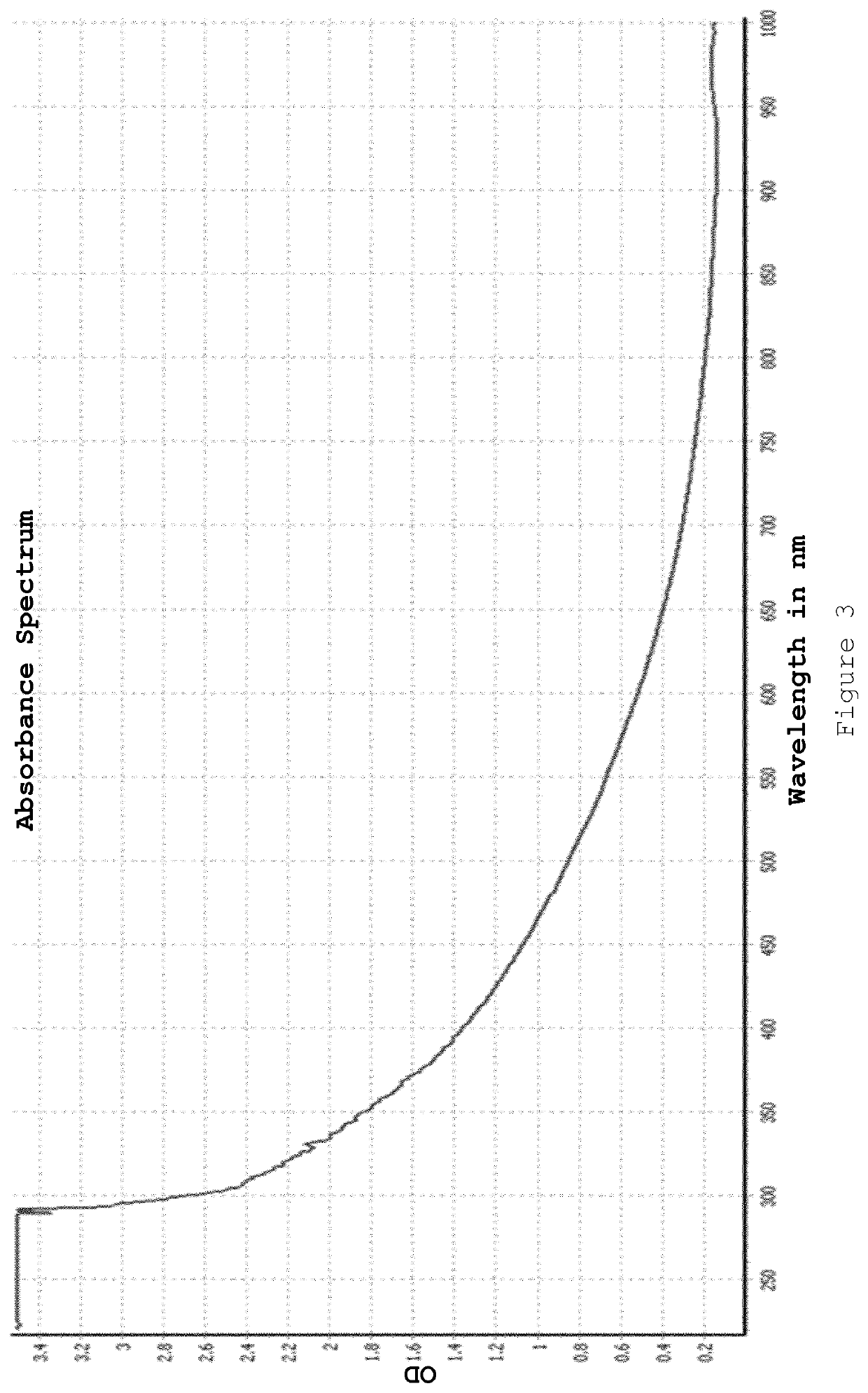
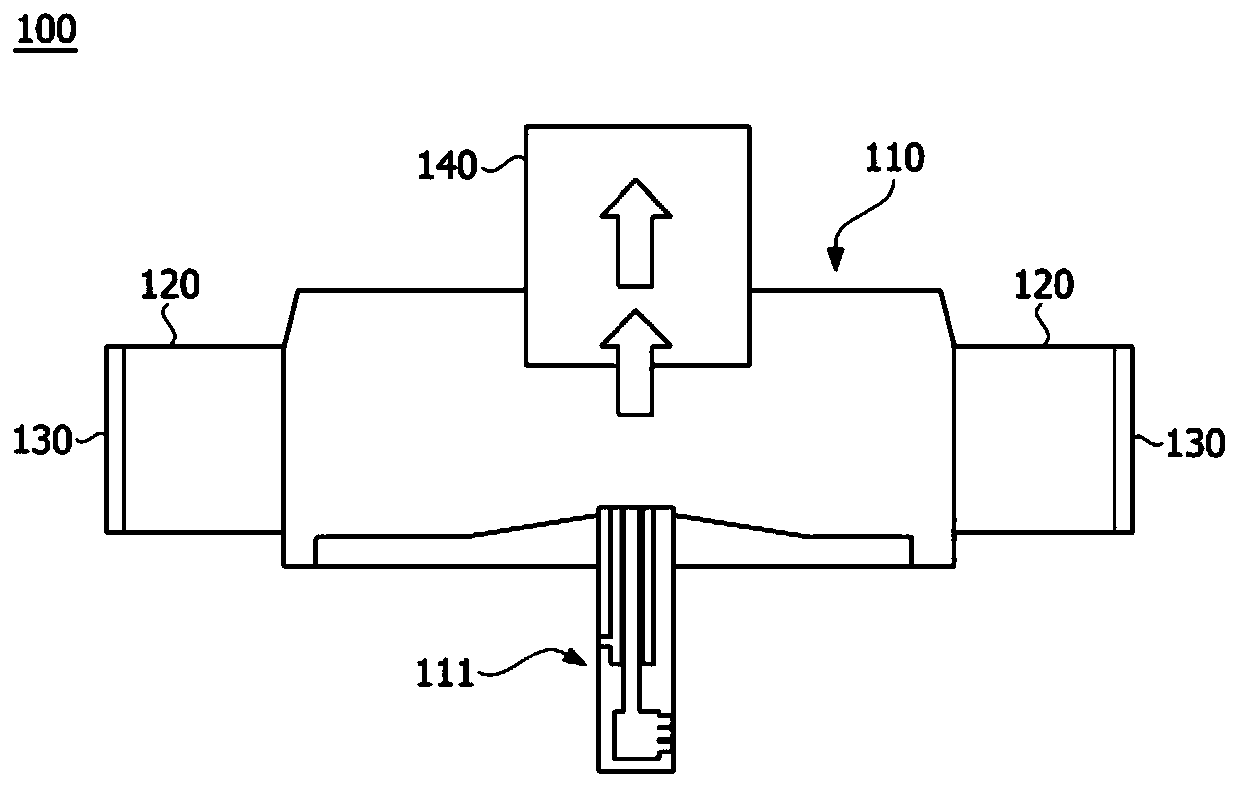
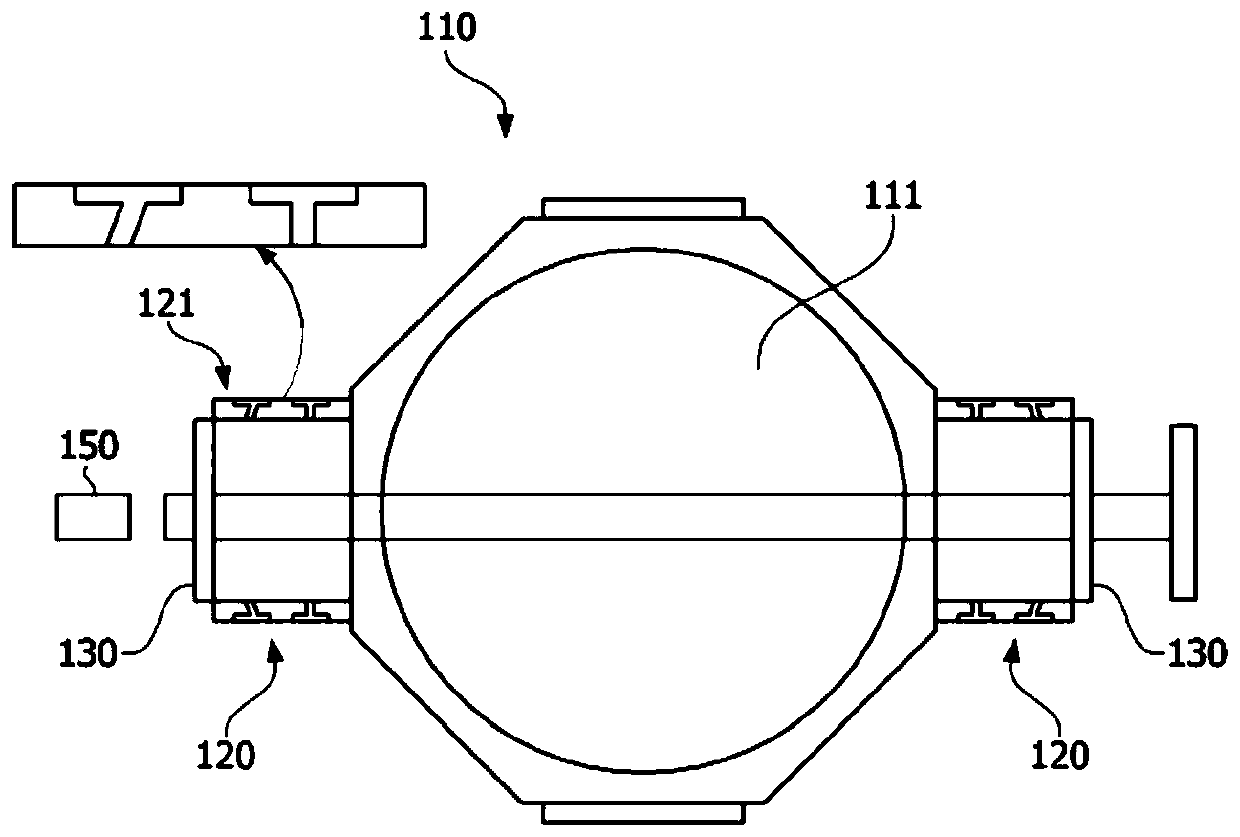
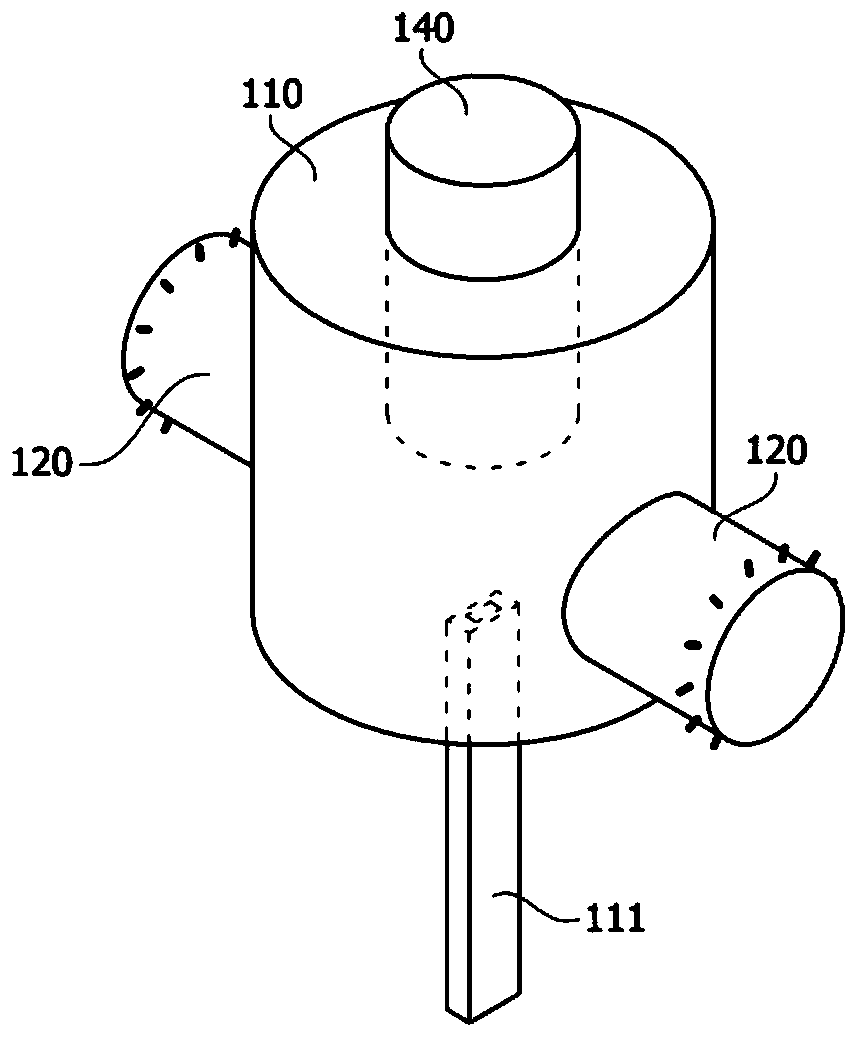
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Nanoparticle Production" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nanoparticle production and corresponding structures
InactiveUS20060147369A1Material nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsProduction rateNanoparticle Production
Methods are described that have the capability of producing submicron / nanoscale particles, in some embodiments dispersible, at high production rates. In some embodiments, the methods result in the production of particles with an average diameter less than about 75 nanometers that are produced at a rate of at least about 35 grams per hour. In other embodiments, the particles are highly uniform. These methods can be used to form particle collections and / or powder coatings. Powder coatings and corresponding methods are described based on the deposition of highly uniform submicron / nanoscale particles.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
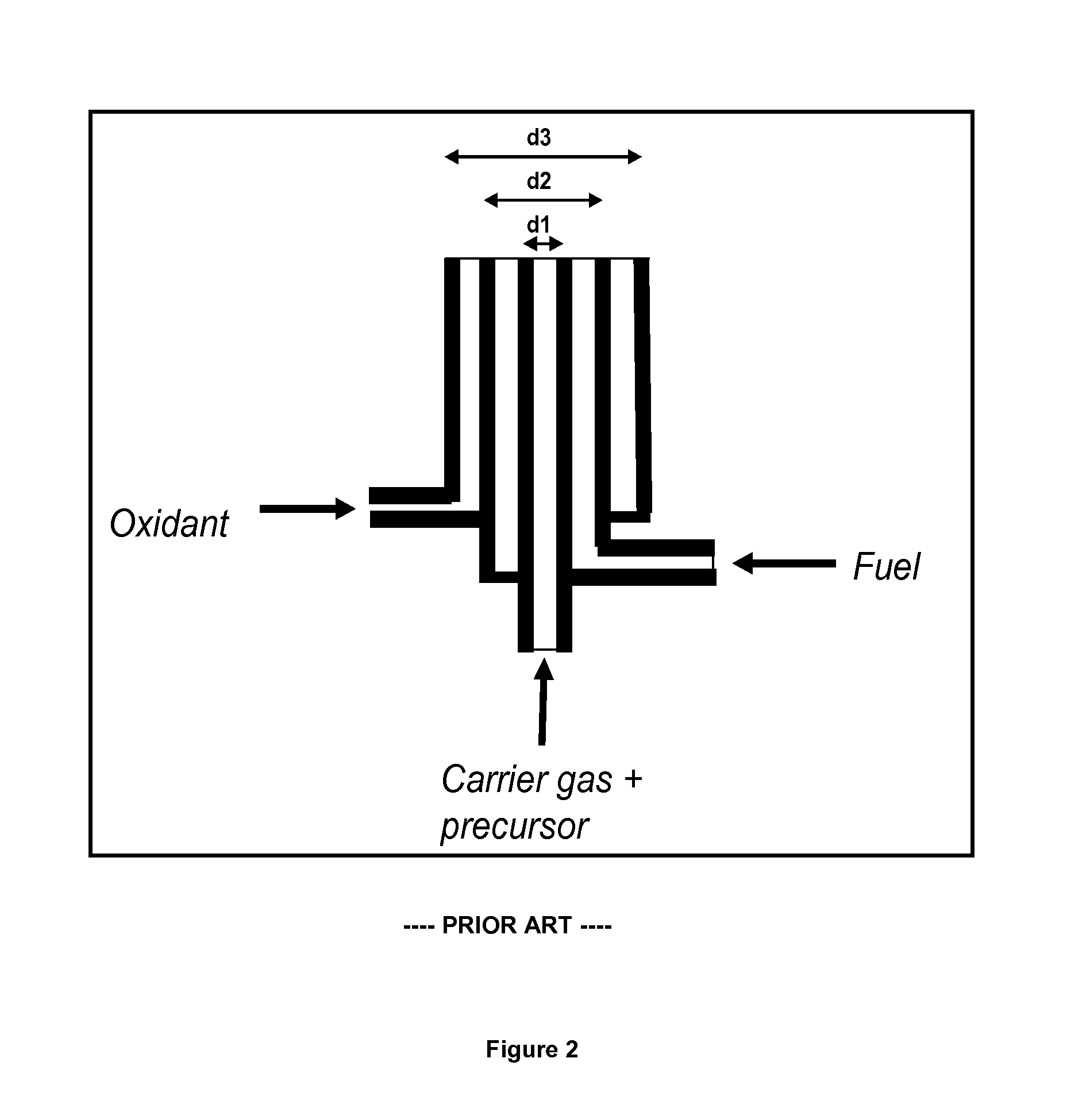
High-throughput particle production using a plasma system
InactiveUS20140263190A1Molten spray coatingArc welding apparatusNanoparticle ProductionProcess engineering
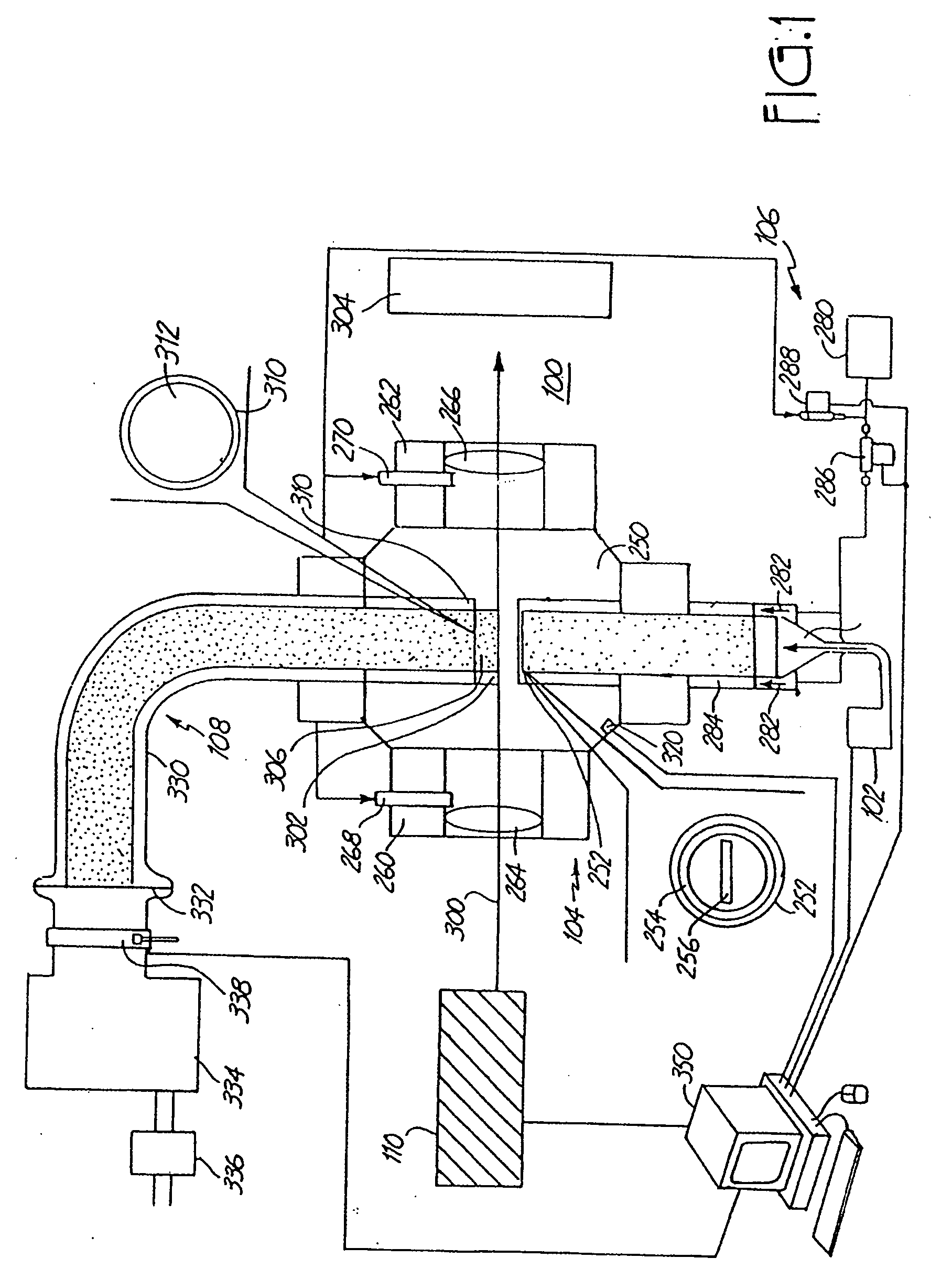
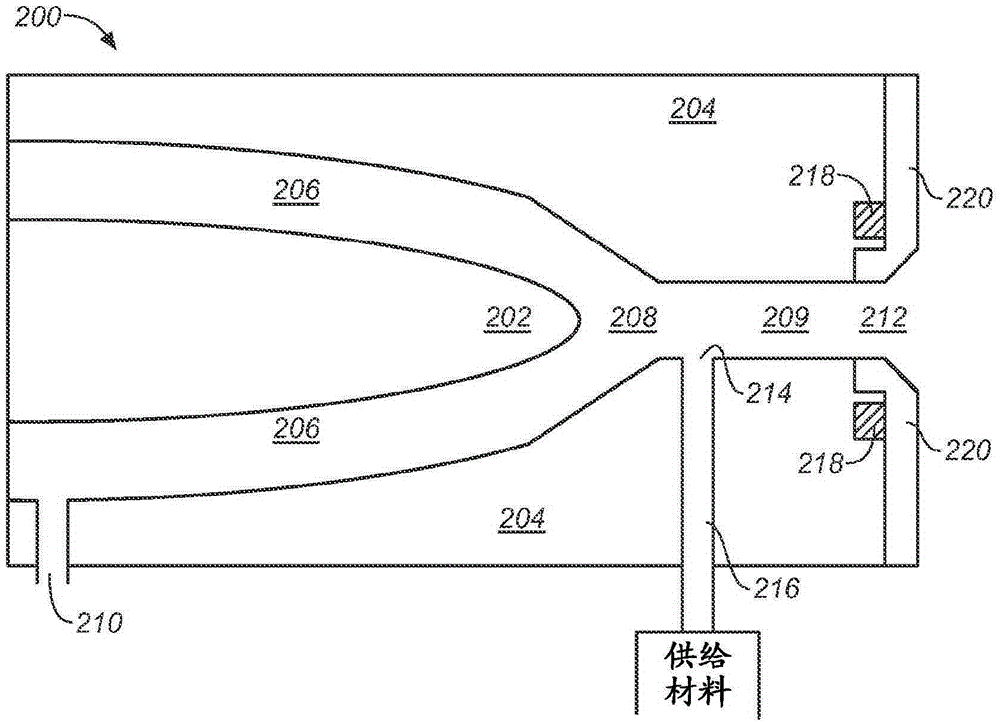
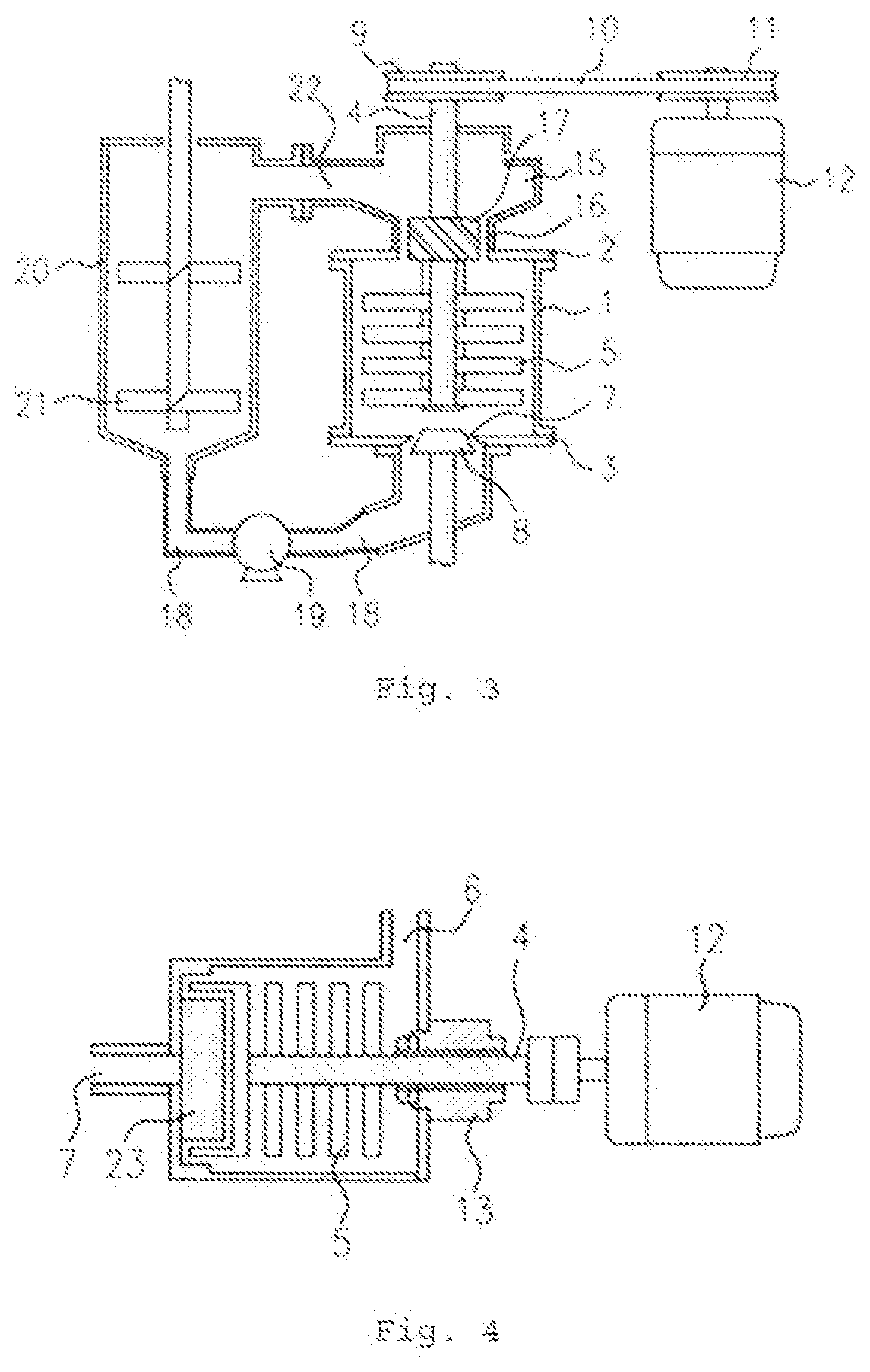
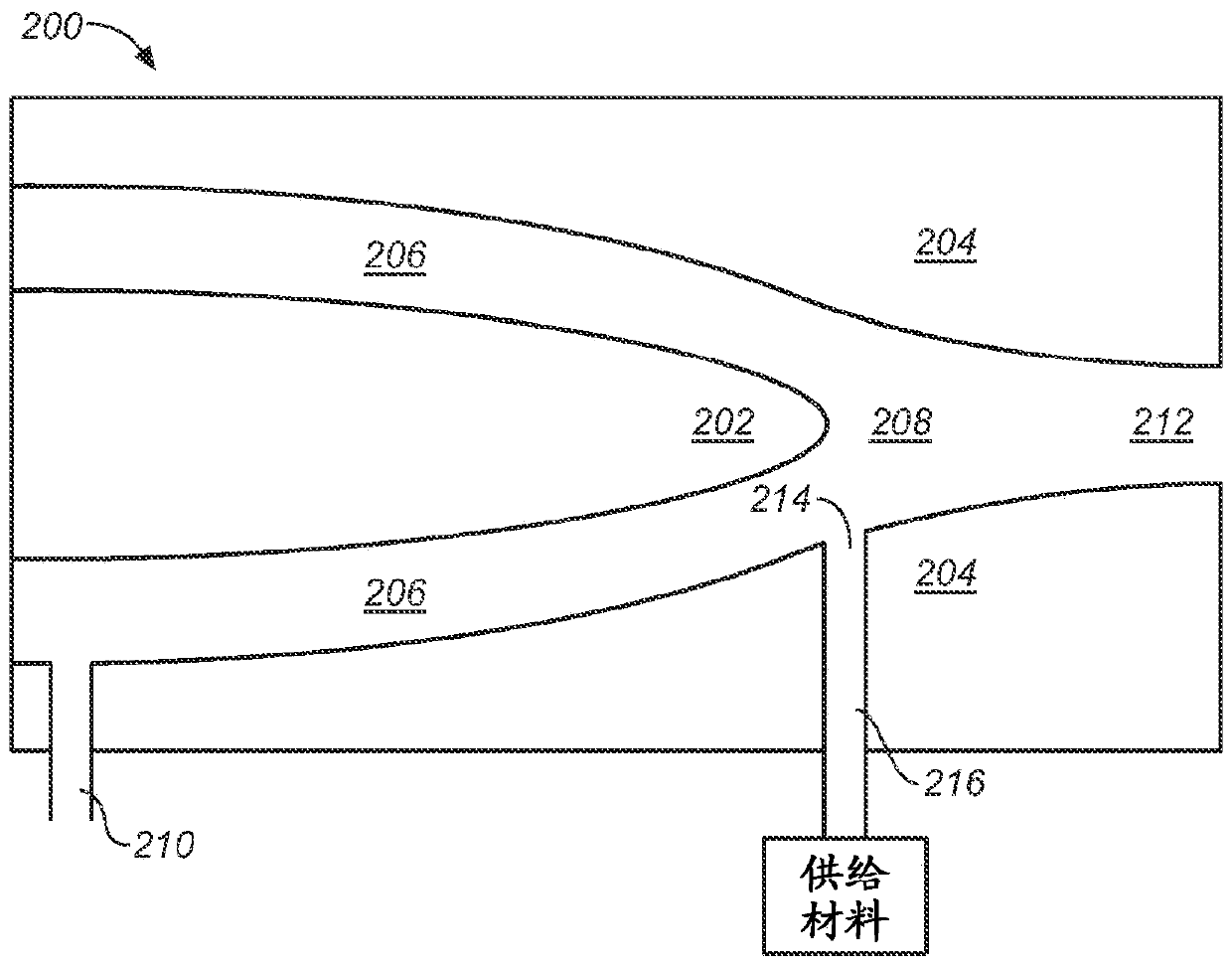
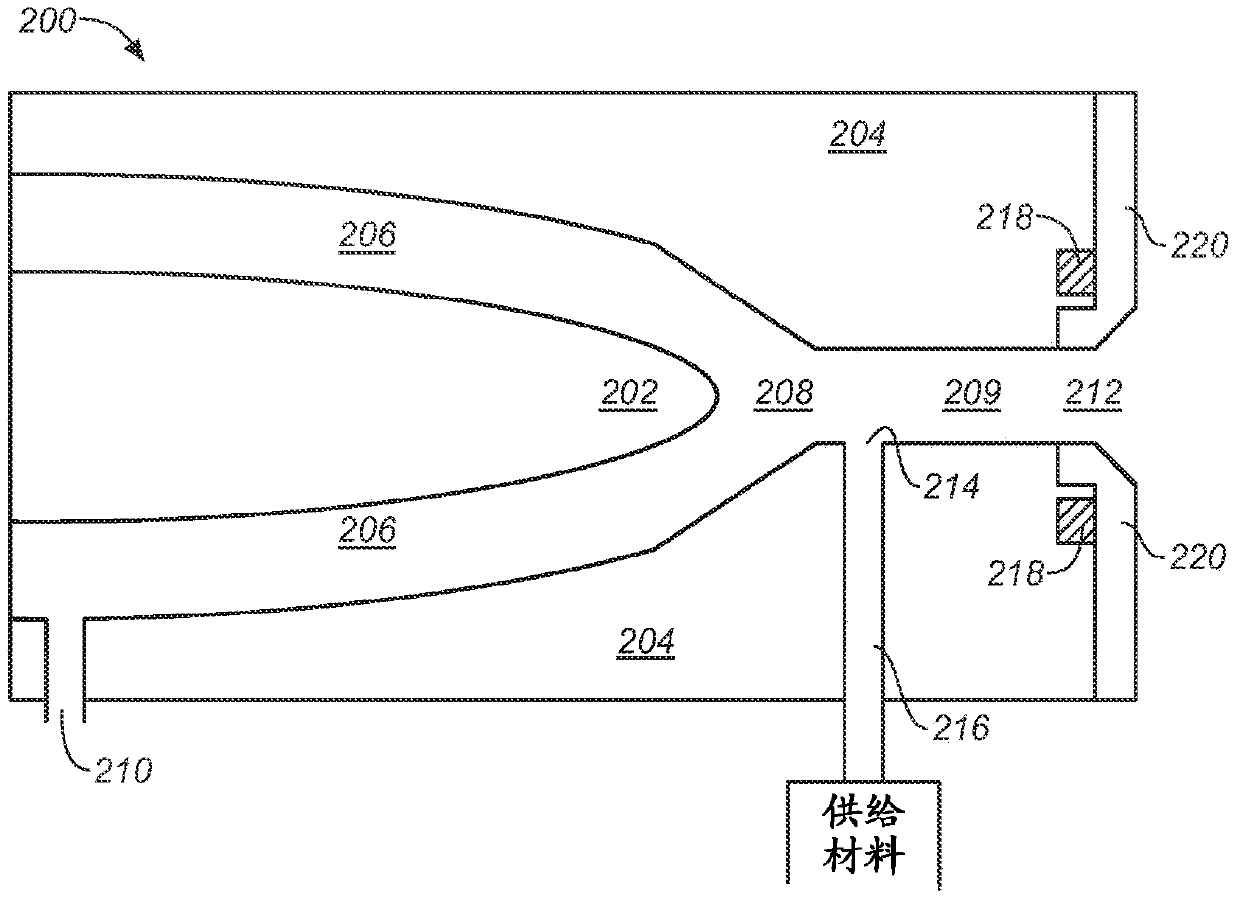
The present disclosure relates to a nanoparticle production system and methods of using the system. The nanoparticle production system includes a plasma gun including a male electrode, a female electrodes and a working gas supply configured to deliver a working gas in a vortexing helical flow direction across a plasma generation region. The system also includes a continuous feed systems, a quench chamber, a cooling conduit that includes a laminar flow disruptor, a system overpressure module, and a conditioning fluid purification and recirculation system.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
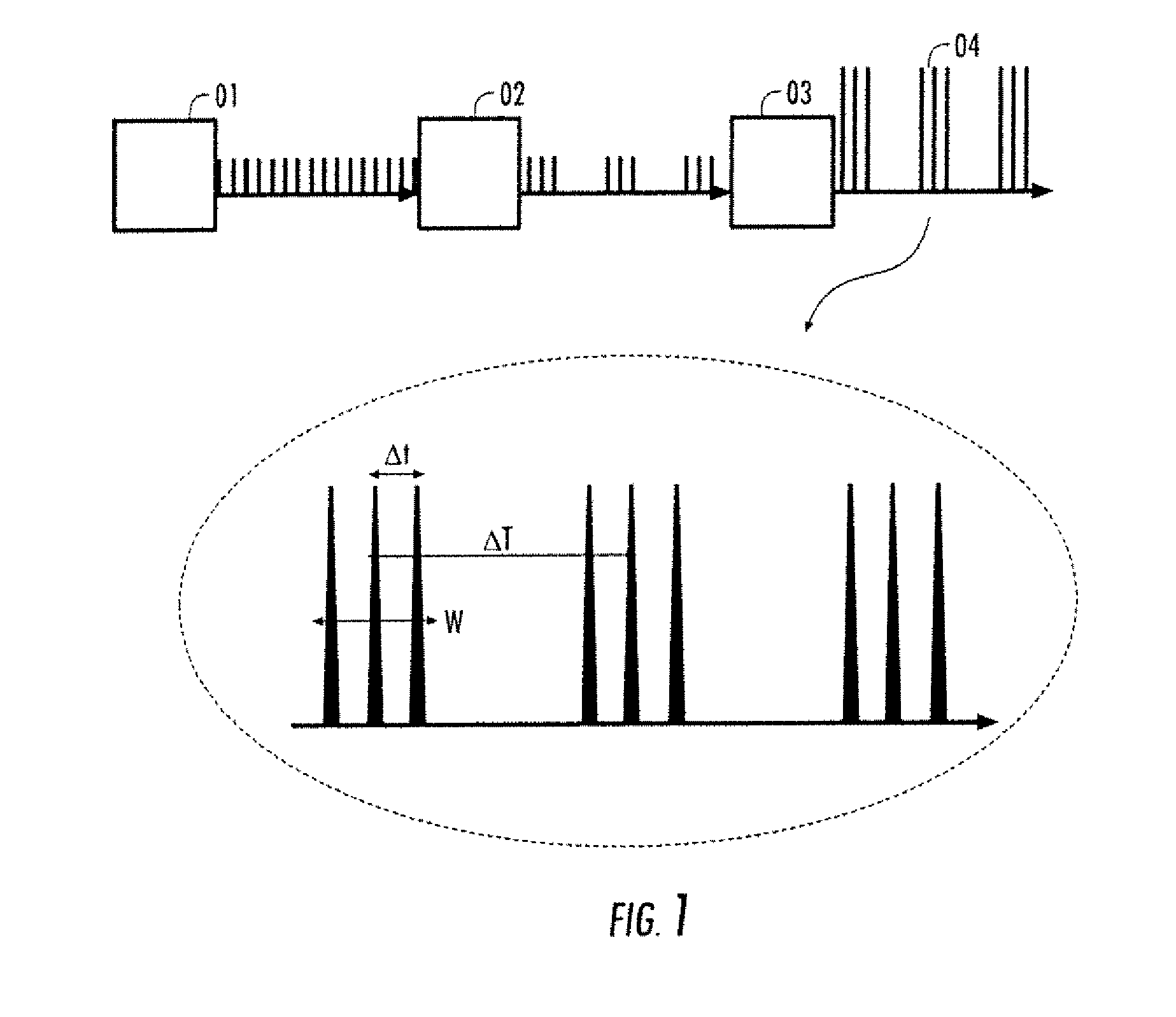
Nanoparticle production in liquid with multiple-pulse ultrafast laser ablation
