Patents
Literature
1181results about "Power reduction by control/clock signal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Integrated circuit communication techniques
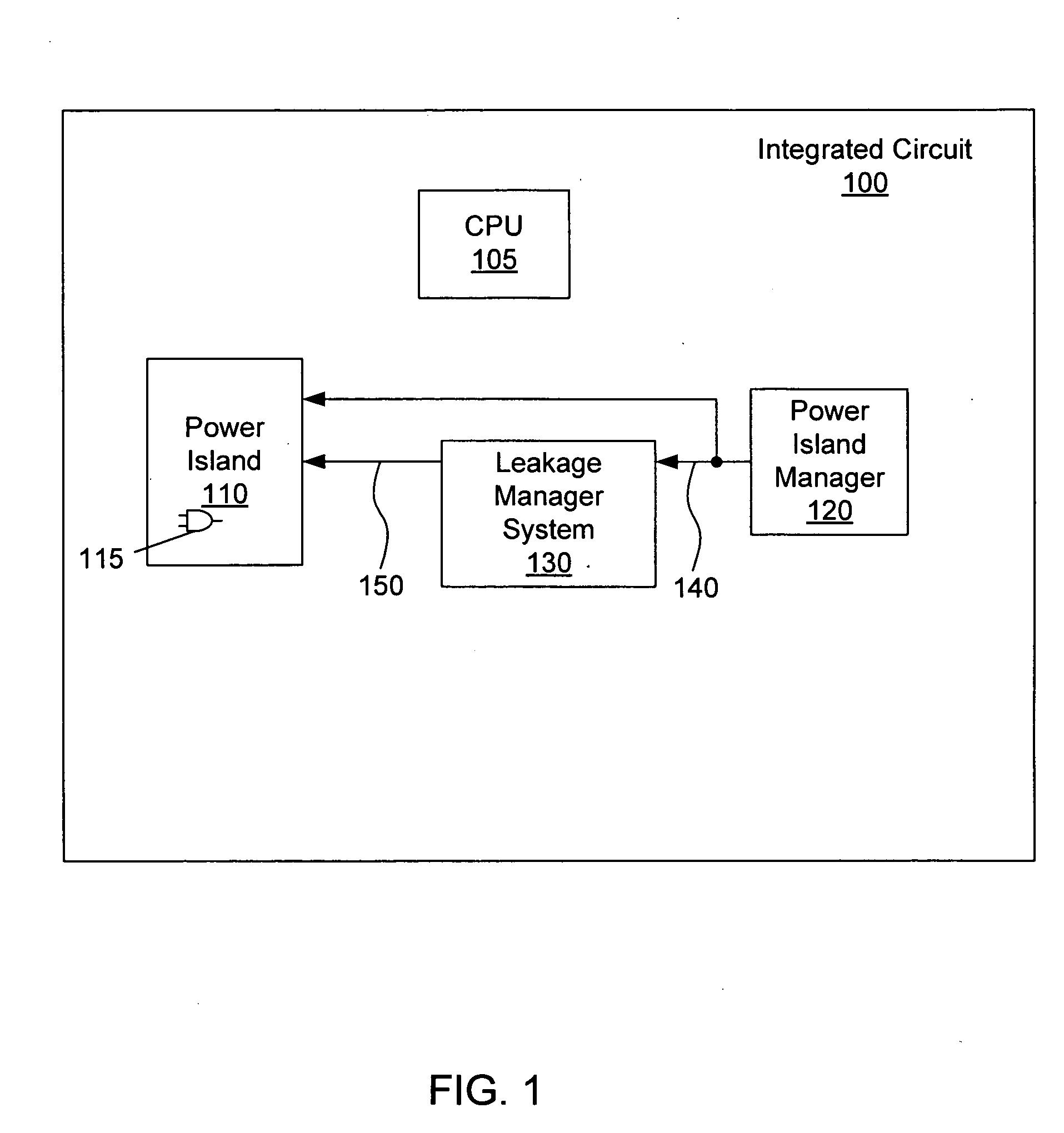
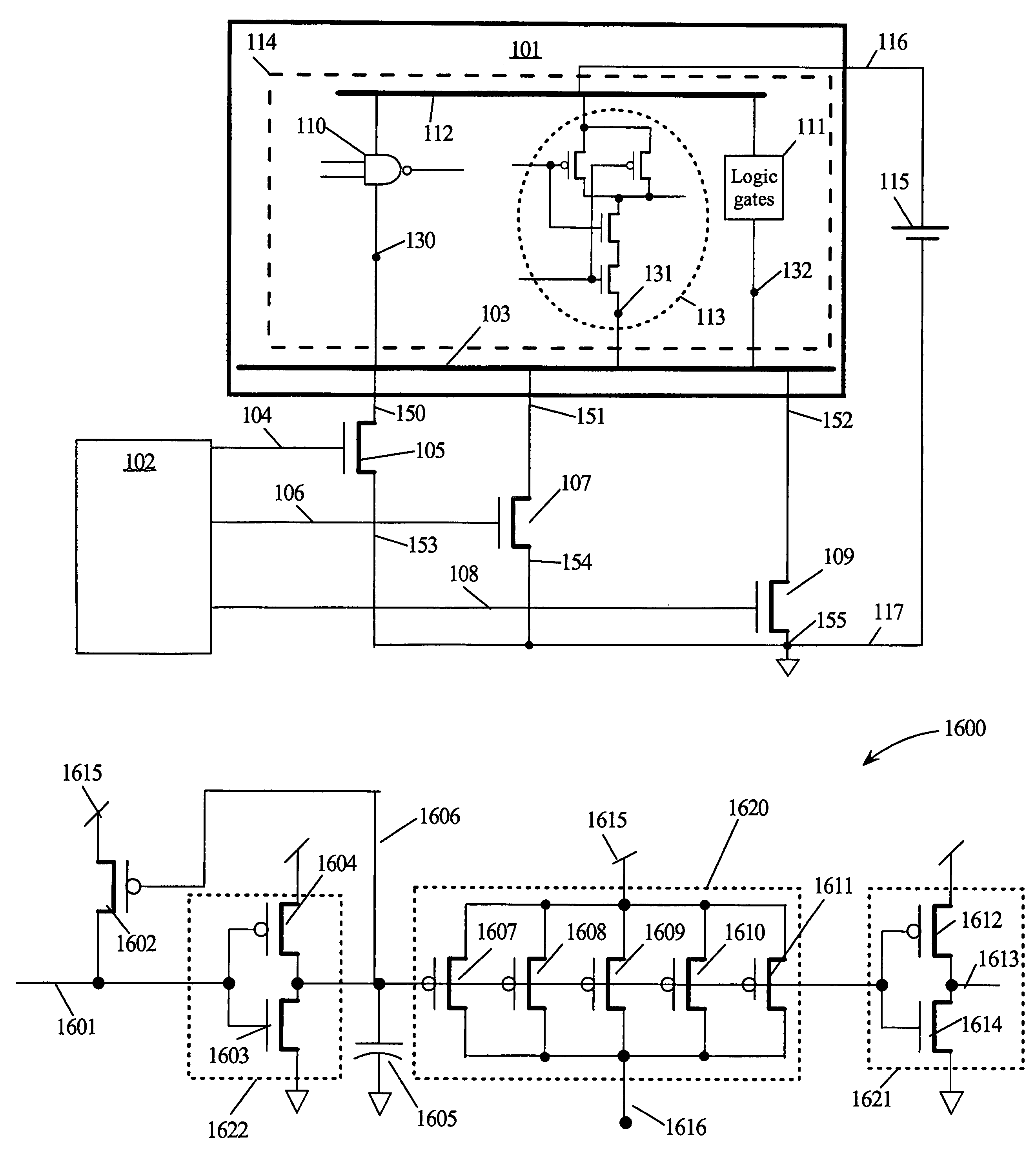
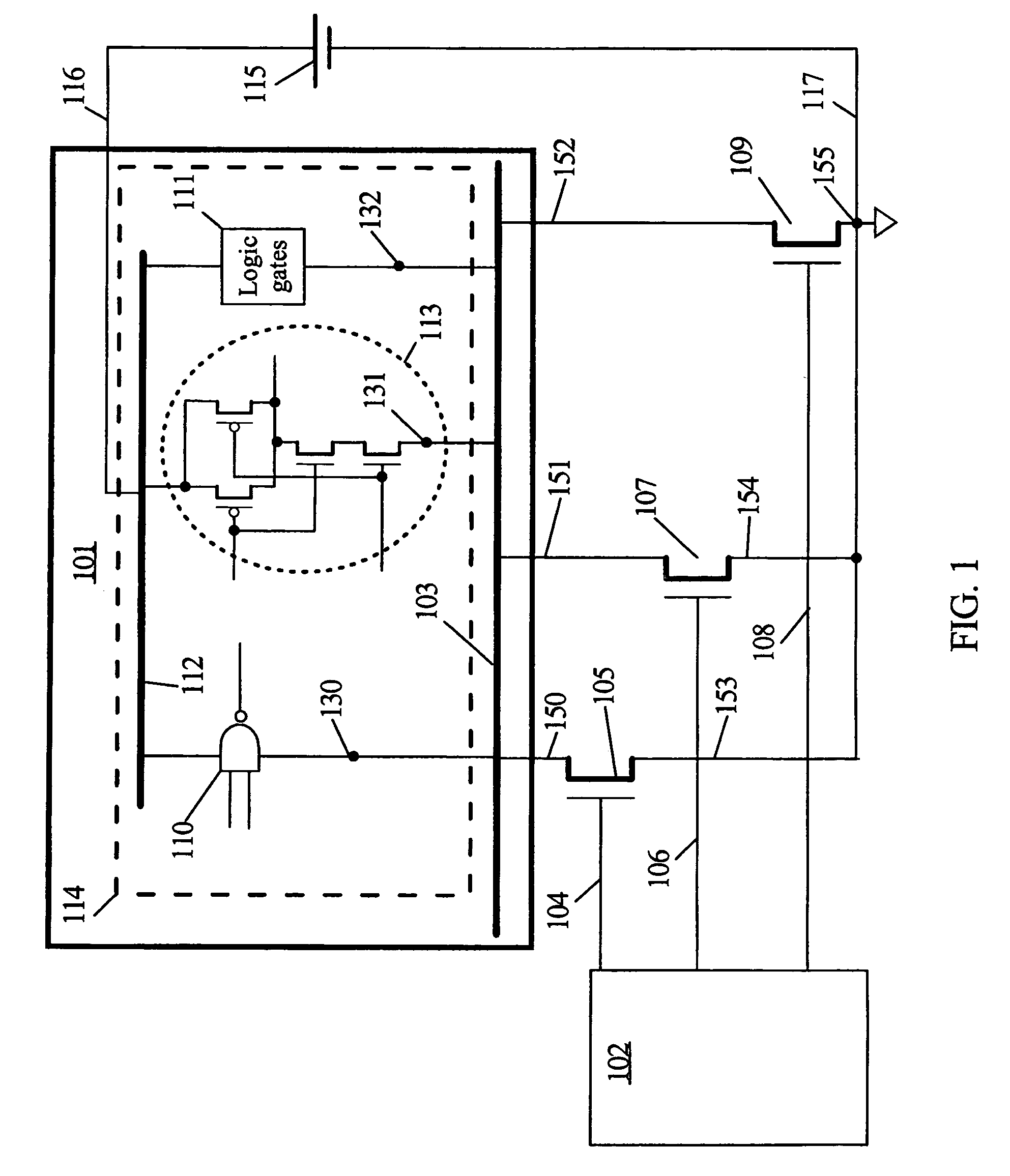
ActiveUS7439773B2Reduce the required powerReduce power consumptionReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalEngineeringSemiconductor
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Logic circuit and semiconductor device
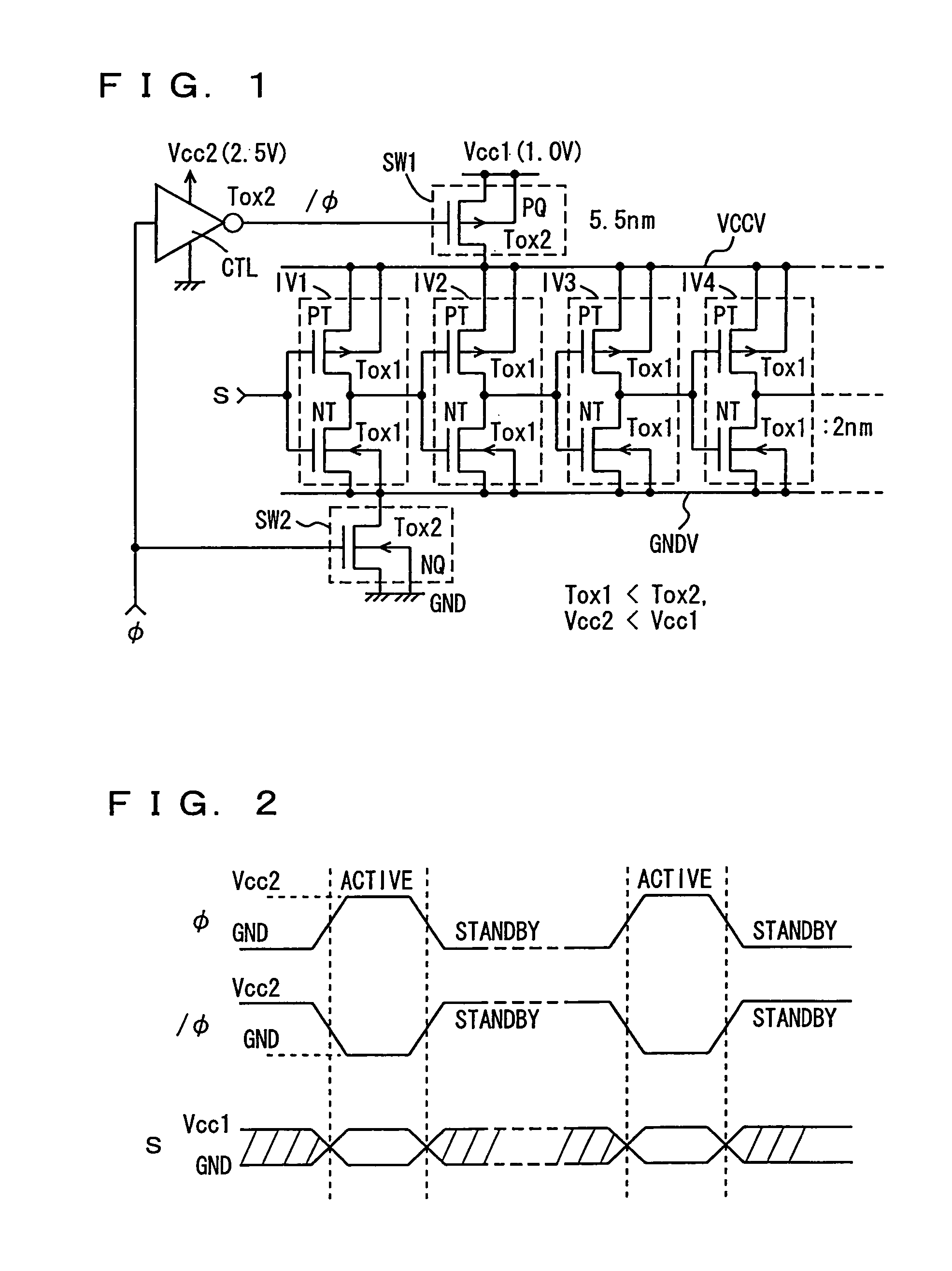
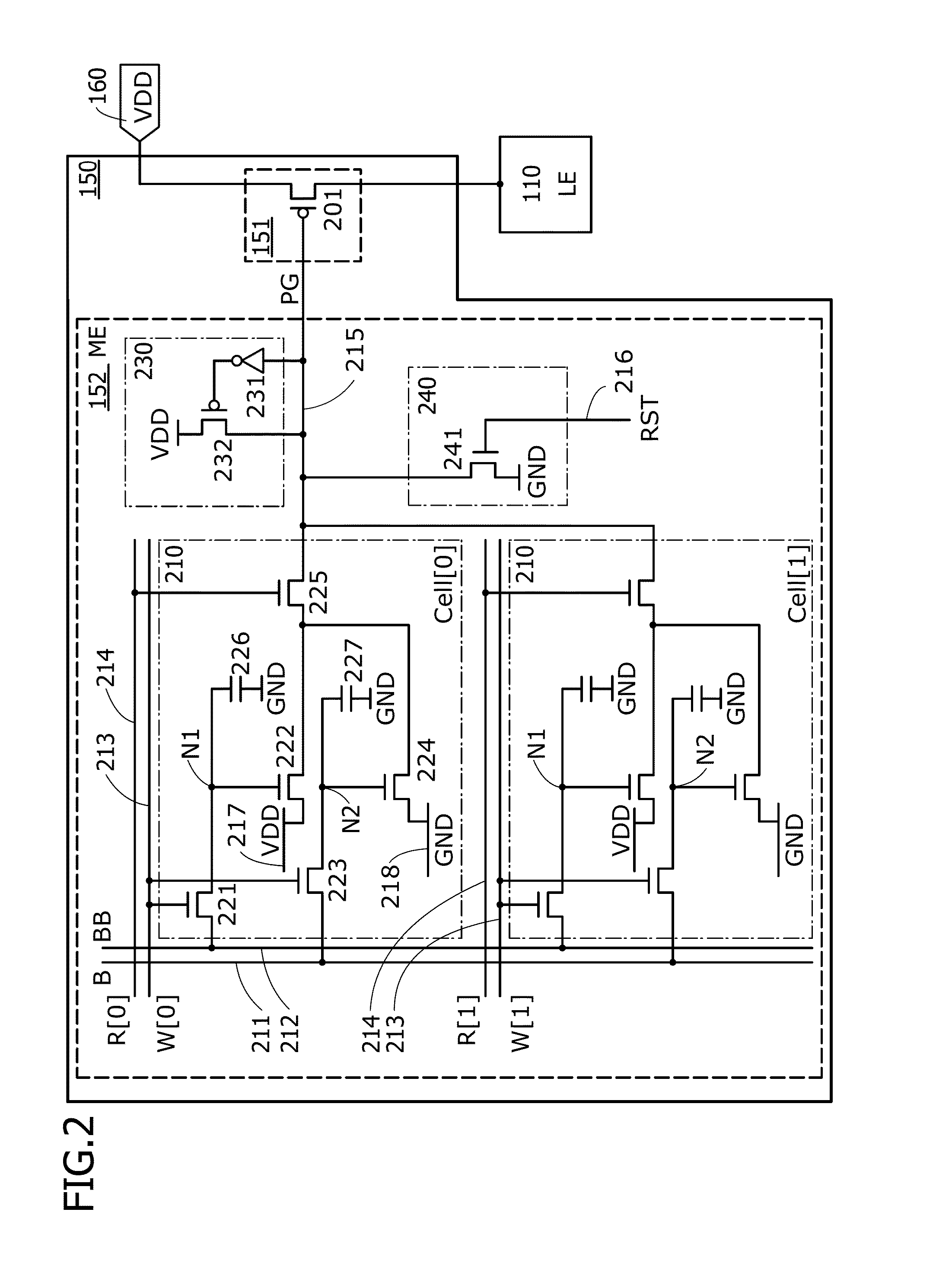
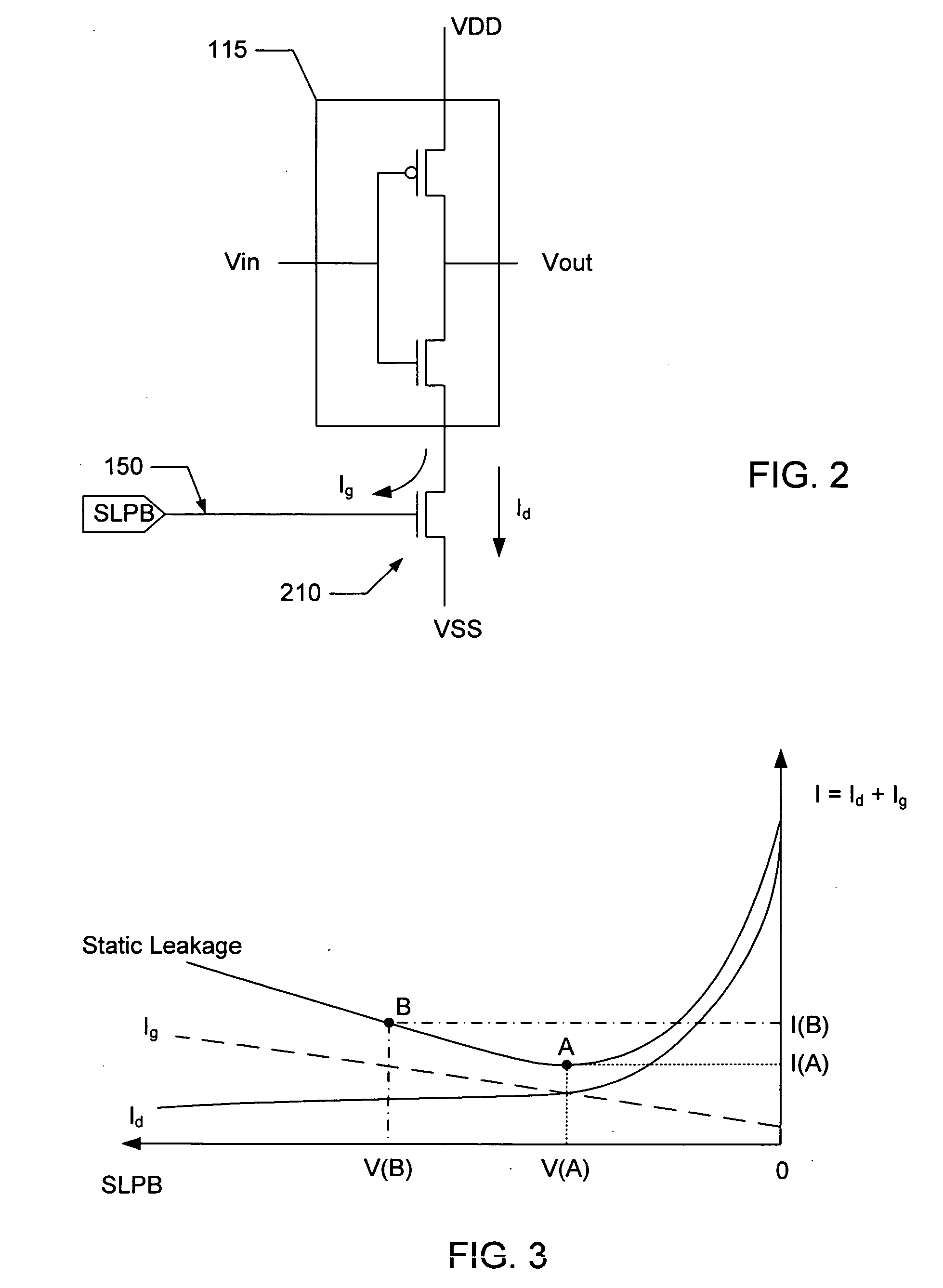
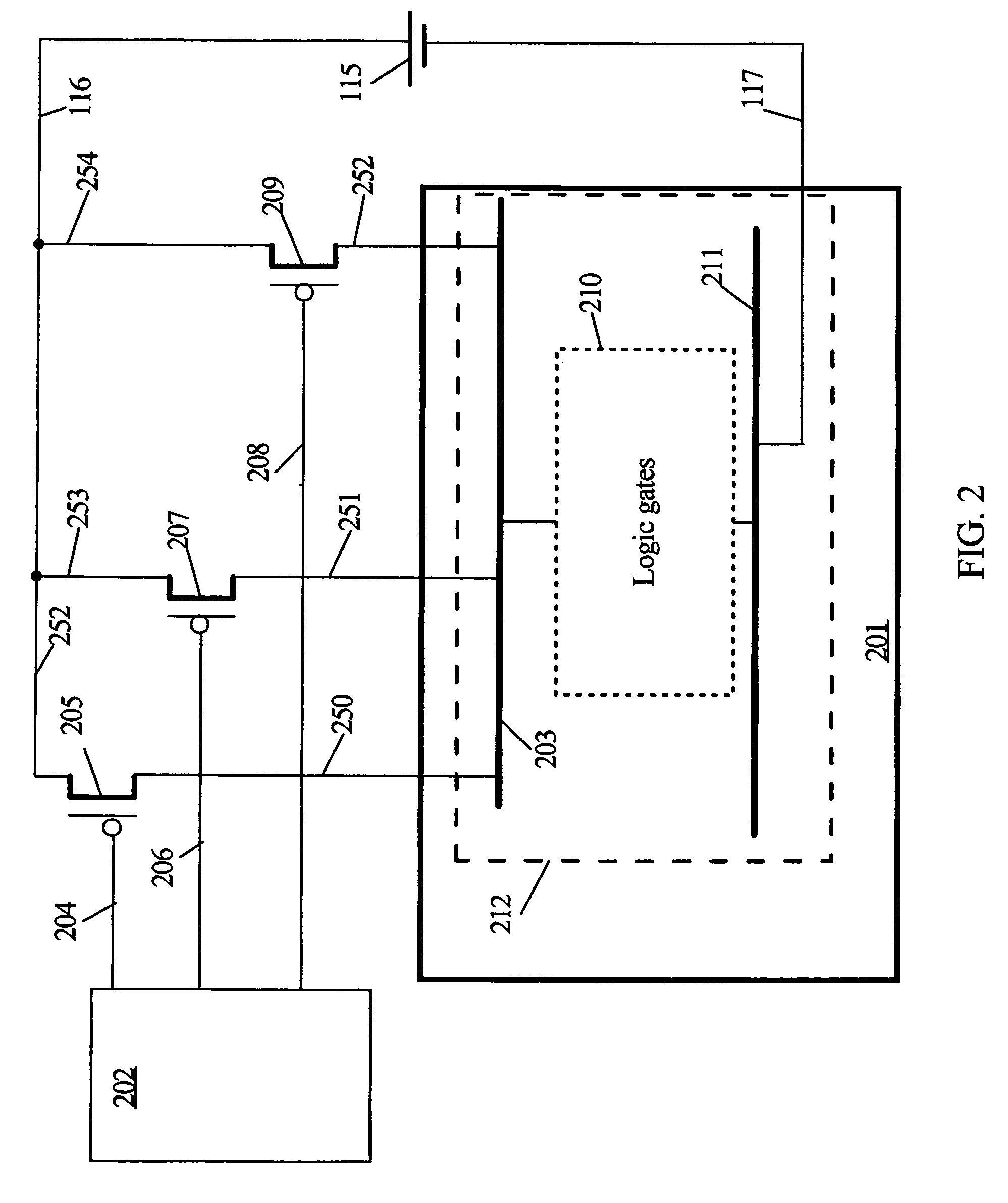
ActiveUS8207756B2Reduce dynamic power consumptionLeakage of highTransistorPower reduction by control/clock signalHydrogen concentrationPower semiconductor device
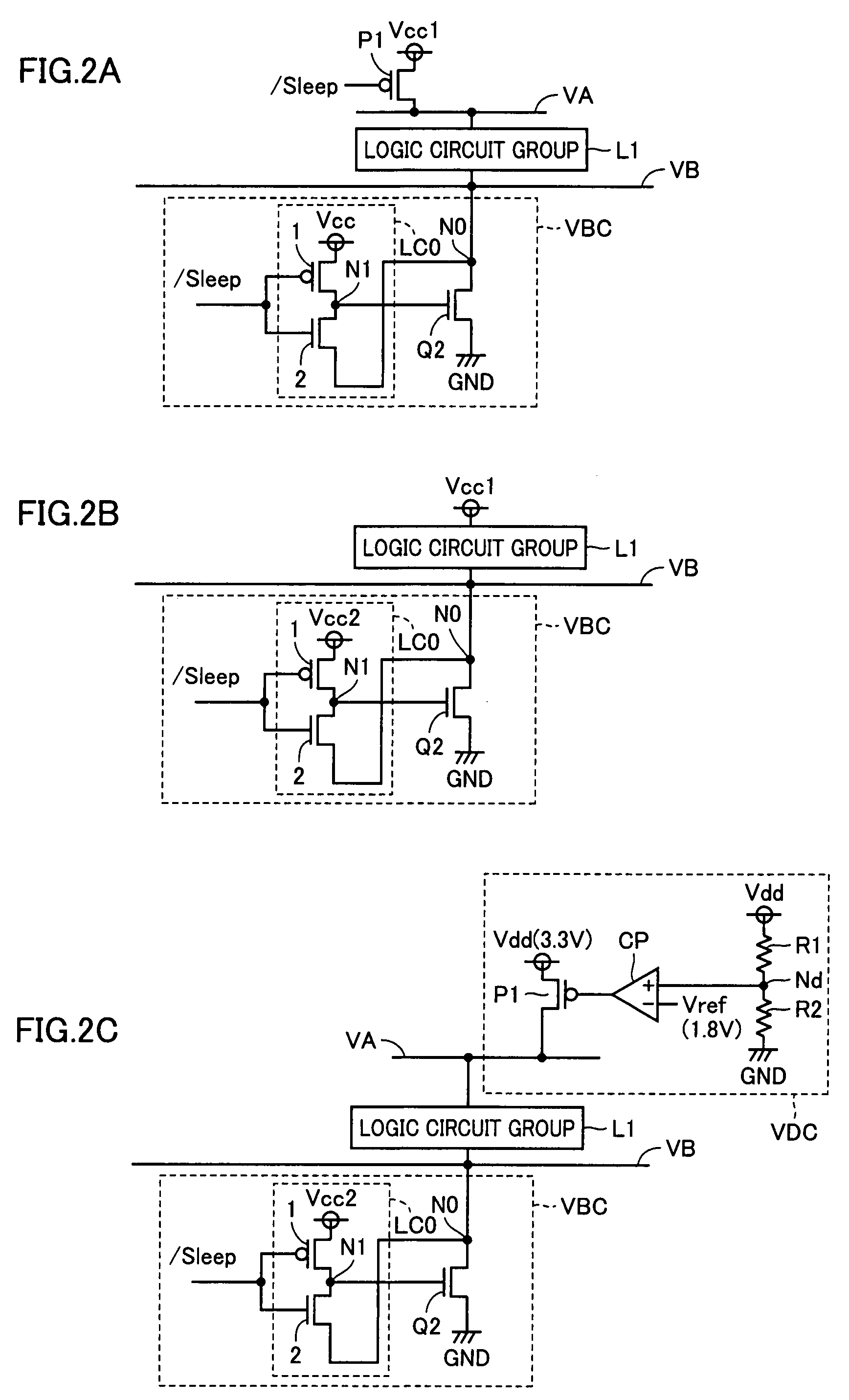
In a logic circuit where clock gating is performed, the standby power is reduced or malfunction is suppressed. The logic circuit includes a transistor which is in an off state where a potential difference exists between a source terminal and a drain terminal over a period during which a clock signal is not supplied. A channel formation region of the transistor is formed using an oxide semiconductor in which the hydrogen concentration is reduced. Specifically, the hydrogen concentration of the oxide semiconductor is 5×1019 (atoms / cm3) or lower. Thus, leakage current of the transistor can be reduced. As a result, in the logic circuit, reduction in standby power and suppression of malfunction can be achieved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Switched backgate bias for FET
InactiveUS6232793B1Reliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalHemt circuitsEngineering
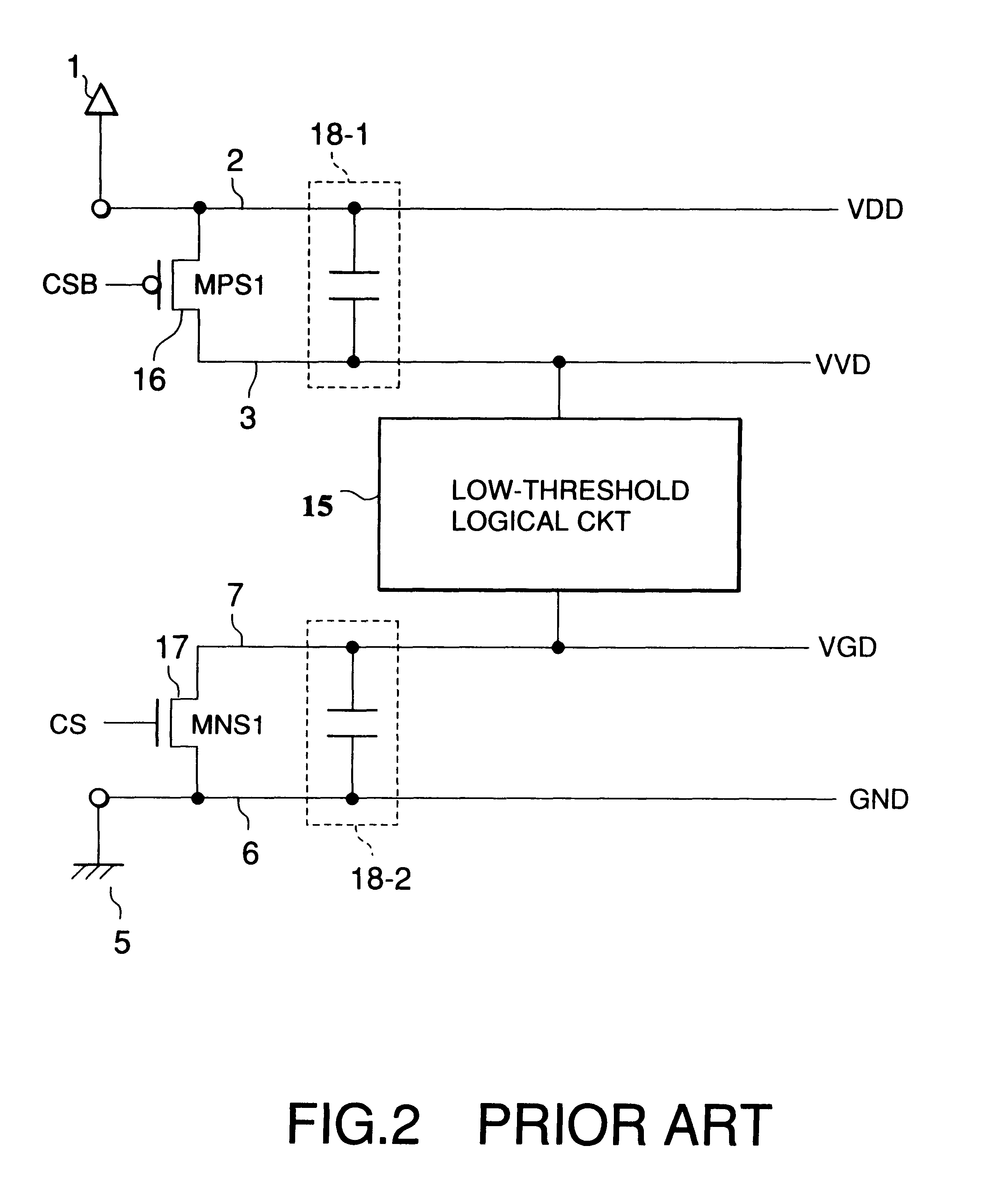
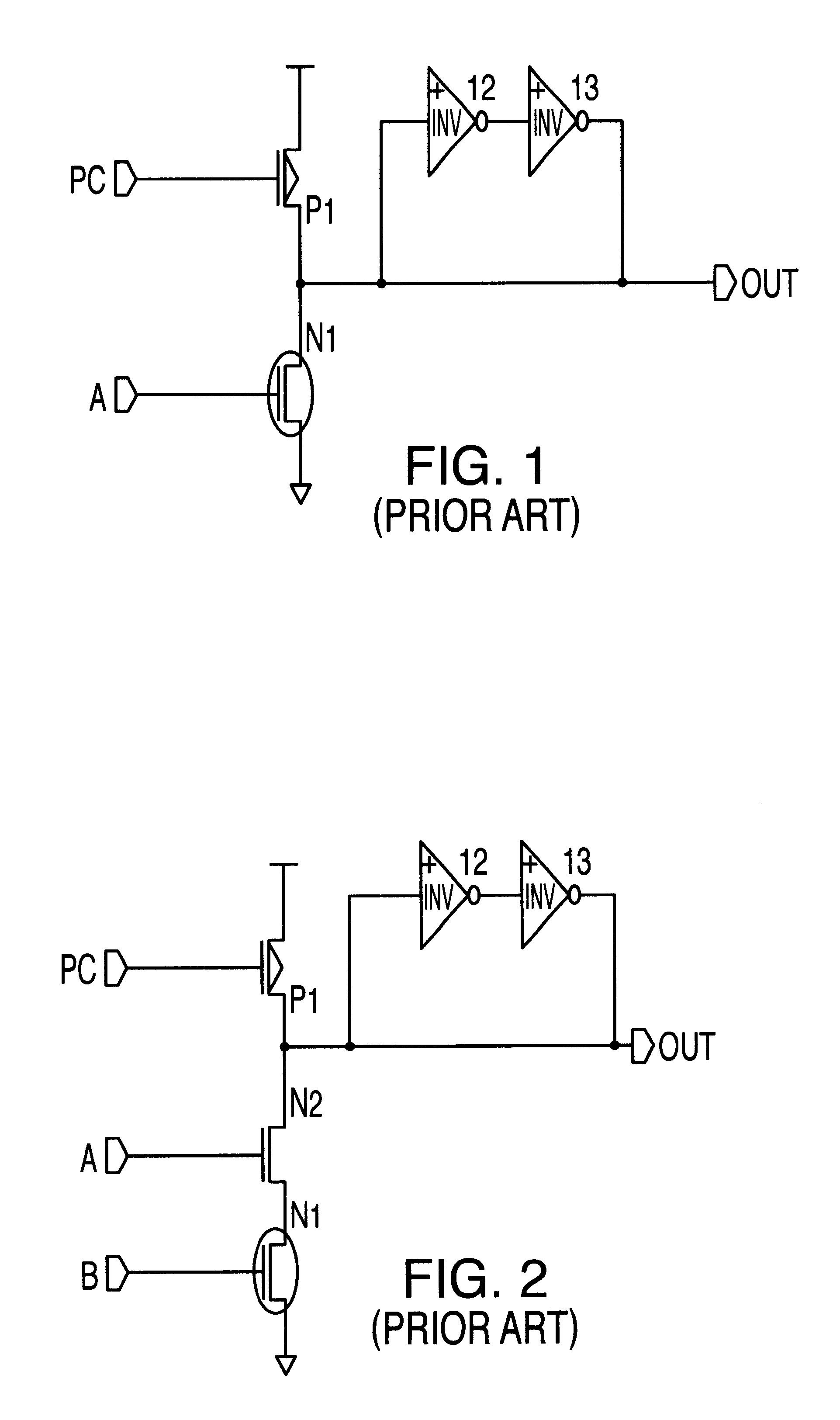
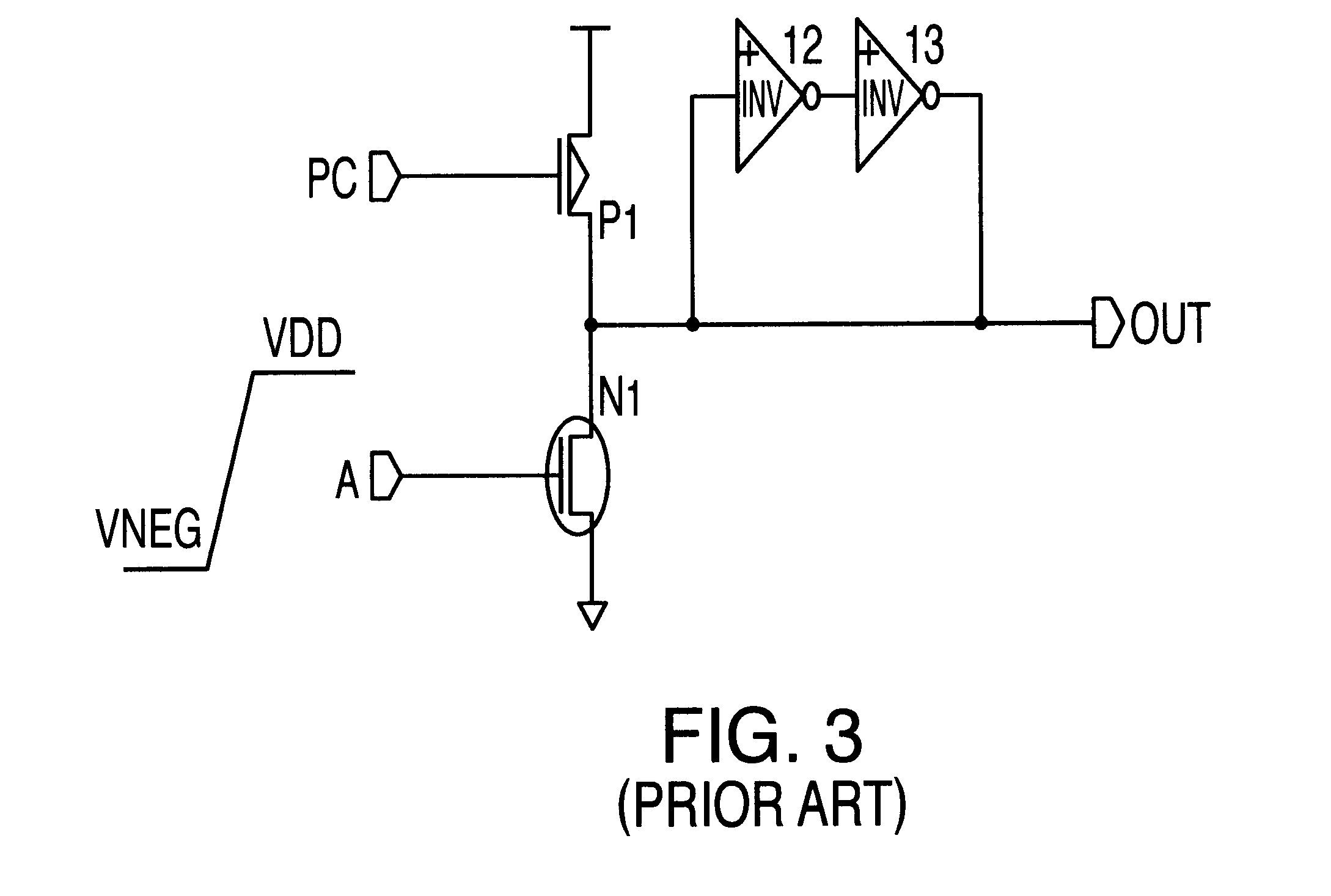
