Patents
Literature
97 results about "Static noise margin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
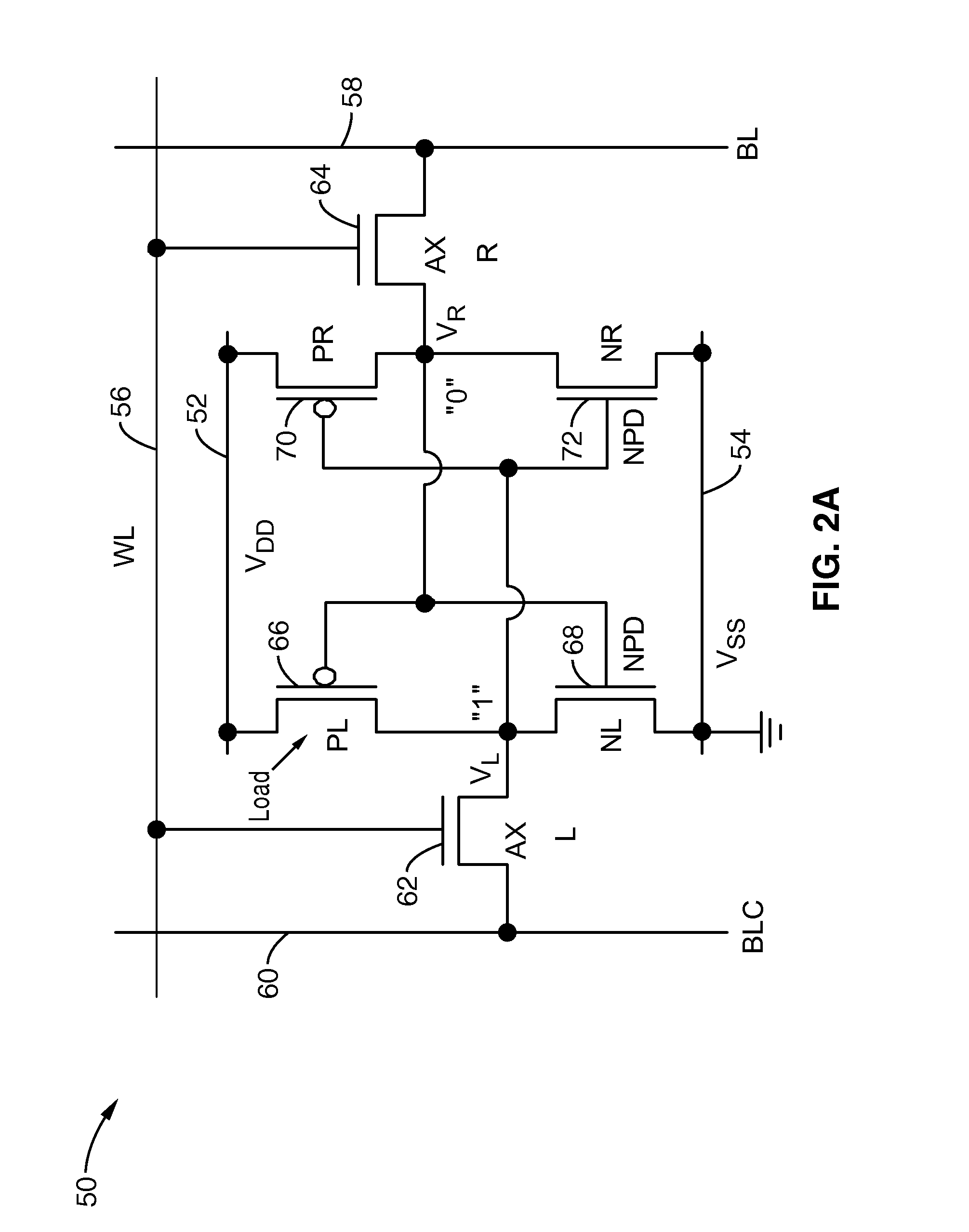
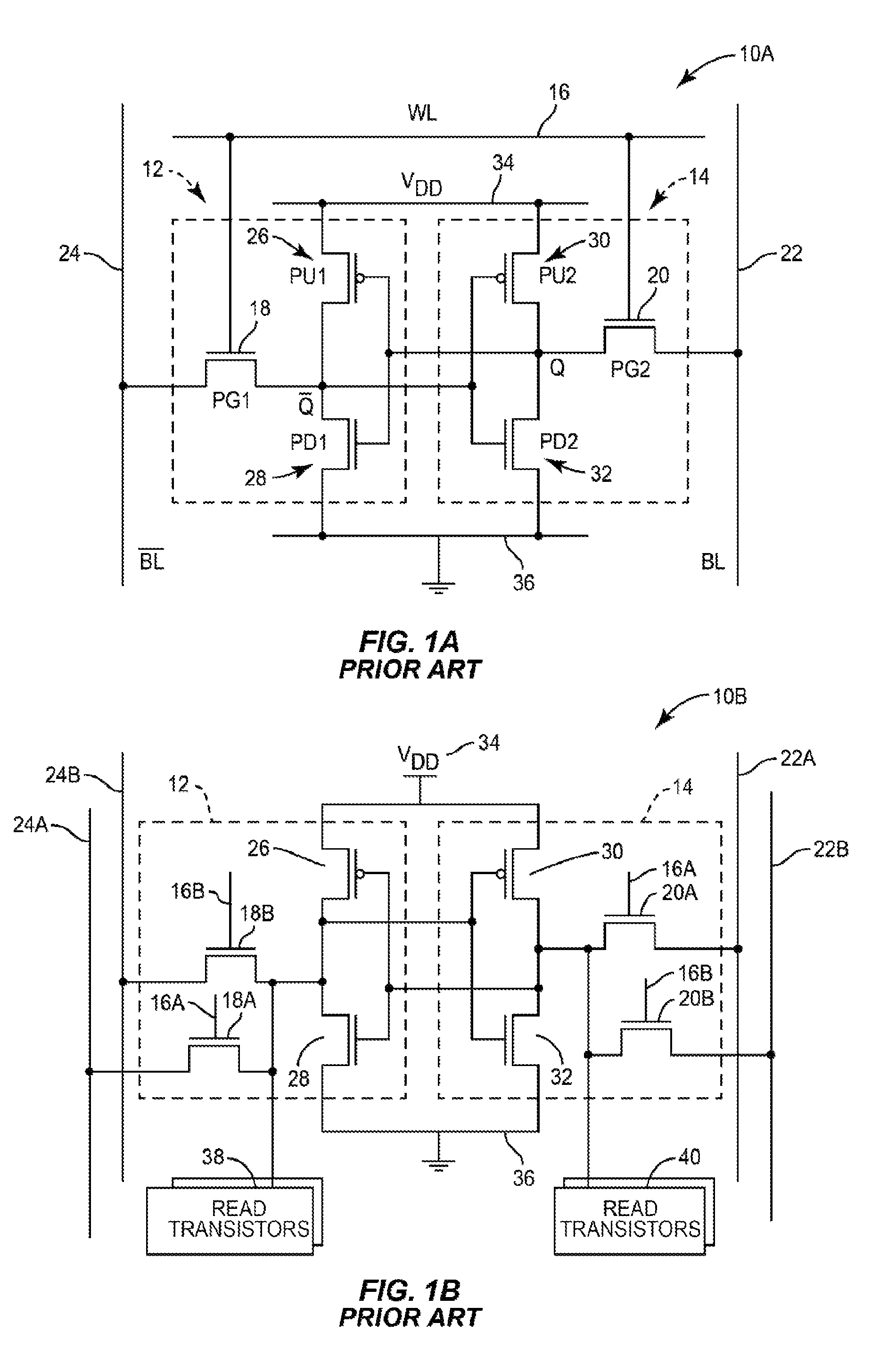
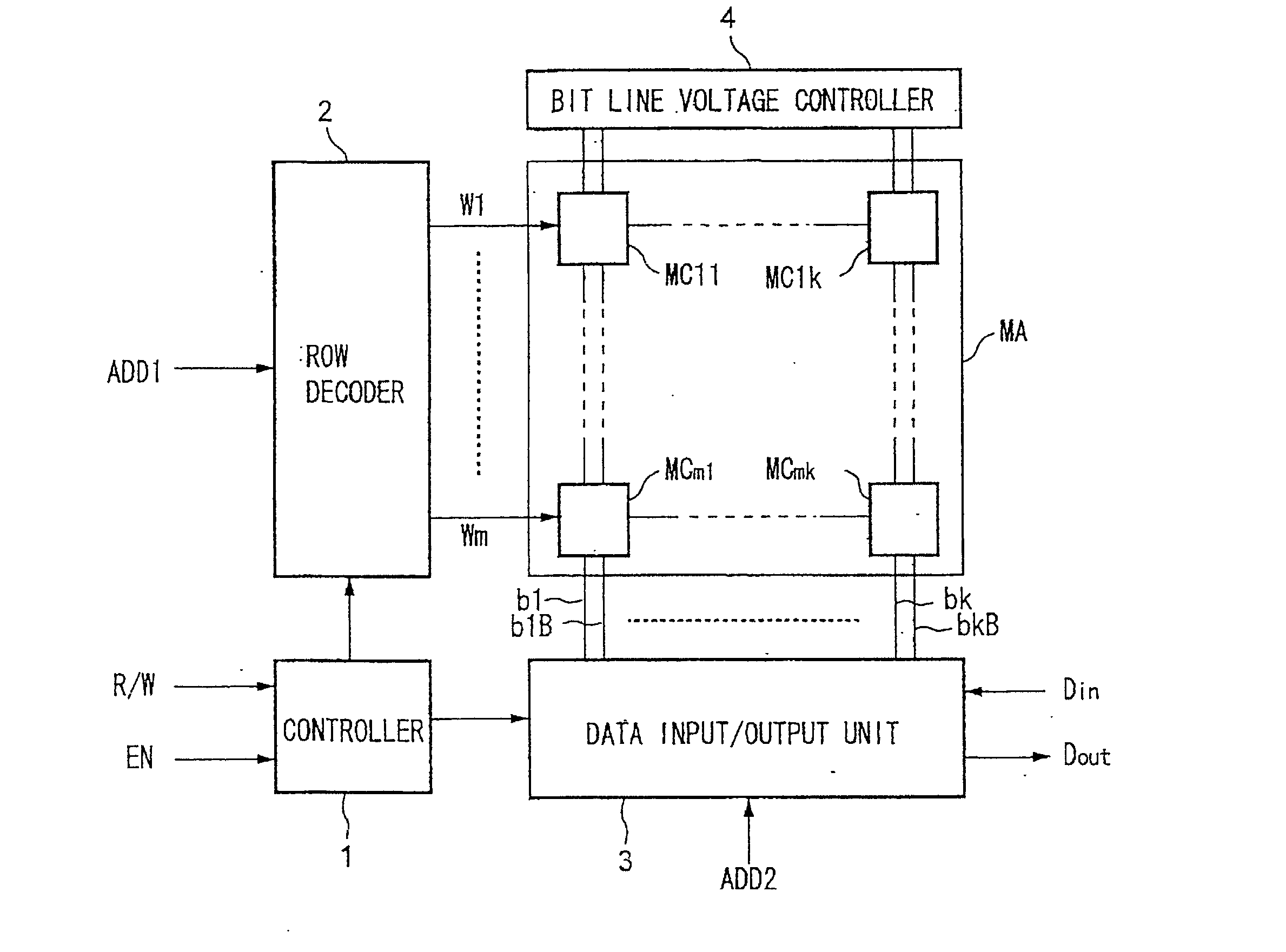
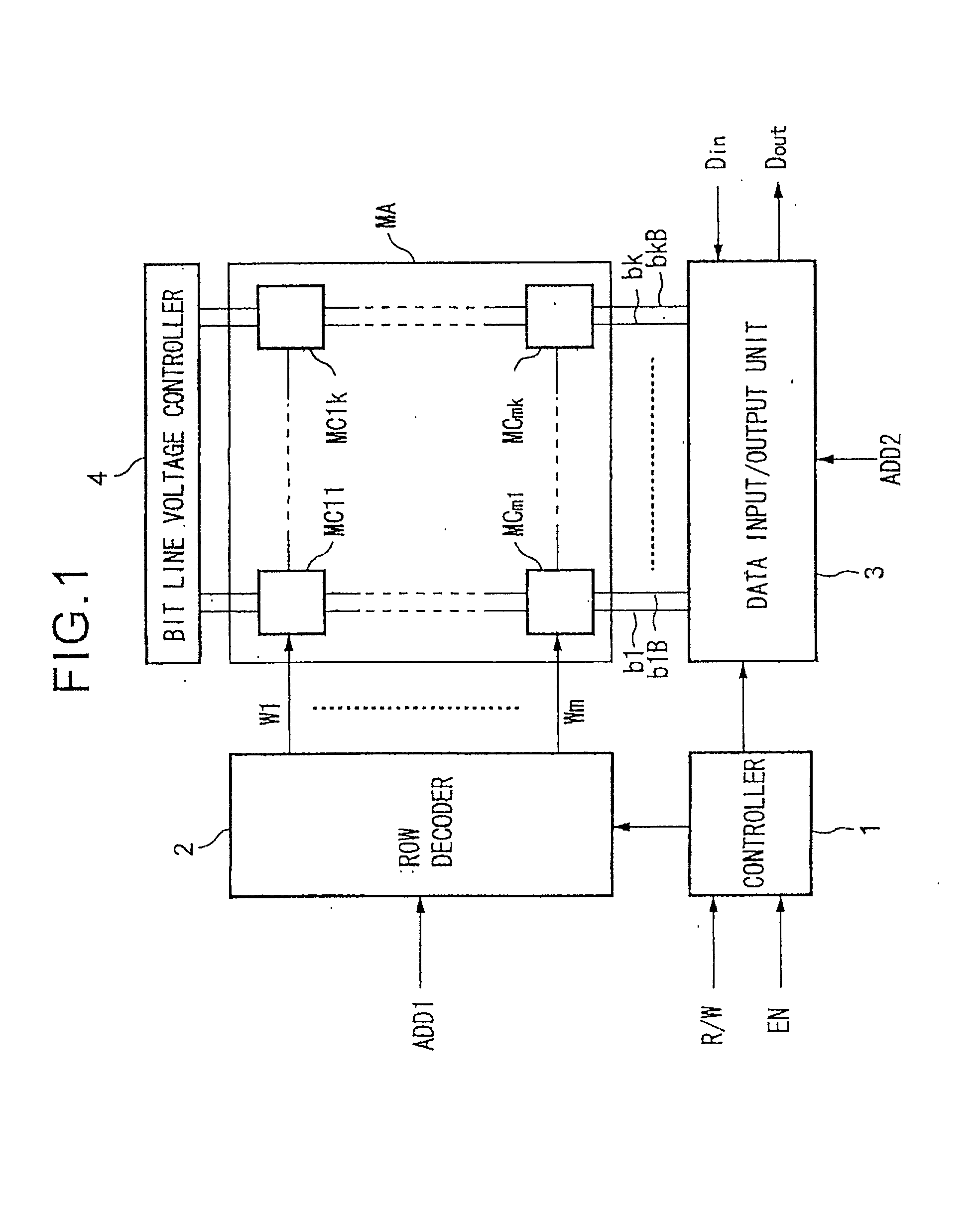
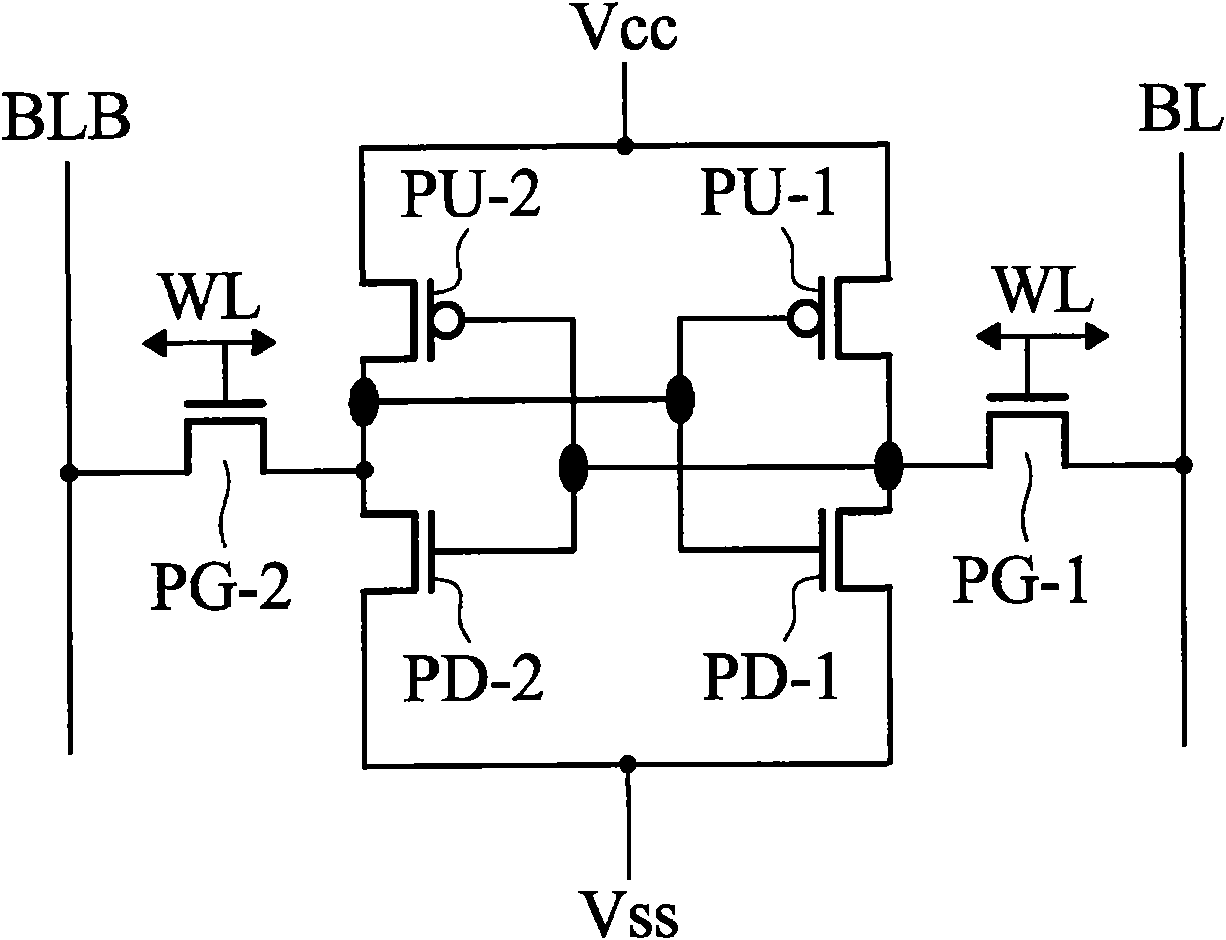
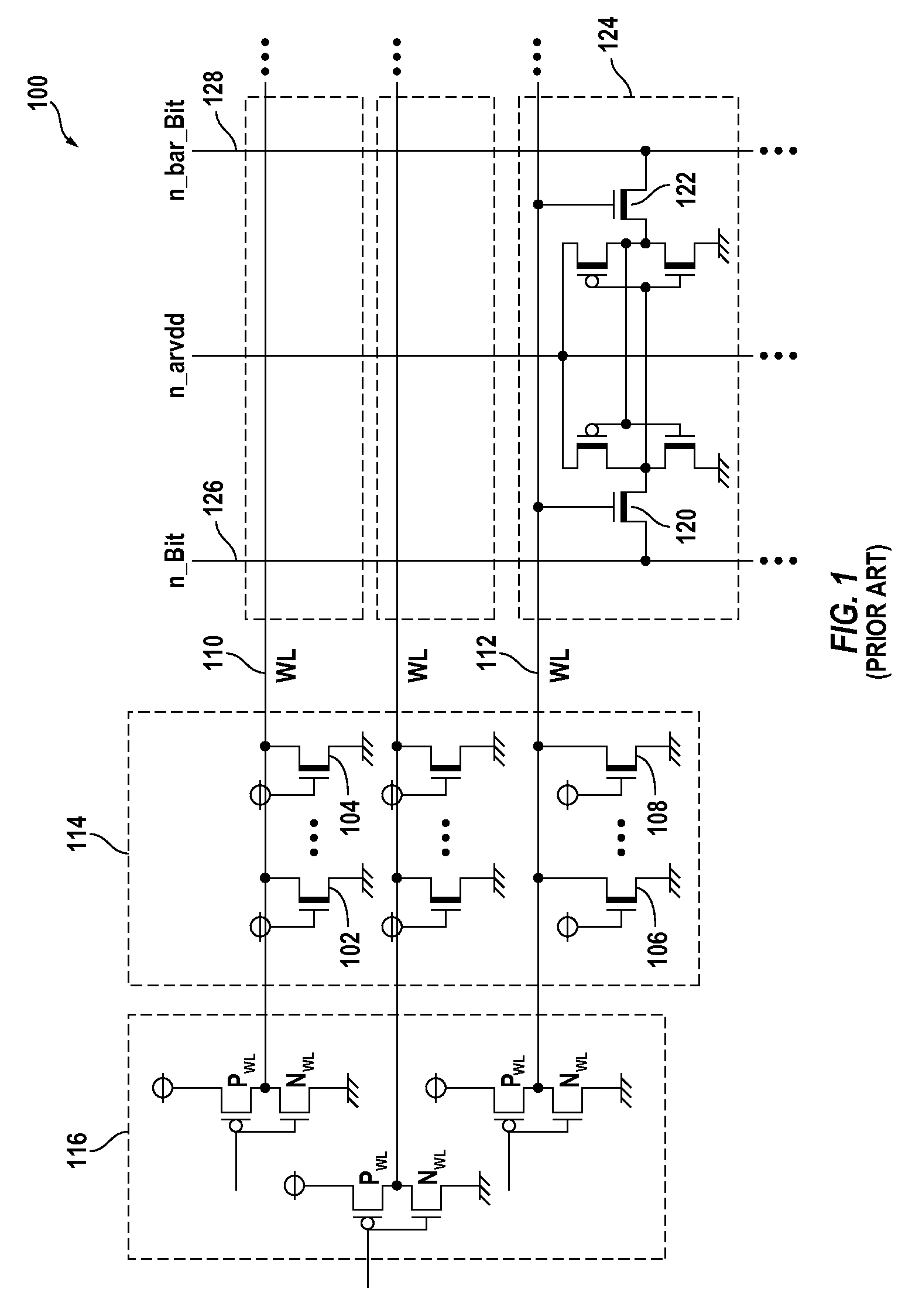
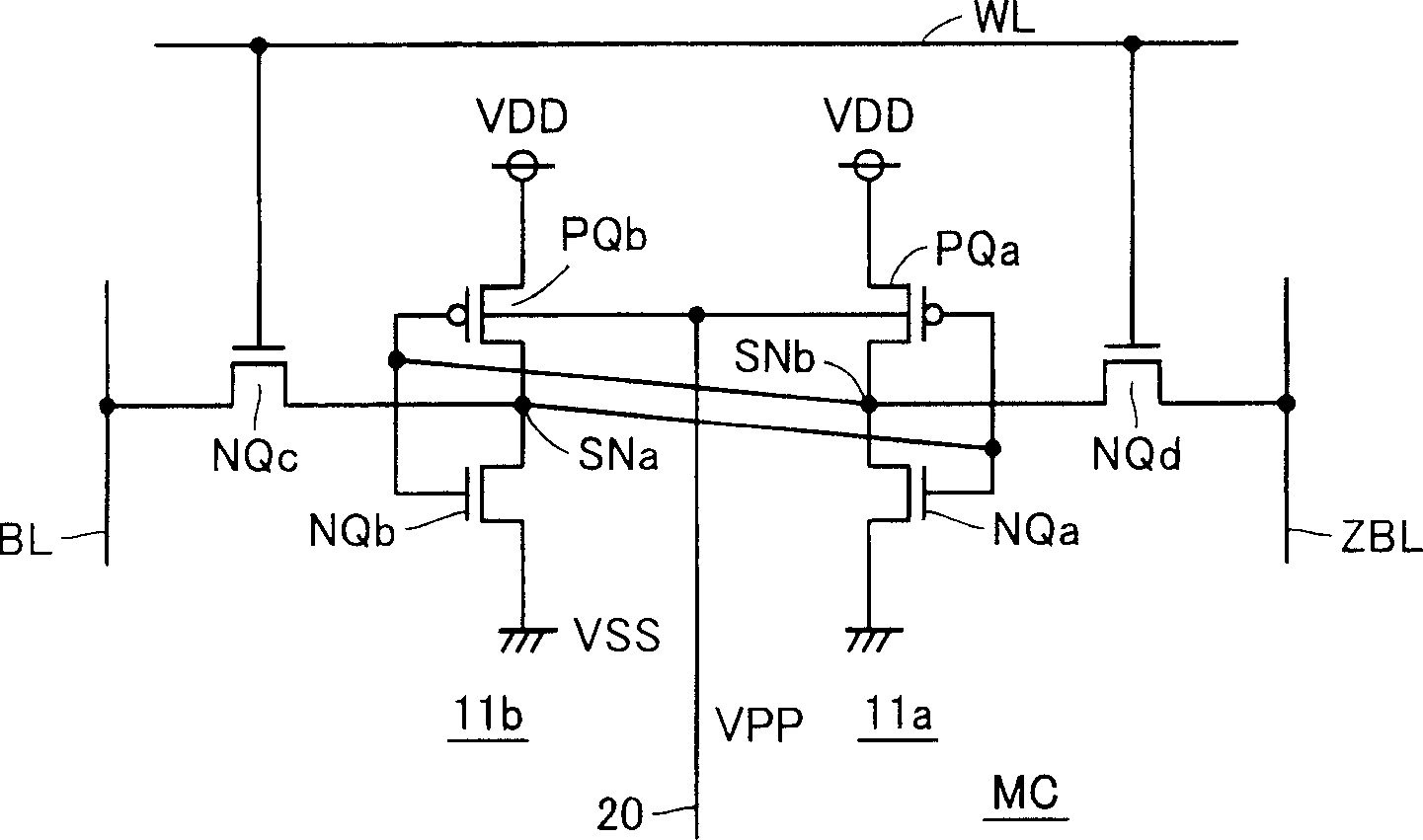
Semiconductor memory device with memory cells operated by boosted voltage
InactiveUS6795332B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLow voltageStatic noise margin
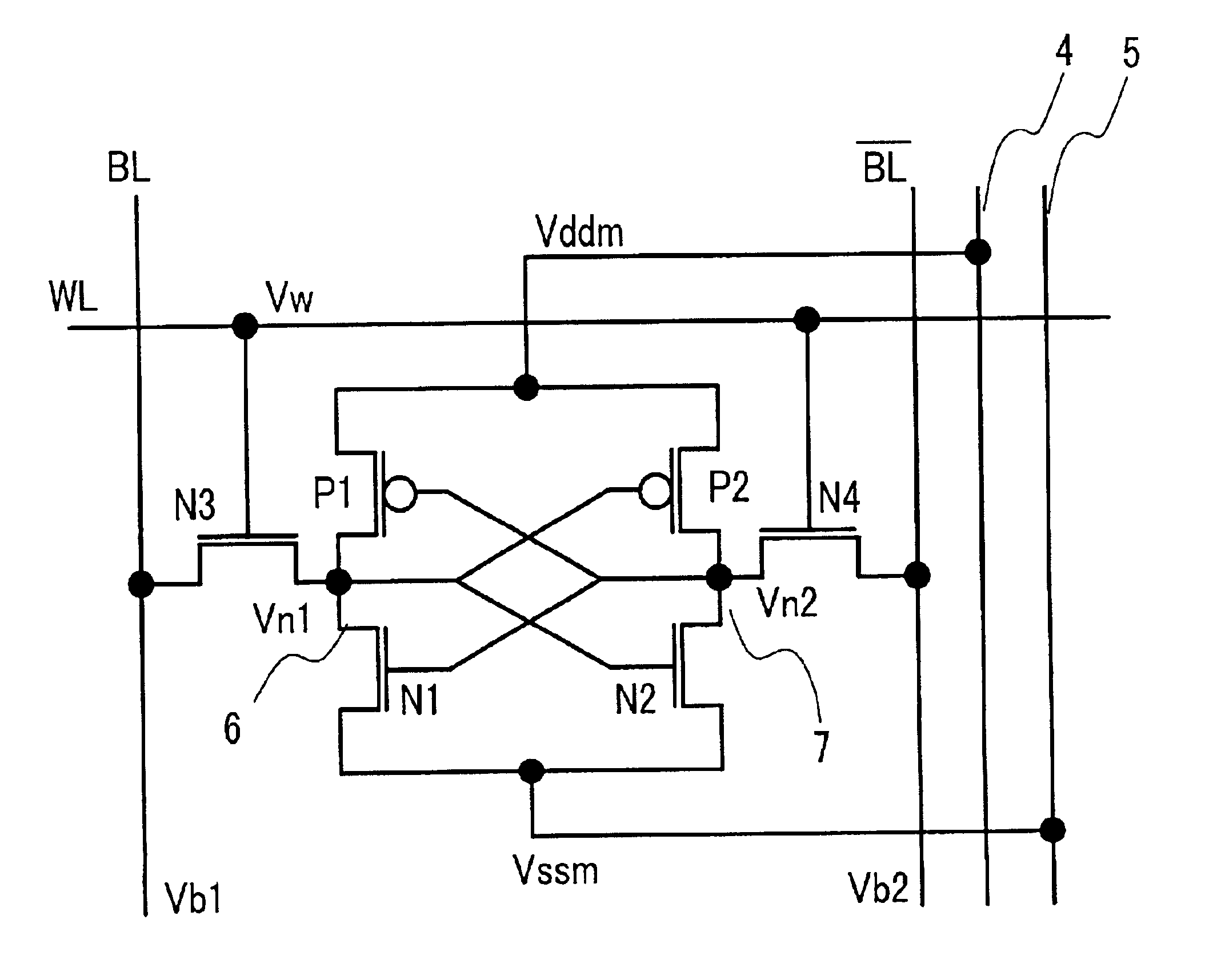
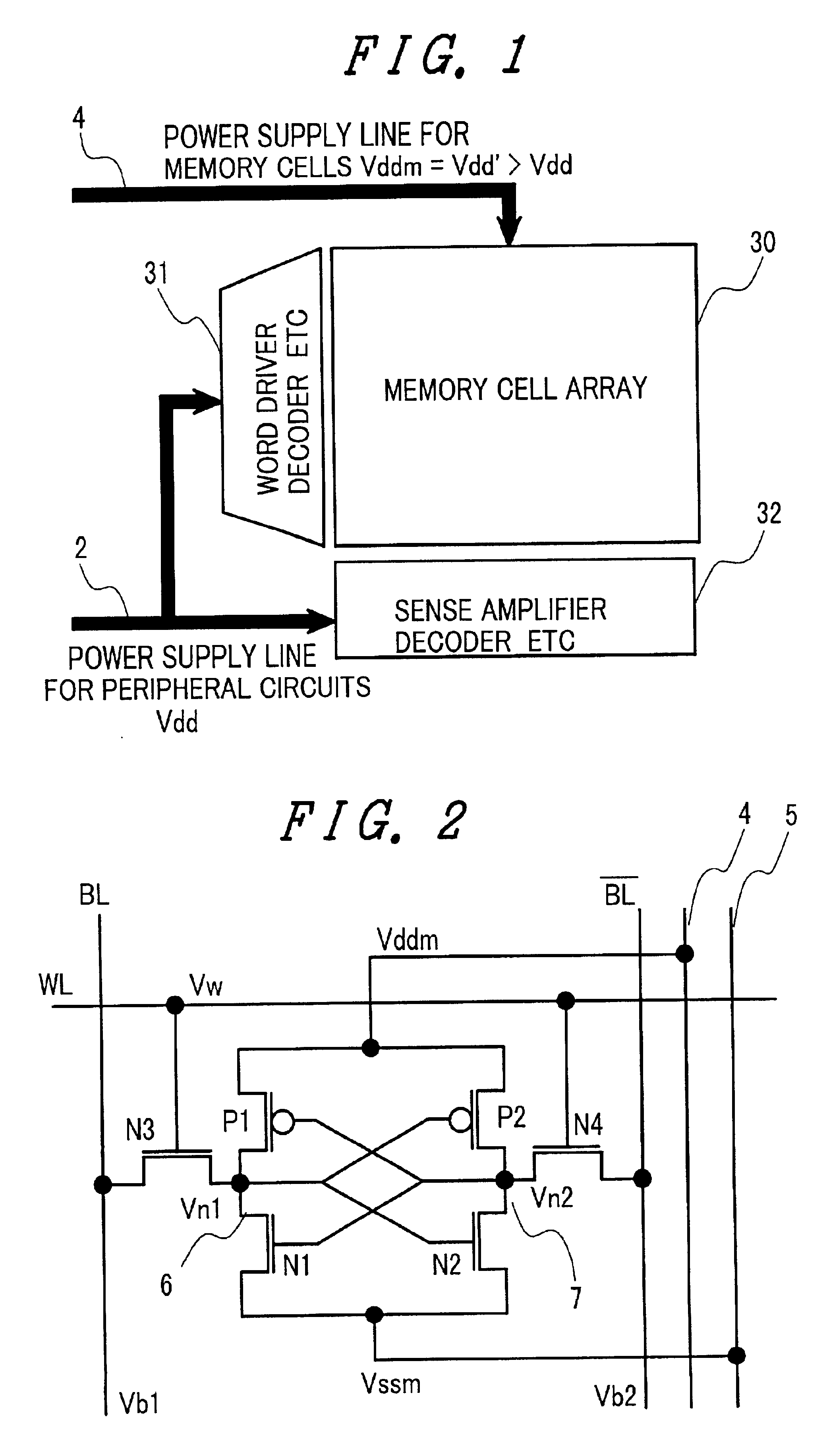
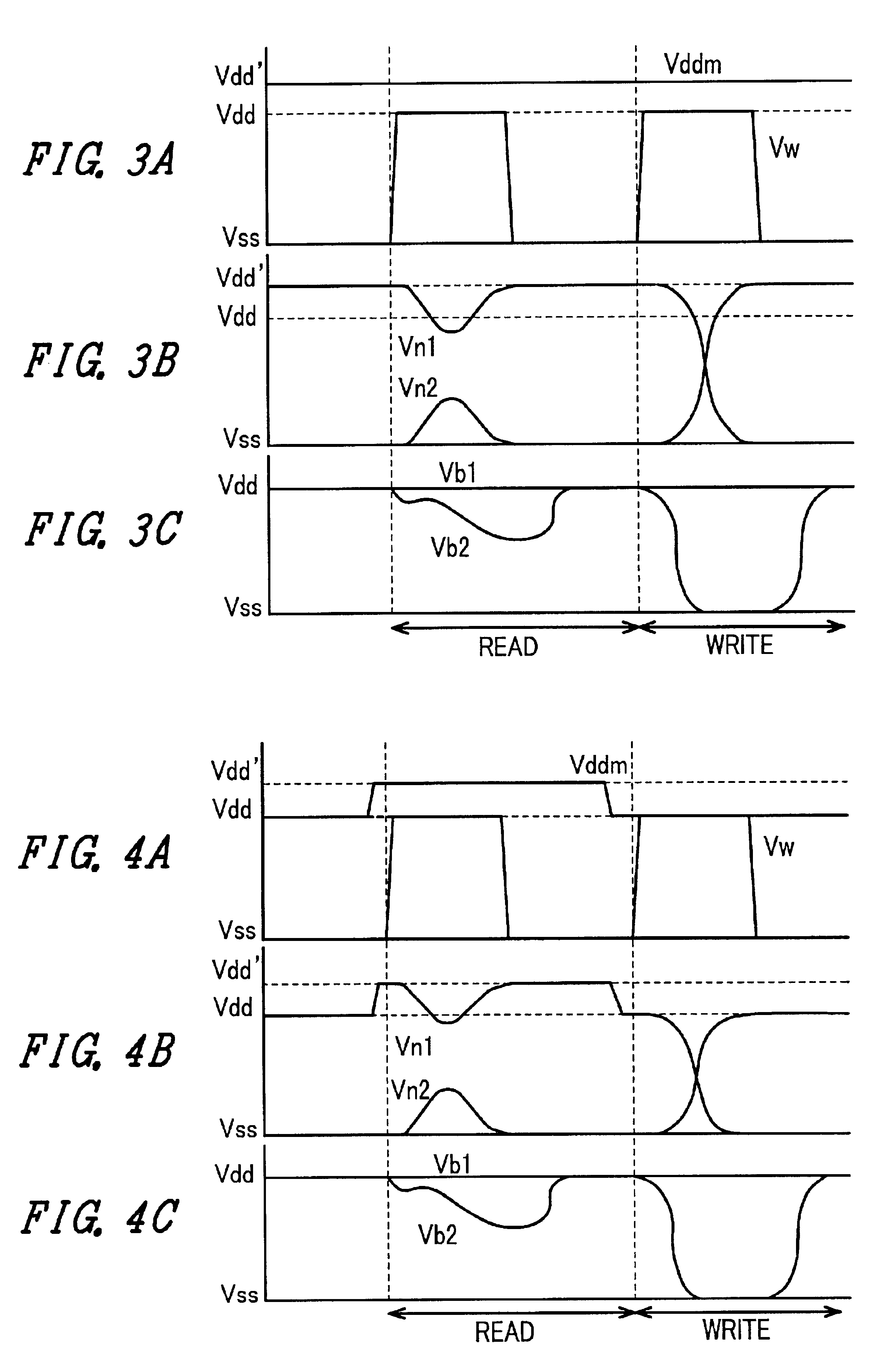
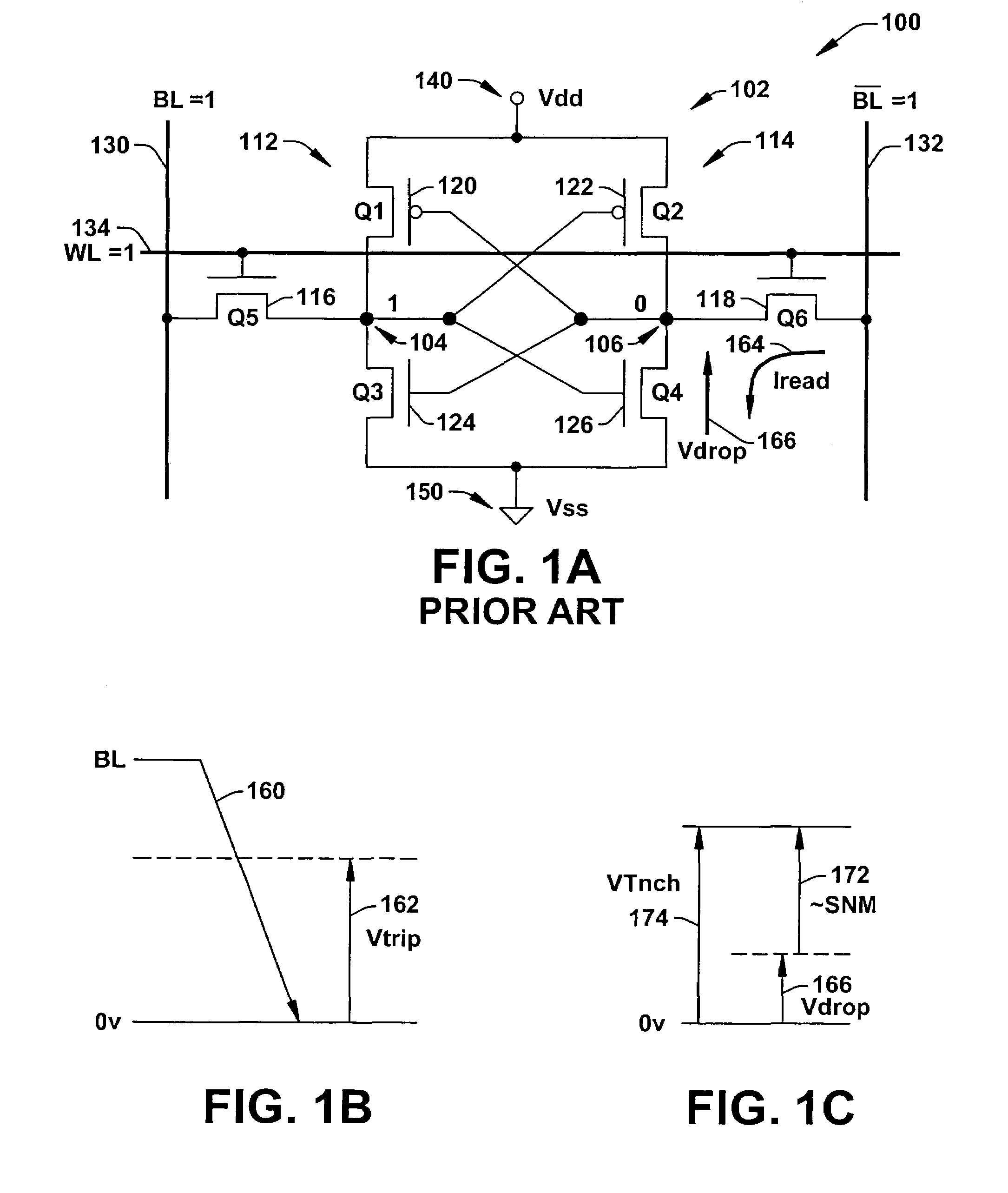
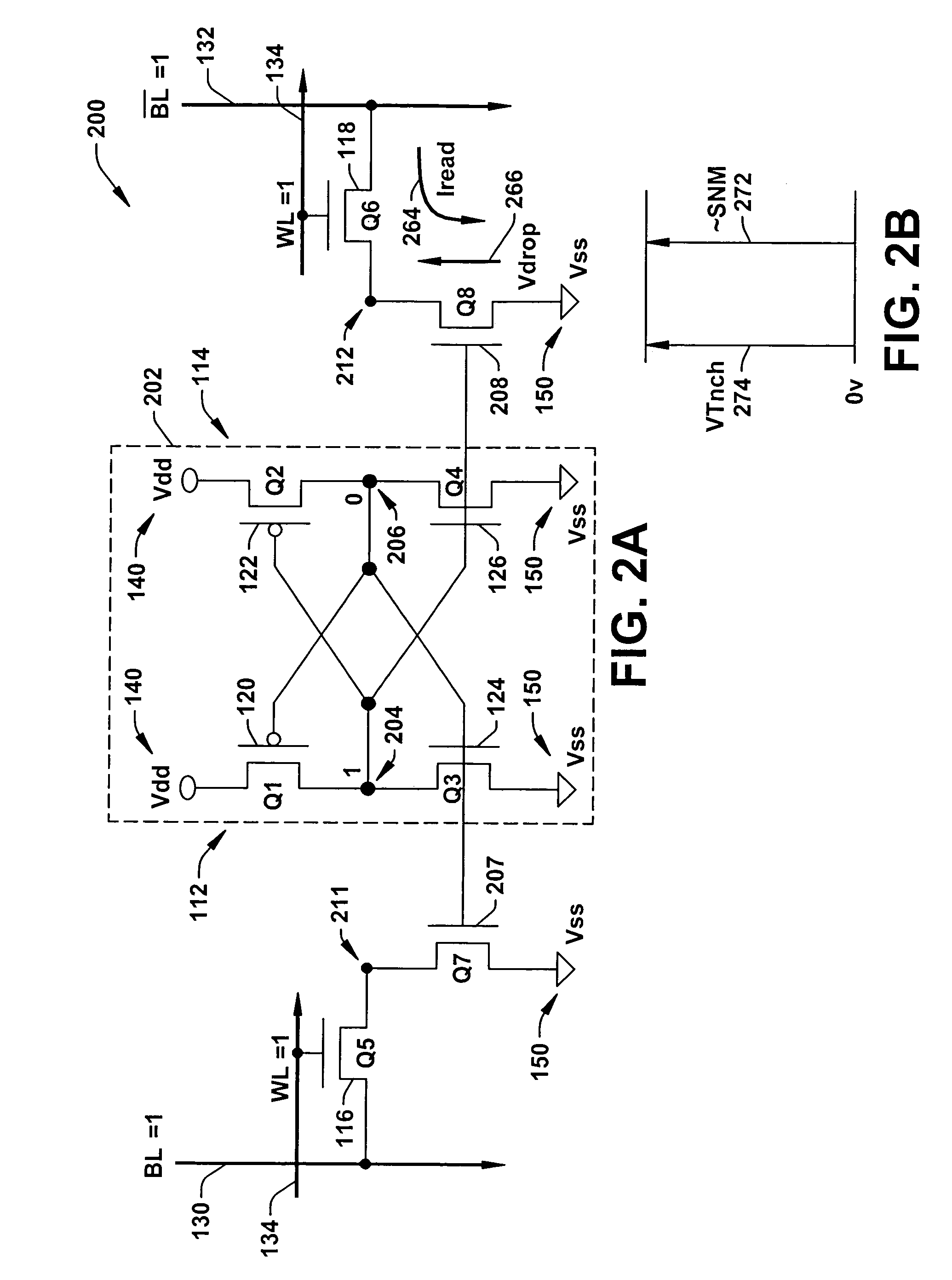
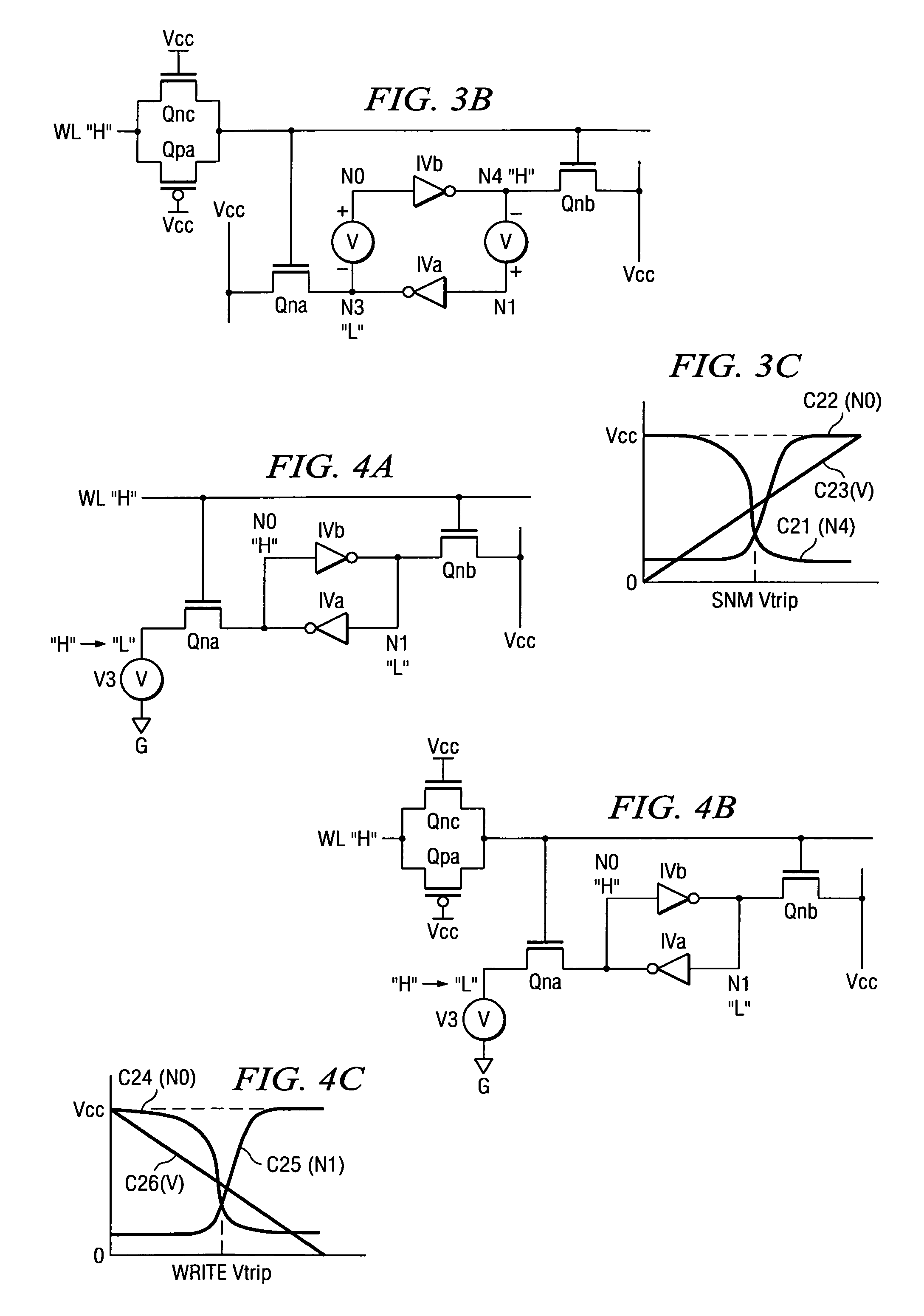
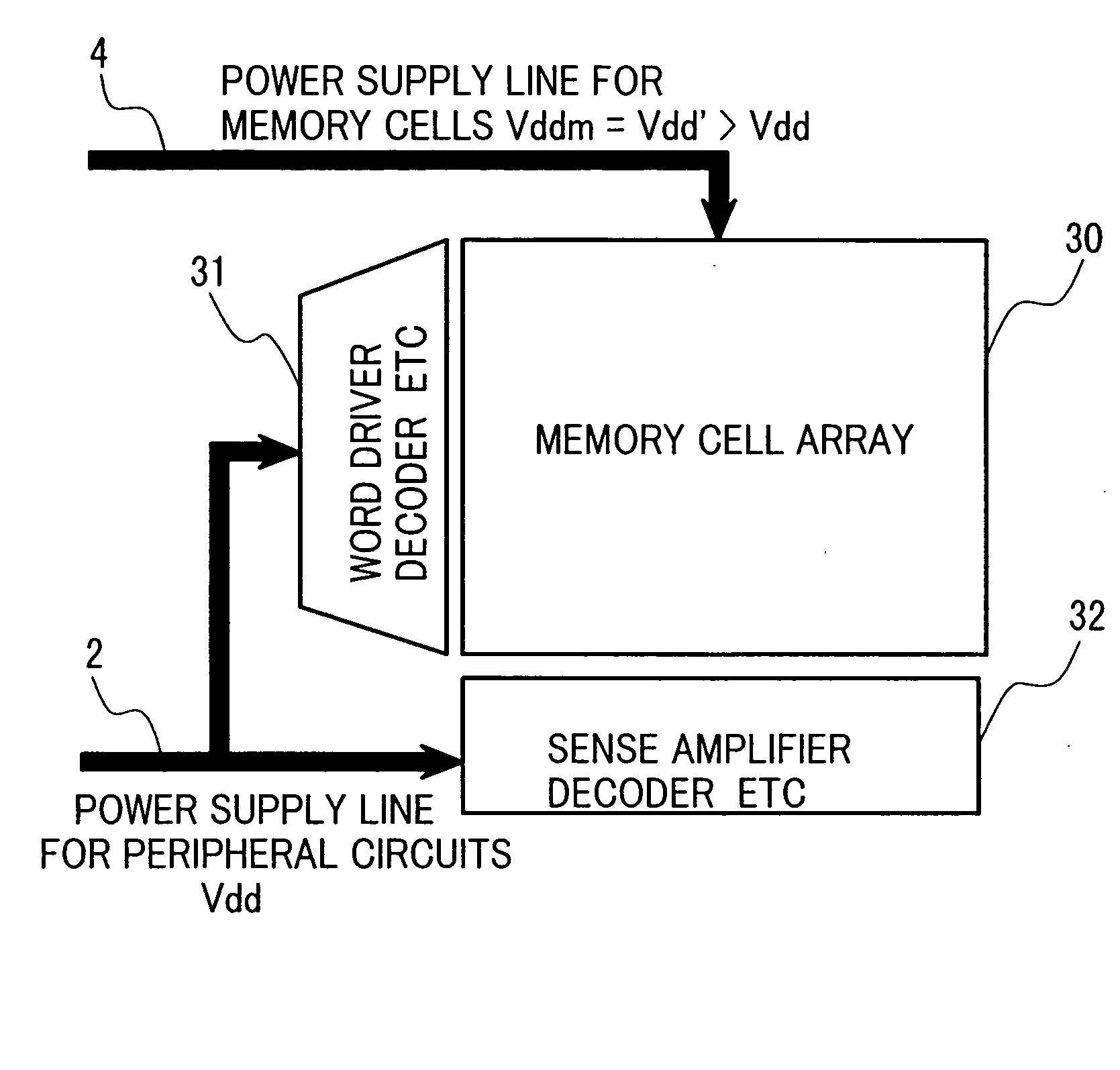
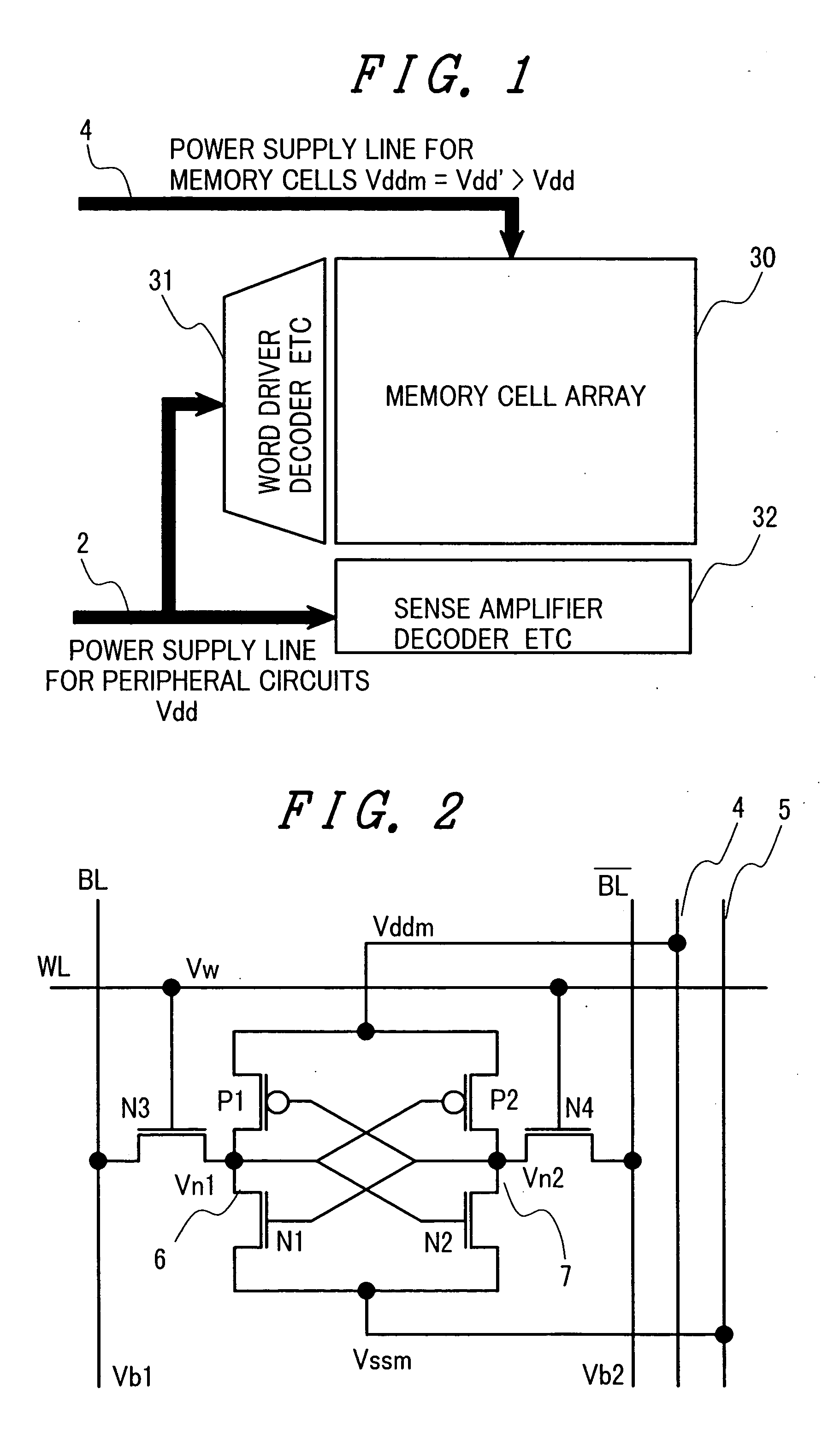
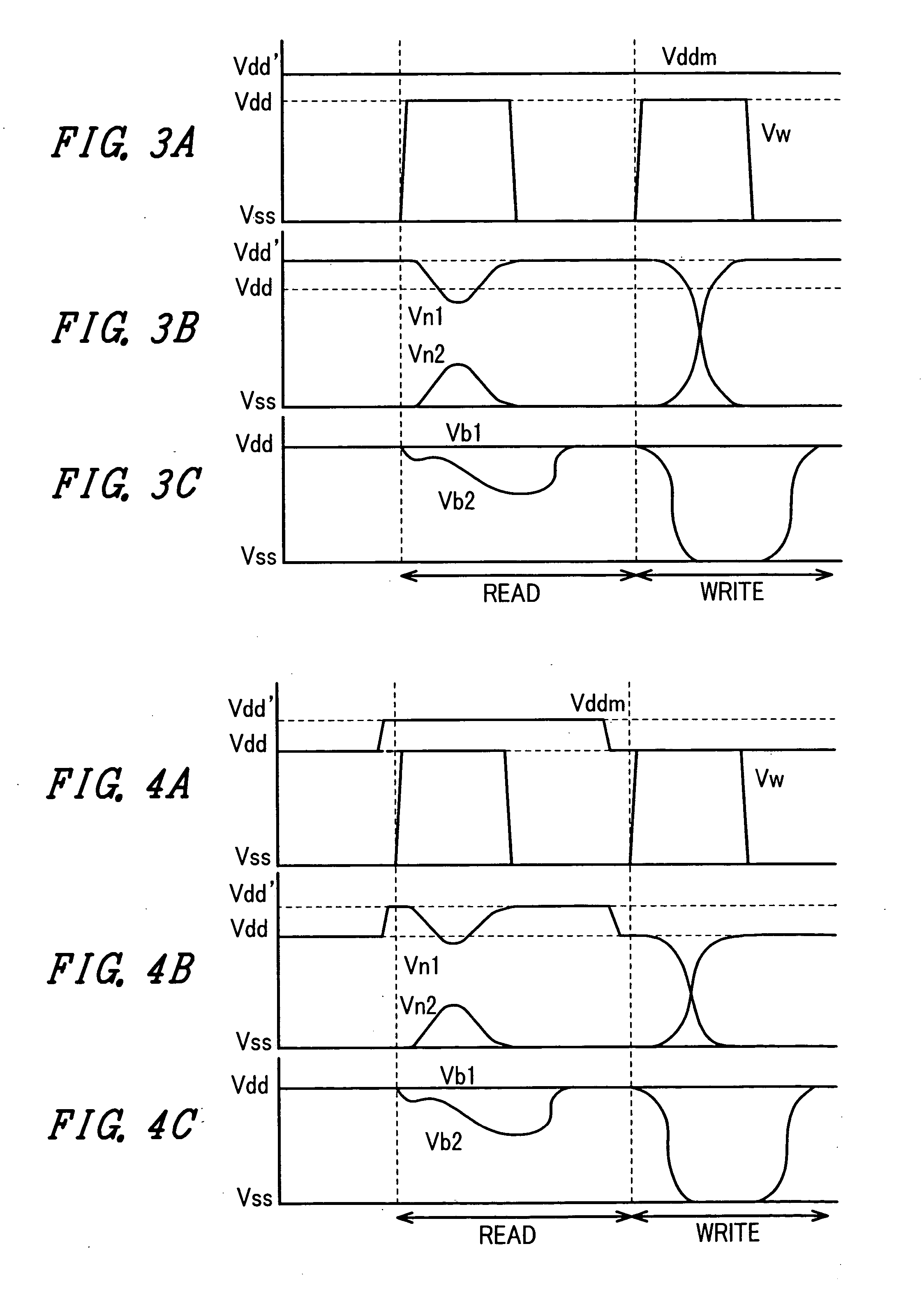
A memory using an SRAM memory cell intended for low-voltage operation is designed to decrease the threshold value of MOB transistors constituting the memory cell without substantial decrease in the static noise margin, which is the operational margin of the memory cell. To this end, a voltage Vdd' higher than a power supply voltage Vdd of a power supply line for peripheral circuits is supplied from a power supply line for memory cells as a power supply voltage for memory cells. Since the conductance of driver MOB transistors is in-creased, the threshold voltage of the MOB transistors within the memory cells can be reduced without reducing the static noise margin. Further the ratio of width between the driver MOS transistor and a transfer MOB transistor can be set to 1, thereby allowing a reduction in the memory cell area.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
