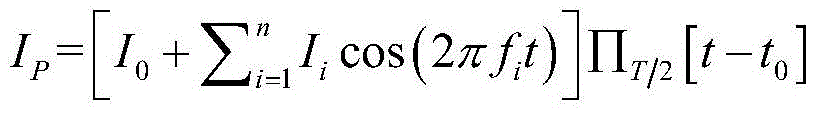Patents
Literature
224results about How to "Reduce laser power" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
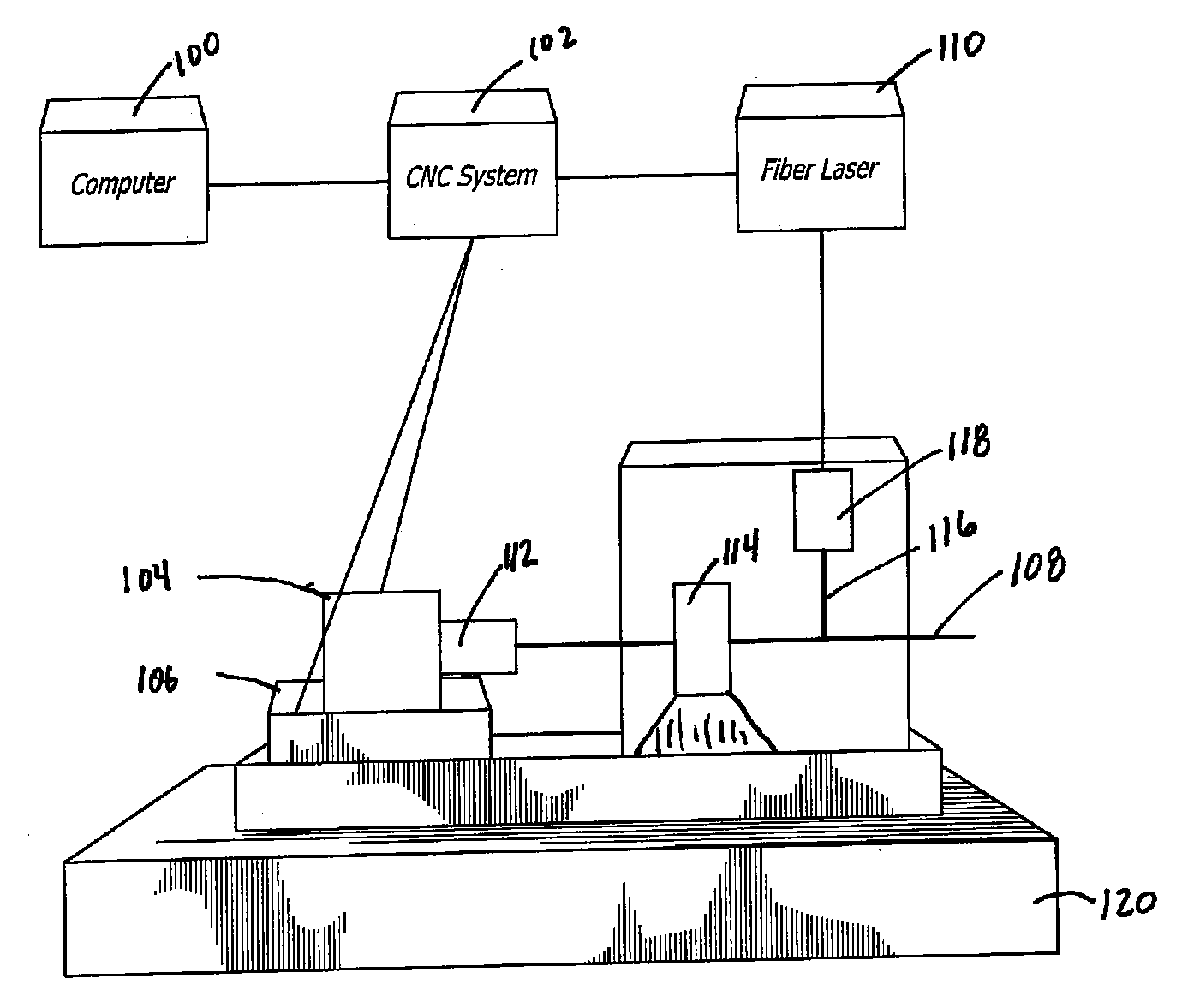
Pulsed Synchronized Laser Cutting of Stents
InactiveUS20070228023A1High resolutionMinimal heat build-upStentsSpecial data processing applicationsPulse controlInsertion stent
A system for pulsed synchronized laser cutting of stents and / or other medical products includes a numerical controller and a machine for moving a tube of material during cutting. A pulsed fiber laser is configured to cut the tube into, for example, a stent, the numerical controller being in communication with the machine and configured to send movement control information to the machine. The numerical controller may also receive movement speed information from the machine. The numerical controller is also in communication with the pulsed fiber laser and is configured to send pulse control information to the pulsed fiber laser. The numerical controller is configured to cause average laser power to decrease by decreasing frequency of laser pulses as stent cutting speed decreases, and to cause average laser power to increase by increasing frequency of laser pulses as stent cutting speed increases.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Method for operation of laser
This invention relates to a method for operation of an irradiation laser whereby laser pulse sequences or pulses of varying length are modified during application such that the comparability of recorded transients is retained.
Owner:MEDIZINISCHES LASERZENTRUM LUEBECK GMBH
Continuous coating installation, methods for producing crystalline solar cells, and solar cell
InactiveUS20100024865A1Improve throughputIncrease powerCellsFinal product manufactureElectrical batteryLaser crystallization
A continuous coating installation is disclosed. The installation includes a vacuum chamber having a supply opening for supplying a substrate to be coated and a discharge opening for discharging the coated substrate. The installation also includes a physical vapour deposition device for coating a surface of the substrate, and a laser crystallization system for simultaneously illuminating at least one sub-partial area of a currently coated partial area of the surface of the substrate with at least one laser beam. The installation further includes a transport device for transporting the substrate in a feedthrough direction from the supply opening to the discharge opening and for continuously or discontinuously moving the substrate during the coating thereof in the feedthrough direction.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH +1
Laser sintering method with increased process precision, and particles used for the same
InactiveUS20060159896A1Reduces temperature inhomogeneityReduce laser powerGlass/slag layered productsWood layered productsMaterials scienceRapid prototyping
In the rapid prototyping method of selective laser sintering, temperature gradients occur inside and between individual layers, leading to component deformation which is intolerable at least for high-quality components. The air of the invention is to provide a method for selective laser sintering, whereby the temperature inside the built-up particle cake is as homogeneous as possible. To this end, particles containing at least one material having a maximum softening temperature of approximately 70° C. are used.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Optical recording medium and method for its initialization
InactiveUS20030008235A1Reduce laser powerRadiation applicationsLayered productsLight beamRecording layer
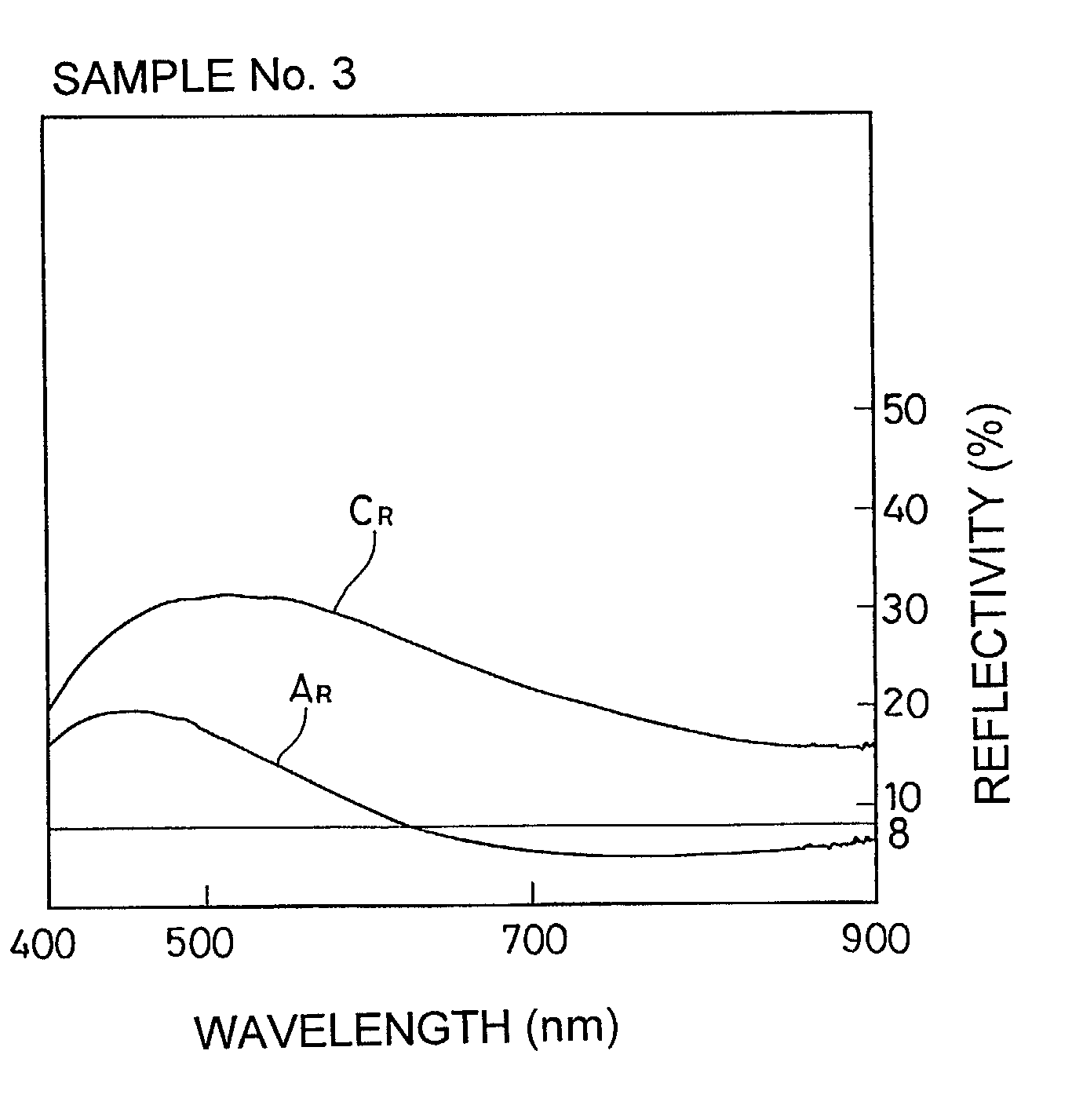
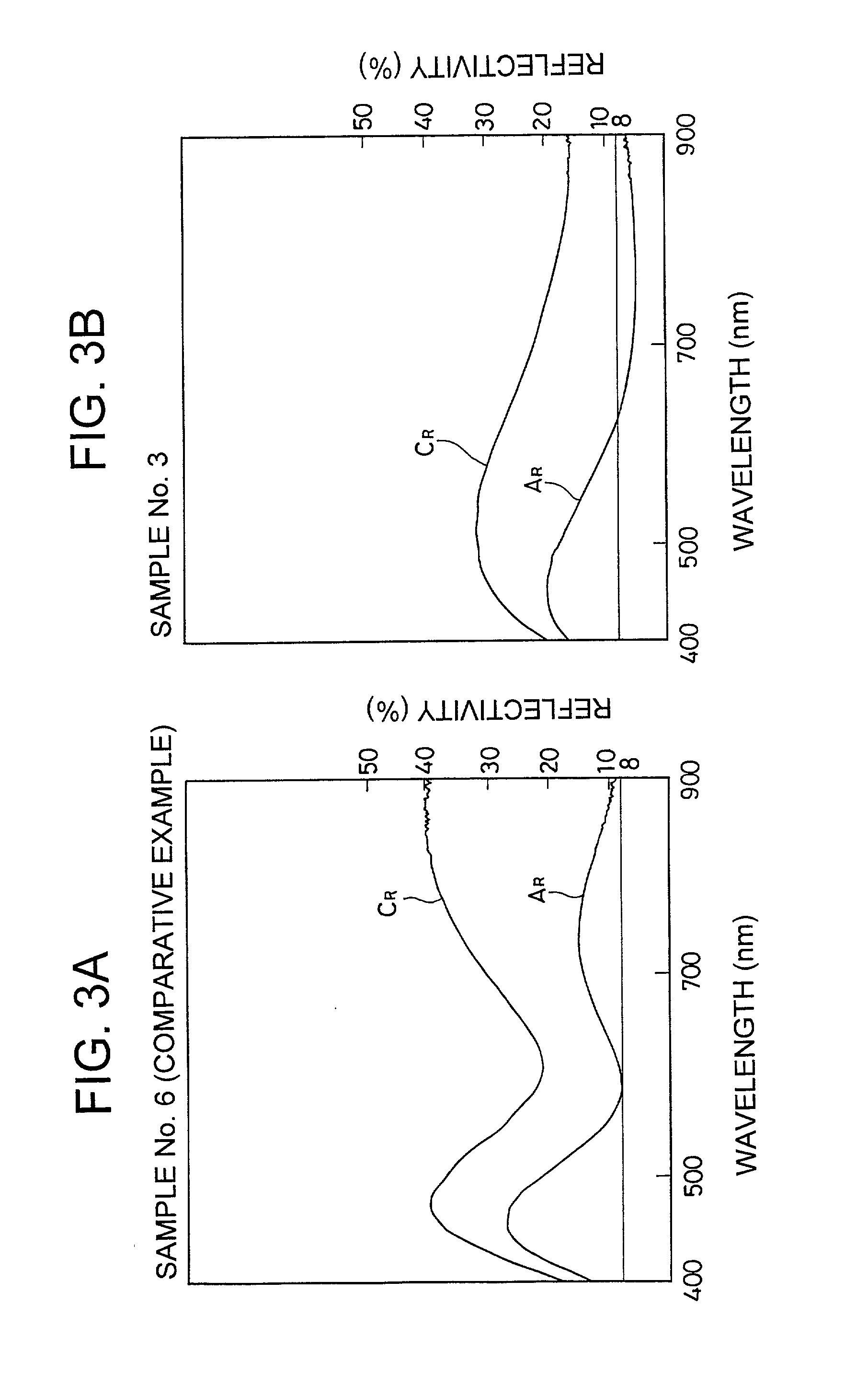
A phase change optical recording medium is provided wherein the power of the laser beam per unit area required in the initialization is reduced. The optical recording medium has a phase change recording layer satisfying the relations: A.sub.I.ltoreq.8.0%, and C.sub.I / A.sub.I.gtoreq.3.0 when the medium is initialized with a light beam having a wavelength .lambda..sub.I, and said recording layer exhibits a reflectivity A.sub.I in amorphous region and a reflectivity C.sub.I in crystalline region at said wavelength .lambda..sub.I.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Scanner system
InactiveUS7046266B1Reduce laser powerLose sensitivityElectrographic process apparatusPhotomechanical exposure apparatusSerial scanningLight beam
A method of scanning for writing a pattern on a surface, including providing a scanning beam comprised of a plurality of independently addressable sub-beams, scanning the surface with the scanning beam a plurality of times, the sub-beams scanning the surface side-by-side in the cross-scan direction, each sub-beam being modulated to reflect information to be written, and overlapping the beams in successive scans in the cross scan direction such that all written areas of the surface are written on during at least two scans.
