Patents
Literature
369 results about "Standby current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Standby current is the current that a device draws when it is not actively performing its function. This current would be measured in amperage, and commonly amperes, milliamperes or microamperes would be the units of measurement.
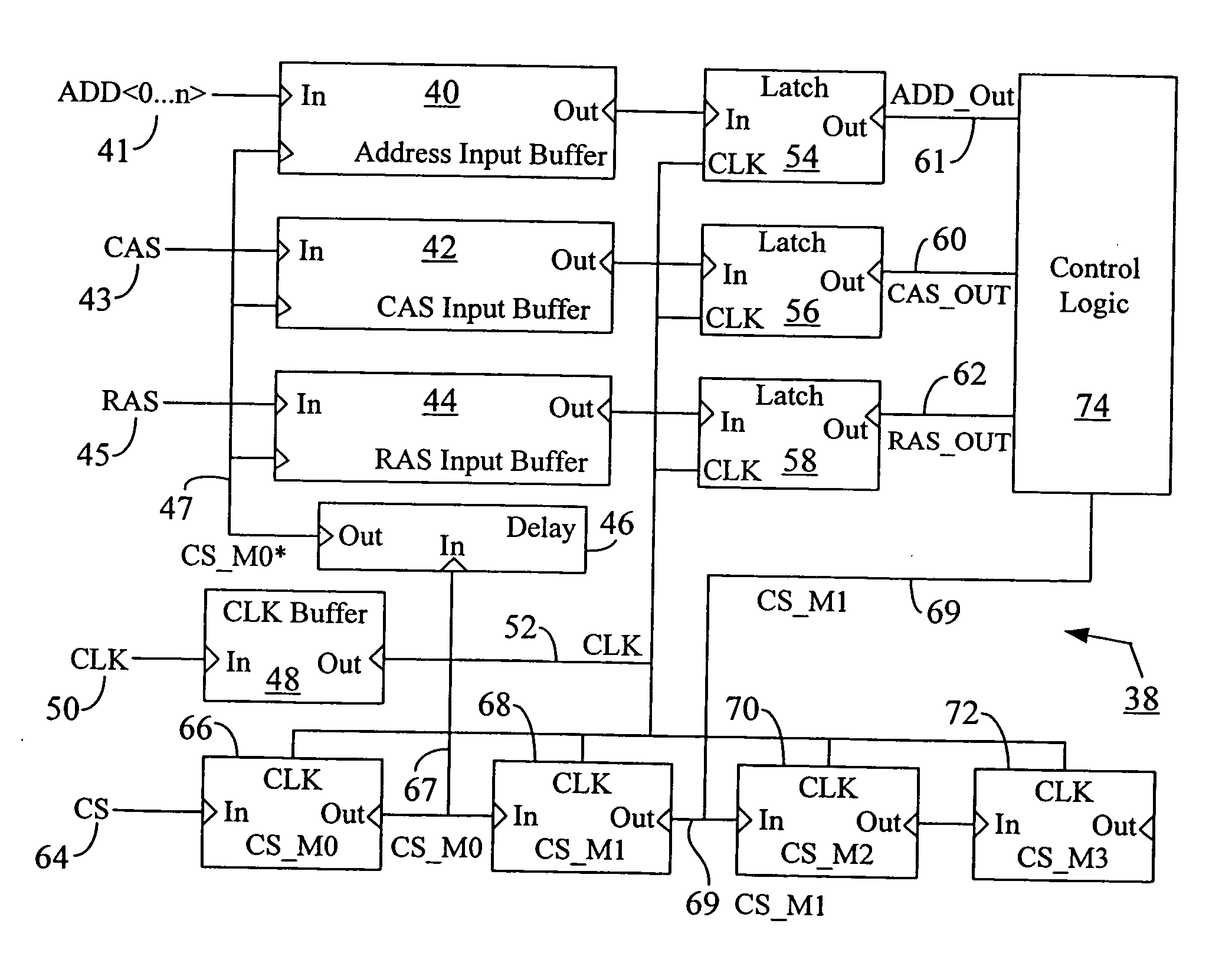
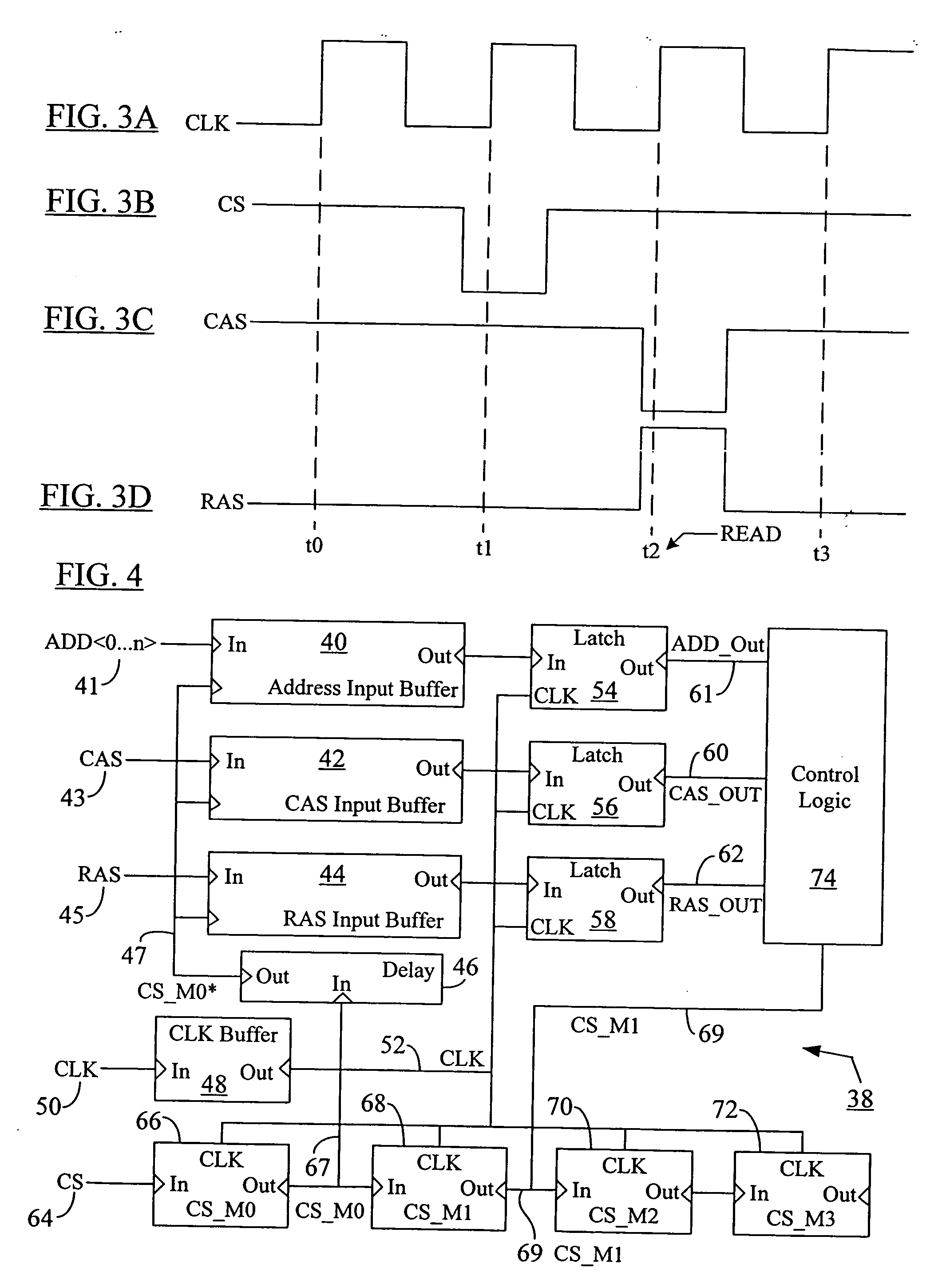
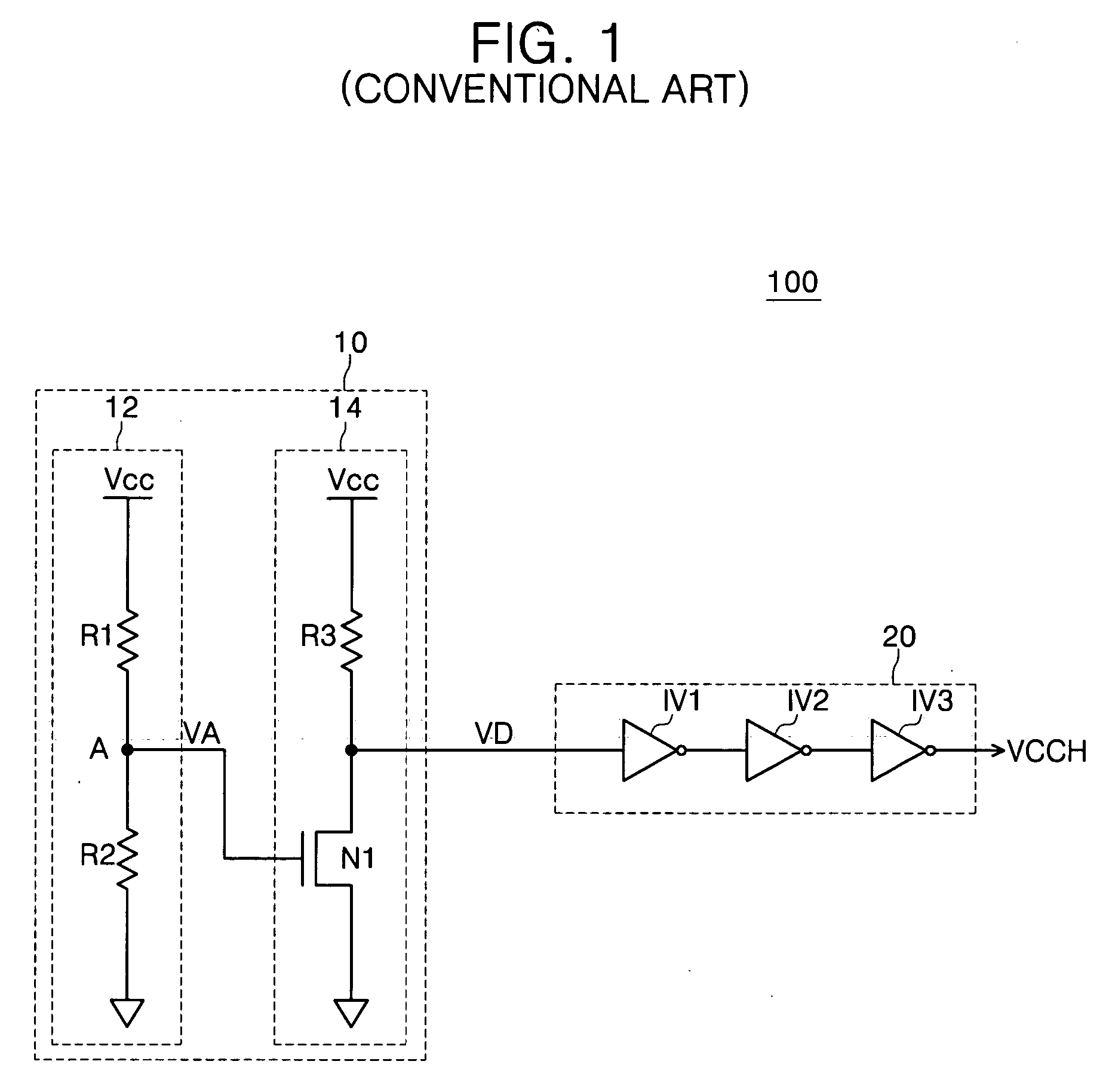
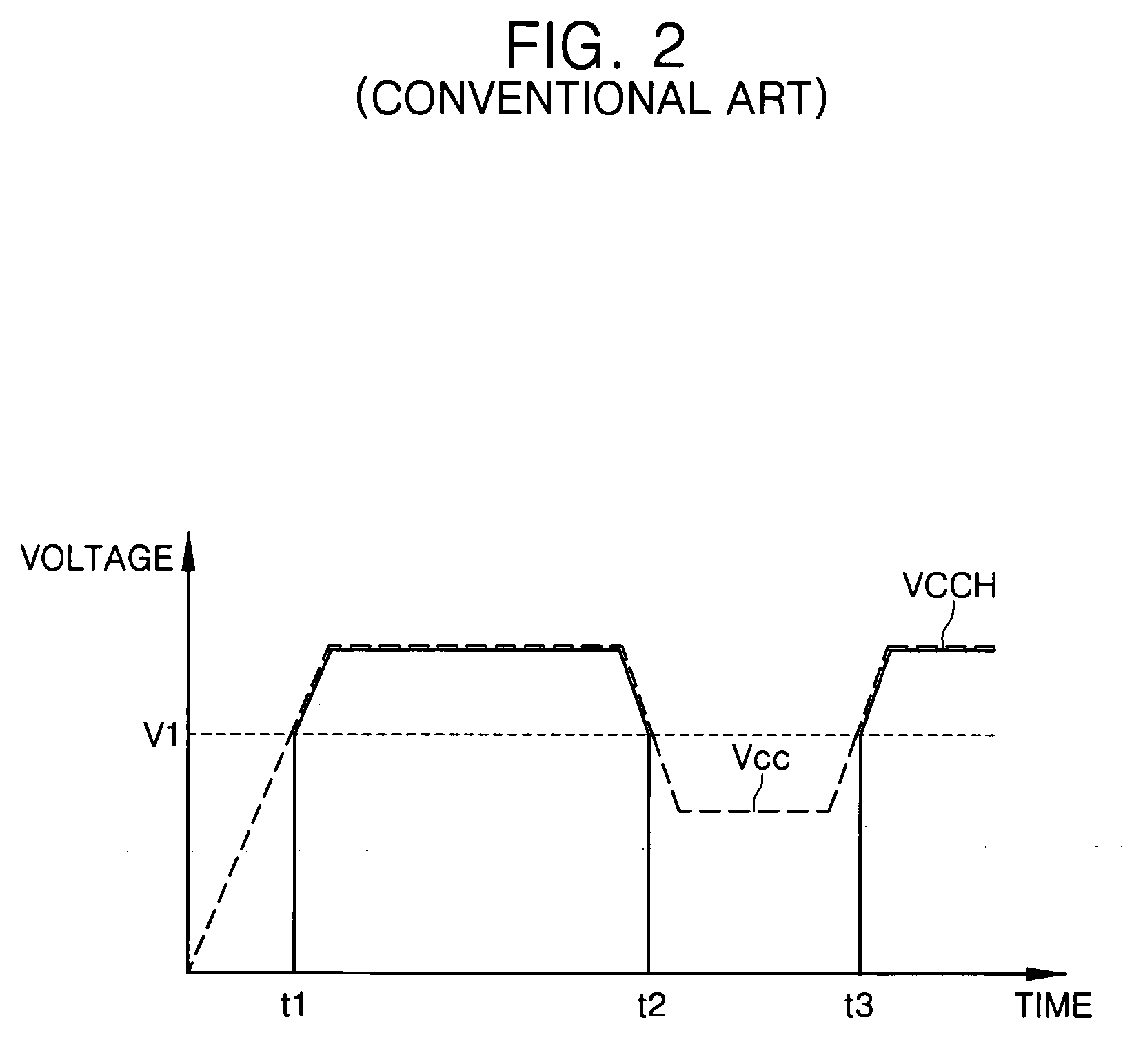
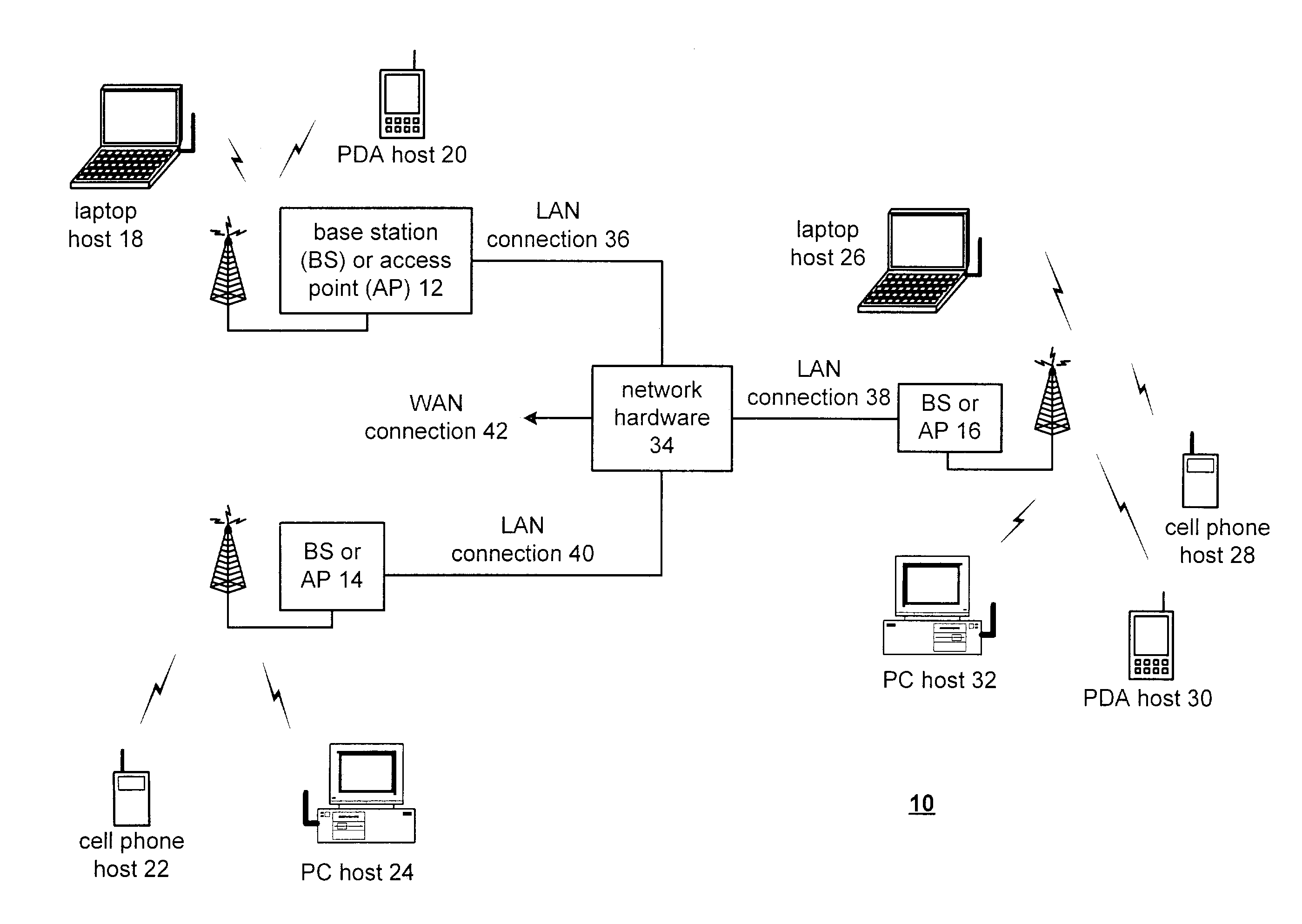
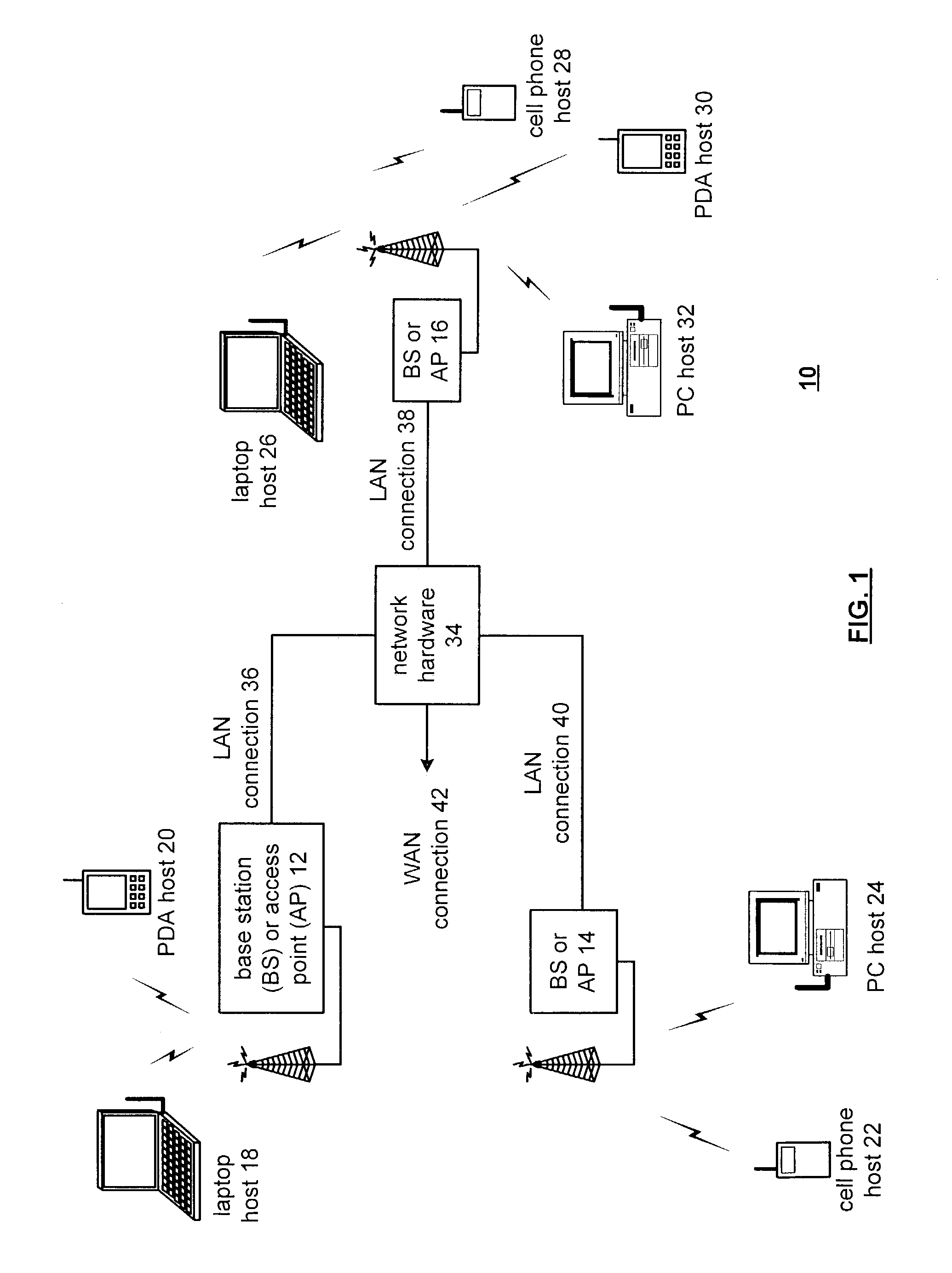
Low power chip select (CS) latency option
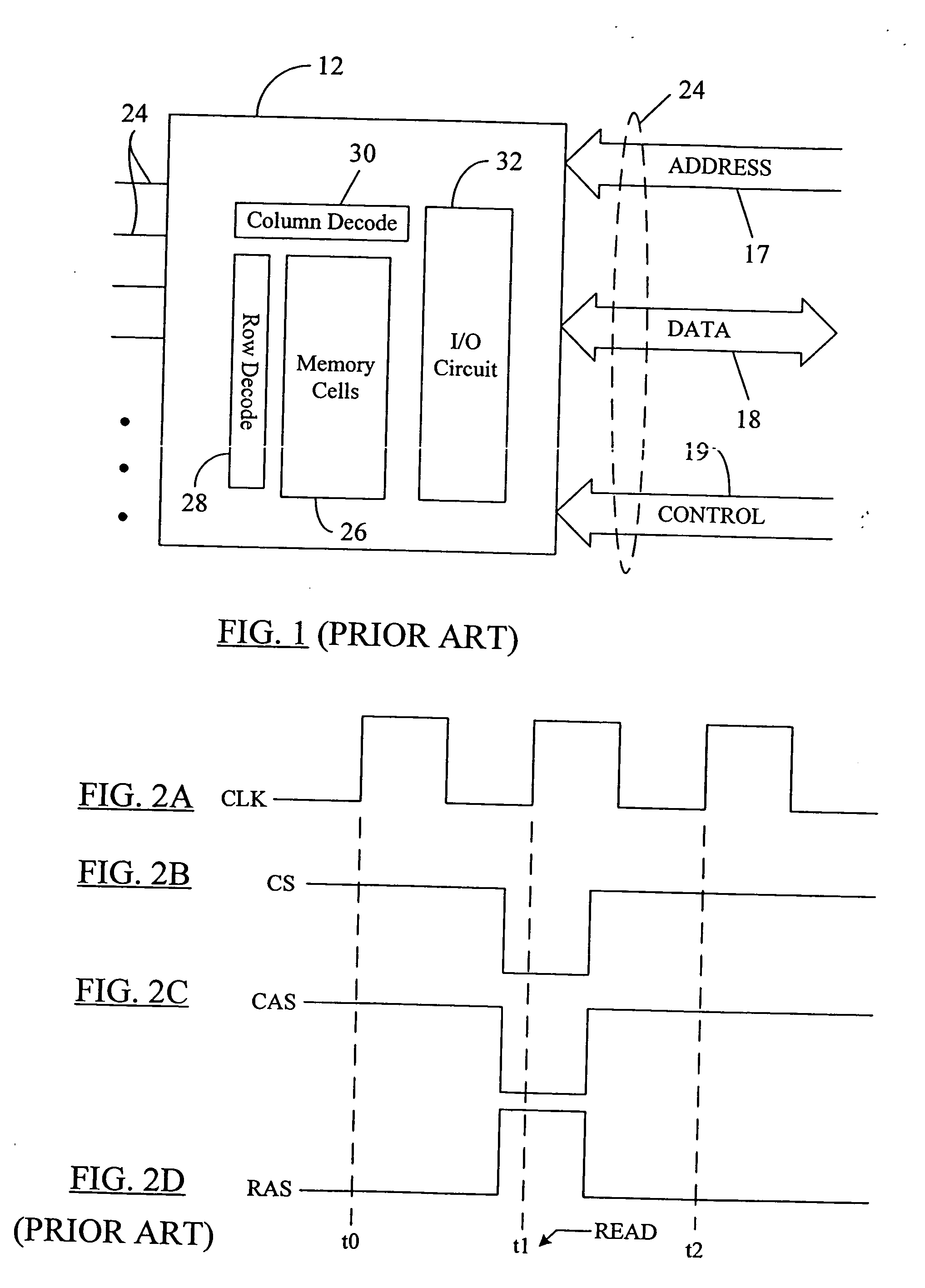
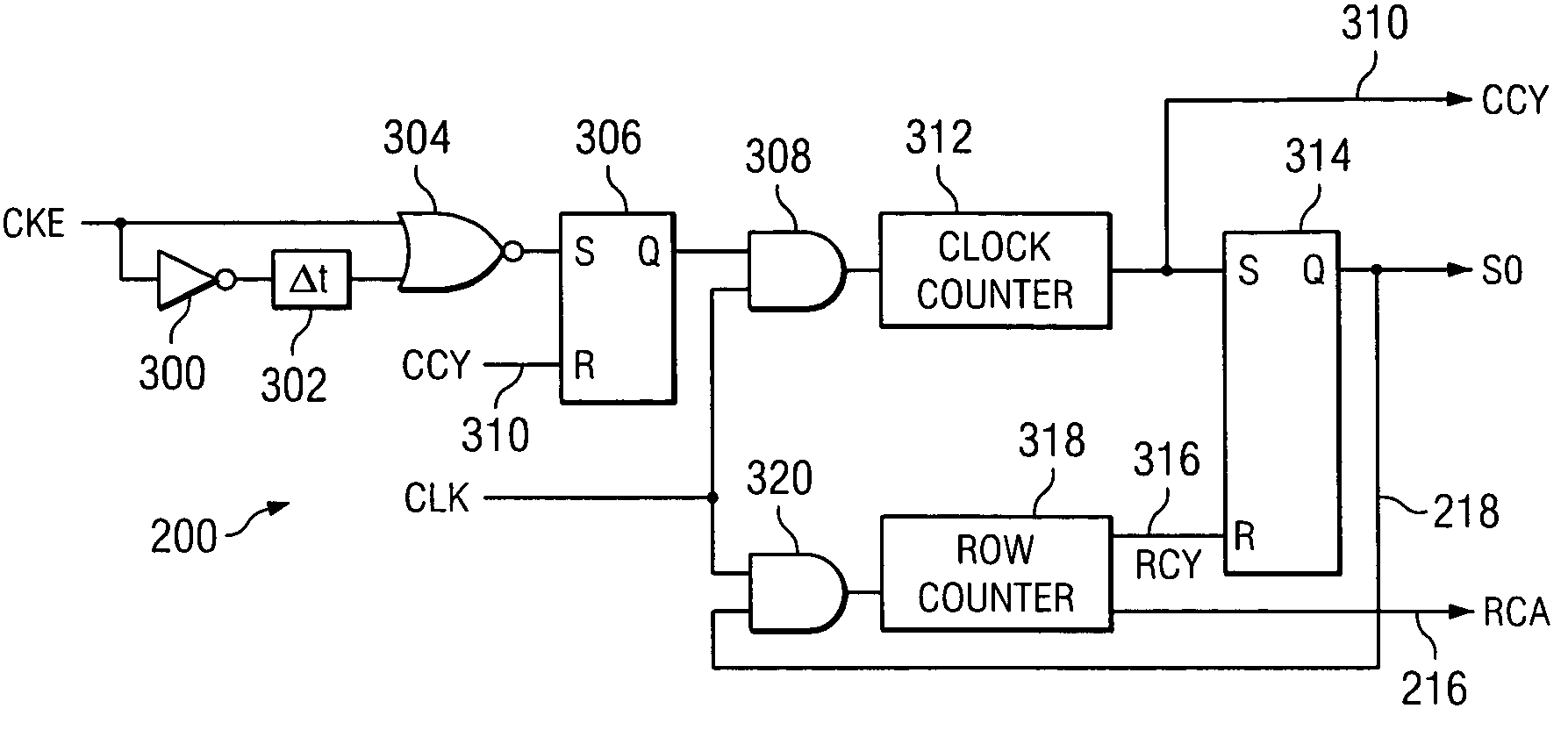
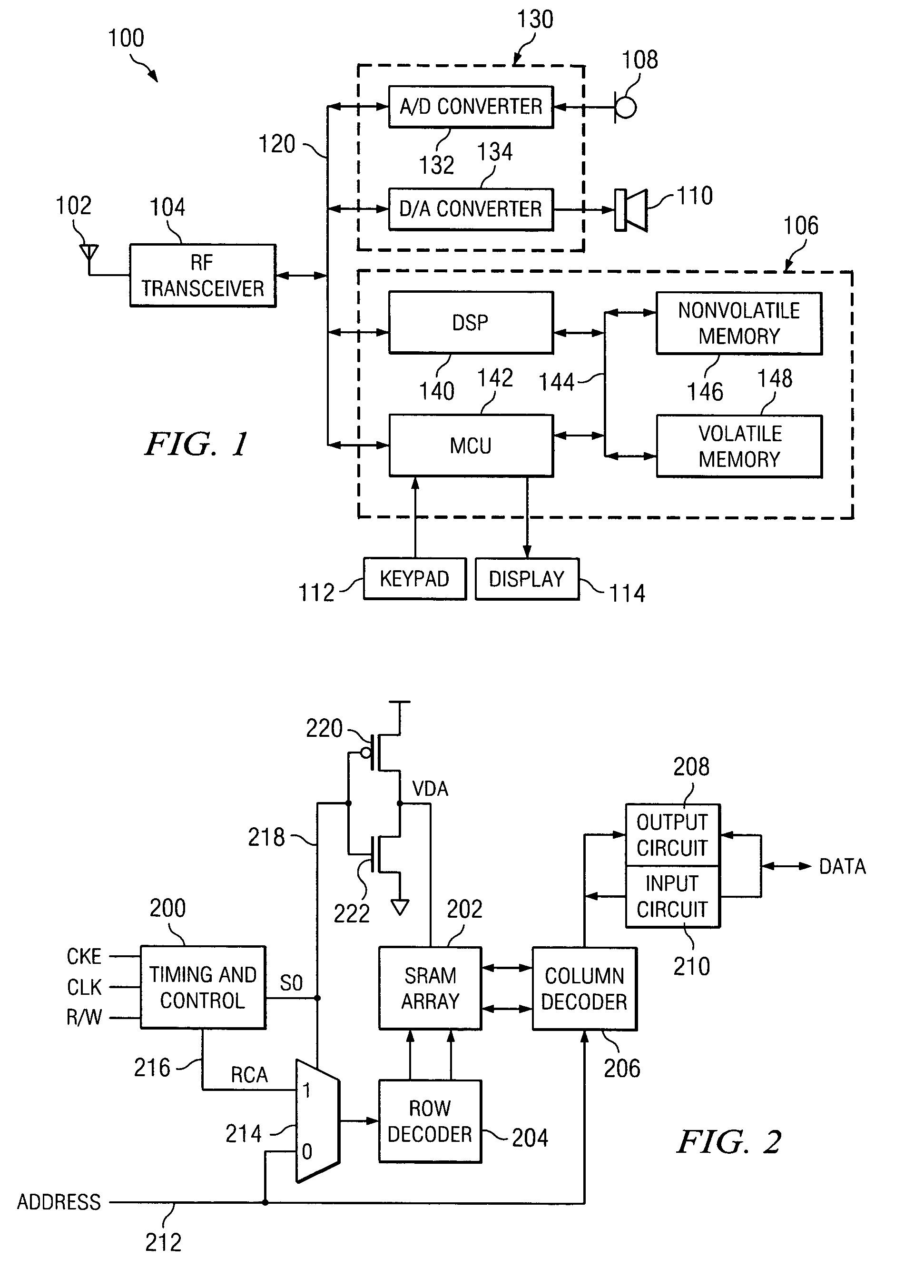
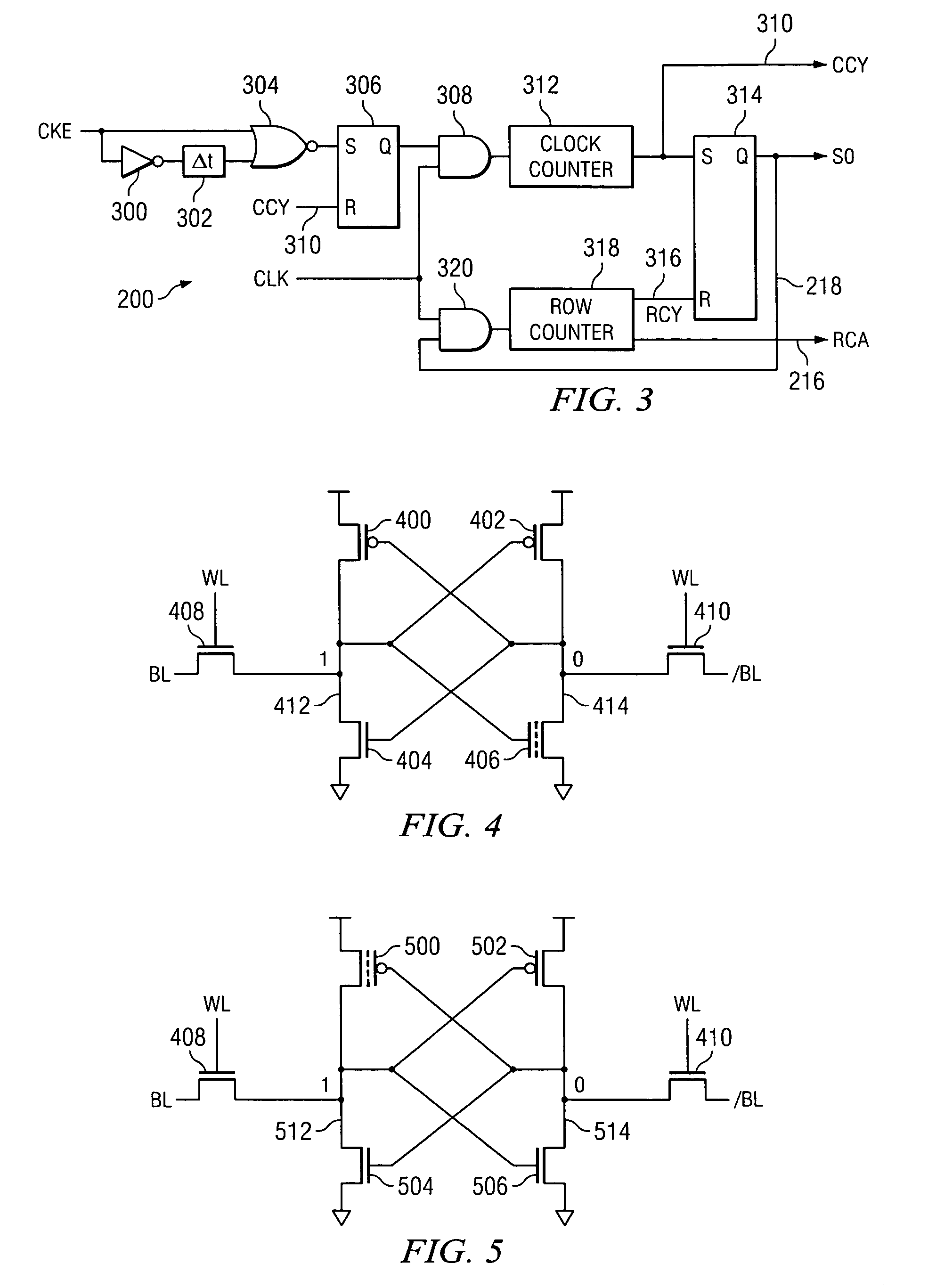
A system and method to reduce standby currents in input buffers in an electronic device (e.g., a memory device) is disclosed. The input buffers may be activated or deactivated by the state of a chip select (CS) signal. In case of a memory device, the active and precharge standby currents in memory input buffers may be reduced by turning off the input buffers when the CS signal is in an inactive state. A memory controller may supply the CS signal to the memory device at least one clock cycle earlier than other control signals including the RAS (row address strobe) signal, the CAS (column address strobe) signal, the WE (write enable) signal, etc. A modified I / O circuit in the memory device may internally delay the CS signal by at least one clock cycle to coincide its timing with the RAS / CAS signals for normal data access operation whereas the turning on / off of the memory input buffers may be performed by the CS signal received from the memory controller on the previous cycle. Thus, activation and deactivation of memory input buffers may be performed without forcing the memory device into power down mode and without employing complex circuits for power management. Because of the rules governing abstracts, this abstract should not be used to construe the claims.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
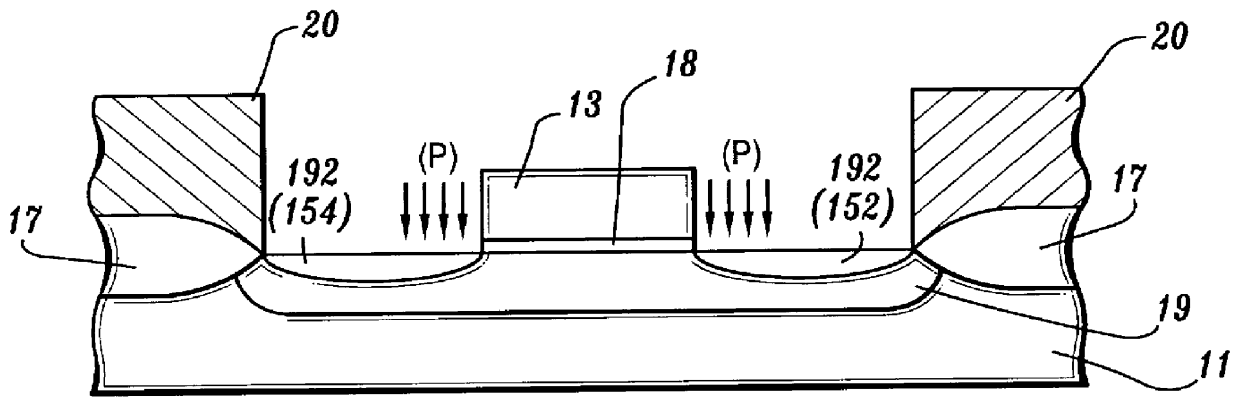
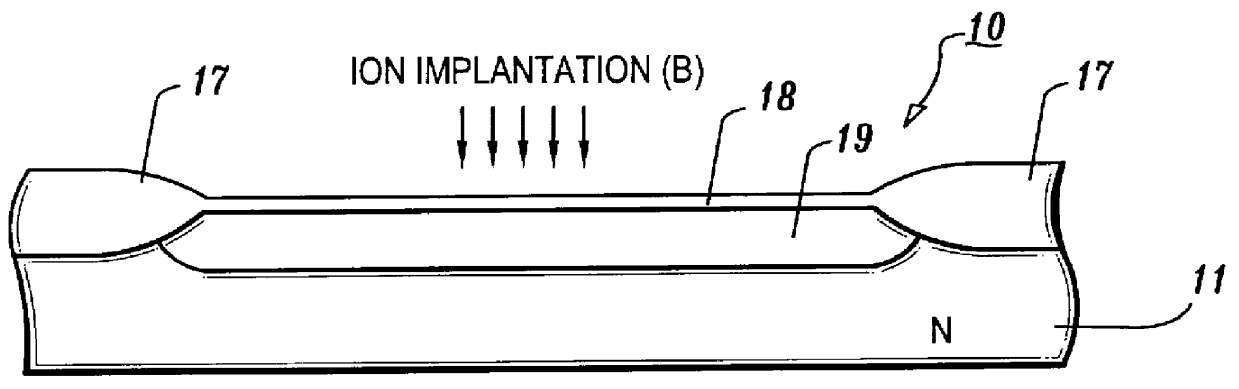
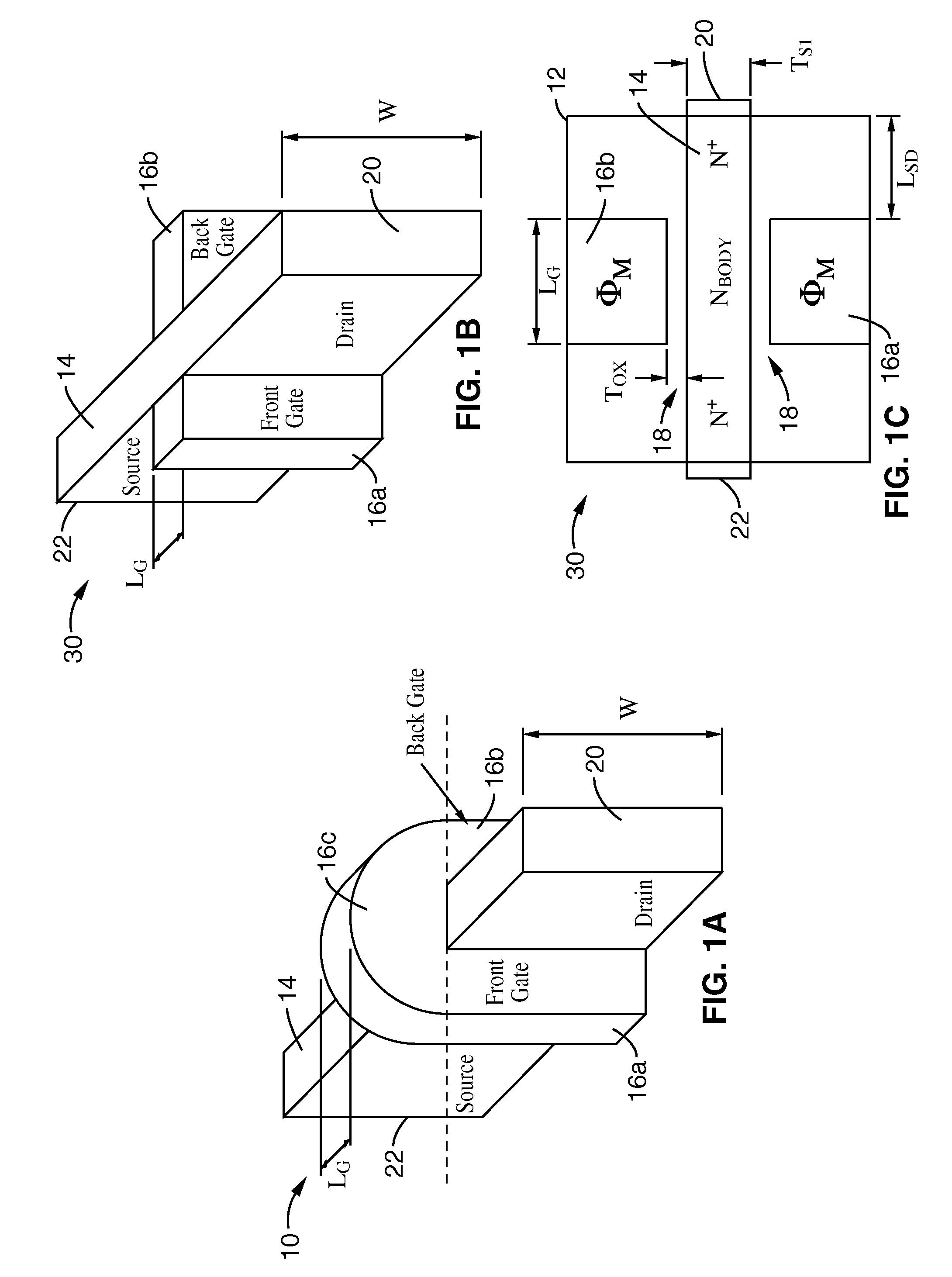
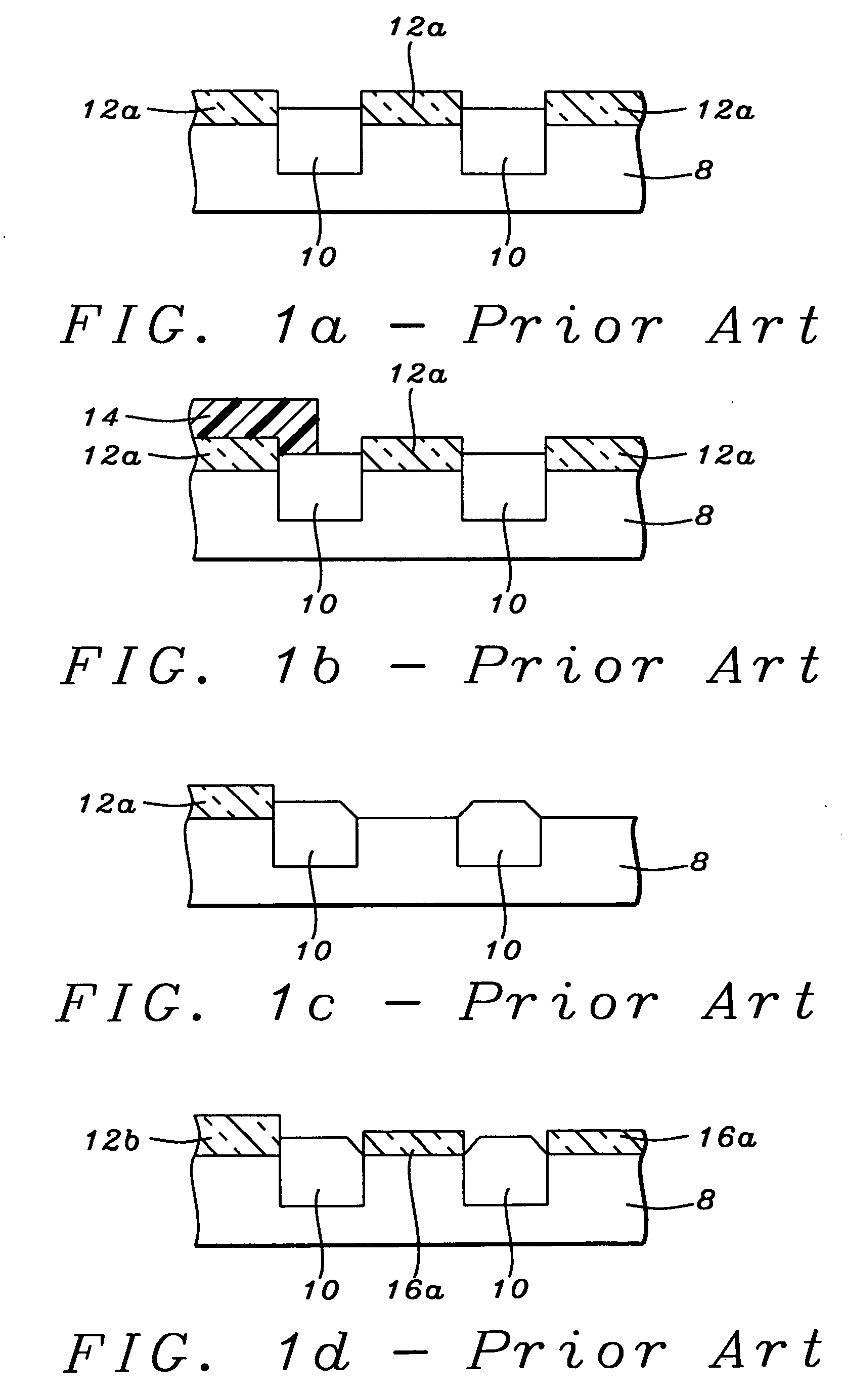
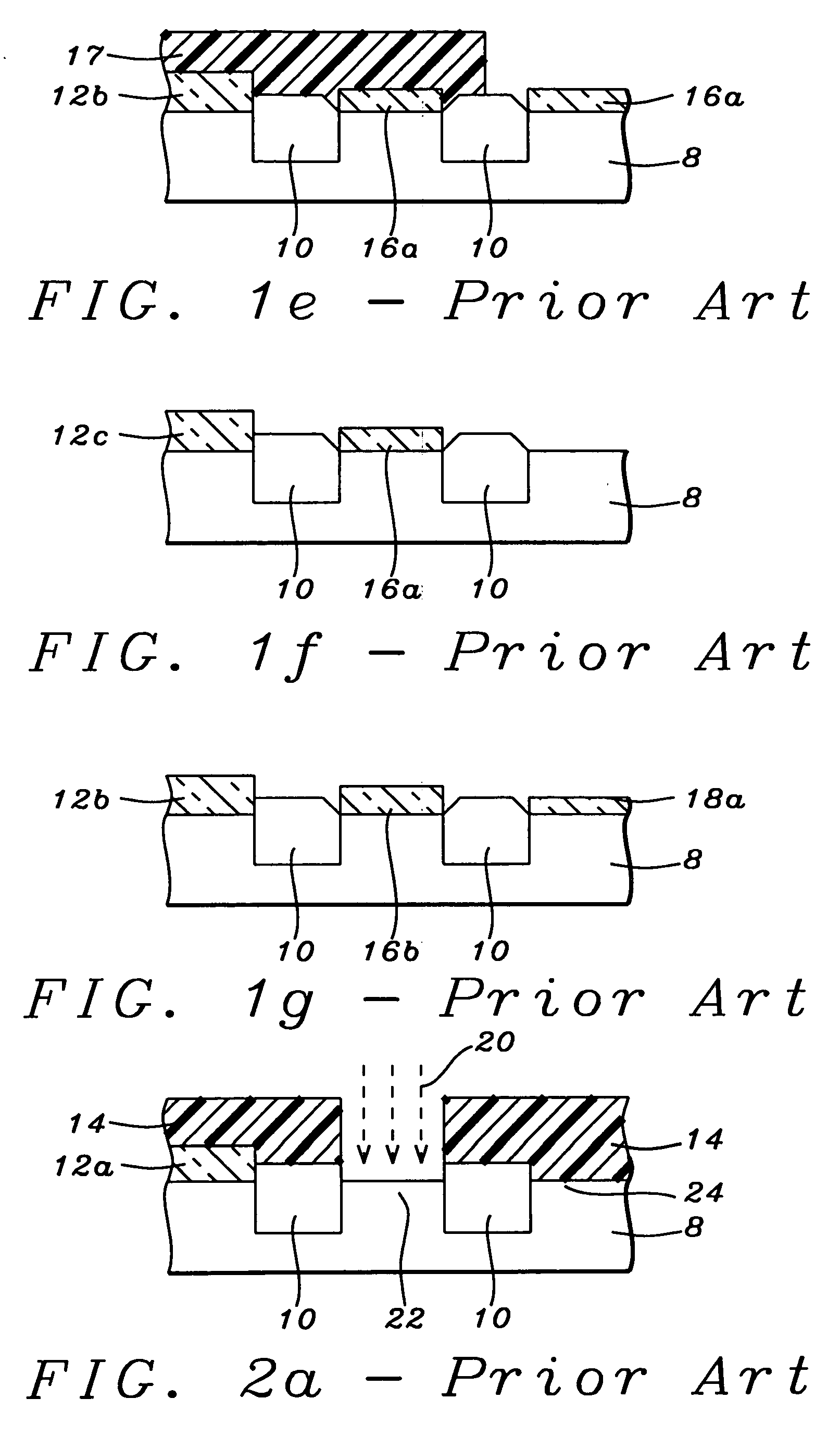
Semiconductor device having opposite-polarity region under channel
InactiveUS6163053ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical polarityEngineering
A semiconductor device and fabrication method thereof are provided, which include an opposite-polarity region formed in a predetermined location under a gate channel region, having a conductive property opposite to that of a surrounding well region. The gate voltage is controlled so that a second depleted layer region is induced concurrently with the opposite-polarity region by the applied gate voltage and can be coupled with a first depleted region which is formed under the channel region and is controllable by the applied gate voltage. In this structure of the semiconductor device, drain current of the device is rendered more responsive to the applied gate voltage, and leakage currents at a certain applied drain voltage and at zero gate voltage are reduced, thereby reducing the standby currents of the semiconductor device.
Owner:RICOH KK
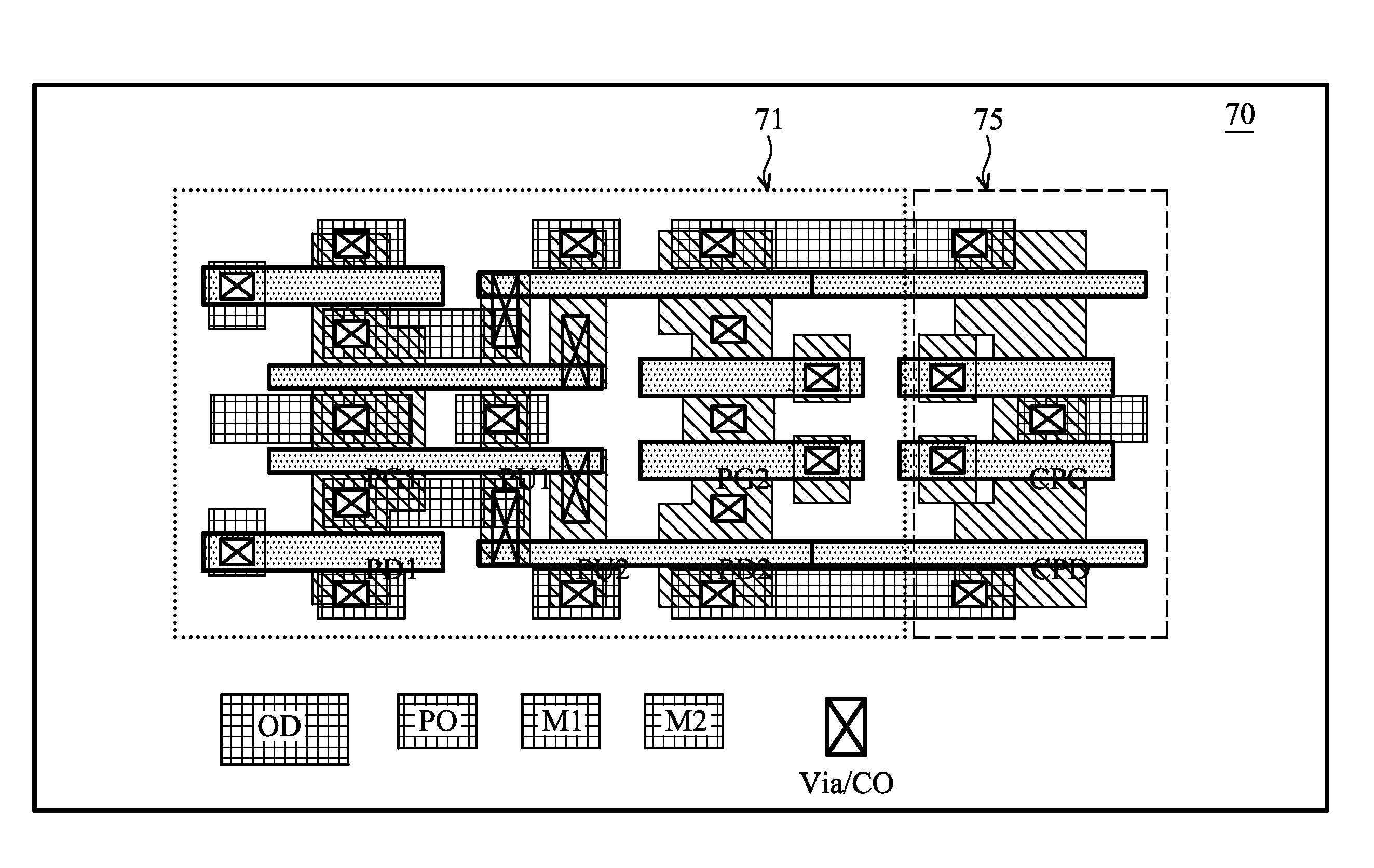
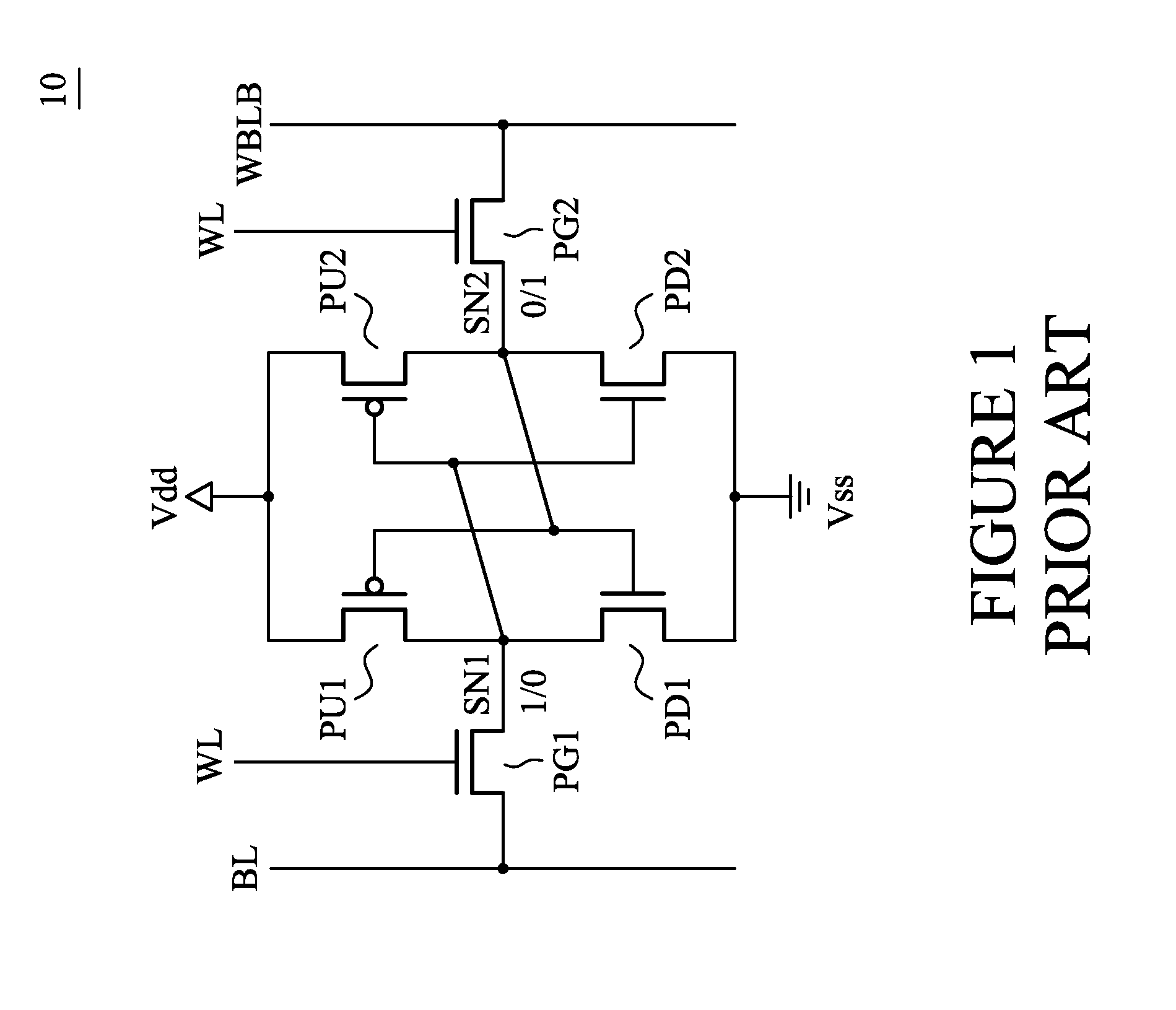
Methods and apparatus for SRAM bit cell with low standby current, low supply voltage and high speed
ActiveUS8294212B2Data stabilityLower average currentTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricGate dielectric
