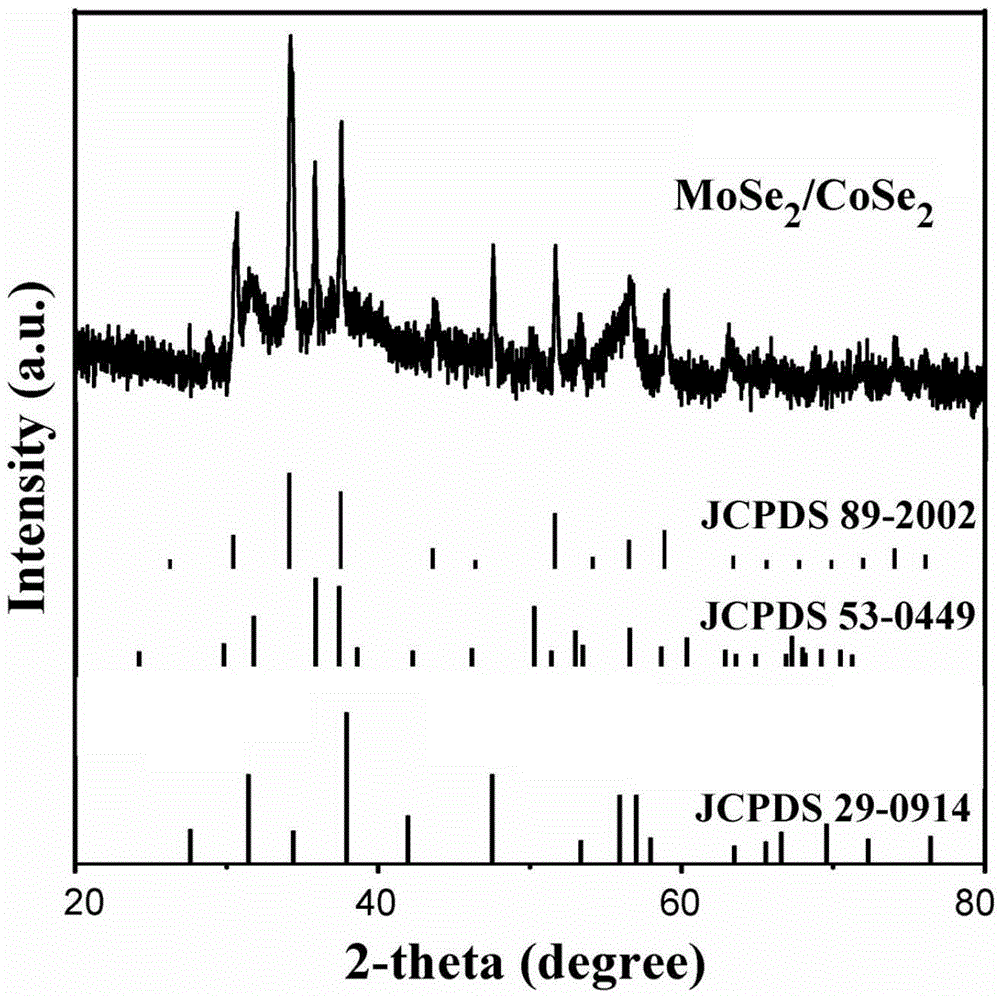
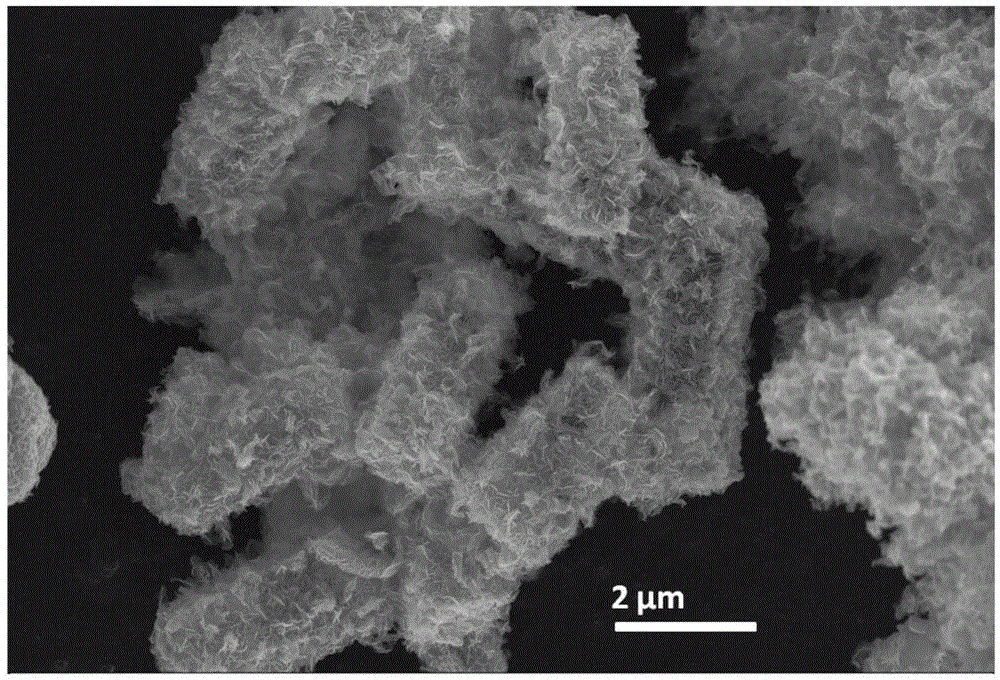
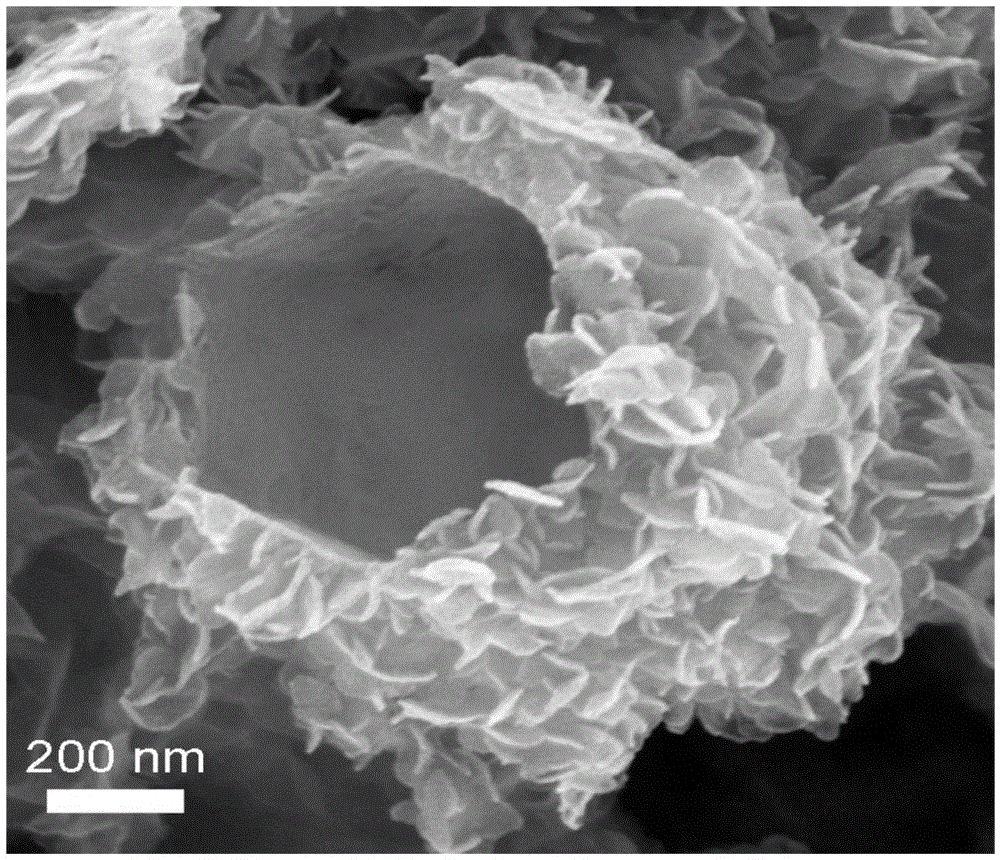
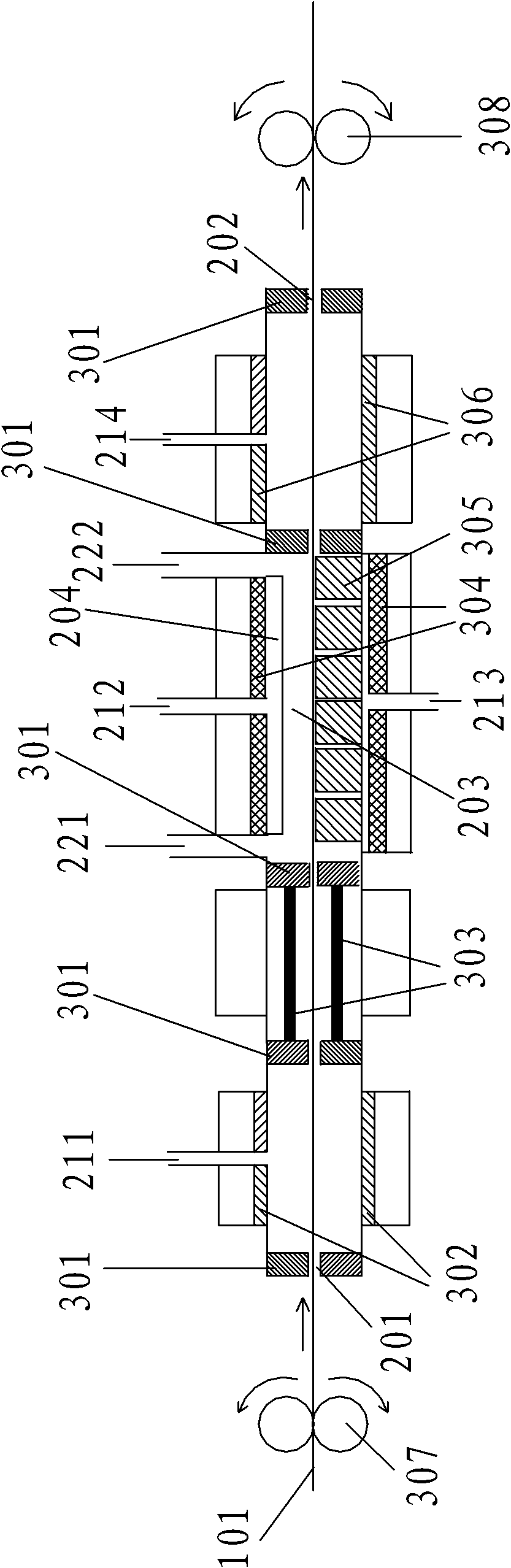
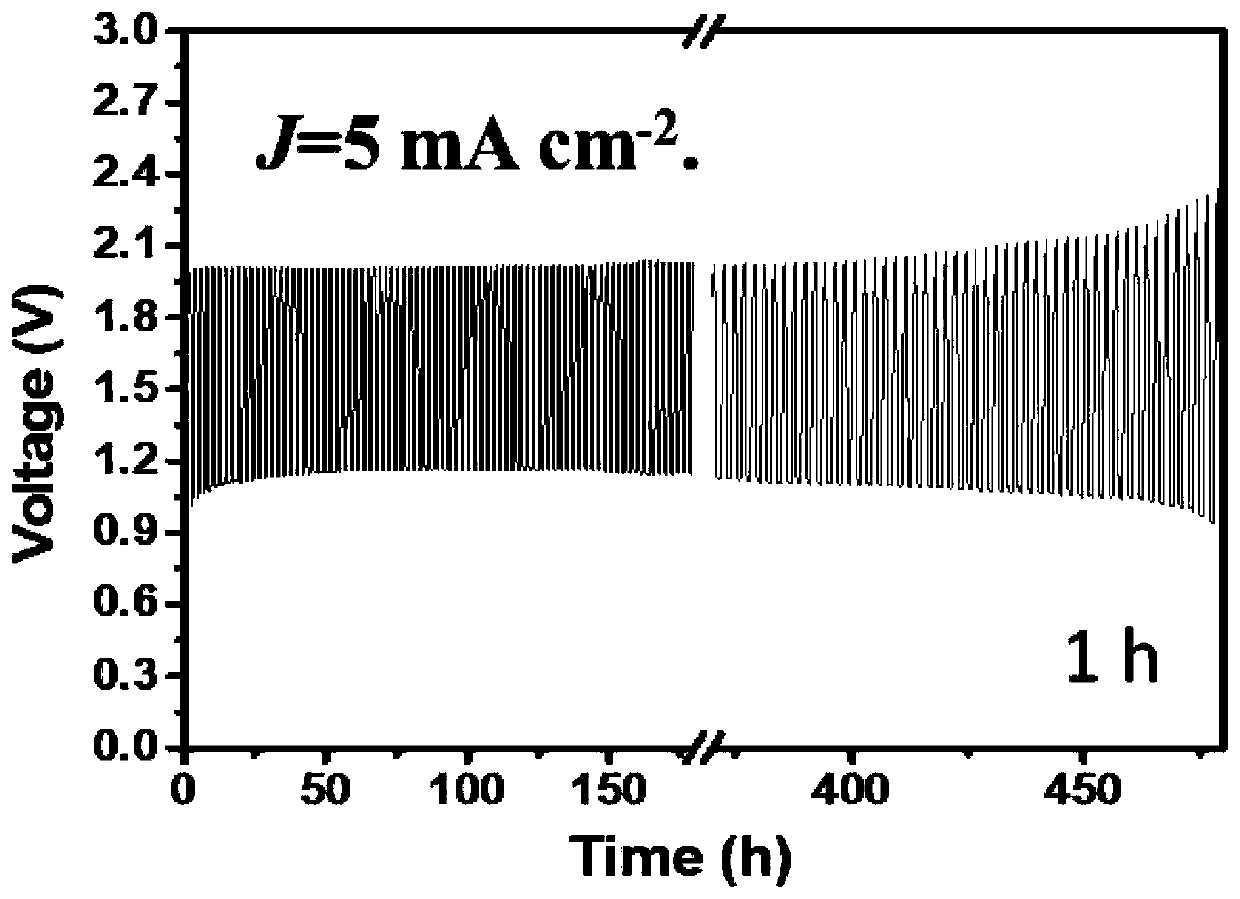
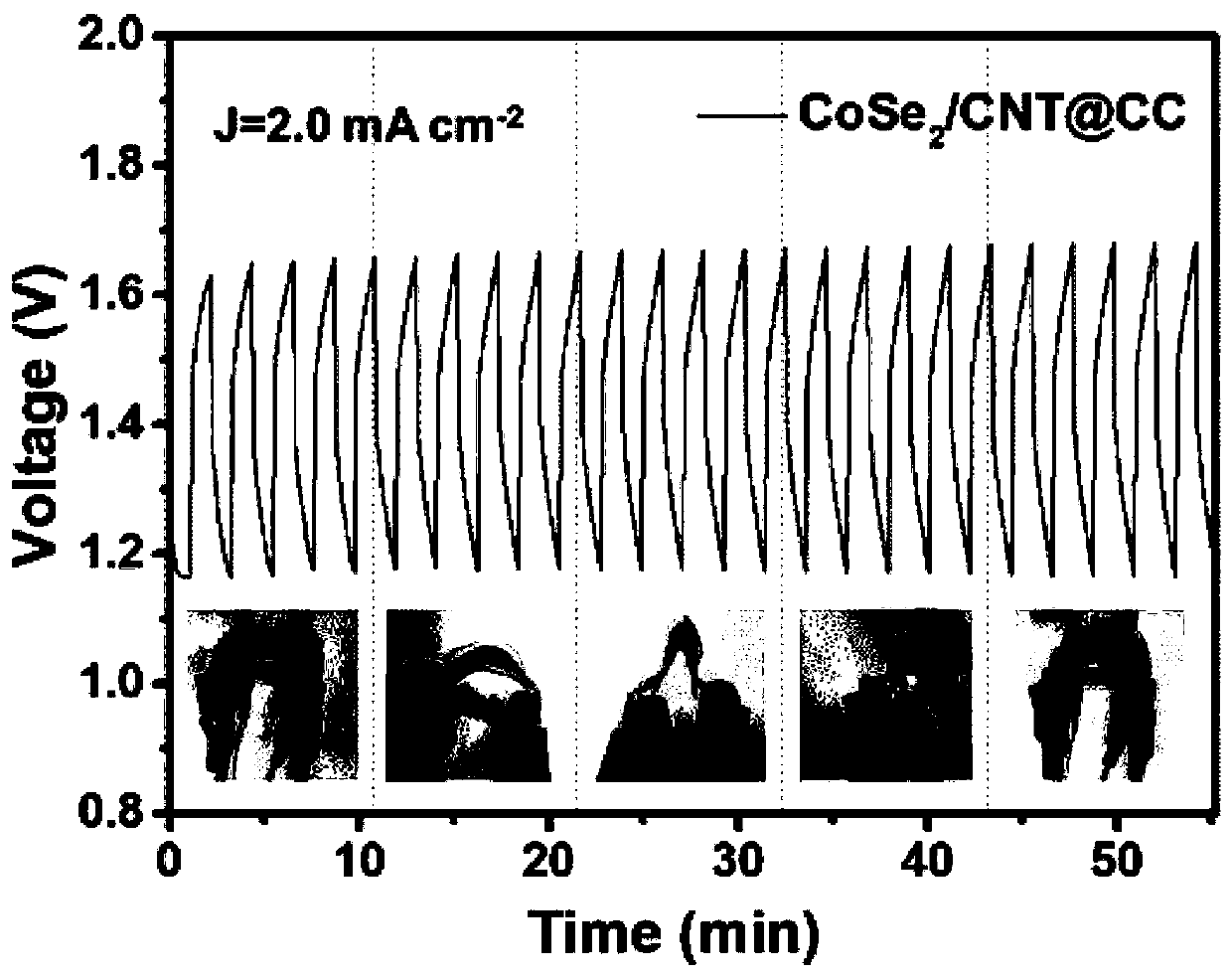
Patents
Literature
529 results about "Diselenide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Diselenide may refer to: Diselane, H-Se-Se-H Carbon diselenide, CSe₂, a yellow-orange oily liquid with pungent odour Diphenyl diselenide, –Se–Se– Metal dichalcogenide, e.g. Manganese diselenide, Molybdenum diselenide, Tungsten diselenide, Titanium diselenide
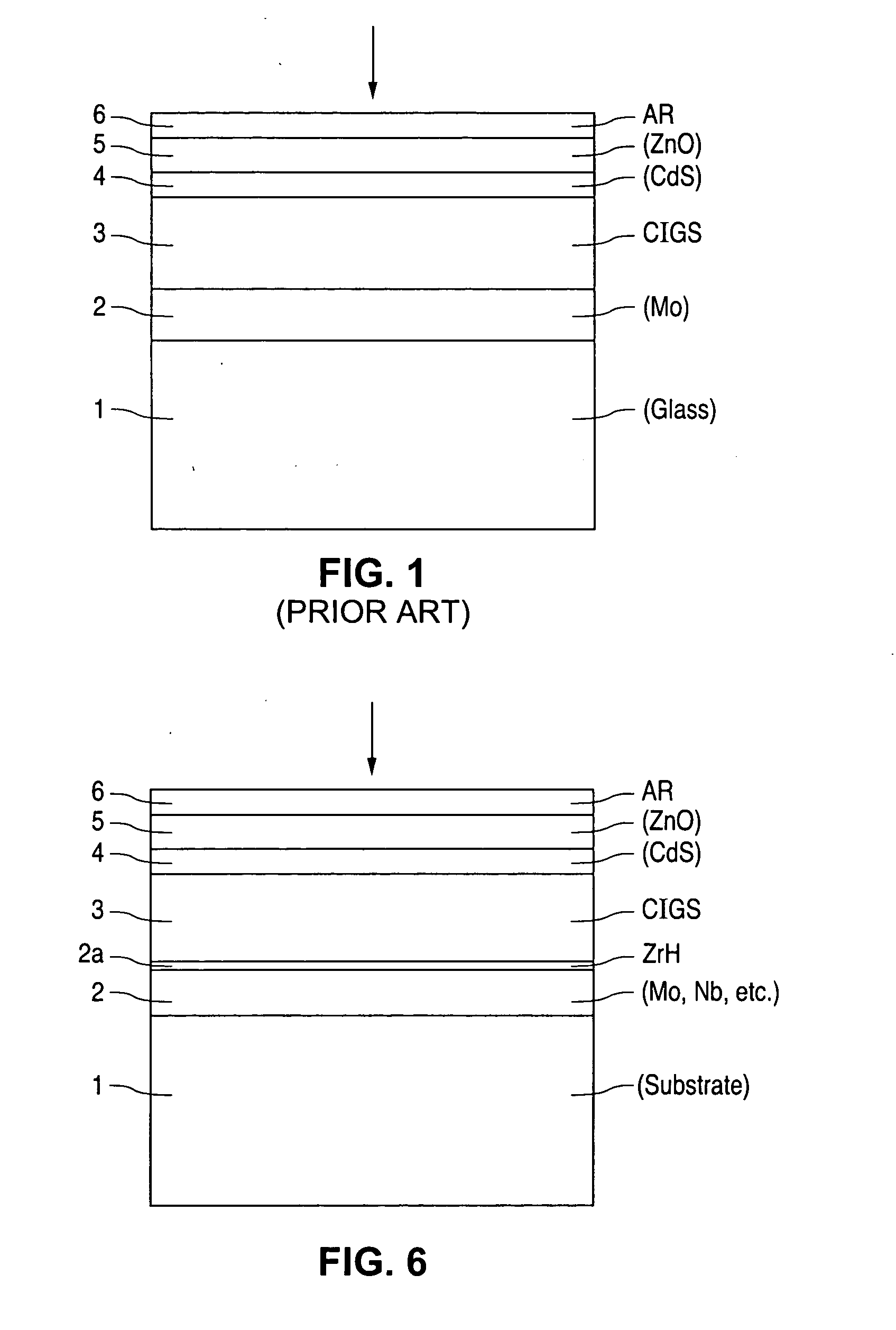
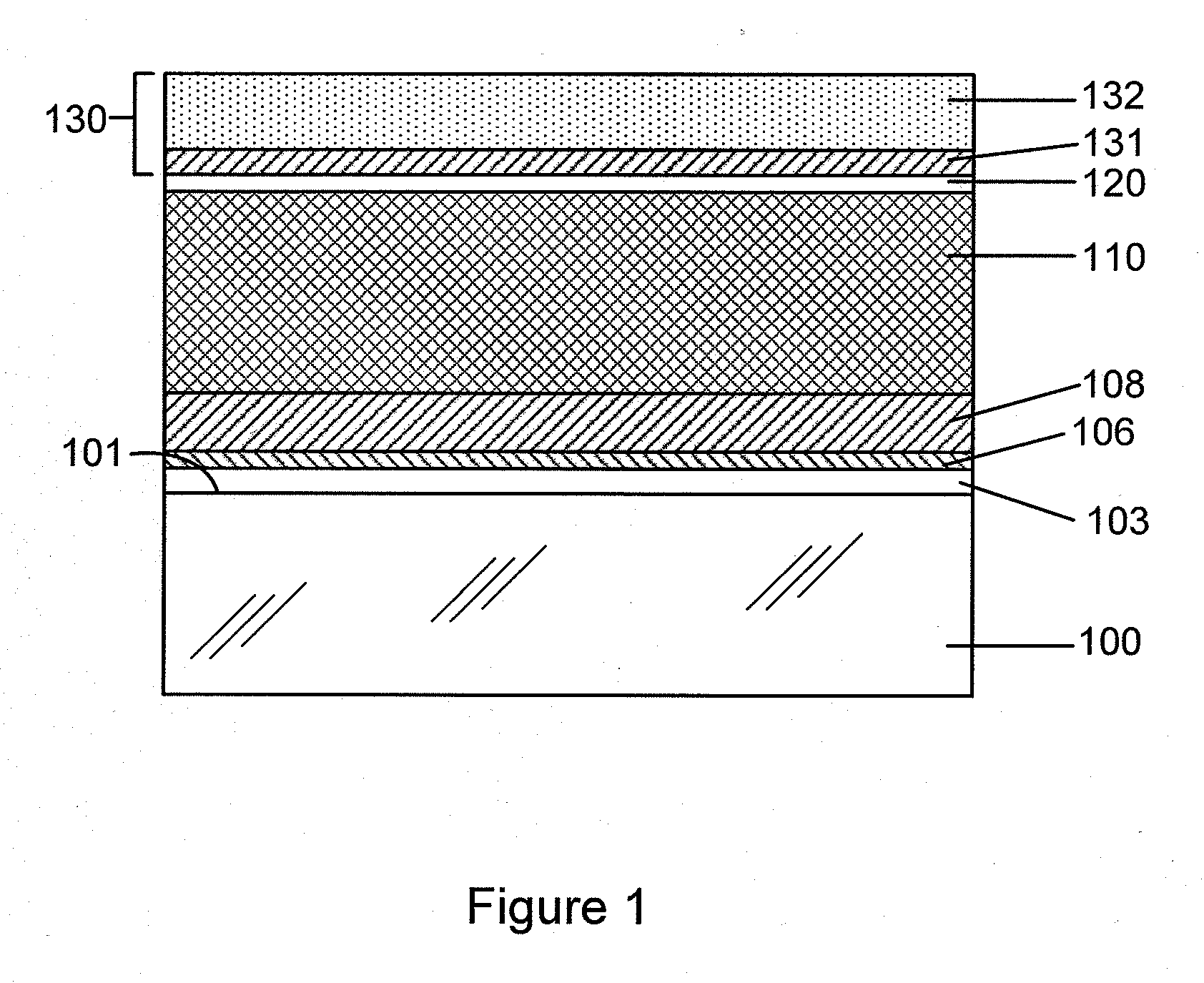
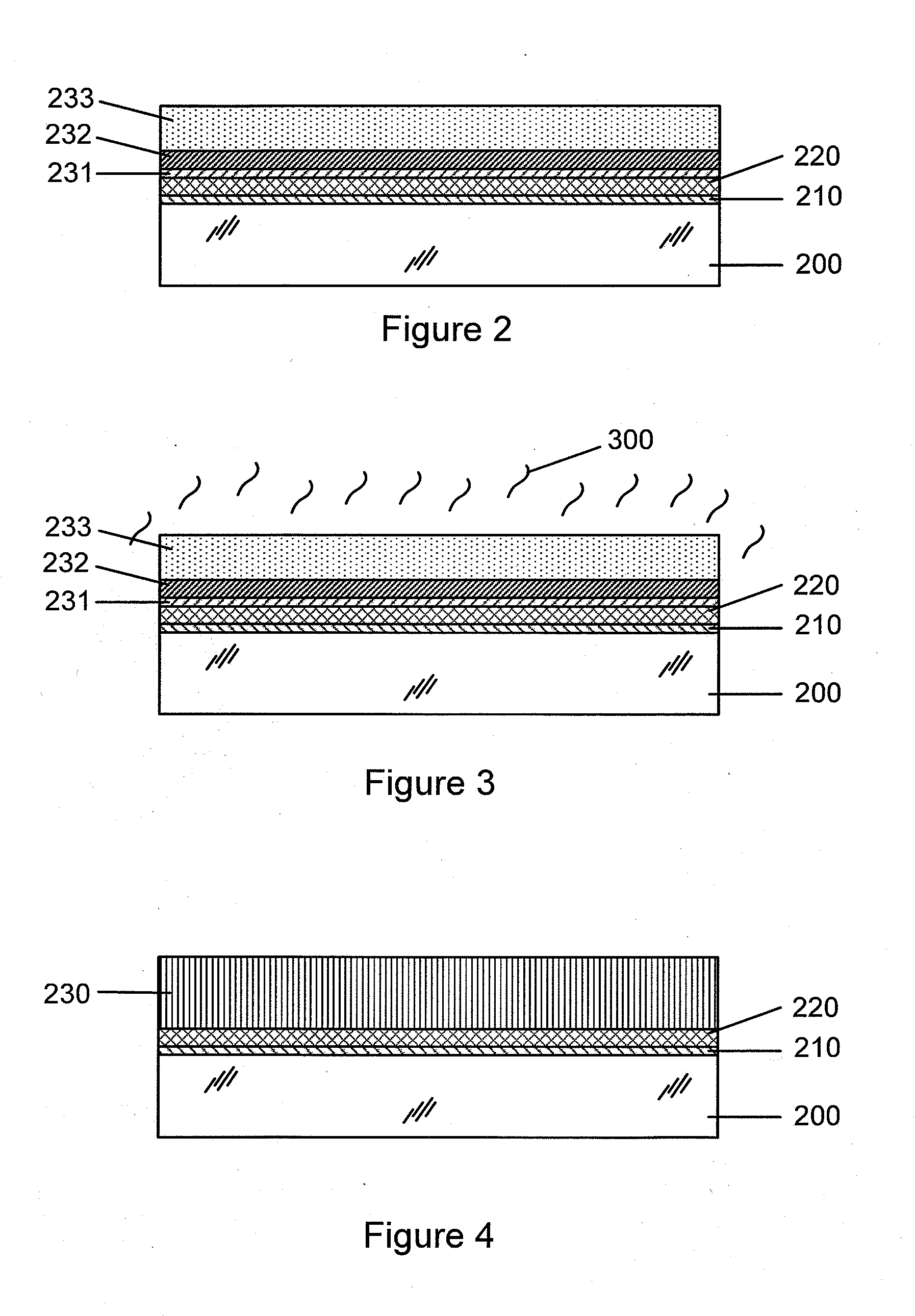
Thin-film solar cells
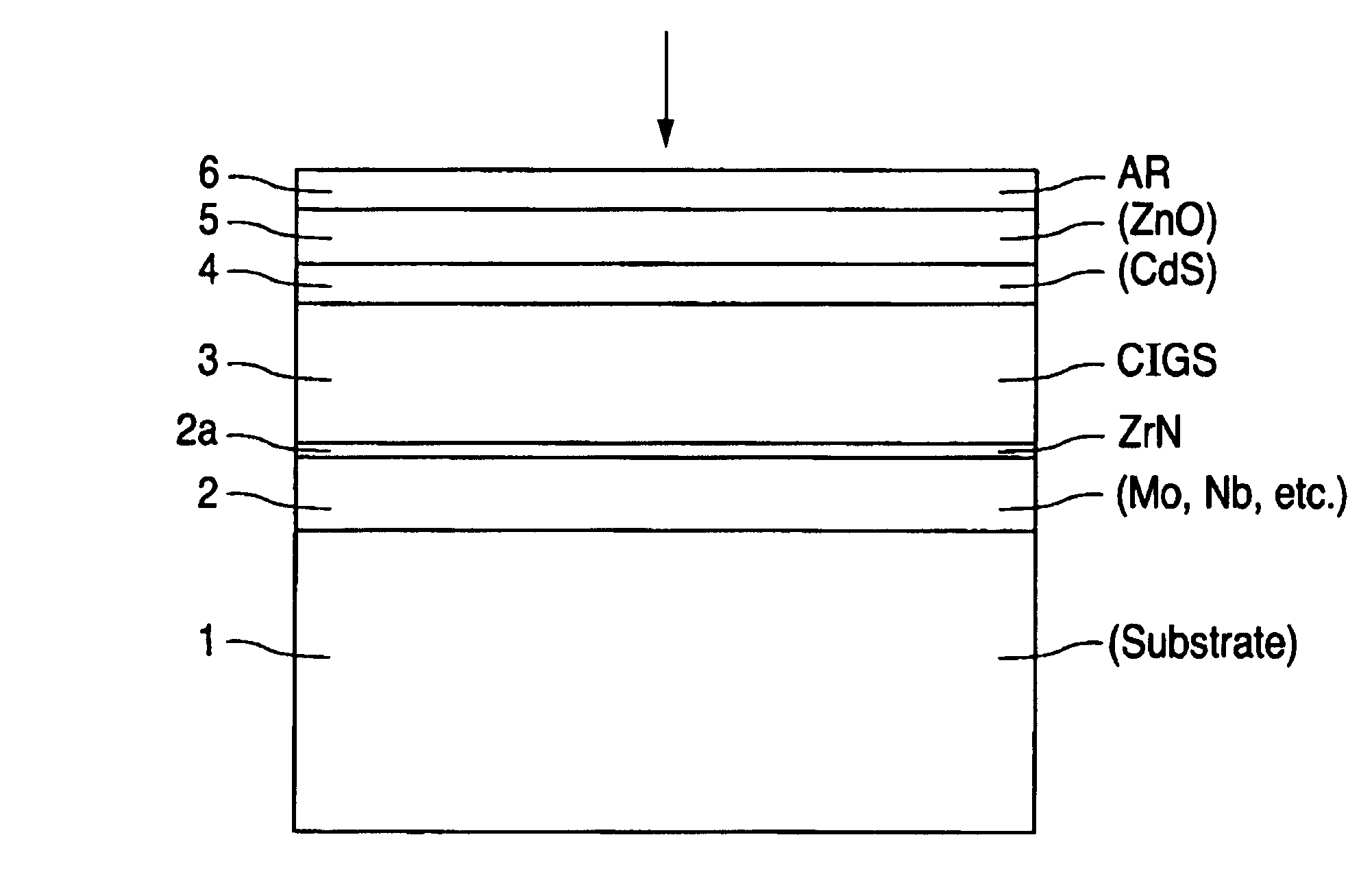
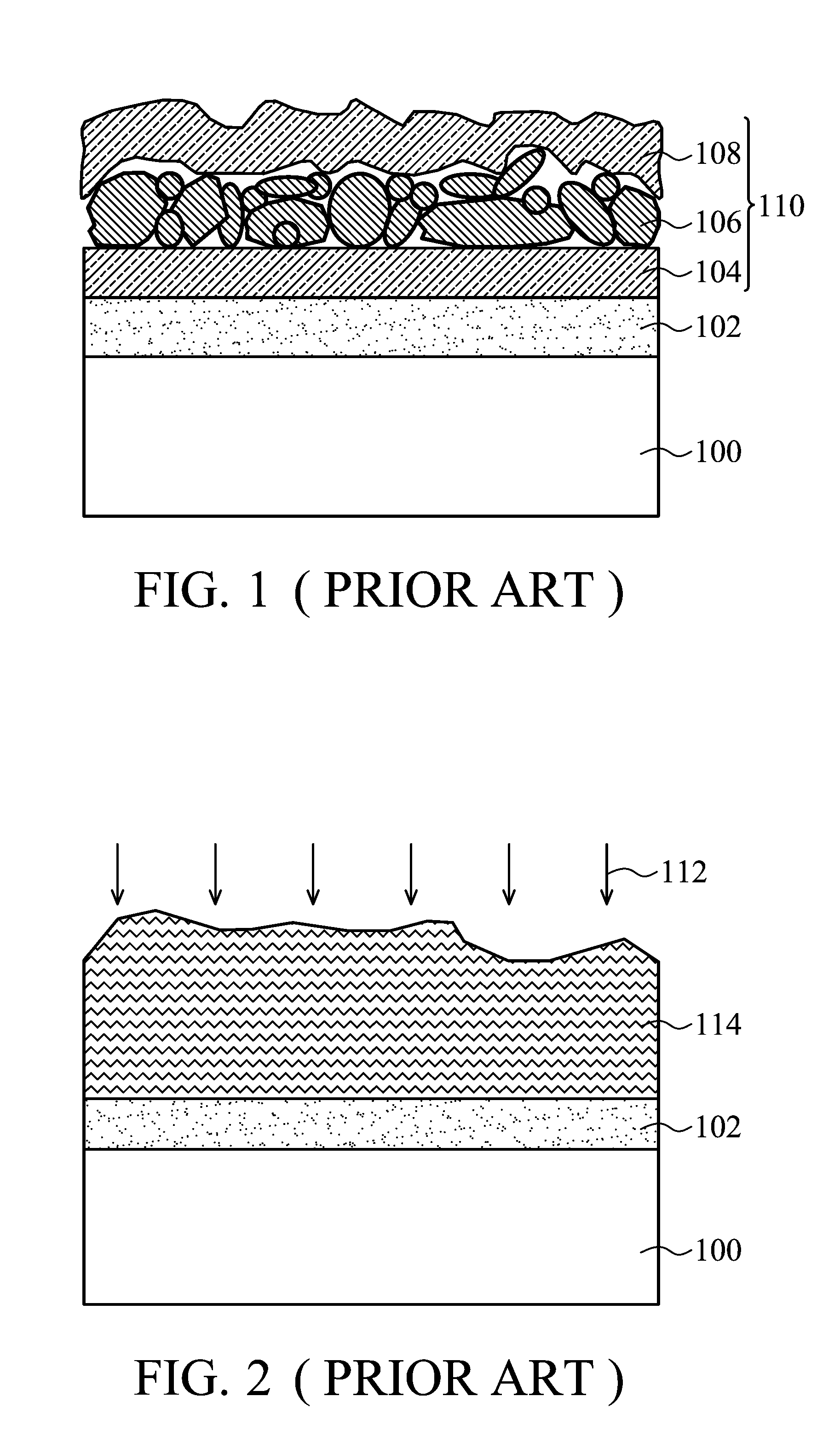
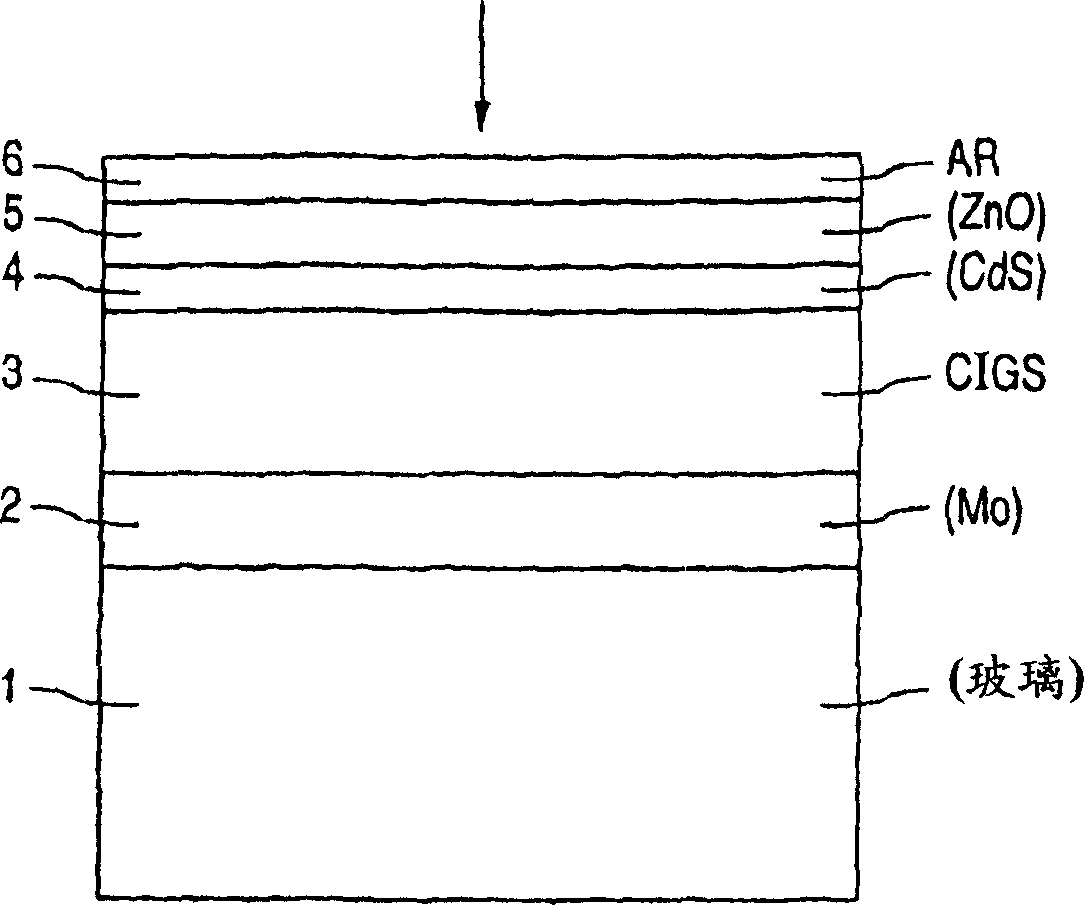
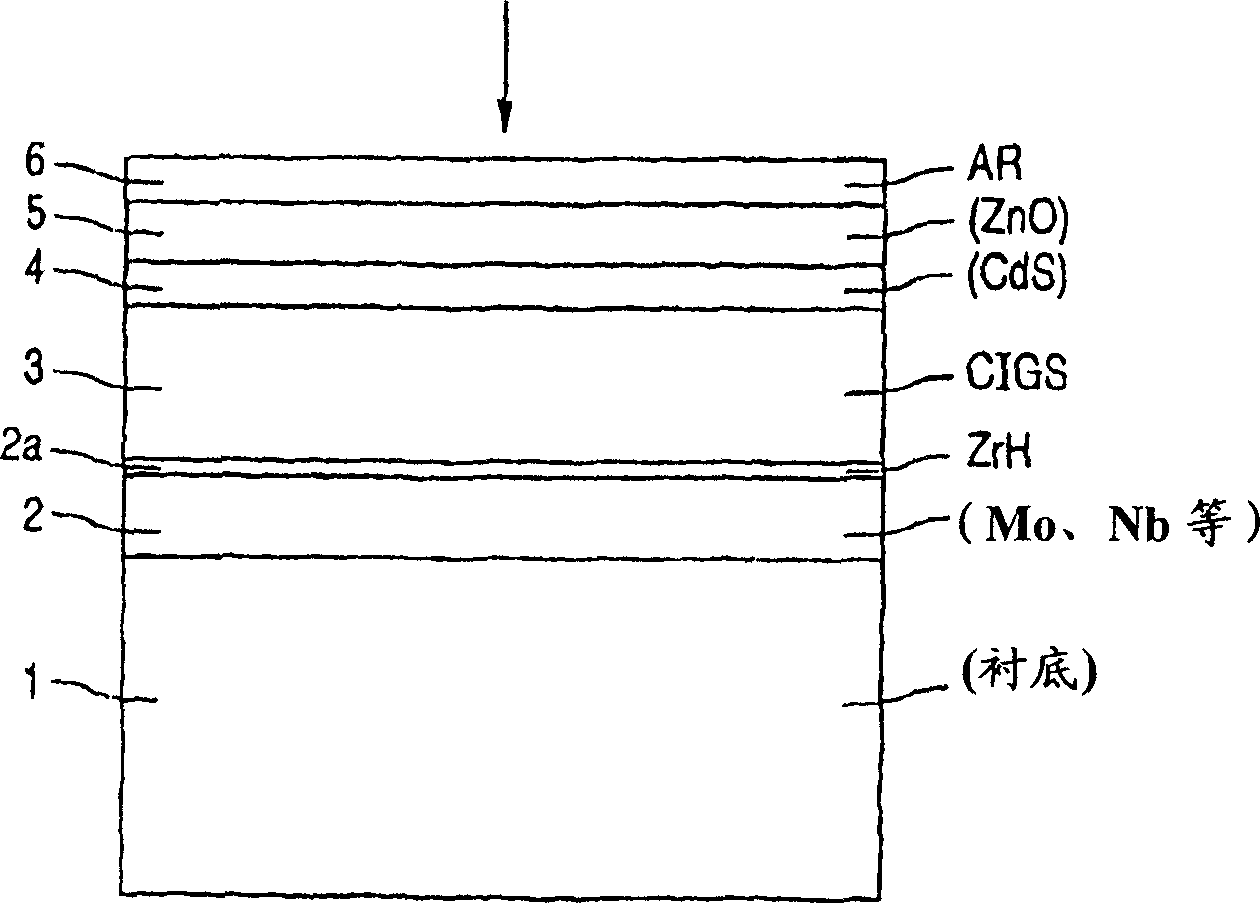
InactiveUS6974976B2Increase reflectionInhibition formationFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingIndiumElectrical battery
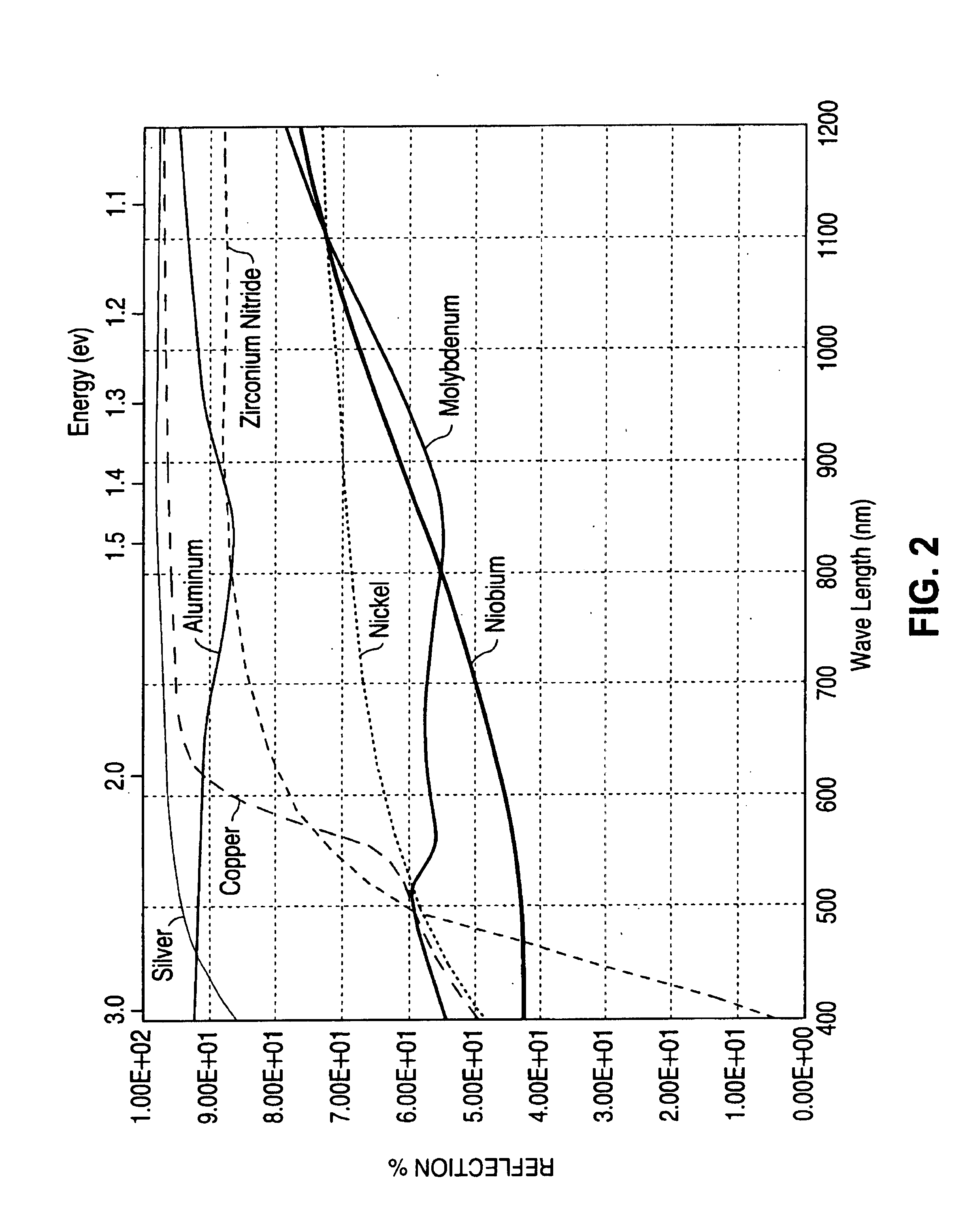
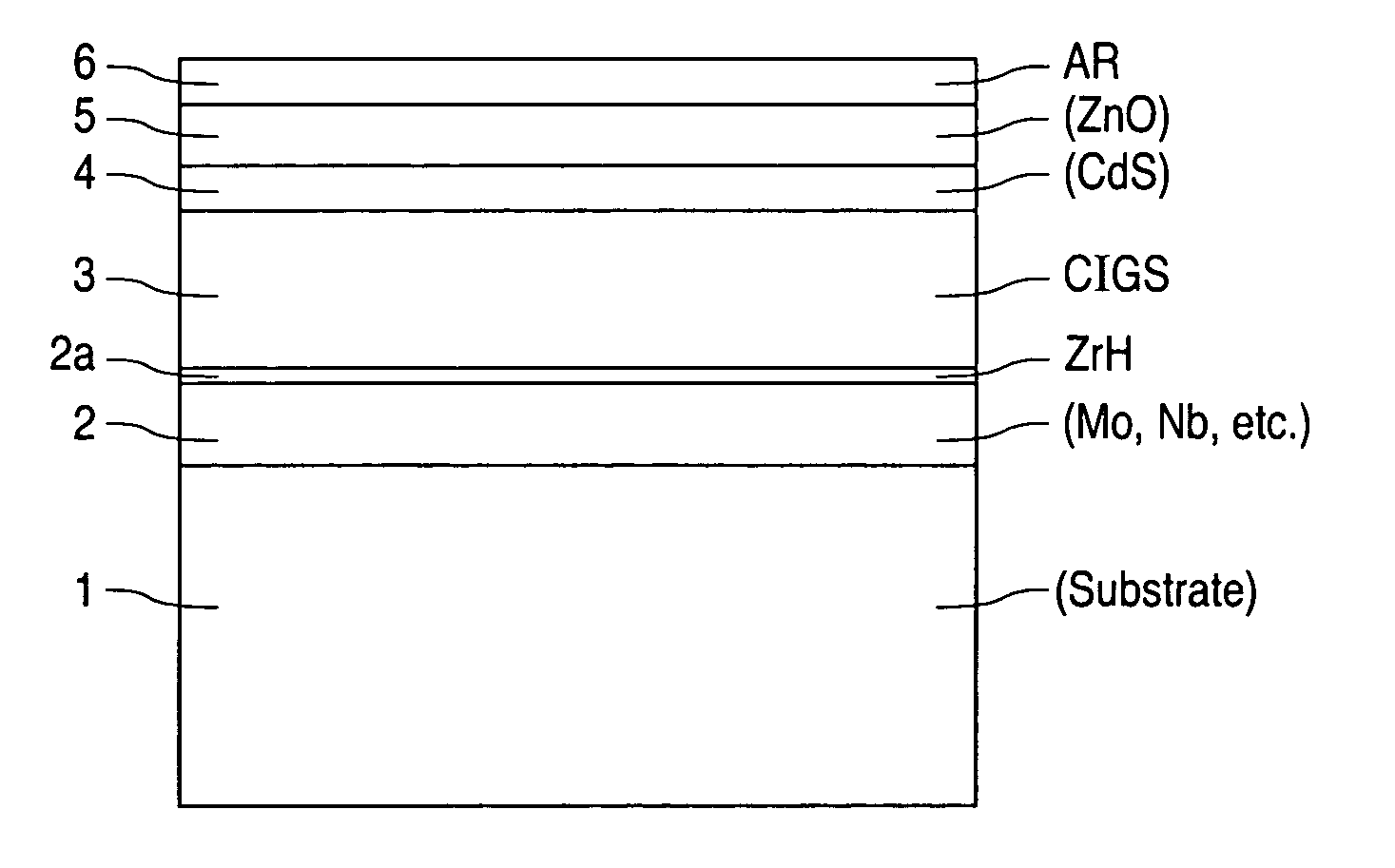
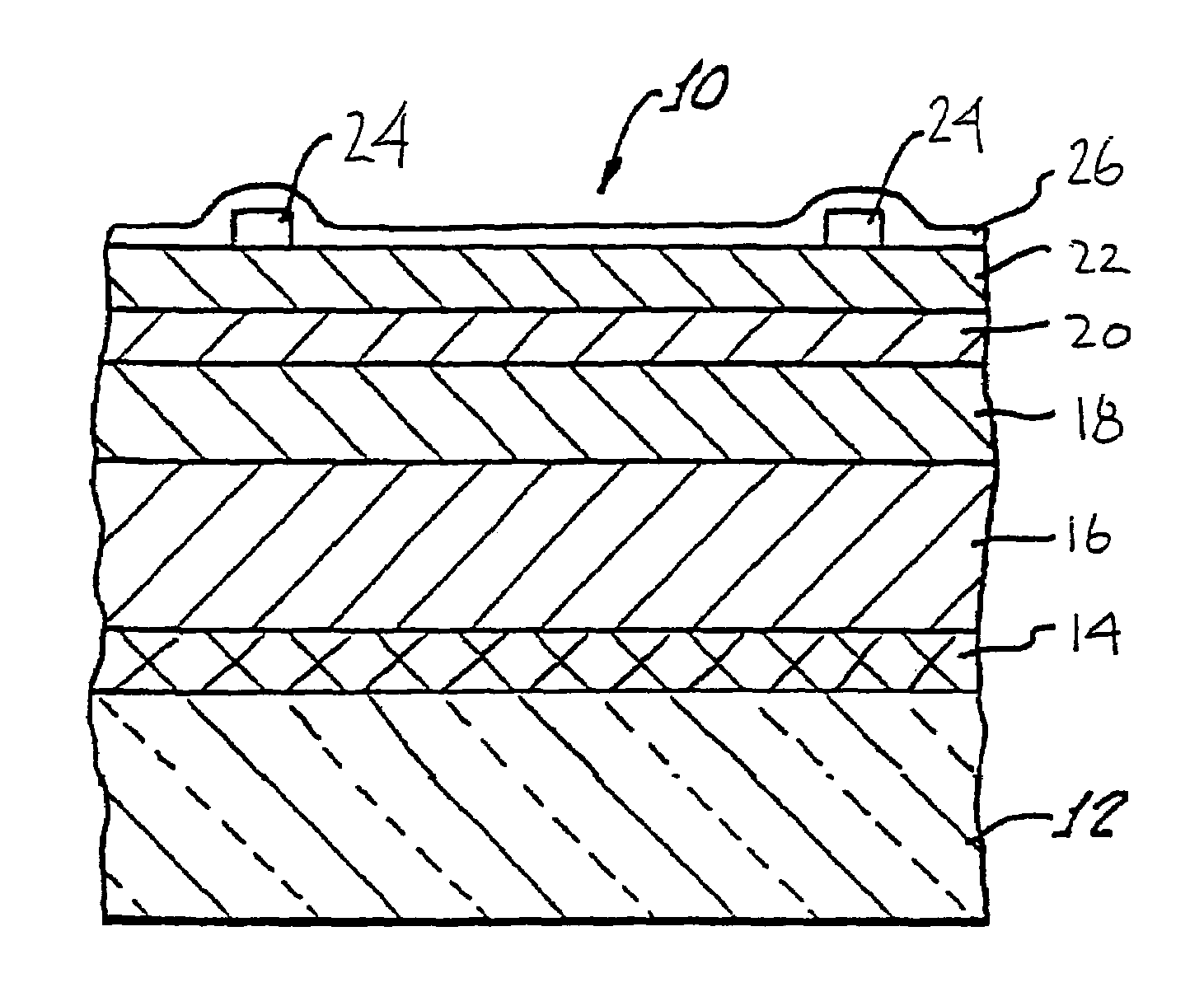
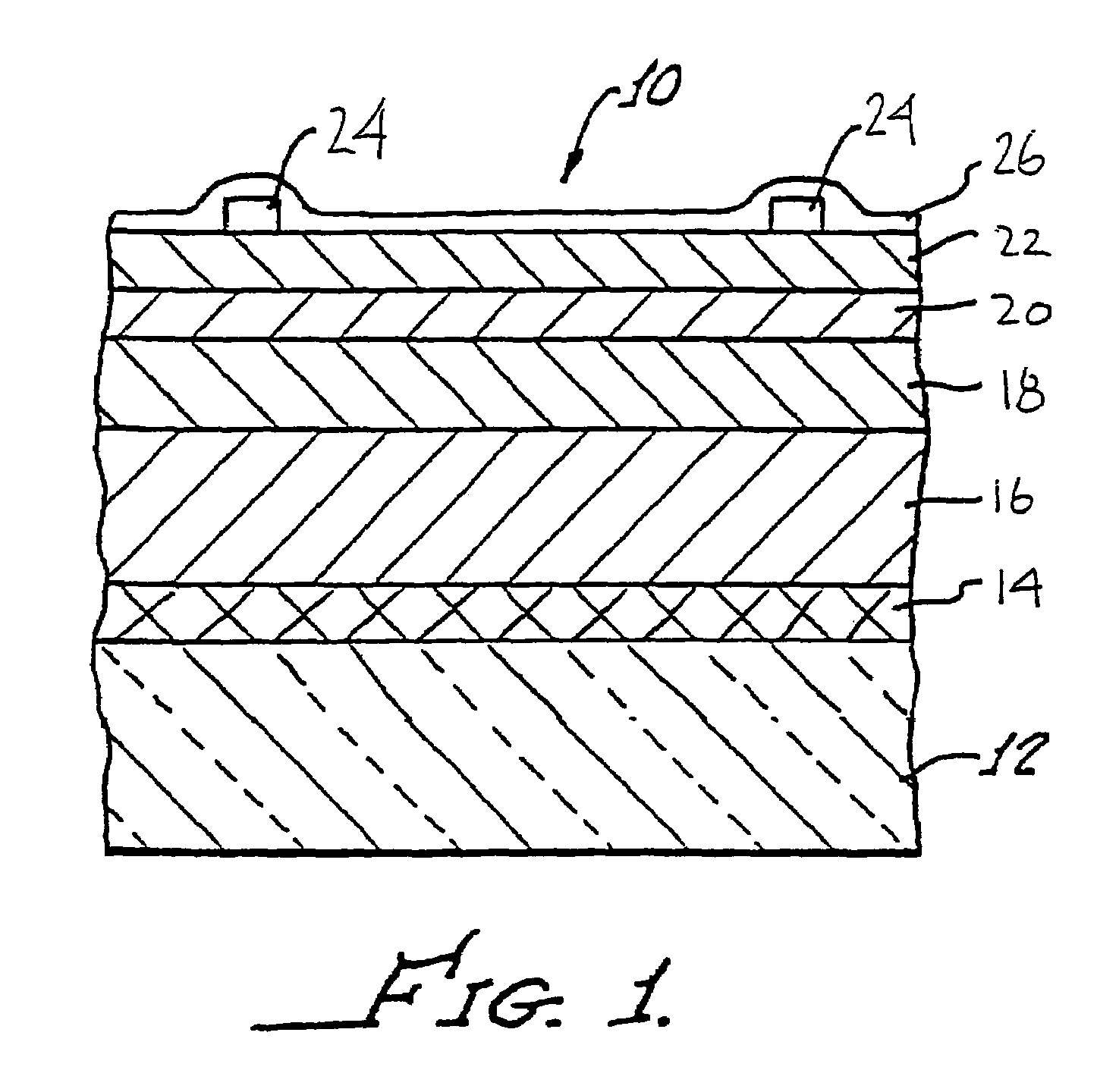
A method of manufacturing improved thin-film solar cells entirely by sputtering includes a high efficiency back contact / reflecting multi-layer containing at least one barrier layer consisting of a transition metal nitride. A copper indium gallium diselenide (Cu(InXGa1−X)Se2) absorber layer (X ranging from 1 to approximately 0.7) is co-sputtered from specially prepared electrically conductive targets using dual