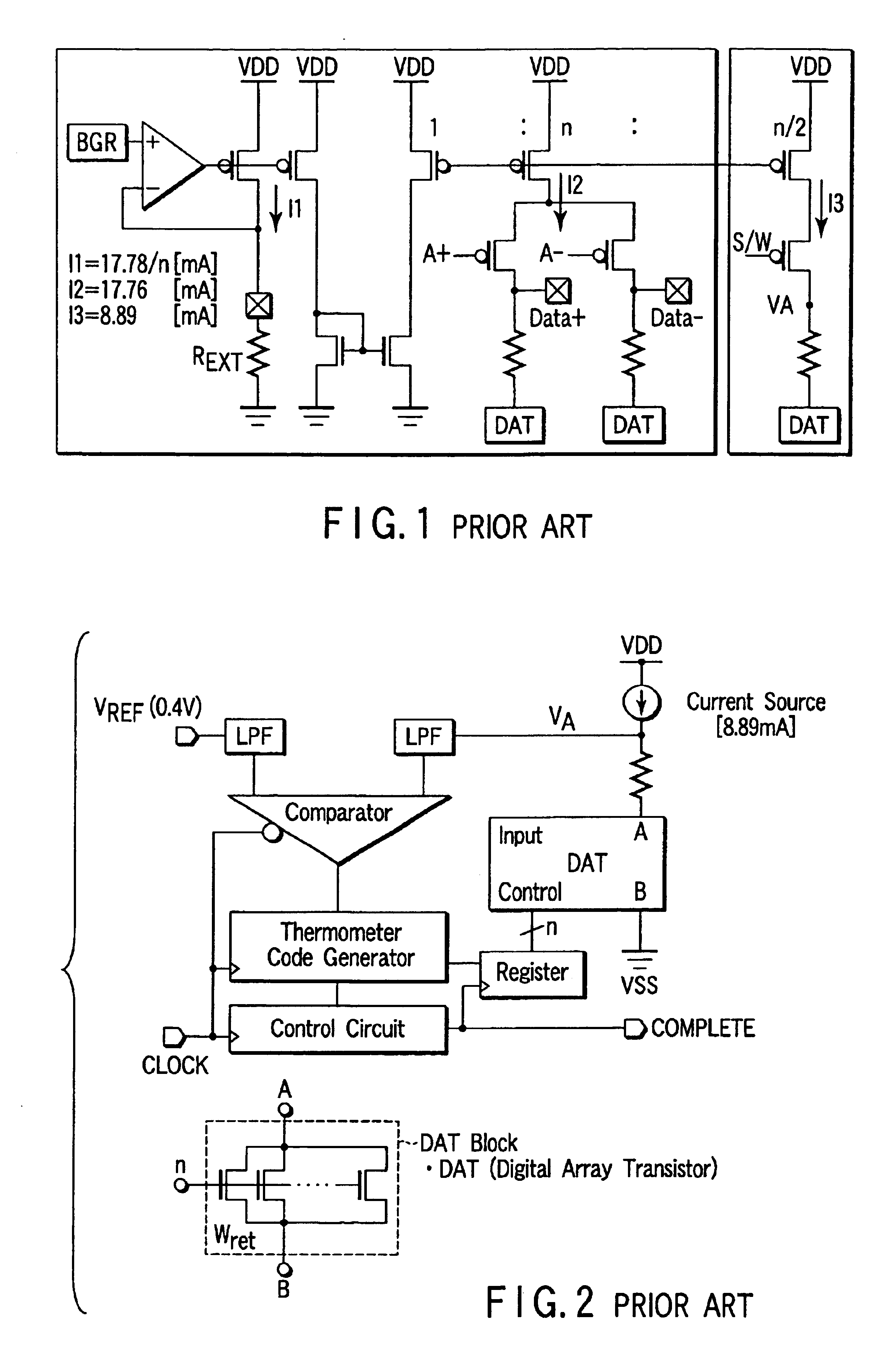
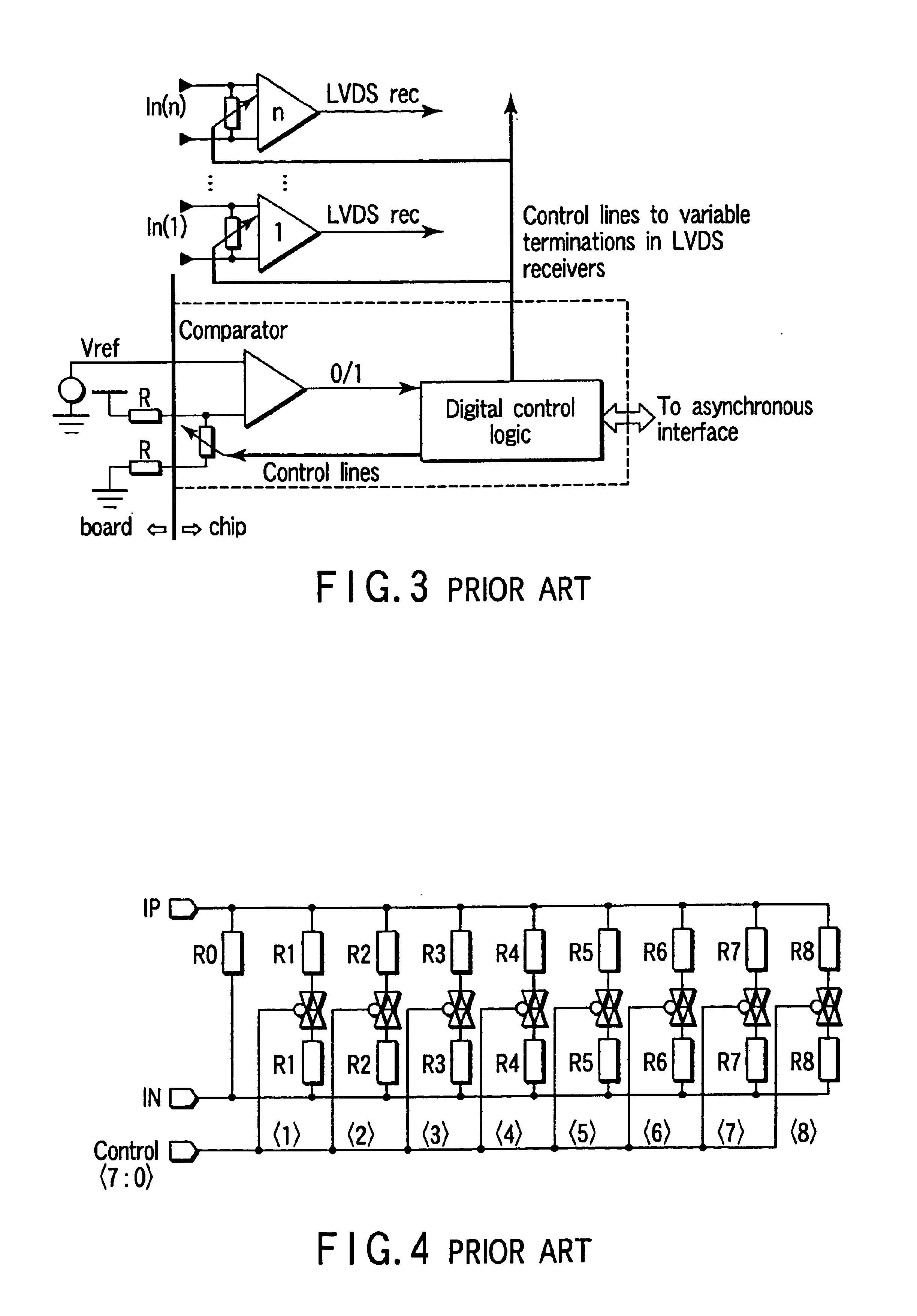
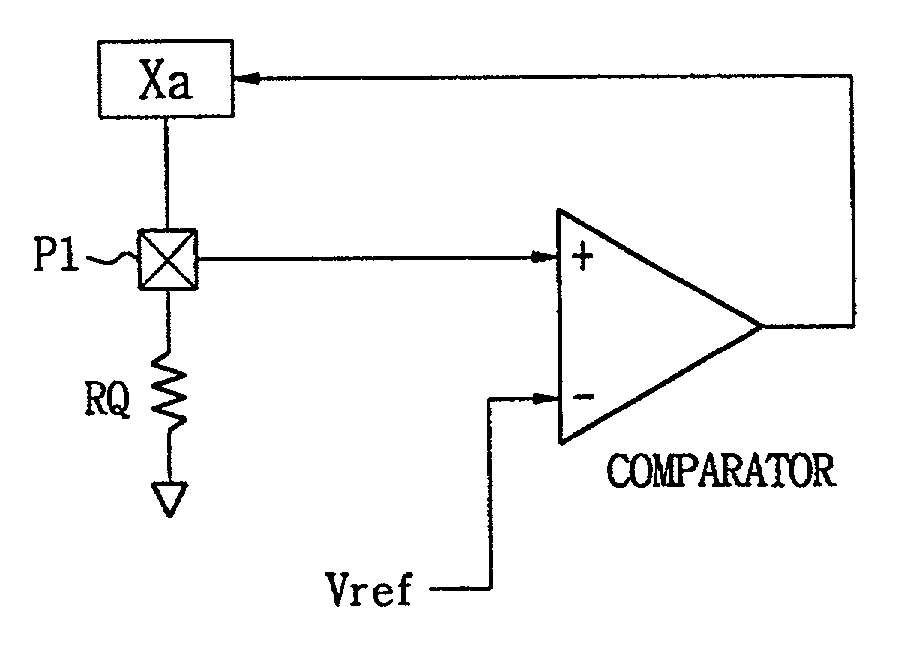
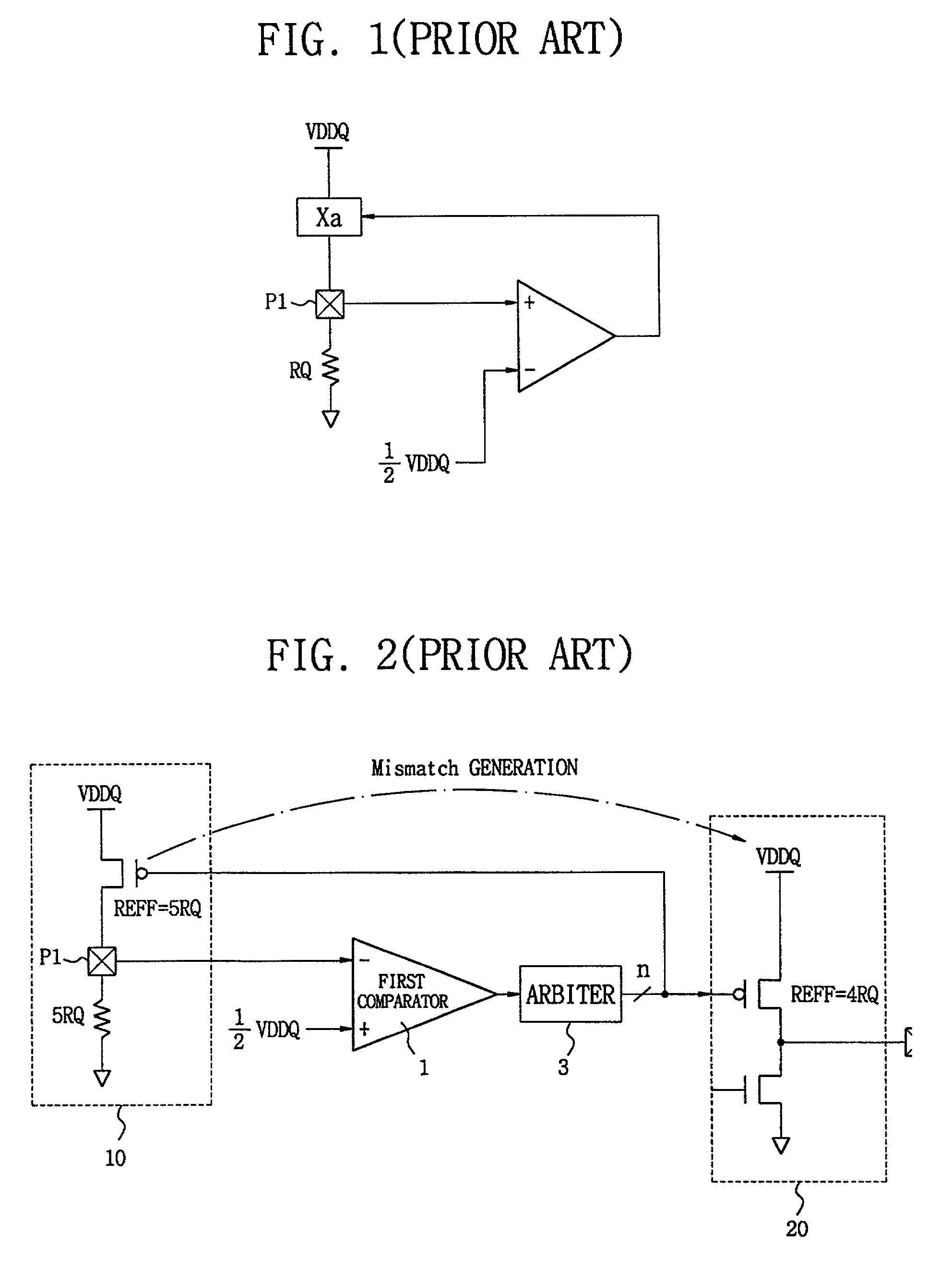
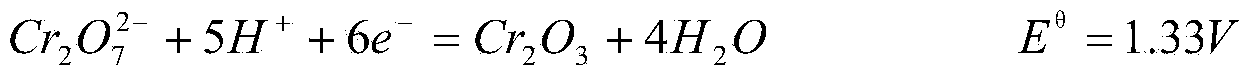Patents
Literature
327 results about "External resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Internal resistance is the resistance within the battery or any other voltage source that causes a drop in source voltage when current is present. On the other hand, external resistance is the resistance present in the external circuit.
Reversible electrochemical mirror (REM) state monitoring
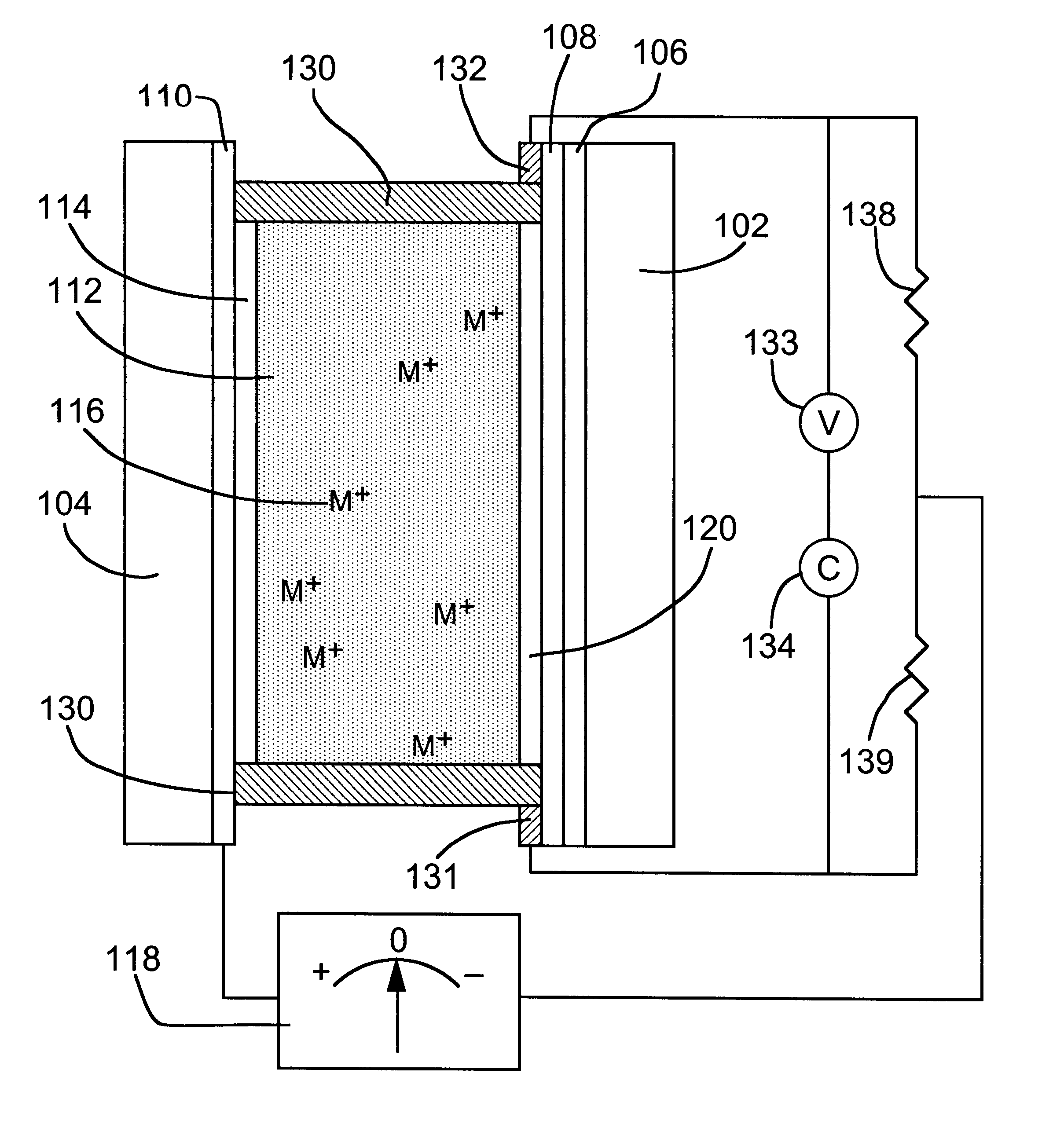
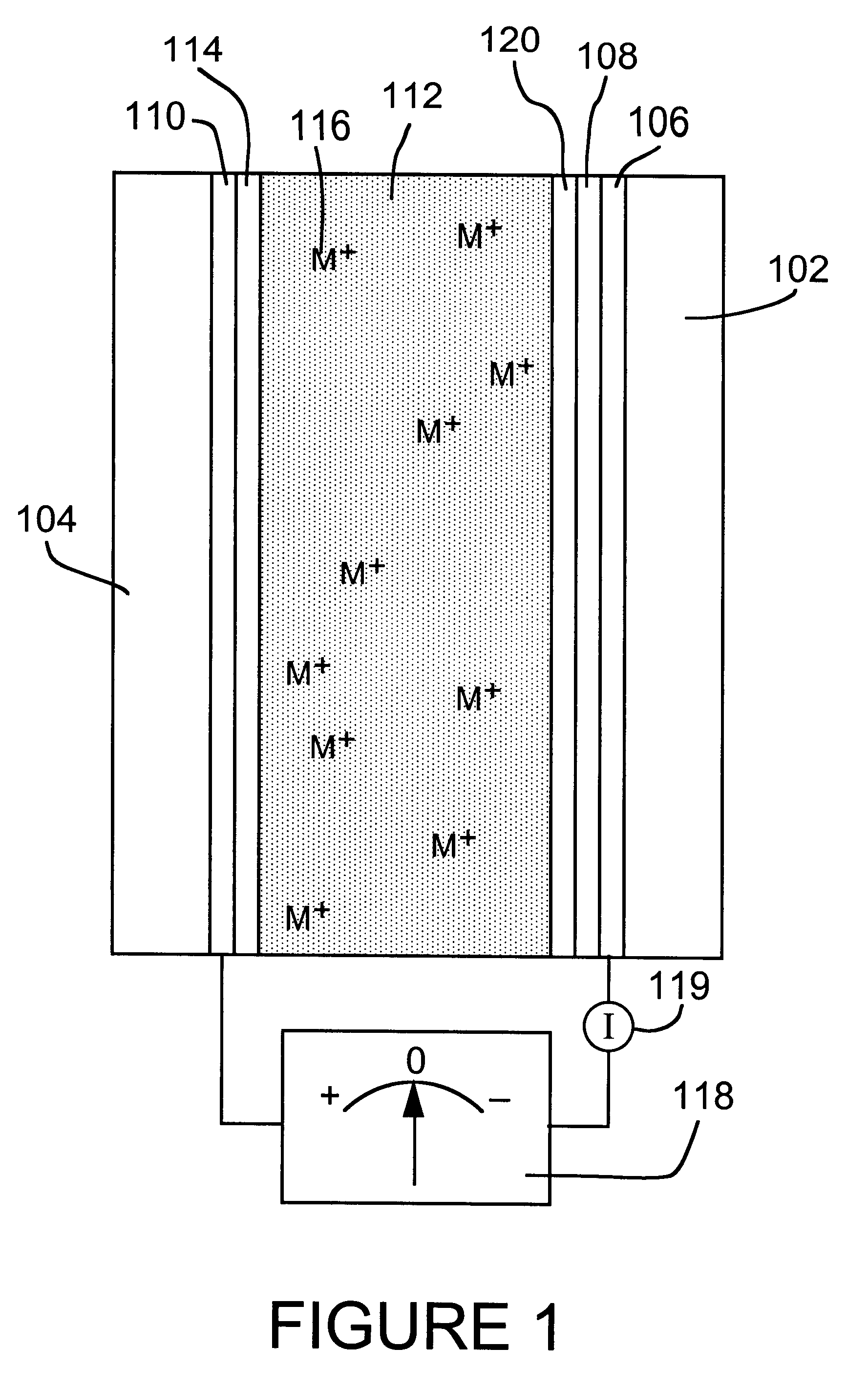
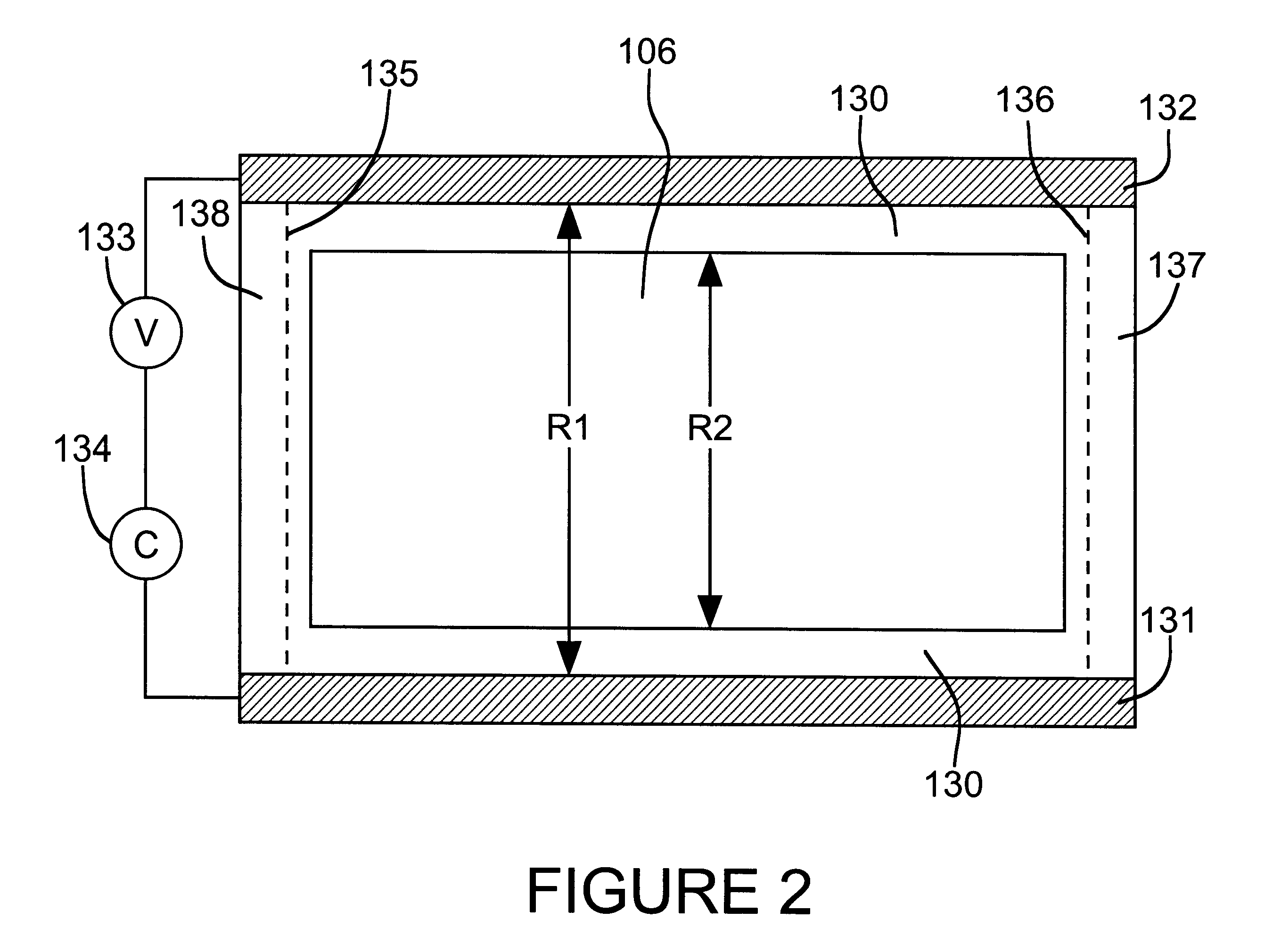
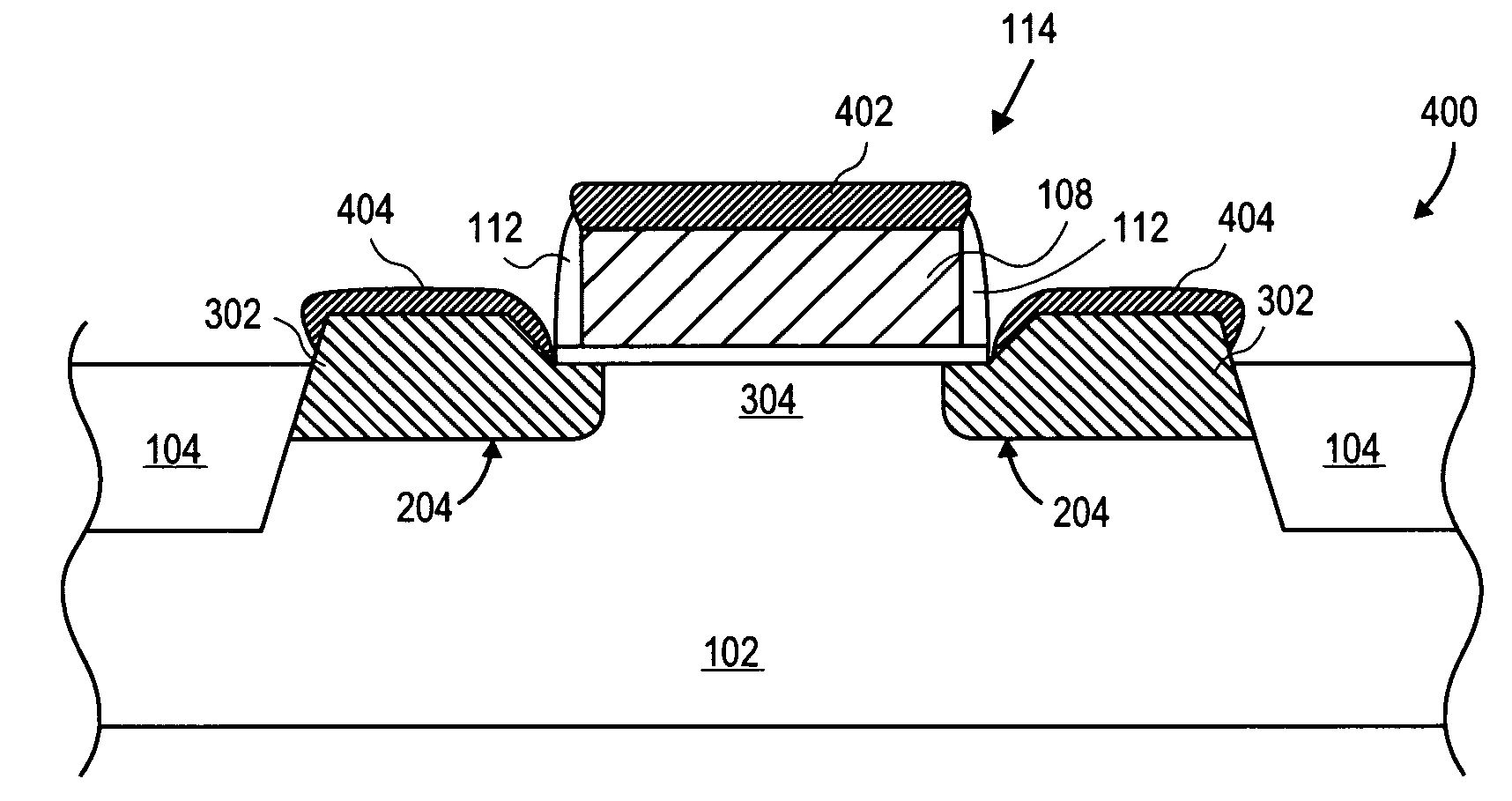
Reversible electrochemical mirror (REM) devices typically comprise a conductive oxide mirror electrode that is substantially transparent to radiation of some wavelengths, a counter electrode that may also be substantially transparent, and an electrolyte that contains ions of an electrodepositable metal. A voltage applied between the two electrodes causes electrodeposition of a mirror deposit on the mirror electrode and dissolution of the mirror deposit on the counter electrode, and these processes are reversed when the polarity of the applied voltage is changed. Such REM devices provide precise control over the reflection and transmission of radiation and can be used for a variety of applications, including smart windows and automatically adjusting automotive mirrors. According to the present invention, measurements of the sheet resistance of the mirror electrode in a REM device are correlated with the thickness of electrodeposited mirror metal and can be used to monitor the reflectance of the device. Sheet resistance measurements can be performed while the mirror state of the device is being switched if adequate isolation between the measurement and switching circuits is provided. This can be accomplished by use of external resistors or more sophisticated circuitry, or by taking advantage of the relatively high sheet resistance of the mirror electrode itself. Monitoring the reflectance of REM devices according to this invention provides significant cost and performance advantages.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
Method for forming an integrated circuit
ActiveUS7402872B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesContact resistanceEpitaxial silicon
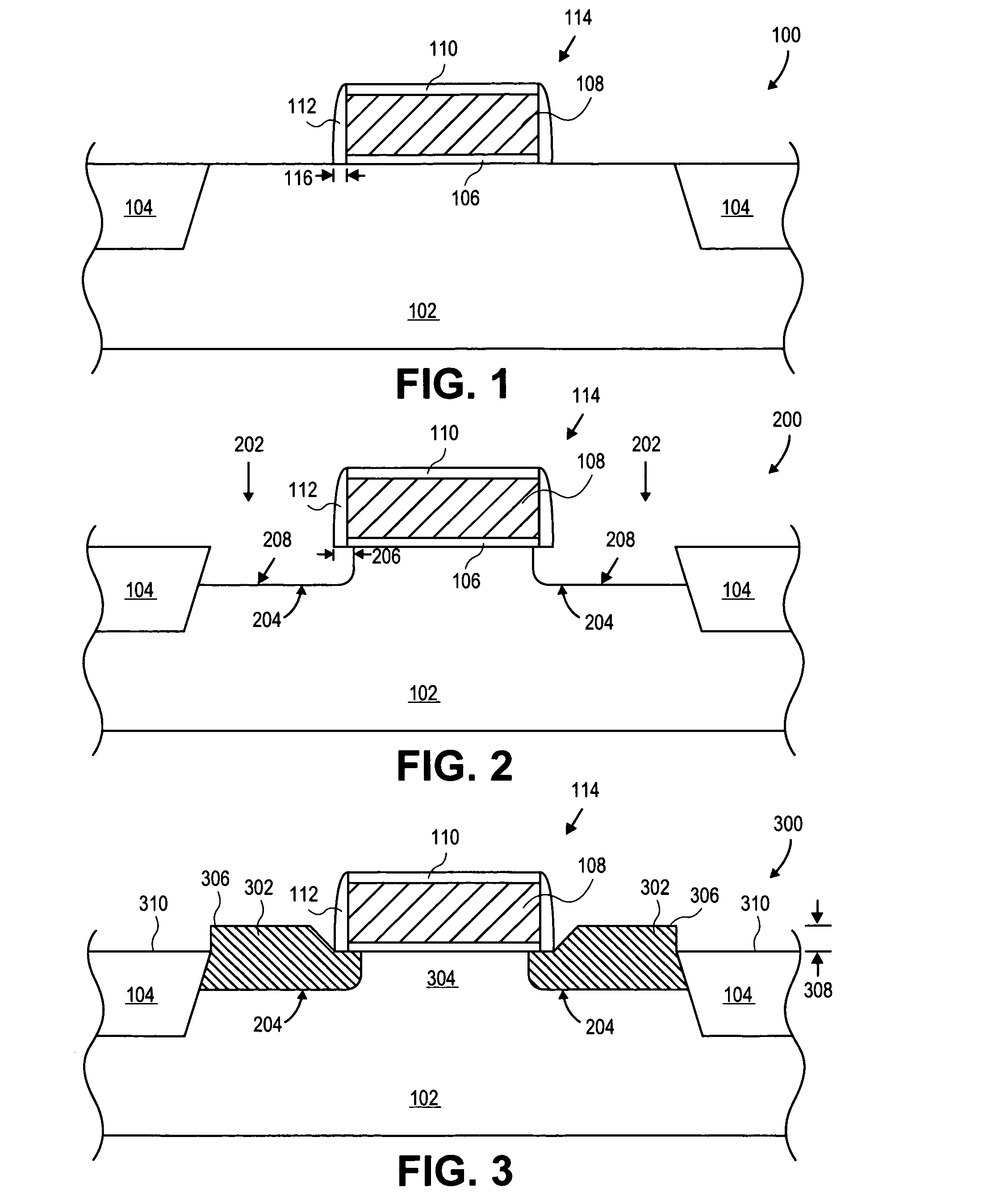
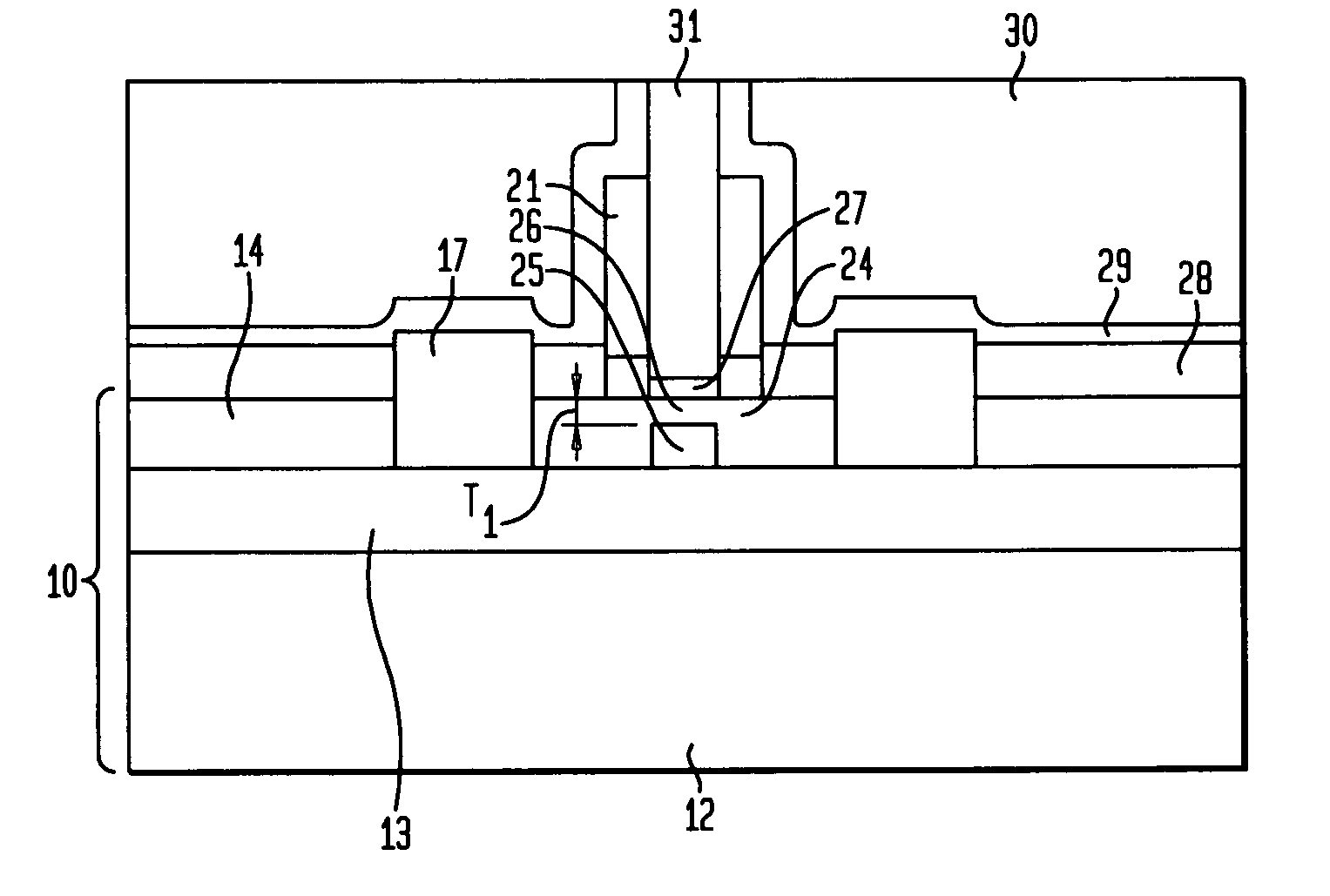
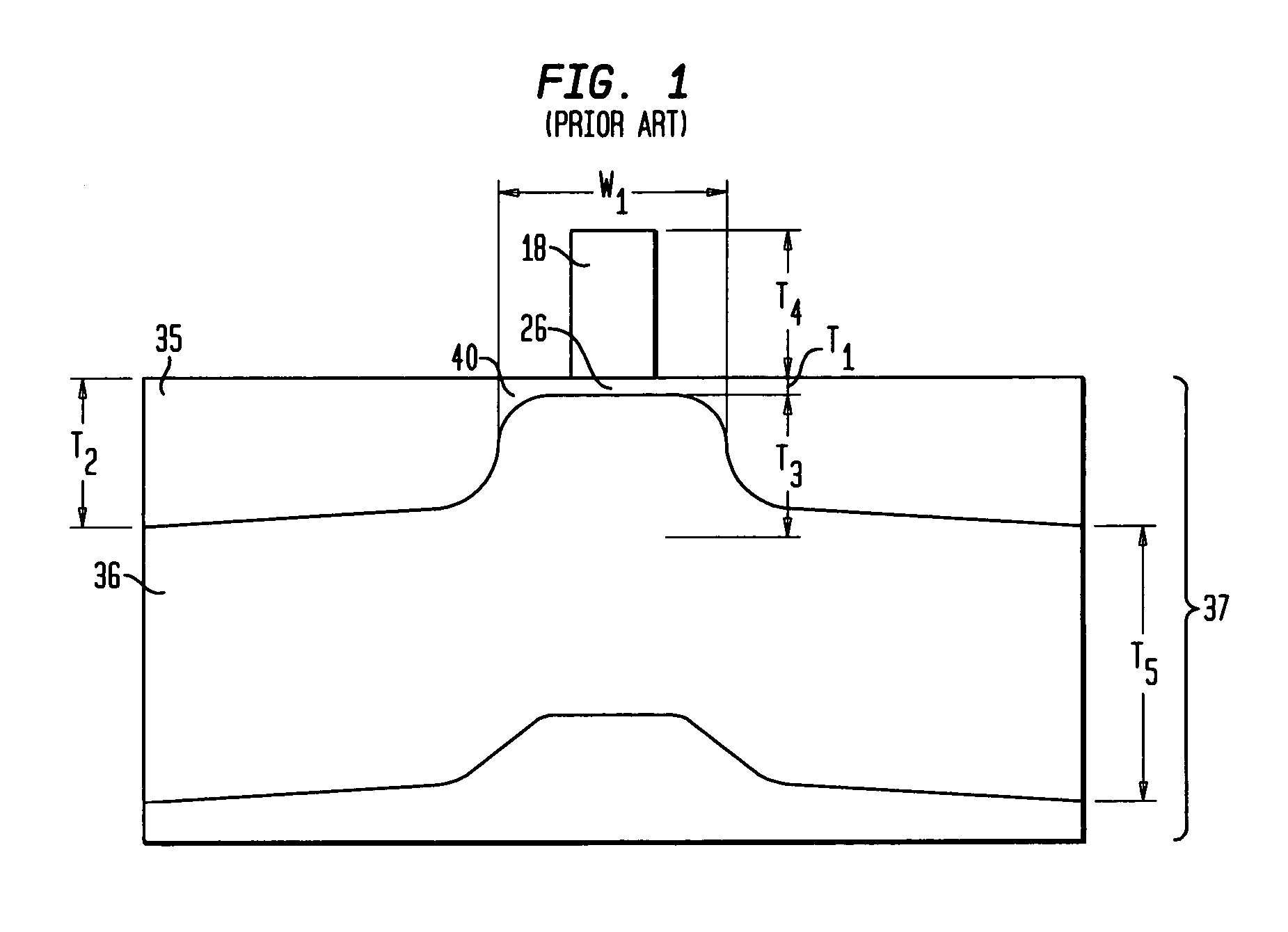