ActiveUS20110192714A1Improve productivityNanotechTransportation and packagingNanoparticle ProductionNanosecond
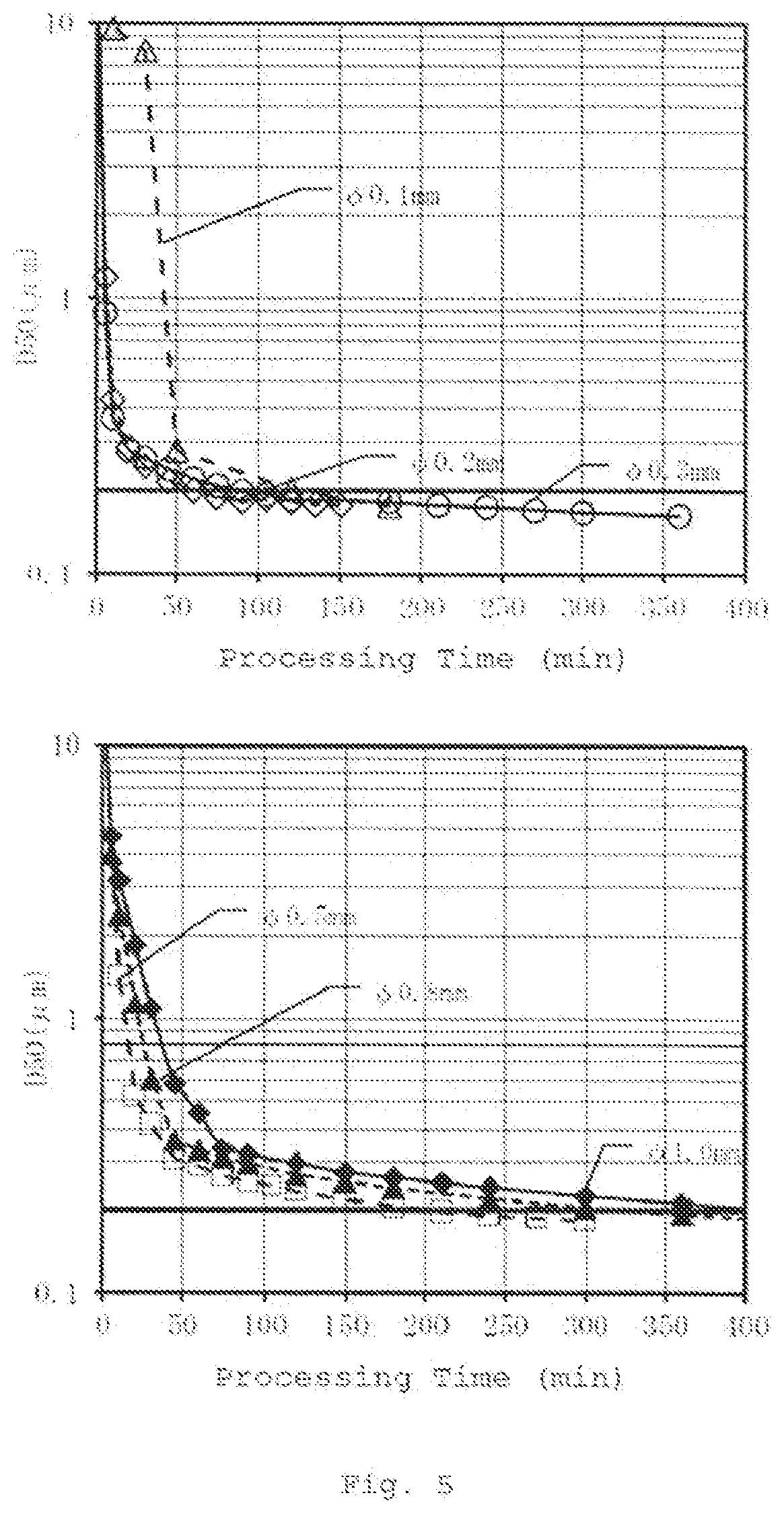
A method for generating nanoparticles in a liquid comprises generating groups of ultrafast laser pulses, each pulse in a group having a pulse duration of from 10 femtoseconds to 200 picoseconds, and each group containing a plurality of pulses with a pulse separation of 1 to 100 nanoseconds and directing the groups of pulses at a target material in a liquid to ablate it. The multiple pulse group ablation produces nanoparticles with a reduced average size, a narrow size distribution, and improved production efficiency compared to prior pulsed ablation systems.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Paclitaxel-based antitumor formulation
InactiveUS20070020337A1Simplifies plantFinal yieldPowder deliveryBiocideNanoparticle ProductionAlbumin solution
Antitumor formulation based on nanoparticles of paclitaxel and human serum albumin as obtained by the addition of a biocompatible acid to an aqueous albumin solution before this is mixed with paclitaxel during the nanoparticle production process, the injectable solutions of this formulation having a pH between 5.4 and 5.8 and having stability and inalterability with time.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Apparatus and method for nanoparticle and nanotube production and use therefor for gas storage
InactiveUS20040258604A1Avoid saturationIncrease productionMaterial nanotechnologyHydrogenNanoparti clesNanotube
There is provided a method for the enhanced production of fullerenes, nanotubes and nanoparticles. The method relies upon the provision of a hydrocarbon liquid which is converted by a suitable energy source to a synthesis gas such as acetone, ethylene, methane or carbon monoxide, the synthesis gas(es) forming the precursors need for fullerene, nanotube or nanoparticle production. The nanotubes formed by the method described are in general terms shorter and wider than conventionally produced nanotubes. An improved apparatus for production of the fullerenes and nanocarbons is also disclosed wherein a moveable contactor is attached to a first electrode with a sealable chamber, and is spaced from the second electrode such that an electric arc can pass between them.
