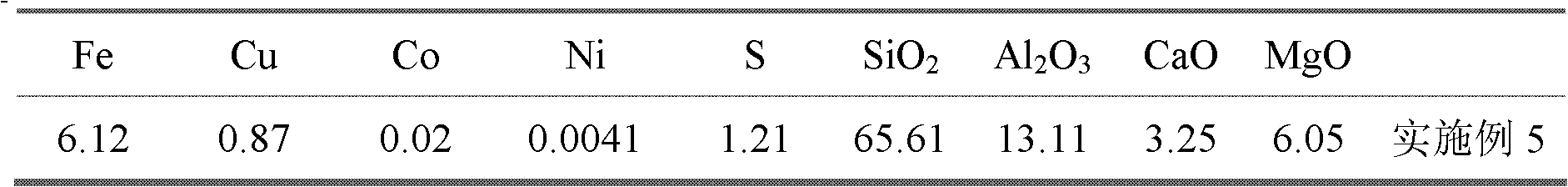
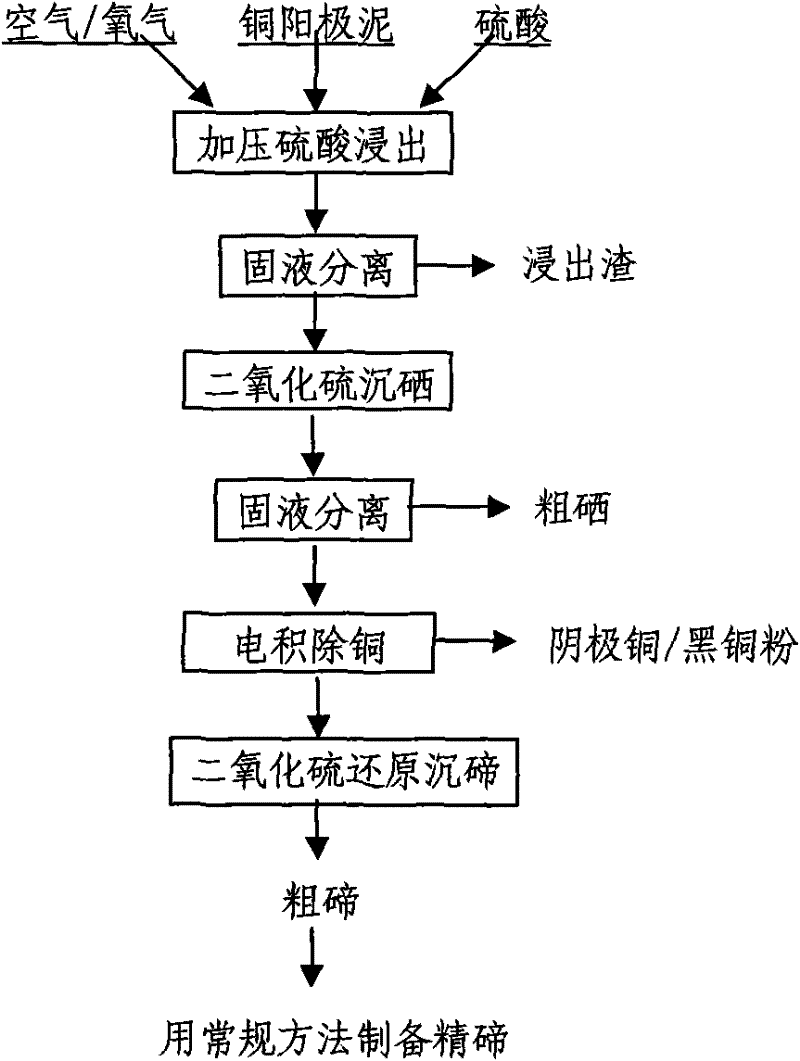
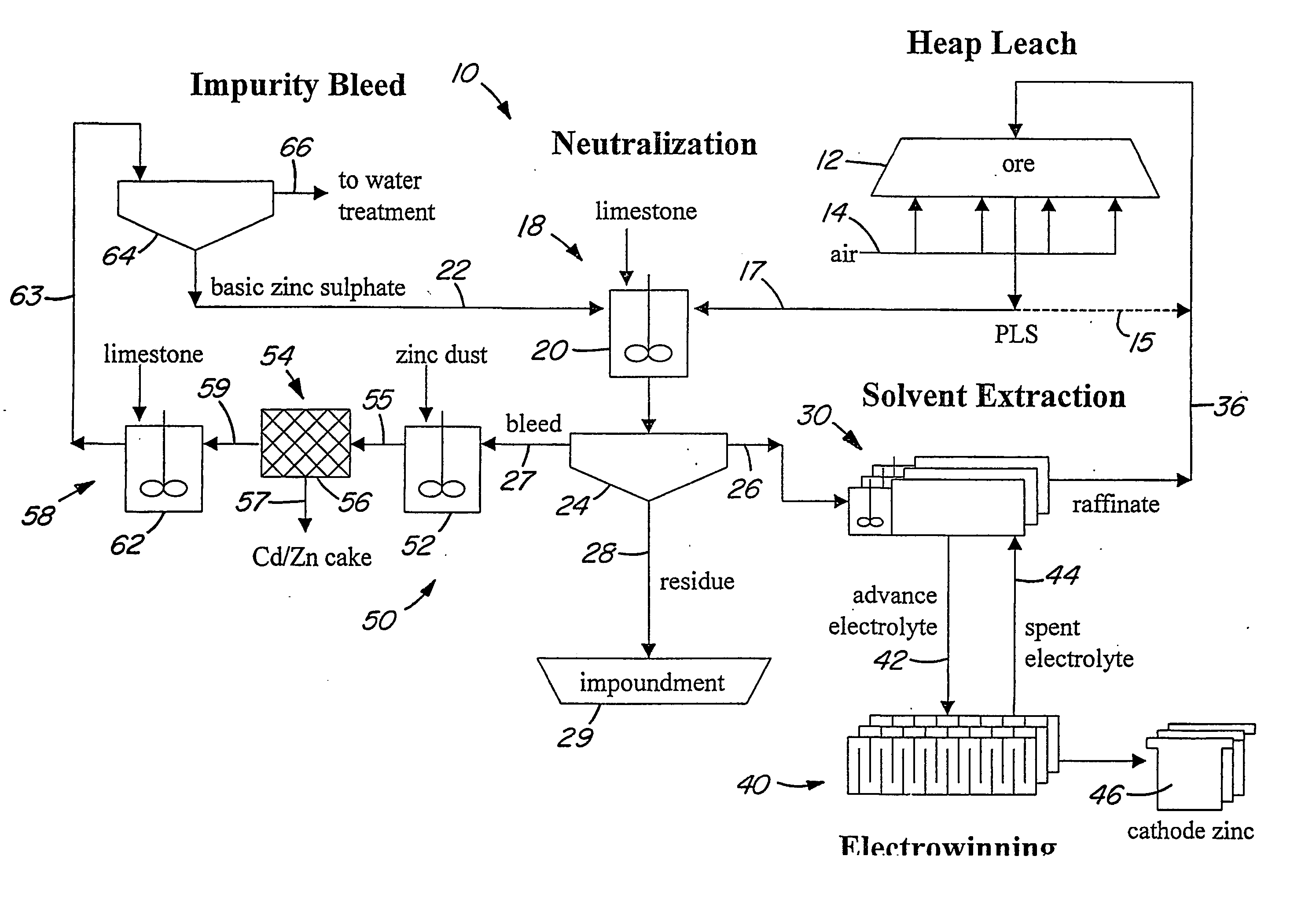
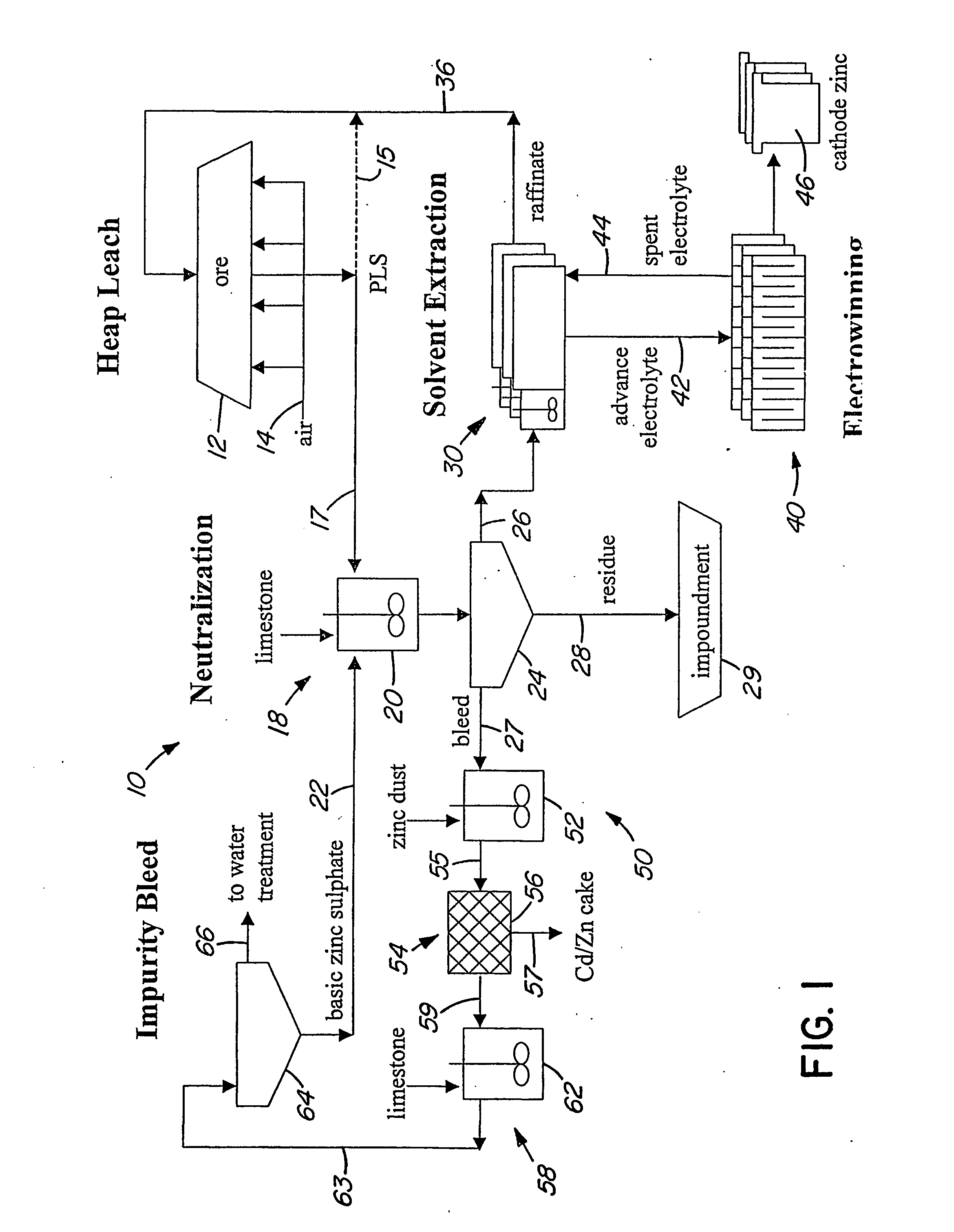
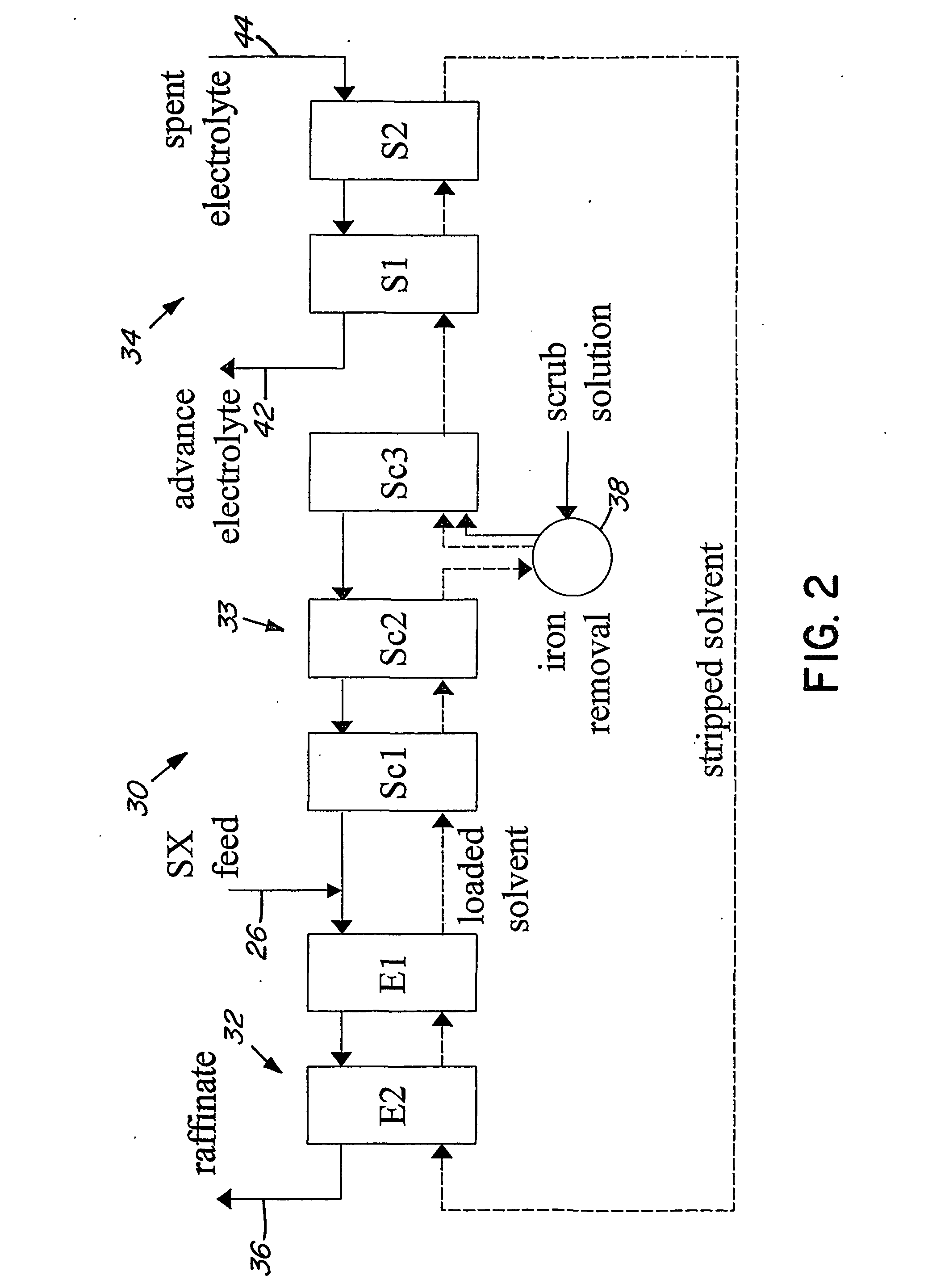
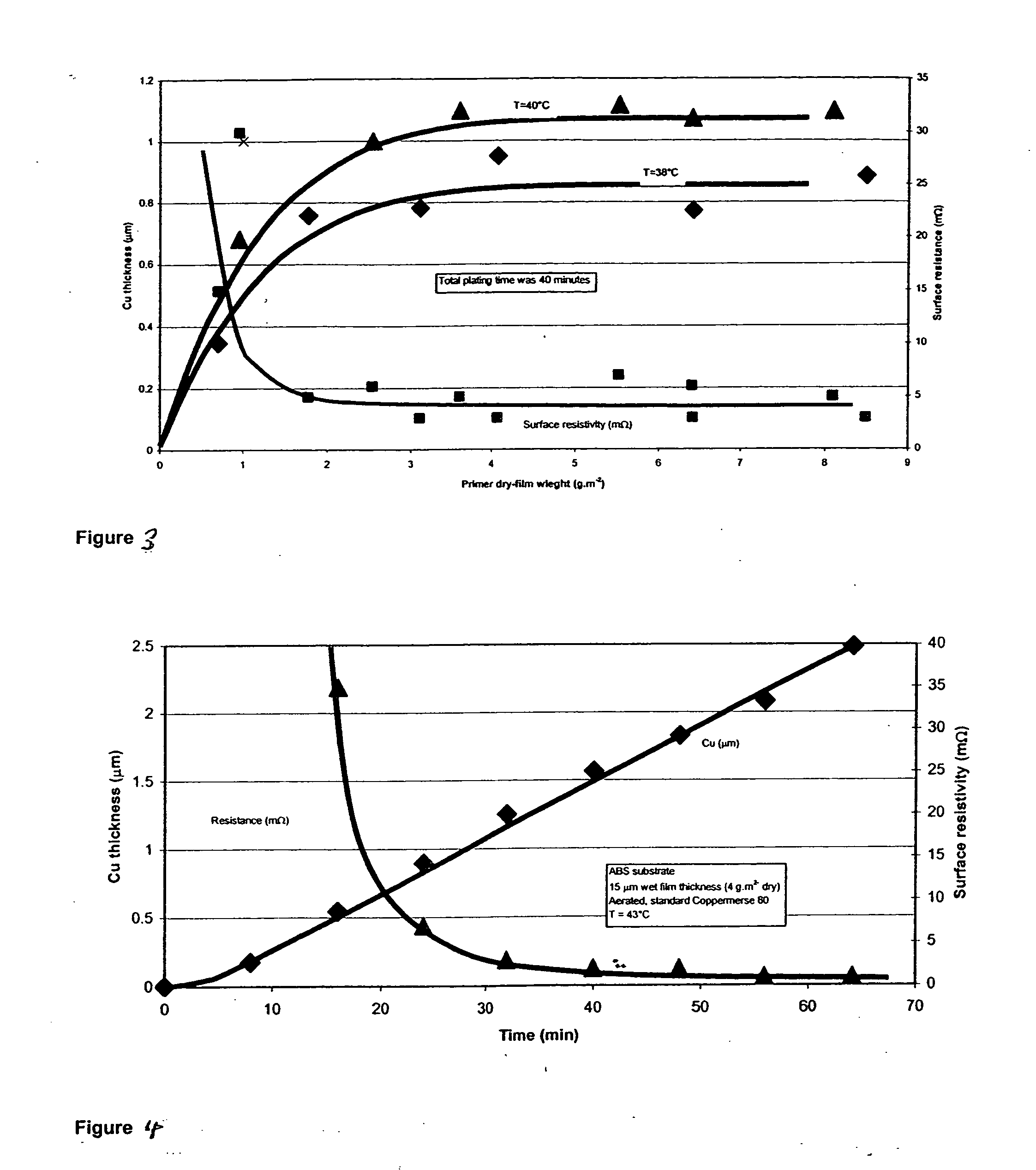
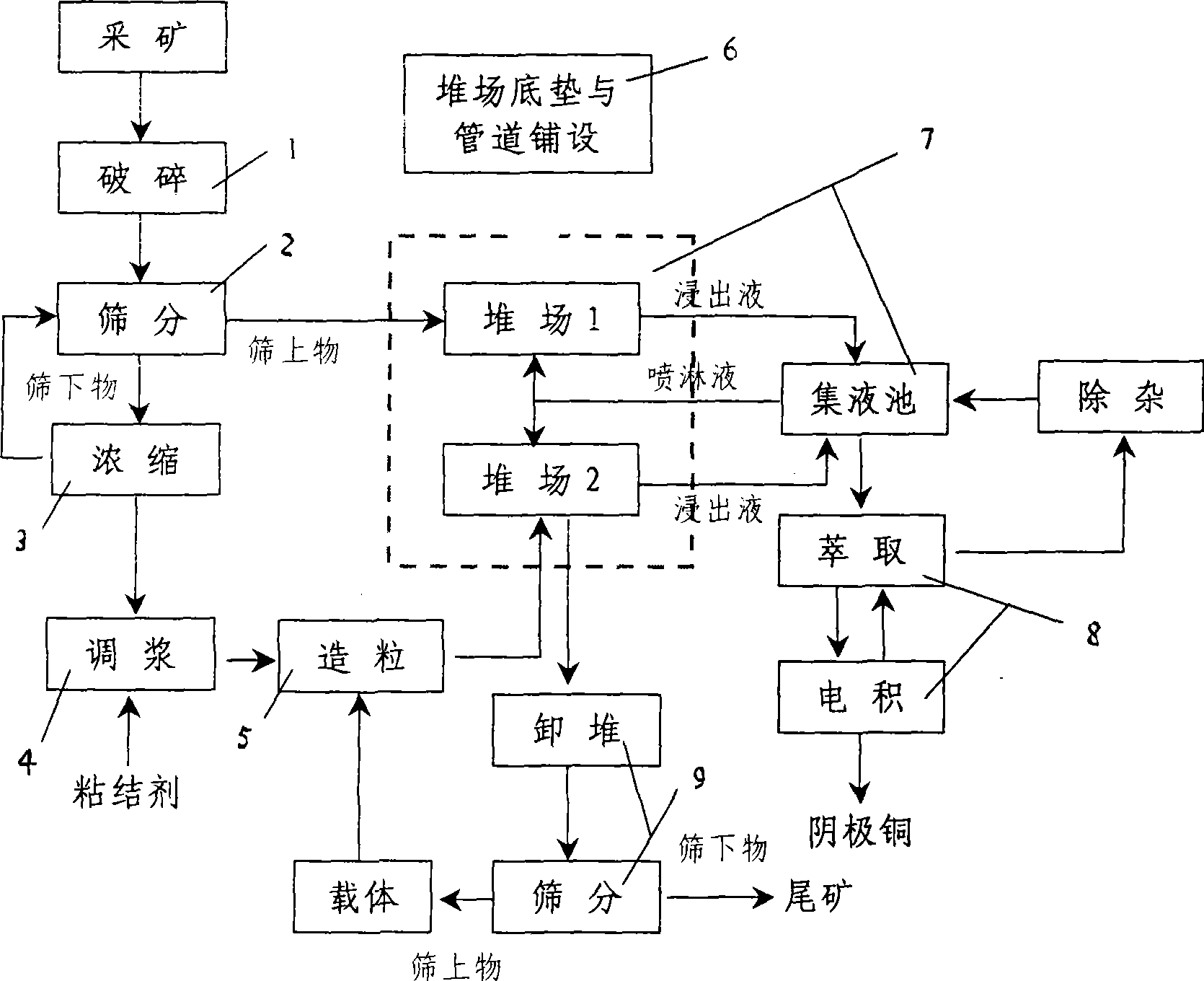
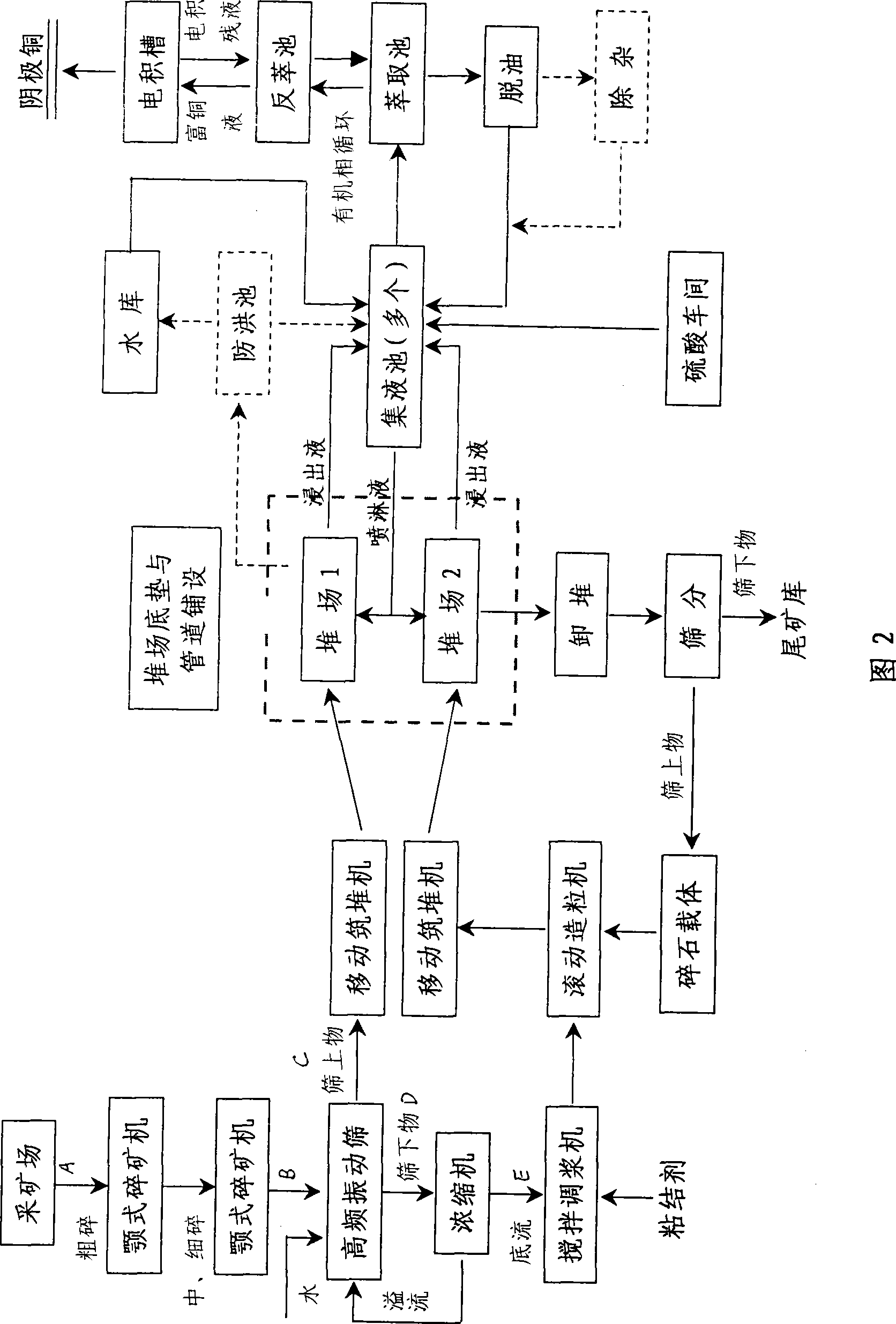
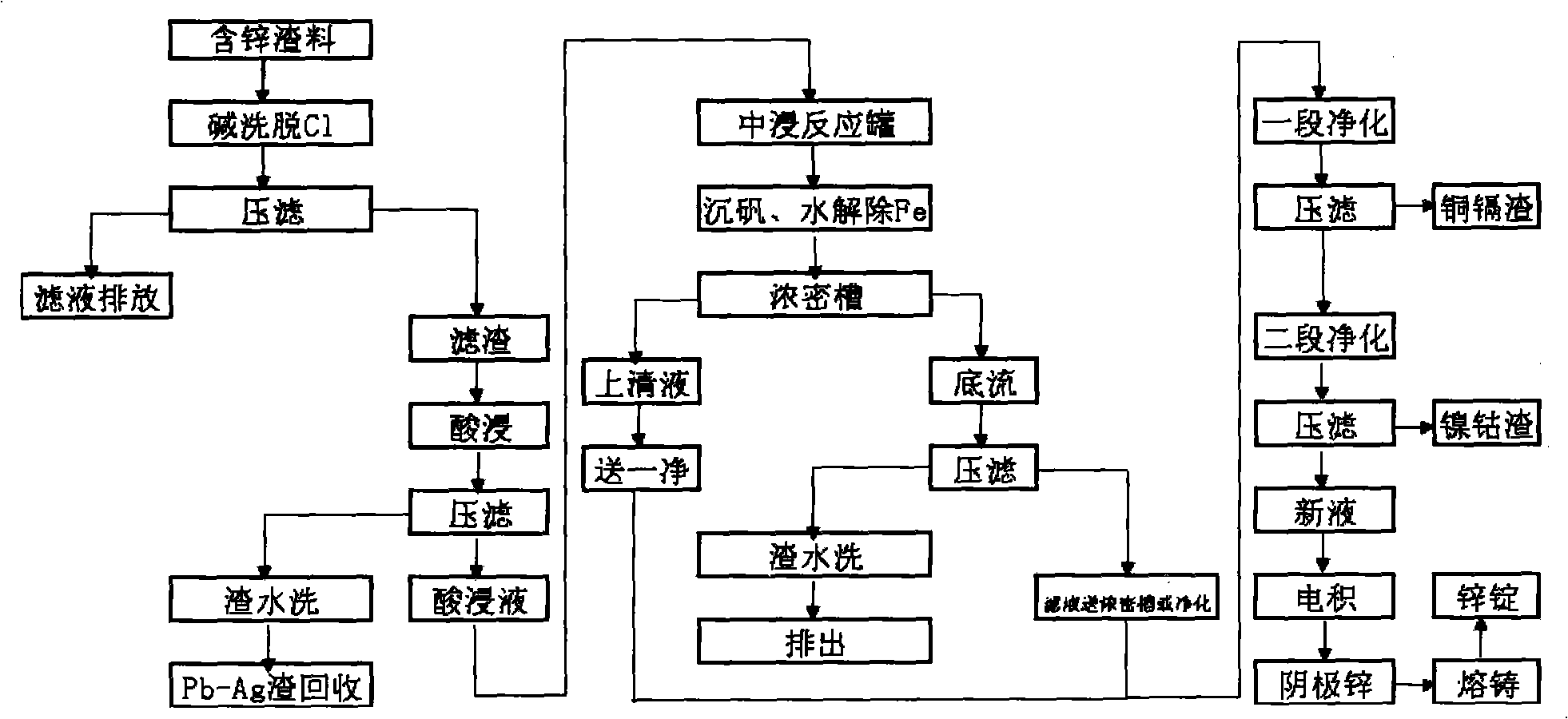
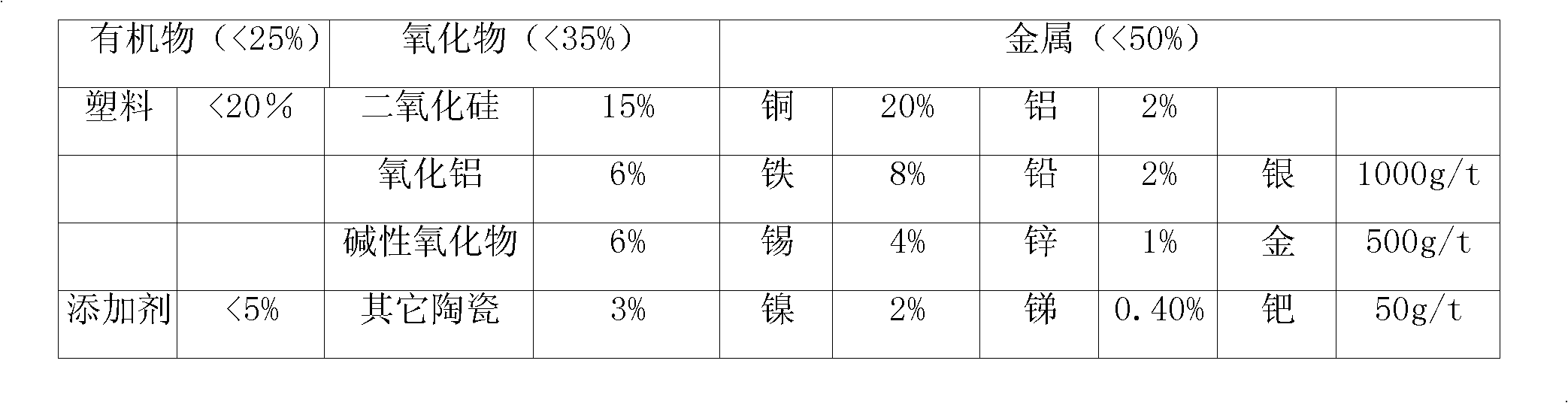
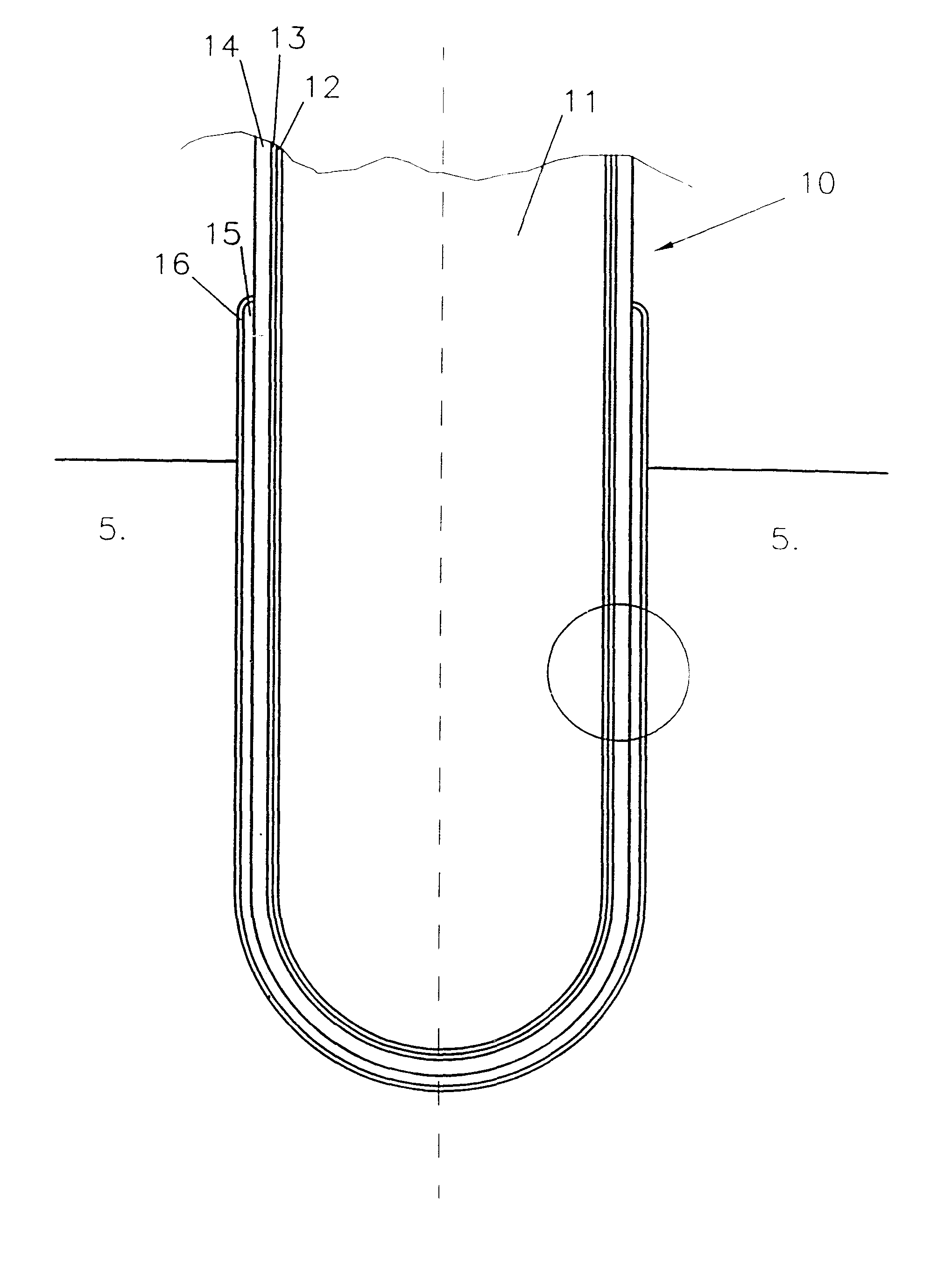
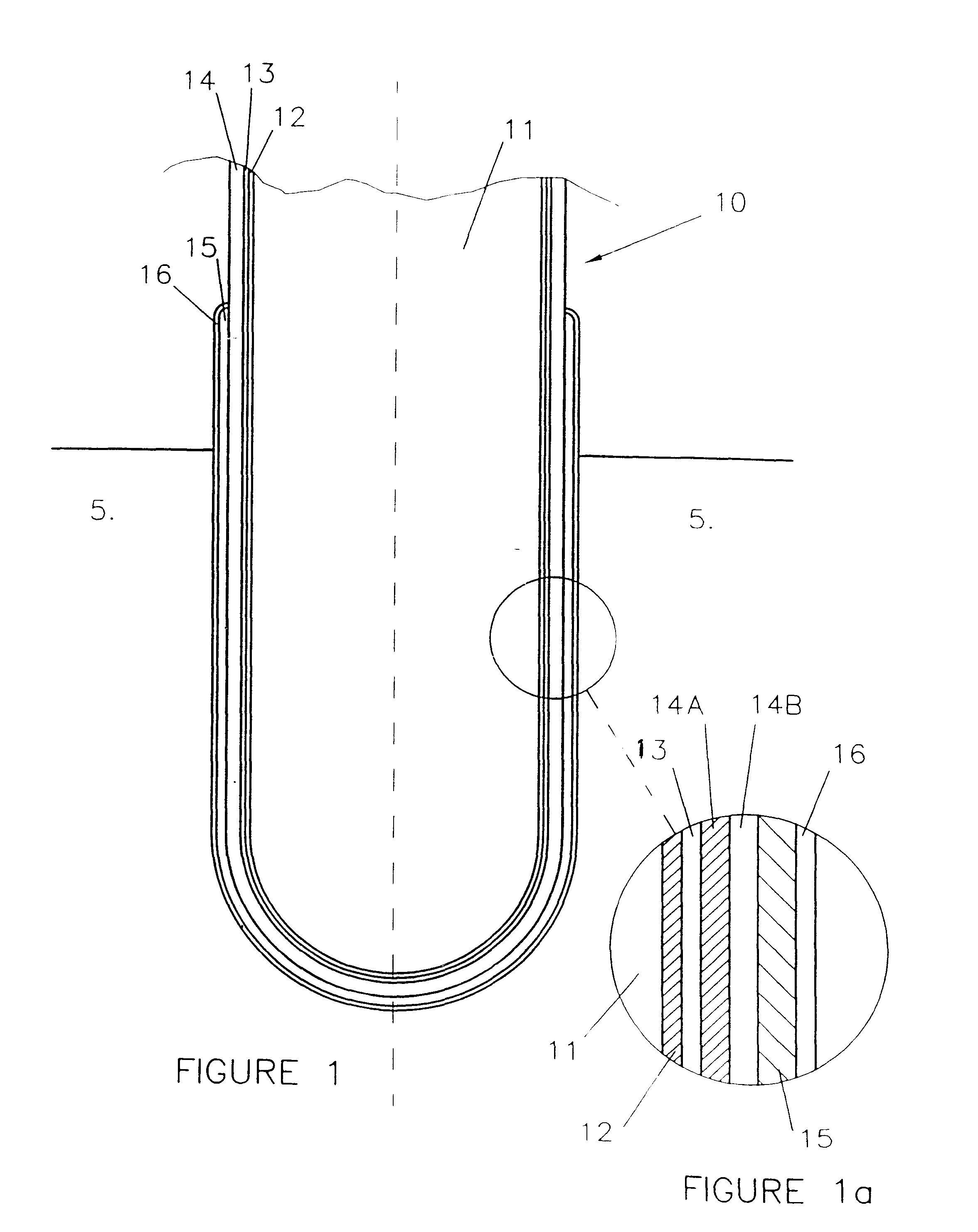
Patents
Literature
542 results about "Electrowinning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electrowinning, also called electroextraction, is the electrodeposition of metals from their ores that have been put in solution via a process commonly referred to as leaching. Electrorefining uses a similar process to remove impurities from a metal. Both processes use electroplating on a large scale and are important techniques for the economical and straightforward purification of non-ferrous metals. The resulting metals are said to be electrowon.