A method is described for manufacturing an n-MOS semiconductor transistor. Recesses are formed in a semiconductor substrate adjacent a gate electrode structure. Silicon is embedded in the recesses via a selective epitaxial growth process. The epitaxial silicon is in-situ alloyed with substitutional carbon and in-situ doped with phosphorus. The silicon-carbon alloy generates a uniaxial tensile strain in the channel region between the source and drain, thereby increasing electron channel mobility and the transistor's drive current. The silicon-carbon alloy decreases external resistances by reducing contact resistance between source / drain and silicide regions and by reducing phosphorous diffusivity, thereby permitting closer placement of the transistor's source / drain and channel regions.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
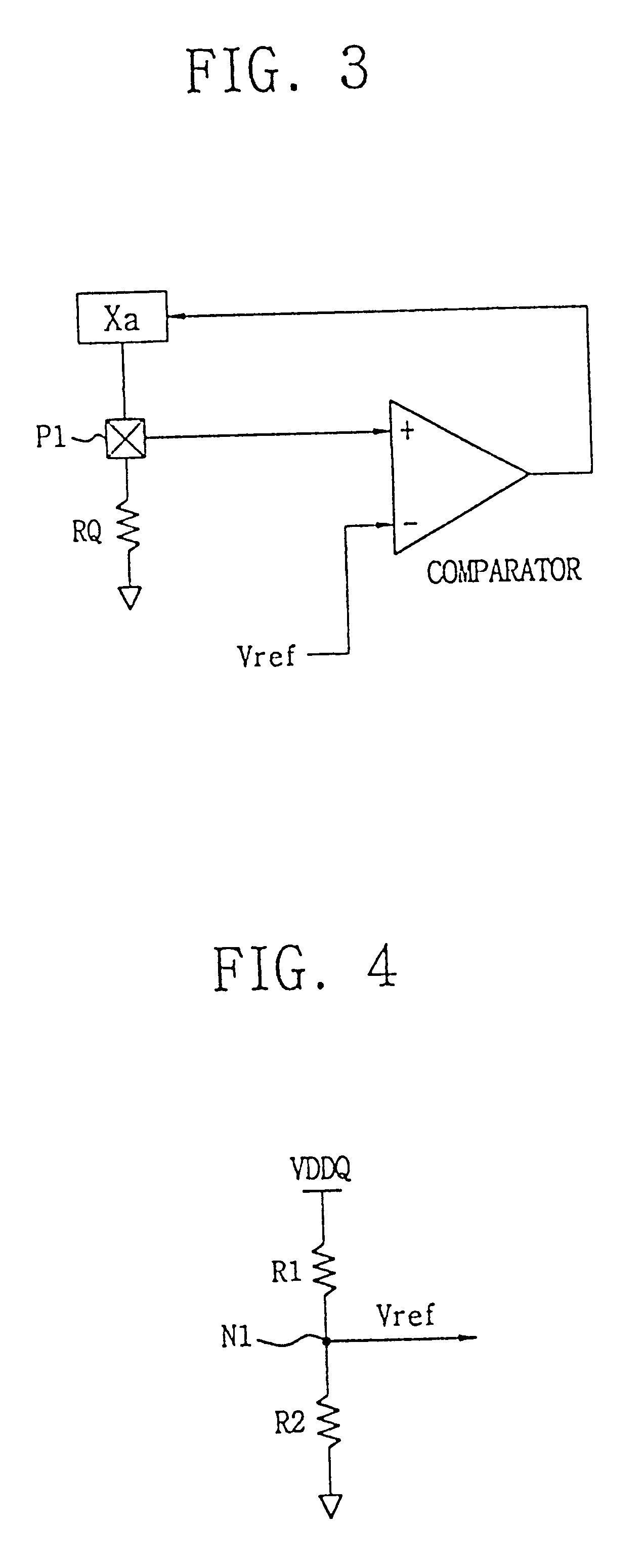
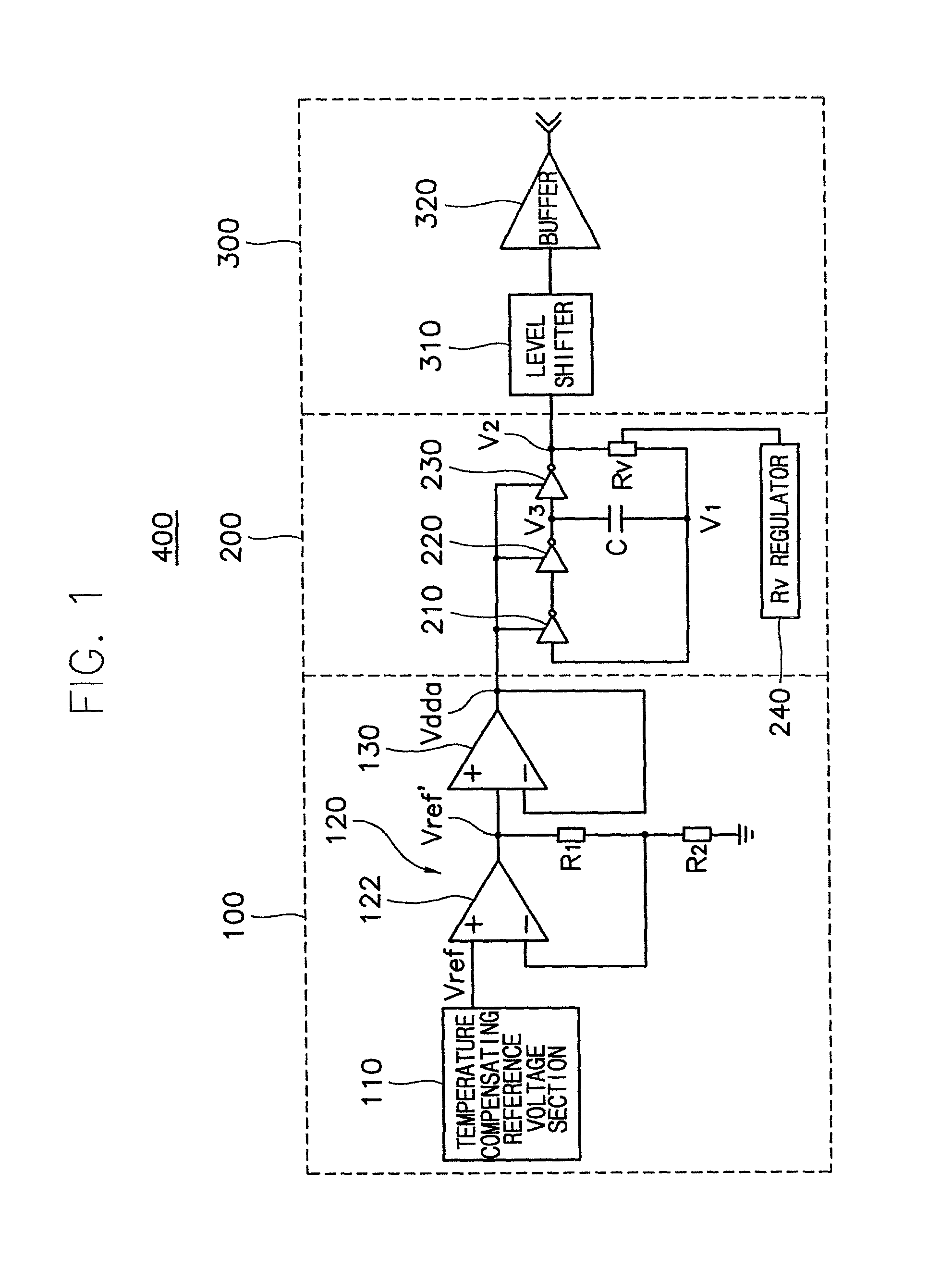
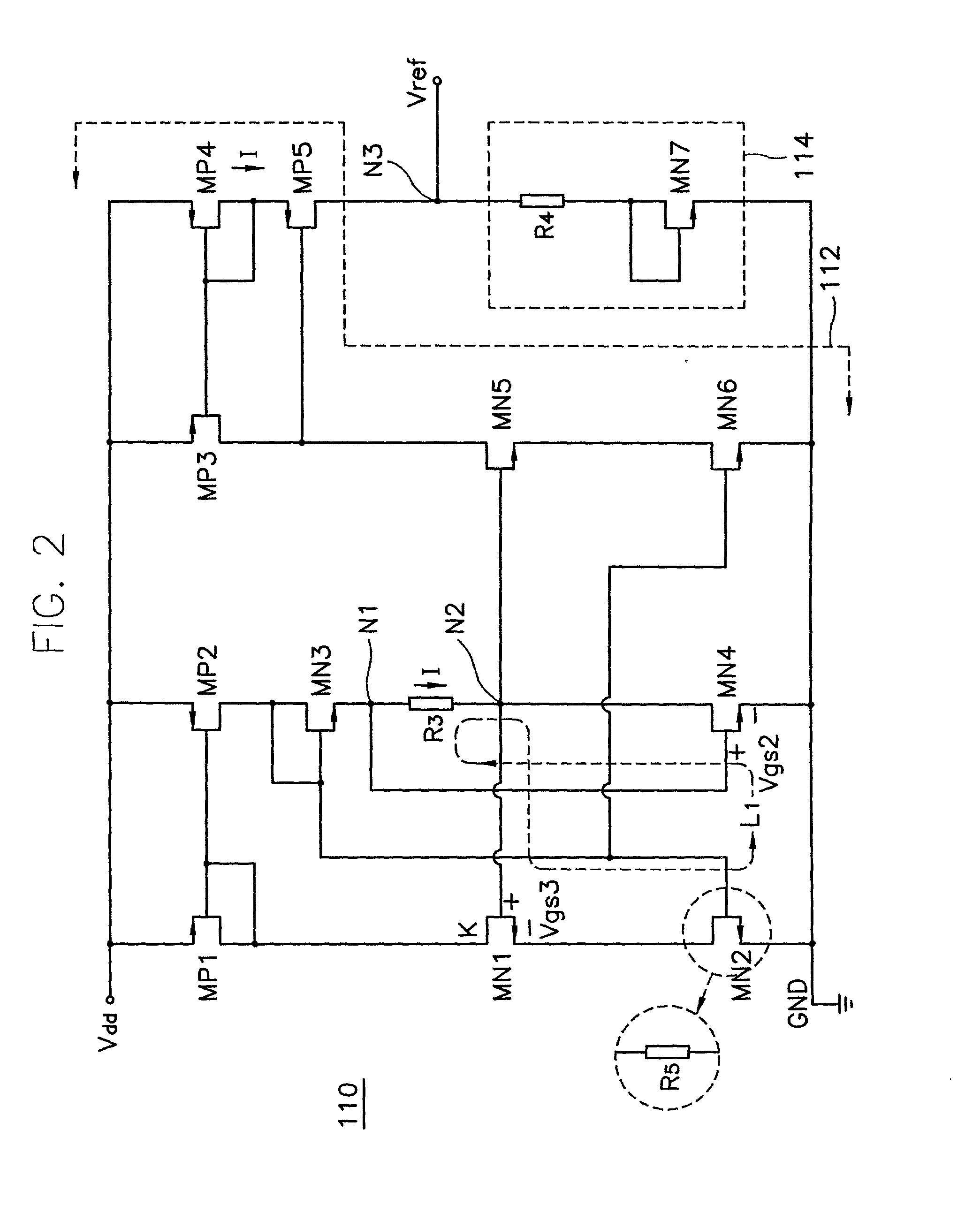
Programmable impedance control circuit
InactiveUS6525558B2Multiple-port networksImpedence matching networksElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage generator
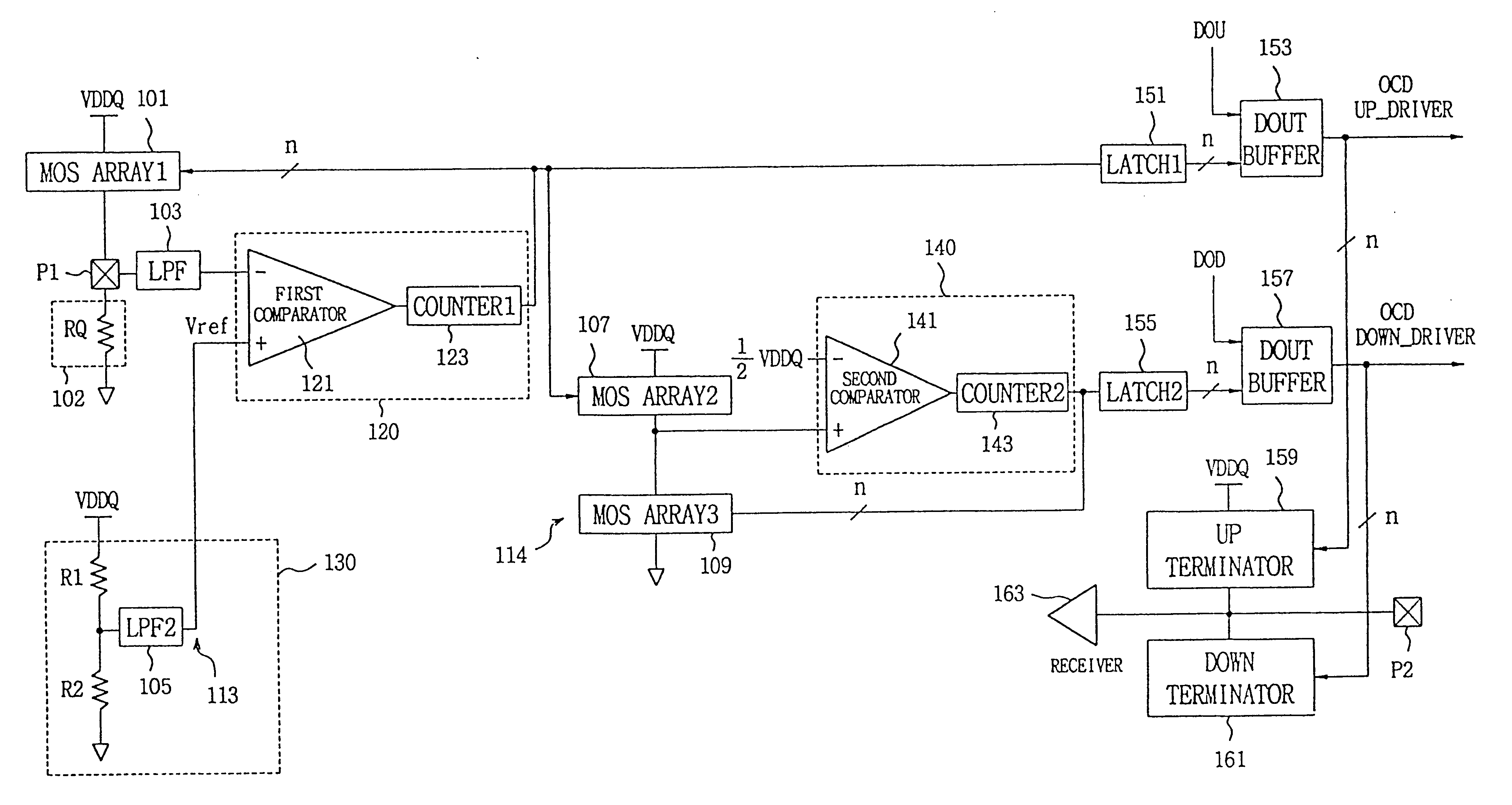
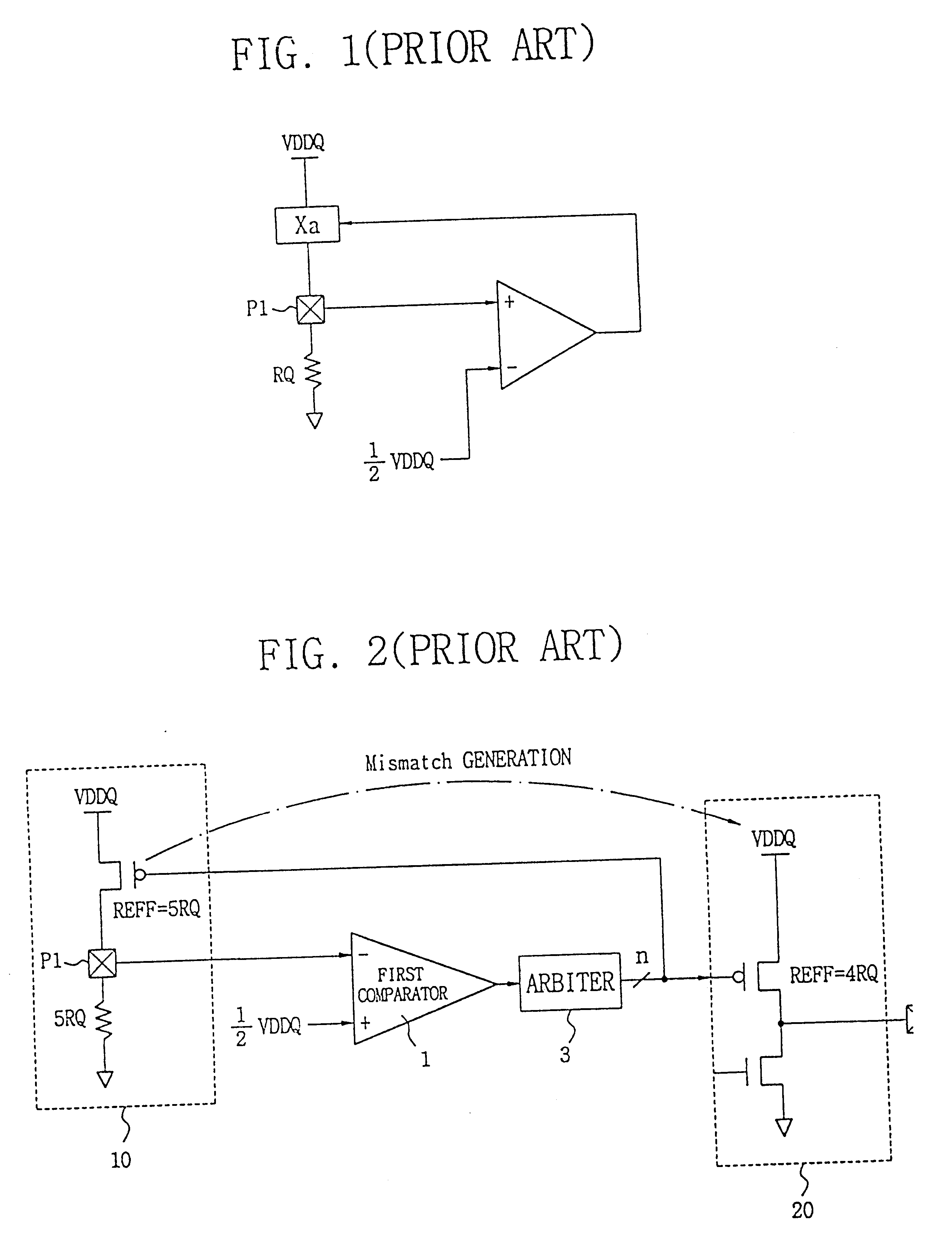
Disclosed is a programmable impedance control circuit, comprising a voltage divider, the voltage divider comprising an MOS array supplied with a first voltage and an external resistance having an external impedance equal to N times said external resistance. The voltage divider outputs a second voltage. A reference voltage generator is provided for generating a third voltage corresponding to N / (N+M) times said first voltage as a reference voltage for said second voltage, and wherein M times internal impedance is used for N times external impedance (N=M or N<> M).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for forming an integrated circuit
ActiveUS20060131665A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesContact resistanceEpitaxial silicon
A method is described for manufacturing an n-MOS semiconductor transistor. Recesses are formed in a semiconductor substrate adjacent a gate electrode structure. Silicon is embedded in the recesses via a selective epitaxial growth process. The epitaxial silicon is in-situ alloyed with substitutional carbon and in-situ doped with phosphorus. The silicon-carbon alloy generates a uniaxial tensile strain in the channel region between the source and drain, thereby increasing electron channel mobility and the transistor's drive current. The silicon-carbon alloy decreases external resistances by reducing contact resistance between source / drain and silicide regions and by reducing phosphorous diffusivity, thereby permitting closer placement of the transistor's source / drain and channel regions.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
