Patents
Literature
1875 results about "Silicon-germanium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
SiGe (/ˈsɪɡiː/ or /ˈsaɪdʒiː/), or silicon-germanium, is an alloy with any molar ratio of silicon and germanium, i.e. with a molecular formula of the form Si₁₋ₓGeₓ. It is commonly used as a semiconductor material in integrated circuits (ICs) for heterojunction bipolar transistors or as a strain-inducing layer for CMOS transistors. IBM introduced the technology into mainstream manufacturing in 1989. This relatively new technology offers opportunities in mixed-signal circuit and analog circuit IC design and manufacture. SiGe is also used as a thermoelectric material for high temperature applications (>700 K).
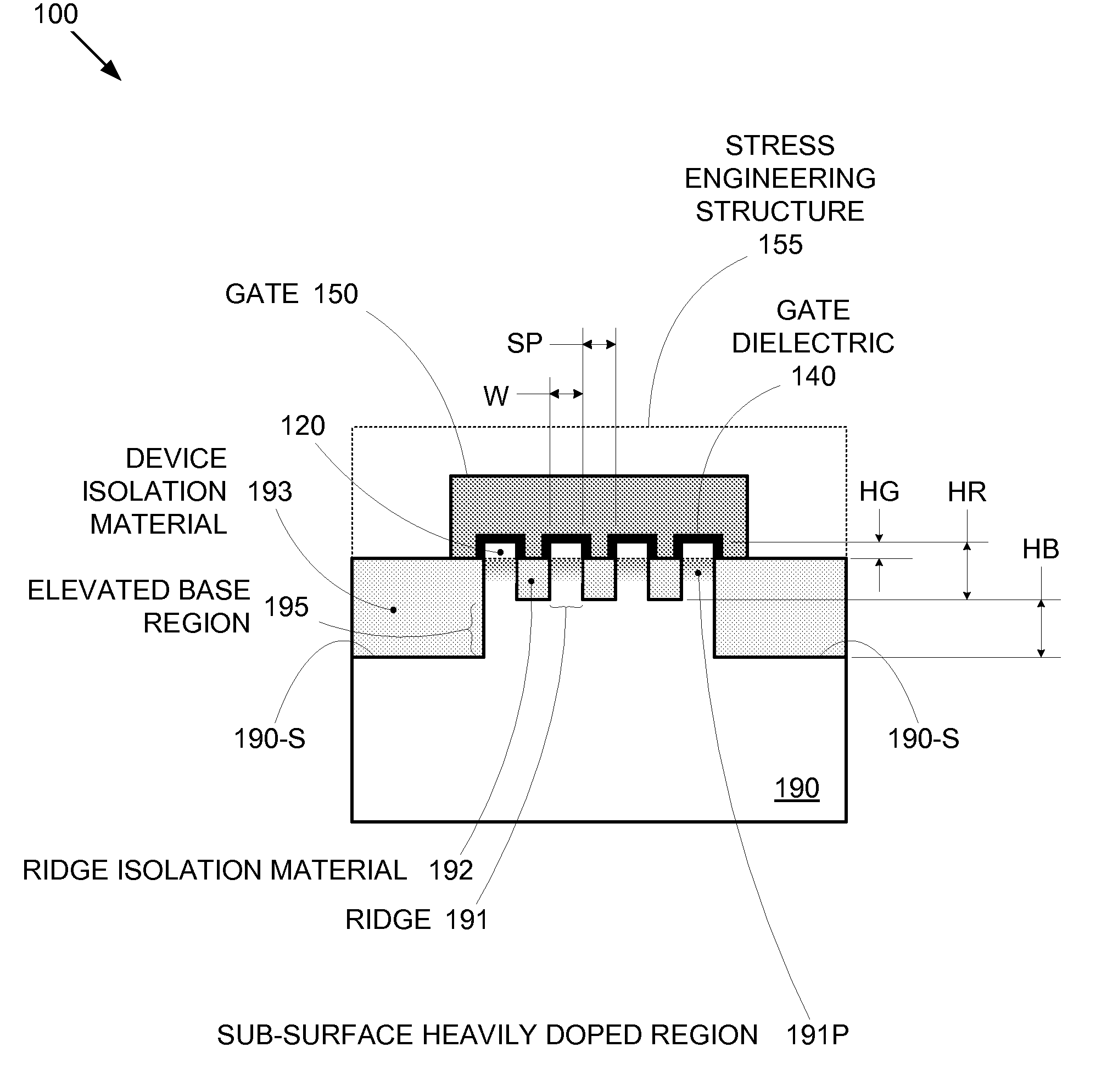
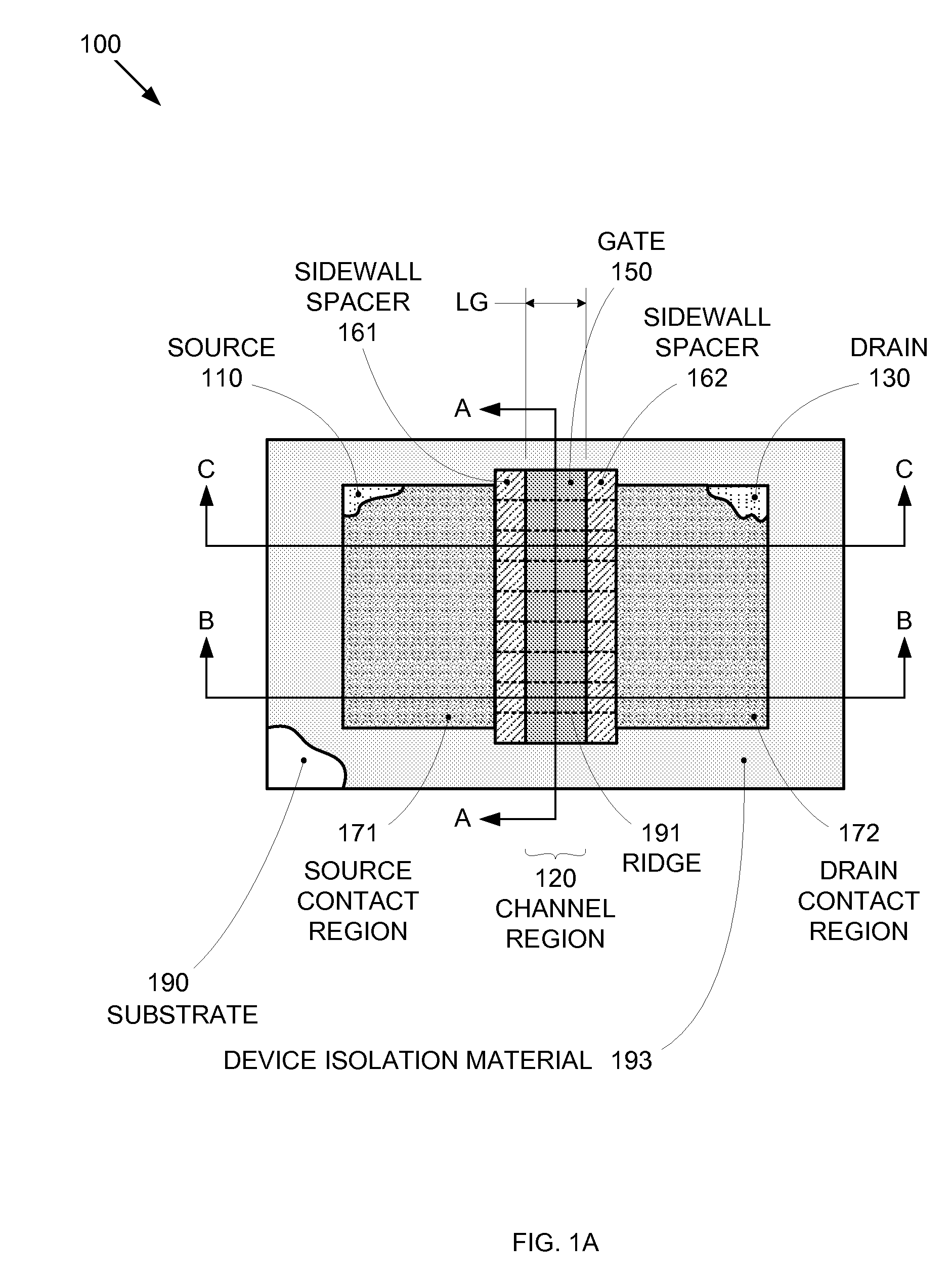
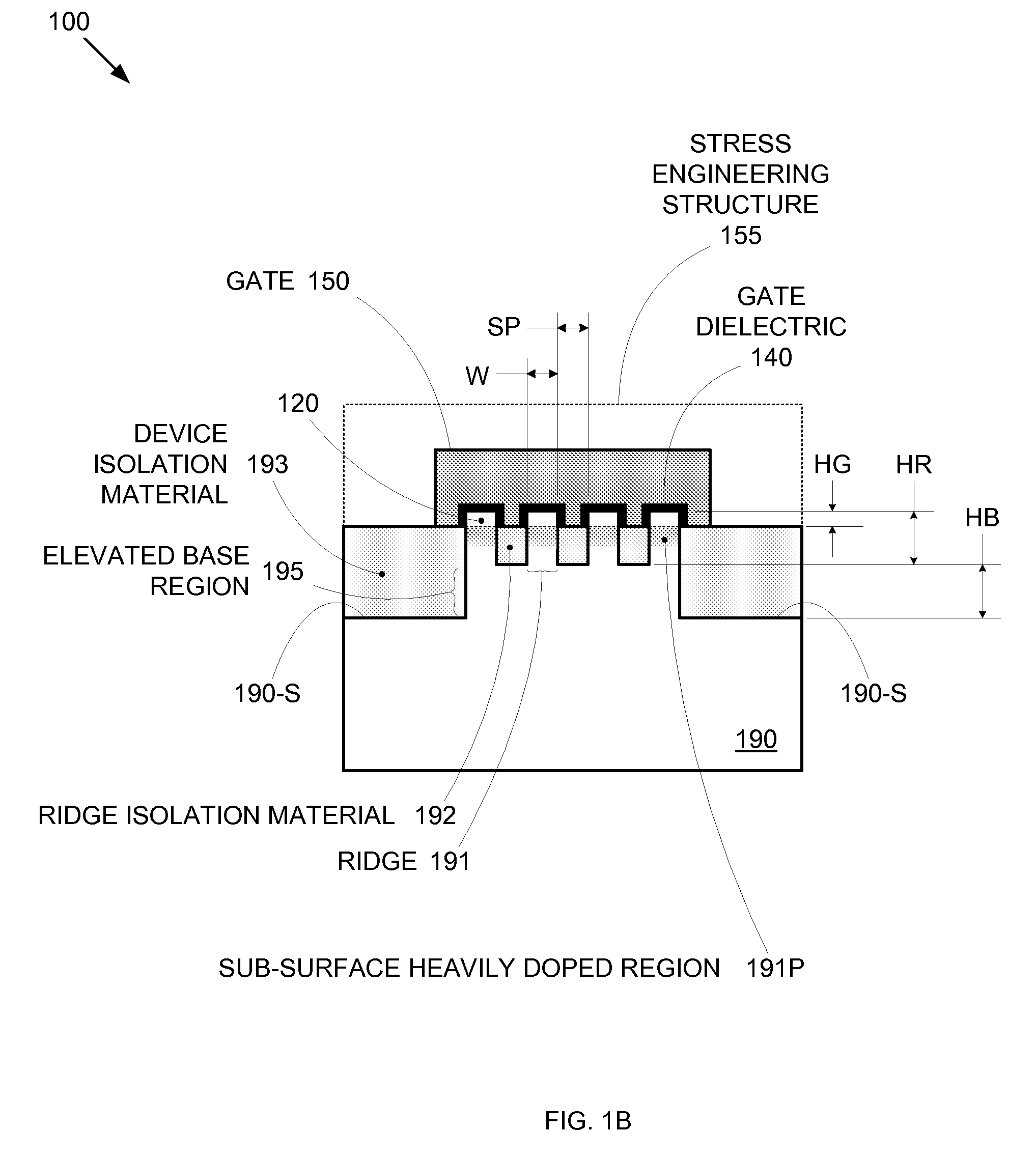
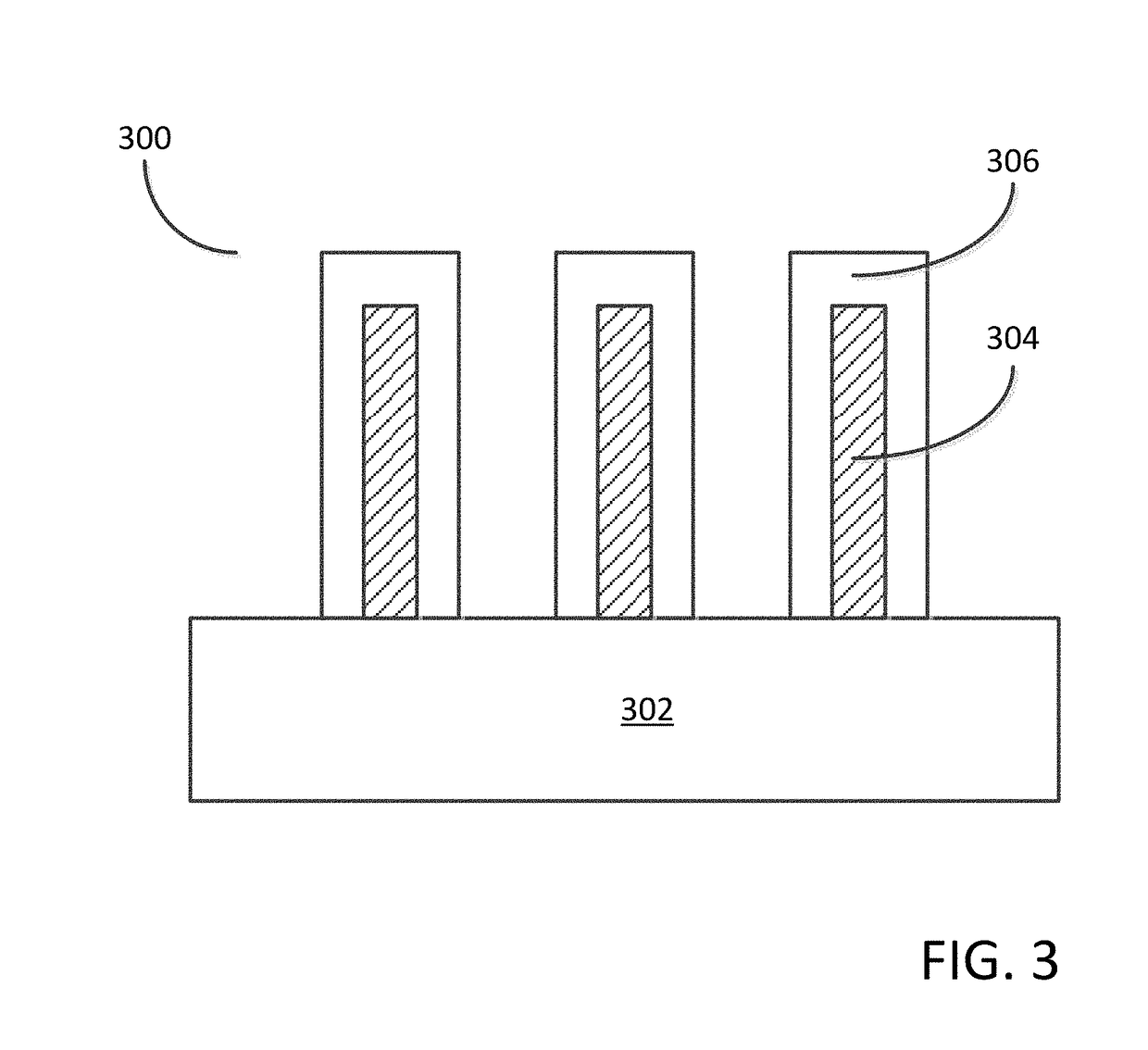
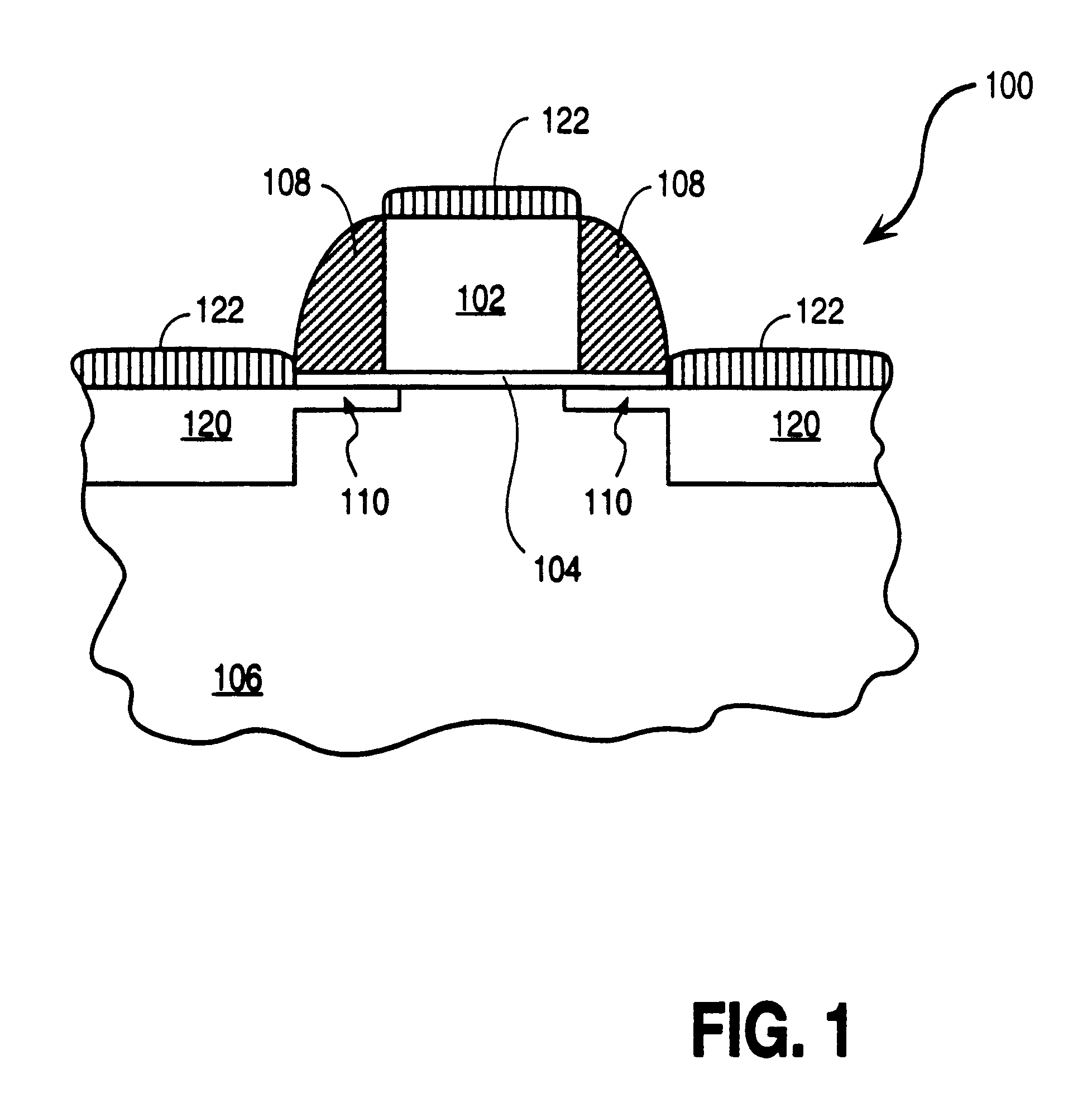
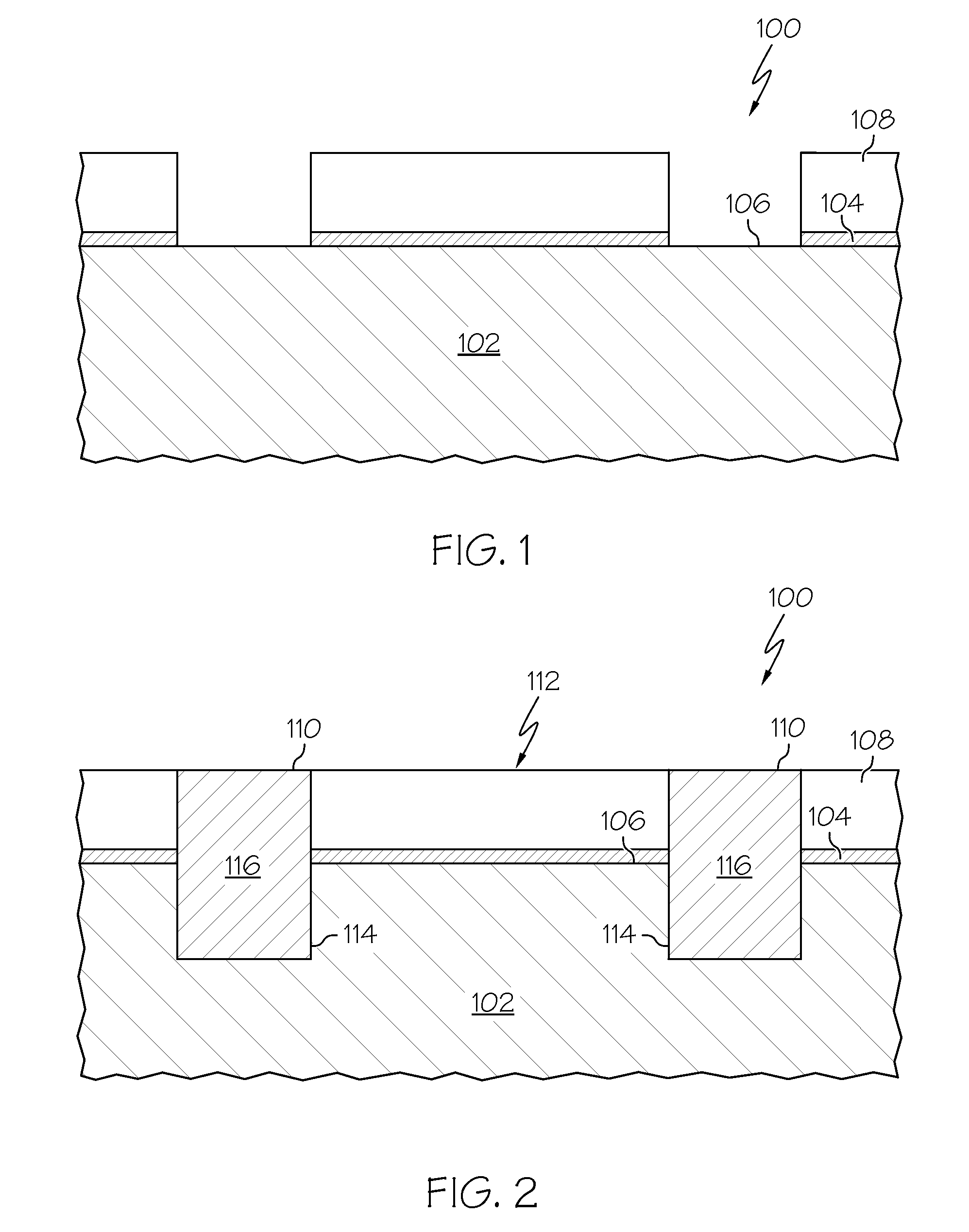
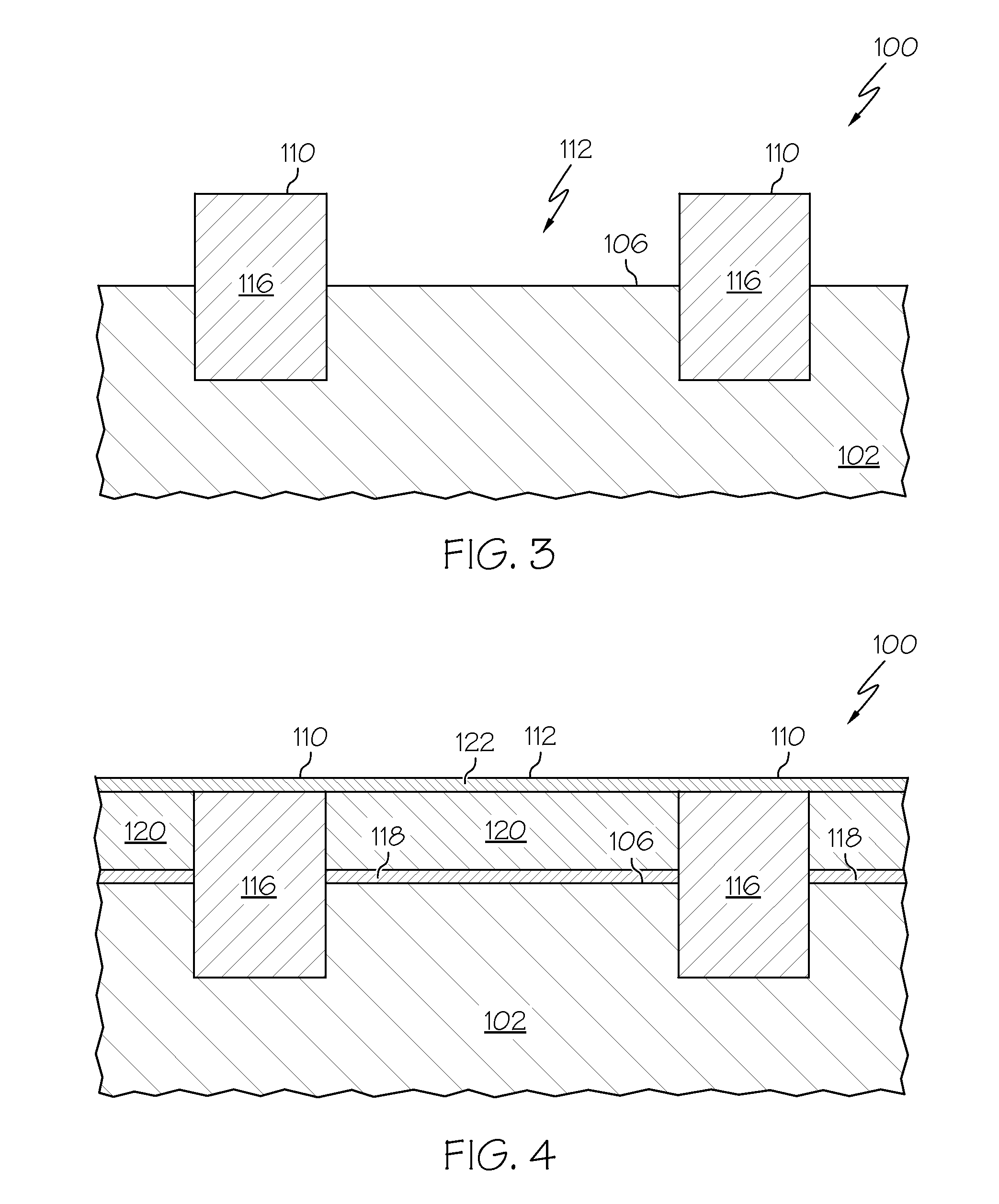
Enhanced Segmented Channel MOS Transistor with Multi Layer Regions
ActiveUS20070120156A1Increase costImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETPerformance enhancement
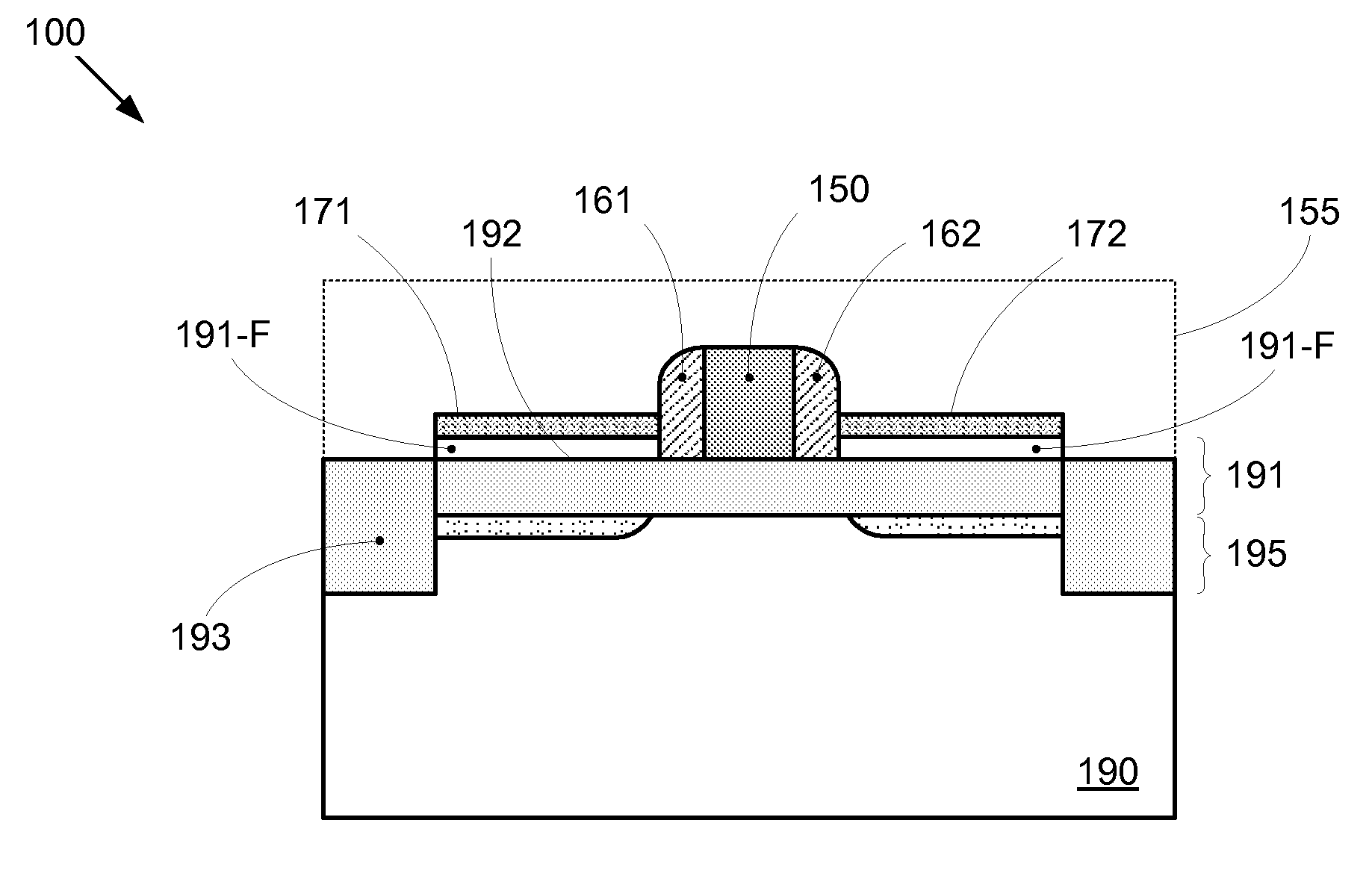
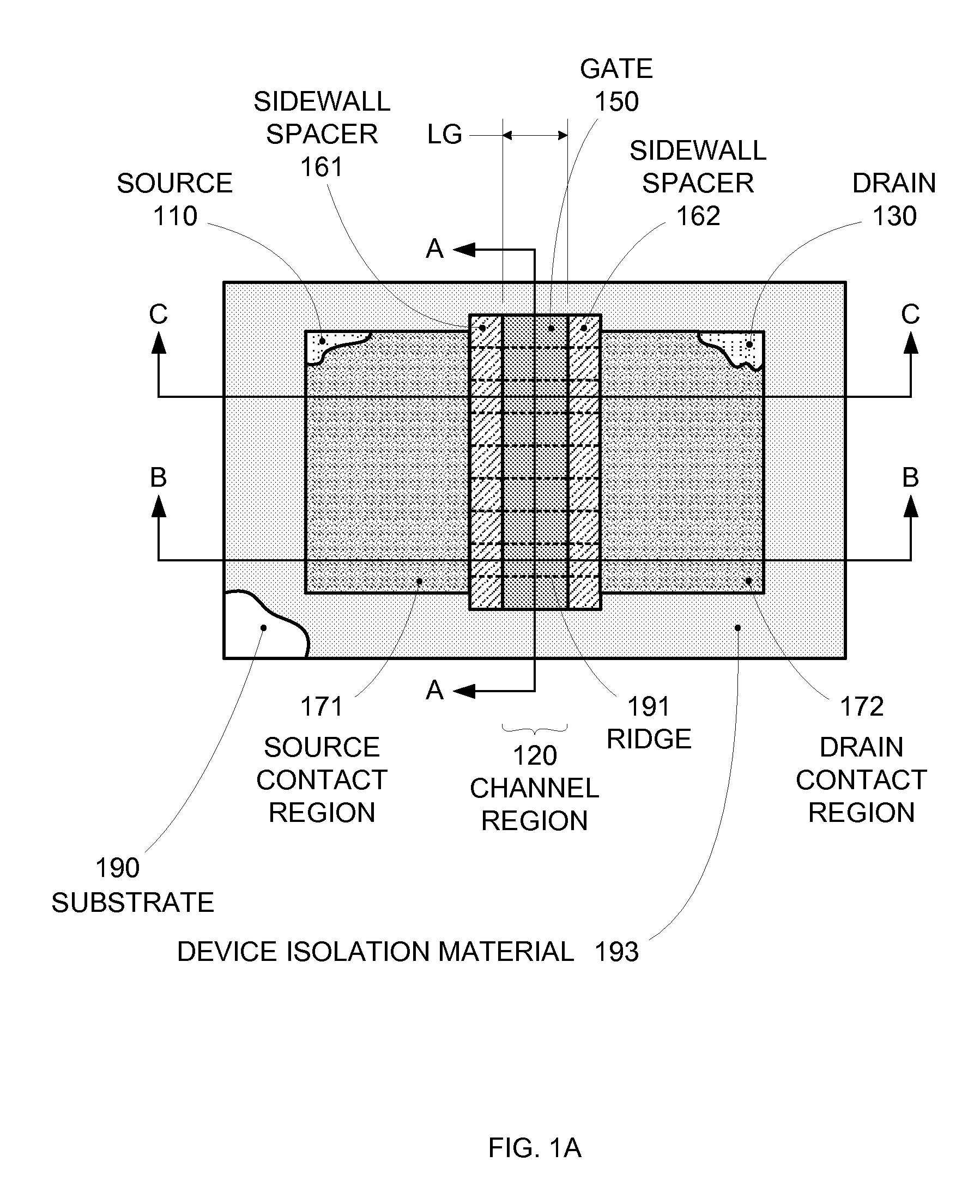
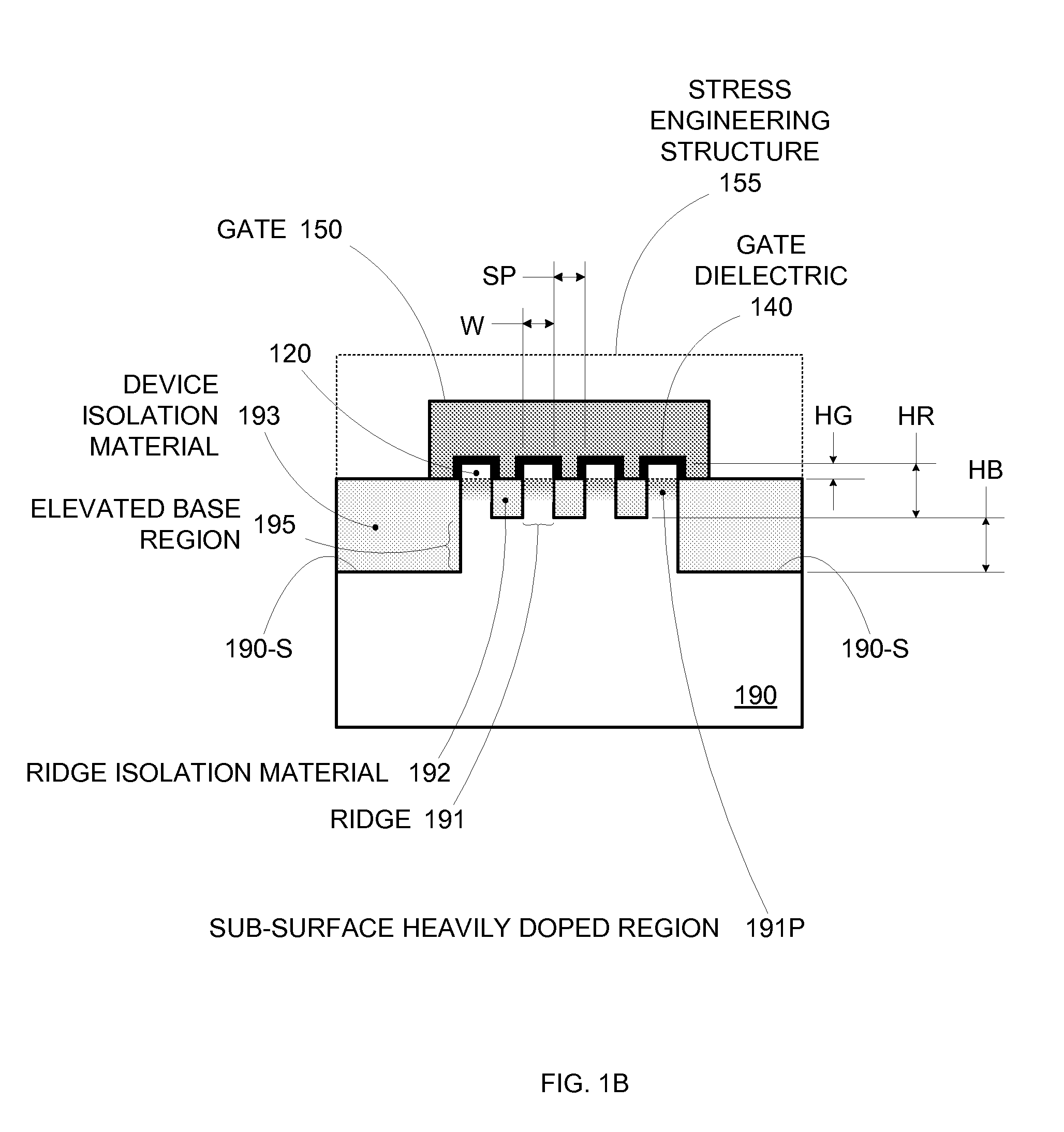
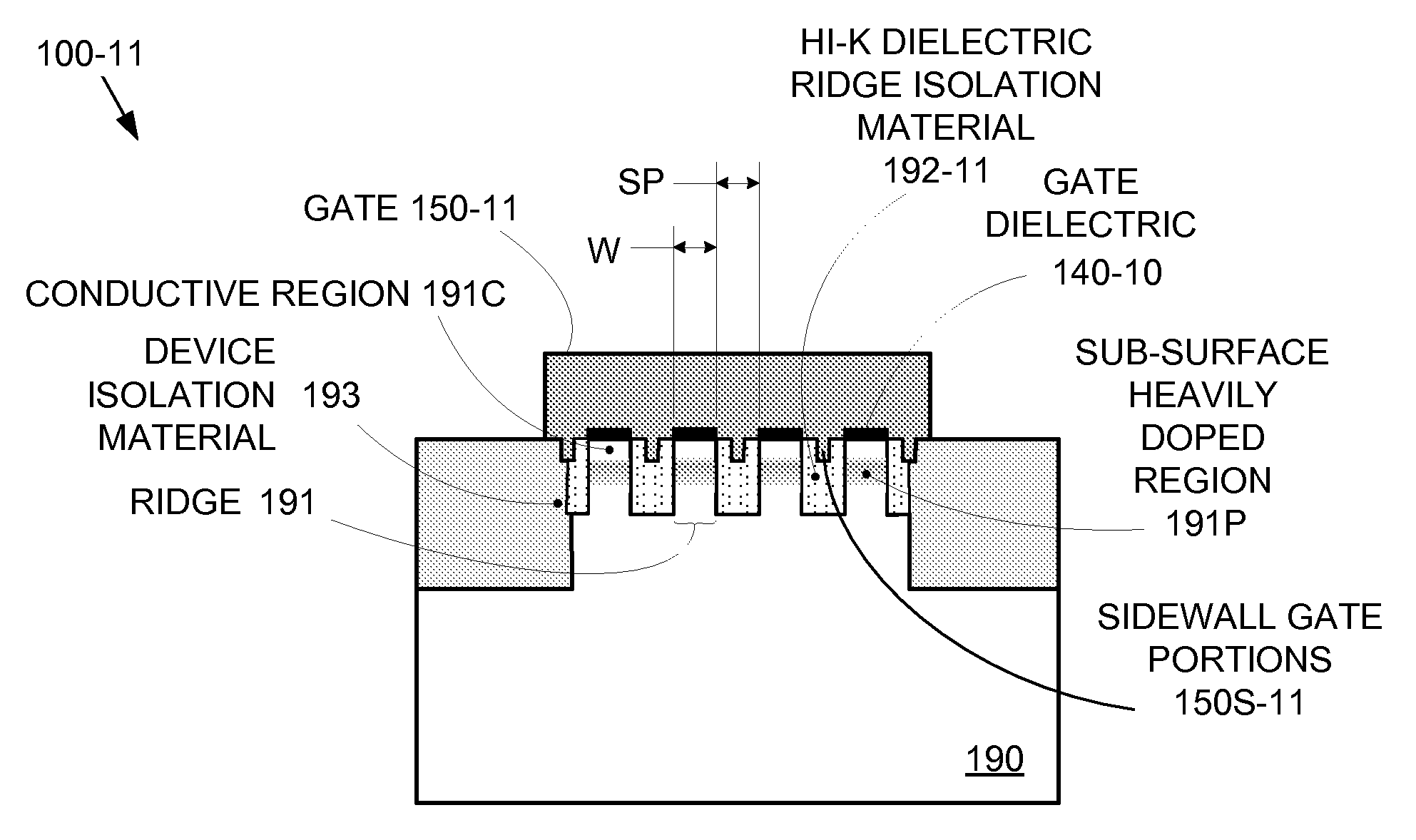
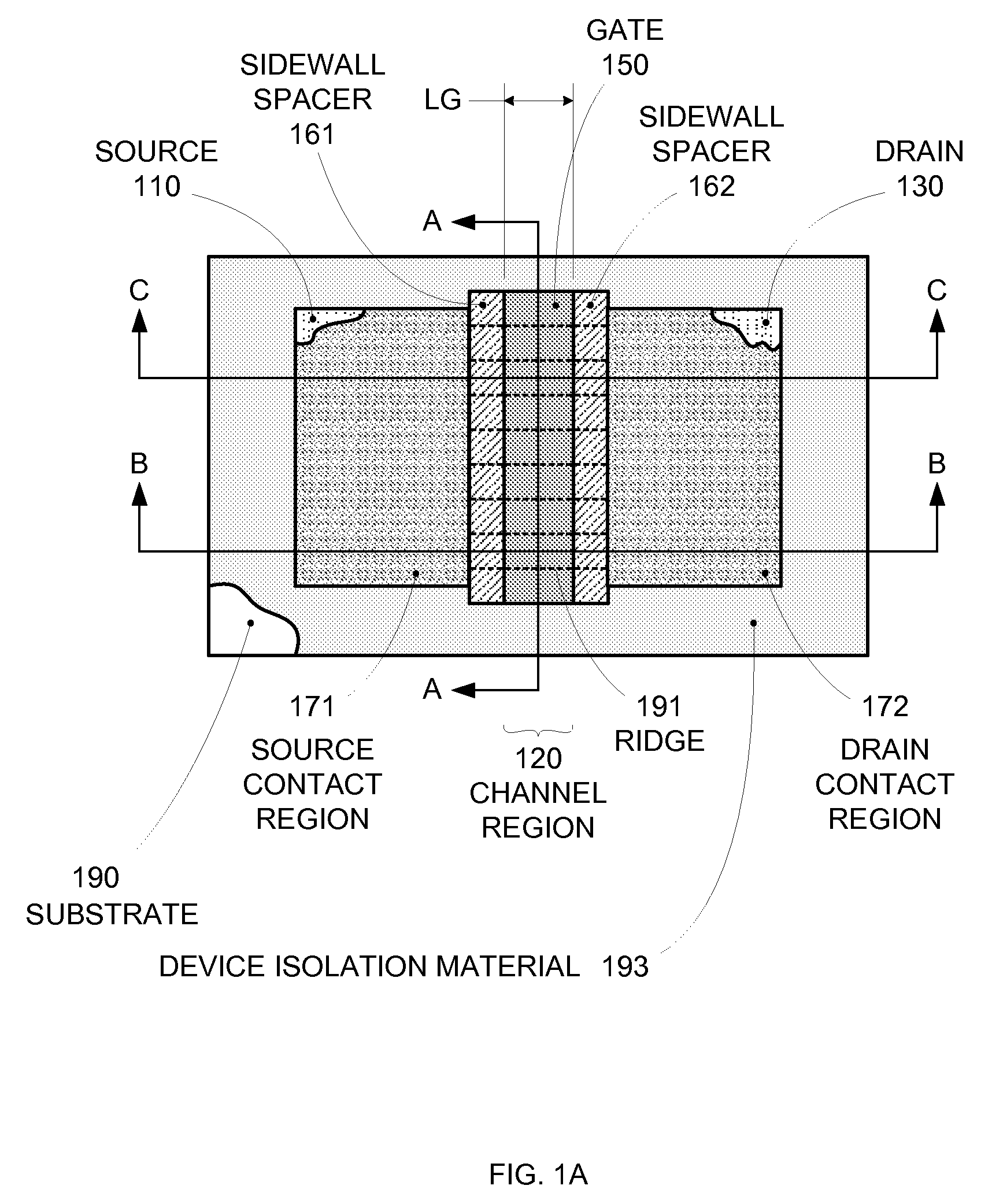
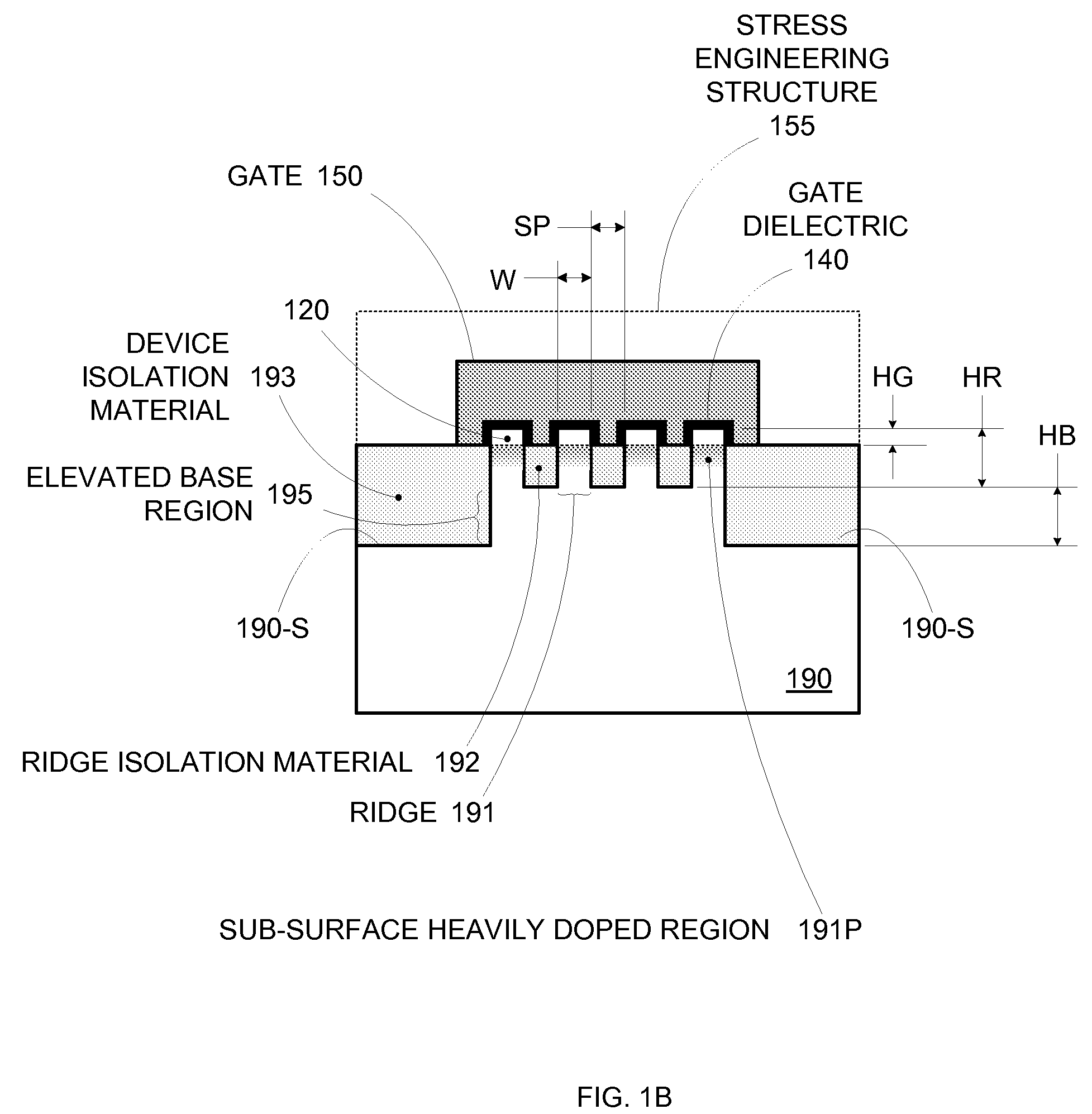
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Inorganic Bulk Multijunction Materials and Processes for Preparing the Same
InactiveUS20110220874A1Material nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureAlloySemiconductor nanocrystals
A nanostructured composite material comprising semiconductor nanocrystals in a crystalline semiconductor matrix. Suitable nanocrystals include silicon, germanium, and silicon-germanium alloys, and lead salts such as PbS, PbSe, and PbTe. Suitable crystalline semiconductor matrix materials include Si and silicon-germanium alloys. A process for making the nanostructured composite materials. Devices comprising nanostructured composite materials.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
