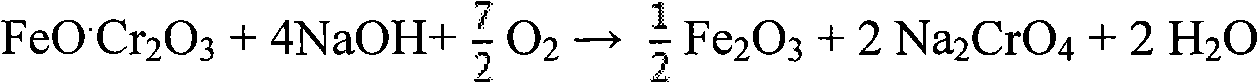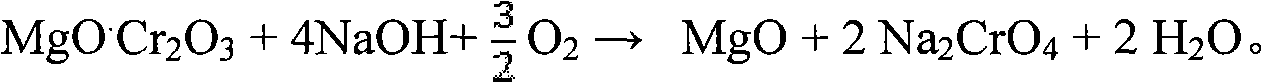Patents
Literature
2450 results about "Hydrometallurgy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hydrometallurgy is a method for obtaining metals from their ores. It is a technique within the field of extractive metallurgy involving the use of aqueous chemistry for the recovery of metals from ores, concentrates, and recycled or residual materials. Metal chemical processing techniques that complement hydrometallurgy are pyrometallurgy, vapour metallurgy and molten salt electrometallurgy. Hydrometallurgy is typically divided into three general areas...
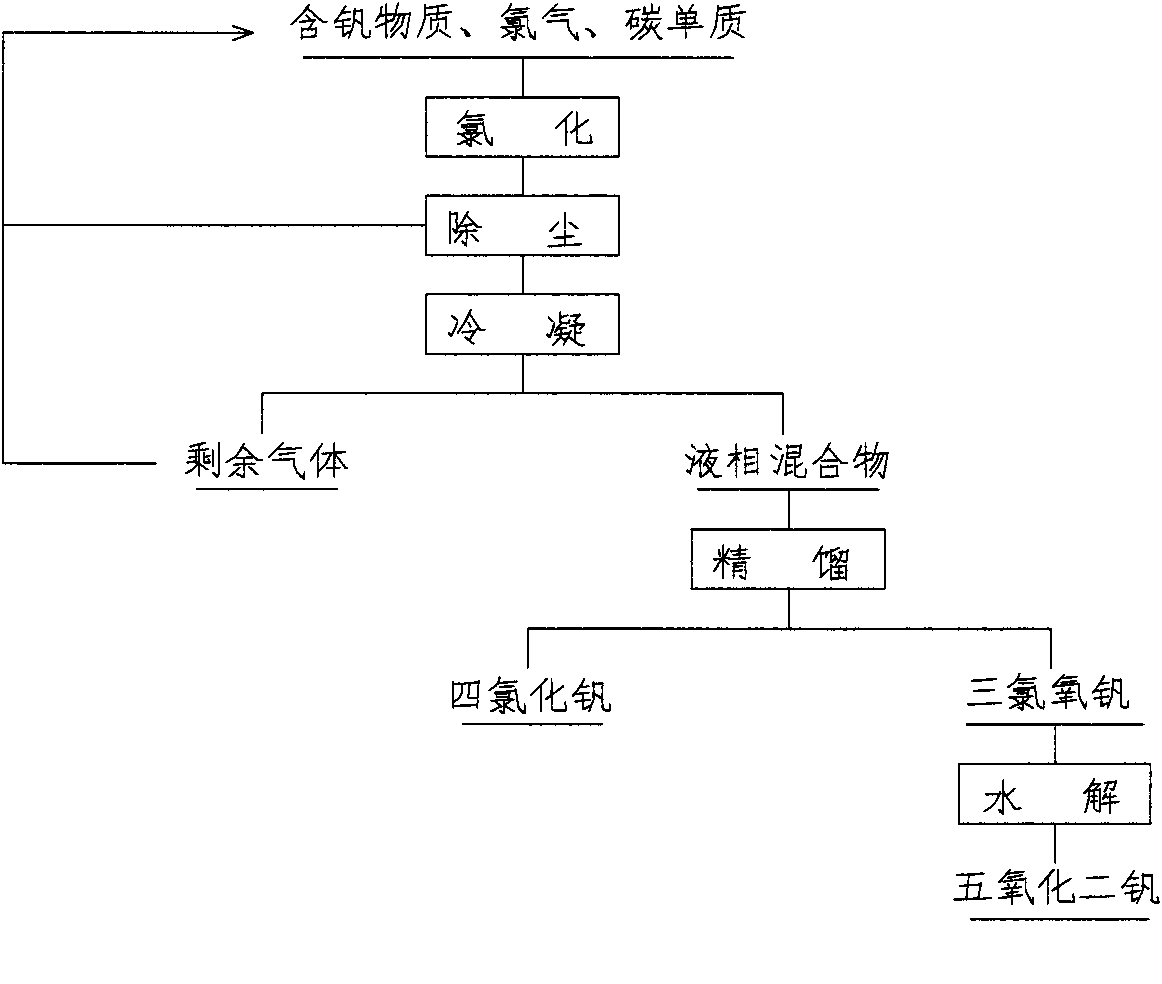
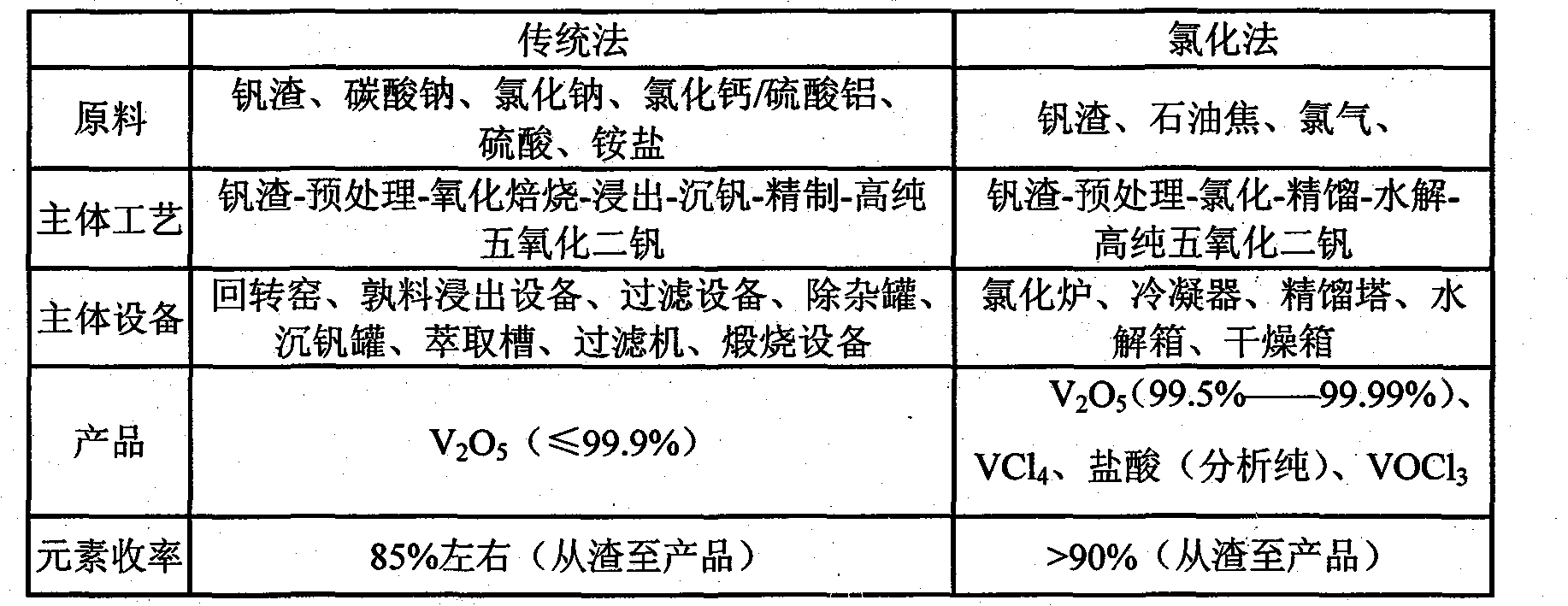
Method for producing high-purity vanadium pentoxide by chlorination
The invention discloses a novel method for extracting and converting a substance containing vanadium into high-purity vanadium pentoxide by chlorination. The high-purity vanadium pentoxide process comprises batching, chlorination, dedusting, condensation, rectification, hydrolysis, filtering, drying and postprocessing. Raw materials comprise the substance containing vanadium and a carbon elementary substance and the weight ratio of the substance containing vanadium to the carbon elementary substance is 1: (0.05-0.25). The raw materials are evenly mixed, dried and put in a reactor and the high-purity vanadium pentoxide is obtained through successive chlorination, hydrolysis, postprocessing and the like. The novel method for producing high-purity vanadium pentoxide instead of a traditional method reduces industrial harmful waste water produced during a traditional hydrometallurgy process, and cyclic utilization of chlorine is achieved after the chlorine is processed. The whole production process is easy in process and basically free of produced wastes, and has certain economic benefit and social benefit. The purity of the vanadium pentoxide powder obtained by the method is 99.5%-99.99%.
Owner:刘艳梅
Method for preparing high purity vanadium pentoxide through using ammonium metavanadate
The invention which relates to a method for preparing high purity vanadium pentoxide through using ammonium metavanadate belongs to the wet metallurgy field. The method comprises the following steps: heating and dissolving crude ammonium metavanadate in water, adjusting the pH value to 8-10 with an alkali after dissolving, adding an impurity removing agent to remove impurities, filtering to obtain a sodium metavanadate solution, adding ammonia water or an ammonium salt to the sodium metavanadate solution to precipitate to obtain an ammonium metavanadate precipitate, dehydrating the ammonium metavanadate precipitate, carrying out water washing on the precipitate through using a dilute ammonium salt solution, dehydrating after the wash washing, and roasting to obtain the high purity vanadium pentoxide. Vanadium pentoxide produced through adopting the method of the invention has the advantages of high purity and less impurities, and completely satisfies production requirements of high-end products; and the method of the invention has the advantages of short process flow, simple equipment, low cost and high benefit, and is suitable for the large-scale industrial production.
Owner:崇阳县恒通工贸有限公司
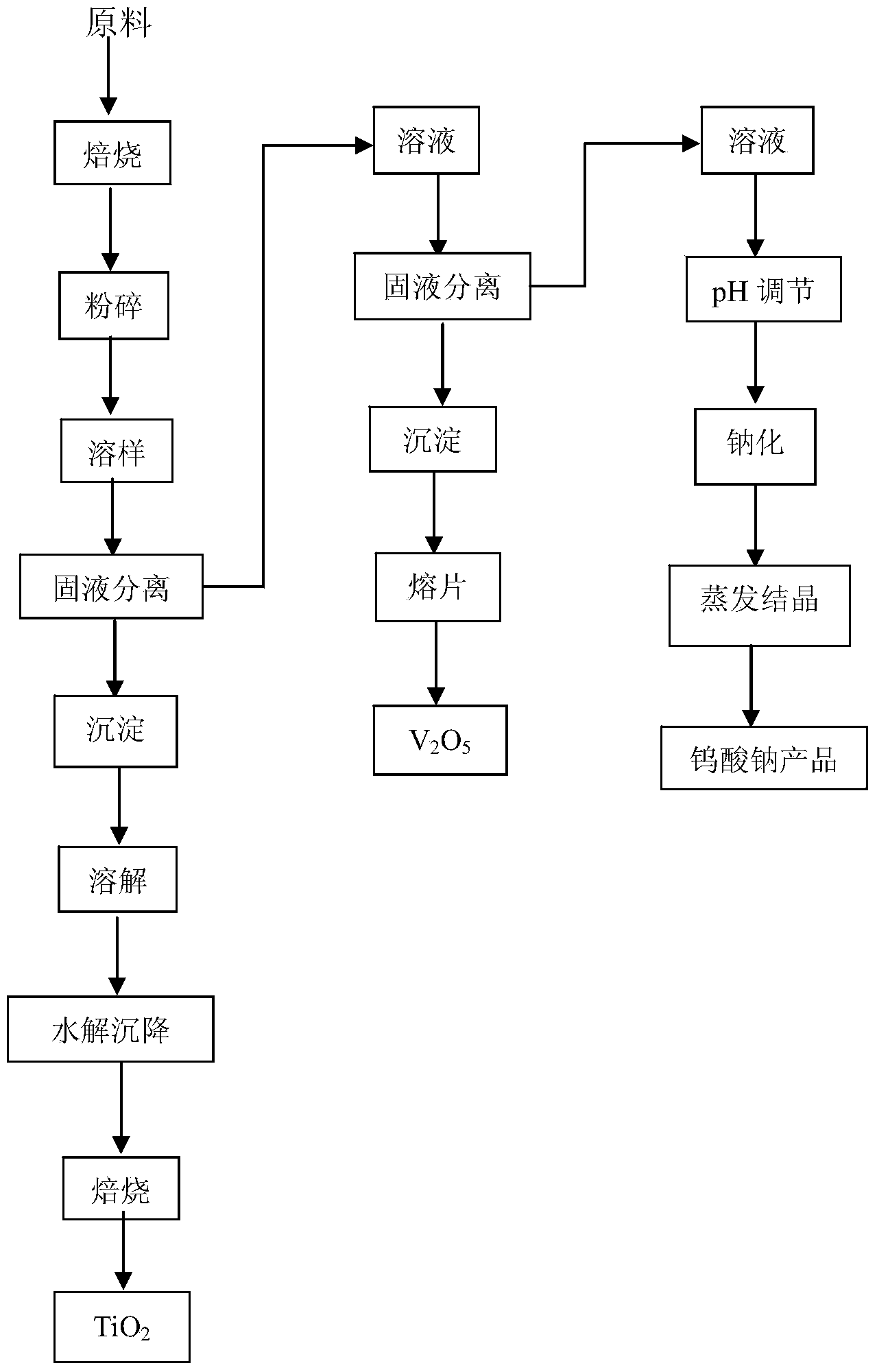
Recovery method for SCR waste flue gas denitration catalyst
ActiveCN103526031AEasy to operateSimple requirementsProcess efficiency improvementPtru catalystRefining (metallurgy)
The invention relates to a recovery method for an SCR waste flue gas denitration catalyst, and adopts a hydrometallurgy process. After the SCR waste flue gas denitration catalyst is smashed and subjected to pre-calcination treatment, a NaOH solution is added according to a ratio for dissolution. After the catalyst is dissolved, solid-liquid separation is performed, sulfuric acid is added into the obtained precipitation, and the precipitation is steeped, precipitated, hydrolyzed, subjected to salt treatment, and calcinated to obtain TiO2. Sulfuric acid is added into the solution obtained from the first solid-liquid separation to adjust the pH value, excess ammonium nitrate is added to precipitate vanadium, and second solid-liquid separation is performed. Ammonium metavanadate obtained from filtration is subjected to pre-calcination to obtain a V2O5 finished product. Hydrochloric acid is added into the solution obtained from the second solid-liquid separation to adjust the pH value, and NaCl is added to obtain sodium tungstate. The sodium tungstate is subjected to purification, filtration, ion exchange, and other processes to separate impurities, and subjected to evaporative crystallization to obtain a sodium tungstate finished product. The method provided by the invention is simple in technology, general in equipment, easily available in raw material, low in cost and high in recovery rate.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
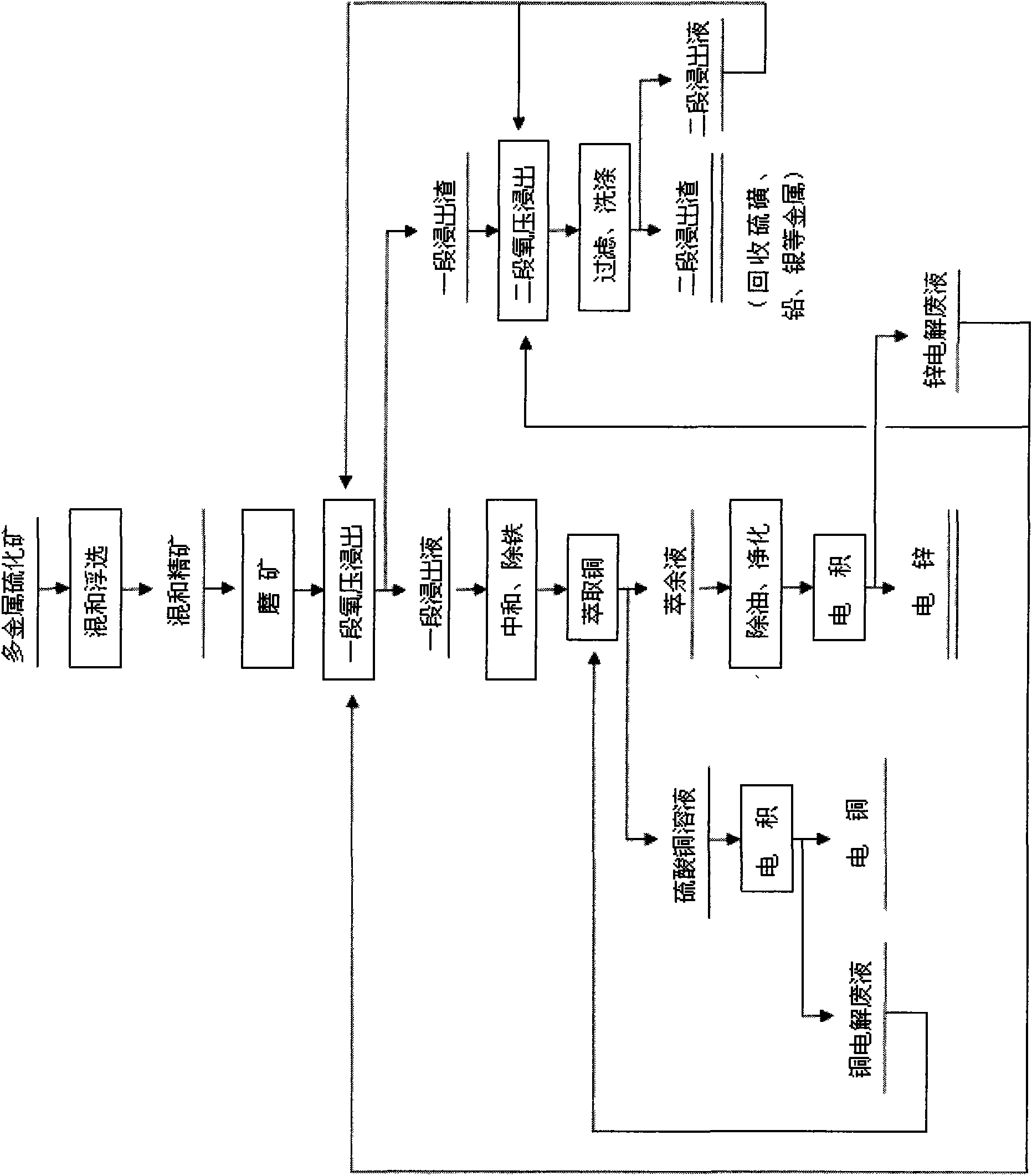
Comprehensive recovery method of complex polymetal sulphide ore containing copper, lead and zinc
InactiveCN101643857AHigh recovery rateSimple processSulfur preparation/purificationFlotationRecovery methodLead smelting
The invention discloses a comprehensive recovery method of complex polymetal sulphide ore containing copper, lead and zinc and adopts dressing-metallurgy combination method and hydrometallurgy-pyrometallurgy combination method to recover metals. The recovery method comprises the following steps: first performing bulk flotation to the complex polymetal sulphide ore, fine grinding the obtained concentrate, leaching by using two-step counter flow oxygen pressure leaching process, extracting and separating copper and zinc from the obtained leachate, electrodepositing the strip liquor of copper-loaded organic phase to obtain cathode copper, cleaning the obtained raffinate and electrodepositing to obtain cathode zinc; pressurizing leaching residue to perform flotation separation and obtain sulfur concentrate and lead silver residue, distilling sulfur concentrate to obtain sulfur; performing lead smelting process to lead silver residue to obtain electrolytic lead product and lead anodic slime; and comprehensively recovering noble metals such as gold, silver and the like from lead anodic slime. The method can greatly improve the metal recovery rate, resource utilization and the economic efficiency of mines and generate a lot of sulfur so as to obviously reduce the sulfur dioxide pollution to the atmosphere.