cylindrical rotary magnetron technology. The band gap of the absorber layer can be graded by varying the gallium content, and by replacing the gallium partially or totally with aluminum. Alternately the absorber layer is reactively sputtered from metal alloy targets in the presence of hydrogen selenide gas. RF sputtering is used to deposit a non-cadmium containing window layer of ZnS. The top transparent electrode is reactively sputtered aluminum doped ZnO. A unique modular vacuum roll-to-roll sputtering machine is described. The machine is adapted to incorporate dual cylindrical rotary magnetron technology to manufacture the improved solar cell material in a single pass.
Owner:BEIJING APOLLO DING RONG SOLAR TECH
Manufacturing apparatus and method for large-scale production of thin-film solar cells
ActiveUS20050109392A1Cheap productionLow costPV power plantsFinal product manufactureIndiumElectrical battery
A method of manufacturing improved thin-film solar cells entirely by sputtering includes a high efficiency back contact / reflecting multi-layer containing at least one barrier layer consisting of a transition metal nitride. A copper indium gallium diselenide (Cu(InXGa1-x)Se2) absorber layer (X ranging from 1 to approximately 0.7) is co-sputtered from specially prepared electrically conductive targets using dual cylindrical rotary magnetron technology. The band gap of the absorber layer can be graded by varying the gallium content, and by replacing the gallium partially or totally with aluminum. Alternately the absorber layer is reactively sputtered from metal alloy targets in the presence of hydrogen selenide gas. RF