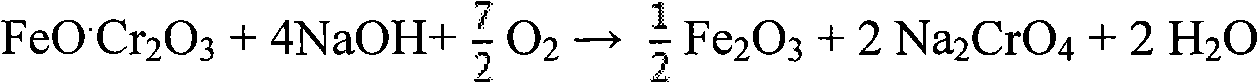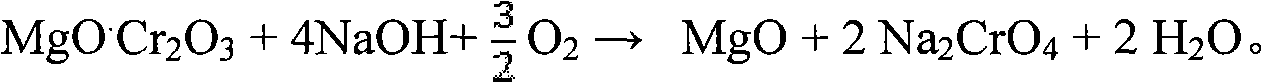Patents
Literature
2272results about How to "Improve leaching rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for directly roasting and processing spent lithium ion batteries and recycling valuable metals
InactiveCN101519726AImprove leaching rateEasily brokenProcess efficiency improvementCobaltSodium sulfate
The invention relates to a method for directly roasting and treating spent lithium ion batteries and recycling valuable metals, in particular to a method for recycling and treating spent lithium ion batteries using lithium cobalt oxide as an anode material. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, remove organic binder on an organic diaphragm material and an electrode material in the batteries by roasting at a temperature of 500 DEG C to 850 DEG C; crushing and mixing the roasted battery material with sodium sulfate (or potassium sulfate) and concentrated sulfuric acid before size mixing; carrying out secondary heat treatment in an electric stove at a temperature of 350 DEG C to 600 DEG C to convert metals in the spent lithium ion batteries, such as cobalt, copper, lithium, and the like into easily water-soluble sulfate which is leached by water or a dilute sulphuric acid solution; then, using an organic extracting agent to respectively extract the cobalt and the copper from a leaching solution and obtain a cobalt product and a copper product; using sodium carbonate to precipitate the metal lithium from the leaching solution after the cobalt and the copper are removed; and enabling the leaching solution to return treatment heat so as to secondarily treat materials. The invention has a metal leaching rate higher than 99.5 percent and a metal recovery rate higher than 99 percent.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Method for recycling copper, nickel, chromium, zinc and iron from plating sludge
The invention relates to a method for recycling copper, nickel, chromium, zinc and iron from plating sludge, belonging to the technical field of chemical engineering and metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: acid leaching, vulcanizing for separation and enrichment, hot-pressure leaching, extracting for separation, hot-press oxidizing chromium, purifying chromium solution, extracting ferric chloride and the like. The method has obvious advantages of strong adaptability to different kinds of plating sludge, high utilization of metal resources, high value-added content of product,less process waste residue, thorough deintoxication and the like.
Owner:YANGZHOU NINGDA NOBLE METAL CO LTD
Leaching and recycling method for metals in anode waste materials of lithium-ion batteries
ActiveCN104868190AWide range of applicationsImprove leaching rateWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingScrapMetal leaching
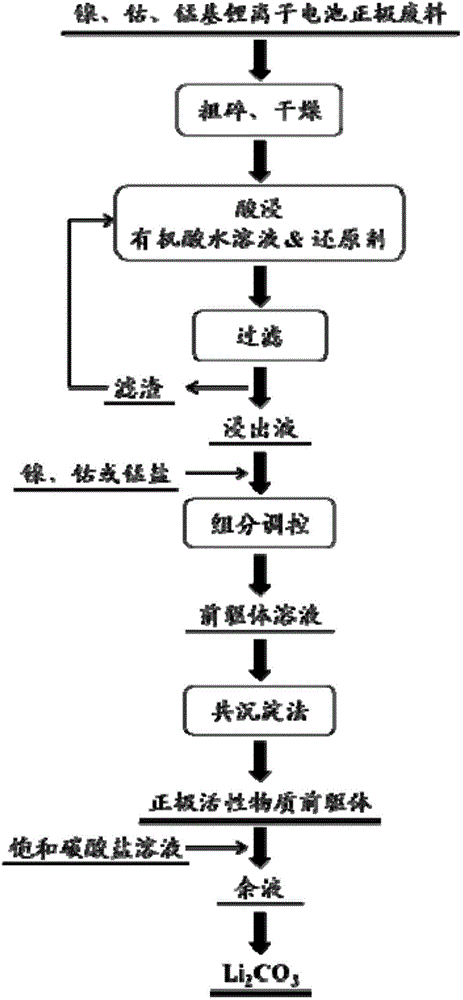
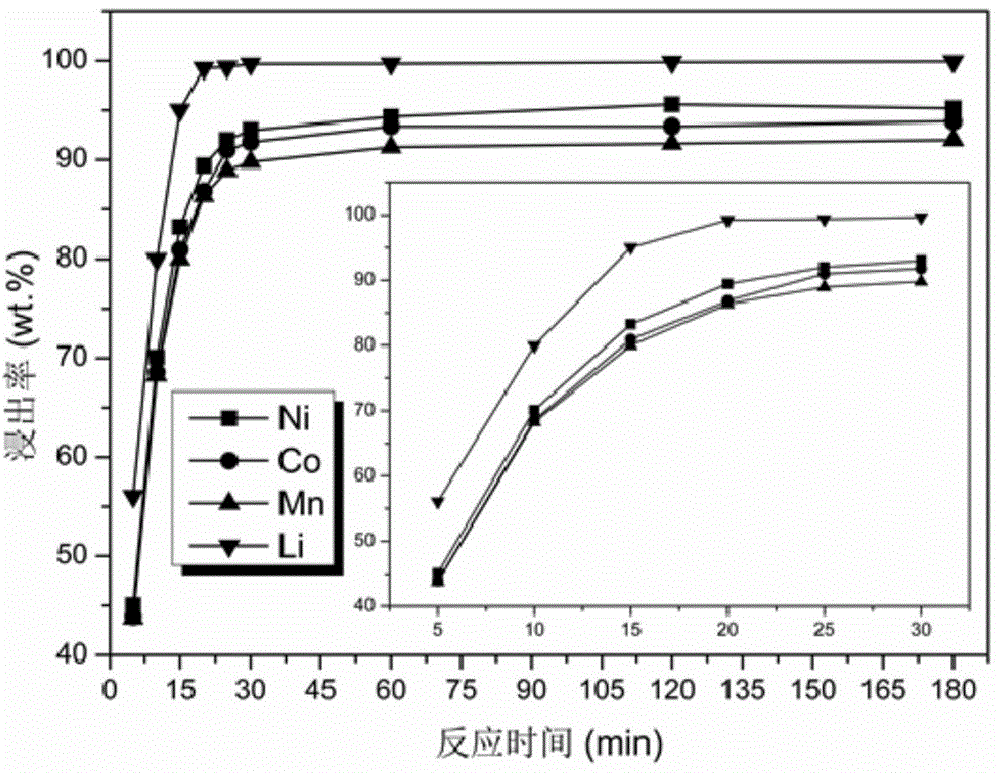
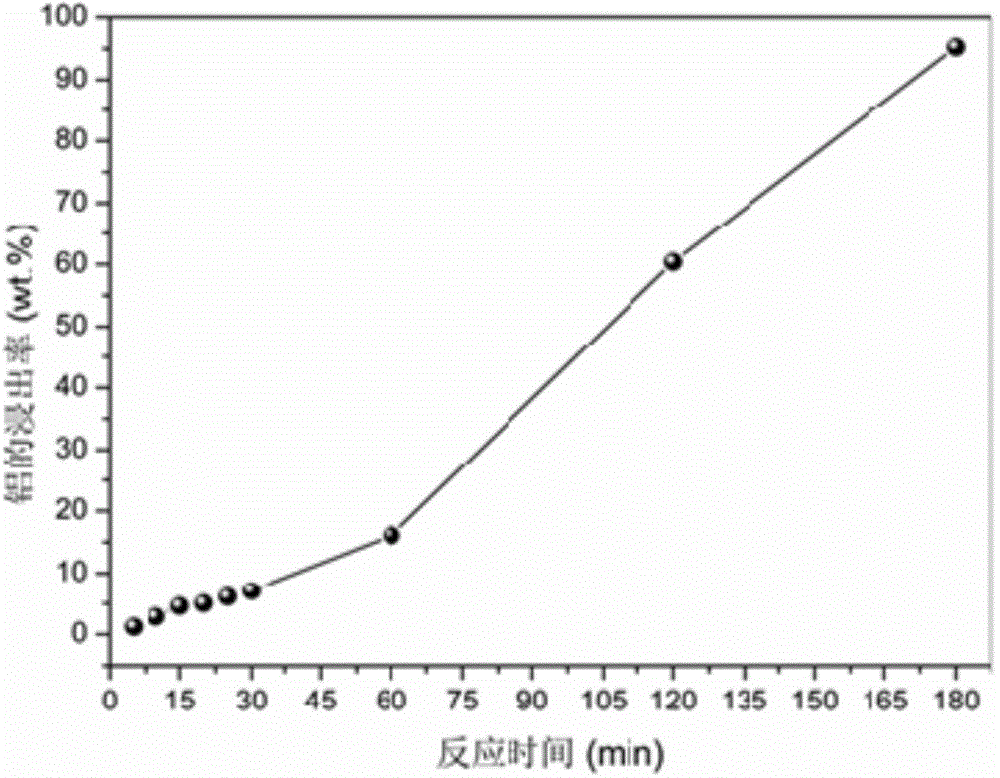
The invention provides a leaching and recycling method for metals in anode waste materials of lithium-ion batteries. The leaching method comprises the steps that: the anode waste materials of the lithium-ion batteries react with organic acid solution containing a reducing agent; after reaction, solid-liquid separation is carried out and leaching solution and filter residues are obtained, so that the leaching of the metals in the anode waste materials of the lithium-ion batteries is realized. Based on the leaching method, the invention provides a recycling method for the anode waste materials of the lithium-ion batteries based on closed-loop circulation of metals. The leaching method for the metals in the anode waste materials of the lithium-ion batteries has the advantages of high metal leaching rate, short leaching time, low processing cost and wide application range; secondary pollution and complex process for separating and purifying various metals in the leaching solution are avoided; according to the recycling method for the metals in the anode waste materials of the lithium-ion batteries, the technological process is short and the closed-loop circulation of the metals is realized.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
