Patents
Literature
50607results about "Laser beam welding apparatus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
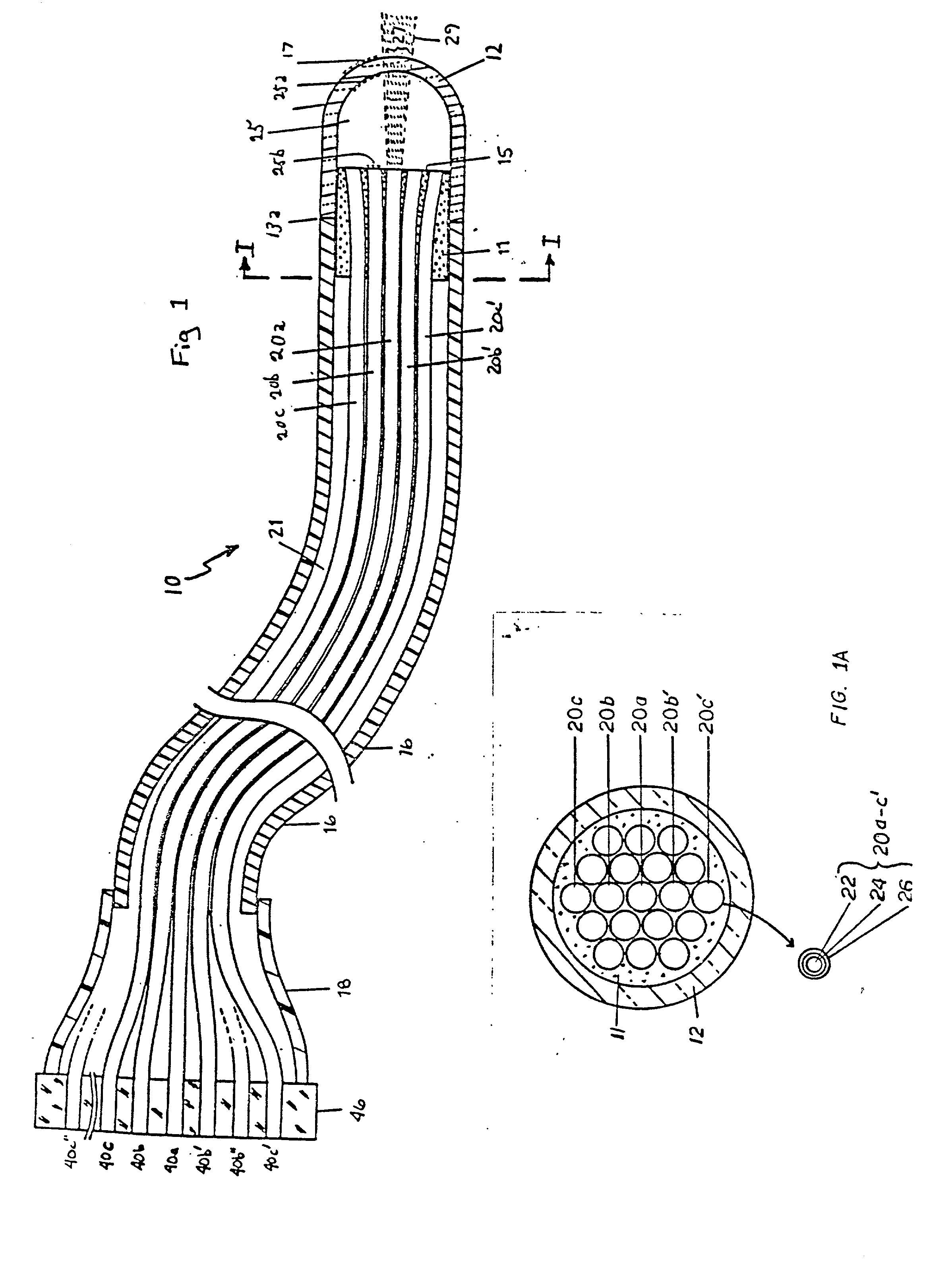
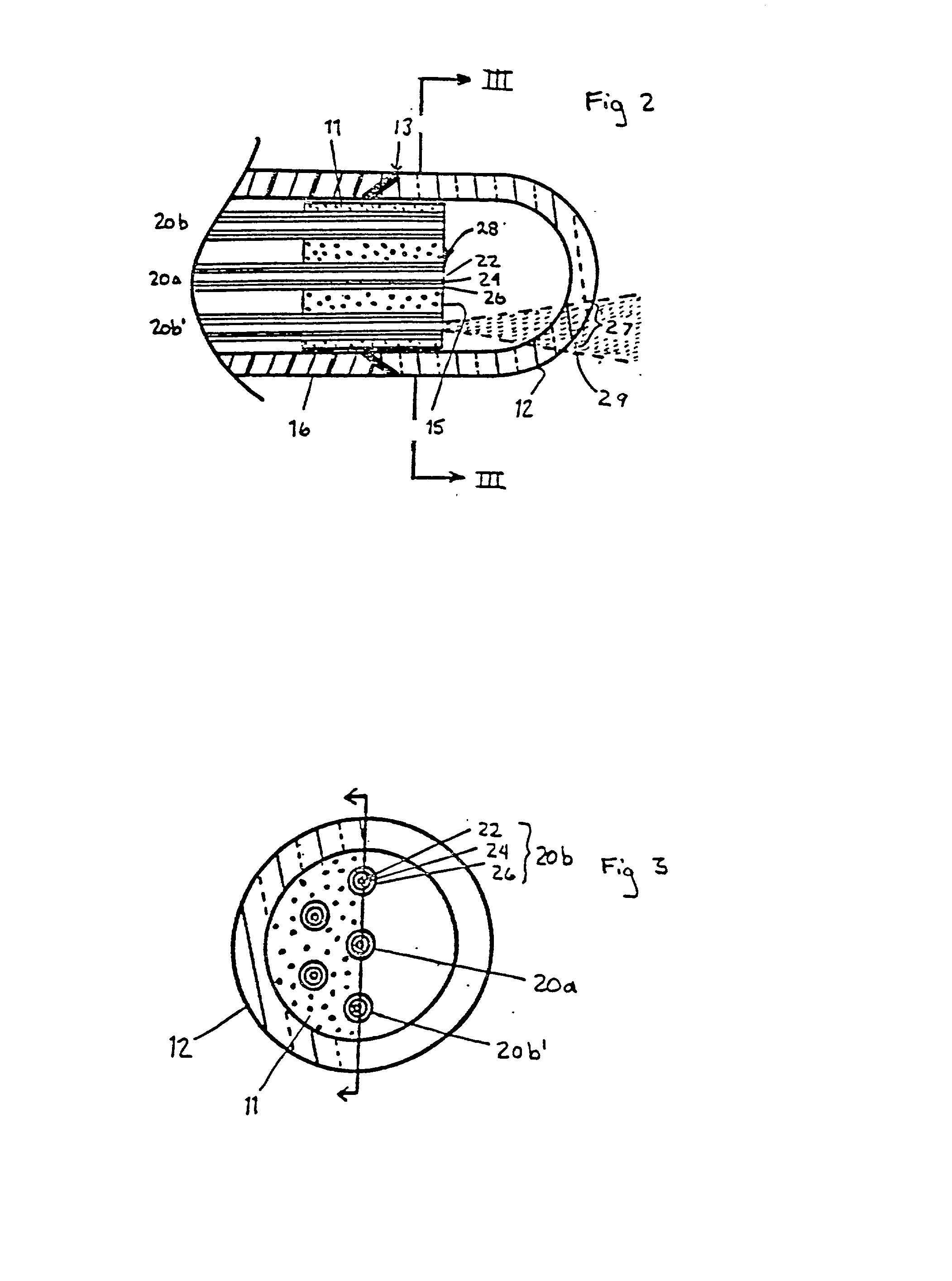
Tear and abrasion resistant expanded material and reinforcement
InactiveUS20070207186A1Increase flexibilityLess complex manufacturing processStentsSurgeryDiseaseEngineering
The present invention is a more durable expanded material that enables thinner wall thicknesses and a more flexible reinforcement suitable for stenting. The present invention is especially useful in the construction of grafts, stents, and stent-grafts which are used, for example, in repairing or replacing blood vessels that are narrowed or occluded by disease, aneurismal blood vessels, or other medical treatments. The inventive material and configurations allow expansion or contraction in size or adjustment in size in an incremental manner so that the optimum size, shape, and fit with other objects can be obtained. The present invention is also optionally capable of more accurately delivering one or more active ingredients such as drugs over longer periods of time. The present invention optionally includes surface modifications and additives that increase the surface adhesion of active ingredients, coatings, or combinations thereof. Finally, the present invention optionally includes growing cells on the inventive material so that the expanded material, reinforcement, or combinations thereof are useful, for example, in producing lab-grown blood vessels or organs.
Owner:SCANLON JOHN JAMES +1
Methods and devices to design and fabricate surfaces on contact lenses and on corneal tissue that correct the eye's optical aberrations
Methods and devices are described that are needed to design and fabricate modified surfaces on contact lenses or on corneal tissue that correct the eye's optical aberrations beyond defocus and astigmatism. The invention provides the means for: 1) measuring the eye's optical aberrations either with or without a contact lens in place on the cornea, 2) performing a mathematical analysis on the eye's optical aberrations in order to design a modified surface shape for the original contact lens or cornea that will correct the optical aberrations, 3) fabricating the aberration-correcting surface on a contact lens by diamond point turning, three dimensional contour cutting, laser ablation, thermal molding, photolithography, thin film deposition, or surface chemistry alteration, and 4) fabricating the aberration-correcting surface on a cornea by laser ablation.
Owner:BROOKFIELD OPTICAL SYST
Analyte sensors and methods of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20110027127A1Hot-dipping/immersion processesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteEngineering
Analyte sensors and methods of manufacturing same are provided, including analyte sensors comprising multi-axis flexibility. For example, a multi-electrode sensor system 800 comprising two working electrodes and at least one reference / counter electrode is provided. The sensor system 800 comprises first and second elongated bodies E1, E2, each formed of a conductive core or of a core with a conductive layer deposited thereon, insulating layer 810 that separates the conductive layer 820 from the elongated body, a membrane layer deposited on top of the elongated bodies E1, E2, and working electrodes 802′, 802″ formed by removing portions of the conductive layer 820 and the insulating layer 810, thereby exposing electroactive surface of the elongated bodies E1, E2.
Owner:DEXCOM
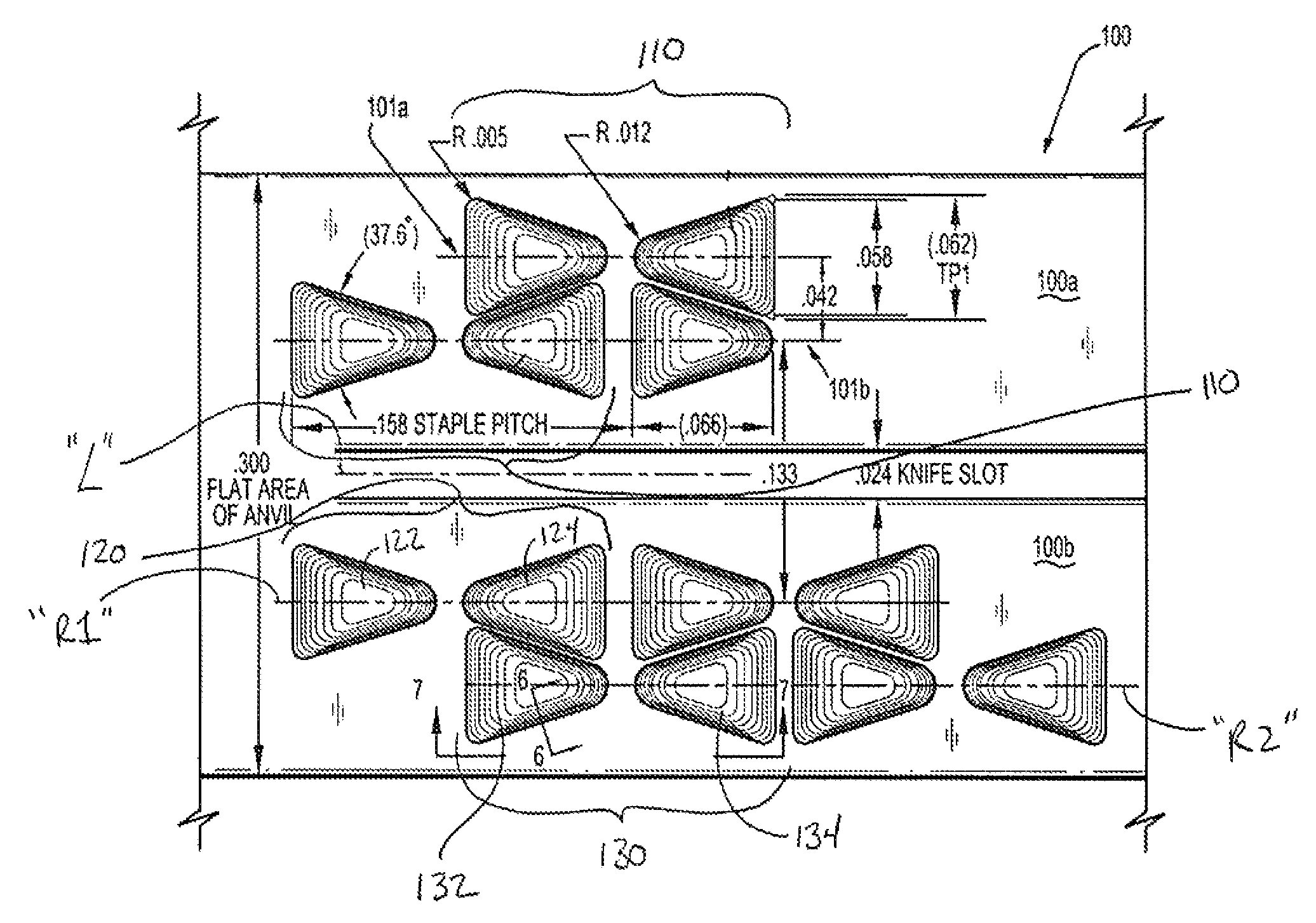
Method for forming staple pockets of a surgical stapler
A system and method for forming a staple pocket, e.g., on the anvil portion of a surgical stapler device. A laser-machining system may include a laser-emitting device that is configured to emit a laser beam or beams for forming staple pockets on the anvil of a surgical stapler. The staple pockets of an anvil may be formed successively or simultaneously. The anvil of the surgical stapler is mounted in a mounting mechanism so as to control its movement, and the laser-emitting device is controlled by a control module, which may control any aspect of the laser-machining operation, e.g., the intensity of the laser beam, the movement of the laser-emitting device relative to the anvil, etc. The control module may be a processor that includes software that provides instructions for the operation of the control module, and may be programmable by a user for inputting parameters, e.g., shape, arrangement, etc., corresponding to the staple pockets.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Laser-produced porous structure
The present invention disclosed a method of producing a three-dimensional porous tissue in-growth structure. The method includes the steps of depositing a first layer of metal powder and scanning the first layer of metal powder with a laser beam to form a portion of a plurality of predetermined unit cells. Depositing at least one additional layer of metal powder onto a previous layer and repeating the step of scanning a laser beam for at least one of the additional layers in order to continuing forming the predetermined unit cells. The method further includes continuing the depositing and scanning steps to form a medical implant.
Owner:UNIV OF LIVERPOOL +1
Analyte sensors and methods of manufacturing same
Analyte sensors and methods of manufacturing same are provided, including analyte sensors comprising multi-axis flexibility. For example, a multi-electrode sensor system 800 comprising two working electrodes and at least one reference / counter electrode is provided. The sensor system 800 comprises first and second elongated bodies E1, E2, each formed of a conductive core or of a core with a conductive layer deposited thereon, insulating layer 810 that separates the conductive layer 820 from the elongated body, a membrane layer deposited on top of the elongated bodies E1, E2, and working electrodes 802′, 802″ formed by removing portions of the conductive layer 820 and the insulating layer 810, thereby exposing electroactive surface of the elongated bodies E1, E2.
Owner:DEXCOM
Analyte sensor
InactiveUS20110024307A1Substantial linearityImmobilised enzymesHot-dipping/immersion processesContinuous measurementAnalyte
Devices and methods are provided for continuous measurement of an analyte concentration. The device can include a sensor having a plurality of sensor elements, each having at least one characteristic that is different from other sensor(s) of the device. In some embodiments, the plurality of sensor elements are each tuned to measure a different range of analyte concentration, thereby providing the device with the capability of achieving a substantially consistent level of measurement accuracy across a physiologically relevant range. In other embodiments, the device includes a plurality of sensor elements each tuned to measure during different time periods after insertion or implantation, thereby providing the sensor with the capability to continuously and accurately measure analyte concentrations across a wide range of time periods. For example, a sensor system 180 is provided having a first working electrode 150 comprising a first sensor element 102 and a second working electrode 160 comprising a second sensor element 104, and a reference electrode 108 for providing a reference value for measuring the working electrode potential of the sensor elements 102, 104.
