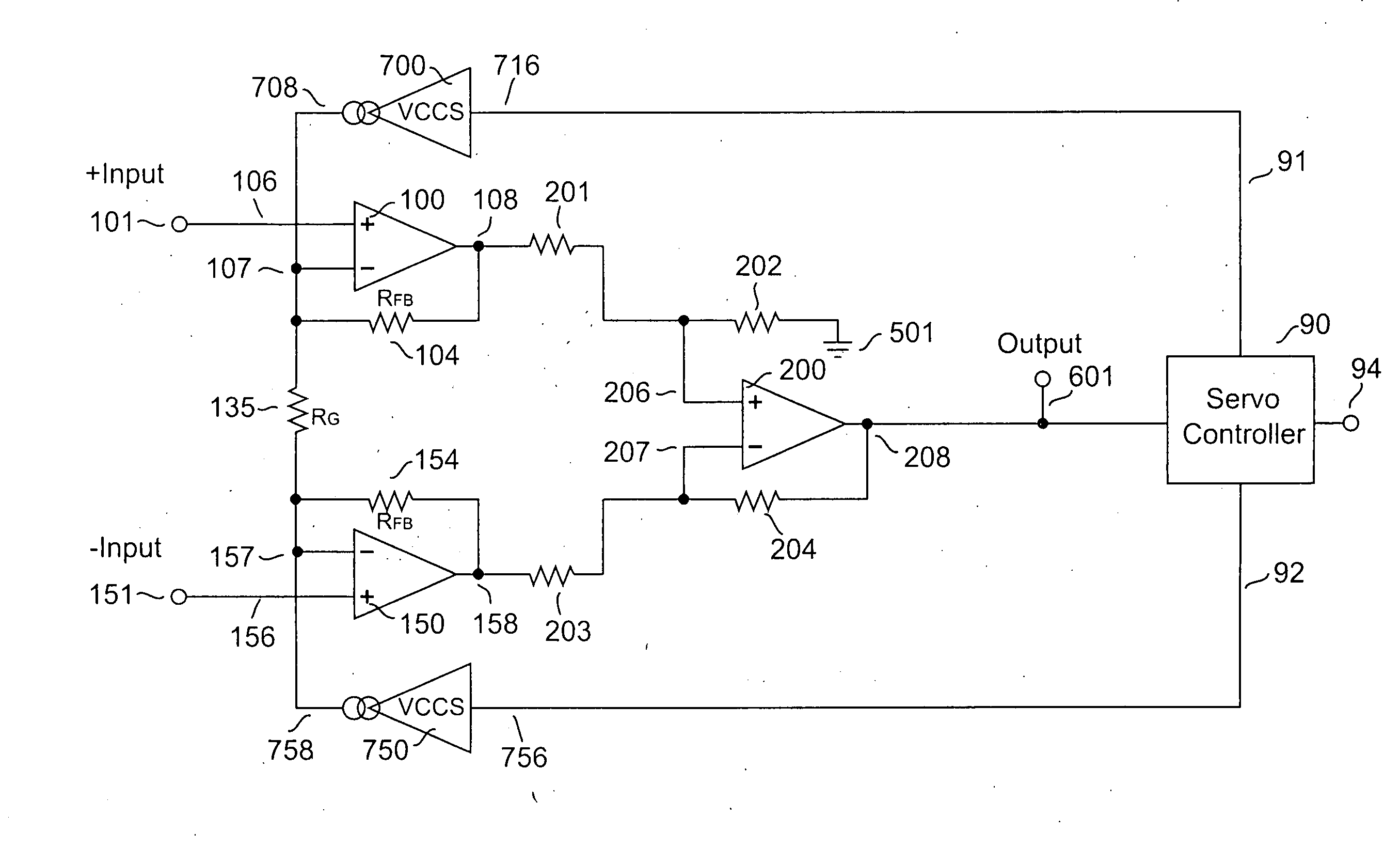
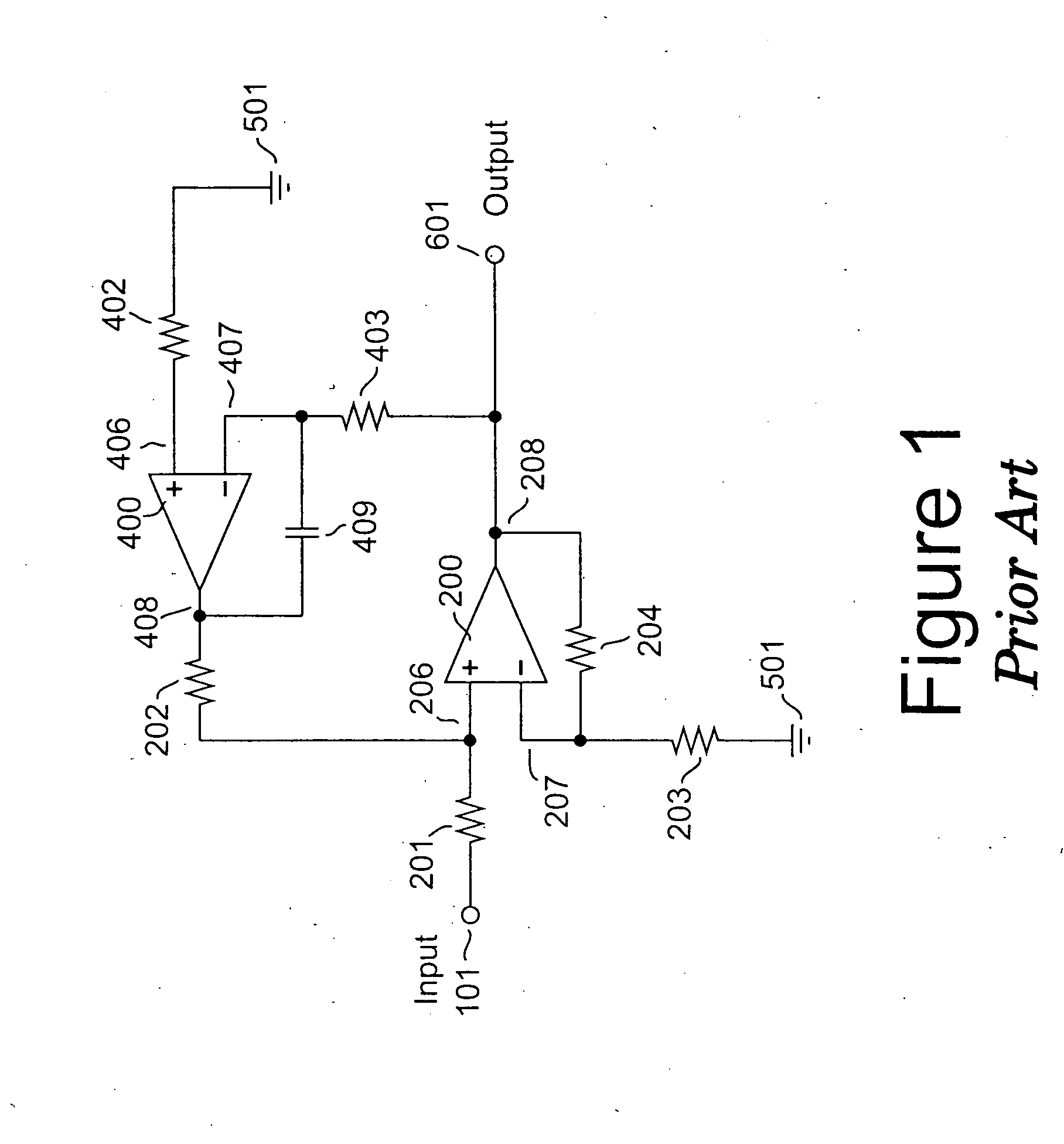
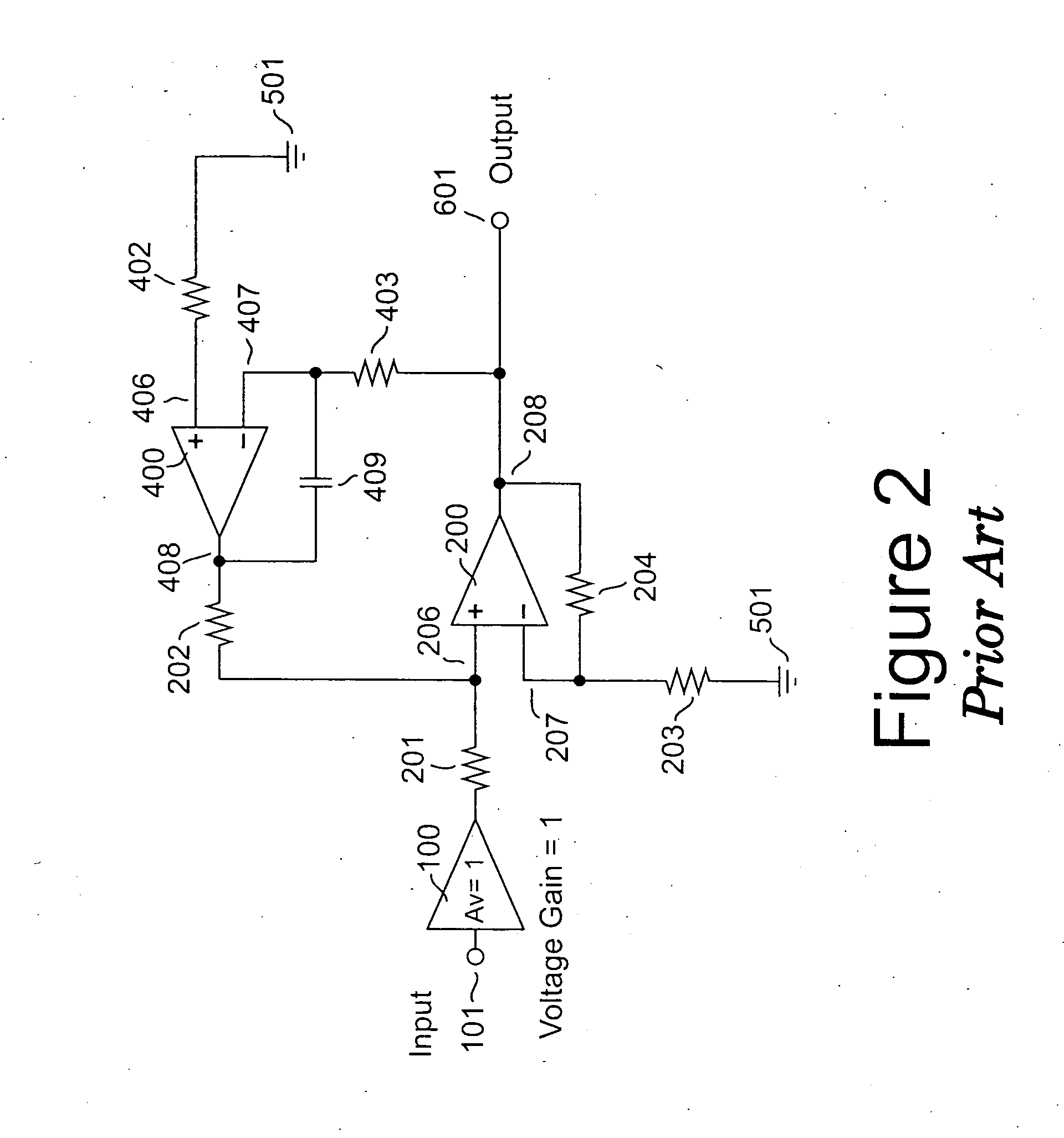
Amplifier system with current-mode servo feedback
InactiveUS7253680B2Maximize dynamic rangeAccurately amplify any subsequent variations in the input signalNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier combinationsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Audio power amplifier
A system and method for compensating an amplifier apparatus for low frequency and / or DC components of an externally applied input signal as well as for any voltage offsets contributed by the amplifier circuitry. Band-limited servo feedback is applied to predetermined nodes in the forward gain path to null out unwanted signal components, leaving a residual signal that, when amplified, will be centered around ground, so that the full dynamic range of the amplifier system may be utilized. Consequently, the signal-to-noise ratio available at the output of the amplifier system will be maximized. The servo compensation may either operate in continuous time, or it may be held constant once a suitable level of compensation has been established, or it may be adjusted from time to time to accommodate slow variations of the average DC component of the input signal.
Owner:BIOURJA ENERGY SYSTEMS LLC
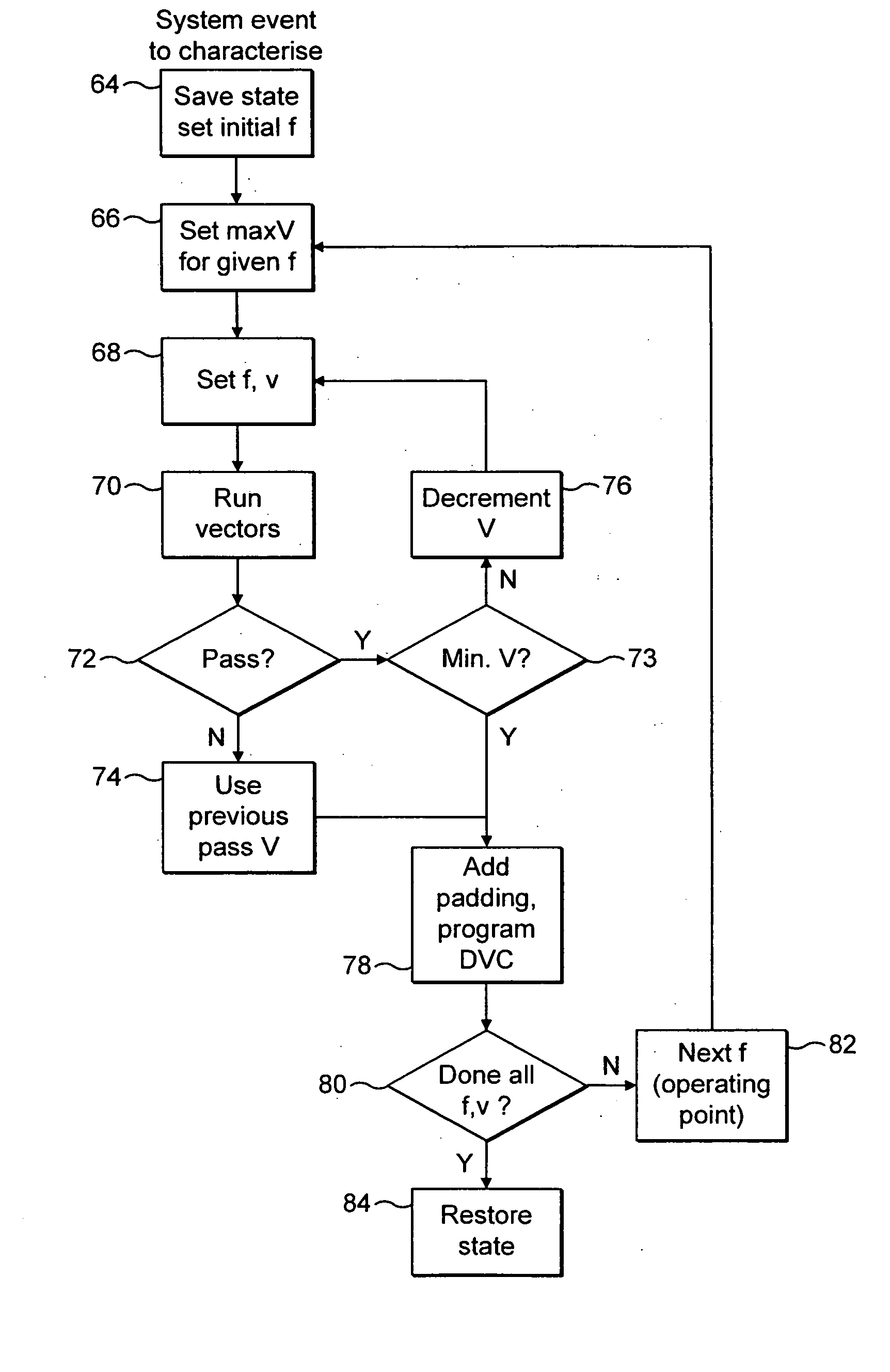
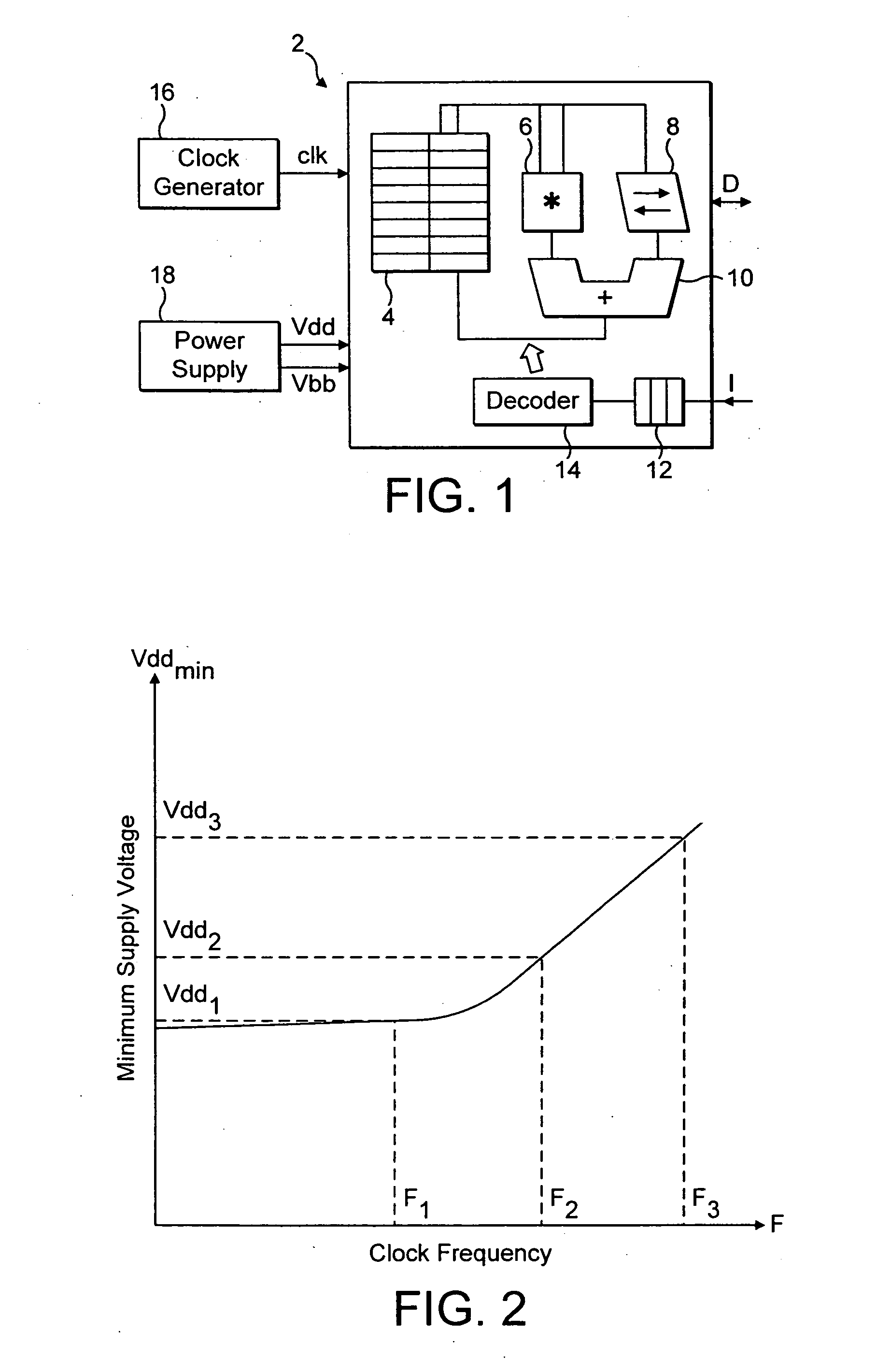
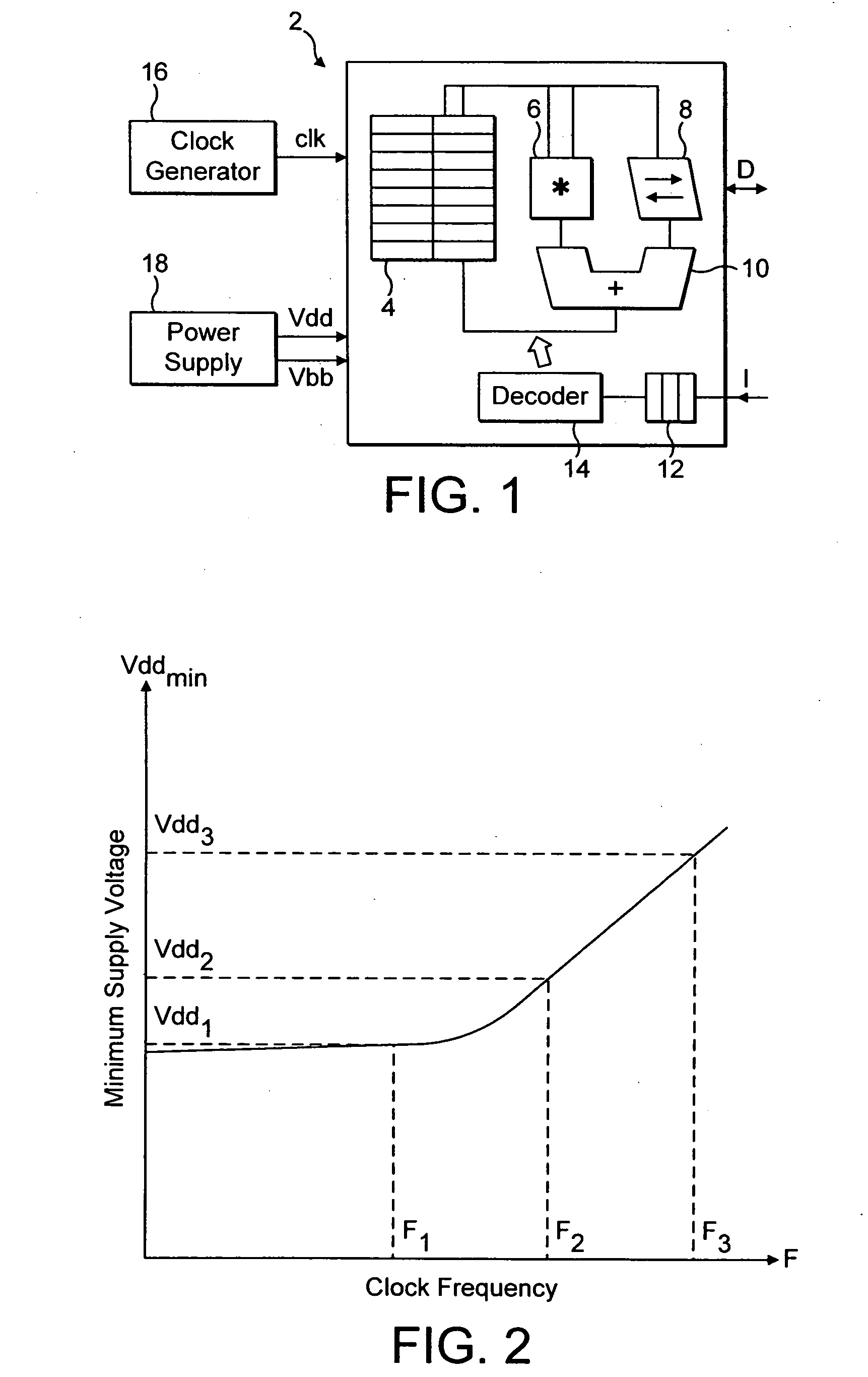
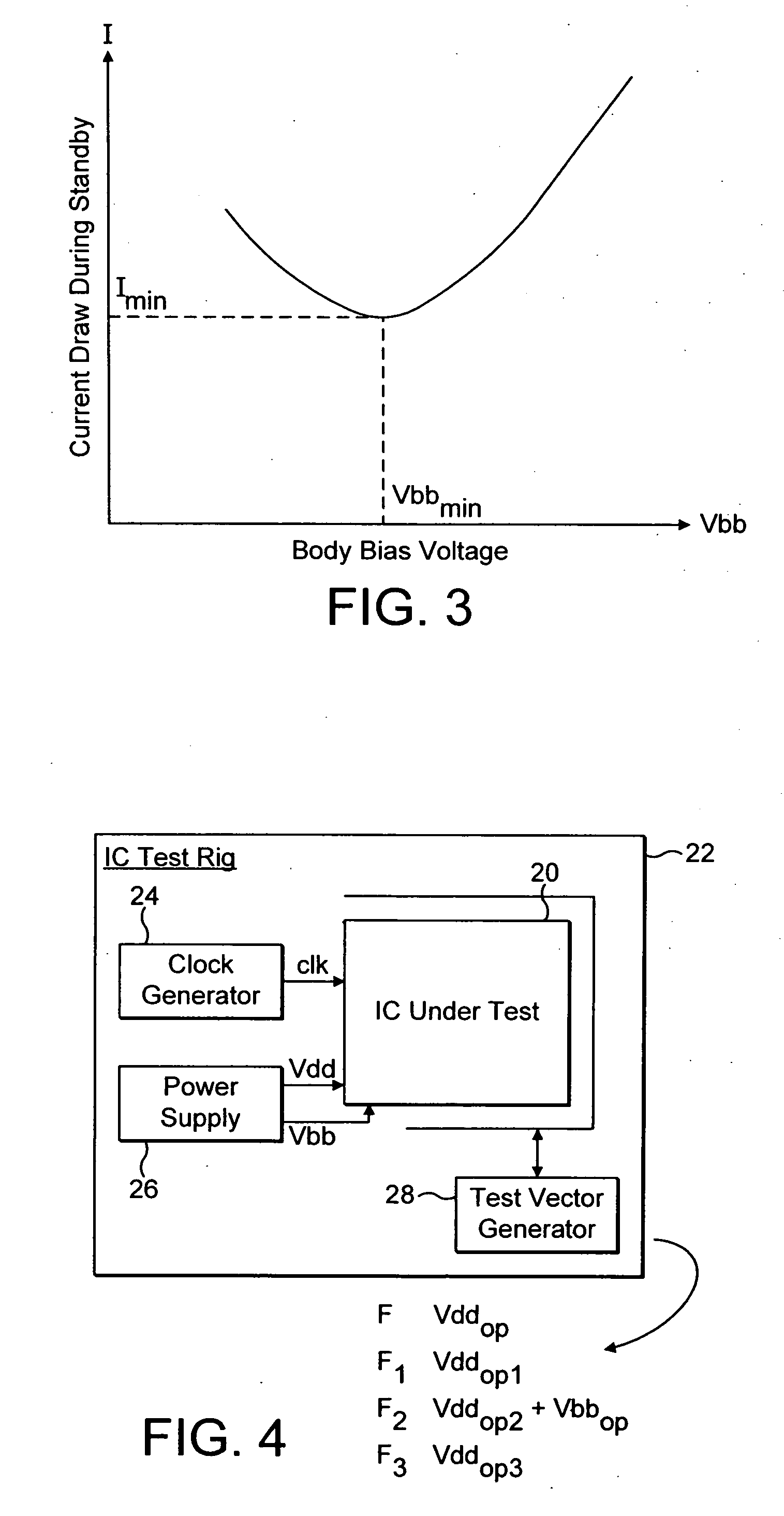
Operating voltage determination for an integrated circuit
ActiveUS20060074576A1Easy to useHigh voltageEnergy efficient ICTCurrent/voltage measurementClock rateTest vector
Owner:ARM LTD
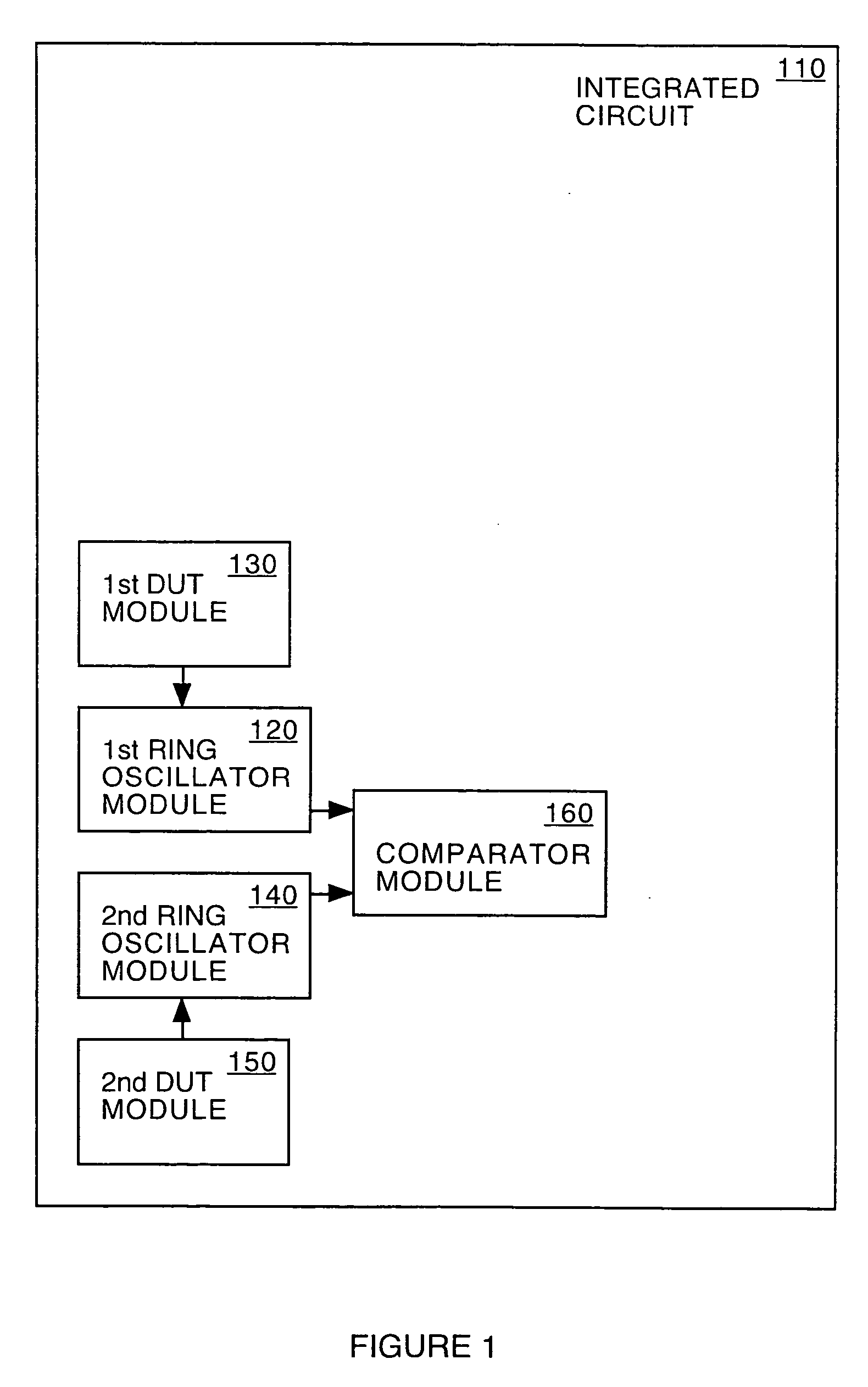
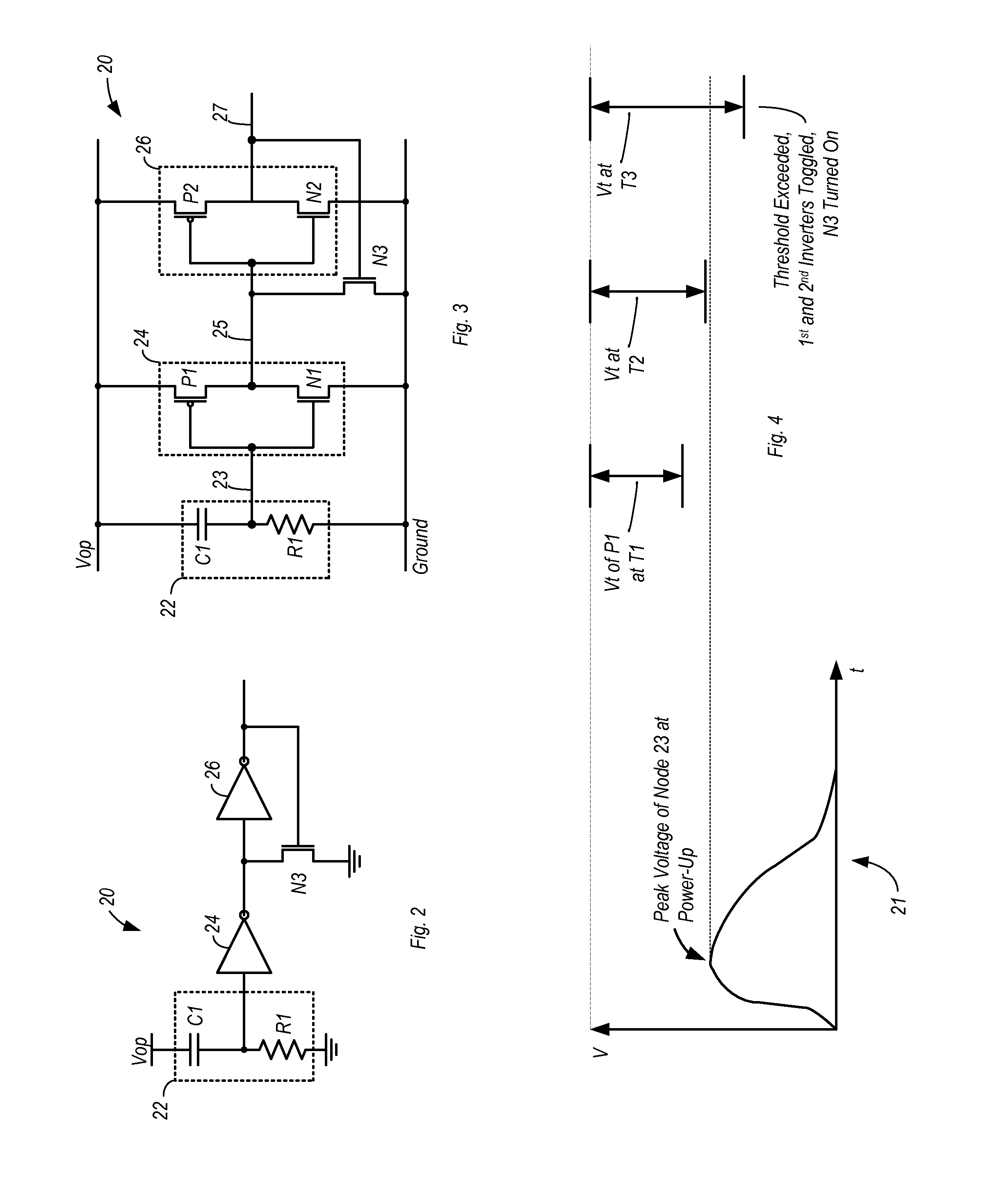
System and method for measuring time dependent dielectric breakdown with a ring oscillator
InactiveUS20050212547A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectricityGate leakage current
An integrated circuit, in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, includes a first device under test (DUT) module coupled to a first ring oscillator module and a second DUT module coupled to a second ring oscillator module. A dielectric layer of the first DUT is stressed during a first mode, thereby causing time dependent dielectric breakdown in the first dielectric layer. A dielectric layer of the second DUT is maintained as a reference. The operating frequency of the first ring oscillator