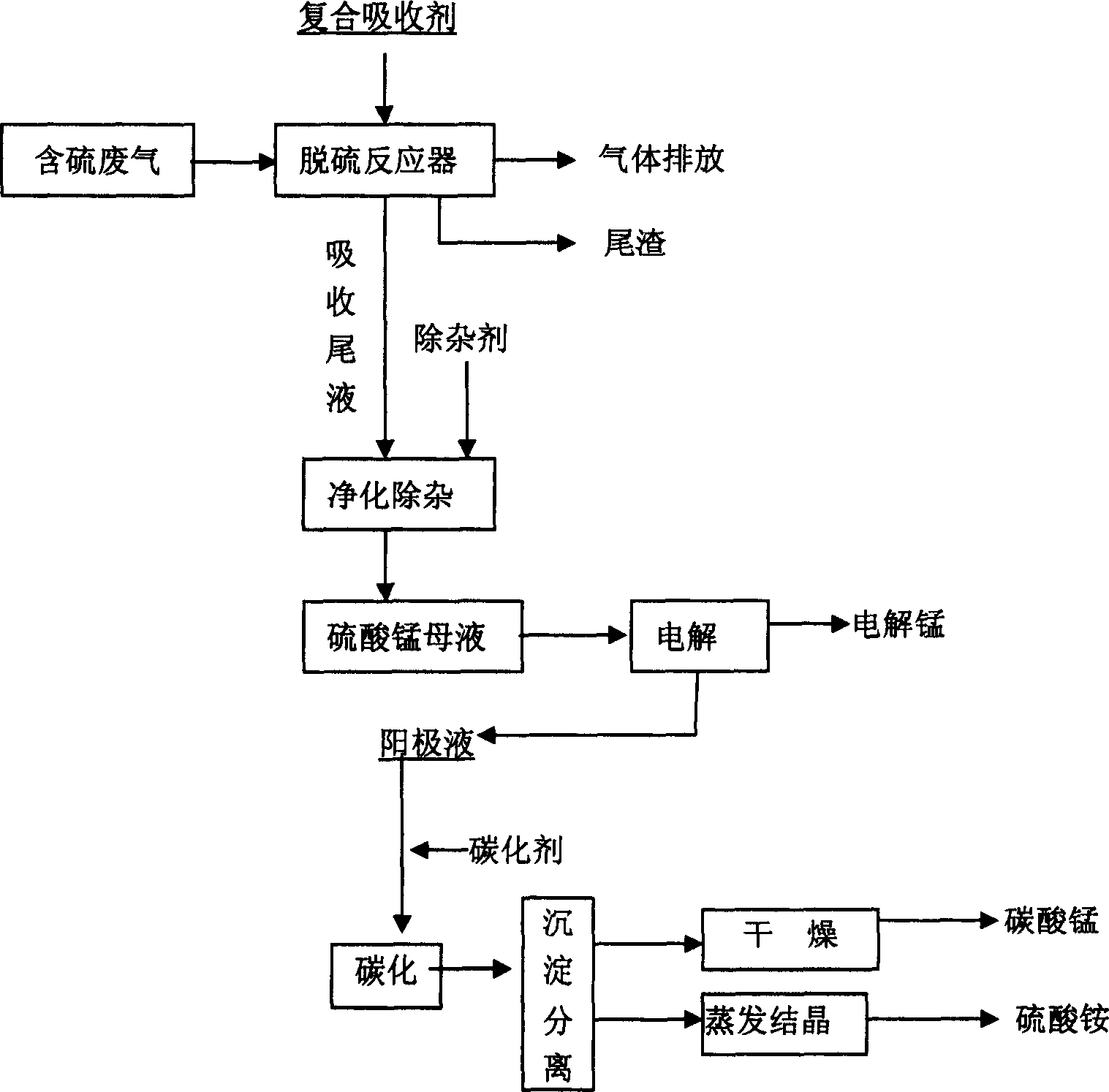
Waste gas desulfurizing method with composite absorbant comprising pyrolusite and pH buffering agent
ActiveCN1772345ARich reservesLow pricePhotography auxillary processesDispersed particle separationPyrolusiteElectrolysis
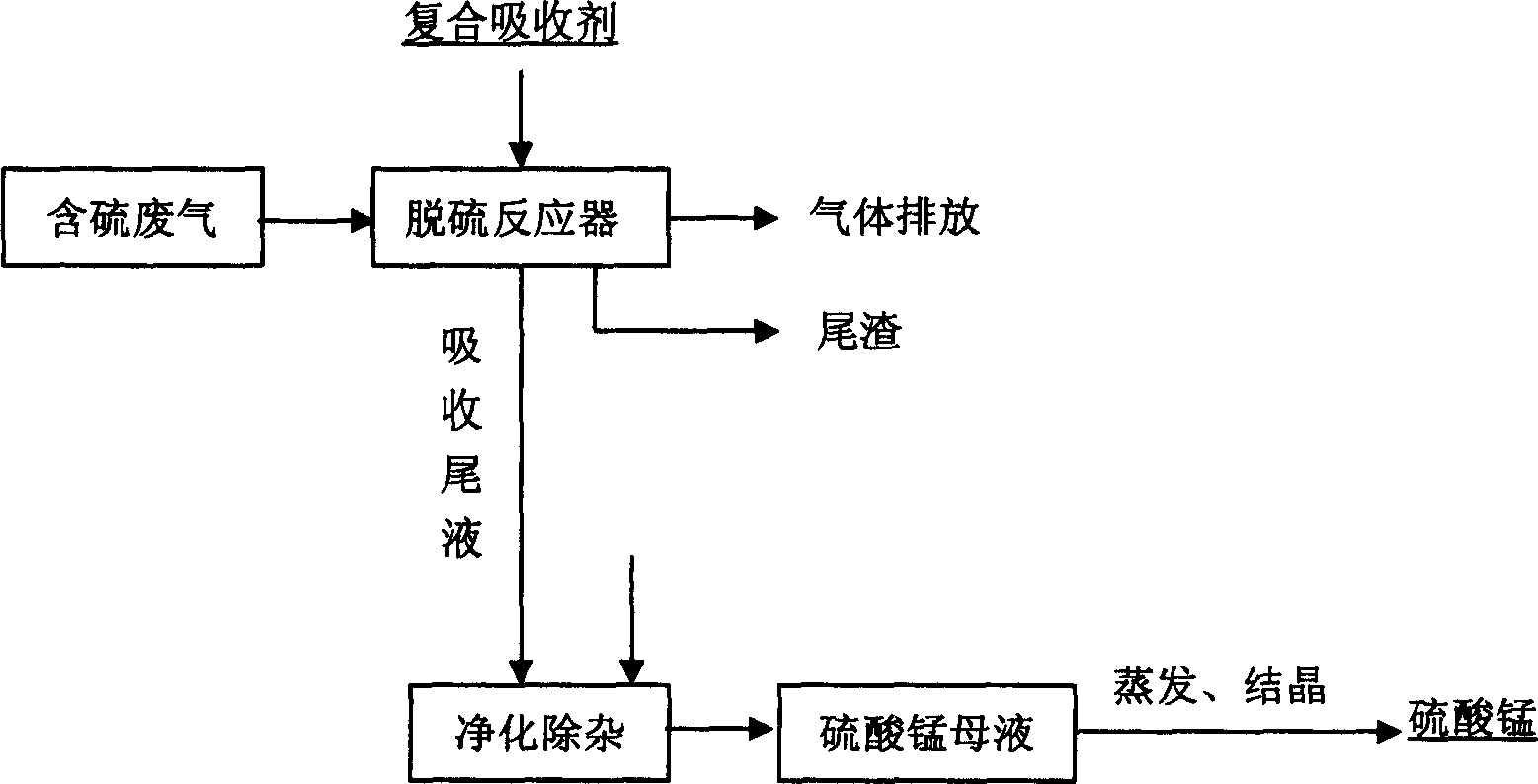
The present invention is method of comprehensively utilizing waste SO2 gas resource and pyrolusite, and the method includes utilizing the composite absorbent comprising pyrolusite slurry and pH buffering agent to produce oxidation-reduction and neutralizing reaction with waste SO2 gas to eliminate SO2 from the waste gas, purifying the absorbed tail liquid to obtain manganese sulfate product through direct evaporating crystallization or metal manganese product through DC electrolysis, and treating the anode liquid to obtain high purity manganese carbonate product and ammonium sulfate product. The present invention realizes treatment of waste with waste to recover sulfur resource and comprehensively utilize pyrolusite. The method of the present invention is reasonable and has no secondary pollution.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
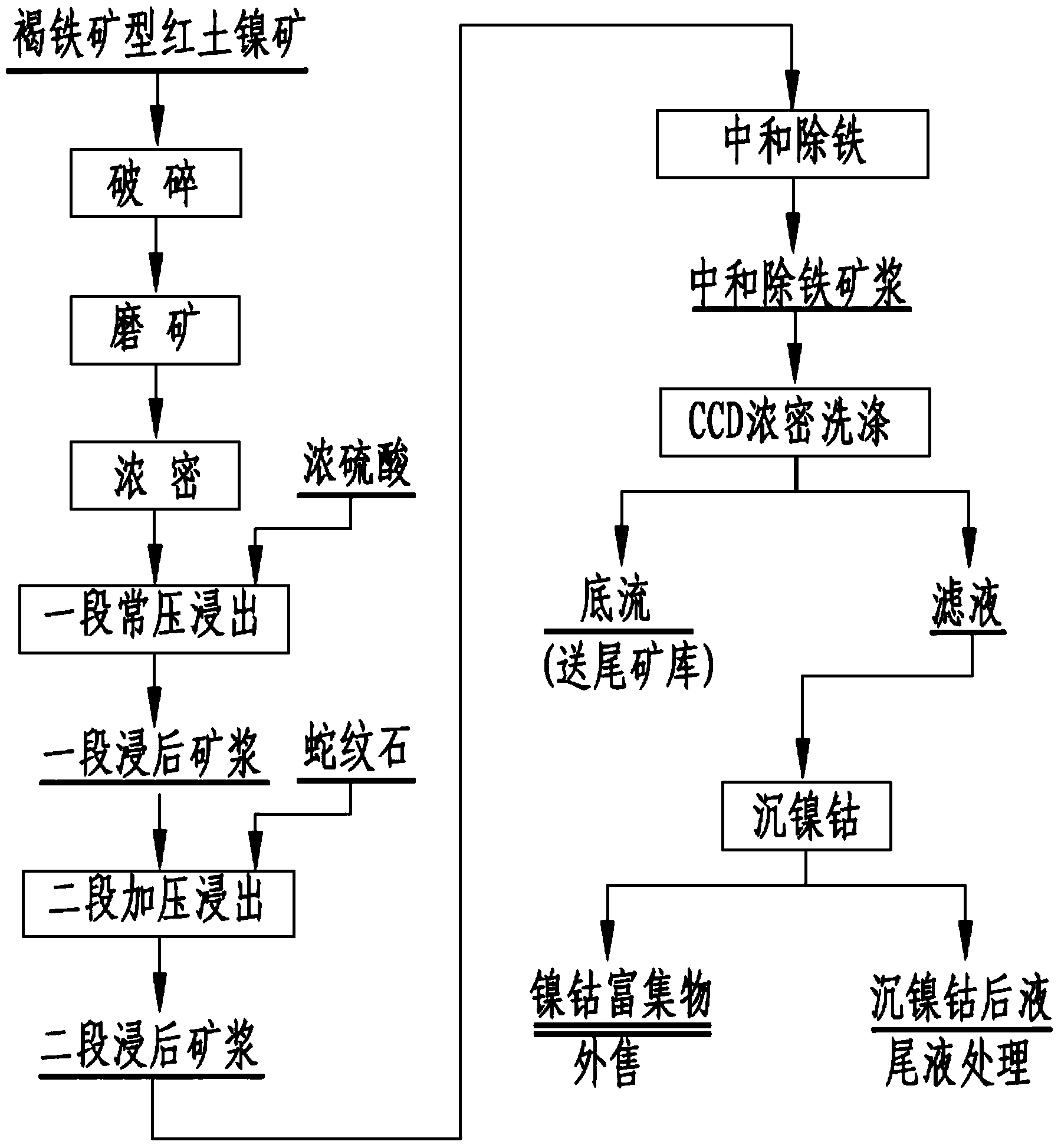
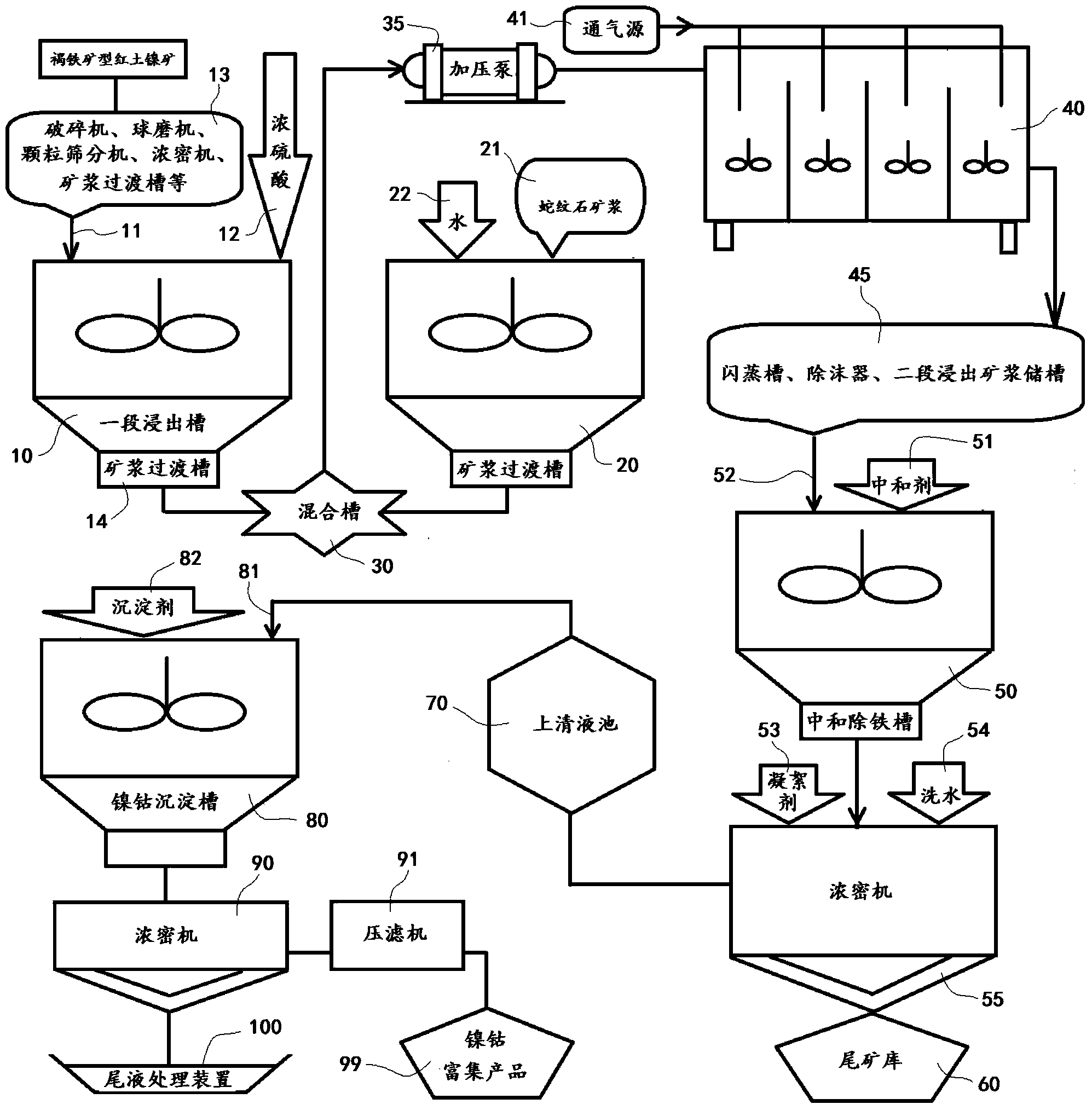
Laterite-nickel ore combination leaching process
InactiveCN103614571AWide adaptabilityImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementMagmaHigh pressure
The invention relates to a laterite-nickel ore combination leaching process, which comprises that: limonite type laterite-nickel ore is subjected to crushing grading, and then is added with concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out primary stage normal pressure stirring self-heating leaching, serpentine type laterite-nickel ore is subjected to crushing grinding, the obtained serpentine type laterite-nickel ore and the primary stage leached ore magma are concurrently conveyed to a pressure kettle, and serpentine is leached by using the primary stage normal pressure leaching residual acid and the acid produced through iron precipitation in the pressure kettle, or mixing type laterite-nickel ore is subjected to grading, the obtained fine particle-grade ore is added with concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out primary stage normal pressure stirring leaching, ore on the sieve is subjected to crushing grinding, the grinded ore and the primary stage leached ore magma are concurrently conveyed to a pressure kettle, and coarse particle-grade ore leaching is performed by using the primary stage normal pressure leaching residual acid and the acid produced through iron precipitation in the pressure kettle. According to the invention, the process has characteristics of no special requirements on ore types and grades, wide raw material adaptability, investment reduction, energy consumption reduction, production cost reduction, and simple process, wherein the Ni recovery rate and the Co recovery rate of the whole process of the present invention are respectively more than 90% and 88%, and are higher than the Ni recovery rate and the Co recovery rate of the treatment method in the existing non-high-pressure acid leaching technology.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Production method for improving summer green tea quality
A production method for improving quality of summer green tea comprises picking summer fresh tea, spreading at 18-22deg.C for 20-25h, evaporation deenzyming under 0.03kg / m2-0.05kg / m2 for 40-60s, cooling to normal temperature, sprinkling tannase and / or cellulase aqueous solution 0.5-1.5wt. parts for per 45 fresh tea, twisting, unblocking, oven drying, and parching, wherein the enzyme liquid contains tannase and cellulase equal to 15000 u / g tannase powder and cellulase powder 50mg.The method is suitable for improving quality of summer tea with two or three leaves and a bud. The method reduces the content of ester-catechin in summer tea, increases the content of amino acid and soluble sugar, reduces astringency of the tea, and improves the taste of tea, thereby making full use of material of summer tea and improving effectiveness of operations of tea garden.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