Owner:WESTERN MINING CO LTD
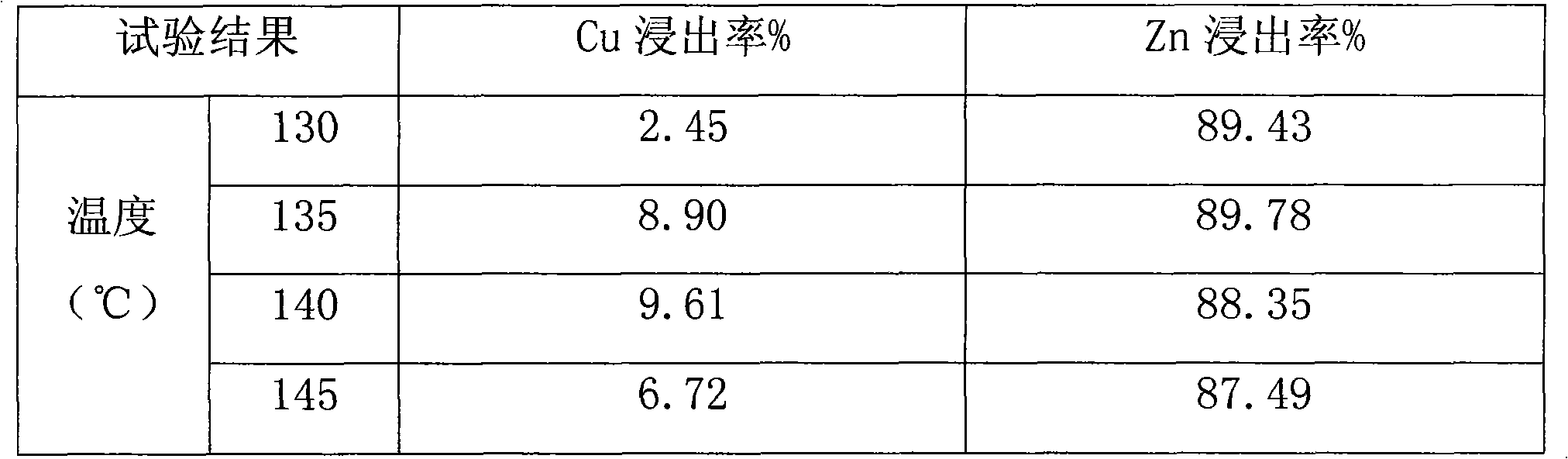
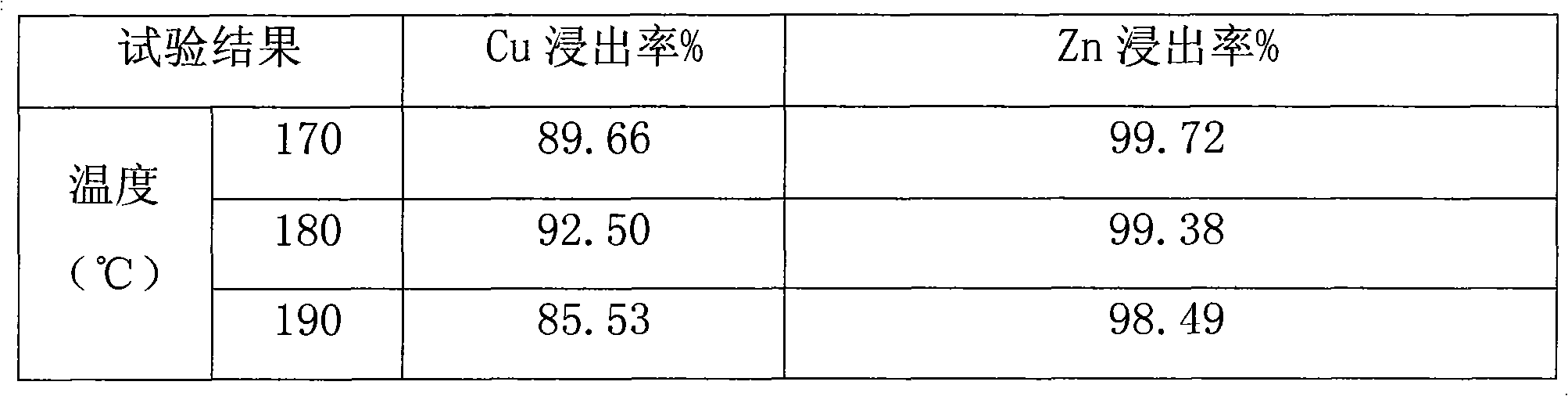
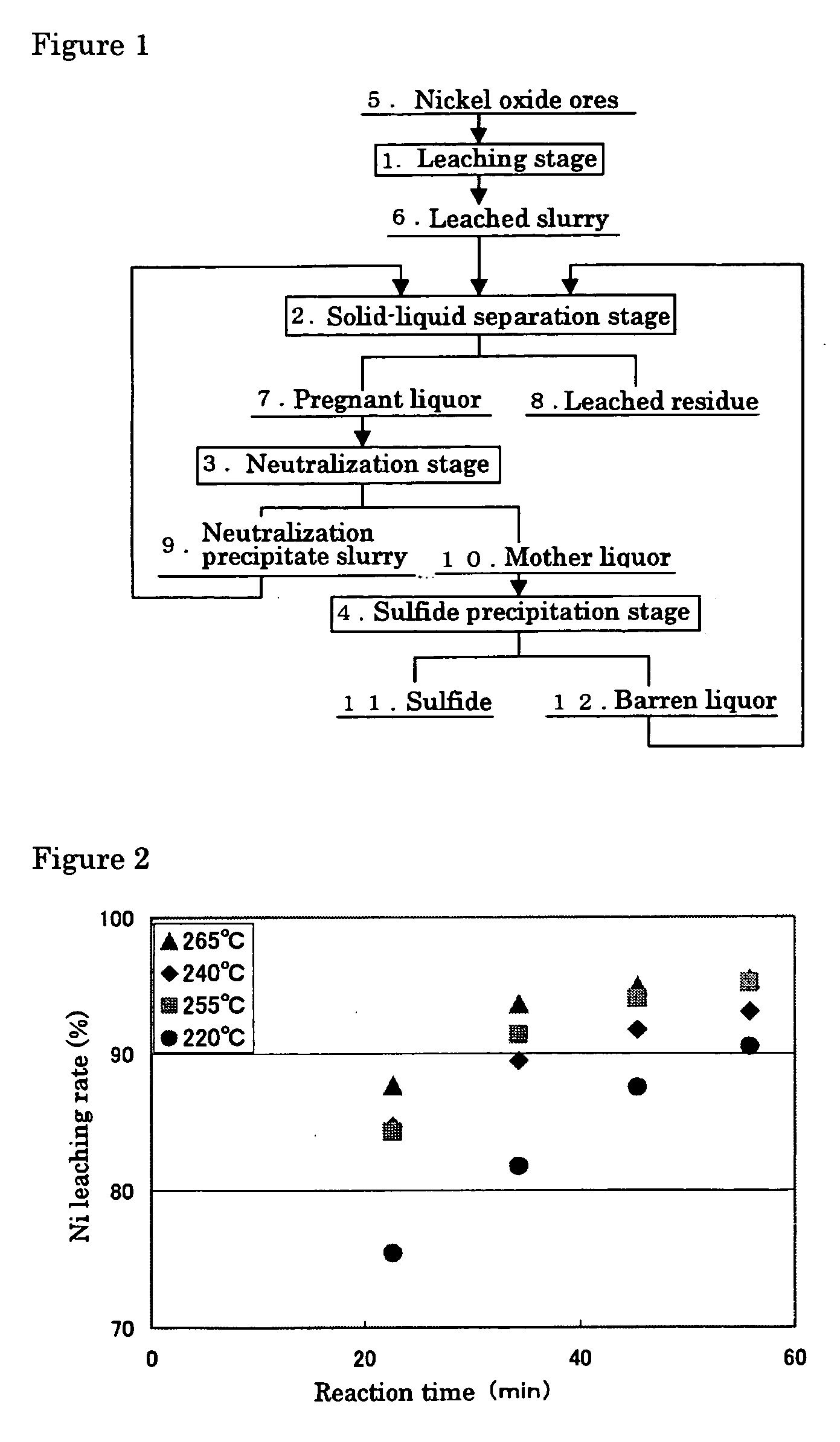
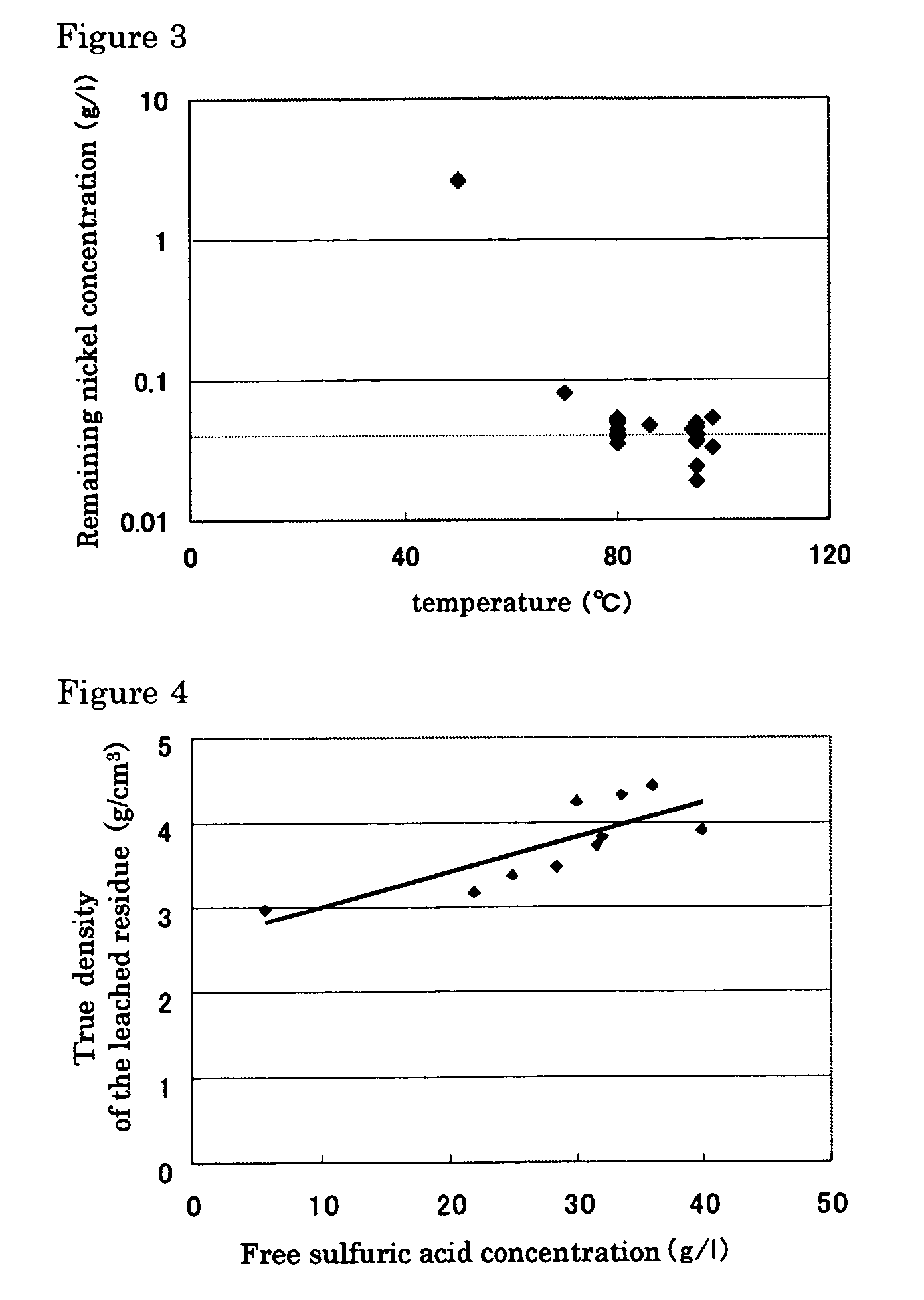
Hydrometallurgical process of nickel oxide ore
InactiveUS20050265910A1Simple and efficient processSimplified leaching stageSolvent extractionIron compoundsSlurryHydrometallurgy
A hydrometallurgical process based on pressure leaching at elevated temperature for recovering nickel from nickel oxide ores, characterized by a simplified and efficient process as a whole, realizing a simplified leaching stage, reduced neutralizer consumption and precipitate production in the neutralization stage, and efficient use of recycled water. The hydrometallurgical process of the present invention, comprising a leaching stage which stirs the slurried ore in the presence of sulfuric acid at 220 to 280° C. to produce the leached slurry; solid-liquid separation stage which washes the leached slurry in multi-stages to produce the pregnant liquor and leached residue, the former containing nickel and cobalt; neutralization stage which treats the pregnant liquor in the presence of calcium carbonate incorporated to keep the pH level at 4 or less, while suppressing oxidation of the liquor, to produce the neutralization precipitate slurry and mother liquor for nickel recovery, the former containing trivalent iron; and a sulfide precipitation stage which blows hydrogen sulfide gas into the mother liquor to produce the sulfide solution and barren liquor, the former containing nickel and cobalt.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
Method for preparing titanium solution by wet-processing on vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrates
ActiveCN103276207ASolve unexploitable puzzlesImprove resource utilizationProcess efficiency improvementSlagResource utilization
The invention belongs to the wet-process metallurgical filed and in particular relates to a method for preparing titanium solution by wet-processing on vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrates. The method for preparing titanium solution by wet-processing on vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrates comprises the following steps of: (1), mixing the vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate with hydrochloric acid, and leaching to obtain an intermediate sizing agent; (2), filtering the intermediate sizing agent to obtain leaching liquor and leaching residues; (3), carrying out water-washing on the leaching slag to obtain washing water and washing slag; (4), carrying out fused-salt reaction on the washing slag to obtain fused-salt reaction materials; (5), carrying out water-washing and filtering on the fused-salt reaction materials to obtain water-washing materials; (6), carrying out acid pickling on the water-washing materials to obtain sizing agent, and filtering to obtain the acid-pickled sizing agent; (7), carrying out acid dissolving on the acid-pickled materials by using a sulfuric acid solution to obtain acid-dissolved materials; and (8), adding the acid-dissolved materials to the sulfuric acid solution for extracting, and filtering to obtain extracting solution which is the titanium solution. According to the method for preparing titanium solution by wet-processing on vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrates disclosed by the invention, the titanium in the iron concentrate is sufficiently utilized, so that the titanium resource utilization rate is high and the recovery rate of the titanium in the titanium concrete is higher than 90%.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
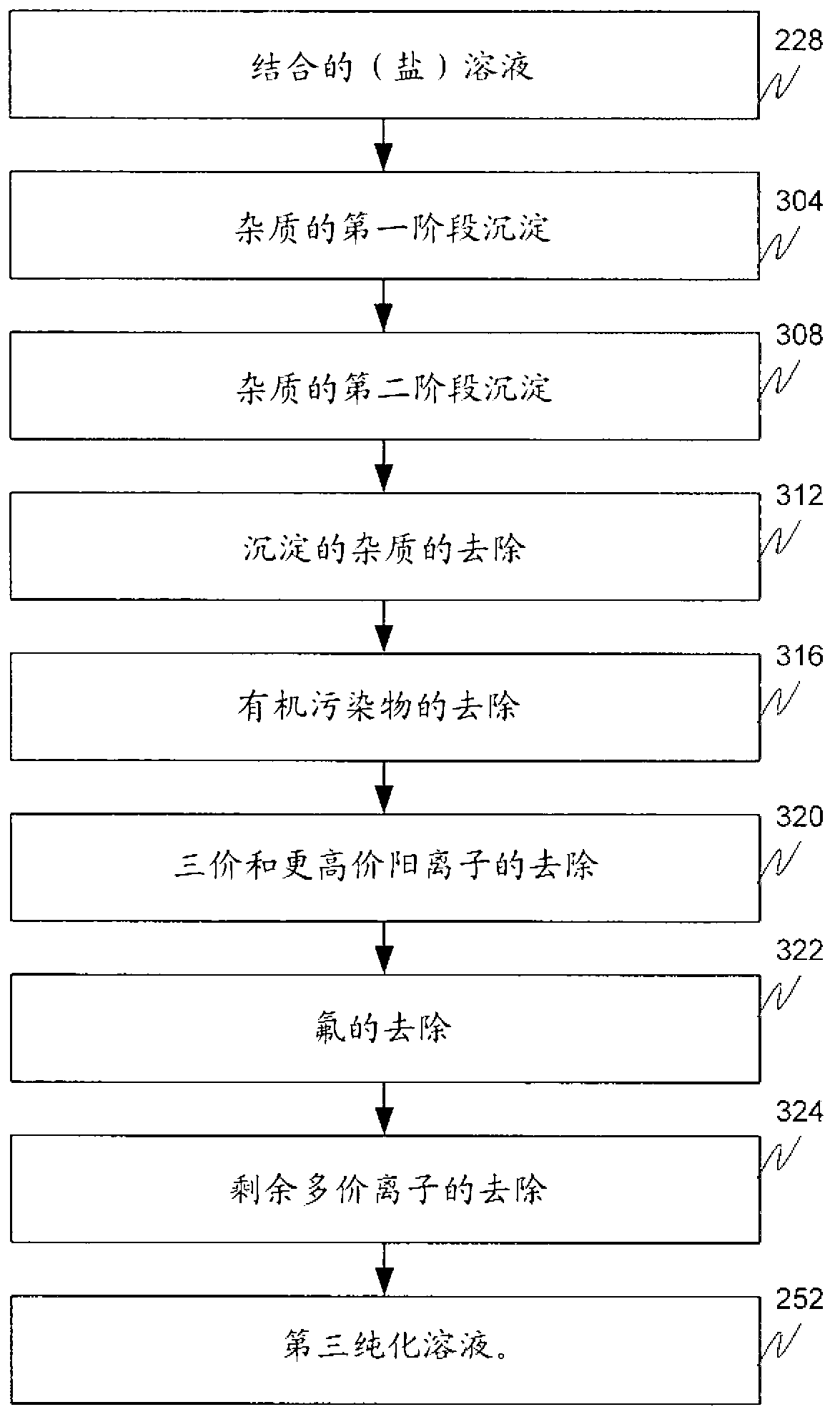
Method of purifying acid leaching solution by precipitation and oxidation
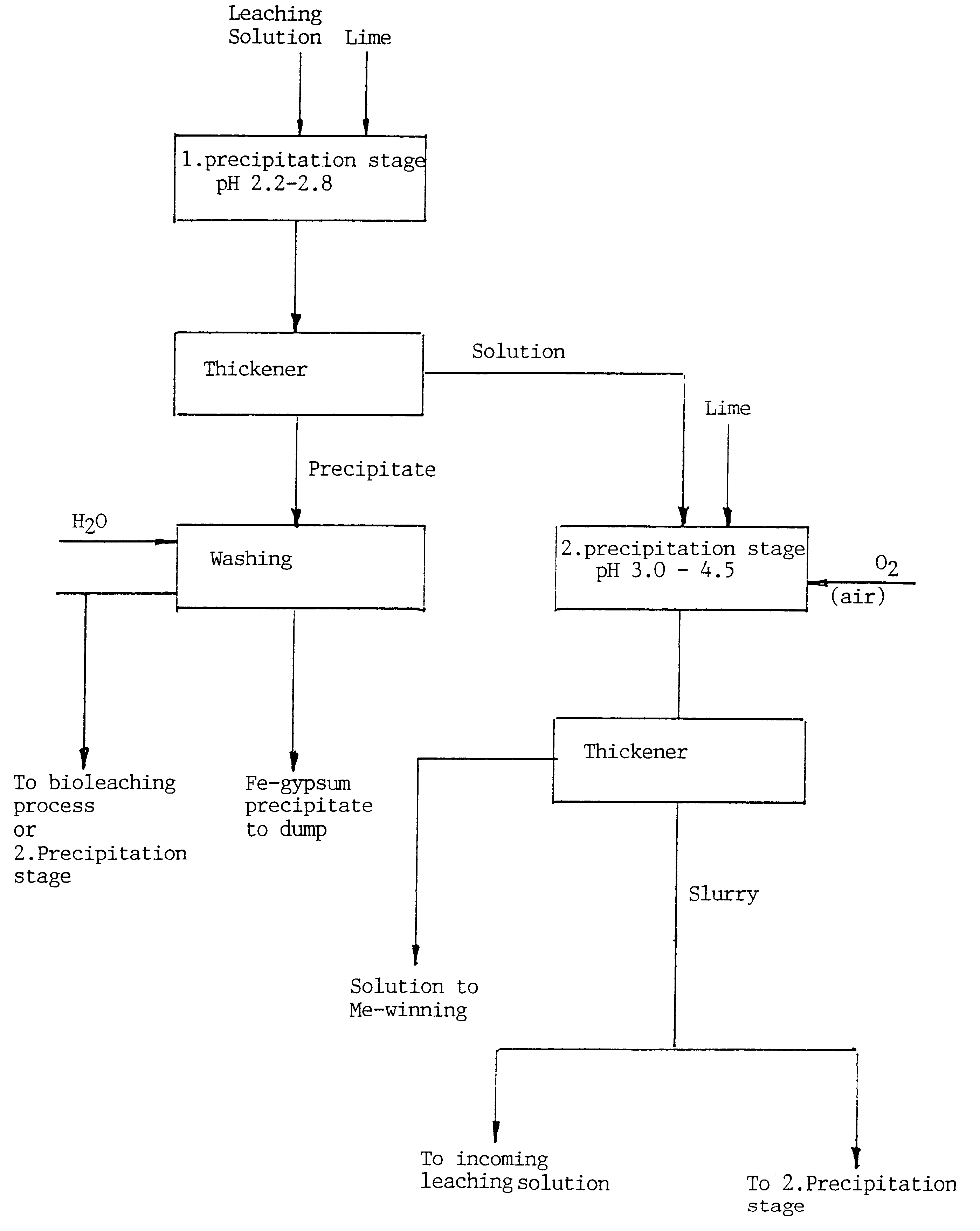
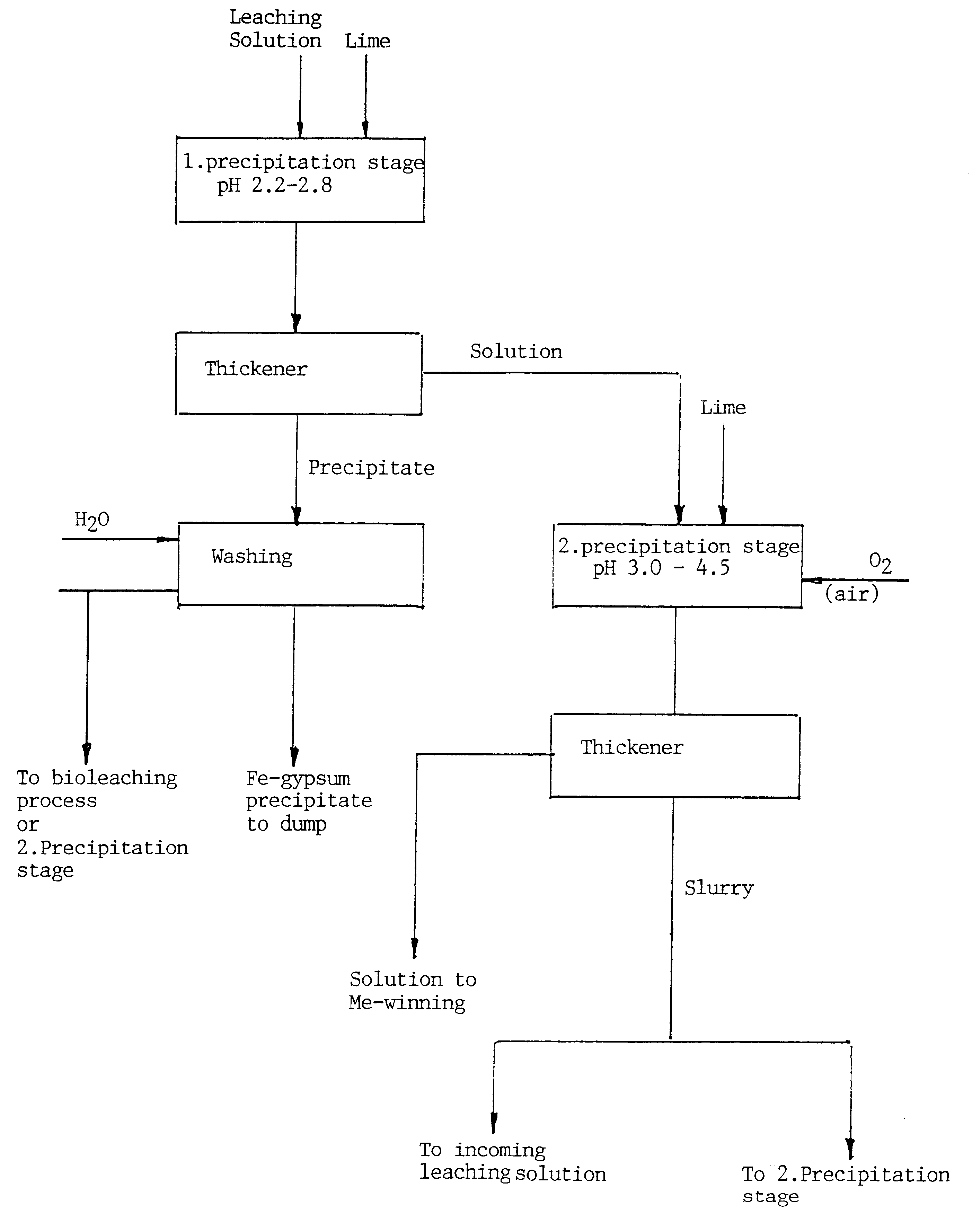
A method of purifying an acid leaching solution obtained by processing hydrometallurgically material that contains valuable metals and also Fe3+ and Fe2+, and possibly also arsenic in solution. The major part of the Fe3+-content and the arsenic is precipitated out in a first stage, by adding pH-elevating agent to the leaching solution. The precipitate formed in the first precipitation stage is extracted from the solution and removed from the process. The solution is oxidised in a second precipitation stage while adding a further pH-elevating agent for oxidation of Fe2+ and precipitation of resultant Fe3+ and any arsenic still present. The resultant precipitate and any residual solid pH-elevating agent are then extracted from the solution and returned in the process to more acid conditions, and the thus purified solution is then processed to win its valuable metal content in a manner per se. The pH is suitably raised during the first stage to a value in the range of 2.2-2.8, and in the second stage to a value in the range of 3.0-4.5. The oxidising process in the second stage is suitably effected by injecting air into the solution and by preferably using lime or limestone as the pH-elevating agent. Solid material extracted from the second stage is returned beneficially to the first stage. Some of the solid material taken from each precipitation stage can be recycled within respective stages as a nucleating agent.
