Patents
Literature
1690results about "Vanadium oxides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
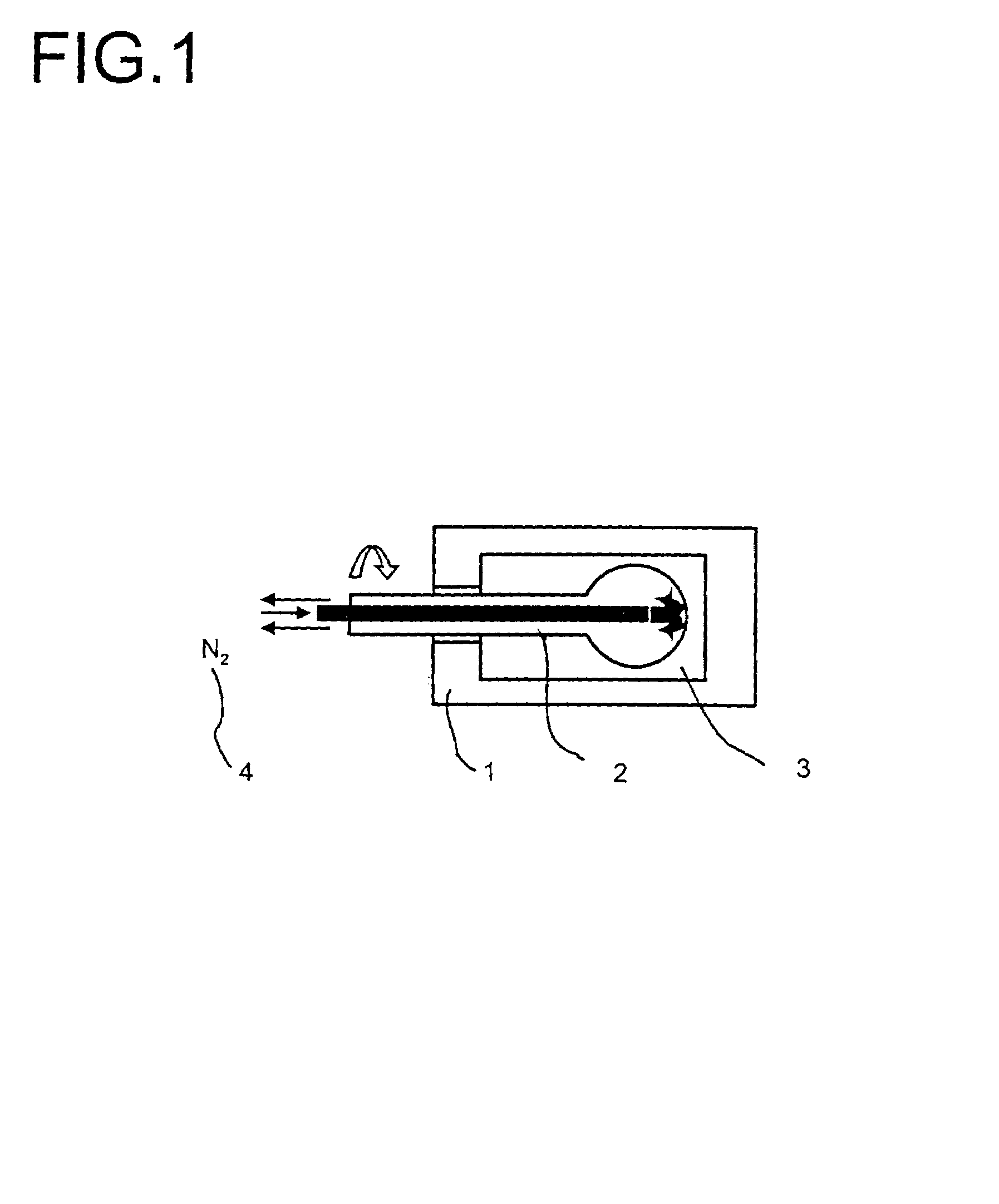
Modified oxygen reduced valve metal oxides
InactiveUS6639787B2Maintain good propertiesWear minimizationOxide/hydroxide preparationLiquid electrolytic capacitorsFluidized bedPhysical chemistry
Owner:GLOBAL ADVANCED METALS USA
Niobium suboxide powder
ActiveUS20050013765A1High currentReduce residual currentOxide/hydroxide preparationLiquid electrolytic capacitorsCapacitorTungsten
A niobium suboxide powder comprising 100 to 600 ppm of magnesium is described. The niobium suboxide powder may (alternatively or in addition to 100 to 600 ppm of magnesium) further include 50 to 400 ppm of molybdenum and / or tungsten. The niobium suboxide powder is suitable for the production of: capacitors having an insulator layer of niobium pentoxide; capacitor anodes produced from the niobium suboxide powder; and corresponding capacitors.
Owner:TANIOBIS GMBH
Process for producing niobium suboxide
ActiveUS20050019581A1Increase capacityIncrease volumeLiquid electrolytic capacitorsTantalum compoundsHydrogenNiobium
A method is described for preparing a niobium suboxide represented by the formula, NbOx, in which 0.7<x<1.3. The method involves reacting NbOy (in which y<1.8<2.1) with a stoichiometric amount of niobium metal, in the presence of hydrogen. The niobium suboxide produced by such method may be used to fabricate anodes for solid electrolyte capacitors.
