Patents
Literature
1255 results about "Gallium arsenide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
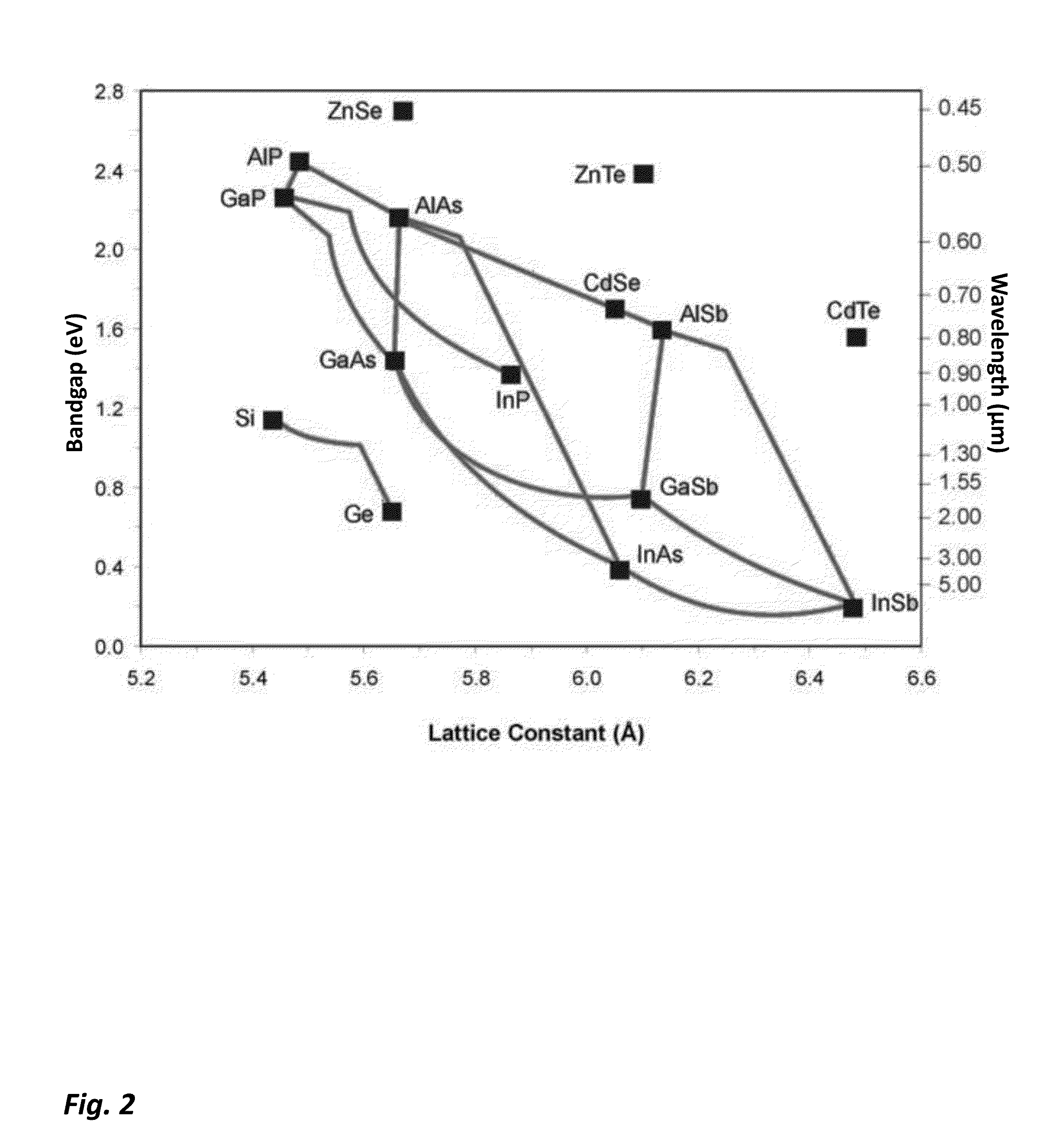
Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is a compound of the elements gallium and arsenic. It is a III-V direct band gap semiconductor with a zinc blende crystal structure. Gallium arsenide is used in the manufacture of devices such as microwave frequency integrated circuits, monolithic microwave integrated circuits, infrared light-emitting diodes, laser diodes, solar cells and optical windows.
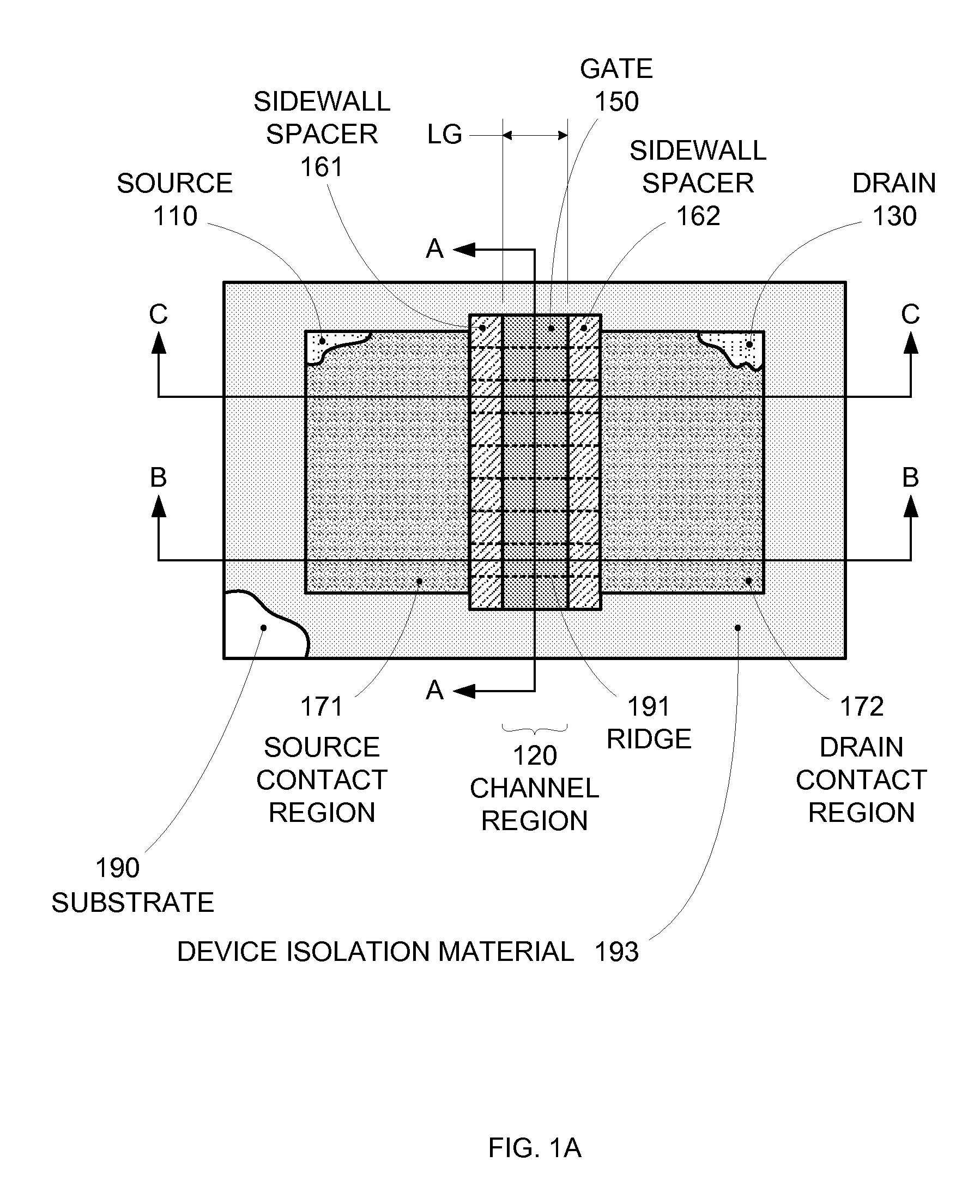
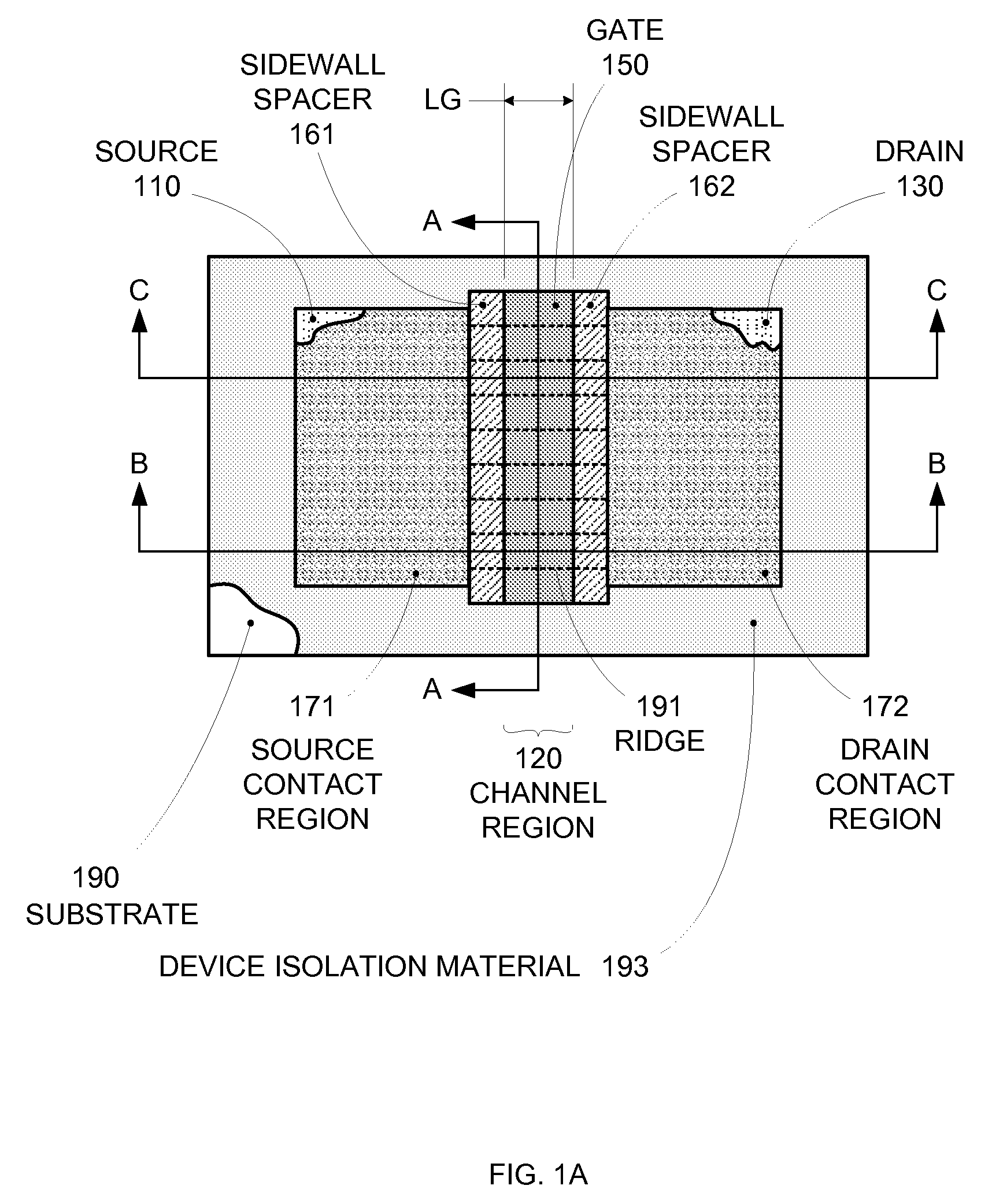
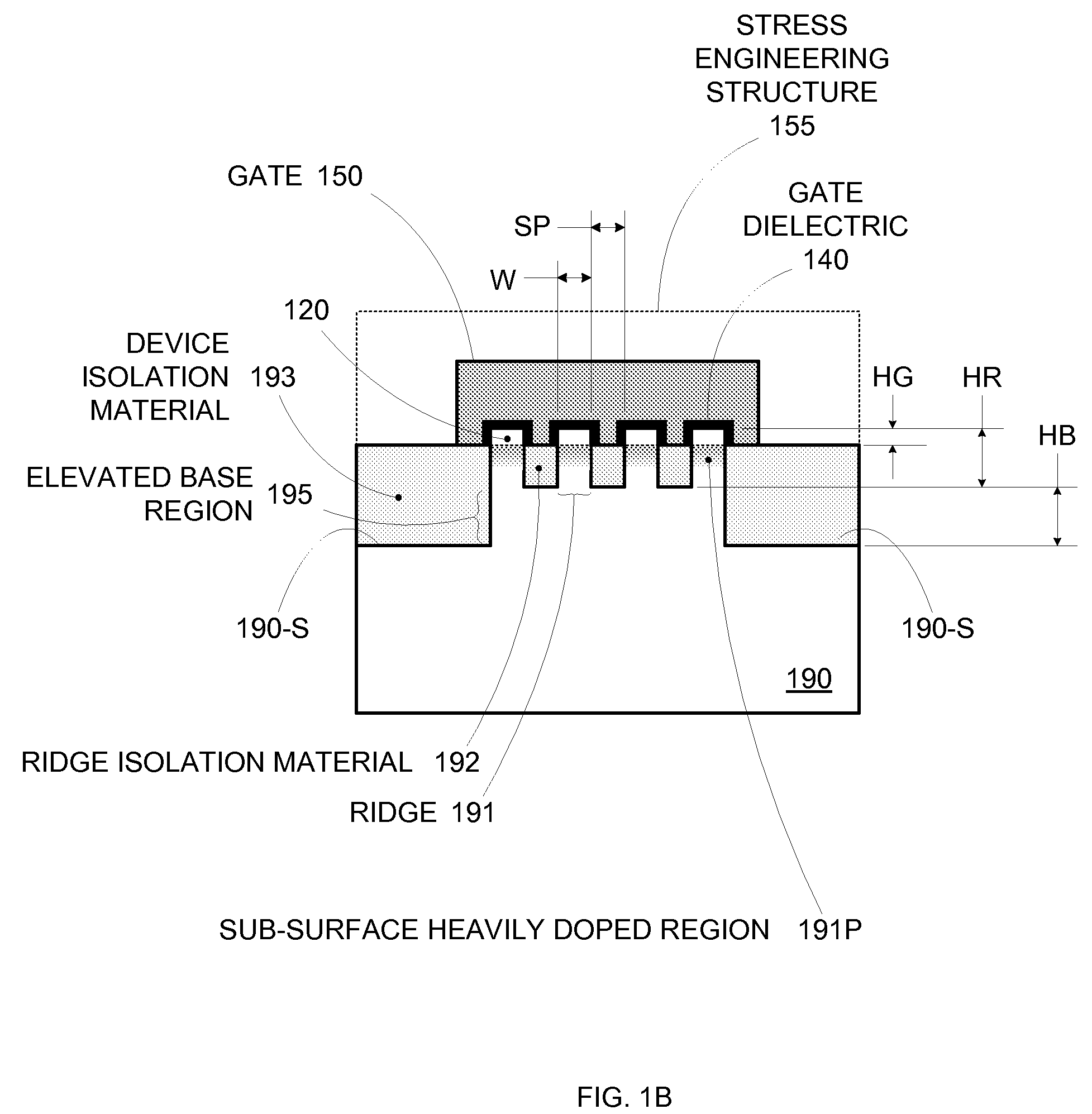
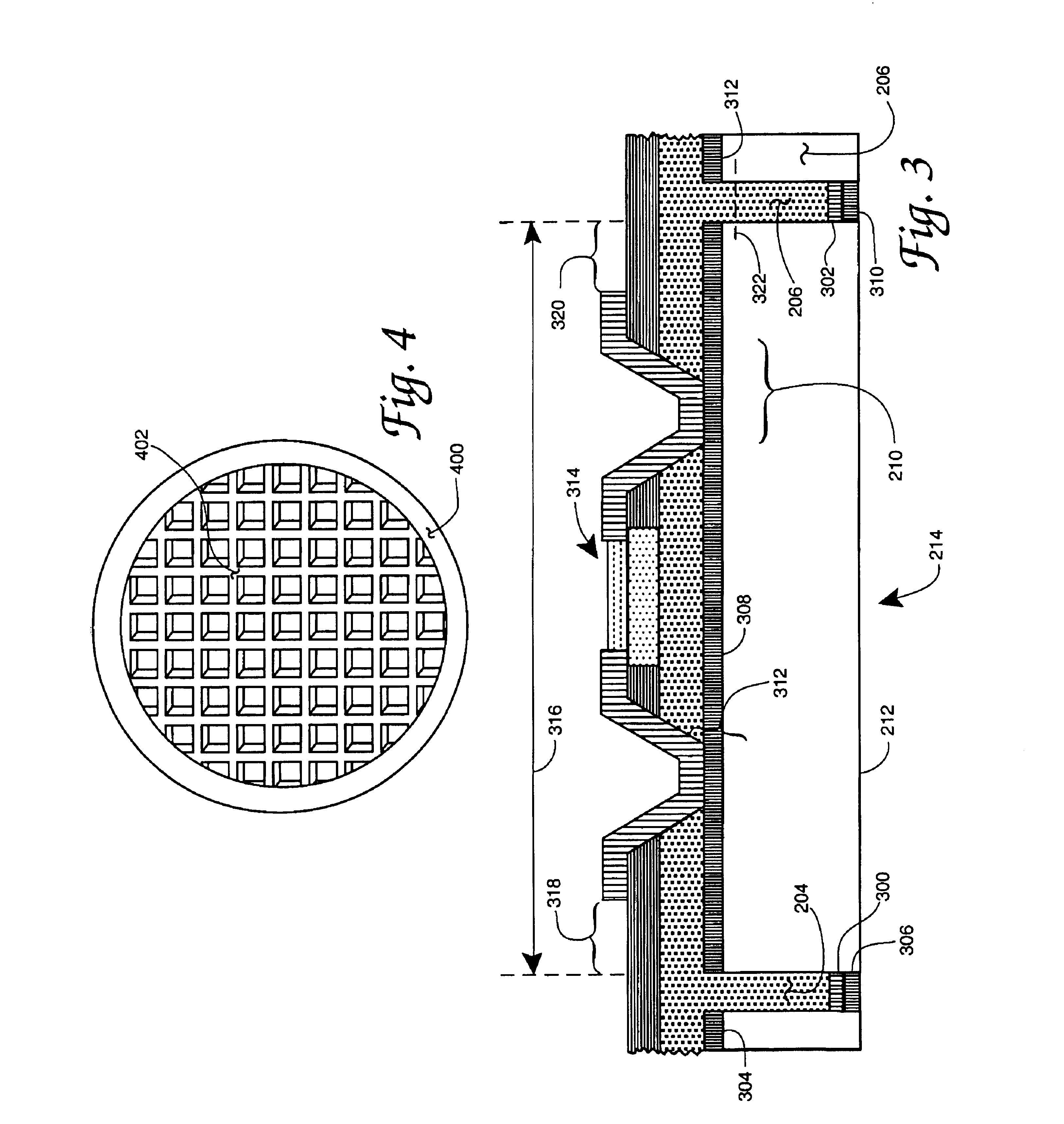
Enhanced Segmented Channel MOS Transistor with Multi Layer Regions
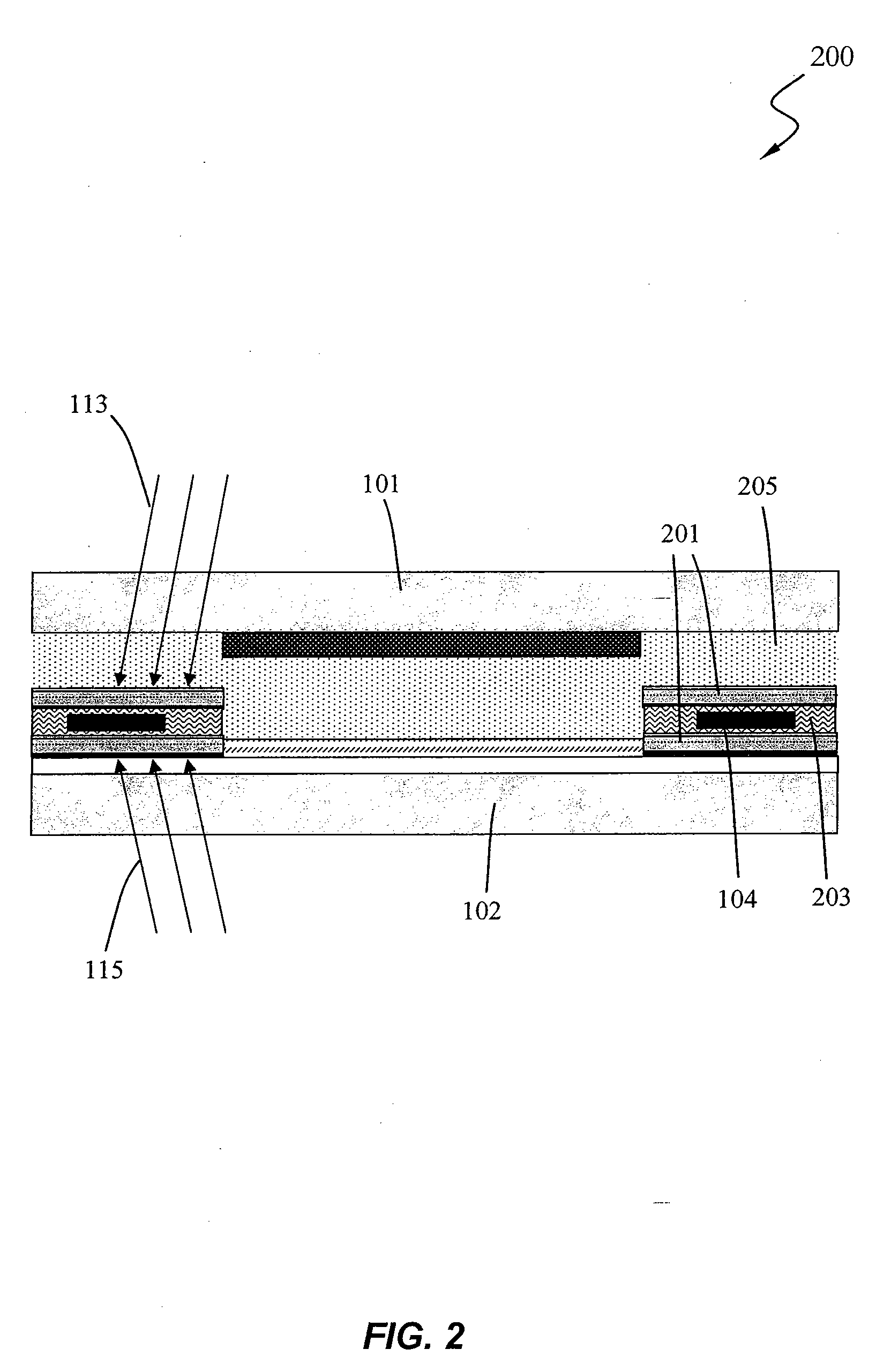
ActiveUS20070120156A1Increase costImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETPerformance enhancement
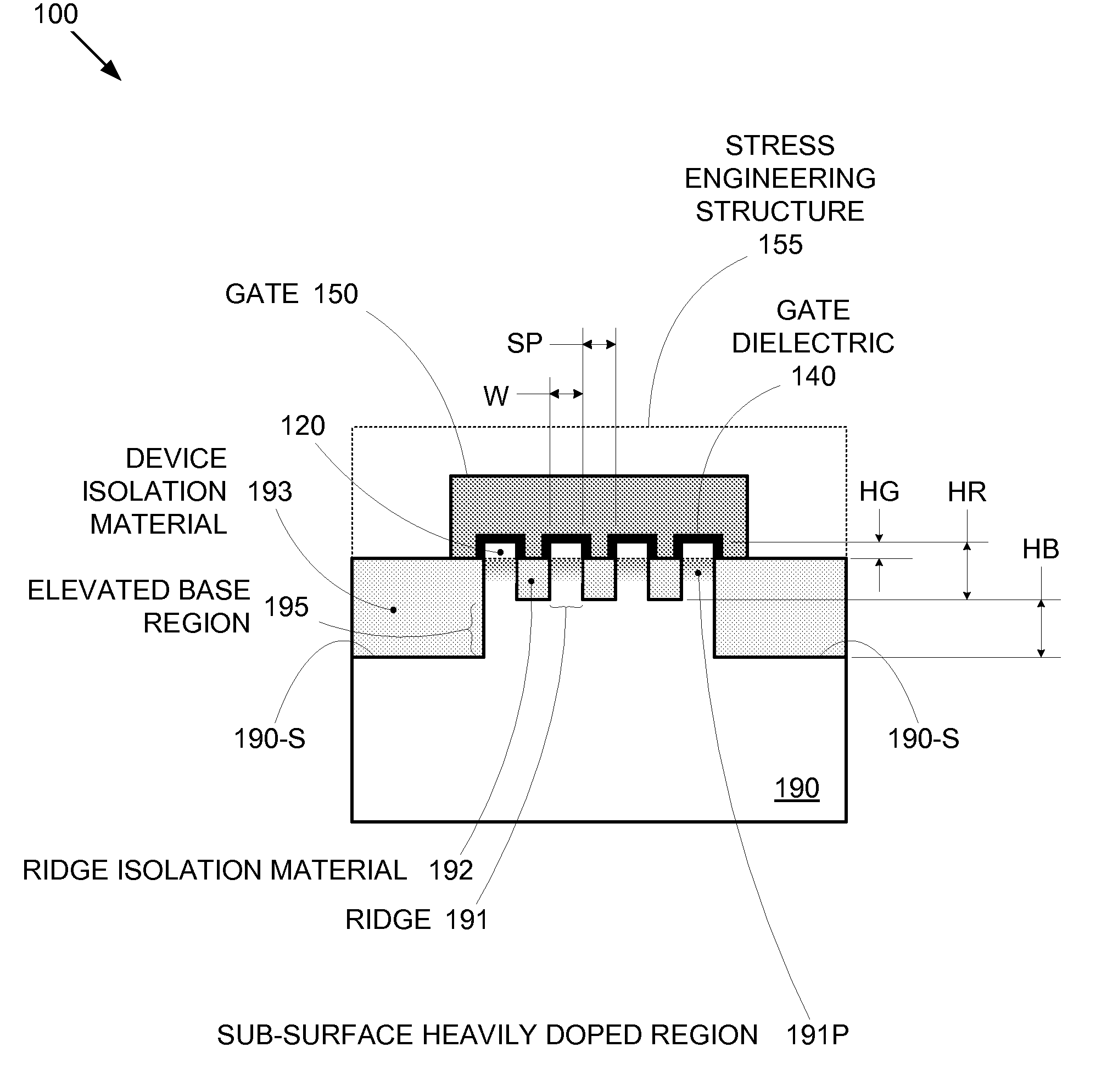
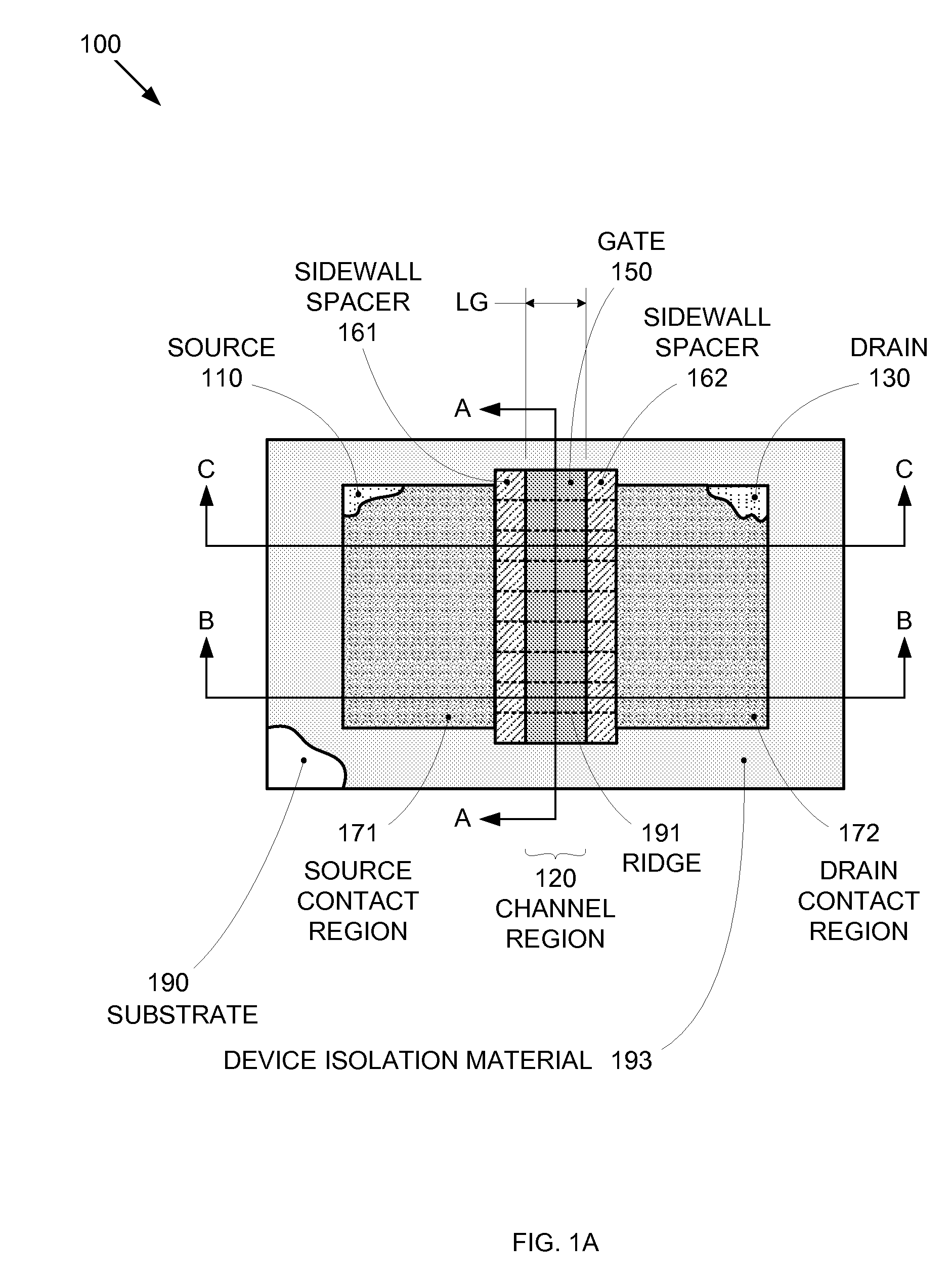
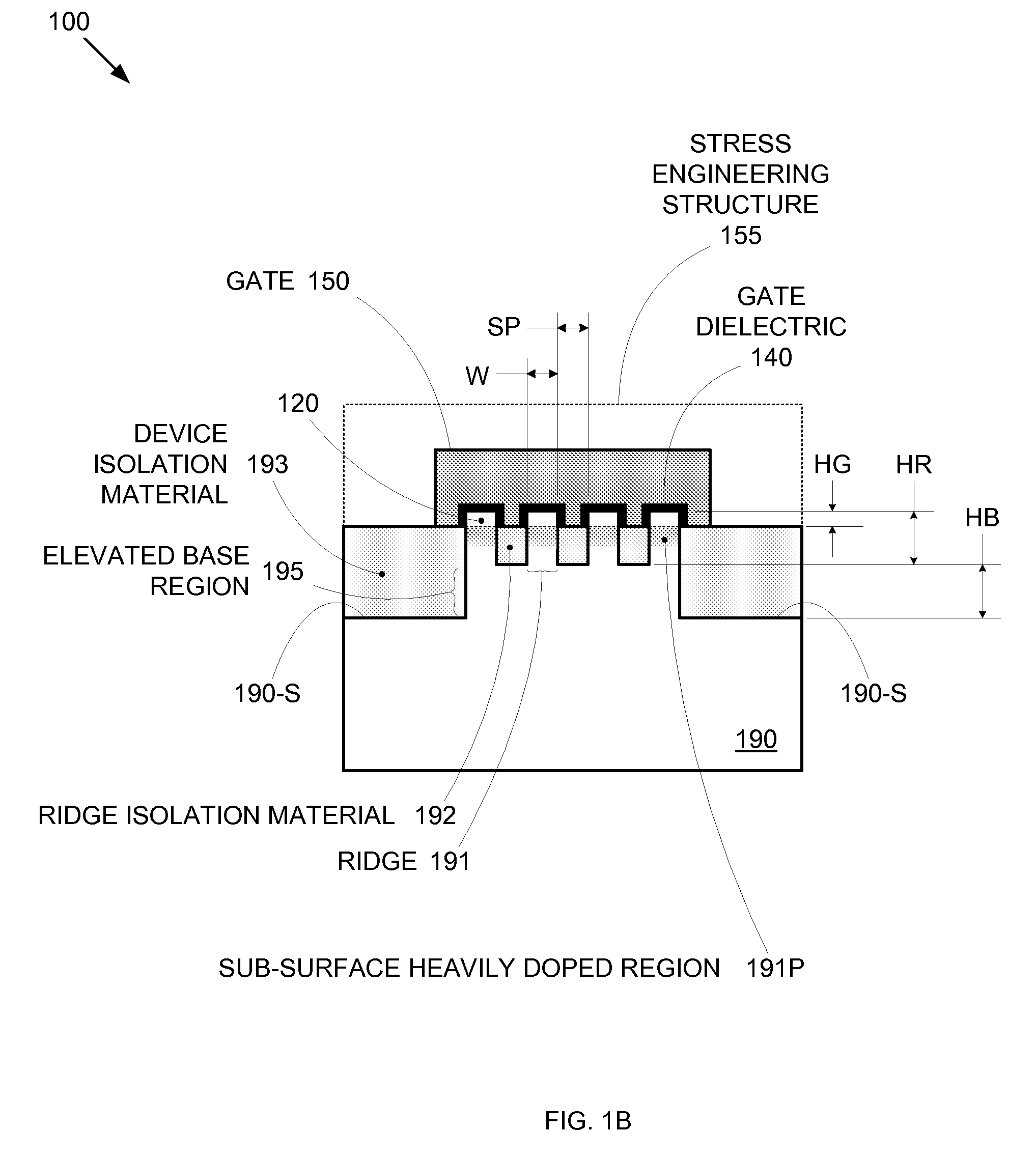
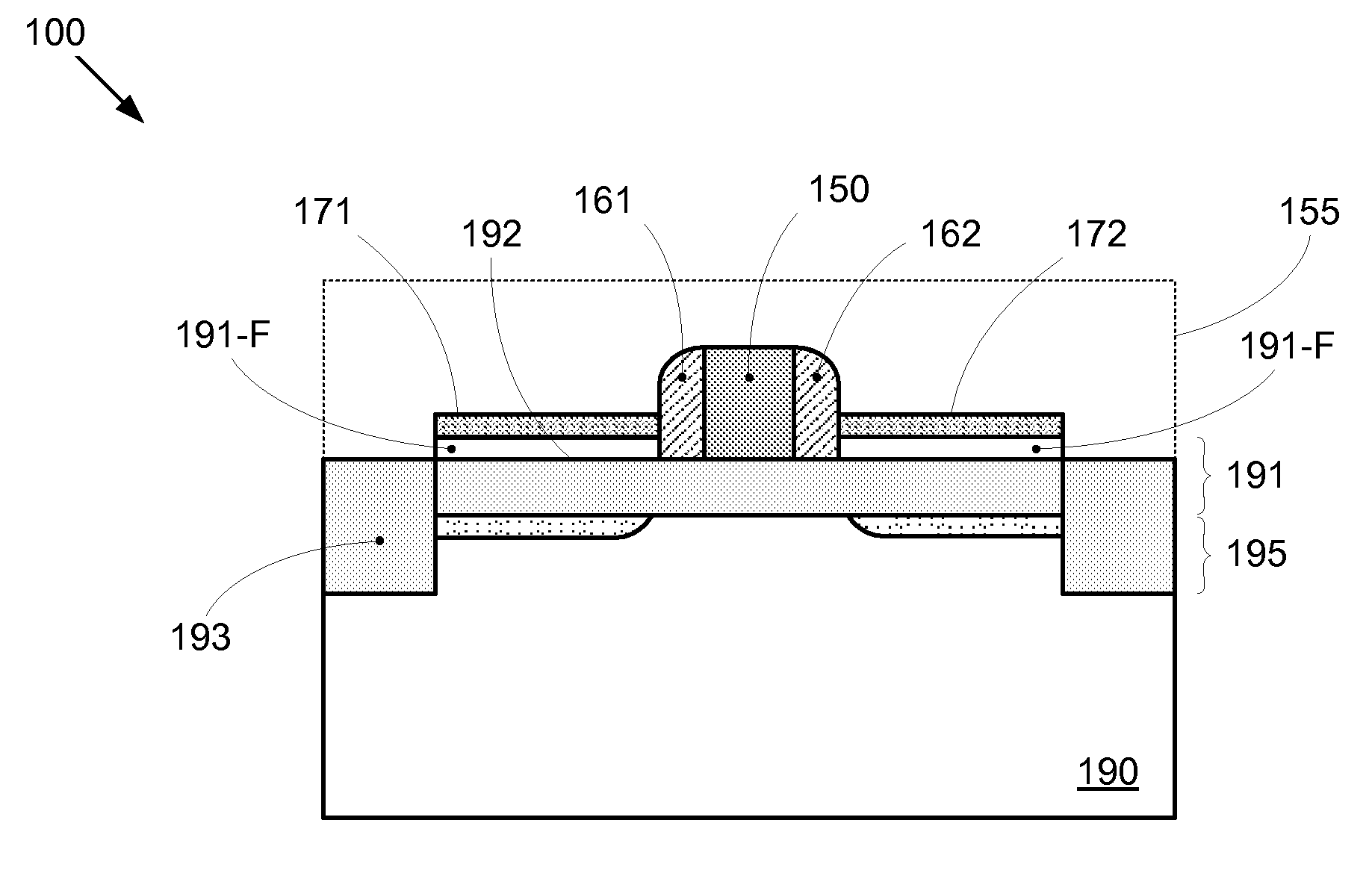
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
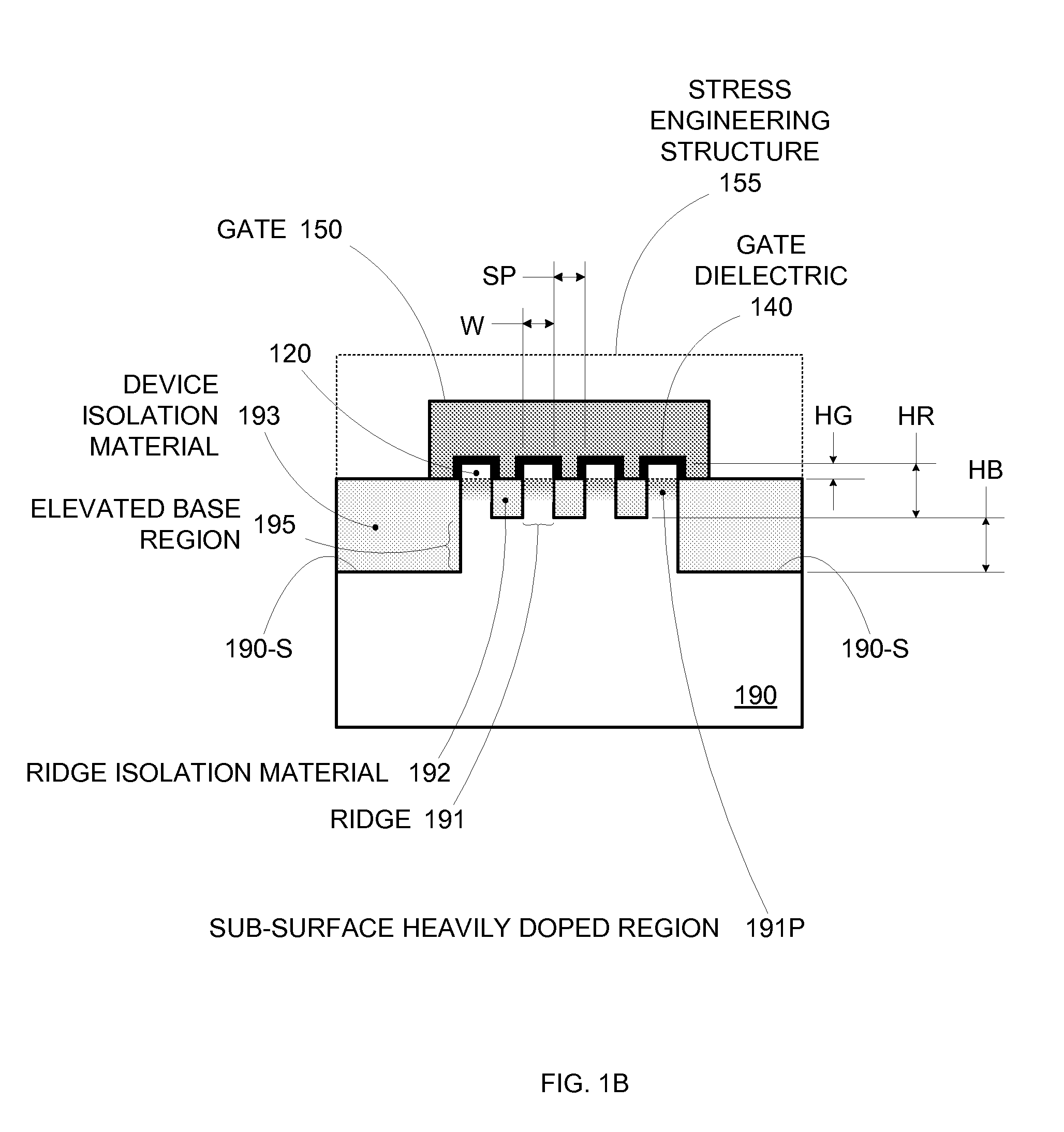
Enhanced Segmented Channel MOS Transistor with High-Permittivity Dielectric Isolation Material
ActiveUS20070122953A1Increase costImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
