Patents
Literature
4707 results about "Voltage generator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A voltage generator is a device that converts potential and kinetic energy into electrical energy.
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
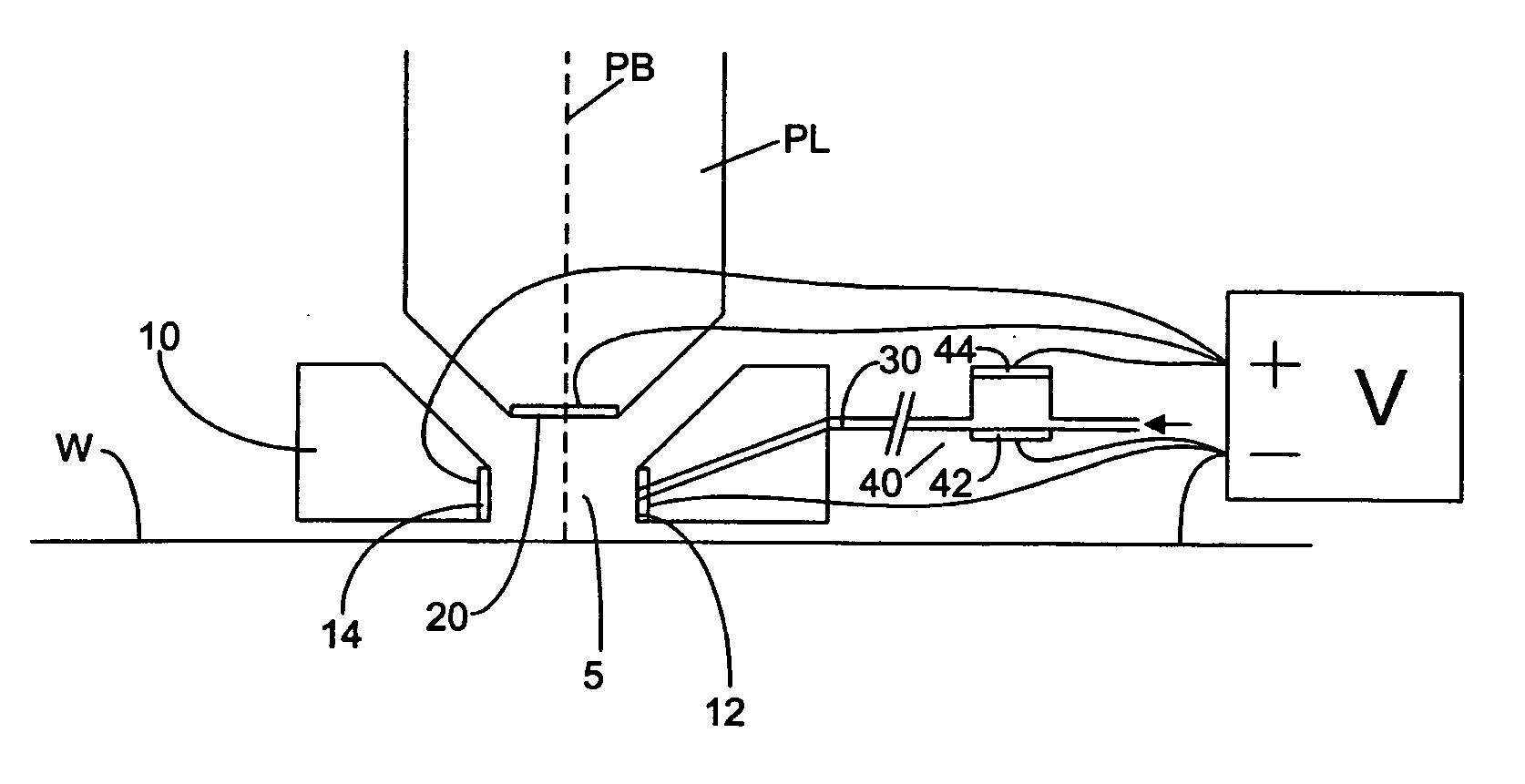
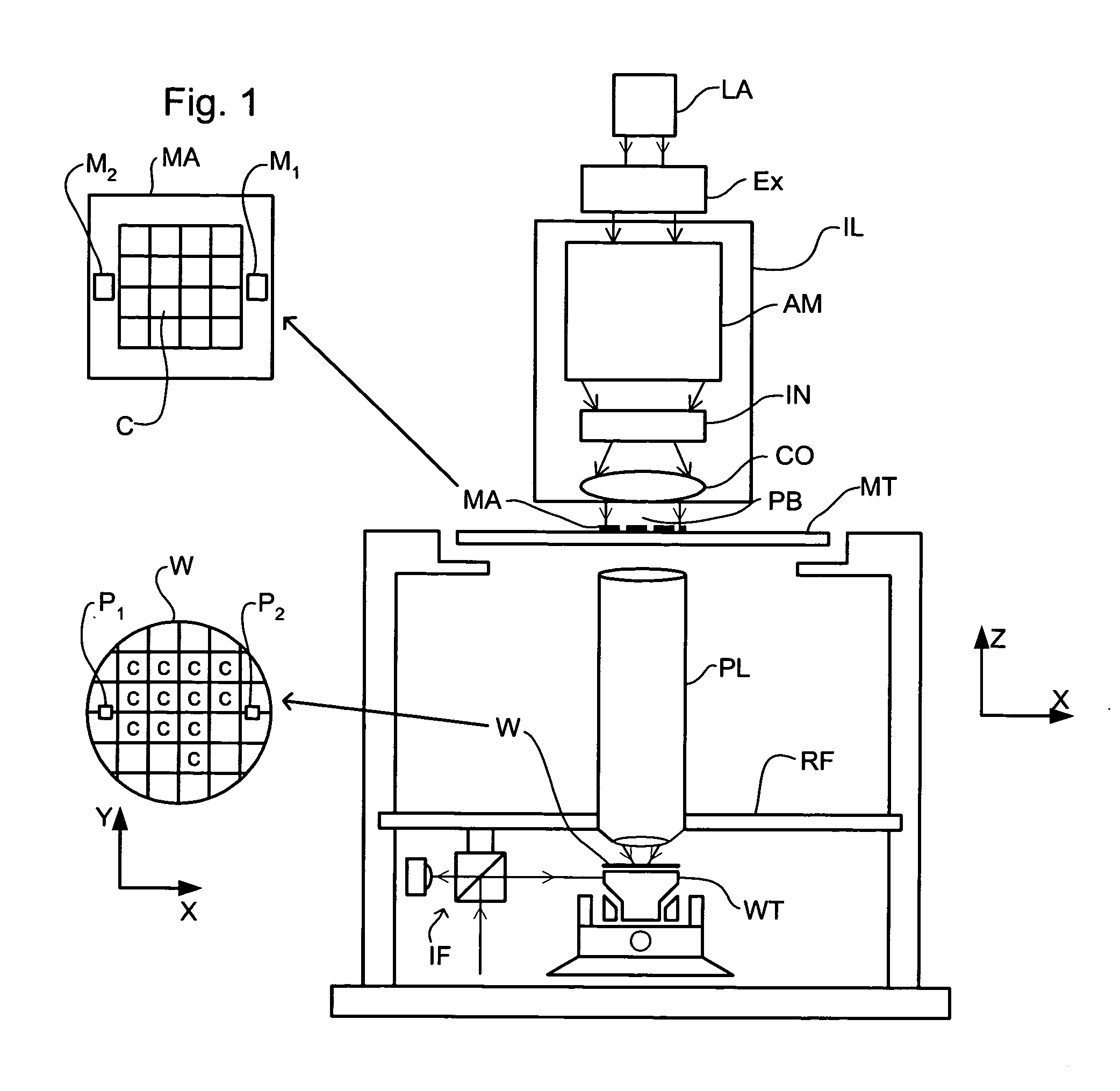
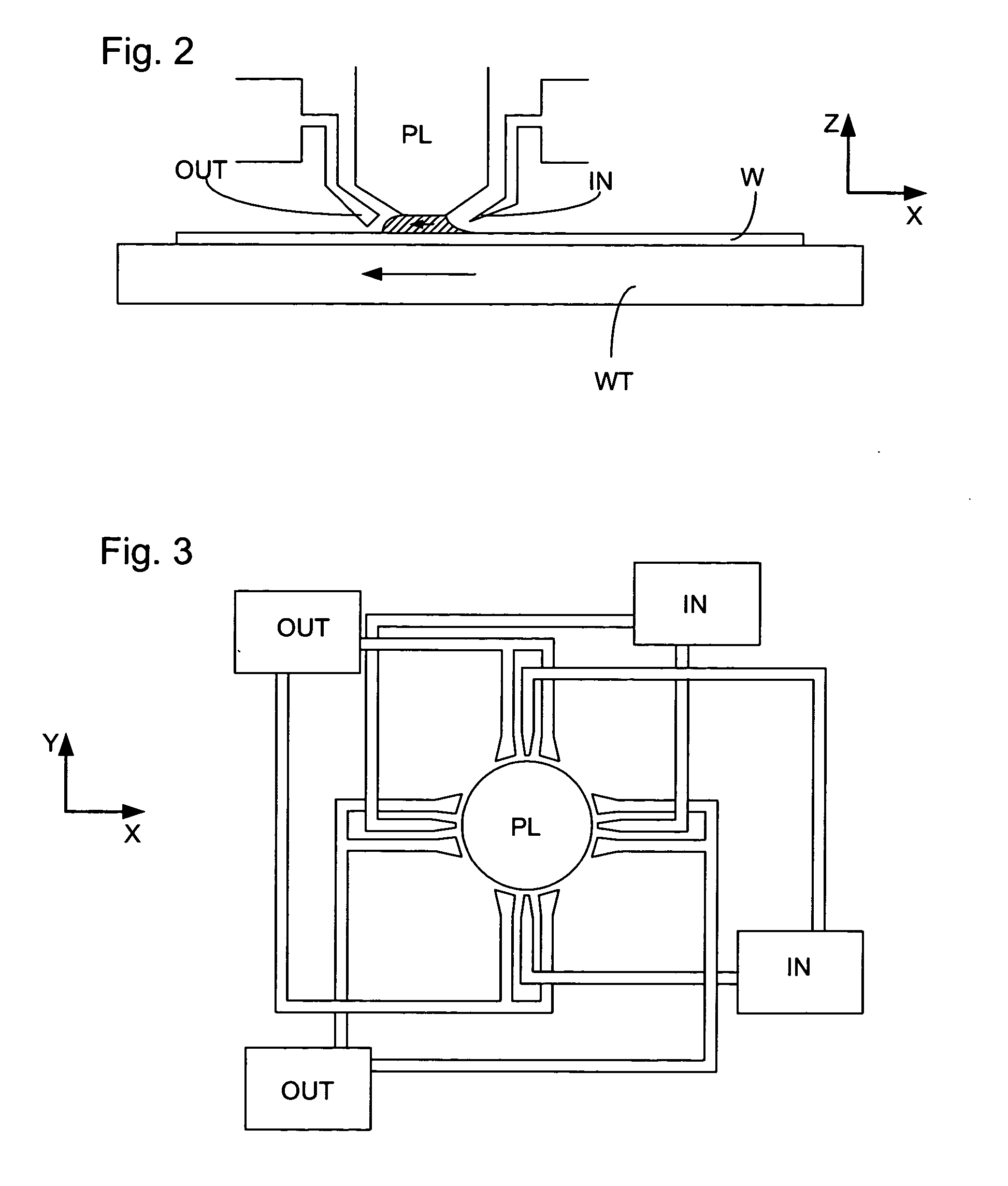
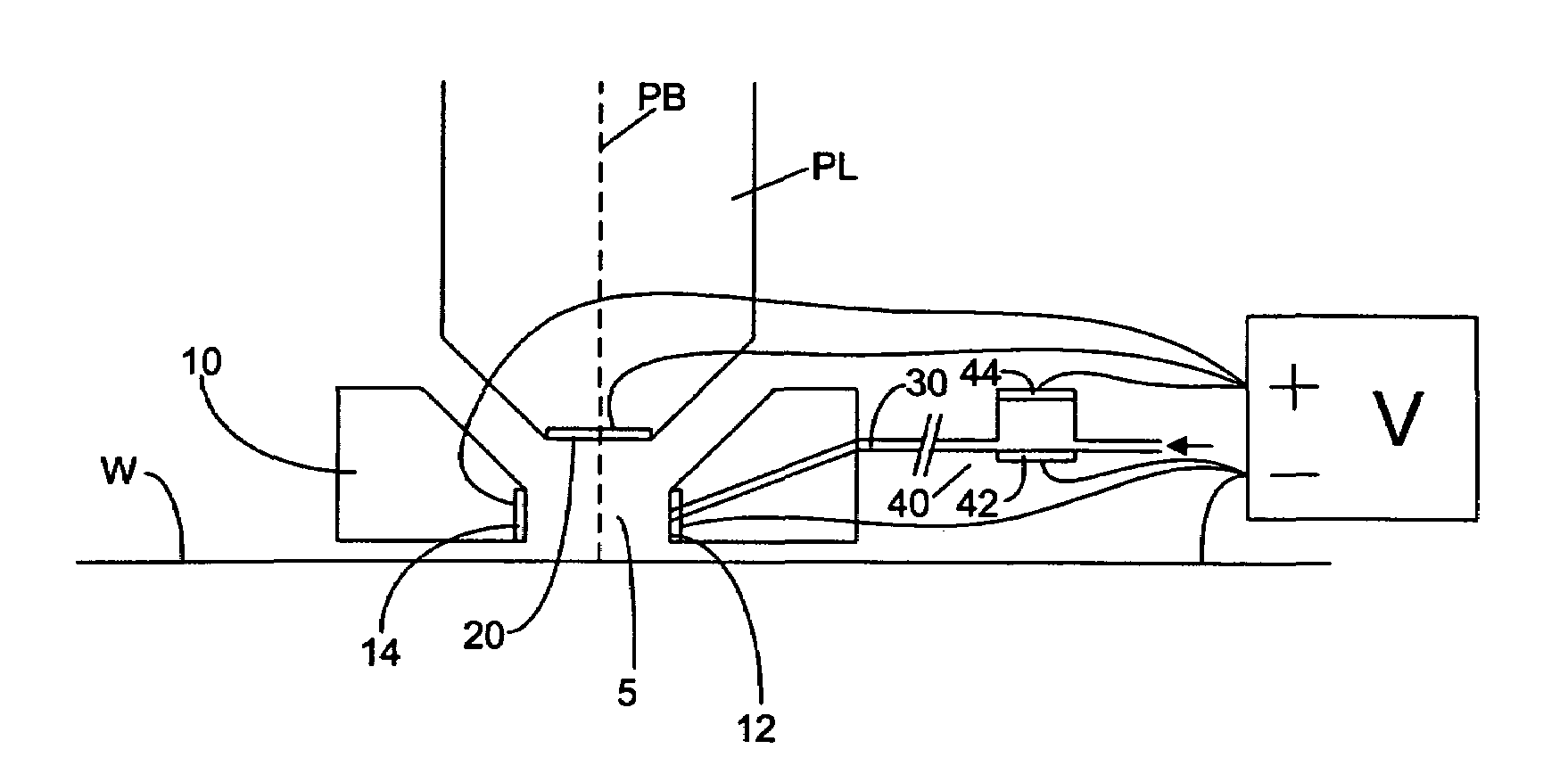
ActiveUS20050174549A1Reduce the impactReduce impactSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusVoltage generatorPotential difference
An immersion lithographic apparatus includes a voltage generator or power source that applies a potential difference to an object in contact with the immersion liquid such that bubbles and / or particles in the immersion liquid are either attracted or repelled from that object due to the electrokinetic potential of the surface of the bubble in the immersion liquid.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
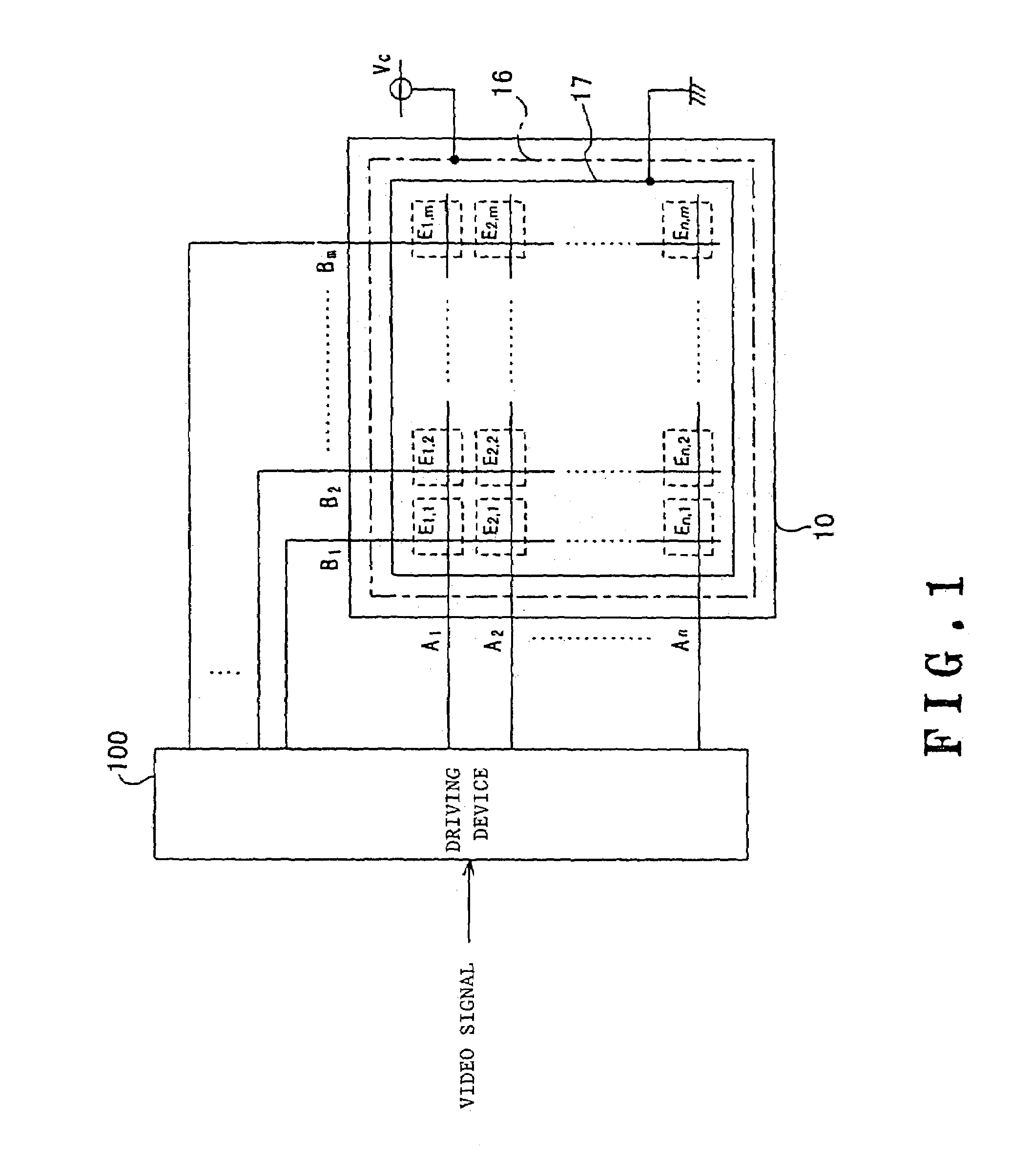
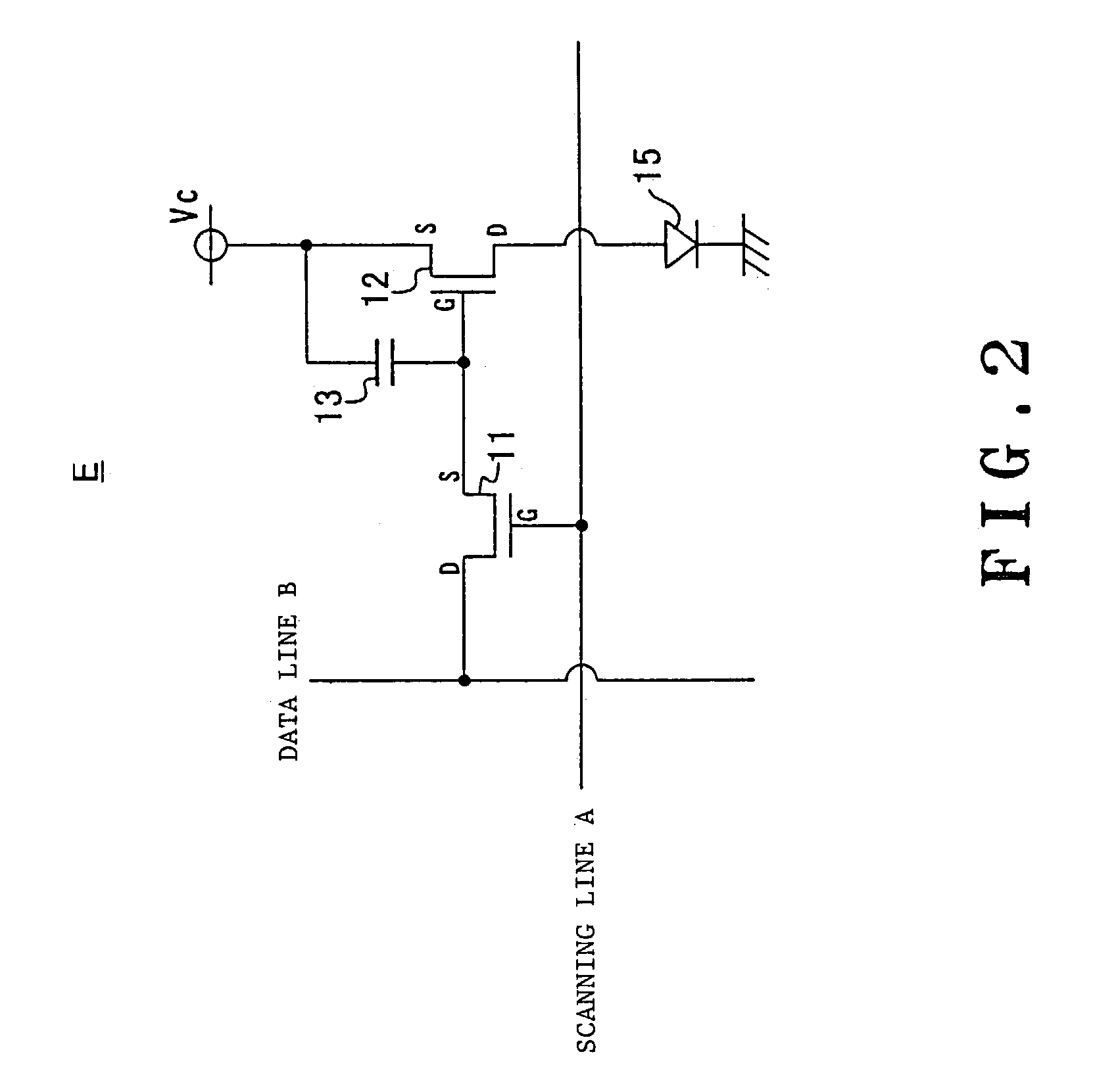
Panel display driving device and driving method
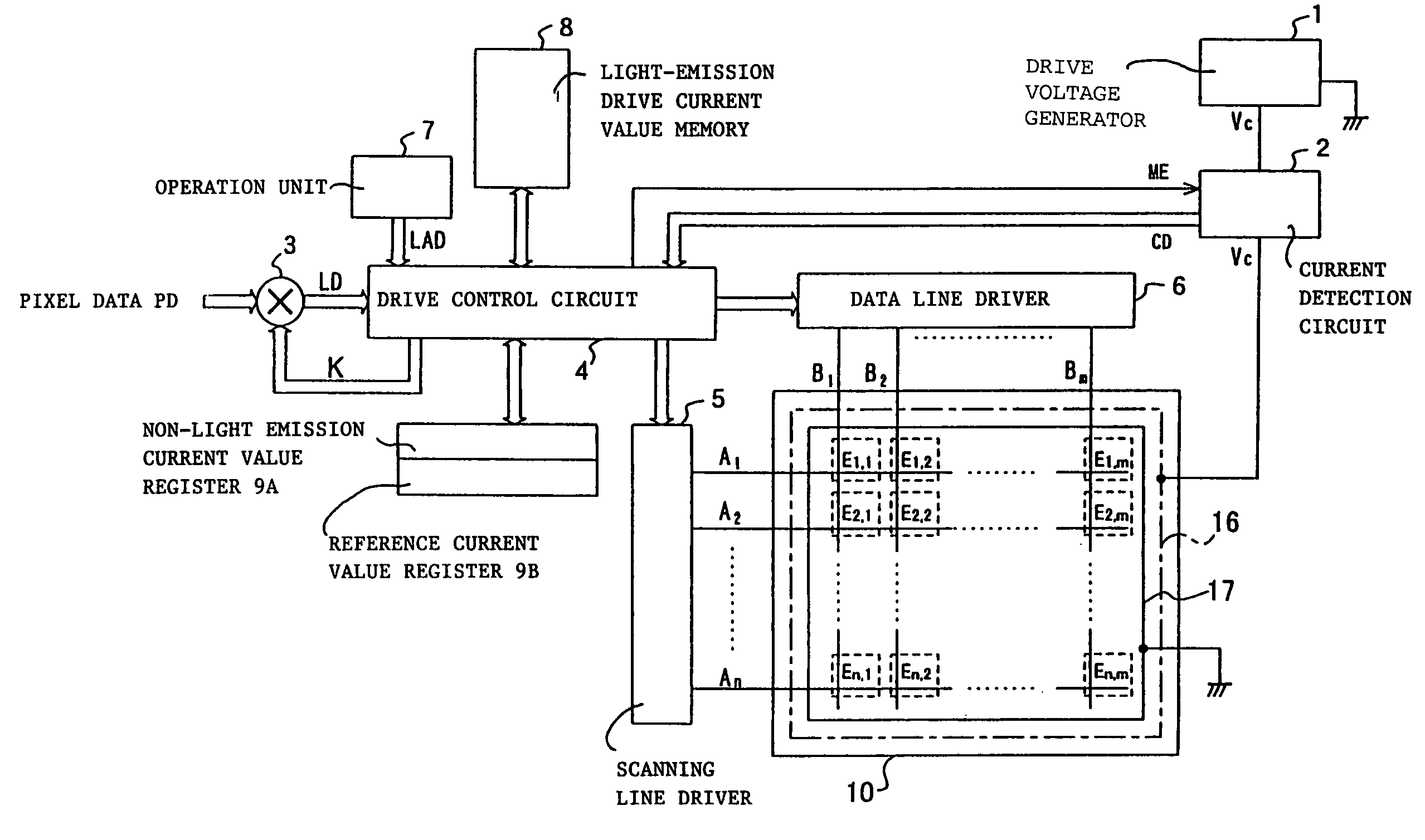
ActiveUS7274363B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDriving currentVoltage generator
A display panel driving device and driving method for providing high quality images without irregular luminance even after long-time use. The value of the light-emission drive current flowing when causing each light-emission elements bearing each pixel to independently emit light in succession is measured, then the luminance is corrected for each input pixel data based on the above light-emission drive current values, associated with the pixels corresponding to the input pixel data. According to another aspect, the voltage value of the drive voltage is adjusted in such a manner that one value among each measured light-emission drive current value becomes equal to a predetermined reference current value. According to a further aspect, the current value is measured while an off-set current component corresponding to a leak current of the display panel is added to the current outputted from the drive voltage generator circuit and the resultant current is supplied to each of the pixel portions.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Display apparatus, display driving apparatus and method for driving same
ActiveUS20080074413A1Current/voltage measurementCathode-ray tube indicatorsVoltage converterVoltage generator
A light-emitting element capable of emitting light having a preferred gradation level depending on display data. During a precharge period, a data driver applies a precharge voltage to a capacitor via a data line. After the application of the precharge voltage, a voltage converter reads a first reference voltage Vref(t1) and a second reference voltage Vref(t2) to generate a compensation voltage based on a difference between the respective reference voltages. Based on the compensation voltage, a voltage calculator compensates an original gradation level voltage Vorg having a value in accordance with display data generated by a gradation level voltage generator. The voltage calculator generates a compensated gradation level voltage Vpix corresponding to a variation amount of an element characteristic for a transistor Tr13 for driving light emission to apply the compensated gradation level voltage Vpix to a data line Ld.