A semiconductor circuit or a MOS-DRAM wherein converting means is provided that converts substrate potential or body bias potential between two values for MOS-FETs in a logic circuit, memory cells, and operating circuit of the MOS-DRAM, thereby raising the threshold voltage of the MOS-FETs when in the standby state and lowering it when in active state. The converting means includes a level shift circuit and a switch circuit. The substrate potential or body bias potential is controlled only of the MOS-FETs which are nonconducting in the standby state; this configuration achieves a reduction in power consumption associated with the potential switching. Furthermore, in a structure where MOS-FETs of the same conductivity type are formed adjacent to each other, MOS-FETs of SOI structure are preferable for better results.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit device with low power consumption and simple manufacturing steps
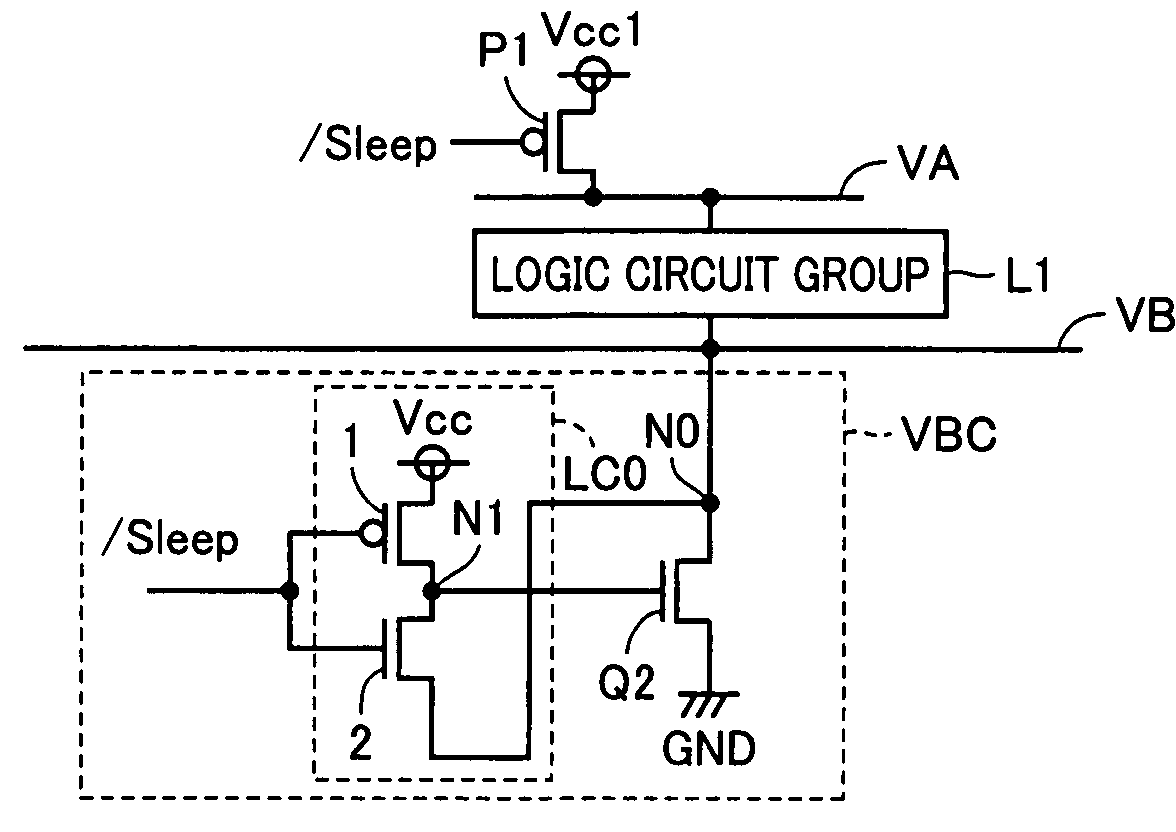
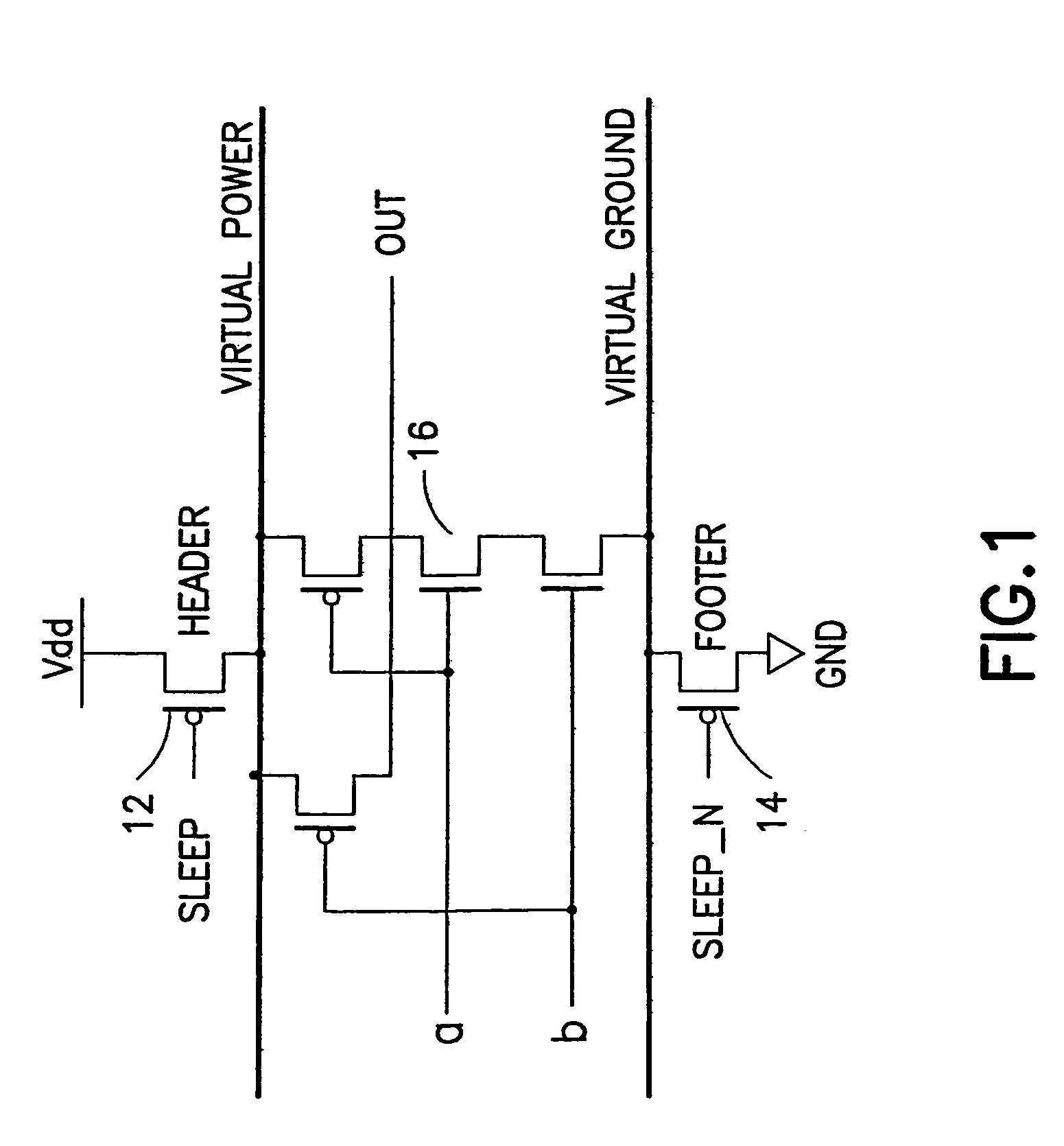
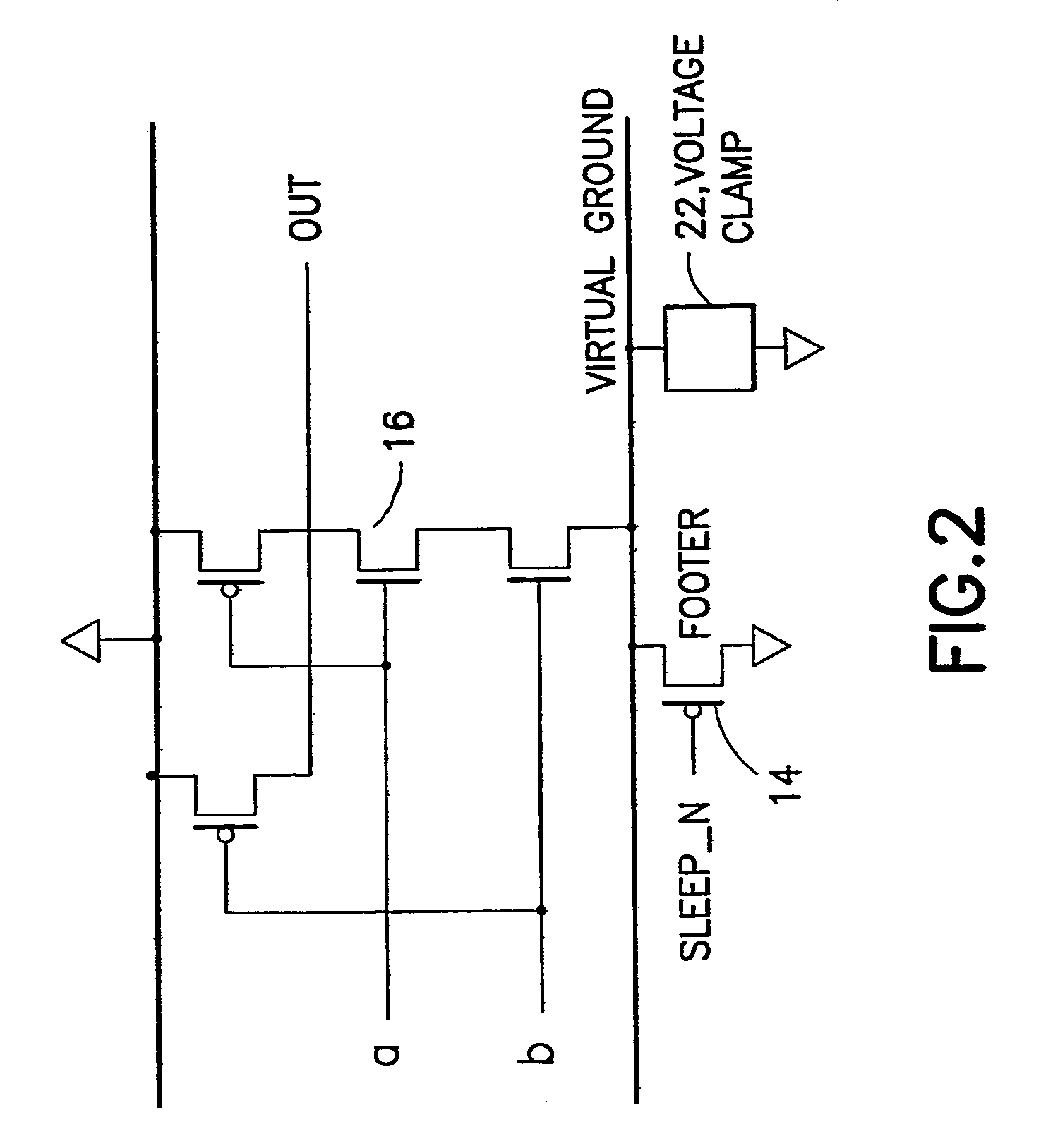
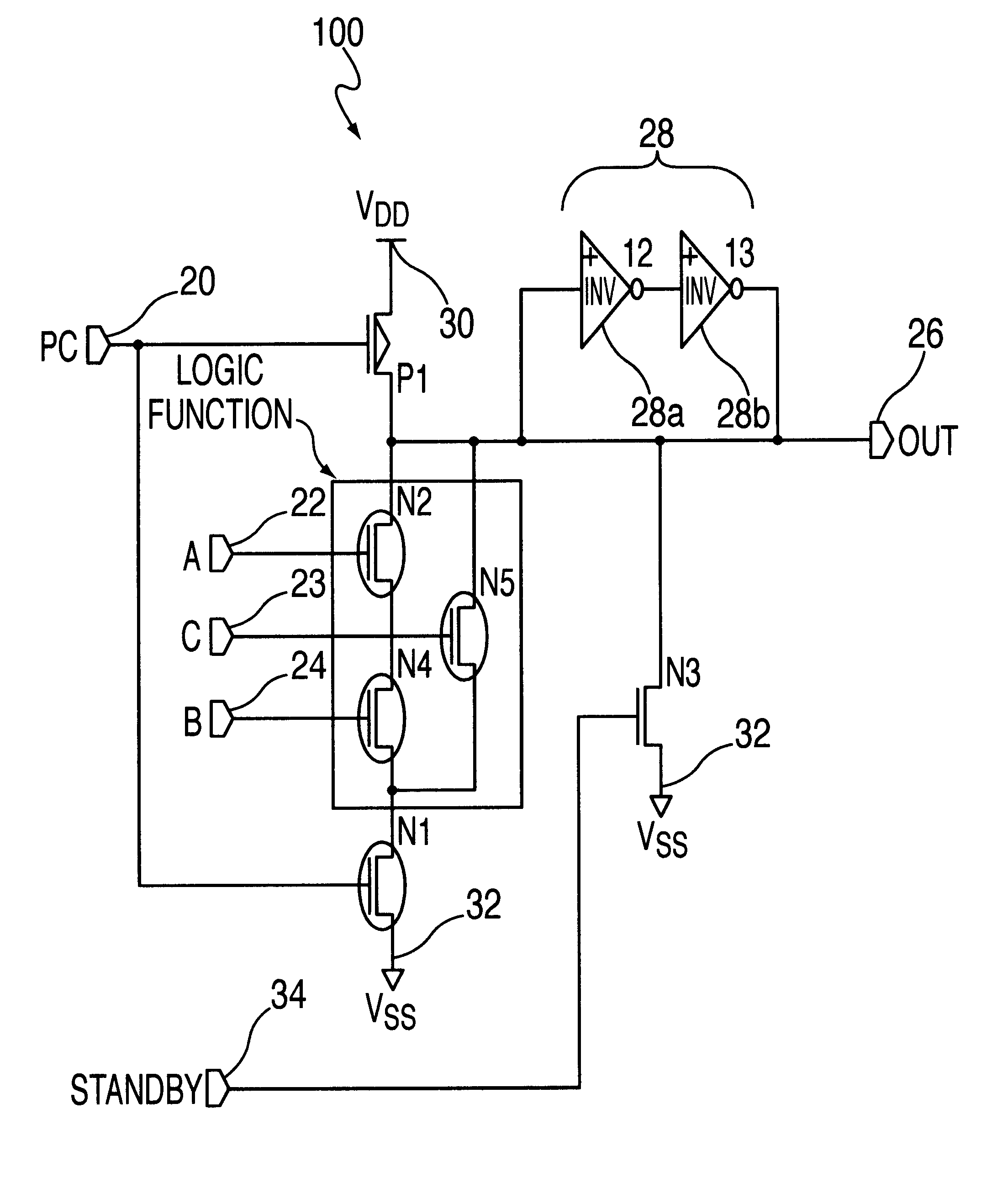
InactiveUS6208171B1Reduce manufacturing stepsProduction costPower reduction by control/clock signalLogic circuits characterised by logic functionPotential clampBack bias
In a semiconductor integrated circuit, a control transistor 4 and a potential clamp circuit 9 are arranged between a power supply line 2 and a virtual power supply line 3. Even in a sleeve mode where the control transistor 4 is turned off, the potential clamp circuit 9-1 clamps the virtual power supply line 3 at a certain potential to hold a potential state (high level or low level) of each node of a logical circuit. At this time, each FET forming the logical circuit is applied with a back bias so that a threshold voltage Vt becomes higher than that in an active mode. Therefore, a leakage current can be decreased. In the semiconductor integrated circuit, the threshold voltage Vt of the control transistor 4 can be selected to be equal to that of one FET of the complementary FET forming the logical circuit. Therefore, the layout area and the number of manufacturing steps can be reduced.