module, during a second mode, is a function of a gate leakage current of the stressed dielectric layer. The operating frequency of the second ring oscillator module, during the second mode, is a function of a gate leakage current the reference dielectric layer. The integrated circuit may also include a comparator module for generating an output signal as a function of a difference between the operating frequency of the first and second ring oscillator modules.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
Semiconductor leakage current detector and leakage current measurement method, semiconductor leakage current detector with voltage trimming function and reference voltage trimming method, and semiconductor integrated circuit thereof
ActiveUS7446549B2Shorten test timeLow costMultiple input and output pulse circuitsDirection of current indicationCapacitanceReference current
A semiconductor leakage current detector of the present invention includes a first analog switch which causes a current to be measured to flow or to be cut off, a second analog switch which causes a reference current to flow or to be cut off, an integral capacitance element which is connected by the first analog switch and the second analog switch and is charged with the current to be measured or the reference current, a discharge unit which discharges the integral capacitor, and a comparison unit which compares the reference voltage with each of an integral voltage generated in the integral capacitor by a reference current after the discharge of the integral capacitor and an integral voltage generated in the integral capacitance element by the current to be measured after the discharge of the integral capacitor.
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
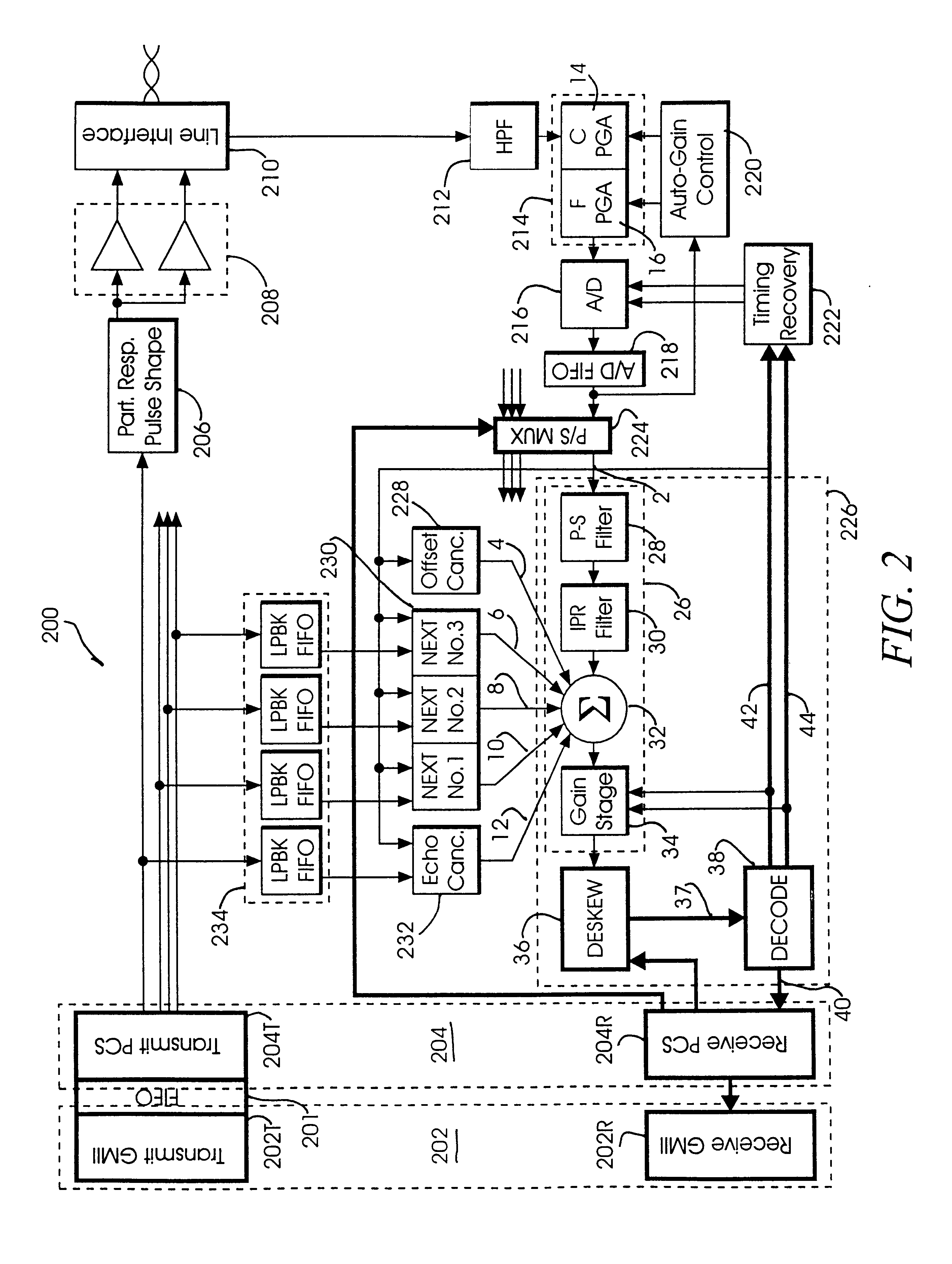
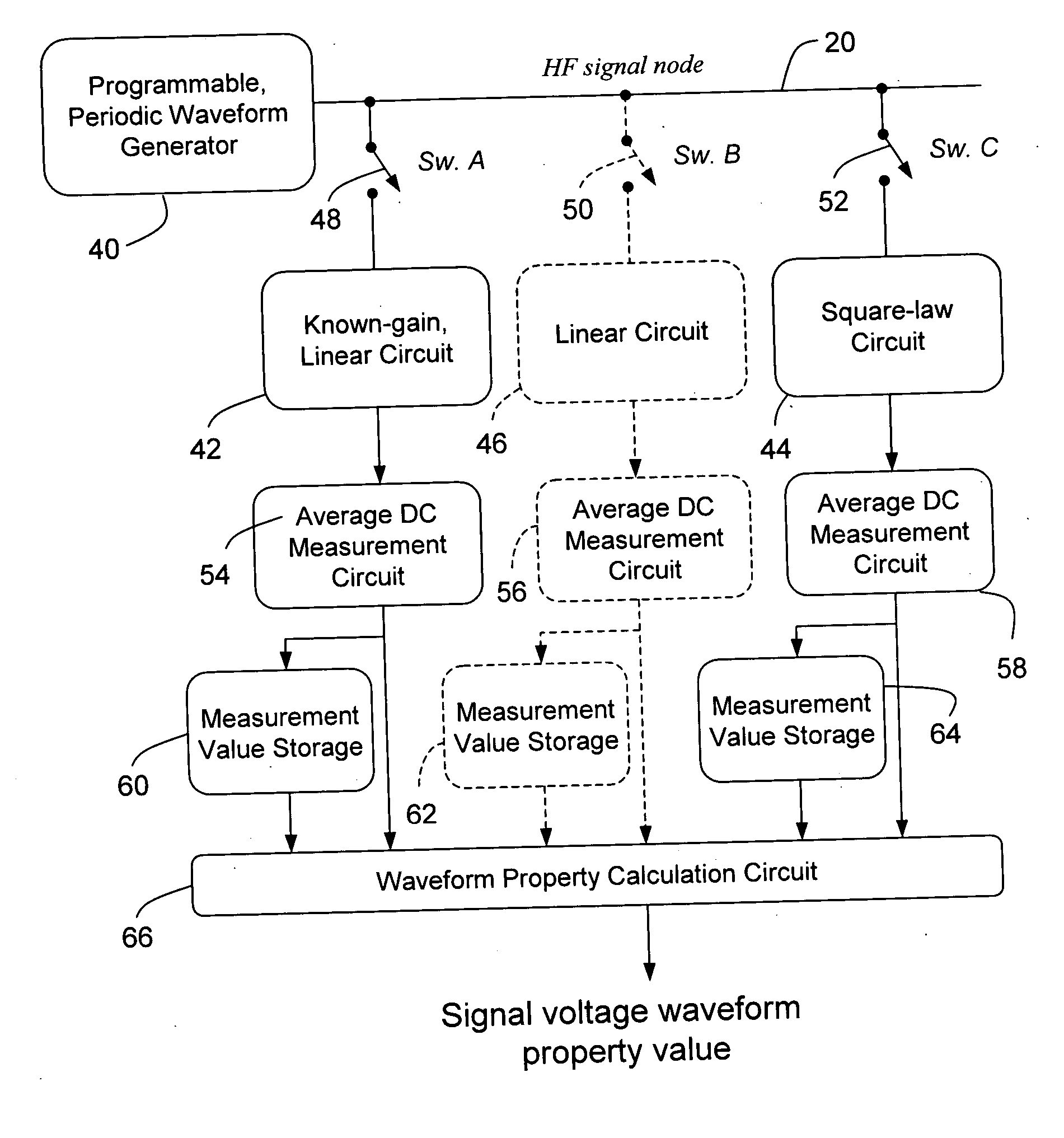
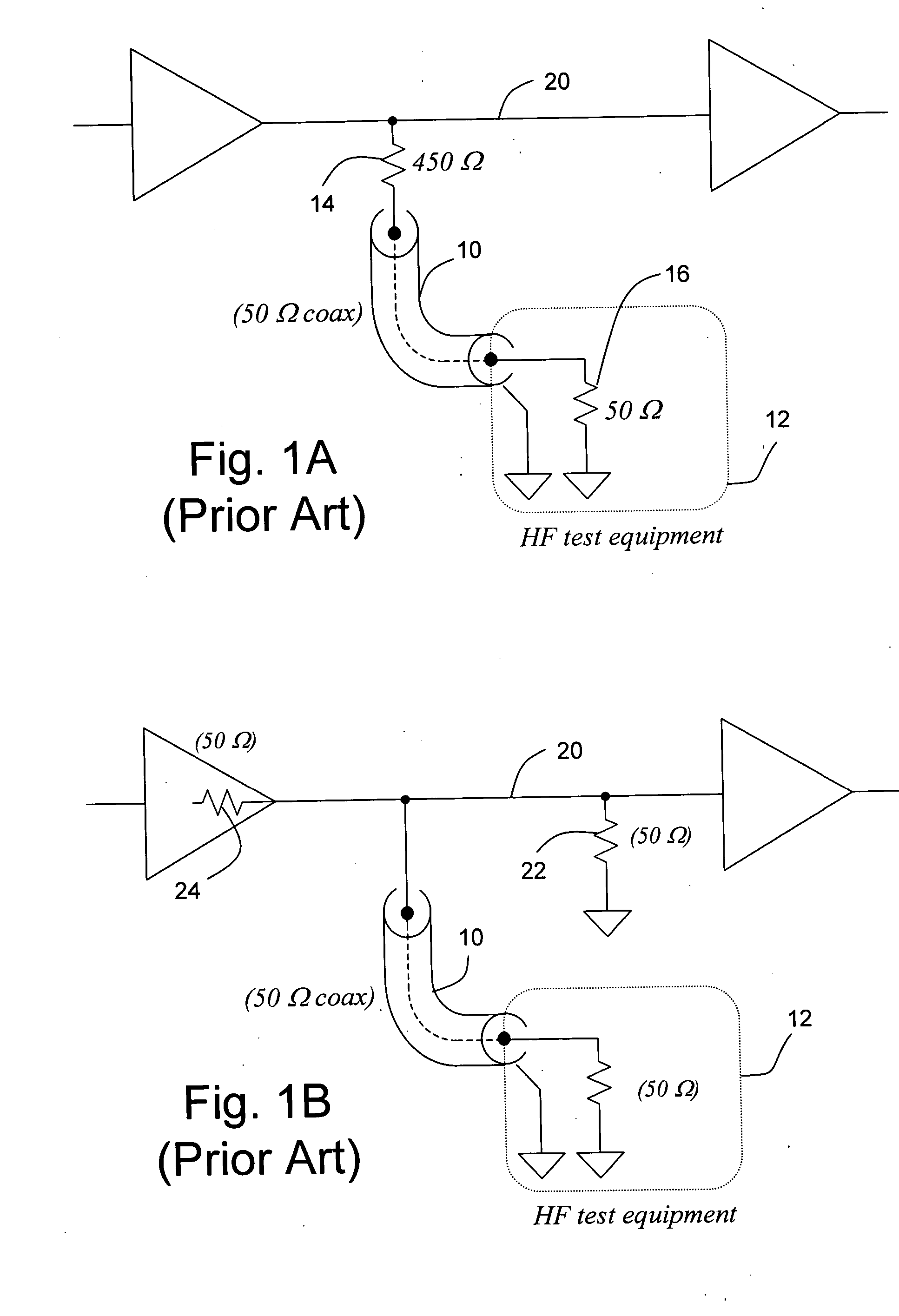
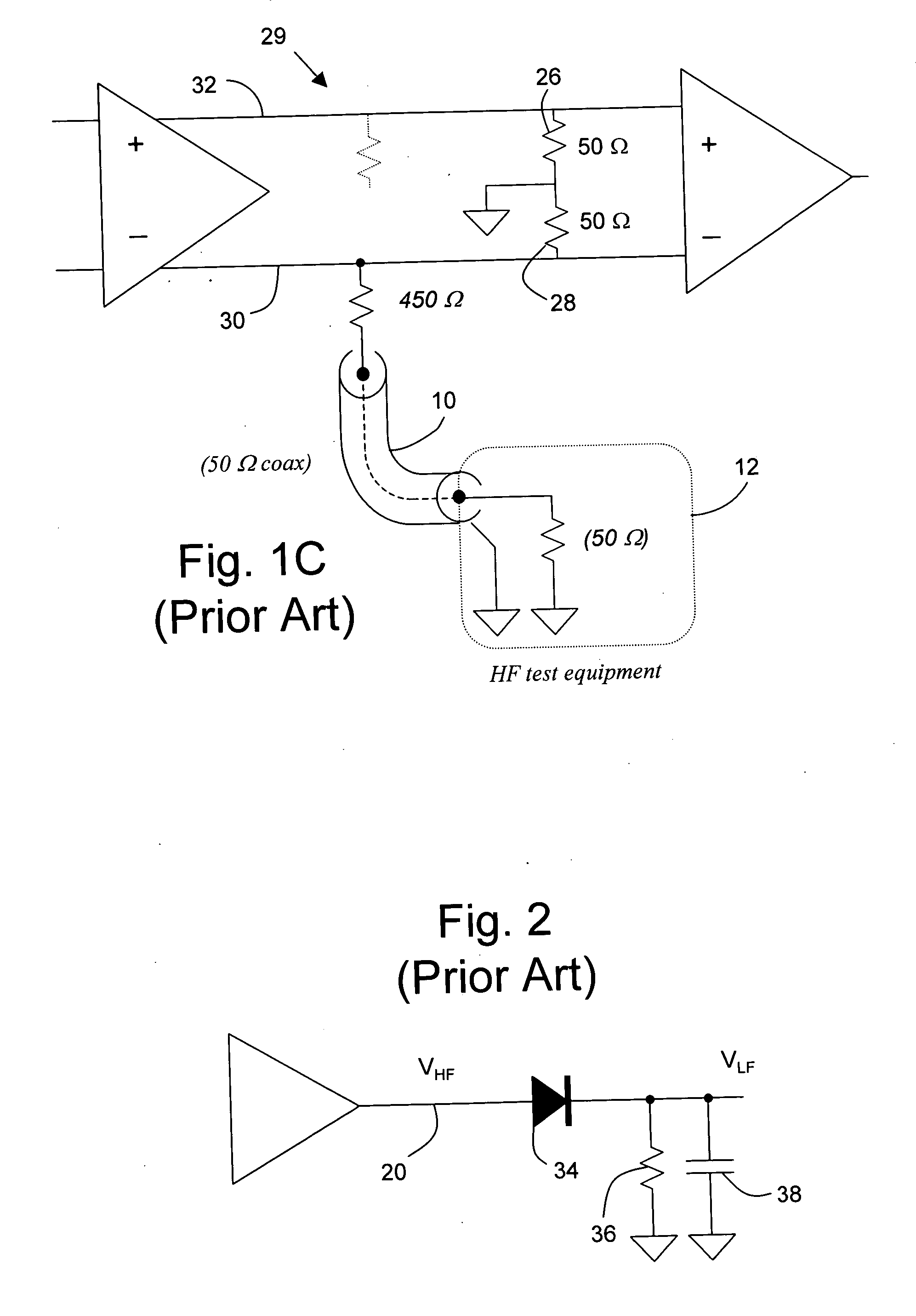
Circuit and method for low frequency testing of high frequency signal waveforms
A method of deducing properties of the shape of a waveform comprises (a) generating a signal based on a periodic pattern of logic levels; (b) measuring a DC level that is proportional to the average level of the signal and a DC level that is proportional to the average of the signal level squared; (c) repeating steps (a) and (b) one or more times; and (d) calculating a property value of the shape of the waveform based on a plurality of measurements.