sputtering is used to deposit a non-cadmium containing window layer of ZnS. The top transparent electrode is reactively sputtered aluminum doped ZnO. A unique modular vacuum roll-to-roll sputtering machine is described. The machine is adapted to incorporate dual cylindrical rotary magnetron technology to manufacture the improved solar cell material in a single pass.
Owner:BEIJING APOLLO DING RONG SOLAR TECH
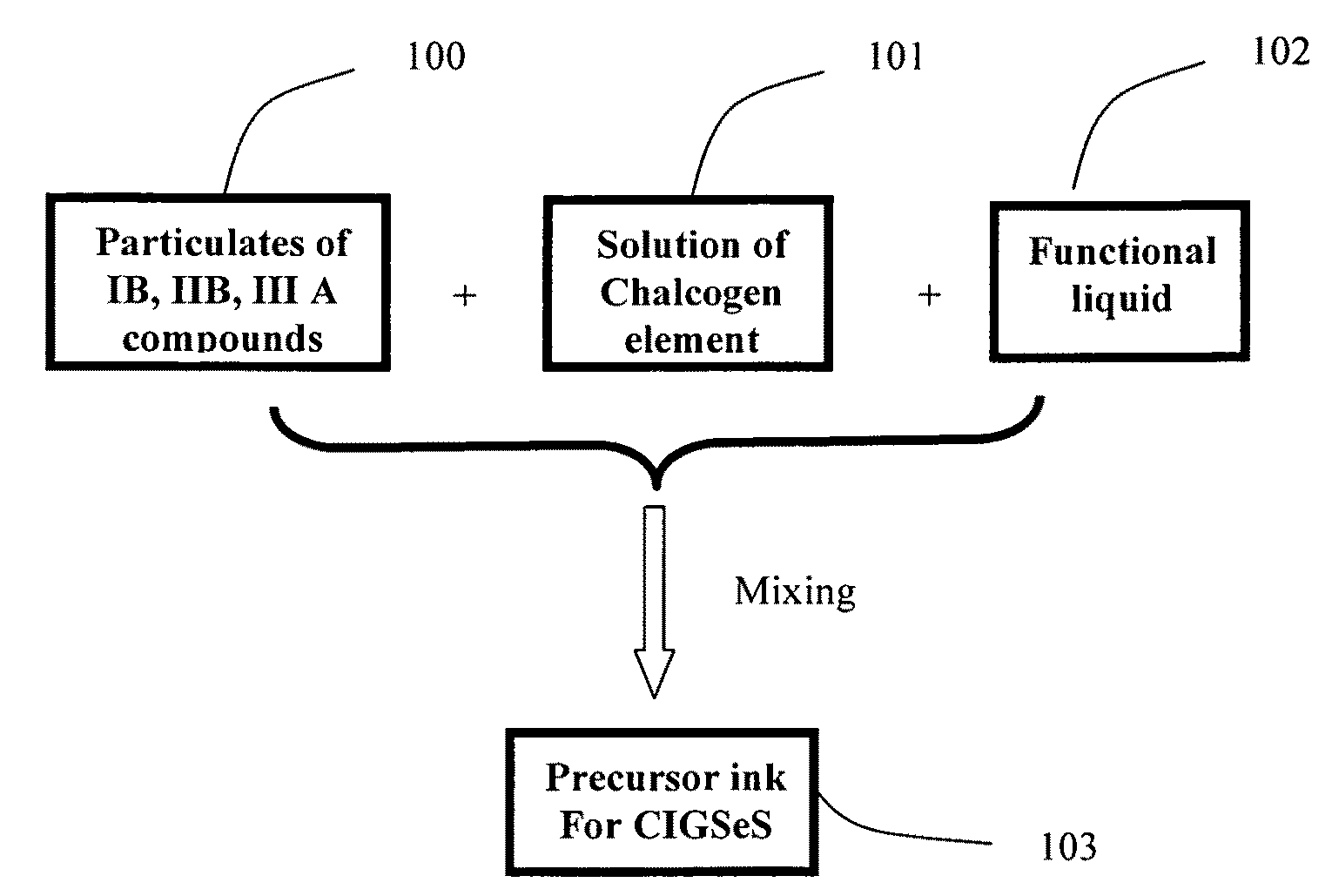
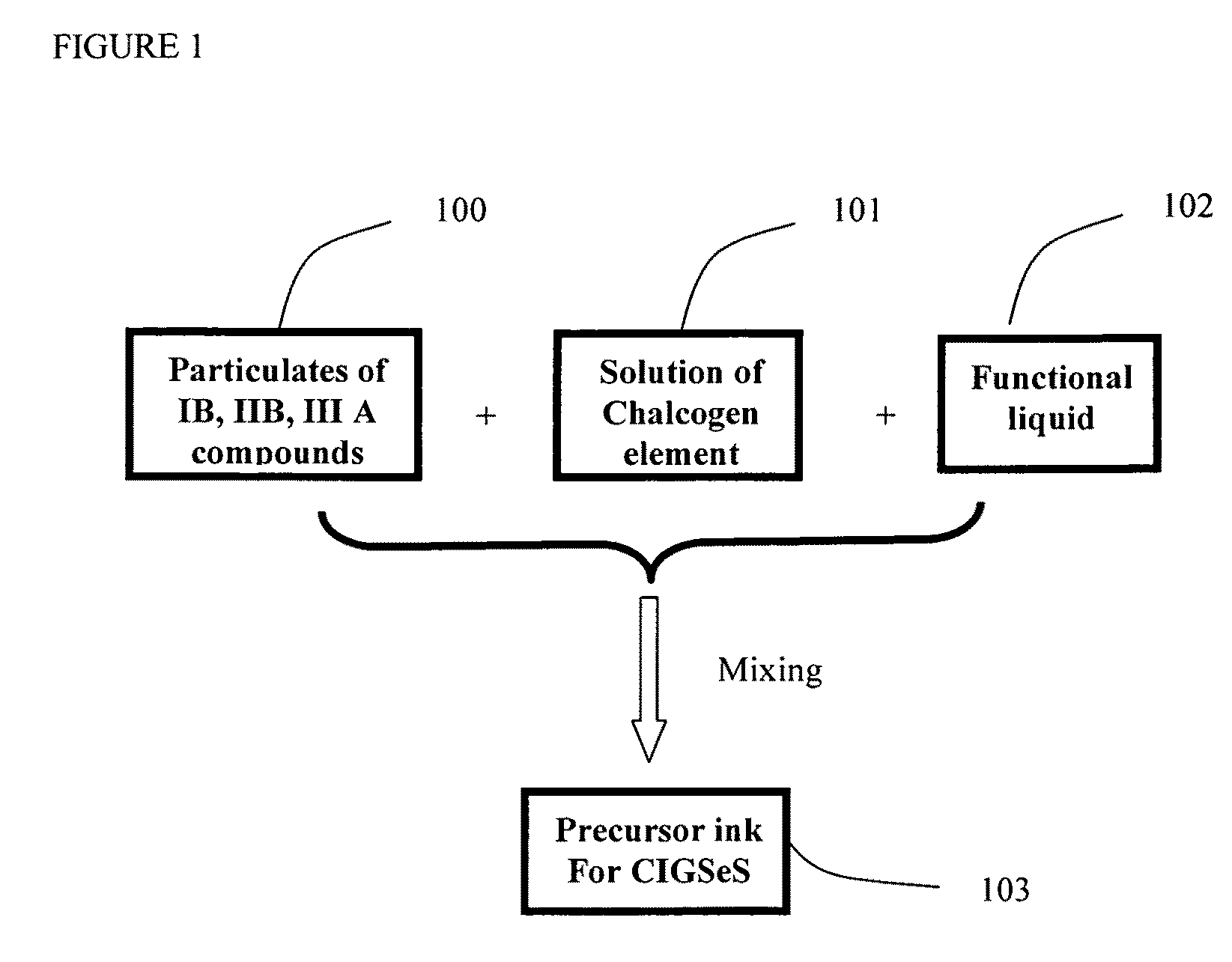
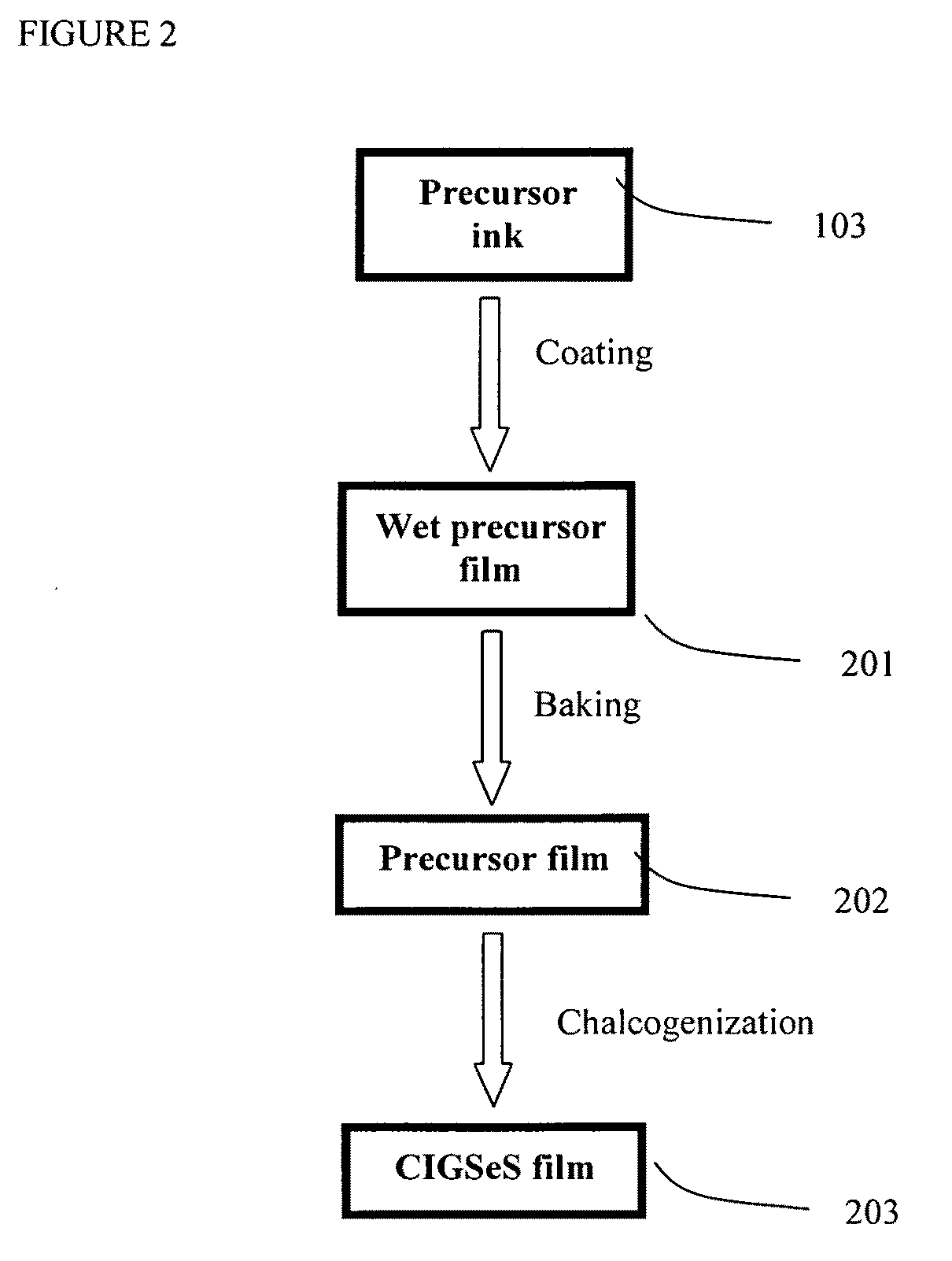
Precursor ink for producing IB-IIIA-VIA semiconductors
InactiveUS20090260670A1Overcome disadvantagesFinal product manufacturePV power plantsIndiumSemiconductor thin films
Copper indium diselenide, copper indium gallium diselenide, and other IB-IIIA-VIA compounds are produced by the liquid deposition on a substrate of a precursor-containing ink, followed by heating to produce the desired material. The precursor containing ink is a mixture of three parts. The first part is plurality of particulates of metal compounds of IB, IIIA. The second part is chalcogen source of selenium, sulfur, or organic chalcogen compounds dissolved in a liquid organic solvent. The third part solution function as viscosity adjustment, as introduction of dopant of sodium ion and / or as ink stabilizer. The precursor ink can be coated on substrate at room temperature and it can be transferred into copper indium (gallium) chalcogenide semiconductor thin film upon baking and a chalcogenization process. The resulting thin film semiconducting material can be incorporated into photovoltaic and other electronic devices.