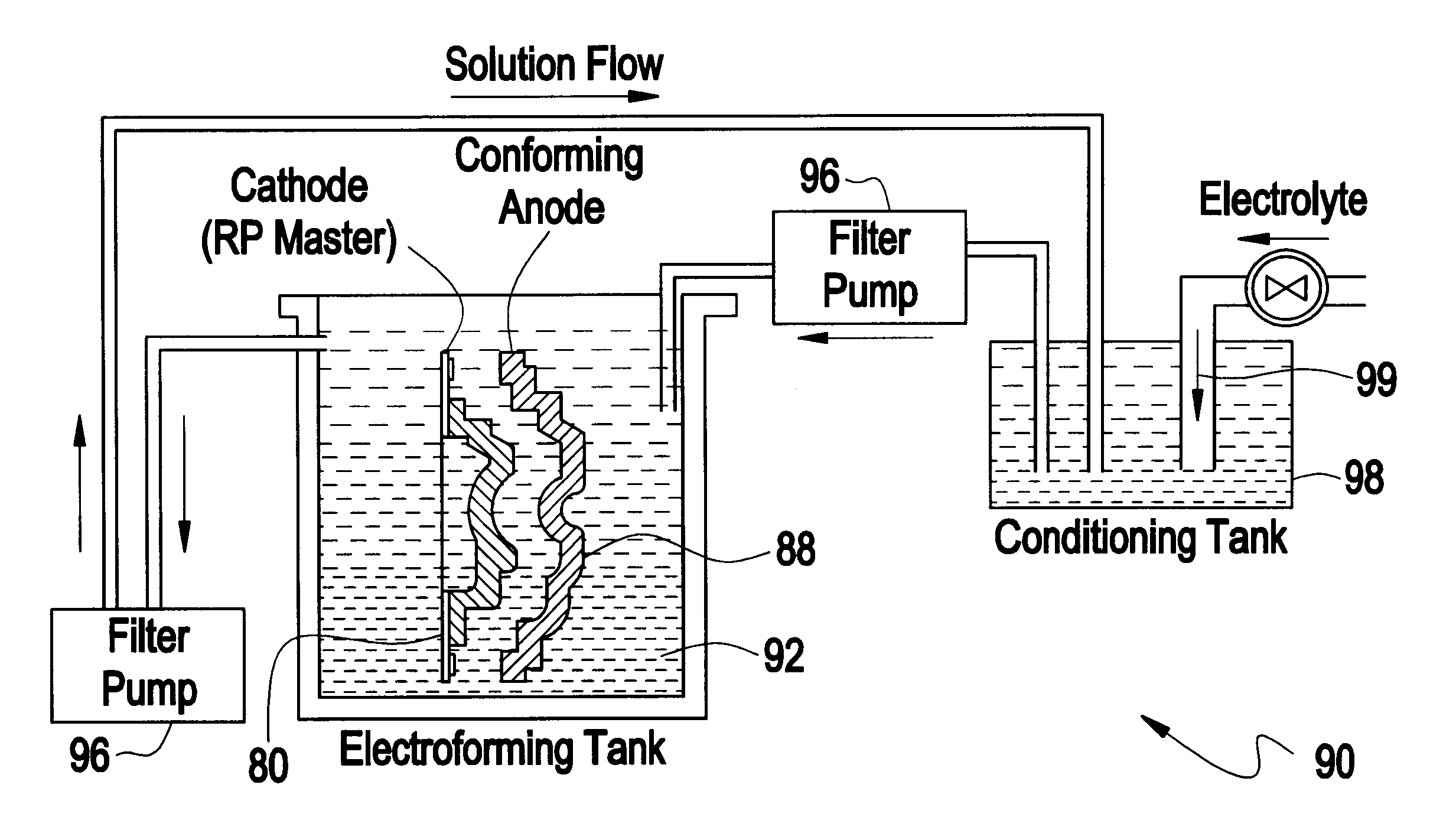
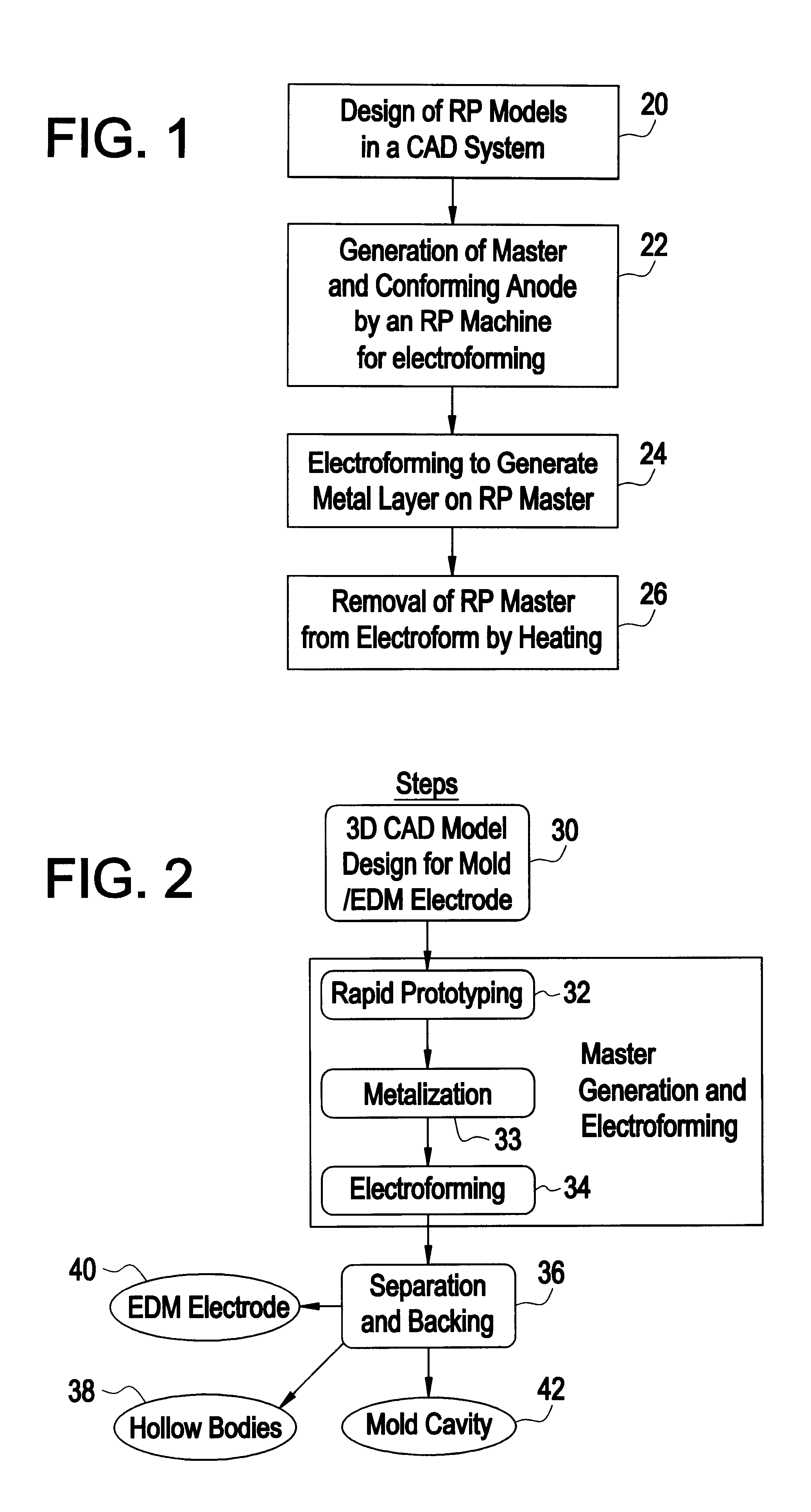
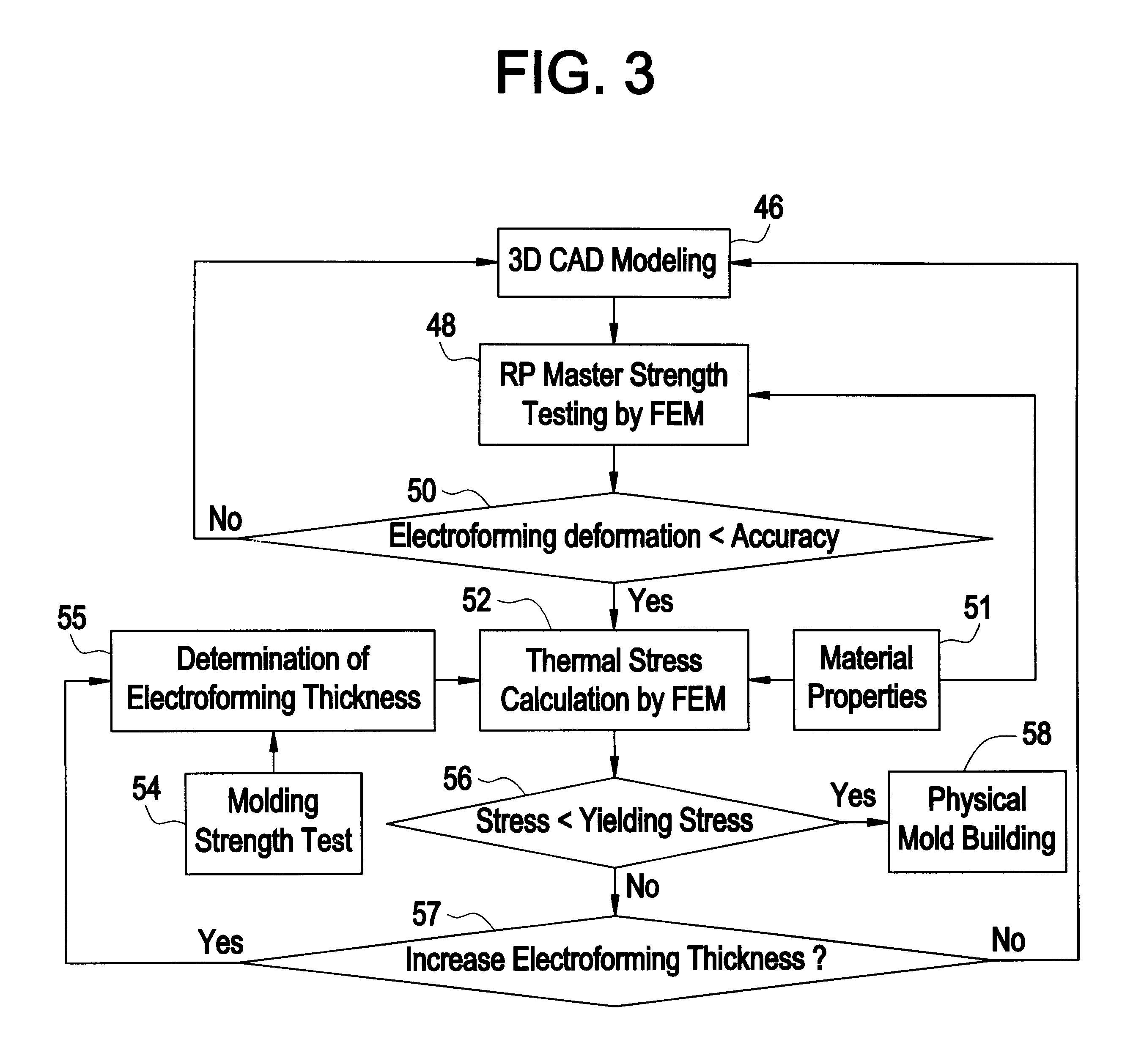
Rapid production of engineering tools and hollow bodies by integration of electroforming and solid freeform fabrication
InactiveUS6409902B1Stay in shapeAvoid insufficient thicknessAdditive manufacturing apparatusFoundry mouldsElectrolysisElement analysis
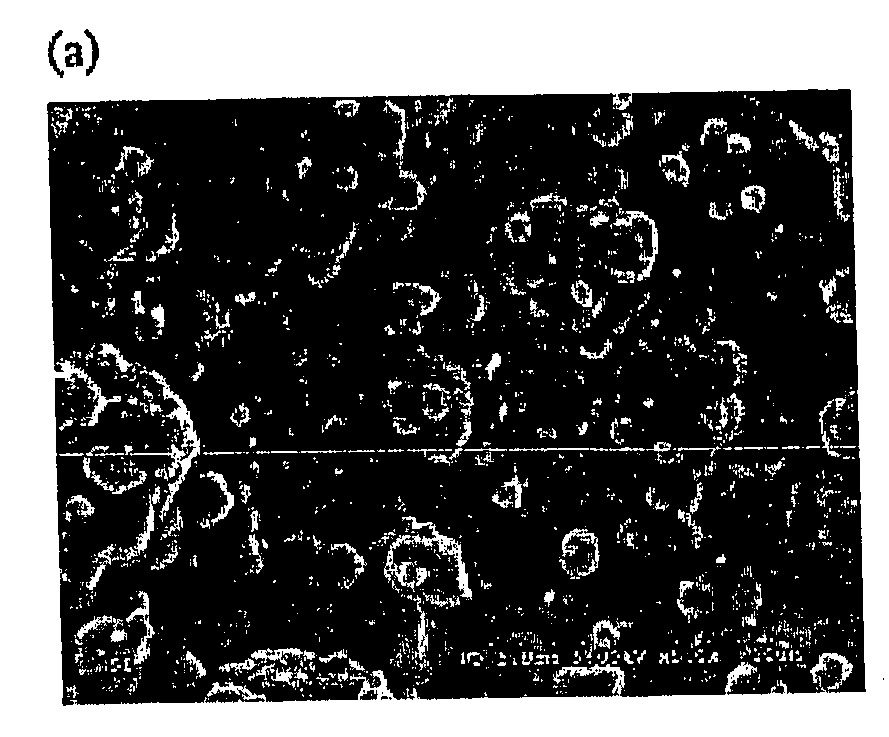
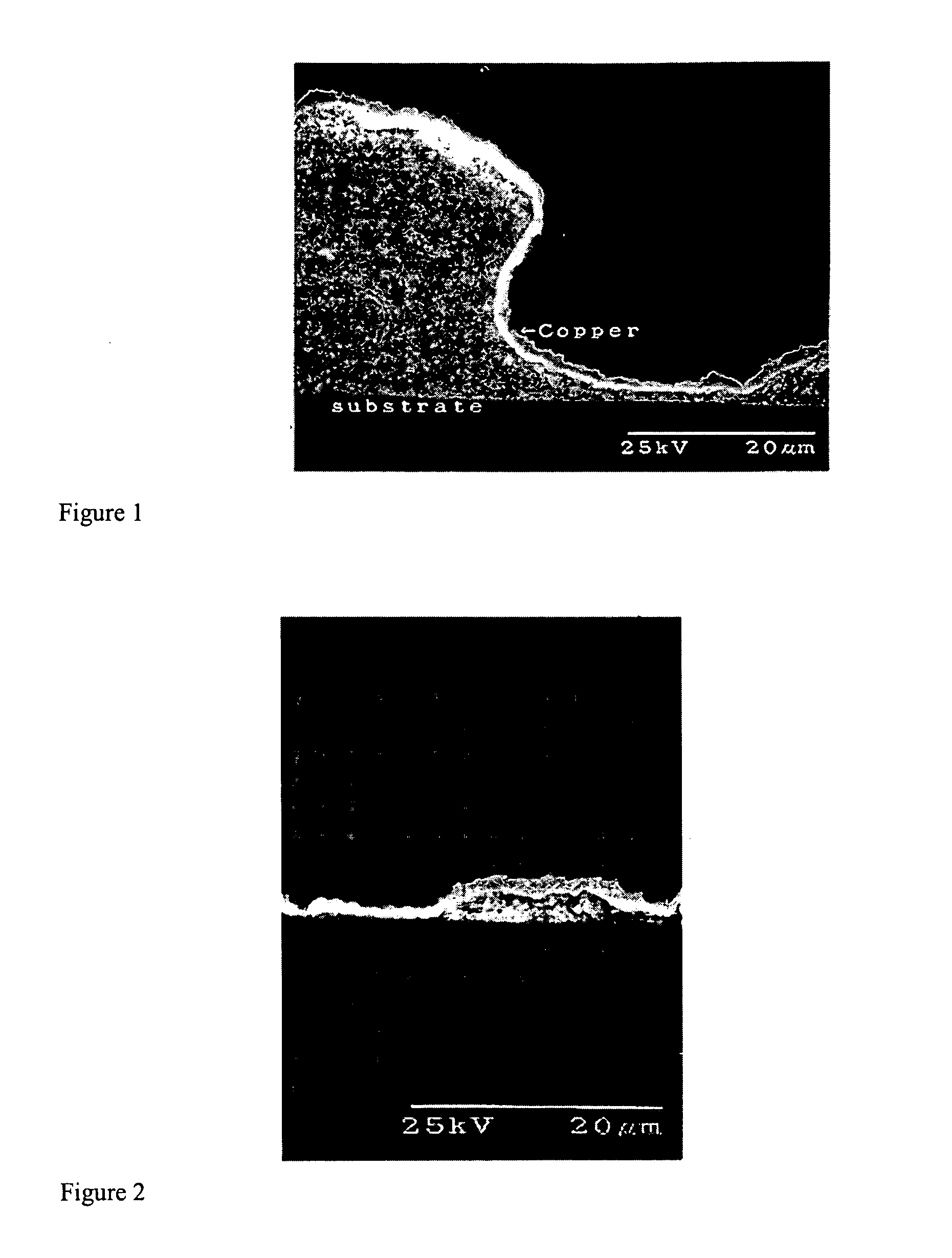
This invention describes a rapid tooling process that integrates solid freeform fabrication (SFF) with electroforming to produce metal tools including molds, dies, and electrical discharge machining (EDM) electrodes. An SFF part is metalized by electroless plating and then placed in an electroplating solution, where metal is deposited upon the part by electrolysis. When the desired thickness of metal has been reached, the SFF part is removed from the metal shell. The shell is then optionally backed with other materials to form a mold cavity, and EDM electrode, or other desired parts for tooling. Thermomechanical modeling and numerical simulation with finite element analysis (FEA) is used to determine the geometry of the SFF part and the electroform thickness for minimizing the manufacturing time and cost while satisfy the tooling requirement.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
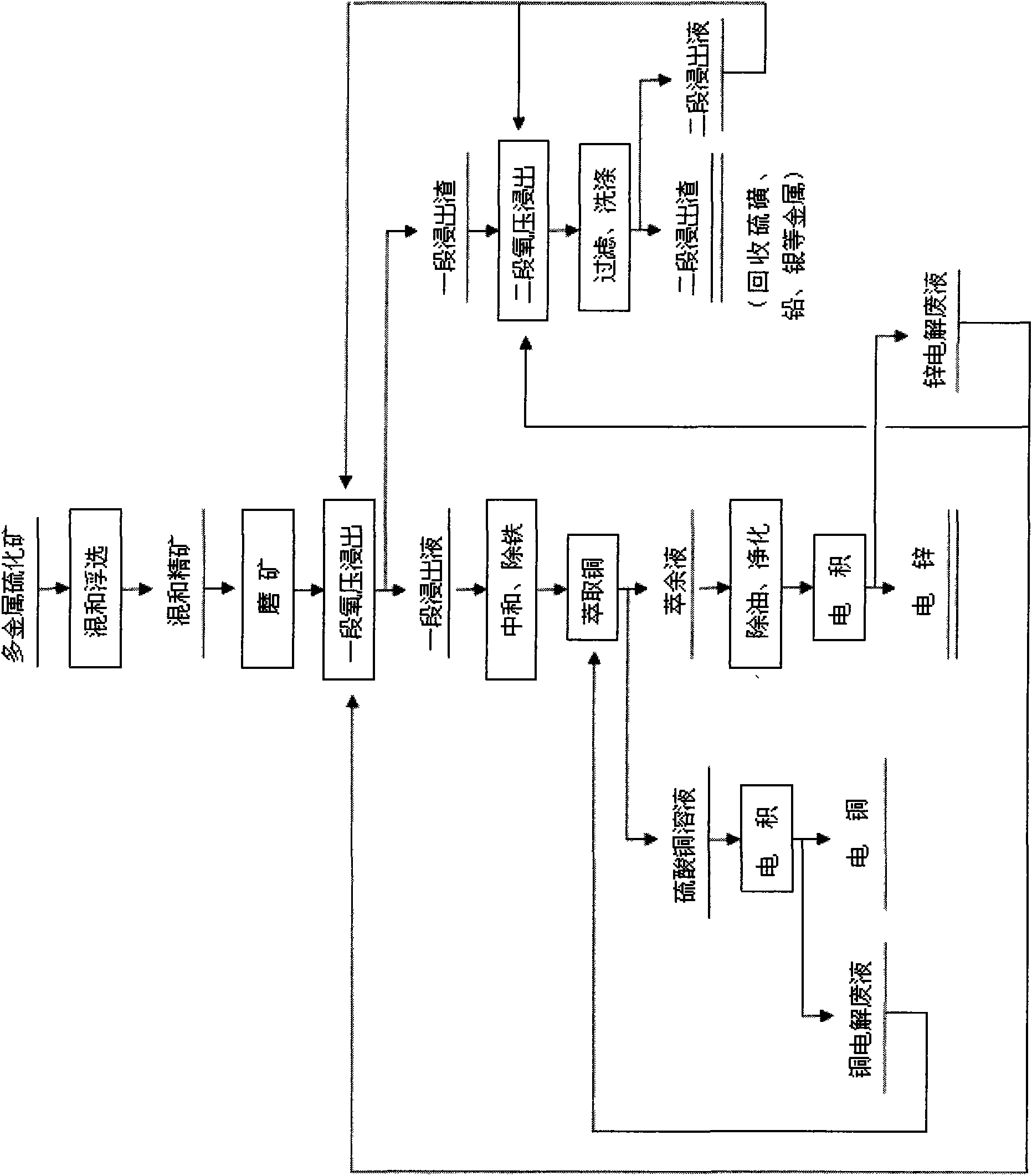
Comprehensive recovery method of complex polymetal sulphide ore containing copper, lead and zinc
InactiveCN101643857AHigh recovery rateSimple processSulfur preparation/purificationFlotationRecovery methodLead smelting
The invention discloses a comprehensive recovery method of complex polymetal sulphide ore containing copper, lead and zinc and adopts dressing-metallurgy combination method and hydrometallurgy-pyrometallurgy combination method to recover metals. The recovery method comprises the following steps: first performing bulk flotation to the complex polymetal sulphide ore, fine grinding the obtained concentrate, leaching by using two-step counter flow oxygen pressure leaching process, extracting and separating copper and zinc from the obtained leachate, electrodepositing the strip liquor of copper-loaded organic phase to obtain cathode copper, cleaning the obtained raffinate and electrodepositing to obtain cathode zinc; pressurizing leaching residue to perform flotation separation and obtain sulfur concentrate and lead silver residue, distilling sulfur concentrate to obtain sulfur; performing lead smelting process to lead silver residue to obtain electrolytic lead product and lead anodic slime; and comprehensively recovering noble metals such as gold, silver and the like from lead anodic slime. The method can greatly improve the metal recovery rate, resource utilization and the economic efficiency of mines and generate a lot of sulfur so as to obviously reduce the sulfur dioxide pollution to the atmosphere.
