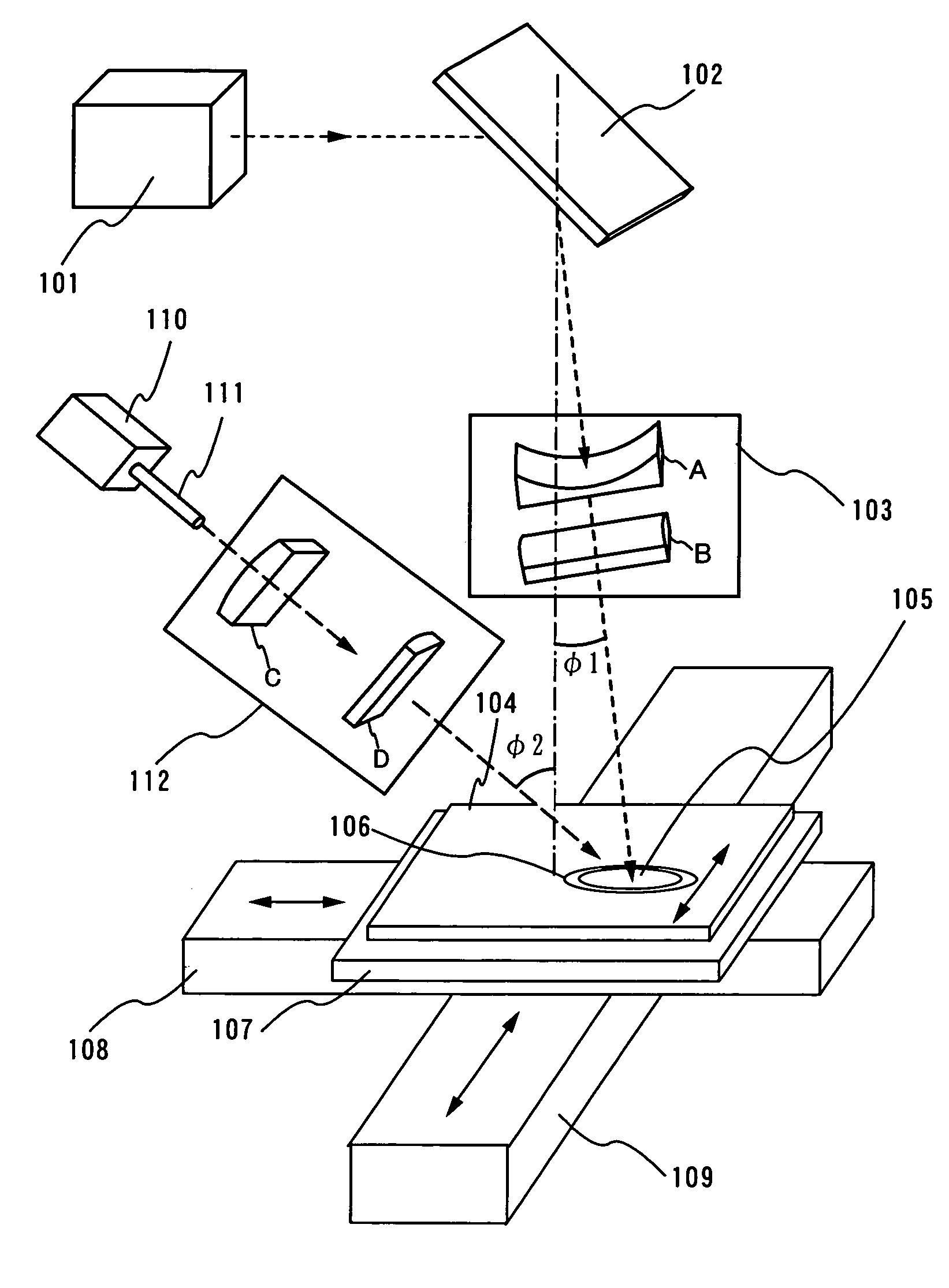
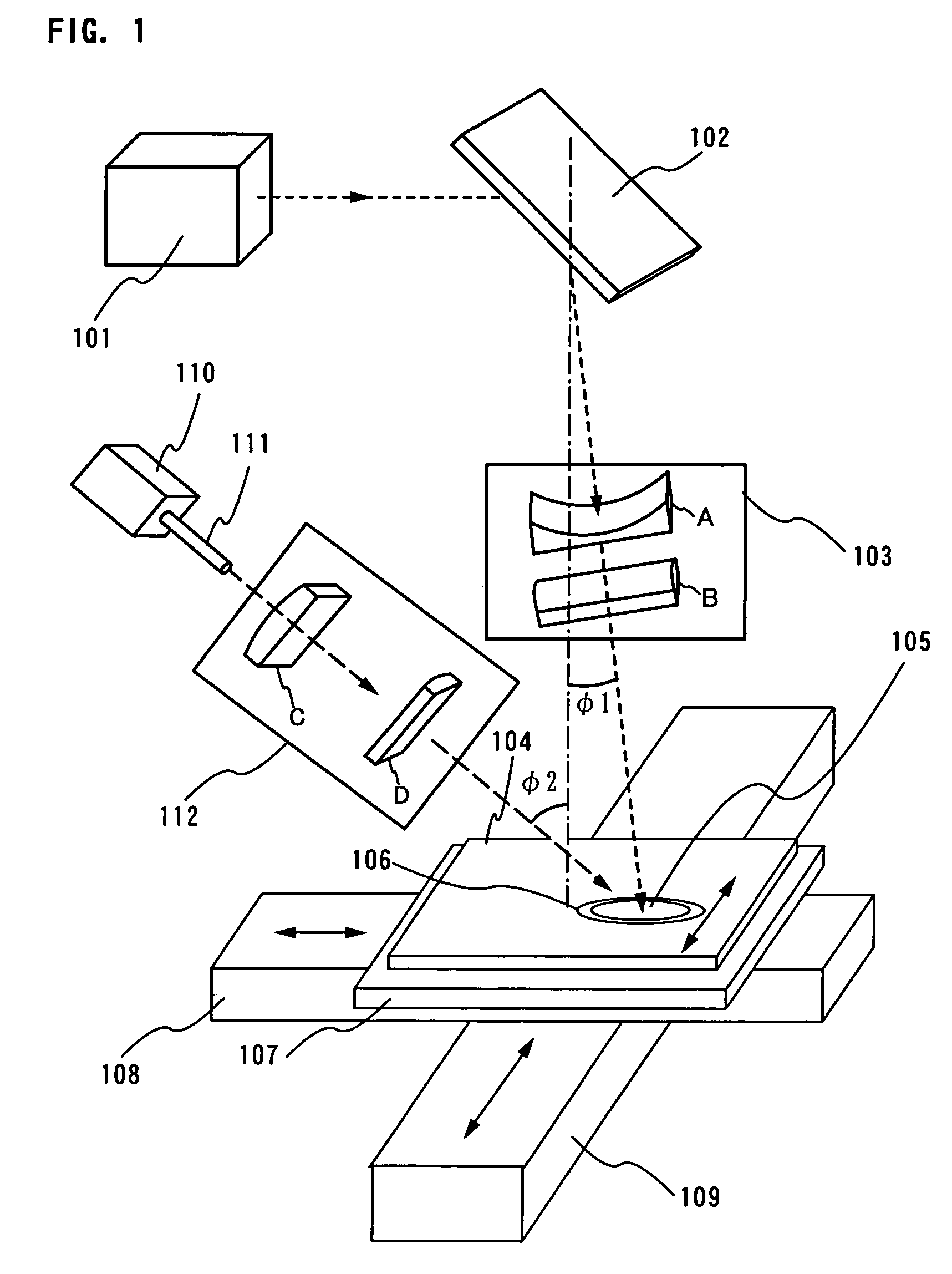
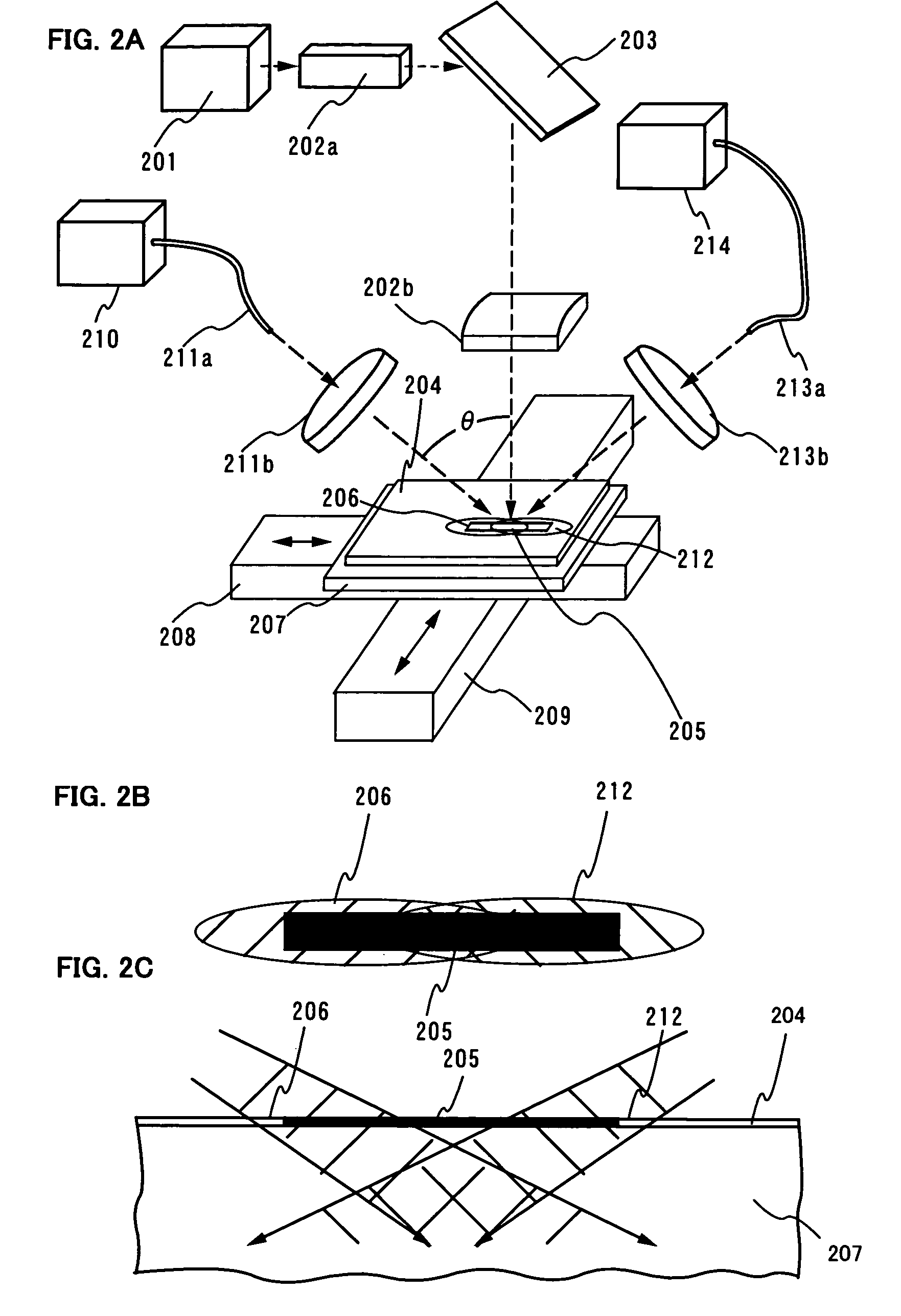
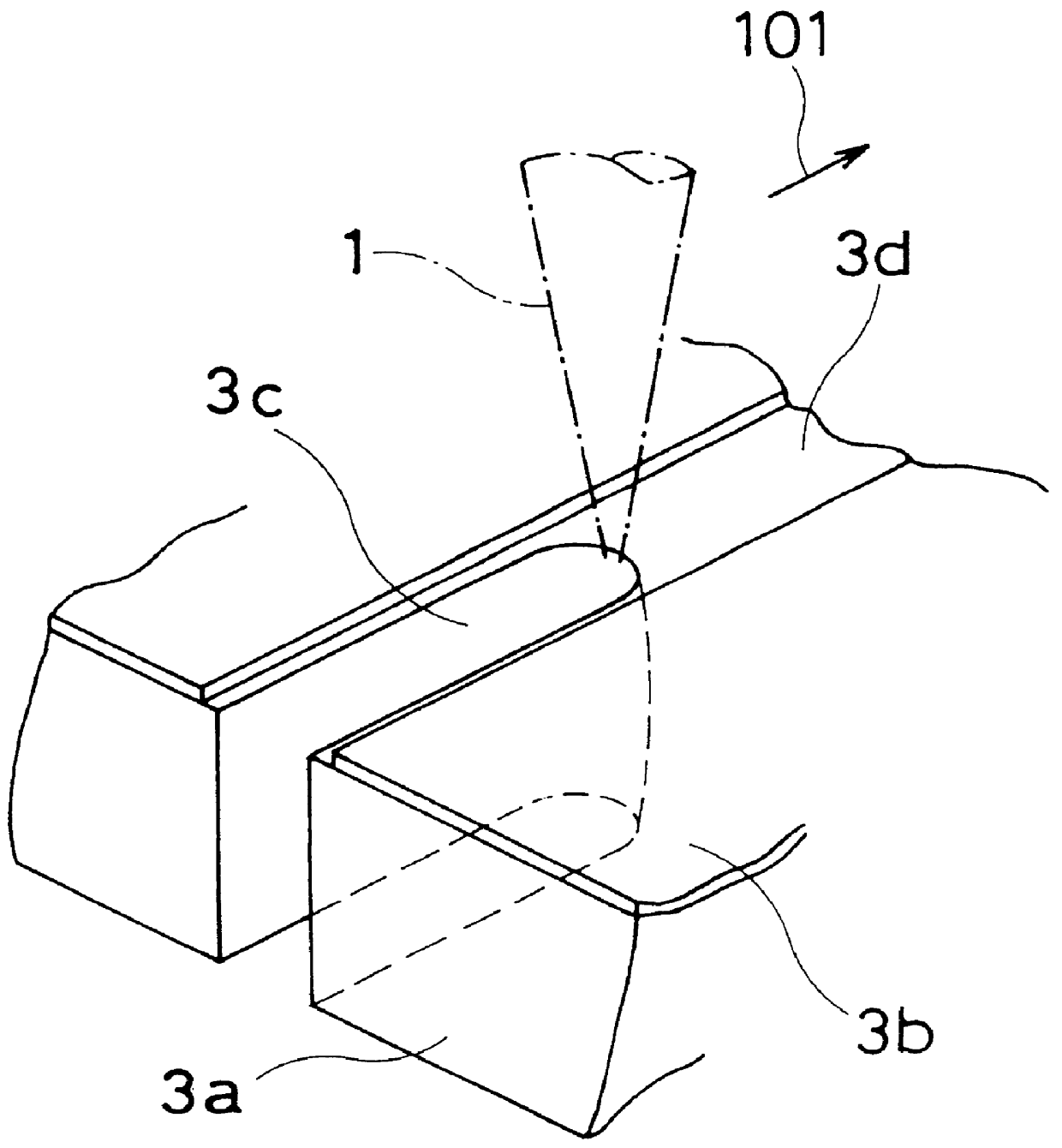
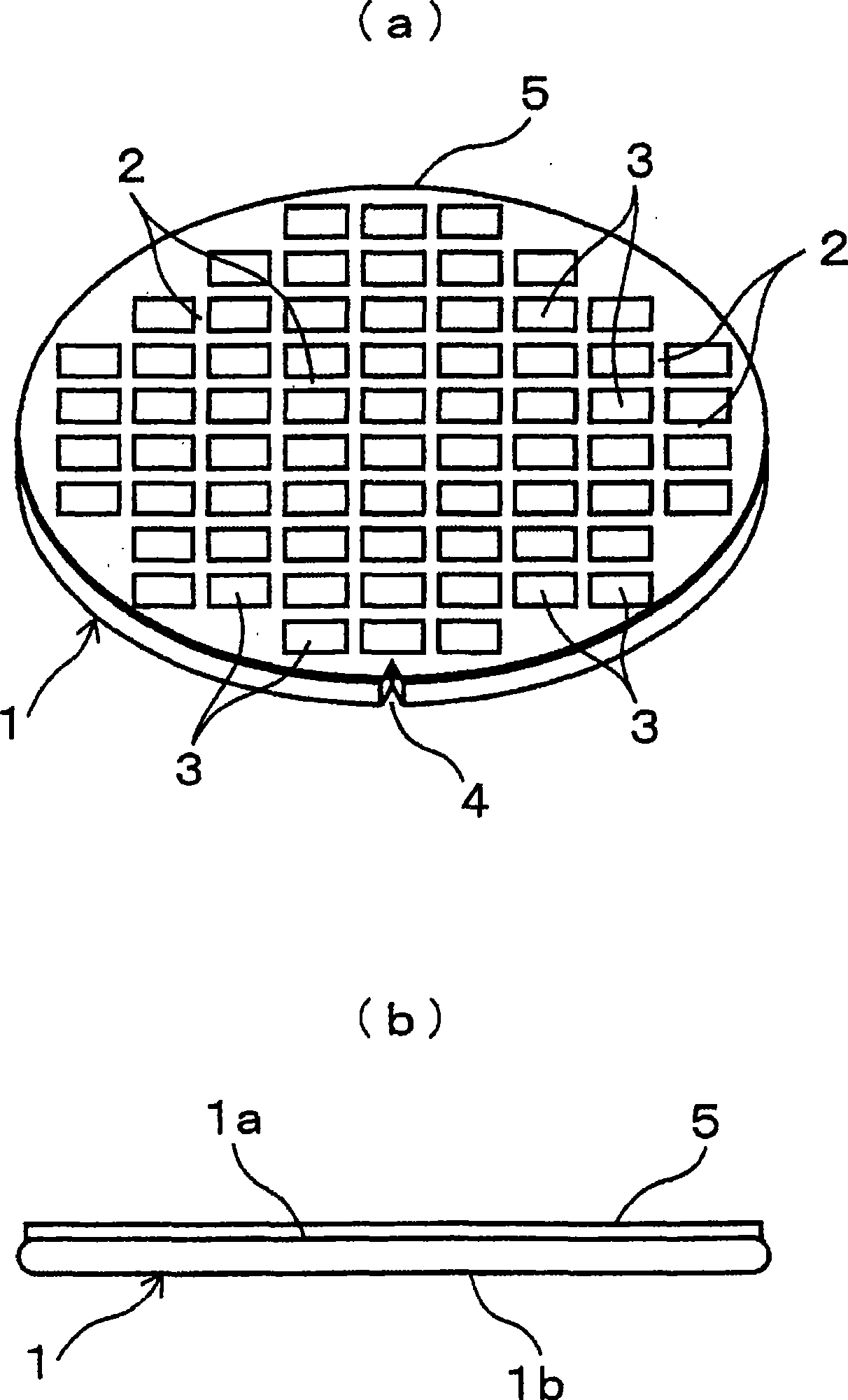
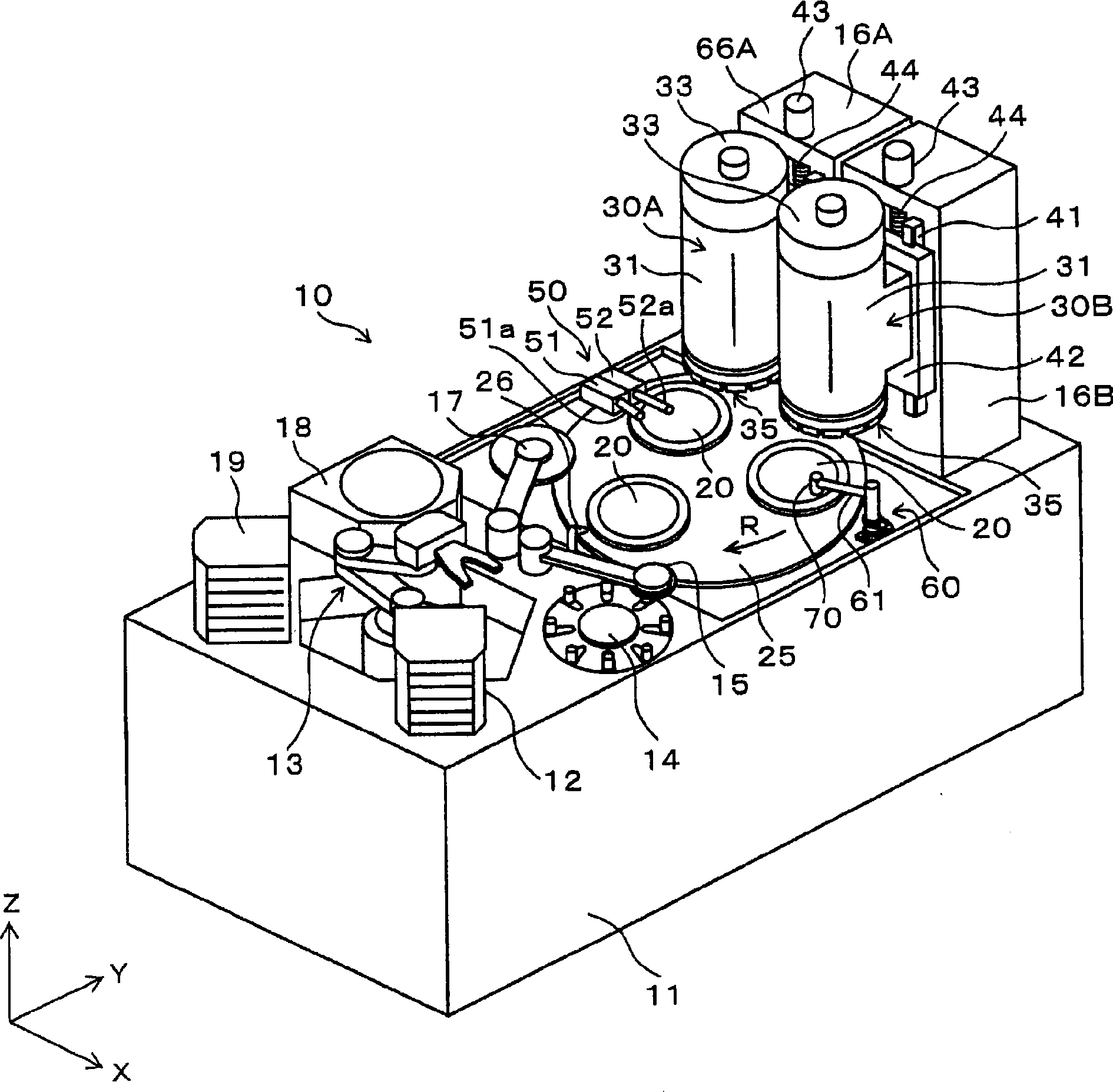
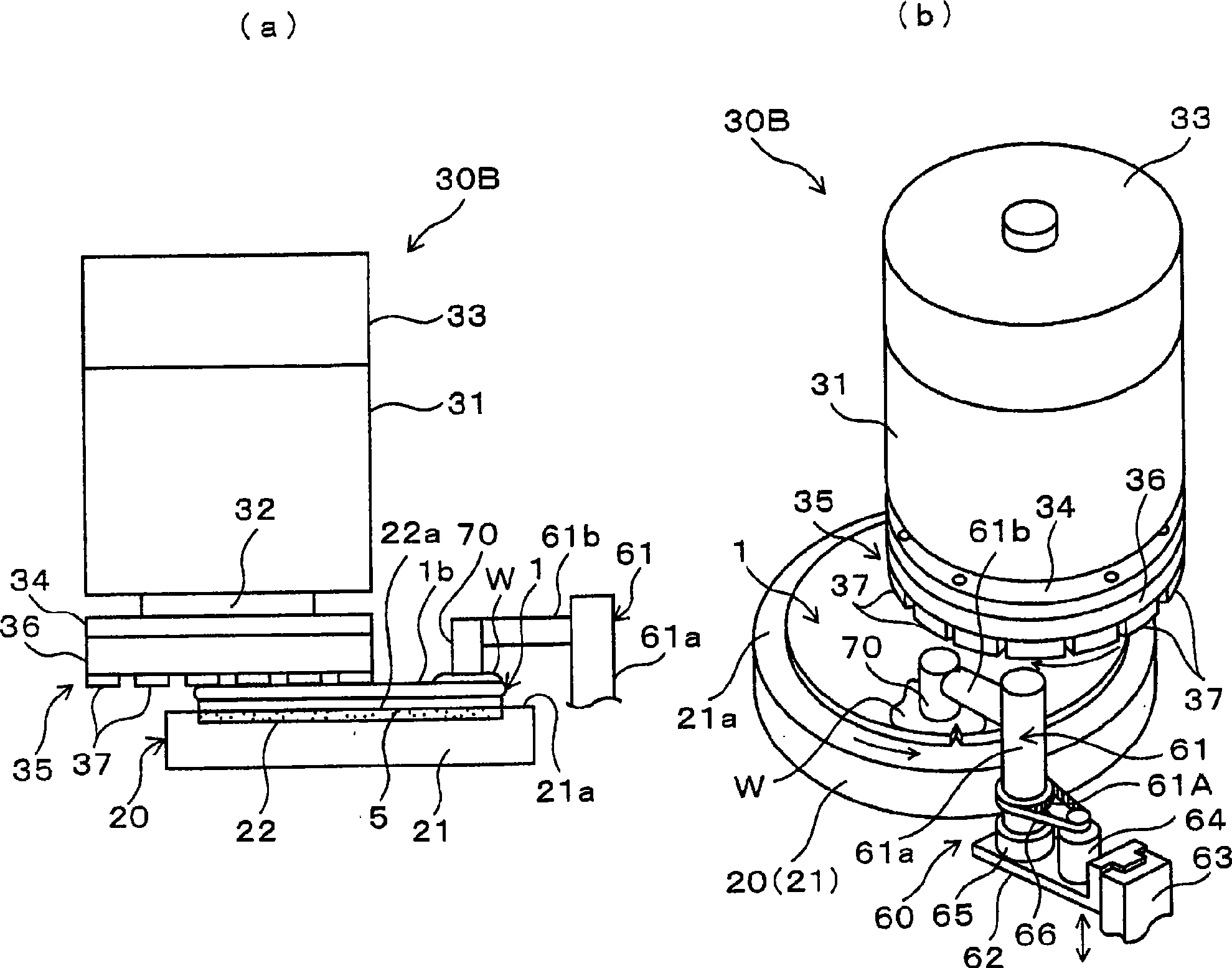
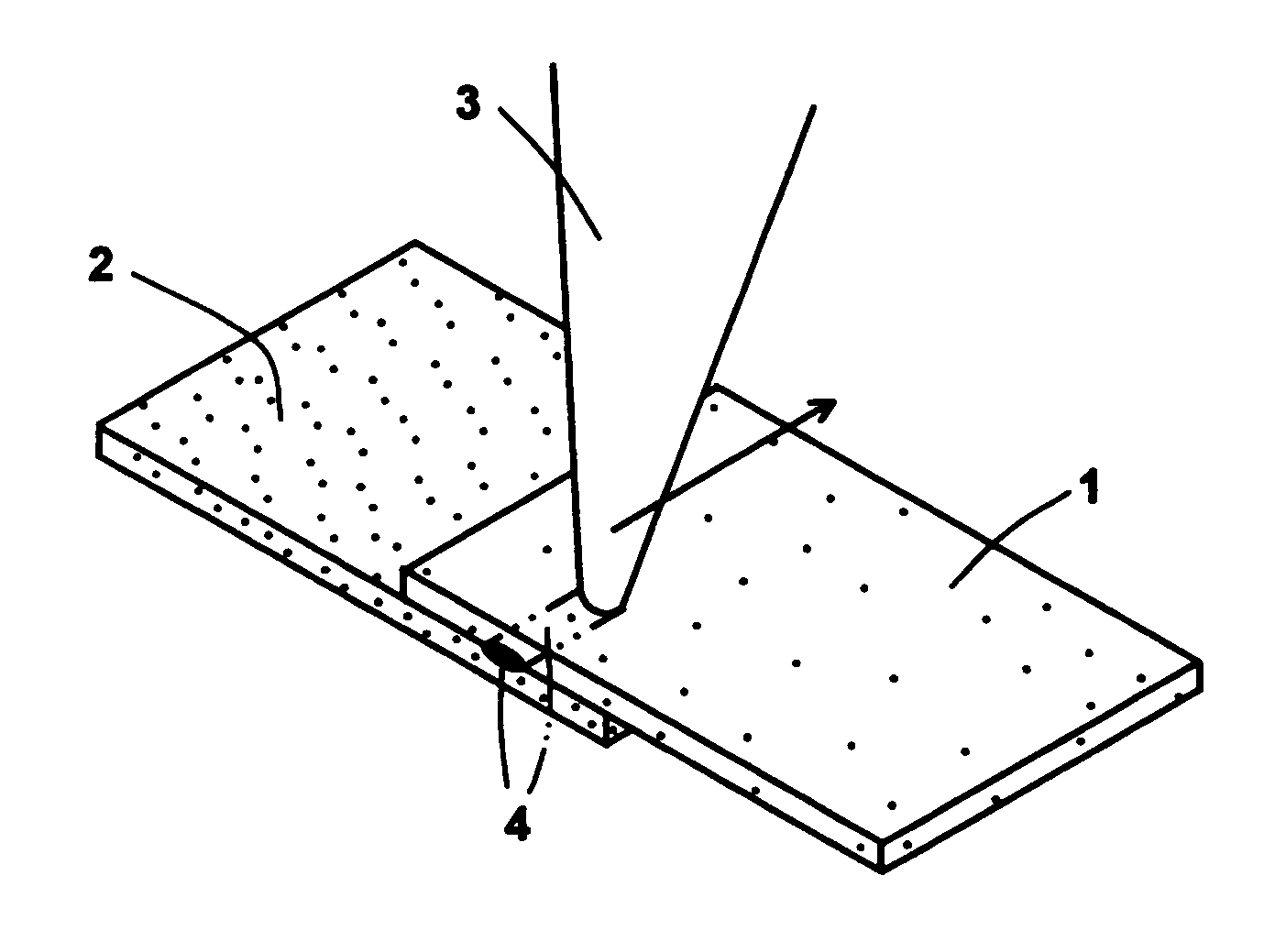
Patents
Literature
635 results about "Irradiation laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Laser cutting device, laser cutting method, and laser cutting system
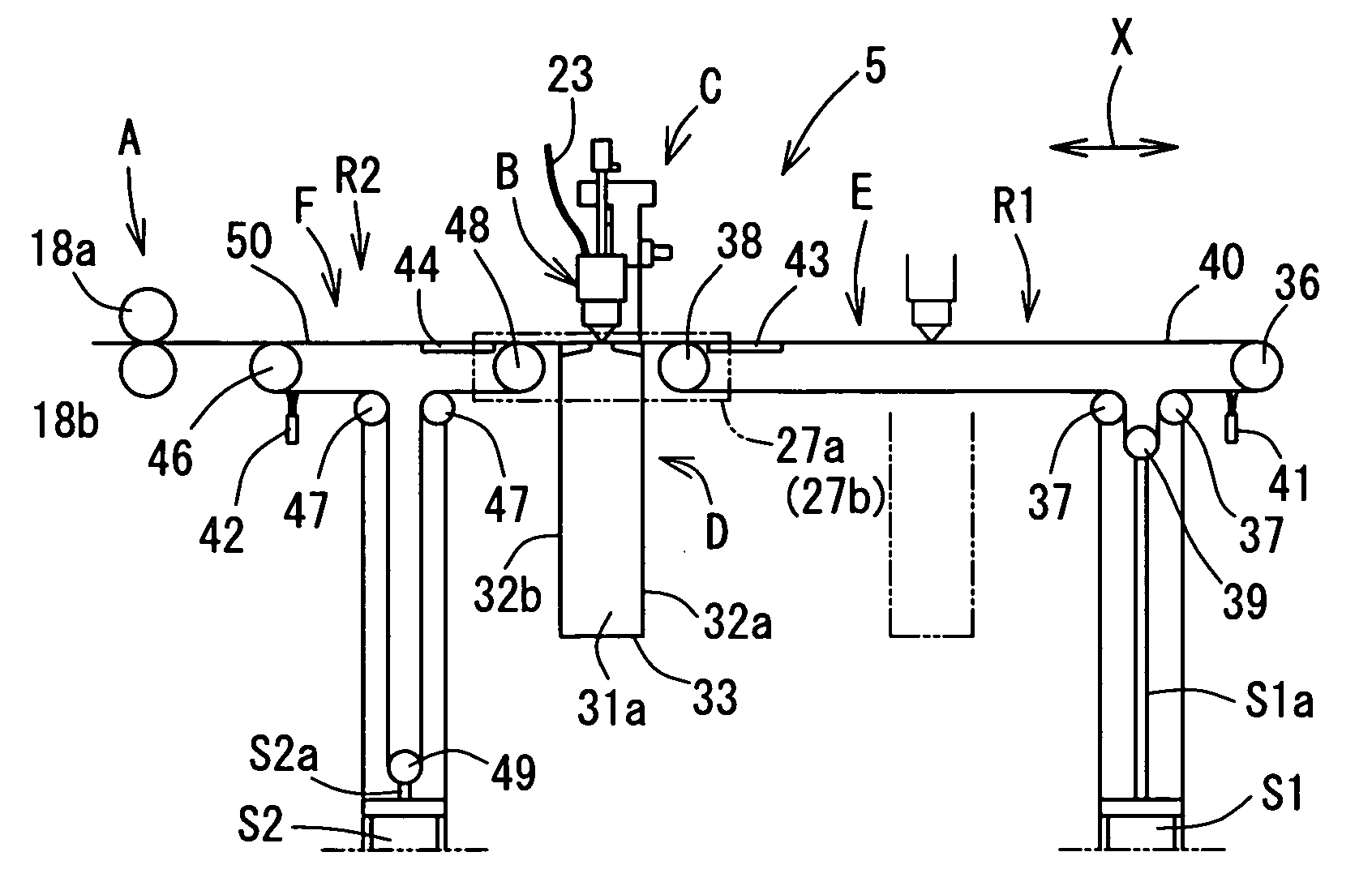
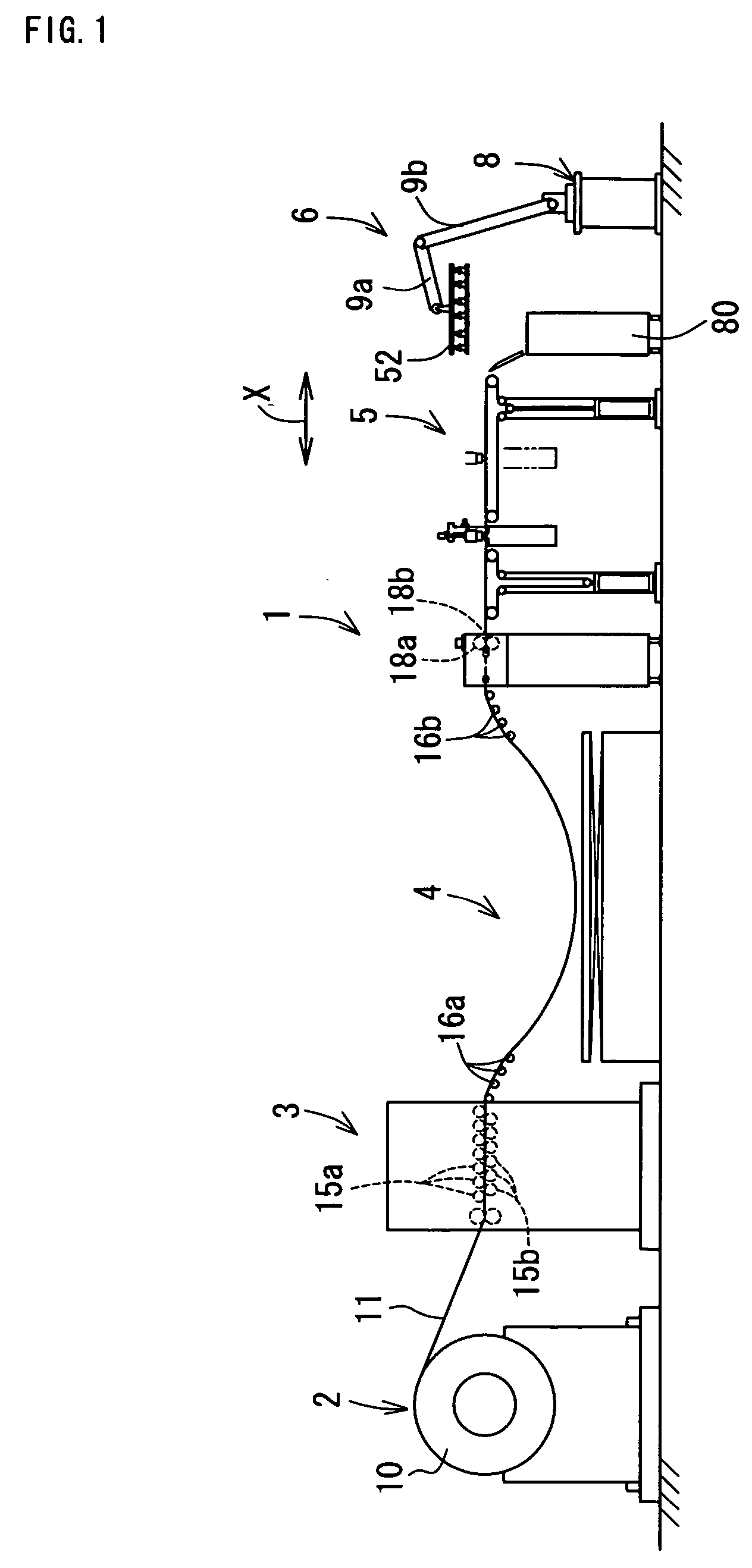
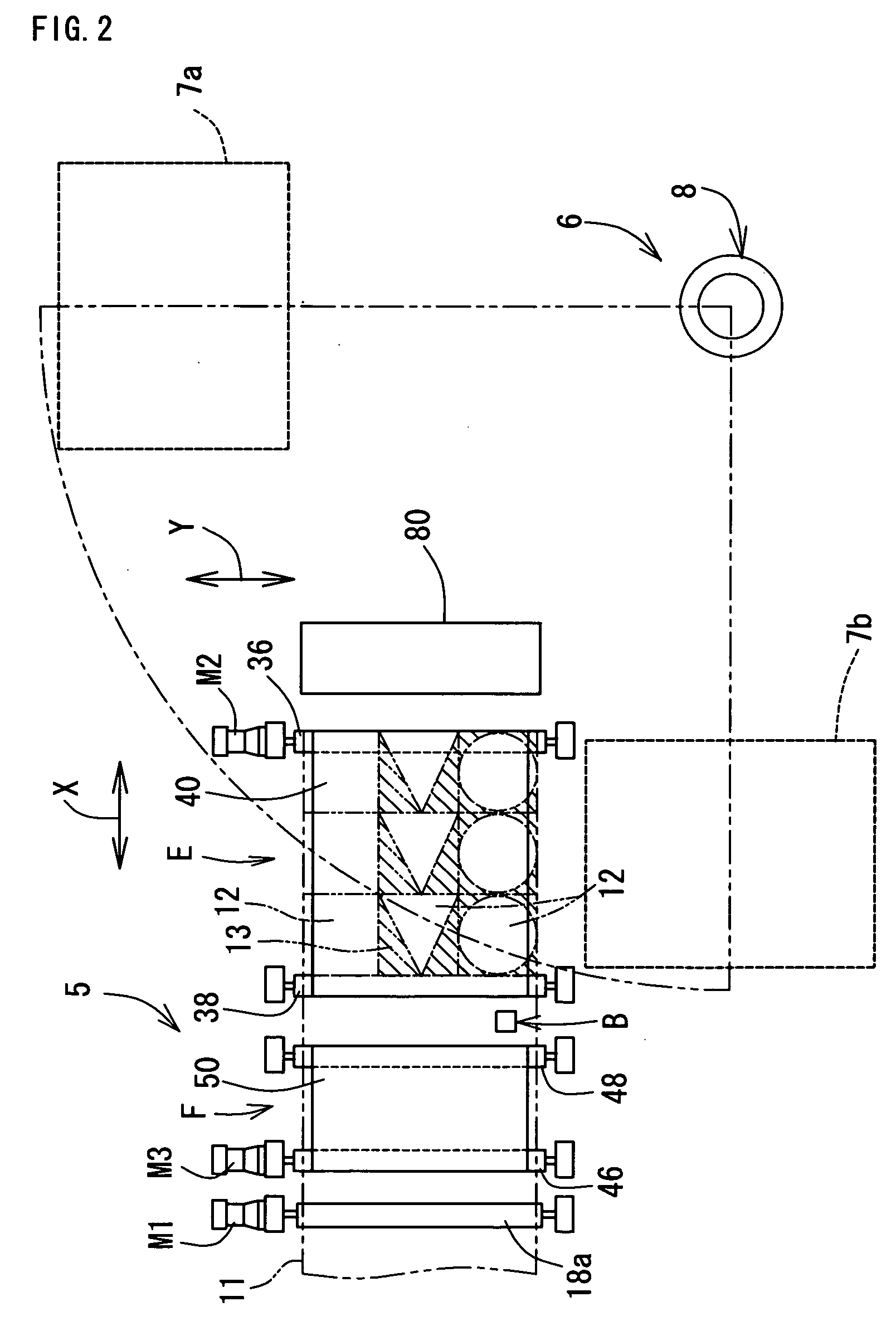
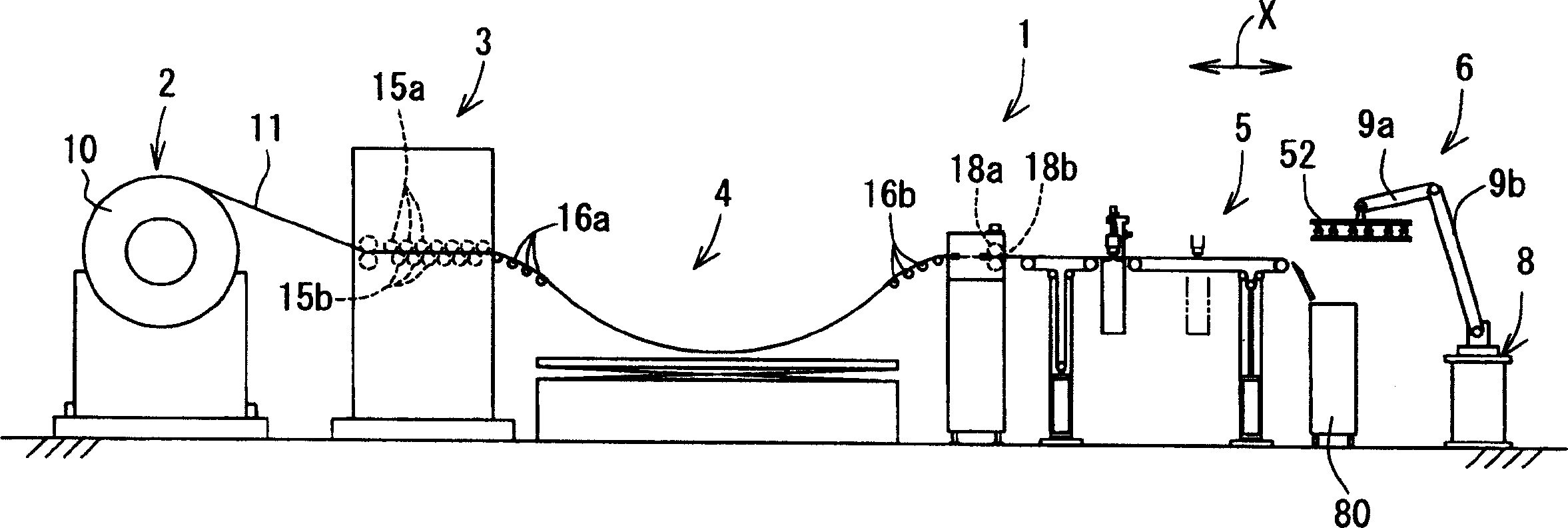
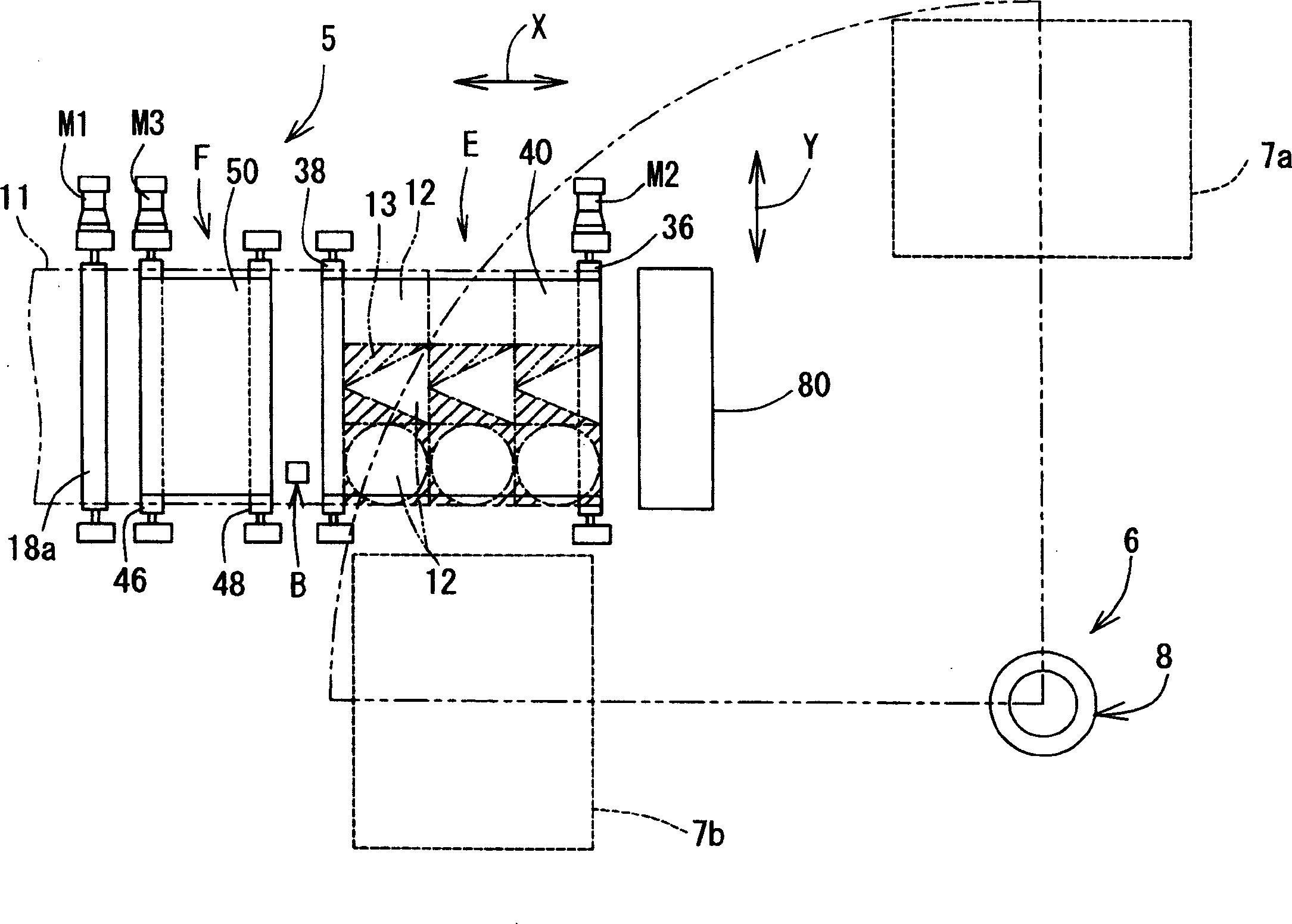
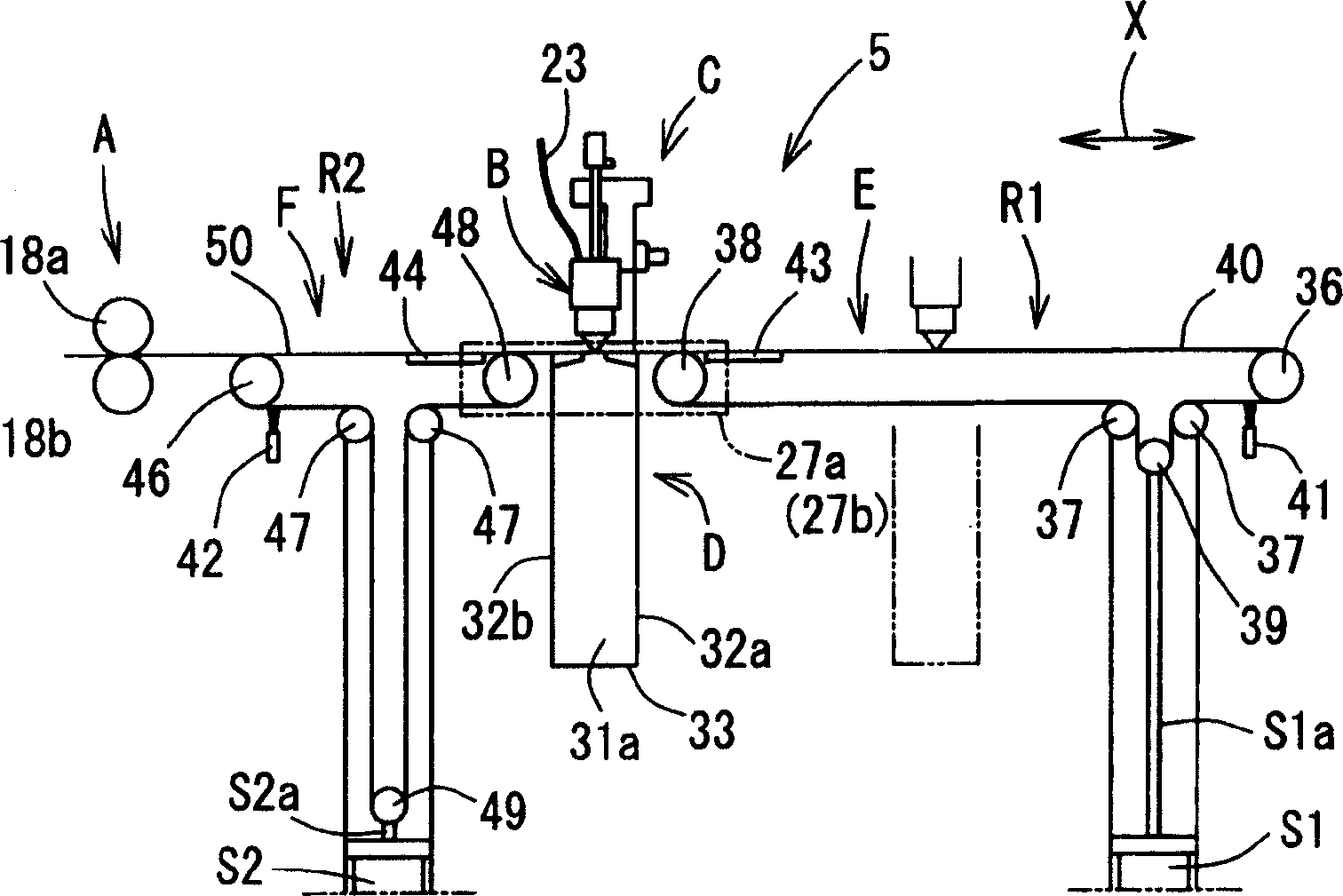
InactiveUS20060118529A1Avoid dust adhesionEasy to controlConveyorsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser cuttingLaser light
It is an object of the present invention to provide a laser cutting device, a method for laser cutting and a laser cutting system with which it is possible to perform laser cutting of parts of various shapes through easy control, to prevent adhesion of dust or similar and scratches being formed in cut parts, and to send out such parts while reliably supporting the same. The present laser cutting device 5 is comprised with a material transferring means A that transfers a sheet-like material 11 in a feeding direction, a processing head B that is capable of irradiating laser light towards the material, a head moving means C that makes the processing head move in the feeding direction X and a width direction Y of the material, an upstream-sided supporting means (belt conveyer mechanism F) that supports the material on an upstream side of a downward portion of the processing head and that expands and contracts a supporting region R2 for the material accompanying movements of the processing head in the feeding direction, and a downstream-sided supporting means (belt conveyer mechanism E) that supports cut parts on a downstream side of a downward portion of the processing head and that expands and contracts a supporting region R1 for the cut parts accompanying movements of the processing head in the feeding direction.