Owner:LI XIAO CHANG CHARLES
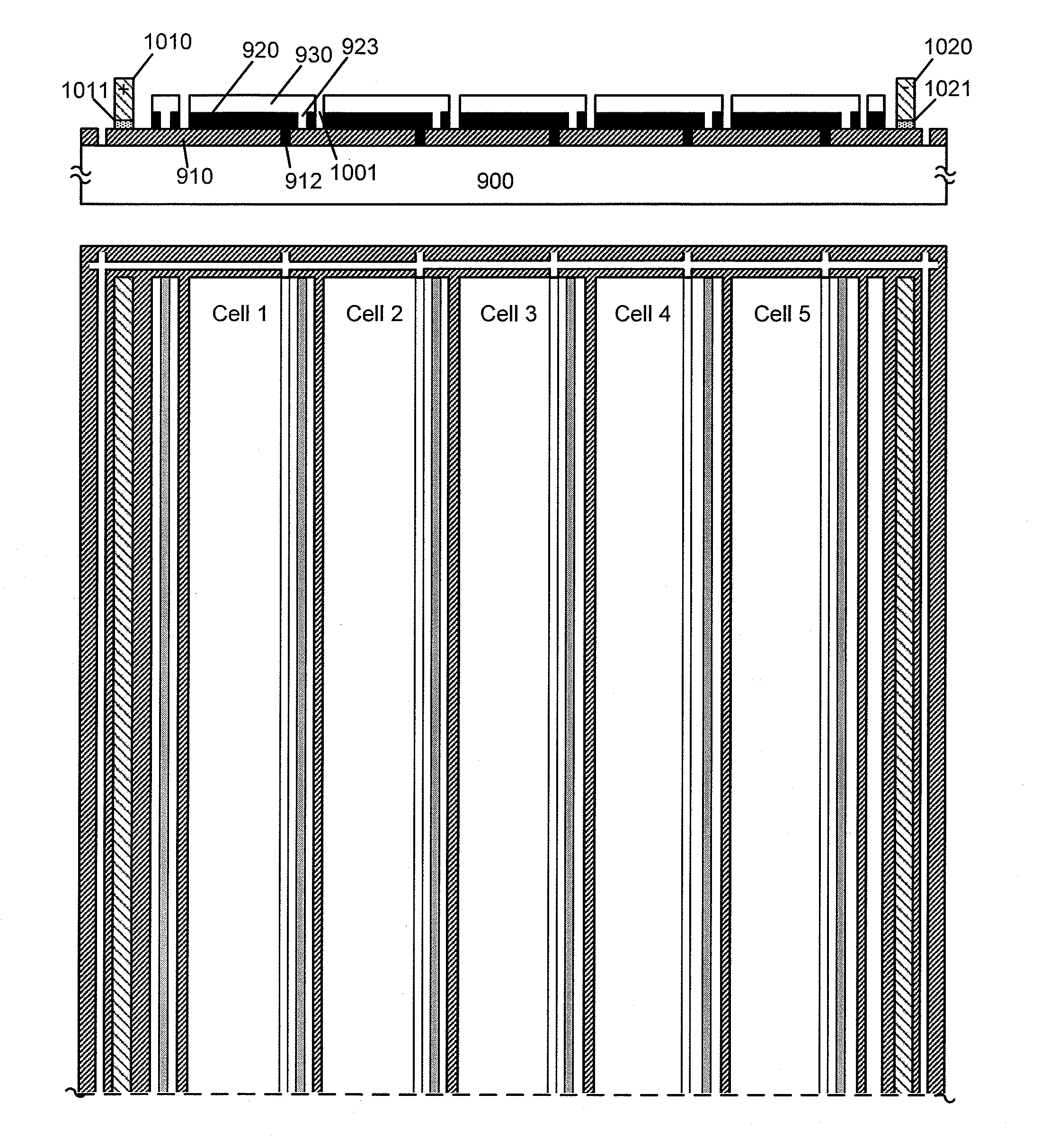
Single Junction CIGS/CIS Solar Module
InactiveUS20110259395A1Low costSimplified thin-film processPV power plantsFinal product manufactureIndiumEngineering
A high efficiency thin-film photovoltaic module is formed on a substrate. The photovoltaic module includes a plurality of stripe shaped photovoltaic cells electrically coupled to each other and physically disposed in parallel to the length one next to another across the width. Each cell includes a barrier material overlying the surface and a first electrode overlying the barrier material. Each cell further includes an absorber formed overlying the first electrode. The absorber includes a copper gallium indium diselenide compound material characterized by an energy band-gap of about 1 eV to 1.1 eV. Each cell additionally includes a buffer material overlying the absorber and a bi-layer zinc oxide material comprising a high resistivity transparent layer overlying the buffer material and a low resistivity transparent layer overlying the high resistivity transparent layer.
Owner:CM MFG
Preparation of CIGS-based solar cells using a buffered electrodeposition bath
InactiveUS7297868B2Easy to handleLightweight productionElectrolytic coatingsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumSolar cell
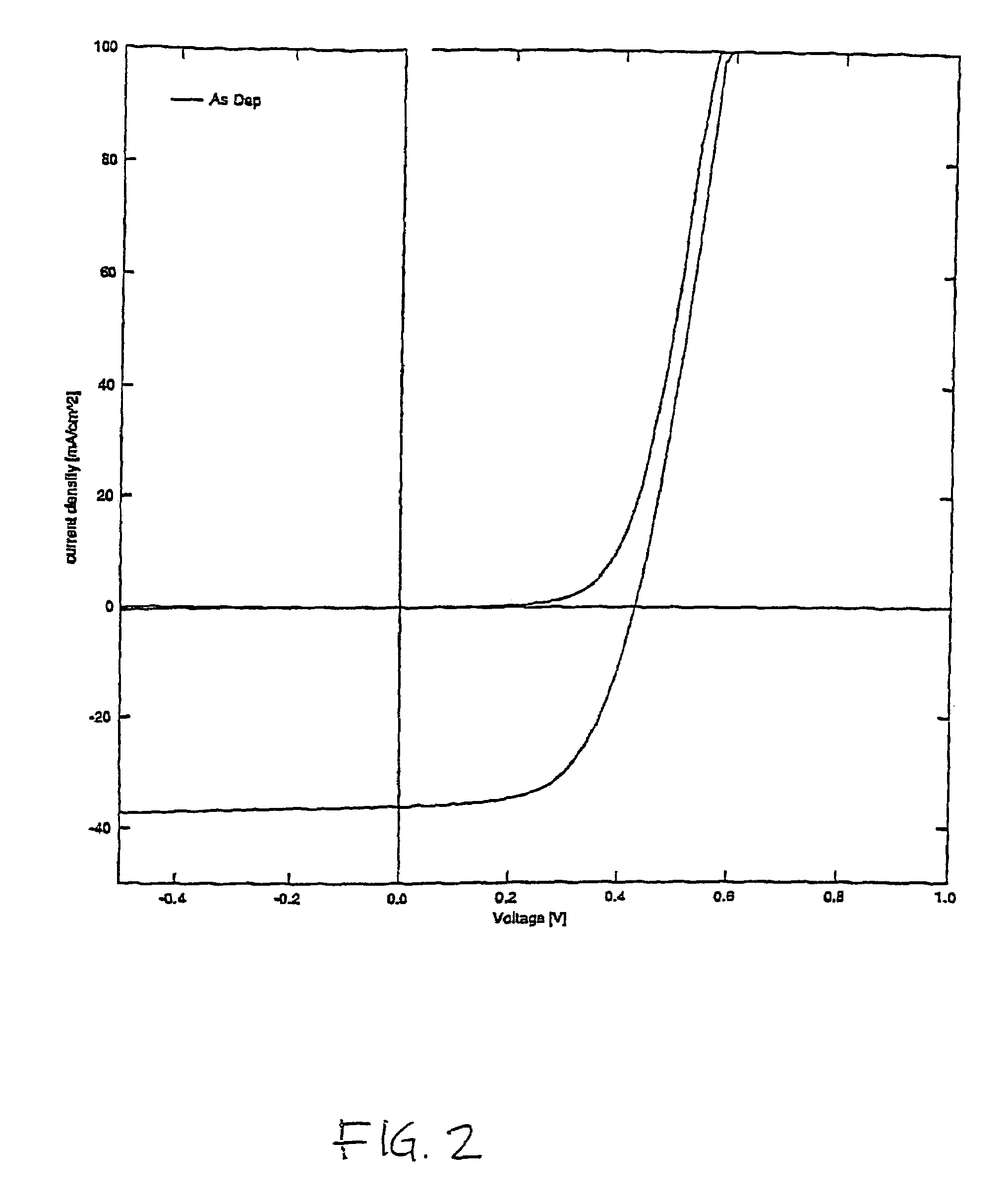
A photovoltaic cell exhibiting an overall conversion efficiency of at least 9.0% is prepared from a copper-indium-gallium-diselenide thin film. The thin film is prepared by simultaneously electroplating copper, indium, gallium, and selenium onto a substrate using a buffered electro-deposition bath. The electrodeposition is followed by adding indium to adjust the final stoichiometry of the thin film.
Owner:DAVIS JOSEPH & NEGLEY
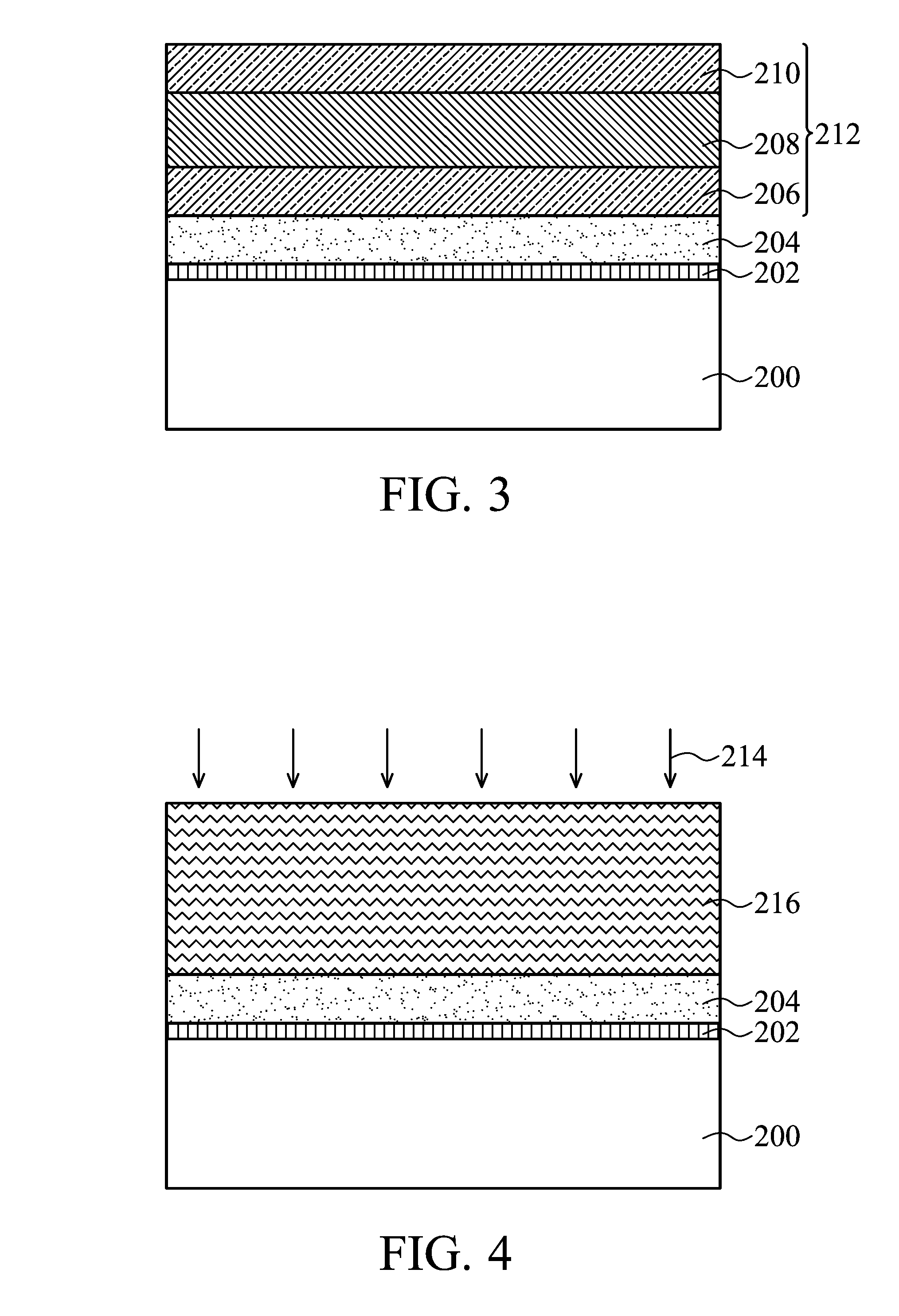
Methods for fabricating copper indium gallium diselenide (CIGS) compound thin films
InactiveUS20100297835A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingIndiumCopper
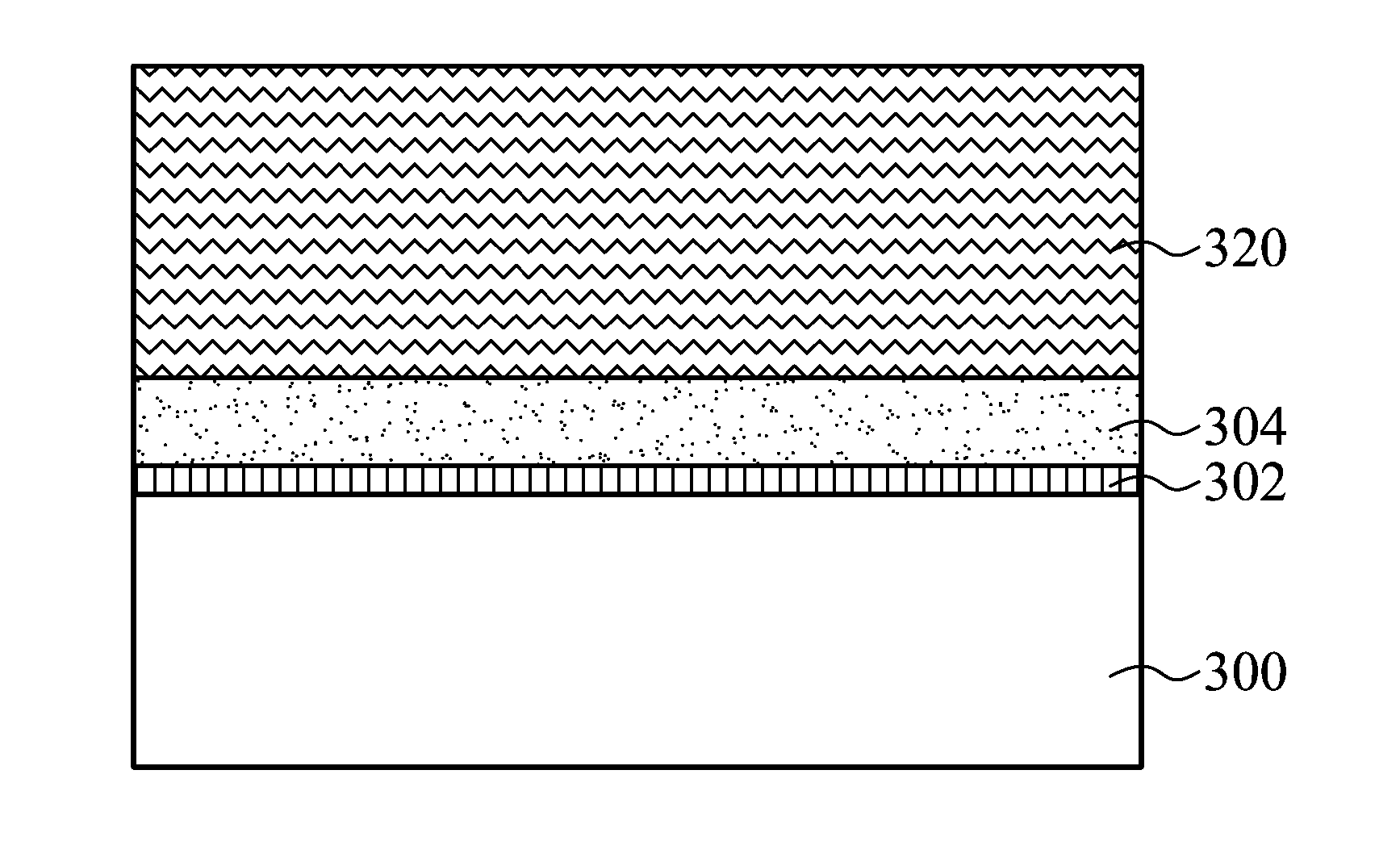
A method for fabricating a copper-indium-gallium-diselenide (CIGS) compound thin film is provided. In this method, a substrate is first provided. An adhesive layer is formed over the substrate. A metal electrode layer is formed over the adhesive layer. A precursor stacked layer is formed over the metal electrode layer, wherein the precursor stacked layer includes a plurality of copper-gallium (CuGa) alloy layers and at least one copper-indium (CuIn) alloy layer sandwiched between the plurality of CuGa alloy layers. An annealing process is performed to convert the precursor stacked layer into a copper-indium-gallium (CuInGa) alloy layer. A selenization process is performed to convert the CuInGa alloy layer into a copper-indium-gallium-diselenide (CuInGaSe) compound thin film.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
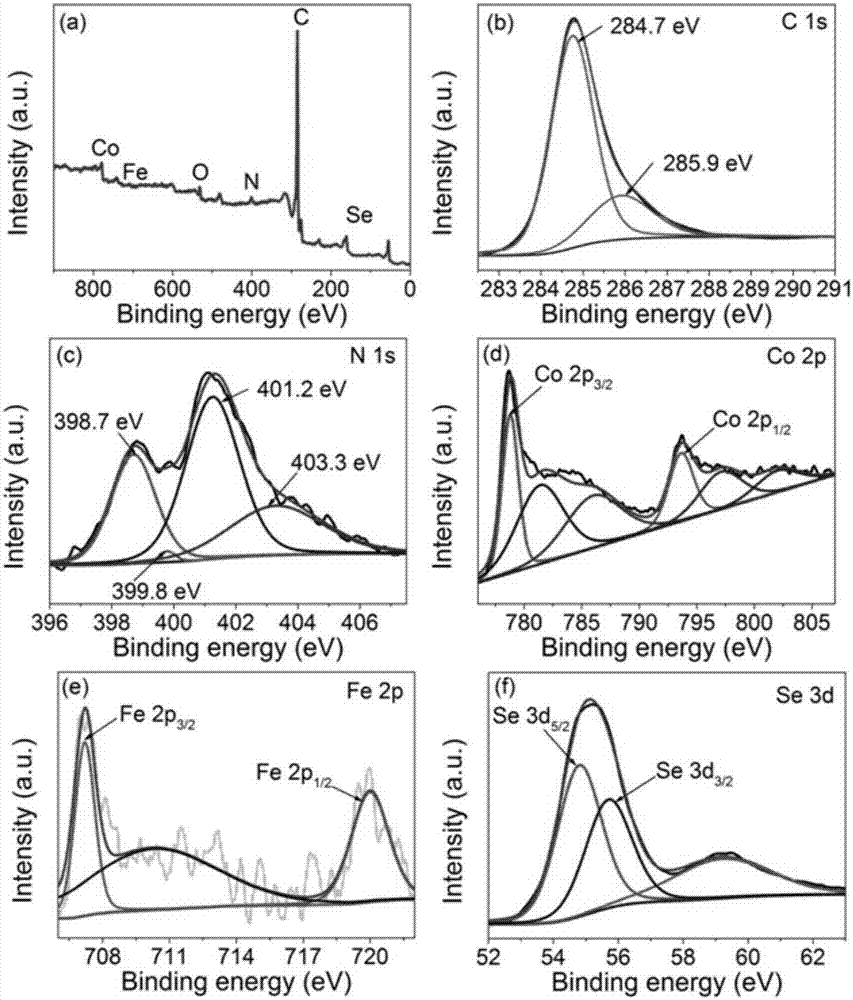
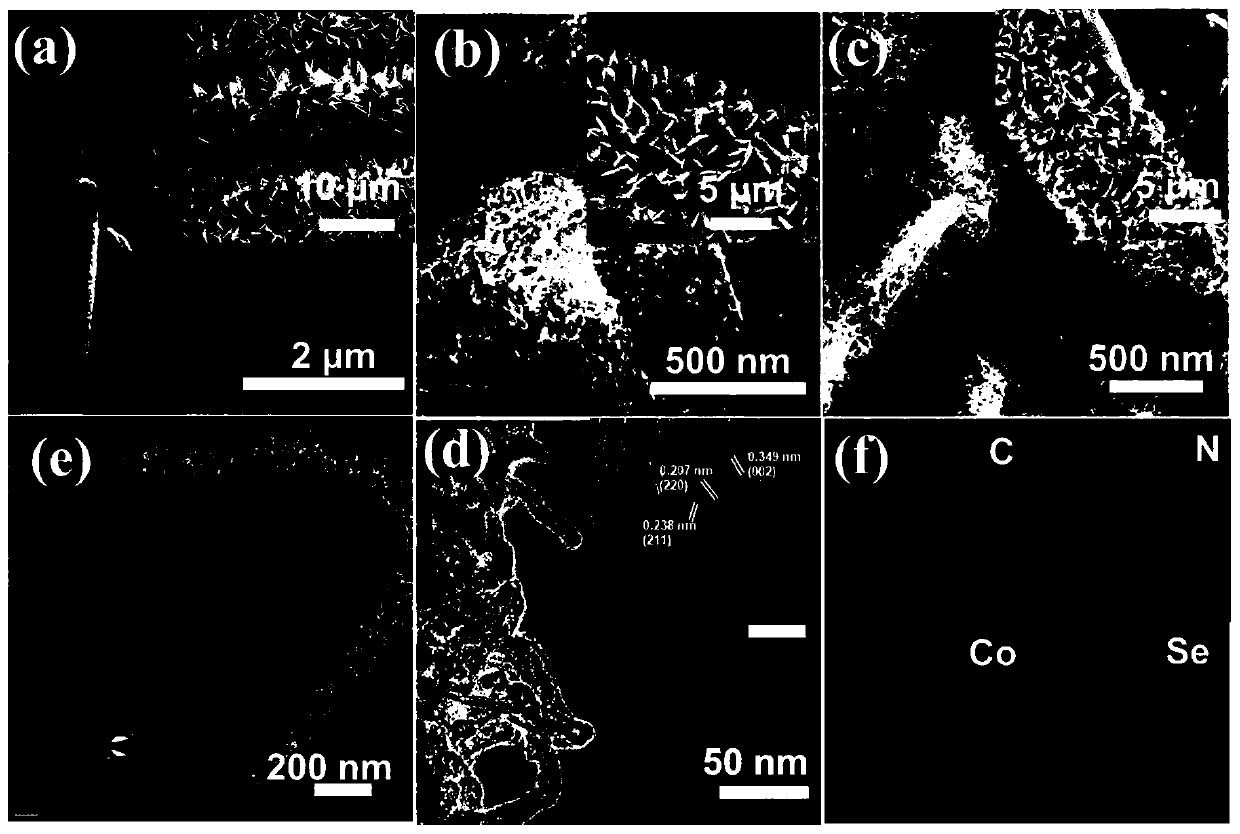
Cobalt selenide/nitrogen-doped carbon composite material and preparation method and application therefor