Owner:DEXCOM
Continuous analyte sensors and methods of making same
InactiveUS20110027458A1Low production costMinimize changesHot-dipping/immersion processesVacuum evaporation coatingAnalyteSolvent
Owner:DEXCOM
Continuous analyte sensors and methods of making same
InactiveUS20110024043A1Low production costMinimize changesHot-dipping/immersion processesPretreated surfacesAnalyteSolvent
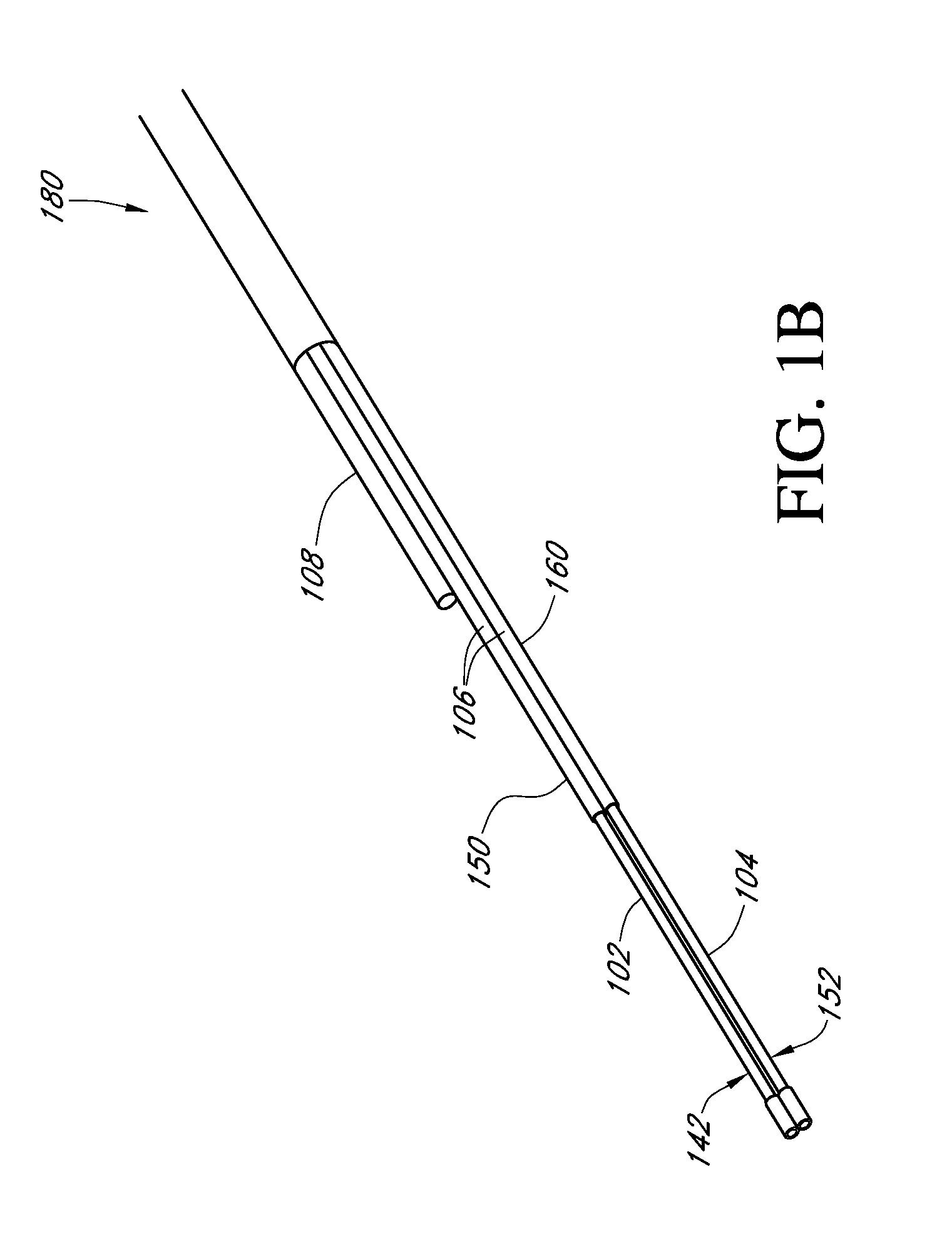
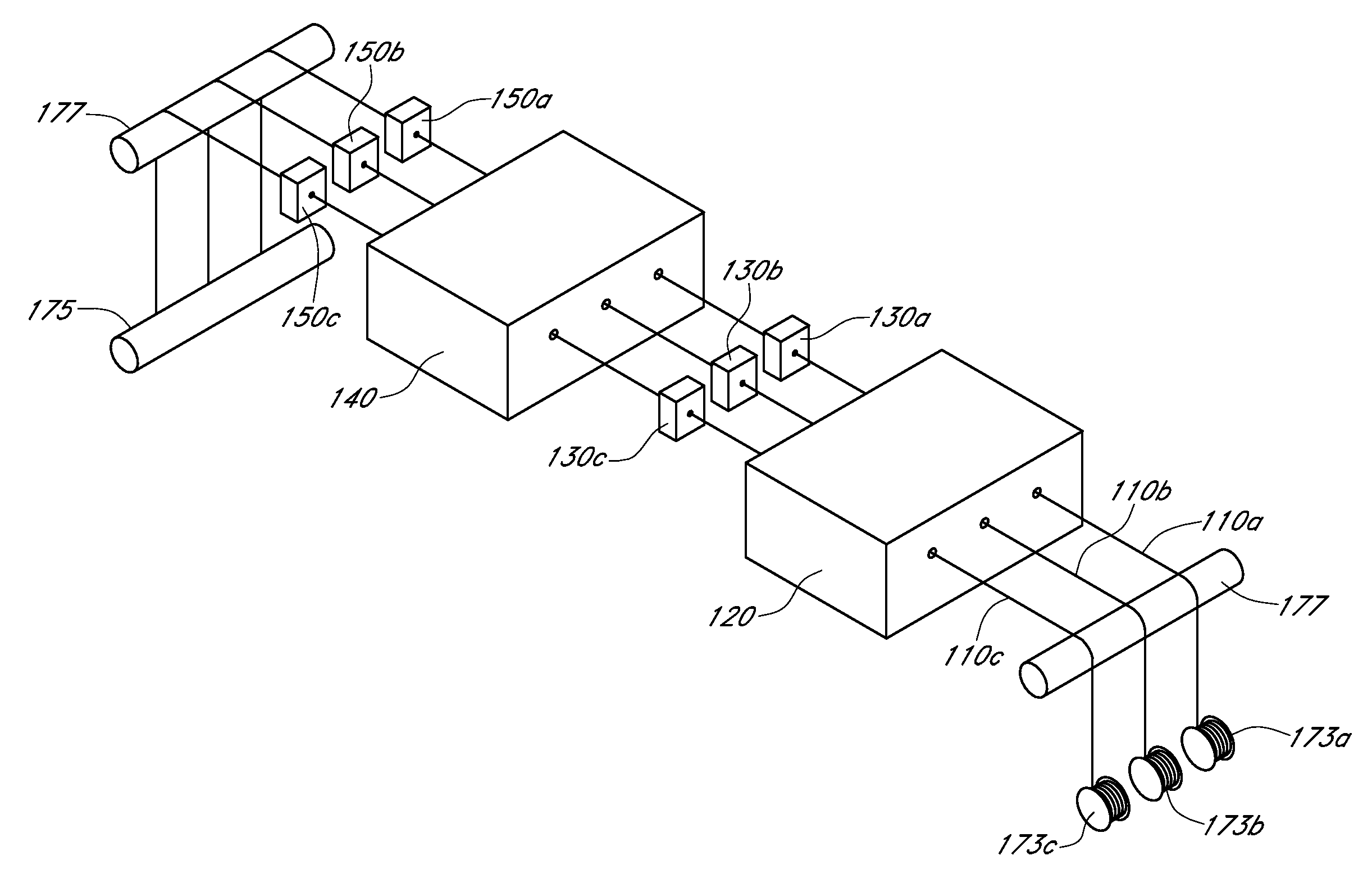
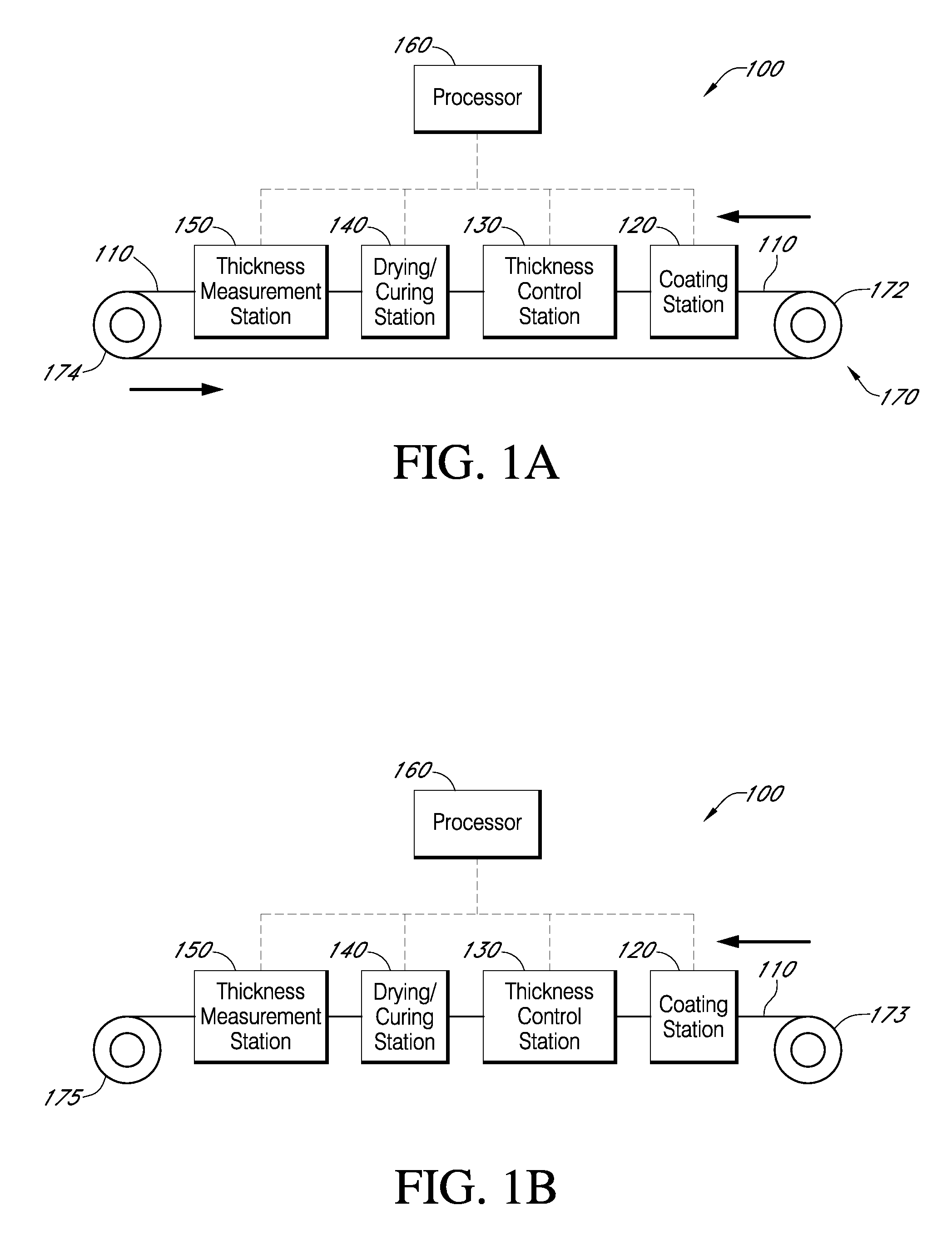
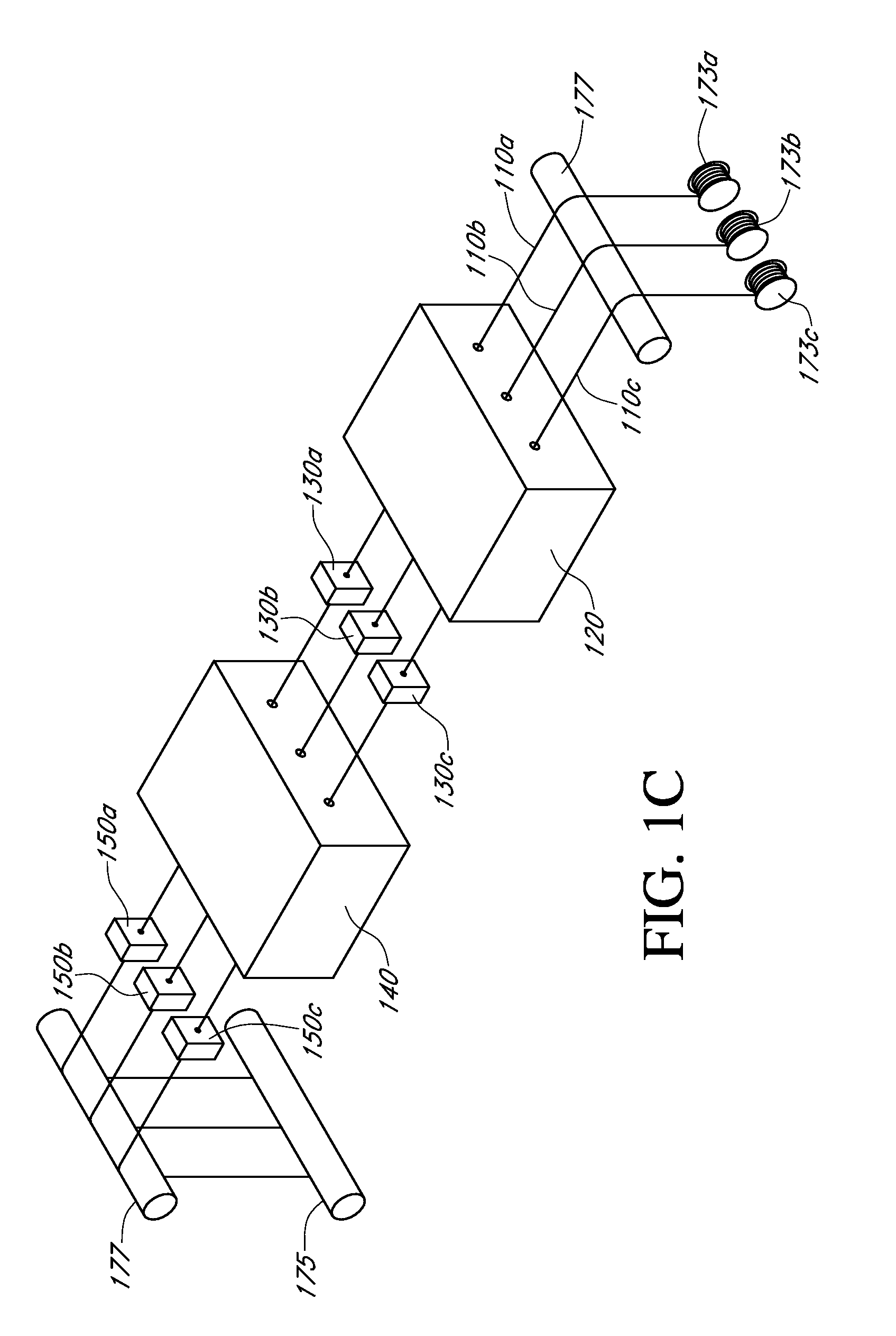
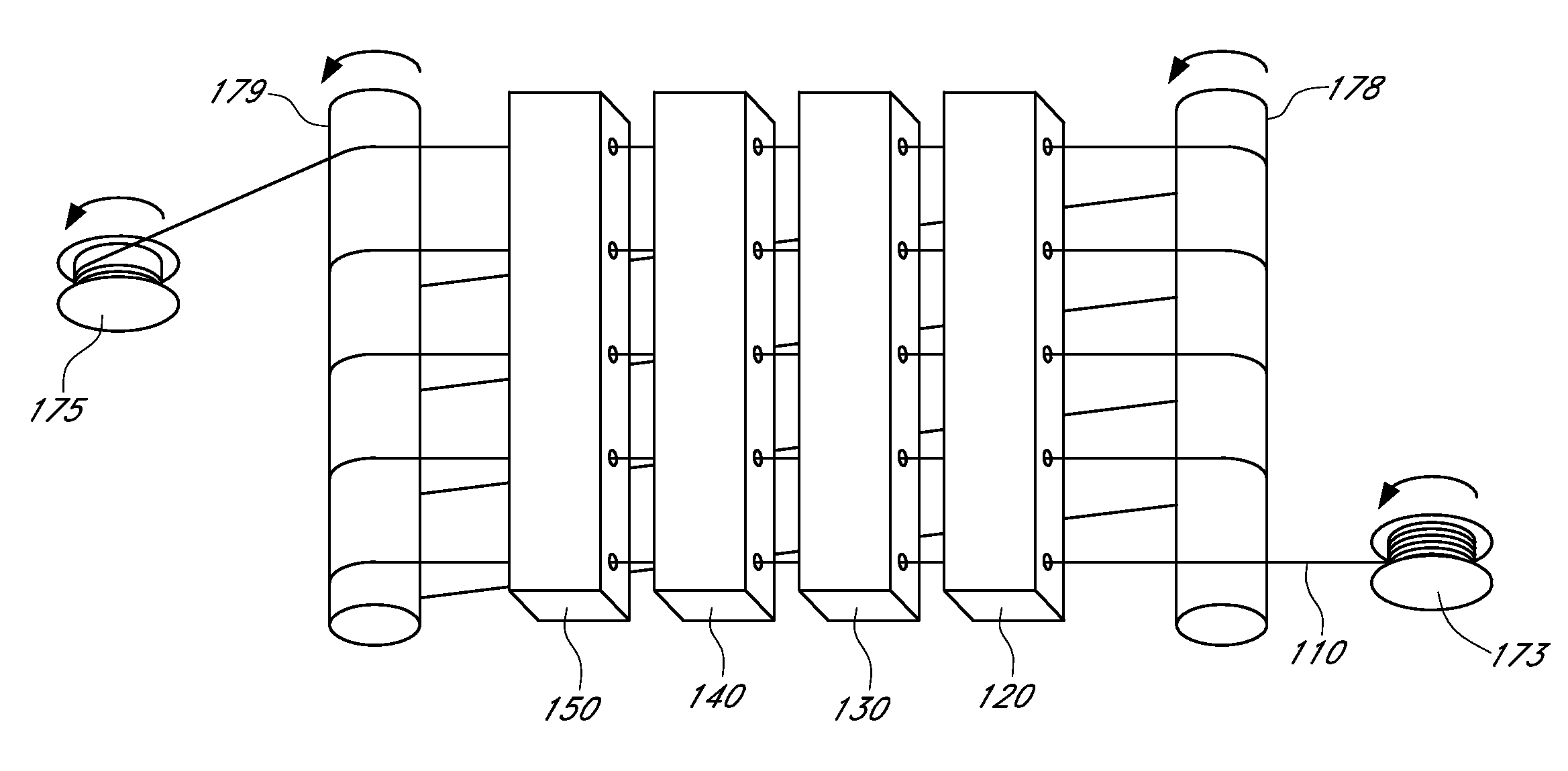
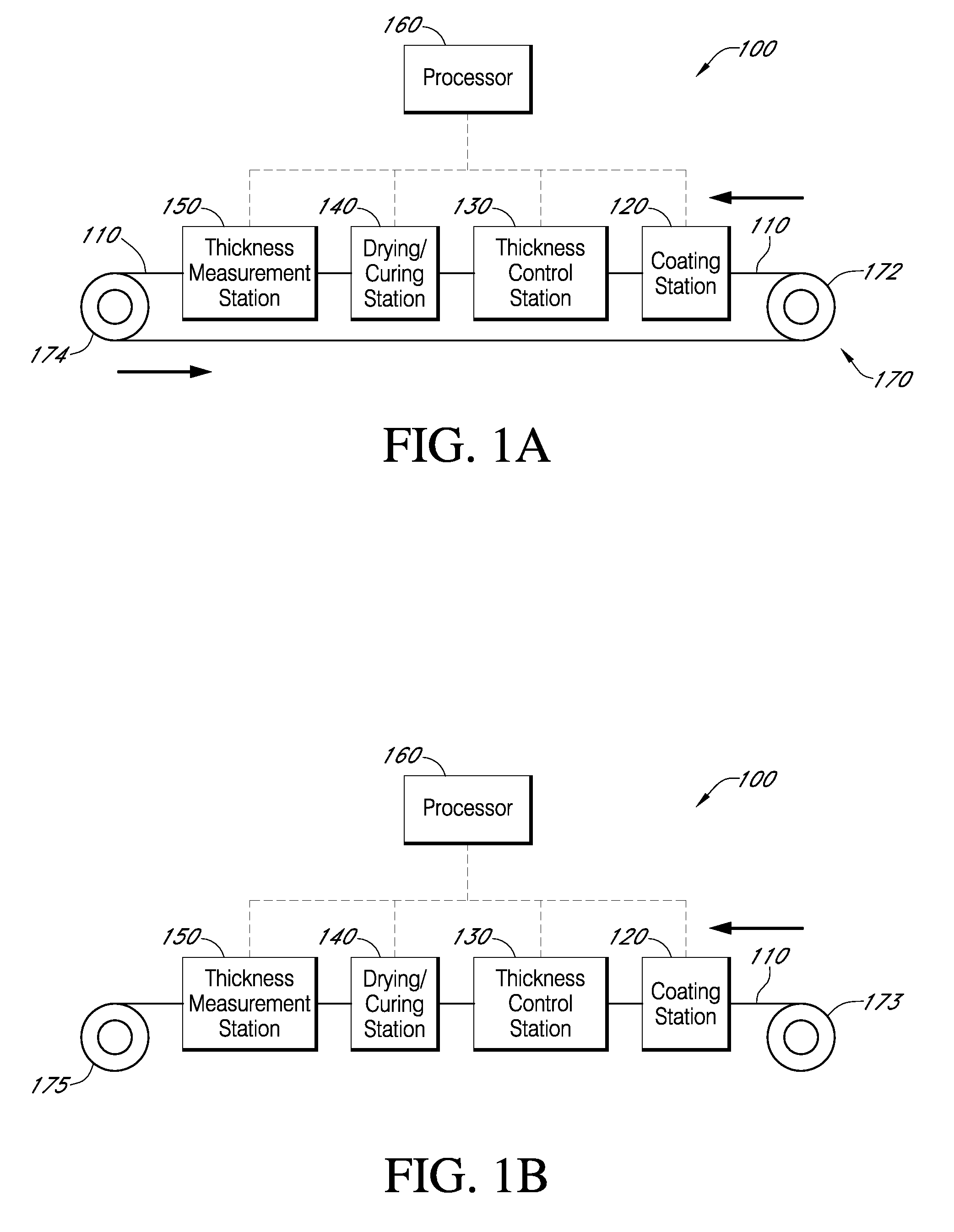
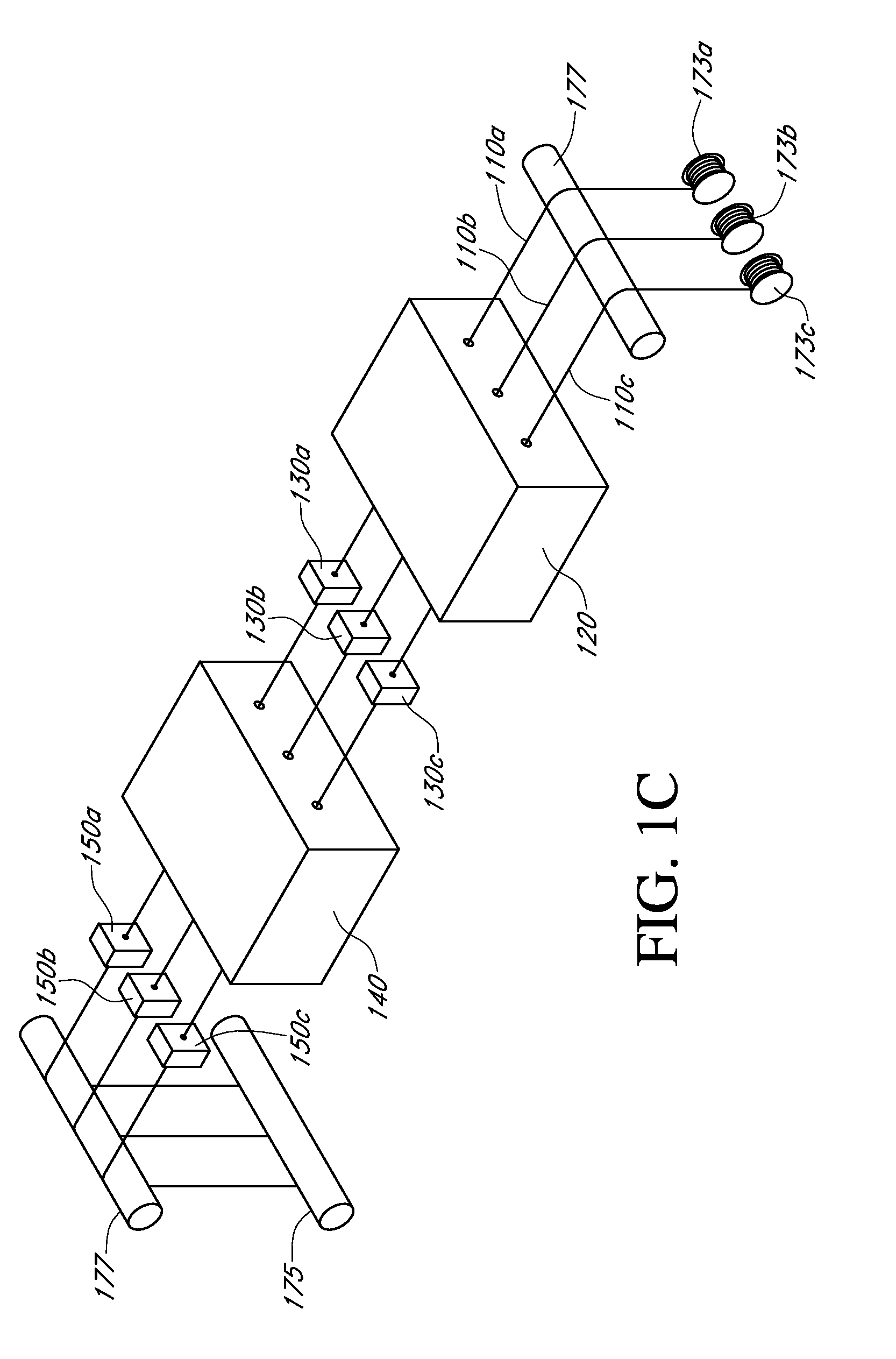
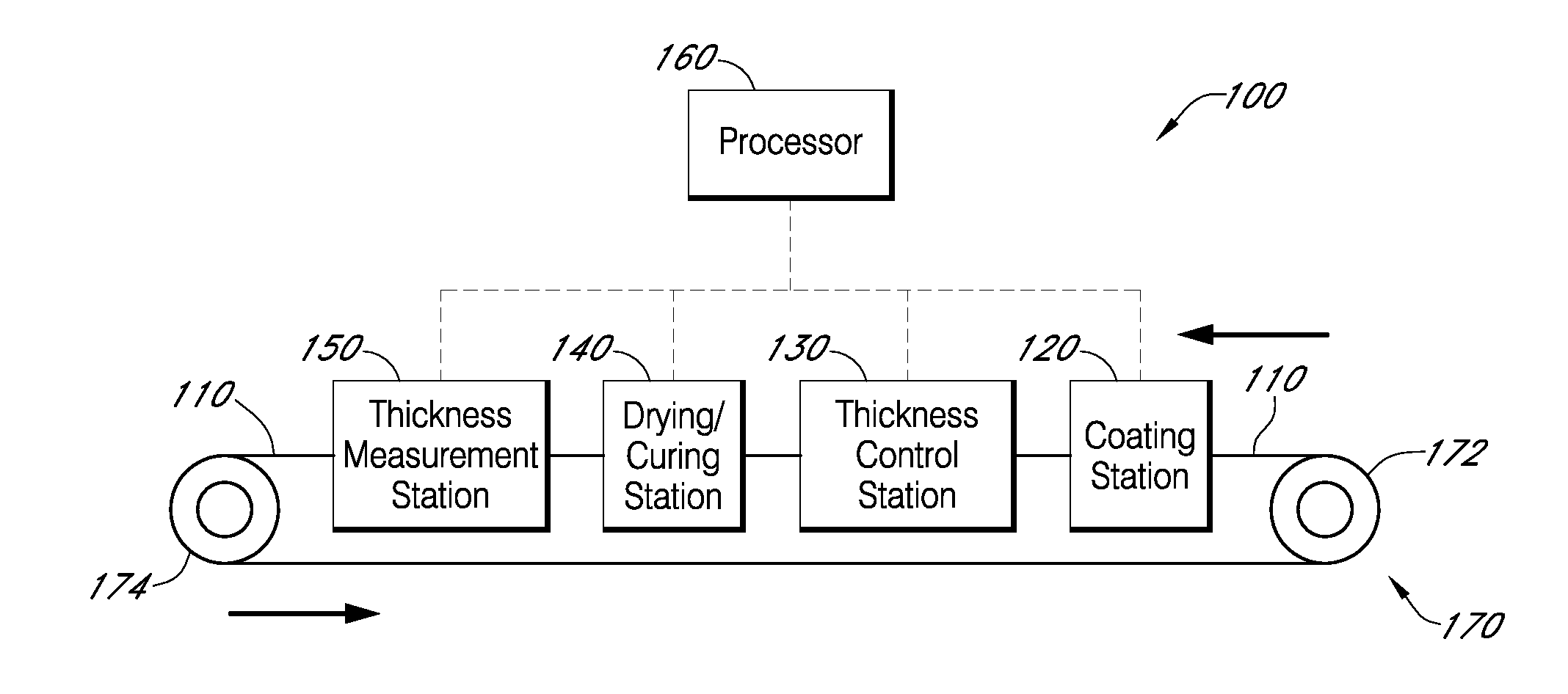
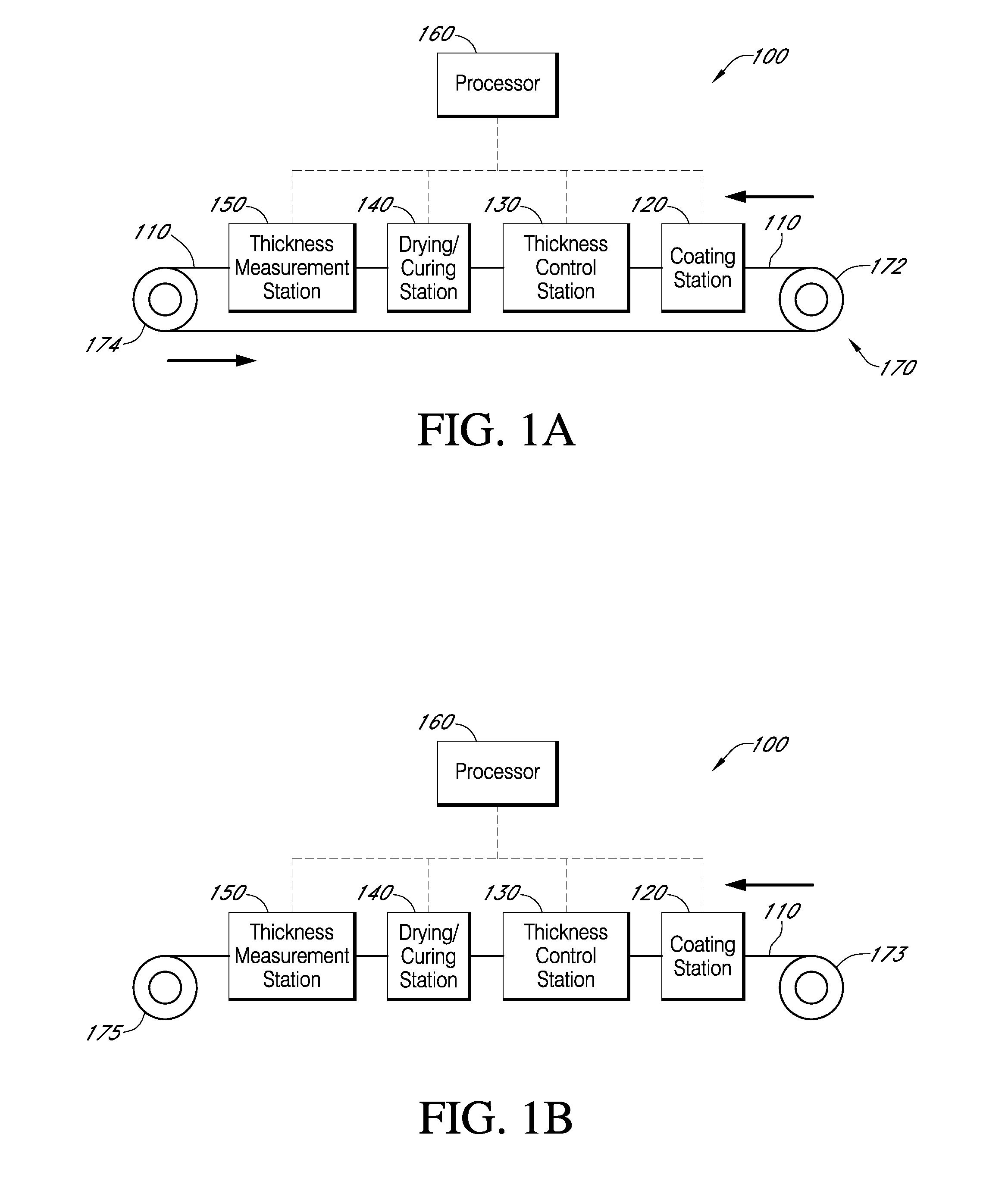
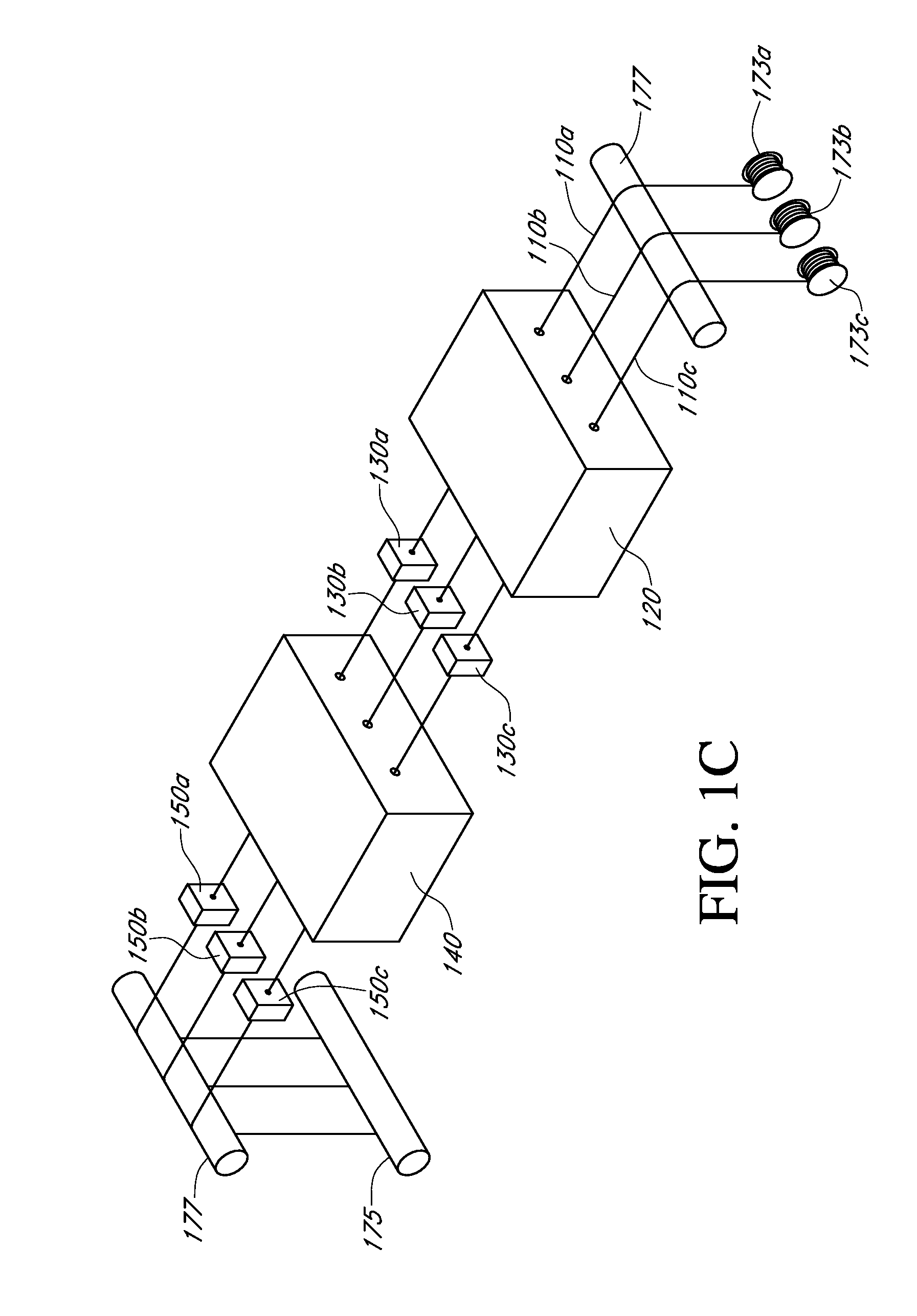
Described here are embodiments of processes and systems for the continuous manufacturing of implantable continuous analyte sensors. In some embodiments, a method is provided for sequentially advancing an elongated conductive body through a plurality of stations, each configured to treat the elongated conductive body. In some of these embodiments, one or more of the stations is configured to coat the elongated conductive body using a meniscus coating process, whereby a solution formed of a polymer and a solvent is prepared, the solution is continuously circulated to provide a meniscus on a top portion of a vessel holding the solution, and the elongated conductive body is advanced through the meniscus. The method may also comprise the step of removing excess coating material from the elongated conductive body by advancing the elongated conductive body through a die orifice. For example, a provided elongated conductive body 510 is advanced through a pre-coating treatment station 520, through a coating station 530, through a thickness control station 540, through a drying or curing station 550, through a thickness measurement station 560, and through a post-coating treatment station 570.