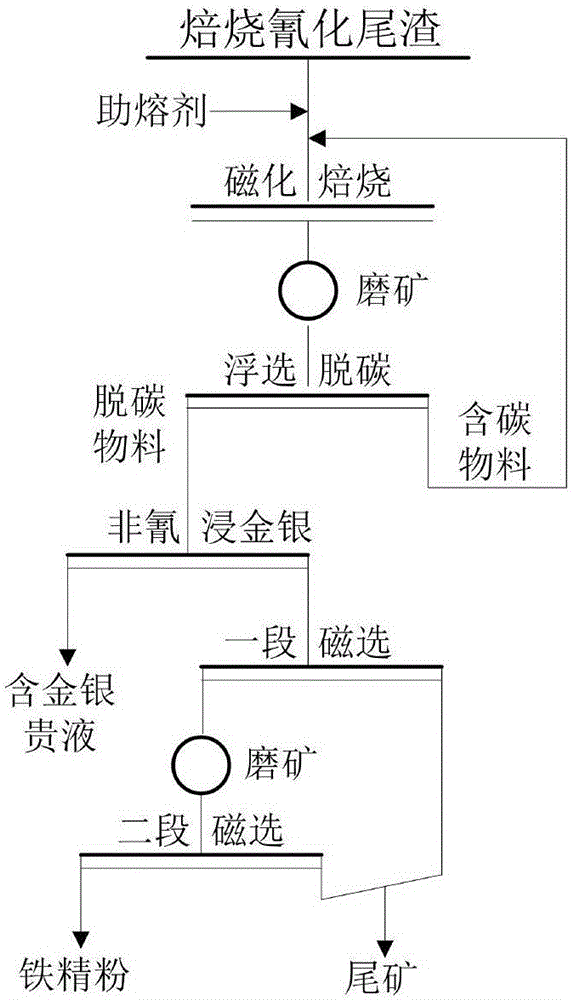
Method for recycling and synchronous harmless treatment of gold, silver and iron in roasting-cyanidation tailings
ActiveCN106498177ARealize harmless treatmentLow toxicityProcess efficiency improvementSilicate mineralsGold leaching
The invention provides a method for recycling and synchronous harmless treatment of gold, silver and iron in roasting-cyanidation tailings, and belongs to the technical field of metallurgical waste residue utilization. The method comprises the following steps: mixing dried roasting-cyanidation tailings with a fluxing agent and a reducing agent; carrying out roasting at 750 to 900 DEG C for 3 to 5 hours; conducting water quenching on hot roasted sand for cooling; carrying out ore grinding and flotation to remove residual carbon; leaching gold and silver with an environment-friendly gold leaching agent; and conducting magnetic separation on the leaching residue to obtain fine iron powder. Containing no highly toxic cyanide, the rejects belong to general industry solid waste. As the fluxing agent is added for magnetic roasting, not only can gold and silver coated with an iron mineral be exposed, but also the fluxing agent can perform a solid-phase reaction with a silicate mineral to generate a dissoluble silicate, and gold and silver coated with the dissoluble silicate can also be exposed after ore grinding. According to the method, gold, silver and iron in the roasting-cyanidation tailings are recycled, harmless treatment is realized synchronously, and the purpose of clean production is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
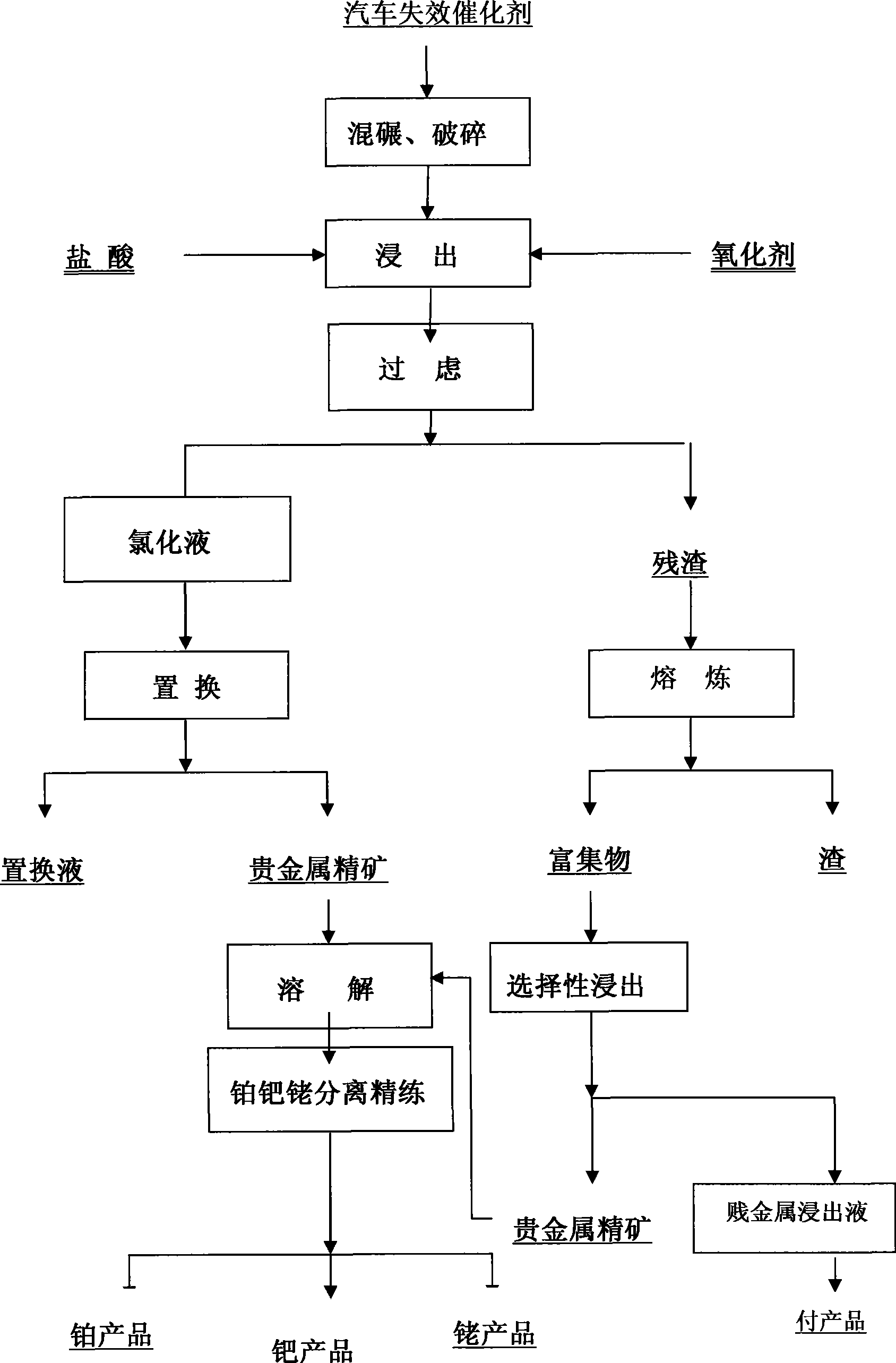
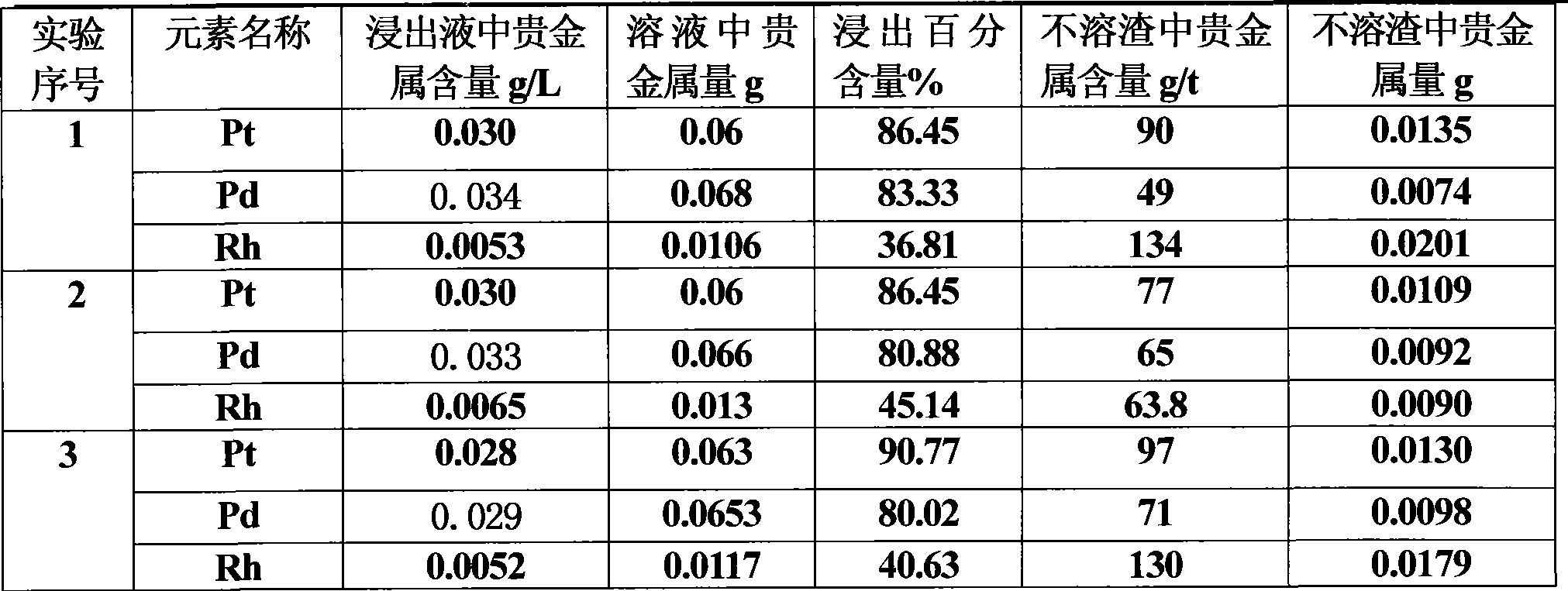
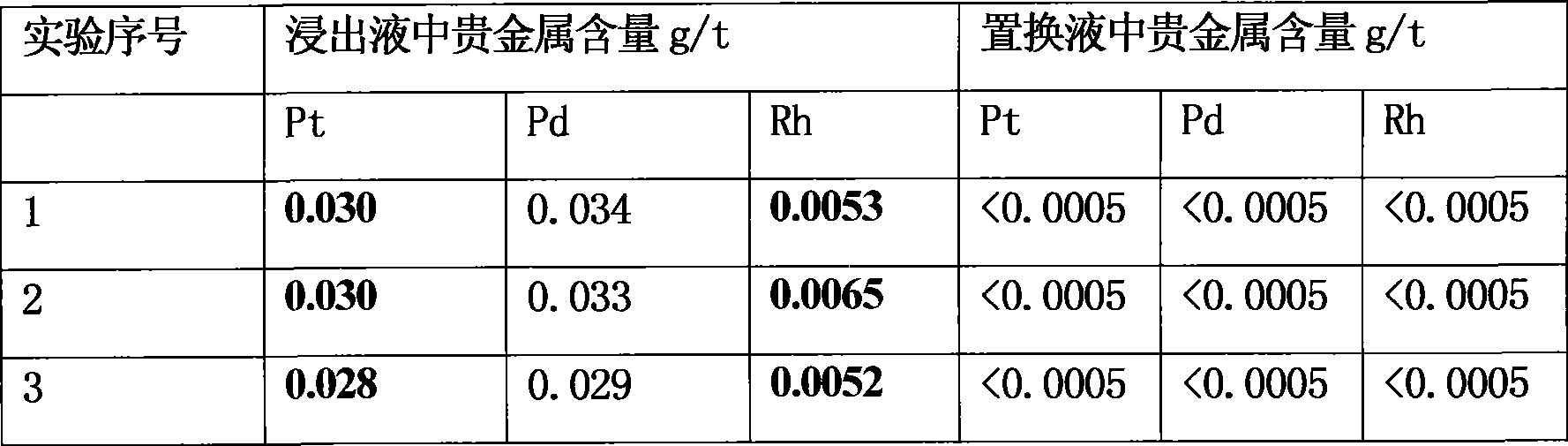
Method for extracting precious metal from auto-exhaust catalyst by hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy complex process
InactiveCN101519725ALoose process conditionsImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionPlatinum
The invention relates to a method for extracting precious metal from a disabled auto-exhaust catalyst, which comprises the following steps: 1. lixiviating precious metal from the disabled auto-exhaust catalyst by a hydrometallurgy process and obtaining precious metal concentrates after permuting lixivium; 2. lixiviating slag, collecting precious metal of the slag by a pyrometallurgy process to obtain a precious metal phase and selectively lixiviating base metal in the precious metal phase to obtain precious metal concentrates; and 3 combining the precious metal concentrates obtained in the first two steps and refining the precious metal concentrates to produce platinum, palladium and rhodium products. The invention compensates the deficiency that the percent recovery of the precious metal is low by simply treating the disabled auto-exhaust catalyst with the hydrometallurgy process and has the advantages that the contents of platinum, palladium and rhodium in the waste slag are smaller than 1g / t and the product purity reaches 99.95 percent.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
Method for in-situ leaching of rare-earth ores from weathering crust elution-deposited rare earth ore
InactiveCN103509944AReduce adsorption consumptionReduce contentProcess efficiency improvementRidgeLandslide
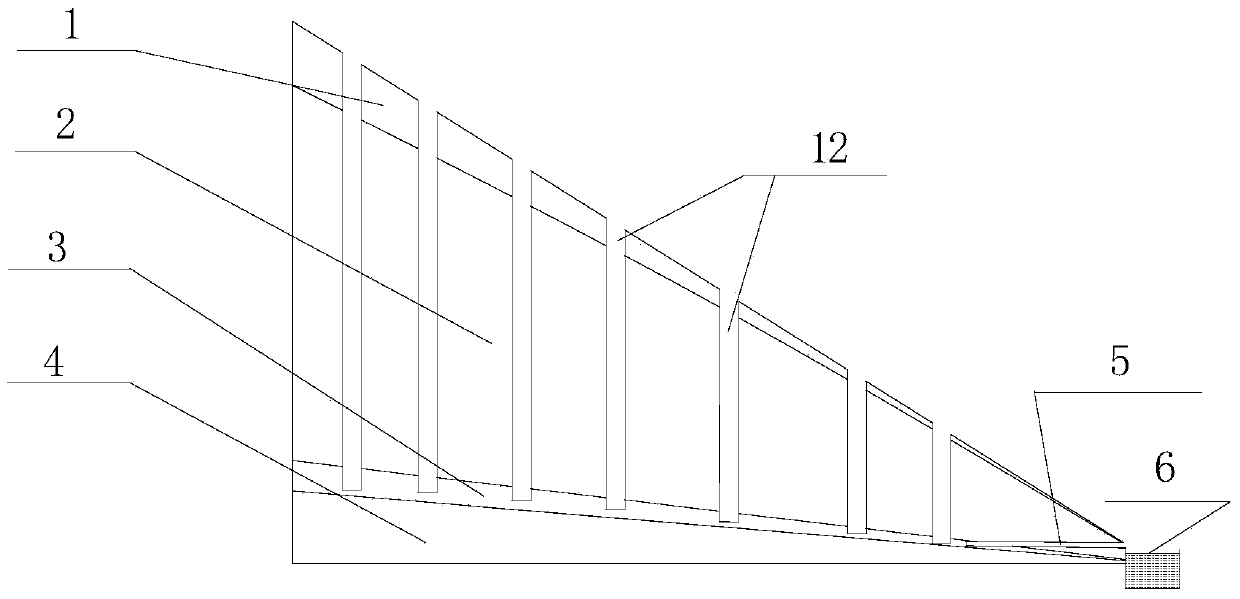
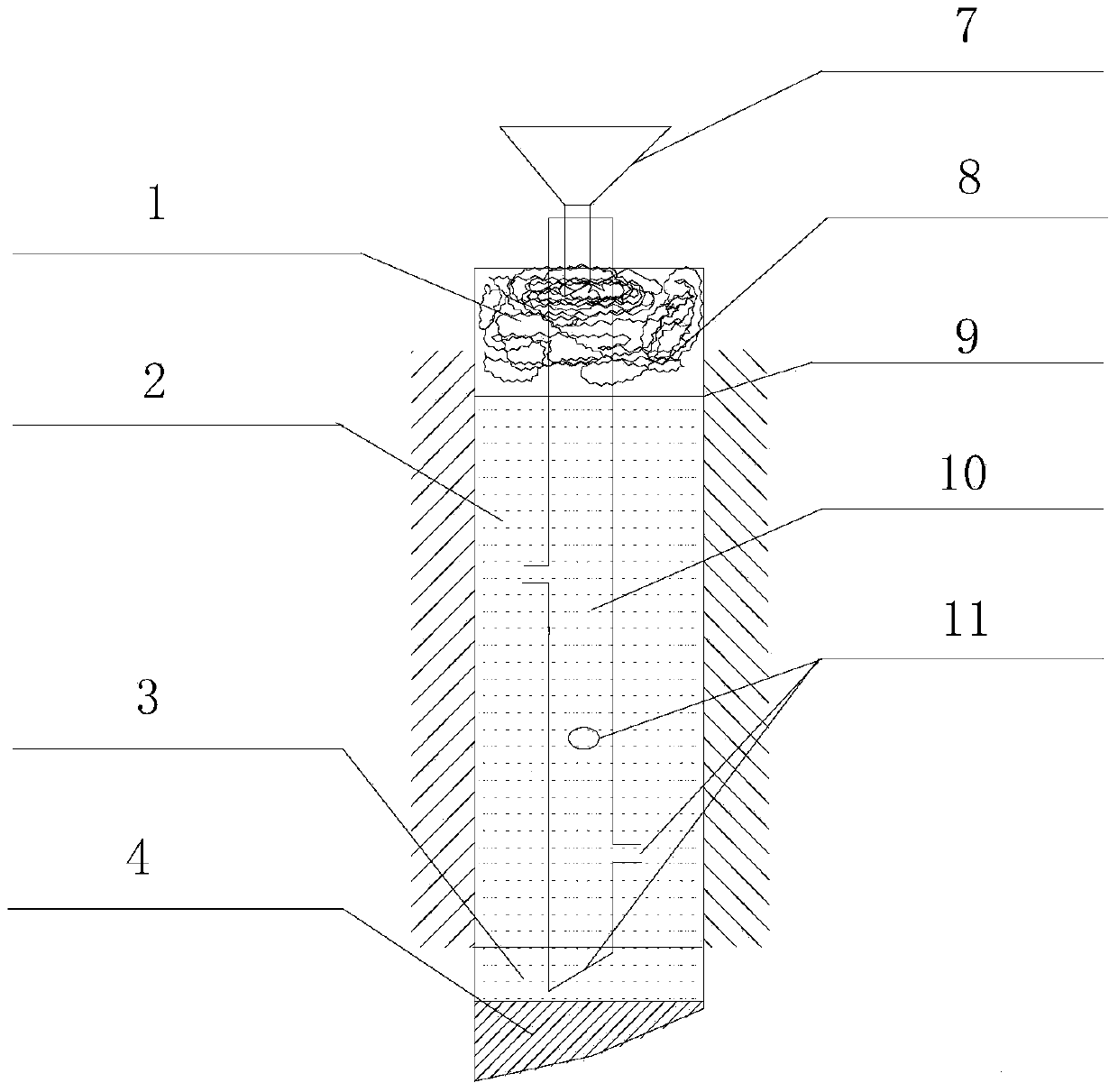
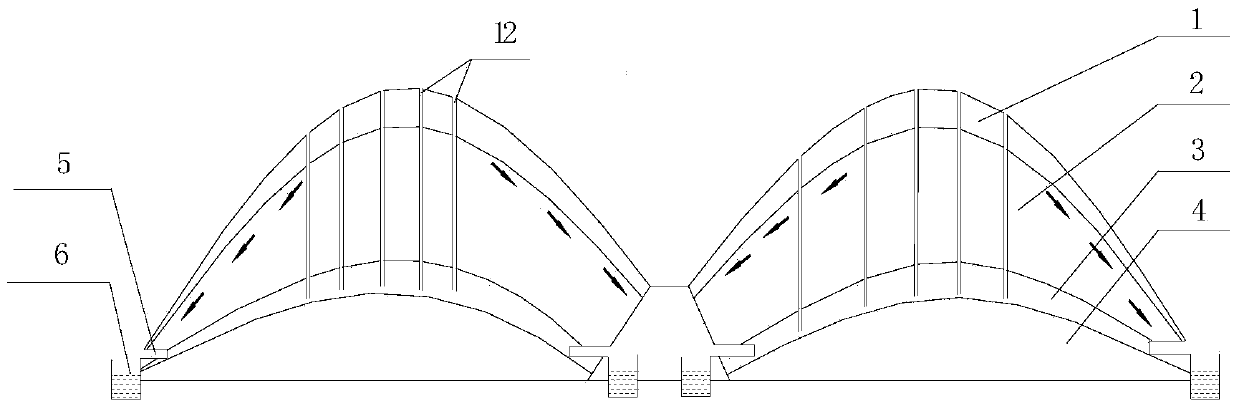