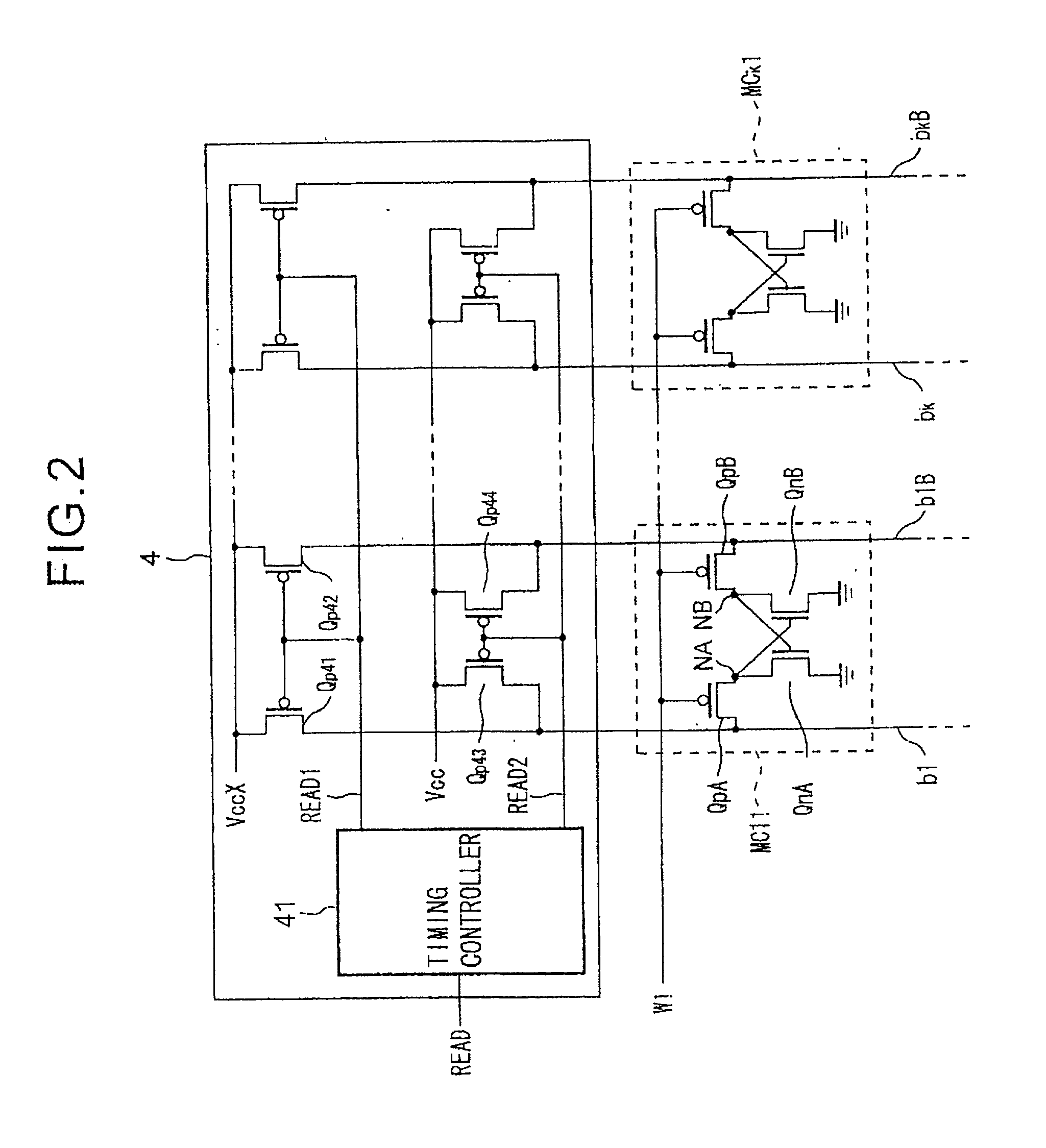
Semiconductor memory device with back gate potential control circuit for transistor in memory cell
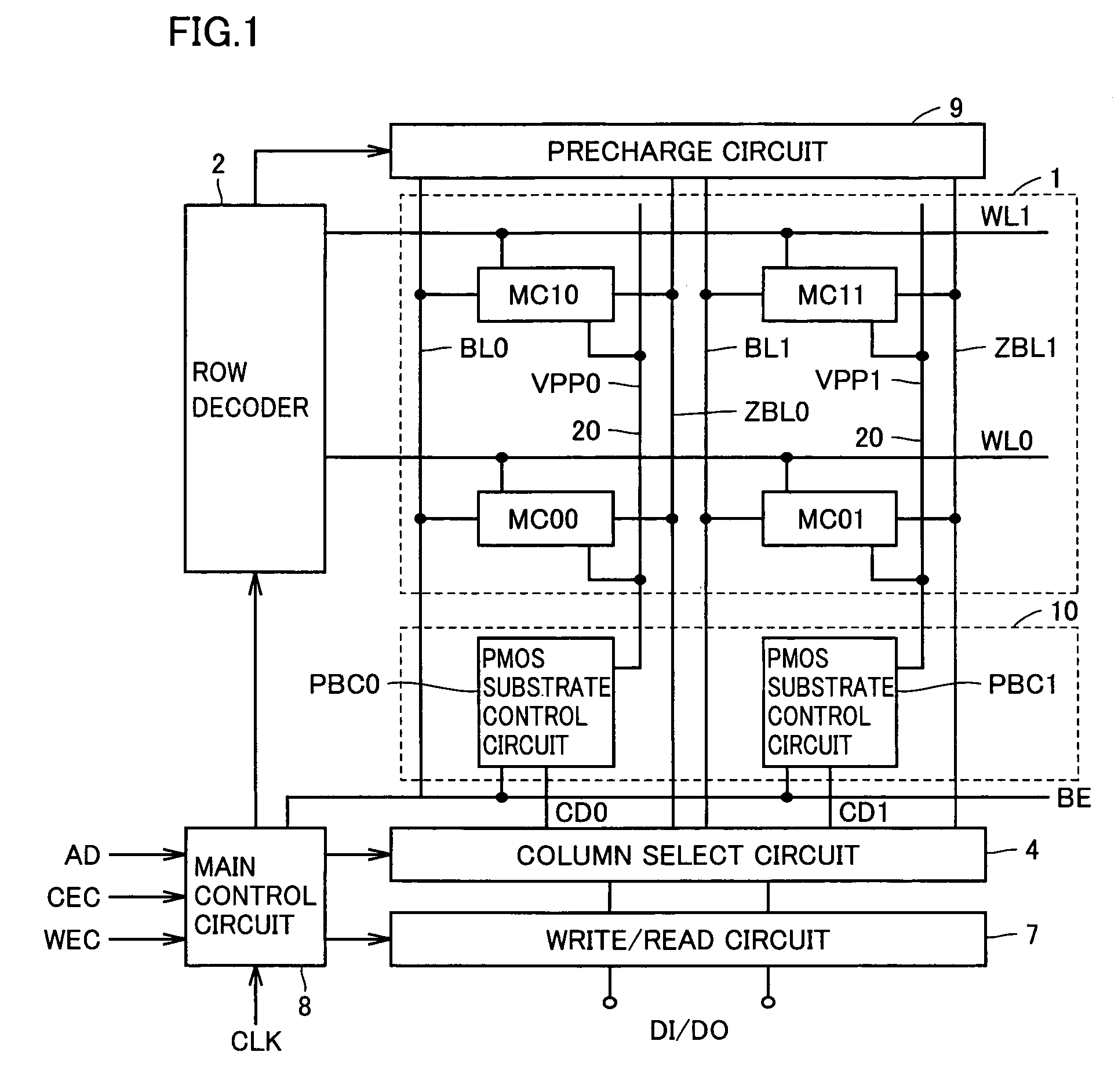
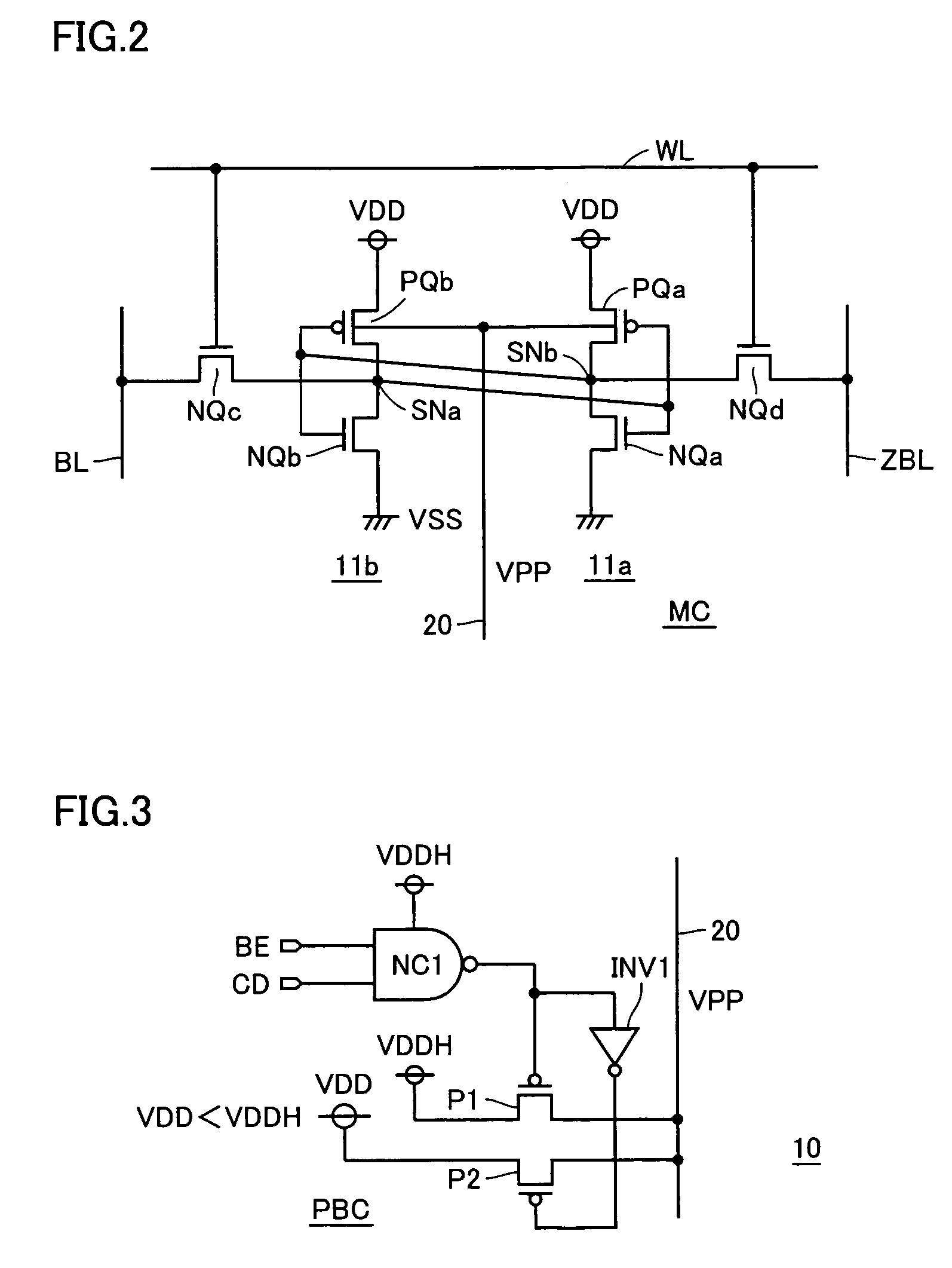
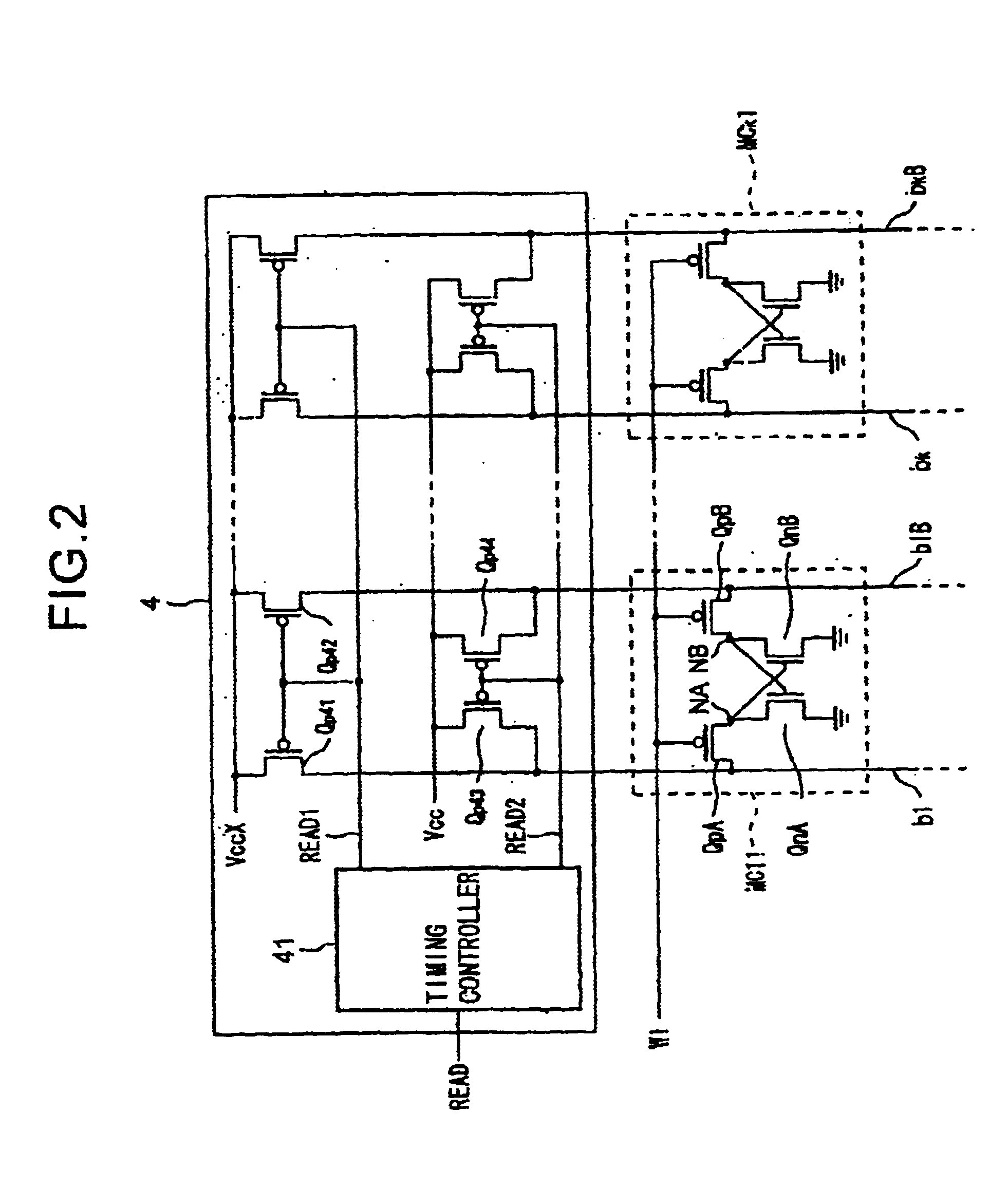
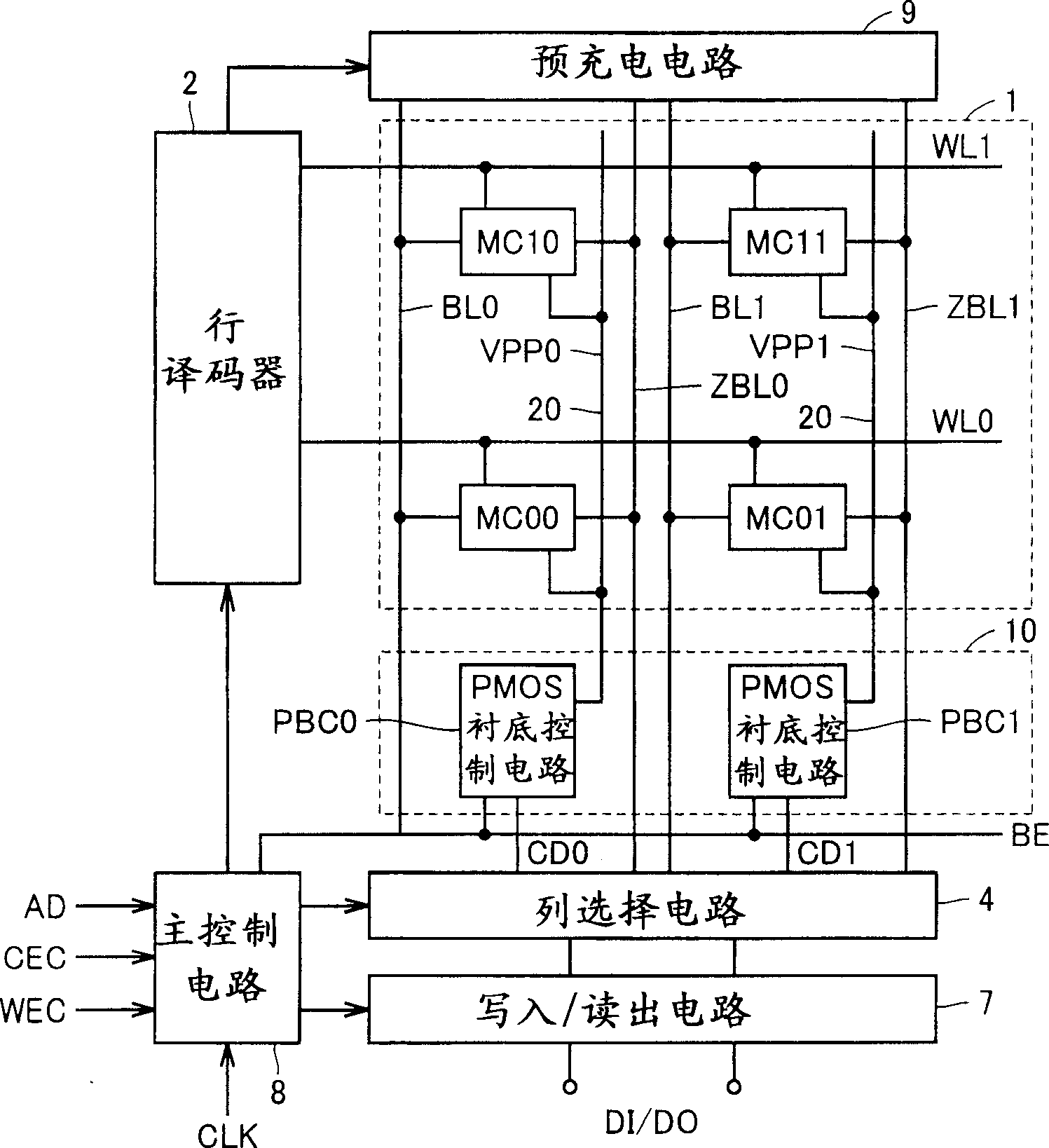
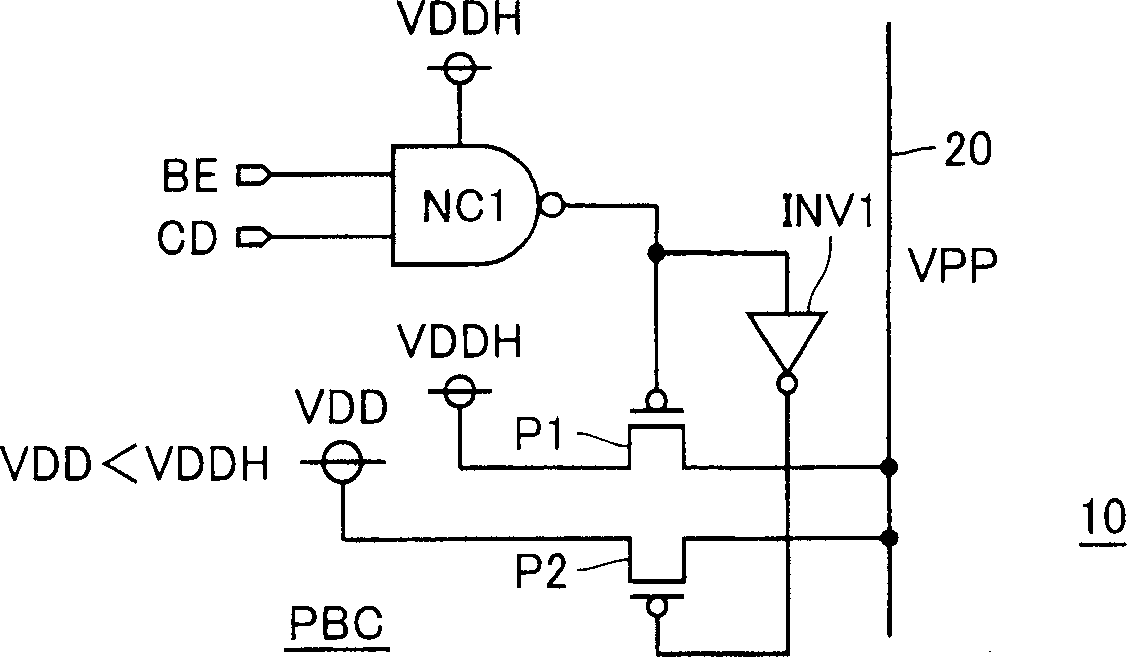
ActiveUS7079413B2High-speed and stable data readingHigh-speed and stable and writingTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringStatic noise margin
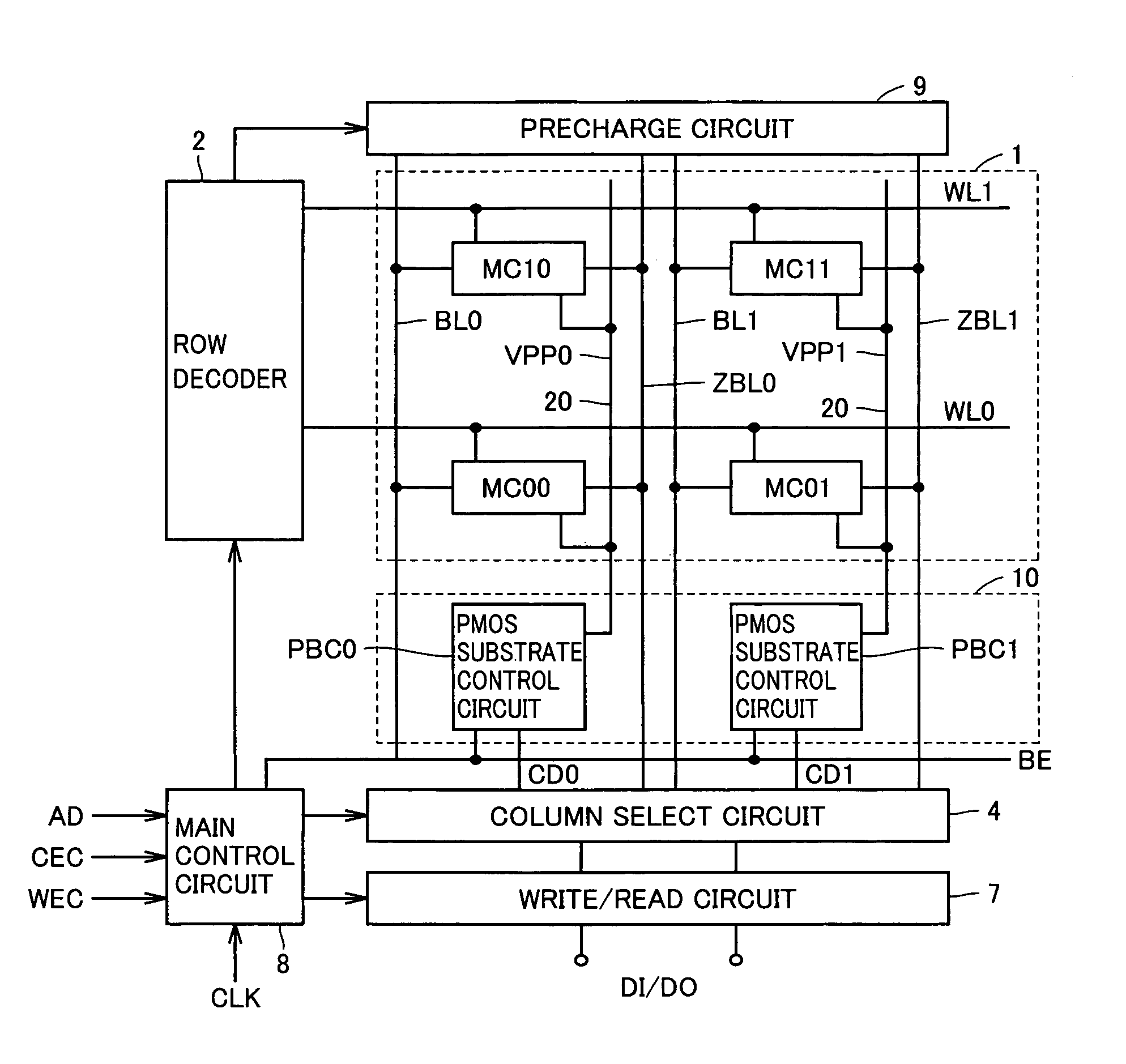
A substrate potential setting circuits are provided which control substrate potentials in units of columns of a memory cell array at least in data writing. Upon data writing, the potential of the substrate region of memory cell transistors on a selected column is changed to reduce the data holding characteristics (static noise margin) to ensure high-speed data writing to the memory cells. Data writing is performed at high speed without impairing stability of data retention.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
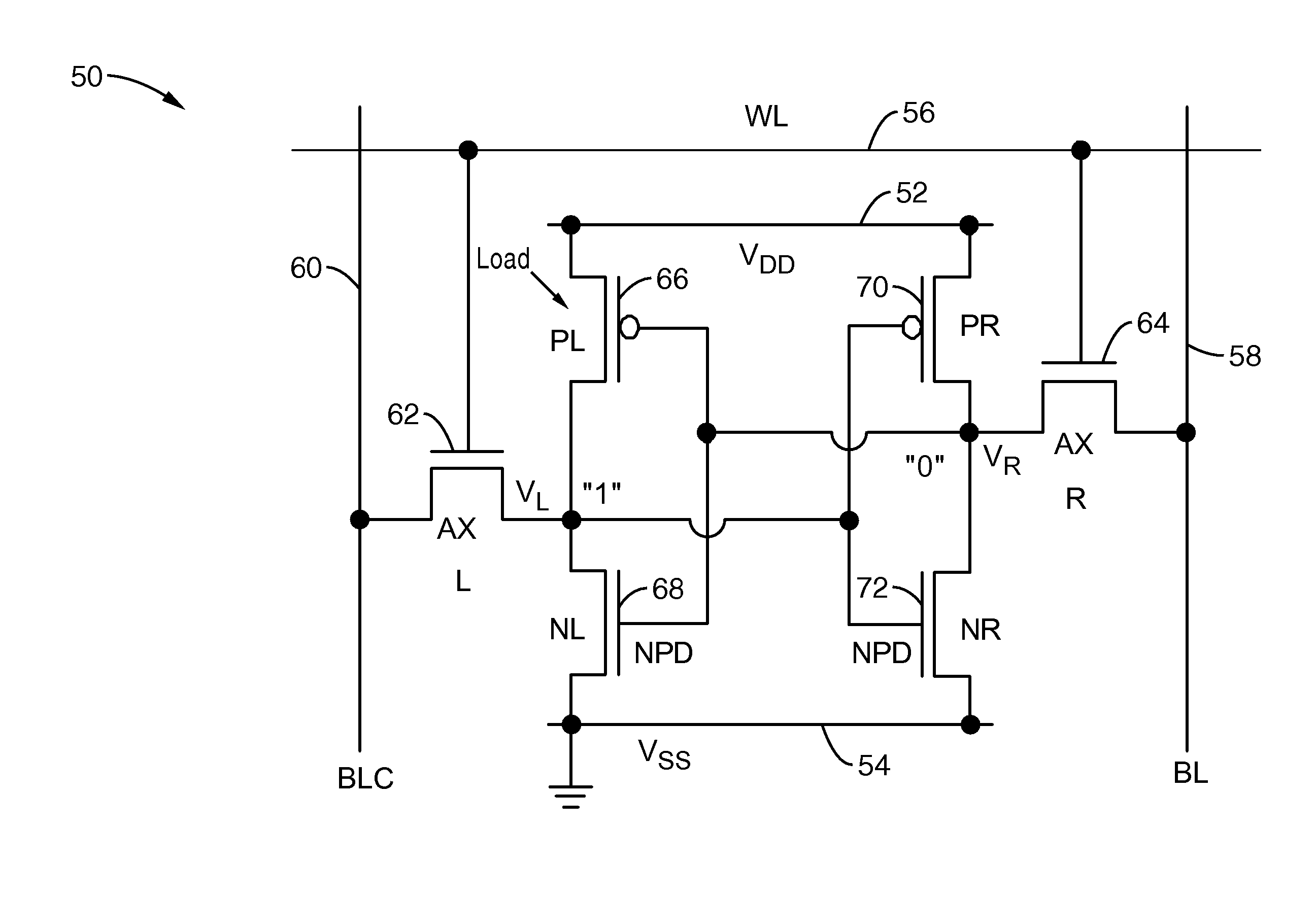
Finfet-based SRAM with feedback
InactiveUS20070183185A1Adequate noise marginReduce leakage currentTransistorSolid-state devicesNoise marginCell design
Intrinsic variations and challenging leakage control in current bulk-Si MOSFETs force undesired tradeoffs to be made and limit the scaling of SRAM circuits. Circuits and mechanisms are taught herein which improve leakage and noise margin in SRAM cells, such as those comprising either six-transistor (6-T) SRAM cell designs, or four-transistor (4-T) SRAM cell designs. The