Owner:TOYOTA STEEL CENT CO LTD
Beam irradiation apparatus, beam irradiation method, and method for manufacturing a thin film transistor
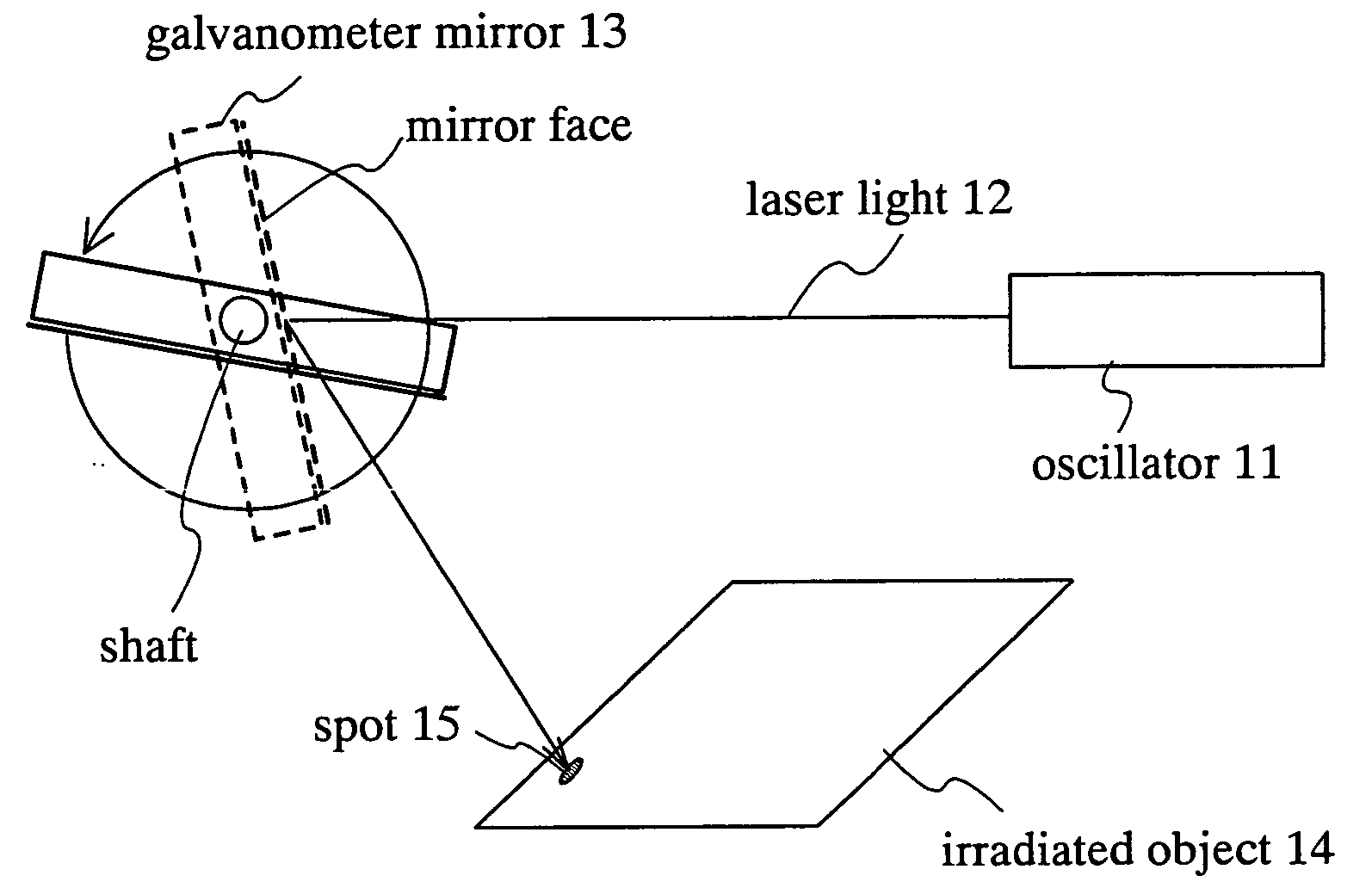
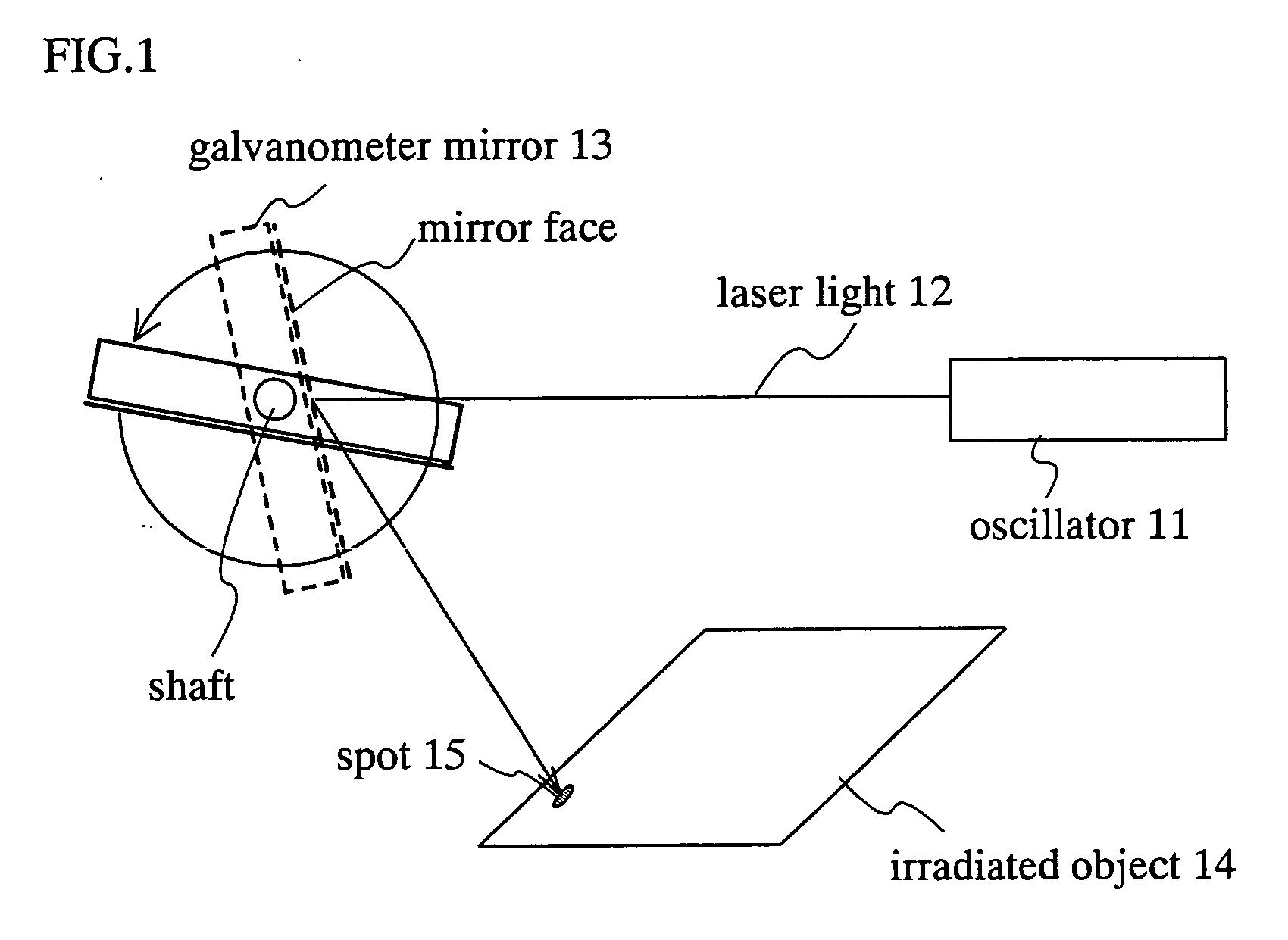
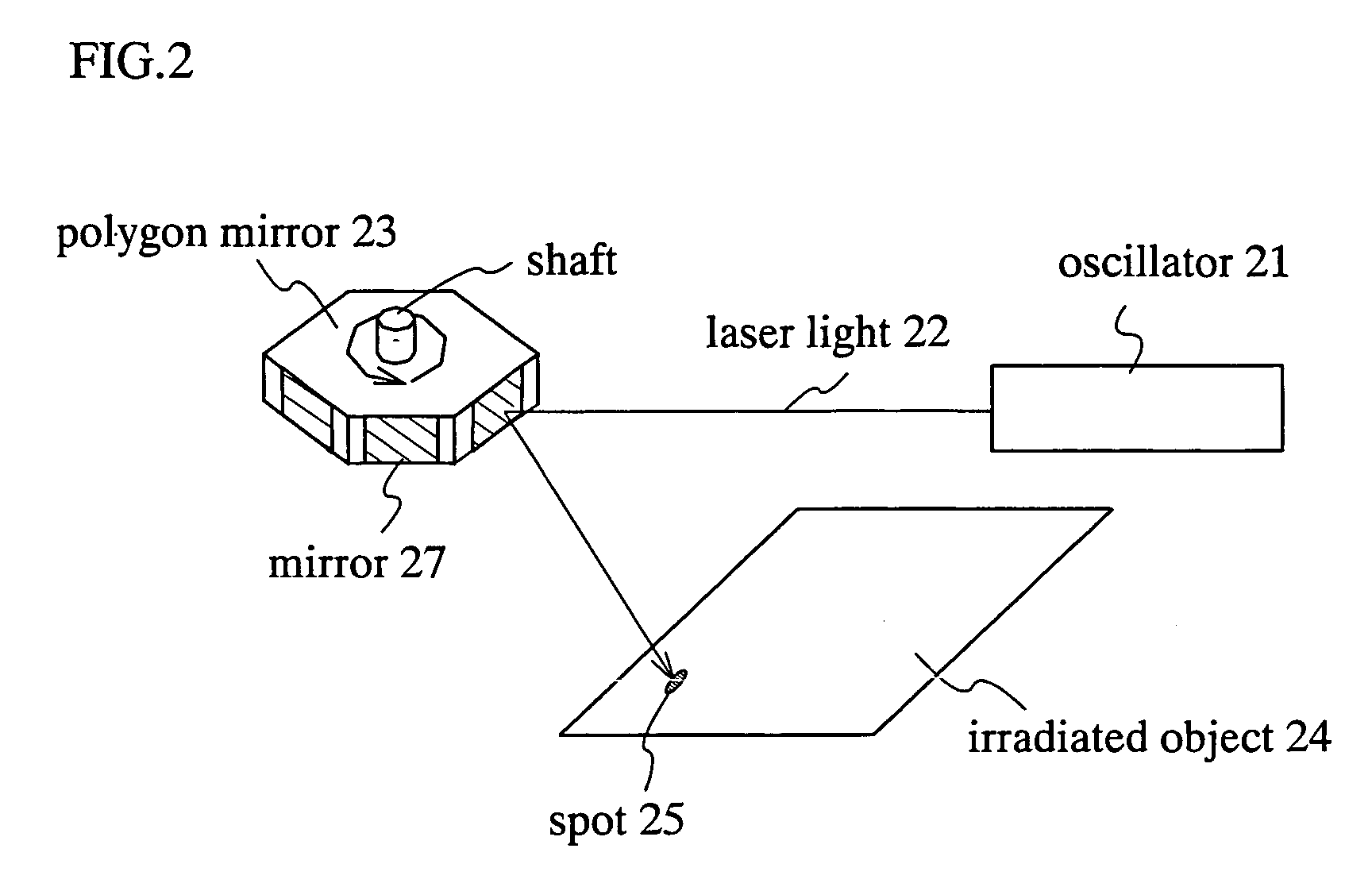
InactiveUS20050036190A1Uniform crystallinityUniform characteristicsLaser beam welding apparatusOptical elementsGalvanometerLight beam
A galvanometer mirror rotates in one direction when the galvanometer mirror is used. A spot can be scanned on an irradiated surface at a more constant speed by rotating the galvanometer mirror and by using the inertia. Moreover, it is preferable to make the galvanometer mirror heavy because the inertia becomes higher so that the spot is scanned at a more constant speed. In addition, in a polygon mirror of this invention, mirrors are arranged so as not to contact each other because a change time of the scanning position between the mirrors is provided. By moving the irradiated object with timing together when the laser light is not irradiated, the laser process can be performed efficiently.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for operation of laser
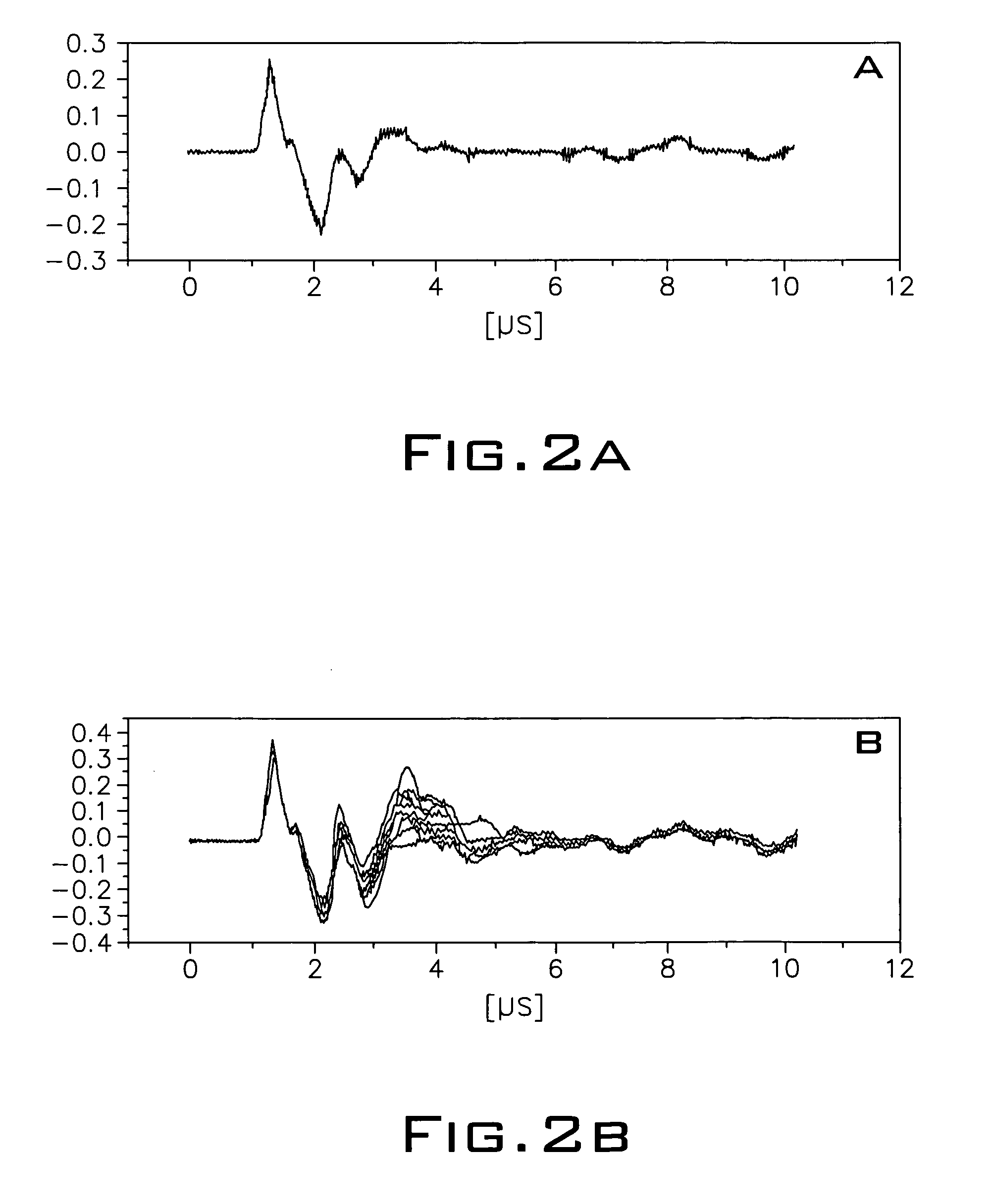
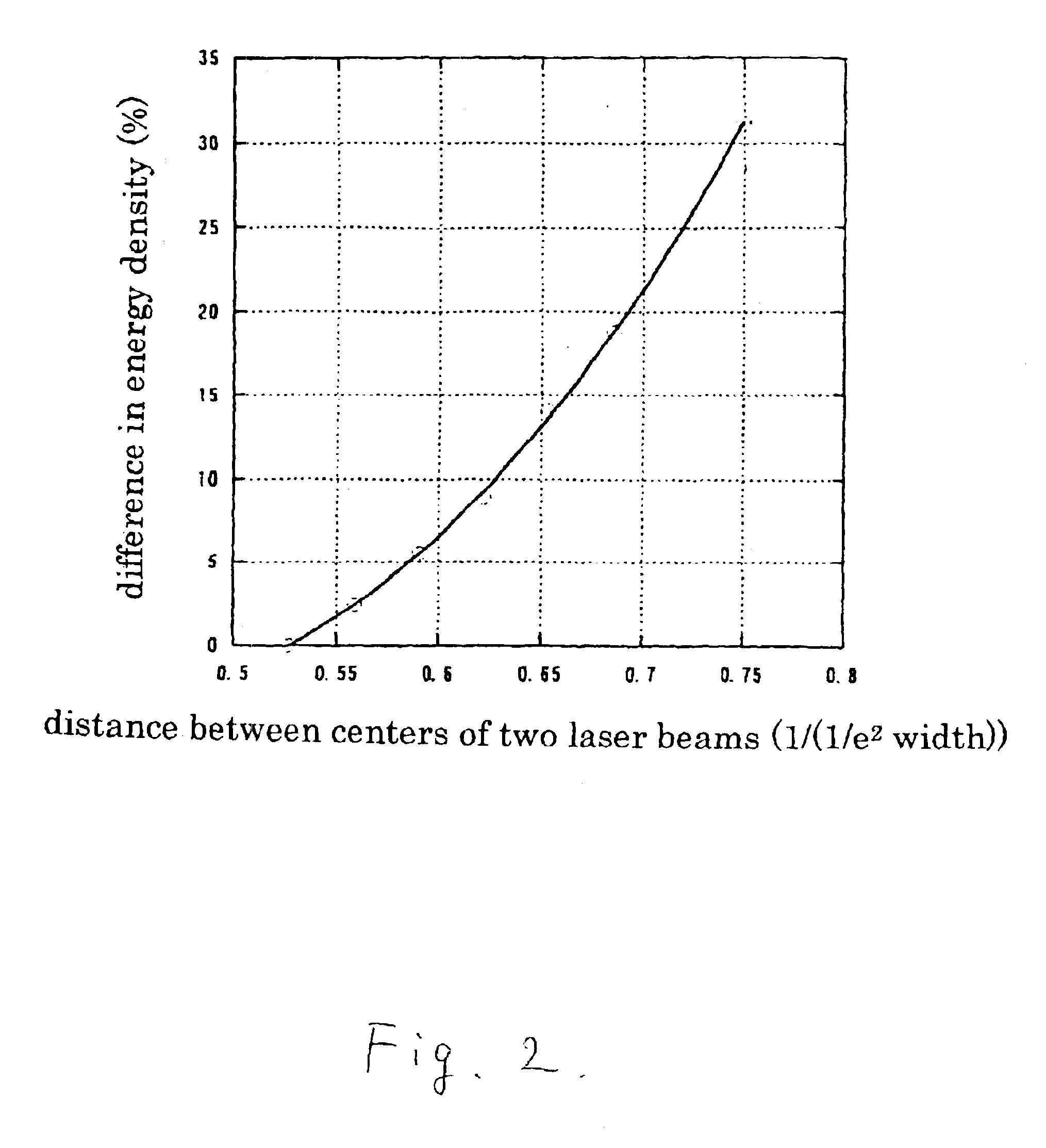
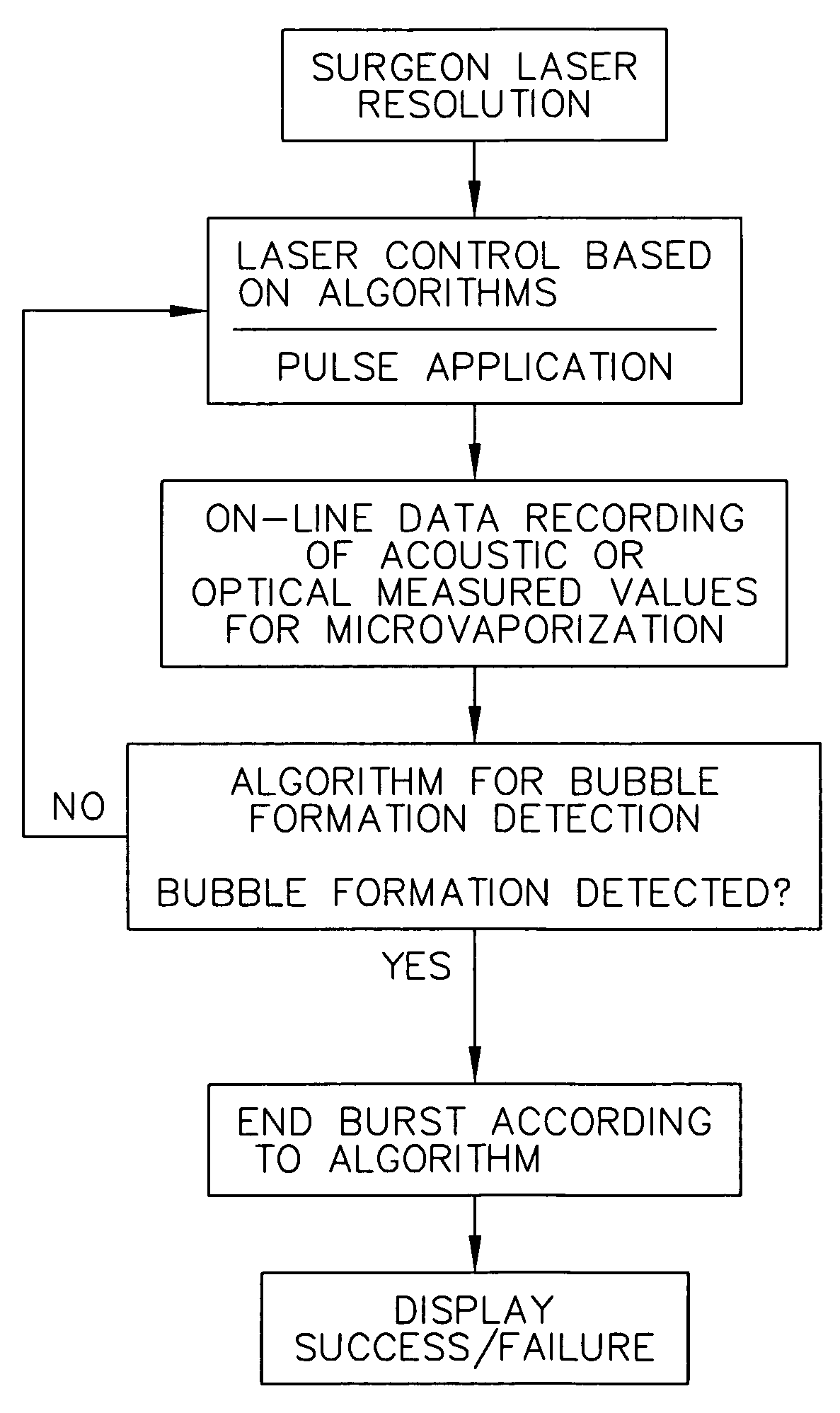
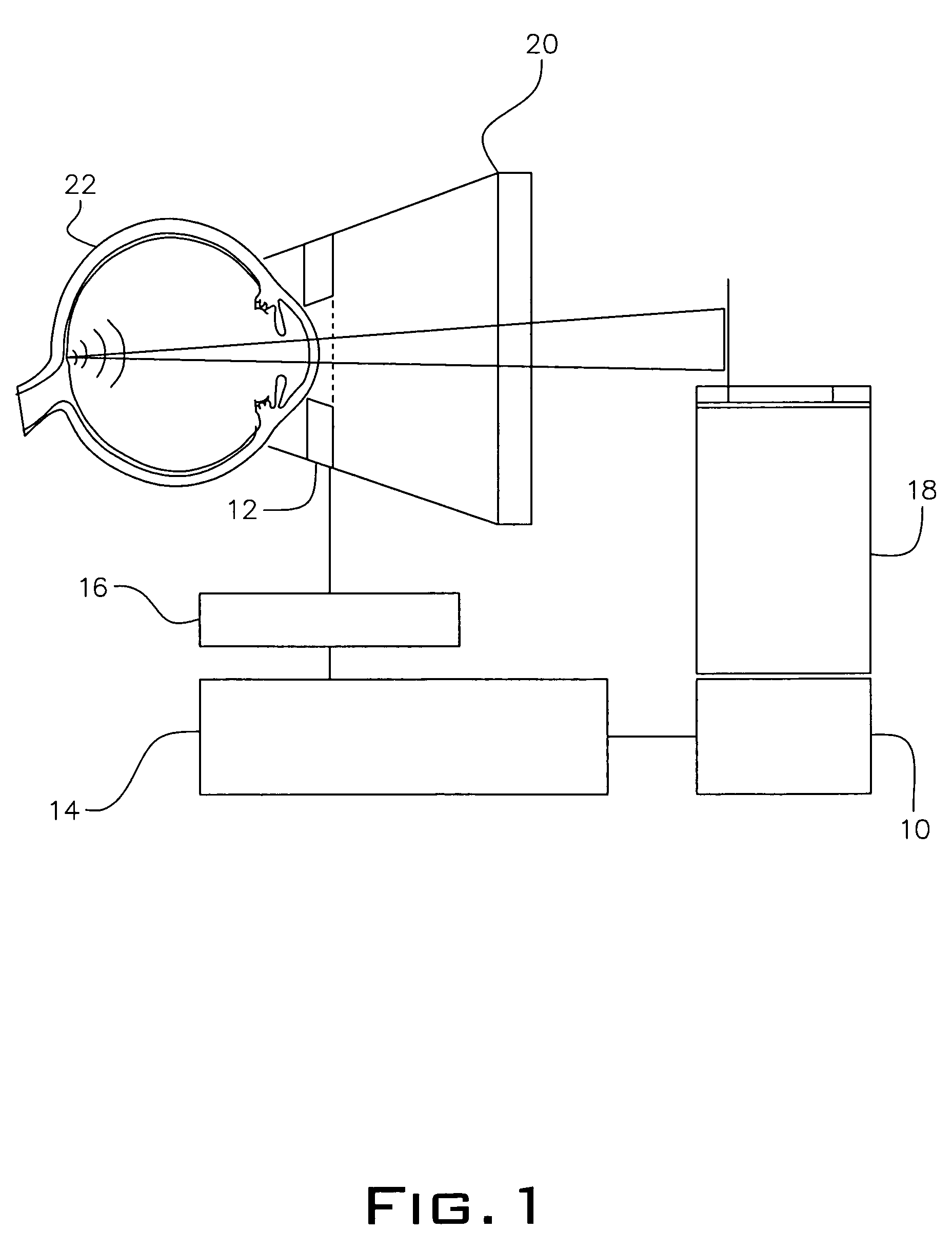
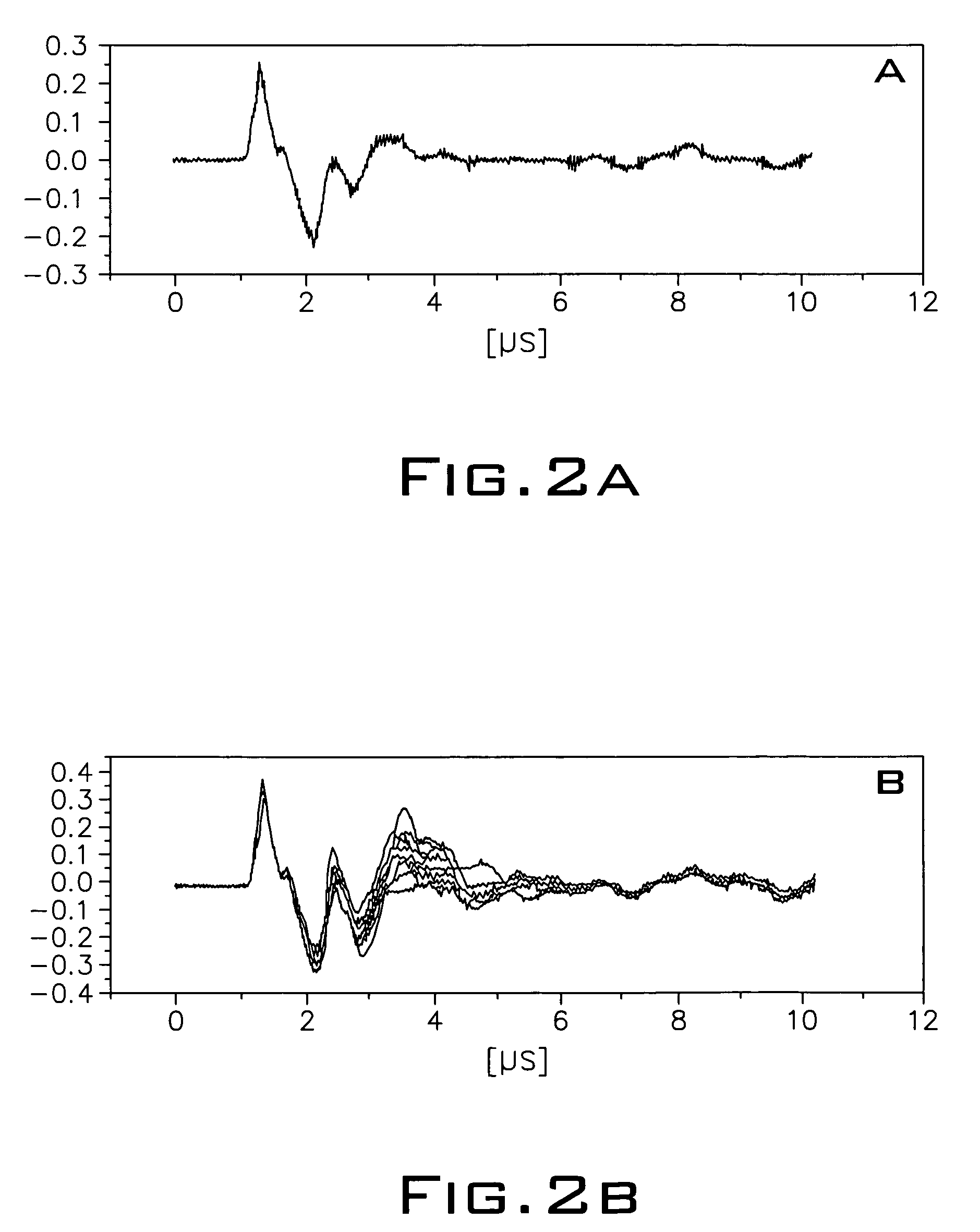
This invention relates to a method for operation of an irradiation laser whereby laser pulse sequences or pulses of varying length are modified during application such that the comparability of recorded transients is retained.
Owner:MEDIZINISCHES LASERZENTRUM LUEBECK GMBH
Method of manufacturing a light emitting device and thin film forming apparatus
InactiveUS20020142697A1Electroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesReverse currentReverse bias
A method of manufacturing a light emitting device is provided in which satisfactory image display can be performed by the investigation and repair of short circuits in defect portions of light emitting elements. A backward direction electric current flows in the defect portions if a reverse bias voltage is applied to the light emitting elements having the defect portions. Emission of light which occurred from the backward direction electric current flow is measured by using an emission microscope, specifying the position of the defect portions, and short circuit locations can be repaired by irradiating a laser to the defect portions, turning them into insulators.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Laser cutting device, laser cutting method and laser cutting system
InactiveCN1652895APrevent adhesionReliable supportConveyorsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesEngineeringLaser cutting
A laser cutting device, comprising a material feeding means for feeding a sheet-like material in a feeding direction, a processing head capable of radiating laser beam toward the material, a head moving means for moving the processing head in a material feeding direction X and a material lateral direction Y, an upstream side support means (belt conveyor mechanism F) for supporting the material on the upstream side of the lower part of the processing head and increasing / decreasing the support area (R2) of the material in the feeding direction according to the movement of the processing head in the feeding direction, and a downstream side support means (belt conveyor mechanism E) for supporting a part cut on the processing side lower part of the processing head and increasing / decreasing the support area (R1) of the cut part in the feeding direction according to the movement of the processing head in the feeding direction.
Owner:TOYOTA STEEL CENT CO LTD
