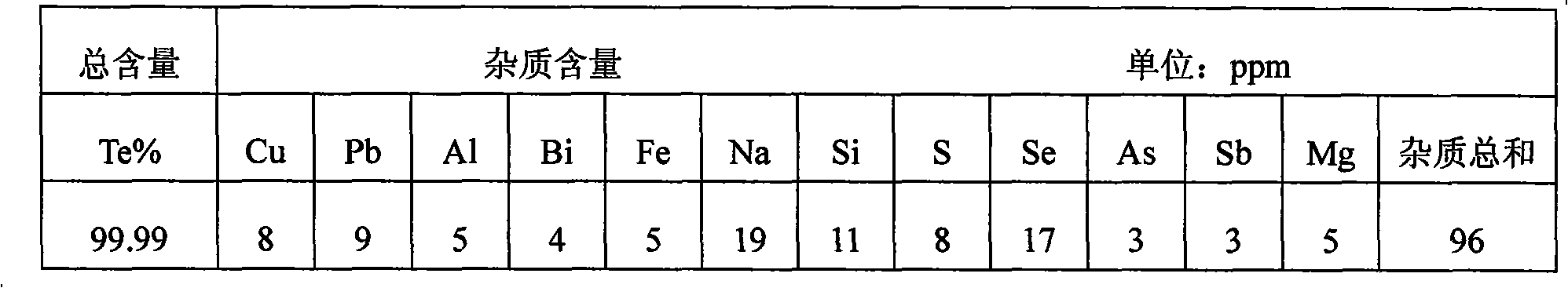
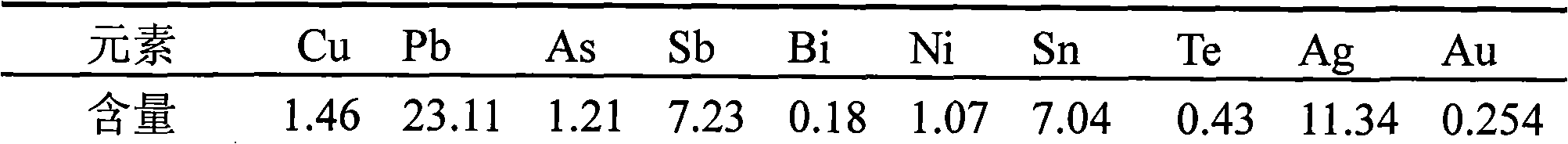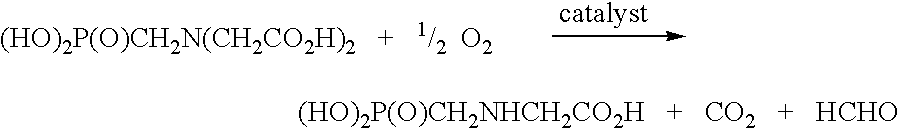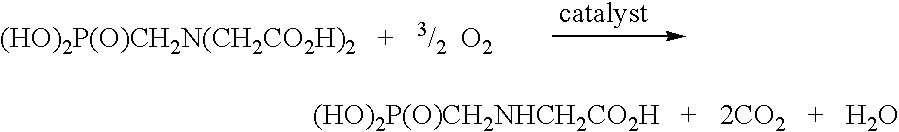Patents
Literature
2642 results about "Tellurium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tellurium is a chemical element with the symbol Te and atomic number 52. It is a brittle, mildly toxic, rare, silver-white metalloid. Tellurium is chemically related to selenium and sulfur, all three of which are chalcogens. It is occasionally found in native form as elemental crystals. Tellurium is far more common in the universe as a whole than on Earth. Its extreme rarity in the Earth's crust, comparable to that of platinum, is due partly to its formation of a volatile hydride that caused tellurium to be lost to space as a gas during the hot nebular formation of Earth, and partly to tellurium's low affinity for oxygen, which causes it to bind preferentially to other chalcophiles in dense minerals that sink into the core.
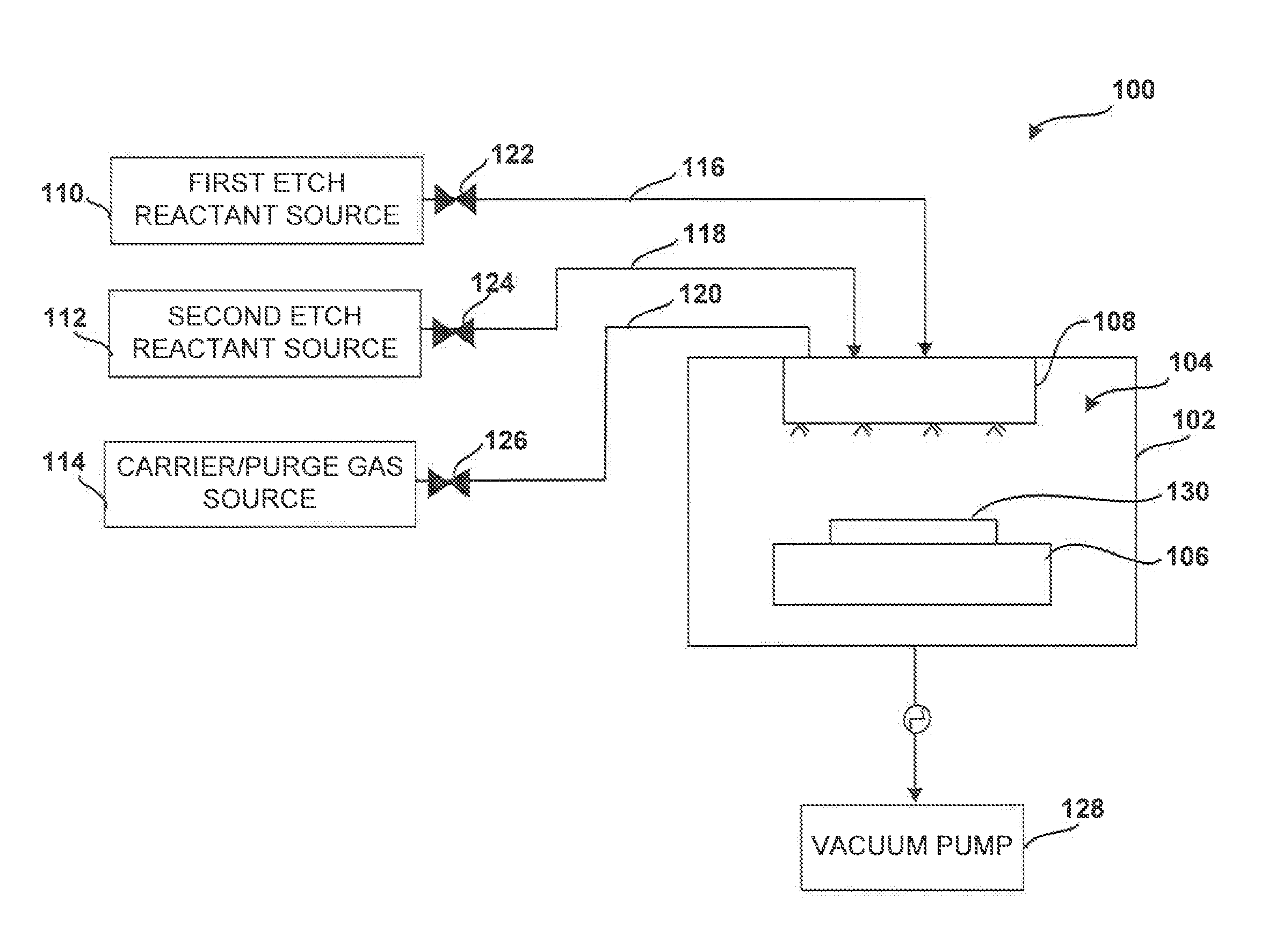
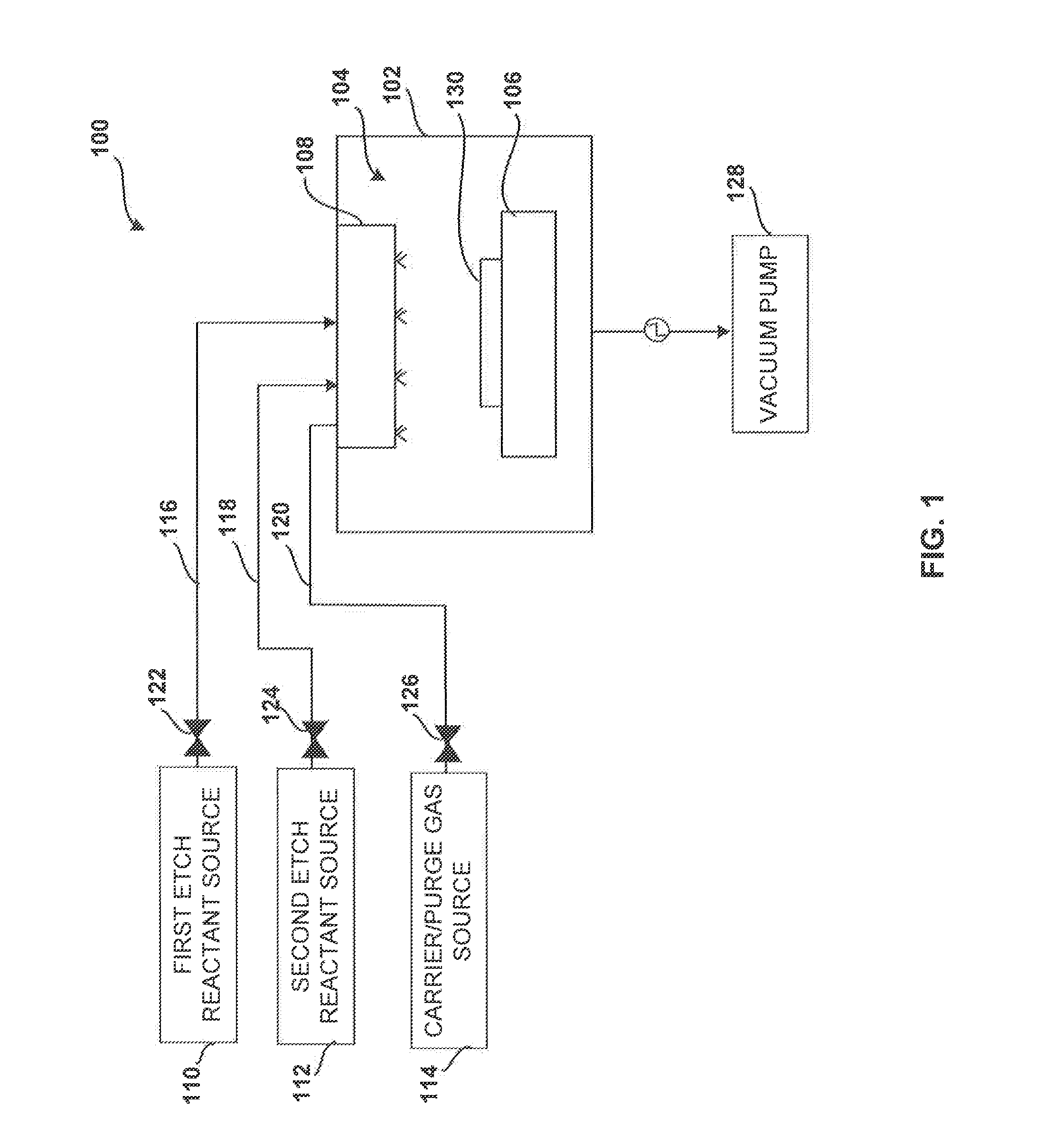
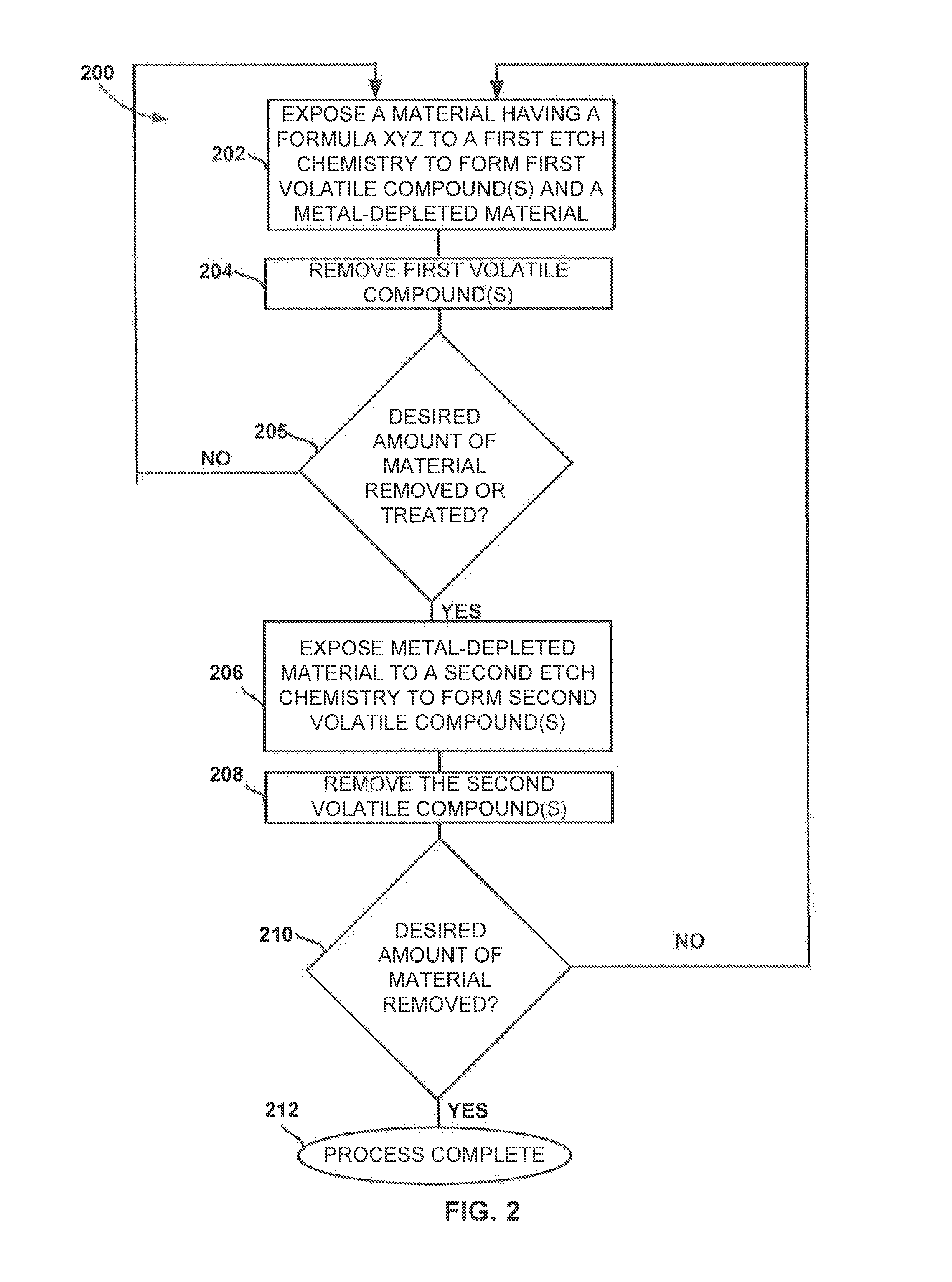
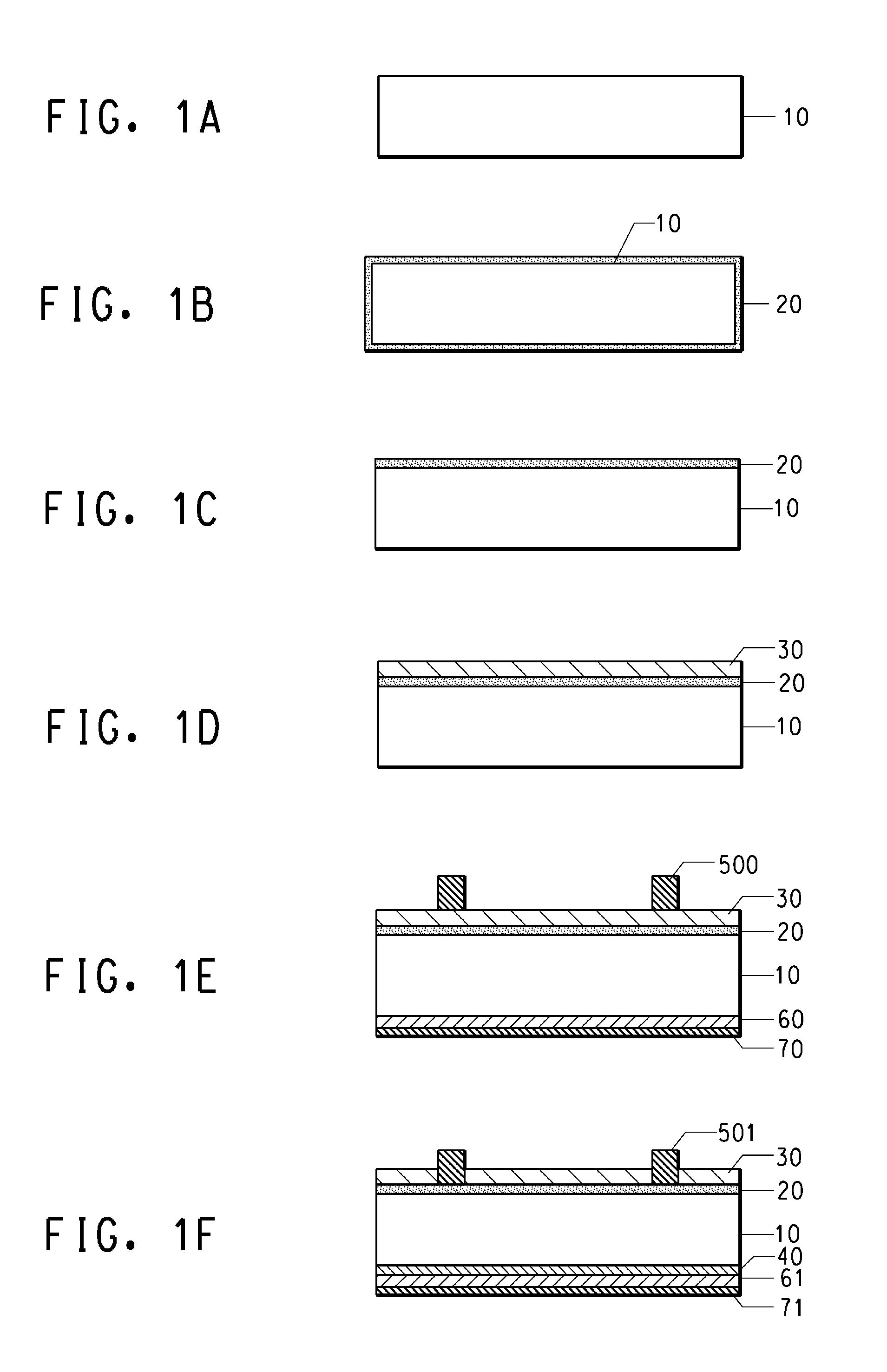
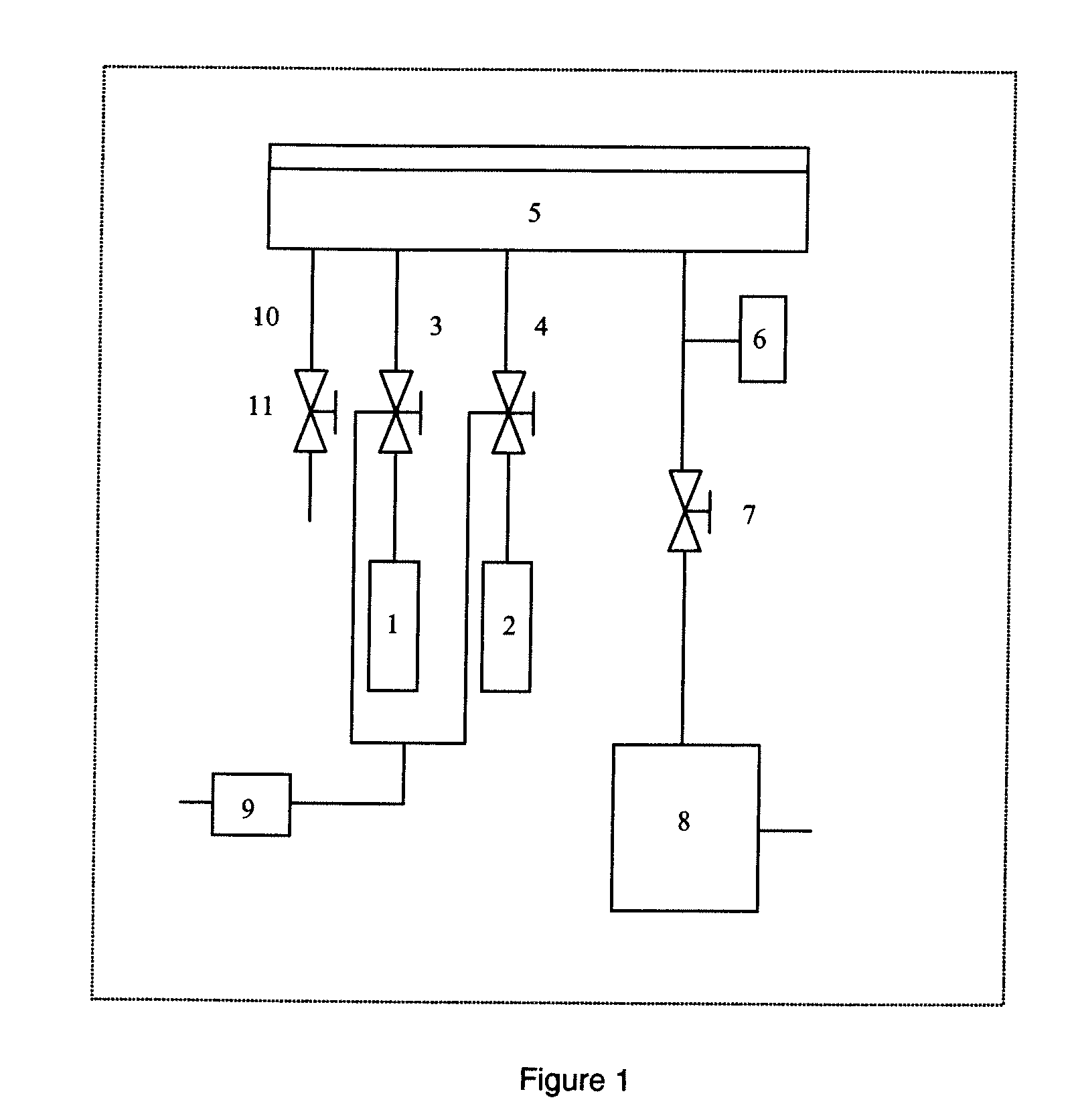
Multi-step method and apparatus for etching compounds containing a metal
ActiveUS20140217065A1Reduce harmReduce formationDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSulfurChemical compound