inventive SRAM cells utilize a feedback means coupling a portion of the storage node to a back-gate of an access transistor. Preferably feedback is coupled in this manner to both access transistors. SRAM cells designed with this built-in feedback achieve significant improvements in cell static noise margin (SNM) without area penalty. Use of the feedback scheme also results in the creation of a practical 4-T FinFET-based SRAM cell that achieves sub-100 pA per-cell standby current and offers similar improvements in SNM as the 6-T cell with feedback.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
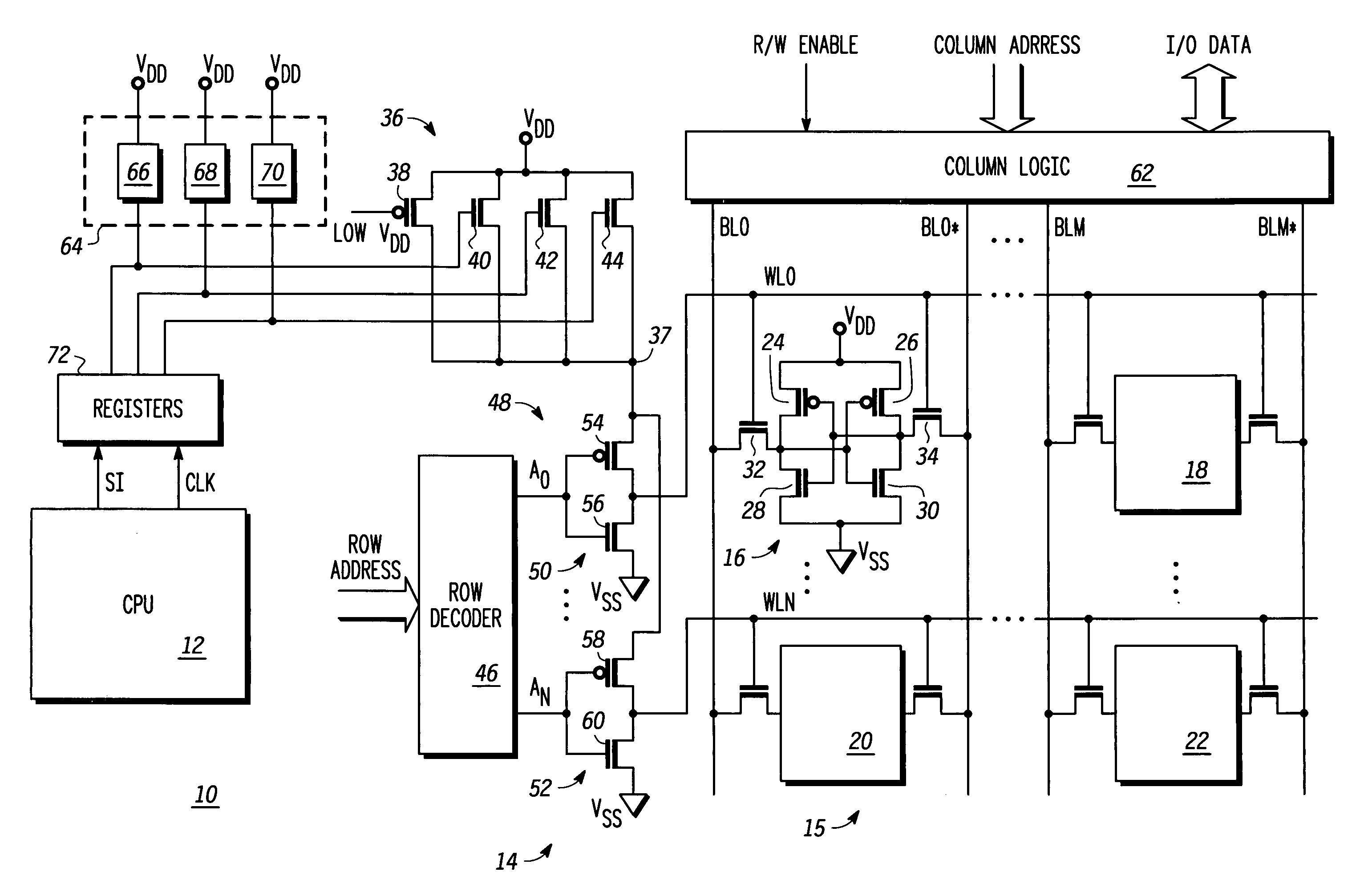
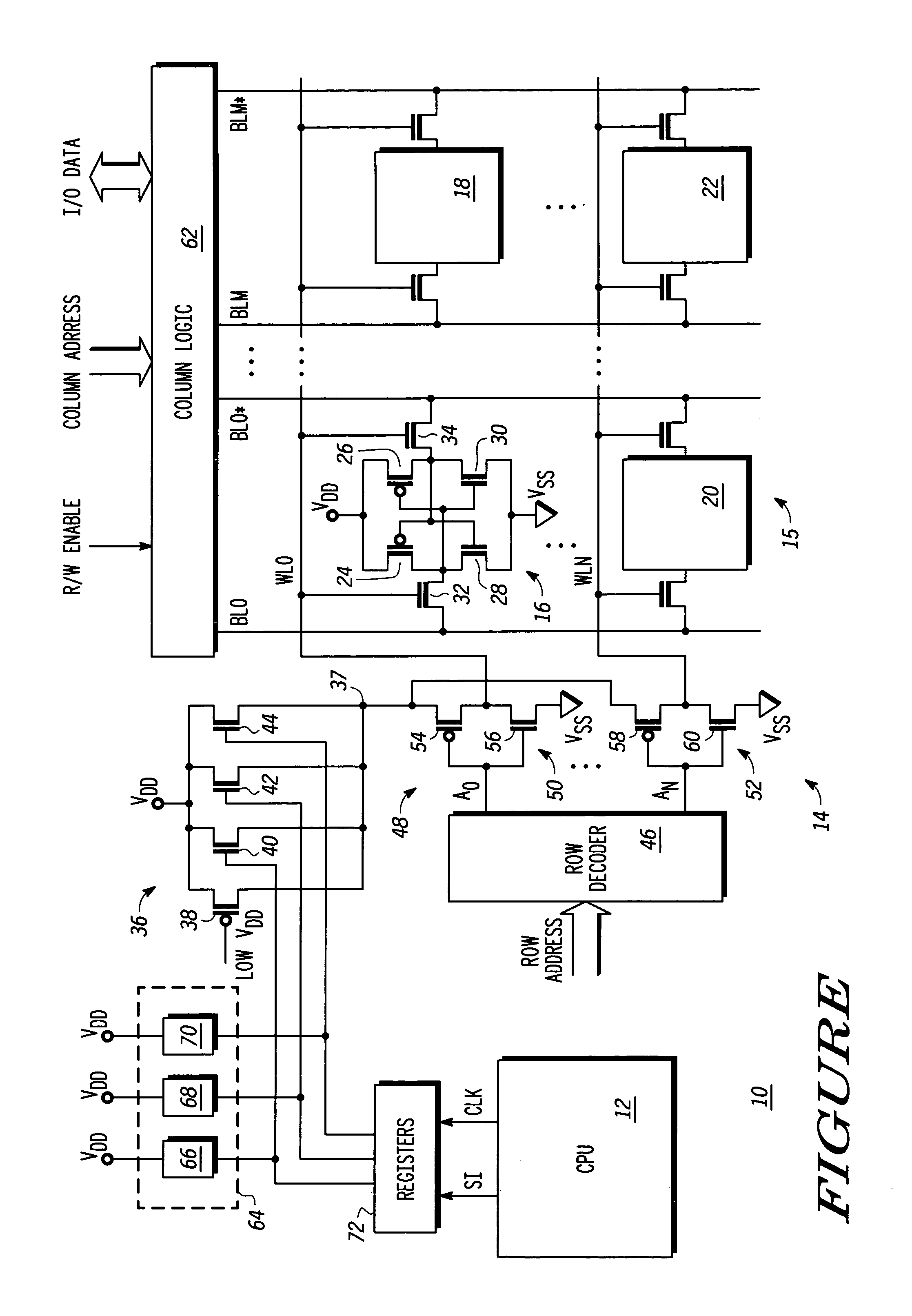
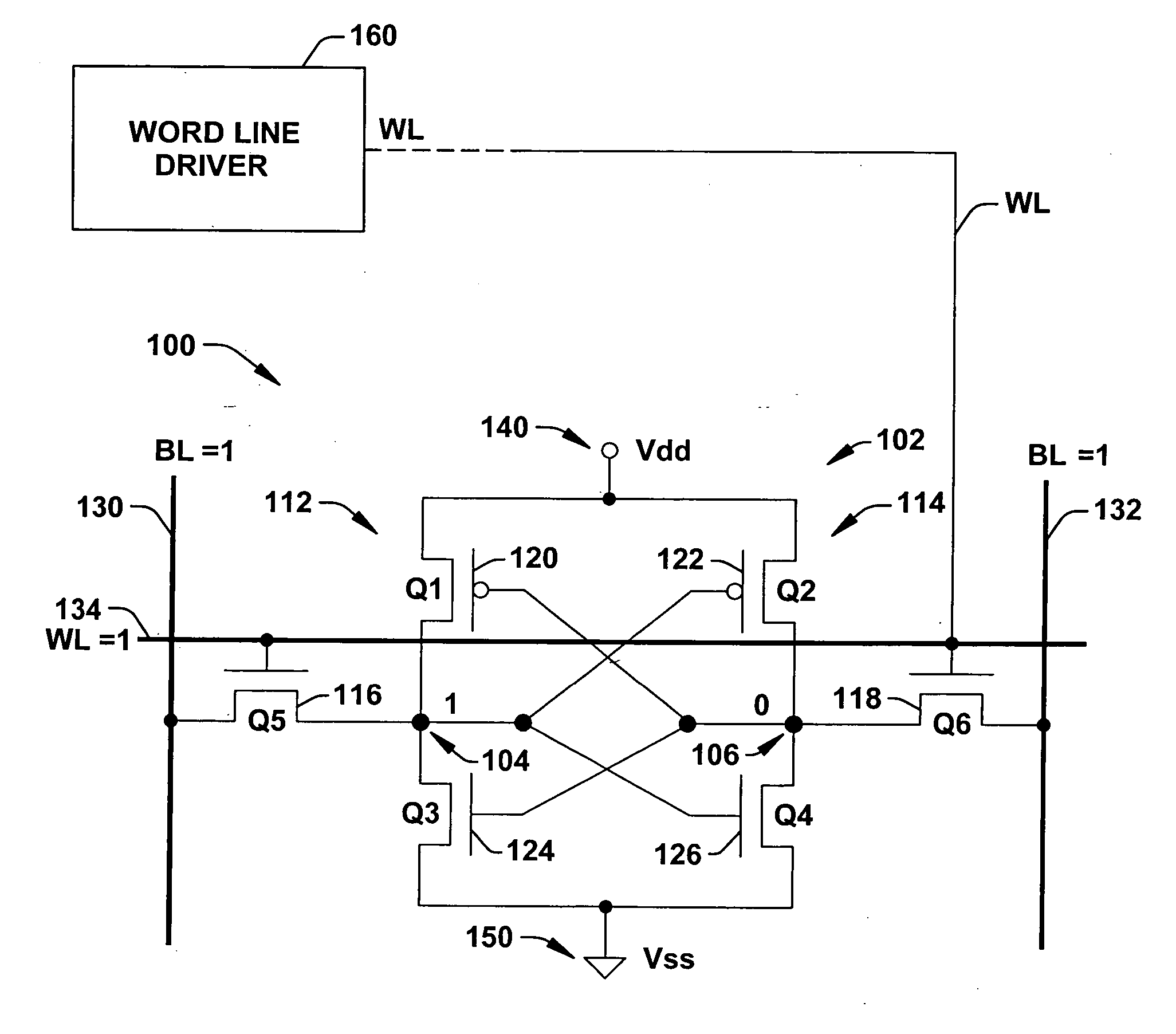
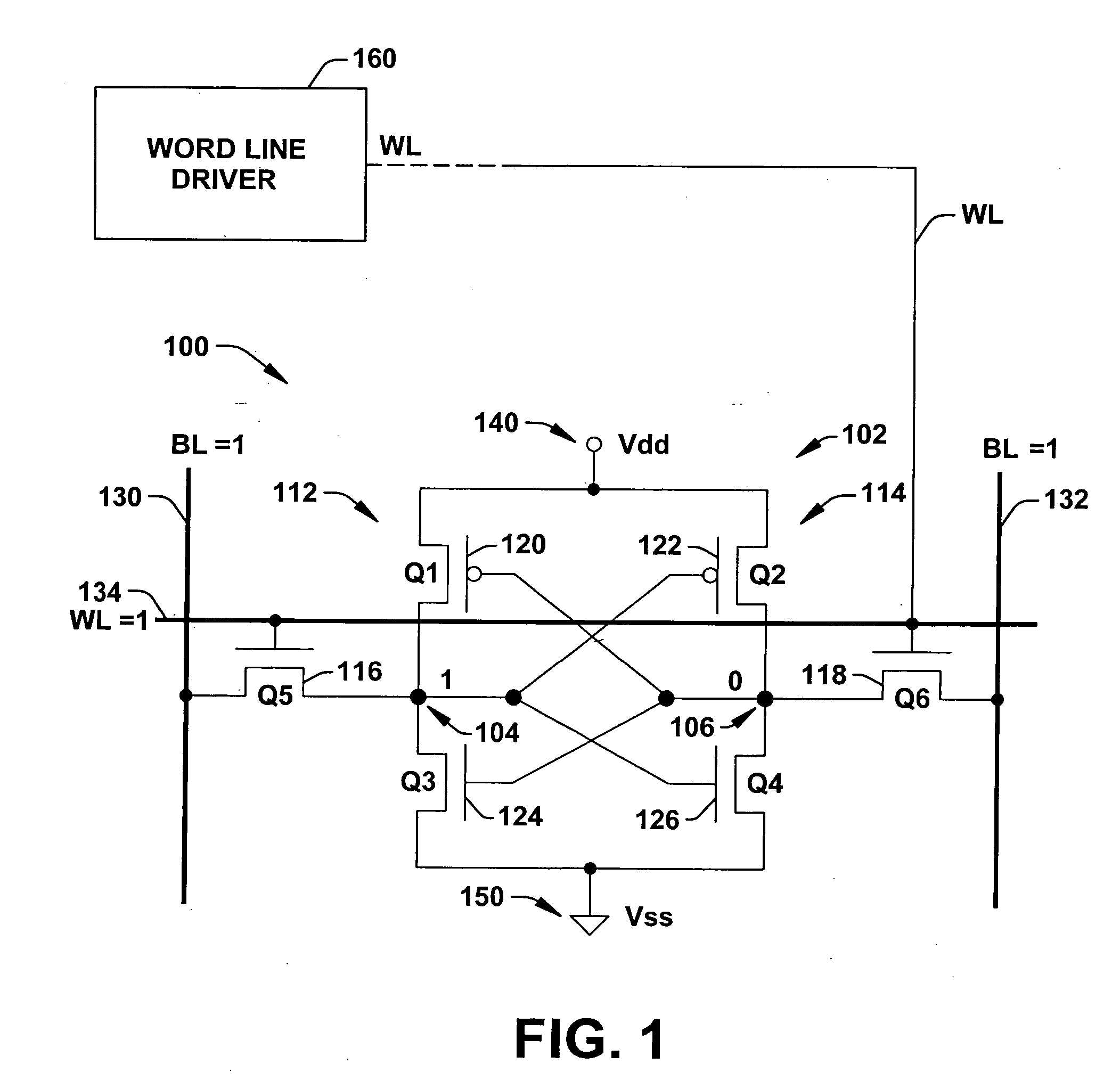
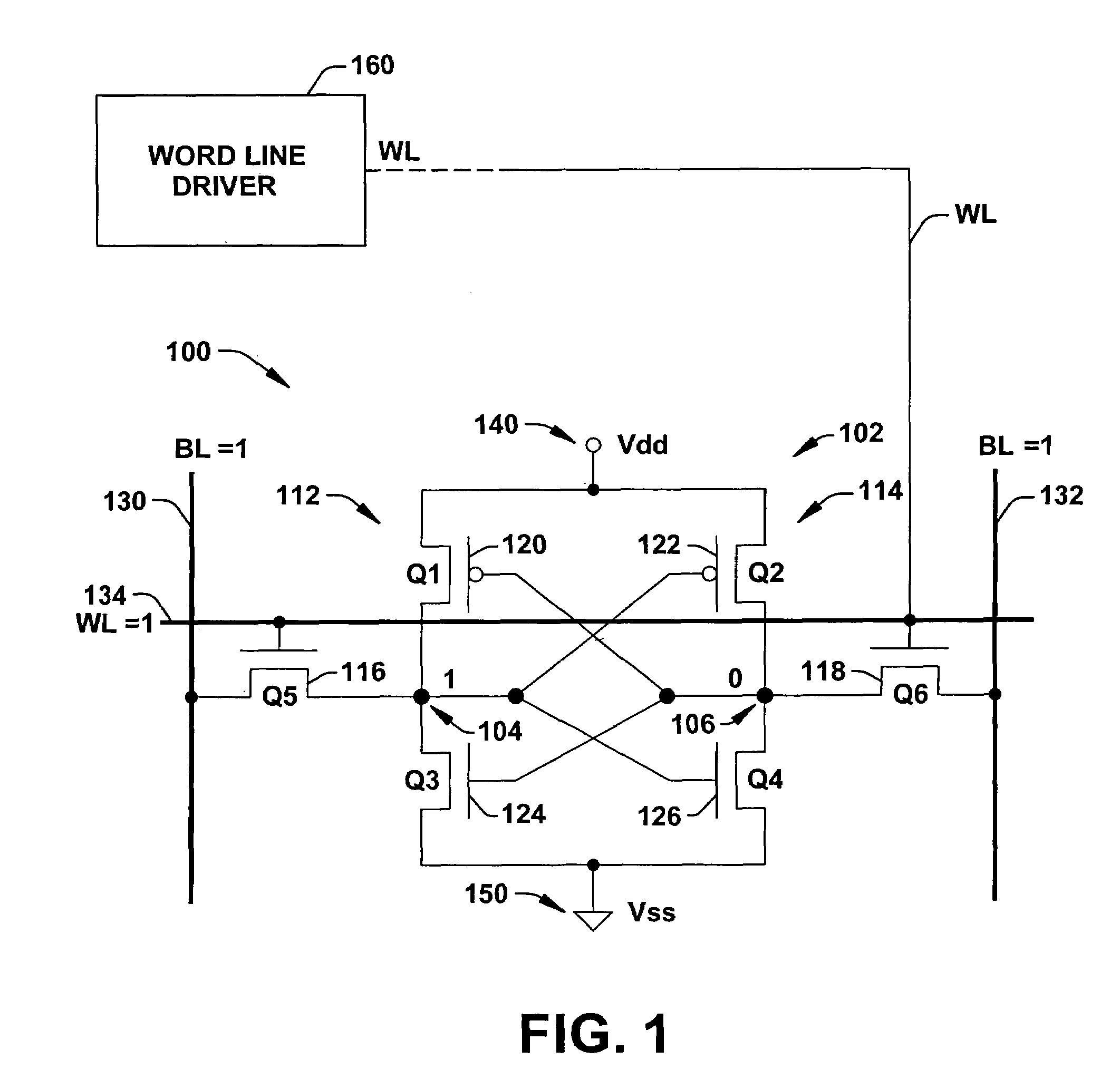
Word line driver circuit for a static random access memory and method therefor
ActiveUS7085175B2Improve static noise marginReduce decreaseRead-only memoriesDigital storageStatic random-access memoryLow voltage
A static random access memory (14) has a normal mode of operation and a low voltage mode of operation. A memory array (15) includes memory cells (16) coupled to a first power supply node (VDD) for receiving a power supply voltage. A plurality of word line drivers is coupled to word lines of the memory array (15) and to a second power supply node (37). A word line driver voltage reduction circuit (36) has an input coupled to the first power supply node (VDD) and an output coupled to the second power supply node (37) for reducing a voltage on the output in relation to a voltage on the input in response to a low power supply voltage signal, and thus improving a static noise margin of the memory cells (16).