Owner:DEXCOM
Continuous analyte sensors and methods of making same
InactiveUS20110027453A1Low production costMinimize changesHot-dipping/immersion processesPharmaceutical containersAnalyteSolvent
Described here are embodiments of processes and systems for the continuous manufacturing of implantable continuous analyte sensors. In some embodiments, a method is provided for sequentially advancing an elongated conductive body through a plurality of stations, each configured to treat the elongated conductive body. In some of these embodiments, one or more of the stations is configured to coat the elongated conductive body using a meniscus coating process, whereby a solution formed of a polymer and a solvent is prepared, the solution is continuously circulated to provide a meniscus on a top portion of a vessel holding the solution, and the elongated conductive body is advanced through the meniscus. The method may also comprise the step of removing excess coating material from the elongated conductive body by advancing the elongated conductive body through a die orifice. For example, a provided elongated conductive body 510 is advanced through a pre-coating treatment station 520, through a coating station 530, through a thickness control station 540, through a drying or curing station 550, through a thickness measurement station 560, and through a post-coating treatment station 570.
Owner:DEXCOM
Precision spray processes for direct write electronic components
InactiveUS6251488B1Keep for a long timeIncrease probabilityMolten spray coatingVacuum evaporation coatingElectrical resistance and conductanceElectronic component
This invention combines the precision spray process with in-flight laser treatment in order to produce direct write electronic components. In addition to these components, the process can lay down lines of conductive, inductive, and resistive materials. This development has the potential to change the approach to electronics packaging. This process is revolutionary in that components can be directly produced on small structures, thus removing the need for printed circuit boards.
Owner:OPTOMEC DESIGN CO
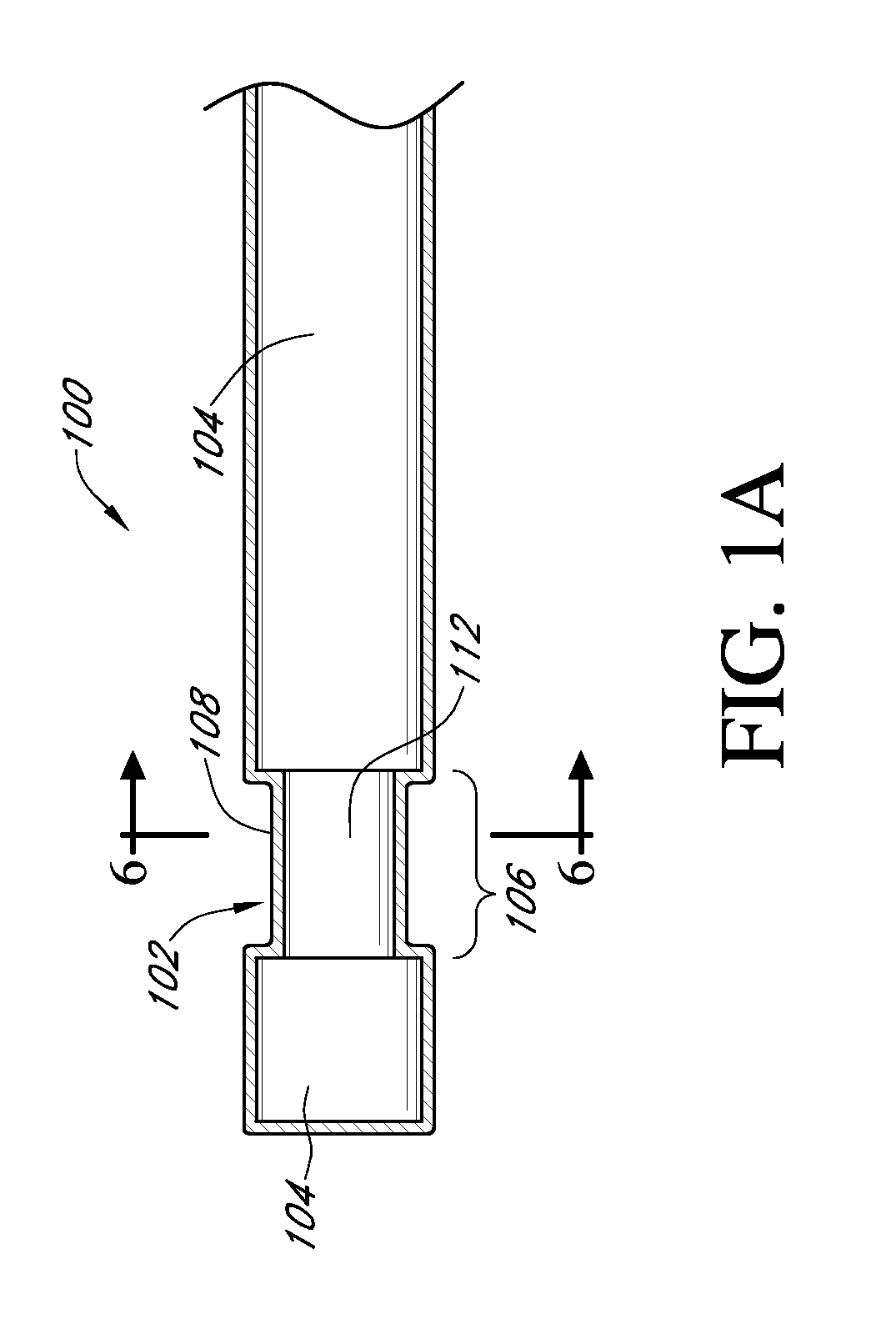
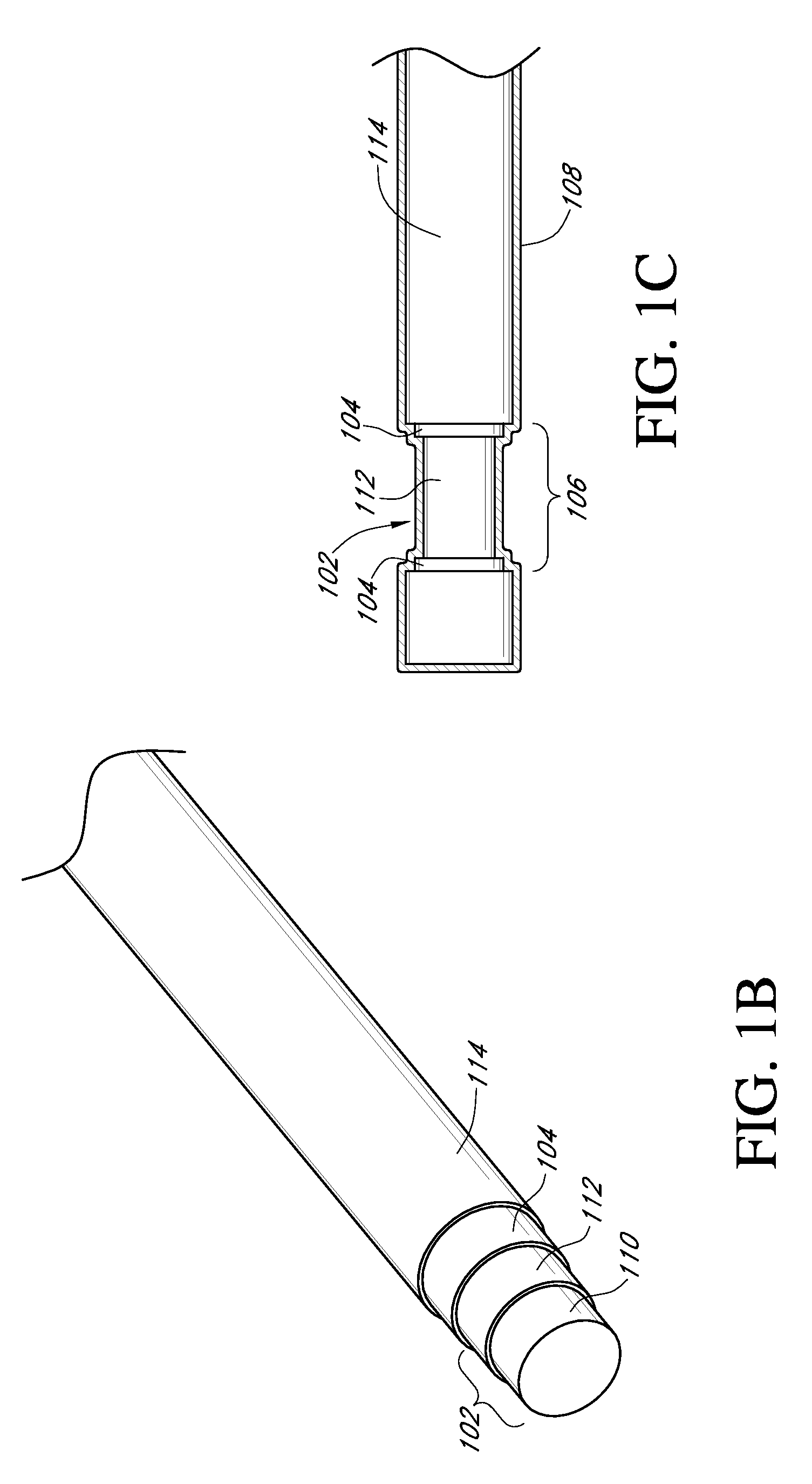
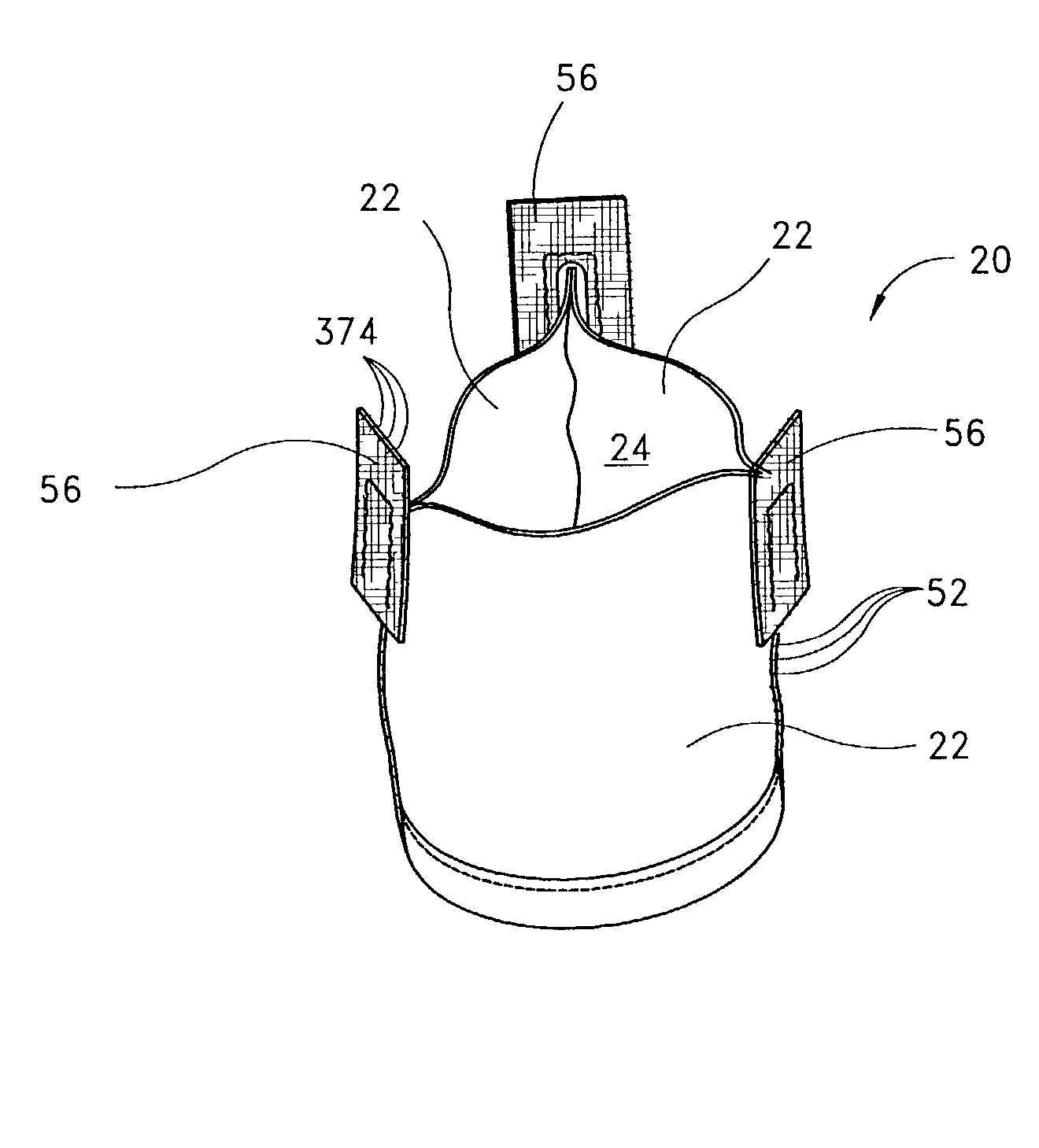
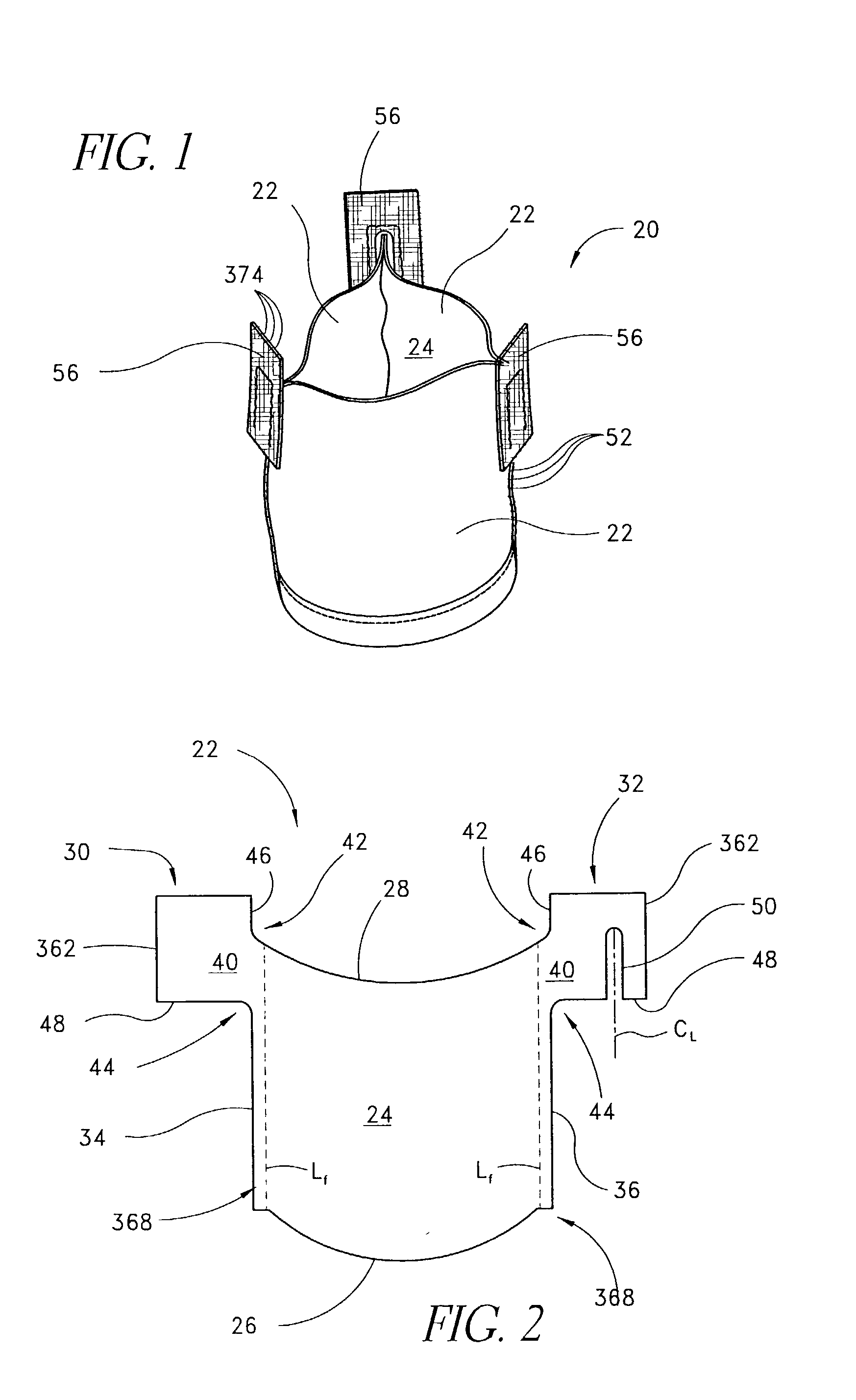
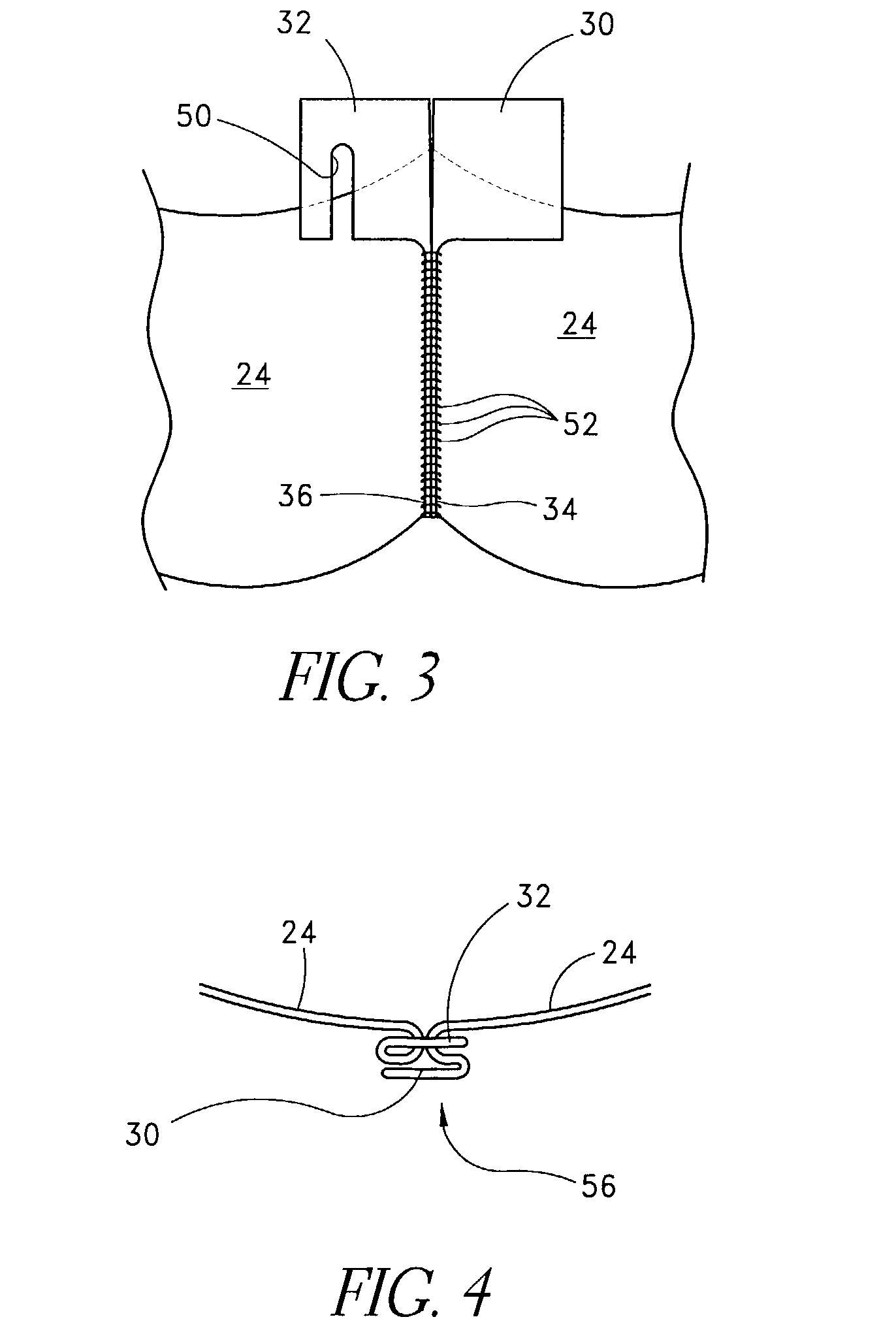
Method of cutting material for use in implantable medical device
A method of cutting material for use in an implantable medical device employs a plotted laser cutting system. The laser cutting system is computer controlled and includes a laser combined with a motion system. The laser precisely cuts segments out of source material according to a predetermined pattern as designated by the computer. The segments are used in constructing implantable medical devices. The cutting energy of the laser is selected so that the cut edges of the segments are melted to discourage delamination or fraying, but communication of thermal energy into the segment beyond the edge is minimized to avoid damaging the segment adjacent the edge.