Owner:BOLIDEN MINERAL
Method for recovering valuable metal from electroplating sludge
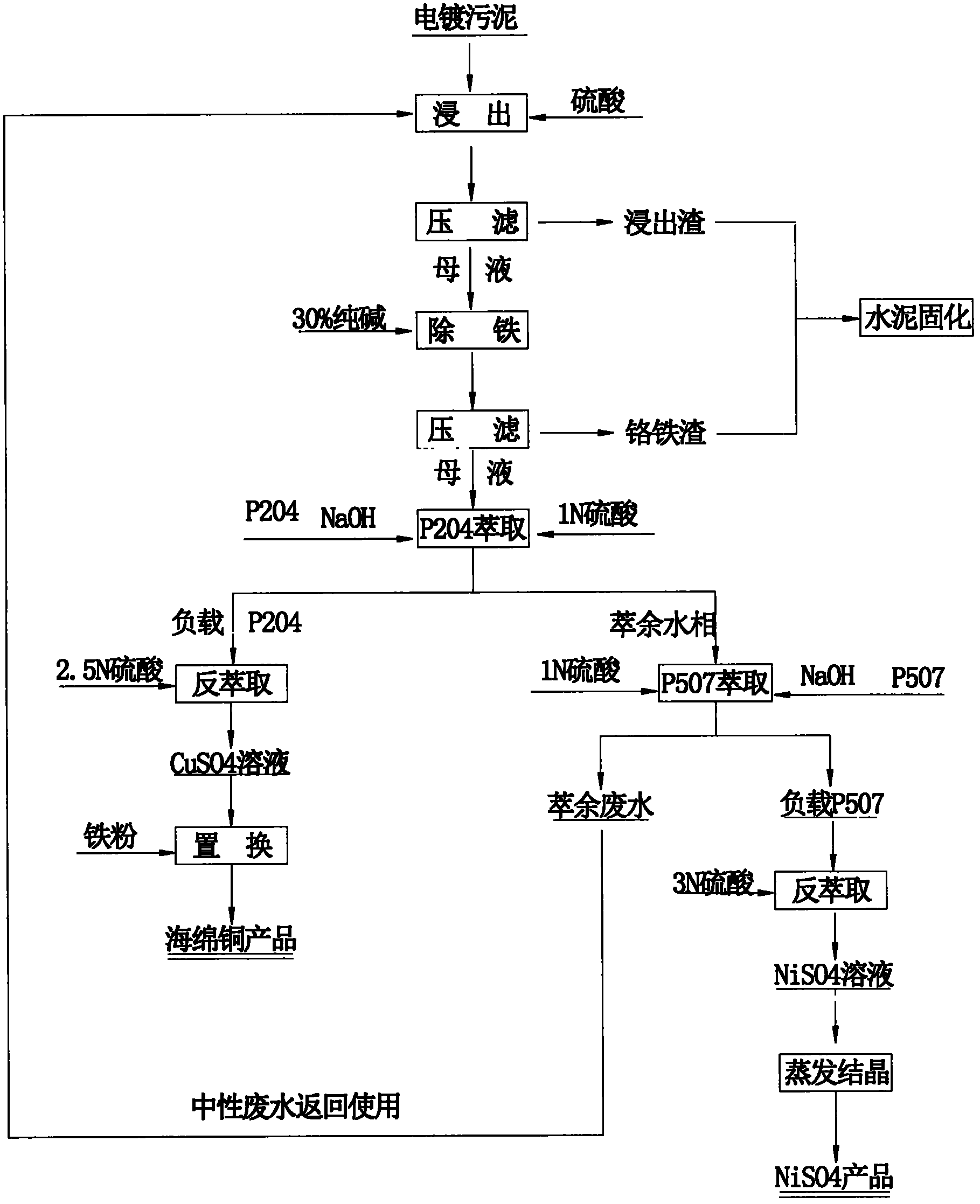
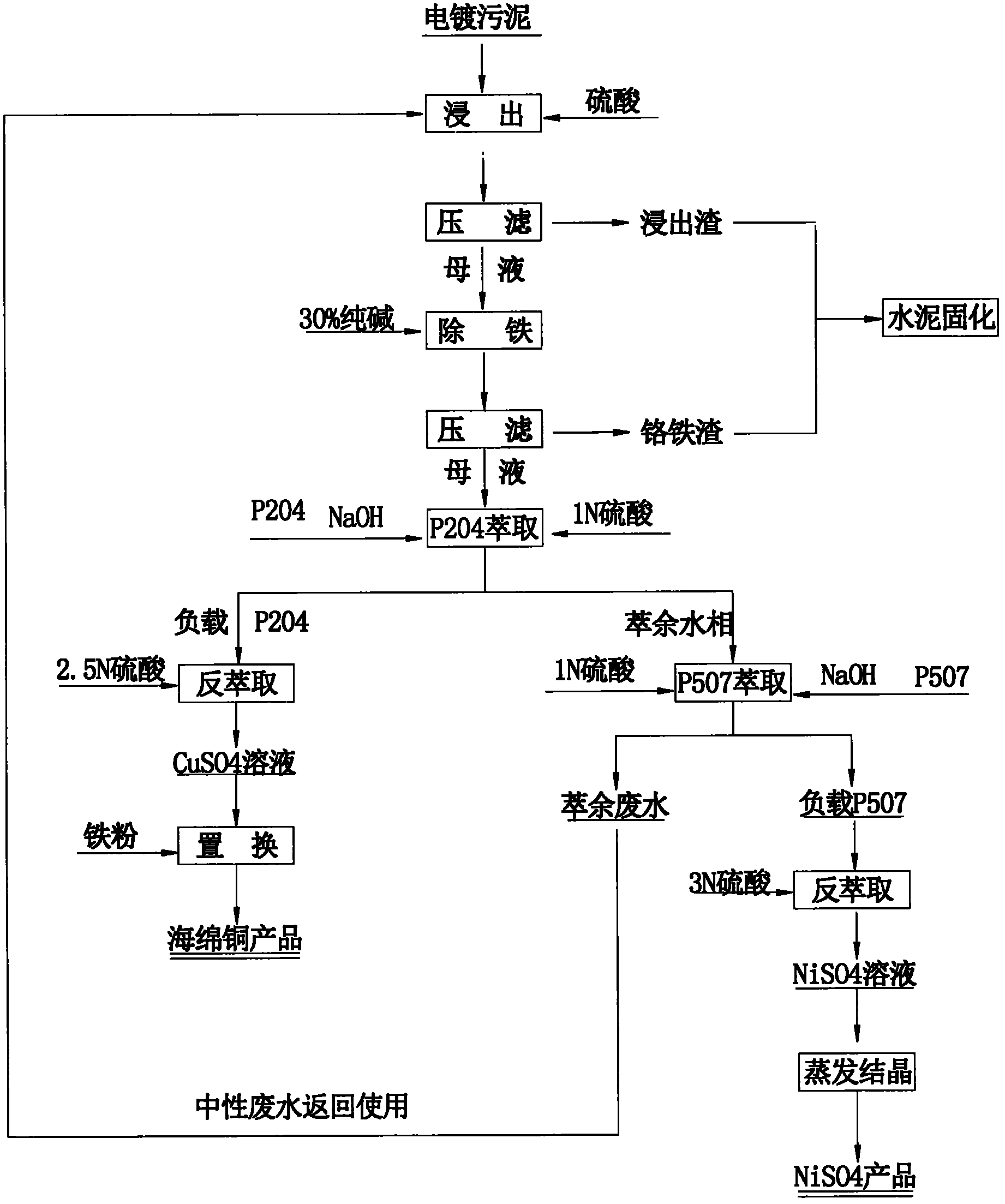
The invention relates to a method for recovering valuable metals from electroplating sludge. Electroplating sludge is used as a raw material; advanced theories and scientific means of leaching principle, redox principle, extraction principle, iron filing displacement principle and evaporation crystallization principle in a wet method metallurgy are integrally utilized; and a technology of ''acid decomposition of electroplating sludge-leachate purification to remove ferrochrome-P204 impurity removal-P507 enrichment-condensation crystallization'' is employed. Meanwhile, calcium and magnesium are removed by an extraction method, which substitutes a traditional sodium fluoride method for removing calcium and magnesium. A recovery rate of nickel reaches 95%, and copper content of recovered copper sponge is larger than 80%. Besides, acid dissolved slag and purifying slag can be solidified to reach requirements of environmental protection and will not cause secondary pollution; waste water can be recycled and has a strong technological versatility. The method is suitable for treating various routine electroplating sludge, has easily controllable technical conditions and low operating cost and is easy for realizing large scale production; therefore, the method is a practical novel technology for treating electroplating sludge in a way of quantitative reduction, harmlessness and resource.
Owner:朱小红
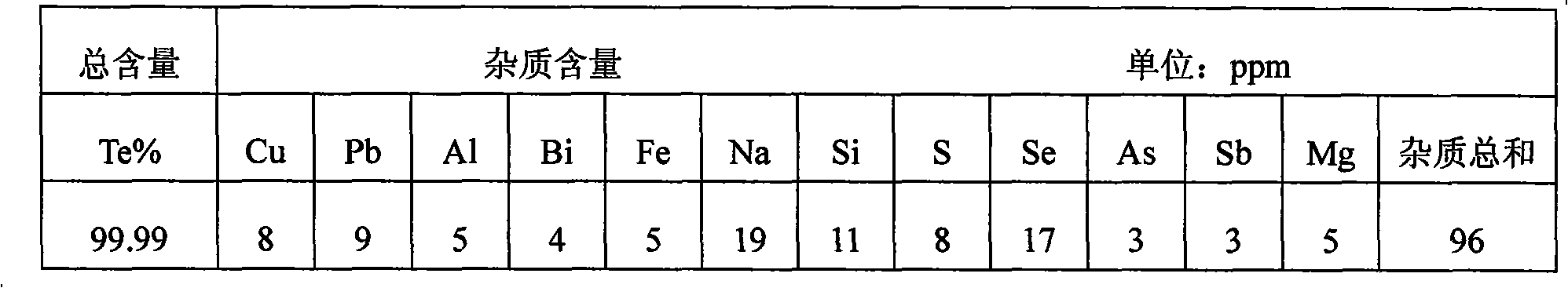
Method for extracting refined tellurium from tellurium-contained smelting slag
InactiveCN101565174AImprove leaching rateReduce invalid consumptionElemental selenium/telluriumSlagTe element
The invention relates to a method for extracting refined tellurium from tellurium-contained smelting slag, which is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps of: oxidizing and leaching inorganic acid, replacing noble metal with a copper plate, depositing the copper by sodium sulfide, counteracting and depositing tellurium, alkaline leaching coarse TeO2, removing impurities by Na2S, concentrating and electrowinning. The method has the advantages of high recovery rate for tellurium, comprehensive and effective recovery of other useful metals, and suitably treating the tellurium-contained waste slag with high water content and small granularity generated in the metallurgy process by a wet-method.
Owner:YONGXING XINTAI SILVER IND
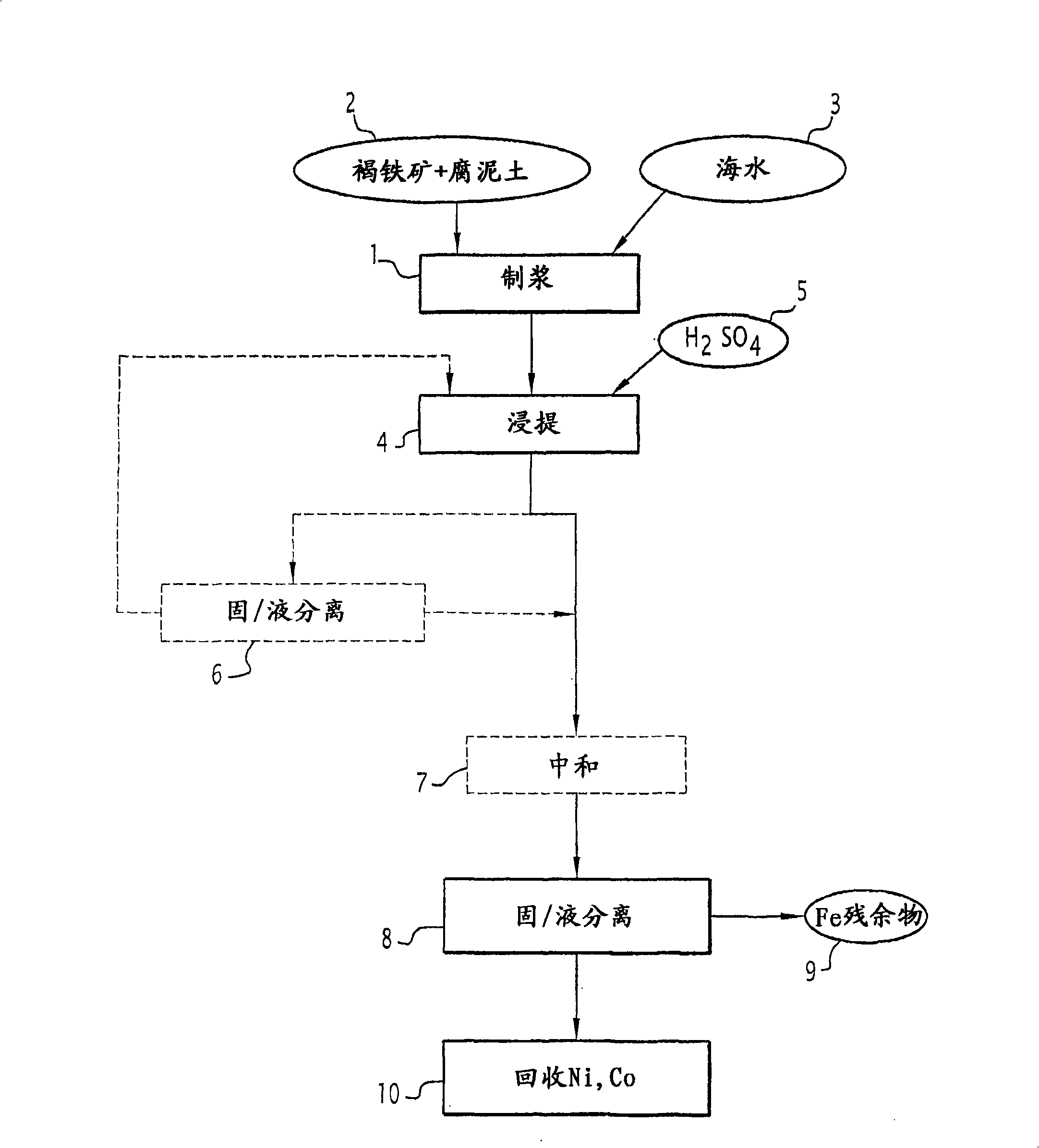
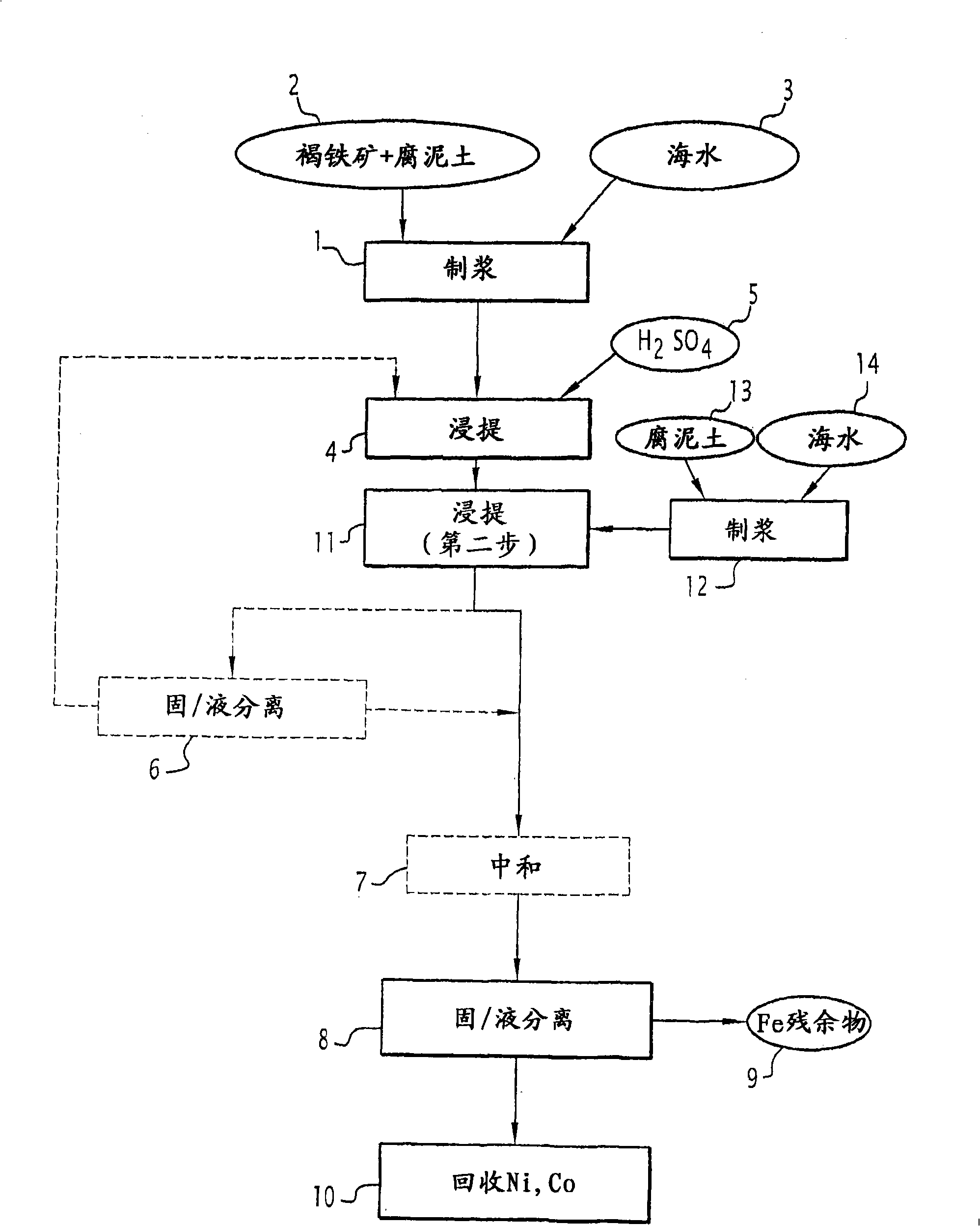
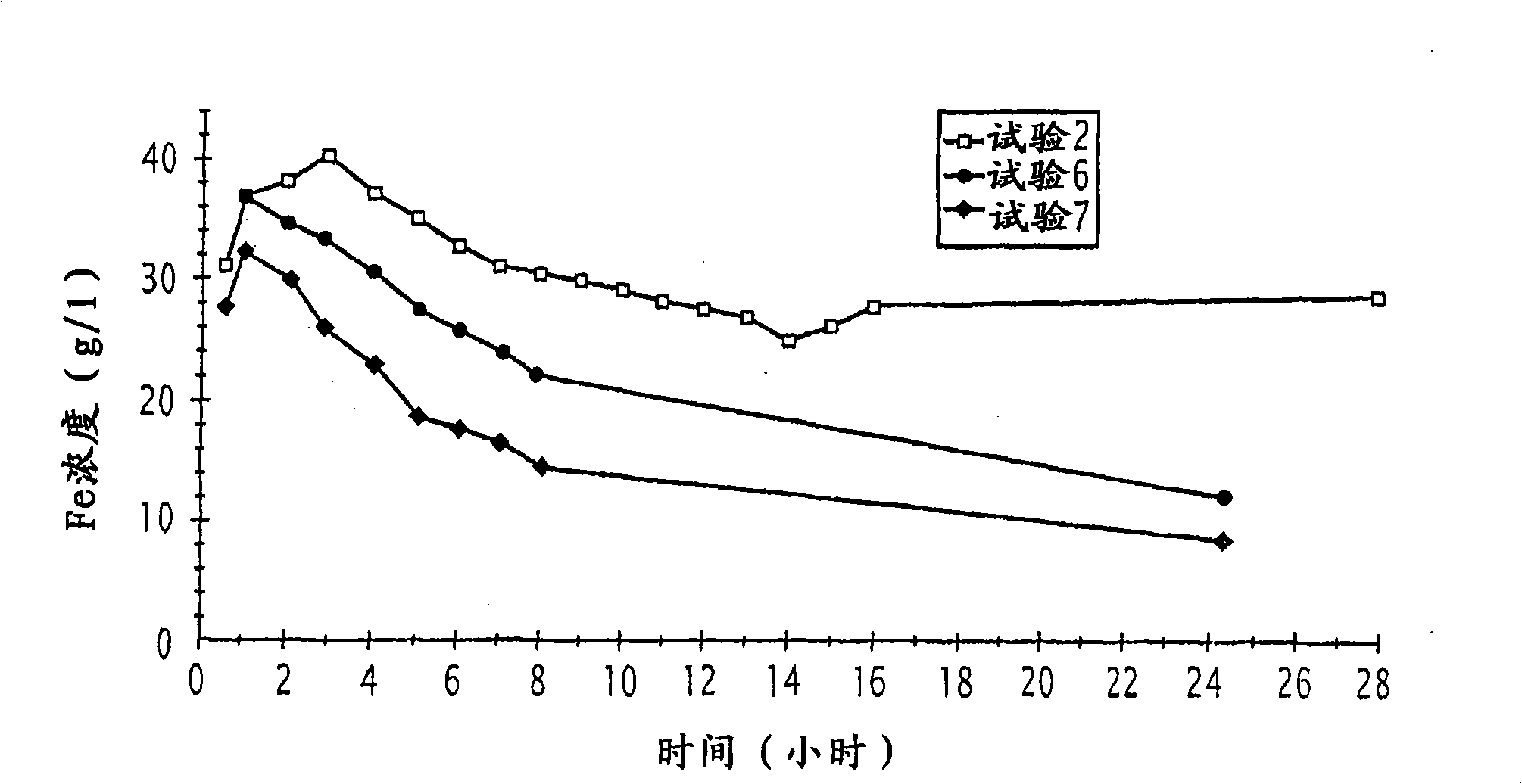
Process for the hydrometallurgical treatment of a lateritic nickel/cobalt ore and process for producing nickel and/or cobalt intermediate concentrates or commercial products using it
ActiveCN101541985ASimple structureShorten the durationProcess efficiency improvementBoiling pointHydrometallurgy
Process for the treatment of a lateritic nickel / cobalt ore consisting of a mixture (2) of limonite and saprolite, characterized in that: the mixture (2) in the presence of an iron-precipitating agent is made into a pulp (1), having a solids content of between 10 and 40% by weight; the pulp undergoes a leaching operation (4) with sulphuric acid (5), at a temperature between 70 DEG C and the boiling point and at atmospheric pressure; and a solid-liquid separation (8) is carried out so as to obtain an iron-containing solid residue (9) and a solution containing nickel and cobalt ions. Process for producing nickel and / or cobalt intermediate concentrates or commercial products using the above process.