A system and method for etching a material, including a compound having a formulation of XYZ, wherein X and Y are one or more metals and Z is selected from one or more Group 13-16 elements, such as carbon, nitrogen, boron, silicon, sulfur, selenium, and tellurium, are disclosed. The method includes a first etch process to form one or more first volatile compounds and a metal-depleted layer and a second etch process to remove at least a portion of the metal-depleted layer.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Chemical manufacture of nanostructured materials
InactiveUS6872330B2High strengthIncrease volumeMaterial nanotechnologyOxide/hydroxide preparationInorganic compoundTe element
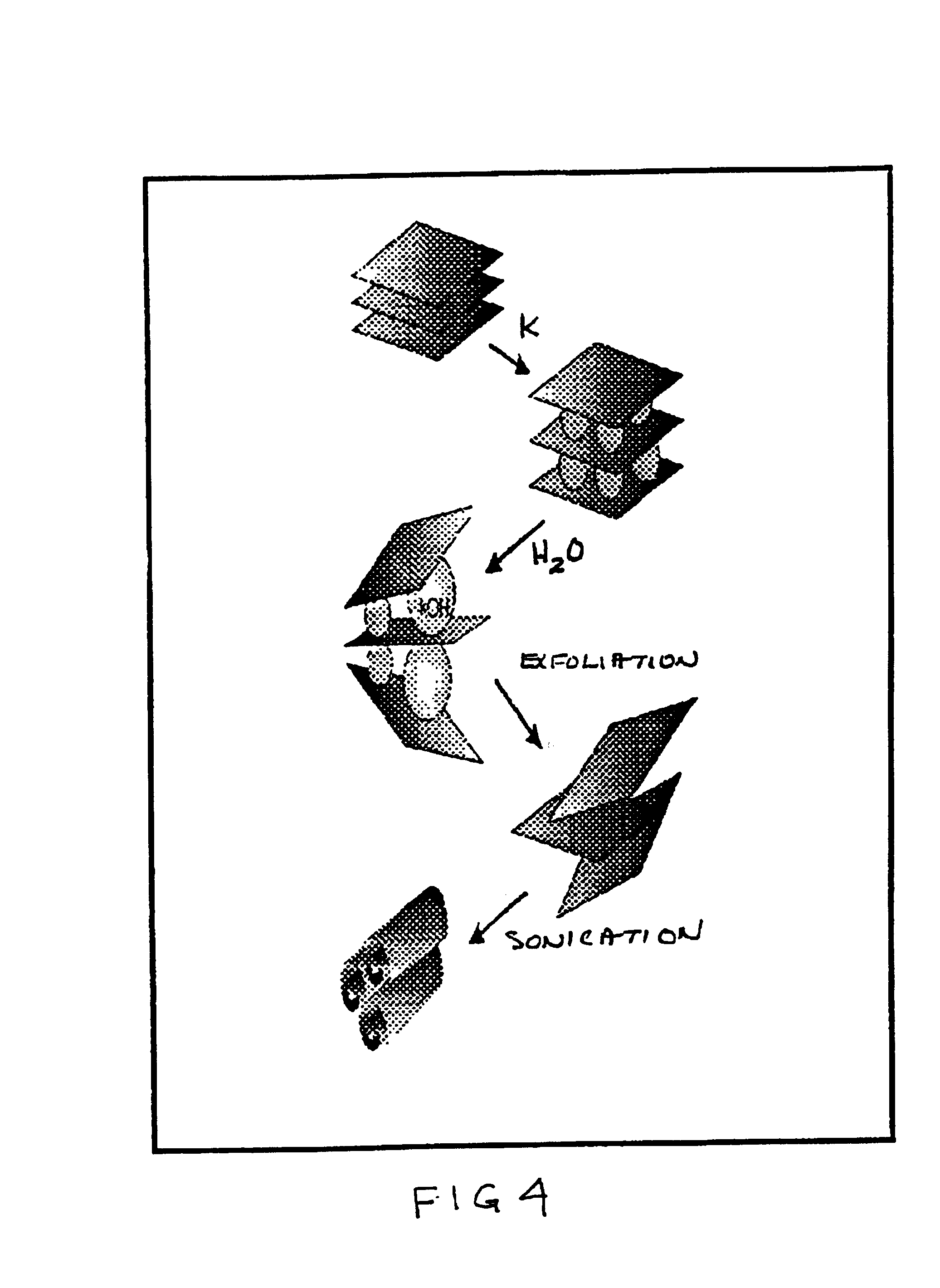
A low temperature chemical route to efficiently produce nanomaterials is described. The nanomaterials are synthesized by intercalating ions into layered compounds, exfoliating to create individual layers and then sonicating to produce nanotubes, nanorods, nanoscrolls and / or nanosheets. It is applicable to various different layered inorganic compounds (for example, bismuth selenides / tellurides, graphite, and other metal complexes, particularly transition metal dichalcogenides compounds including oxygen, sulfur, tellurium or selenium).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Thick-film pastes containing lead-tellurium-boron-oxides, and their use in the manufacture of semiconductor devices
The present invention provides a thick-film paste for printing the front side of a solar cell device having one or more insulating layers. The thick-film paste comprises an electrically conductive metal and a lead-tellurium-boron-oxide dispersed in an organic medium.