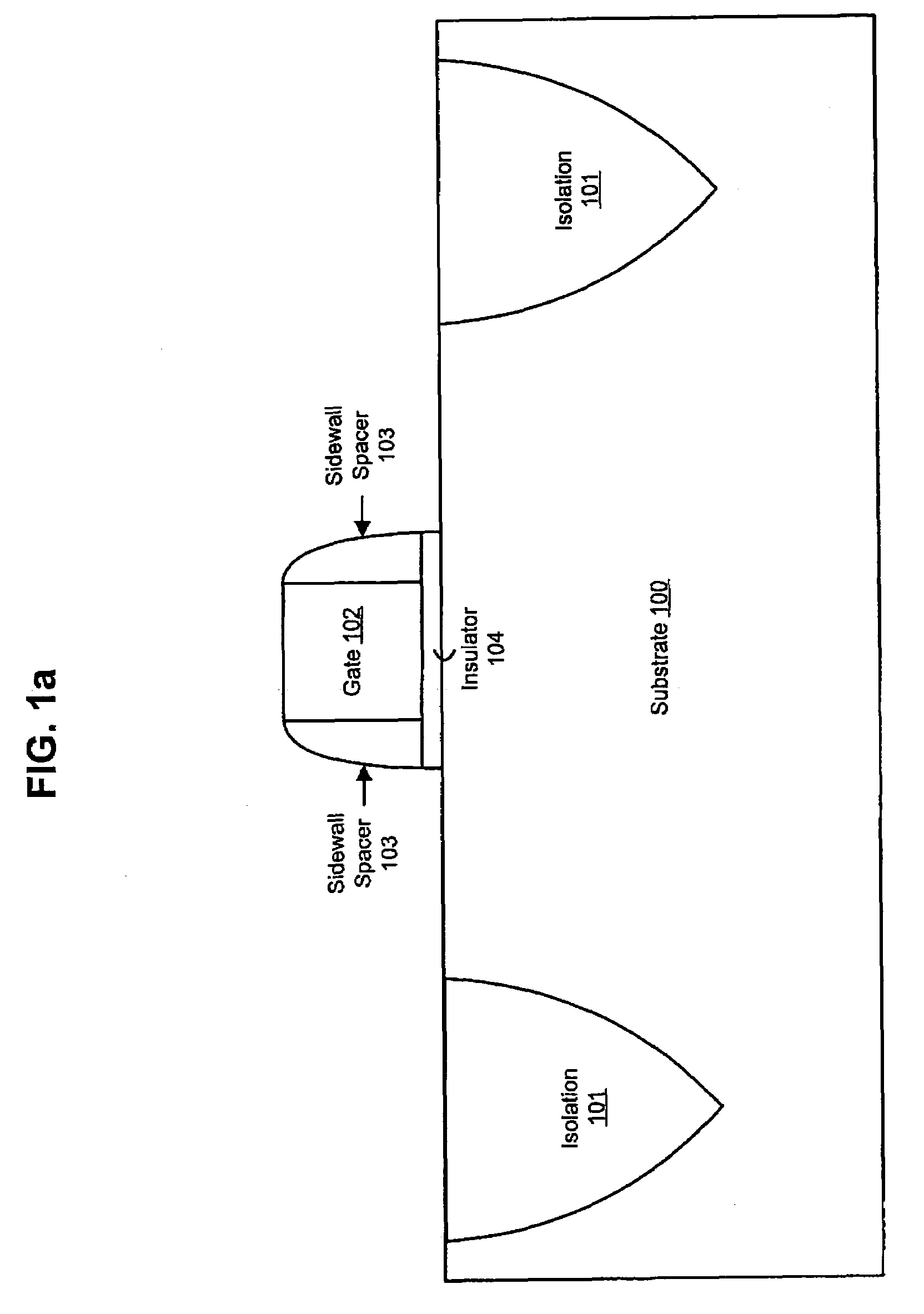
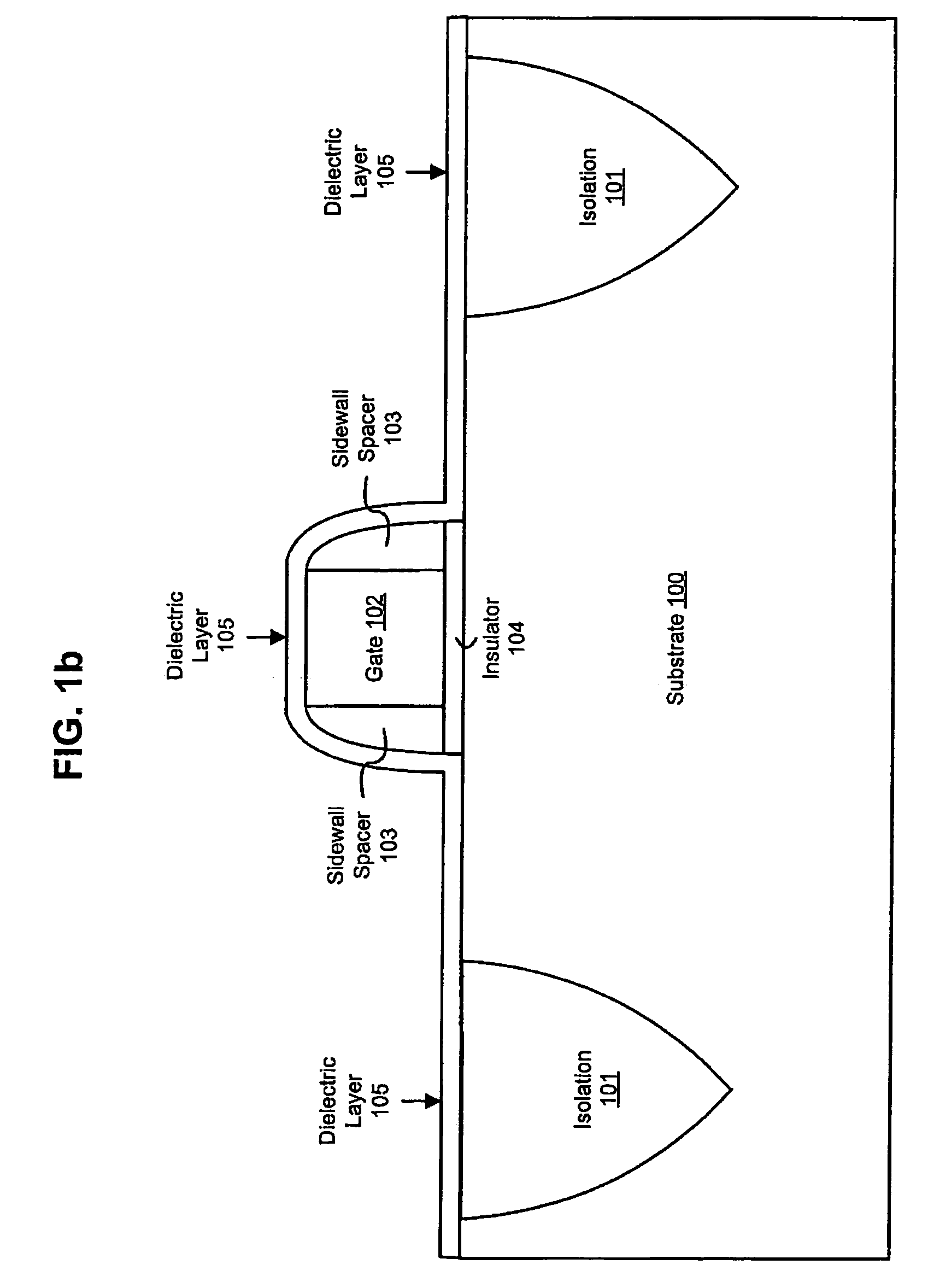
Ultra-thin Si channel MOSFET using a self-aligned oxygen implant and damascene technique
The present invention provides a thin channel MOSFET having low external resistance. In broad terms, a silicon-on-insulator structure comprising a SOI layer located atop a buried insulating layer, said SOI layer having a channel region which is thinned by the presence of an underlying localized oxide region that is located on top of and in contact with said buried insulating layer; and a gate region located atop said SOI layer, wherein said localized oxide region is self-aligned with the gate region. A method for forming the inventive MOSFET is also provided comprising forming a dummy gate region atop a substrate; implanting oxide forming dopant through said dummy gate to create a localized oxide region in a portion of the substrate aligned to the dummy gate region that thins a channel region; forming source / drain extension regions abutting said channel region; and replacing the dummy gate with a gate conductor.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Variable impedance output driver circuit using analog biases to match driver output impedance to load input impedance
InactiveUS6133749AInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsDriver circuitElectrical resistance and conductance
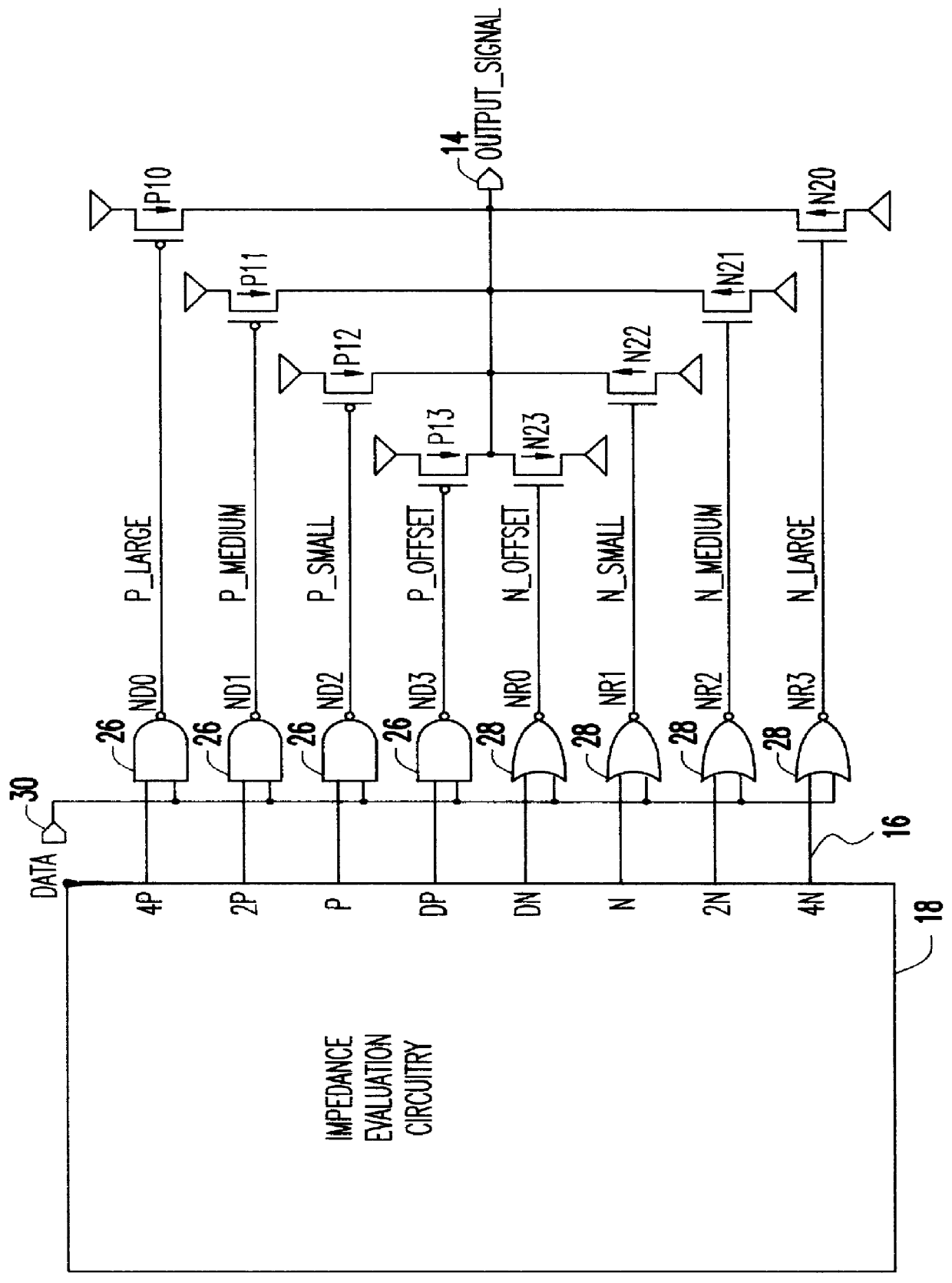
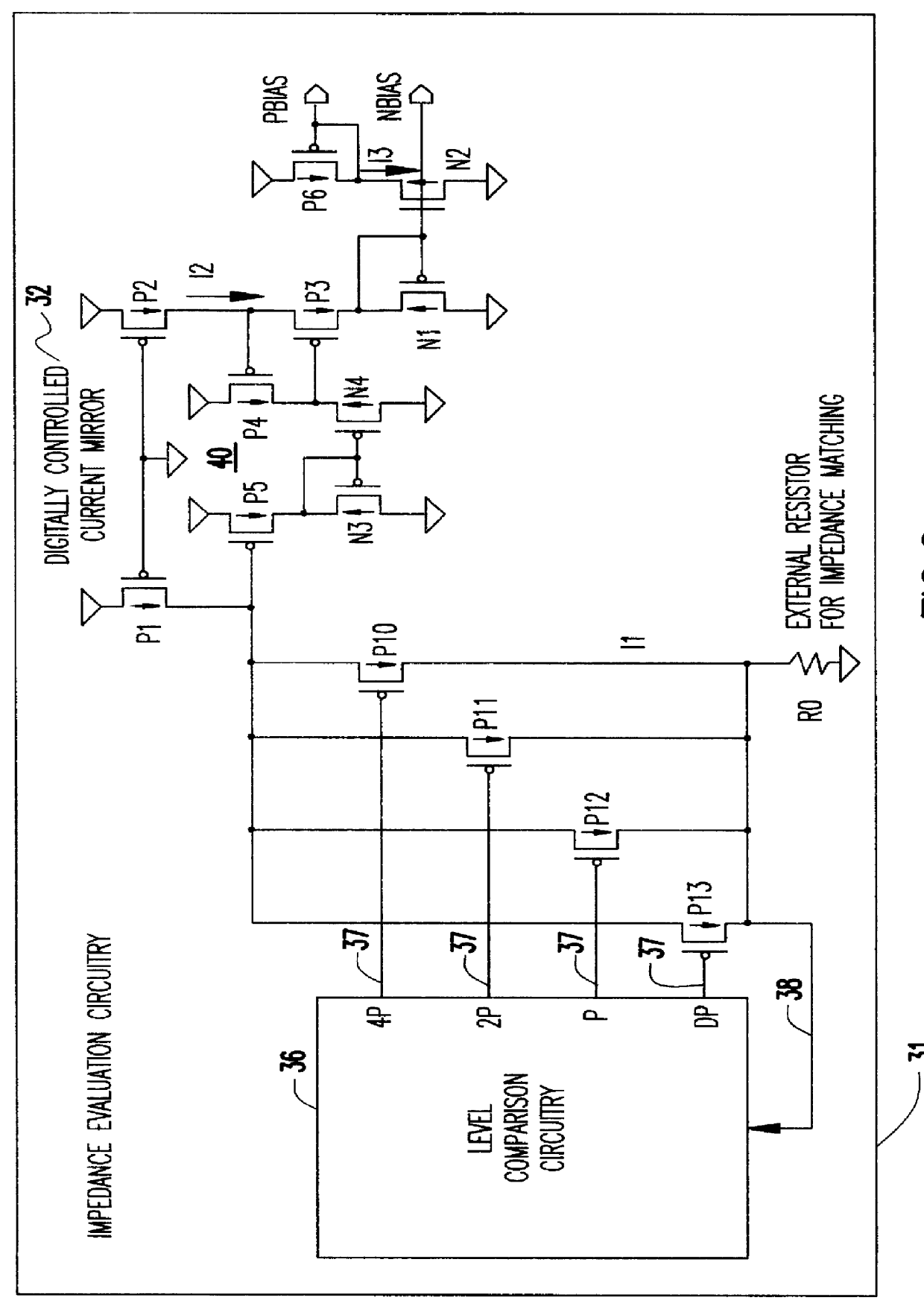
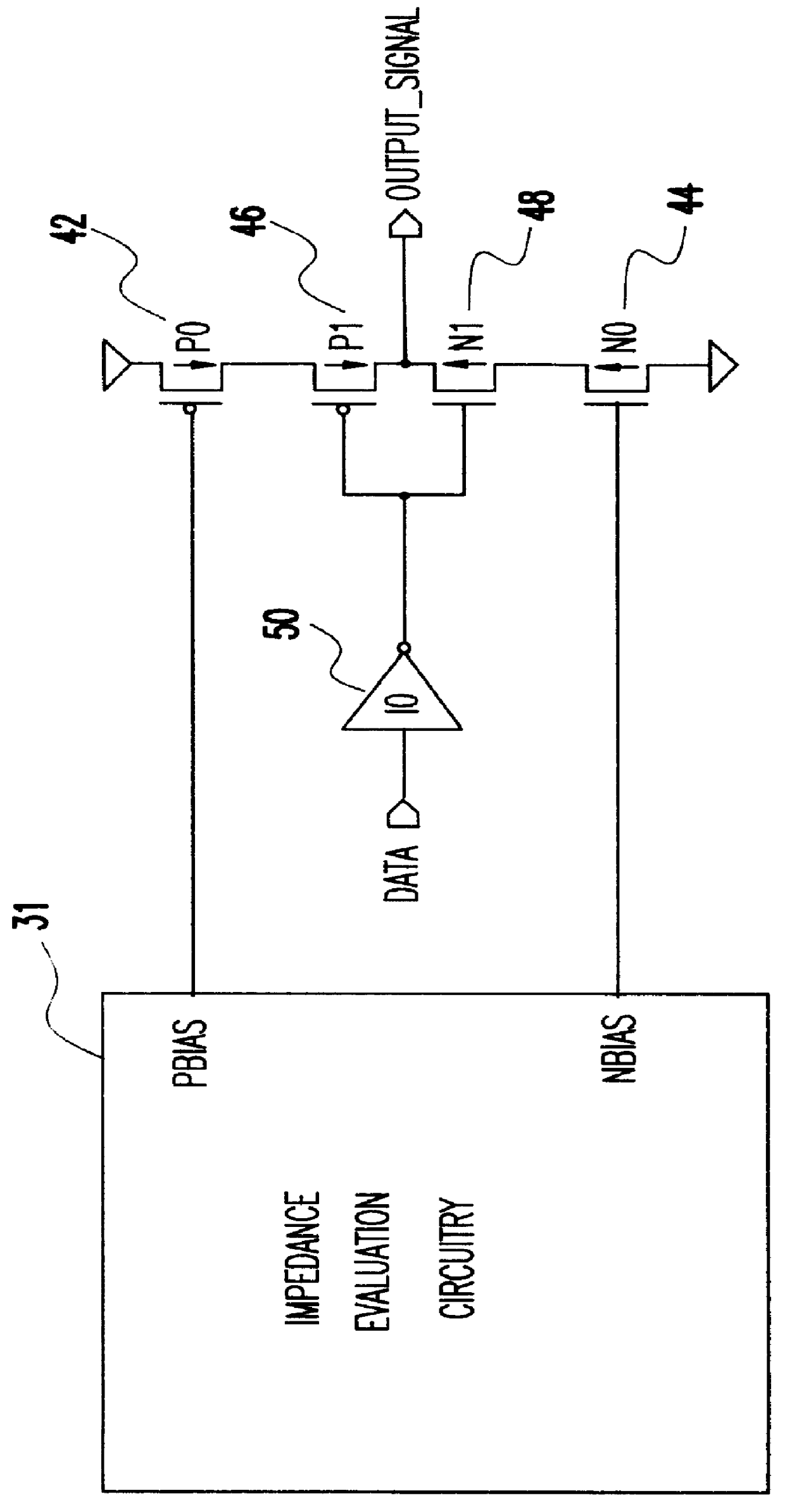
A programmable variable impedance output driver circuit uses analog biases to match driver output impedance to load input impedance. A current mirror is used to obtain a measurement of an external resistance value for matching the impedance of a driven load. The mirrored current generates the voltage "NBIAS" when passed through the resistively connected NFET. Similarly, the current is again mirrored and passed through a resistively connected PFET resulting in the voltage "PBIAS". The analog bias voltages, NBIAS and PBIAS are used to vary the impedance of complementary FETs in an impedance matched driver for a high degree of dI / dt control. The driver provides a high degree of flexibility because its turn-on and turn-off characteristics do not depend on a combination of digital control signals connected directly to the driving FETs as in the prior art. Instead, the PBIAS and NBIAS signals provide analog controls which may be applied to single transistors whose impedance changes as PBIAS and NBIAS increase or decrease.