Owner:ERAMET
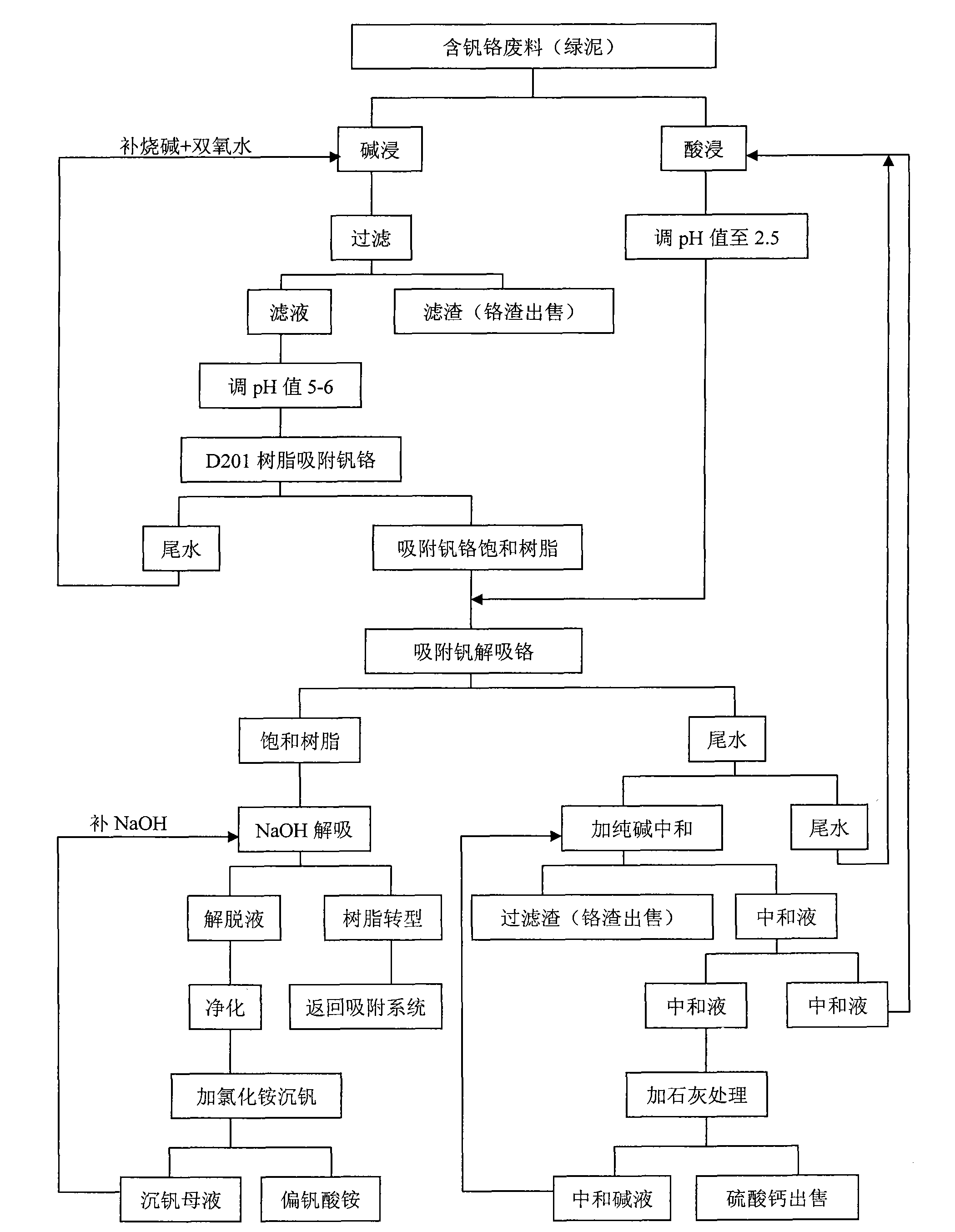
Method for separating and recovering vanadium and chrome from vanadium and chrome-containing waste
InactiveCN101538652ALess investmentMature production processProcess efficiency improvementDesorptionIon exchange
The invention relates to the field of chemical hydrometallurgy, in particular relates to a method for separating and recovering vanadium and chrome from a vanadium and chrome-containing waste. The method comprises the following steps: (1) alkaline leaching; (2) adsorption of alkaline leaching liquid; (3) acid leaching; (4) ion exchange; (5) desorption and devanadation; and (6) vanadium precipitation. The method has the advantages that: (1) the method has lower cost than a primary and secondary compound amine extraction process; (2) the method has short process flow, convenient operation, easy control, easy mastering and mature production process of recovering vanadium and chrome once the vanadium and chrome are separated; (3) the method has low production cost, and excluding sales revenue from chrome residues and calcium sulphate, the cost of fine vanadium is only 50000-60000 yuan / t; (4) the vanadium and the chrome are completely separated by the method; and (5) the method produces no secondary pollution, all the production processes are performed at normal temperature and has no roasting fume, and industrial water is recycled and subject to zero discharge; produced neutralization residues are of high-quality chrome residues and calcium sulphate and can be sold to chemical plants and cement plants as a raw material.
Owner:杨秋良 +1
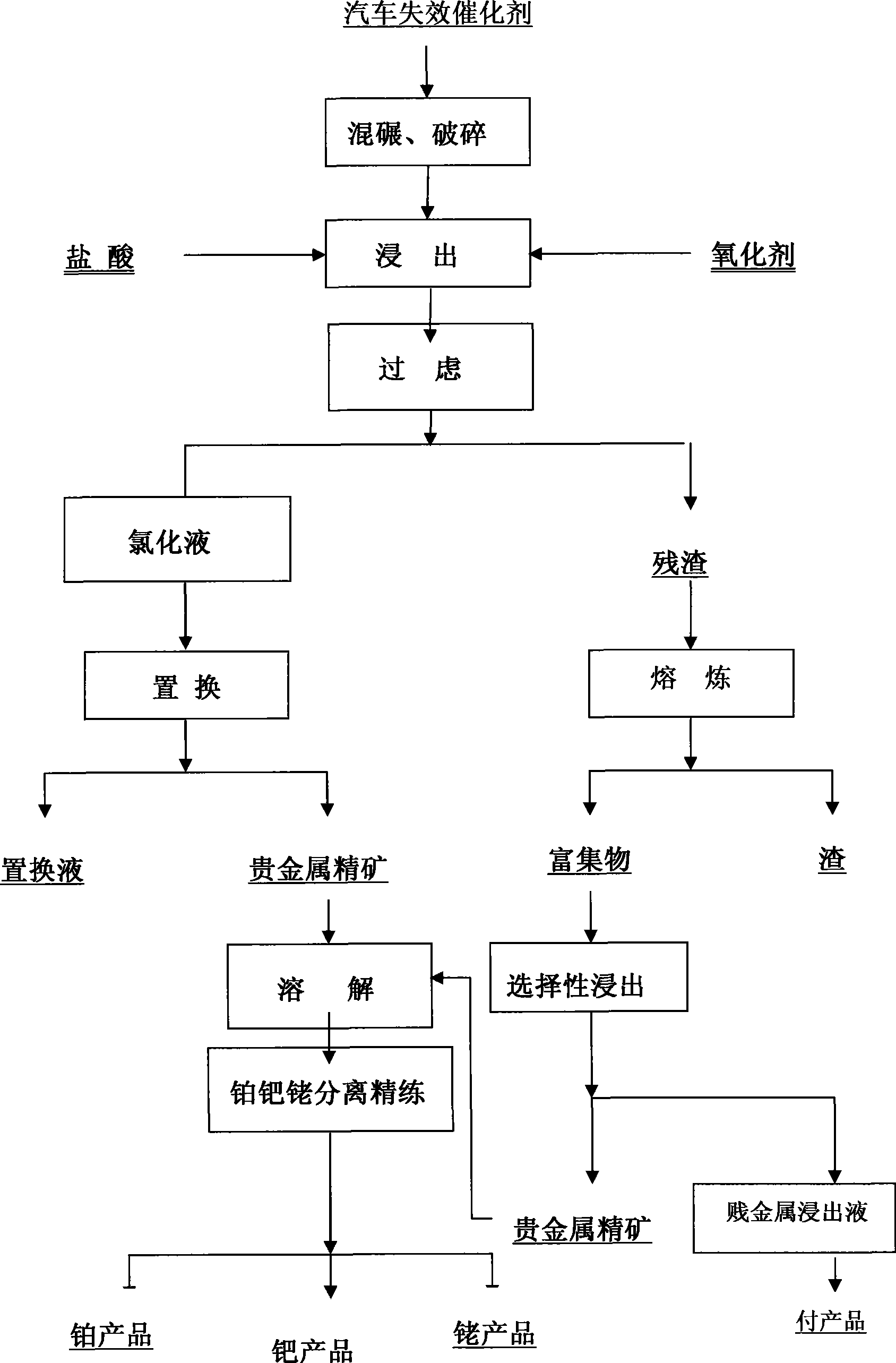
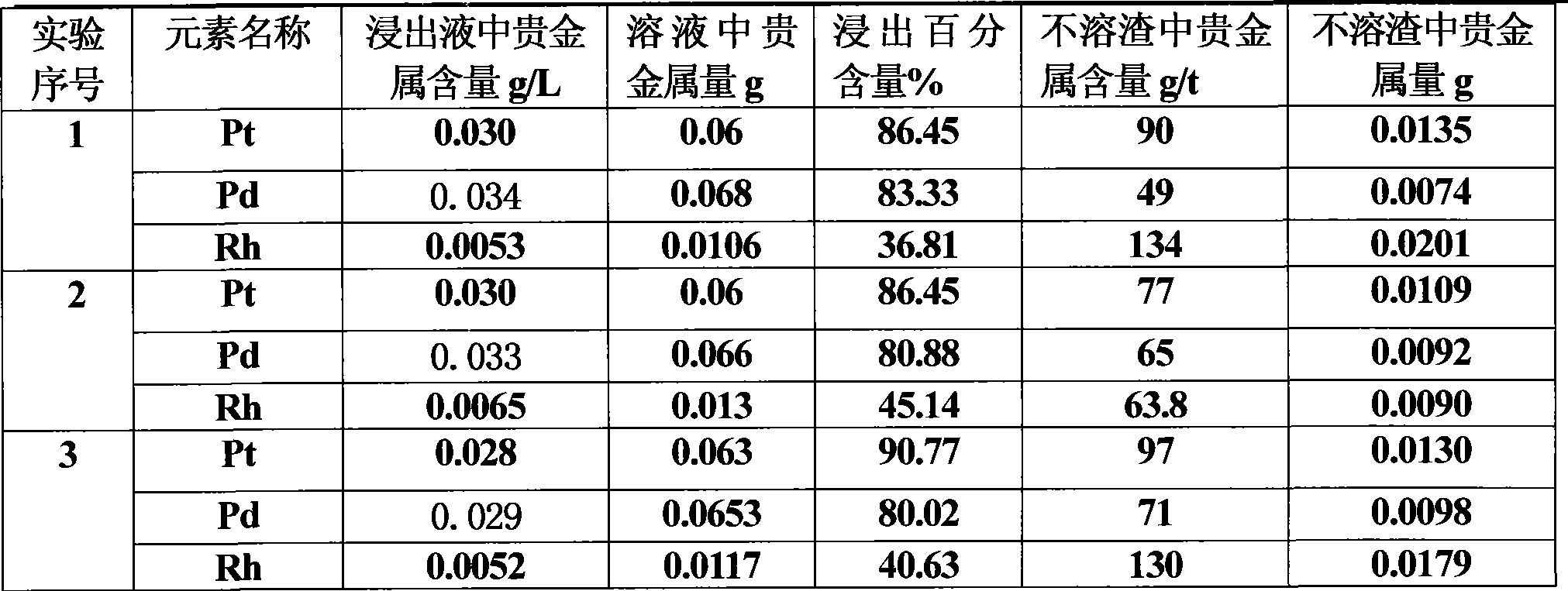
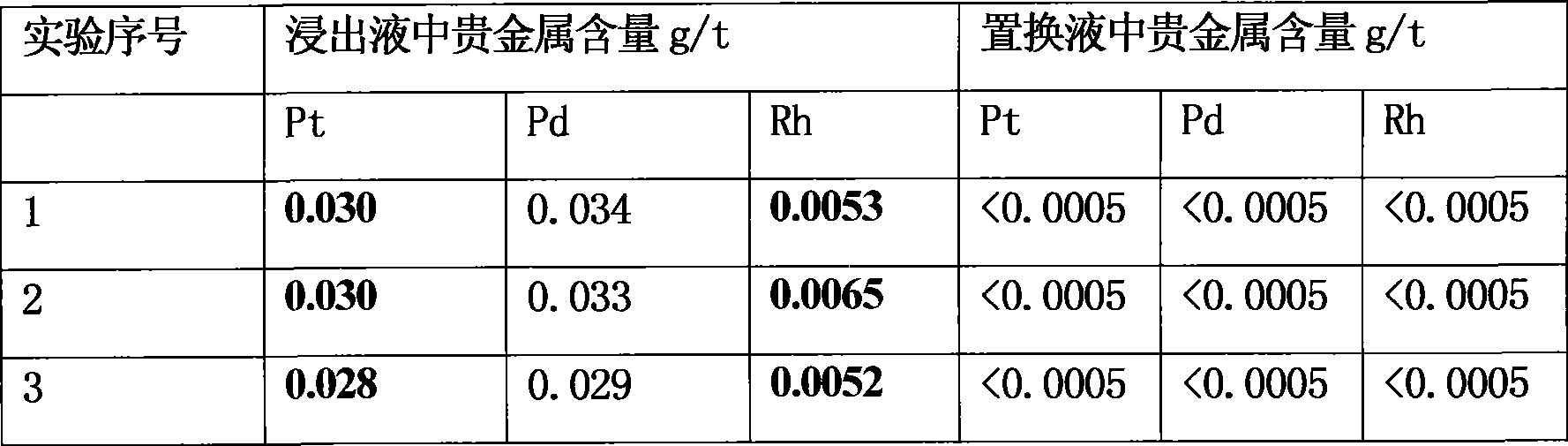
Method for extracting precious metal from auto-exhaust catalyst by hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy complex process
InactiveCN101519725ALoose process conditionsImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionPlatinum
The invention relates to a method for extracting precious metal from a disabled auto-exhaust catalyst, which comprises the following steps: 1. lixiviating precious metal from the disabled auto-exhaust catalyst by a hydrometallurgy process and obtaining precious metal concentrates after permuting lixivium; 2. lixiviating slag, collecting precious metal of the slag by a pyrometallurgy process to obtain a precious metal phase and selectively lixiviating base metal in the precious metal phase to obtain precious metal concentrates; and 3 combining the precious metal concentrates obtained in the first two steps and refining the precious metal concentrates to produce platinum, palladium and rhodium products. The invention compensates the deficiency that the percent recovery of the precious metal is low by simply treating the disabled auto-exhaust catalyst with the hydrometallurgy process and has the advantages that the contents of platinum, palladium and rhodium in the waste slag are smaller than 1g / t and the product purity reaches 99.95 percent.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
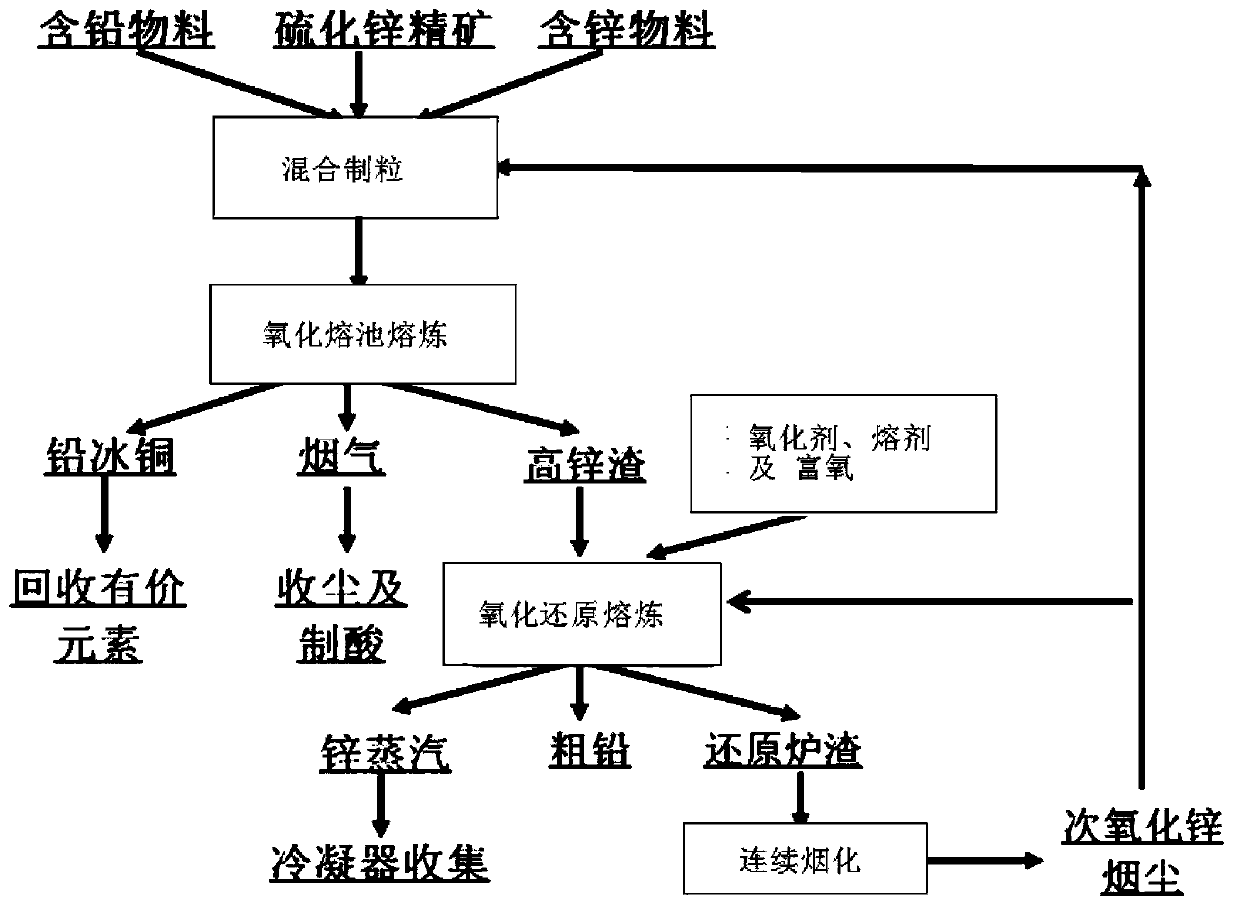
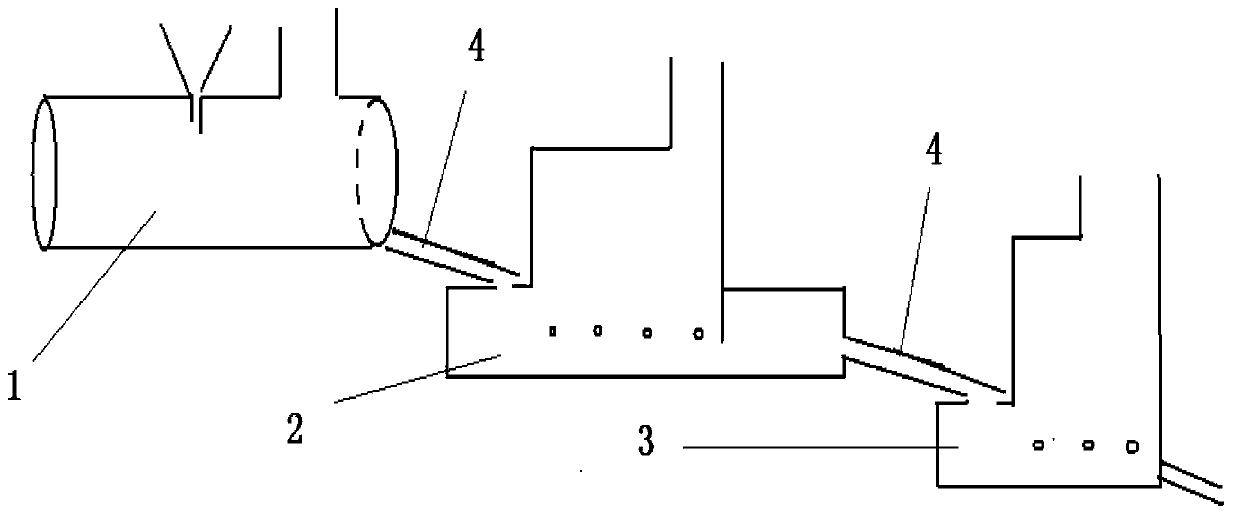
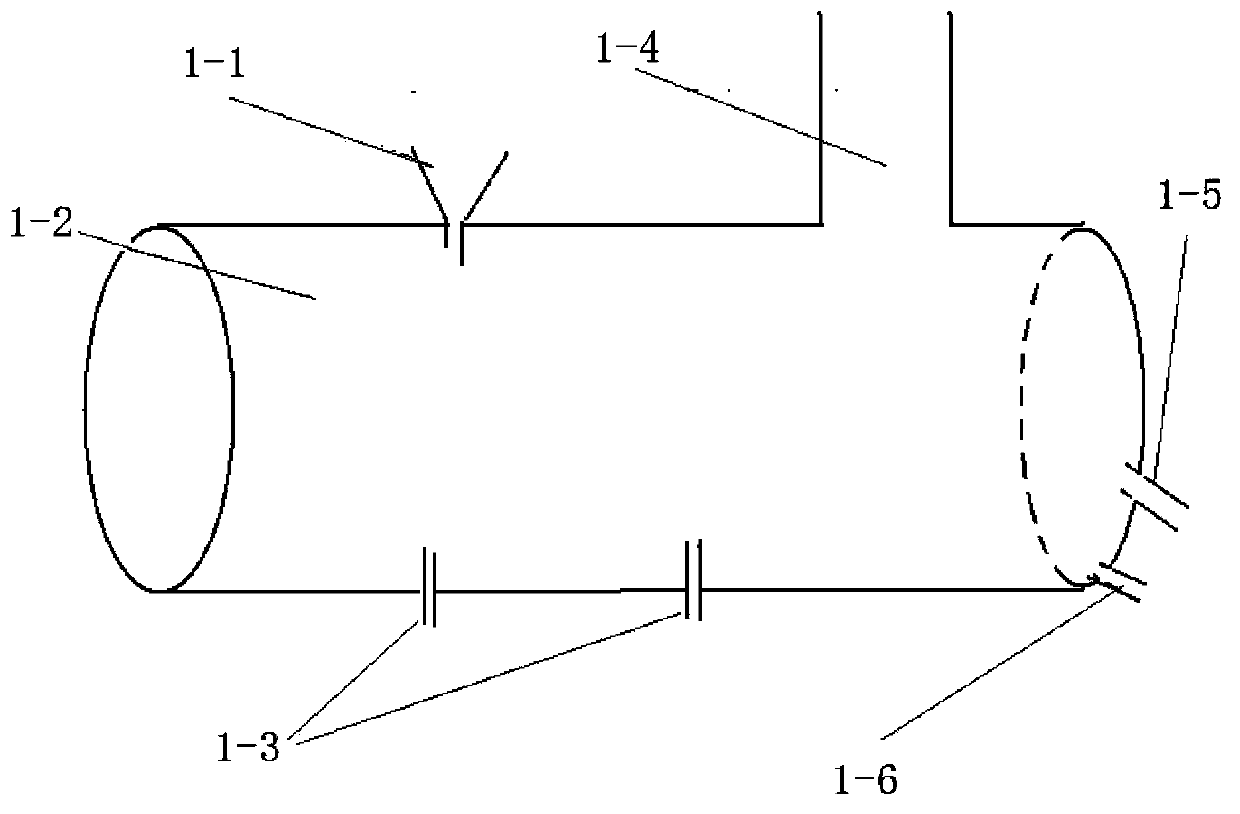
Bath smelting method and apparatus of zinc sulfide concentrate and lead-zinc containing materials
InactiveCN103388081AMeet the requirements of smeltingReduce energy consumptionMelting tankHigh concentration