Owner:LOGICVISION
Method and apparatus for use in IDDQ integrated circuit testing
InactiveUS6144214AComprehensive understandingSmall footprintMarginal circuit testingIndividual semiconductor device testingMOSFETIntegrated circuit
PCT No. PCT / US96 / 18426 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 13, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 13, 1998 PCT Filed Nov. 15, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 18481 PCT Pub. Date May 22, 1997A built in current sensor circuit (BICS) for use in integrated circuit testing utilizing the Quiescent Power Supply testing technique comprised of a detecting transistor, an s-ram cell and a buffer cell electrically coupled in a cascaded configuration to perform a comparator function, a reference source comprised of a current generating transistor and a voltage level setting transistor, and an active output load comprised of a single p-MOSFET sized to draw a unique amount of current when a respective circuit under test is determined to be defective., whereby the additional current drawn by the active output load is readily observable on the bias line by an external standard off-the-shelf current monitor. The built in current sensor circuit thereby alleviates the excessive use of area overhead in deep submicron integrated circuits and the need for separately propagating a defect signal to an output pin.
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
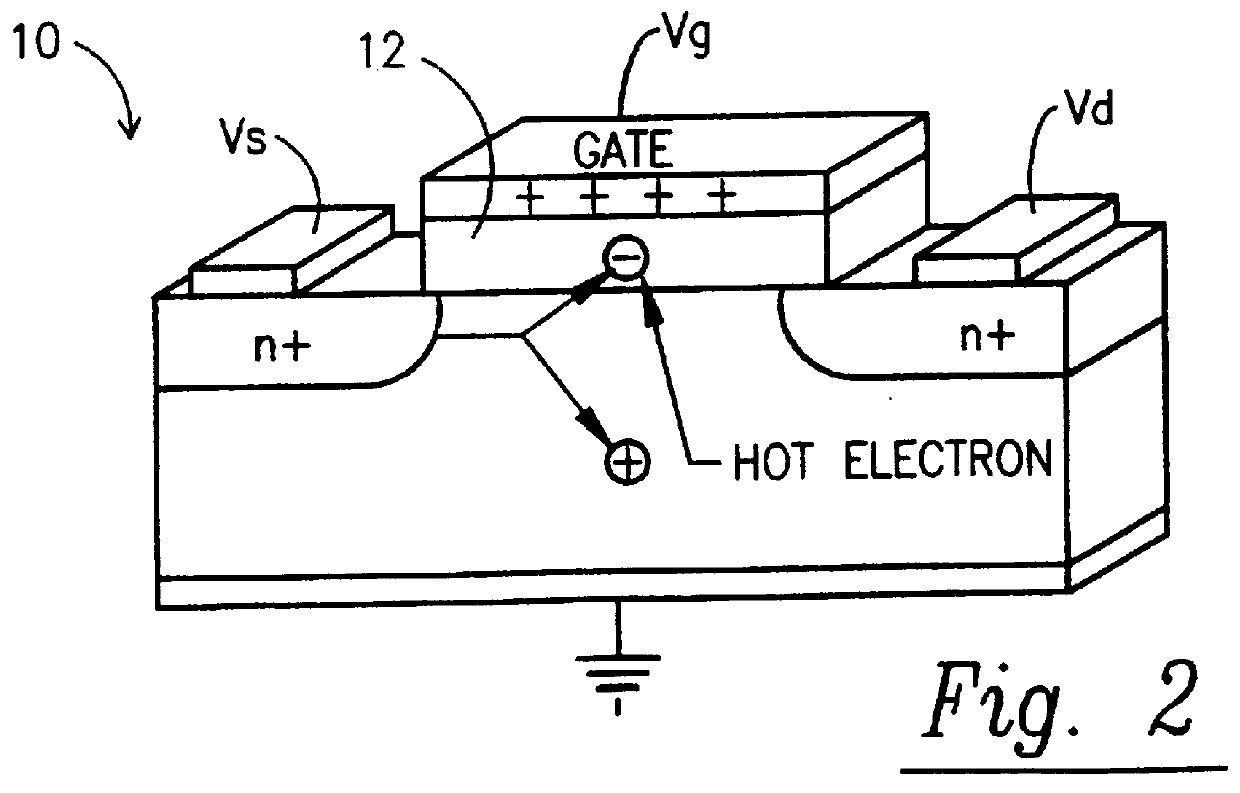
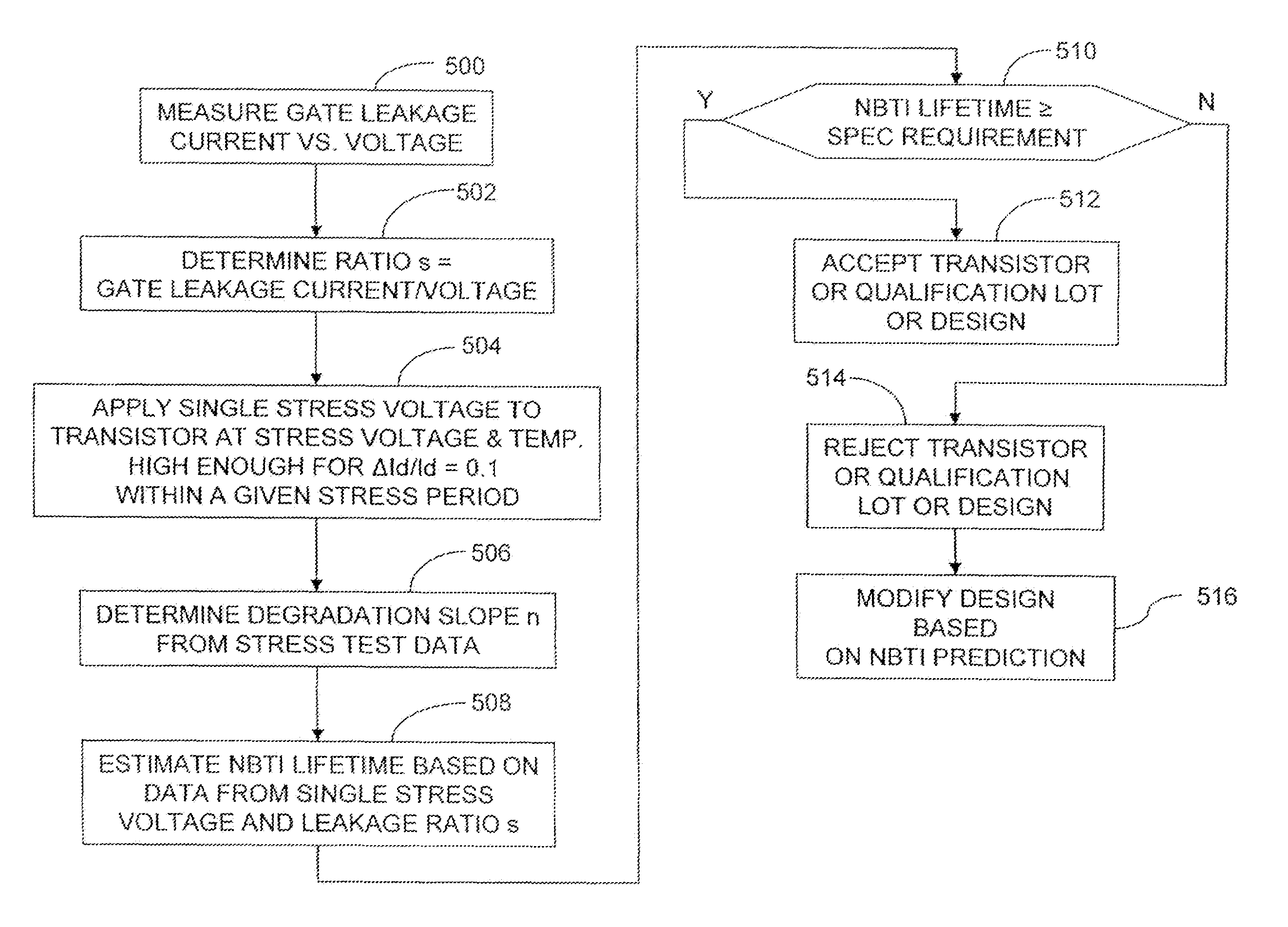
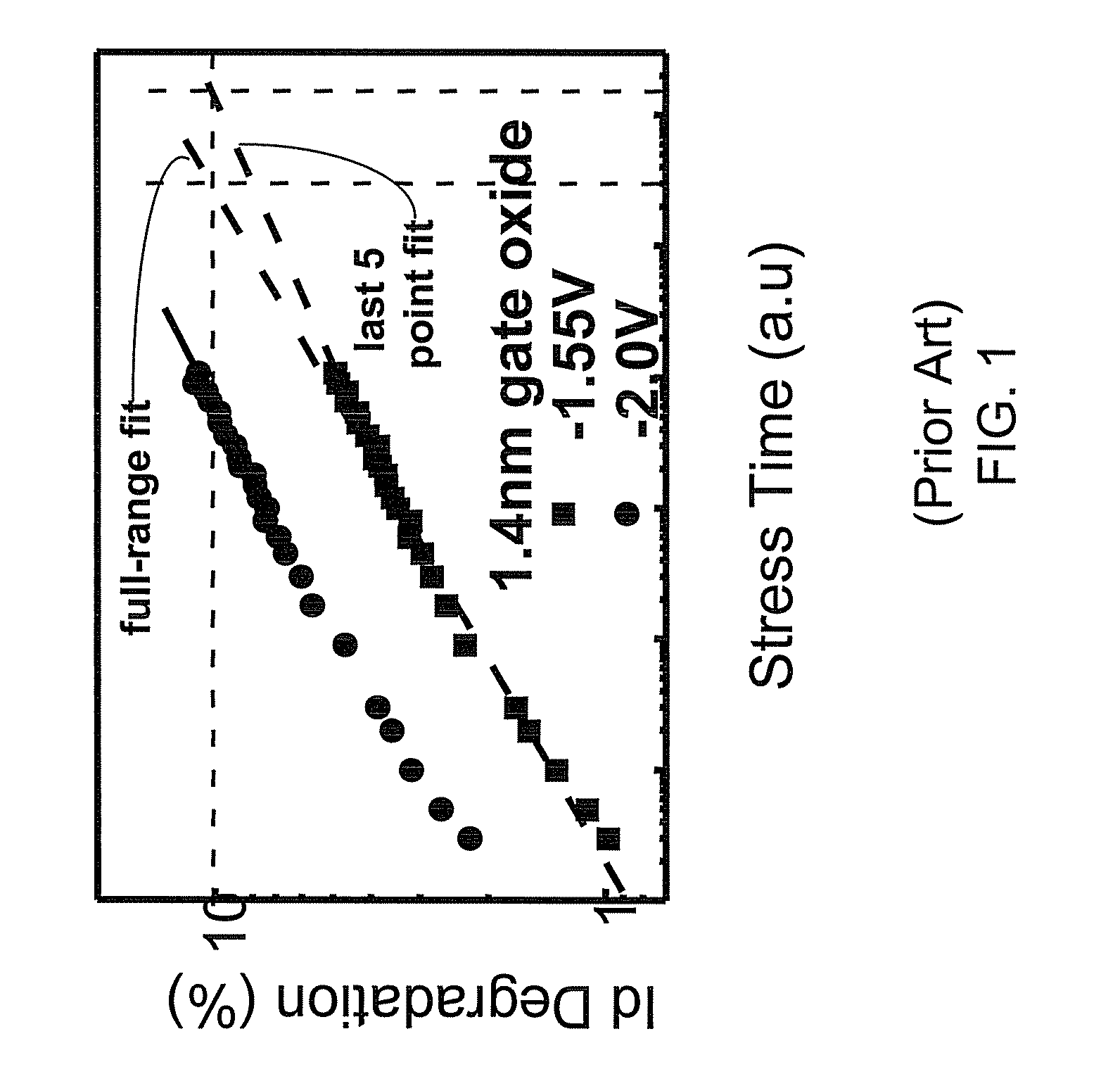
Method of NBTI prediction
InactiveUS7268575B1Semiconductor operation lifetime testingMarginal circuit testingGate leakage currentDriving current
A method includes measuring a gate leakage current of at least one transistor. A single stress bias voltage is applied to the at least one transistor at a given temperature for a stress period t. The stress bias voltage causes a 10% degradation in a drive current of the transistor at the given temperature within the stress period t. A negative bias temperature instability (NBTI) lifetime τ of the transistor is estimated based on the measured gate leakage current and a relationship between drive current degradation and time observed during the applying step.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
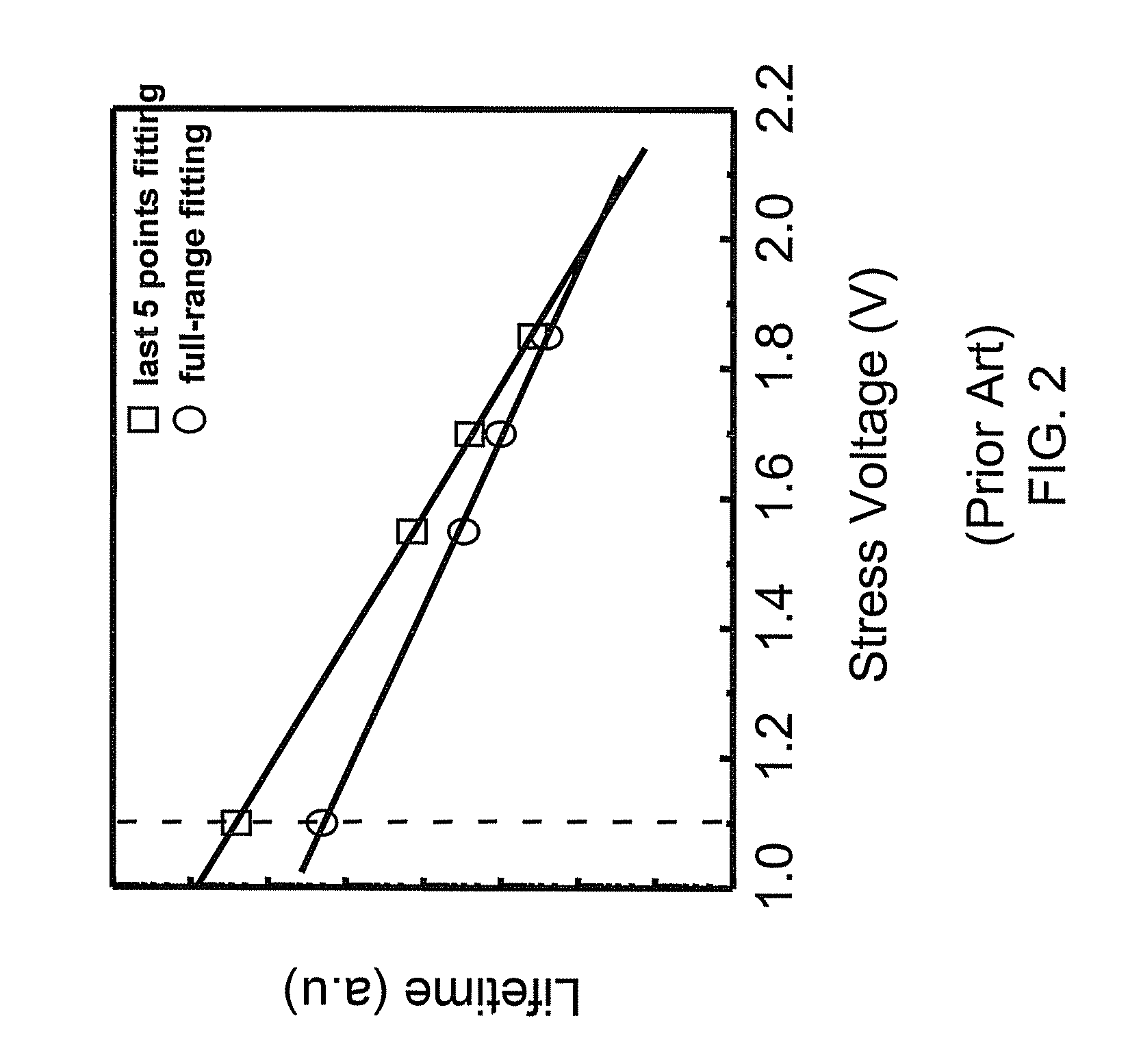
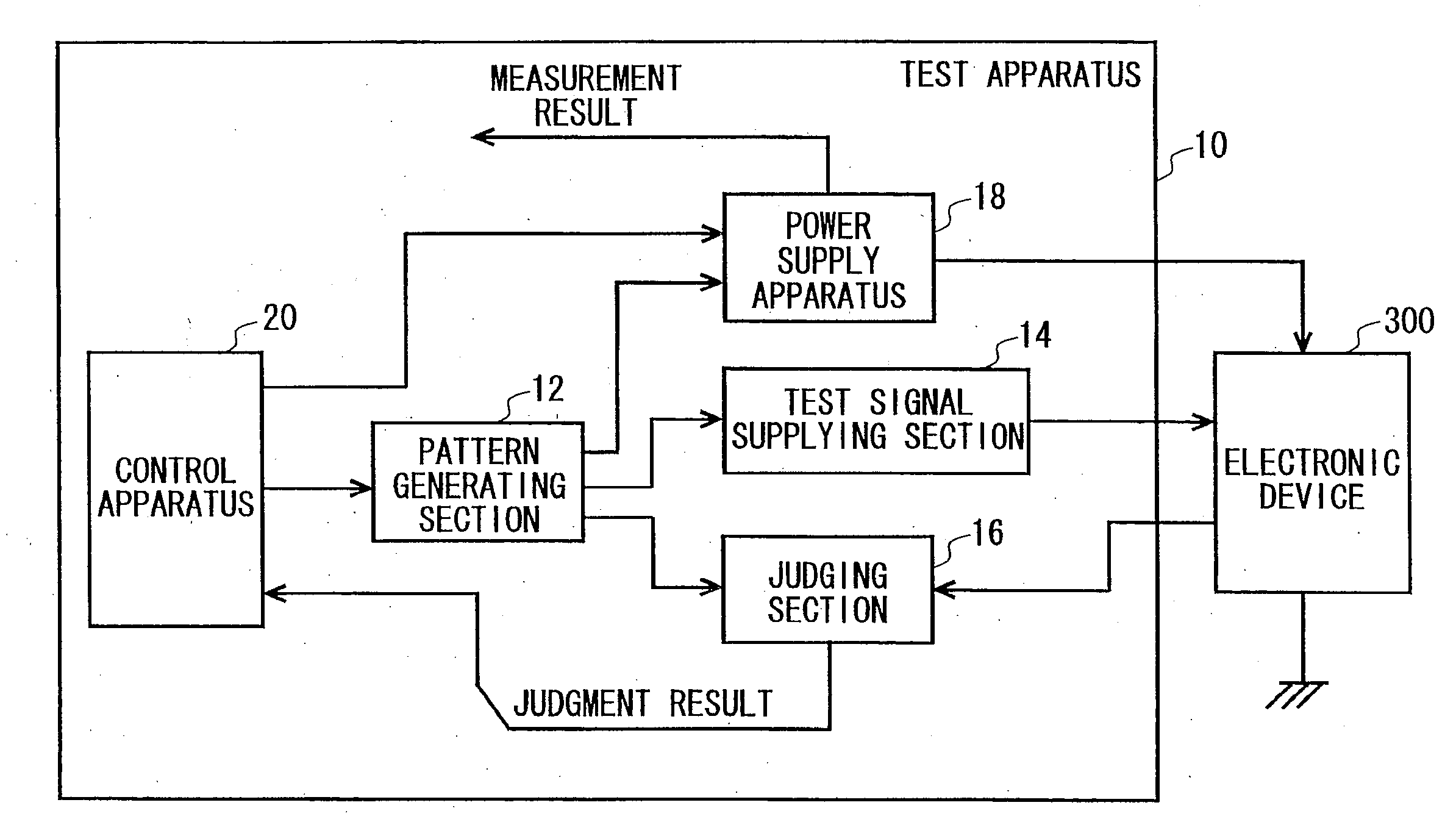
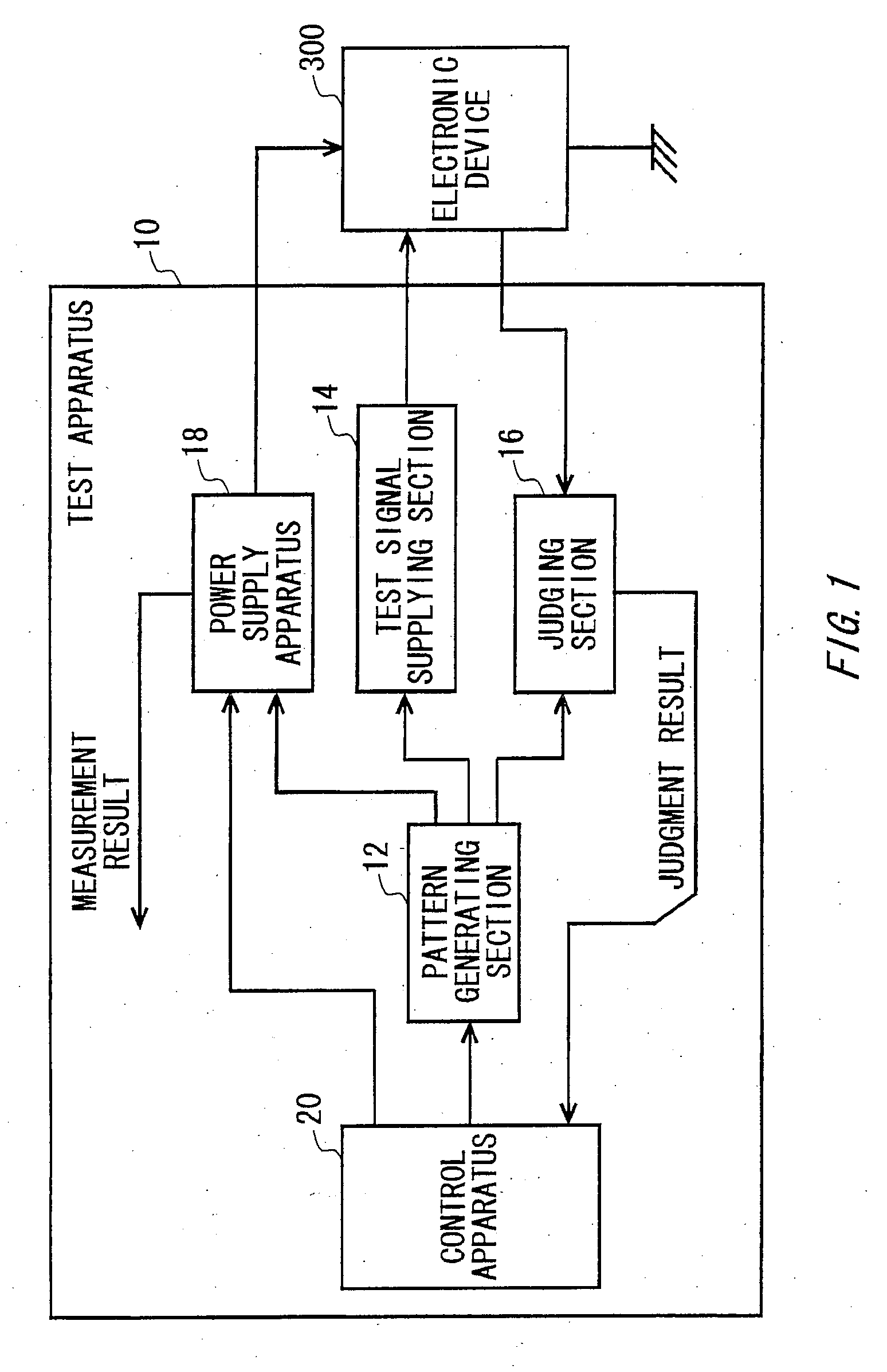
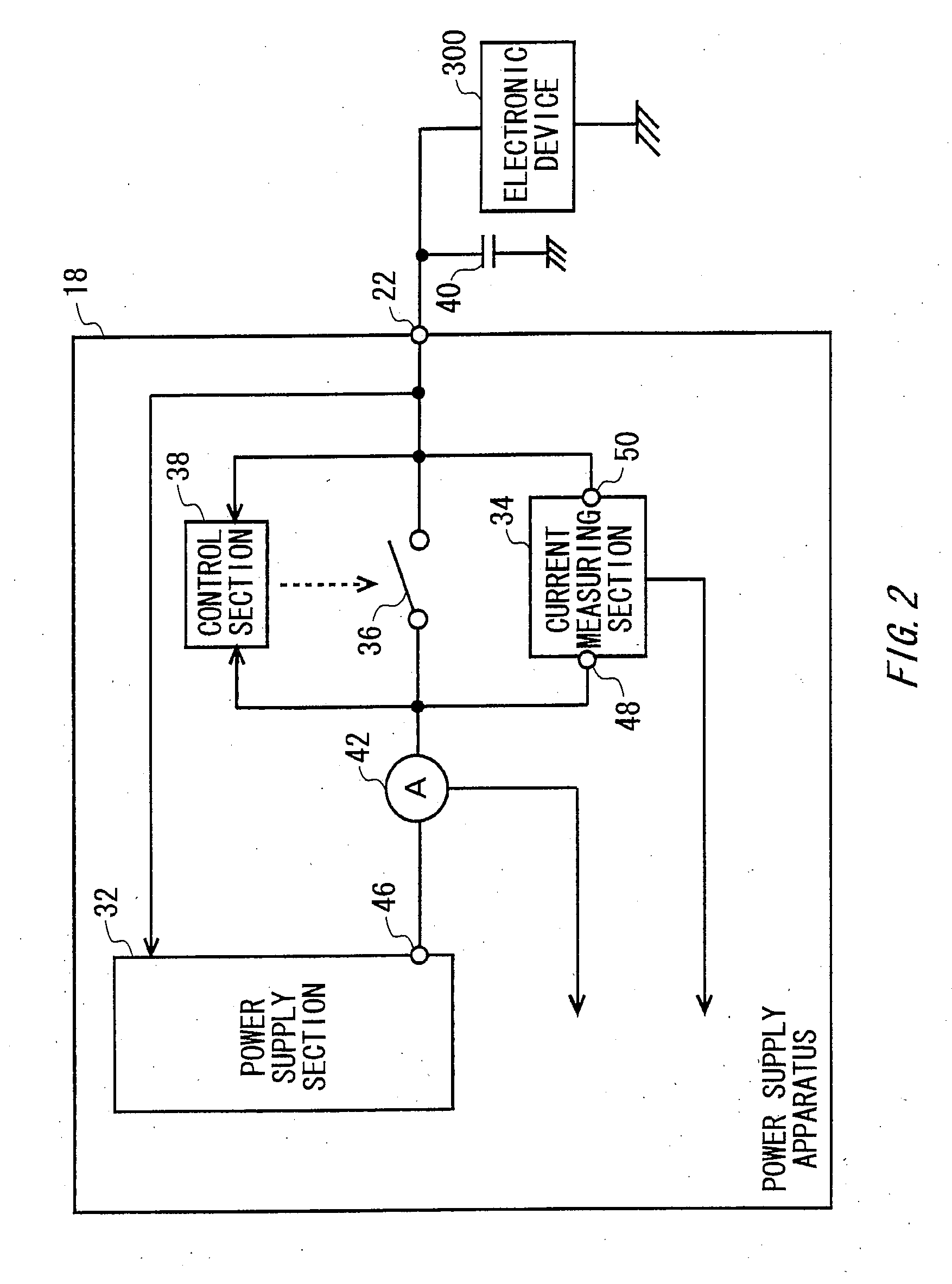
Measurement apparatus, test apparatus and measurement method
InactiveUS20100007327A1Current/voltage measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceMeasurement deviceEngineering