Owner:ROSSETER HLDG
High-throughput particle production using a plasma system
InactiveUS20160030910A1Chemical/physical/physico-chemical reactor detailsChemical/physical/physico-chemical nozzle-type rreactorsNanoparticle ProductionProcess engineering
The present disclosure relates to a nanoparticle production system and methods of using the system. The nanoparticle production system includes a plasma gun including a male electrode, a female electrodes and a working gas supply configured to deliver a working gas in a vortexing helical flow direction across a plasma generation region. The system also includes a continuous feed system, a quench chamber, a cooling conduit that includes a laminar flow disruptor, a system overpressure module, and a conditioning fluid purification and recirculation system.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
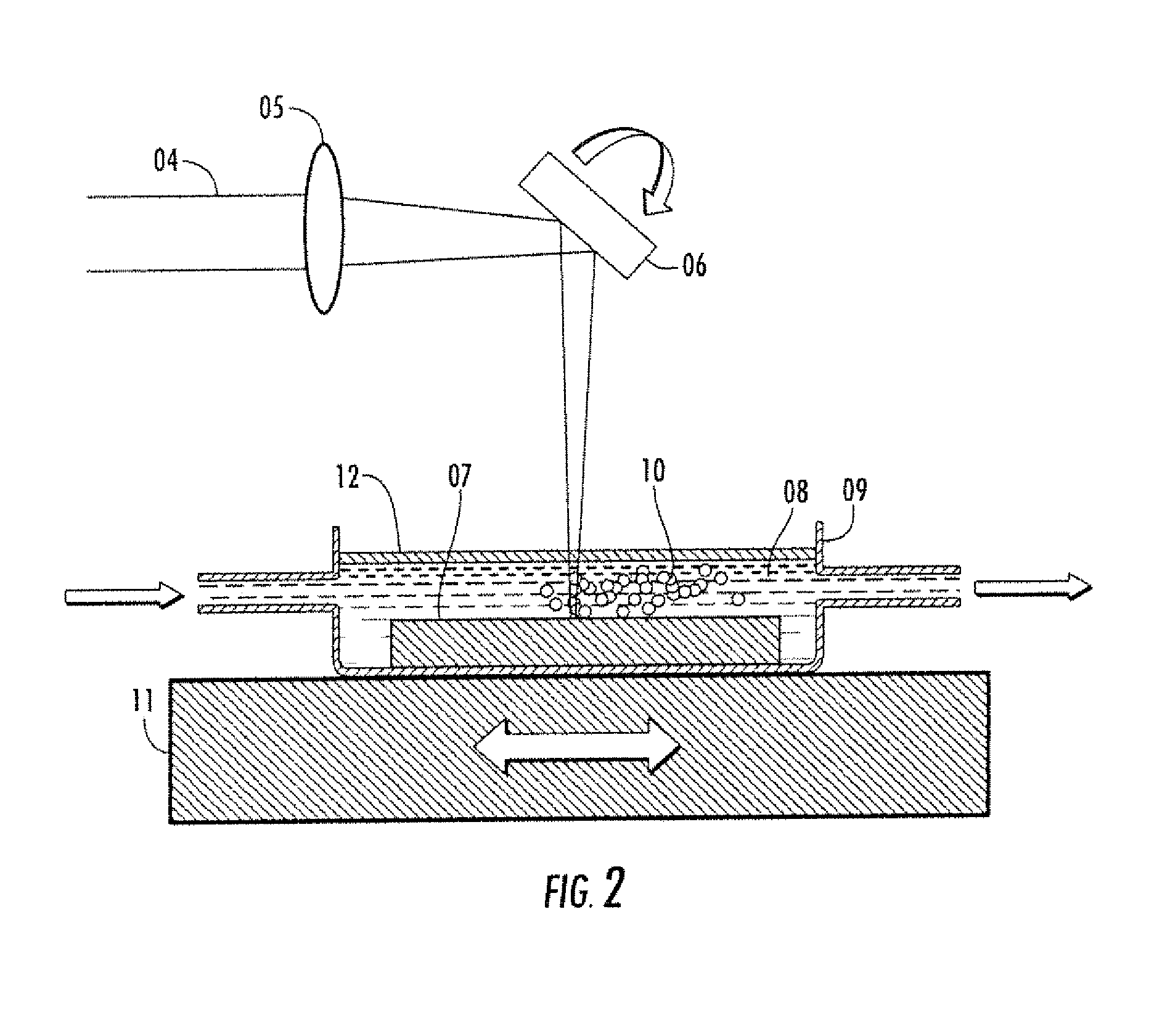
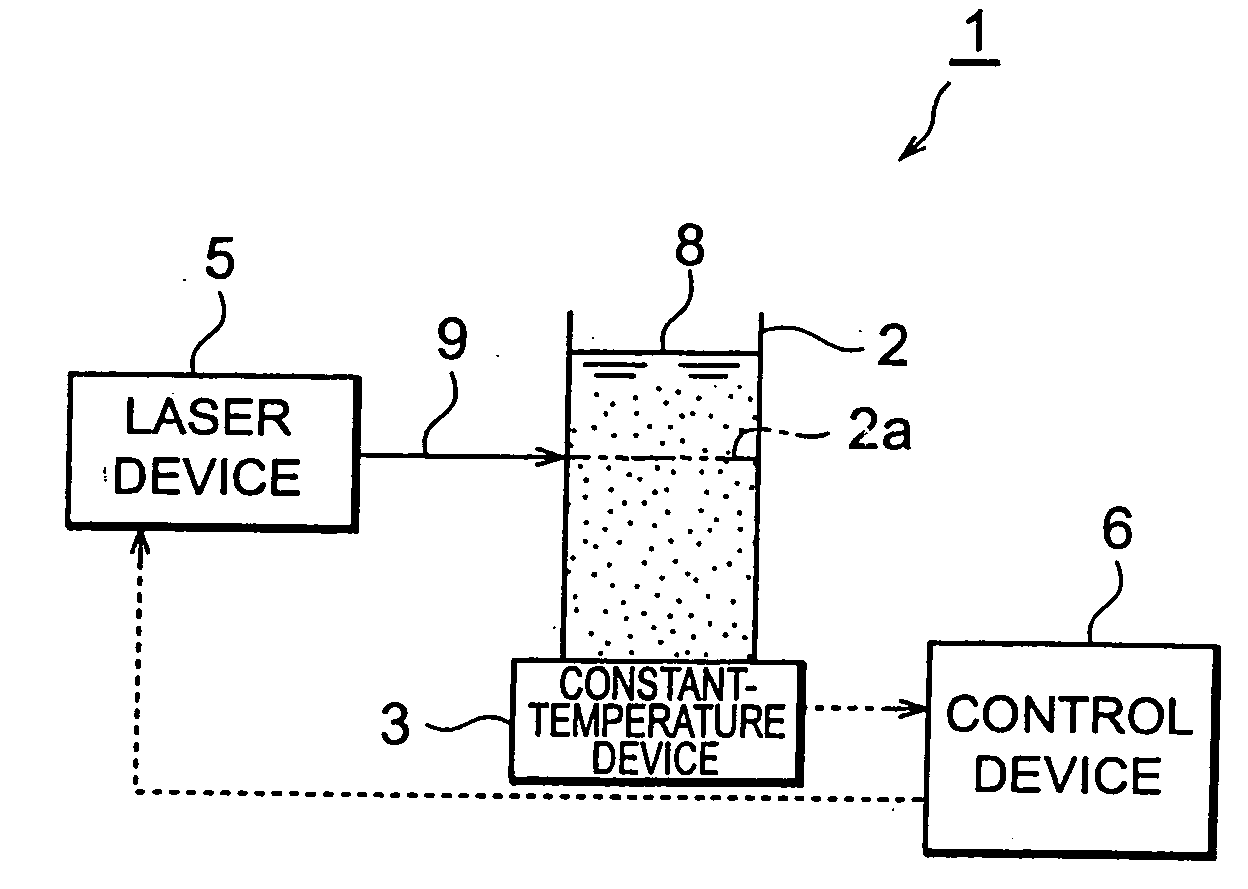
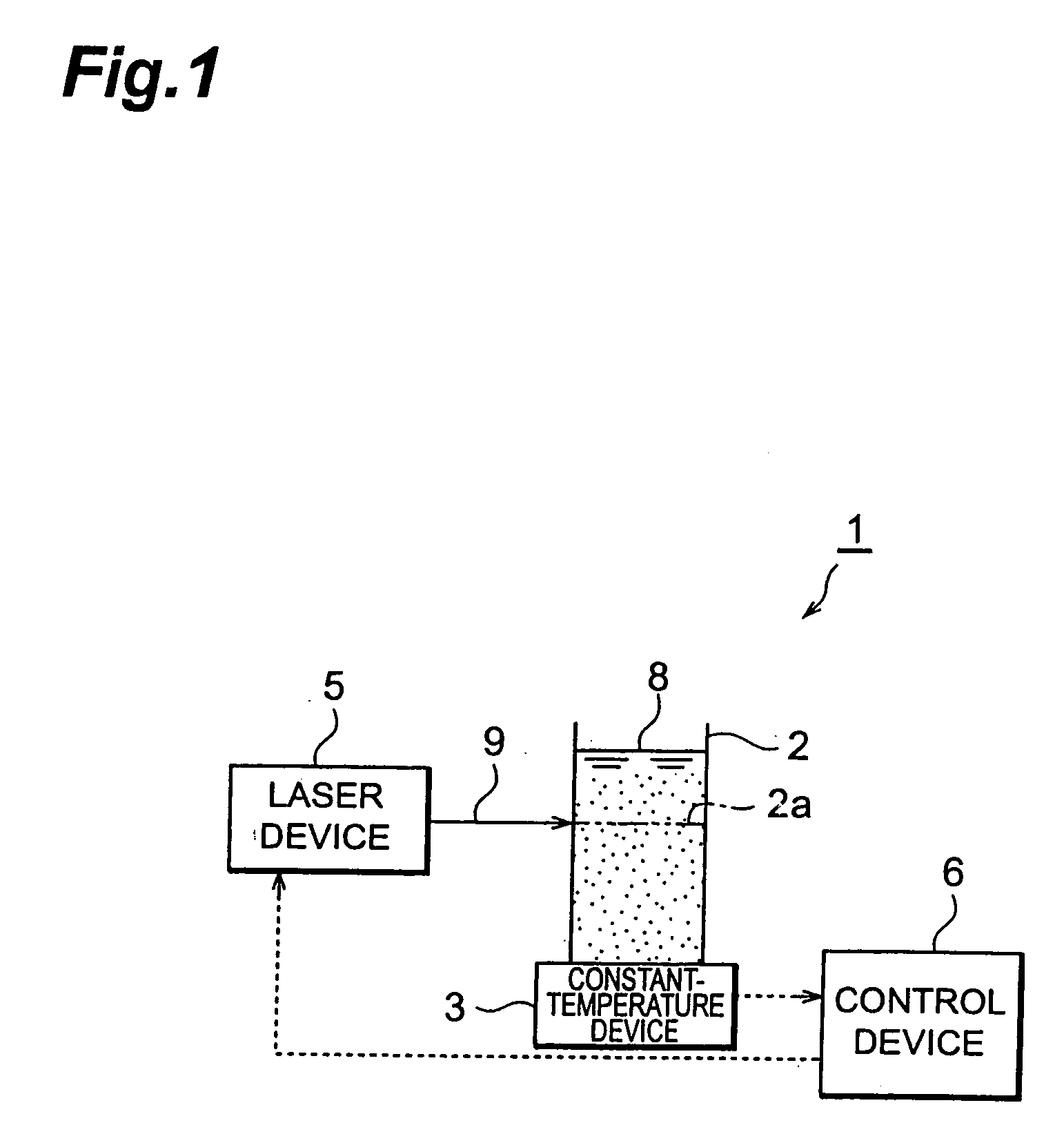
Process for producing nanoparticle apparatus therefor and method of storing nanoparticle
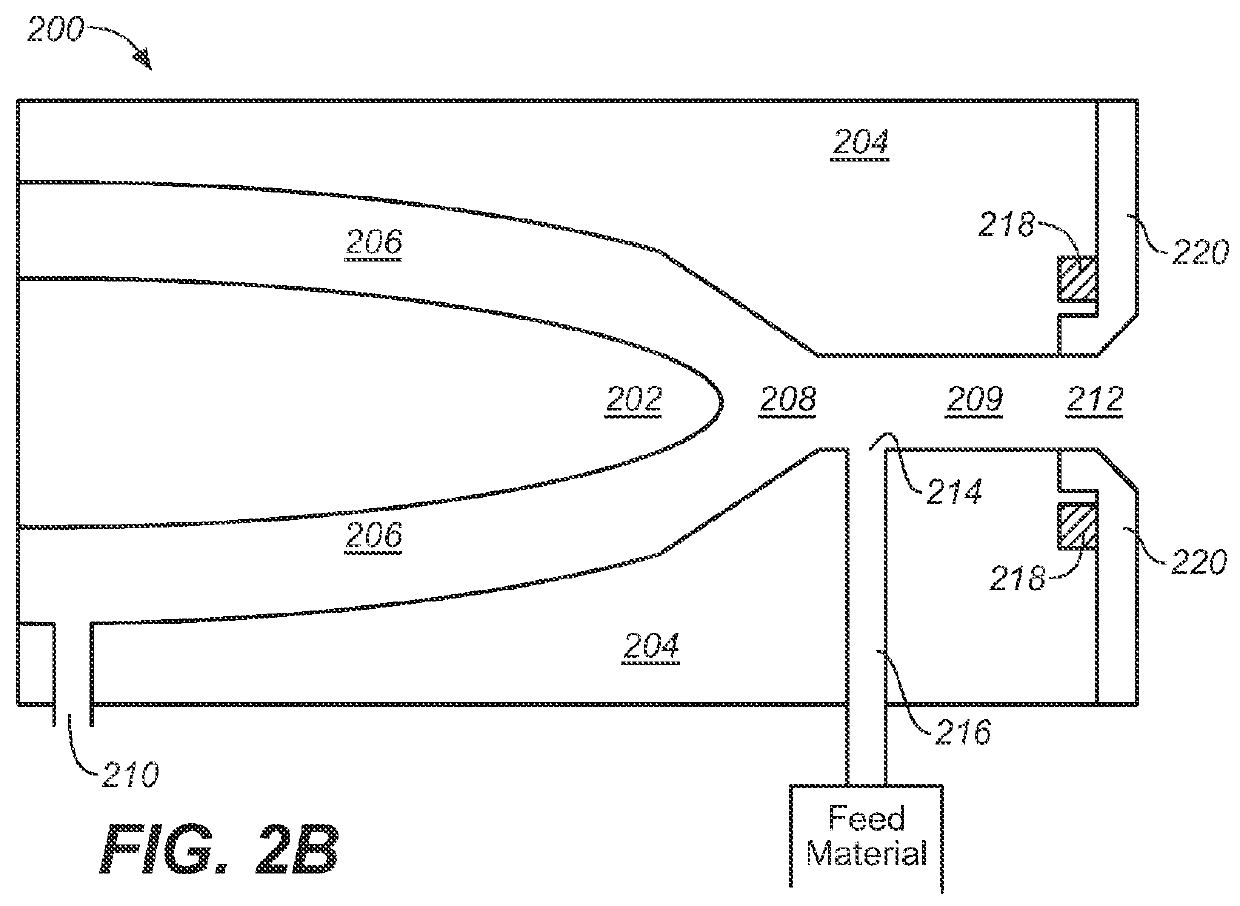
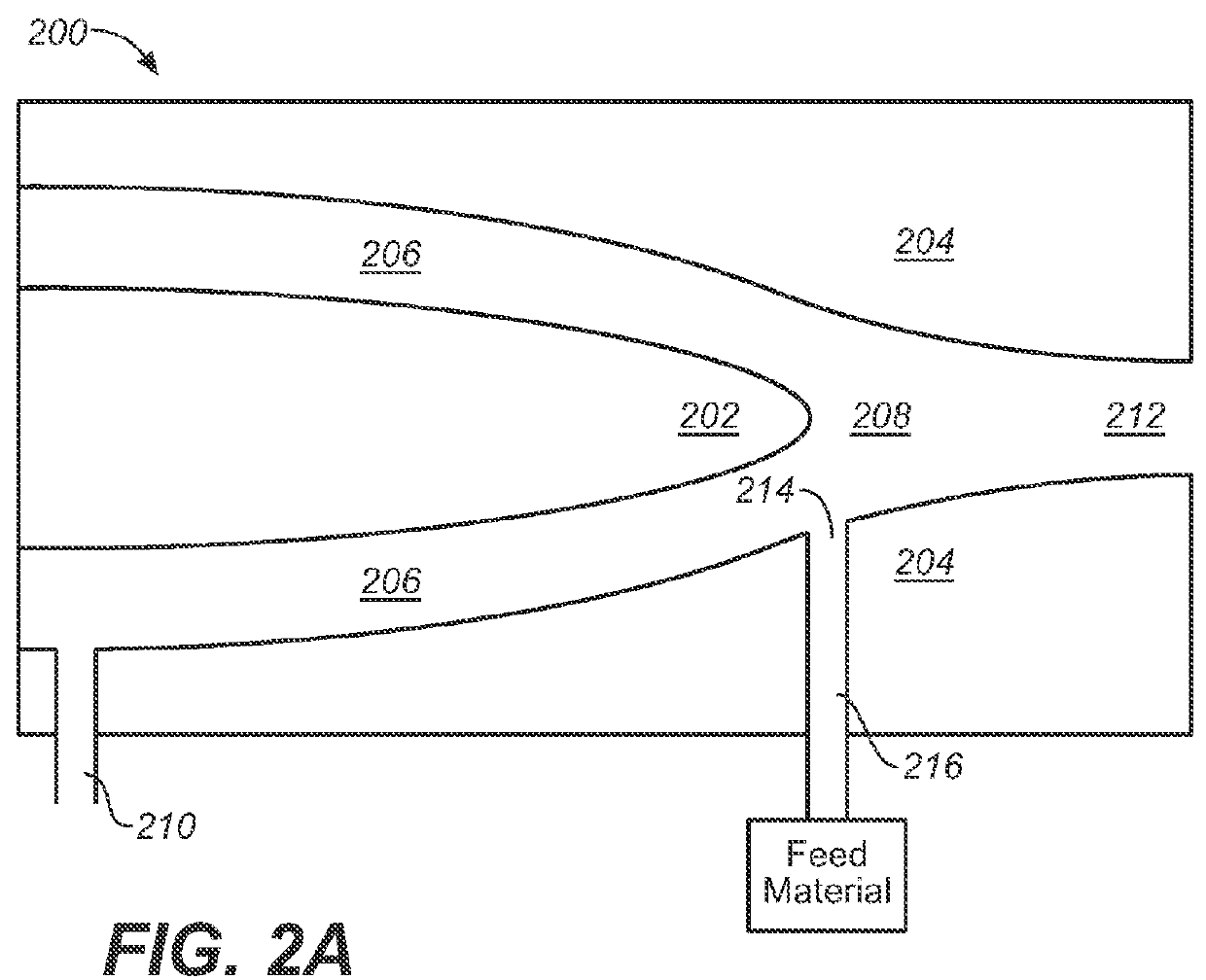
InactiveUS20060103060A1Improve efficiencyEfficient executionLaser detailsInorganic pigment treatmentNanoparticle ProductionSuspended particles
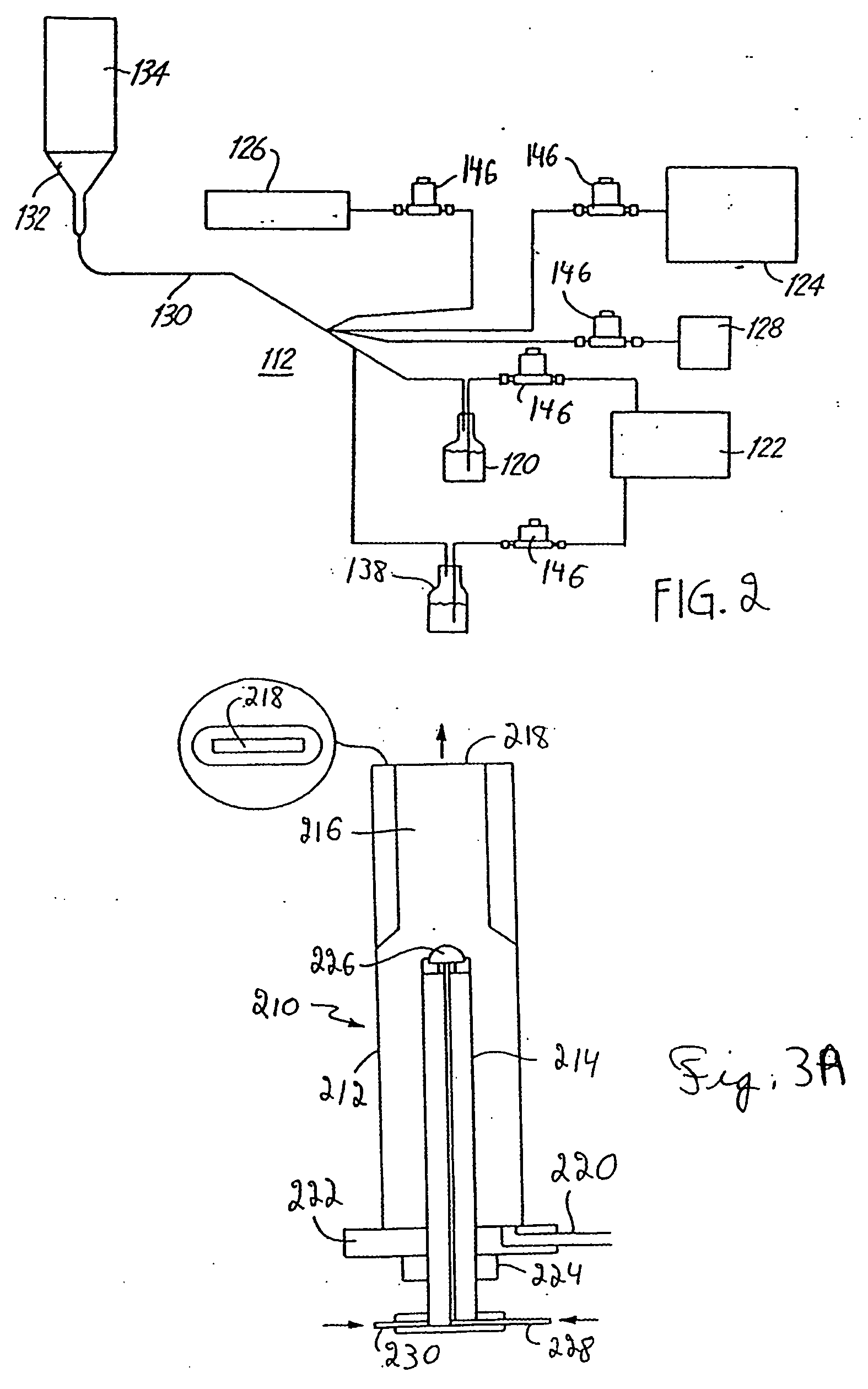
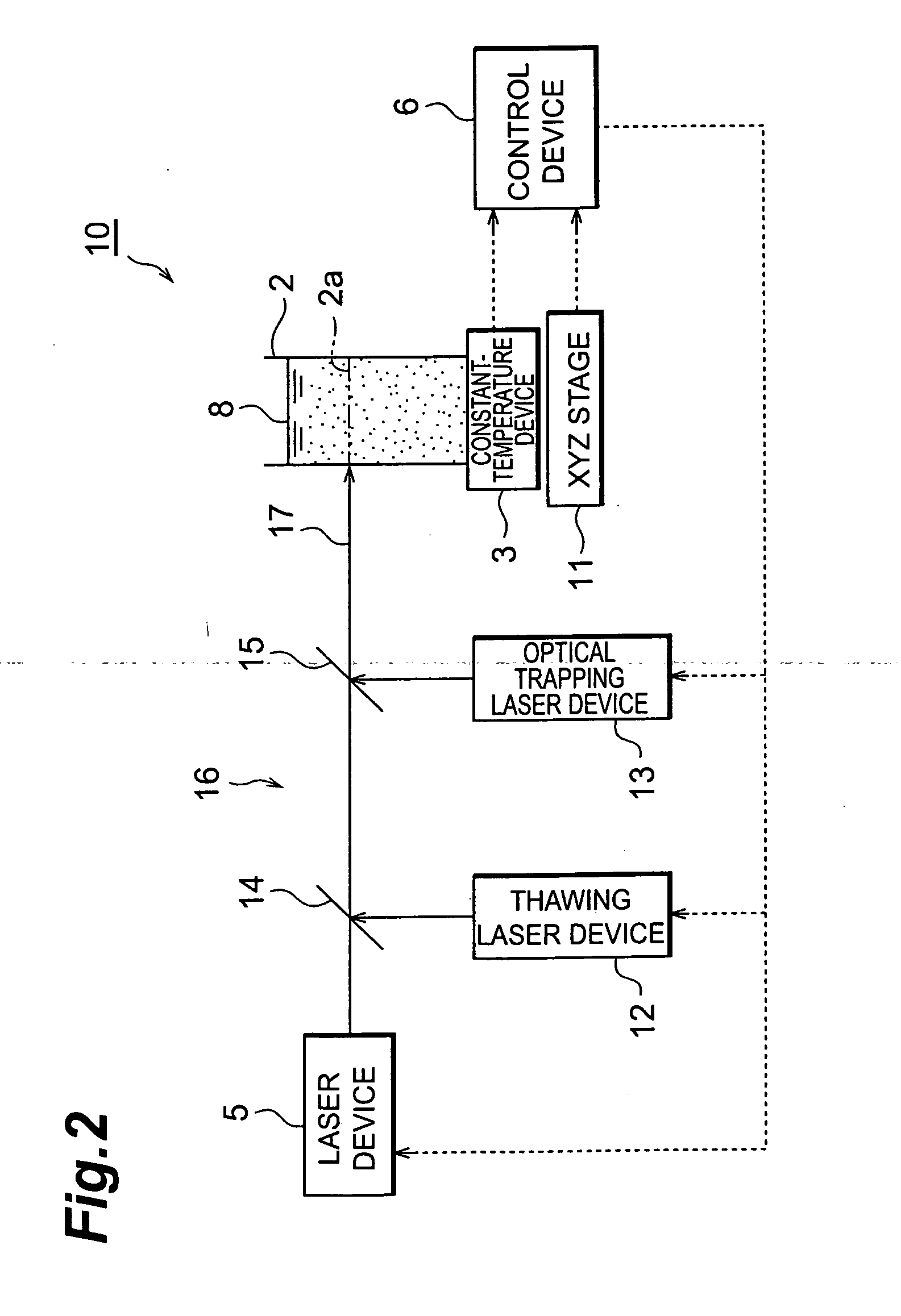
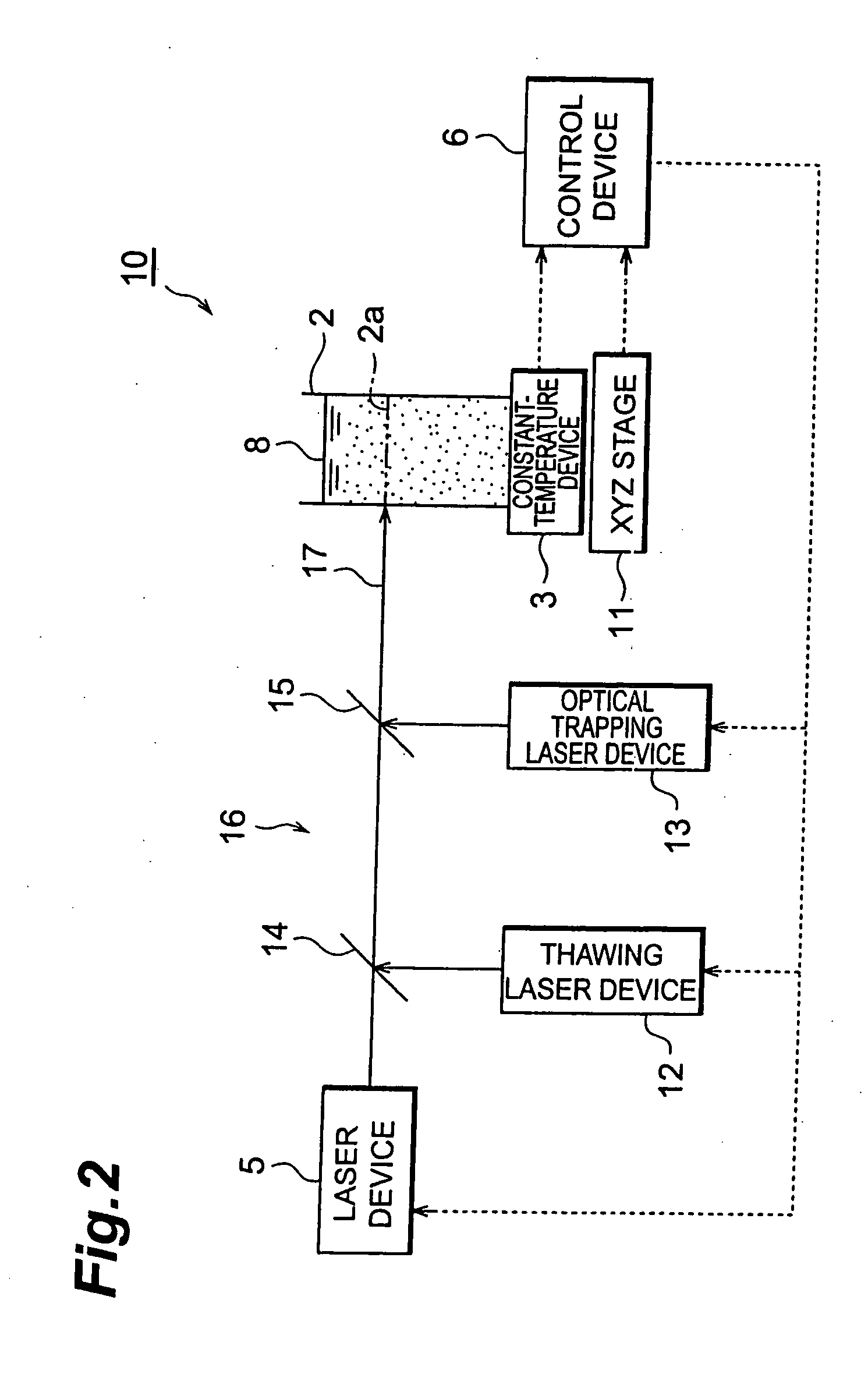
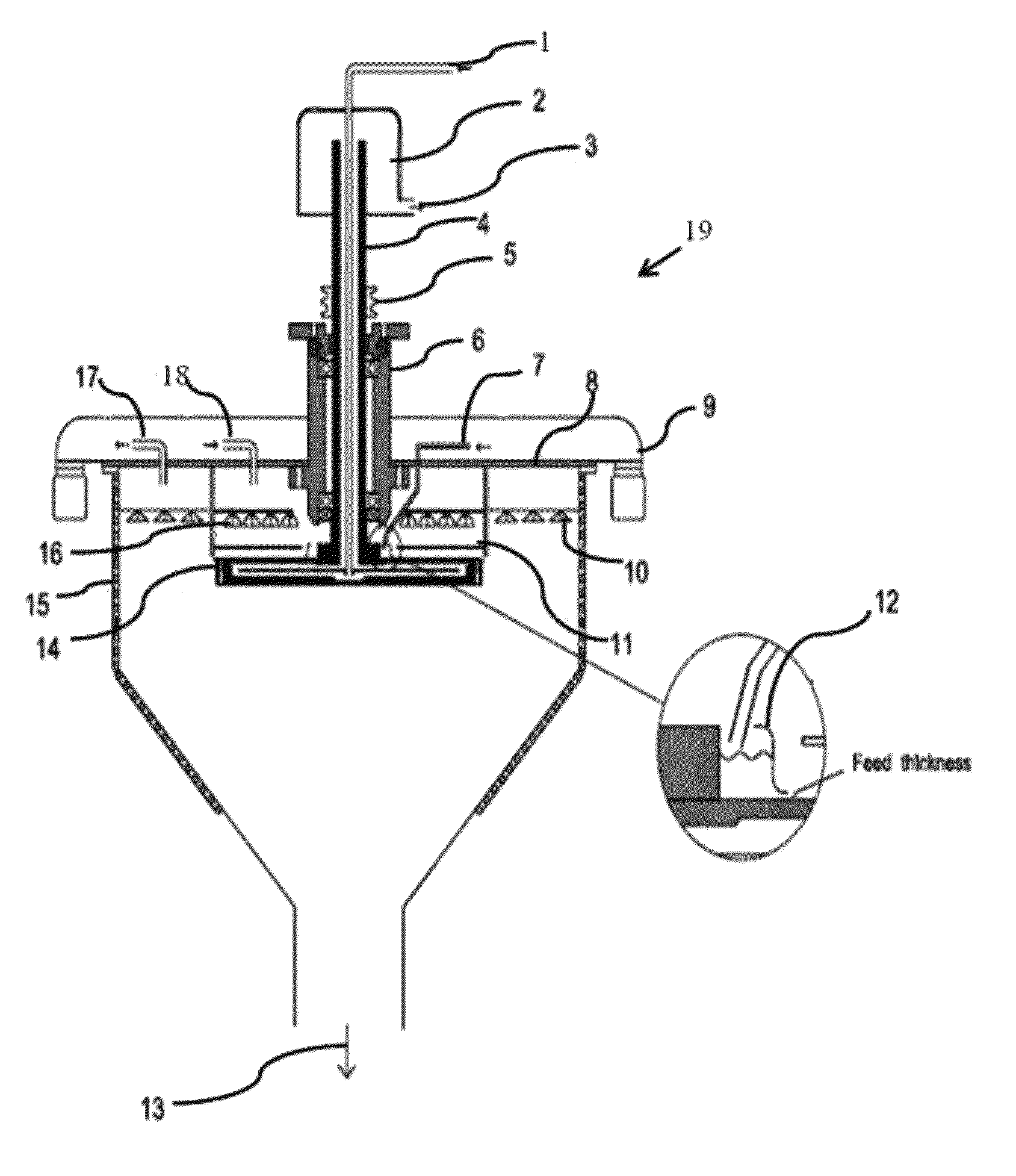
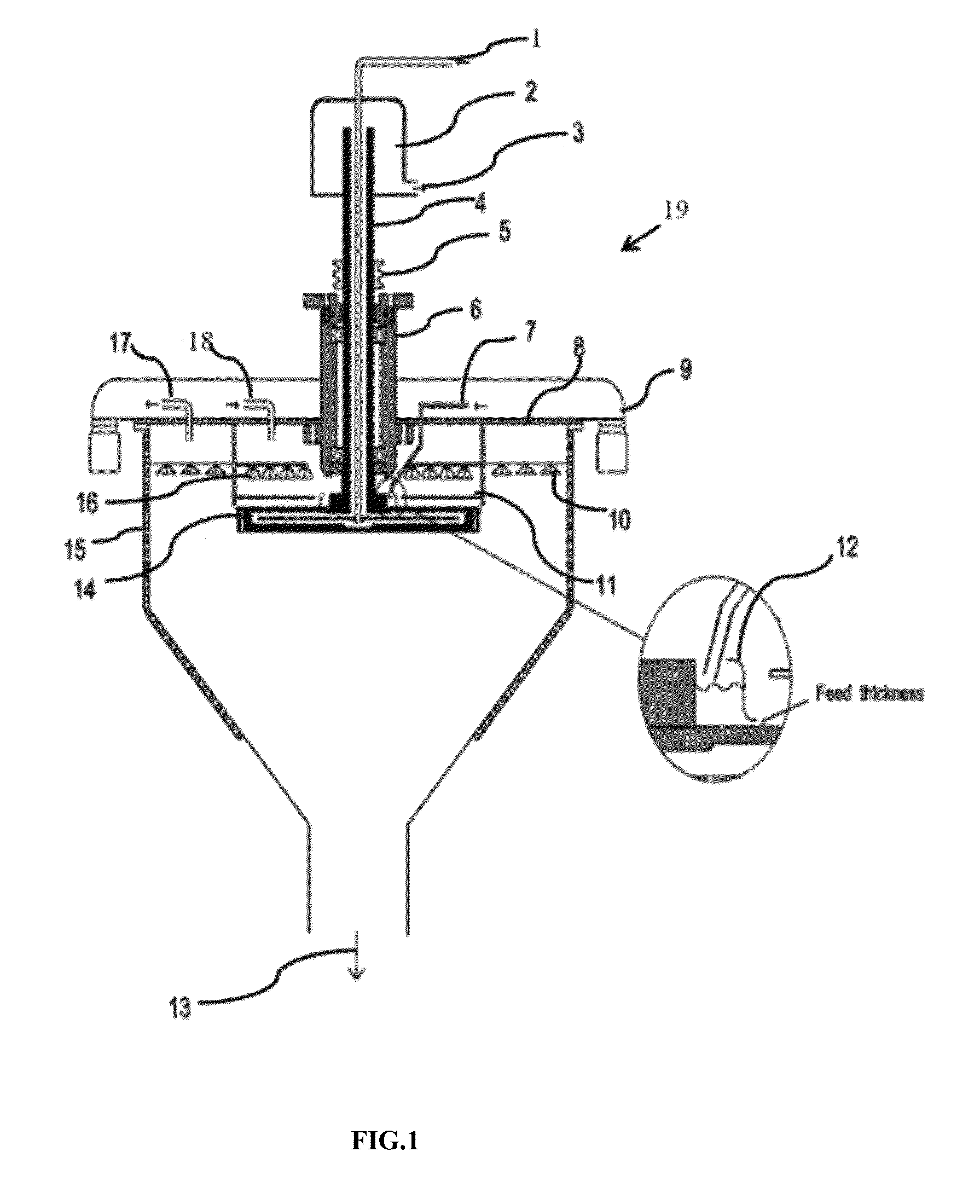
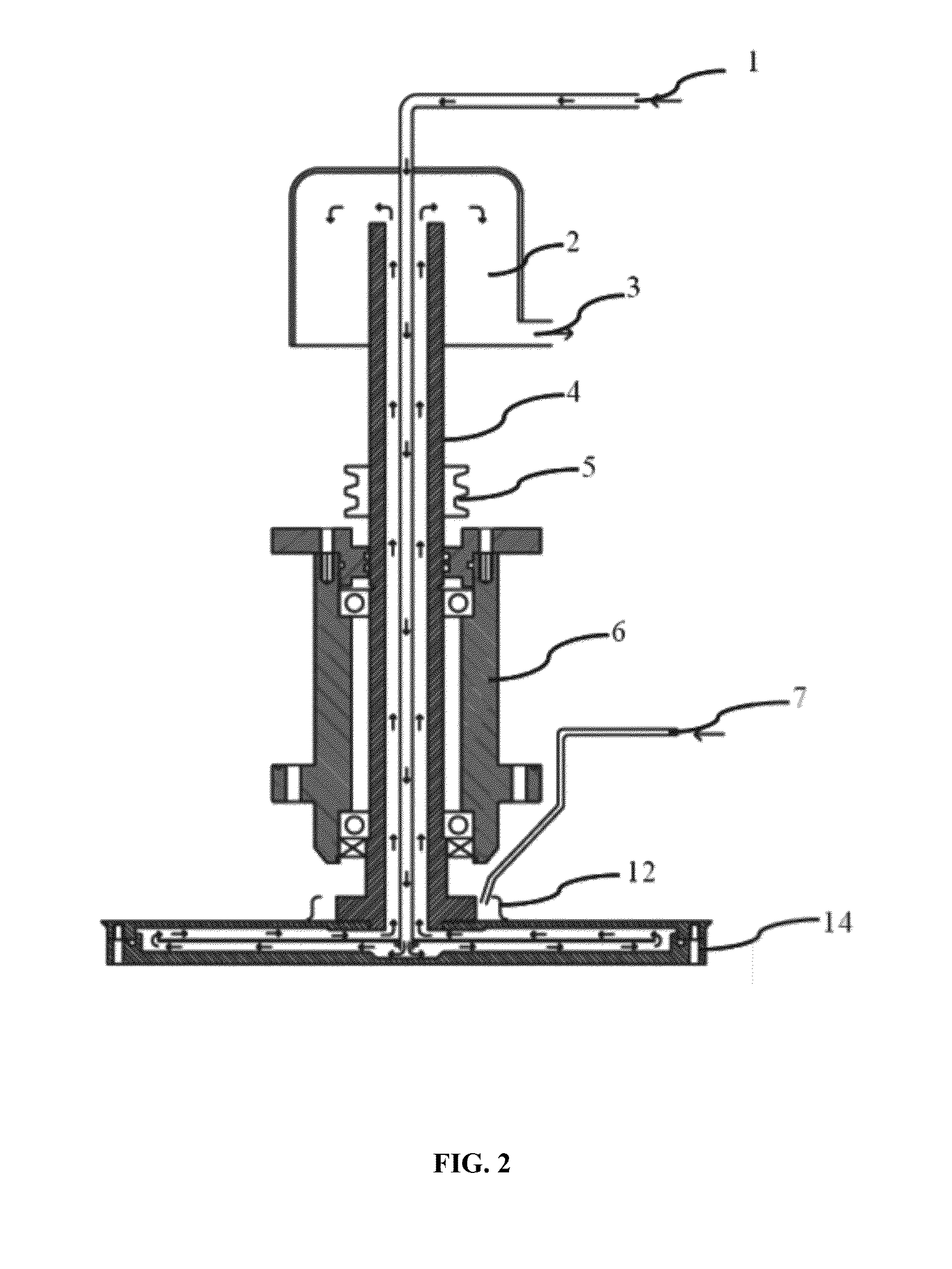
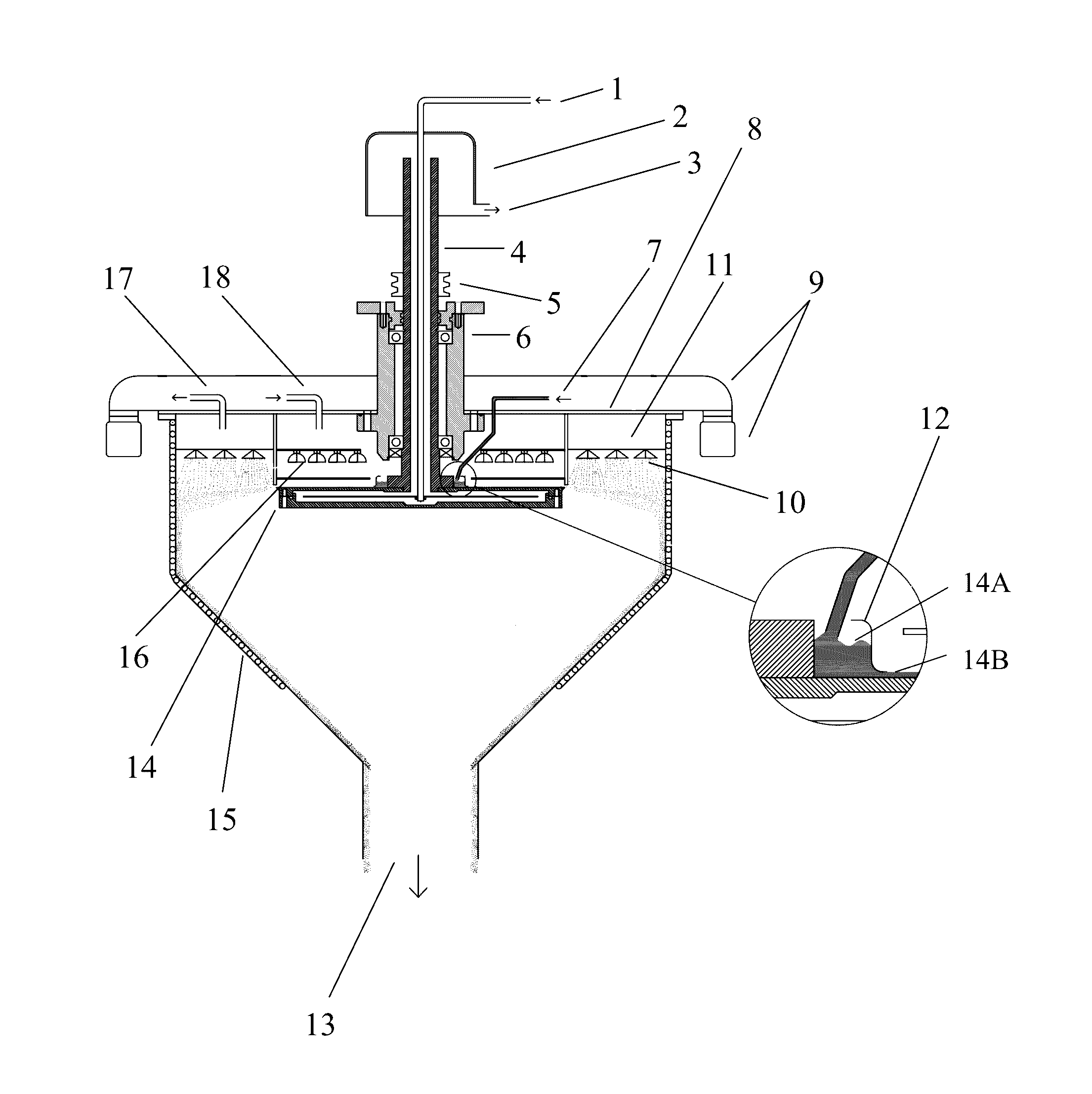
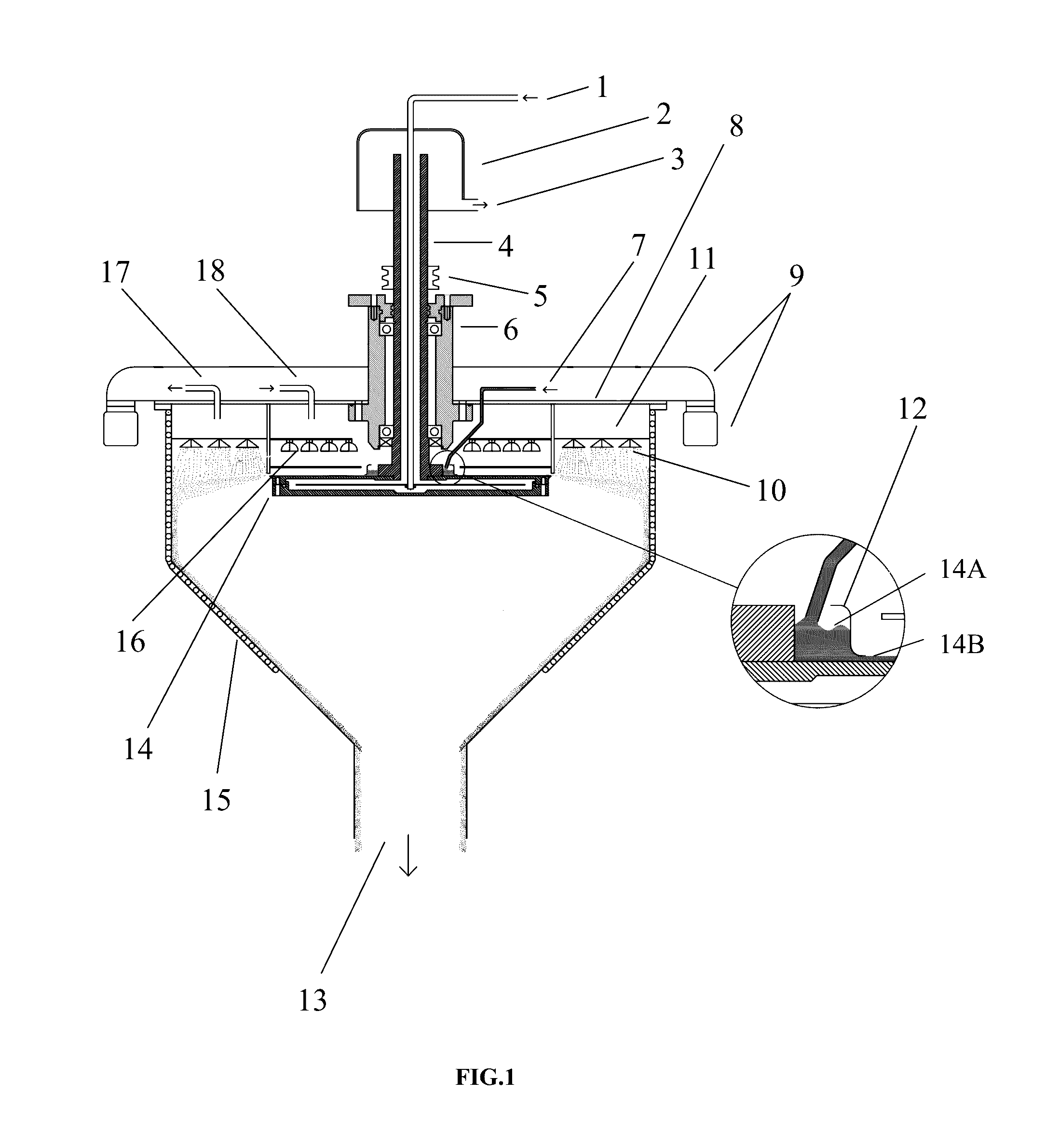
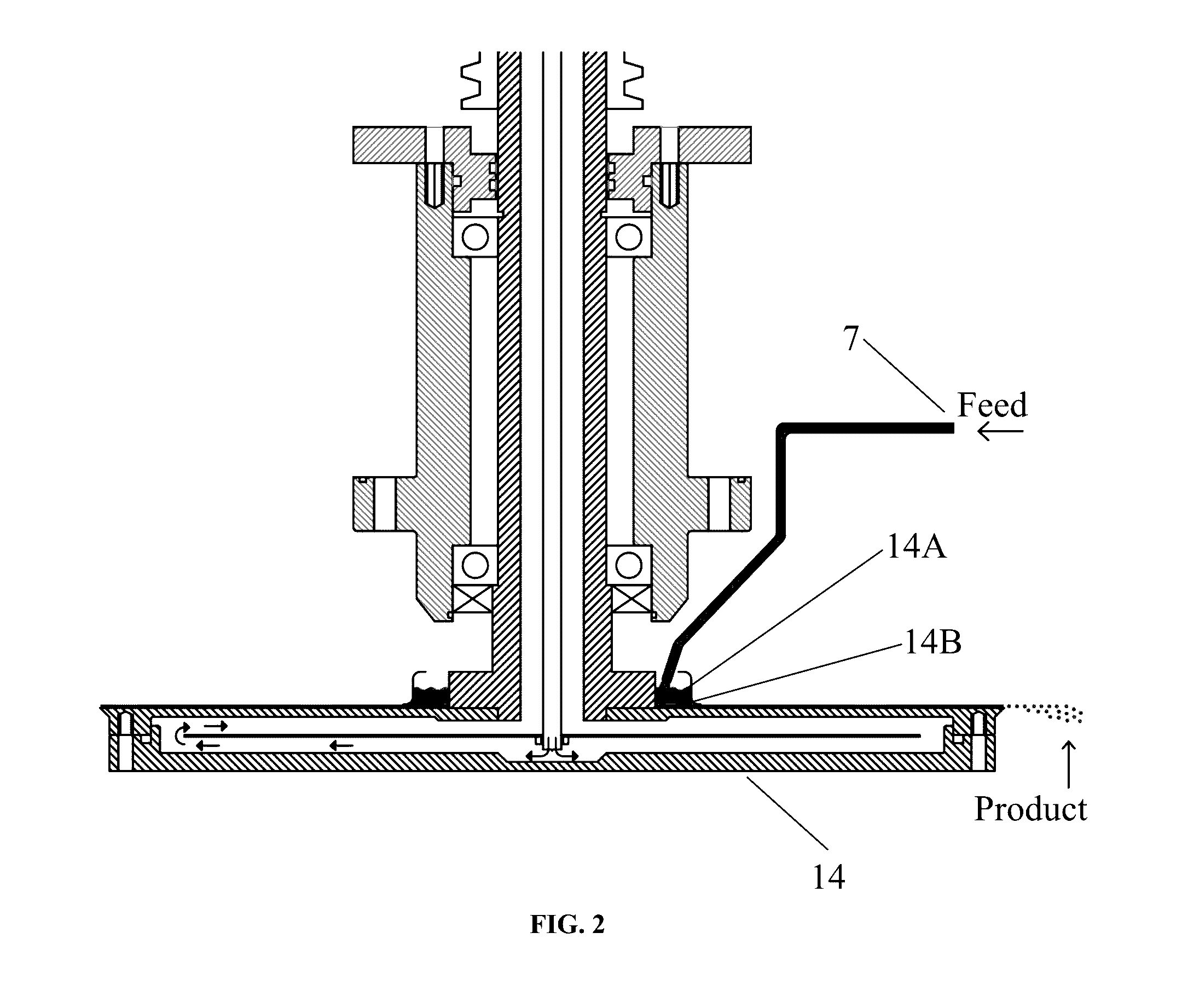
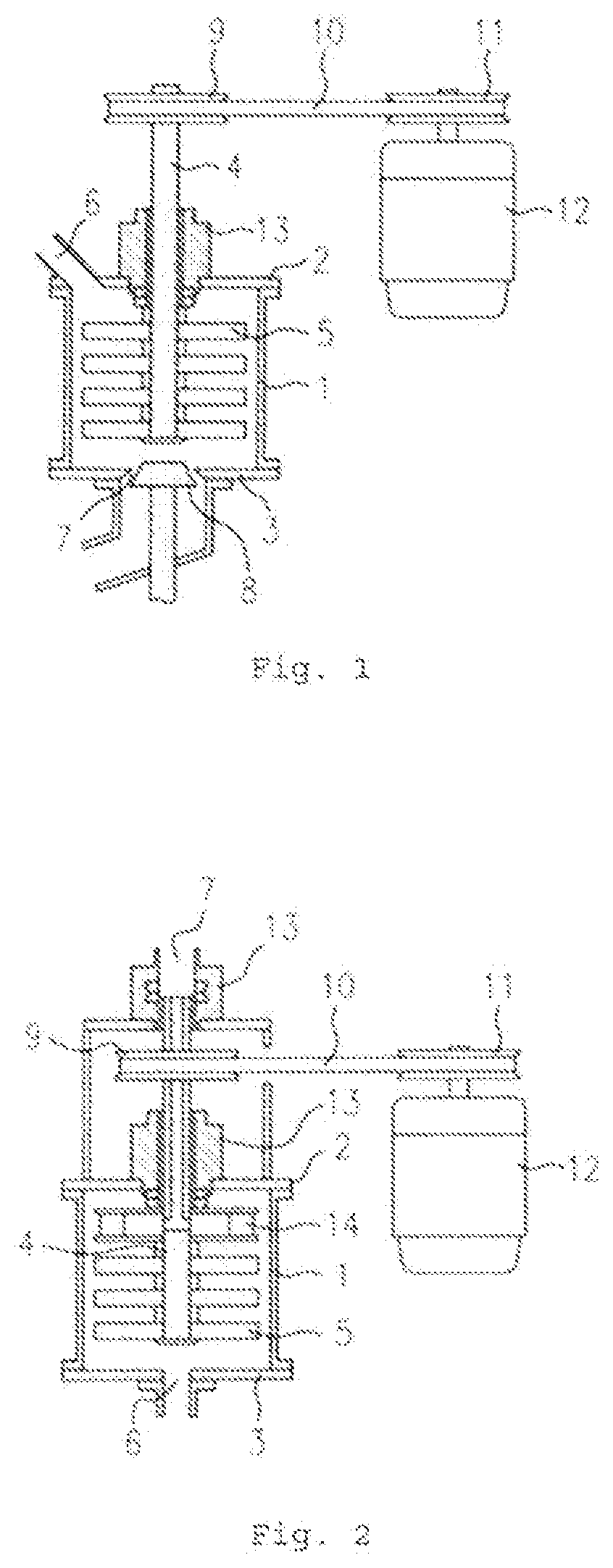
With this invention, in a nanoparticle production method, wherein nanoparticles are produced by irradiating a laser light irradiation portion 2a of a to-be-treated liquid 8 with a laser light, in which suspended particles are suspended, to pulverize the suspended particles in laser light irradiation portion 2a, laser light irradiation portion 2a of to-be-treated liquid 8 is cooled. In this case, by the cooling of to-be-treated liquid 8, the respective suspended particles are cooled in their entireties. When the portion 2a of this to-be-treated liquid 8 is irradiated with the laser light, the laser light is absorbed at the surfaces of the suspended particles at portion 2a. Since to-be-treated liquid 8 is cooled during this process, significant temperature differences arise between the interiors and surfaces of the suspended particles and between the surfaces of the suspended particles and the to-be-treated liquid at laser light irradiation portion 2a, and highly efficient nanoparticulation is realized.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Method for manufacturing a nanoparticle, method for manufacturing a light-emitting element having the nanoparticle, and method for manufacturing a display substrate having the nanoparticle
ActiveUS9109153B2Improve productivityToxic reductionMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanoparticle ProductionPolyethylene glycol
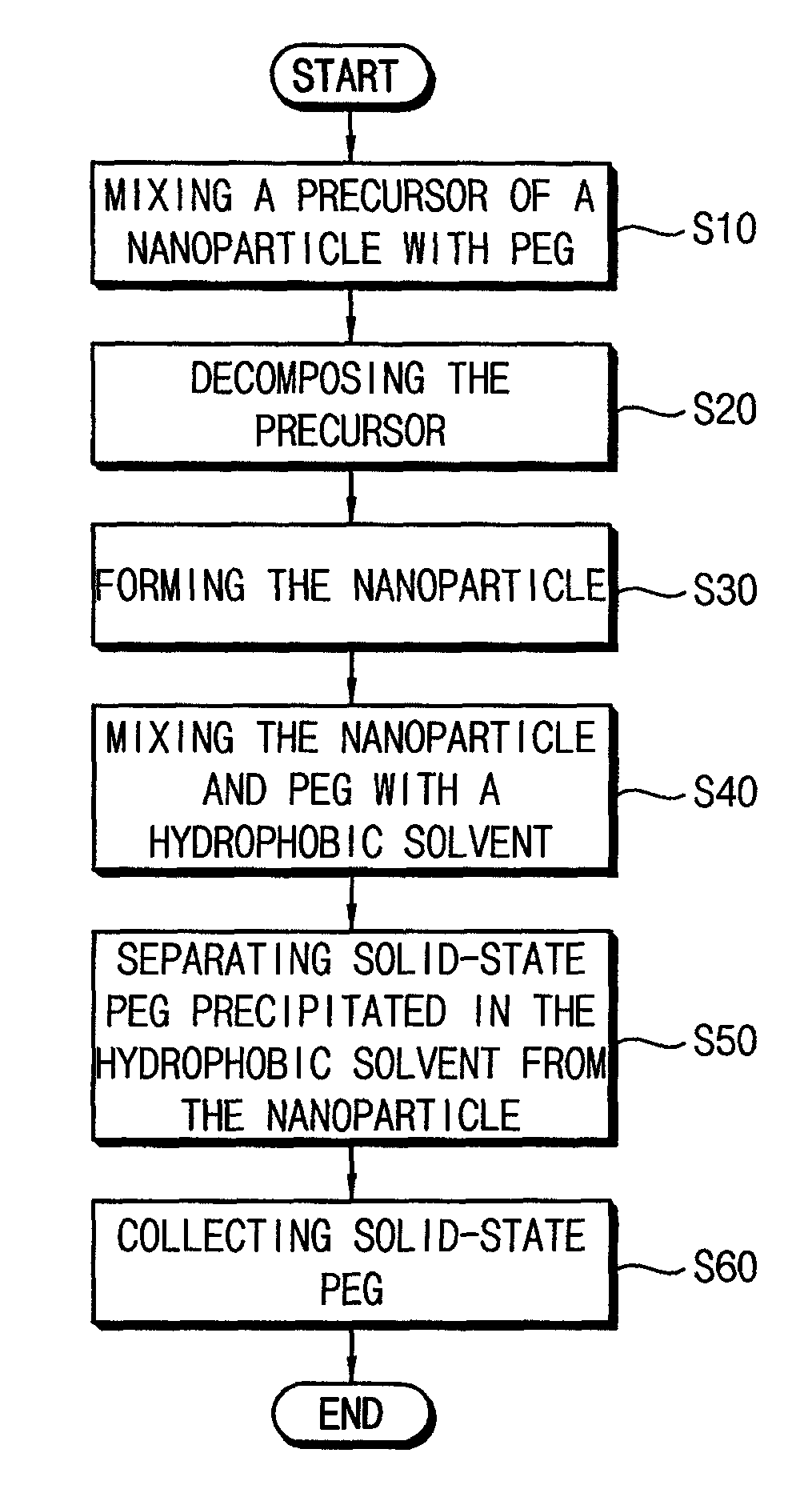
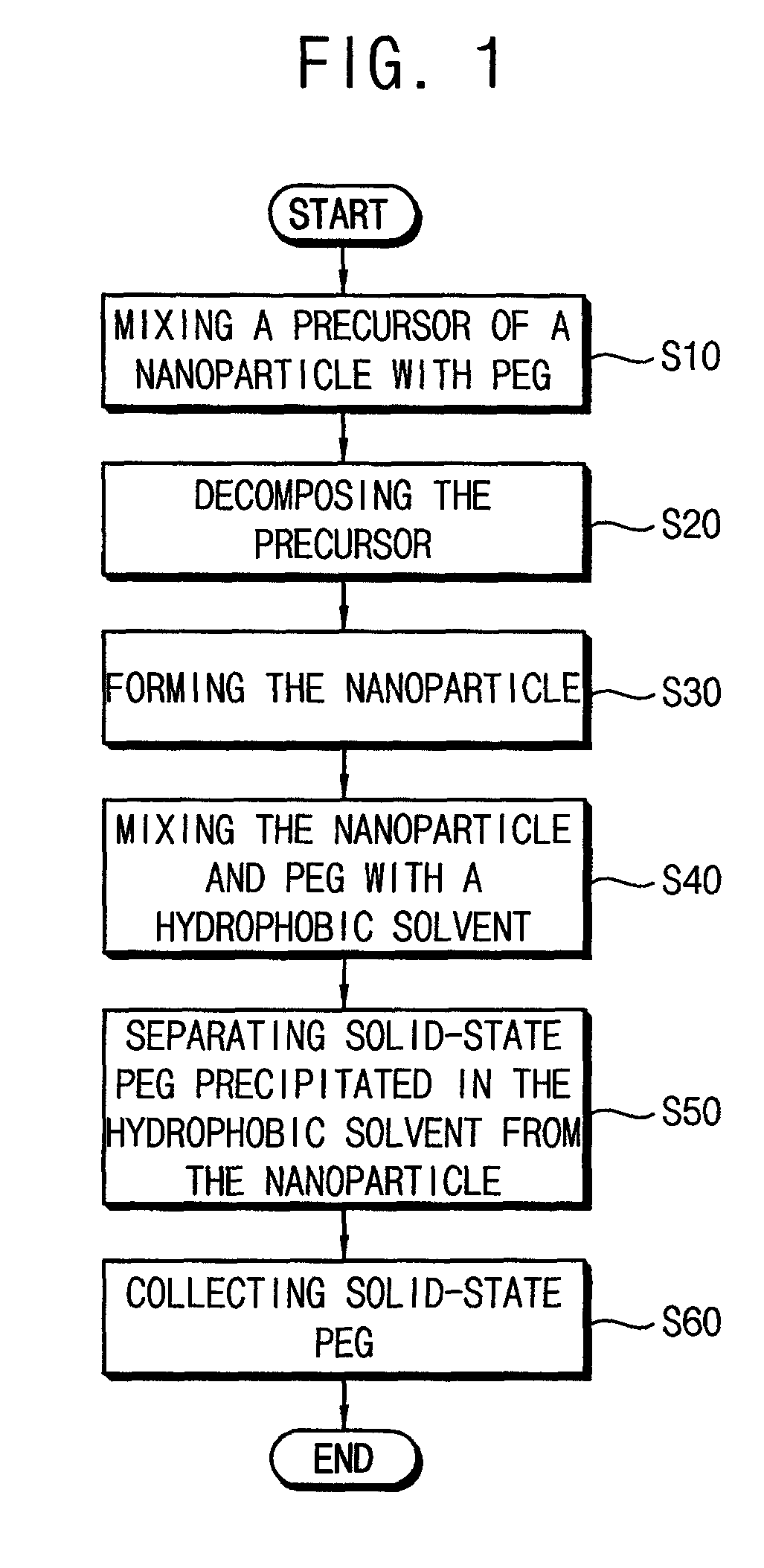