Owner:SOLAS OLED LTD
Integrated circuit structure including three-dimensional memory array
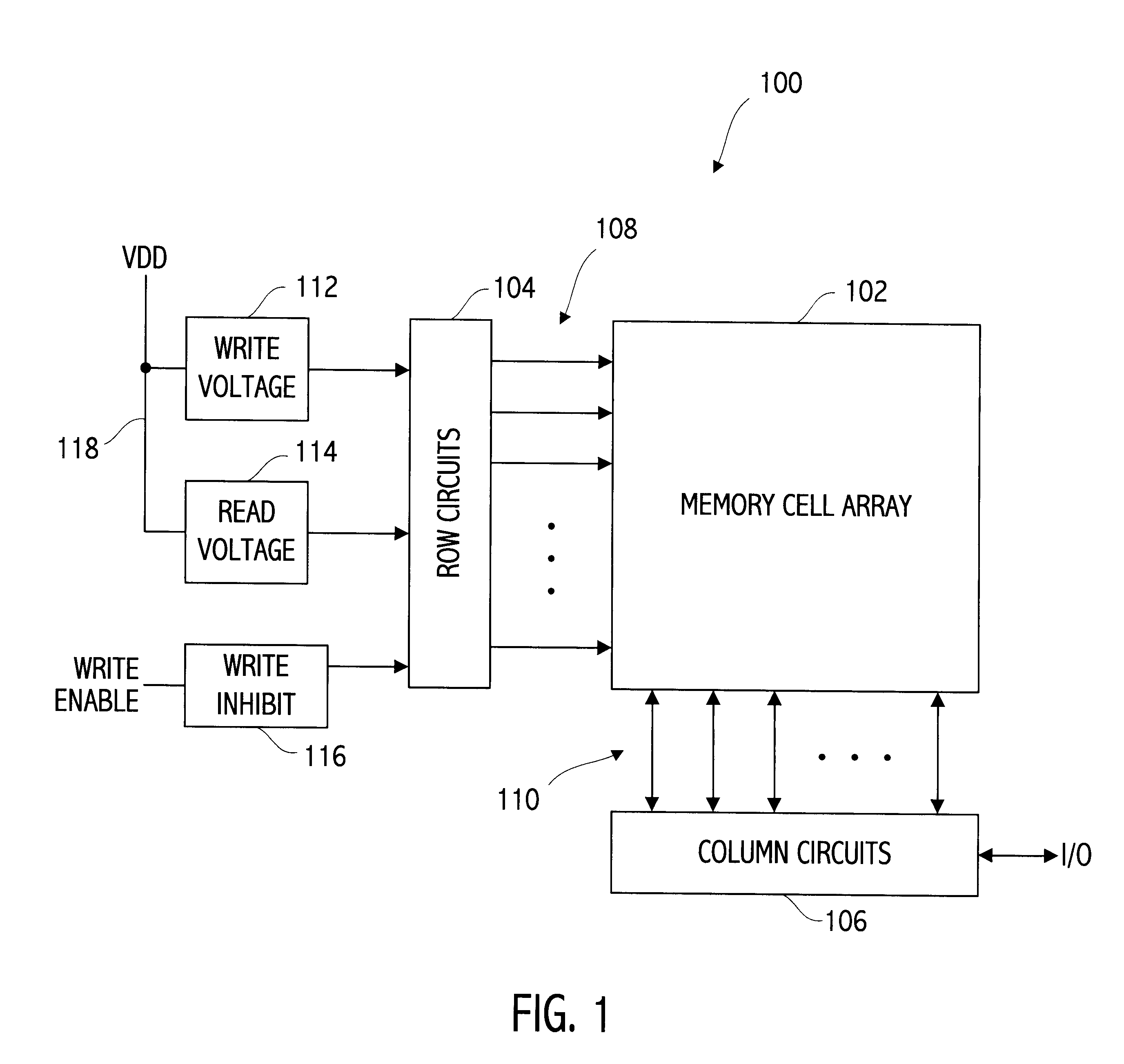
An integrated circuit device includes a three-dimensional memory array and array terminal circuitry for providing to selected memory cells of the array a write voltage different from a read voltage. Neither voltage is necessarily equal to a VDD power supply voltage supplied to the integrated circuit. The write voltage, particularly if greater than VDD, may be generated by an on-chip voltage generator, such as a charge pump, which may require an undesirably large amount of die area, particularly relative to a higher bit density three-dimensional memory array formed entirely in layers above a semiconductor substrate. In several preferred embodiments, the area directly beneath a memory array is advantageously utilized to layout at least some of the write voltage generator, thus locating the generator near the selected memory cells during a write operation.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
ActiveUS7050146B2Reduce impactMinimize impactSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusVoltage generatorPotential difference
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
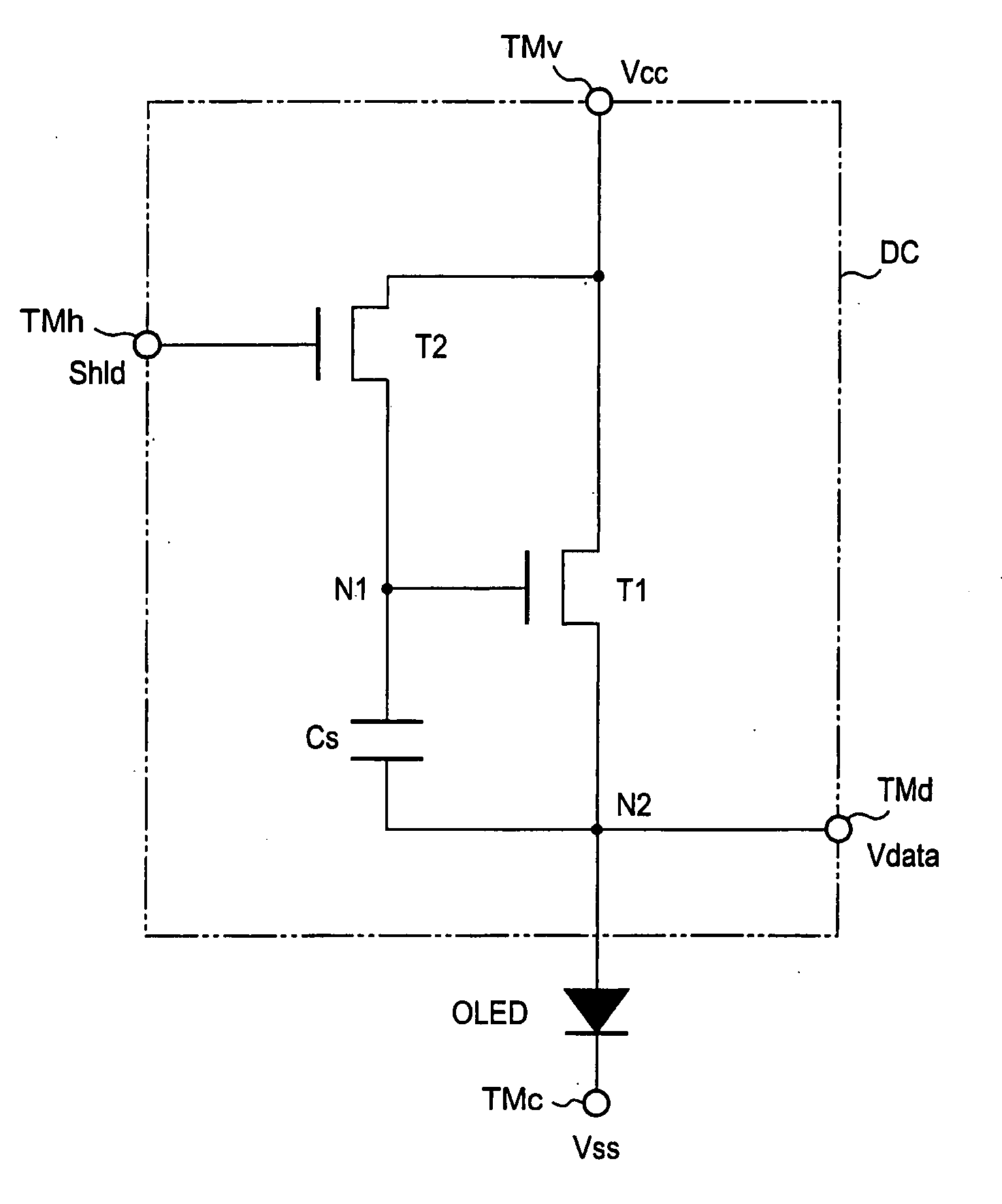
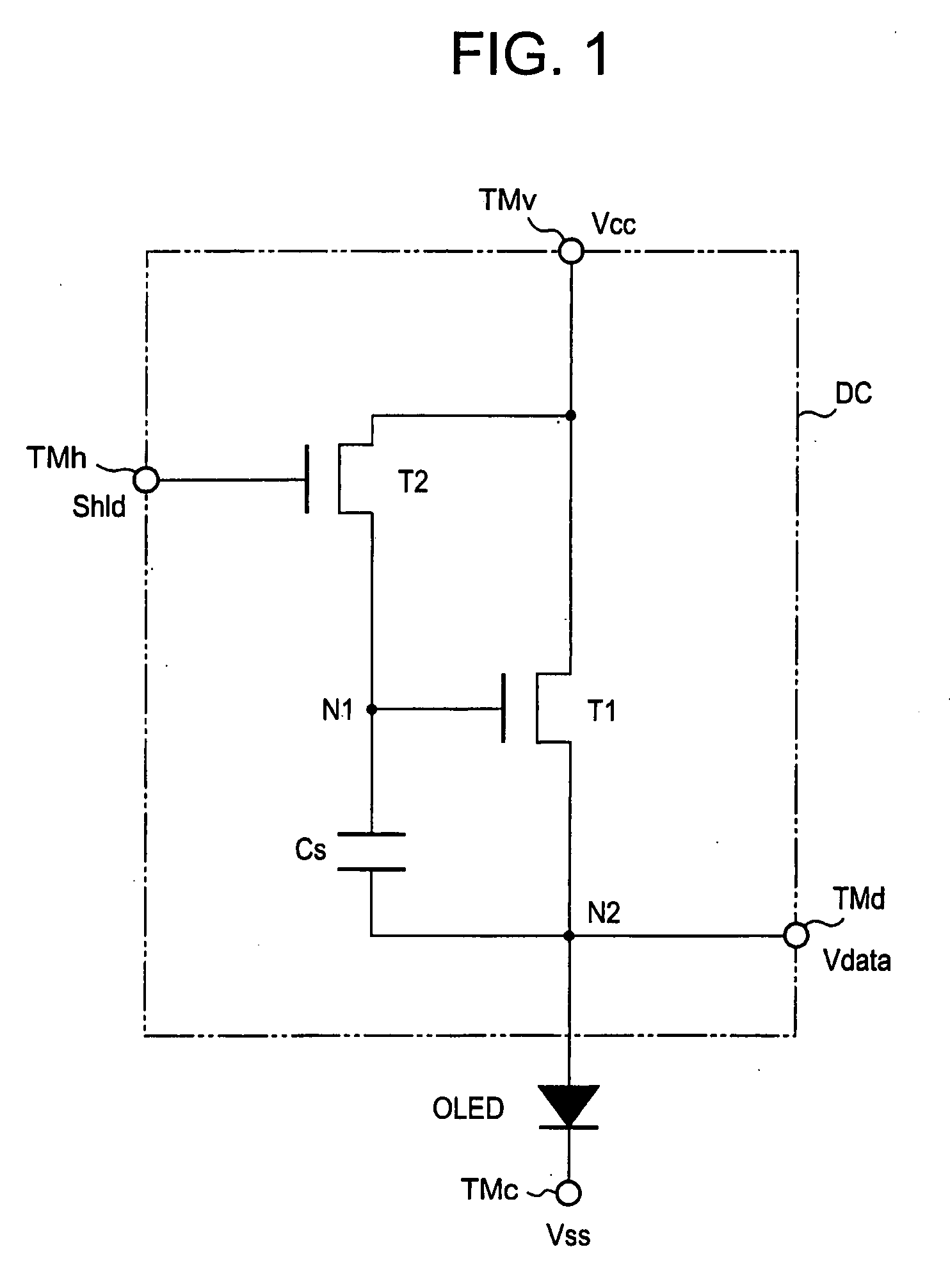
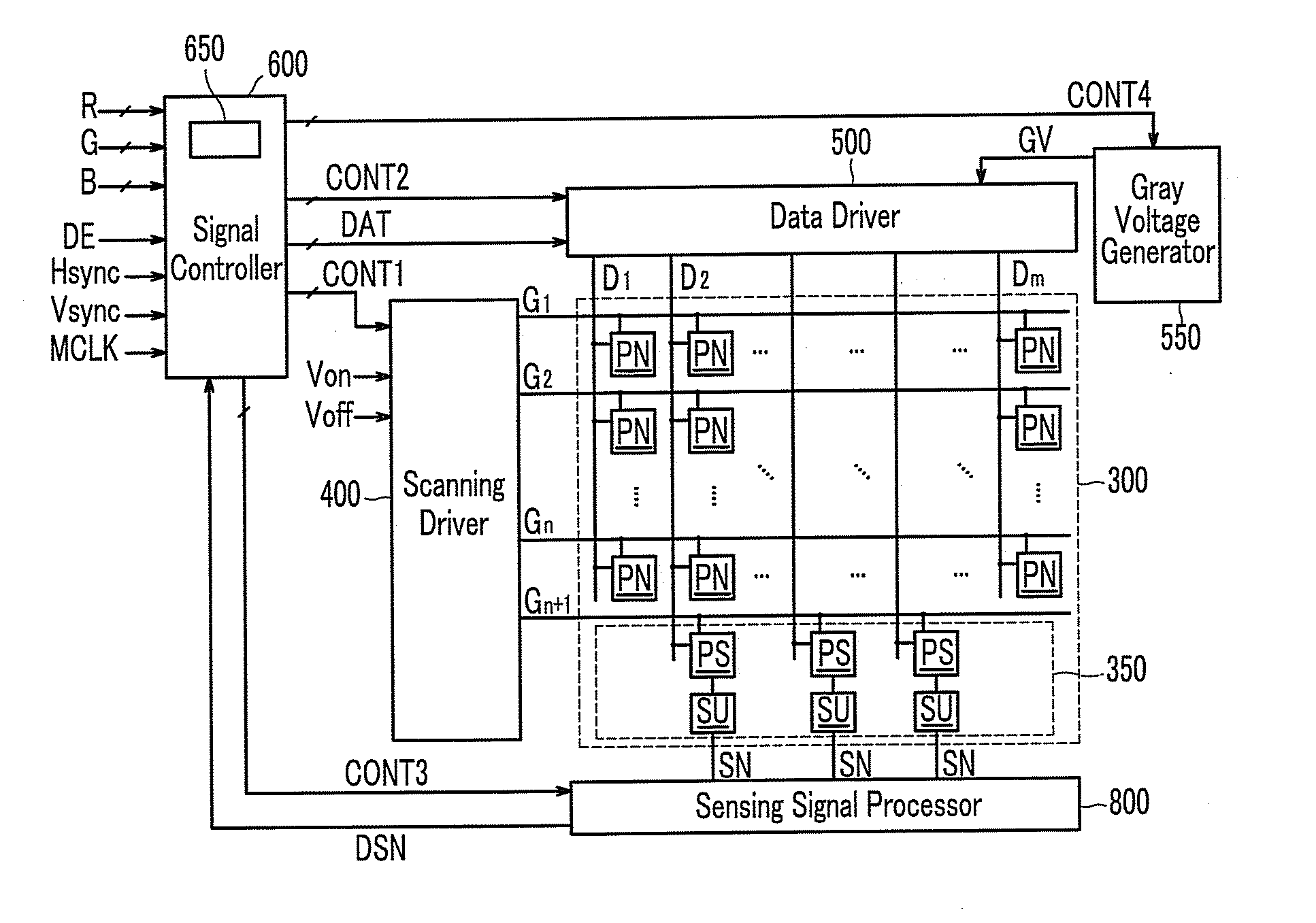
Display device and driving method thereof
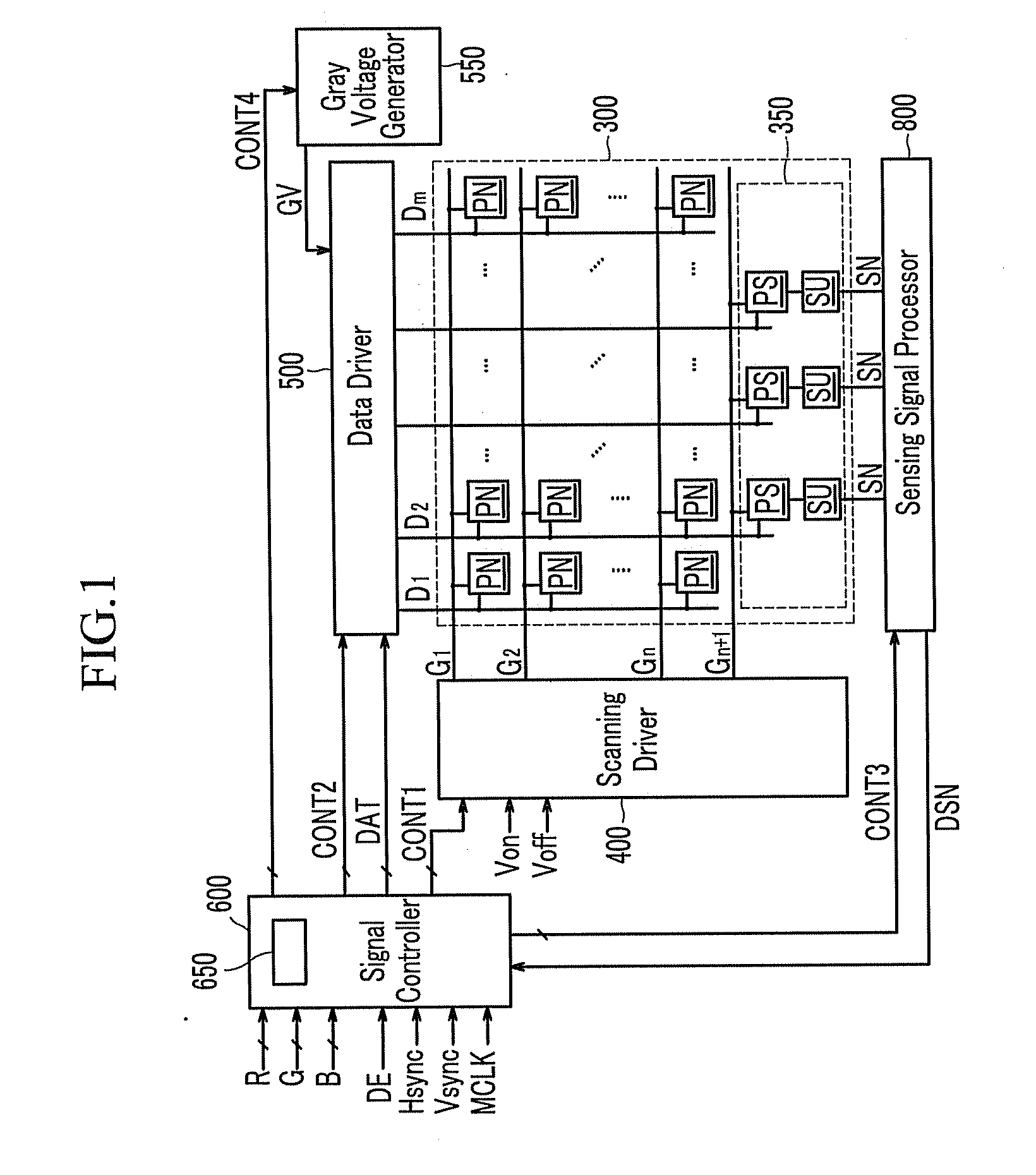
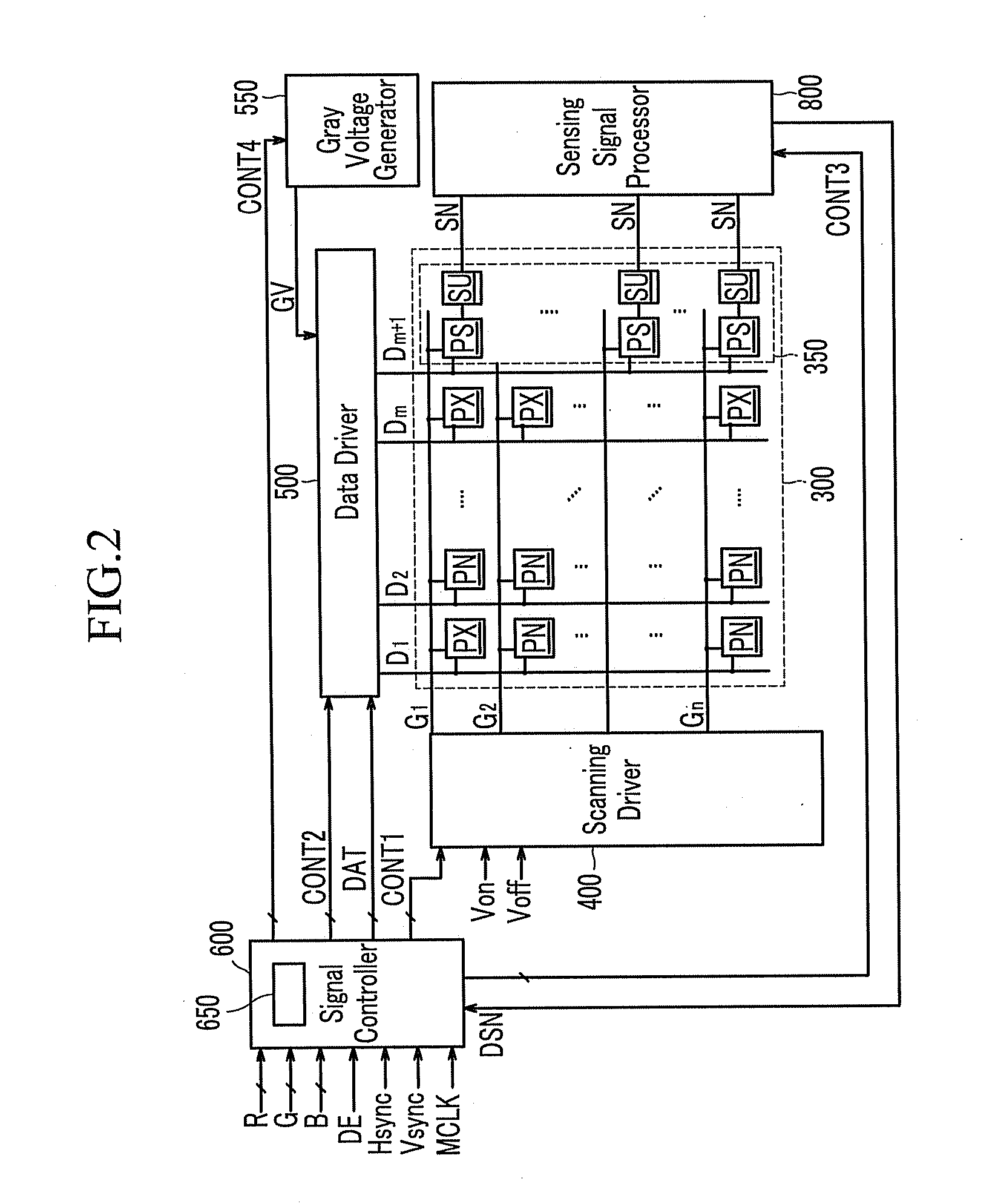
A display device includes: a plurality of pixels comprising normal pixels and sample pixels; a plurality of sensing units which sense luminance of the sample pixels and generate sensing signals based on the sensed luminance; a gray voltage generator which generates a plurality of reference gray voltages having values depending on the sensing signals; and a data driver which generates normal data voltages for the normal pixels and sample data voltages for the sample pixels.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Mobile power generation system including dual voltage generator
InactiveUS20190067991A1Reduce system weightEliminate needSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsMechanical energy handlingElectricityVoltage generator
Mobile power generation system and methods for dual-voltage generation include providing a trailer including a rear end, a front end, a bottom end, and a top end, a gas turbine housed inside the trailer, and an electrical generator coupled to the gas turbine to generate electricity and housed inside the trailer. The electrical generator is at least a dual-voltage generator configured to provide an auxiliary power to generator parasitic loads and a main primary load output power and comprising one or more taps configured to provide the auxiliary power to generator parasitic loads. The electrical generator is at least a dual-voltage generator comprising three-phase circuitry including three lines and one or more taps configured to provide auxiliary power to generator parasitic loads, ends of the three lines configure to provide a main primary load output power.
Owner:ON POWER INC
Electro-phoretic display apparatus and driving method thereof
ActiveUS9082352B2Effectively loweringImage degradationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingVoltage generatorElectrophoresis
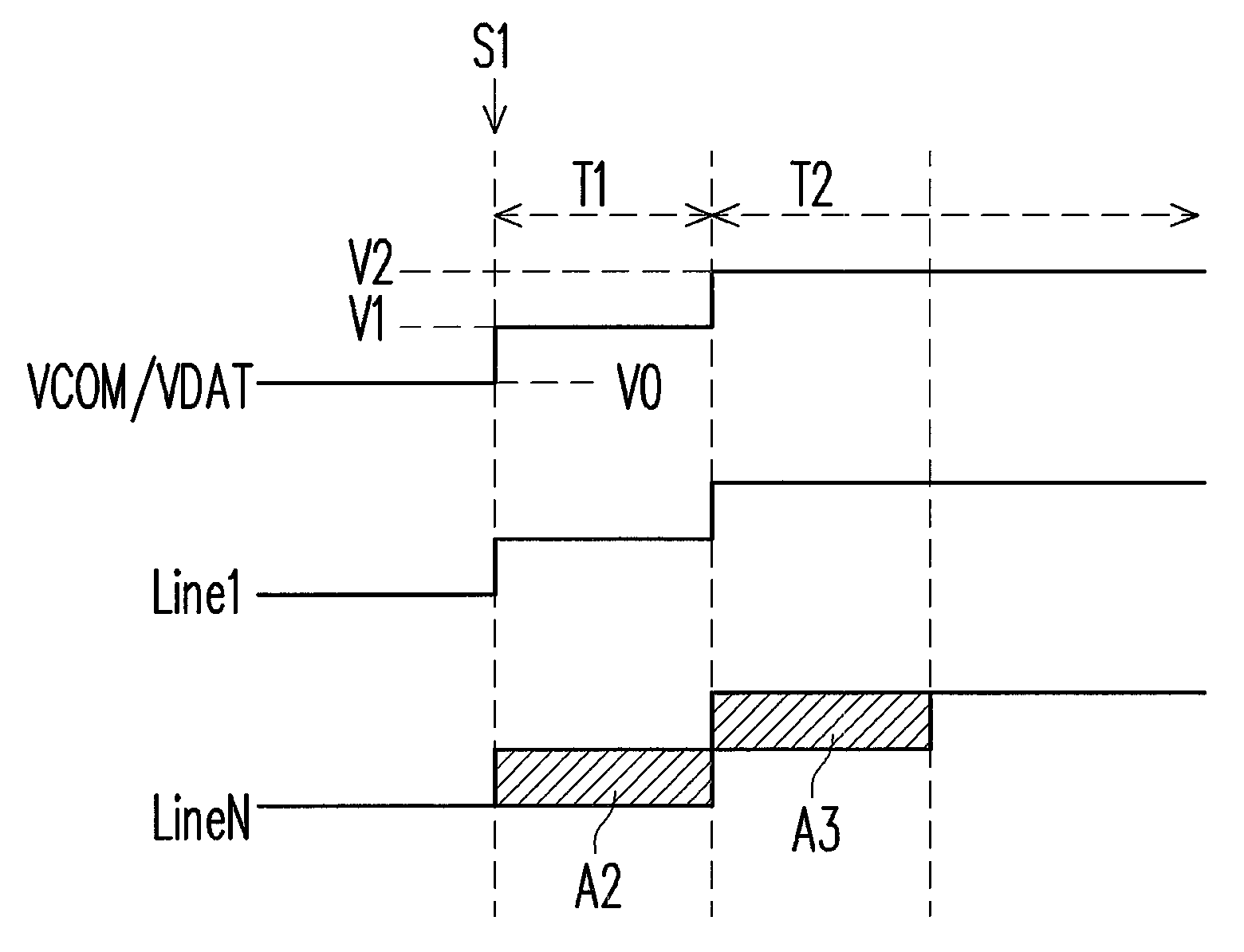
A driving method for an electro-phoretic display apparatus is disclosed. The method includes generating a common voltage by a common voltage generator held at a first voltage level before a polarity transfer, generating the common voltage held at a second voltage level when the polarity transfer starts during a first timing period, and generating the common voltage transfers held at a third voltage level during a second timing period after the first timing period, in which the second voltage level is between the first and the third voltageE levels.
Owner:YUANHAN MATERIALS INC
Method for operating an inverter, and inverter
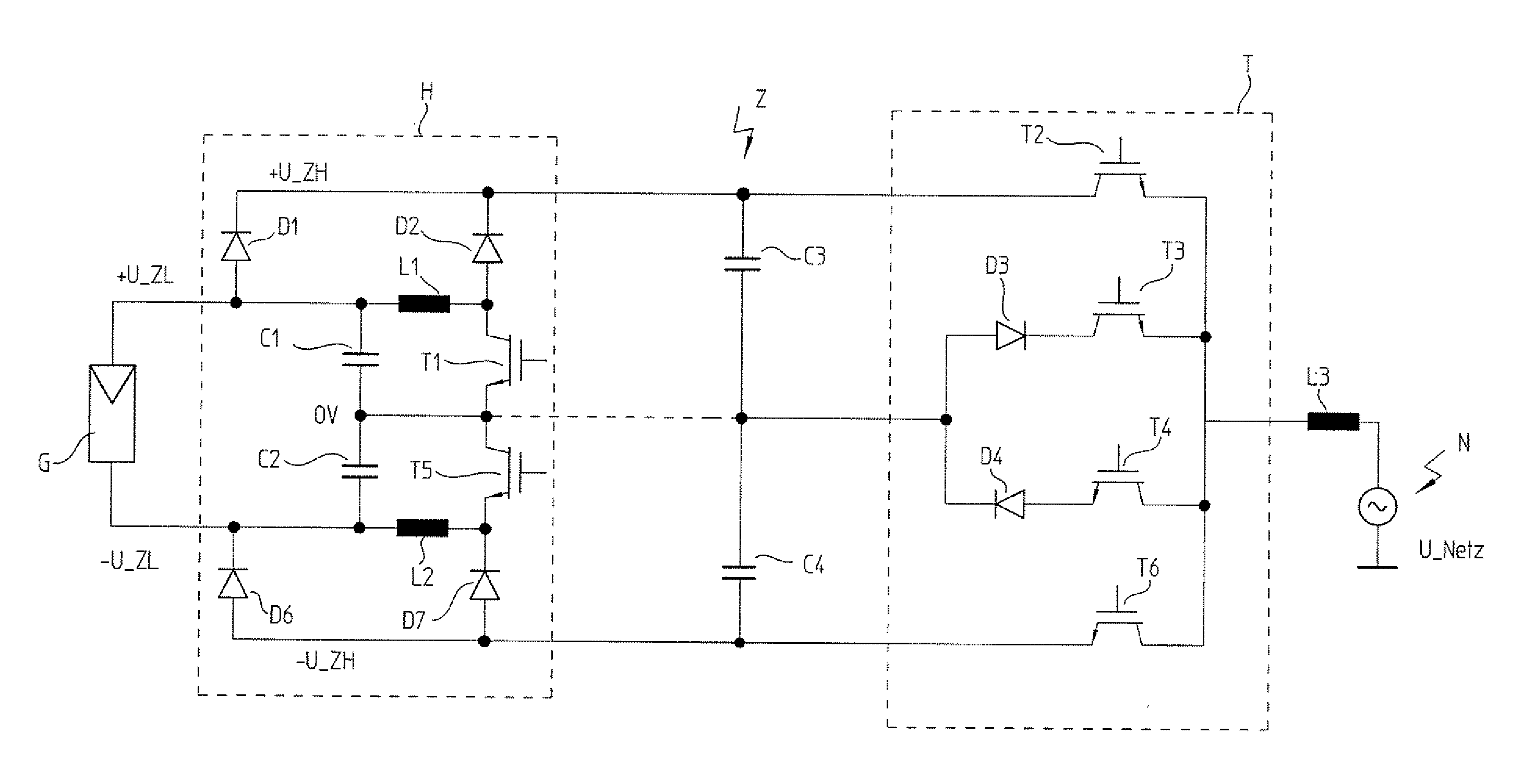
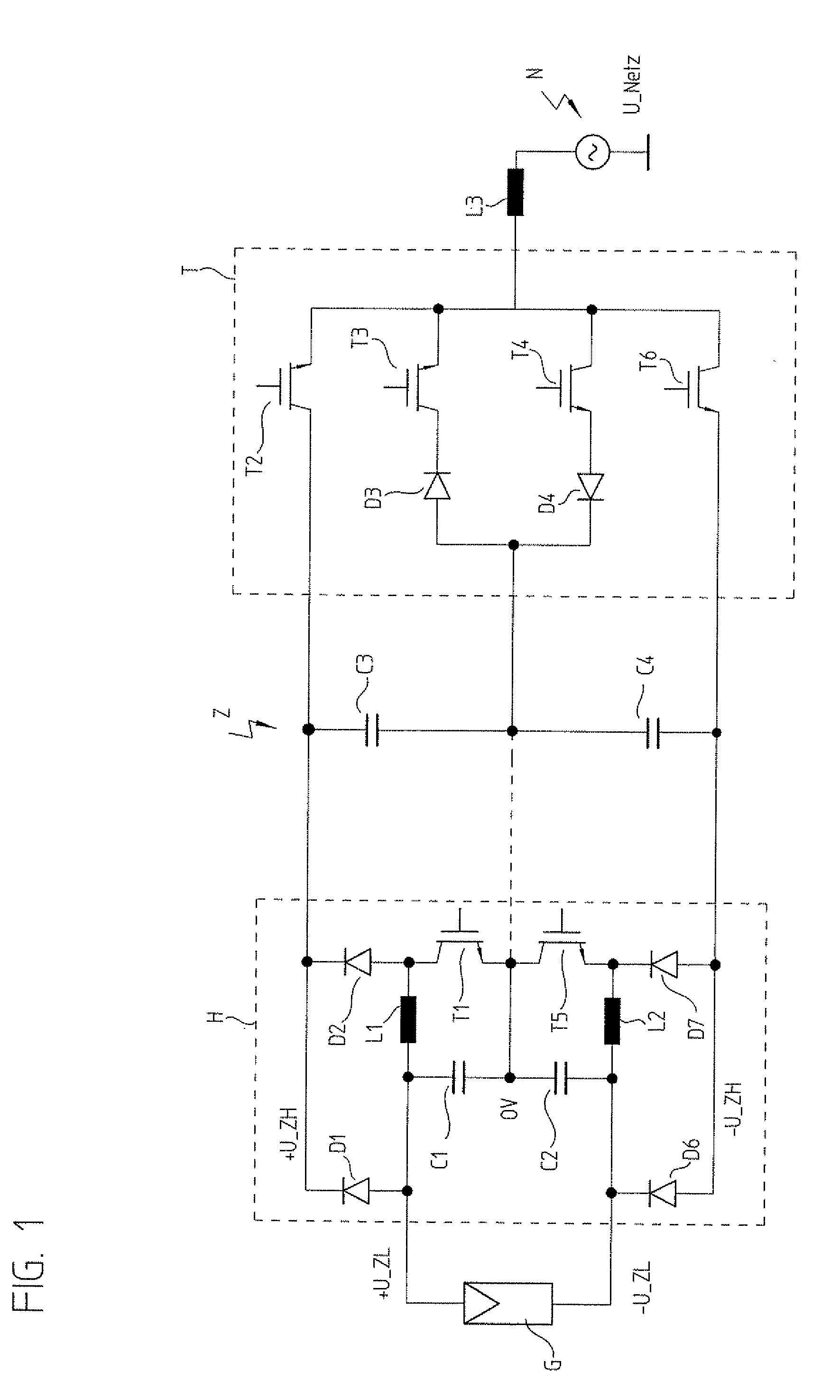
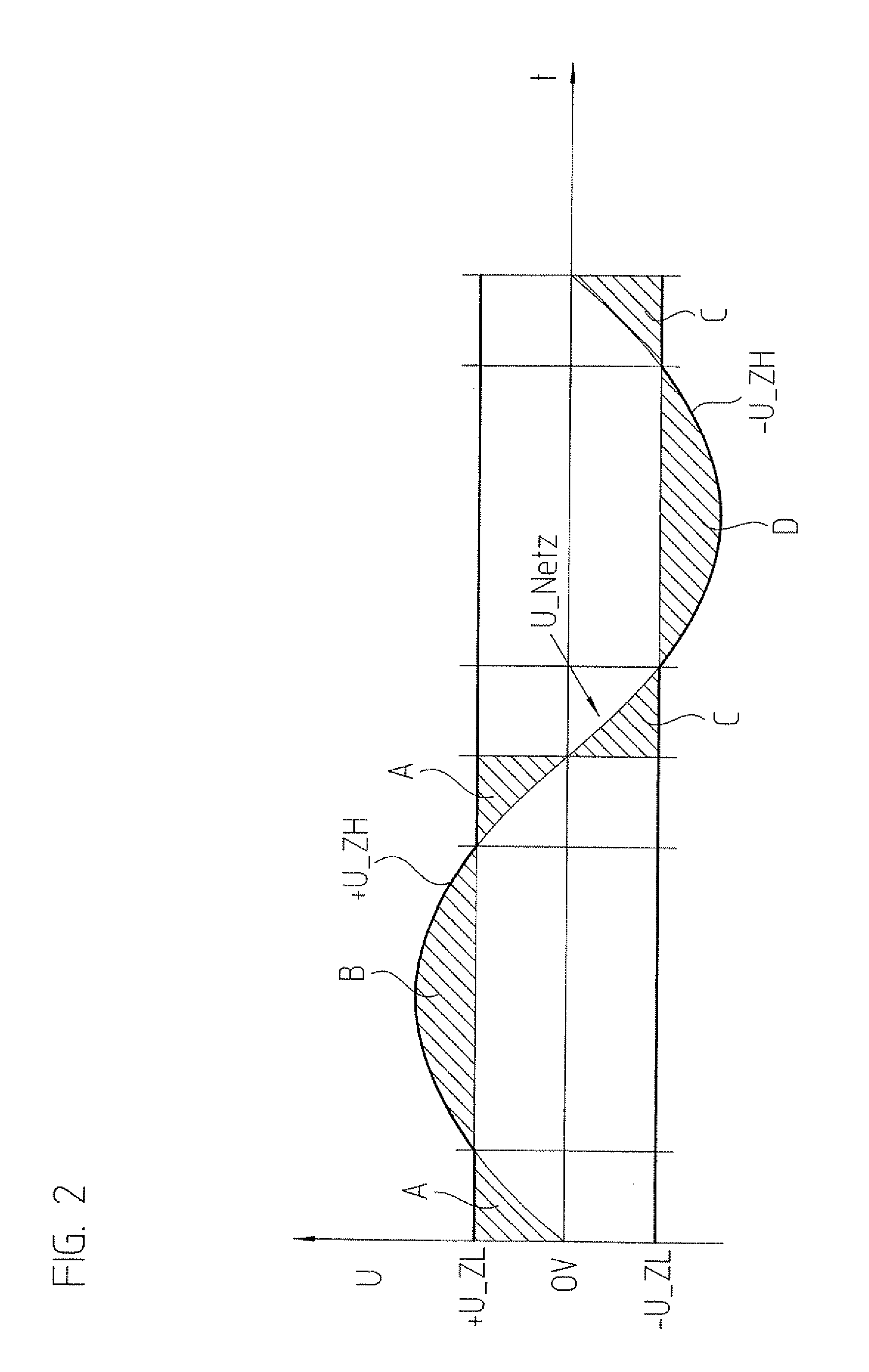
InactiveUS20110080147A1Improve efficiencySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationVoltage generatorLow voltage
In an inverter and a method for operating an inverter, the inverter includes a step-up converter circuit, a dynamic intermediate circuit, and a step-down converter circuit for converting a direct voltage of a direct voltage generator or string into an alternating voltage for supplying a network. The step-up converter circuit increases the direct voltage if the latter is lower than a peak-to-peak maximum of the network voltage, and the step-down converter circuit lowers a dynamic intermediate circuit voltage, as needed, to a lower voltage currently required in the network. The step-up converter circuit dynamically increases the direct voltage to the value currently required in the network and in the process temporarily supplies an approximately sinusoidal voltage curve for the intermediate circuit voltage.