Circuits and methods for providing an SRAM or CAM bit cell. In one embodiment, a bit cell portion with thicker gate oxides in the storage cell transistors, and thinner gate oxides in a read port section having transistors are disclosed. The use of the thick gate oxides in the storage cell transistors provides a stable storage of data and lower standby leakage current. The use of the thinner gate oxides in the read port transistors provides fast read accesses and allows a lower Vcc,min in the read port. The methods used to form the dual gate oxide thickness SRAM cells have process steps compatible with the existing semiconductor manufacturing processes. Embodiments using high k gate dielectrics, dual gate dielectric materials in a single bit cell, and using finFET and planar devices in a bit cell are described. Methods for forming the structures are disclosed.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
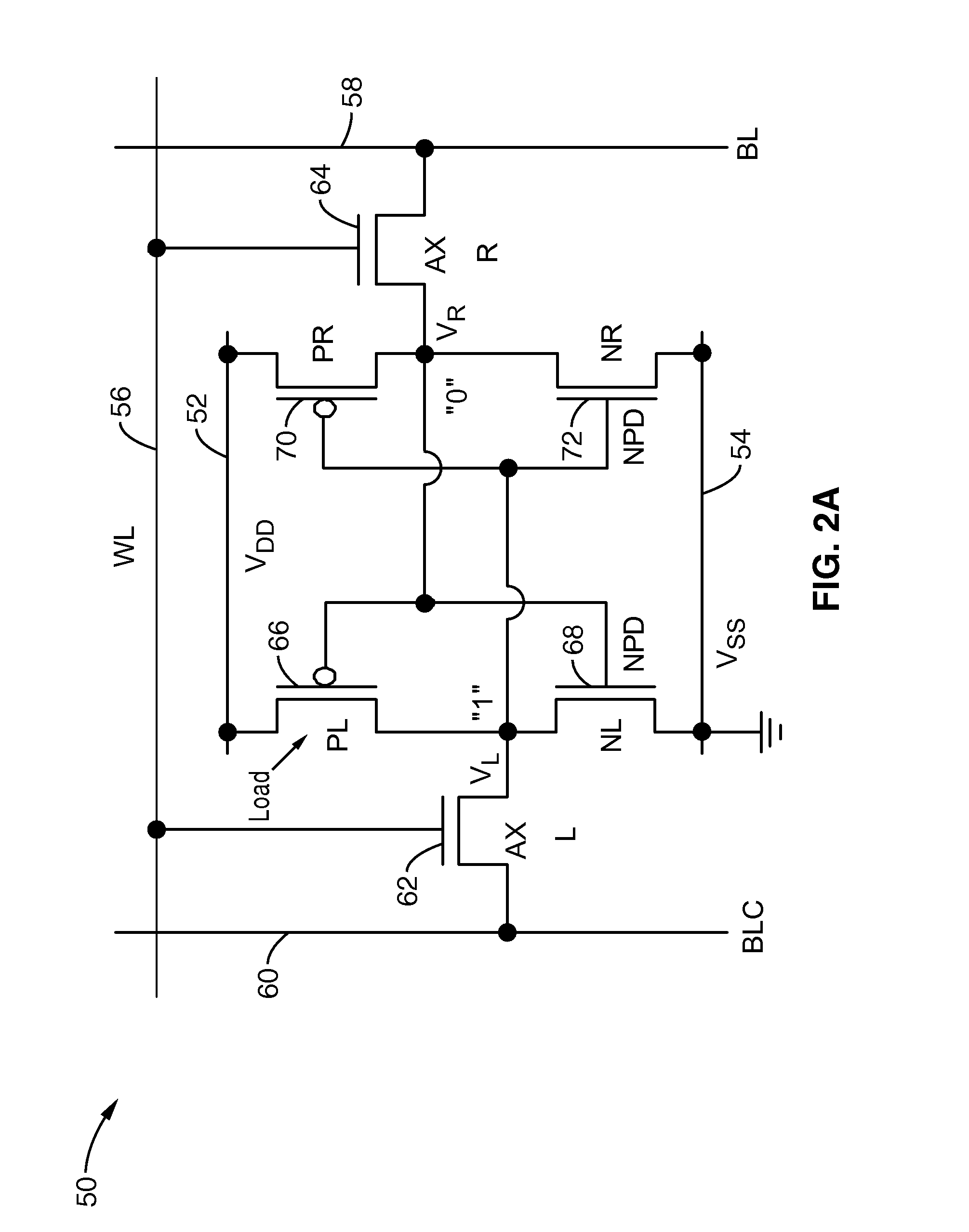
Static random access memory device and method of reducing standby current
A semiconductor storage device includes first and second additional FETs disposed in parallel on one of potential lines for supplying first and second drive potentials to each SRAM memory cell. The gate terminal of the first additional FET is supplied with a selection signal through a selection signal supply line to turn on the first additional FET, when the memory cell is selected. The gate terminal of the second additional FET is supplied with a bias potential through a bias supply line, wherein the bias potential has first and second levels respectively corresponding to non-selection and selection of the memory cell.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Methods and Apparatus for SRAM Bit Cell with Low Standby Current, Low Supply Voltage and High Speed
ActiveUS20110068400A1Data stabilityLower average currentTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricGate dielectric
Circuits and methods for providing an SRAM or CAM bit cell. In one embodiment, a bit cell portion with thicker gate oxides in the storage cell transistors, and thinner gate oxides in a read port section having transistors are disclosed. The use of the thick gate oxides in the storage cell transistors provides a stable storage of data and lower standby leakage current. The use of the thinner gate oxides in the read port transistors provides fast read accesses and allows a lower Vcc,min in the read port. The methods used to form the dual gate oxide thickness SRAM cells have process steps compatible with the existing semiconductor manufacturing processes. Embodiments using high k gate dielectrics, dual gate dielectric materials in a single bit cell, and using finFET and planar devices in a bit cell are described. Methods for forming the structures are disclosed.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Finfet-based SRAM with feedback
InactiveUS20070183185A1Adequate noise marginReduce leakage currentTransistorSolid-state devicesNoise marginCell design
Intrinsic variations and challenging leakage control in current bulk-Si MOSFETs force undesired tradeoffs to be made and limit the scaling of SRAM circuits. Circuits and mechanisms are taught herein which improve leakage and noise margin in SRAM cells, such as those comprising either six-transistor (6-T) SRAM cell designs, or four-transistor (4-T) SRAM cell designs. The inventive SRAM cells utilize a feedback means coupling a portion of the storage node to a back-gate of an access transistor. Preferably feedback is coupled in this manner to both access transistors. SRAM cells designed with this built-in feedback achieve significant improvements in cell static noise margin (SNM) without area penalty. Use of the feedback scheme also results in the creation of a practical 4-T FinFET-based SRAM cell that achieves sub-100 pA per-cell standby current and offers similar improvements in SNM as the 6-T cell with feedback.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
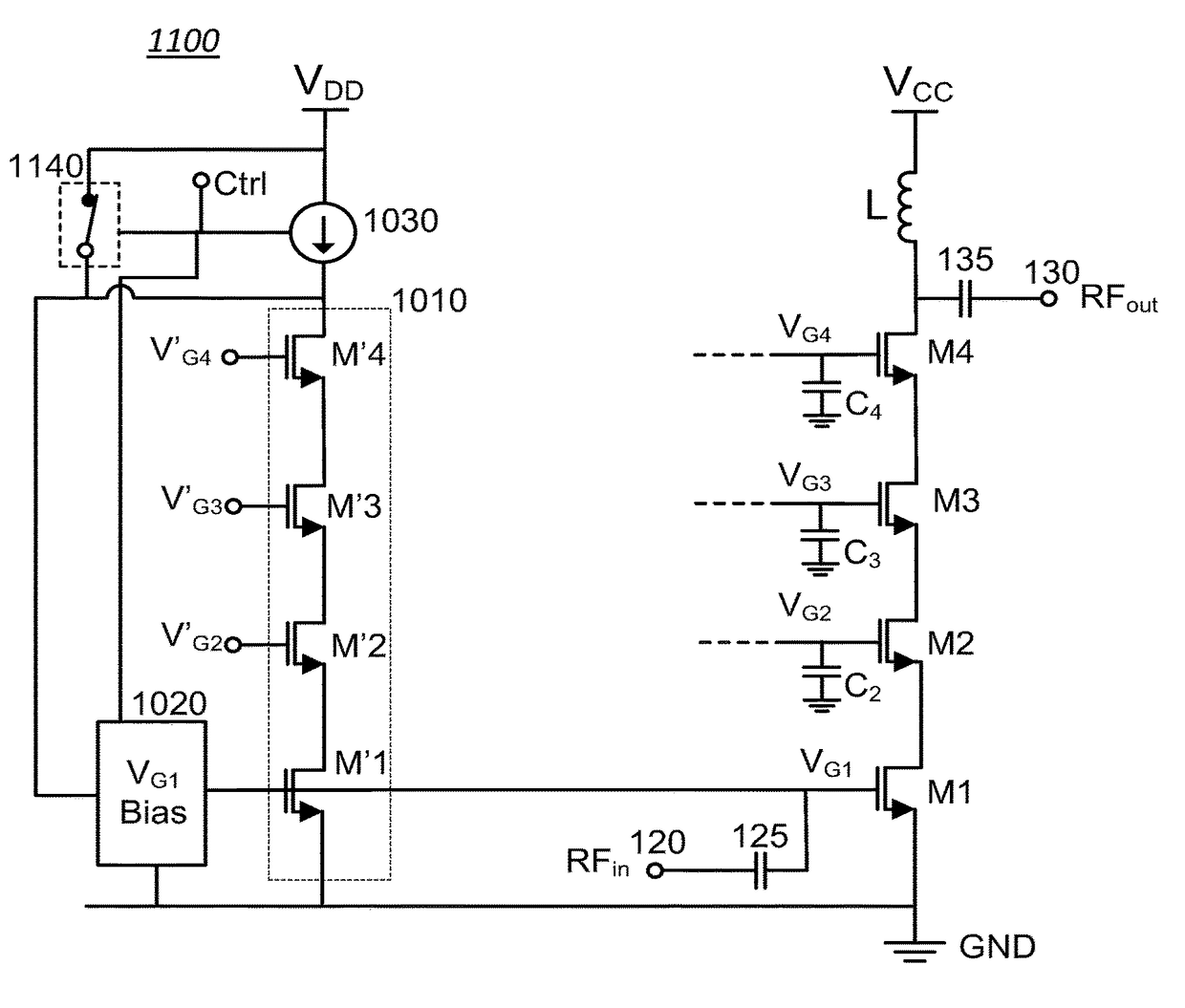
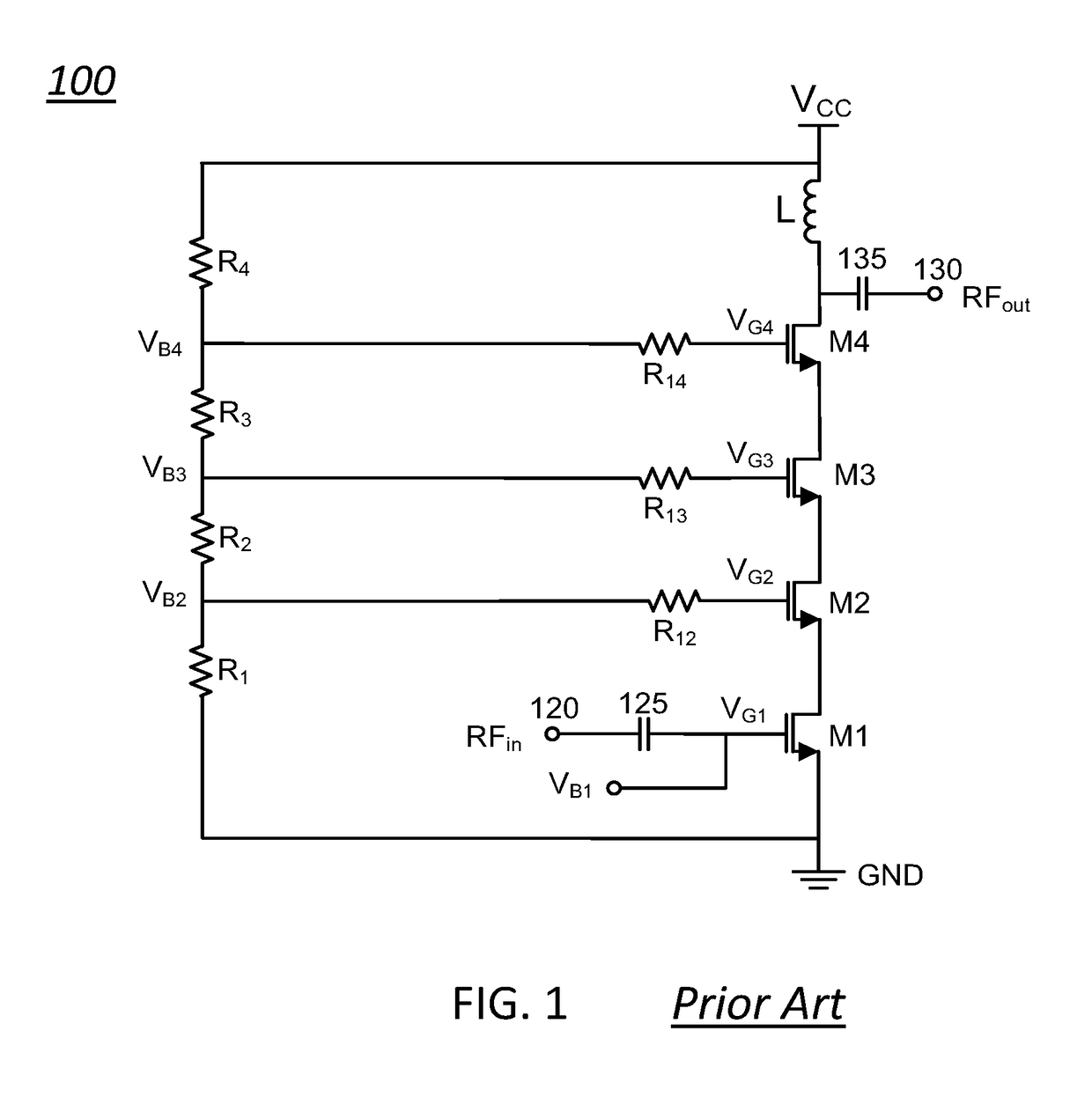
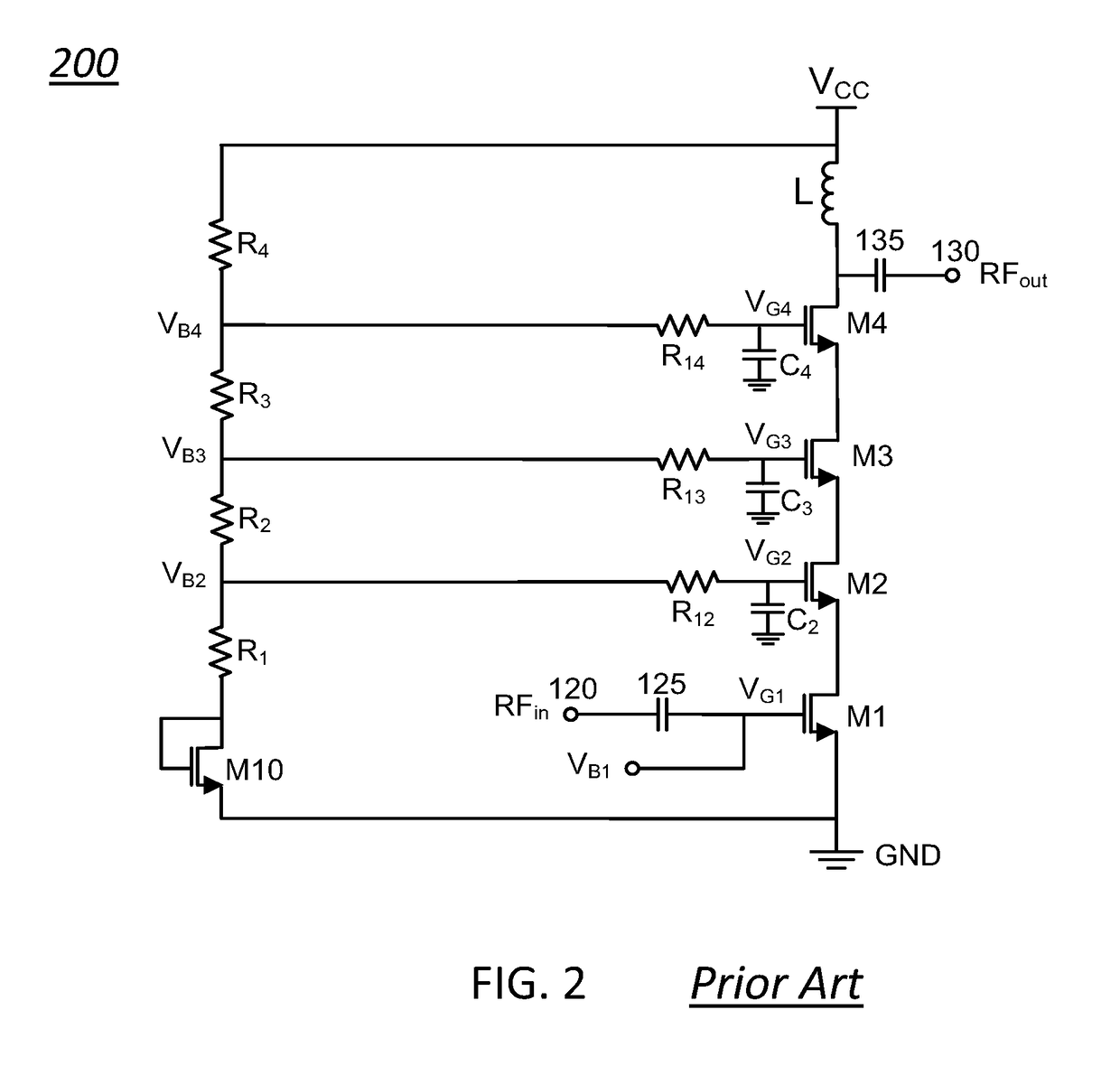
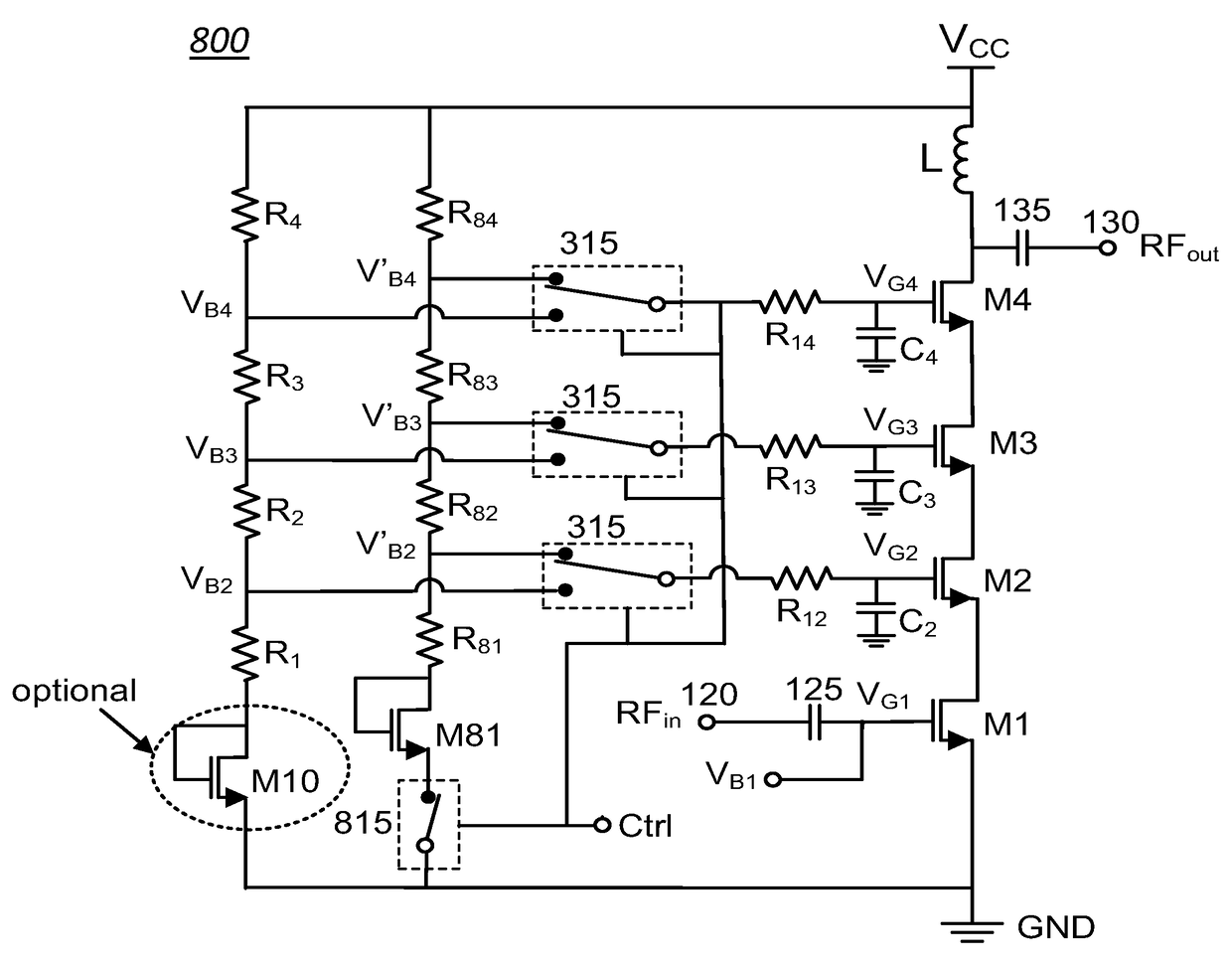
Standby voltage condition for fast RF amplifier bias recovery
ActiveUS9837965B1Promote recoveryReduce power consumptionHigh frequency amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierTransistor
Various methods and circuital arrangements for biasing one or more gates of stacked transistors of an amplifier are possible where the amplifier is configured to operate in at least an active mode and a standby mode. Circuital arrangements can reduce bias circuit standby current during operation in the standby mode while allowing a quick recovery to normal operating conditions of the amplifier. Biasing an input transistor of the stacked transistors can be obtained by using a replica stack circuit.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
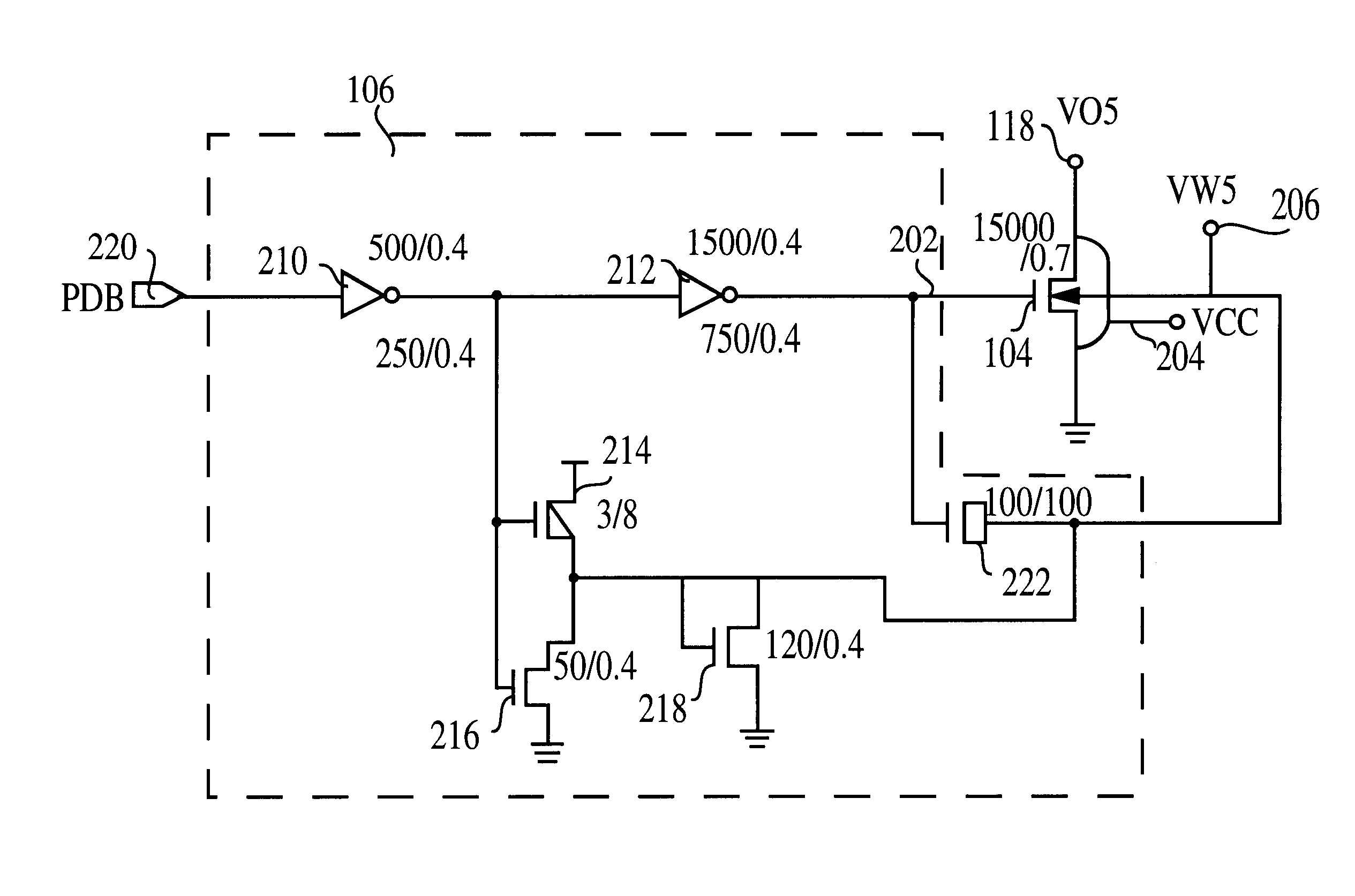
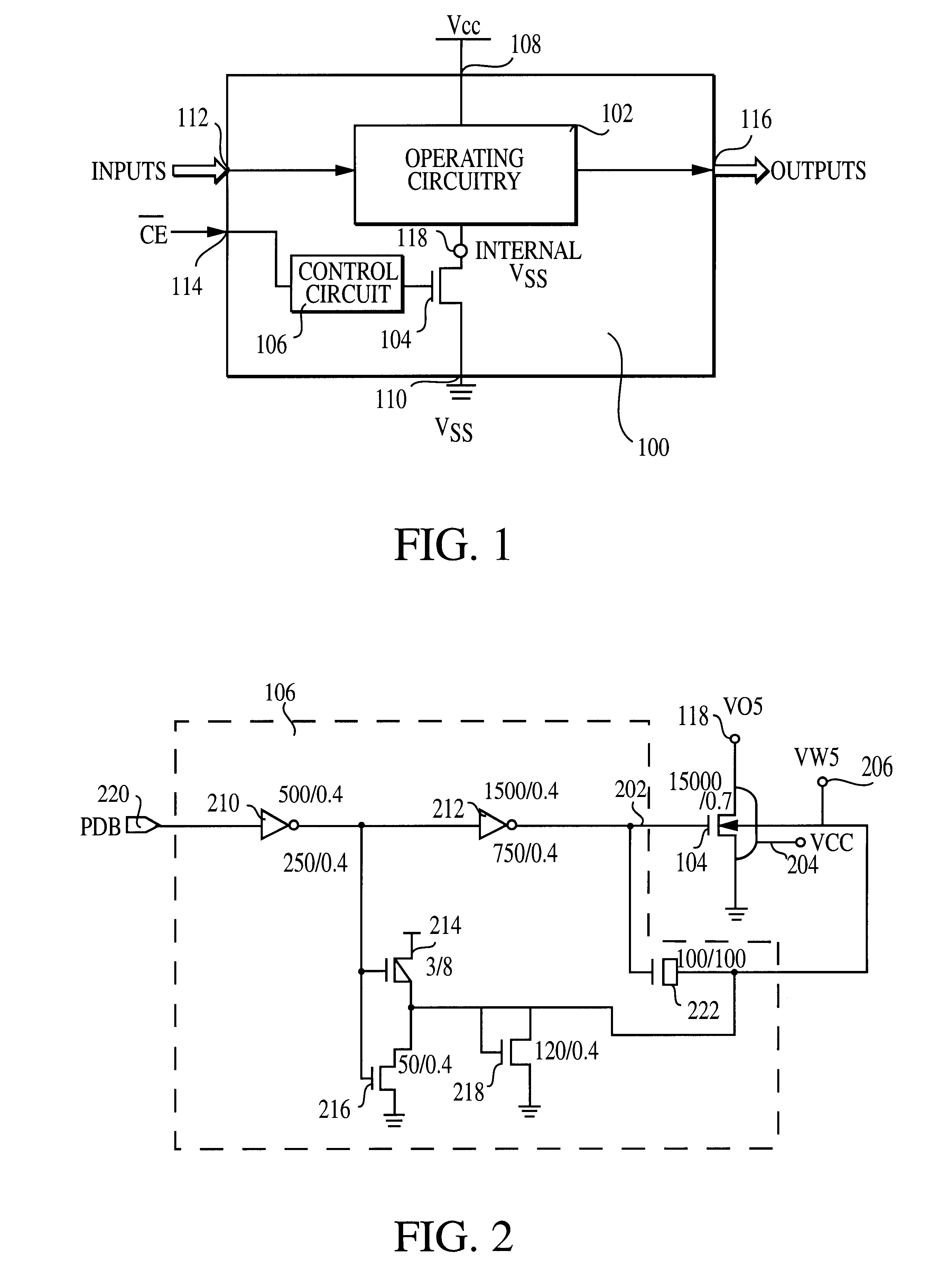
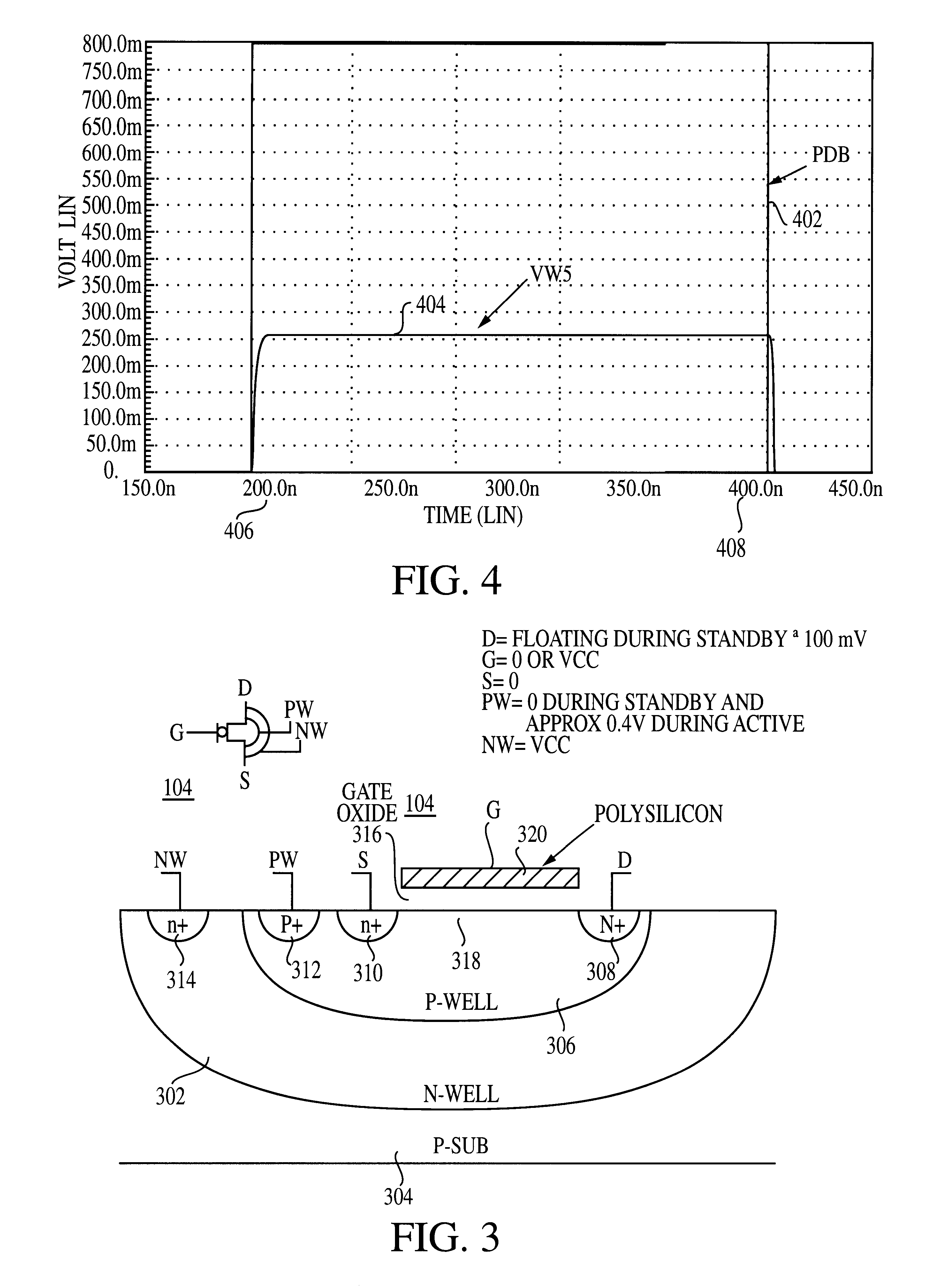
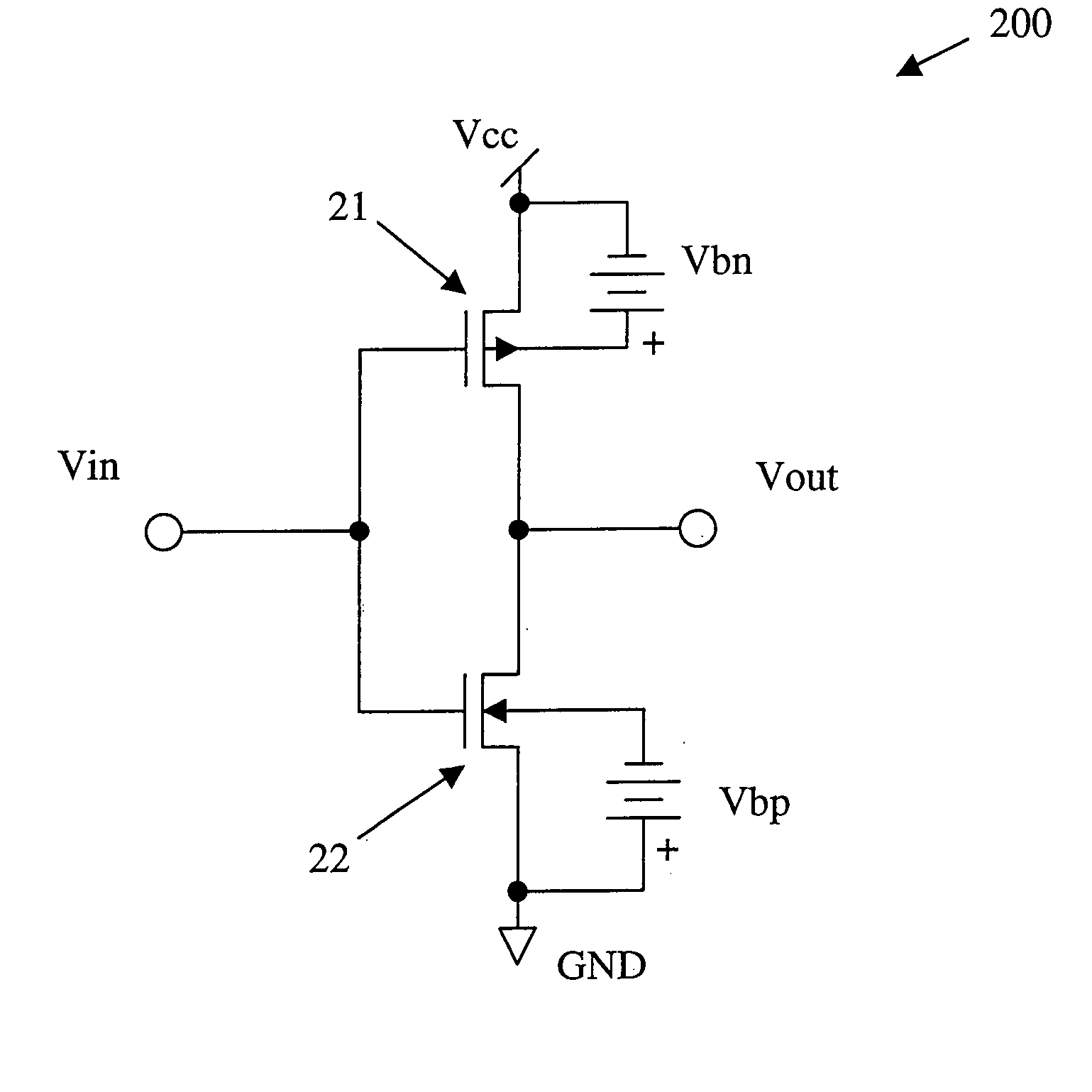
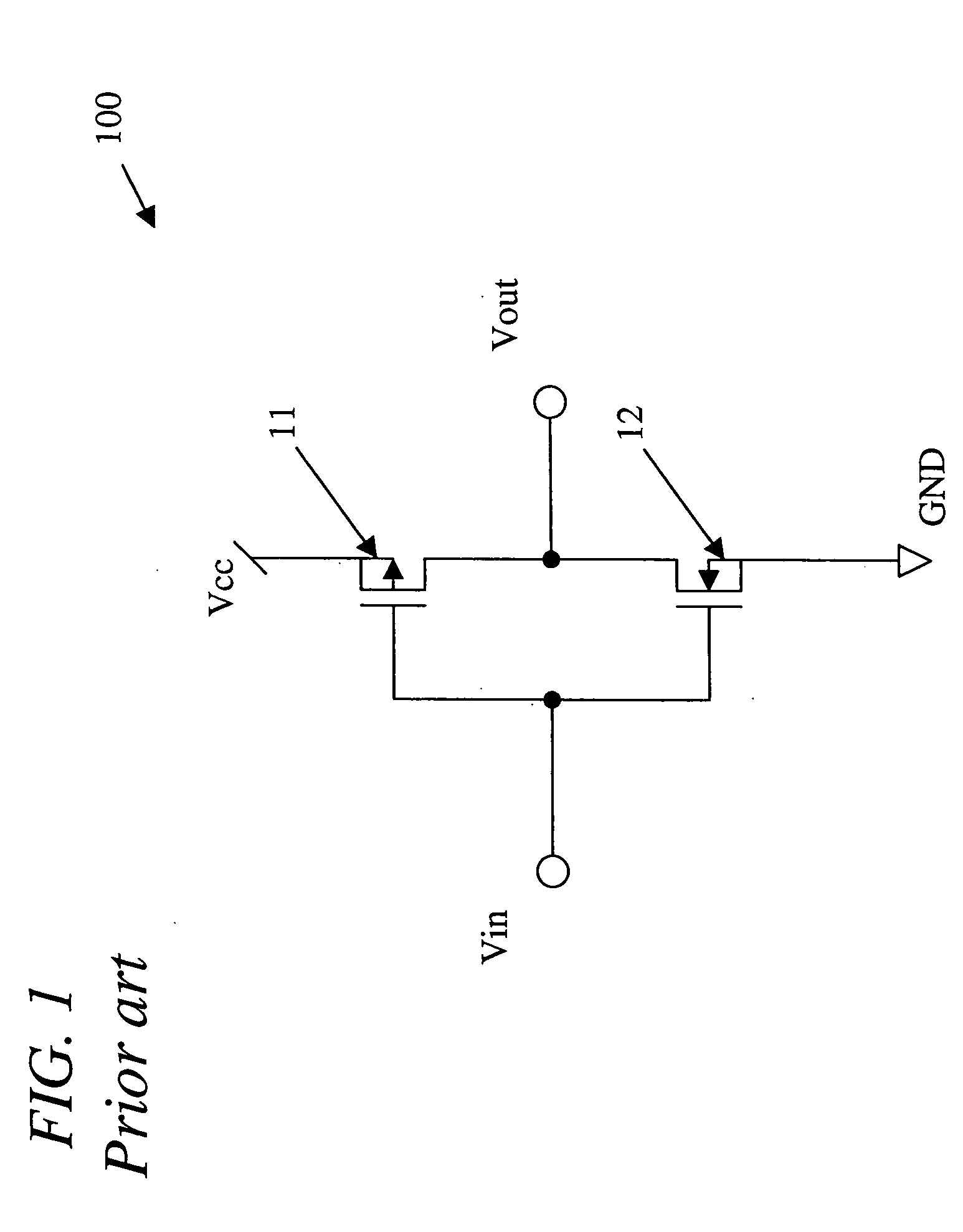
Use of biased high threshold voltage transistor to eliminate standby current in low voltage integrated circuits
InactiveUS6225852B1Turn fasterLower threshold voltagePower reduction by control/clock signalElectric pulse generator detailsStandby currentLow voltage cmos
An integrated circuit (100) includes a first input (108) to receive a first operating voltage Vcc and a second input (110) to receive a second operating voltage Vss. Operating circuitry (102) of the integrated circuit is coupled to the first input to power the operating circuitry. A transistor (104) is coupled between the second input and the operating circuitry to selectively provide the second operating voltage to the operating circuitry of the integrated circuit. The well containing the transistor is biased to provide a reverse body effect and reduce the threshold voltage of the transistor to allow operation at very low Vcc.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Gate drivers for stacked transistor amplifiers
ActiveUS9843293B1Reduce leakage currentMaintaining voltage complianceAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierEngineering
Various methods and circuital arrangements for biasing one or more gates of stacked transistors of an amplifier are possible where the amplifier is configured to operate in at least an active mode and a standby mode. Circuital arrangements can reduce bias circuit and stacked transistors standby current during operation in the standby mode and to reduce impedance presented to the gates of the stacked transistors during operation in the active mode while maintaining voltage compliance of the stacked transistors during both modes of operation.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
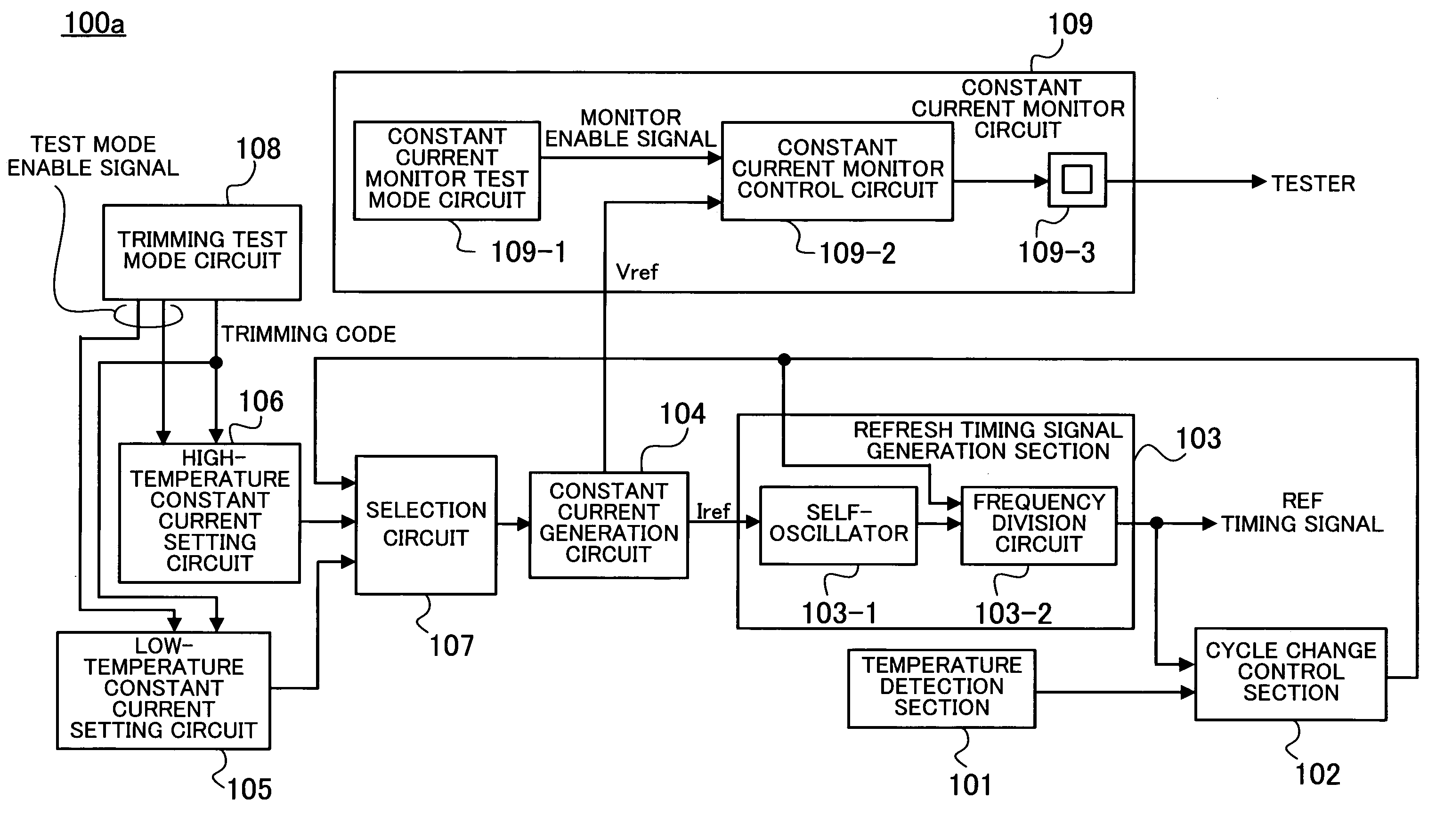
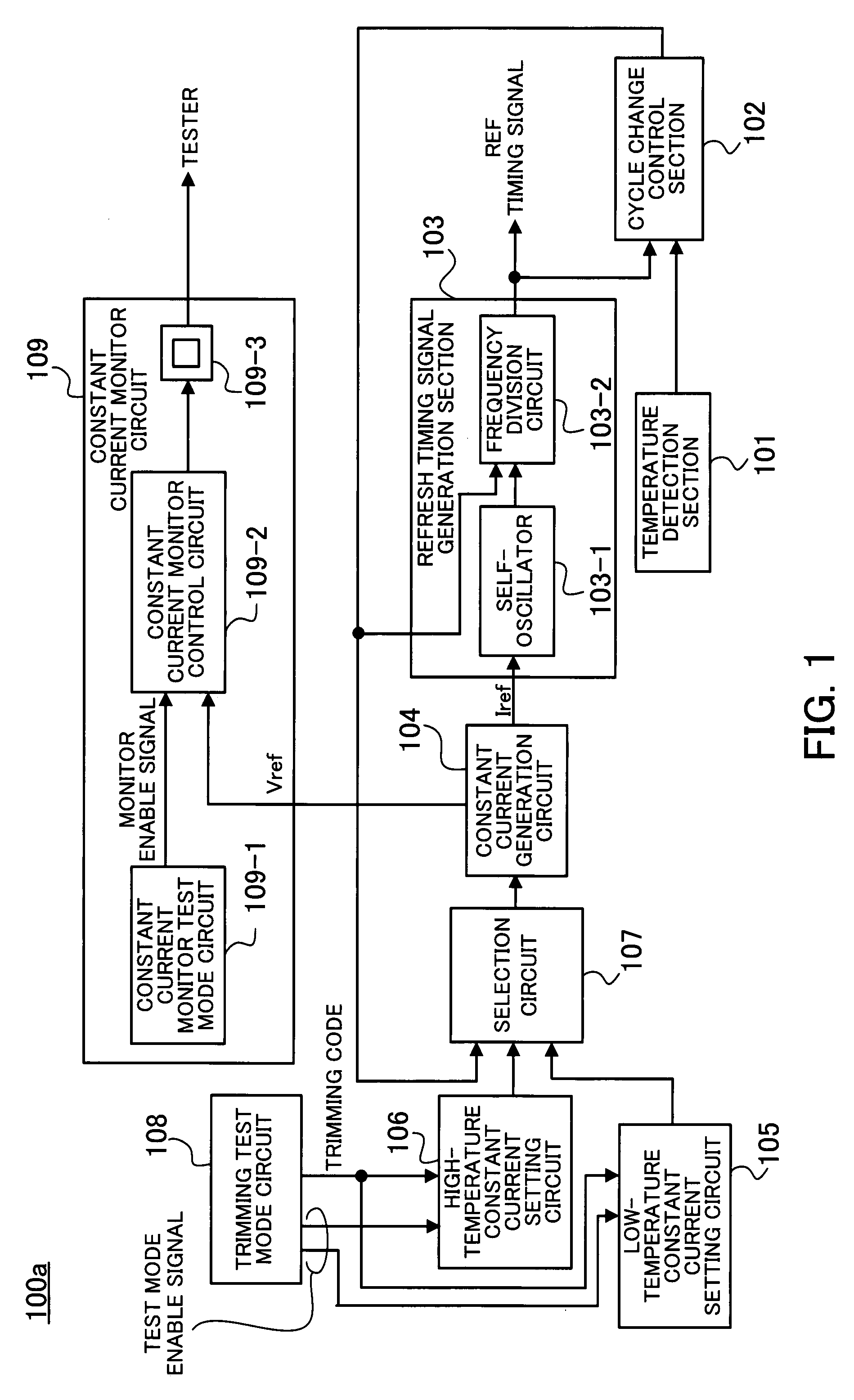
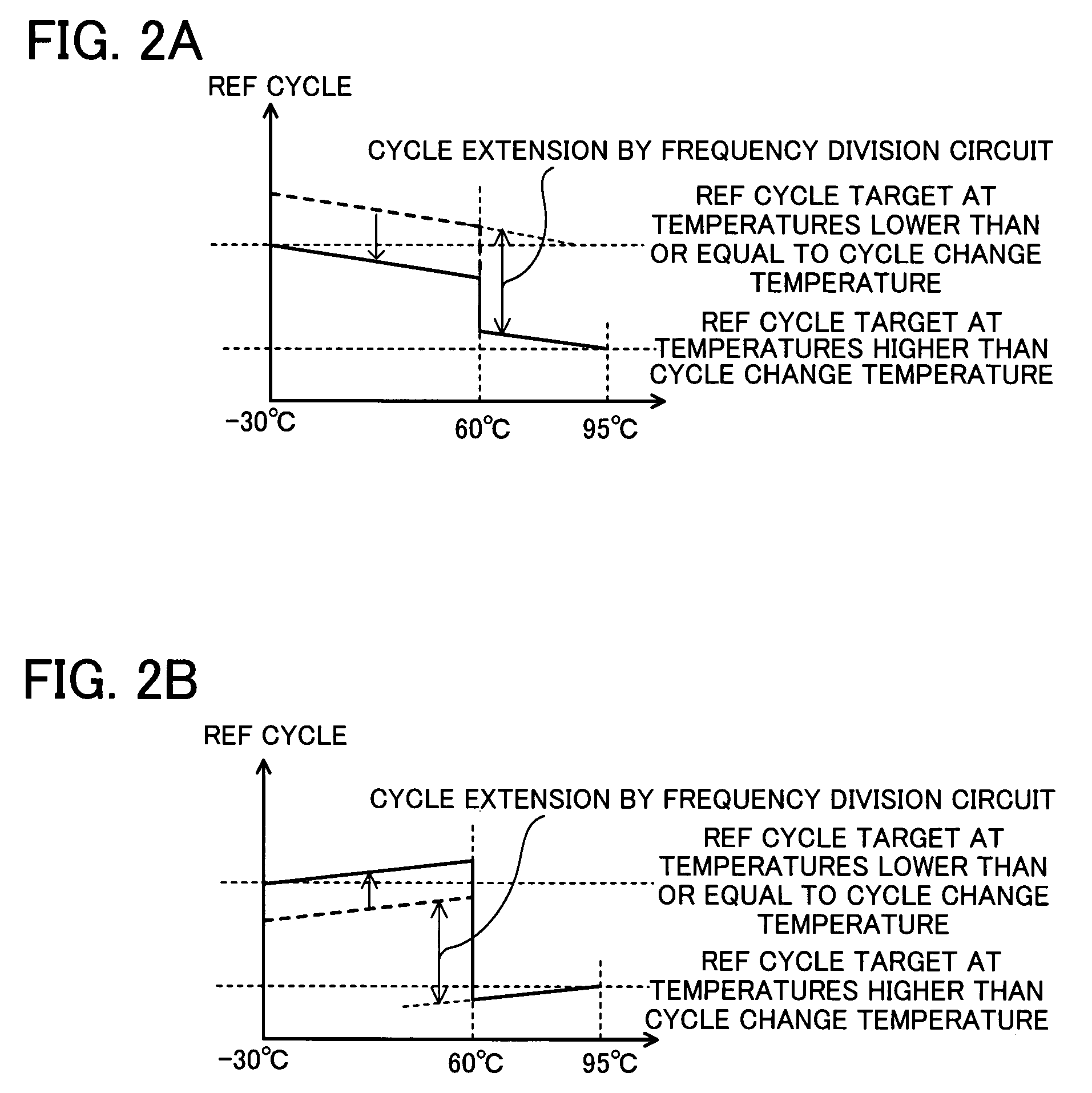
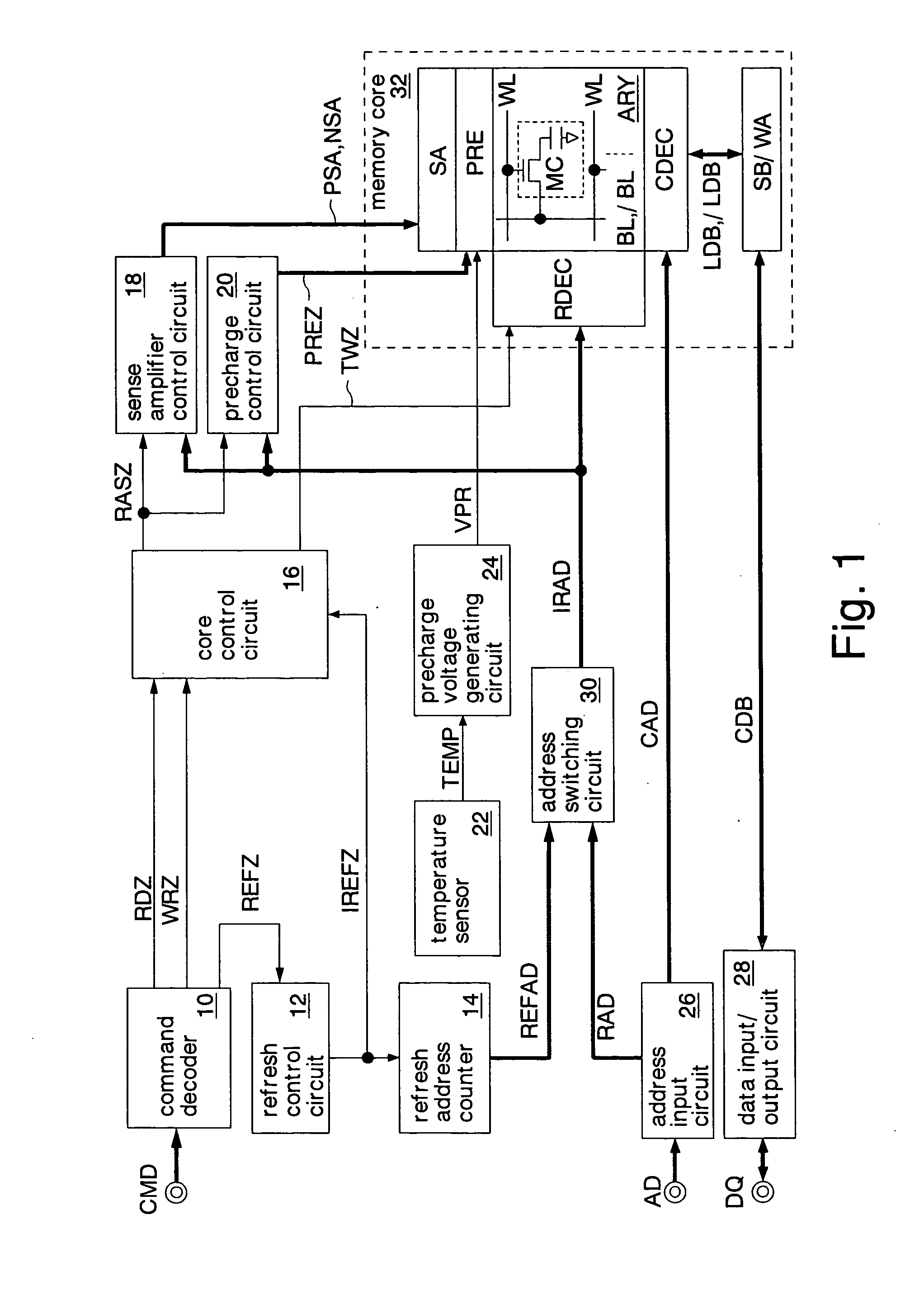
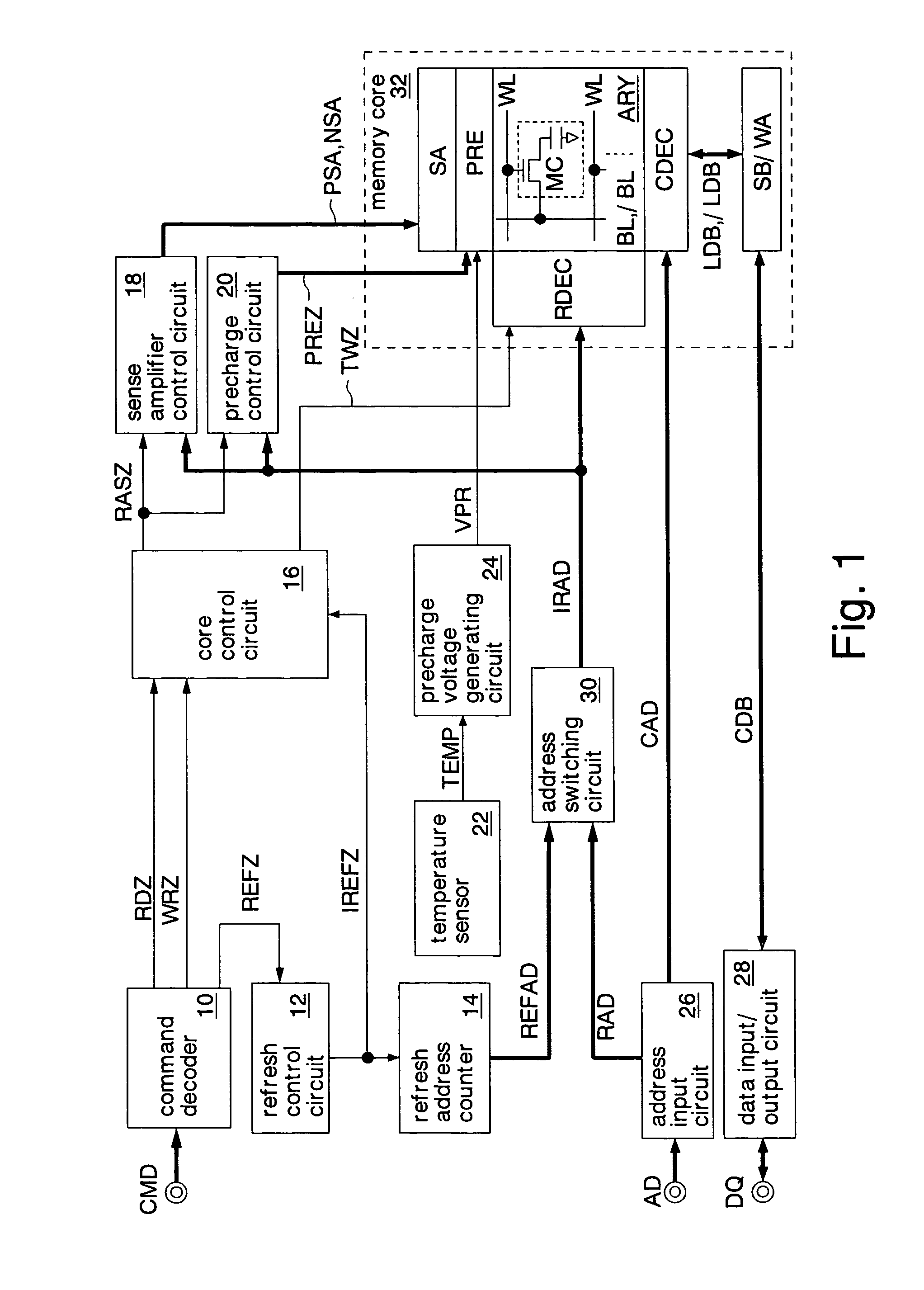
Semiconductor memory and refresh cycle control method
A semiconductor memory and a refresh cycle control method that reduce a standby current by properly changing a refresh cycle according to the temperature of the semiconductor memory. A temperature detection section detects the temperature of the semiconductor memory. A cycle change control section sends a cycle change signal for changing a refresh cycle when the temperature of the semiconductor memory reaches a predetermined cycle change temperature. A refresh timing signal generation section generates a refresh timing signal and changes the cycle of the refresh timing signal in response to the cycle change signal. A constant current generation circuit generates an electric current for generating the refresh timing signal. A low-temperature constant current setting circuit designates the level of the electric current generated in the case that the temperature of the semiconductor memory is lower than or equal to the cycle change temperature. A high-temperature constant current setting circuit designates the level of the electric current generated in the case that the temperature of the semiconductor memory is higher than the cycle change temperature.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
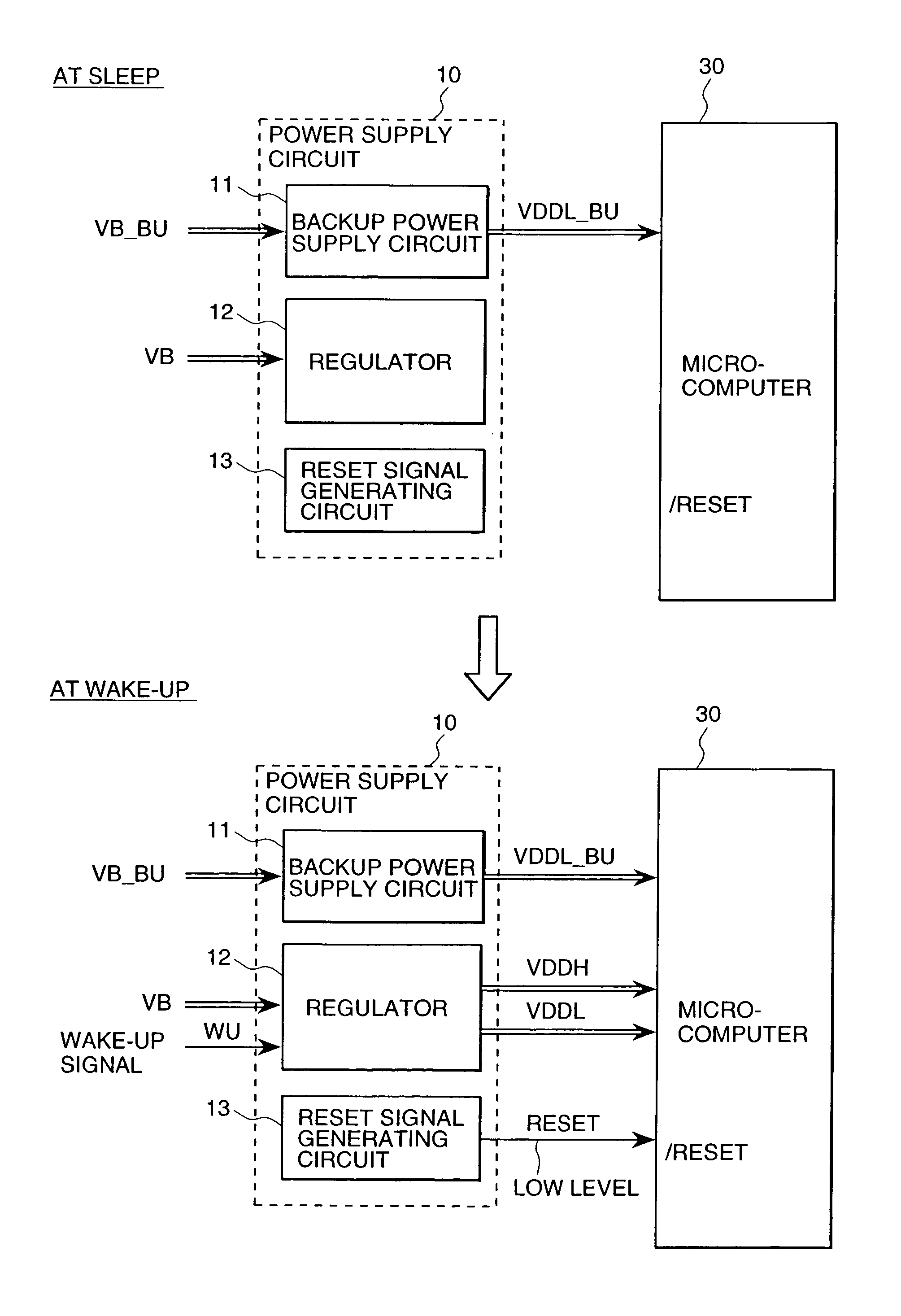
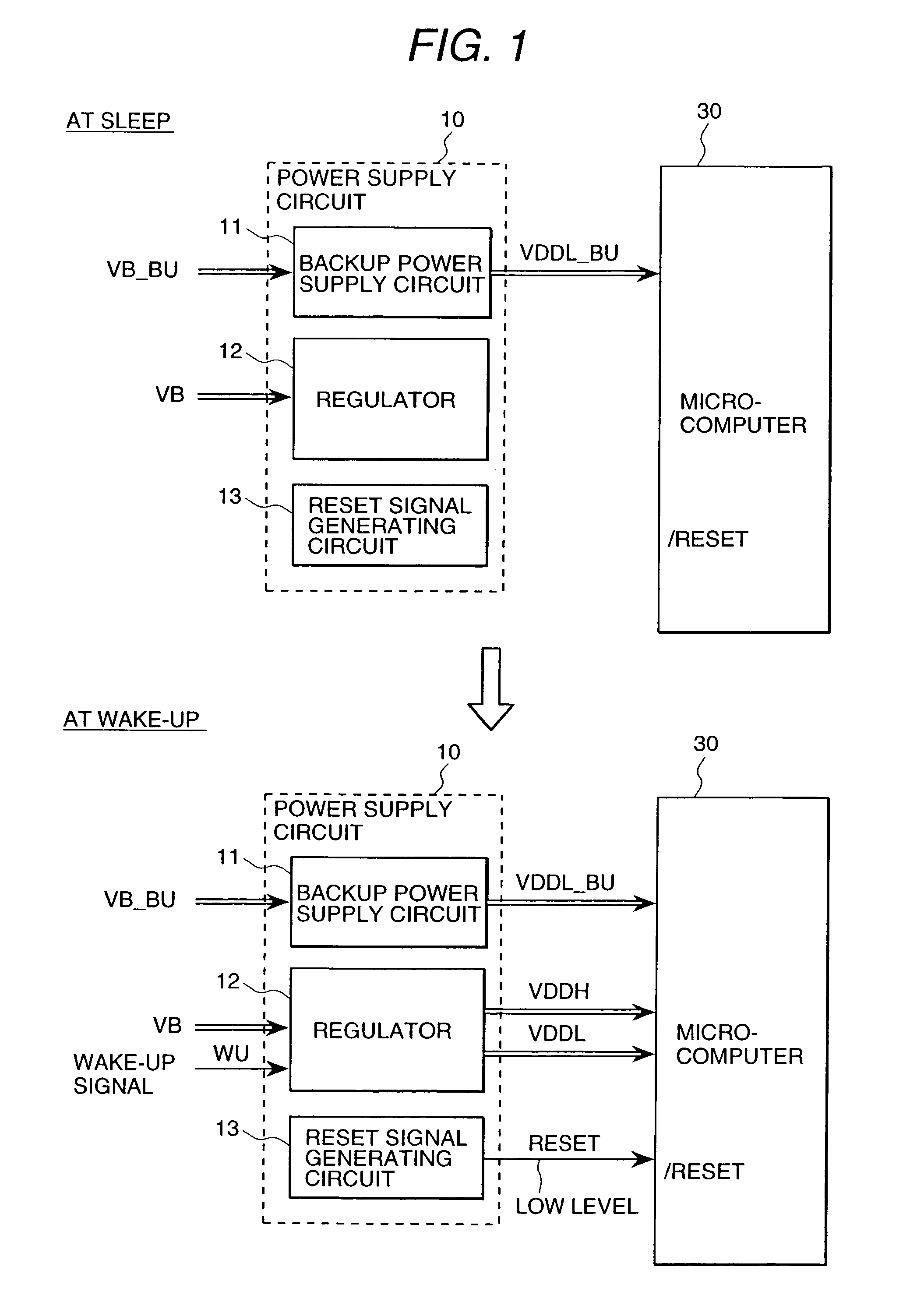
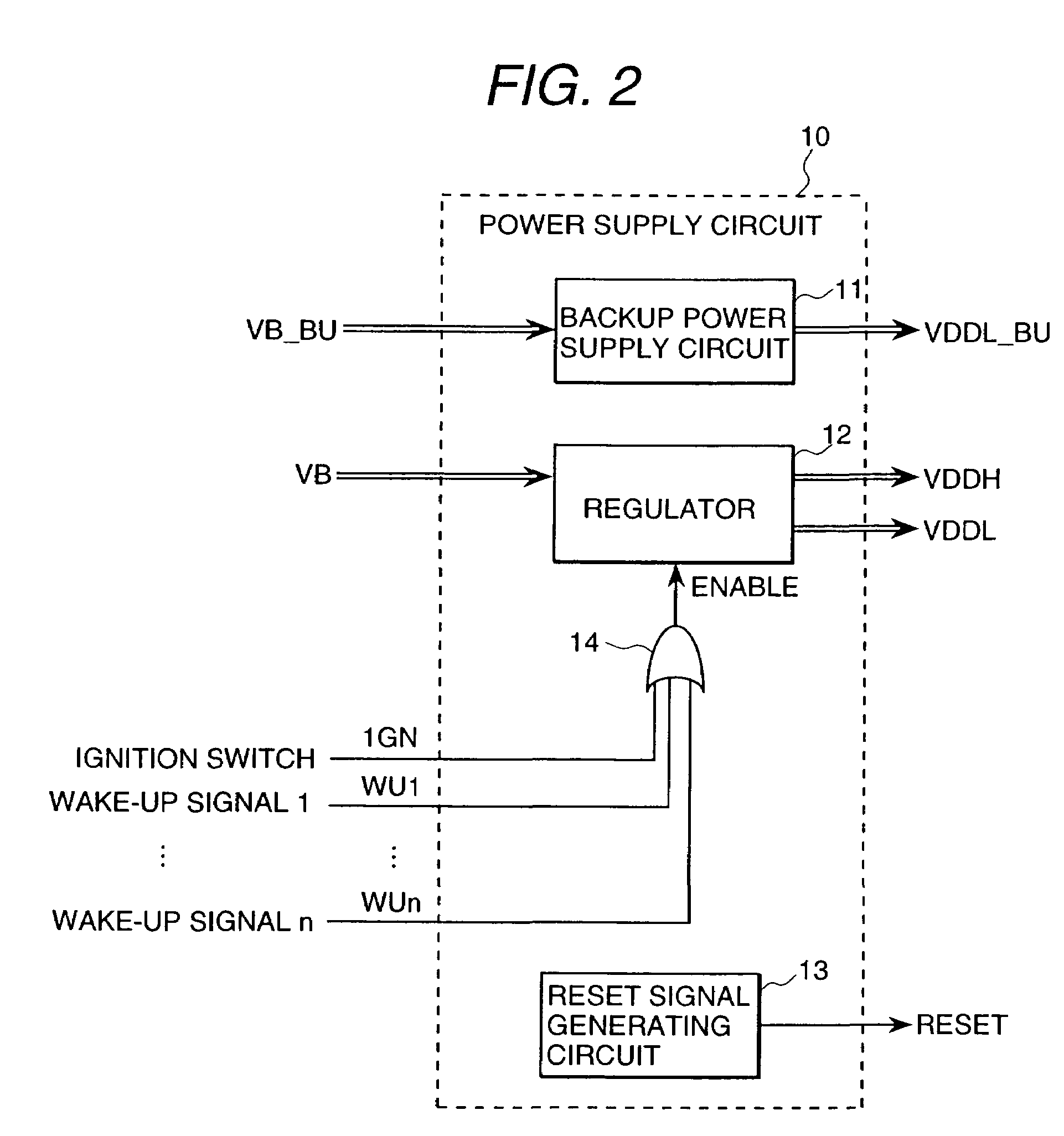
Electrical control unit for an automobile