InactiveCN105609322AEasy to operateGood repeatabilityMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrodesCapacitanceCarbon composites
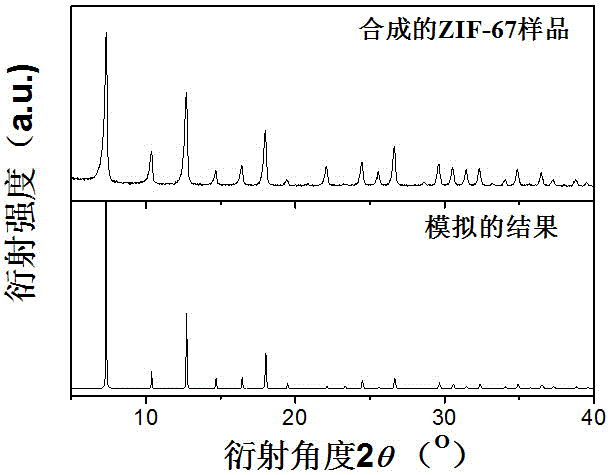
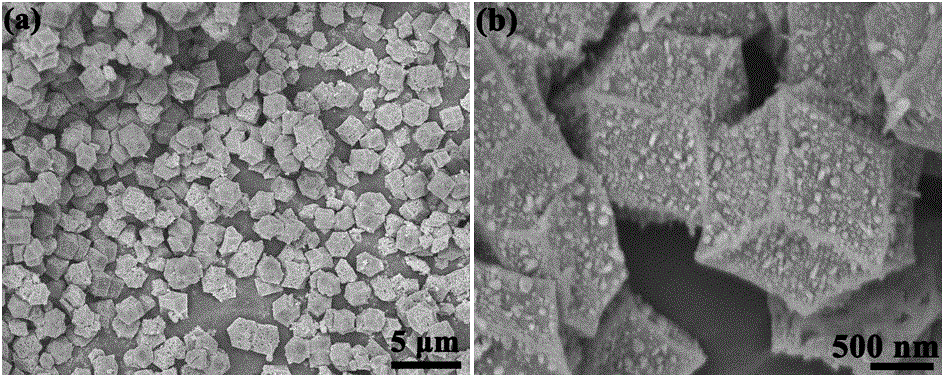
The invention provides a cobalt selenide / nitrogen-doped carbon composite material and a preparation method and an application therefor, and belongs to the technical fields of nanomaterial preparation and application. An organic metallic framework ZIF-67 is taken as a template for preparing the cobalt selenide / nitrogen-doped carbon composite material; the material adopts a rhombic dodecahedron shape with controllable sizes; and cobalt selenide is cobalt selenide or cobalt diselenide nanoparticles uniformly dispersed on a nitrogen-doped carbon framework. The compound has a good mesoporous structure and excellent conductivity; and when the composite material is used as the electrode material for a supercapacitor, a high specific capacitance and high stability are achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
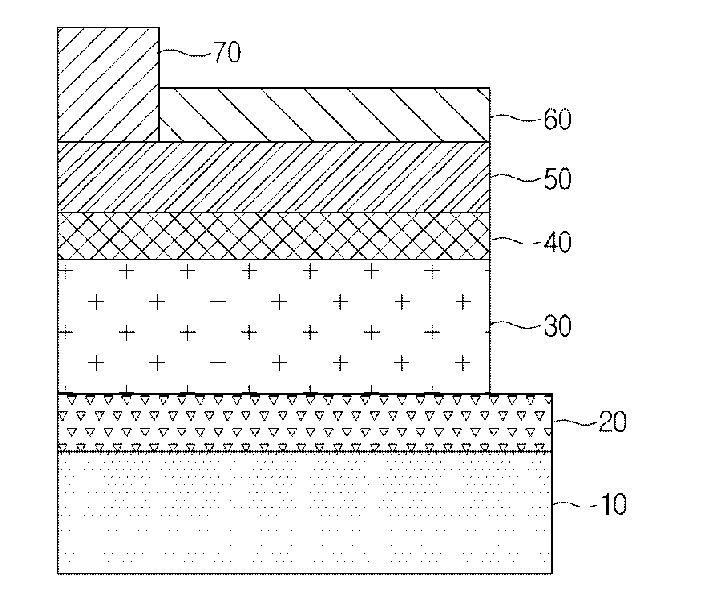
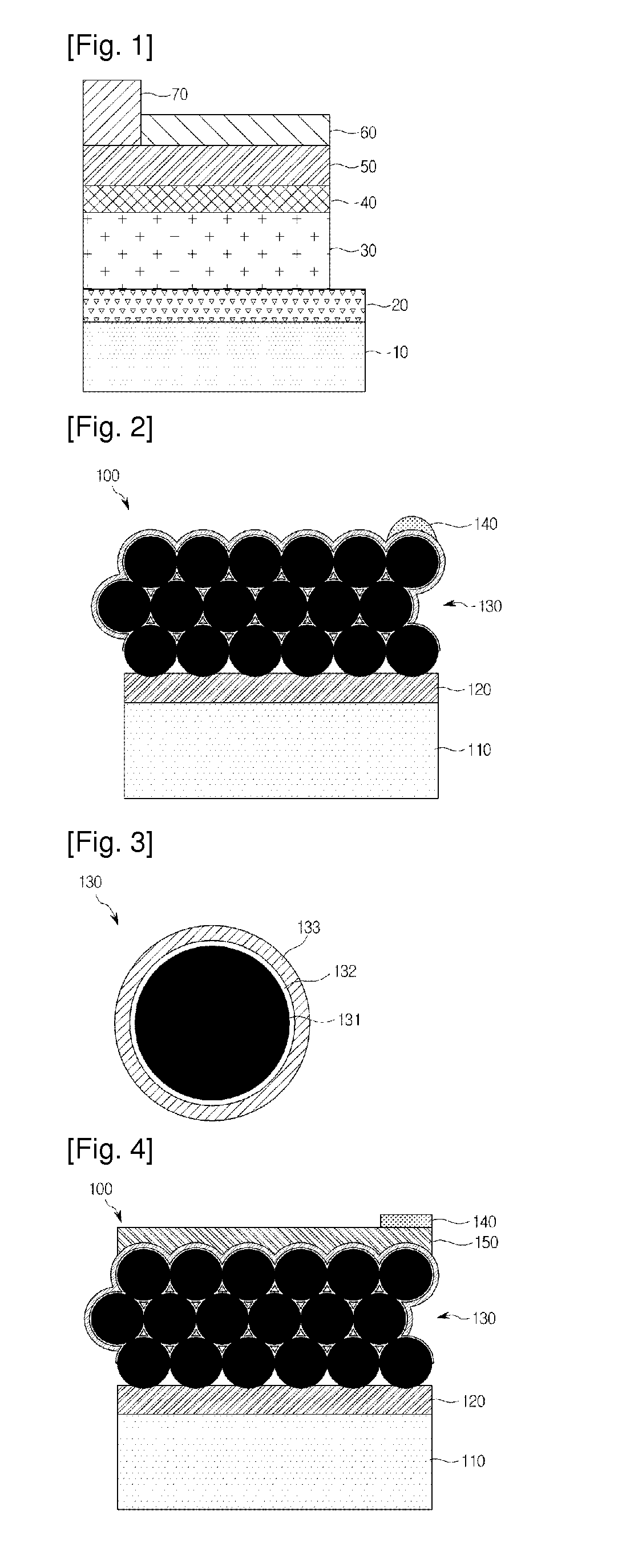
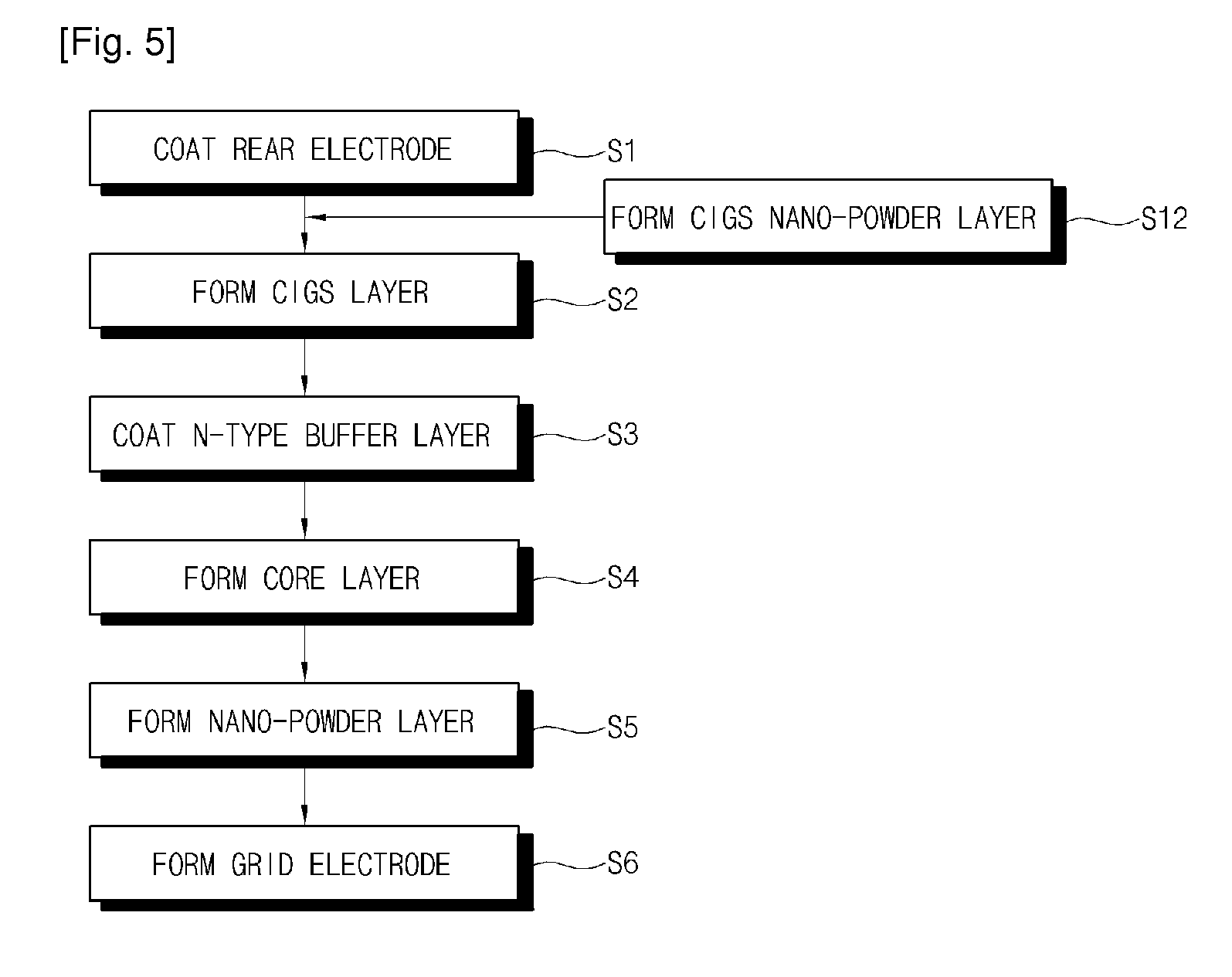
Bulk heterojunction solar cell and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20110024793A1Reduce manufacturing costHigh power outputFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionIndium
Provided are a bulk heterojunction solar cell, including: a substrate; a rear electrode formed on a top surface of the substrate; a core layer comprising a copper indium gallium diselenide (CIGS) layer in which a CIGS powder is formed on a top surface of the rear electrode to be porous, an n-type buffer layer coated on the CIGS powder, and an n-type ZnO layer coated on the n-type buffer layer; and a grid electrode formed on a top surface of the core layer, and a method of manufacturing the same. A porous p-type semiconductor layer is formed by sintering CIGS powders, and then, the n-type semiconductor is coated on the surface of the CIGS powders by using a wet method such that a much larger junction area than a physical size of the solar cell is formed and a power output of the solar cell can be greatly increased.
Owner:RES COOPERATION FOUND OF YEUNGNAM UNIV
Method for preparing hollow ball of sulfide and oxide of nickel
ActiveCN103058289ASimplified protocolEasy to operateNanotechnologyNickel oxides/hydroxidesCysteine thiolateTe element
The invention discloses a method for preparing a hollow ball of sulfide and oxide of nickel. The method comprises the following steps: (1), adopting ultrasonic or mechanical stirring to disperse nickel nitrate, L-cysteine and urea uniformly in deionized water; (2), transferring the mixed liquid into a reaction kettle, and reacting for 8 to 48 hours at a temperature of 140 DEG C to obtain a nickel disulphide hollow ball; (3), calcinating nickel disulphide at different temperatures to obtain hollow balls of nickel monosulfide and nickel oxide respectively; and (4), under hydrothermal condition, reacting nickel disulphide with selenium source and tellurium source respectively for 4 to 48 hours at a temperature of 140 DEG C to obtain hollow balls of nickel diselenide and nickel telluride. According to the method, raw materials are cheap, easy to obtain, and convenient to compound; the required devices are simple; no pollution is caused in the production process; and the large scale production can be realized rapidly.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
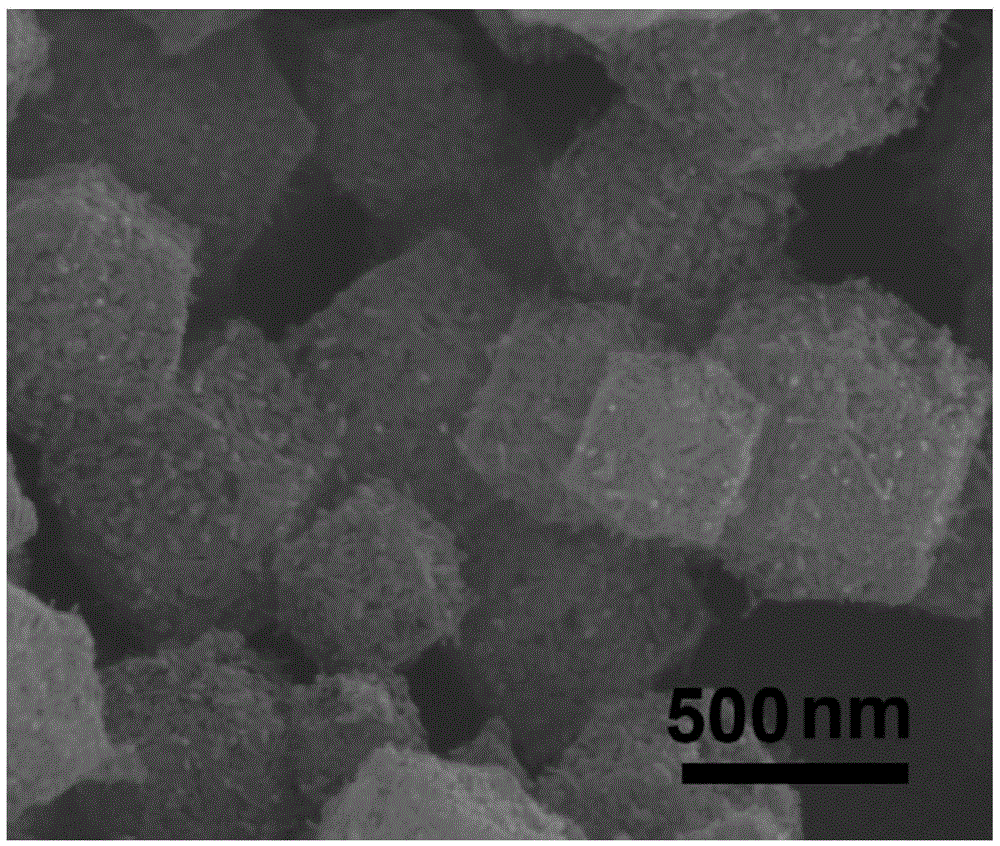
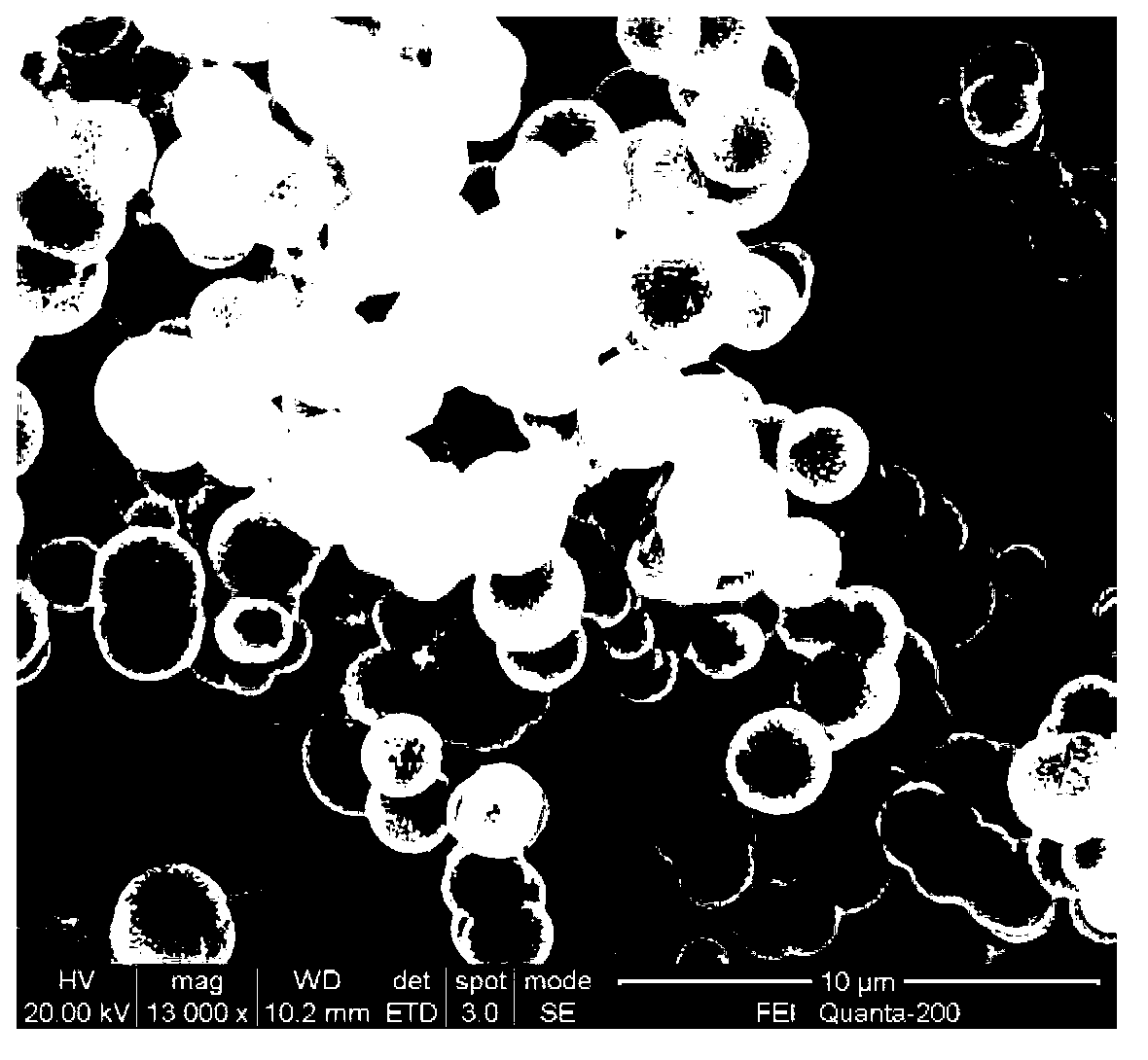
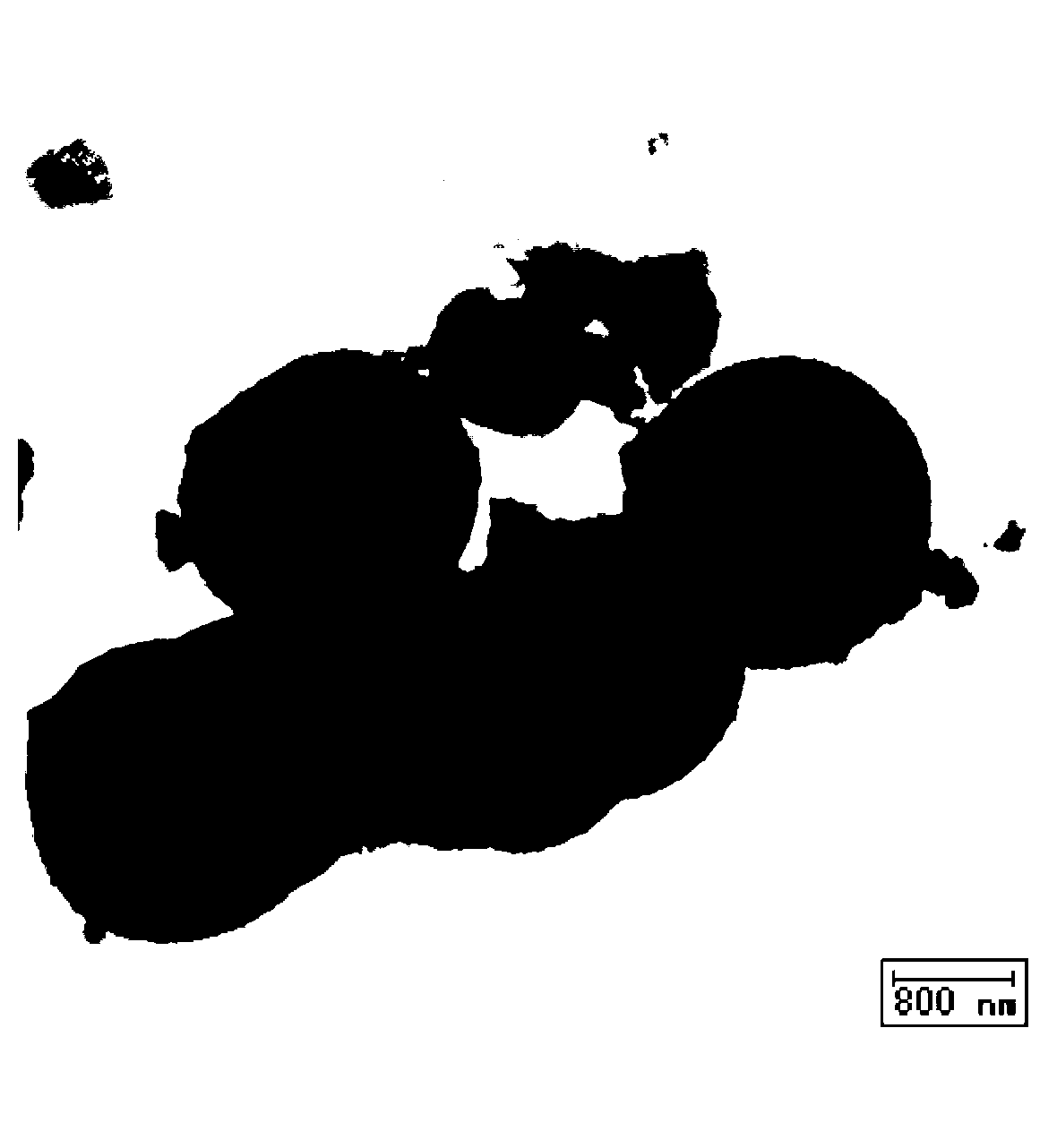
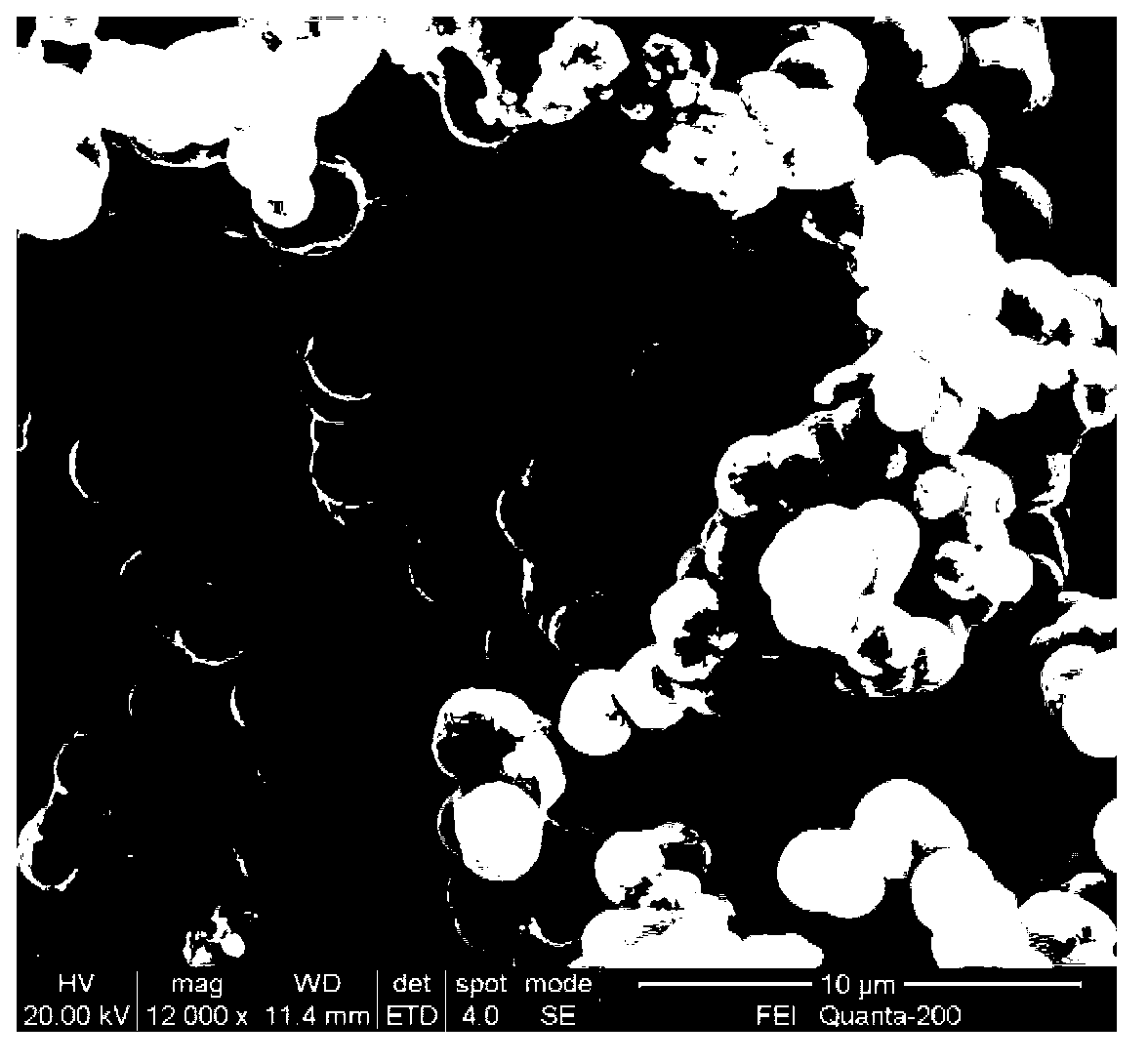
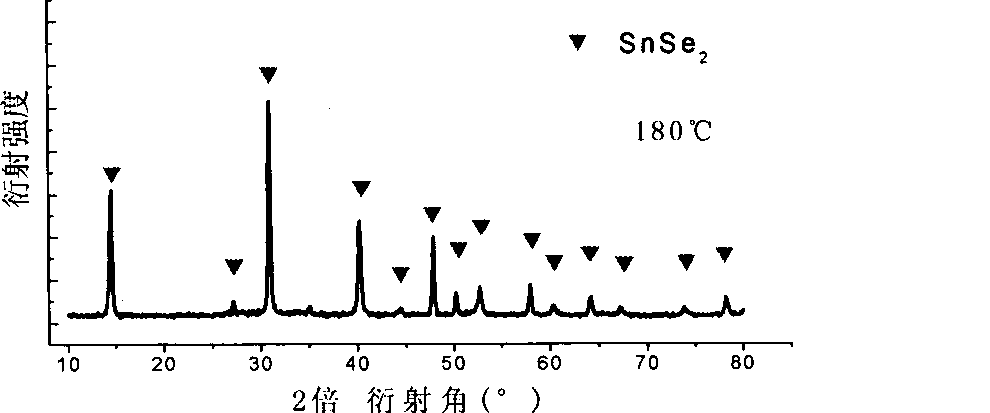
Preparation of high-purity tin diselenide nano-plate
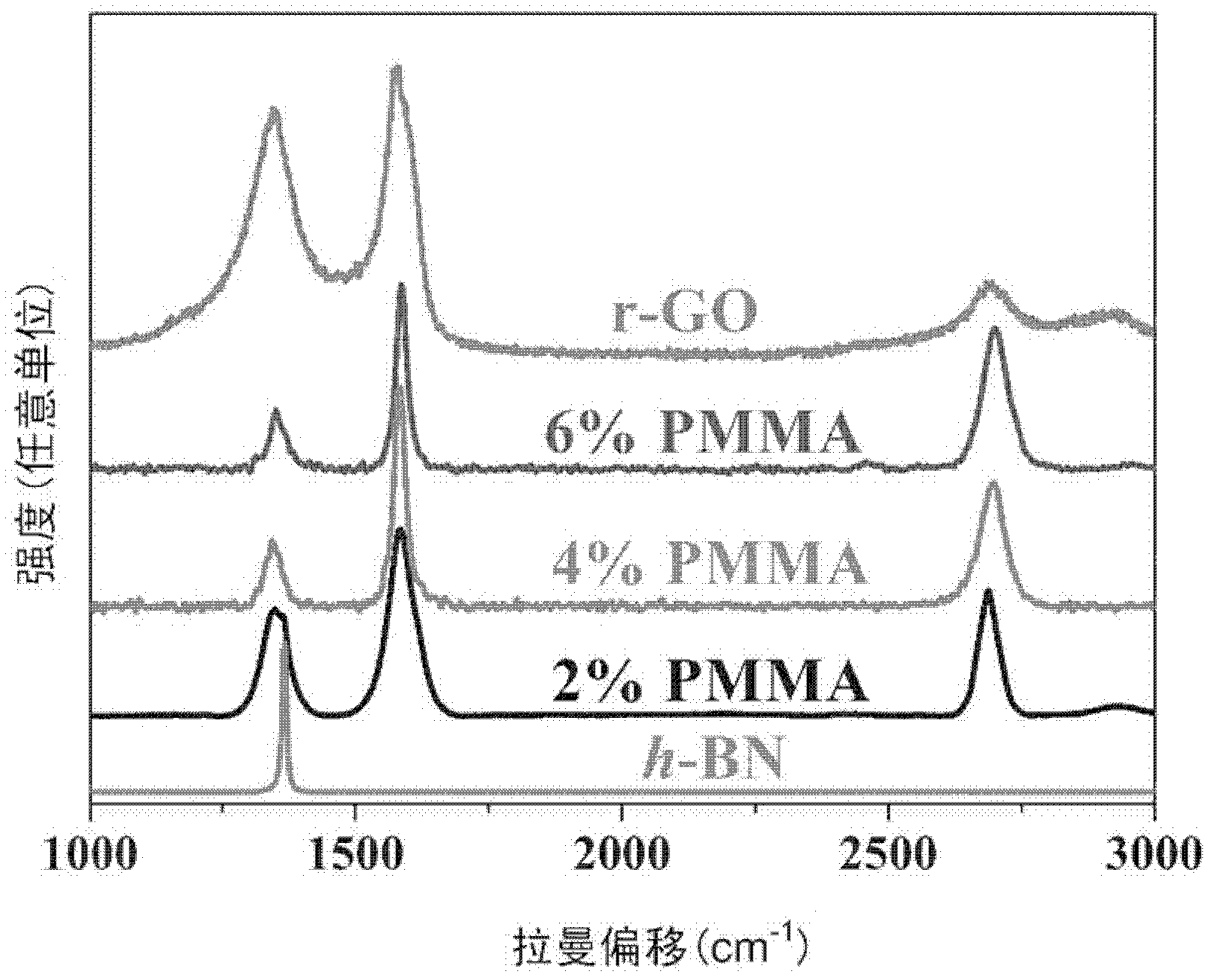
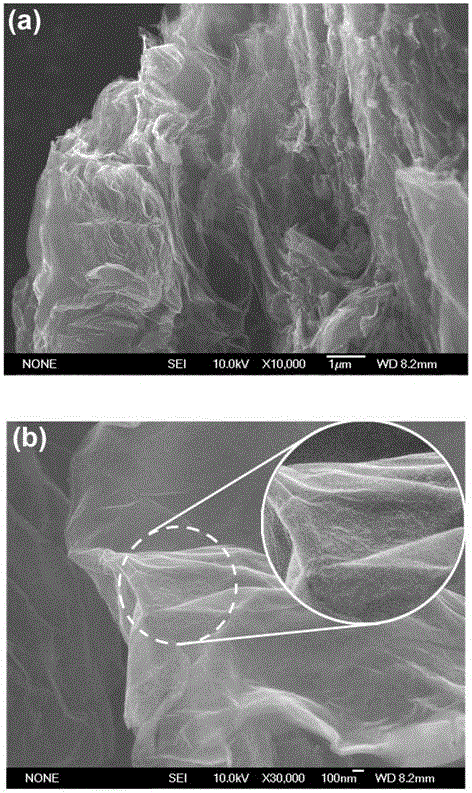
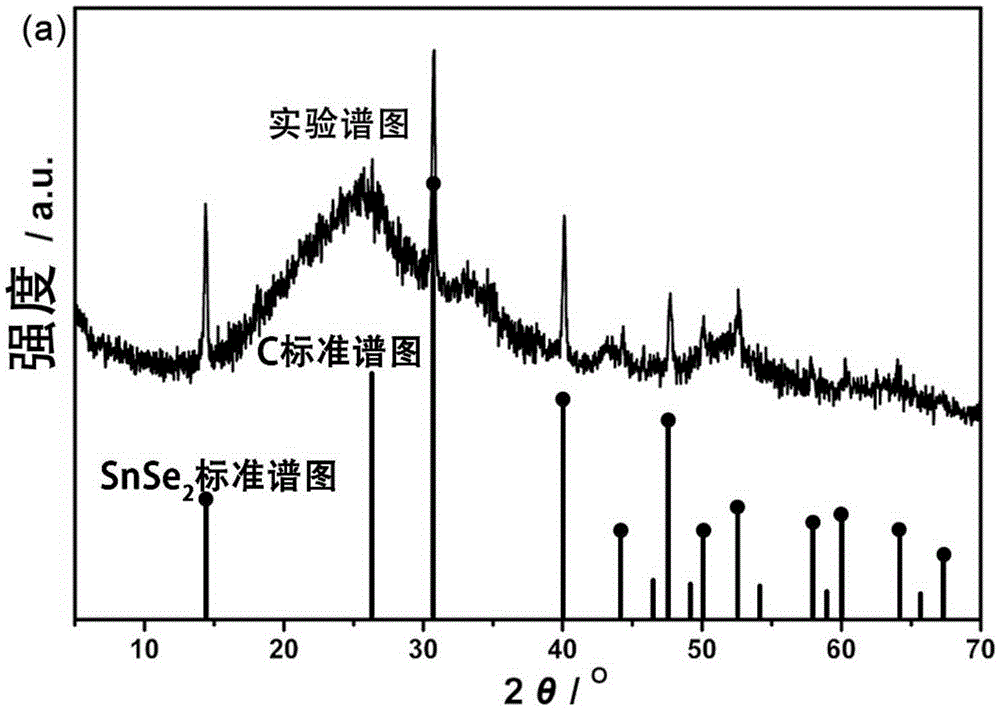
InactiveCN101412505AUniform thicknessUniform shapeBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsChemical synthesisHydrazine compound
The invention provides a preparation method for a high-purity tin diselenide nanometer piece, and relates to the technical field of hydrothermal chemical synthesis nanometer material process. According to the invention, three solid powders of SnCL2.2H2O, SeO2 and NaOH, hydrazine, and ammonia water are adopted to prepare the tin diselenide nanometer piece through the steps of reaction, heating, washing, drying and the like. The obtained tin diselenide has high purity, good dispersibility, and a regular and even shape. The technical process is safe; and the auxiliary solution and products of the process can be easily treated without pollution. Therefore, the method has broad application prospects.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
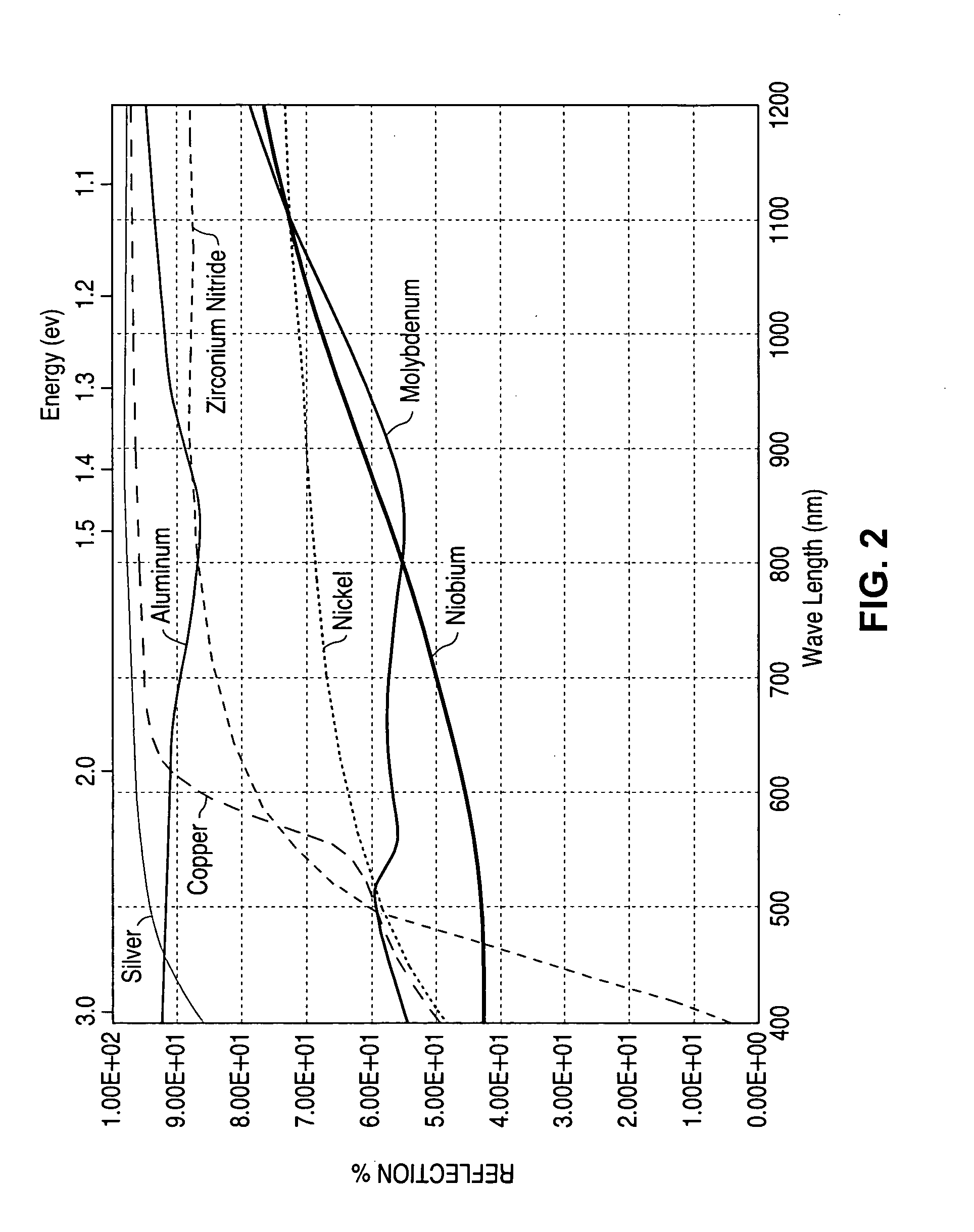
Method and Apparatus for In-Line Process Control of the Cigs Process
ActiveUS20080254202A1High precisionControl compositionFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingIndiumSolar cell
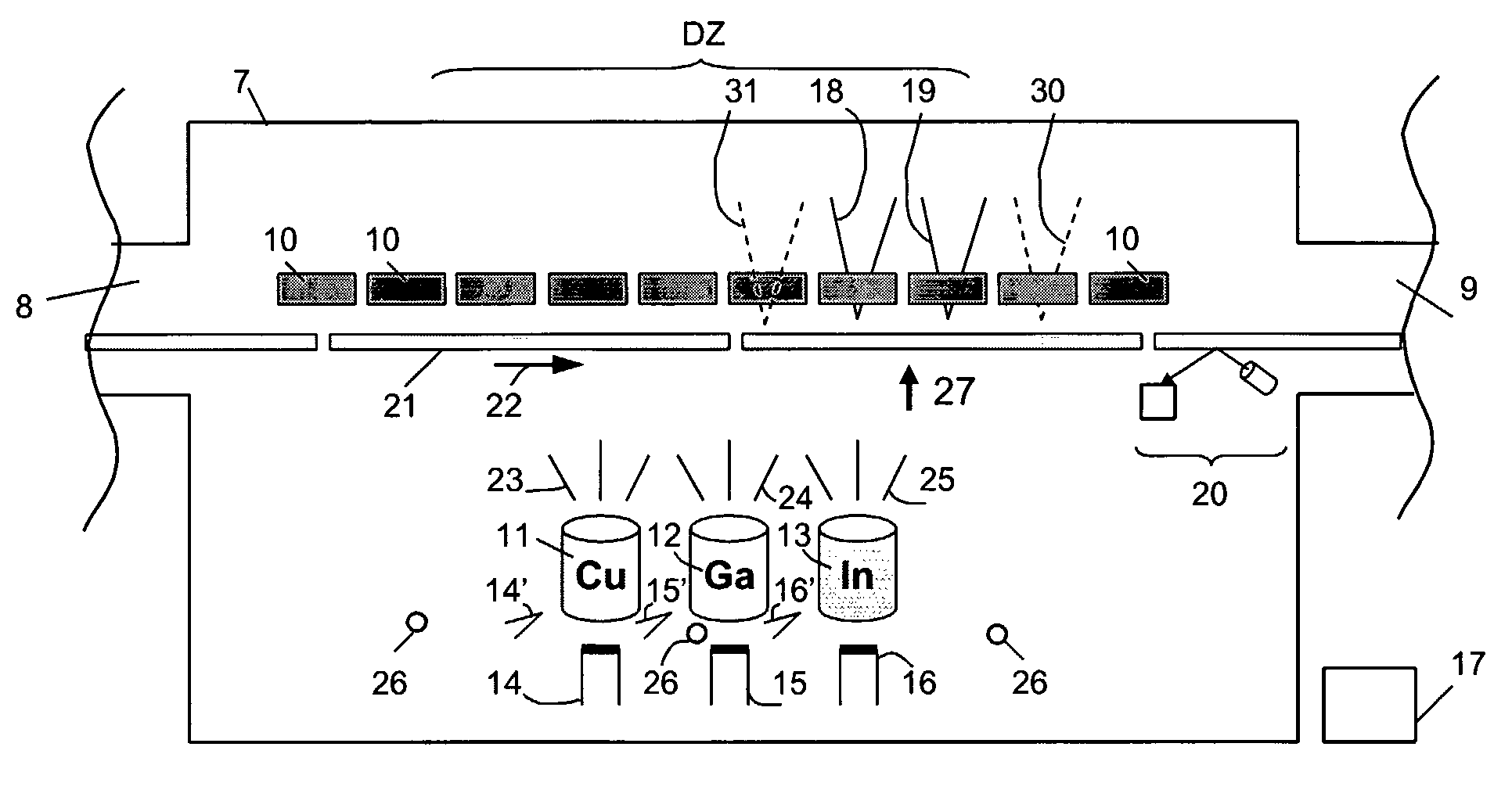
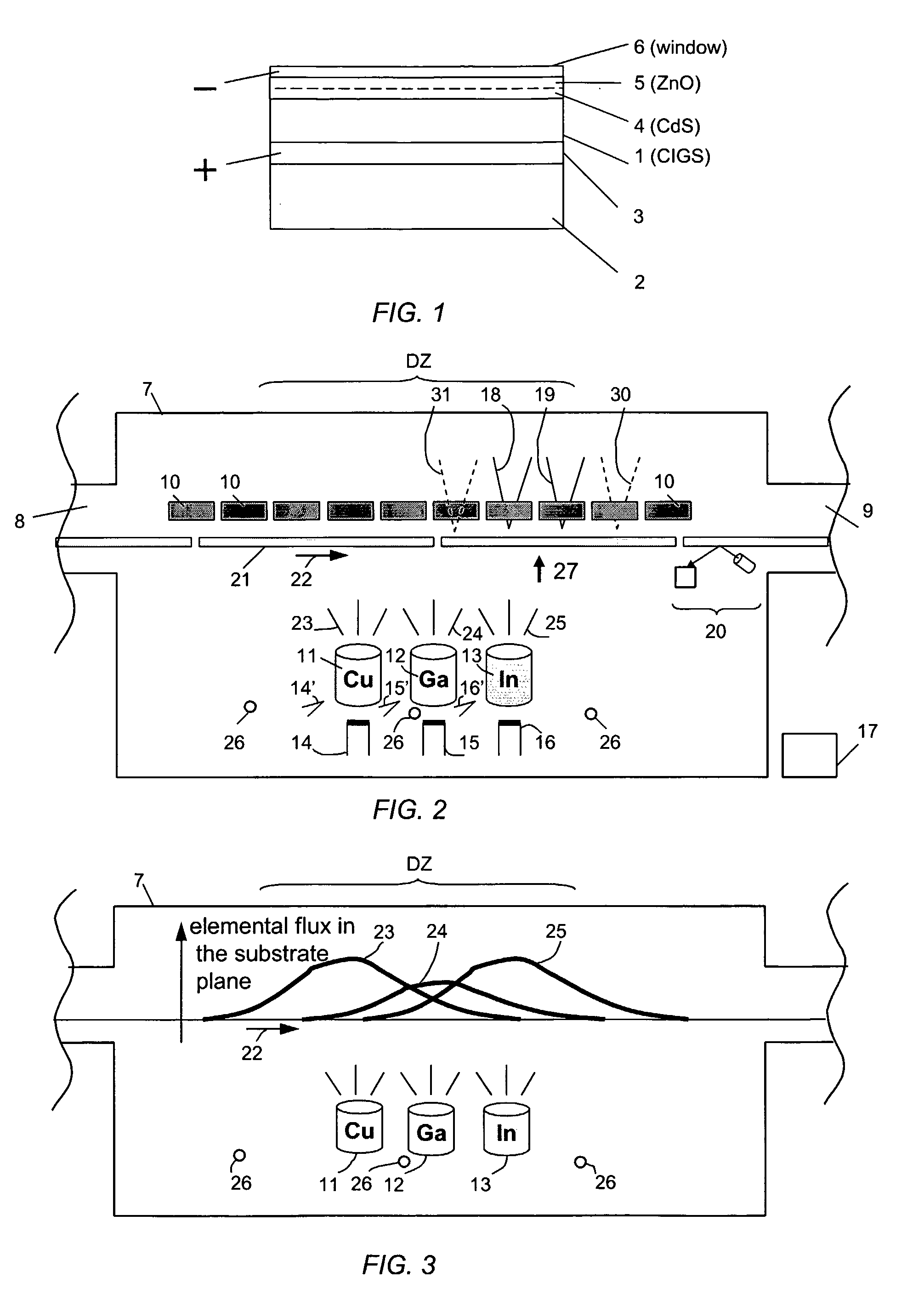
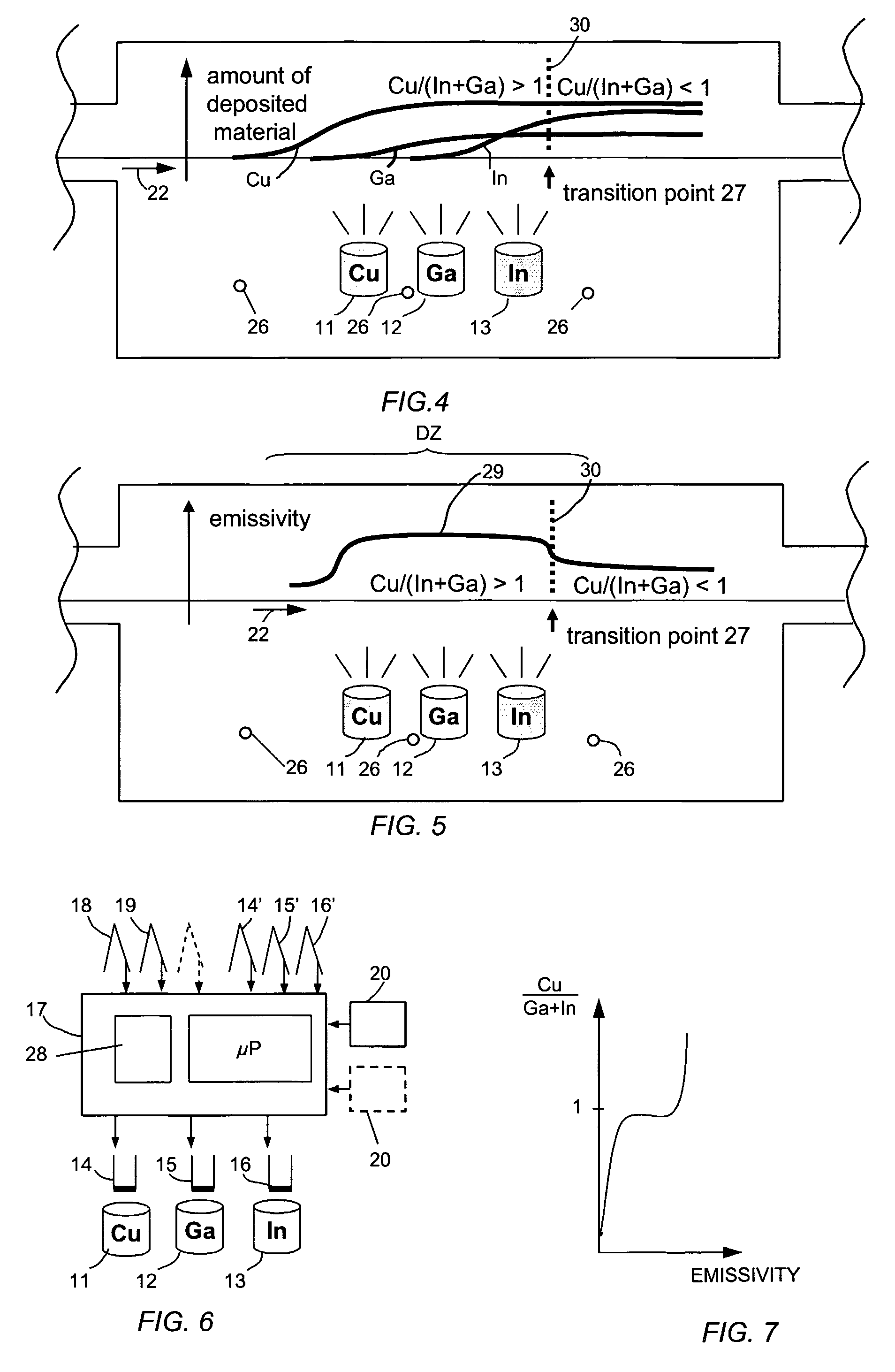
An in-line production apparatus and a method for composition control of copper indium gallium diselenide (CIGS) solar cells fabricated by a co-evaporation deposition process. The deposition conditions are so that a deposited Cu-excessive overall composition is transformed into to a Cu-deficient overall composition, the final CIGS film. Substrates with a molybdenum layer move through the process chamber with constant speed. The transition from copper rich to copper deficient composition on a substrate is detected by using sensors which detect a physical parameter related to the transition. A preferred embodiment sensors are provided that detect the composition of elements in the deposited layer. A controller connected to the sensors adjusts the fluxes from the evaporant sources in order provide a CIGS layer with uniform composition and thickness over the width of the substrate.