Owner:3F THERAPEUTICS
Copper conductor annealing process employing high speed optical annealing with a low temperature-deposited optical absorber layer
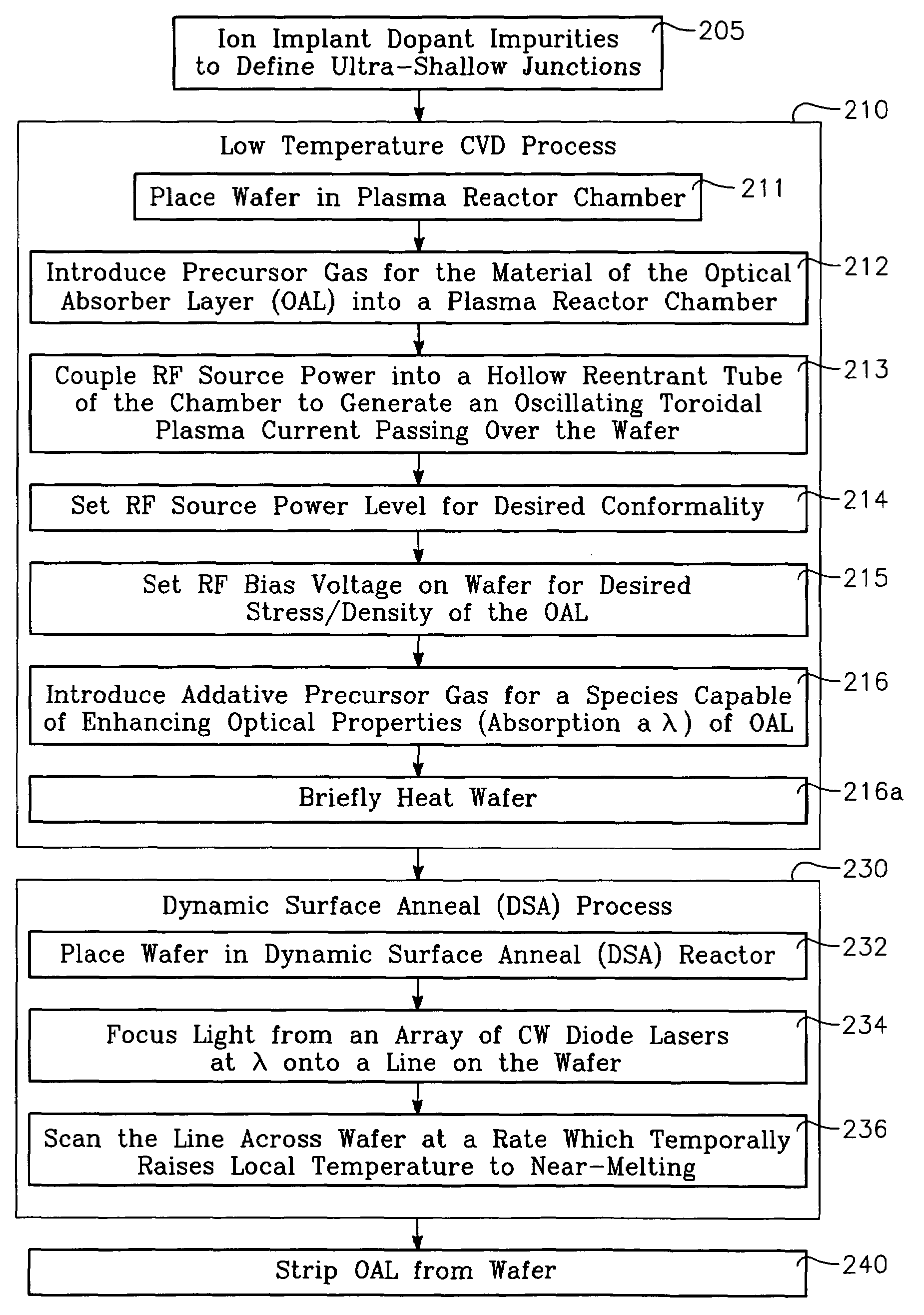
InactiveUS7335611B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesCopper conductorLow temperature deposition
A method of forming a conductor in a thin film structure on a semiconductor substrate includes forming high aspect ratio openings in a base layer having vertical side walls, depositing a dielectric barrier layer comprising a dielectric compound of a barrier metal on the surfaces of the high aspect ratio openings including the vertical side walls, depositing a metal barrier layer comprising the barrier metal on the first barrier layer, depositing a main conductor species seed layer on the metal barrier layer and depositing a main conductor layer. The method further includes annealing the main conductor layer by (a) directing light from an array of continuous wave lasers into a line of light extending at least partially across the thin film structure, and (b) translating the line of light relative to the thin film structure in a direction transverse to the line of light. The method of Claim 1 further comprising, prior to the annealing step, depositing an amorphous carbon optical absorber layer on the main conductor layer. The step of depositing an amorphous carbon optical absorber layer includes introducing a carbon-containing process gas into a reactor chamber containing the substrate in a process zone of the reactor, applying RF source power to an external reentrant conduit of the reactor to generate a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current passing through the process zone and applying a bias voltage to the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Laser ablation process and apparatus
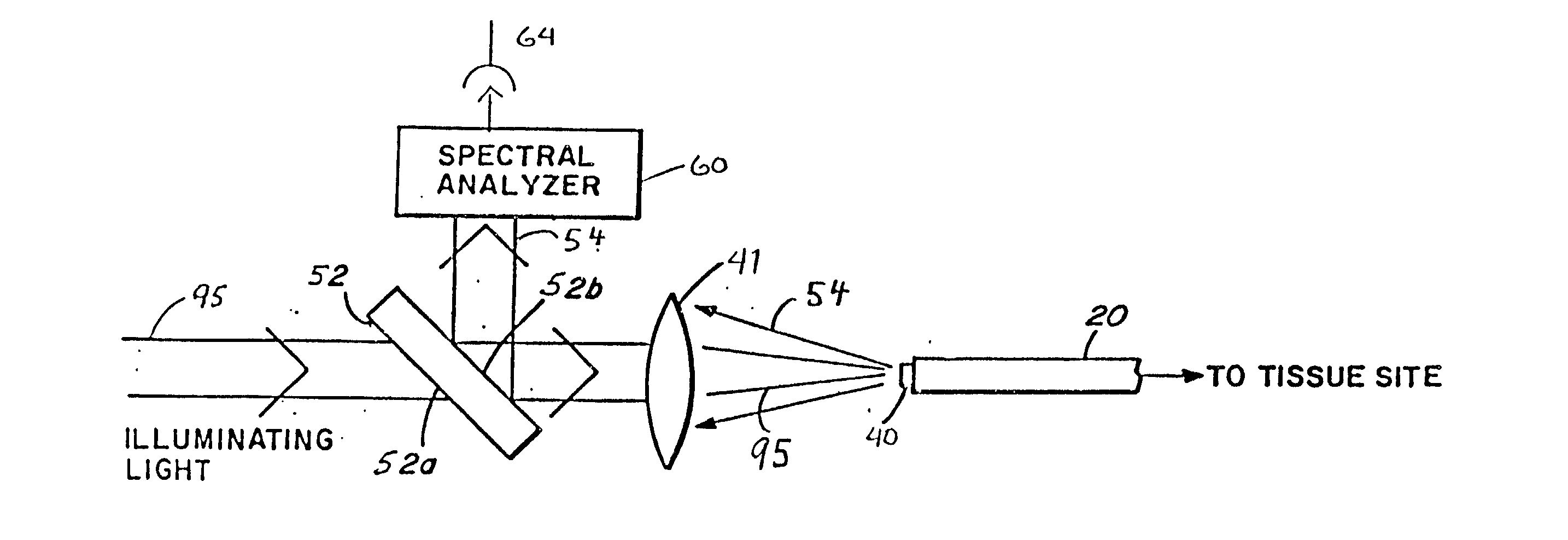
InactiveUS20020045811A1Reduce Fresnel reflectionMaximize transmitted lightControlling energy of instrumentDiagnostics using spectroscopyFiberLaser light
A laser catheter is disclosed wherein optical fibers carrying laser light are mounted in a catheter for insertion into an artery to provide controlled delivery of a laser beam for percutaneous intravascular laser treatment of atherosclerotic disease. A transparent protective shield is provided at the distal end of the catheter for mechanically diplacing intravascular blood and protecting the fibers from the intravascular contents, as well as protecting the patient in the event of failure of the fiber optics. Multiple optical fibers allow the selection of tissue that is to be removed. A computer controlled system automatically aligns fibers with the laser and controls exposure time. Spectroscopic diagnostics determine what tissue is to be removed.