Owner:DR JOHANNES HEIDENHAIN GMBH
Voltage up-conversion circuit using low voltage transistors
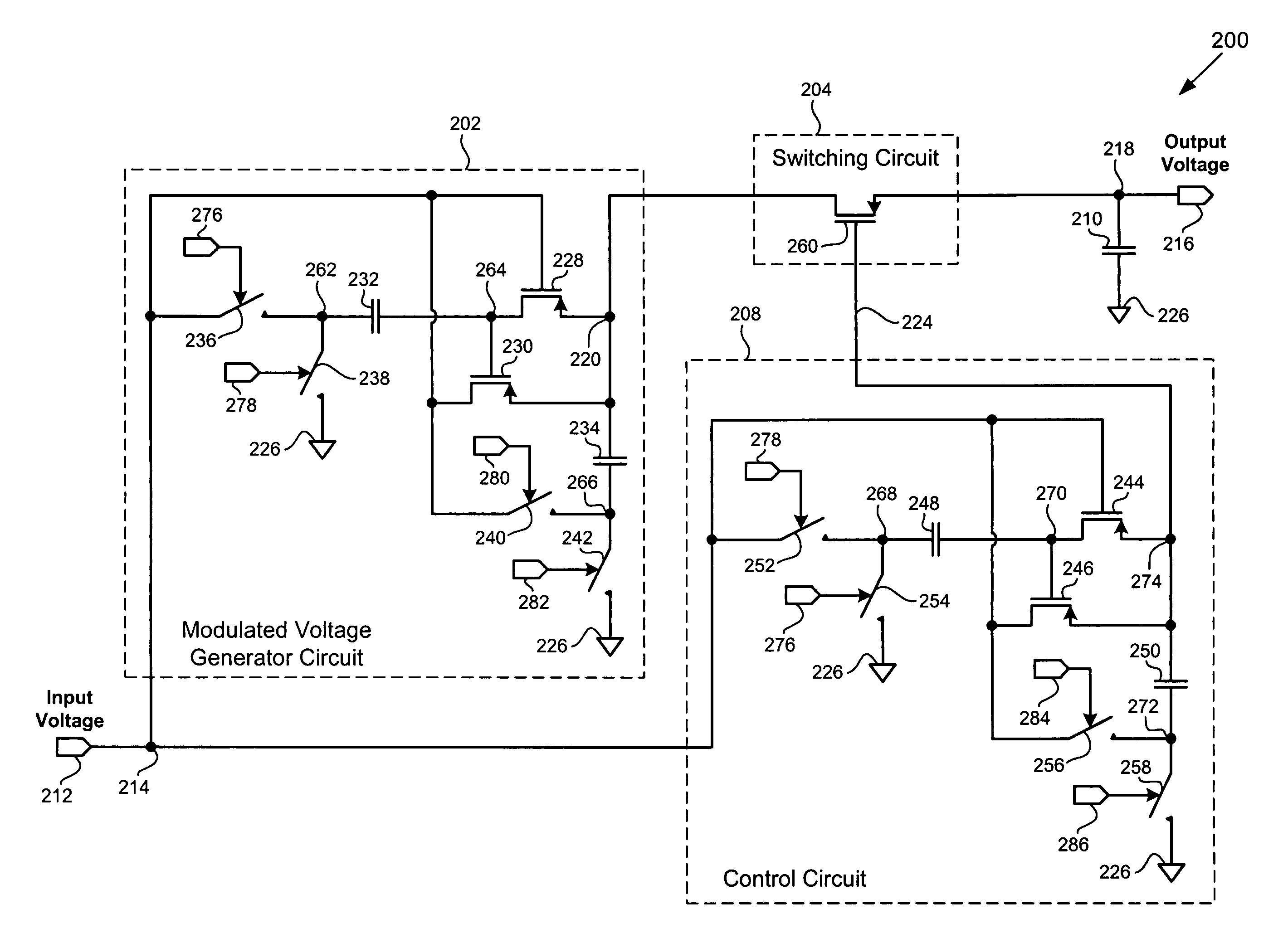
ActiveUS7408330B2Low costApparatus without intermediate ac conversionLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsVoltage generatorLow voltage
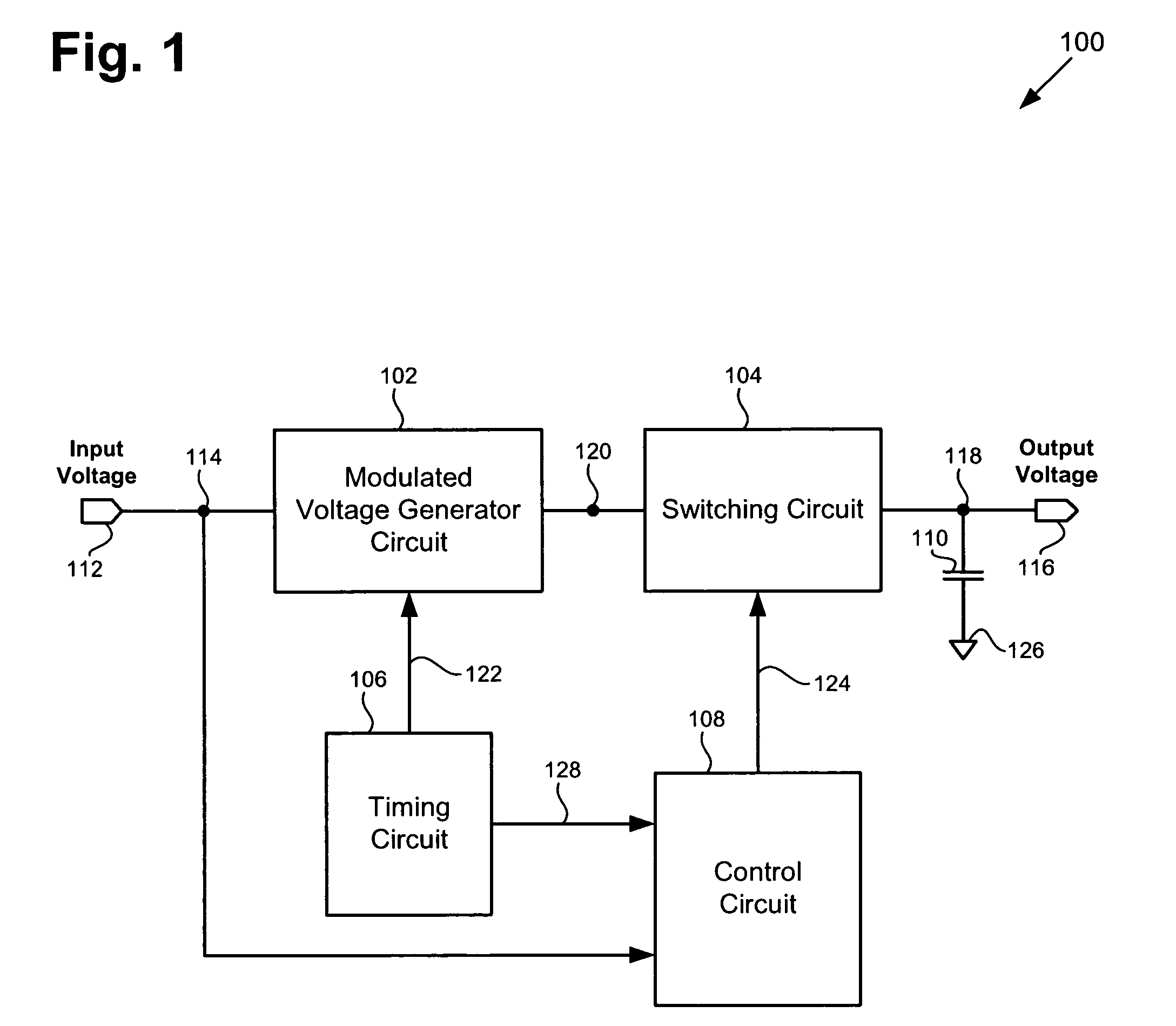
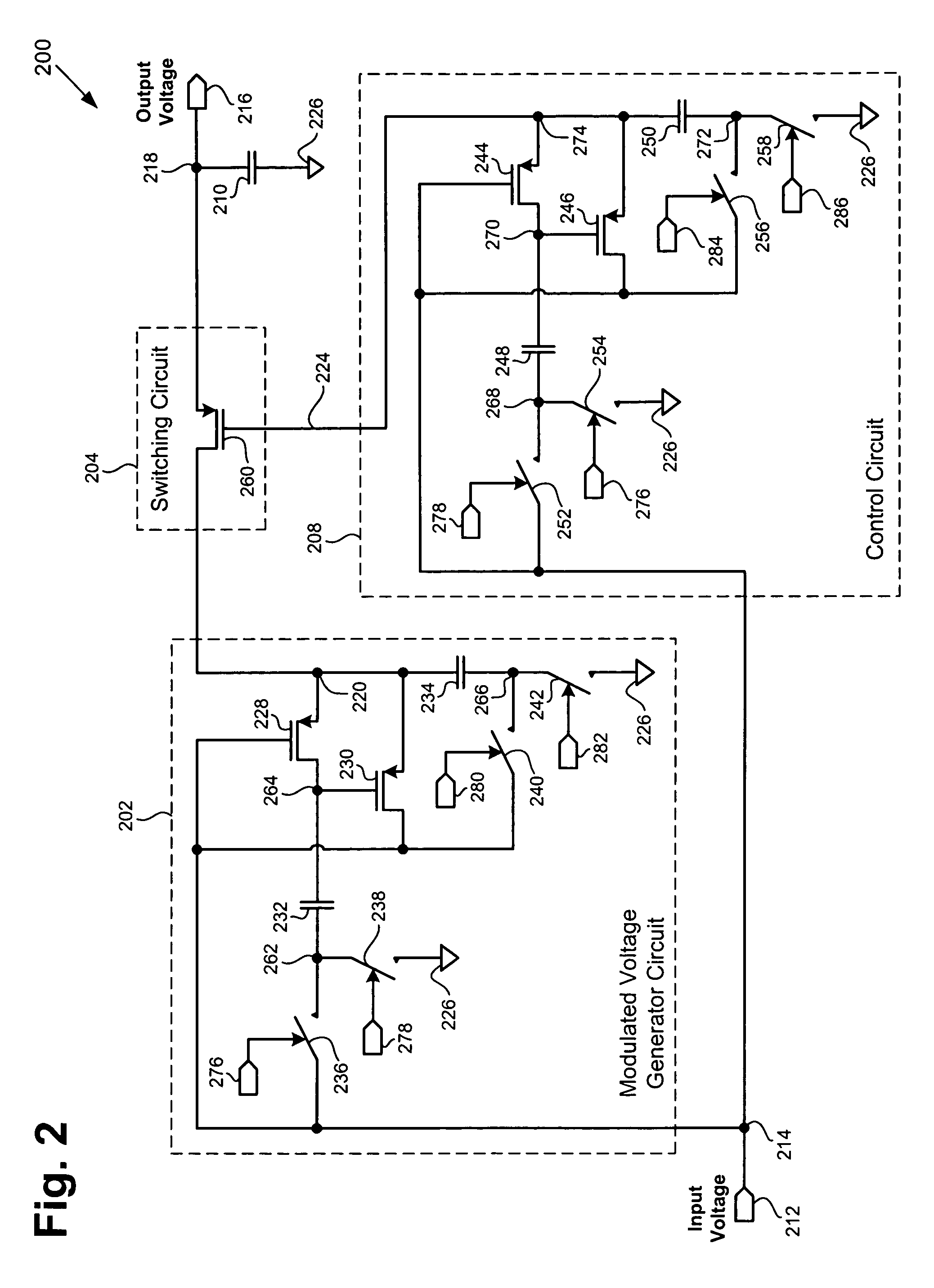
According to one exemplary embodiment, a voltage up-conversion circuit includes a modulated voltage generator circuit, where the modulated voltage generator circuit is configured to receive an input voltage and generate a modulated voltage, and where the modulated voltage generator circuit includes at least one transistor. The voltage up-conversion circuit further includes a switching circuit coupled to the modulated voltage generator circuit, where the switching circuit is configured to couple the modulated voltage to a load capacitor when the modulated voltage is at a high level and decouple the modulated voltage to the load capacitor when the modulated voltage is at a low level. In the voltage up-conversion circuit, the load capacitor reaches a voltage greater a breakdown voltage of the at least one transistor in the modulated voltage generator circuit. The breakdown voltage can be a reliability breakdown voltage.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Disk drive controlling a voice coil motor during an emergency unload
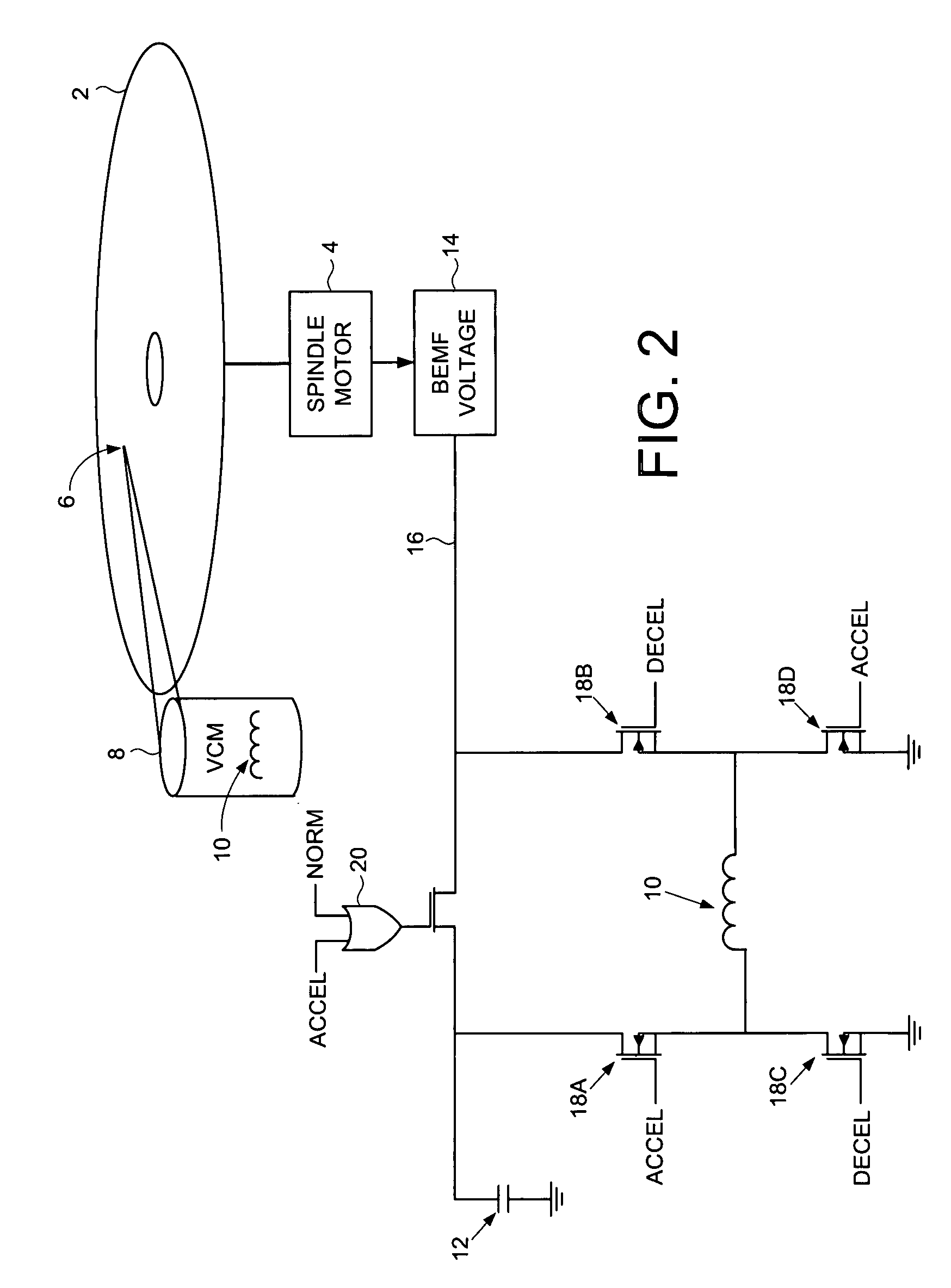
ActiveUS7548392B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageVoltage generatorElectric machine
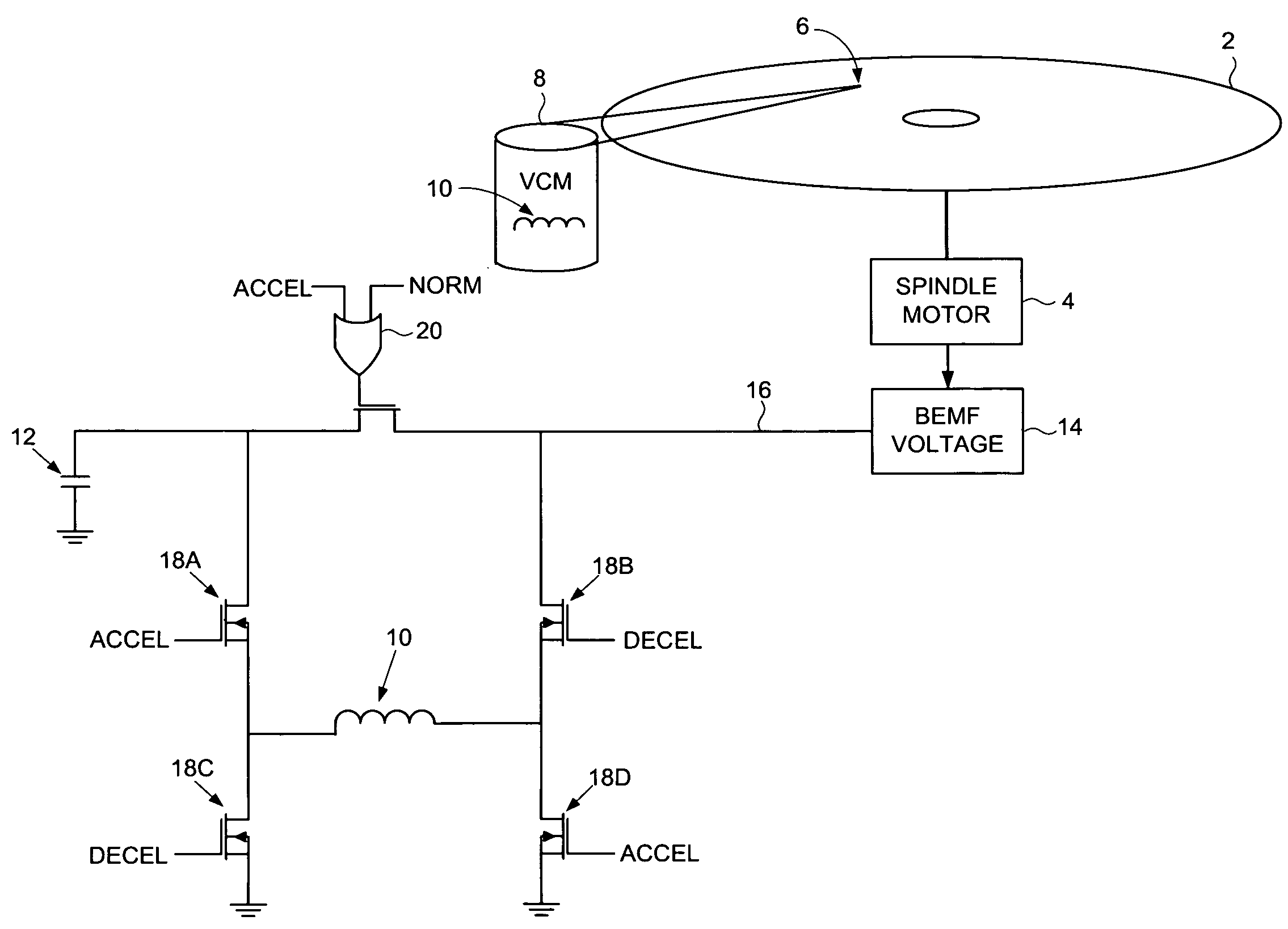
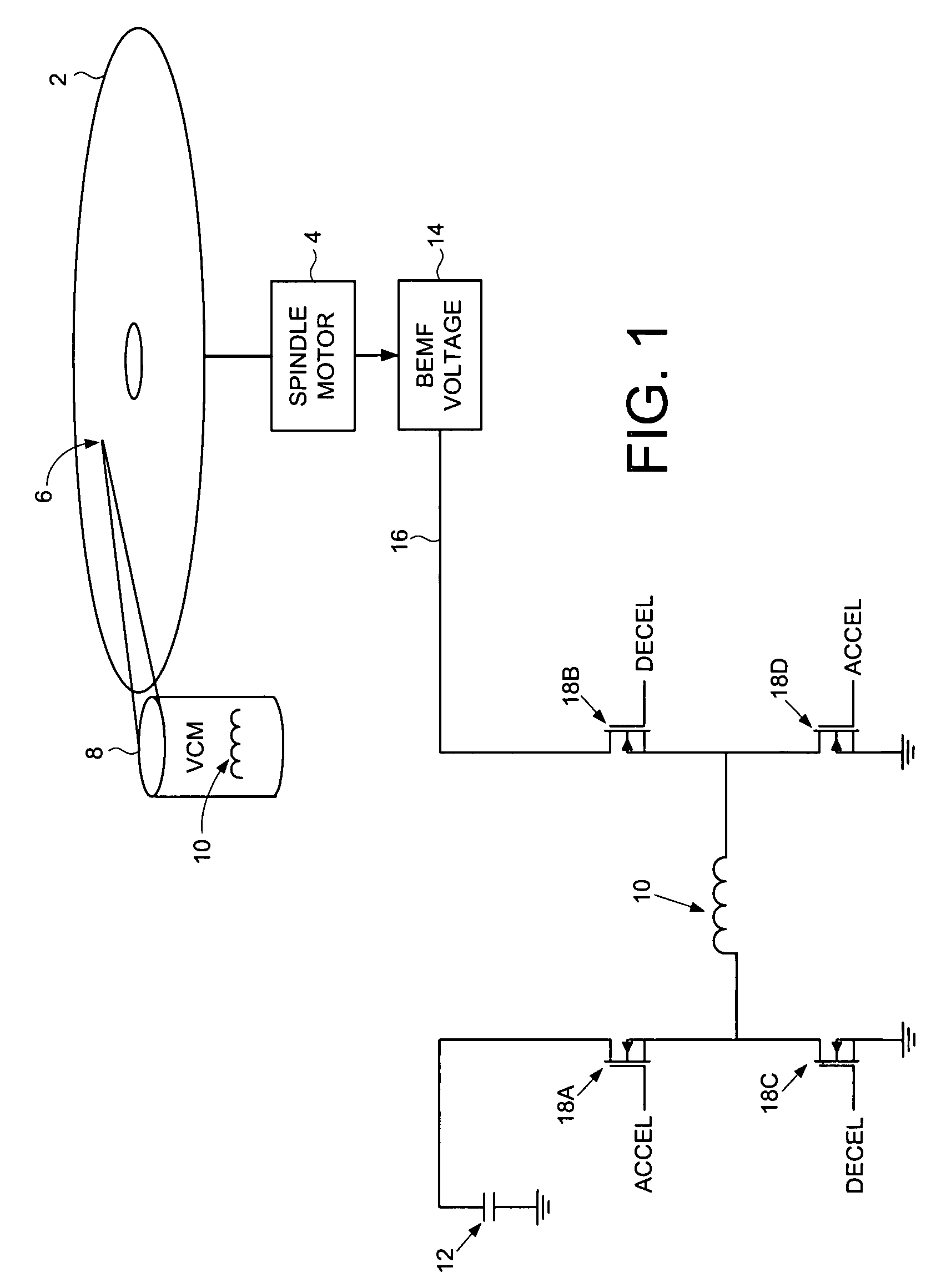
A disk drive is disclosed including a disk, a spindle motor operable to rotate the disk, a head, and a voice coil motor (VCM) operable to actuate the head over the disk, wherein the VCM comprises a voice coil. The disk drive further comprises a capacitor, and a back electromotive force (BEMF) voltage generator operable to generate a BEMF voltage from the spindle motor. The disk drive further comprises switching circuitry operable to connect the voice coil to the capacitor while accelerating the VCM, and to disconnect the voice coil from the capacitor and connect the voice coil to the BEMF voltage while decelerating the VCM.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
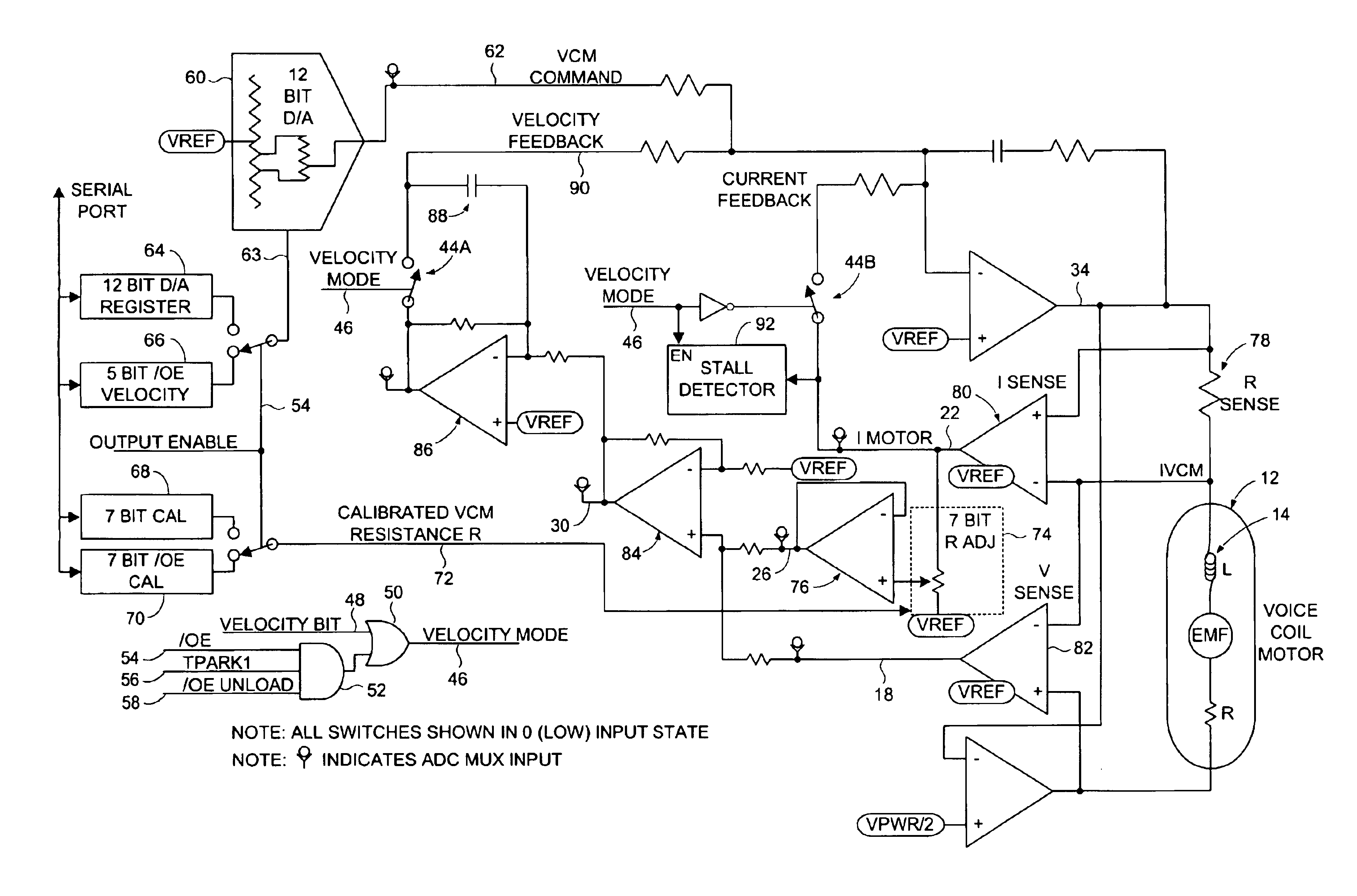
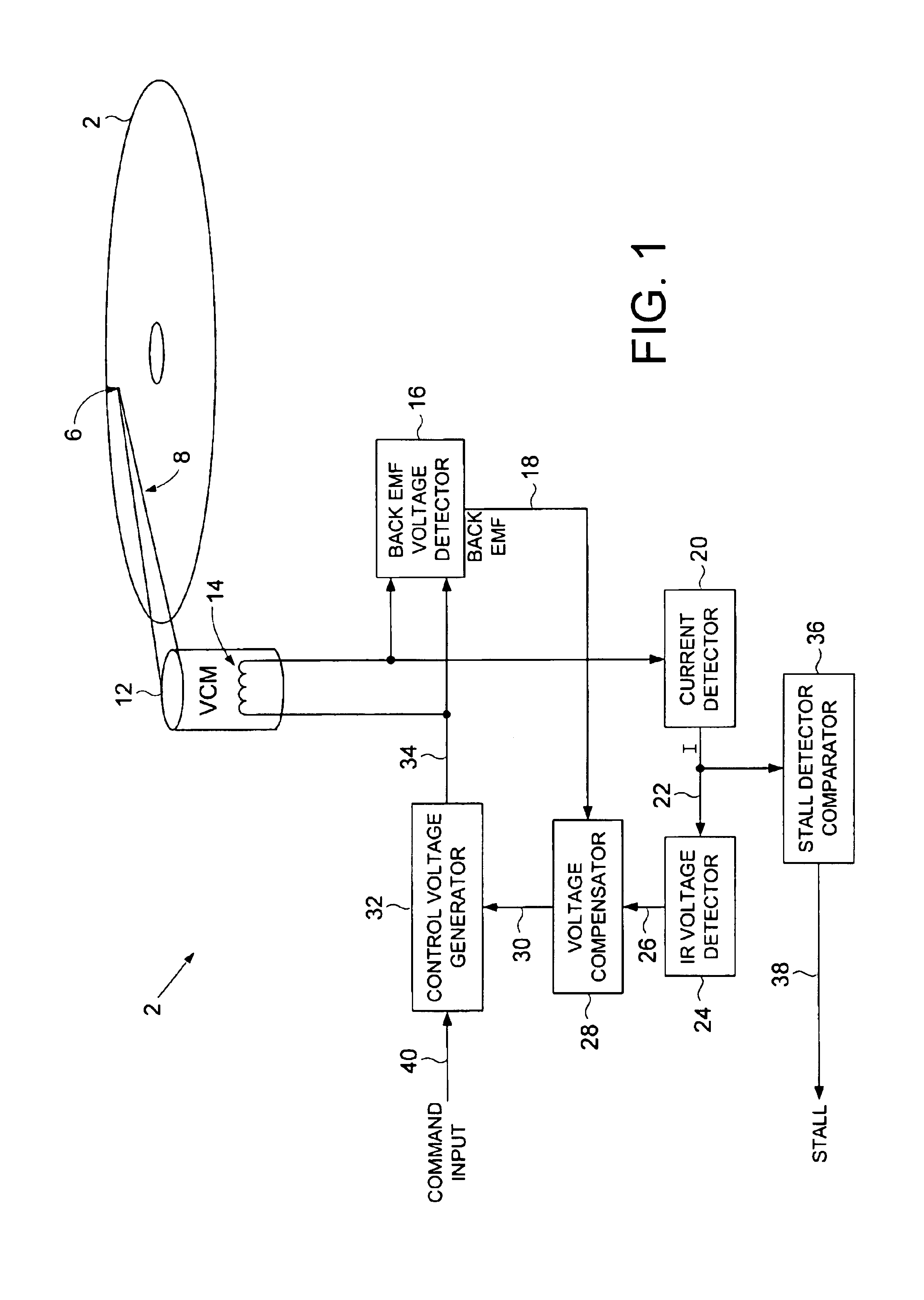
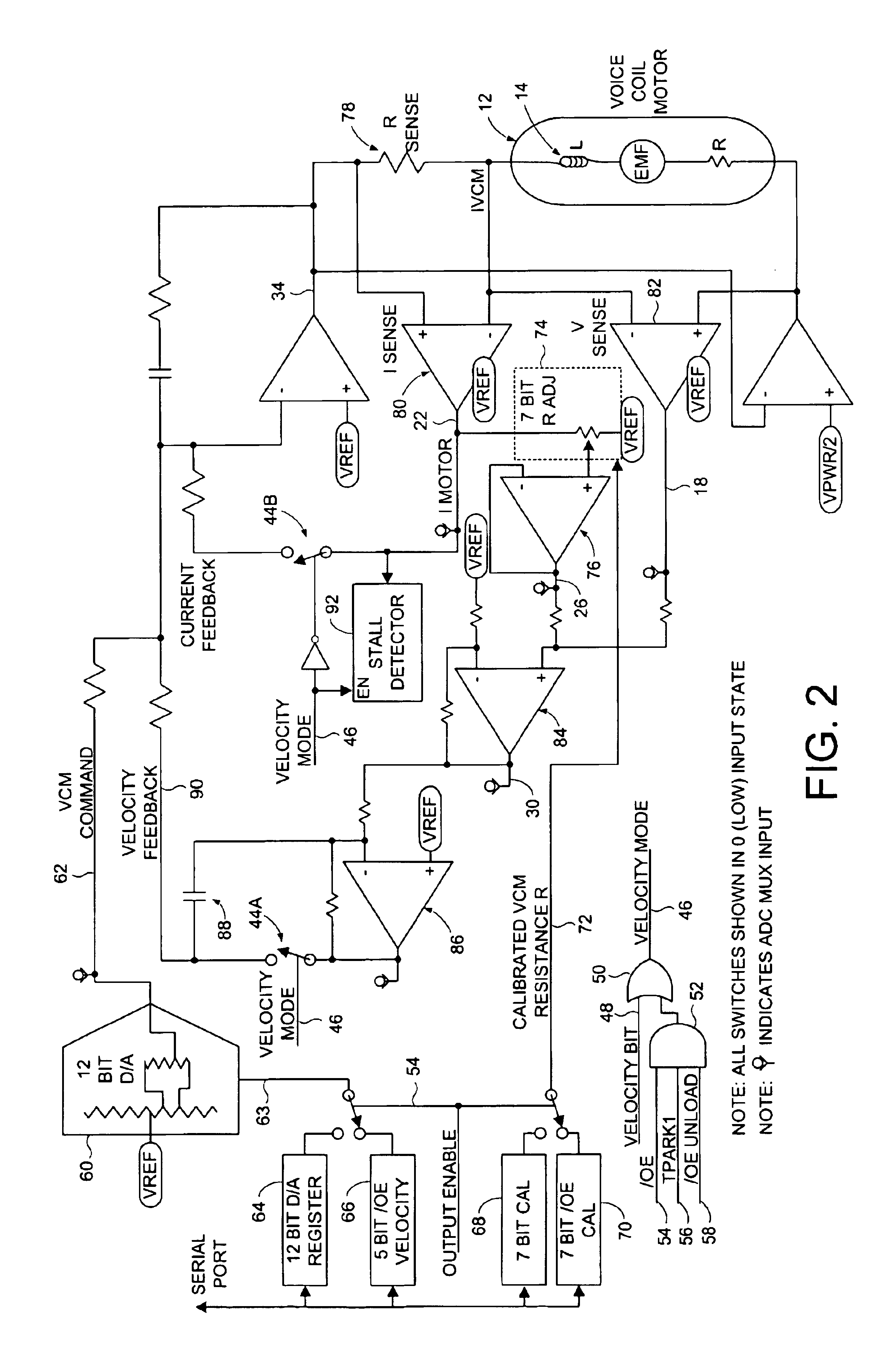
Disk drive comprising VCM stall detector for velocity control of an actuator arm
InactiveUS6867944B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageVoltage generatorElectric machine