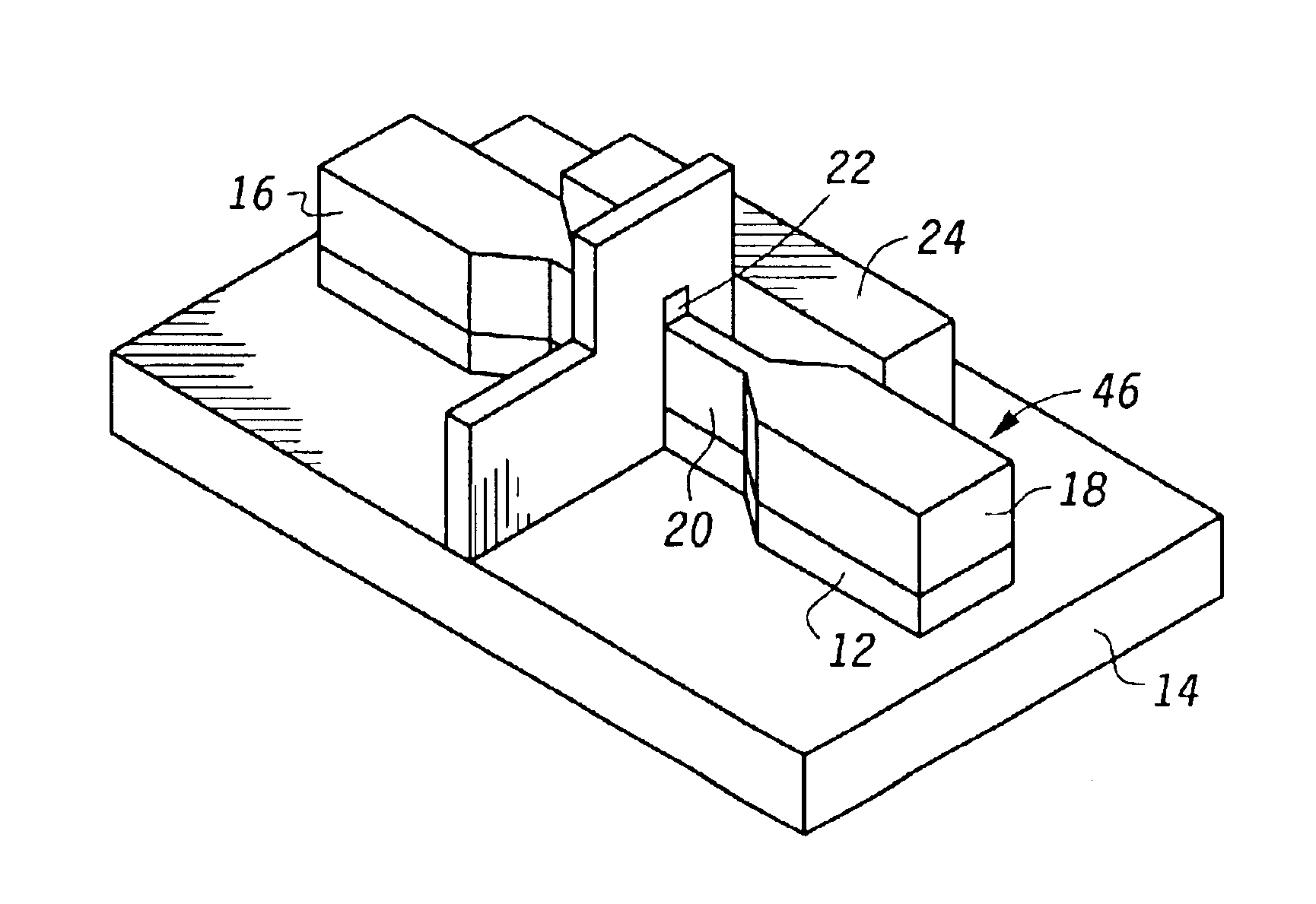
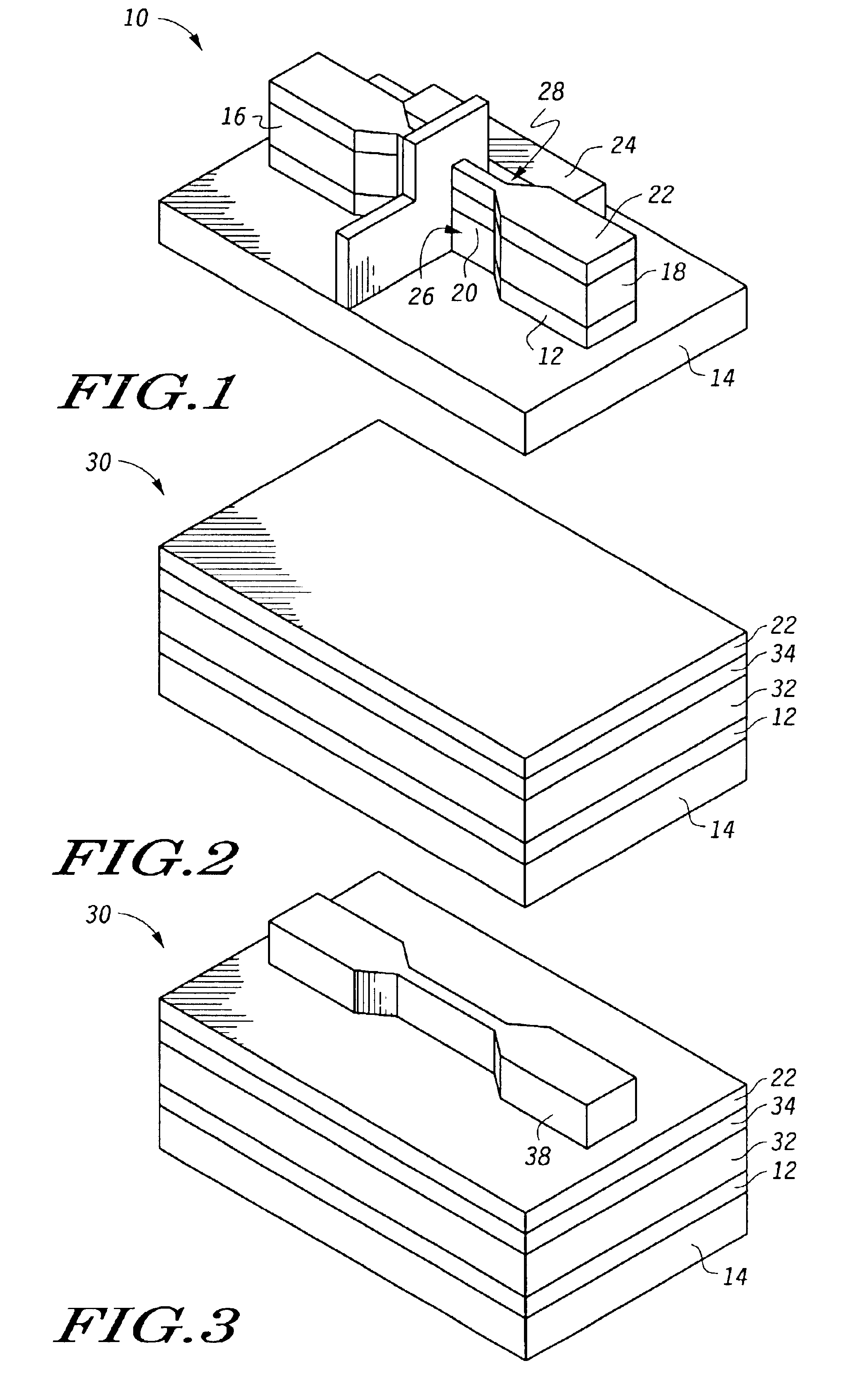
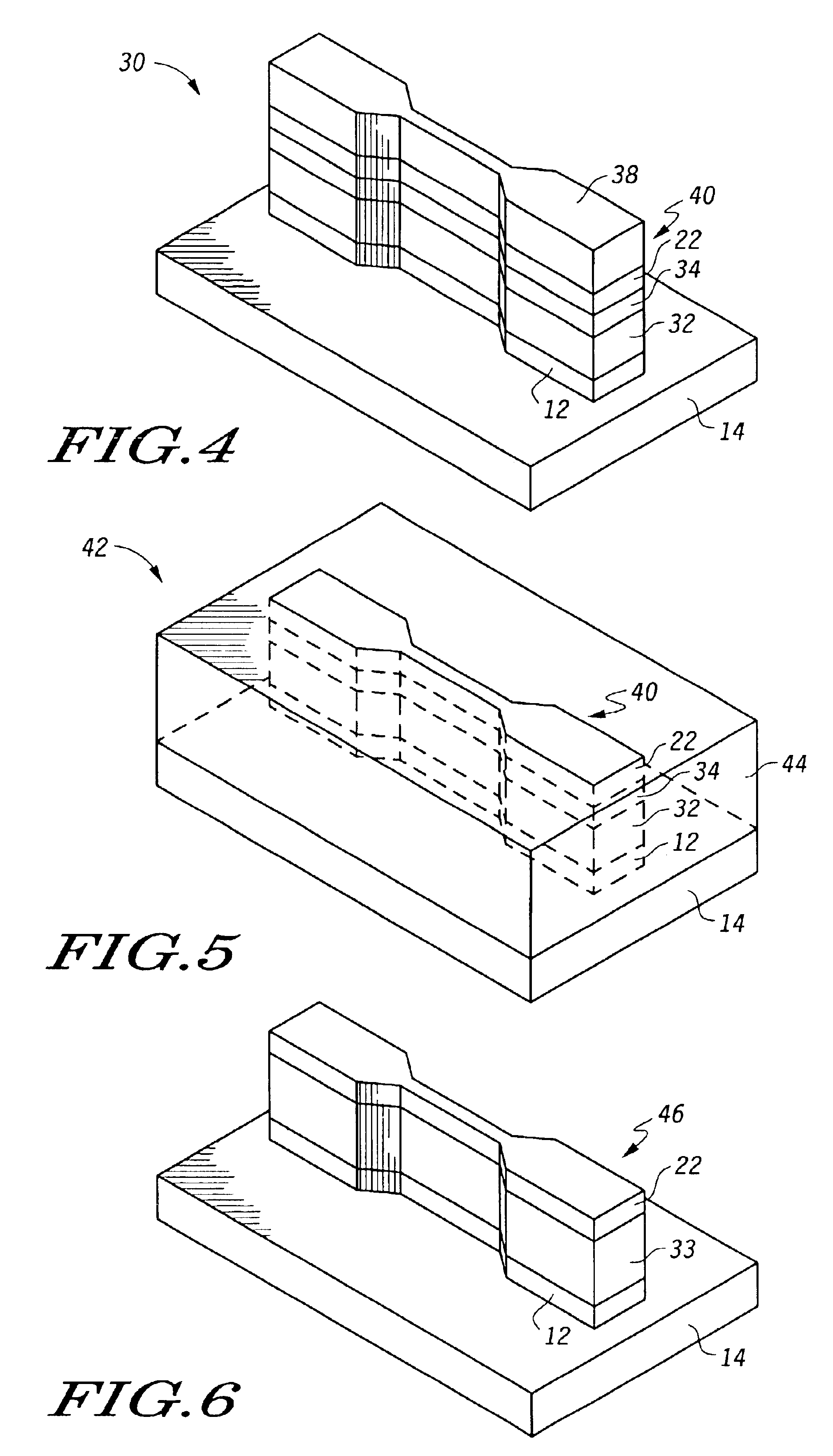
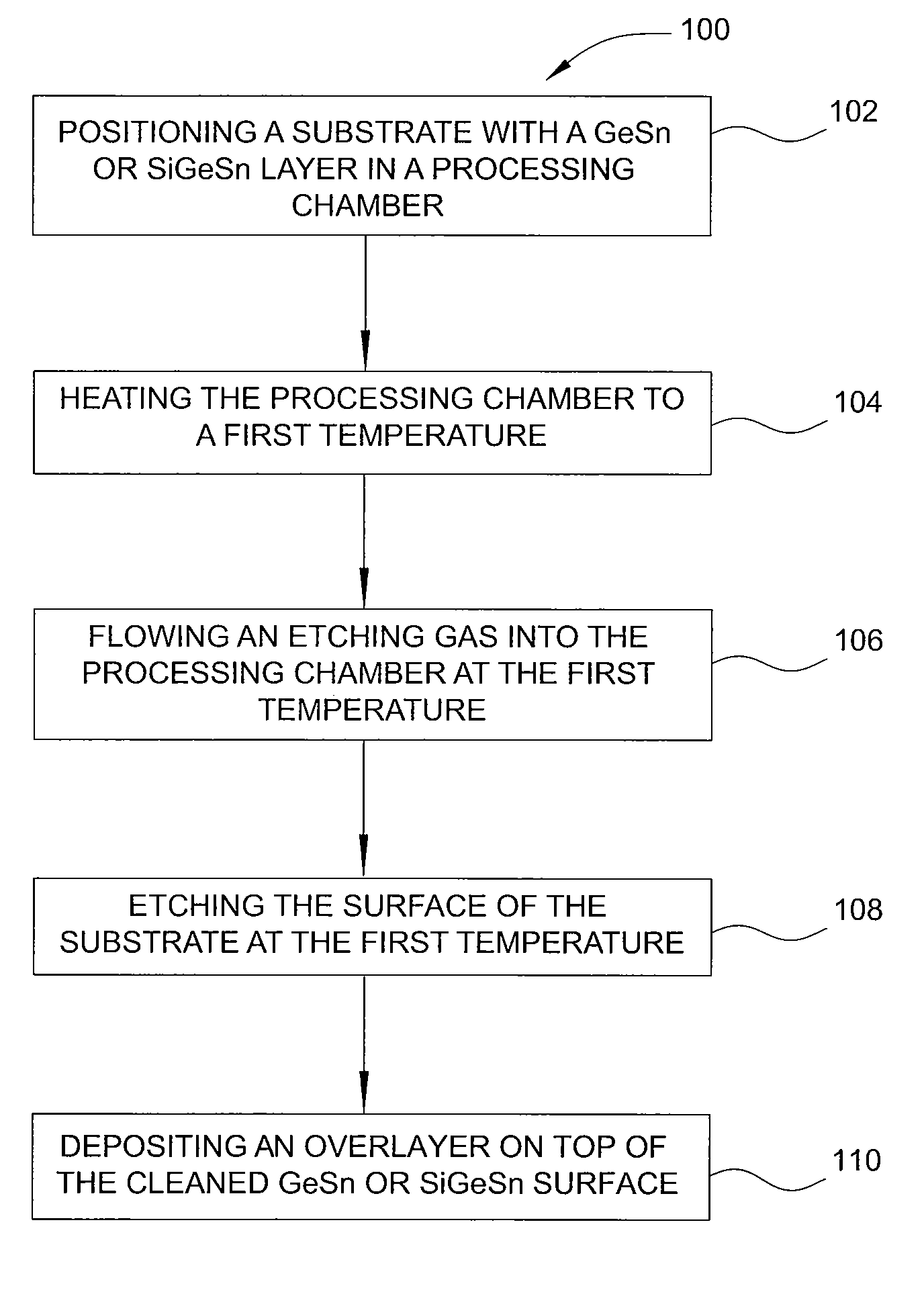
Method of epitaxial germanium tin alloy surface preparation
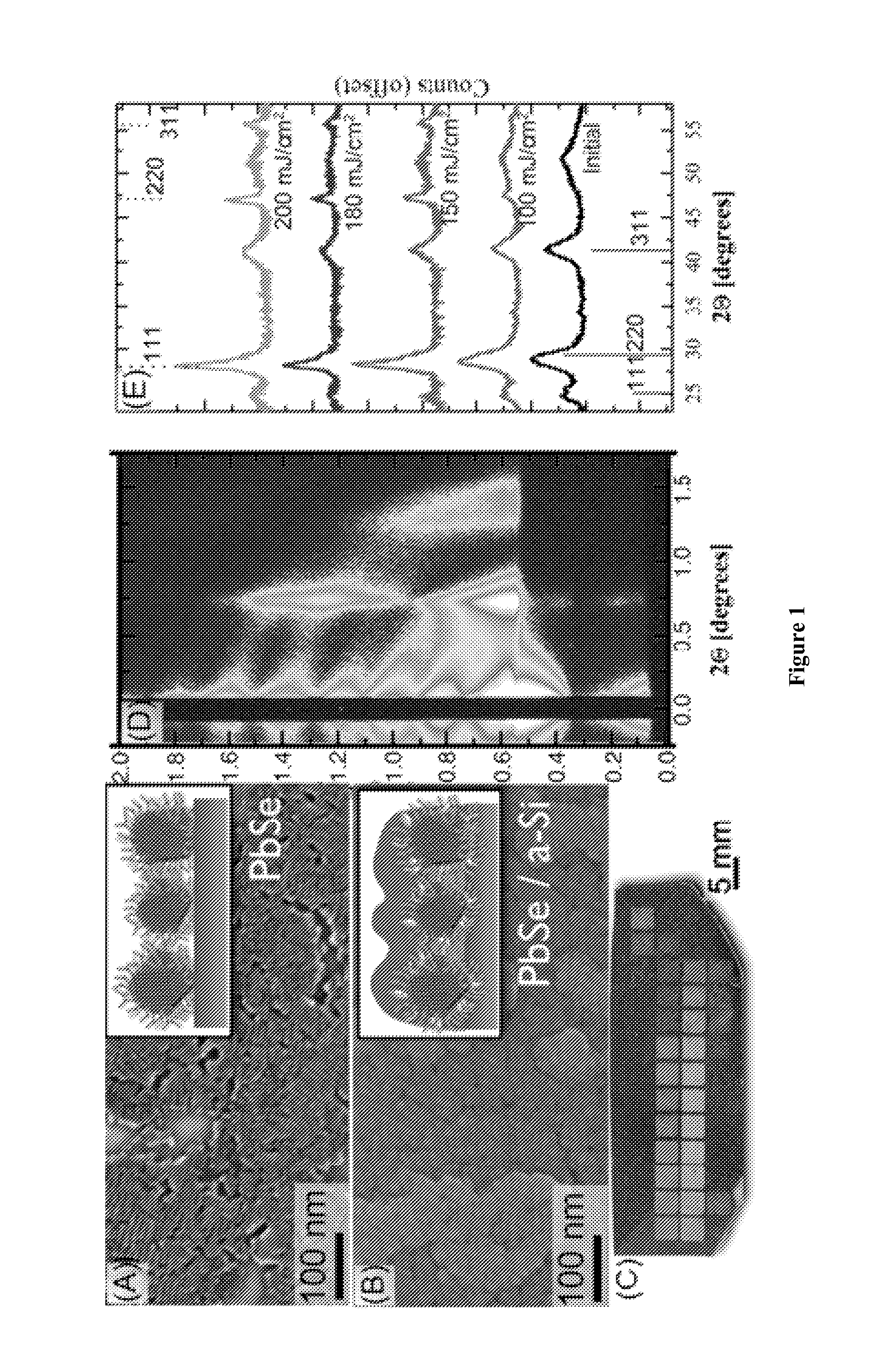
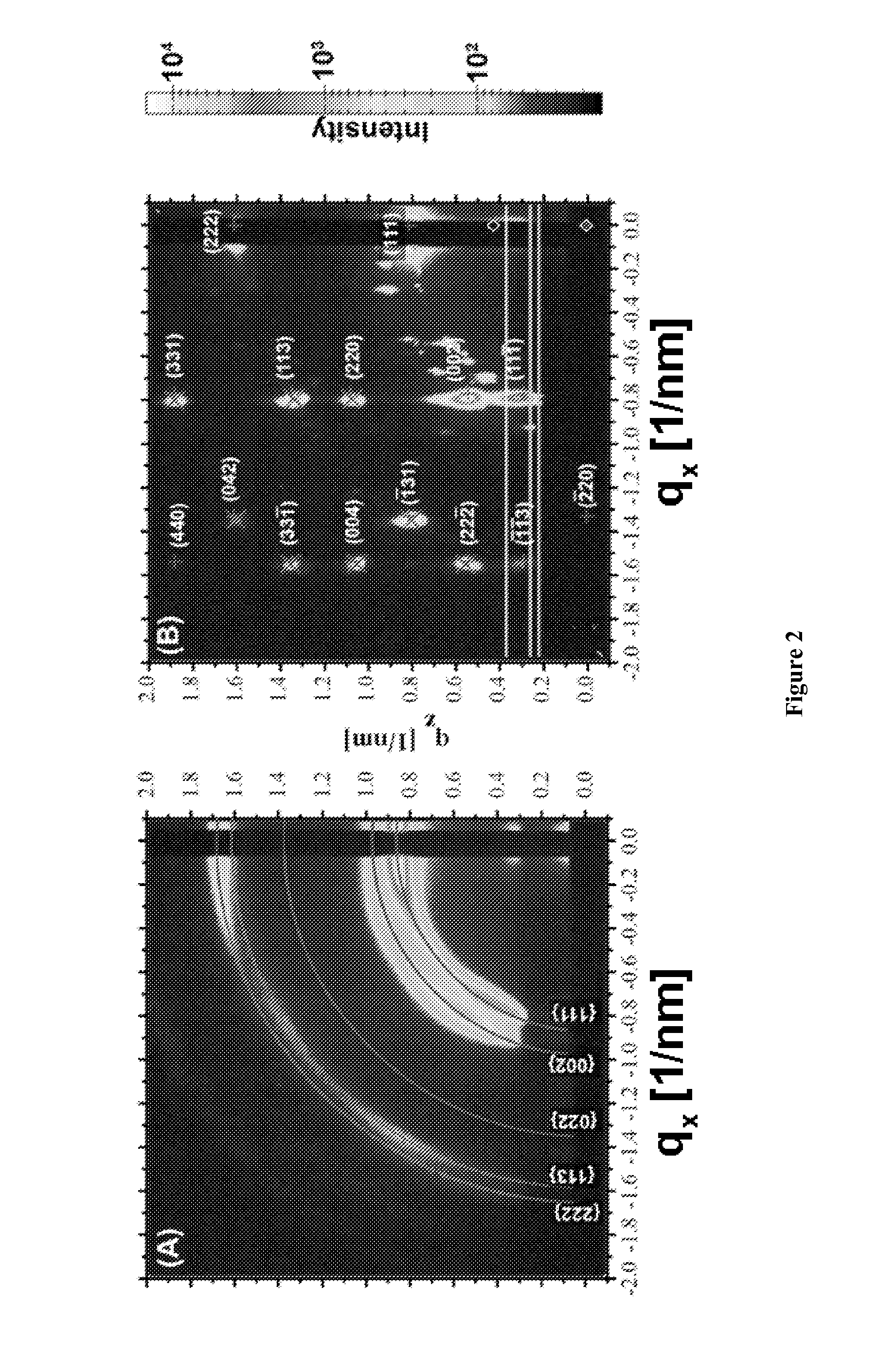
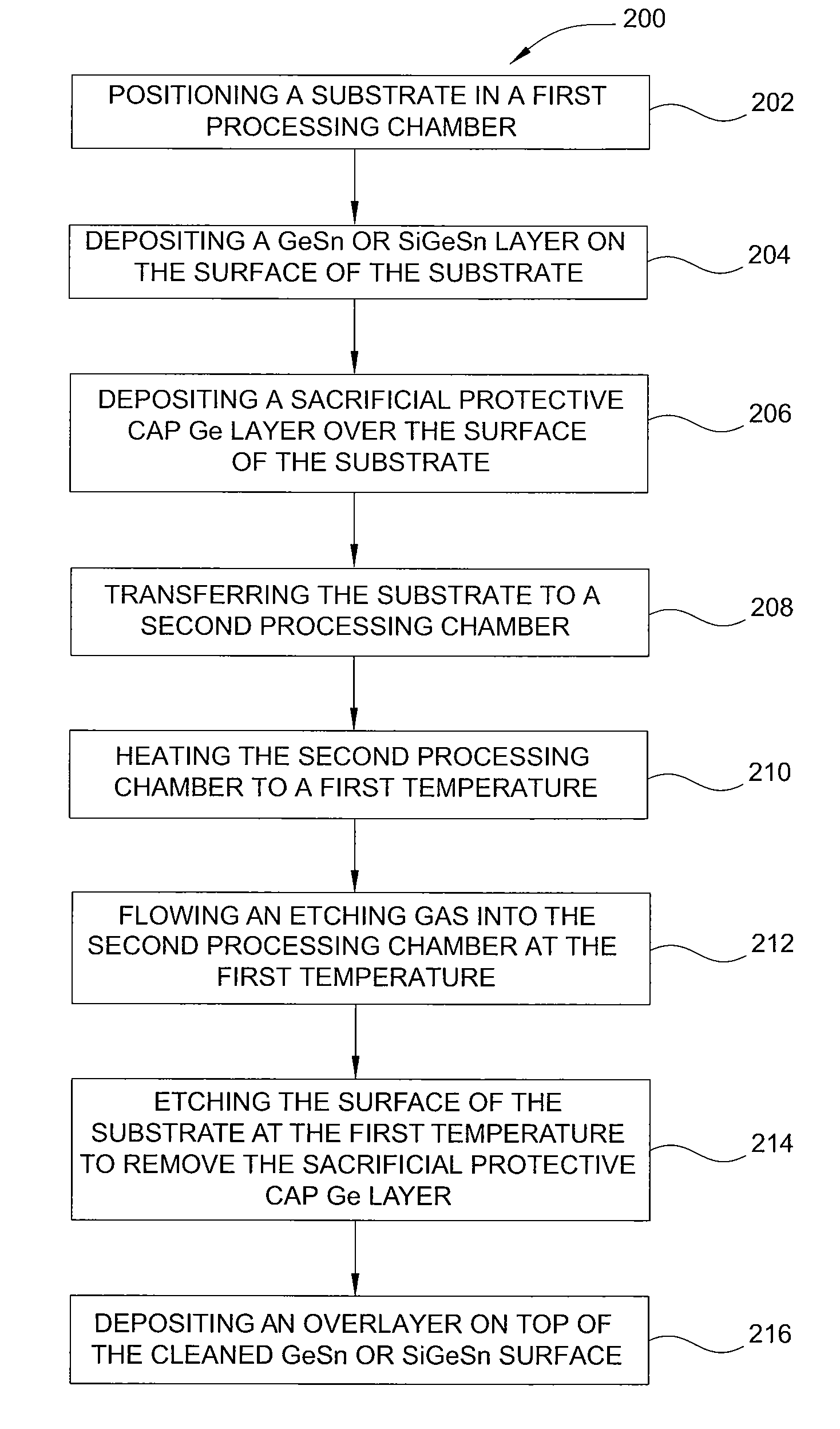
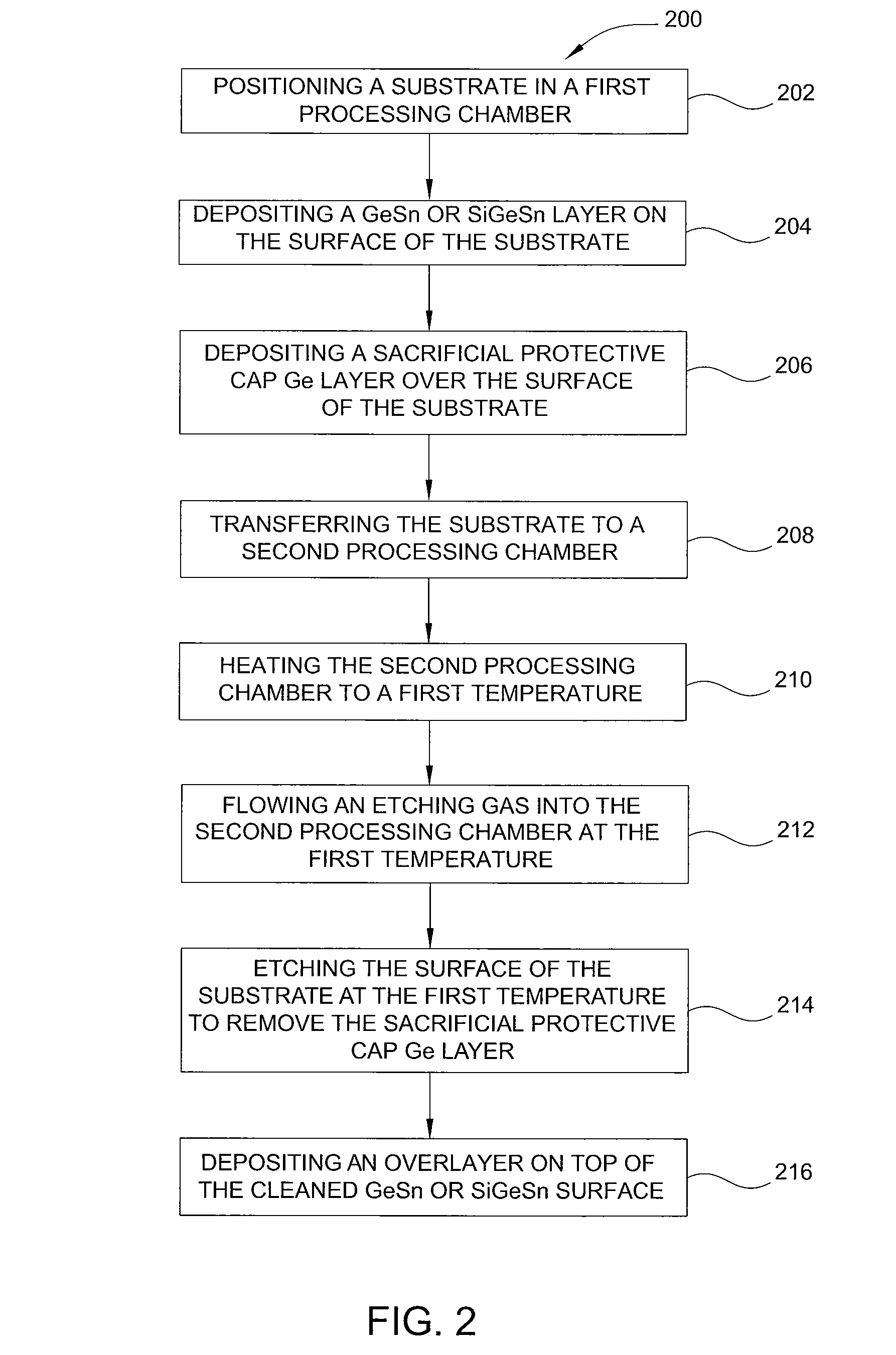
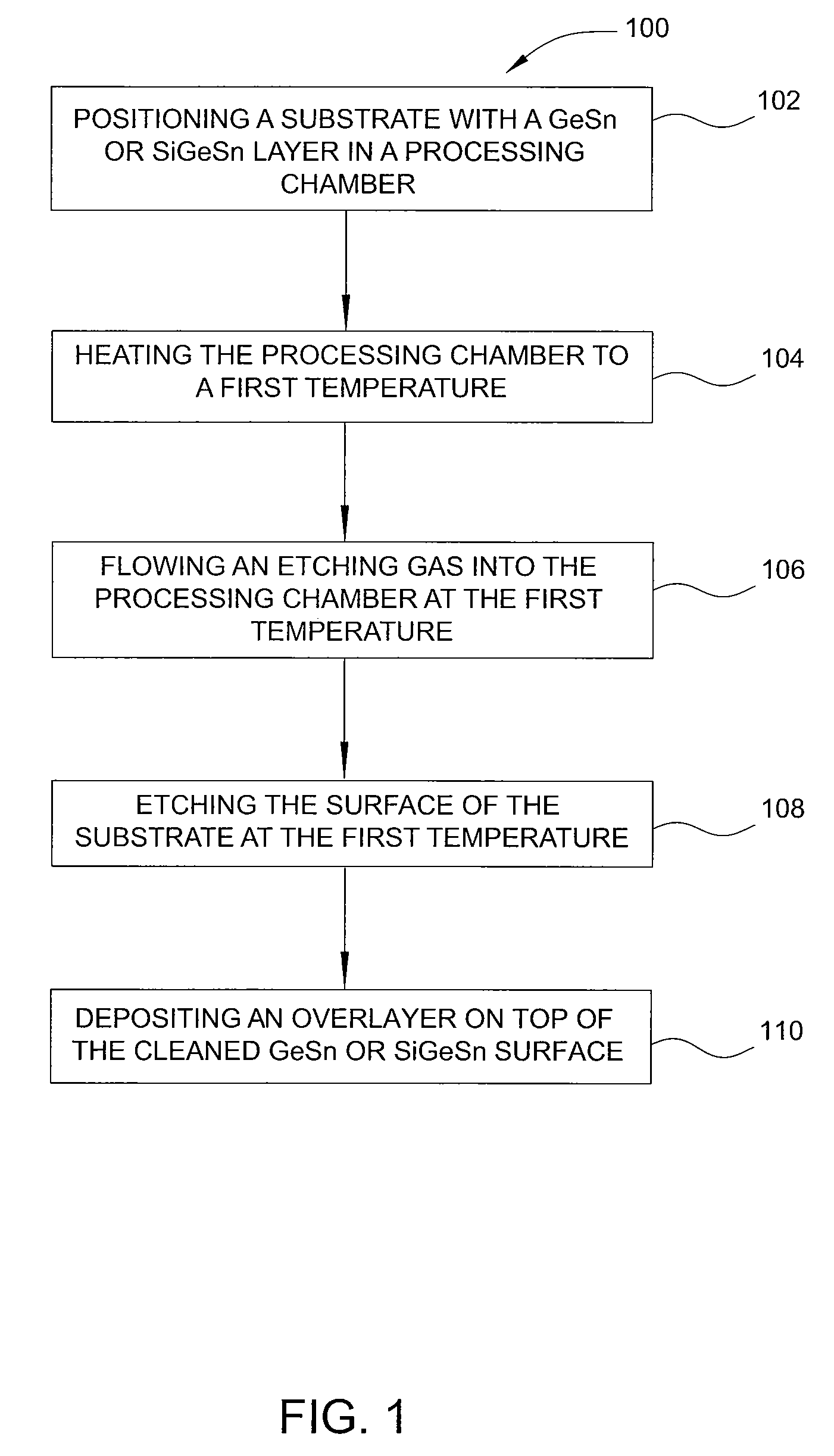
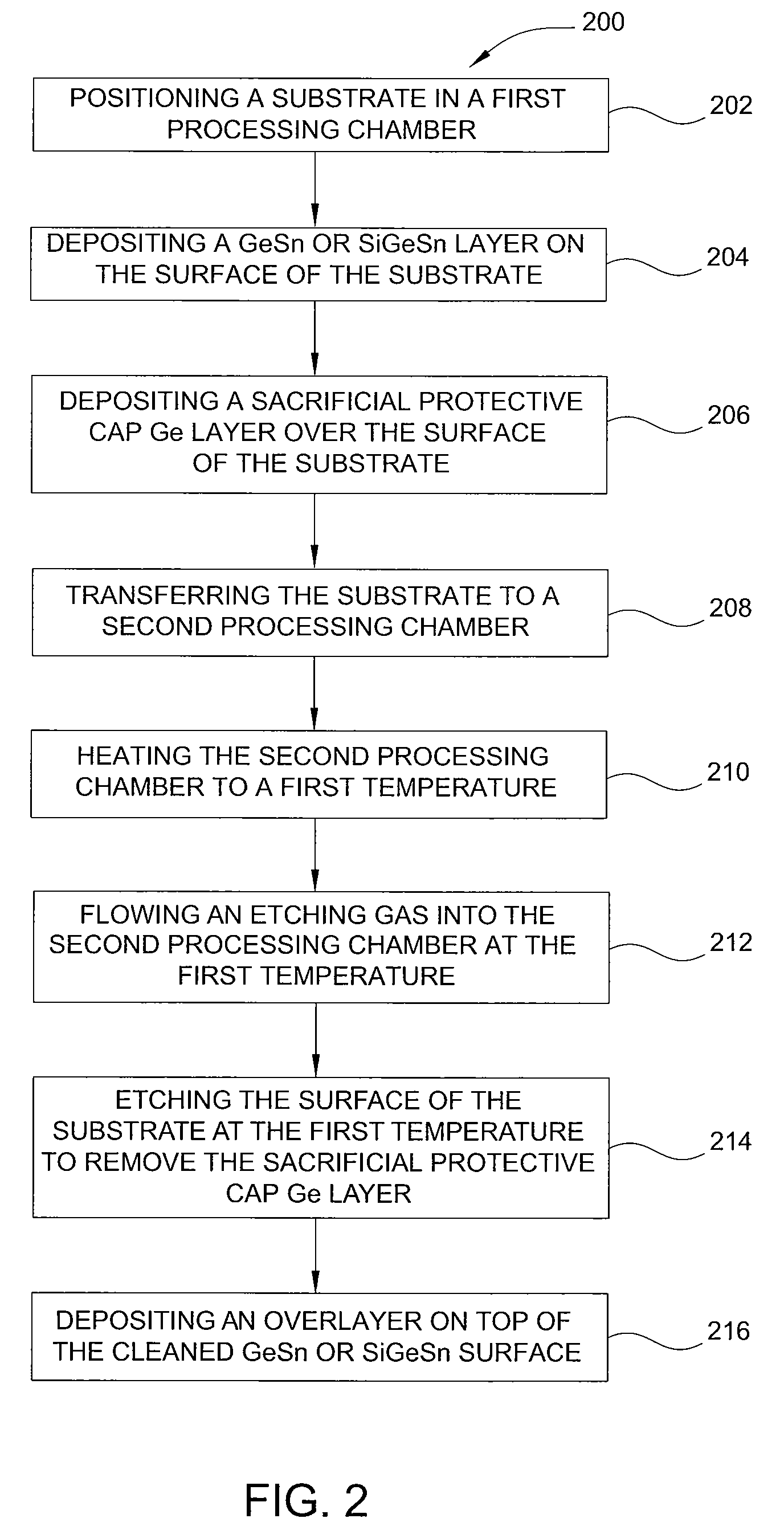
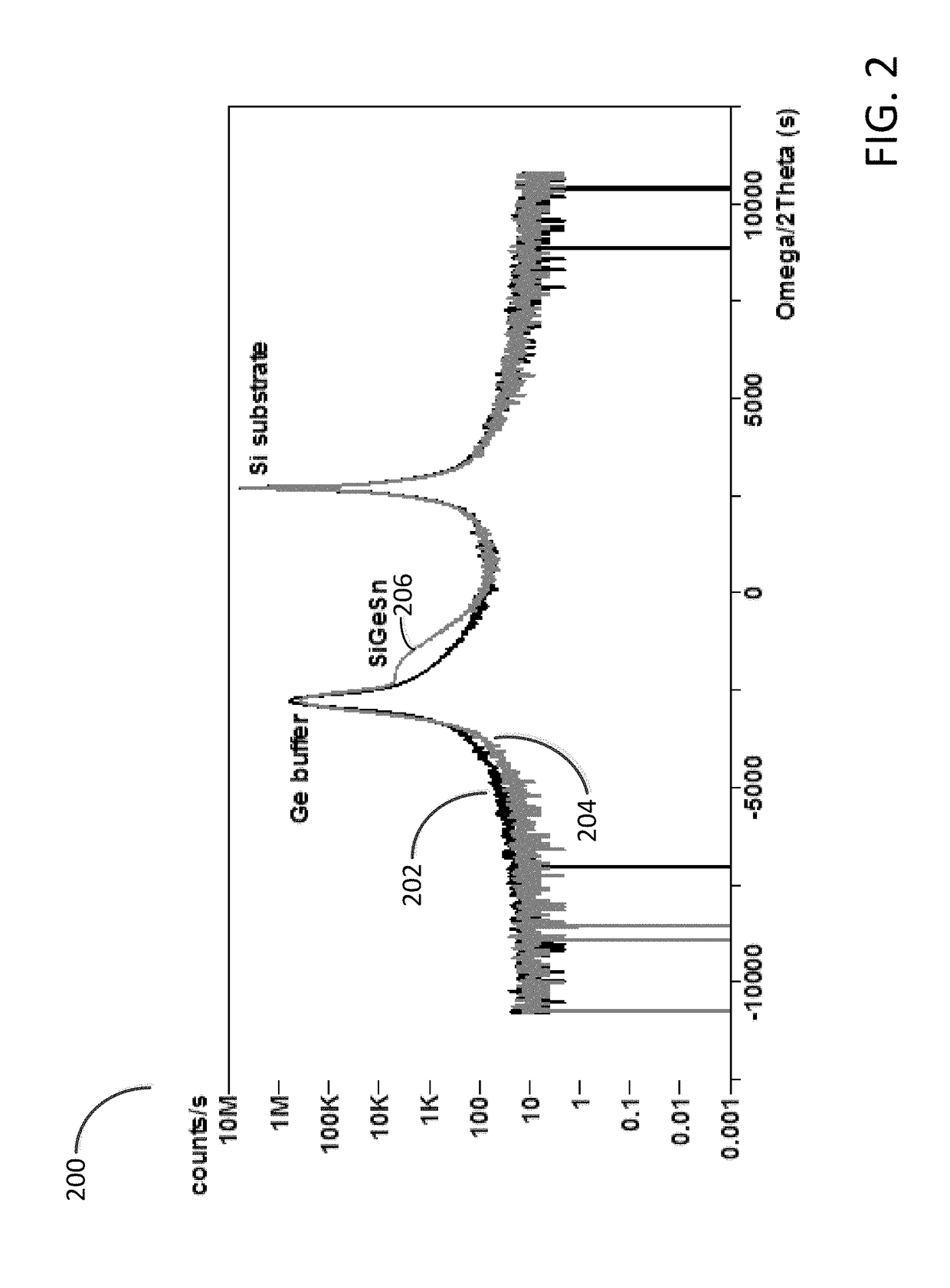
ActiveUS20130288480A1Increase temperatureStop the flowSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationEtchingRapid thermal annealing
Methods of preparing a clean surface of germanium tin or silicon germanium tin layers for subsequent deposition are provided. An overlayer of Ge, doped Ge, another GeSn or SiGeSn layer, a doped GeSn or SiGeSn layer, an insulator, or a metal can be deposited on a prepared GeSn or SiGeSn layer by positioning a substrate with an exposed germanium tin or silicon germanium tin layer in a processing chamber, heating the processing chamber and flowing a halide gas into the processing chamber to etch the surface of the substrate using either thermal or plasma assisted etching followed by depositing an overlayer on the substantially oxide free and contaminant free surface. Methods can also include the placement and etching of a sacrificial layer, a thermal clean using rapid thermal annealing, or a process in a plasma of nitrogen trifluoride and ammonia gas.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Enhanced Segmented Channel MOS Transistor with High-Permittivity Dielectric Isolation Material
ActiveUS20070122953A1Increase costImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Enhanced segmented channel MOS transistor with high-permittivity dielectric isolation material