Owner:LASER IMAGING SYST
Method and apparatus for processing substrates using a laser
ActiveUS20120067858A1Improve bending strengthProcessing quality is constantFine working devicesGlass severing apparatusPulse durationSemiconductor
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for processing substrates, such as glass and semiconductor wafers. The method comprises directing to the substrate from a laser source a plurality of sequential focused laser pulses having a predetermined duration, pulsing frequency and focal spot diameter, the pulses being capable of locally melting the substrate, and moving the laser source and the substrate with respect to each other at a predetermined moving velocity so that a structurally modified zone is formed to the substrate. According to the invention, the pulse duration is in the range of 20-100 ps, pulsing frequency at least 1 MHz and moving velocity adjusted such that the distance between successive pulses is less than ⅕ of the diameter of the focal spot. The invention can be utilized, for example, for efficient dicing, scribing and welding of materials which are normally transparent.
Owner:CORELASE
Phototherapy method for irradiating biological tissue with a series of laser pulse sequences
This invention relates to a method for operation of an irradiation laser whereby laser pulse sequences or pulses of varying length are modified during application such that the comparability of recorded transients is retained.
Owner:MEDIZINISCHES LASERZENTRUM LUEBECK GMBH
Stone-plastic composite powder for laser sintering 3D manufacturing technology and preparation method of stone-plastic composite powder
ActiveCN103881371ALow costReduce consumptionAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresManufacturing technologyNylon 12
The invention provides stone-plastic composite powder for laser sintering 3D manufacturing technology and a preparation method of the stone-plastic composite powder, and relates to composite powder for laser sintering 3D manufacturing technology as well as a preparation method and a use method of the composite powder. The stone-plastic composite powder provided by the invention is used for solving the technical problems of low strength of a sintered workpiece prepared from a wood-plastic composite material and a rice husk powder-hot melt adhesive composite material for the existing laser sintering, and high cost of a sintered workpiece prepared from metal powder or ceramic powder. The stone-plastic composite powder for laser sintering 3D manufacturing technology provided by the invention is composed of nylon 12 powder and limestone powder. The preparation method comprises the steps of adding the nylon 12 powder and the limestone powder into a ceramic grinding tank for grinding and mixing to obtain the stone-plastic composite powder. During laser sintering, a laser beam scans a sub-region in a manner of scanning on a horizontal plane, and the laser power is 15-20 W, so that the laser power is low. The stone-plastic composite powder provided by the invention is applied to the laser sintering 3D manufacturing field.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +2
Laser double-side synchronous welding system with skin-skeleton structure
InactiveCN102059455AIncrease flexibilityEasy to adjustLaser beam welding apparatusLight beamEngineering
The invention discloses a laser double-side synchronous welding system with a skin-skeleton structure, relating to a laser double-side synchronous welding system. The laser double-side synchronous welding system aims to solve the problems that a spectroscope is easy to damage by ablation because the traditional welding device with double light beams needs high laser power, and also solve the problems of inconvenience of regulation of laser incident angle, narrow regulation range and limited selection on defocussing amount during welding. The sleeve of the laser double-side synchronous weldingsystem is sleeved on a third pipe barrel; a bearing is arranged between the sleeve and the third pipe barrel; a calibration loop is sleeved on the third pipe barrel; a first junction plate and a wirefeeder are connected by a second junction plate; a heightening block is screwed on the lower end of a fourth pipe barrel; an air cutter is provided with at least one side blowing body hole; a nozzle and a third junction plate are connected via a flexible pipe; two welding devices are oppositely arranged above a clamping device of a test piece to be welded; and a skin-skeleton is clamped on the clamping device of a test piece to be welded. The laser double-side synchronous welding system is suitable for welding the skin-skeleton structure.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Apparatus and method for dynamic cellular probing and diagnostics using holographic optical forcing array