Owner:KITTRELL CARTER +2
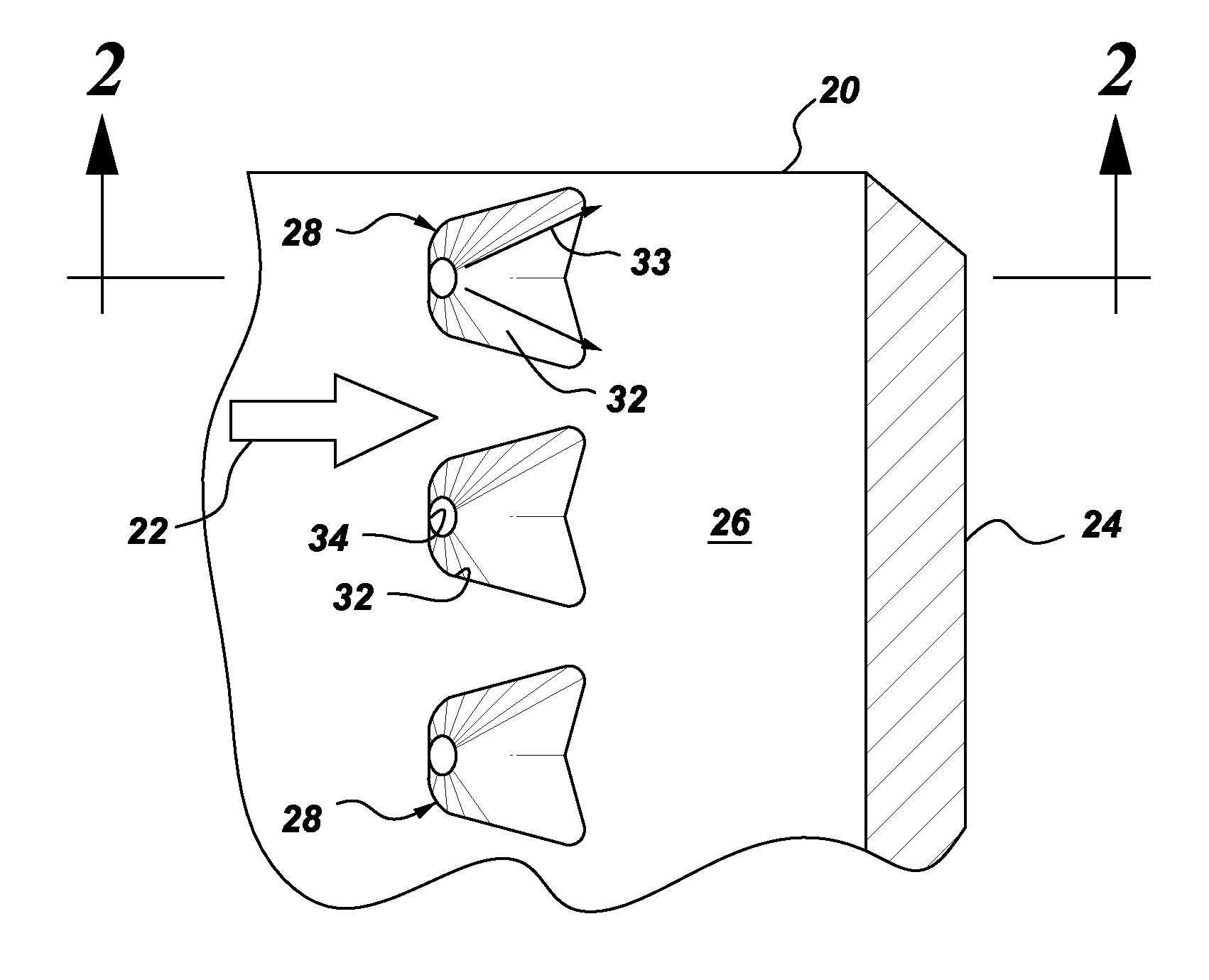
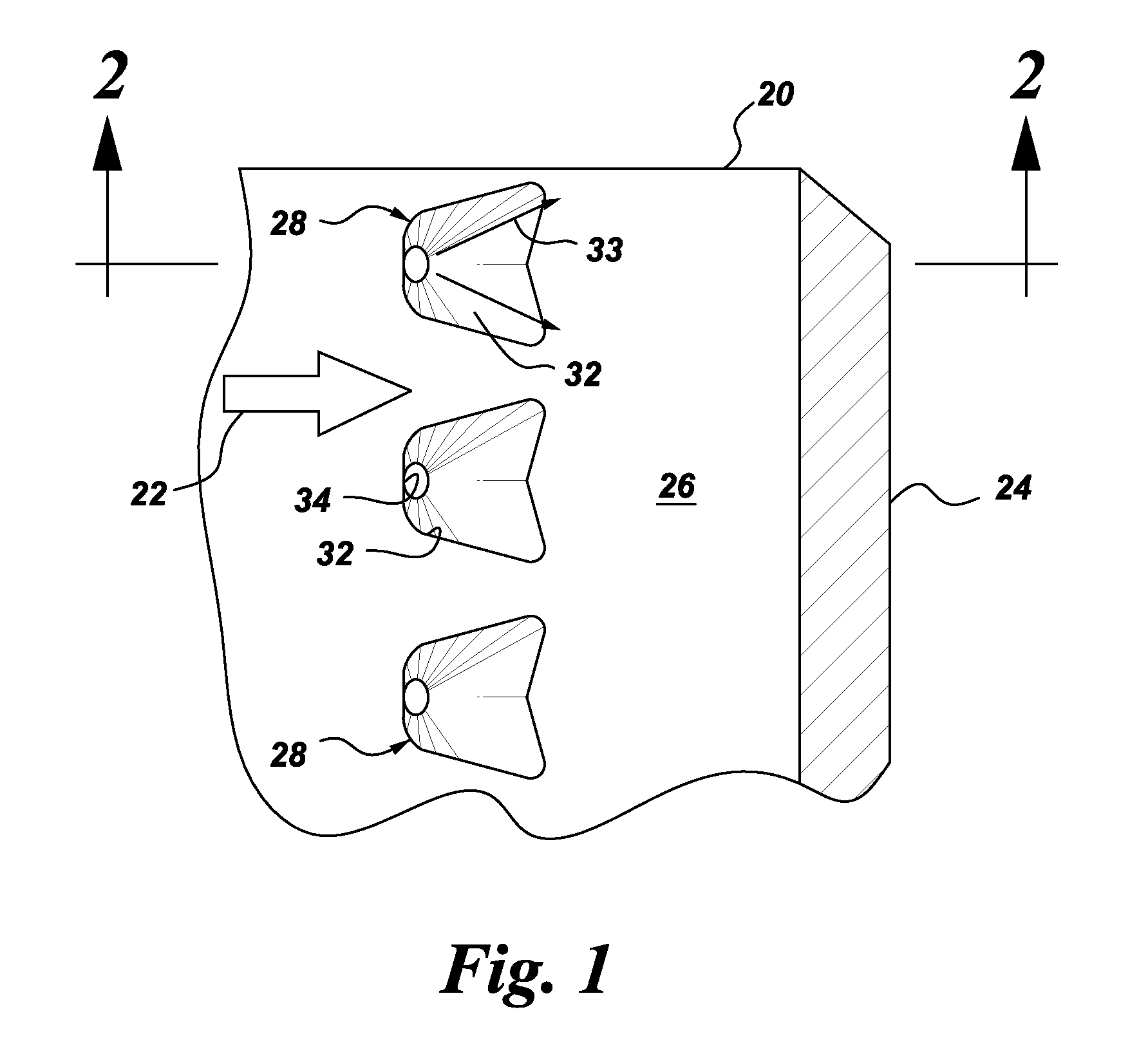
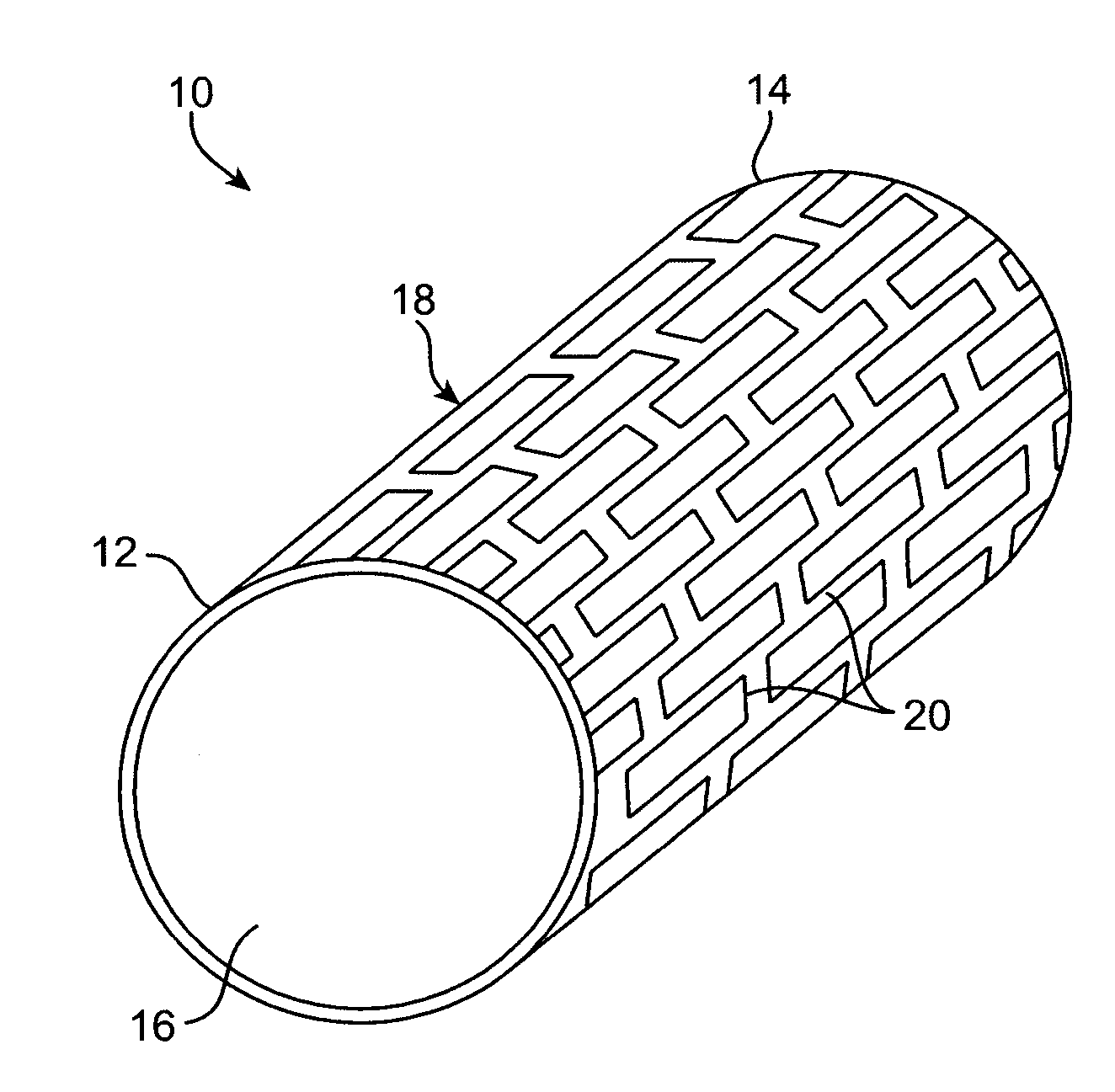
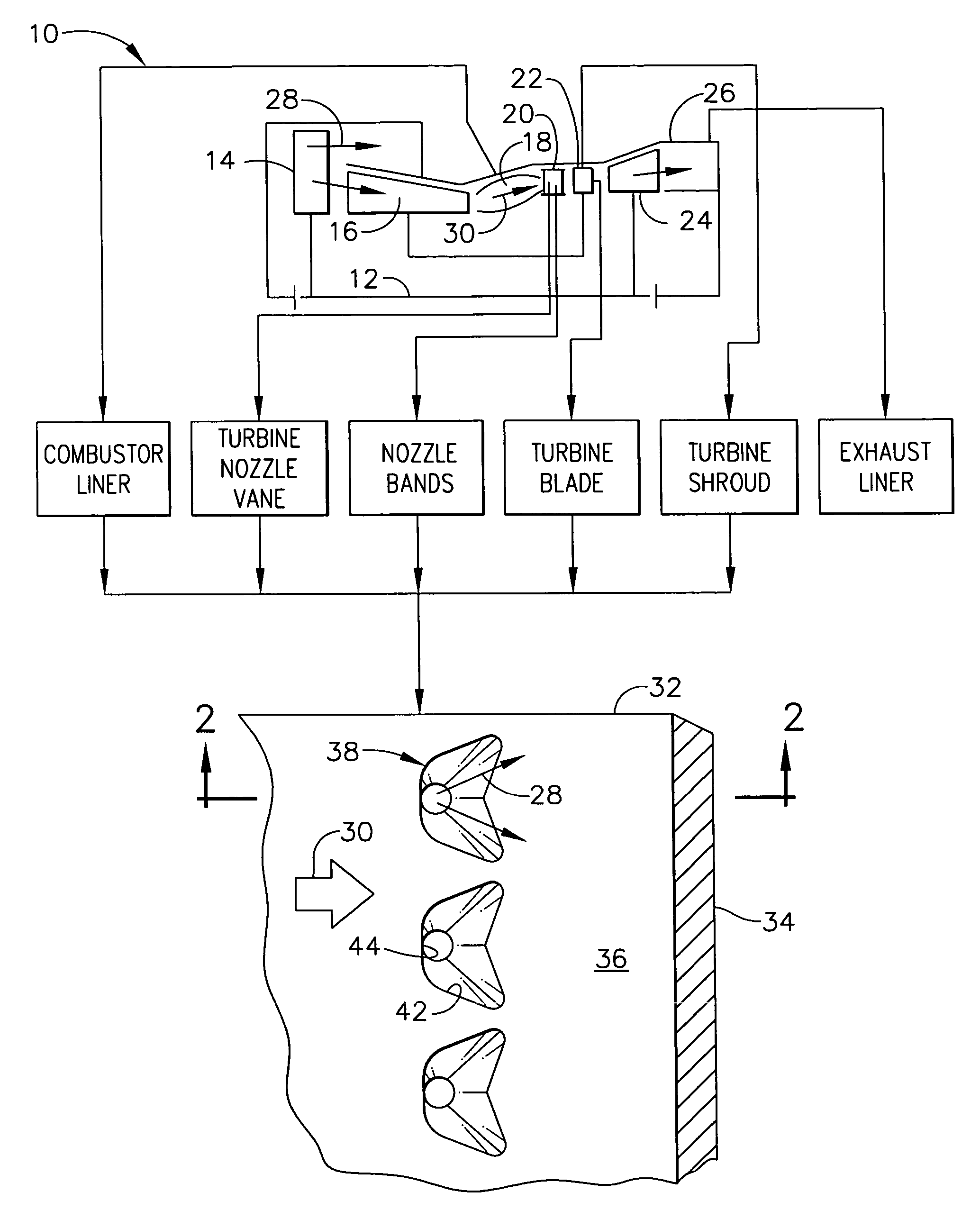
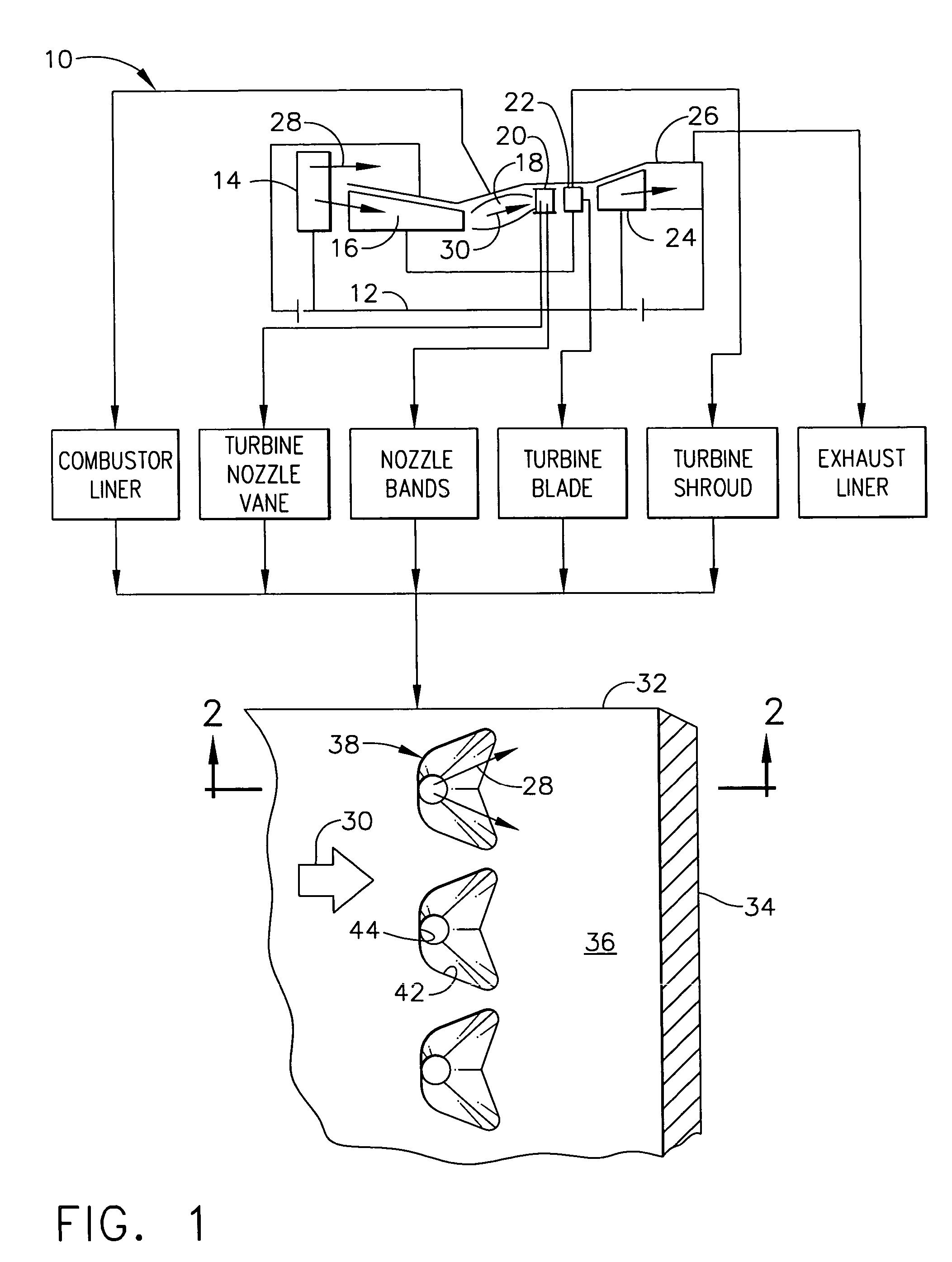
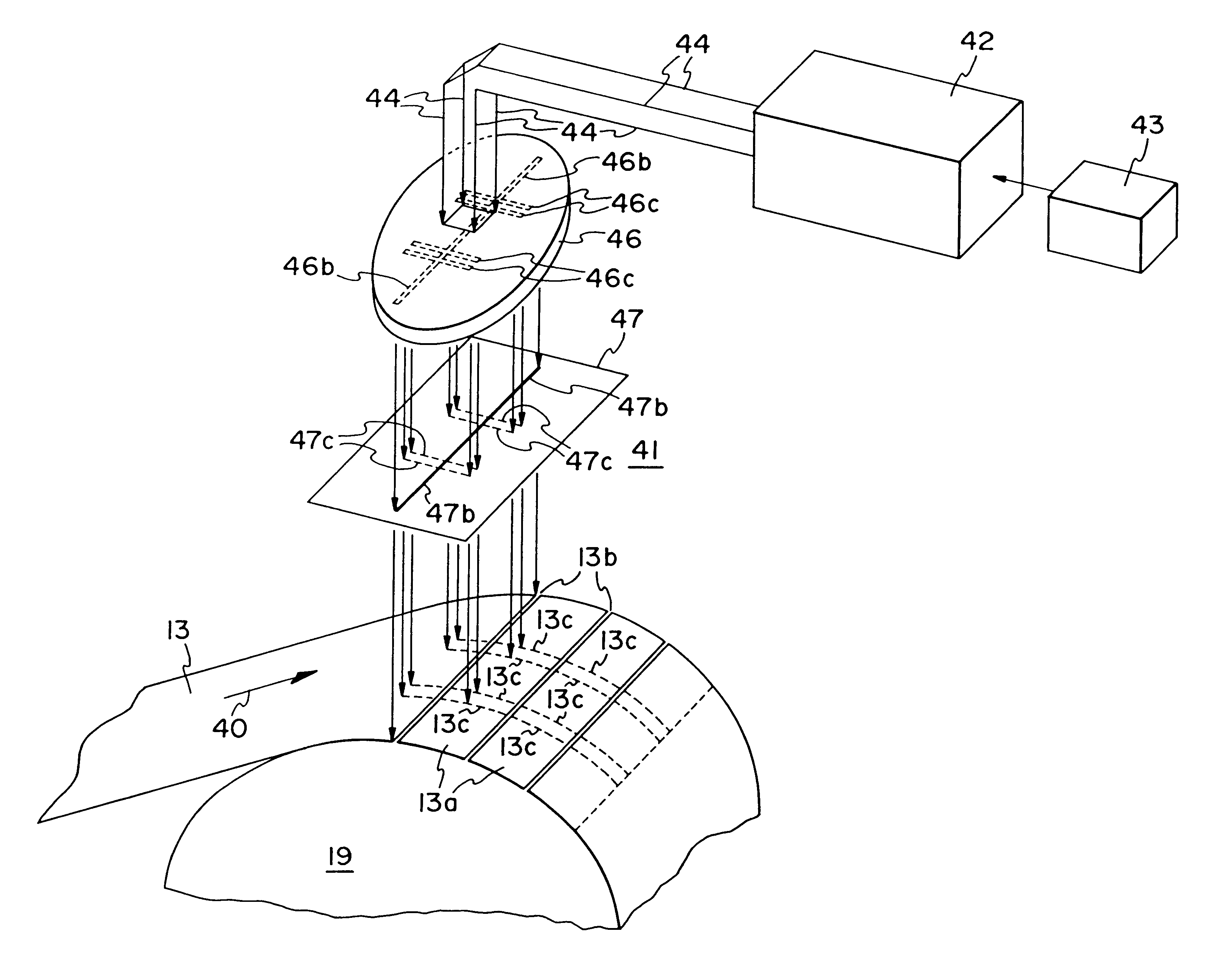
Articles which include chevron film cooling holes, and related processes
An article is described, including an inner surface which can be exposed to a first fluid; an inlet; and an outer surface spaced from the inner surface, which can be exposed to a hotter second fluid. The article further includes at least one row or other pattern of passage holes. Each passage hole includes an inlet bore extending through the substrate from the inlet at the inner surface to a passage hole-exit proximate to the outer surface, with the inlet bore terminating in a chevron outlet adjacent the hole-exit. The chevron outlet includes a pair of wing troughs having a common surface region between them. The common surface region includes a valley which is adjacent the hole-exit; and a plateau adjacent the valley. The article can be an airfoil. Related methods for preparing the passage holes are also described.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Tissue remover and method
InactiveUS6669685B1Fine and smooth incisionEasy to controlMedical devicesFluid jet surgical cuttersMedicineCutting force
An electromagnetically induced cutting mechanism provides accurate cutting operations on soft tissues. The electromagnetically induced cutter is adapted to interact with atomized fluid particles. A tissue remover comprises an aspiration cannula housing a fluid and energy guide for conducting electromagnetically induced cutting forces to the site within a patient's body for aspiration of soft tissue. The cannula is provided with a cannula distal end. The proximal end of the cannula is provided with fluid flow connection to an aspiration source. Separated soft tissue and fluid are aspirated through the cannula distal end and the cannula by an aspiration source at the proximal end of the cannula.
Owner:BIOLASE TECH INC
Method of cutting material for use in implantable medical device
A method of cutting material for use in an implantable medical device employs a plotted laser cutting system. The laser cutting system is computer controlled and includes a laser combined with a motion system. The laser precisely cuts segments out of source material according to a predetermined pattern as designated by the computer. The segments are used in constructing implantable medical devices. The cutting energy of the laser is selected so that the cut edges of the segments are melted to discourage delamination or fraying, but communication of thermal energy into the segment beyond the edge is minimized to avoid damaging the segment adjacent the edge.