ActiveUS7605449B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
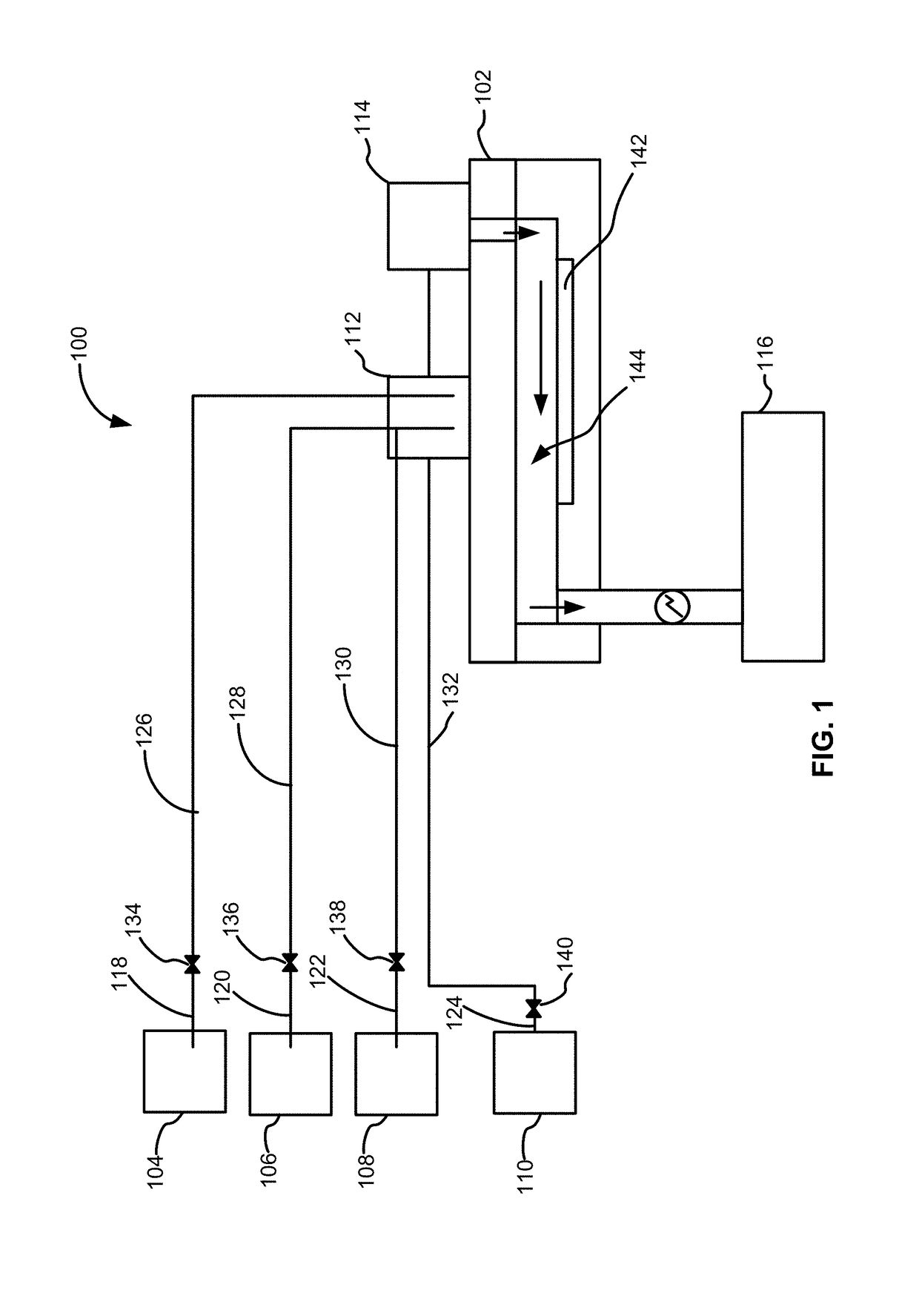
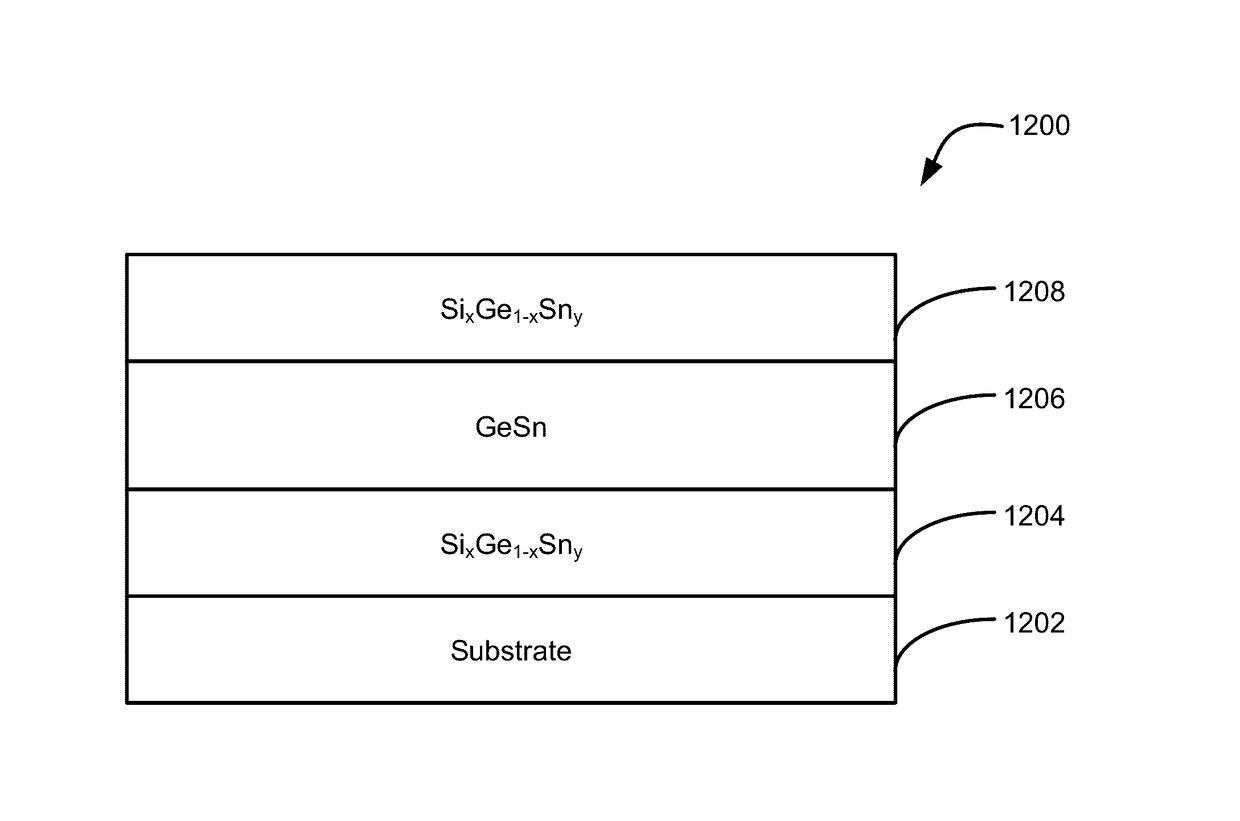
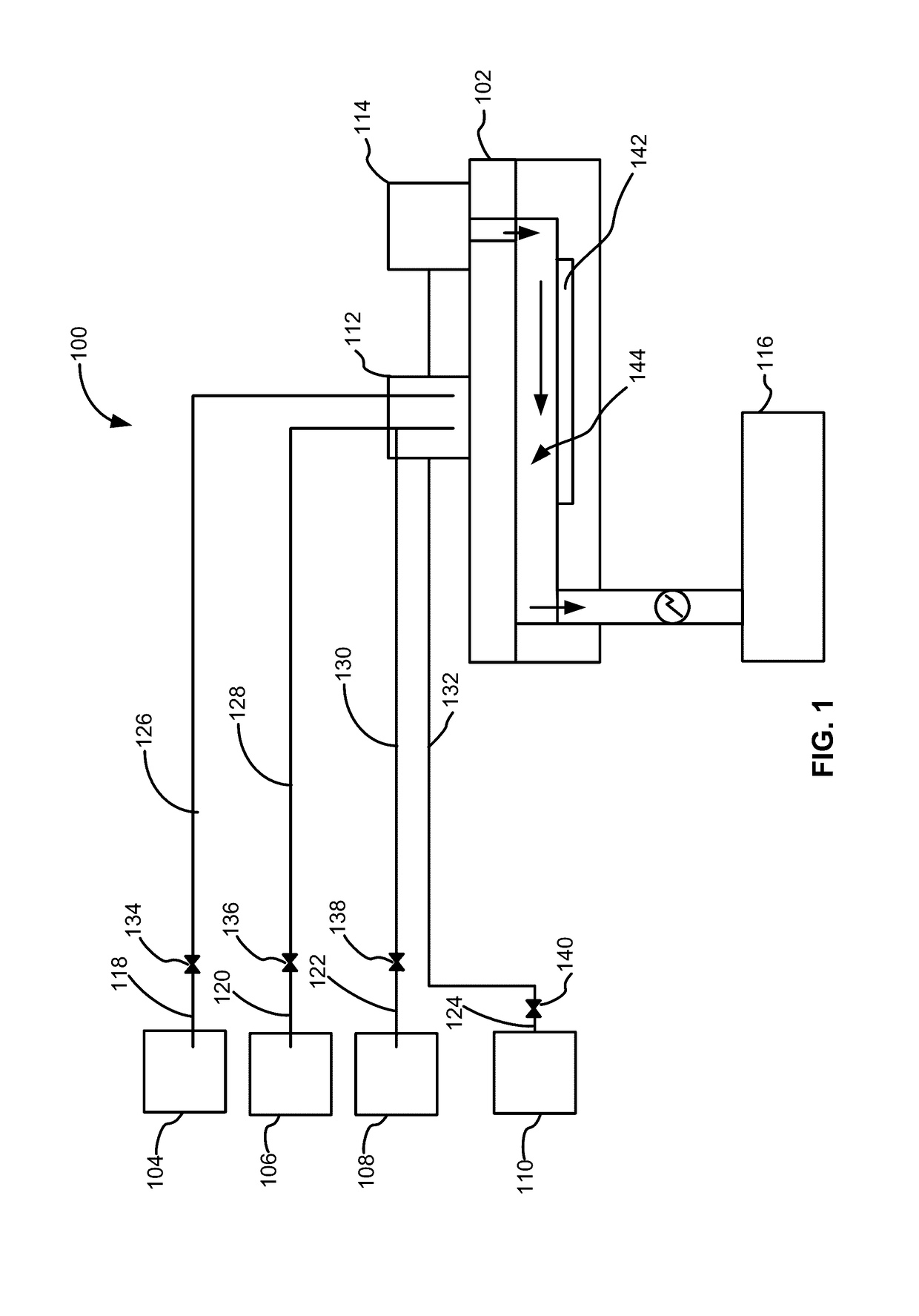
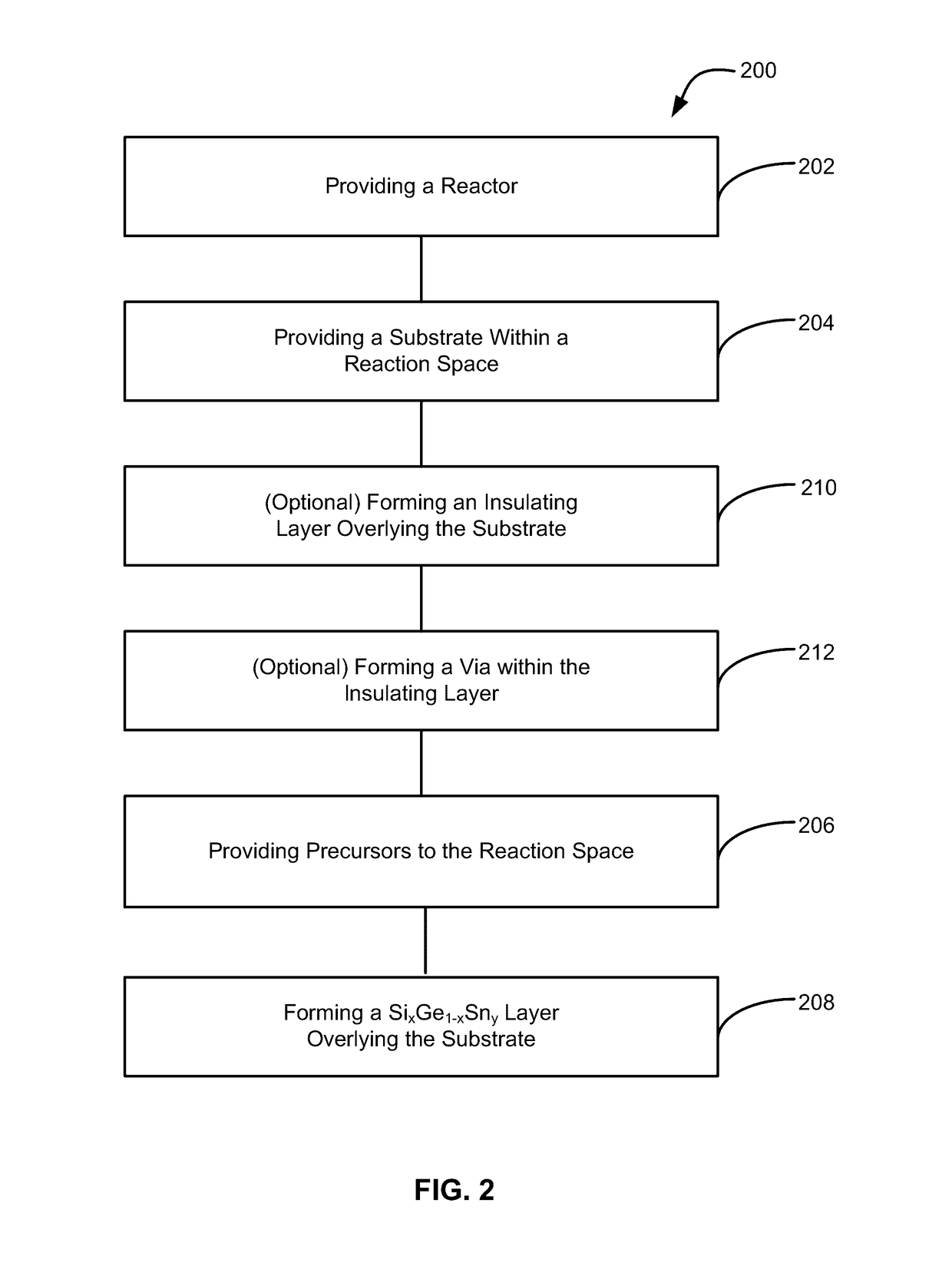
Methods of forming silicon germanium tin films and structures and devices including the films
ActiveUS9905420B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh volume manufacturingChemical vapor deposition
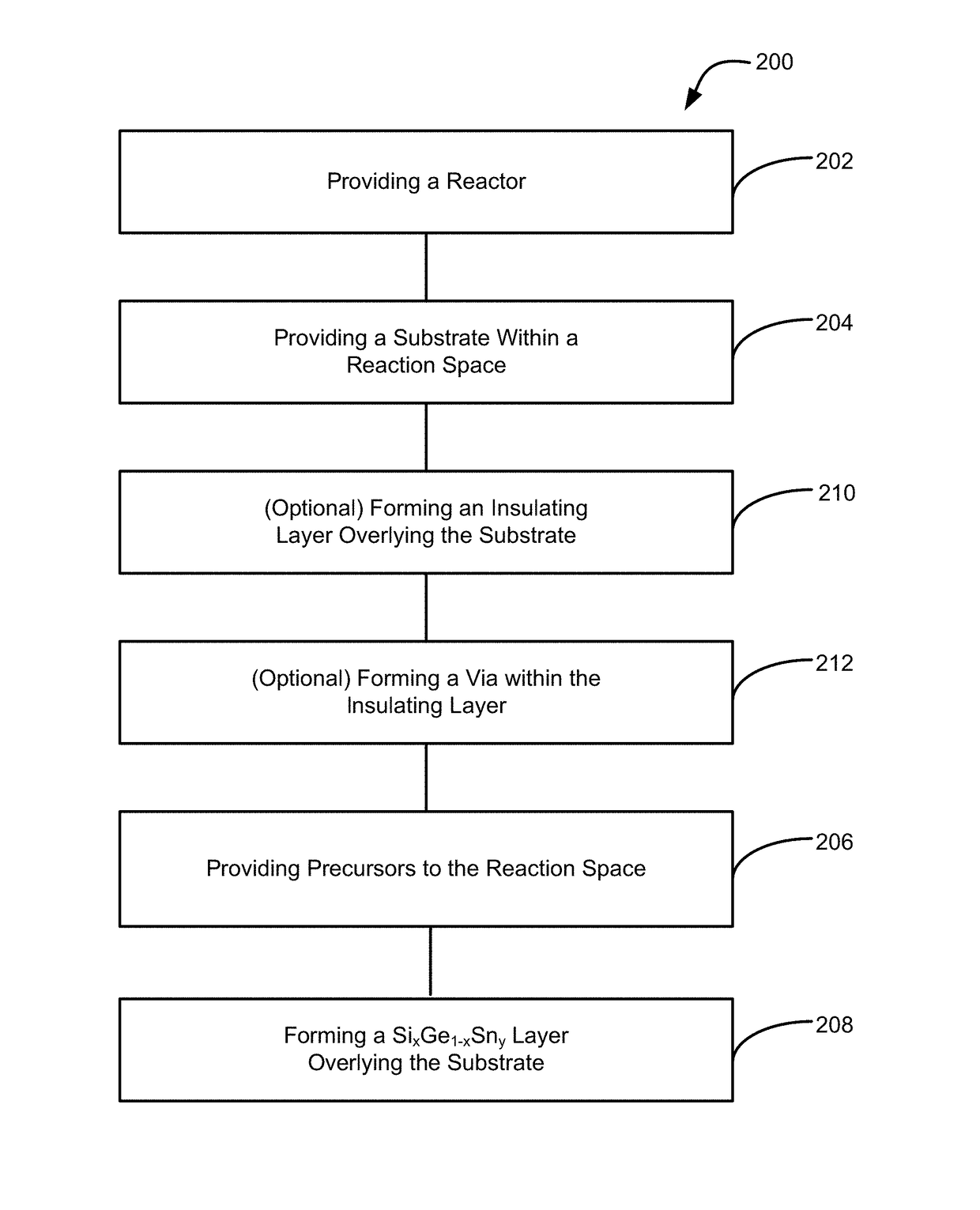
Methods of forming silicon germanium tin (SixGe1-xSny) films are disclosed. Exemplary methods include growing films including silicon, germanium and tin in an epitaxial chemical vapor deposition reactor. Exemplary methods are suitable for high volume manufacturing. Also disclosed are structures and devices including silicon germanium tin films.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
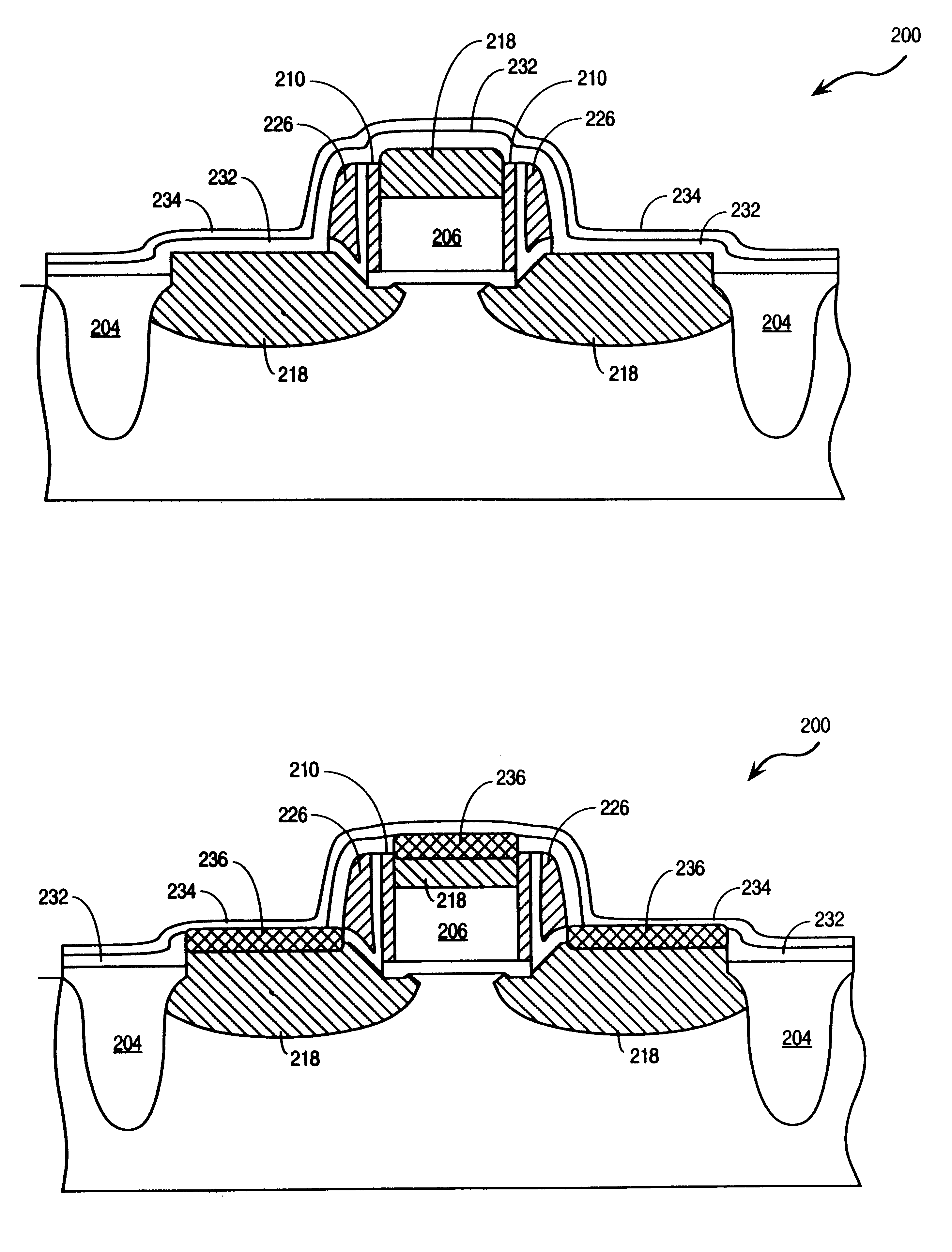
SOI SiGe-Base Lateral Bipolar Junction Transistor
ActiveUS20120139009A1Great current densityNoise minimizationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarrier scatteringParasitic capacitance
A lateral heterojunction bipolar transistor (HBT) is formed on a semiconductor-on-insulator substrate. The HBT includes a base including a doped silicon-germanium alloy base region, an emitter including doped silicon and laterally contacting the base, and a collector including doped silicon and laterally contacting the base. Because the collector current is channeled through the doped silicon-germanium base region, the HBT can accommodate a greater current density than a comparable bipolar transistor employing a silicon channel. The base may also include an upper silicon base region and / or a lower silicon base region. In this case, the collector current is concentrated in the doped silicon-germanium base region, thereby minimizing noise introduced to carrier scattering at the periphery of the base. Further, parasitic capacitance is minimized because the emitter-base junction area is the same as the collector-base junction area.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods of selective deposition of heavily doped epitaxial SiGe