InactiveUS20090128825A1Quick and sterile measurementTechnique is very sensitiveHolographic optical componentsMaterial analysis by optical meansPhase shiftedPhysics
The present invention utilizes a holographic optical forcing array for dynamic cellular probing and diagnostics. A holographic optical trapping system generates optical forces on objects so that deformations thereof may be quantified. In one embodiment, digital holography is used to generate an interference pattern, and an analysis thereof determines the phase profile which yields a measurement of the objects' shape deformation using only one image. In another embodiment, phase-stepped holography allows the phase profile of an object to be measured using only one image, by using a holographic optical element to make phase-shifted replicas of the beam in space. In another embodiment, the optical forcing array applies optical forces to beads placed on the objects' surface, deforming the objects. The beads' position is determined by applying Mie theory, and analysis thereof yields the three dimensional position of the beads, and a measurement of the deformation displacement on the objects' surface.
Owner:ARRYX INC
Thermally-assisted recording (TAR) head with conductive layer between the near-field transducer and the write pole
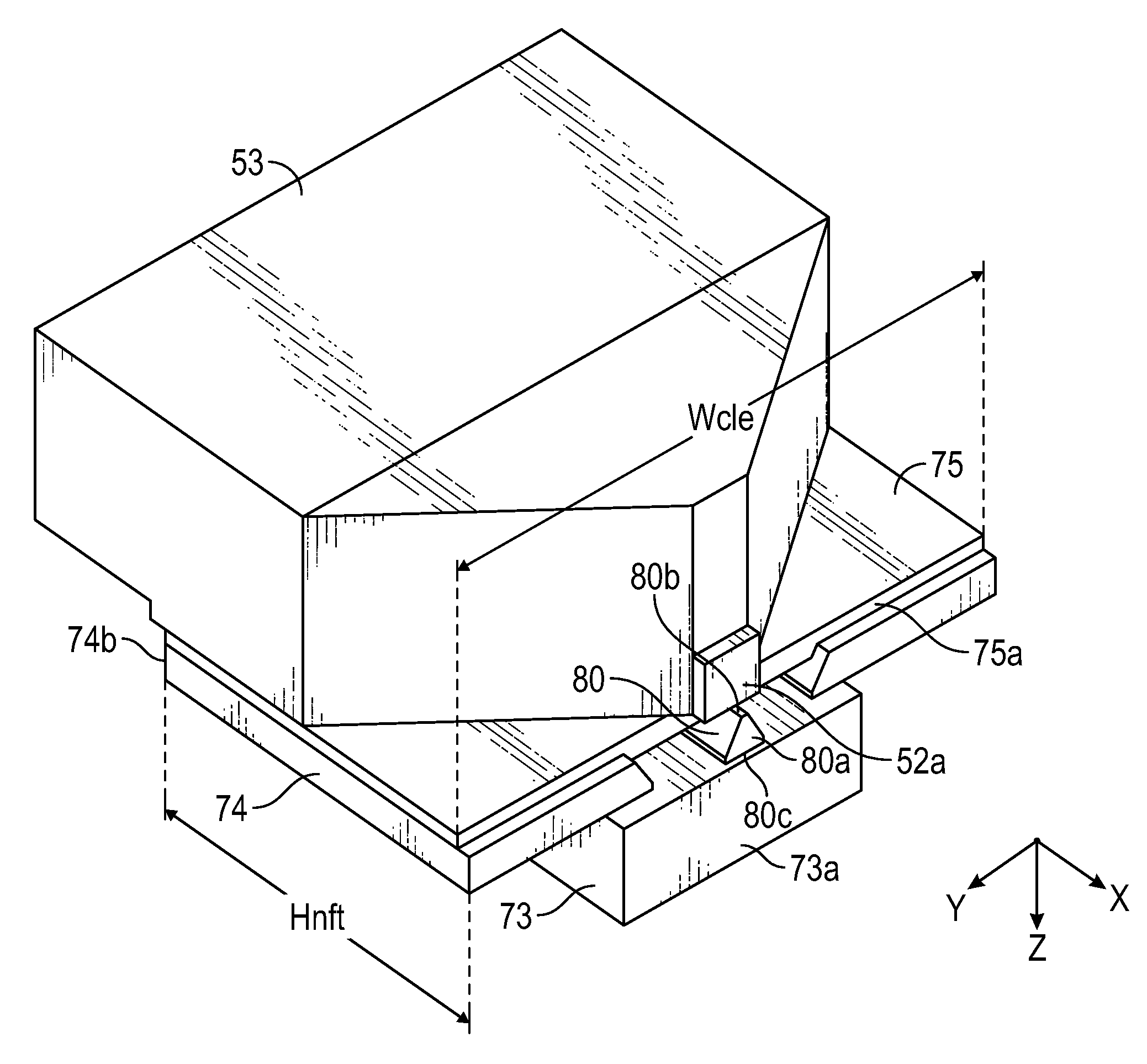
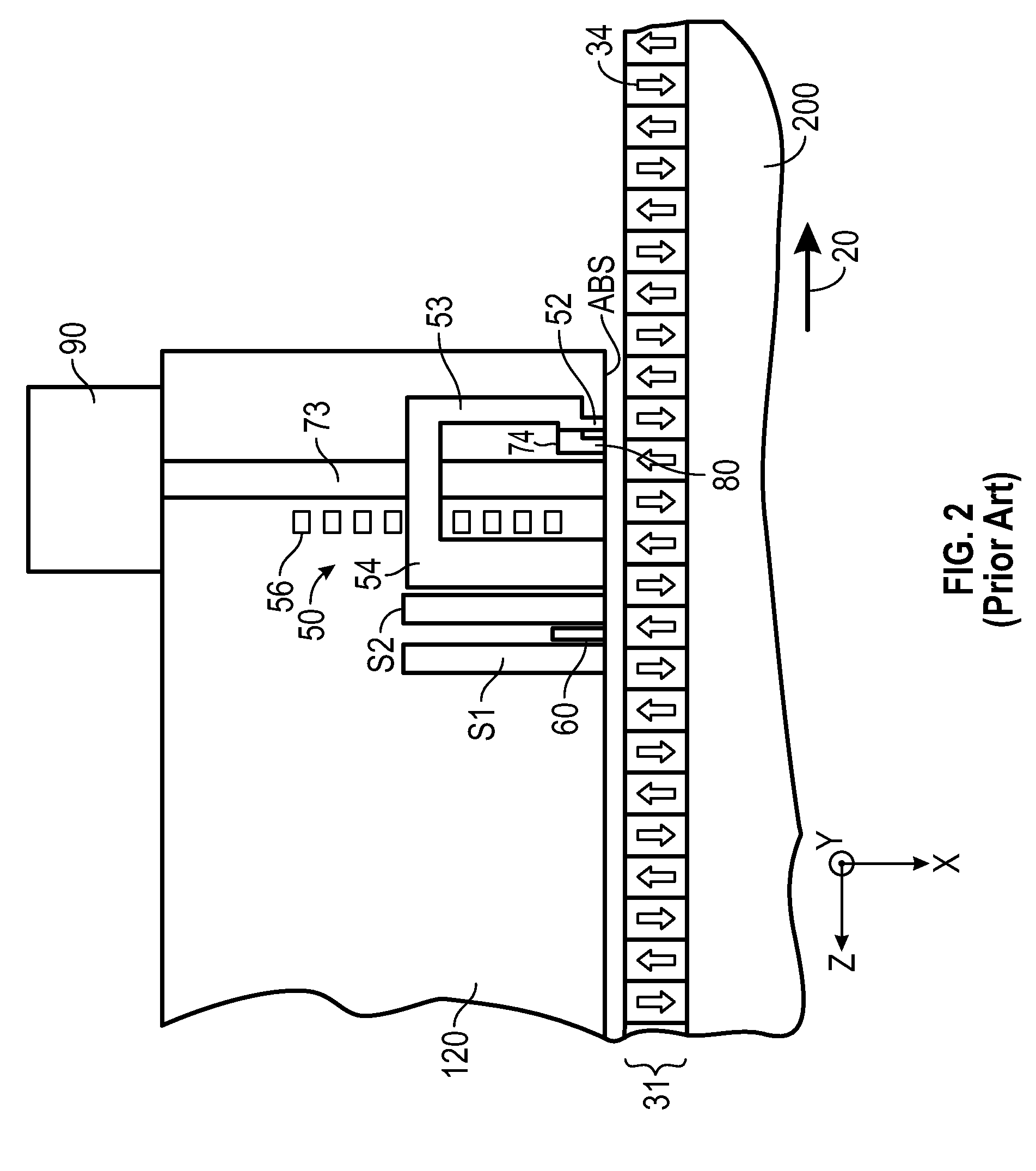
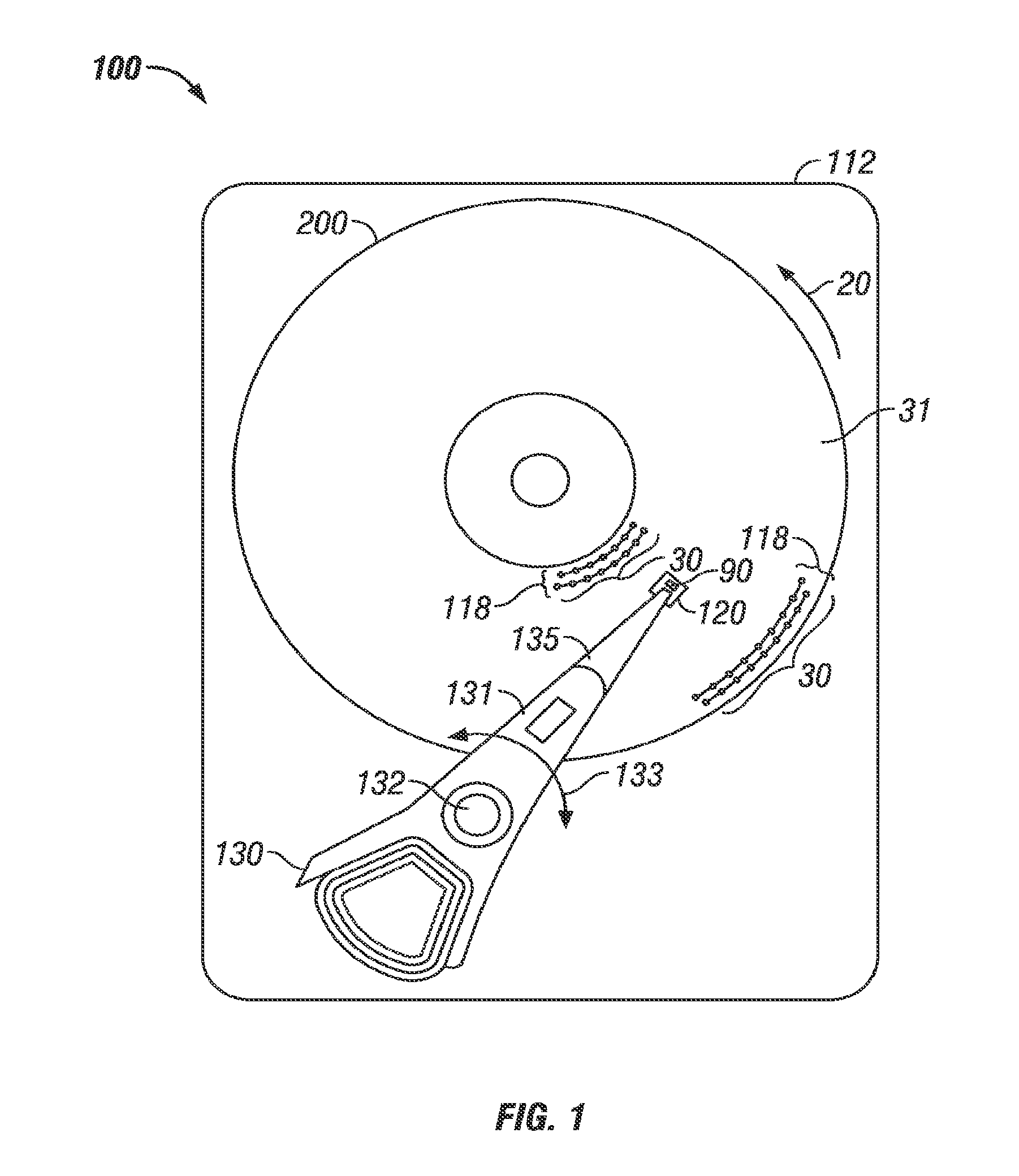
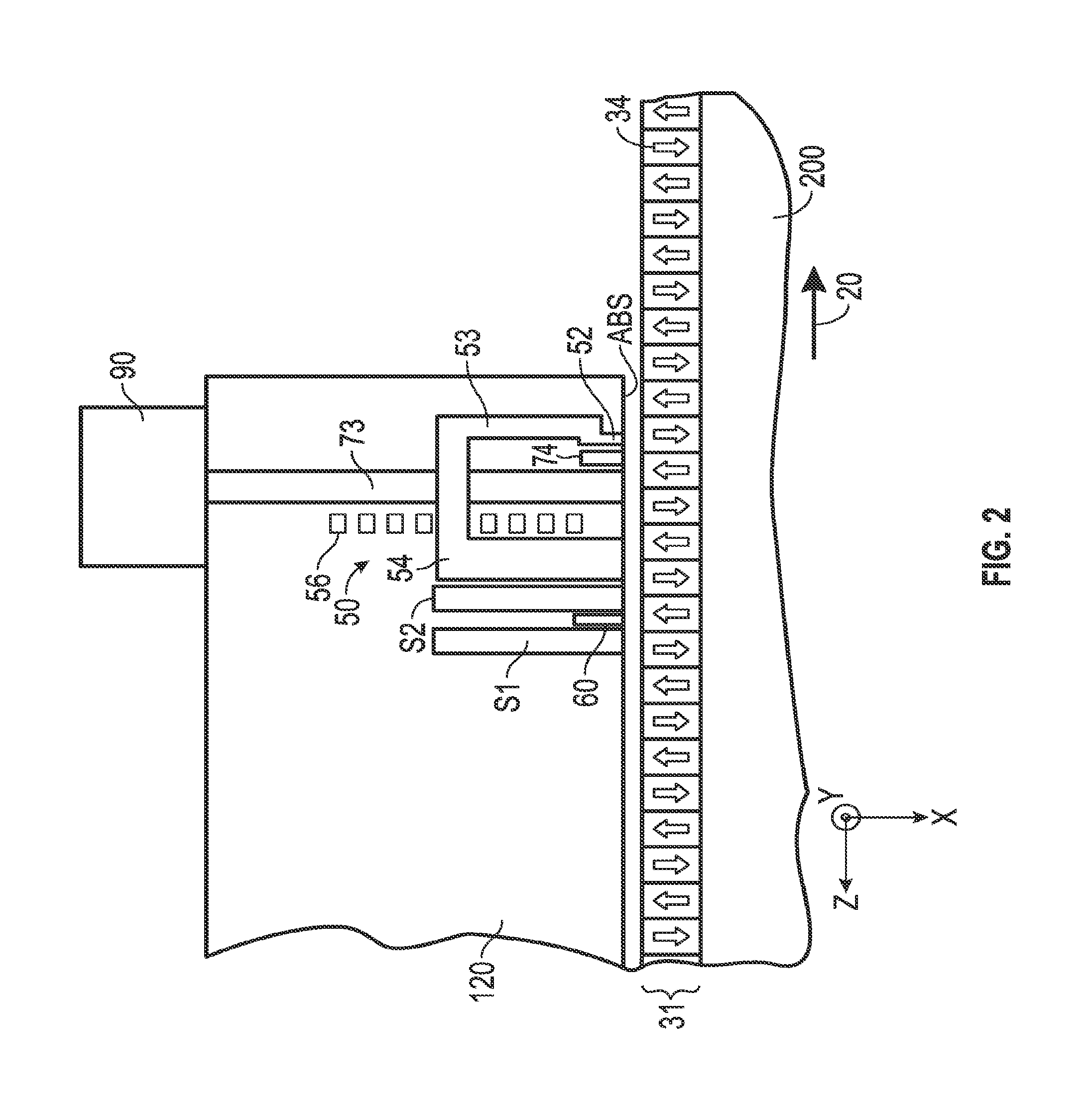
ActiveUS8619516B1Reduce laser powerReduce temperature riseCombination recordingRecord information storageAir bearingTransducer
A thermally-assisted recording (TAR) head for recording data in data tracks of a TAR disk is supported on an air-bearing slider and includes the magnetic write pole, a near-field transducer (NFT), an optical waveguide that directs laser light to the NFT, and an electrically conductive layer between and in contact with the NFT and the write pole. The NFT has an output tip having a generally triangularly-shaped end at the slider's air-baring surface (ABS). The electrically conductive layer is located between the NFT and the write pole and contacts both the NFT output tip and the write pole. The electrically conductive layer has a contact edge that is generally parallel with the ABS but recessed from the NFT output tip end and a cross-track width greater than the cross-track width of the NFT output tip end.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
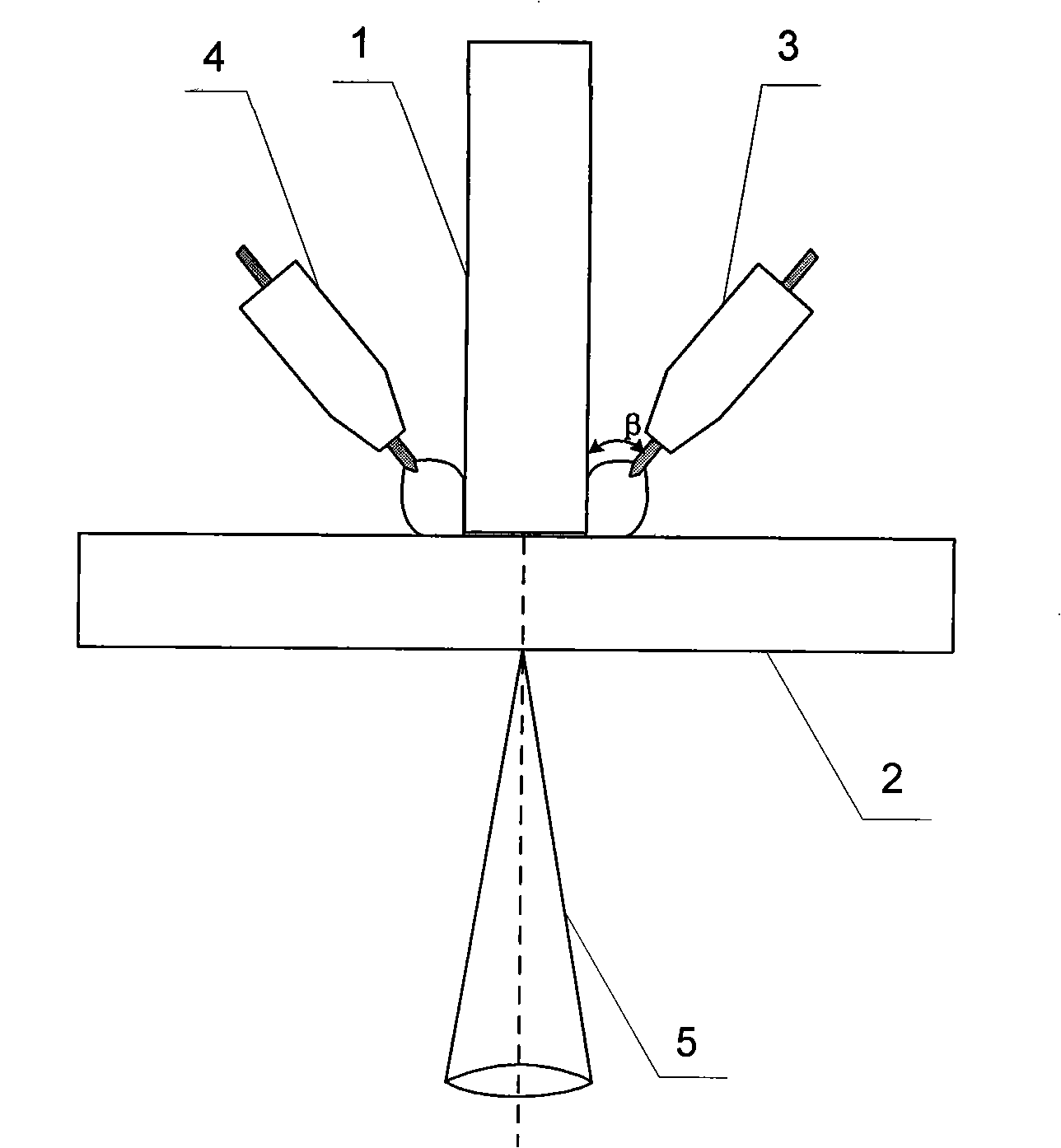
Laser-double arc double sided compound welding method of T shaped joint
InactiveCN101306492AImprove energy utilizationReduce laser powerArc welding apparatusLaser beam welding apparatusElectric arcLight beam
A laser and double-electric-arc double-faced composite welding method for a T-type joint relates to a welding method for laser and electric arc composite welding, and particularly relates to applying the laser and the double-electric-arc double-faced composite welding to a workpiece with a T-type joint to be welded. The invention aims to solve the problems that the single laser penetration welding has strict requirement to the seam fit-up gap and smaller fusion diameter of the faying surface, which results in low shear strength of the seam; and the laser wire filling welding or the double-beam laser synchronous welding process has strict requirement and high cost in the prior T-type joint welding. The laser beams are vertically incident for penetration welding from the top surface of a top plate along the seam formed by the contact of a vertical slab and the top plate of the T-type joint, at the same time, a first electric arc welding gun and a second electric arc welding gun carry out synchronous welding from the two sides of the seam, and the first electric arc welding gun and the second electric arc welding gun are remained to be arranged symmetrically on the left and the right sides of the vertical slab. Compared with the single laser welding, the composite welding method of the invention has the advantages that the capacity usage ratio is improved by more than 30%, the welding speed is increased by more than twice, and the welding efficiency is improved by two to three times.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