The present invention may be regarded as a disk drive comprising a disk, a head, an actuator arm for actuating the head radially over the disk, and a voice coil motor (VCM) for rotating the actuator arm about a pivot, the VCM comprising a coil comprising a VCM resistance R. A back EMF voltage detector measures a back EMF voltage across the coil, and a current detector detects a current I flowing through the coil. An IR voltage detector, responsive to the current I detected by the current detector, detects an IR voltage proportional to the current I times the VCM resistance R. A voltage compensator substantially cancels the IR voltage from the measured back EMF voltage to generate a compensated back EMF voltage. A control voltage generator, responsive the compensated back EMF voltage, generates a control voltage applied to the coil to generate the current I flowing through the coil. A stall detector compares the current I detected by the current detector to a threshold, wherein a VCM stall condition is detected if the current I exceeds the threshold for a predetermined interval.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
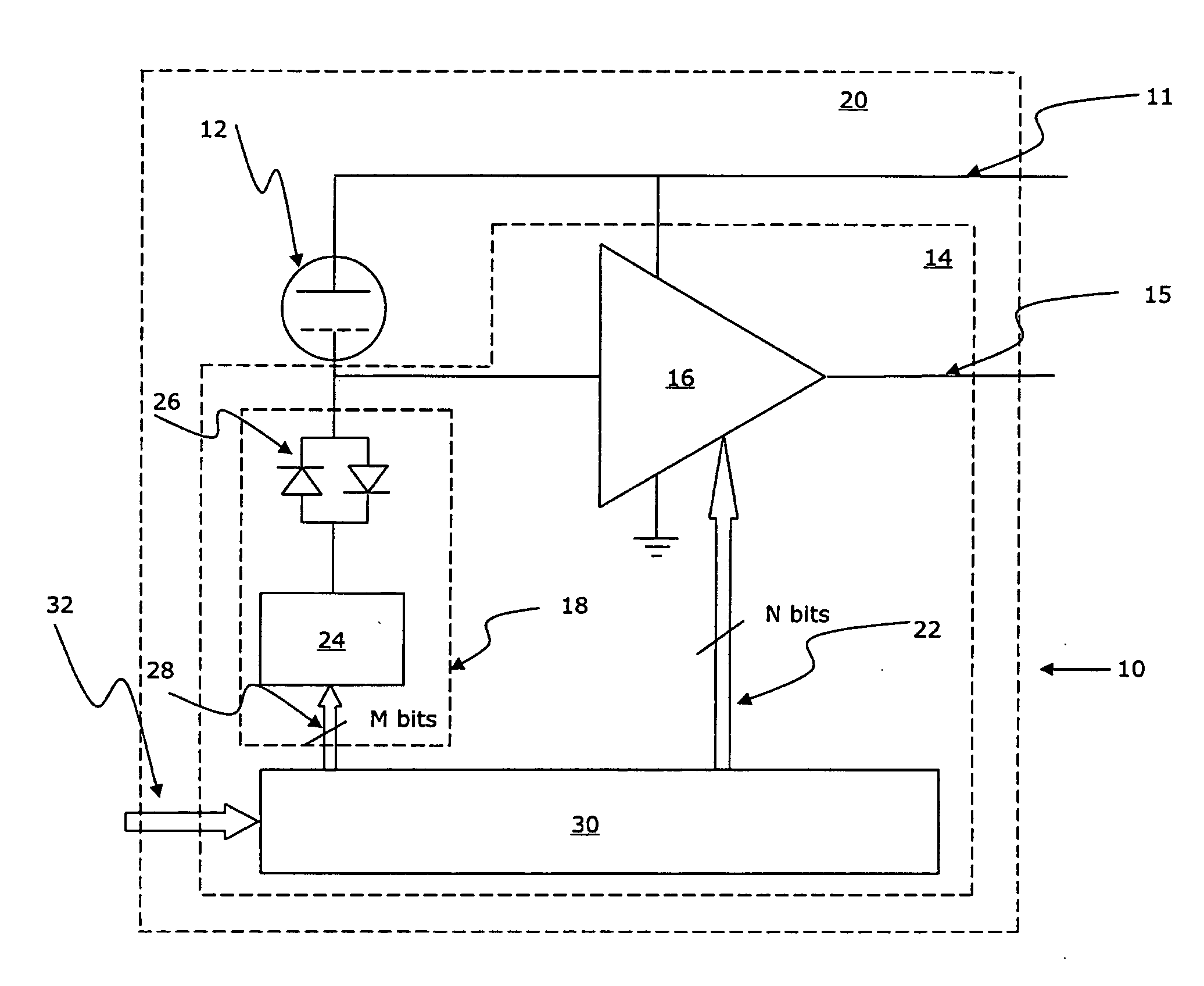
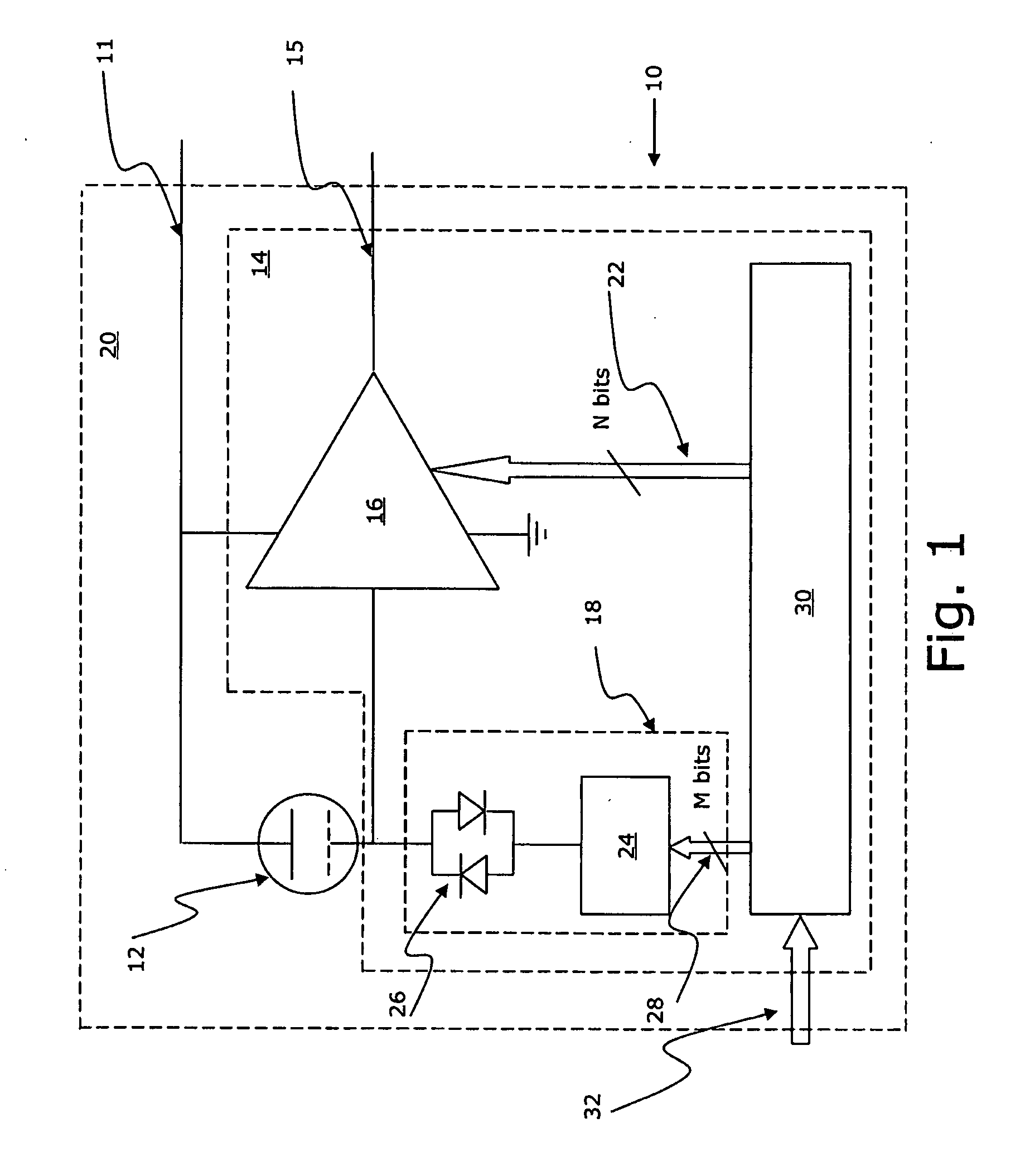
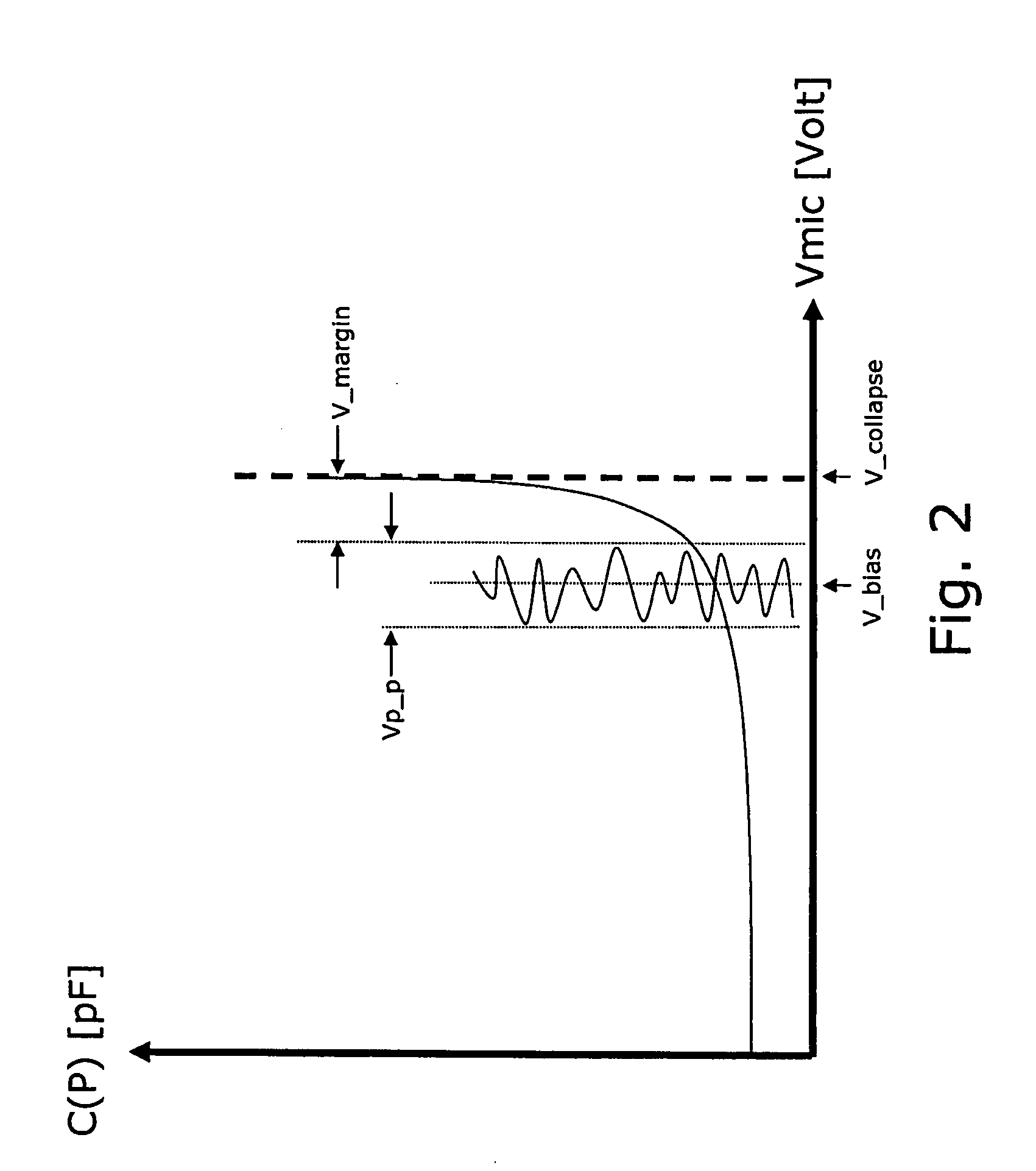
Calibrated microelectromechanical microphone
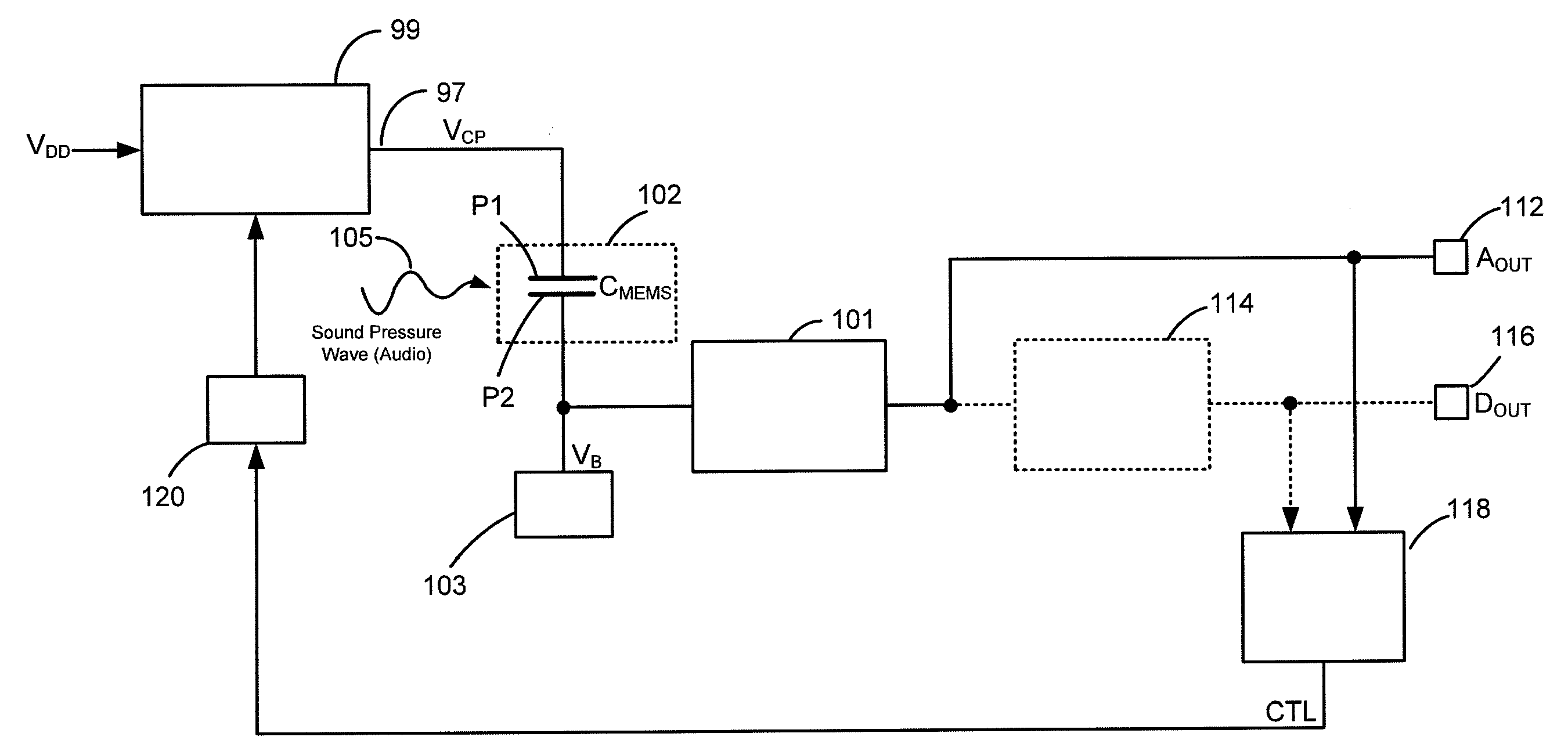
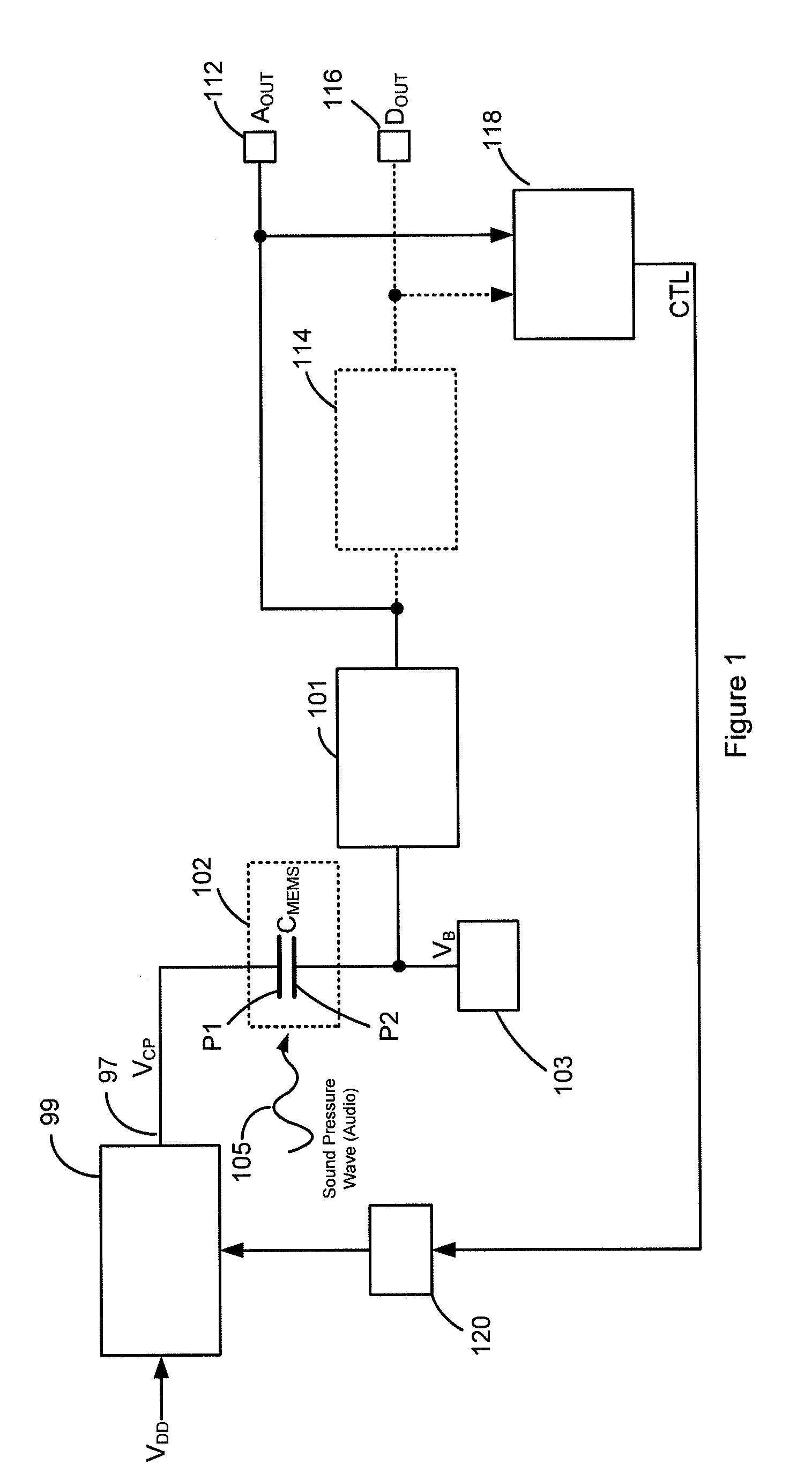
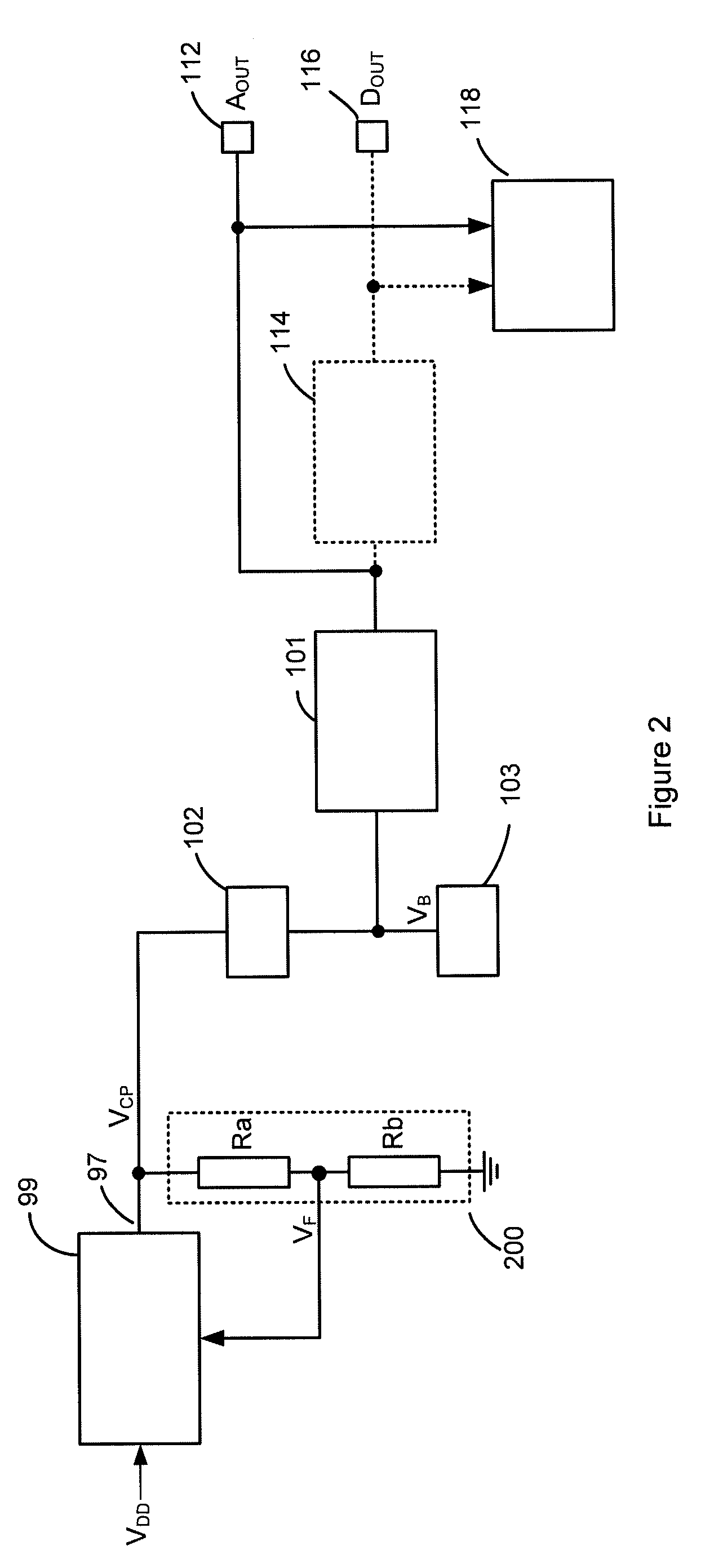
ActiveUS20080075306A1Improve production yieldMaximize sensitivitySemiconductor electrostatic transducersElectrostatic transducer microphonesVoltage generatorAudio power amplifier
A MEMS microphone comprising a MEMS transducer having a back plate and a diaphragm as well as controllable bias voltage generator providing a DC bias voltage between the back plate and the diaphragm. The microphone also has an amplifier with a controllable gain, and a memory for storing information for determining a bias voltage to be provided by the bias voltage generator and the gain of the amplifier.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Cold-cathode ion source with a controlled position of ion beam
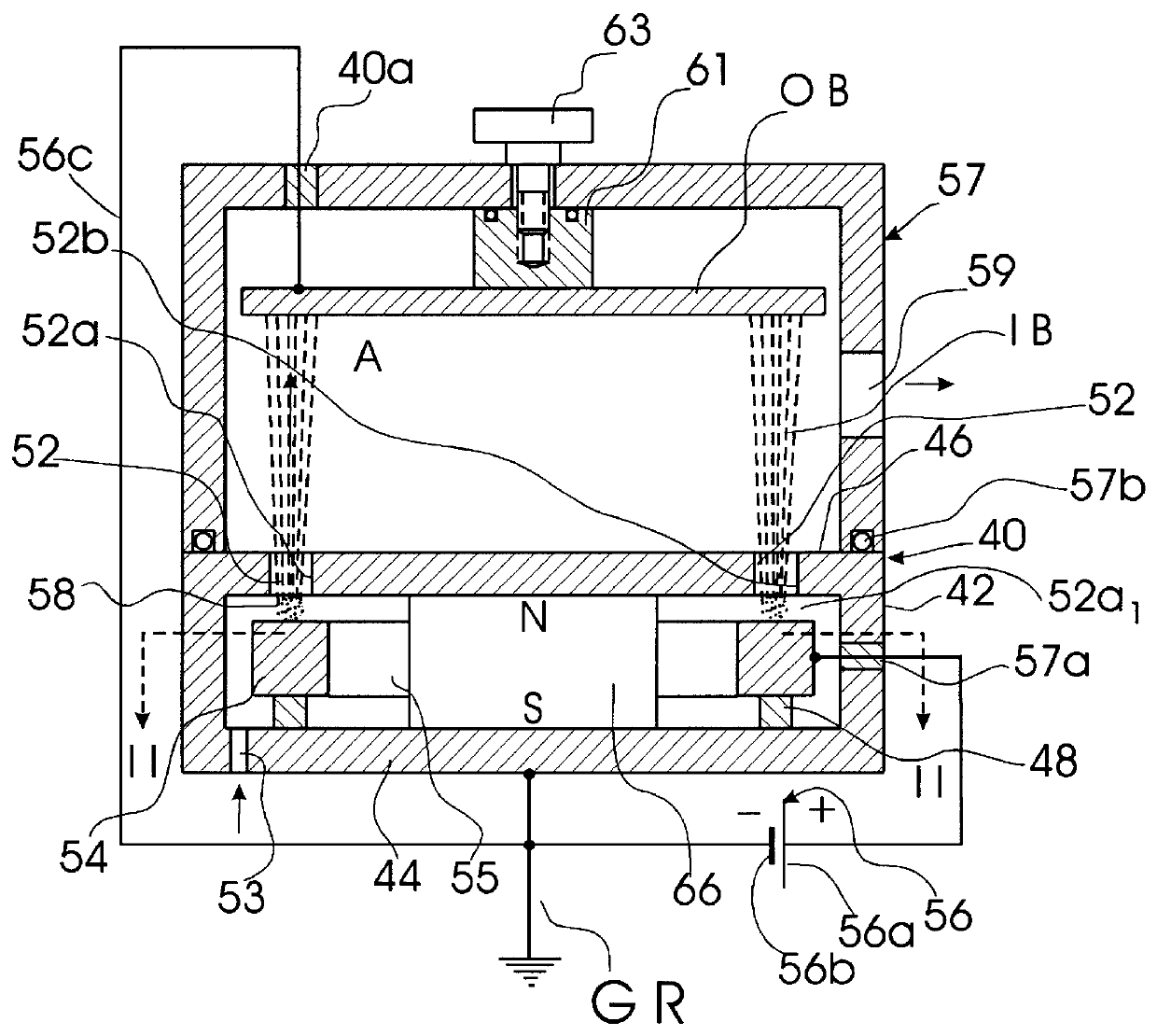
A cold-cathode ion source with a closed-loop ion-emitting slit which is provided with means for generating a cyclically-variable, e.g., alternating or pulsating electric or magnetic field in an anode-cathode space. These means may be made in the form of an alternating-voltage generator which generates alternating voltage on one of the cathode parts that form the ion-emitting slit, whereas the other slit-forming part is grounded. The alternating voltage deviates the ion beam in the slit with the same frequency of the alternating voltage. In accordance with another embodiment, the aforementioned means may be an electromagnetic coil which generates a magnetic field which passes through the ion-emitting slit, thus acting on the condition of the spatial-charge formation and, hence, on concentration of ions in the ion beam. The cold-cathode ion source may be of any type, i.e., with the ion beam emitted in the direction perpendicular to the direction of drift of electrons in the ion-emitting slit or with the direction of emission of the beam which coincides with the direction of electron drift.