Method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6962860B2Shorten time takenIncrease speedTransistorSolid-state devicesPhysicsOptoelectronics
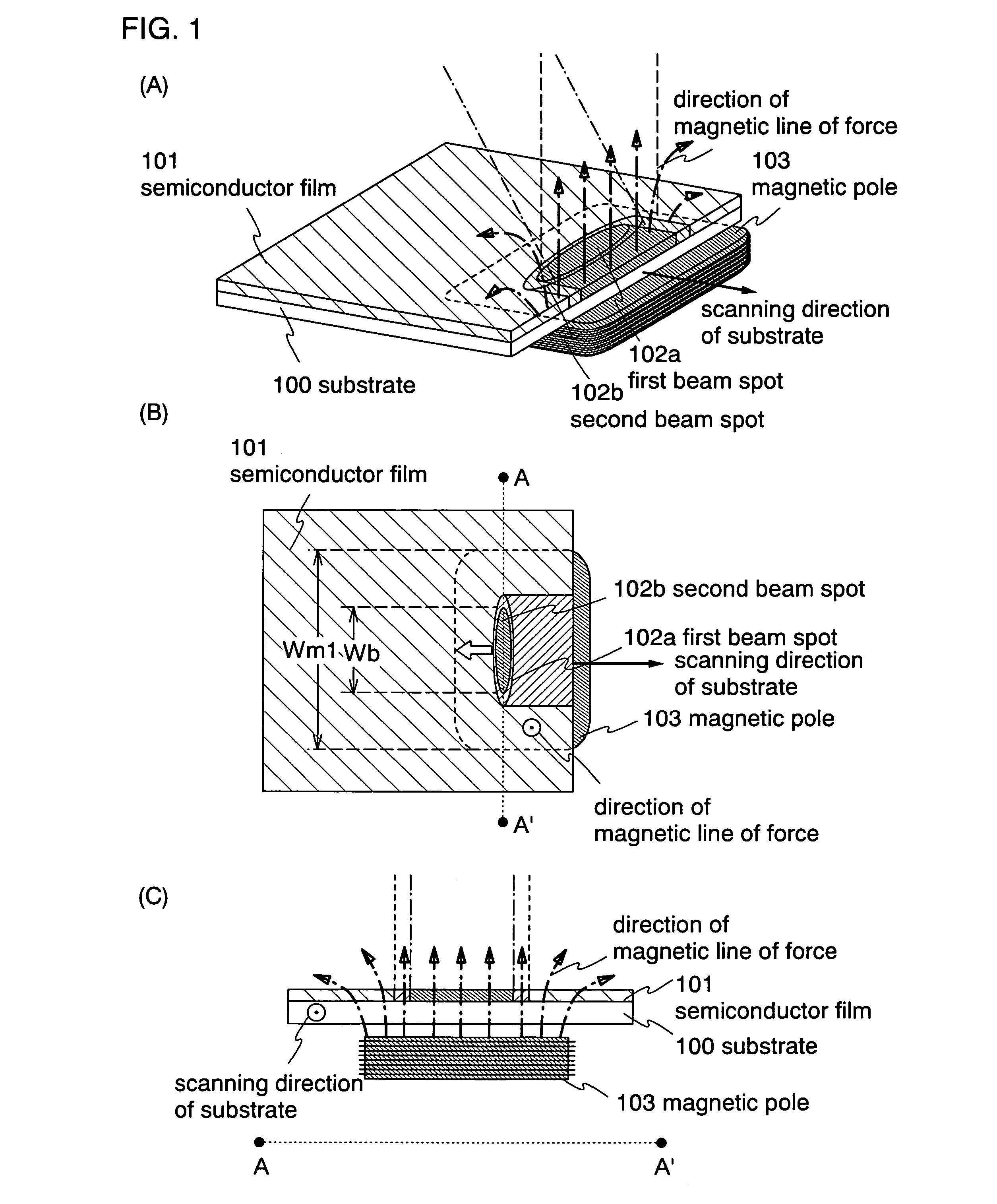
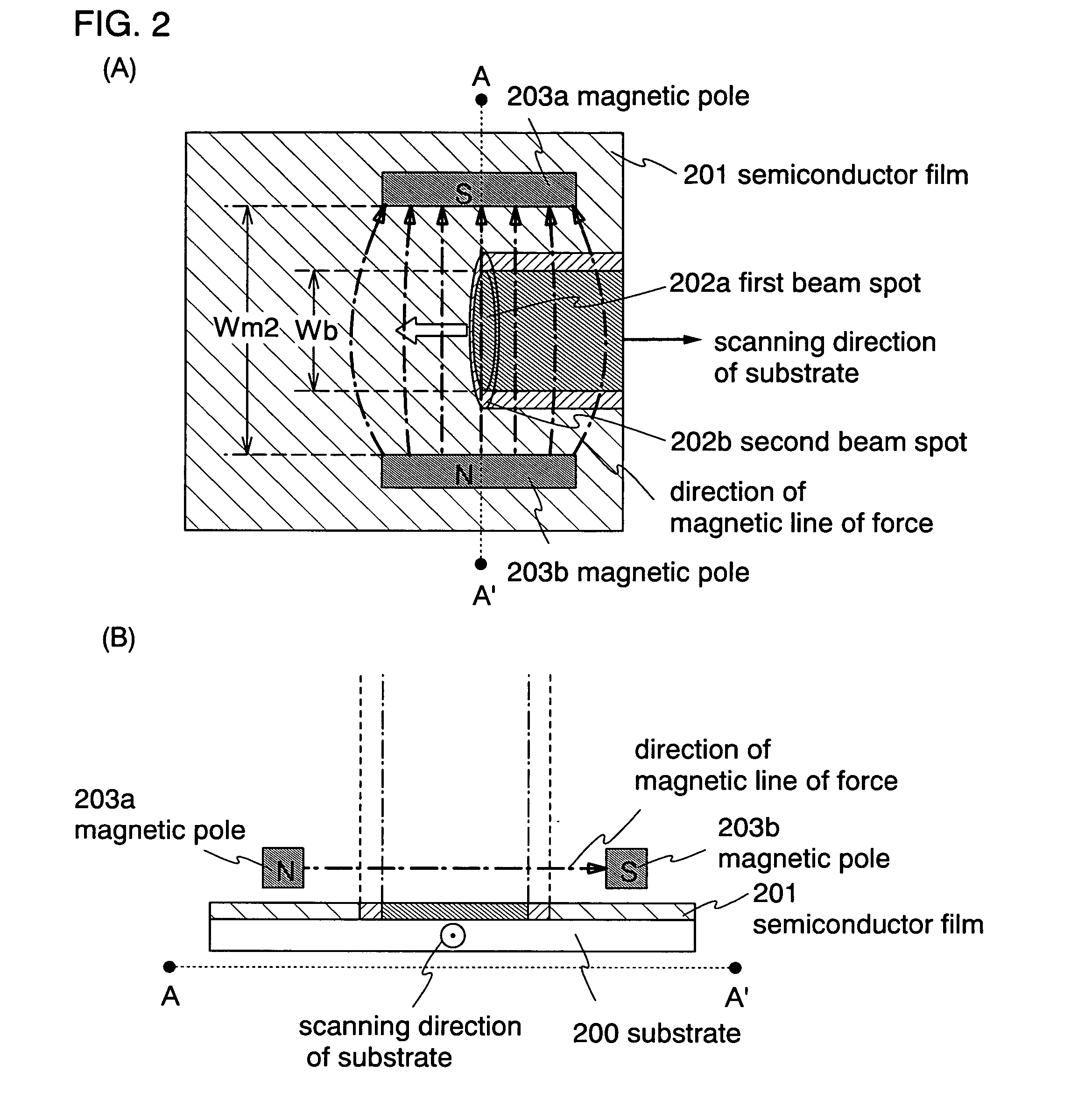
To provide a continuous-oscillating laser apparatus capable of improving the efficiency of substrate treatment, a method of irradiating a laser beam, and a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device using the laser apparatus. Of the entire semiconductor film, a portion that needs to be left on the substrate after patterning is identified according to a mask. Then, a portion to be scanned by respective lasers are defined, so that a laser beam is irradiated twice in different scanning directions to a portion to be obtained at least through patterning and beam spots are impinged upon the scanned portion, thereby partially crystallizing the semiconductor film. In other words, in the invention, it is arranged in such a manner that a laser beam is not irradiated by scanning a laser beam across the entire semiconductor film but by scanning a laser beam twice at least to the absolutely necessary portion. According to the above arrangement, it is possible to save the time to irradiate a laser beam in waste to the semiconductor film at a portion to be removed through patterning, and the crystalline characteristics of the semiconductor film obtained after the patterning can be further enhanced.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Non-contact type dynamic measuring device and method for wheel diameter based on laser and method thereof
ActiveCN101219672ASimple measuring principlePractical measurement principleWheel-rims surveying/measuringMeasurement deviceOptoelectronics
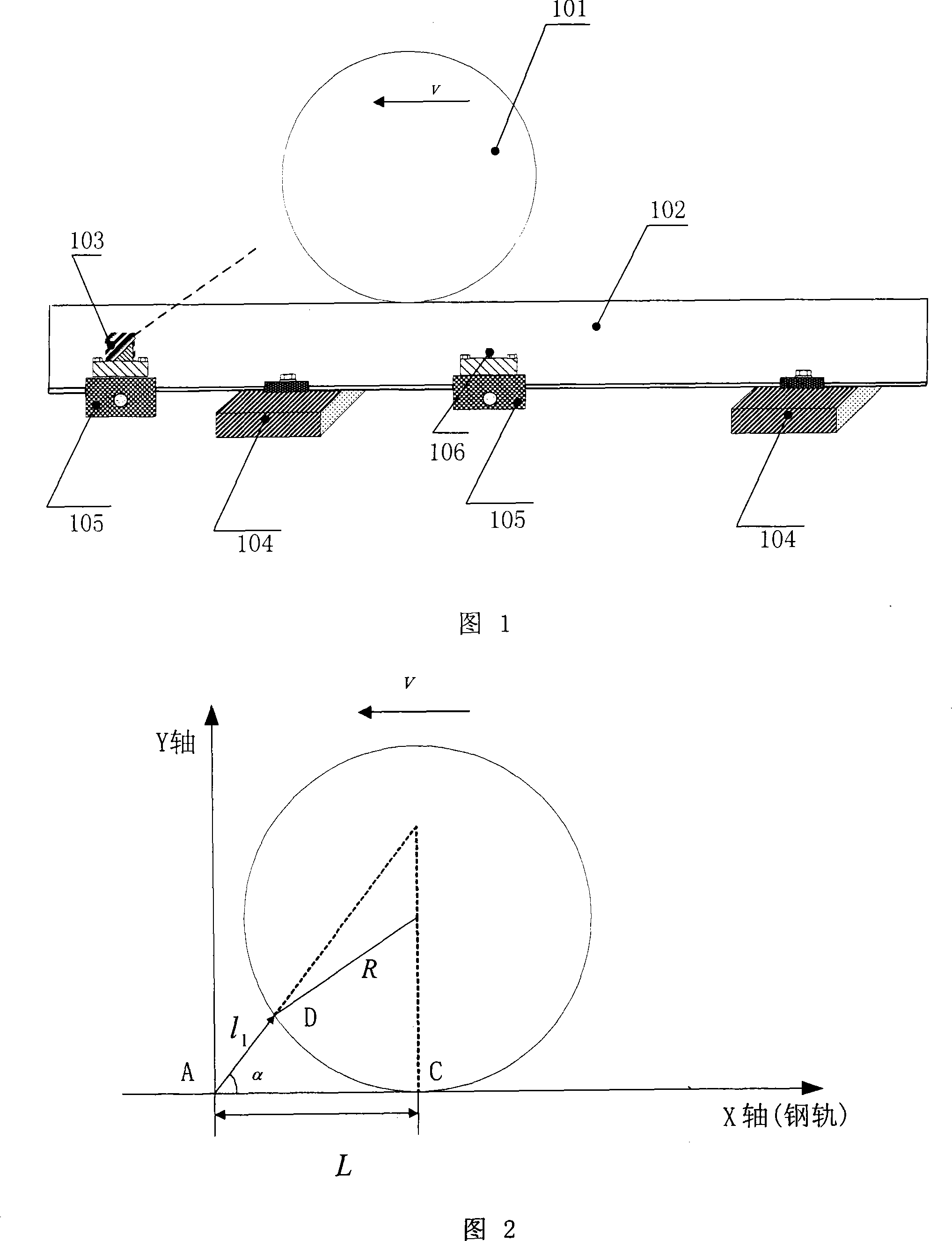
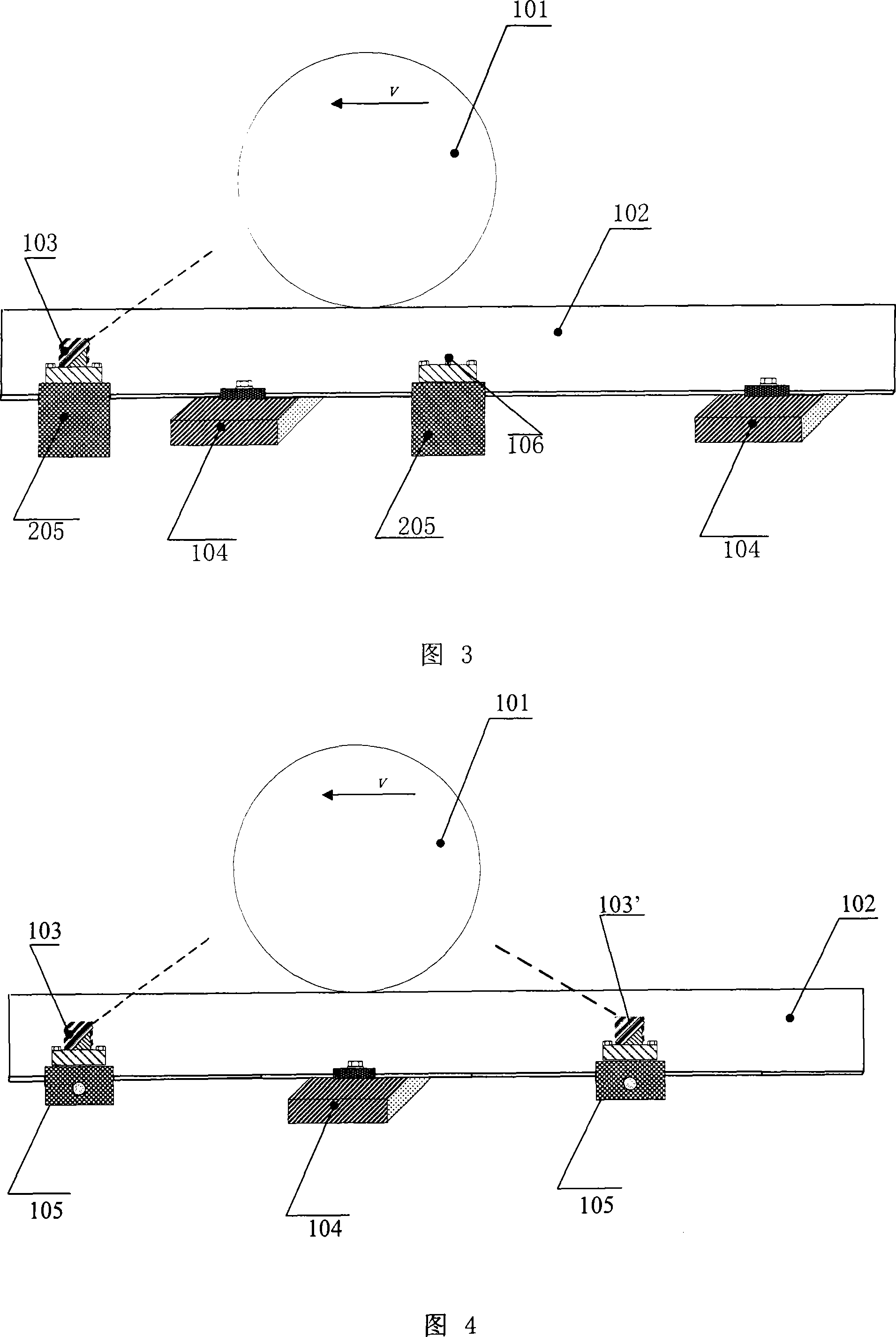
The invention discloses a non-contact dynamic measuring device for a wheel diameter based on laser and a method thereof. The measuring device consists of a laser displacement sensor, a wheel positioning sensor or two laser displacement sensors; the two sensors are arranged along the direction of a steel rail. When the two laser displacement sensors are applied, light spots of irradiation laser can directly irradiate onto two opposite surfaces of the measured wheel; the two laser displacement sensors respectively and continuously measure the distance between each sensor and corresponding point on a tread of the wheel; the reading data of distance in each laser displacement sensor is recorded when the sum of the distance measured by the two laser displacement sensors is basically unchanged, to calculate the diameter of the train wheel. The invention requires two sensors at most, and measurement principle is simple and practical.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Laser irradiation apparatus and method of fabricating semiconductor device
InactiveUS20040259387A1Suppress of stateSuppress unevennessTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHarmonicNitrogen
According to the present invention, oxygen and nitrogen are effectively prevented from mixing into the semiconductor film by doping Ar or the like in the semiconductor film in advance, and by irradiating the laser light in the atmosphere of Ar or the like. Therefore, the variation of the impurity concentration due to the fluctuation of the energy density can be suppressed and the variation of the mobility of the semiconductor film can be also suppressed. Moreover, in TFT formed with the semiconductor film, the variation of the on-current in addition to the mobility can be also suppressed. Furthermore, in the present invention, the first laser light converted into the harmonic easily absorbed in the semiconductor film is irradiated to melt the semiconductor film and to increase the absorption coefficient of the fundamental wave.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Recording/reading method for an optical recording medium using an irradiating a laser beam