ActiveUS20050079691A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantSelective deposition
The invention generally teaches a method for depositing a silicon film or silicon germanium film on a substrate comprising placing the substrate within a process chamber and heating the substrate surface to a temperature in the range from about 600° C. to about 900° C. while maintaining a pressure in the range from about 0.1 Torr to about 200 Torr. A deposition gas is provided to the process chamber and includes SiH4, an optional germanium source gas, an etchant, a carrier gas and optionally at least one dopant gas. The silicon film or the silicon germanium film is selectively and epitaxially grown on the substrate. One embodiment teaches a method for depositing a silicon-containing film with an inert gas as the carrier gas. Methods may include the fabrication of electronic devices utilizing selective silicon germanium epitaxial films.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20080042165A1Increase speedImprove mobilityThyristorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThyratronSemiconductor
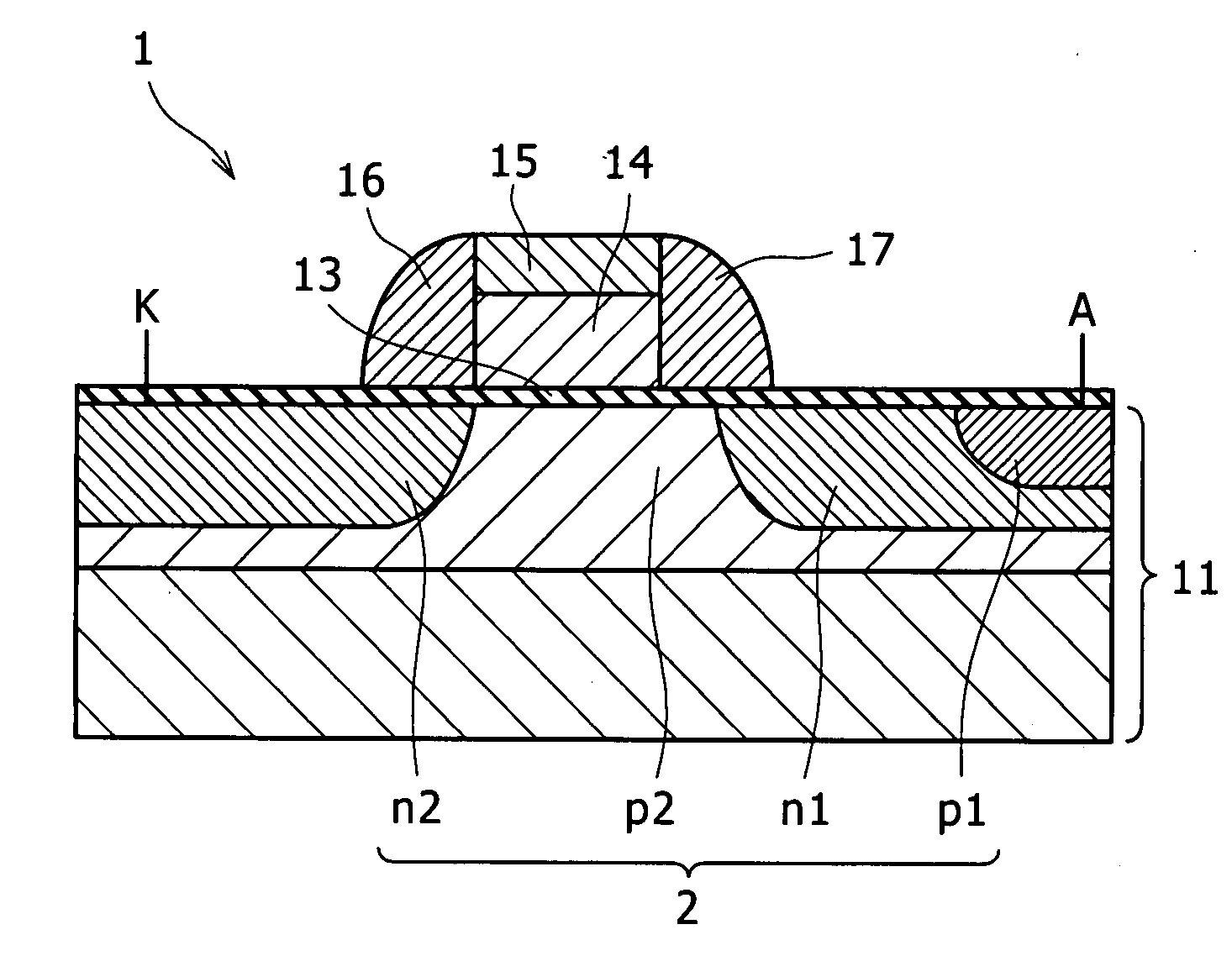
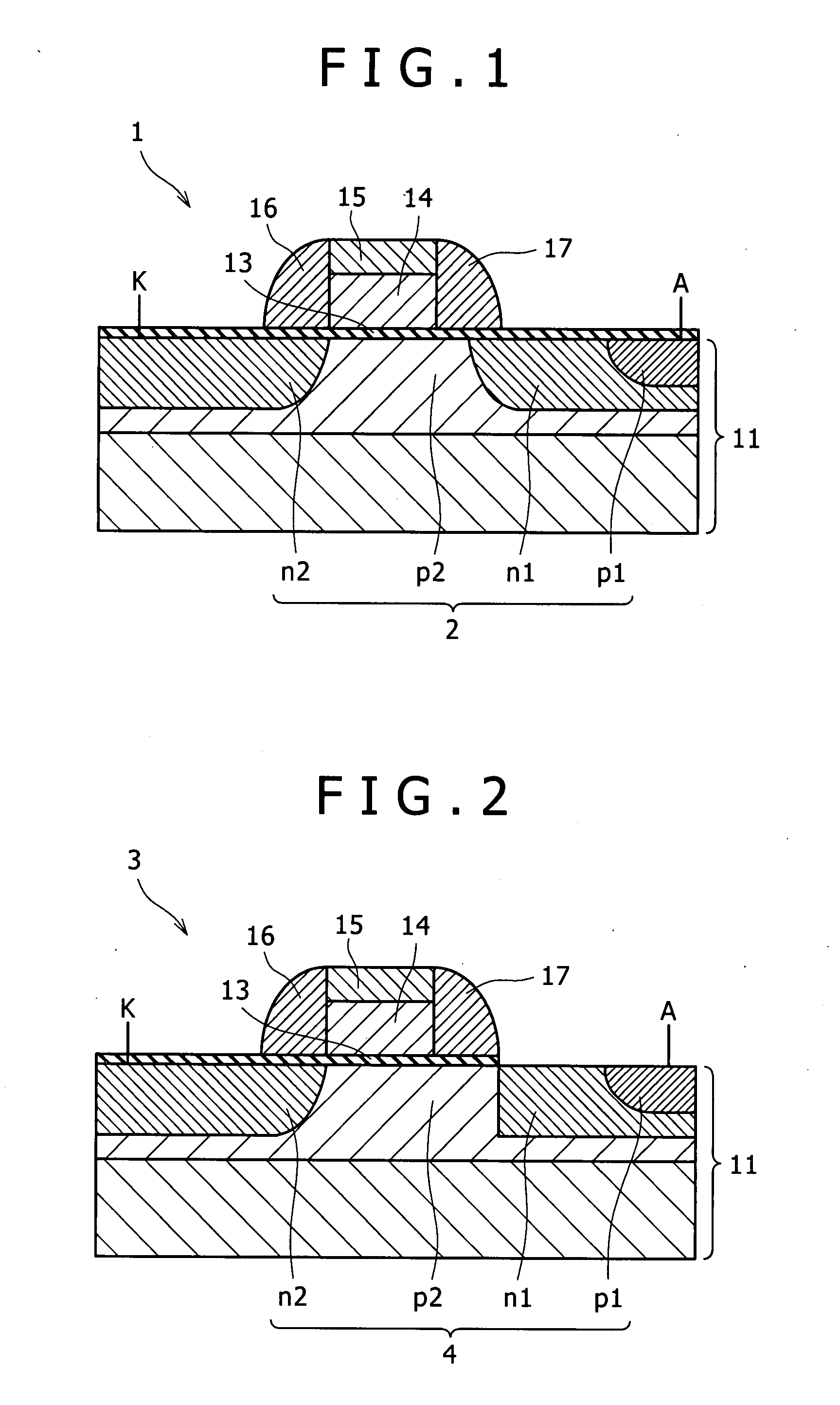
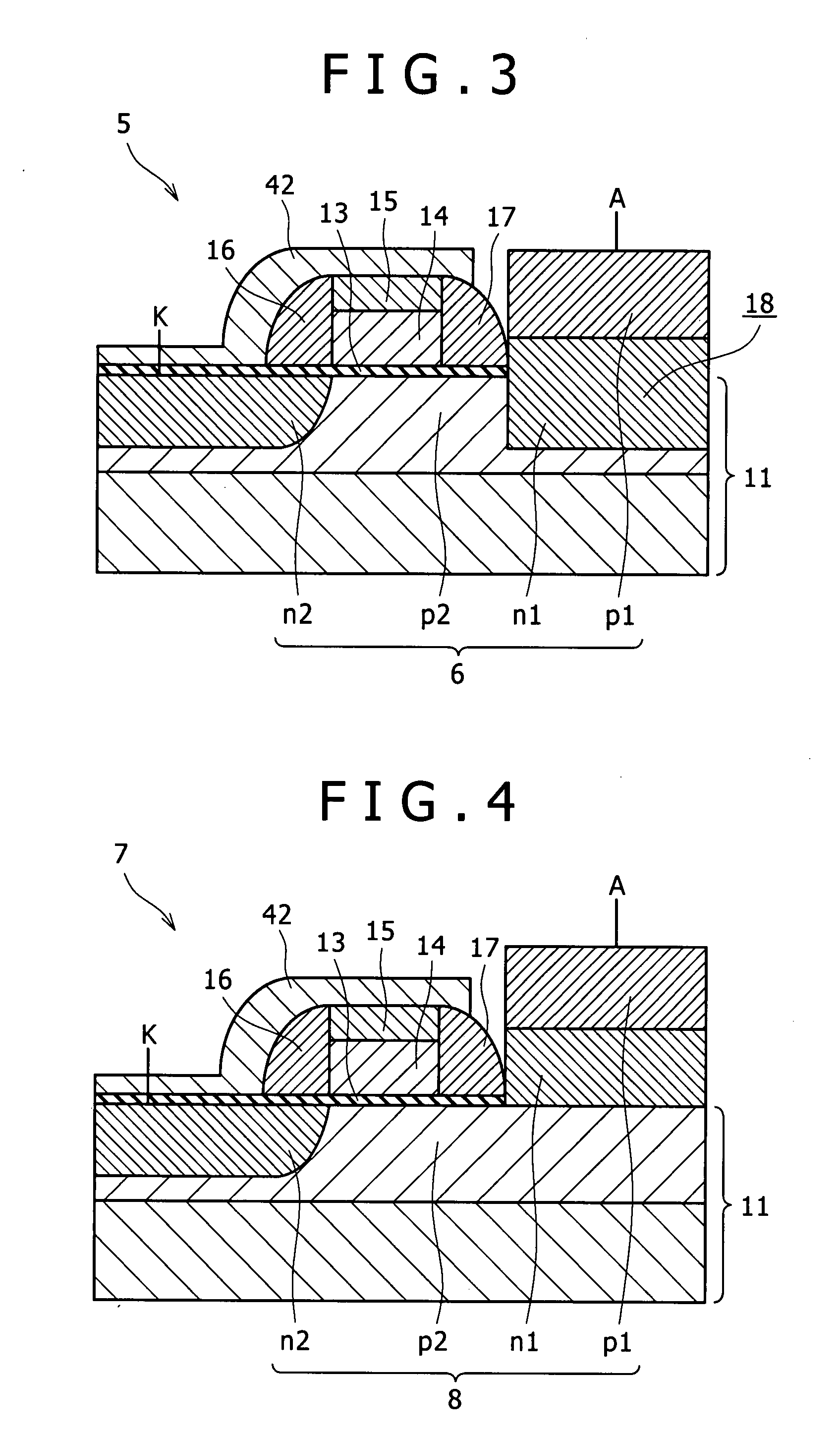
A semiconductor device includes a thyristor configured to be formed through sequential joining of a first region of a first conductivity type, a second region of a second conductivity type opposite to the first conductivity type, a third region of the first conductivity type, and a fourth region of the second conductivity type, and have a gate formed over the third region. The first to fourth regions are formed in a silicon germanium region or germanium region.