Owner:NEC CORP
Low power consumption MIS semiconductor device
InactiveUS7042245B2Total current dropSimple circuit configurationTransistorReliability increasing modificationsCurrent consumptionLogic gate
A logic gate is constructed of an insulated gate field effect transistor (MIS transistor) having a thin gate insulation film. An operation power supply line to the logic gate is provided with an MIS transistor having a thick gate insulation film for switching the supply and stop of an operation power source voltage. A voltage of the gate of the power source switching transistor is made changing in an amplitude greater than an amplitude of an input and an output signal to the logic gate. Current consumption in a semiconductor device configured of MIS transistor of a thin gate insulation film can be reduced and an power source voltage thereof can be stabilized.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Low power consumption MIS semiconductor device
InactiveUS7355455B2Total current dropSimple circuit configurationTransistorReliability increasing modificationsCurrent consumptionLogic gate
A logic gate is constructed of an insulated gate field effect transistor (MIS transistor) having a thin gate insulation film. An operation power supply line to the logic gate is provided with an MIS transistor having a thick gate insulation film for switching the supply and stop of an operation power source voltage. A voltage of the gate of the power source switching transistor is made changing in an amplitude greater than an amplitude of an input and an output signal to the logic gate. Current consumption in a semiconductor device configured of MIS transistor of a thin gate insulation film can be reduced and an power source voltage thereof can be stabilized.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device
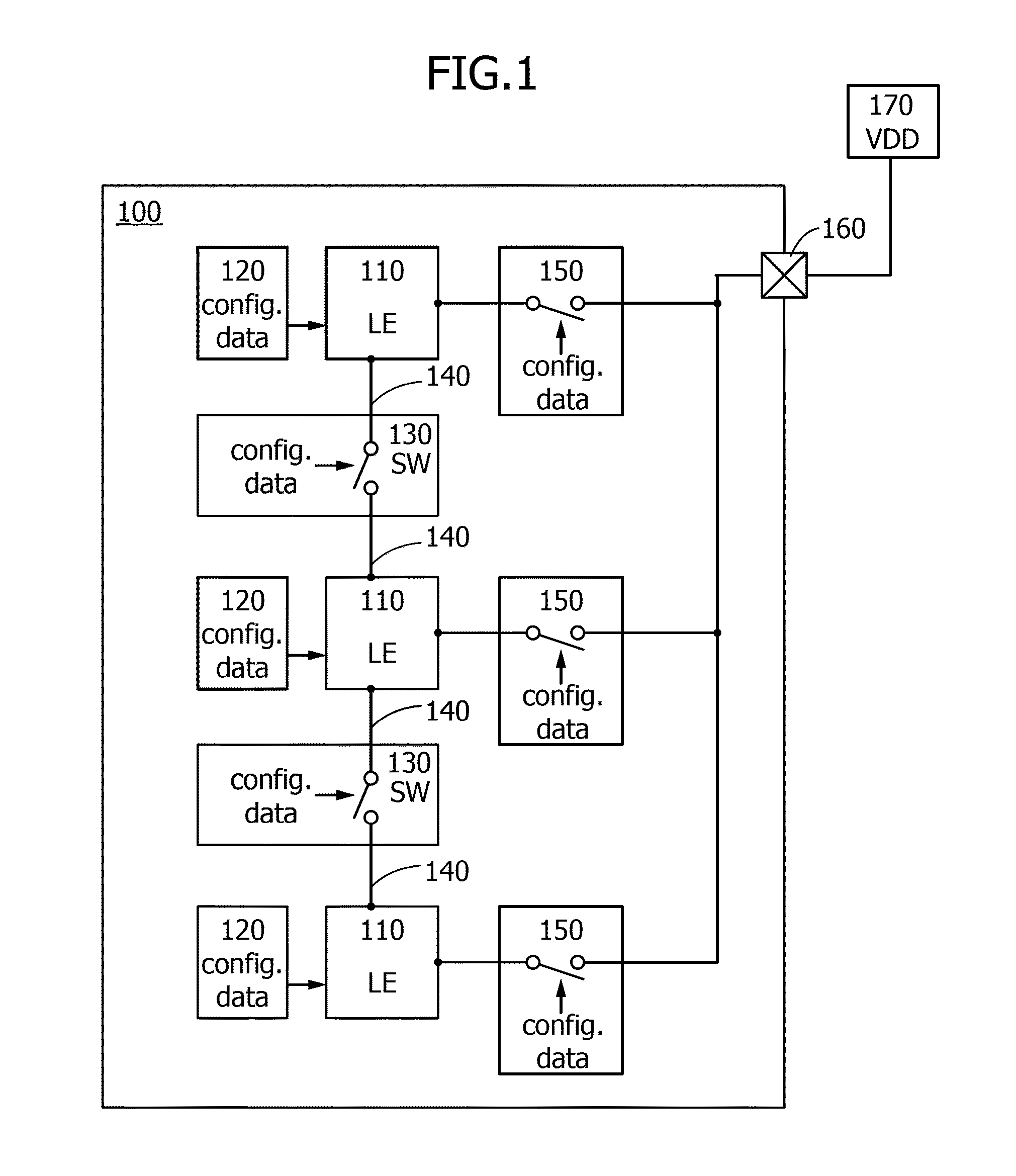
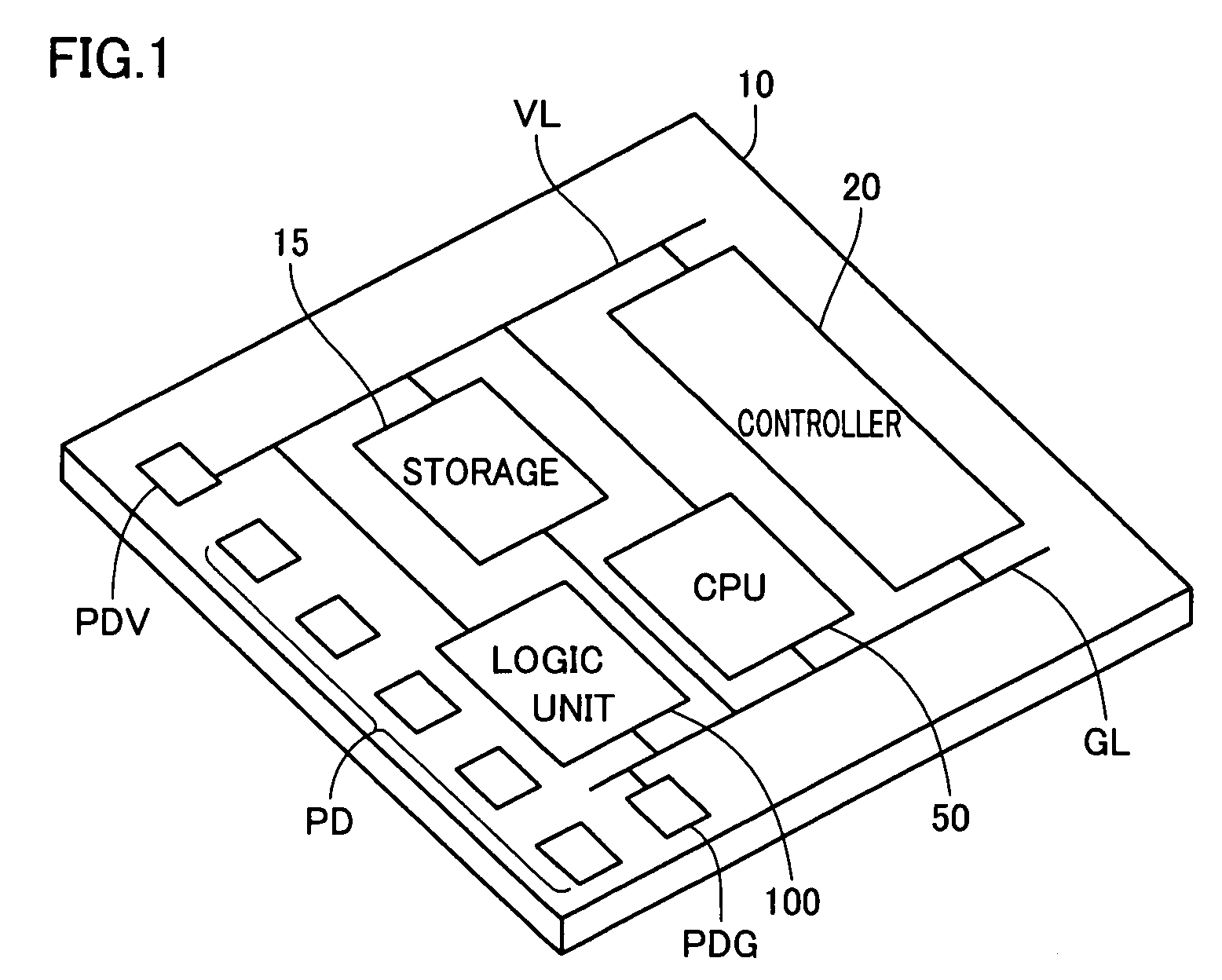
ActiveUS20140159771A1Less influenceImprove reliabilityPower reduction by control/clock signalSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceControl signal
A programmable logic device (PLD) that can control whether to supply power in each logic element is provided. The PLD includes at least a programmable logic element, a terminal to which a potential is input from an external power source, a switch controlling conduction between the terminal and the logic element, and a memory outputting a control signal for setting the conduction state of the switch. The memory stores pieces of configuration data for setting the conduction state of the switch. Any one of the pieces of configuration data is output as the control signal from the memory to the switch.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Logic circuit and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110102018A1Reduce hydrogen concentrationTotal current dropTransistorPower reduction by control/clock signalHydrogen concentrationPower semiconductor device
In a logic circuit where clock gating is performed, the standby power is reduced or malfunction is suppressed. The logic circuit includes a transistor which is in an off state where a potential difference exists between a source terminal and a drain terminal over a period during which a clock signal is not supplied. A channel formation region of the transistor is formed using an oxide semiconductor in which the hydrogen concentration is reduced. Specifically, the hydrogen concentration of the oxide semiconductor is 5x1019 (atoms / cm3) or lower. Thus, leakage current of the transistor can be reduced. As a result, in the logic circuit, reduction in standby power and suppression of malfunction can be achieved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
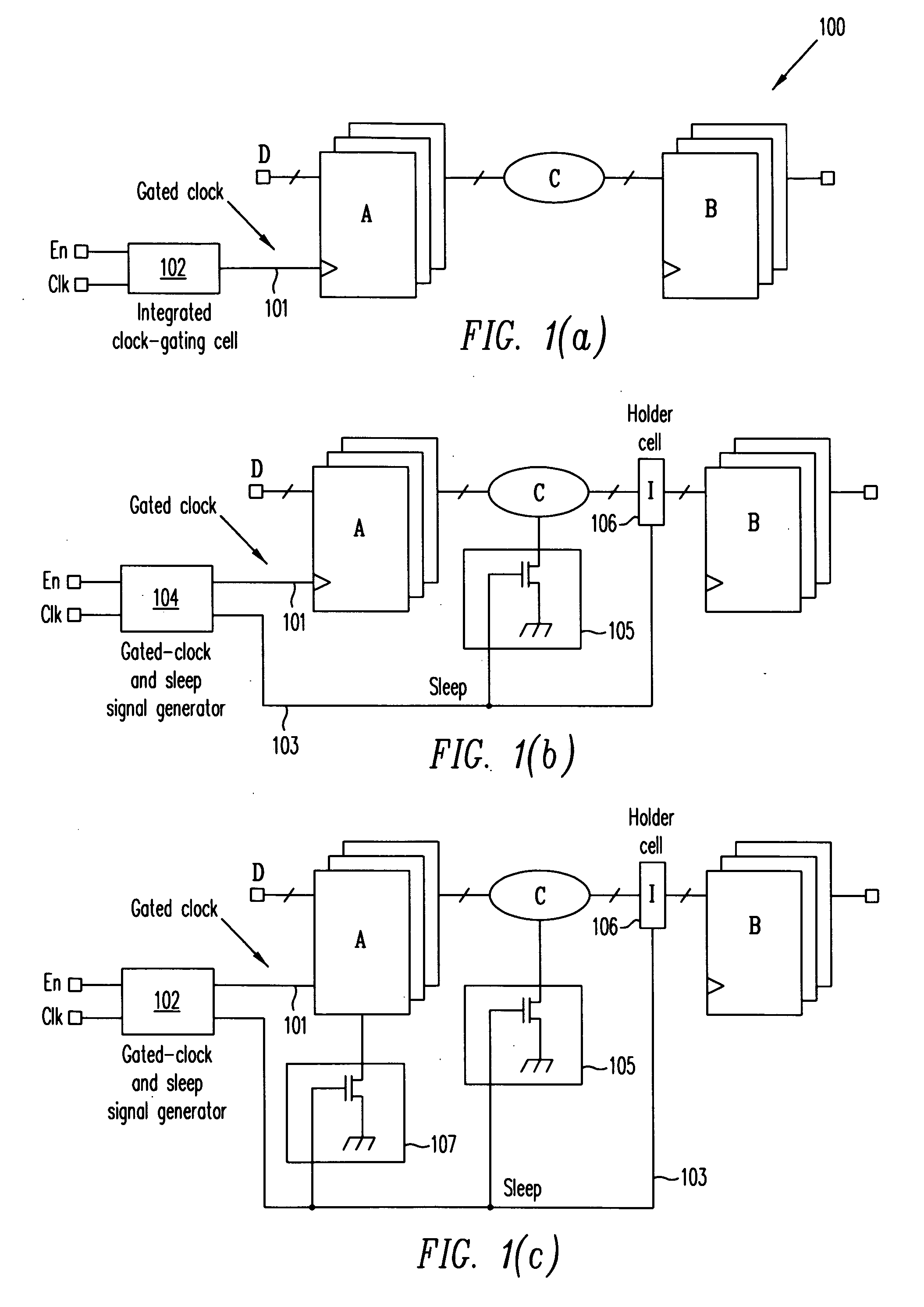