Owner:SOLIBRO RES AB
Method and device for scribing a thin film photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS20110240118A1Increase productionIncrease powerVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIndiumAluminum doped zinc oxide
The present invention is a method for scribing a thin film solar cell that includes a soda lime glass substrate, a film of molybdenum (Mo), a film of copper indium gallium diselenide (GIGS), a buffering layer, a layer of zinc oxide (i-ZnO), a layer of aluminum doped zinc oxide (n-ZnO:Al or AZO), a first scribe, a conductive link and a second scribe. The method steps include producing the first scribe on the Mo film, depositing the CICS film, the buffering layer and the zinc oxide layer onto the Mo film, producing the second scribe on the CICS film, the zinc oxide layer and the buffering layer above the Mo film, depositing and filling a first insulating material into the first scribe. and depositing a second insulating material that covers the solar cell while filling the first scribe forming a conduction layer.
Owner:BEATTY PAUL HANLON JAMES
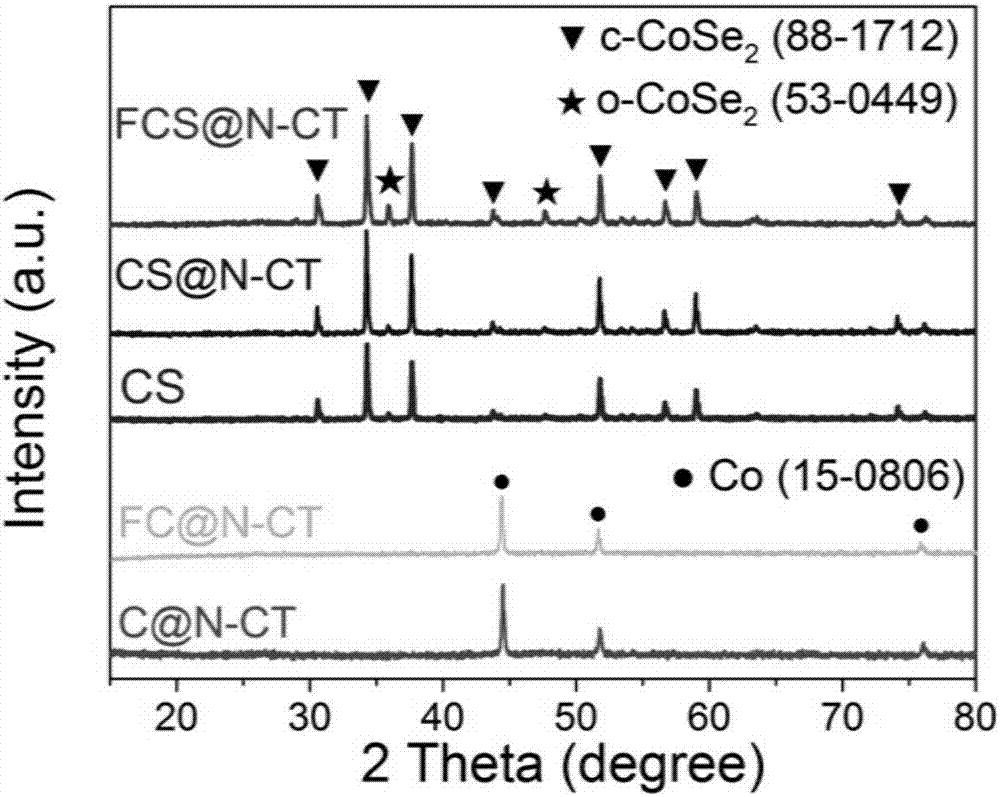
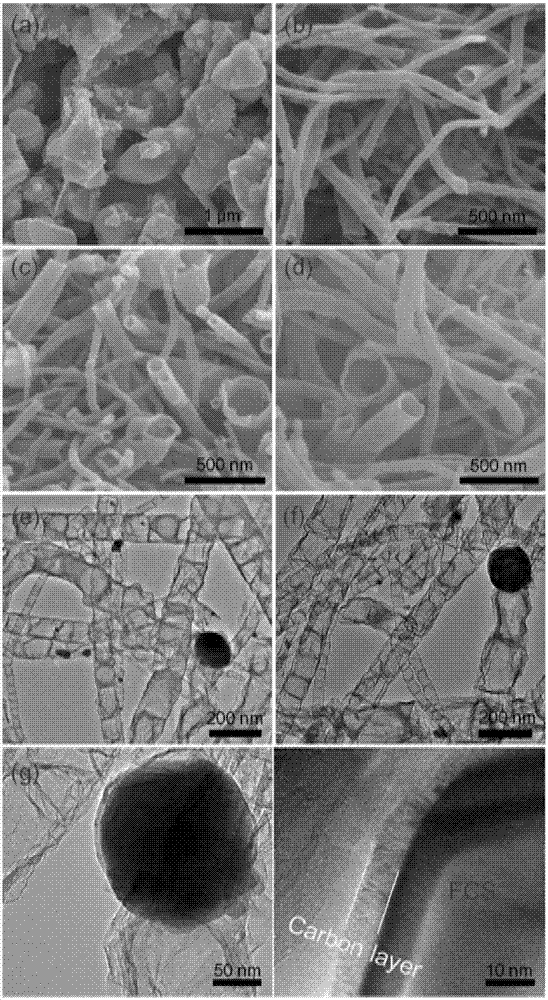
Oxygen evolution Fe-doped cobalt diselenide@N-CT compound catalyst and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107051568AHigh catalytic activityHigh OER catalytic performanceOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsElectrodesDecompositionOxygen evolution
The invention discloses an oxygen evolution Fe-doped cobalt diselenide@N-CT compound catalyst and a preparation method and application thereof. The compound catalyst comprises Fe-doped CoSe2 nano particles coated by an N-doped carbon nanotube. The preparation method includes: evaporating and drying the solution of cobalt acetate, iron nitrate and urea, and performing high-temperature treatment to obtain the Fe-doped CoSe2 nano particles coated by the N-doped carbon nanotube; mixing the Fe-doped CoSe2 nano particles coated by the N-doped carbon nanotube with Se powder to obtain a mixture, and performing selenylation on the mixture under protective atmosphere to obtain the compound catalyst. The preparation method has the advantages that the method is simple, low in cost and beneficial to industrial production; the prepared Fe-doped CoSe2@N-CT (recorded as FCS@N-CT) compound catalyst is applicable to electrocatalytic water decomposition, and the compound catalyst is good in comprehensive performance as compared with a commercial RuO2 catalyst and is promising in application prospect.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Manufacturing apparatus and method for large-scale production of thin-film solar cells
InactiveCN1703782ALow costFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumManufactured apparatus
A method of manufacturing improved thin-film solar cells entirely by sputtering includes a high efficiency back contact / reflecting multi-layer containing at least one barrier layer consisting of a transition metal nitride. A copper indium gallium diselenide (Cu(InxGa1-x)Se2) absorber layer (X ranging from 1 to approximately 0.1) is co-sputtered from specially prepared electrically conductive targets using dual cylindrical rotary magnetron technology. The band gap of the absorber layer can be graded by varying the gallium content, and by replacing the gallium partially or totally with aluminum. Alternately the absorber layer is reactively sputtered from metal alloy targets in the presence of hydrogen selenide gas. RF sputtering is used to deposit a non-cadmium containing window layer of ZnS. The top transparent electrode is reactively sputtered aluminum doped ZnO. A unique modular vacuum roll-to-roll sputtering machine is described. The machine is adapted to incorporate dual cylindrical rotary magnetron technology to manufacture the improved solar cell material in a single pass.
Owner:BEIJING APOLLO DING RONG SOLAR TECH
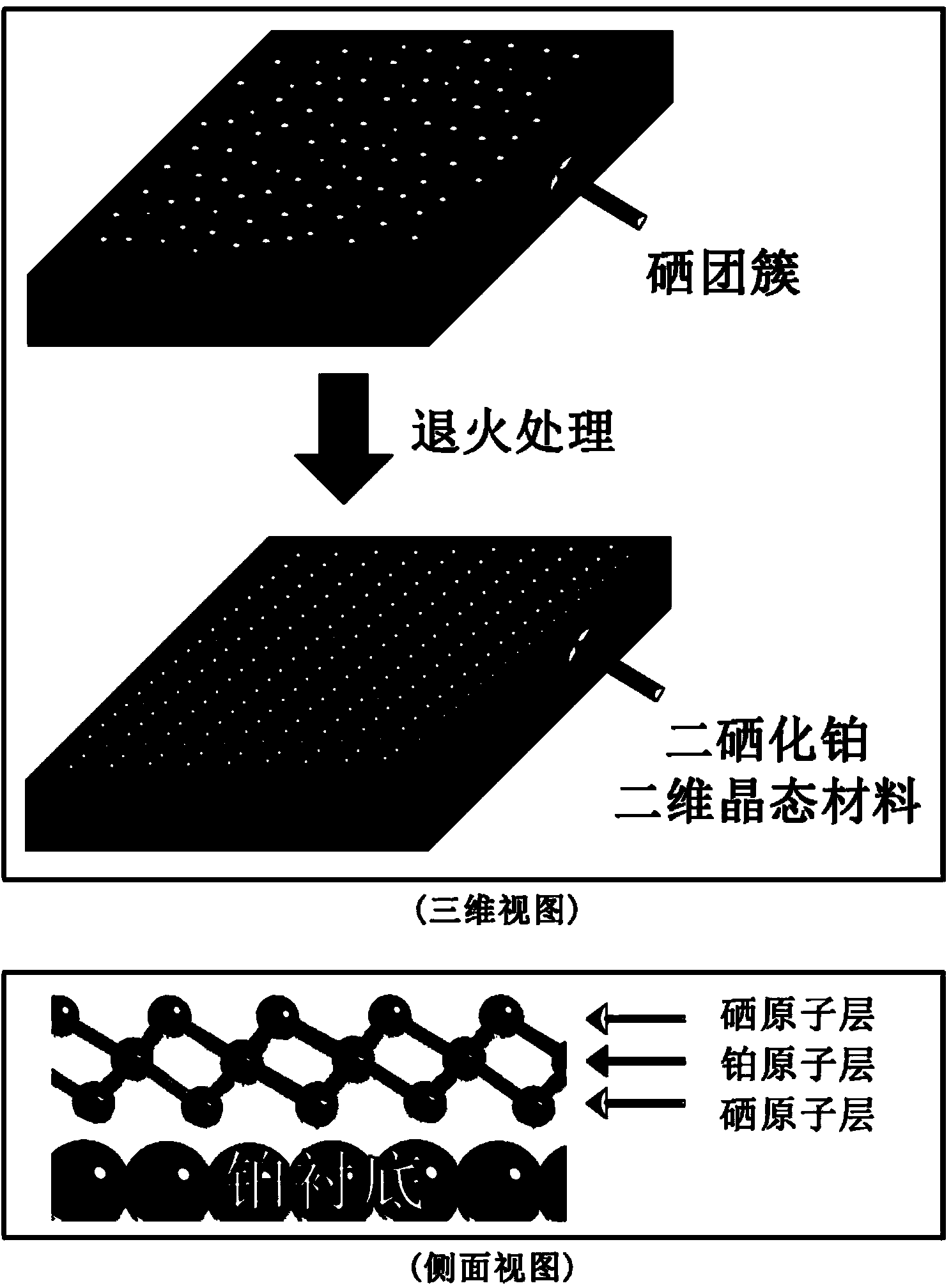
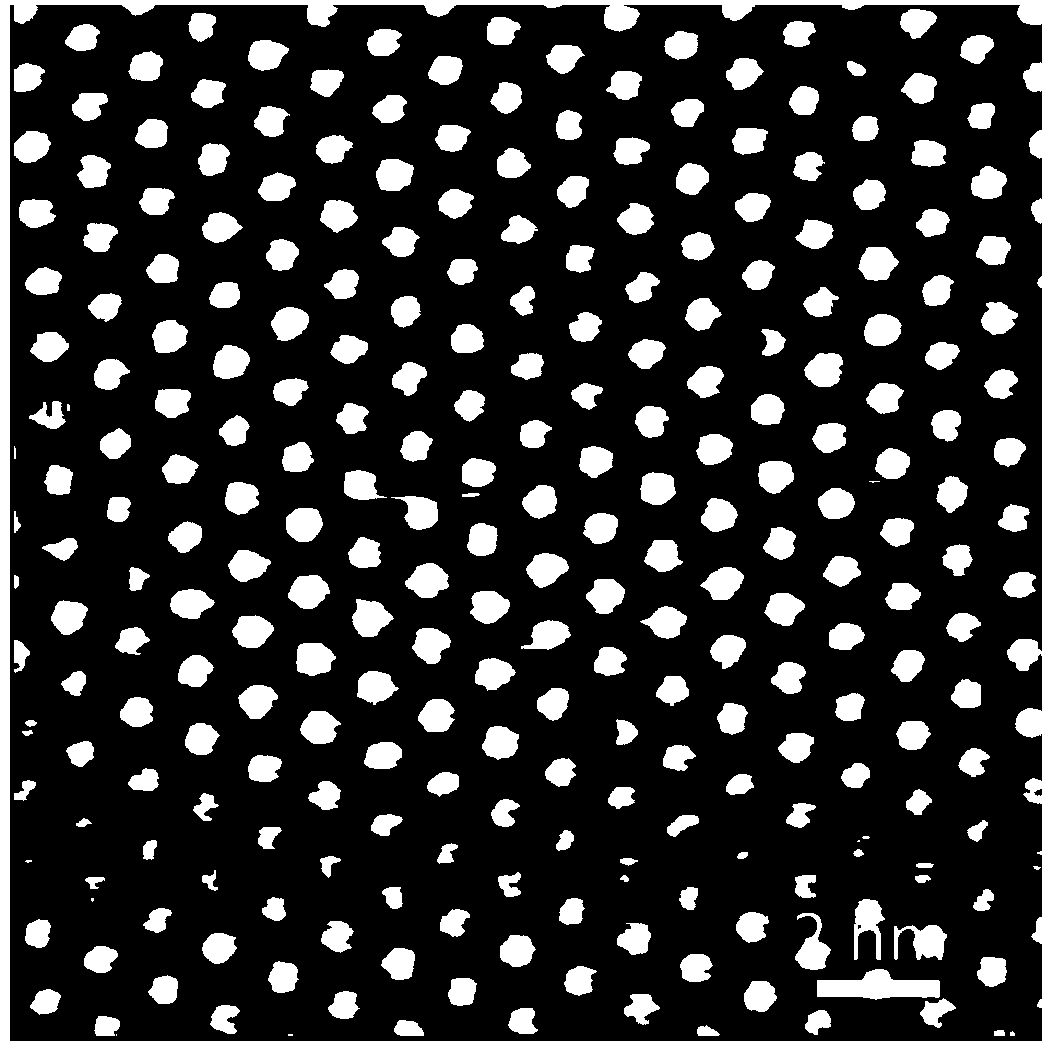
Platinum diselenide crystal material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104233214ABroaden the field of studyImprove electronic propertiesVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingTitanium diselenideSe element
The invention discloses a platinum diselenide crystal material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) under a vacuum environment, evaporating and depositing a proper amount of high purity selenium on a metal platinum substrate; and 2) carrying out an annealing treatment, so that selenium atoms covering the surface of the substrate and platinum atoms on the substrate interact to form a two-dimensional ordered crystalline state membrane structure in a sandwich arrangement of selenium-platinum-selenium so as to obtain the platinum diselenide crystal material. The inorganic two-dimensional crystalline state material is a new member of a transitional metal disulfide compound family, expands the field of research on non-carbon based two-dimensional crystal materials, and has a wide application potential in future information electronics and apparatus development and research. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the platinum diselenide two-dimensional crystalline state material with a big area and a high quality is grown on a molecular beam epitaxial method, so that the electronic properties of the platinum diselenide crystalline state material and related applications and development are favorably researched.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
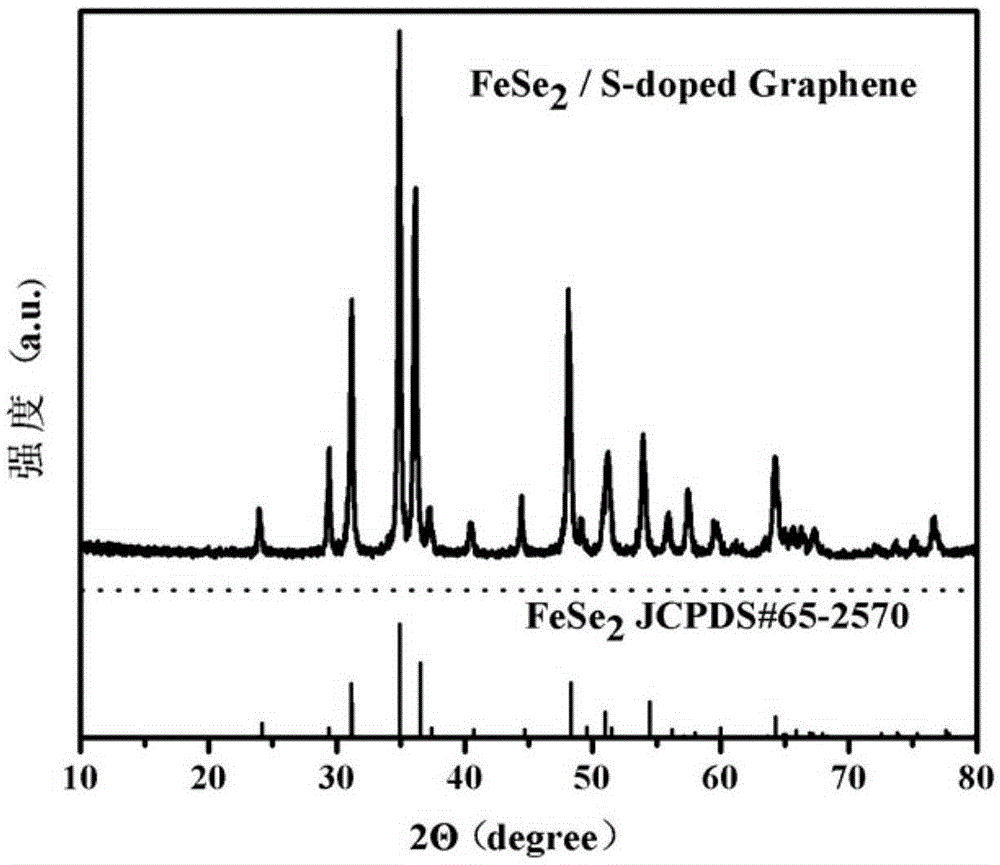
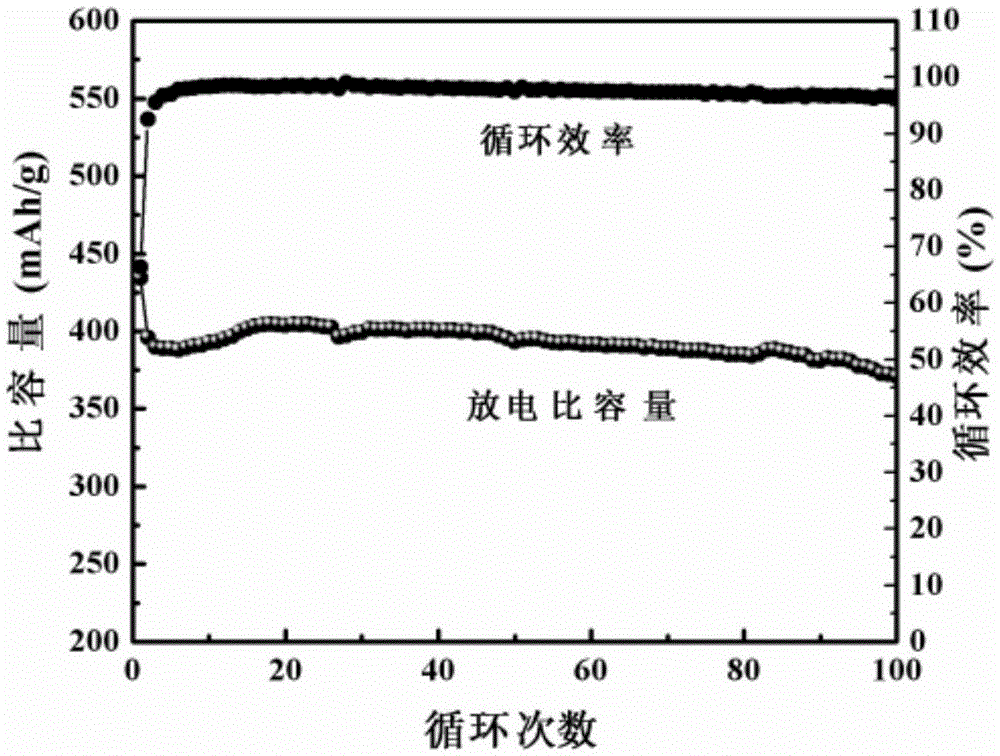
Iron diselenide/sulfur-doped graphene anode composite material for sodium-ion battery and preparation method of iron diselenide/sulfur-doped graphene anode composite material
ActiveCN105390674AAvoid irregular topographyAvoid reunionCell electrodesSecondary cellsSe elementMaterials science
The invention discloses an iron diselenide / sulfur-doped graphene anode composite material for a sodium-ion battery and a preparation method of the iron diselenide / sulfur-doped graphene anode composite material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving a sulfur source, a selenium-containing inorganic matter, an iron-containing inorganic salt and citric acid or sodium citrate into a graphene oxide solution; dropwise adding hydrazine hydrate to form a light black solution, adding the light black solution to a hydrothermal reaction kettle for reaction, and naturally cooling the product after the reaction is ended; and carrying out repeated washing, suction filtration and drying on a reaction sediment with distilled water and absolute ethyl alcohol, so as to obtain the iron diselenide / sulfur-doped graphene composite material. According to the iron diselenide / sulfur-doped graphene composite material prepared by the method, iron diselenide nano-particles are evenly distributed on the surface of the sulfur-doped graphene and the iron diselenide / sulfur-doped graphene composite material has excellent electrochemical properties as a sodium-ion battery anode material. The iron diselenide / sulfur-doped graphene anode composite material is prepared by a simple hydrothermal process; synchronous sulfur doping, graphene oxide reduction and graphene oxide and iron diselenide recombination can be achieved; and the iron diselenide / sulfur-doped graphene anode composite material is simple in preparation technology and low in cost, and has a wide industrial application prospect.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for preparing visible light self-repairing waterborne polyurethane coating material with double selenium bonds on main chain
ActiveCN106497385AAchieve self-healingAchieve brokenPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPhotochemistryDiselenide
The invention discloses a method for preparing a visible light self-repairing waterborne polyurethane coating material with double selenium bonds on a main chain. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing an isocyanate end capped polyurethane prepolymer with double selenium bonds on a main chain from raw materials of diisocyanate, dihydroxyethyl diselenide, macromolecule dihydric alcohol and dimethylolpropionic acid; secondly, adding triethylamine for neutralization, further adding a proper amount of deionized water for rapid emulsification, slowly adding a diamine chain extender which is diluted with water, and performing emulsification chain expansion under a condition that the rotation speed is greater than 1200r / min, thereby obtaining the visible light self-repairing waterborne polyurethane coating material with the double selenium bonds on the main chain. On the basis of the visible light reversibility characteristic of double-selenium dynamic covalent bonds, the waterborne polyurethane coating material with the double selenium bonds on the main chain is capable of achieving self-repairing of cracks and broken parts under radiation of gentle visible illumination, so that the service life of the material can be greatly prolonged, the potential safety hazard in use can be reduced, and a relatively long service life can be achieved for the waterborne polyurethane coating material. The waterborne polyurethane coating material with double selenium bonds on the main chain is applicable to coating of leather, textiles, paper, furniture, wall surfaces and the like, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
One-dimensional conductive nanomaterial-based conductive film having the conductivity thereof enhanced by a two-dimensional nanomaterial
InactiveUS20140212672A1Improve conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyConductive layers on insulating-supportsMolybdenum tellurideNiobium
A one-dimensional conductive nanomaterial-based conductive film having the conductivity thereof enhanced by a two-dimensional nanomaterial in which the conductive film includes a substrate, a one-dimensional conductive nanomaterial layer formed on the substrate, and a two-dimensional nanomaterial layer formed on the one-dimensional conductive nanomaterial layer, wherein the one-dimensional conductive nanomaterial layer includes a one-dimensional conductive nanomaterial formed of at least one selected from a carbon nanotube, a metal nanowire, and a metal nanorod, and the two-dimensional nanomaterial layer includes a two-dimensional nanomaterial formed of at least one selected from graphene, boron nitride, tungsten oxide (WO3), molybdenum sulfide (MoS2), molybdenum telluride (MoTe2), niobium diselenide (NbSe2), tantalum diselenide (TaSe2), and manganese dioxide (MnO2). A two-dimensional nanomaterial, such as graphene may be stacked on a one-dimensional conductive nanomaterial such as a carbon nanotube or a metal nanowire to enhance the conductivity of the one-dimensional conductive nanomaterial film.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Method for preparing graphene powder and graphene transparent conductive film by oxyhydrogen flame method
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-quality graphene powder and a graphene transparent conductive film. The method comprises that through an oxyhydrogen flame rapid heating method, organics are decomposed into high-activity carbon atoms; and the high-activity carbon atoms are re-configurated into graphene on an insulating substrate or a catalyst substrate. Through the method, high-quality graphene can directly grow on the insulating substrate, and through an ultrasonic method, high-quality graphene powder without a support substrate is obtained. Compared with the traditional chemical stripping method for preparing graphene, the method has simple processes, a low cost, less defects and good conductivity and can produce high-quality graphene. The method can be used for preparing the graphene transparent conductive film on a catalyst film substrate. The graphene transparent conductive film has quality and conductivity approximate to the optimal values of a graphene transparent conductive film obtained by the traditional CVD method. Graphene obtained by the method has wide application prospects in fields of photoelectric devices such as copper indium gallium diselenide, cadmium telluride and dye-sensitized solar cells, panel displays, super capacitors, field emission materials, and lithium ion batteries.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nanometer tin diselenide/graphene composite material and its preparation method and use
ActiveCN105304878AUniform particle sizeHigh bonding strengthMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesSodium-ion batteryNanostructure
The invention discloses a nanometer tin diselenide / graphene composite material. The nanometer tin diselenide / graphene composite material is characterized in that tin diselenide particles with the average particle size of 3-10nm grow on the graphene surface. Nanometer tin diselenide and graphene have high binding strength, tin diselenide nanometer particles have good crystallization structures, graphene slice layers are disorderedly stacked to form a 3D skeleton, and nano-scale tunnels and a good charge transmission network are provided. The nanometer tin diselenide / graphene composite material is used as a cell cathode material and has good charge and discharge performances and stability. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the nanometer tin diselenide / graphene composite material. In synthesis, an ionic liquid is used and through improvement of binding strength of a metal sulfur nanometer structure and a carbon material, effective compounding of the carbon material and tin diselenide is realized and a high-performance lithium ion battery and sodion battery cathode material is obtained.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for surface modification of copper indium gallium diselenide (Cu(In, Ga)Se2) film
InactiveCN102694068AEfficient removalIncrease the open circuit voltageFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesIndiumNew energy