Owner:TANIOBIS GMBH
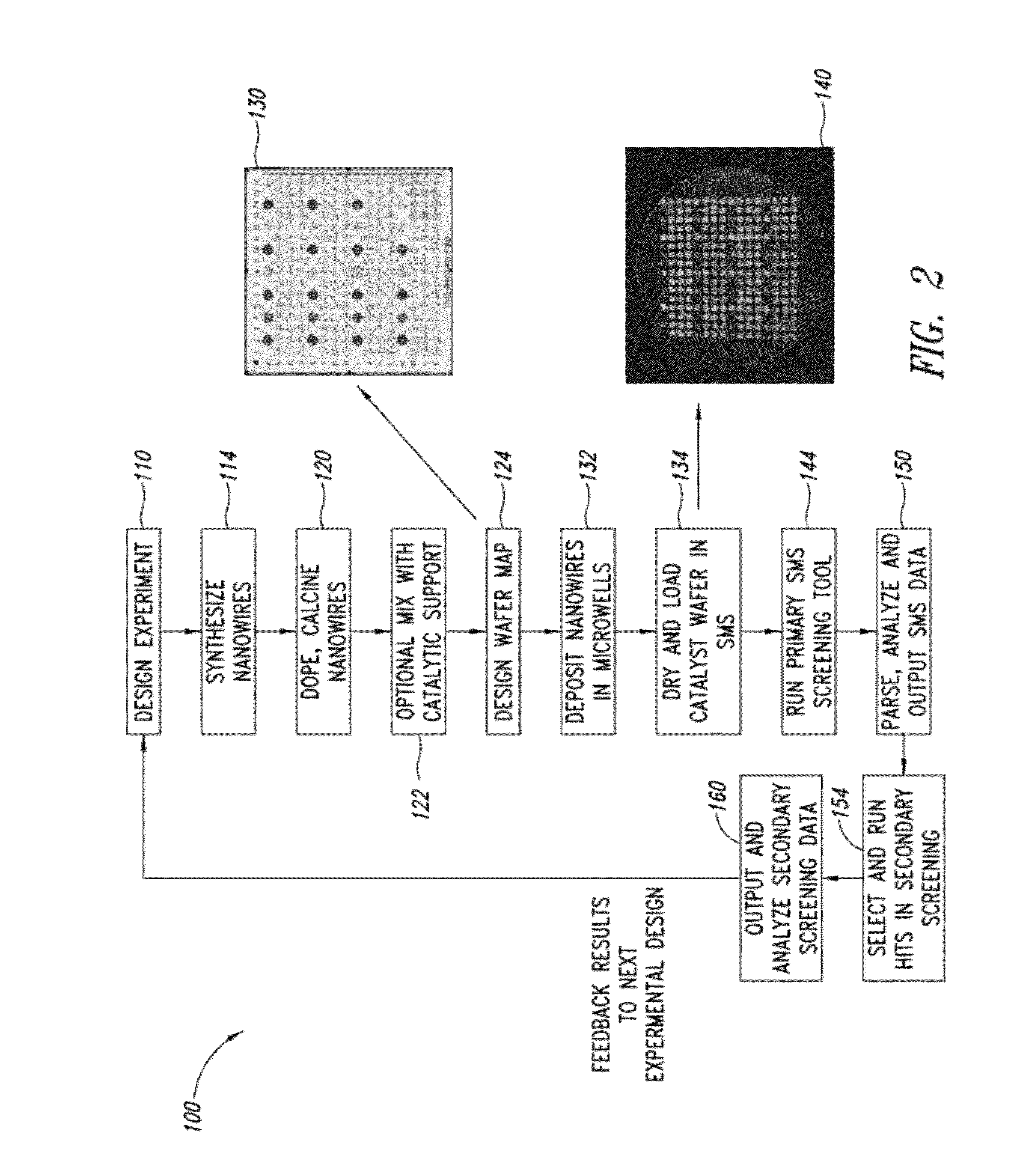
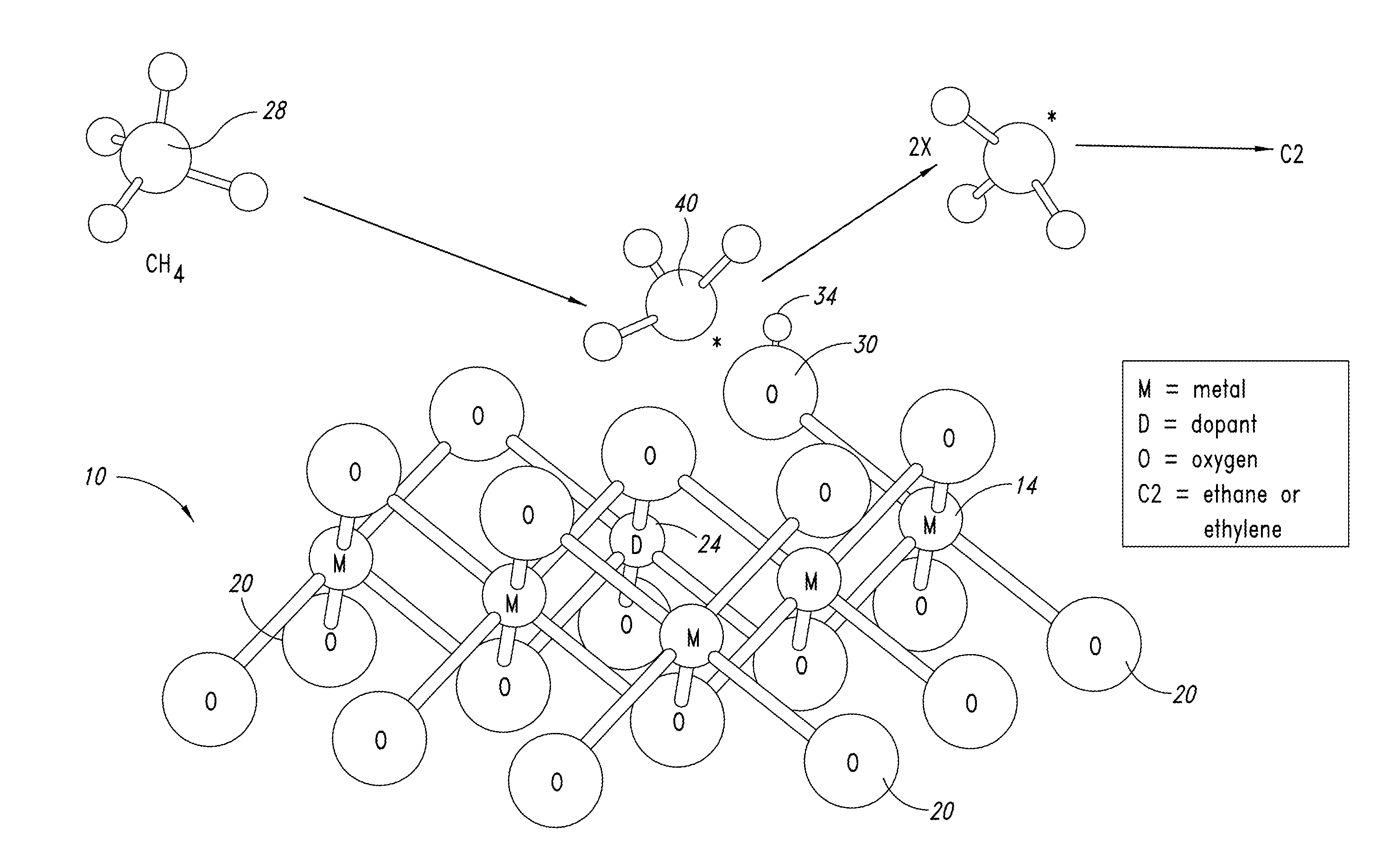
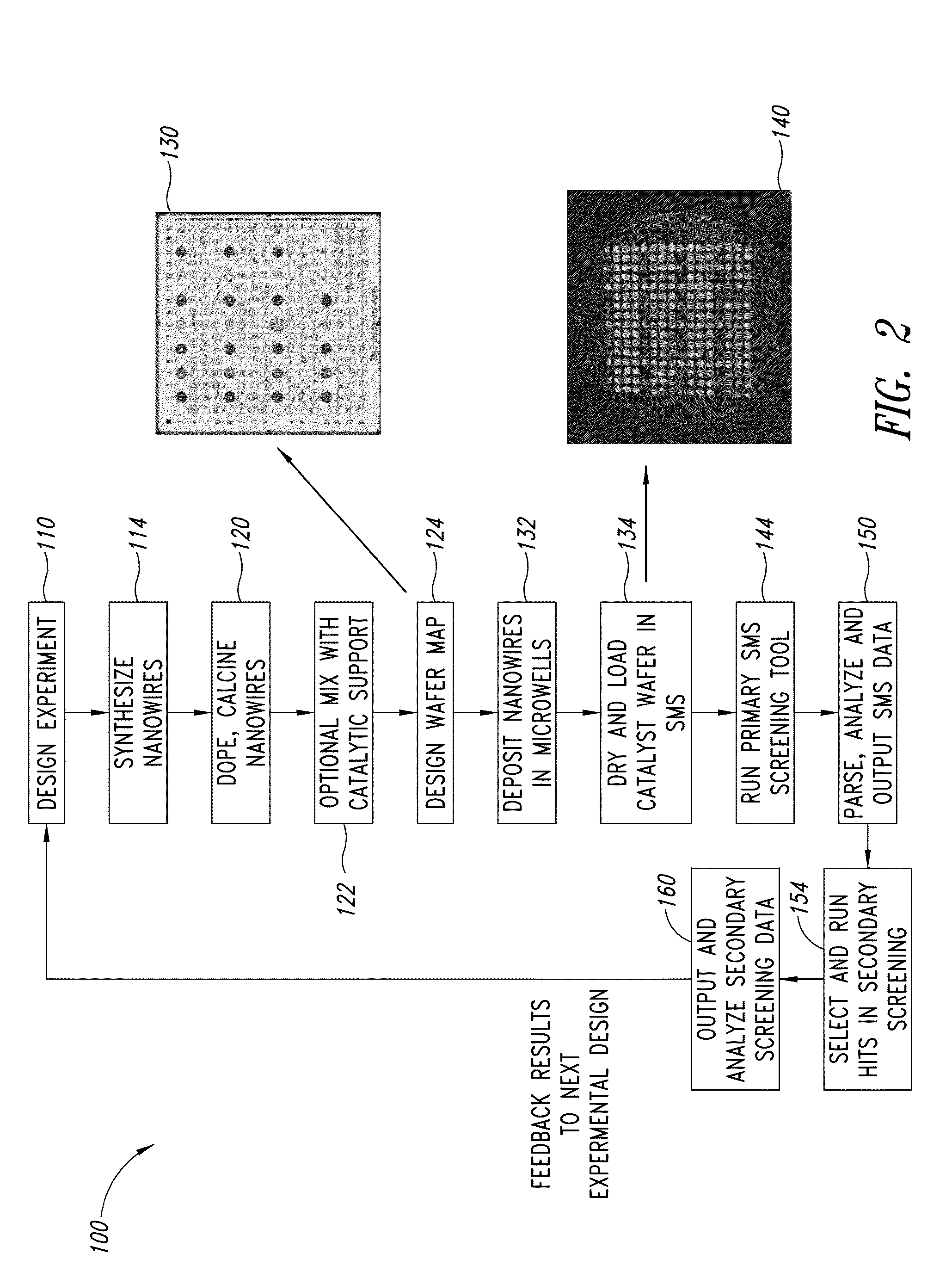
Nanowire catalysts
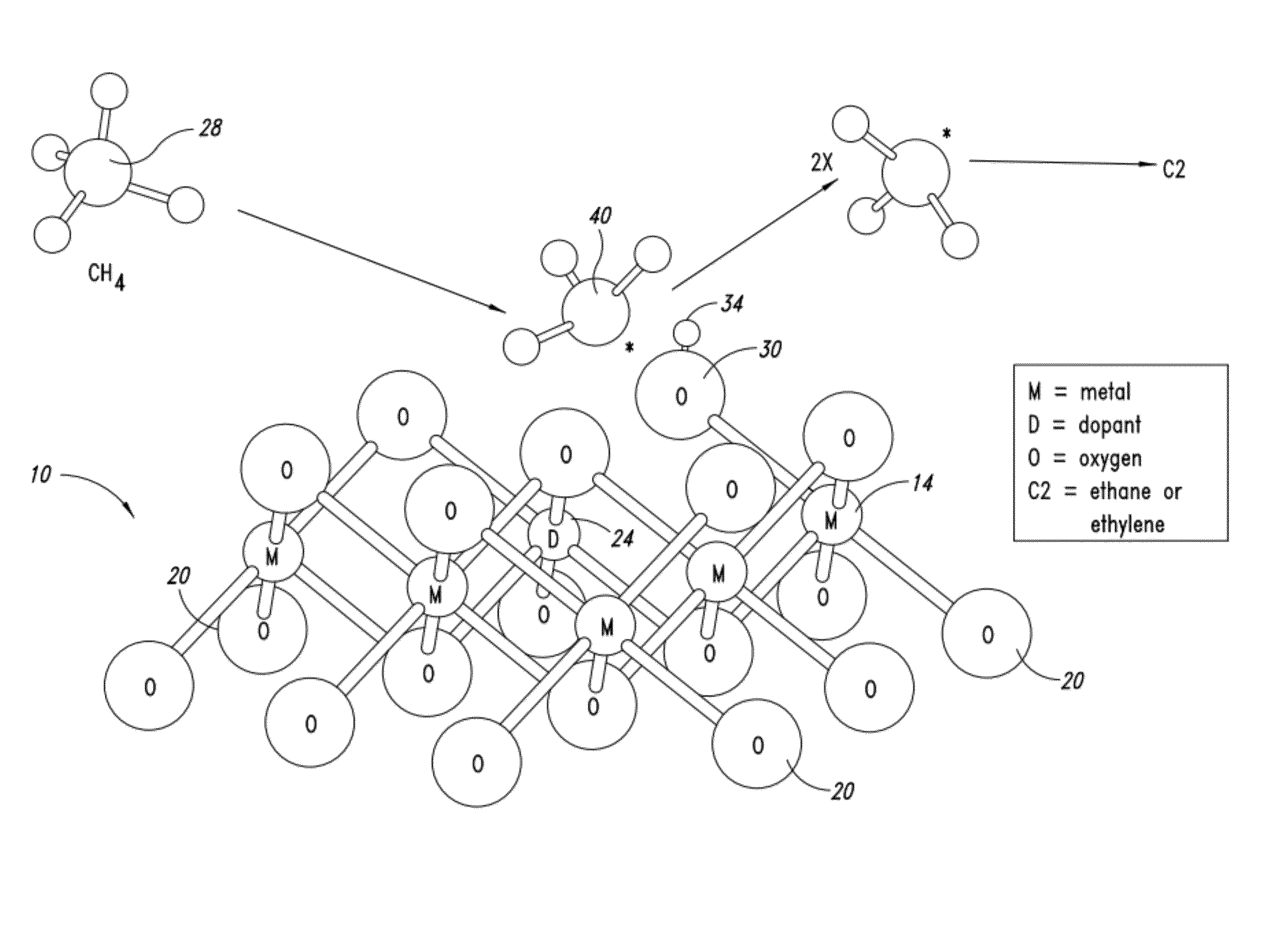
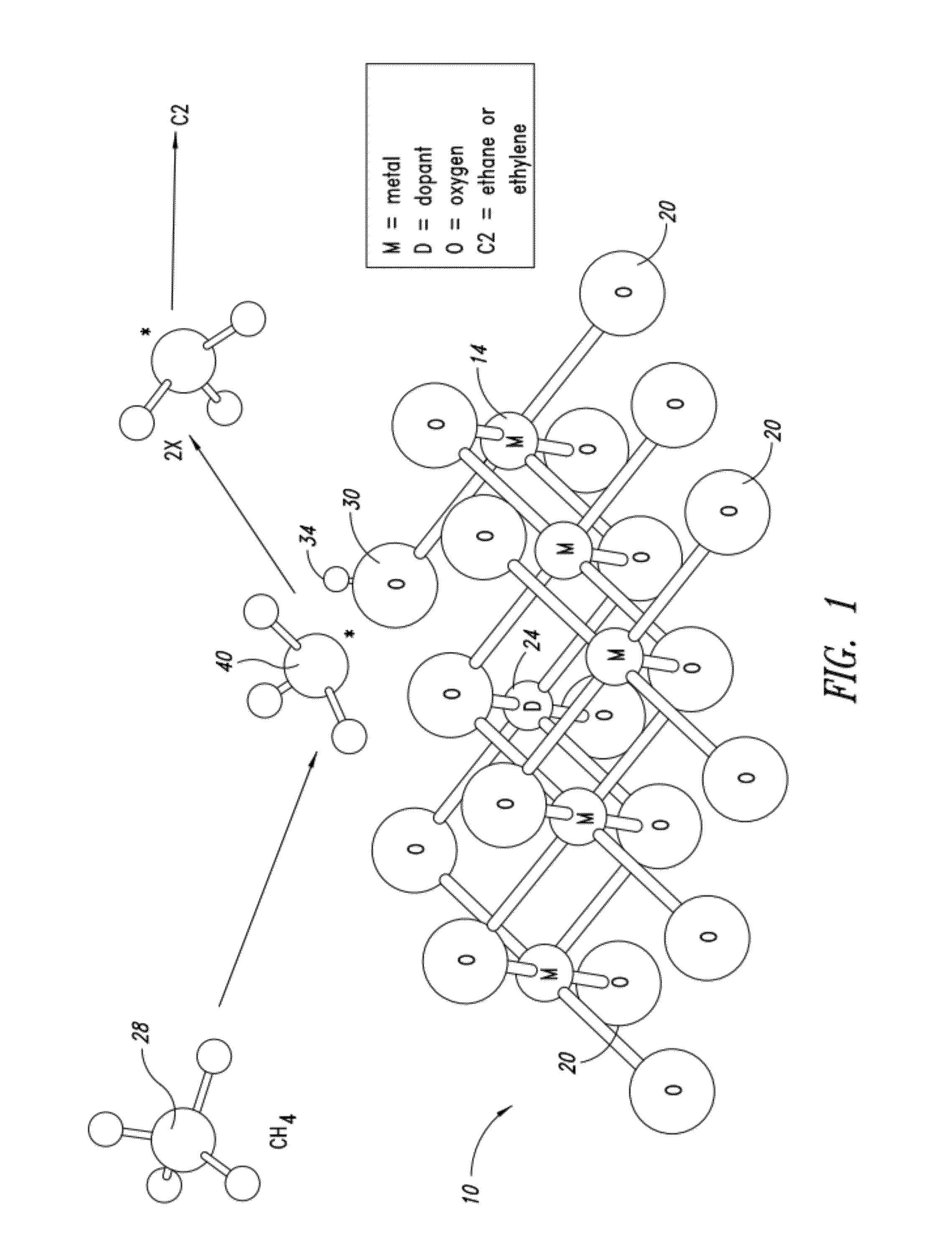
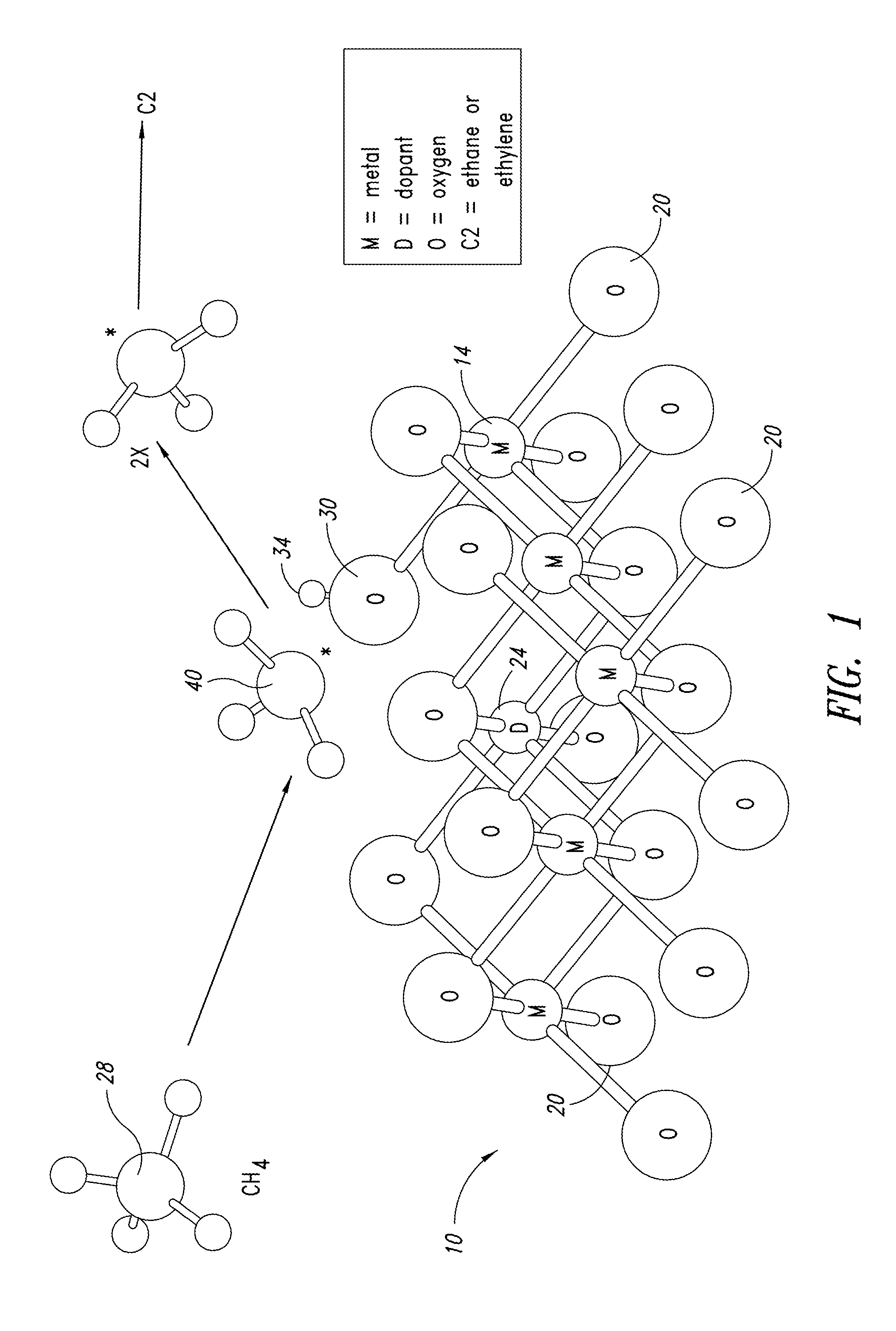
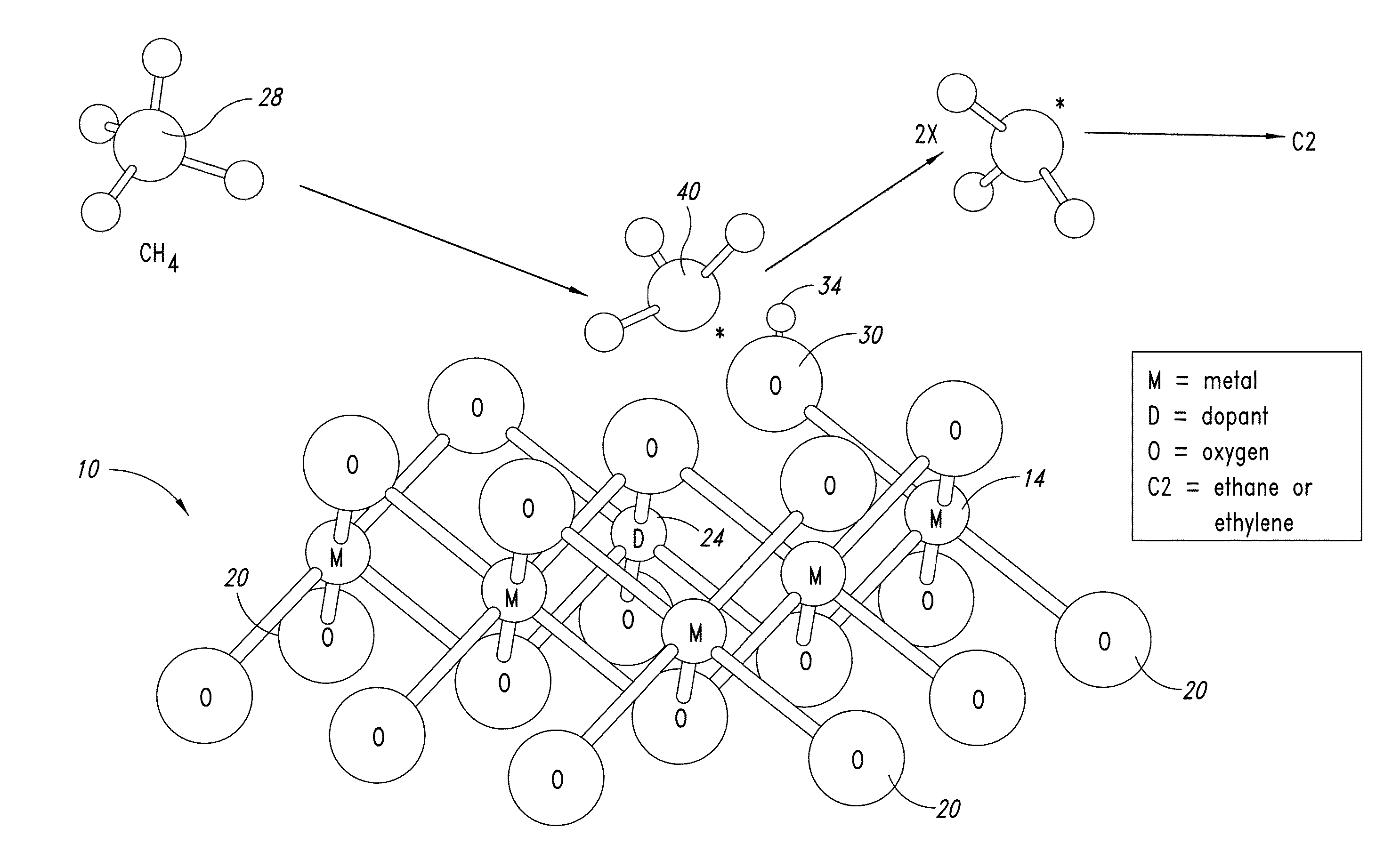
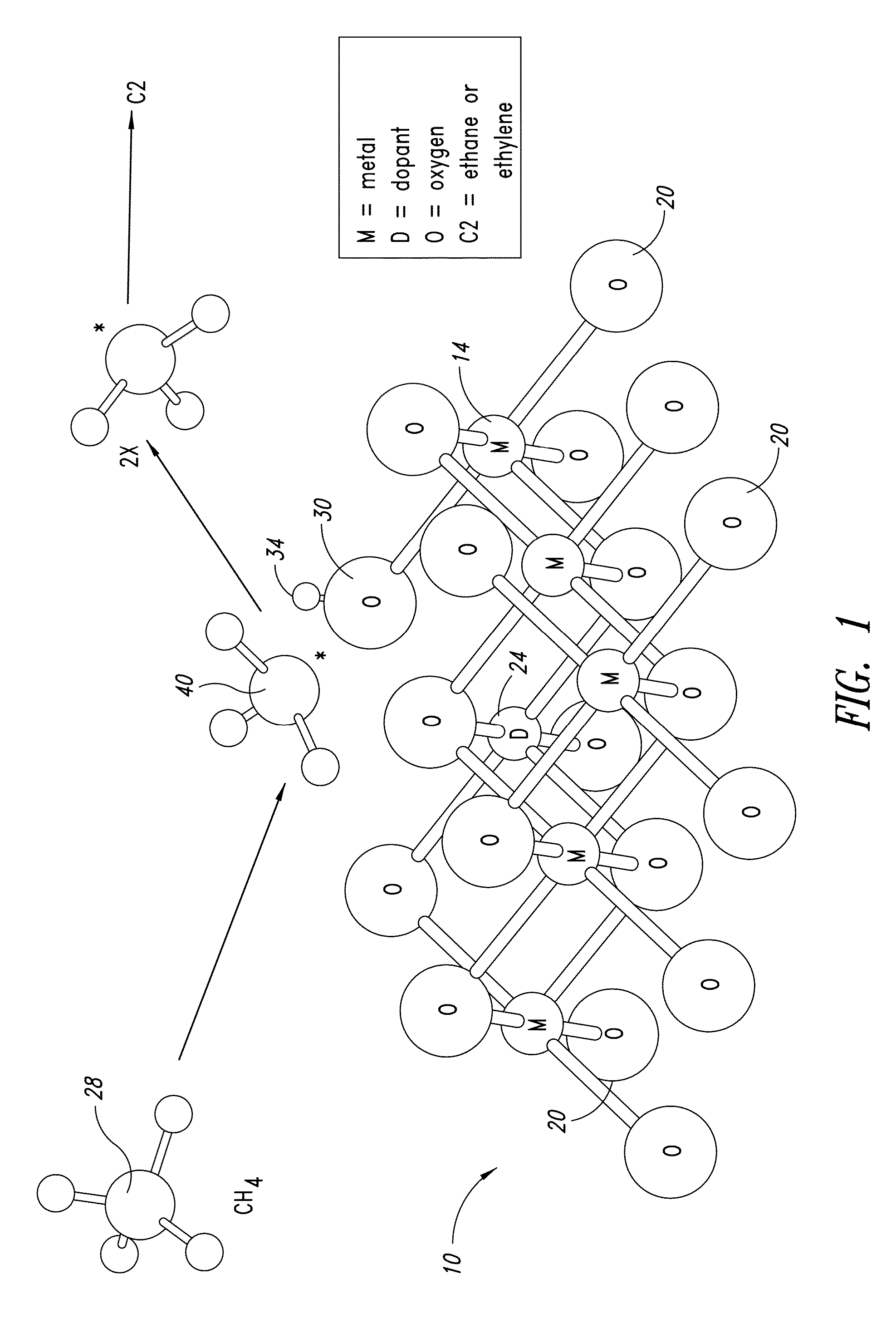
Nanowires useful as heterogeneous catalysts are provided. The nanowire catalysts are useful in a variety of catalytic reactions, for example, the oxidative coupling of methane to ethylene. Related methods for use and manufacture of the same are also disclosed.
Owner:SILURIA TECH INC
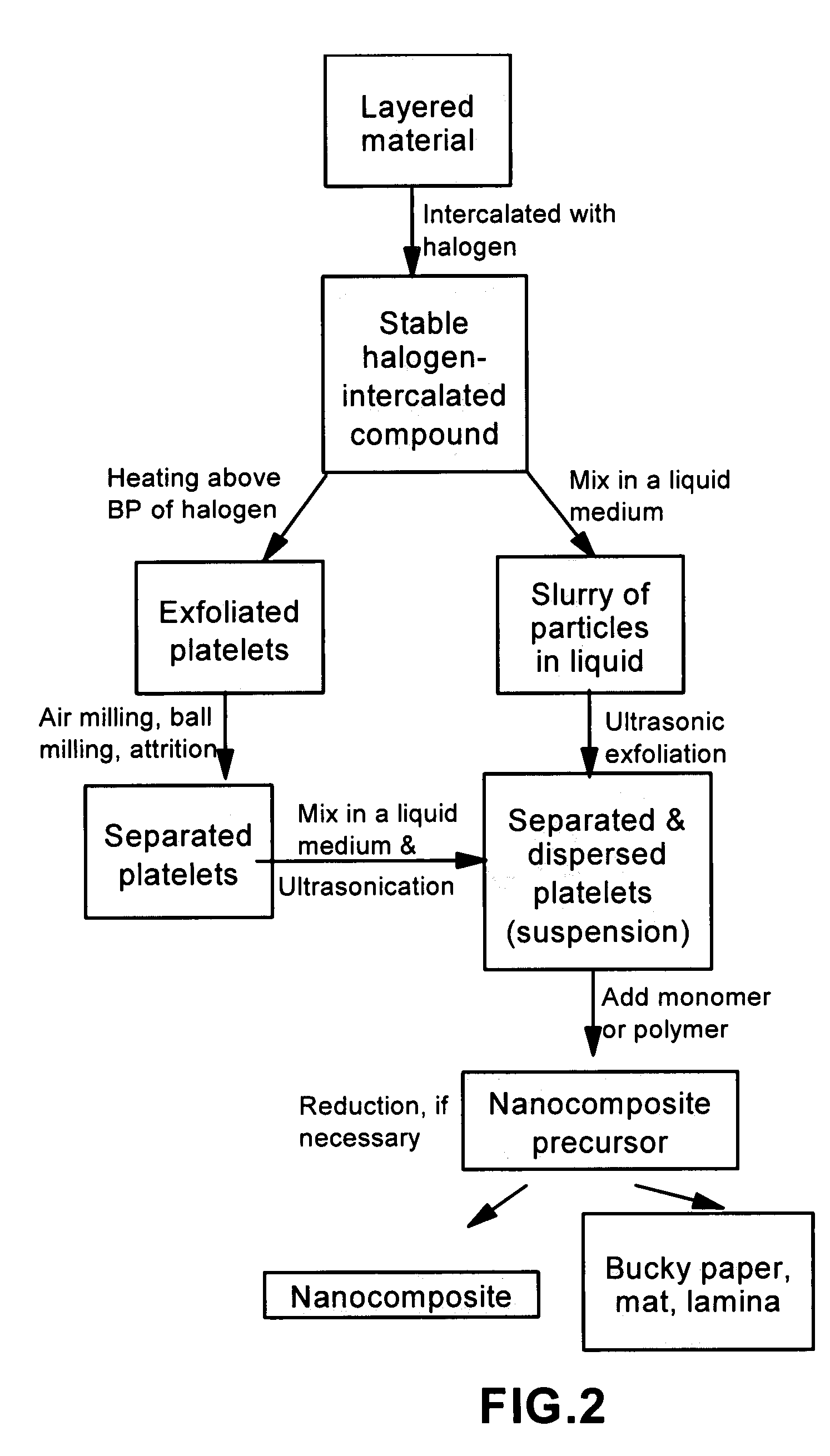
Method of producing nano-scaled graphene and inorganic platelets and their nanocomposites
ActiveUS20080206124A1Readily captured and re-usedReduce impactCarbon compoundsSelenium/tellurium compundsLiquid mediumPhysical chemistry
Disclosed is a method of exfoliating a layered material (e.g., graphite and graphite oxide) to produce nano-scaled platelets having a thickness smaller than 100 nm, typically smaller than 10 nm, and often between 0.34 nm and 1.02 nm. The method comprises: (a) subjecting the layered material in a powder form to a halogen vapor at a first temperature above the melting point or sublimation point of the halogen at a sufficient vapor pressure and for a duration of time sufficient to cause the halogen molecules to penetrate an interlayer space of the layered material, forming a stable halogen-intercalated compound; and (b) heating the halogen-intercalated compound at a second temperature above the boiling point of the halogen, allowing halogen atoms or molecules residing in the interlayer space to exfoliate the layered material to produce the platelets. Alternatively, rather than heating, step (a) is followed by a step of dispersing the halogen-intercalated compound in a liquid medium which is subjected to ultrasonication for exfoliating the halogen-intercalated compound to produce the platelets, which are dispersed in the liquid medium. The halogen can be readily captured and re-used, thereby significantly reducing the impact of halogen to the environment. The method can further include a step of dispersing the platelets in a polymer or monomer solution or suspension as a precursor step to nanocomposite fabrication.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Multimetal oxide materials
Owner:BASF SE
Nanowire catalysts and methods for their use and preparation
ActiveUS20130165728A1Material nanotechnologyManganese oxides/hydroxidesNanowireOxidative coupling of methane
Nanowires useful as heterogeneous catalysts are provided. The nanowire catalysts are useful in a variety of catalytic reactions, for example, the oxidative coupling of methane to C2 hydrocarbons. Related methods for use and manufacture of the same are also disclosed.