Owner:3F THERAPEUTICS
Degradable implantable medical devices
InactiveUS20060229711A1Reduce probabilityLower resistanceStentsBlood vesselsVascular implantBlood vessel
Devices and methods are provided for an implantable medical device which is degradable over a clinically relevant period of time. The medical devices may have the form of implants, graft implants, vascular implants, non vascular implants, wound closure implants, sutures, drug delivery implants, biologic delivery implants, urinary tract implants, inter-uterine implants, organ implants, bone implants including bone plates, bone screws, dental implants, spinal disks, or the like. In preferred embodiments, the implantable medical device comprises an implantable luminal prosthesis, such as vascular and non-vascular stents and stents grafts.
Owner:ELIXIR MEDICAL CORP
Method for controlling configuration of laser induced breakdown and ablation
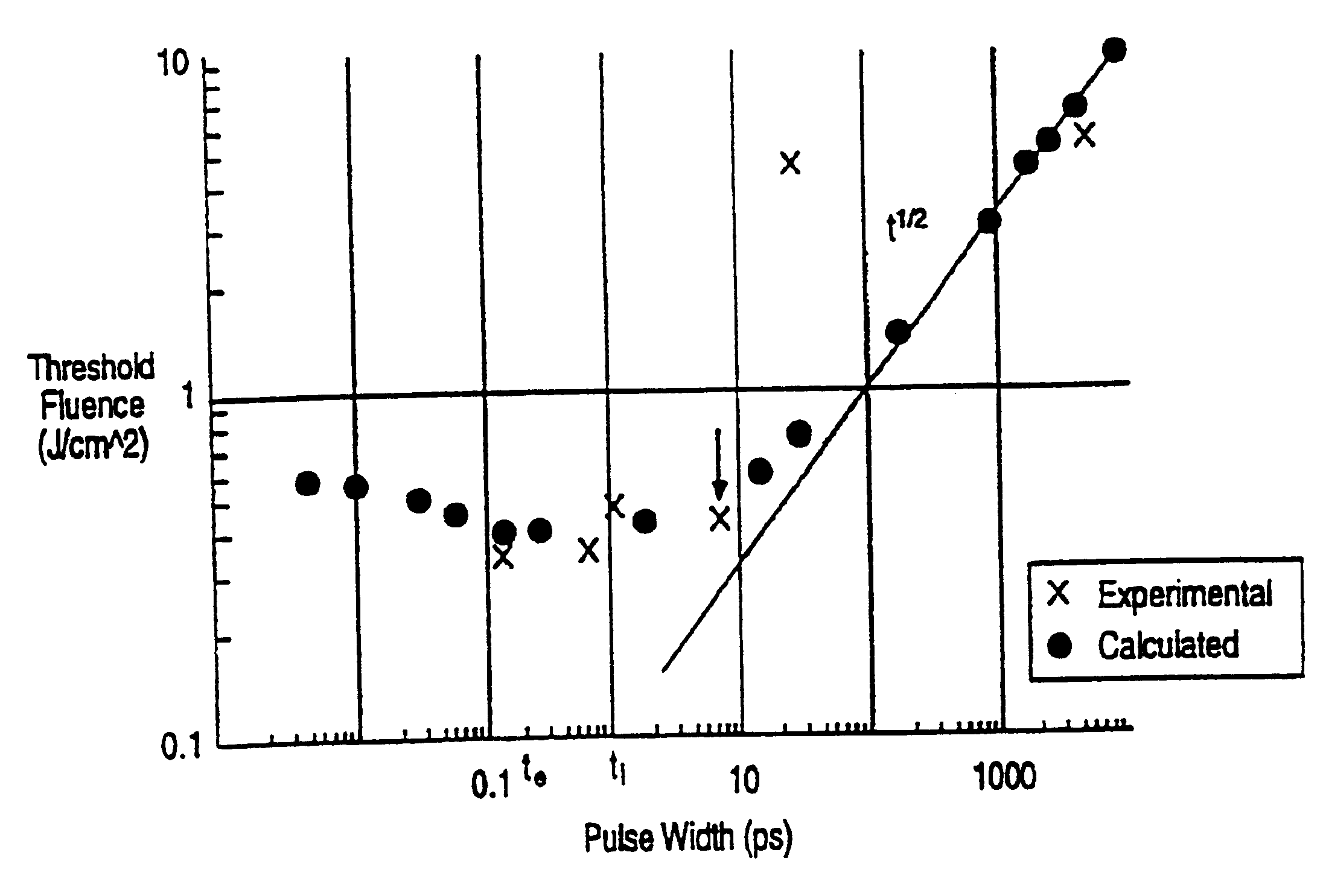
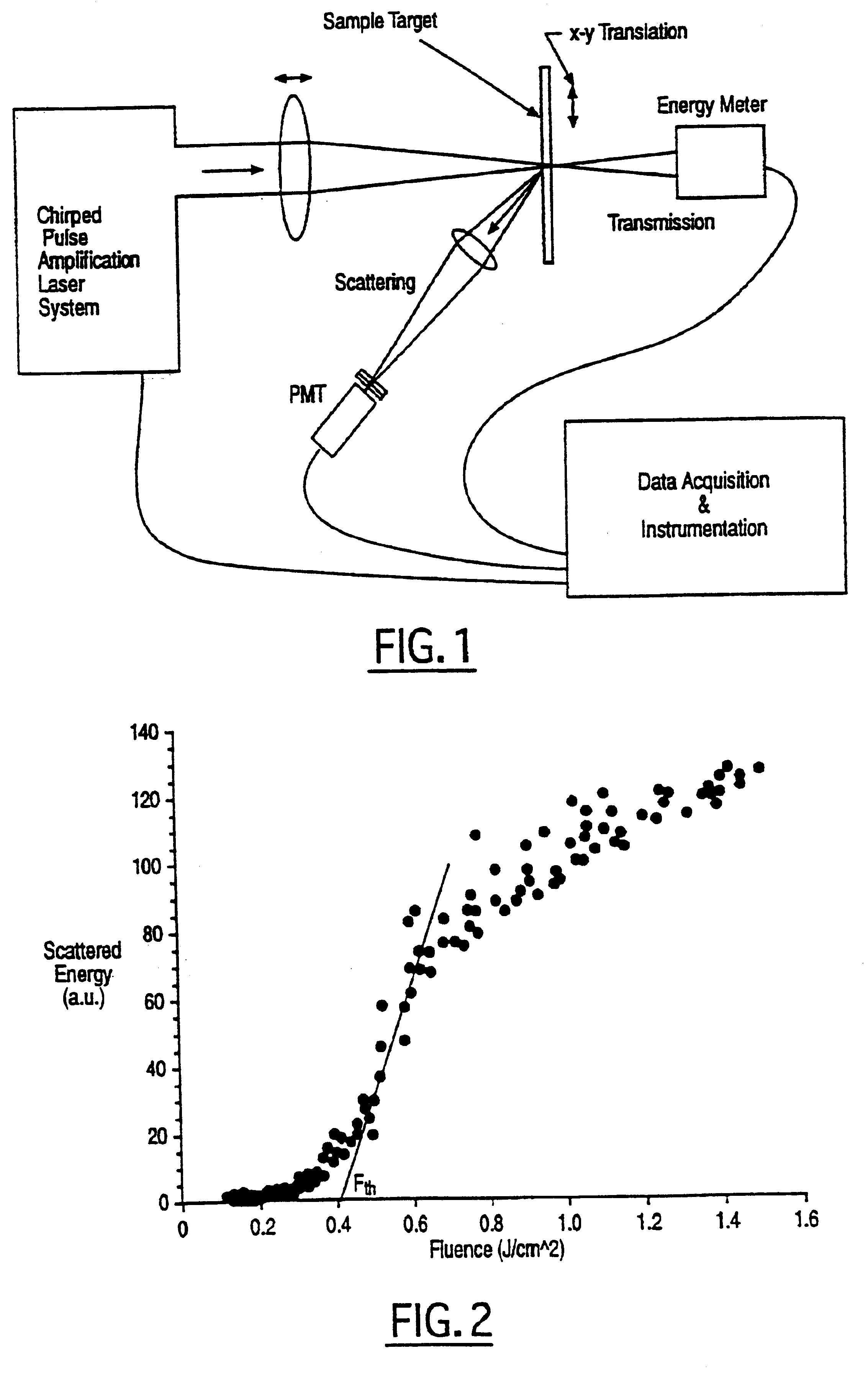
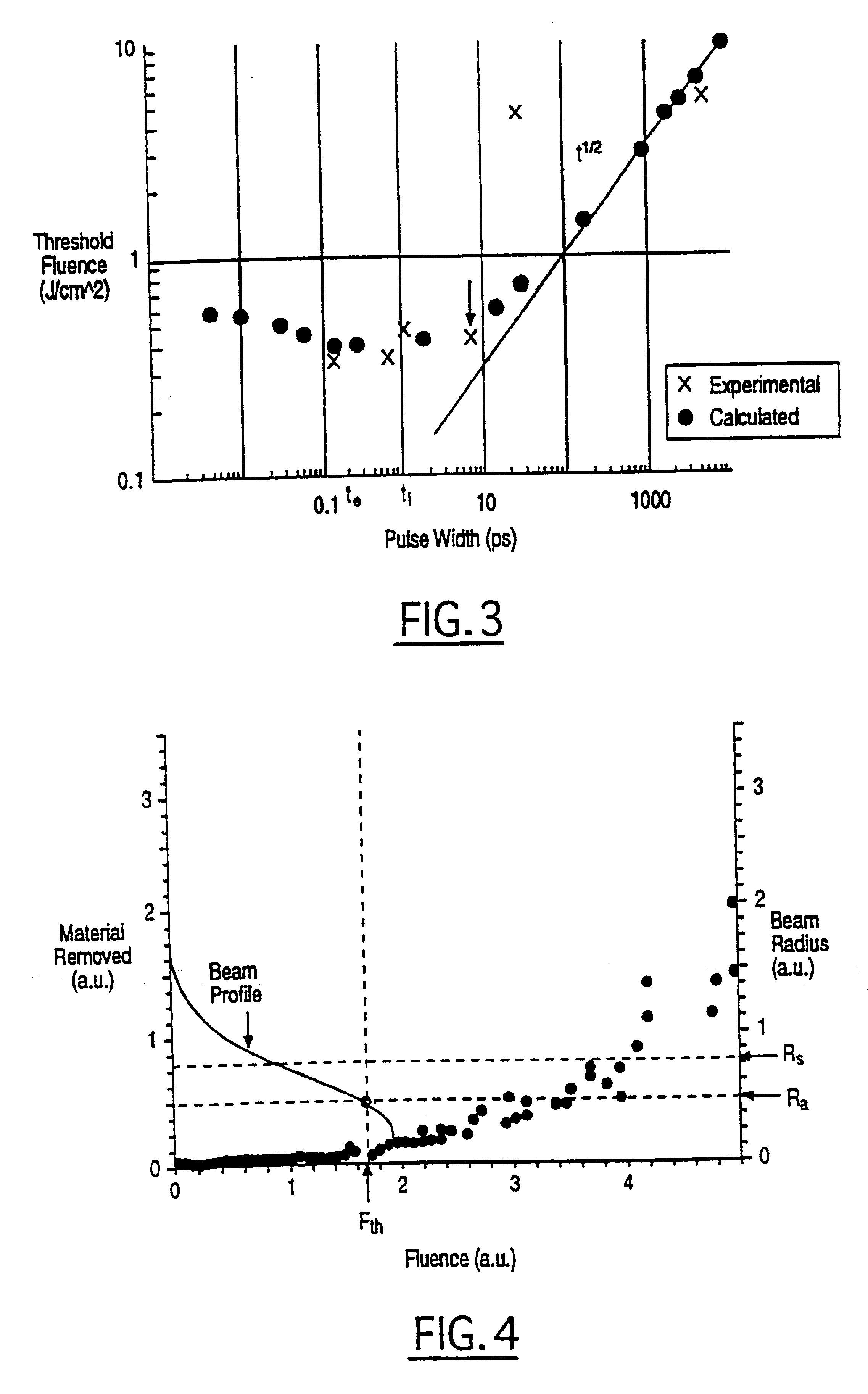
In one aspect the invention provides a method for laser induced breakdown of a material with a pulsed laser beam where the material is characterized by a relationship of fluence breakdown threshold (Fth) versus laser beam pulse width (T) that exhibits an abrupt, rapid, and distinct change or at least a clearly detectable and distinct change in slope at a predetermined laser pulse width value. The method comprises generating a beam of laser pulses in which each pulse has a pulse width equal to or less than the predetermined laser pulse width value. The beam is focused to a point at or beneath the surface of a material where laser induced breakdown is desired.The beam may be used in combination with a mask in the beam path. The beam or mask may be moved in the x, y, and Z directions to produce desired features. The technique can produce features smaller than the spot size and Rayleigh range due to enhanced damage threshold accuracy in the short pulse regime.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Laser-produced porous surface
ActiveUS20070142914A1Promote bone ingrowthGood stiffness characteristicsAdditive manufacturing apparatusMolten spray coatingLight beamMetal powder
A method of forming an implant having a porous tissue ingrowth structure and a bearing support structure. The method includes depositing a first layer of a metal powder onto a substrate, scanning a laser beam over the powder so as to sinter the metal powder at predetermined locations, depositing at least one layer of the metal powder onto the first layer and repeating the scanning of the laser beam.