The invention discloses a method for in-situ leaching of rare-earth ores from a weathering crust elution-deposited rare earth ore. The method comprises the following steps: holes are drilled in an ore body and drilled from a humus layer, a completely weathering layer to a half weathering layer of the ore body, a guide pipe with an opened upper part and an opened lower part is inserted into the holes and reaches the half weathering layer, and an ore leaching liquid is injected into the guide pipe; a diversion trench is formed in a bedrock to be used for guiding the rare earth leaching liquid into a liquid collecting reservoir; holes are distributed in a net shape along the ridge of the ore body, and the distance between every two holes is 2-3 m; a hopper is mounted at the upper end of the guide pipe, a fixing device is arranged on the guide pipe passing through the humus layer. The method has the advantages that the content of leached rare earth mother liquid impurities is reduced, the subsequent rare earth mother liquid treatment is facilitated, the geological hazards caused by the ore body landslide due to water swelling of clay minerals with high content of the humus layer are reduced, ammonium chloride can be used as a leaching agent, and under the premise of not increasing the impurity removal cost, the rare earth leaching rate is improved, and the selection range of the leaching agent is widened.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Fungal alpha-amylase-containing beer complex enzyme and preparation method thereof
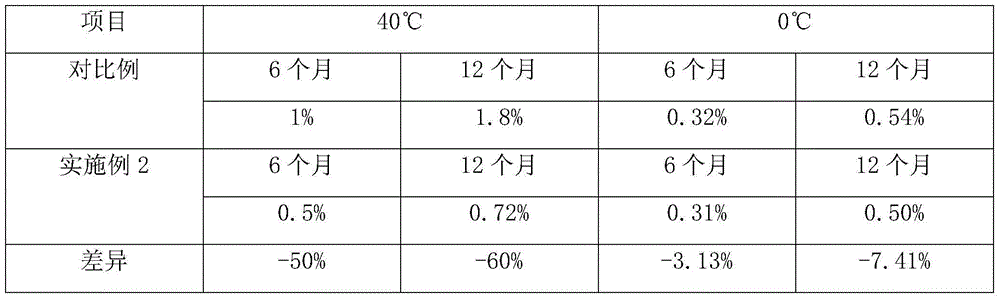
ActiveCN104651335AEnsure food safetyIncrease profitOxidoreductasesGlycosylasesAntioxidantAlpha-amylase
The invention discloses a fungal alpha-amylase-containing beer complex enzyme and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of enzyme preparation processing. The high-activity fungal alpha-amylase and other food grade enzyme preparations, plant extracts, antioxidants, protective agents, activating agents and the like can be scientifically compounded by taking concentrated maltase and concentrated malt juice powder as main raw materials; the prepared beer complex enzyme is complete in proteases, high in enzyme activity, difficult to deactivate, mellow in malt aroma, and capable of providing abundant nitrogen source for malt juice, wherein the activity of fungal alpha-amylase in fermenting liquor during the preparation of fungal alpha-amylase is 17000-21000 U / mL. The complex enzyme can be stored for 12 months under the conditions of 0DEG C and 40DEG C, the single enzyme activity loss in the complex enzyme are respectively 0.50% and 0.72%, the enzyme deactivation caused by environment change, and inappropriate operation methods during packaging, storage, transportation, use and the like can be effectively prevented, especially the enzyme deactivation caused by high temperature can be prevented.
Owner:湖南新鸿鹰生物工程有限公司
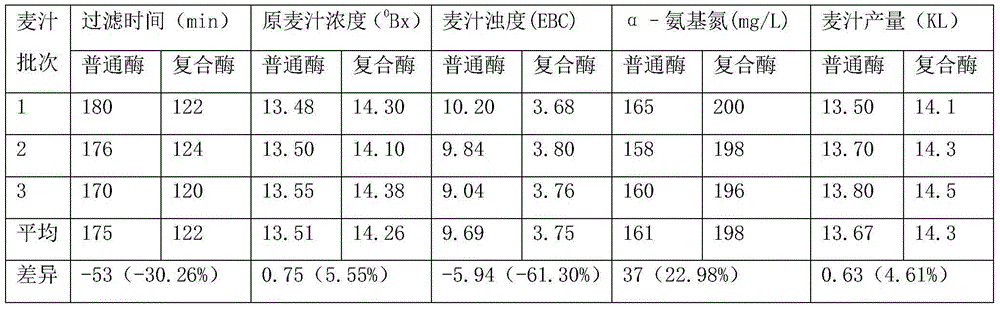
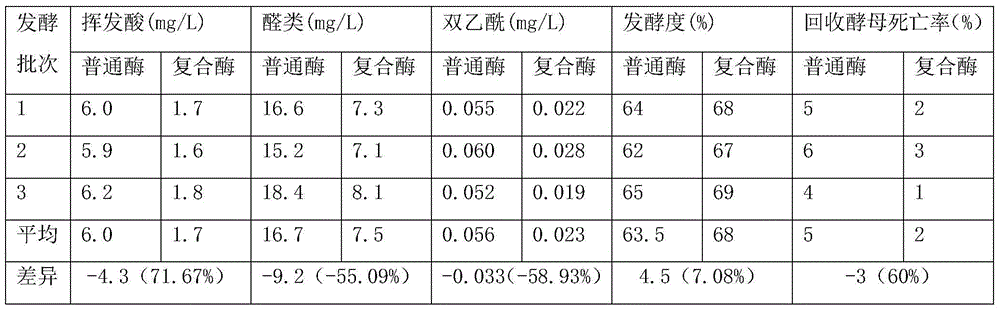
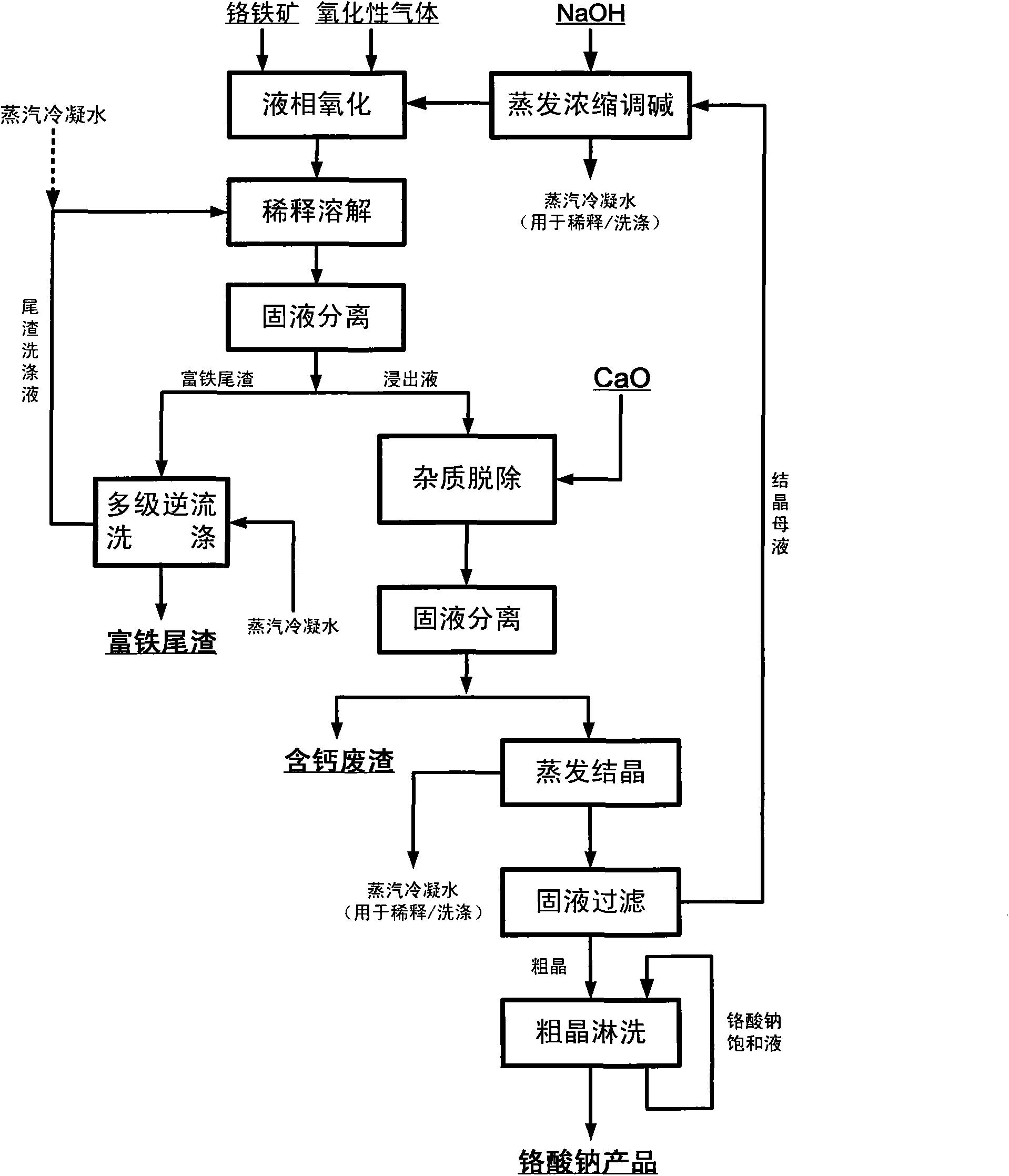
Method for pollution-free production of sodium chromate by pressure leaching of chromite
ActiveCN101817561AObvious superioritySimple ingredientsChromates/bichromatesReaction temperatureHydrometallurgy
The invention belongs to the field of chromite hydrometallurgy and chromium chemical industry, and in particular relates to a method for the pollution-free production of sodium chromate by pressure leaching of chromite. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) reacting the chromite with oxidizing gas in solution of NaOH; 2) diluting the product obtained by the step 1) and making subcrystalline sodium chromate to fully enter a liquid phase; 3) performing solid-liquid separation on the solid-liquid mixed slurry obtained by the step 2); 4) adding calcium oxide into the obtained diluent for removing impurities; and 5) evaporating and crystallizing the obtained solution without the impurities to obtain a sodium chromate crystal and crystallization mother solution; after the solid-liquid separation, rinsing the sodium chromate crystal by using saturated solution of sodium chromate; and drying to obtain a qualified sodium chromate product. The method has the advantages of simple reaction system component, no difficultly separated phase introduced in the system, contribution to high-efficiency separation of the sodium chromate, great reduction in reaction temperature, low energy consumption, effective reduction in production cost of the sodium chromate, and high chromium leaching yield.