An electrical control unit for an automobile of which standby current is smaller. In an electrical control unit for an automobile having a microcomputer, an input circuit, a driver circuit, and a power supply circuit, which is started by a wake-up signal from the circuit other than the ignition switch even when the ignition switch of the automobile is cut off, the microcomputer is started by shifting the power supply circuit from an inert state to an active state to generate the voltage for operating the microcomputer, and the predetermined processing is executed.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
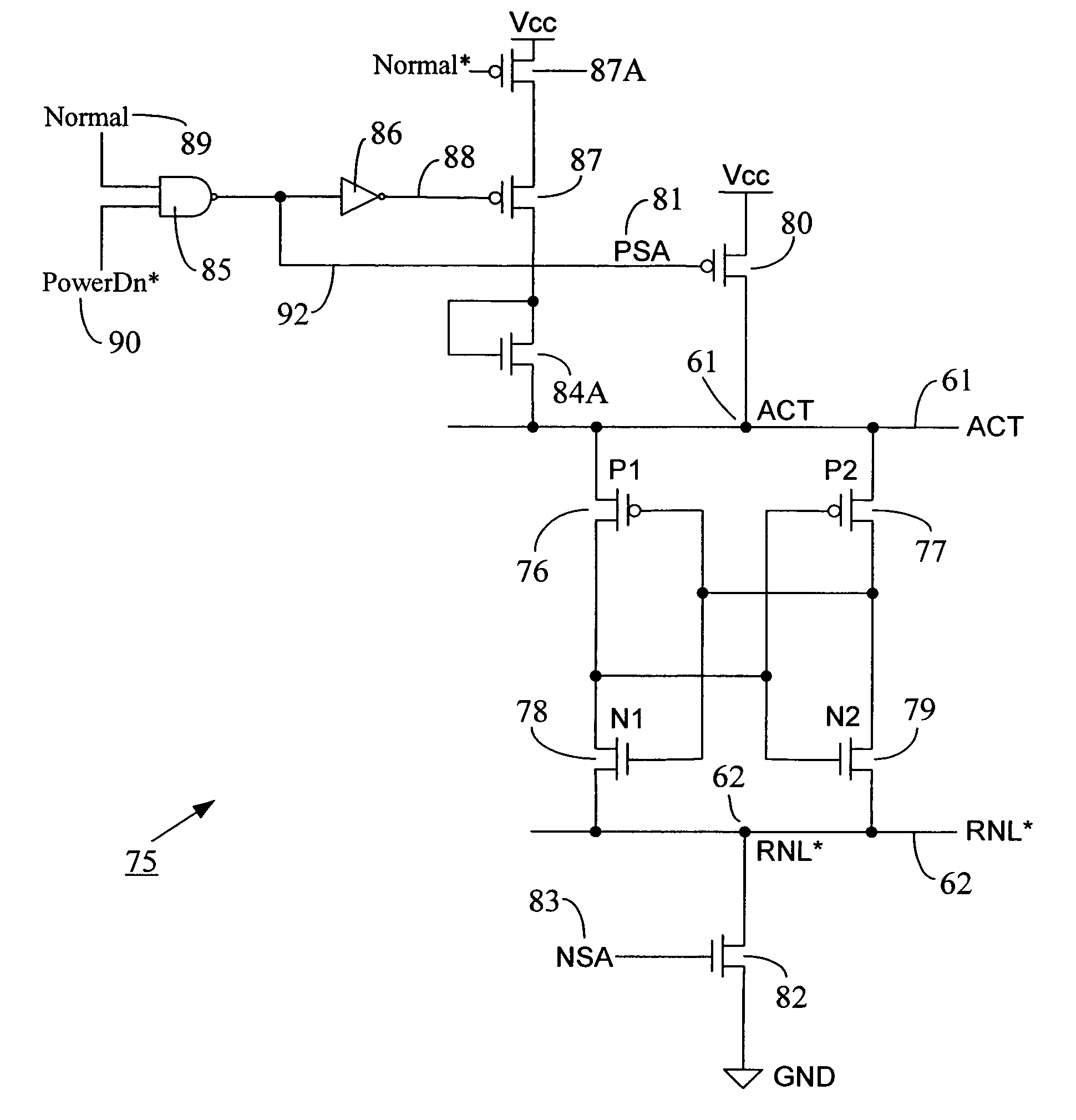
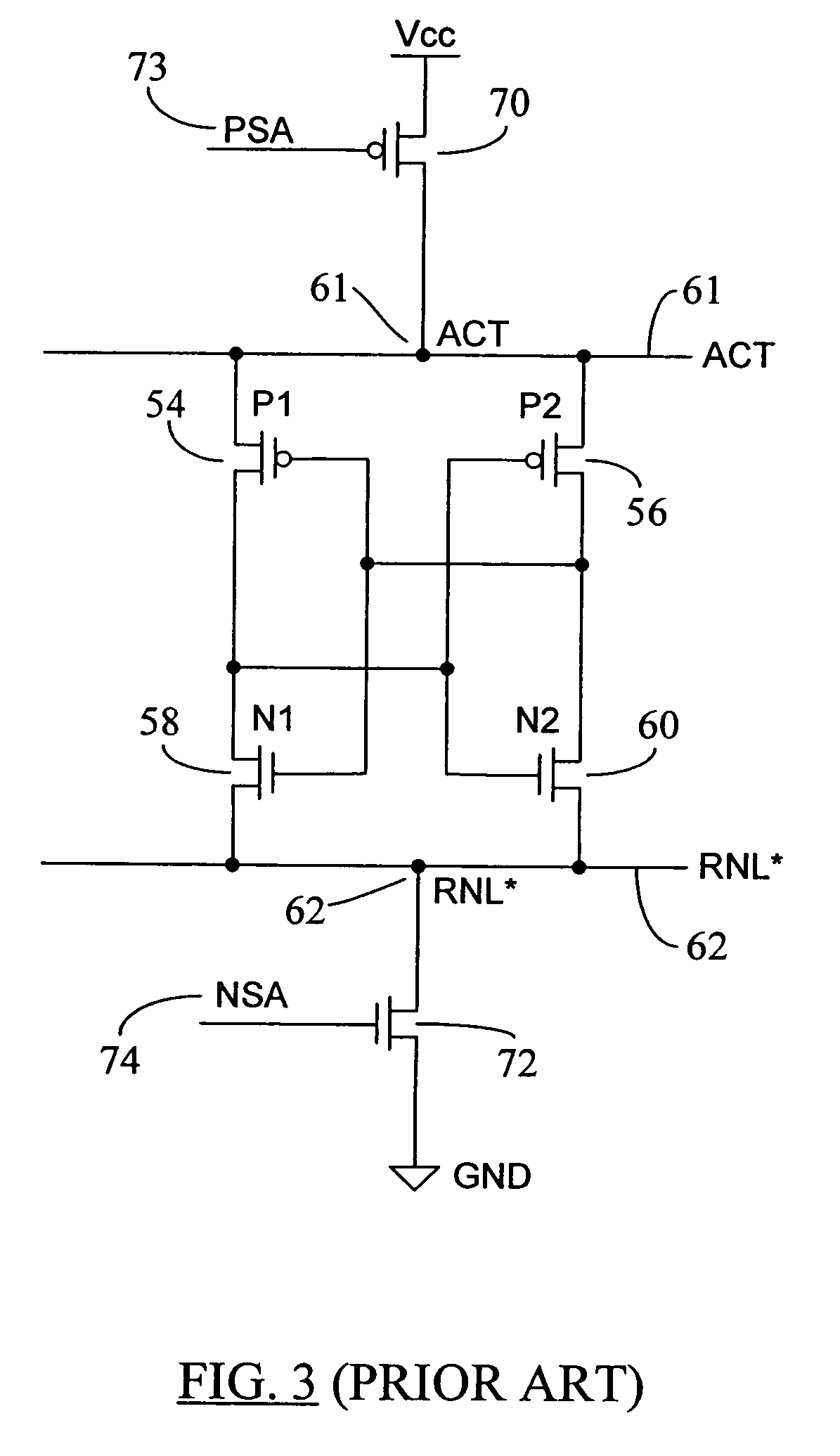
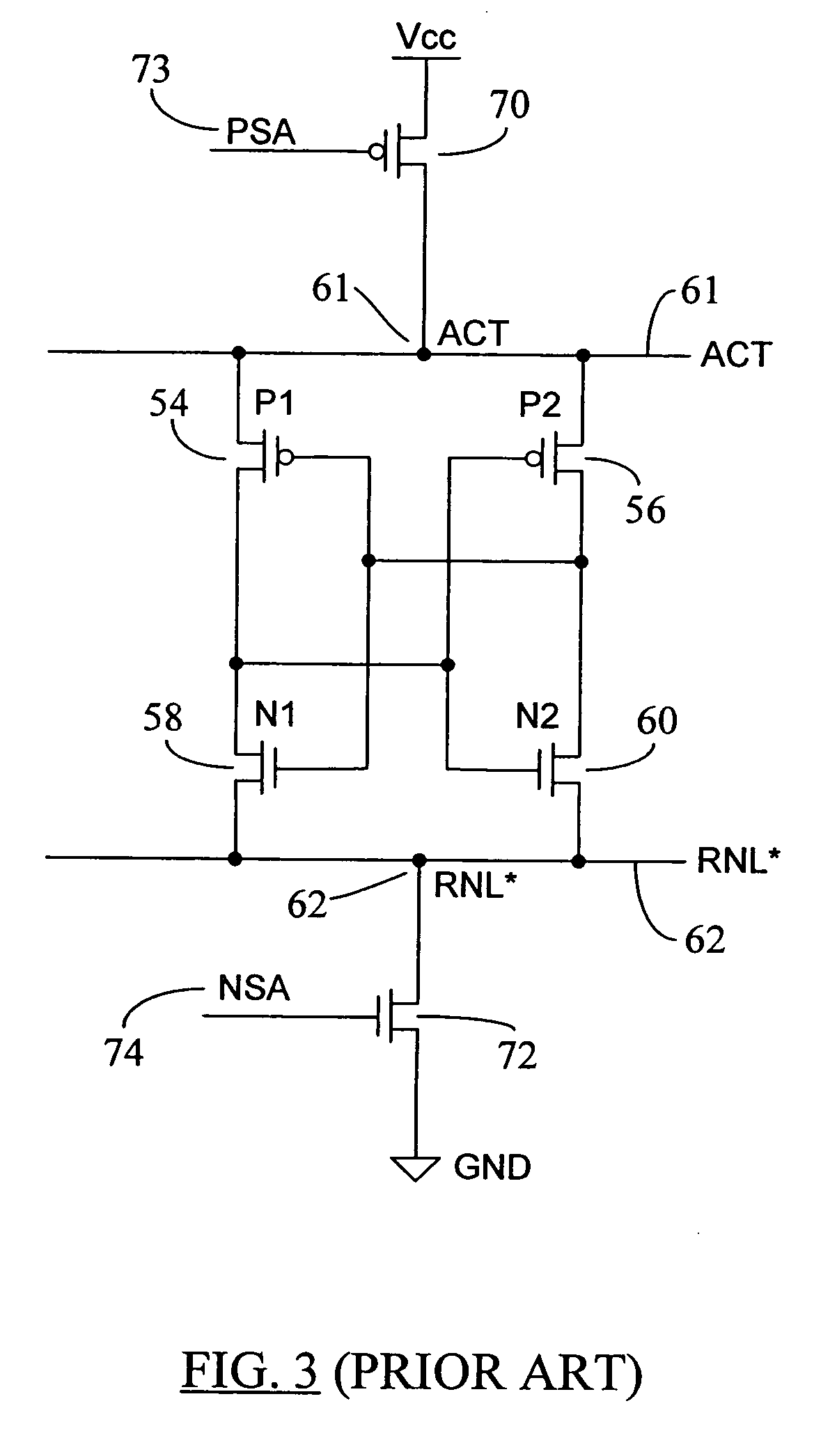
Low voltage sensing scheme having reduced active power down standby current
ActiveUS7372746B2Reduces active power down standby leakage currentReduce voltageDigital storageControl lineEngineering
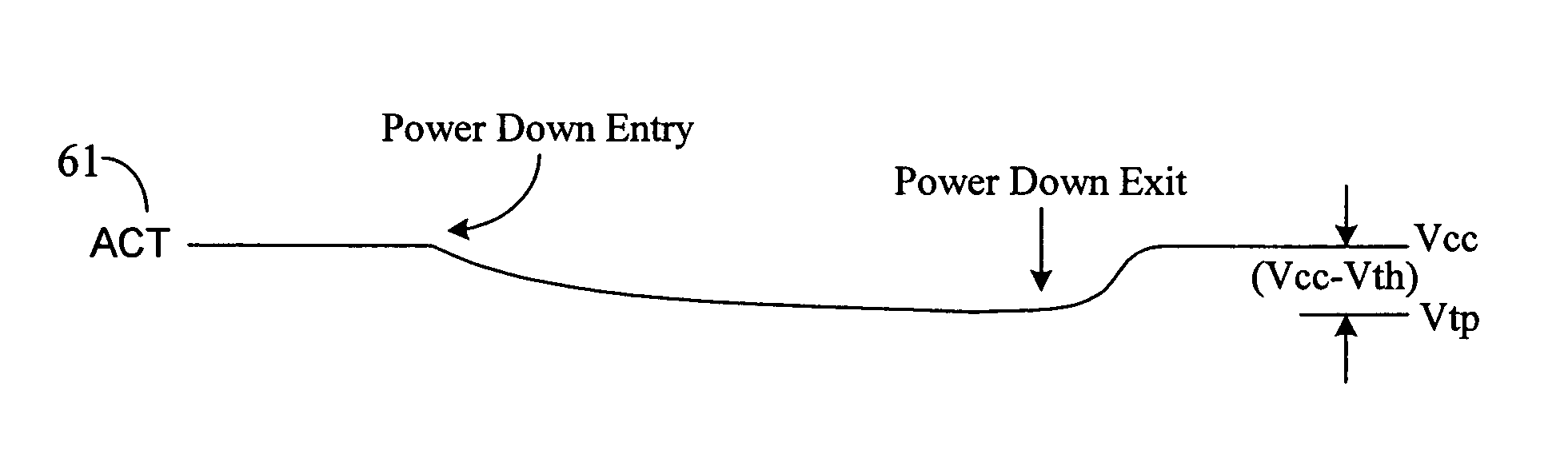
A low voltage sensing scheme reduces active power down standby leakage current in a memory device. During memory's active power down state, the leak current may increase because of the use of P and Nsense amplifiers having low threshold voltages (Vth) for low Vcc sensing of data signals. A clamping device or diode is used between a Psense amplifier control line (e.g. ACT) and Vcc and / or between an Nsense amplifier control line (e.g. RNL*) and Vss (ground potential). The clamping diode is not enabled during normal memory operations, but is turned on during active power down mode to reduce leakage current through ACT and / or RNL* nodes. The clamping device connected to the ACT node may reduce the voltage on the ACT line during power down mode, whereas the clamping device connected to the RNL* node may increase the voltage on the RNL* line during power down mode to reduce sense amplifier leakage current through these nodes.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Semiconductor memory
ActiveUS20070091703A1Easy switch controlPrevent circuit scaleDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
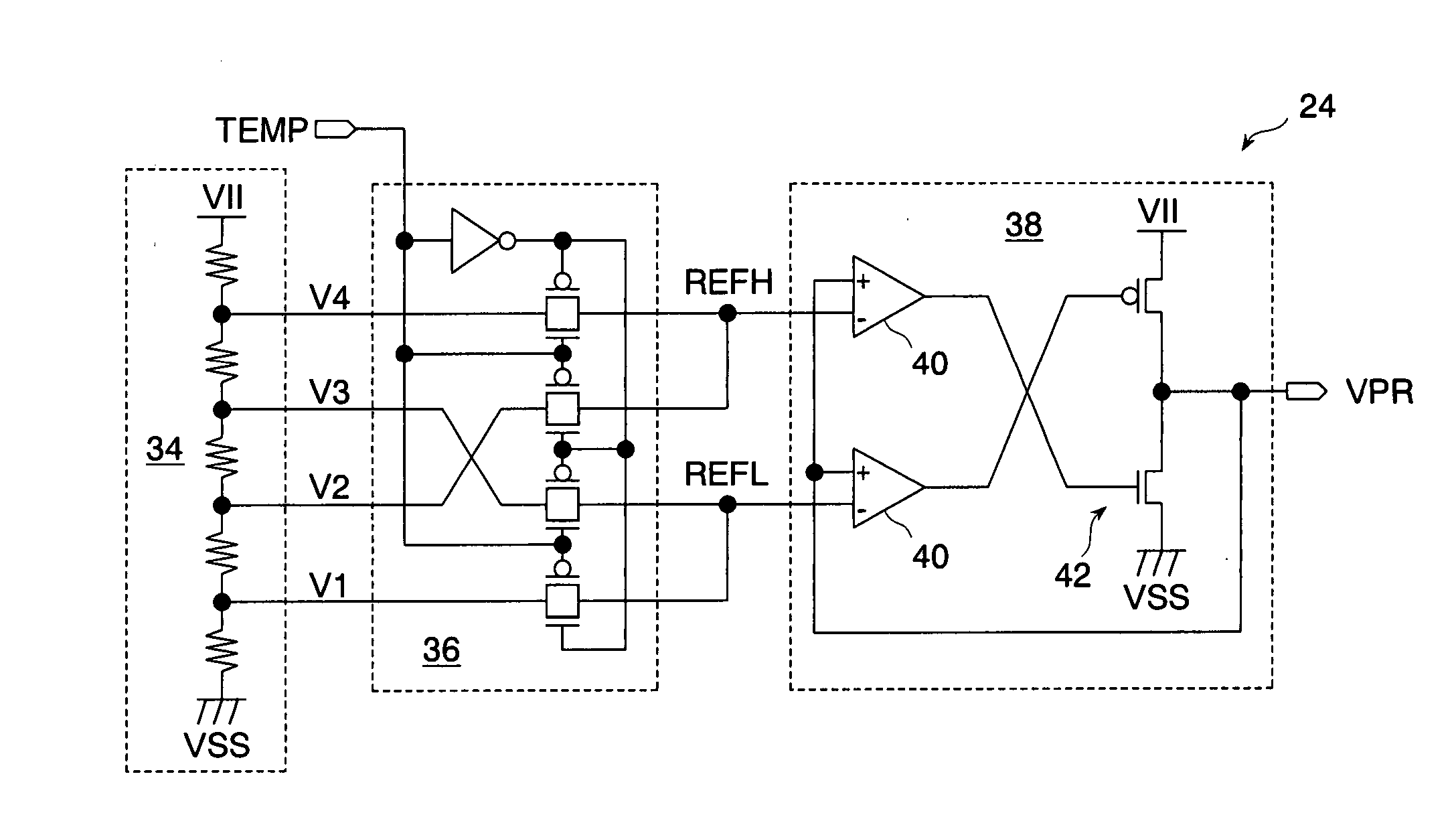
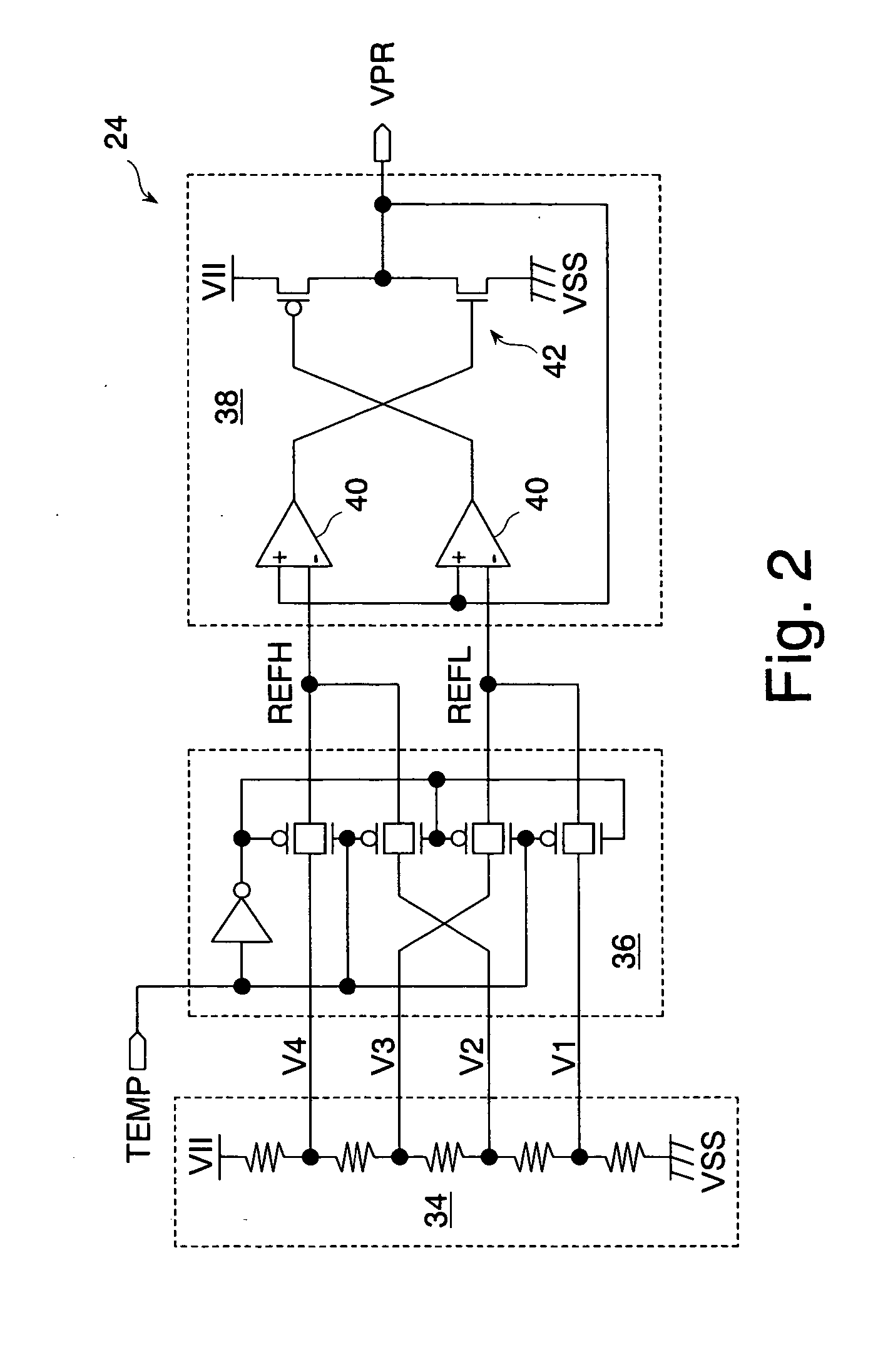
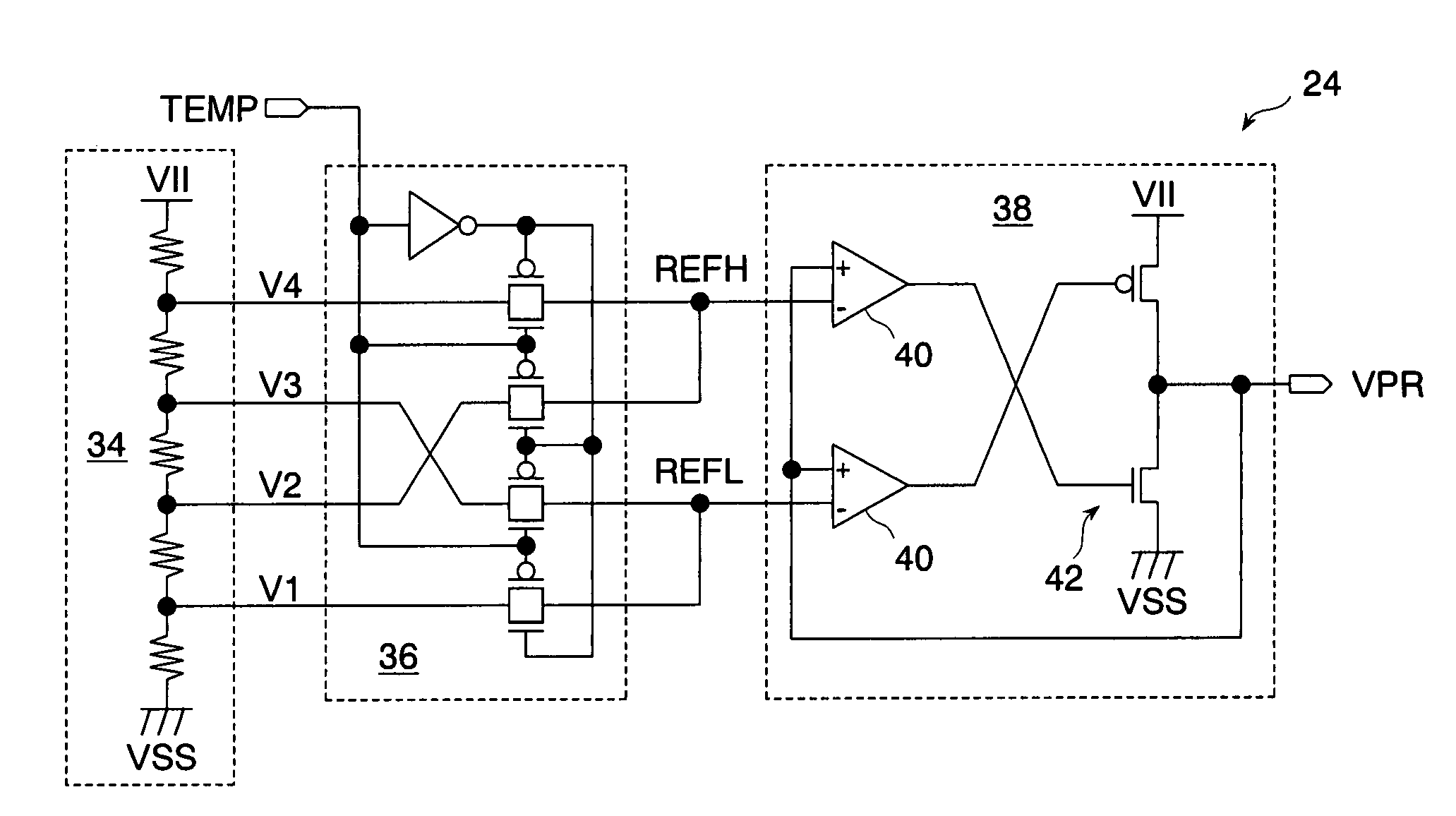
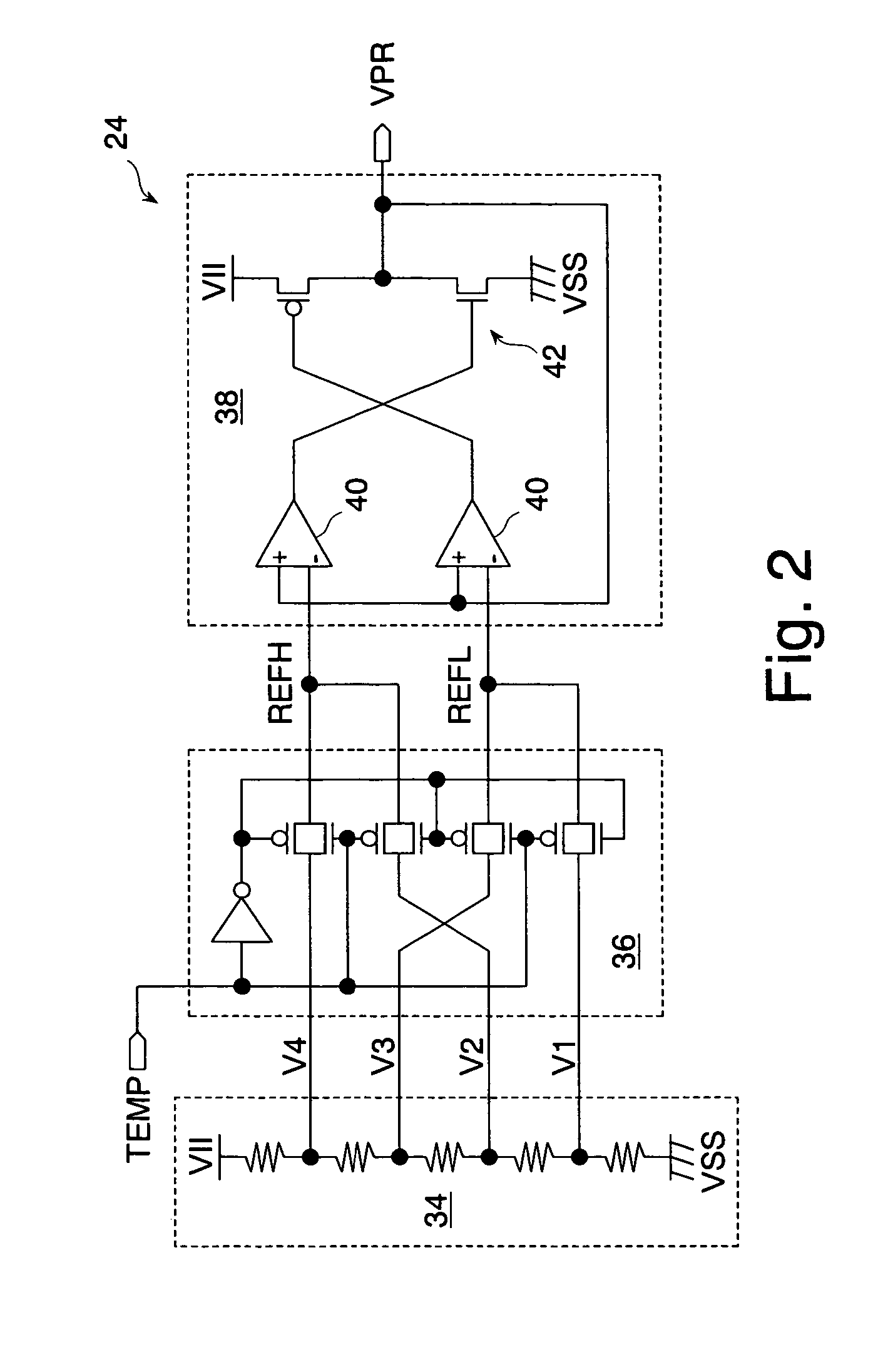
A precharge voltage generating circuit outputs any of a plurality of kinds of precharge voltages in accordance with an ambient temperature. A precharge circuit supplies the precharge voltage to a bit line during the nonaccess of a dynamic memory cell. A sense amplifier amplifies a difference between the voltage of a data signal read from the dynamic memory cell onto the bit line and the supplied precharge voltage. The precharge voltage is altered in accordance with the ambient temperature, whereby the read margin of the sense amplifier can be changed, and the worst value of the data retaining time of the memory cell can be improved. As a result, the frequency of refreshing of the memory cell can be lowered, reducing power consumption and a standby current.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
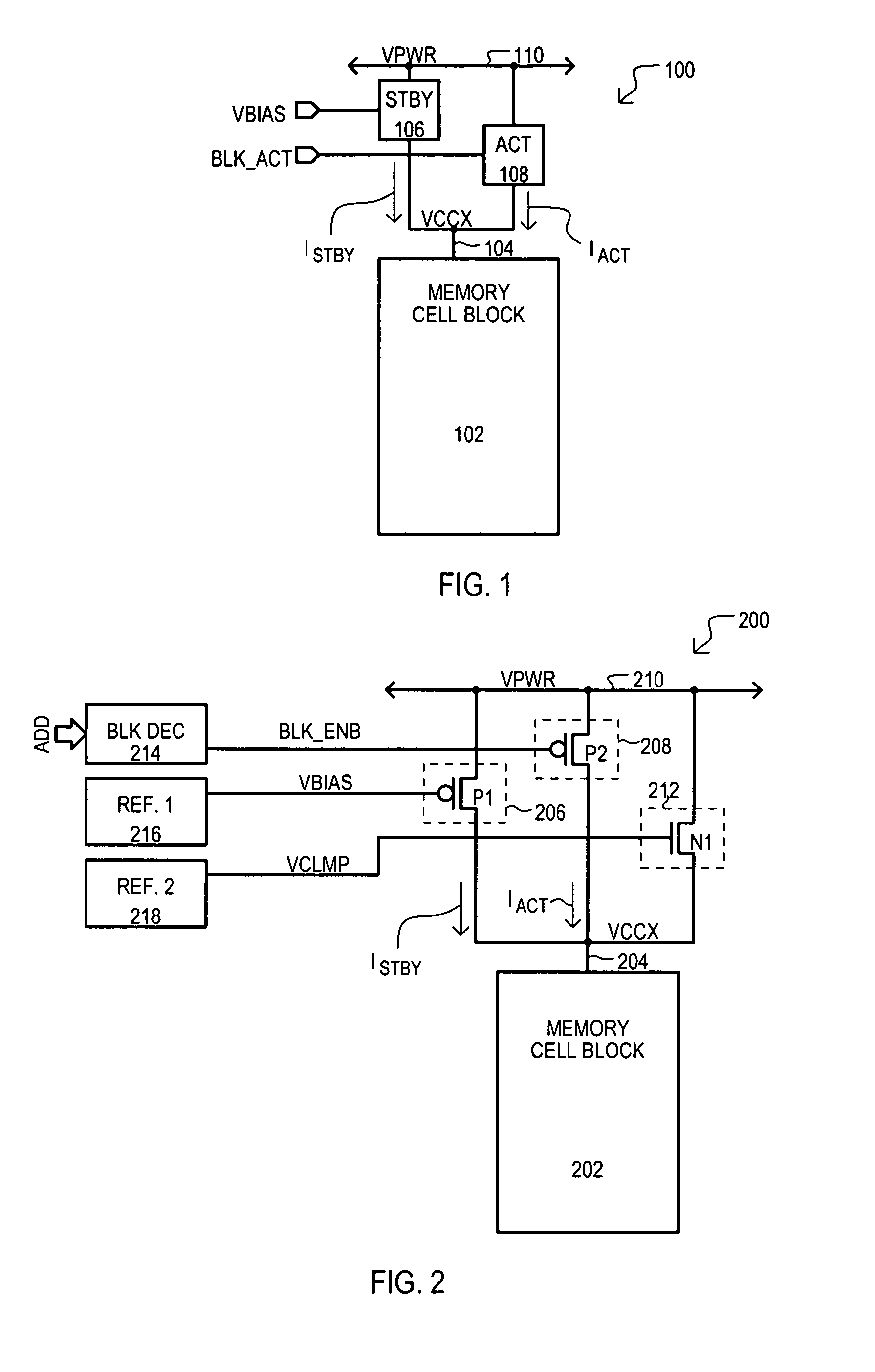
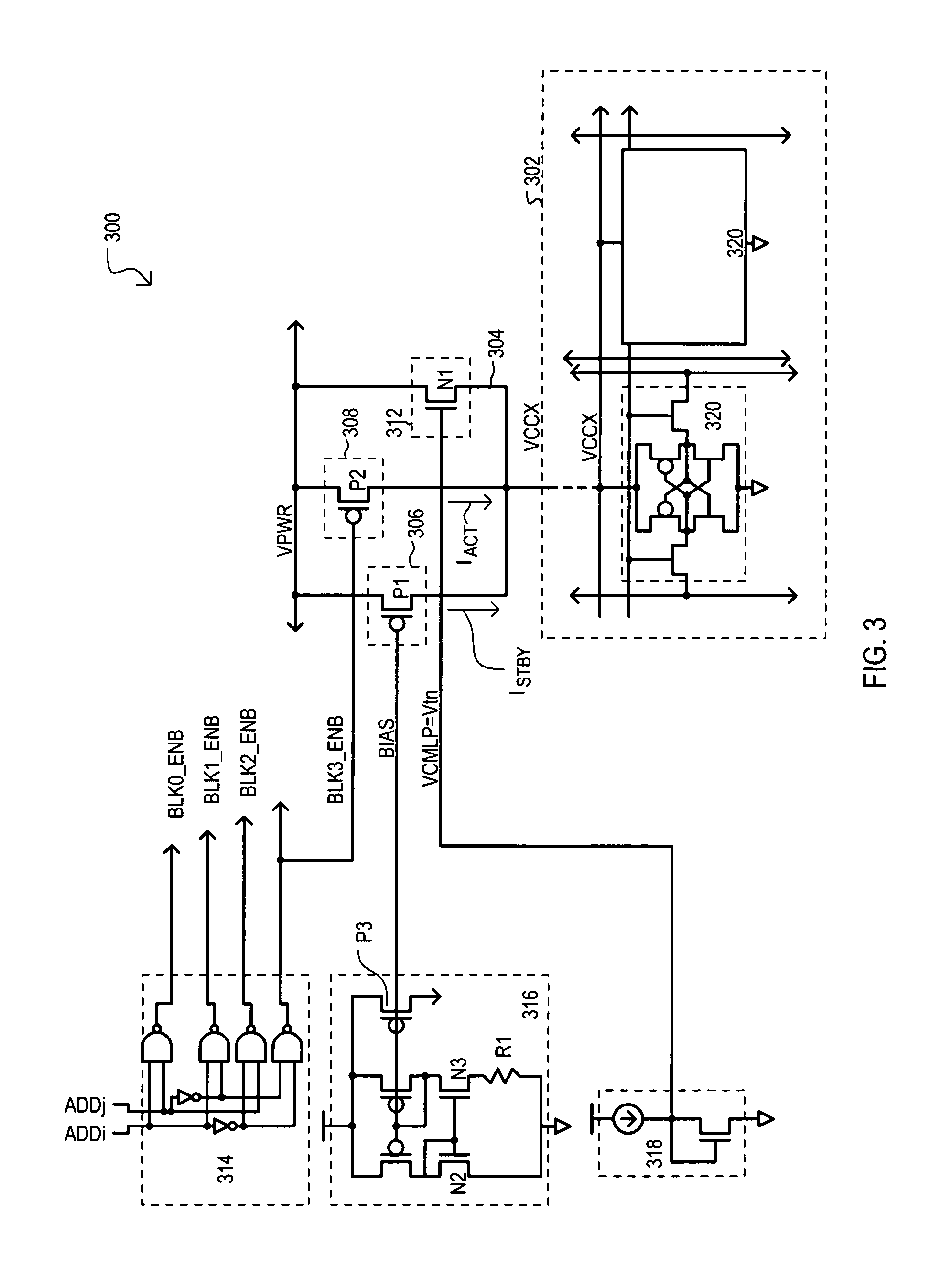
Current source architecture for memory device standby current reduction
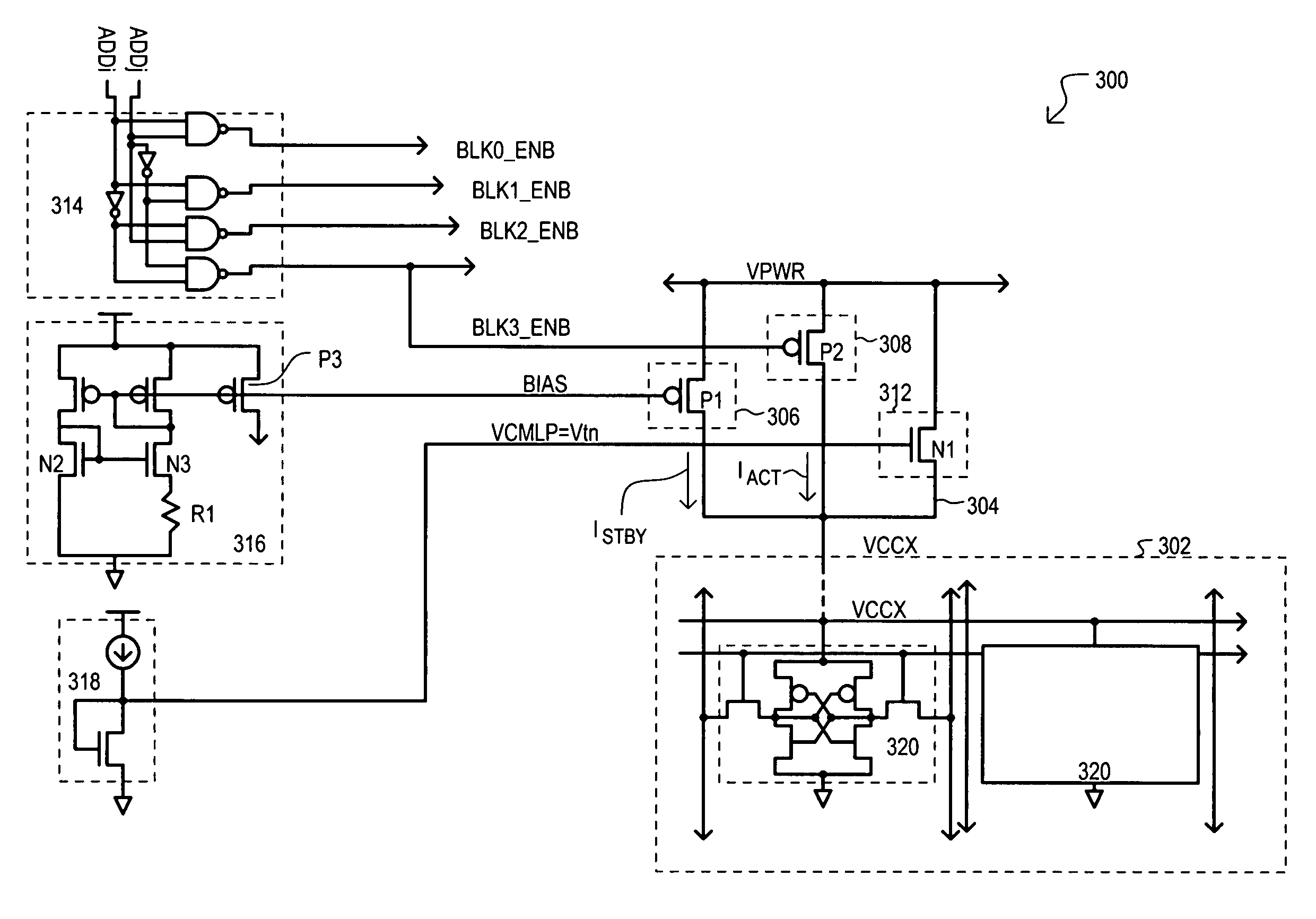
A memory device (200) can include a memory cell block (202), a standby current source (206), an active current source (208), and a clamping device (212). In a standby mode, a standby current source (206) can provide constant standby current ISTBY to memory cell block (202) via block supply node (204). In an active mode, active current source (208) can provide current to accommodate current necessary for active operations (e.g., accessing the memory cell block). A clamping circuit (212) can provide additional current in the event a block supply node (204) potential VCCX collapses due to the presence of micro-defects. In addition, compensation for process variation can be achieved by a self regulating well (454) to source (404) back bias that can modulate the threshold voltage of p-channel transistors of memory cells within the well (454), reducing overall leakage.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