Owner:ADVANCED ION TECH
AD converter
InactiveUS8106806B2Reduce power consumptionReduce areaElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersVoltage generatorAudio power amplifier
Owner:SONY CORP
Blood circuit for a dialysis machine and corresponding dialysis machine
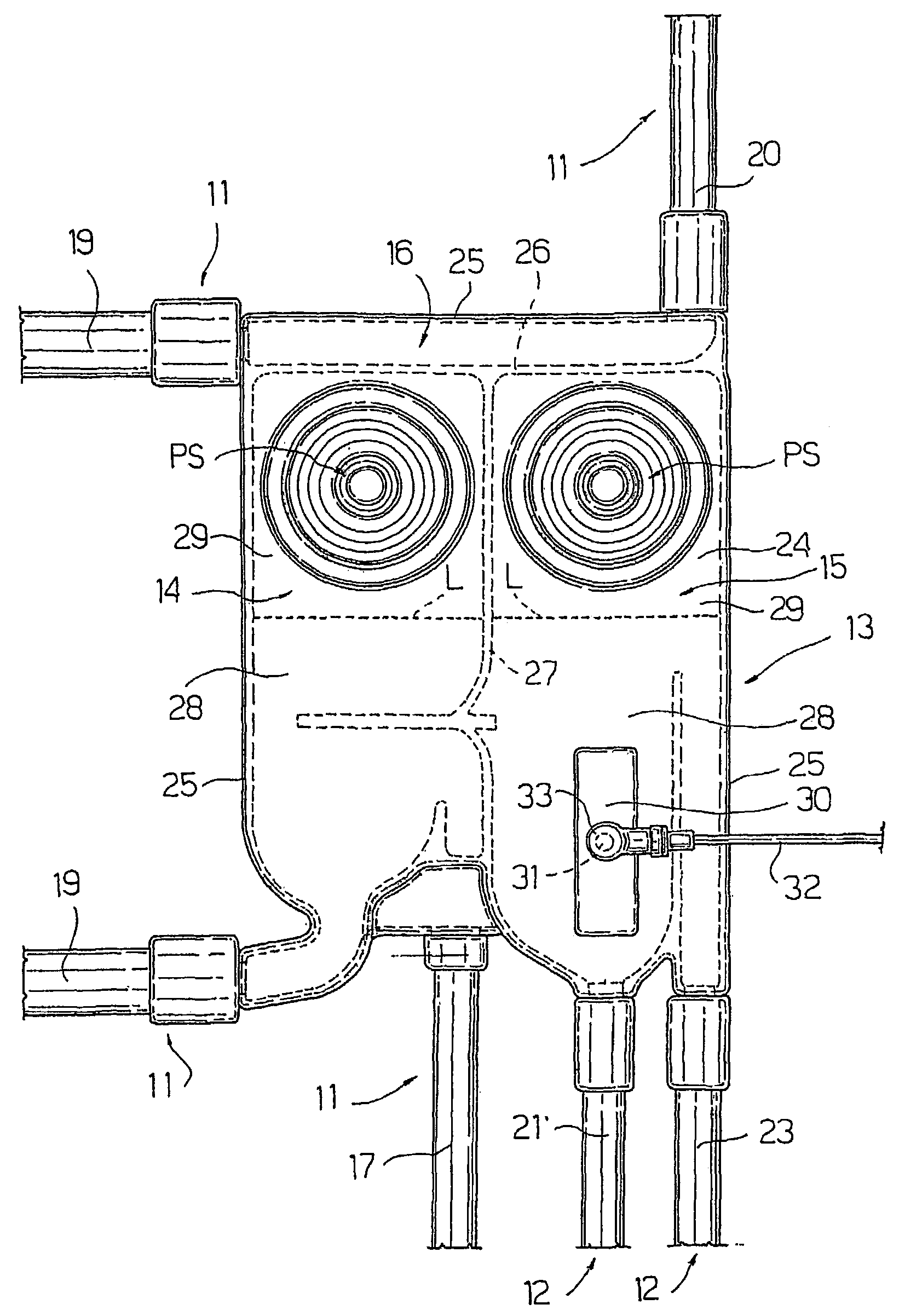
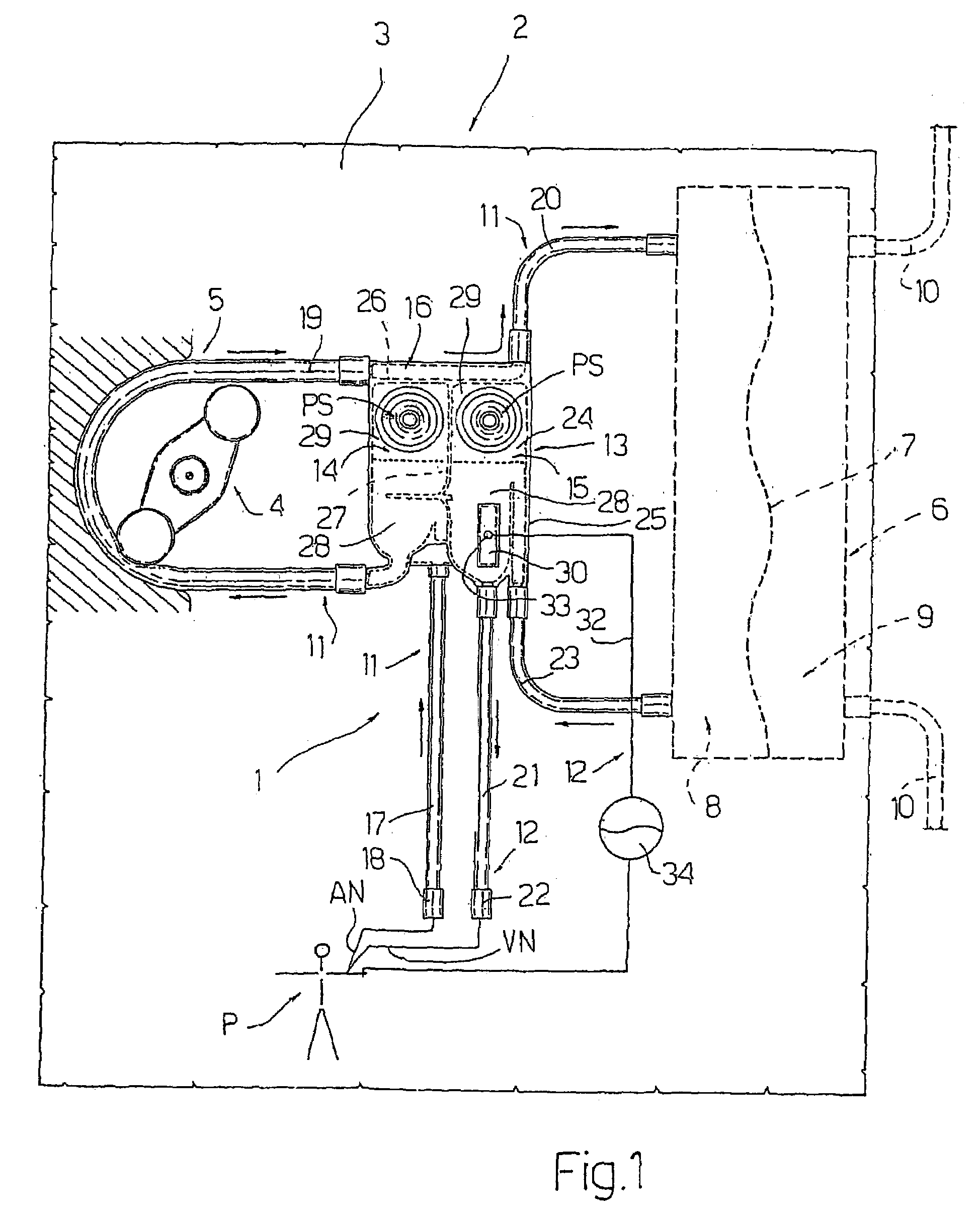
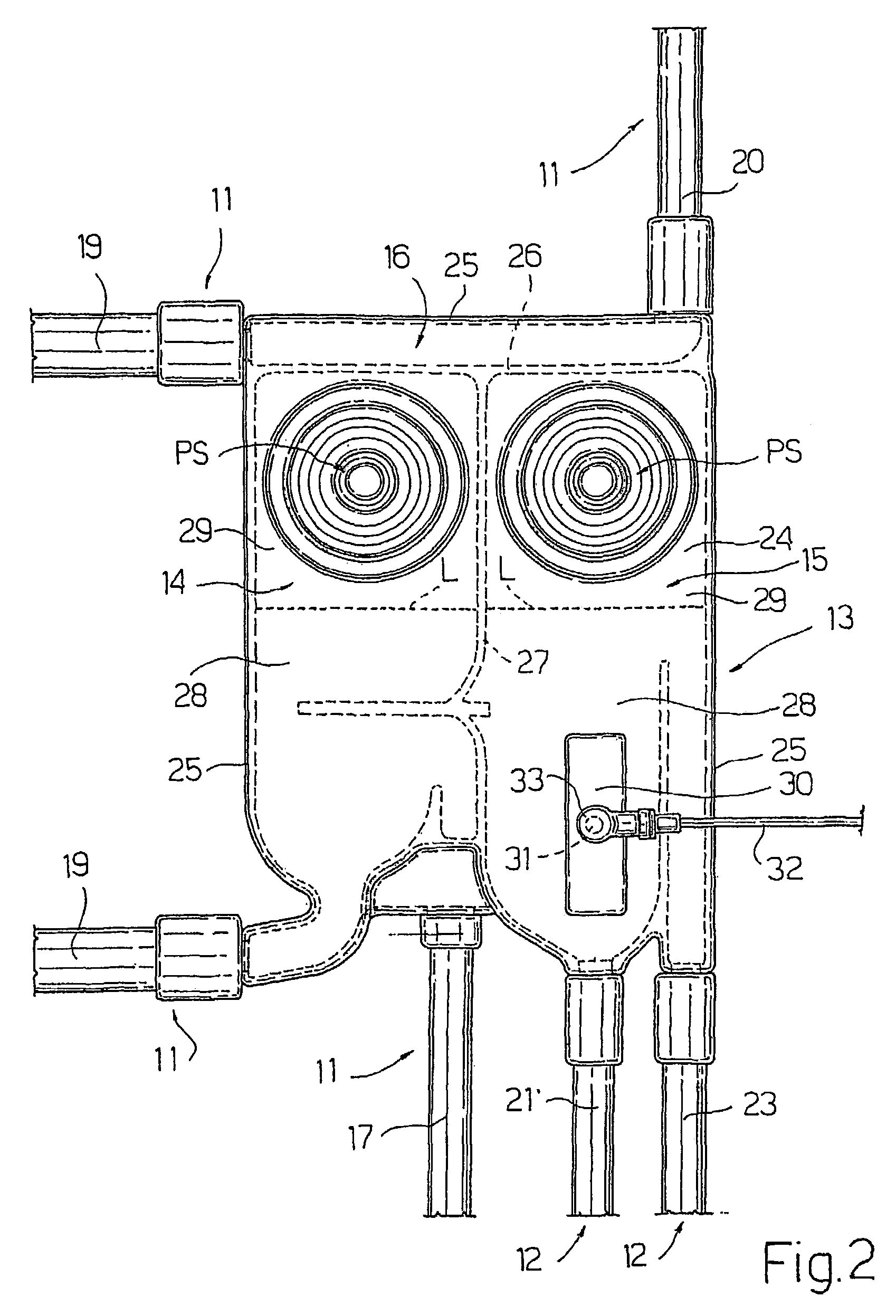
InactiveUS7115107B2Practical and convenientSimple methodSemi-permeable membranesOther blood circulation devicesDielectricVoltage generator
A blood circuit (1) for a dialysis machine is made form plastic material and is provided with a metallic plate (30), which is applied to an external face of the blood circuit (1) and is connectable to a voltage generator (34) in such a way as to form a capacitor, in which the plate (30) and the blood act as the capacitor plates and the plastic material acts as the dielectric.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
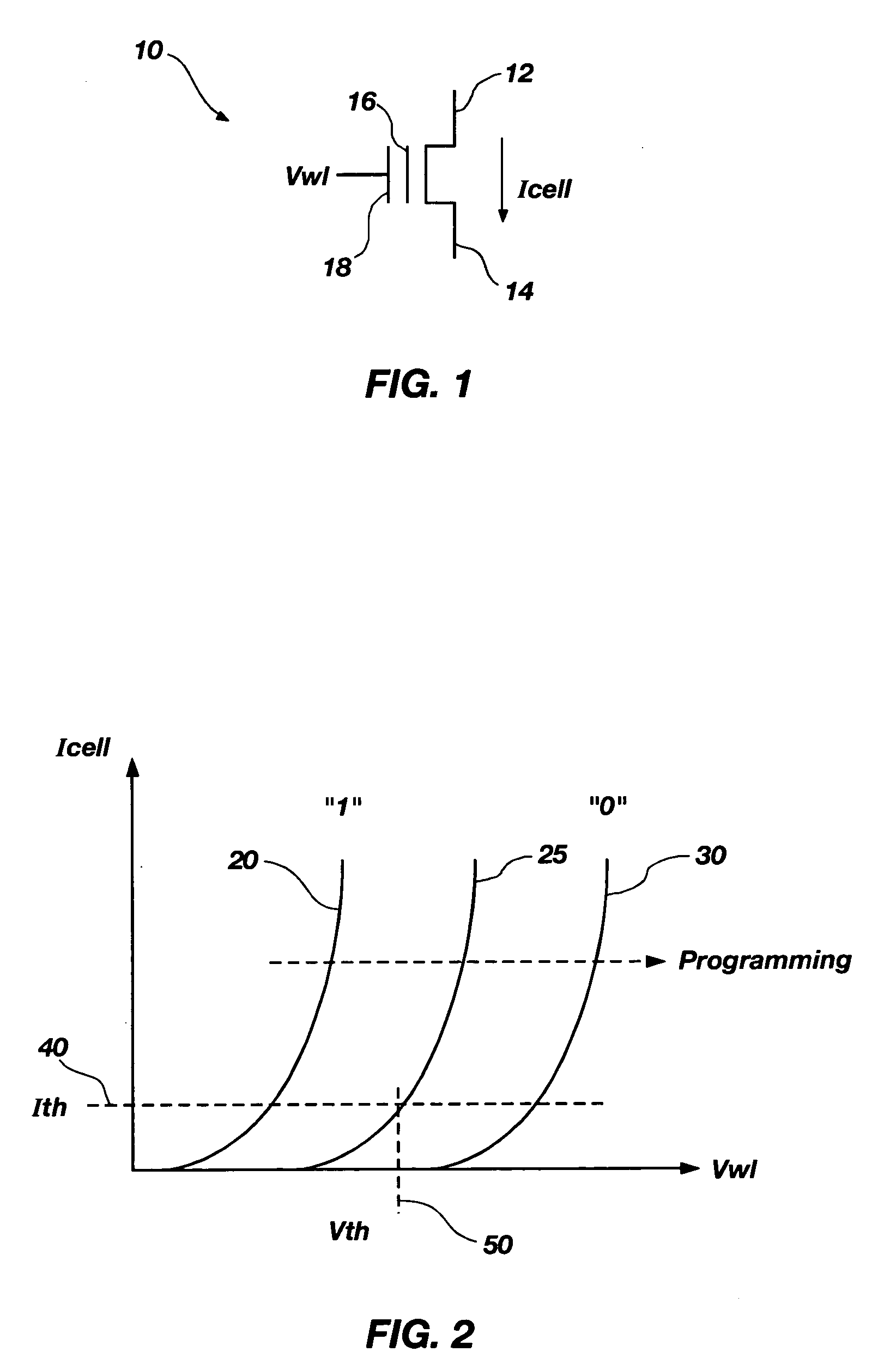
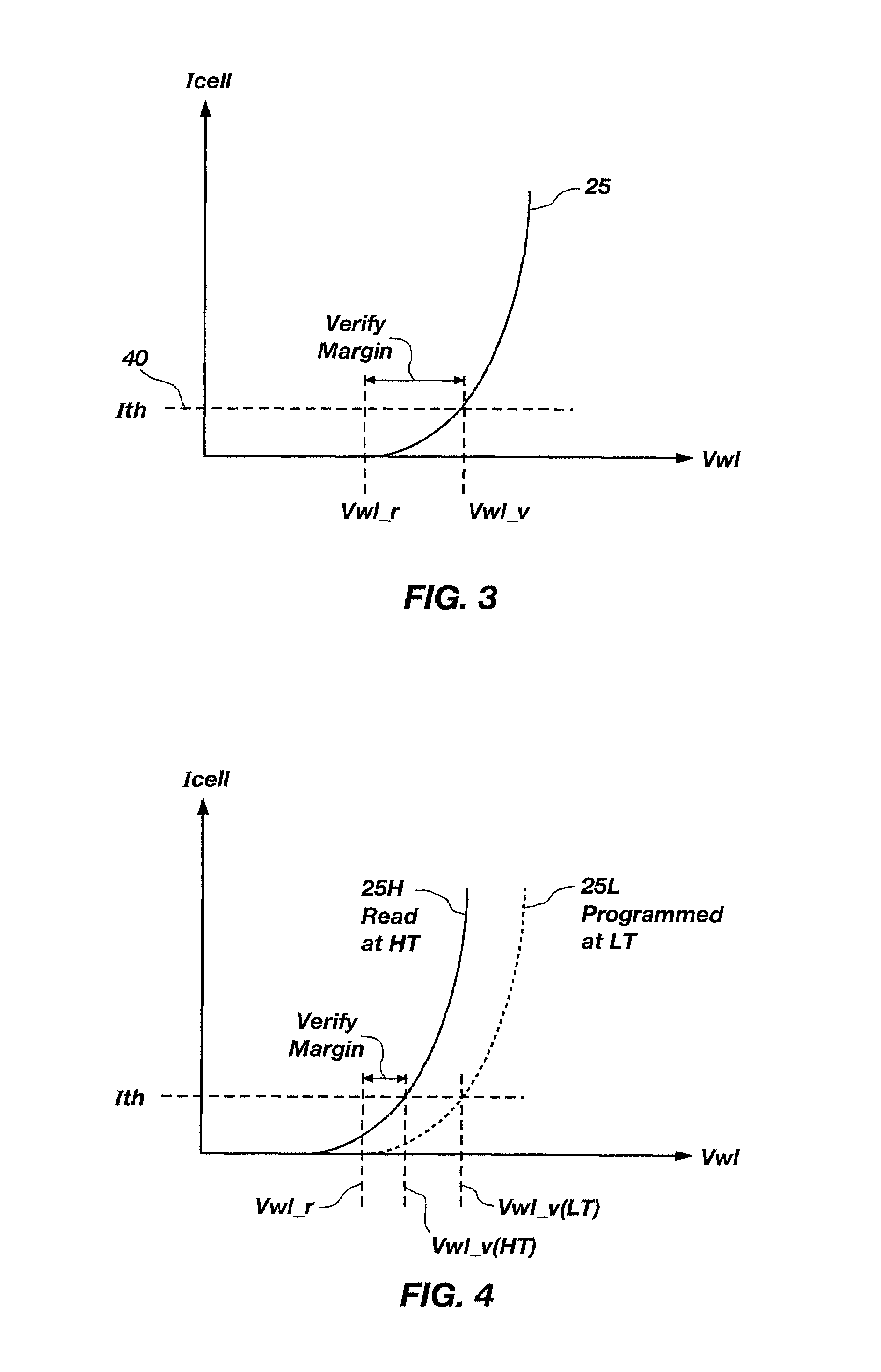
Method and apparatus for generating temperature-compensated read and verify operations in flash memories
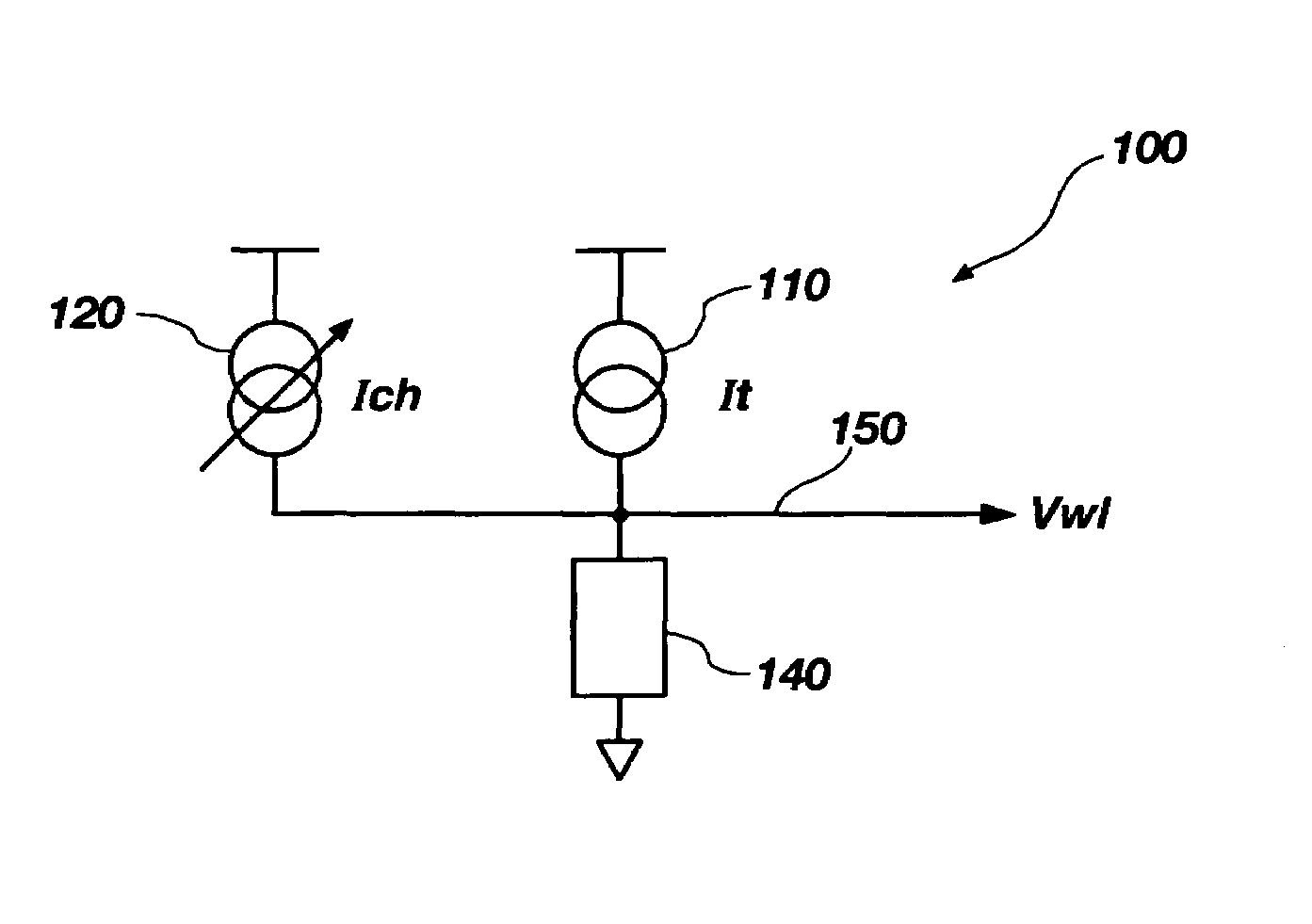
Methods and an apparatuses for generating a word-line voltage are disclosed. A word-line voltage generator includes a first current source, an adjustable current source, adjustable current sink, and a voltage converter, all operably coupled to a current sum node. The first current source generates a first current having a temperature coefficient substantially equal to a temperature coefficient of at least one bit cell. The adjustable current source generates a second current that is substantially independent of a temperature change. The adjustable current sink sinks a third current that is substantially independent of a temperature change. The voltage converter is configured for generating a word-line signal having a word-line voltage proportional to a reference current, wherein the reference current comprises the first current, plus the second current, and minus the third current.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
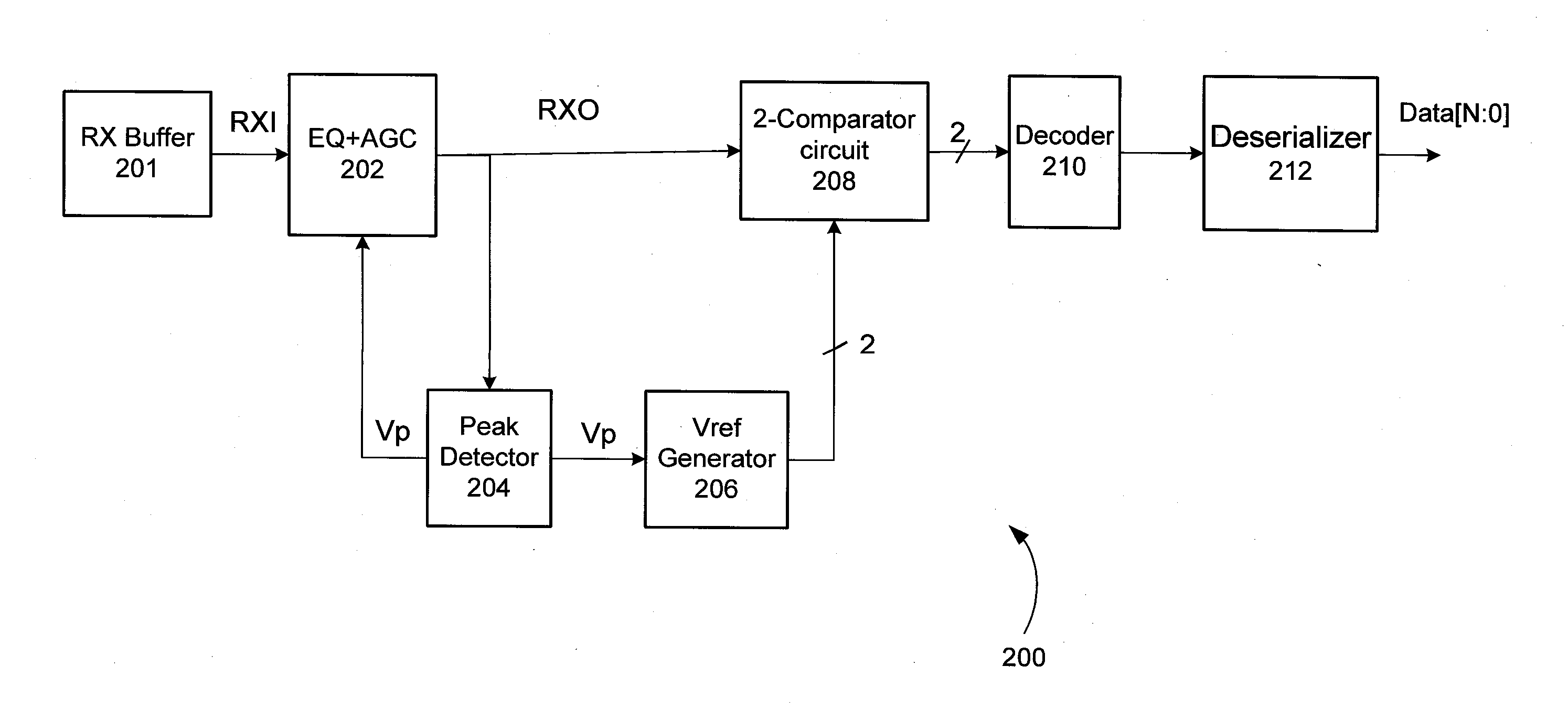
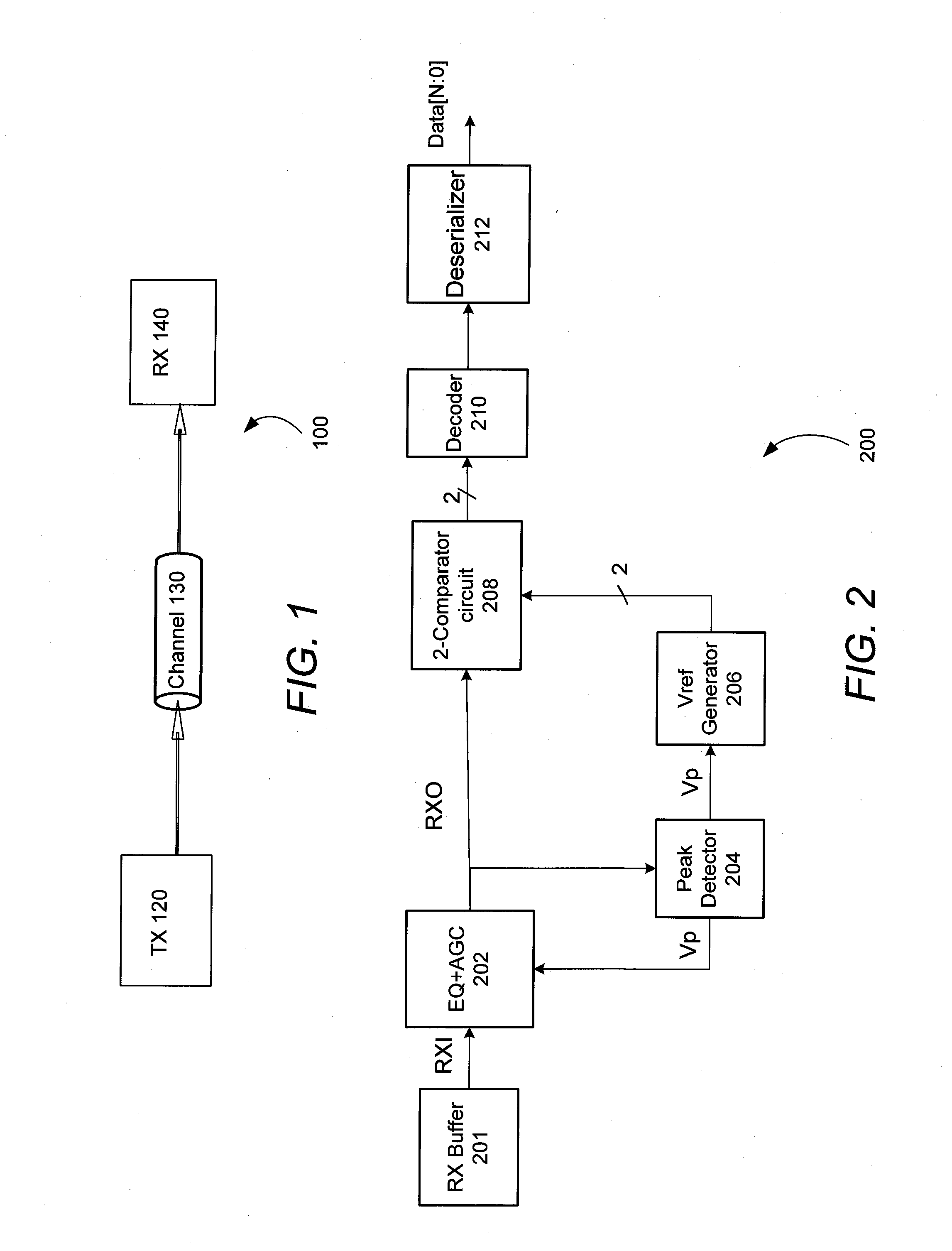
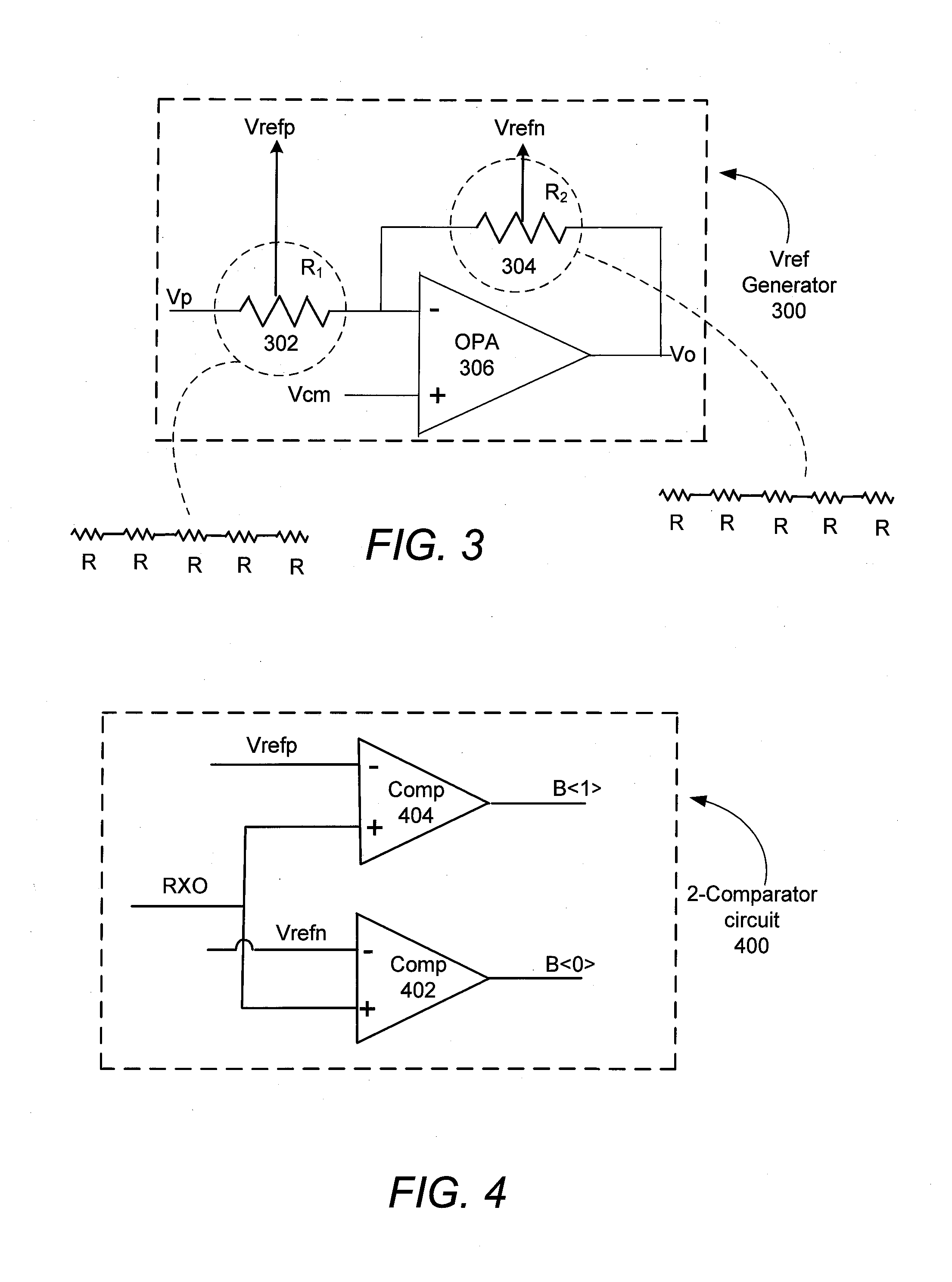
Multi-level amplitude signaling receiver
ActiveUS20130195155A1Dc level restoring means or bias distort correctionLine balance variation compensationVoltage generatorComparators circuits
One embodiment relates to a receiver circuit for multi-level amplitude signaling which includes at least three amplitude levels for each symbol period. The receiver circuit includes a peak detector, a reference voltage generator, and a comparator circuit. The peak detector is arranged to detect a peak voltage of the multi-level amplitude signal, and the reference voltage generator uses the peak voltage to generate multiple reference voltages. The comparator circuit uses the multiple reference voltages to detect an amplitude level of the multi-level amplitude signal. Other embodiments and features are also disclosed.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
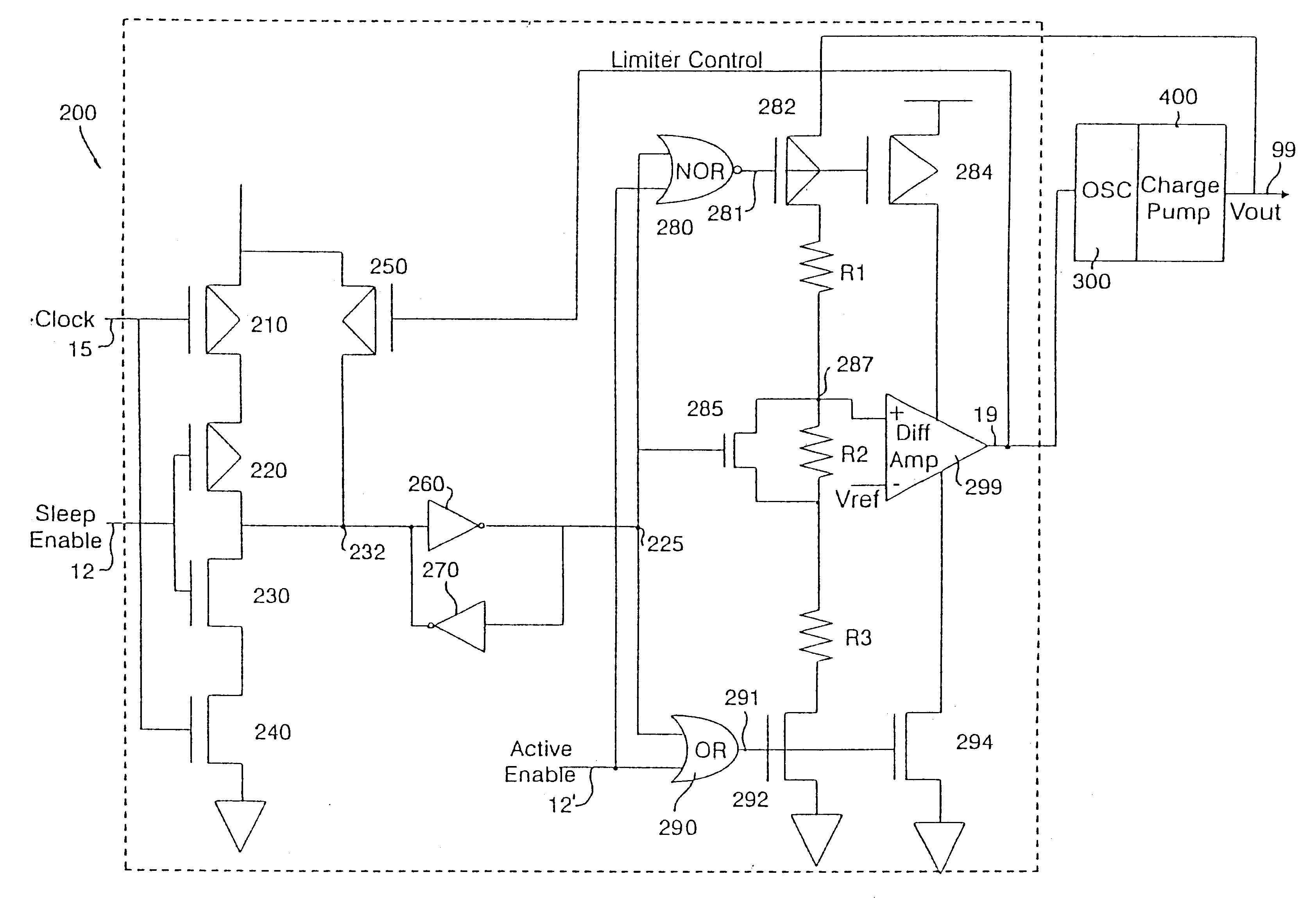
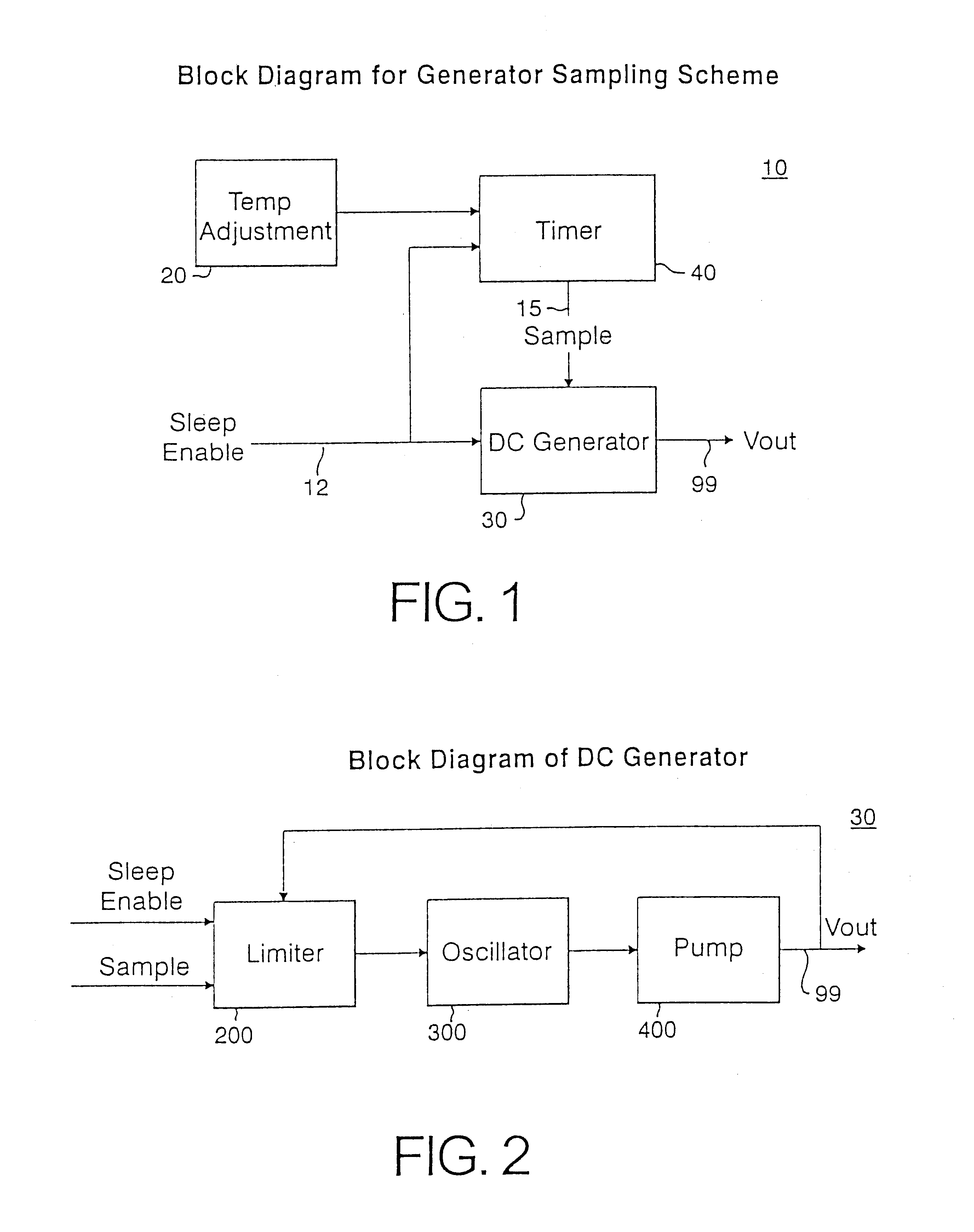
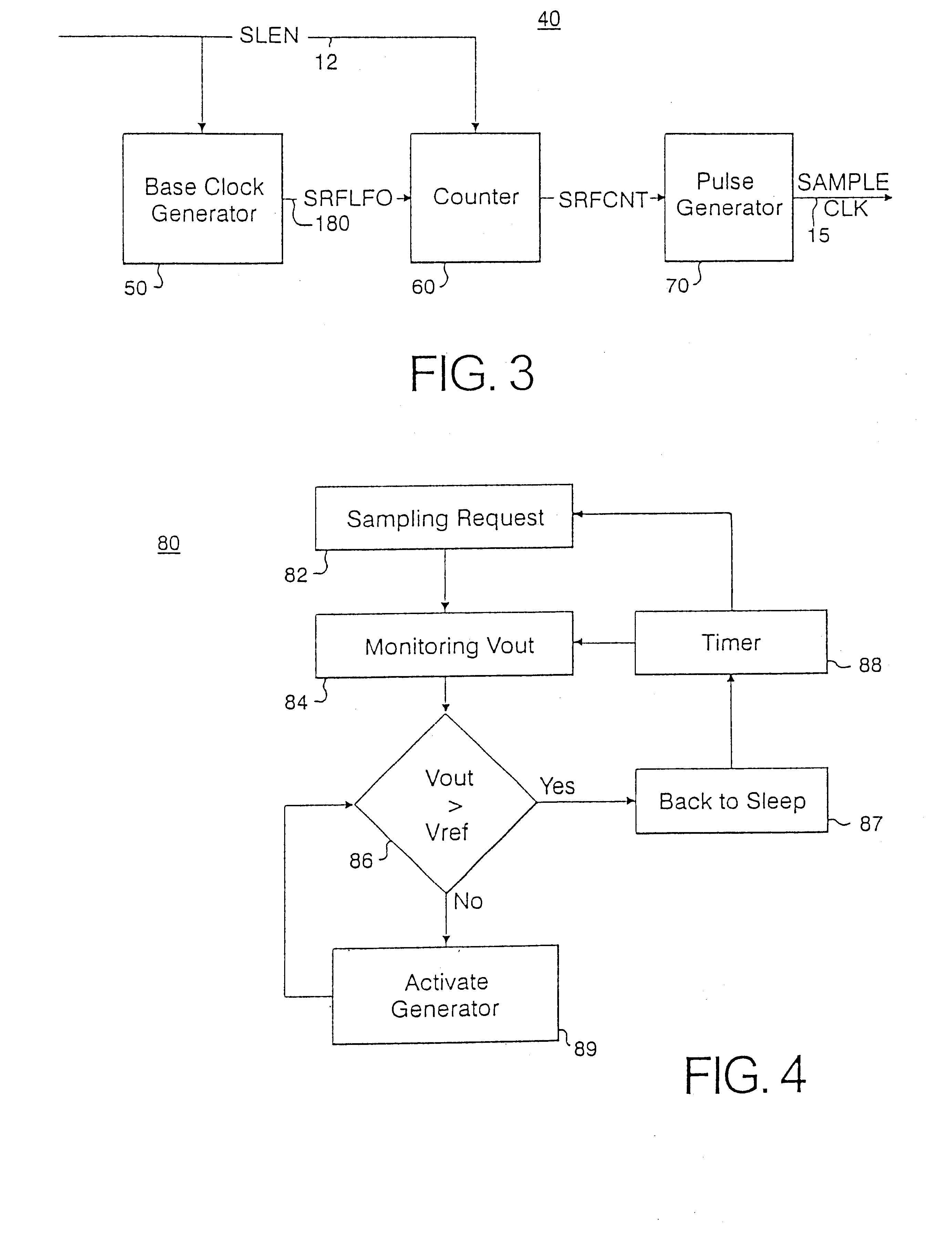
Self-refresh on-chip voltage generator
InactiveUS6411157B1Lower Level RequirementsReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityVoltage generator
A voltage control system and methodology for maintaining internally generated voltage levels in a semiconductor chip. The method comprises the steps of intermittently sampling an internal voltage supply level during a low power or "sleep" mode of operation; comparing the internal voltage supply level against a predetermined voltage reference level; and, activating a voltage supply generator for increasing the internal voltage supply level when the internal voltage supply level falls below the predetermined voltage reference level. The voltage supply generator is subsequently deactivated when the voltage supply level is restored to the predetermined voltage reference level. The sampling cycle may be appropriately tailored according to chip condition, chip temperature, and chip size. In one embodiment, the voltage control system and methodology is implemented in DRAM circuits during a refresh operation. The voltage levels that are suitable for sampling including DRAM band-gap reference voltage, boost wordline line voltage, wordline low voltage, bitline high voltage and bitline equalization voltages.