In an optical recording medium of a single-sided incident type having a plurality of recording layers, recording / reading conditions (for example, tracking polarity, recording pulse strategy, recording recommended power, etc.) can be instantaneously switched according to each of the recording layer, and recording or reading of information can be accurately and surely performed under recording / reading conditions adapted to each recording layer. A control unit reads out layer information from one recording layer of the optical recording medium in which the layer information is recorded in each of the plural layers, on which recording or reading of information can be performed by irradiating a laser beam from one side thereof (layer information reading step), and controls so that recording or reading is performed under recording / reading conditions adapted to a recording layer specified on the basis of the layer information (recording controlling step).
Owner:CMC MAGNETICS CORPORATION
Method for manufacturing semiconductor substrate, semiconductor device and electronic device
InactiveUS20090115028A1Improve flatnessEasy to optimizeTransistorSolid-state devicesHydrogenSingle crystal
A semiconductor substrate including a single crystal semiconductor layer with a buffer layer interposed therebetween is manufactured. A semiconductor substrate is doped with hydrogen to form a damaged layer containing a large amount of hydrogen. After the single crystal semiconductor substrate and a supporting substrate are bonded, the semiconductor substrate is heated so that the single crystal semiconductor substrate is separated along a separation plane. The single crystal semiconductor layer is irradiated with a laser beam from the single crystal semiconductor layer side to melt a region in the depth direction from the surface of the laser-irradiated region of the single crystal semiconductor layer. Recrystallization progresses based on the plane orientation of the single crystal semiconductor layer which is solid without being melted; therefore, crystallinity of the single crystal semiconductor layer is recovered and the surface of the single crystal semiconductor layer is planarized.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and a manufacturing method of the same
InactiveUS20070037321A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialLiquid state
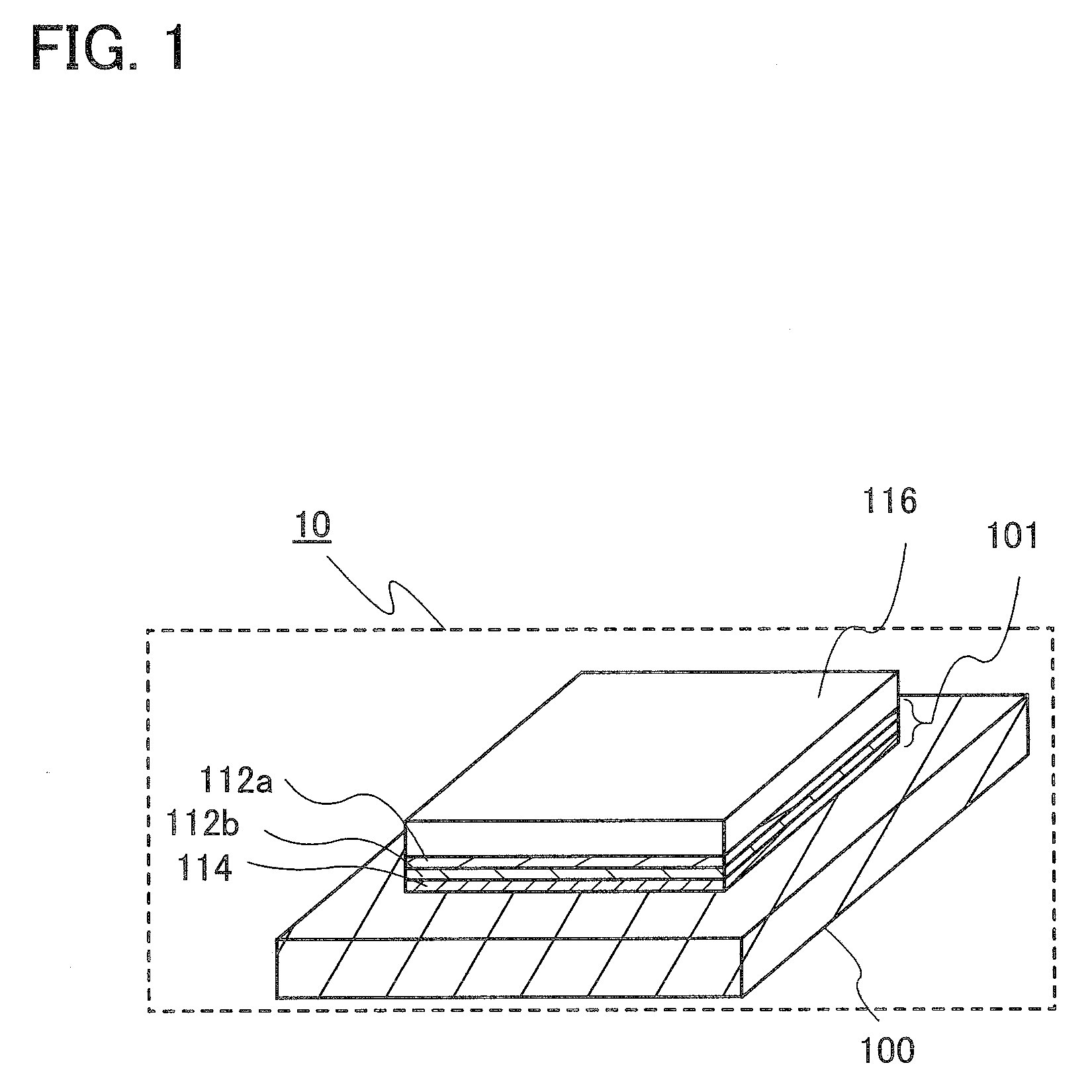
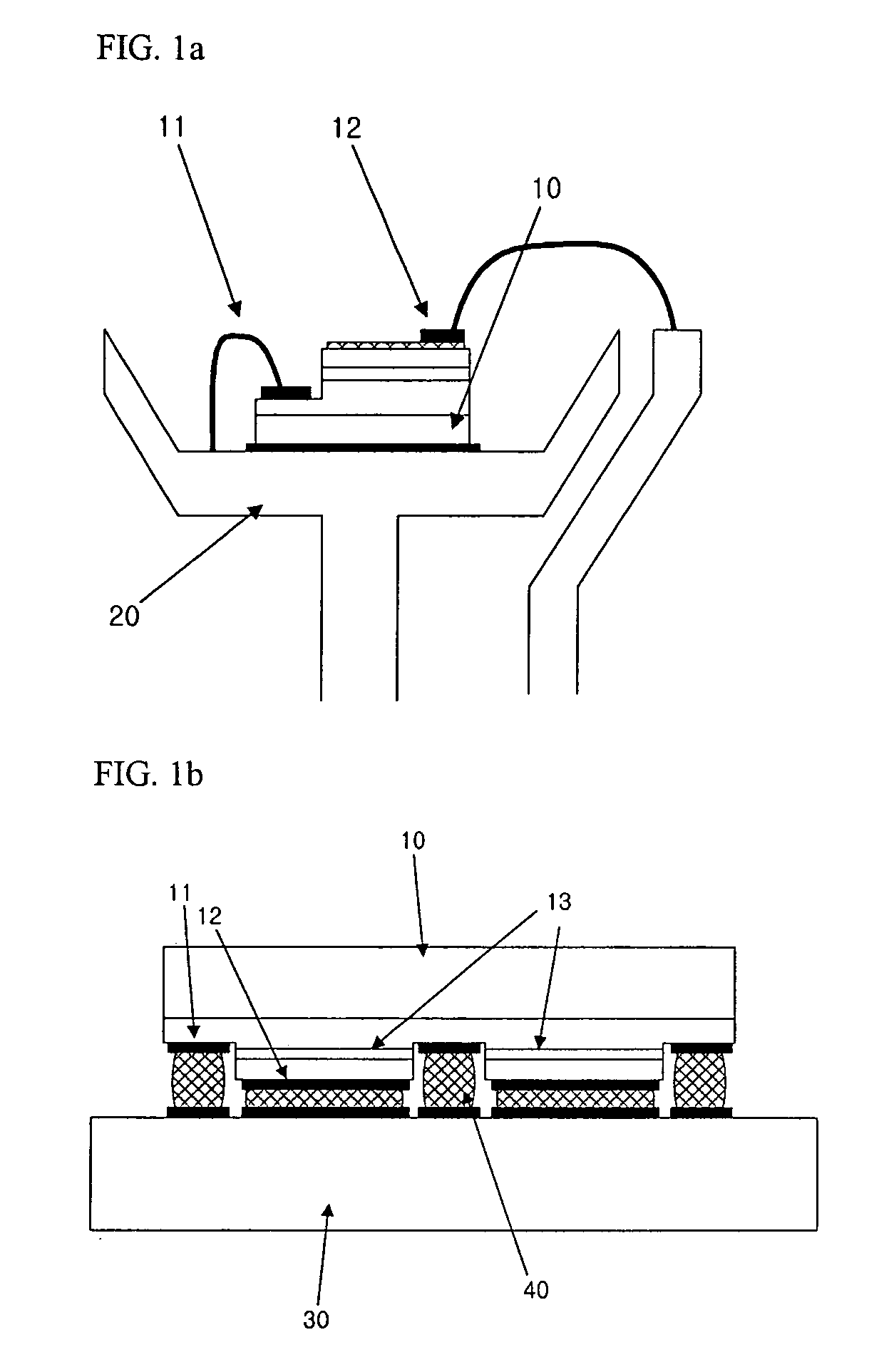
The semiconductor device having the structure which laminated the chip in many stages is made thin. A reforming area is formed by irradiating a laser beam, where a condensing point is put together with the inside of the semiconductor substrate of a semiconductor wafer. Then, after applying the binding material of liquid state to the back surface of a semiconductor wafer by a spin coating method, this is dried and a solid-like adhesive layer is formed. Then, a semiconductor wafer is divided into each semiconductor chip by making the above-mentioned reforming area into a division origin. By pasting up this semiconductor chip on the main surface of an other semiconductor chip by the adhesive layer of the back surface, the semiconductor device having the structure for which the semiconductor chip was laminated by many stages is manufactured.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method for fabricating a semiconductor device
InactiveUS7037811B1Improve featuresHigh crystallinityTransistorSolid-state devicesAtmospheric airAmorphous silicon