Automatic extension of clock gating technique to fine-grained power gating
ActiveUS20070024318A1Reduce dynamic power consumptionPower reduction by control/clock signalLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsTime criticalEngineering
A method extends a clock-gating technique to provide a sleep signal for controlling switch circuits that reduce active leakage power. Using this extension of the clock-gating technique, fine-grained power-gating is achieved. The method automatically identifies, at an RTL or a gate level, the logic circuits that can be power-gated. The method of the present invention derives a sleep signal for fine-grained power-gating that may be applicable to both time-critical and non-time-critical designs.
Owner:ANSYS
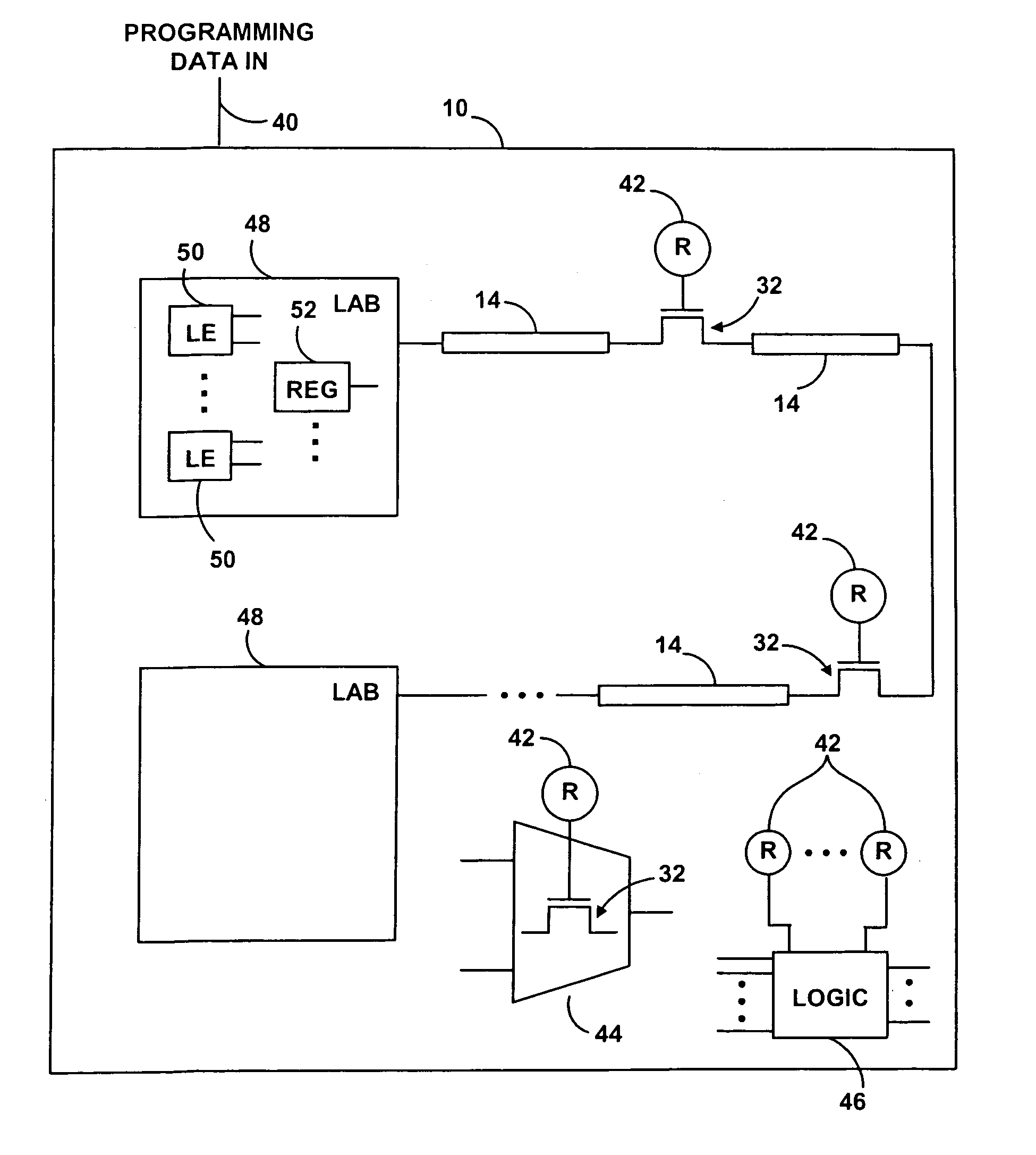
Integrated circuits with reduced standby power consumption
ActiveUS6940307B1Improved standby power consumption propertyReduce power consumptionPower reduction by control/clock signalLogic circuits characterised by logic functionProgrammable logic deviceStandby power
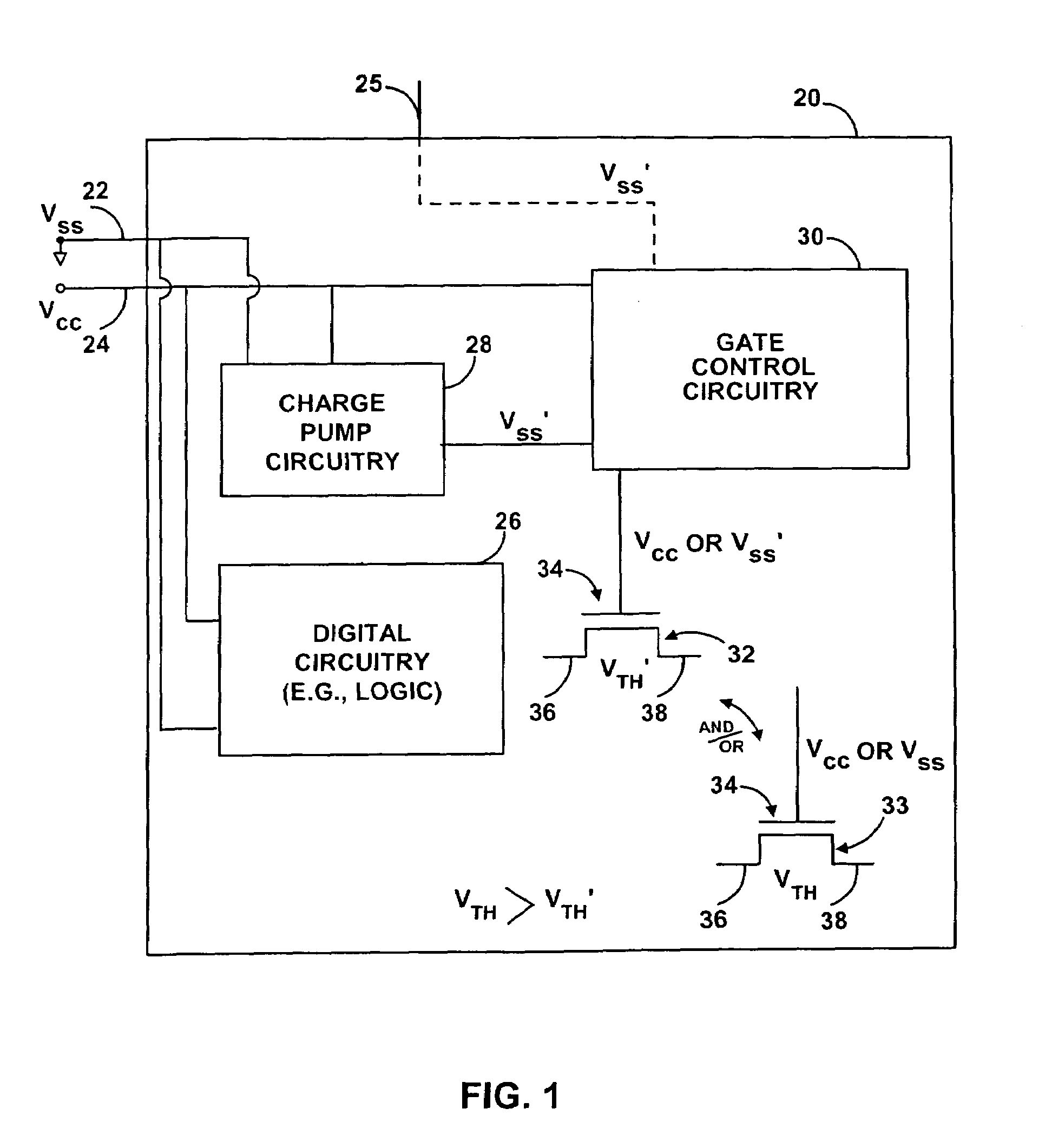
Integrated circuit standby power consumption may be reduced using a reverse-bias transistor control arrangement that reduces transistor leakage current. Integrated circuit transistors may be turned off using a reverse bias voltage rather than a ground voltage. A charge pump circuit on the integrated circuit may be used to generate the reverse bias voltage. The reverse bias voltage may also be provided from an external source. The integrated circuit may be a programmable logic device in which logic is configured by providing programming data to configuration cells. The configuration cells may be used to apply either a positive power supply voltage to a given transistor to turn that transistor on or to provide the reverse bias voltage to that transistor to turn that transistor off.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
ActiveUS20070139072A1Reduce leakage currentReduce power consumptionReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalDrain currentDouble gate
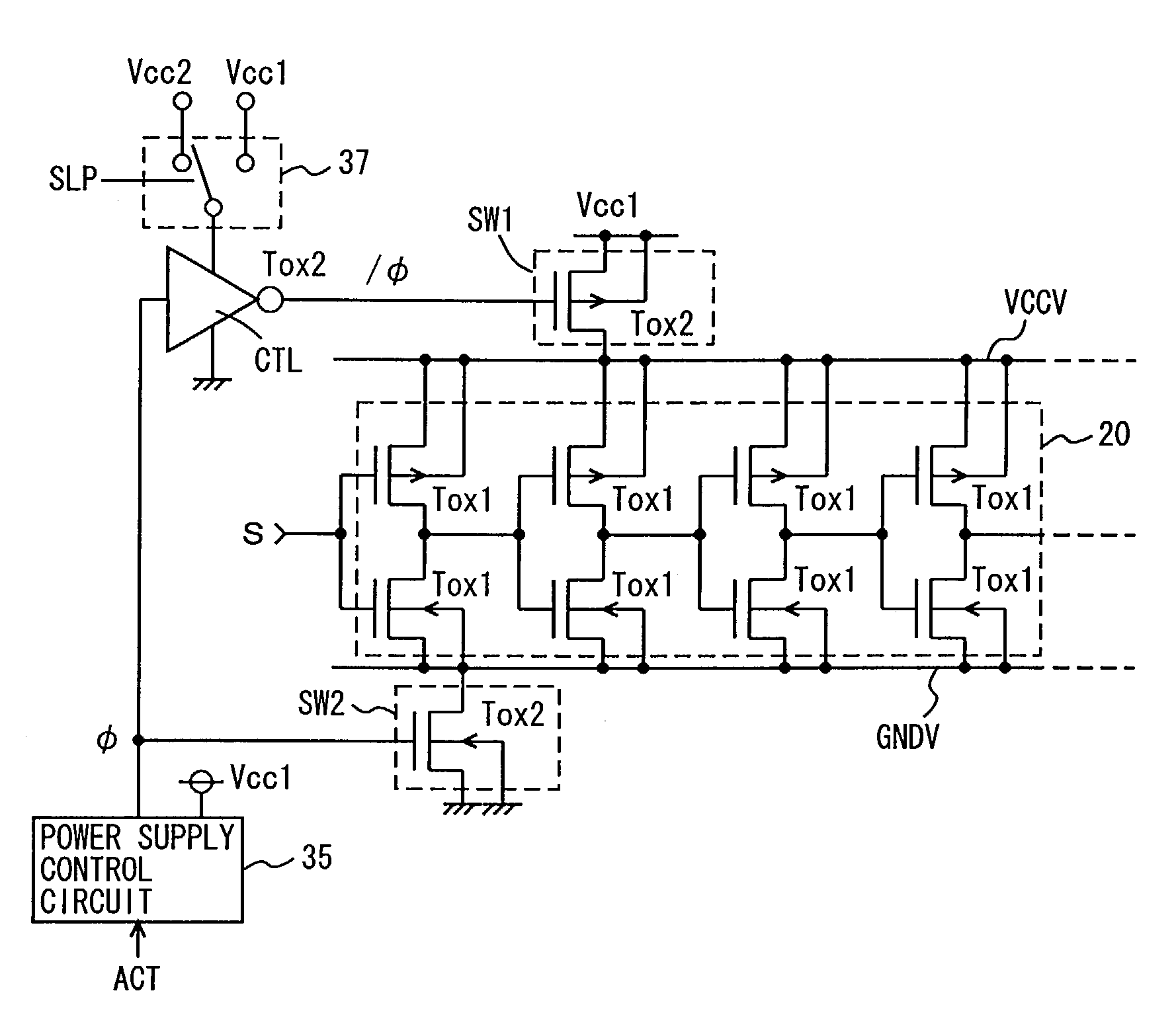
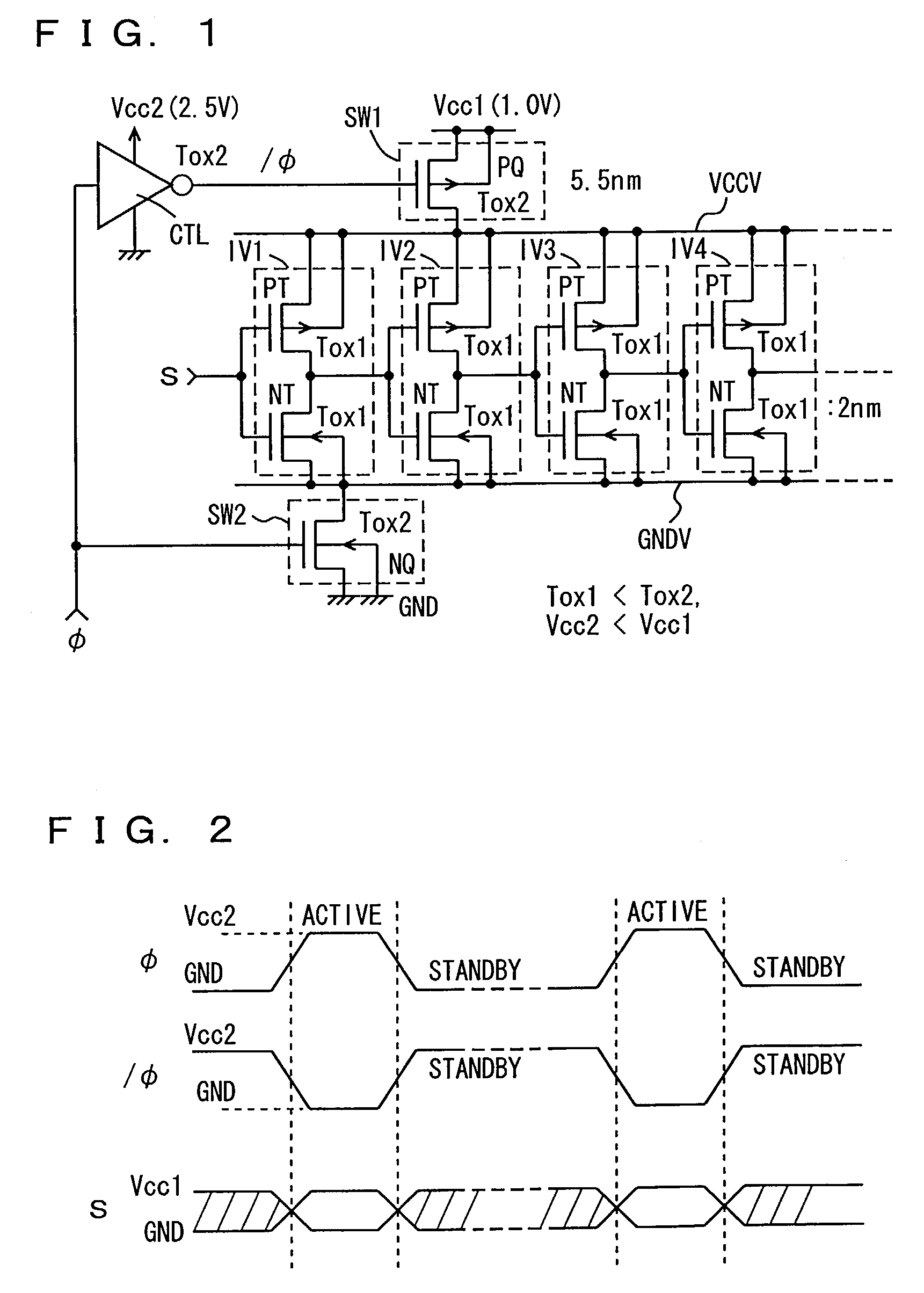
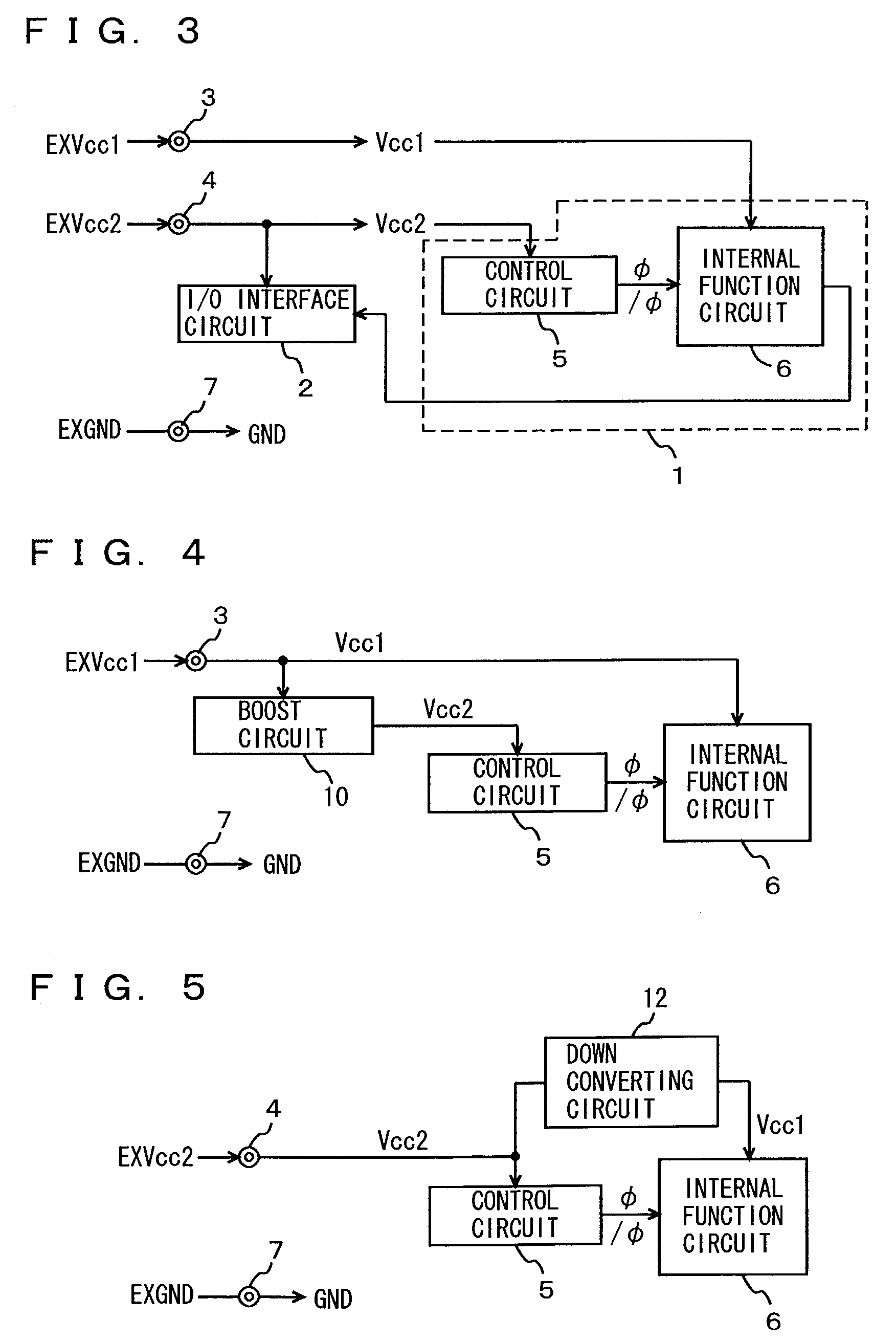
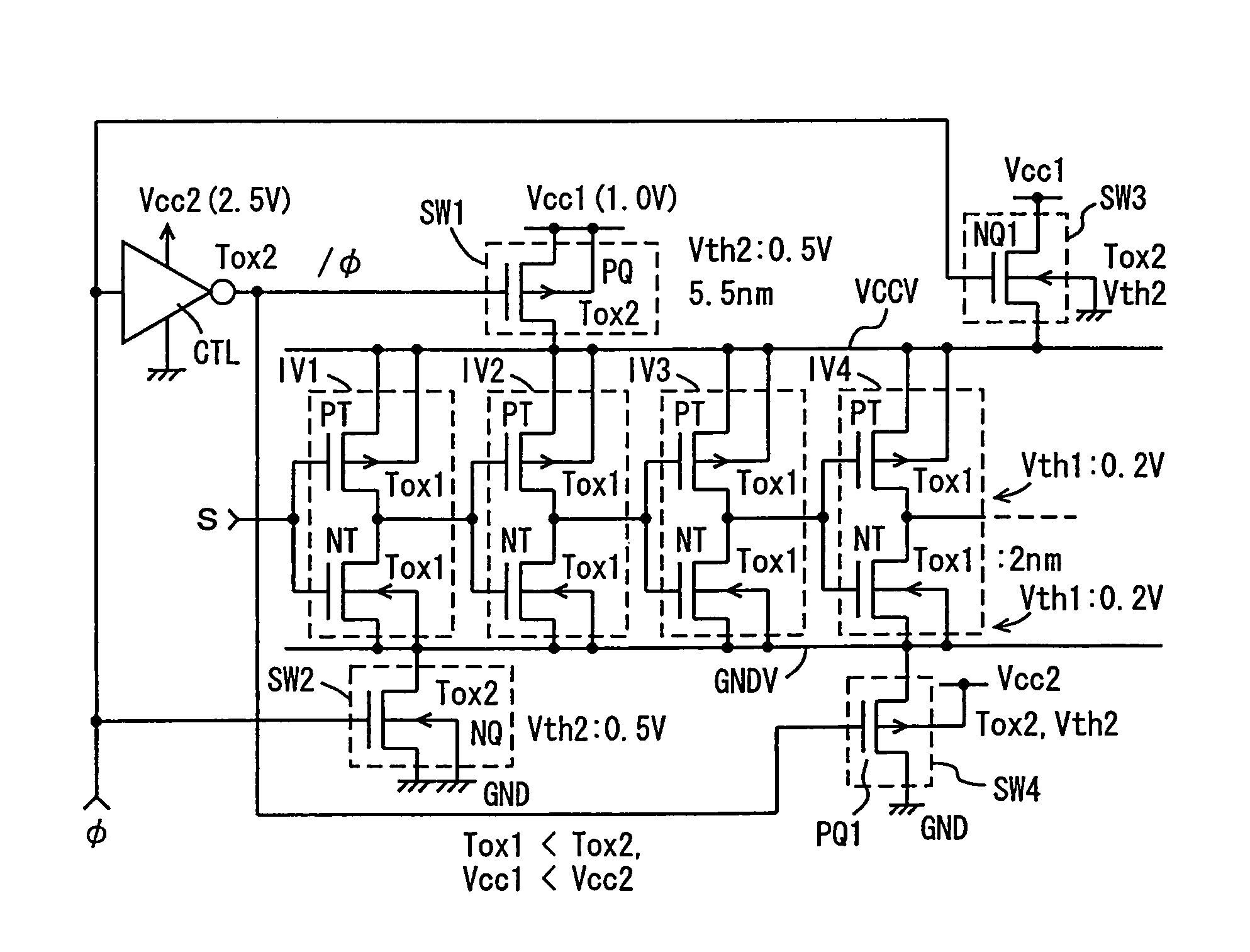
An object of the present invention is to provide a technique of reducing the leakage current of a drive circuit for driving a circuit that must retain a potential (or information) when in its standby state. A semiconductor integrated circuit device of the present invention includes a drive circuit for driving a circuit block. This drive circuit is made up of a double gate transistor with gates having different gate oxide film thicknesses. When the circuit block is in its standby state, the gate of the double gate transistor having a thinner gate oxide film is turned off and that having a thicker gate oxide film is turned on. This arrangement allows a reduction in the leakage currents of both the circuit block and the drive circuit while allowing the drive circuit to deliver or cut off power to the circuit block.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
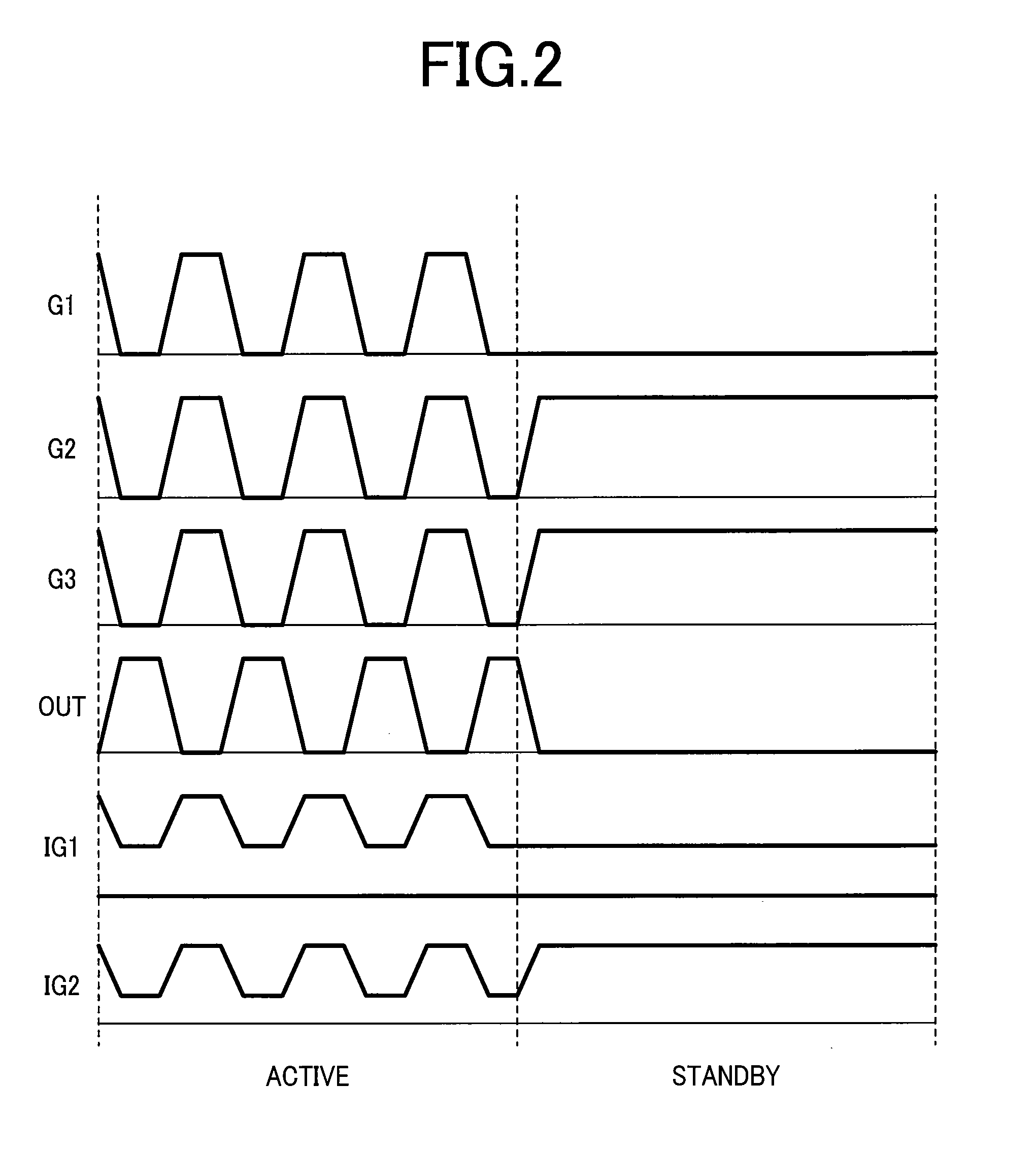
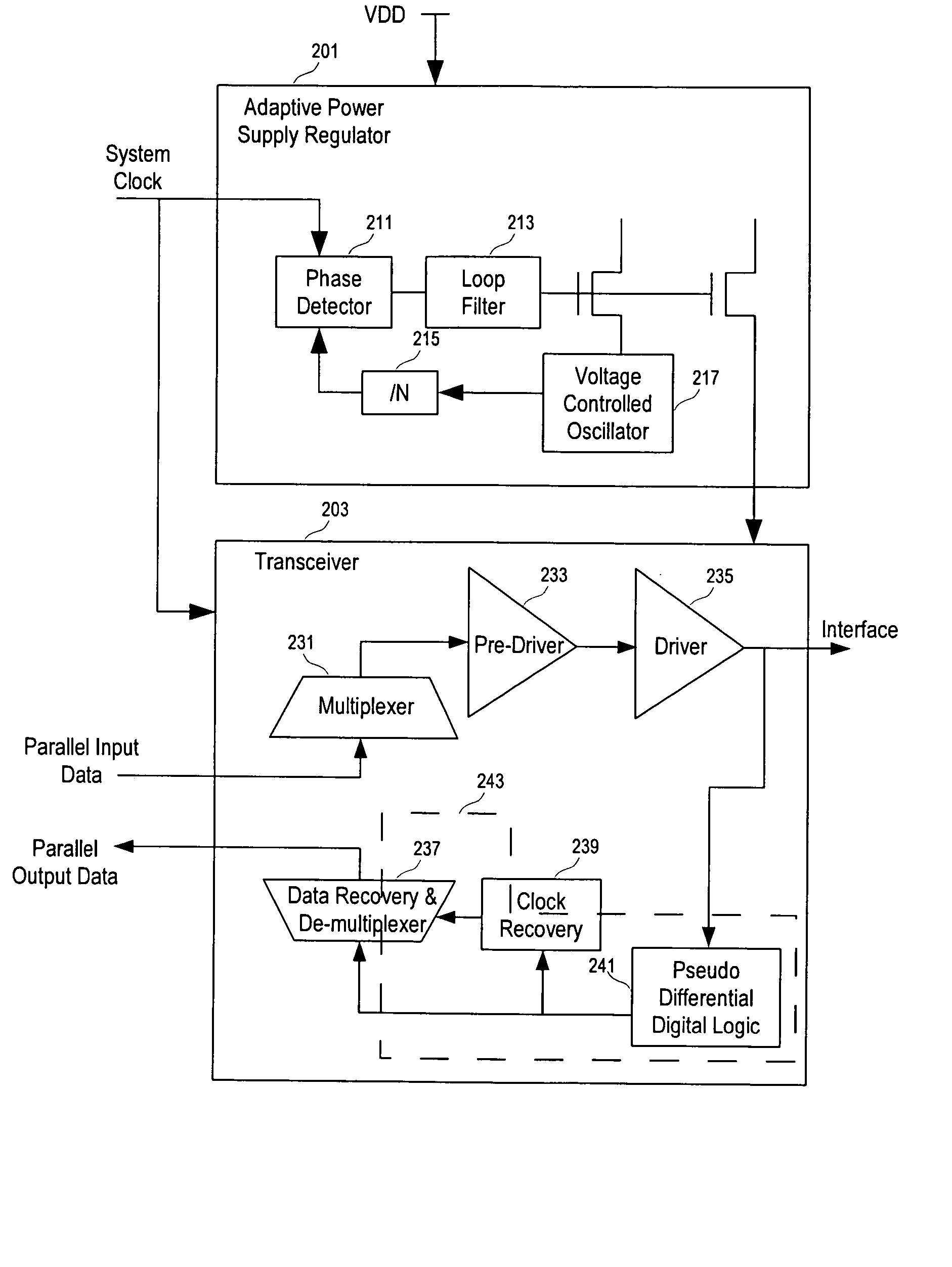
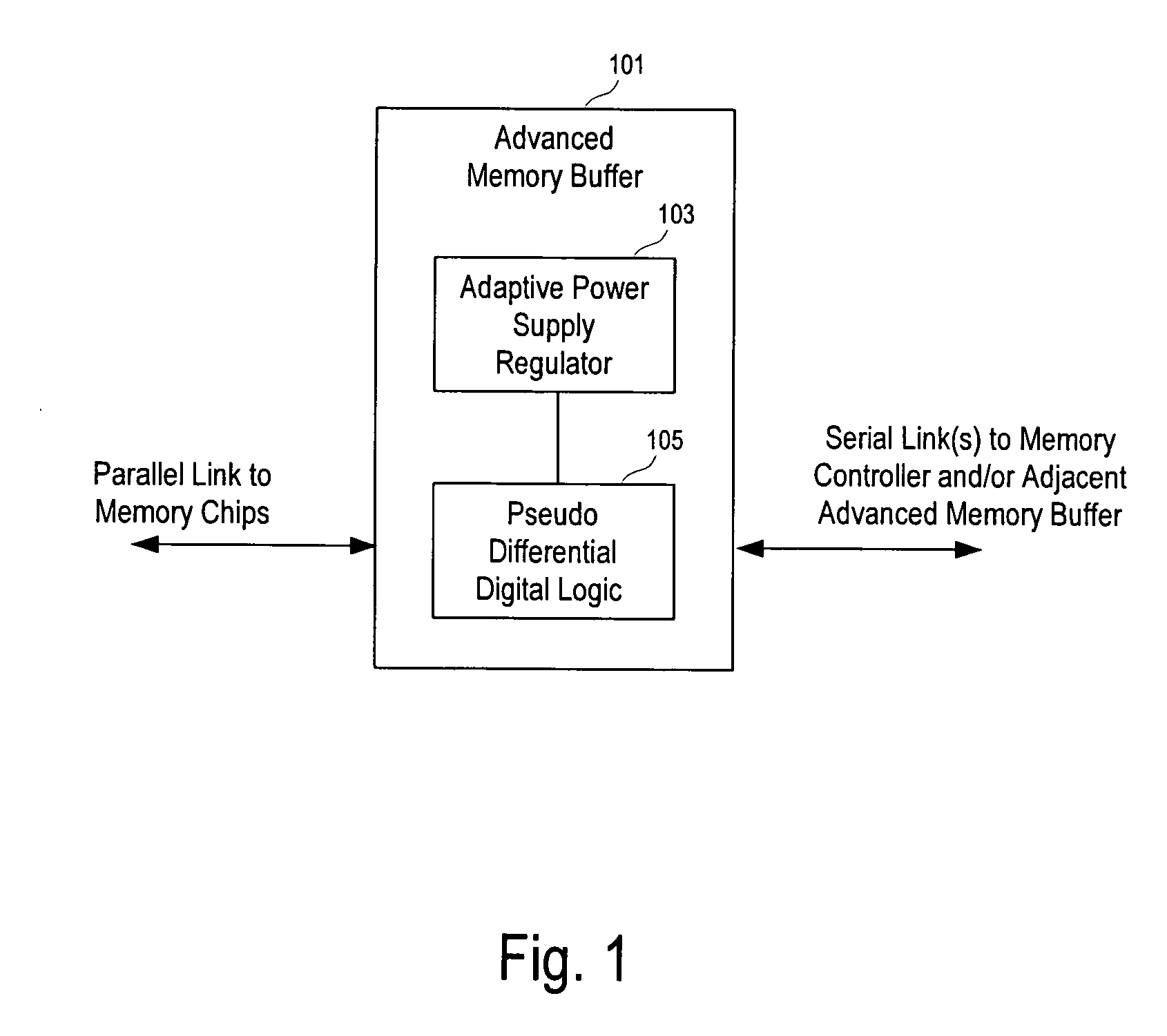
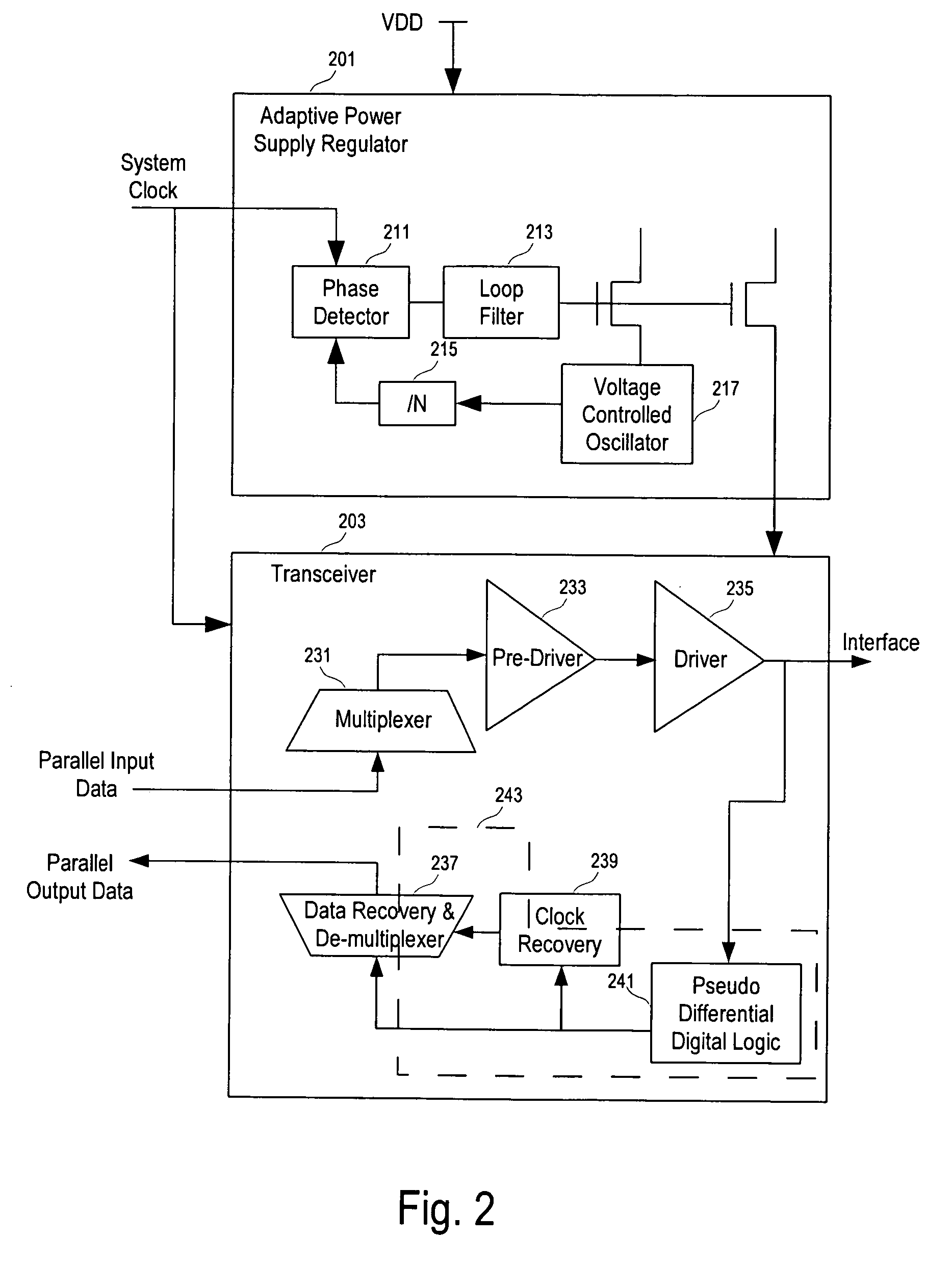
High speed transceiver with low power consumption
ActiveUS20070109019A1Electric signal transmission systemsPower reduction by control/clock signalTransceiverHigh velocity
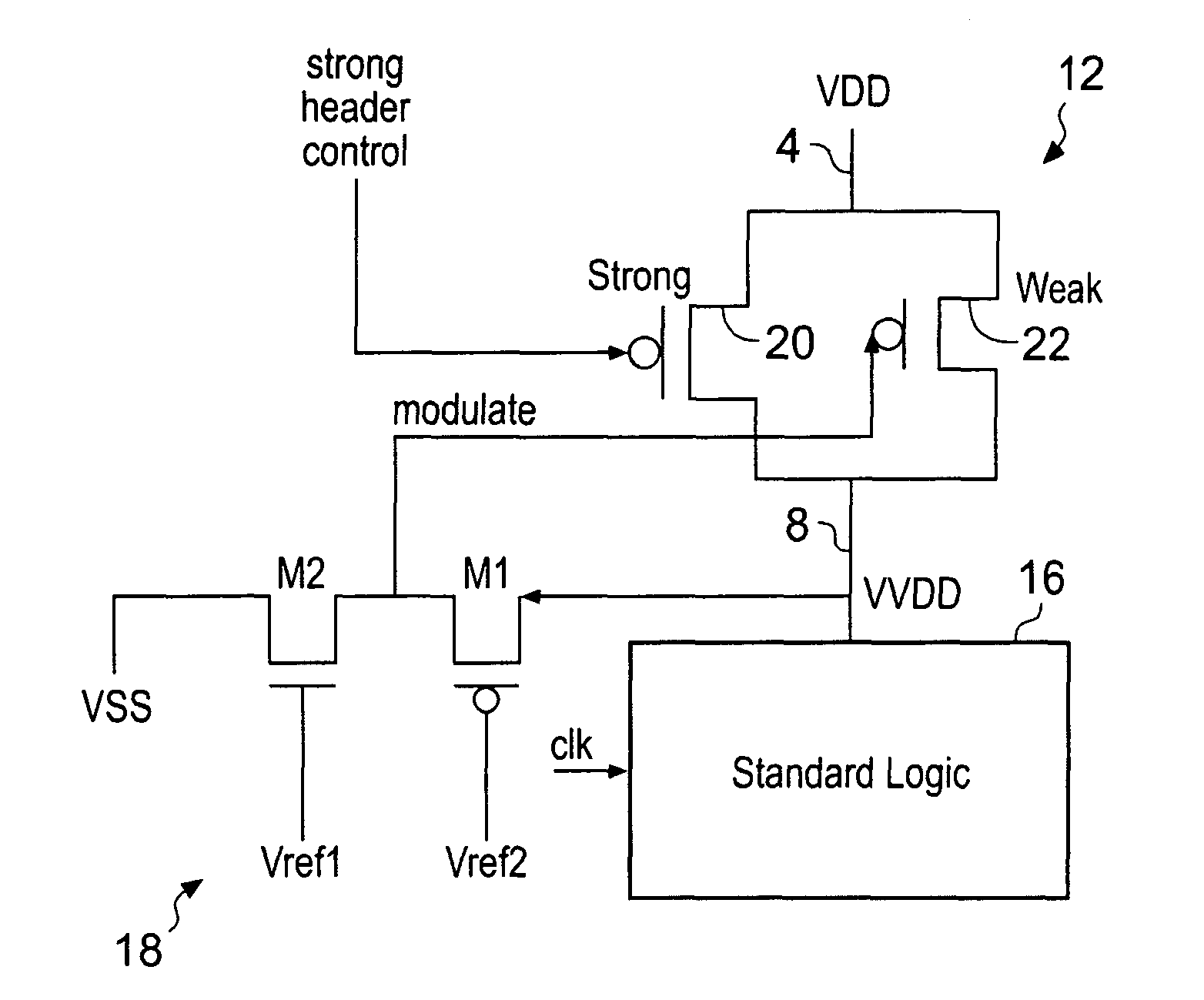
High-speed and low-power consumption CMOS receivers using adaptively-regulated power supply and pseudo differential digital logic to: 1) reduce the power consumption of the transceiver; and, 2) increase the power supply rejection (PSR) during processing the data.