Owner:LUMMUS TECH LLC
Polymer templated nanowire catalysts
InactiveUS20130158322A1Improve drawing legibilityMaterial nanotechnologyManganese oxides/hydroxidesNanowirePolymer science
Nanowires useful as heterogeneous catalysts are provided. The nanowire catalysts are prepared by polymer templated methods and are useful in a variety of catalytic reactions, for example, the oxidative coupling of methane to ethane and / or ethylene. Related methods for use and manufacture of the same are also disclosed.
Owner:SILURIA TECH INC
Process for producing niobium suboxide
ActiveUS7341705B2Increase capacityLiquid electrolytic capacitorsTantalum compoundsNiobiumPhysical chemistry
A method is described for preparing a niobium suboxide represented by the formula, NbOx, in which 0.7<x<1.3. The method involves reacting NbOy (in which y<1.8<2.1) with a stoichiometric amount of niobium metal, in the presence of hydrogen. The niobium suboxide produced by such method may be used to fabricate anodes for solid electrolyte capacitors.
Owner:TANIOBIS GMBH
Niobium suboxide powder
ActiveUS7381396B2Reduce residual currentReduce volatilityOxide/hydroxide preparationLiquid electrolytic capacitorsTungstenSuboxide
A niobium suboxide powder comprising 100 to 600 ppm of magnesium is described. The niobium suboxide powder may (alternatively or in addition to 100 to 600 ppm of magnesium) further include 50 to 400 ppm of molybdenum and / or tungsten. The niobium suboxide powder is suitable for the production of: capacitors having an insulator layer of niobium pentoxide; capacitor anodes produced from the niobium suboxide powder; and corresponding capacitors.
Owner:TANIOBIS GMBH
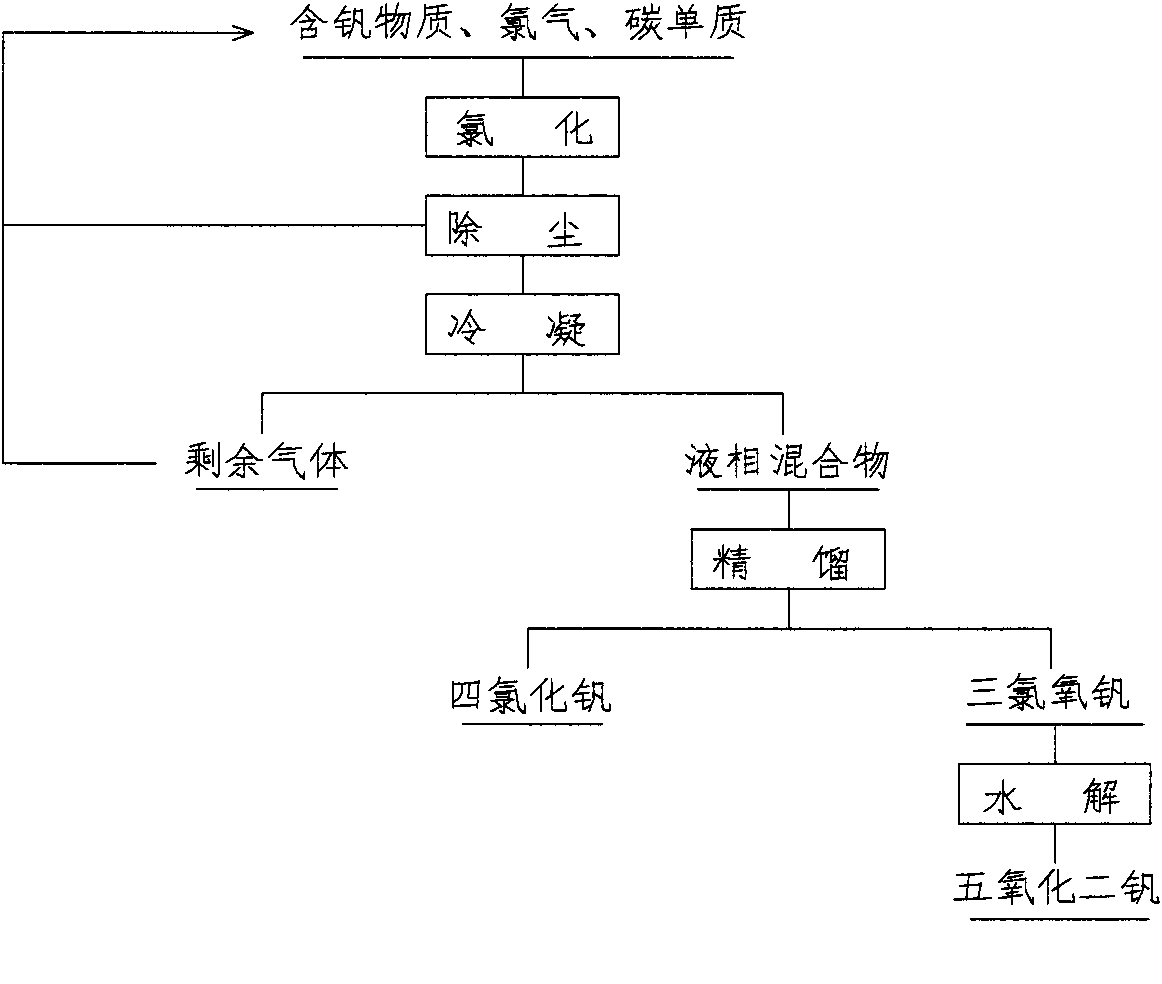
Method for producing high-purity vanadium pentoxide by chlorination
The invention discloses a novel method for extracting and converting a substance containing vanadium into high-purity vanadium pentoxide by chlorination. The high-purity vanadium pentoxide process comprises batching, chlorination, dedusting, condensation, rectification, hydrolysis, filtering, drying and postprocessing. Raw materials comprise the substance containing vanadium and a carbon elementary substance and the weight ratio of the substance containing vanadium to the carbon elementary substance is 1: (0.05-0.25). The raw materials are evenly mixed, dried and put in a reactor and the high-purity vanadium pentoxide is obtained through successive chlorination, hydrolysis, postprocessing and the like. The novel method for producing high-purity vanadium pentoxide instead of a traditional method reduces industrial harmful waste water produced during a traditional hydrometallurgy process, and cyclic utilization of chlorine is achieved after the chlorine is processed. The whole production process is easy in process and basically free of produced wastes, and has certain economic benefit and social benefit. The purity of the vanadium pentoxide powder obtained by the method is 99.5%-99.99%.
Owner:刘艳梅
Heavy oil reforming method, an apparatus therefor, and gas turbine power generation system
InactiveUS20060011511A1Reduce equipment costsReduce runningThermal non-catalytic crackingHydrogenScavengerCombustor
Owner:HOKARI NOBUYUKI +4
Sintered bodies based on niobium suboxide
Disclosed are sintered bodies that include: (a) 30 to 100 mol % of NbOx, wherein 0.5<x<1.5; and (b) 0 to 70 mol % of MgO. The sintered bodies may be used as inert apparatuses in the production of niobium suboxide powder or niobium suboxide anodes, or as chemically resistant components in chemical apparatuses.