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Laser irradiation apparatus, laser irradiation method, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS7125761B2Fully absorbedImprove annealing efficiencyTransistorSolid-state devicesSingle crystalLaser annealing
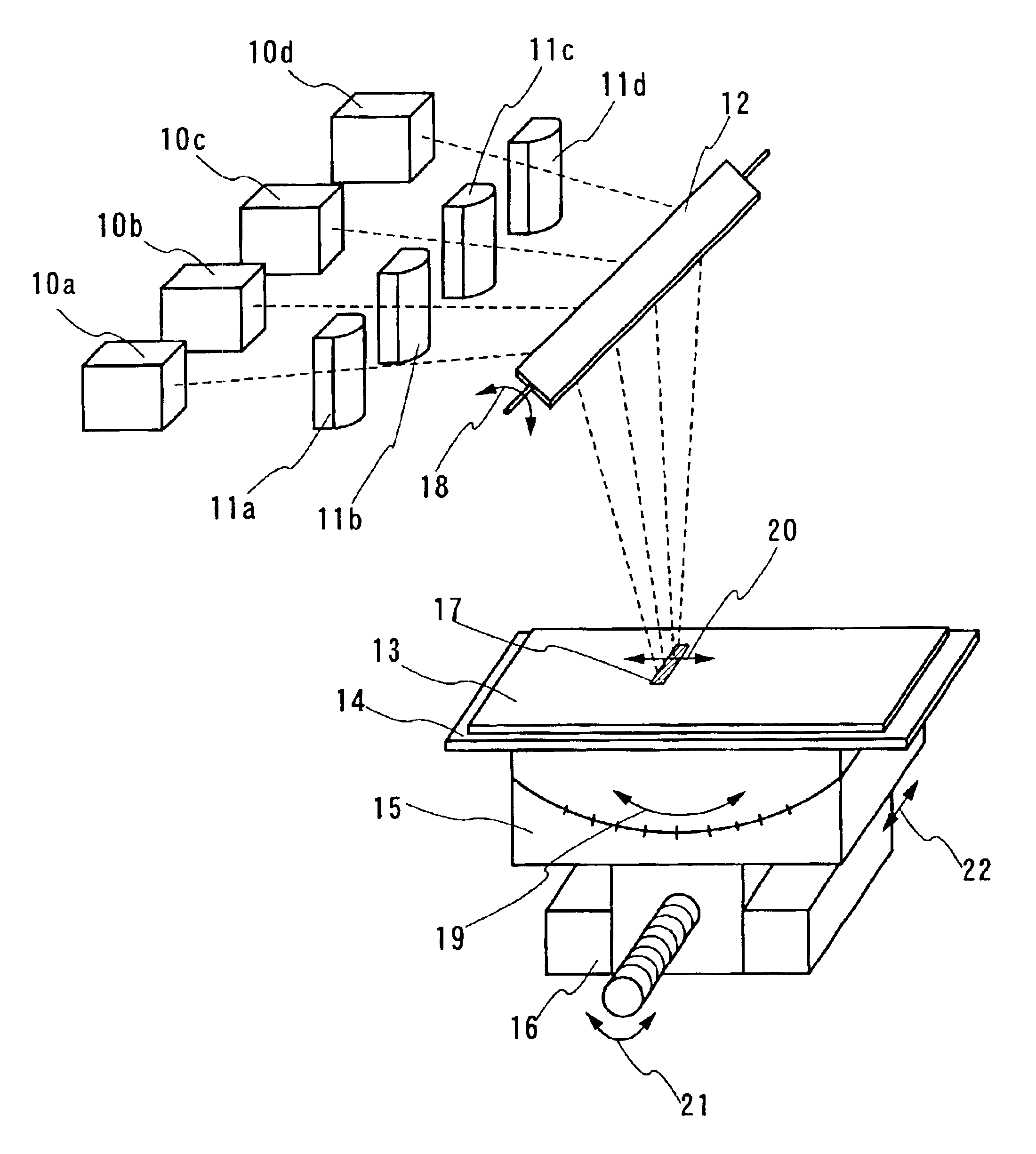
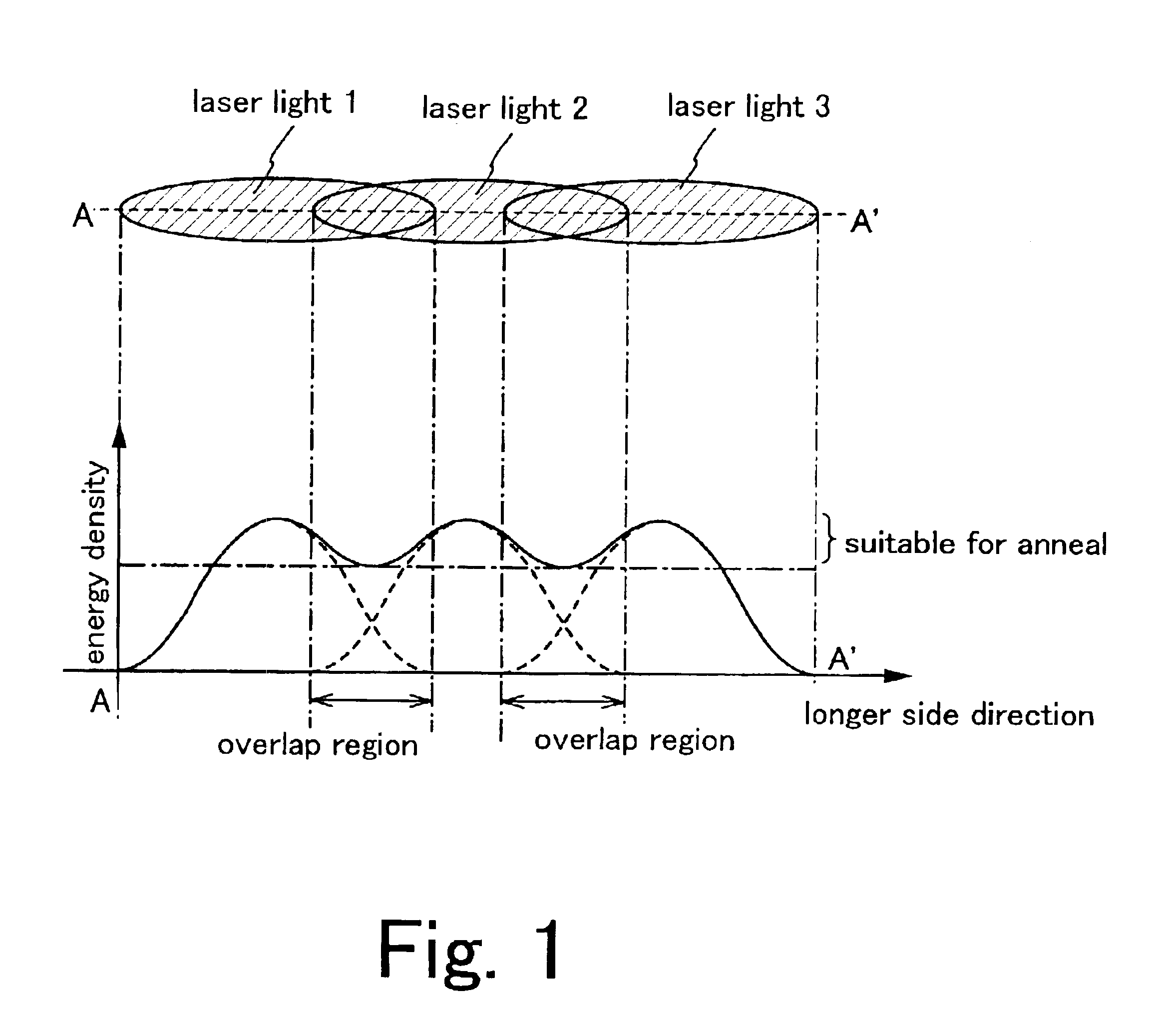
An aggregation of crystals extending long in the scanning direction (a long crystal grain region) is formed when a continuous wave laser oscillator (a CW laser oscillator) is employed for annealing the semiconductor film in the manufacturing process of a semiconductor device. The long crystal grain region has a characteristic similar to that of single crystal in the scanning direction, but there is restriction for high integration because of the small output of the CW laser oscillator. pa In order to solve the problem, a pulsed laser beam 1 having a wavelength absorbed sufficiently in the semiconductor film is used in combination with a laser beam 2 having a high output and having a wavelength absorbed sufficiently in the melted semiconductor film. After irradiating the laser beam 1 to melt the semiconductor widely, the laser beam 2 is irradiated to the melted region. And then the laser beam 2 and the semiconductor film are moved relatively while keeping the melting state so as to form the long crystal grain region. The laser beam 2 keeps to be irradiated to the semiconductor film until the laser beam 1 is irradiated, and the output of the laser beam 2 is attenuated when the laser beam 1 is irradiated so as not to give the energy more than is needed so that the very uniform laser annealing becomes possible. Thus the long crystal grain region having a width 10 times as broad as the conventional one can be formed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Laser beam machining apparatus and corresponding method which employs a laser beam to pretreat and machine a workpiece
InactiveUS6040549AWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusLight beamLaser beam machining
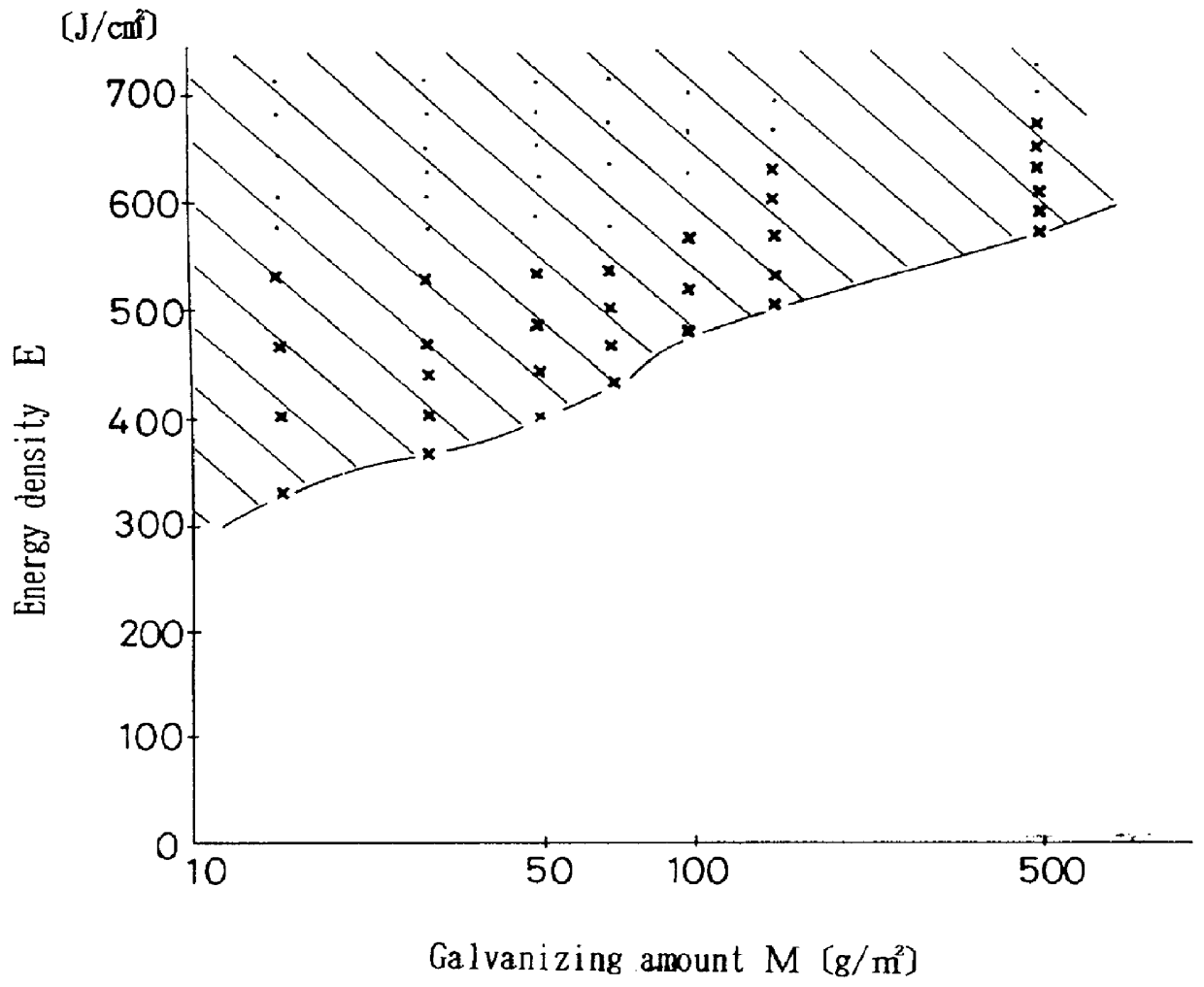
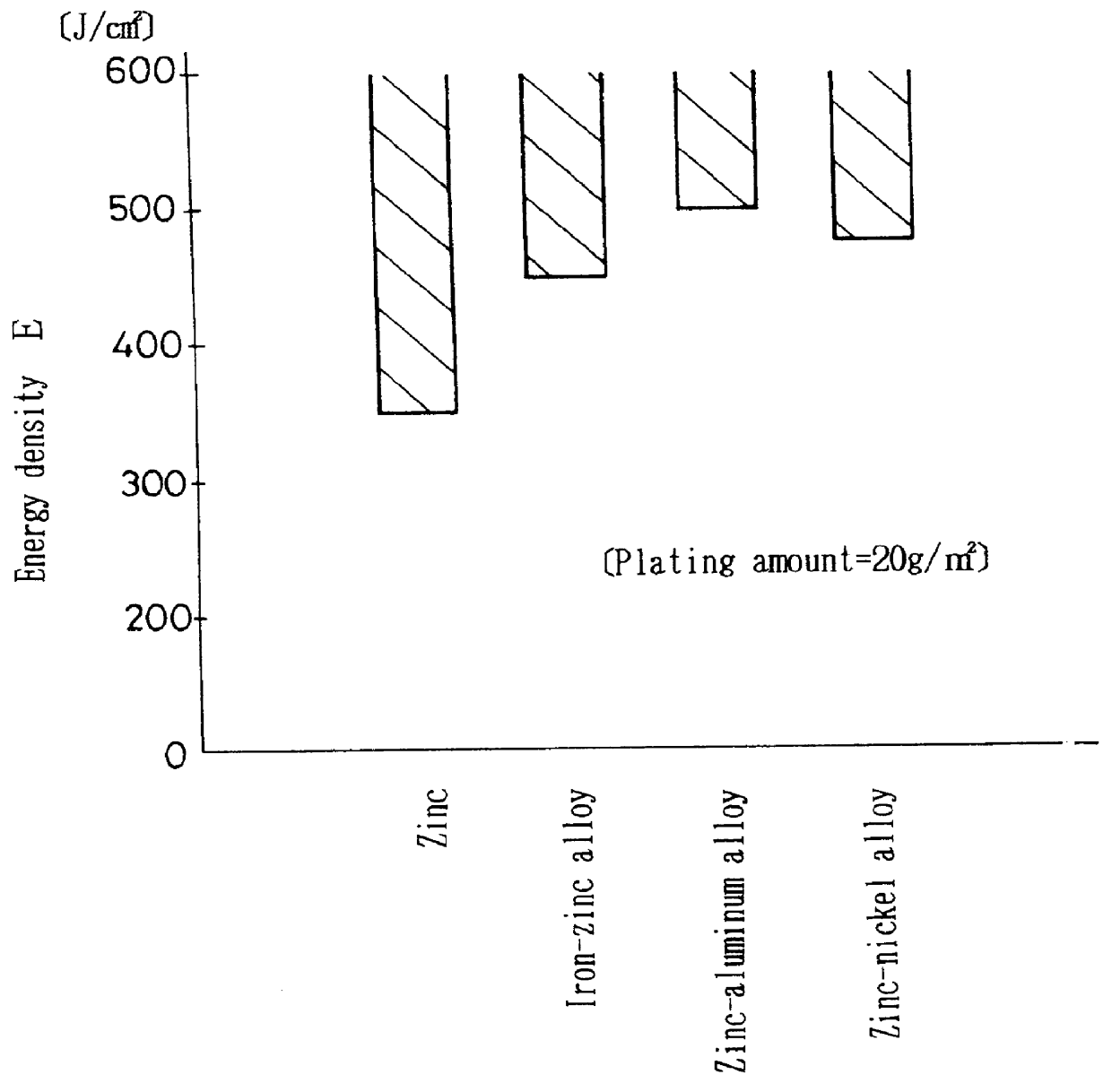
A laser beam machining is carried out by irradiating beforehand the laser beam along a final locus for a main machining, under such a condition as to obtain an energy density for removing a galvanized layer as a surface substance of a work. Thereafter, the laser beam is irradiated to a bare area on which the zinc has been removed, while changing only the energy density according to a cutting condition to cut the work.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Laser Irradiation Device, Laser Irradiation System, and Method for Removing Coating or Adhering Matter
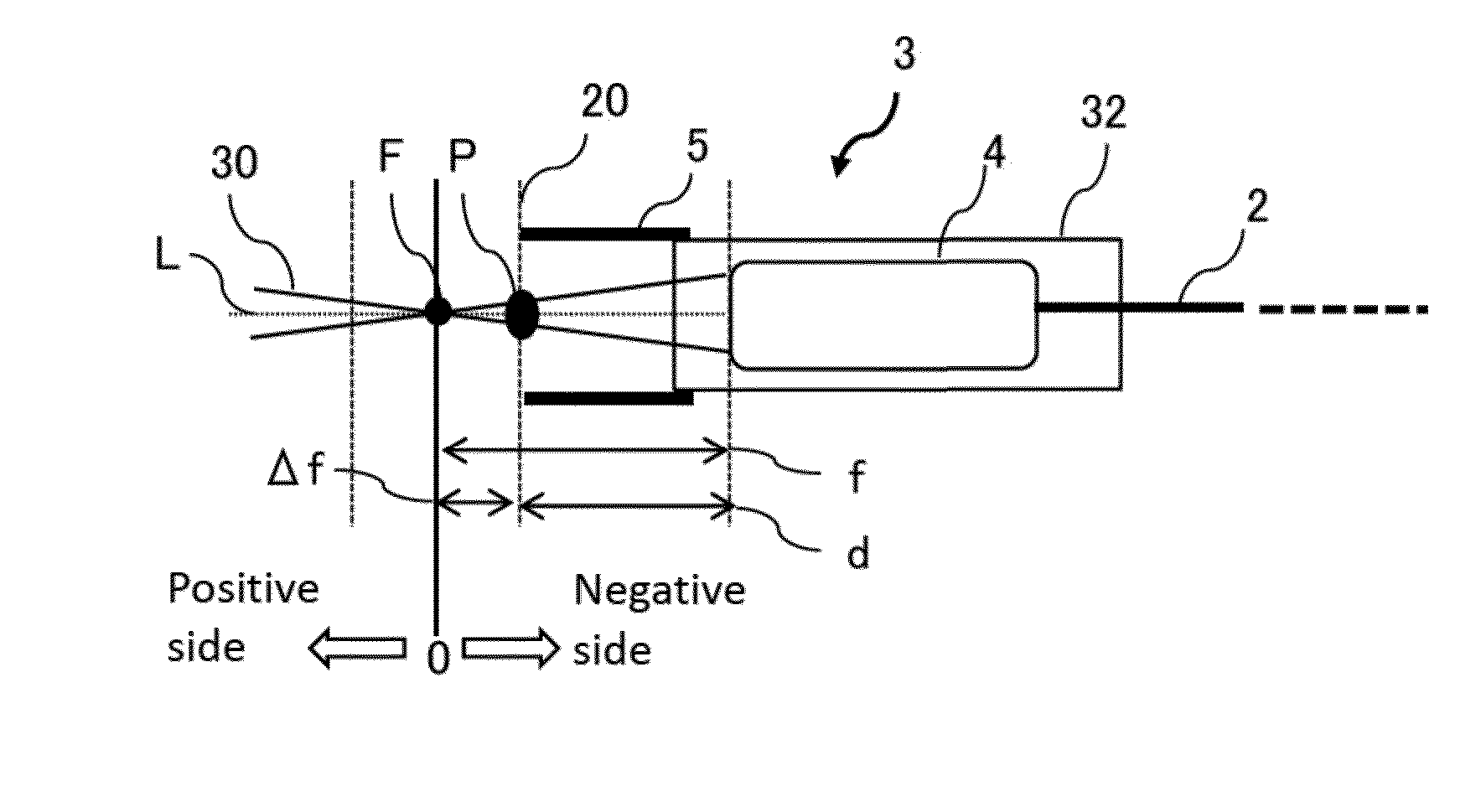
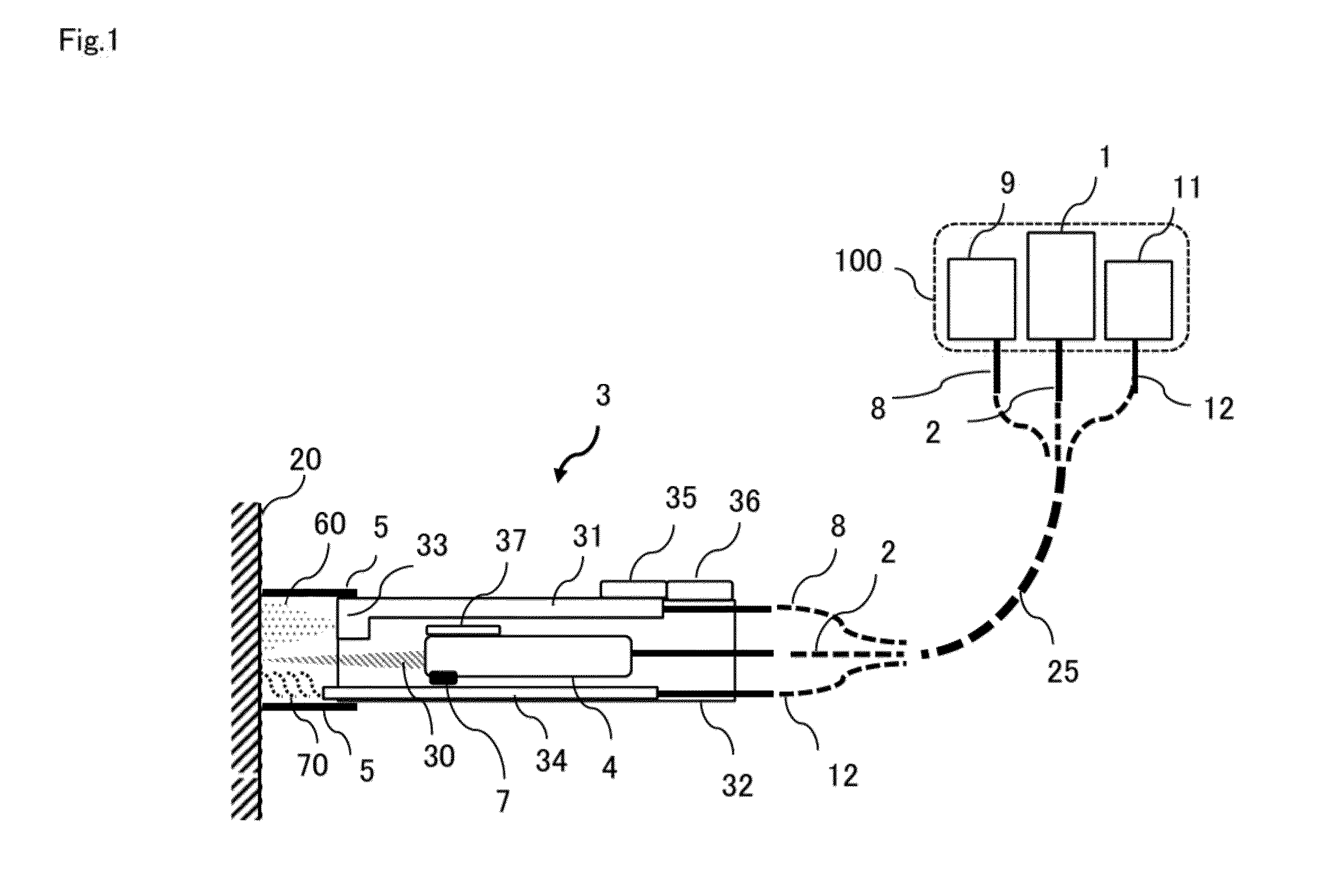
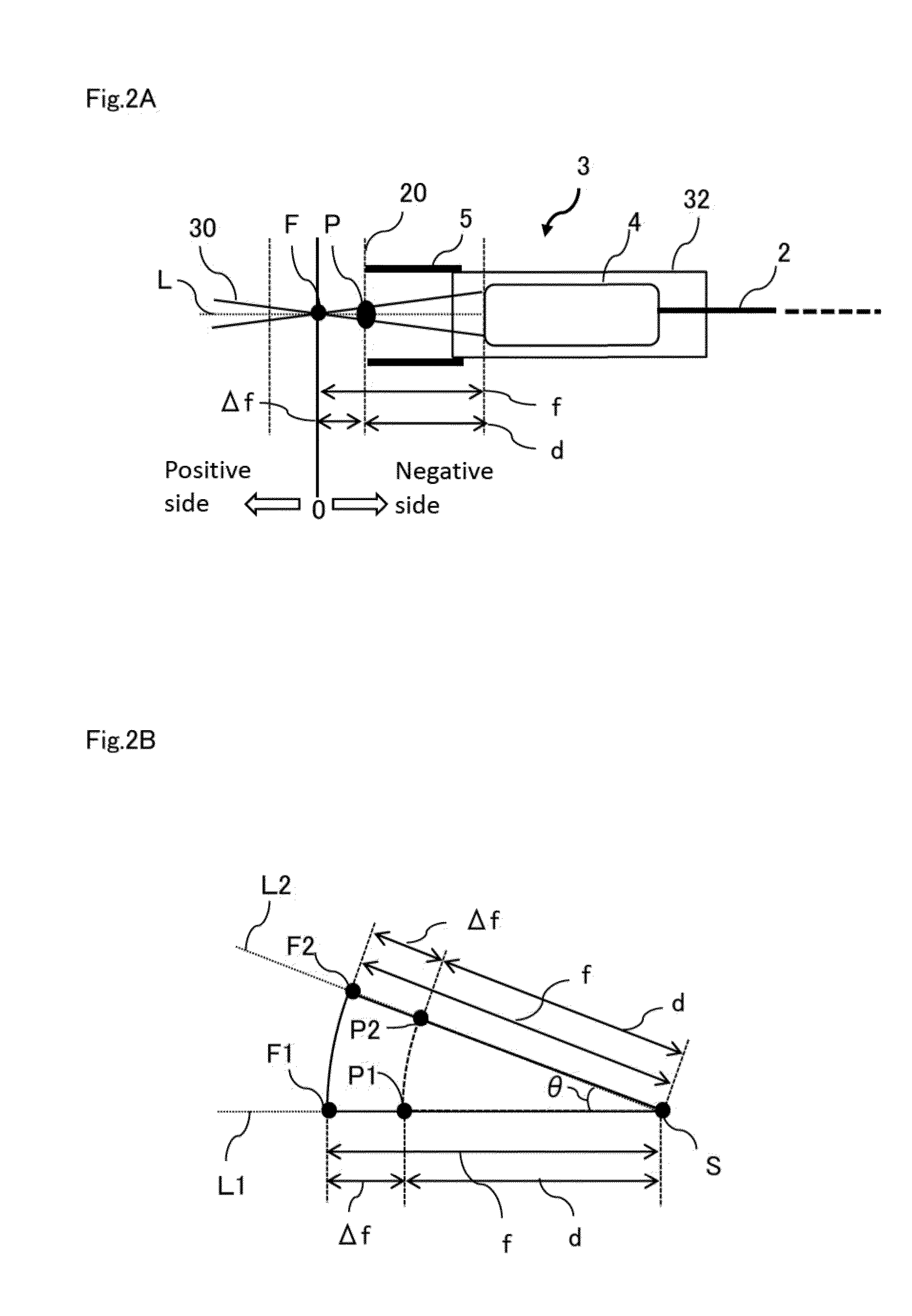
ActiveUS20150076125A1Effective treatmentLow costNuclear energy generationEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesOptical axisIrradiation laser
In order to provide a laser irradiation system, a method for removing a coating, and a laser irradiation apparatus capable of efficiently removing a coating on a surface of a structure and recovering the removed substance using suction, a laser head (3) is configured from an optical system (4) for irradiating laser beam (30), a suctioning means (33) for suctioning removed matter (60) produced at the point where the laser beam (30) is directed, and an attachment (5) configured to be capable of abutting a surface (20) of a structure, the optical system (4) being operated to scan the irradiation point of the laser beam so as to draw a trajectory of a circle having a radius r1 around the optical axis of the laser beam (30) on a surface substantially perpendicular to the optical axis.