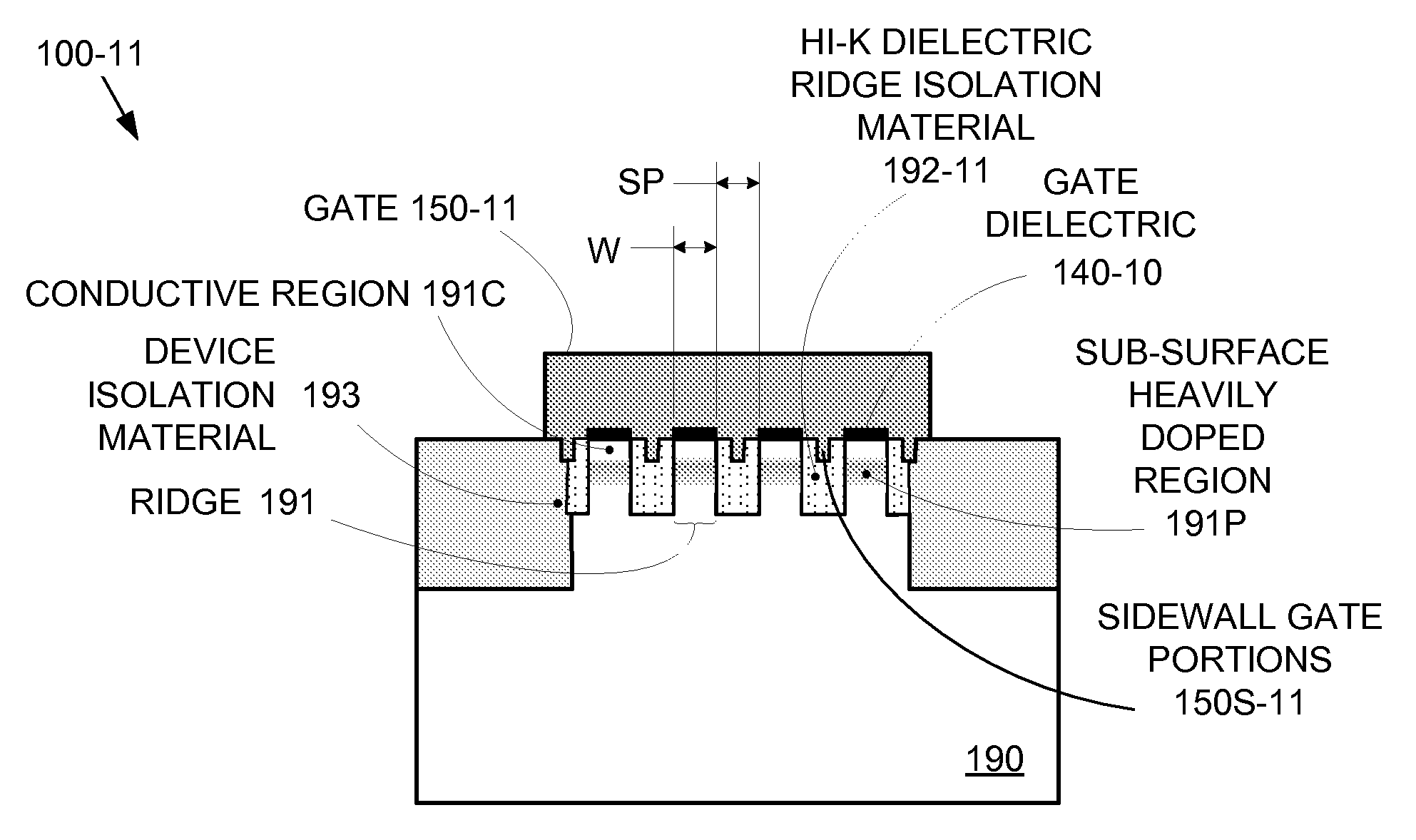
Enhanced segmented channel MOS transistor with high-permittivity dielectric isolation material
ActiveUS7605449B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
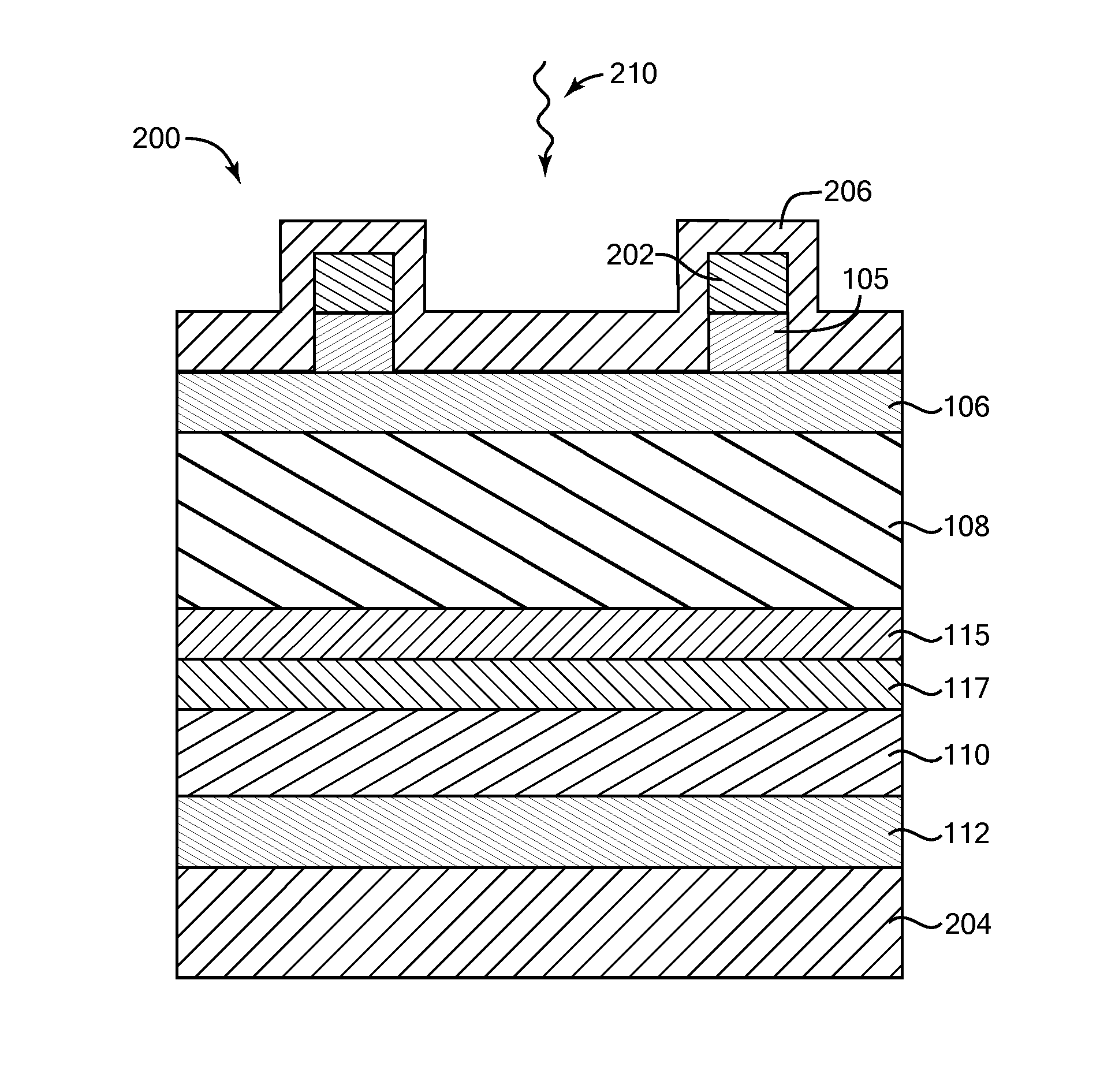
Linearity improvements of semiconductor substrate based radio frequency devices
ActiveUS7868419B1Effectively layerPrevent capacitance changeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceHigh density
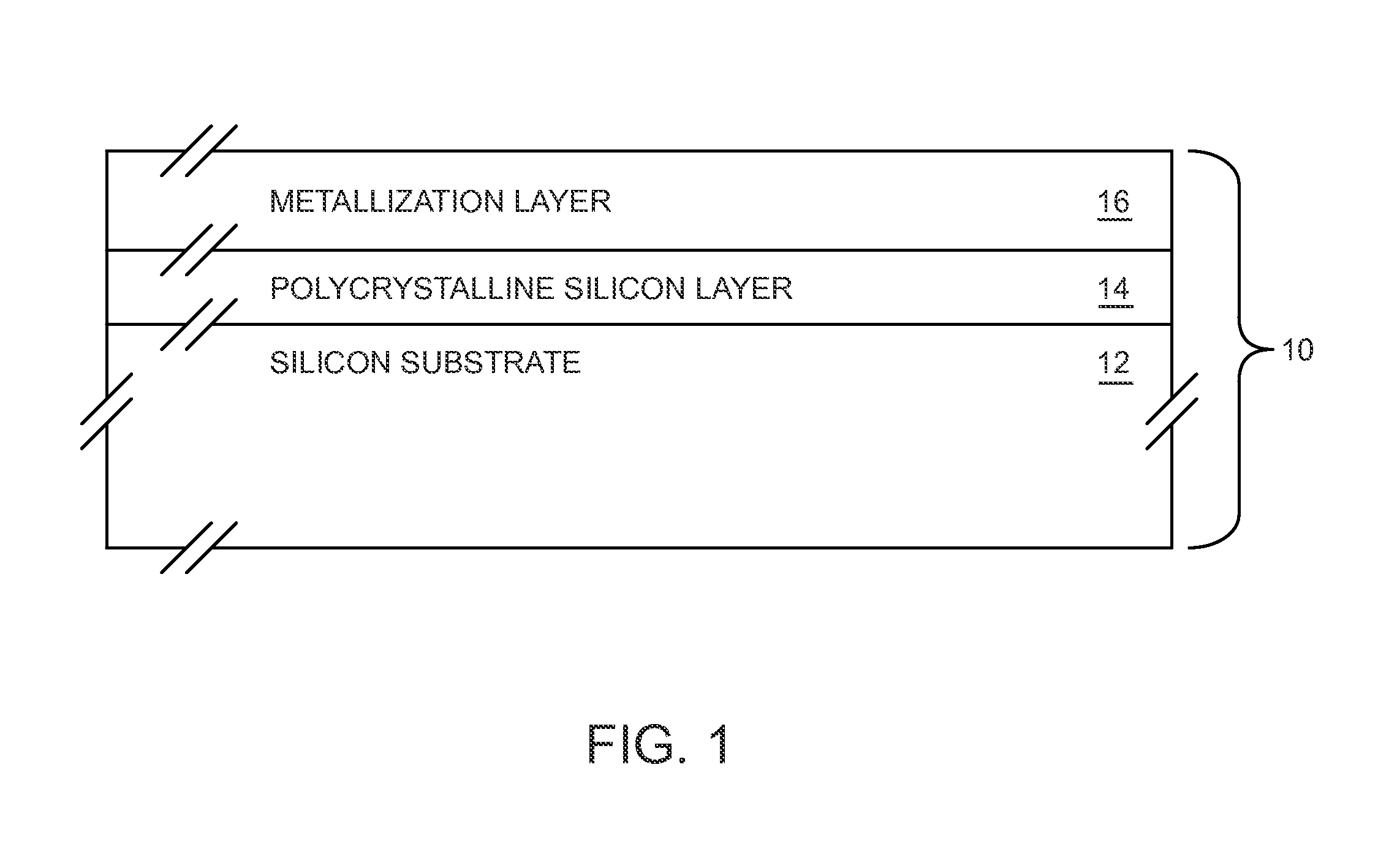
The present invention relates to using a trap-rich layer, such as a polycrystalline Silicon layer, over a semiconductor substrate to substantially immobilize a surface conduction layer at the surface of the semiconductor substrate at radio frequency (RF) frequencies. The trap-rich layer may have a high density of traps that trap carriers from the surface conduction layer. The average release time from the traps may be longer than the period of any present RF signals, thereby effectively immobilizing the surface conduction layer, which may substantially prevent capacitance and inductance changes due to the RF signals. Therefore, harmonic distortion of the RF signals may be significantly reduced or eliminated. The semiconductor substrate may be a Silicon substrate, a Gallium Arsenide substrate, or another substrate.