Owner:WESTERN MINING CO LTD
Method for recovering valuable metals from waste printed circuit board
ActiveCN101787547ASolve pollutionReduce energy consumptionPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisFiltration
The invention discloses a method for recovering valuable metals from a waste printed circuit board. The method comprises the following steps: sorting and crushing the printed circuit board, evenly mixing powder containing multiple metal parts with a fluxing agent, and smelting at low temperature for 1-3.5h; adding hot water into smelting products for leaching; evaporating and concentrating filtrate after filtration, and then returning evaporation mother liquor to the water leaching process step; using solution after leaching for swirl electrodeposition of metal silver, and adding 5-25% of HNO3 into filter residue for leaching; filtering the solution after electrodeposition, and adding 1-5 times of the weight of aqua regia into the filter residue for leaching; using the solution after leaching by the aqua regia for the swirl electrodeposition of gold, adding saturated NH4Cl into the solution after the electrodeposition for reaction, then filtering, using ammonium chloroplatinate for refining the filter residue, obtaining sponge platinum, adding methanoic acid into the solution after precipitation, and carrying out reaction for obtaining crude palladium powder. The method can extract copper, nickel, silver, gold, platinum, palladium and other main products and other by-products, realize the maximization of reutilization of value metal resources in the waste printed circuit board and solve the environmental pollution problem; and the adoption of the swirl electrolysis technology can realize low energy consumption, low reagent consumption, short process flow and simple operation.
Owner:HUNAN JIANG YE MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH CO LTD
Multi-layer non-carbon metal-based anodes for aluminum production cells and method
InactiveUS6077415AImprove electrochemical activitySolution to short lifeMachining electrodesIsotope separationElectrical batteryOxygen ions
A composite, high-temperature resistant, non-carbon metal-based anode of a cell for the electrowinning of aluminium comprises a metal-based core structure of low electrical resistance, for connecting the anode to a positive current supply, coated with a series of superimposed, adherent, electrically conductive layers. These layers consist of at least one layer on the core structure constituting a barrier substantially impervious to monoatomic oxygen and molecular oxygen; one or more intermediate, protective layers on the oxygen barrier layer which remain inactive in the reactions for the evolution of oxygen gas; and an electrochemically active layer for the oxidation reaction of oxygen ions present at the anode / electrolyte interface into nascent monoatomic oxygen, as well as for subsequent reaction for the formation of gaseous biatomic oxygen. The active layer on the outermost intermediate layer is slowly consumable during electrolysis and protects the intermediate protective layer by inhibiting its dissolution into the electrolyte.
Owner:MOLTECH INVENT
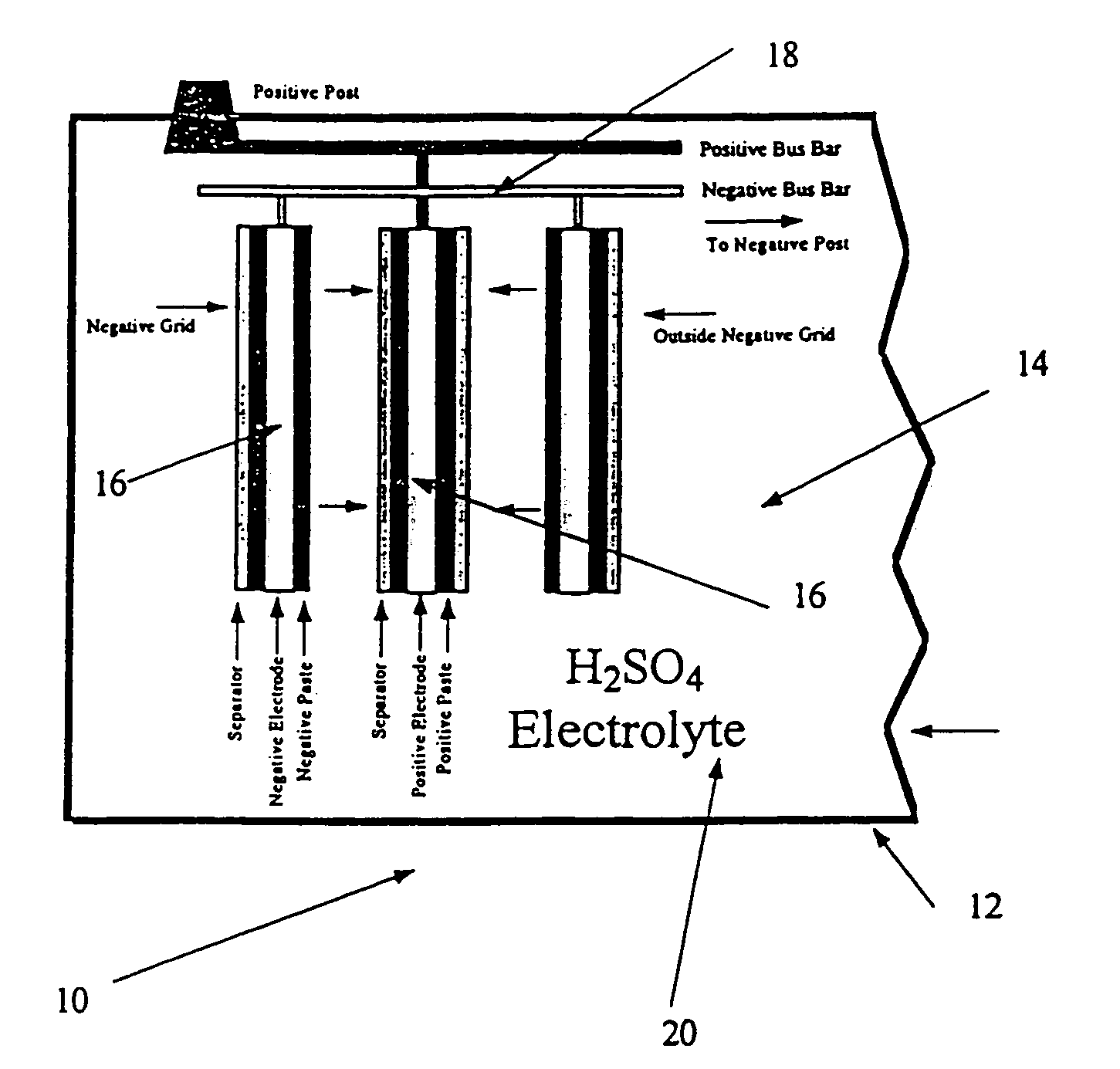
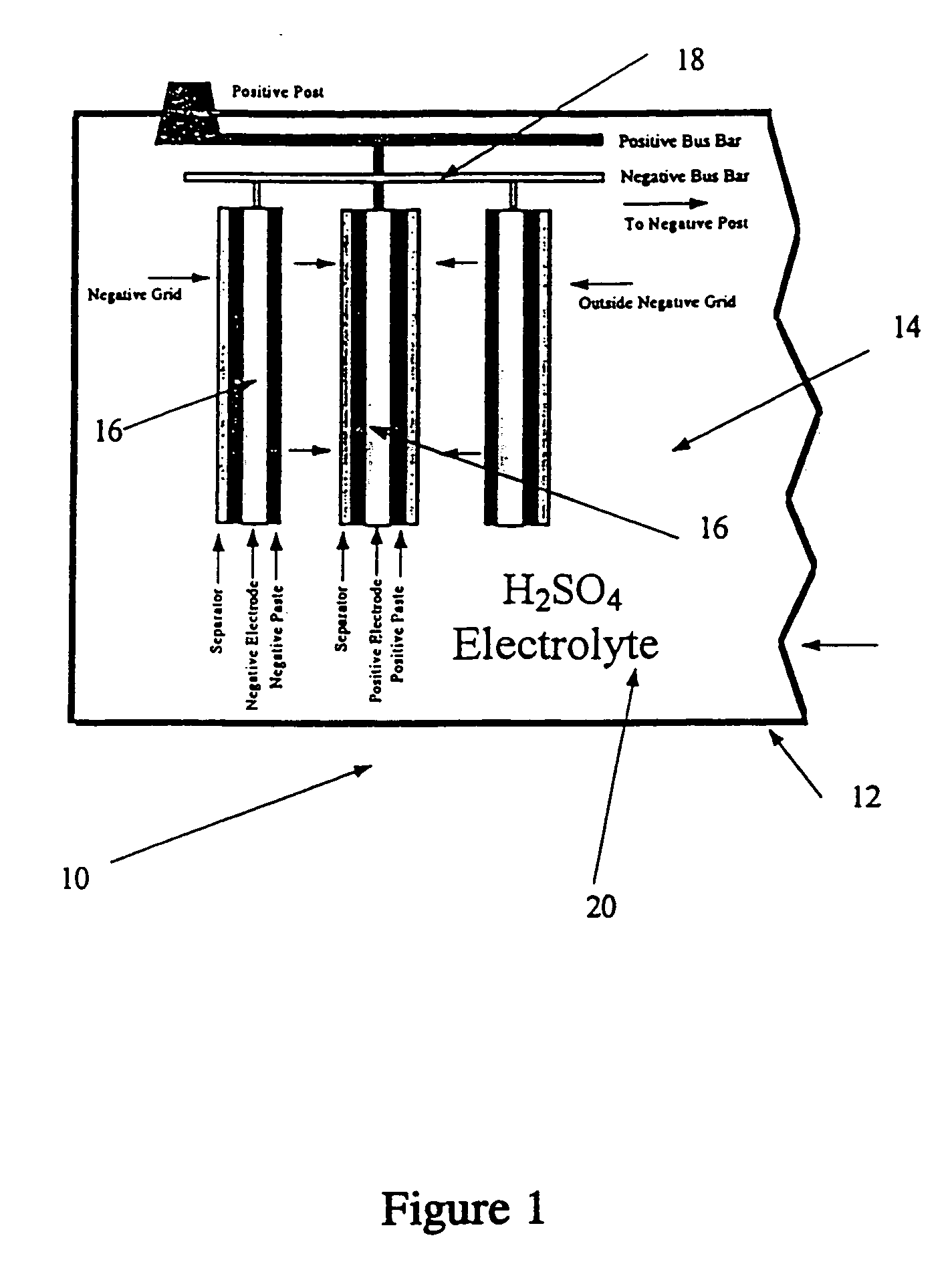
Thermo-mechanical treated lead and lead alloys especially for current collectors and connectors in lead-acid batteries
InactiveUS20040112486A1Improvement in lead-acid battery performanceSmall sizeElectrode carriers/collectorsElectrolysisMetallurgy
Recrystallized lead and lead alloy positive current collectors and connectors such as straps and lugs for use e.g. in lead acid batteries and electrowinning anodes, having an increased percentage of special grain boundaries in at least part of the microstructure, which have been provided by a process comprising of (i) cold or hot rolling or cold or hot extrusion or (ii) steps of deforming the lead or lead alloy, and subsequently annealing the lead or lead alloy. Either a single cycle of working and annealing can be provided, or a plurality of such cycles can be provided. The amount of deformation, the recrystallization time and temperature, and the number of repetitions of such steps are selected to ensure that a substantial increase in the population of special grain boundaries is provided in the microstructure, to improve resistance to creep, intergranular corrosion and intergranular cracking of the current collectors and connectors during battery service, and result in extended battery life and the opportunity to reduce the size and weight of the battery.
Owner:AUST KARL T +5
Method for extracting refined tellurium from tellurium-contained smelting slag
InactiveCN101565174AImprove leaching rateReduce invalid consumptionElemental selenium/telluriumSlagTe element
The invention relates to a method for extracting refined tellurium from tellurium-contained smelting slag, which is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps of: oxidizing and leaching inorganic acid, replacing noble metal with a copper plate, depositing the copper by sodium sulfide, counteracting and depositing tellurium, alkaline leaching coarse TeO2, removing impurities by Na2S, concentrating and electrowinning. The method has the advantages of high recovery rate for tellurium, comprehensive and effective recovery of other useful metals, and suitably treating the tellurium-contained waste slag with high water content and small granularity generated in the metallurgy process by a wet-method.