Owner:IBM CORP
On-chip termination with calibrated driver strength
InactiveUS7221193B1Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
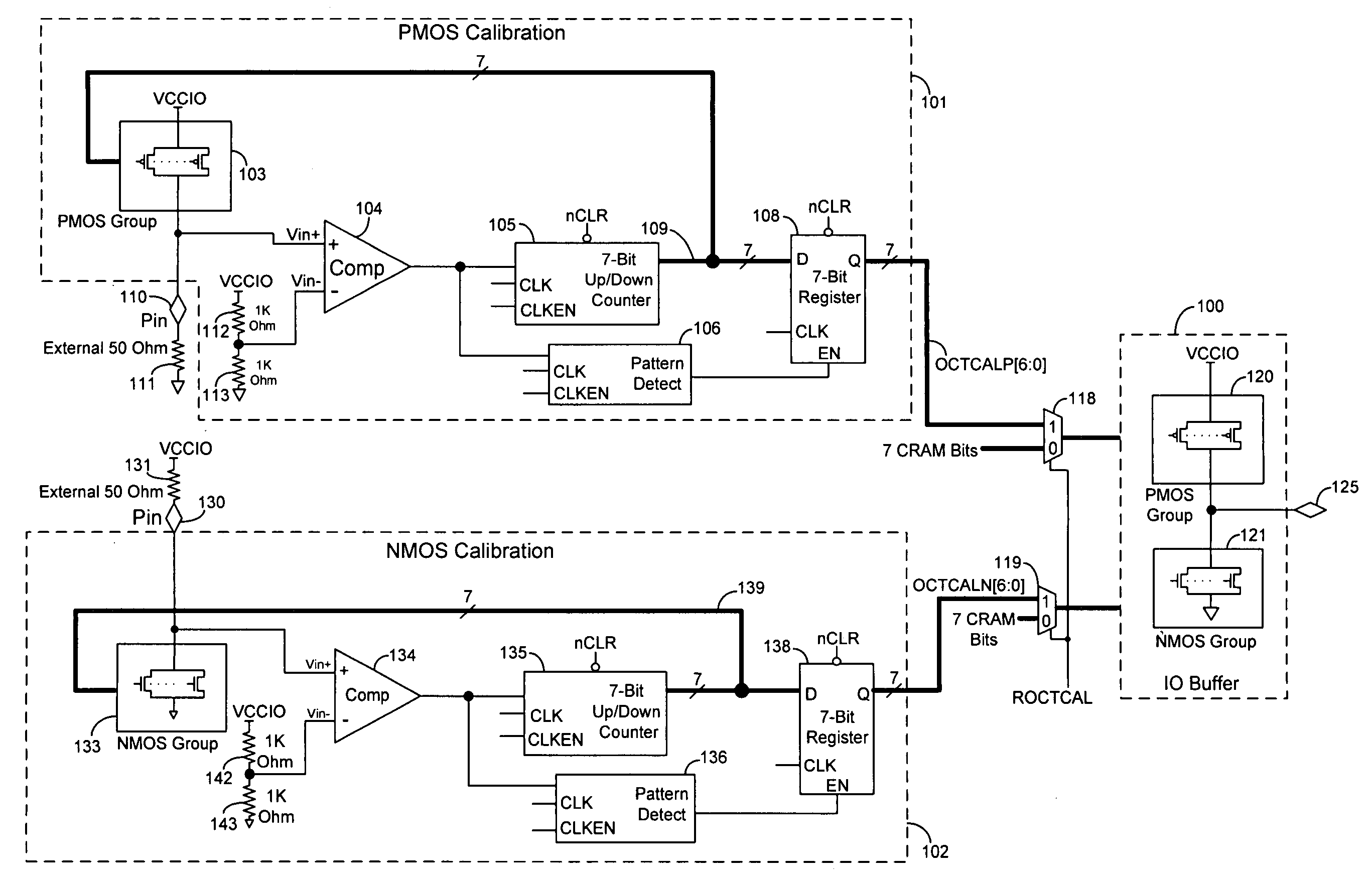
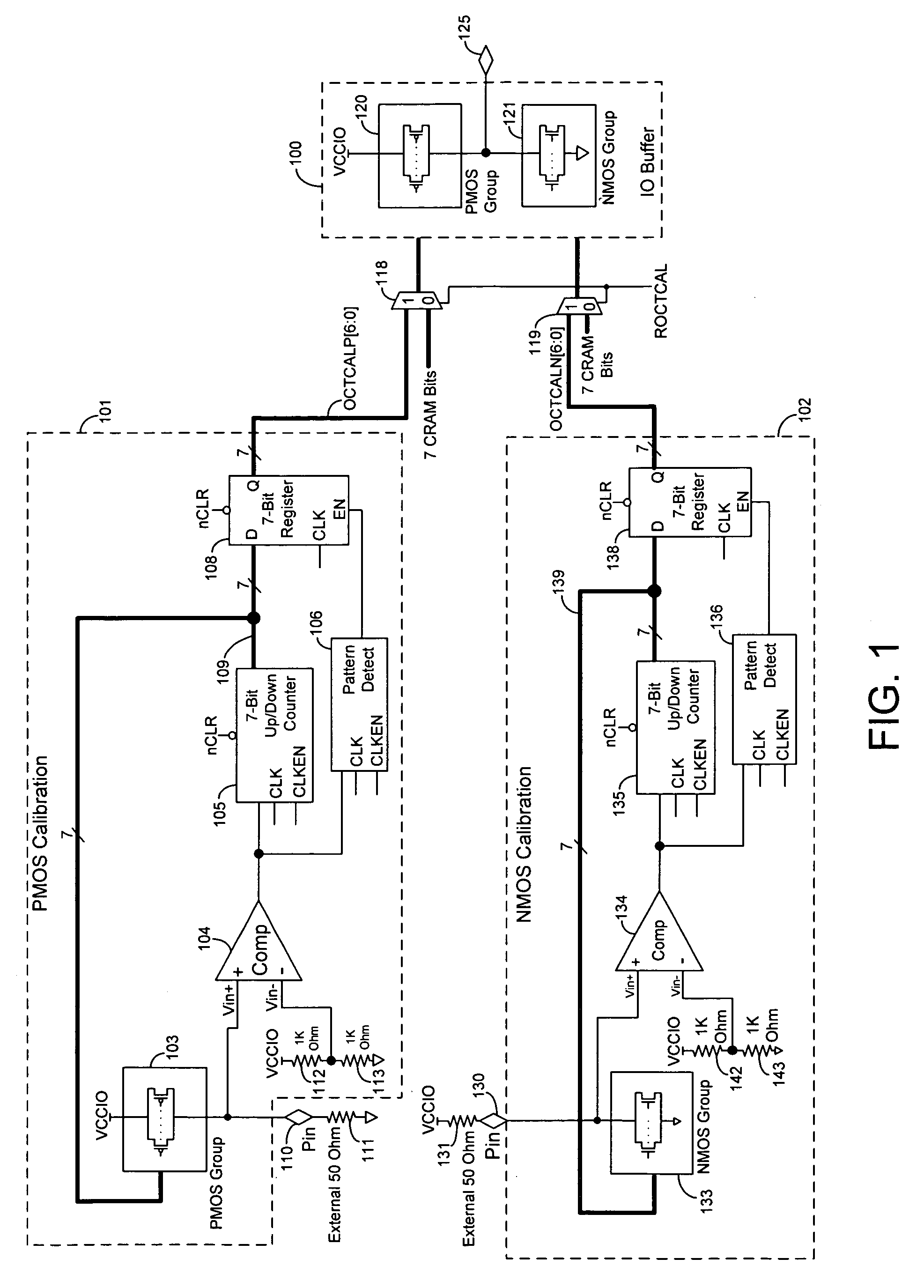
Techniques are provided for controlling an on-chip termination resistance in an input or output (IO) buffer using calibration circuits. Each calibration circuit monitors the voltage between an external resistor and a group of on-chip transistors. When the effective resistance of the group of transistors matches the external resistance, the calibration circuit causes the effective resistance of drive transistors in the IO buffer to match the effective resistance of the group of on-chip transistors.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Micropower RC oscillator
InactiveUS6462625B2Logic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsGenerator stabilizationElectrical resistance and conductanceClosed loop
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Mosfet including asymmetric source and drain regions
InactiveUS20130049115A1Increasing the thicknessLower resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETCapacitance
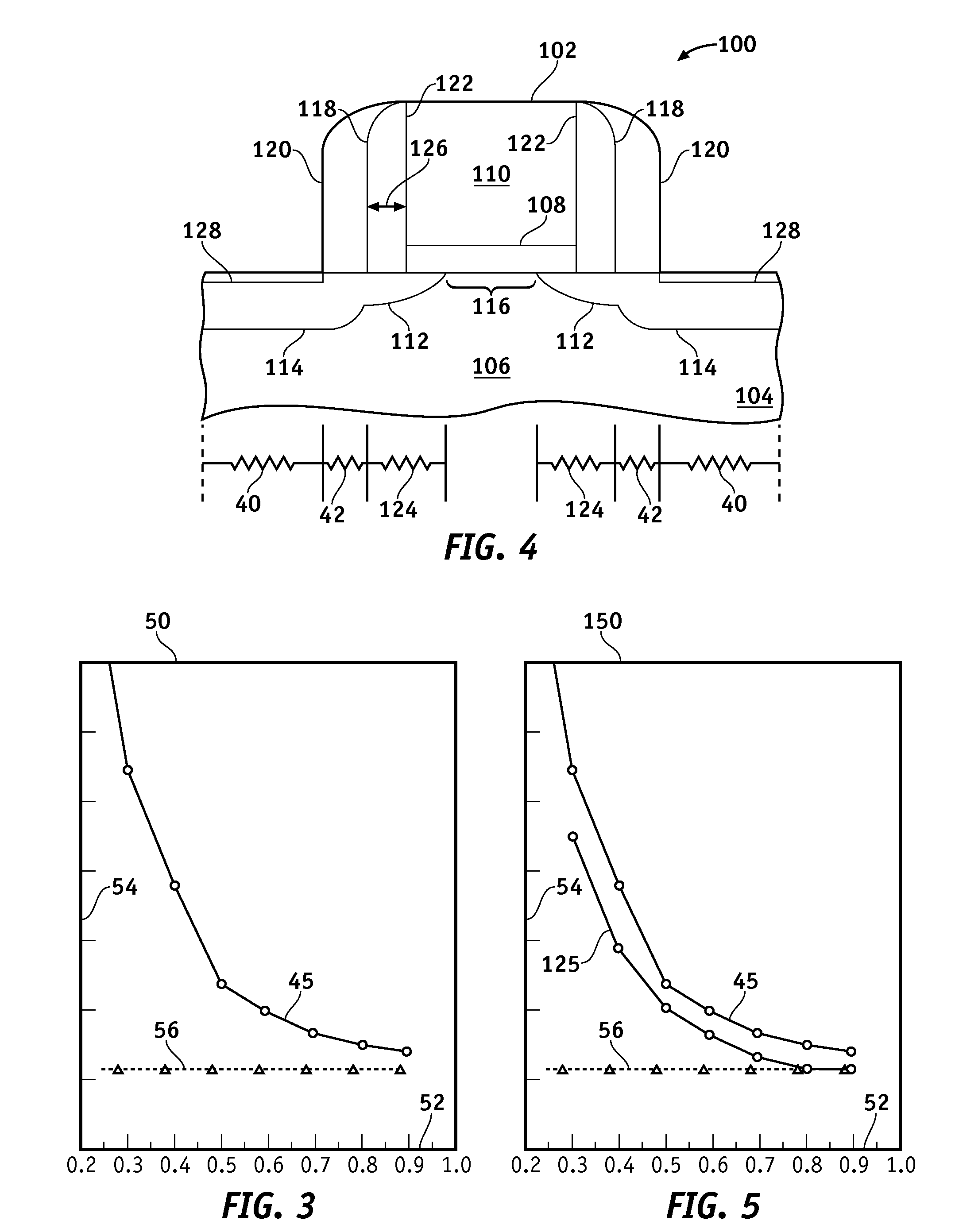
At least one drain-side surfaces of a field effect transistor (FET) structure, which can be a structure for a planar FET or a fin FET, is structurally damaged by an angled ion implantation of inert or electrically active dopants, while at least one source-side surface of the transistor is protected from implantation by a gate stack and a gate spacer. Epitaxial growth of a semiconductor material is retarded on the at least one structurally damaged drain-side surface, while epitaxial growth proceeds without retardation on the at least one source-side surface. A raised epitaxial source region has a greater thickness than a raised epitaxial drain region, thereby providing an asymmetric FET having lesser source-side external resistance than drain-side external resistance, and having lesser drain-side overlap capacitance than source-side overlap capacitance.
Owner:IBM CORP
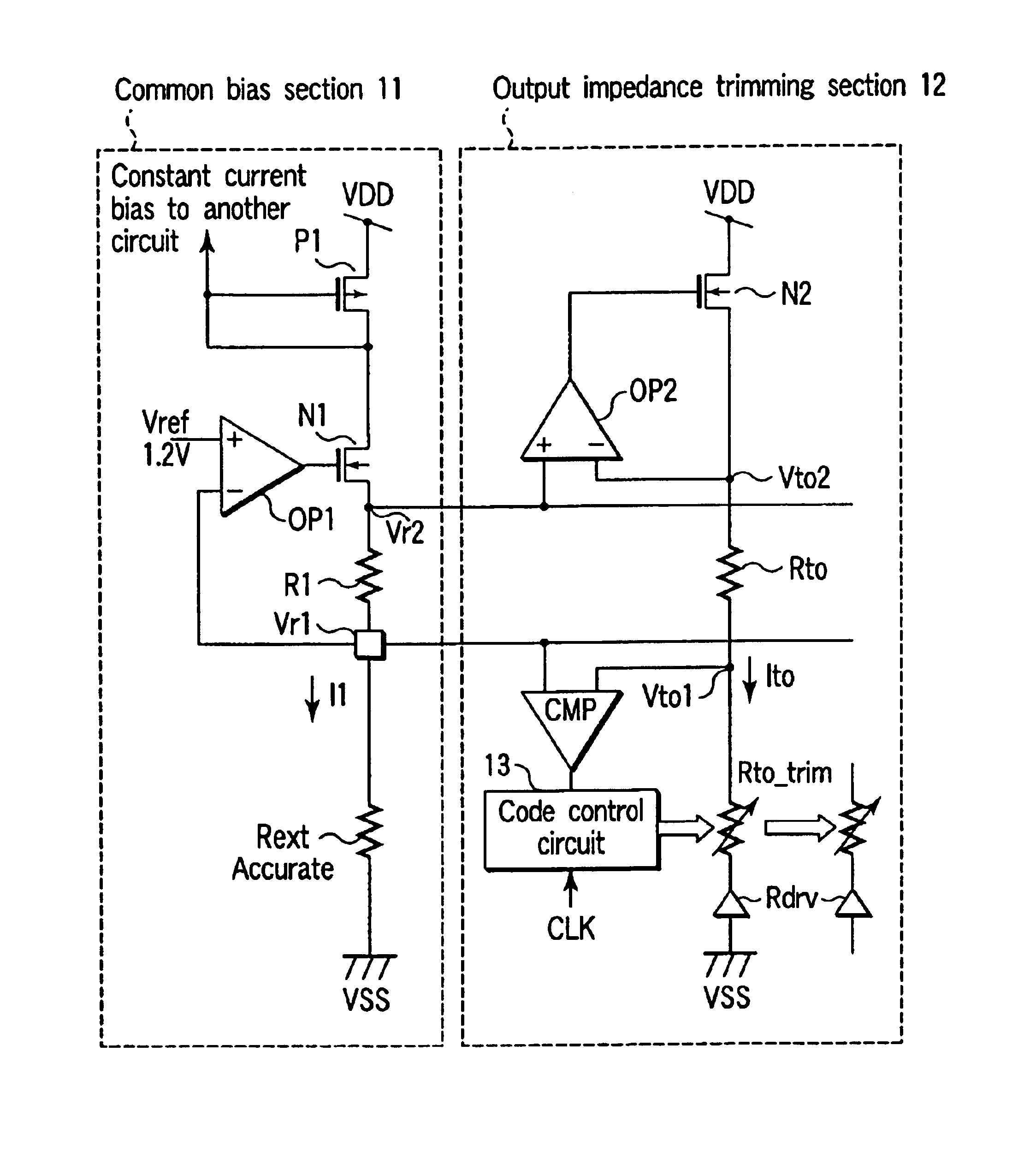
Impedance trimming circuit
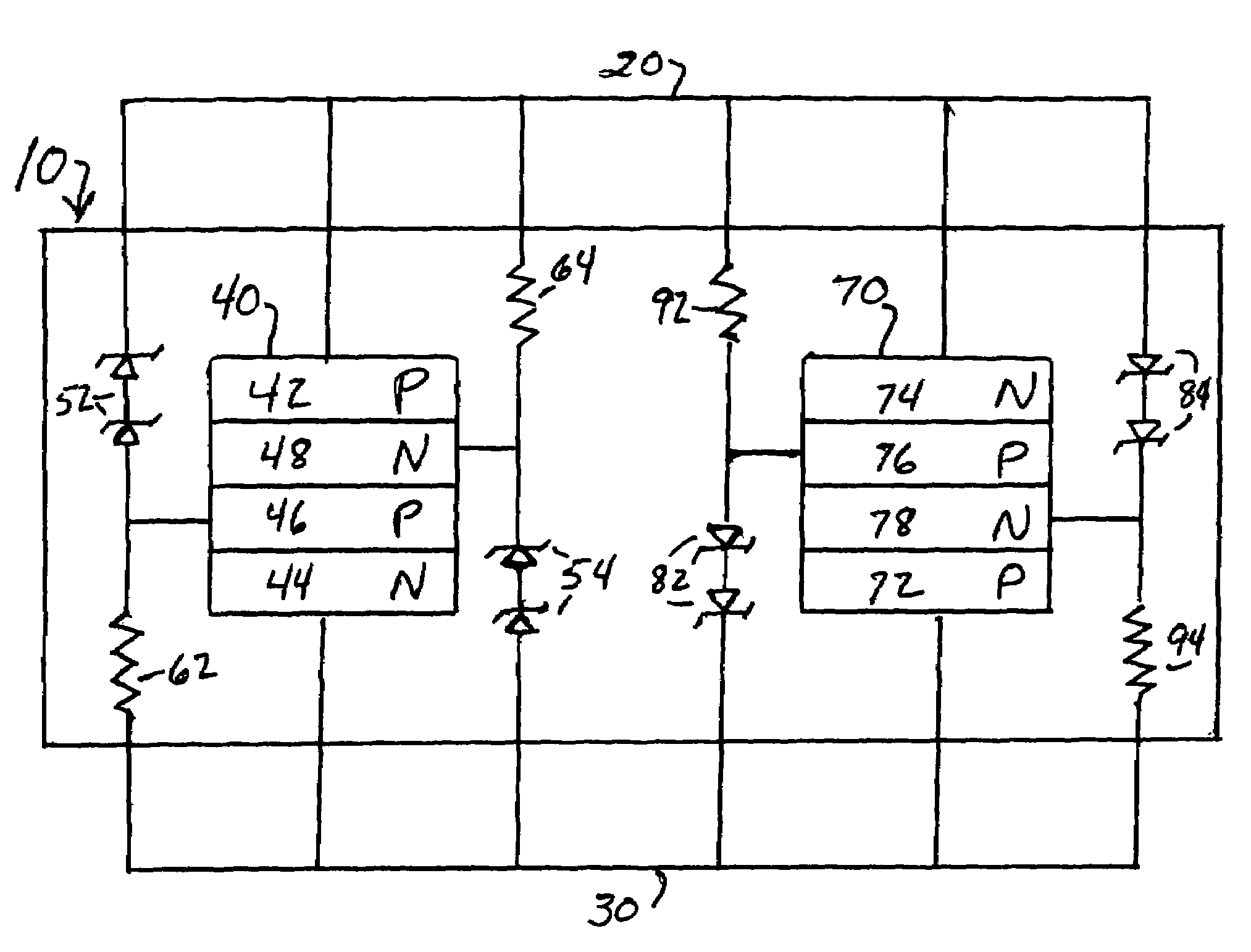
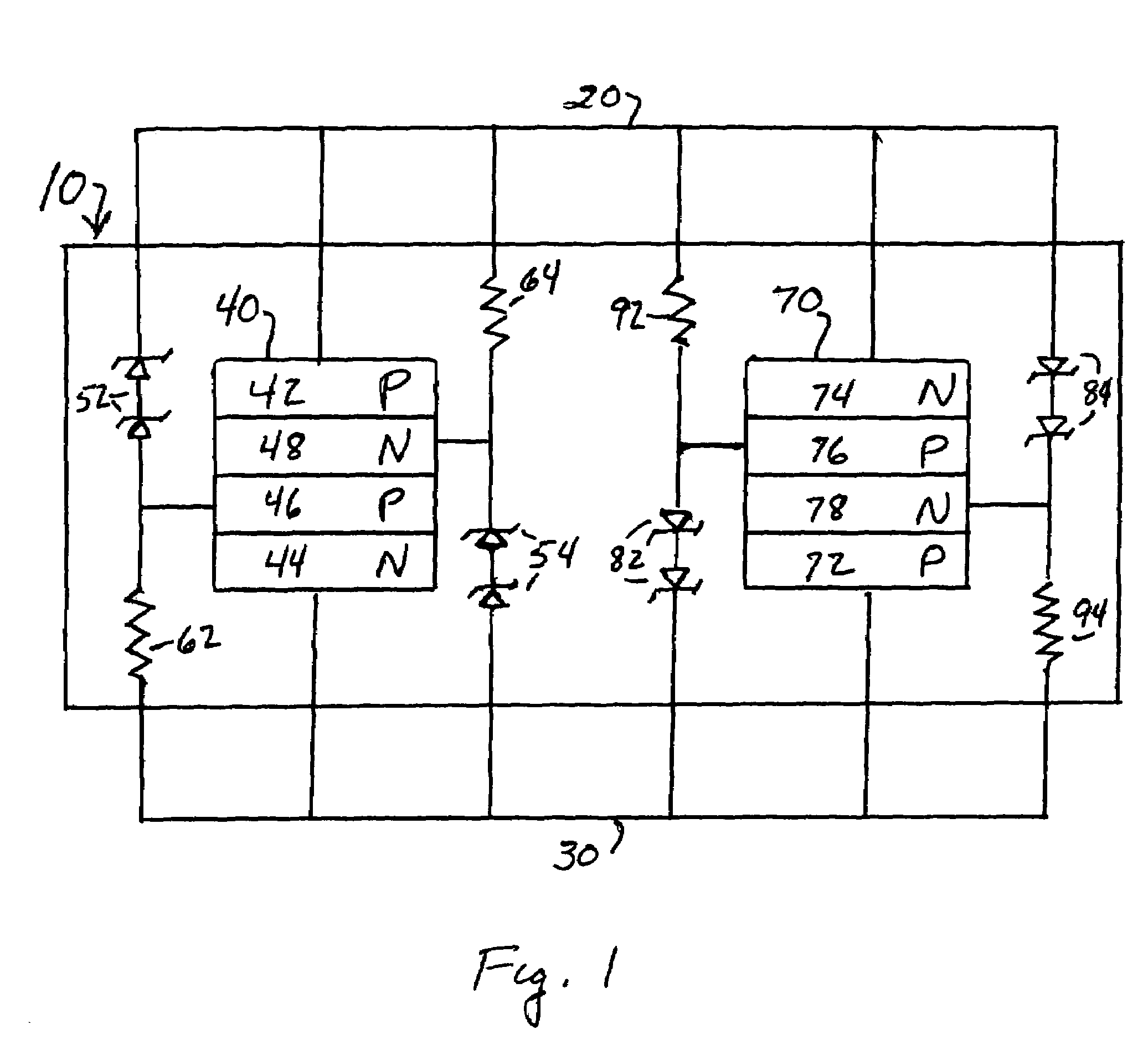
InactiveUS6836170B2Reliability increasing modificationsImpedence matching networksExternal resistanceVoltage reference
A common bias section is composed of a first series circuit having an internal resistor and an external resistor connected in series and an operational amplifier having a first input terminal connected to a reference voltage, a second input terminal connected to a Vr1 node, and an output terminal connected to the series circuit. An impedance trimming section is composed of a series circuit having an internal resistor and an impedance dummy resistor connected in series, a comparator CMP having a first input terminal connected to the Vr1 node and a second input terminal connected to a Vto1 node, a code control circuit which uses a clock signal to latch an output signal from the comparator to generate a plurality of switching codes, and a switching circuit which switch a resistance value of the impedance dummy resistor.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Programmable impedance control circuit
InactiveUS20020063576A1Multiple-port networksReliability increasing modificationsVoltage generatorElectrical resistance and conductance
Disclosed is a programmable impedance control circuit, comprising a voltage divider, the voltage divider comprising an MOS array supplied with a first voltage and an external resistance having an external impedance equal to N times said external resistance. The voltage divider outputs a second voltage. A reference voltage generator is provided for generating a third voltage corresponding to N / (N+M) times said first voltage as a reference voltage for said second voltage, and wherein M times internal impedance is used for N times external impedance (N=M or N<> M).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Impedance matching circuit, high speed semiconductor integrated circuit employing the same and computer system employing the integrated circuit
InactiveUS6188237B1Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsComputerized systemImpedance matching
A high speed impedance matching circuit suitable for use in high speed semiconductor integrated circuits matches the output impedance of a semiconductor device to the impedance of other devices such a computer system bus thereby reducing signal reflections caused by impedance mismatches and which can adversely affect the operation of a high speed computer system. The impedance of an output buffer is matched to the impedance of an external resistor.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Wind-powered pneumatic engine and a motor vehicle equipped with the engine
InactiveUS20070284155A1Improve energy efficiencyIncrease profitAuxillary drivesWind motor controlEngineeringEnergy expenditure
A wind-powered pneumatic engine including one or more impeller chambers and one or more impellers disposed in the impeller chambers is provided. One or more air inlets for receiving external wind resistance airflow are disposed on the impeller chambers, and the external wind resistance airflow entering the air inlets drives the impellers to operate to generate power output. The wind-powered pneumatic engine further includes an air-jet system for jetting HPCA into the impeller chambers, and the internal high-pressure compressed air jetted by the air-jet system in conjunction with the external wind resistance airflow entering the air inlets drives the impellers to operate to generate power output. In the present invention, the external resistance airflow around a motor vehicle moving at a speed is converted into power for use, which greatly reduces energy consumption and improves the moving speed of a motor vehicle. A motor vehicle equipped with wind-powered pneumatic engine is also provided.