Owner:QORVO US INC
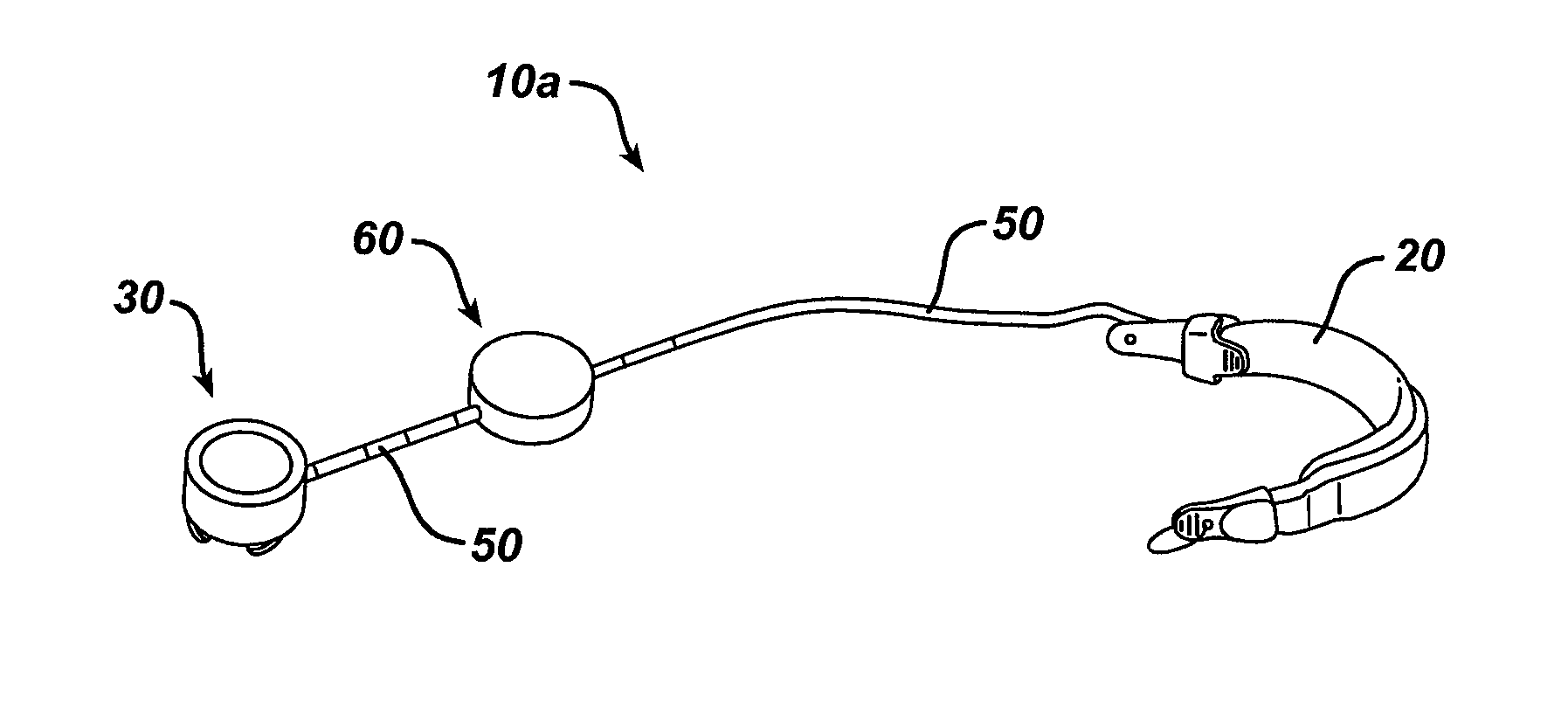
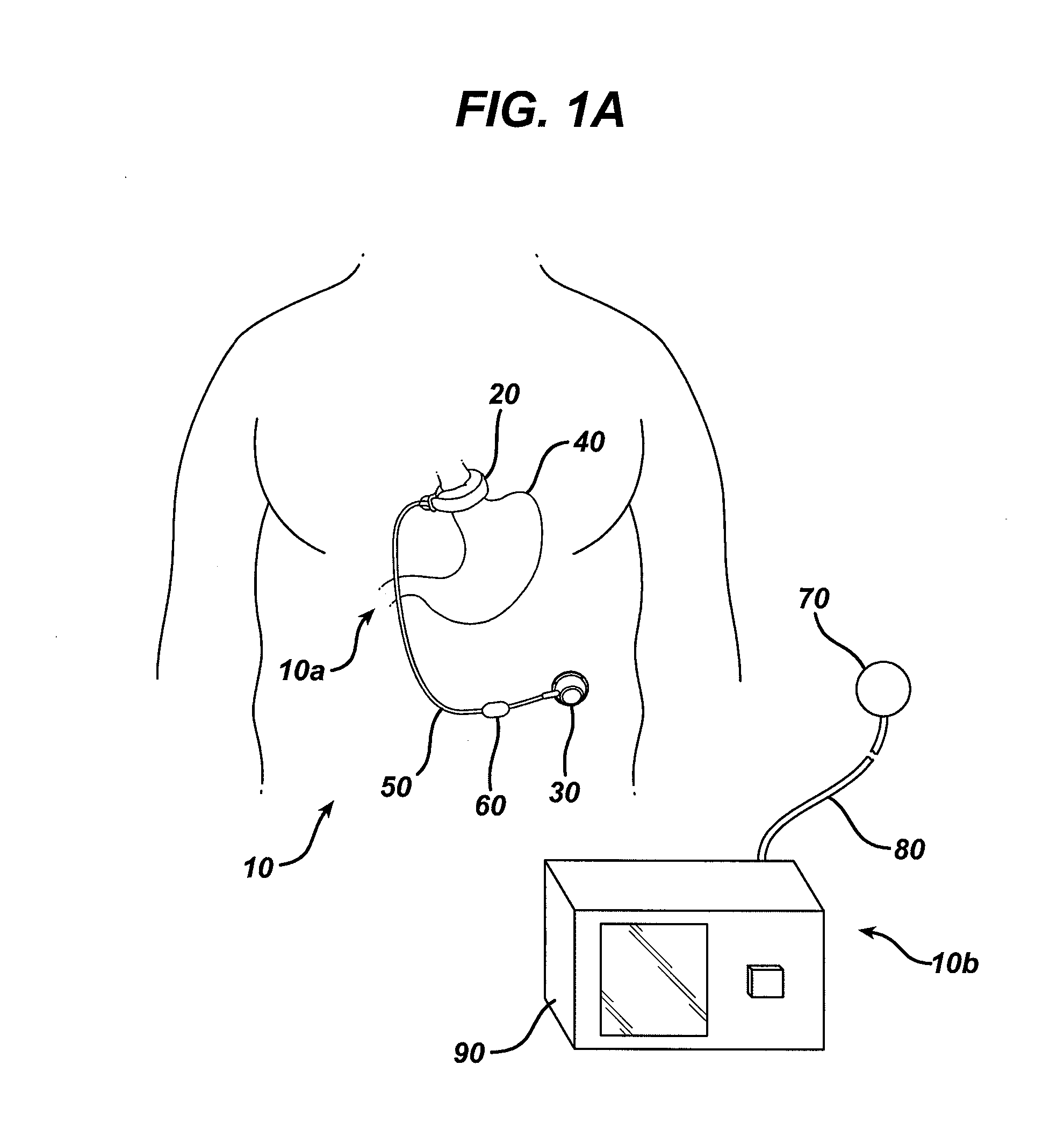
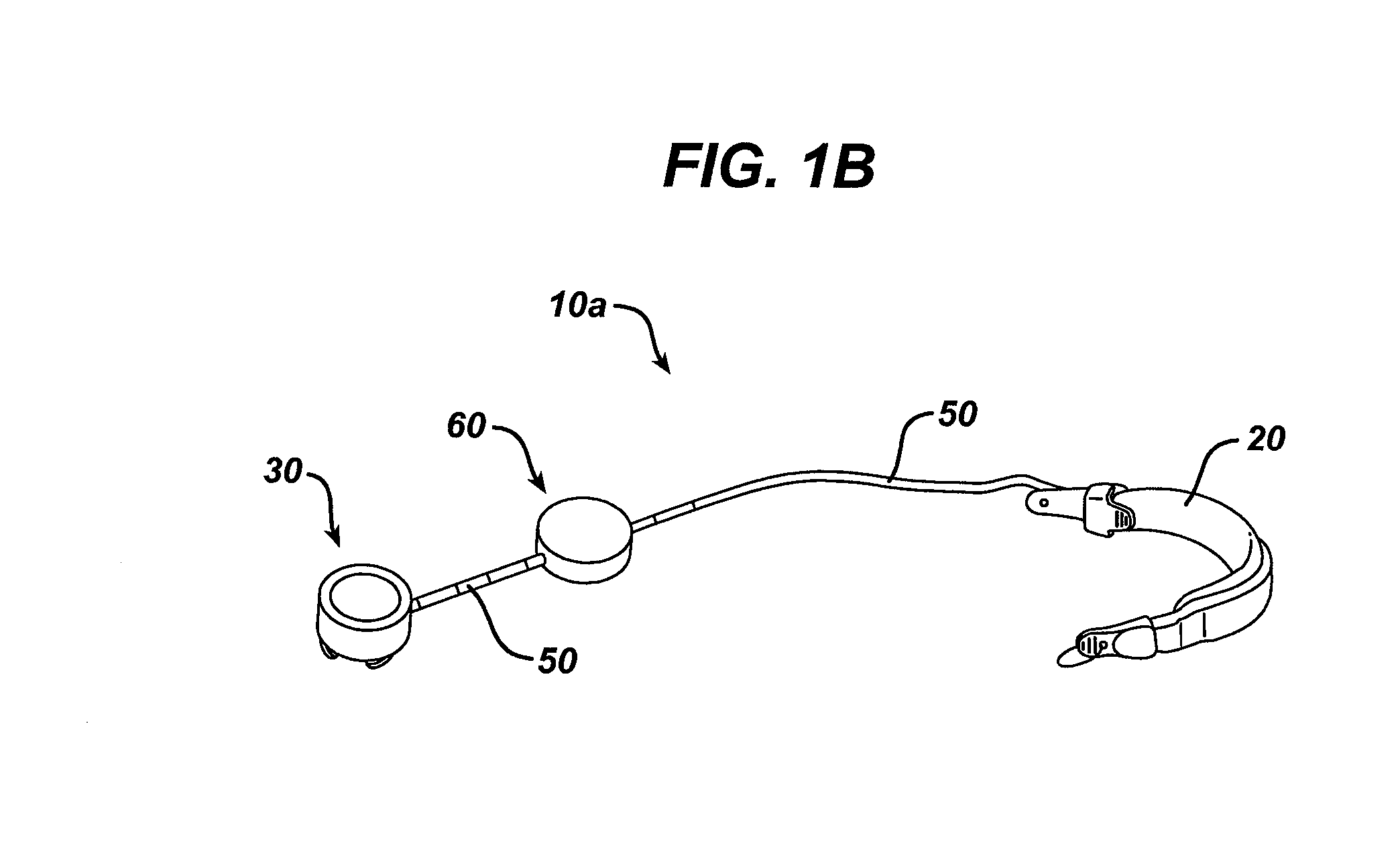
System and method of sterilizing an implantable medical device
An implantable system having internal circuitry configured to withstand a pre-determined amount of sterilization radiation is provided. In general, the system includes an internal control module in electrical communication with an implantable medical device. The internal control module can include a circuit board configured to withstand radiation and / or any number of integrated circuits (e.g., application specific integrated circuits) wherein the circuits or at least some portion thereof are fabricated so as to withstand some amount of radiation. For example, some portion of the circuitry can be fabricated utilizing radiation compliant material(s), silicon-on-insulator technology, and / or gallium arsenide technology. Additionally, the circuitry can include various components which are inherently resistant to such radiation (e.g., components fabricated utilizing magnetic field based technology, surface acoustical wave devices, etc.). A method of sterilizing an implantable medical device via radiation is also provided.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
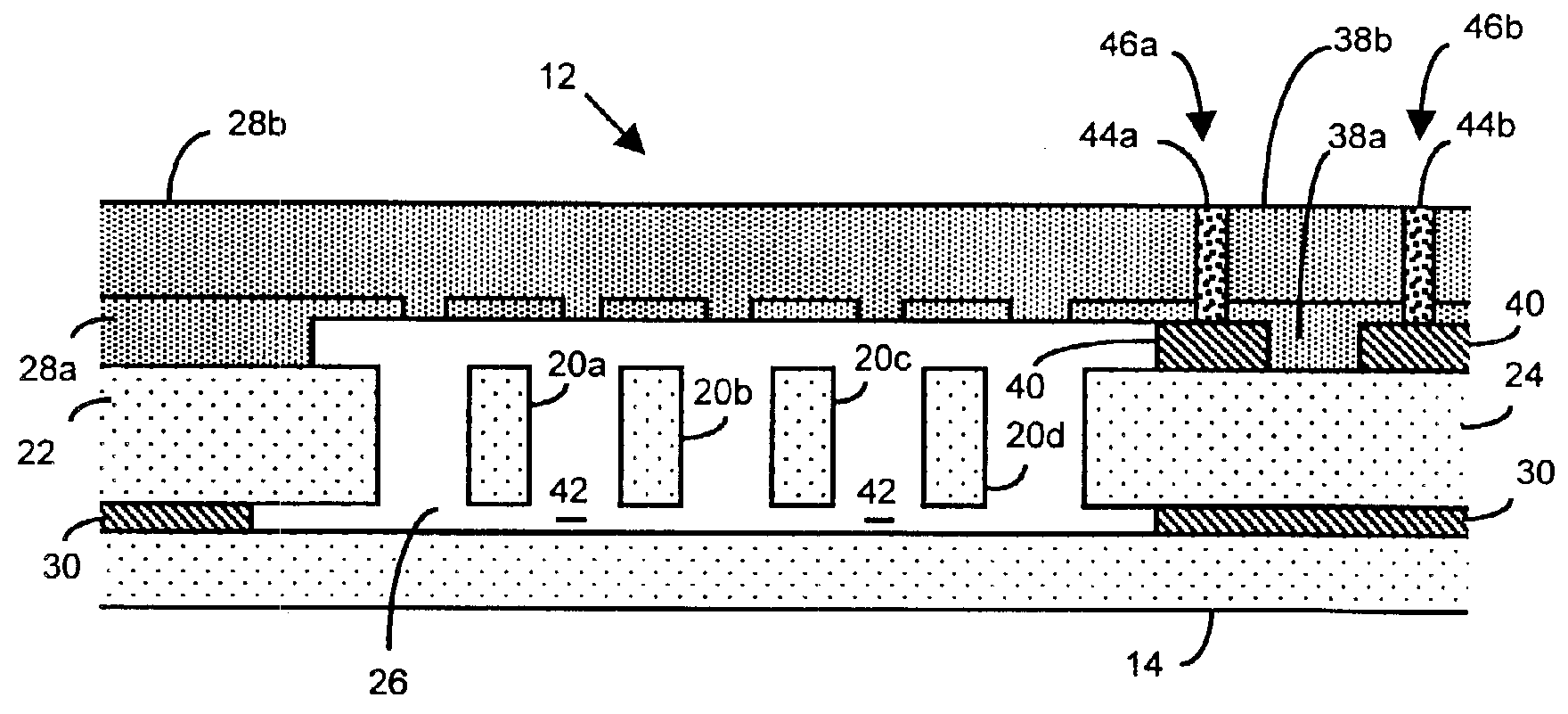
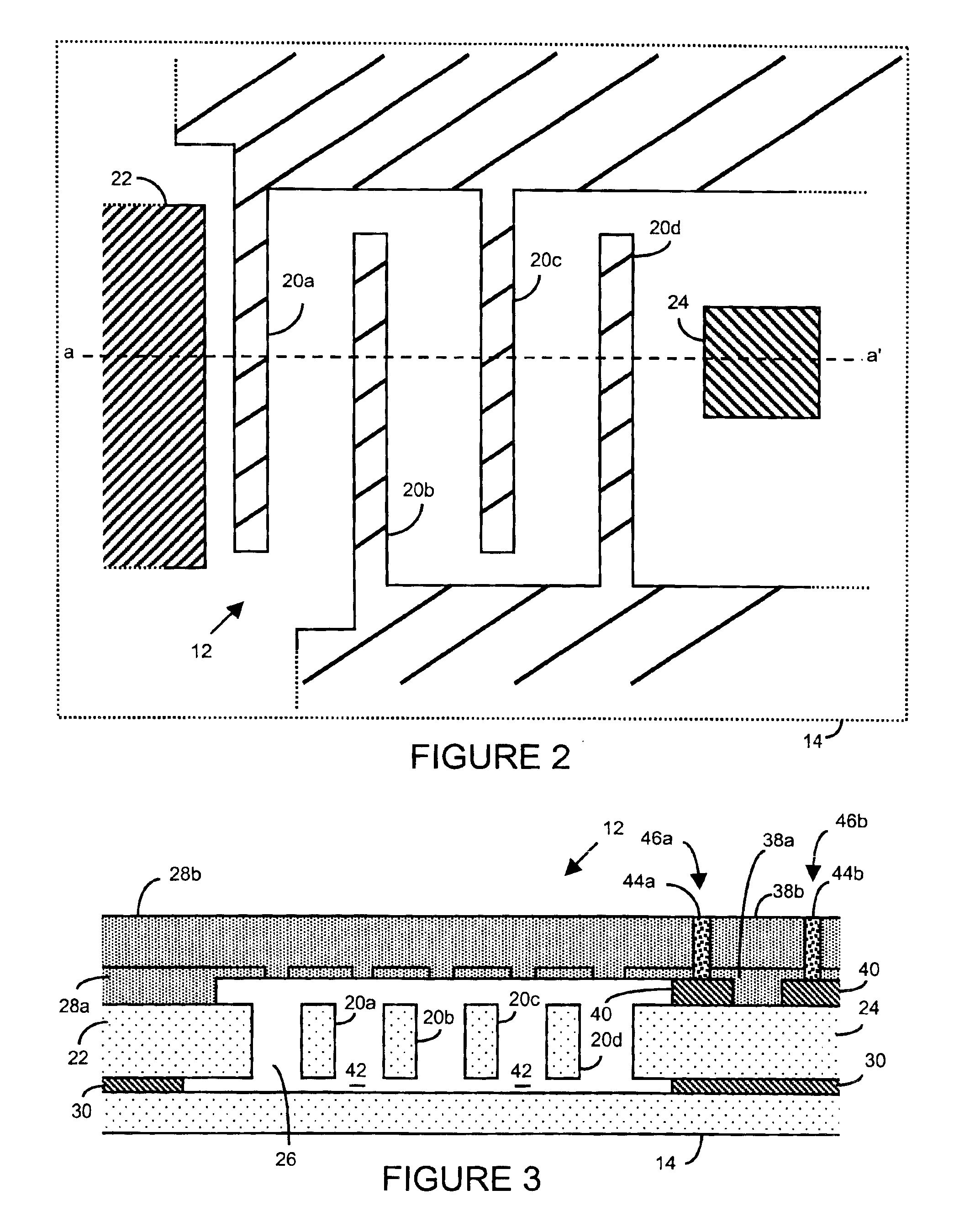
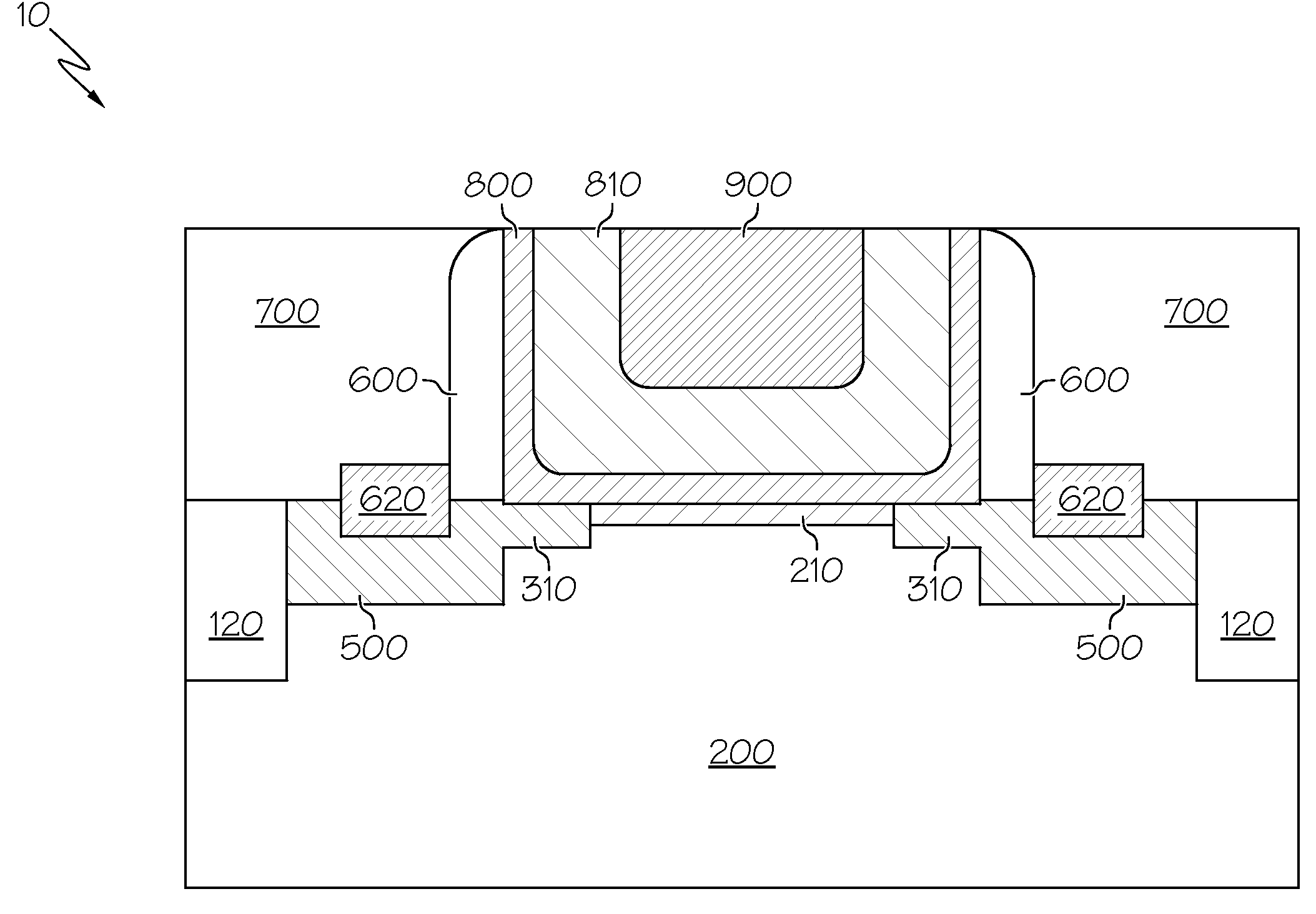
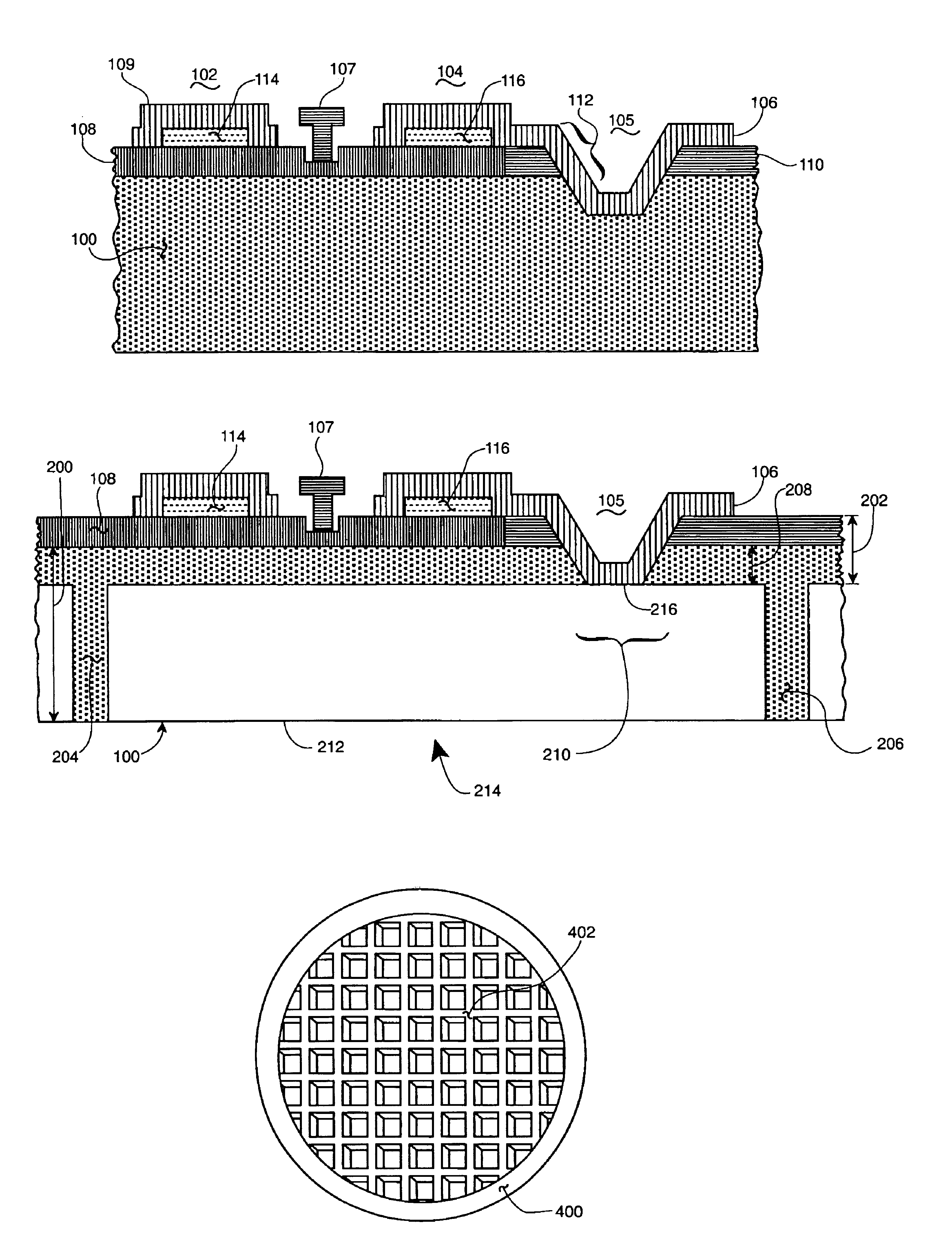
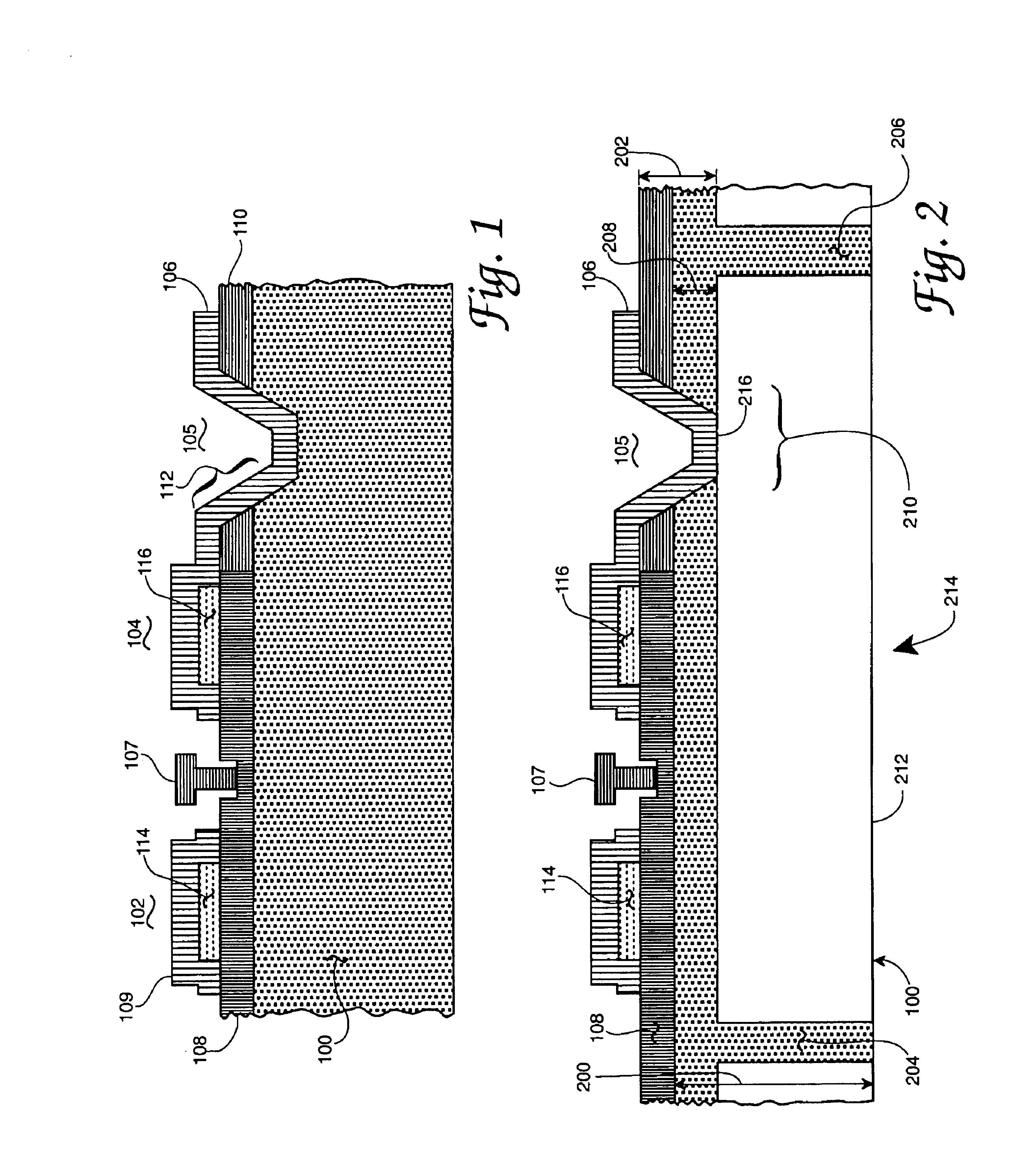
Method of fabricating microelectromechanical systems and devices having trench isolated contacts
InactiveUS6936491B2Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSolid-state devicesEngineeringMicroelectromechanical systems
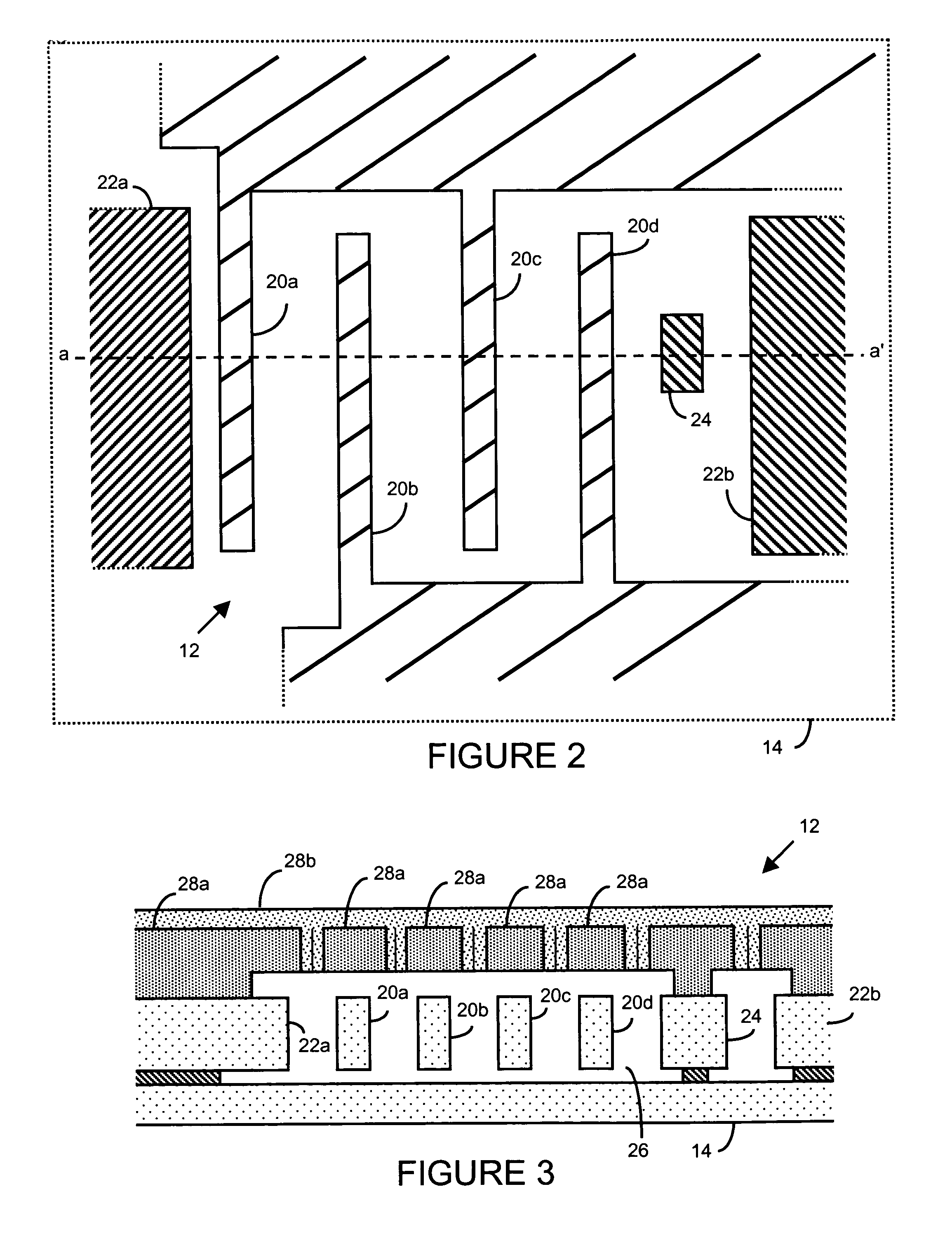
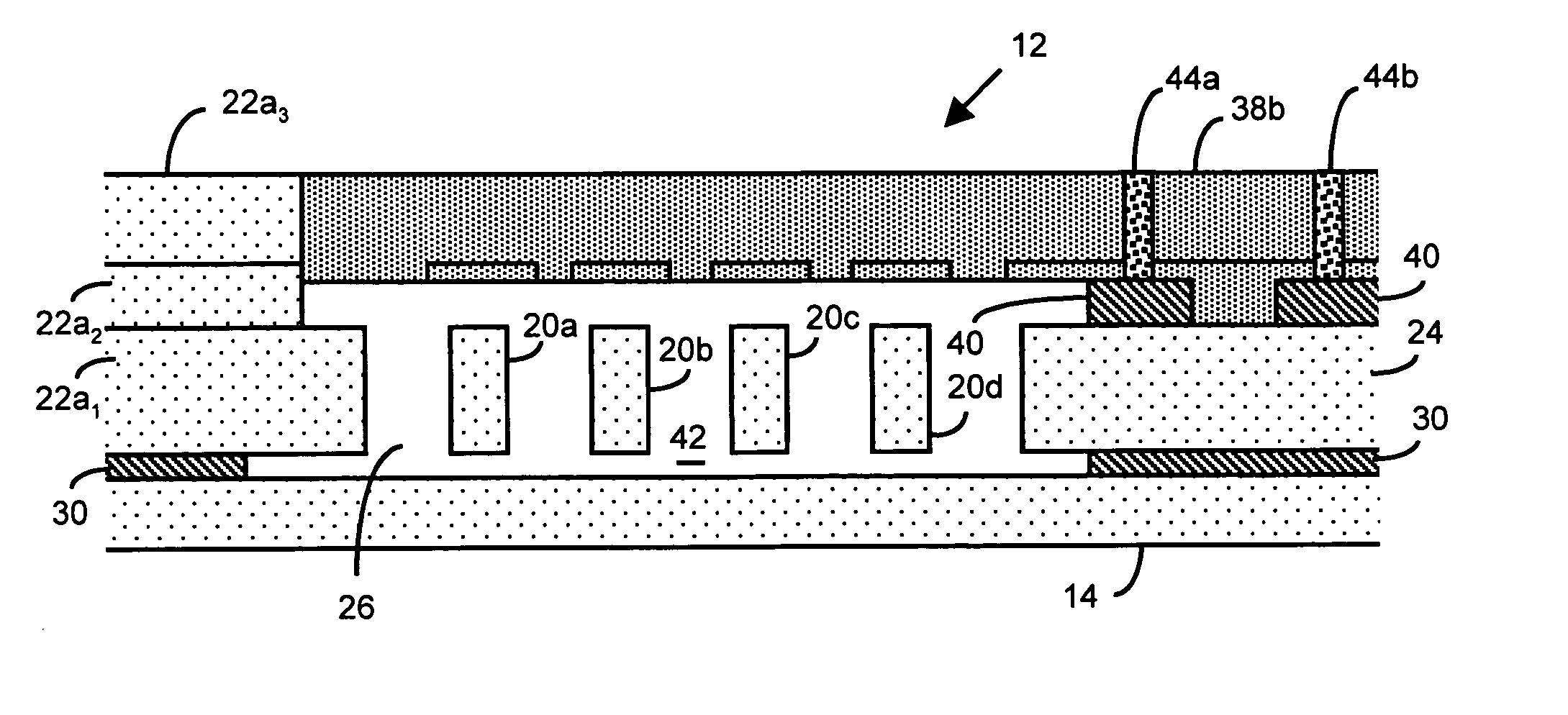
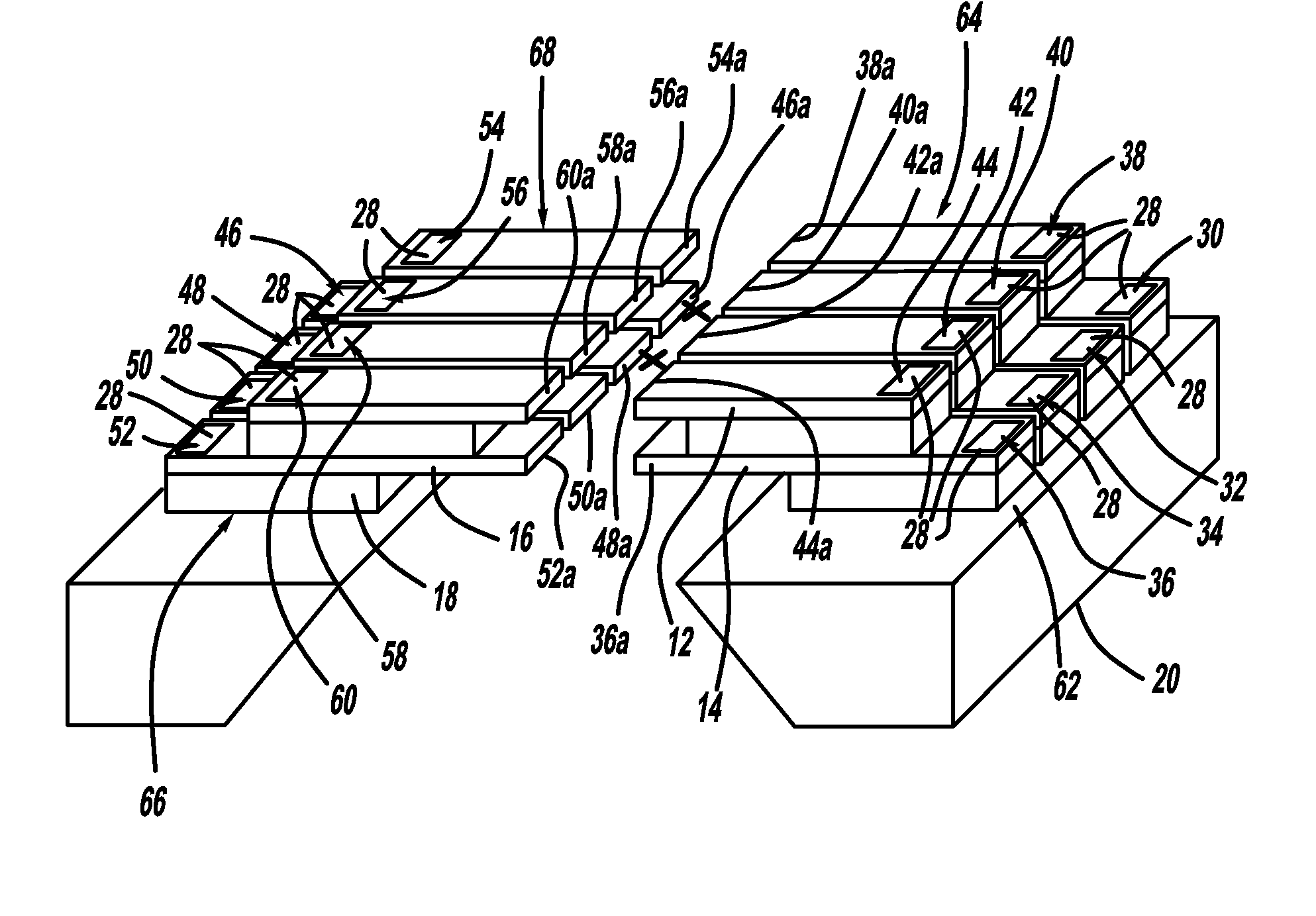
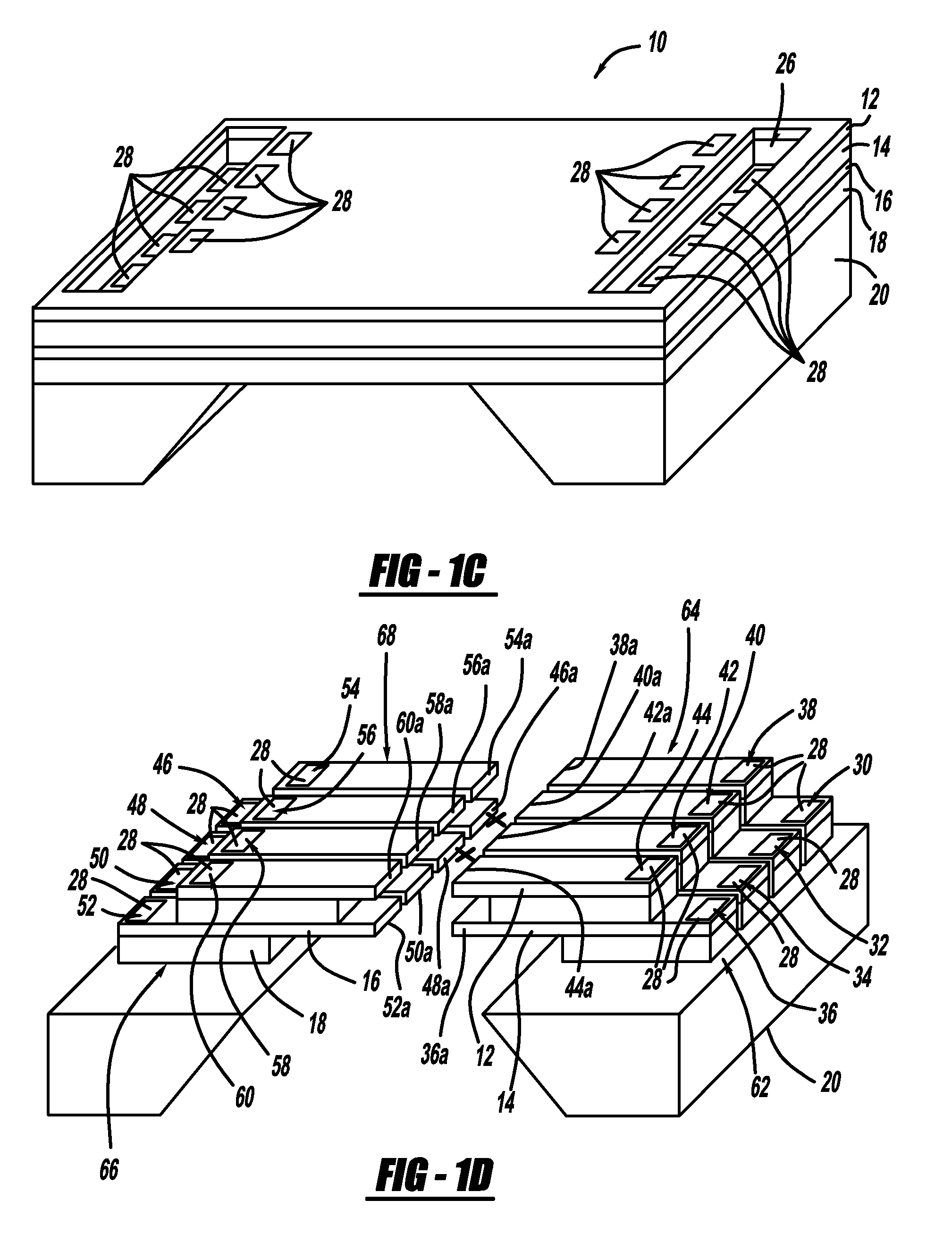
There are many inventions described and illustrated herein. In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a MEMS device, and technique of fabricating or manufacturing a MEMS device, having mechanical structures encapsulated in a chamber prior to final packaging and a contact area disposed at least partially outside the chamber. The contact area is electrically isolated from nearby electrically conducting regions by way of dielectric isolation trench that is disposed around the contact area. The material that encapsulates the mechanical structures, when deposited, includes one or more of the following attributes: low tensile stress, good step coverage, maintains its integrity when subjected to subsequent processing, does not significantly and / or adversely impact the performance characteristics of the mechanical structures in the chamber (if coated with the material during deposition), and / or facilitates integration with high-performance integrated circuits. In one embodiment, the material that encapsulates the mechanical structures is, for example, silicon (polycrystalline, amorphous or porous, whether doped or undoped), silicon carbide, silicon-germanium, germanium, or gallium-arsenide.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Structures and methods for high efficiency compound semiconductor solar cells
InactiveUS20130337601A1Eliminate and reduce cost and scaling disadvantageLow costFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsThin layer
Methods and structures are provided for the growth and separation of a relatively thin layer crystalline compound semiconductor material containing III-V device layers, including but not limited to Gallium Arsenide (GaAs), on top of a crystalline silicon template wafer. Solar cell structures and manufacturing methods based on the crystalline compound semiconductor material are described.