Owner:IBM CORP
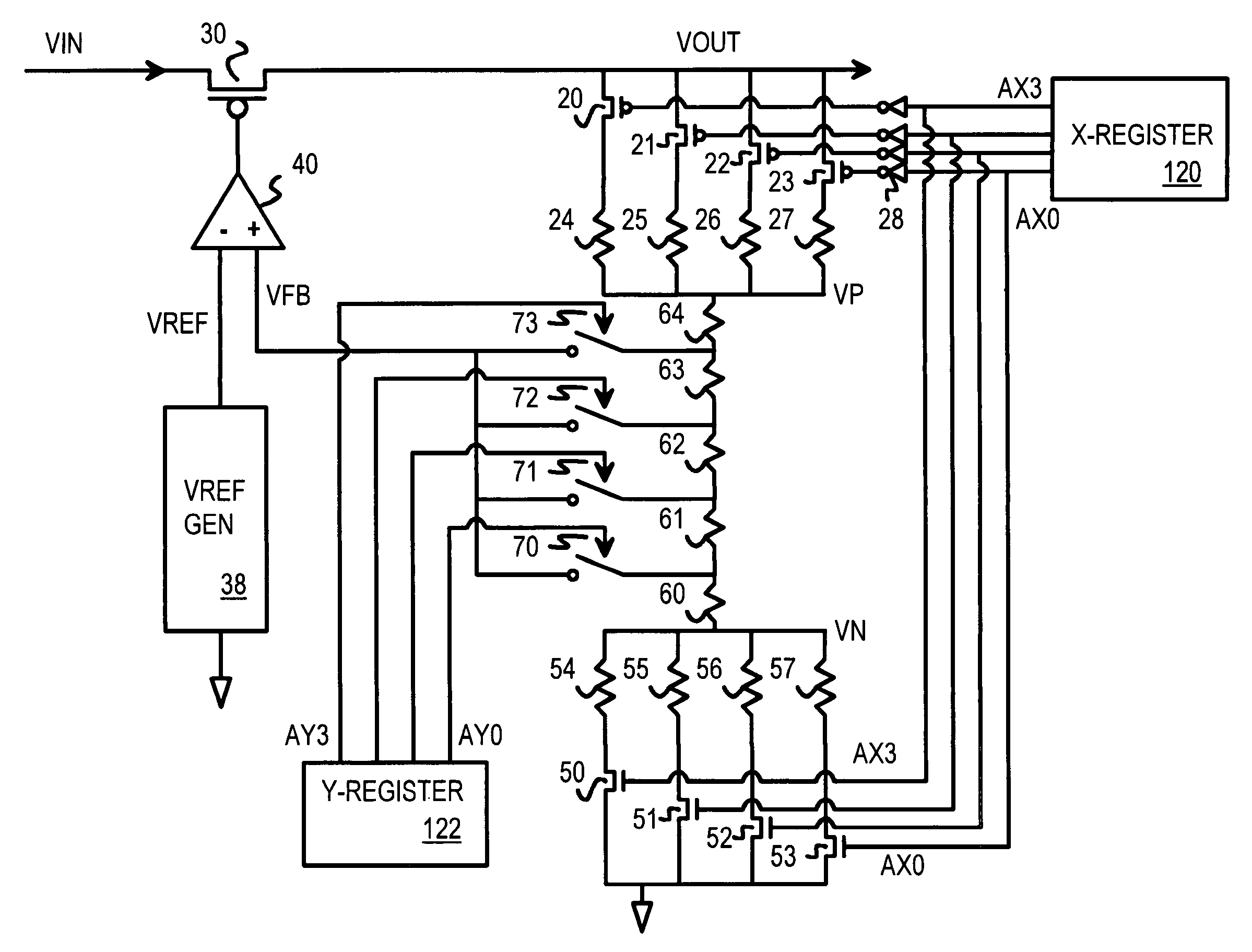
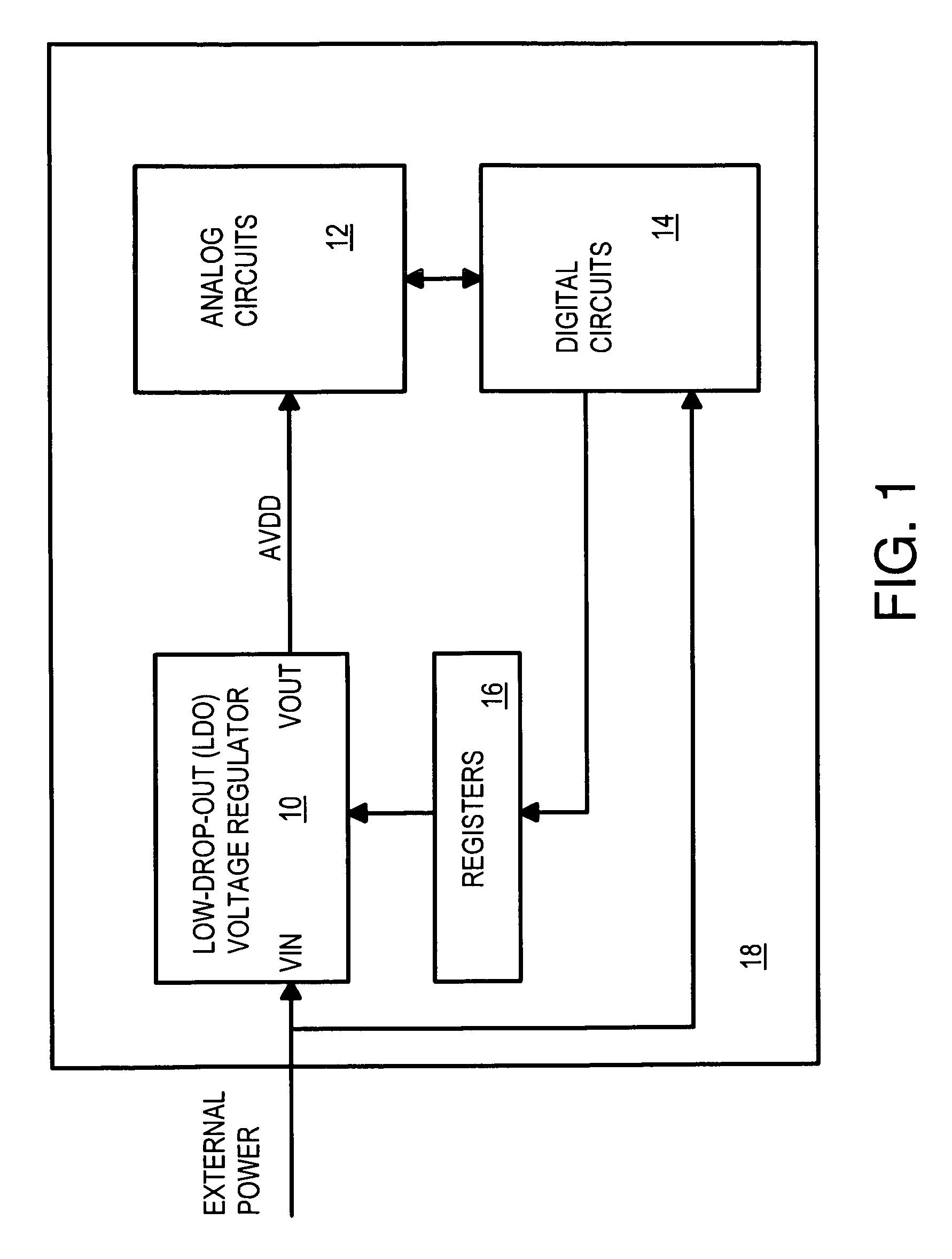
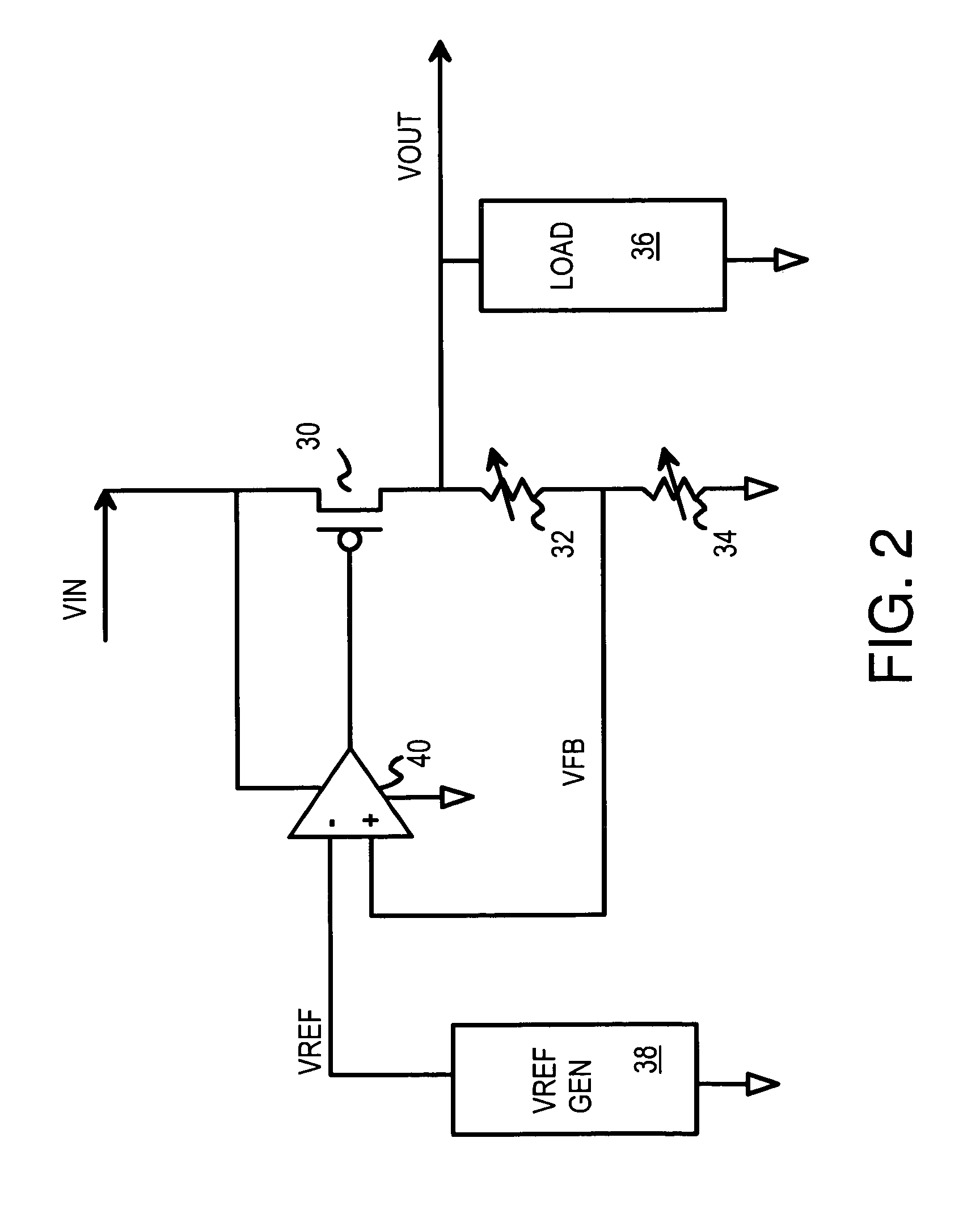
Low dropout voltage regulator with programmable on-chip output voltage for mixed signal embedded applications
ActiveUS7619402B1Multiple-port networksOne-port networksElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage generator
A programmable voltage generator has software-programmable registers that may be decoded to generate control bits that turn on select transistors that control a variable resistor network. An external power voltage is input to a regulator transistor, which has a channel resistance controlled by a gate voltage. The channel resistance of the regulator transistor produces a regulated voltage as an output. An op amp compares a reference voltage to a feedback voltage to generate the gate voltage. The feedback voltage is taken from a tap within the variable resistor network. The variable resistor network has select transistors that select one resistor between the regulated voltage and an upper node, and that select one resistor between a lower node and ground. Switches select a tap within a series of resistors between the upper and lower nodes. Y (fine) control bits select the tap while X (coarse) control bits enable select transistors.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Apparatus and method for biasing a transducer
ActiveUS20100166228A1No unnecessary loadingLimiting stepSemiconductor electrostatic transducersApparatus without intermediate ac conversionVoltage generatorMems microphone
An apparatus comprising a capacitive transducer, for example a MEMS microphone. A first voltage generator is connected to receive a first voltage (VDD*) and generate a second voltage (VCP) for biasing the capacitive transducer. A control circuit is adapted to, in use, control the first voltage (VDD*) based on a calibration value, wherein a different calibration value would lead to a different first voltage level and the calibration value is set such that an input signal of known amplitude produces an output signal of predetermined amplitude.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
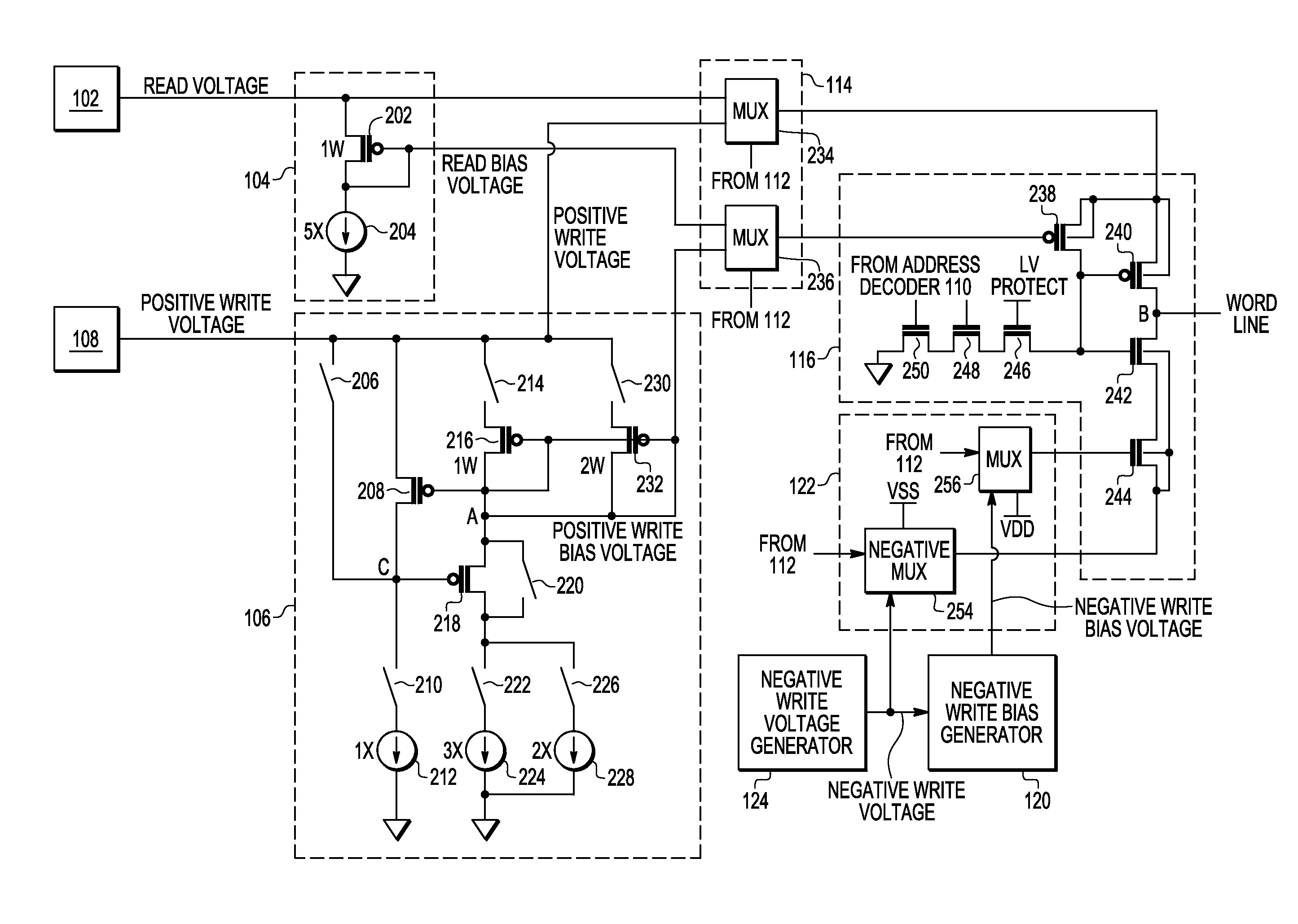
Flash memory with bias voltage for word line/row driver
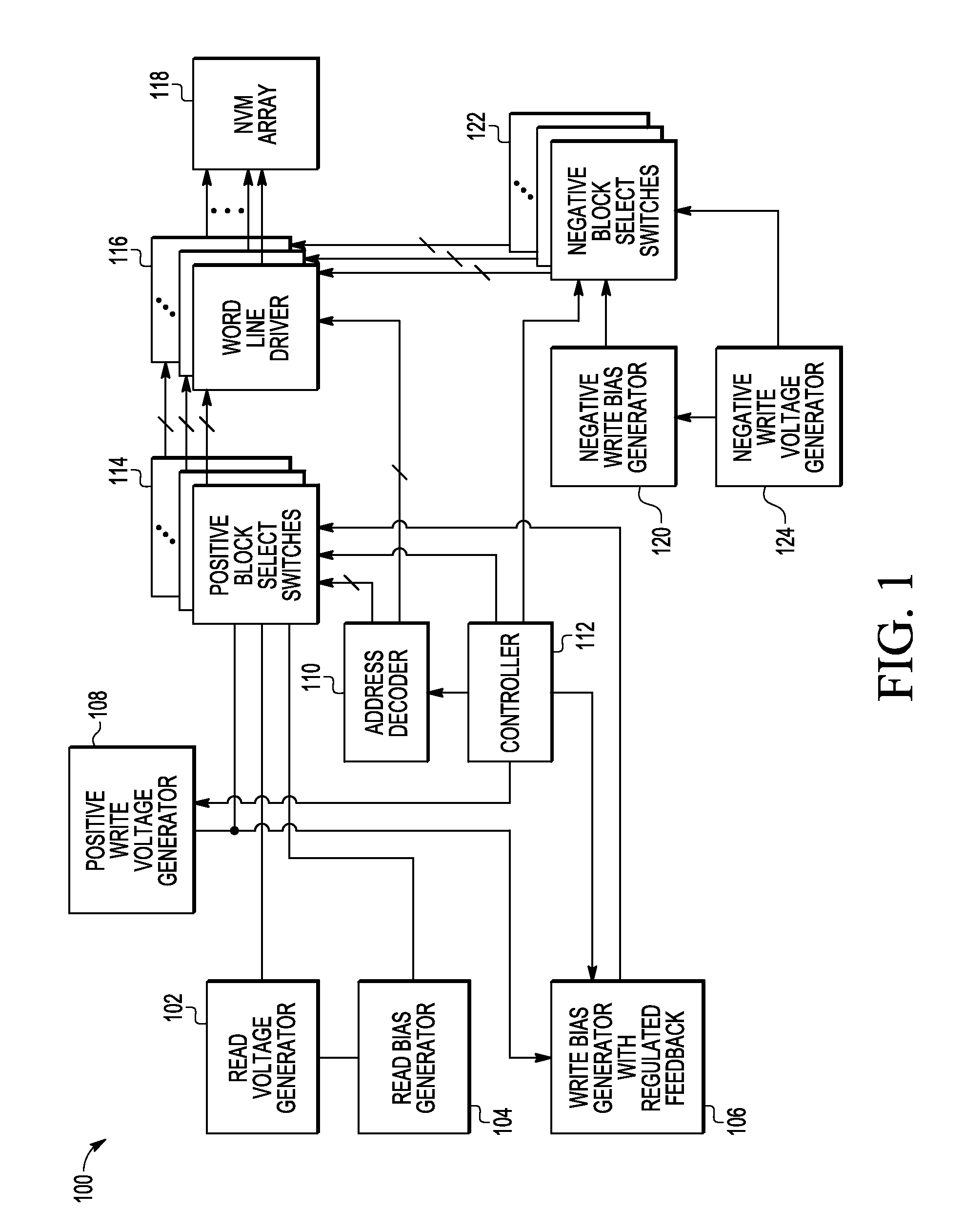
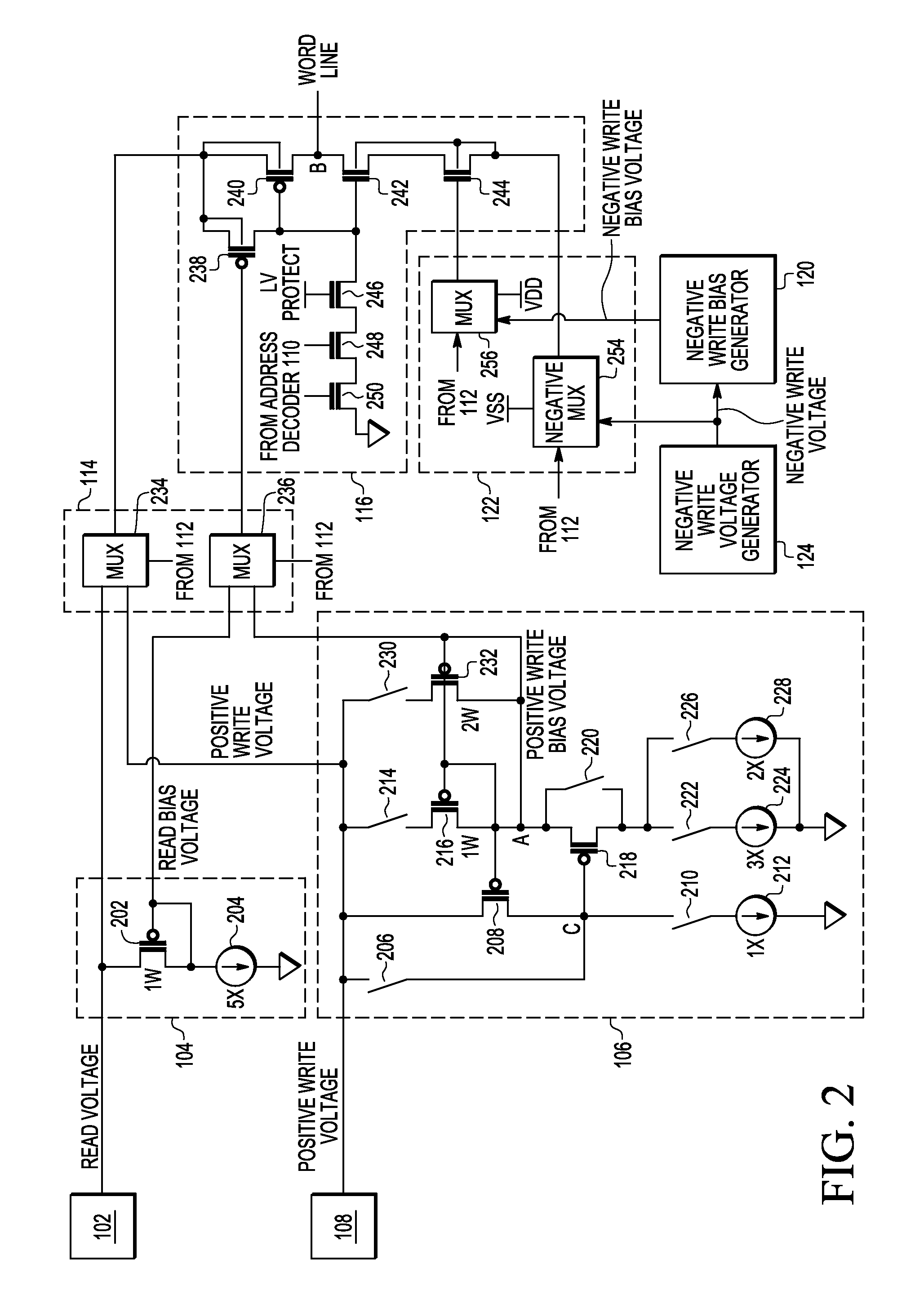
A memory device includes a word line driver circuit, a write voltage generator for providing a write voltage to the word line driver during a write operation to memory cells coupled to the word line driver circuit, and a write bias generator including an output node for providing a write bias voltage that is different from the write voltage to the word line driver circuit during a write operation to memory cells coupled to the word line driver circuit. The write bias voltage is used to reduce current drawn by the word line driver circuit from the write voltage generator during a write operation to memory cells coupled to the word line driver circuit.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Programmable impedance control circuit