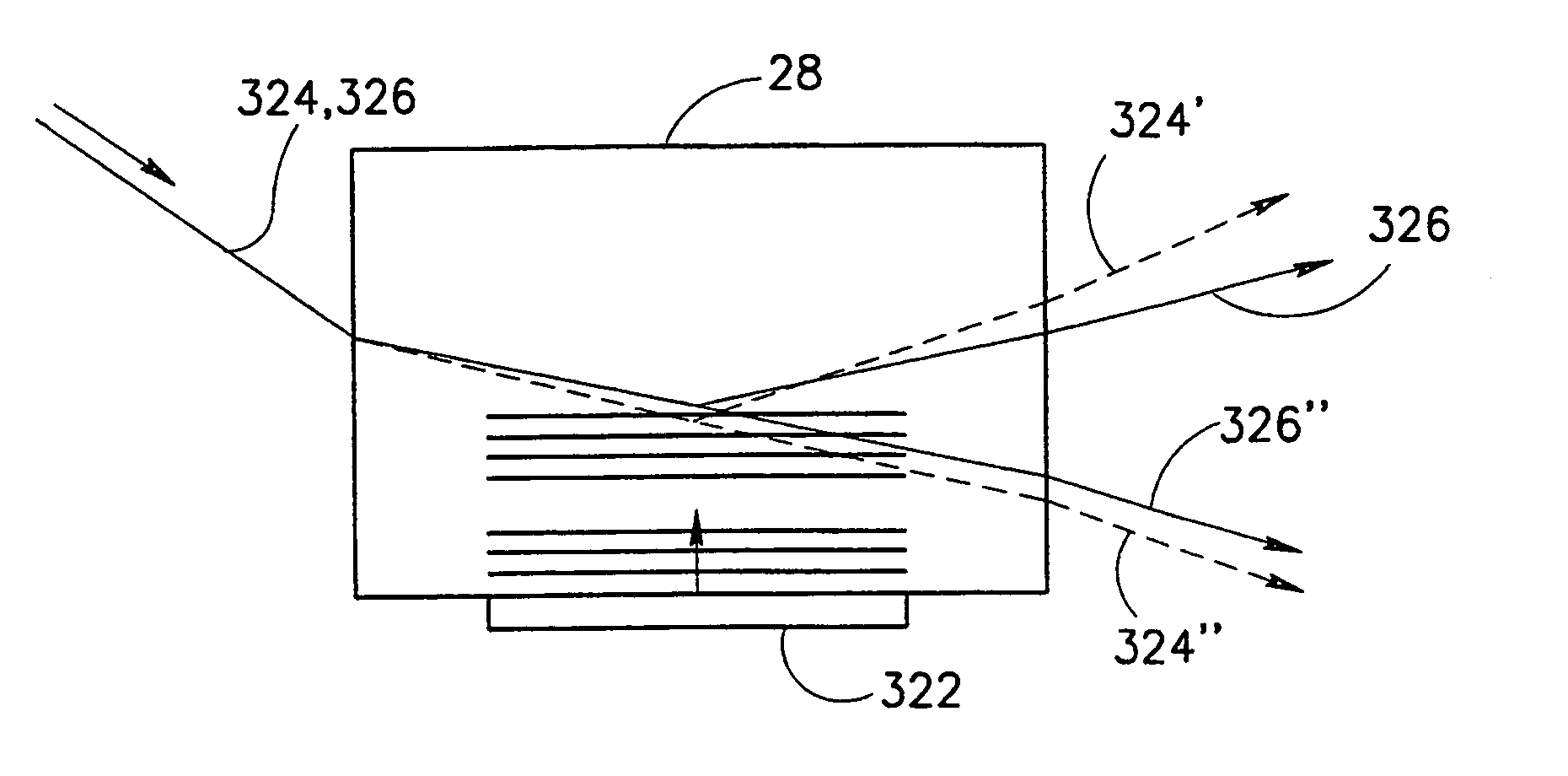
Peak power and speckle contrast reduction for a single layer pulse
InactiveUS7187500B2Reduce laser powerEasy to splitPhotomechanical apparatusGenerators/motorsLeading edgeGrating
A system and method for reducing peak power of a laser pulse and reducing speckle contrast of a single pulse comprises a plurality of elements oriented to split and delay a pulse or pulses transmitted from a light emitting device. The design provides the ability to divide the pulse into multiple pulses by delaying the components relative to one another. Reduction of speckle contrast entails using the same or similar components to the power reduction design, reoriented to orient received energy wherein angles between the optical paths are altered such that the split or divided light energy components strike the target at different angles or different positions. An alternate embodiment for reducing speckle contrast is disclosed wherein a single pulse is passed in an angular orientation through a grating to create a delayed portion of the pulse relative to the leading edge of the pulse.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Method for removing laser welding pores of medium-thick D406A ultra-high-strength steel
InactiveCN105328342AReduce couplingReduce cooling rateLaser beam welding apparatusMaterials scienceSoldering process
The invention provides a method for removing laser welding pores of a medium-thick D406A ultra-high-strength steel, and aims at solving the problem of pores of a medium-thick D406A ultra-high-strength steel plate in welding. The method comprises the following steps: grinding and cleaning a part to be welded; assembling; setting backing weld and filling weld process parameters; controlling the welding process parameters through a robot integration system; arcing through TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas Welding) electric arc; stabilizing the electric arc for 1 to 2 seconds; controlling a laser to emit laser; finally controlling a robot to drive a laser working head and a TIG welding gun to work together to finish the welding process. According to the method, different pore inhibiting measures are carried out for backing weld and filling weld.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
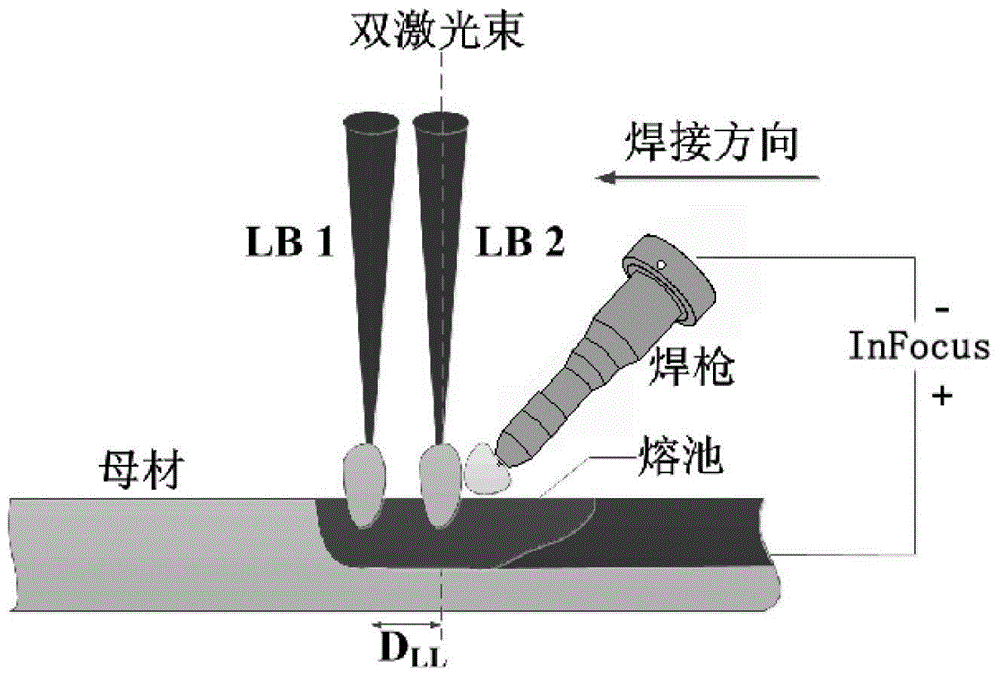
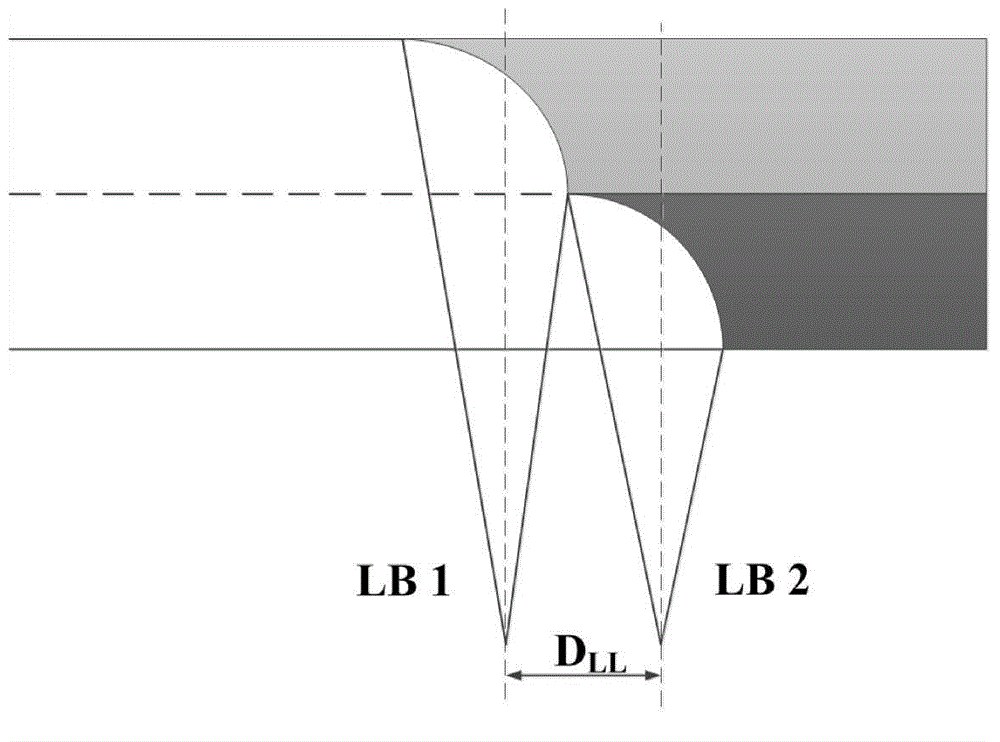
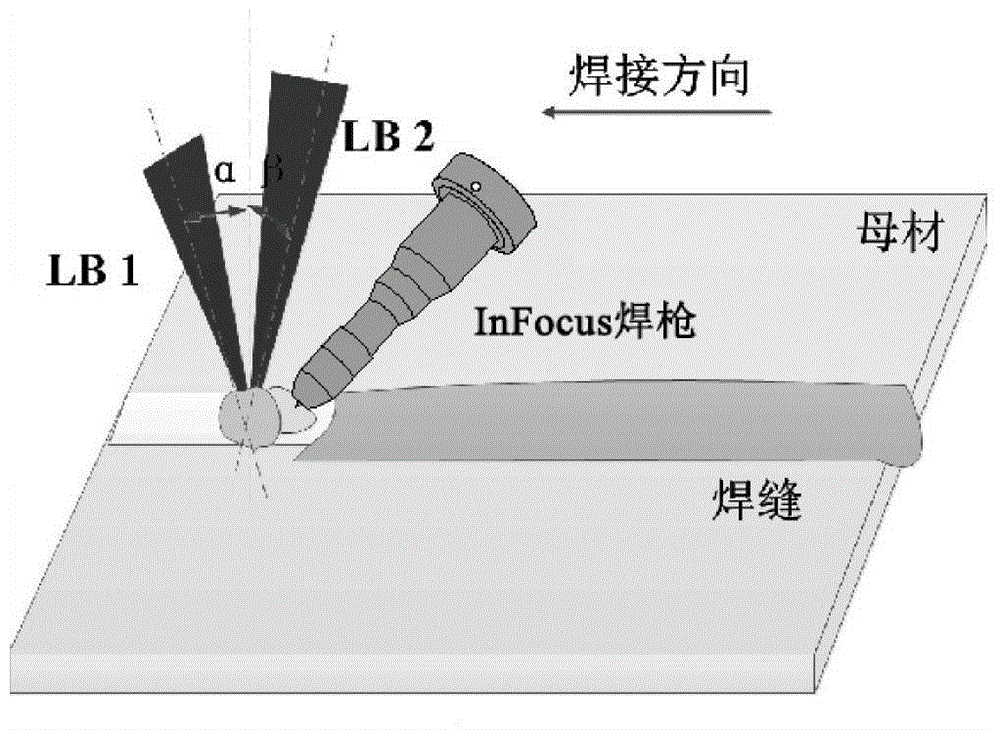
Bifocus laser and InFocus arc hybrid welding method
InactiveCN104985327AImprove energy utilizationIncrease weld penetrationLaser beam welding apparatusElectric arcEngineering
The invention discloses a bifocus laser and InFocus arc hybrid welding method, and relates to a welding method. The method includes the steps that (1) a to-be-welded workpiece is polished or washed; (2) the spot diameter is set to range from 0.1 mm to 0.5 mm, and the defocusing amount ranges from -3 mm to +3 mm; (3) welding parameters are set, wherein the arc current ranges from 50 A to 900 A, an included angle formed between a welding gun and the vertical direction ranges from 25 degrees to 55 degrees, the welding speed ranges from 100 mm / min to 1000 mm / min, the wire feeding speed ranges from 100 mm / min to 600 mm / min, the protection gas is inert gas, and the flow of the protection gas ranges from 15 L / min to 30 L / min; and (4) a switch is started, and laser-InFocus arc welding is carried out. According to bifocus lasers and InFocus, as the InFocus arc fusion depth is larger, and a key hole can be formed through welding, when a medium-thickness plate is welded, the lasers can directly act on the bottom of the key hole generated by the InFocus arc, and the fusion depth is continuously increased.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Thermally-assisted recording (TAR) head with waveguide having tapered region coupled to near-field transducer
ActiveUS8619514B1Reduce laser powerSmall sizeCombination recordingRecord information storageAir bearingTar
A thermally-assisted recording (TAR) head for recording data in data tracks of a TAR disk has an air-bearing slider that supports a near-field transducer (NFT) and an optical waveguide that directs laser light to the NFT. The NFT has an output end at the slider's air-bearing surface (ABS) located between the write pole and the optical waveguide in the along-the-track direction. The NFT output end is generally triangularly shaped with an apex facing the write pole and a back edge wider than the apex in the cross-track axis direction facing the waveguide. The surface of the waveguide facing the NFT back edge is tapered, with a width in the cross-track axis direction at a region recessed from the ABS and a smaller width in the cross-track axis direction at an end near the ABS.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