Owner:MONTAGE TECH HLDG CO LTD
Adaptive supply voltage body bias apparatus and method thereof
InactiveUS20050225376A1Power reduction in field effect transistorsPower reduction by control/clock signalMaster controllerSelf adaptive
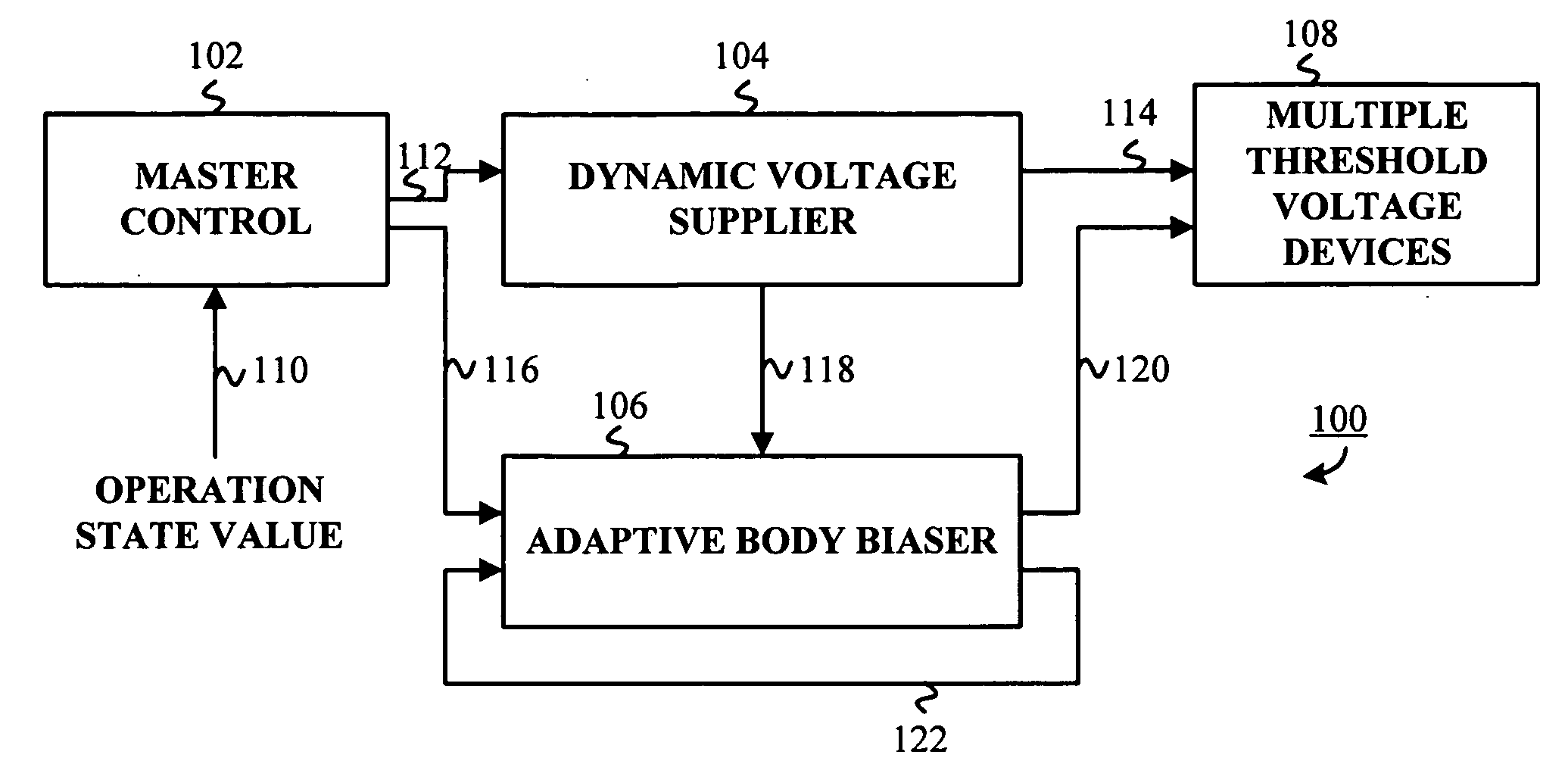
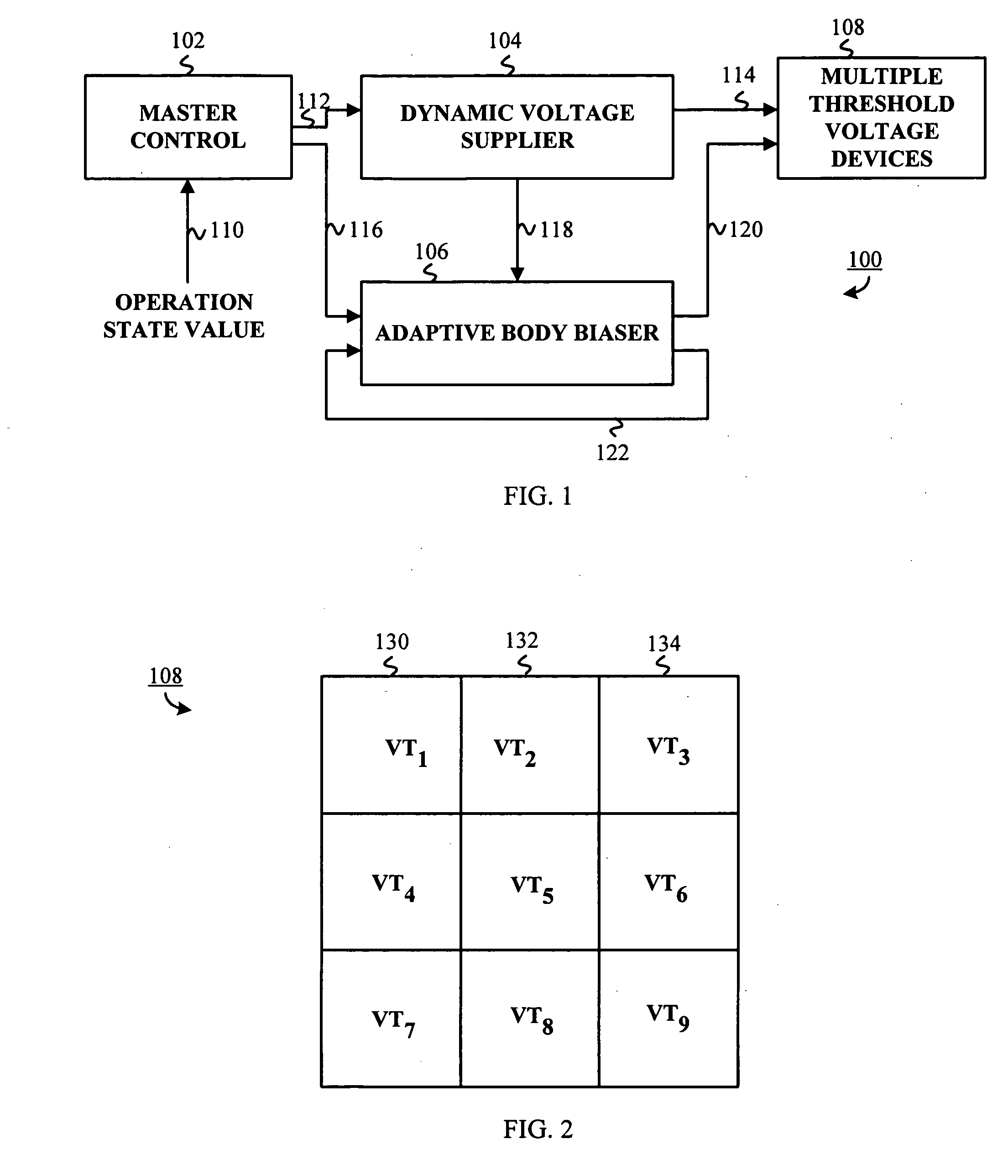
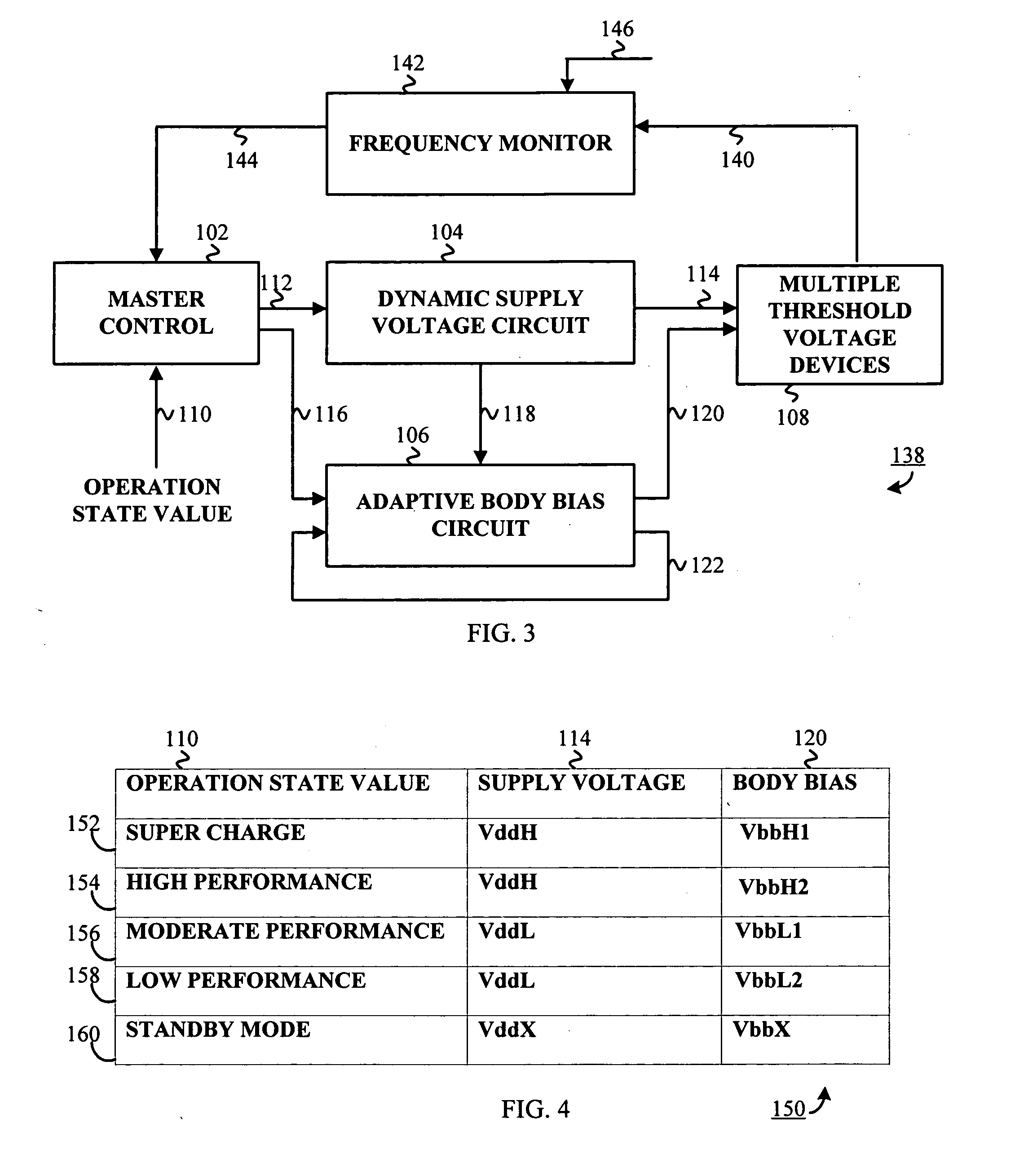
An adaptive supply voltage and body bias apparatus includes a master controller including an operation state value. The apparatus and method includes a dynamic voltage supplier coupled to the master controller operative to receive a supply voltage indicator. The apparatus and method includes an adaptive body biaser coupled to the master controller operative to receive a body bias indicator. Furthermore, the apparatus and method includes a plurality of computing devices each having one of a plurality of threshold voltages. The plurality of computing devices are operative to receive the supply voltage from the dynamic voltage supplier and a bias voltage from the adaptive body biaser for optimized power supply in conjunction with reduction of power leakage in view of the varying threshold voltage of the computing devices.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
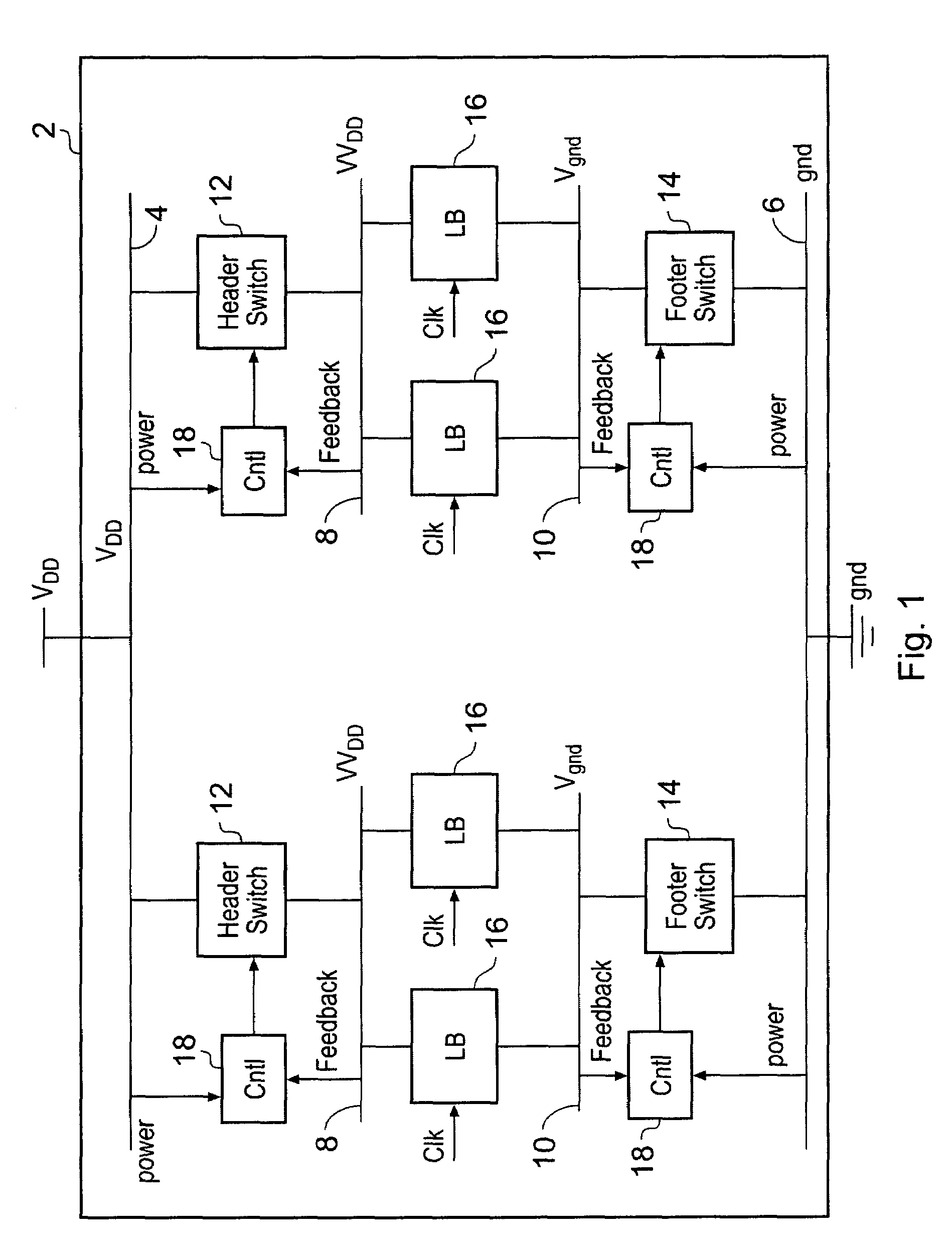
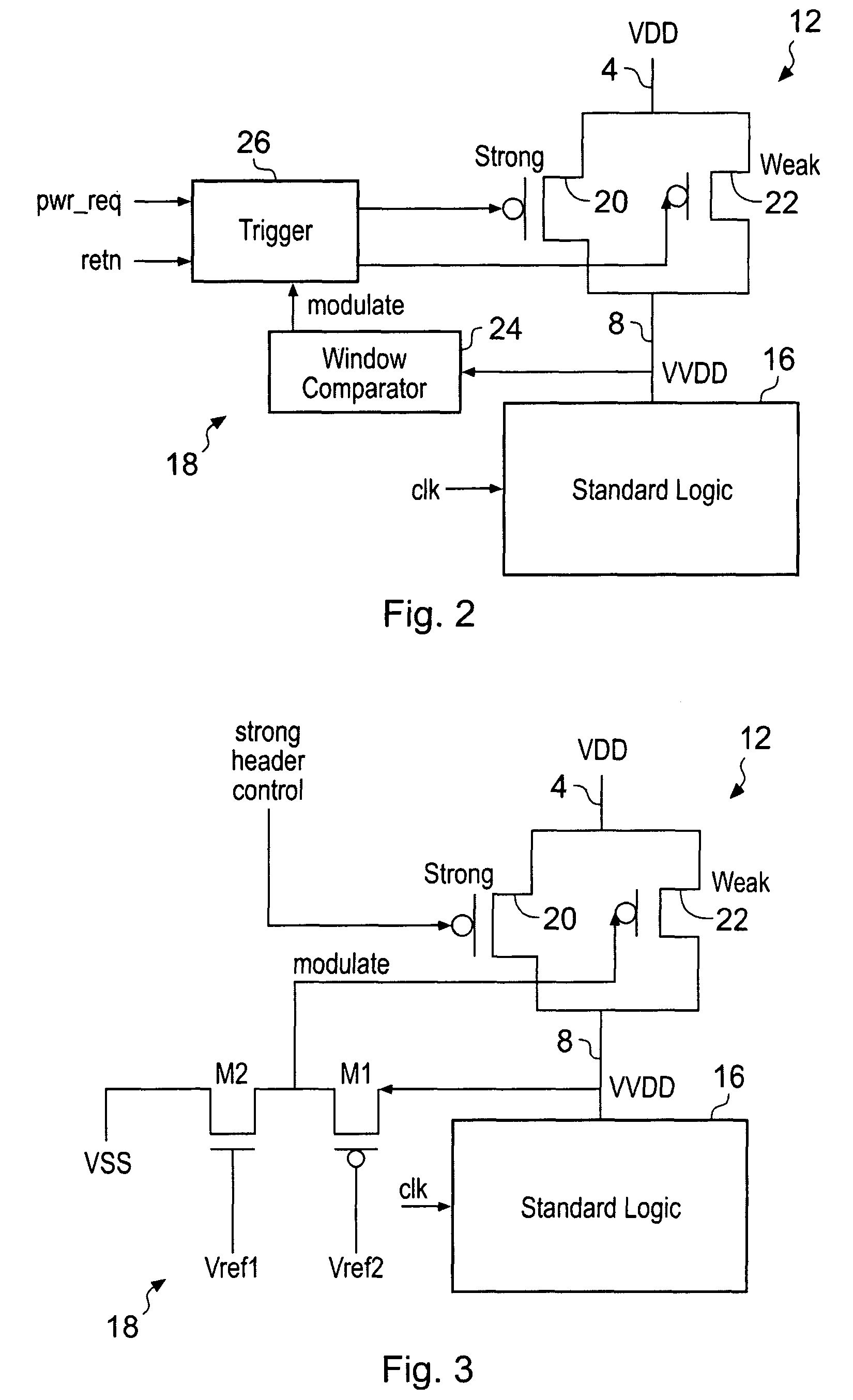
Virtual power rail modulation within an integrated circuit
InactiveUS7737720B2Reduce power consumptionReliability increasing modificationsDc network circuit arrangementsVirtual powerFeedback control
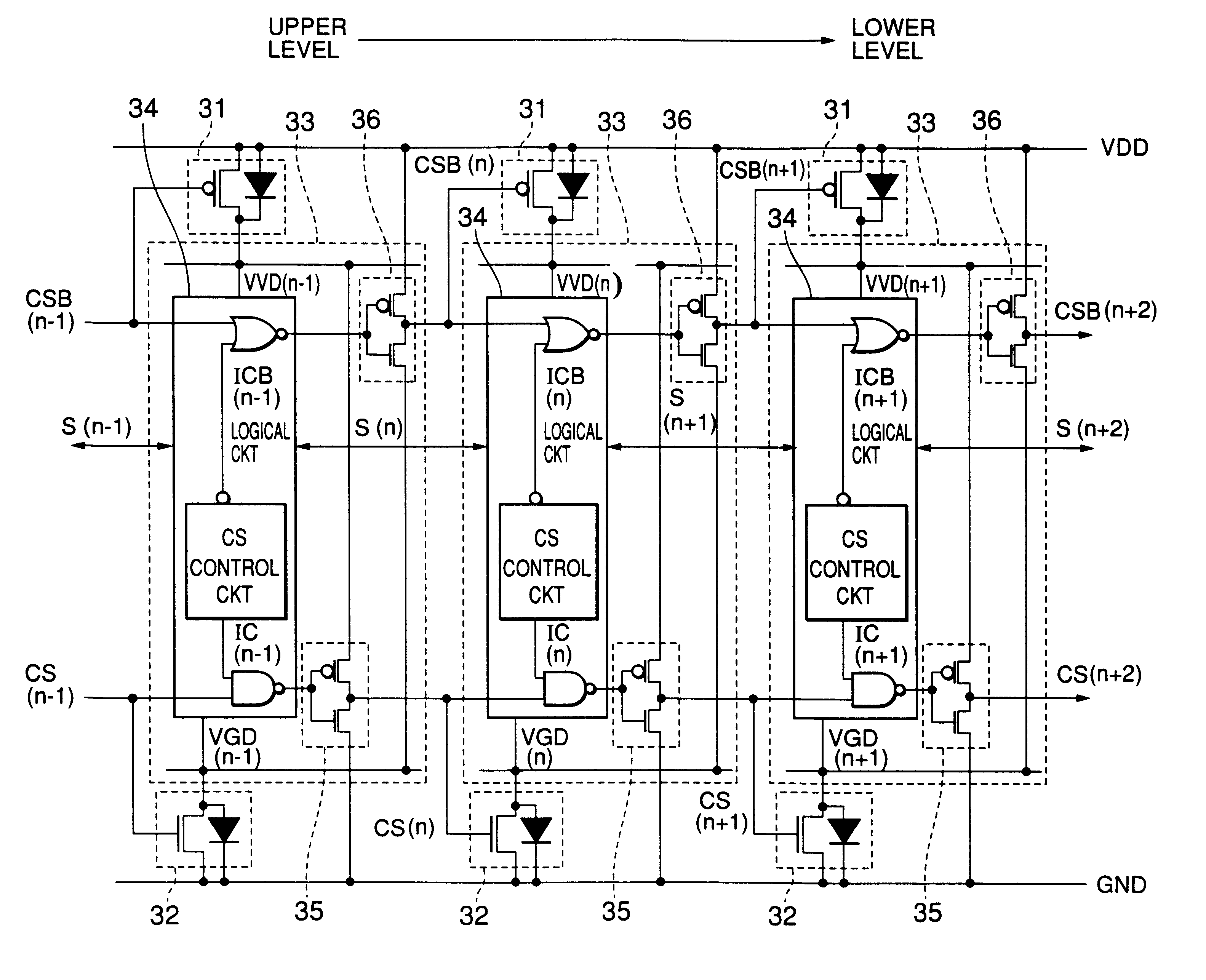
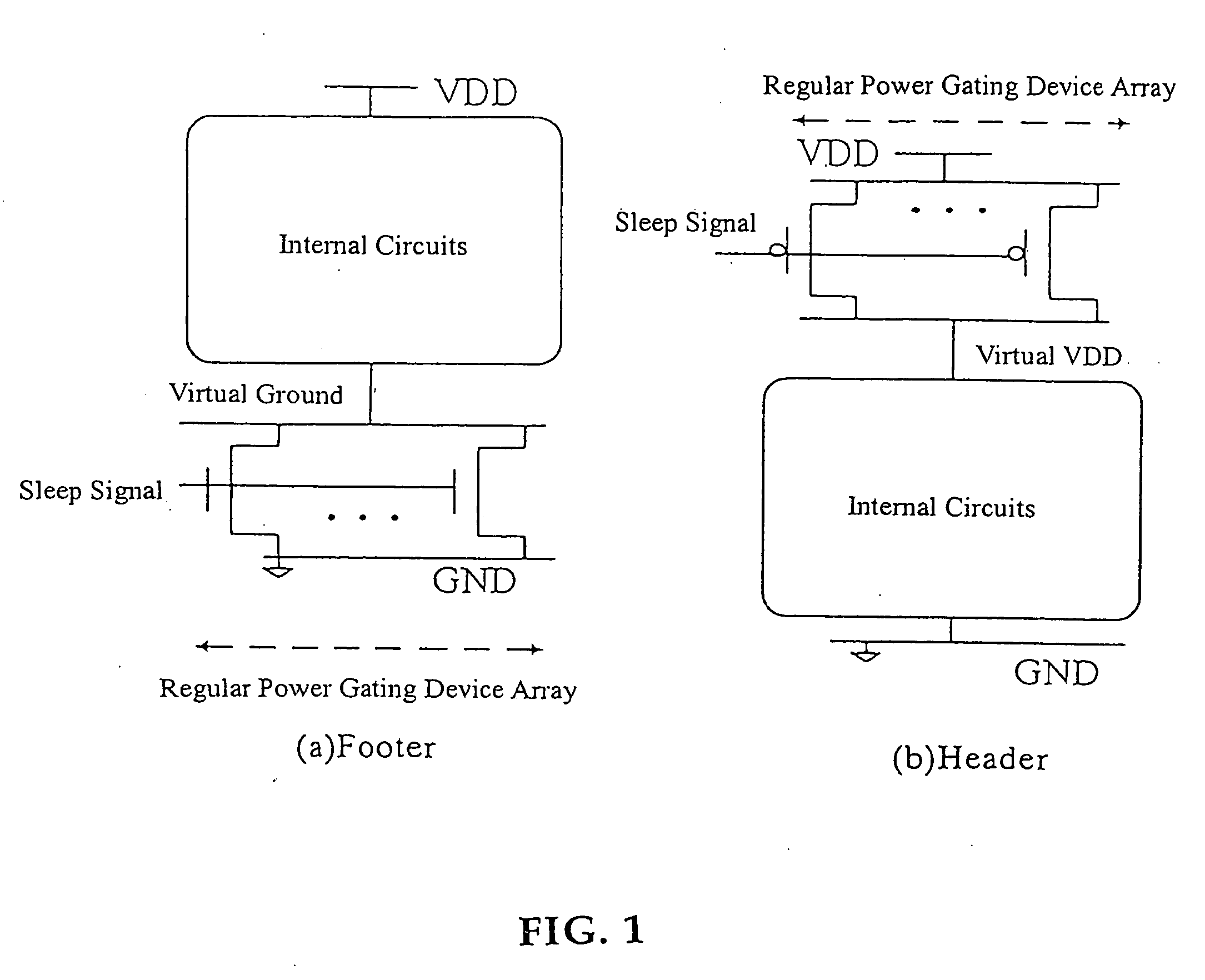
An integrated circuit is provided with logic blocks which draw their power from virtual supply rails. These virtual supply rails are connected by switch blocks to main supply rails. The switch blocks are subject to modulation to maintain the virtual supply rails at an intermediate voltage level such that a reduced voltage difference is applied across the logic block. This intermediate voltage level is used in a state retention mode in which the clock signal clk to the logic block is stopped and state signal values are maintained therein using this reduced virtual power rail derived voltage difference. When it is desired to resume processing then the full virtual rail voltages are restored by rendering the switch blocks fully conductive and then the clock is restarted. The switch blocks which are modulated by controllers which use feedback control based upon the sensed virtual rail voltages (VVdd and Vgnd) while drawing their own power from the normal supply rails (Vdd and gnd).
