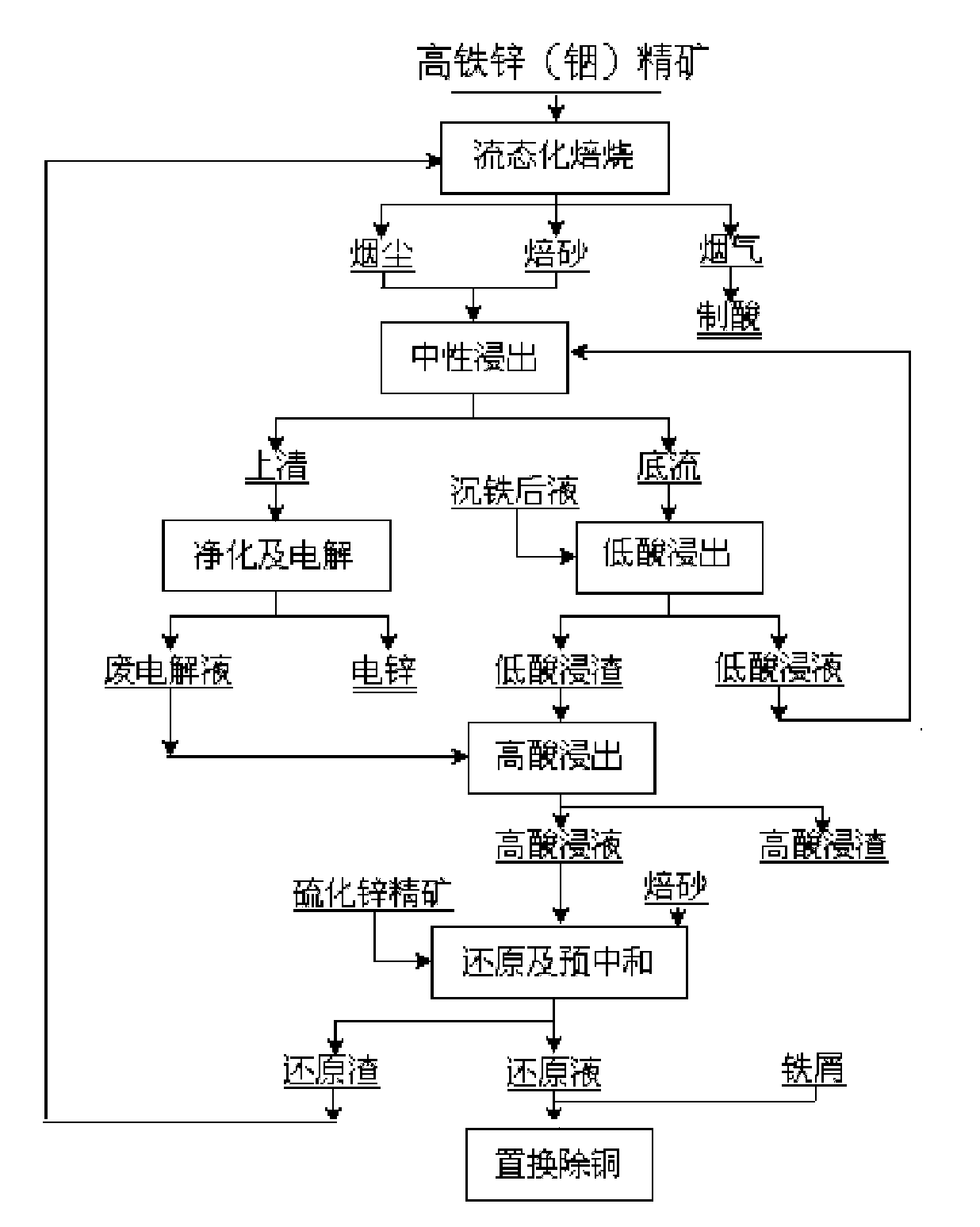
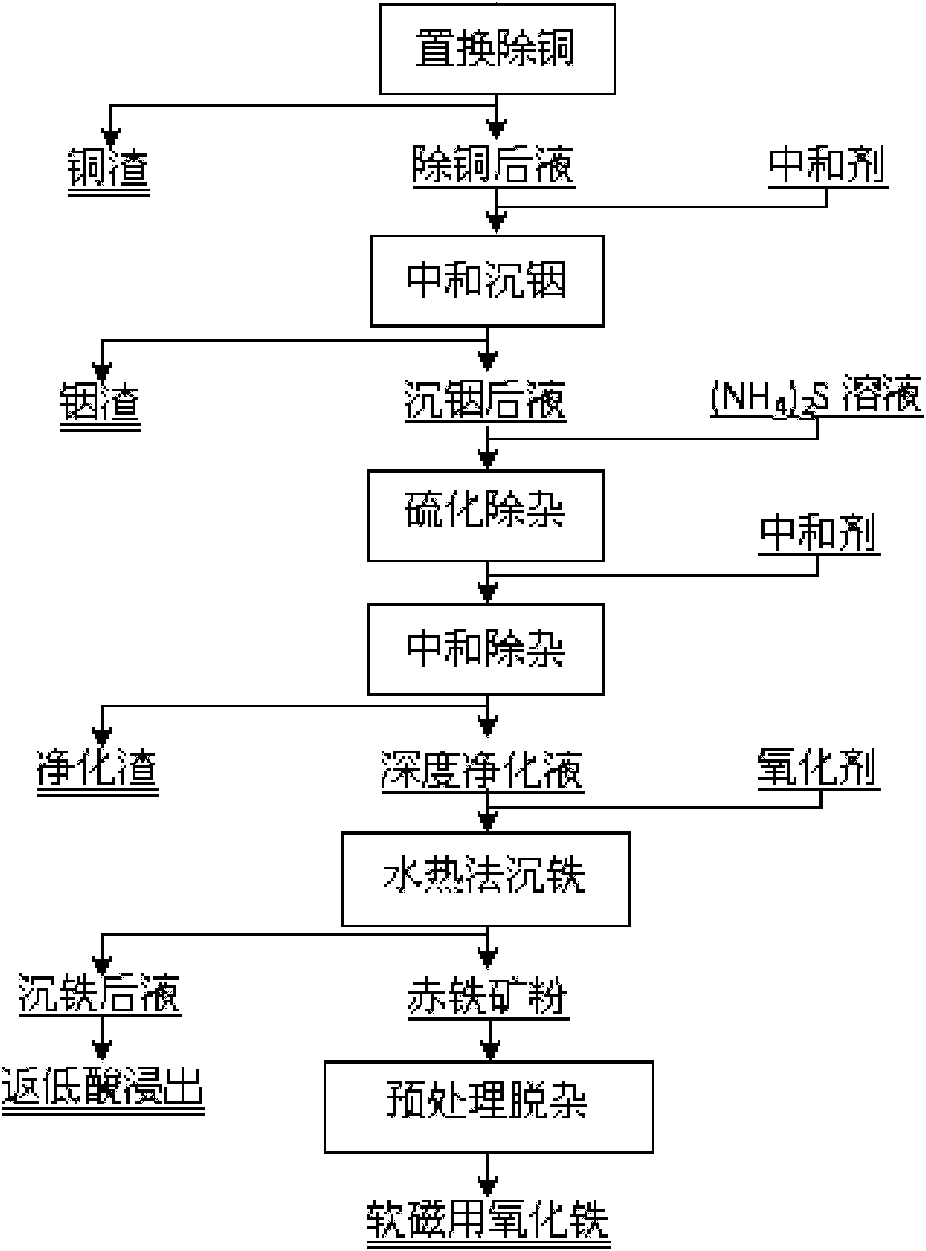
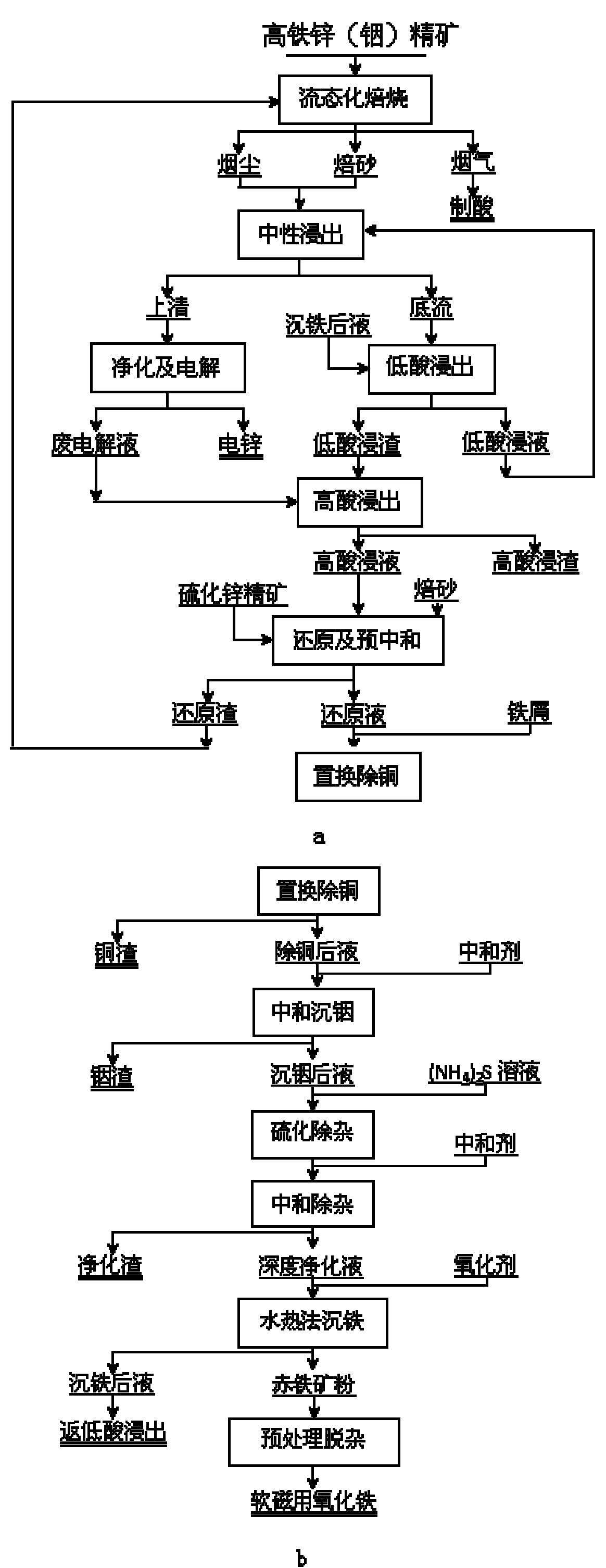
Method for extracting indium and preparing iron oxide by slag-free zinc hydrometallurgy of zinc concentrate
A technology for hydro-smelting zinc and zinc concentrate, which is applied in the directions of iron oxide, iron oxide/iron hydroxide, and process efficiency improvement, can solve the problems of long iron-zinc separation process and large amount of extractant, and achieves the Effective use of difficult problems, short separation process, and simple process methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] 1. Using the high-indium and low-acid leaching slag produced by a certain factory as raw material, the following components were obtained (g L -1 ) copper removal solution: Zn: 69.37, In: 0.123, Cu: 0.002, Fe: 21.4, Pb: 0.008.
[0021] 2. Slowly add 160g of basic zinc carbonate neutralizer containing Zn 57% to the above 5000mL copper removal solution, and keep stirring. When the pH value of the solution is stable at 4.5, raise the temperature to 50°C, and continue stirring for 30 minutes. After filtering, 5050mL of indium sinking liquid was obtained, and its chemical