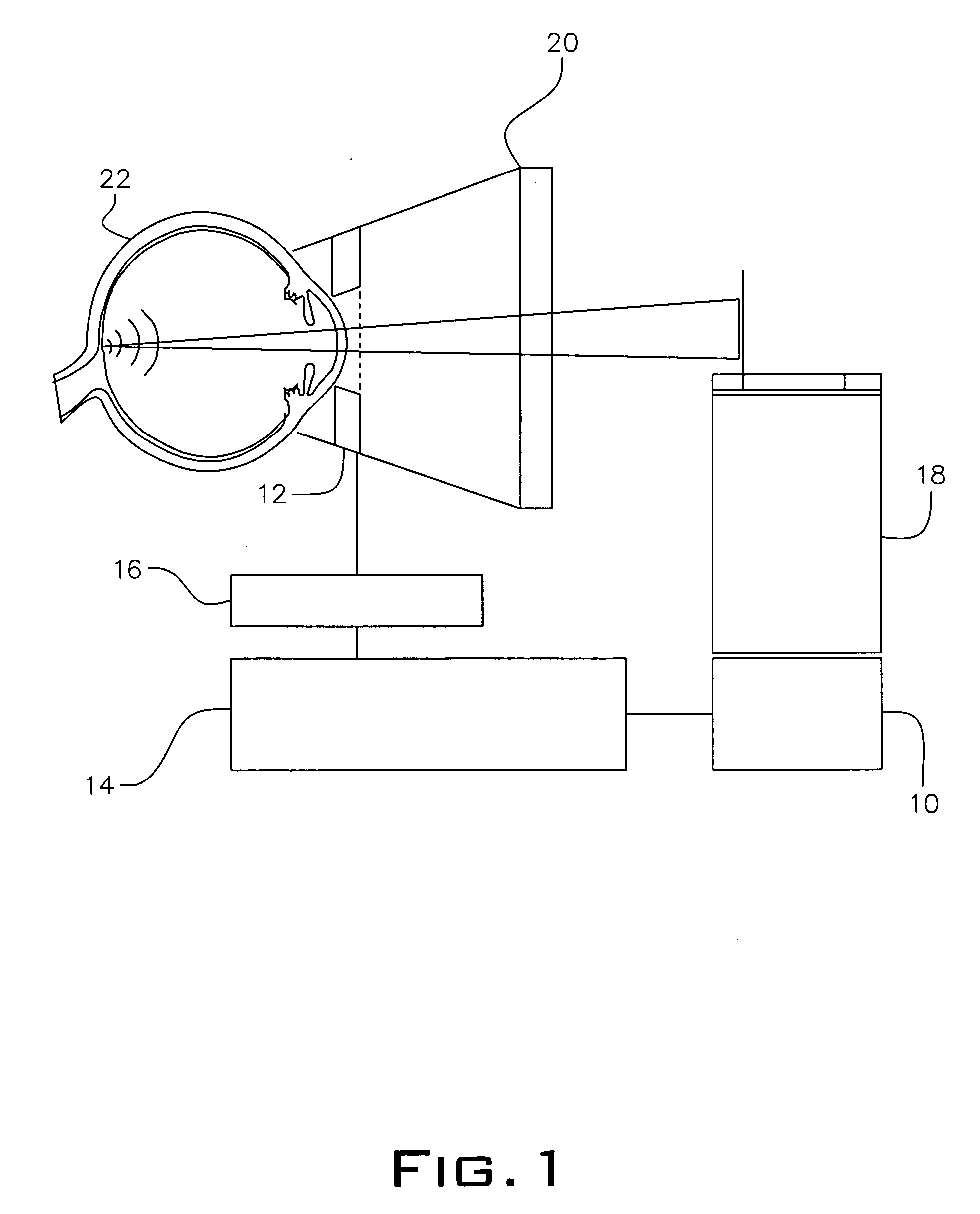
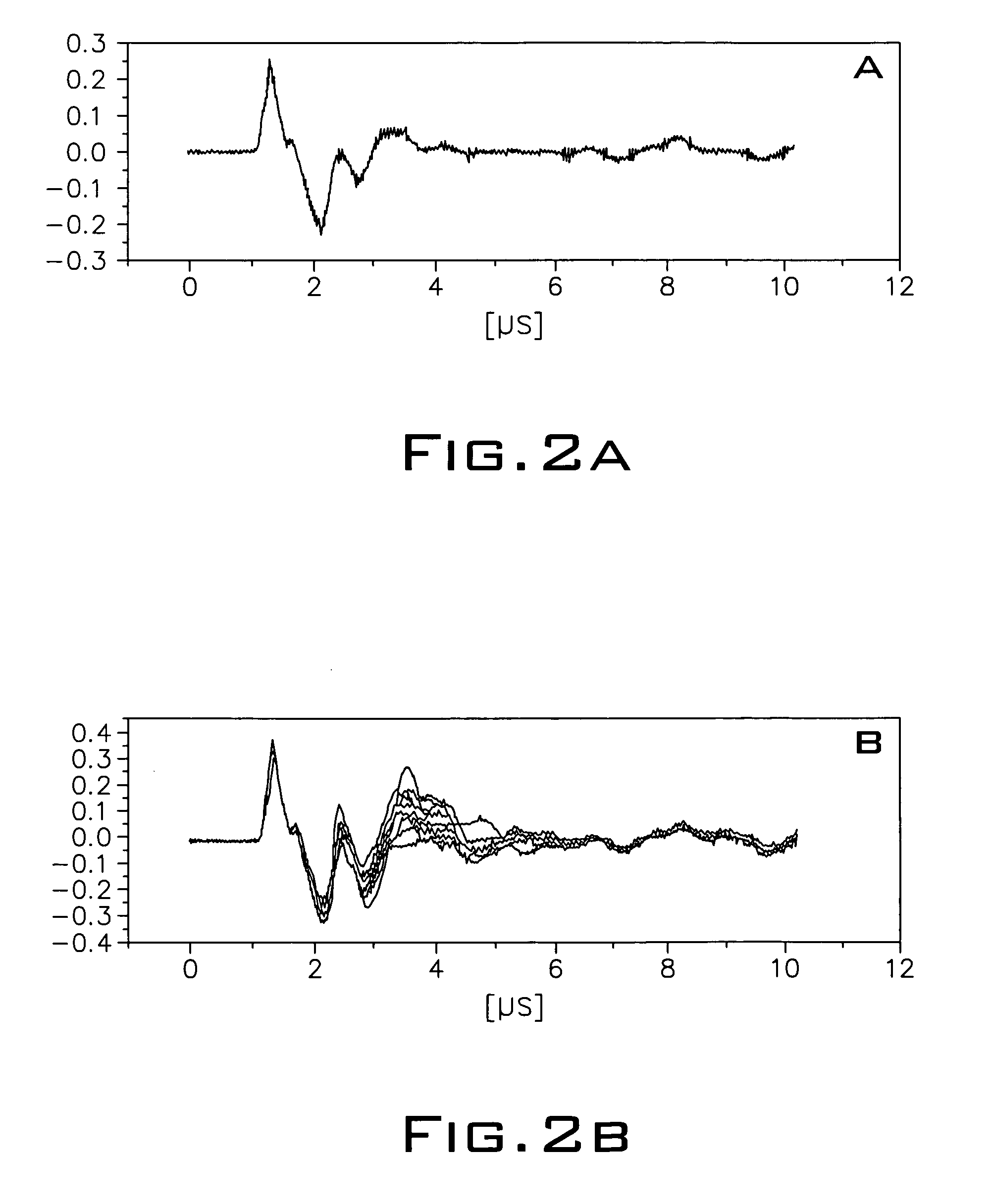
Fundus optical full-field microangiography imaging device and method
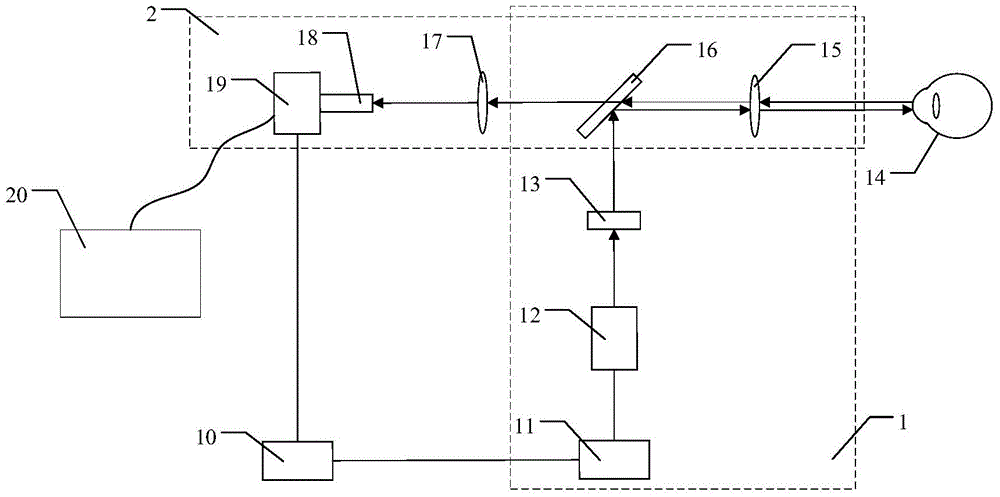
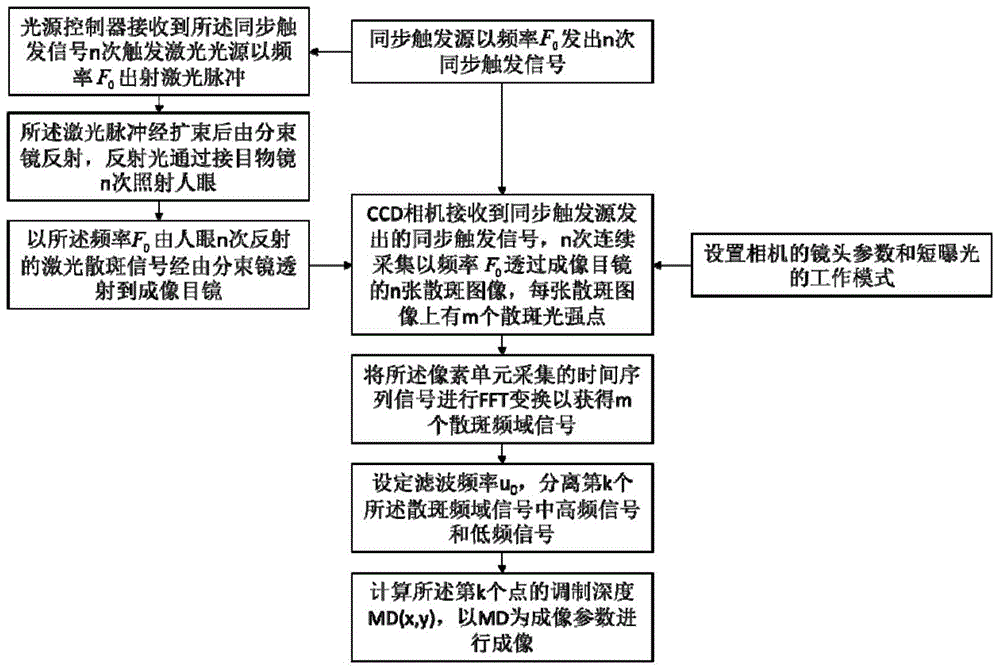
ActiveCN105769117ARestore clarityReal-time monitoringDianostics using fluorescence emissionSensorsOptical pathPhysics
The invention relates to a fundus optical full-field microangiography imaging device and method. The device comprises a fundus illumination optical path, a fundus imaging optical path, a synchronous triggering source and a data processing system, wherein the fundus illumination optical path and the fundus imaging optical path are synchronously triggered by the synchronous triggering source; the fundus illumination optical path comprises a light source controller, a laser light source, a beam expanding lens, a beam splitter lens and an eye piece objective lens which are sequentially connected; and the fundus imaging optical path comprises an eye piece objective lens, a beam splitter lens, an imaging ocular lens, a lens and a COMS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) camera which are sequentially connected. The device and the method have the advantages that the light source gives out laser at the same frequency as the sampling frame rate of the camera; the realization of the fundus microvessel imaging is ensured; and meanwhile, the laser power is reduced, so that the value reaches the range capable of being borne by human eyes. The method and the device can realize the fundus optical full-field microangiography imaging. The method has the advantages that a contrast agent is not needed; the resolution ratio, the signal-to-noise ratio and the detection depth are high; and the fundus blood capillary can be rebuilt.
Owner:佛山市灵觉科技有限公司
Laser surface treatment
ActiveUS20060213880A1Reduce reflection lossReduce laser powerLaser detailsChemical vapor deposition coatingPeriodic IntervalLaser energy density
A laser surface treatment for reducing reflection loss on the surface of an optical material is provided. A metal film is formed on the surface of the optical material, and then the metal film is removed from the optical material by irradiation of an ultra-intense short-pulse laser beam having a pulse width of 1 femtosecond to 100 picoseconds, so that a fine periodic structure is formed on the surface of the optical material exposed by the removal of the metal film. The obtained fine periodic structure has asperities with a periodic interval of preferably 50 to 1000 nm, which can be controlled by changing the laser energy density.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD +1
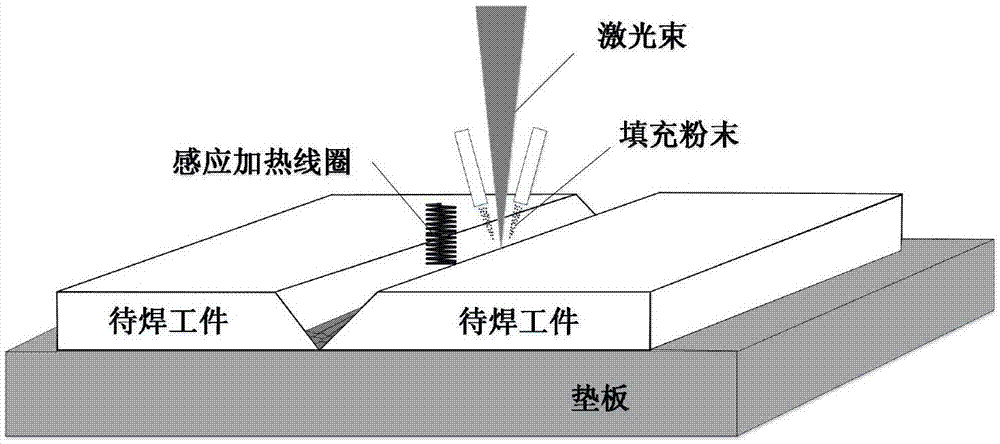
Connecting method assisted by electro-magnetic induction synchronous preheating and based on laser additive manufacturing
ActiveCN105436707AAlleviate crack sensitivity tendencyPromote absorptionLaser beam welding apparatusMicro structureSuperalloy
The invention relates to a connecting method, in particular to a connecting method assisted by electro-magnetic induction synchronous preheating and based on laser additive manufacturing. The problems that Ti-Al system intermetallic compound materials, high-temperature alloy, aluminum alloy and the like are sensitive to laser welding cracks, materials serious in laser reflection are prone to defects like cracks during welding, and the laser utilization rate is small are solved. The method includes the steps that a workpiece to be welded is machined, ground and cleaned; process parameters are set, and welding is carried out. An electro-magnetic induction coil serves as a preheating heat source, the crack sensitivity tendency of the materials in the welding process is relieved, the defects that the materials are low in laser adsorption rate, large in energy consumption in the welding process and the like are effectively relieved, and the laser utilization rate is improved. Meanwhile, the welding joint and peripheral materials are heated in an induction mode, the temperature gradient of the area around the welding joint in the welding process is reduced, the micro structure after welding can be effectively improved, and the performance of a welding connector is improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