Owner:H C STARCK GMBH
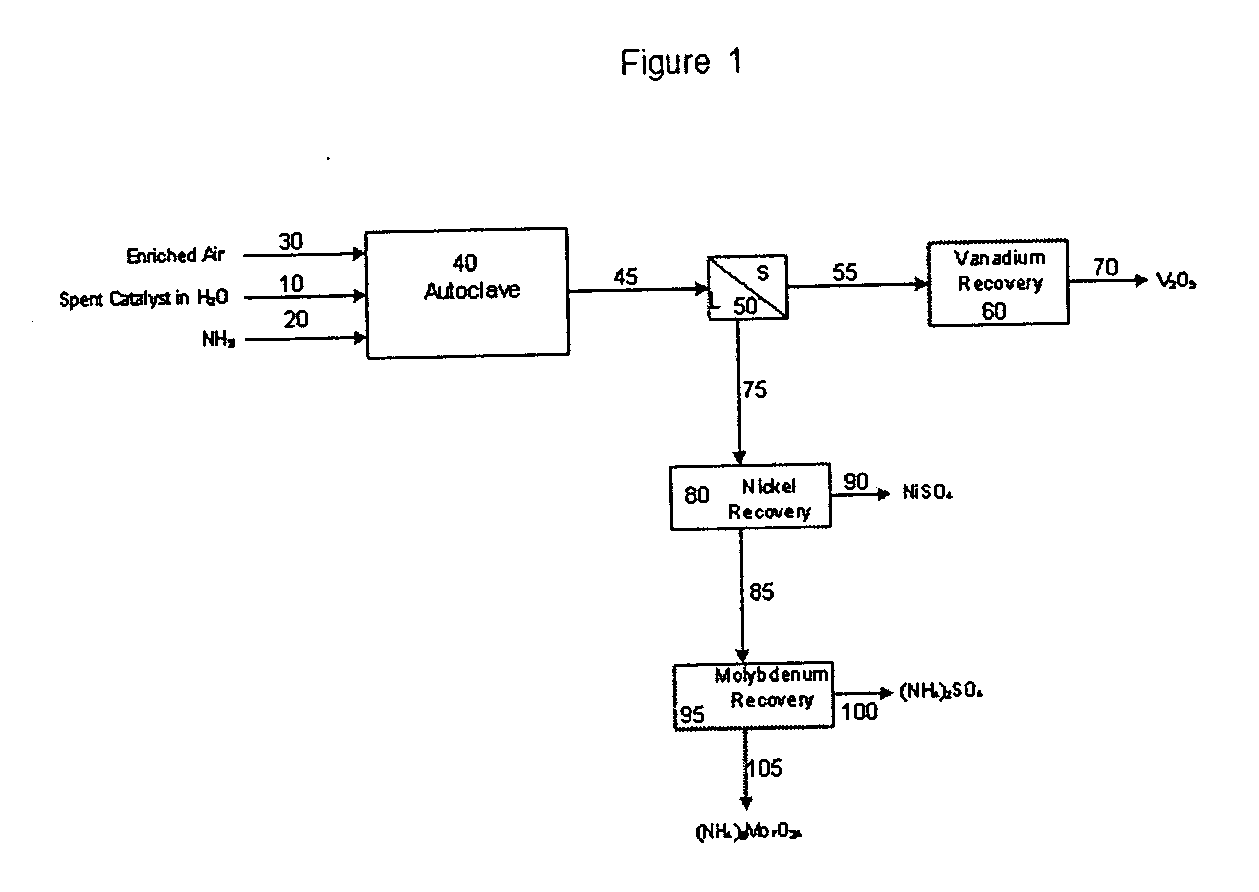
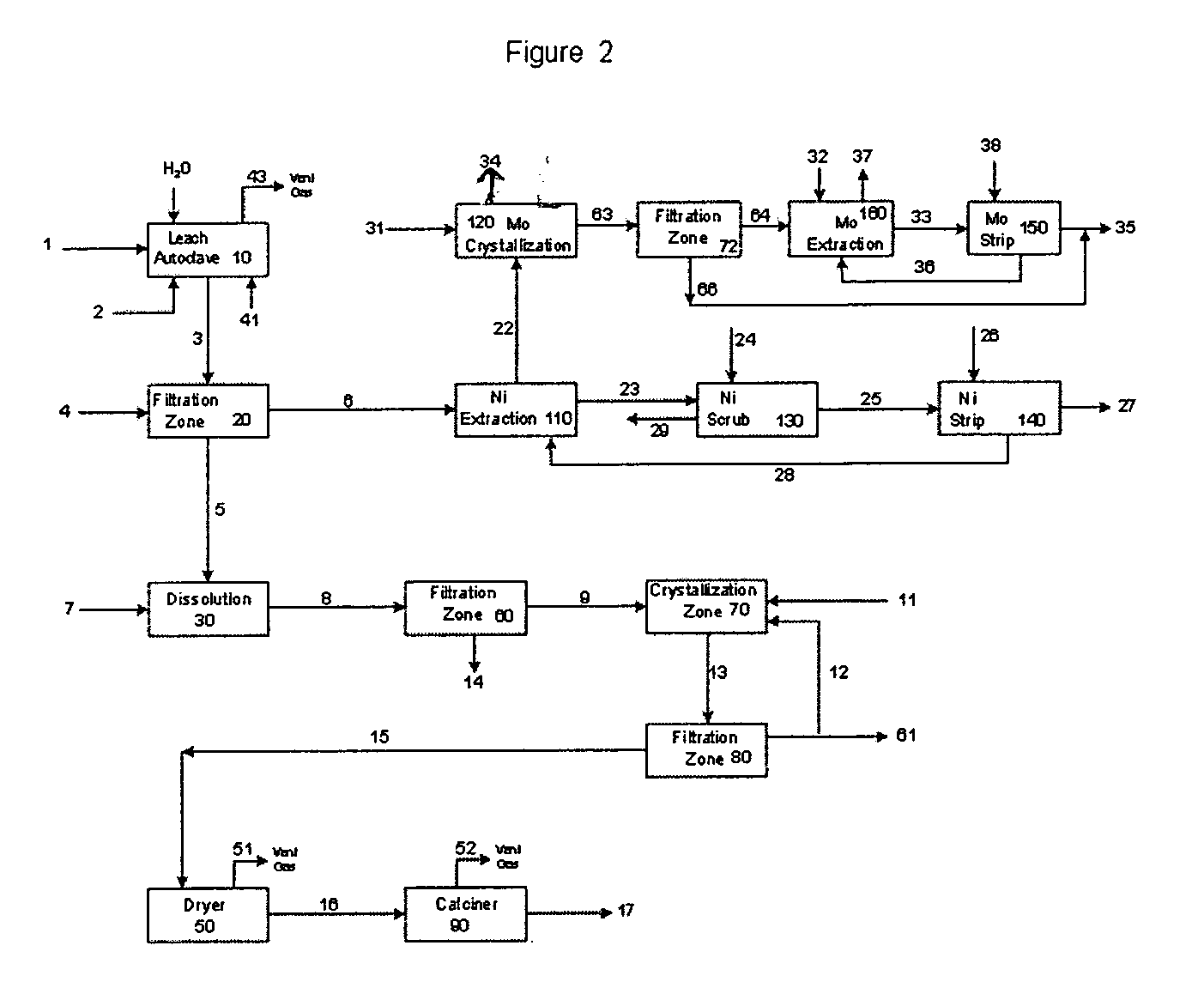
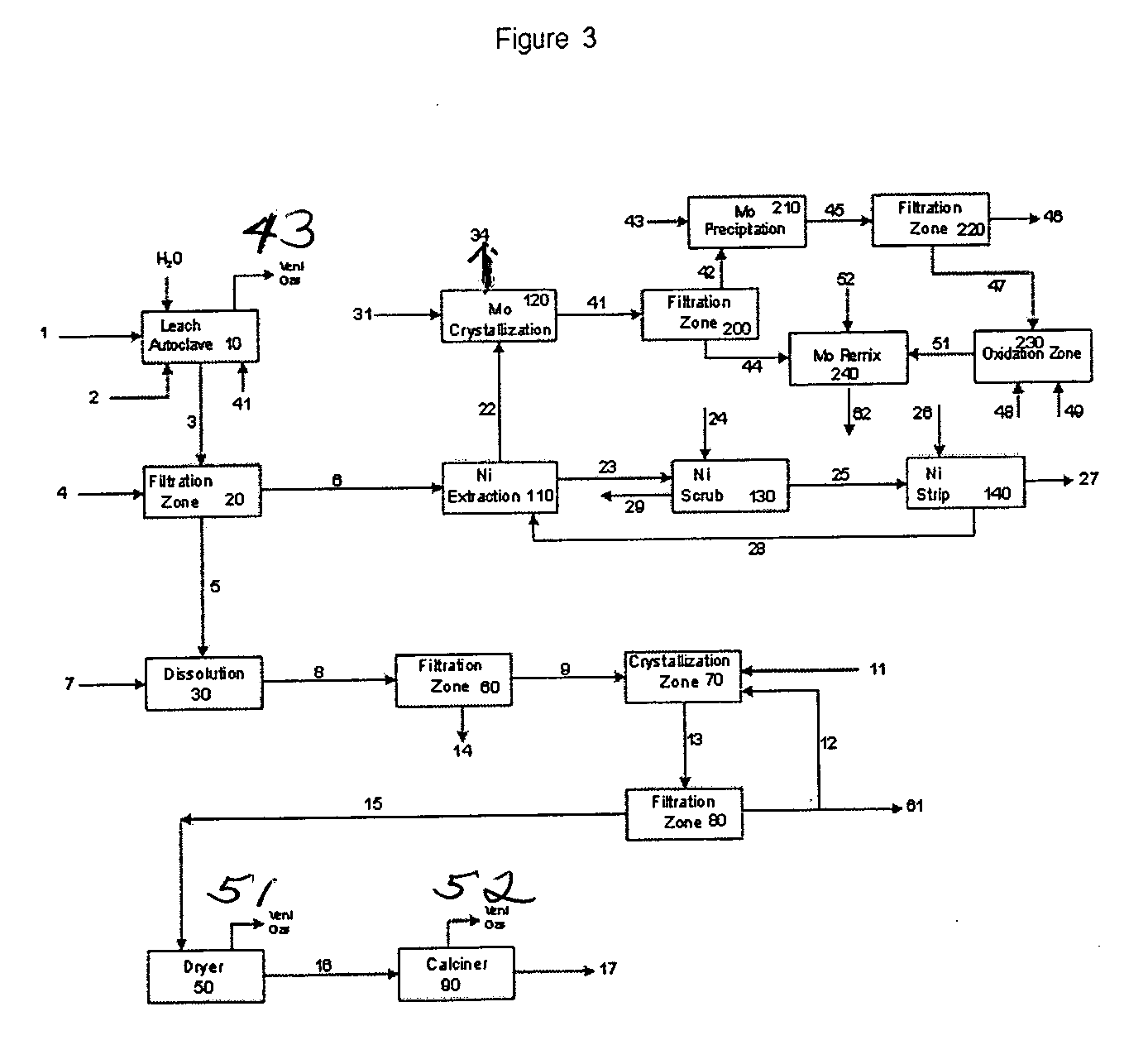
Process for metals recovery from spent catalyst
The process of this invention is directed to the removal of metals from an unsupported spent catalyst. The catalyst is subjected to leaching reactions. Vanadium is removed as a precipitate, while a solution comprising molybdenum and nickel is subjected to further extraction steps for the removal of these metals. Molybdenum may alternately be removed through precipitation.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Method for extracting tungsten, titanium and vanadium from waste SCR (selective catalytic reduction) catalyst
InactiveCN102936049ASolve the pollution of the environmentLow equipment requirementsTungsten oxides/hydroxidesTitanium dioxideSlagStrong acids
The invention discloses a method for extracting tungsten, titanium and vanadium from a waste SCR (selective catalytic reduction) catalyst, which comprises the following steps: crushing the waste SCR catalyst, adding a strongly alkaline solution, and reacting; filtering, separating, then adding strong acid into the sodium tungstate and sodium vanadate mixed solution, and reacting to obtain tungstic acid and a sodium salt and vanadic acid mixed solution; regulating the pH value of the sodium salt and vanadic acid mixed solution until precipitate is separated out, thus obtaining ammonium vanadate; then adding sulfuric acid into the tungsten-and-vanadium-removed SCR catalyst, and reacting to obtain a titanyl sulfate solution and solids such as aluminum slag and the like; then adding water into the titanyl sulfate solution, and hydrolyzing to obtain titanic acid and a waste acid solution; and finally, respectively calcining the obtained ammonium vanadate, tungstic acid and titanic acid to obtain vanadium pentoxide, tungsten trioxide and titanium dioxide. According to the invention, tungsten, titanium and vanadium can be extracted from the SCR catalyst through the reaction with strong alkali and strong acid at a low temperature, the equipment requirement is low, the energy consumption is low, some products having added values can be coproduced, and no secondary pollution is generated, thereby facilitating popularization and application.
Owner:成都新智金森环保科技有限公司
Method for producing vanadium pentoxide by utilizing vanadium slag
The invention discloses a process for producing vanadic anhydride by vanadium slag. The steps of the process comprise as follows: a, adding alkali metal salt in the vanadium slag, and mixing with each other uniformly, a mixture is obtained. b, laying the mixture obtained by step a into a calcining furnace to oxidize and calcine, vanadium slag grog is obtained. c, the calcined vanadium slag is discharged out of the furnace, fast cooling and performing water immersion. d, filtering the mixture obtained by step c, filter liquor is obtained. e, removing impurities in the filter liquor. f, adjusting the pH value of the filter liquor obtained by step e, adding ammonium salt to precipitate vanadium and filtering the filter liquor, then, ammonium peroxovanadate filter cake and ammonium metavanadate filter cake are obtained. g, calcining the filter cake after vanadium precipitation obtained by step f, and vanadic anhydride is obtained, wherein the content of the vanadic anhydride in the vanadium slag used in step a is 2.0%-8.0%. The invention has the advantages of simple and easy, low facility request, convenient operation and low cost, further, the residual quantity of the vanadic anhydride in waste slag is 0.55%-1.0%, which has fine economic benefit and social benefit.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP +1
Vanadium dioxide-doped powder and dispersion, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102120615ASimple processLow costVanadium oxidesCoatingsVanadium dioxideChemical composition
The invention relates to vanadium dioxide-doped powder, vanadium dioxide-doped dispersion, and a preparation method and application thereof. The chemical compositions of the vanadium dioxide-doped powder shown as V1-xMxO2 (x is more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.5, and M is a doped element used for controlling the size and appearance of the vanadium dioxide-doped powder.). The vanadium dioxide-doped powder has uniform grain size and high dispersibility.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing high purity vanadium pentoxide through using ammonium metavanadate
The invention which relates to a method for preparing high purity vanadium pentoxide through using ammonium metavanadate belongs to the wet metallurgy field. The method comprises the following steps: heating and dissolving crude ammonium metavanadate in water, adjusting the pH value to 8-10 with an alkali after dissolving, adding an impurity removing agent to remove impurities, filtering to obtain a sodium metavanadate solution, adding ammonia water or an ammonium salt to the sodium metavanadate solution to precipitate to obtain an ammonium metavanadate precipitate, dehydrating the ammonium metavanadate precipitate, carrying out water washing on the precipitate through using a dilute ammonium salt solution, dehydrating after the wash washing, and roasting to obtain the high purity vanadium pentoxide. Vanadium pentoxide produced through adopting the method of the invention has the advantages of high purity and less impurities, and completely satisfies production requirements of high-end products; and the method of the invention has the advantages of short process flow, simple equipment, low cost and high benefit, and is suitable for the large-scale industrial production.