Owner:NXP USA INC
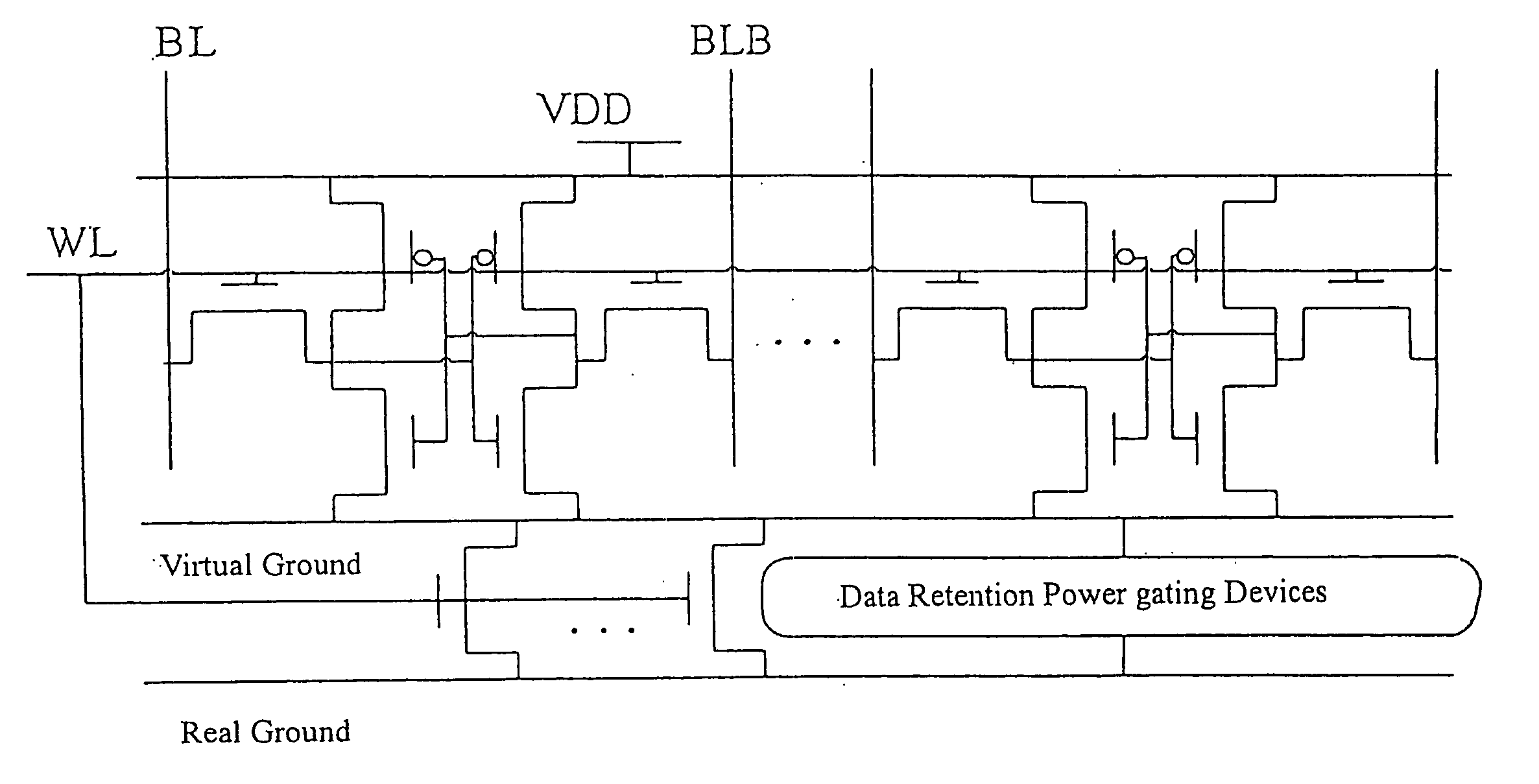
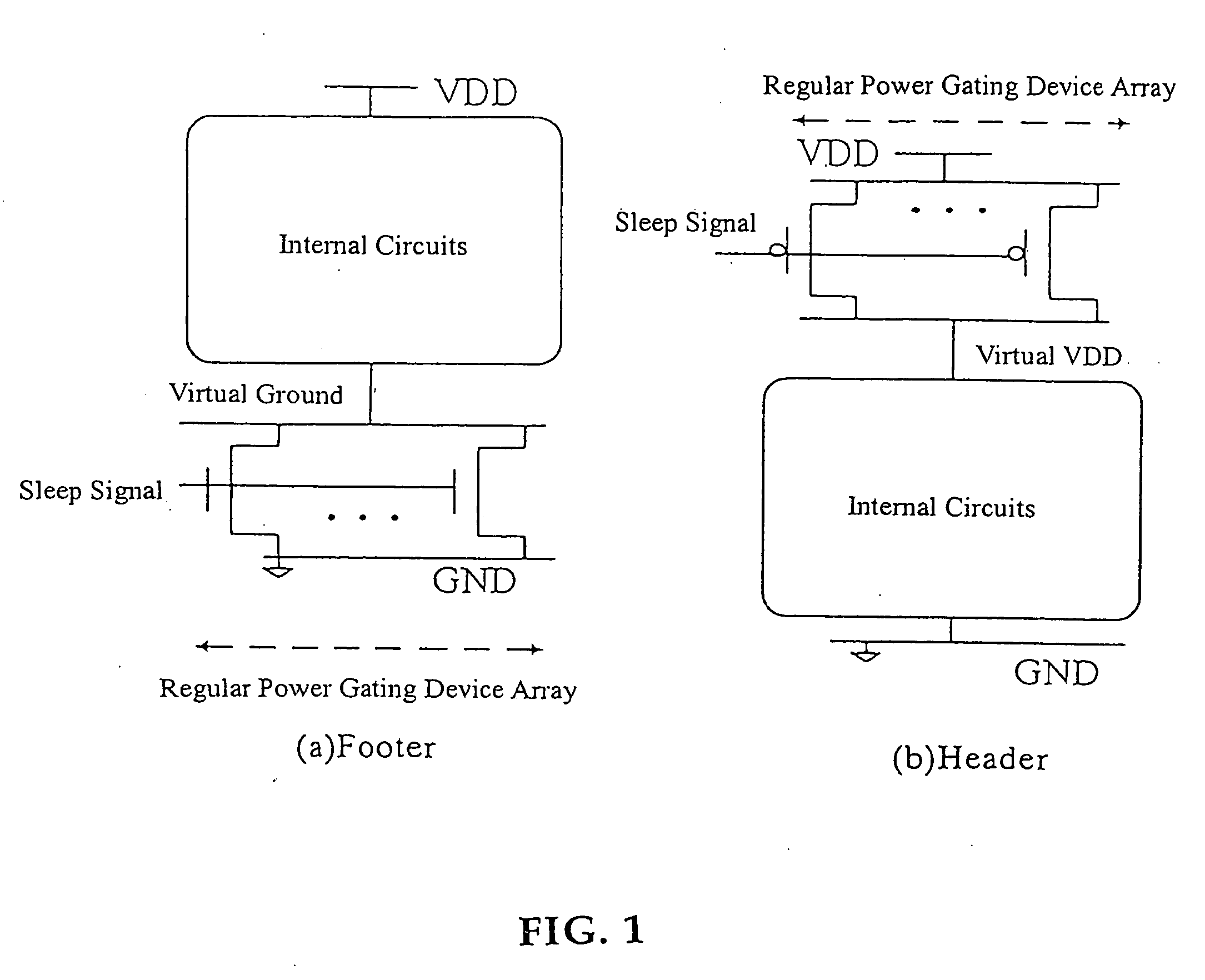
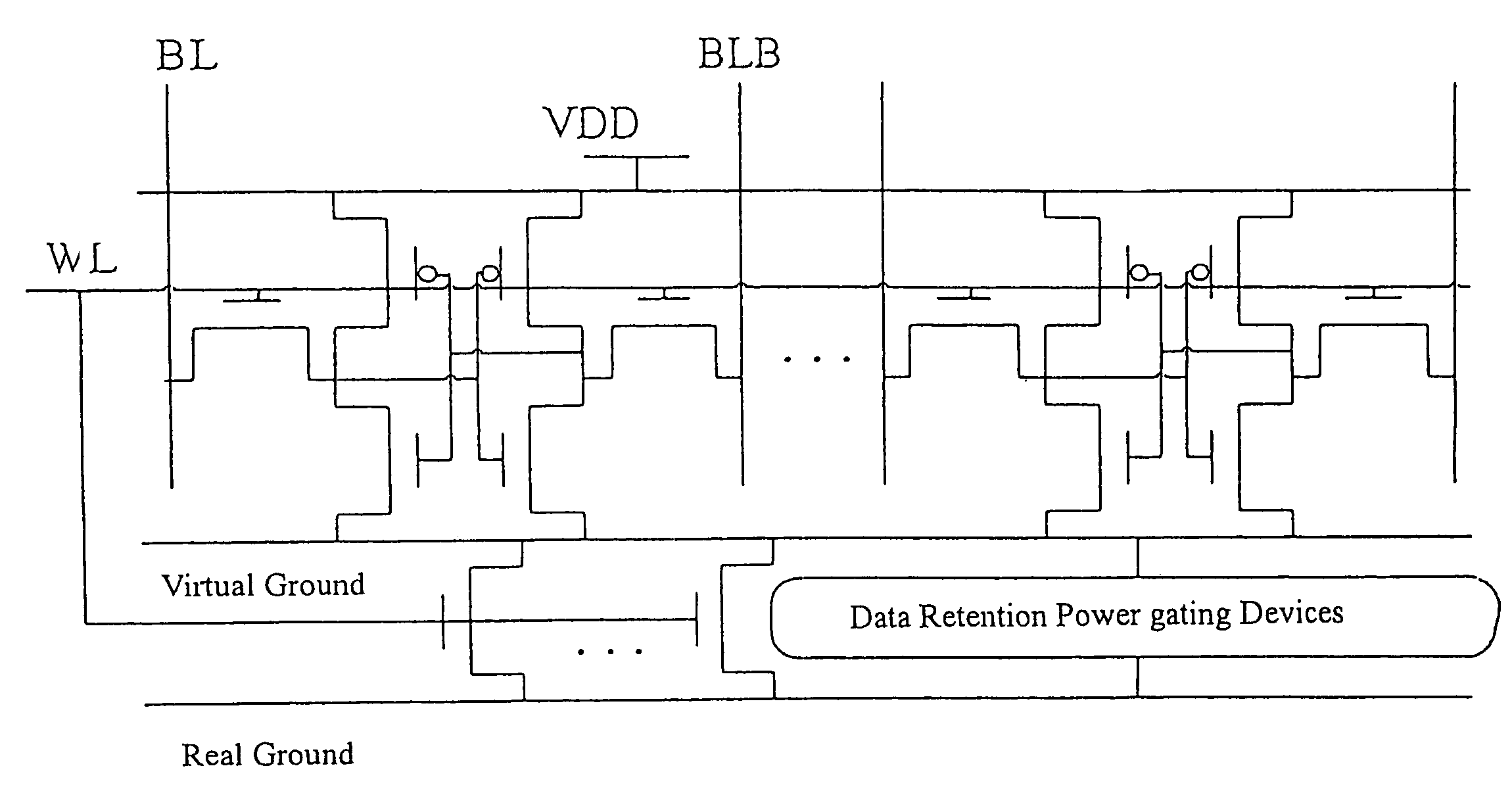
Power gating structure having data retention and intermediate modes
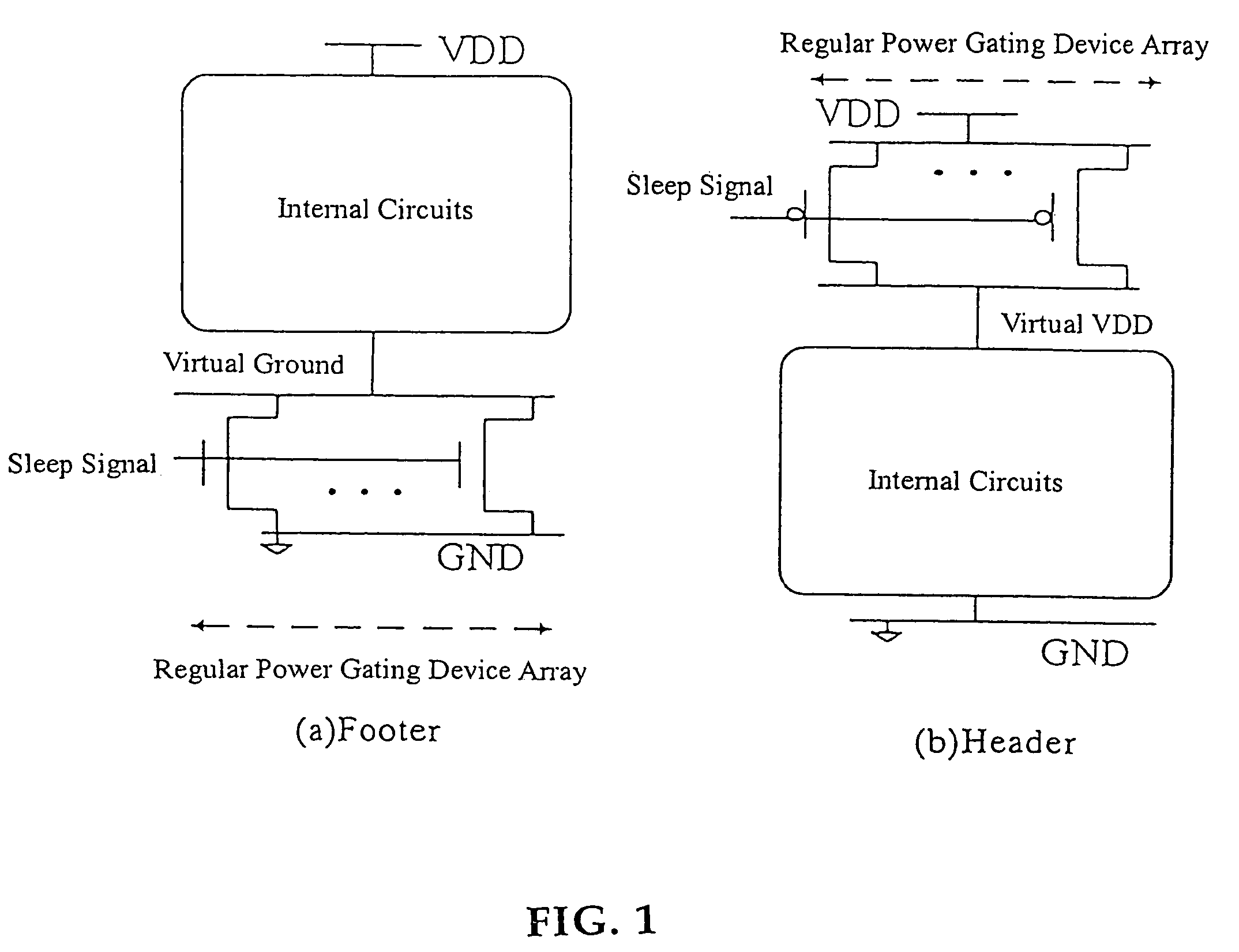
InactiveUS20060119393A1Reduce leakage currentExtend lifetime of battery packReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalStatic noise marginOperation mode
The present invention provides a power gating structure having data retention and intermediate modes and able to operate under multiple modes. A conventional power gating structure has only turn-on and turn-off functions, and is used to suppress a leakage current problem which has become more and more serious in advance manufacture processes, under a turn-off mode. However, in a memory circuit, such as latch, register and SRAM, when the power gate is turned off, a new power gating structure is required for data retention. The power gating structure of the present invention can be set into one of 4 different operational modes: a data retention mode for maintaining the static noise margin of the memory, an intermediate mode for reducing the interference on ground and power levels, an active mode used when the circuit operates in normal condition, and a standby mode used when the circuit does not operate.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
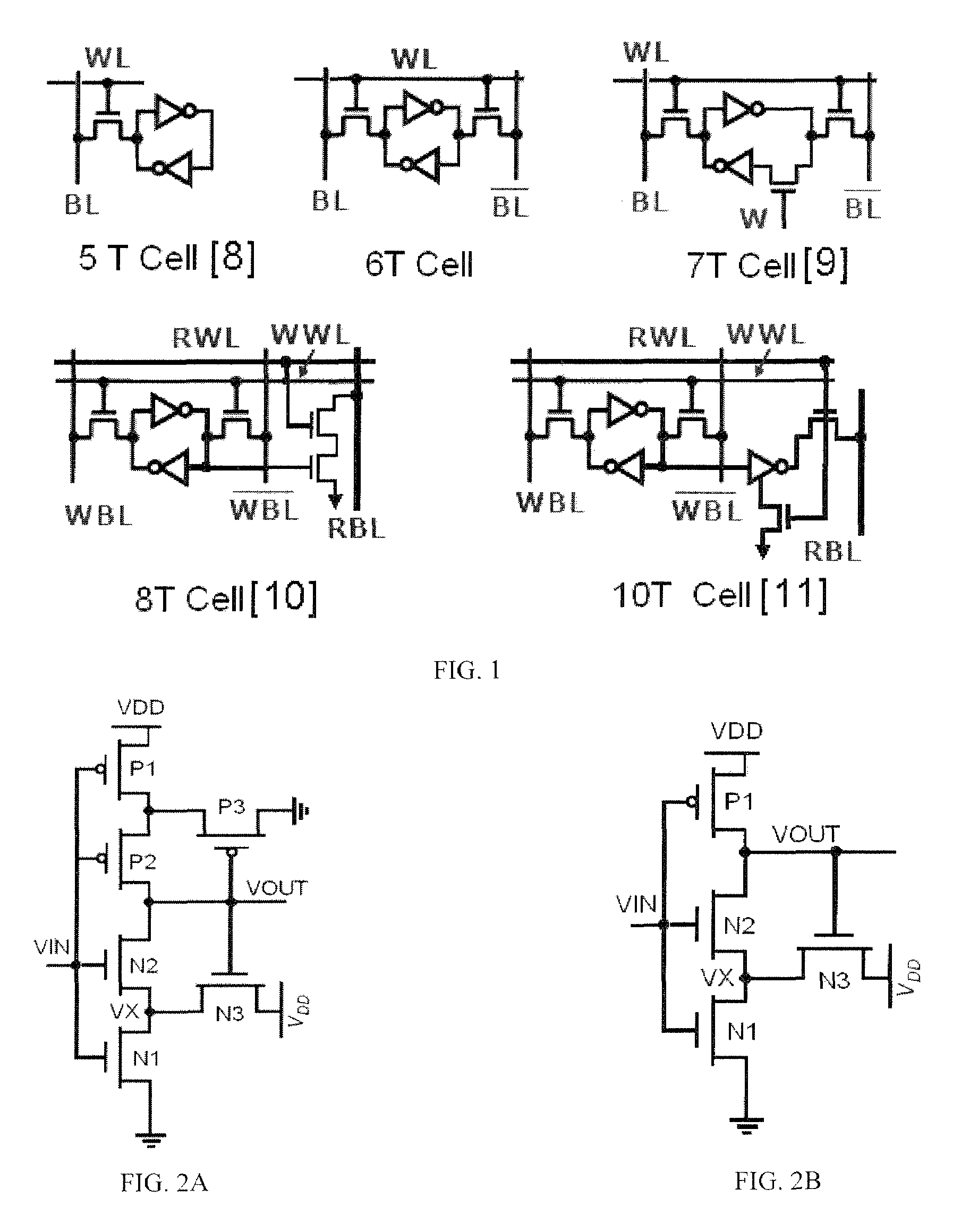
Memory cell with built-in process variation tolerance
InactiveUS7672152B1Less sensitive to process variationIncreased process variation toleranceDigital storageSub thresholdStatic random-access memory
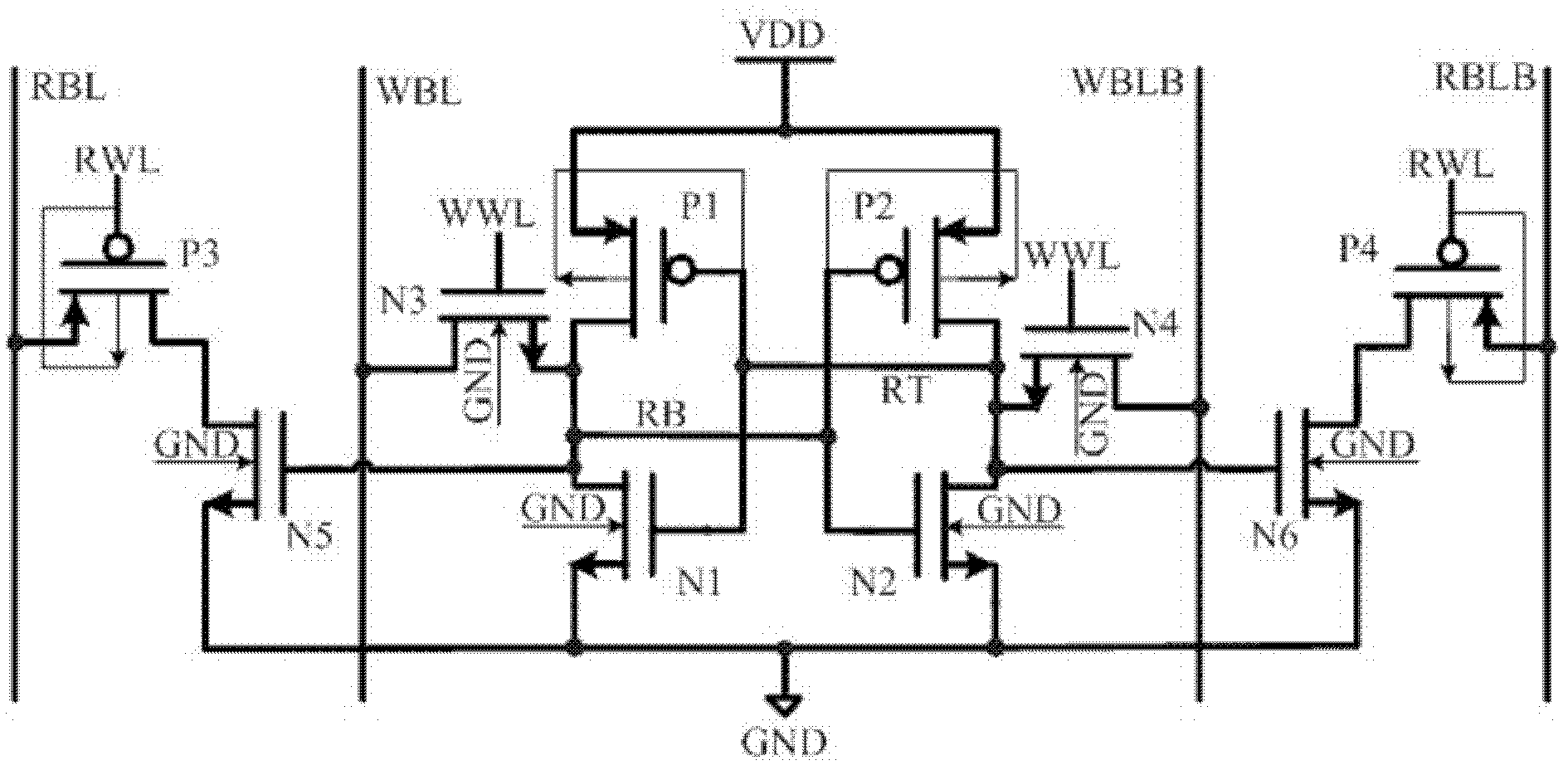
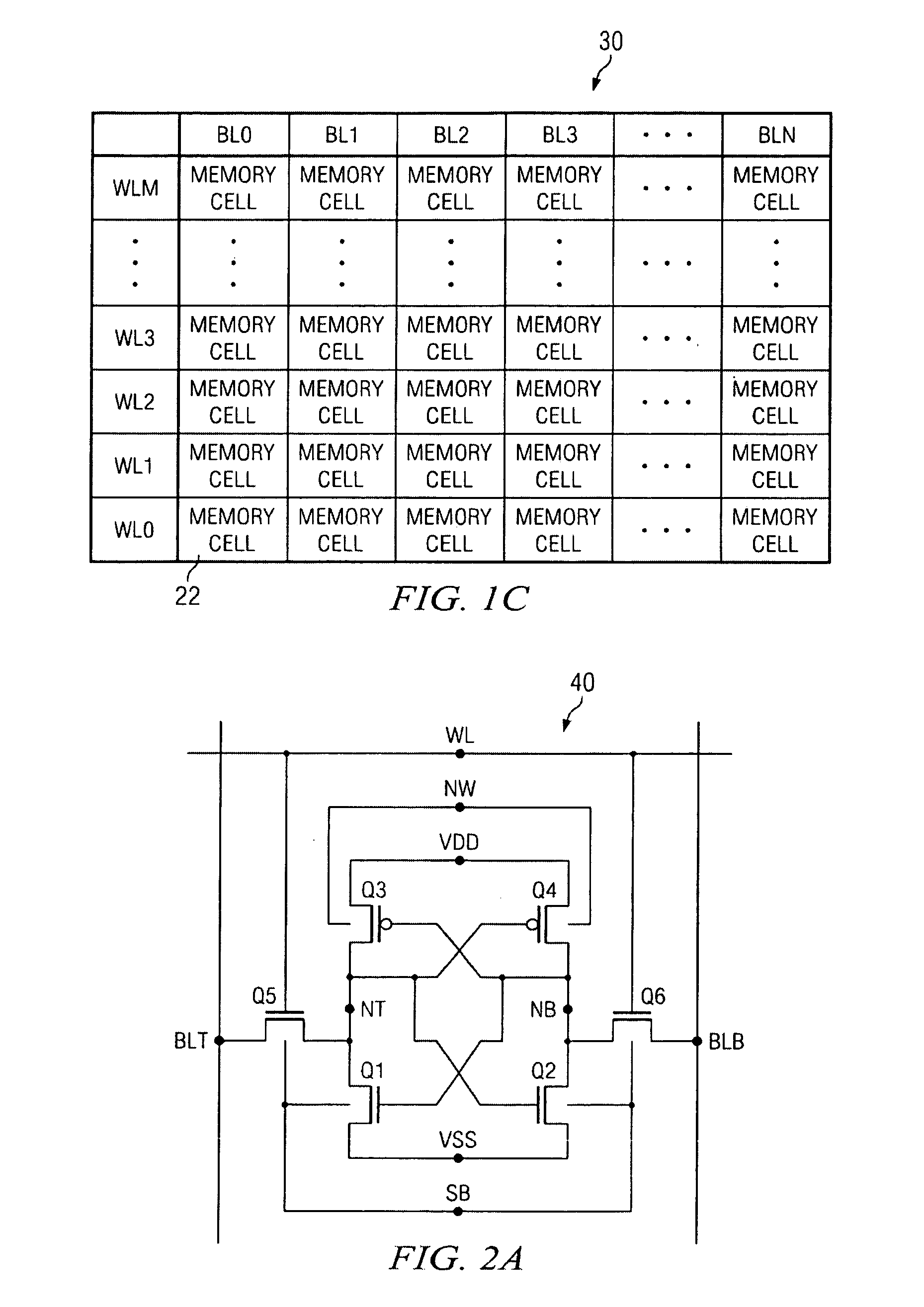
A Schmitt Trigger (ST) based, fully differential, 10-transistor (10T) SRAM (Static Random Access Memory) bitcell suitable for sub-threshold operation. The Schmitt trigger based bitcell achieves 1.56× higher read static noise margin (SNM) (VDD=400 mV) compared to a conventional 6T cell. The robust Schmitt trigger based memory cell exhibits built-in process variation tolerance that gives tight SNM distribution across the process corners. It utilizes fully differential operation and hence does not require any architectural changes from the present 6T architecture. The 10T bitcell has two cross-coupled Schmitt trigger inverters which each consist of four transistors, including a PMOS transistor and two NMOS transistors in series, and an NMOS feedback transistor which is connected between the inverter output and the junction between the series-connected NMOS transistors. Each inverter has one associated NMOS access transistor.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Semiconductor integrated circuit device having static random access memory mounted thereon
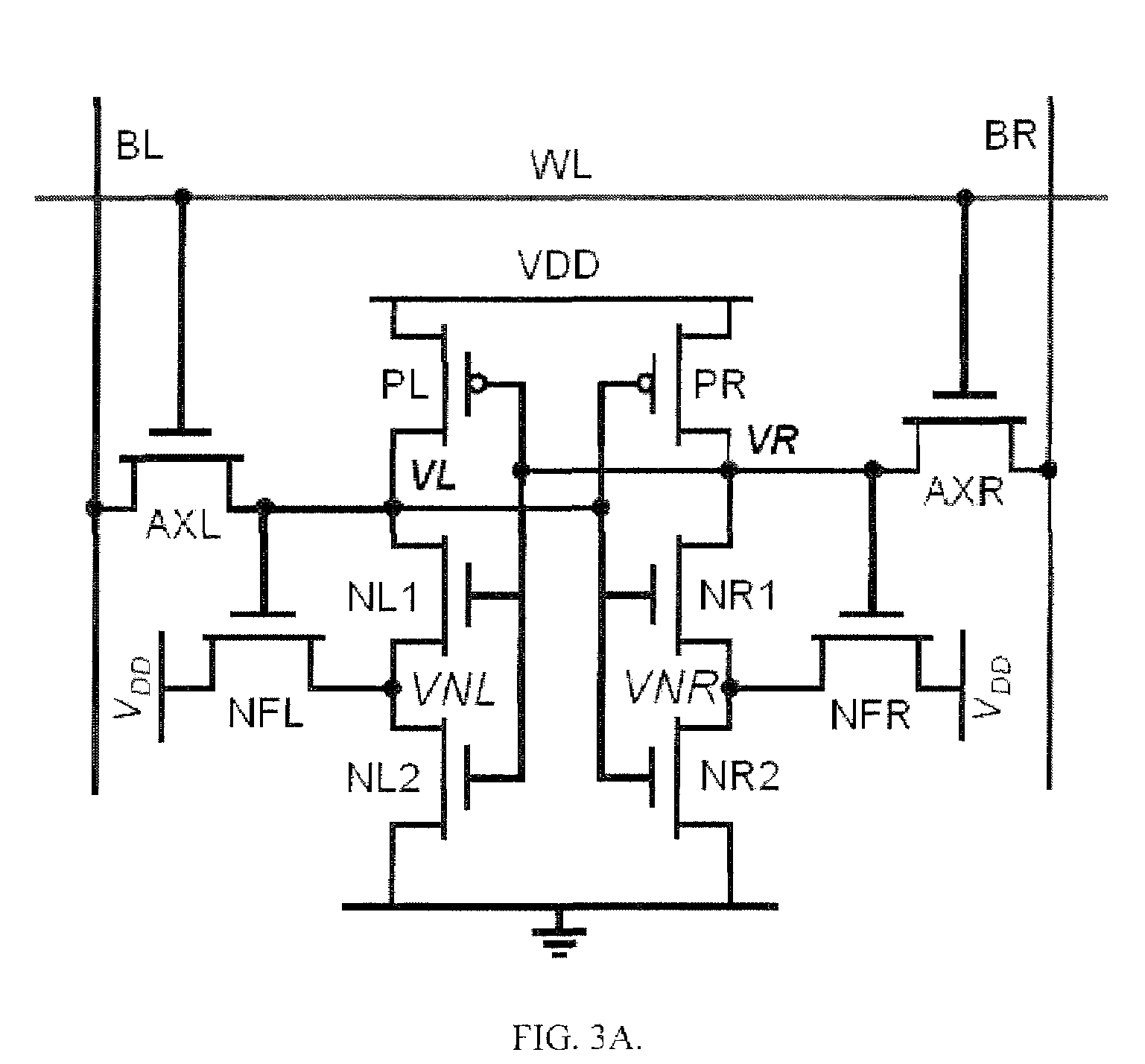
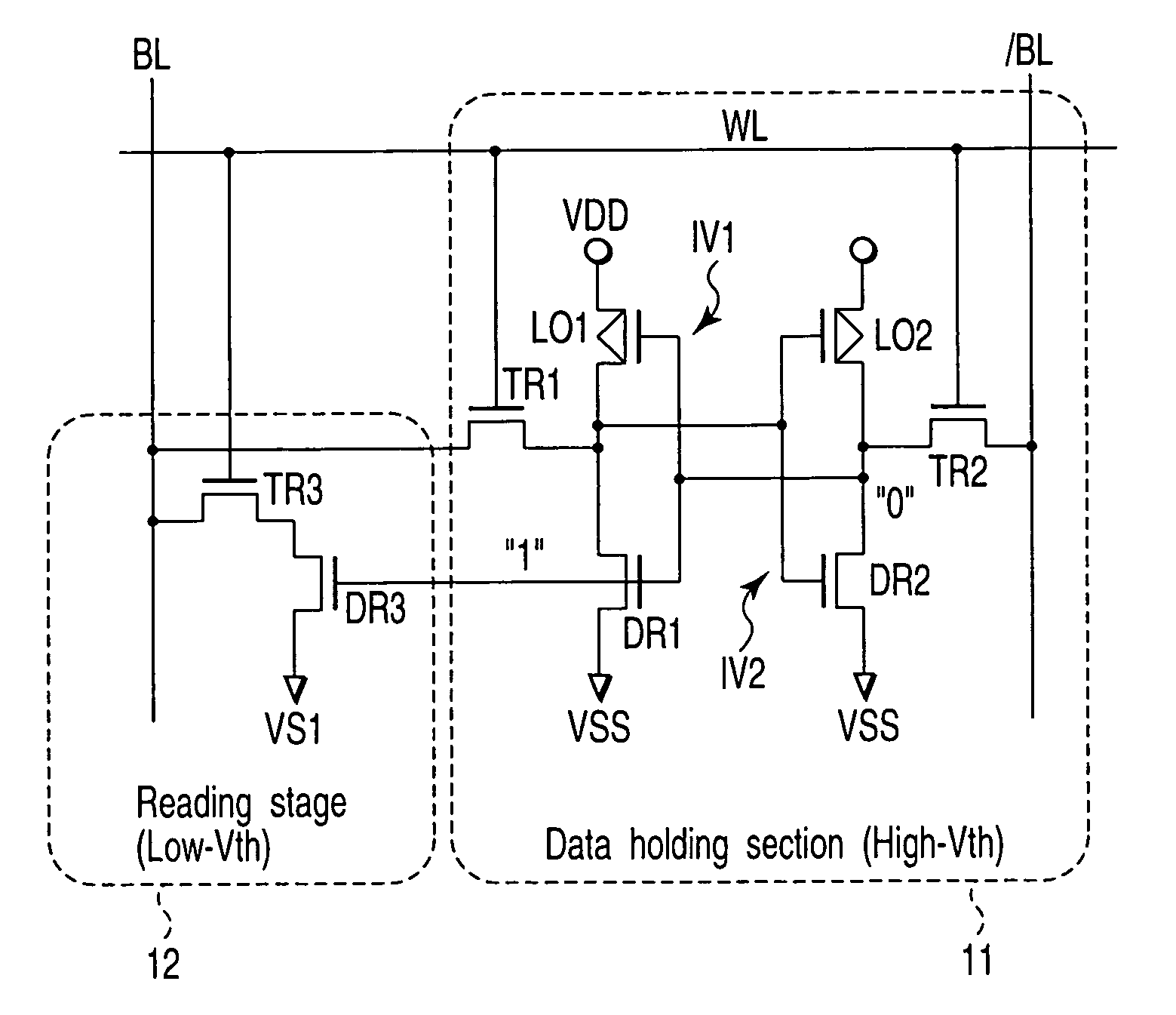
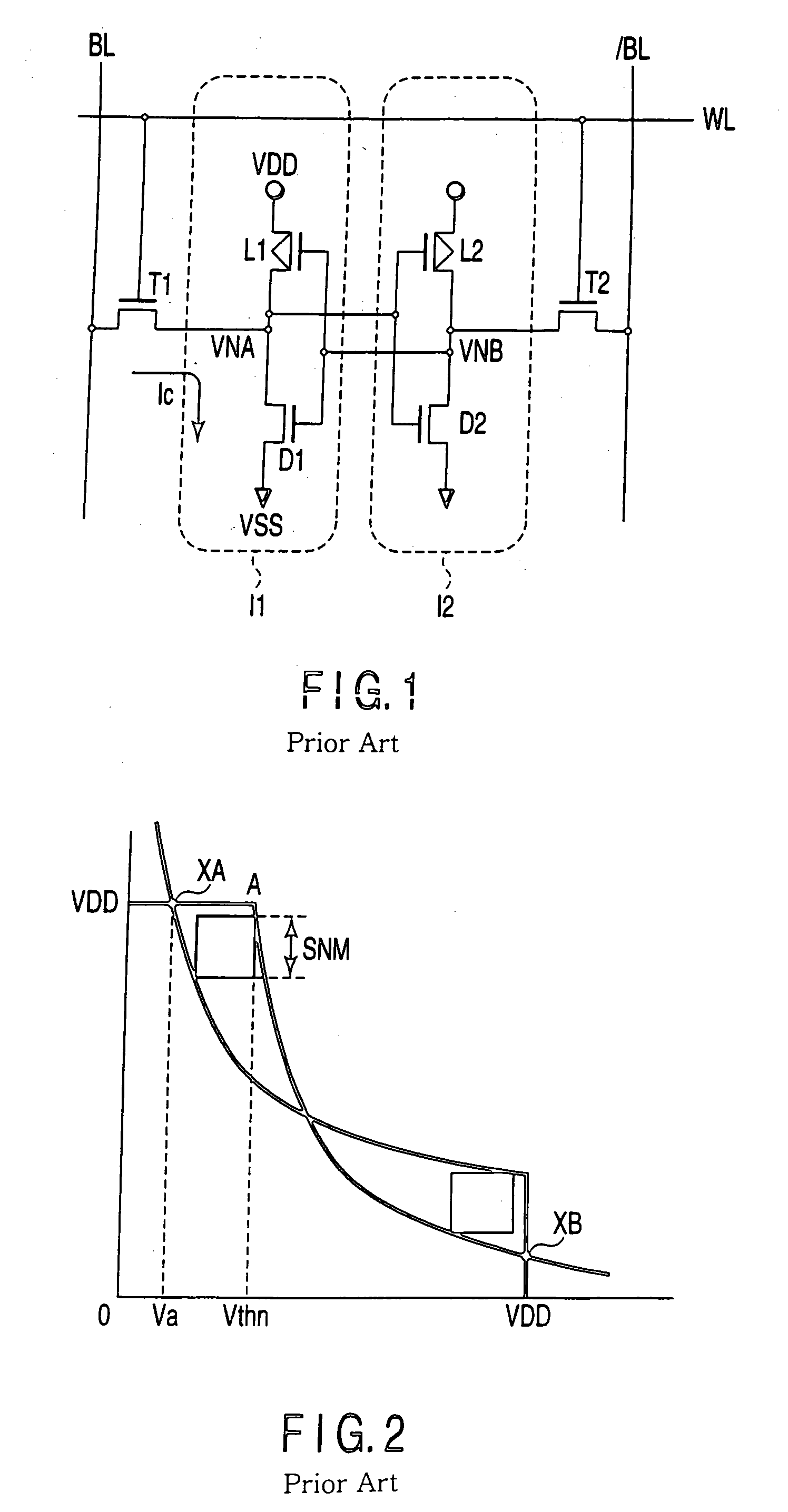
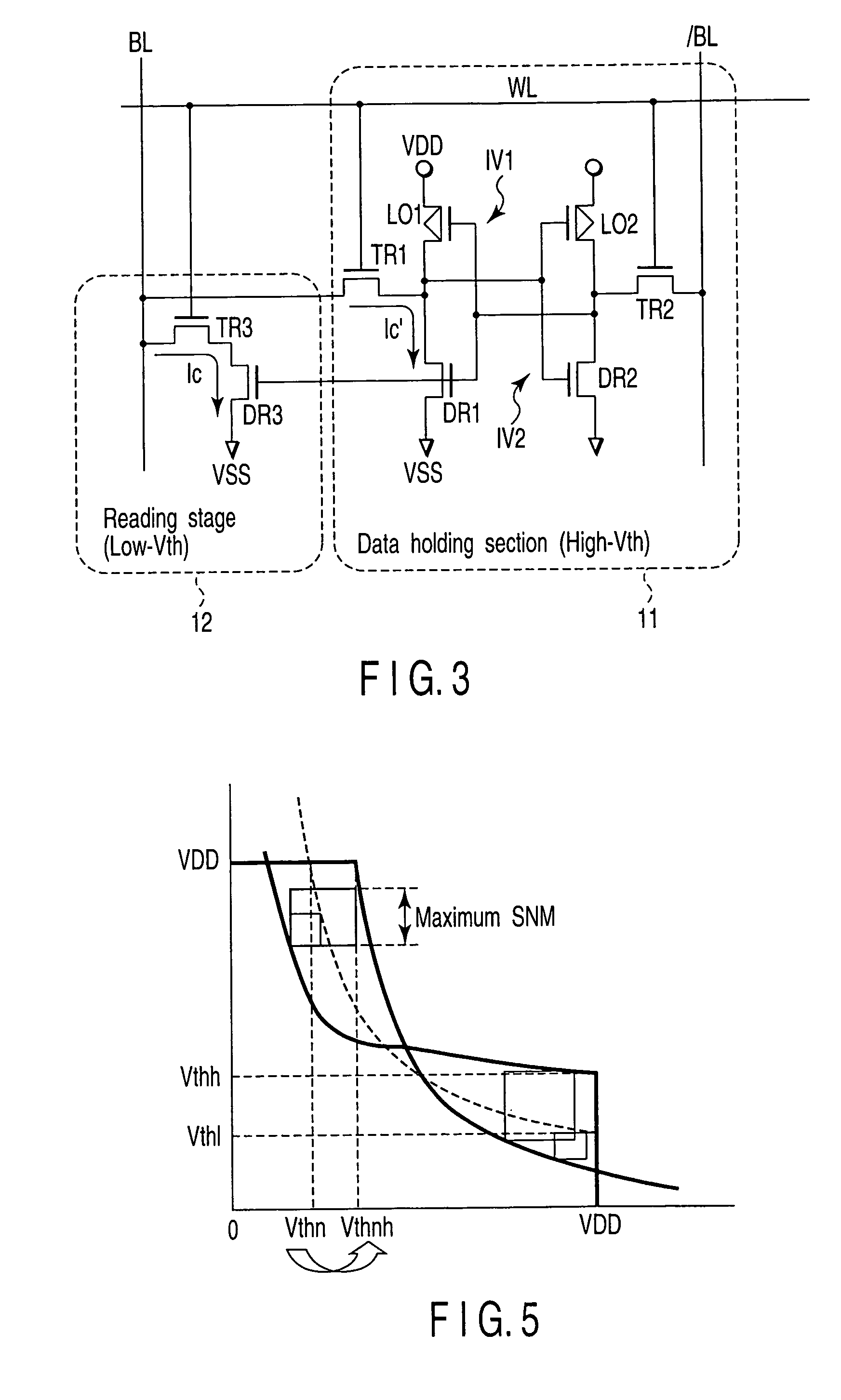
A semiconductor integrated circuit device is configured by eight transistors including the six transistors configuring the data holding section and the two NMOS transistors configuring the reading stage. The threshold voltage of the NMOS transistors configuring the reading stage is set low and the threshold voltage of the six transistors configuring the data holding section is set higher than the threshold voltage of the NMOS transistors configuring the reading stage. The cell current flowing from the bit line to the ground terminal can be set large and the large static noise margin (SNM) can be attained.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
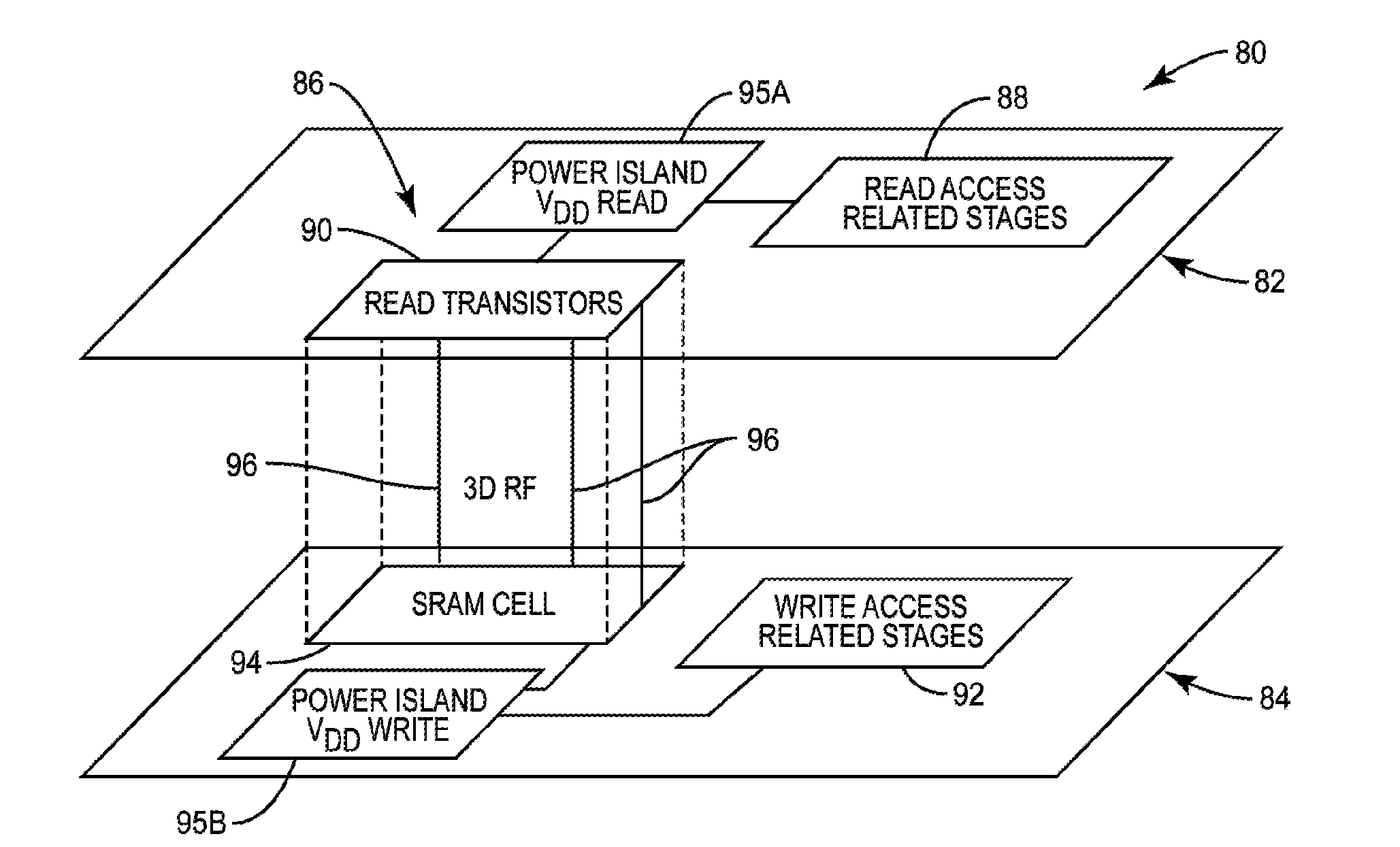
Three-dimensional (3D) memory cell separation among 3D integrated circuit (IC) tiers, and related 3D integrated circuits (3DICS), 3Dic processor cores, and methods
ActiveUS20140269022A1High device packing densityLower latencyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device details3d integrated circuitComputer architecture
A three-dimensional (3D) memory cell separation among 3D integrated circuit (IC) (3DIC) tiers is disclosed. Related 3DICs, 3DIC processor cores, and methods are also disclosed. In embodiments disclosed herein, memory read access ports of a memory block are separated from a memory cell in different tiers of a 3DIC. 3DICs achieve higher device packing density, lower interconnect delays, and lower costs. In this manner, different supply voltages can be provided for the read access ports and the memory cell to be able to lower supply voltage for the read access ports. Static noise margins and read / write noise margins in the memory cell may be provided as a result. Providing multiple power supply rails inside a non-separated memory block that increases area can also be avoided.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Power gating structure having data retention and intermediate modes