Owner:CONG YANG
Internal waverider hypersonic inlet and design method based on random shock form
InactiveCN101392685AImprove export aerodynamic performanceReduce windward external resistanceTurbine/propulsion air intakesShock waveRadial position
The invention provides an internal waverider-derived hypersonic inlet based on arbitrary shockwave shape and a design method thereof. The structure of the internal waverider-derived hypersonic inlet comprises an inlet contraction section and an inlet insulation section; wherein the inlet contracting section is inward contracted in three-dimension; hypersonic velocity incoming flow forms irregular initial incident three-dimensional shockwave at the inlet; and the shockwave closes the three-dimensional inlet surface completely. The design method comprises the following steps: an internally contracted axisymmetric basic flow field used as a base is formed by the combination of ICFA flow field and partial Buesemann flow field; and after shapes of shockwave sections with different centers of curvature and directions of curvature are appointed, flown line tracing of the basic flow field with different centers and different radial positions is carried out on a plane in each circle of the hypersonic inlet to obtain the internal waverider-derived hypersonic inlet based on arbitrary shockwave shape. The internal waverider-derived hypersonic inlet and the method have the advantages of ensuring that the hypersonic inlet captures the incoming flow in full flow, increasing thrust force of an engine while reducing overflow resistance, improving pneumatic performance of an outlet of the hypersonic inlet, reducing windward external resistance of the hypersonic inlet, and improving starting performance of low-mach number of the hypersonic inlet.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
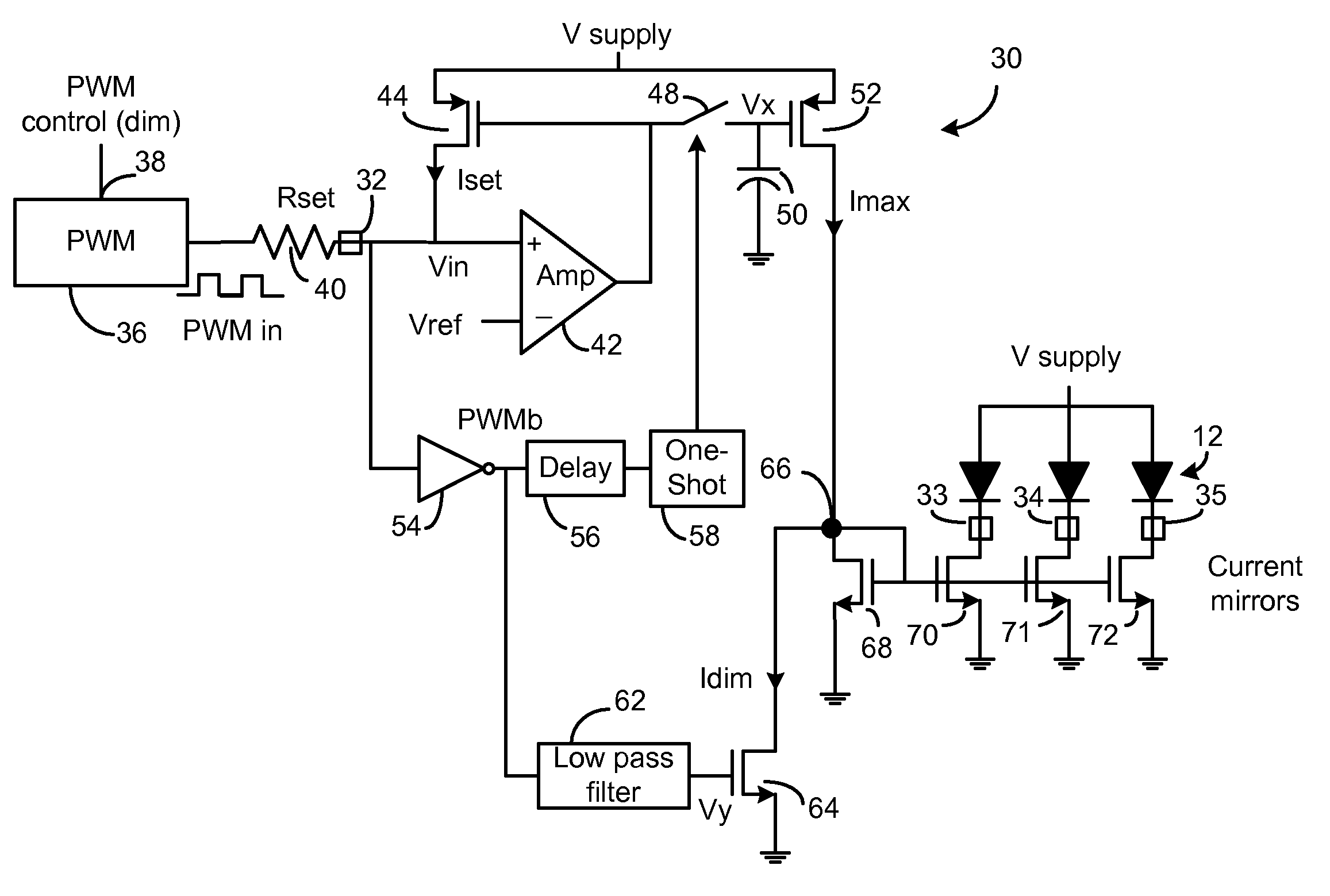
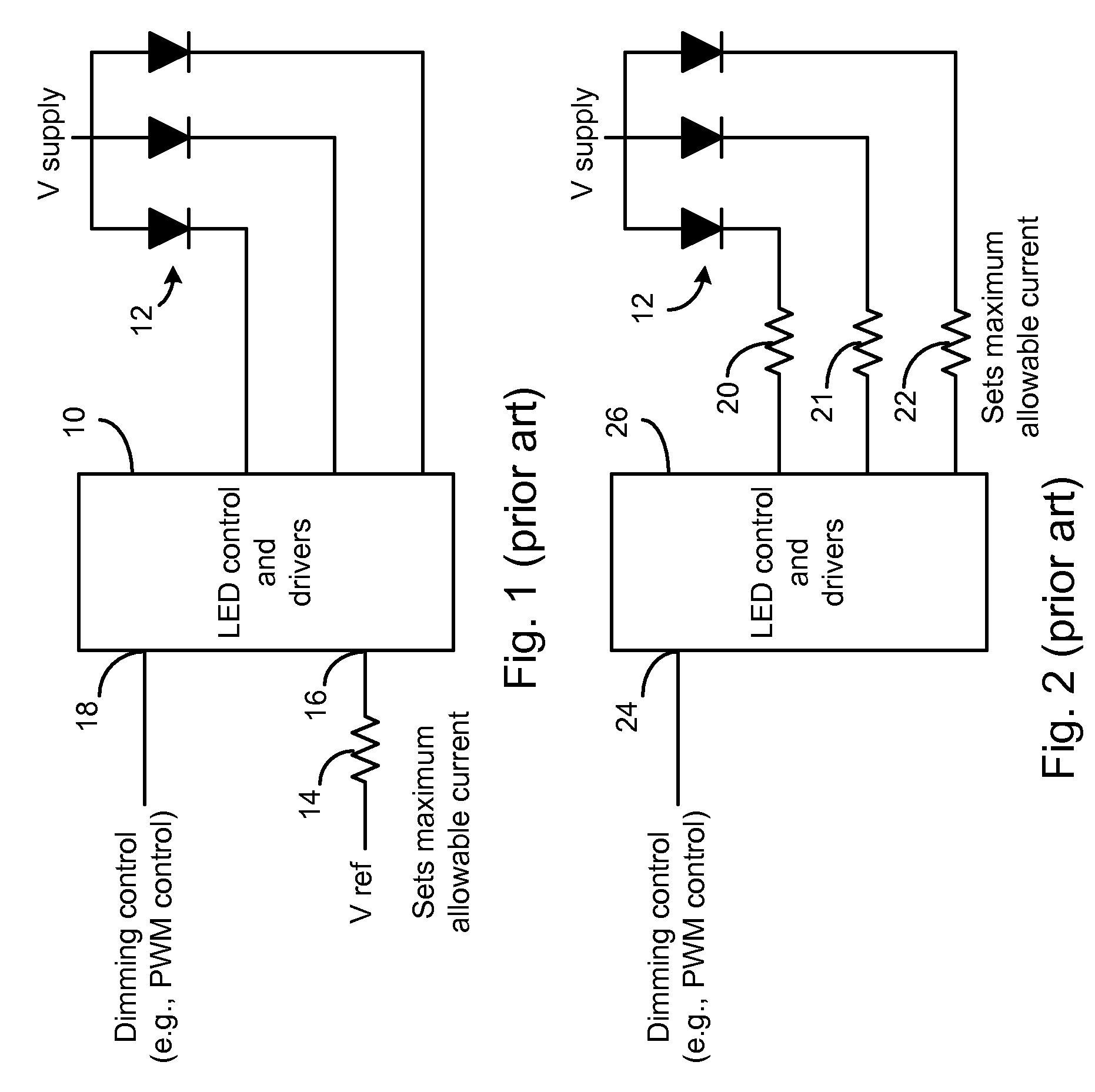
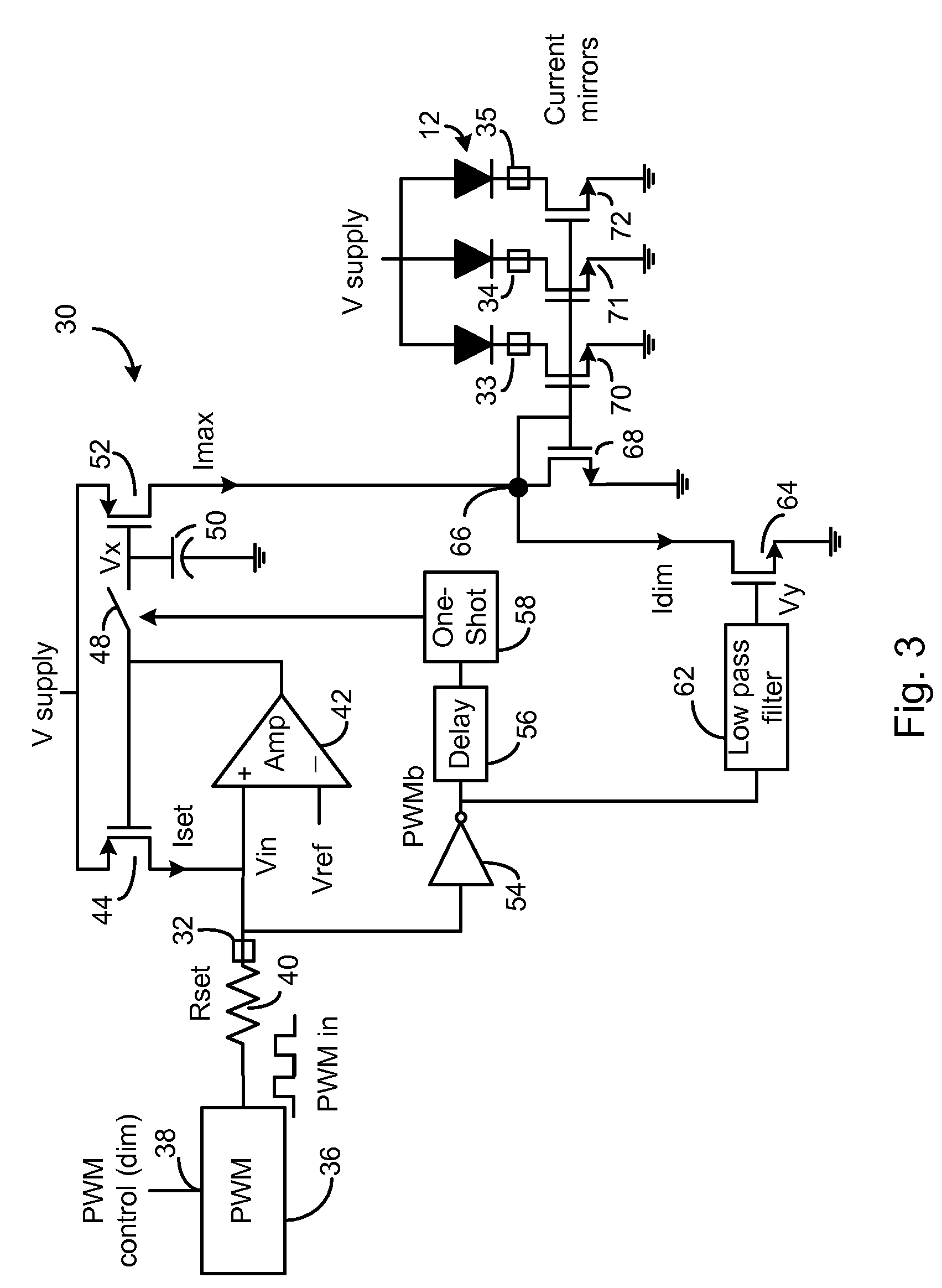
LED Controller IC Using Only One Pin to Dim and Set a Maximum LED Current
ActiveUS20090033243A1Reduce signalingIncrease currentElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesPulse sequenceFeedback control
An LED driver IC is described that uses a single pin to both set the maximum current through one or more driven LEDs and variably control the brightness of the LEDs. A single resistor is connected to the control pin of the IC, where the value of the resistor sets the maximum current through the LEDs. A PWM source, outputting a pulse train at a particular duty cycle, is connected to the other end of the resistor, where the duty cycle controls the LED brightness level. When the PWM signal is low (e.g. ground), a sample and hold circuit connects the output of a feedback control voltage to an Imax current source to set a maximum current based on the external resistor value. An inverse of the duty cycle of the PWM controller controls a current Idim that is subtracted from the maximum current Imax set by the resistor. This difference current is used to control drivers for the LEDs.
Owner:MICREL
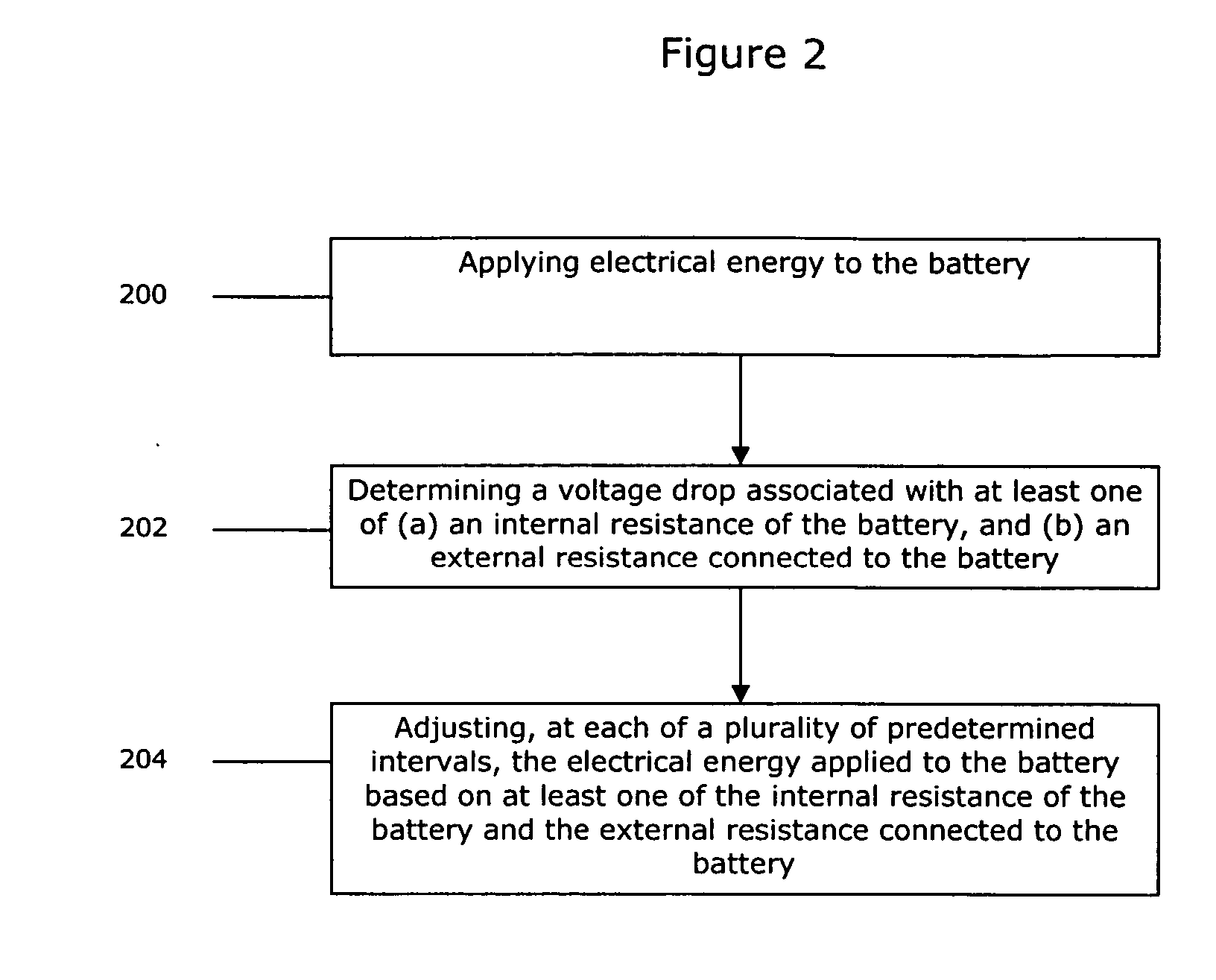
Method of charging a battery
InactiveUS20050194933A1Batteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerElectrical resistance and conductanceInternal resistance
A method of charging a battery having an internal resistance and an external resistance connected to the battery includes applying electrical energy to the battery. The method also includes adjusting, at a plurality of predetermined intervals, the electrical energy applied to the battery based on at least one of the internal resistance of the battery and the external resistance connected to the battery.