In a method for manufacturing a nanoparticle, a precursor (e.g., transition metal complex) mixed with polyethylene glycol (PEG) is thermally decomposed. A nanoparticle is formed from the thermal decomposition. PEG is cost effective and less toxic than chemicals that are conventionally used for nanoparticle production, so that costs for manufacturing the nanoparticle may be decreased. Further, PEG may be reused to produce more nanoparticles.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND +1
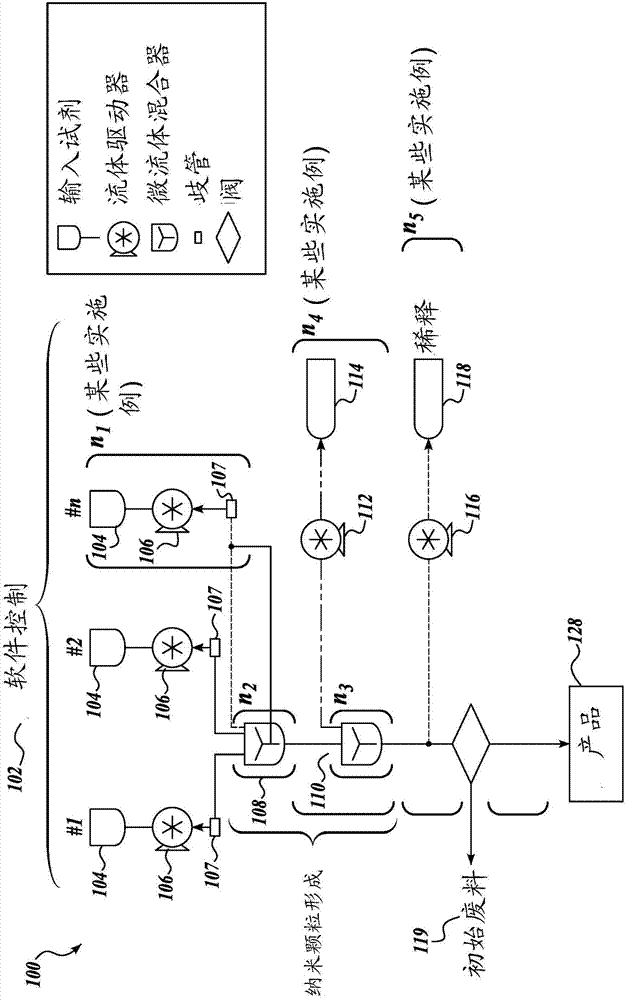
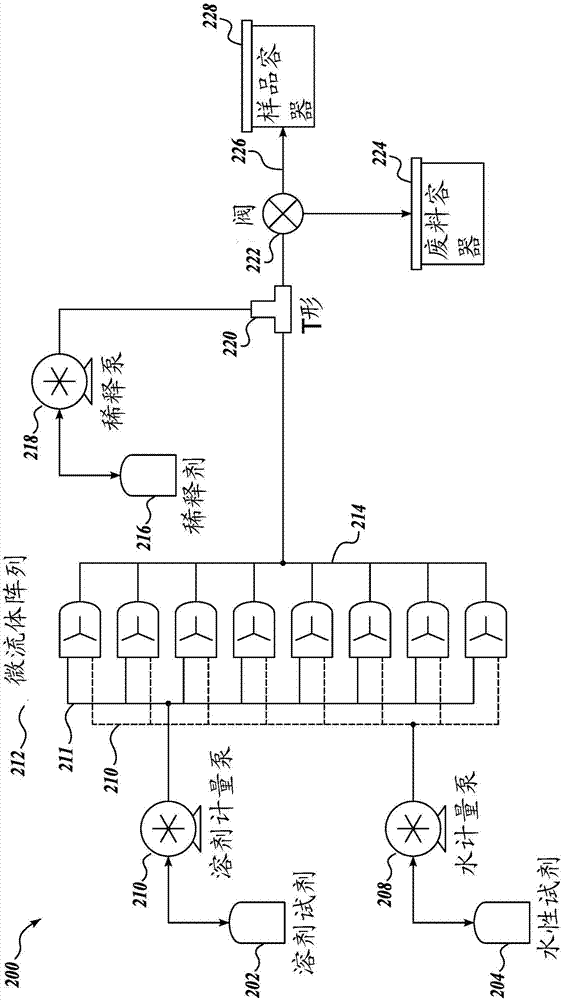
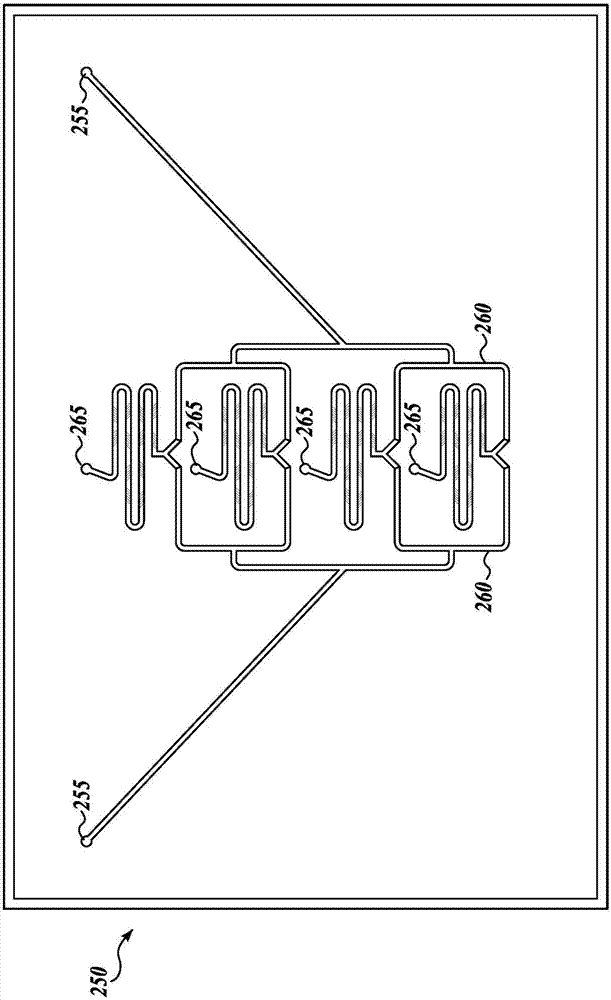
Continuous flow microfluidic system
The present disclosure is directed towards improved systems and methods for large-scale production of nanoparticles used for delivery of therapeutic material. The apparatus can be used to manufacturea wide array of nanoparticles containing therapeutic material including, but not limited to, lipid nanoparticles and polymer nanoparticles. In certain embodiments, continuous flow operation and parallelization of microfluidic mixers contribute to increased nanoparticle production volume.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Nanoparticle production in liquid with multiple-pulse ultrafast laser ablation
ActiveUS8858676B2Easy particle size controlImprove production efficiencyNanotechTransportation and packagingNanoparticle ProductionNanosecond
A method for generating nanoparticles in a liquid comprises generating groups of ultrafast laser pulses, each pulse in a group having a pulse duration of from 10 femtoseconds to 200 picoseconds, and each group containing a plurality of pulses with a pulse separation of 1 to 100 nanoseconds and directing the groups of pulses at a target material in a liquid to ablate it. The multiple pulse group ablation produces nanoparticles with a reduced average size, a narrow size distribution, and improved production efficiency compared to prior pulsed ablation systems.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
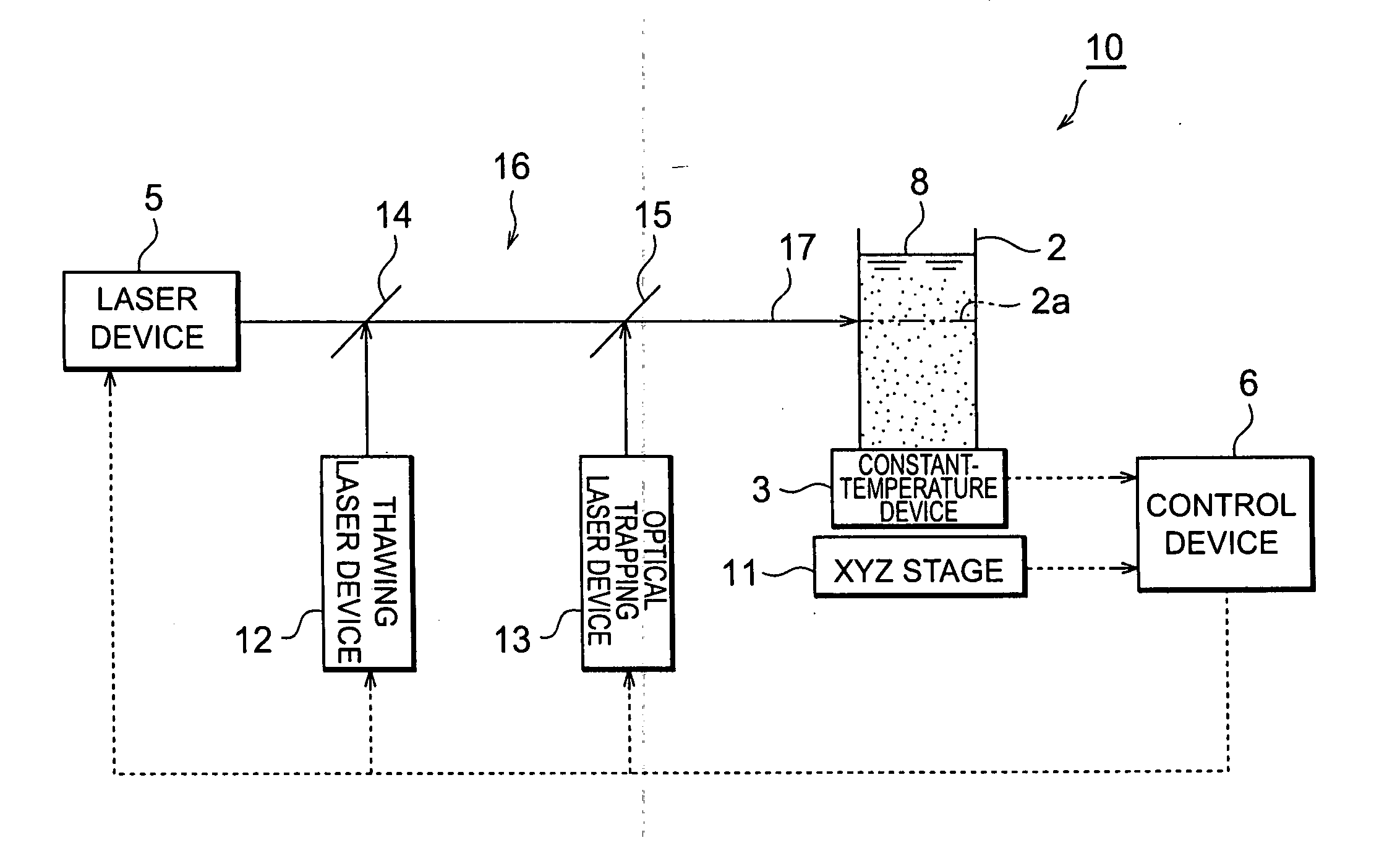
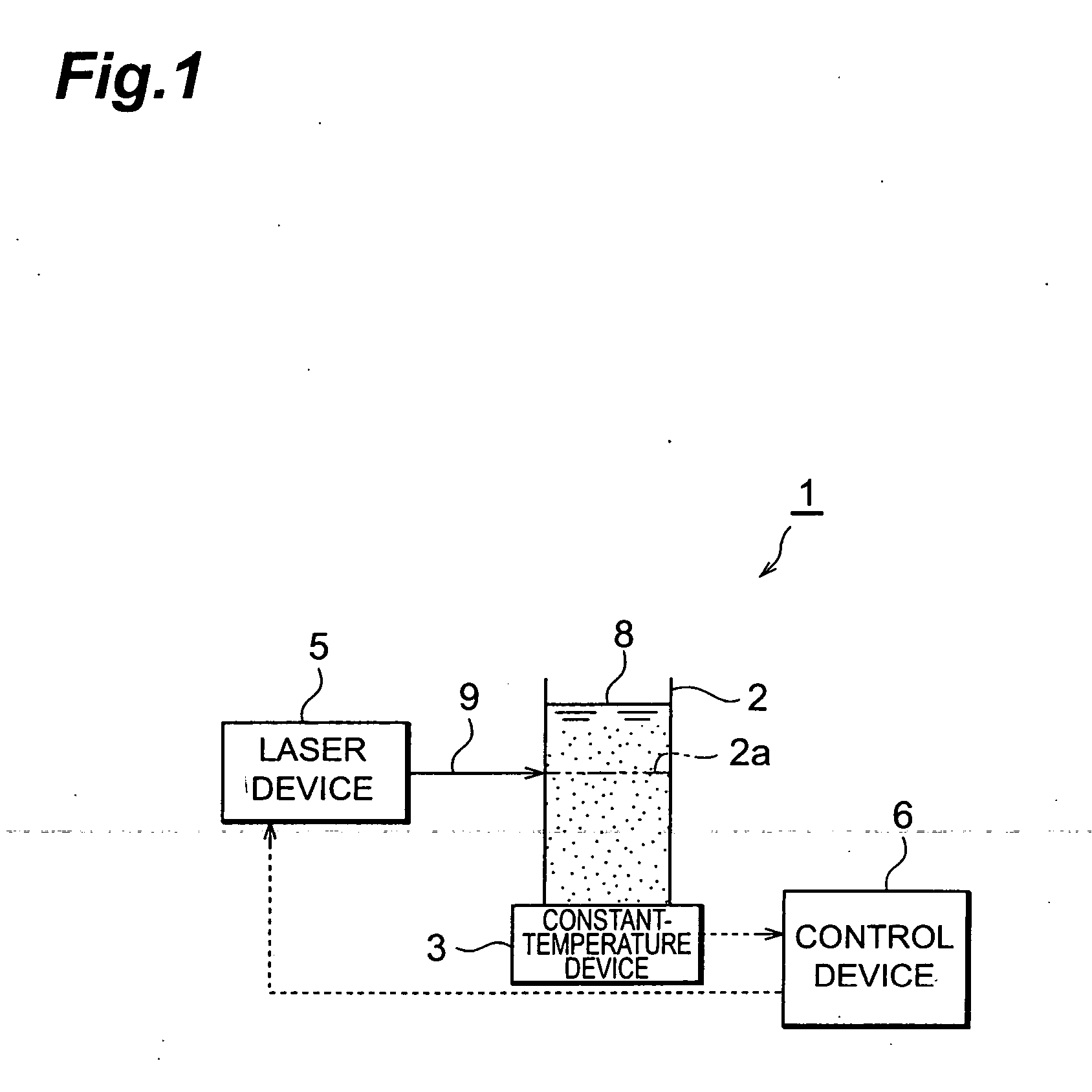
Nanoparticle production method and production device and nanoparticle preservation method
InactiveUS20080265070A1Improve efficiencyEasy to crushLaser detailsInorganic pigment treatmentSuspended particlesNanoparticle Production
With this invention, in a nanoparticle production method, wherein nanoparticles are produced by irradiating a laser light irradiation portion 2a of a to-be-treated liquid 8 with a laser light, in which suspended particles are suspended, to pulverize the suspended particles in laser light irradiation portion 2a, laser light irradiation portion 2a of to-be-treated liquid 8 is cooled. In this case, by the cooling of to-be-treated liquid 8, the respective suspended particles are cooled in their entireties. When the portion 2a of this to-be-treated liquid 8 is irradiated with the laser light, the laser light is absorbed at the surfaces of the suspended particles at portion 2a. Since to-be-treated liquid 8 is cooled during this process, significant temperature differences arise between the interiors and surfaces of the suspended particles and between the surfaces of the suspended particles and the to-be-treated liquid at laser light irradiation portion 2a, and highly efficient nanoparticulation is realized.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Humulus lupulus polysaccharide nanoparticles and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113234552ASmall particle sizeImprove distributionBeer brewingAgainst vector-borne diseasesNanoparticle ProductionPolyelectrolyte