The invention discloses a bath smelting method and an apparatus of zinc sulfide concentrate and lead-zinc containing materials. The smelting method comprises the following steps: mixing lead-zinc-containing mixed materials according to a certain proportion and pelletizing; and then, adding the pelletized materials into an oxidation furnace having a lead-containing high-zinc-slag bath with proper ingredients and smelting points, and blowing oxygen-enriched air into the bath for generating an oxidation reaction with the pelletizing materials to generate high-concentration SO2 flue gas and lead-containing high-zinc slag, wherein the SO2 flue gas is used for preparing acid, the lead-containing high-zinc slag is continuously discharged from the oxidation furnace into a reduction furnace bath, zinc in the lead-containing high-zinc slag is reduced into zinc vapor to be collected, and the lead is reduced into metal lead and such precious metals as gold and silver in the raw materials are captured and gathered at the bottom part of the bath to be discharged. The bath smelting method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of short flow, strong raw material adaptability, low energy consumption, environment friendliness, efficient source utilization and the like and is expected to solve the current treatment difficulty of high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate, zinc oxide ores, iron and steel plant zinc dust and gold-containing iron ores and the long-term pollution problems of zinc slag of hydrometallurgy.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
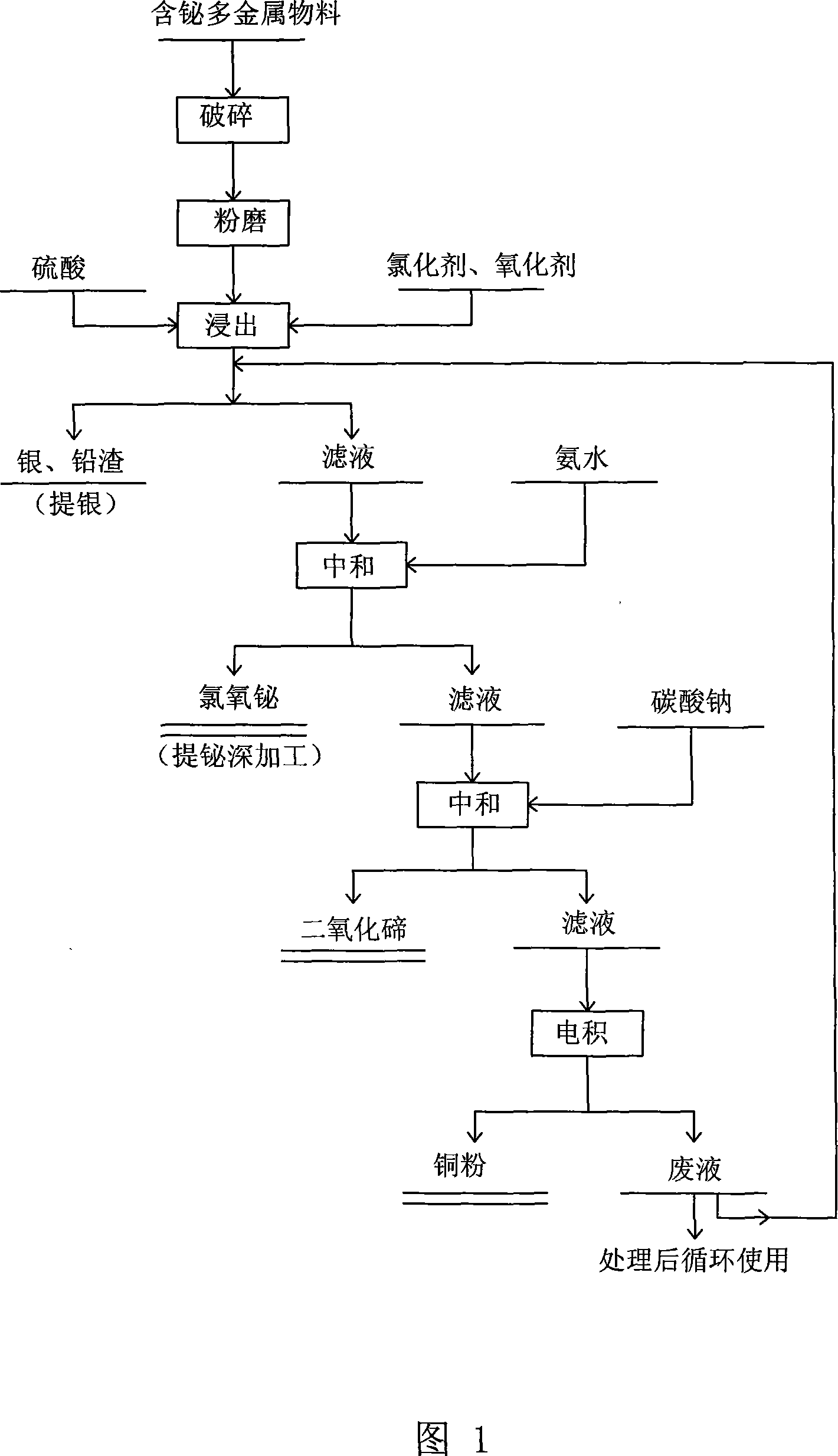
Comprehensive extraction of valent metal from bismuth-containing polymetallic material
InactiveCN101029353AHigh recovery rateImprove product added valuePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementSesquioxideTe element
A method for extracting metal from bismuth-contained multi-metal material is carried out by leaching out copper and tellurium from bismuth-contained multi-metal by sulfuric acid, adding into chlorinating agent and oxidant to leach out metal bismuth, extracting silver from leaching-out slag with AgCl, PbSO4 and PbC12, adding ammonia water into leaching-out liquid, adjusting pH value to 1.5 to obtain bismuth oxychloride slag with 70% bismuth content, smelting into coarse bismuth by firing method or machining to obtain high-purity bismuth sesquioxide, adjusting pH value to 4.5 by Na2CO3, depositing tellurium to obtain tellurium dioxide and copper-contained solution, and electrically depositing to obtain copper powder with copper-contained content90%. It adopts wetting and firing metallurgical technology, has higher metal recovery rate and excellent leaching-out separation effect and effluent circulating utilization and no environmental pollution.
Owner:HUNAN JINWANG BISMUTH
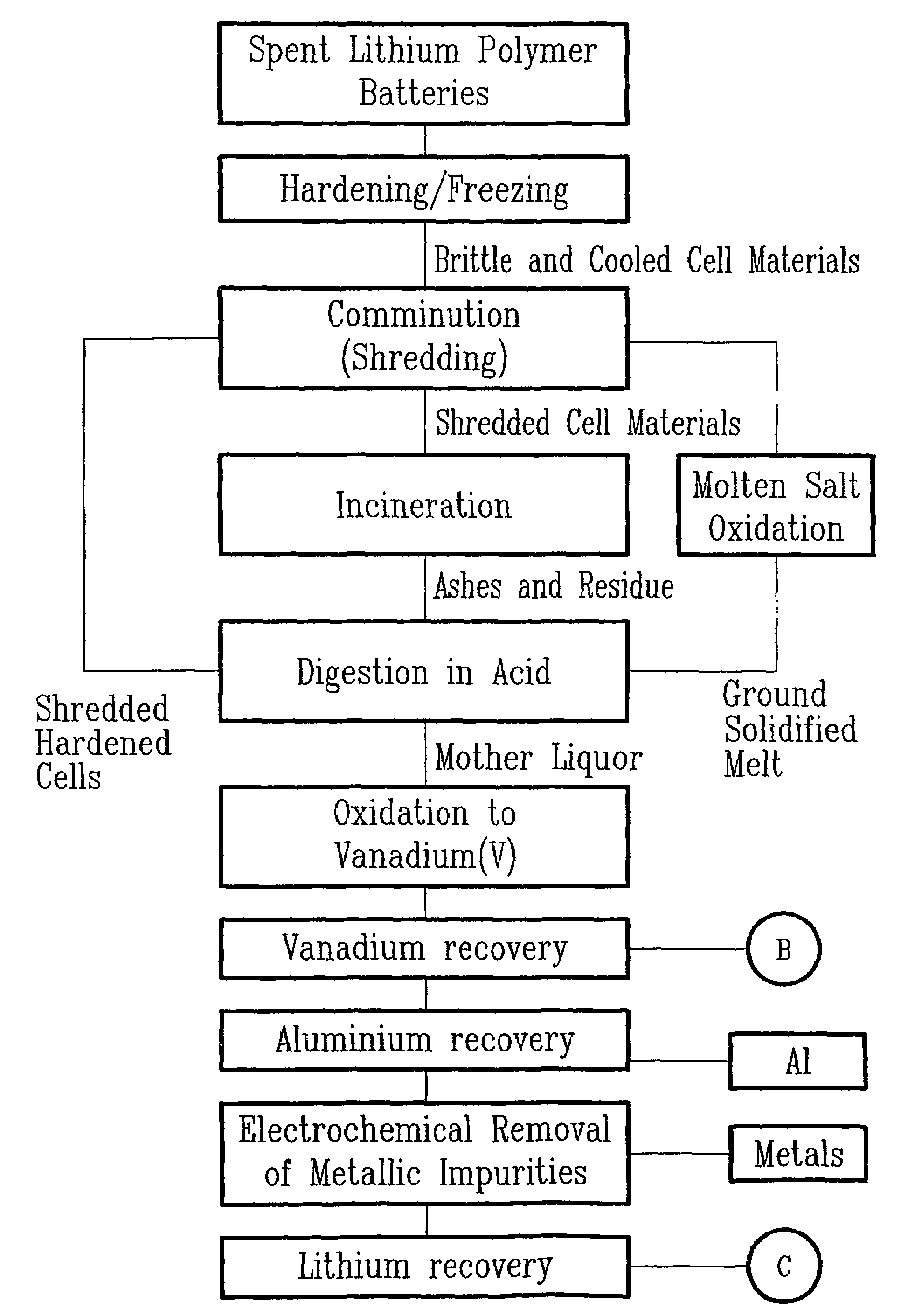
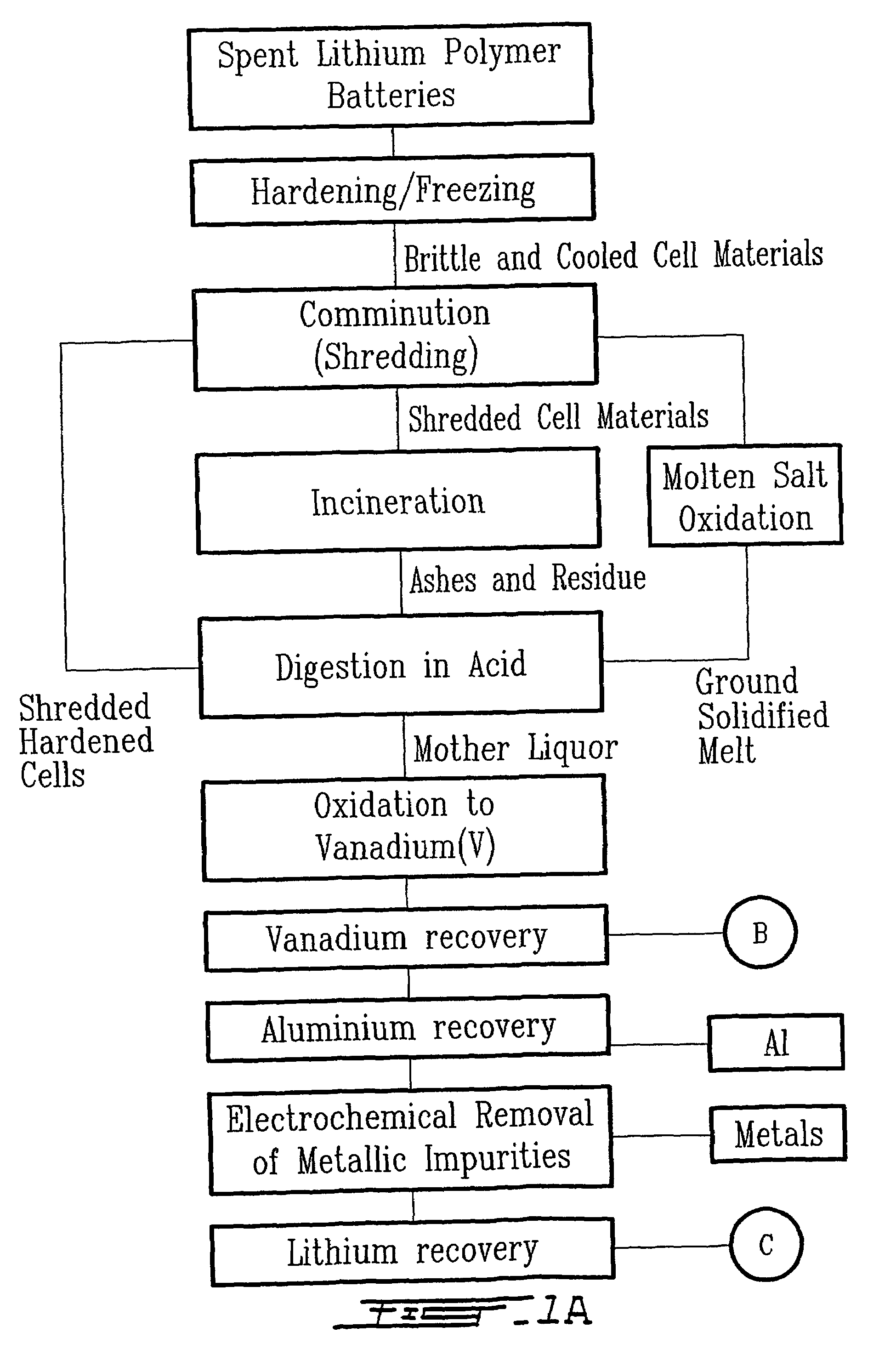
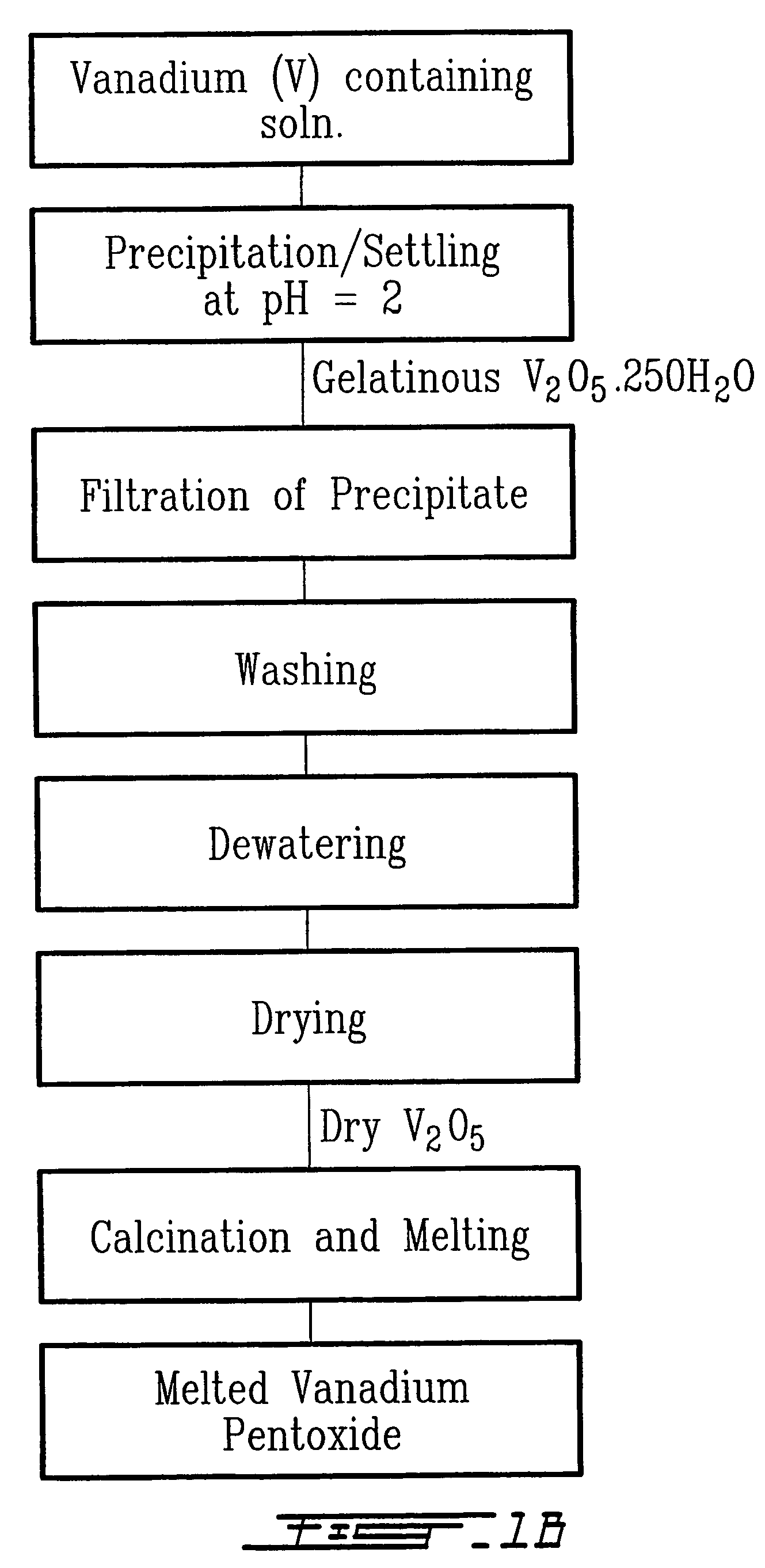
Method for recycling spent lithium metal polymer rechargeable batteries and related materials
The method relates to a pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical process for the recovery and recycling of lithium and vanadium compounds from a material comprising spent rechargeable lithium batteries, particularly lithium metal gel and solid polymer electrolyte rechargeable batteries. The method involves providing a mass of the material, hardening it by cooling at a temperature below room temperature, comminuting the mass of cooled and hardened material, digesting with an acid its ashes obtained by incineration, or its solidified salts obtained by molten salt oxidation, or the comminuted mass itself, to give a mother liquor, extracting vanadium compounds from the mother liquor, separating heavy metals and aluminium therefrom, and precipitating lithium carbonate from the remaining solution.