InactiveUS7190187B2Maintain efficiencyActive powerReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalEngineeringOperation mode
The present invention provides a power gating structure having data retention and intermediate modes and able to operate under multiple modes. A conventional power gating structure has only turn-on and turn-off functions, and is used to suppress a leakage current problem which has become more and more serious in advance manufacture processes, under a turn-off mode. However, in a memory circuit, such as latch, register and SRAM, when the power gate is turned off, a new power gating structure is required for data retention. The power gating structure of the present invention can be set into one of 4 different operational modes: a data retention mode for maintaining the static noise margin of the memory, an intermediate mode for reducing the interference on ground and power levels, an active mode used when the circuit operates in normal condition, and a standby mode used when the circuit does not operate.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Memory array with a delayed wordline boost
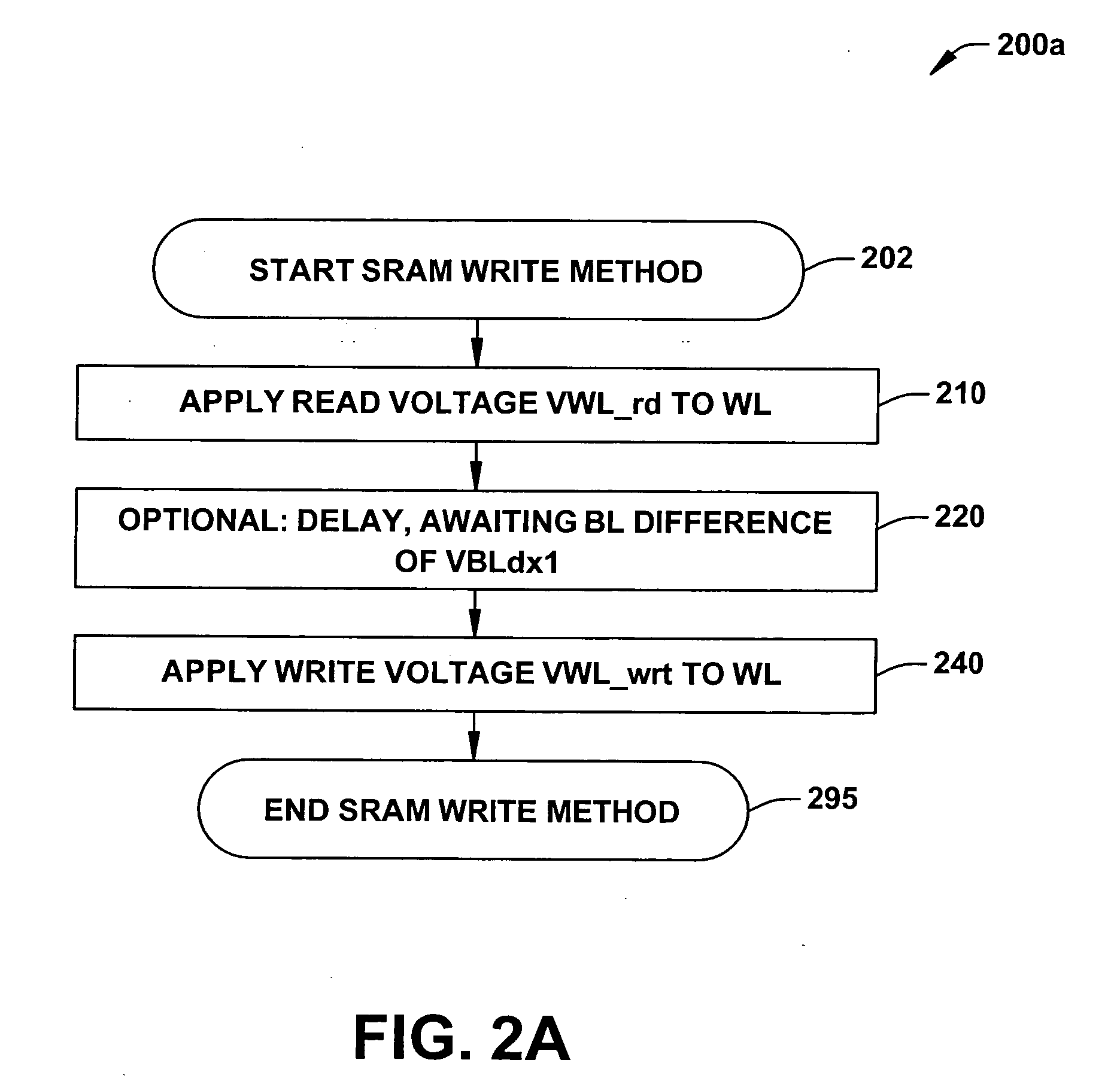
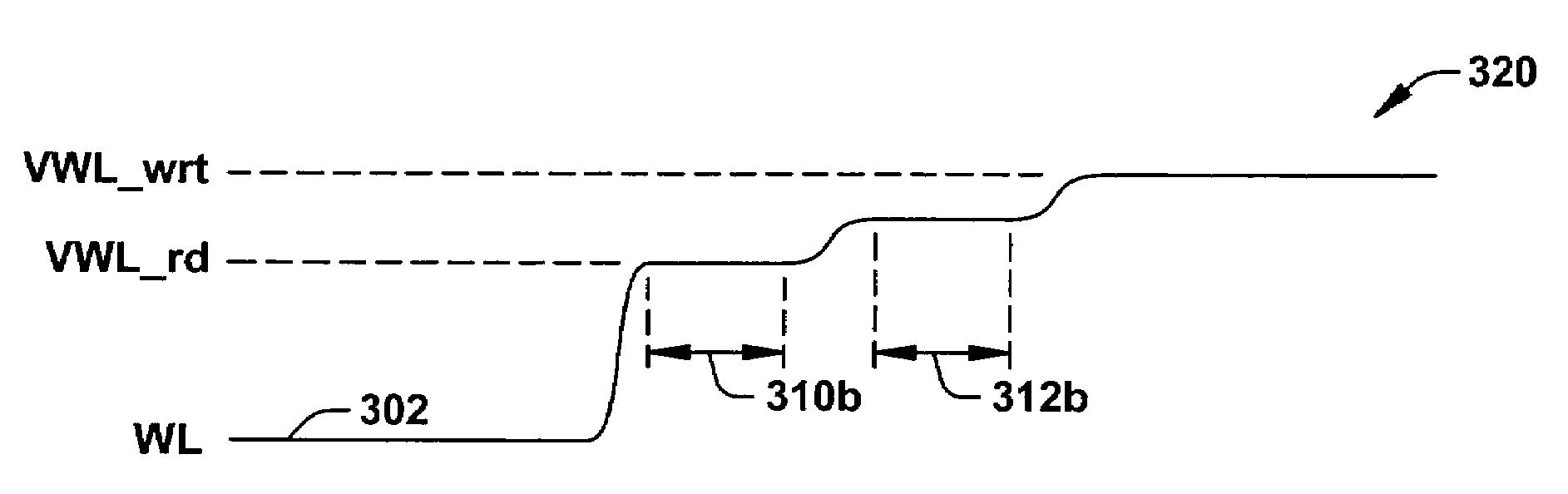
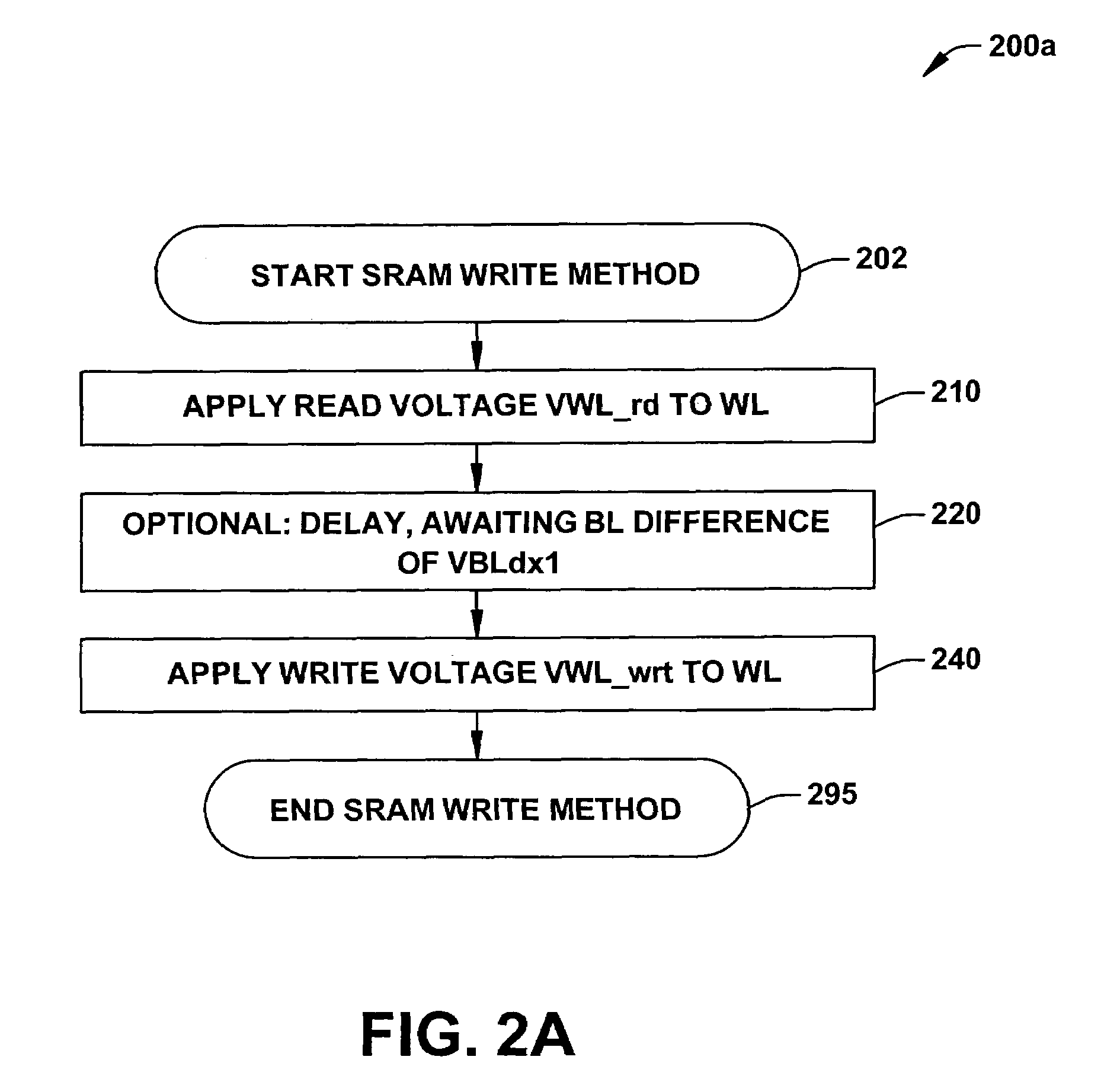
ActiveUS20070025169A1Least riskImprove static noise marginDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
Methods and a circuit for writing to an SRAM memory cell of an array are discussed that provide improved static noise margin, and minimal risk of data upsets during write operations. The write method first rapidly raises the wordline to a lower read voltage level for access, then after a time delay that allows the cells in the selected row to establish a stabilizing differential voltage on the associated bitlines, raises the wordline voltage to a boosted or higher write voltage level. An SRAM bitline enhancement circuit may also be utilized in association with the SRAM memory array and writing method, for enhancing the differential voltage produced by an SRAM memory cell of the array on associated first and second bitlines of the array of conventional SRAM cells (e.g., a conventional 6T differential cell). In one implementation, the SRAM bitline enhancement circuit comprises a half-latch or a sense amplifier connected to associated bitline pairs of the array for amplifying the differential voltage.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
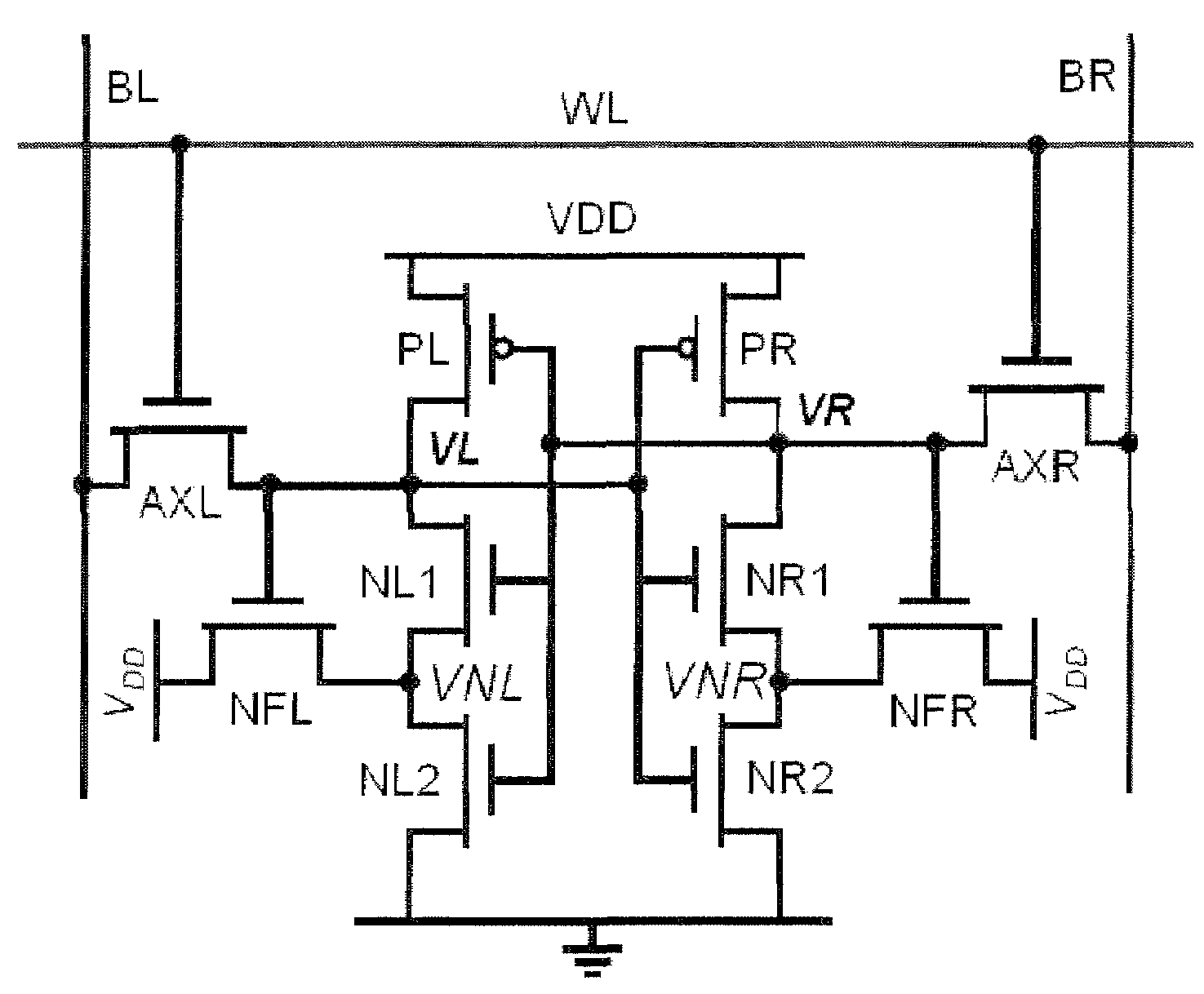
SRAM cell with independent static noise margin, trip voltage, and read current optimization
ActiveUS7385840B2Well formedData becomes unstableDigital storageComputer architectureStatic noise margin
An SRAM memory cell structure utilizing a read driver transistor and a column select write transistor, and a method of operating the same. The SRAM memory cell comprises first and second cross-coupled inverters, having a first and second latch nodes, respectively. The cell further comprises a first write pass transistor connected between the first latch node of the first inverter and a first pass node, and a first wordline pass transistor connected between the first pass node and a first bitline. The cell also includes a first read driver connected between the first pass node and a source potential, and a control terminal of the first read driver connected to the second latch node of the second inverter.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
SRAM cell with independent static noise margin, trip voltage, and read current optimization
ActiveUS20070025140A1Well formedData becomes unstableDigital storageStatic noise marginUnit structure
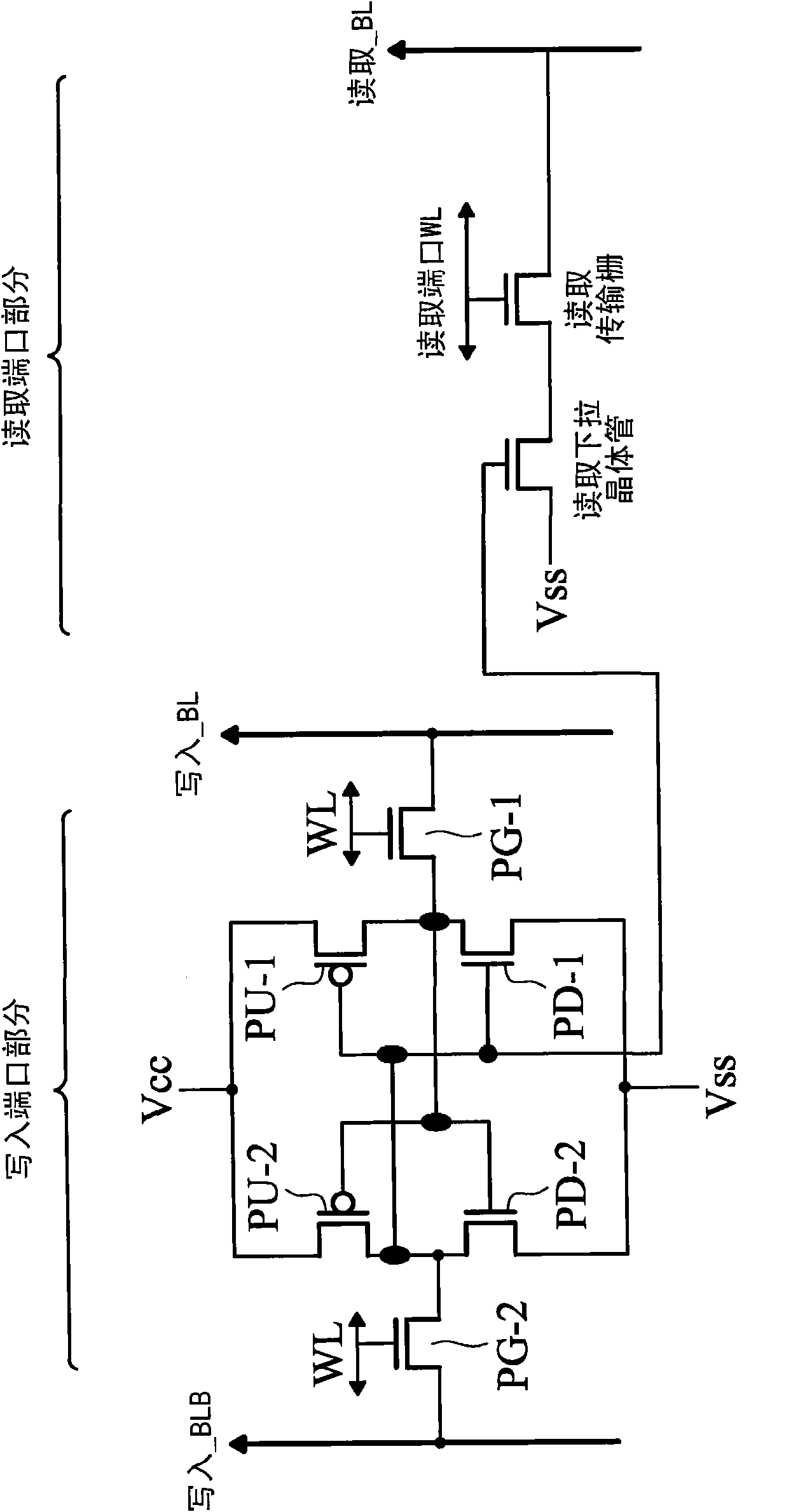
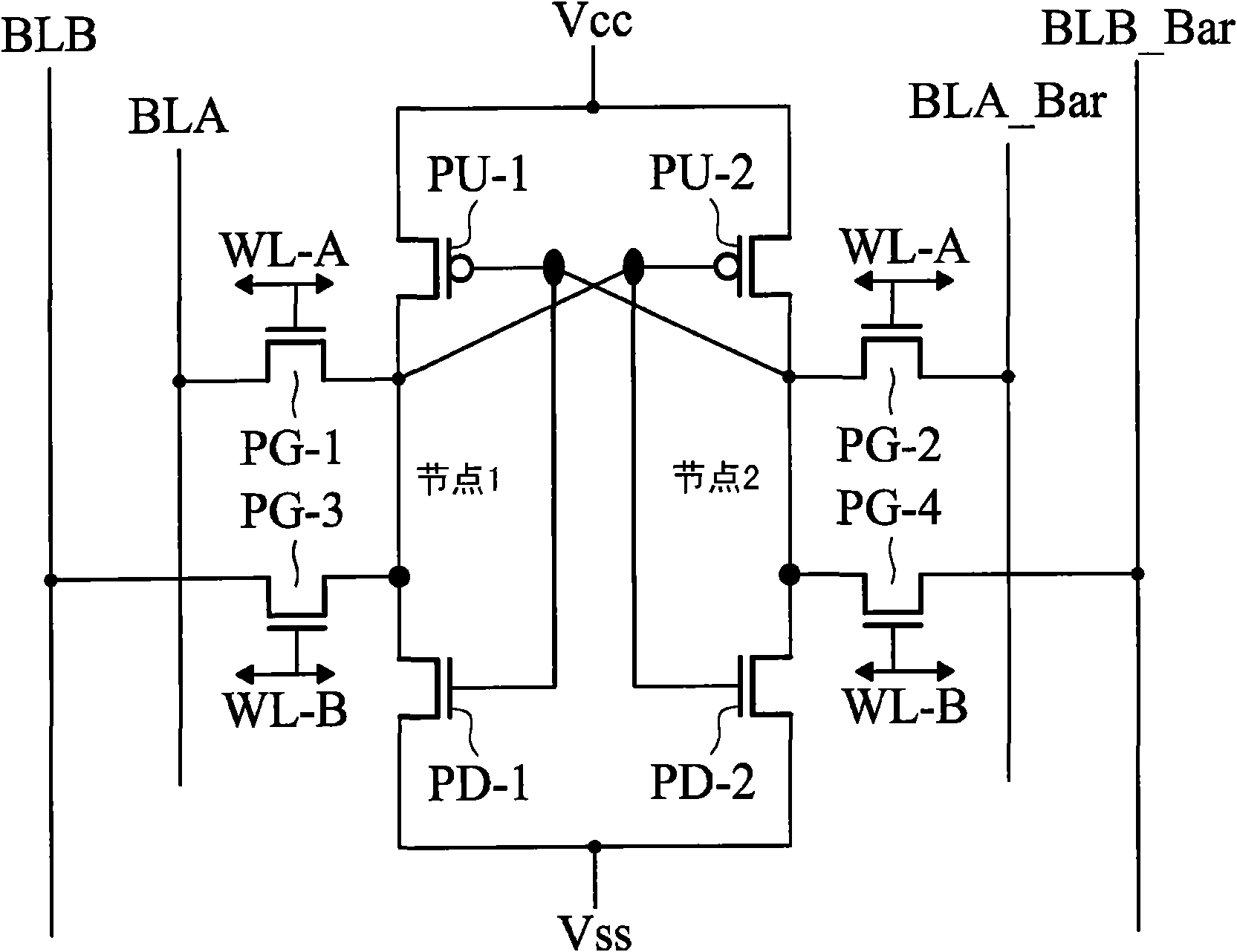
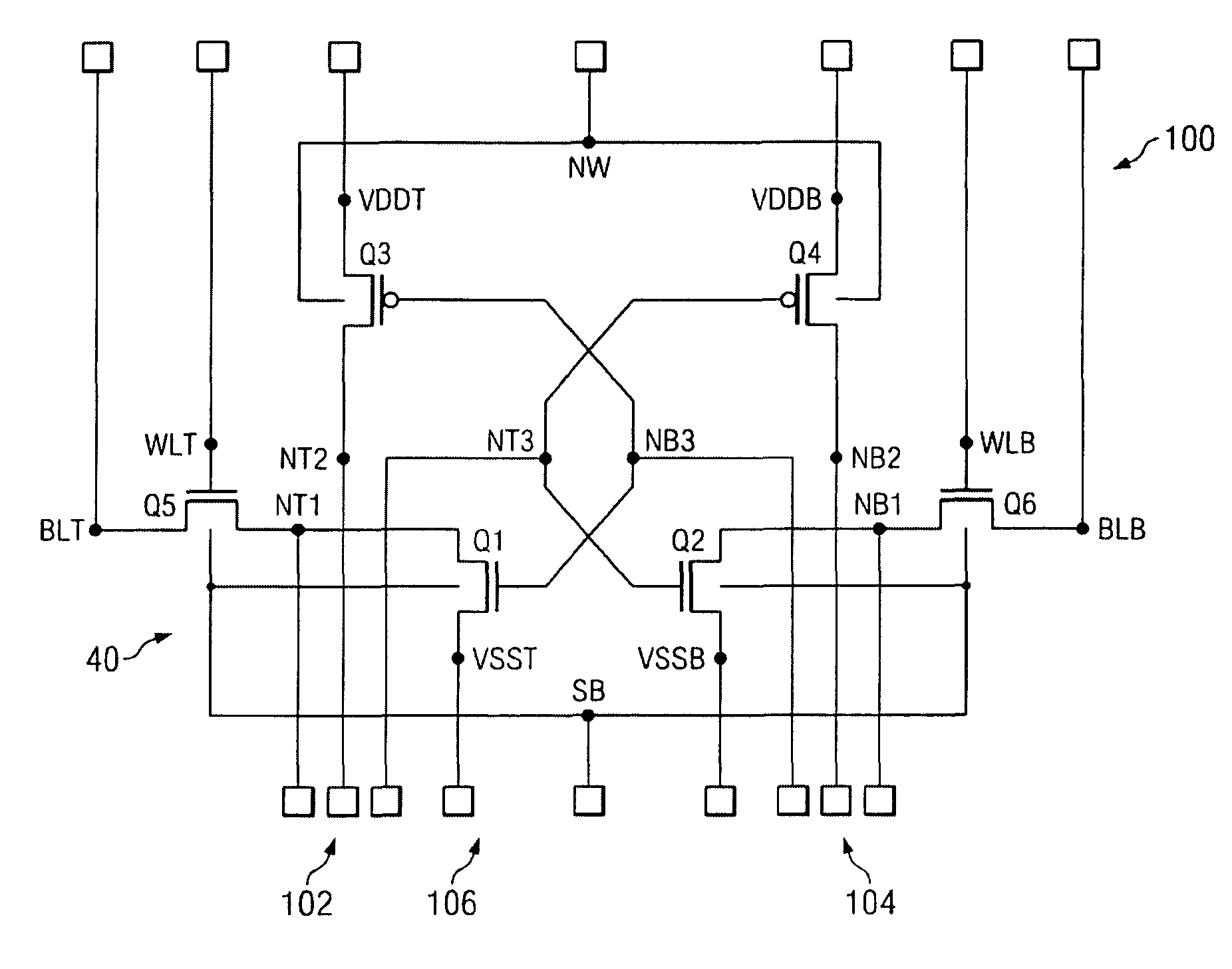