The invention discloses humulus lupulus polysaccharide nanoparticles and application thereof in functional beer production, and belongs to the technical field of food. The preparation method of the humulus lupulus polysaccharide nanoparticles comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a chitosan-acetic acid solution, and adjusting the pH value to 3-5; (2) preparing a humulus lupulus polysaccharide solution, and adjusting the pH to be consistent with the chitosan-acetic acid solution; (3) preparing a functional factor solution; (4) under a stirring condition, dropwise adding the functional factor solution into the chitosan-acetic acid solution, then dropwise adding the humulus lupulus polysaccharide solution, and controlling the mass ratio of chitosan to humulus lupulus polysaccharide to be (2: 1)-(1: 2), and obtaining the chitosan-humulus lupulus polysaccharide embedded functional factor nanoparticles. The nanoparticles prepared through polyelectrolyte complexation between humulus lupulus polysaccharide and chitosan can effectively embed functional factors. The functional beer product produced based on the nanoparticles can effectively reduce the loss of functional factors in the storage process.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Method and system for enhancing polymerization and nanoparticle production
InactiveUS20130127080A1Increase polymerization rateIncrease productionGranulation by liquid drop formationAuxillary shaping apparatusNanoparticle ProductionProcess engineering
The various embodiments herein provide a system and method for enhancing polymerization and nanoparticles production using a disc reactor. The system comprises of a rotating disc comprising a first surface and a second surface arranged longitudinally along a single axis of rotation, a shaft attached to the rotating disc, a ring provided across the first surface and the second surface of the rotating disc, at least one feed inlet for providing a feed solution, a fluid inlet for providing a heat transfer fluid, a fluid outlet for exiting the heat transfer fluid, a product collector for collecting the produced nanoparticles and a product outlet for exiting the produced nanoparticles. The feed solution flows from the first surface to the second surface of the rotating disc due to centrifugal forces and gets accumulated on the product collector and exits from the disc reactor through the product outlet.
Owner:REZA YOUSSEFI REZA +1
Gastroenteric tumor targeted magnetic adriamycin albumin nanoparticles manufactured through pressurization and vibration packing method
InactiveCN107669660AAvoid scatterEvenly dispersedOrganic active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsTumor targetTumor targeted