Owner:YONGXING XINTAI SILVER IND
Porous non-carbon metal-based anodes for aluminium production cells
InactiveUS6113758AEliminate carbon-generated pollutionReduces high cell operating costMachining electrodesElectrical-based machining electrodesFiberCuprate
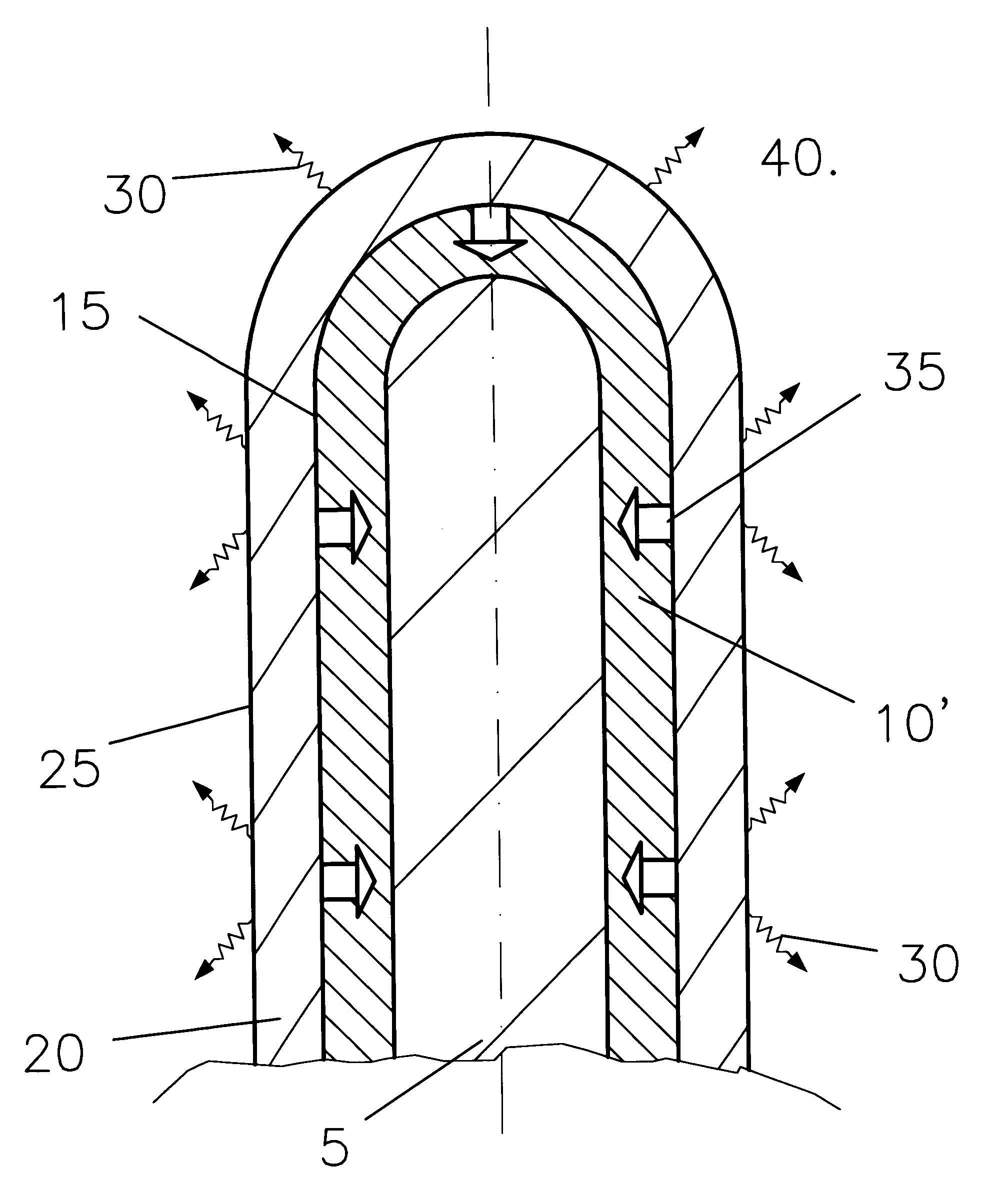
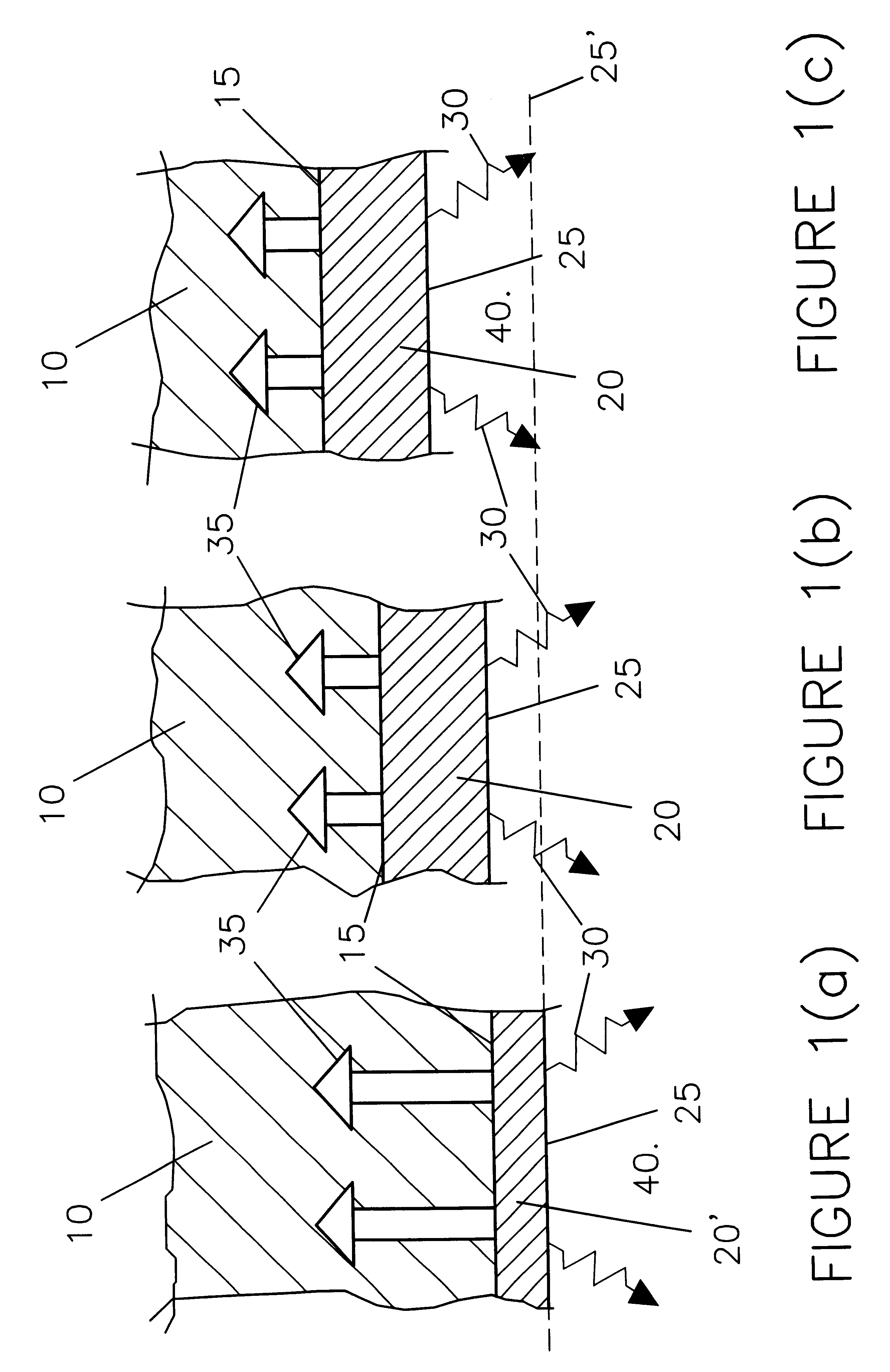
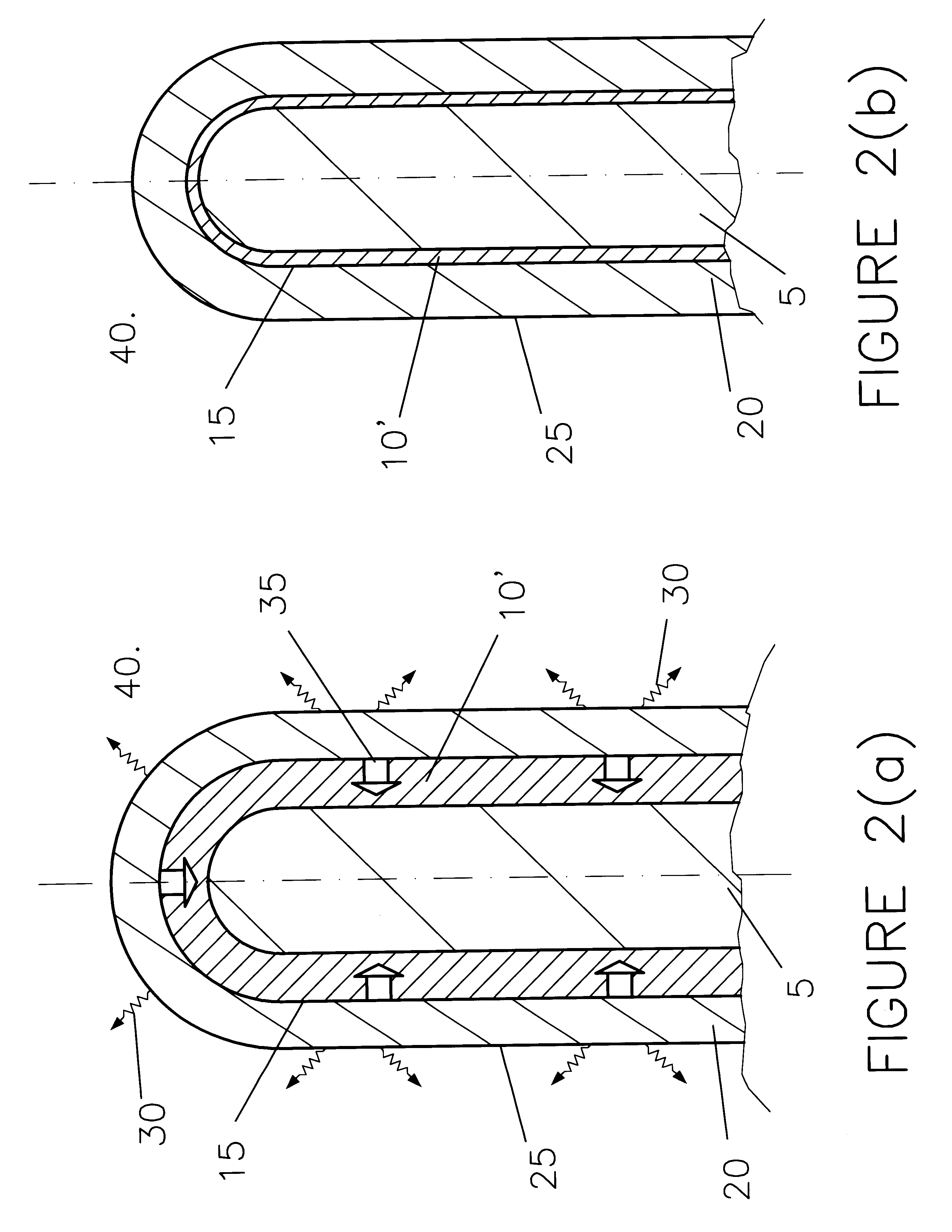
A non-carbon, metal-based anode (10) of a cell for the electrowinning of aluminium, comprising an electrically conductive, high temperature resistant and oxidation resistant metal structure (11) in the form of a wire mesh or net, a foraminate sheet, a fibrous network, a reticulated skeletal structure, or a porous structure having voids, recesses and / or pores which are filled or partly filled with an electrochemically active filling (12), such as oxides, oxyfluorides, phosphides, carbides, cobaltites and cuprates making the surface of the anode (10) conductive and electrochemically active for the oxidation of oxygen ions present at the anode surface / electrolyte (5) interface.
Owner:MOLTECH INVENT
Surface oxidised nickel-iron metal anodes for aluminium production
InactiveUS20050205431A1Reduce solubilityPremature depletionIsotope separationElectrodesElectrolysisSurface oxidation
An anode for the electrowinning of aluminium by the electrolysis of alumina in a molten fluoride electrolyte has an electrochemically active integral outside oxide layer obtainable by surface oxidation of a metal alloy which consists of 20 to 60 weight % nickel; 5 to 15 weight % copper; 1.5 to 5 weight % aluminium; 0 to 2 weight % in total of one or more rare earth metals, in particular yttrium; 0 to 2 weight % of further elements, in particular manganese, silicon and carbon; and the balance being iron. The metal alloy of the anode has a copper / nickel weight ratio in the range of 0.1 to 0.5, preferably 0.2 to 0.3.
Owner:MOLTECH INVENT
Method of electrolytically depositing a pharmaceutical coating onto a conductive osteal implant
InactiveUS20080011613A1Electrolytic inorganic material coatingPretreated surfacesCalcium biphosphateConductive materials
A method of electrolytically depositing a pharmaceutical coating onto a conductive osteal implant. The implant is submerged into an electrolytic cell containing an electrolysis solution of the pharmaceutical and acts as a cathode. When current is applied to the electrolytic cell, the pharmaceutical coating forms on the implant. The pharmaceutical can comprise bisphosphonates, including calcium salts. The implants can comprise any conductive material suitable for use as an osteal implant. The implants can also be electrolytically coated with calcium phosphate before coating with a pharmaceutical.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
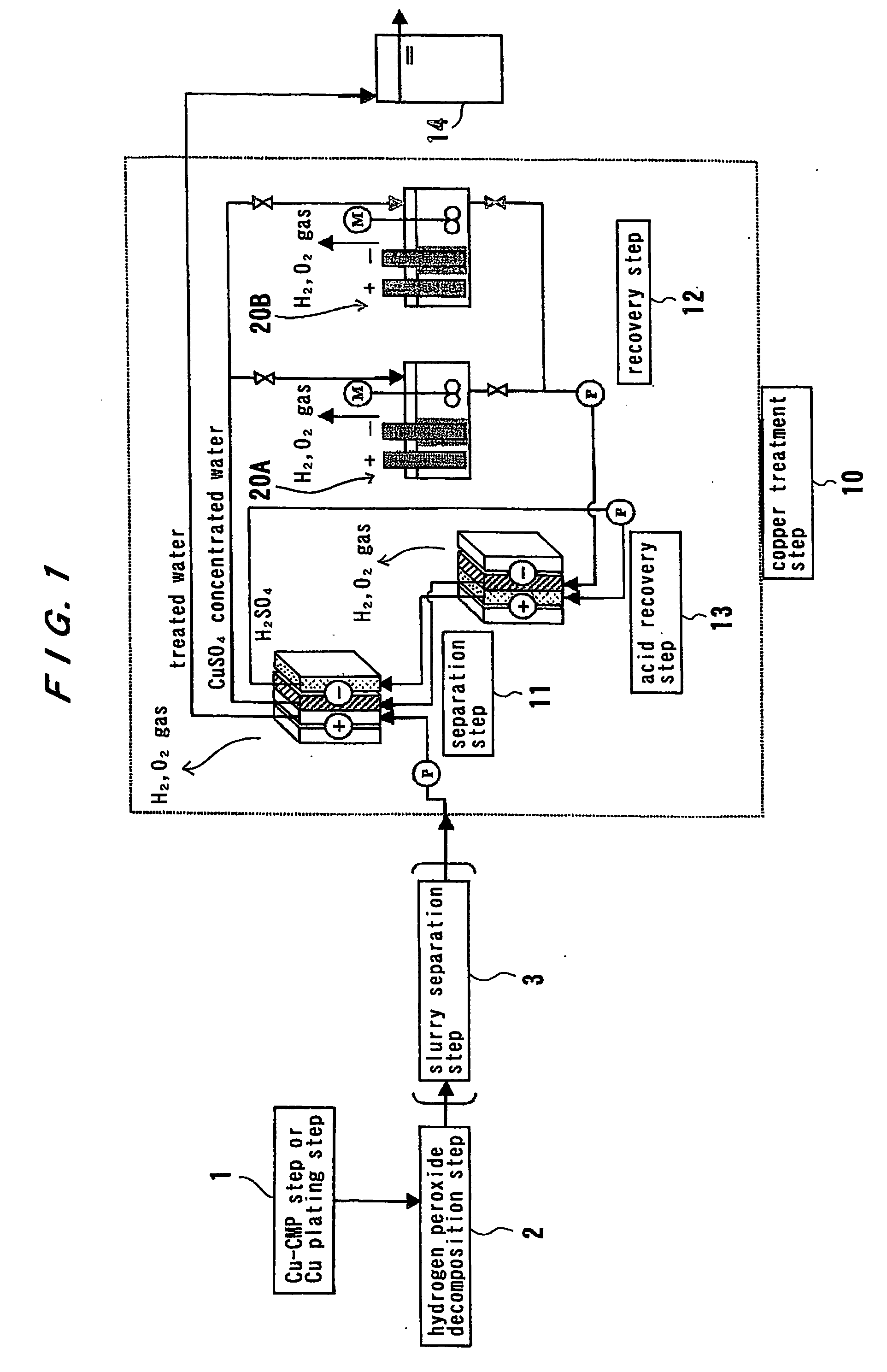
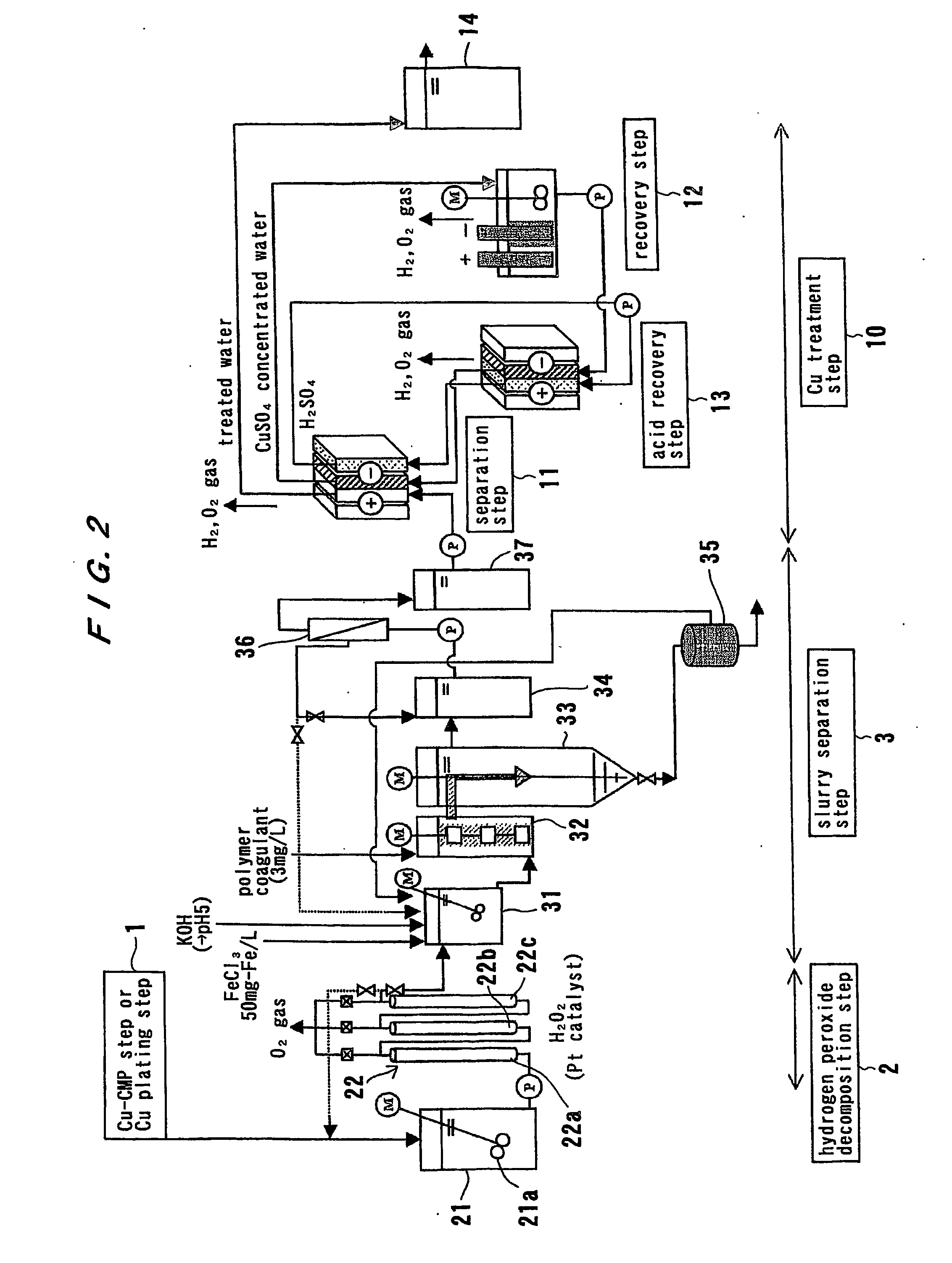
Method and apparatus for treating waste water
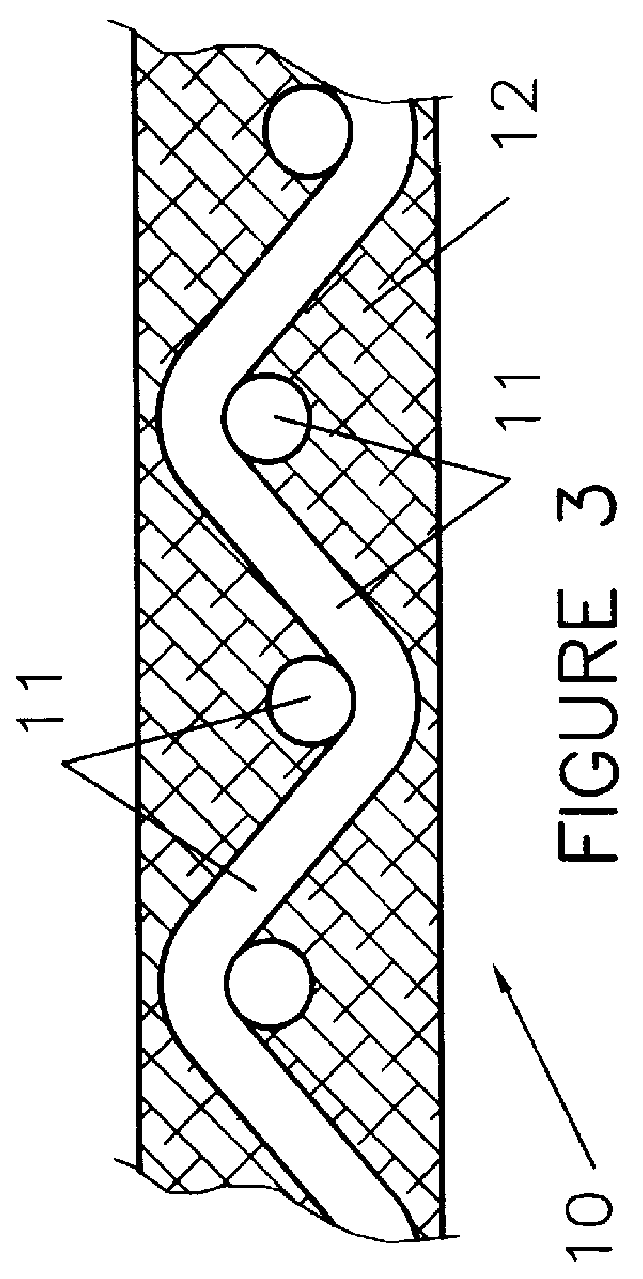
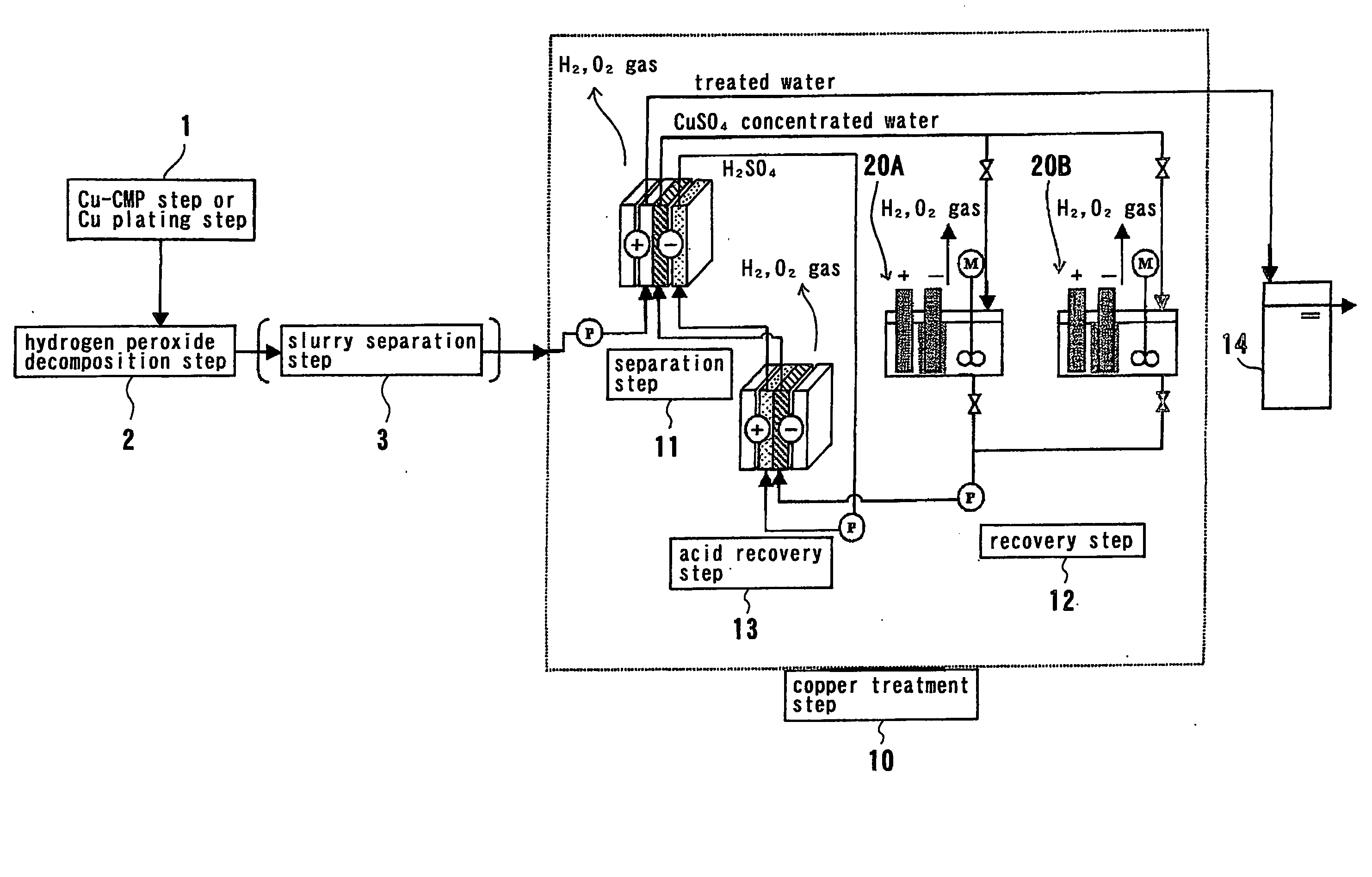
InactiveUS20060243604A1Large specific surface areaImprove gas separation performanceLiquid separation by electricityVolume/mass flow measurementElectrolysisCopper
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for removing and recovering metal such as copper from various kinds of waste water containing copper. A method for treating waste water includes treating waste water in a copper treatment step (10) comprising a combination of electrodialysis operation and electrolytic deposition operation to produce treated water (107) having a lowered copper concentration, and recovering copper from the waste water.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Device for recovering copper in old electronic printed circuit board and method
InactiveCN101538722AElectrolytic deposition achievedAvoid pollutionPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisVolumetric Mass Density
The invention provides a device for recovering copper in an old electronic printed circuit board by a suspension electrolysis method and a method. The suspension electrolysis device which comprises a groove body, a stirrer, a cathode and an anode is adopted; wherein, the anode is an anode basket, and a membrane is arranged between the anode basket and the cathode. The formulation of electrolyte used for recovering the copper in the old electronic printed circuit board comprises 10-50g / L of Cu<2+>, 100-180g / L of H2SO4 and 10-30mg / L of Cl<->; the mass ratio between the raw material of the circuit board and the electrolyte is 1:5-1:10, and the density of cathode current is 2-4A / dm<2>. The copper produced by the method takes the metal in the old electronic printed circuit board as the main raw material, and prepared by the suspension electrolysis method. The suspension electrolysis method utilizes the oxidization of the anode and anode energy in the electrolytic deposition process, can realize electrolytic deposition of the metal under the conditions of low cell voltage and low energy consumption, and has remarkable advantages in the aspects of metal separation and environmental pollution prevention.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Slow consumable non-carbon metal-based anodes for aluminium production cells
InactiveUS6248227B1Eliminate carbon-generated pollutionReduce frequencyMachining electrodesIsotope separationElectrolysisAlloy