Owner:崇阳县恒通工贸有限公司
Method for producing vanadium trioxide by adopting fluidized bed reactor
ActiveCN101880059AImprove efficiencySuitable for mass productionVanadium oxidesCombustion chamberFluidized bed
The invention relates to a method for producing vanadium trioxide by adopting a fluidized bed reactor, belonging to the field of the chemical industry and metallurgy. Heat is provided for reaction by a mode of preheating the materials containing vanadium to be 400-550 DEG C, the materials containing vanadium are preheated by adopting a two-stage cyclonic preheater, and high-temperature smoke generated by a combustion chamber provides heat. Gas with heat value of being larger than 1250kcal / Nm<3> is adopted to be reduced for 5-20 minutes at the temperature of 700-850 DEG C, and a vanadium trioxide product with vanadium grade of being more than 66% can be obtained. The method has the advantages of high reduction efficiency, good energy utilization and suitability for large-scale production of vanadium trioxide.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Clean production process for vanadium oxide
ActiveCN101412539ASolve difficult environmental problemsSolve the technical problem of not being able to obtain high-quality vanadium productsVanadium oxidesProcess efficiency improvementSlagWastewater
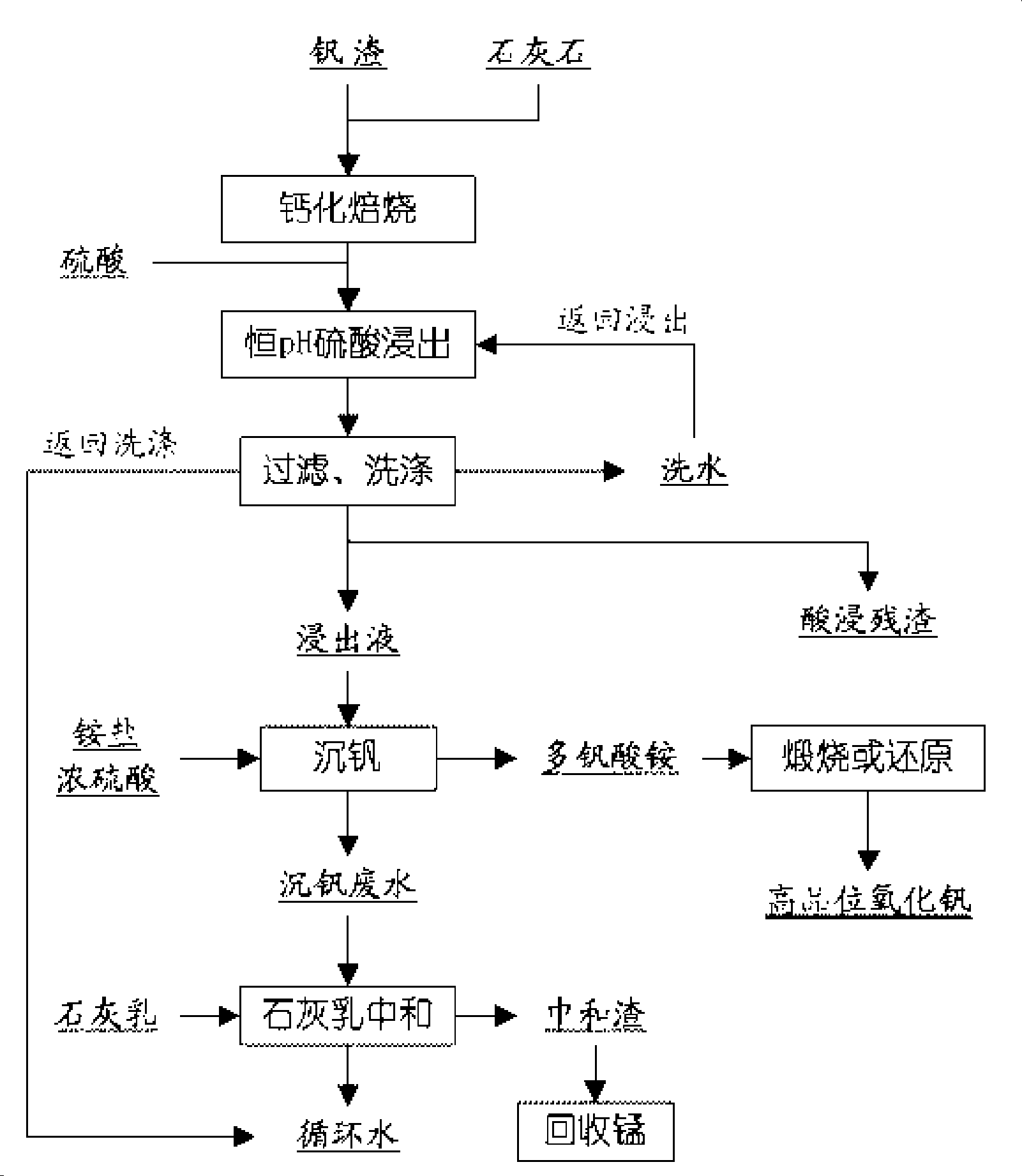
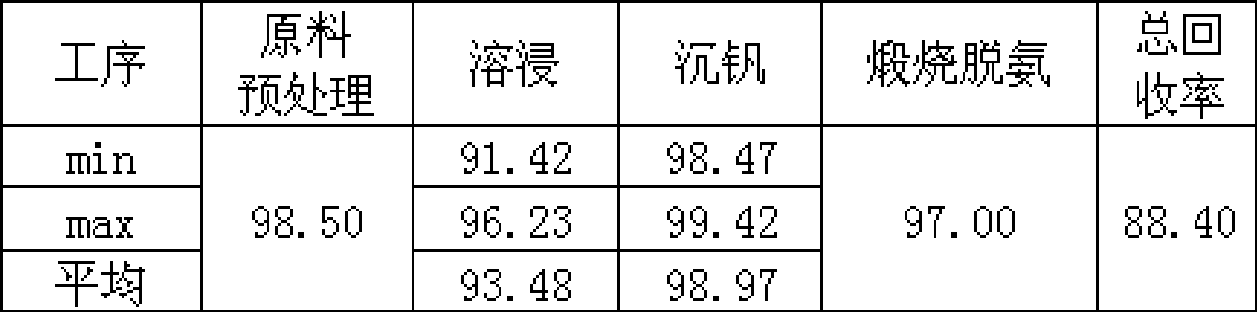
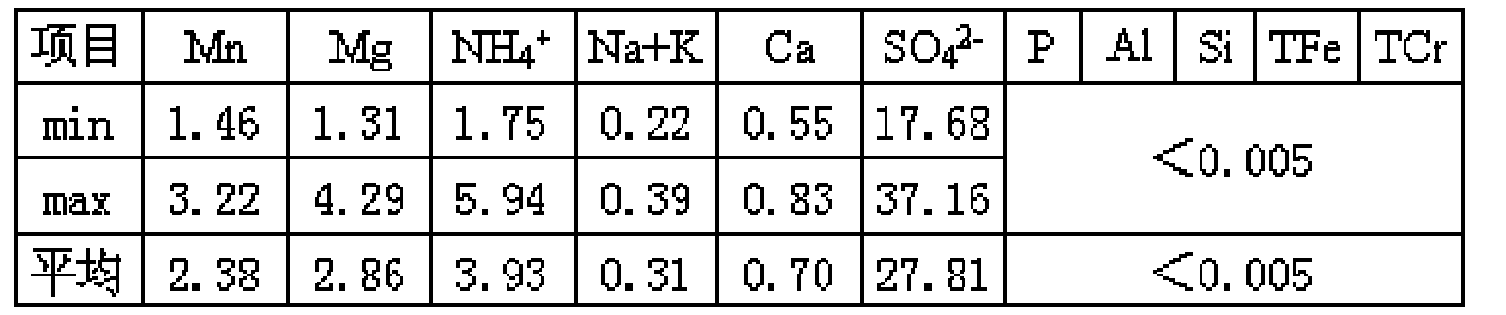
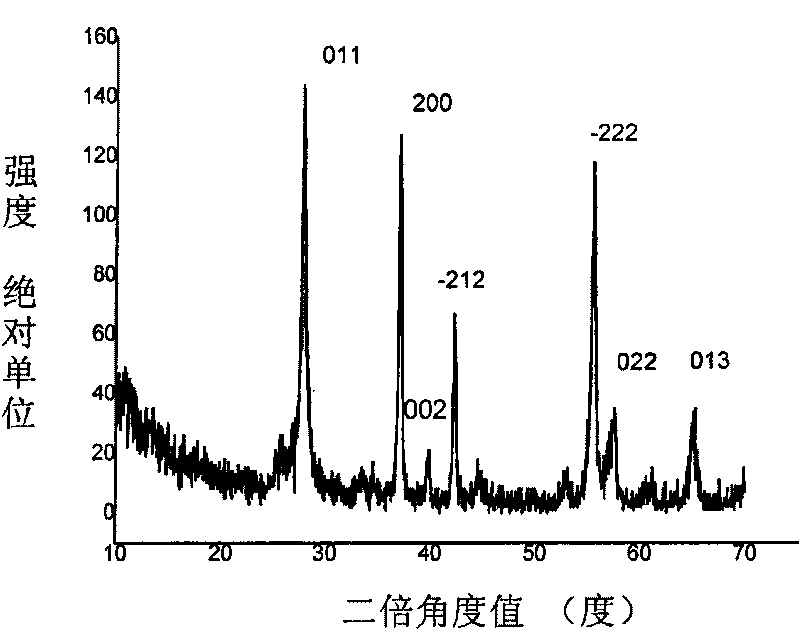
The invention relates to a method for cleanly producing vanadium oxide, which belongs to the field of extraction of vanadium oxide. The technical problems to be solved by the invention is to provide the method for cleanly producing the vanadium oxide which not only can obtain a high-quality vanadium product, but also can ensure that vanadium waste water can be reclaimed. The method for producing the vanadium oxide comprises the following steps: preparing roasting raw materials, calcification roasting; infiltrating, separating solid and liquid, precipitating vanadium by ammonium salt, calcining for deaminating or reducing, and the like. Waste water after vanadium extraction can be returned to a system for recycling after the waste waster is subjected to neutralizing treatment by lime cream so as to realize zero drainage of the waste water. The method also improves the reclamation rate of vanadium to be superior to that of the prior process, and reduces production cost. Through combining with other technologies, the method can change extracted slag and other waste into secondary resource to be used once again, and realize clean production.