The invention relates to gastrointestinal tumor-targeted magnetic doxorubicin-albumin nanoparticles prepared by a compression-vibration wrapping method. The high polymer coating layer on the surface of magnetic doxorubicin albumin nanoparticles is uneven, and the surface of a single magnetic doxorubicin albumin nanoparticle is partially coated with a polymer coating layer, and some parts are not coated with a polymer polymer In the production process of the above magnetic doxorubicin albumin nanoparticles, the magnetic doxorubicin albumin nanoparticles powder is uniformly dispersed and laid on a flat, smooth surface with sufficient surface strength and surrounded by a circle. On the plane, another flat, smooth and hard enough circular surface is pressed on the magnetic doxorubicin albumin nanoparticle powder for pre-pressurization, the two circular planes have equal areas, and the upper surface is embedded in the lower surface circle; Then vibrate, pressurize to the required pressure while vibrating, and then drop the solution of high molecular polymer drop by drop around the magnetic doxorubicin albumin nanoparticle powder. .
Owner:锡山区东港全宝机械经营部
Method for producing antibacterial silk through adding nanoparticles
ActiveCN111357719AGood dispersionReduce dosageAccessory food factorsWorking-up animal fodderNanoparticle ProductionPolymer science
The invention discloses a method for producing antibacterial silk through adding nanoparticles. The method comprises the following steps of evenly spraying a dispersion liquid of amino acid surface-modified nanoparticles on silkworm food, or directly mixing the amino acid surface-modified nanoparticles with the silkworm food evenly to obtain the silkworm food containing nanoparticles; feeding silkworms with the silkworm food containing the nanoparticles from the fifth instar of the silkworms until the silkworms stop eating; and spinning silk and cocooning by the silkworms and obtaining an antibacterial silk fiber containing the amino acid surface-modified nanoparticles. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the silk fiber and related products with excellent antibacterial property can be obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Method for preparing polymer emulsion of optical anode of dye sensitization battery
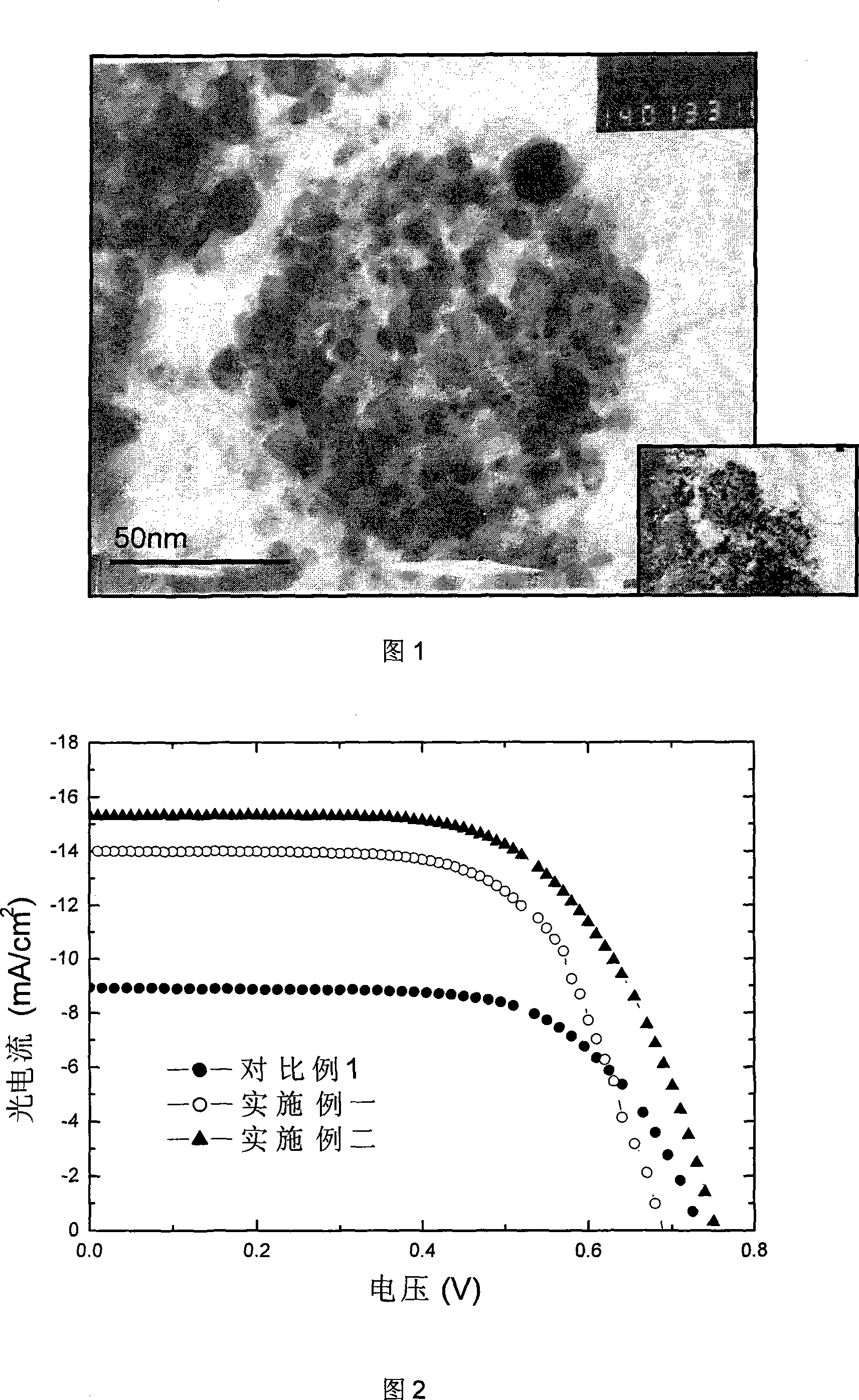
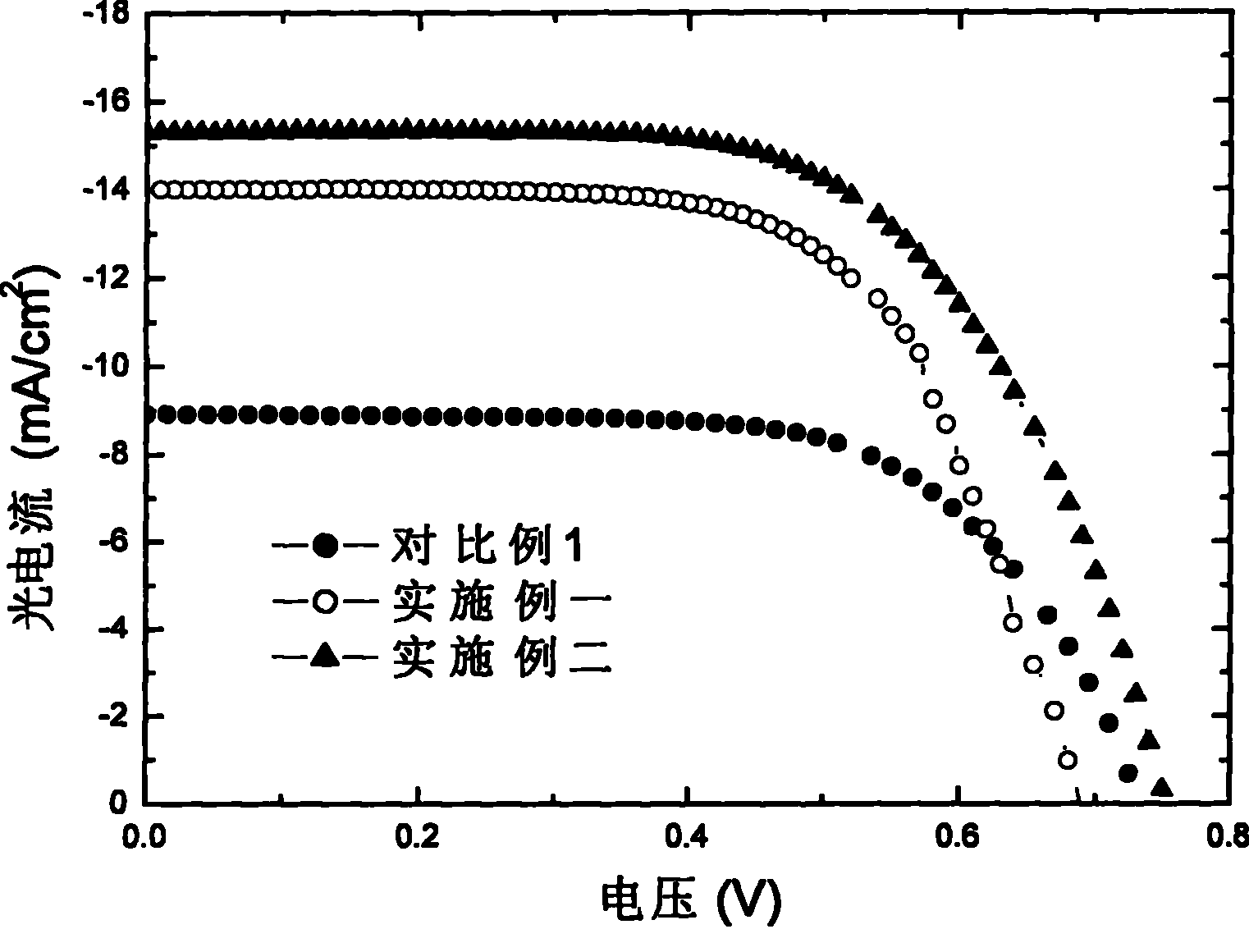
ActiveCN101471397BFavorable for multi-scale adsorptionImprove adsorption capacityLight-sensitive devicesFinal product manufactureMetal oxide nanoparticlesTransformation efficiency
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
High-throughput particle production using a plasma system
The present disclosure relates to a nanoparticle production system and methods of using the system. The nanoparticle production system includes a plasma gun including a male electrode, a female electrodes and a working gas supply configured to deliver a working gas in a vortexing helical flow direction across a plasma generation region. The system also includes a continuous feed system, a quench chamber, a cooling conduit that includes a laminar flow disruptor, a system overpressure module, and a conditioning fluid purification and recirculation system.