Owner:SOLAR PASTE LLC
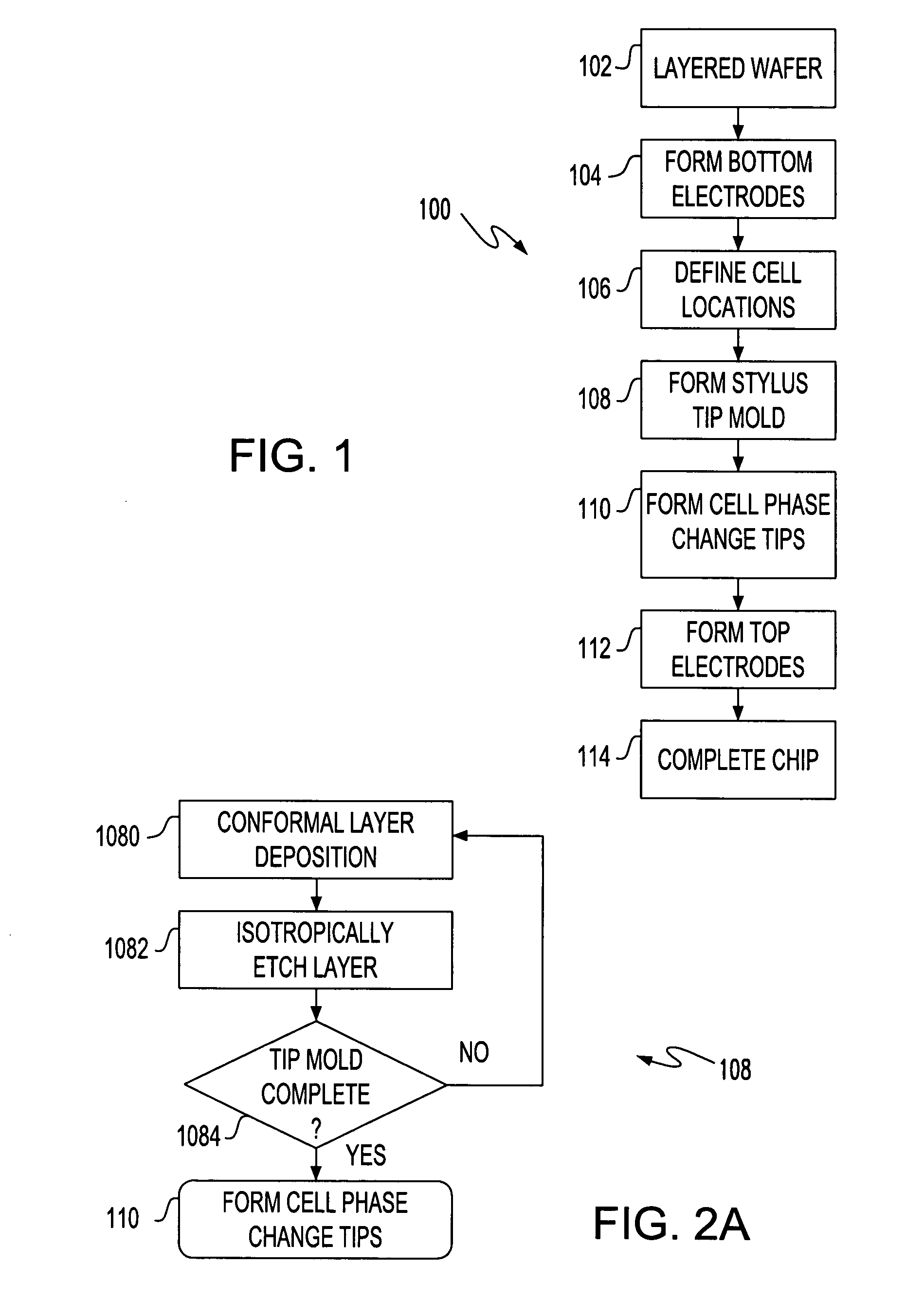
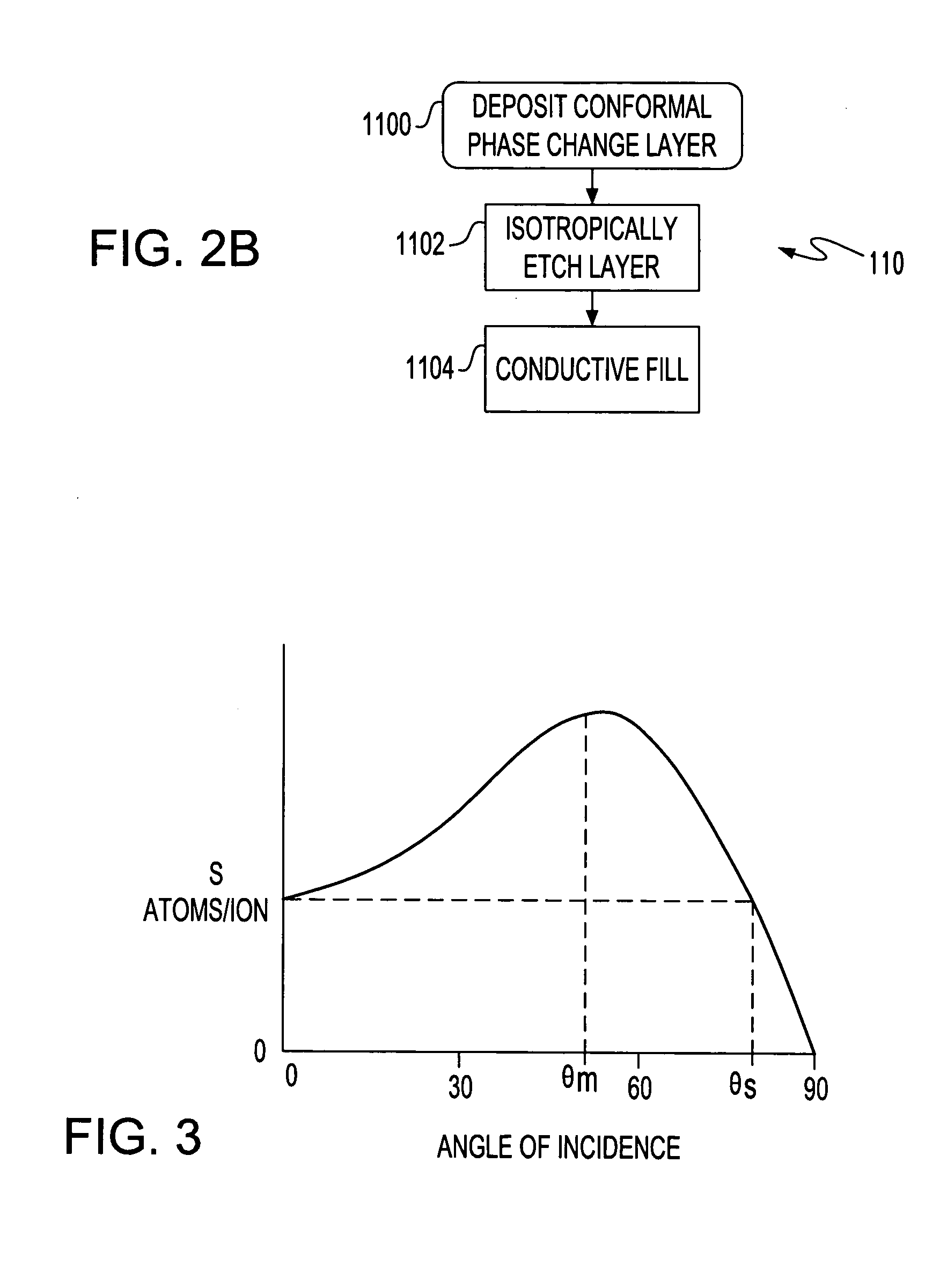
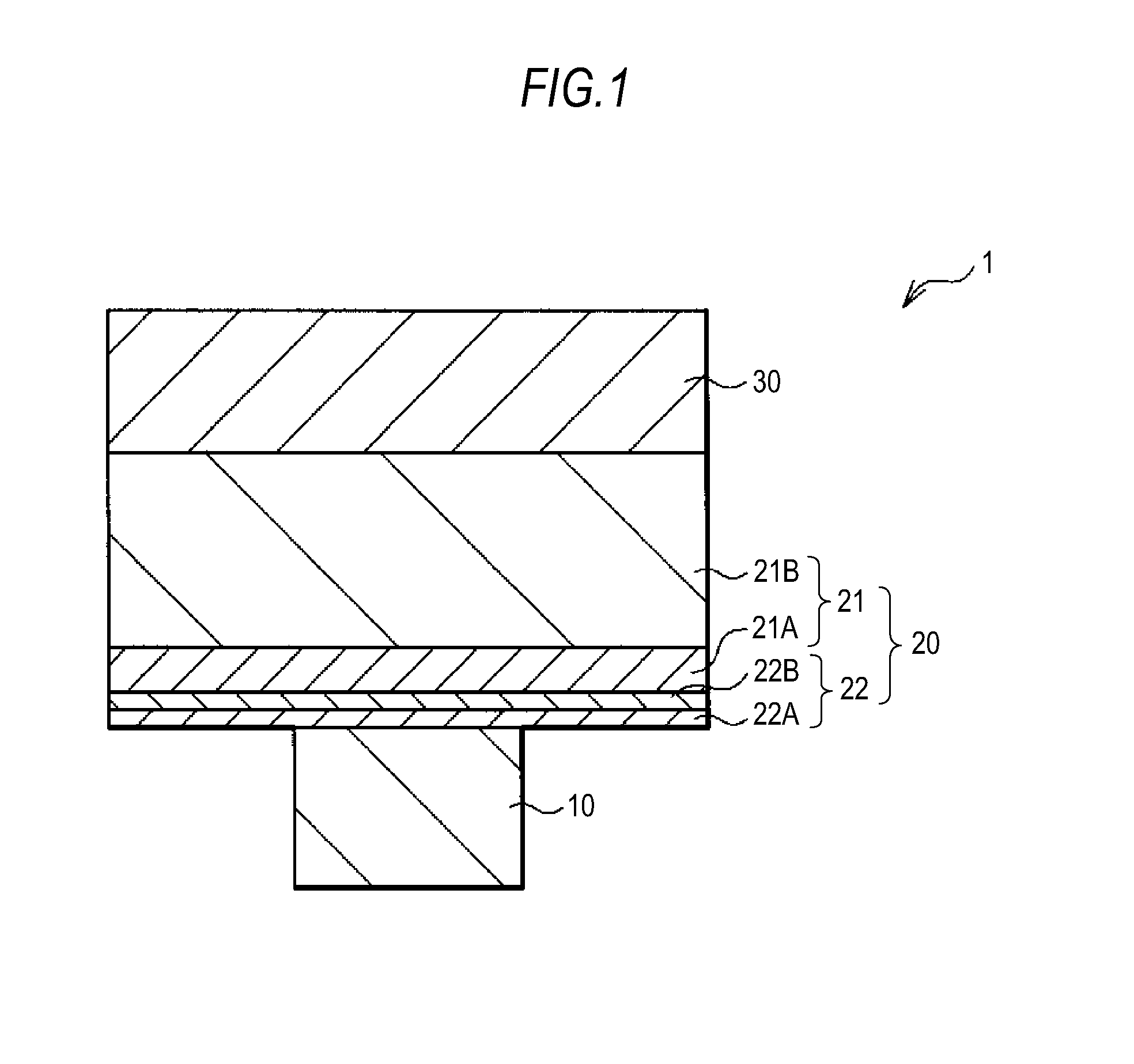
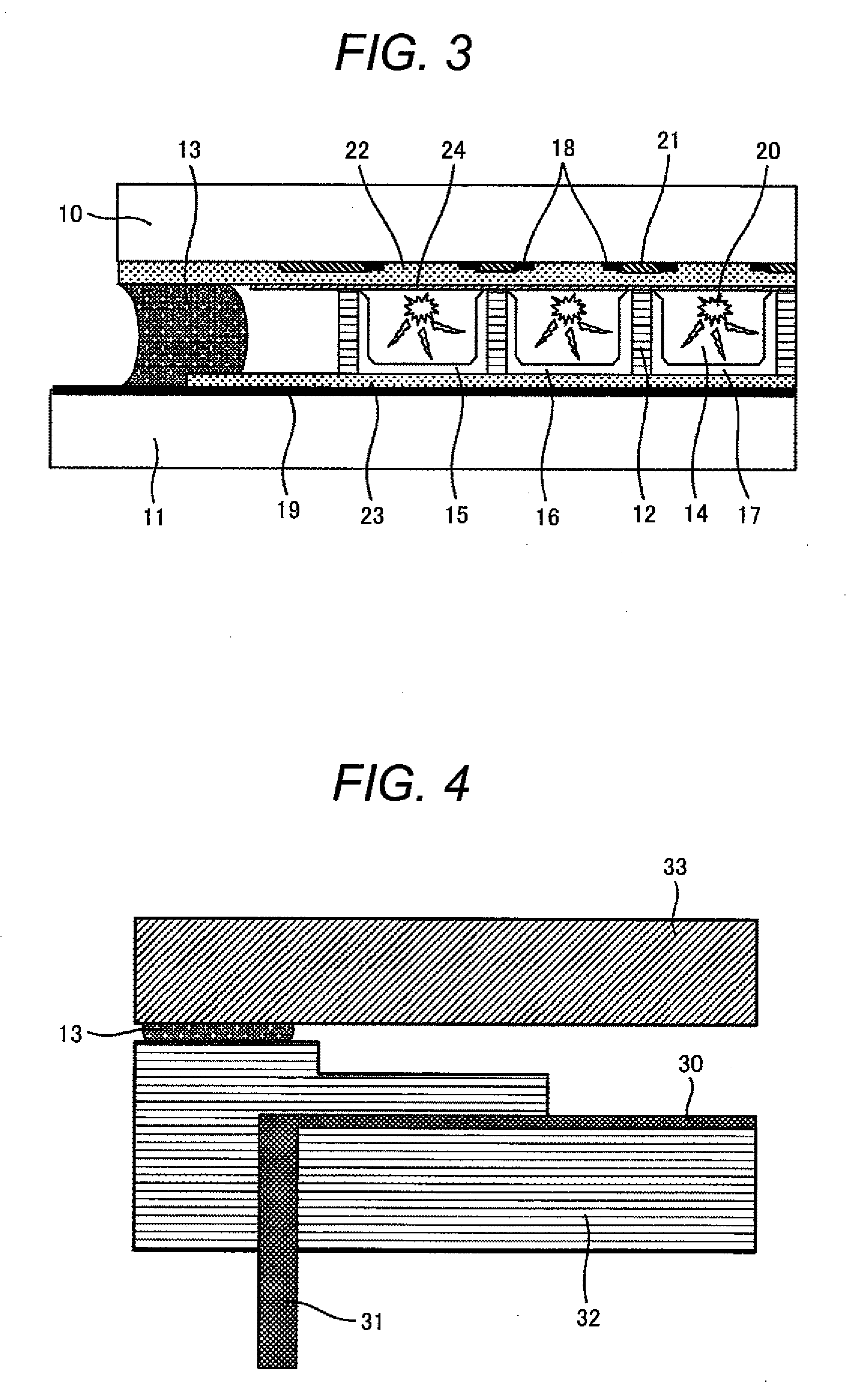
Phase change tip storage cell
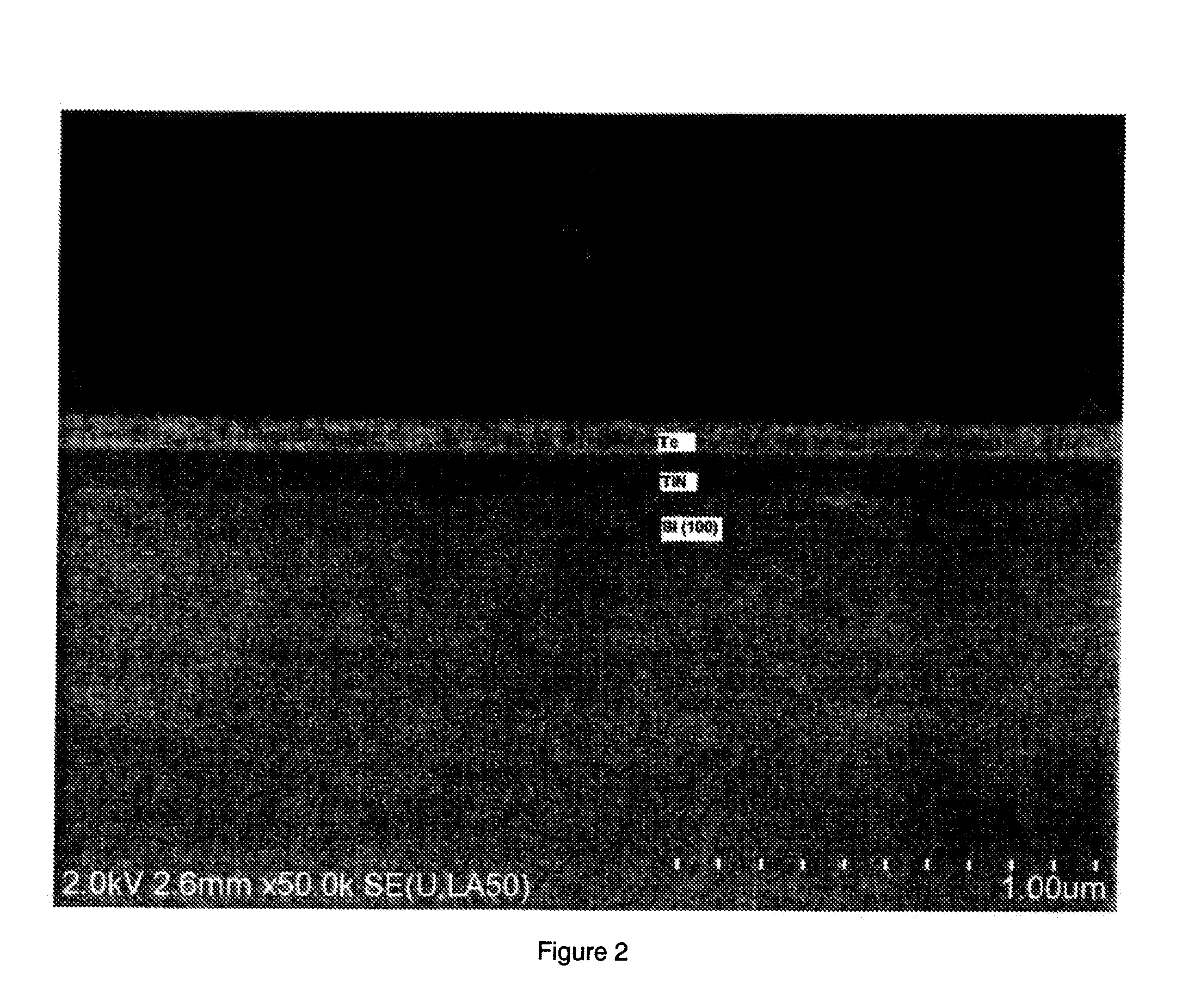
ActiveUS20050127349A1Reduce the required powerSolid-state devicesDigital storageTitanium nitrideTe element
A storage cell, integrated circuit (IC) chip with one or more storage cells that may be in an array of the storage cells and a method of forming the storage cell and IC. Each storage cell includes a stylus, the tip of which is phase change material. The phase change tip may be sandwiched between an electrode and conductive material, e.g., titanium nitride (TiN), tantalum nitride (TaN) or n-type semiconductor. The phase change layer may be a chalcogenide and in particular a germanium (Ge), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) (GST) layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Memory component, memory device, and method of operating memory device
InactiveUS20110194329A1Avoid reactionImprove repetition durabilitySolid-state devicesDigital storageLow resistanceTellurium
A memory component includes: a first electrode; a memory layer; and a second electrode which are provided in that order, wherein the memory layer includes an ion source layer containing aluminum (Al) together with at least one chalcogen element selected from the group consisting of tellurium (Te), sulfur (S), and selenium (Se), and a resistance variable layer provided between the ion source layer and the first electrode and containing an aluminum oxide and at least one of a transition metal oxide and a transition metal oxynitride having a lower resistance than the aluminum oxide.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Method of fabricating a thin film
InactiveUS20060172083A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenChemical reaction
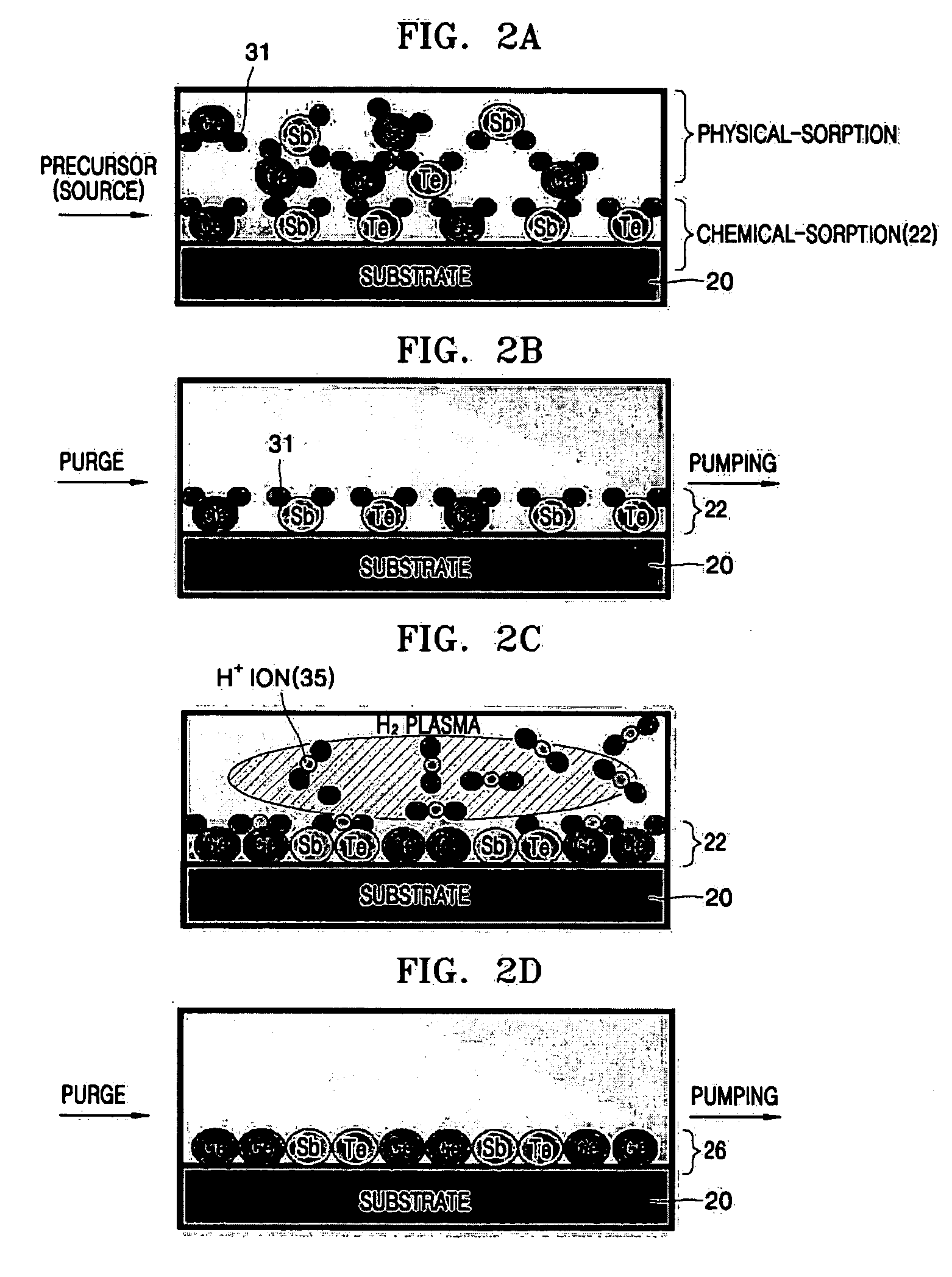
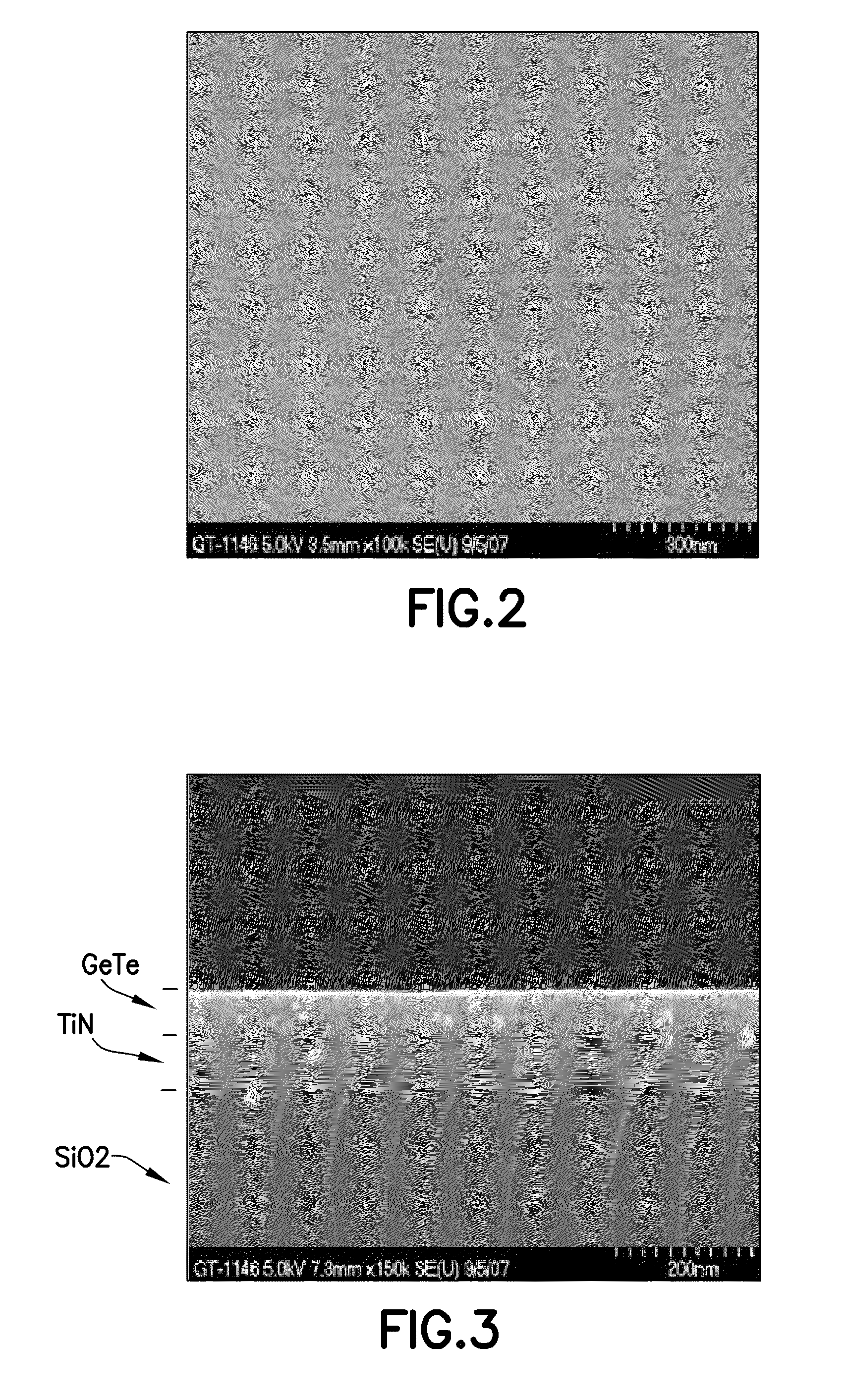
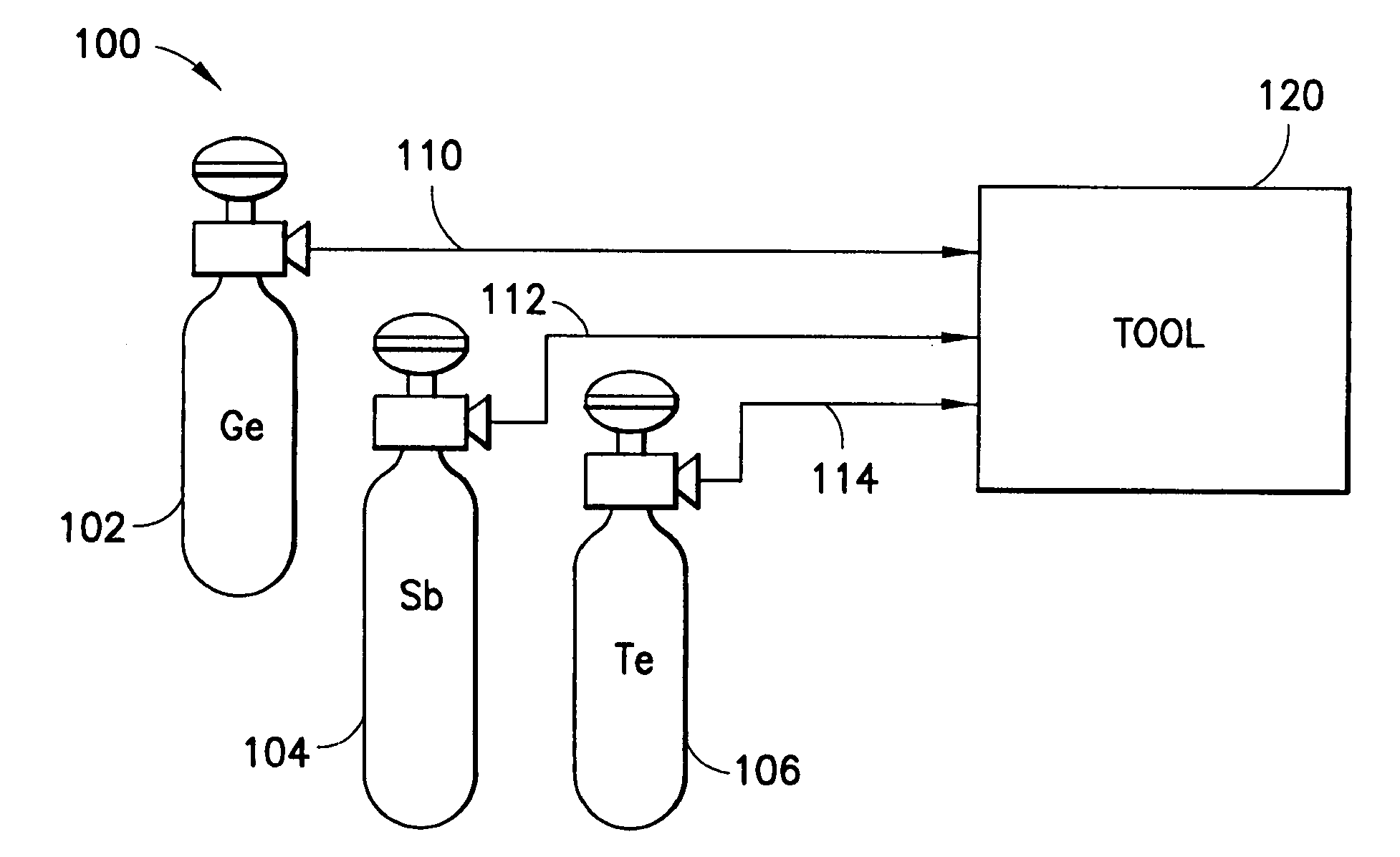
Methods of fabricating a thin film. An example method includes forming a GeSbTe thin film on a surface of a substrate by chemically reacting a first precursor including germanium (Ge), a second precursor including antimony (Sb), and a third precursor including tellurium (Te) in a reaction chamber and processing the surface of the GeSbTe thin film with hydrogen plasma. Another example method includes injecting at least one precursor into a reactor chamber and depositing the at least one precursor onto a substrate within the reactor chamber using a chemical vapor deposition process so as to form the thin film.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
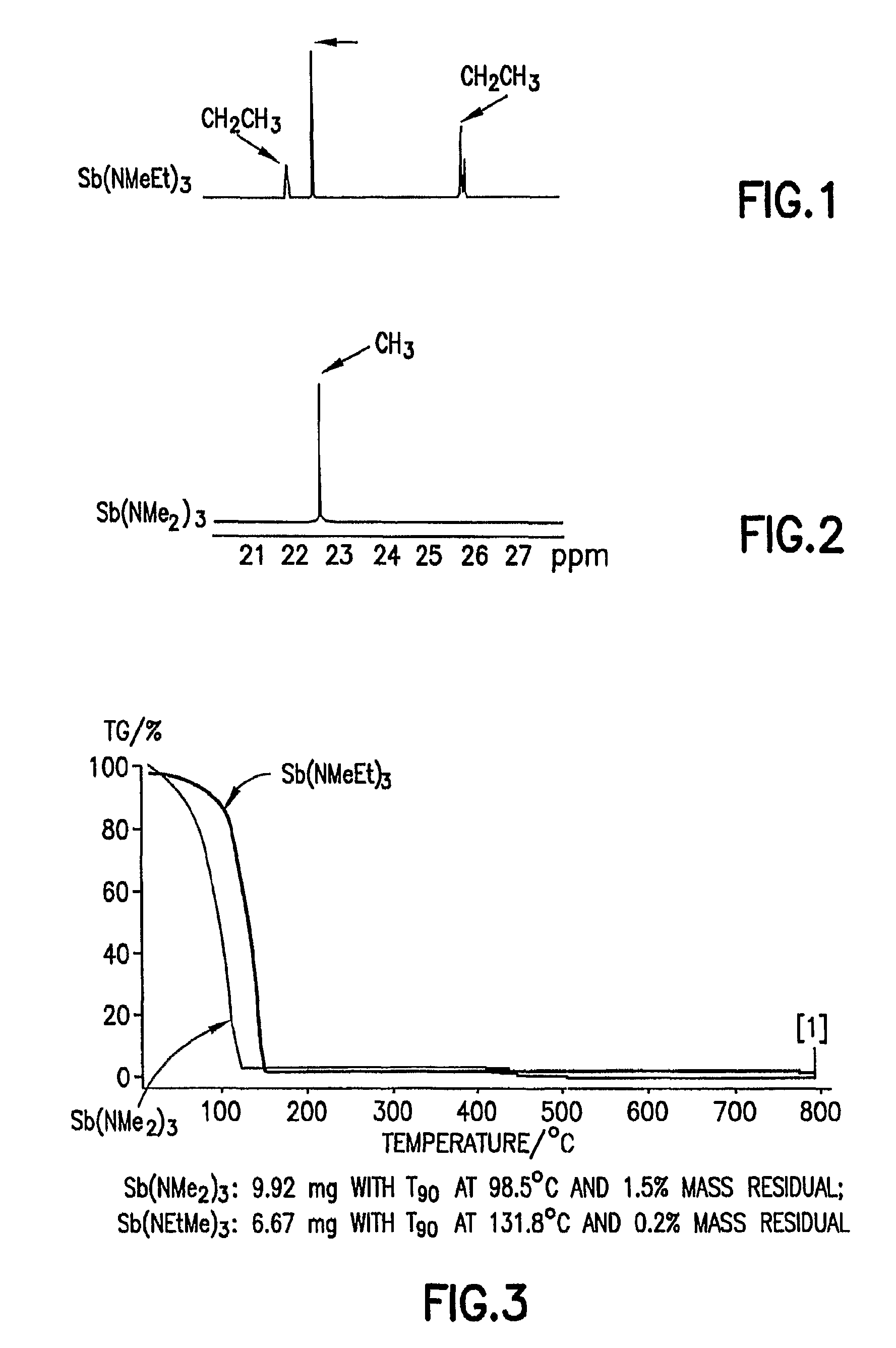
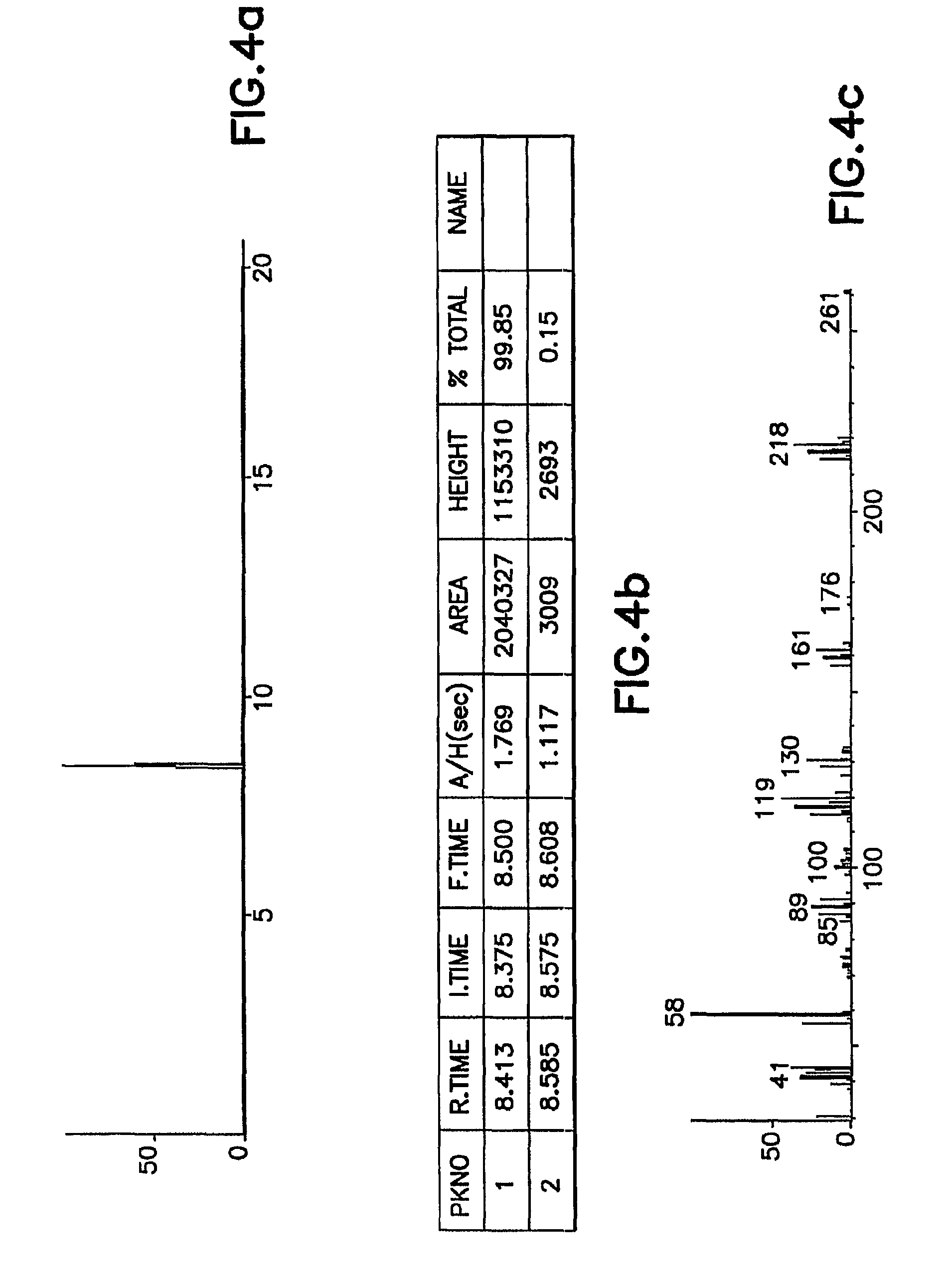
Antimony and germanium complexes useful for cvd/ald of metal thin films
ActiveUS20090305458A1Group 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesGermanium organic compoundsPhase-change memoryTe element