Owner:攀钢集团西昌钒制品科技有限公司
Method of preparing intelligent energy-saving vanadium dioxide by hydrothermal method
InactiveCN101700909ALow costRaw materials are cheap and easy to getChemical industryVanadium oxidesVanadium dioxideAlkalinity
The invention relates to a method of preparing vanadium dioxide by hydrothermal method. The method comprises the following steps: adding oxidant, reducing agent or acidity and alkalinity adjusting agent in a hydrothermal kettle containing proper amount of aqueous solution of the source of vanadium, then placing the hydrothermal kettle in a 40-300 DEG C of oven to perform heat preservation for 30 minutes to 5 days, and centrifuging to collect vanadium dioxide after the reaction is completely finished. The preparation method provided by the invention has simple process, low cost and high yield, the mass production can be realized and the purity of the obtained intelligent energy-saving vanadium dioxide nano-powder is high. Vanadium dioxide doped powder can further be obtained by adding proper amount of compound containing tungsten, molybdenum, manganese, chromium or titanium in the aqueous solution of the source of vanadium to realize wider industrial applications. The control of different appearances of vanadium dioxide nano-powder can be realized by controlling the categories of the source of vanadium and the dosage of oxidant, reducing agent or acidity and alkalinity adjusting agent.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Preparation method of one-step hydrothermal synthesis of carbon/molybdenum disulfide composite microsphere
InactiveCN1994896AUniform particle sizeSimple methodVanadium oxidesMolybdenum sulfidesSucroseMicrosphere
The invention discloses a making method of carbon / molybdenum disulfide composite microball through water heat method, which comprises the following steps: dissolving molybdate in the deionized water to form 0.02-0.1m solution; adding thioacetamide or sulfourea as sulfur source with molar rate of thioacetamide or sulfourea and molybdate at 31-51; stirring evenly; adding glucose or sucrose as carbon source with the molar rate of glucose or sucrose and molybdate at 51-251; stirring completely; transmitting solution into water heat reacting autoclave to react under 200-240 deg. c for 20-24h; cooling naturally; separating; washing; drying to obtain the product.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method of high-purity vanadium pentoxide
InactiveCN102923775AEfficient removalReduce pollutionVanadium oxidesMetal impuritiesAmmonium metavanadate
The invention discloses a preparation method of high-purity vanadium pentoxide. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: returning and dissolving coarse vanadium in aqueous alkali, and filtering the solution to remove metal impurities, which are subjected to precipitation reaction with the aqueous alkali, in the coarse vanadium, thus obtaining a primary returned solution; slowly pouring the primary returned solution into a sulfuric acid solution, adjusting the pH value of the solution to be 1.0-2.0 to obtain a liquid-solid mixture, and performing solid-liquid separation on the liquid-solid mixture; filtering and washing precipitates obtained from the solid-liquid separation of the mixture, and returning and dissolving the mixture into the aqueous alkali, thus obtaining a secondary returned solution; adding ammonium sulfate into the secondary returned solution for precipitating vanadium, and filtering the solution to obtain ammonium metavanadate; and processing the ammonium metavanadate to obtain the high-purity vanadium pentoxide. The preparation method adopting multiple stages of returned dissolving can be used for effectively removing the metal canon impurities of the vanadium pentoxide, and further obtaining the high-purity vanadium pentoxide with the metal canon impurity contents of less than 0.001% and the vanadium pentoxide content of 99.99%.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
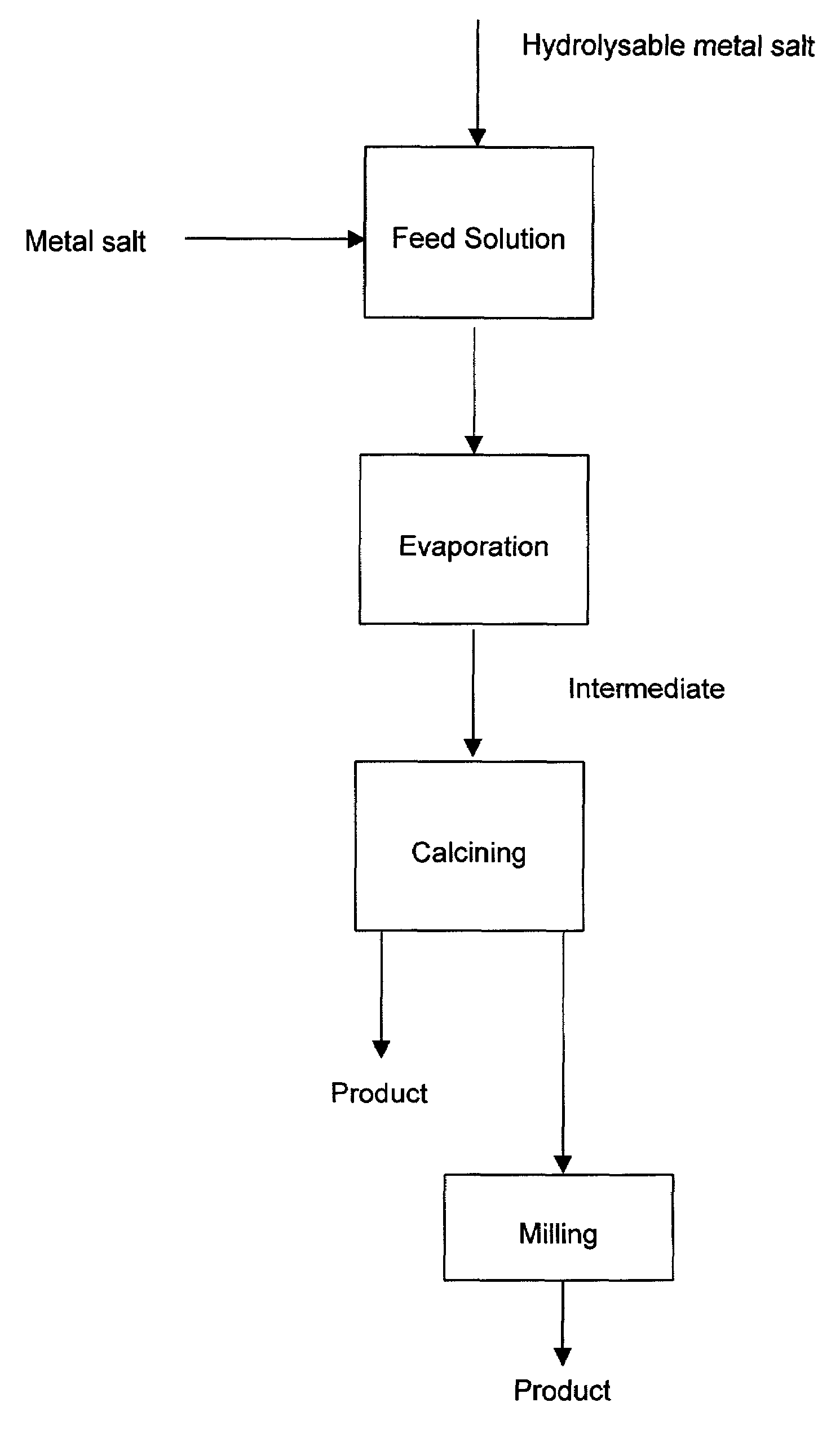
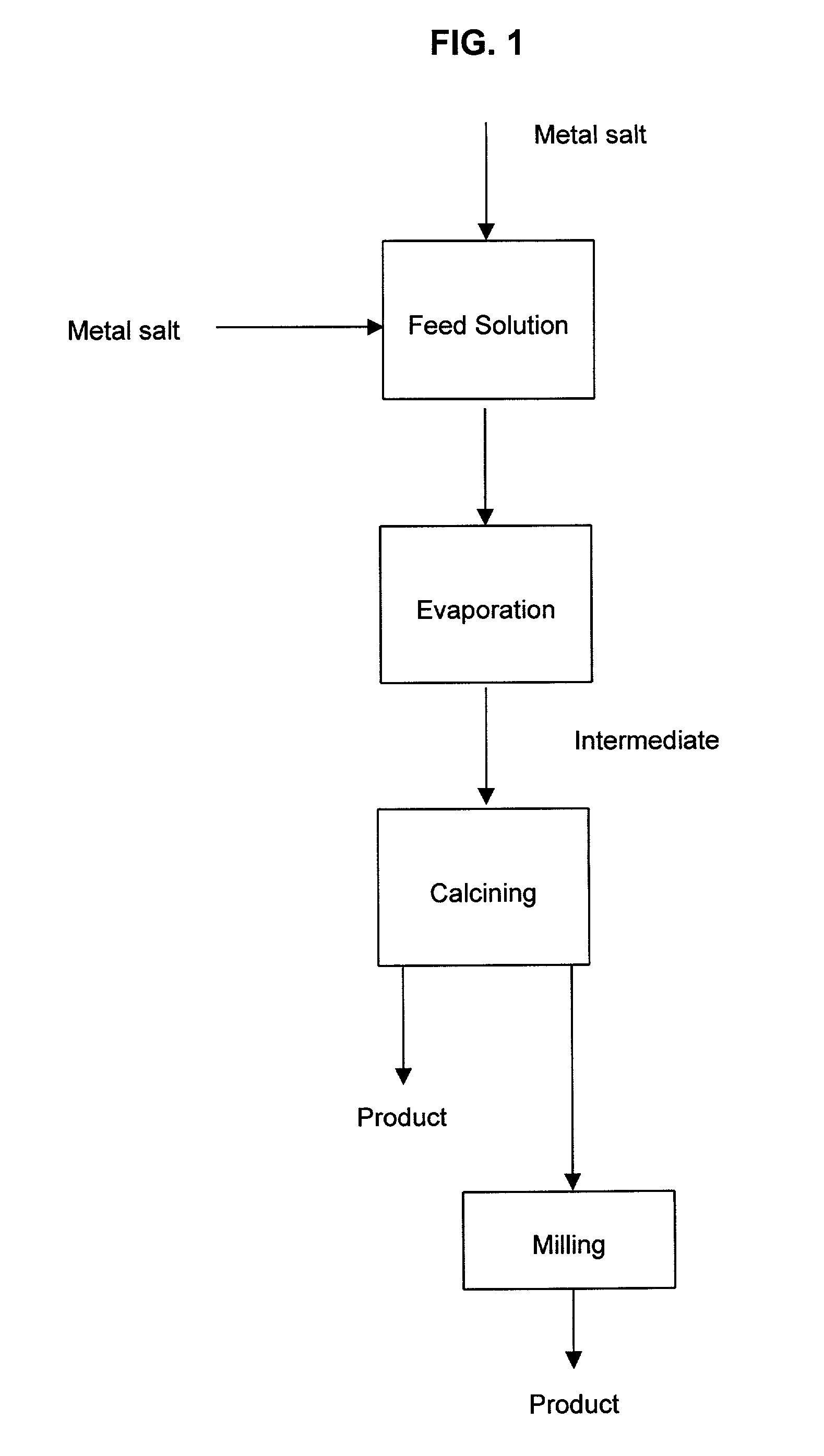
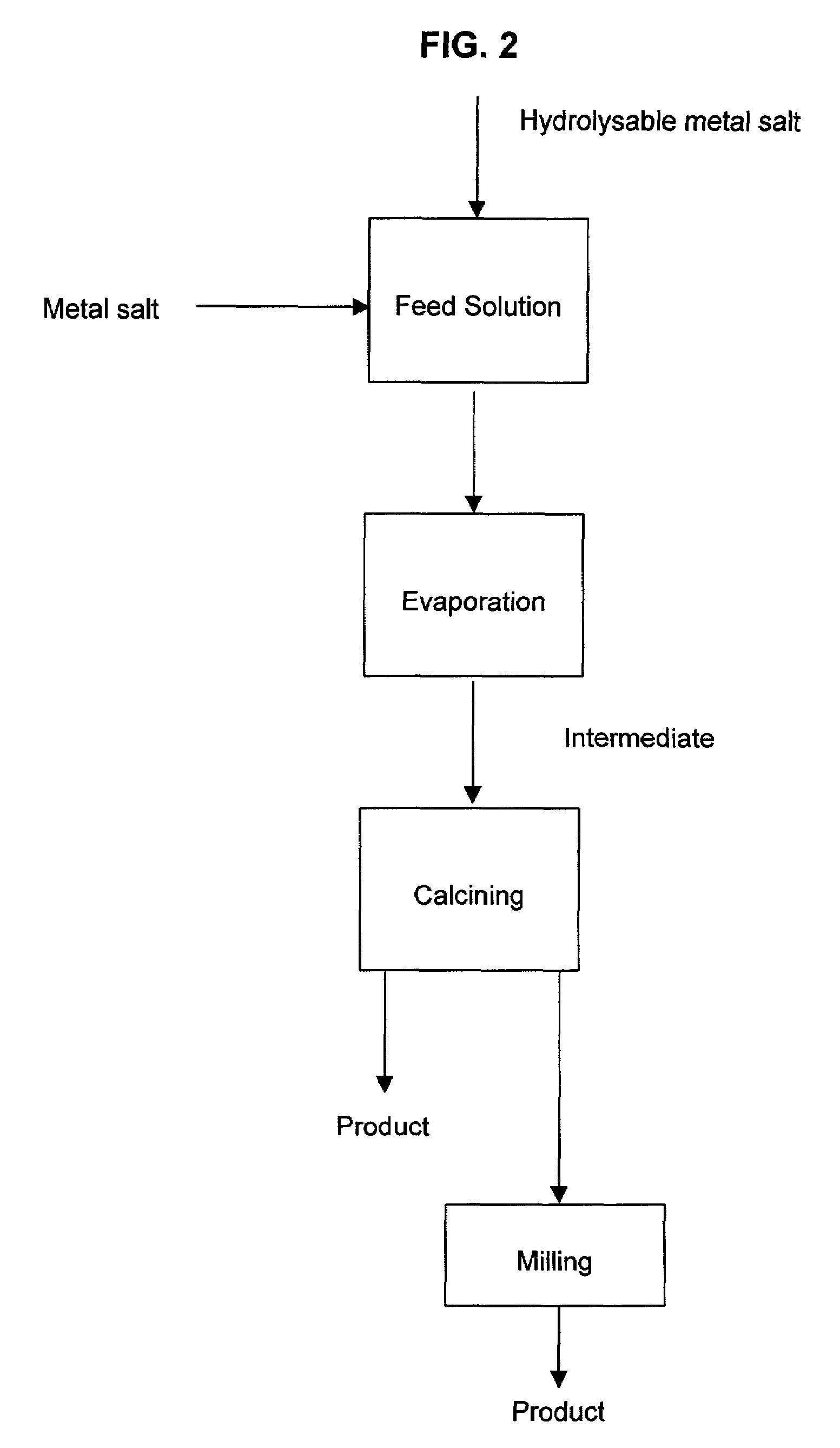
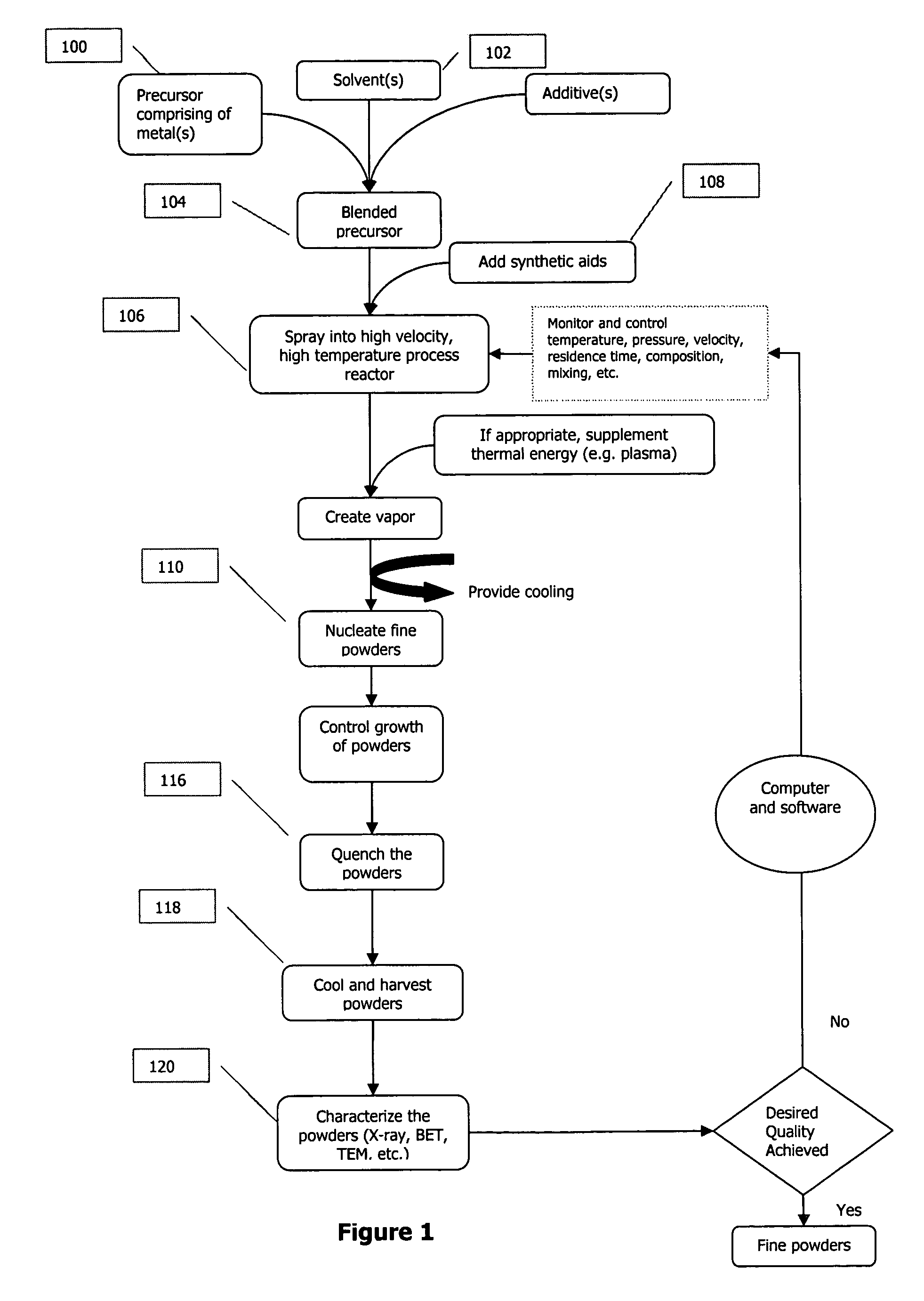
Method for producing mixed metal oxides and metal oxide compounds
A process to produce mixed metal oxides and metal oxide compounds. The process includes evaporating a feed solution that contains at least two metal salts to form an intermediate. The evaporation is conducted at a temperature above the boiling point of the feed solution but below the temperature where there is significant crystal growth or below the calcination temperature of the intermediate. The intermediate is calcined, optionally in the presence of an oxidizing agent, to form the desired oxides. The calcined material can be milled and dispersed to yield individual particles of controllable size and narrow size distribution.