An SRAM memory cell structure utilizing a read driver transistor for isolating the read current from the latch nodes of the cell during read operations and a column select write transistor for selection of a single cell during write operations, and a method of operating the same is discussed. The SRAM memory cell structure (single-ended or differential cell) allows independent optimization of the static noise margin, trip voltage, and read current, thereby avoiding some of the static noise margin and trip voltage problems of conventional SRAM cells (e.g., a conventional 6T differential cell). In one implementation, the SRAM memory cell comprises a 7T single-ended cell including first and second cross-coupled inverters, having a first and second latch nodes, respectively. The cell further comprises a first write pass transistor connected between the first latch node of the first inverter and a first pass node, and a first wordline pass transistor connected between the first pass node and a first bitline. The cell also includes a first read driver connected between the first pass node and a source potential, and a control terminal of the first read driver connected to the second latch node of the second inverter. Beneficially, the read current conducts through the first read driver to avoid upsetting the data state at the latch node. Further, a differential 10T SRAM memory cell for coupling to a complimentary pair of bitlines is discussed, having all the elements mentioned above used in the exemplary 7T cell.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
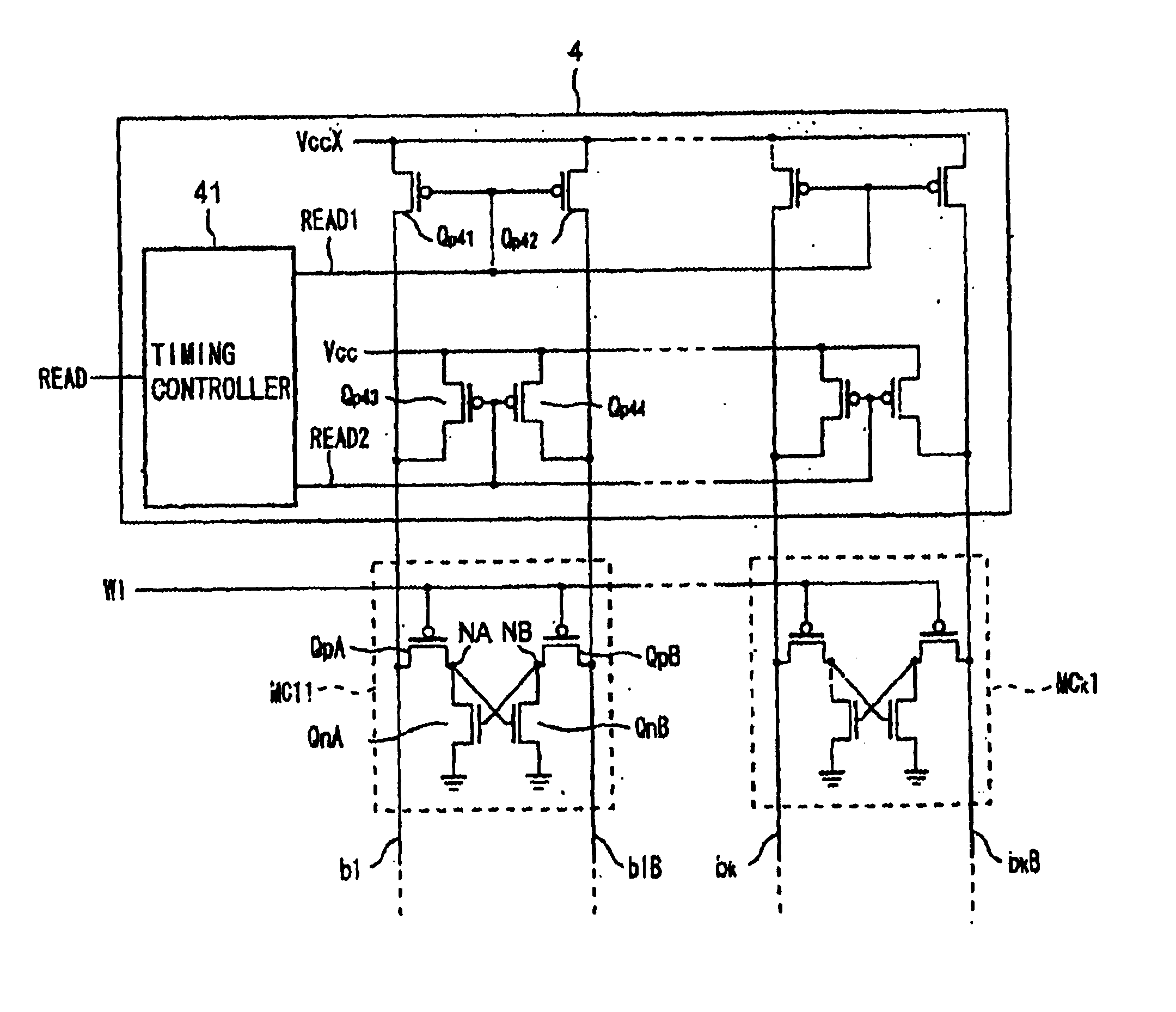
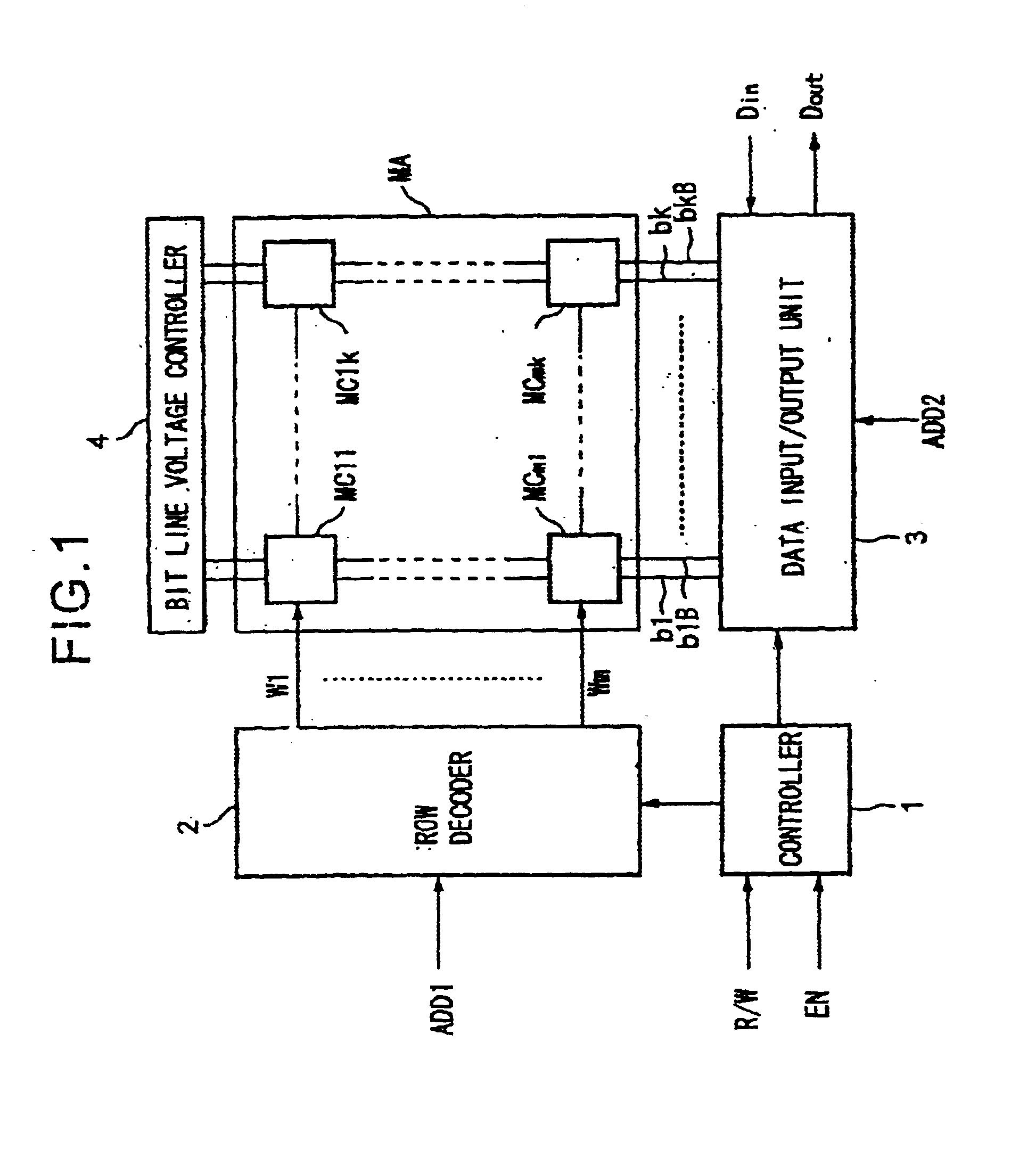
Method of reading stored data and semiconductor memory device
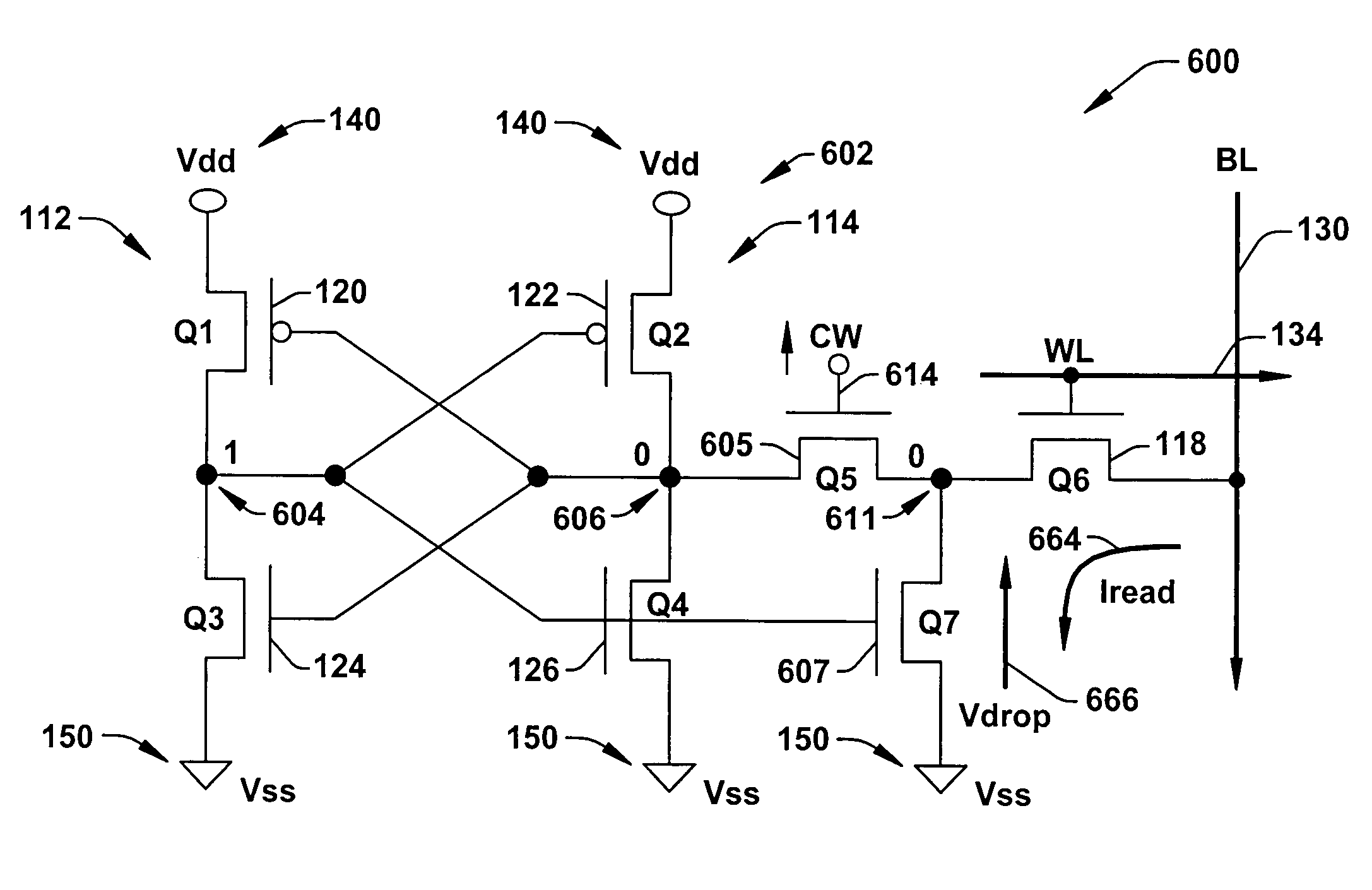
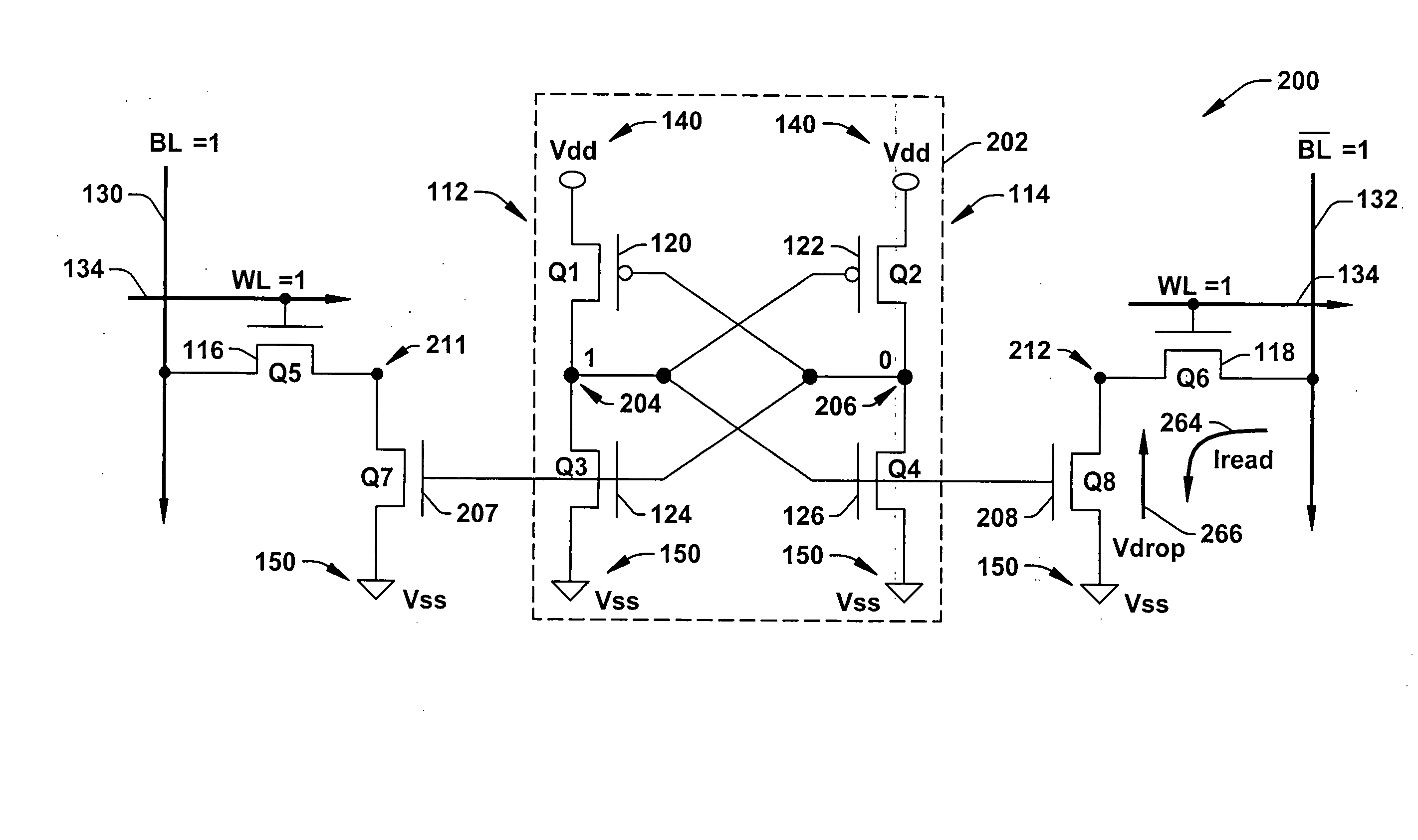
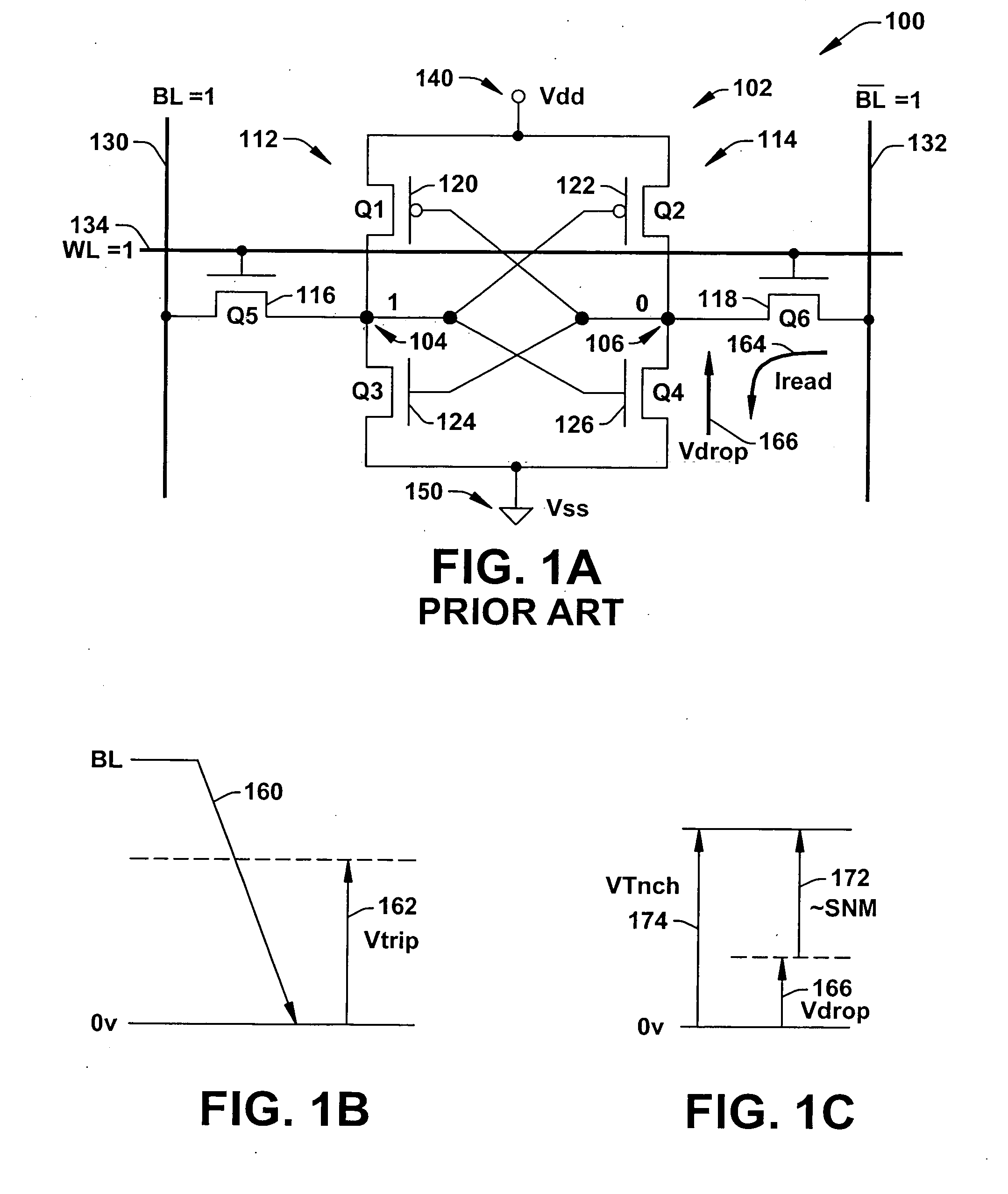
InactiveUS20020159312A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBit lineVoltage drop
A method of reading stored data in a semiconductor memory device able to suppress the reduction in the static noise margin accompanying a voltage drop of a power supply voltage, and able to improve the degree of integration of the circuit, that is, a method of reading stored data of a semiconductor memory device which has a first storage node and a second storage node, a first transistor having a control terminal connected to the first storage node and having a pair of input / output terminals connected between the second storage node and a reference potential, a second transistor having a control terminal connected to the second storage node and having a pair of input / output terminals connected between the first storage node and the reference potential, a third transistor having a pair of input / output terminals connected between the first storage node and a first bit line and having a control terminal connected to a word line, and a fourth transistor having a pair of input / output terminals connected between the second storage node and a second bit line and having a control terminal connected to the word line, comprising the steps of applying a first voltage to the first bit line and the second bit line in a period for holding the stored data, and activating the word line and applying a second voltage higher than the first voltage to the first bit line and the second bit line at the time of reading the stored data, and a semiconductor memory device using the same.
Owner:SONY CORP
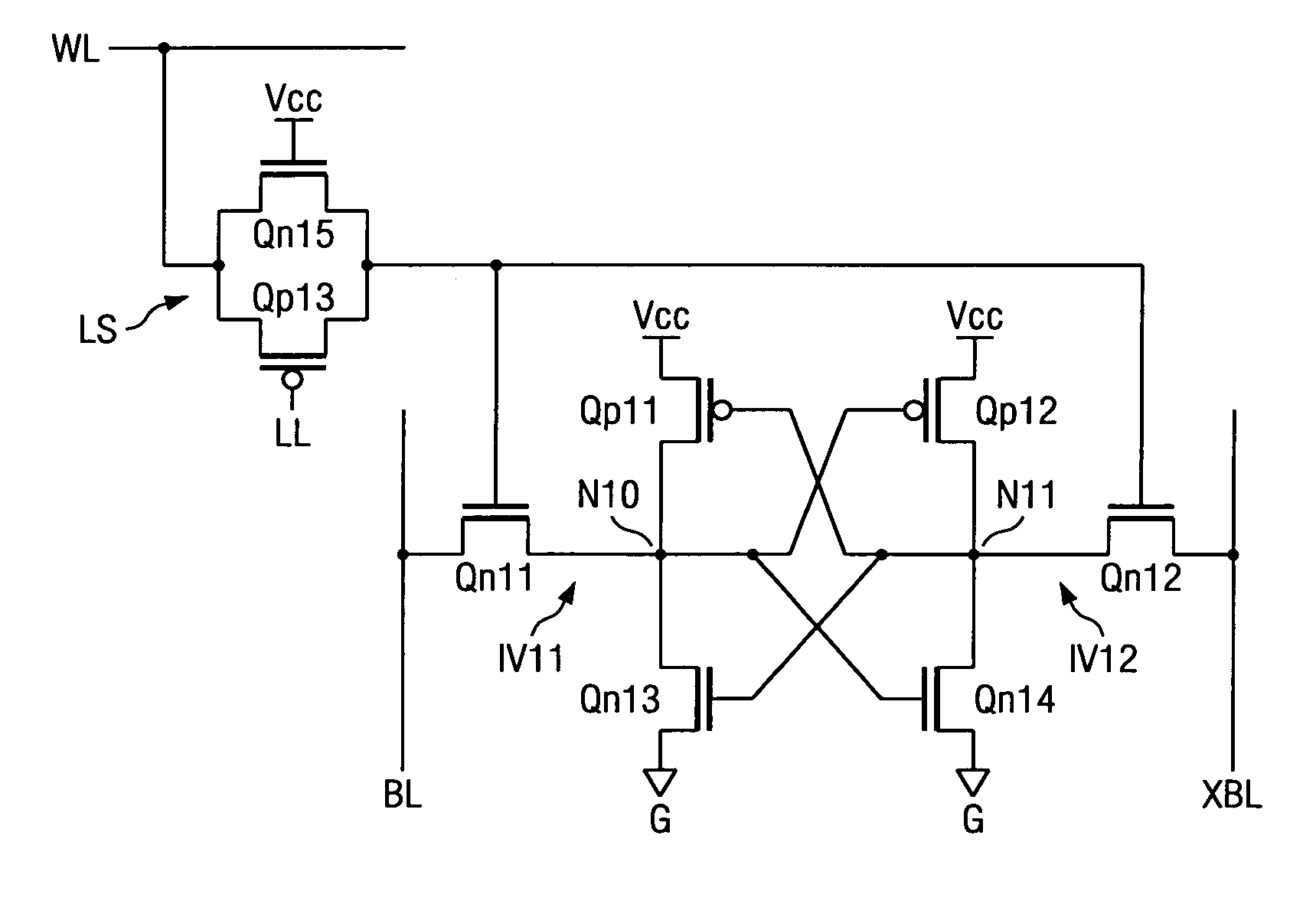
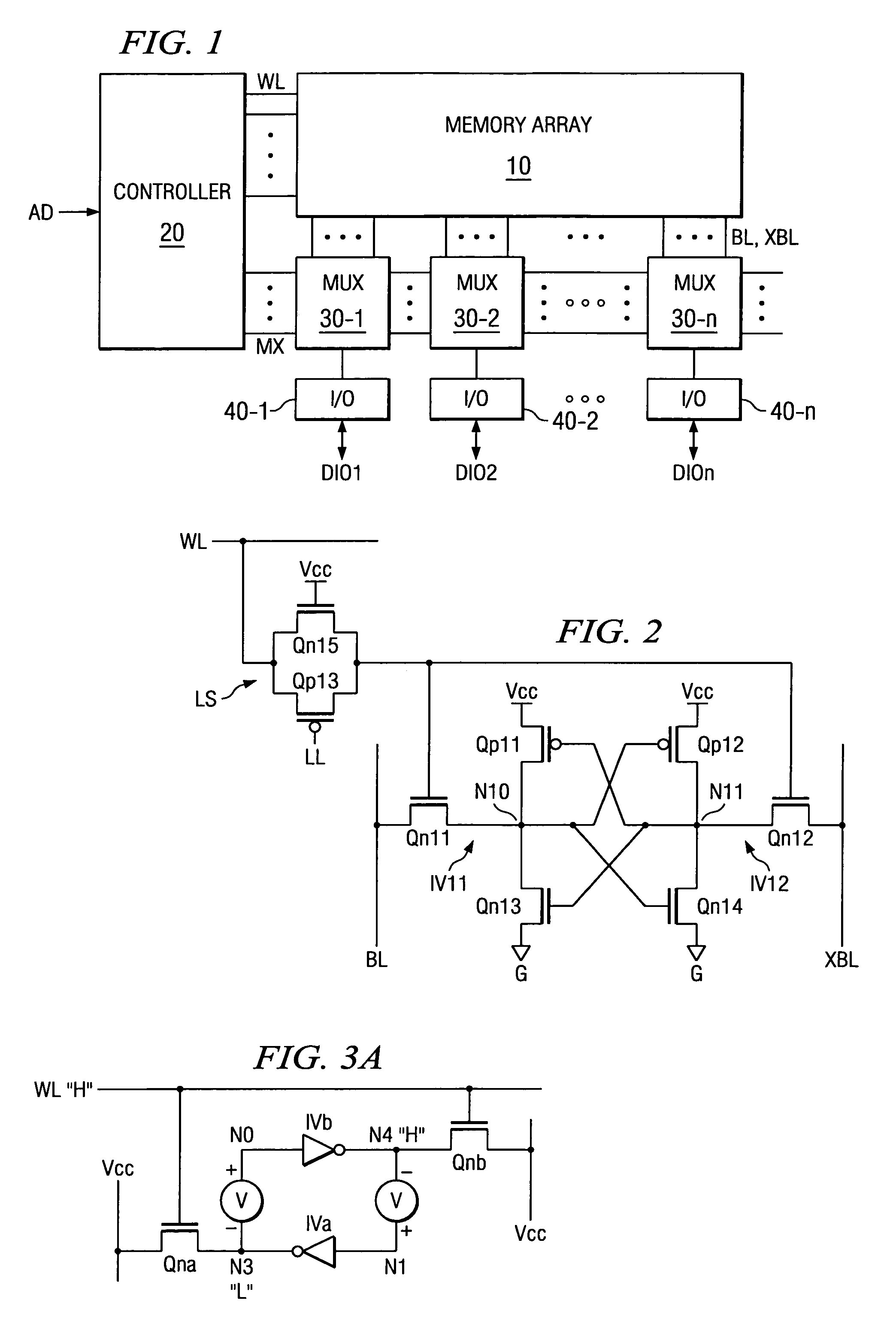
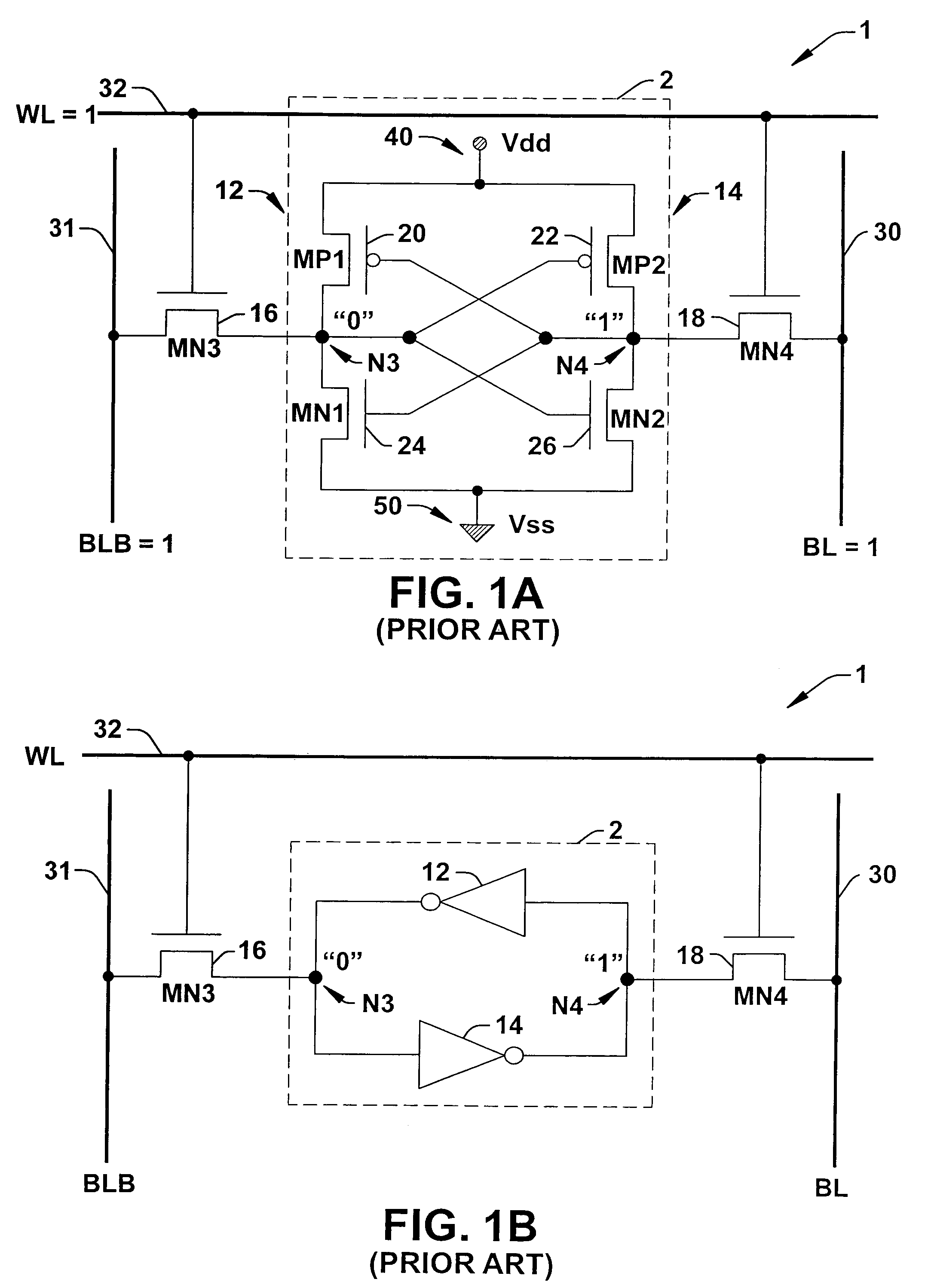
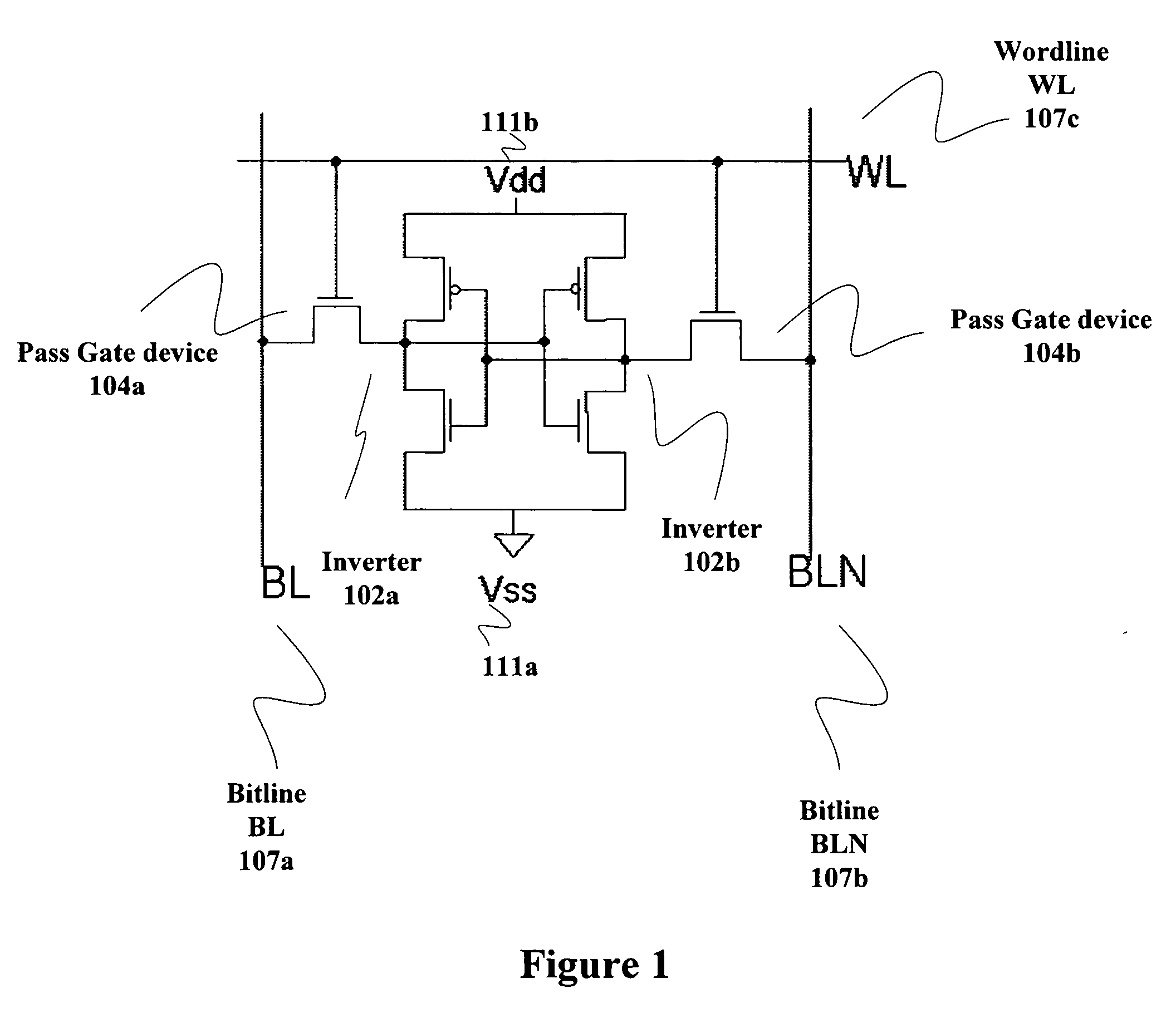
Static memory cell and SRAM device
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
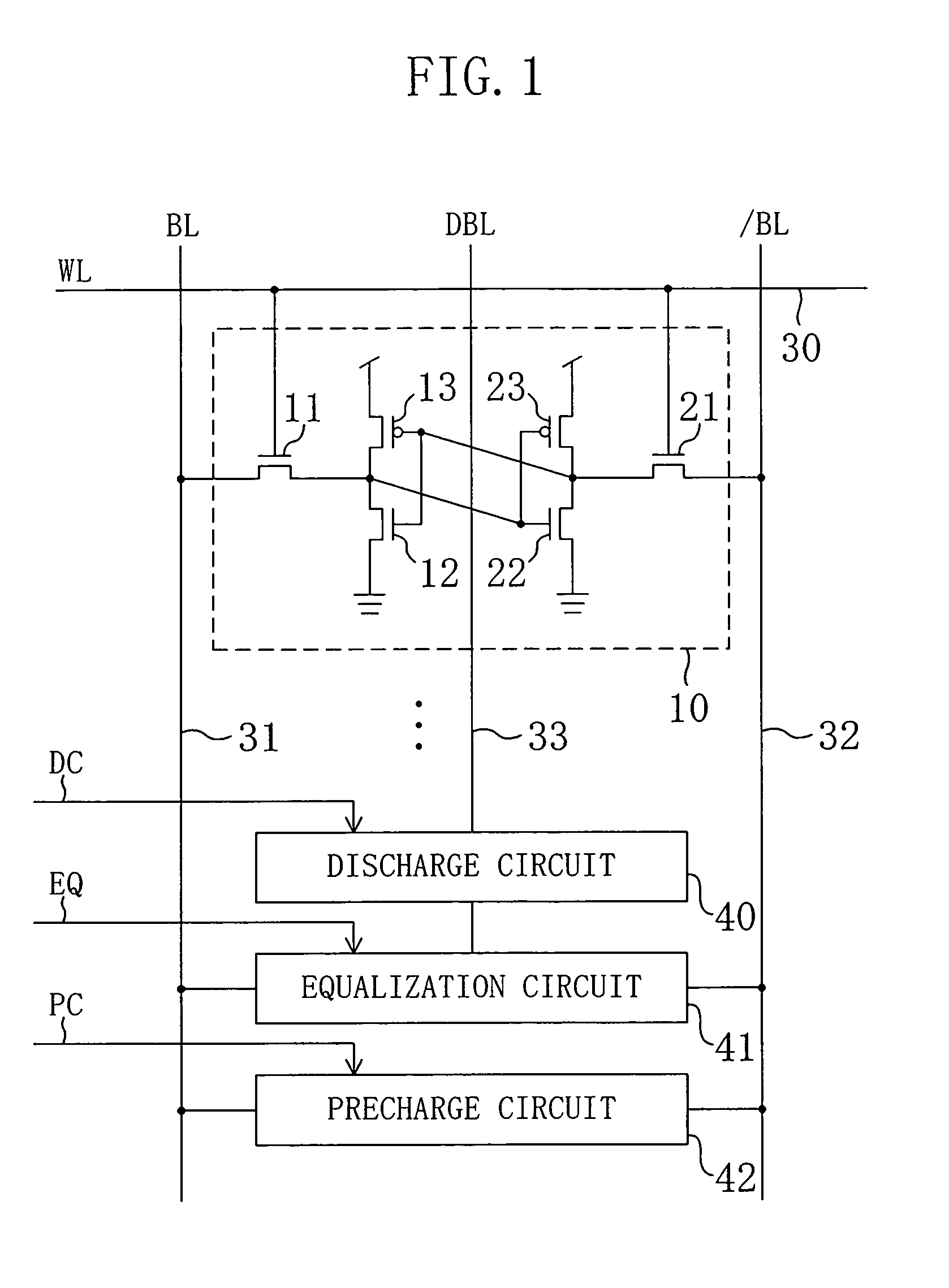
Semiconductor memory device with memory cells operated by boosted voltage
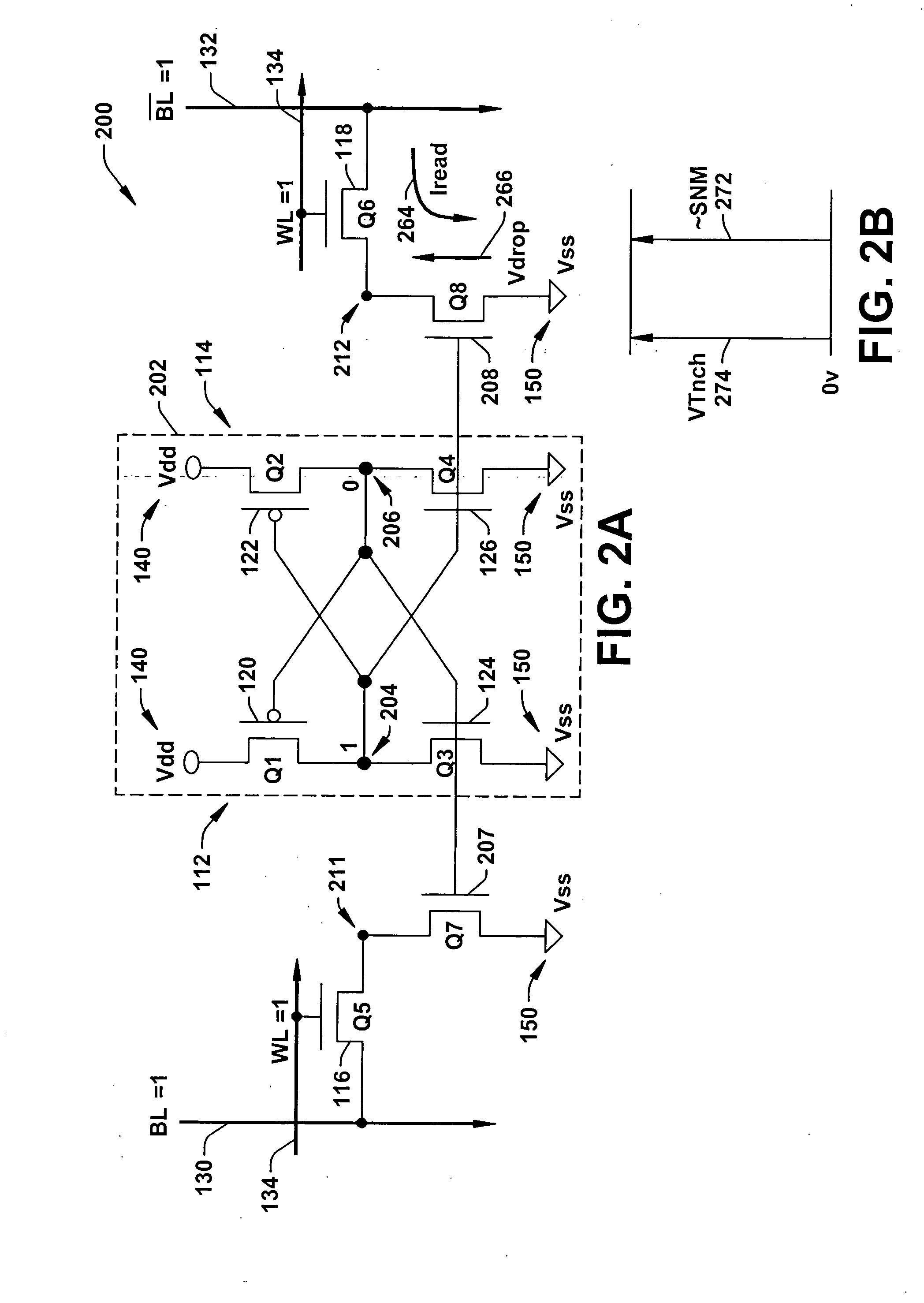
InactiveUS20050024917A1Reduced operating requirementsStatic noise marginSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLow voltageEngineering
A memory using an SRAM memory cell intended for low-voltage operation is designed to decrease the threshold value of MOS transistors constituting the memory cell without substantial decrease in the static noise margin, which is the operational margin of the memory cell. To this end, a voltage Vdd′ higher than a power supply voltage Vdd of a power supply line for peripheral circuits is supplied from a power supply line for memory cells as a power supply voltage for memory cells. Since the conductance of driver MOS transistors is increased, the threshold voltage of the MOS transistors within the memory cells can be reduced without reducing the static noise margin. Further the ratio of width between the driver MOS transistor and a transfer MOS transistor can be set to 1, thereby allowing a reduction in the memory cell area.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Embedded sram structure and chip
ActiveCN102034825AImprove reliabilityGood compatibilityTransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryComputer architecture
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