Provided is a measurement apparatus that measures a current flowing through a load, including a power supply section that outputs a current supplied to the load; a current measuring section that measures a load current flowing between the load and the power supply section; a switch that is connected in parallel with the current measuring section between the load and the power supply section; and a control section that disconnects the switch during measurement of the load current and connects the switch when the load current falls outside of a predetermined reference range.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
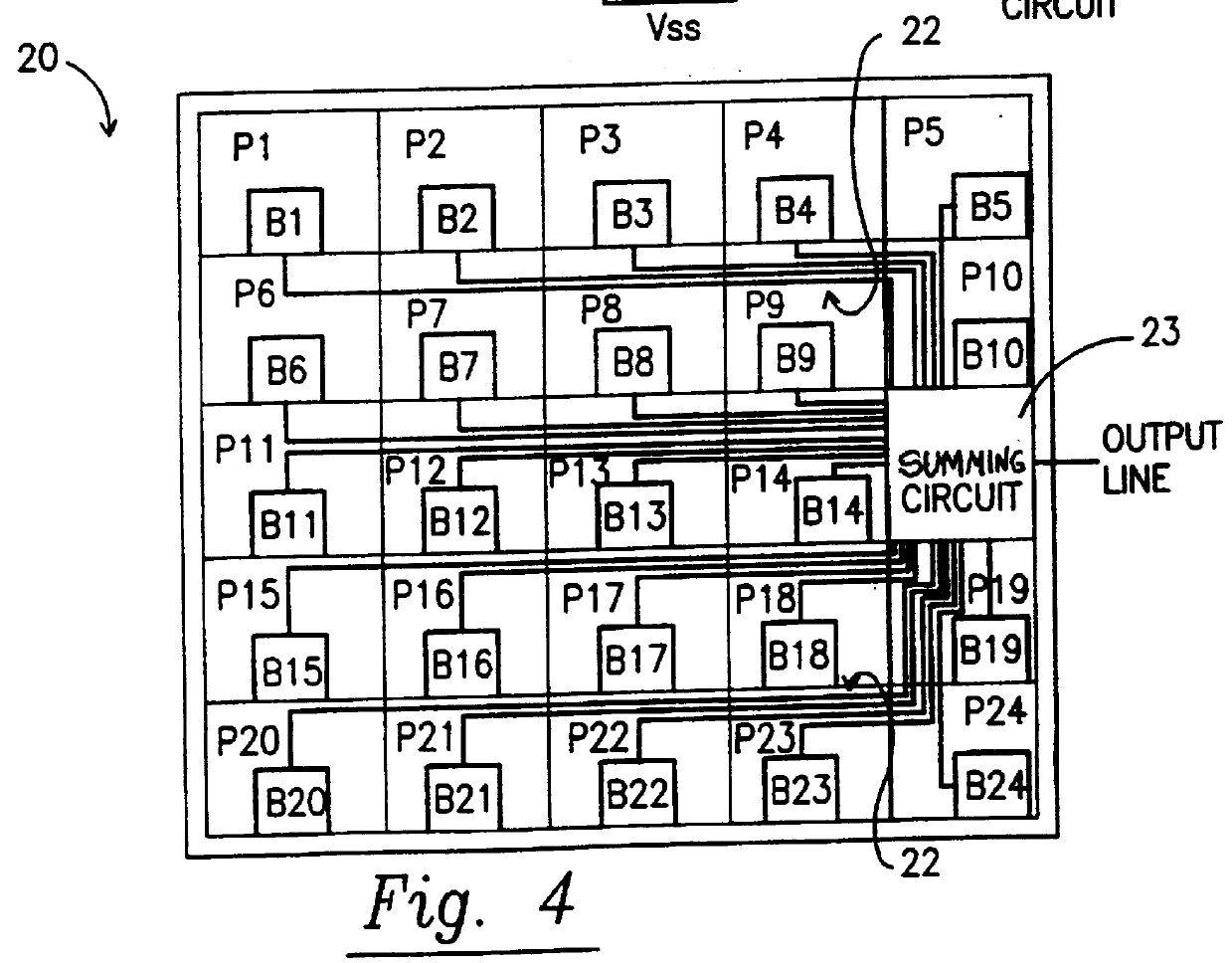
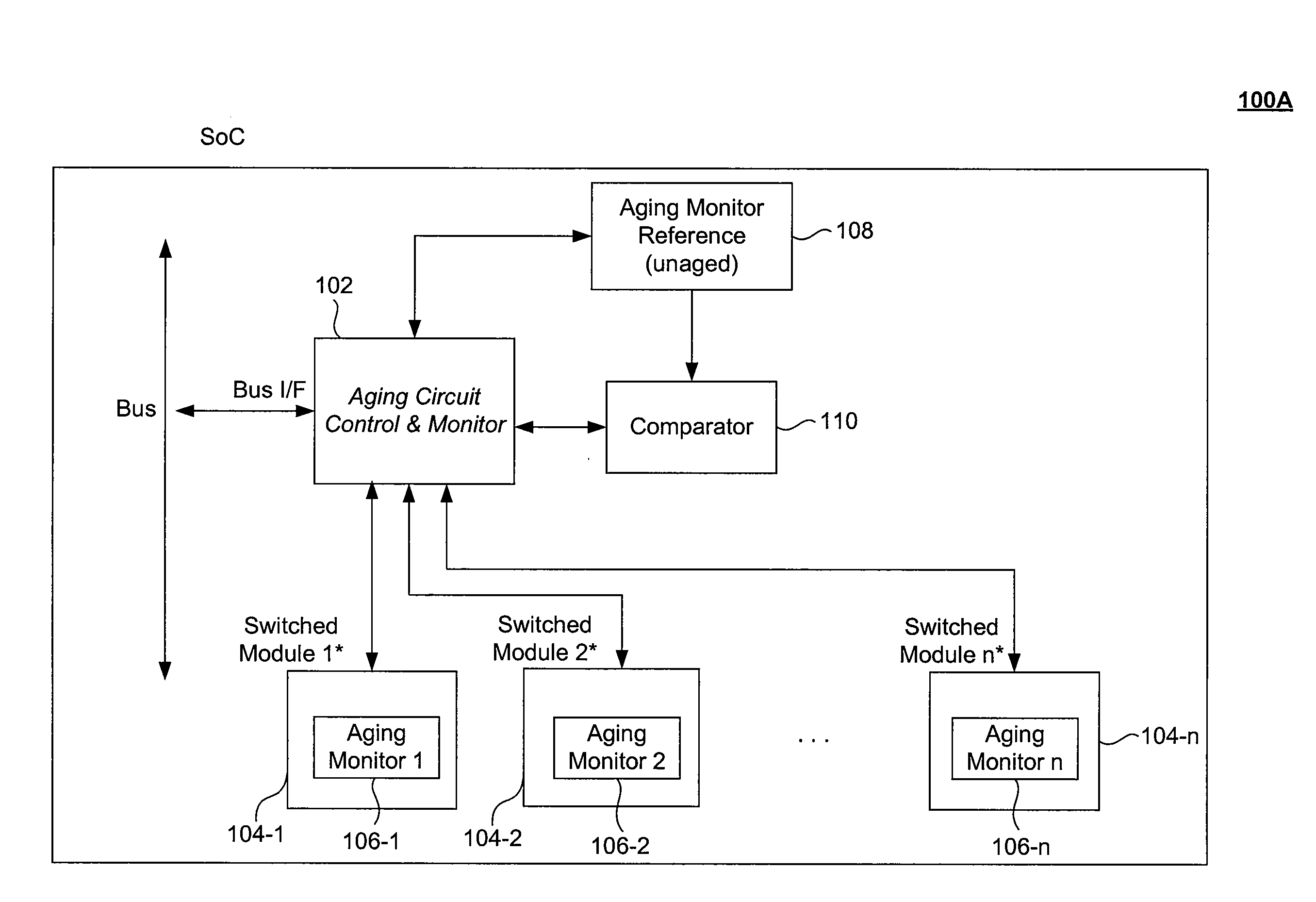
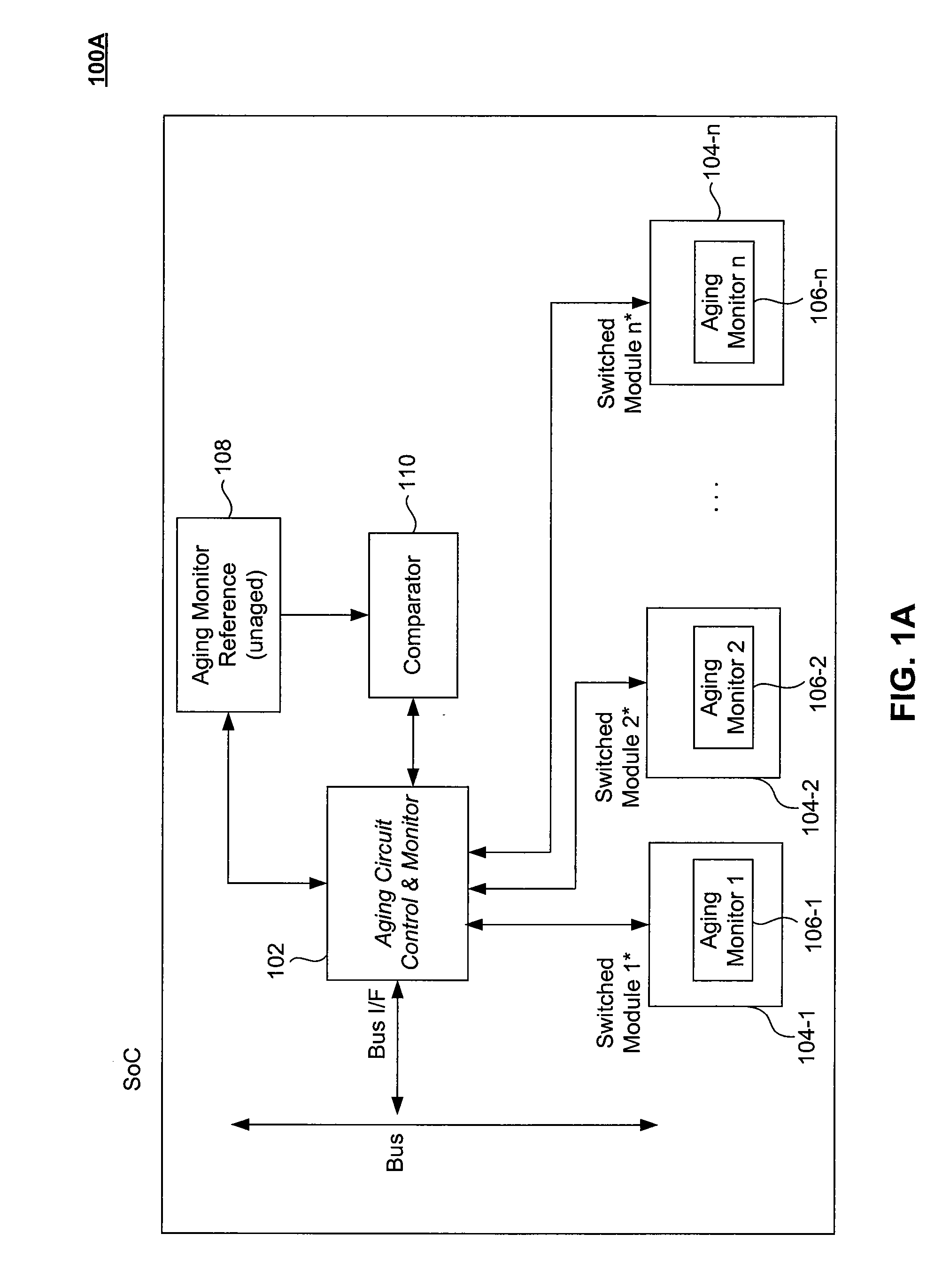
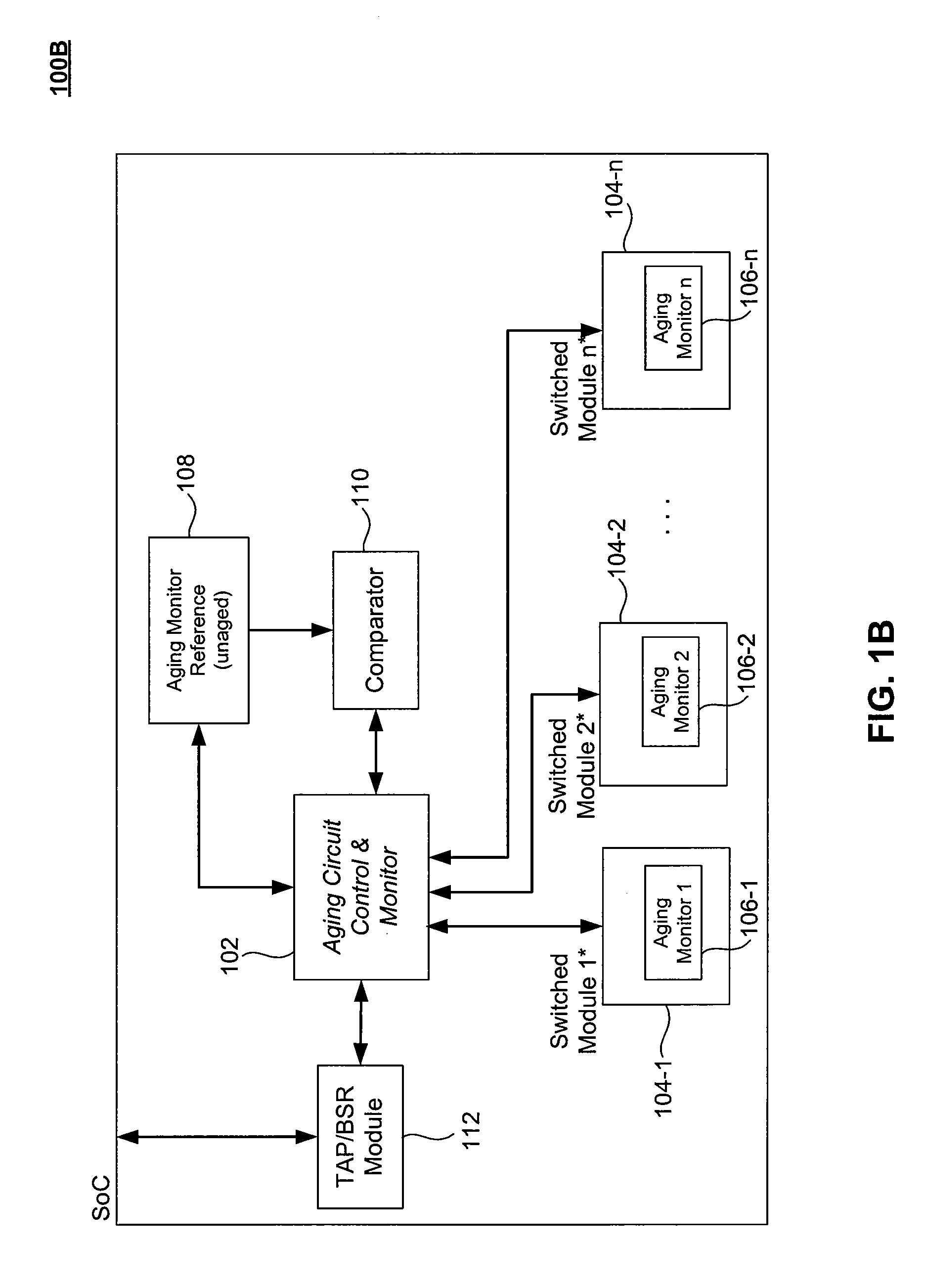
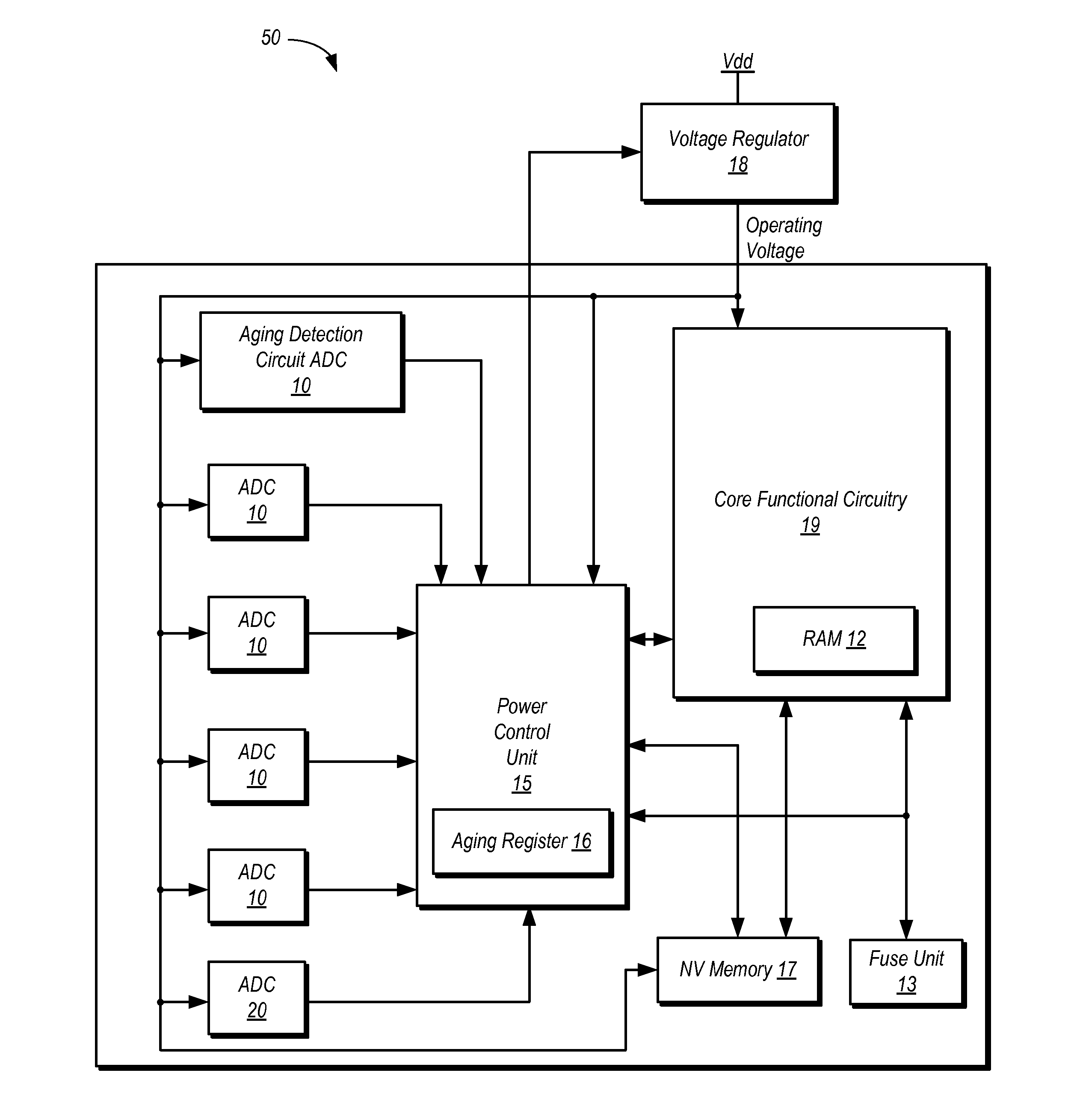
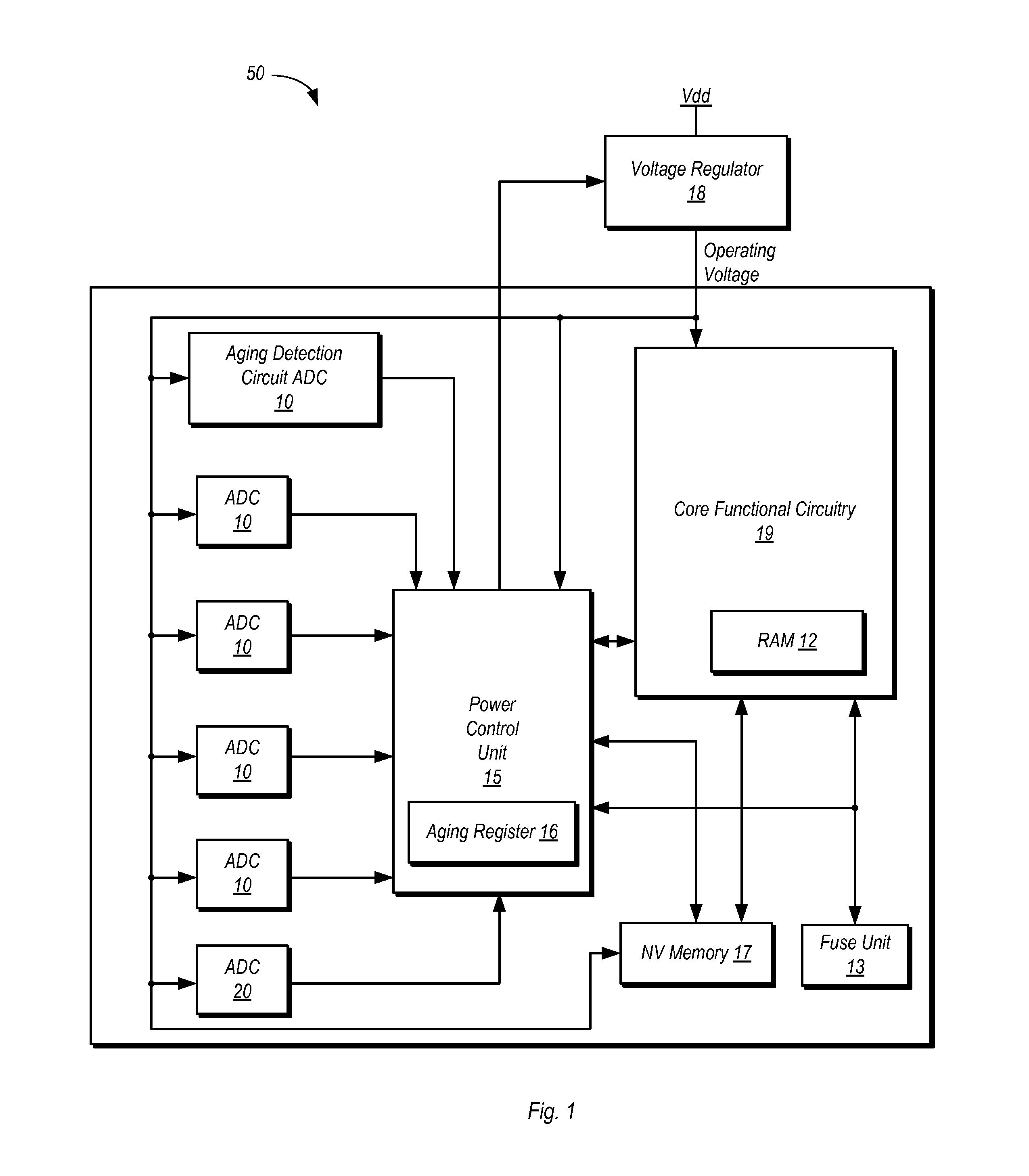
Adaptive Device Aging Monitoring and Compensation
InactiveUS20110181315A1Marginal circuit testingIndividual semiconductor device testingGranularityEngineering
Improved device aging monitoring and compensation schemes are presented herein. In particular, embodiments enable quantitative measurement of actual aging experienced by a device up to the instant of measurement, rather than rely on static a priori estimation of aging effects under worst case conditions. As such, embodiments provide adaptive device aging monitoring and compensation schemes. In addition, embodiments allow for aging monitoring and compensation to be performed at a desired granularity, whereby aging monitoring and compensation can be performed at a chip, module, or sub-module level. Further, embodiments inherently compensate for the effects of aging on passive components (e.g., parasitics of interconnect wires, capacitors, etc.) in addition to active device aging.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method and system for identifying and locating defects in an integrated circuit
InactiveUS7043389B2Reduce impactDigital circuit testingResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical resistance and conductancePower grid
A method and system for detecting and locating defects in an integrated circuit. A time-varying input signal is applied to the integrated circuit, power signals produced at a plurality of respective ordered connections in response to the input signal are measured, and one or more defects in the integrated circuit are identified from the power signals so measured. A system is provided having a probe for connecting to the die of an integrated circuit prior to final packaging, a testing system for applying transient input signals to the die and acquiring die power signal measurements in response thereto, and a data processor for determining whether the power signal measurements indicate the presence of a defect in the die. Also provided is a method for reducing the effect of contact resistance from test probe connections. As a way of implementing the approach of the method and system there is also provided an integrated circuit having a plurality of ordered connections to the power grid and a plurality of calibration circuits associated with respective ordered connections so as to selectively inject transient signals onto the power grid at respective locations.