Antimony, germanium and tellurium precursors useful for CVD / ALD of corresponding metal-containing thin films are described, along with compositions including such precursors, methods of making such precursors, and films and microelectronic device products manufactured using such precursors, as well as corresponding manufacturing methods. The precursors of the invention are useful for forming germanium-antimony-tellurium (GST) films and microelectronic device products, such as phase change memory devices, including such films.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Low softening point glass composition, bonding material using same and electronic parts
ActiveUS20100180934A1Flow on effectReduce softeningAddress electrodesConductive layers on insulating-supportsTe elementAntimony
Owner:RESONAC CORP
Field emission phase change diode memory
InactiveUS7057923B2Reduce the required powerSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical batteryEngineering
A storage cell that may be a memory cell, and integrated circuit (IC) chip including an array of the memory cells and a method of forming the IC. Each storage cell is formed between a top an bottom electrode. Each cell includes a phase change layer that may be a chalcogenide and in particular a germanium (Ge), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) or GST layer. The cell also includes a stylus with the apex of the stylus contacting the GST layer. The apex may penetrate the GST layer
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Amorphous ge/te deposition process
ActiveUS20090112009A1Silicon organic compoundsGermanium organic compoundsPhase-change memoryTe element
Germanium, tellurium, and / or antimony precursors are usefully employed to form germanium-, tellurium- and / or antimony-containing films, such as films of GeTe, GST, and thermoelectric germanium-containing films. Processes for using these precursors to form amorphous films are also described. Further described is the use of [{nBuC(iPrN)2}2Ge] or Ge butyl amidinate to form GeTe smooth amorphous films for phase change memory applications.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Low temperature deposition of phase change memory materials
InactiveUS20090124039A1Silicon organic compoundsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsLow temperature depositionPhase-change memory
A system and method for forming a phase change memory material on a substrate, in which the substrate is contacted with precursors for a phase change memory chalcogenide alloy under conditions producing deposition of the chalcogenide alloy on the substrate, at temperature below 350° C. with the contacting being carried out via chemical vapor deposition or atomic layer deposition. Various tellurium, germanium and germanium-tellurium precursors are described, which are useful for forming GST phase change memory films on substrates.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Non-Isoelectronic Surfactant Assisted Growth In Inverted Metamorphic Multijunction Solar Cells
InactiveUS20090229658A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor materialsLattice mismatch