Owner:TOYOKOH
Optical recording method, optical recording medium, optical recording medium recording device, optical recording device, optical disk, optica disk recording/reproducing device
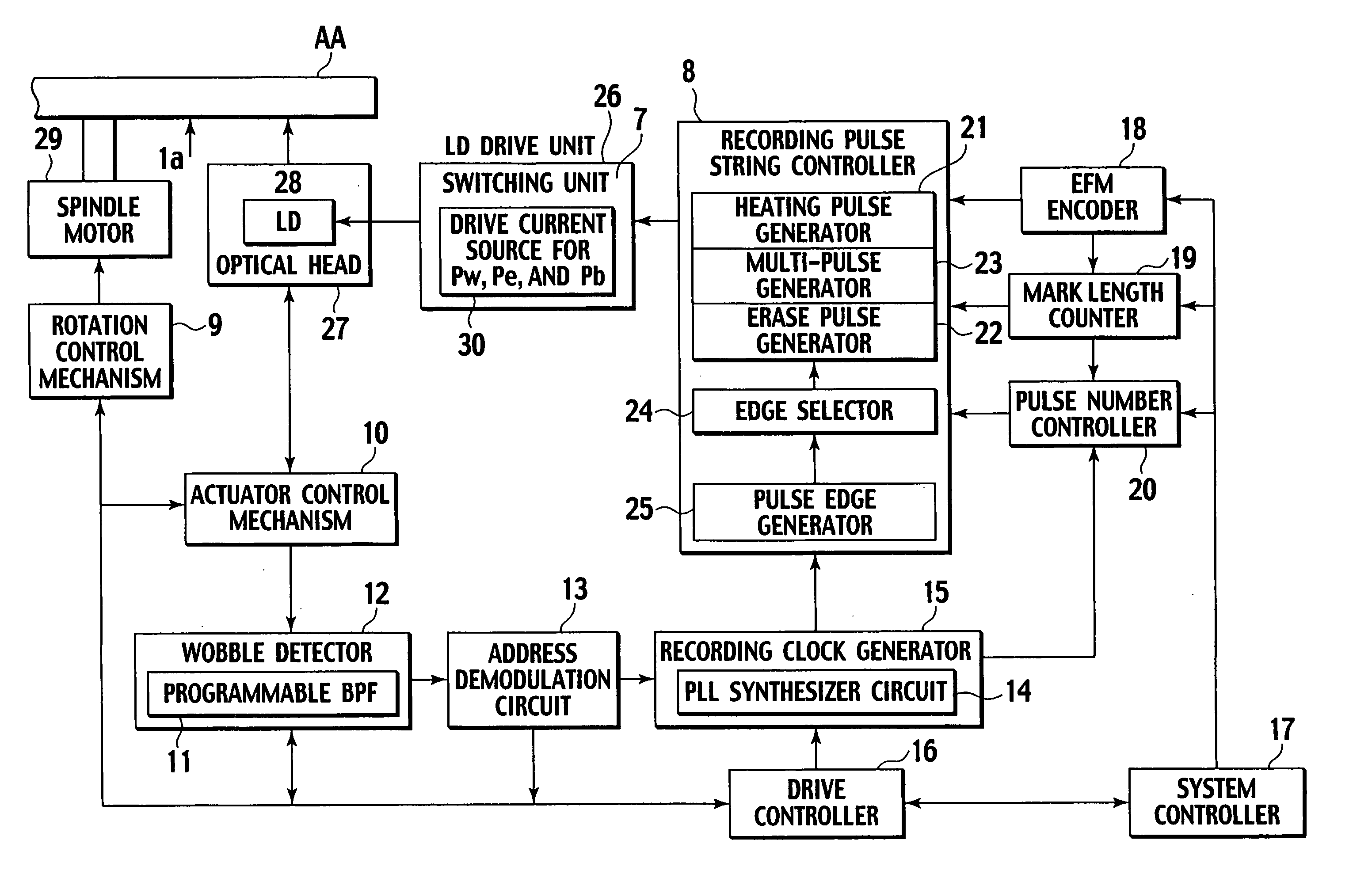
InactiveUS20060140094A1Relatively low linear speedRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsEngineeringIrradiation laser
A mark having a length nT (n being an integer equal to or greater than 3 and T being a clock period) is formed by modulating irradiation laser power with three values of recording power Pw, erase power Pe, and bias power Pb (Pw>Pe>Pb). Constant strength periods (At) of the recording power Pw are set as AtT, A1T, . . . and AmT and constant strength periods (Bt) of the bias power Pb are set as BtT, B1T, . . . BmT, and CT (C=−1 to 3). The application of laser is divided into pulses in order of AtT, BtT, A1T, B1T, . . . , AmT, BmT, and CT (m=(n−k) / 2, k=3 (if n is an odd number), or k=4 (if n is an even number)). (Here, the constant strength period of the recording power Pw for n=3, n=4, n≧5 (odd number), and n≧6 (even number) is set as At3, At4, Atod, and Atev, the constant strength period of the bias power Pb for n=3, n=4, n≧5 (odd number), and n≧6 (even number) is set as Bt3, Bt4, Btod, and Btev, and then, At3+Bt3=Atod+Btod=Am+Bm=2T and At4+Bt4=Atev+Btev=3T).
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Laser ray transmitting colored thermoplastic resin composition and method of laser welding
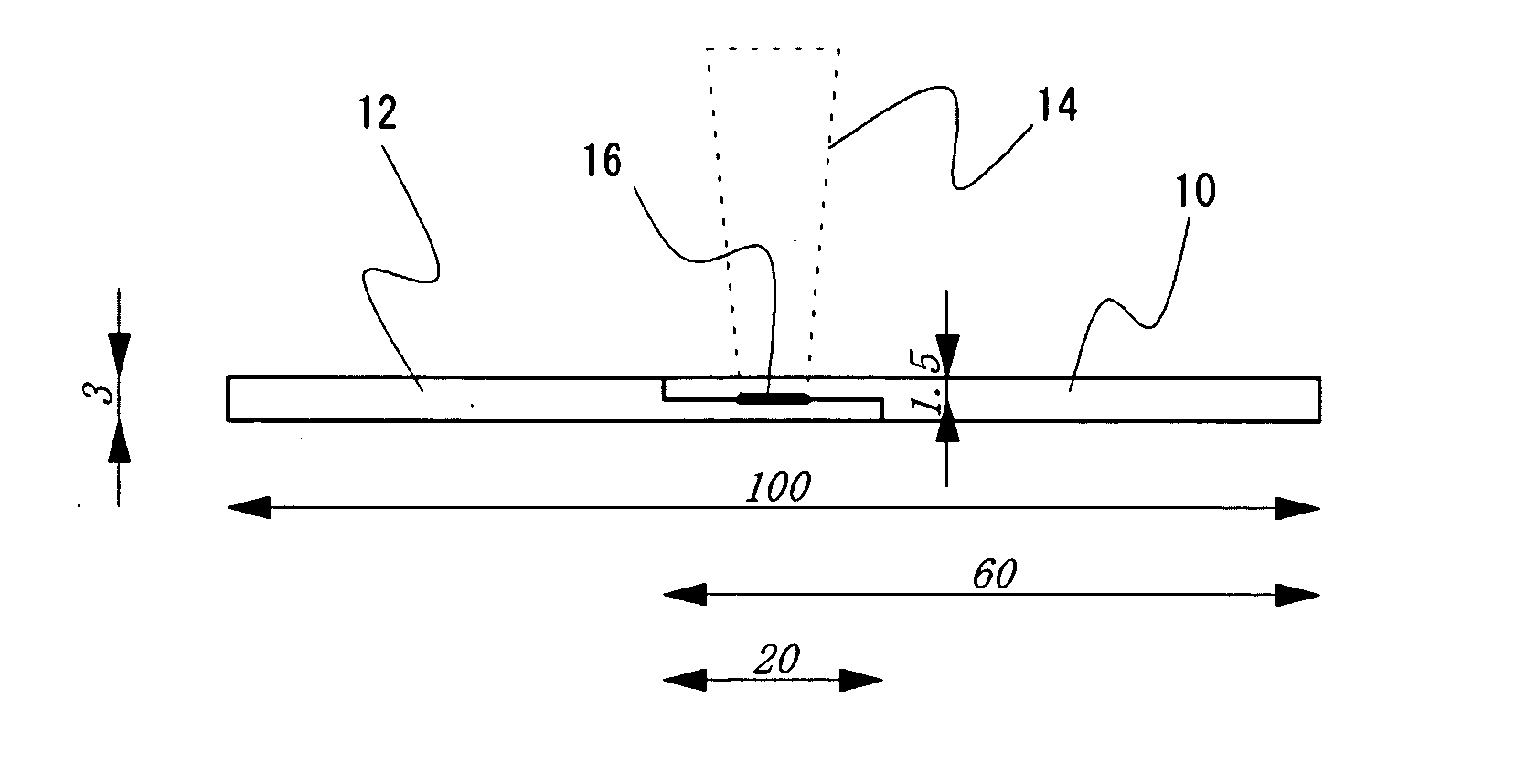
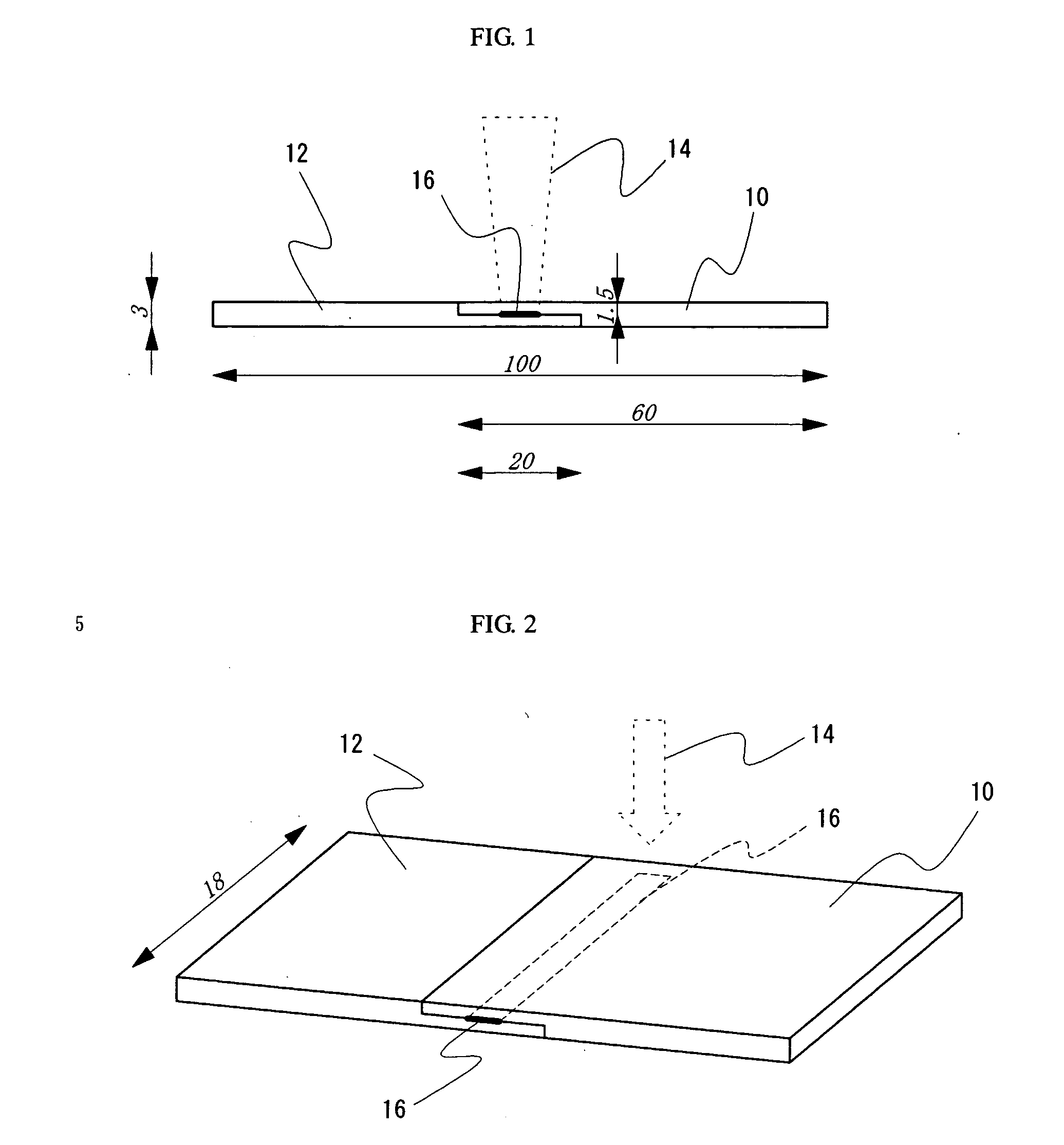
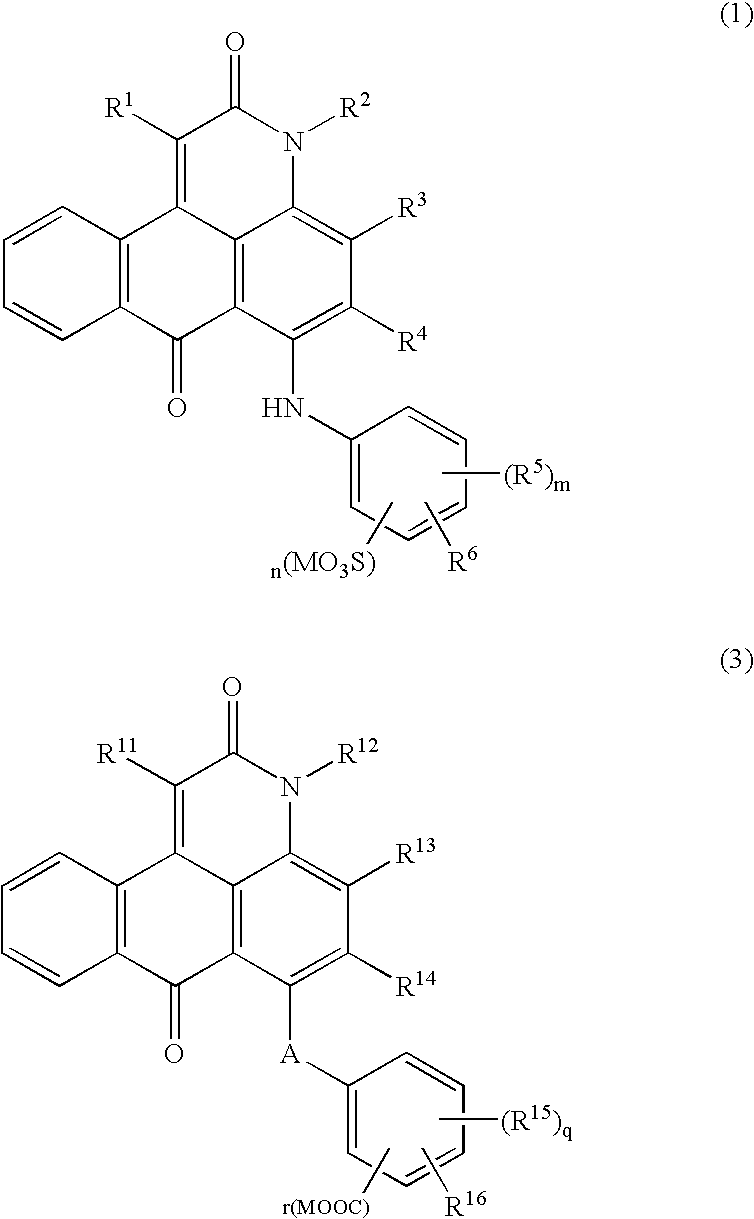
InactiveUS20050003301A1High fastnessGood anti-migration propertyPhotomechanical apparatusPhotosensitive material auxillary/base layersOptoelectronicsIrradiation laser
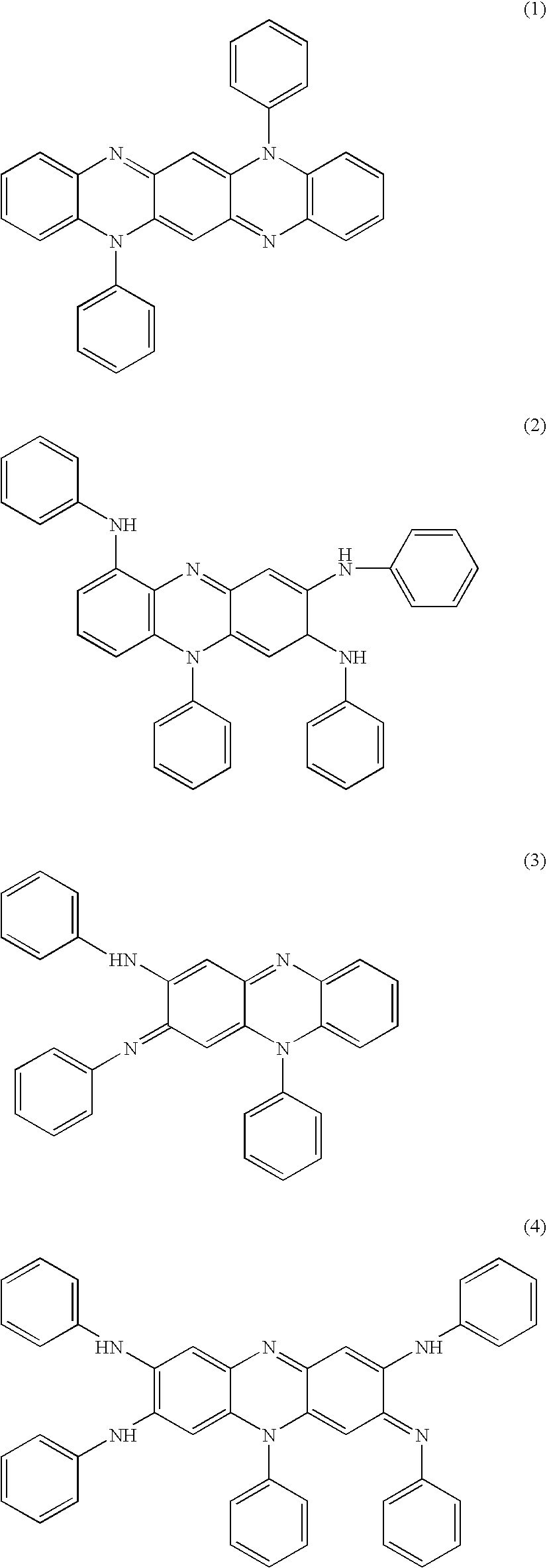
A laser ray transmitting colored thermoplastic resin composition containing an anthrapyridone acid dye represented by formula (1) or (3); method of laser welding wherein a contact portion of a laser ray transmitting material of the laser ray transmitting colored thermoplastic resin composition and a laser absorbent material is welded by irradiating laser ray so that the laser ray transmits the laser ray transmitting material and is absorbed in the laser absorbent material with the laser ray transmitting material and the laser absorbent material in contact with each other.
Owner:ORIENT CHEM INDS
Method for manufacturing GaN-based light emitting diode using laser lift-off technique and light emitting diode manufactured thereby
InactiveUS20060124939A1Shine wellSimple manufacturing processSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDischarge efficiencyCrystal structure
A simplified manufacturing process for massive production of LEDs that have superior light emitting efficiency and superior heat discharging efficiency. The method employs a laser lift-off technique instead of the flip-chip bonding technique and it does not require a photolithography process, thereby substantially reducing the process steps and enhancing the heat discharging efficiency. The LED chips are formed as unit chips before irradiating the laser, thereby increasing the yield and realizing the mass production by preventing cleavage of the crystal structures. Heat discharging efficiency is also increased by roughening the surface of an n-type GaN layer. The light emitting area can be widened 30% more than in the flip-chip technique. Thus, the present invention serves to increase the light output and the heat discharging area, thereby drastically enhancing the performance of manufacturing high-output LEDs.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Laser beam irradiating apparatus, laser beam irradiating method, and method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6897889B2Reduce weightIncreased durabilityTransistorInking apparatusLight beamIrradiation laser
A laser beam irradiating apparatus capable of achieving uniform annealing efficiently by employing a simple optical system using laser beams having attenuated regions is disclosed. It is possible to provide a method of irradiating a laser beam using the laser beam irradiating apparatus, and to provide a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device including the laser beam irradiating method in the fabrication sequence thereof.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Phototherapy method for irradiating biological tissue with a series of laser pulse sequences
This invention relates to a method for operation of an irradiation laser whereby laser pulse sequences or pulses of varying length are modified during application such that the comparability of recorded transients is retained.