Owner:GALAXY POWER
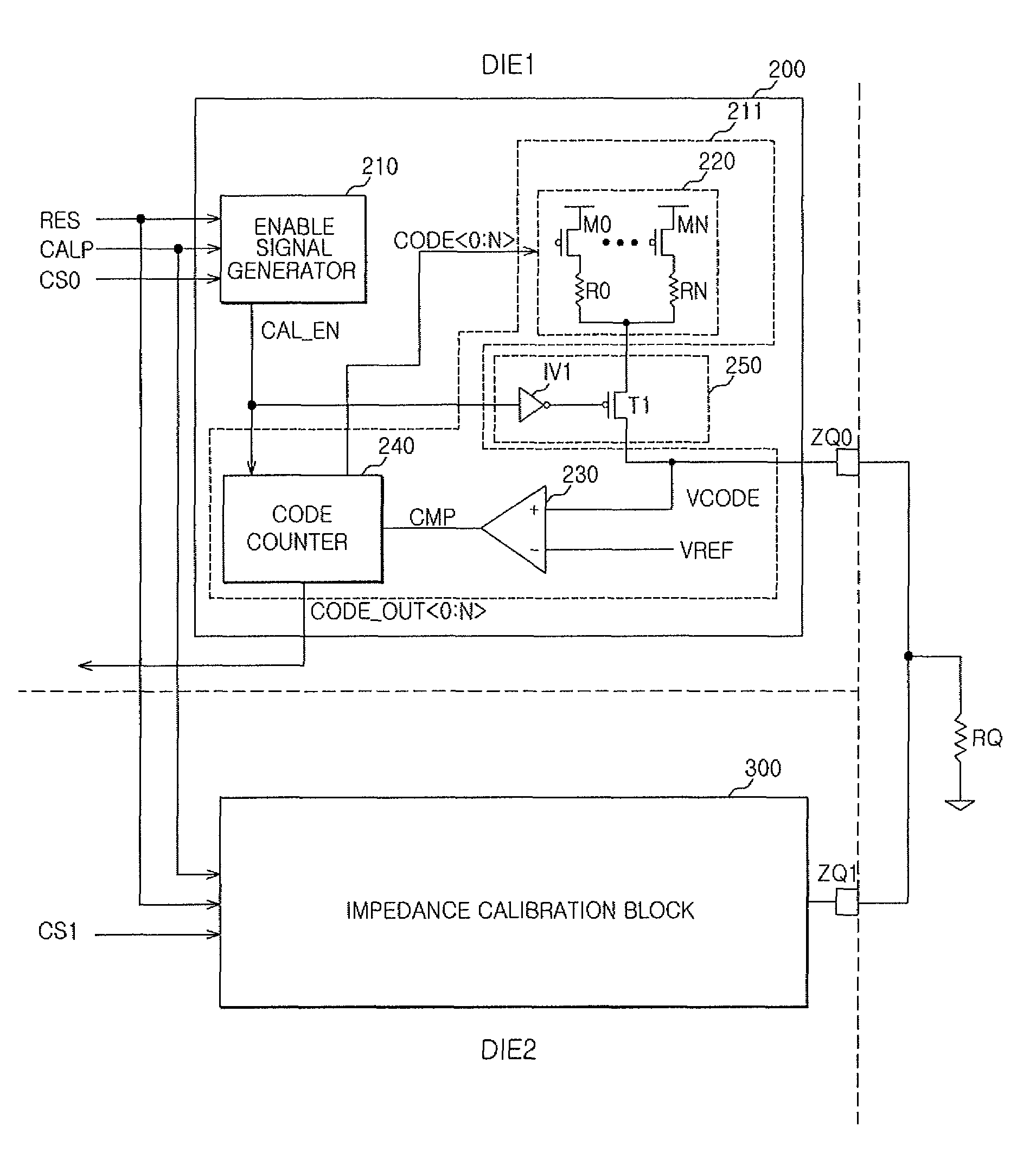
Circuit for calibrating impedance and semiconductor apparatus using the same
ActiveUS7990174B2Improve layout marginReliability increasing modificationsSolid-state devicesSignal generatorExternal resistance
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
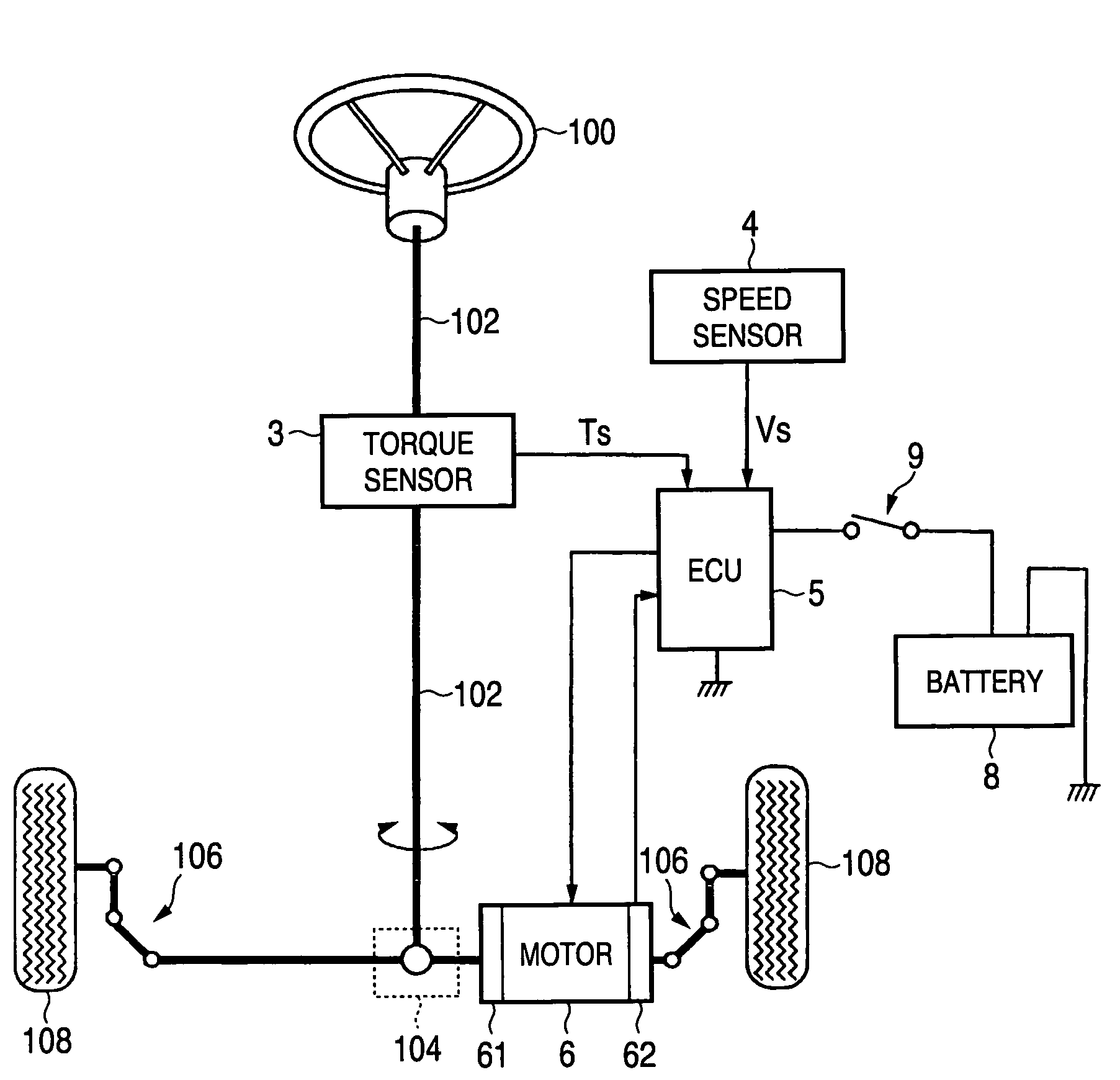
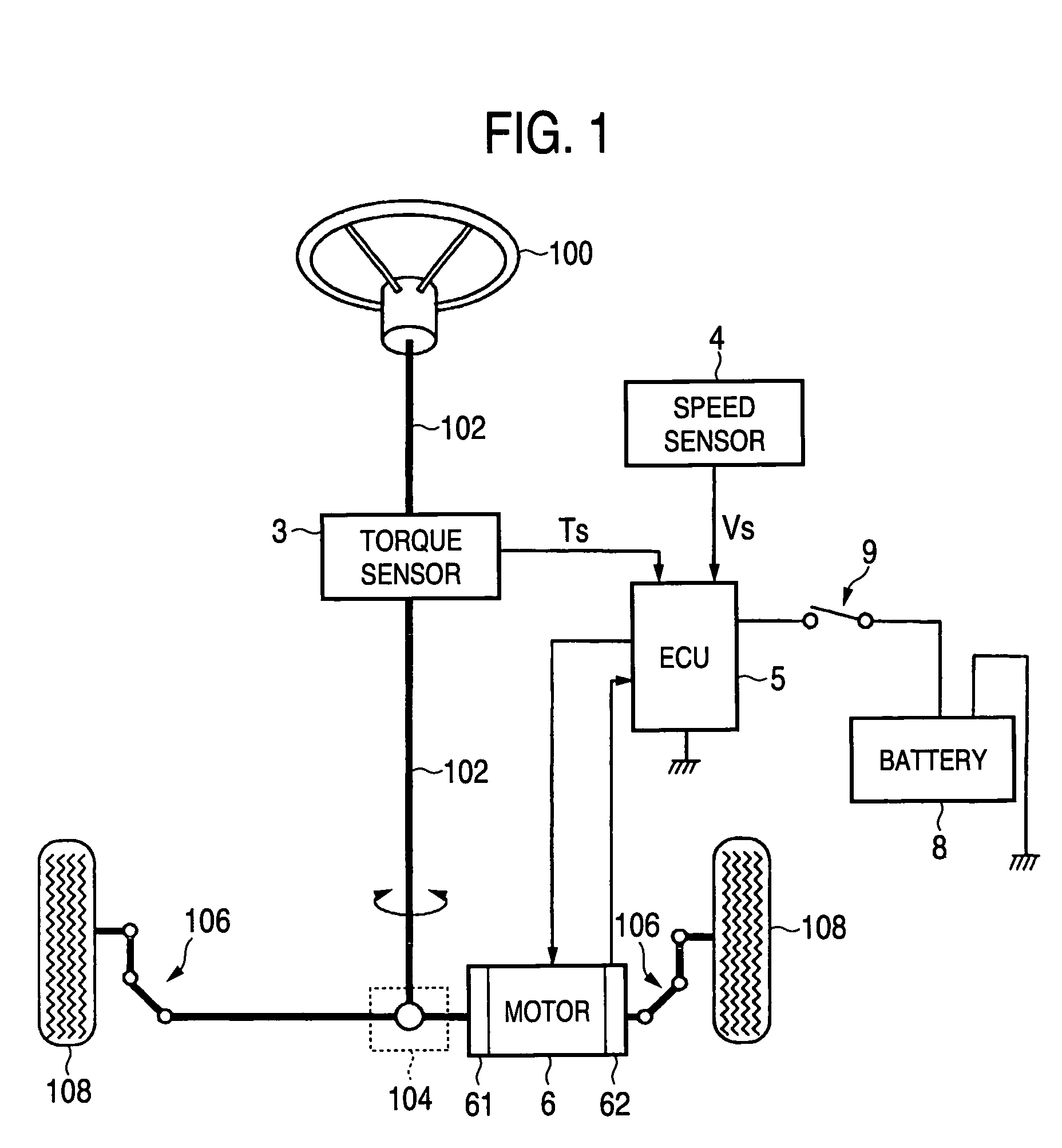
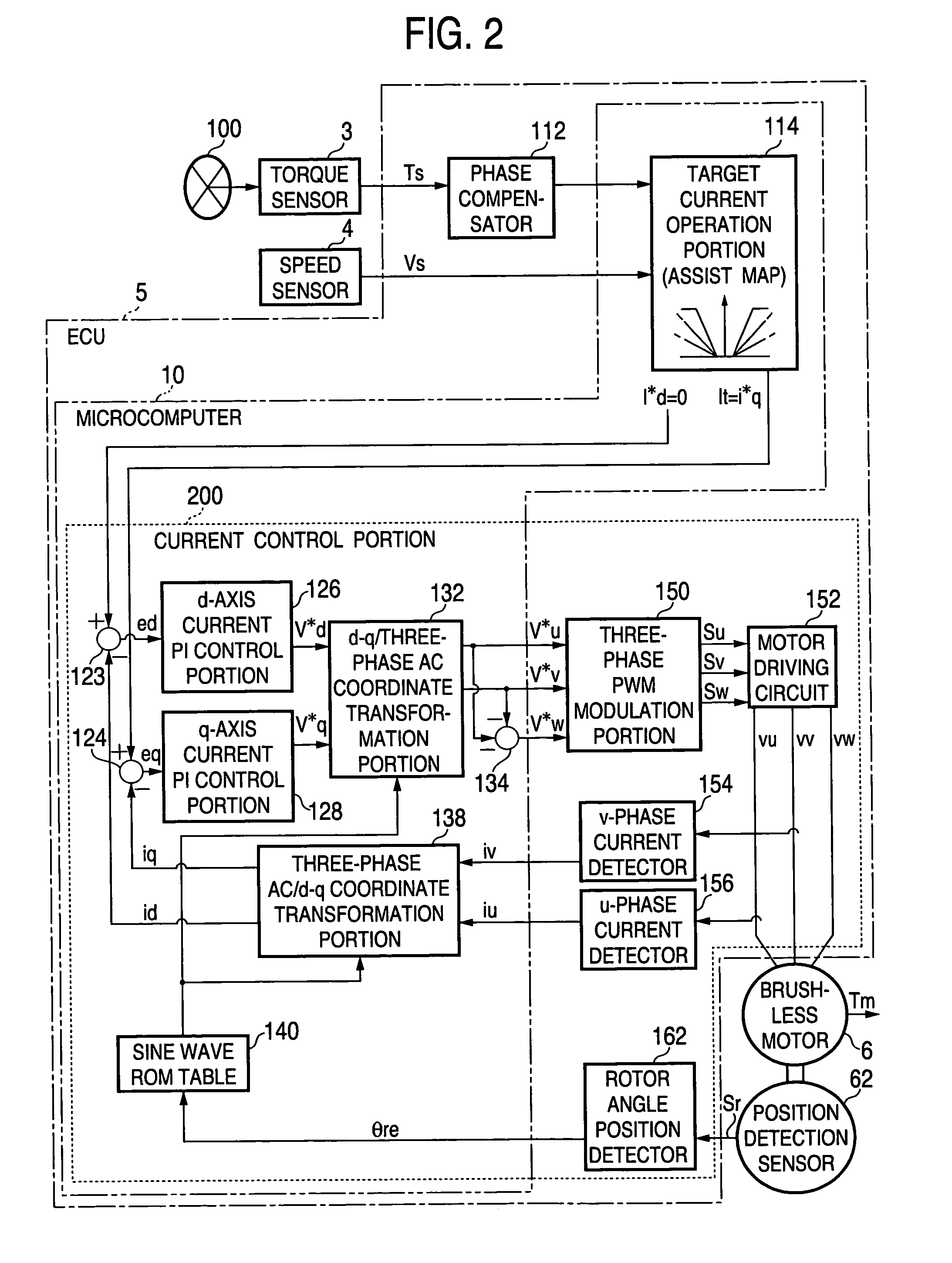
Electric power steering apparatus
ActiveUS7240761B2Improve responseReduce controlElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlElectric power steeringElectrical resistance and conductance
In a current control system for a cylindrical permanent magnet synchronous motor as the drive source of an electric power steering apparatus, proportional gain Kdp and integral gain Kdi of a d-axis current PI control portion 126 are respectively set to K1·Ld and K1·Rd on the basis of d-axis inductance Ld and d-axis resistance Rd of the motor. Further, proportional gain Kqp and integral gain Kqi of a q-axis current PI control portion 128 are respectively set to K2·Lq and K2·Rq on the basis of q-axis inductance Lq and q-axis resistance Rq of the motor (K1 and K2 are optional coefficients). In this case, both of the d-axis resistance Rd and the q-axis resistance Rq have values resulting from adding the external resistance R′ including wiring resistance to the internal resistance R of the motor.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Wind-powered pneumatic engine and a motor vehicle equipped with the engine
InactiveUS7641005B2Improve overall utilizationShorten speedAuxillary drivesWind motor controlEngineeringHigh pressure
A wind-powered pneumatic engine including one or more impeller chambers and one or more impellers disposed in the impeller chambers is provided. One or more air inlets for receiving external wind resistance airflow are disposed on the impeller chambers, and the external wind resistance airflow entering the air inlets drives the impellers to operate to generate power output. The wind-powered pneumatic engine further includes an air-jet system for jetting HPCA into the impeller chambers, and the internal high-pressure compressed air jetted by the air-jet system in conjunction with the external wind resistance airflow entering the air inlets drives the impellers to operate to generate power output. In the present invention, the external resistance airflow around a motor vehicle moving at a speed is converted into power for use, which greatly reduces energy consumption and improves the moving speed of a motor vehicle. A motor vehicle equipped with wind-powered pneumatic engine is also provided.
Owner:CONG YANG
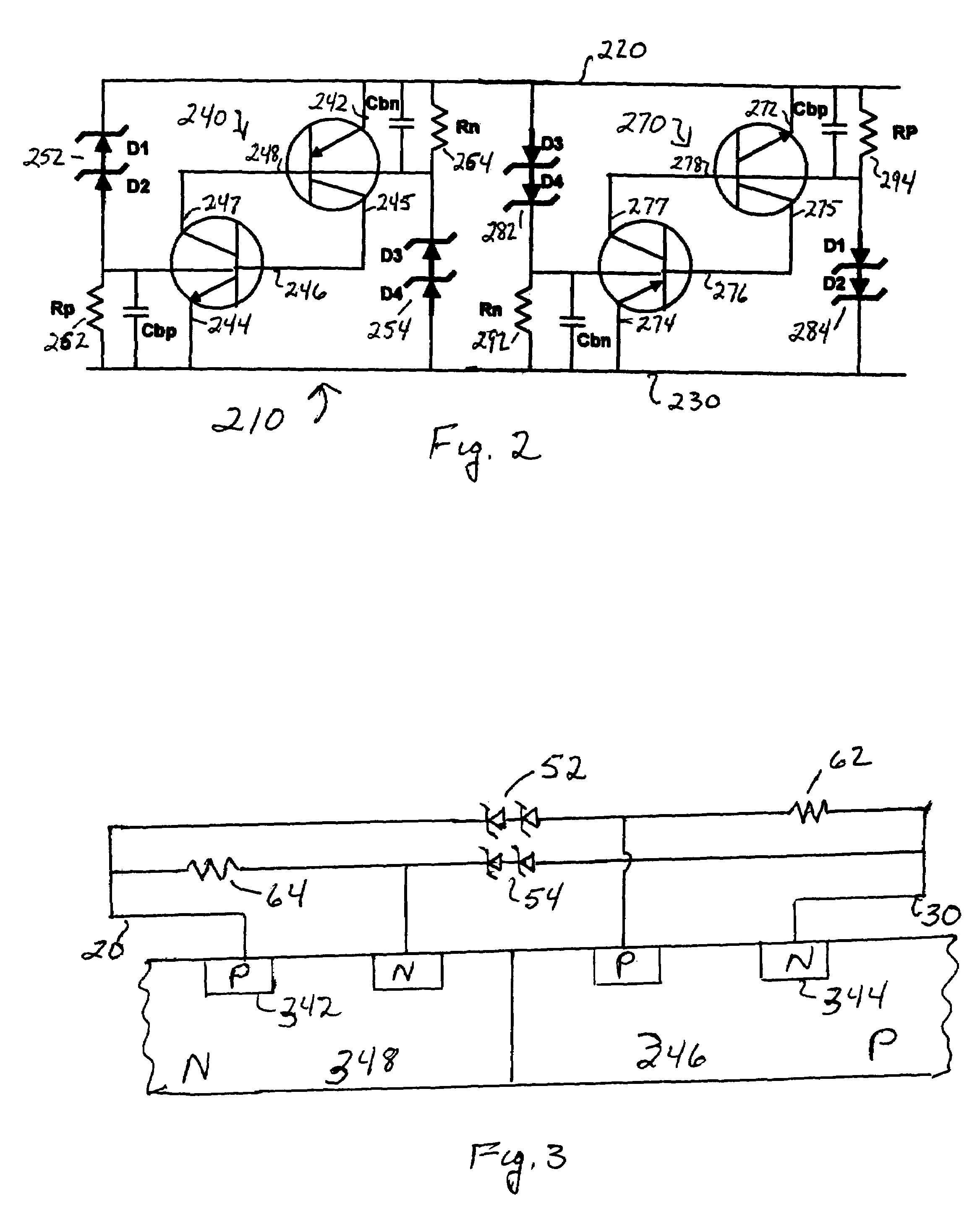
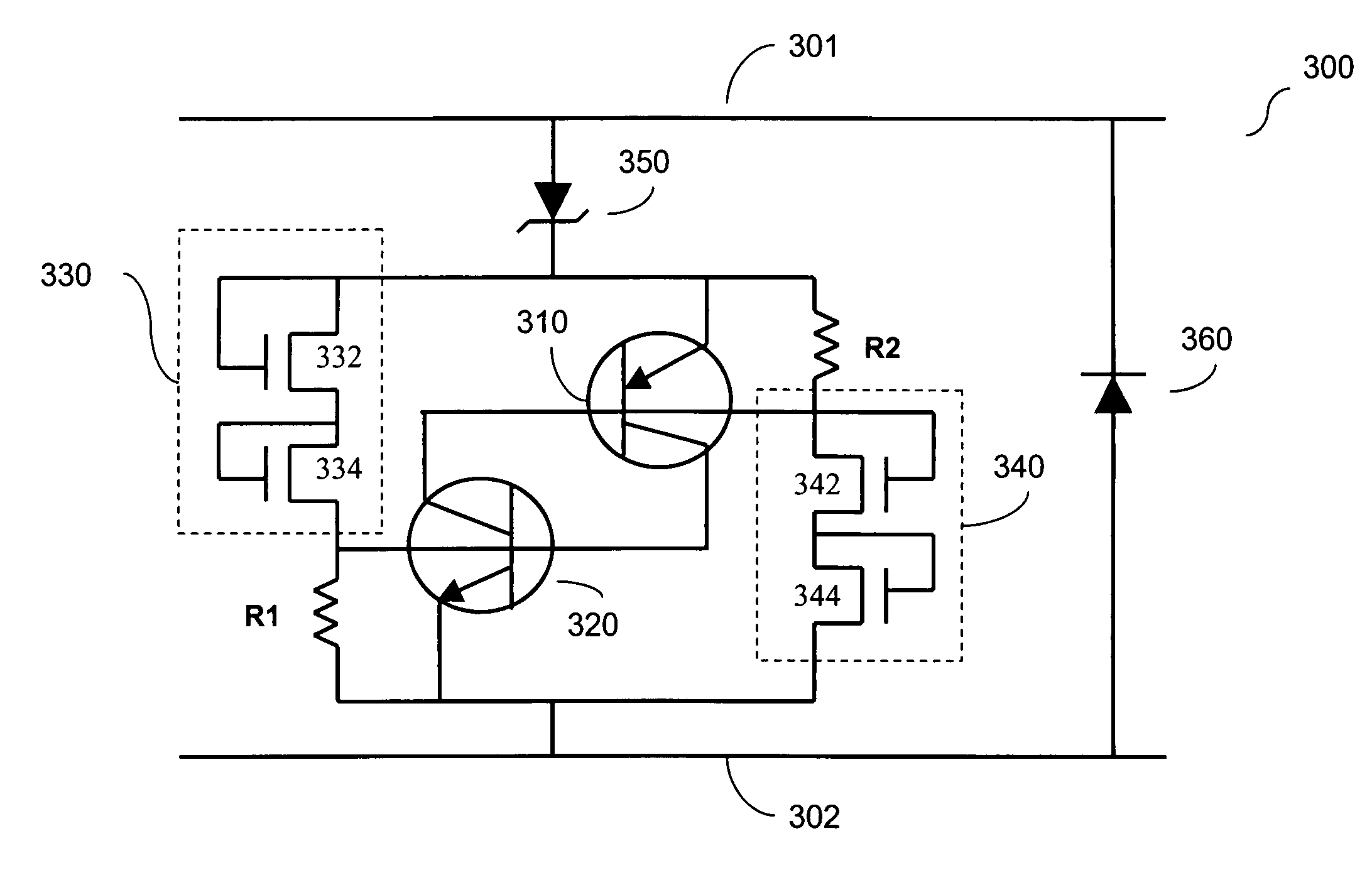
Fast and compact SCR ESD protection device for high-speed pins
InactiveUS7471493B1Reduce latencyMaximize currentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPre-chargeZener diode
A pair of SCR devices connected in antiparallel between first and second nodes. Each SCR device comprises an NPN and a PNP bipolar transistor. Reverse-biased Zener diodes are used for triggering the NPN bipolar transistor in each SCR device when it breaks down in an ESD event. Advantageously, additional Zener diodes are provided for pre-charging the PNP transistor of each SCR device at the same time, thereby reducing the delay time for turning on the PNP bipolar transistor. In addition, the breakdown current of the Zener diodes is preferably maximized by reducing the P-well and N-well resistance of the SCRs. This is achieved by connecting external resistances between the base of each bipolar transistor and the node to which the emitter of the transistor is connected.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