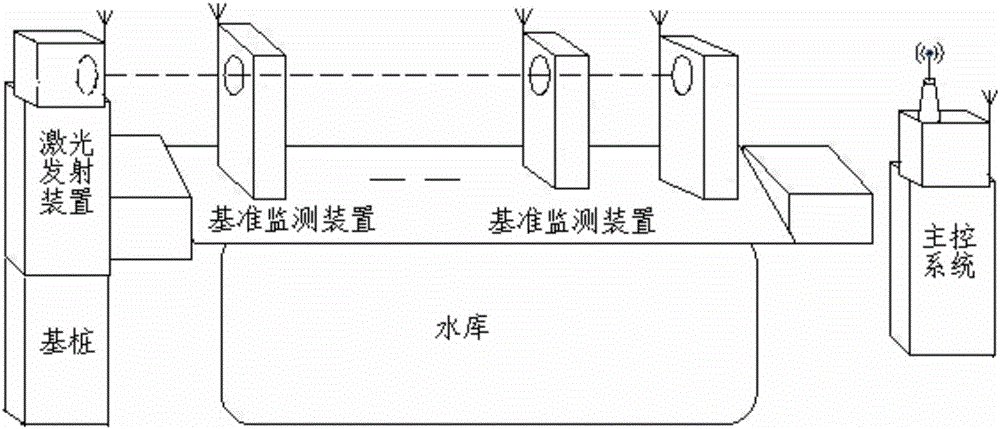
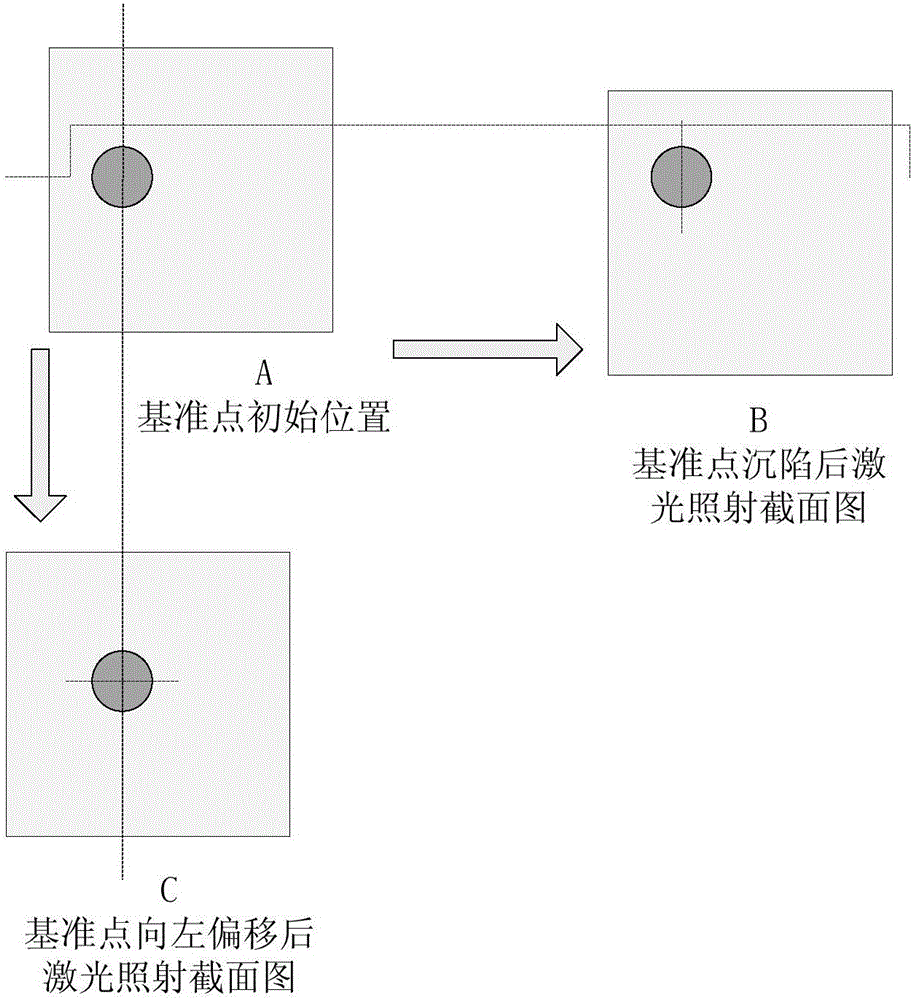
Reservoir dam deformation monitoring method and system
InactiveCN106595506AHigh measurement accuracyRealize automatic monitoring functionUsing optical meansLight spotControl system
The invention relates to a reservoir dam deformation monitoring method and system. The monitoring method includes the following steps that: 1) a reservoir dam deformation monitoring device is set; 2) the initial circular light spot images of each reference point are obtained; and 3) reservoir dam deformation monitoring is carried out. The reservoir dam deformation monitoring system includes a laser emitting device, reference point detecting devices and a main control system; the laser emitting device is arranged at one end of a dam and is used for emitting collimating laser light adopted as a reference line; a plurality of reference points with equal intervals are arranged one a ray with the laser emitting device adopted as an end point; one reference point detecting device is arranged at each reference point; the reference point detecting devices are used for detecting the subsidence and horizontal displacement of the dam; and the main control system is connected with the laser emitting device and the reference point detecting devices through a wireless communication mode and is used for transmitting detection commands, receiving detected data and performing analysis processing on the detected data. With the reservoir dam deformation monitoring method and system of the invention adopted, the automatic detection of the subsidence and horizontal displacement of the dam can be realized, the measurement accuracy of the reservoir dam is improved, and monitoring costs can be reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
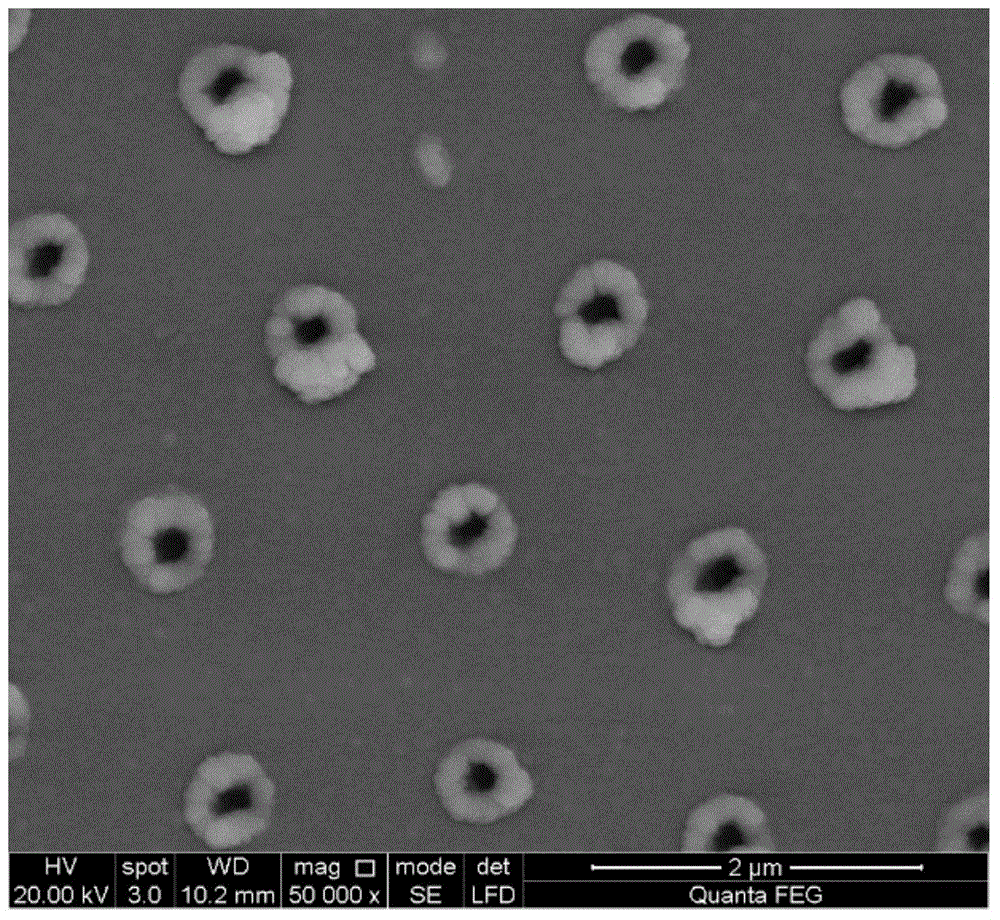
Quick preparing method for large-area surface Raman spectrum enhancing monocrystalline silicon substrate
InactiveCN104949959APrecise control of densityExtended cycleVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingWater bathsSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
The invention relates to a quick preparing method for a large-area surface Raman spectrum enhancing monocrystalline silicon substrate and belongs to the field of SERS substrate preparing. The quick preparing method comprises the steps that the surface of monocrystalline silicon is covered with a microballoon array which is periodically and densely arranged; microballoon left on the surface is removed through laser scanning or irradiating; the monocrystalline silicon is immersed into a sodium hydroxide water solution including alcohol, corrosion is carried out for 10-30 s in the environment with the water bath temperature ranging from 70 DEG C to 80 DEG C, the monocrystalline silicon is taken out and cleaned with deionized water, and the monocrystalline silicon with the microstructure array is obtained, wherein in the water solution, the sodium hydroxide accounts for 5%-10% by mass, and alcohol accounts for 8%-10% by mass; silver film deposition is carried out on the surface of the corroded monocrystalline silicon through magnetron sputtering, and the deposition thickness ranges from 50 nm to 200 nm. By means of the quick preparing method, the periodic and uniform microstructure array can be quickly, easily and conveniently prepared, and the performance of an SERS substrate can be controlled by controlling the morphology dimension feature of the microstructure array and the thickness of a silver film. Meanwhile, the method is high in reproducibility and low in cost, and prepared SERS substrate is stable in performance and capable of being repeatedly used.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
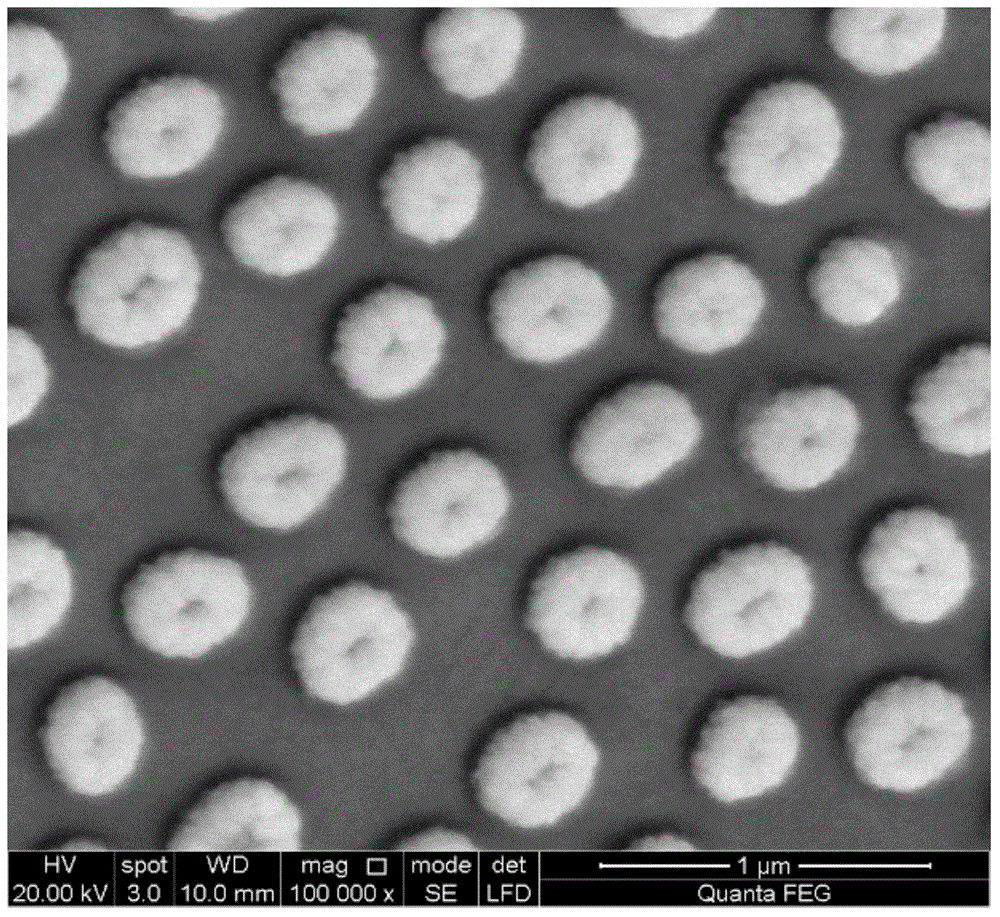
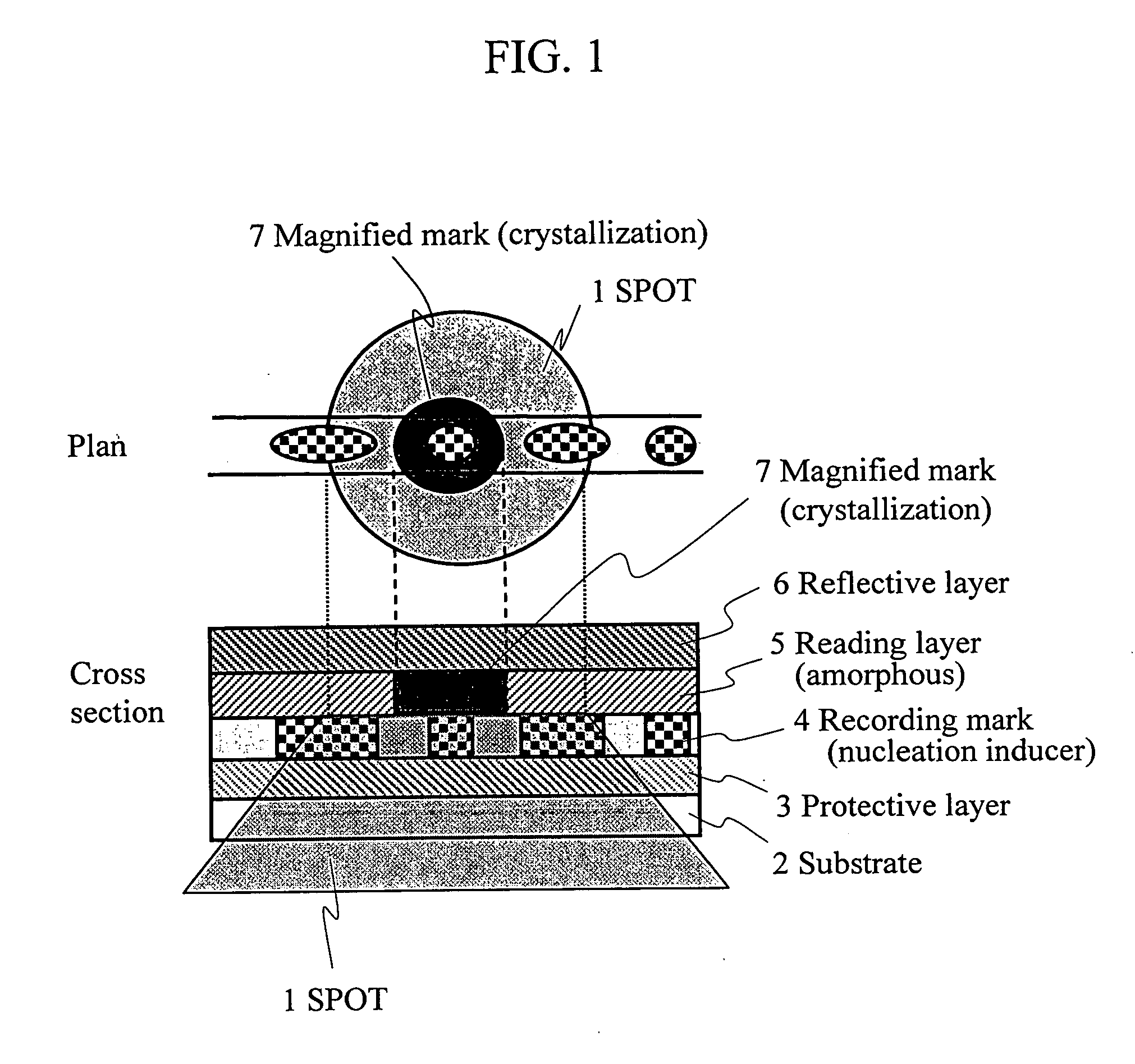
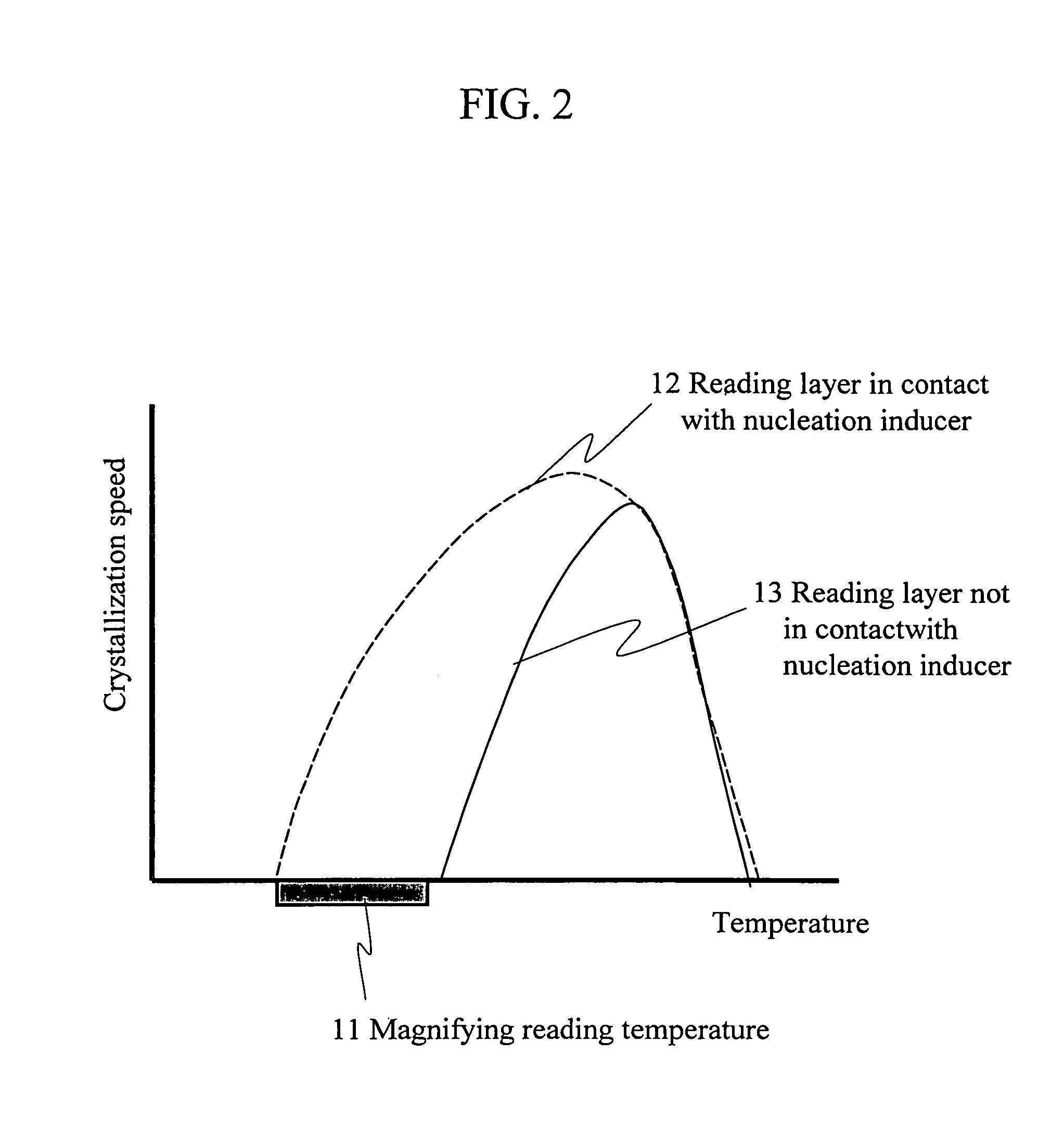
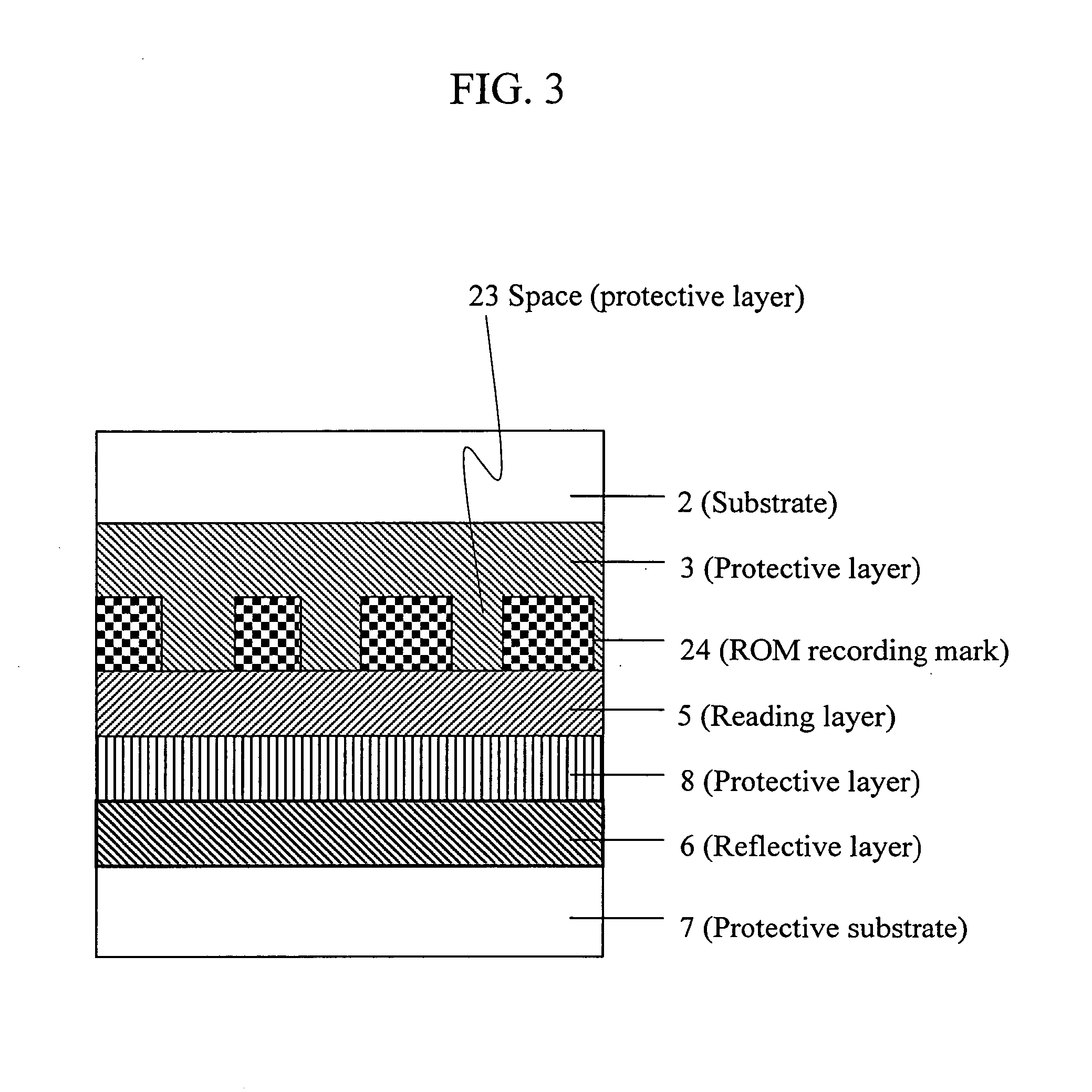
Information reproduction method and information recording medium
InactiveUS20060040088A1Less-expensiveReduce laser powerLayered productsRecord information storageRecording layerNucleation