Owner:ALTAIR NANOMATERIALS INC
Nanoparticle production and corresponding structures
InactiveUS20060147369A1Material nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsProduction rateNanoparticle Production
Methods are described that have the capability of producing submicron / nanoscale particles, in some embodiments dispersible, at high production rates. In some embodiments, the methods result in the production of particles with an average diameter less than about 75 nanometers that are produced at a rate of at least about 35 grams per hour. In other embodiments, the particles are highly uniform. These methods can be used to form particle collections and / or powder coatings. Powder coatings and corresponding methods are described based on the deposition of highly uniform submicron / nanoscale particles.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
Titanium comprising nanoparticles and related nanotechnology
ActiveUS7232556B2Increase volumeLow cost productionNitrogen compoundsGermanium dioxideNanoparticleTitanium metal
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Method for preparing vanadium pentoxide
InactiveCN1843938AMeet the needs of domestic chemical productionVanadium oxidesCalcium hydroxideSodium aluminate
The invention relates to a method for preparing vanadic anhydride. It comprises following steps: employing ammonium vanadate, vanadic anhydride of technical grade or waste catalyst discharged in sulfuric acid preparation process; treating with ammonium hydroxide, sulfuric acid and ammonium chloride, washing with water; getting fine active vanadic anhydride; removing foreign matter with ammonium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, sodium aluminate, sodium silicate, sulfuric acid and ammonium chloride; washing with water again; drying; calcing at 670 Deg. C and getting high-purity vanadic anhydride. The invention is characterized in that it makes use of current material to prepare chemical materials urgently needed by industrial production, and saves a large amount of foreigh exchange.
Owner:宿素满
Method of preparing high-purity vanadium pentoxide from roasting-method vanadium solution
The invention discloses a method of preparing high-purity vanadium pentoxide from roasting-method vanadium solution. The method comprises the following steps: adding a purifying agent into the roasting-method vanadium solution, wherein the purifying agent is polyaluminium chloride, magnesium chloride or calcium chloride, or the purifying agent is polyaluminium chloride and magnesium chloride, or polyaluminium chloride and calcium chloride; uniformly stirring the roasting-method vanadium solution containing the purifying agent, standing for settling, then filtering, and adding ammonium salt into the filtrate to precipitate vanadium; and finally, calcining meta-ammonium and deaminizing to prepare vanadium pentoxide with the purity being higher than 99.5%. Polyaluminium chloride serving as the purifying agent can be used for polymerizing jellies with several molecules into large particles with several tens of thousands of molecules, even hundreds of thousands of molecules. The large-particle molecular polymer is easy to settle in the vanadium solution and can be separated from the solution. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the consumption of polyaluminium chloride is low, the flocculation process is simple, the flocculation capacity is strong, the flocculation speed is high, pollution is hardly caused and the cost is low.
Owner:贵州义信矿业有限公司
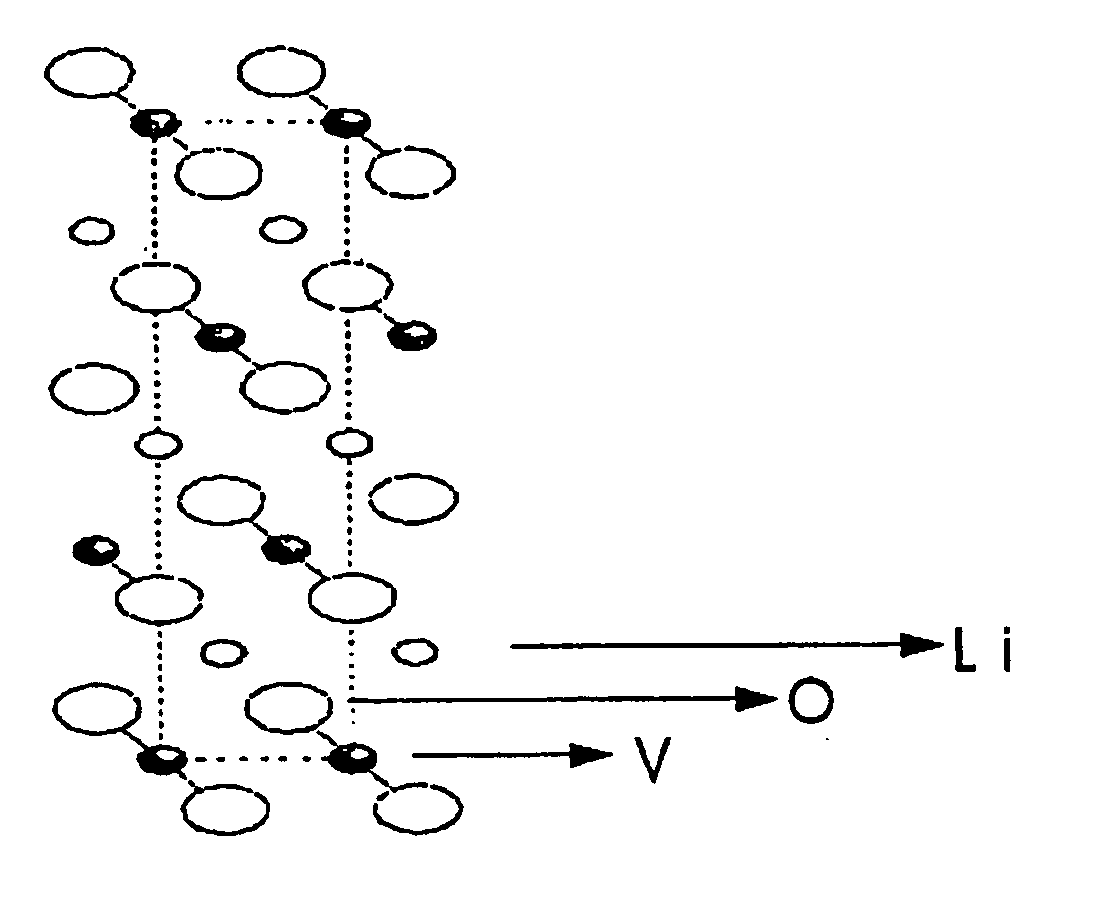
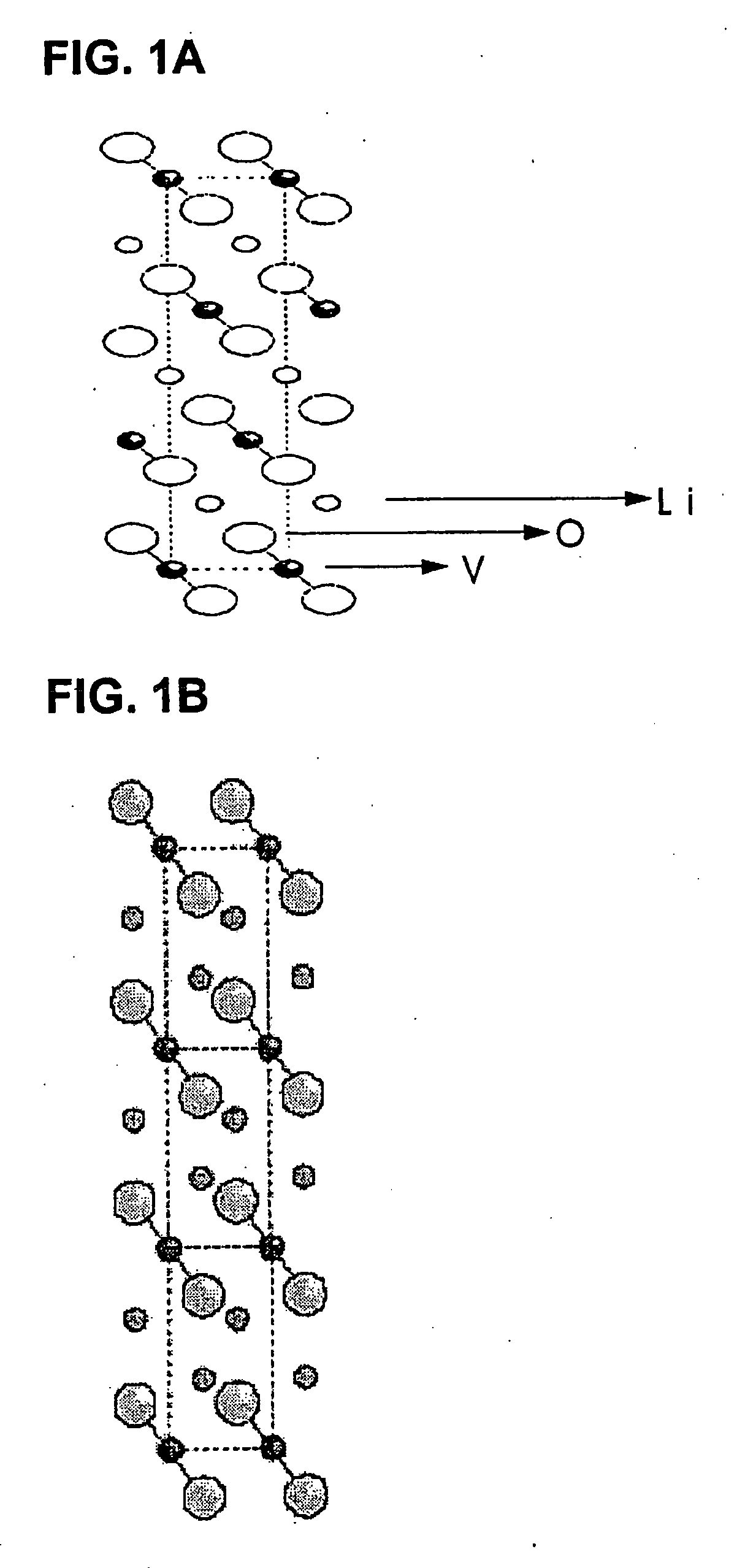
Negative active material for non-aqueous electrolyte battery, method of preparing same, and non-aqueous electrolyte battery comprising same
InactiveUS20050079417A1Improve security featuresNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsMolybdeum compoundsPhysical chemistryNon aqueous electrolytes
A negative active material of a non-aqueous electrolyte battery includes a compound represented by formula 1: LixMyVzO2+d (1) where 0.1≦x≦2.5, 0<y≦0.5, 0.5≦z≦1.5, 0≦d≦0.5, and M is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Al, Cr, Mo, Ti, W, and Zr.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Method for preparing rutile phase hypovanadic oxide powder
The invention relates to a method for preparing rutile-phase vanadium dioxide powder, in particular to a method for preparing rutile-phase vanadium dioxide powder through a hydrothermal method. The method for preparing rutile-phase vanadium dioxide powder adopts the conditions of different vanadium materials, dopants and doping ratios, and the like, to obtain rutile-phase vanadium dioxide powders with good crystallization performance and in shapes of grains, nanometer rods and snowflake-shaped grains. The temperature for transforming the powder from semiconductor phase to conductor phase can be reduced approximately to the room temperature.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com