A non-carbon, metal-based slow-consumable anode of a cell for the electrowinning of aluminium self-forms during normal electrolysis an electrochemically-active oxide-based surface layer (20). The rate of formation (35) of the layer (20) is substantially equal to its rate of dissolution (30) at the surface layer / electrolyte interface (25) thereby maintaining its thickness substantially constant, forming a limited barrier controlling the oxidation rate (35). The anode (10) usually comprises an alloy of iron with at least one of nickel, copper, cobalt or zinc which during use forms an oxide surface layer (20) mainly containing ferrite.
Owner:MOLTECH INVENT
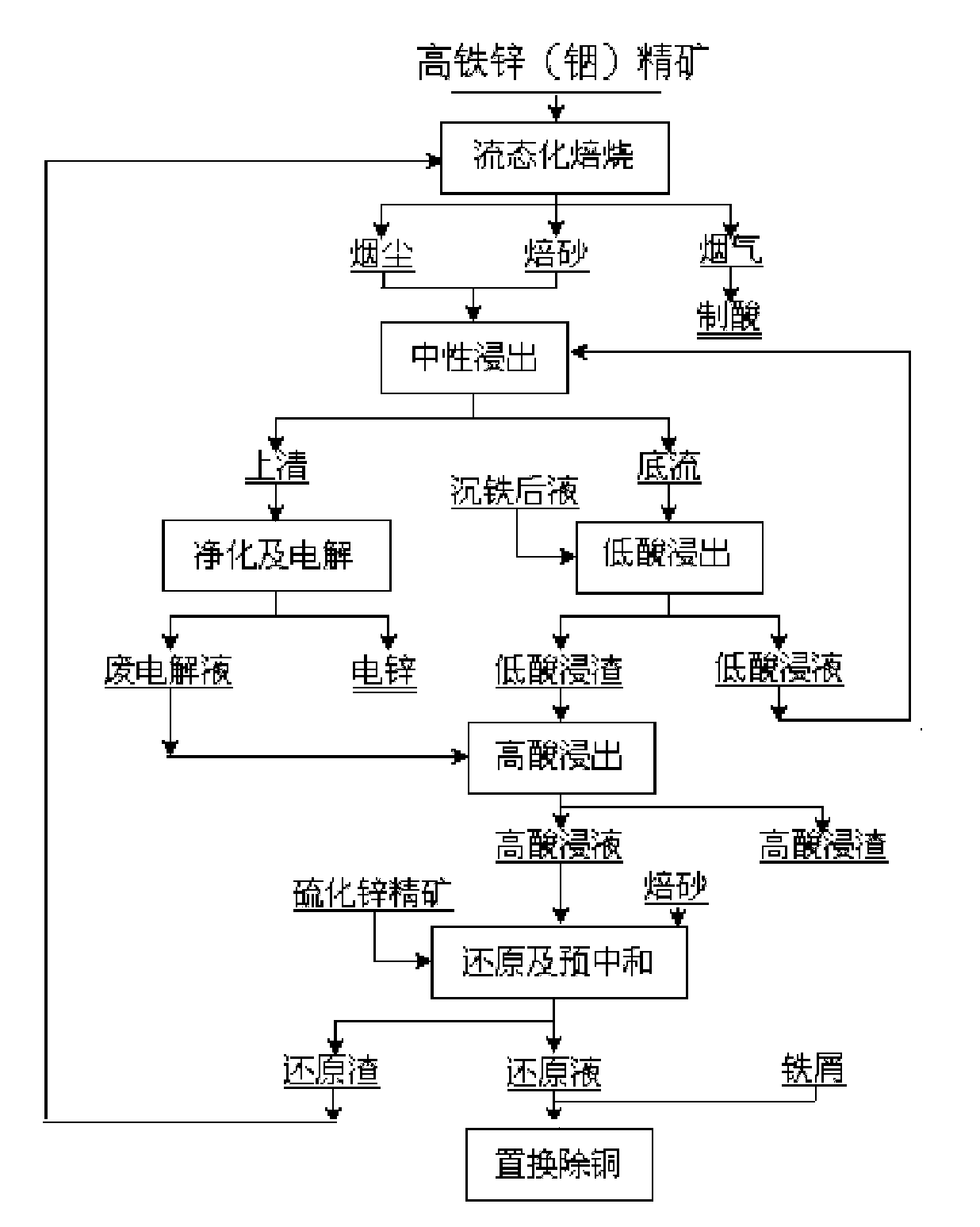
Method for extracting indium and preparing iron oxide by slag-free zinc hydrometallurgy of zinc concentrate
InactiveCN101886272AHigh recovery rateOvercome the problem of efficient usePhotography auxillary processesFerric oxidesIndiumSlag
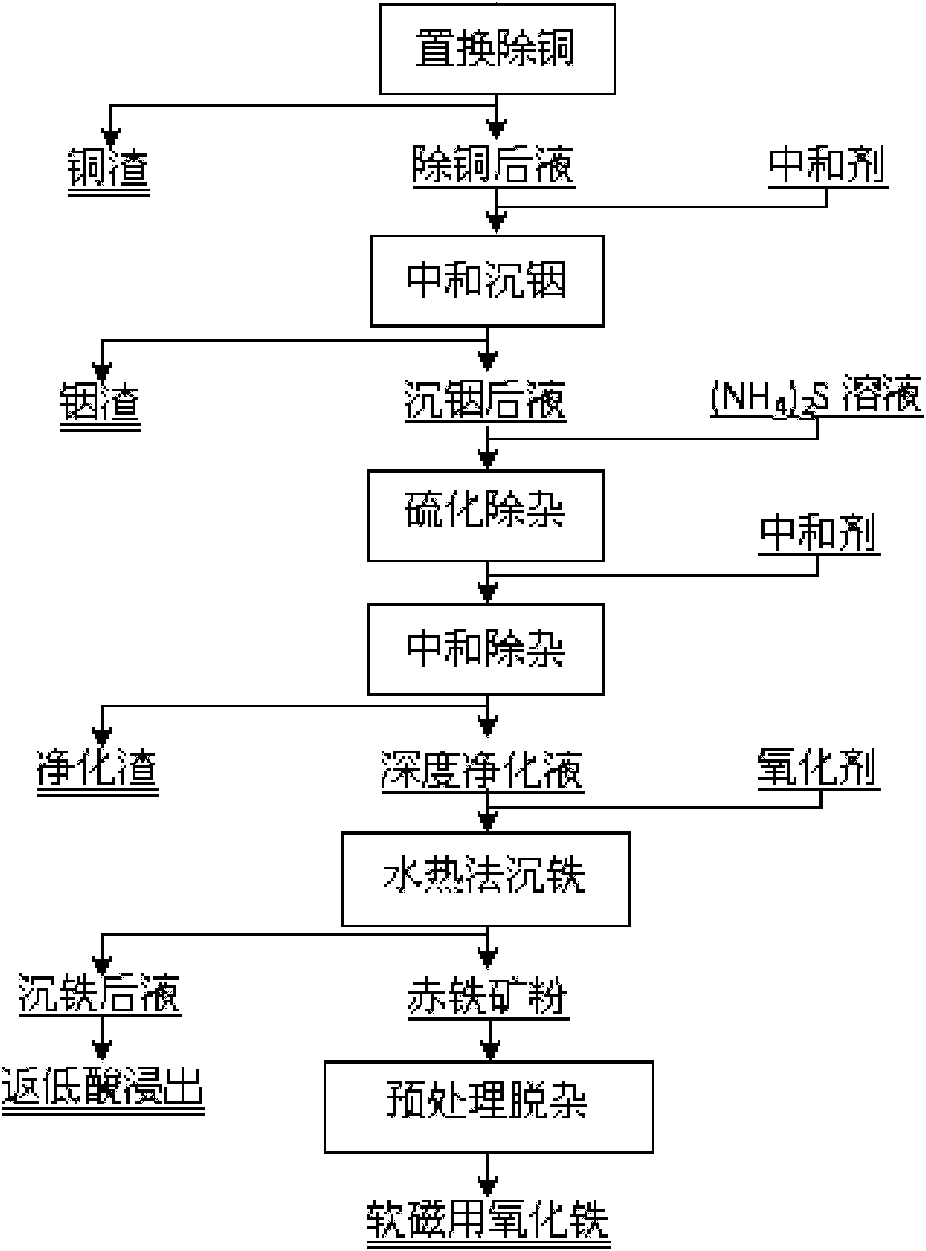
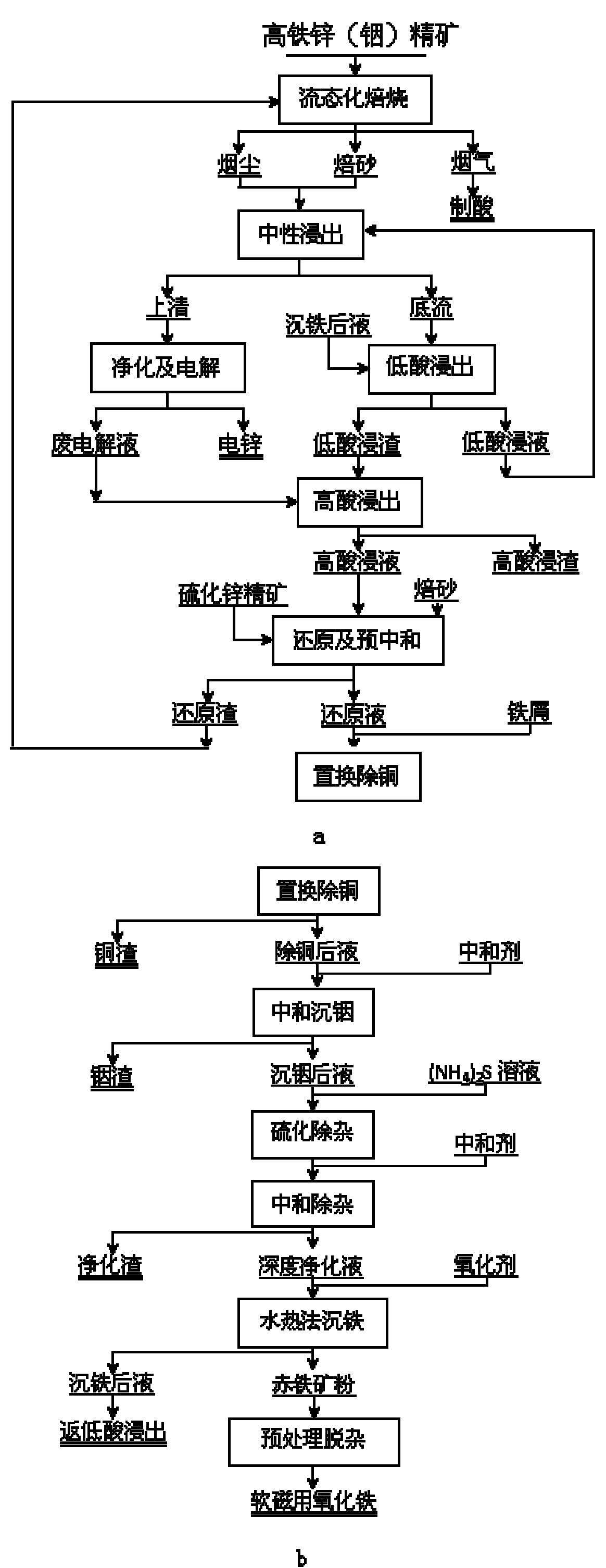
The invention relates to a method for extracting indium and preparing iron oxide by slag-free zinc hydrometallurgy of zinc concentrate, which comprises the following steps of: 1, performing fluidized bed roasting, neutral leaching, low acid leaching, purification and electrodeposition on the zinc concentrate to prepare electric zinc; 2, performing high acid leaching, reduction, preneutralization and displacement to remove copper on low acid leaching residue and waste electrolyte after the electrodeposition to prepare the electric zinc; 3, neutralizing the liquid from which the copper is removed to settle the indium; 4, vulcanizing the liquid in which the indium is settled to remove heavy metal and then adding lime milk to neutralize the liquid to obtain deeply purified liquid; 5, settling iron in the deeply purified liquid by a hydrothermal method to obtain hematite powder; and 6, removing impurities from the hematite powder to obtain soft magnetic iron oxide. In the method, the indium is settled by neutralizing and the iron is settled by the hydrothermal method, so that the indium is separated from the iron, the indium is separated from the zinc, the hematite powder is formed, and the requirement of the soft magnetic iron oxide is met through impurity removal treatment. The method has the advantages of simple process, high recovery rate of the indium and the zinc, short flow for separating the iron from the zinc, high purity of the iron, environmental friendliness, suitability for industrial application, and capability of replacing the conventional slag-free zinc hydrometallurgy process for extracting the indium and making effective use of the iron resource in the zinc concentrate in a form of the soft magnetic iron oxide.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for recycling tin from waste tin-stripping solution based on tin-stripping solution of hydrochloric acid-tin salt system
ActiveCN103741142AAvoid the Cons of PollutionStrong oxidation abilityPhotography auxillary processesSolution treatmentTetrachloride
The invention discloses a method for efficiently recycling tin from a waste tin-stripping solution based on a tin-stripping solution of a hydrochloric acid-tin salt system. According to the tin-stripping solution, the components and the contents are as follows: 110-230g / L of tin tetrachloride, 70-220g / L of hydrochloric acid, 10-30g / L of iron chloride, 0.5-2.5g / L of a stabilizing agent, 5-30g / L of an accelerant and 2-5g / L of a brightener. The waste tin-stripping solution obtained by tin stripping is subjected to diaphragm electrodeposition treatment by using a cathode room and an anode room of an anion diaphragm electrolytic cell to recycle tin, the tin tetrachloride and ferric trichloride. According to the method for treating the waste tin-stripping solution, not only can the tin be effectively recycled from the waste tin-stripping solution, but also the tin tetrachloride and ferric trichloride can be regenerated and returned to prepare the waste tin-stripping solution to use; the problems of resource wastes, serious environment pollution and the like of a traditional waste tin-stripping solution treatment method are completely avoided.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
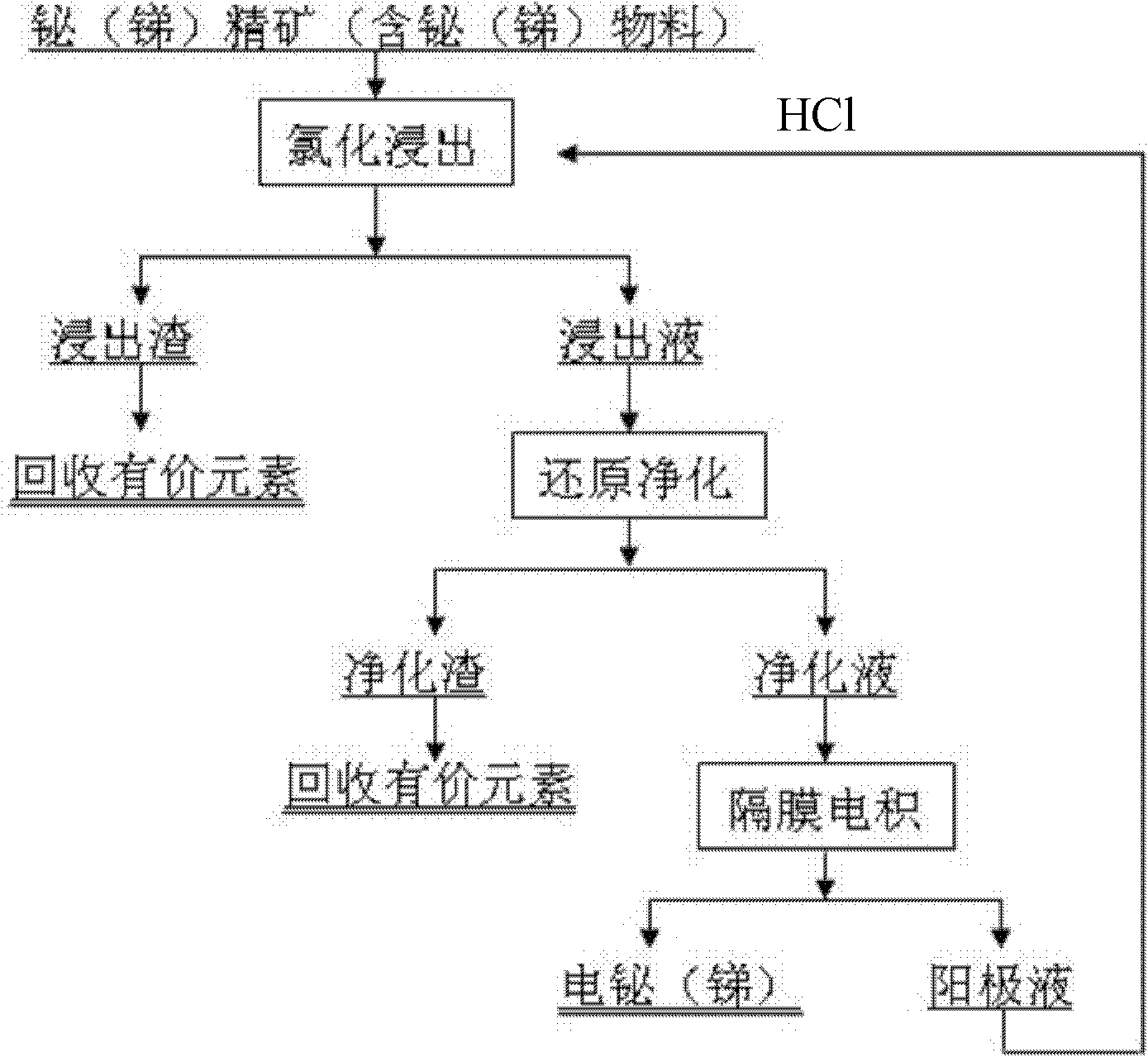
Clean metallurgical method for bismuth or stibium by wet method
ActiveCN101775619AInhibition releaseEfficient separationPhotography auxillary processesClosed loopMaterials science
The invention discloses a clean metallurgical method for bismuth or stibium by a wet method, comprising steps of leaching, purifying, diaphragm electrodepositing and the like. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, selectively leaching the bismuth (or the stibium) from bismuth concentrate (or stibium concentrate); then, purifying and reducing leachate; and finally, extracting the bismuth (or stibium) by adopting diaphragm electrodeposition. The electro-bismuth (or electro-stibium) is obtained on a negative plate, and oxidant solution is obtained in an anode chamber. The oxidant solution can be used as the oxidant required in the leaching step, and is returned to the leaching process. The method achieves closed loop circulation of the technical process, recycled oxidant, better solves the problems of high consumption, severe equipment corrosion, low metal reclamation, difficult comprehensive reclamation of other valuable metals, large discharge of wastewater and the like universally existing in the prior wet bismuth (or stibium) extracting process. The method is particularly suitable for treating low-grade difficult-treatment complicated bismuth (stibium) mineral or bismuth (stibium) containing materials, and has outstanding advantages of strong raw material adaptability and high metal reclamation.