Disclosed are an information reproduction method and an information recording medium that allow reproducing information below a diffraction limit. A recording layer formed with recording marks consisting of a nucleation inducer and a reading layer are provided. When a reading beam is irradiated, a predetermined area of the reading layer is crystallized based on the recording mark of the recording layer such that the area is magnified to a size larger than the recording mark, and information is thus reproduced. Information of the recording marks below the diffraction limit can be reproduced without using a special information reproduction apparatus.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Nylon/graphene/carbon fiber composite powder and preparation method thereof, and application of composite powder to selective laser sintering technology
ActiveCN107936547AUniform particle size distributionAvoid reunionAdditive manufacturing apparatusHeat-exchange elementsFiberSelective laser sintering
The invention discloses a nylon / graphene / carbon fiber composite powder and a preparation method thereof, and application of the composite powder to selective laser sintering technology. The preparation method comprises the following steps: subjecting nylon powder and graphene powder to double-liquid-phase mixing so as to prepare nylon / graphene composite powder; and then mechanically mixing the nylon / graphene composite powder with carbon fibers, a flow promoting agent and an antioxidant so as to obtain the nylon / graphene / carbon fiber composite powder. The invention provides the preparation method for the nylon / graphene / carbon fiber composite powder. A laser-sintered member prepared from the nylon / graphene / carbon fiber composite powder through selective laser sintering has good conductivity,good thermal conductivity and excellent mechanical properties.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
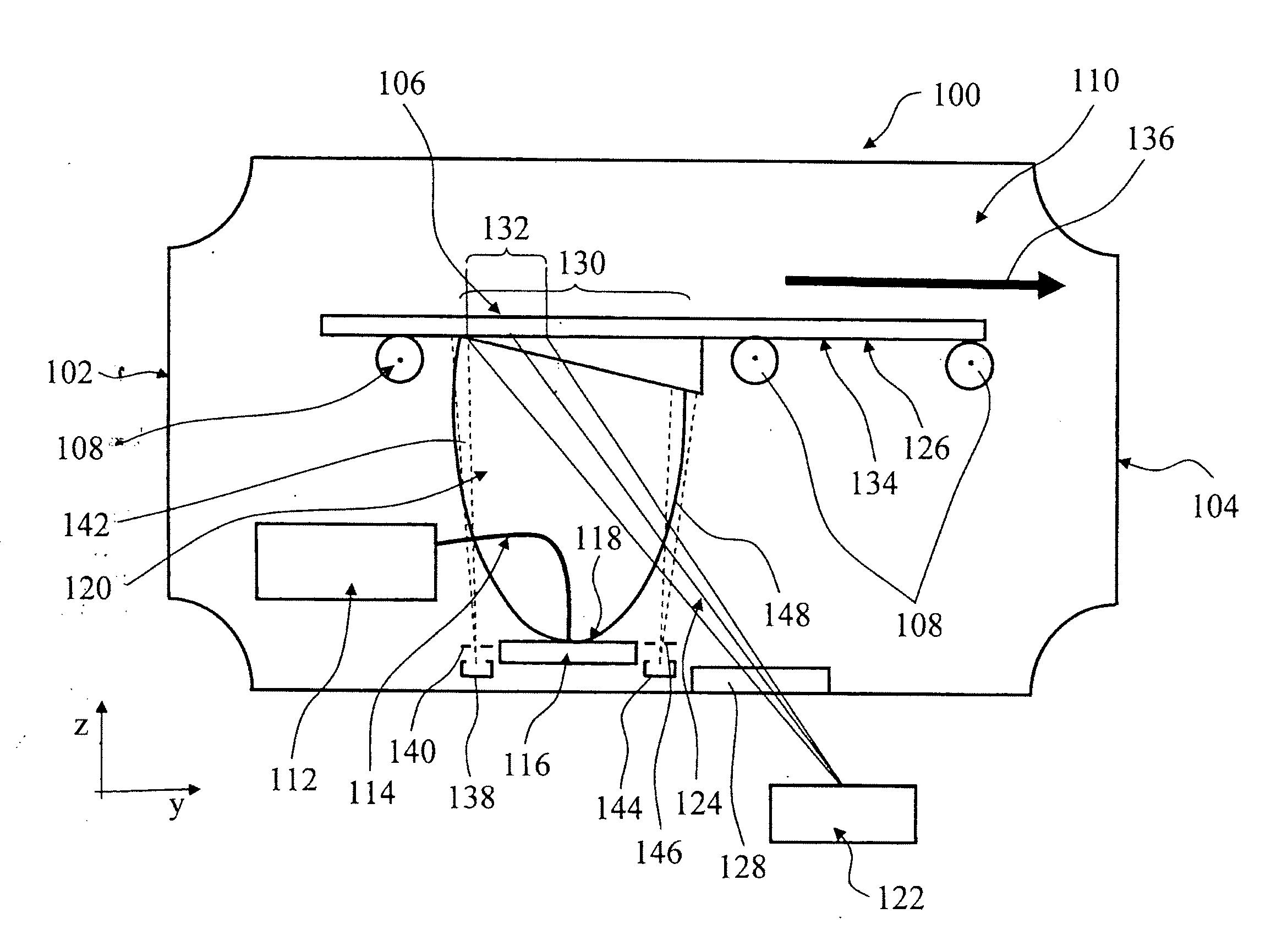
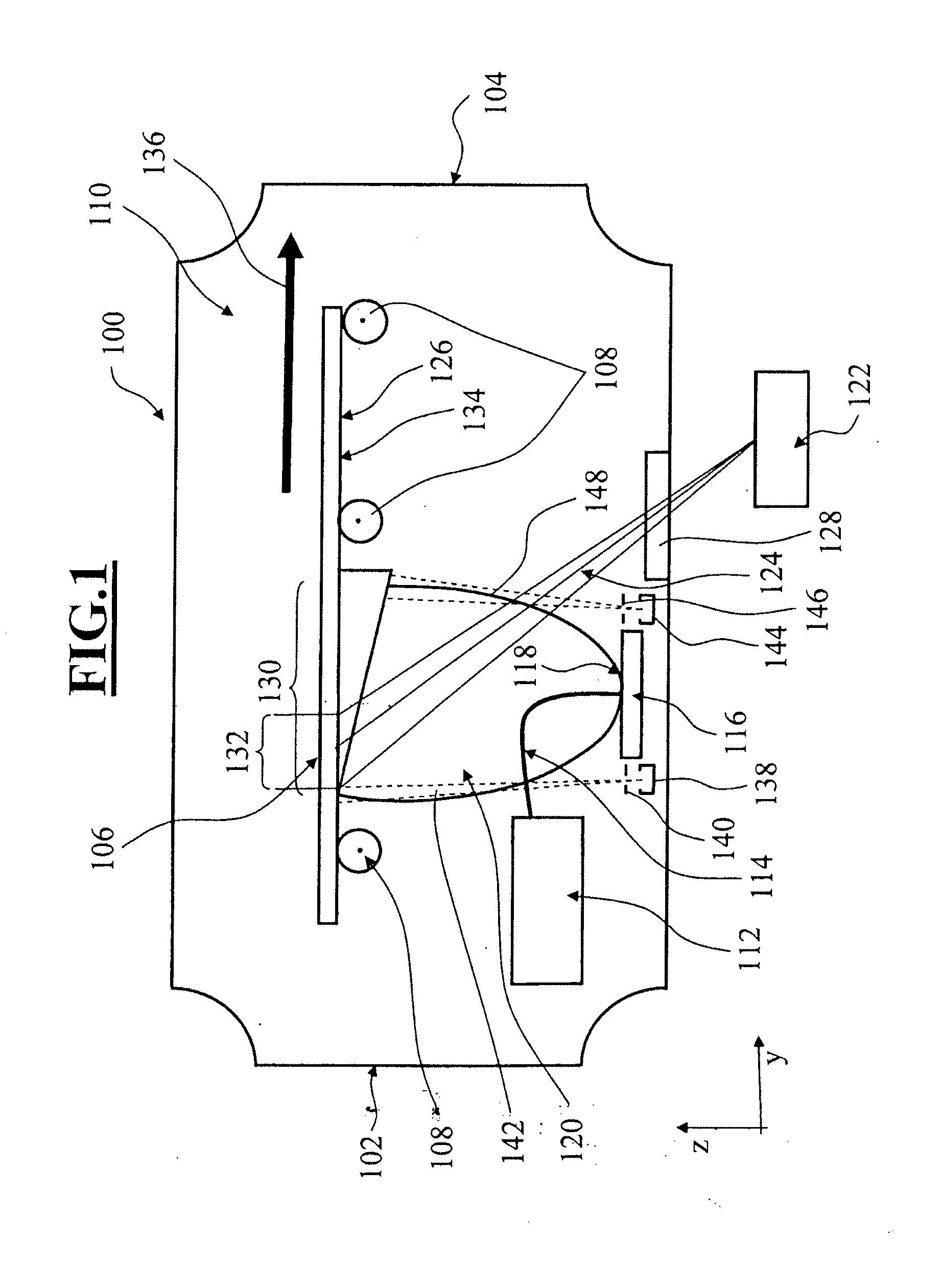
Method and apparatus for processing substrates using a laser
ActiveUS9701581B2Powerful method and apparatus for processing substratesPromote absorptionFine working devicesGlass severing apparatusPulse durationSemiconductor
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for processing substrates, such as glass and semiconductor wafers. The method comprises directing to the substrate from a laser source a plurality of sequential focused laser pulses having a predetermined duration, pulsing frequency and focal spot diameter, the pulses being capable of locally melting the substrate, and moving the laser source and the substrate with respect to each other at a predetermined moving velocity so that a structurally modified zone is formed to the substrate. According to the invention, the pulse duration is in the range of 20-100 ps, pulsing frequency at least 1 MHz and moving velocity adjusted such that the distance between successive pulses is less than ⅕ of the diameter of the focal spot. The invention can be utilized, for example, for efficient dicing, scribing and welding of materials which are normally transparent.
Owner:CORELASE
Porous titanium interbody fusion cage and method for preparing same
ActiveCN106667626APromote bone fusionExcellent anti-fatigue mechanical propertiesSpinal implantsSpinal cagePore diameter
The invention discloses a porous titanium interbody fusion cage. The porous titanium interbody fusion cage is a structural component, and titanium alloy materials are integrally printed by the aid of a 3D (three-dimensional) printer to form the structural component. The porous titanium interbody fusion cage comprises a support structure and a pore structure. The support structure is used for bearing external load, and the pore structure is used for guiding new bone ingrowth. The volume of the support structure ranges from 5% to 20% of the total volume of the porous titanium interbody fusion cage. The pore structure is outwardly exposed on the upper side, the lower side, the front side, the rear side and the right side of the porous titanium interbody fusion cage in an open manner, and open growth spaces can be provided for effective growth of bones and the like. The porous titanium interbody fusion cage has the advantages that laser power, the scanning speeds and the scanning interval are controlled when a method for preparing the porous titanium interbody fusion cage is implemented, and accordingly the porous titanium interbody fusion cage can be integrally formed, has appropriate pore diameters and is high in porosity and good in strength; functions of two functional components of the porous titanium interbody fusion cage can be independently implemented by the functional components, the two functional components further can be matched with each other, and accordingly interbody therapy effects can be realized.