A method of forming a multifunction solar cell including an upper subcell, a middle subcell, and a lower subcell, the method including: providing a substrate for the epitaxial growth of semiconductor material; forming a first solar subcell on the substrate having a first band gap; forming a second solar subcell over the first solar subcell having a second band gap smaller than the first band gap; forming a graded interlayer over the second subcell using a non-isoelectronic surfactant such as selenium or tellurium, the graded interlayer having a third band gap greater than the second band gap; and forming a third solar subcell over the graded interlayer having a fourth band gap smaller than the second band gap such that the third subcell is lattice mismatched with respect to the second subcell.
Owner:EMCORE SOLAR POWER
Compositions and methods for CMP of phase change alloys
The present invention provides a chemical-mechanical polishing (CMP) composition suitable for polishing a substrate comprising a phase change alloy (PCA), such as a germanium-antimony-tellurium (GST) alloy. The composition comprises not more than about 6 percent by weight of a particulate abrasive material in combination with an optional oxidizing agent, at least one chelating agent, and an aqueous carrier therefor. The chelating agent comprises a compound or combination of compounds capable of chelating a phase change alloy or component thereof (e.g., germanium, indium, antimony and / or tellurium species) that is present in the substrate, or chelating a substance that is formed from the PCA during polishing of the substrate with the CMP composition. A CMP method for polishing a phase change alloy-containing substrate utilizing the composition is also disclosed.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS INC
Lead-free free-cutting copper alloys
A lead-free free-cutting copper alloy having 69 to 79 percent, by weight, of copper; greater than 3 percent, by weight, of silicon; and a remaining percent, by weight, of zinc. The alloy preferable has greater than 3.0 percent and less than or equal to 4.0 percent, by weight, of silicon; and at least one element selected from among 0.02 to 0.4 percent, by weight, of bismuth, 0.02 to 0.4 percent, by weight, of tellurium, and 0.02 to 0.4 percent, by weight, of selenium. The alloy also preferable has at least one element selected from among 0.3 to 3.5 percent, by weight, of tin, 1.0 to 3.5 percent, by weight, of aluminum, and 0.02 to 0.25 percent, by weight, of phosphorus. In further embodiments, the alloy has at least one element selected from among 0.02 to 0.15 percent, by weight, of antimony, and 0.02 to 0.15 percent, by weight, of arsenic.
Owner:MITSUBISHI SHINDOH CO LTD
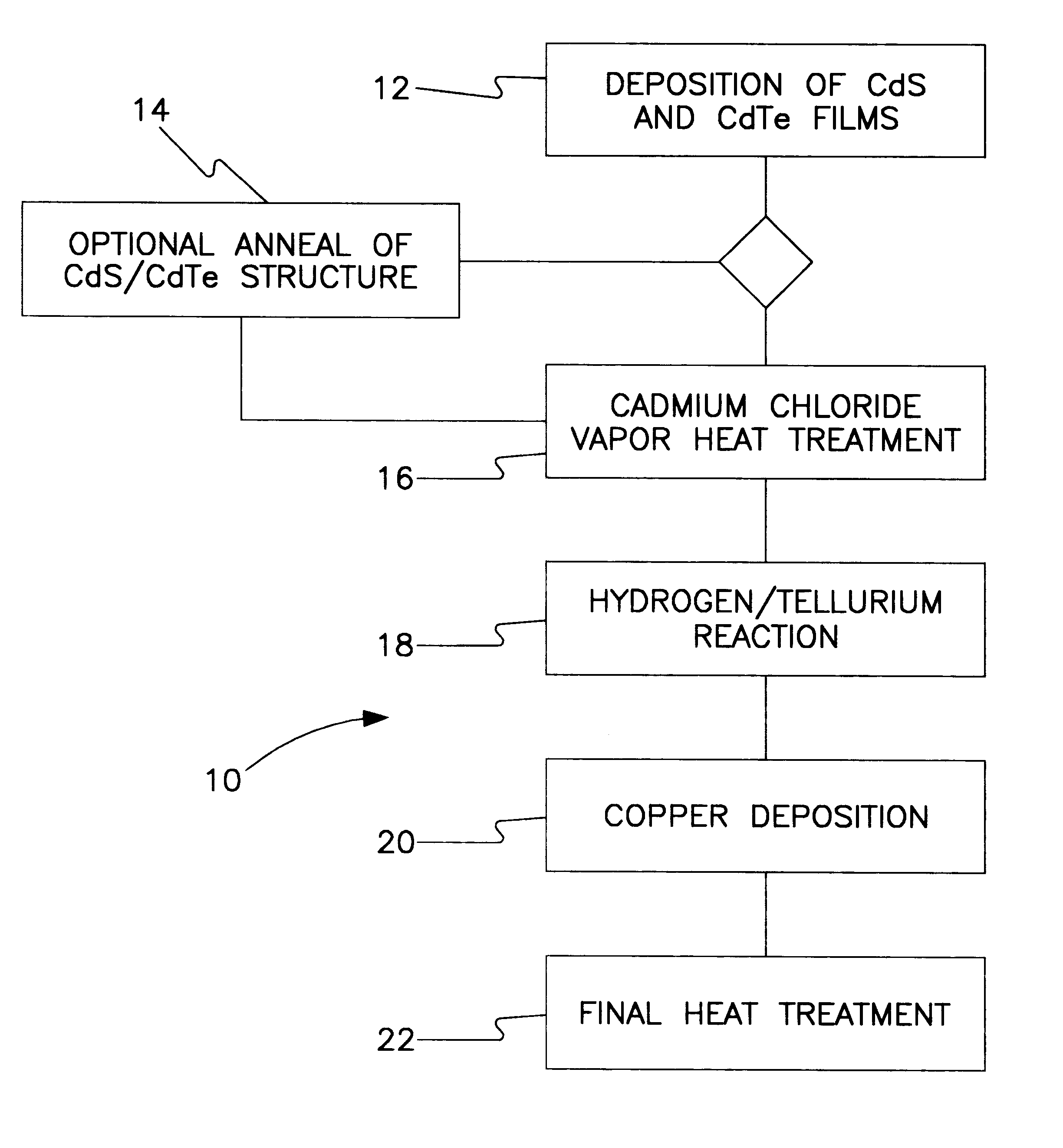
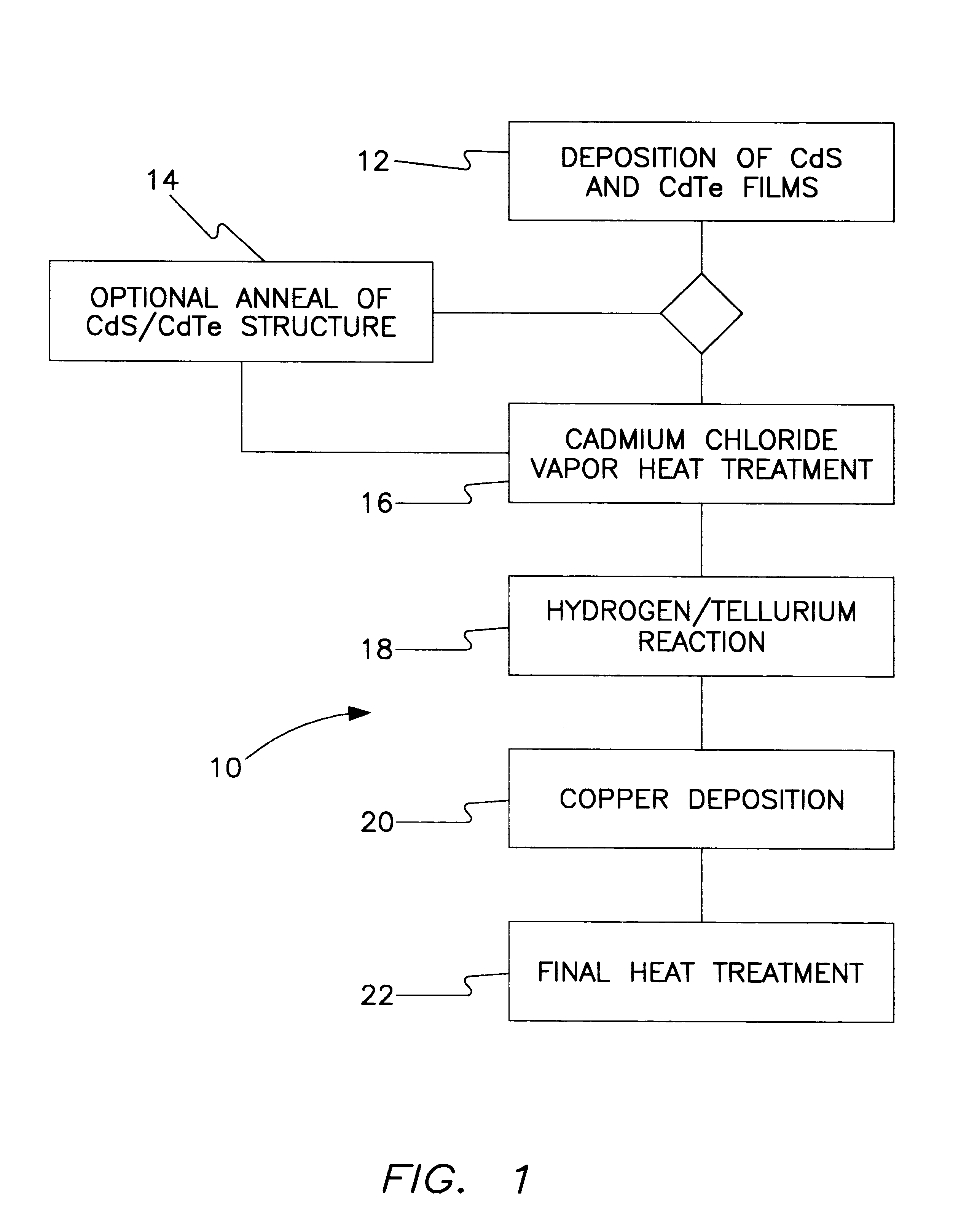
All-vapor processing of p-type tellurium-containing II-VI semiconductor and ohmic contacts thereof
InactiveUS6251701B1Reduce manufacturing costReduce pollutionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOhmic contactTellurium compounds
An all dry method for producing solar cells is provided comprising first heat-annealing a II-VI semiconductor; enhancing the conductivity and grain size of the annealed layer; modifying the surface and depositing a tellurium layer onto the enhanced layer; and then depositing copper onto the tellurium layer so as to produce a copper tellurium compound on the layer.