Owner:HUBEI ZHENHUA CHEMICAL CO LTD
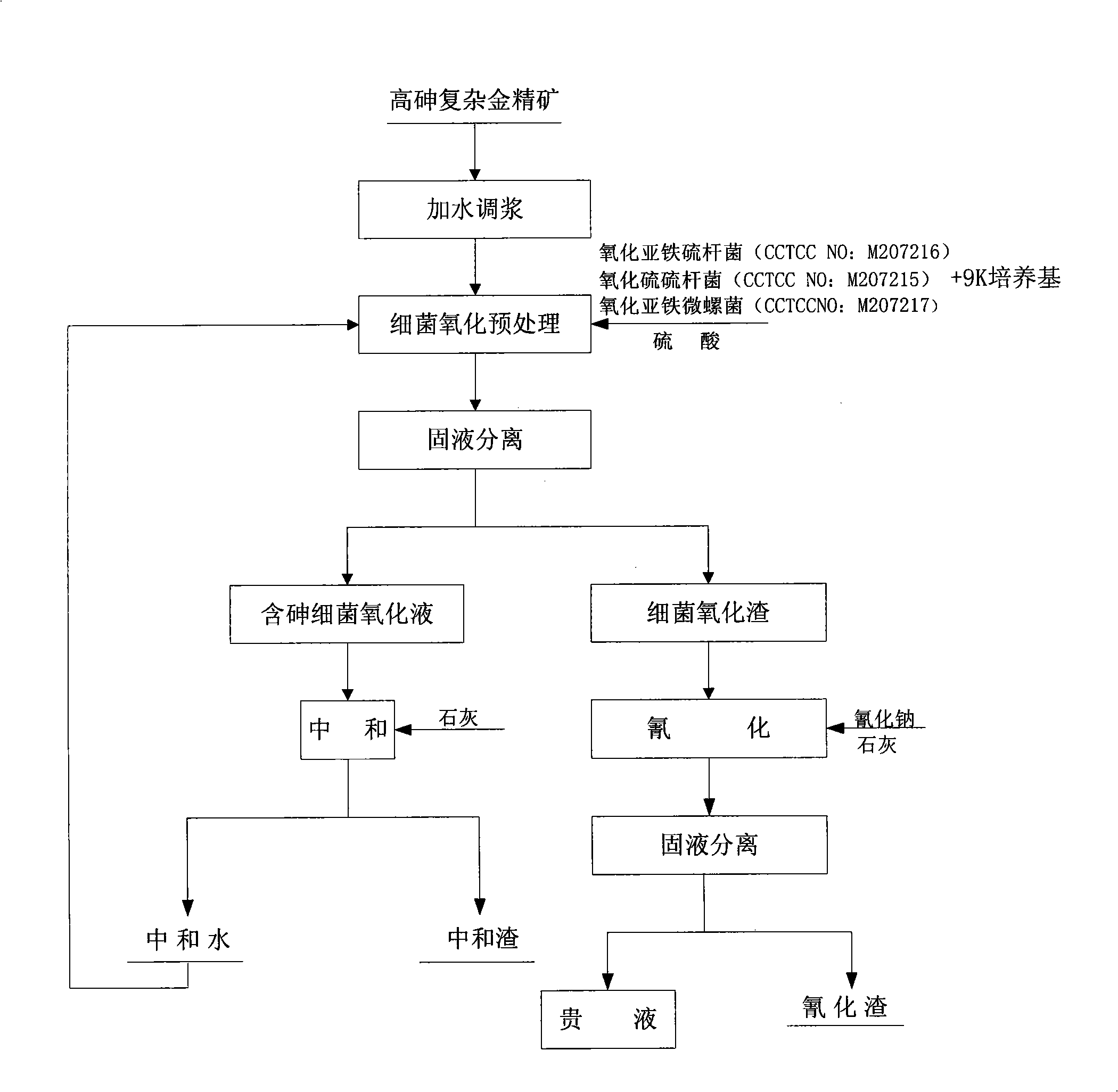
Cyanidation aurum-extracting method for preprocessing high-arsenic complex refractory gold ore by oxidation with arsenic resistant strains
InactiveCN101333599AIncrease growth temperatureStable temperatureProcess efficiency improvementThiobacillus ferrooxidansResistant strain
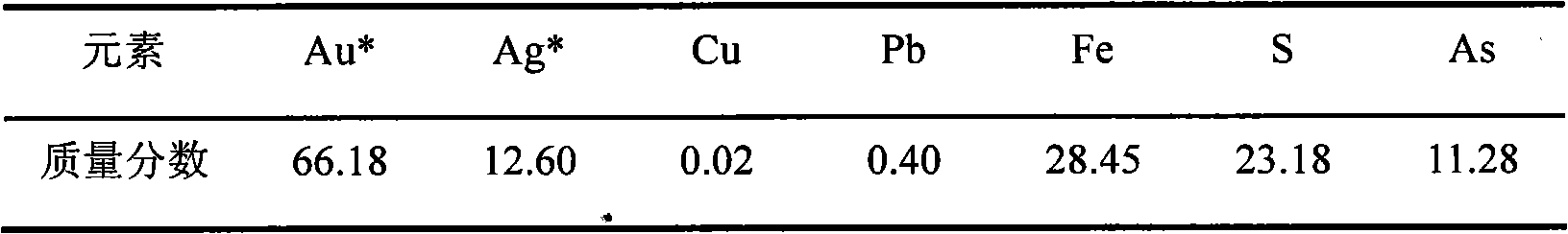
Disclosed is a cyaniding gold extraction method for pre-treating high-arsenic complex refractory gold ore by arsenic-resistant bacteria oxidation, comprising five steps of arsenic-resistant bacteria culture, flotation concentrate mixing, bacterial oxidation of flotation concentrates, solid-liquid separation and cyaniding gold extraction. The cyaniding gold extraction method adopts specific arsenic-resistant bacteria which are prepared by mixing Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, Thiobacillus thiooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans, and conducts oxidation pretreatment of high-arsenic complex refractory gold ore. The high-arsenic complex gold ore containing 8 to 20 percent of arsenic can be pretreated, and the arsenic removal rate is 85 to 98 percent. The leaching rate of gold is up to 90 to 95 percent after cyaniding leaching. The cyaniding gold extraction method adopts unique bacteria for leaching ores, greatly saves cooling cost, conducts direct oxidation of high-arsenic complex gold ore containing 8 to 20 percent of arsenic, and has advantages of being widely adaptable, simple in operation, environmentally friendly and remarkably beneficial.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Leaching process of zinc oxide ore
InactiveCN1477217AImprove leaching rateAvoid enteringProcess efficiency improvementLiquid wastePregnant leach solution
The present invention relates to a leaching-out method of zinc ore containing high iron and silicone. It includes the following steps: (1). neutral leaching-out, simultaneously adding zinc oxide powder and solution containing sulfuric acid and stirring, progressively raising pH value to 5-5.2 from initial 3.0-3.5, and purifying the reacted neutral leach and using it for electrolysis, and using the leached slag make next leaching-out; (2). low acid leaching-out, in the leached slag adding sulfuric acid solution and stirring, controlling pH value and making it progressively be reduced to 1.5-3.0 from 5-5.2; and (3). circulating waste liquor, solid-liquid separating second leached material, and returning the waste liquor contaiing sulfuric acid into neutral leaching-out stage of zinc oxide ore.
Owner:YUNNAN XIANGYUNFEILONG RESOURCES RECYCLING TECH CO LTD
Comprehensive recovery for bullion ore with various metals
InactiveCN1818098AImprove leaching rateSolve difficult preprocessing problemsProcess efficiency improvementMaceralArsenic
The invention opened a recovery method for the polymetallic bullion ore of high sulphur, carbon and arsenic. It solves the problem of extracting gold interfering by the sulphur and carbon. The chlorination extracting system is proper not only to sulfide mineral but also to the polymetallic accompanying mineral. Also it can recovery the accompanying metal less than 8h, so it has improved the extracting ratio. The process is easy to do and low cost.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Preparation method for tea extract
The invention discloses a preparation method for a tea extract, belonging to the technical field of extraction of effective components of tea leaves. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out low-temperature rapid freezing treatment on high-quality commercial tea leaves; then immediately crushing; then combining a high-voltage pulsed electric field (PEF for short) technology, an ultrasonic treatment technology and a low-temperature enzymolysis technology; and carrying out low-temperature extraction in a whole process. According to the preparation method for the tea extract, the loss of effective components, caused by high-temperature processing, is avoided, and the extraction rate of the effective components of the tea leaves is also improved. The process is simple and low in cost; the introduction amount of extraneous food additives, processing auxiliary agents and chemical substances is reduced; the natural nutritional ingredient and the flavor of the tea leaves are kept to the greatest extent, the low-carbon production is realized and the environment is protected.
Owner:LVJIN DEV FUJIAN
Method of bulk infusion extracting nickel cobalt from low grade red soil nickel ore
InactiveCN1718787AImprove leaching rateNo pollutionProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionGranularity
A process for extracting Ni and Co from the low-grade Ni-contained laterite ore includes such steps as crushing to make its average granularity less than 2 cm, stacking the ore particles with granularity of 100 mesh-1.5 cm, proportionally mixing others, adding them to the stack, shrinkling acidic extracting liquid, collecting the extracting liquid, and concentrating until the concentration of Ni ions is 2-4g / L.
Owner:广西赛可昱新材料科技有限公司
Method for separating and recovering nickel, cobalt, magnesium, iron and silicon from nickel-bearing laterite
InactiveCN101525690AImprove leaching rateHigh dissolution rateProcess efficiency improvementSlagLaterite
A method for separating and recovering nickel, cobalt, magnesium, iron and silicon from nickel-bearing laterite is disclosed; nickel, cobalt, magnesium and iron therein are leached out by using high-temperature peracid, leachate is pre-neutralized via serpentine powder, after the pre-neutralization, the leachate is neutralized by magnesite powder for de-ironing, and the scum is delivered for ironmaking after being dewatered by smoke gases in a fluidized bed furnace for making sulfuric acid, the de-ironed clear nickel liquid uses magnesite powder to precipitate nickel carbonate, and the precipitated liquid is concentrated and crystallized to obtain magnesium sulfate heptahydrate. The leached slag mainly contains silicon and can be used for making white carbon black. The invention can sufficiently recover and utilize nickel, cobalt, magnesium, iron and silicon in the nickel-bearing laterite, and the invention is simple in technology, low in energy consumption and pollution-free on environment.