composition was (g·L -1 ): In: 0.005, Zn: 73.57, Fe: 17.7, Al: 6.4, Pb: 0.006. The indium slag was 16.75g, containing 3.5% In, the indium precipitation rate was 95.33%, and the recovery rates of iron and zinc were 98.22% and 96.50%, respectively.
[0022] 3. Take 5000mL of the above-mentioned indium sinking liquid, adjust the pH value to 3, and slowly add S8% (NH 4 ) 2 S solution 7.5mL, vulcanize and re...
Embodiment 2
[0026] 1. Using the high-indium and low-acid leaching slag produced by a certain factory as raw material, the following components were obtained (g L -1 ) copper removal solution: Zn: 69.83, In: 0.131, Cu: 0.003, Fe: 21.5, Pb: 0.039.
[0027] 2. Slowly add 160g of basic zinc carbonate neutralizer containing Zn 57% to the above 5000mL copper removal solution, and keep stirring. When the pH value of the solution is stable at 5, raise the temperature to 30°C and continue stirring for 60min. After filtering, 5336mL of indium sinking liquid was obtained, and its chemical composition was (g·L -1 ): In: 0.005, Zn: 60.96, Fe: 19.97, Al: 7.8, Pb: 0.007. The indium slag was 25.68g, containing 2.4% In, the indium precipitation rate was 94.12%, and the recovery rates of iron and zinc were 99.13% and 93.16%, respectively.