Low voltage sensing scheme having reduced active power down standby current
ActiveUS20070041257A1Reduces active power down standby leakage currentReduce voltageDigital storageLow voltageControl line
A low voltage sensing scheme reduces active power down standby leakage current in a memory device. During memory's active power down state, the leak current may increase because of the use of P and Nsense amplifiers having low threshold voltages (Vth) for low Vcc sensing of data signals. A clamping device or diode is used between a Psense amplifier control line (e.g. ACT) and Vcc and / or between an Nsense amplifier control line (e.g. RNL*) and Vss (ground potential). The clamping diode is not enabled during normal memory operations, but is turned on during active power down mode to reduce leakage current through ACT and / or RNL* nodes. The clamping device connected to the ACT node may reduce the voltage on the ACT line during power down mode, whereas the clamping device connected to the RNL* node may increase the voltage on the RNL* line during power down mode to reduce sense amplifier leakage current through these nodes. Because of the rules governing abstracts, this abstract should not be used to construe the claims.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
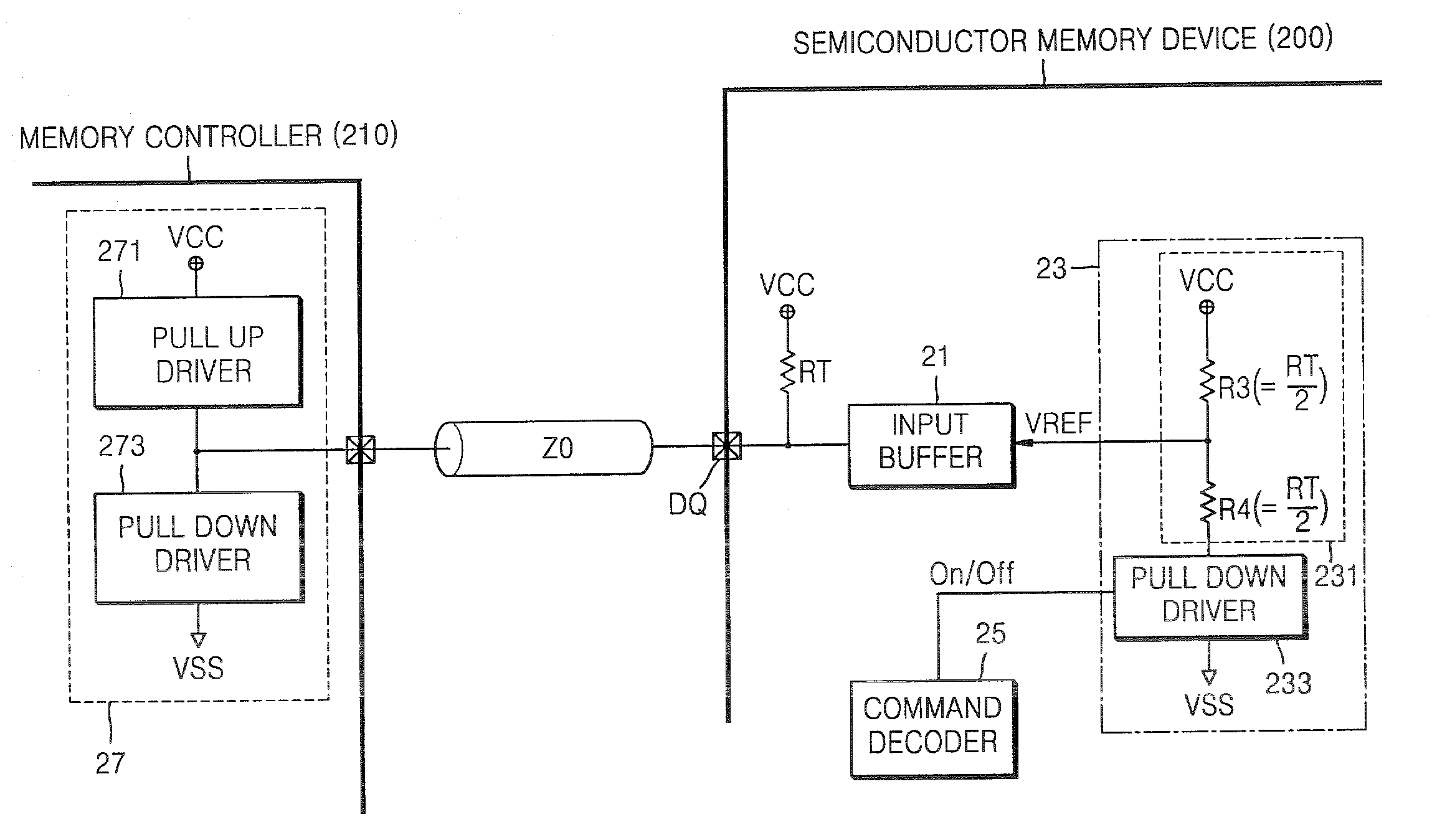
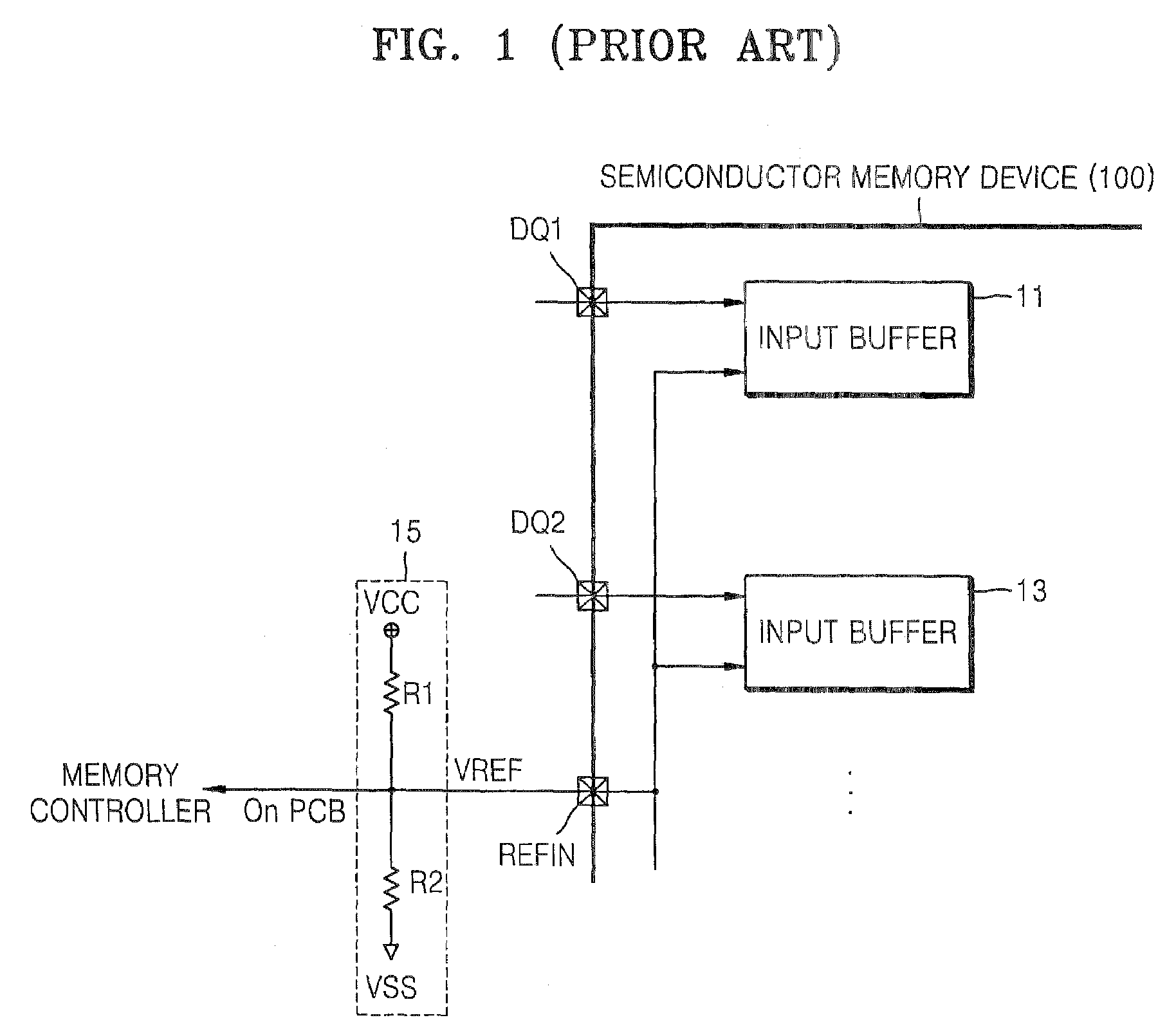
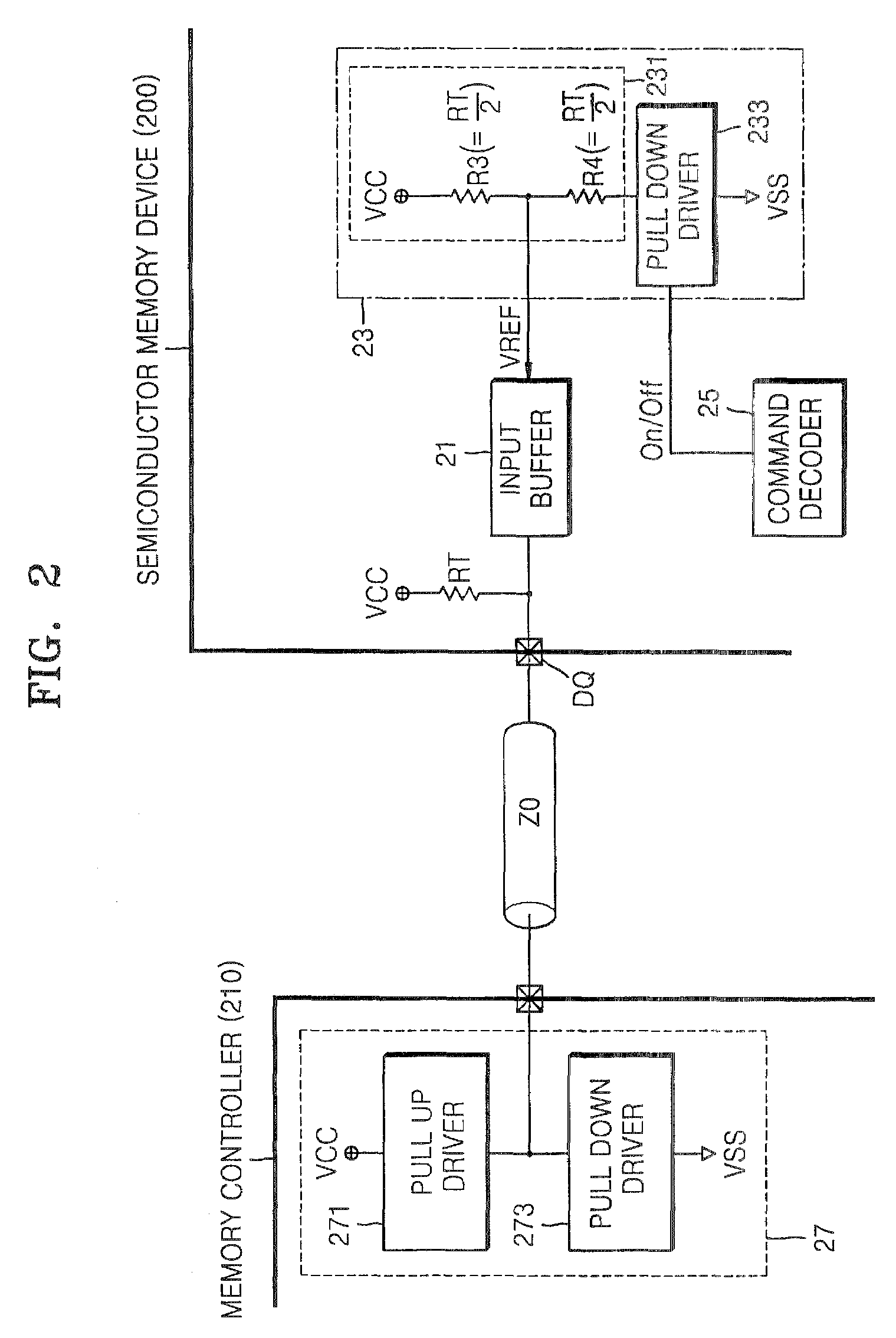
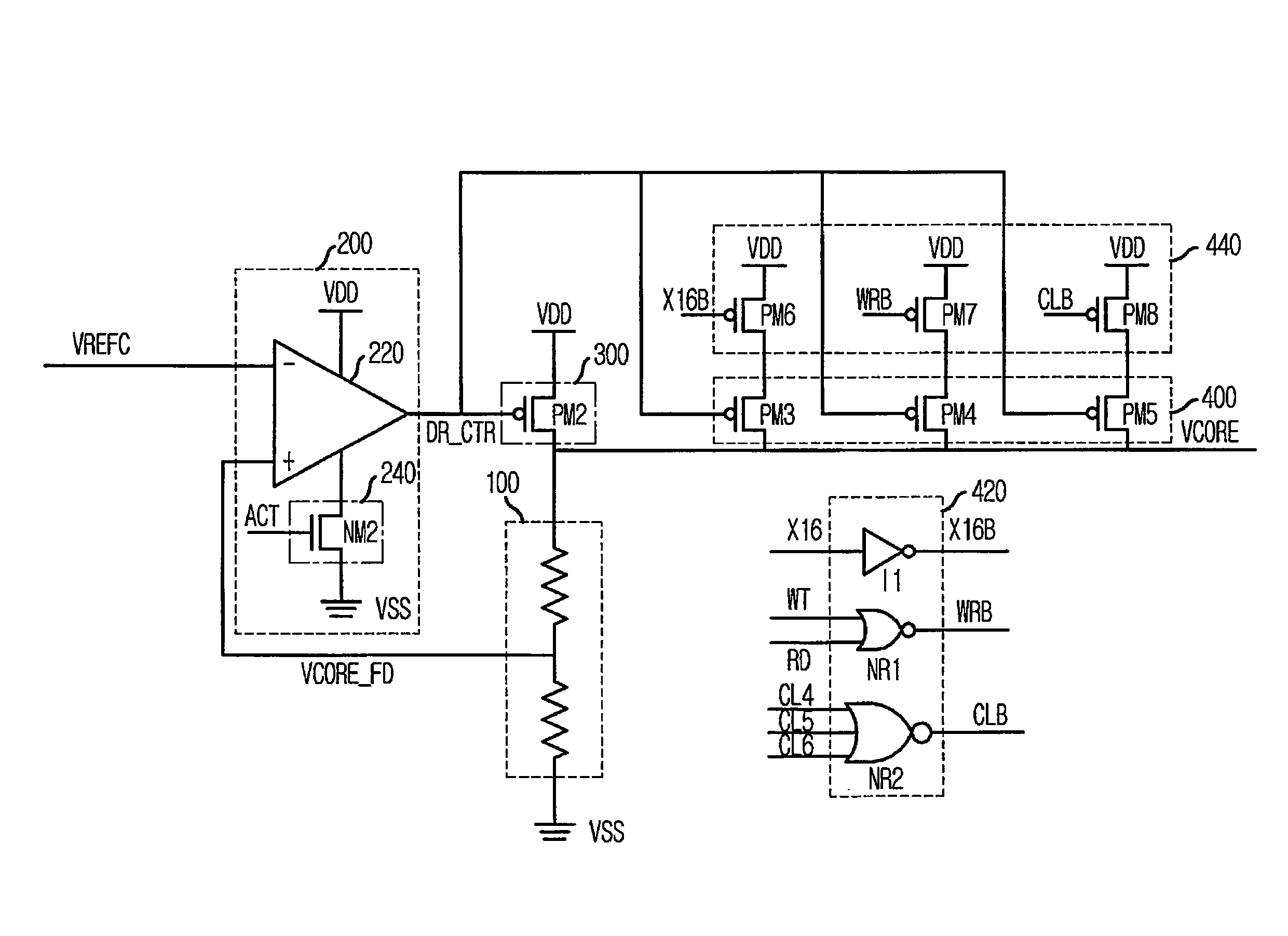
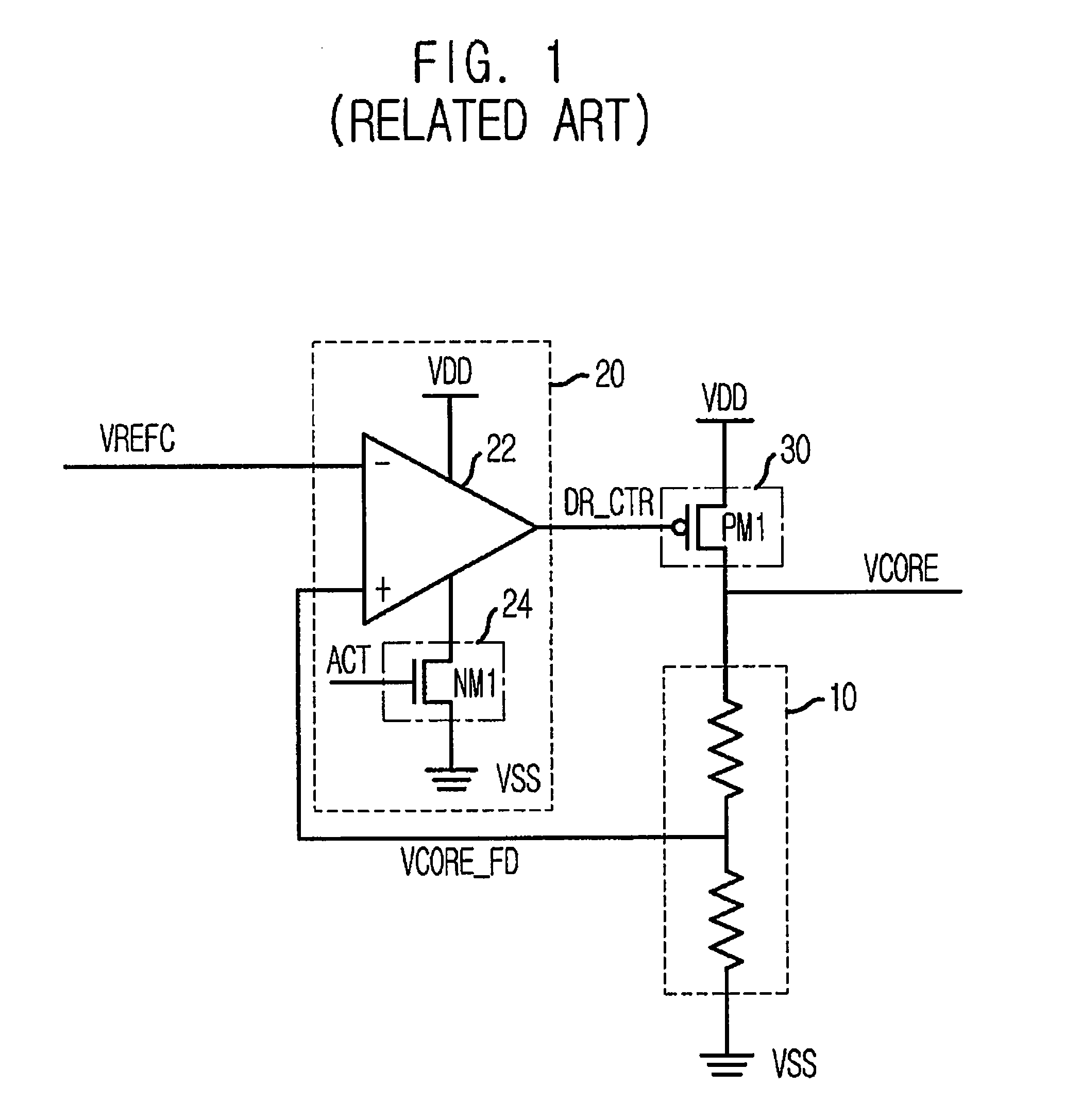
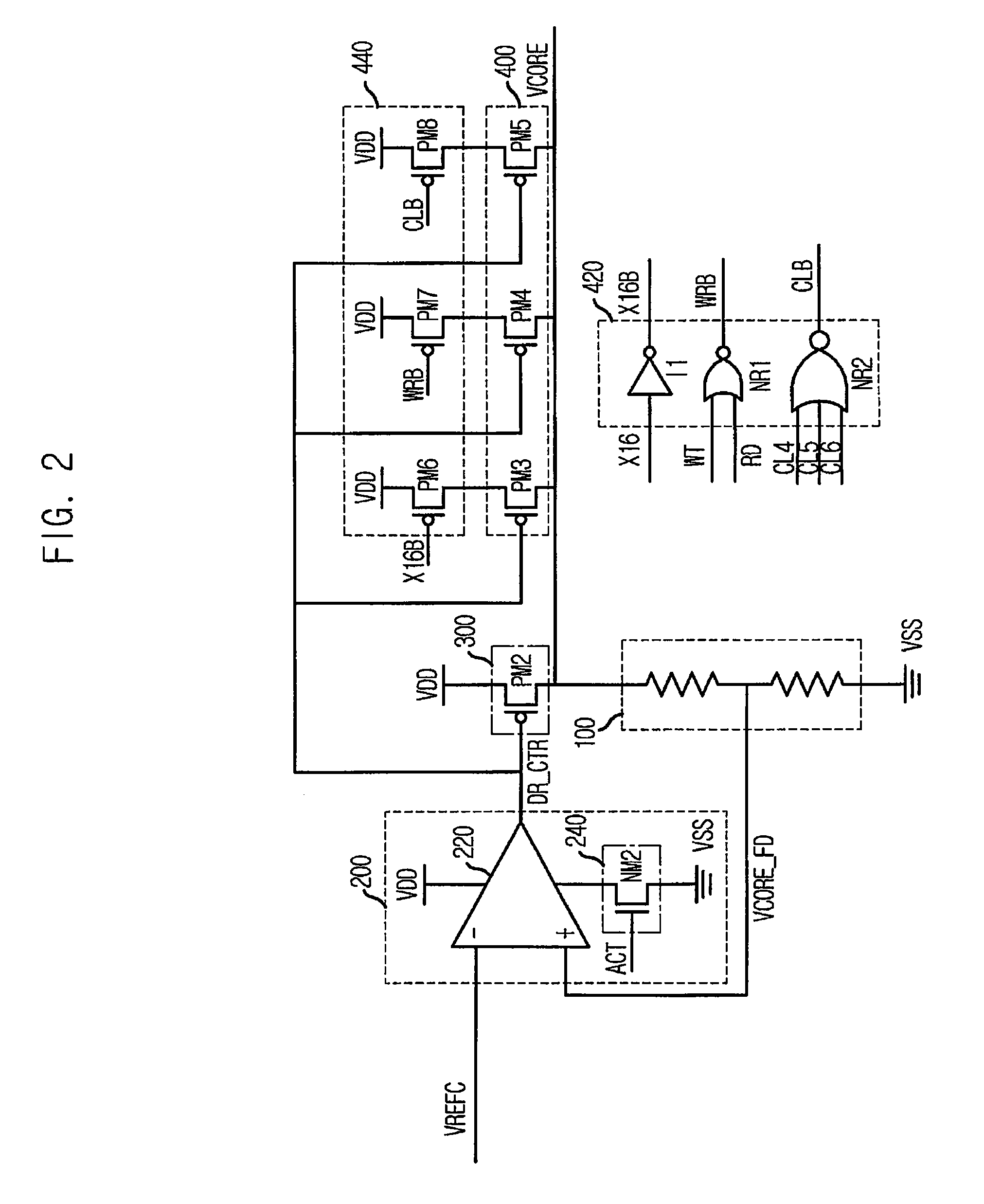
Internal reference voltage generating circuit for reducing standby current and semiconductor memory device including the same
InactiveUS7515487B2Reduced pin countReliability increasing modificationsElectronic switchingDividing circuitsEngineering
An internal reference voltage generating circuit that reduces a standby current and the number of pins of a semiconductor memory device, in which a reference voltage is provided to an input buffer that receives a signal through an input to which an on die transmitor resistor is connected, includes: a voltage dividing circuit outputting the reference voltage by a power voltage; a pull down driver connected to an end of the voltage dividing circuit; and a calibration control circuit comparing a voltage level of the input and a voltage level of an end of the voltage dividing circuit, and controlling the on resistor value of the pull down driver according to a result of the comparison. The internal reference voltage generating circuit is operated while the memory controller inputs a signal into a mode register set (MRS) to enable the internal reference voltage generating circuit and the output signal of the MRS is activated.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Internal voltage generator
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
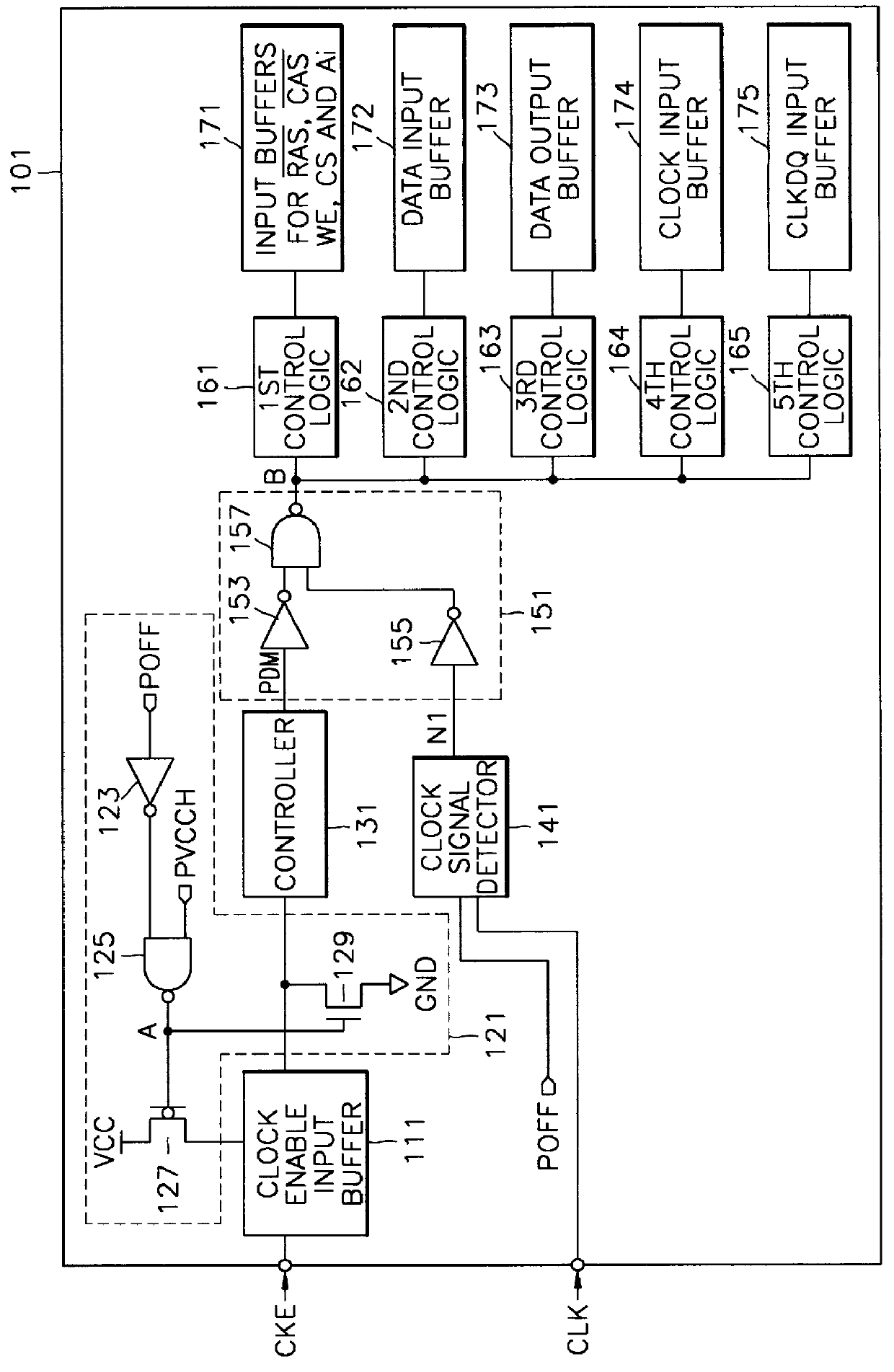
Integrated circuit memory devices having automatically induced standby modes and methods of operating same
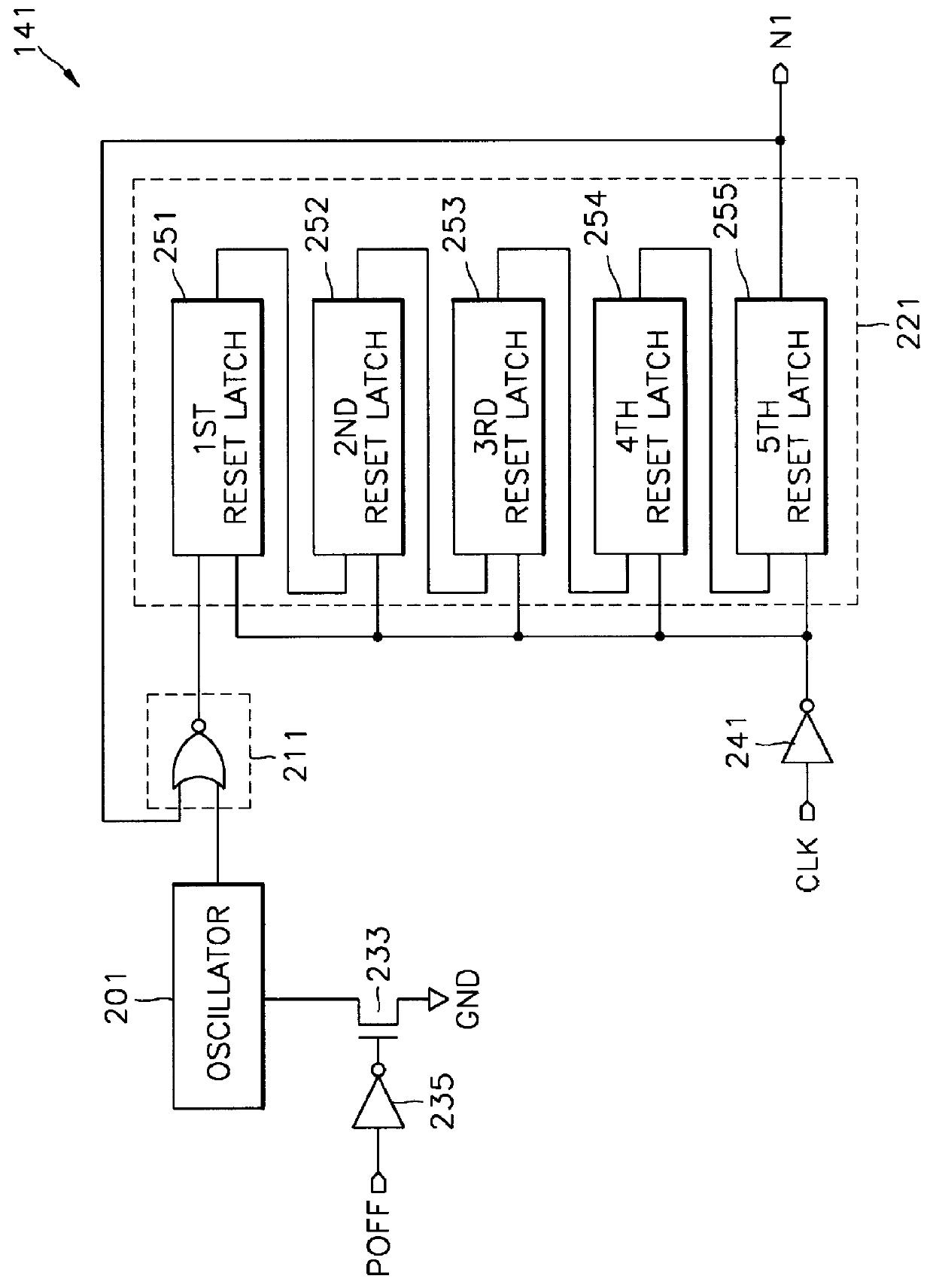
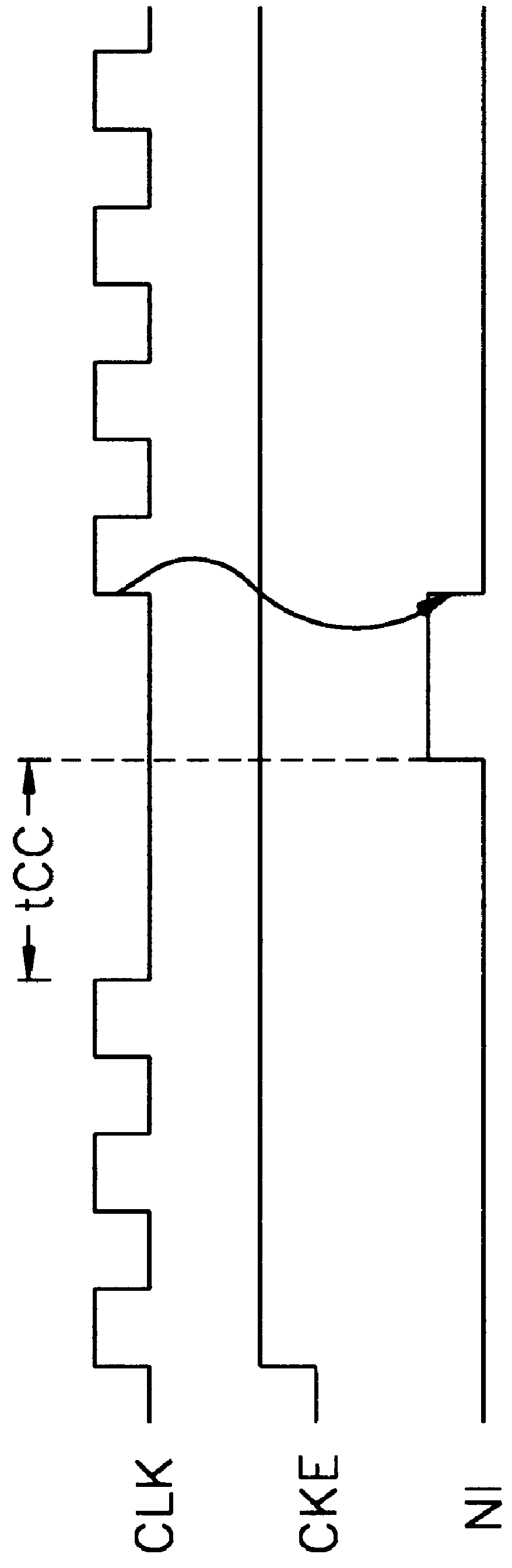
Integrated circuit memory devices monitor clock signal transitions and automatically induce a power saving standby mode of operation if the clock signal becomes inactive for a designated amount of time. The memory devices include at least one buffer having an active mode and an inactive standby mode and a standby current control circuit. This control circuit disposes the at least one buffer in its inactive standby mode whenever a power down signal is in a first logic state or whenever the power down signal is in a second logic state at a point in time when a clock signal has continuously been in an inactive state for a duration greater than twice its period. The control circuit may comprise a clock signal detector having N serially-connected latches therein which are reset whenever the clock signal transitions from the inactive state to an active state. The clock signal detector is responsive to the power down signal and comprises an oscillator which is active whenever the power down signal is in the second logic state and inactive whenever the power down signal is in the first logic state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Background scanning method for WLAN client devices