Owner:广西冶金研究院有限公司 +1
Technology for extracting tellurium dioxide from tellurium-containing smelting slag
ActiveCN102992280AImprove leaching rateReduce dosageWaste processingSolid waste disposalSlagMaterials science
The invention relates to a technology for extracting tellurium dioxide from tellurium-containing smelting slag. The technology comprises the following steps: ball-milling tellurium slag, leaching by water, carrying out reduction alkali leaching, vulcanizing, carrying out silicon removal purification, and neutralizing to precipitate tellurium. The method has the advantages of tellurium leaching rate improvement, reduction of the alkali application amount in the leaching operation, and production cost reduction. The method is characterized in that sodium hydrosulphite is adopted as a transition agent to transit insoluble high-valence tellurium to low-valence tellurium, so the leaching rate leaching rate is increased. The total tellurium leaching rate can reach above 90% under a suitable technological condition; and after recovering tellurium through neutralizing, the TeO2 grade of the smelting slag can reach above 50%, and the content of tellurium in the waste liquid obtained after the neutralizing is 0.1-0.3g / L. The method also has the advantages of further enrichment of copper, lead, bismuth, antimony and precious metals in the leaching slag, realization of the resource reuse, production cost reduction, and energy saving, and is of great importance to the resource recovery and the environmental protection.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
Method of preparing high purity copper by bacteria leaching primary sulfide ore
InactiveCN101033508AEnhanced synergistic leachingIncrease leaching ratePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementSulfurThin layer
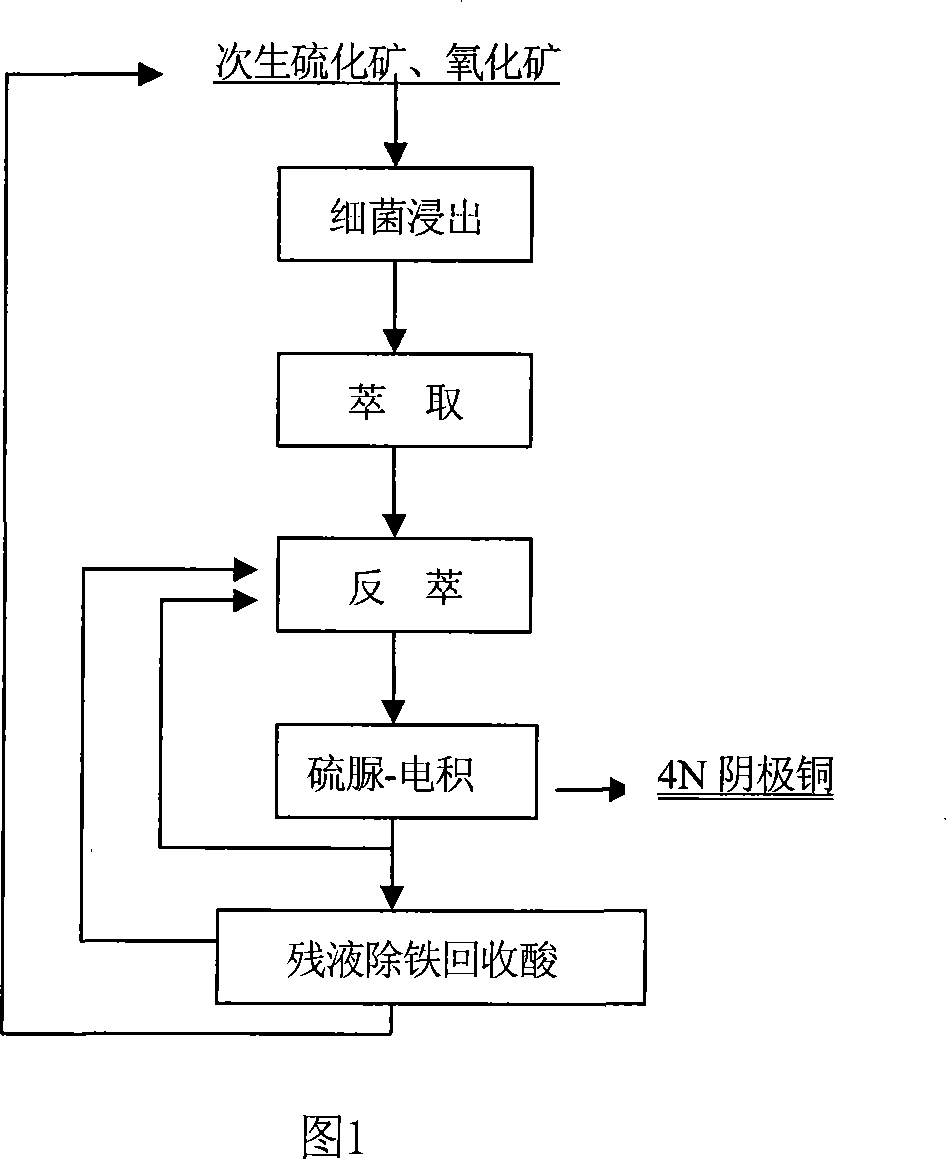
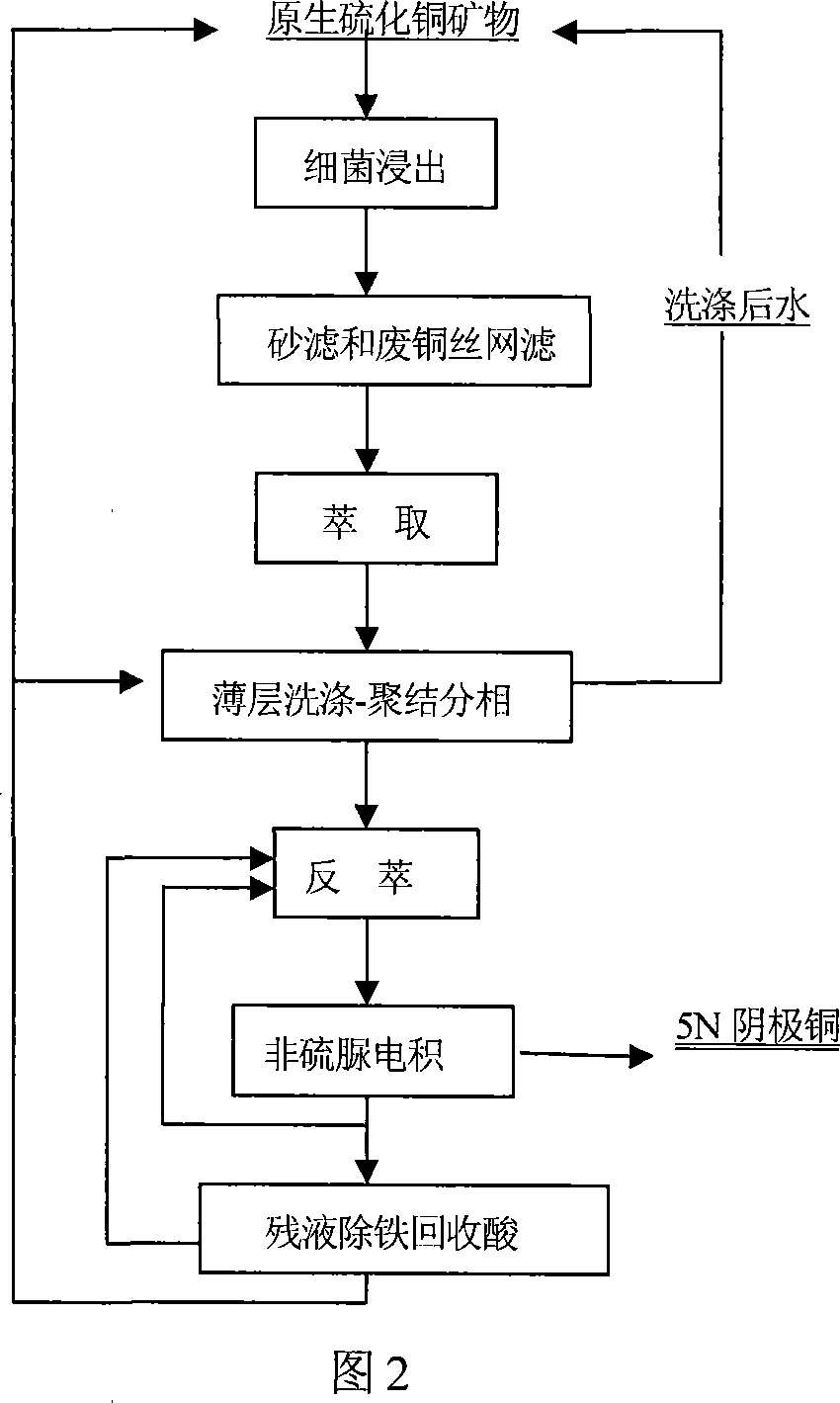
The invention relates to a method of preparing high pure copper from the leachate of primary sulfide ore bacteria, including: it leaches the primary sulfide ores and its mixture by using the mixture of middle and mesophilic bacterias. It filters and extracts the bacterial leaching solution, and conducts thin-layer wash-condensate, coalescence phase, and back-extraction electrowinning for the organic phase load. The invention uses hybrid strains of bacteria and sub-culture techniques to enhance the synergy of the bacterial leaching role and the minerals leaching rate, uses gelatin and other additives without sulfur element to reduce the sulfur impurities.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for recovering valuable elements in waste lithium ion battery electrode material
ActiveCN107955879AReduce sorting costsReduce recycling costsWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementSlagElectrical battery
The invention discloses a method for recovering valuable elements in waste lithium ion battery electrode materials. The method comprises steps of roasting the waste lithium ion battery electrode materials in an inert gas atmosphere, the roasting temperature is 200 -600 DEG C, the time is 30-360 minutes, and the roasting slag is obtained; mixing the obtained roasting slag and an acidic solution with [H+] concentration of 0.5~8 mol / L according to the mass ratio of 1:3~10; leaching at the leaching temperature of 30-90 DEG C and leaching time of 1-8 hours, leach liquor and leach residues are filtered to be obtained; the leach liquor is used for recovering nickel, cobalt, manganese, aluminum and lithium, and the leach residues are used for preparing negative electrode materials. According to the method for recovering valuable elements in waste lithium ion battery electrode materials, a leaching reducing agent does not need to be additionally added, the battery sorting and recycling costs are reduced, the positive and the negative electrode materials can be recovered at the same time, and the economic benefits of lithium battery recovery can be improved.
Owner:INST OF RESOURCES UTILIZATION & RARE EARTH DEV GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI
Isolation technology and process for extracting Ni and Co from nickel-containing high-cobalt hydroxide
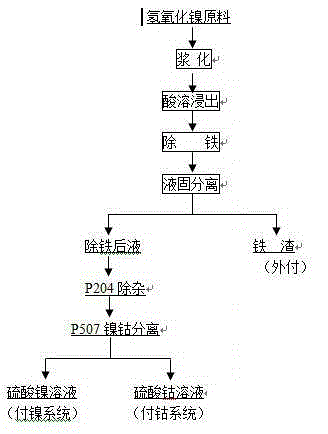
InactiveCN105274332AImprove leaching rateEasy to separateProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionPhysical chemistry
The sulfuric acid total leaching process is adopted in an isolation technology and process for extracting nickel and cobalt from nickel-containing high-cobalt hydroxide, so that a high Ni and Co leaching rate is guaranteed. By means of the processes of sulfuric acid leaching, impurity removal, extraction, and Ni-Co isolation, leaching agents rich in metallic nickel and metallic cobalt are obtained, the leaching agents are directly fed into an electro-deposited nickel and electro-deposited cobalt production system, and accordingly metallic nickel and metallic cobalt are isolated and extracted. The obtained leaching agents rich in metallic nickel and metallic cobalt can directly enter the electro-deposited nickel and electro-deposited cobalt production system. In addition, the process for extracting nickel and cobalt from nickel-containing high-cobalt hydroxide is simple, efficient, environment-friendly and suitable for treating nickel-containing high-cobalt hydroxide.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Moderate thermophilic enriched substance used for mineral leaching of copper pyrites
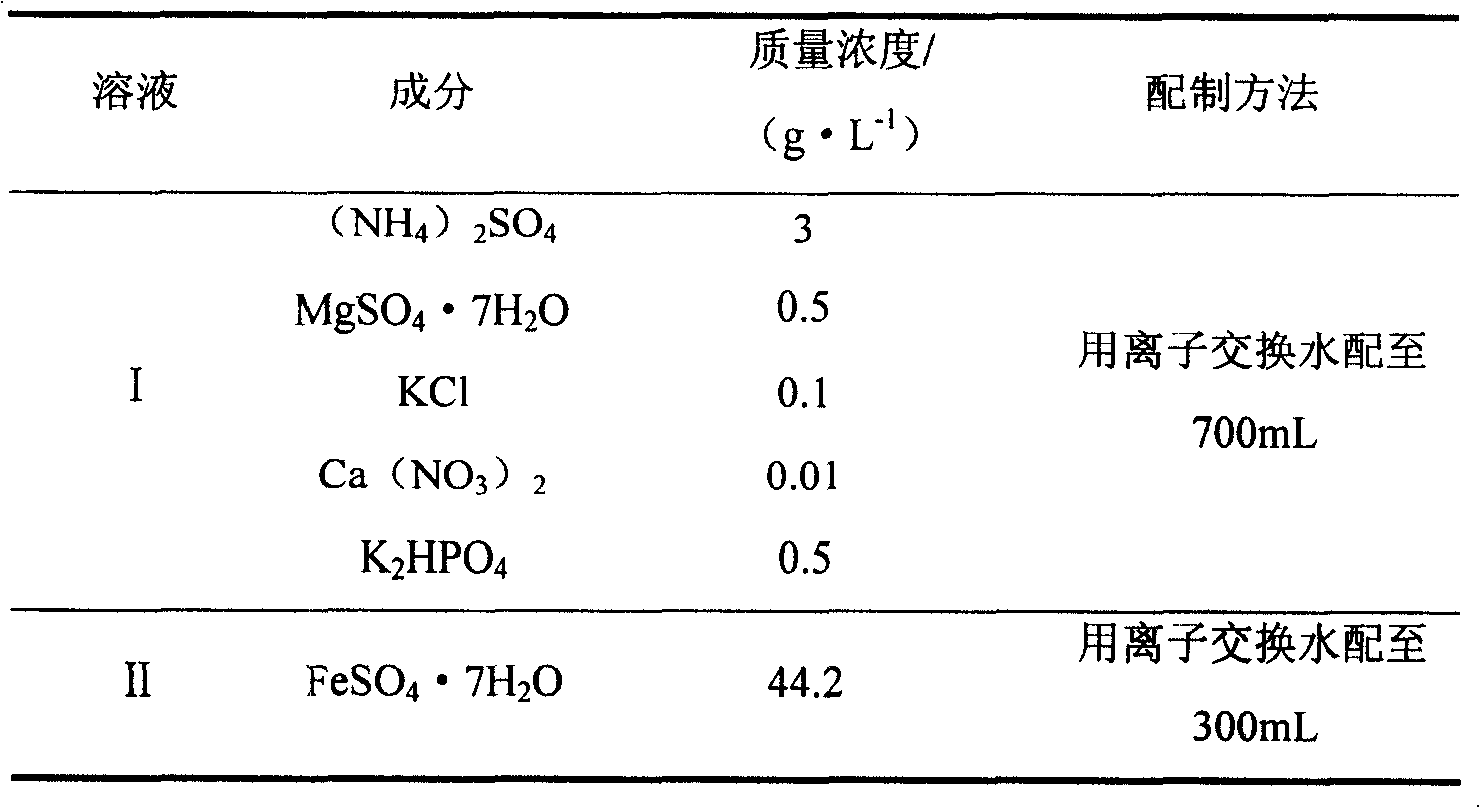
InactiveCN101560485APromote leachingReduce inhibitionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationFerroplasma thermophilum