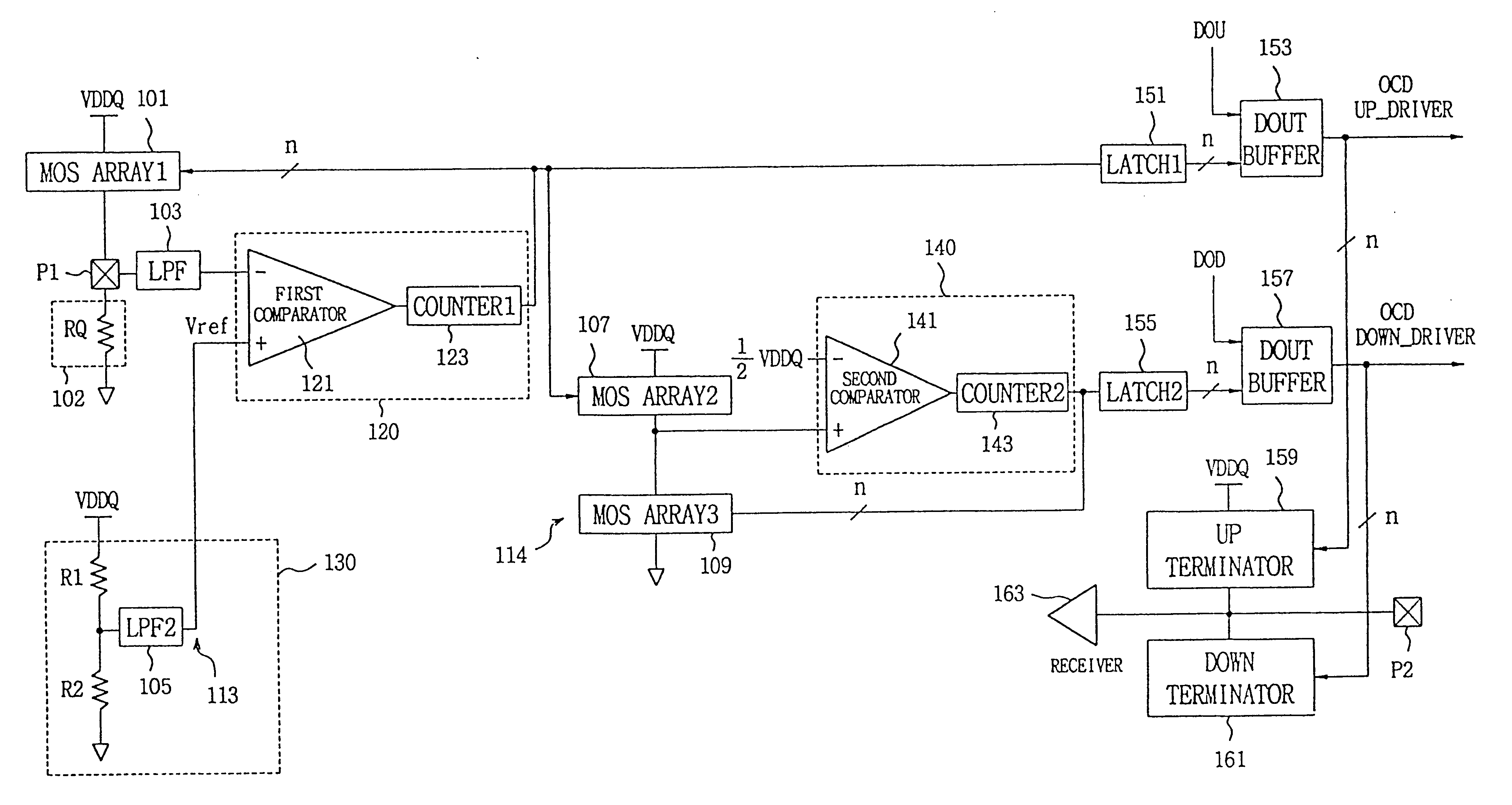
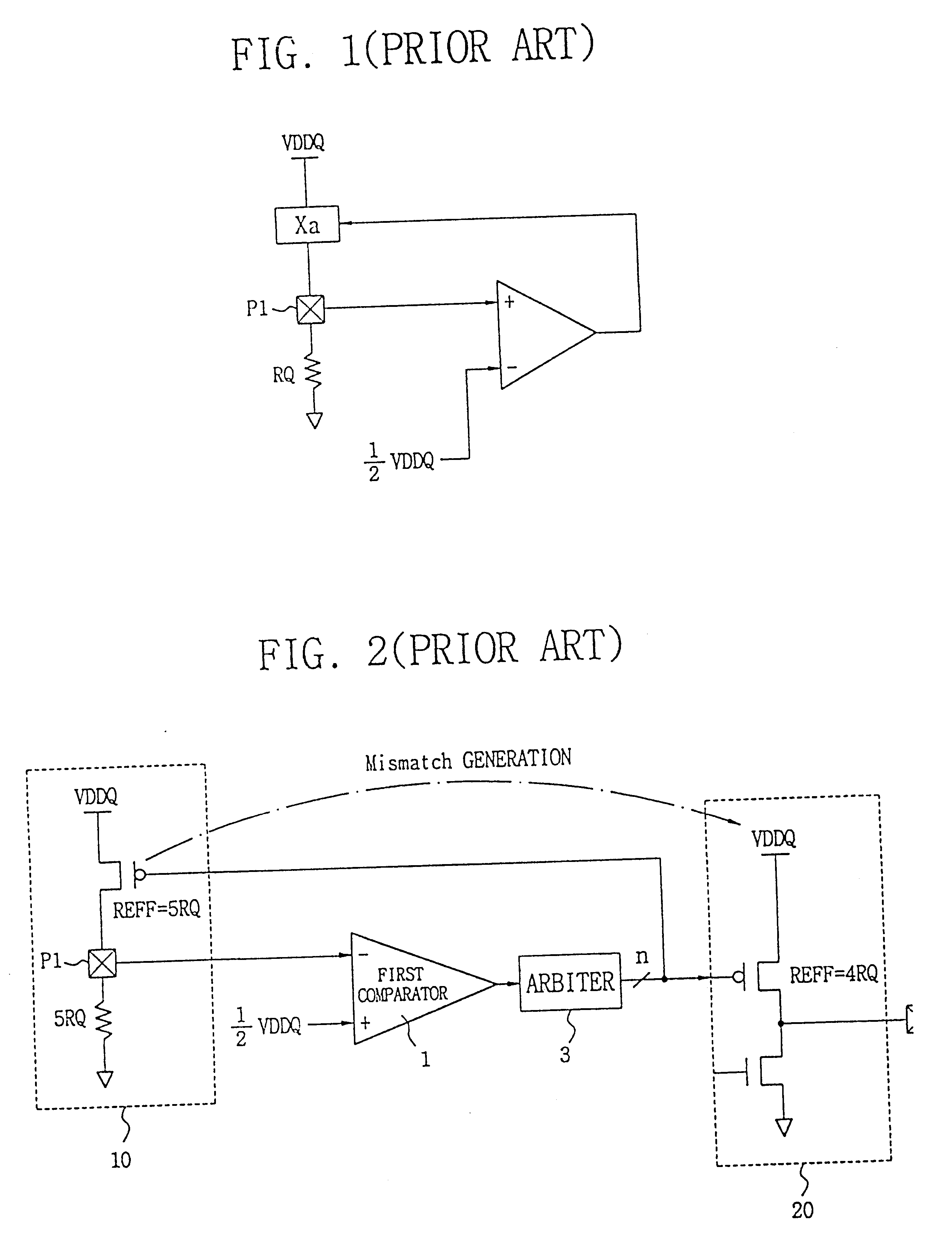
InactiveUS6525558B2Multiple-port networksImpedence matching networksElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage generator
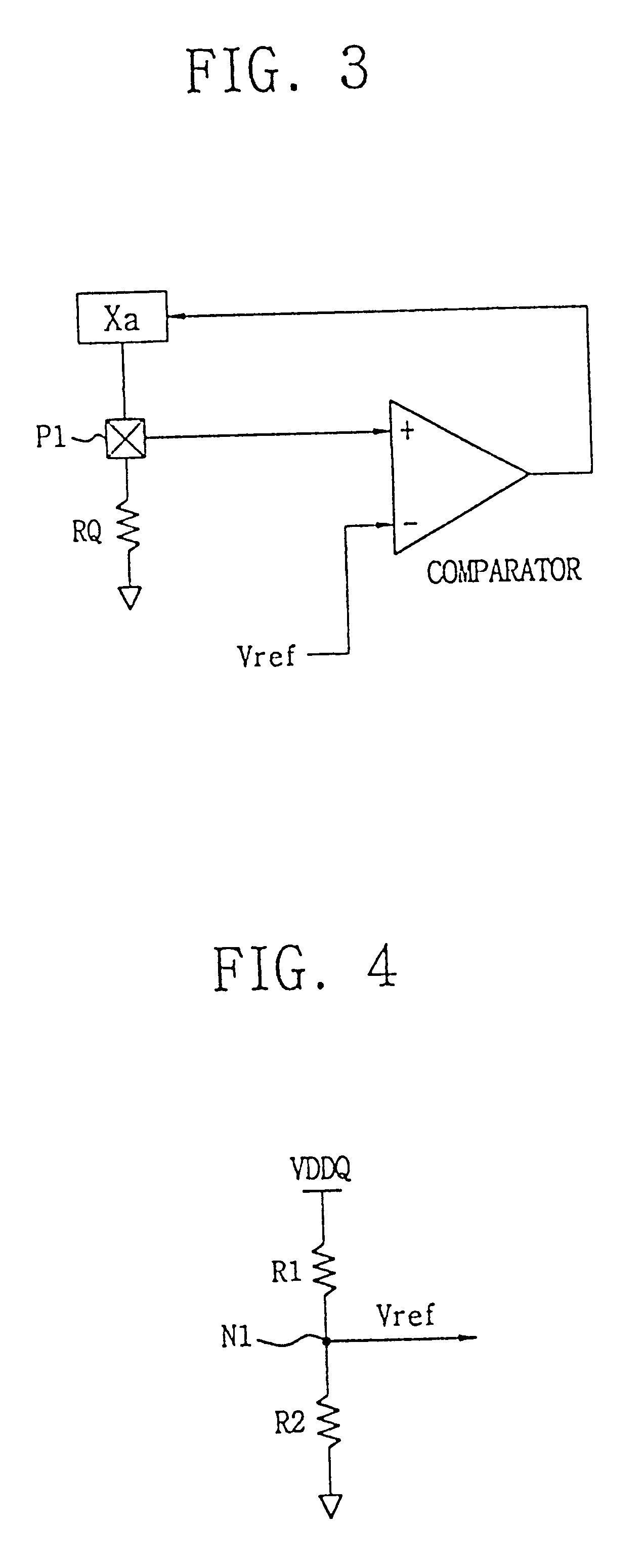
Disclosed is a programmable impedance control circuit, comprising a voltage divider, the voltage divider comprising an MOS array supplied with a first voltage and an external resistance having an external impedance equal to N times said external resistance. The voltage divider outputs a second voltage. A reference voltage generator is provided for generating a third voltage corresponding to N / (N+M) times said first voltage as a reference voltage for said second voltage, and wherein M times internal impedance is used for N times external impedance (N=M or N<> M).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Liquid Crystal Display Device and Driving Method Thereof
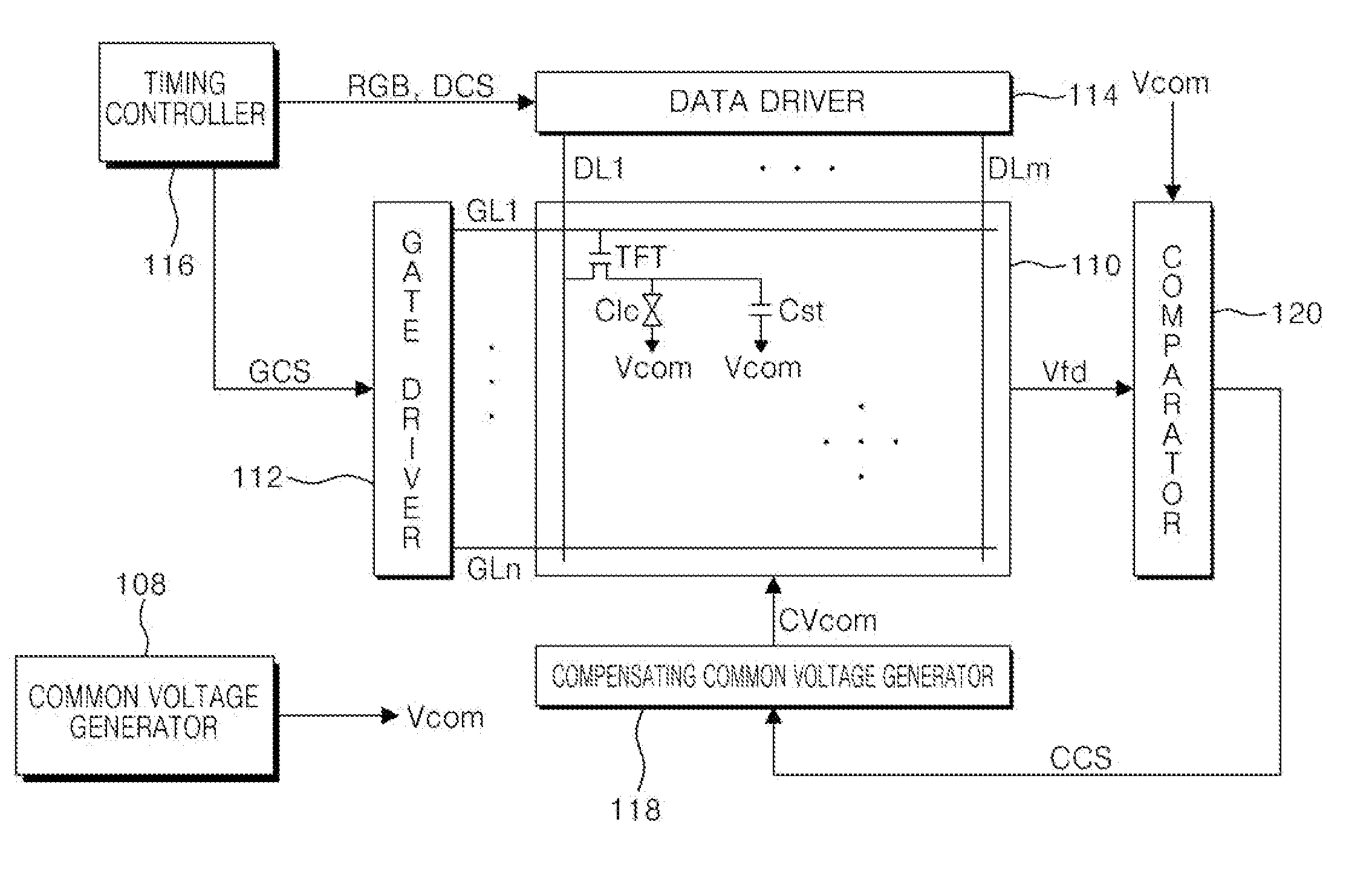
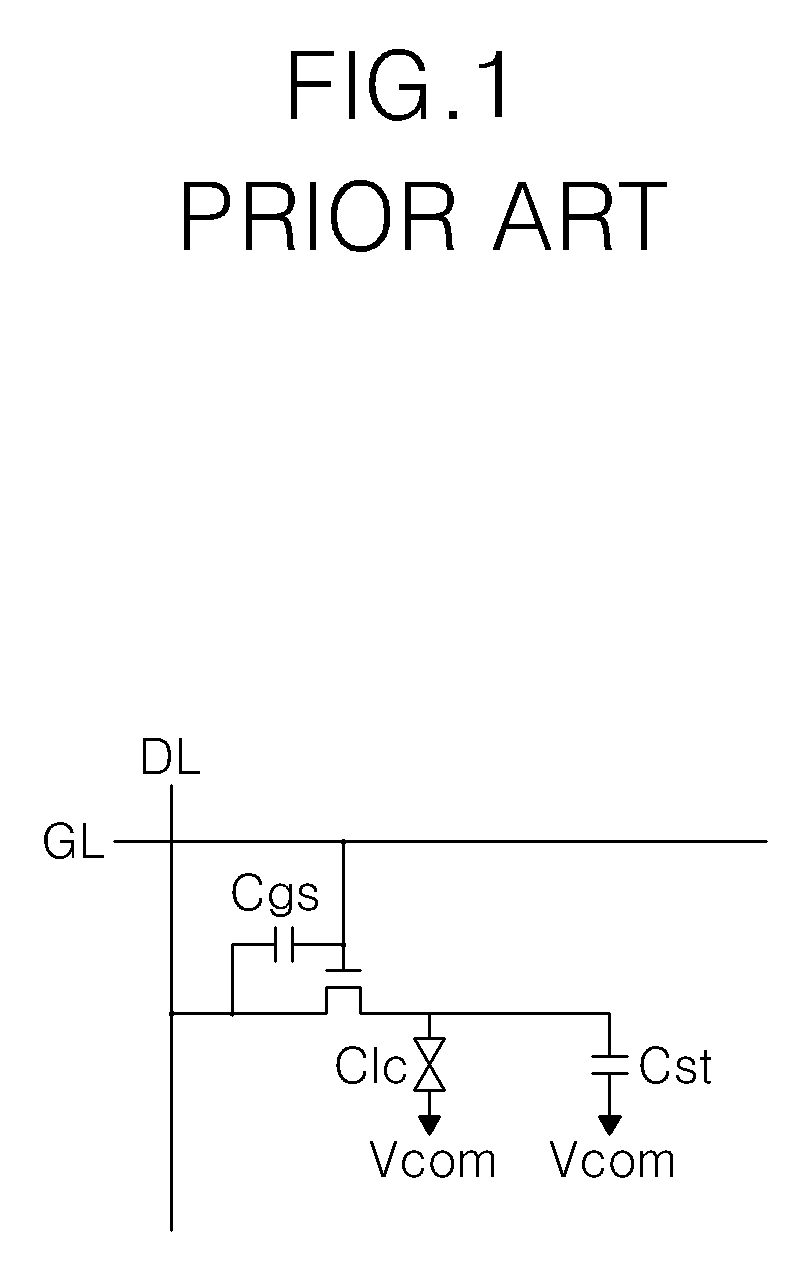
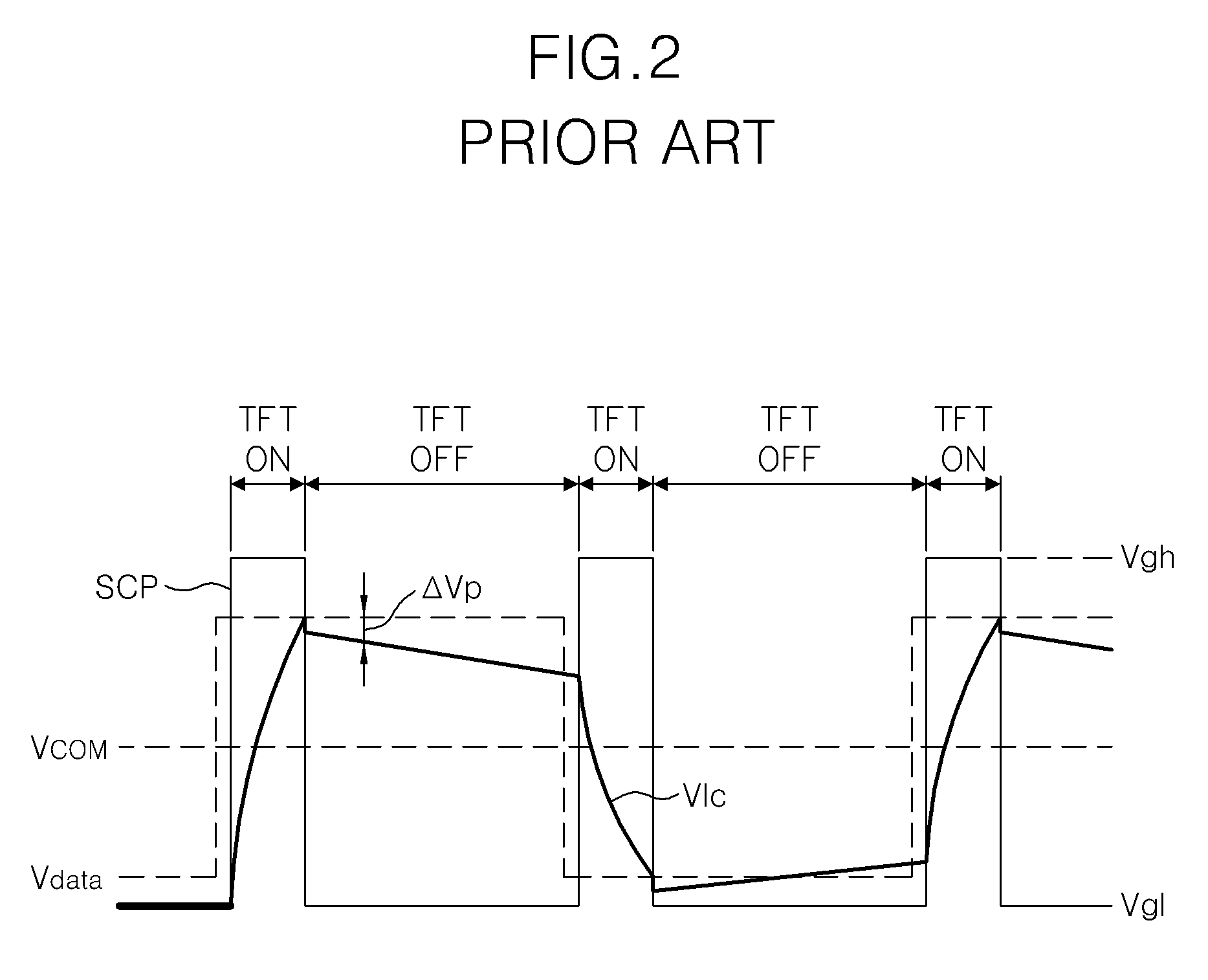
InactiveUS20070024560A1Minimizing deteriorationStatic indicating devicesVoltage generatorImage quality
Disclosed is a liquid crystal display (LCD) device which is capable of minimizing deterioration in picture quality caused by a kickback voltage, and a driving method thereof. The LCD device includes an LCD panel having a plurality of liquid crystal cells to which a pixel voltage signal is supplied, and a compensating common voltage generator for generating different compensating common voltages according to a pixel voltage signal which is fed back from the LCD panel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
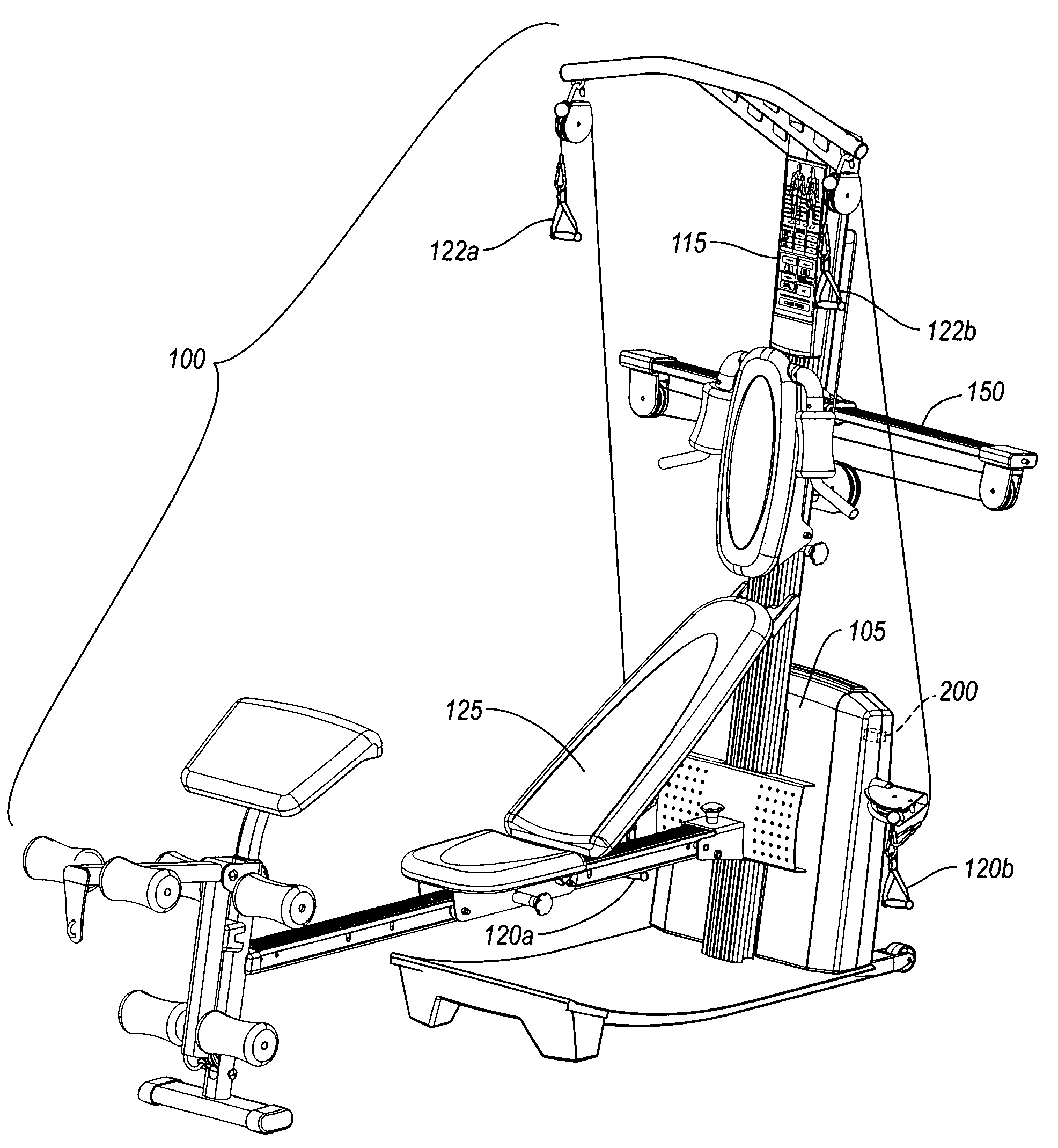
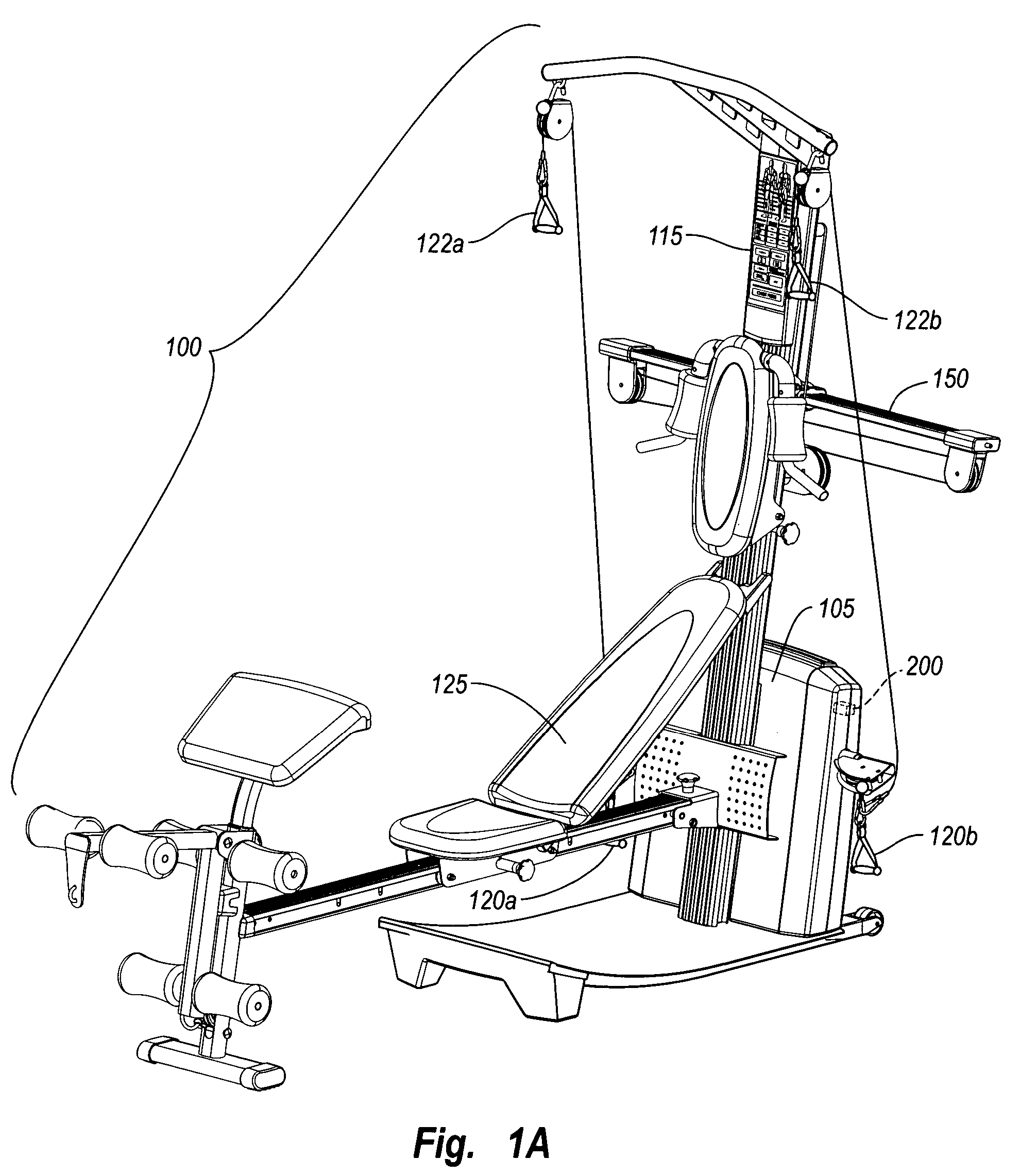
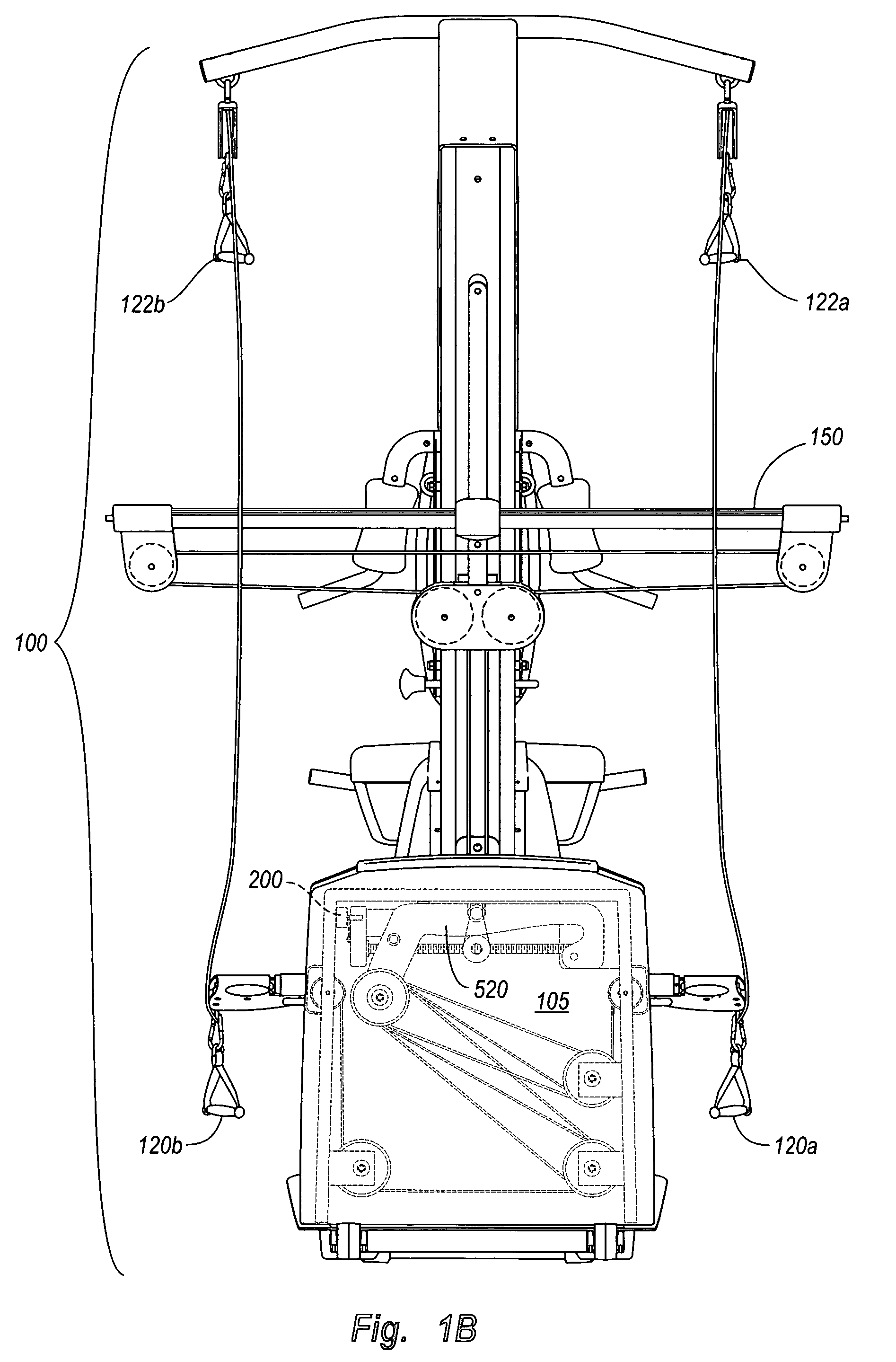
Repetition sensor in exercise equipment
ActiveUS7628737B2Accurately monitor shortDetection speedClubsResilient force resistorsSports equipmentEngineering
An exercise repetition sensor comprises an electricity generator, such as an electricity generator, which is coupled to an exercise system, where the electricity generator is capable of sensing exercise movements of any size or intensity on the exercise system. The electricity generator can be based on a number of electrical, magnetic, or optical sensing principles. For example, an electricity generator comprising an electricity generator includes a spindle that is coupled to one or more parts that move in proportion to an applied force. The voltage-generator generates an electrical current as the spindle moves, and sends the electrical current to an electronic display interface. In one embodiment, the voltage-generator sends a positive direct current through one of two circuit wires to the electronic console, such that the electronic console can immediately identify that the user has performed an exercise repetition.