Owner:SONY CORP
Methods of forming silicon germanium tin films and structures and devices including the films
ActiveUS20170154770A1Low throughput timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh volume manufacturingChemical vapor deposition
Methods of forming silicon germanium tin (SiGexGe1−xSny) films are disclosed. Exemplary methods include growing films including silicon, germanium and tin in an epitaxial chemical vapor deposition reactor. Exemplary methods are suitable for high volume manufacturing. Also disclosed are structures and devices including silicon germanium tin films.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
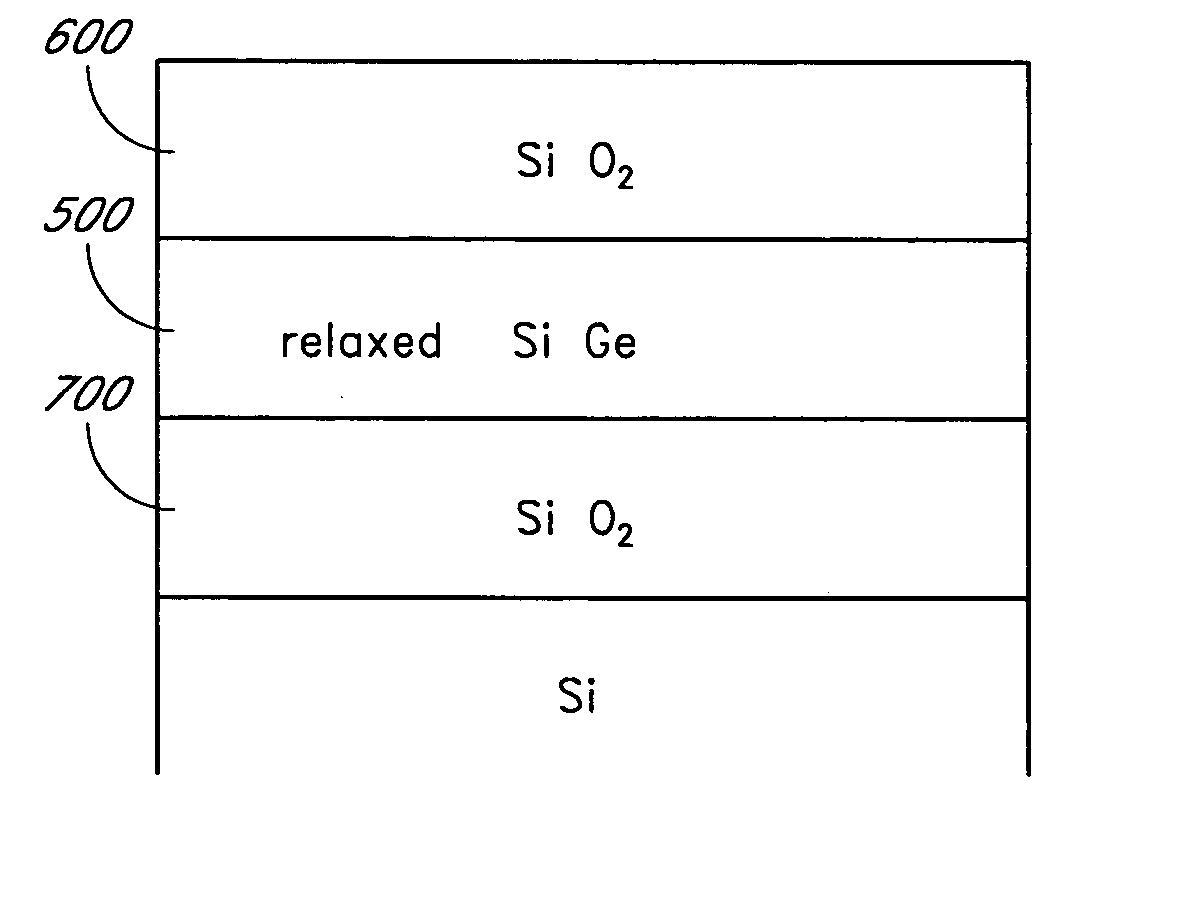
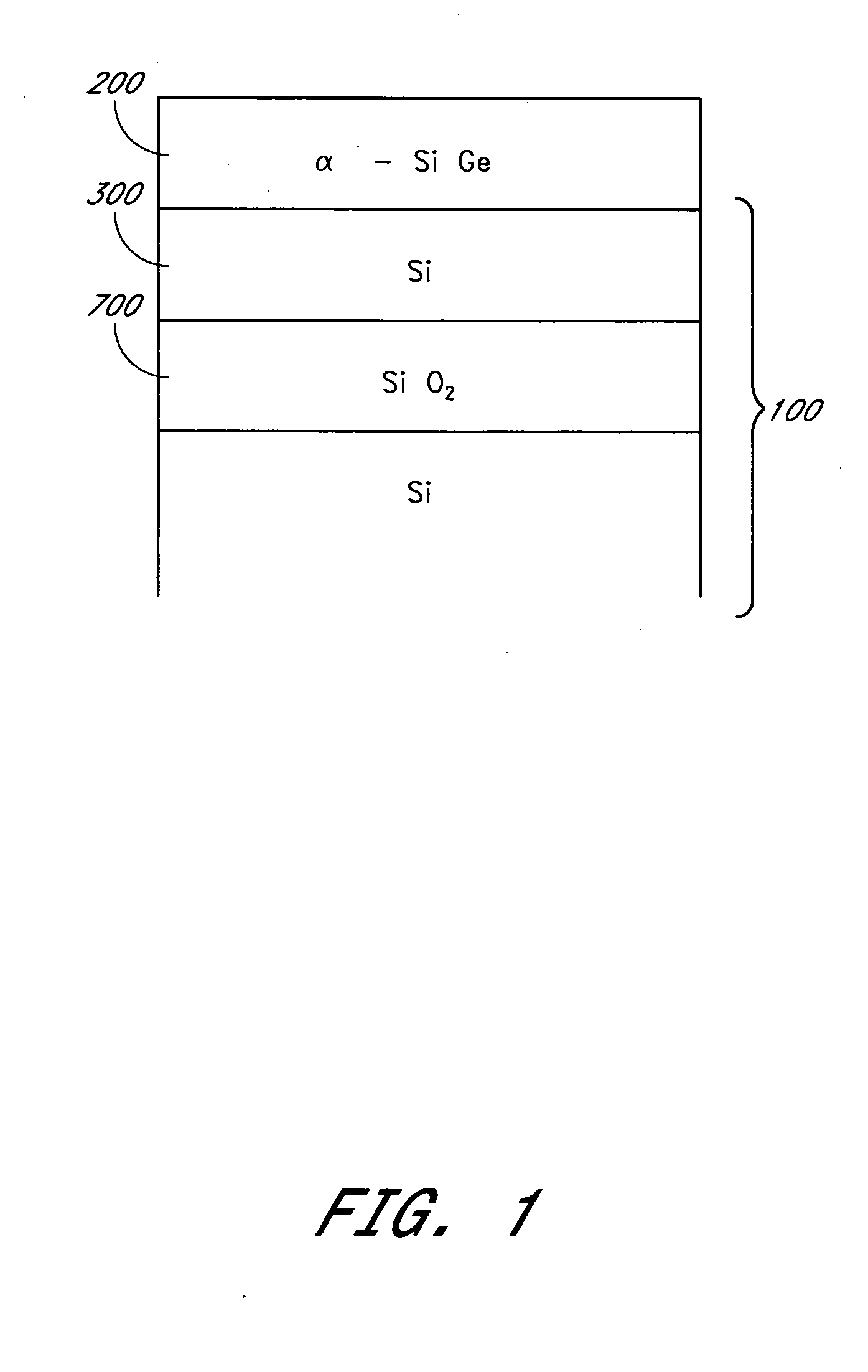
Deposition of silicon germanium on silicon-on-insulator structures and bulk substrates
Methods are provided for producing SiGe-on-insulator structures and for forming strain-relaxed SiGe layers on silicon while minimizing defects. Amorphous SiGe layers are deposited by CVD from trisilane and GeH4. The amorphous SiGe layers are recrystallized over silicon by melt or solid phase epitaxy (SPE) processes. The melt processes preferably also cause diffusion of germanium to dilute the overall germanium content and essentially consume the silicon overlying the insulator. The SPE process can be conducted with or without diffusion of germanium into the underlying silicon, and so is applicable to SOI as well as conventional semiconductor substrates.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
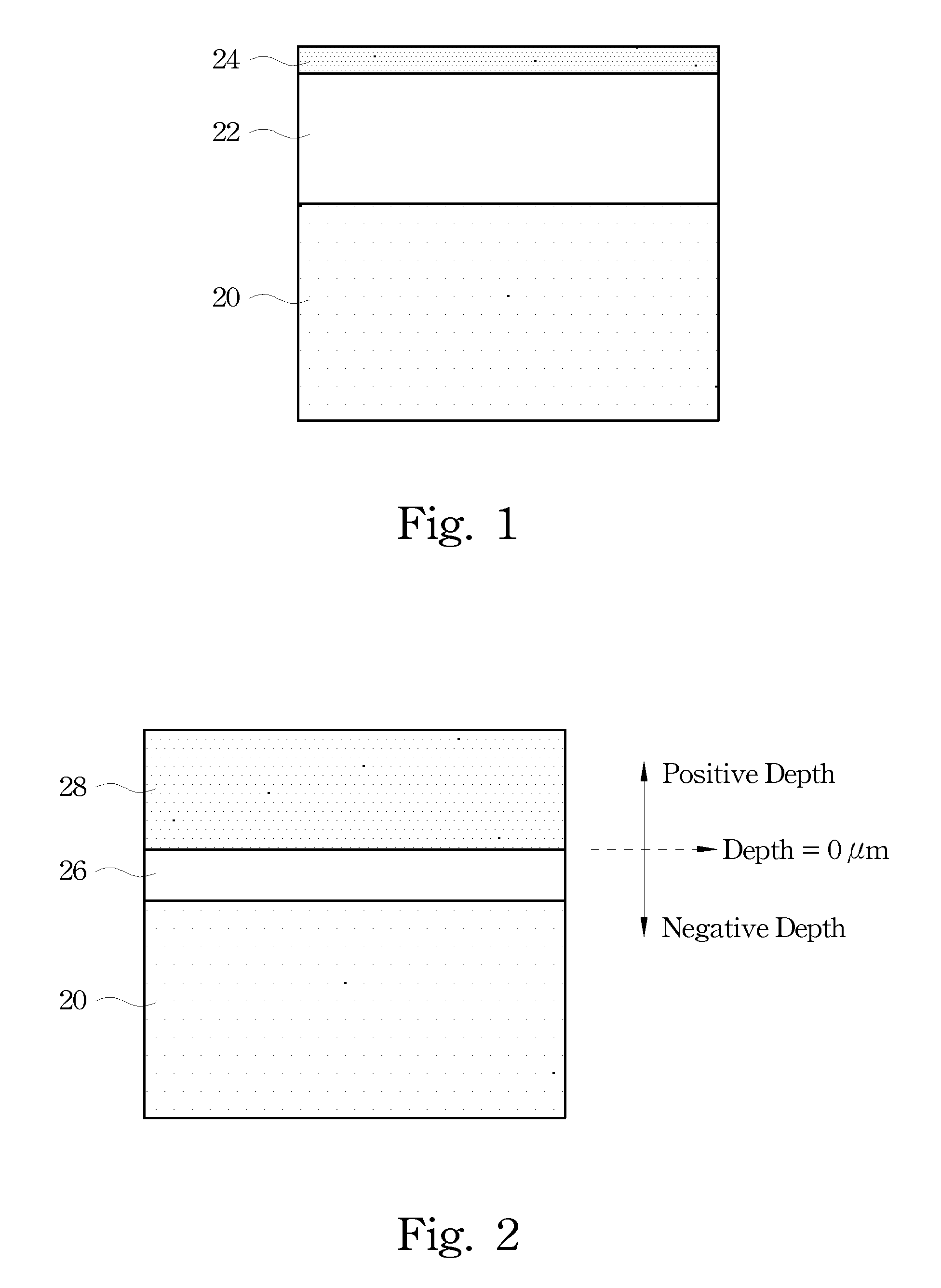
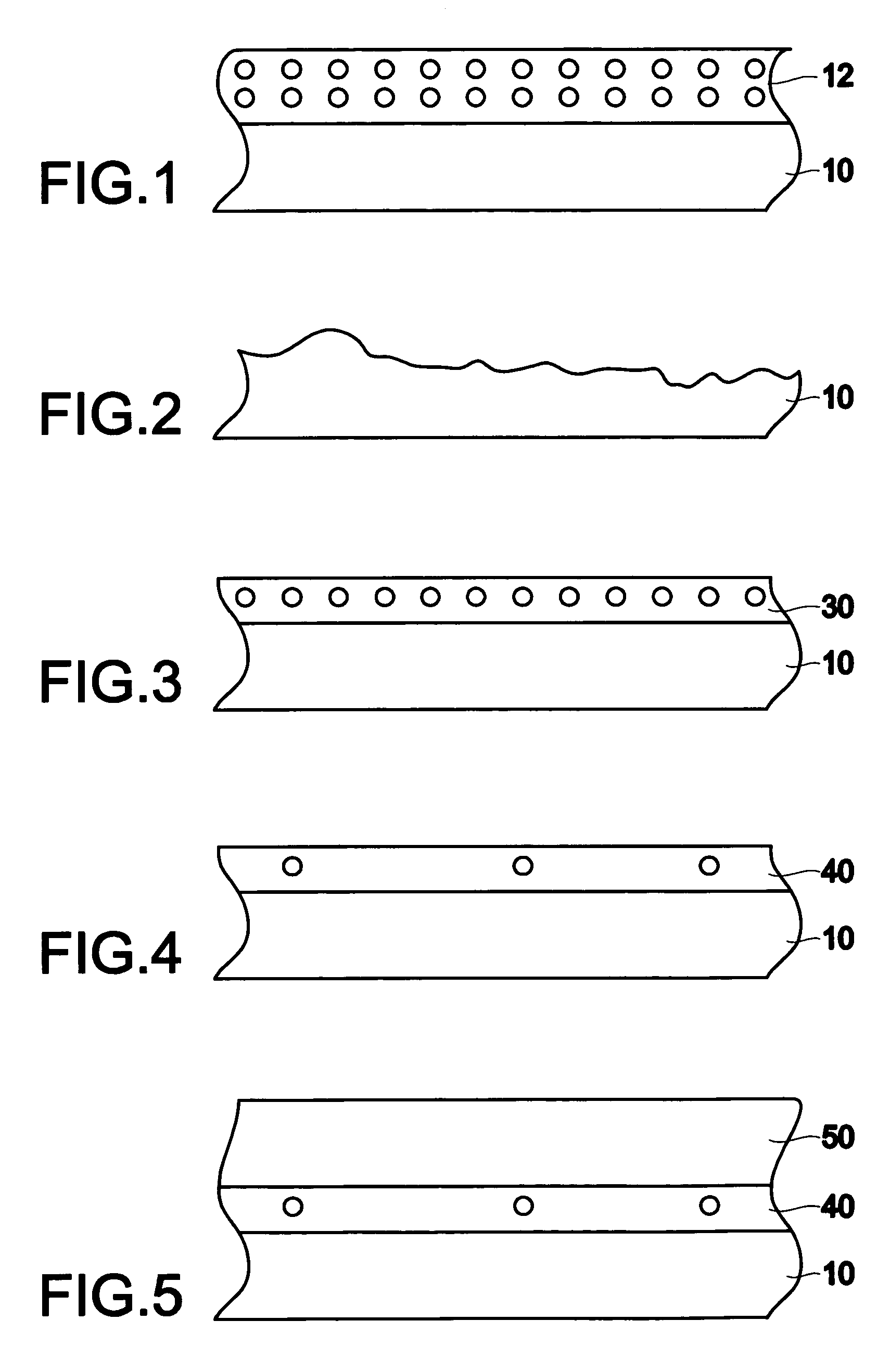
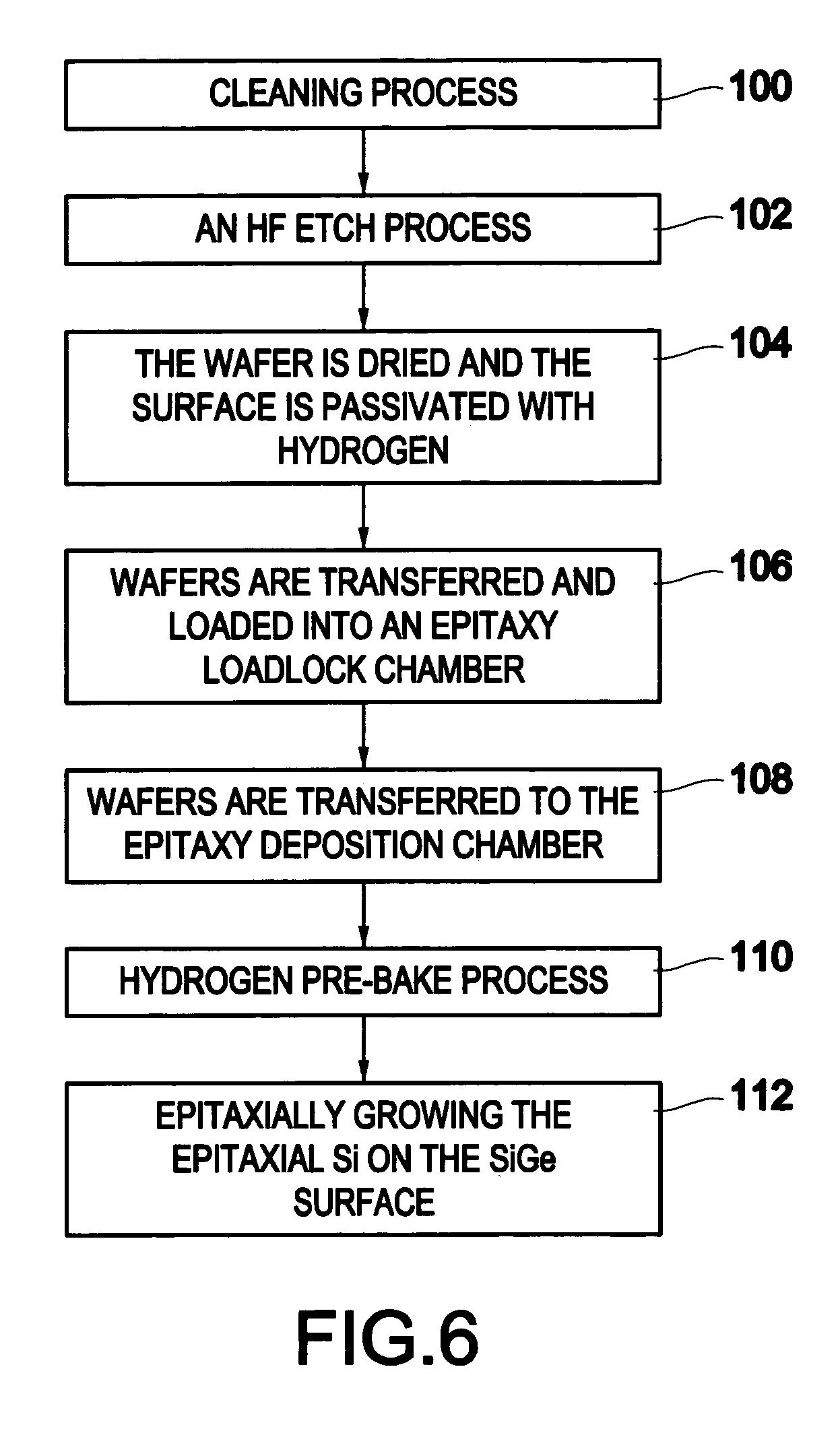
Method of preventing surface roughening during hydrogen pre-bake of SiGe substrates using chlorine containing gases
InactiveUS20050148162A1Prevent surfaceAvoid creatingPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPartial oxidationSilicon on insulator
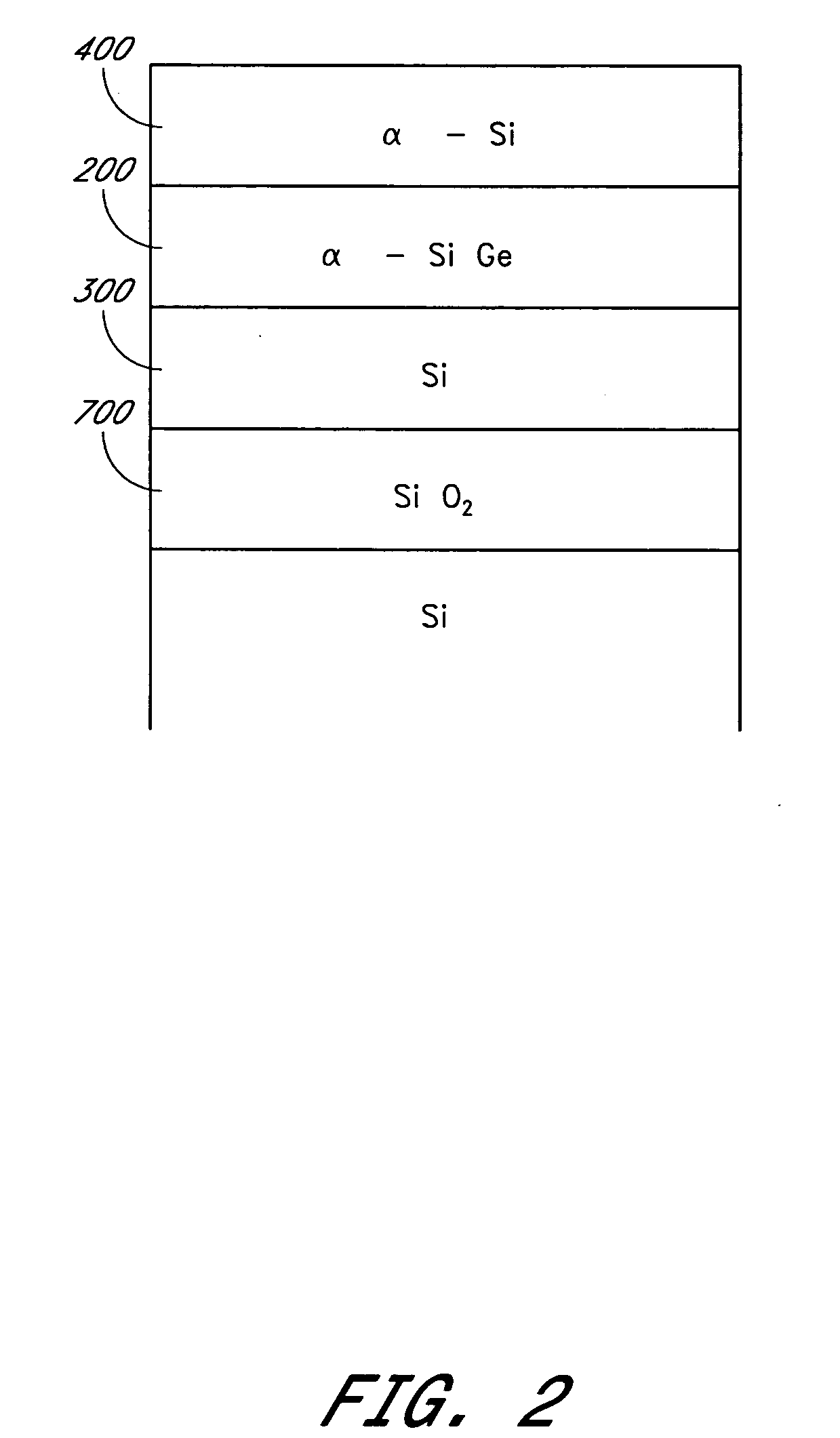
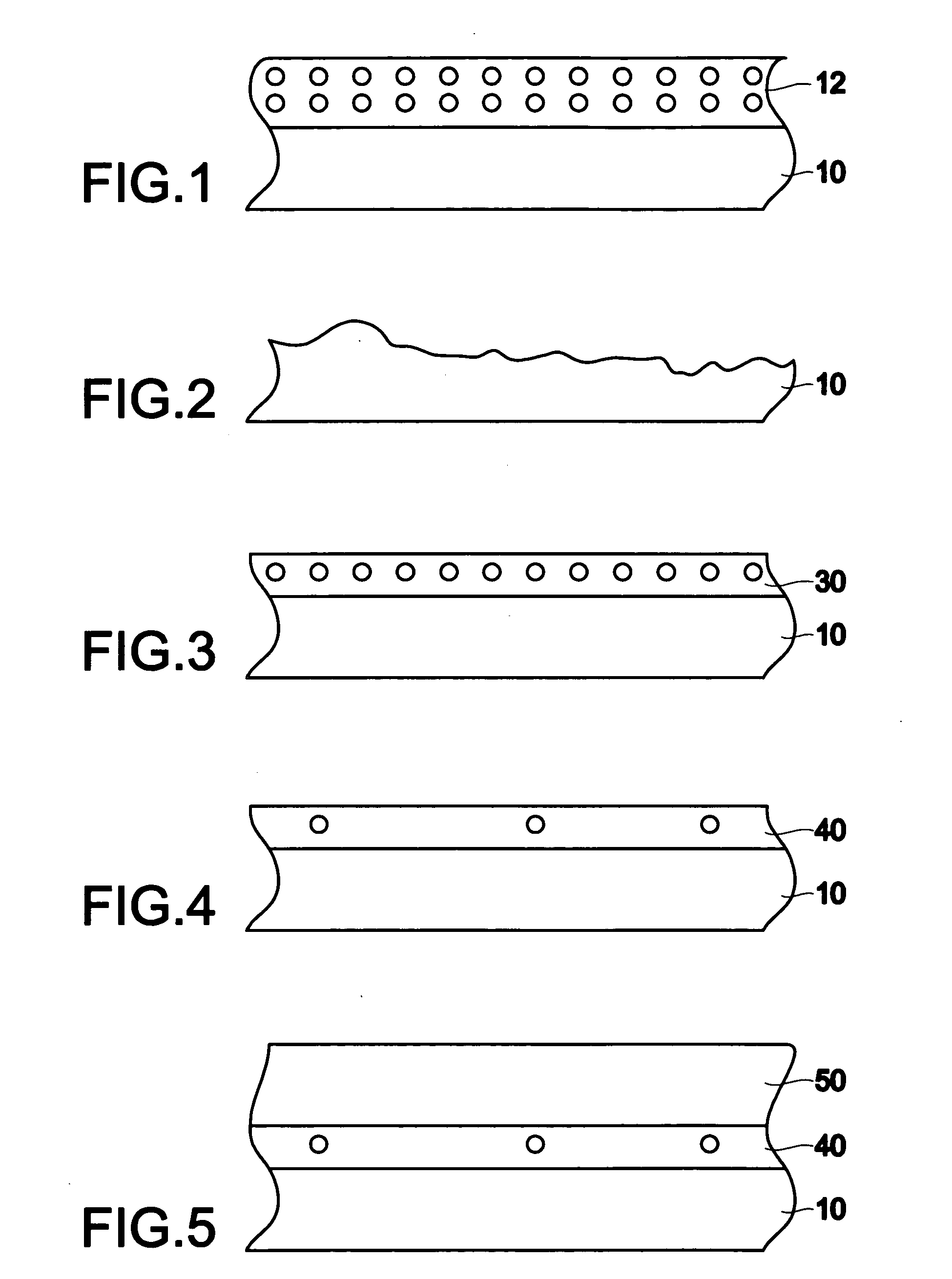
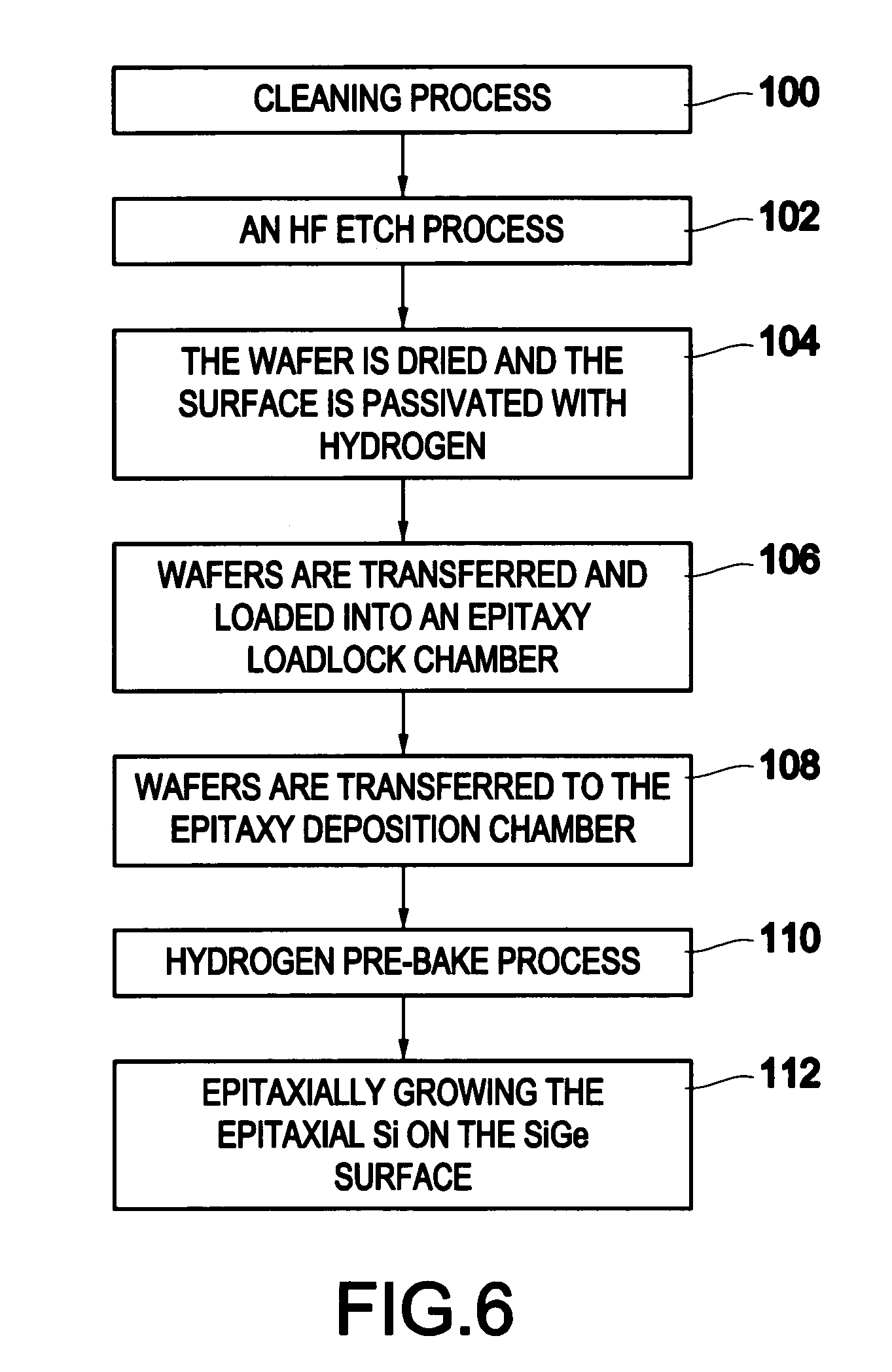
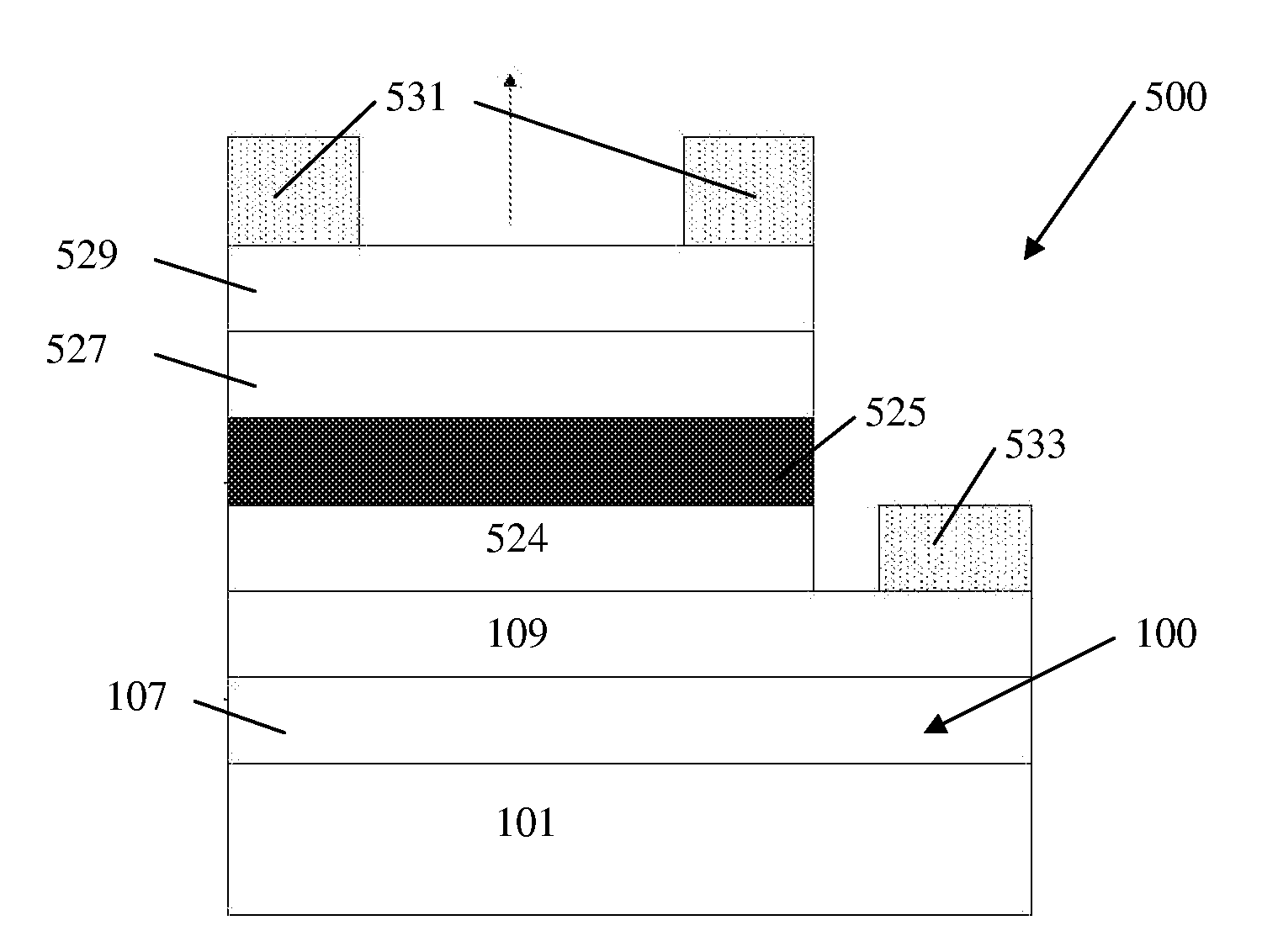
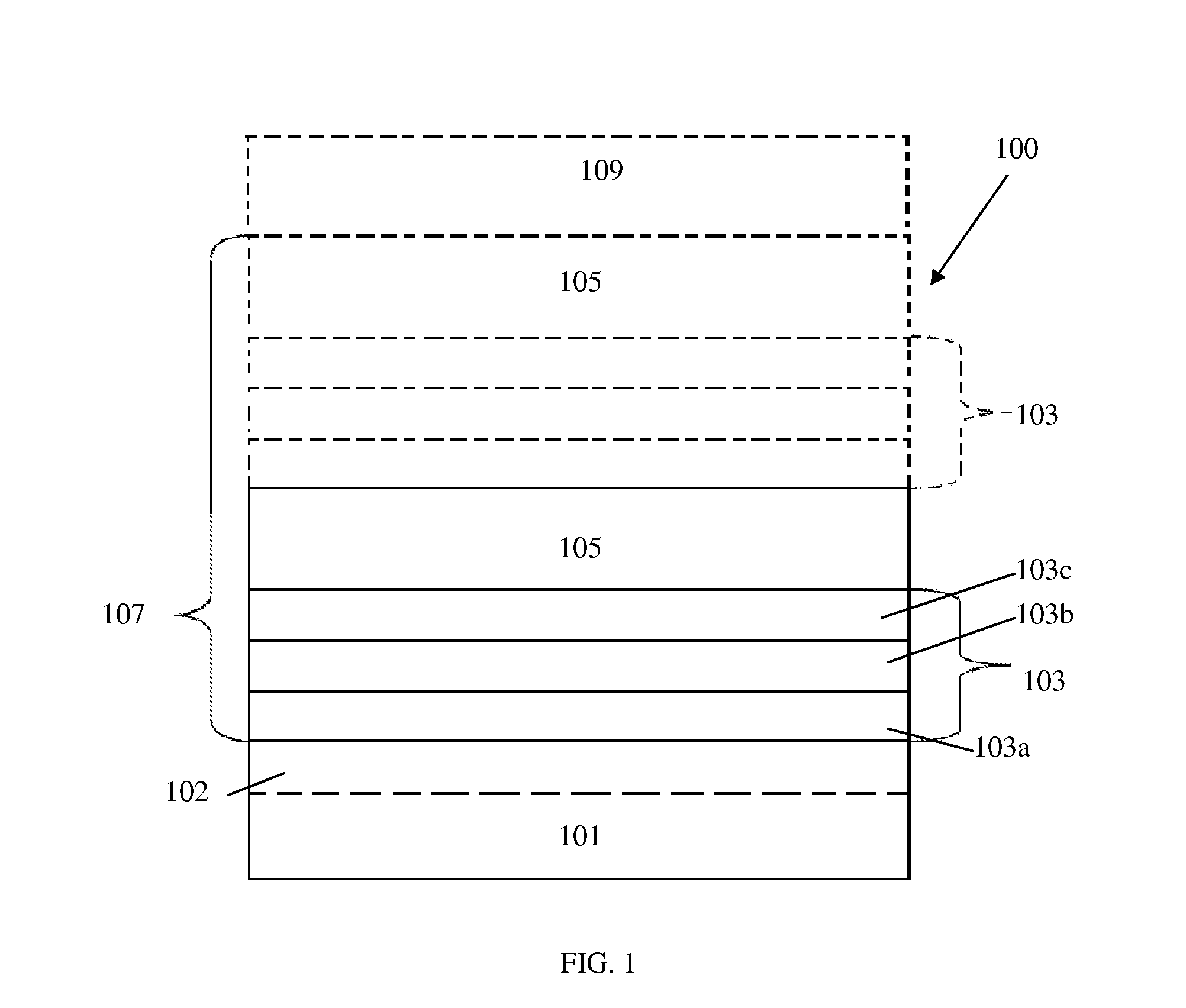
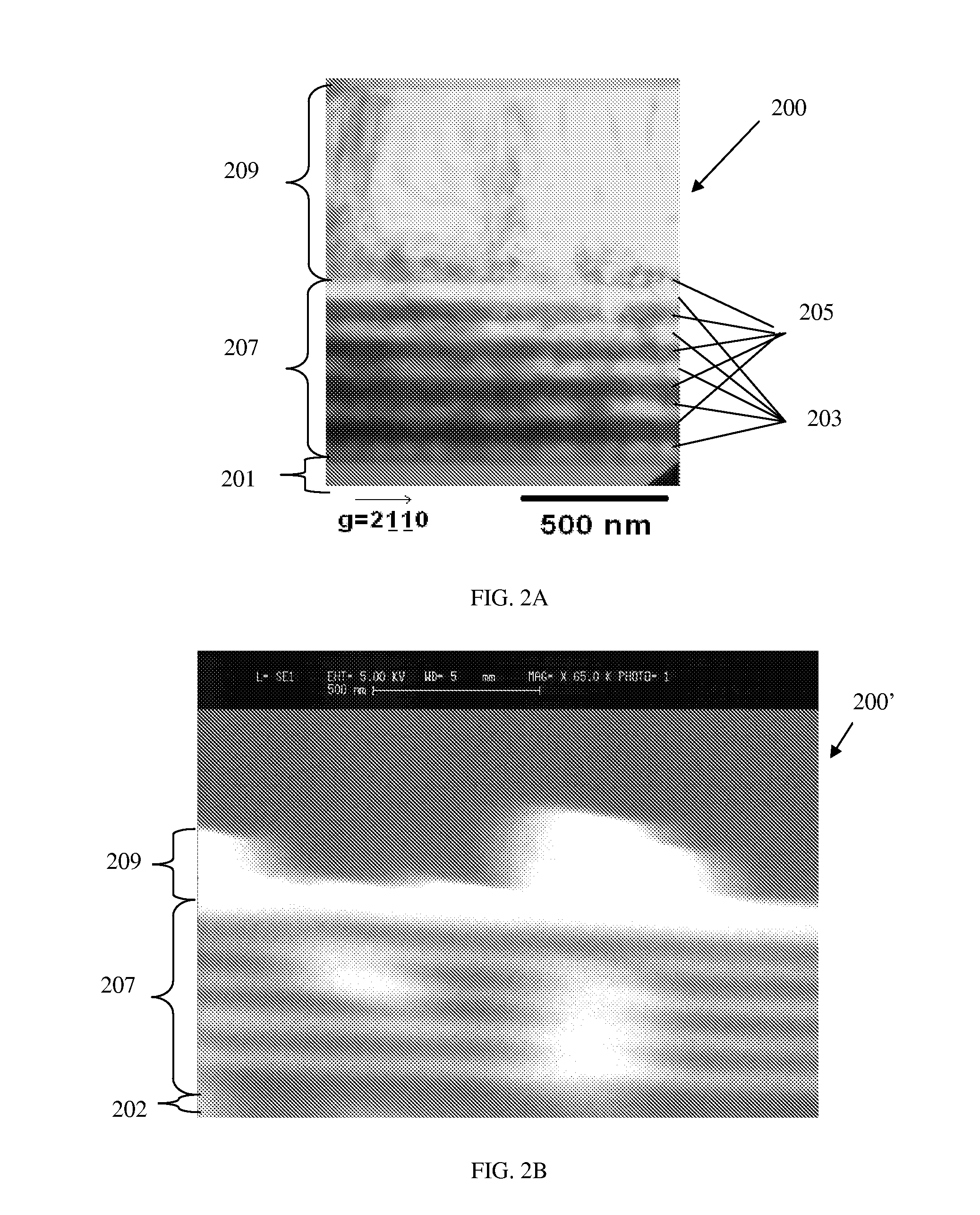
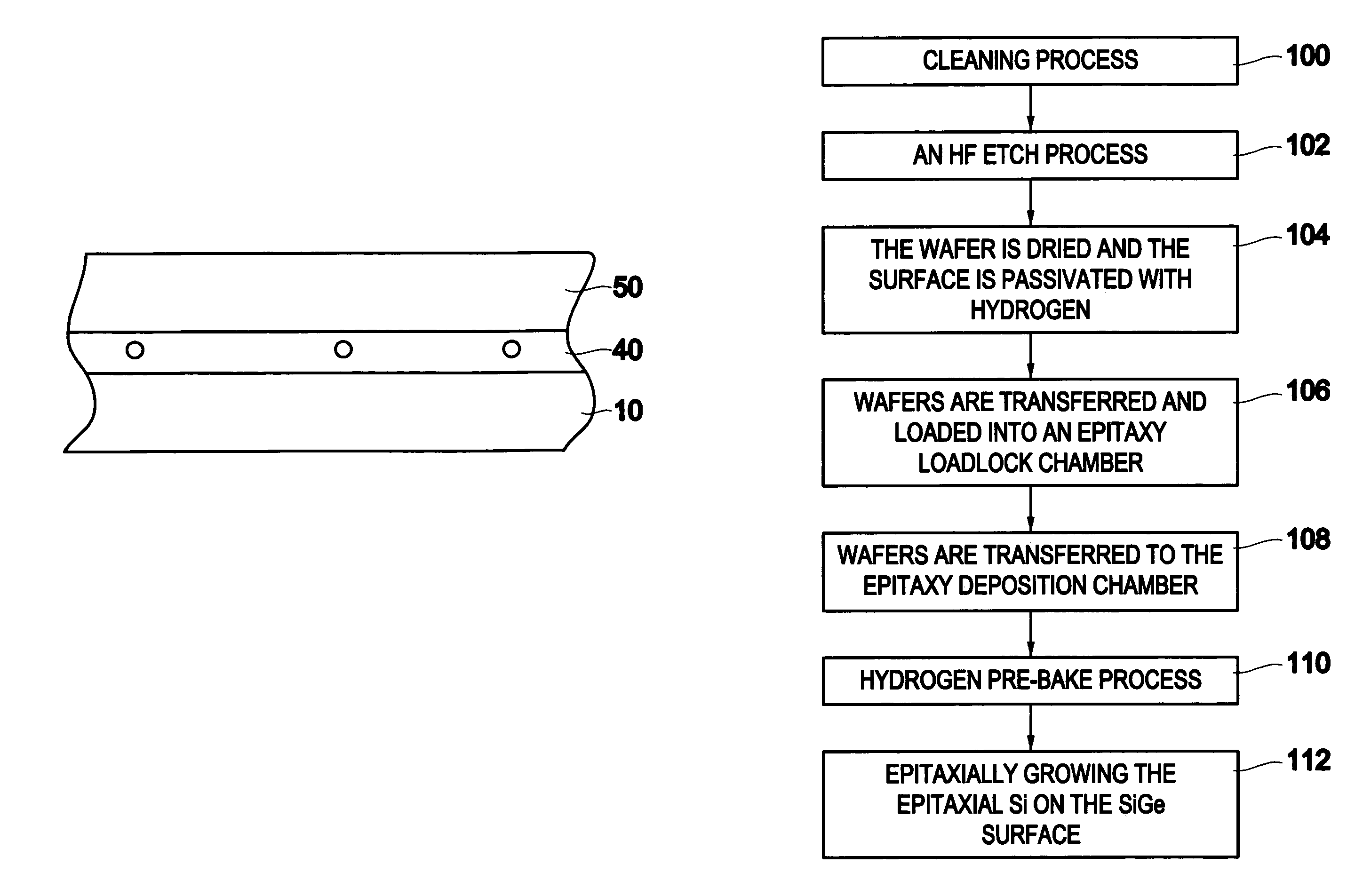
The invention forms an epitaxial silicon-containing layer on a silicon germanium, patterned strained silicon, or patterned thin silicon-on-insulator surface and avoids creating a rough surface upon which the epitaxial silicon-containing layer is grown. In order to avoid creating the rough surface, the invention first performs a hydrofluoric acid etching process on the silicon germanium, patterned strained silicon, or patterned thin silicon-on-insulator surface. This etching process removes most of oxide from the surface, and leaves only a sub-monolayer of oxygen (typically 1×1013-1×1015 / cm2 of oxygen) at the silicon germanium, patterned strained silicon, or patterned thin silicon-on-insulator surface. The invention then performs a hydrogen pre-bake process in a chlorine containing environment which heats the silicon germanium, strained silicon, or thin silicon-on-insulator surface sufficiently to remove the remaining oxygen from the surface. By introducing a small amount of chlorine containing gases, the heating processes avoid changing the roughness of the silicon germanium, patterned strained silicon, or patterned thin silicon-on-insulator surface. Then the process of epitaxially growing the epitaxial silicon-containing layer on the silicon germanium, patterned strained silicon, or patterned silicon-on-insulator surface is performed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for forming a double-gated semiconductor device
A method for forming a polysilicon FinFET (10) or other thin film transistor structure includes forming an insulative layer (12) over a semiconductor substrate (14). An amorphous silicon layer (32) forms over the insulative layer (12). A silicon germanium seed layer (44) forms in association with the amorphous silicon layer (32) for controlling silicon grain growth. The polysilicon layer arises from annealing the amorphous silicon layer (32). During the annealing step, silicon germanium seed layer (44), together with silicon germanium layer (34), catalyzes silicon recrystallization to promote growing larger crystalline grains, as well as fewer grain boundaries within the resulting polysilicon layer. Source (16), drain (18), and channel (20) regions are formed within the polysilicon layer. A double-gated region (24) forms in association with source (16), drain (18), and channel (20) to produce polysilicon FinFET (10).
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
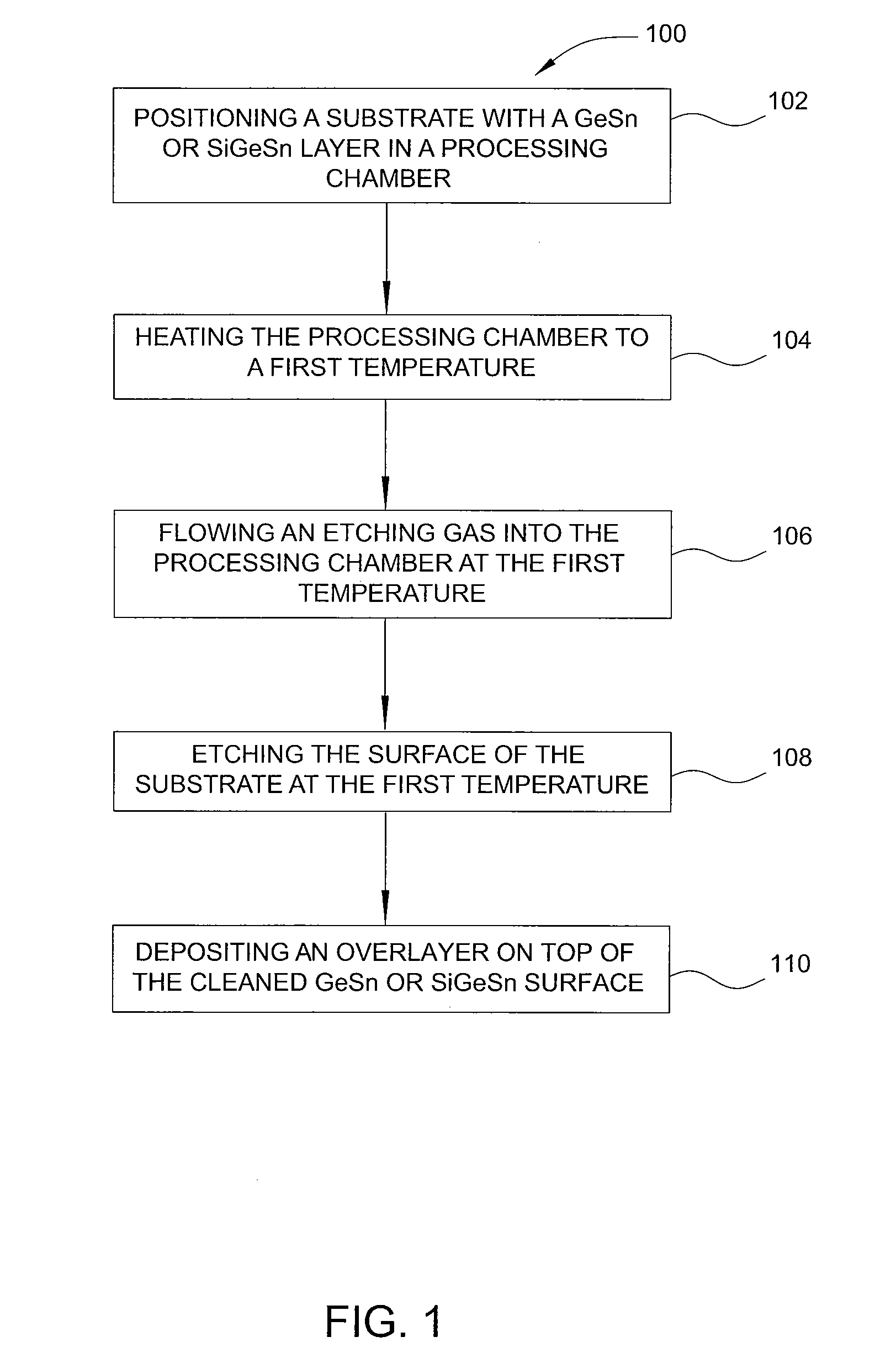
Method of epitaxial germanium tin alloy surface preparation
Methods of preparing a clean surface of germanium tin or silicon germanium tin layers for subsequent deposition are provided. An overlayer of Ge, doped Ge, another GeSn or SiGeSn layer, a doped GeSn or SiGeSn layer, an insulator, or a metal can be deposited on a prepared GeSn or SiGeSn layer by positioning a substrate with an exposed germanium tin or silicon germanium tin layer in a processing chamber, heating the processing chamber and flowing a halide gas into the processing chamber to etch the surface of the substrate using either thermal or plasma assisted etching followed by depositing an overlayer on the substantially oxide free and contaminant free surface. Methods can also include the placement and etching of a sacrificial layer, a thermal clean using rapid thermal annealing, or a process in a plasma of nitrogen trifluoride and ammonia gas.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method to form upward pointing p-i-n diodes having large and uniform current