ActiveUS20100080134A1Increase currentExtension of timePower managementError preventionPower modeClient-side
Background scan for 802.11 client devices allows them to keep most of its components in low power mode when certain criteria are not met. A method for changing dynamically those criteria according to the air data traffic conditions is described in the present invention. This increases the time the system remains in sleep mode and consequently improves the standby current consumption to portable 802.11 enabled media.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Circuit and method for reducing SRAM standby power
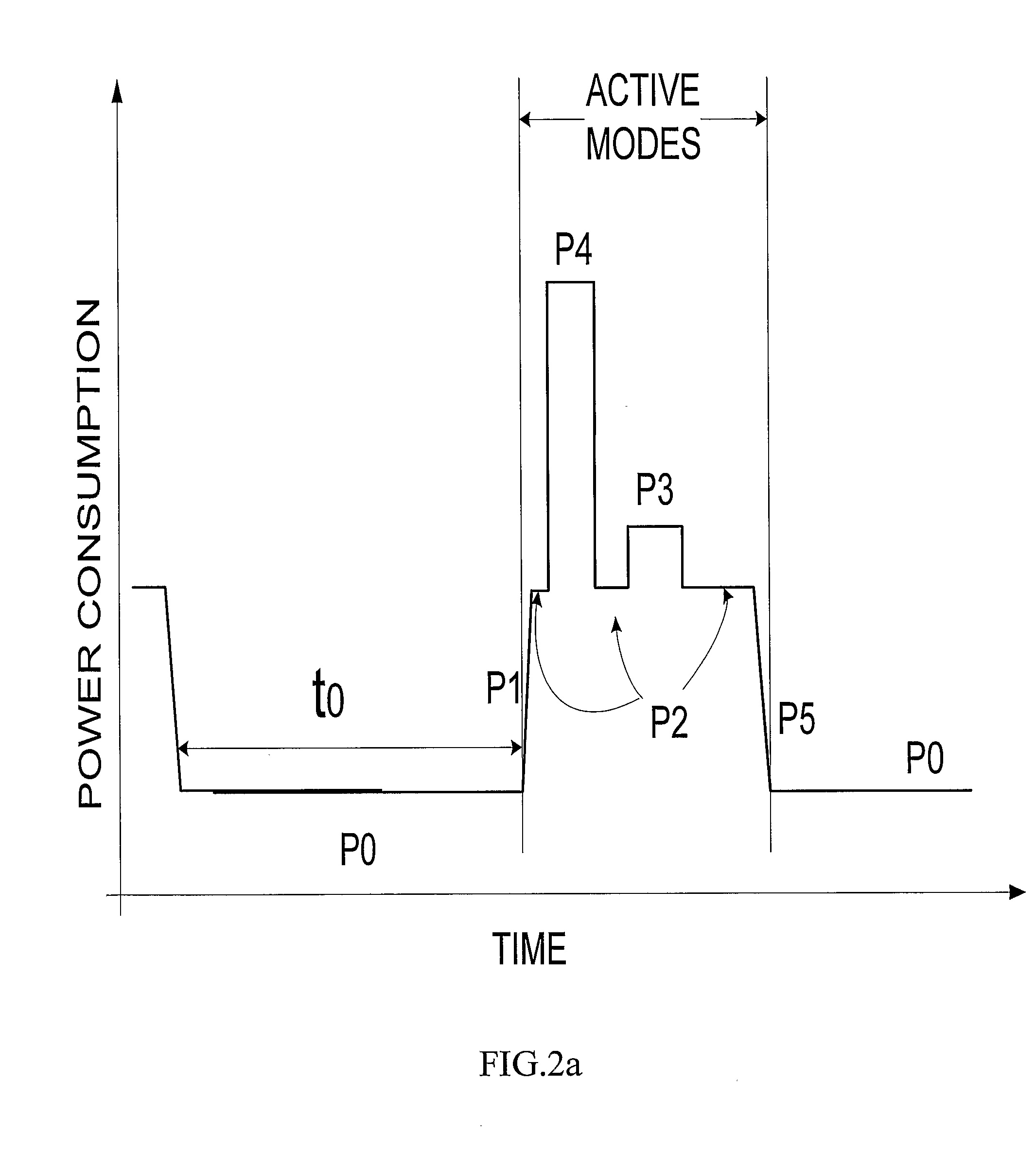
A method of operating a memory circuit to reduce standby current is disclosed. The method includes applying a first voltage (Vdd) to a power terminal (224) of a memory cell having a first (612) and a second (614) data terminal. A data bit is stored in a memory cell (600,602,604,606). A second voltage (VDA) different from the first voltage is applied to the power terminal. A third voltage (Ground) is applied to the first and second data terminals. The first voltage is applied to the power terminal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System and Method of Battery Monitoring
InactiveUS20180236890A1Accurately reportPractical and convenientElectric devicesLead-acid accumulatorsBattery state of chargeDriver/operator
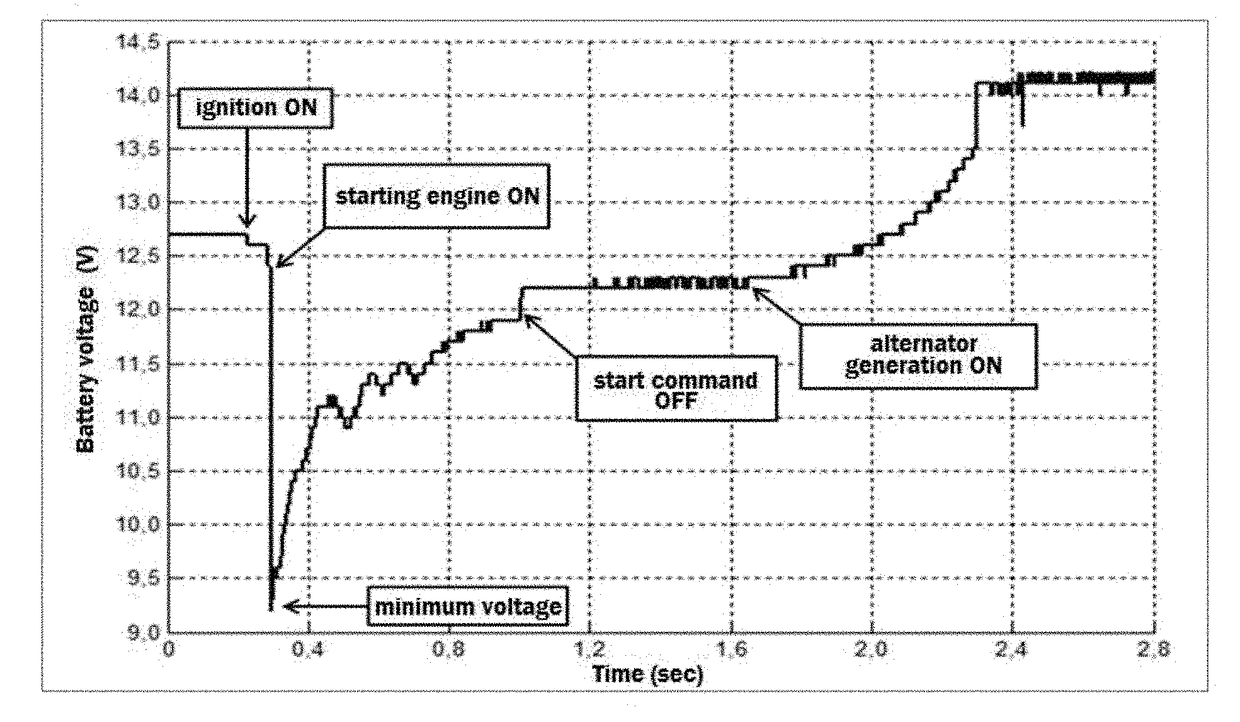
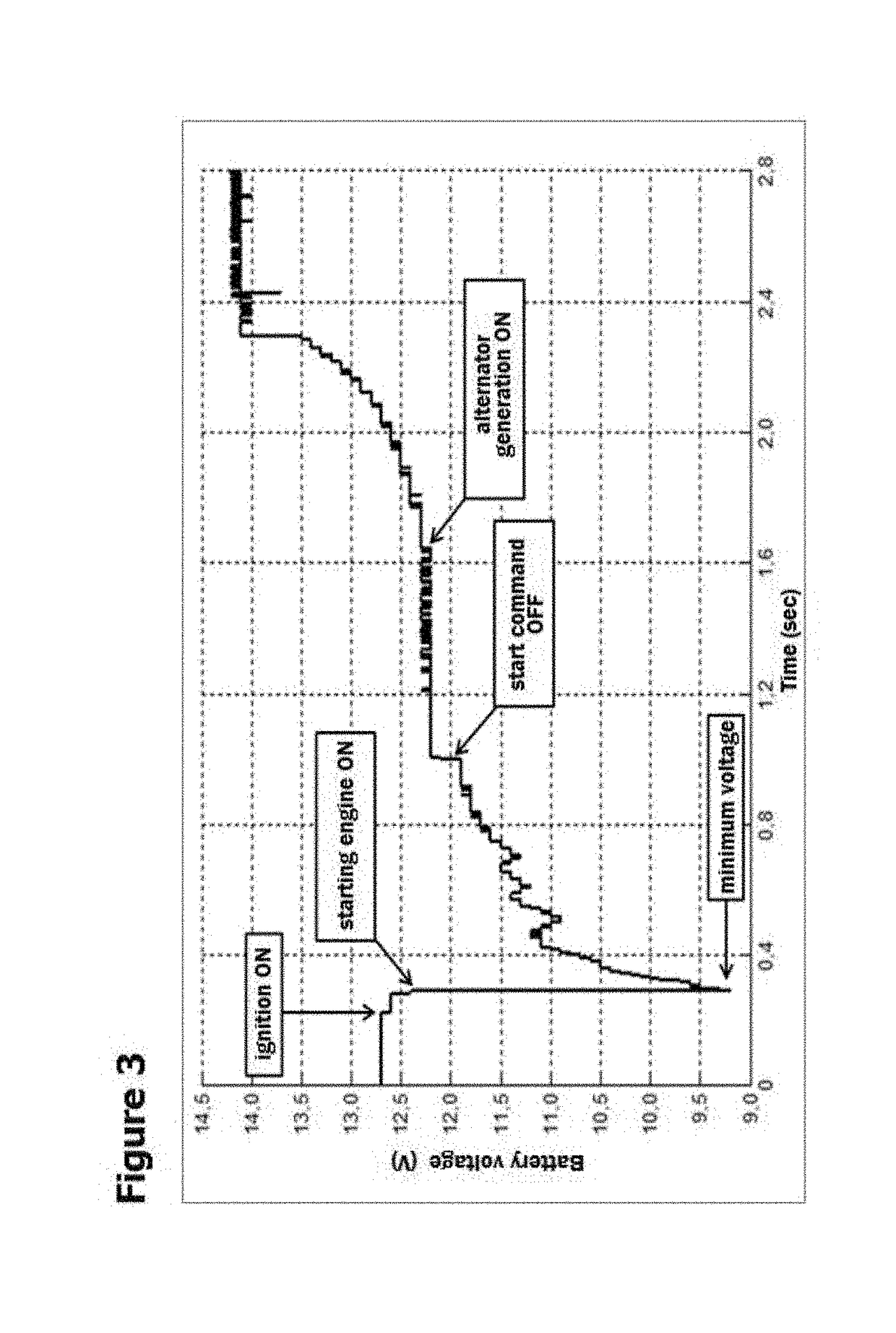
It is herein described a battery monitoring system, in particular for a vehicle battery, which comprises the steps of: calculating, based on the battery voltage (1), the parameters of the battery state of health (SoH), battery state of charge (SoC) and stand-by current (IOD); comparing the battery state of health (SoH), the battery state of charge (SoC) and stand-by current (IOD) parameters with their previously established limits; and providing a warning sign when any parameter is different from its previously pre-defined limit. The system allows monitoring a vehicle battery (1) beginning from its installation and provides the driver indications about the necessity of maintenance or replacement thereof, exclusively based on the battery voltage, measured at specific times of the vehicle operation.
Owner:FCA FIAT CHRYSLER AUTOMOVEIS BRASIL
Power-up reset circuit
A power-up reset circuit with reduced power consumption. The resistance of the power-up reset circuit may be adjusted during a power-up operation. The standby current may thereby be reduced, which may reduce the power consumption in the power-up reset circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
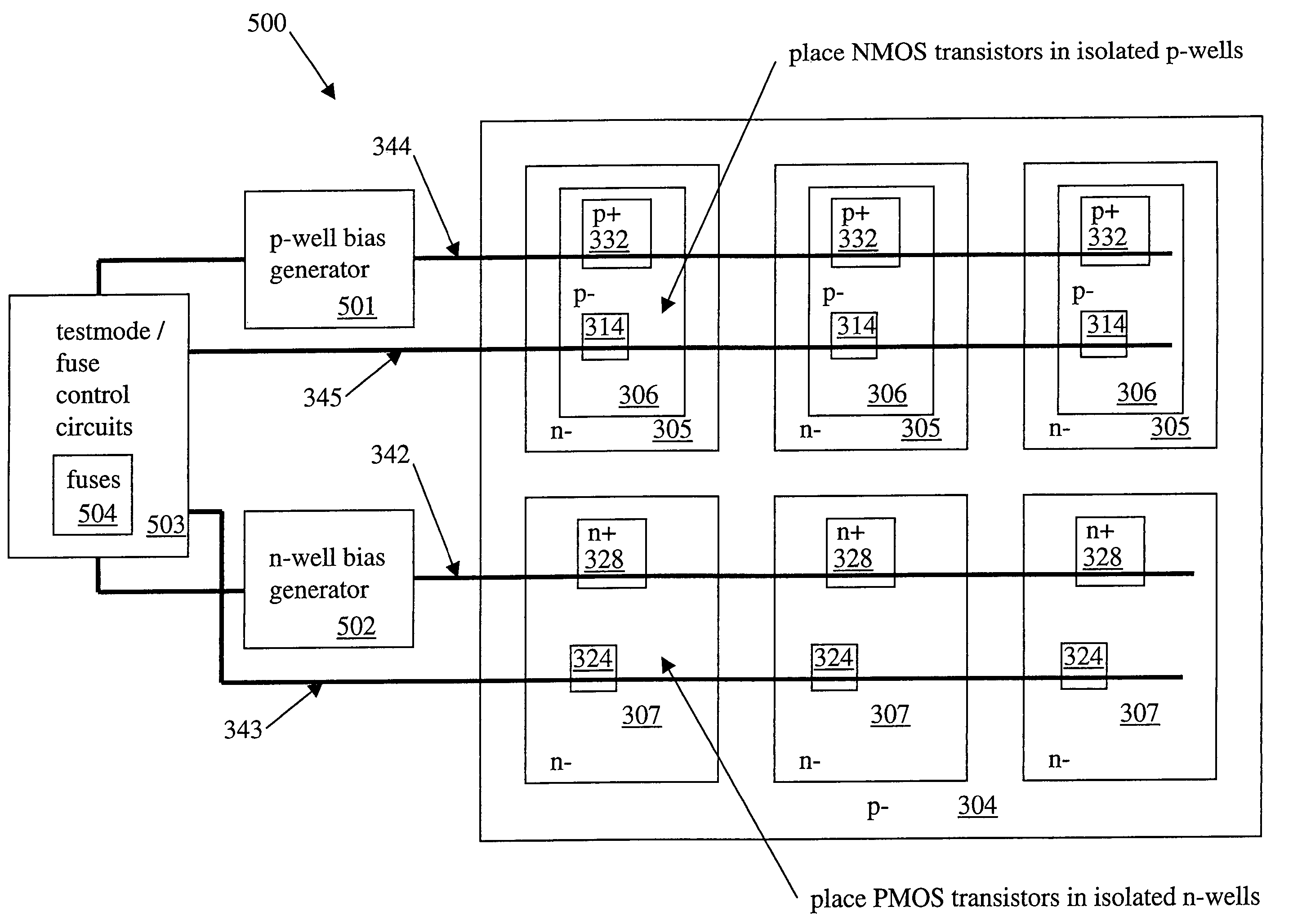
Standby current reduction over a process window with a trimmable well bias
InactiveUS20050280083A1High densityLow costTransistorPower reduction in field effect transistorsMOSFETOhmic contact
An integrated circuit device including a plurality of MOSFETs of similar type and geometry is formed on a substrate with an ohmic contact, and an adjustable voltage source on the die utilizing clearable fuses is coupled between the ohmic contact and the sources of the MOSFETs. After die processing, a post-processing test is performed to measure an operating characteristic of the die such as leakage current or switching speed, and an external voltage source is applied and adjusted to control the operating characteristic. The on-die fuses are then cleared to adjust the on-die voltage source to match the externally applied voltage. The operating characteristic may be determined by including a test circuit on the die to exhibit the operating characteristic such as a ring oscillator frequency. This approach to controlling manufacturing-induced device performance variations is well suited to efficient manufacture of small feature-size circuits such as DRAMs.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Semiconductor device including internal voltage generation circuit