Owner:BEAMREACH SOLAR INC
Flexible 3-D Photonic Device
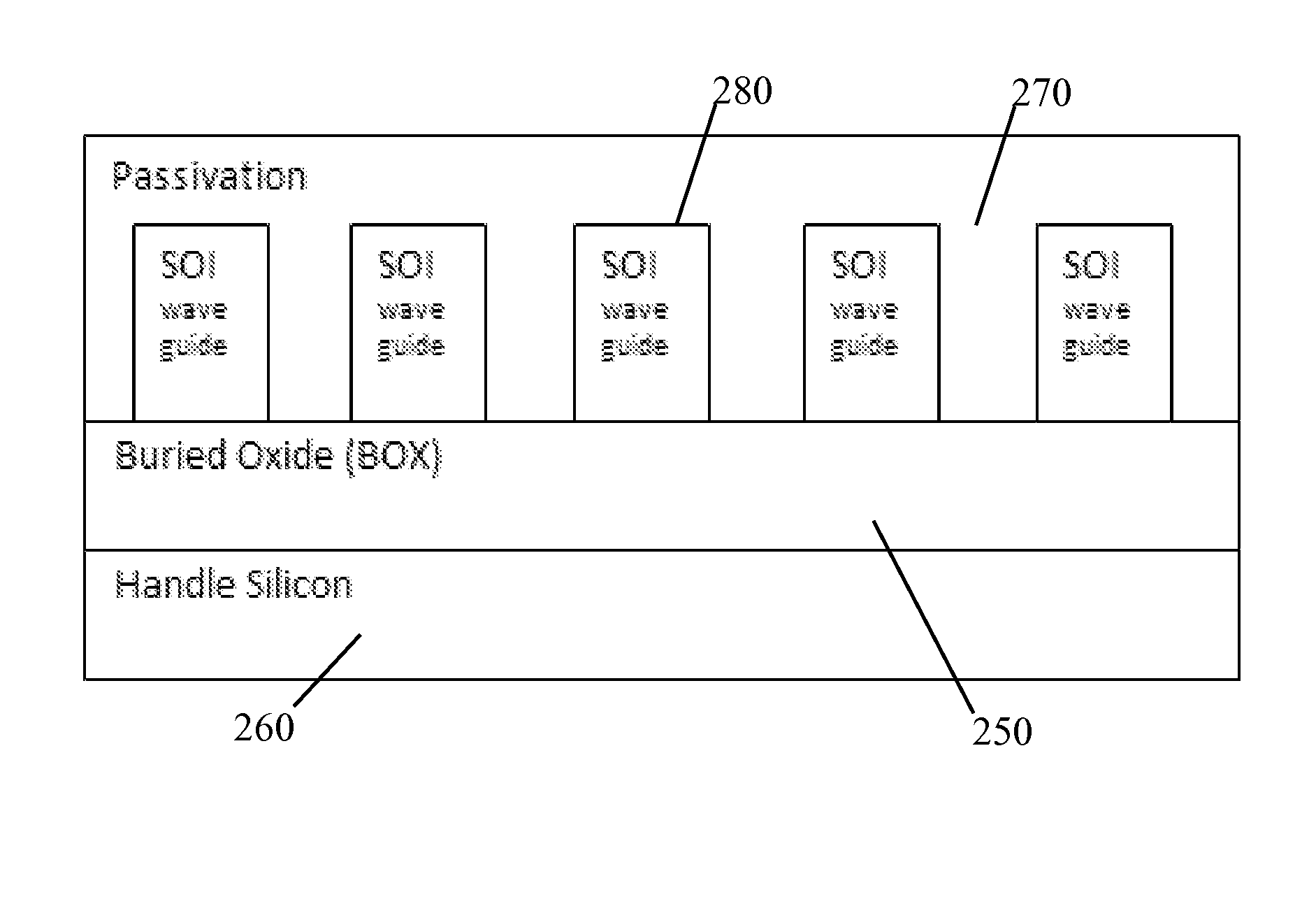
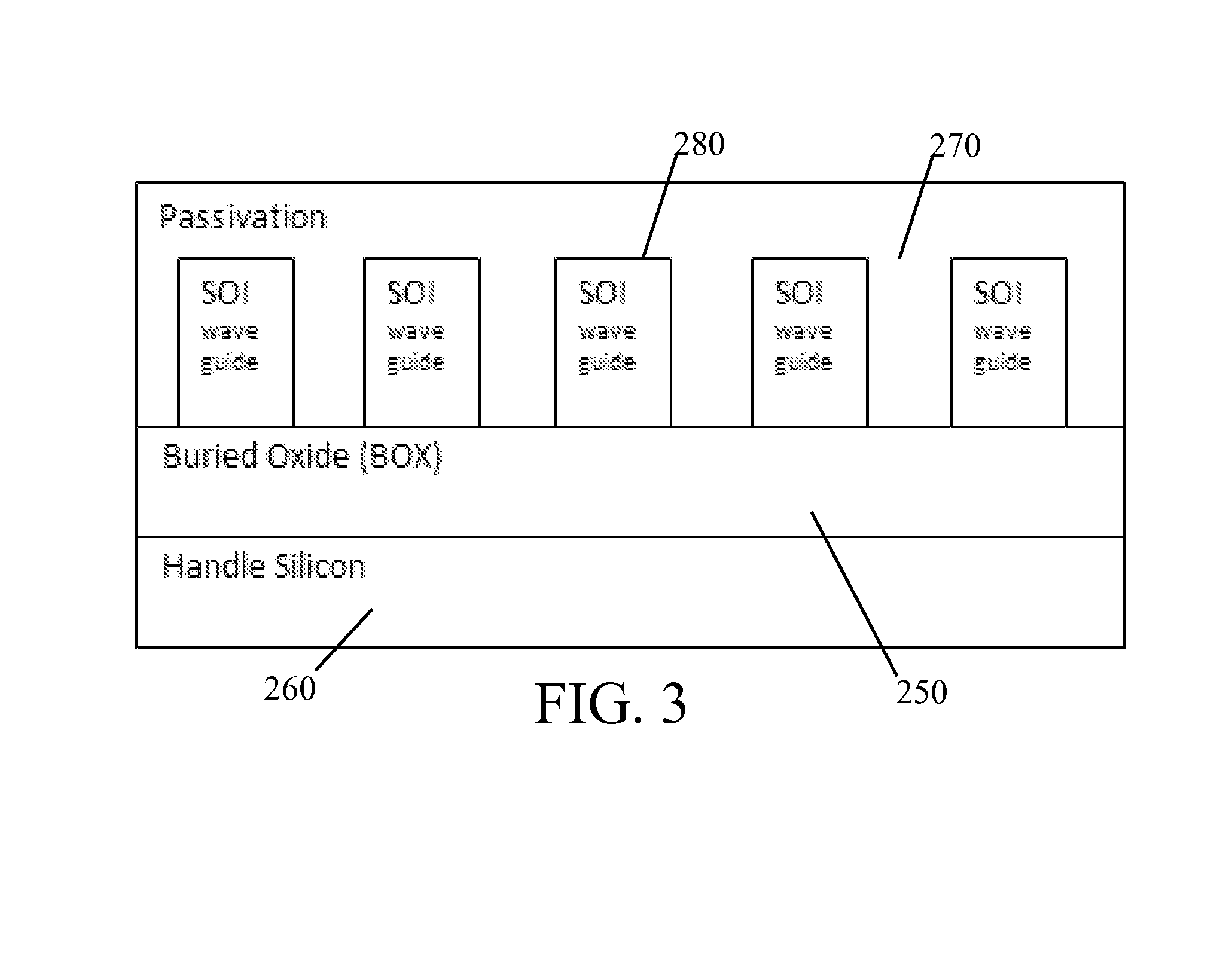
ActiveUS20140219604A1Function increaseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical waveguide light guidePolymerPhoton
Three-dimensional flexible photonic integrated circuits on silicon are fabricated in semiconductor wafer form and then transferred to Silicon-on-Polymer (SOP) substrates. SOP provides flexibility for conformal mounting with devices capable of maintaining performance when dynamically deformed to allow routing of light in x, y and z directions. Bonding a wafer or individual die of III-V semiconductor, such as Gallium Arsenide or similar photonic material, to the flexible silicon creates an active region for lasers, amplifiers, modulators, and other photonic devices using standard processing. Mounting additional photonic devices to the opposite side of a flexible photonic waveguide produces a stack for three-dimensional devices. Multiple flexible photonic waveguides may be stacked to increase functionality by transferring light between stacked waveguides. The flexible photonic circuit allows for integration of photonic devices such as low threshold lasers, tunable lasers, and other photonic integrated circuits with flexible Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) integrated circuits.
Owner:AMERICAN SEMICON
Treatment method of film quality for the manufacture of substrates
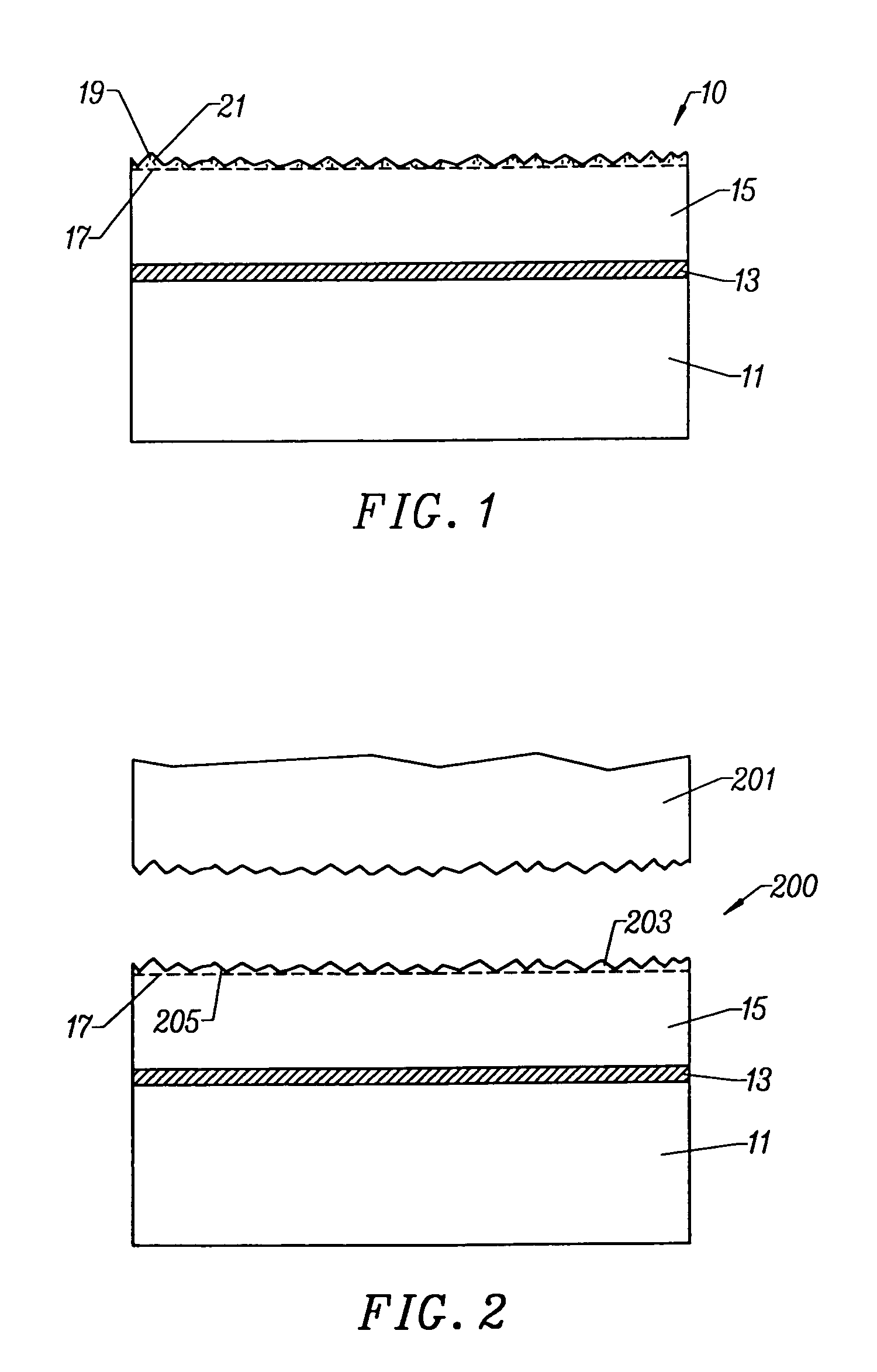
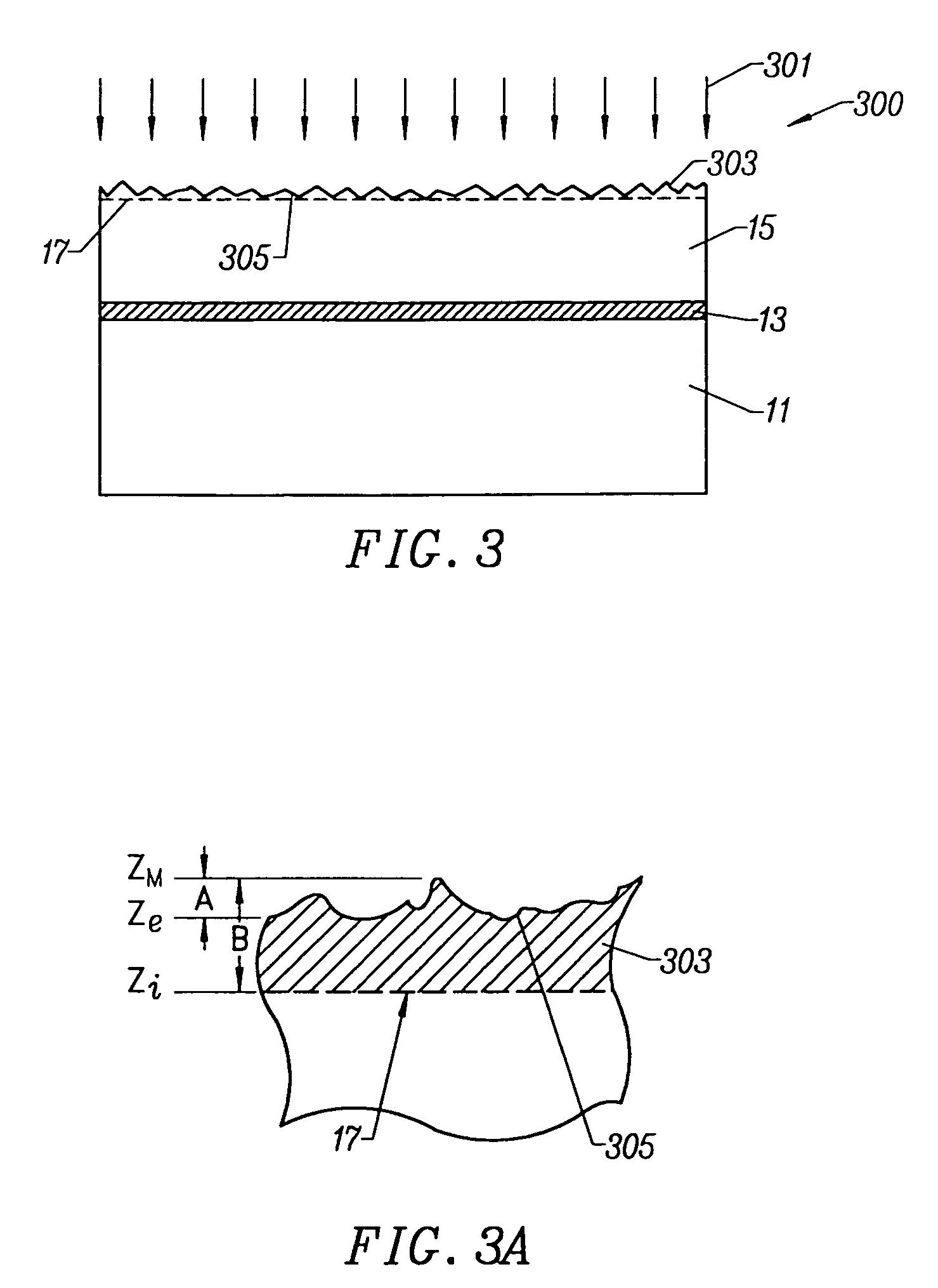
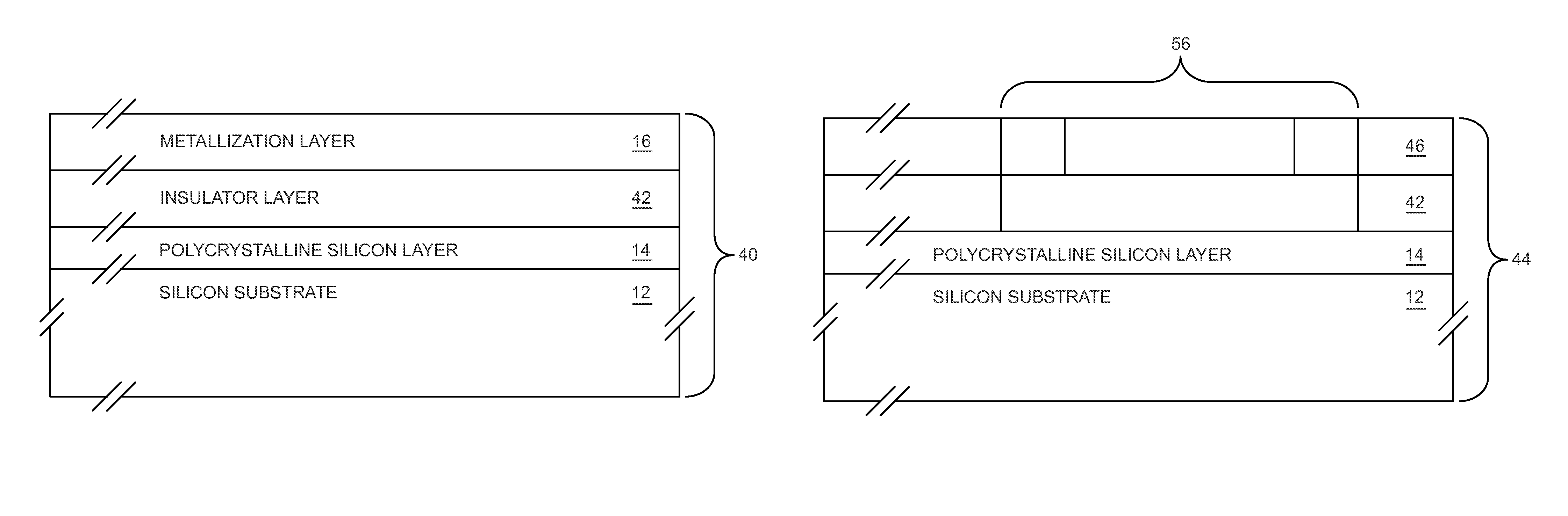
InactiveUS6969668B1Improve crystal structureReduce defectsDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface roughnessGallium nitride
A method of fabricating substrates, e.g., bulk wafers, silicon on insulator wafers, silicon on saphire, optoelectronic substrates. The method includes providing a substrate (e.g., silicon, gallium arsenide, gallium nitride, quartz). The substrate has a film characterized by a non-uniform surface, which includes a plurality of defects. At least some of the defects are of a size ranging from about 100 Angstroms and greater. The method also includes applying a combination of a deposition species for deposition of a deposition material and an etching species for etching etchable material. The combination of the deposition species and the etching species contact the non-uniform surface in a thermal setting to reduce a level of non-uniformity of the non-uniform surface by filling a portion of the defects to smooth the film of material. The smoothed film of material is substantially free from the defects and is characterized by a surface roughness of a predetermined value.
Owner:SILICON GENERAL CORPORATION
Linearity improvements of semiconductor substrate based radio frequency devices
ActiveUS8076750B1Effectively immobilizing the surface conduction layerPrevent capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceRelease time
The present invention relates to using a trap-rich layer, such as a polycrystalline Silicon layer, over a semiconductor substrate to substantially immobilize a surface conduction layer at the surface of the semiconductor substrate at radio frequency (RF) frequencies. The trap-rich layer may have a high density of traps that trap carriers from the surface conduction layer. The average release time from the traps may be longer than the period of any present RF signals, thereby effectively immobilizing the surface conduction layer, which may substantially prevent capacitance and inductance changes due to the RF signals. Therefore, harmonic distortion of the RF signals may be significantly reduced or eliminated. The semiconductor substrate may be a Silicon substrate, a Gallium Arsenide substrate, or another substrate.