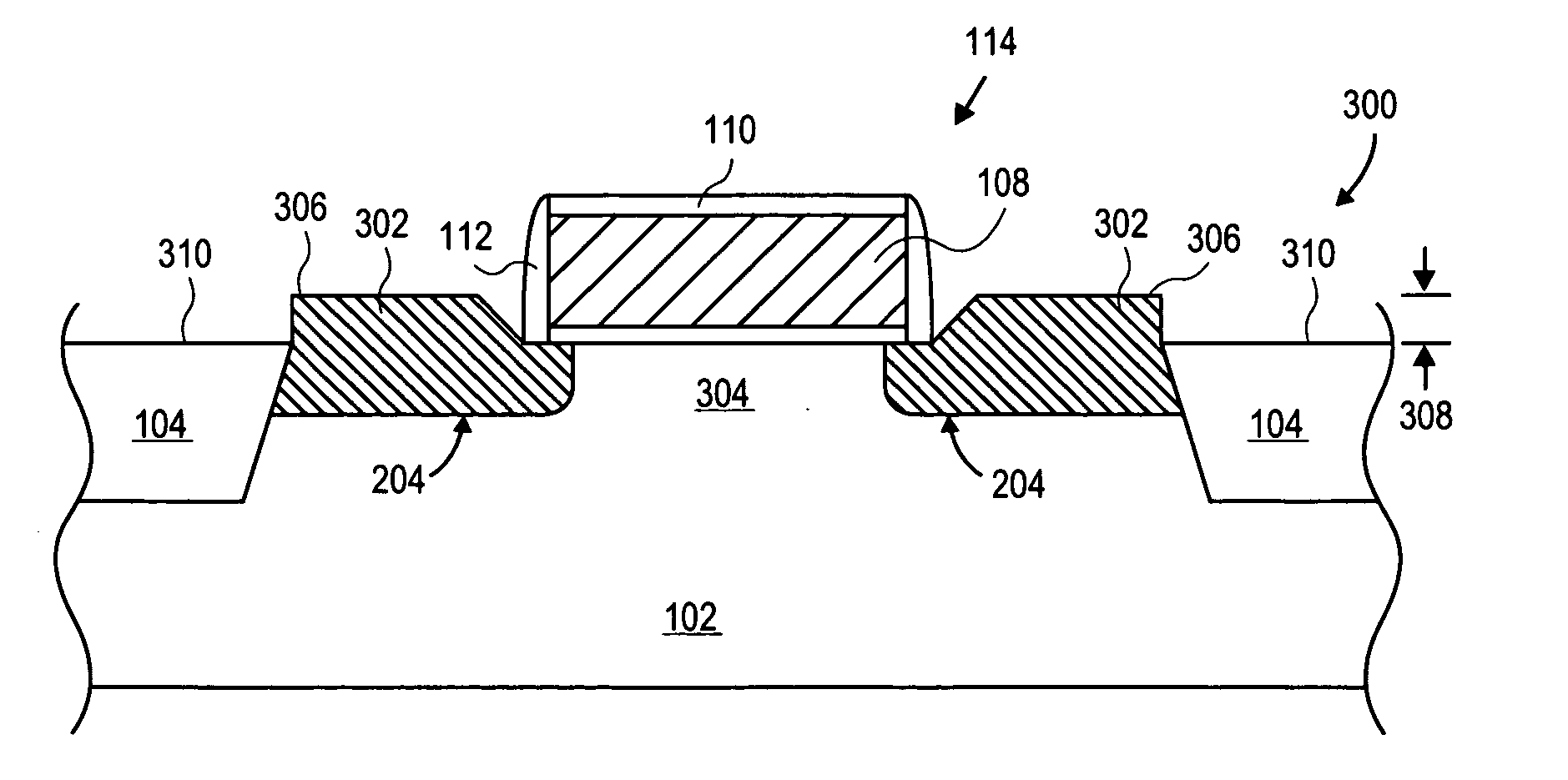
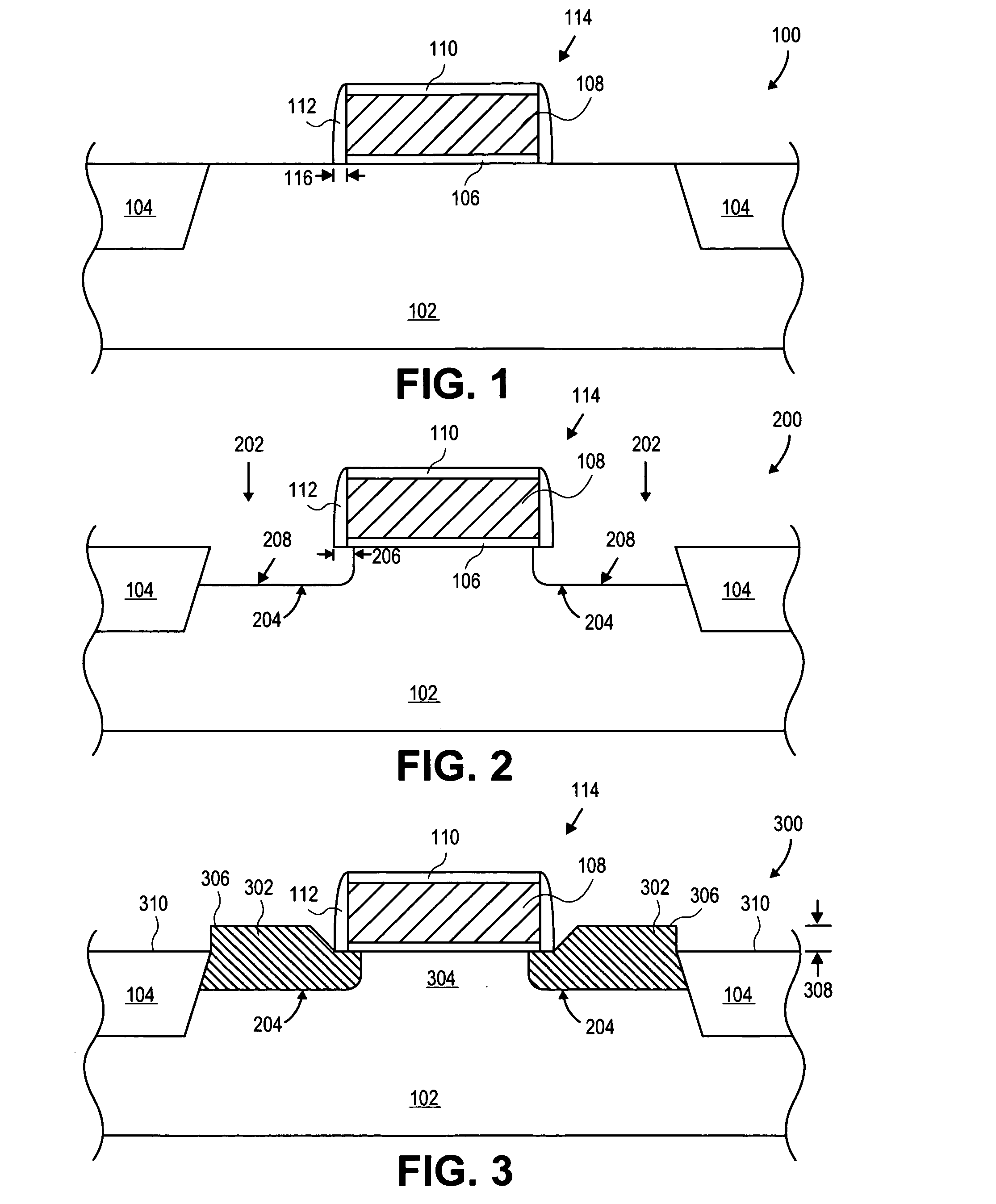
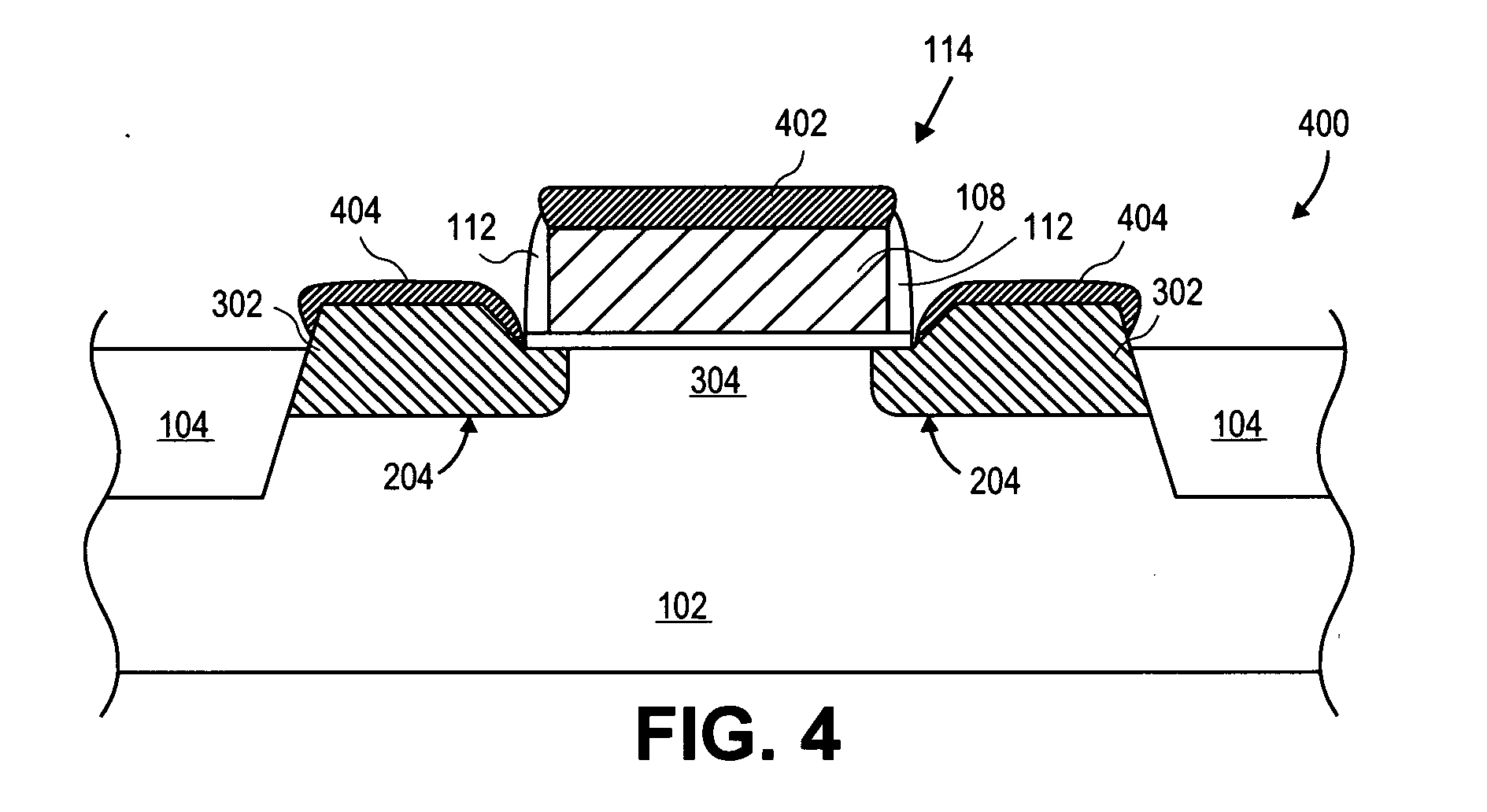
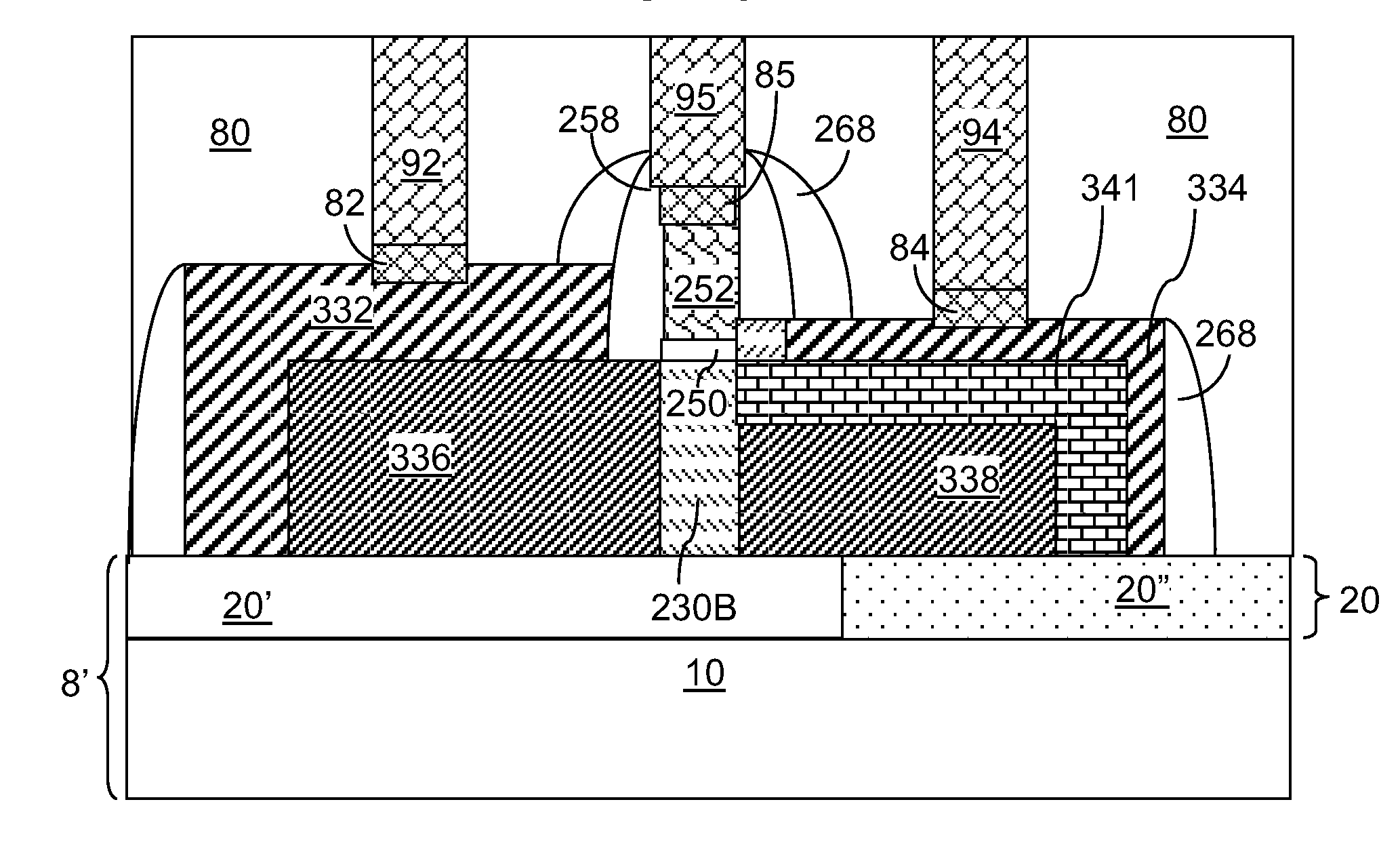
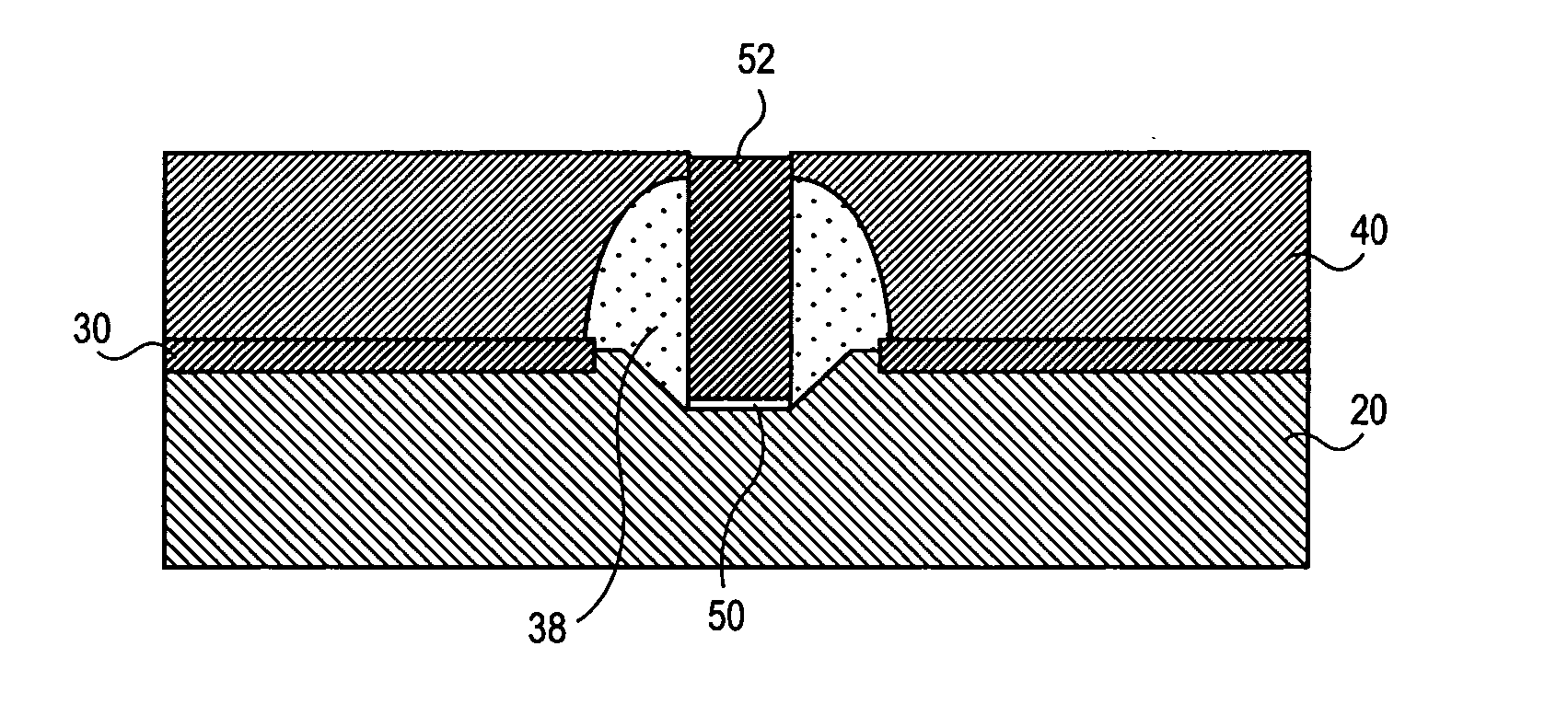
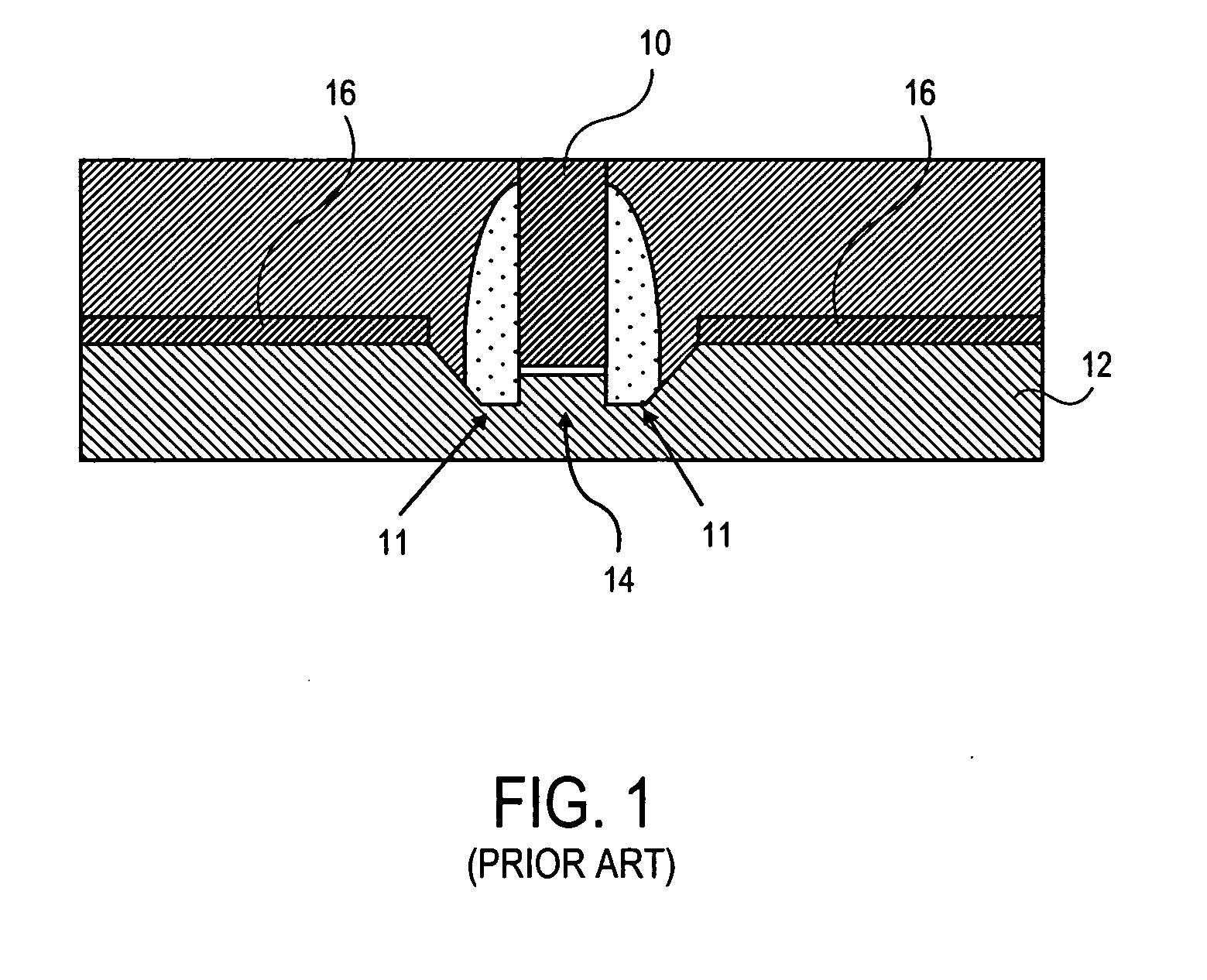
Method and structure for reducing the external resistance of a three-dimensional transistor through use of epitaxial layers
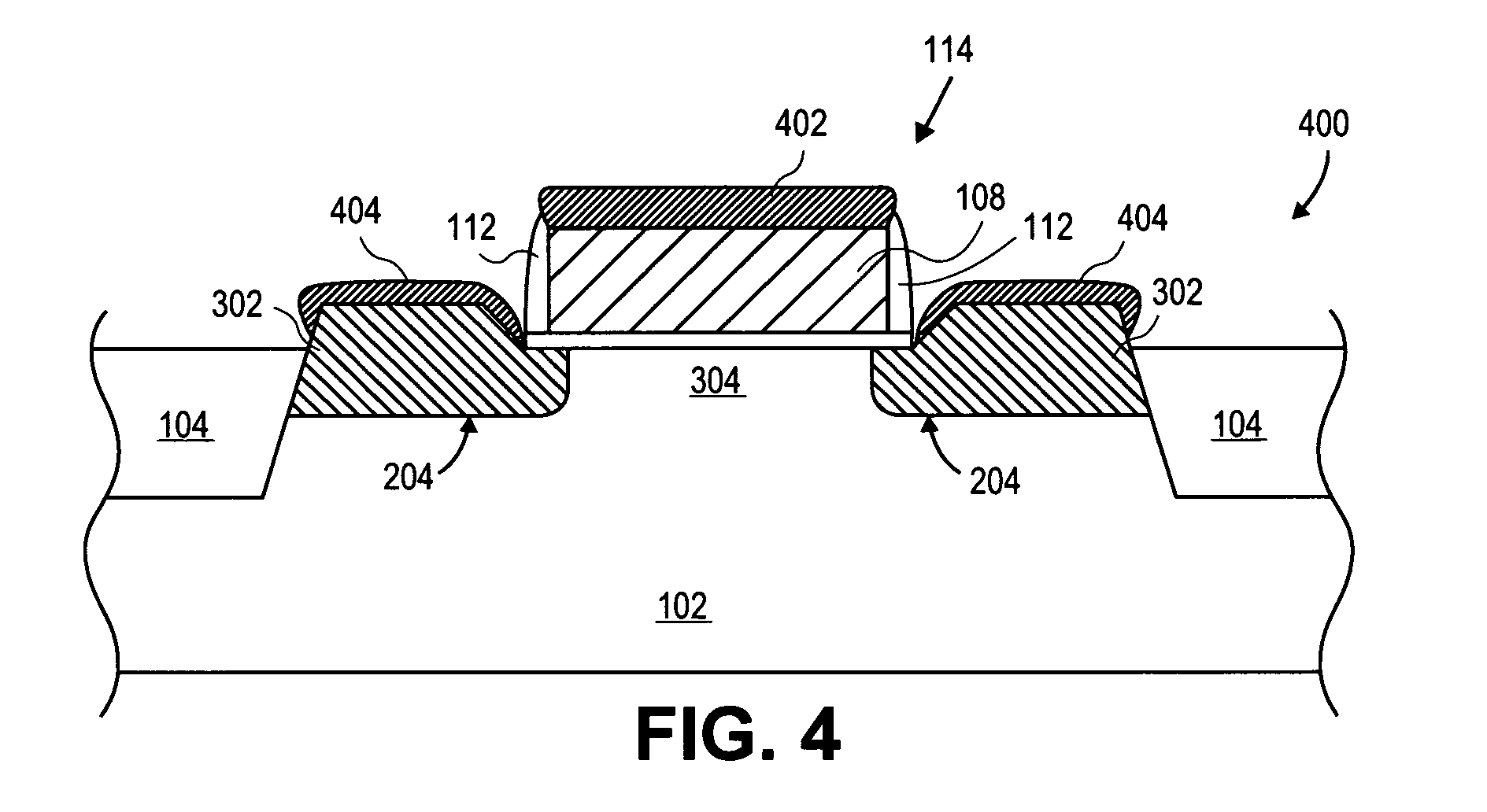
The fabrication of a tri-gate transistor formed with a replacement gate process is described. A nitride dummy gate, in one embodiment, is used allowing the growth of epitaxial source and drain regions immediately adjacent to the dummy gate. This reduces the external resistance.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Micropower RC oscillator
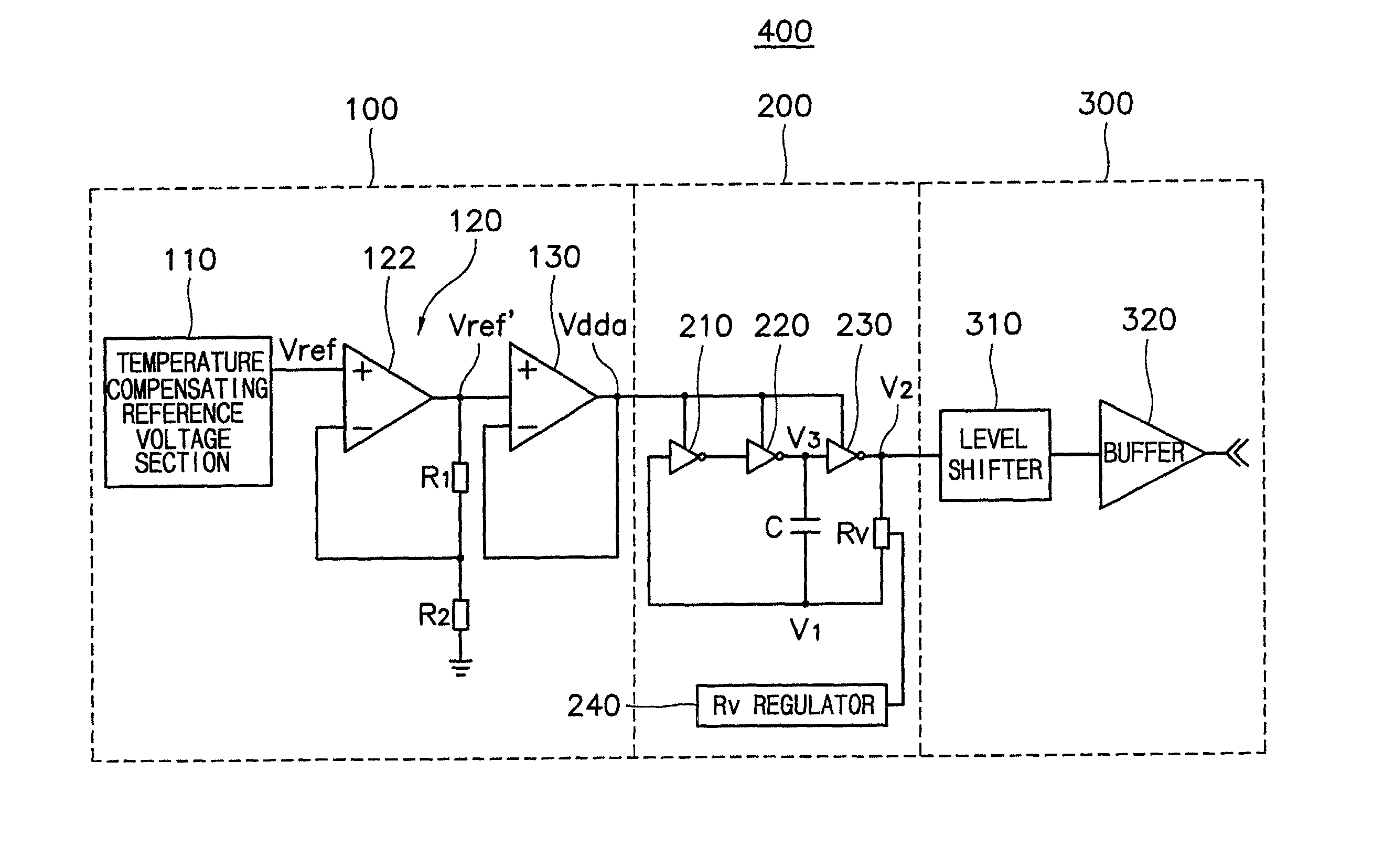
InactiveUS20020000889A1Pulse automatic controlLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsLevel shiftingElectrical resistance and conductance
A micropower RC oscillator having stable frequency characteristics with varying temperature includes a number of inverting circuits which are driven by an external driving voltage and connected in series with each other and an RC circuit having a resistor disposed in between a head-inverter and a tail inverter to form a closed loop and a capacitor disposed between the tail-inverter and the head-inverter. The resistor comprises a plurality of unit resistors constituting of a P+ diffusion resistor and a polysilicon resistor having opposing characteristics with respect to temperature variation at a predetermined ratio. A resistance regulator controls the resistance of the resistor by decoding an external resistance setting data to select a unit resistor that determines the oscillation frequency effectively. A driving voltage circuit receives a reference signal having the voltage level which is stable against the temperature variation by using a current source and a load having opposing characteristics with respect to the temperature variation and provides as a driving voltage of the RC oscillating circuit after increasing a fan-out capacity of the reference signal. An output level shifting circuit can be added to the rear side of the RC oscillating circuit to adjust the voltage level of the oscillation signal with the appropriate standard required at a receiving end.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
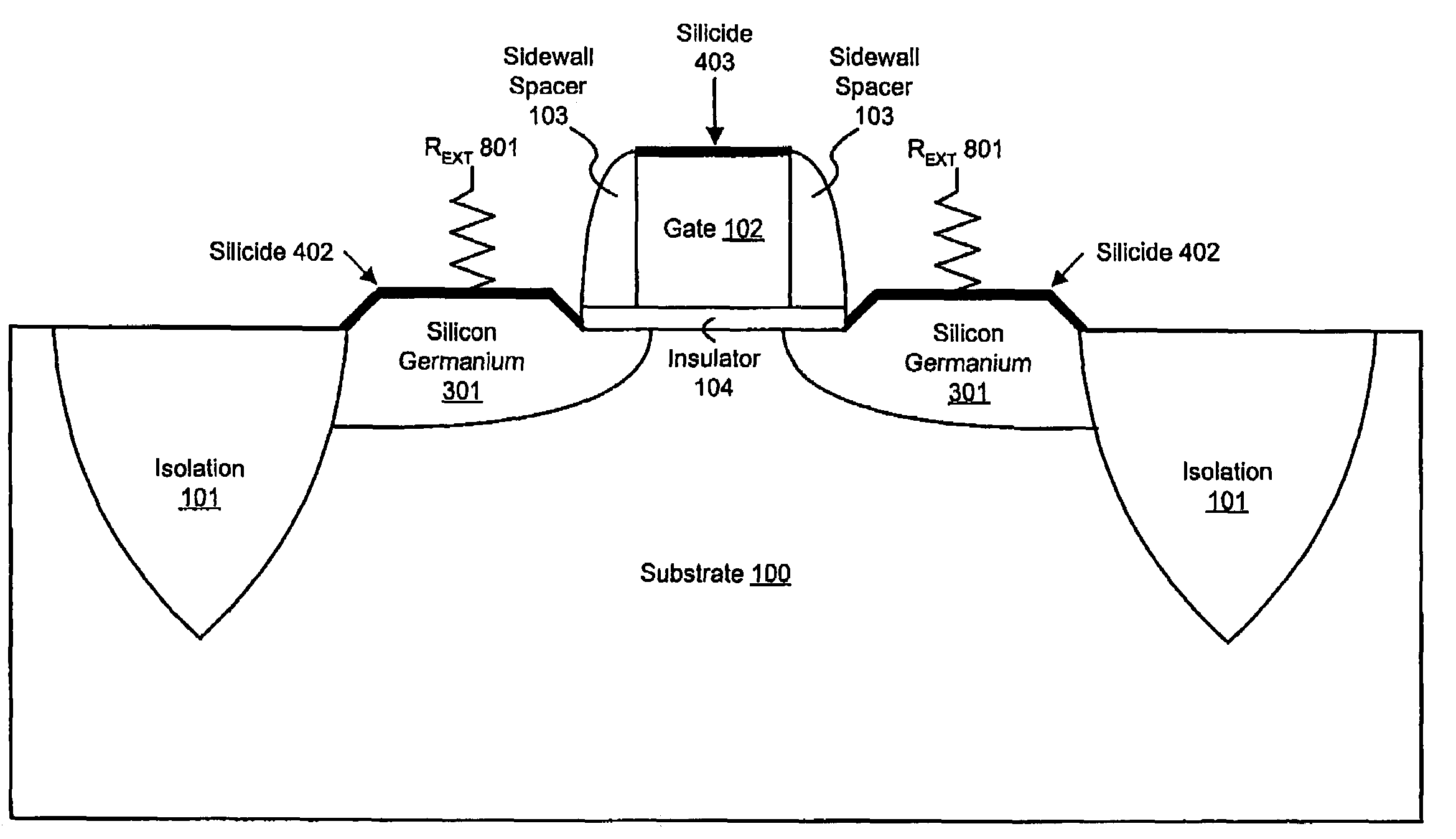
Method for improving transistor performance through reducing the salicide interface resistance
ActiveUS7274055B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSalicideCharge carrier mobility
An embodiment of the invention reduces the external resistance of a transistor by utilizing a silicon germanium alloy for the source and drain regions and a nickel silicon germanium self-aligned silicide (i.e., salicide) layer to form the contact surface of the source and drain regions. The interface of the silicon germanium and the nickel silicon germanium silicide has a lower specific contact resistivity based on a decreased metal-semiconductor work function between the silicon germanium and the silicide and the increased carrier mobility in silicon germanium versus silicon. The silicon germanium may be doped to further tune its electrical properties. A reduction of the external resistance of a transistor equates to increased transistor performance both in switching speed and power consumption.