Owner:AVESTOR
Method for extracting high-valence manganese from manganese carbonate ore
This invention has provided one kind of method to leach high price manganese from manganese carbonateore, which belongs to the hydrometallurgy domain. It takes the glucose or the plant biomass and sulfuric acid as reducing agent of high pricemanganese in manganese carbonate ore, adopting microwave radiation glucose to promote high price manganese to revert, the concrete step includes: Takes 1 copy 100-200 sieve manganese carbonateore, add 10 -20 copy water to modulate the pulp; Again add 60% density sulfuric acid to pulp, the load ratio of mineral powder and sulfuric acid is 1: 6 -9; Simultaneously, add glucose or plant biomass, the load ratio of mineral powder and glucose or plant biomass is 10 -15: 1, stir evenly; radiate under 500 -1000W microwave, stir and respond for 4-10min, leach temperature is controlled at 50degree C-60 degree C, then get lixivium by filtering. This invention has the merits of lower reaction temperature, reducing acid consume and reduce leaching time of the manganese ore, high thermal using and respond rapidly.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
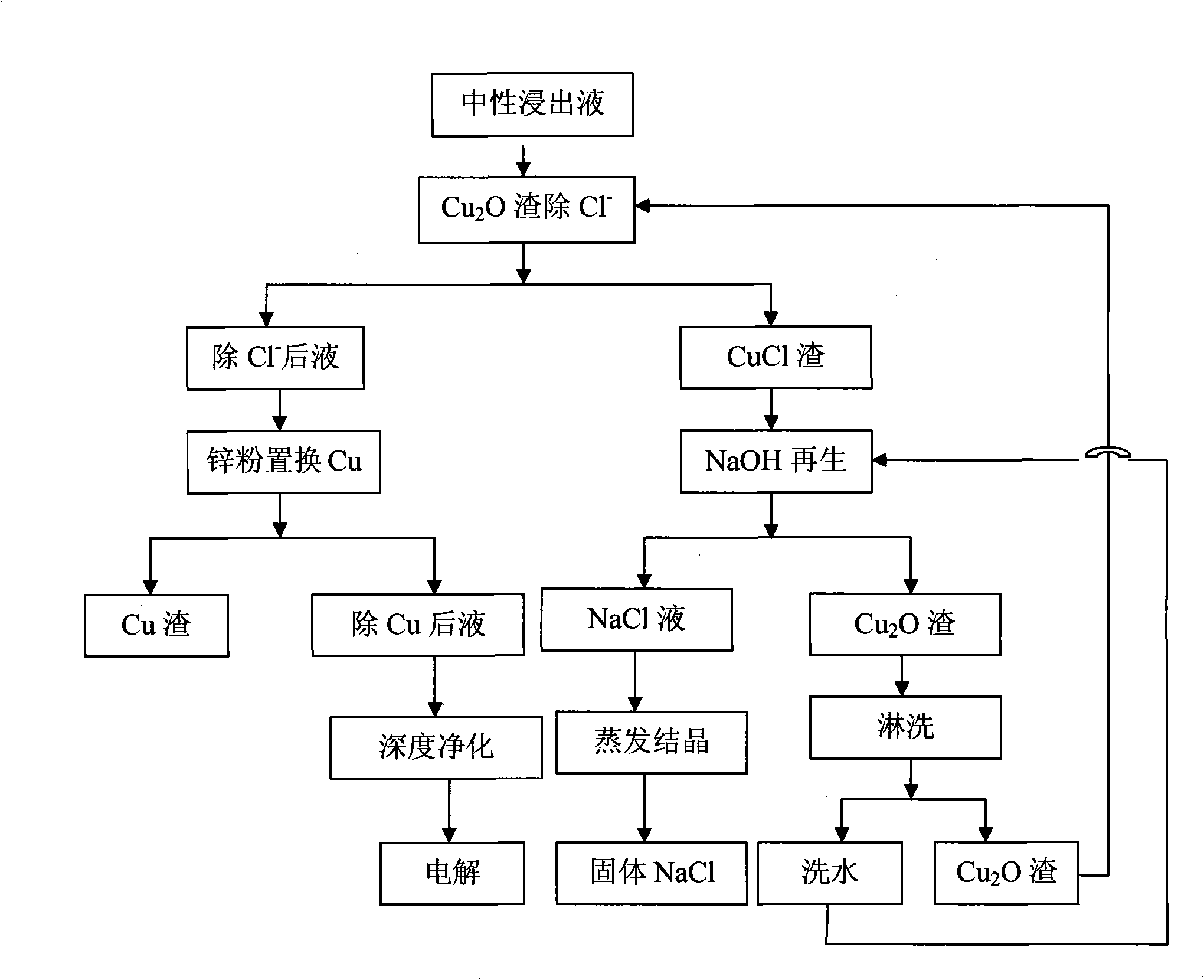
Dechlorination process from zinc electrolytic solution
ActiveCN101285119ALow costLow efficiencyProcess efficiency improvementHigh concentrationElectrolysis
The invention relates to a dechlorination method for zinc electrolytic solution, in particular to a dechlorination method for high concentration chloridion neutral lixivium of zinc hydrometallurgy. The method comprises the following steps that: the zinc electrolytic neutral lixivium with chloridion is in the dilute sulphuric acid condition with Cu2O and pH value of between 2.0 and 3.5, obtained Cu2SO4 through dissolving and Cl-1 react to obtain CuCl precipitate which is difficult to dissolve; CuCl is separated and then reacts with alkaline solution to obtain Cu2O which can be circularly used; and the chloride becomes solid chloride through evaporating and crystallizing. The dechlorination method for zinc electrolytic solution has the advantages of low technological cost, high efficiency, high extraction yield of regenerant and easy operation.
Owner:YUNNAN XIANGYUNFEILONG RESOURCES RECYCLING TECH CO LTD
Method for extracting chromium and vanadium from vanadium slag at low temperature and normal pressure
ActiveCN105400967ALow reaction temperatureReduce reaction energy consumptionSlagReaction temperature
The invention relates to the field of vanadium slag hydrometallurgy and vanadium chemical engineering, in particular to a method for extracting chromium and vanadium from vanadium slag at a low temperature and the normal pressure. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, burdening, wherein the vanadium slag and a NaOH solution are mixed to form reaction slurry; secondly, reaction, oxide gas is led into the reaction slurry through a micro-hole arrangement device to carry out normal-pressure oxidative leaching, and after the reaction, solid-liquid mixed slurry of a solution containing NaOH, Na3VO4, Na2CrO4, water soluble impurity components and iron-rich tailings is obtained; thirdly, solid-liquid separation; fourthly, impurity removing; fifthly, sodium vanadate crystallization; and sixthly, sodium chromate crystallization. According to the method, chromium and vanadium efficient common extraction can be achieved, the extraction efficiency of both chromium and vanadium can be higher than 85%, more importantly, after the micro-hole gas distribution manner is adopted, the oxygen solubility can be obviously improved, the reaction temperature and alkali concentration are obviously reduced compared with those of an existing vanadium extraction method, the operation safety is greatly improved, and reaction energy consumption is reduced.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
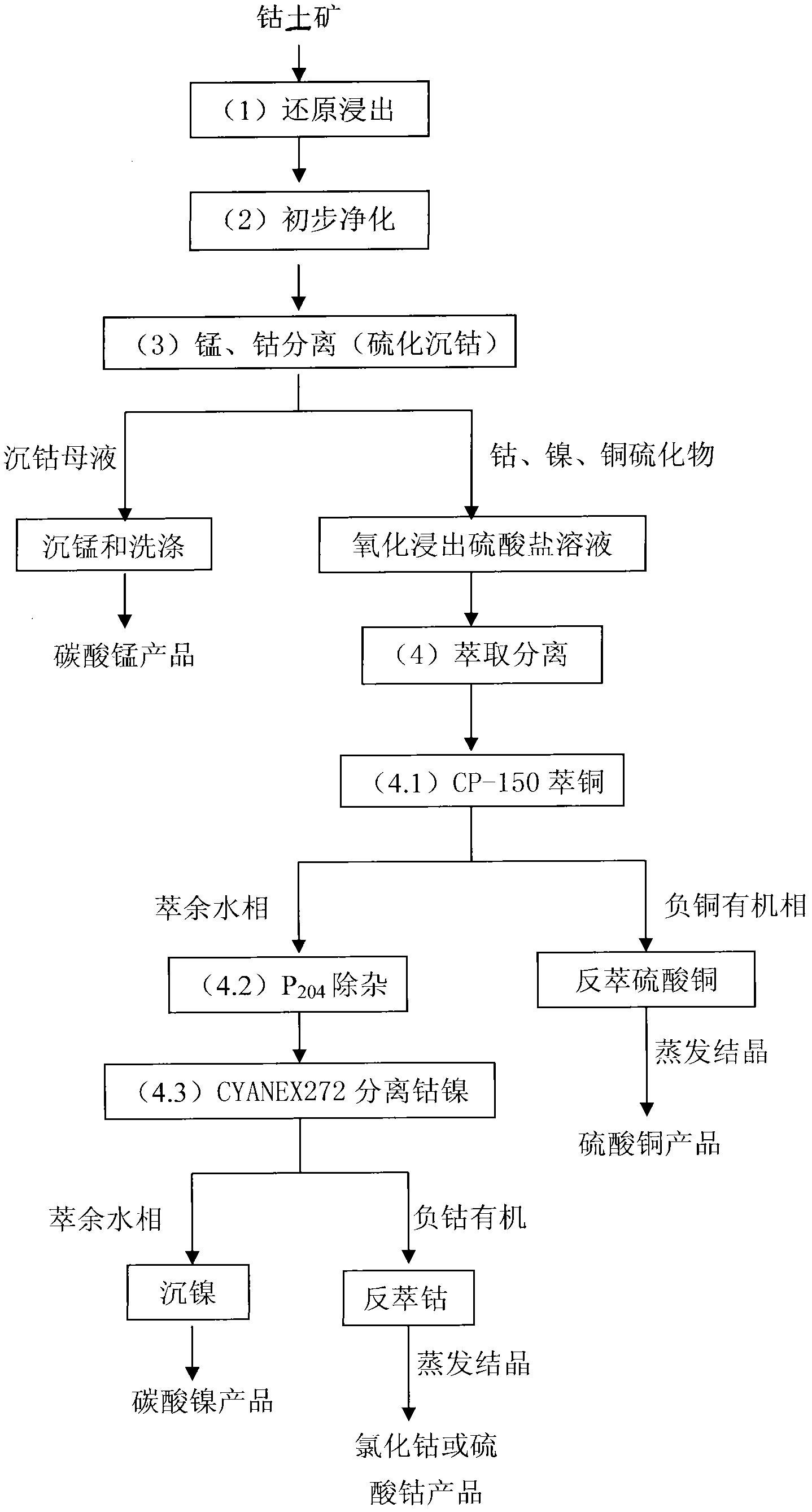
Processing method for comprehensively recovering high manganese asbolite
InactiveCN102021331AIncrease costLow recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementManganeseHydrometallurgy
The invention discloses a processing method for comprehensively recovering high manganese asbolite, belonging to the field of hydrometallurgy. In the processing method, the high manganese asbolite is processed through four processing steps comprising (1) reduction leaching, (2) primary cleaning, (3) manganese and cobalt separation and (4) extraction separation to obtain a product manganese carbonate, copper sulfate, nickel carbonate or cobaltous sulfate. The processing method has the advantages that the source of raw materials is wide, the process and equipment are simple, the operation is stable, the energy consumption is low, the production cost is low, the practicability is wide, and the economic effect and the society effect are obvious.
Owner:HAINAN ZHONGDAO ENERGY DEV
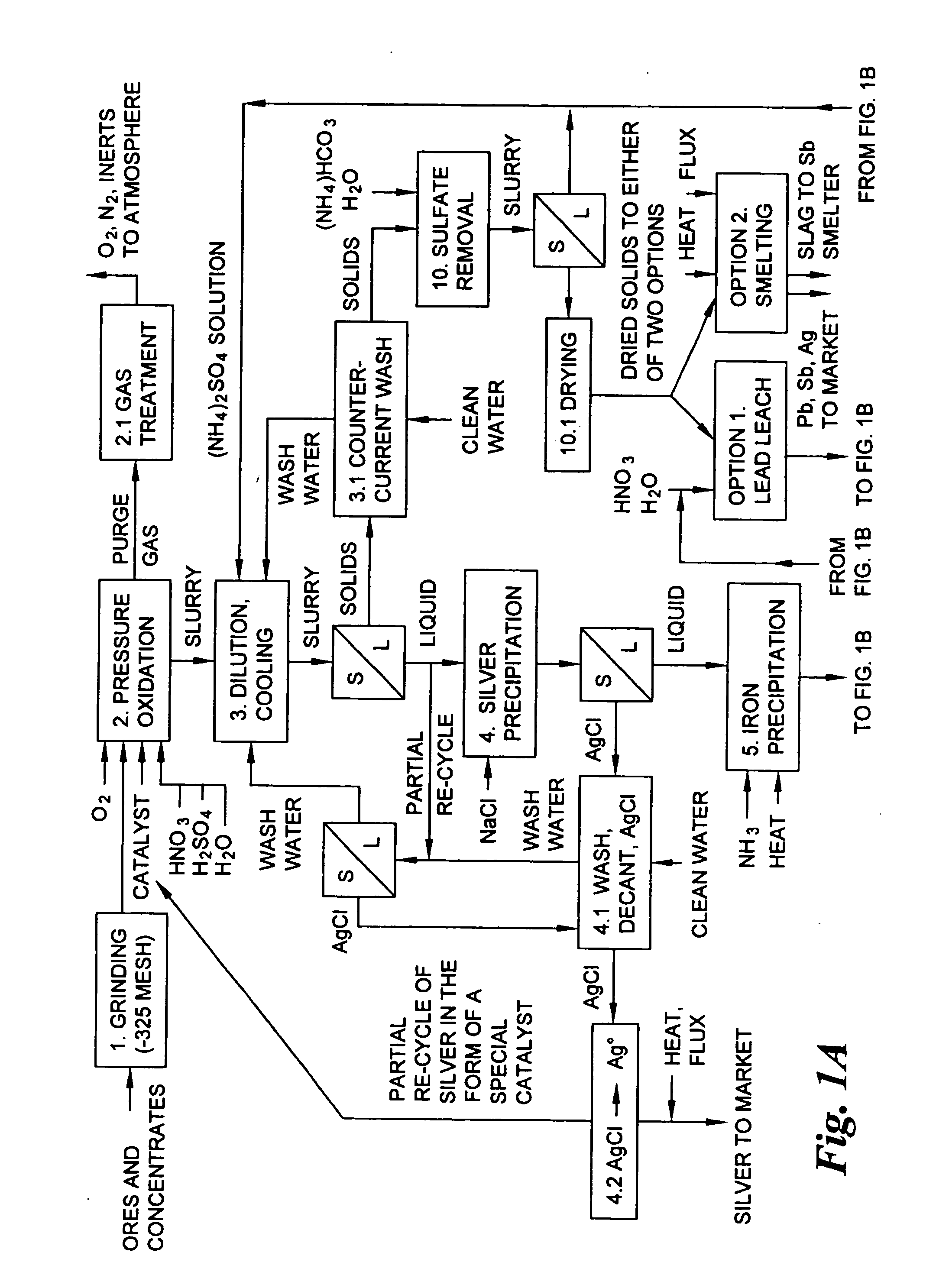
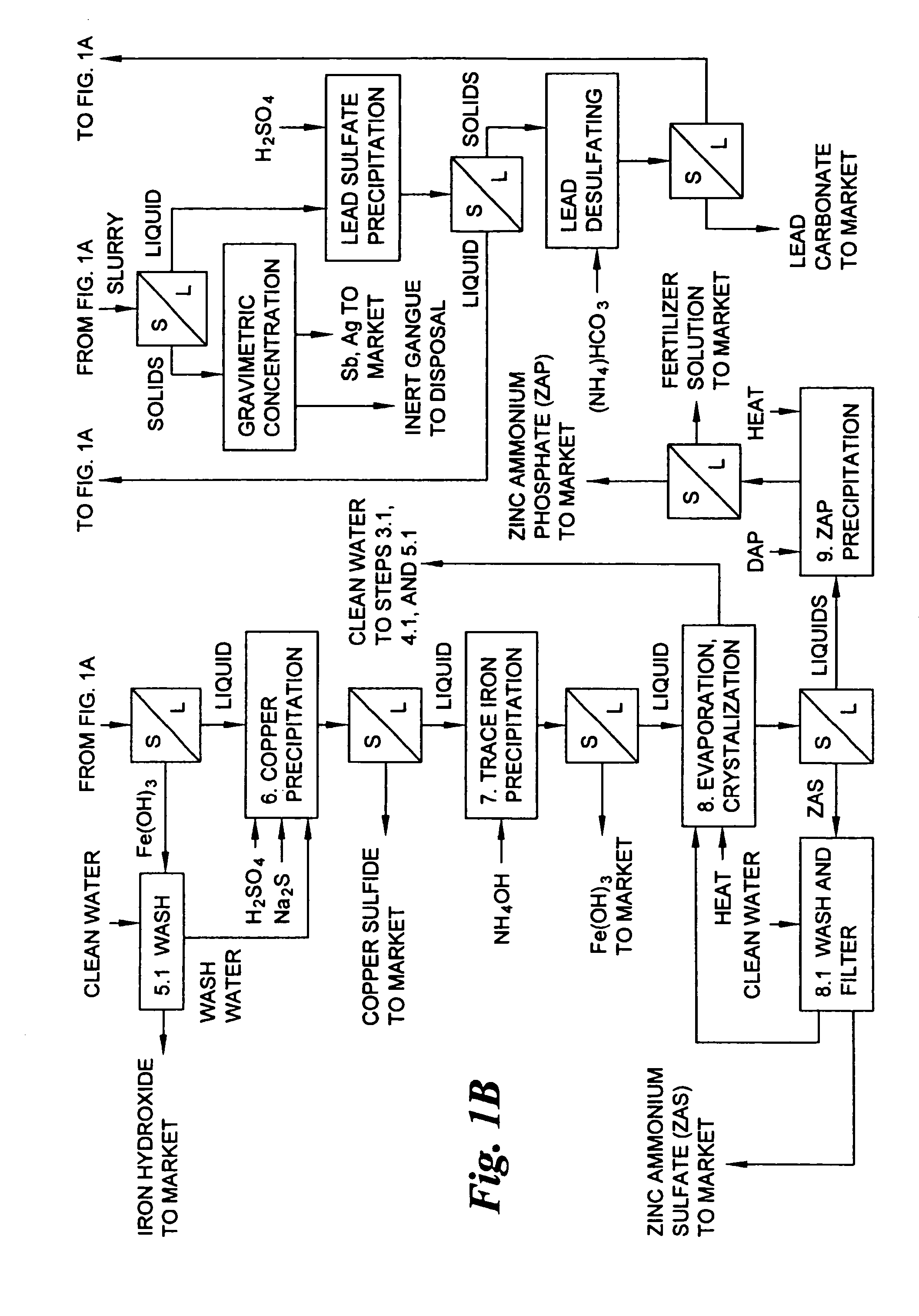
Hydrometallurgical process for the treatment of metal-bearing sulfide mineral concentrates
InactiveUS20070098609A1Improve efficiencyReduce the amount requiredSolvent extractionGold compoundsAmmonium compoundsMetallic sulfide
A hydrometallurgical process for the treatment of complex silver-bearing sulfide ores and concentrates that recovers substantially all silver, lead, antimony, zinc, copper and sulfur, along with the chemical reagents utilized during the process. Finely ground ores and concentrates are leached under heat and pressure with water, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, oxygen, and a catalyst, and are further treated to recover silver in the form of silver chloride; iron in the form of iron hydroxide; copper and all traces of soluble toxic metals as sulfides; zinc as zinc ammonium sulfate and specifically nitric acid, sulfuric acid, oxygen, ammonia, and ammonium compounds as valuable fertilizer products.
Owner:ROYAL SILVER PANAMA
Beneficiation process of polymetallic ore containing betafite
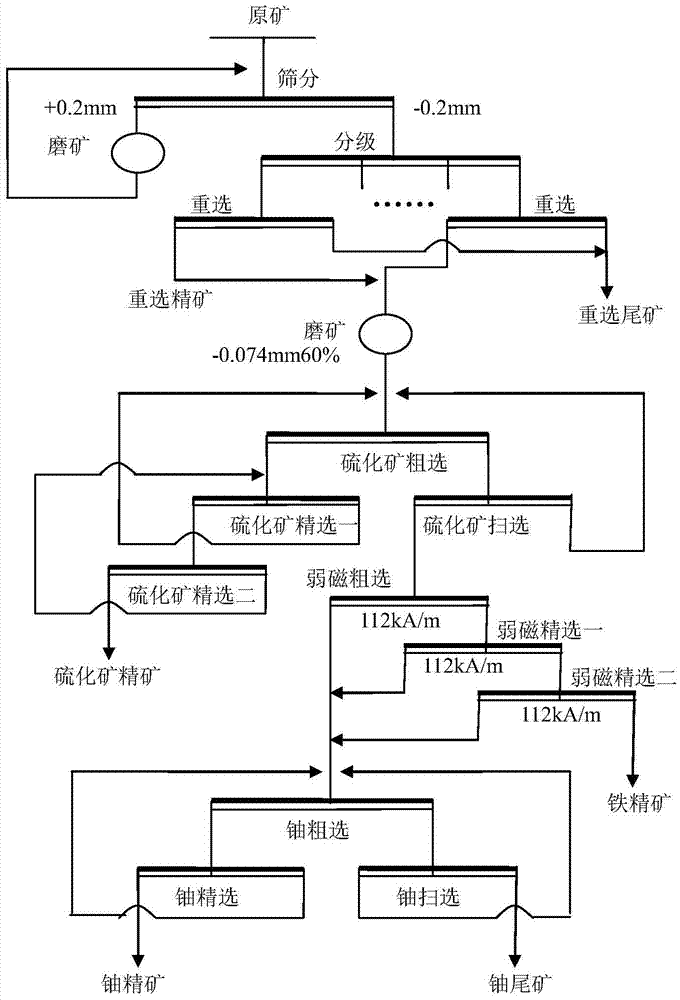
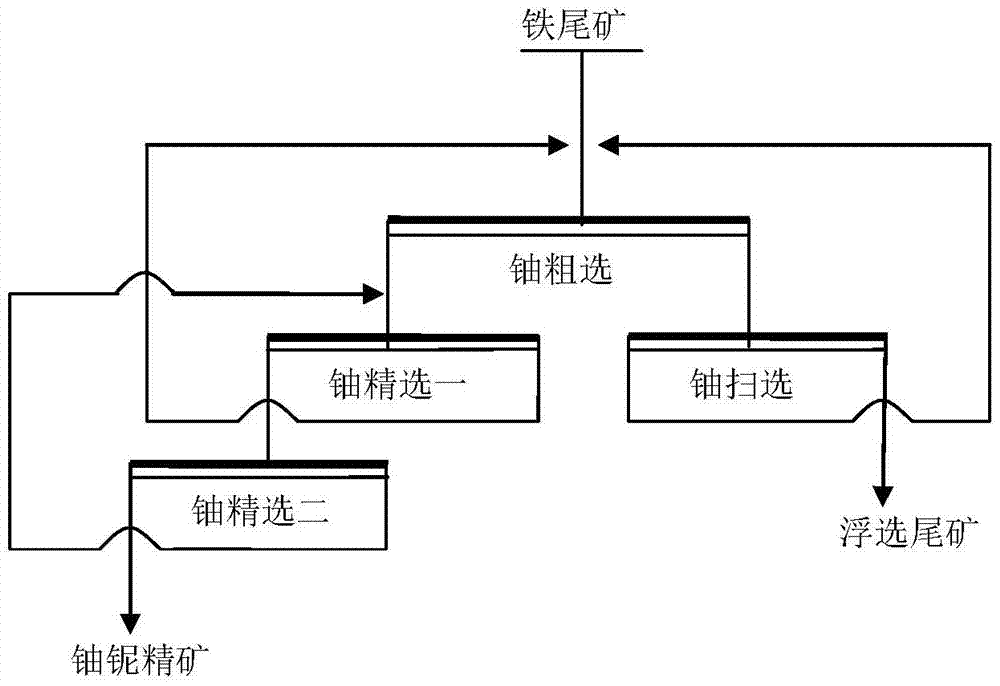
This invention belongs to the technical field of beneficiation, is suitable for beneficiation of polymetallic ore containing betafite, and particularly relates to a beneficiation process of polymetallic ore containing betafite. According to the beneficiation process of the polymetallic ore containing the betafite, the low-grade polymetallic ore containing the betafite is economically developed and utilized, and the process relates to a combined technological process of gravity concentration, magnetic separation and flotation. Firstly, ore is subjected to gravity concentration after ore grinding and classification, after gravity concentrate is reground, sulfide ore is subjected to flotation and iron minerals are subjected to magnetic separation, and sulfide concentrate and iron concentrate can be obtained; secondly, uranium-rich ore pulp after iron removed is then subjected to flotation so that the betafite can be recycled, by adding a betafite efficient collecting agent, the direct flotation technology of the betafite is adopted, and the high-grade and high-recovery-rate uranium concentrate can be obtained; when the uranium concentrate is subjected to subsequent hydrometallurgy processing for uranium extraction, the handling capacity can be greatly reduced, the hydrometallurgy cost is substantially reduced, and the economic benefits are remarkably improved; and by means of beneficiation, the sulfide ore, the iron minerals and other associated useful components can be comprehensively recycled, and resources are fully utilized.