[0028] 3. Take 5000mL of the above-mentioned indium sinking liquid, adjust the pH value to 3, and slowly add S8% (NH 4 ) 2 S solution 3.8mL, vulcanize and remove im...
Embodiment 3
[0032] 1. Using the high-indium and low-acid leaching slag produced by a certain factory as raw material, the following components were obtained (g L -1 ) copper removal solution: Zn: 63.61, In: 0.172, Cu: 0.012, Fe: 39.8, Pb: 0.037.
[0033] 2. Slowly add 160g of basic zinc carbonate neutralizer containing Zn 57% to the above 5000mL copper removal solution, and keep stirring. When the pH value of the solution is stable at 4, raise the temperature to 70°C and continue stirring for 2 hours. After filtering, 5410mL of indium sinking solution was obtained, and its chemical composition was (g·L -1 ): In: 0.008, Zn: 72.3, Fe: 35.04, Pb: 0.035. The indium slag was 22.07g, containing 3.7% In, the indium precipitation rate was 94.96%, and the recovery rates of iron and zinc were 95.37% and 98.71%, respectively.
[0034] 3. Take 5000mL of the above-mentioned indium sinking liquid, adjust the pH value to 3, and slowly add S8% (NH 4 ) 2 S solution 11.2mL, vulcanize and remove impurit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com