ActiveUS20070216467A1Run at high speedLower average currentRead-only memoriesElectronic switchingEngineeringPower circuits
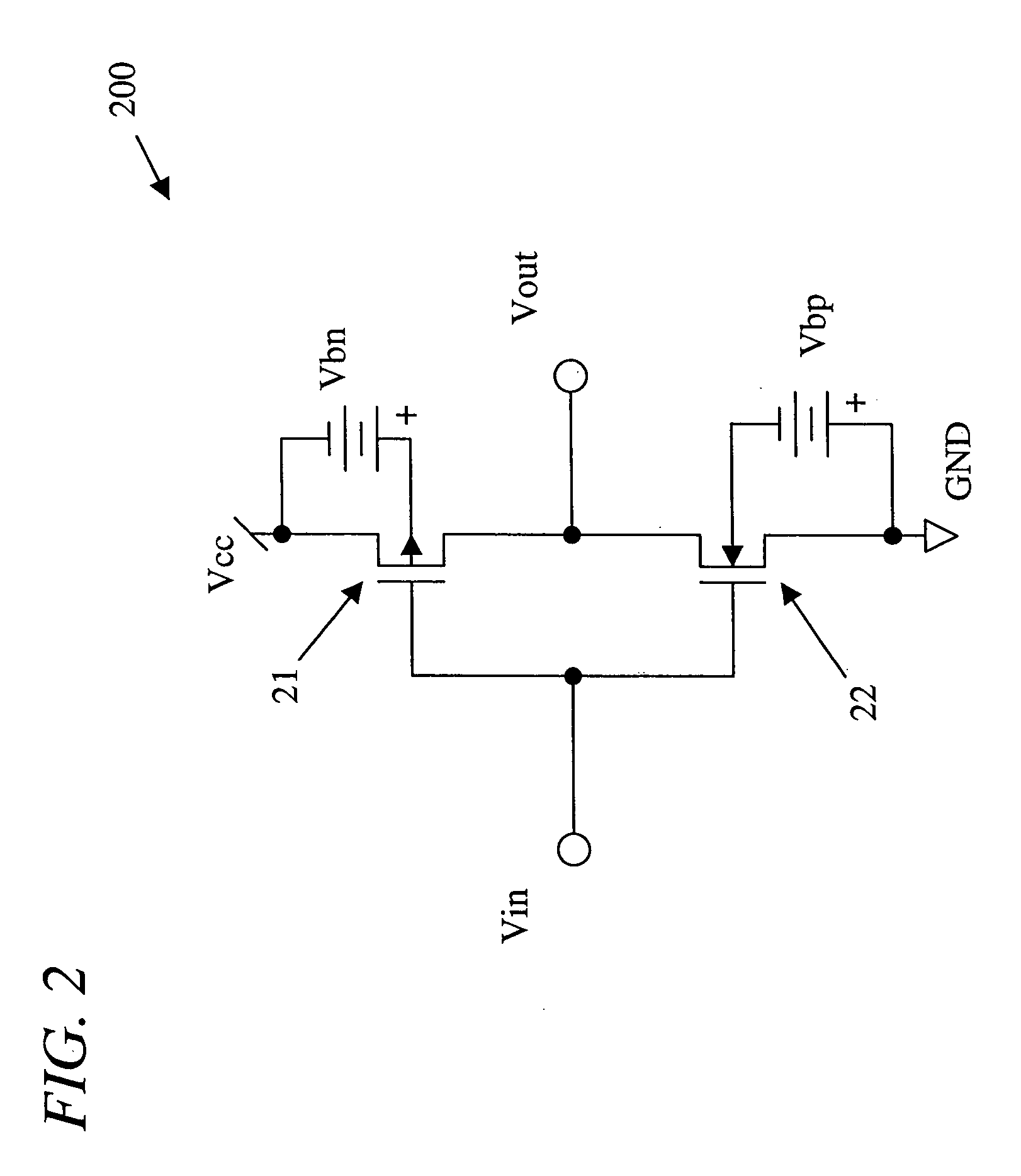
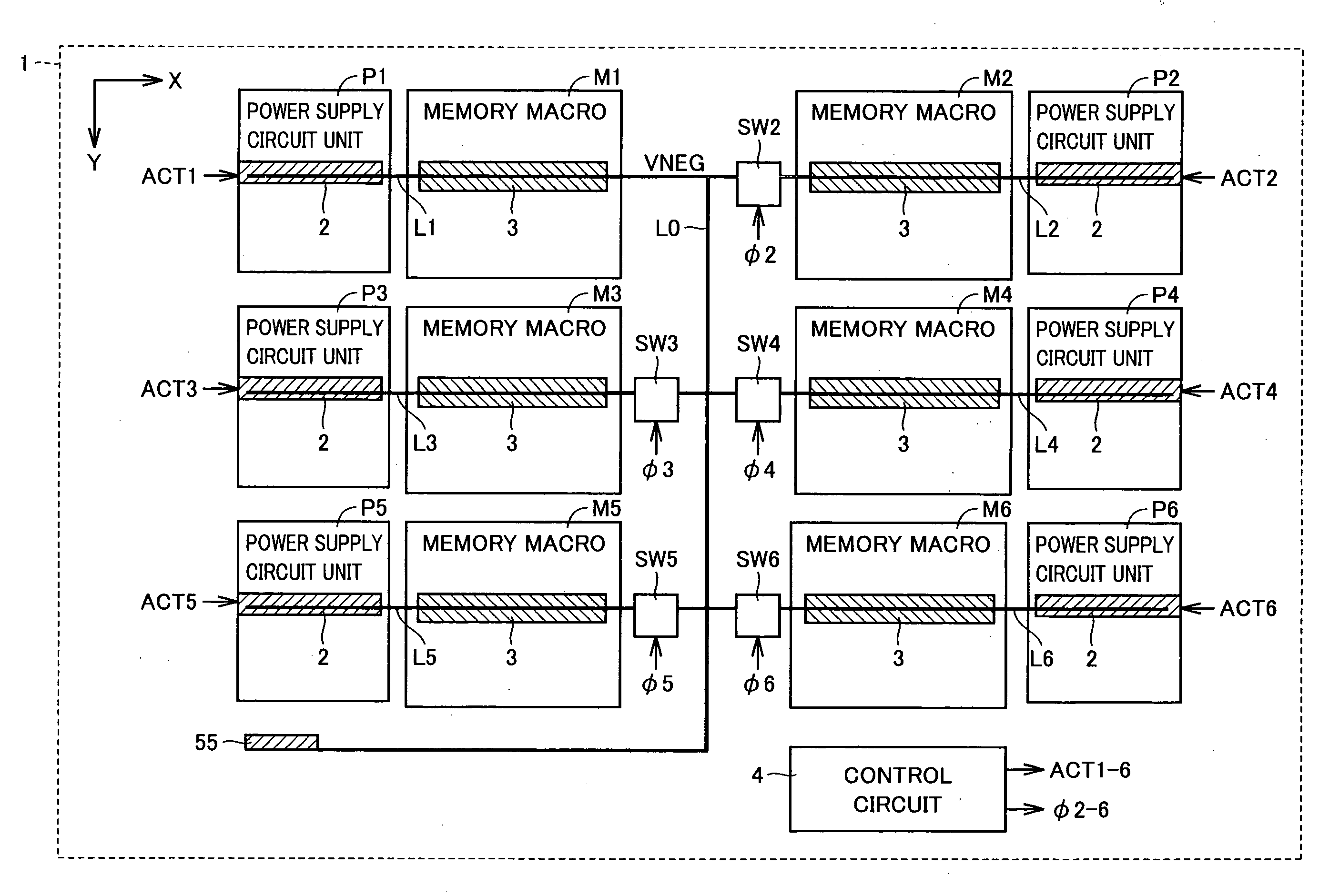
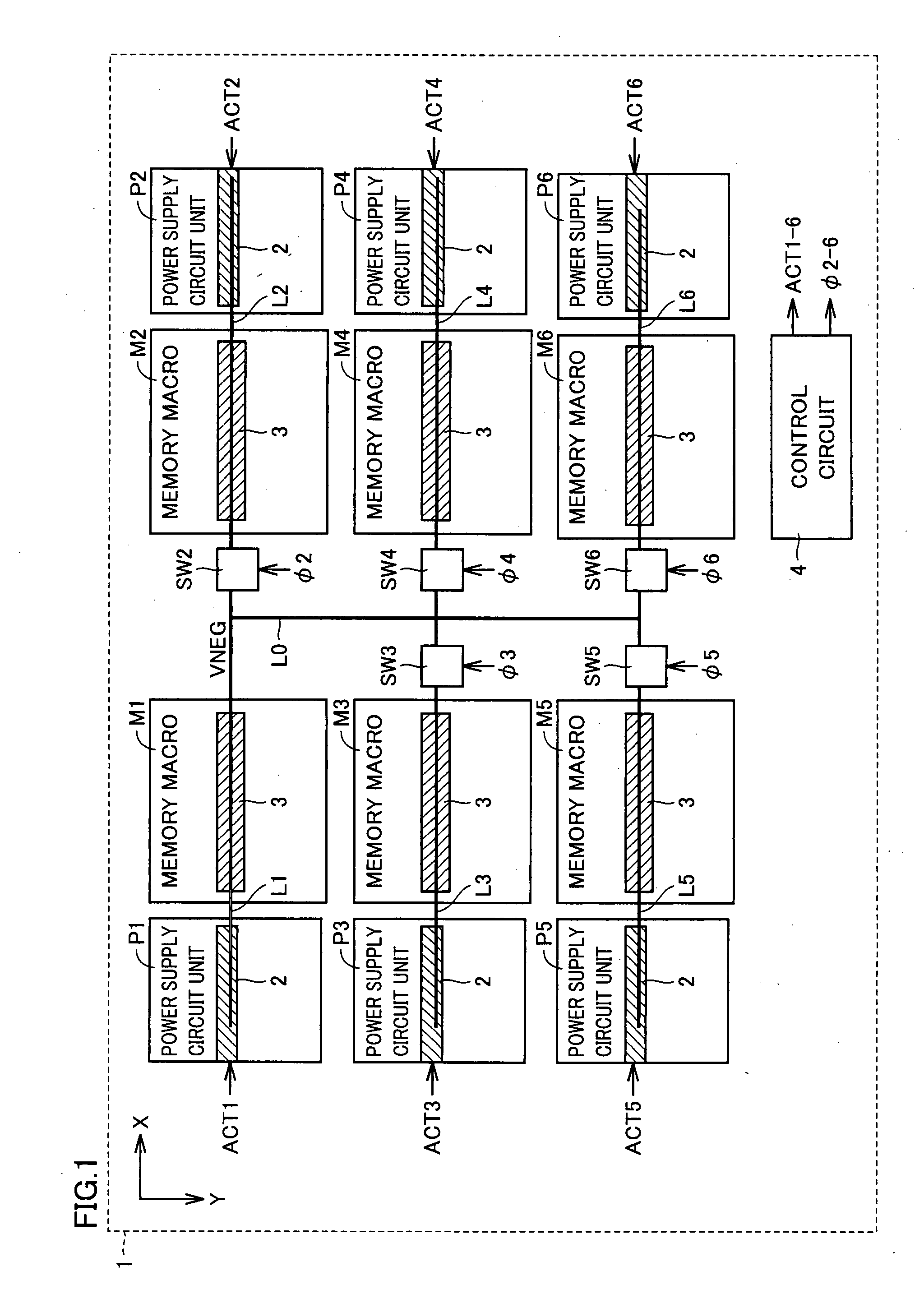
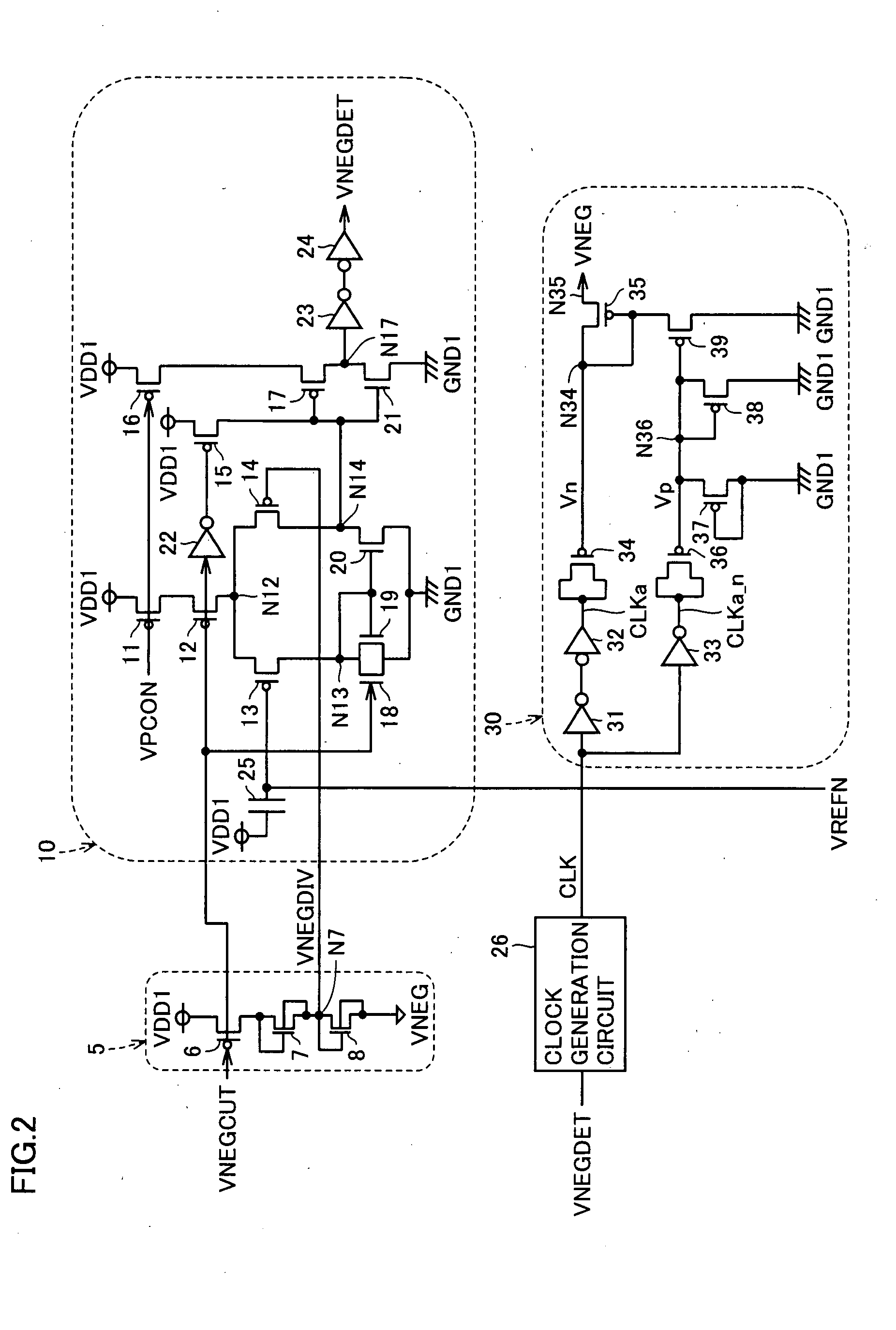
A semiconductor integrated circuit device has a negative voltage generation circuit provided at each power supply circuit unit for six memory macros. Therefore, the response with respect to variation in a negative voltage is increased. In a standby mode, a negative voltage supply line for the six memory macros is connected by a switch circuit, and only a negative voltage generation circuit of one power supply circuit unit among six negative voltage generation circuits of the six power supply circuit units is rendered active. Thus, increase in standby current can be prevented.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
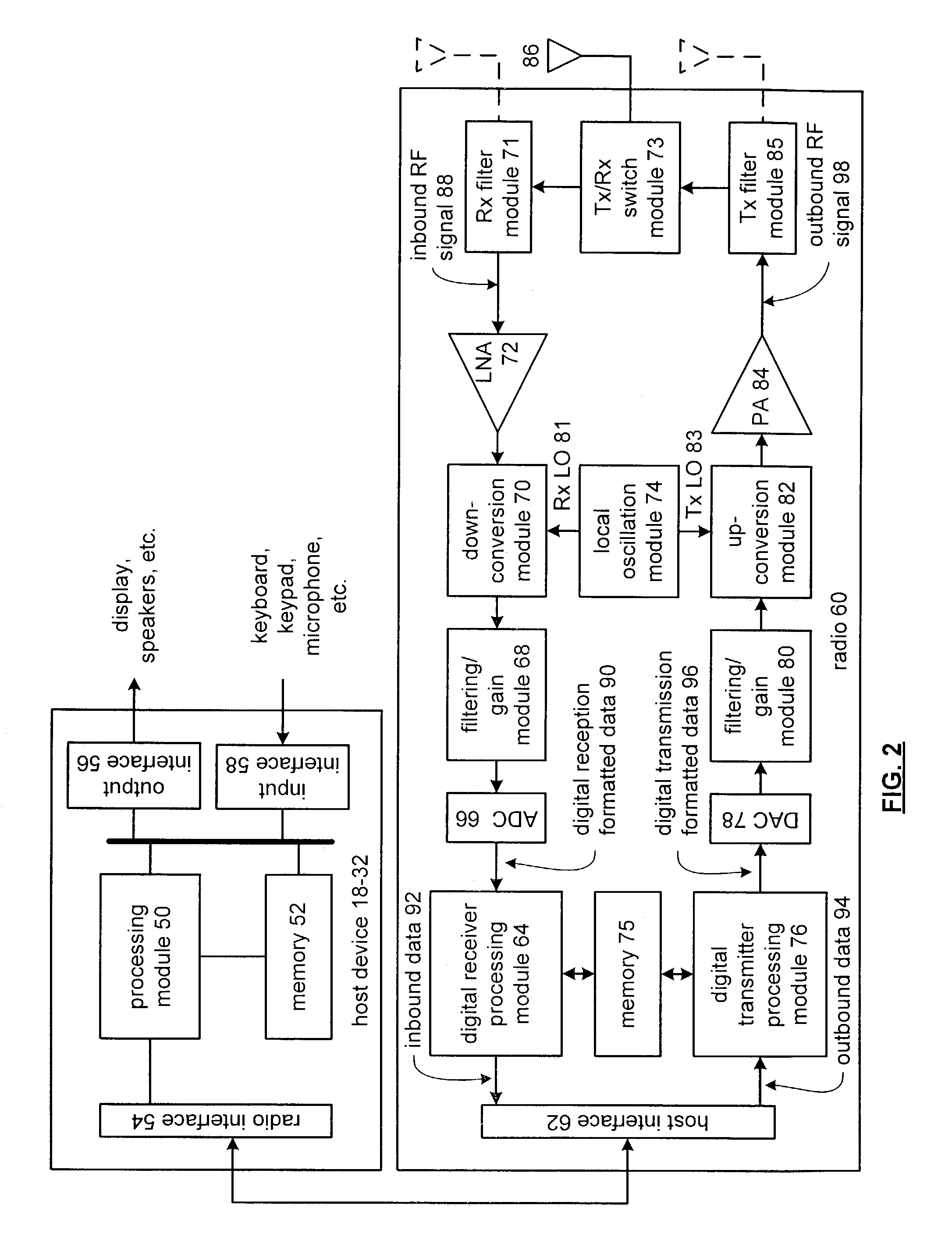
High gain, highly linear mixer
InactiveUS7107025B2Reduce switchingImprove linearityMultiple input and output pulse circuitsPush-pull amplifiersFrequency mixerEngineering
A high gain, highly linear mixer includes an input section, mixing section, at least one tuning component, and at least one stand by current source. The input section is operably coupled to receive an input voltage signal and perform a linear transconductance thereon to produce an input current signal. The mixing section is operably coupled to mix a local oscillation with the input current to produce a mixed current signal. The tuning component is operably coupled to the mixing section and to convert the mixed current signal into a mixed voltage signal that function as the output of the mixer. The standby current source is operably coupled to the mixing section and provides a standby current to the mixing section.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
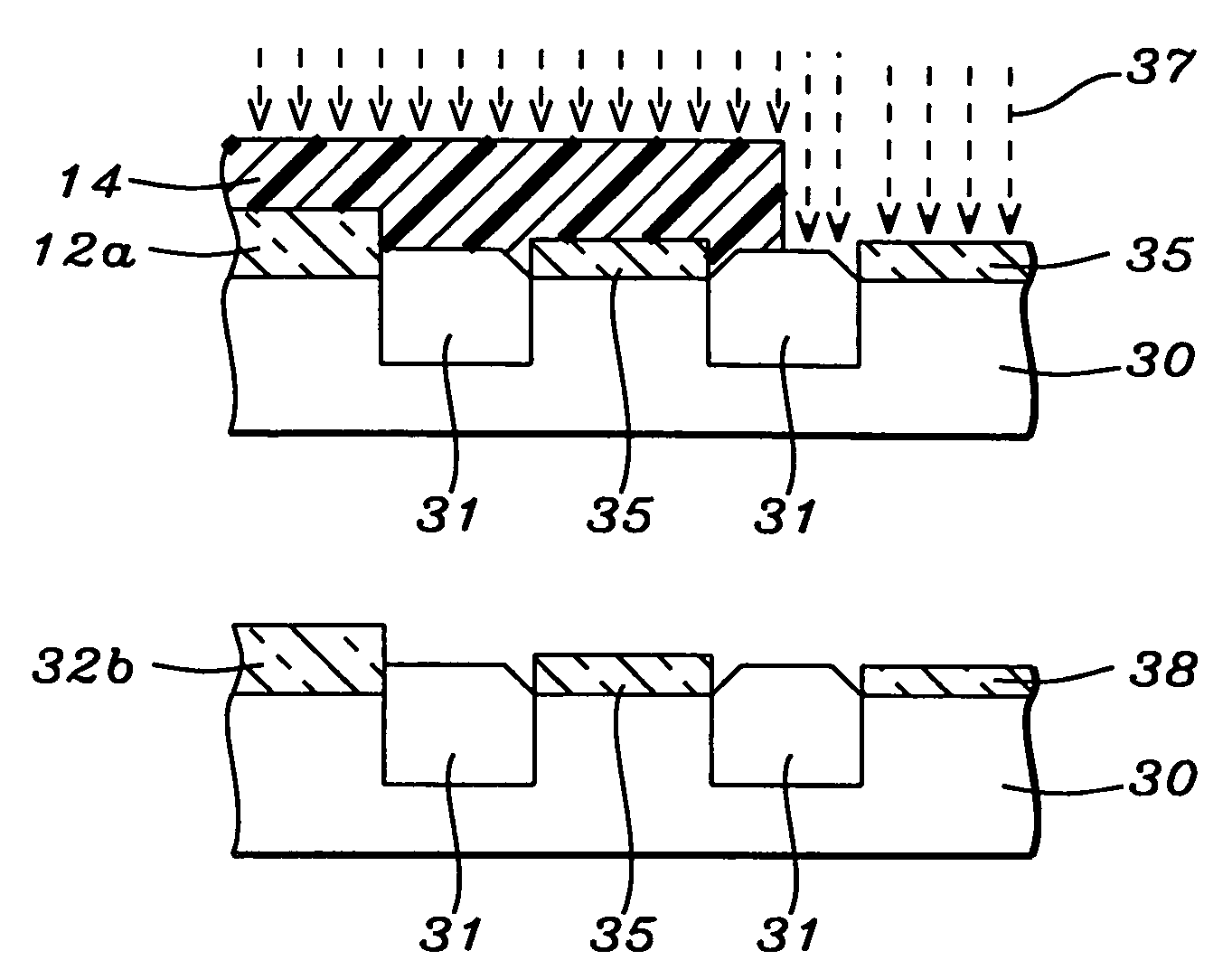
Method of generating multiple oxides by plasma nitridation on oxide
InactiveUS7118974B2Little and no effect integrityAvoid degradation in device performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantPlasma nitridation
A method of forming multiple gate oxide thicknesses on active areas that are separated by STI isolation regions on a substrate. A first layer of oxide is grown to a thickness of about 50 Angstroms and selected regions are then removed. A second layer of oxide is grown that is thinner than first growth oxide. For three different gate oxide thicknesses, selected second oxide growth regions are nitridated with a N2 plasma which increases the dielectric constant of a gate oxide and reduces the effective oxide thickness. To achieve four different gate oxide thicknesses, nitridation is performed on selected first growth oxides and on selected second growth oxide regions. Nitridation of gate oxides also prevents impurity dopants from migrating across the gate oxide layer and reduces leakage of standby current. The method also reduces corner loss of STI regions caused by HF etchant.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
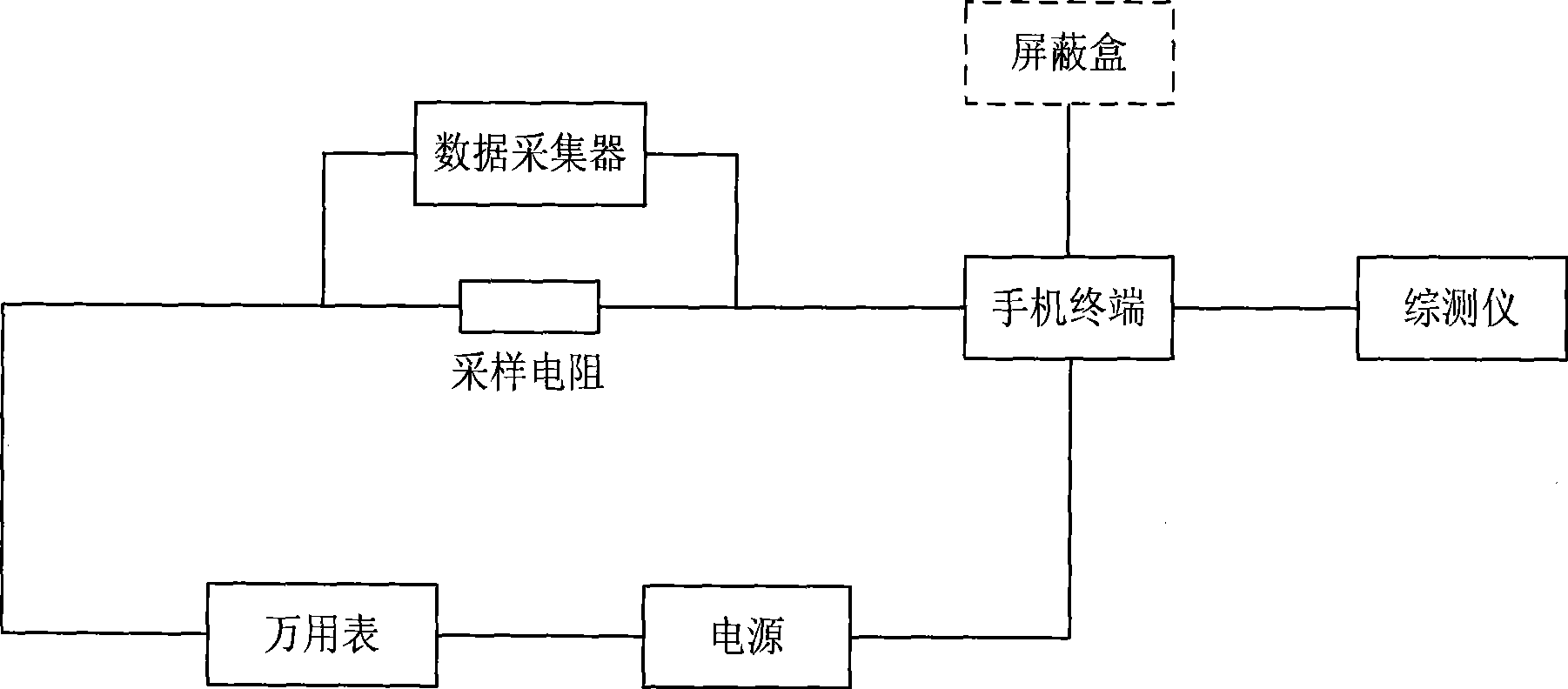
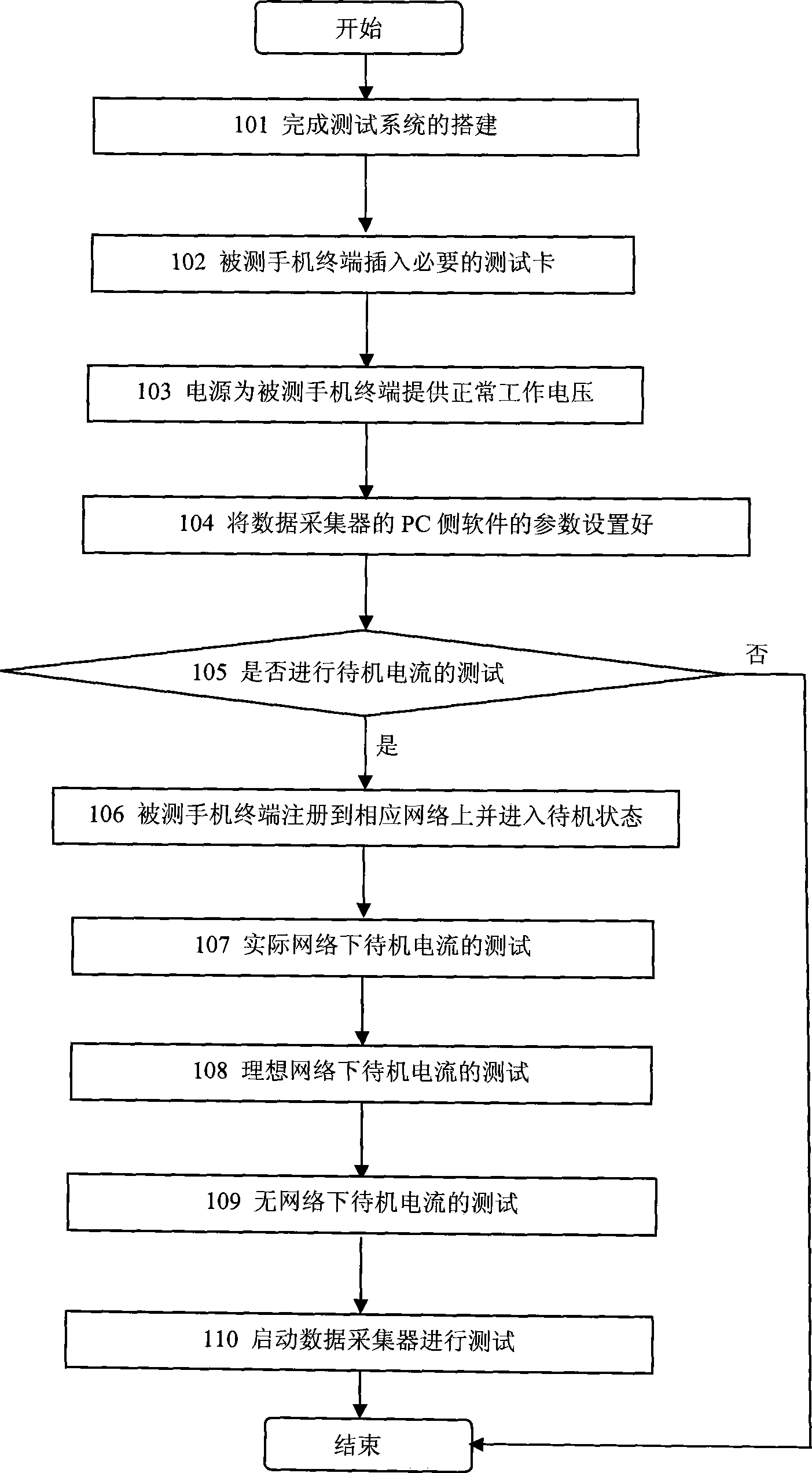
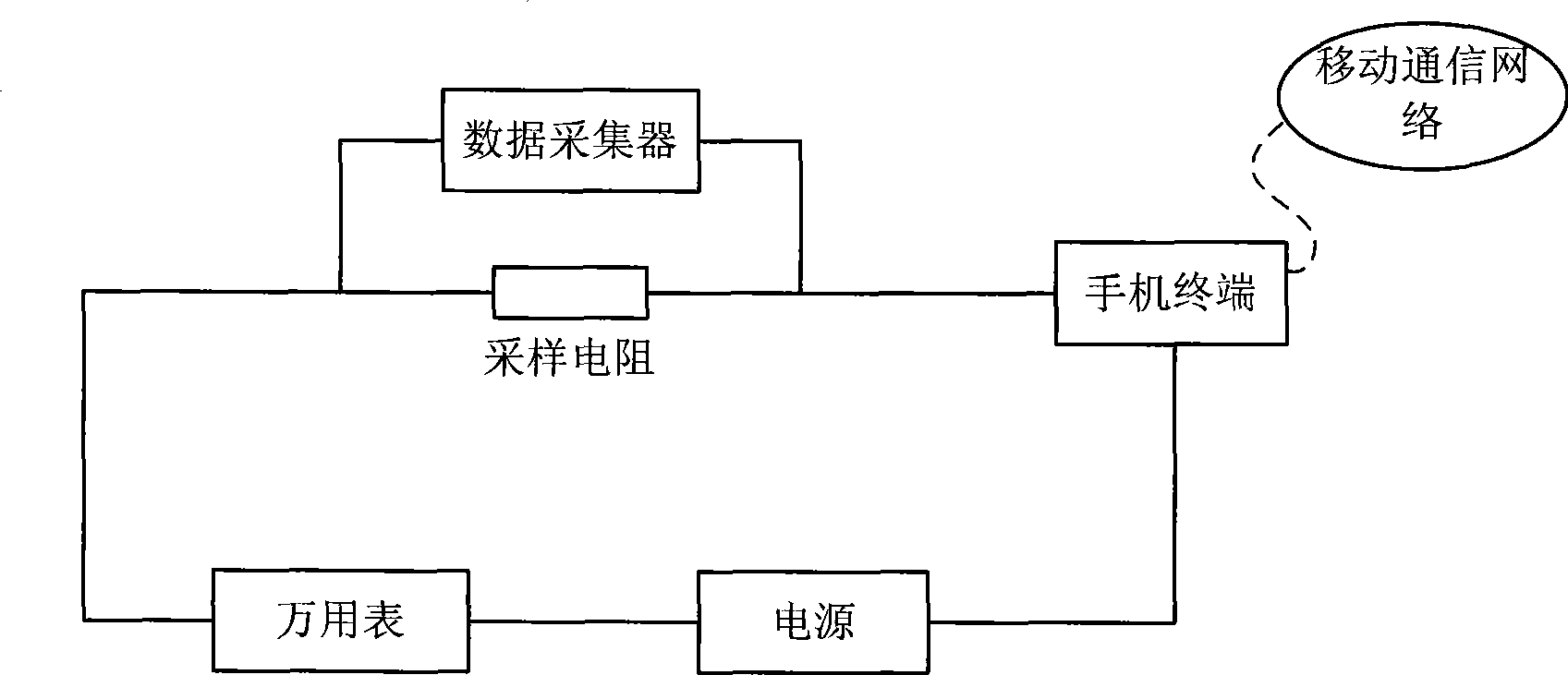
Test system and method for standby current of mobile terminal
InactiveCN101399864AHigh precisionReduce complexitySubstation equipmentTransmission monitoringElectrical resistance and conductanceData acquisition