Owner:BEIJING RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING AND METALLURGY
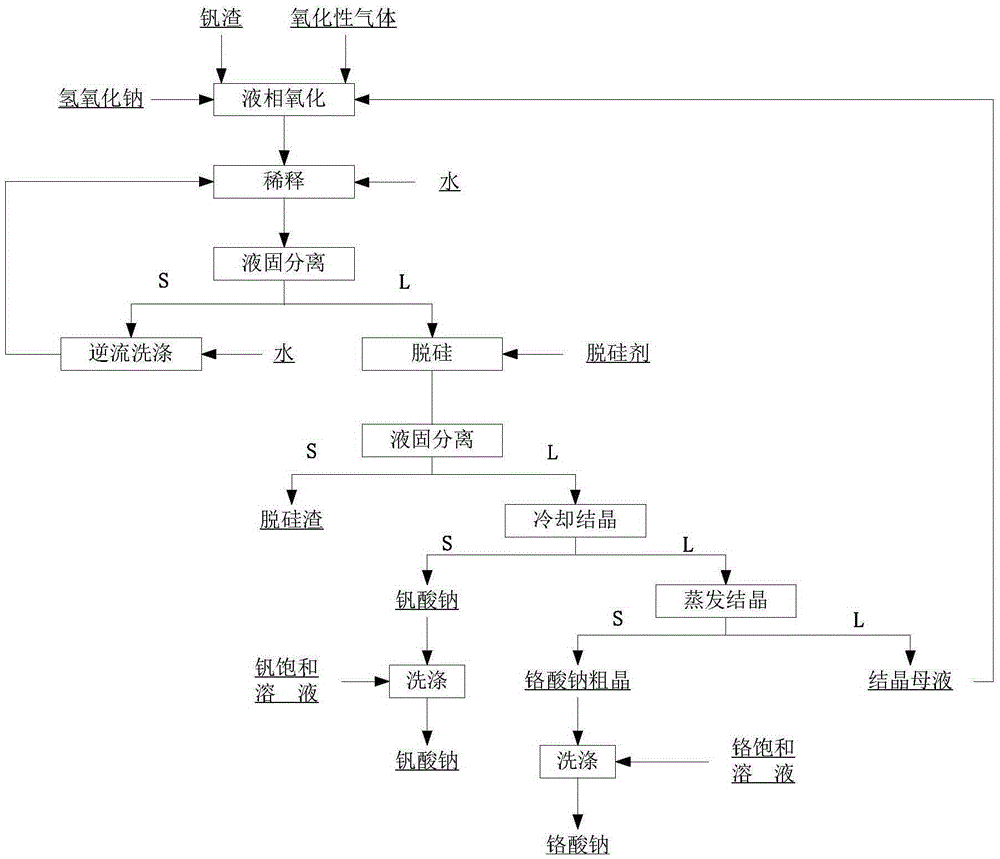
Method for pollution-free production of sodium chromate by pressure leaching of chromite
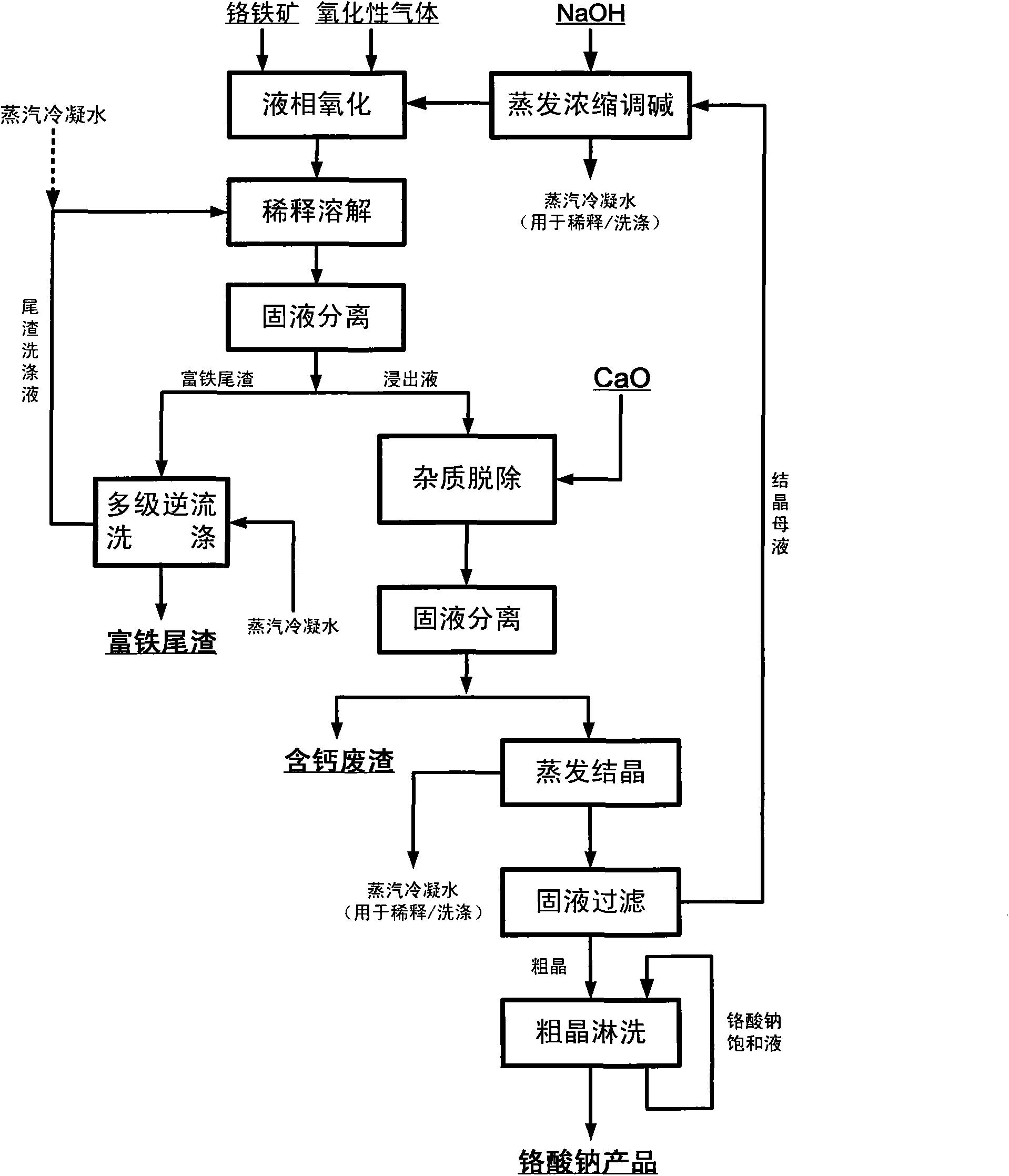
ActiveCN101817561AObvious superioritySimple ingredientsChromates/bichromatesReaction temperatureHydrometallurgy
The invention belongs to the field of chromite hydrometallurgy and chromium chemical industry, and in particular relates to a method for the pollution-free production of sodium chromate by pressure leaching of chromite. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) reacting the chromite with oxidizing gas in solution of NaOH; 2) diluting the product obtained by the step 1) and making subcrystalline sodium chromate to fully enter a liquid phase; 3) performing solid-liquid separation on the solid-liquid mixed slurry obtained by the step 2); 4) adding calcium oxide into the obtained diluent for removing impurities; and 5) evaporating and crystallizing the obtained solution without the impurities to obtain a sodium chromate crystal and crystallization mother solution; after the solid-liquid separation, rinsing the sodium chromate crystal by using saturated solution of sodium chromate; and drying to obtain a qualified sodium chromate product. The method has the advantages of simple reaction system component, no difficultly separated phase introduced in the system, contribution to high-efficiency separation of the sodium chromate, great reduction in reaction temperature, low energy consumption, effective reduction in production cost of the sodium chromate, and high chromium leaching yield.
Owner:HUBEI ZHENHUA CHEMICAL CO LTD
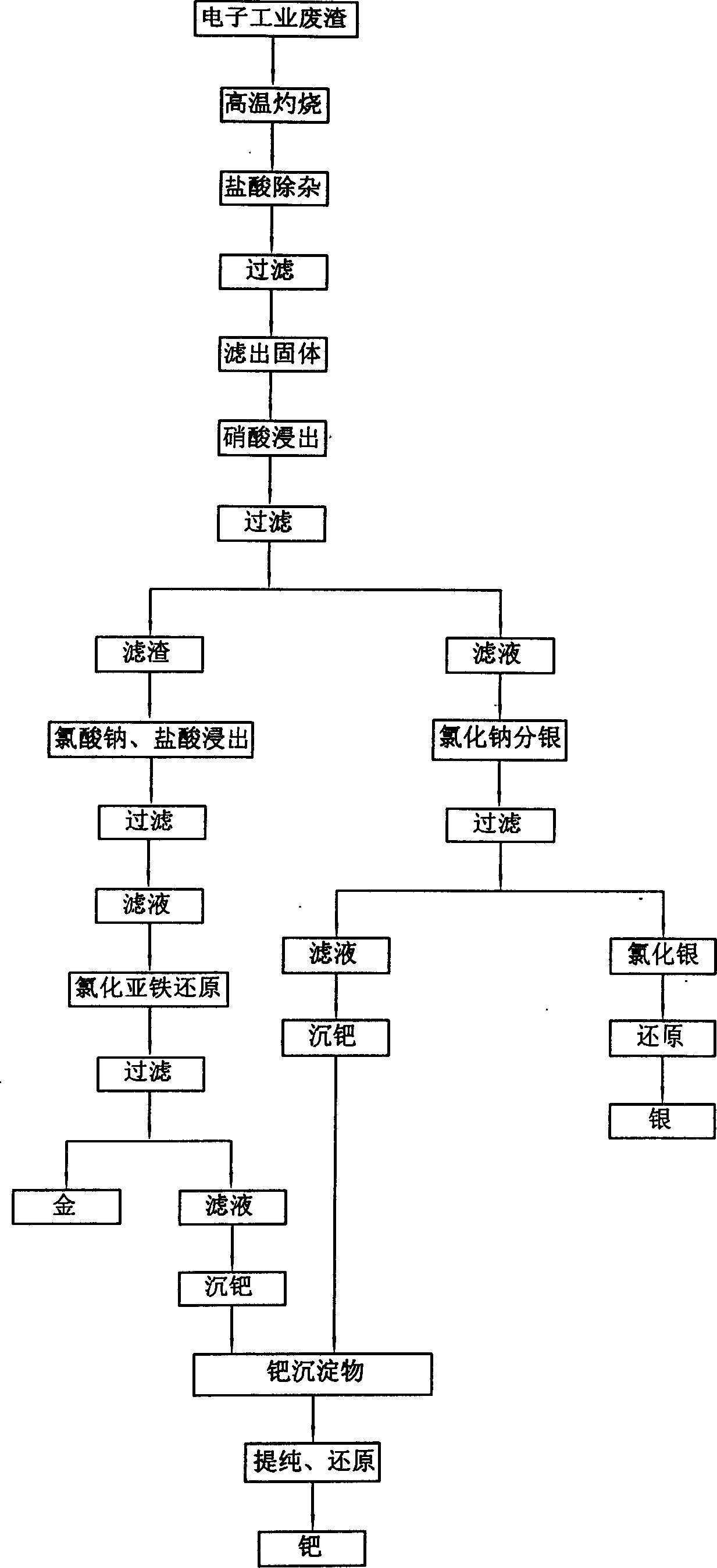
Technological process for extracting gold, silver and palladium from electronic industry waste
InactiveCN1603432AEfficient extractionAvoid interferenceProcess efficiency improvementHydrometallurgyOrganic matter
The invention discloses a kind withdraws golden, the silver, the arrowhead used in ancient times technique from the electronics industry waste residue, he solved the organic matter to withdraw the process to the precious metal the disturbance, realized the minute using the hydrometallurgy technology step to withdraw golden, the silver, the arrowhead used in ancient times goal. The technique has the operating environment well, the cost is inexpensive, the precious metal first experience higher merit which withdraws.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Leaching process of zinc oxide ore
InactiveCN1477217AImprove leaching rateAvoid enteringProcess efficiency improvementLiquid wastePregnant leach solution
The present invention relates to a leaching-out method of zinc ore containing high iron and silicone. It includes the following steps: (1). neutral leaching-out, simultaneously adding zinc oxide powder and solution containing sulfuric acid and stirring, progressively raising pH value to 5-5.2 from initial 3.0-3.5, and purifying the reacted neutral leach and using it for electrolysis, and using the leached slag make next leaching-out; (2). low acid leaching-out, in the leached slag adding sulfuric acid solution and stirring, controlling pH value and making it progressively be reduced to 1.5-3.0 from 5-5.2; and (3). circulating waste liquor, solid-liquid separating second leached material, and returning the waste liquor contaiing sulfuric acid into neutral leaching-out stage of zinc oxide ore.
Owner:YUNNAN XIANGYUNFEILONG RESOURCES RECYCLING TECH CO LTD
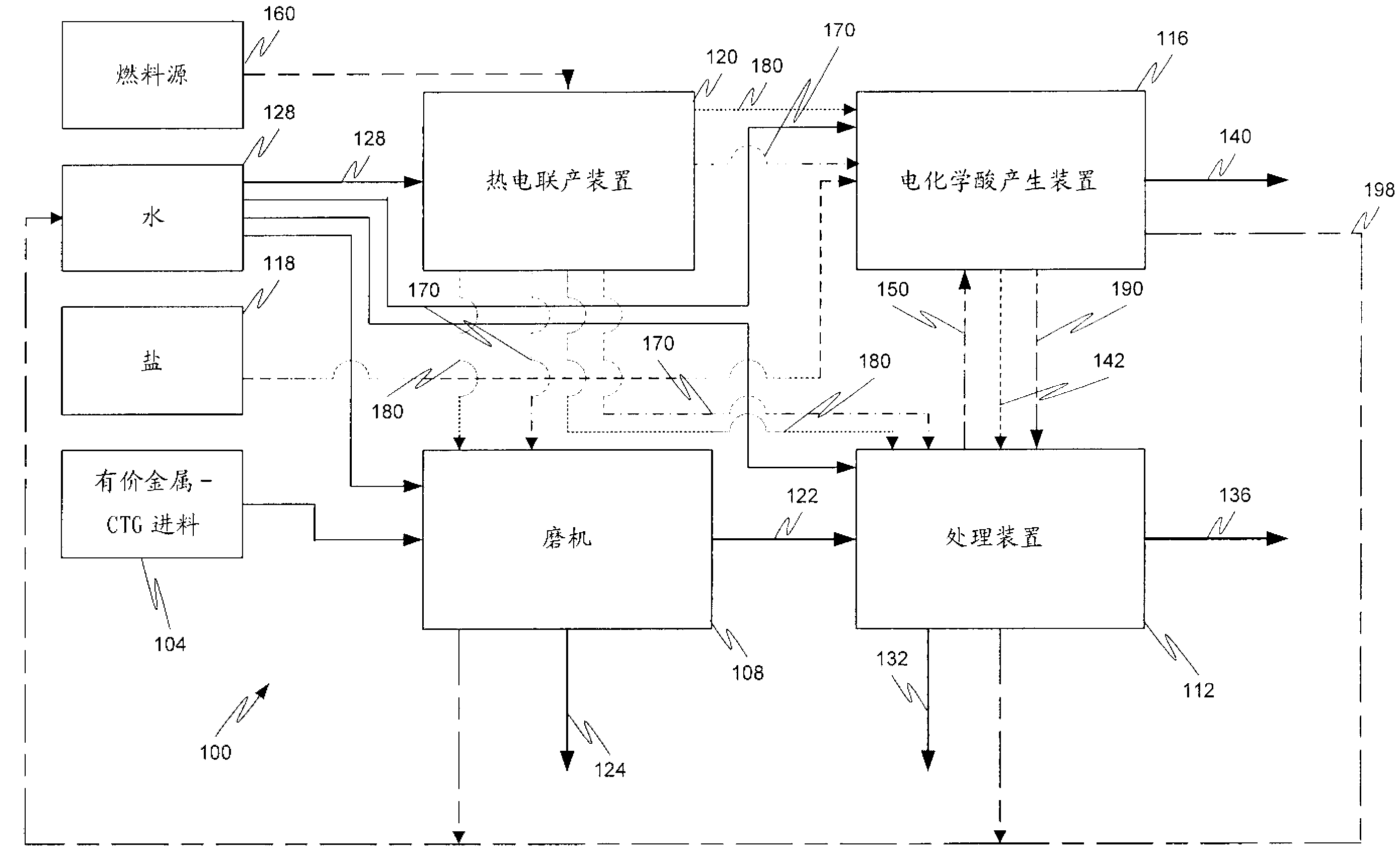
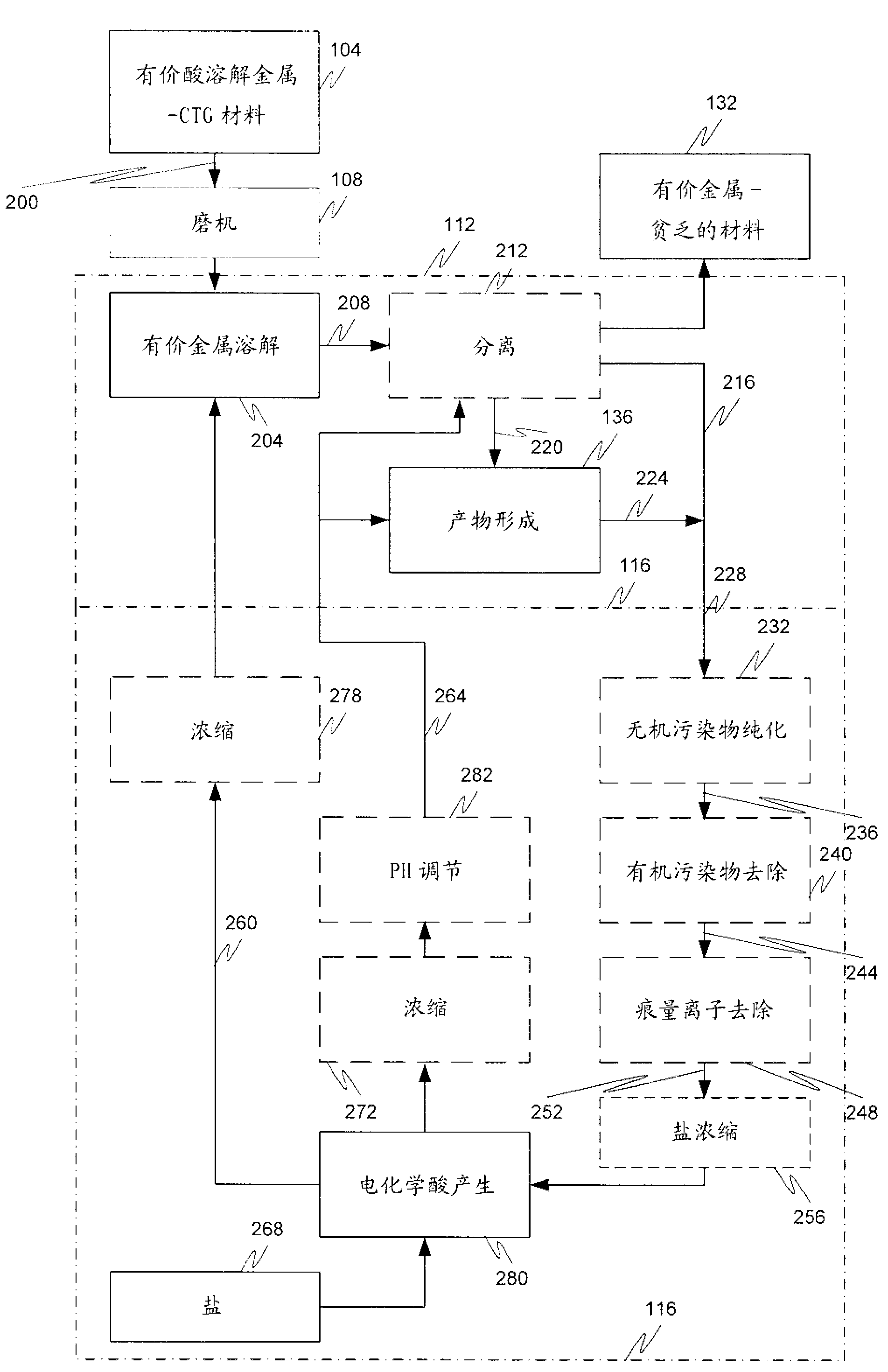
Hydrometallurgical process and method for recovering metals
InactiveCN102939397AReduce demandAvoid demandCerium oxides/hydroxidesEnergy inputMineral processingMetal
A mineral processing facility is provided that includes a cogen plant to provide electrical energy and waste heat to the facility and an electrochemical acid generation plant to generate, from a salt, a mineral acid for use in recovering valuable metals.