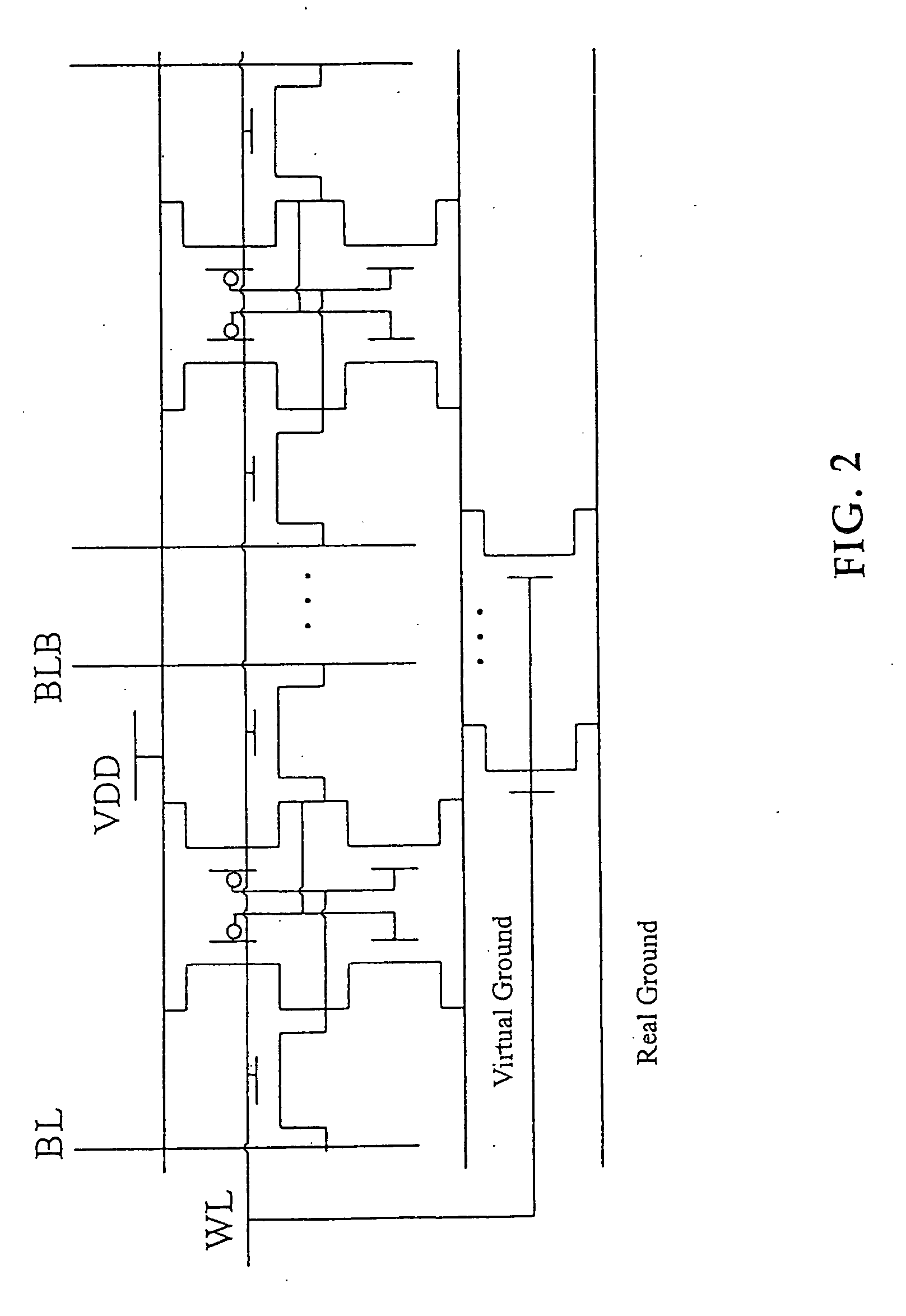
Semiconductor memory device
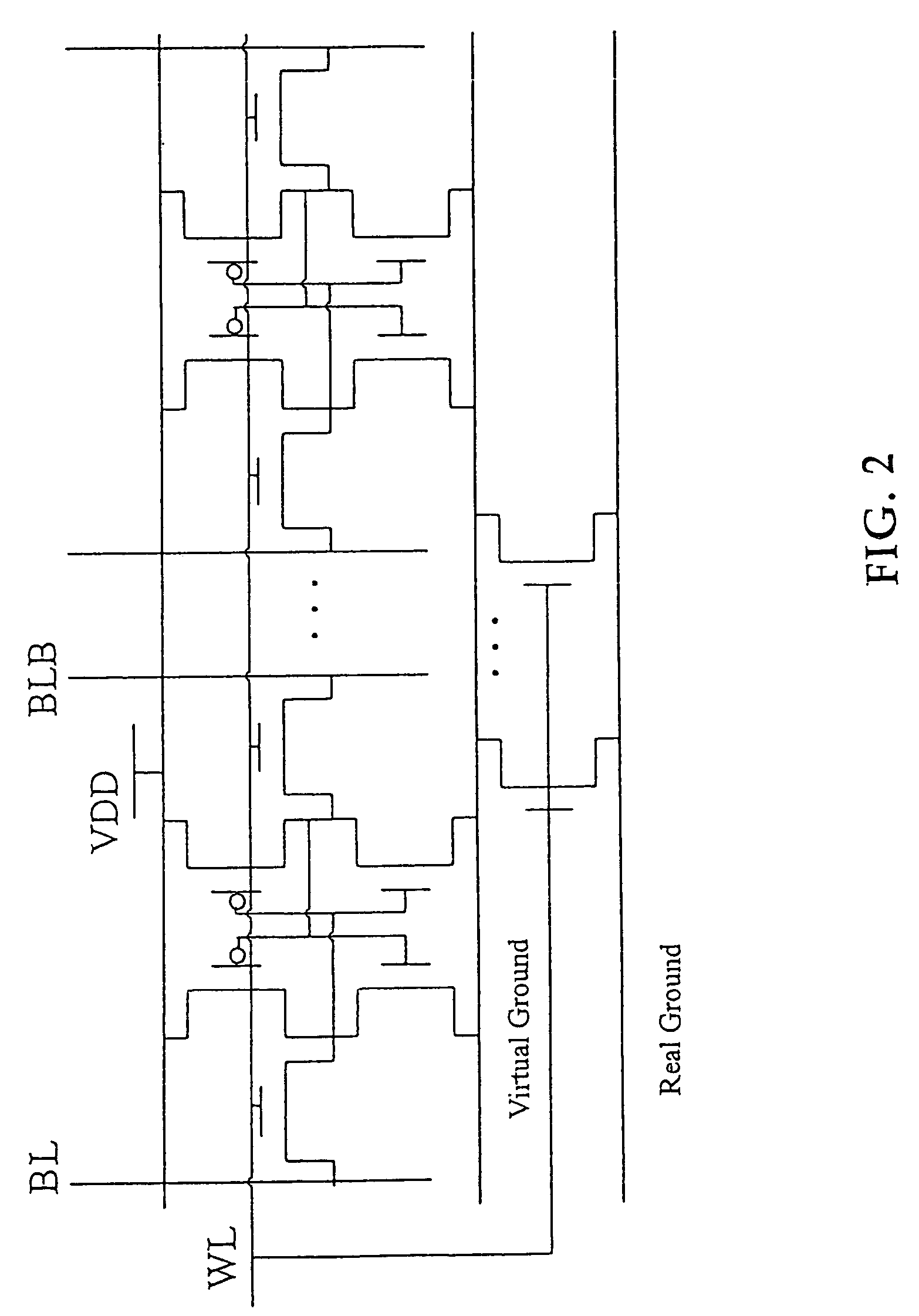
InactiveUS6982899B2Reduce voltageAvoid failureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringStatic noise margin
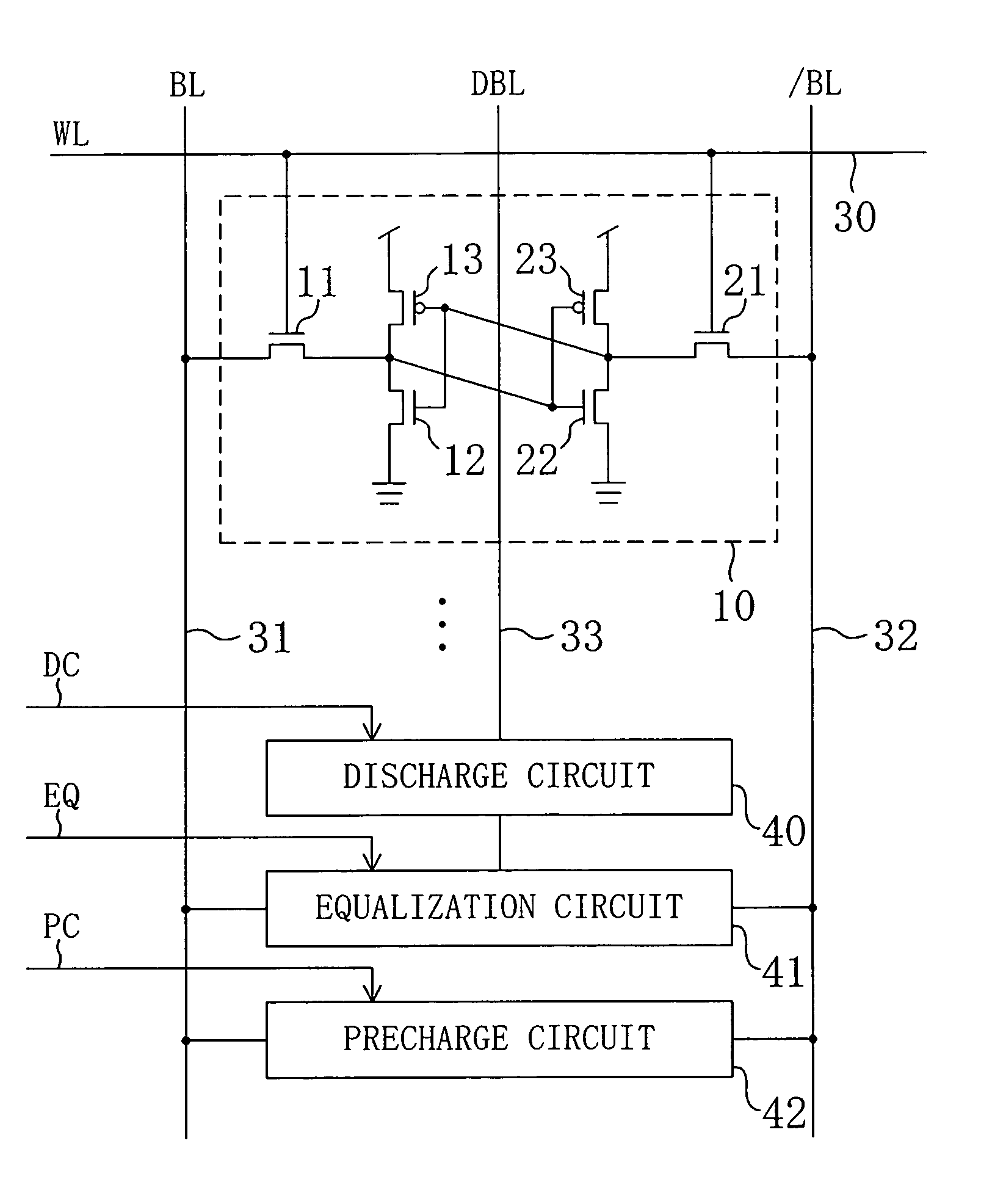
A dummy bit line is provided between a pair of bit lines. The pair of bit lines is set at a power supply voltage and the dummy bit line is set at a ground voltage, and then the pair of bit lines and the dummy bit line are equalized. When a word line is activated in subsequent read operation, the pair of bit lines is at an intermediate potential lower than the power supply voltage, so that an apparent current drive capability of an access transistor decreases, and the static noise margin of a memory cell increases.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Memory array with a delayed wordline boost
Methods and a circuit for writing to an SRAM memory cell of an array are discussed that provide improved static noise margin, and minimal risk of data upsets during write operations. The write method first rapidly raises the wordline to a lower read voltage level for access, then after a time delay that allows the cells in the selected row to establish a stabilizing differential voltage on the associated bitlines, raises the wordline voltage to a boosted or higher write voltage level. An SRAM bitline enhancement circuit may also be utilized in association with the SRAM memory array and writing method, for enhancing the differential voltage produced by an SRAM memory cell of the array on associated first and second bitlines of the array of conventional SRAM cells (e.g., a conventional 6T differential cell). In one implementation, the SRAM bitline enhancement circuit comprises a half-latch or a sense amplifier connected to associated bitline pairs of the array for amplifying the differential voltage.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
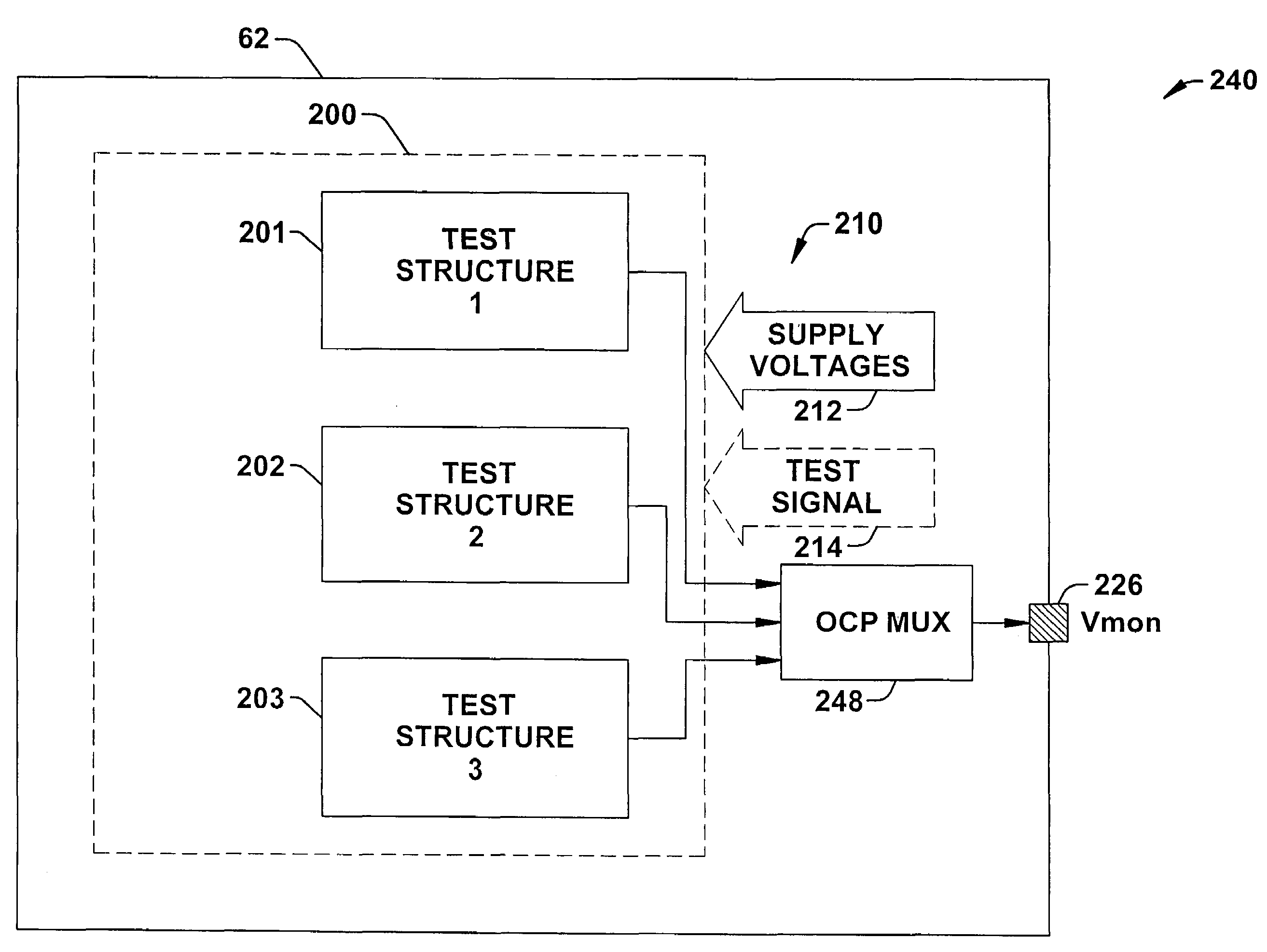
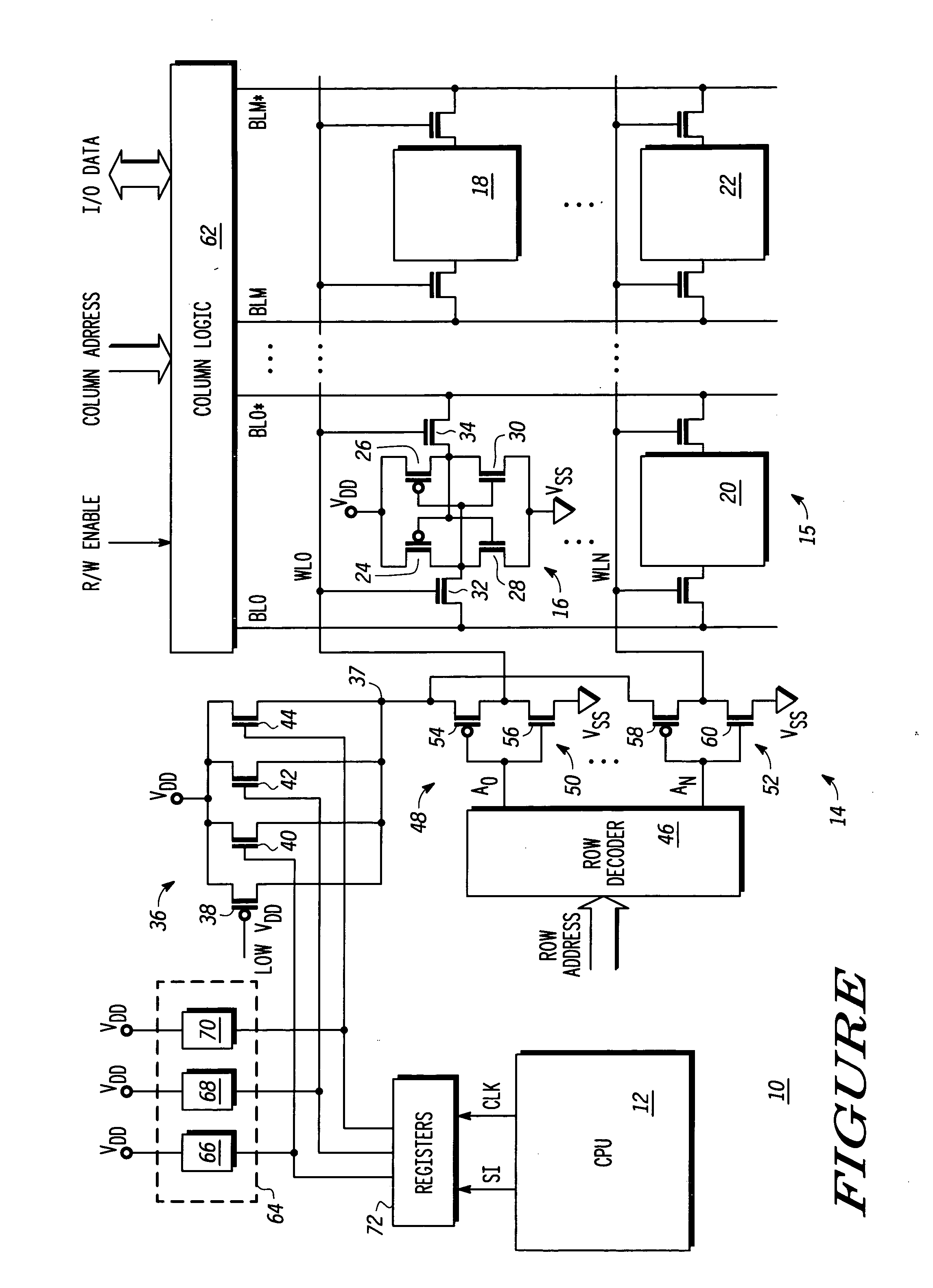
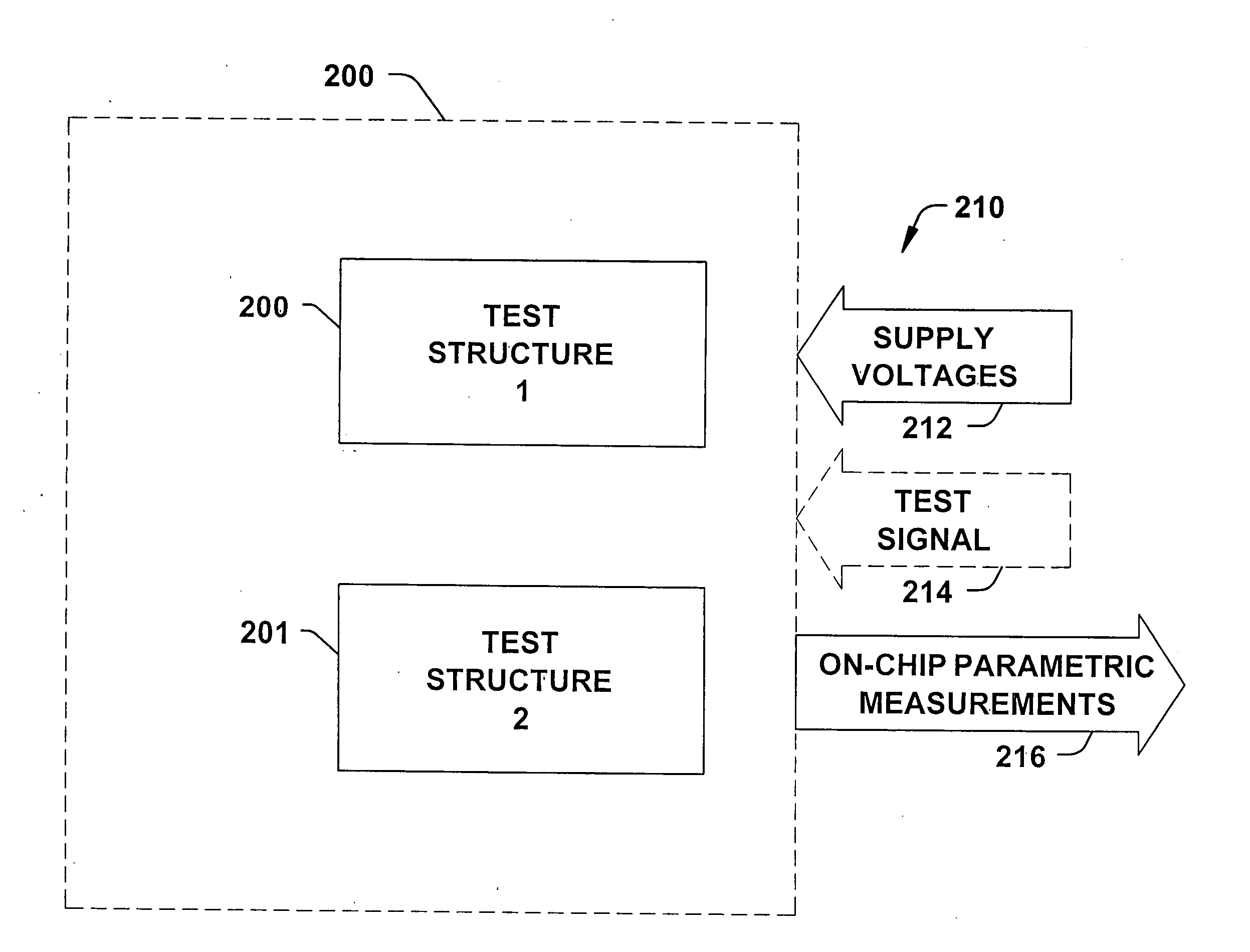
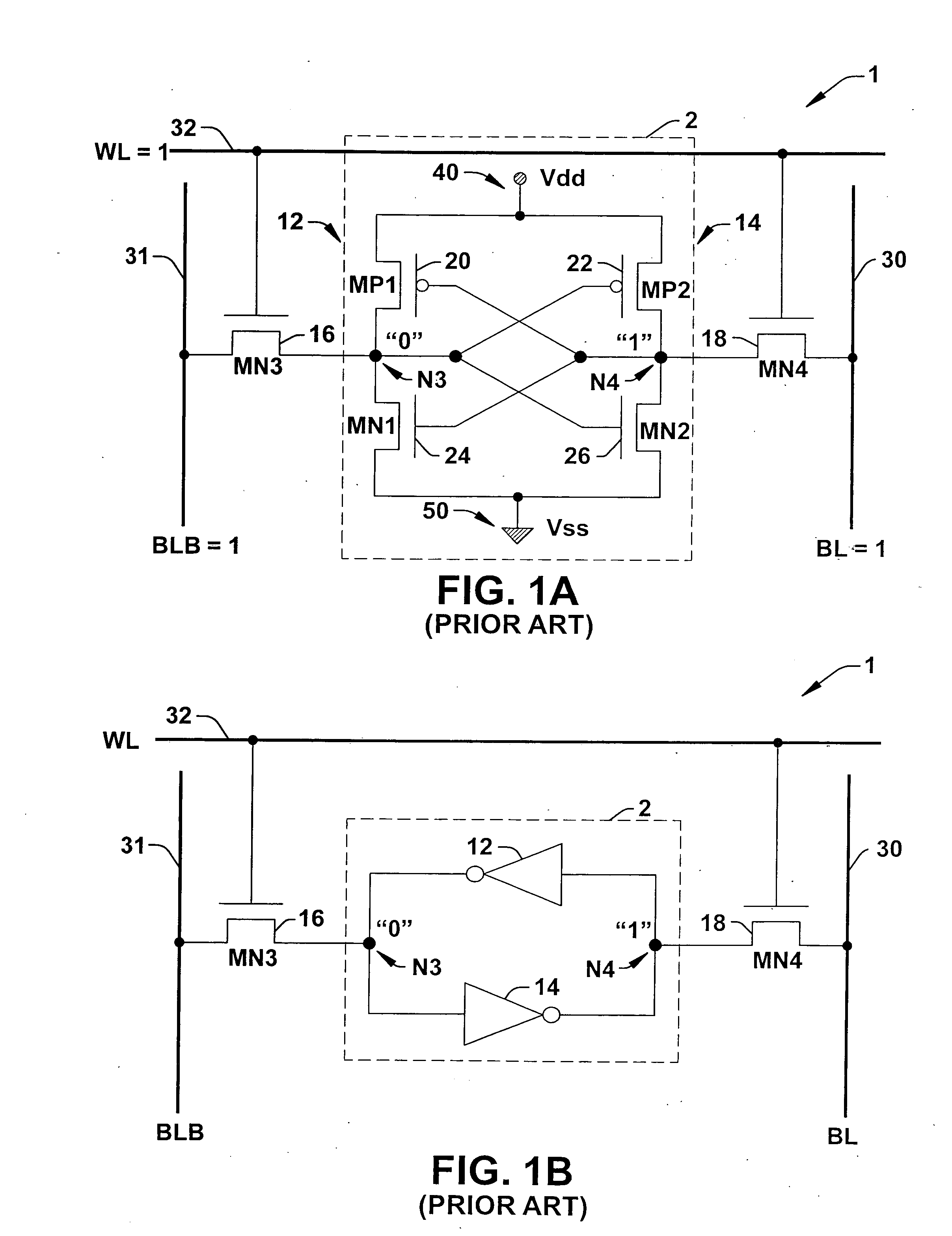
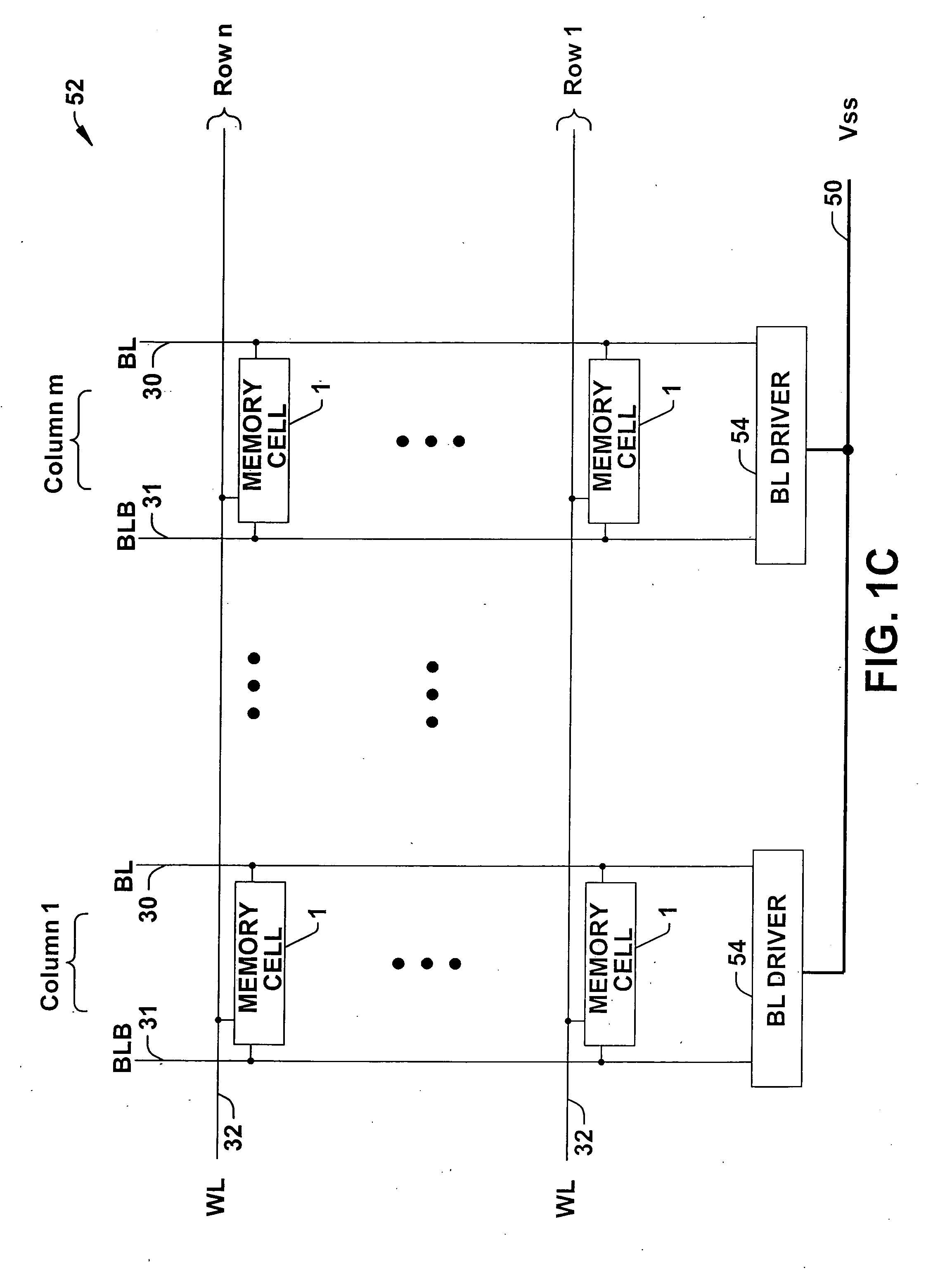
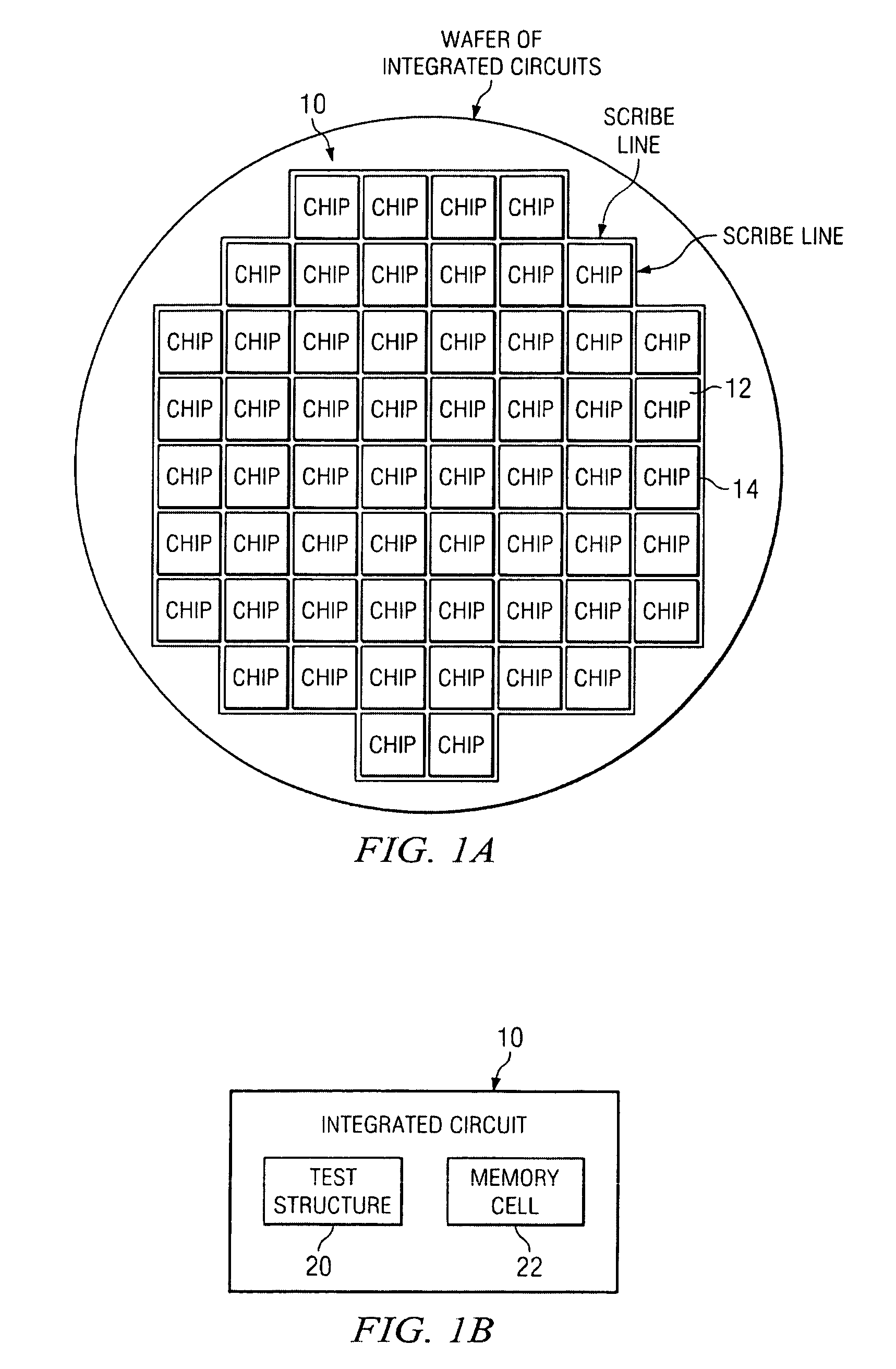
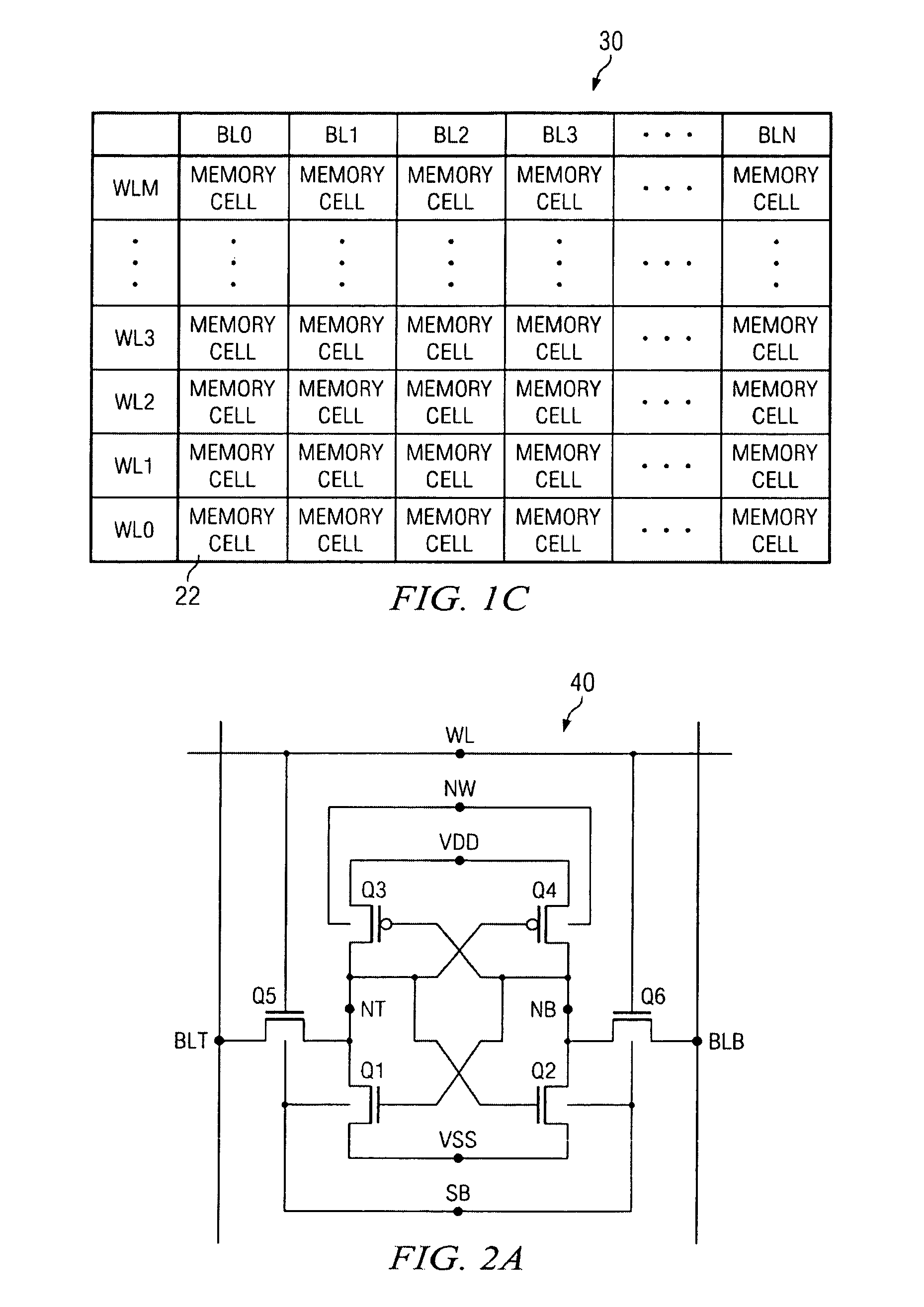
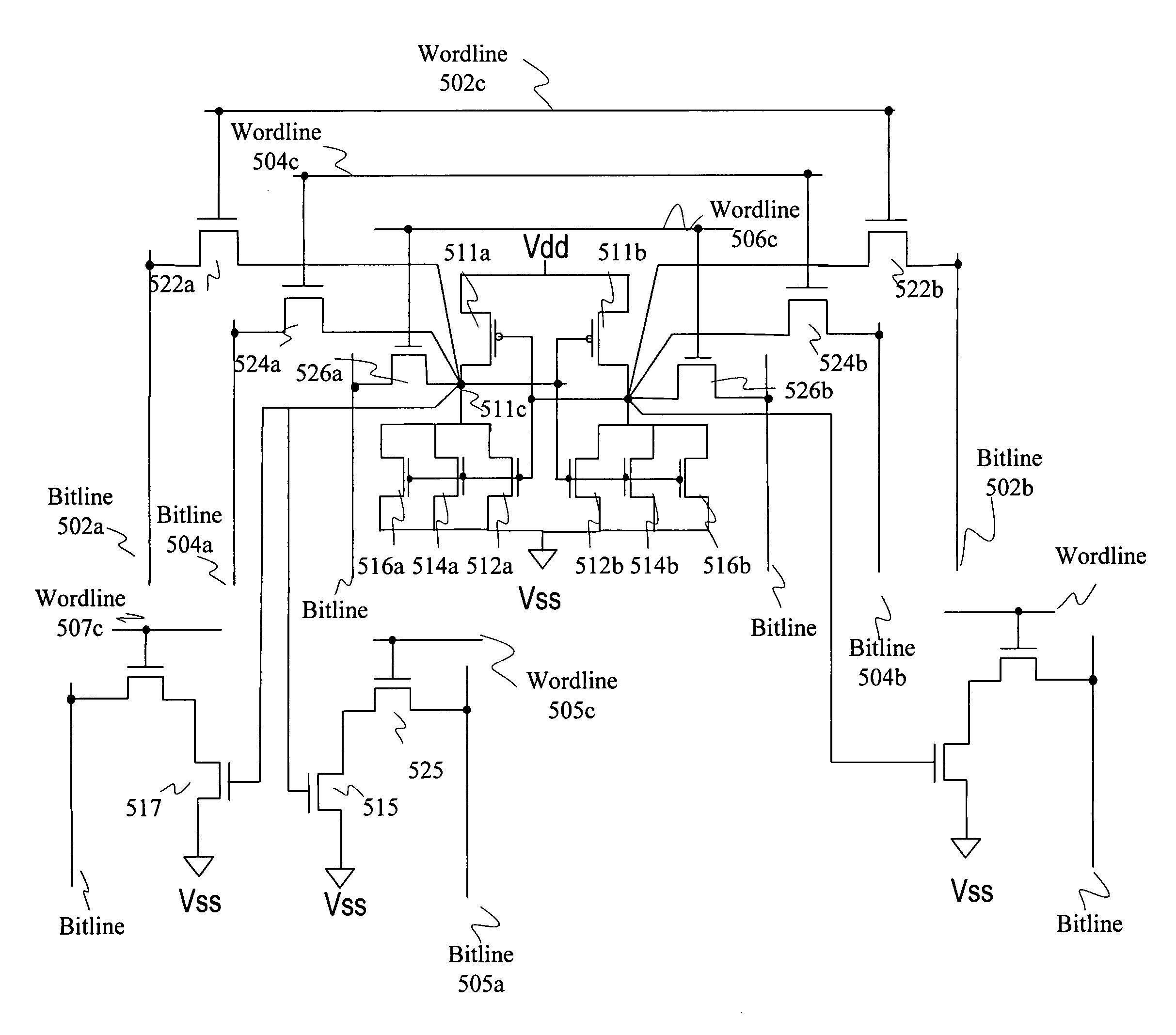
SRAM static noise margin test structure suitable for on chip parametric measurements
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method of Screening Static Random Access Memory Cells for Positive Bias Temperature Instability
ActiveUS20130058177A1Efficient and accurate identificationYield minimizationDigital storageStatic random-access memorySemiconductor materials
A method of screening complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor CMOS integrated circuits, such as integrated circuits including CMOS static random access memory (SRAM) cells, for n-channel transistors susceptible to transistor characteristic shifts over operating time. For the example of SRAM cells formed of cross-coupled CMOS inverters, static noise margin and writeability (Vtrip) screens are provided. Each of the n-channel transistors in the CMOS SRAM cells are formed within p-wells that are isolated from p-type semiconductor material in peripheral circuitry of the memory and other functions in the integrated circuit. Forward and reverse body node bias voltages are applied to the isolated p-wells of the SRAM cells under test to determine whether such operations as read disturb, or write cycles, disrupt the cells under such bias. Cells that are vulnerable to threshold voltage shift over time can thus be identified.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Word line driver circuit for a static random access memory and method therefor
ActiveUS20060104107A1Improve static noise marginReduce decreaseRead-only memoriesDigital storageStatic random-access memoryLow voltage
A static random access memory (14) has a normal mode of operation and a low voltage mode of operation. A memory array (15) includes memory cells (16) coupled to a first power supply node (VDD) for receiving a power supply voltage. A plurality of word line drivers is coupled to word lines of the memory array (15) and to a second power supply node (37). A word line driver voltage reduction circuit (36) has an input coupled to the first power supply node (VDD) and an output coupled to the second power supply node (37) for reducing a voltage on the output in relation to a voltage on the input in response to a low power supply voltage signal, and thus improving a static noise margin of the memory cells (16).