Owner:SDC MATERIALS
Improved paclitaxel-based antitumor formulation
InactiveCN1935121AImprove stabilityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsNanoparticle ProductionAlbumin solution
Antitumor formulation based on nanoparticles of paclitaxel and human serum albumin as obtained by the addition of a biocompatible acid to an aqueous albumin solution before this is mixed with paclitaxel during the nanoparticle production process, the injectable solutions of this formulation having a pH between 5.4 and 5.8 and having stability and inalterability with time.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Method and system for enhancing polymerization and nanoparticle production
InactiveUS9573297B2Increase productionIncrease polymerization rateGranulation by liquid drop formationAuxillary shaping apparatusNanoparticle ProductionProcess engineering
The various embodiments herein provide a system and method for enhancing polymerization and nanoparticles production using a disc reactor. The system comprises a rotating disc comprising a first surface and a second surface arranged longitudinally along a single axis of rotation, a shaft attached to the rotating disc, a ring provided on top of the first surface of the rotating disc, at least one feed inlet for providing a feed solution, a fluid inlet for providing a heat transfer fluid, a fluid outlet for exiting the heat transfer fluid, a product collector for collecting the produced nanoparticles and a product outlet for exiting the produced nanoparticles. The feed solution flows from the first surface to the second surface of the rotating disc due to centrifugal forces and gets accumulated on the product collector and exits from the disc reactor through the product outlet.
Owner:REZA YOUSSEFI REZA +1
Organic nanoparticle production method and organic nanoparticles
PendingUS20220287985A1Avoid pollutionReduce componentsOrganic chemistryNanotechnologyNanoparticle ProductionPhysical chemistry
Provided is an organic nanoparticle production method comprising a step in which a mixture of beads having an average particle size at least 0.15 mm and no more than a value (mm) calculated by the formula 1.07−0.11×[outer peripheral speed of the stirring rotor (m / sec)] and a slurry containing organic particles is stirred by a stirring rotor rotating at an outer peripheral speed of 7 m / sec or less in a vessel of a wet bead mill.
Owner:HIROSHIMA METAL & MACHINERY
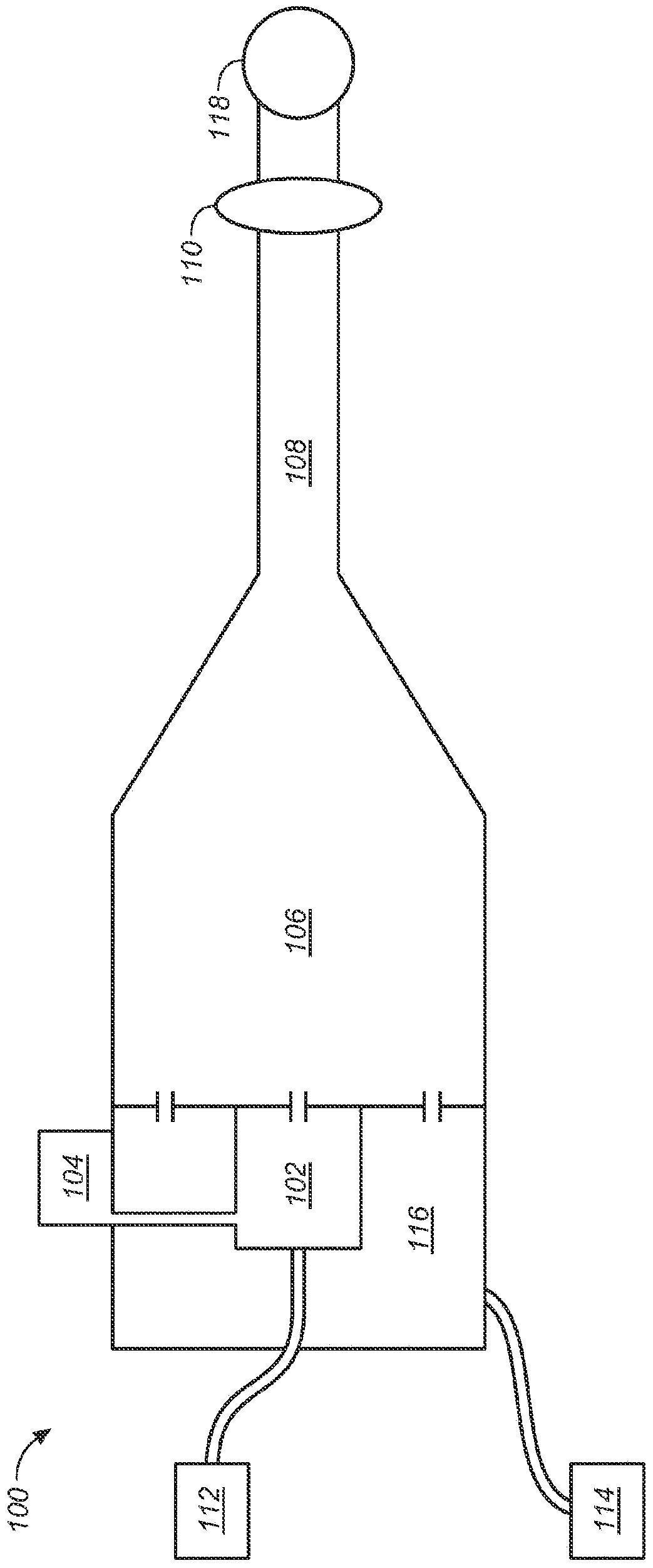
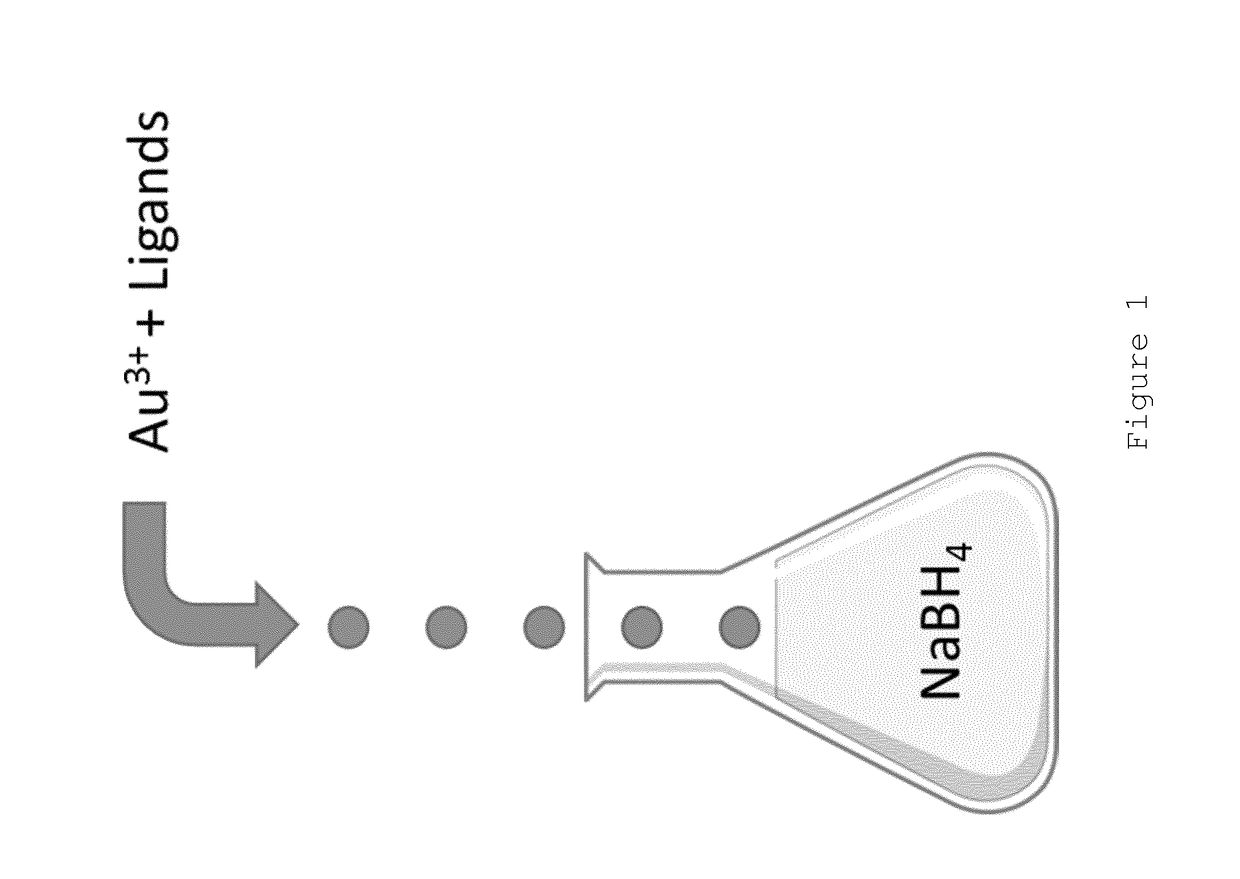
Nanoparticle production
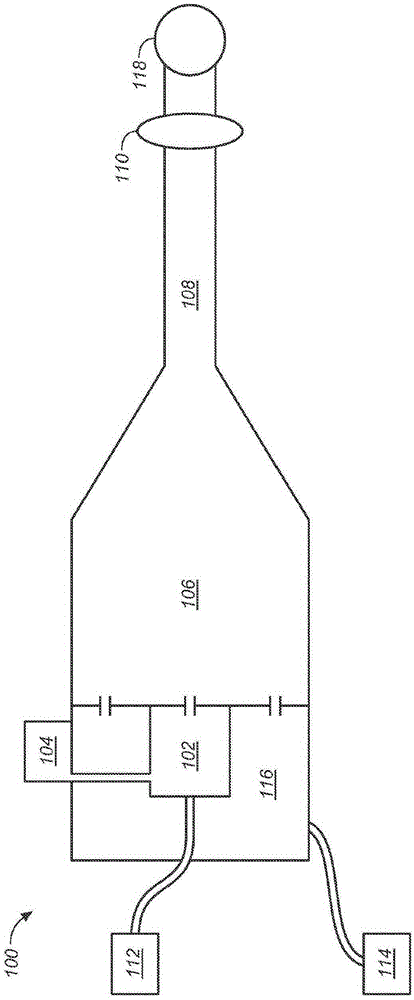
ActiveUS11090626B2Quick mixUniform propertyPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsNanoparticle ProductionSelf-assembly
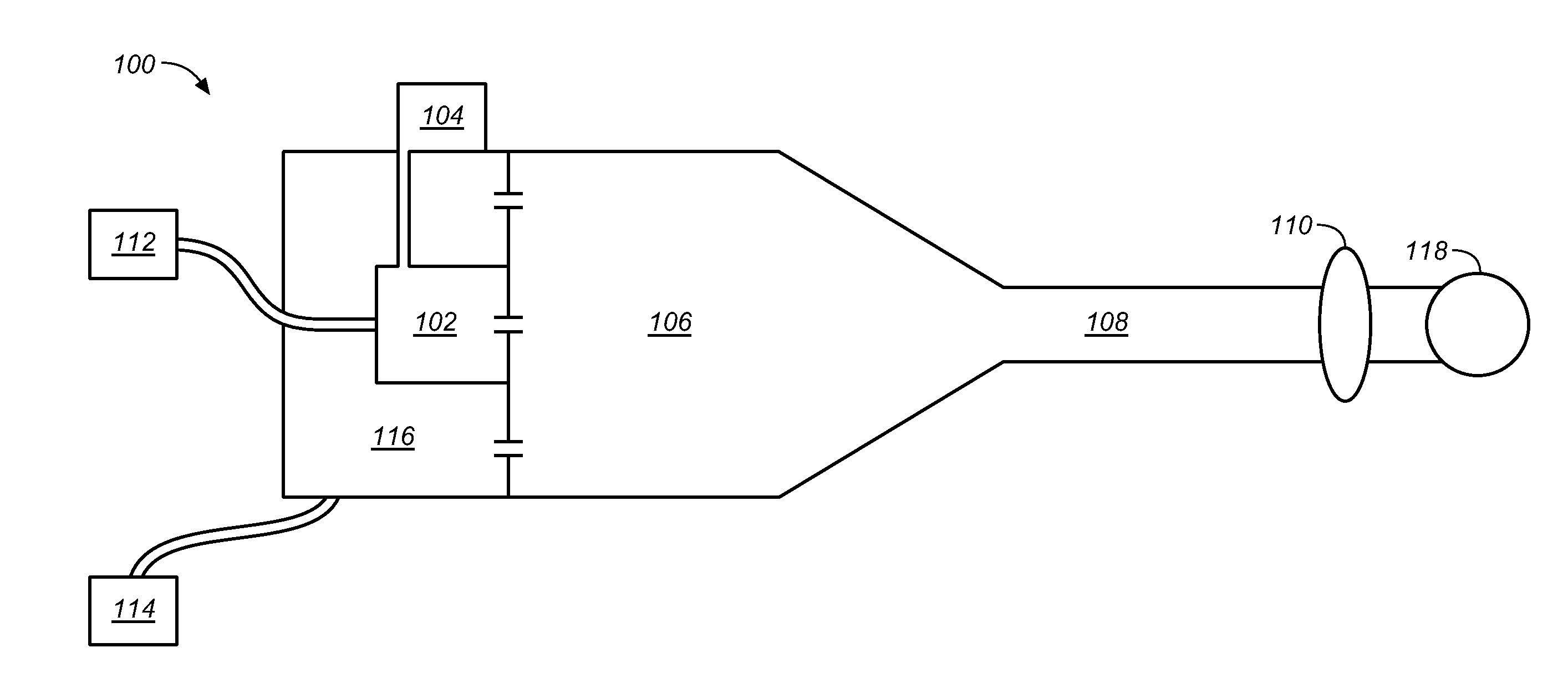
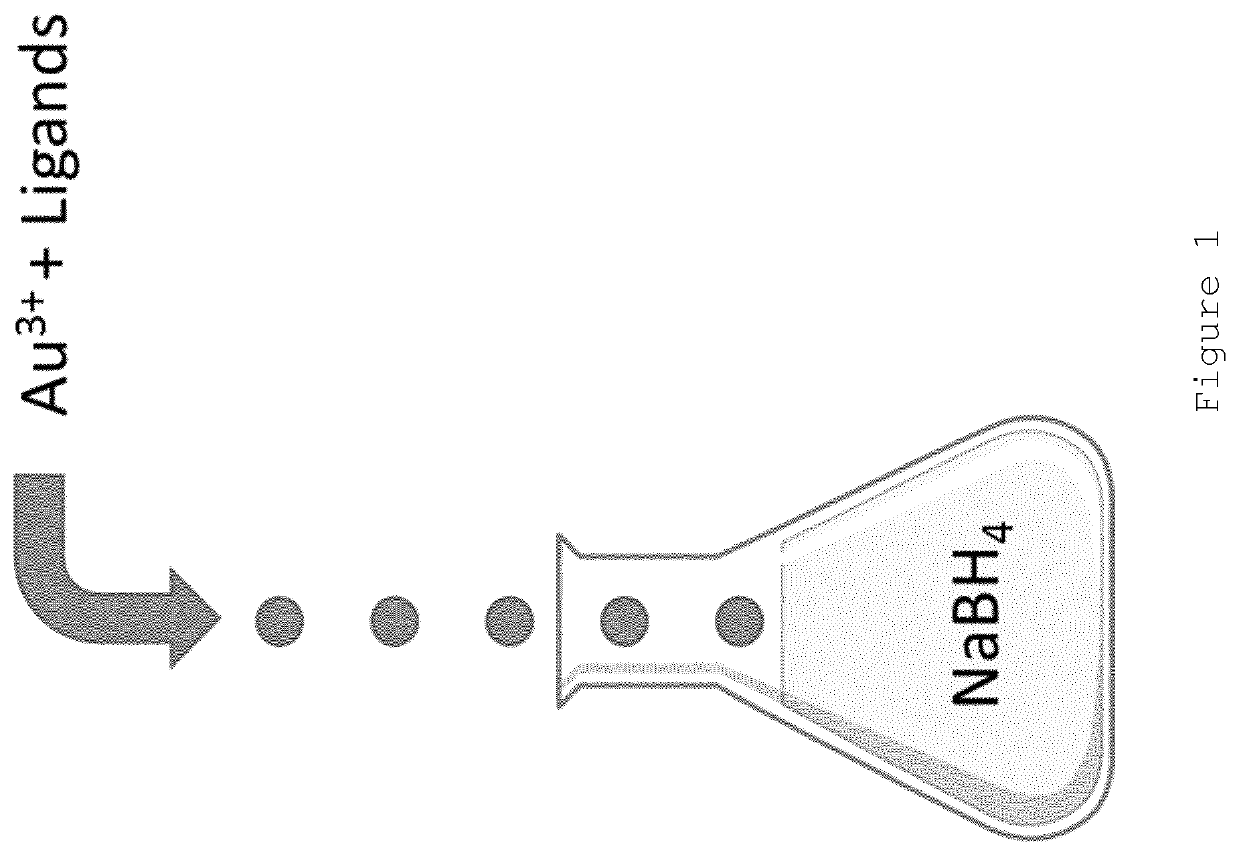
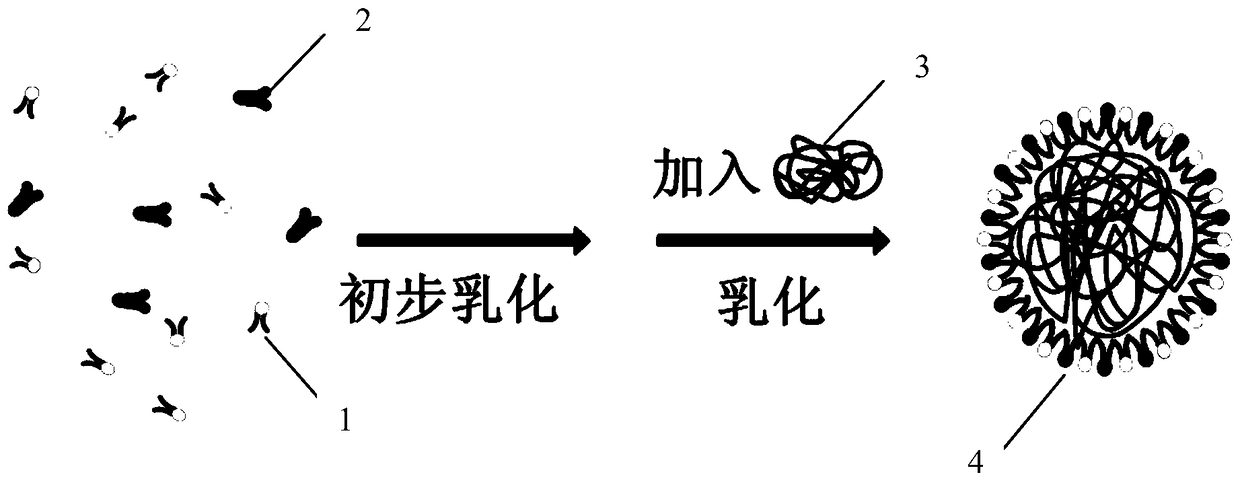
The present invention provides a process for producing nanoparticles, comprising: providing a first liquid comprising a metal salt and at least one species of ligand having a functional group capable of binding to a metal surface, providing a second liquid comprising a reducing agent; providing at least one liquid droplet generator operable to generate liquid droplets, causing the at least one liquid droplet generator to form liquid droplets of the first liquid, passing the liquid droplets through a gas to contact the second liquid so as to cause the metal salt and the at least one species of ligand to come into contact with the reducing agent, thereby causing self-assembly of nanoparticles, said nanoparticles having a core of said metal and a corona comprising a plurality of said ligands covalently bound to the core. Also provided are nanoparticles produced by the process of the invention and use of such nanoparticles in medicine.