Owner:U S DEPT OF ENGERGY
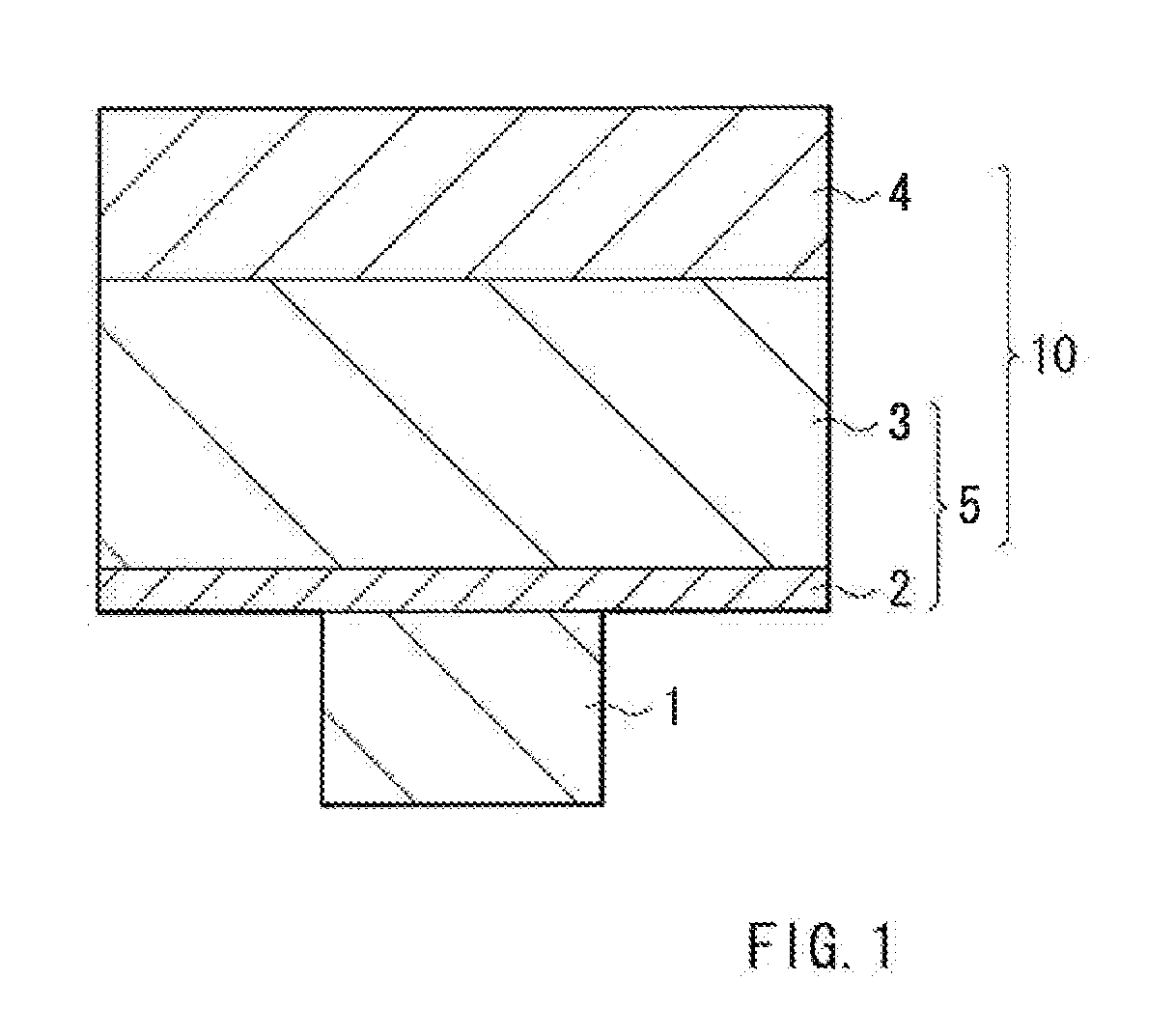
Memory element and memory device
ActiveUS20100195371A1Improve retentionMaintain performanceSolid-state devicesDigital storageHigh resistanceSulfur
The capability of retaining a resistance value of a stored state and an erased state is improved in a resistance variation-type memory device. A memory layer 5 including a high-resistance layer 2 and an ion source layer 3 is provided between a lower electrode 1 and an upper electrode 4. The ion source layer 3 contains Al (aluminum) as an additive element together with an ion conductive material such as S (sulfur), Se (selenium), and Te (tellurium) (chalcogenide element) and a metal element to be ionized such as Zr (zirconium). Since Al is included in the ion source layer 3, the high-resistance layer which includes Al (Al oxide) is formed on an anode in erasing operation. Thus, a retaining property in a high-resistance state improves, and at the same time, an operating speed is improved.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method of forming a phase changeable material layer, a method of manufacturing a phase changeable memory unit, and a method of manufacturing a phase changeable semiconductor memory device
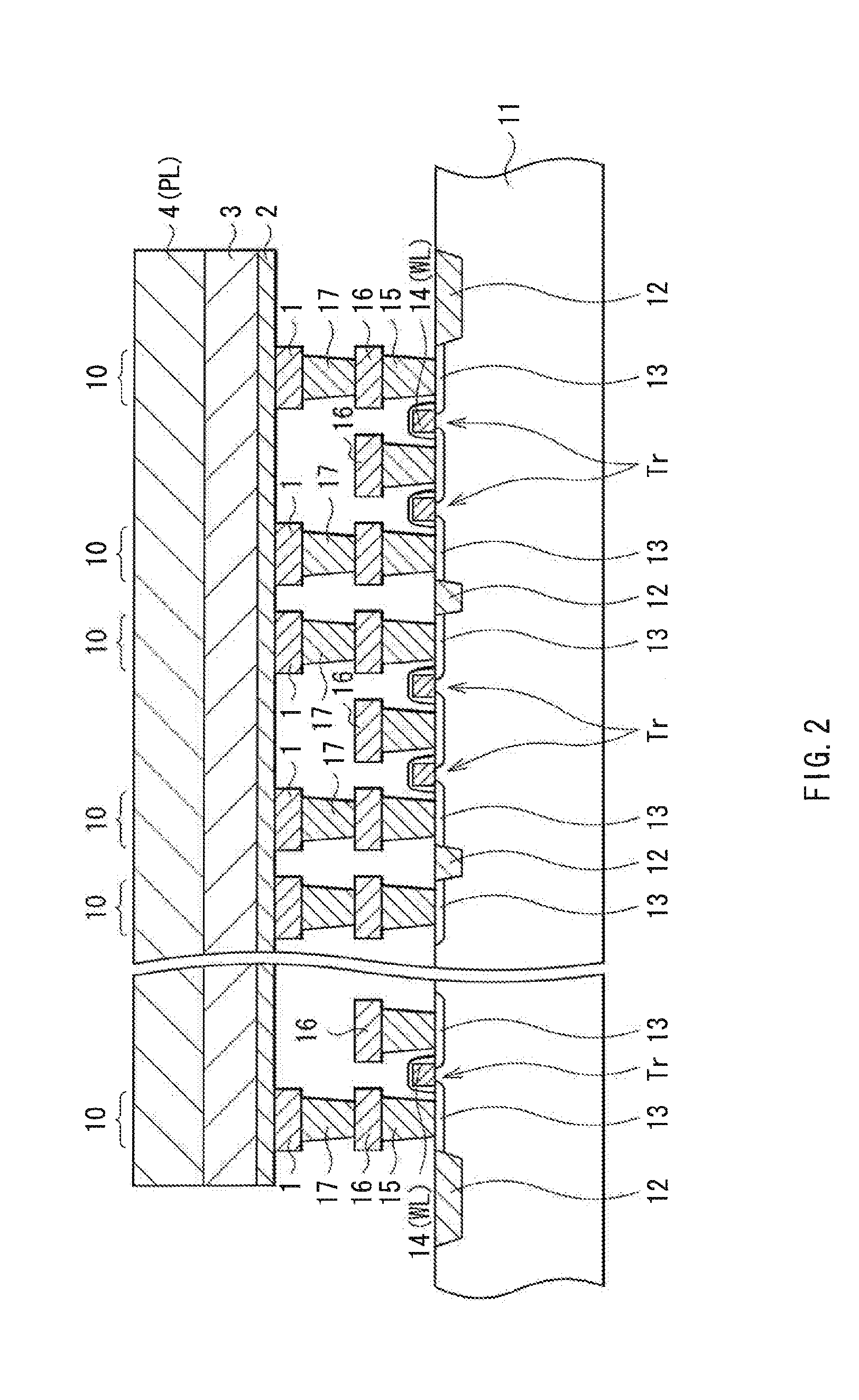
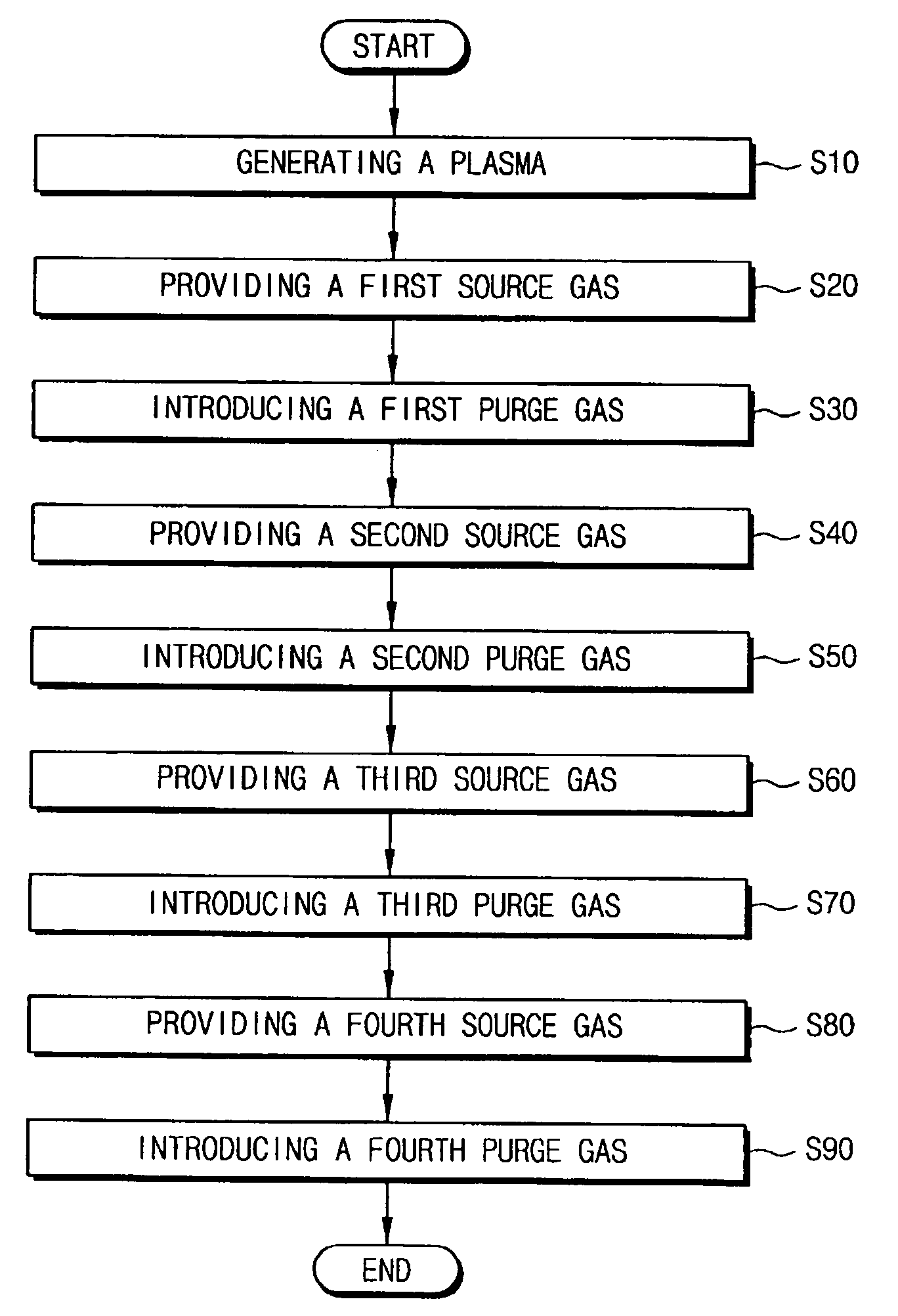
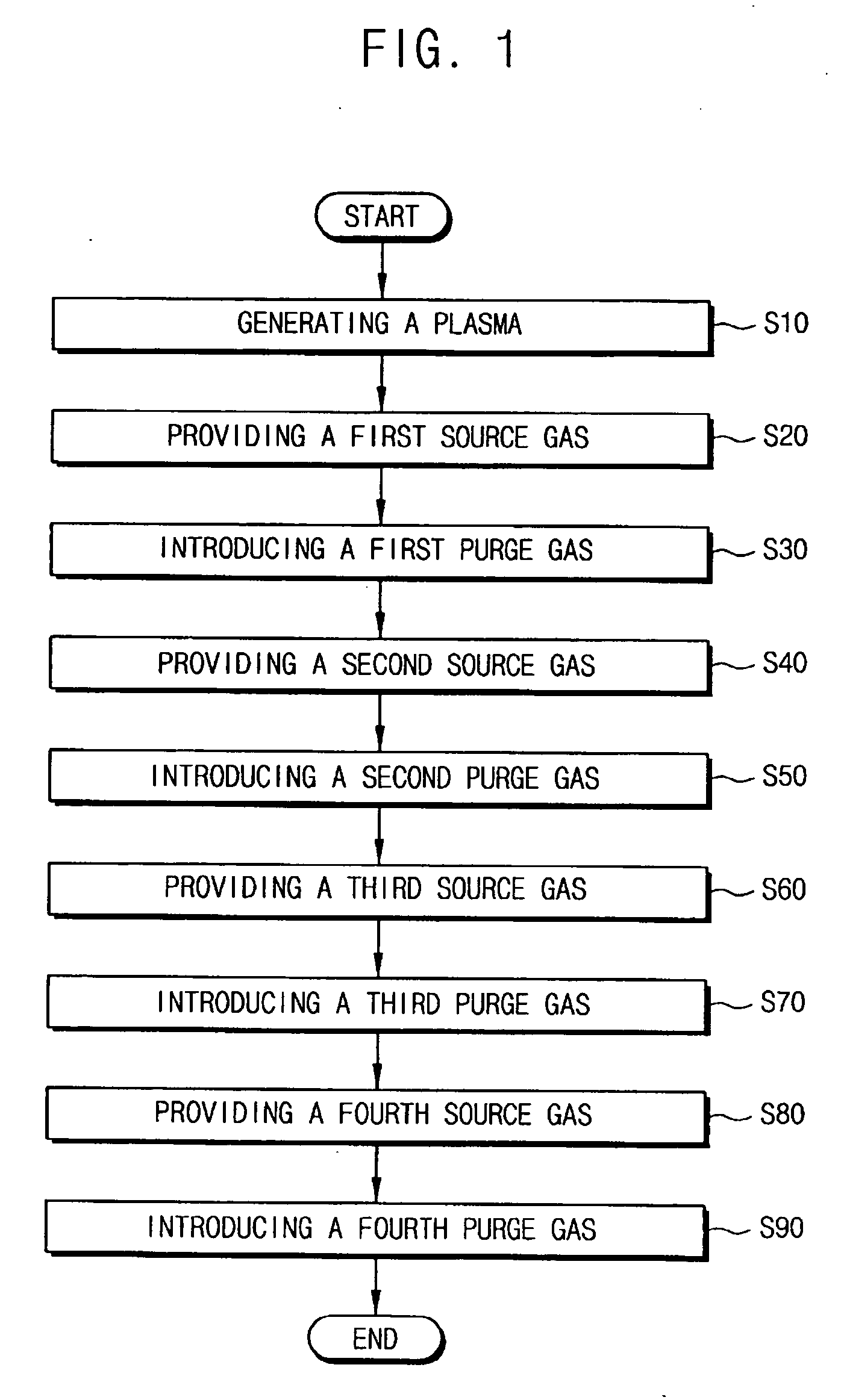
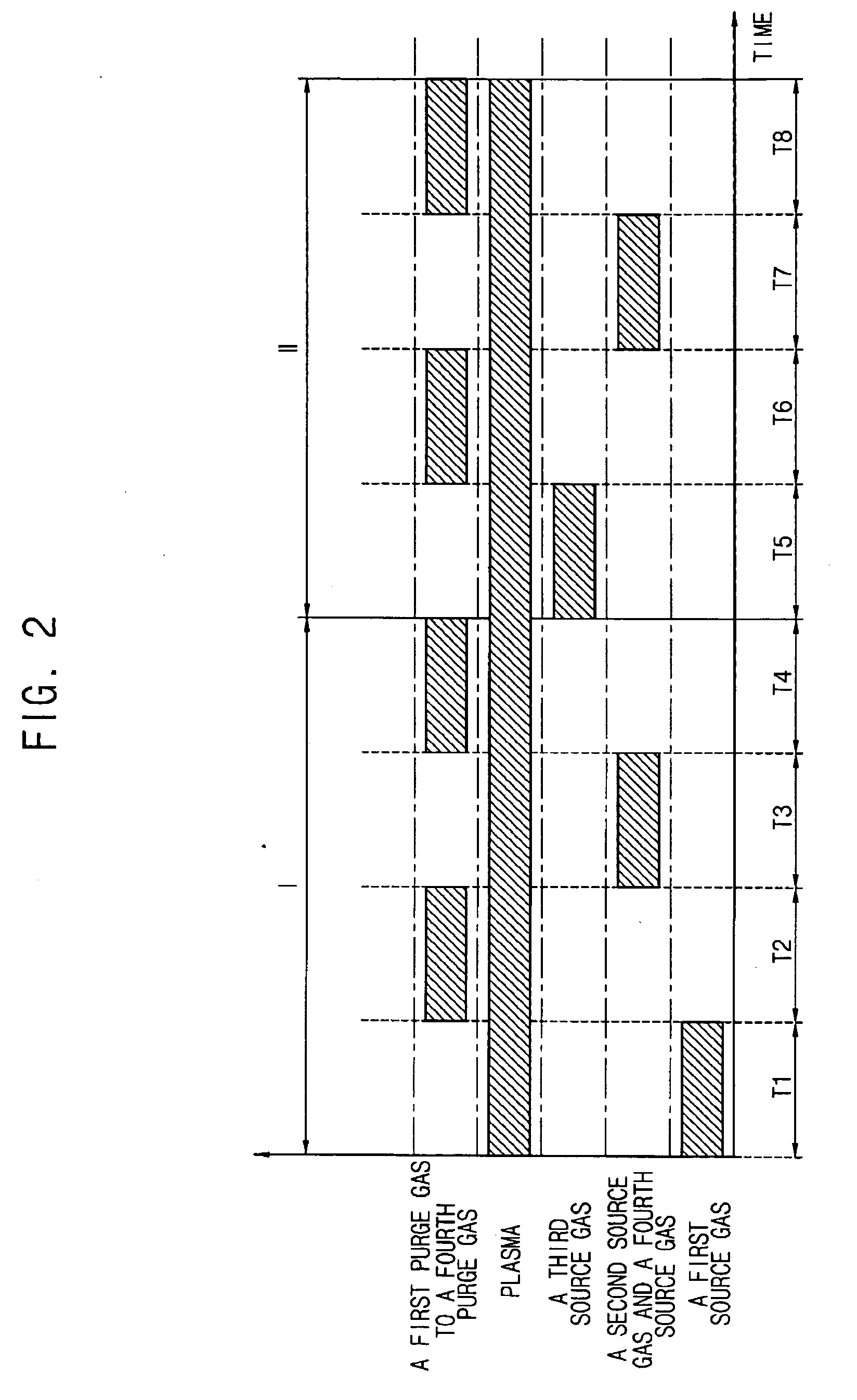
ActiveUS20070054475A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTe elementPhase-change material
A phase changeable material layer usable in a semiconductor memory device and a method of forming the same are disclosed. The method includes forming a plasma in a chamber having a substrate disposed therein, providing a first source gas including a germanium based material to form a first layer including the germanium based material on the substrate while maintaining the plasma in the chamber, providing a second source gas including a tellurium based material to react with the first layer to form a first composite material layer including a germanium-tellurium composite material on the substrate while maintaining the plasma in the chamber, providing a third source gas including an antimony based material to form a second layer including the antimony based material on the first composite material layer while maintaining the plasma in the chamber, and providing a fourth source gas including tellurium based material to react with the second layer including antimony based material to form a second composite material layer including an antimony-tellurium composite material on the first composite material layer. Accordingly, the phase changeable material layer may be formed at a low temperature and power to have desirable electrical characteristics.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