Owner:NXP USA INC
SRAM static noise margin test structure suitable for on chip parametric measurements
A set of memory cell test structures and a method are disclosed for assessment of the static noise margin (SNM) of a memory cell or an array of such cells, for example, of SRAM cells of an integrated circuit device, using discrete point measurement structures provided either on-chip or within the scribe lines. In one embodiment, the set of memory structures comprises first and second test structures, individually comprising a memory cell, having one or more left and right half-bit test structures having hard-wired connections between select nodes of each memory cell half-bit and one or more voltage supplies. The half-bits of the first test structure are configured for measuring respective left and right standby SNM values, and the half-bits of the second test structure are configured for measuring respective left and right cell ratio values at respective output nodes of the structures, using applied supply voltages for on-chip assessment of the static noise margin of the memory cells. The method applies the supply voltages to select nodes of the test structures, measures left and right standby SNM values at a first test structure, measures left and right cell ratio values at a second test structure, determines a first difference between the left half-bit standby SNM value and the right half-bit cell ratio value, determines a second difference between the right half-bit standby SNM value and the left half-bit cell ratio value, and determines a smaller one of the first and second difference values proportional to an SNM value of the cell.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
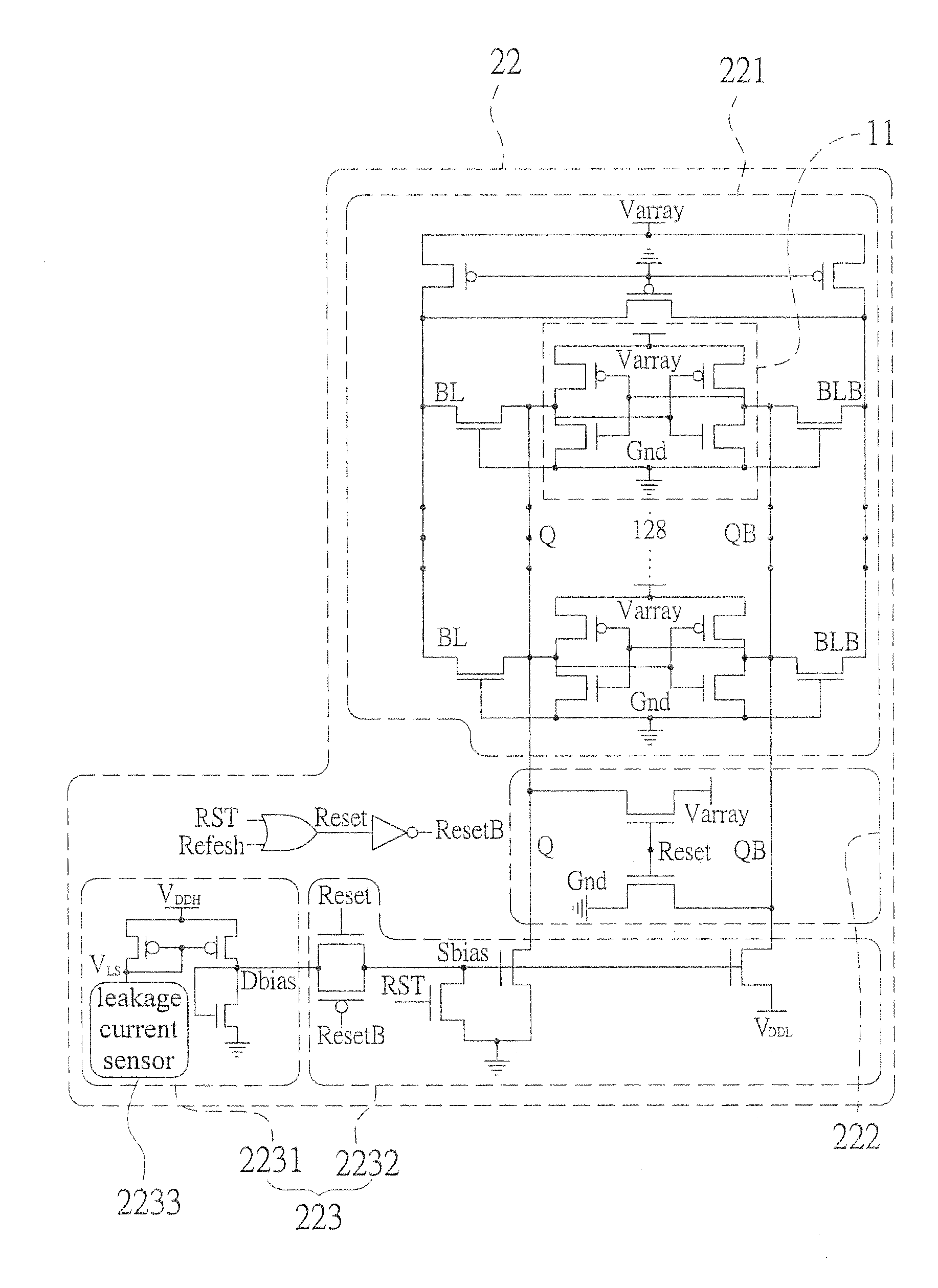
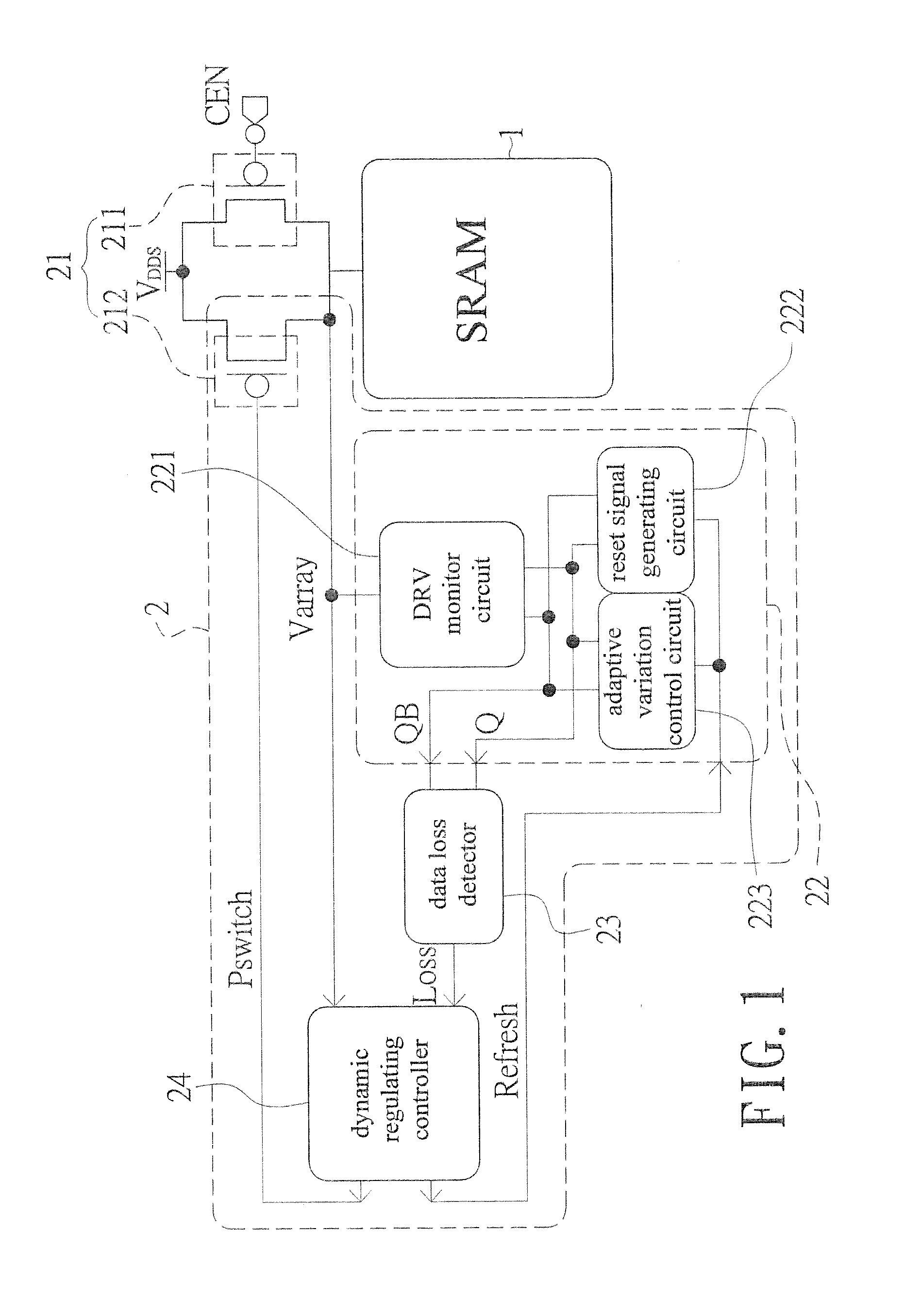
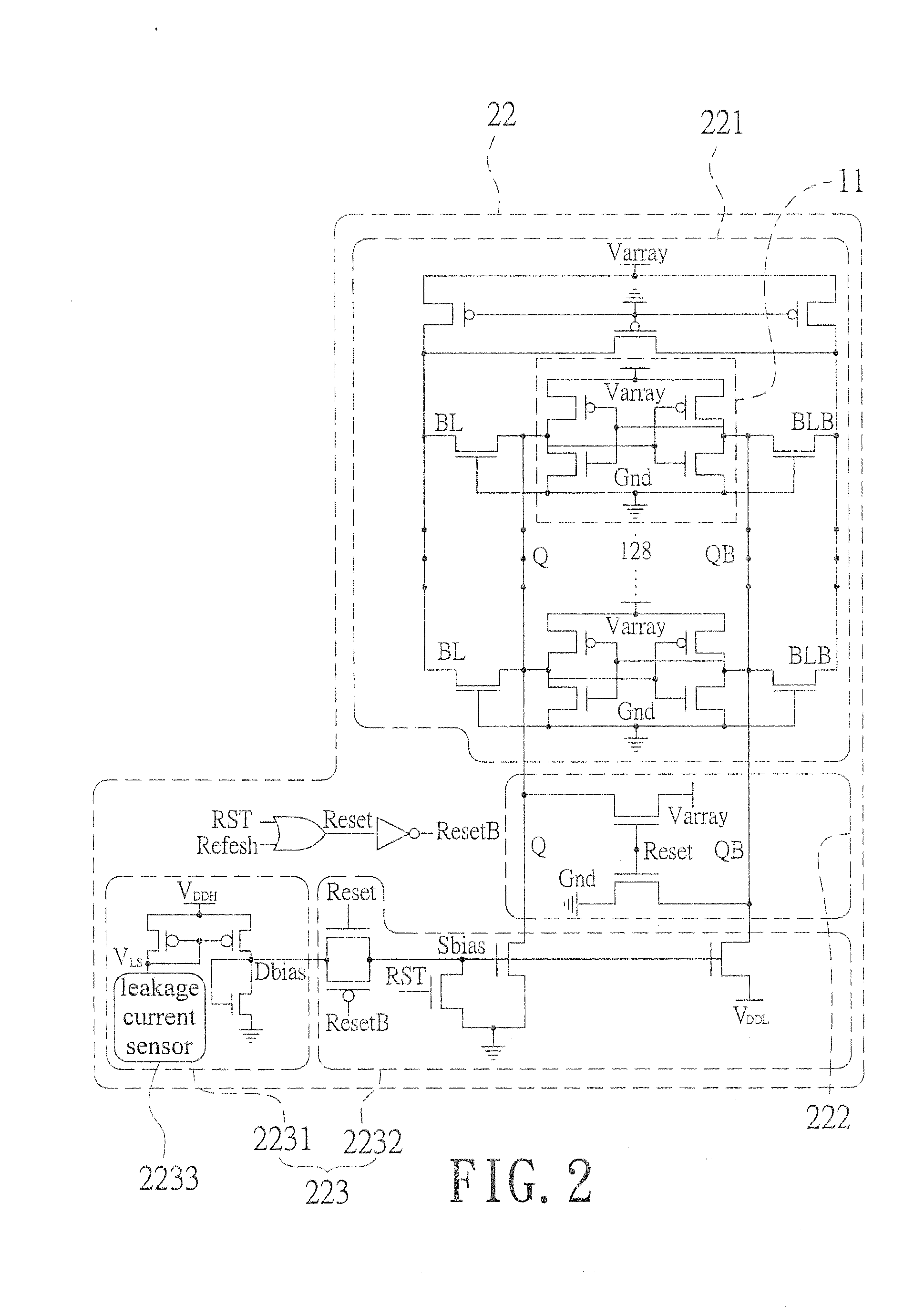
Adaptive data-retention-voltage regulating system for SRAM
InactiveUS20150092477A1Reduce leakage powerReduce power supply voltageDigital storagePower supply for data processingData retention voltageStatic random-access memory
An adaptive data-retention-voltage regulating system for static random-access memory (SRAMs) is revealed. The system includes a power supply unit, a data-retention-voltage (DRV) monitor cell for monitoring static noise margin (SNM) of SRAM, a data loss detector for generating a data loss signal, and a dynamic regulating controller that receives the data loss signal for generating a refresh signal and a switch signal. The DVR monitor cell consists of a DRV monitor circuit mounted with a plurality of memory cells, a reset signal generating circuit for resetting the DRV monitor circuit, and an adaptive variation control circuit that generates noise bias according to leakage current to adjust reaction speed of the DRV monitor circuit correspondingly.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
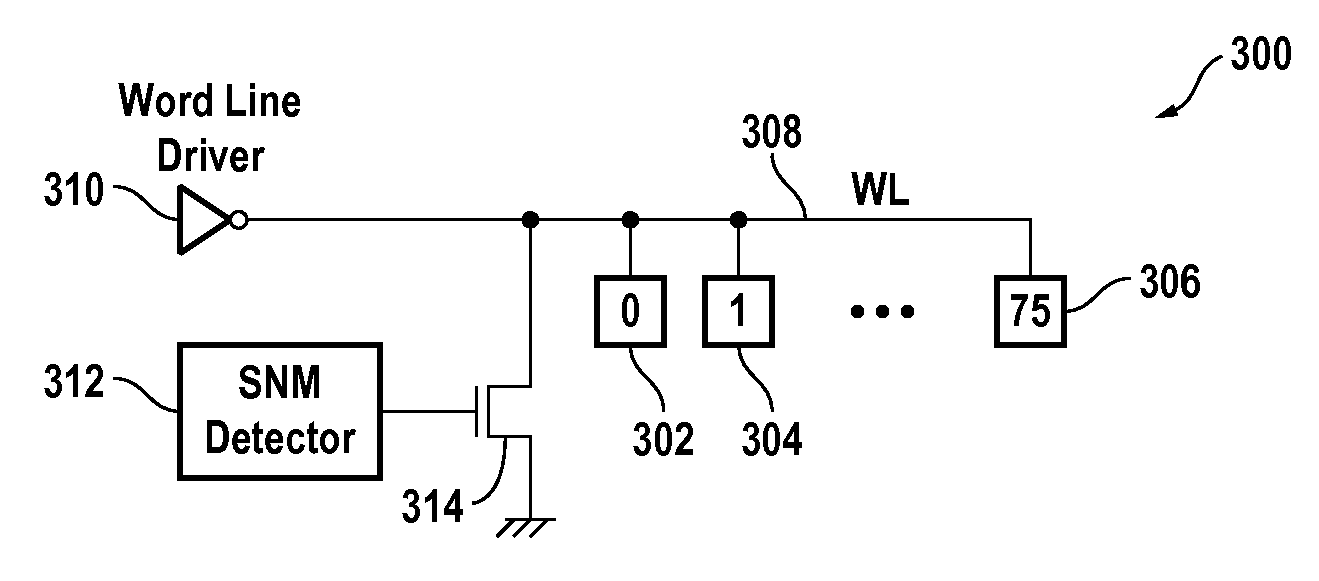
Integrated circuit with improved static noise margin
A static random access memory (“SRAM”) has a plurality of SRAM cells connected to a word line. A static noise margin (“SNM”) detector controls a pull-down transistor that selectively couples the word line to a ground path. The SNM detector is configured to produce a first output signal in response to a SNM event that couples the word line to the ground path, and otherwise produces a second output signal that de-couples the word line from the ground path.
Owner:XILINX INC
Method of reading stored data and semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS6738283B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVoltage dropStatic noise margin
A semiconductor memory device includes a smaller number of elements. A method for reading stored data within the semiconductor memory device suppresses the reduction in the static noise margin accompanying a voltage drop of a power supply voltage, and improves the degree of integration of the circuit.
Owner:SONY CORP
Semiconductor memory device
InactiveCN1542847AStatic Noise Margin OptimizationTransistorSolid-state devicesComputer architectureStatic noise margin
A substrate potential setting circuits are provided which control substrate potentials in units of columns of a memory cell array at least in data writing. Upon data writing, the potential of the substrate region of memory cell transistors on a selected column is changed to reduce the data holding characteristics (static noise margin) to ensure high-speed data writing to the memory cells. Data writing is performed at high speed without impairing stability of data retention.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Double-bit-line sub-threshold storage unit circuit
InactiveCN102543157AReduce capacitanceReduce in quantityDigital storageOxide semiconductorStatic noise margin
The invention discloses a double-bit-line sub-threshold storage unit circuit which employs double-end read-write operation. The double-bit-line sub-threshold storage unit circuit comprises a first phase inverter and a second phase inverter, wherein the two phase inverters are connected to form a cross coupling; and by employing a double-bit-line structure of separating read bit lines from write bit lines, two storage nodes of the cross coupling are respectively connected to two write bit lines through an N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) tube, and another two storage nodes of the cross coupling are respectively connected to two read bit lines through the NMOS tube and a P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) tube. The double-bit-line sub-threshold storage unit circuit has the advantages that: by employing a PMOS substrate regulation technology, substrate ends of all PMOS tubes are connected to gate ends, so on the premise that additional management power consumption is not improved and the performance is not reduced, the energy consumption of dynamic operation and the leakage power consumption of static operation of a system can be reduced simultaneously, the static noise margin of a storage unit is improved, and the performance of the system is optimized.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Method for memory cell characterization using universal structure
ActiveUS7924640B2Accurate measurementComplete characterizationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementUniversal structureSource type
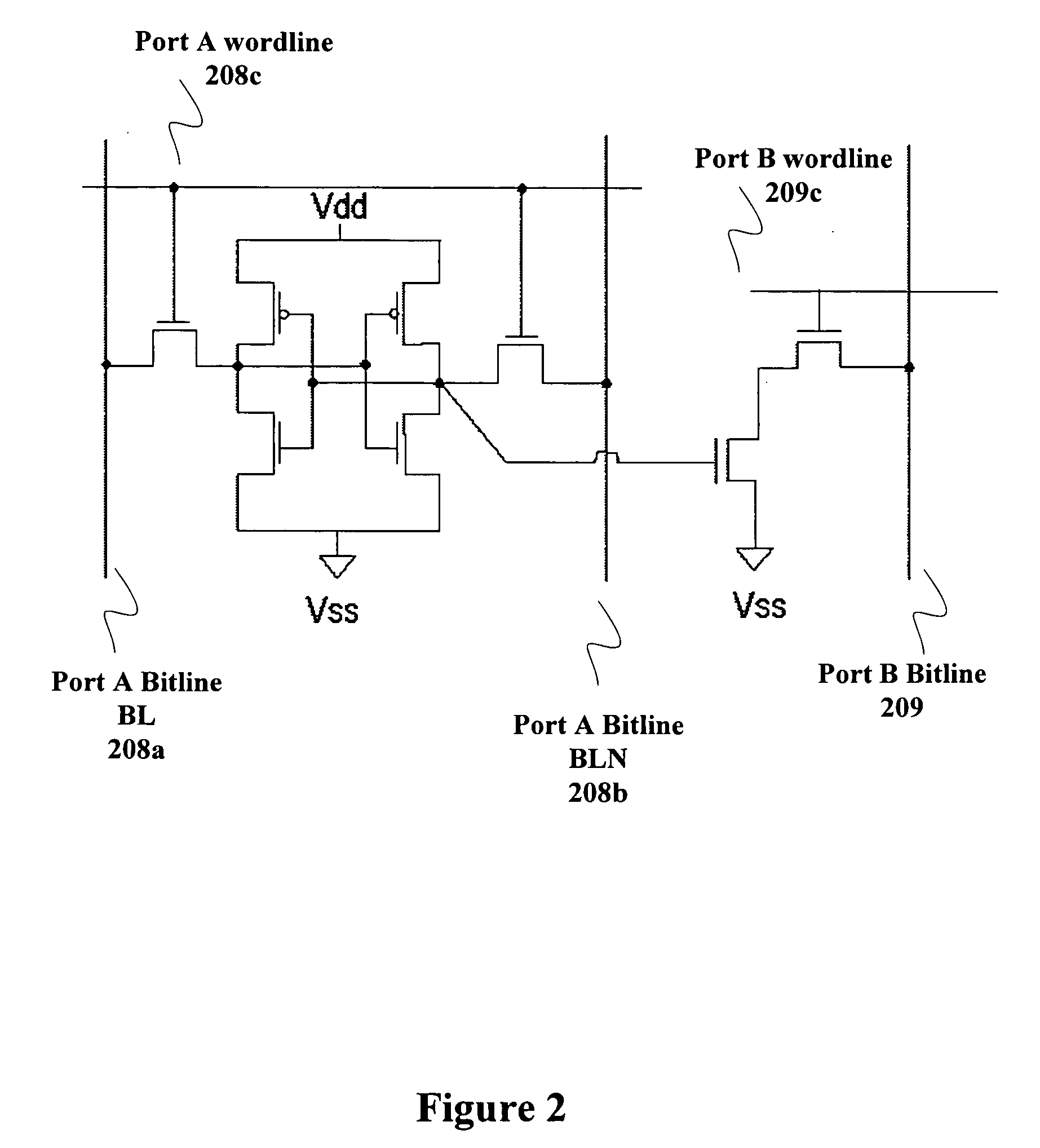
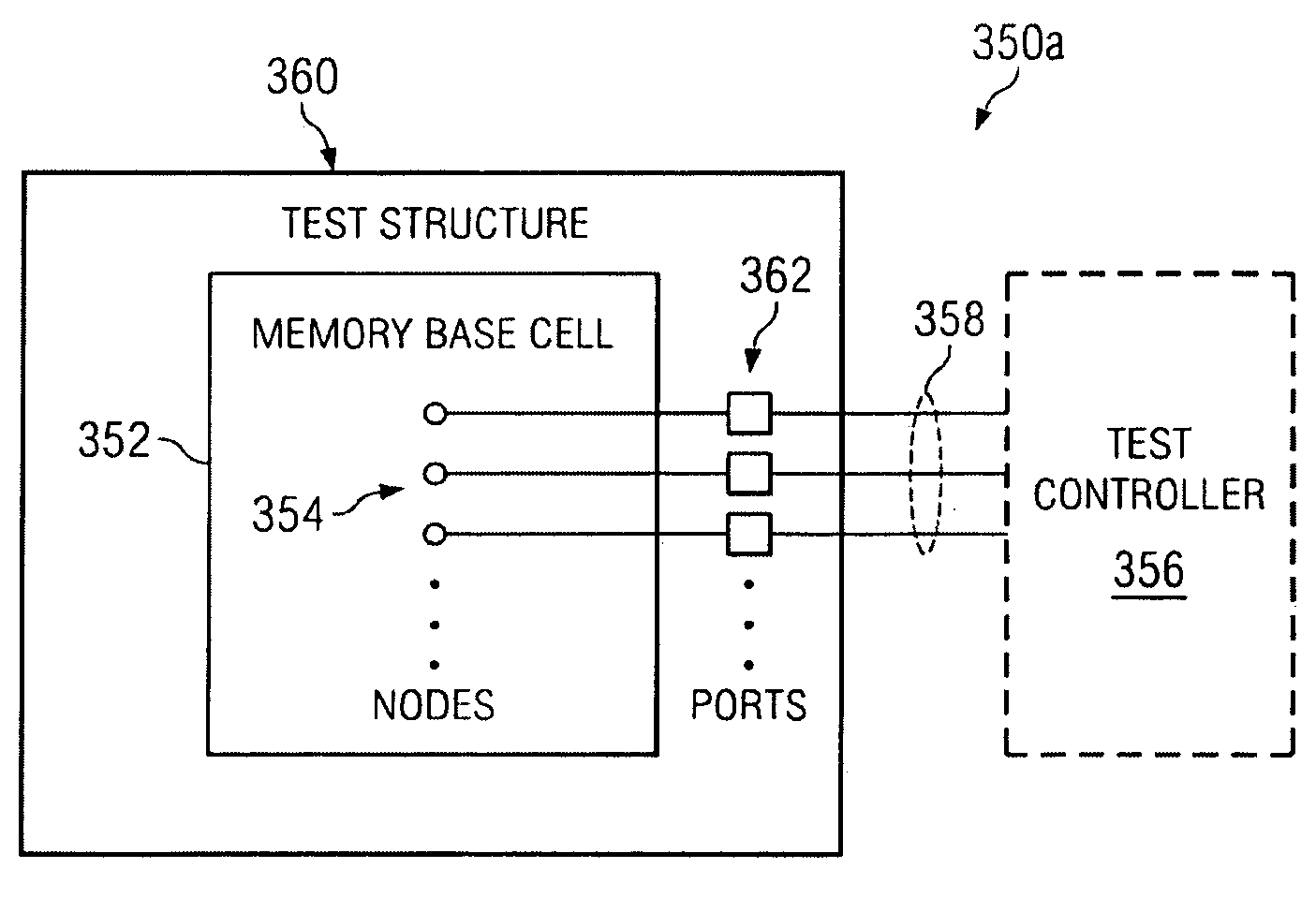
A test method includes providing an integrated circuit, where the integrated circuit includes a memory base cell, where the memory base cell includes a first storage node set, a second storage node set, a set of other nodes, and a set of circuit elements each having a plurality of terminals, where the set of other nodes includes a first data node for accessing the first storage node set, a first access control node for controlling the access of the first storage node set, a first supply node for supplying the first storage node set, and a second supply node for supplying the second storage node set, where the first and second supply nodes are of the same sinking or sourcing type. The method further includes conducting a circuit element test on a circuit element in the set of circuit elements, where in the circuit element test the first and second supply nodes are not connected together, each terminal of the circuit element is directly forced with an electrical quantity, and an electrical quantity is directly measured from a terminal of the circuit element. Further, the method includes conducting at least one of a static noise margin test or a full cell test on the memory base cell.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Modular design of multiport memory bitcells
InactiveUS20080013383A1Reduce complexityEasy interconnectionTransistorSolid-state devicesAccess timeWrite margin
The present invention provides a system and method for designing and modularly expanding multiport bitcells. A modular design approach is described that reduces the complexity of designing multiport bitcells while complying with DFM rules across various semiconductor fabrication providers. The modular design may be parsed into modules such as read port modules, write port modules, and pull-up modules that may be easily interconnected to build a multiport bitcell. These modules may also be independently sized and assembled to achieve desired read margins, write margins, static noise margins as well as read access times and write times.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method for memory cell characterization using universal structure
ActiveUS20080148116A1Accurate measurementComplete characterizationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSource typeUniversal structure
A test method includes providing an integrated circuit, where the integrated circuit includes a memory base cell, where the memory base cell includes a first storage node set, a second storage node set, a set of other nodes, and a set of circuit elements each having a plurality of terminals, where the set of other nodes includes a first data node for accessing the first storage node set, a first access control node for controlling the access of the first storage node set, a first supply node for supplying the first storage node set, and a second supply node for supplying the second storage node set, where the first and second supply nodes are of the same sinking or sourcing type. The method further includes conducting a circuit element test on a circuit element in the set of circuit elements, where in the circuit element test the first and second supply nodes are not connected together, each terminal of the circuit element is directly forced with an electrical quantity, and an electrical quantity is directly measured from a terminal of the circuit element. Further, the method includes conducting at least one of a static noise margin test or a full cell test on the memory base cell.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com