Owner:QORVO US INC
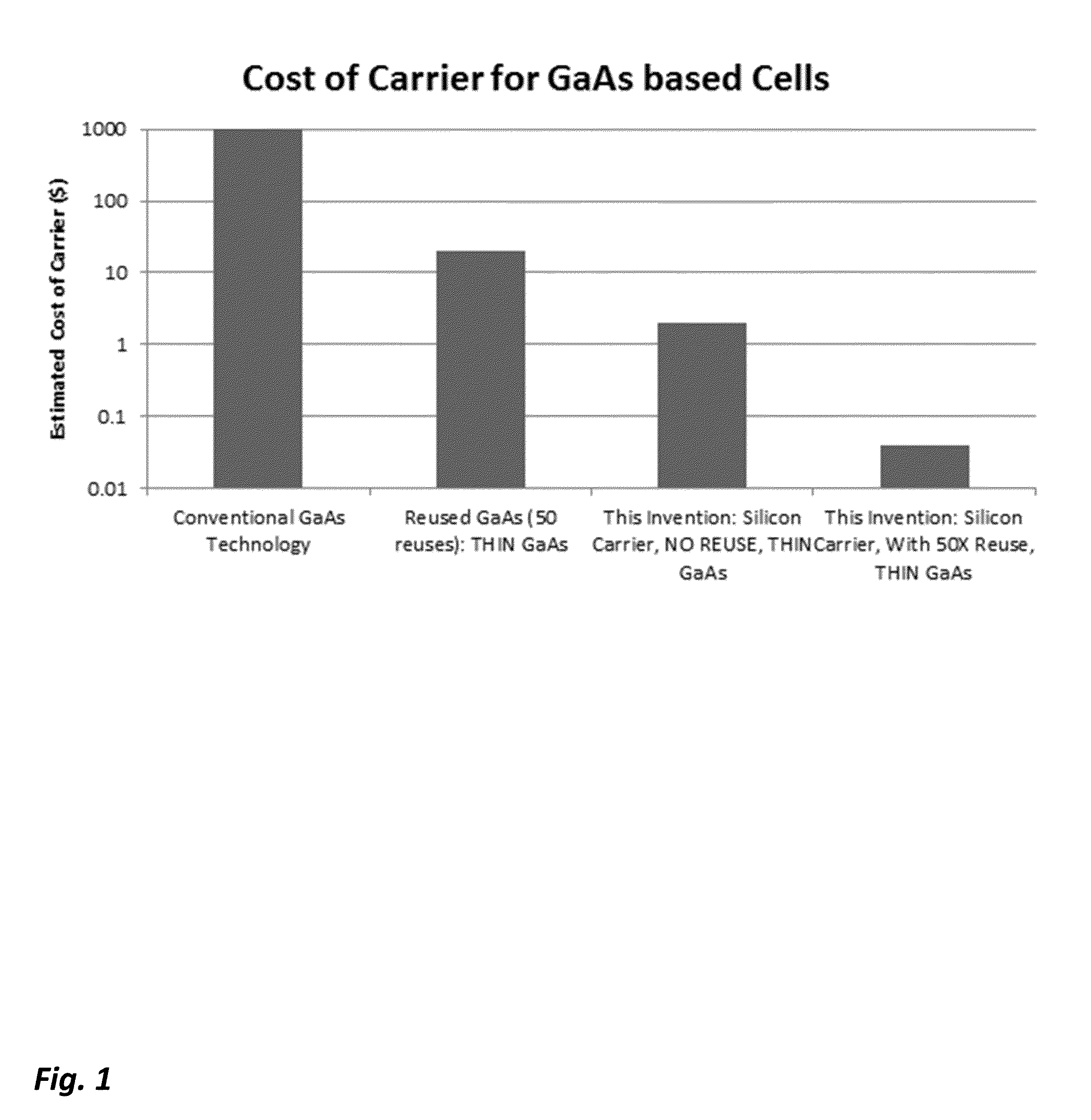
Growth substrates for inverted metamorphic multijunction solar cells
ActiveUS7785989B2Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsSolar cell
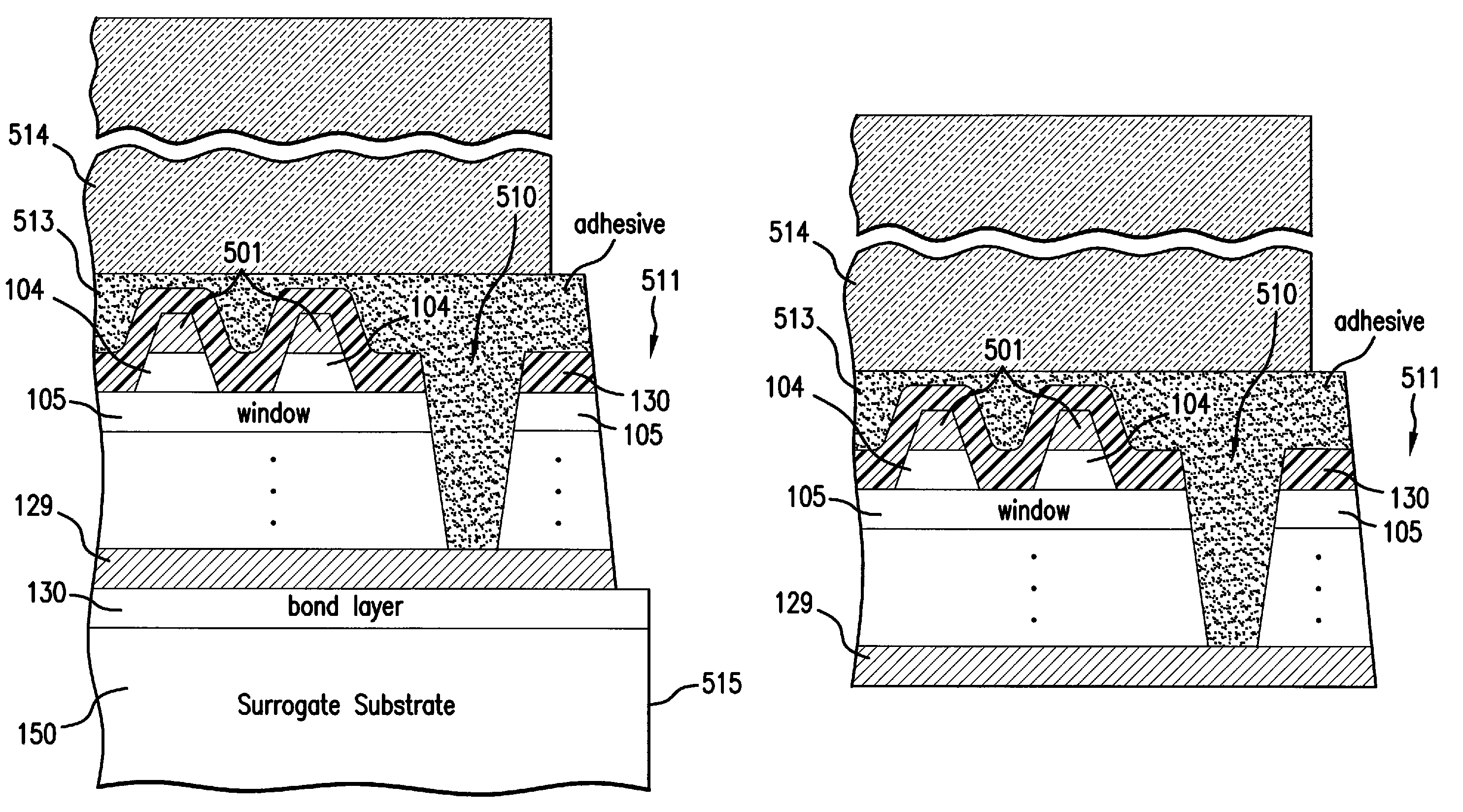
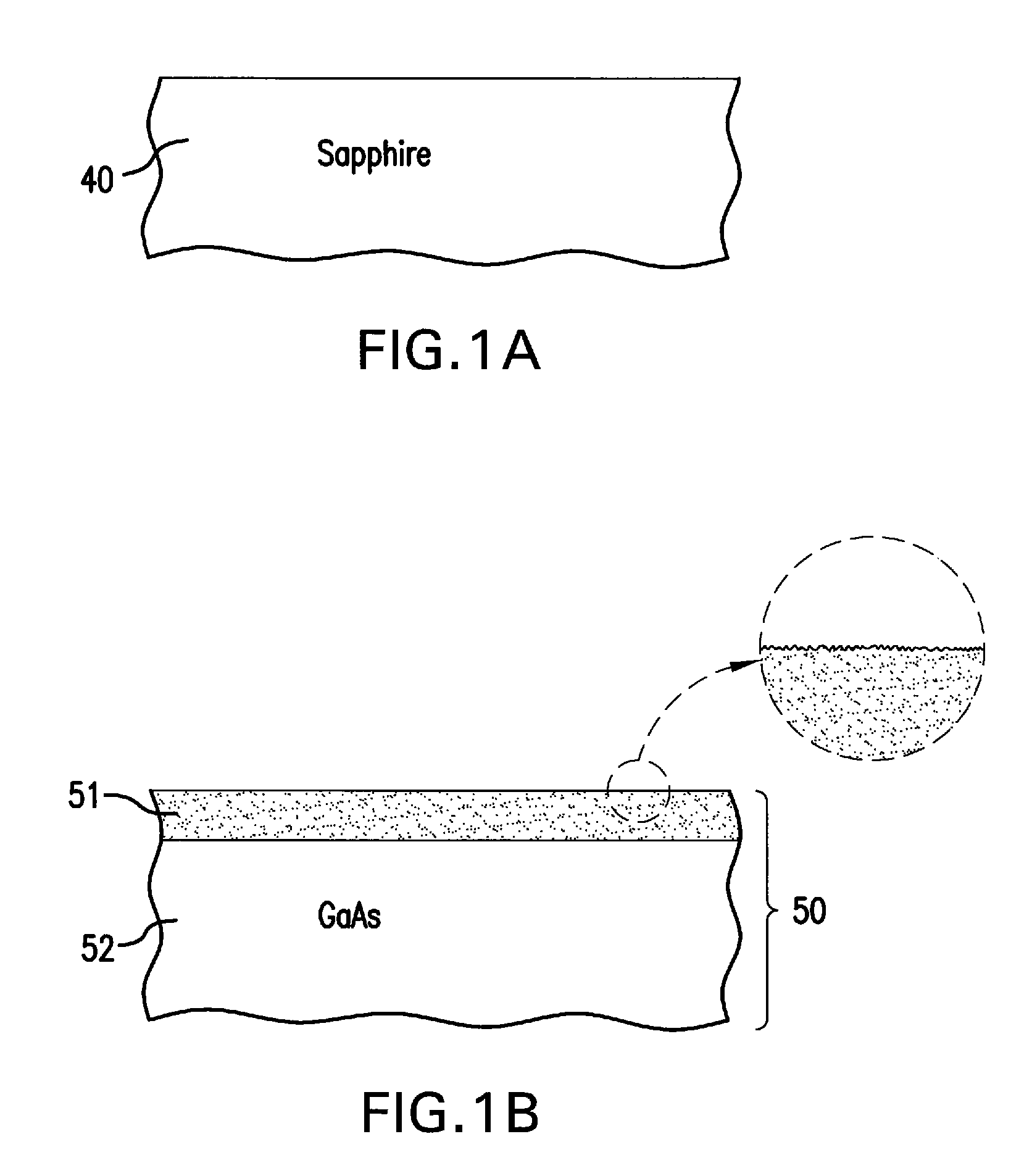
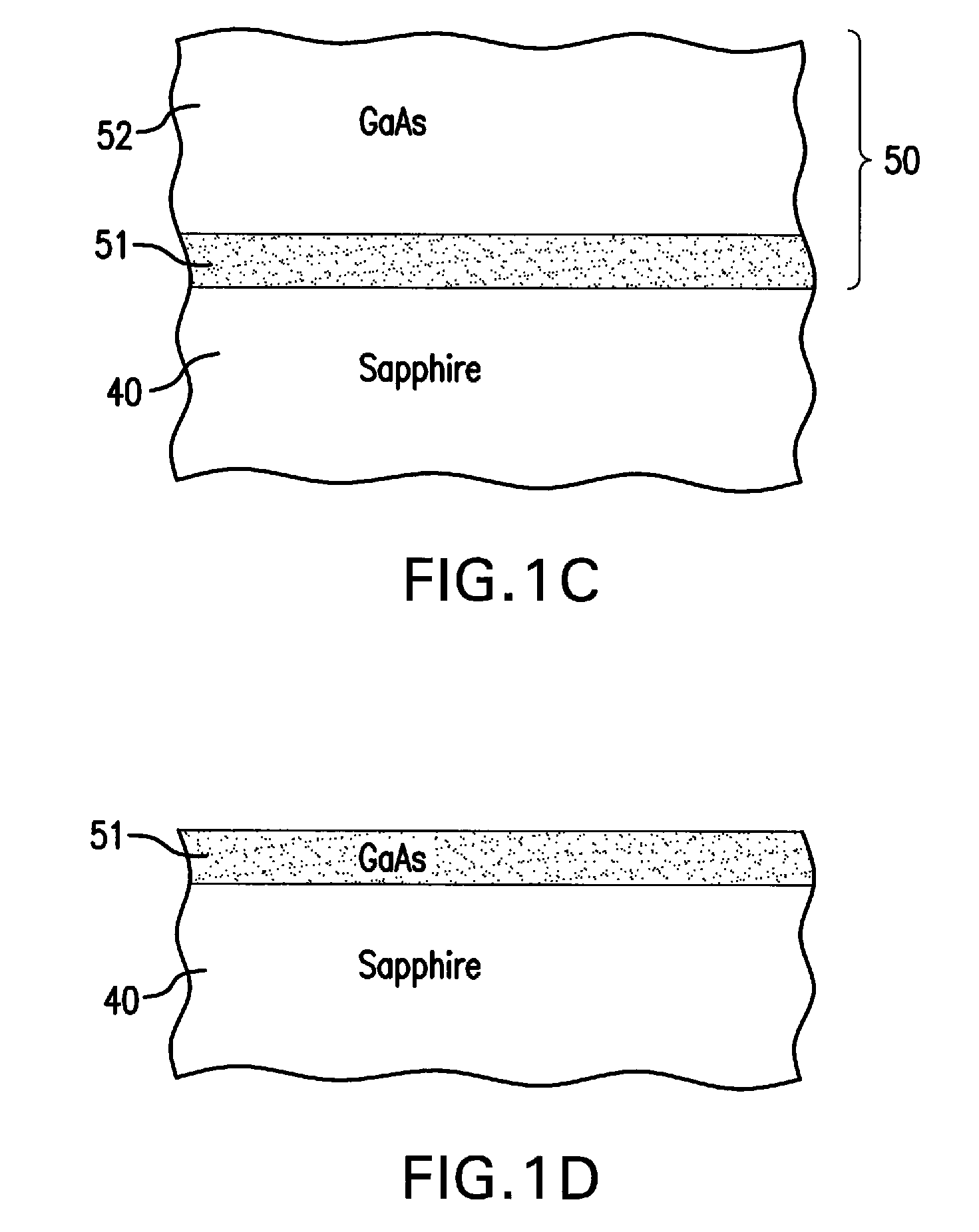
A method of manufacturing a solar cell by providing a gallium arsenide carrier with a prepared bonding surface; providing a sapphire substrate; bonding the gallium arsenide carrier and the sapphire substrate to produce a composite structure; detaching the bulk of the gallium arsenide carrier from the composite structure, leaving a gallium arsenide growth substrate on the sapphire substrate; and depositing a sequence of layers of semiconductor material forming a solar cell on the growth substrate. For some solar cells, the method further includes mounting a surrogate second substrate on top of the sequence of layers of semiconductor material forming a solar cell; and removing the growth substrate.
Owner:SOLAERO TECH CORP
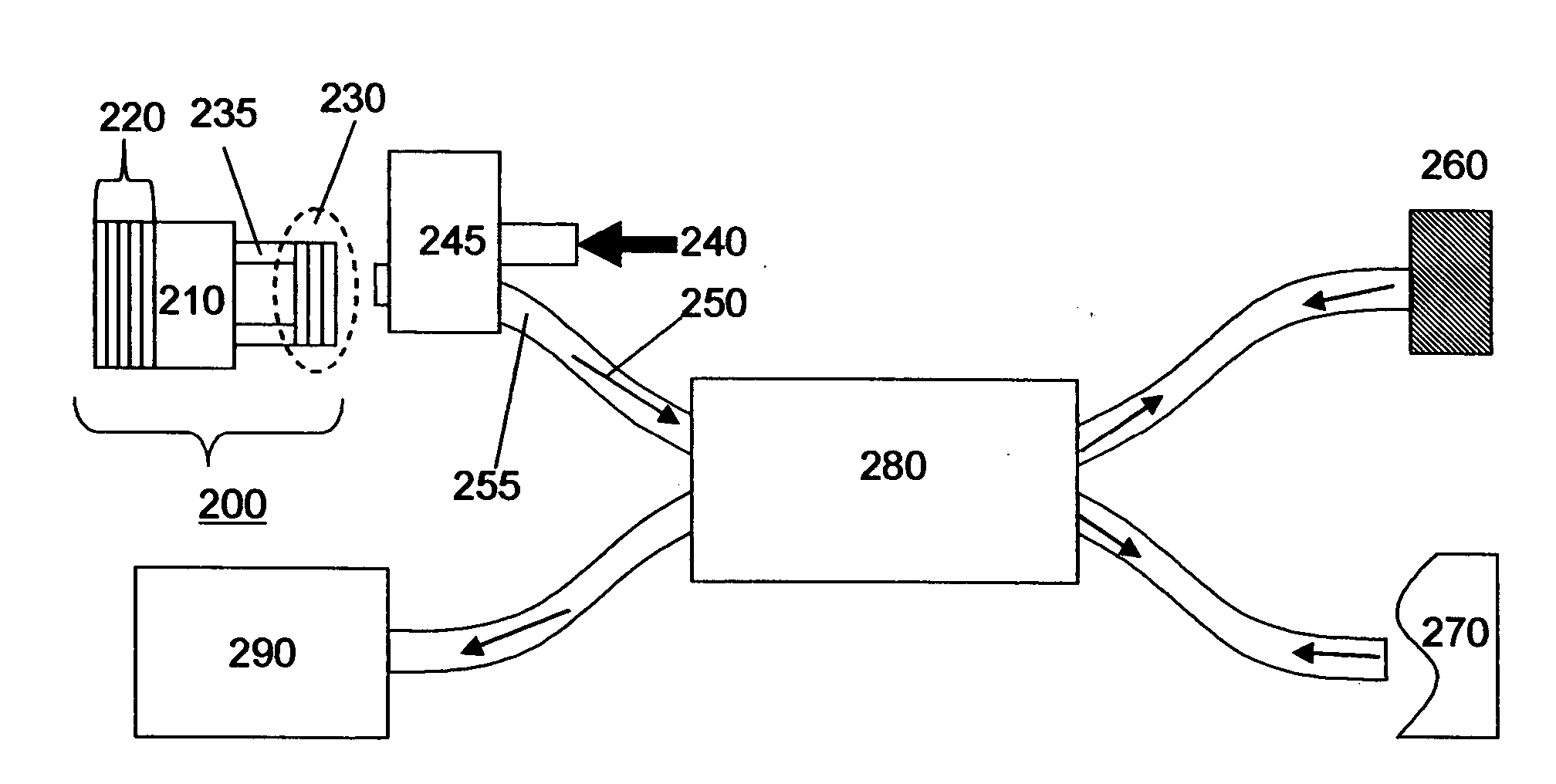
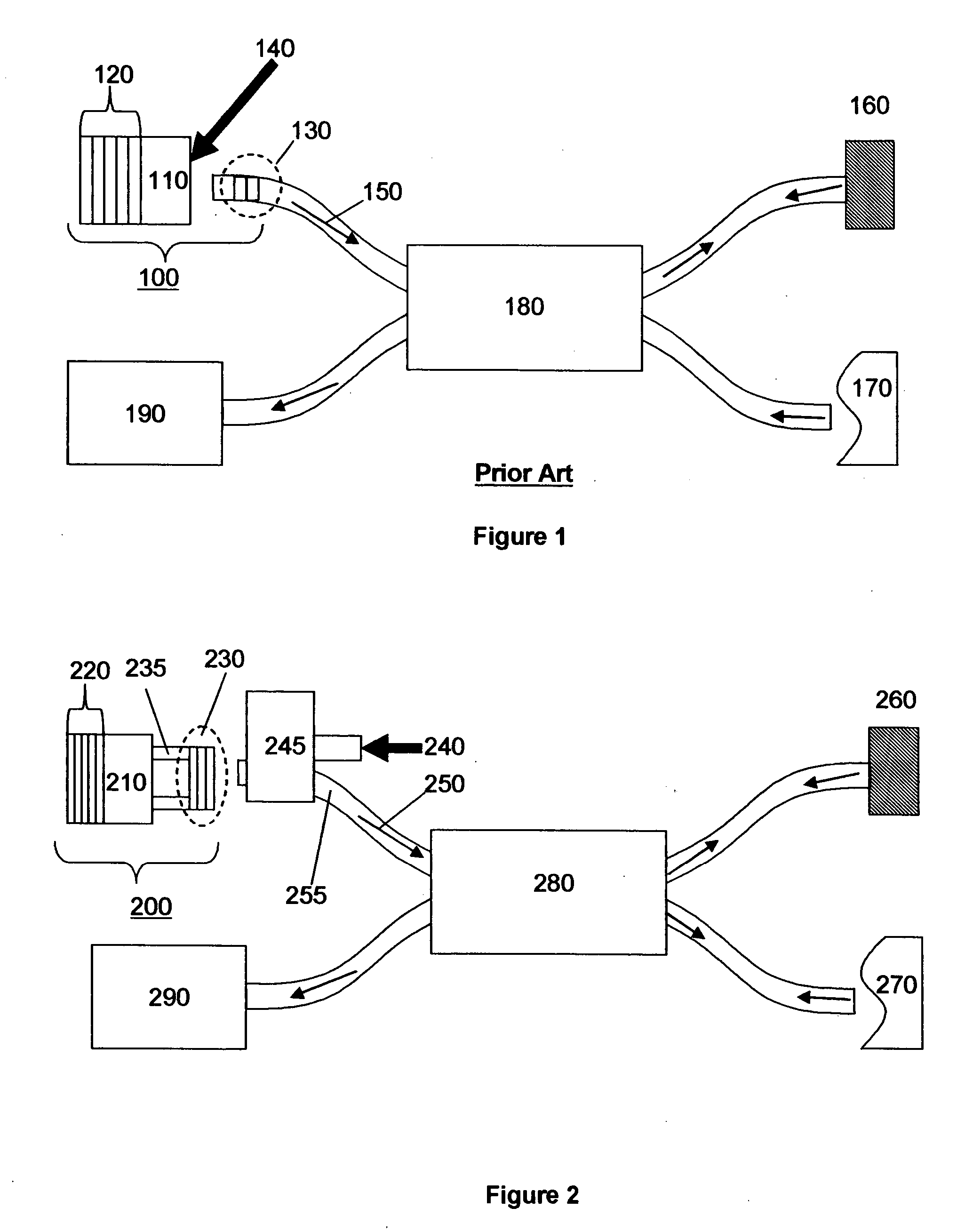
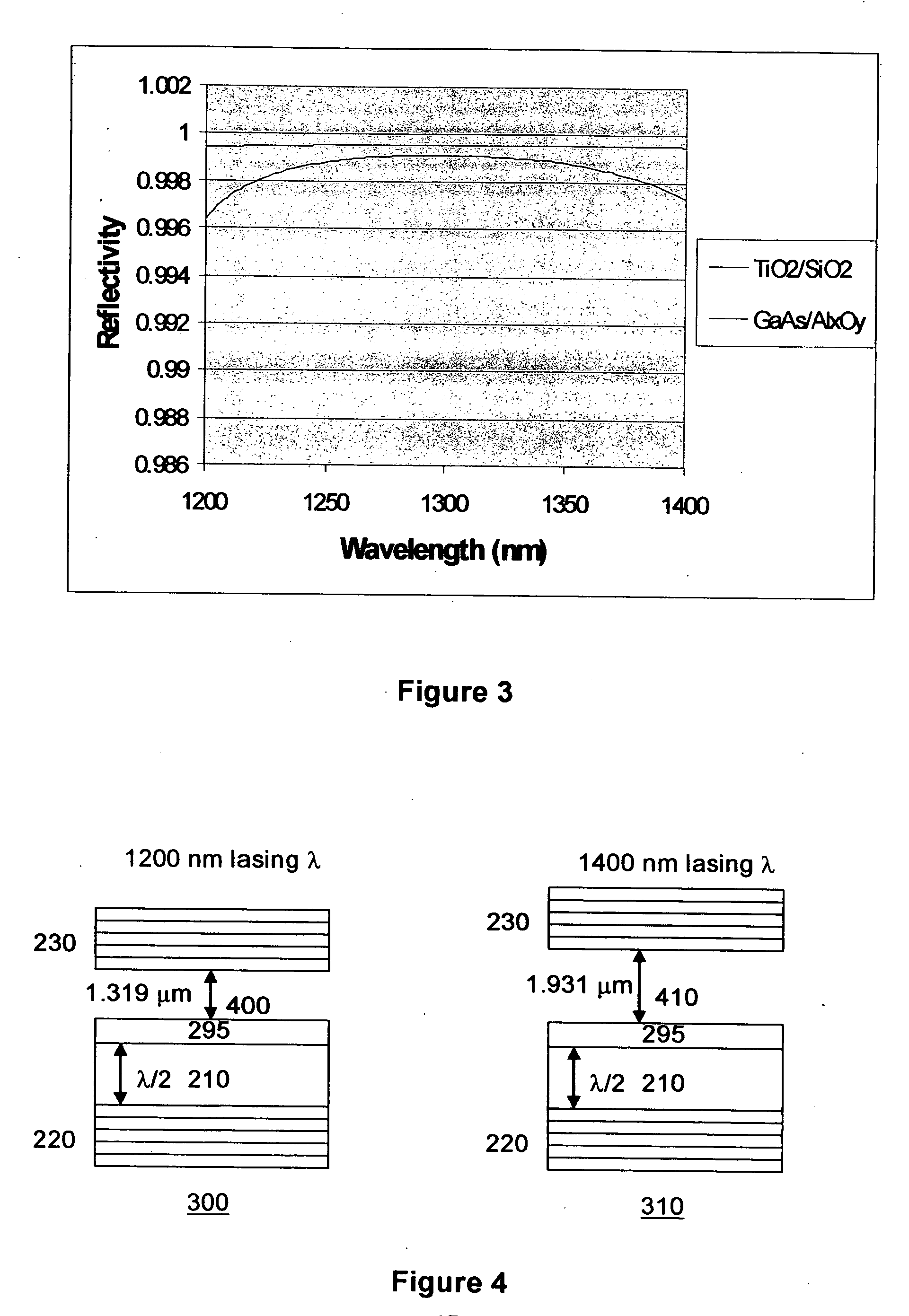
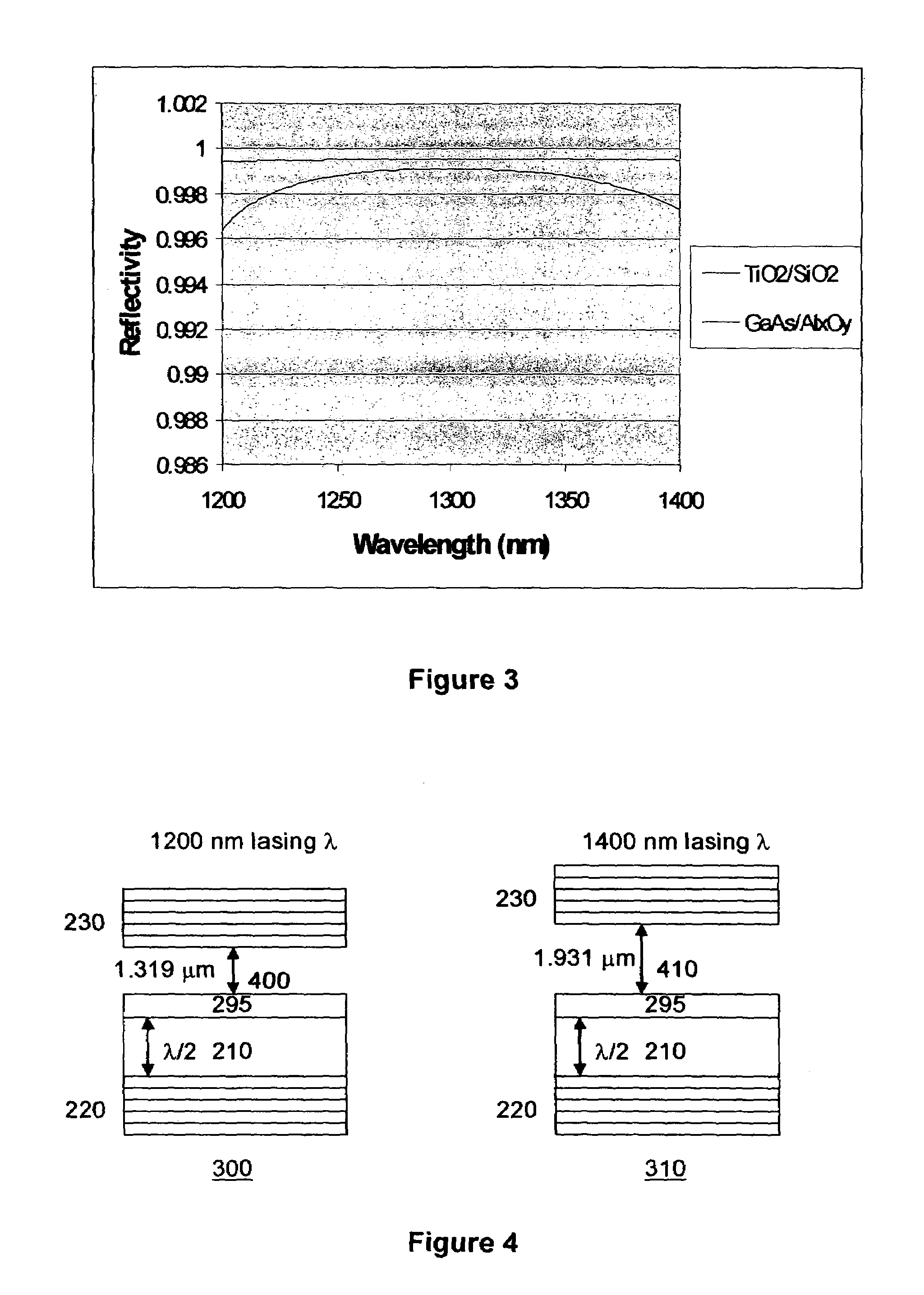
System for swept source optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS20070183643A1Broaden effective gain bandwidthLaser detailsDiagnostics using lightVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserTomography
A swept source Optical coherence tomography system (SSOCT) comprises a vertical cavity surface-emitting laser with an integrated MEMs tunable mirror movable by electro-static deflection. The MEMs tunable VCSEL offers scan rates greater than 100 khz and tuning ranges approaching 200 nm around 1300 nm and 150 nm around 850 nm. In the preferred embodiment of this invention, a bottom mirror of the VCSEL is comprised of a Aluminum Gallium Arsenide / Aluminum Oxide DBR stack, and a movable top mirror is comprised of a TiO2 / SiO2 DBR stack. A MEMs tunable VCSEL at 1300 nm is preferably pumped through the top mirror in a wavelength range between 1050 and 1120 nm, and a MEMs tunable VCSEL at 850 nm is preferably pumped through the top mirror in a wavelength range between 700 nm and 730 nm.
Owner:PRAEVIUM RES
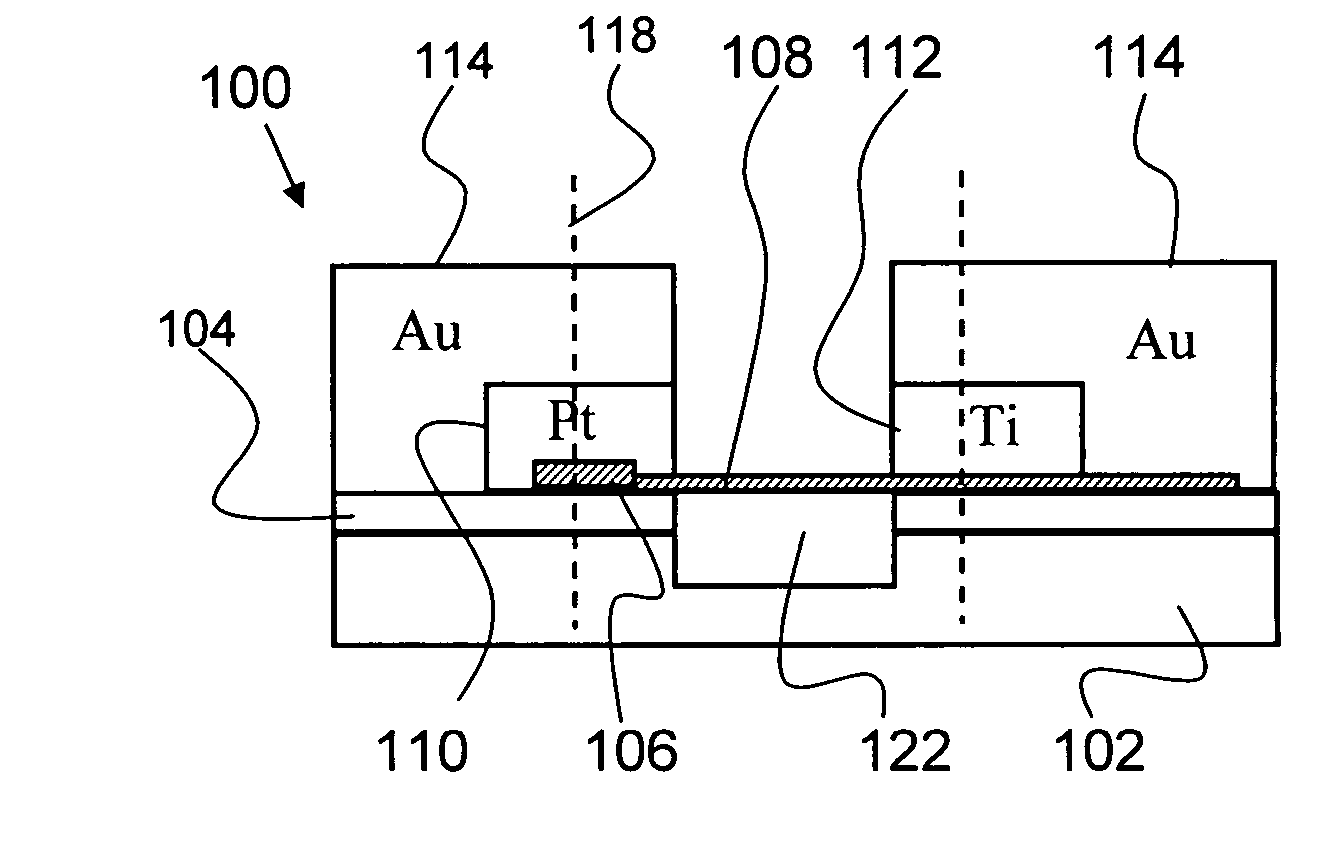
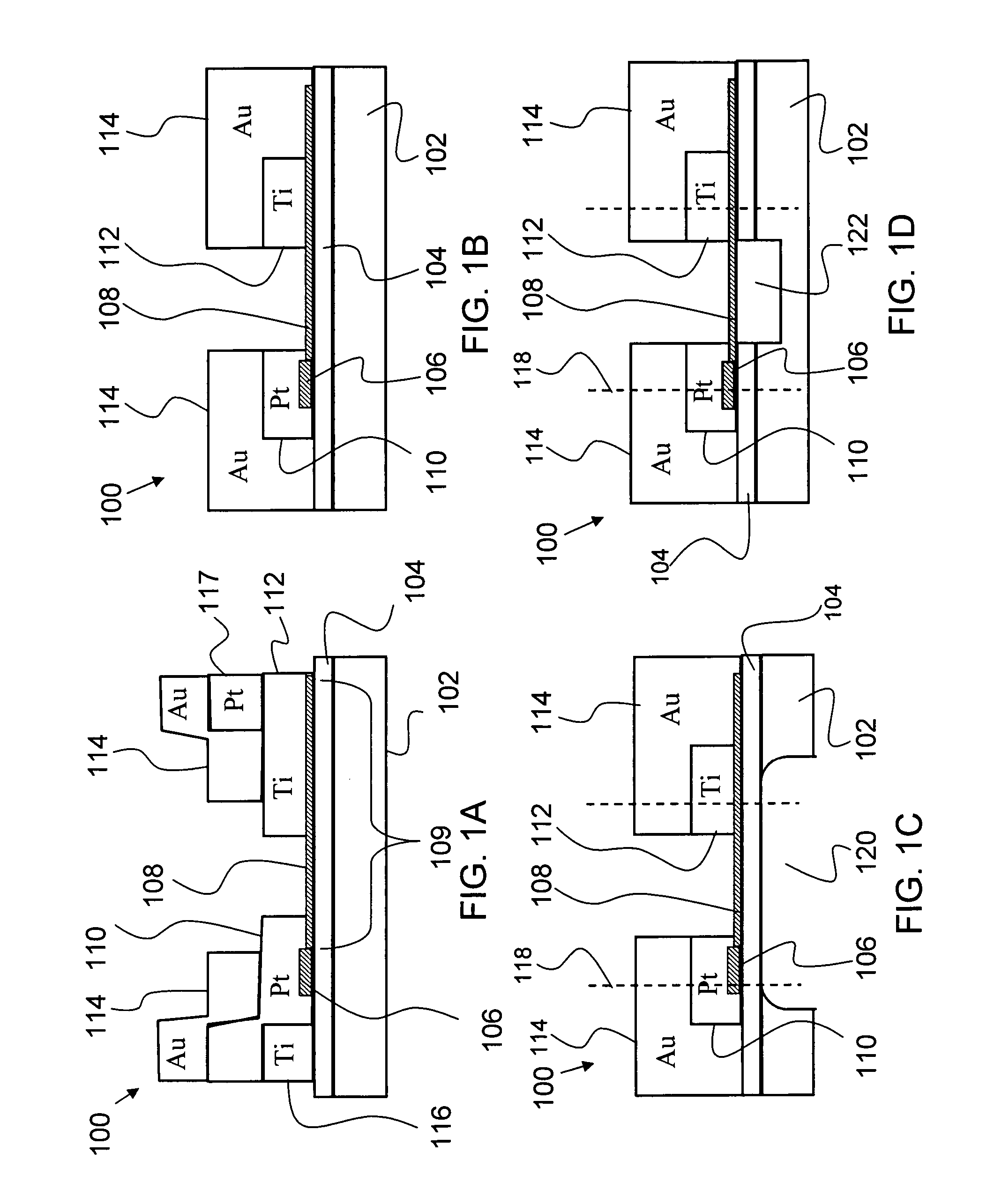
Fabrication of self-aligned gallium arsenide MOSFETs using damascene gate methods
ActiveUS7435636B1Improve featuresShorten the lengthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETEngineering
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method and Structure for Integrated Solar Cell LCD Panel
InactiveUS20070102035A1Improve fill rateIncrease cell areaPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringSolar cell
The present invention relates to a method and device for integrating solar cell on LCD panels for photovoltaic electricity generation for portable electronic devices. According to one embodiment of the present invention, the black matrix region on the color filter substrate in a LCD panel is replaced by a solar cell region. A lens array substrate is coupled between the light source layer and the TFT to focus the backlight to increase the solar cell layer area while maintaining high fill ratio of the LCD pixels. The solar cell material is selected from at least silicon, a single crystal silicon, poly-crystalline silicon, amorphous silicon, gallium arsenide, cadmium telluride, copper indium diselenide, organic / inorganic, or hybrid cells. The substrate material is selected from glass, metal, plastic or polymer.