Owner:PLUSQUELLIC JAMES FRANCIS
Method and system for monitoring test signals for semiconductor devices
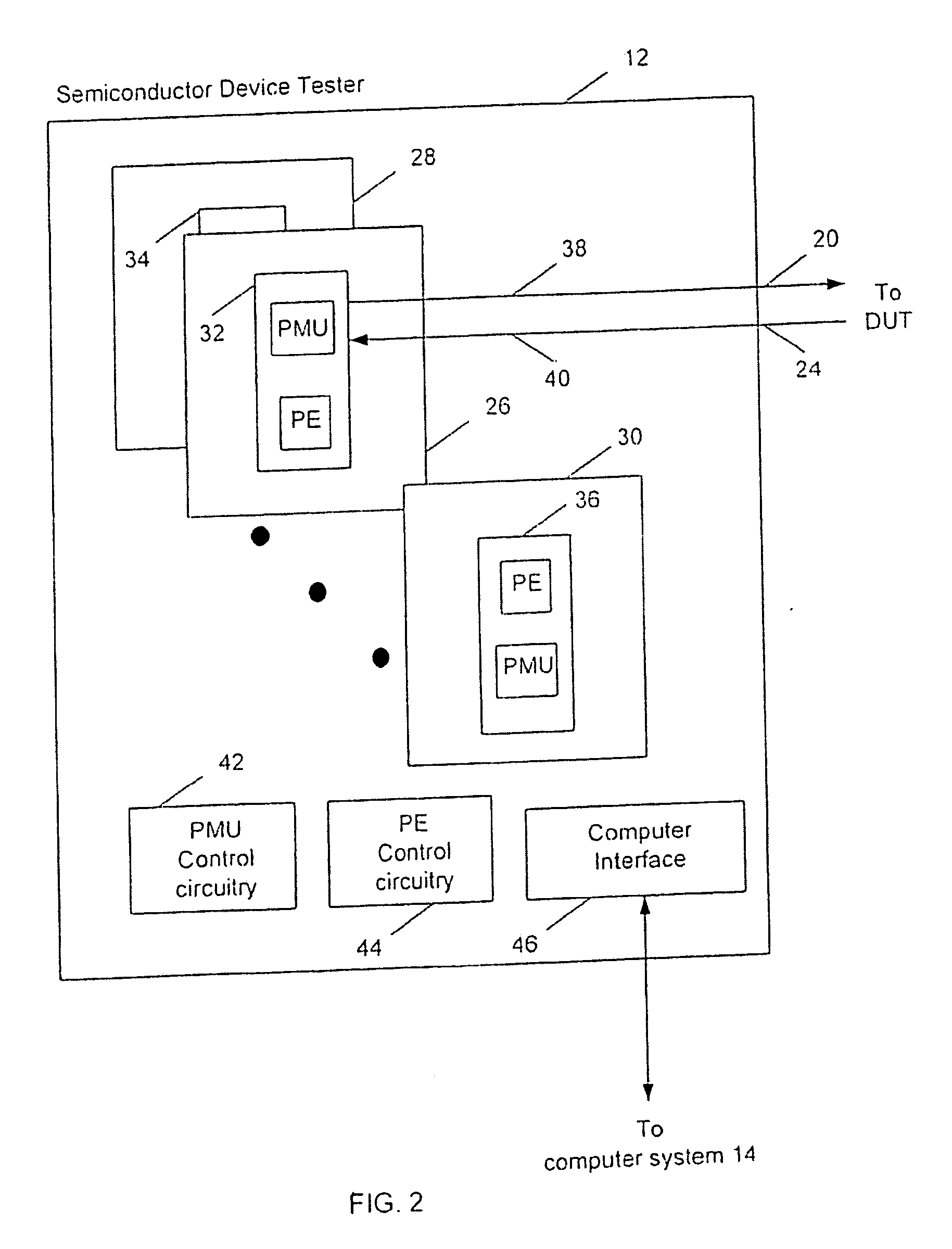
A semiconductor device tester includes a parametric measurement unit (PMU) driver circuit that provides a DC test signal for testing a semiconductor device, and a feedback circuit that senses the DC test signal at an output of the PMU driver circuit and sends the sensed DC test signal to an input of the PMU driver circuit for compensating the DC test signal.
Owner:TERADYNE
Transmitter voltage and receiver time margining
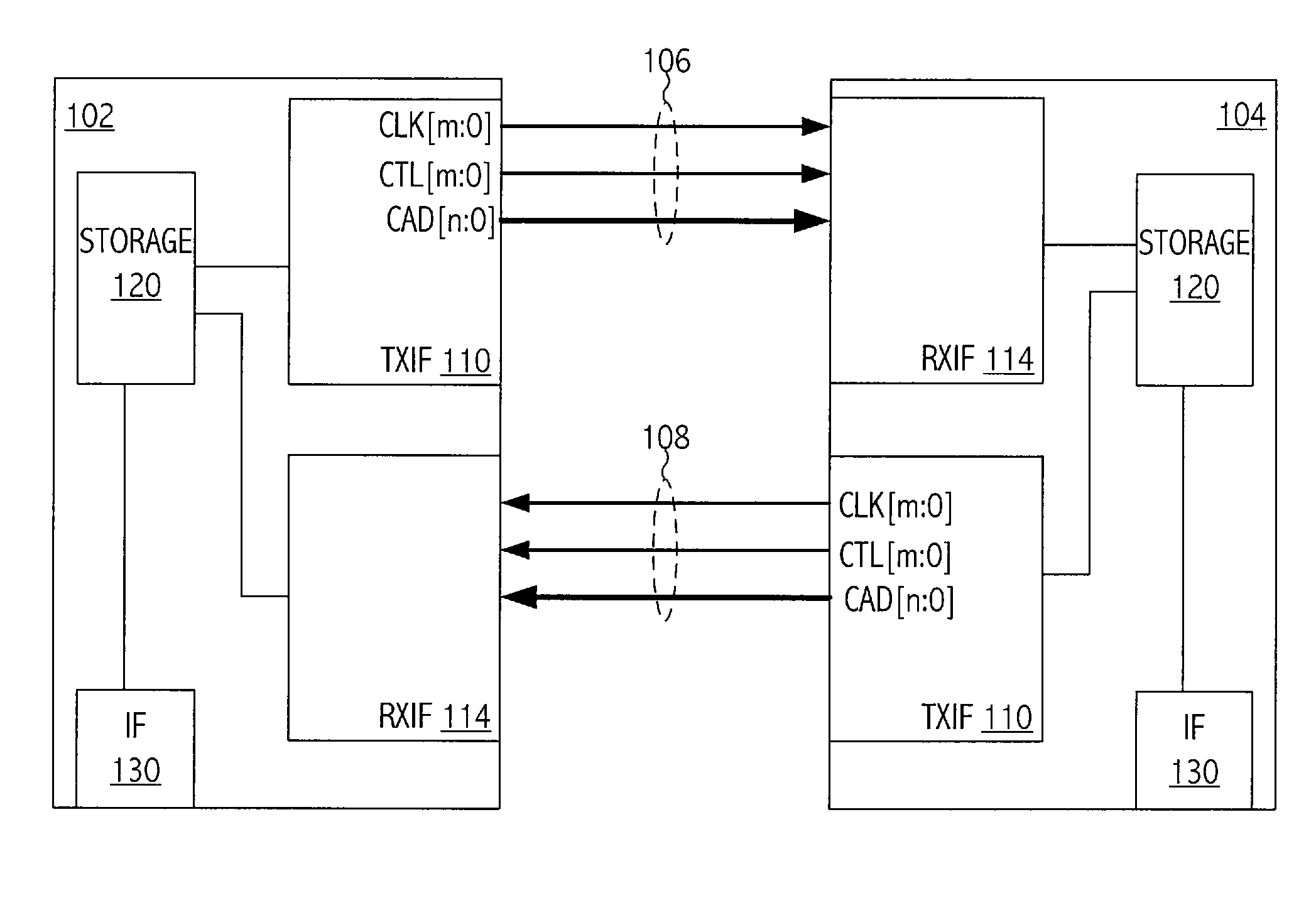
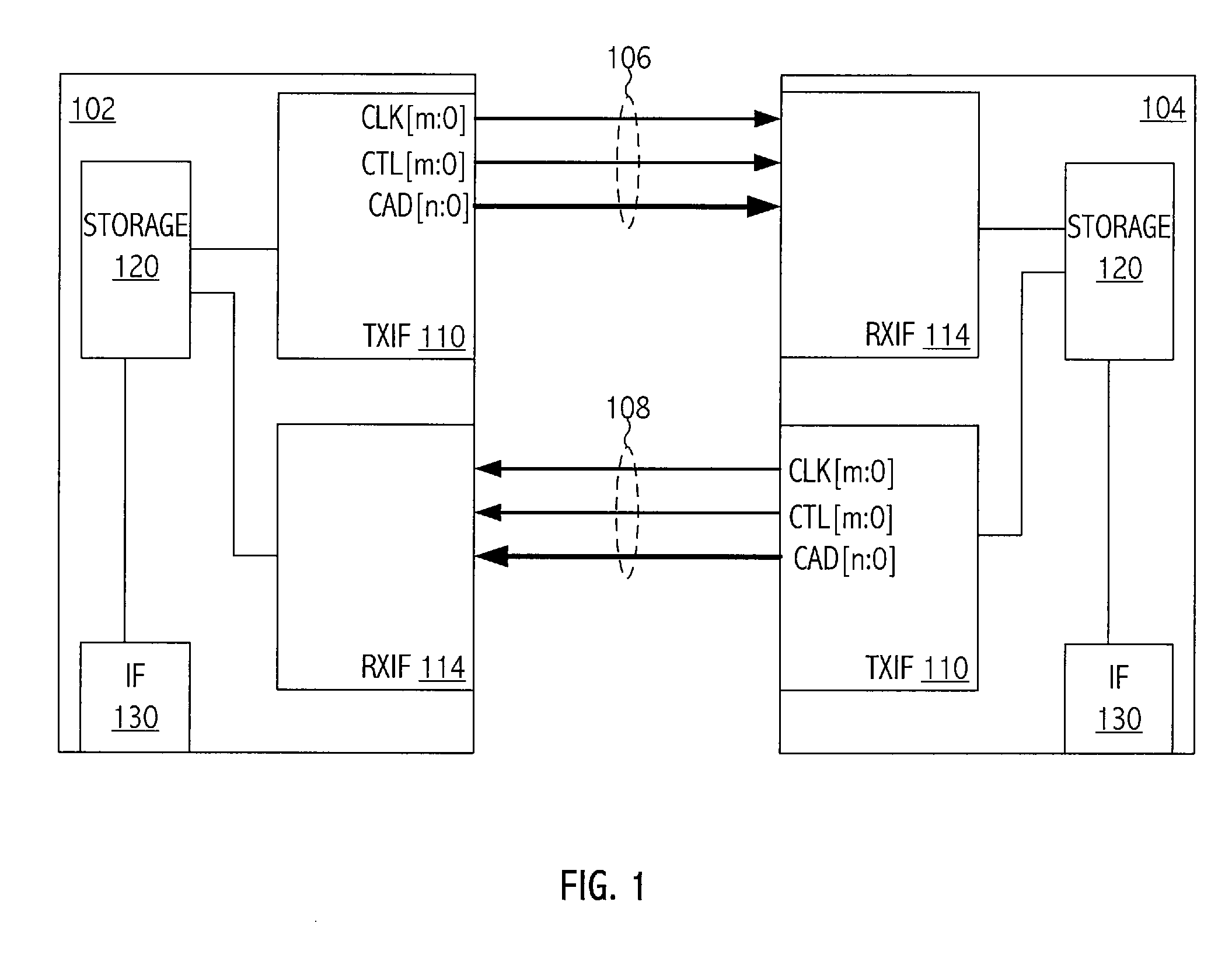
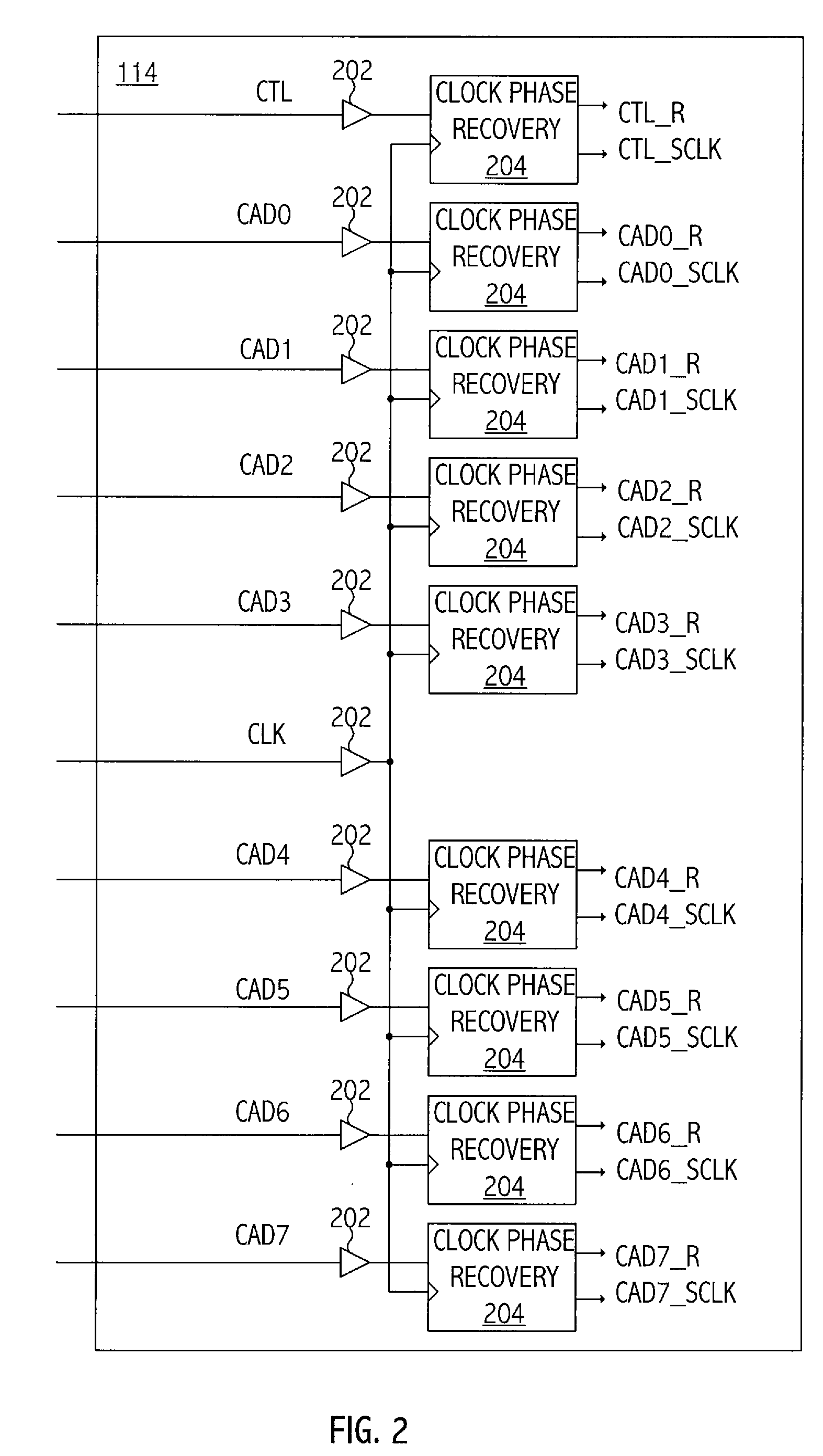
ActiveUS20070230513A1Analog circuit testingError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCommunication interfaceTiming margin
A technique for characterizing a communications interface includes determining a voltage margin and a timing margin of the interface based on data sampled by a sampling device of a receiver of the interface. In at least one embodiment of the invention, a method for determining margin associated with a receiver circuit of an integrated circuit includes periodically sampling a signal over a time period by a receiver sampling circuit of the receiver circuit to generate a sampled version of the signal. The method includes incrementally varying a value of the parameter associated with the signal. The varying of the parameter is through a range of values of the parameter over the time period. The method includes determining a margin value of the receiver circuit associated with the parameter based, at least in part, on the sampled version of the signal.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Integrated circuit with leakage control and method for leakage control
InactiveUS20050149799A1Improved leakage power controlReduce leakage powerPower reduction by control/clock signalDigital circuit testingPower modeState variable
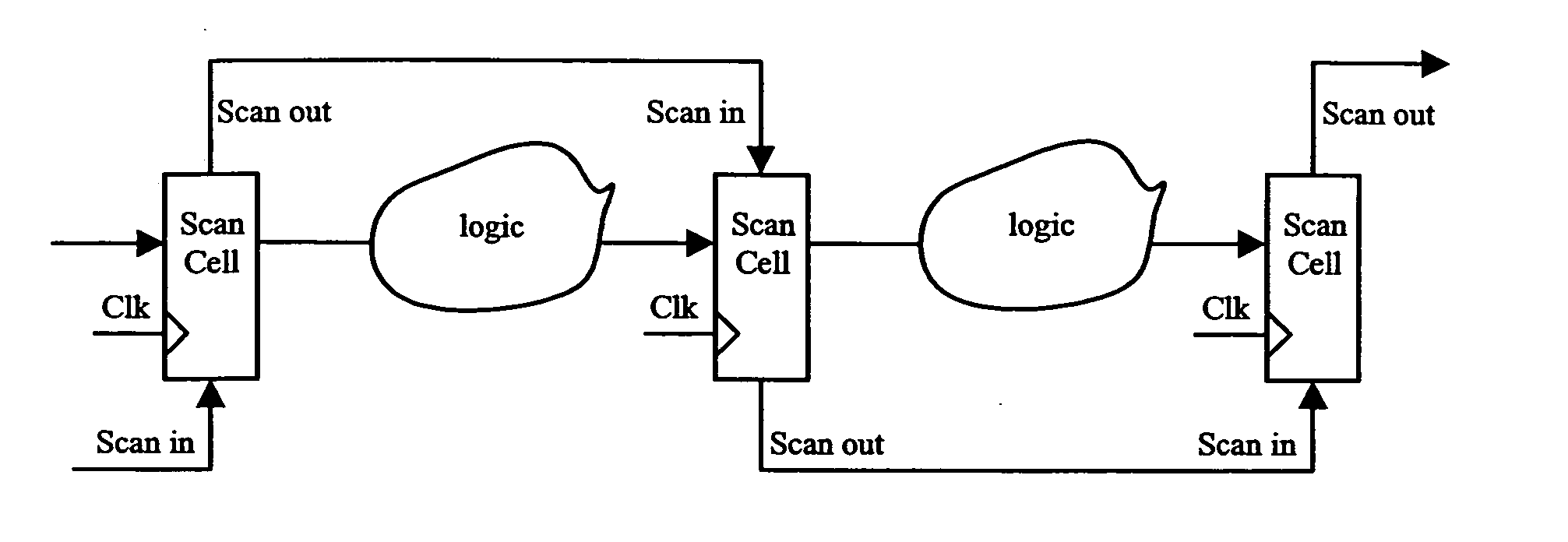
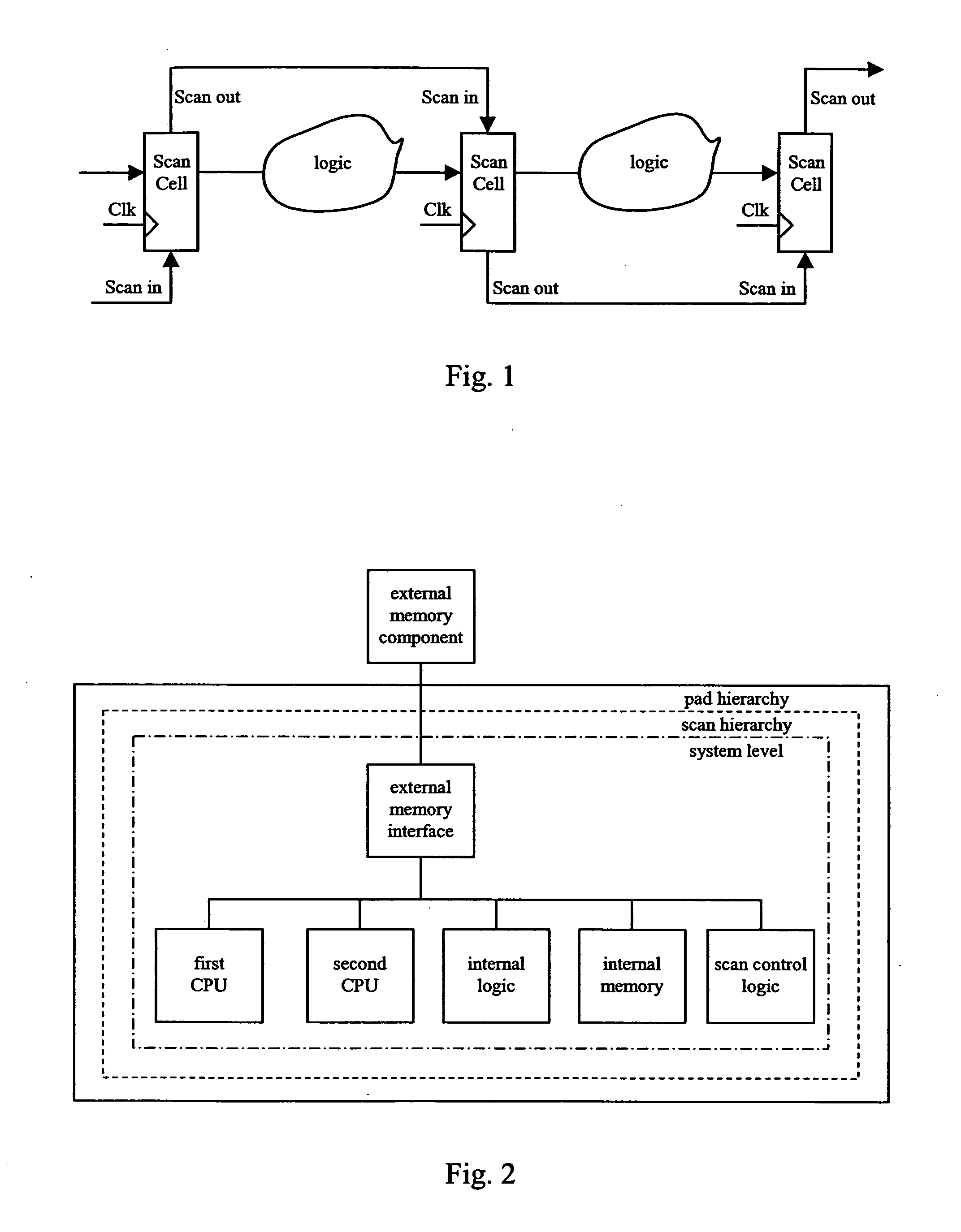
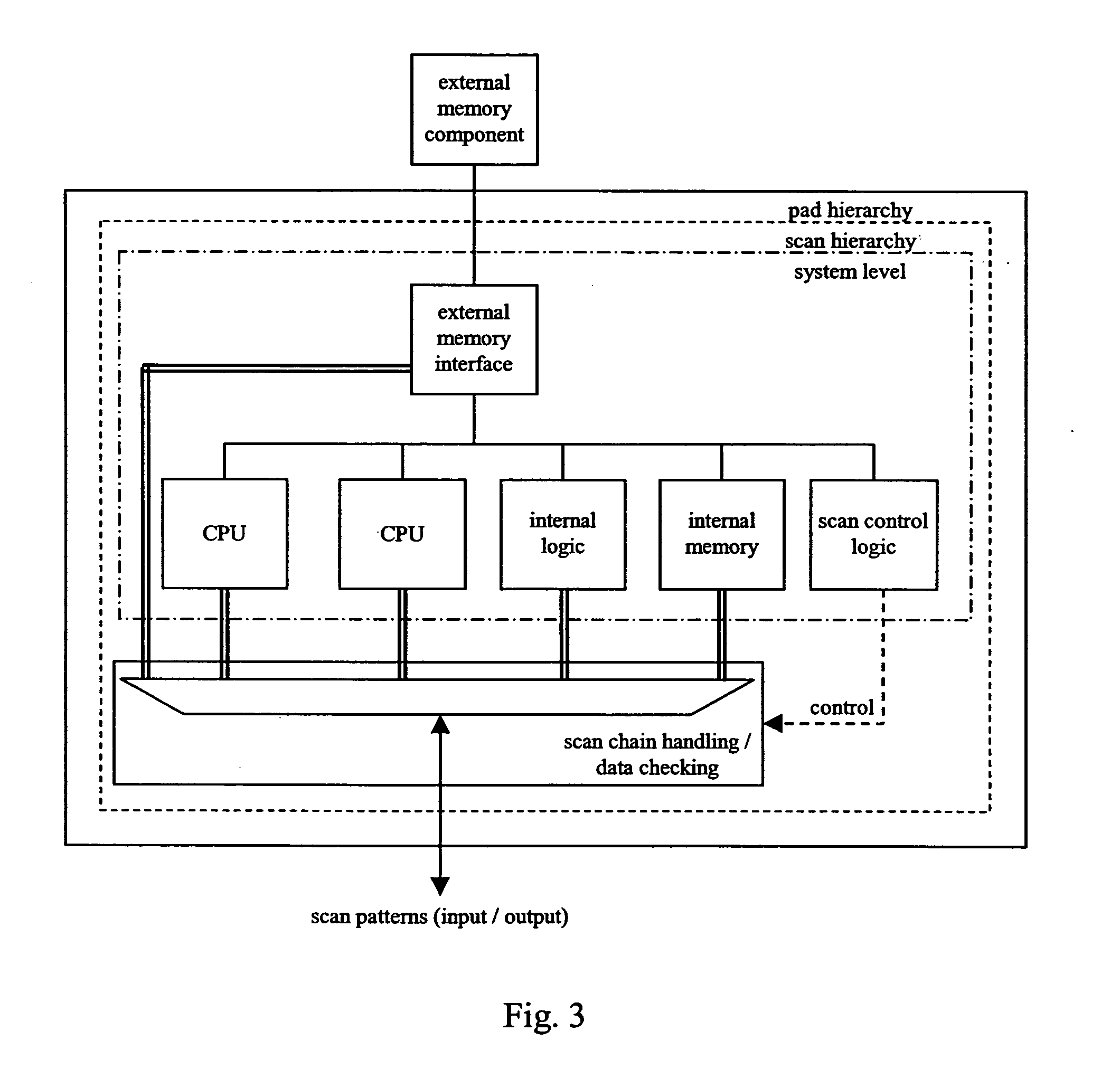
The present invention relates to integrated circuit with reduced leakage power and in particular to a methodology for retaining an operational state of at least a part of the integrated circuit while the part is in standby / low power mode. In detail, the inventive methodology is based on the use of scan chains being implemented in the integrated circuit for production testing purposes. Via the scan chains circuit-internal state-variable memory element content is read out and / or written in such that the operational state of for instance a specific part (power domain) of the integrated circuit may be captured on the basis of the circuit internal contents, retained in an adequately provided data storage and afterwards scanned into the specific part of the integrated circuit to restore the operational state thereof.