Owner:ARM LTD
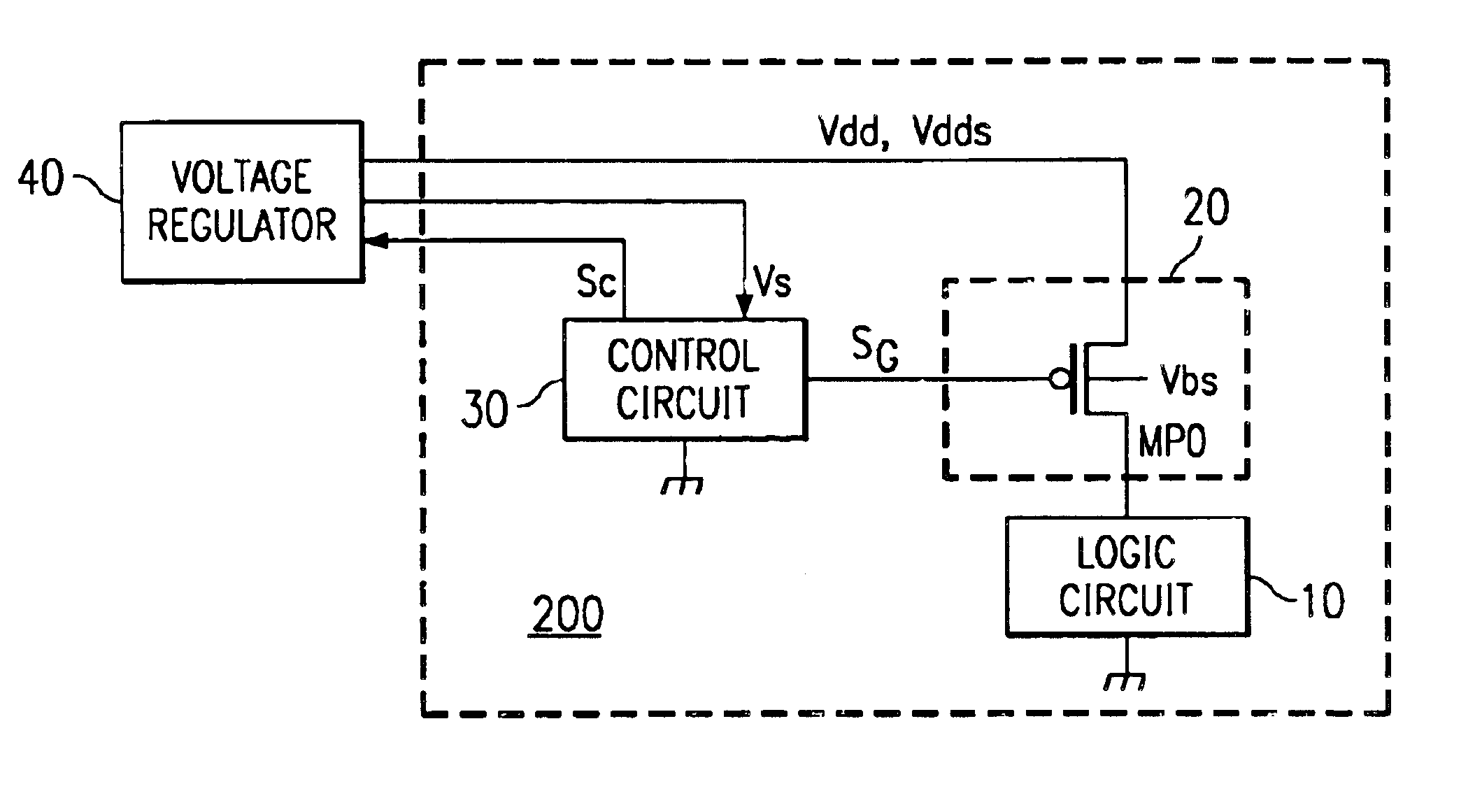
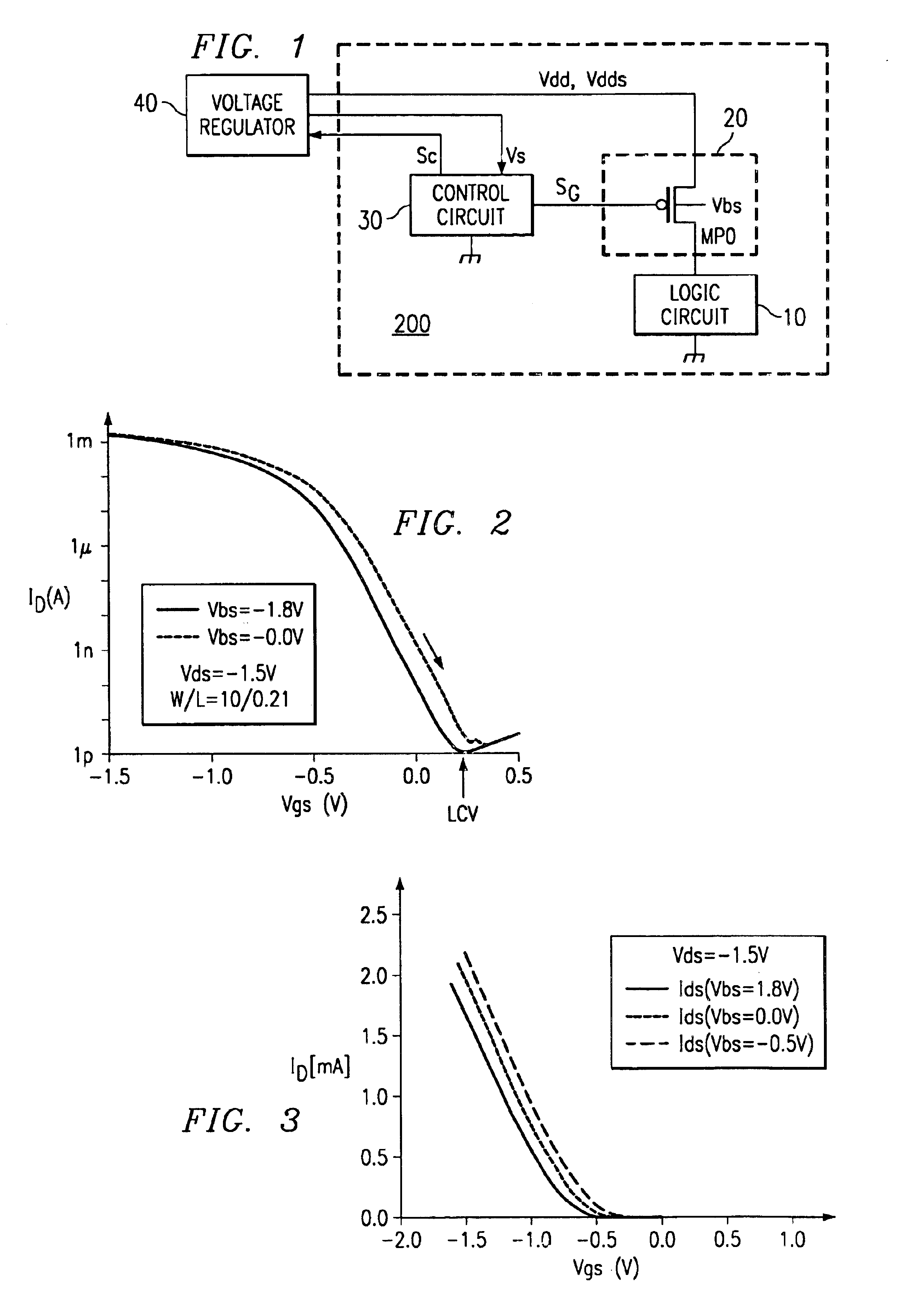
Suppressing the leakage current in an integrated circuit
InactiveUS6864708B2Lower levelPower reduction by control/clock signalSolid-state devicesDrain currentGate oxide
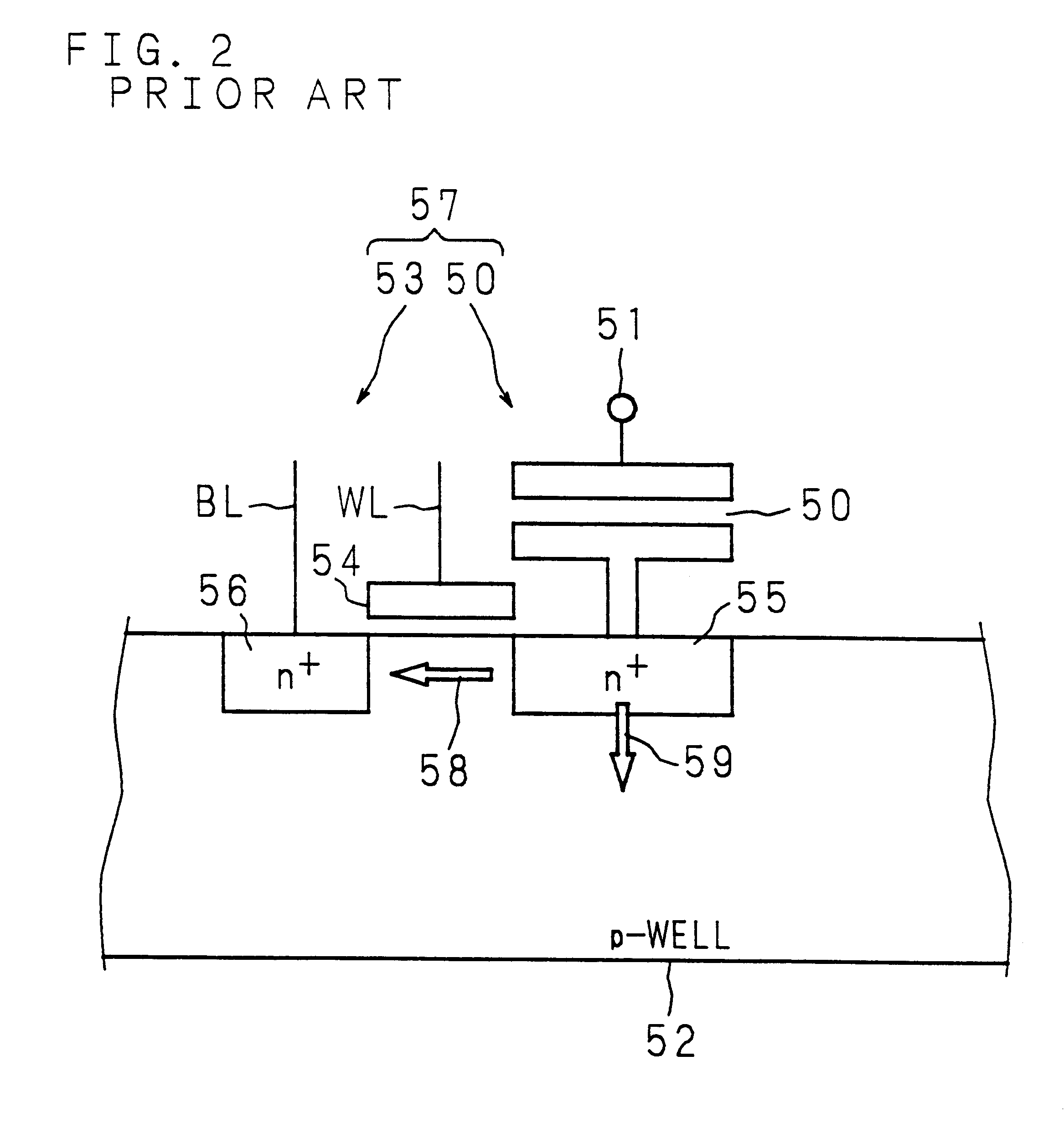
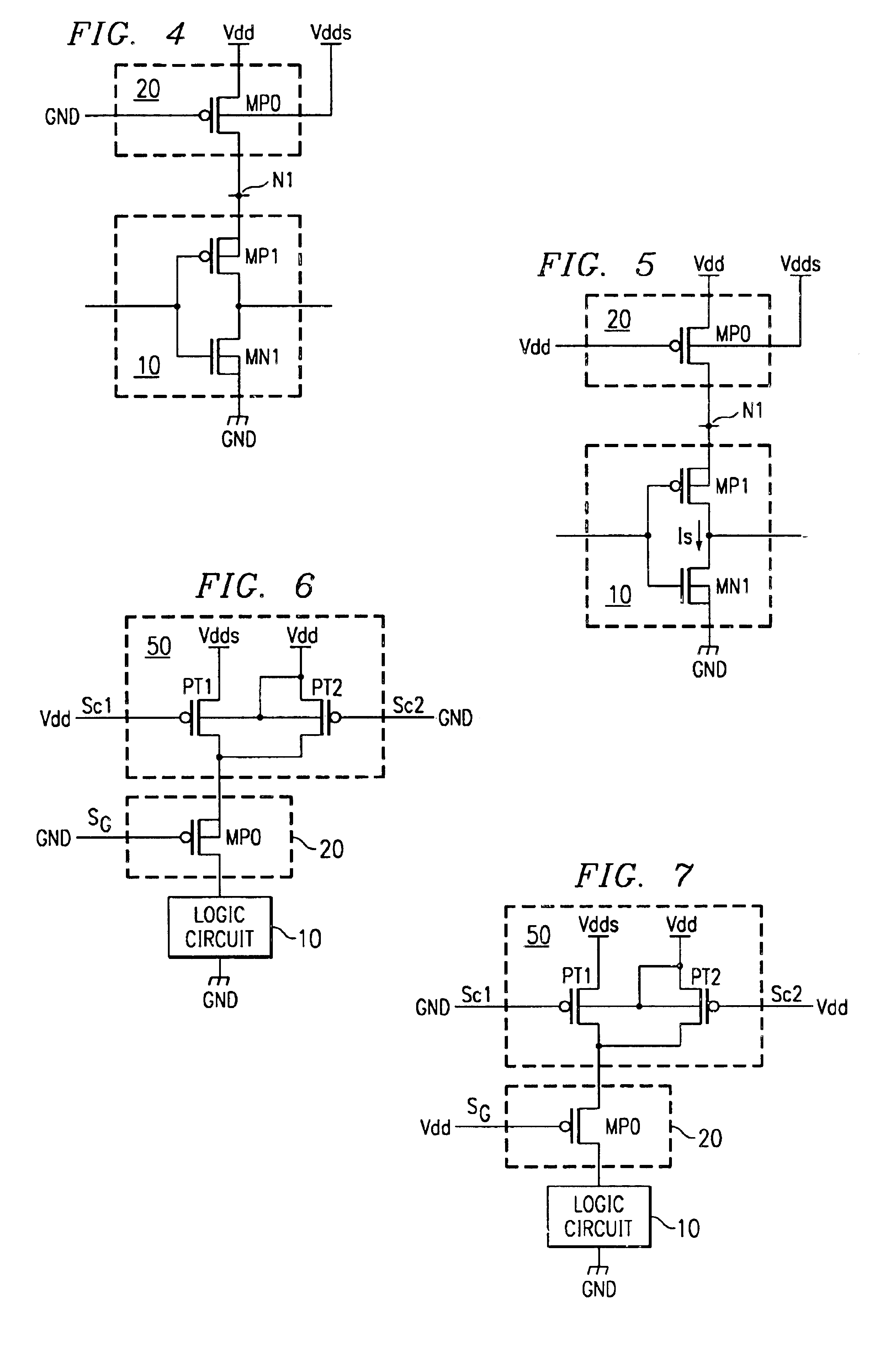
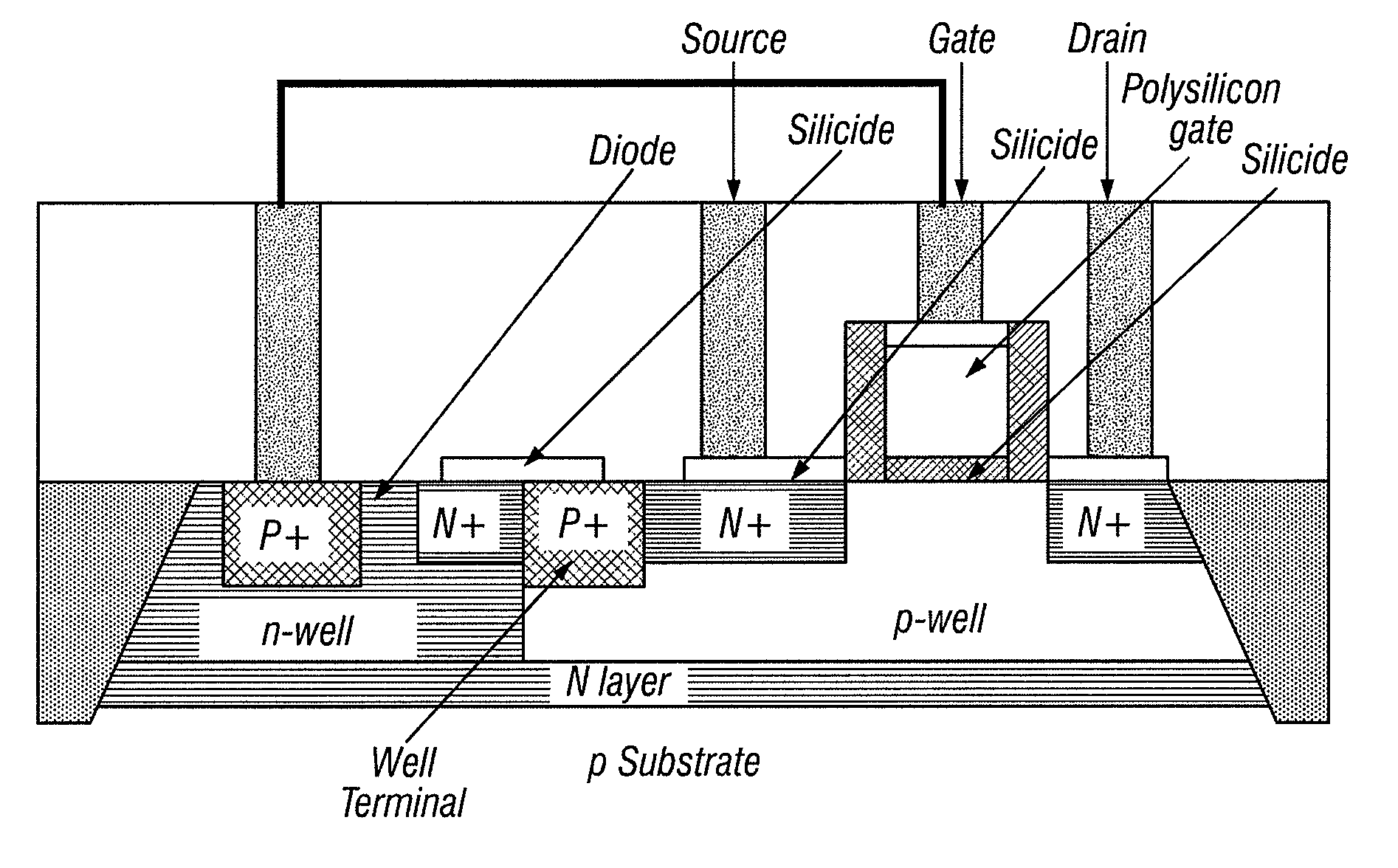
A semiconductor integrated circuit wherein the circuit area can be minimized, and defects can be detected reliably during a standby status while maintaining the reliability of a gate oxide film. Switching circuit 20 is provided between logic circuit 10 and source voltage Vdd supply terminal. While in an operating status, 0 V voltage is applied to the gate of transistor MP0 of switching circuit 20, and bias voltage VB equal to or slightly lower than source voltage Vdd is applied to its channel region in order to reduce the threshold voltage of transistor MP0 and increase its current driving capability. While in a standby status, a voltage equal to source voltage Vdd is applied to the gate of transistor MP0, a voltage lower than the source voltage is applied to the source, and bulk bias voltage VB equal to or higher than source voltage Vdd is applied to the channel region in order to minimize the drain current of transistor MP0, so that current path of logic circuit 10 is cut off, and the occurrence of leakage current is suppressed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Use of biased high threshold voltage transistor to eliminate standby current in low voltage integrated circuits
InactiveUS6225852B1Turn fasterLower threshold voltagePower reduction by control/clock signalElectric pulse generator detailsStandby currentLow voltage cmos
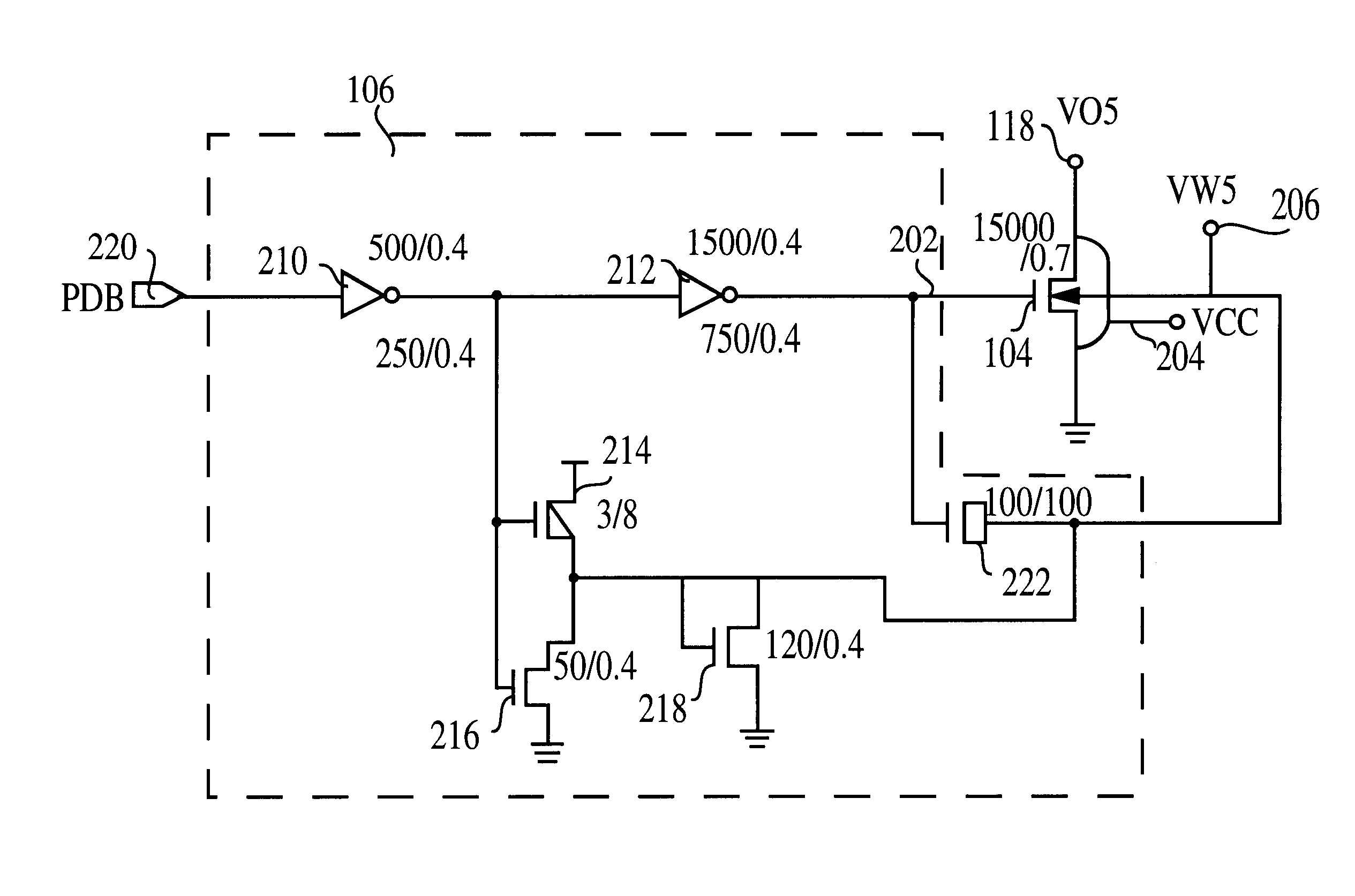
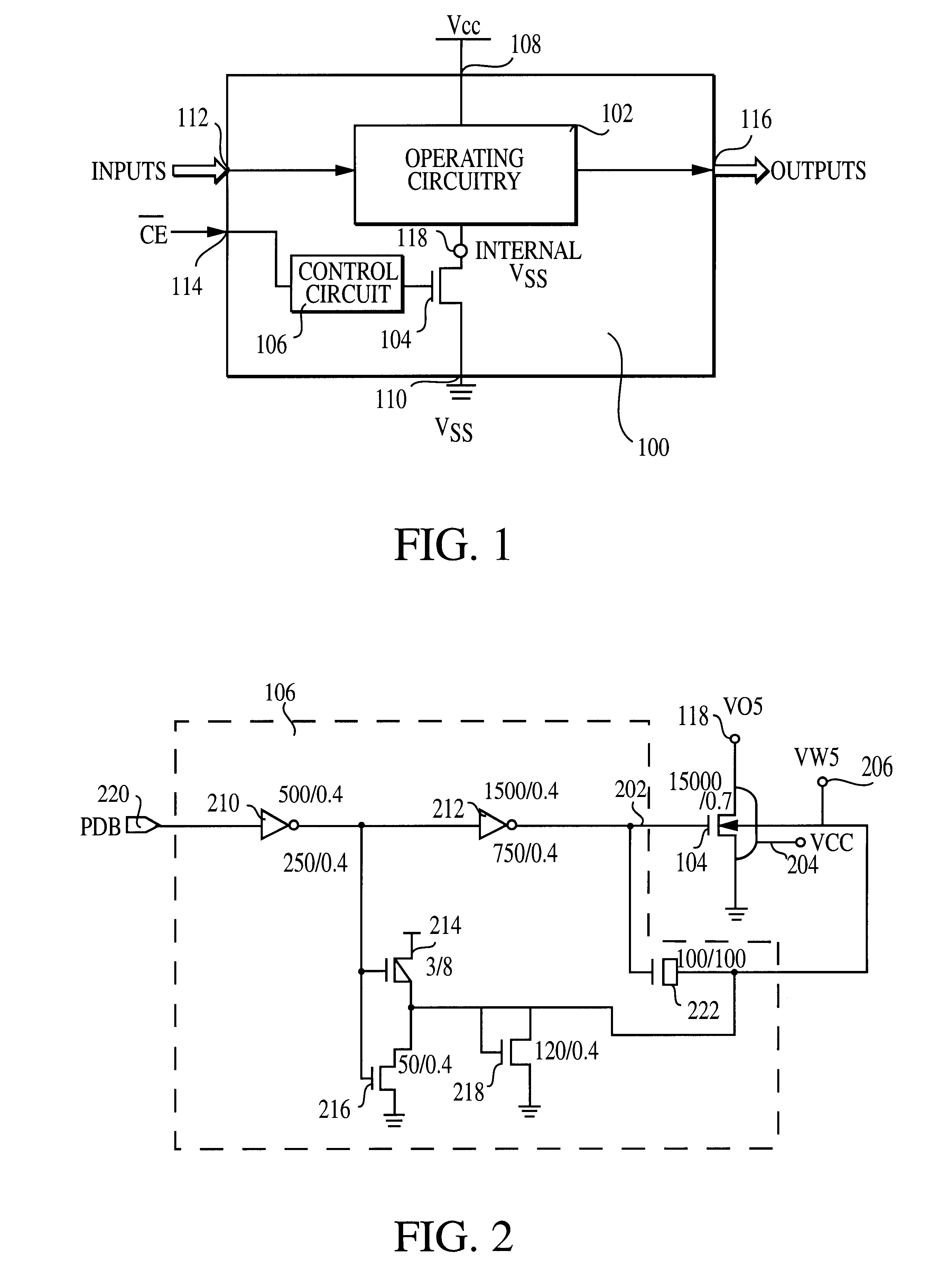
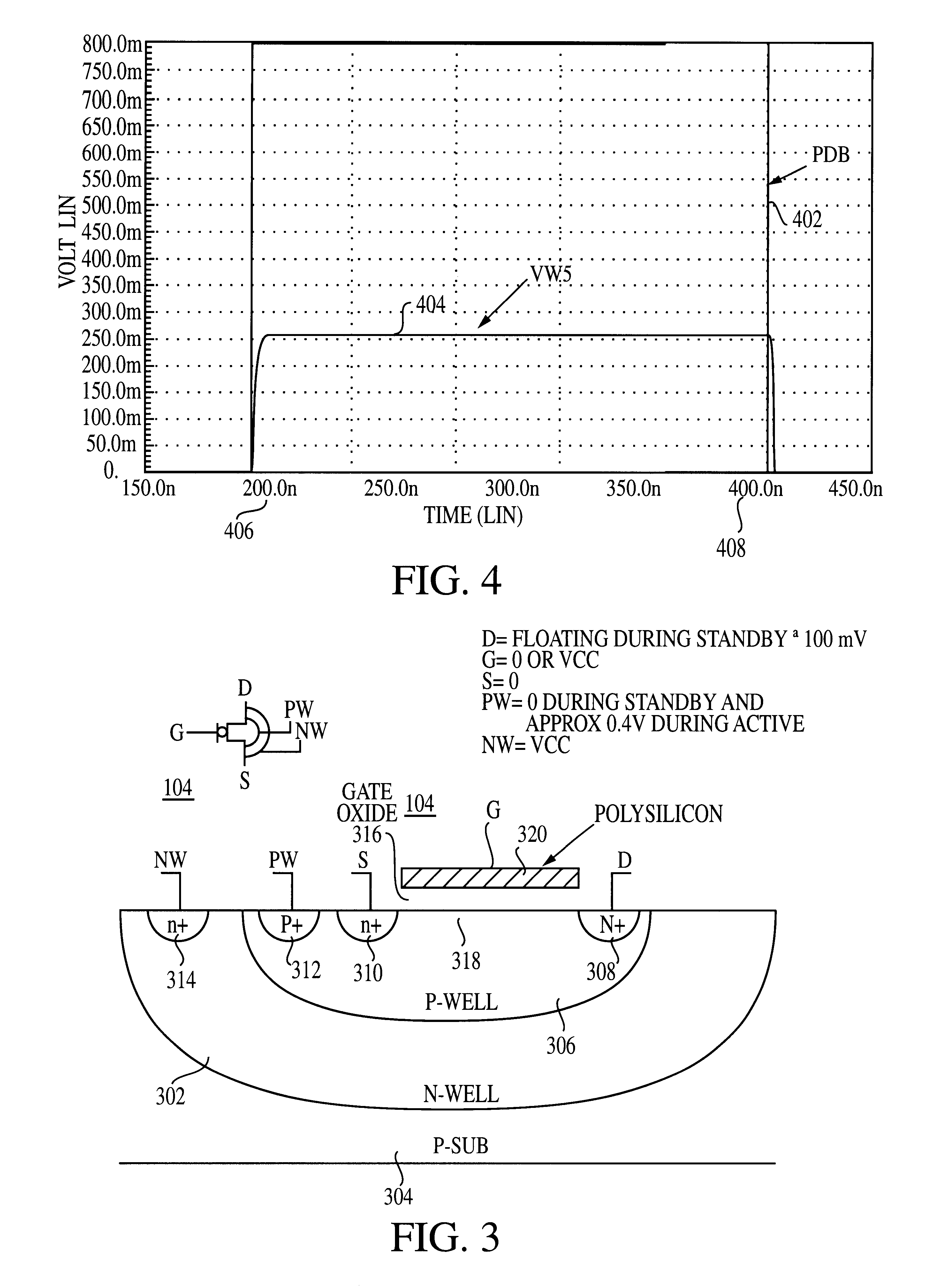
An integrated circuit (100) includes a first input (108) to receive a first operating voltage Vcc and a second input (110) to receive a second operating voltage Vss. Operating circuitry (102) of the integrated circuit is coupled to the first input to power the operating circuitry. A transistor (104) is coupled between the second input and the operating circuitry to selectively provide the second operating voltage to the operating circuitry of the integrated circuit. The well containing the transistor is biased to provide a reverse body effect and reduce the threshold voltage of the transistor to allow operation at very low Vcc.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Clock network fishbone architecture for a structured ASIC manufactured on a 28 NM CMOS process lithographic node
InactiveUS8629548B1Low levelEasy constructionPower reduction in field effect transistorsPower reduction by control/clock signalLogic cellAnd logic unit
A clock architecture for a Structured ASIC chip, manufactured using a CMOS process is shown. A via-configurable logic block (VCLB) architecture in the Structured ASIC has a core region containing memory and logic cells arranged in columns that are supplied by a clock network having a global clock network tree and a low-level clock mesh to distribute the global clock signal in a repeating pattern. The clock mesh has a fishbone configuration in outline and allows for scalable expansion of the clock network. In one embodiment 36 global clocks may be provided to the Structured ASIC, with four clocks per logic cell. The VCLB Structured ASIC chip is manufactured on a 28 nm CMOS process lithographic node, having several metal layers but preferably is programmable on a single via layer.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Systems and methods for minimizing static leakage of an integrated circuit
ActiveUS20060006929A1Minimize static leakageReduce complexityPower reduction by control/clock signalElectric variable regulationEngineeringLogic gate
To minimize static leakage of an integrated circuit, a charge pump generates a negative voltage to be applied to a “sleep” transistor cascaded to a logic gate of the integrated circuit. An adaptive leakage controller determines continuously or periodically whether to adjust the negative voltage to minimize the static leakage. A negative voltage regulator adjusts the negative voltage depending on the determination. Some embodiments determine whether to adjust the negative voltage by monitoring one or more parameters of the sleep transistor. Some embodiments determine whether to adjust the negative voltage by monitoring one or more parameters of an emulated sleep transistor.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
Semiconductor device reducing power consumption in standby mode
InactiveUS7436205B2Reduce power consumptionReduce in quantityReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalElectricityControl signal
A voltage supply control circuit is arranged between a true ground voltage and a pseudo ground line. In an active mode, first and second control signals are at the “H” and “L” levels, respectively. In response to this, a first switch is turned on so that a first node is electrically coupled to a power supply voltage, and attains the “H” level. Further, a second switch is turned on to couple electrically the ground voltage to a second node. In a standby mode, the first and second control signals are at the “L” and “H” levels, respectively. In response to this, a third switch is turned on to couple electrically the first and second nodes together. Since the power supply voltage was electrically coupled to the first node according to the turn-on of the first switch in the active mode, the path of the control signal including the first node to the switch has accumulated charged charges.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Power gating structure having data retention and intermediate modes
InactiveUS20060119393A1Reduce leakage currentExtend lifetime of battery packReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalStatic noise marginOperation mode
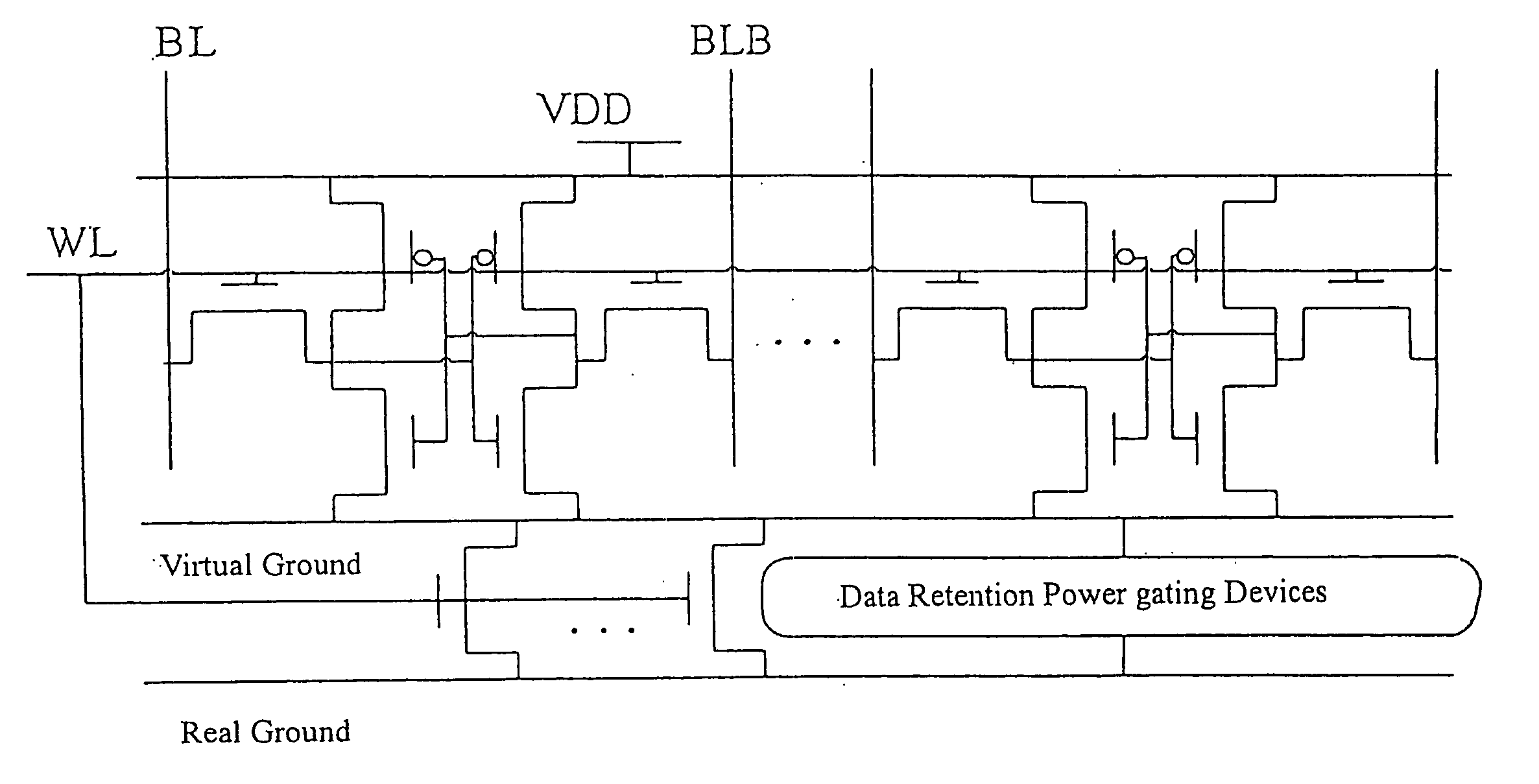
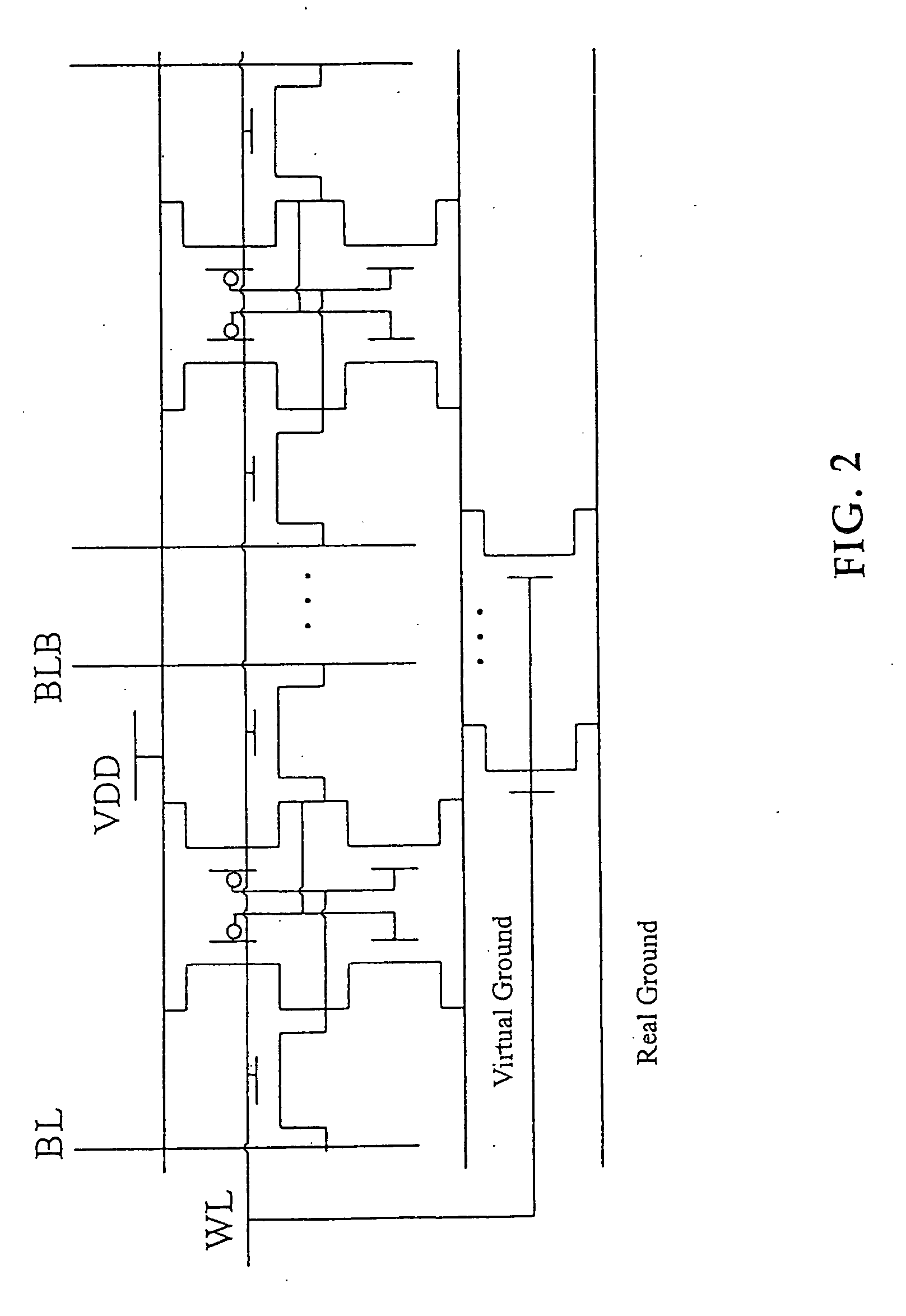