Owner:INTEL CORP
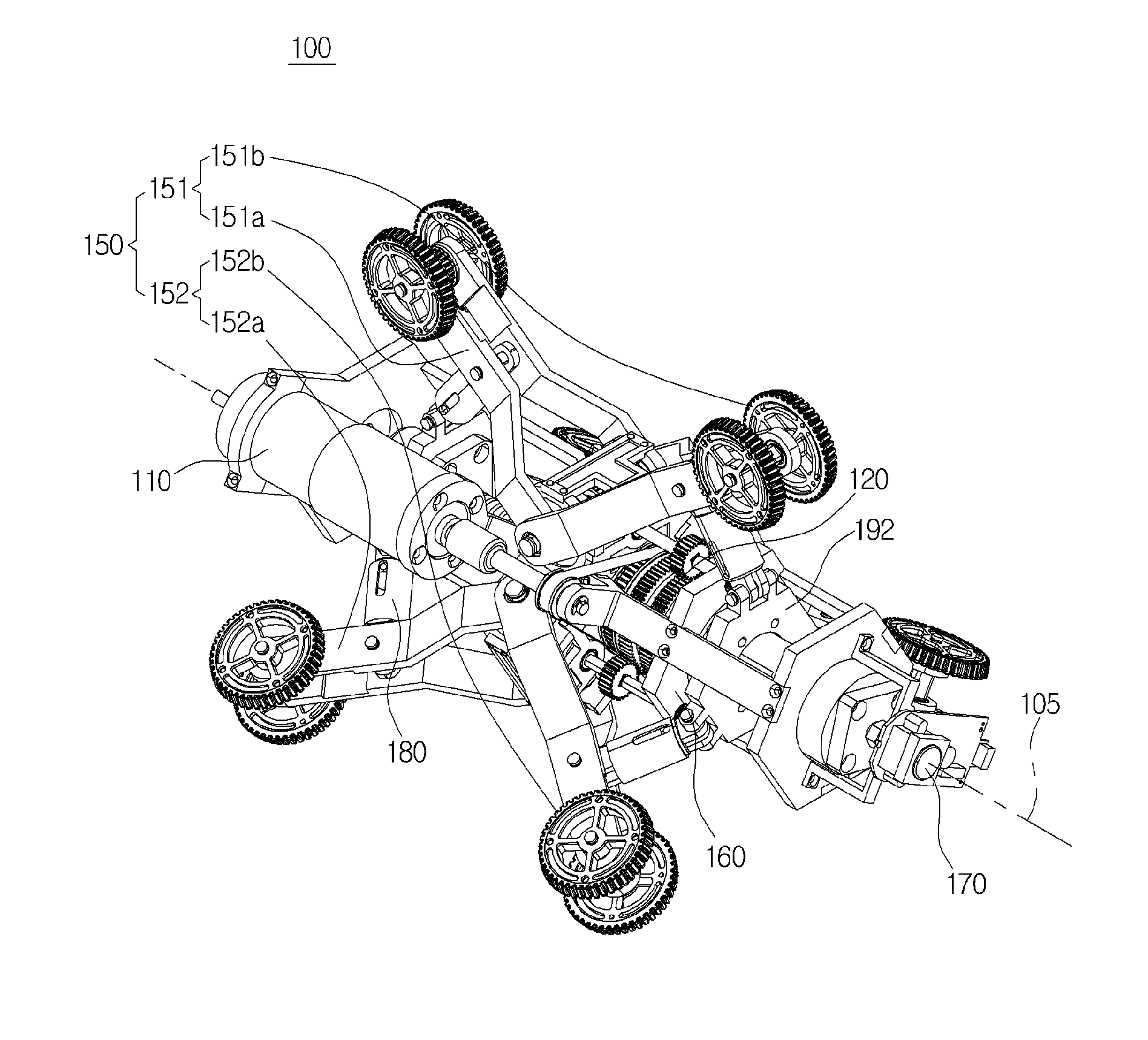
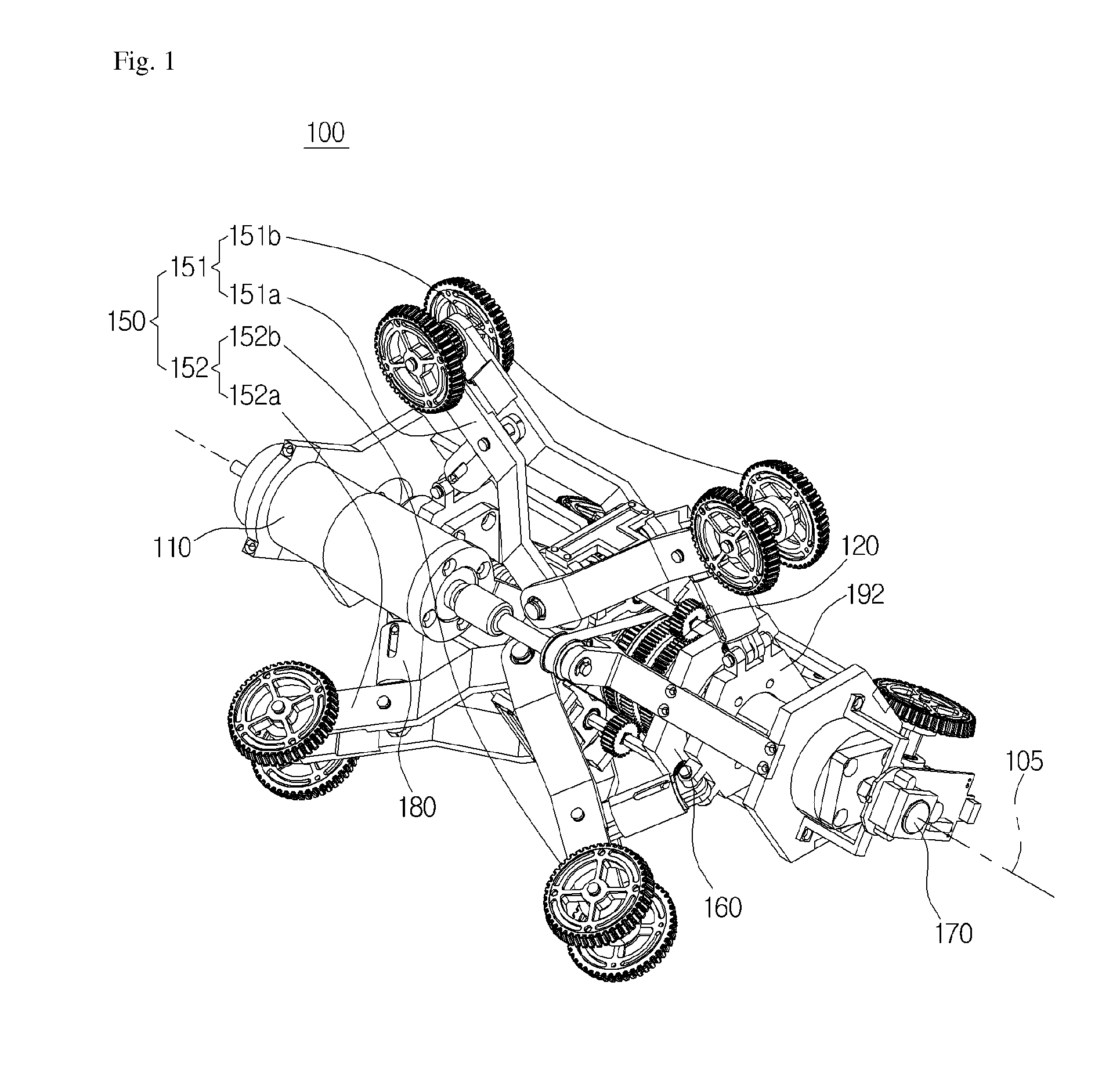
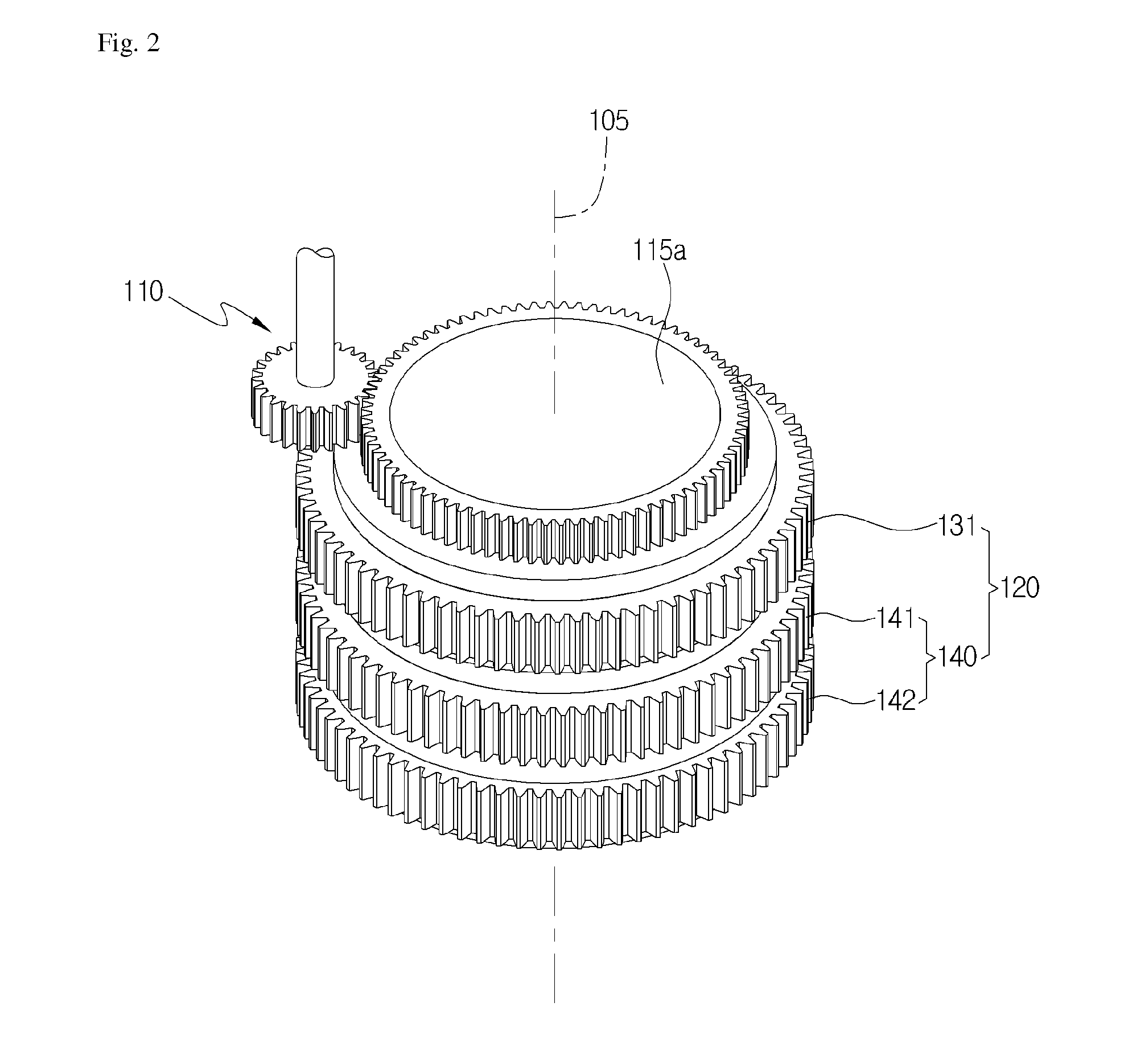
Robot using multi-output differential gear
Provided herein is a robot using a multi-output differential gear, the robot comprising a driver; a differential gear configured to receive a driving power from the driver, and to drive in an interlocked manner with the driving power to generate at least three outputs differentiated from the driving power; and a motion section configured to drive in an interlocked manner with an output generated from the differential gear, and to apply an external resistance to the differential gear.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
Method and device for regulating train speed
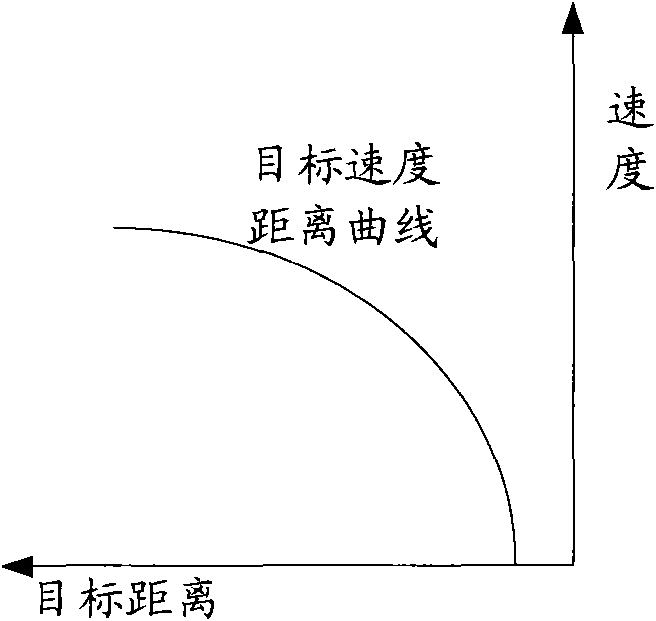
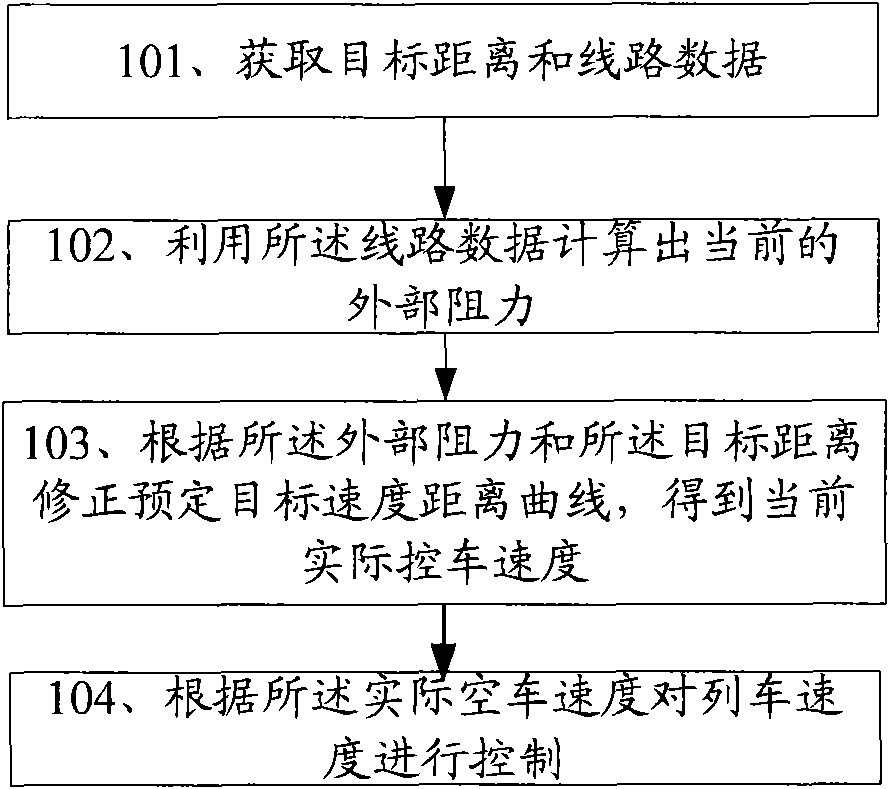
InactiveCN101875361AGuaranteed safe operationSmall amount of calculationSpeed controllerAutomatic systemsEngineeringSafe operation
The invention discloses a method for regulating train speed, comprising the steps of: acquiring target distance and line data; calculating the current external resistance by using the line data; modifying a predetermined target speed distance curve according to the external resistance and the target distance to obtain the current actual train control speed; and controlling the train speed according to the actual train control speed. The embodiment of the invention also provides a corresponding device. By prestoring an ideal train control curve which only takes the brake performance of the train into account without considering the external resistance, the actual train control speed can be obtained just by modifying the current train control speed in the ideal train control curve in each train control period, thereby reducing the calculated amount, shortening the train control period and ensuring the safe operation of the train.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Fast trigger ESD device for protection of integrated circuits
ActiveUS7408754B1Low hold voltageLow trigger voltageTransistorEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentThin oxideSilicon-controlled rectifier
The present invention provides an ESD device for protecting thin oxide layers in transistors or capacitors in an integrated circuit. In one embodiment, the ESD device includes a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR), the SCR including a PNP bipolar transistor and a NPN bipolar transistor. The ESD device further includes first and second trigger devices coupled to the SCR and configured to simultaneously turn on the PNP bipolar transistor and the NPN bipolar transistor in response to an ESD pulse on the ESD device. The base of the NPN bipolar transistor is floating to allow a first external resistor to be connected between the base and emitter of the NPN bipolar transistor. A second external resistor can be connected between the base and emitter of the PNP bipolar transistor.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Mos transistors having high-k offset spacers that reduce external resistance and methods for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20080258225A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate stackEngineering
MOS transistors having high-k spacers and methods for fabricating such transistors are provided. One exemplary method comprises forming a gate stack overlying a semiconductor substrate and forming an offset spacer about sidewalls of the gate stack. The offset spacer is formed of a high-k dielectric material that results in a low interface trap density between the offset spacer and the semiconductor substrate. First ions of a conductivity-determining impurity type are implanted into the semiconductor substrate using the gate stack and the offset spacer as an implantation mask to form spaced-apart impurity-doped extensions.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
High-side driver circuit
ActiveUS20130241601A1Improve the problemLower performance requirementsTransistorElectronic switchingDriver circuitVoltage source
The present invention provides a high-side driver circuit including a power transistor, the first transistor, the second transistor, the second capacitor, the second diode, a start-up circuit. The start-up circuit is coupled between a resistor and the second capacitor to complete a gate driving circuit. And, the aforementioned resistor can either be the gate resistance of the power transistor or an external resistor. The design of start-up circuit enables the functionality of the bootstrap capacitor of being charged to a designate voltage level. Thus, the depletion-mode transistor can be controlled to turn on / off without a floating voltage source or a negative voltage source.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
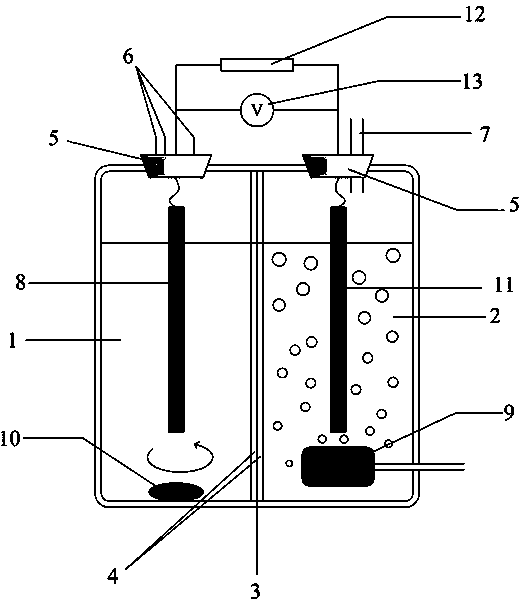
Microbial fuel cell based method for treatment and detection of chromium-containing electroplating wastewater
InactiveCN104386826AAvoid toxic effectsNo pollution in the processTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsHigh concentrationSodium acetate
The invention discloses a microbial fuel cell based method for treatment and detection of chromium-containing electroplating wastewater. The steps include: 1) injecting anaerobic sludge and a sodium acetate solution into an anode chamber of a two-chambered microbial fuel cell to inoculate microorganisms, injecting a cathode liquid into a cathode chamber, and connecting resistance at the cathode and the anode to form a closed loop, reacting the cell in a thermotank, injecting sodium acetate into the anode chamber each day till the output voltage is stable; 2) changing the anode chamber solution to an oxygen removed anode liquid, and changing the cathode solution to chromium-containing wastewater; and 3) after starting, adjusting the pH value of wastewater, injecting the wastewater into the cathode chamber, connecting the external resistance and starting the treatment process. The method provided by the invention realizes no direct contact of microorganisms and hexavalent chromium, avoids poisoning of hexavalent chromium on microorganisms, and makes microbiological treatment of high concentration hexavalent chromium wastewater become possible. The standard redox potential of hexavalent chromium is 1.33V, the microbial fuel cell is utilized to treat hexavalent chromium wastewater, and the purposes of synchronous wastewater treatment and electric energy recovery are realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
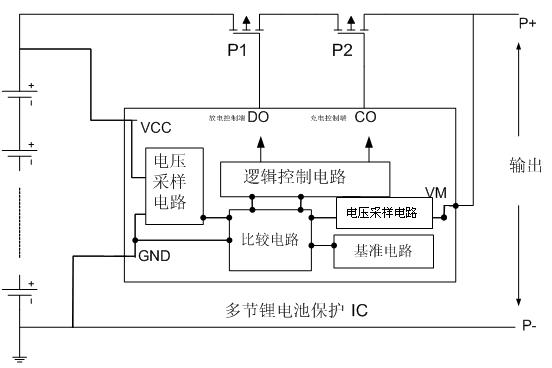
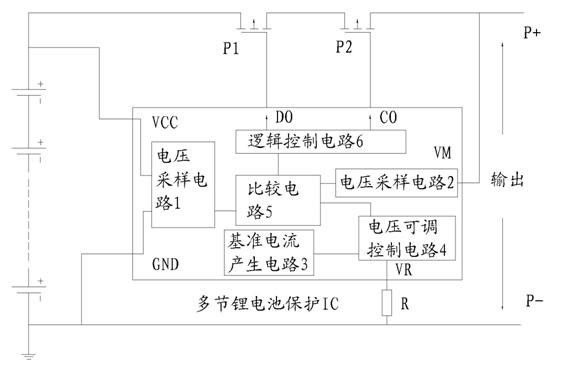
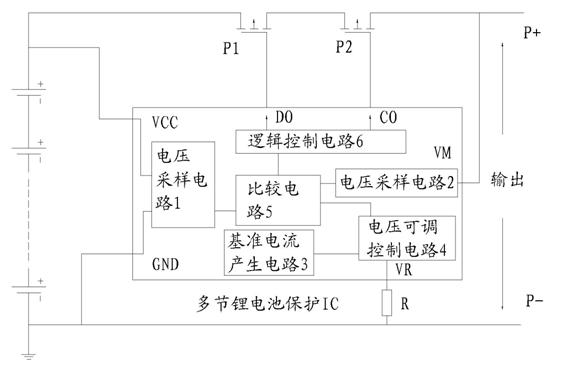
Integrated circuit (IC) with adjustable protection threshold for protecting a plurality of lithium batteries
The invention mainly discloses an IC with adjustable protection threshold for protecting a plurality of lithium batteries. The IC comprises a chip power supply terminal VCC, a discharge circuit current detection terminal VM, a chip ground potential terminal GND, an outlaid MOSFET charging control terminal CO, an outlaid MOSFET discharge control terminal DO, and an external resistance terminal VR arranged on a chip, wherein an outlaid adjustable resistor R is connected with a chip power supply grounding end; and the protection threshold can be adjusted by adjusting the resistance of the outlaid adjustable resistor. The IC solves the problem of limited protection threshold of the prior IC for protecting the plurality of lithium batteries, and can achieve the adjustable over-voltage and over-current protection threshold.
Owner:宿松县市场监督管理局市场监督检验所
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com