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Operating voltage determination for an integrated circuit
ActiveUS20050107967A1Easy to useReduce the likelihood of failureEnergy efficient ICTCurrent/voltage measurementClock rateEngineering
Owner:ARM LTD
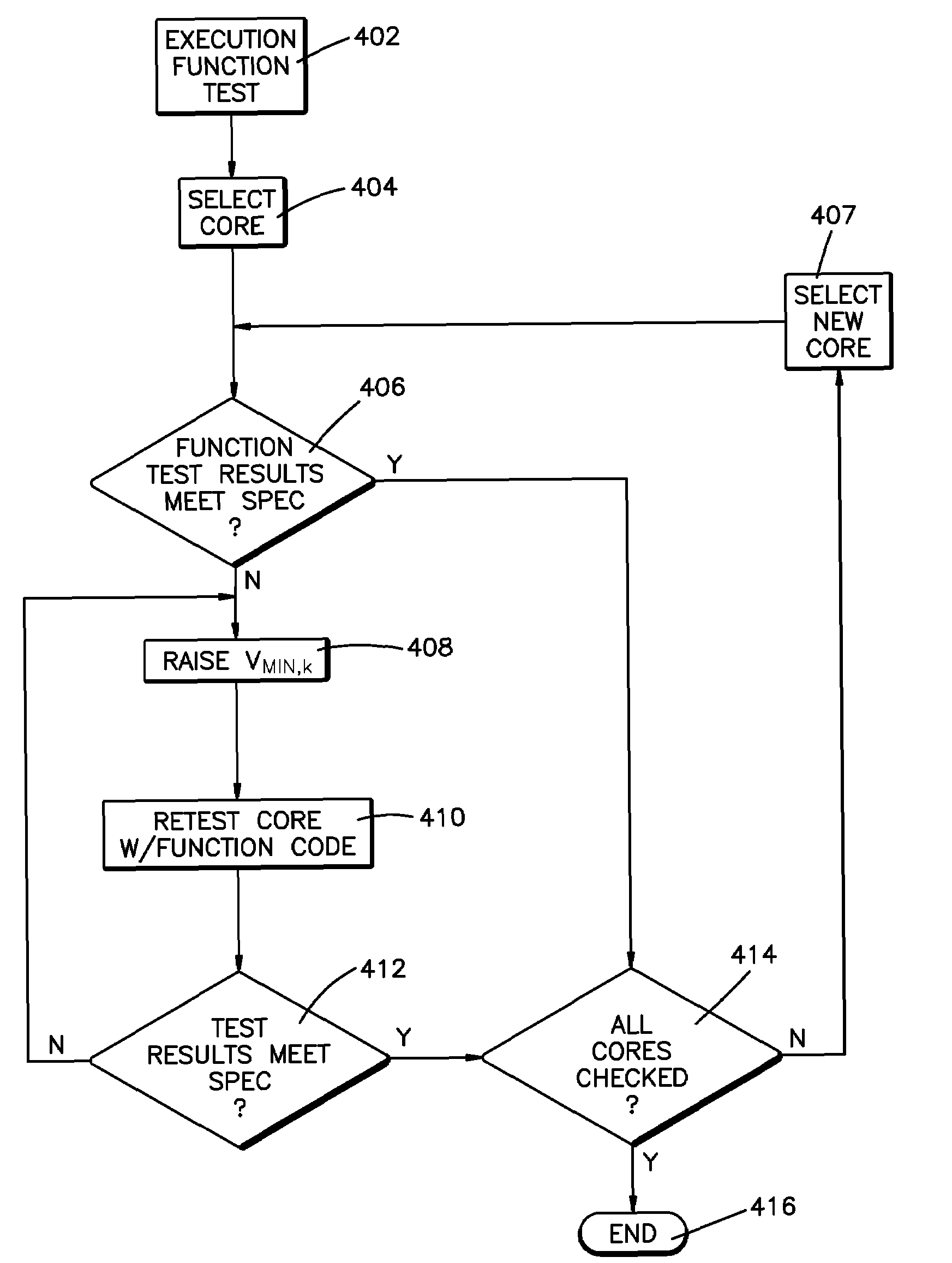
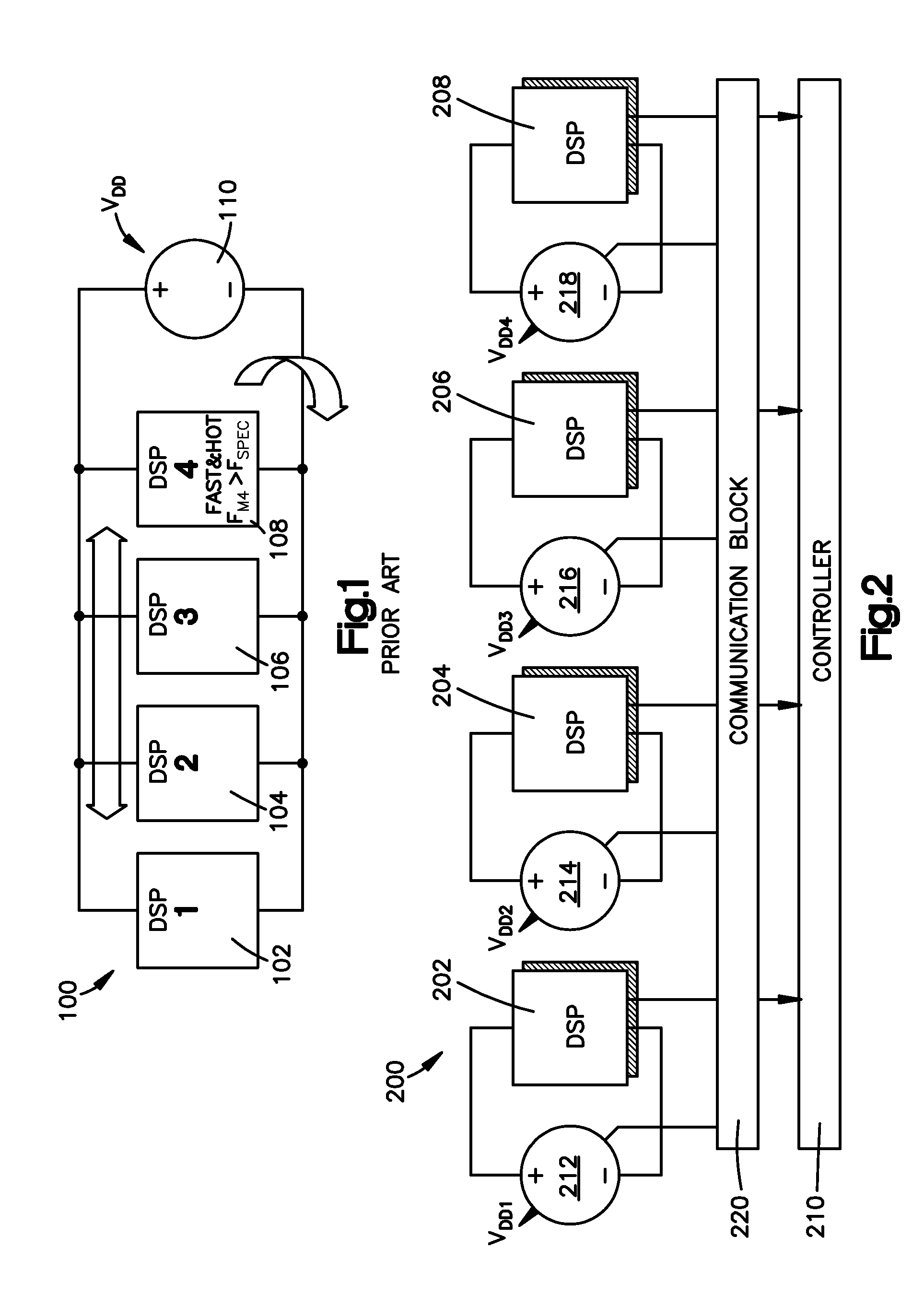
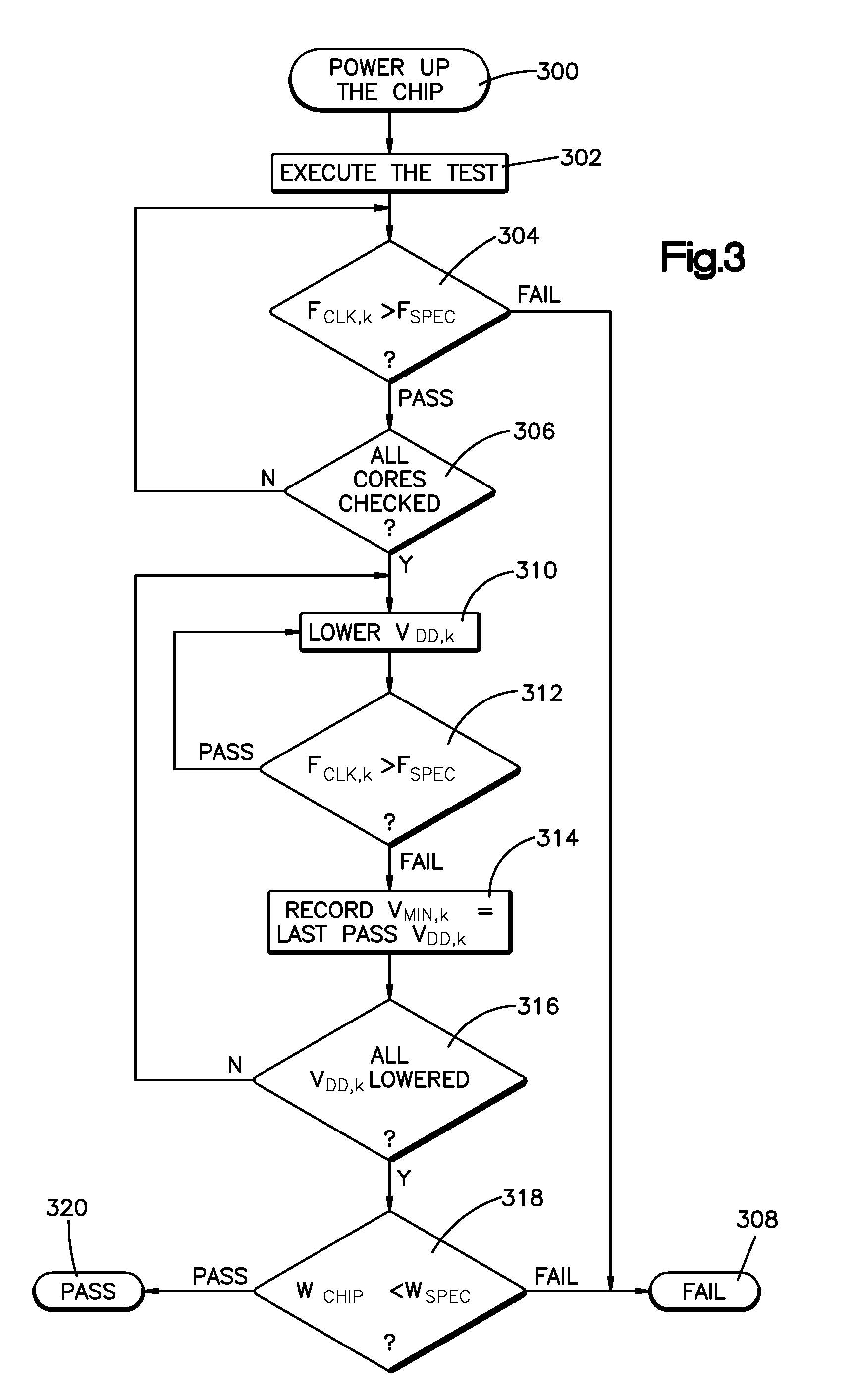
Method and system for testing processor cores
Systems, methods and program codes are provided for testing multi-core processor chip structures. Individual processor core power supply voltages are provided through controlling individual power supplies for each core, in one aspect to ensure that one or more cores operate at clock rates in compliance with one or more performance specifications. In one example, a first power supply voltage supplied to a first processing core differs from a second core power supply voltage supplied to a second processing core, both cores operating in compliance with a reference clock rate specification. Core power supply voltages may be selected from ordered discrete supply voltages derived by progressively raising or lowering a first supply voltage, optionally wherein the selected supply voltage also enables the core to operate within another performance specification.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
Amplifier system with current-mode servo feedback
InactiveUS20050116773A1Maximize dynamic rangeAccurately amplify any subsequent variations in the input signalNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierCurrent mode
A system and method for compensating an amplifier apparatus for low frequency and / or DC components of an externally applied input signal as well as for any voltage offsets contributed by the amplifier circuitry. Band-limited servo feedback is applied to predetermined nodes in the forward gain path to null out unwanted signal components, leaving a residual signal that, when amplified, will be centered around ground, so that the full dynamic range of the amplifier system may be utilized. Consequently, the signal-to-noise ratio available at the output of the amplifier system will be maximized. The servo compensation may either operate in continuous time, or it may be held constant once a suitable level of compensation has been established, or it may be adjusted from time to time to accommodate slow variations of the average DC component of the input signal.