The present invention provides a power gating structure having data retention and intermediate modes and able to operate under multiple modes. A conventional power gating structure has only turn-on and turn-off functions, and is used to suppress a leakage current problem which has become more and more serious in advance manufacture processes, under a turn-off mode. However, in a memory circuit, such as latch, register and SRAM, when the power gate is turned off, a new power gating structure is required for data retention. The power gating structure of the present invention can be set into one of 4 different operational modes: a data retention mode for maintaining the static noise margin of the memory, an intermediate mode for reducing the interference on ground and power levels, an active mode used when the circuit operates in normal condition, and a standby mode used when the circuit does not operate.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
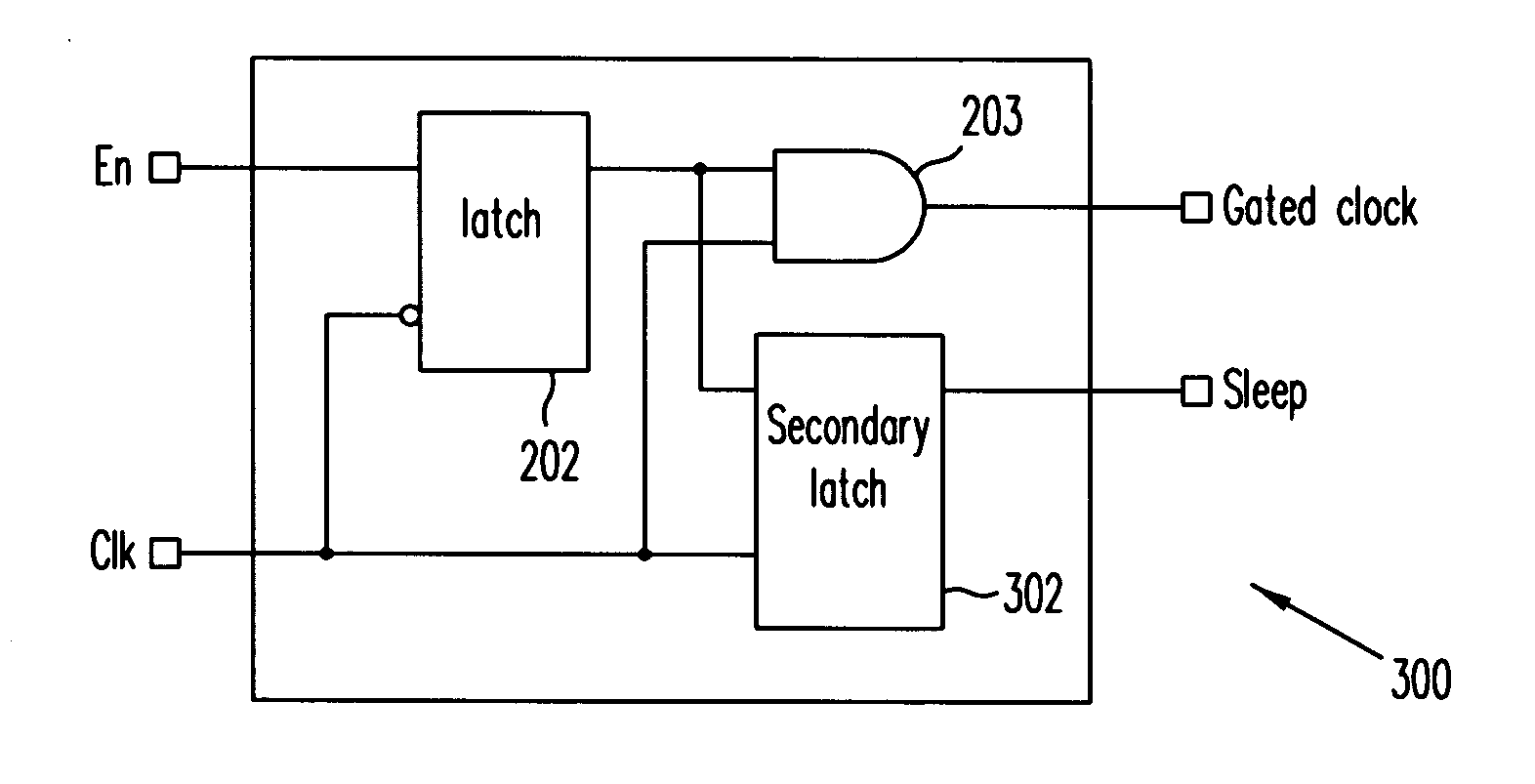
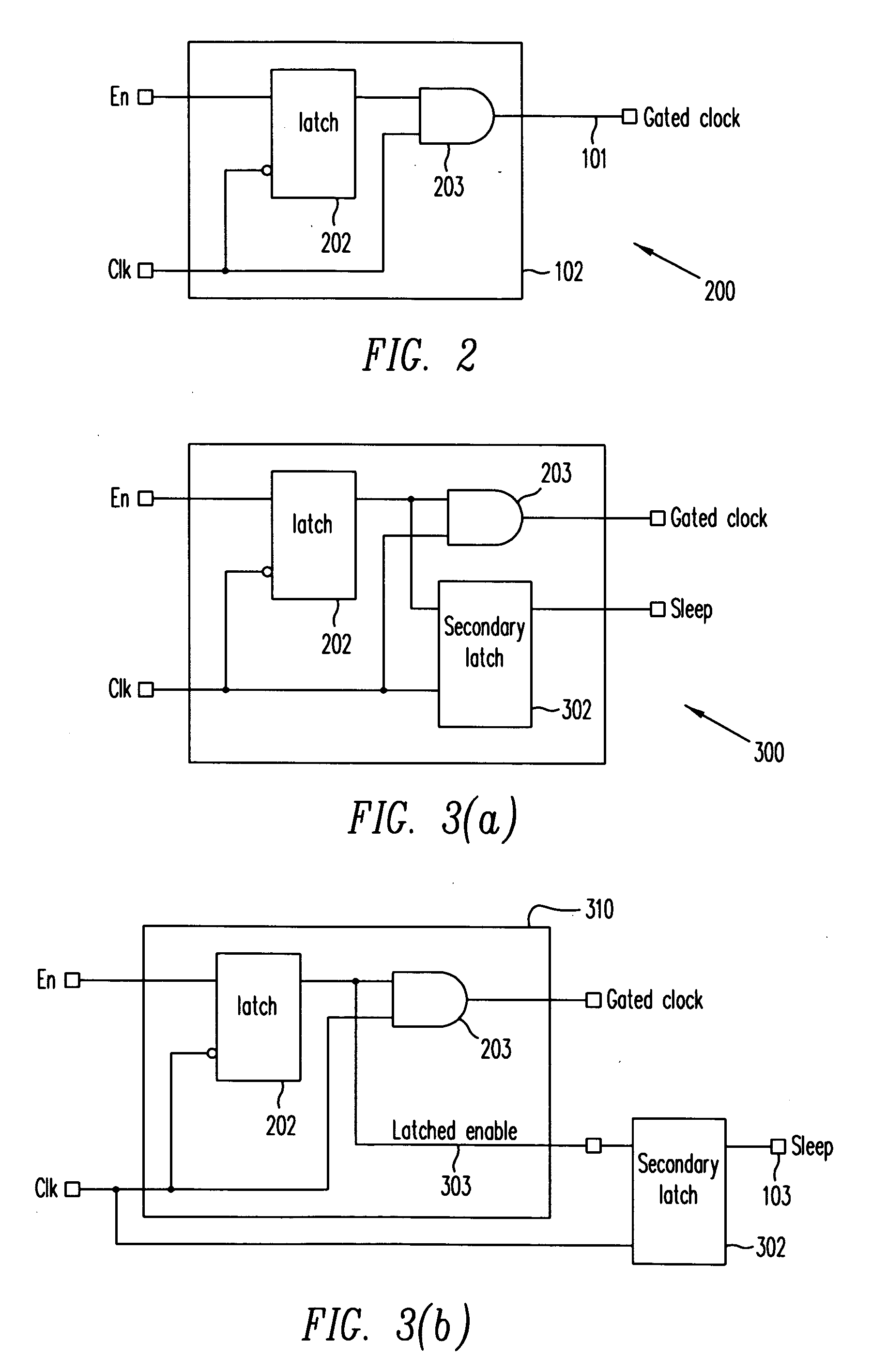
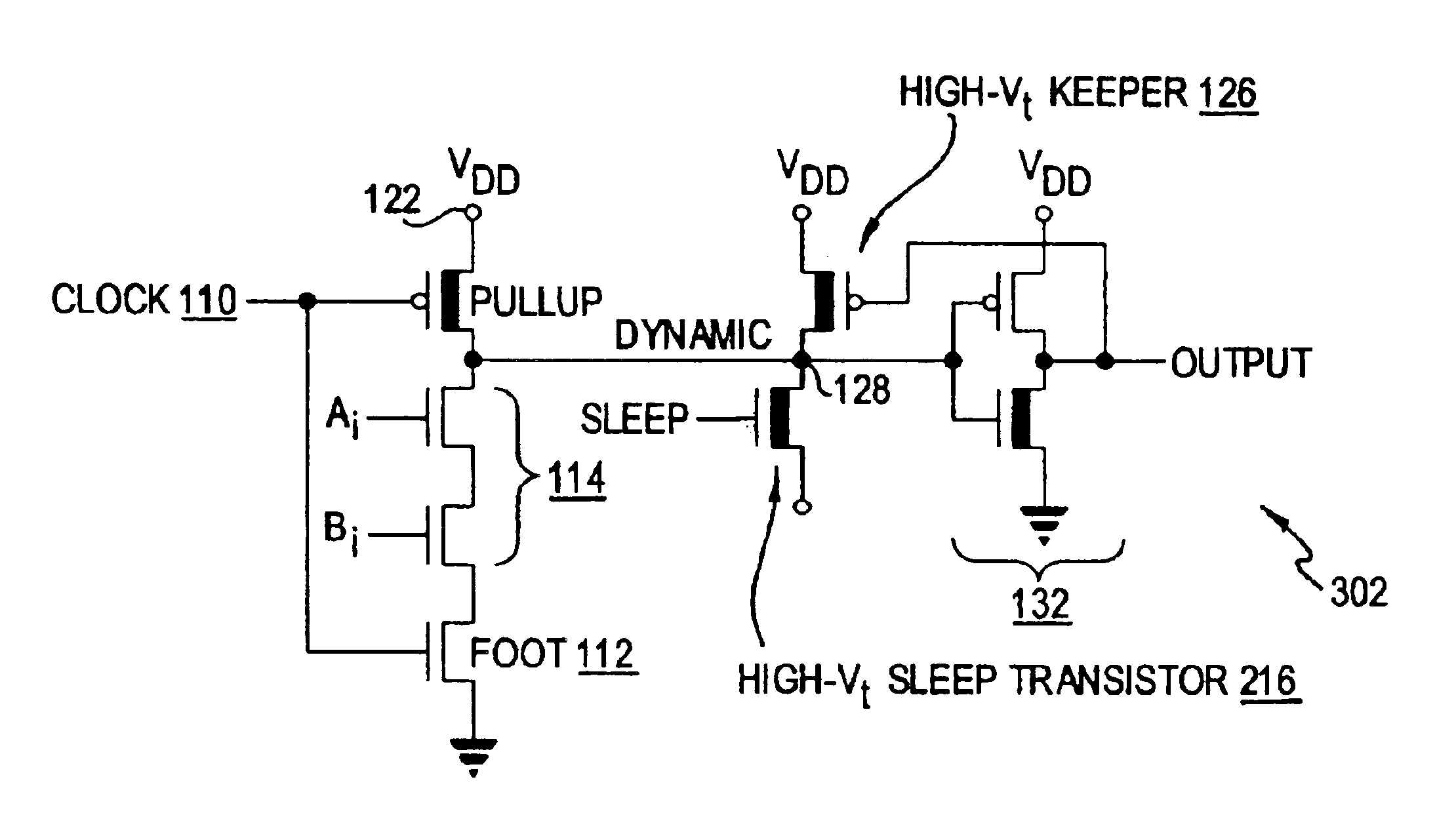
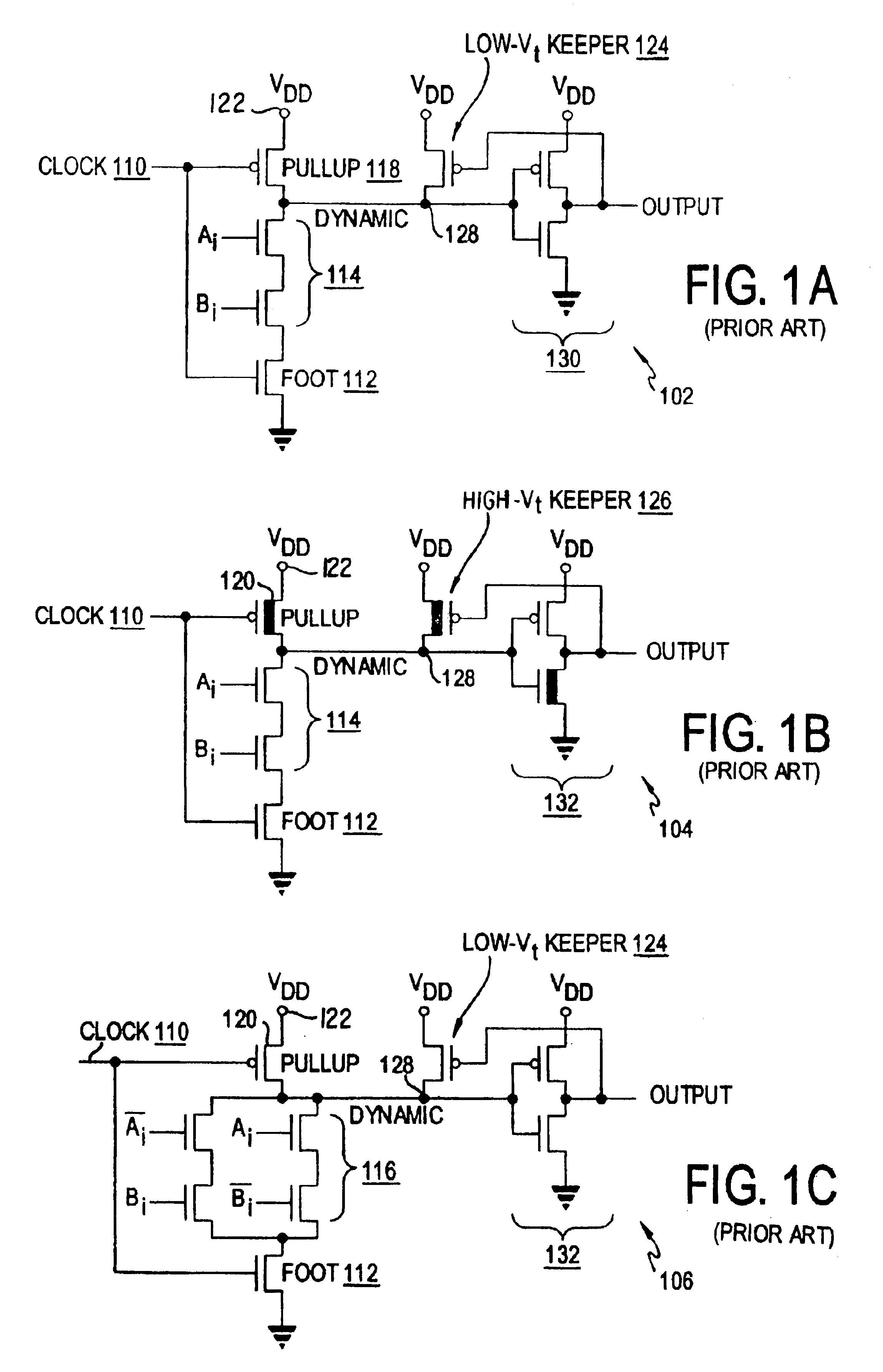
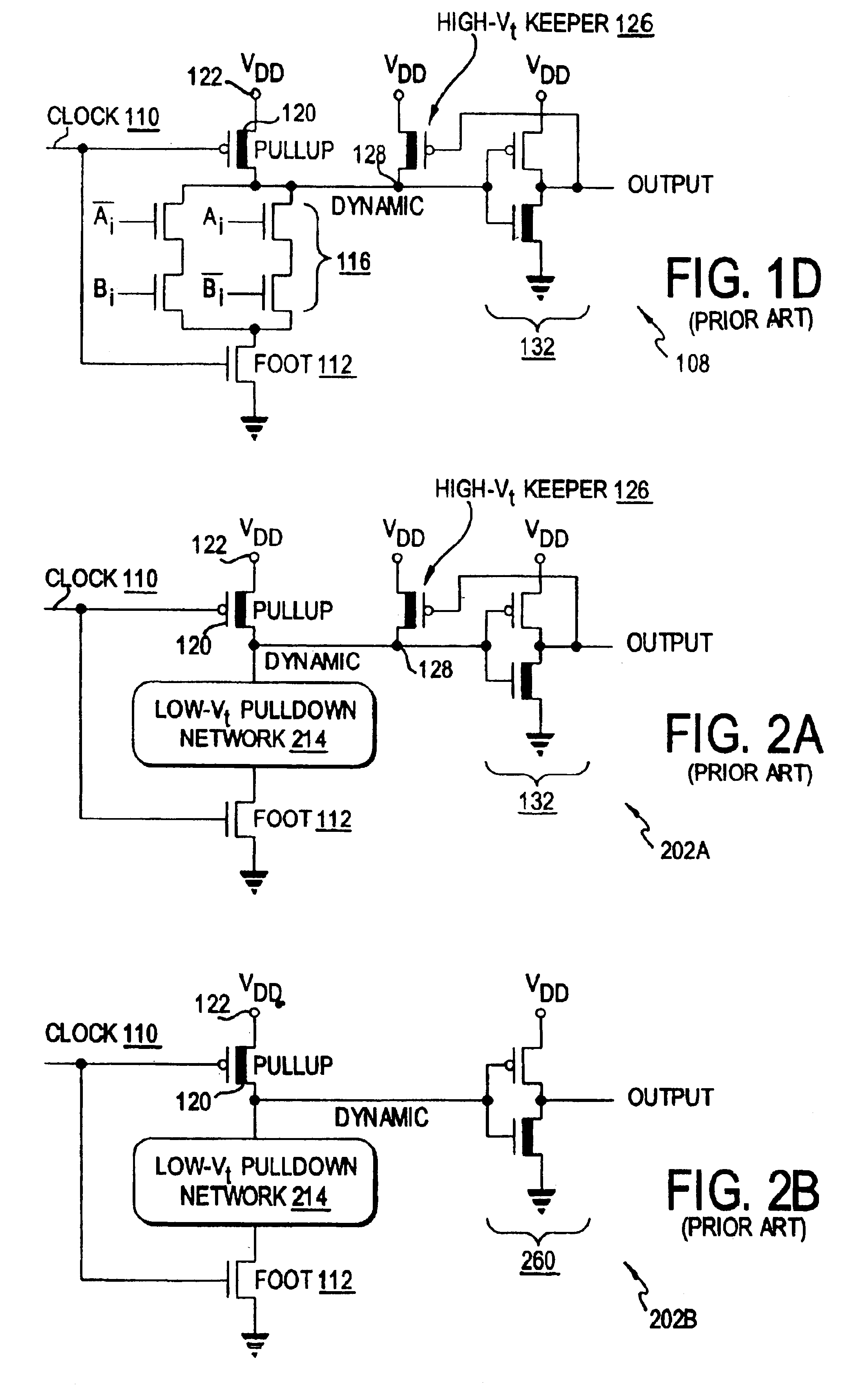
Clock gating system and method
ActiveUS7902878B2Reduce in quantityReduce areaPower reduction by control/clock signalGenerating/distributing signalsEngineeringLogic circuitry
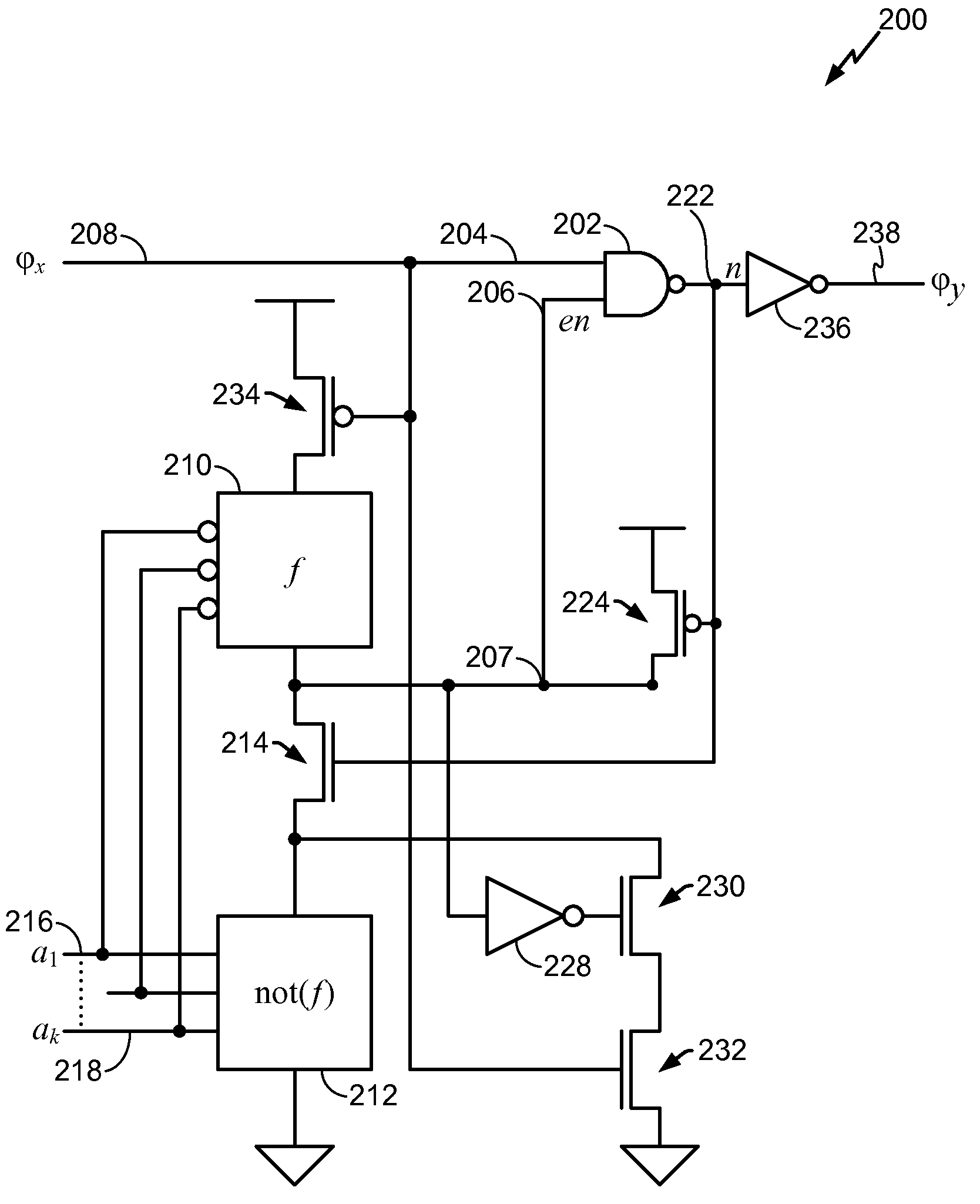
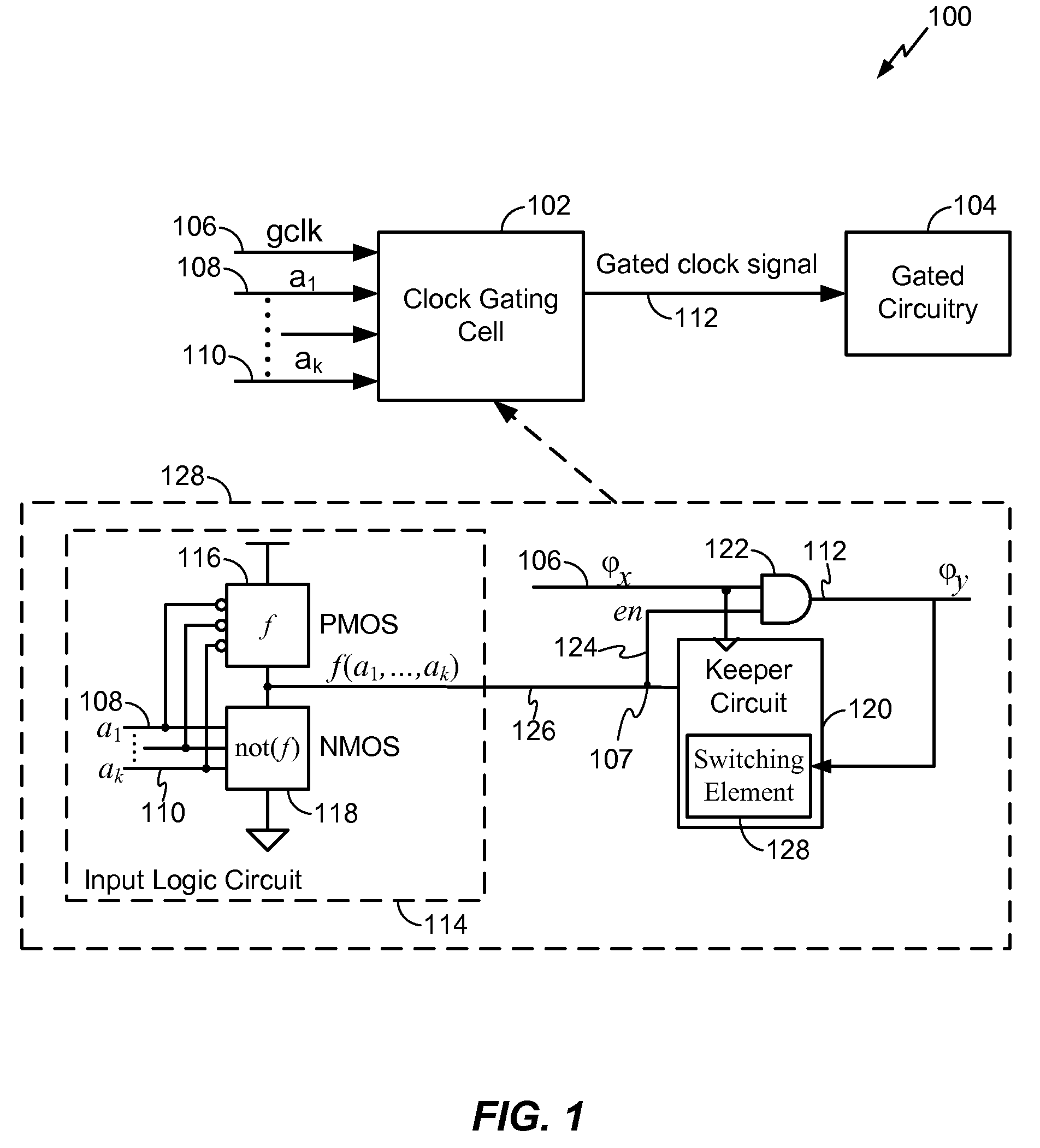
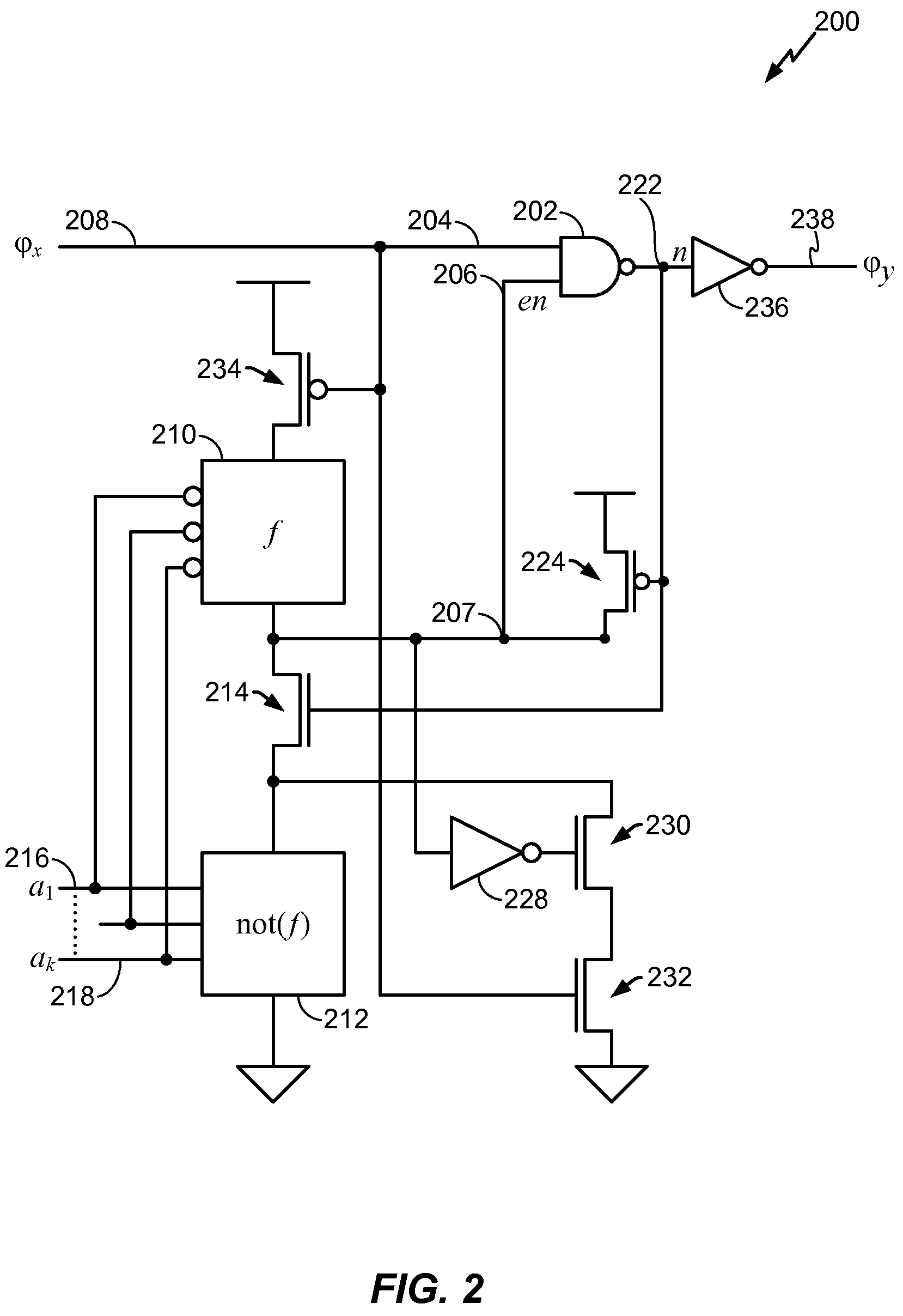
A clock gating system and method is disclosed. In a particular embodiment, the system includes an input logic circuit having at least one input to receive at least one input signal and having an output at an internal enable node. A keeper circuit includes at least one switching element that is responsive to a gated clock signal and is coupled to the internal enable node to selectively hold a logical voltage level at the internal enable node. The system further includes a gating element responsive to an input clock signal and to the logical voltage level at the internal enable node to generate the gated clock signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Apparatus and method for improving drive-strength and leakage of deep submicron MOS transistors
InactiveUS7683433B2Increase drive strengthReduce leakage currentTransistorInput/output impedence modificationCMOSEngineering
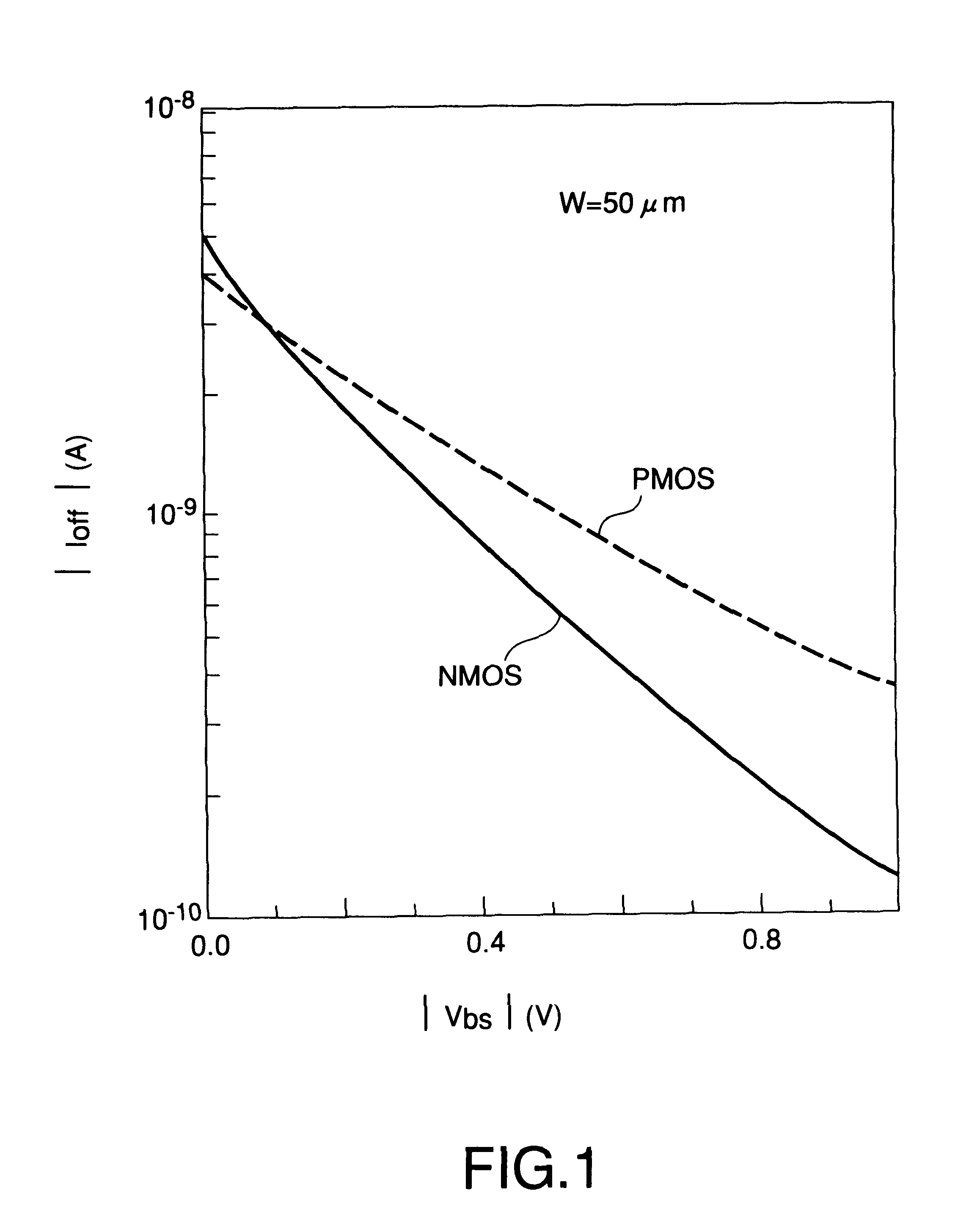
An apparatus and method of manufacture for metal-oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistors is disclosed. Devices in accordance with the invention are operable at voltages below 2V. The devices are area efficient, have improved drive strength, and have reduced leakage current. A dynamic threshold voltage control scheme comprised of a forward biased diode in parallel with a capacitor is used, implemented without changing the existing MOS technology process. This scheme controls the threshold voltage of each transistor. In the OFF state, the magnitude of the threshold voltage of the transistor increases, keeping the transistor leakage to a minimum. In the ON state, the magnitude of the threshold voltage decreases, resulting in increased drive strength. The invention is particularly useful in MOS technology for both bulk and silicon on insulator (SOI) CMOS. The use of reverse biasing of the well, in conjunction with the above construct to further decrease leakage in a MOS transistor, is also shown.
Owner:SEMI SOLUTIONS LLC
Power supply detection circuit biased by multiple power supply voltages for controlling a signal driver circuit
ActiveUS7397296B1Power reduction by control/clock signalPulse automatic controlDriver circuitCapacitance
A power supply detection circuit biased by at least two power supply voltages for controlling a signal driver circuit. Upstream and downstream amplifiers, powered by upstream and downstream power supply voltages, respectively, process an original control signal to produce a differential signal via output signal electrodes. Capacitances coupling respective ones of the output signal electrodes to the downstream power supply voltage and the circuit reference potential discharge and charge respective ones of the output signal electrodes in relation to initial receptions of the upstream and downstream power supply voltages and original control signal, following which voltage clamp circuitry maintains such discharged and charged states pending reception of the original control signal in a predetermined state.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
InactiveUS20050104133A1Cell height can be increasedRestricted degrees of freedomTransistorPower reduction by control/clock signalEngineeringSemiconductor
In a low power consumption mode in which prior data is retained upon power shutdown, the return speed thereof is increased. While use of an existent data retaining flip-flop may be considered, this is not preferred since it increases area overhead such as enlargement of the size of a cell. A power line for data retention for power shutdown is formed with wirings finer than a usual main power line. Preferably, power lines for a data retention circuit are considered as signal lines and wired by automatic placing and mounting. For this purpose, terminals for the power line for data retention are previously designed by providing the terminals therefor for the cell in the same manner as in the existent signal lines. Additional layout for power lines is no longer necessary for the cell, which enables a decrease in the area and design by an existent placing and routing tool.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Dual threshold voltage and low swing domino logic circuits
InactiveUS6900666B2Lowering standby leakage energyReducing leakage energyPower reduction in field effect transistorsPower reduction by control/clock signalDomino logicGate voltage
A domino logic circuit is configured to reduce power consumption. In a first embodiment, a sleep switch grounds the dynamic node during sleep mode. In a second embodiment, a low-swing circuit at the output reduces the output and keeper transistor gate voltage swings. A third embodiment combines those two techniques.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
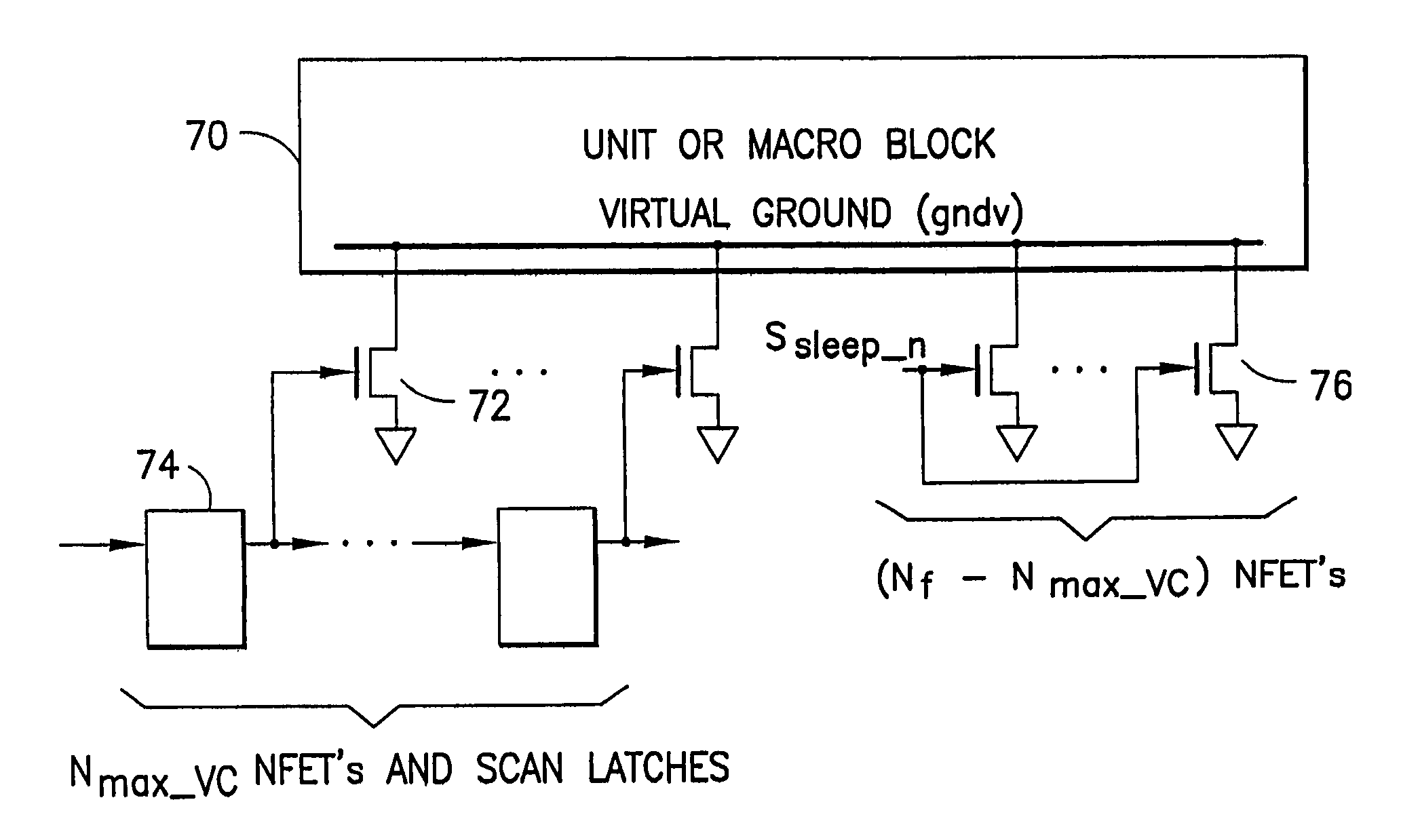
Power gating techniques able to have data retention and variability immunity properties
ActiveUS7126370B2Reduce power consumptionReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalManufacturing variabilityEngineering