Owner:MOLYCORP MINERALS
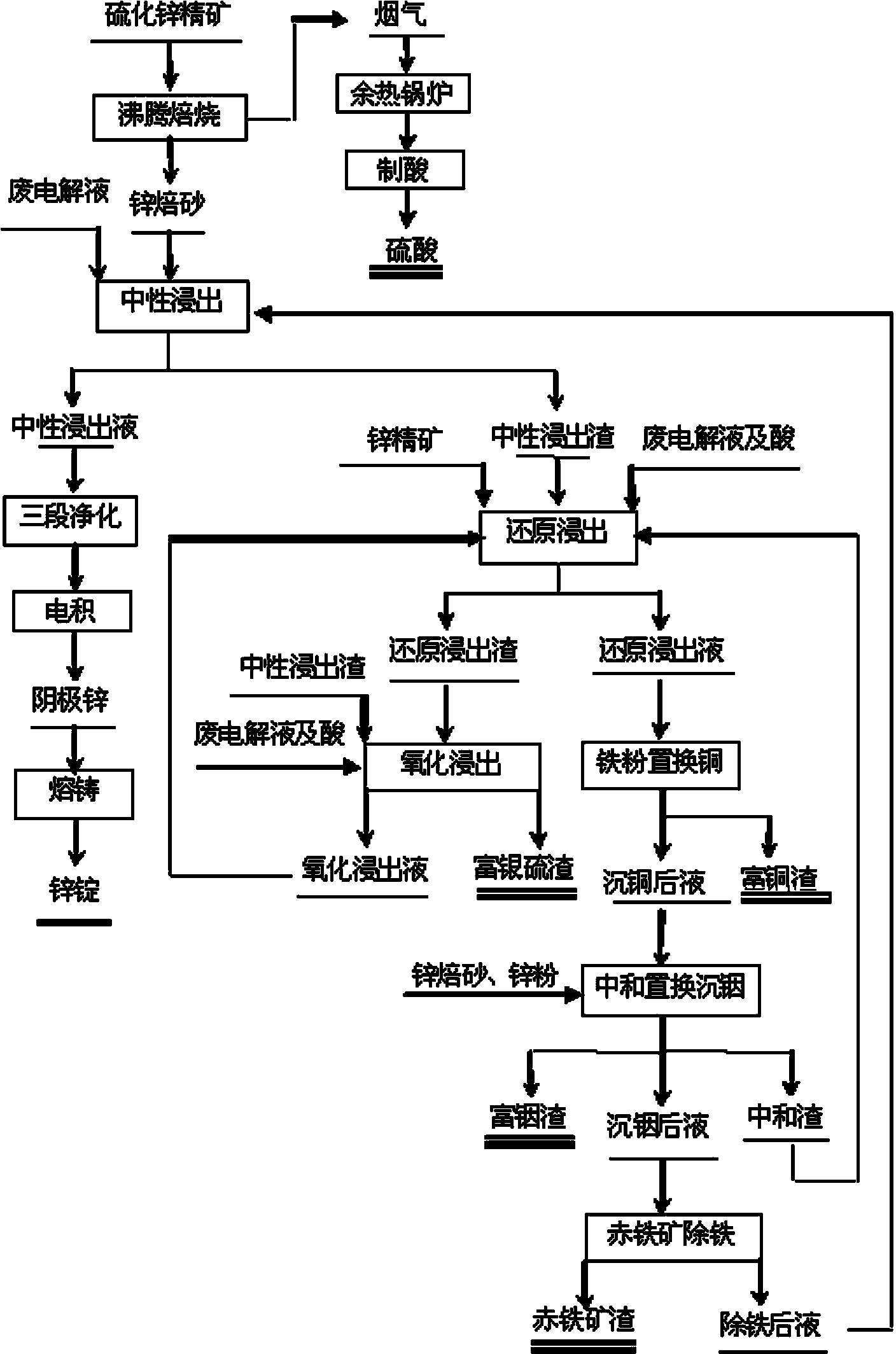
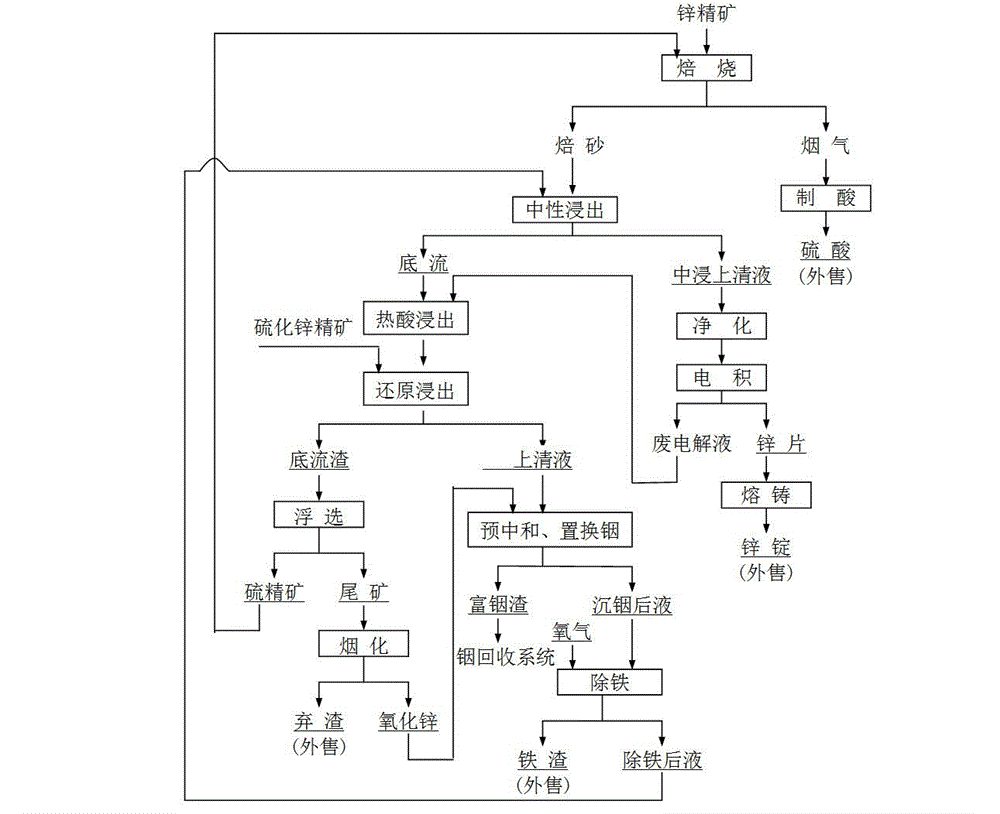
Method for individually processing high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate
ActiveCN103409622AThe process is highly targetedHigh enrichment ratioProcess efficiency improvementIndiumHydrometallurgy
The invention belongs to the technical field of hydrometallurgy, and particularly relates to a method for individually processing high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate. The method comprises a step of subjecting the high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate to calcination in a fluidized bed combustion boiler to obtain zinc calcine; a step of subjecting the zinc calcine to neutral leaching to produce neutral leaching solution and neutral leaching residue; a step of, after the neutral leaching residue and the high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate are mixed, successively performing reduction leaching and oxidation leaching, and circulating oxidation leaching solution to the reduction leaching to produce reduction leaching solution and silver-rich sulfur residue; a step of replacing the reduction leaching solution by using iron powder to precipitate copper and to produce copper-rich slag and solution after copper precipitation; a step of subjecting the solution after copper precipitation to pre-neutralization by using the zinc calcine, and then replacing by using zinc powder to precipitate indium and to produce indium-rich slag and solution after indium precipitation; and a step of bubbling oxygen into the solution after indium precipitation, heating and removing iron to obtain iron removal solution and hematite slag. The hematite slag can be utilized as a raw material for ironmaking. The method has strong pertinence, short technological process and high metal recovery yield, and the method is clean, efficient, energy-saving and environmental friendly. Separation and comprehensive utilization of zinc, indium, copper and iron are achieved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH TECH IND SALES MANAGEMENT
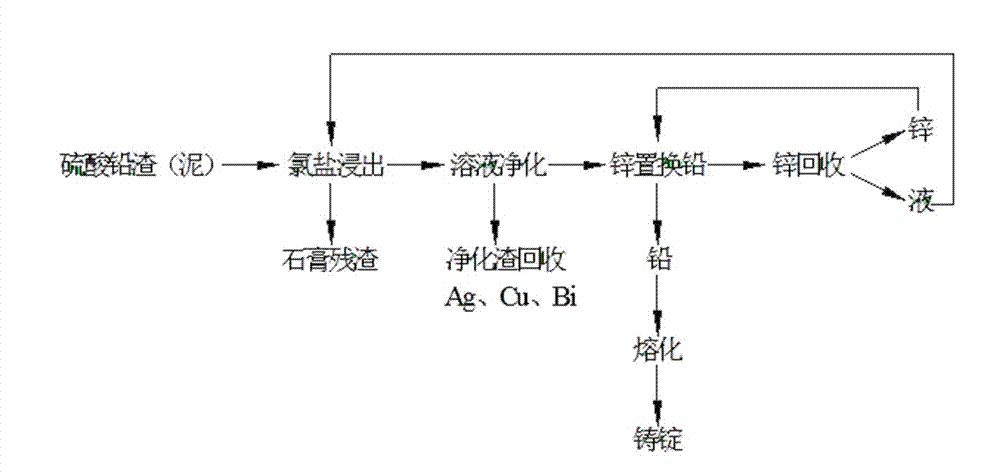
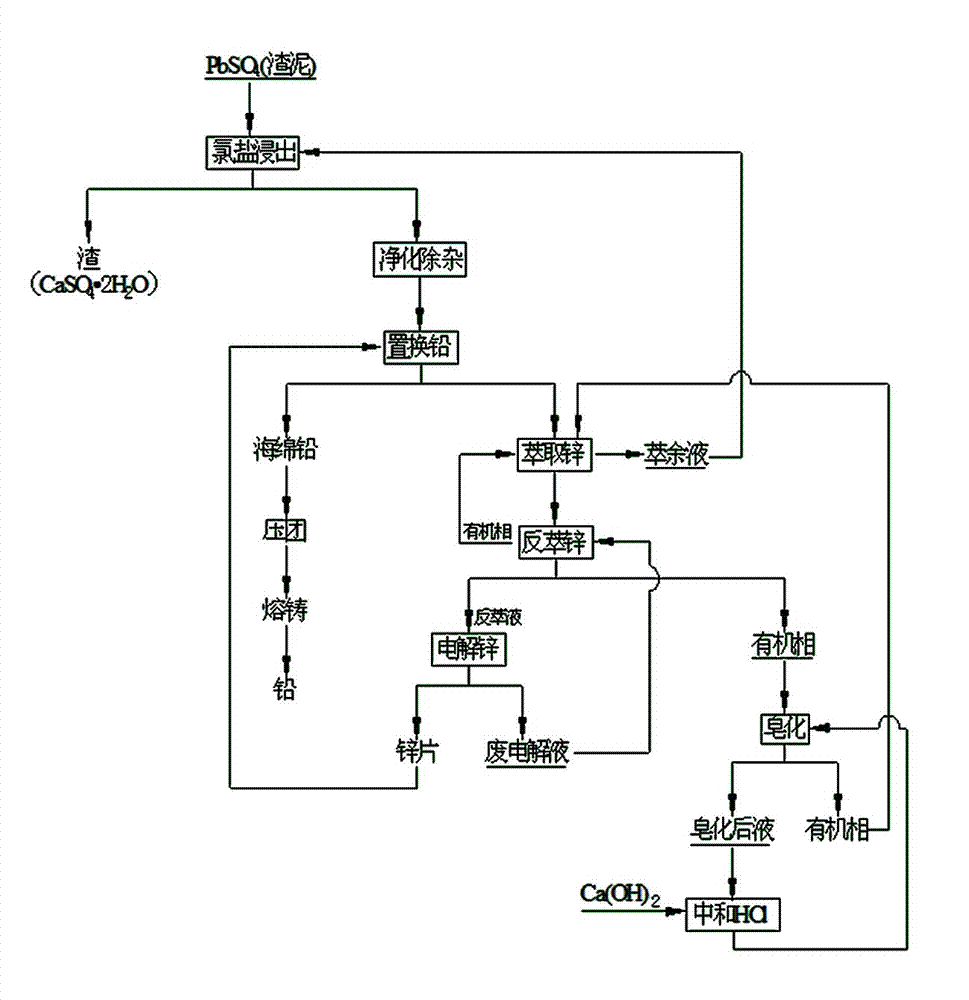
Lead hydrometallurgical technology through utilizing lead sulfate
The invention discloses a lead hydrometallurgical technology through utilizing lead sulfate, belongs to a hydrometallurgical technology, and relates to a technology which adopts a full-hydrometallurgical technology to produce lead through lead sulfate residuals or lead storage battery lead slime which is additionally produced in a zinc hydrometallurgical process. The method comprises steps of: with CaCl2 and NaCl as a leaching solvent; leaching high leaching residuals generated by zinc hydrometallurgy and containing lead sulfate, lead skims generated by leaching zinc out of lead-containing zinc oxides or the lead slimes generated by dismantling lead-acid storage batteries; using zinc to replace lead in the leaching solution; recovering zinc from the replacing solution; returning the recovered zinc to a lead replacement process; and circulating a Cl<->-containing liquid after zinc recovery to a lead sulfate chloride leaching process. The technology has the characteristics of low energy consumption, low cost and easiness in popularization and application; and smoke pollutions such as lead fume, lead dust and SO2 are thoroughly eliminated by utilizing the technology.
Owner:YUNNAN XIANGYUNFEILONG RESOURCES RECYCLING TECH CO LTD
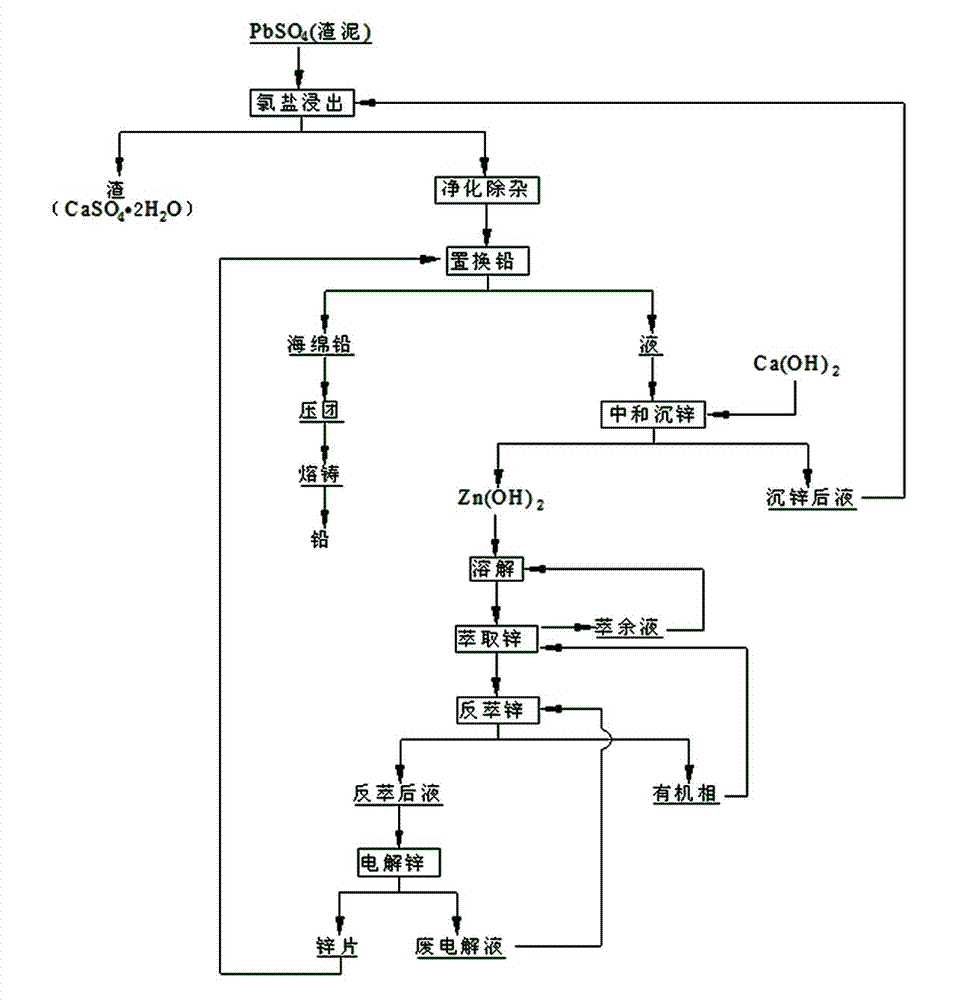
Zinc hydrometallurgy production process
InactiveCN102876888AReduce lossesHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementCement factoryIndium
The invention relates to a zinc hydrometallurgy production process. According to the zinc hydrometallurgy production process provided by the invention, reduction leached supernate is subjected to preneutralization, then zinc dust is added for replacing indium, after the indium is separately removed, oxygen with the concentration being not lower than 98 percent is filled into liquid obtained after the indium is deposited, controlling the temperature in the range of 160 to 200 DEG C and controlling the pressure in the range of 1,000 to 2,000kPa, so that iron precipitates in the liquid obtained after the indium is deposited enter slags. The iron removed liquid obtained by the zinc hydrometallurgy production process has the iron content being lower than 1.2g / l, the iron removed liquid can be directly returned to be subjected to neutral leaching, and the system has stable production working conditions and is beneficial to stable production; in the iron slags obtained by the zinc hydrometallurgy production process, the zinc content is lower than 1 percent, the zinc loss is low and the zinc recovery rate is high; the iron slags can be directly sold to a cement plant and an iron and steel plant to be used as the raw materials without being stacked in a slag field, so that the zinc hydrometallurgy production process is beneficial to environmental-protection and the comprehensive utilization of resources and mineral resources are saved.
Owner:广西华锡集团股份有限公司 +1
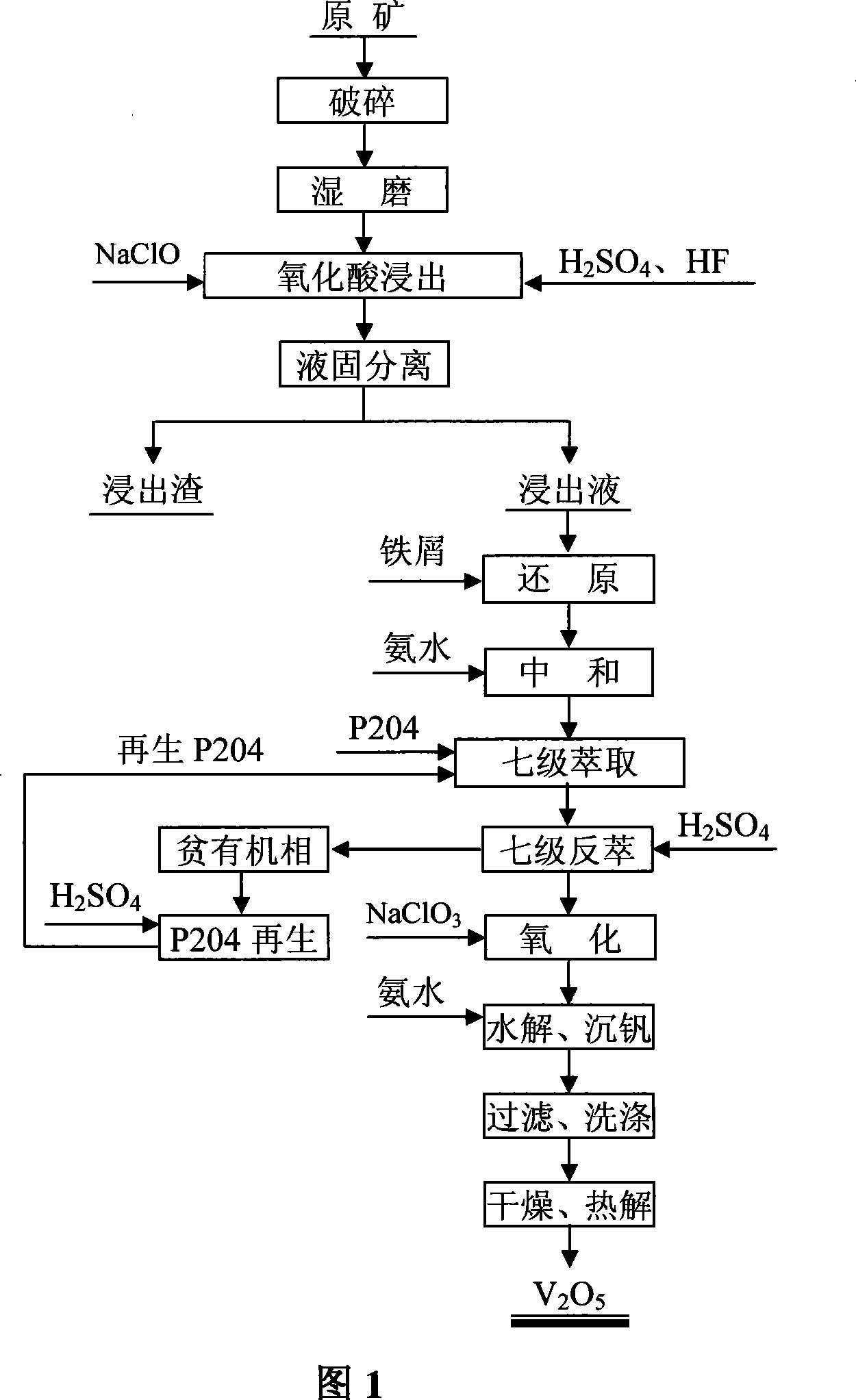
Method for coproducing vanadium pentoxide from vanadium-containing stone coal ore and fluorite
InactiveCN101239740ASolve the problem of leaching and extracting vanadiumSimplification of smelting processVanadium oxidesSulfateChemical combination
The present invention provides a preparing method of vanadic oxide by coal mine containing vanadium and fluorite. The invention belongs to vanadic hydrometallurgy technology, especially a melting technique of directly lixiviating and separating vanadium from coal mine containing vanadium. Acylvanadium sulfate is prepared by mixing coal mine containing vanadium, fluorite mine and sulphuric acid, then pumped in the reactive tank, further chemical combination and dissolving, acylvanadium sulfate enters in solution, qualified vanadic oxide is prepared. The invention adopts whole wet to process coal mine containing vanadium,recovering and utilizing vanadium, the method has a simple process, strength process, high metal recovery rate, easy to separate object metal, small consumption agent, integrated valuable metal and lower pollution.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
All-wet process pretreatment method for copper anode mud
InactiveCN103966450AReduce processingHigh enrichment rateProcess efficiency improvementPretreatment methodHydrometallurgy
The invention relates to a wet-process metallurgy technology in the metallurgical field and particularly relates to an all-wet process pretreatment method for copper anode mud. The all-wet process pretreatment method is as follows: firstly, carrying out hot acid leaching onto copper anode mud, leaching metals such as copper, selenium, sliver, barium, and the like and adding in liquor, leaving gold, tellurium, tin, platinum and platinum-family metals in leaching residue; by virtue of alkali leaching of hot acid leaching residue, leaching and enriching metals such as tellurium, lead, arsenic, and the like in liquor; carrying out chlorination on the obtained tellurium-separating residue for separating gold, enriching the gold, the platinum and the platinum-family metals in the liquor, enriching the tin and the antimony in residue; diluting the hot acid leaching liquor by water, enriching the copper and the selenium in diluted liquor, dissolving obtained precipitates by nitric acid, and filtering to obtain barium sulfate molten slag and sliver nitrate liquor. The all-wet process pretreatment method disclosed by the invention cancels a sulfating and roasting process which is high in energy consumption and great in pollution in the conventional copper anode mud treatment method, removes and openly recycles barium by the hot acid leaching before extracting the gold and the sliver, reduces treatment amount of the copper anode mud, and improves recovery rate of gold and sliver.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com