Owner:BIOURJA ENERGY SYST LLC
Smart capture for ATPG (automatic test pattern generation) and fault simulation of scan-based integrated circuits
InactiveUS7124342B2Improve performanceHigh simulationError detection/correctionMarginal circuit testingHemt circuitsAutomatic test pattern generation
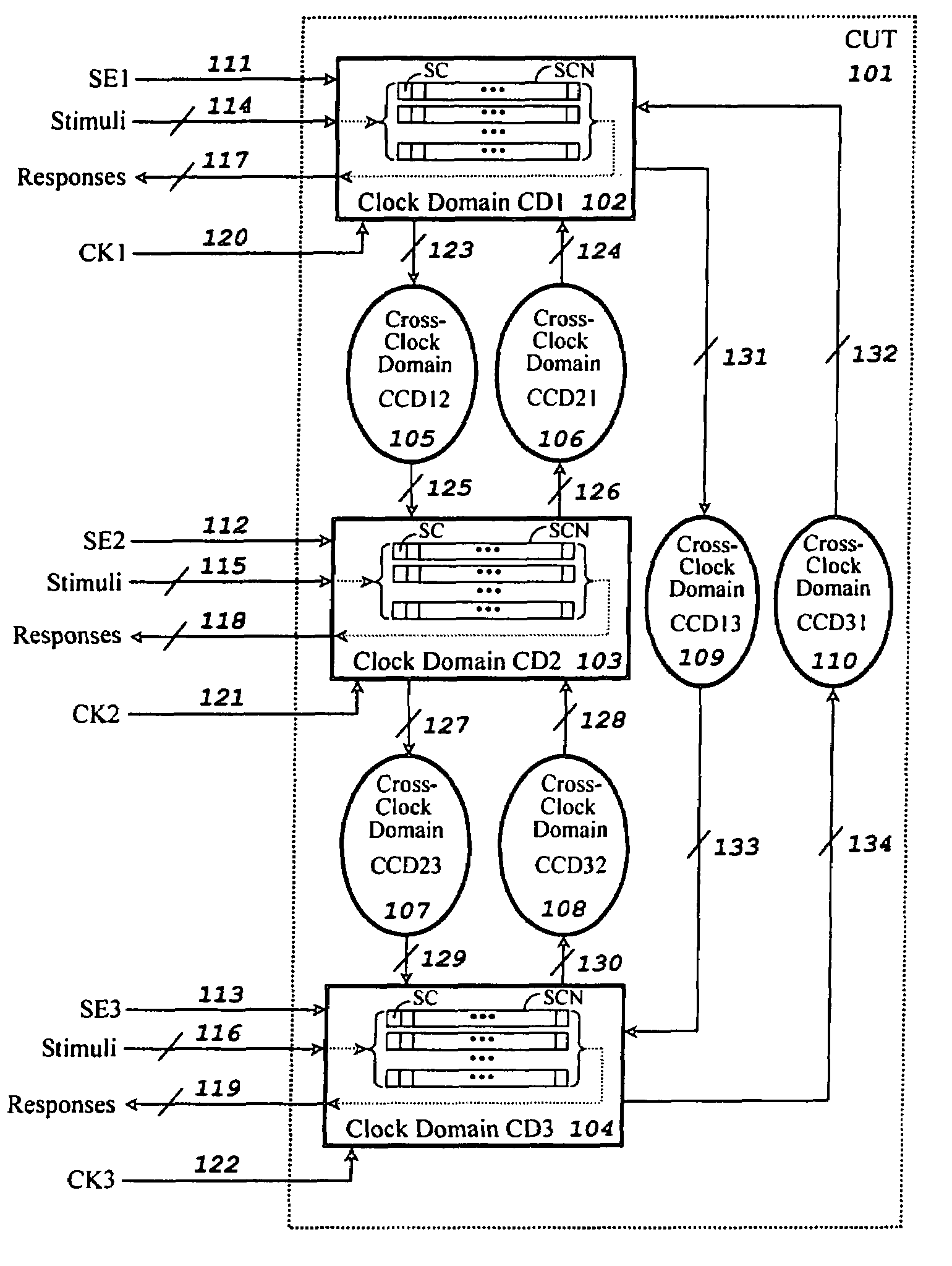
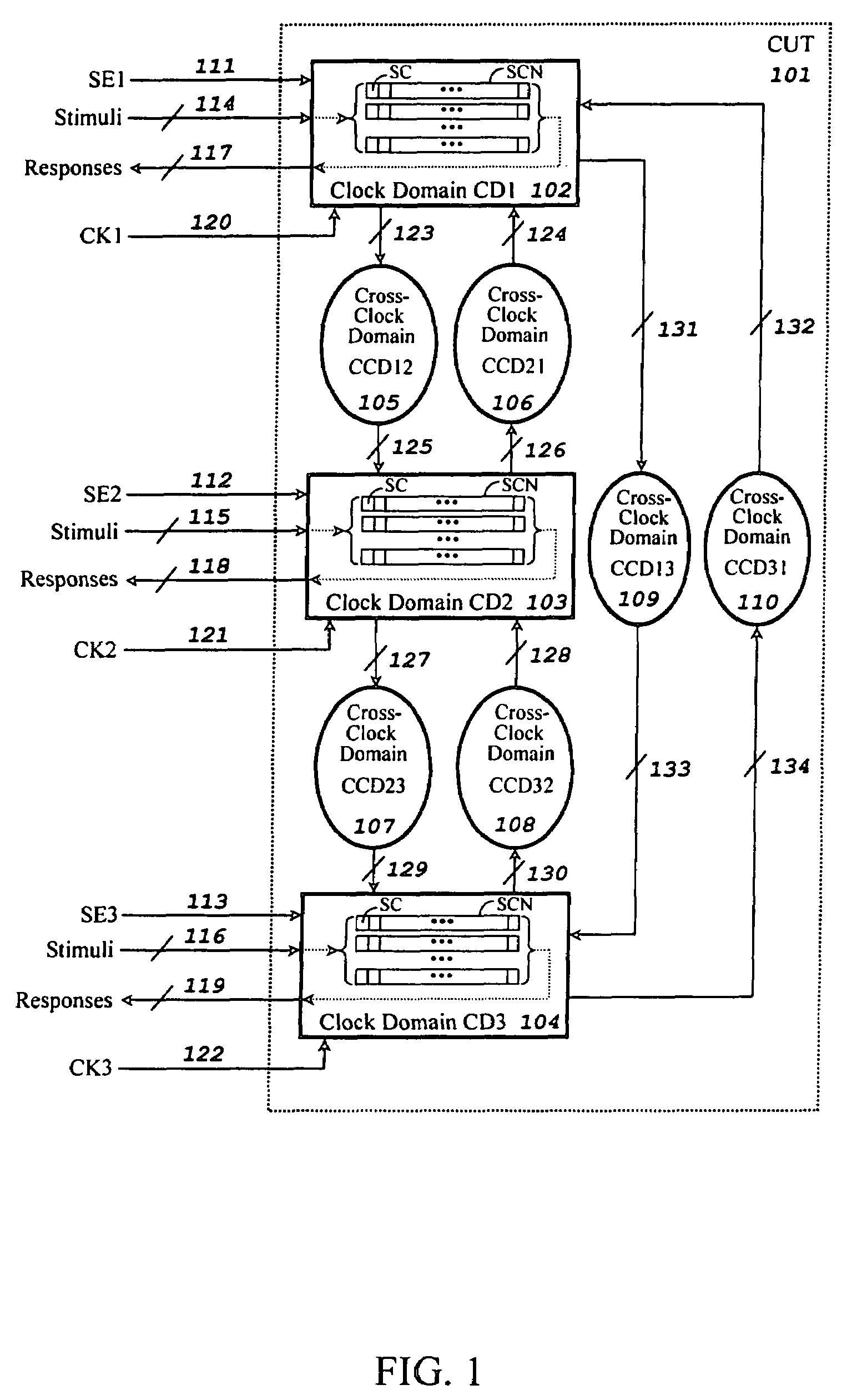
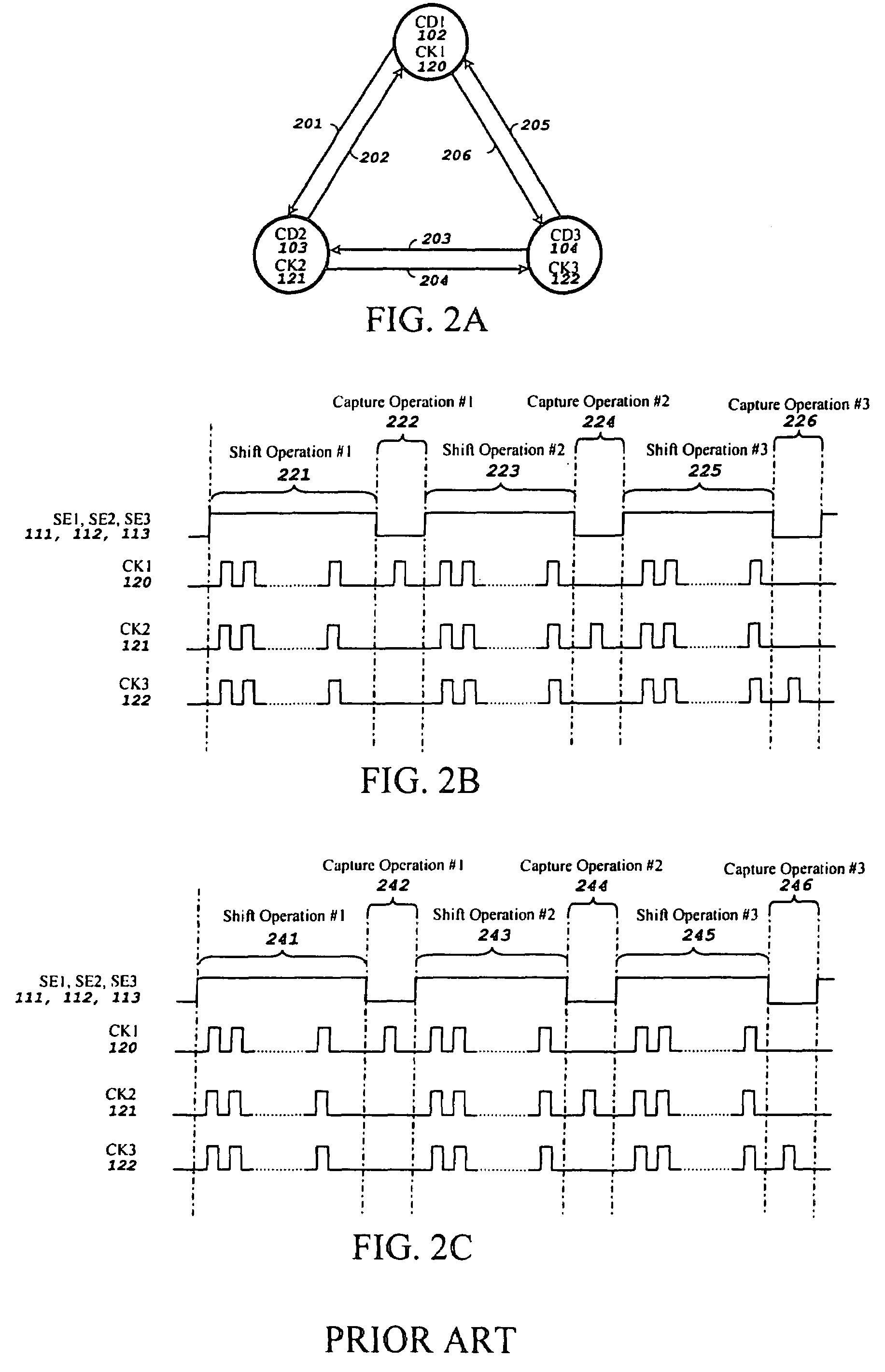
A method for generating stimuli and test responses for testing faults in a scan-based integrated circuit in a selected scan-test mode or a selected self-test mode, the scan-based integrated circuit containing a plurality of scan chains, N clock domains, and C cross-clock domain blocks, each scan chain comprising multiple scan cells coupled in series, each clock domain having one capture clock, each cross-clock domain block comprising a combinational logic network. The method comprises compiling the scan-based integrated circuit into a sequential circuit model; specifying input constraints on the scan-based integrated circuit during a shift and capture operation; specifying a clock grouping to map the N clock domains into G clock domain groups, where N>G>1; transforming the sequential circuit model into an equivalent combinational circuit model according to the input constraints and the clock grouping; and generating the stimuli and test responses on the equivalent combinational circuit model according to the input constraints.
Owner:SYNTEST TECH
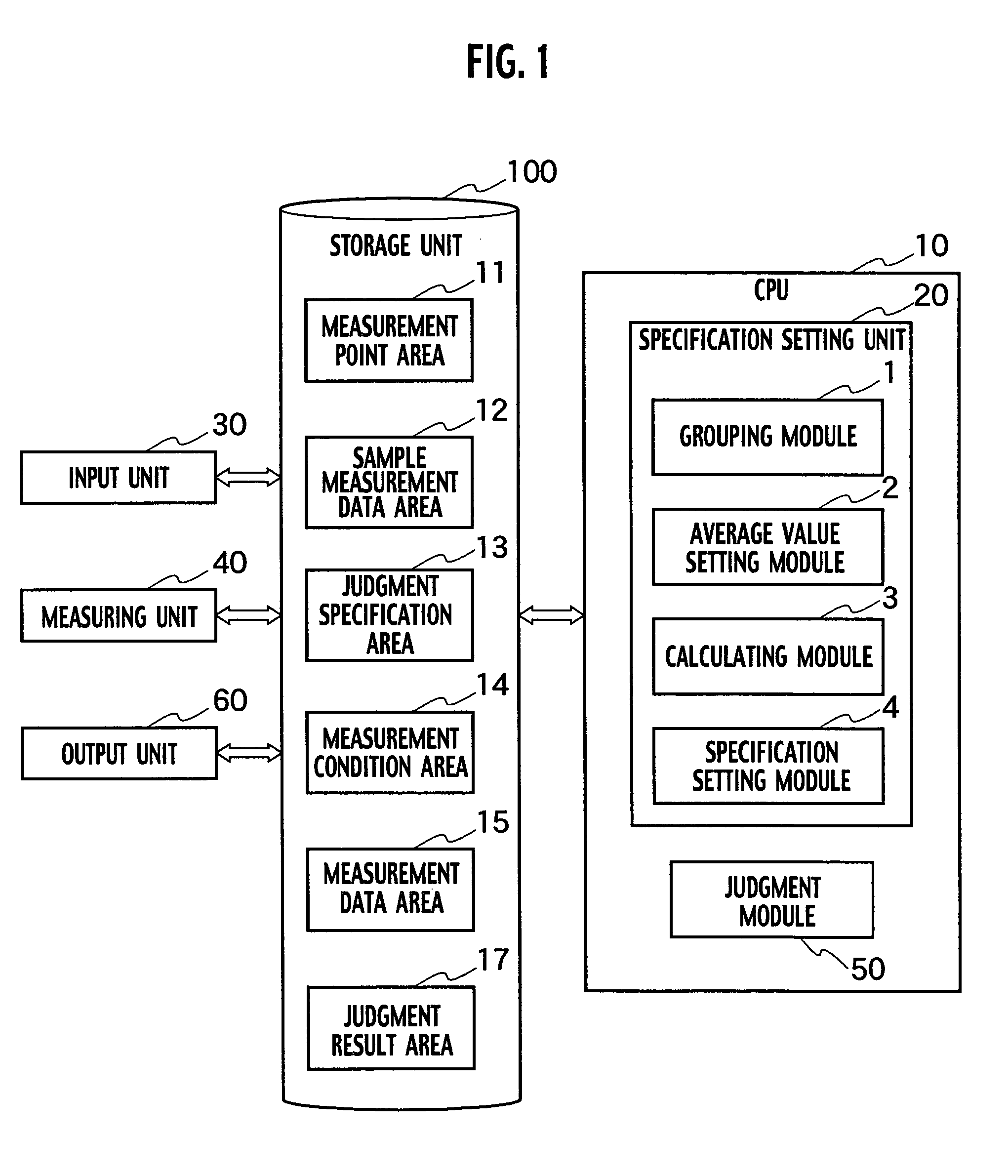
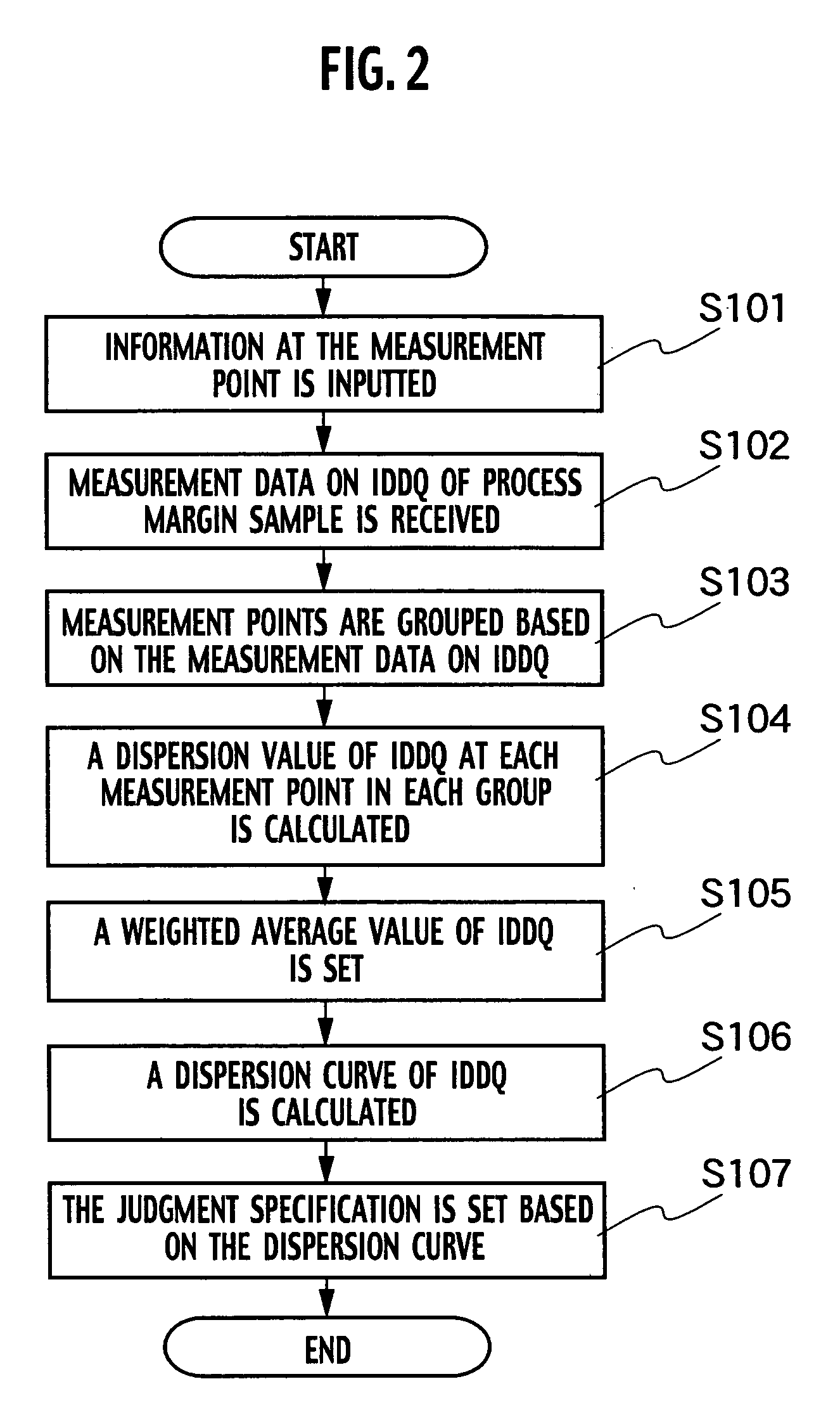
Test system, test method and test program for an integrated circuit by IDDQ testing
InactiveUS7096140B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceValue setMeasurement point
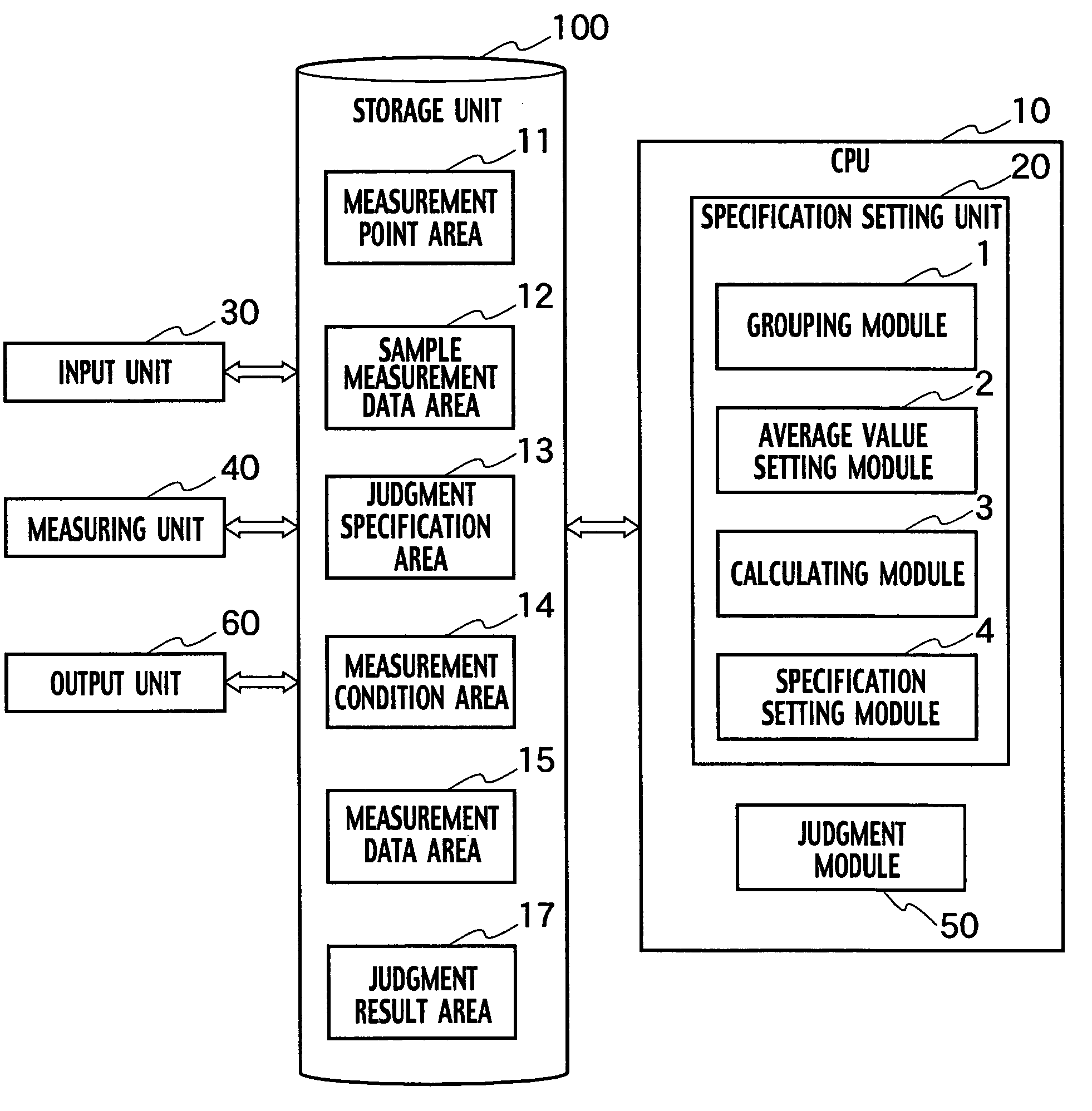
A test system for an integrated circuit includes a grouping module grouping measurement points on basis of values of the quiescent supply current and setting measurement point groups; an average value setting module setting a weighted average value minimizes the sum of dispersion of the quiescent supply current; a calculating module calculating a maximum estimated value of dispersion of the quiescent supply current on the basis of the weighted average value; and a judgment module judging whether the integrated circuit passes or fails the judgment specification.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
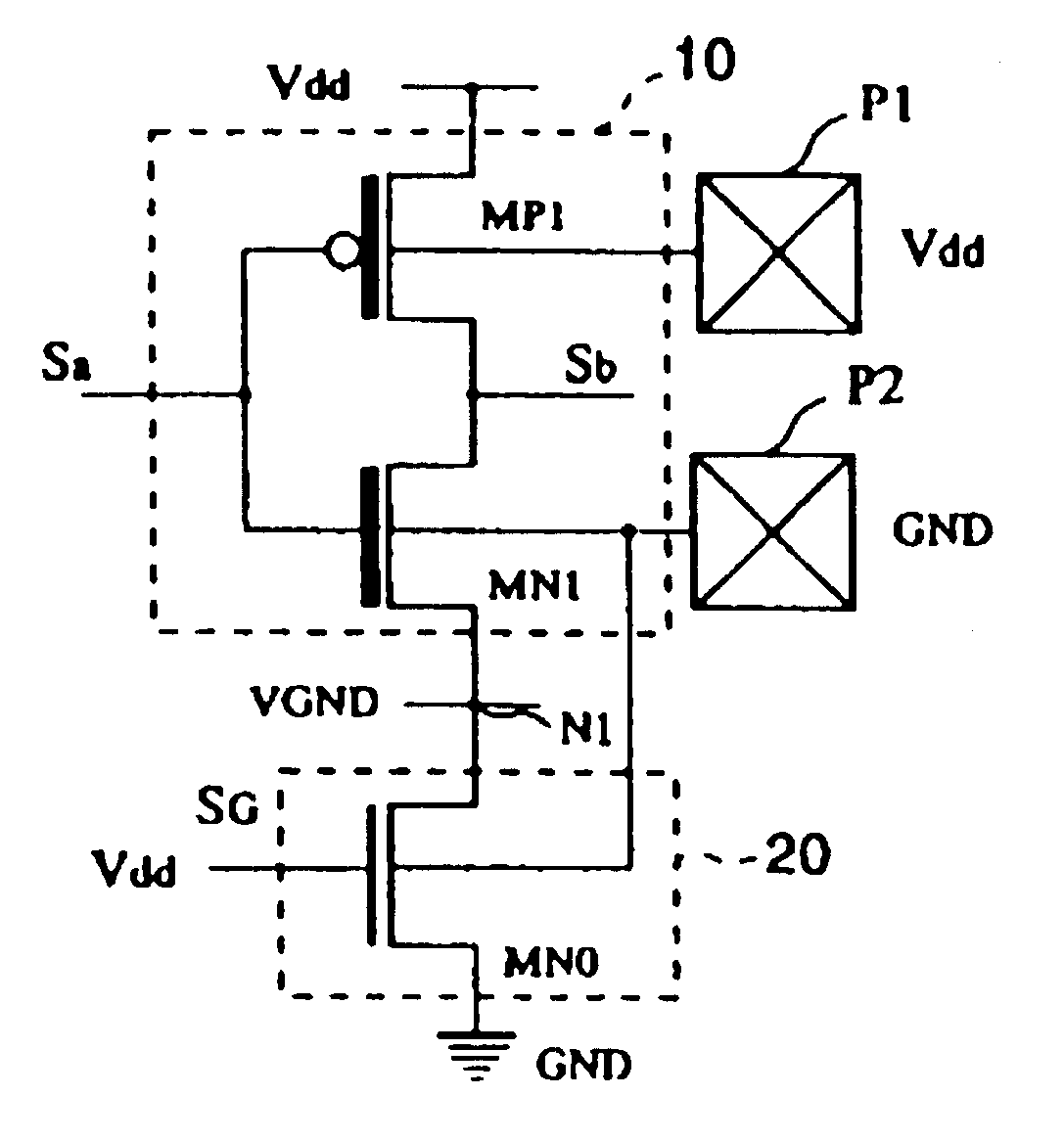
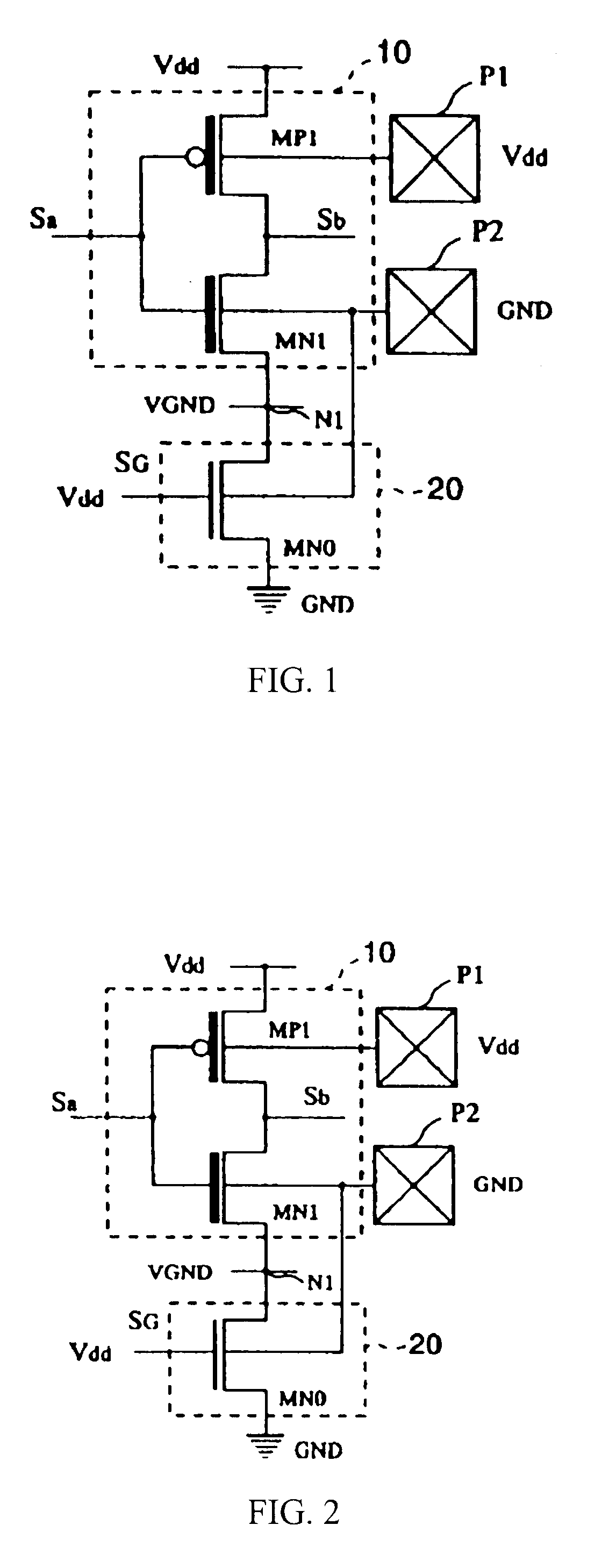
Semiconductor integrated circuit
The objective of this invention is to provide a type of semiconductor integrated circuit which can lessen solution in the circuit area to the minimum necessary level, and can lessen the leakage current in the standby state so as to cut the power consumption, and which allows Iddq test to determine whether it is passed or defective. Logic circuit 10 composed of low threshold voltage transistors and switching circuit 20 composed of transistors having the standard threshold voltage are set. In the operation, the switching circuit is turned ON, and a driving current is fed to logic circuit 10. On the other hand, in the standby mode, the switching circuit is turned OFF, and the path of the leakage current is cut off to lessen generation of the leakage current. In the case of Iddq test, different bulk bias voltages are applied to the channel regions of PMOS transistors and NMOS transistors from an IC tester through pads P1 and P2. In this way, the leakage current can be lessened on a low level, and whether the semiconductor integrated circuit is passed or defective can be judged from the results of the current measurement.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
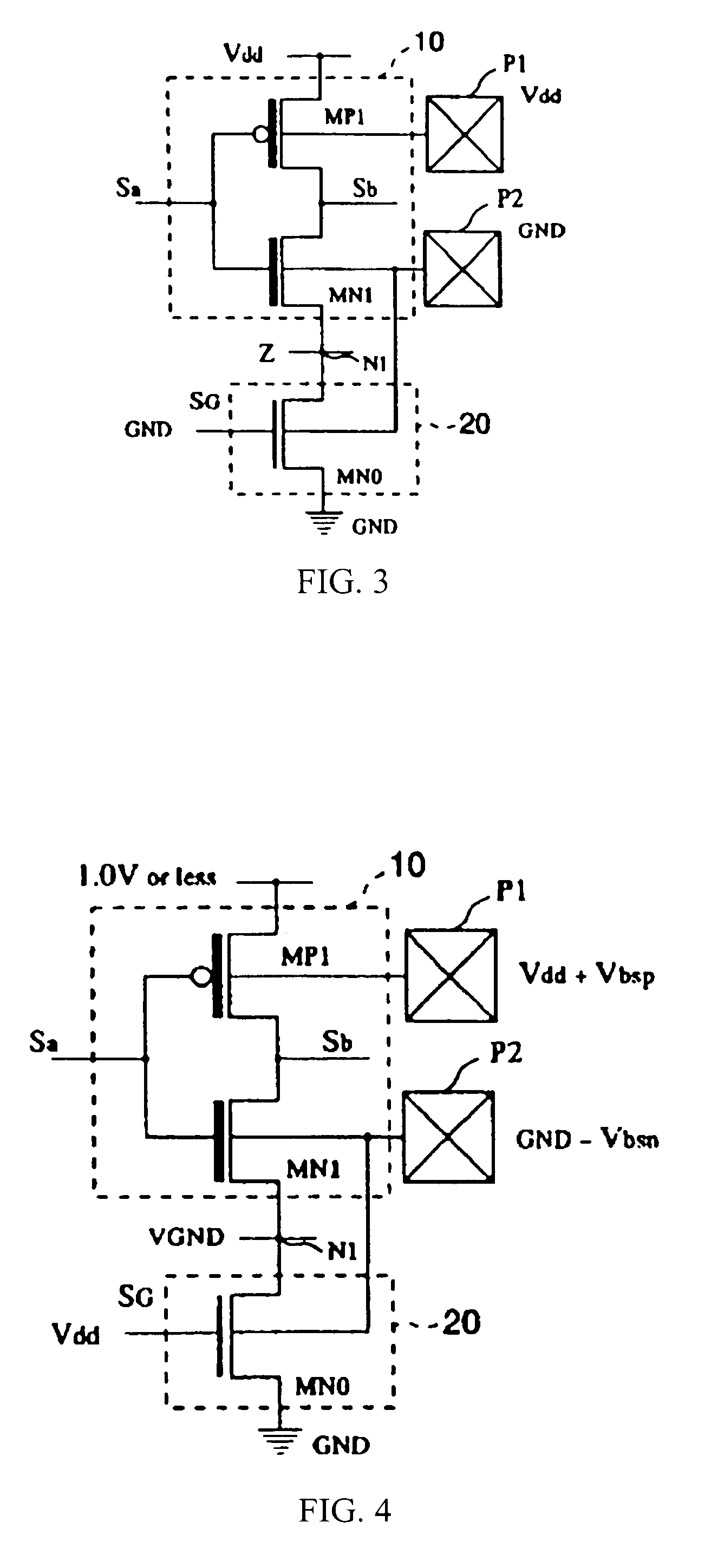
Compensating for Aging in Integrated Circuits
ActiveUS20140022008A1Easy to operateHigh voltagePower supply for data processingMemory systemsEngineeringOperating life