A power gated semiconductor integrated circuit comprises: (1) logic circuit to be power gated, said logic circuit having a virtual ground rail; (2) footer device disposed between said virtual ground rail and a ground rail for reducing power consumption of said logic circuit; and (3) virtual rail voltage clamp disposed electrically in parallel with said footer device for limiting the voltage at the virtual ground rail, the virtual rail voltage clamp comprising at least one NFET. A total of Nf NFETs are connected to the virtual ground rail of the integrated circuit for use as both virtual rail voltage clamps and footer devices. A quantity of Nmax-VC NFETs are scanned and perform the function of voltage clamps and the remaining (Nf−Nmax-VC) NFETs perform power gating. Manufacturing variability immunity and tuning of the variability immunity is achieved by adjusting the quantity Nmax-VC based upon testing of the manufactured integrated circuit.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Low-power high-performance storage circuitry
InactiveUS6888202B2TransistorPower reduction by control/clock signalThreshold voltageIntegrated circuit
An integrated circuit is provided comprising a latch circuit including, a first inverter including a first high threshold voltage PMOS transistor and a first high threshold voltage NMOS transistor with a first data node comprising interconnected source / drains (S / D) of the first PMOS and NMOS transistors; a second inverter including a second high threshold voltage PMOS transistor and a second high threshold voltage NMOS transistor with a second data node comprising interconnected source / drains (S / D) of the second PMOS and NMOS transistors; wherein the gates of the first PMOS and first NMOS transistors are coupled to the second data node; wherein the gates of the second PMOS and second NMOS transistors are coupled to the first data node; a first low threshold voltage access transistor including a first S / D coupled to the first data node and to the gate of the second PMOS transistor and to the gate of the second NMOS transistor and including a second S / D coupled to a first data access node and including a gate coupled to a first access control node; and a second low threshold voltage access transistor including a first S / D coupled to the second data node and to the gate of the first PMOS transistor and to the gate of the first NMOS transistor and including a second S / D coupled to a second data access node and including a gate coupled to a second access control node.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Switch driver with slew rate control
ActiveUS20060033551A1Total current dropReduced magnitudePower reduction by control/clock signalElectronic switchingDriver circuitCapacitance
System and method for providing power to circuitry while avoiding a large transient current. A preferred embodiment comprises a distributed switch (such as switch arrangement 400) with a plurality of switches (such as switch 405) coupling a power supply to the circuitry. Each switch is individually controlled by a control signal and is turned on sequentially. Also coupled to each switch is a pre-driver circuit (such as pre-driver circuit 410). The pre-driver circuit comprises a potential adjust circuit (such as potential adjust circuit 505) that rapidly adjusts a voltage potential at the switch and a rate adjust circuit (such as the rate adjust circuit 520) that accelerates the power ramp-up across the switch once transient currents are no longer a concern. Adjusting the voltage potential so that the switch operates in a saturation mode increases an effective capacitance across the switch and thereby retarding the power ramp-up across the switch.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Power-gating cell for virtual power rail control
ActiveUS7276932B2Eliminate delaysReliability increasing modificationsMajority/minority circuitsControl signalPower grid
Virtual power-gated cells (VPC) are configured with control circuitry for buffering control signals and a power-gated block (PGB) comprising two or more NFETs for virtual ground rail nodes and PFETs for virtual positive rail nodes. Each VPC has a control voltage input, a control voltage output, a node coupled to a power supply voltage potential, and a virtual power-gated node that is coupled and decoupled from the power supply potential in response to logic states on the control input. The control signals are buffered by non-power-gated inverters before being applied to the input of a PGB. VPCs may propagate a control signal that is in phase with or inverted from a corresponding control signal at the control input. VPCs may be cascaded to create virtual power rails in chains and power grids. The control signals are latched at the cell boundaries or latched in response to a clock signal.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method of reducing sub-threshold leakage in circuits during standby mode
InactiveUS6522171B2Minimizes or reduces sub-threshold current leakagePower reduction by control/clock signalDigital storageSub thresholdSubthreshold leakage current
A dynamic logic circuit having reduced sub-threshold leakage current during standby mode comprises a connection to at least one upper power rail, a connection to a lower power rail, a precharge node, and an output node adapted to be charged to the potential of the upper power rail after a precharge signal is received at the precharge node. A latch on the output node is provided to maintain the potential at the output node, along with at least one input node for receiving at least one evaluation signal to maintain the potential at the output node to the voltage of the upper power rail or reduce the potential at the output node to the potential of the lower power rail. A device is coupled to the output node to set the output node to a potential which minimizes the sub-threshold leakage upon receipt of a standby signal to maintain the potential at the output node at the potential of the upper power rail or at the potential of the lower power rail.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG +1
Popular searches
Electric pulse generator Pulse shaping Pulse duration/width modulation Logic circuit coupling/interface arrangements Baseband systems Computation using denominational number representation Energy efficient computing Logic circuits using dielectric elements Semiconductor devices Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com