Owner:IFIT INC
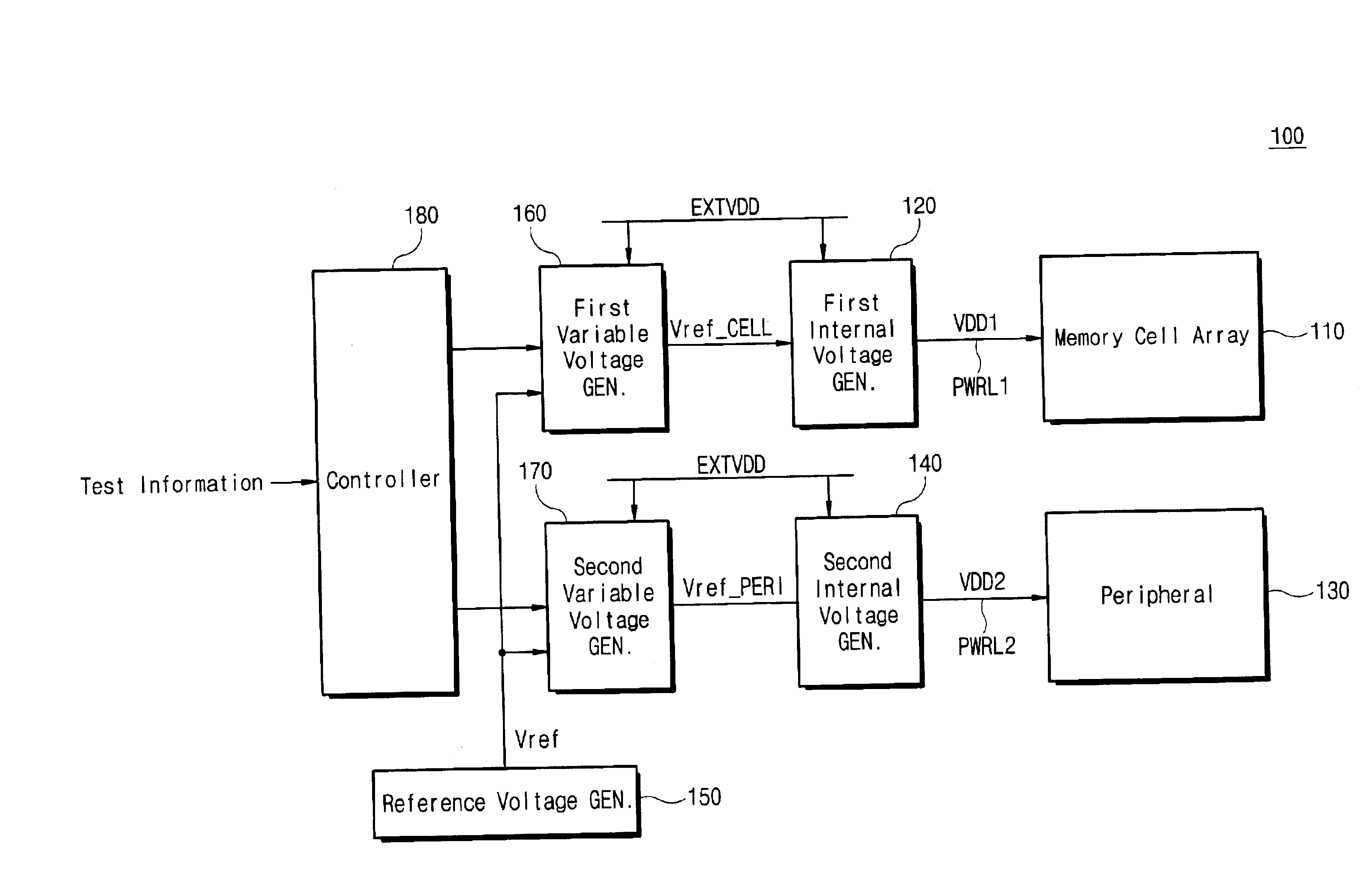
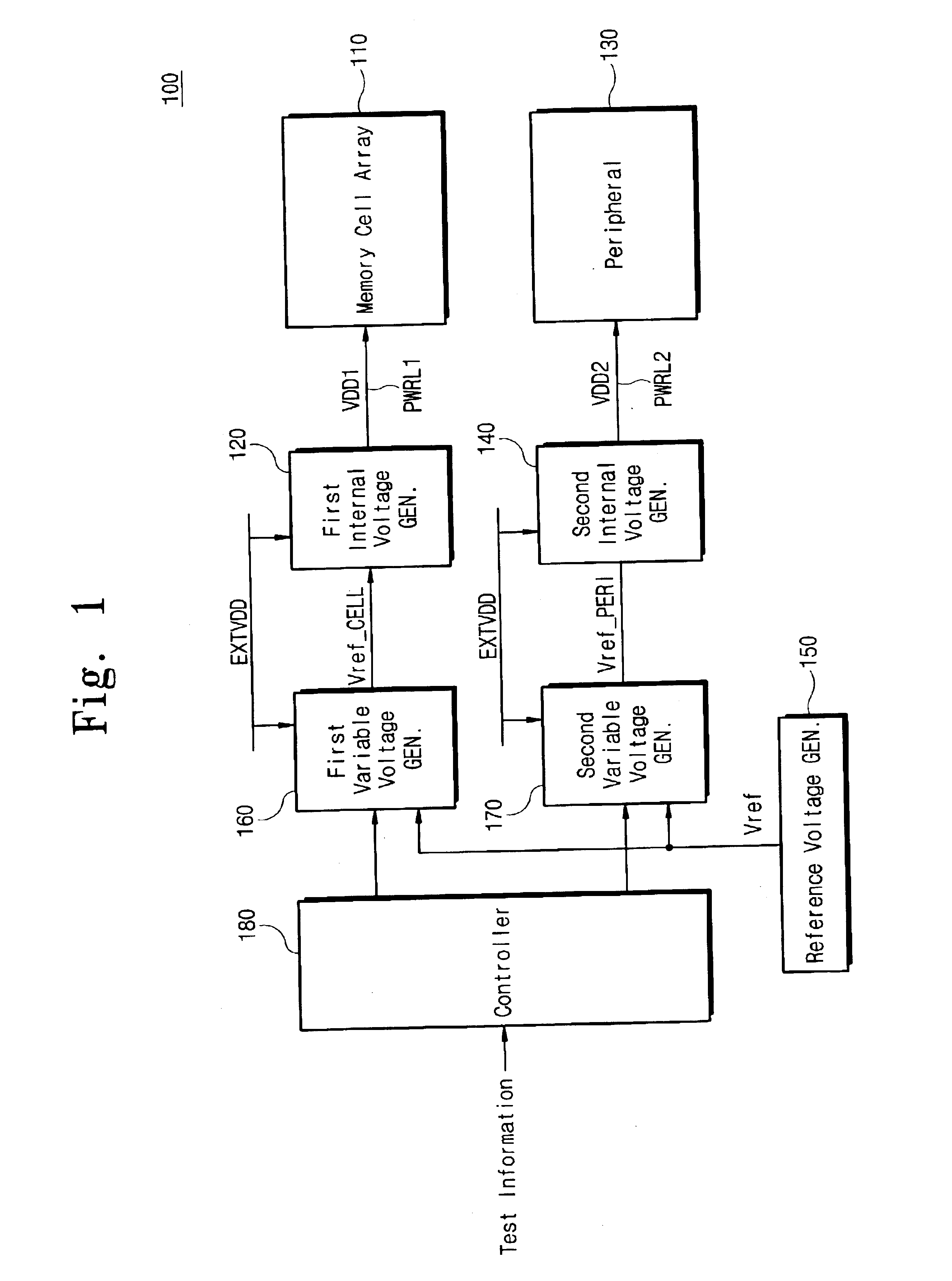
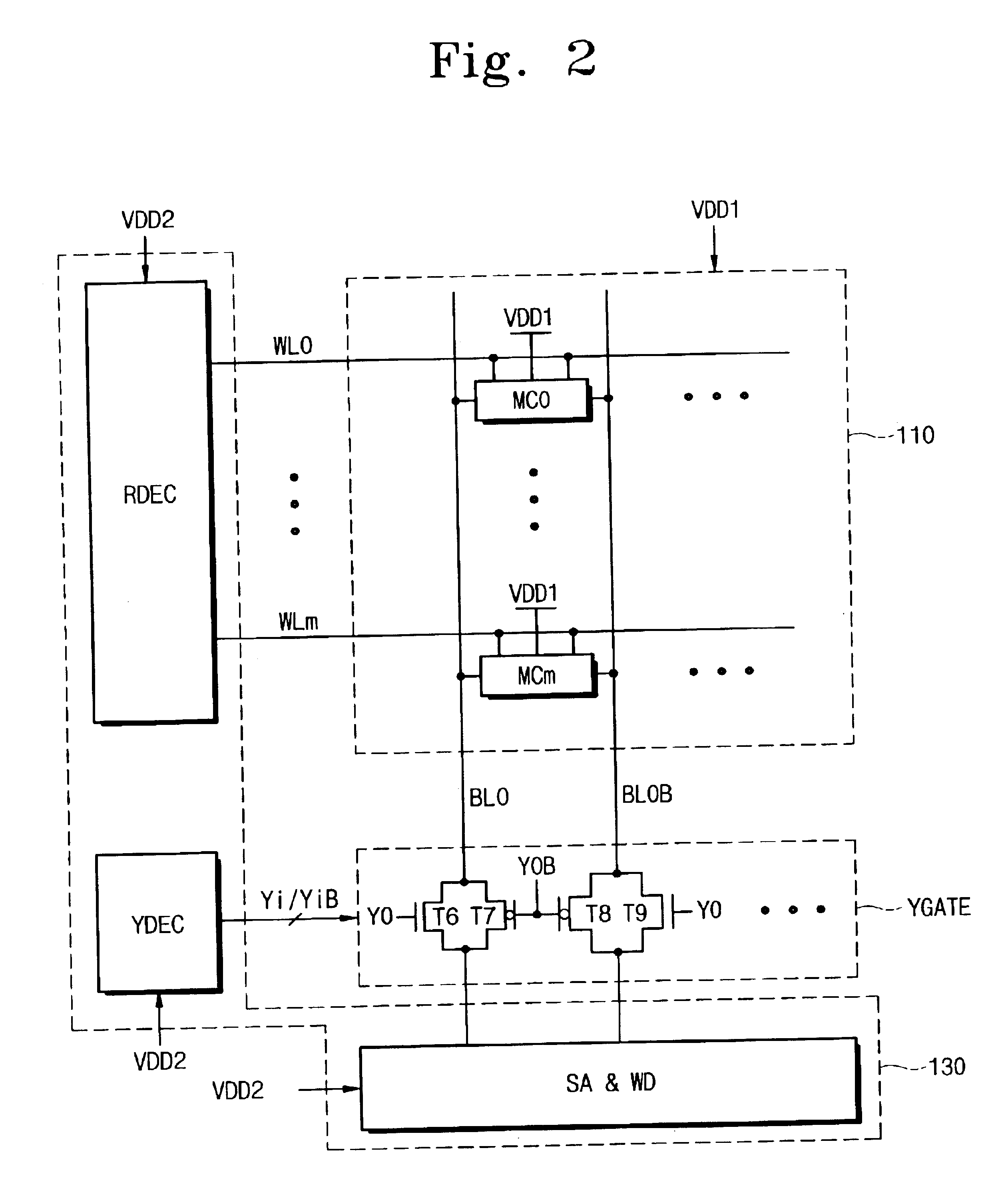
Semiconductor memory device with internal voltage generators for testing a memory array and peripheral circuits
A semiconductor memory device which includes an internal voltage generator circuit for adjusting an external power supply voltage and generating first and second internal power supply voltages. The first internal power supply voltage is supplied to a memory cell array via a first power supply line, and the second internal power supply voltage is supplied to a peripheral circuit via a second power supply line. A control circuit controls the internal voltage generator circuit so that the levels of the first and second internal power supply voltages vary depending on a mode of operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for manipulation of cells and cell-like structures focused electric fields in microfludic systems and use thereof
InactiveUS7018819B2Understand natureOvercomes shortcomingHybrid cell preparationOther foreign material introduction processesVoltage generatorEngineering
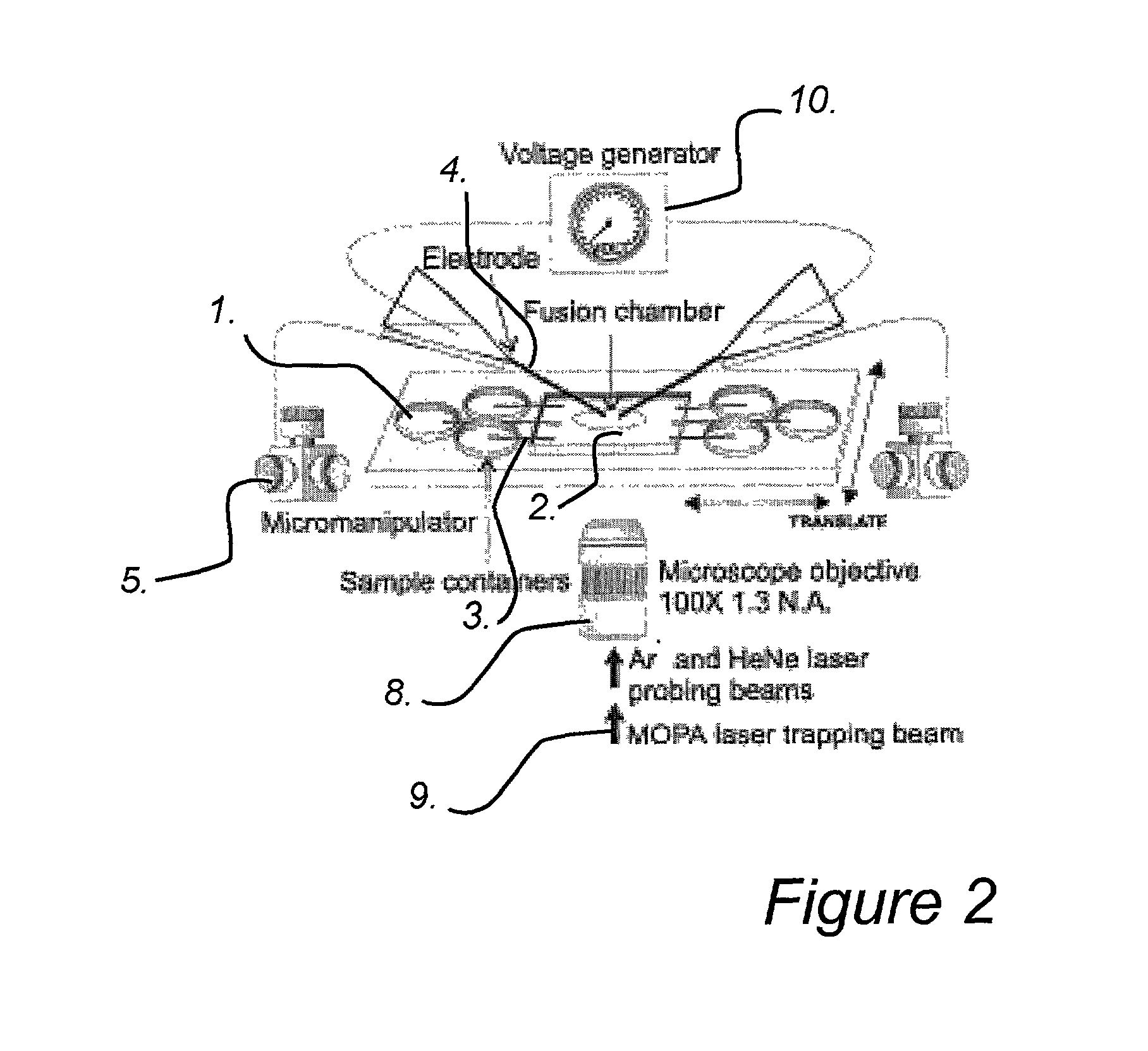
An apparatus and method are disclosed for electromanipulation of at least one cell or cell-like structure having cell-like membranes, the method comprising the steps: (a) at least one cell or cell-like structure is transported from one or more sample containers located on a chip through microchannel(s) located on said chip into a chamber located on said chip, wherein said chamber contains electrode(s) connected to a voltage generator, wherein said microchannel provides a fluid contact between the sample containers, (b) said cell or cell-like structure(s) is placed close to said at least one electrode, and (c) an electrical field is applied and focused on said cell or cell-like structure(s), said electrical field being of a strength sufficient to obtain pore-formation or fusion of said at least one cell or cell-like structure with another cell or cell-like structure(s) present in said chamber.
Owner:CELLECTRICON
Liquid crystal display, driving apparatus, digital-analog converter and output voltage amplifier thereof
InactiveUS8294657B2Reduce areaLow costCathode-ray tube indicatorsDifferential amplifiersVoltage generatorAudio power amplifier
The present invention relates to a liquid crystal display, a driving device thereof, a digital to analog converter, and an output voltage amplifying circuit. The present invention provides a liquid crystal display driving device including a reference gray voltage generator for generating a plurality of reference gray voltages, and a data driver for generating a plurality of gray voltages based on the plurality of reference gray voltages and applying a data signal that is generated by selecting a gray voltage corresponding to m-bit video signals applied from the outside from among the plurality of gray voltages to the pixel The data driver includes: a voltage generator for selecting a first gray voltage and a second gray voltage corresponding to bit values of (m−k) bits from among the video signal from among the plurality of gray voltages, and outputting the first and second gray voltages; an output voltage generator for outputting 2k voltages determined as one of the first and second gray voltages corresponding to bit values of k bits from among the video signal; and an output voltage amplifier for generating the data signal by combining the 2k voltages, and applying the data signal to a plurality of pixels. According to the present invention, a liquid crystal display having a small cost and area can be realized.
Owner:MC TECH CO LTD
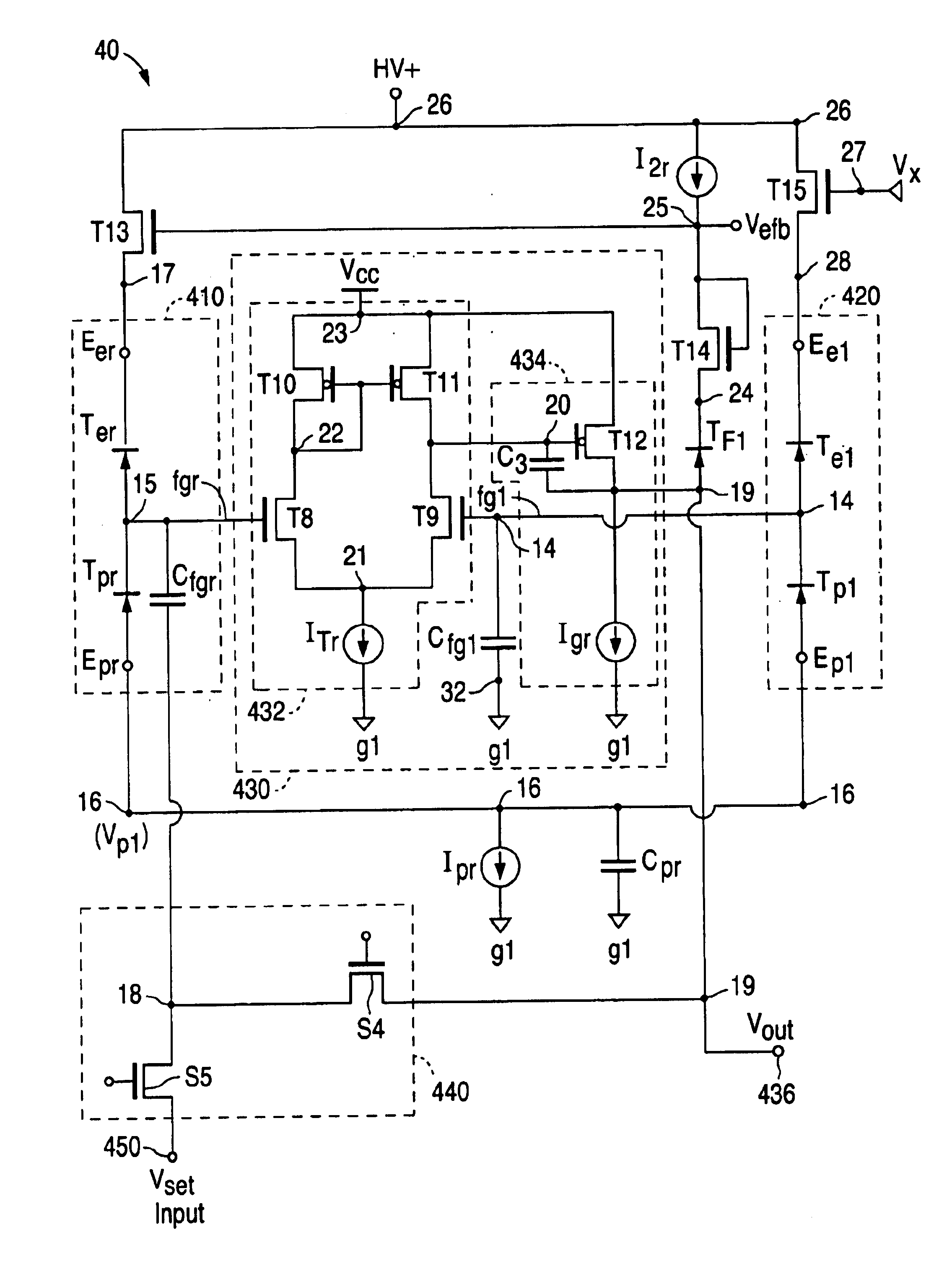
Output voltage compensating circuit and method for a floating gate reference voltage generator
An apparatus and method is provided for adjusting a reference voltage at an output terminal of a floating gate reference voltage generator circuit in order to improve the accuracy of the reference voltage at an input terminal of a load circuit. The apparatus and method compensates for the voltage drop produced between the output terminal of the reference voltage generator circuit and the input terminal of the load circuit, and includes a capacitor for capacitively coupling the voltage at the input terminal of said load circuit to a floating gate, and a differential amplifier operatively coupled to the floating gate which acts in response to the capacitively coupled load circuit input voltage to adjust the voltage at the output terminal such that the voltage at the input terminal of the load circuit becomes equal to the reference voltage.
Owner:XICOR
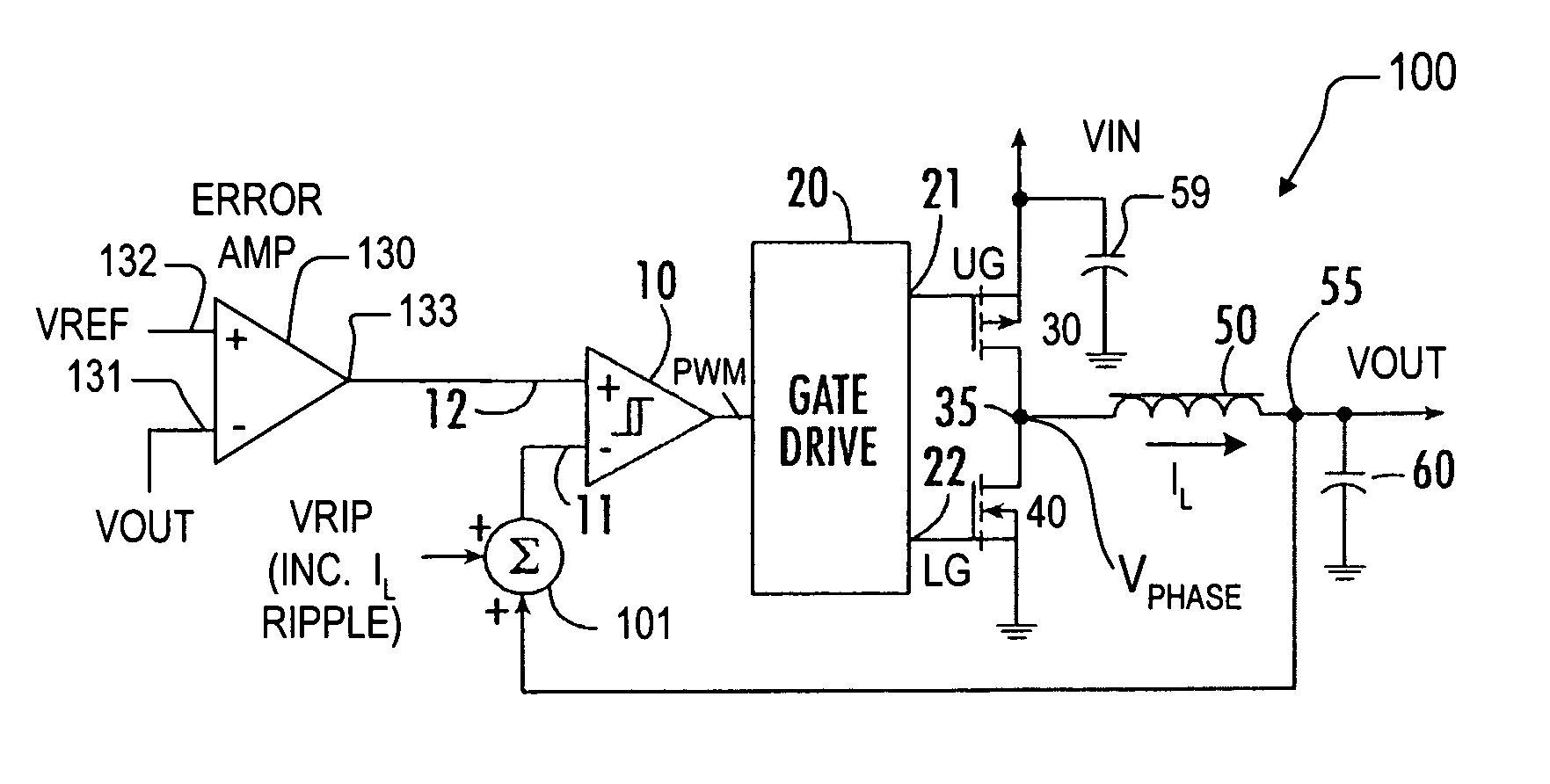
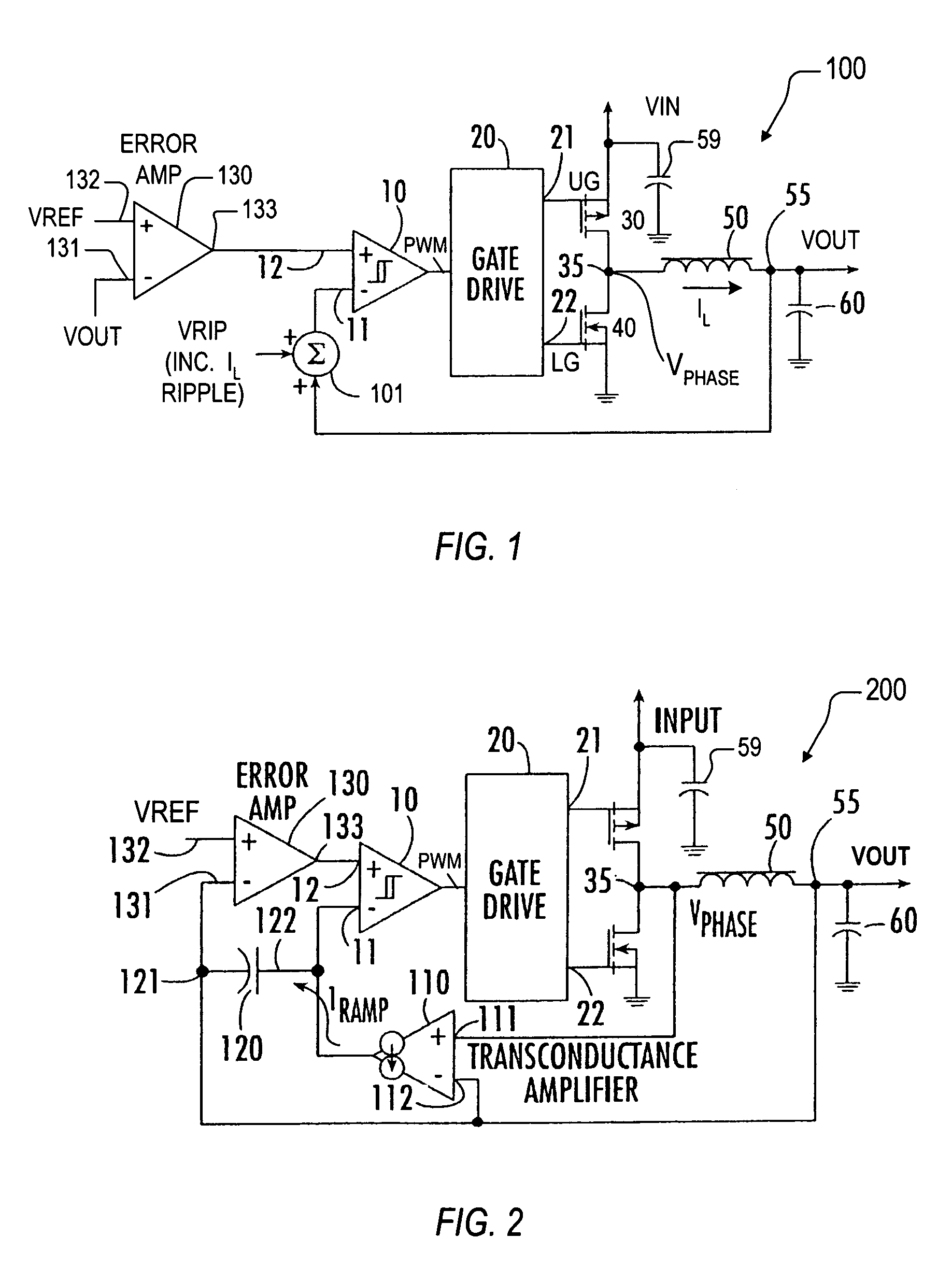
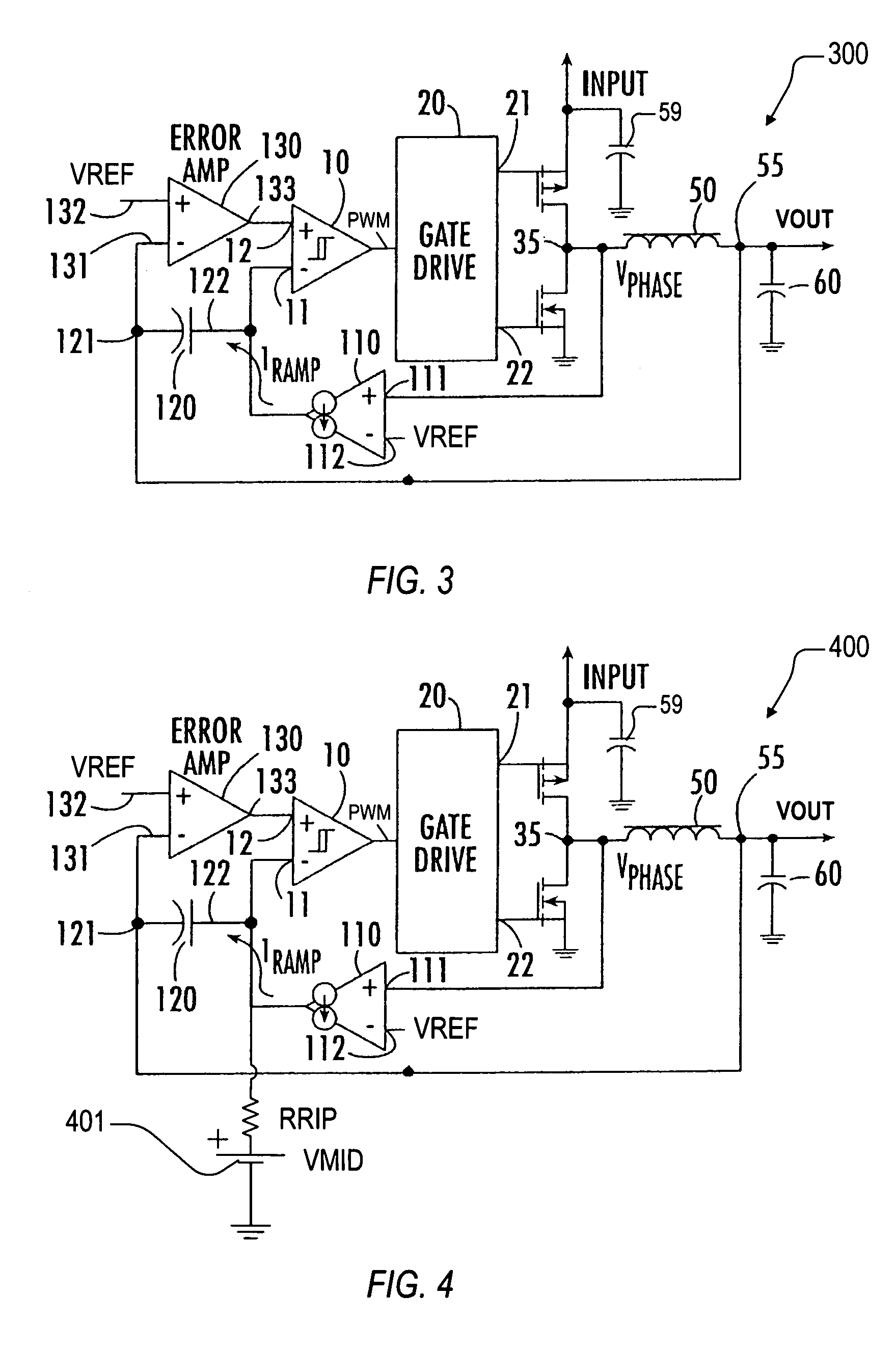
Synthetic ripple regulator
InactiveUS7132820B2Low output rippleCompensation is simpleDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationVoltage generatorInductor
A synthetic ripple regulator including a synthetic ripple voltage generator that generates a synthetic ripple voltage indicative of the ripple current through an output inductor. The regulator uses the synthetically generated ripple voltage to control toggling of a hysteretic comparator for developing the pulse width modulation (PWM) signal that controls switching of the regulator. In a non-limiting implementation, a transconductance amplifier monitors the phase node voltage of the inductor and supplies an inductor voltage-representative current to a ripple capacitor, which produces the synthetic ripple voltage. Using the replicated inductor current for ripple regulation results in low output ripple, input voltage feed forward, and simplified compensation.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com