A method is disclosed to form an upward-pointing p-i-n diode formed of deposited silicon, germanium, or silicon-germanium. The diode has a bottom heavily doped p-type region, a middle intrinsic or lightly doped region, and a top heavily doped n-type region. The top heavily doped p-type region is doped with arsenic, and the semiconductor material of the diode is crystallized in contact with an appropriate silicide, germanide, or silicide-germanide. A large array of such upward-pointing diodes can be formed with excellent uniformity of current across the array when a voltage above the turn-on voltage of the diodes is applied. This diode is advantageously used in a monolithic three dimensional memory array.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Multiple gate semiconductor device and method for forming same
In accordance with an embodiment of the invention, a FinFET device is disclosed which comprises a strained silicon channel layer formed on, at least, the sidewalls of a strain-relaxed silicon-germanium body.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Strained silicon fin structure
InactiveUS20060113522A1Suppression of short channel effectsIncrease currentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriving currentLattice mismatch
Disclosing is a strained silicon finFET device having a strained silicon fin channel in a double gate finFET structure. The disclosed finFET device is a double gate MOSFET consisting of a silicon fin channel controlled by a self-aligned double gate for suppressing short channel effect and enhancing drive current. The silicon fin channel of the disclosed finFET device is a strained silicon fin channel, comprising a strained silicon layer deposited on a seed fin having different lattice constant, for example, a silicon layer deposited on a silicon germanium seed fin, or a carbon doped silicon layer deposited on a silicon seed fin. The lattice mismatch between the silicon layer and the seed fin generates the strained silicon fin channel in the disclosed finFET device to improve hole and electron mobility enhancement, in addition to short channel effect reduction characteristic inherently in a finFET device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
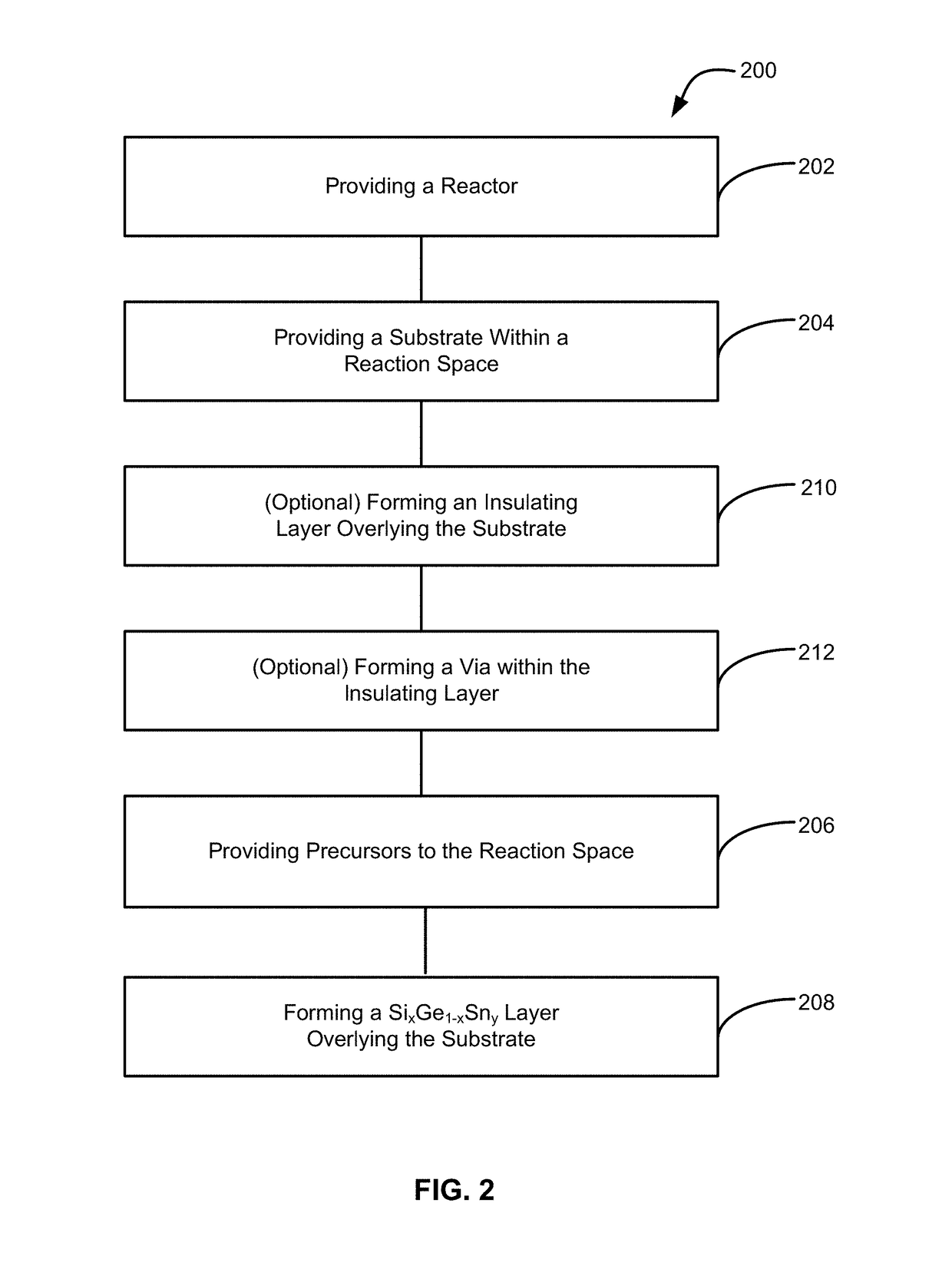
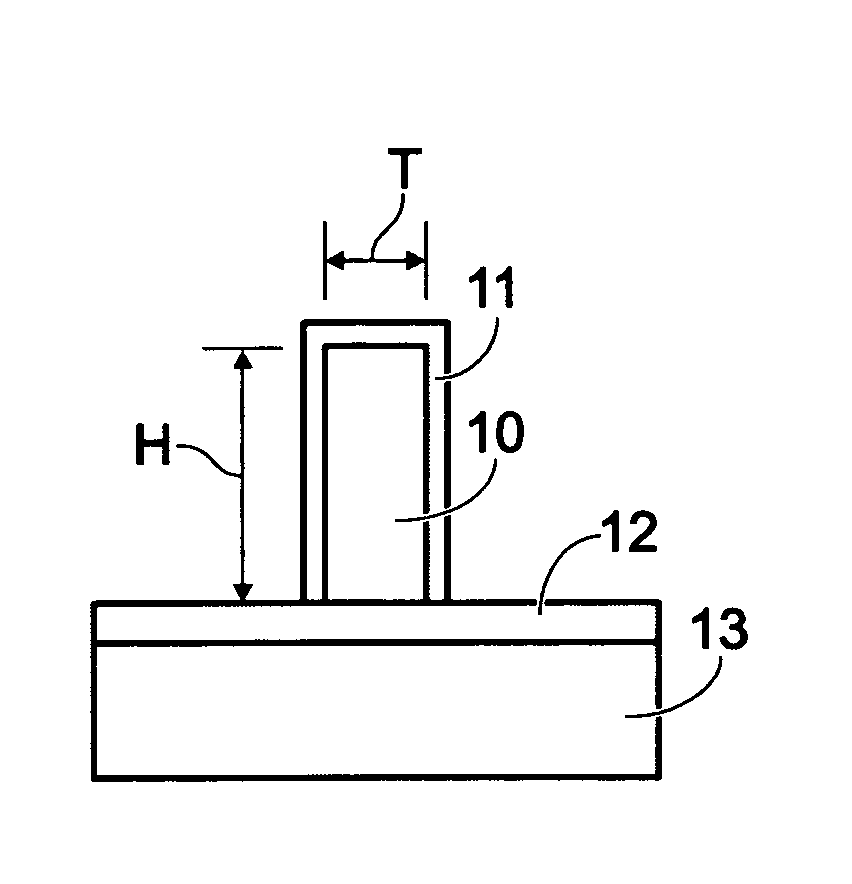
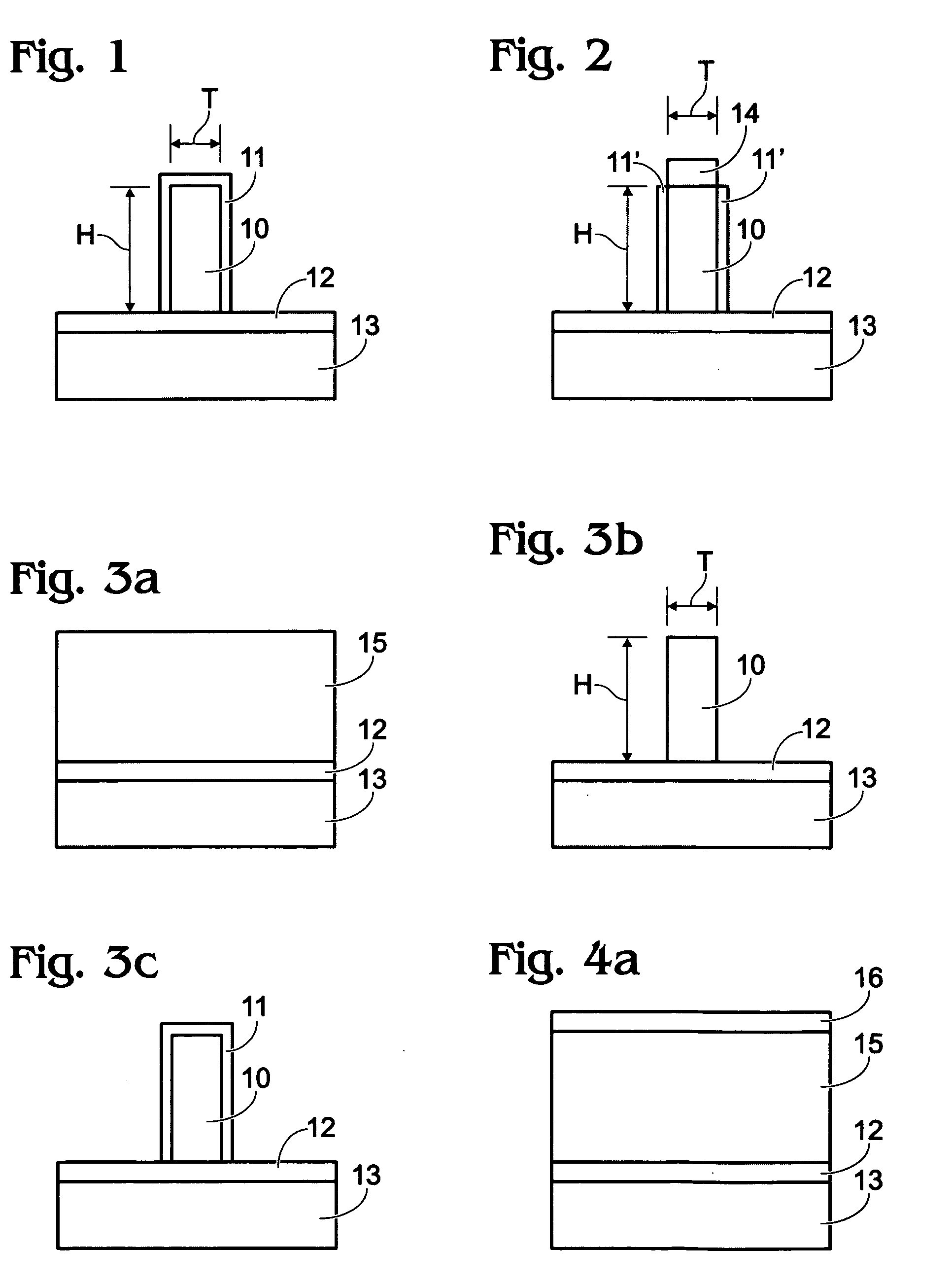
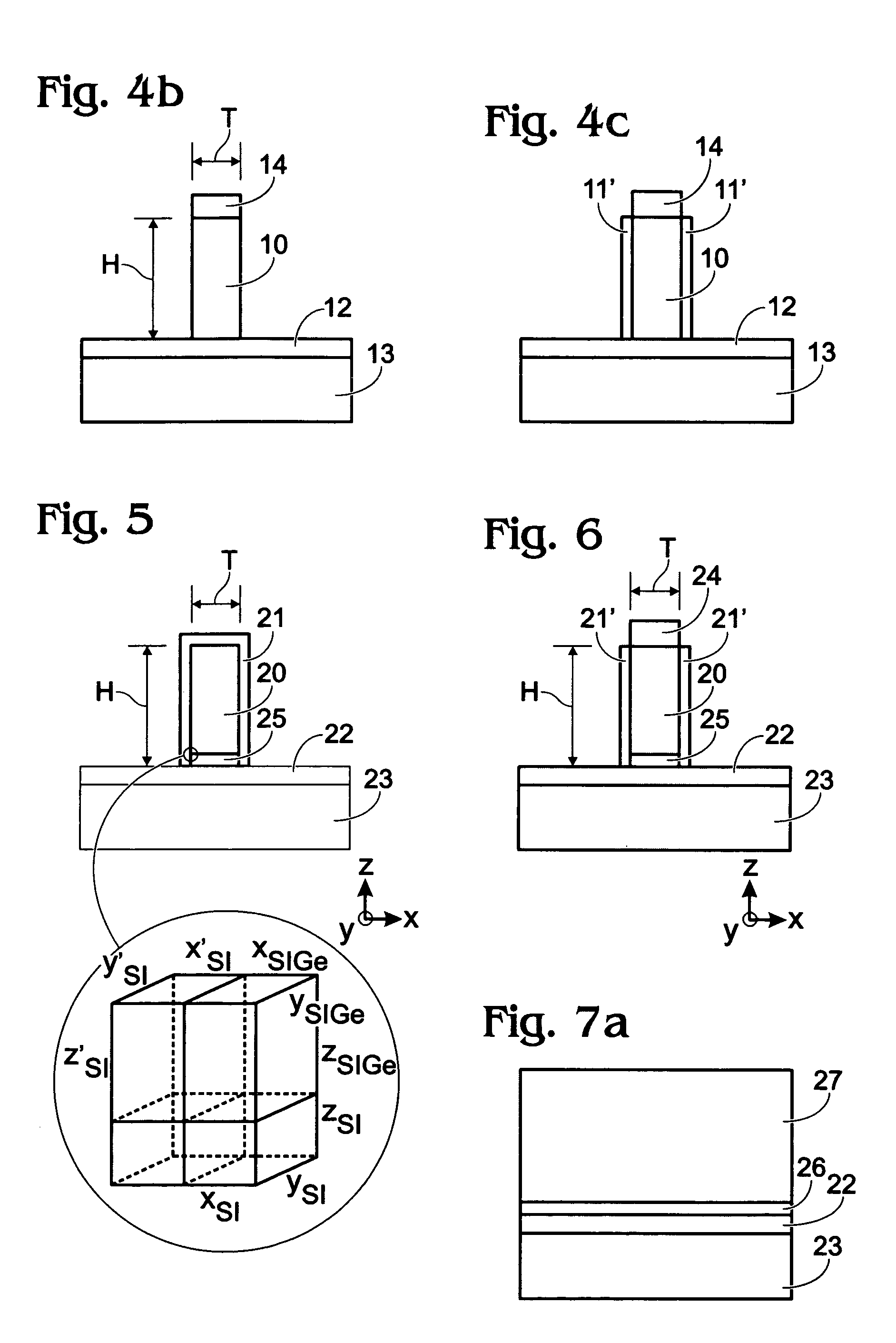
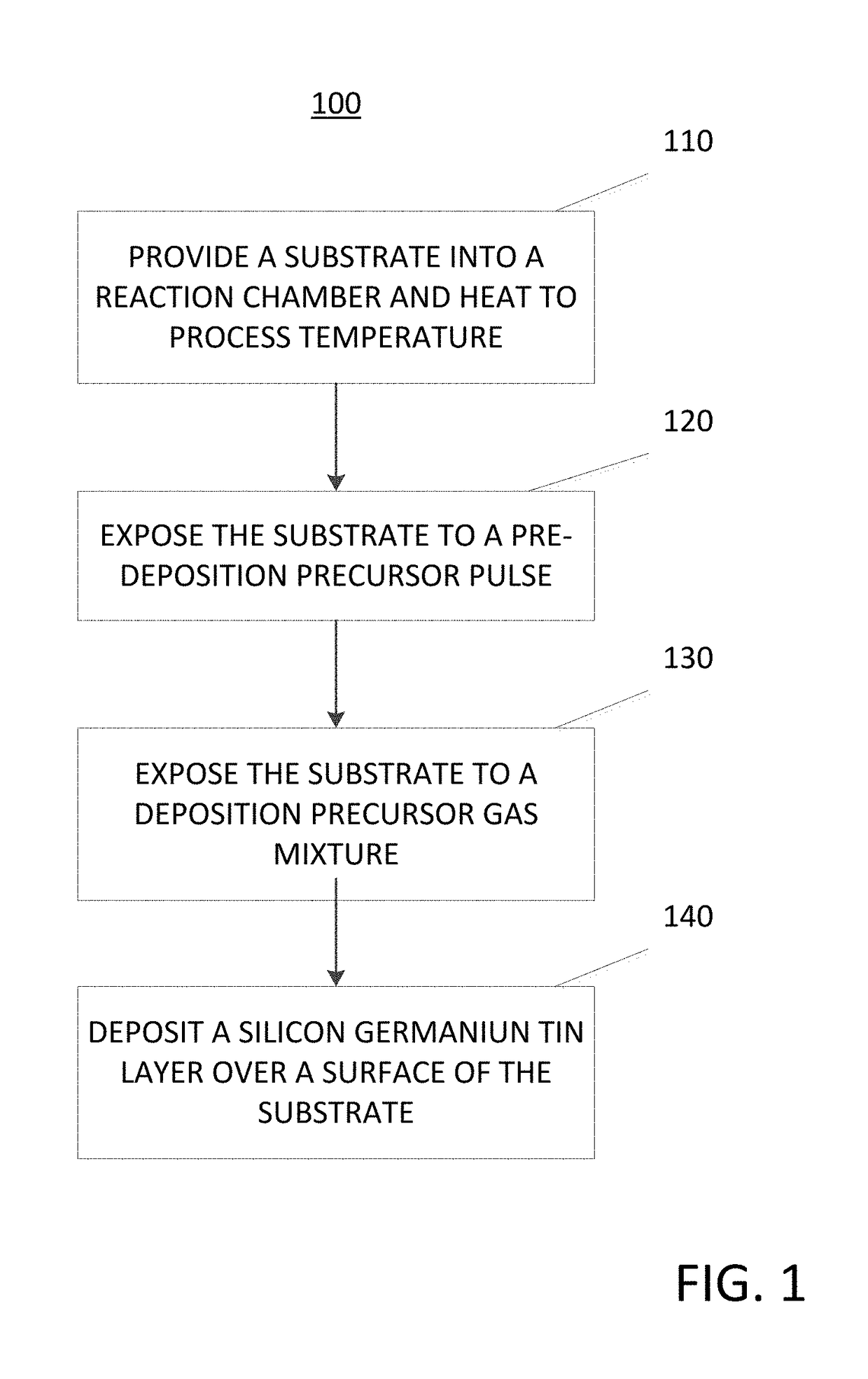
Methods for forming a silicon germanium tin layer and related semiconductor device structures
ActiveUS20190013199A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingTetrachlorideGermane
A method for forming a forming a silicon germanium tin (SiGeSn) layer is disclosed. The method may include, providing a substrate within a reaction chamber, exposing the substrate to a pre-deposition precursor pulse, which comprises tin tetrachloride (SnCl4), exposing the substrate to a deposition precursor gas mixture comprising a hydrogenated silicon source, germane (GeH4), and tin tetrachloride (SnCl4), and depositing the silicon germanium tin (SiGeSn) layer over a surface of the substrate. Semiconductor device structures including a silicon germanium tin (SiGeSn) layer formed by the methods of the disclosure are also provided.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Germanium FinFETs having dielectric punch-through stoppers
InactiveUS8048723B2High carrier mobilityTotal current dropSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structureComposite substrate
A method of forming a semiconductor structure includes providing a composite substrate, which includes a bulk silicon substrate and a silicon germanium (SiGe) layer over and adjoining the bulk silicon substrate. A first condensation is performed to the SiGe layer to form a condensed SiGe layer, so that the condensed SiGe layer has a substantially uniform germanium concentration. The condensed SiGe layer and a top portion of the bulk silicon substrate are etched to form a composite fin including a silicon fin and a condensed SiGe fin over the silicon fine. The method further includes oxidizing a portion of the silicon fin; and performing a second condensation to the condensed SiGe fin.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Methods for forming a semiconductor structure and related semiconductor structures
ActiveUS20190131124A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structureSilicon oxide
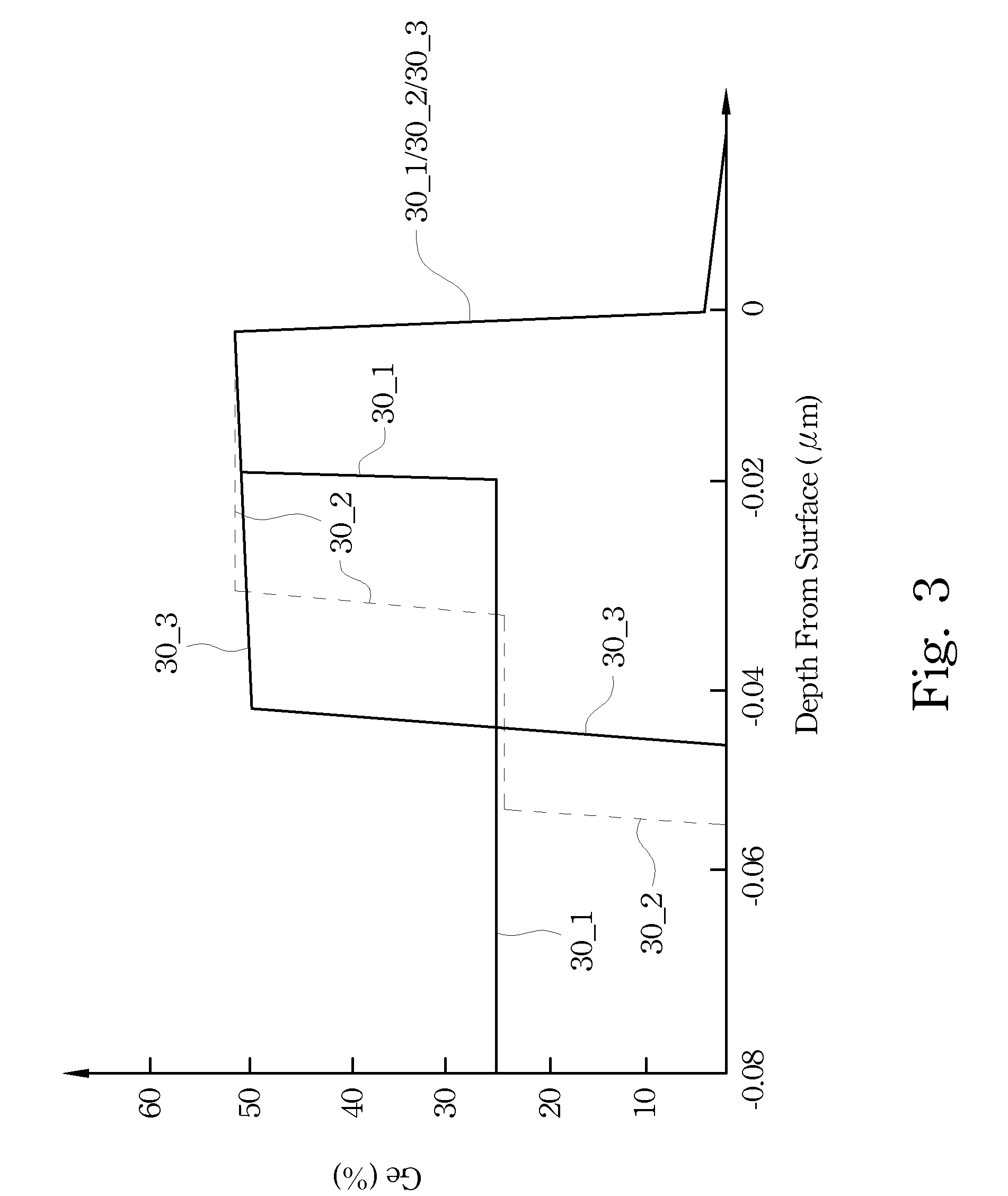
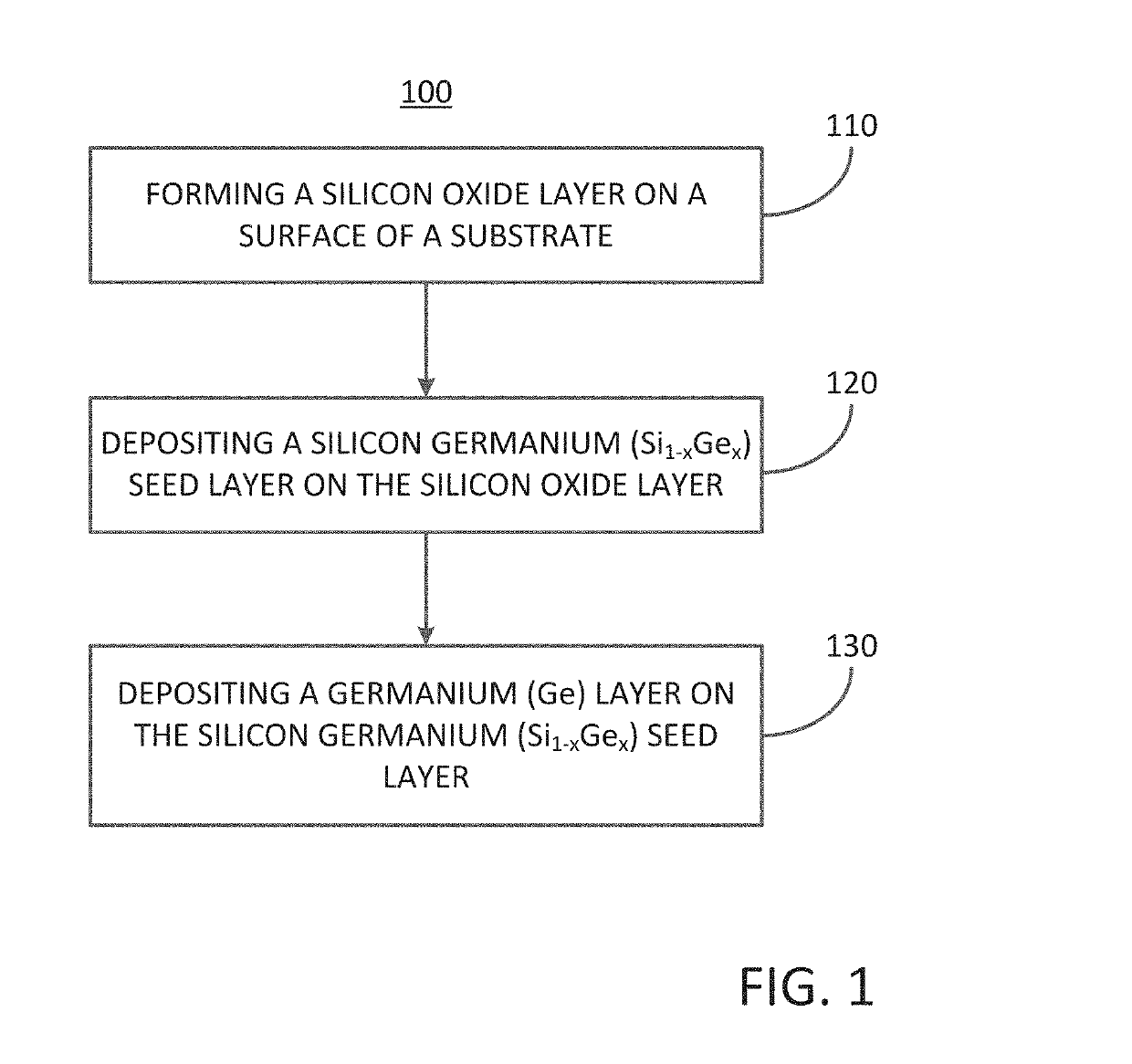
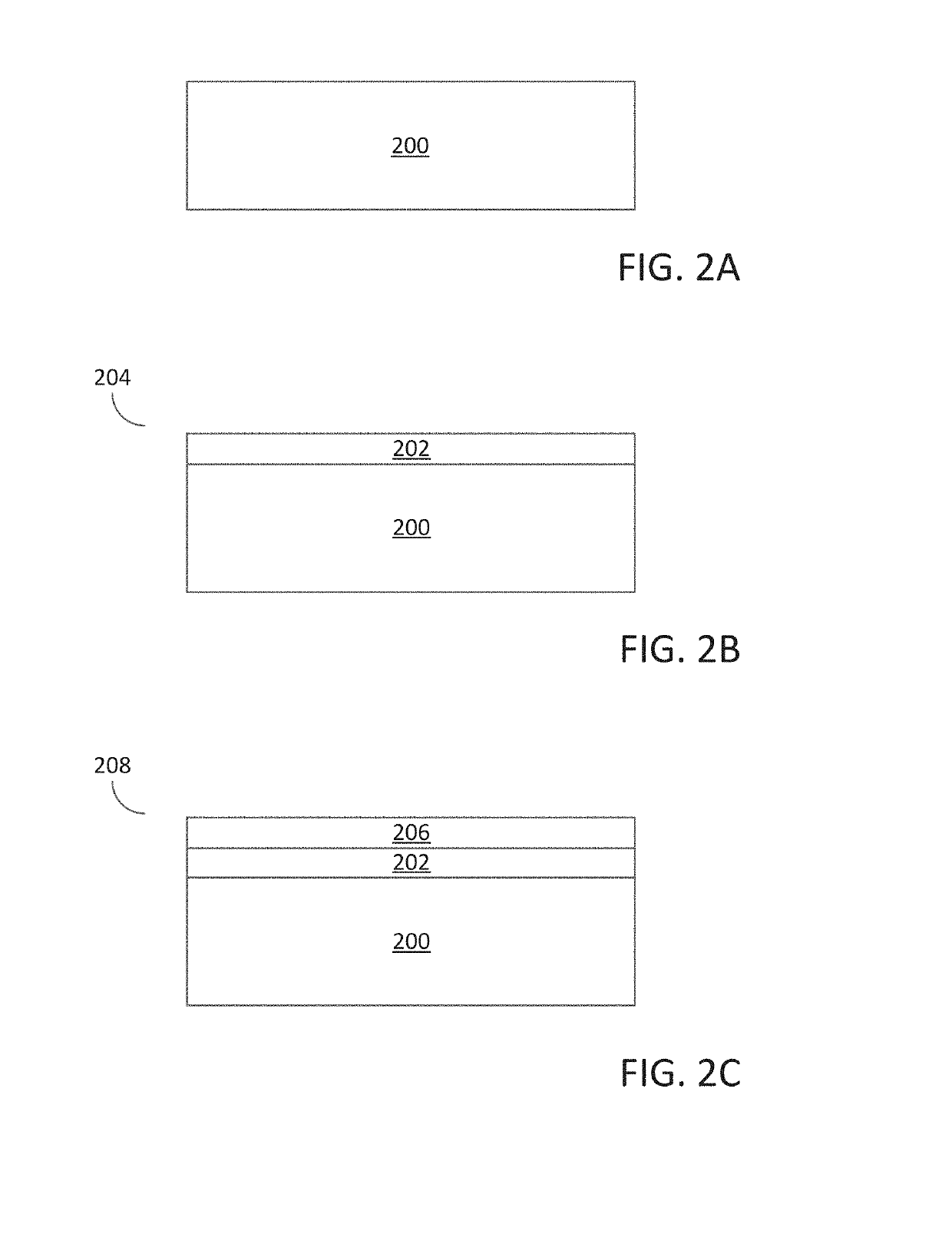
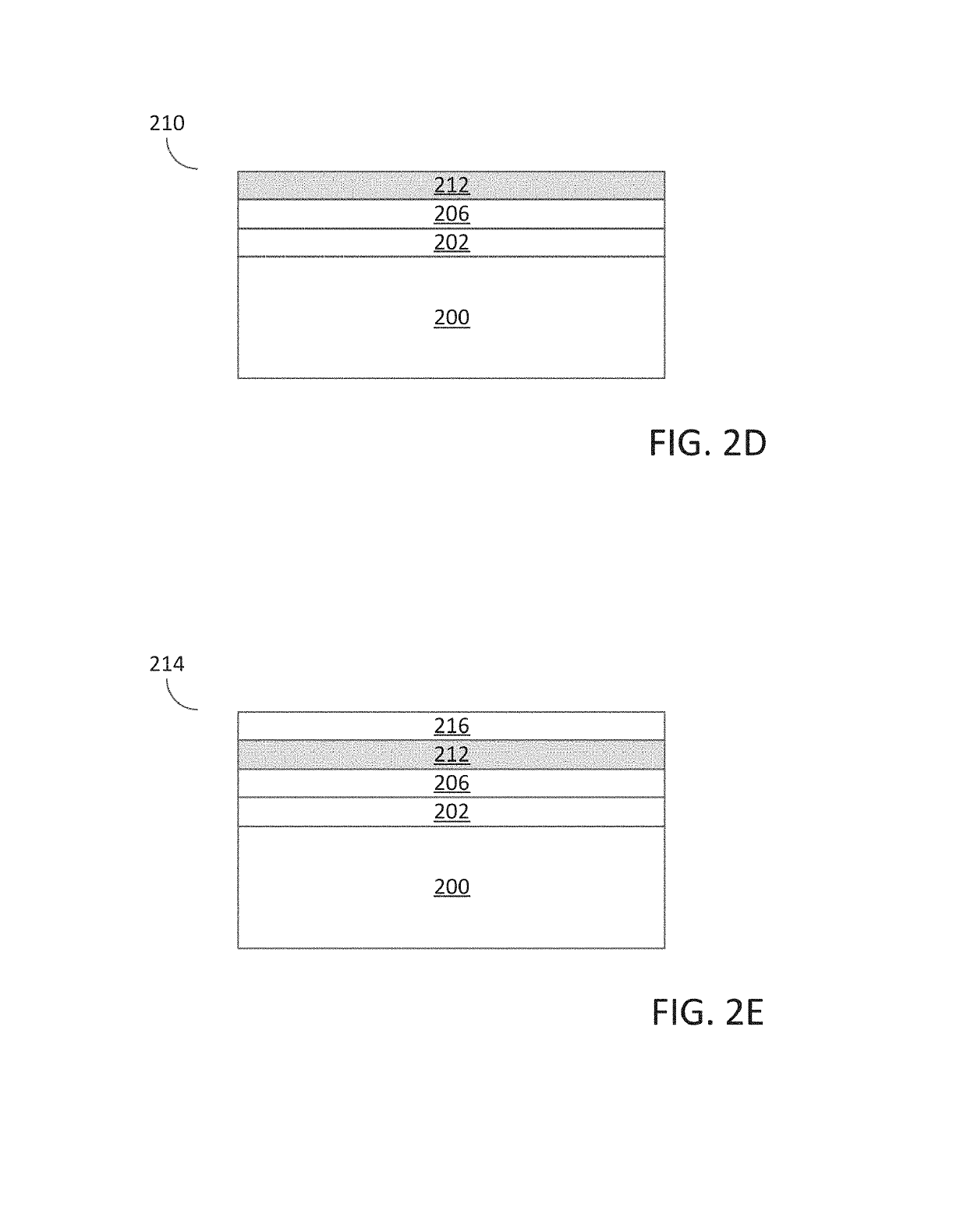
A method for forming a forming a semiconductor structure is disclosed. The method may include: forming a silicon oxide layer on a surface of a substrate, depositing a silicon germanium (Si1-xGex) seed layer directly on the silicon oxide layer, and depositing a germanium (Ge) layer directly on the silicon germanium (Si1-xGex) seed layer. Semiconductor structures including a germanium (Ge) layer deposited on silicon oxide utilizing an intermediate silicon germanium (Si1-xGex) seed layer are also disclosed.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Group iii-nitride growth on silicon or silicon germanium substrates and method and devices therefor