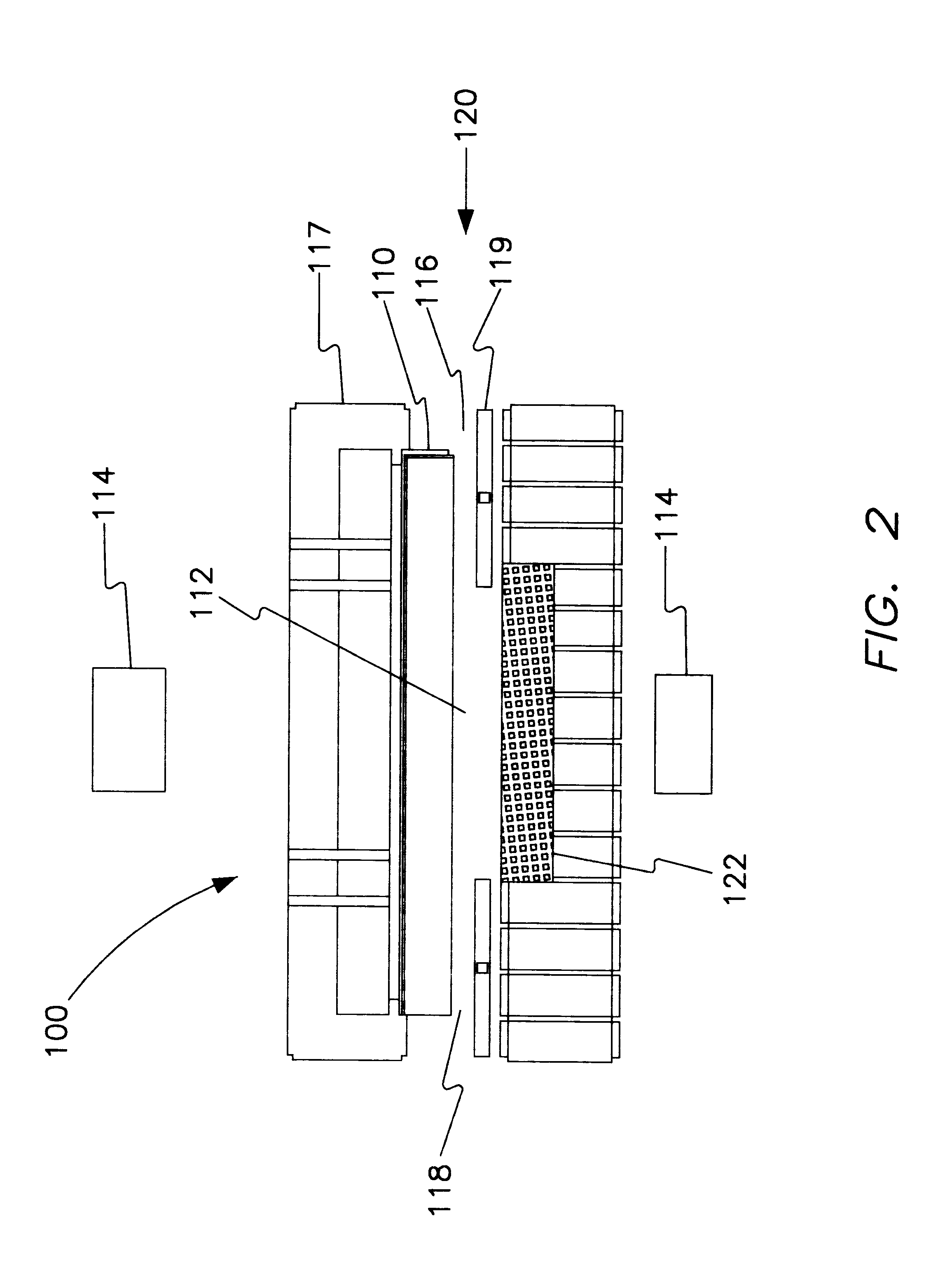
Continuous deposition process and apparatus for manufacturing cadmium telluride photovoltaic devices
InactiveUS20100184249A1Refined grain sizeAvoid condensationCellsVacuum evaporation coatingGas phaseSource material
A continuous deposition process and apparatus for depositing semiconductor layers containing cadmium, tellurium or sulfur as a principal constituent on transparent substrates to form photovoltaic devices as the substrates are continuously conveyed through the deposition apparatus is described. The film deposition process for a photovoltaic device having an n-type window layer and three p-type absorber layers in contiguous contact is carried out by a modular continuous deposition apparatus which has a plurality of processing stations connected in series for depositing successive layers of semiconductor films onto continuously conveying substrates. The fabrication starts by providing an optically transparent substrate coated with a transparent conductive oxide layer, onto which an n-type window layer formed of CdS or CdZnS is sputter deposited. After the window layer is deposited, a first absorber layer is deposited thereon by sputter deposition. Thereafter, a second absorber layer formed of CdTe is deposited onto the first absorber layer by a novel vapor deposition process in which the CdTe film forming vapor is generated by sublimation of a CdTe source material. After the second absorber layer is deposited, a third absorber layer formed of CdHgTe is deposited thereon by sputter deposition. The substrates are continuously conveyed through the modular continuous deposition apparatus as successive layers of semiconductor films are deposited thereon.
Owner:CHEN YUNG TIN
Thick-film pastes containing lead-tellurium-lithium- oxides, and their use in the manufacture of semiconductor devices
The present invention provides a thick-film paste for printing the front side of a solar cell device having one or more insulating layers. The thick-film paste comprises an electrically conductive metal, and a lead-tellurium-lithium-oxide dispersed in an organic medium.