The invention discloses a testing system and a testing method for a standby current of a movable terminal; the testing system includes a sampling resistance, a multimeter, a power and a movable terminal which are connected in series for forming a testing loop as well as a data collector connected in parallel with the sampling resistance; the invention further includes a comprehensive measuring device connected with the movable terminal and a shielding box which shields the movable terminal inside the shielding box. During testing, the movable terminal is arranged in a testing network environment and the movable terminal is started into a standby state; then the testing is started, the voltage at the two ends of the sampling resistance connected in series with the movable terminal is collected in real time by the data collector; the voltage data of the whole standby measuring process is preserved; after the measurement is finished, a real time standby current value in the whole standby process is obtained according to the relation formula of the voltage that I is equal to U / R; and the average standby current value during the standby measuring process is further obtained by an integral mean of (1 / t) multiply the integral of f from 0 to t. The invention has the advantages of high technical precision, high flexibility and being capable of tracing the state change of a mobile phone terminal.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Semiconductor memory having a precharge voltage generation circuit for reducing power consumption
ActiveUS7580303B2Reduce power consumptionData Retention Time EnhancementDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
A precharge voltage generating circuit outputs any of a plurality of kinds of precharge voltages in accordance with an ambient temperature. A precharge circuit supplies the precharge voltage to a bit line during the nonaccess of a dynamic memory cell. A sense amplifier amplifies a difference between the voltage of a data signal read from the dynamic memory cell onto the bit line and the supplied precharge voltage. The precharge voltage is altered in accordance with the ambient temperature, whereby the read margin of the sense amplifier can be changed, and the worst value of the data retaining time of the memory cell can be improved. As a result, the frequency of refreshing of the memory cell can be lowered, reducing power consumption and a standby current.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Multiple valued dynamic random access memory cell and thereof array using single electron transistor
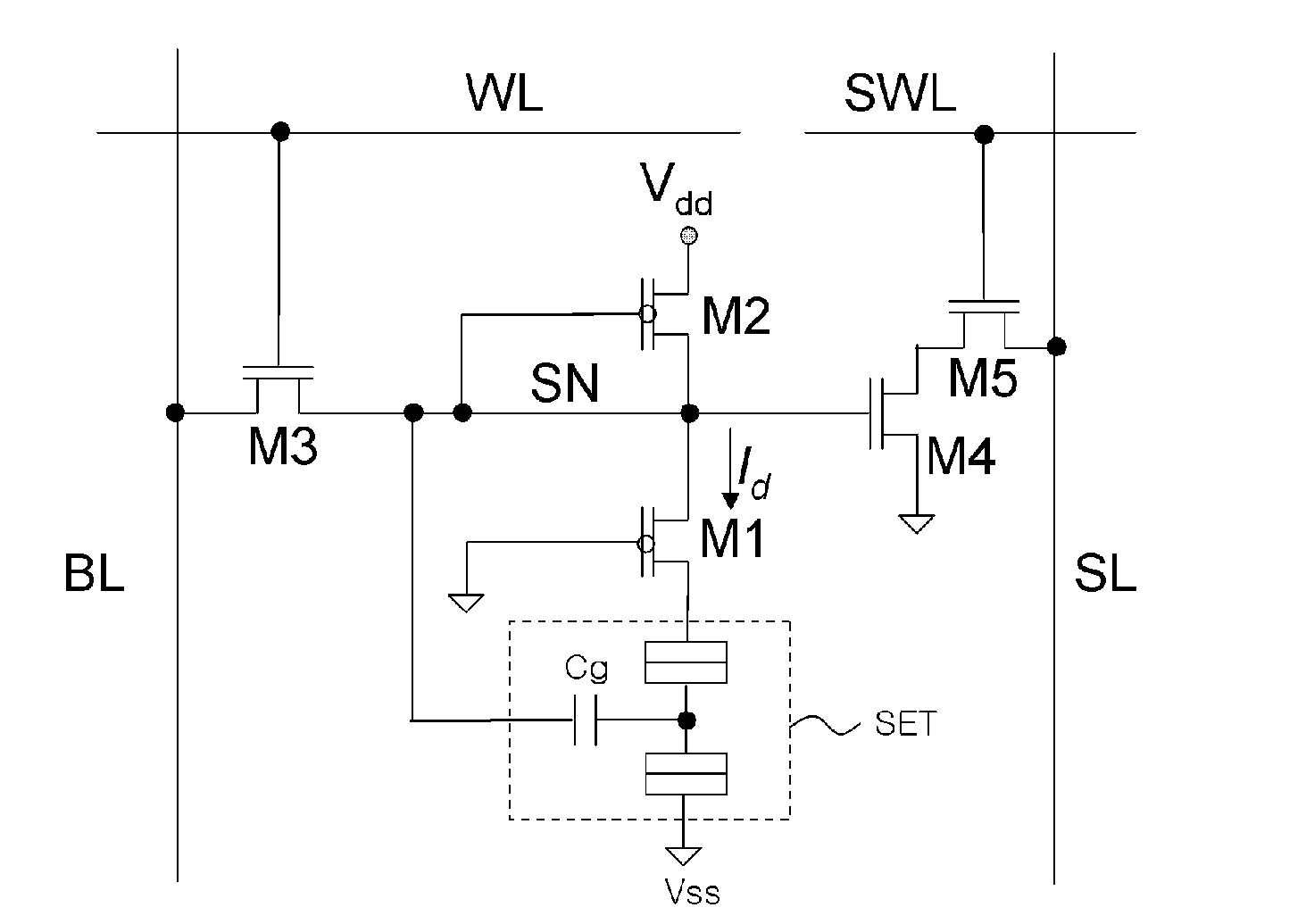
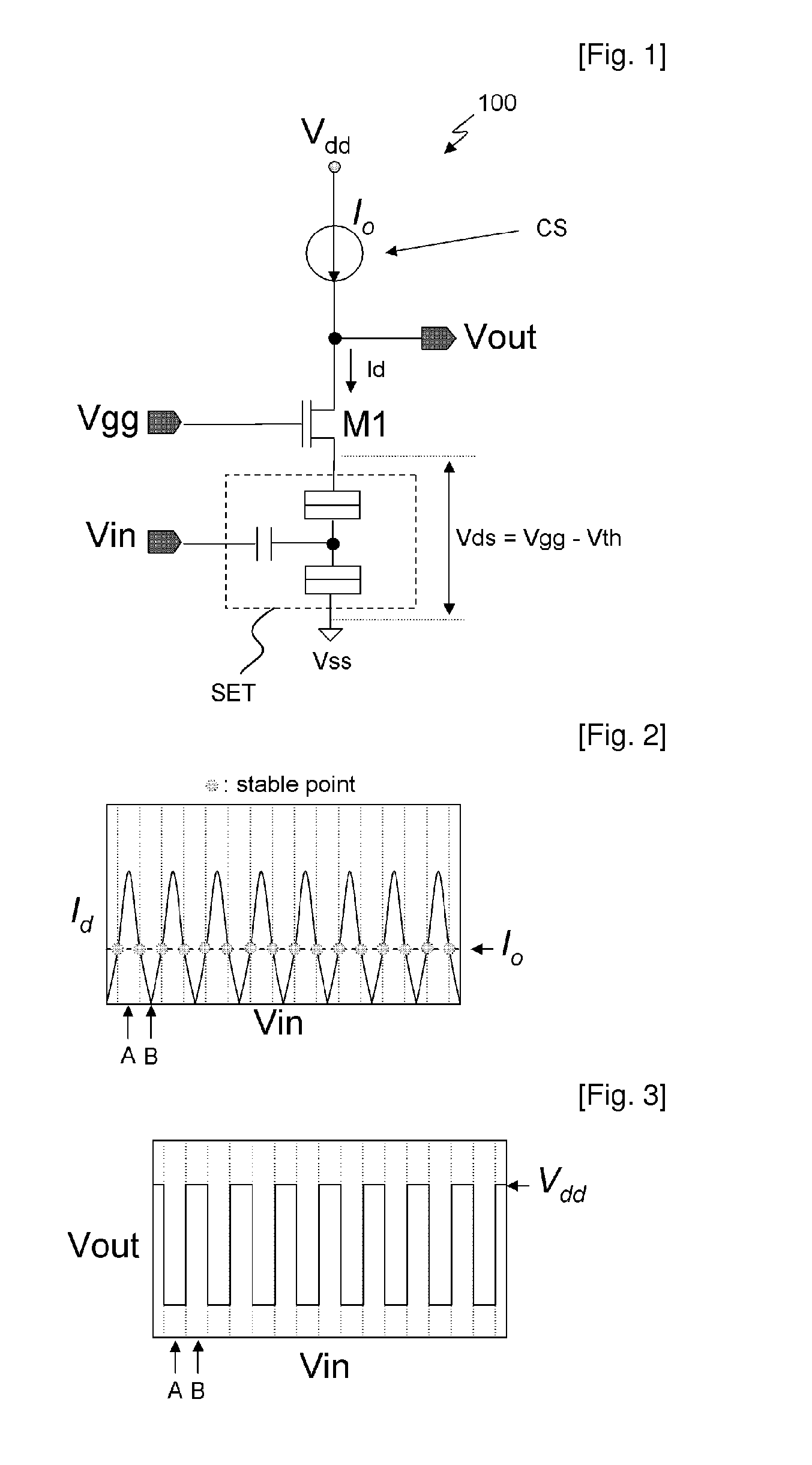
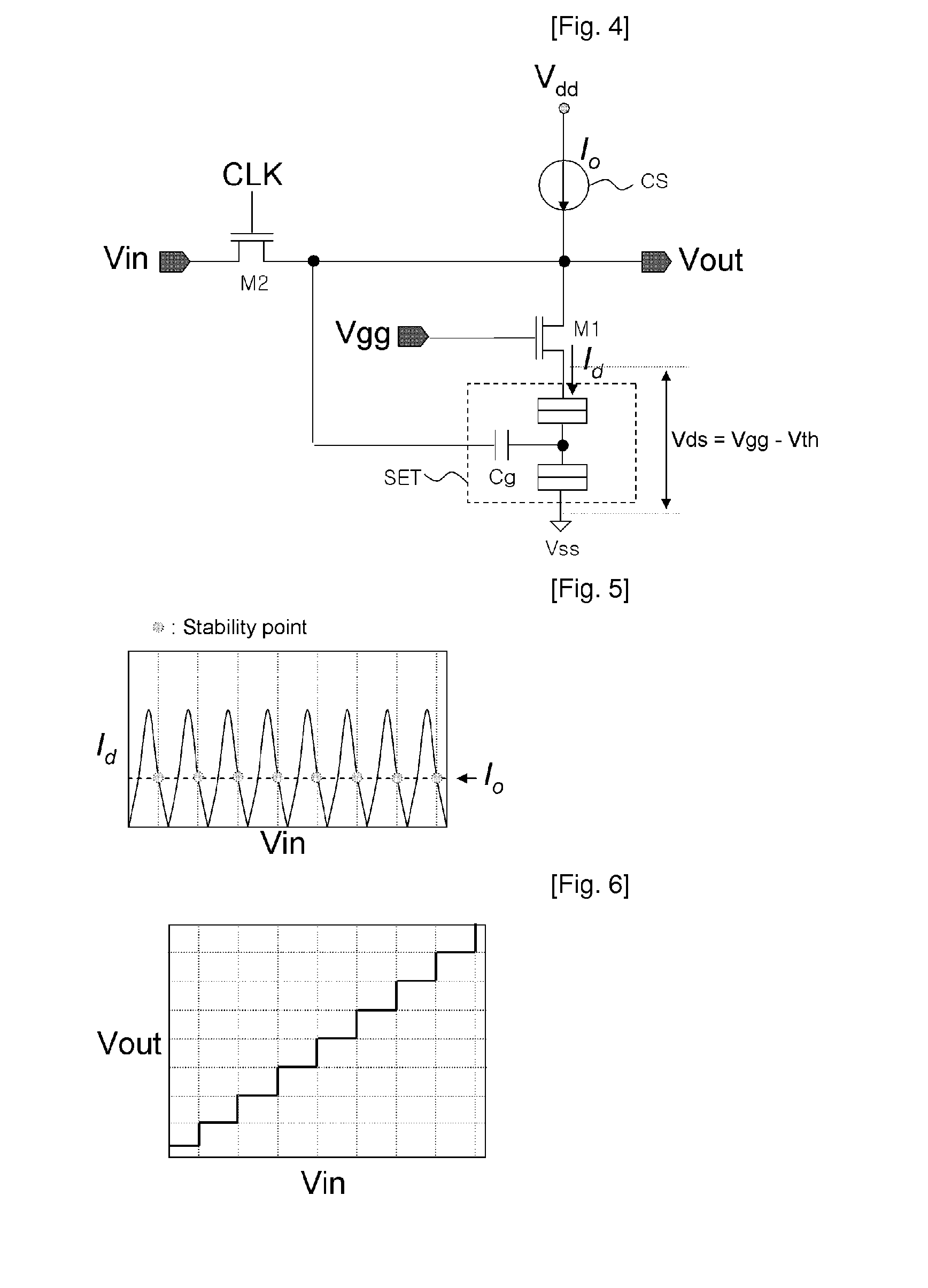
InactiveUS20100118597A1Total current dropReduce power consumptionDigital storageStatic random-access memoryTerminal voltage
Provided is a multi-valued dynamic random access memory (DRAM) cell using a single electron transistor (SET). The multi-valued DRAM cell using the SET applies different refresh signals to a load current transistor for controlling current supply to the SET and a voltage control transistor for controlling a terminal voltage of the SET and refreshes a data value stored in the SET by a predetermined period to reduce standby current and stably supply a voltage low enough to satisfy a coulomb-blockade condition to the terminal of the SET.
Owner:NANOCHIPS
Standby current reduction over a process window with a trimmable well bias
InactiveUS7060566B2High densityLow costTransistorPower reduction in field effect transistorsMOSFETOhmic contact
An integrated circuit device including a plurality of MOSFETs of similar type and geometry is formed on a substrate with an ohmic contact, and an adjustable voltage source on the die utilizing clearable fuses is coupled between the ohmic contact and the sources of the MOSFETs. After die processing, a post-processing test is performed to measure an operating characteristic of the die such as leakage current or switching speed, and an external voltage source is applied and adjusted to control the operating characteristic. The on-die fuses are then cleared to adjust the on-die voltage source to match the externally applied voltage. The operating characteristic may be determined by including a test circuit on the die to exhibit the operating characteristic such as a ring oscillator frequency. This approach to controlling manufacturing-induced device performance variations is well suited to efficient manufacture of small feature-size circuits such as DRAMs.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com