Owner:MEDIZINISCHES LASERZENTRUM LUEBECK GMBH
Cold air power spraying and coating method containing laser irradiation
ActiveCN101153393ALow critical speedReduce hardnessHeat inorganic powder coatingOptoelectronicsLaser beams
The invention relates to the cold gas dynamic spray technology and the laser technology, in particular to a cold gas dynamic spray method comprising laser irradiation, wherein, compressed gas which carries with metallic powder impacts against the surface of a plaque at supersonic speed to form a circular spray spot on the surface of the plaque; meanwhile, an elliptic irradiation laser speckle is formed directly ahead of the circular spray spot through laser beam irradiation; moreover, the elliptic irradiation laser speckle and the circular spray spot are partly overlapped. The invention can substantially reduce the particle critical speed during cold gas dynamic spray and increases splicing efficiency and strength to ensure structural stability of spray particles, thereby improving coating performance.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Manufacturing method of structural body, droplet discharging head and droplet discharging device
InactiveUS20050142812A1Avoid complex processLow costDecorative surface effectsWriting implementsEngineeringLaser beams
Provided is technology capable of avoiding complex processes and high costs while securing the protection of the functional unit upon forming a device including a glass substrate. A manufacturing method of a structural body structured with a bonding body formed from a glass substrate and a semiconductor substrate, including a first step of forming a first functional unit as a structural element of the structural body on one face of the glass substrate; a second step of bonding the semiconductor substrate to one face of the glass substrate so as to cover the first functional unit; a third step of forming an affected zone extending in the thickness direction of the glass substrate by irradiating a laser beam from the other face side of the glass substrate and scanning the focal point of the laser beam in the thickness direction of the glass substrate; and a fourth step of forming a hole in the glass substrate by etching the glass substrate and removing the portion along the affected zone.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method for measuring thickness of substrate and equipment for processing substrate
ActiveCN101372090AWon't hurtThere will be no adverse conditions of bending strength dropSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementLapping machinesInterior spaceEngineering
The invention provides a method for measurement of thickness of a substrate and a processing device for the substrate, when thickness of the substrate is measured by interference of a laser, a stable measurement value is attainable and is not influenced by processing water. A cylindrical shield (74) is connectively arranged on an opening of a laser head portion (70), a wafer (1) is irradiated by the laser (L) from a laser irradiation end (71) on condition that an interior space (75) of the shield (74) is filled with the water 9W) supplied from a water supply pipe (76). The laser (L) irradiates the end (71) to irradiate the wafer (1). The laser (L) irradiates the wafer (1) by permeating through a glass plate (73) of the laser head portion (70) and the water (W) in the interior space (75), thickness of the wafer (1) is detected by means of an interference wave that is generated by reflective lights of a lower surface (surface (1a)) and a processing surface (back (1b)) of the wafer (1). Entry of the grinding water (the processing water) to a laser irradiation region is cut off to maintain the laser irradiation in a fixed state.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Laser-welded article
InactiveUS20070065659A1Improve welding strengthGood lookingLayered productsThin material handlingExothermic weldingIrradiation laser
A laser-welded article comprises: an integral construction of piled workpieces, that are welded by exothermic through irradiating laser and include thermoplastic resin, comprises of a laser-transmissible-absorptive molded workpiece including a thermoplastic resin and 0.001 to 0.3 weight % of colorant consisting of nigrosine which has an absorption coefficient: ε for a ray of 940 nm ranging form 4000 to 7000, that transmits laser partially and absorbs laser partially, and a laser-absorptive molded workpiece including a thermoplastic resin and 0.1 to 5 weight % of diverse colorant comprising of nigrosine and / or carbon black, that absorbs the laser.
Owner:ORIENT CHEM INDS
Laser lap welding method
InactiveUS20120211474A1Inhibition formationIncreased space requirementLaser beam welding apparatusOptical axisIrradiation laser
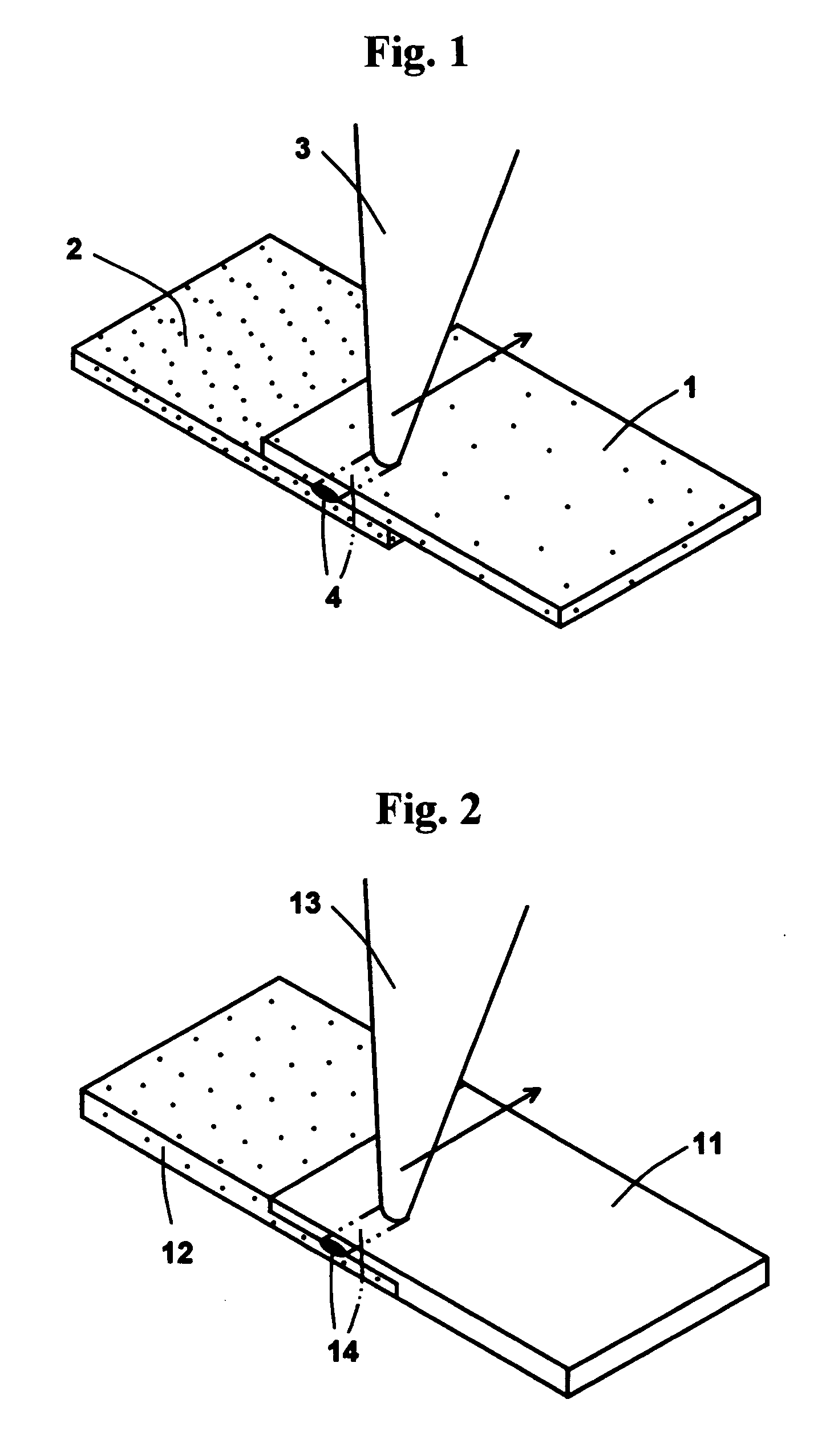
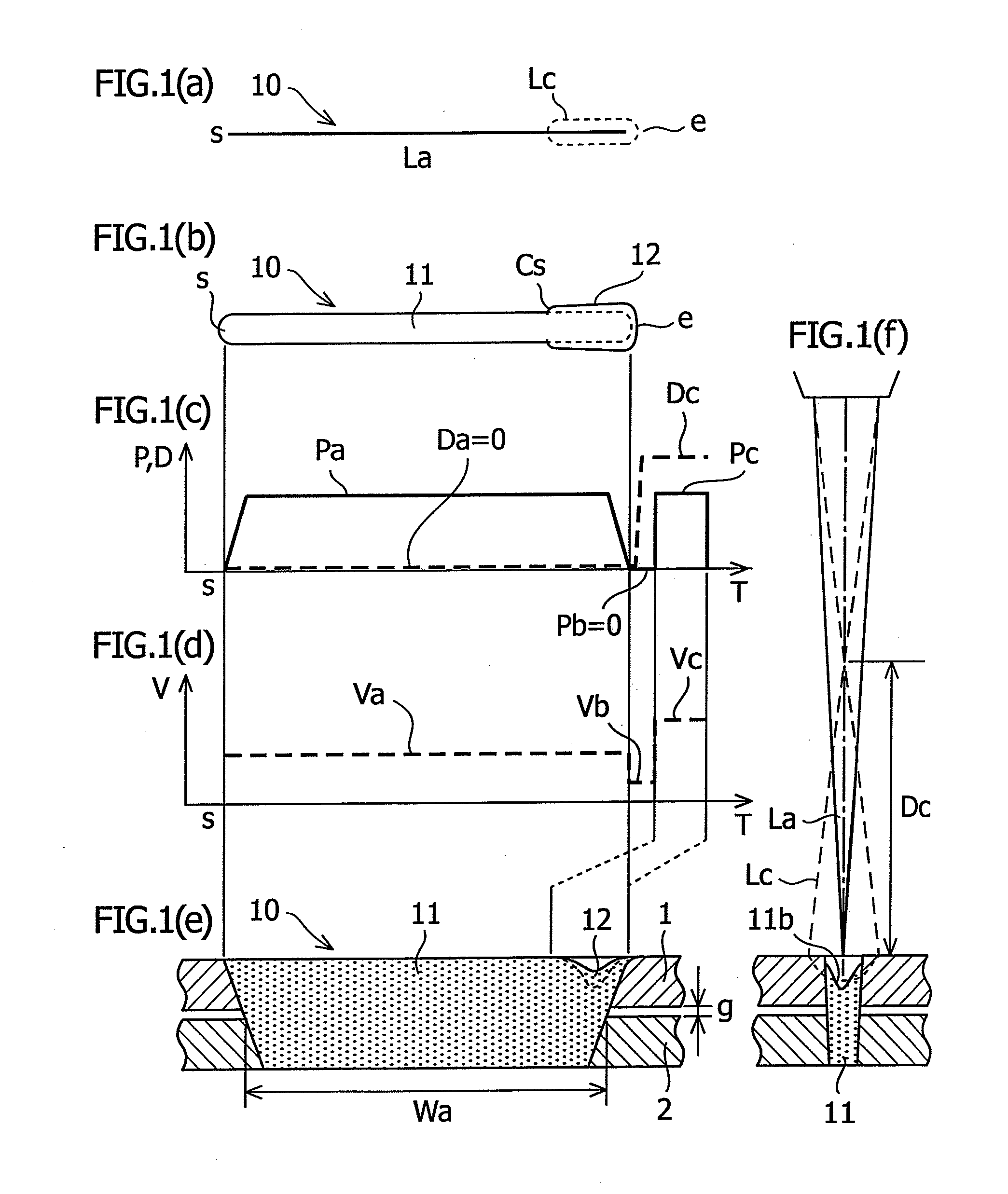
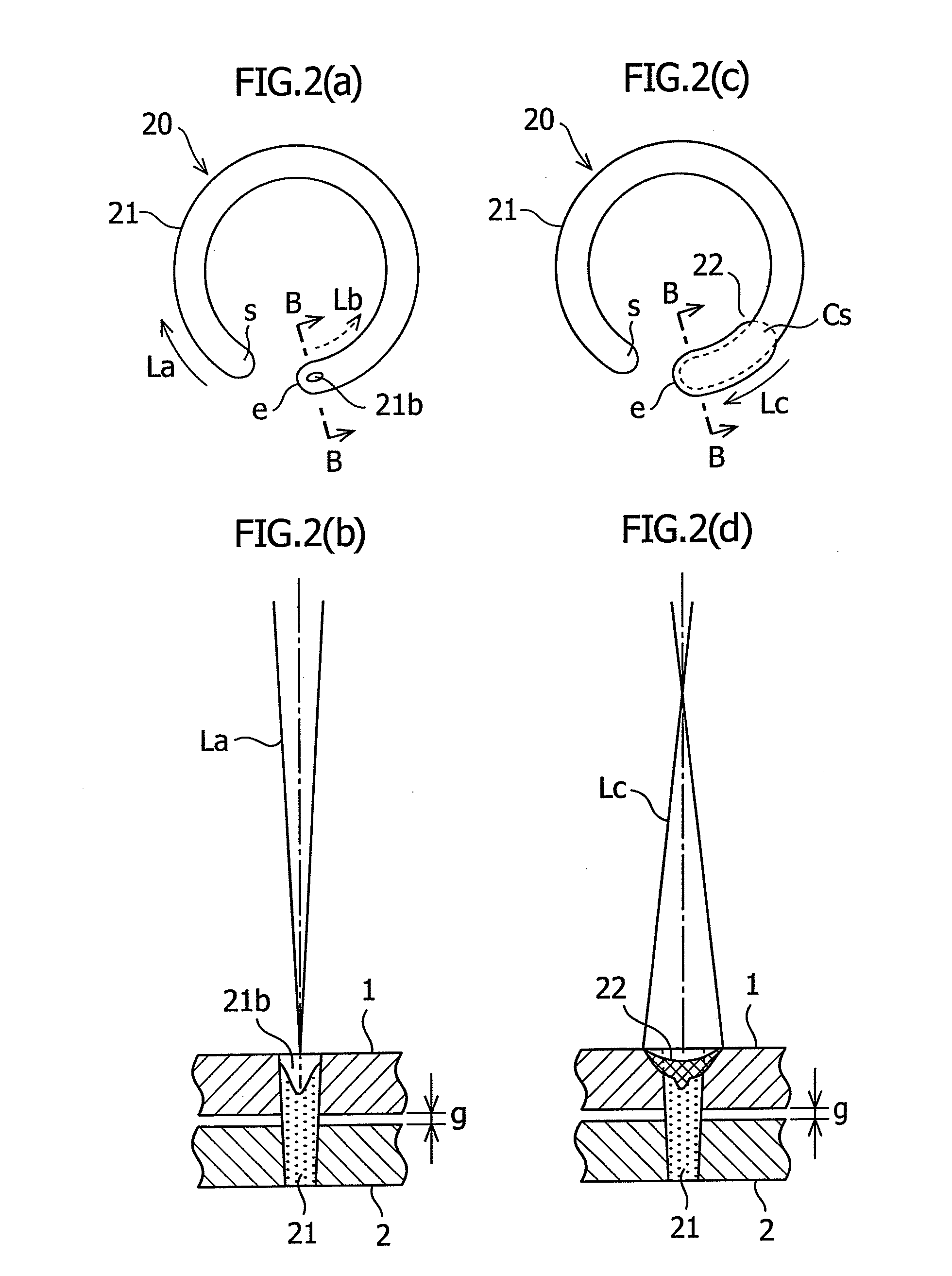
To provide a laser lap welding method including: performing lap welding (11; 21) by irradiating a laser beam (La) on a plurality of overlapped workpieces (1, 2); and irradiating, after a very short interruption time period of the laser beam irradiation, a defocused laser beam (Lc) on a terminating end (12; 22) of the lap welding. Preferably, the laser lap welding method including: interrupting the irradiation of the laser beam for a very short time period and moving, during the interruption time period, the optical axis of the laser beam from the terminating end of the lap welding to the side of the starting end of the lap welding; and irradiating a defocused laser beam from the position to which the optical axis of the laser beam is moved, to the terminating end of the lap welding.
Owner:SUZUKI MOTOR CORP
Laser processing device
ActiveCN102091869AEffective guidanceInhibition byWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesLaser processingIrradiation laser
The invention provides a laser processing device, which is capable of effectively collecting and discharging dust like debris generated by irradiating laser ray from a condenser to an object to be processed. The laser ray irradiation component comprises a laser ray oscillator, a condenser having a condensing lens for condensing laser rays, and a dust discharging component which is disposed at the end of the condenser near the downstream side of the laser ray irradiation direction. The dust discharging component comprises a dust collector, consisting of an upstream sidewall, a downstream sidewall and an outer sidewall. The upstream sidewall is provided with a first opening which enables the laser ray irradiated from the condenser to pass and acquire air obtain. The downstream sidewall is provided with a second opening which enables the laser ray irradiated through the first opening to pass and suck dust. The outer sidewall is connected to the upstream sidewall and the downstream sidewall, forming a dust collecting room. The outer sidewall is provided with an exhaust outlet enabling the dust collecting room and a suction source to commutate with each other. An outer air acquiring channel which enables the first opening to communicated with the outer air is disposed between the dust collector and the condenser.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Powder metal cladding nozzle
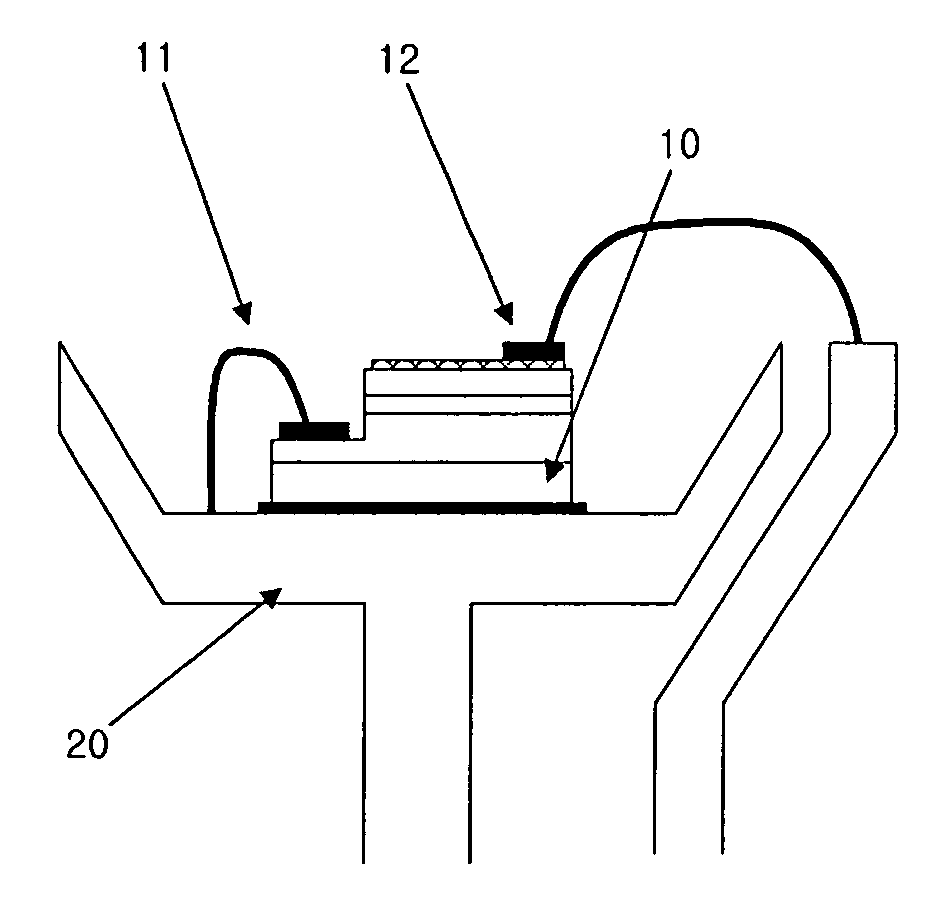
ActiveUS7626136B2Easily form and maintainImprove milling efficiencyLiquid surface applicatorsLiquid spraying apparatusLaser processingMetallurgy
A powder metal cladding nozzle which is coaxially attached to a laser processing head that irradiates a process portion (W) with a laser beam (L) and that discharges powder metal (P) to a laser beam irradiation portion in the process portion (W). The powder metal cladding nozzle includes a body portion (2) that has a ring-shaped powder metal holding space (7) in which the powder metal (P) is held; and a nozzle portion (3) that is connected to the body portion (2) and that has plural discharge passages (18) which are communicated with the powder metal holding space (7) and which open at an outlet (19) for discharging the powder metal (P). The powder metal holding space (7) is formed in the body portion (2) and is divided into plural powder metal holding regions corresponding to plural supply passages (10) that open into the powder metal holding space (7) and that supply the powder metal (P) to the powder metal holding space (7).
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
Multi-irradiation laser quenching method and device
The invention discloses a laser quenching method and device. According to the method, single heating in the conventional laser quenching technology is changed into multi-irradiation heating, or even high-frequency multi-irradiation heating by combining multi-irradiation heating with a quick scanning function of a rotating mirror; the heat conduction process caused by input of laser energy is injected into the surface of a workpiece within short heating time in a multi-stacking mode, so that the accumulation of the laser energy absorbed by a metal base body is increased, and the accumulation of the heat conduction depth is also increased. The device comprises a laser device, a control system, a light guide system, a mechanical motion device and a laser processing head. Even if technical parameters adopt high laser power, and when the scanning speed is high, and an irradiation interval exists, the surface temperature of the metal is always controlled to be below a melting point, and heat can be effectively and continuously expanded from the surface of the workpiece into the workpiece; and therefore, on the premise that the surface of the metal is prevented from being melted, the depth of an austenitizing region on the surface of the workpiece is increased, and the laser quenching efficiency is obviously improved.
Owner:WUHAN HIVALUE INTELASER LTD
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device, and laser irradiation apparatus
InactiveUS20050026401A1Improve mobilityUniform characteristicsTransistorFrom solid stateGrid patternDevice material
It is an object of the present invention to provide a method for manufacturing a crystalline semiconductor film comprising the steps of crystallizing with the use of the metal element for promoting the crystallization to control the orientation and irradiating the laser once to form a crystalline semiconductor film having a small crystal grain arranged in a grid pattern at a regular interval. In the present invention made in view of the above object, a ridge forms a grid pattern on a surface of the crystalline semiconductor film in such a way that a crystalline semiconductor film is formed by adding the metal element for promoting the crystallization to the amorphous semiconductor film and the pulsed laser whose polarization direction is controlled is irradiated thereto. As the means for controlling the polarization direction, a half-wave plate or a mirror is used.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method of forming microstructure, laser irradiation device, and substrate
InactiveUS20130029093A1Easy to controlConstant speedDecorative surface effectsLayered productsOptoelectronicsPicosecond
A method of forming a microstructure includes a Step (A) of forming a modified region in a substrate by irradiating a laser beam having a pulse duration on the order of picoseconds or shorter on a region where a pore-like microstructure is to be provided, and scanning a focal point at which the laser beam is converged; and a Step (B) of forming a microstructure by performing an etching process on the substrate in which the modified region has been formed, and removing the modified region, where a linear polarized laser beam is used as the laser beam in the Step (A), and the laser beam is irradiated so that an orientation of a linear polarization has a certain direction with respect to a direction of scanning the focal point.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com