Owner:XIAI CHARLES YANG
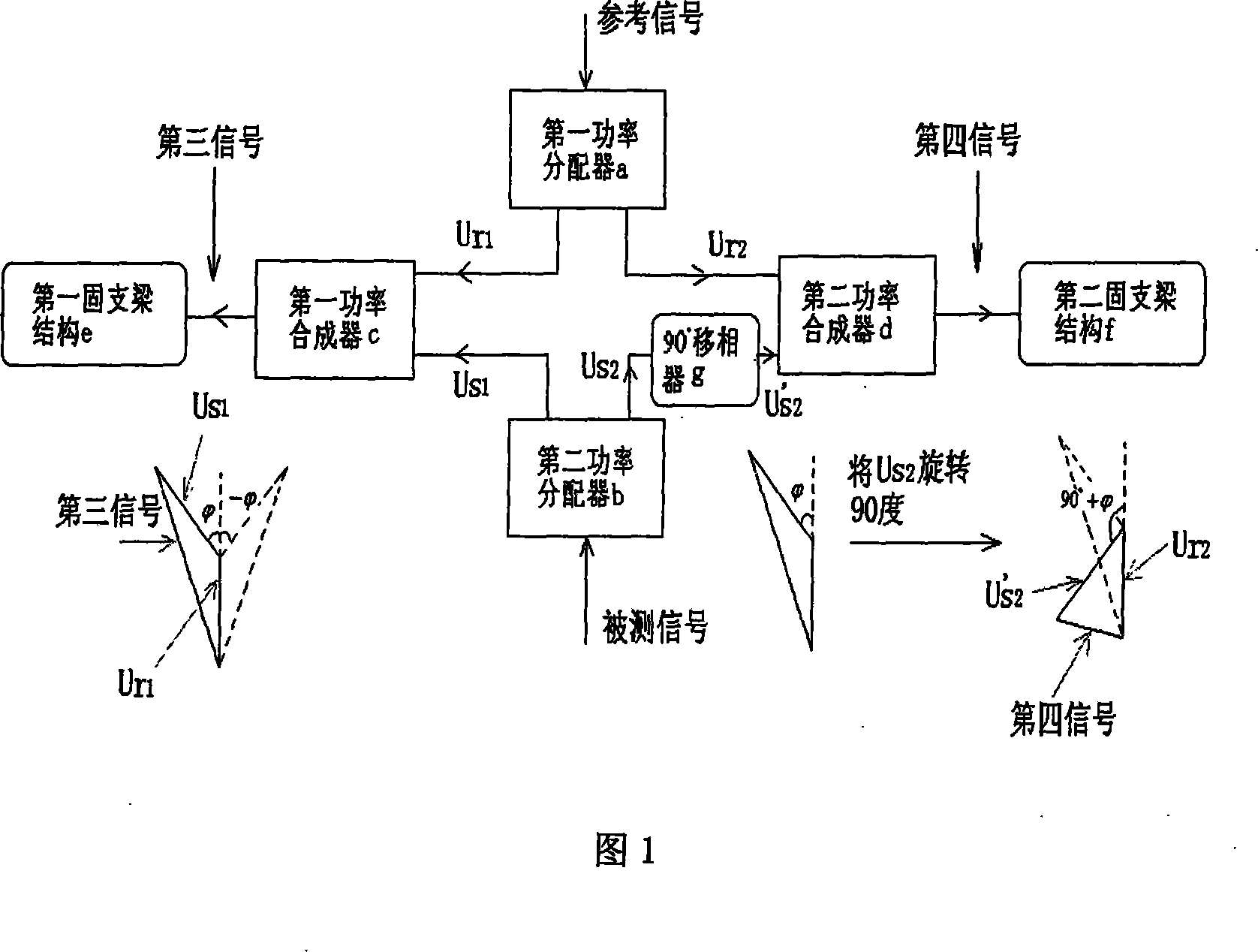
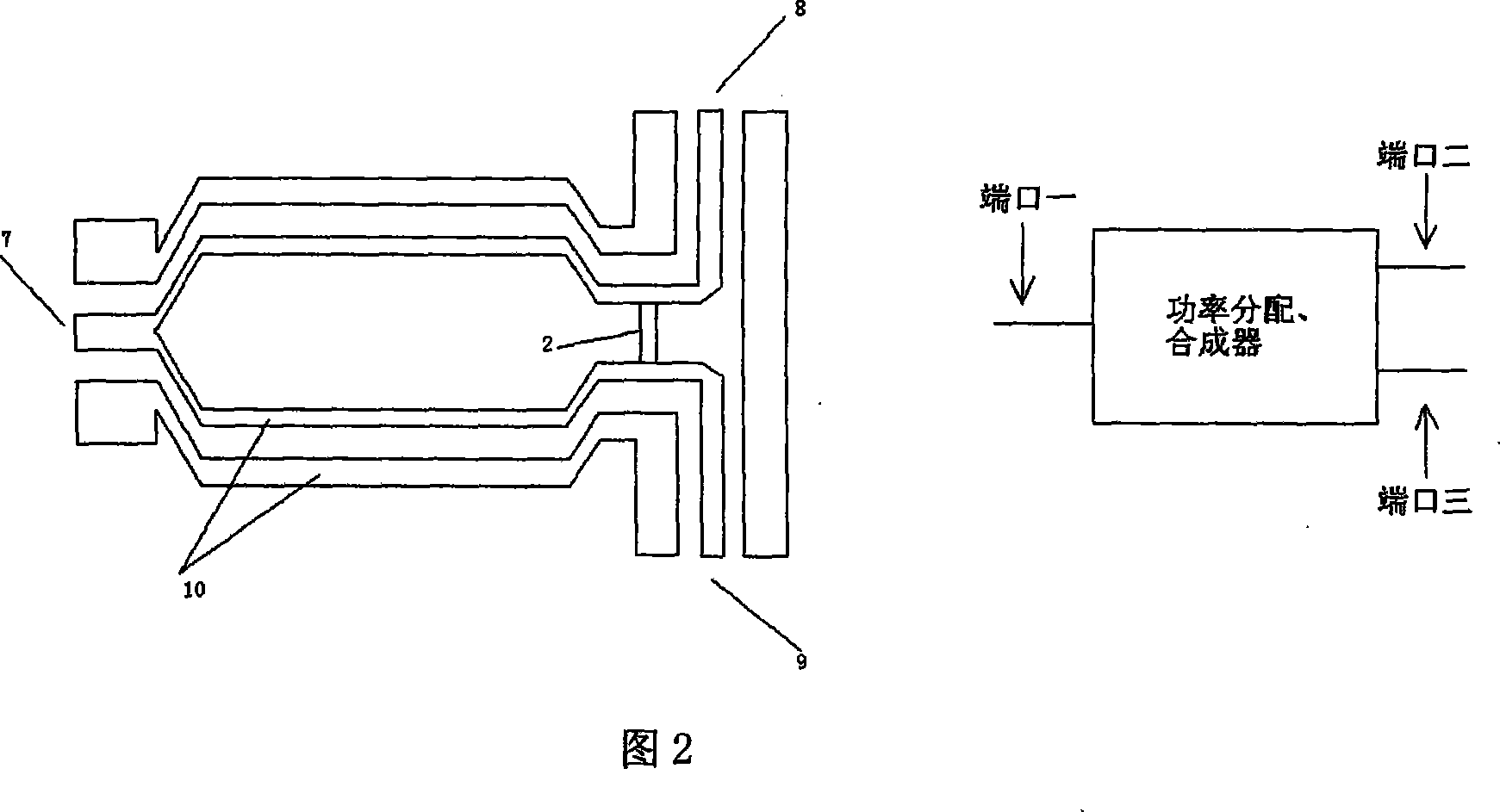
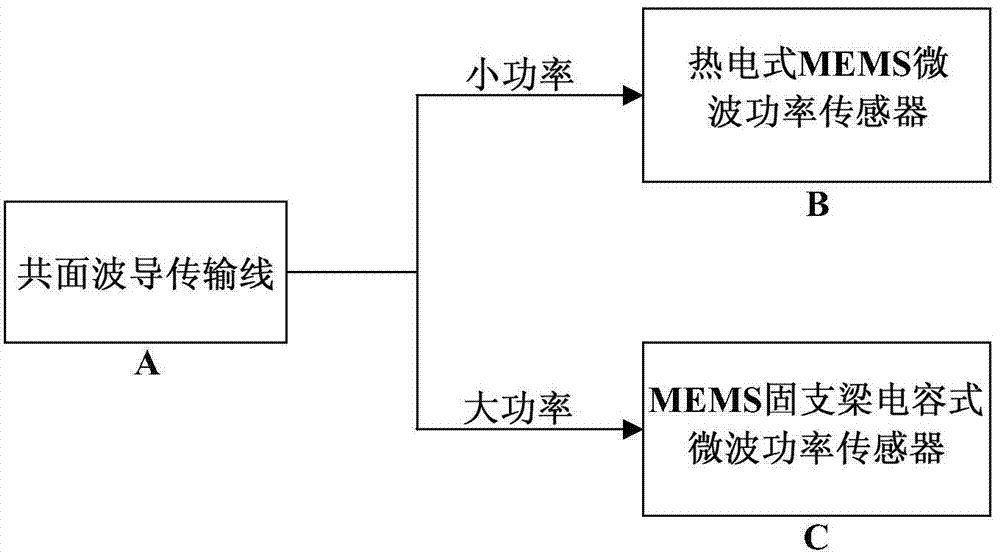
Wireless-receiving system for detecting microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency and preparation method thereof
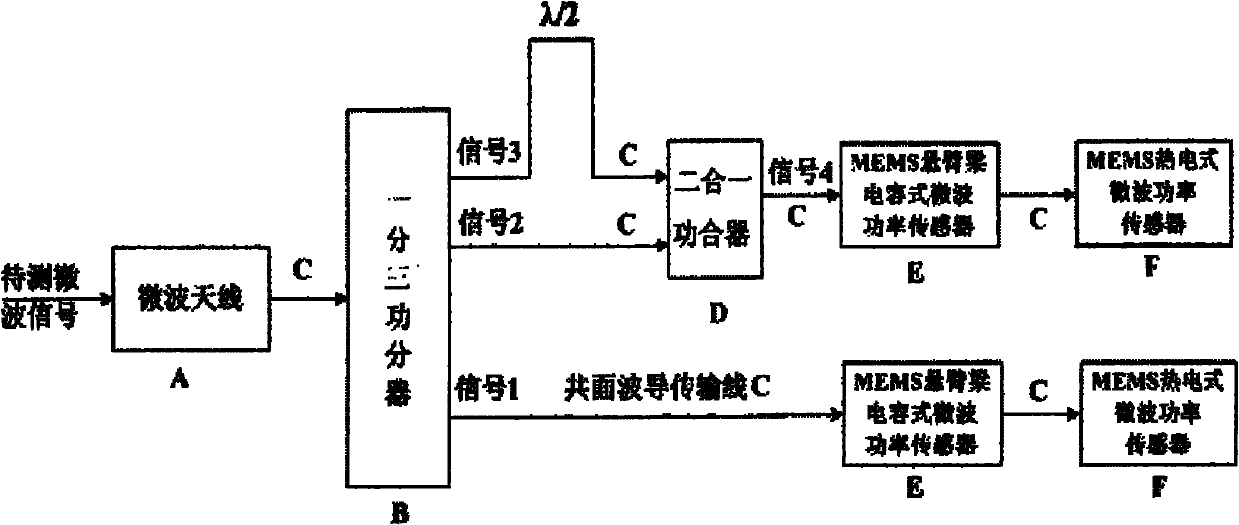
InactiveCN101788605ARealize wireless receptionTo achieve the purpose of wireless detectionTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPower combinerPhase difference
The invention relates to a wireless-receiving system for detecting microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency and a preparation method thereof. The wireless-receiving system for detecting the microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency has quite simple structure, large measurement magnitude range, no direct-current power consumption and easy integration. In the system for detecting the microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency, gallium arsenide is used as a substrate, wherein a microwave antenna (A), a one-three power splitter (B), a coplanar waveguide transmission line (C), a two-in-one power combiner (D), an MEMS cantilever capacitive microwave power sensor (E) and an MEMS thermoelectric microwave power sensor (F) are designed on the substrate; and then a phase difference between a signal 3 and a signal 2 after the signal 3 passes through the coplanar waveguide transmission line with the length of lambda / 2 can be determined according to a law of cosines. Because the phase difference corresponds to the frequency of the signal, the frequency of the signal can be measured.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
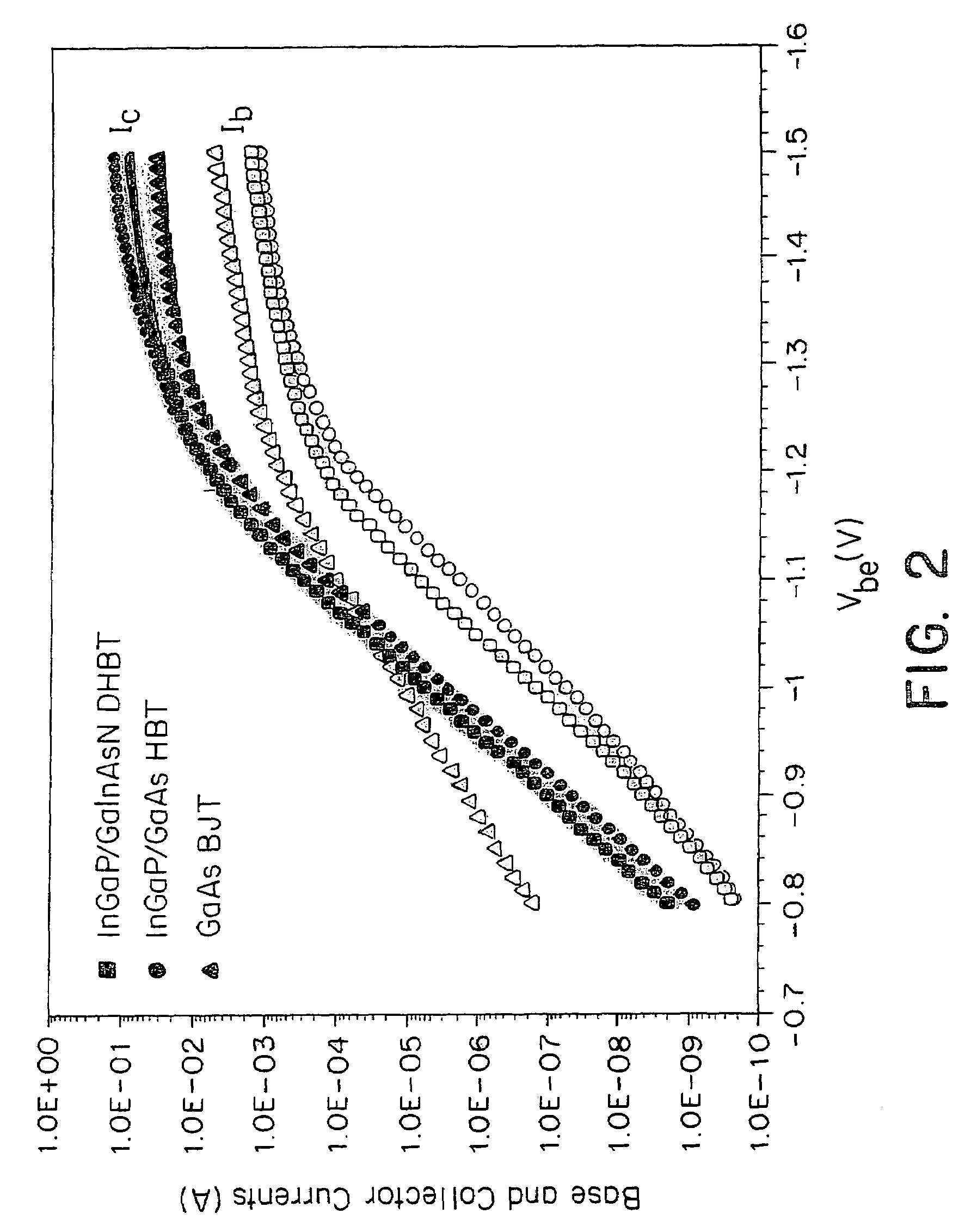
Bipolar transistor with lattice matched base layer
InactiveUS7186624B2Reduce gapLow resistivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionDopant
A semiconductor material which has a high carbon dopant concentration and is composed of gallium, indium, arsenic and nitrogen is disclosed. The material is useful in forming the base layer of gallium arsenide based heterojunction bipolar transistors because it can be lattice matched to gallium arsenide by controlling the concentration of indium and nitrogen. The disclosed semiconductor materials have a low sheet resistivity because of the high carbon dopant concentration obtained.
Owner:IQE KC
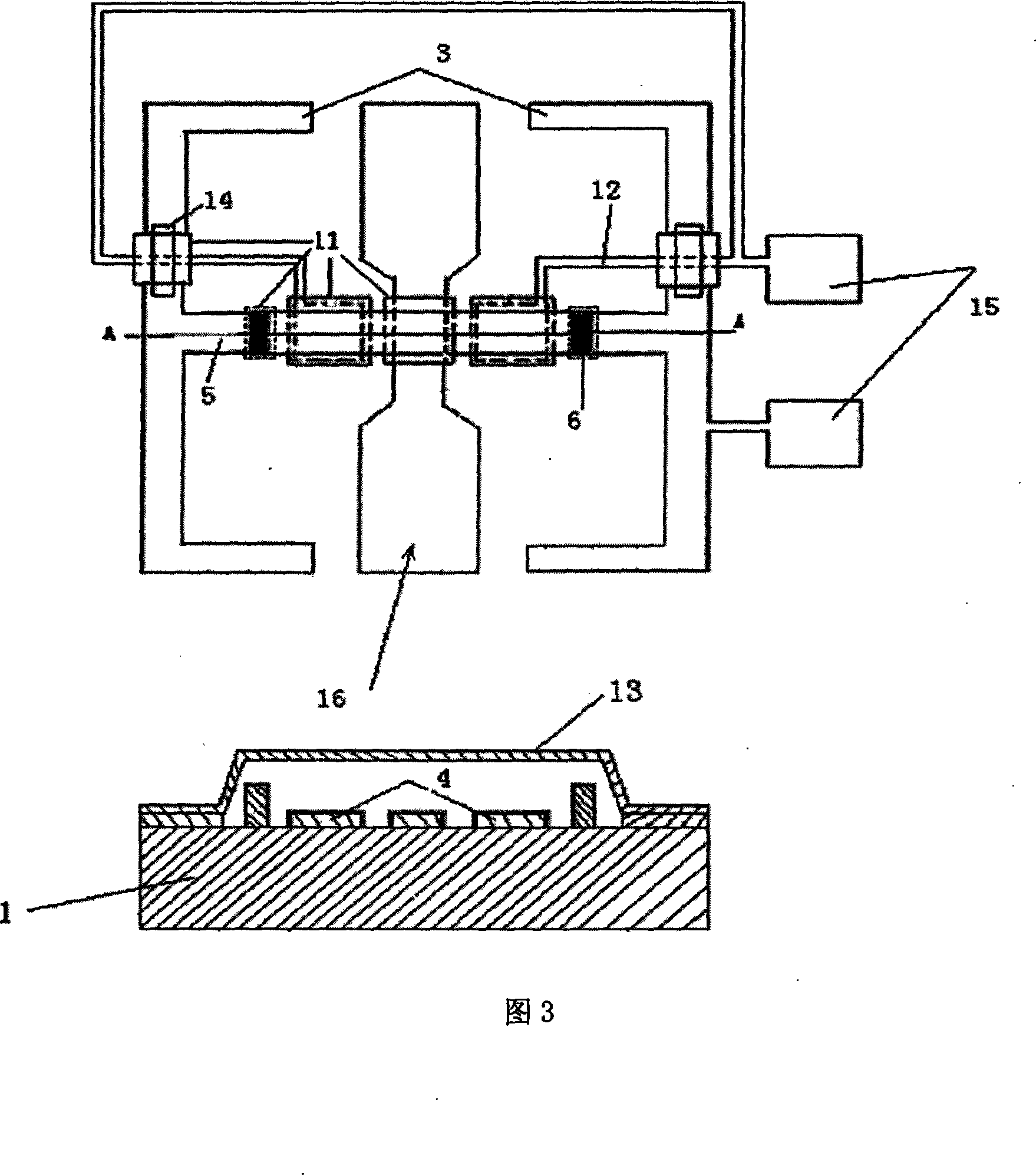
Microelectronic machinery orthogonal double channels microwave phase online detector and manufacturing method therefor
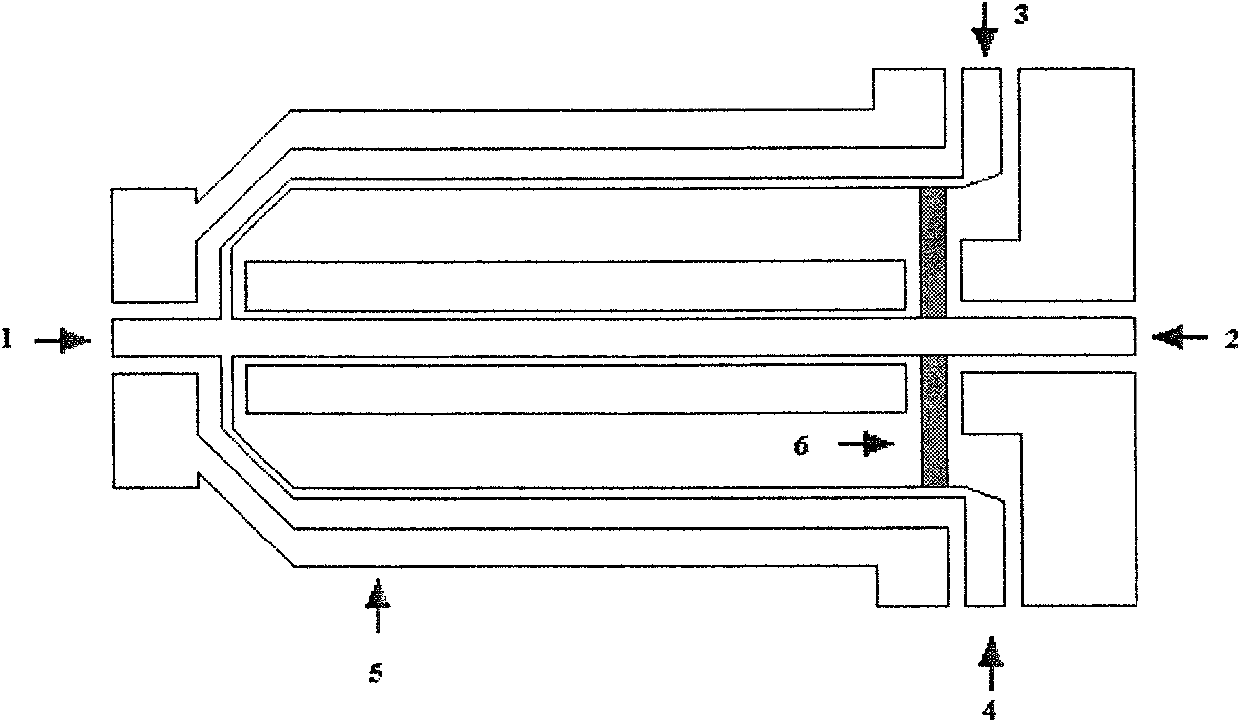
InactiveCN101034122AIncreaseIncreased bandwidthElectromagentic field characteristicsCapacitancePower combiner
this invention relates to power in direct-current circuits. The invention takes gallium arsenide as foundation (1). On the foundation has power divider, power synthesizer, 90deg phaser, solid beam structure. Power divider and power synthesizer composed by port one (7), port two(8), port three(8), dissymmetry coplane band line(10), nitride tantalum electric resistance. Solid beam structure includes signal input port(16), pier(5), solid beam(13), pedestal structure(6), sensing electrode(4), sensing electrode leader(12), capacitance detecting port(15), air bridge(14). There are nitriding silicon medium layer on the transmission line, pedestal structure and sensing electrode under solid beam, and sensing electrode leader under Air Bridge.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Microwave power detection system based on parallel-connected MEMS (micro-electromechanical system) cantilever beams and preparation method of microwave power detection system
ActiveCN104655921AHigh sensitivityGood compatibilityElectric devicesElectric power measurementCapacitanceMicrowave power
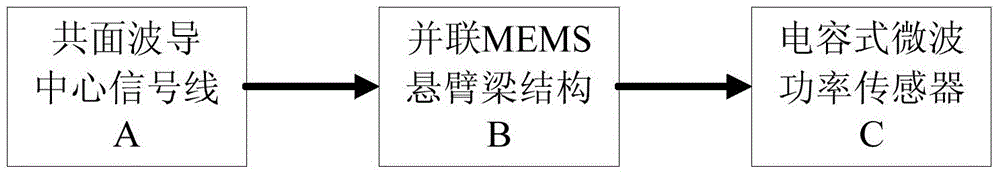
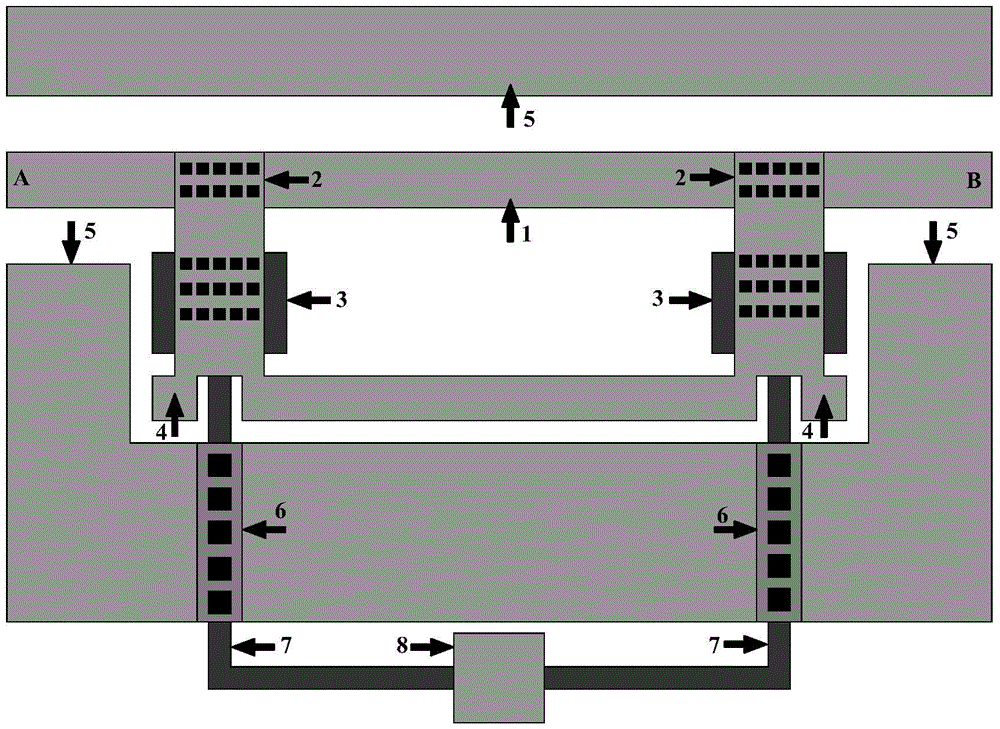
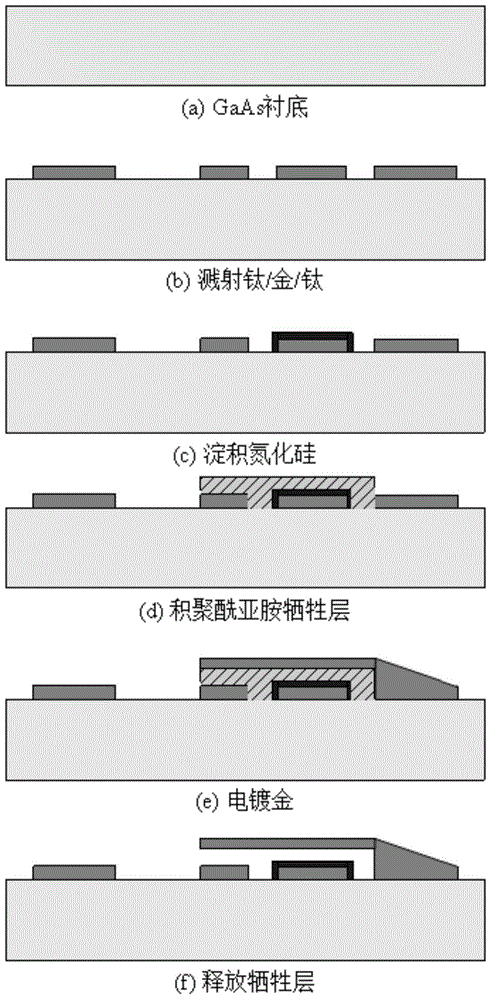
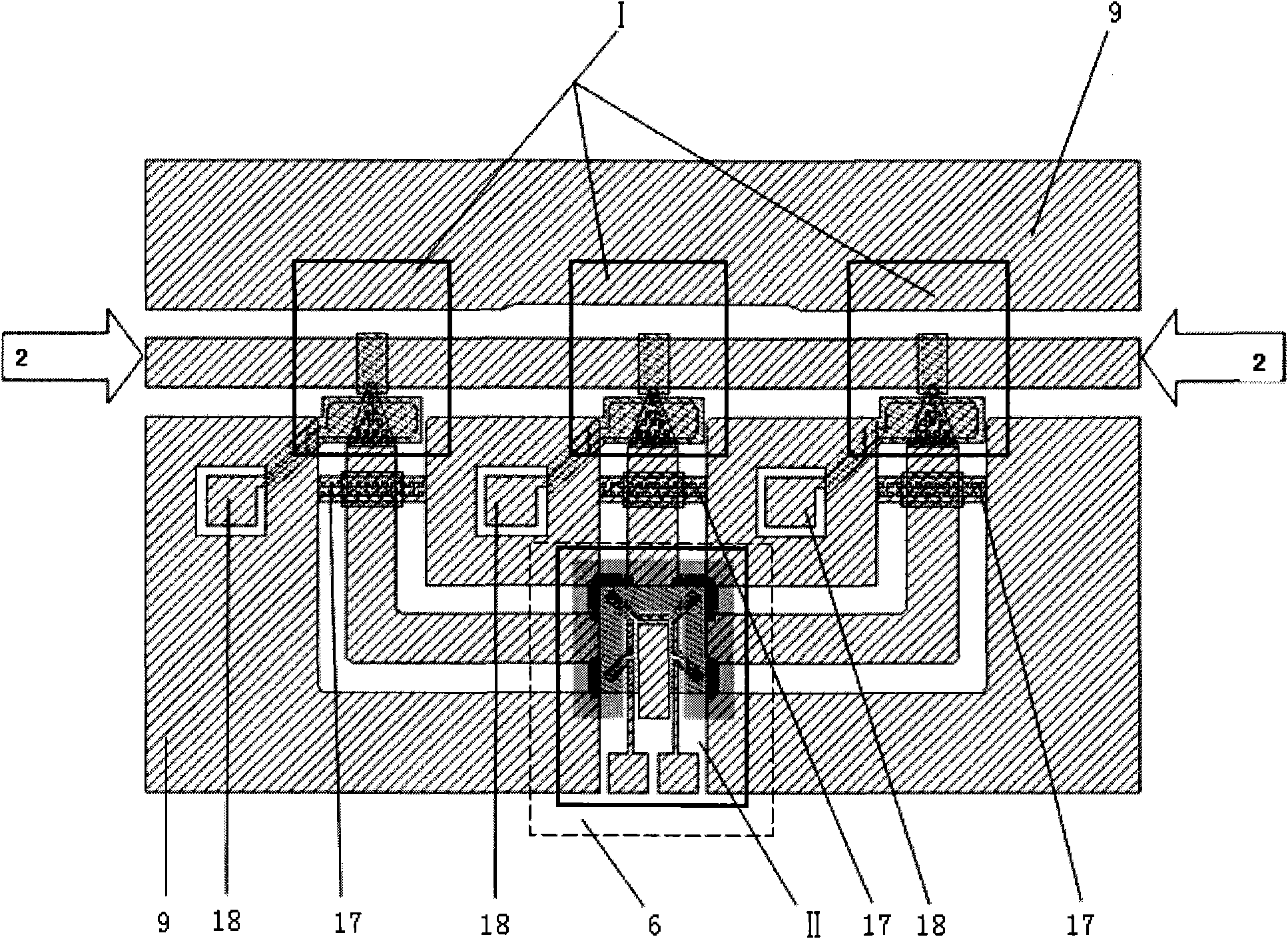
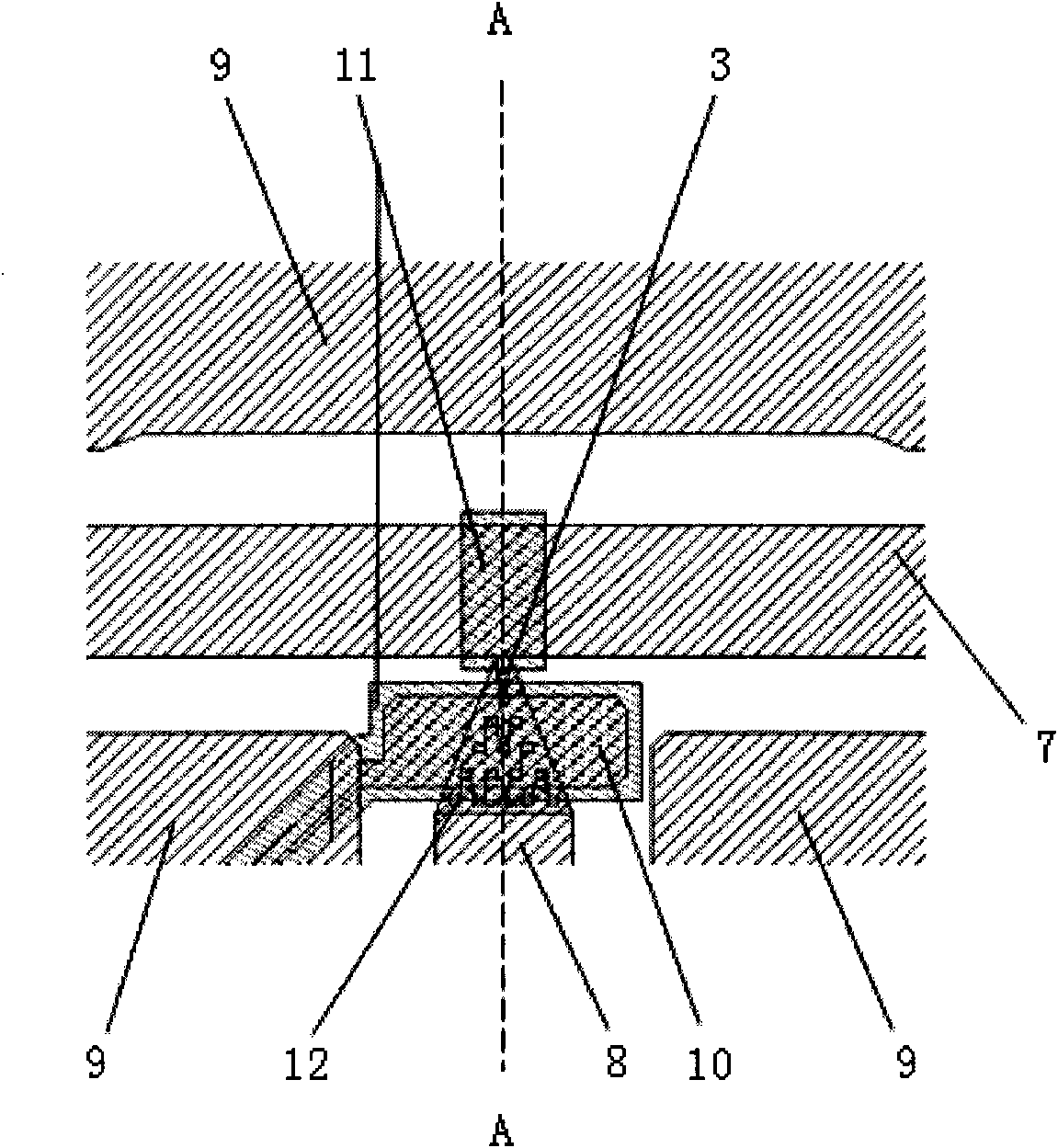
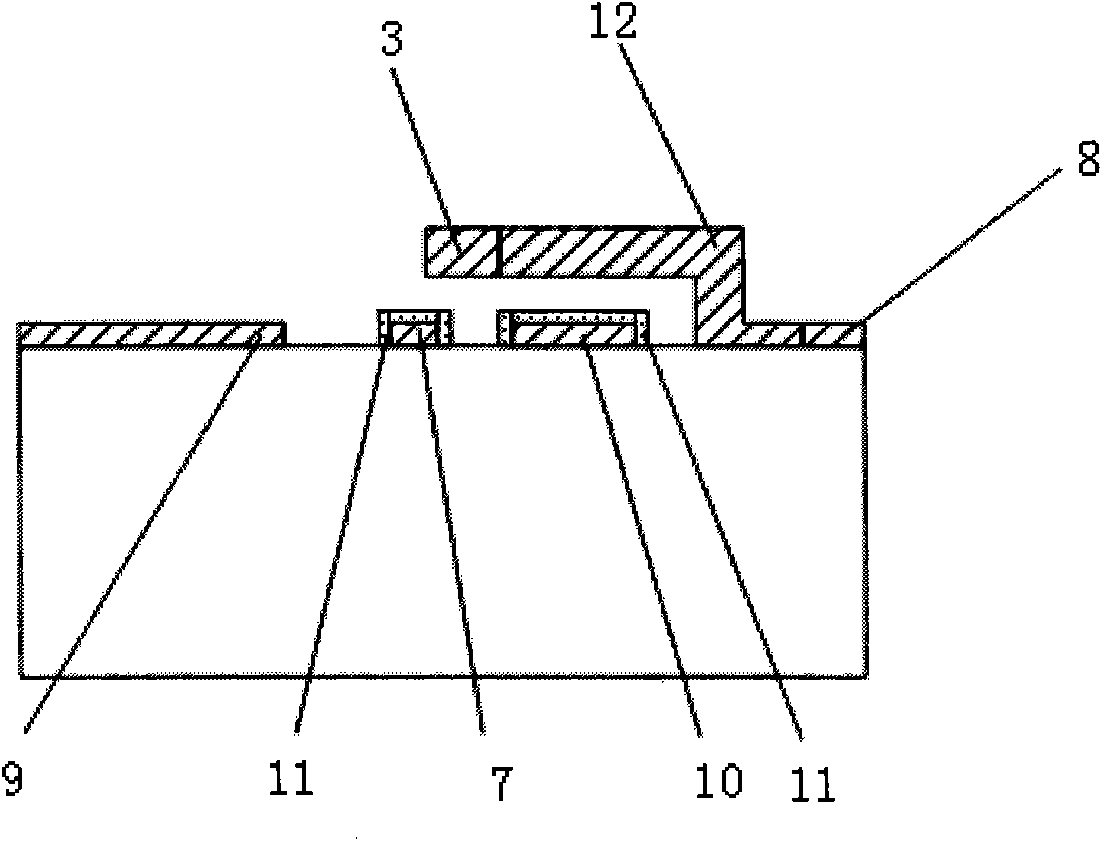
The invention discloses a microwave power detection system based on parallel-connected MEMS (micro-electromechanical system) cantilever beams and a preparation method of the microwave power detection system. The method is used for on-line measurement, electrostatic force can be generated between each MEMS cantilever beam and a transmission line in a center signal line transmission process, the cantilever beams are pulled downwards, and an interval between each cantilever beam and a corresponding test electrode becomes smaller, so that capacitance values are changed and microwave power in one-to-one correspondence with the capacitance values is obtained by measuring the changed capacitance values. The microwave power detection system based on the parallel-connected MEMS cantilever beams comprises a gallium arsenide substrate, wherein a plane-waveguide center signal line (A), a parallel-connected MEMS cantilever beam structure (B) and a capacitance type microwave power sensor (C) are arranged on the substrate. When a microwave signal is transmitted on the plane-waveguide center signal line, the two parallel-connected MEMS cantilever beams generate displacement under the action of the electrostatic force, and the to-be-measured power is detected by the capacitance type microwave power sensor.
Owner:南京尔芯电子有限公司
System for swept source optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS7468997B2Broaden effective gain bandwidthLaser detailsDiagnostics using lightVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserTomography
Owner:PRAEVIUM RES
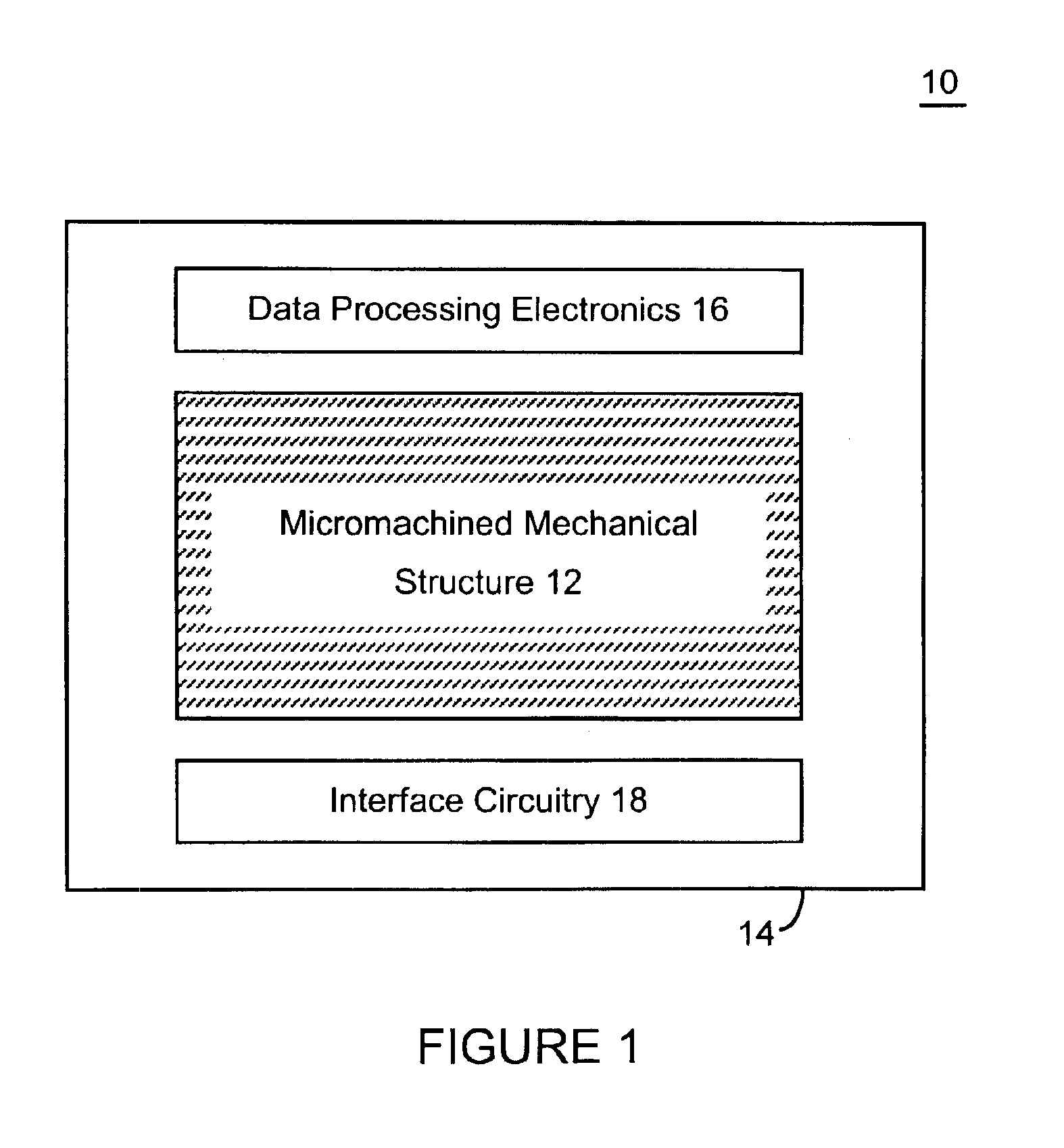
Microelectromechanical systems and devices having thin film encapsulated mechanical structures
InactiveUS7075160B2Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMicroelectromechanical systemsEngineering