InactiveUS20080128745A1Laser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A structure including a Si1-xGex substrate and a distributed Bragg reflector layer disposed directly onto the substrate. The distributed Bragg reflector layer includes a repeating pattern that includes at least one aluminum nitride layer and a second layer having the general formula AlyGa1-yN. Another aspect of the present invention is various devices including this structure. Another aspect of the present invention is directed to a method of forming such a structure comprising providing a Si1-xGex substrate and depositing a distributed Bragg reflector layer directly onto the substrate. Another aspect of the present invention is directed to a photodetector or photovoltaic cell device, including a Si1-xGex substrate device, a group III-nitride device and contacts to provide a conductive path for a current generated across at least one of the Si1-xGex substrate device and the group III-nitride device upon incident light.
Owner:NAVY U S A AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE THE
Method of preventing surface roughening during hydrogen prebake of SiGe substrates
InactiveUS6958286B2Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRough surfaceHydrofluoric acid
The invention forms an epitaxial silicon-containing layer on a silicon germanium, patterned strained silicon, or patterned thin silicon-on-insulator surface and avoids creating a rough surface upon which the epitaxial silicon-containing layer is grown. In order to avoid creating the rough surface, the invention first performs a hydrofluoric acid etching process on the silicon germanium, patterned strained silicon, or patterned thin silicon-on-insulator surface. This etching process removes most of oxide from the surface, and leaves a first amount of oxygen (typically 1×1013−1×1015 / cm2 of oxygen) on the silicon germanium, patterned strained silicon, or patterned thin silicon-on-insulator surface. The invention then performs a hydrogen pre-bake process which heats the silicon germanium, patterned strained silicon, or patterned thin silicon-on-insulator surface sufficiently to remove additional oxygen from the surface and leave a second amount of oxygen, less than the first amount, on the silicon germanium, patterned strained silicon, or patterned thin silicon-on-insulator surface. The heating process leaves an amount of at least 5×1012 / cm2 of oxygen (typically, between approximately 1×1013 / cm2 and approximately 5×1013 / cm2 of oxygen) on the silicon germanium, patterned strained silicon, or patterned thin silicon-on-insulator surface. By leaving a small amount of oxygen on the silicon germanium, patterned strained silicon, or patterned silicon-on-insulator surface, the heating processes avoid changing the roughness of the silicon germanium, patterned strained silicon, or patterned thin silicon-on-insulator surface. Then the process of epitaxially growing the epitaxial silicon-containing layer on the silicon germanium, patterned strained silicon, or patterned silicon-on-insulator surface is performed.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Cobalt salicidation method on a silicon germanium film
A method of forming a cobalt germanosilicide film is described. According to the present invention a silicon germanium alloy is formed on a substrate. A cobalt film is then formed on the silicon germanium alloy. The substrate is then heated to a temperature of greater than 850° C. for a period of time less than 20 seconds to form a cobalt germanium silicide film.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Process for etching silicon with selectivity to silicon-germanium
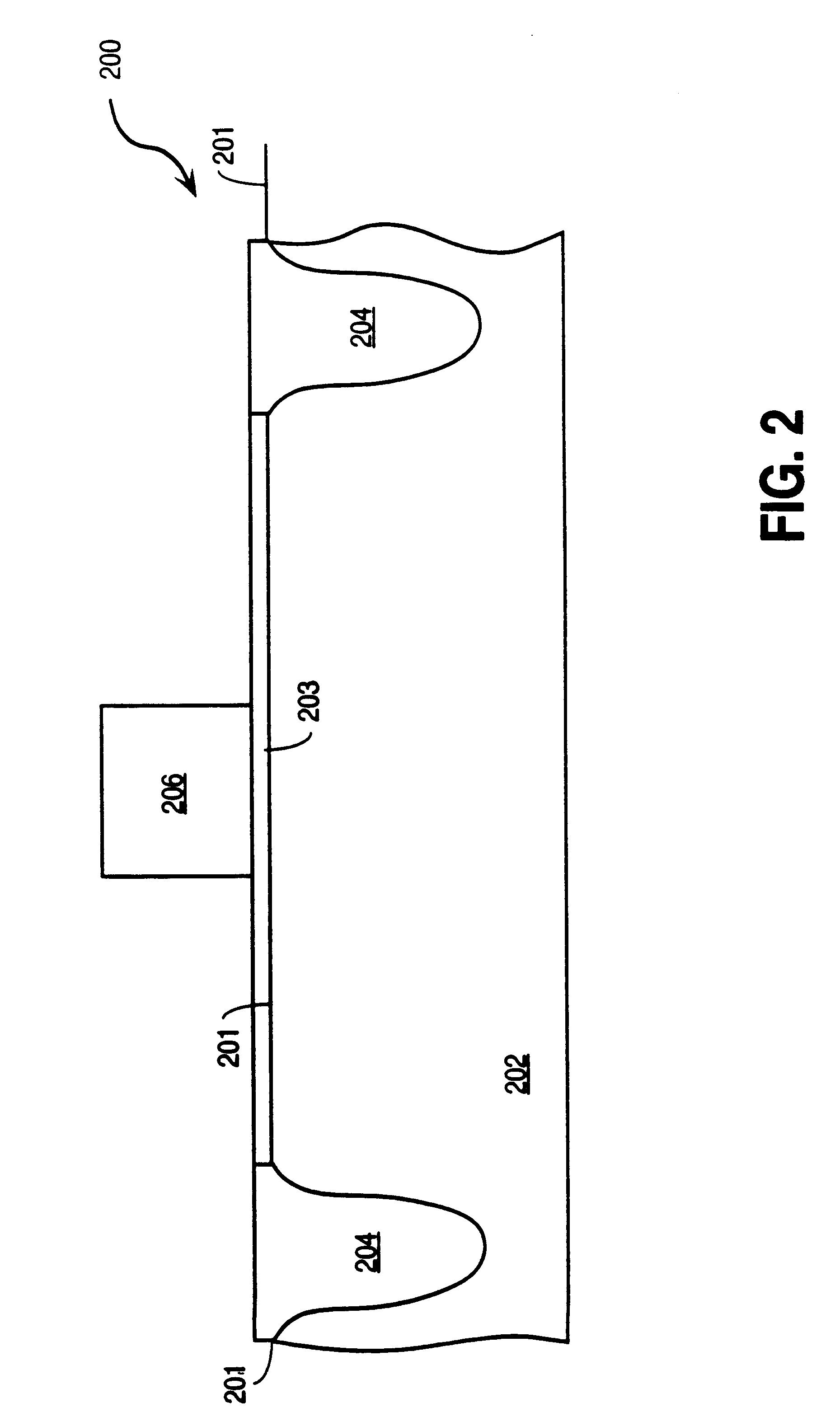
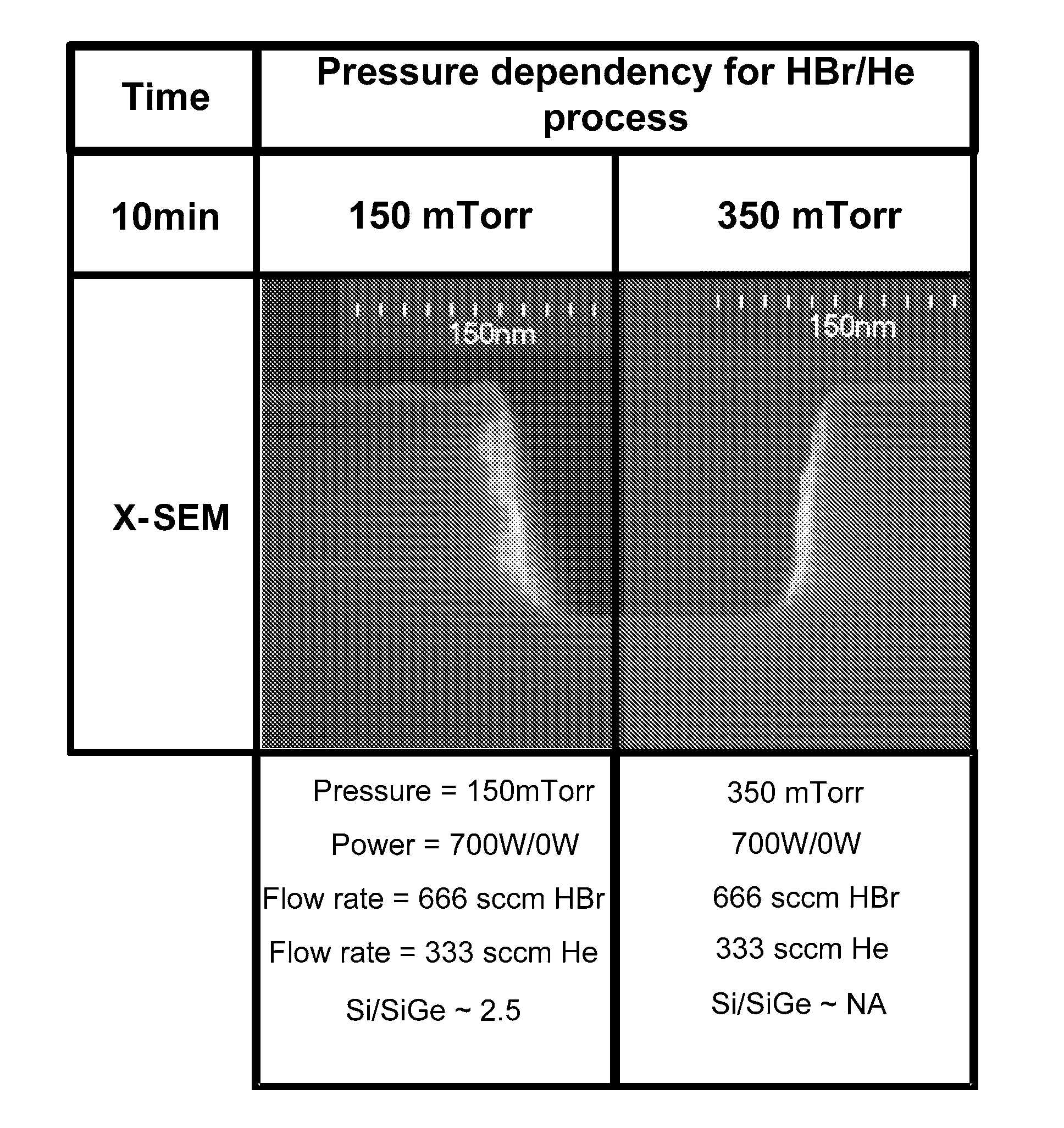
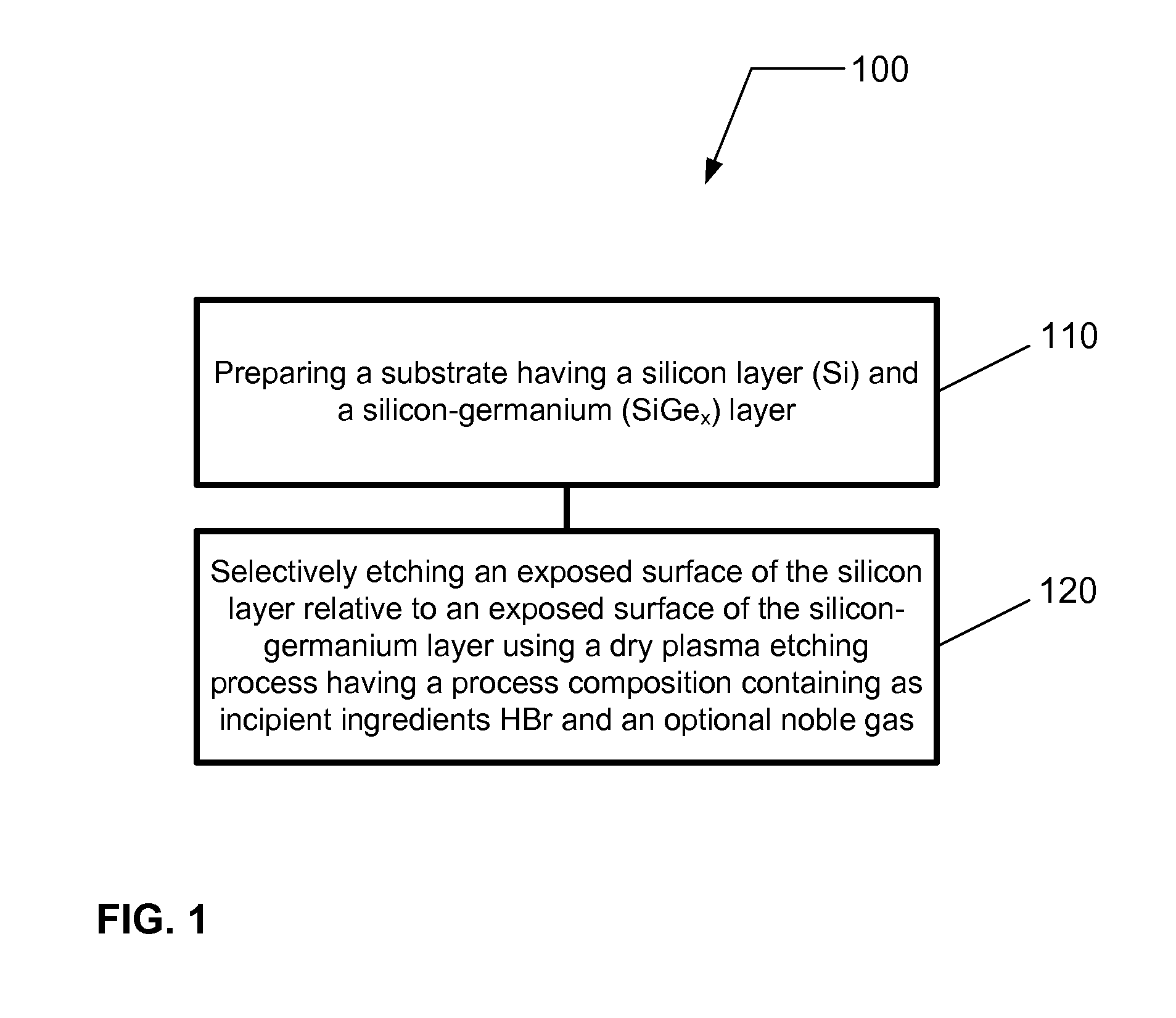
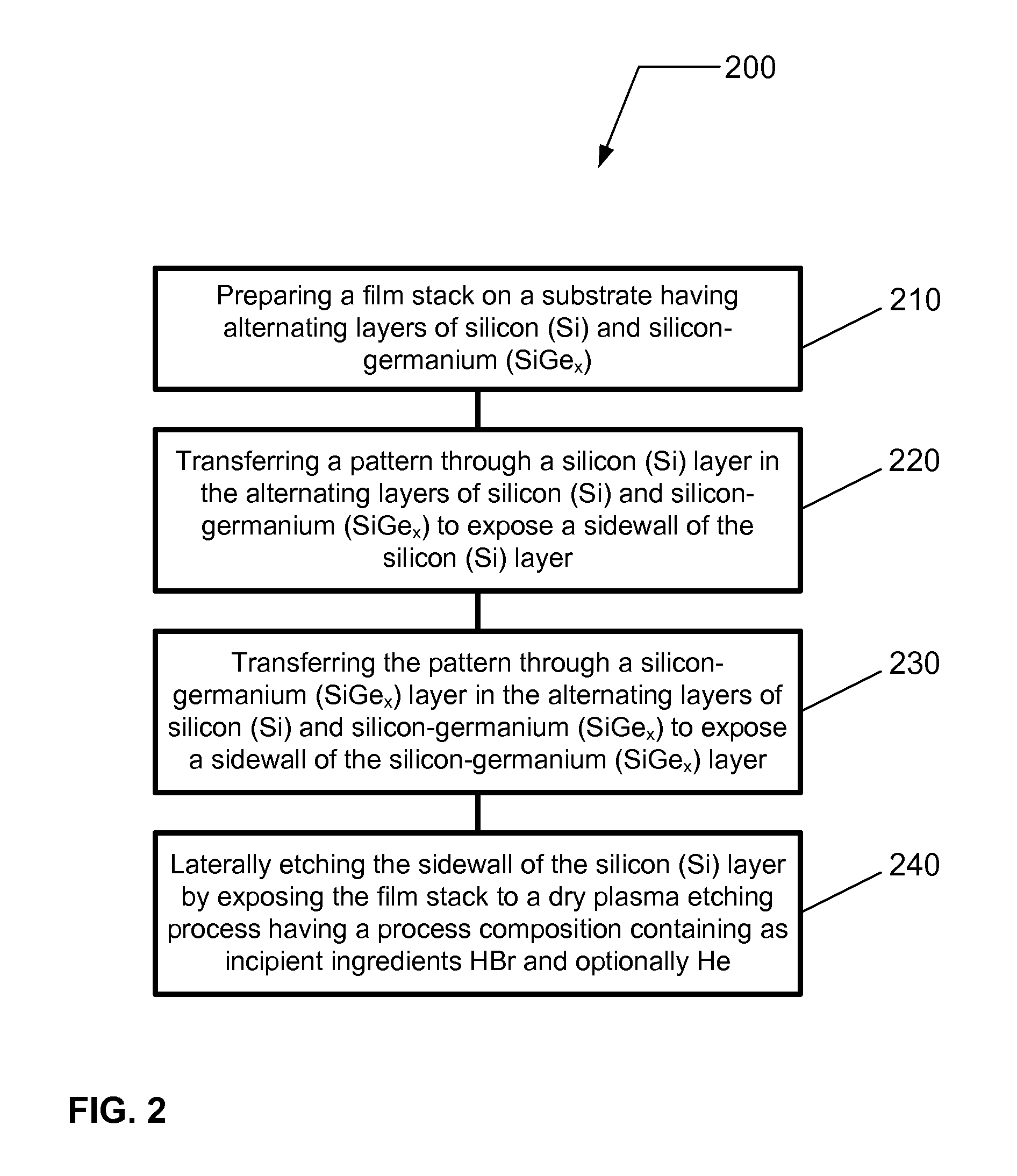
ActiveUS20120129354A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma etchingSilicon-germanium
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Deposited semiconductor structure to minimize N-type dopant diffusion and method of making
ActiveUS20060087005A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantSemiconductor structure
In deposited silicon, n-type dopants such as phosphorus and arsenic tend to seek the surface of the silicon, rising as the layer is deposited. When a second undoped or p-doped silicon layer is deposited on n-doped silicon with no n-type dopant provided, a first thickness of this second silicon layer nonetheless tends to include unwanted n-type dopant which has diffused up from lower levels. This surface-seeking behavior diminishes when germanium is alloyed with the silicon. In some devices, it may not be advantageous for the second layer to have significant germanium content. In the present invention, a first heavily n-doped semiconductor layer (preferably at least 10 at % germanium) is deposited, followed by a silicon-germanium capping layer with little or no n-type dopant, followed by a layer with little or no n-type dopant and less than 10 at % germanium. The germanium in the first layer and the capping layer minimizes diffusion of n-type dopant into the germanium-poor layer above.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Methods for fabricating a finfet integrated circuit on a bulk silicon substrate