Owner:CHANGZHOU WASTON MEDICAL APPLIANCE CO LTD
Laser drilling machining method
InactiveCN106112280AStrong melting abilityBlowout preventionLaser beam welding apparatusSpray nozzleLaser cutting
The invention relates to a laser drilling machining method. The laser drilling machining method comprises the following steps of step 1: preparing a workpiece (1) to be cut and removing impurities from the surface of the workpiece (1); step 2: connecting a vacuum hood (3) onto a laser cutting head (6), and enabling the distance from a cutting spray nozzle (5) and the the vacuum hood to the upper surface of the workpiece (1) to be adjustable; step 3: moving the laser cutting head above the workpiece, enabling the cutting spray nozzle to keep a certain distance from the surface of the workpiece and enabling the vacuum hood to keep a certain distance from the surface of the workpiece; setp 4: supplying dry compressed air from an air inlet port (4) of the vacuum hood; step 5: supplying drilling auxiliary gas from an auxiliary gas inlet port (7) of the laser cutting head; and step 6: starting a laser cutting system and enabling a laser beam (2) to radiate the upper surface of the workpiece vertically to complete the drilling process. According to the method, a partial vacuum environment is formed by the simple cyclonic-type vacuum hood, so that the problem can be avoided that large amounts of molten metal is injected upward and therefore a hole bursts, and the drilling efficiency and stability can be greatly improved.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Laser joining apparatus and laser joining method
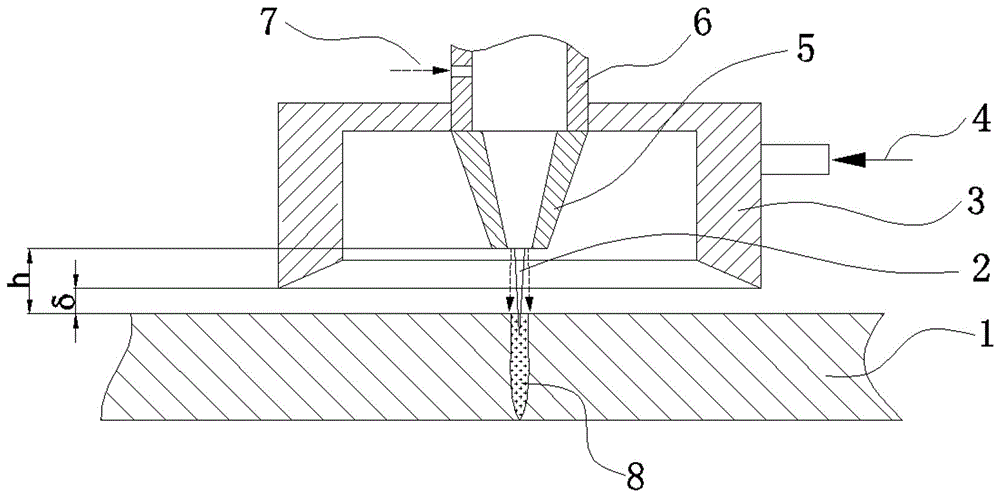
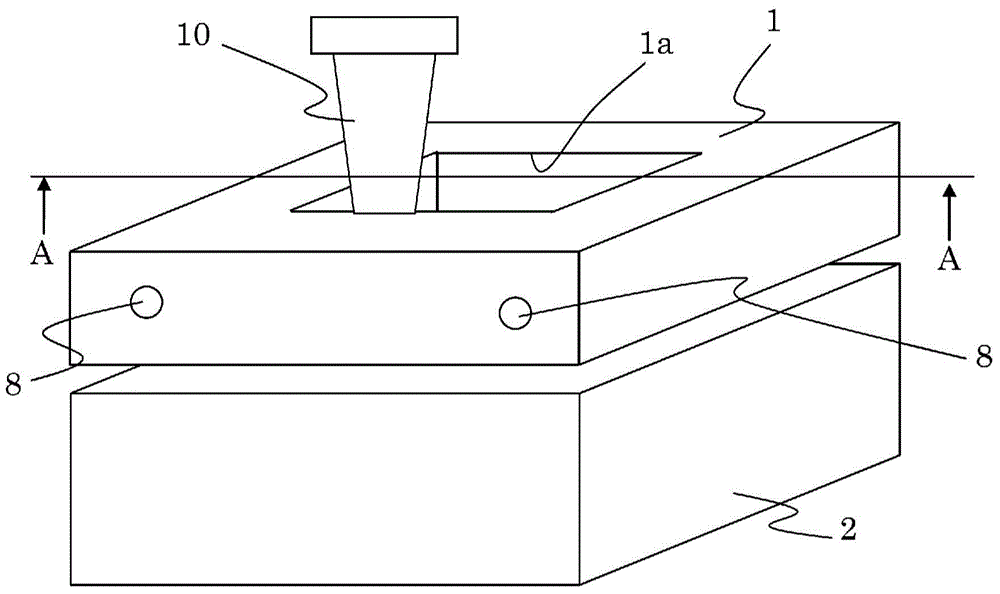
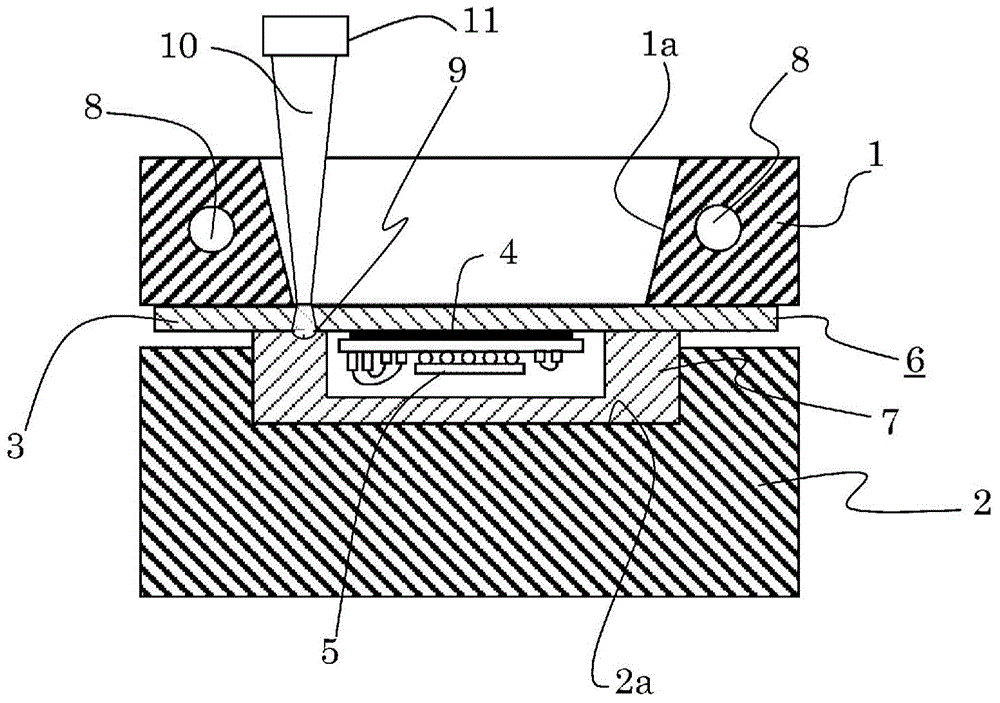
InactiveCN104968483AReduce restrictionsImprove reliabilityWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesMetallic materialsLaser beams
Provided is a laser joining apparatus for joining a metal material and a resin housing made from a thermoplastic resin, wherein the laser joining apparatus enhances the efficiency of heat conduction and reduces the output of the laser beam. A joining apparatus that heat-joins the joint surfaces of a resin housing (7) and a metal material (3) by applying a laser to the surface of the metal material (3) on the opposite side of the joint surface, wherein the resin housing (7) and metal material (3) are positioned and fixed by an upper mold (1) and a lower mold (2) and the joint surfaces of the resin housing (7) and metal material (3) are brought into close contact by pressing the upper mold (1). At this time, the metal material (3) is preheated by a heater (8). A laser beam is applied thereafter from a hole (1a) in the upper mold (1). The efficiency of heating the metal material (3) using the laser can be enhanced, the laser output can be reduced, and the cost of joining can be vastly reduced by heating the resin housing (7) and metal material (3) to a predetermined temperature using the heater (8) and pressurizing the joint surfaces using the upper mold (1) and lower mold (2).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
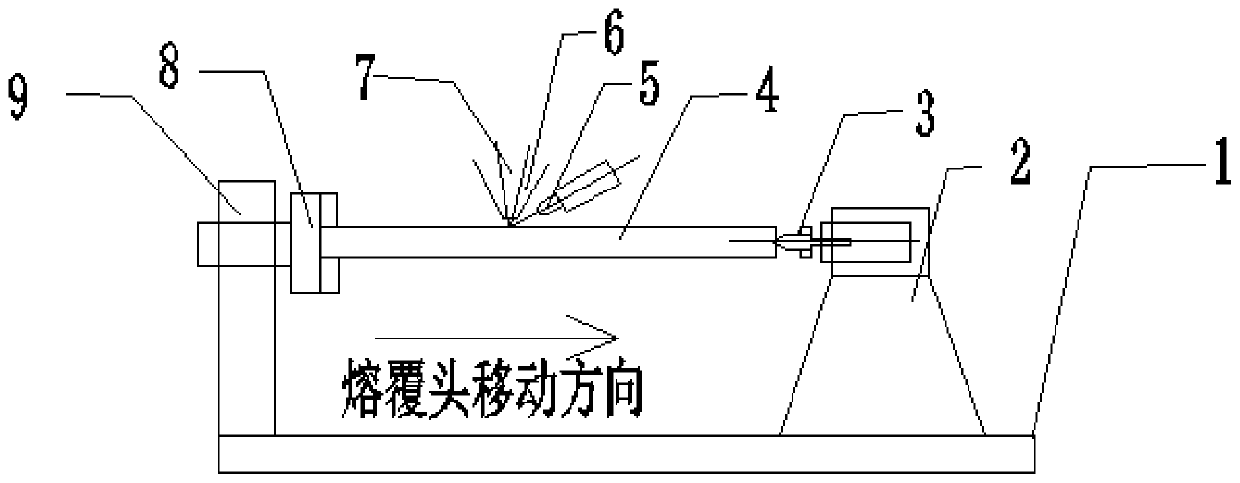
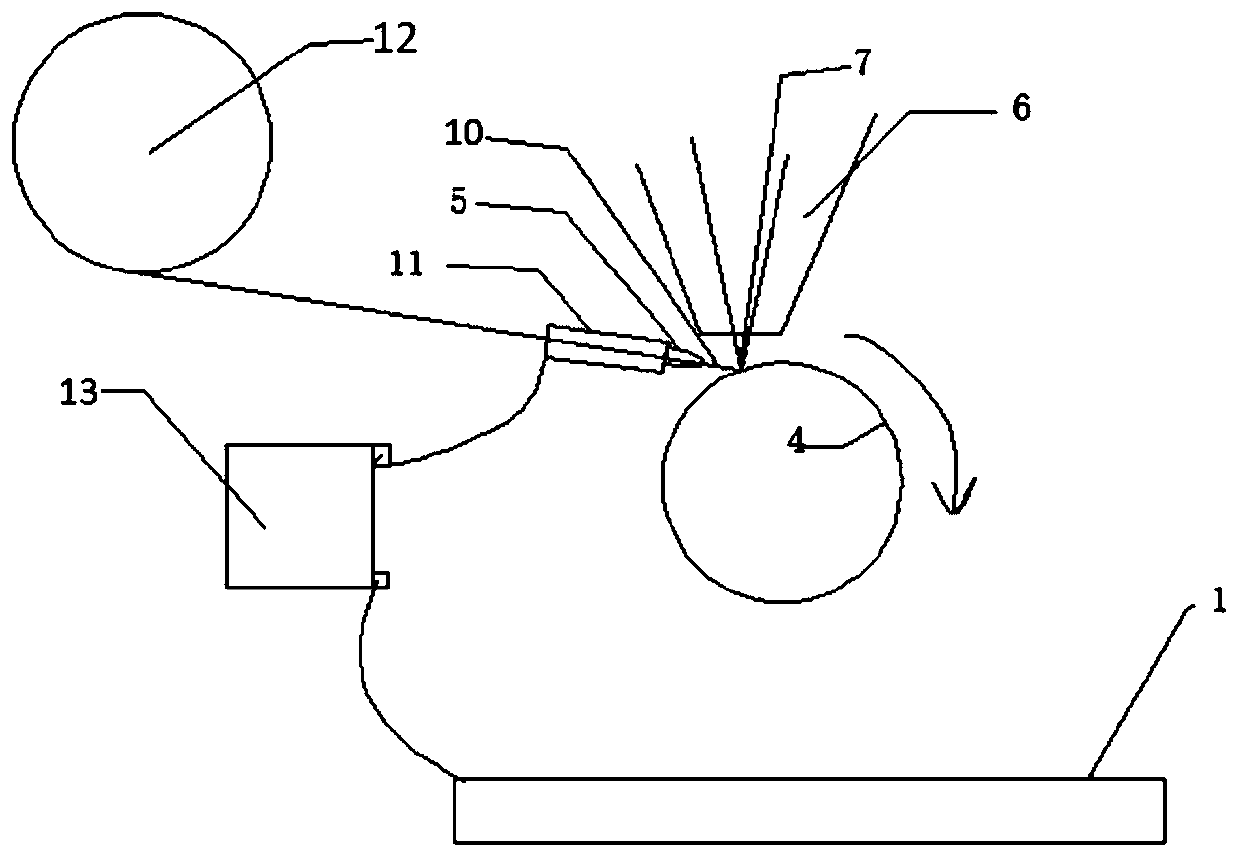
Laser cladding device and method for slender shaft-like workpieces
InactiveCN111020565ALow heat inputReduce the risk of cladding deformationMetallic material coating processesThermal dilatationEngineering
The invention provides a laser cladding device and method for slender shaft-like workpieces. The laser cladding is performed by preheating a wire, and the wire is preheated when entering a molten pool, so that the absorption rate of materials to laser is effectively improved; laser power 50% lower than that of ordinary laser cladding is used for wire cladding, so that the heat input of the workpieces is reduced; a movable center is arranged on the tail part of a cladding machine, and the maximum stroke of the movable center is 8mm, it is guaranteed that the workpieces can be expanded and contracted in the axial direction when the workpieces are thermally expanded in the cladding process, and deformation of the workpieces due to excessive stress caused by thermal expansion is avoided; and the segmented cladding technology is used in the cladding operation, excessive concentration and accumulation of heat is effectively avoided, the slender workpieces are dispersed by heat in the laser cladding process, and the cladding deformation of the slender workpieces is effectively reduced. According to the laser cladding device and method for the slender shaft-like workpieces, the applicationof laser cladding technology in the surface treatment process of slender shaft-like workpieces is promoted, and the broad prospect for popularization and application is achieved.
Owner:SHAANXI TIANYUAN MATERIALS PROTECTION TECH
Laser beam irradiation apparatus and substrate sealing method
ActiveUS20140174664A1Scanning speed can not be increasedReduce laser powerMechanical working/deformationElectrical apparatusLight beamOptoelectronics
Provided is a laser beam apparatus for sealing a first substrate and a second substrate by irradiating a sealant between the first substrate and the second substrate using a laser beam, the laser beam apparatus including a controller, wherein the controller is configured to defocus the laser beam and to move a scanning central axis of the laser beam across a sealing path of the sealant.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com