There are many inventions described and illustrated herein. In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a MEMS device, and technique of fabricating or manufacturing a MEMS device, having mechanical structures encapsulated in a chamber prior to final packaging. The material that encapsulates the mechanical structures, when deposited, includes one or more of the following attributes: low tensile stress, good step coverage, maintains its integrity when subjected to subsequent processing, does not significantly and / or adversely impact the performance characteristics of the mechanical structures in the chamber (if coated with the material during deposition), and / or facilitates integration with high-performance integrated circuits. In one embodiment, the material that encapsulates the mechanical structures is, for example, silicon (polycrystalline, amorphous or porous, whether doped or undoped), silicon carbide, silicon-germanium, germanium, or gallium-arsenide.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Microelectromechanical systems having trench isolated contacts, and methods for fabricating same
ActiveUS20050156260A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsElectricityEngineering
There are many inventions described and illustrated herein. In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a MEMS device, and technique of fabricating or manufacturing a MEMS device, having mechanical structures encapsulated in a chamber prior to final packaging and a contact area disposed at least partially outside the chamber. The contact area is electrically isolated from nearby electrically conducting regions by way of dielectric isolation trench that is disposed around the contact area. The material that encapsulates the mechanical structures, when deposited, includes one or more of the following attributes: low tensile stress, good step coverage, maintains its integrity when subjected to subsequent processing, does not significantly and / or adversely impact the performance characteristics of the mechanical structures in the chamber (if coated with the material during deposition), and / or facilitates integration with high-performance integrated circuits. In one embodiment, the material that encapsulates the mechanical structures is, for example, silicon (polycrystalline, amorphous or porous, whether doped or undoped), silicon carbide, silicon-germanium, germanium, or gallium-arsenide.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
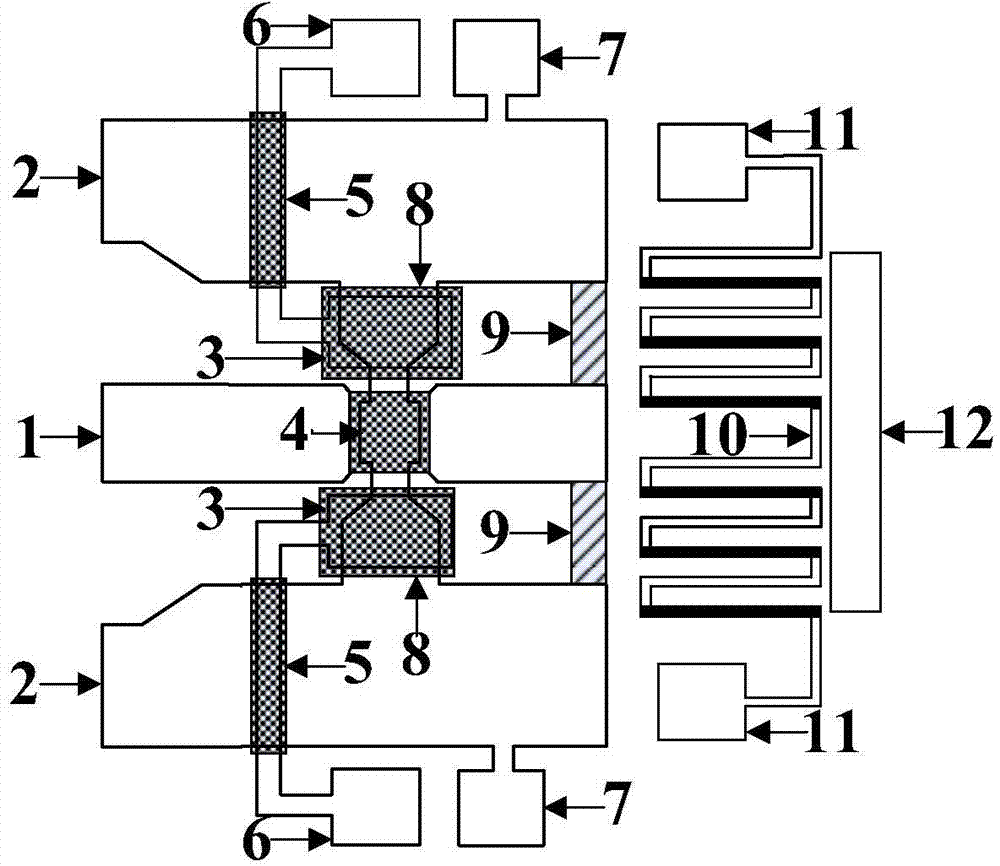
Microelectronic mechanical dual channel microwave power detection system and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103777066ALarge dynamic rangeProtection from being burnedTelevision system detailsImpedence networksPower sensorThermopile
The invention discloses a dual channel microwave power detection system based on a microelectronic mechanical microwave power sensor and a preparation method thereof. The system has the advantages of simple structure, large measurement range and no direct current power consumption. The system is based on a gallium arsenide substrate. A coplanar waveguide transmission line (A), a thermoelectric MEMS microwave power sensor (B) and an MEMS clamped beam capacitor type microwave power sensor (C) are designed on the substrate. When the power of a microwave signal is small, the thermoelectric MEMS microwave power sensor carries out detection according to the one-to-one corresponding relationship between the thermopile output voltage and the microwave power. When the power of the microwave signal is large, the MEMS clamped beam capacitor type microwave power sensor carries out detection. A square mass block is designed on an MEMS clamped beam above the coplanar waveguide transmission line. The area with the coplanar waveguide transmission line is increased, and at the same time the weight of the center position of the MEMS clamped beam is increased. Static power is more likely to cause large deformation of the MEMS clamped beam, and the system sensitivity is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Nanotube Schottky diodes for high-frequency applications
InactiveUS20060261433A1Lower work functionImprove work functionNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEvaporationNanotube
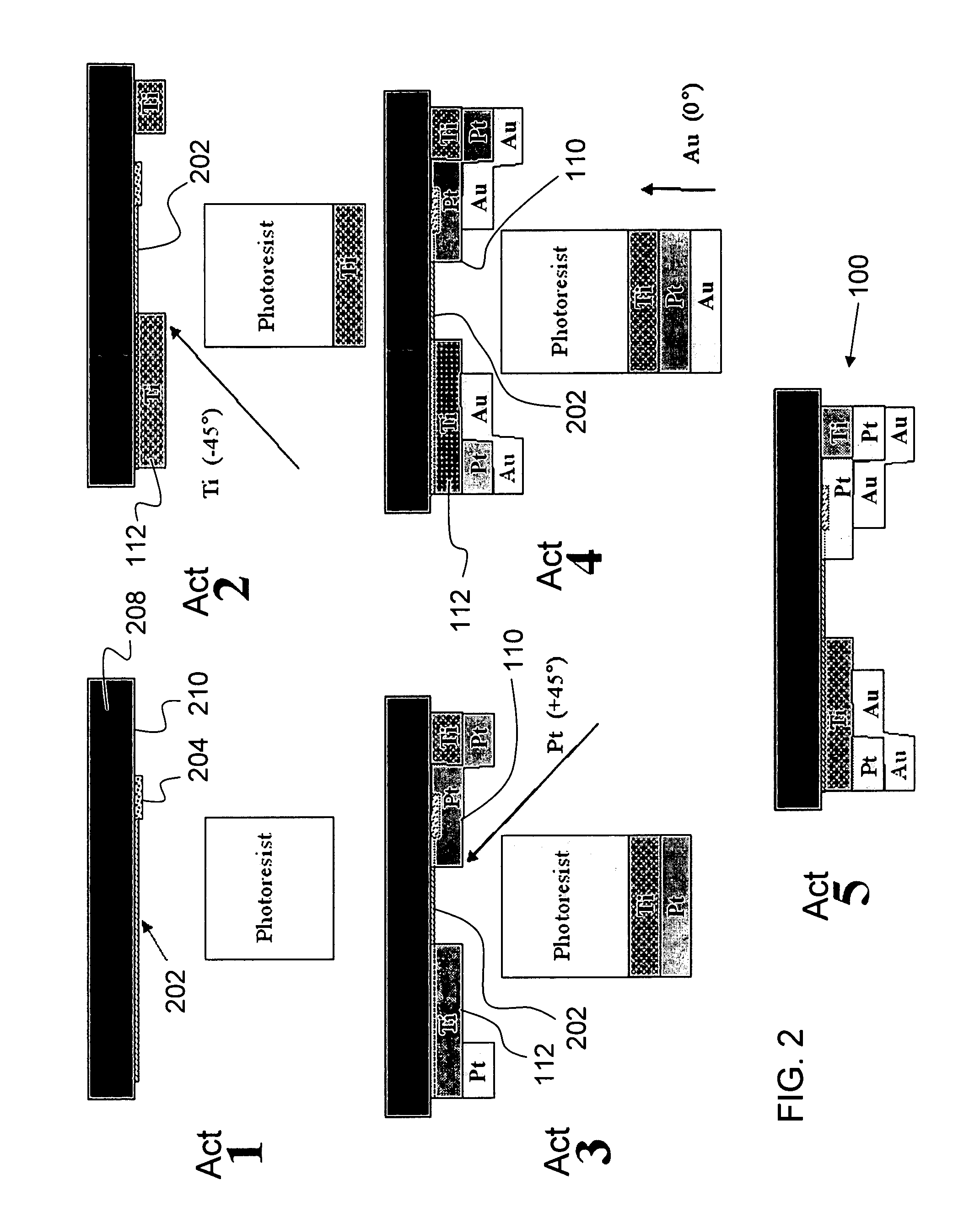
Described is a Schottky diode using semi-conducting single-walled nanotubes (s-SWNTs) with titanium Schottky and platinum Ohmic contacts for high-frequency applications. The diodes are fabricated using angled evaporation of dissimilar metal contacts over an s-SWNT. The devices demonstrate rectifying behavior with large reverse-bias breakdown voltages of greater than −15 V. In order to decrease the series resistance, multiple SWNTs are grown in parallel in a single device, and the metallic tubes are burnt-out selectively. At low biases, these diodes showed ideality factors in the range of 1.5 to 1.9. Modeling of these diodes as direct detectors at room temperature at 2.5 terahertz (THz) frequency indicates noise equivalent powers (NEP) comparable to that of the state-of-the-art gallium arsenide sold-state Schottky diodes, in the range of 10-13 W / square-root (√) Hz.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
MEMS (Micro Electronic Mechanical System) cantilever beam type online microwave power sensor and production method thereof
InactiveCN101915870AReduce lossHigh sensitivityDecorative surface effectsPower measurement by thermal methodsCouplingMonitoring system
The invention discloses an MEMS (Micro Electronic Mechanical System) cantilever beam type online microwave power sensor and a production method thereof. The microwave power sensor comprises a gallium arsenide substrate, a mainline CPW (Co-Planer Waveguide), a subline CPW, an MEMS cantilever beam type structure and a terminal microwave power monitoring system, wherein the MEMS cantilever beam type structure comprises a cantilever beam and an anchor area; the cantilever beam stretches across the mainline CPW signal line, and the fixed end of the cantilever beam is fixed on the anchor area; the anchor area is connected with the terminal microwave power monitoring system through the subline CPW signal line; and a drive electrode is arranged below the cantilever beam type structure. The MEMS cantilever beam type online microwave power sensor not only has the advantages of the terminal type microwave power sensor, such as low loss and high sensitivity, but also has the advantages of online microwave power measurement, realization of monitoring and not monitoring, integration of the online microwave power sensors with various kinds of coupling factors, and compatibility with the gallium arsenide monolithic microwave integrated circuit.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