Owner:SOLAR PASTE LLC
Antimony and germanium complexes useful for CVD/ALD of metal thin films
ActiveUS7838329B2Group 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesGermanium organic compoundsPhase-change memoryTe element
Antimony, germanium and tellurium precursors useful for CVD / ALD of corresponding metal-containing thin films are described, along with compositions including such precursors, methods of making such precursors, and films and microelectronic device products manufactured using such precursors, as well as corresponding manufacturing methods. The precursors of the invention are useful for forming germanium-antimony-tellurium (GST) films and microelectronic device products, such as phase change memory devices, including such films.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Method for preprocessing anode sludge and recovering dissipated metal
InactiveCN101338368AHigh recovery rateSimple processSelenium/tellurium compundsProcess efficiency improvementAcetic acidSludge
The invention relates to a method for pre-processing anode mud and recycling rare metals. The invention carries out pre-processing on the anode mud of copper and lead ions and recycling the rare metals; firstly the anode mud is extracted by an acid liquid; a primary acid extraction liquid and the primary decopper anode mud are obtained by filtering; the primary decopper anode mud after being stirred and grinded with sodium carbonate is extracted by metric acid or acetic acid to obtain the deleading anode mud; after sulfated roasting for steaming selenium is carried out on the primary decopper anode mud or the deleading anode mud, the steaming selenium anode mud is extracted by the acid liquid; a secondary acid extraction liquid and the secondary decopper anode mud are obtained by filtering. The acid extraction liquid recycles the selenium and Te by reducing or recycles the slag of selenium and Te by directly adding alkali to react in the acid extraction liquid. The secondary acid extraction liquid after recycling the Te by reducing uses alkali or adds water to dilute and adjust the pH value of a filter liquid and obtain the slag of bismuth by filtering. The method of the invention has a simple flow, a high recycling rate of selenium, Te and bismuth; the noble metals can be enriched and the recycling rate of gold and silver can be remarkably improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Multilayer composite metal oxide catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102247862AHigh reactivityHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationAlkaline earth metalCerium
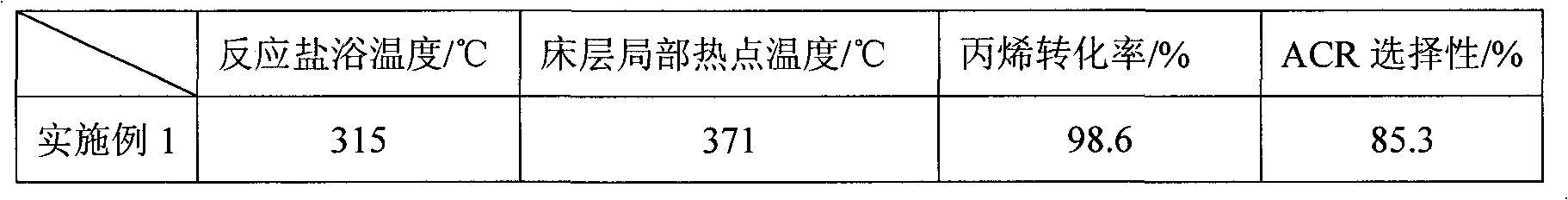
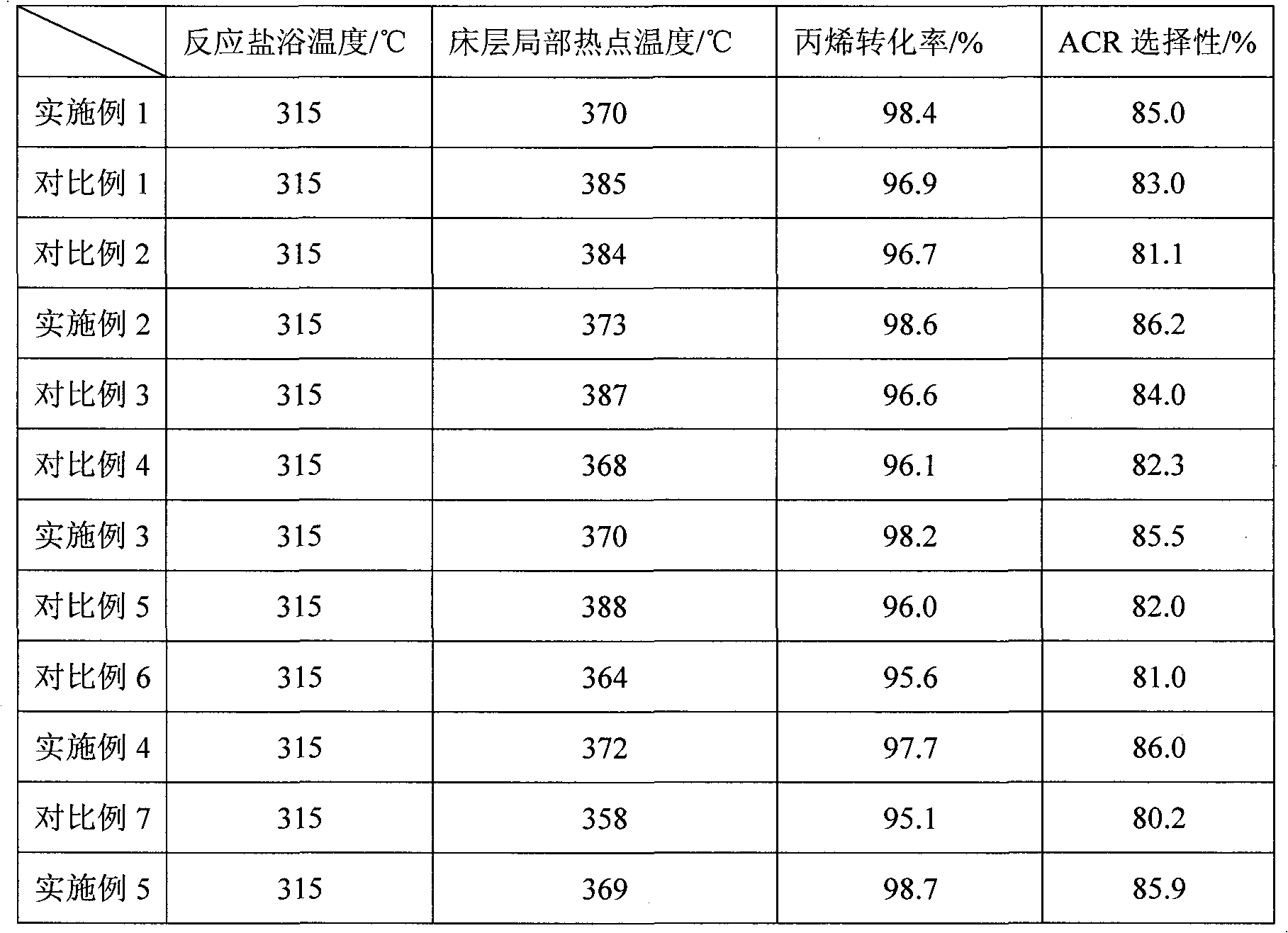
The invention relates to a multilayer composite metal oxide catalyst. The multilayer composite metal oxide catalyst has the general formula as follows: Mo[a]Bi[b]Ni[c]Cs[d]Cu[e]Ti[f]A[g]B[h]C[i]O[j], wherein Mo is molybdenum, Bi is bismuth, Ni is nickel, Cs is cesium, Cu is copper, and Ti is titanium; A is at least one element selected from arsenic, tellurium, manganese, cerium, niobium, zirconium, rubidium, cadmium and germanium; B is at least one element selected from cobalt, boron, strontium, tantalum, alkali metal and alkaline earth metal; C is at least one element selected from vanadium, stannum, gallium, zinc, ferrum, tungsten and stibium; and O is oxygen. The composite metal oxide catalyst has a multilayer structure in which the concentrations of all the elements are reduced progressively from a matrix at the inner layer to the outer layer. The catalyst provided by the invention can effectively reduce the local heat accumulation of single pipe reactors and inhibit the formation of hot spots, and has the characteristics of high reactivity and selectivity and long service life.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Leadless tellurate low melting sealing glass
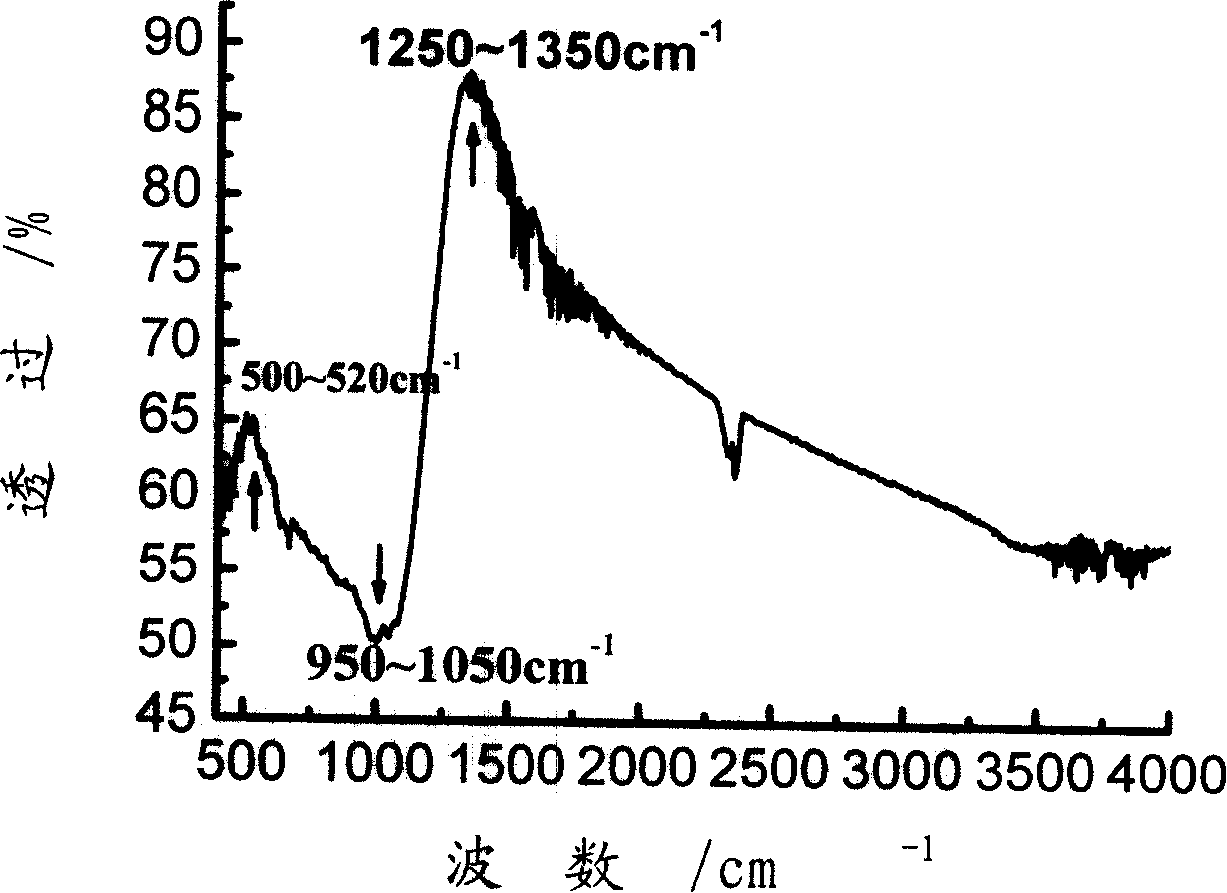
The leadless tellurate low melting glass is used for seal-glass and functional paste-composition binder for sintering. It is characterized by that components (mass percentages): TeO2 10-90%, V205 2-40%, SiO2 0-5%, B203 0-5%, ZnO 0-10%, Bi203 0-20%, Sb203 0-8%, Al203 0-4%, SnO2 0-6%, Ag20 0-10%, BaO 0-5%, MgO+CaO+SrO 0-5% Na20+Li20+K20 0-5%. The infrared absorption spectrum has strong absorption band at 950 to 1050cm-1, and two transmission peaks at 500 to 520cm-1 and 1250 to 1350cm-1 respectively, its sealing temperation is between 350 and 580deg.C.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
Braze alloys
An improved braze alloy is microalloyed to include about 0.0005 wt % to about 0.5 wt % of at least one aggressively surface acting element selected from tellurium (Te), selenium (Se), antimony (Sb), bismuth (Bi), and gallium (Ga), or any combination thereof. The braze alloys may include at least about 30% by weight of at least one base metal selected from the group of silver (Ag), copper (Cu), gold (Au), nickel (Ni), or aluminum (Al). In one example, a silver braze alloy suitable for brazing a cutter to a drill bit body is microalloyed to improve a characteristic of the braze material.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
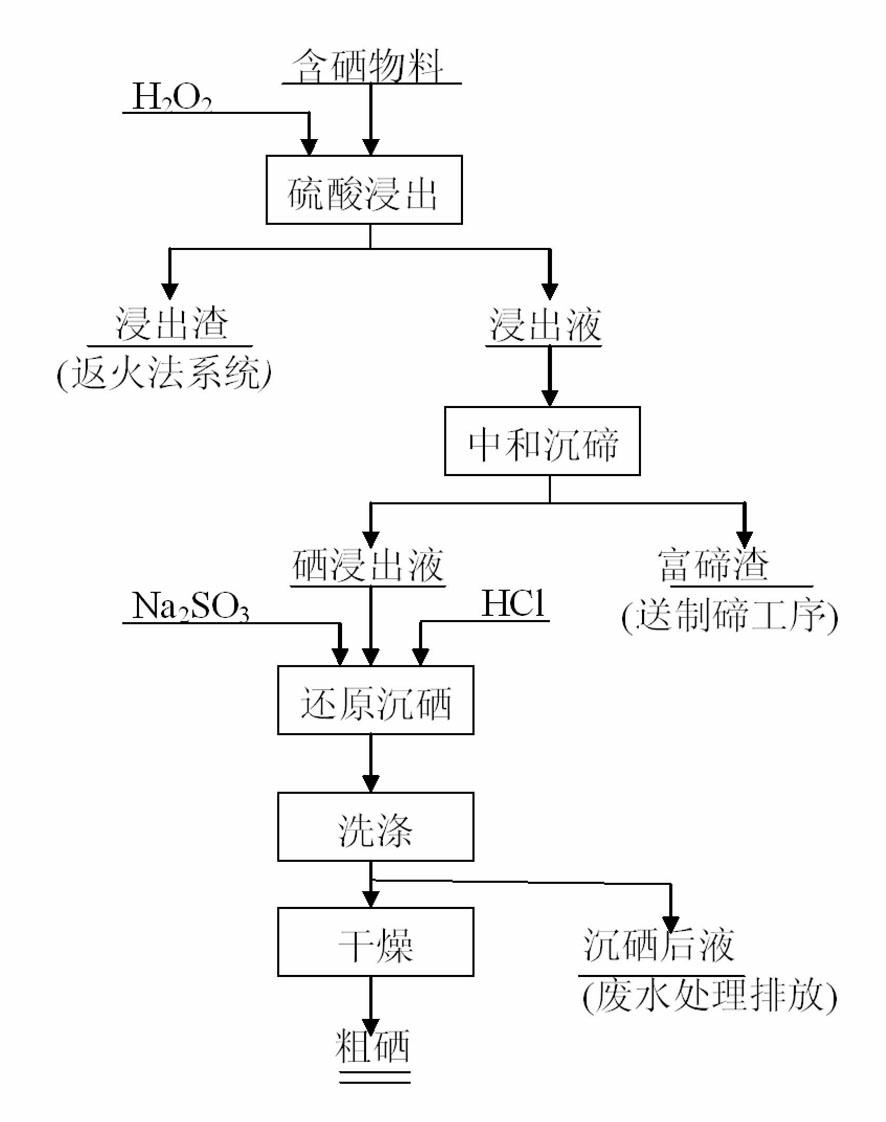
Process for separating and recovering selenium from selenium-containing material
The invention relates to a process for separating and recovering selenium from a selenium-containing material. The process comprises the following steps: dissolving the selenium-containing material into a sulfuric acid solution, adding 10% H2O2 into the mixture, filtering and separating to get leachate and residue containing silver, lead, copper and other valuable metals; separating the selenium from tellurium in the oxidation leachate by using sodium hydroxide; and acidifying the selenium leachate with hydrochloric acid, adding sodium sulfite to reduce the settled selenium, washing and drying to get crude selenium with the grade of not lower than 90%. The crude selenium which is separated by the process is higher in purity and can be directly refined, so that the process flow of recovering selenium is shortened, the recovery rate of selenium is improved, the production cost is reduced and the energy is saved; and the sodium sulfite is used for substituting sulfur dioxide to perform reduction, the control is easy and the environmental pollution is further reduced. The process has very important significance in both aspects of recovering resources and protecting an environment.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
Optical recording medium and process for producing the same, data recording method and data reproducing method for optical recording medium
InactiveUS20060280896A1Excellent signal characteristicEasy to set upLayered productsRecording involving bubble/bump formingTe elementData recording
A supporting substrate 11 and a light-transmitting layer 12, and further between the light-transmitting layer and the supporting substrate 11 a dielectric layer 31, a noble metal oxide layer 23, a dielectric layer 32, a light absorption layer 22 and a dielectric layer 33 in this arranging order when viewed from the light-transmitting layer side are provided. The light absorption layer 22 contains as a main component a material that can be represented by (SbaTe1−a)1−bMAb (wherein MA is an element other than antimony (Sb) and tellurium (Te), 0<a<1 and 0≦b<1), and besides, that is different from an intermetallic compound represented by {(GeTe)c(Sb2Te3)1−c)}dMB1−d (wherein MB is an element other than antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and germanium (Ge), c is ⅓, ½ or ⅔, and 0<d≦1).
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Tellurium Precursors for GST Films in an ALD or CVD Process
The present invention is a process of making a germanium-antimony-tellurium alloy film using a process selected from the group consisting of atomic layer deposition and chemical vapor deposition, wherein a silyltellurium precursor is used as a source of tellurium for the alloy film and is reacted with an alcohol during the deposition process.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Use of tellurium in carbon-supported, noble metal-containing catalysts for liquid phase oxidation reactions
InactiveUS6956005B2High activityHigh selectivityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsCatalyst activation/preparationIminodiacetic acidTe element
An improved catalyst comprising a noble metal and tellurium at the surface of a carbon support is provided. Also provided are novel methods for preparing such catalysts and novel processes for the use of such catalysts in liquid phase oxidation reactions, particularly the oxidation of N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid or a salt thereof.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Method for extracting refined tellurium from tellurium-contained smelting slag
InactiveCN101565174AImprove leaching rateReduce invalid consumptionElemental selenium/telluriumSlagTe element
The invention relates to a method for extracting refined tellurium from tellurium-contained smelting slag, which is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps of: oxidizing and leaching inorganic acid, replacing noble metal with a copper plate, depositing the copper by sodium sulfide, counteracting and depositing tellurium, alkaline leaching coarse TeO2, removing impurities by Na2S, concentrating and electrowinning. The method has the advantages of high recovery rate for tellurium, comprehensive and effective recovery of other useful metals, and suitably treating the tellurium-contained waste slag with high water content and small granularity generated in the metallurgy process by a wet-method.
Owner:YONGXING XINTAI SILVER IND
Medium carbon free-cutting non-quenched-and-tempered steel containing sulfur and tellurium and production technological method thereof
ActiveCN107287504AExcellent machinabilityReduce precipitationProcess efficiency improvementSulfurImpurity
The invention discloses medium carbon free-cutting non-quenched-and-tempered steel containing sulfur and tellurium and a production technological method thereof. The non-quenched-and-tempered steel mainly comprises 0.35%-0.50% of C, 0.10%-0.80% of Si, 0.75%-1.60% of Mn, 0-0.03% of P, 0.02%-0.08% of S, 0-0.08% of Mo, 0-0.025% of Nb, 0.02%-0.12% of V, 0.012%-0.016% of N, 0.02%-0.08% of Te, 0.001%-0.003% of Ca, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. The ratio of the tellurium to the sulfur is 0.25-2.5. According to the free-cutting non-quenched-and-tempered steel disclosed by the invention, occluded foreign substances in the steel can be subjected to modifying treatment by adding the tellurium, the cutting properties, fatigue resistance and the like of the non-quenched-and-tempered steel can be improved obviously, and pollution to the environment can be avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com