Owner:MIDATECH LTD +1
Nanoparticle production reactor
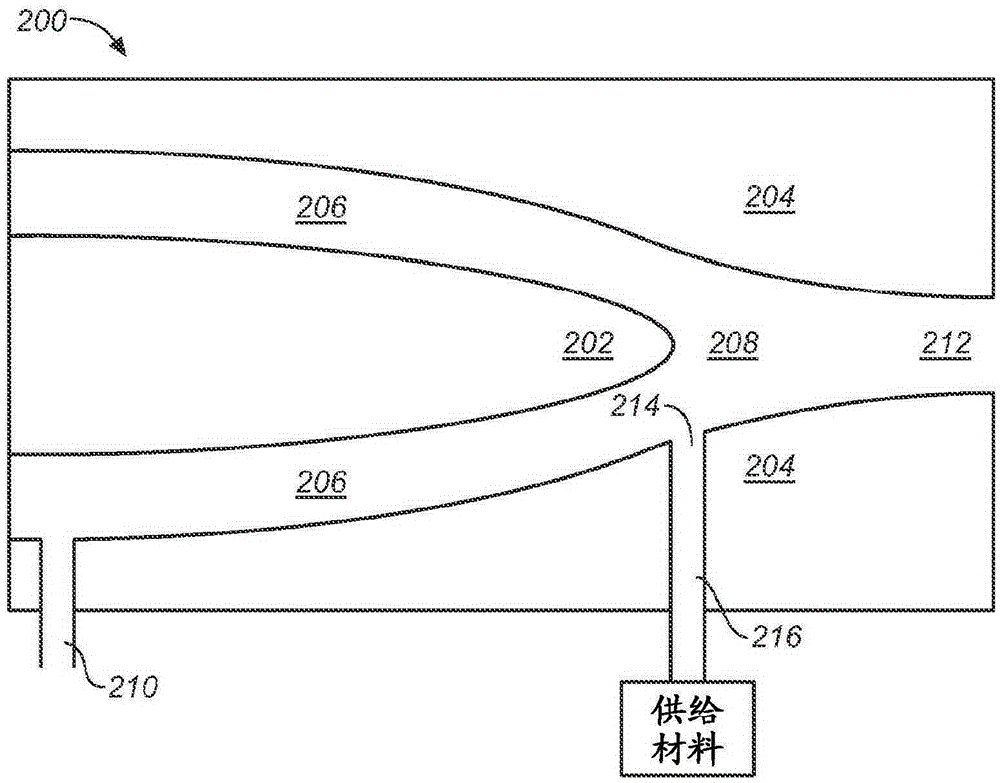
ActiveCN111050898AGreat momentumPrevent inflowChemical liquid solidificationNanotechnologyNanoparticle ProductionEngineering
The present invention relates to a nanoparticle production reactor. An aspect of the present invention provides a nanoparticle production reactor comprising: a main chamber including a first nozzle through which a raw gas is supplied; a lens housing which is connected to the main chamber to allow fluid to move therebetween and includes a second nozzle for supplying flushing gas thereinto; a lens mounted on the lens housing; a light source for emitting a laser such that the laser passes through the lens to reach a raw gas in the main chamber; and a hood for discharging a nanoparticle produced in the main chamber, wherein the lens housing is provided to have at least a partial region having a sectional area decreasing along a direction toward the main chamber.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Nanoparticle production method, production device and automatic production device
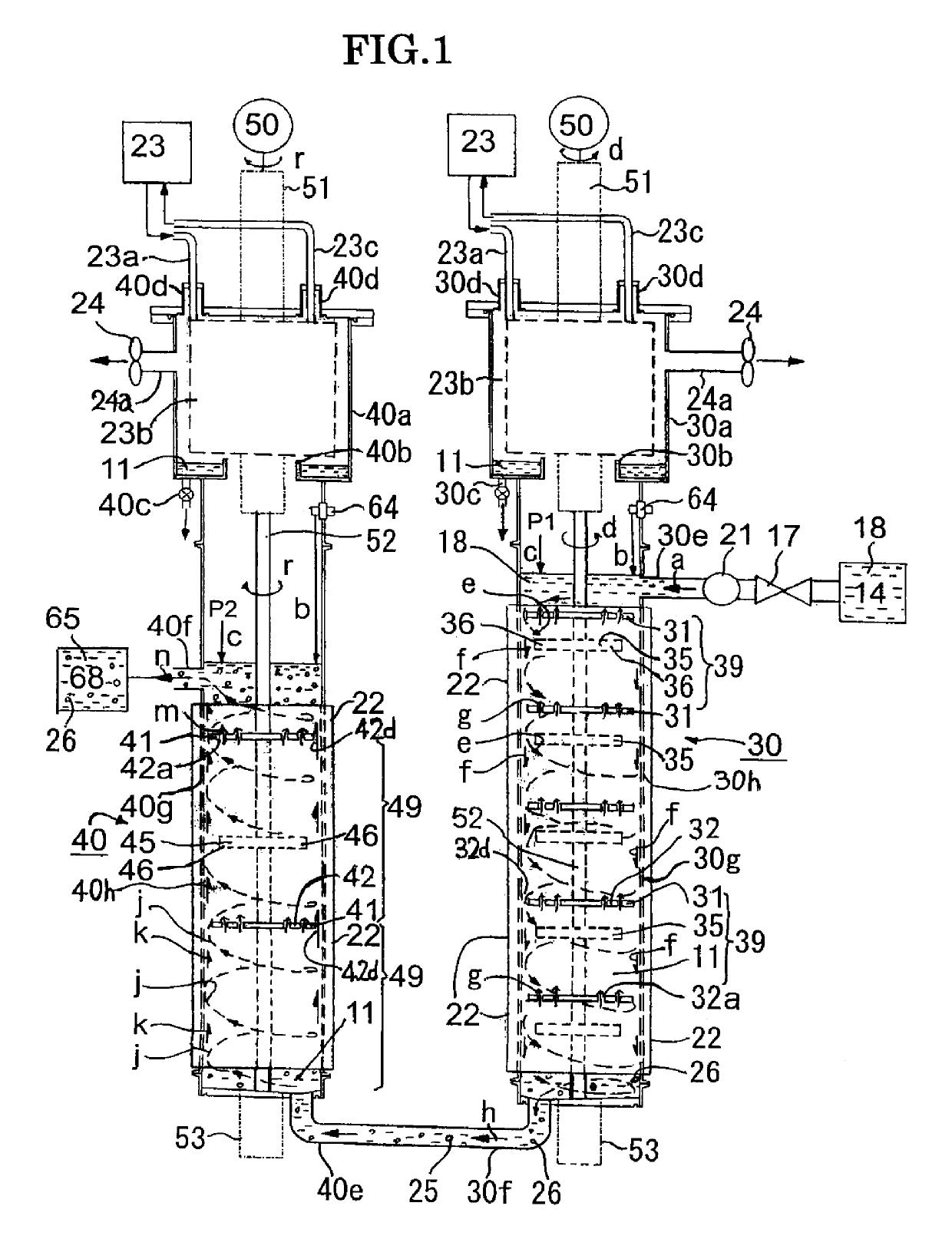
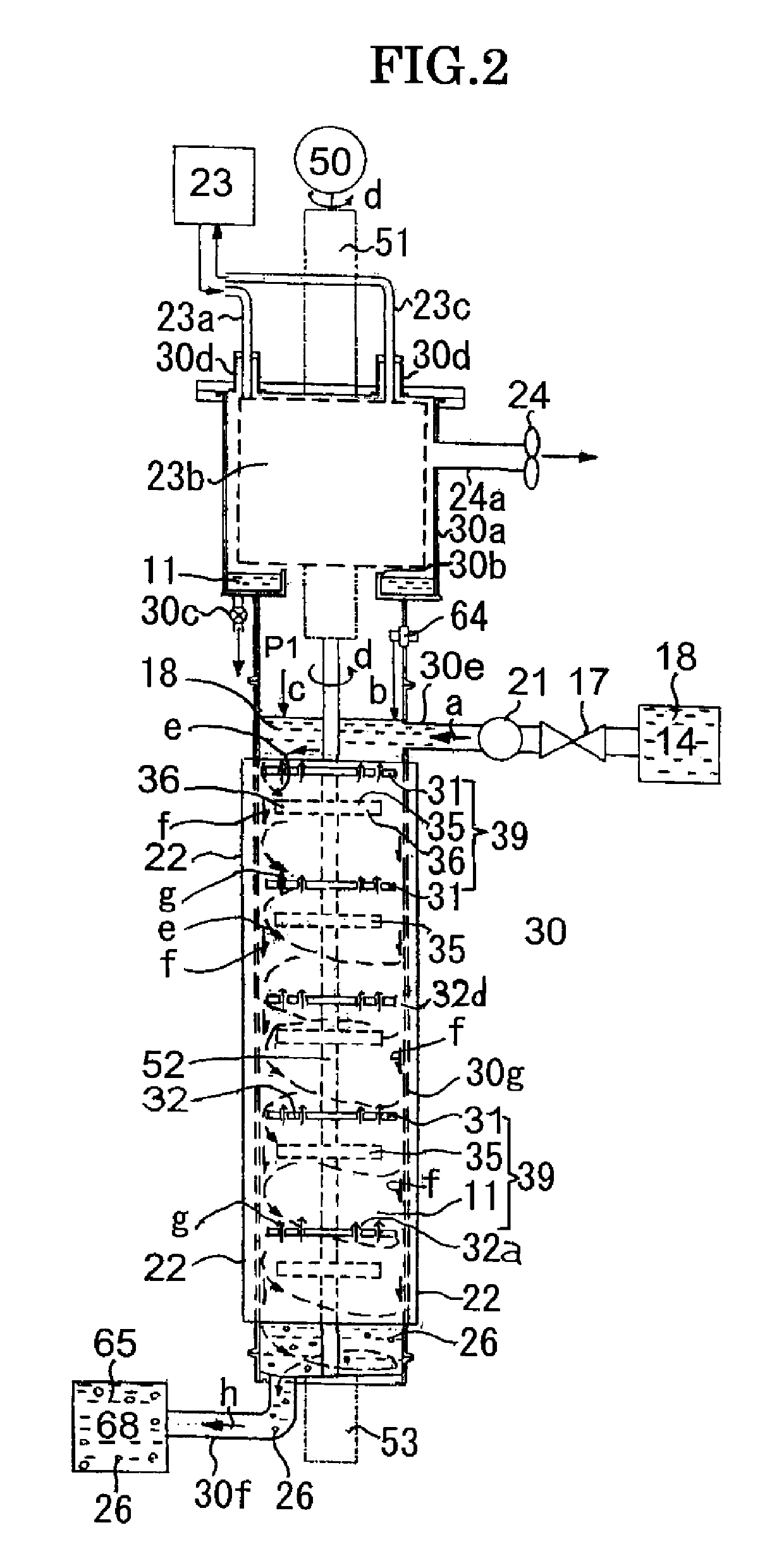
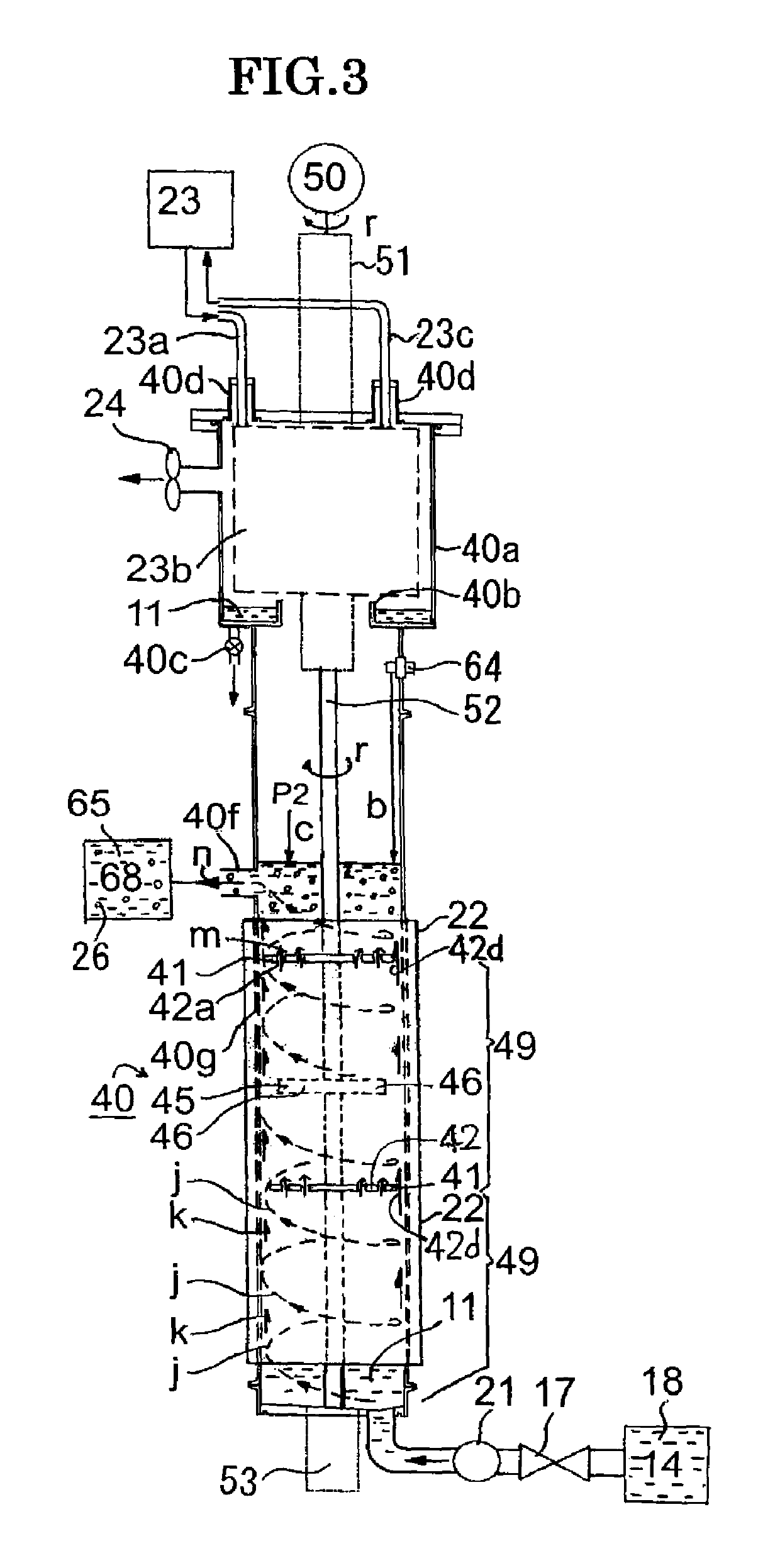
ActiveUS10427220B2Synthesis speedEasy to synthesizeMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingNanoparticle ProductionSolvent
A nanoparticle production apparatus and automatic production apparatus that allow continuous mass production of nanoparticles with a uniform particle diameter and allow freely adjusting the generation time are provided. This nanoparticle production apparatus is characterized by being configured from: reaction tubes (30, 40) which are filled with the same solvent (11) as that in a ingredient liquid (18), which is used in nanoparticle production and comprises an ingredient material (12) mixed into the solvent (11); a heating apparatus (22) which controls the temperature of the solvent (11) in the reaction tubes (30, 40) to the synthesis temperature of the nanoparticles (26); inflow ends (30e, 40e) of the reaction tubes into which the ingredient liquid (18) is supplied; rotors (35, 45) which form spiral flows (e, j) along the inner surface of the outer walls (30h, 40h) of the reaction tubes while mixing the ingredient liquid (18) supplied and the solvent (11) present in the reaction tubes (30, 40); and outflow ends (30f, 40f) of the reaction tubes (30, 40) for forming, in the spiral flows (e, j), nanoparticles (26) from the ingredient material (12) and discharging a generation liquid (65) containing the nanoparticles (26).
Owner:NIHON SUPERIOR CO LTD +1
High-throughput particle production using plasma systems
The present invention relates to a nanoparticle production system and methods of using said system. The nanoparticle production system includes a plasma gun including a male electrode, a female electrode, and a working gas supply configured to deliver working gas across a plasma generation region in a vortex helical flow direction . The system also includes a continuous supply system, a quench chamber, cooling conduits including laminar flow disruptors, a system overpressure module, and a conditioning fluid purification and recirculation system.
Owner:SDC MATERIALS
A kind of cationic phospholipid-polymer nanoparticle and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104523595BHigh endocytosis efficiencyStrong encapsulationGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolymeric surfacePolymer science
The invention provides a cationic phospholipid-polymer nanoparticle, comprising an inner core and an outer shell, the inner core is a polymer, the outer shell is a cationic liposome and a phospholipid, and the cationic liposome and the phospholipid are coated on On the polymer surface, the polymer is polyglycolide lactide or polylactic acid. The cationic phospholipid-polymer nanoparticles have uniform particle size and stable properties, and can carry DNA into cells. The present invention also provides a preparation method of cationic phospholipid-polymer nanoparticles, which adopts a one-step high-pressure homogenization method to prepare cationic phospholipid-polymer nanoparticles, which is simple to operate and can prepare large doses of cationic phospholipid-polymer nanoparticles. The scale-up production and clinical research of the nanoparticles provide a basis, and the preparation method is simple and easy to implement and easy to popularize.
Owner:ZHUHAI INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Reactors for Nanoparticle Production
ActiveCN111050898BGreat momentumPrevent inflowChemical liquid solidificationNanotechnologyNanoparticle ProductionIrradiation laser
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
A device for producing silicon and silicon nitride nanoparticles
The invention relates to the field of silicon and silicon nitride nanoparticle production, in particular to a device for producing silicon and silicon nitride nanoparticle. The device of the present invention adopts that corresponding cones are arranged on the air inlet cover and the quartz cover, and the holes on the outer ring-shaped flat plate part on the quartz cover are reasonably distributed, so that the distribution of the plasma is uniform, and the size distribution of the nanoparticles is Narrower.
Owner:江西紫宸科技有限公司
Molybdenum oxide nanoparticle production device and production method
InactiveCN104495933BLow production costSimple and fast operationMaterial nanotechnologyMolybdenum oxides/hydroxidesNanoparticle ProductionQuenching
The invention relates to a production device and method of molybdenum oxide nanoparticles, aiming to solve the technical problems of unstable product quality, complex production procedures and low production efficiency in the production of molybdenum oxide nanoparticles in the prior art. The production device comprises a gasifying unit, a quenching unit and a collecting unit, wherein the gasifying unit is used for gasifying the precursor material of molybdenum oxide nanoparticles, the quenching unit is used for quenching the gasified molybdenum oxide nanoparticles, and the collecting unit is used for collecting the finished molybdenum oxide nanoparticles. The production device and method have the advantages of high production efficiency and stable product quality.
Owner:江西省鼎力金属有限公司
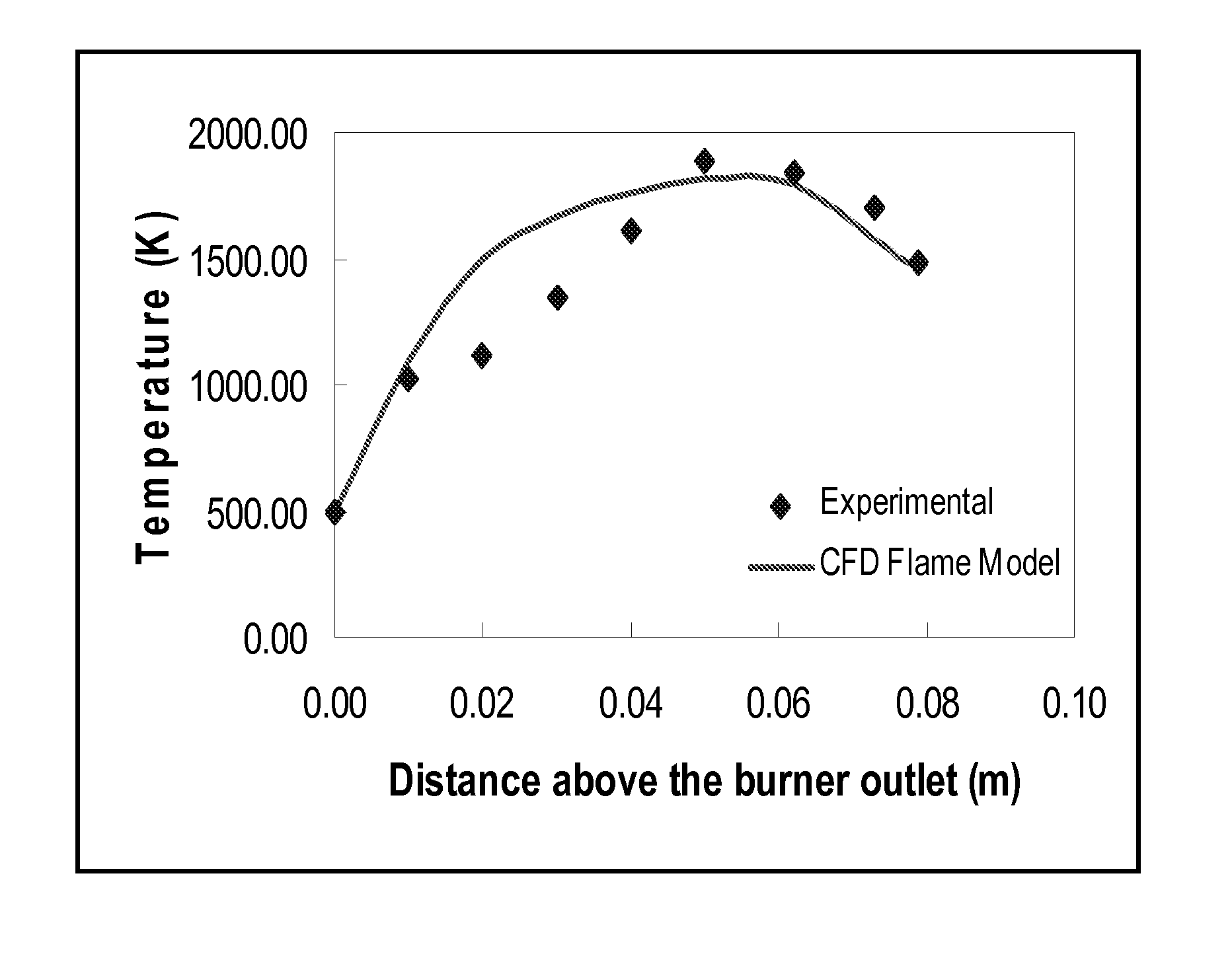
System for optimizing and controlling particle size distribution and for scale-up of nanoparticle production in an aerosol flame reactor
ActiveUS8805586B2Less experimentationLess timeProcess control/regulationElement comparisonNanoparticle ProductionPopulation balance model
The present invention relates to a system for optimizing and controlling the particle size distribution and scale-up of production of nanoparticle in an aerosol flame reactor. The method provides nanoparticles with desired, optimized and controlled particle size and the specific surface area in aerosol reactors using a simulation tool with programmed instructions. The simulation tool couples flame dynamics model and particle population balance model.
Owner:TATA CONSULTANCY SERVICES LTD
Nanoparticle production
ActiveUS20190039039A1Improve uniformityQuick mixPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsNanoparticle ProductionReducing agent
The present invention provides a process for producing nanoparticles, comprising: providing a first liquid comprising a metal salt and at least one species of ligand having a functional group capable of binding to a metal surface, providing a second liquid comprising a reducing agent; providing at least one liquid droplet generator operable to generate liquid droplets, causing the at least one liquid droplet generator to form liquid droplets of the first liquid, passing the liquid droplets through a gas to contact the second liquid so as to cause the metal salt and the at least one species of ligand to come into contact with the reducing agent, thereby causing self-assembly of nanoparticles, said nanoparticles having a core of said metal and a corona comprising a plurality of said ligands covalently bound to the core. Also provided are nanoparticles produced by the process of the invention and use of such nano particles in medicine.
Owner:MIDATECH LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com