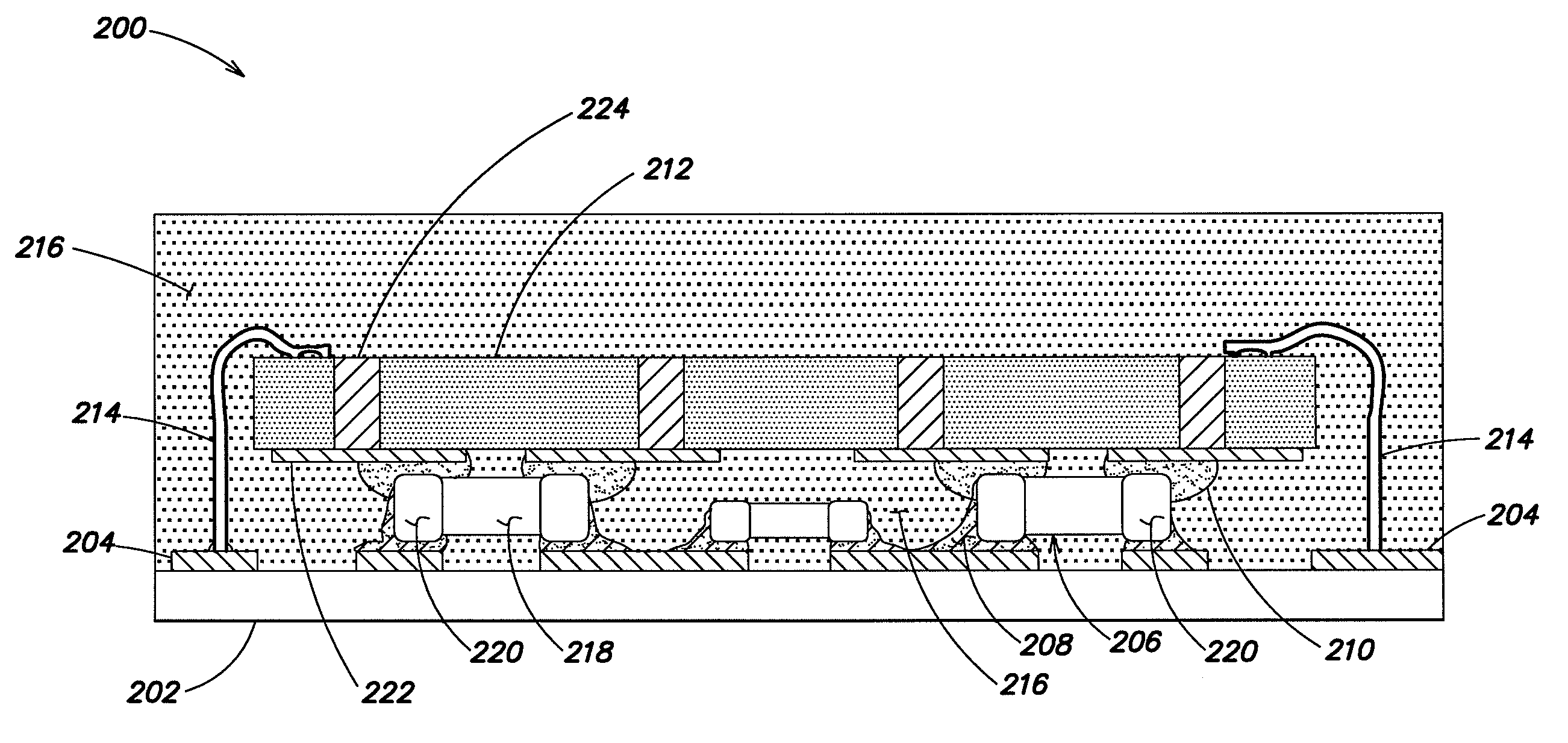
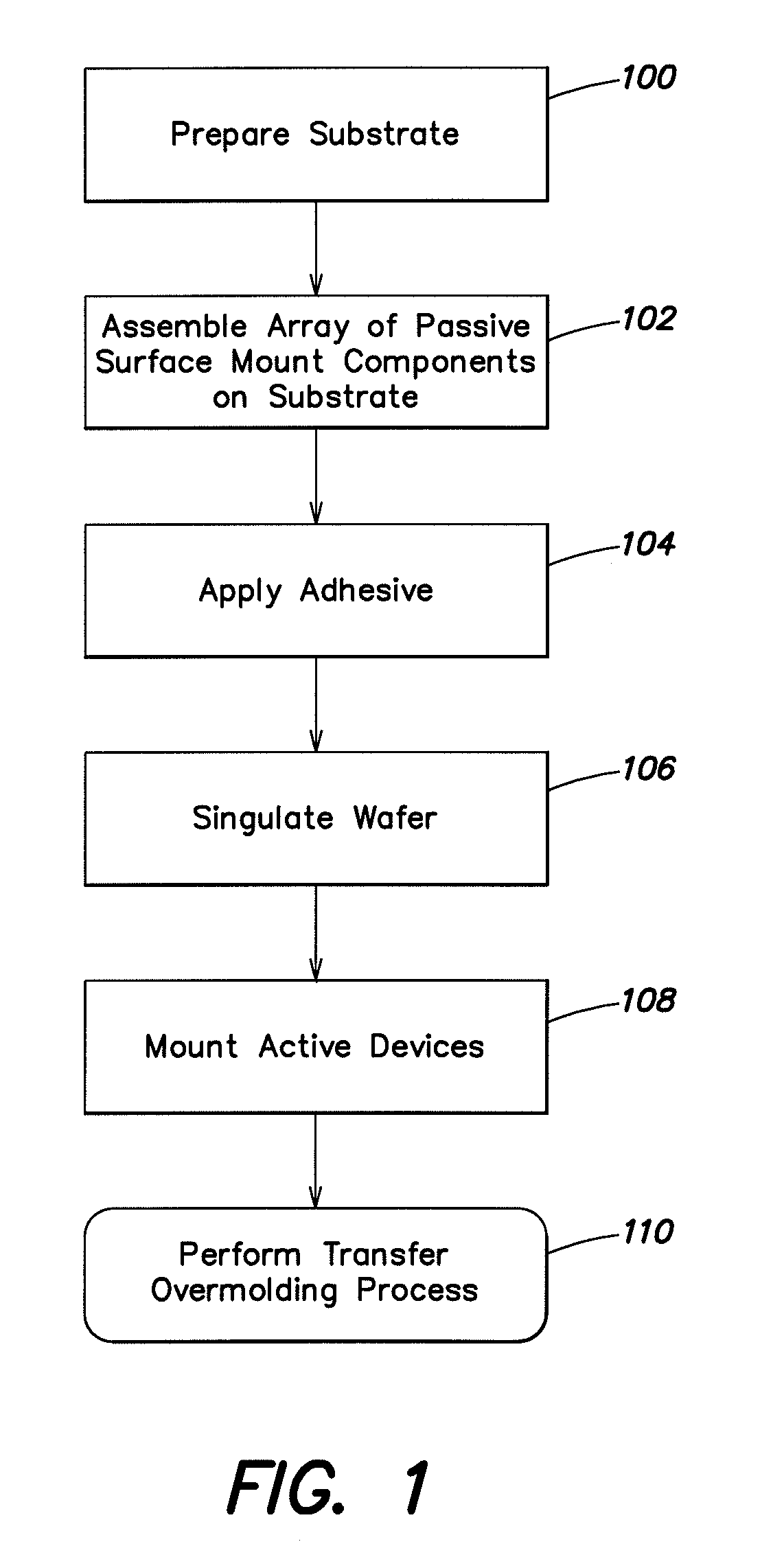
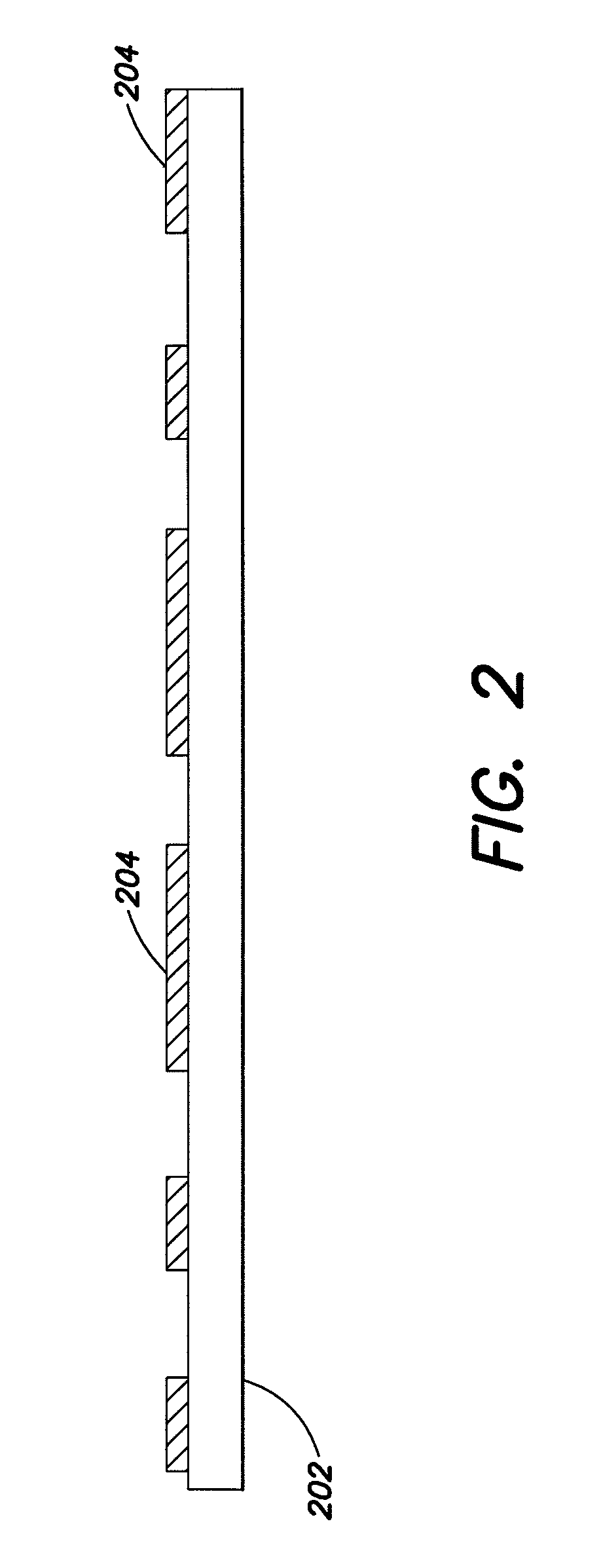
3-d stacking of active devices over passive devices
ActiveUS20090267220A1Increase in board densitySize of substrate can be reducedFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsAdhesiveSurface mounting
Single-die or multi-die packaged modules that incorporate three-dimensional integration of active devices with discrete passive devices to create a package structure that allows active devices (such as, silicon or gallium-arsenide devices) to share the same footprint area as an array of passive surface mount components. In one example, a module includes at least one active device stacked on top of an array of passive surface mount components on a substrate. A conductive or non-conductive adhesive can be used to adhere the active device to the array of passive devices.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
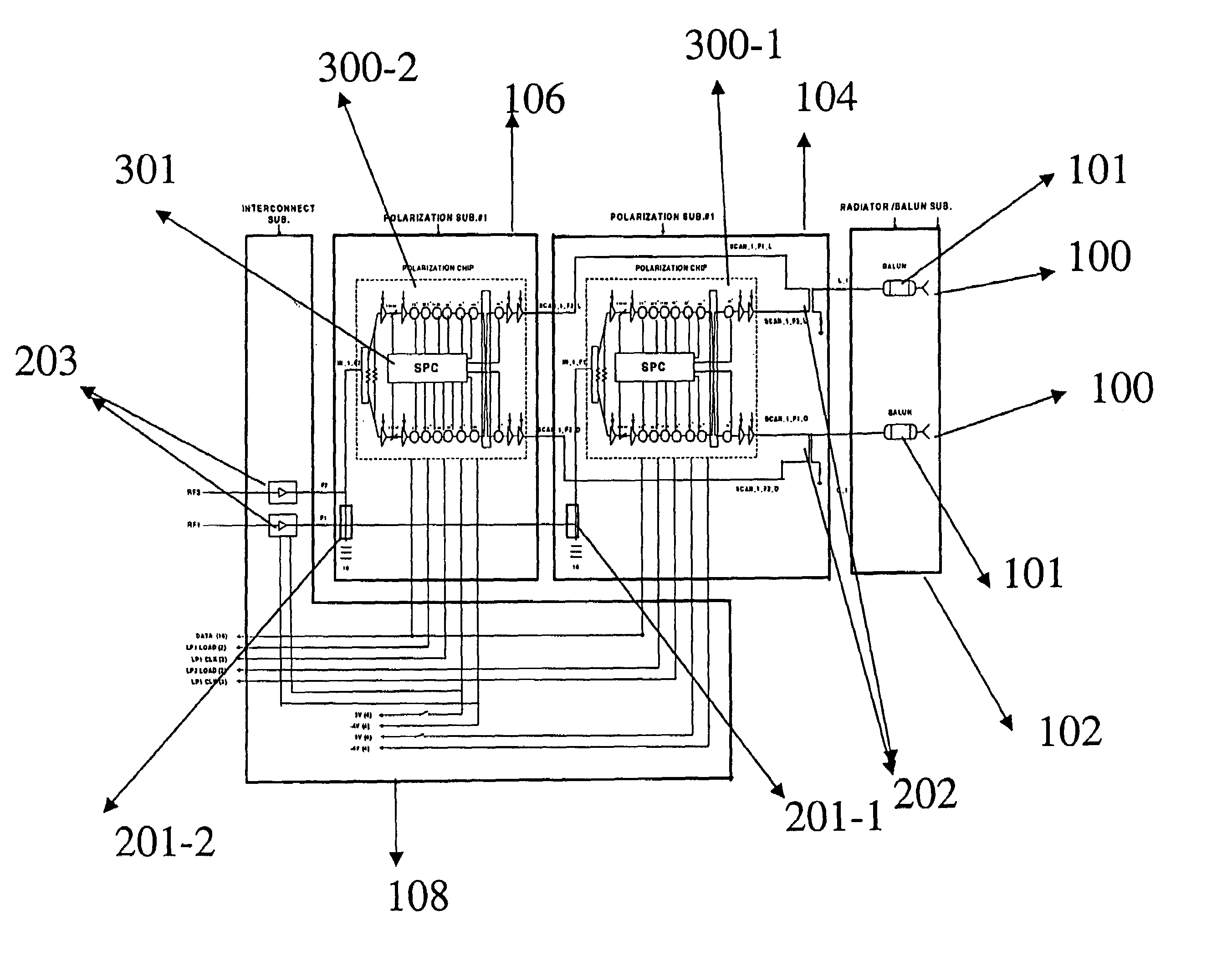
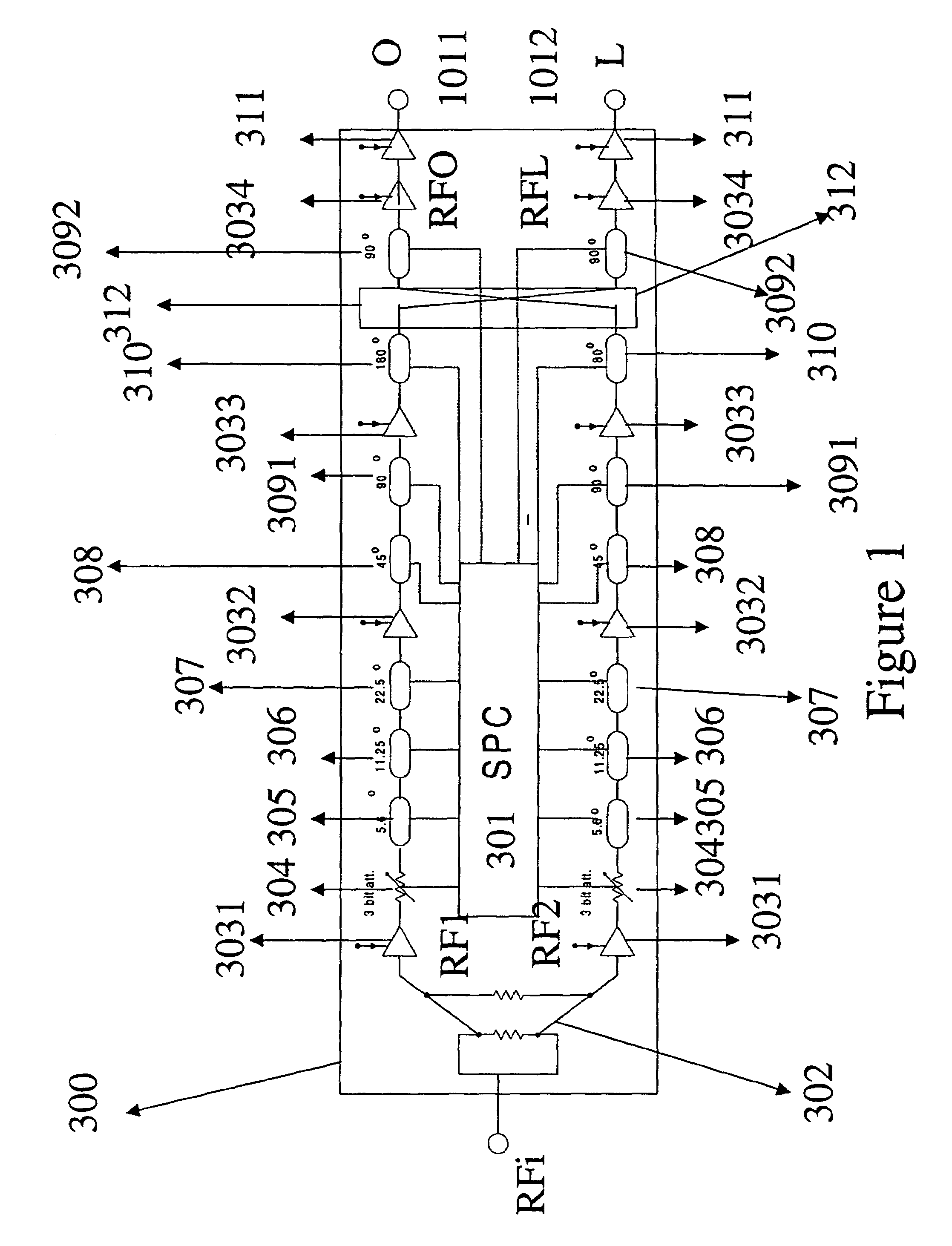
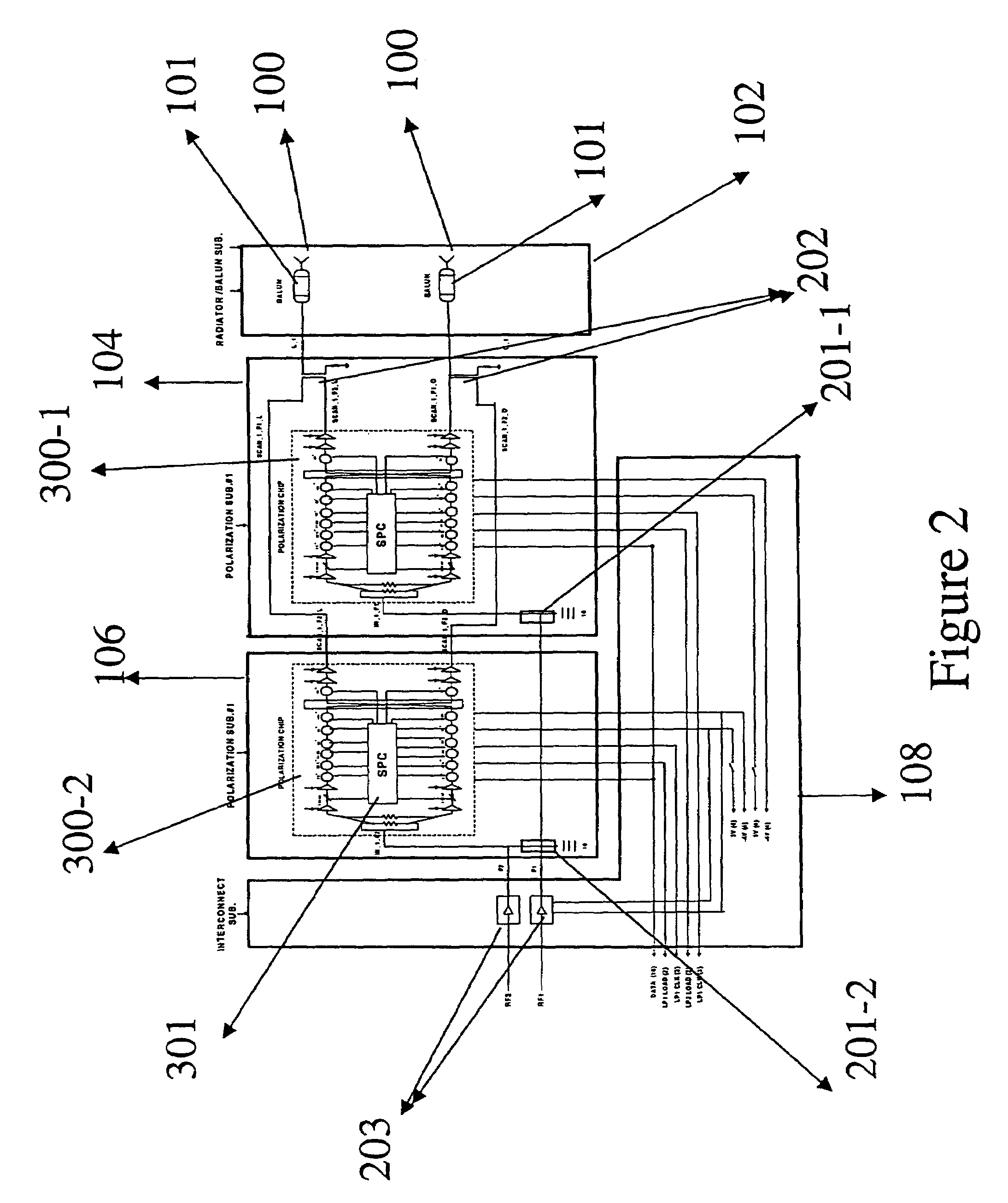
Single ku-band multi-polarization gallium arsenide transmit chip
InactiveUS7009562B2ThinnerLow costSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsActive phaseEngineering
The present invention is a wide band GaAs microwave monolithic integrated circuit (MMIC) transmit chip that is capable of transmitting linearly or circularly polarized signals when connected to a pair of orthogonal cross-polarized antennas. In an active phased-array antenna environment, this transmit chip is capable of transmitting signals with different scan angles. This invention also contains a digital serial to parallel converter that uses TTL signal to control the phase shifter and attenuator circuits that are required for controlling the polarization and scan angle of the transmitted signal.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Stiffened backside fabrication for microwave radio frequency wafers
InactiveUS6884717B1Less fragileNot easy to damageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEtchingSemiconductor materials
An etching based semiconductor wafer thinning arrangement usable as an improved alternative to the usual grinding and polishing wafer thinning. The thinned wafer includes a structurally enhancing wafer backside grid array of original wafer thickness semiconductor material with grid cells surrounding individual thinned wafer areas and serving to improve the strength and physical rigidity characteristics of the thinned wafer. Preferably this grid array is supplemented with an additional, wafer periphery-located, backside ring of semiconductor material also of original wafer thickness. Ability to avoid a wafer front side mounting during thinning accomplishment, fast etching, reduced wafer breakage, enhanced wafer strength and improved wafer handling achieved with the disclosed thinning arrangement all contribute to achieved advantages over conventional wafer thinning. Gallium arsenide or other semiconductor materials are contemplated along with use in radio frequency or other integrated circuit devices of either the single transistor or complete integrated circuit components types.
Owner:SANDVIK AB +1
Self-bypass diode function for gallium arsenide photovoltaic devices
ActiveUS20120199184A1Improve efficiencyIncrease flexibilityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor structureControl manner
Embodiments of the invention generally relate to photovoltaic devices. In one embodiment, a method for forming a gallium arsenide based photovoltaic device includes providing a semiconductor structure, the structure including an absorber layer comprising gallium arsenide. A bypass function is provided in a p-n junction of the semiconductor structure, where under reverse-bias conditions the p-n junction breaks down in a controlled manner by a Zener breakdown effect.
Owner:ALTA DEVICES INC
Ion trap in a semiconductor chip
ActiveUS7411187B2Particle separator tubesDigital data processing detailsMicrometer scaleSemiconductor chip
A micrometer-scale ion trap, fabricated on a monolithic chip using semiconductor micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) technology. A single 111Cd+ ion is confined, laser cooled, and the heating measured in an integrated radiofrequency trap etched from a doped gallium arsenide (GaAs) heterostructure. Single 111Cd+ qubit ions are confined in a radiofrequency linear ion trap on a semiconductor chip by applying a combination of static and oscillating electric potentials to integrated electrodes. The electrodes are lithographically patterned from a monolithic semiconductor substrate, eliminating the need for manual assembly and alignment of individual electrodes. The scaling of this structure to hundreds or thousands of electrodes is possible with existing semiconductor fabrication technology.
Owner:NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY +1
Extremely high-speed switchmode DC-DC converters
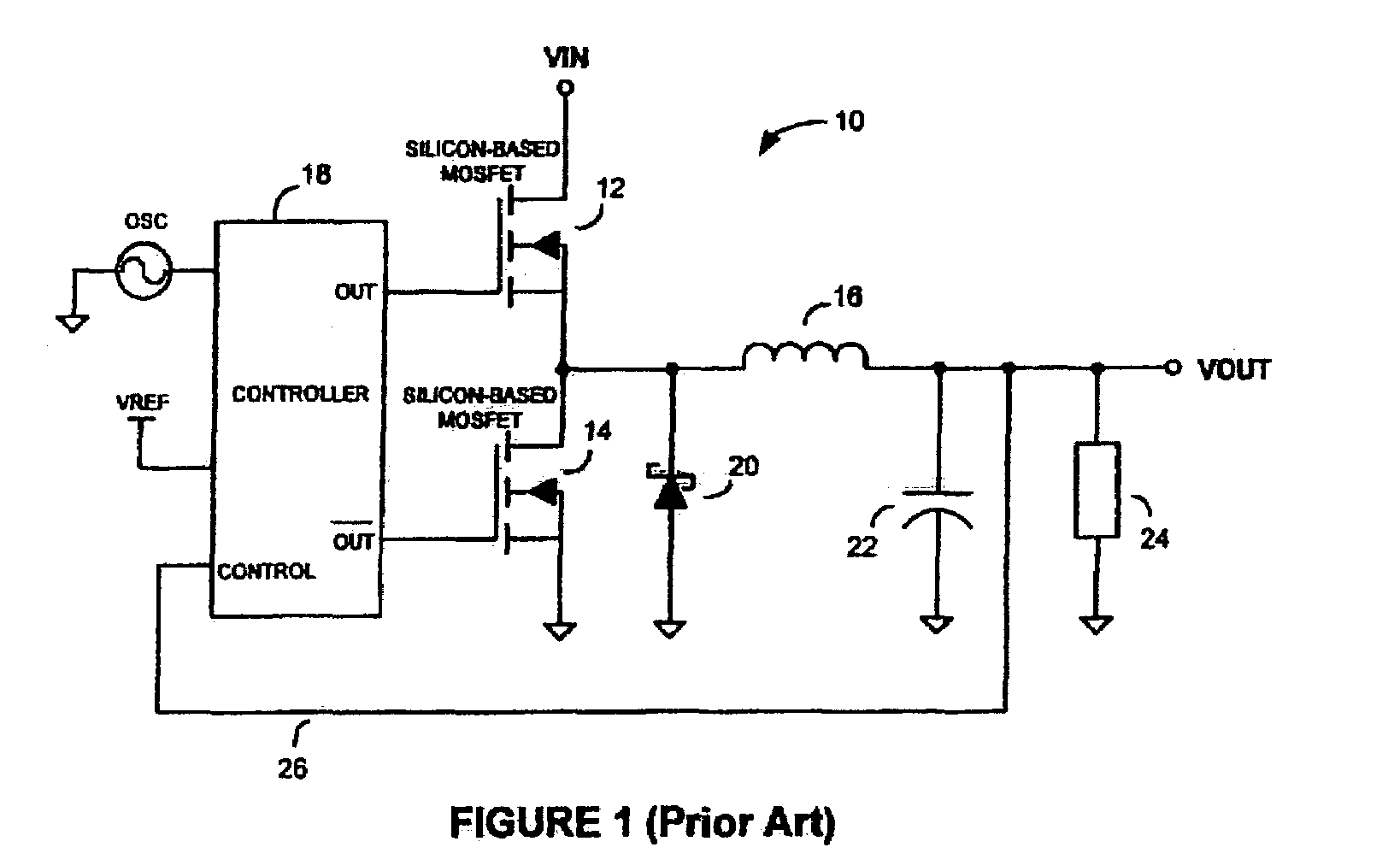
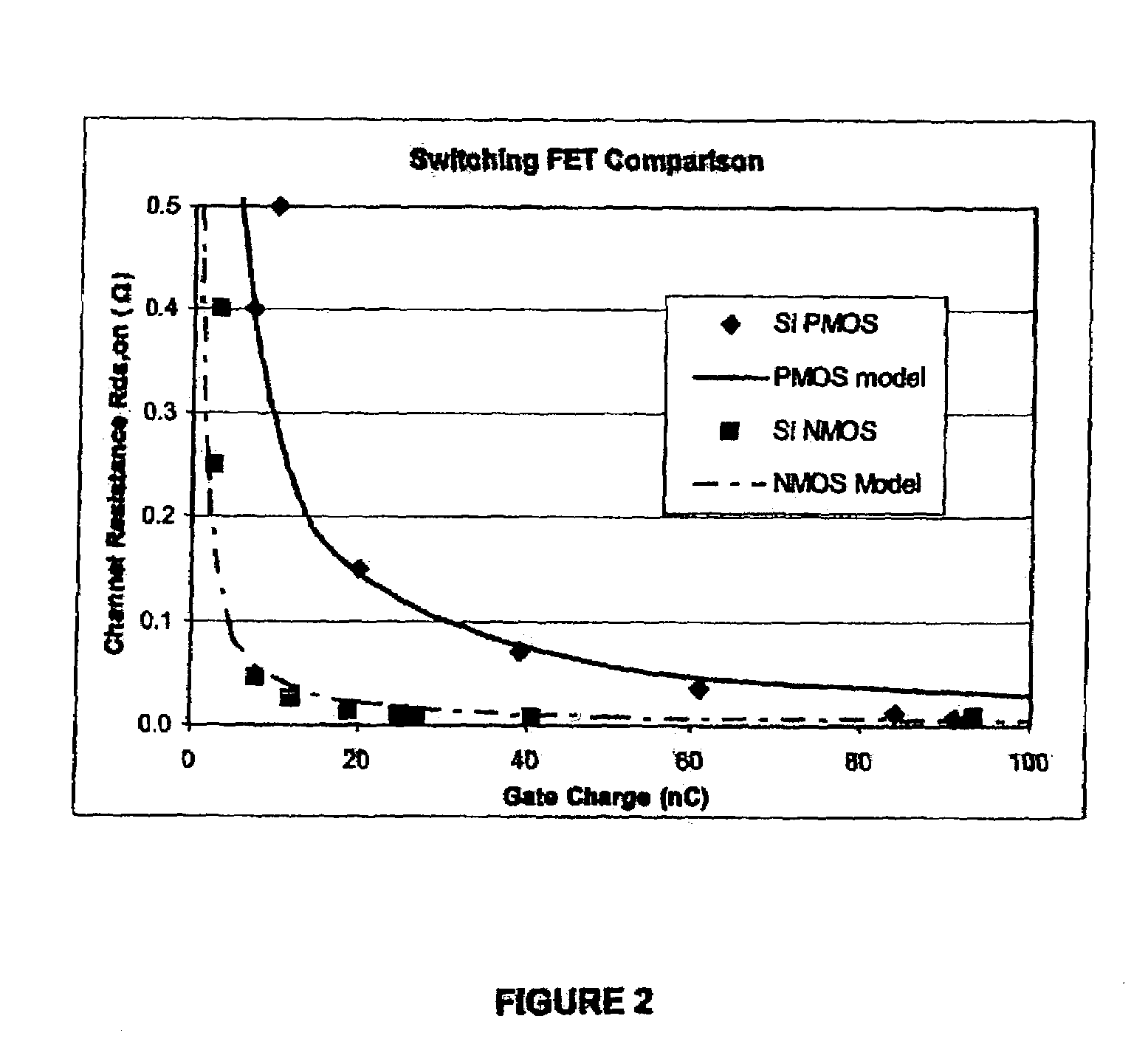
InactiveUS7026797B2Improve efficiencyImproving efficiency and battery savingResonant long antennasEfficient power electronics conversionFigure of meritCMOS
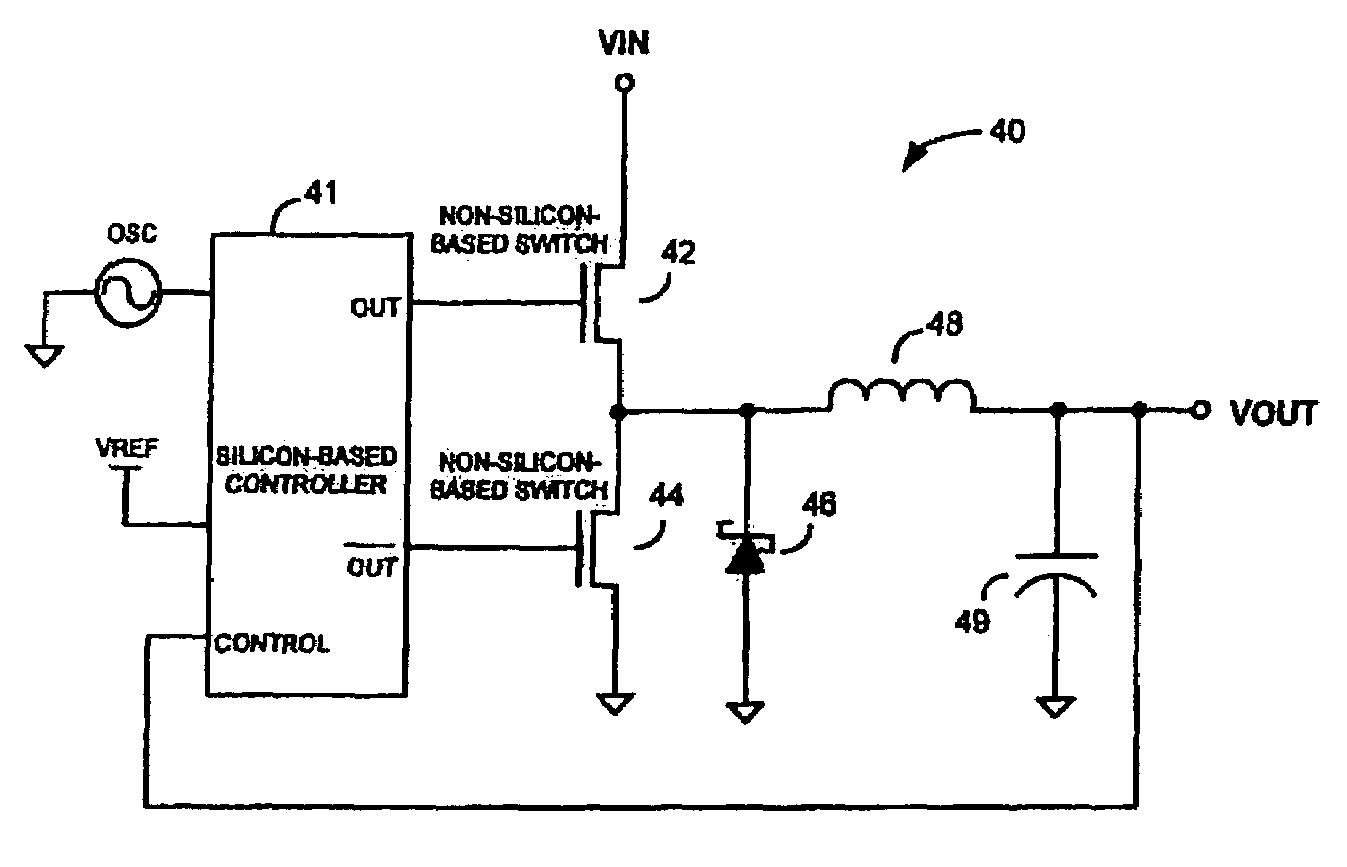
Switchmode DC—DC power converters using one or more non-Silicon-based switching transistors and a Silicon-based (e.g. CMOS) controller are disclosed. The non-Silicon-based switching transistors may comprise, but are not necessarily limited to, III-V compound semiconductor devices such as gallium arsenide (GaAs) metal-semiconductor field effect transistors (MESFETS) or heterostructure FETs such as high electron mobility transistors (HEMTs). According to an embodiment of the invention, the low figure of merit (FoM), τFET, of the non-Silicon-based switching transistors allows the converters of the present invention to be employed in envelope tracking amplifier circuits of wireless devices designed for high-bandwidth technologies such as, for example, EDGE and UMTS, thereby improving the efficiency and battery saving capabilities of the wireless devices.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com