InactiveUS20130005103A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesIntegrated circuitSilicon-germanium
Methods are provided for fabricating a FINFET integrated circuit that includes epitaxially growing a first silicon germanium layer and a second silicon layer overlying a silicon substrate. The second silicon layer is etched to form a silicon fin using the first silicon germanium layer as an etch stop. The first silicon germanium layer underlying the fin is removed to form a void underlying the fin and the void is filled with an insulating material. A gate structure is then formed overlying the fin.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
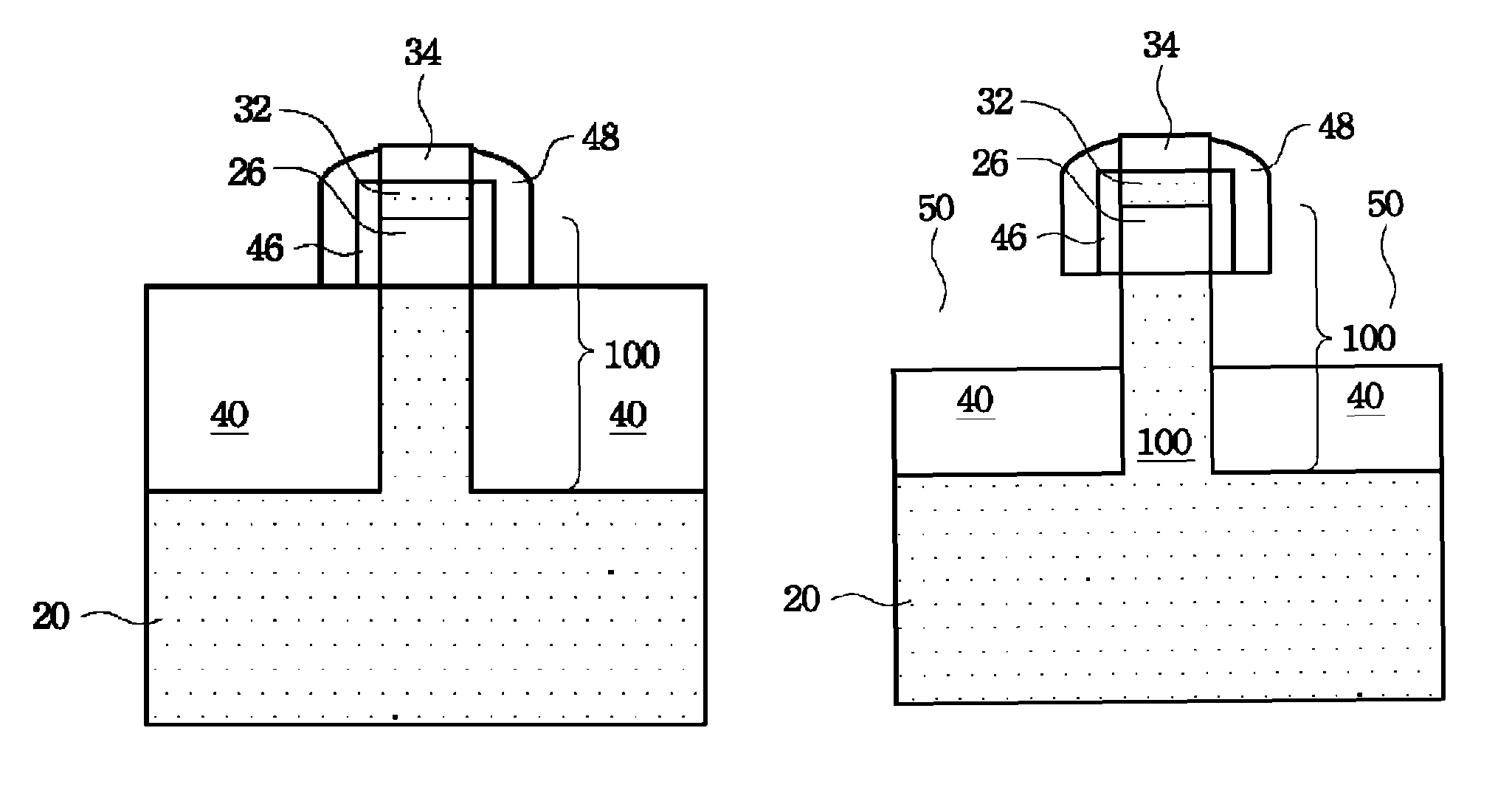
SiGe (silicon germanium) source and drain area manufacturing method
ActiveCN104201108AReduce thicknessAvoid stress relaxationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh concentrationEngineering
The invention discloses a SiGe (silicon germanium) source and drain area manufacturing method. A multi-layer structure which comprises alternately stacked buffer layers and main body layers is formed by a method that the SiGe epitaxial growth of the buffer layer and the main body layers is alternated repeatedly and accordingly the thickness of every high Ge concentration of SiGe main body layer is effectively reduced and shared into every layer of main body layer and accordingly the stress relaxation due to the fact that thickness of every main body layer exceeds the critical thickness is avoided; the Ge content of every layer of SiGe main body layer is further improved to enable the stress of the SiGe source leakage on a channel to be increased; an SiGe process window is enlarged due to the repeated epitaxy and accordingly the process stability is enhanced and accordingly the device performance is improved; the stress can be effectively improved without increase of the process difficulty and accordingly the process is stable and controllable and the cost is low.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT
Structure and method of making strained semiconductor CMOS transistors having lattice-mismatched semiconductor regions underlying source and drain regions
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
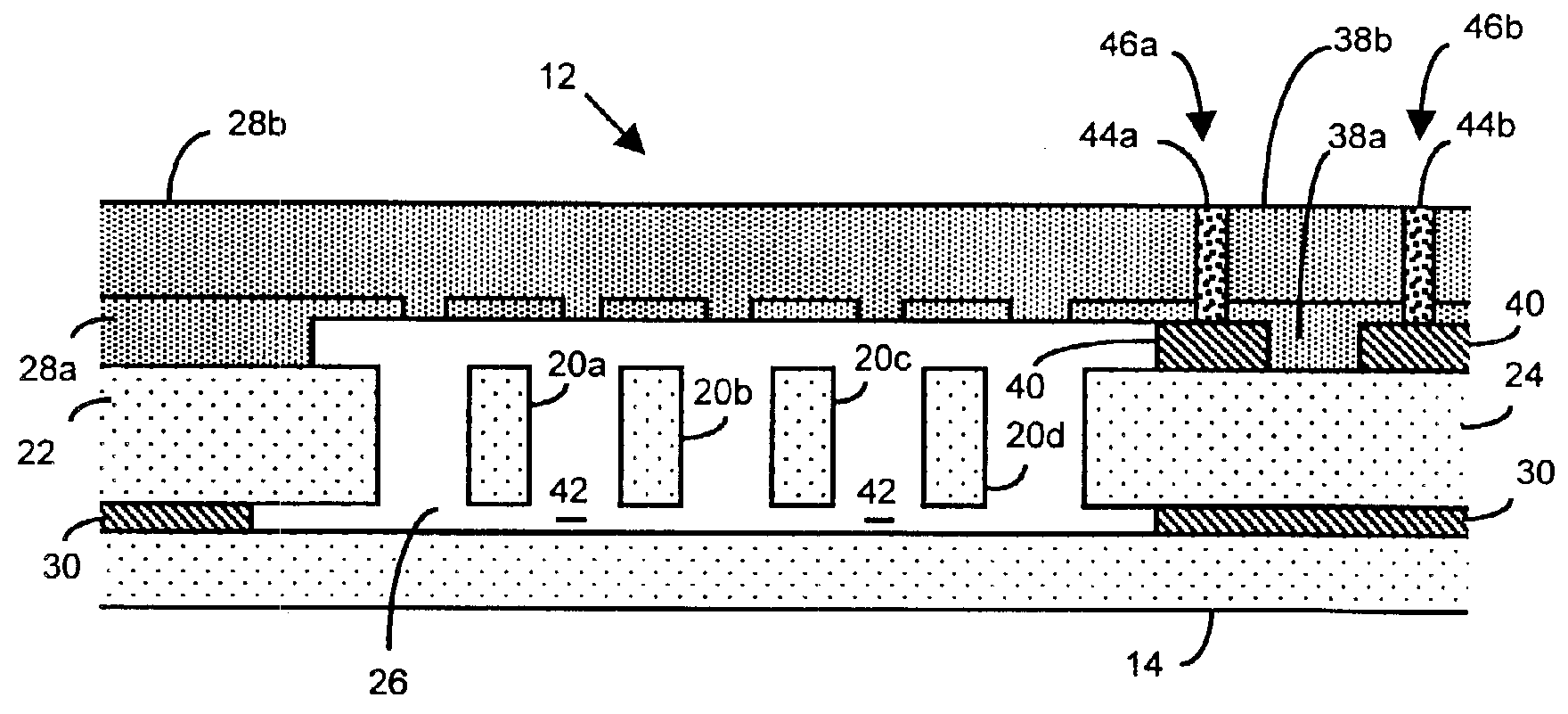
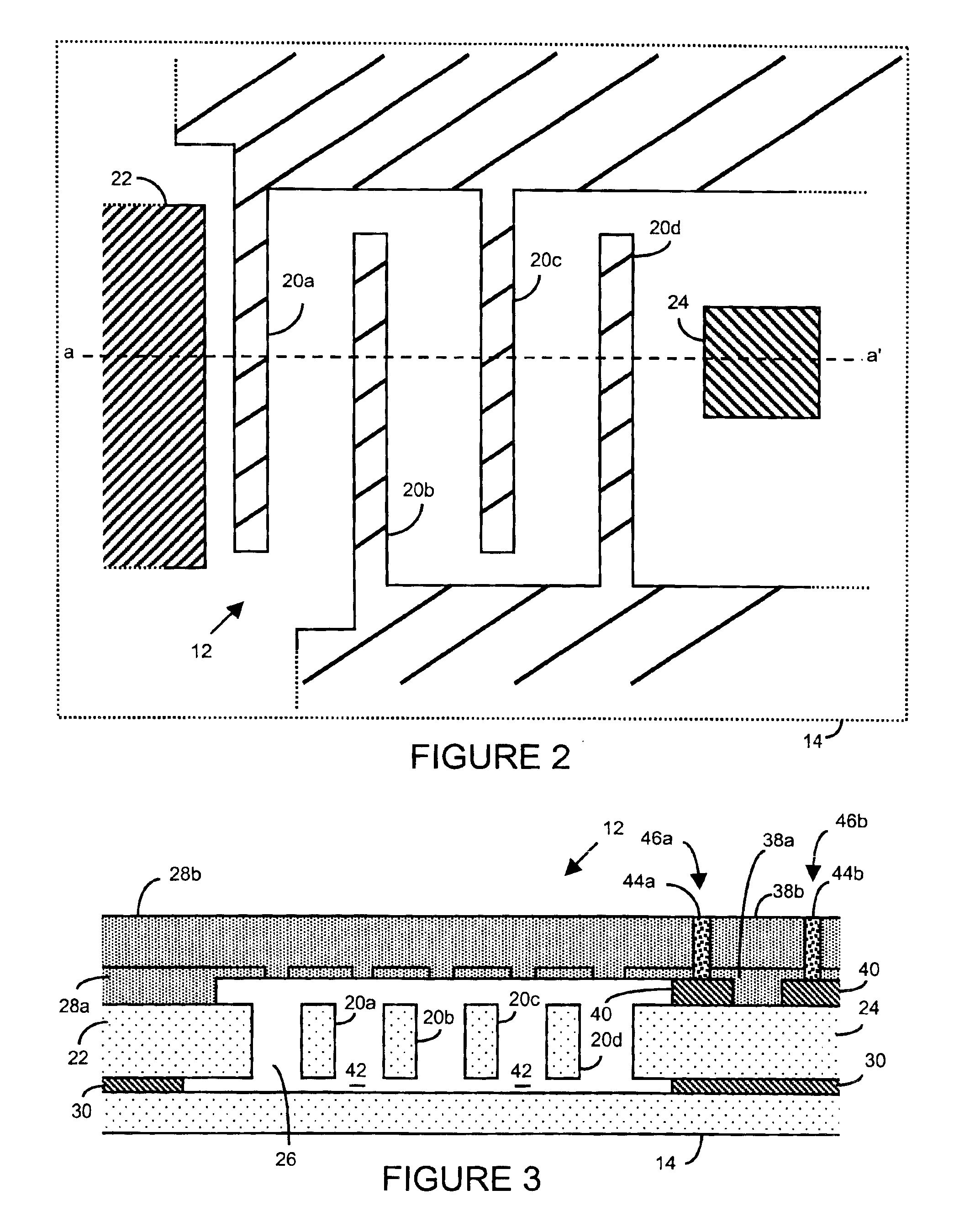
Method of fabricating microelectromechanical systems and devices having trench isolated contacts
InactiveUS6936491B2Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSolid-state devicesEngineeringMicroelectromechanical systems
There are many inventions described and illustrated herein. In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a MEMS device, and technique of fabricating or manufacturing a MEMS device, having mechanical structures encapsulated in a chamber prior to final packaging and a contact area disposed at least partially outside the chamber. The contact area is electrically isolated from nearby electrically conducting regions by way of dielectric isolation trench that is disposed around the contact area. The material that encapsulates the mechanical structures, when deposited, includes one or more of the following attributes: low tensile stress, good step coverage, maintains its integrity when subjected to subsequent processing, does not significantly and / or adversely impact the performance characteristics of the mechanical structures in the chamber (if coated with the material during deposition), and / or facilitates integration with high-performance integrated circuits. In one embodiment, the material that encapsulates the mechanical structures is, for example, silicon (polycrystalline, amorphous or porous, whether doped or undoped), silicon carbide, silicon-germanium, germanium, or gallium-arsenide.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
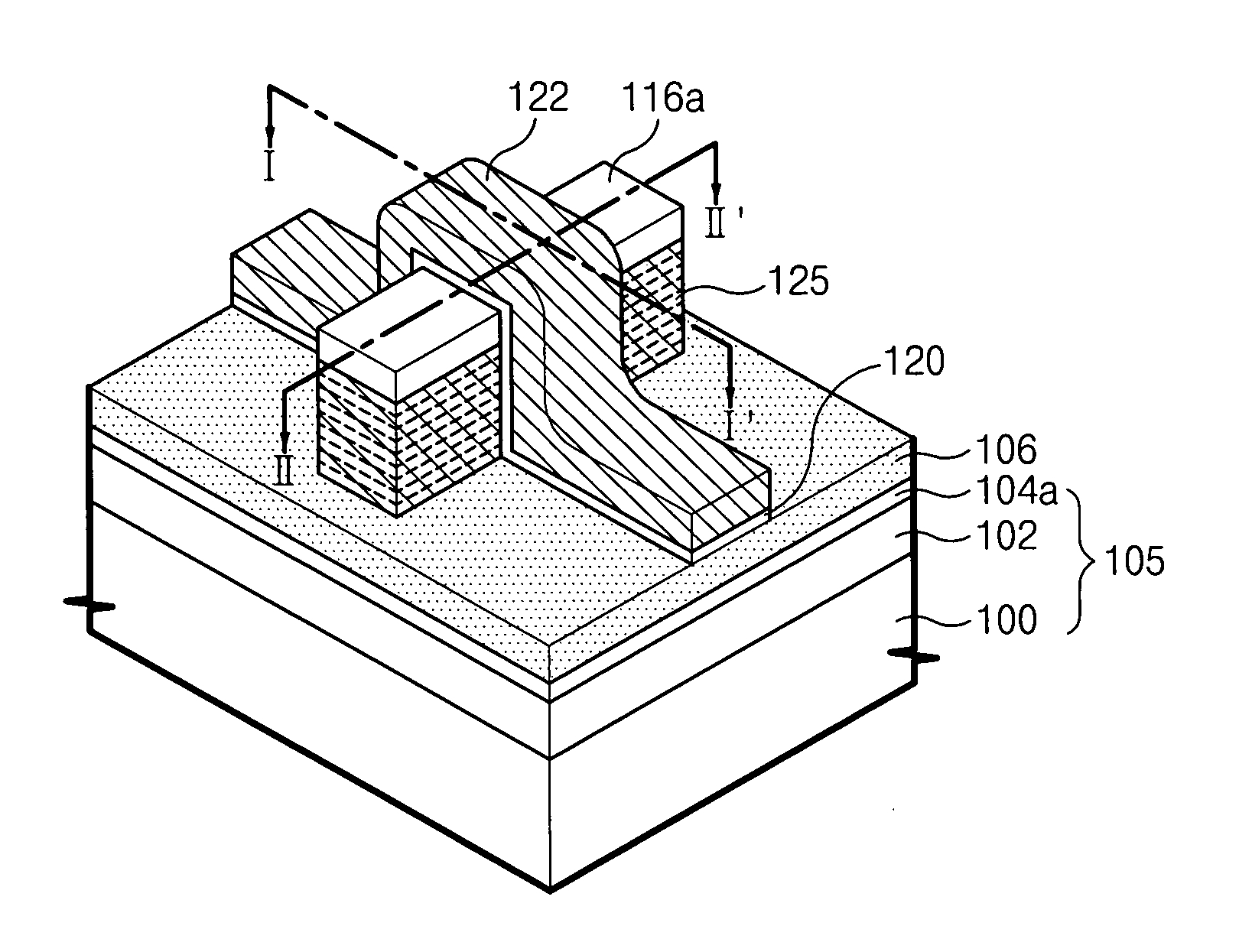
Fin field effect transistors having multi-layer fin patterns and methods of forming the same
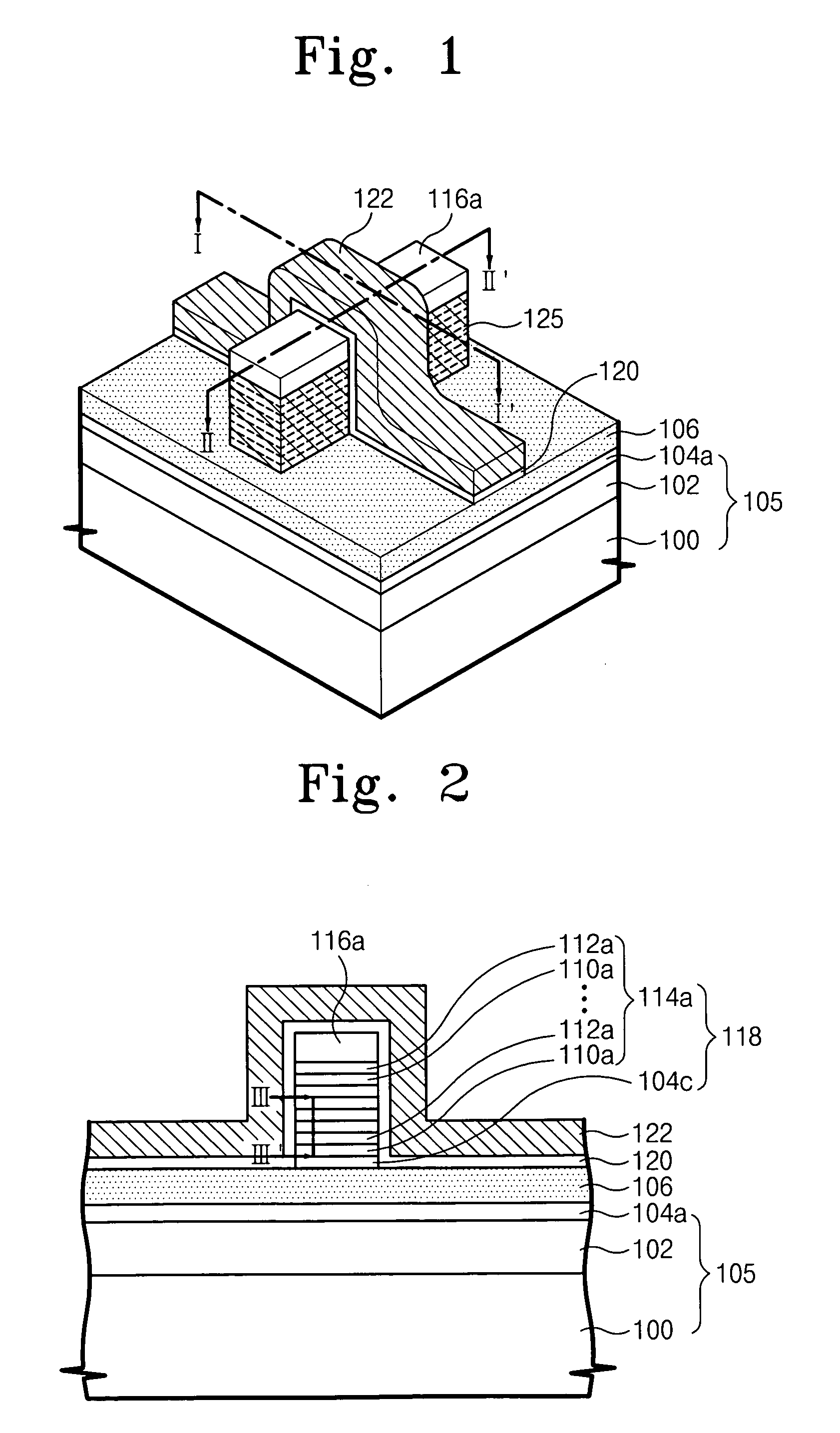
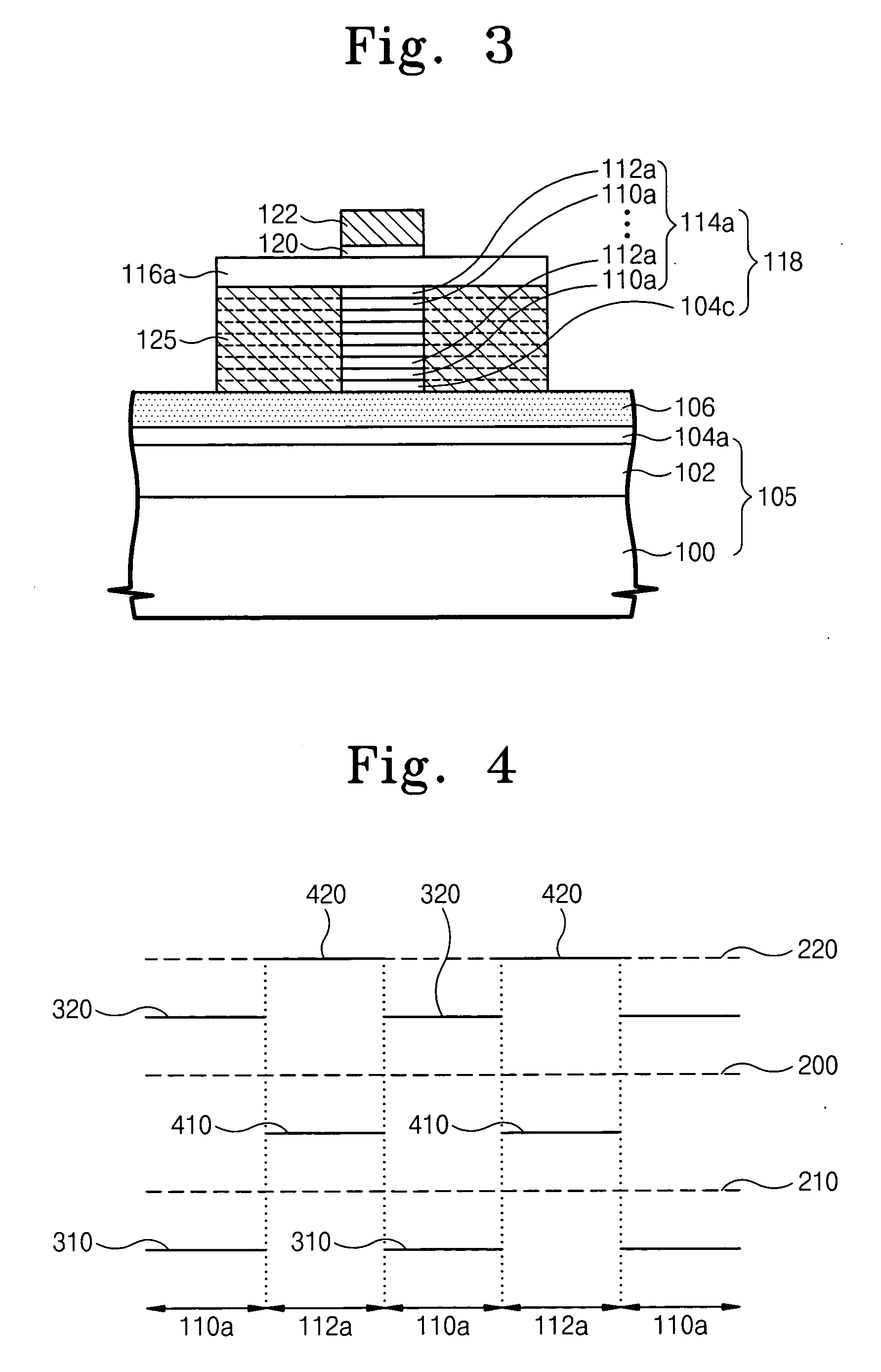
ActiveUS20050184316A1Increase heightRelieve pressureTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarrier signalEngineering
A fin field effect transistor has a fin pattern protruding from a semiconductor substrate. The fin pattern includes first semiconductor patterns and second semiconductor patterns which are stacked. The first and second semiconductor patterns have lattice widths that are greater than a lattice width of the substrate in at least one direction. In addition, the first and second semiconductor patterns may be alternately stacked to increase the height of the fin pattern, such that one of the first and second patterns can reduce stress from the other of the first and second patterns. The first and second semiconductor patterns may be formed of strained silicon and silicon-germanium, where the silicon-germanium patterns can reduce stress from the strained silicon patterns. Therefore, both the number of carriers and the mobility of carriers in the transistor channel may be increased, improving performance of the fin field effect transistor. Related methods are also discussed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com