The invention discloses a method for surface modification of a copper indium gallium diselenide (Cu(In, Ga)Se2) film and relates to the technical field of photoelectric function materials and new energy. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: depositing a metal film or an alloy film with a certain thickness on the (Cu(In, Ga)Se2) film, performing high temperature annealing on the (Cu(In, Ga)Se2) film under reactive atmosphere and carrying out a copper selenium secondary phase (CuxSe) reaction on the surface of the deposited metal or alloy and (Cu(In, Ga)Se2) film to form a copper selenium poly-metal compound with a wide band gap so as to fulfill the aim of removing CuxSe. By the surface modification method, the defect that toxicity exists and the environment cannot be protected in etching the CuxSe by the traditional modification method by adopting KCN (potassium cyanide) are overcome; the method has the advantages of being low in cost and high in reproducibility and being suitable for large-area film growth and the like; and with the adoption of method, the band gap width on the surface of the film can be improved, a gradient band gap is formed, the pn junction interface composition is obviously reduced, and the open-circuit voltage of a device is effectively improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
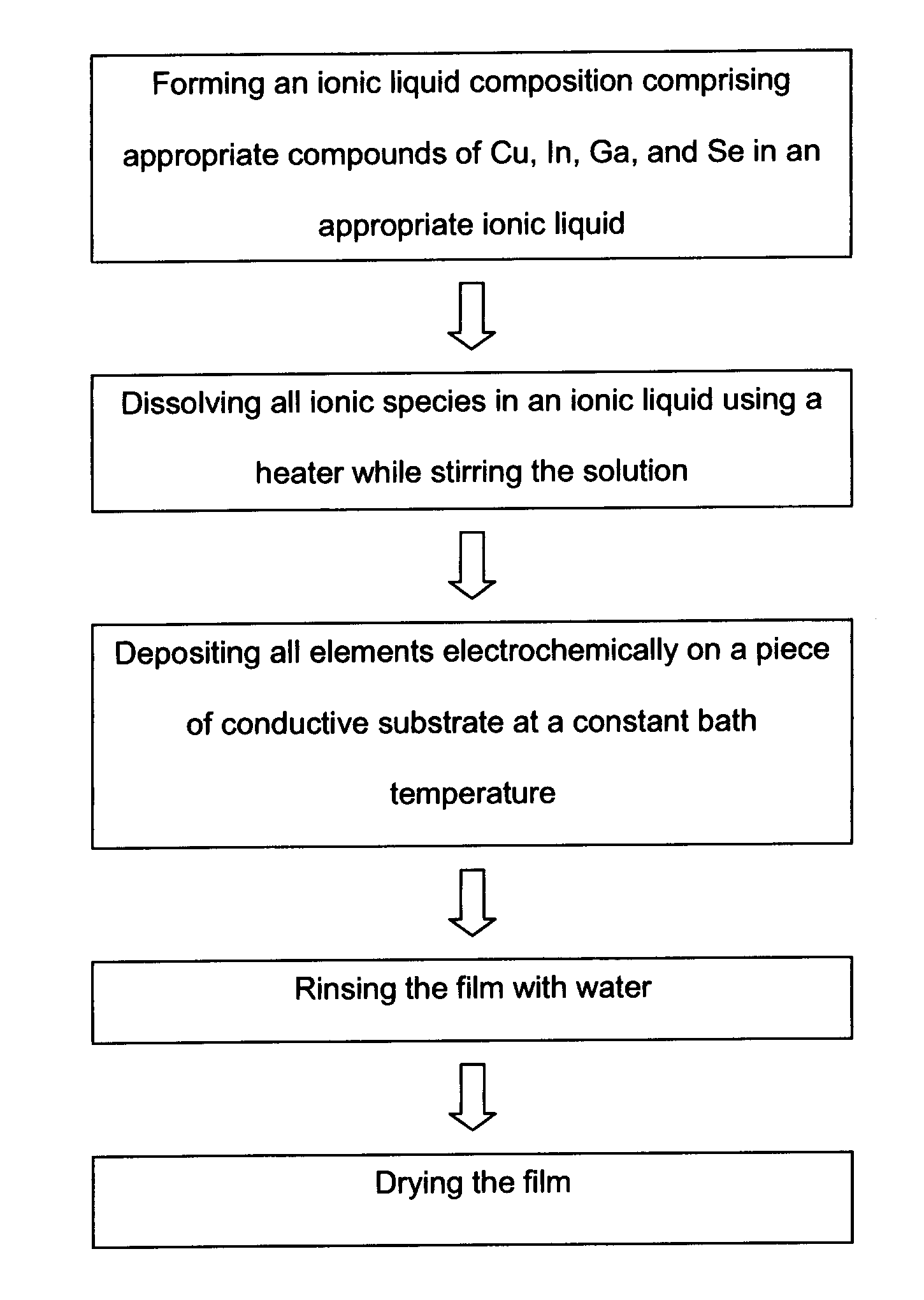
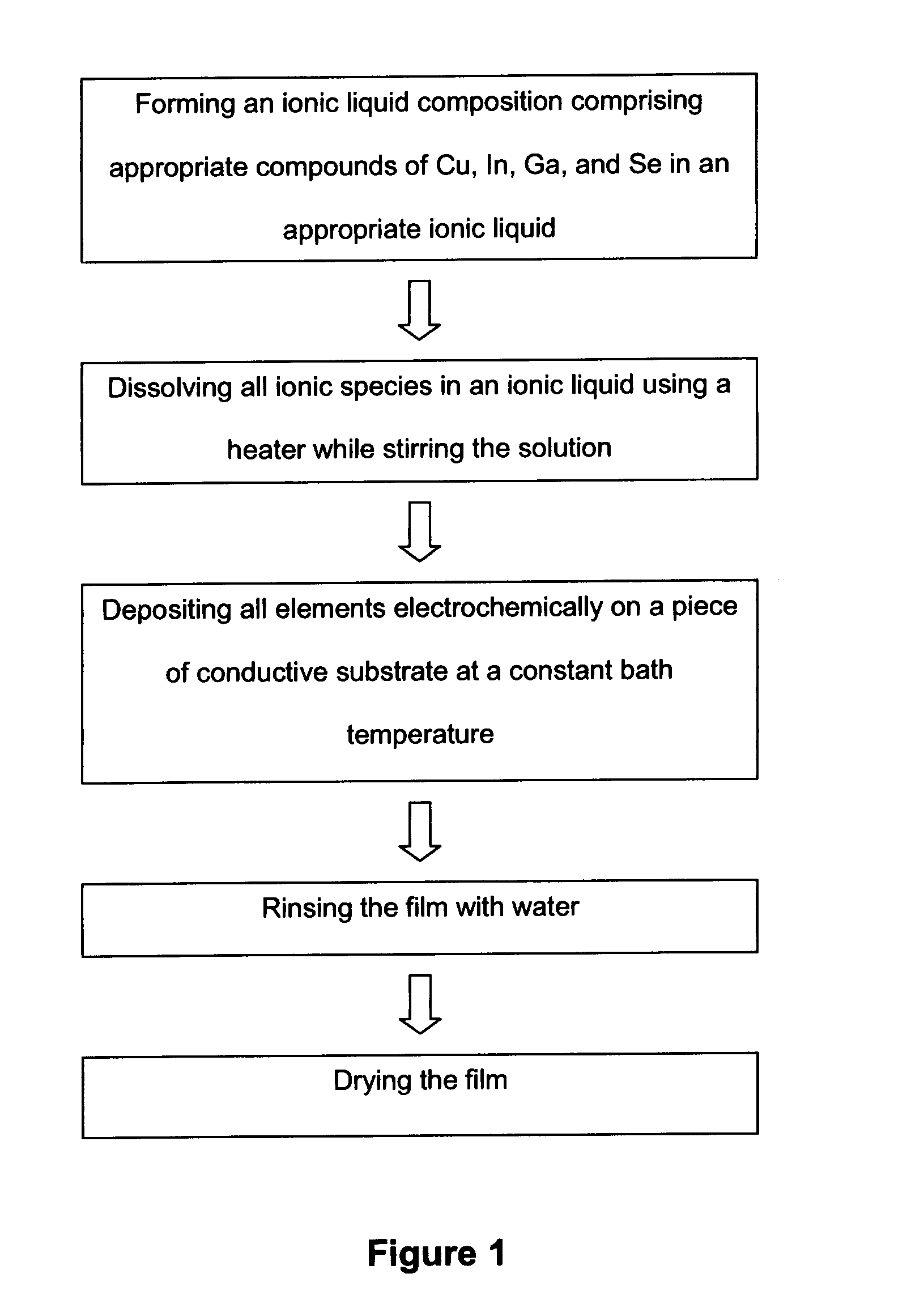
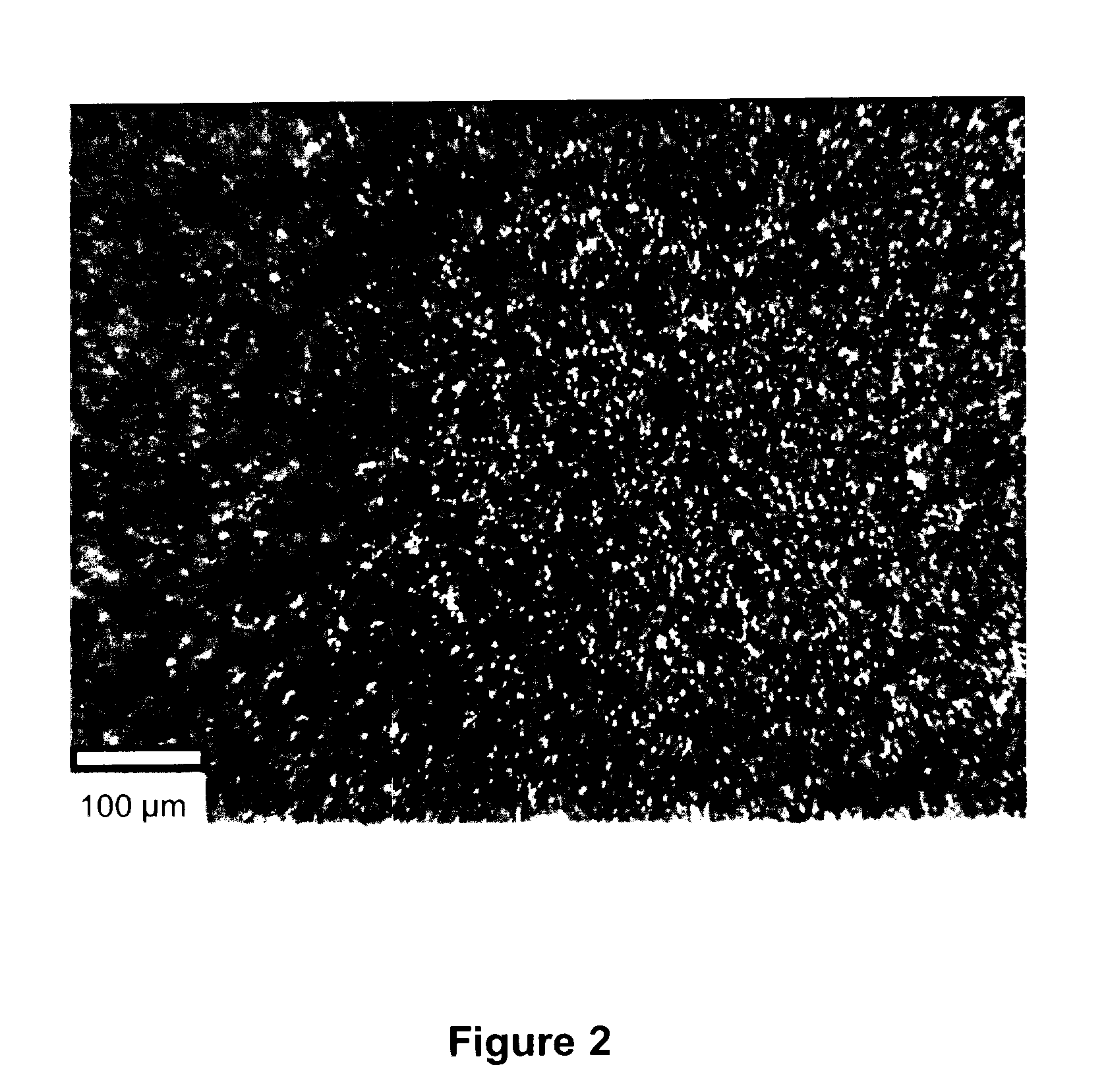
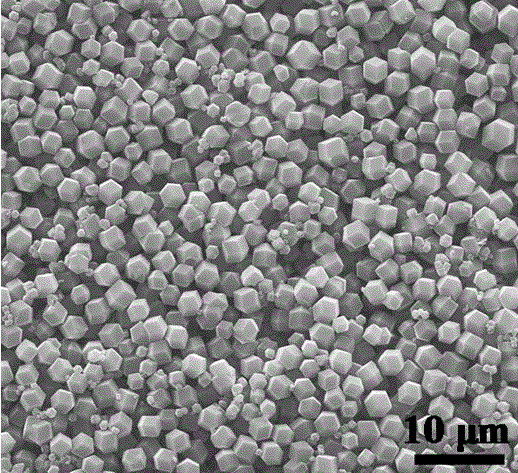
Electrochemical method of producing copper indium gallium diselenide (CIGS) solar cells
InactiveUS20120227811A1Low-cost and high-throughput productionImprove scalabilityFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesIndiumElectrochemistry
The present invention describes a method of producing a photovoltaic solar cell with stoichiometric p-type copper indium gallium diselenide (CuInxGa1-xSe2) (abbreviated CIGS) as its absorber layer and II-IV semiconductor layers as the n-type layers with electrodeposition of all these layers. The method comprises a sequence of novel procedures and electrodeposition conditions with an ionic liquid approach to overcome the technical challenges in the field for low-cost and large-area production of CIGS solar cells with the following innovative advantages over the prior art: (a) low-cost and large-area electrodeposition of CIGS in one pot with no requirement of post-deposition thermal sintering or selenization; (b) low-cost and large-area electrodeposition of n-type II-VI semiconductors for the completion of the CIGS solar cell production; and (c) low-cost and large-area deposition of a buffer layer of CdS or other compounds with a simple chemical bath method.
Owner:CHENGDU ARK ETERNITY PHOTOVOLTAIC TECH COMPANY
Cobalt diselenide/graphite carbon composite material, namely oxygen reduction catalyst, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105552392AThe synthesis method is simpleReduce manufacturing costCell electrodesCarbon compositesGraphite carbon
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical catalysts, and particularly relates to a cobalt diselenide / graphite carbon composite material, namely an oxygen reduction catalyst, and a preparation method thereof. The oxygen reduction catalyst provided by the invention is the cobalt diselenide / graphite carbon composite material and obtained by uniformly embedding cobalt diselenide nano-particles, the diameter of which is several nanometres, in a porous graphite carbon polyhedron. According to the invention, a synthesis method is simple; the production cost is low; large-scale preparation can be realized; compared with cobalt diselenide and a carbon materialwhich are subjected tomechanical mixing, the prepared composite material has the advantages of being high in interface coupling, uniform in cobalt diselenide particle distribution and the like; a carbon substrate has a mesoporous structure; and the oxygen reduction catalytic performance of the oxygen reduction catalyst in an alkaline environment is superior to that of the commercial platinum-carbon catalyst.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Graphene and ferrum diselenide composite material and method for preparing same
InactiveCN102942165ARich sourcesSimple preparation processMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsHydrazine compoundReaction temperature
The invention discloses a graphene and ferrum diselenide composite material and a method for preparing the same. The method for preparing comprises the following steps: selenium-containing inorganic salt and ferrum-containing inorganic salt are put into a stainless steel reactor; hydrazine hydrate and source graphene solution are mixed together and stirred uniformly to form an ink black solution to be added into the reactor, and the reactor is closed so as to carry out reaction; and after the reaction is completed, natural cooling is carried out, reaction precipitate is subjected to repeated washing and suction filtering through distilled water and absolute ethyl alcohol, and after the drying, the product is collected and stored in a drying device. According to the prepared graphene and ferrum diselenide composite material, a graphene sheet wraps ferrum diselenide nanoparticles, the ferrum diselenide is tightly combined with the graphene sheet, so that high specific surface area and excellent magnetic performance are obtained. The method adopts a simple hydrothermal method, the graphene reduction oxide and the composite preparation of the praphene and the ferrum diselenide can be synchronously carried out, and the method has the advantages of simplicity in technology, low reaction temperature, low cost, green, controllability and applicability for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation method of radiation sensitive copolymer carrier for coating radiated nanoparticles and chemotherapy drugs
The preparation method of radiation-sensitive copolymer carrier for coating radiated nanoparticles and / or chemotherapy drugs includes forming a nanosphere by diselenide block copolymers and DSPE-PEG-biomarkers to coat chemotherapy drugs and / or radiated nanoparticles that can be released from the opened nanosphere by protons penetrating tissue during proton therapy. The treatment effect of proton therapy is enhanced by two ways of using the radiated nanoparticles released from an opened nanosphere to produce nuclear fission with the protons for releasing electrons to destroy cancer cells of tumor and the chemotherapy drugs released from the opened nanosphere for distributing among tissue to kill the cancer cells of the tumor.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR ENERGY RES NUCLEAR ENERGY COUNCIL EXECUTIVE YUAN
Preparation method of radiation sensitive copolymer carrier for coating radiated nanoparticles and chemotherapy drugs
The preparation method of radiation-sensitive copolymer carrier for coating radiated nanoparticles and / or chemotherapy drugs includes forming a nanosphere by diselenide block copolymers and DSPE-PEG-biomarkers to coat chemotherapy drugs and / or radiated nanoparticles that can be released from the opened nanosphere by protons penetrating tissue during proton therapy. The treatment effect of proton therapy is enhanced by two ways of using the radiated nanoparticles released from an opened nanosphere to produce nuclear fission with the protons for releasing electrons to destroy cancer cells of tumor and the chemotherapy drugs released from the opened nanosphere for distributing among tissue to kill the cancer cells of the tumor.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR ENERGY RES NUCLEAR ENERGY COUNCIL EXECUTIVE YUAN
Preparation method of molybdenum diselenide/cobalt diselenide nanocomposite
InactiveCN105381807ARaw materials are simpleThe equipment process is simpleMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsMolybdenum diselenideNanocomposite
The present invention provides a preparation method of a molybdenum diselenide / cobalt diselenide nanocomposite, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of inorganic nanocomposites. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding 0.002-0.05 mol / L of molybdate, 0.01-0.1 mol / L of cobalt salt and 0.02-0.5 mol / Lof molybdenum diselenide into deionized water to obtain mixed liquid at first; adding a complexing agent into the mixed liquid, and stirring to obtain emulsion, wherein the volume ratio of the complexing agent and the deionized water is 0.5-2; transferring the emulsion to an autoclave, reacting for 6-24 hours at the temperature of160-240 DEG C, after cooling down the reacted solution, centrifuging, washing and drying to obtain solid powder; and annealing the solid powder for 1-4 hours at the temperature of 400-600 DEG C. The method provided by the present invention has the advantages that raw materials and technological equipment are simple, production cost is low, and the molybdenum diselenide / cobalt diselenide nanocomposite is easy to produce in large scale; and the obtained composite is composed of a micro-tube which is obtained by nanosheets in a self-assembling manner, so that electrocatalytic activity is good.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Selenylation furnace for treating and preparing CIGS (Copper Indium Gallium Diselenide) solar cell absorbing layer and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102185024AAvoid crosstalkAvoid corrosionFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingIndiumNitrogen gas
The invention relates to a selenylation furnace for forming an absorbing layer with a chalcopyrite phase structure by performing continuous and rapid selenization on a prefabricated layer of a flexible CIGS (Copper Indium Gallium Diselenide) solar sell with a solid-sate selenium source method. Both sides of the furnace are provided with transmission devices; the main body of the furnace consists of four parts, i.e., a transition section, a rapid heating region, a high-temperature selenium sulfurization region and a cooling region respectively; the transition region, the rapid heating region and the cooling region are filled with protective atmospheres; the high-temperature selenium sulfurization region is a mixed atmosphere of nitrogen or argon, Se and S steam; a hearth is a long, narrow and flat channel; narrow gaps are formed at an inlet, an outlet and corresponding positions where the regions are in butt joint; a gas curtain formed by inert gas is used for preventing the entrance of air and mixing of gases in different regions; the transition section and the cooling region are provided with water cooling devices; the lower part of the hearth in the high-temperature selenium sulfurization region is provided with an air cushion device for preventing the back face of a substrate from being sulfurized; and a selenium steam supply device of the selenization furnace is used for realizing convenient controllability of the selenium steam.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Flexible thin-film solar photoelectric cell and large-scale continuous automatic production method thereof
ActiveCN102110732AQuality improvementIncrease conversion rateFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingIndiumTitanium oxide
The invention provides a flexible thin-film solar photoelectric cell and a large-scale continuous automatic production method thereof. The solar photoelectric cell comprises an antireflection layer, a transparent upper electrode layer, an isolating layer, a window layer, a protective layer, an absorbing layer, a reflecting layer, a metal back electrode layer, an insulating layer, a substrate layer and a solder flux layer in sequence. The material of the antireflection layer is magnesium fluoride, the material of the transparent upper electrode layer is aluminum zinc oxide, the material of the isolating layer is intrinsic zinc oxide, the material of the window layer is zinc sulfide, the material of the protective layer is sulfur or zinc, the material of the absorbing layer is CIGS (copper indium gallium diselenide) or CIAS (copper indium aluminum diselenide), the material of the reflecting layer is aluminum, the material of the metal back electrode layer is copper-molybdenum-sodium alloy, the material of the insulating layer is titanium oxide, and the material of the substrate layer is stainless steel, copper, aluminum foil or polyimide film. The production method of the flexible thin-film solar photoelectric cell comprises sputtering layer by layer in a closed environment on a continuous automatic production line through a plurality of sputtering methods to form a multilayer structure. The large-scale continuous automatic production method provided by the invention has the advantages of high efficiency, high quality, and low cost.
Owner:江苏航天之光新能源装备有限公司
Cobalt diselenide/nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterial composite electrode catalytic material, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110787819AMass productionThe preparation method is mildFuel and primary cellsPhysical/chemical process catalystsNanotubeCobalt selenide
Relating to the technical field of composite materials, in order to solve the problems of high price and low catalytic activity of electrode catalytic materials in existing zinc-air batteries, the invention provides a cobalt diselenide / nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterial composite electrode catalytic material, a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method includes the steps of: (1) growing Co-MOF on carbon cloth subjected to hydrophilization treatment; (2) growing a nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterial through CVD process to obtain a Co / nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterial; wherein the nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterial is a combination of nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube and nitrogen-doped carbon nanosheet; and (3) carrying out selenylation treatment to obtain the cobalt diselenide / nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterial composite electrode catalytic material. The composite material provided by the invention retains the structural integrity of the cobalt diselenide porous frame / carbon nanosheet array obtained by taking the triangular lamellar MOF crystal as a template, has excellent properties of both the carbon nanotube and the cobalt diselenide porous frame, and has wide application prospects in the fields of adsorption, sensing, energy storage, catalysis and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com