An age compensation method and apparatus for an integrated circuit (IC). An IC may be configured to operate at an initial operating voltage at the beginning of its operational life. Various circuits may be used to detect aging of the IC, and indications of aging may be stored to determine the aging of the IC. The information indicative of the determined aging of the IC may be compared to an aging threshold. If the information indicates that the aging is greater than or equal to the determined aging threshold, the operating voltage of the IC may be increased. This process may be repeated over the life of the IC, increasing the operating voltage as the IC ages. Raising the operating voltage in response to aging may compensate for various age related degradation mechanisms that can occur over the operational life of the IC.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and system for identifying and locating defects in an integrated circuit
InactiveUS20050182584A1Reduce the impactReduce impactDigital circuit testingResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical resistance and conductancePower grid
A method and system for detecting and locating defects in an integrated circuit. A time-varying input signal is applied to the integrated circuit, power signals produced at a plurality of respective ordered connections in response to the input signal are measured, and one or more defects in the integrated circuit are identified from the power signals so measured. A system is provided having a probe for connecting to the die of an integrated circuit prior to final packaging, a testing system for applying transient input signals to the die and acquiring die power signal measurements in response thereto, and a data processor for determining whether the power signal measurements indicate the presence of a defect in the die. Also provided is a method for reducing the effect of contact resistance from test probe connections. As a way of implementing the approach of the method and system there is also provided an integrated circuit having a plurality of ordered connections to the power grid and a plurality of calibration circuits associated with respective ordered connections so as to selectively inject transient signals onto the power grid at respective locations.
Owner:PLUSQUELLIC JAMES FRANCIS
Enhanced loopback testing of serial devices
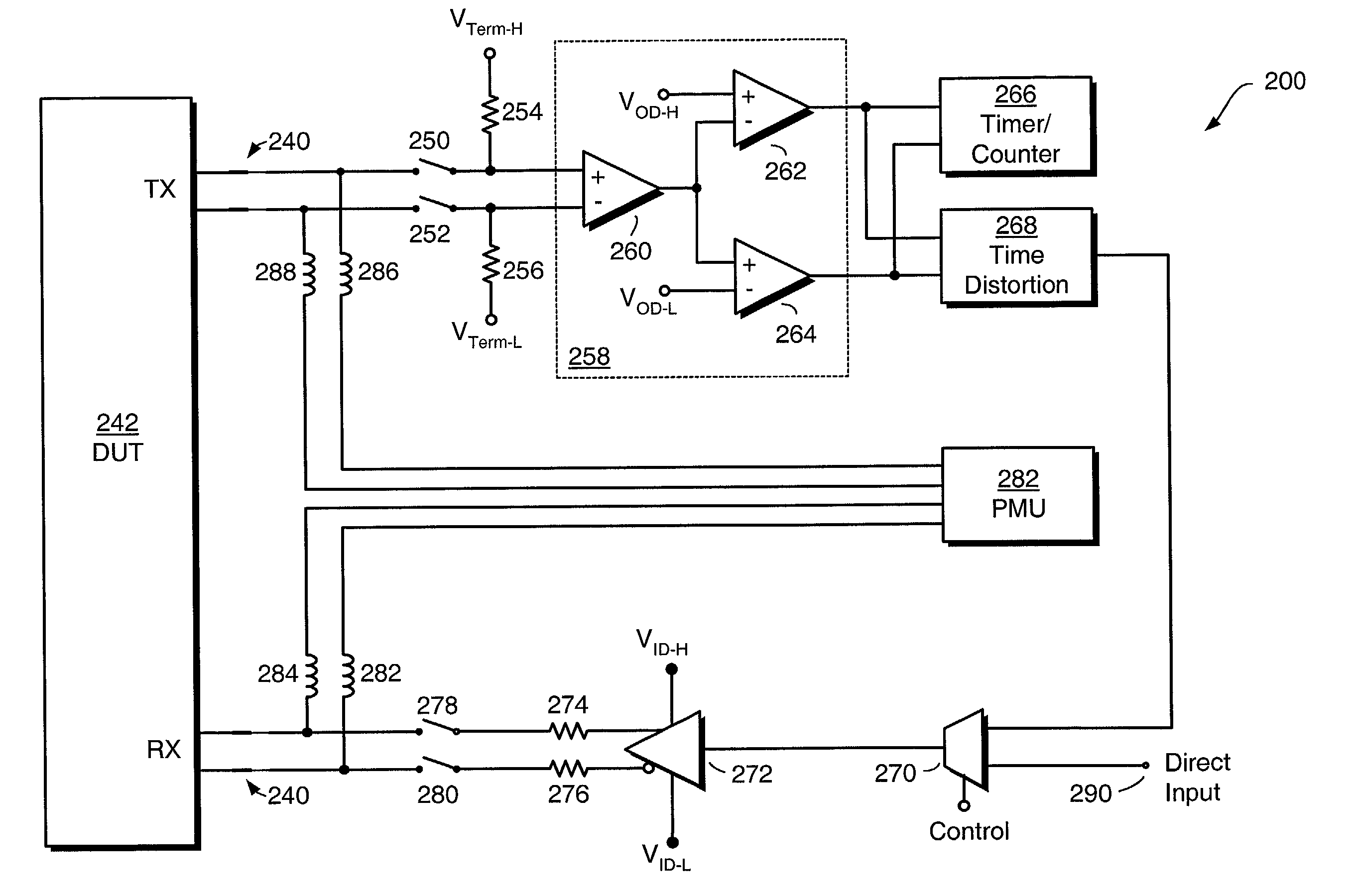
InactiveUS7017087B2Low costDigital circuit testingCorrect operation testingTime distortionEngineering
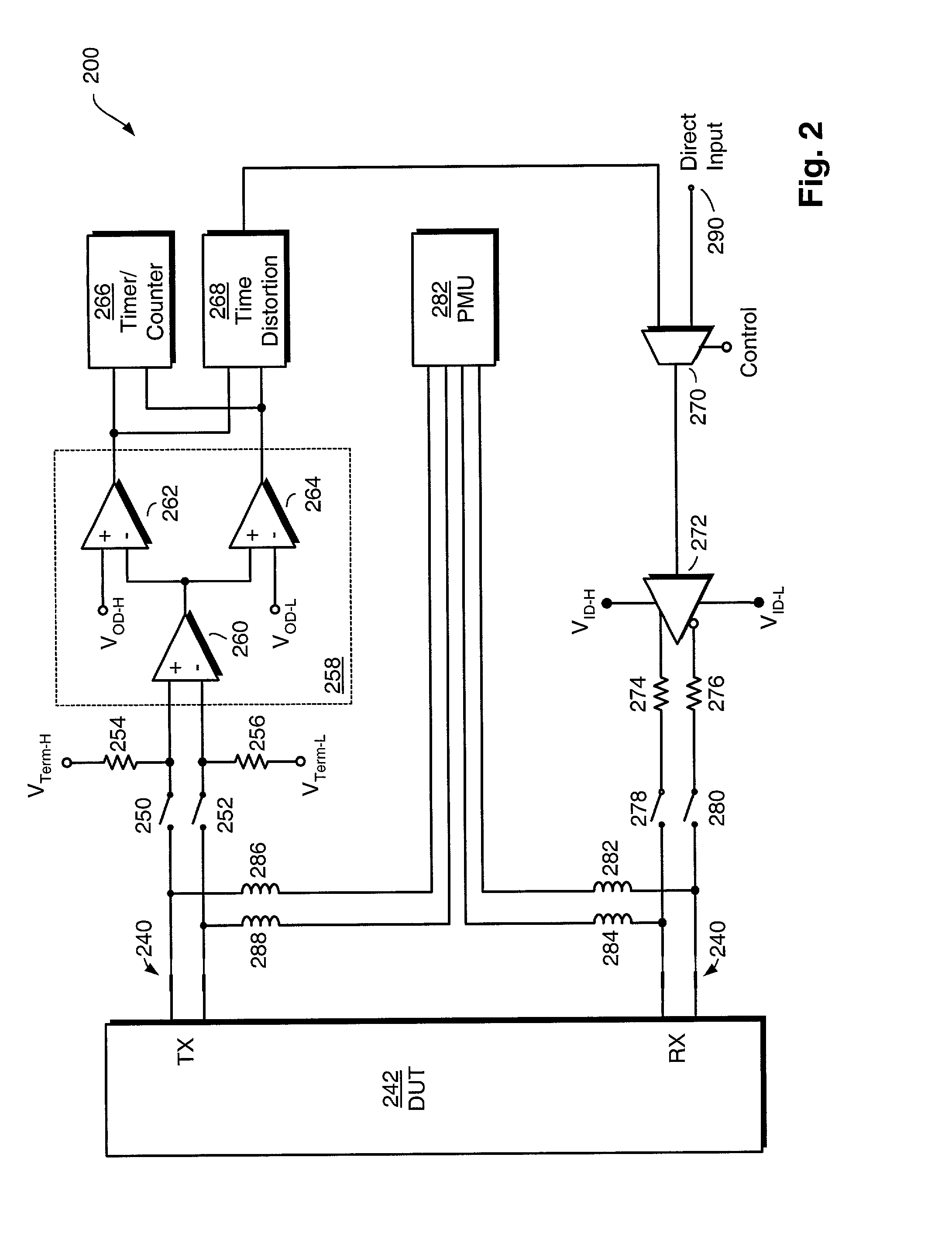
A system and method for economically yet thoroughly testing serial ports of electronic devices includes a receiver and a transmitter. The receiver is coupled to a TX line of a device under test for receiving an input serial bit stream from the device under test. The transmitter is coupled to a RX line of the device under test for providing an output serial bit stream to the device under test. The receiver is coupled to the transmitter for establishing a loopback connection. A time distortion circuit is interposed between the receiver and the transmitter, for adding predetermined amounts of timing distortion to the output serial bit stream. In addition, a selector is interposed between the receiver and the transmitter, for selecting between the receiver and a direct input. The direct input provides an algorithmic test signal that differs from the input serial bit stream received by the receiver. The direct input thus allows a tester to exercise the device under test with a test signal that differs from the signal that the device under test generates. A time measurement circuit measures timing characteristics of the device under test, and a parametric measurement circuit measures steady-state characteristics of the device under test.
Owner:TERADYNE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com