Owner:YIYANG SHENGLI CHEM IND
Biological metallurgy mineral leaching microorganism combined bacterium fluid for copper ore and method for recycling metallic copper
InactiveCN101956071ATake advantage ofProtect environmentProcess efficiency improvementEcological environmentSlag
The invention discloses biological metallurgy mineral leaching microorganism combined bacterium fluid for a copper ore and a method for recycling metallic copper. The method comprises the following steps that: mineral leaching microorganisms after adaptive culture, continuous amplification culture and ore pile adaptive culture are combined and used for mineral leaching, and different leaching methods are adopted aiming at the ore of different objects, which comprise a biological metallurgy processing method for lump ores, powder ores, tailings, copper smelting slags and the like; and the obtained qualified leaching solution is used to prepare two products, namely electrolytic copper by an extraction-electrodeposition method and spongy copper by a short stage displacement method. The method has the advantages of suitability for industrial production under different conditions, efficient utilization of low-grade copper ore resources and capacity of effectively protecting the ecological environment of mine areas and achieving a win-win situation of economic benefit and environmental friendliness.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for extracting tellurium from copper anode sludge
InactiveCN102220489AEasy to separateRaise the gradePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionSludge
The invention discloses a method for extracting tellurium from copper anode sludge and relates to the method for recovering the tellurium from copper-containing tellurium material, in particular to the method for extracting the tellurium from the copper anode sludge. The method is characterized in that the process sequentially comprises the following steps: (1) performing oxygenation, pressurization and sulfuric acid leaching on the copper anode sludge for leaching copper, the tellurium and part of selenium; (2) introducing sulfur dioxide gas into leachate, and precipitating and separating the selenium; (3) performing electrodeposition on a solution after removing the selenium by precipitation and separation, and separating the copper; and (4) introducing the sulfur dioxide gas into the solution after removing the copper by electrodeposition and separation for performing reduction reaction so as to get the deposited crude tellurium. In the method, the selenium deposition and tellurium deposition technology by sulfur dioxide step-by-step reduction is adopted, no copper powder is consumed during the process, the effect of separating the selenium, the tellurium and the copper is good, the grades of the crude tellurium and crude selenium are high, the production cost can be greatly reduce, the process flow is simplified, and convenient conditions are provided for preparing follow-up fine tellurium.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Heap bioleaching process for the extraction of zinc
InactiveUS20050066773A1Sufficient acid contentPrevent precipitationProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionZinc compounds
A method of extracting zinc from a sulphidic ore is provided which comprises bioleaching the ore in a heap with acidophilic microorganisms to produce a pregnant leach solution which is recovered from the bottom of the heap. An integrated process which comprises subjecting the pregnant leach solution to neutralization and solvent extraction to produce a concentrated zinc solution is also provided. Zinc may be recovered from the concentrated solution by means of electrowinning, either in the absence or presence of manganese. Alternatively zinc may be recovered in the form of a zinc compound.
Owner:TECK METALS
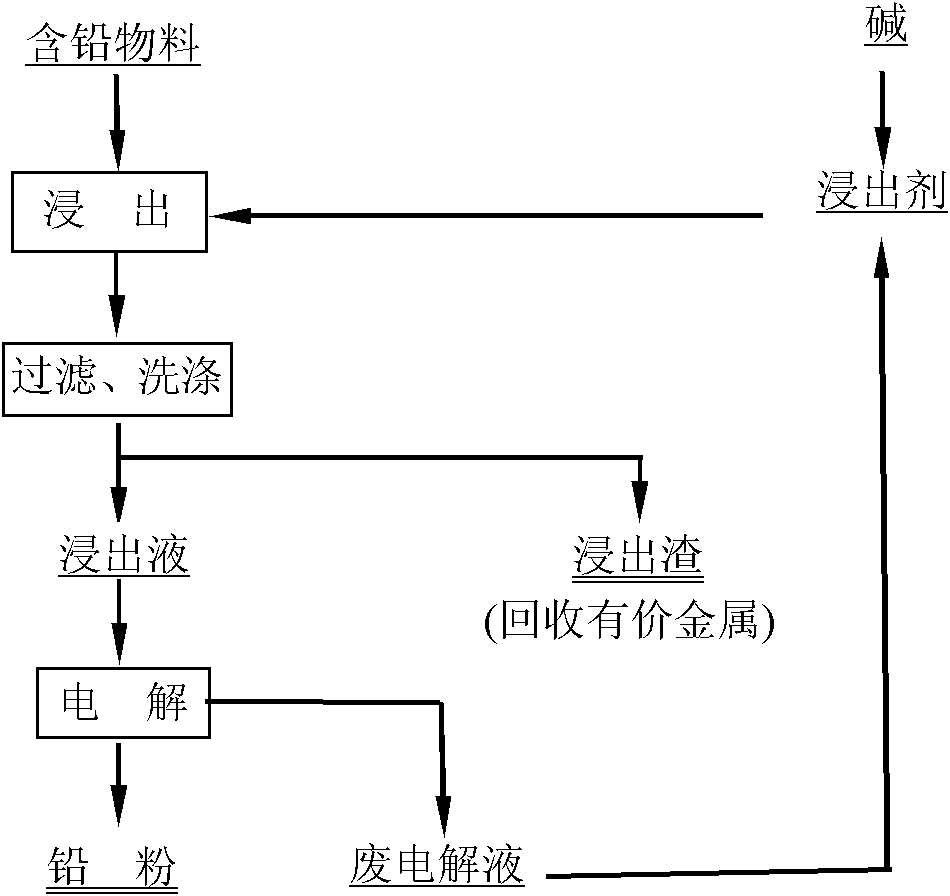
Method for recovering lead from lead-containing material by matching leaching-electrowinning method
InactiveCN102206750AEasy to separateImprove the efficiency of follow-up operationsPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementSlagLead sulfate
The invention discloses a method for recovering lead from a lead-containing material by matching a leaching-electrowinning method. The method comprises the following steps of: selectively leaching the lead from the lead-containing material at the temperature of -95DEG C by using a mixture of 0.005-0.5M ethylenediaminotetraacetateedetate and 0.05-1.0M alkali as a leaching agent, and filtering and separating to obtain a lead-containing solution; and separating out metal lead powder from the solution by using an electrowinning method, blending electrowinning waste liquor, and returning to the leaching step. By leaching lead from secondary zinc oxide soot, the grade of zinc in secondary zinc oxide and the leaching rate of subsequent leaching can be improved, and subsequent treatment is facilitated; and by leaching lead from low-grade lead slag containing lead oxide, lead sulfate or lead chloride, the leached sewage in the slag piling process never contains lead or contains little lead, environment is not affected, the waste is changed into treasure, and the lead can be recovered from the lead slag. The method has the advantages of simple flow, simple operation, low energy consumption and the like, and can be widely used for treating lead-containing secondary zinc oxide materials and low-grade lead slag.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Copper electrolyte adsorption, impurity removal and purification method
ActiveCN104060295AAchieve recyclingEliminate generationPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsPurification methodsSorbent
The invention discloses a copper electrolyte adsorption, impurity removal and purification method which is characterized by comprising the following steps: by taking oxides of antimony or / and bismuth and hydrates thereof as adsorbents, selectively adsorbing impurities As, Sb and Bi from copper electrolyte or from a solution in which cathode copper is produced through electrodeposition of the copper electrolyte or from a crystallizing mother solution obtained after copper sulfate is evaporated, concentrated and crystallized in the copper electrolyte. According to desorption of loaded adsorbents and regeneration of the analyzed solution, the adsorbents and analytical solution can be recycled, and the adsorbed impurities As, Sb and Bi can be recycled. The method has the advantages of simple process, simple and convenient operation, low production cost, good purification effect and the like, side effects on a main process are avoided, a traditional electrodeposition copper and impurity removal copper electrolyte purification process can be completely substituted, black copper sludge and black copper plate in the copper electrolyte purification process are completely eliminated, emission of harmful substances such as AsH3 is avoided, pollution is reduced, and the environment is protected.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
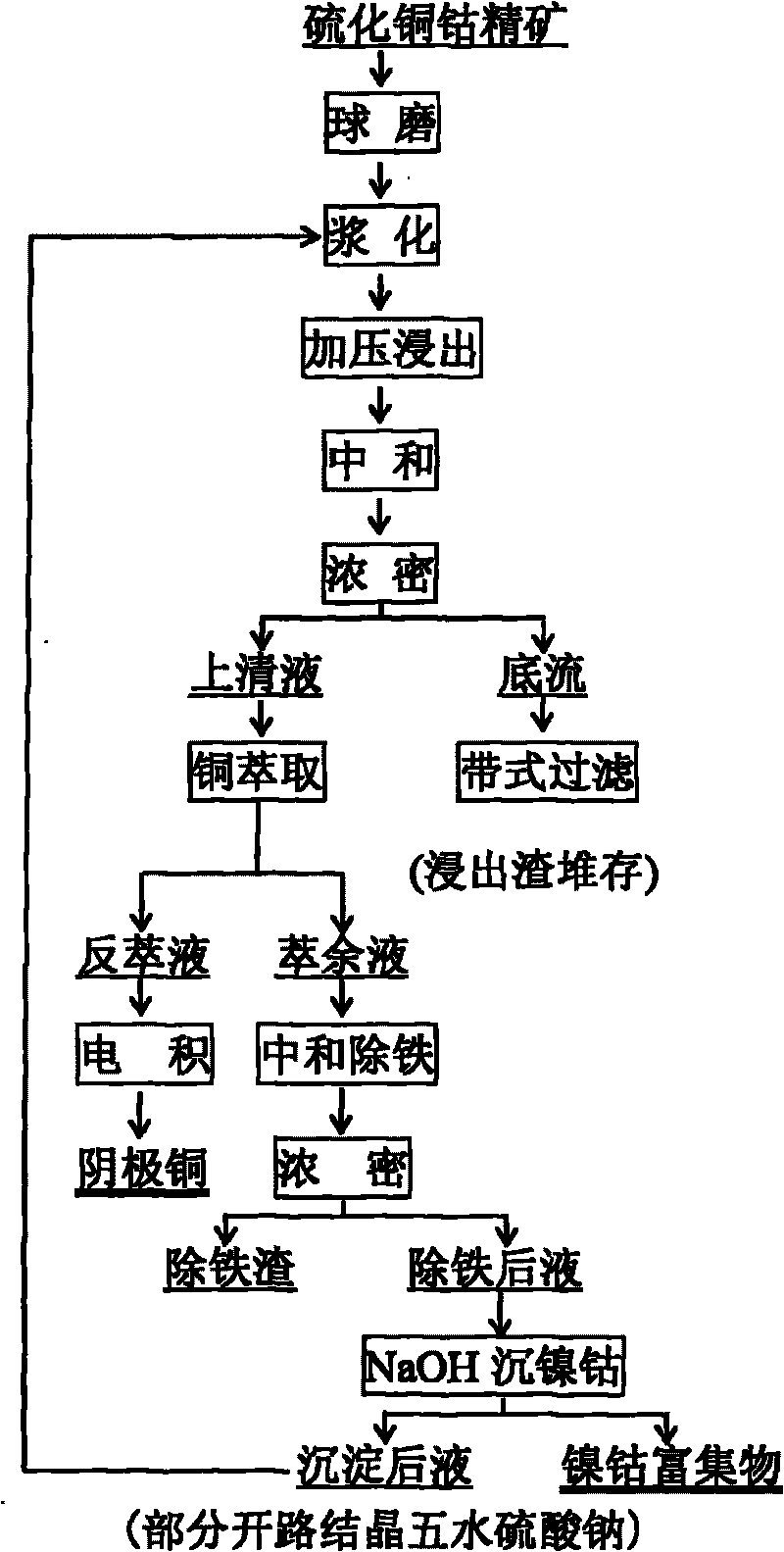
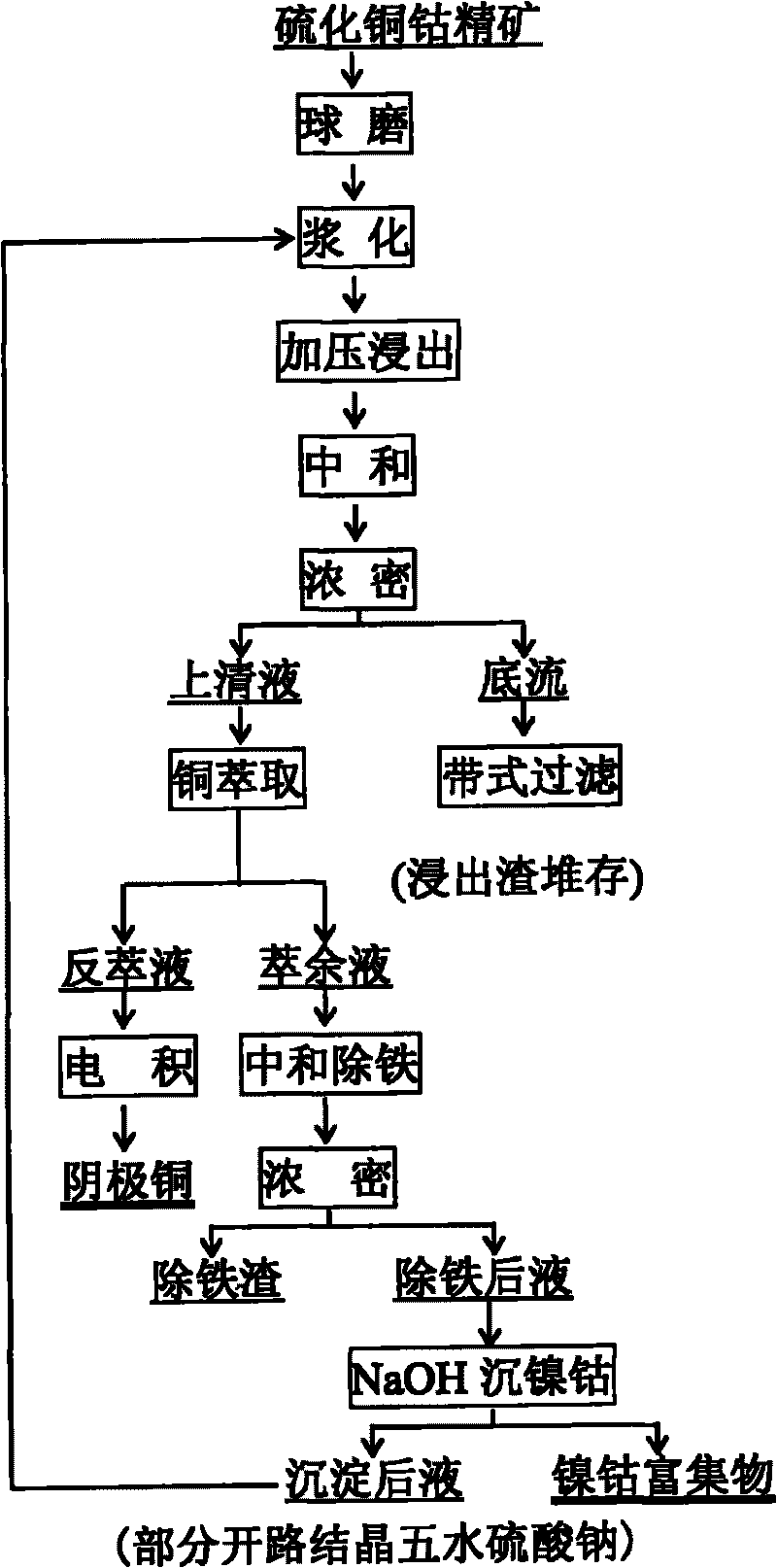
Method for extracting cobalt in copper cobalt sulfide ore
ActiveCN101705371AAchieve recyclingRealize self-heatingPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementRaffinateSulfur containing
The invention provides a method for extracting cobalt in a copper cobalt sulfide ore, and relates to a method for extracting the cobalt in a copper cobalt ore which is in low grade and hard to treat and contains cobalt mineral raw materials. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) crushing and grinding low sulfur containing copper cobalt ore; (2) adding water into the grinded ore material for autoclave leaching; (3) neutralizing and filtering the leached ore pulp, and sending leaching residue into tailing; (4) carrying out copper extraction, extract stripping and strip liquor electrodeposition on the filtered solution to prepare cathode copper; (5) neutralizing copper extracting raffinate to remove iron and aluminum, filter-pressing and separating the neutralized ore pulp, and performing the neutralizing step after the filter-pressed and separated residue is returned to the step (3) for leaching; (6) precipitating cobalt and nickel in filter-pressed and separated solution by adopting sodium hydroxide, wherein the separated precipitate is cobalt nickel hydroxide concentrate; and (7) returning separated after-precipitating solution to the step (2) for the leaching process. The method has simple technical process and less equipment corrosion, and realizes comprehensive reclamation and utilization of valuable metals in the low sulfur containing copper cobalt concentrate.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY +1
Non-carbon anodes for aluminium electrowinning and other oxidation resistant components with slurry-applied coatings
InactiveUS20050178658A1Improve the protective effectImprove propertiesMachining electrodesPretreated surfacesSlurryOxidation resistant
A method of manufacturing a component, in particular an aluminium electrowinning anode, for use at elevated temperature in an oxidising and / or corrosive environment comprises: applying onto a metal-based substrate layers of a particle mixture containing iron oxide particles and particles of a reactant-oxide selected from titanium, yttrium, ytterbium and tantalum oxides; and heat treating the applied layers to consolidate by reactive sintering of the iron oxide particles and the reactant-oxide particles to turn the applied layer into a protective coating made of a substantially continuous reacted oxide matrix of one or more multiple oxides of iron and the metal from the reactant-oxide. The metal-based substrate comprises at its surface during the heat treatment an integral anchorage-oxide of at least one metal of the substrate. The anchorage-oxide anchors the multiple oxide matrix to the substrate by reacting with the iron oxide and / or the reactant-oxide to form an integral multiple bonding oxide of the metal of the integral anchorage-oxide and iron from the iron oxide and / or the metal of the reactant-oxide. The particle mixture can be applied in a colloidal and / or polymeric slurry.