The invention discloses a moderate thermophilic enriched substance used for mineral leaching of copper pyrites, comprising five mineral leaching microorganisms: acidithiobacillus caldus S2, leptospirillum ferriphilum YSK, sulfobacillus acidophilus ZW-1, sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans YN22 and ferroplasma thermophilum L1; the pH value and the temperature which are most suitable for the growth of the enriched substance are respectively 1.4-2.0 and 45-48 DEG C. Compared with the existing microorganisms used for brass bio-heap leaching, the enriched substance not only improves the leaching reaction kinetics and shortens the leaching period, but also reduces the passivation inhibition phenomenon and increases the bioleaching speed and the leaching rate of the copper pyrites; furthermore, the enriched substance can endure high concentration metallic ion at the late stage of bioleaching.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Process for comprehensively developing and utilizing nickel, cobalt, iron and magnesium from laterite-nickel ore
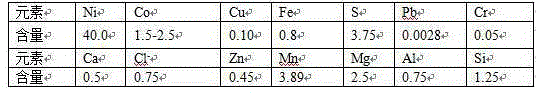
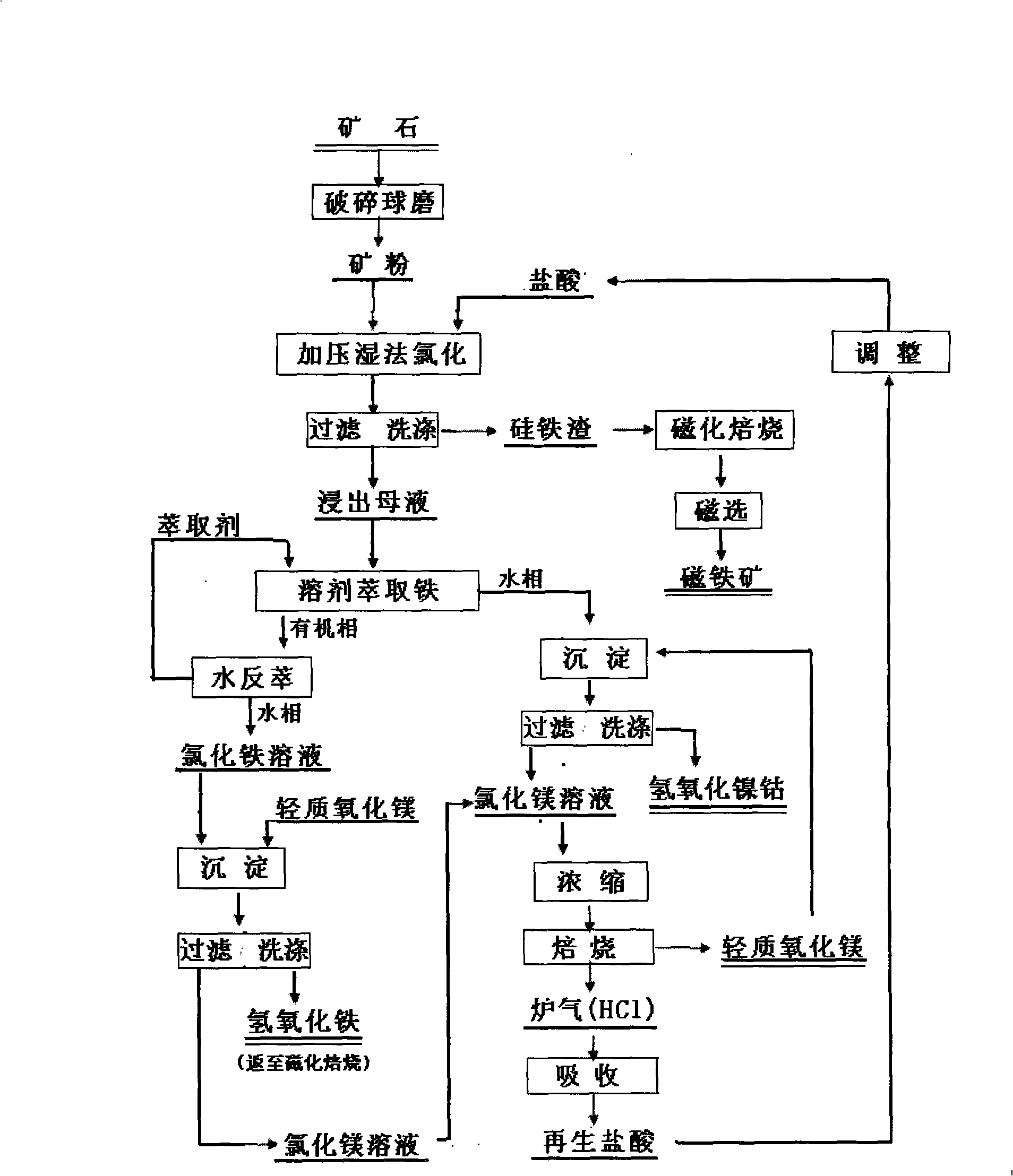
The invention relates to a method for compressively developing and utilizing nickel and cobalt in a lateritic nickel ore. The lateritic nickel ore is used as the raw material; the technical flows of mining, defibrination and ore preparation, pressurizing and wet chlorinating extraction, separating the nickel (cobalt) and iron by extraction, hydrolyzing magnesium chloride with a high temperature, magnetizing and roasting the extracted slag, magnetically separating, etc., and the like, are adopted to extract the middle product of the nickel and cobalt, recycle the light magnesium chloride and the materials used for pudding. The invention is mainly characterized in that the nickel and cobalt in the lateritic nickel ore is firstly and selectively dissolved and extracted by using the pressurized muriatic acid; a depositing method is used on the nickel and cobalt in a liquid to obtain the middle product; the mother liquid after the nickel is deposited is hydrolyzed by high temperature to obtain the light magnesium chloride and the chlorine hydride is recycled to obtain the muriatic acid; a material used for pudding is obtained after the extracted slag is reduced, magnetized, roasted and weakly separated in a magnetic way; the recycling muriatic acid enters the working period of extraction, thereby leading the muriatic acid to closely circulate. The method of the invention comprehensively recycles nickel and cobalt, magnesium and iron and has the advantages of high nickel and cobalt extraction rate, low cost, less investment and closed muriatic acid circulation. The whole technique is simple, clean, environmental friendly and is applicable for industrial production with large scale in particular.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Process for efficiently leaching anode active material of waste lithium battery
InactiveCN101603126AReduce loadReduce pollutionProcess efficiency improvementBattery recyclingElectrical batteryWorking environment
The invention discloses a process for efficiently leaching an anode active material of a waste lithium battery, which is characterized by splitting a waste lithium-ion battery to obtain an anode active material, leaching the active material with a vitriol / hydrogen peroxide mixed solution in counter current in a plurality of sections, and leaching the left residue with hydrochloric acid. The process firstly uses a vitriol / hydrogen peroxide solution system to leach the anode active material and uses hydrochloric acid to leach the left residue. Therefore, poor working environment and heavy environment pollution caused by a large amount of Cl2 generated when independently using the hydrochloric acid to leach are weakened maximally, and the leaching yield of the anode active material is improved to uttermost extent. The leaching yield of the anode active material of the waste lithium battery can be up to 99 percent by the method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
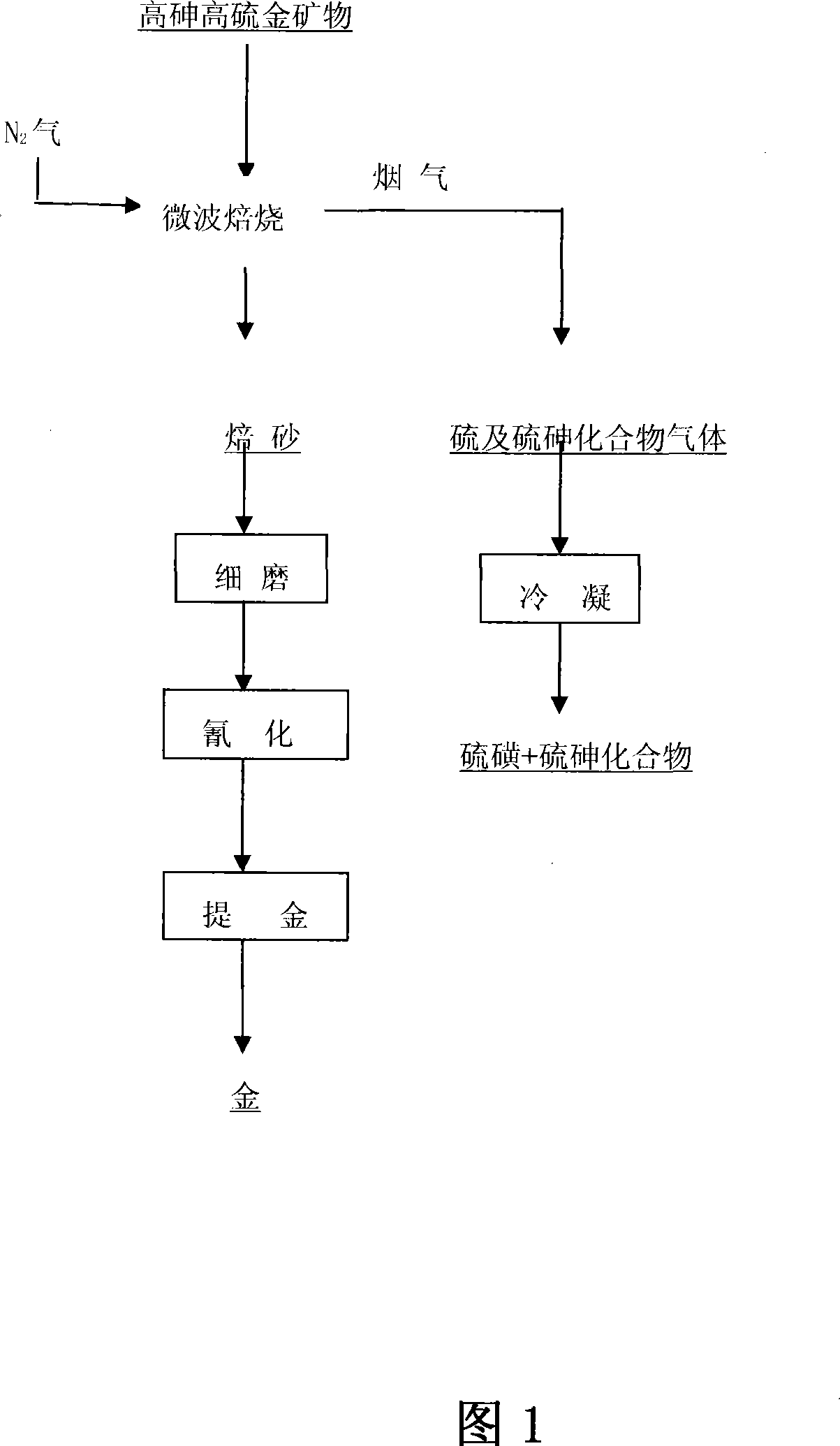
Method for pretreating refractory gold ore by employing microwave calcining
InactiveCN101225467AImprove leaching rateTo achieve the goal of green environmental protectionProcess efficiency improvementNitrogen gasMicrowave irradiation
The invention relates to a method to pre-treat a hard-to-leach gold ores-pyrite by microwave roasting, which is characterized in that the gold ores-pyrite or fine gold ores-pyrite with the granularity being 200 meshes which takes 90% to 95% of the whole gold ores-pyrite is positioned in a reaction chamber of a microwave roasting oven, a nitrogen is filled fully into the reaction chamber, starting the microwave roasting oven, the gold ores-pyrite or fine gold ores-pyrite is radiated and roasted by the microwave in the nitrogen atmosphere, the roasting temperature is 450 to 580 degree centigrade, the power is 4 to 6kw, the microwave roasting oven stops working after roasting for 5 to 20 minutes, a roasted product is made when the roasting gold ore-pyrite is taken out. The method to pre-treat a hard-to-leach gold ores-pyrite by microwave roasting has the advantages of increasing the gold leaching yield of the hard-to-leach gold ores-pyrite up to over 90%, reaching purpose of the environment protection because the sulfur is precipitated as a free sulfur without the recovery process of smoke and dust, and saving the energy because the microwave roasting process is adopted and the pretreatment time is greatly shortened.