Owner:MOLTECH INVENT
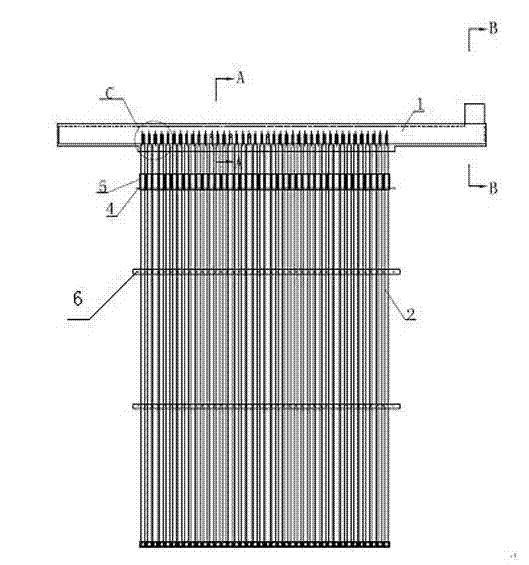
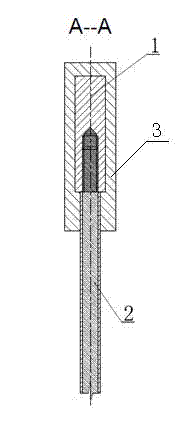
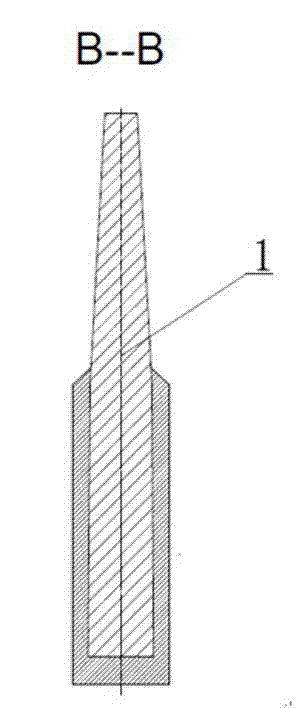
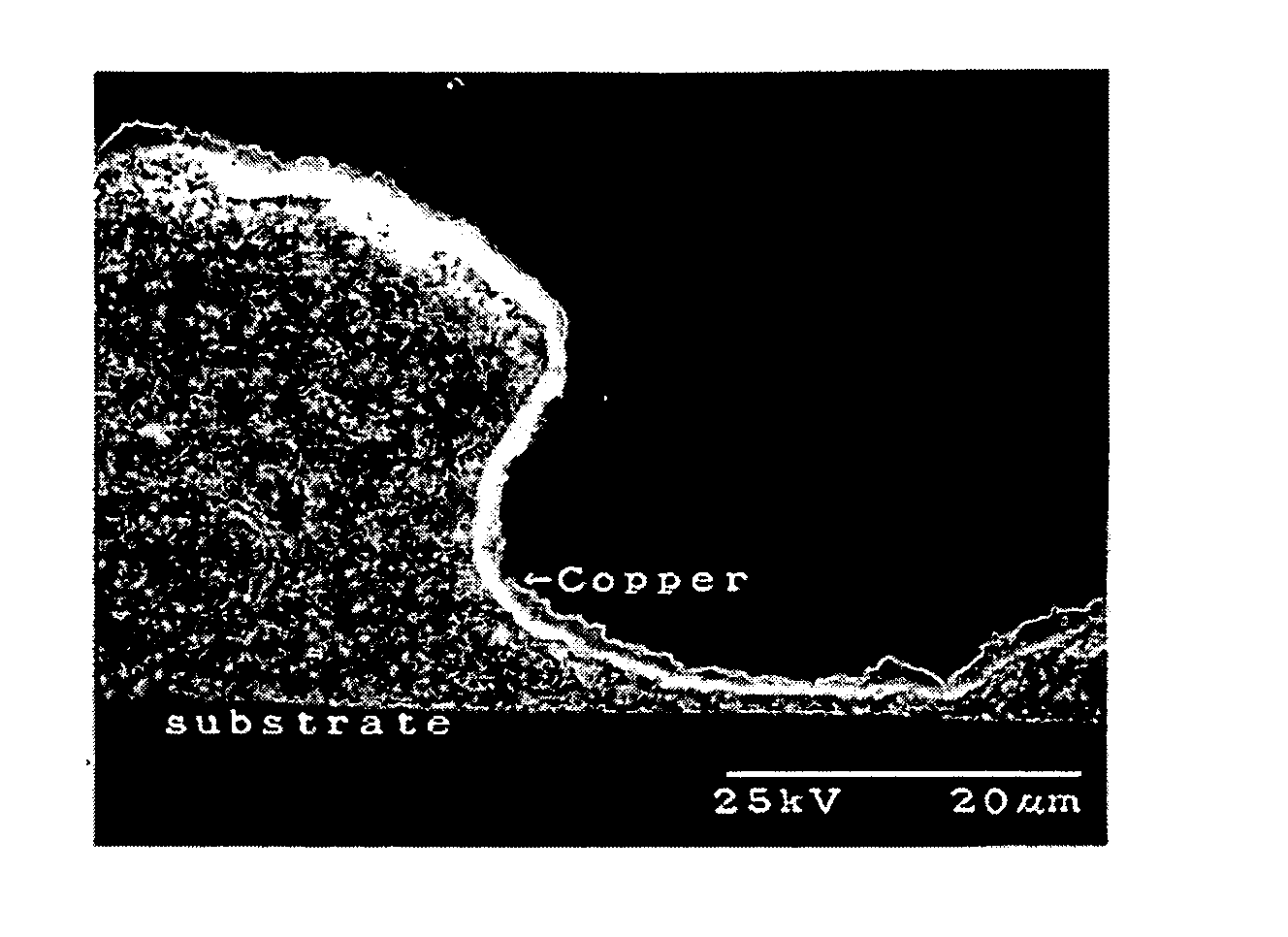
Grate type titanium-based PbO2 electrode for nonferrous metal electrodeposition and preparation method of grate type titanium-based PbO2 electrode
The invention discloses a grate type titanium-based PbO2 electrode for nonferrous metal electrodeposition and a preparation method of the grate type titanium-based PbO2 electrode. The PbO2 electrode comprises an anode consisting of a lead-coated copper conducting bar (1) an a group of titanium rods (2) connected below the lead-coated copper conducting bar, wherein the titanium rods are successively formed by a titanium substrate, a lead silver alloy bottom layer, an alpha-PbO2 composite middle layer and a beta-PbO2 activation surface layer form inside to outside. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out quenching, tapping, sand blasting, deoiling and activating, connecting the titanium substrate with the lead-coated copper conducting bar, electrically depositing a Pb-Ag-TiO2 composite layer on the titanium substrate, plating an alpha-PbO2 composite layer in an alkaline way and plating a beta-PbO2 composite layer in an acidic way to obtain the grate type titanium-based PbO2 electrode for nonferrous metal electrodeposition. The electrode prepared according to the invention has the advantages of good electrocatalytic activity, strong electrode electrical conductivity, low slot voltage in electrodeposition, long service life and low energy consumption.
Owner:KUNMING HENDERA SCI & TECH
Catalyst composition and deposition method
ActiveUS20050025960A1Increase the effective areaSolve the lack of adhesionConductive layers on insulating-supportsMolecular sieve catalystsSimple Organic CompoundsWater dispersible
Compositions and methods for depositing one or more metal or metal alloy films on substrates. The compositions contain a catalyst, one or more carrier particles and one or more water-soluble or water-dispersible organic compounds. Metal or metal alloys may be deposited on the substrates by electroless or electrolytic deposition.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC
Acid heap leaching process for cupric oxide ore
InactiveCN101435021AImprove the level of comprehensive utilizationReduce pollutionPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionClay minerals
The invention provides a new technique of acid heap leaching of copper oxide ore. The copper oxide ore is crushed and screened, then materials on a screen are carried out conventional acid heap leaching operation and the materials under the screen carry out concentration, size mixing and granulation and then are piled and leached; and leachate rich in copper ions is treated by the procedures of extraction, electrodeposition and the like so as to obtain cathode copper sold on the market. After the materials under the screen are concentrated, a binding agent needs to be added for size mixing; after size mixing, ore pulp and prepared acid-proof gravel with the granularity of 5mm to 25mm are mixed for granulation; in the granulation and heap leaching process, the pile height is 3 to 5m, in the heap leaching process, the concentration of dilute sulphuric acid is 0.1 to 2mol / L, the spraying strength is 0.2 to 0.5L / (min.m<2>) and the leaching period is 1 to 2 months. The technique can fully utilize copper oxide ore resource which is hard to be utilized in the past time, contains a large amount of clay mineral and is easy to argillization, improves the level of comprehensive utilization of mines, saves cost and increases profit. The invention is particularly suitable for being applied to the development of copper ore resources, mainly the copper oxide ore, which are hard to treat in all regions of China, in particular to remote regions of the western highlands.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Method for comprehensively recovering copper and indium from lead matte
ActiveCN104357661AAchieving selective leachingAchieve separationProcess efficiency improvementOxygenBall mill
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recovering copper and indium from lead matte. The method comprises the following steps: A, crushing lead matte block materials and then ball-milling to obtain lead matte powder; B, leaching the lead matte powder obtained by ball-milling in an autoclave by using sulfuric acid and continuously introducing oxygen in the leaching process; C, after leaching, carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain leaching residues and leachates containing copper ions and indium ions; D, selectively extracting the copper ions in the leachates by using ZJ988, obtaining copper sulfate enrichment liquid by using a sulfuric acid-copper sulfate solution to perform reverse extraction on loaded organic phase, taking the copper sulfate enrichment liquid as an electrolyte of electro-deposit copper and obtaining cathode copper through a copper sulfate electro-deposition process; E, selectively extracting the indium ions by using P204, then obtaining indium chloride enrichment liquid by using a hydrochloric acid solution to perform reverse extraction on the loaded organic phase and replacing the indium chloride enrichment liquid by using a zinc plate or an aluminum plate to obtain sponge indium. The method has the benefits that the complete separation of the copper from the indium in the lead matte is realized, recovery rate of the valuable metal is high, and the environmental friendliness is realized.
Owner:YUNNAN COPPER CO LTD +1
Method for refining zinc by using slag containing zinc
InactiveCN101580901AReduce wasteImprove protectionProcess efficiency improvementLiquid wasteElectrolysis
The invention provides a method for refining zinc by using slag containing zinc, comprising the steps of washing out chlorine by alkali, acid dipping, removing iron by mediate dipping and purifying electrodeposition. The step of washing out chlorine by alkali comprises the process of using one or a mixture of sodium carbonate, ammonium bicarbonate and sodium hydroxide to wash slag containing zinc by alkali, and then carrying out filter pressing; the step of acid dipping comprises the process of acid dipping slag by electrolytic waste liquid after the filter pressing in the step of washing out chlorine by alkali, and then carrying out filter pressing; the step of removing iron by mediate dipping comprises the process of removing iron from the acid dipping liquid in the step of acid dipping by an alum deposition method and a hydrolyzing method; the step of purifying electrodeposition comprises the process of purifying the liquid without iron after the step of removing iron by mediate dipping and then electrodepositing. The method has simple steps and easy operation, and can recycle the zinc in the slag containing zinc and metal elements such as zinc, copper, cadimium, nickel and cobalt so as to reduce waste of the sources of raw materials and protect environment.
Owner:甘肃世恒有色资源再利用有限公司
Method for extracting valuable metals from electronic waste
InactiveCN101575715AAdaptableMinor metal recoveryPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionSelective leaching
The invention discloses a method for extracting valuable metals from electronic waste. The method comprises the following concrete steps: smashing; oxidant ammoniac leaching; separating organic components; purifying leaching solution and electrodepositing to obtain the final products of organic granules, gold / silver / palladium powder and cathode copper, more concretely, the method comprises the following steps: carrying out the selective leaching on the smashed electronic waste by an oxidant ammoniac system; separating the organic granules on the basis of the characteristic that the organic components in the smashed electronic waste float on the surface layer of the leaching solution, for the density of the organic components is lower, whereas the valuable metals, such as Au, Ag, Pd, Cu, Ni, Cd, Zn and Pb, enter the solution; then, extracting the valuable metals of Au, Ag and Pd from the leaching solution by replacement; and finally obtaining the electrodeposit copper by the electro-deposition method, and extracting the metals of Ni, Pb, Zn and Cd from the electrolyte by the open-circuit method after the enrichment of the electrolyte. The invention has the outstanding advantages of high material adaptability, high metal recovery rate and low environmental pollution, and achieves the balance between the environmental benefit and the economic benefit.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Cells for the electrowinning of aluminium having dimensionally stable metal-based anodes
InactiveUS6372099B1Eliminate pollutionProlong lifeMachining electrodesElectrical-based machining electrodesSolubilityElectrochemistry
A cell for the electrowinning of aluminium comprising one or more anodes, each having a metal-based anode substrate, comprising a metal core covered with an metal layer, an oxygen barrier layer, one or more intermediate layers and an iron layer. The anode substrate is covered with an electrochemically active iron oxide-based outside layer, particularly a hematite-based layer, which remains dimensionally stable during operation in a cell by maintaining in the electrolyte a sufficient concentration of iron species. The cell operating temperature is sufficiently low so the required concentration of iron species in the electrolyte is limited by the reduced solubility of iron species in the electrolyte at the operating temperature, limiting the contamination of the product aluminium by iron to an acceptable level. The iron oxide-based layer is an applied coating or an oxidised surface of a substrate, the surface of which contains iron.
Owner:MOLTECH INVENT
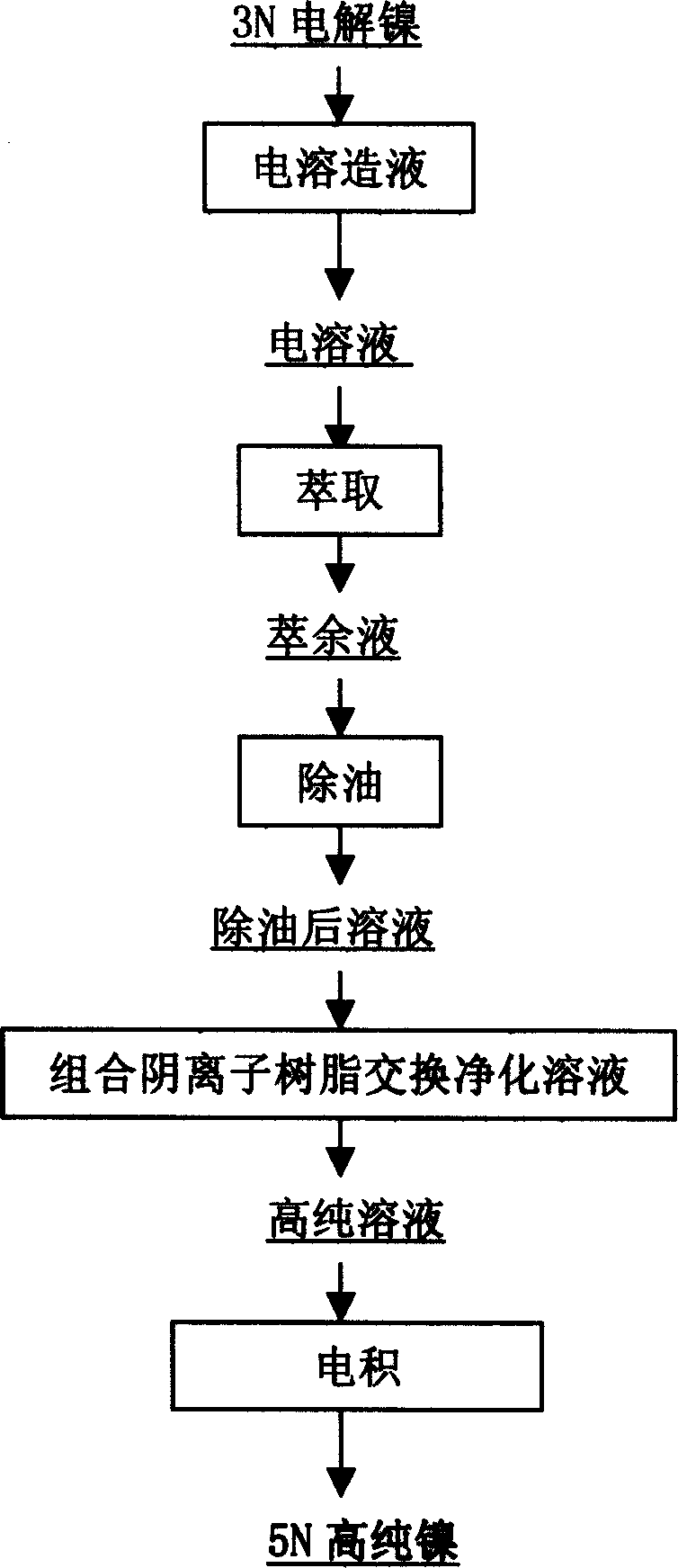
Process for preparing high purity nickel
ActiveCN1587441AImprove detection efficiencyPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementThree stageIon exchange
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com