Owner:SHENYANG LIGONG UNIV
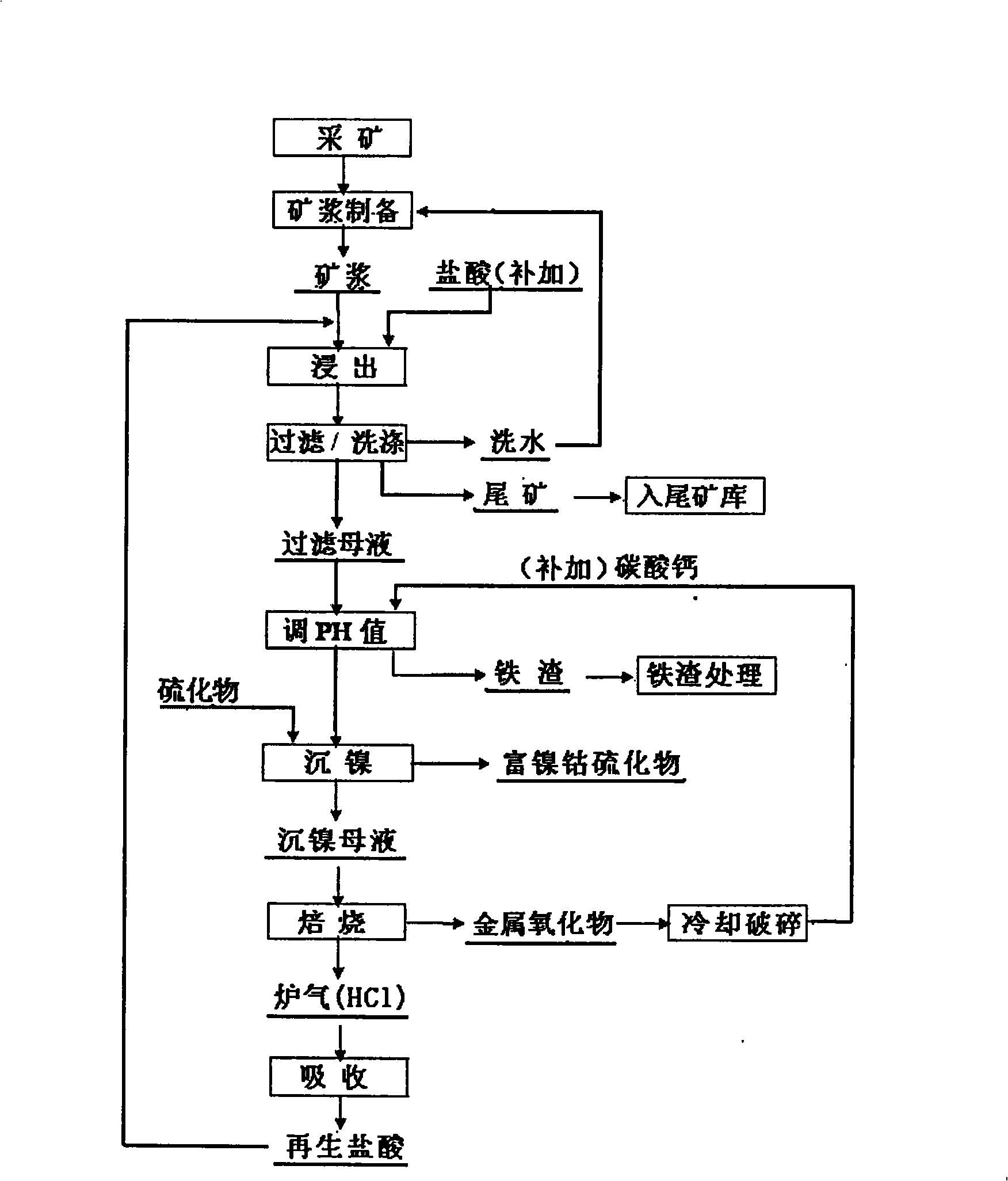
Process for extracting nickel and cobalt from laterite-nickel ore
InactiveCN101338374ARealize closed loop recyclingImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementMetal chlorideSlurry
The invention discloses a method for extracting nickel and cobalt from a lateritic nickel ore which includes the steps of: (1) preparing the slurry of the ore: cracking the ores and preparing the slurry; (2) dipping the ores with muriatic acid: adding the muriatic acid in the slurry of the ore to carry out stirring and extraction under a normal pressure; (3) separating the solid and liquid; (4) neutralizing an extraction liquid; (4) sulfurizing and depositing the nickel; (6) regenerating the muriatic acid: the mother deposition liquid after nickel depositing is concentrated and roasted, the metal chloride in the mother liquid is hydrolyzed into chlorine hydride and metal oxide; the chlorine hydride after being absorbed by water obtains the regenerated muriatic acid and return to the working procedure of ore extraction; the metal oxide after being cracked and grinded returns to the working procedure of neutralizing. The method of the invention has a simple flow and an environment protective technique; the application range to resources is large; besides, the extraction speed is fast; the impurity removing capacity is high; the extraction rate of the nickel and cobalt is high; the method realizes the closed circulation of HCl and the comprehensive utilization of the resources.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for continuously leaching sulfide ore by using synergy of autotrophic ore leaching bacteria and heterotrophic ore leaching bacteria
ActiveCN102329957AEliminate static clingImprove leaching efficiencyPregnant leach solutionSulfidation
The invention discloses a method for continuously leaching sulfide ore by using the synergy of autotrophic ore leaching bacteria and heterotrophic ore leaching bacteria, which comprises two main steps of preparing a compound ore leaching strain and leaching ore by using the compound strain. The step of preparing the compound ore leaching strain comprises the steps of selecting a strain, preparing a culture medium, compositely culturing the strain and domesticating the compound ore leaching strain. The step of leaching ore by using the compound strain comprises the steps of pretreating an ore sample, preparing an ore leaching culture medium, leaching the ore by using the compound ore leaching strain, selecting and adding semiconductor sulfide ore and extracting metals in the leaching liquids. In the method, the characteristic of the semiconductor sulfide ore to provide electrons to promote the ore leaching action of microbes in the electron transition process is utilized, so that the operating cost of the whole process is lowered, the ore leaching efficiency of the process is improved, and the method has broad application prospect in the field of metallurgy.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
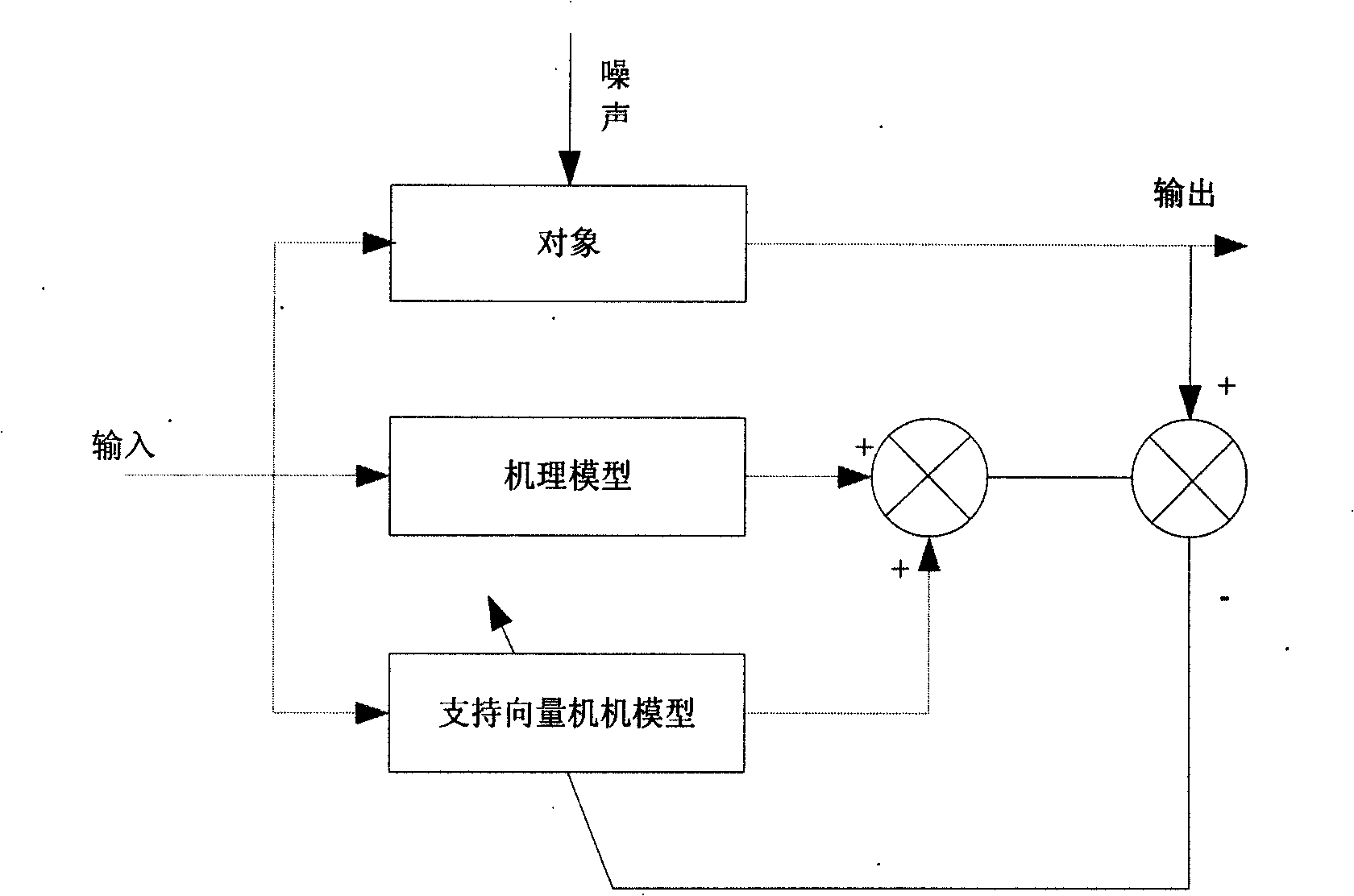
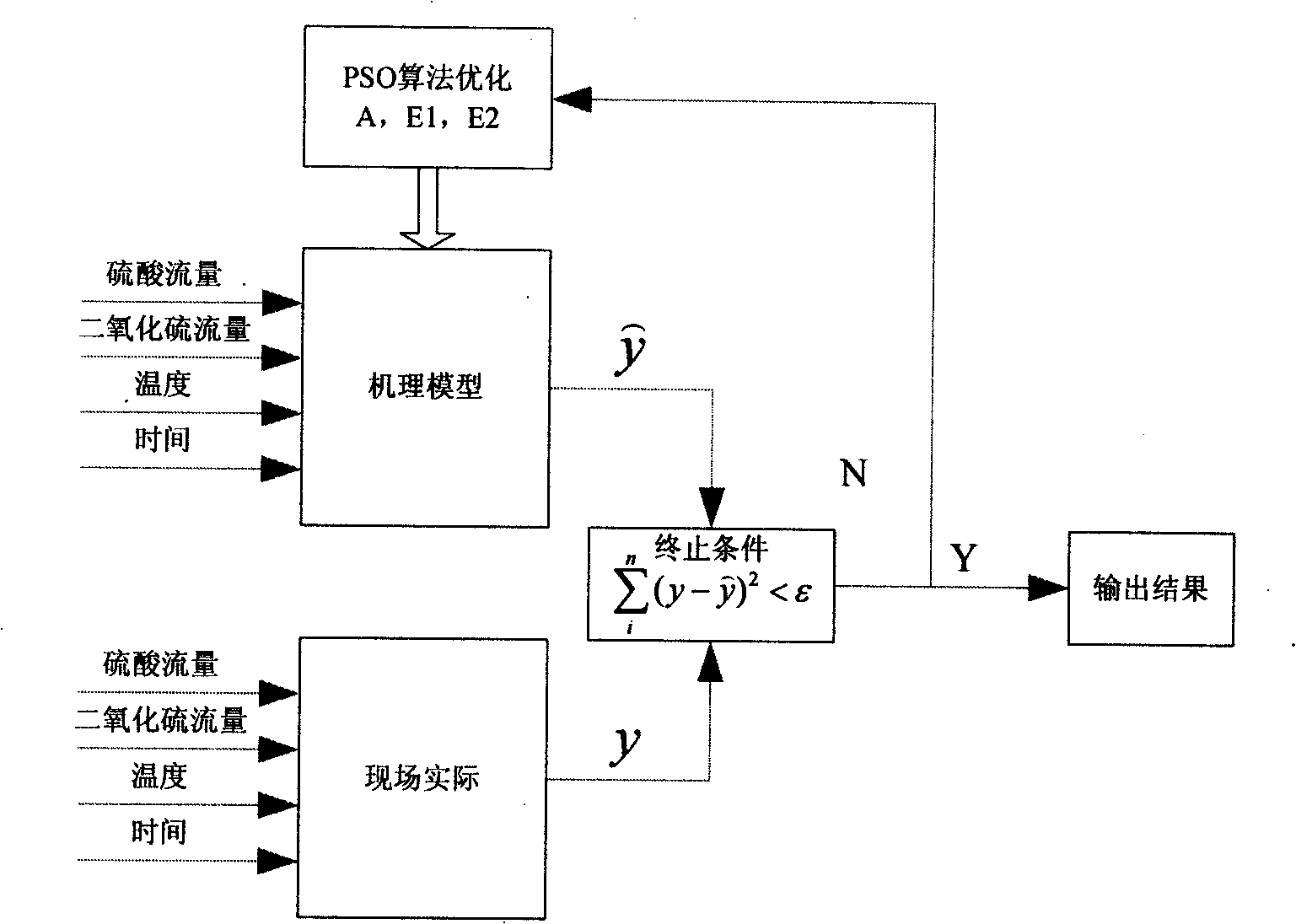
Leaching rate prediction and optimization operation method in wet metallurgical leaching process
InactiveCN101526814AUniform temperature distributionImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementTotal factory controlEnergy balance equationHydrometallurgy
The invention relates to a leaching rate prediction and optimization operation method in the wet metallurgical leaching process. The method comprises the following steps: predicting a leaching rate by an established mixing model and giving optimization operation instructions, wherein an integrative dynamic mechanism model of the leaching process is established, and a material balance equation and an energy balance equation are gradually established in the leaching process on the basis of the ore-leaching dynamic principle of the integrative dynamic mechanism model. The device comprises a leaching rate prediction and optimization operation system in the leaching process, a host computer, a PLC and a field sensing transmitting part which comprises a pH value detecting instrument, a temperature detecting instrument, a flow detecting instrument, and the like. With the technical scheme, the leaching process can be greatly improved, the production can be constantly kept in an optimal state, the consumption of raw materials and energy sources is reduced, the operation period of equipment is prolonged and the relation change between supply and demand on markets can be reflected in time.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Treatment method for rare earth phosphate rock and enrichment method for rare earth
ActiveCN103184356AReduce eutectic adsorptionEasy accessProcess efficiency improvementRare-earth elementEnrichment methods
The invention discloses a treatment method for a rare earth phosphate rock and an enrichment method for rare earth. The treatment method comprises the following steps: mixing the rare earth phosphate rock and phosphoric acid to form mixed slurry; adding concentrated sulfuric acid into the mixed slurry in such a manner that the concentration of Ca<2+> in the mixed slurry is decreased from at least 1 wt% to the equilibrium concentration of Ca<2+> and SO4<2->, then the concentration of SO4<2-> in the mixed slurry is increased from the equilibrium concentration of Ca<2+> and SO4<2-> to at least 2 wt% and the mixed slurry is added during addition of the concentrated sulfuric acid to allow the rare earth phosphate rock to be dissolved so as to obtain hemihydrate gypsum; and subjecting the obtained hemihydrate gypsum to recrystallization to obtain dihydrate gypsum. The enrichment method for rare earth comprises a step of recovering rare earth elements from liquid obtained after recrystallization of the hemihydrate gypsum and / or liquid obtained after heating of the mixed slurry. In the process of generation of the hemihydrate gypsum, the addition speed of the concentrated sulfuric acid is controlled, and SO4<2-> in the mixed slurry is allowed to be insufficient at first and then controlled to be excess, which aids rare earth in entering into the phosphoric acid.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for microbiological leaching of uranium-molybdenum ore and enrichment and separation of uranium and molybdenum
The invention discloses a method for microbiological leaching of uranium-molybdenum ore and enrichment and separation of uranium and molybdenum. The method comprises a microbiological leaching method of uranium-molybdenum ore and an enrichment and separation method of uranium and molybdenum in a leachate; in the leaching method, an oxidizing agent for leaching the uranium-molybdenum ore is biological high iron, namely an acidophilous acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans solution containing the biological high iron. The method comprises the following specific steps: firstly crushing the uranium-molybdenum ore so that the crushed materials with the granularity of above 200 meshes account for more than 50% of the total amount and the crushed materials with the granularity of 30 meshes account for not more than 10% of the total amount; then infiltrating the crushed uranium-molybdenum ore in a biological oxidizing agent solution, carrying out solid-liquid separation after infiltrating, and then carrying out ion exchange on the microbiological leachate of the uranium-molybdenum ore by using 201*7 resins, and carrying out iron elution, uranium elution and molybdenum elution. In the method, the uranium leaching rate is above 80%, the molybdenum leaching rate is within the range from 60% to 70% or above, and the molybdenum leaching rate is increased by 20-30%; the uranium, molybdenum and iron in the leachate are eluted by using a PH1.0 solution by virtue of an ion exchange column, and the removal rate of the iron is above 95%, the adsorption rate of the uranium and the molybdenum is not affected, the uranium and the molybdenum adsorbed on the resin are desorbed by using different desorption reagents step by step, and the recovery rate of the uranium and the molybdenum is above 80%.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com