Owner:UNIV OF LIVERPOOL +1
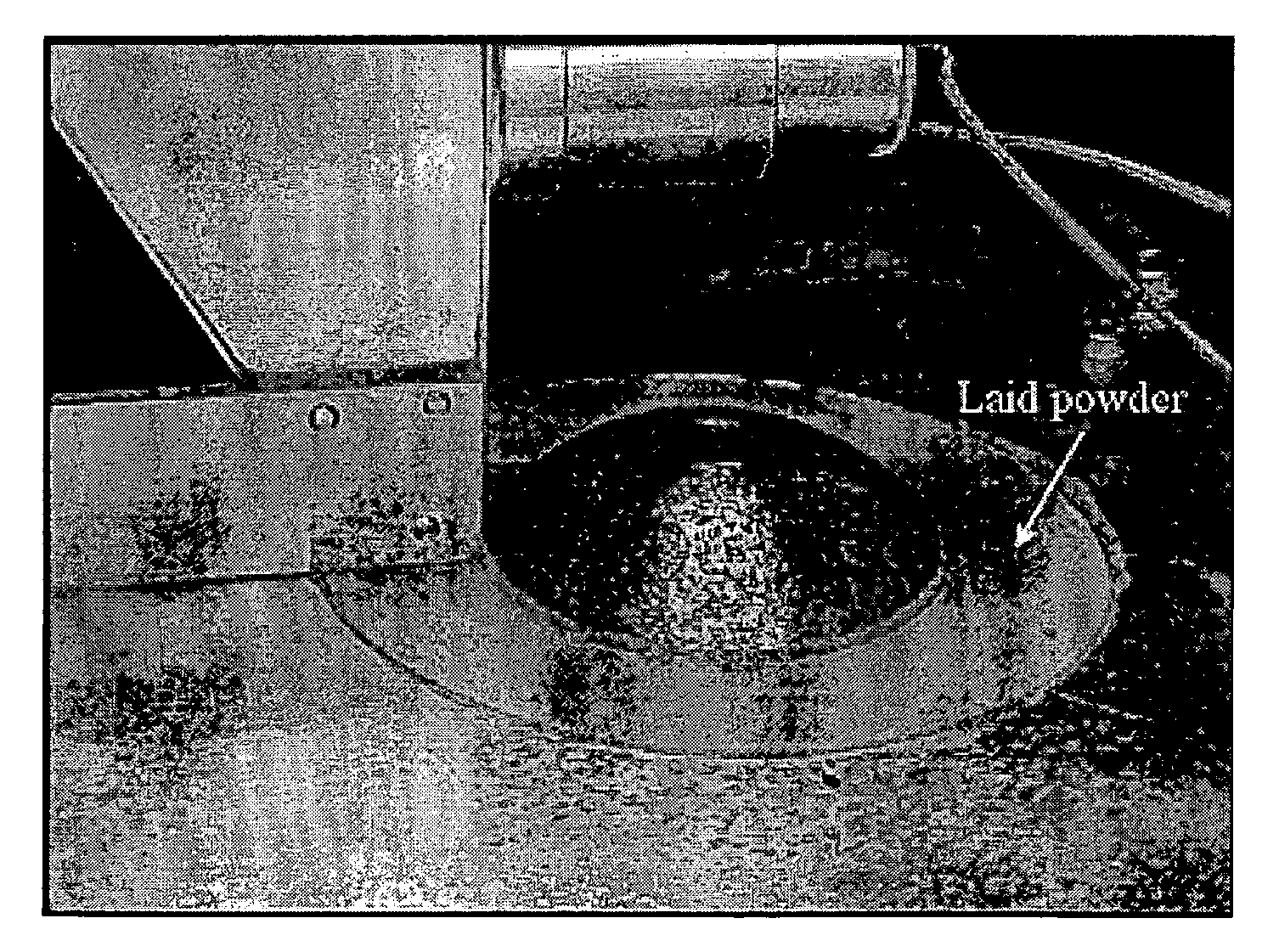
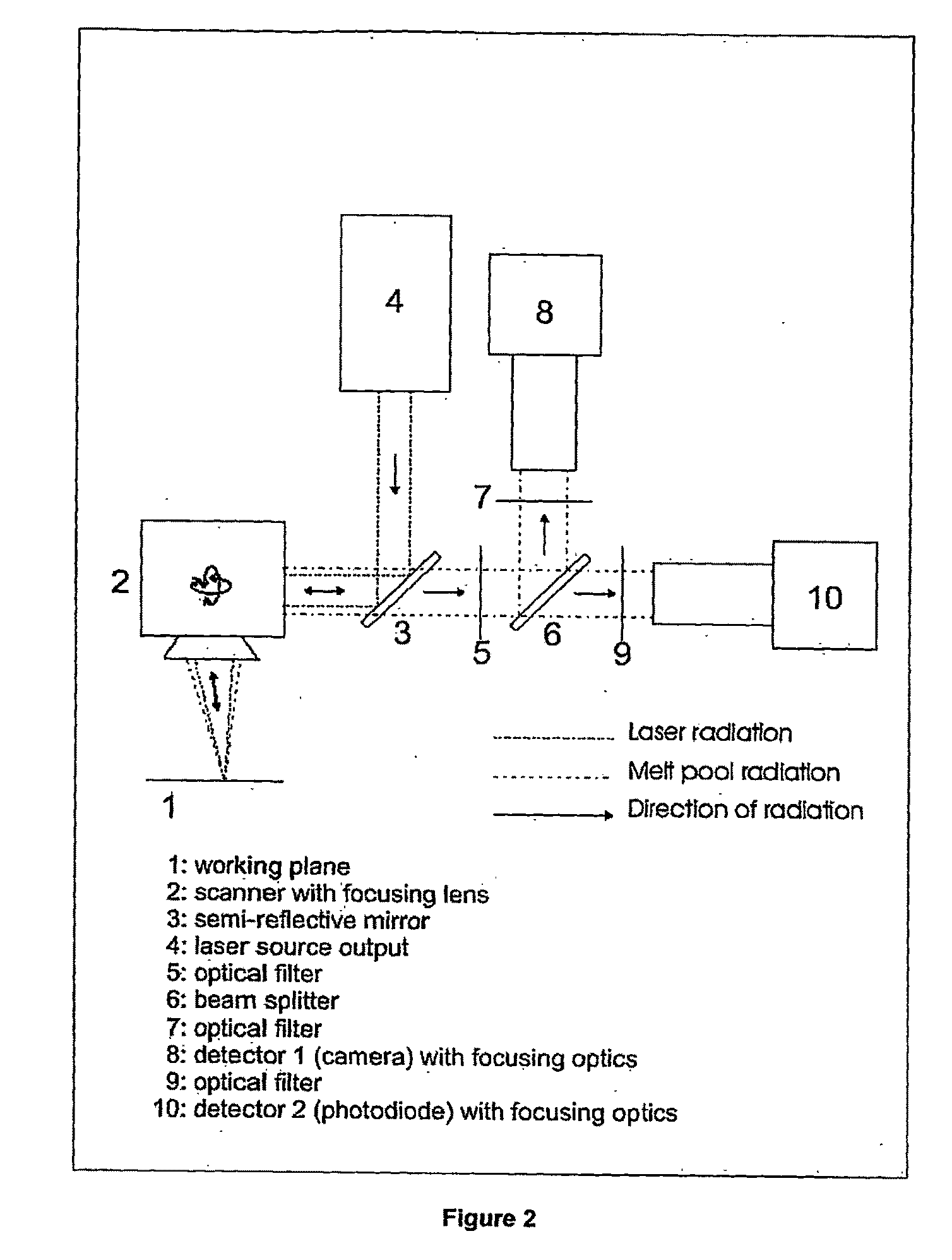
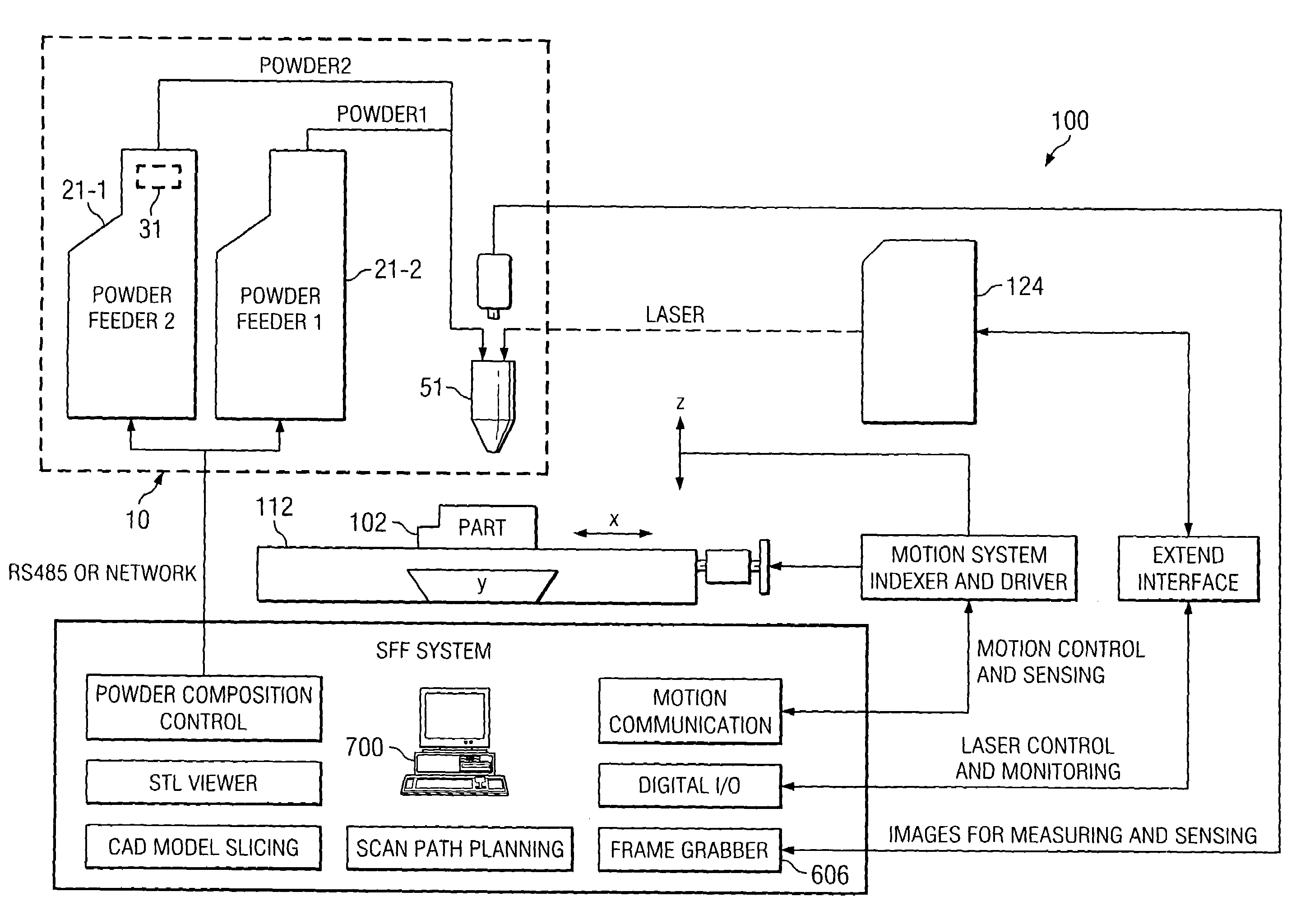
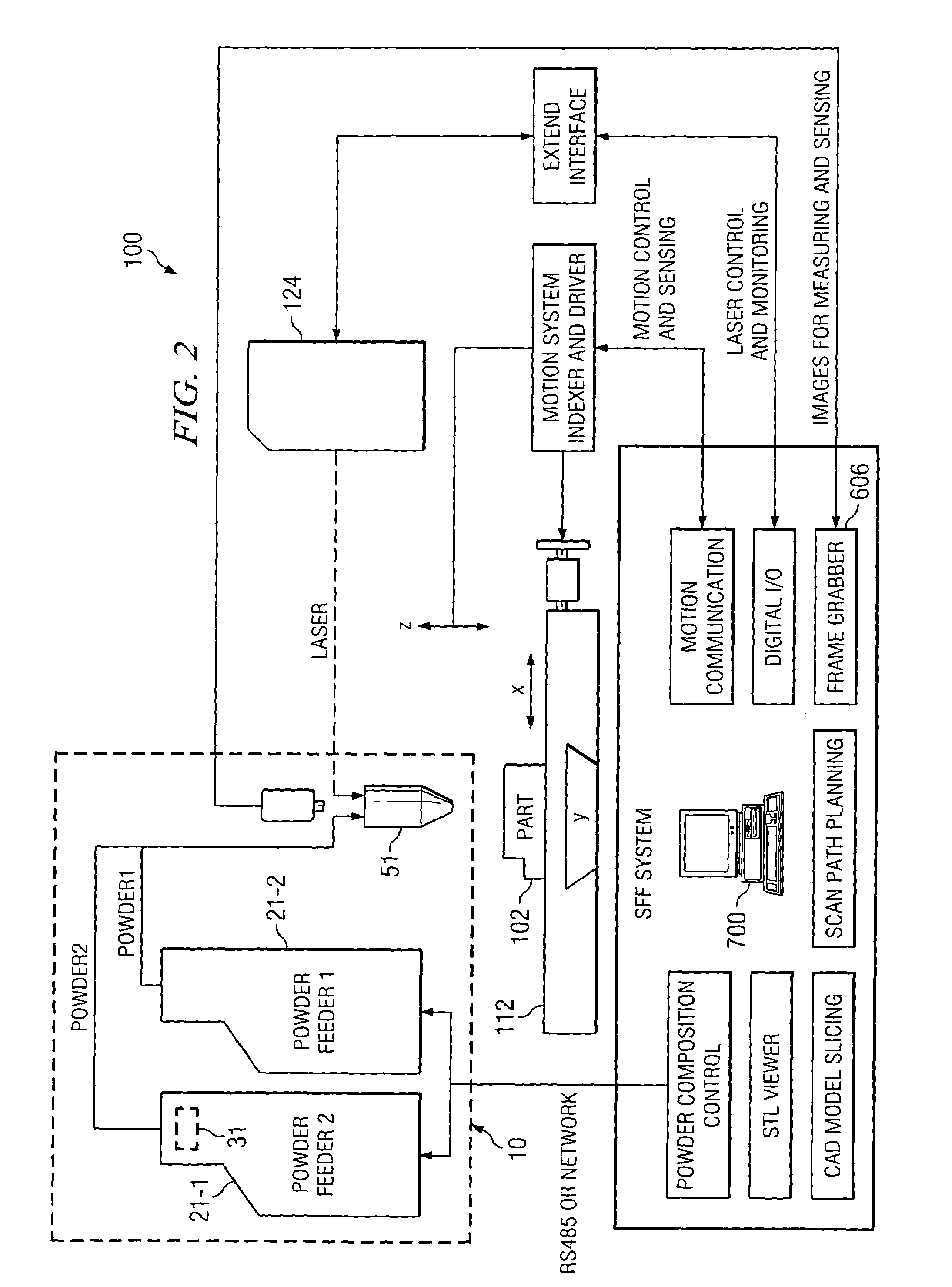
Procedure and apparatus for in-situ monitoring and feedback control of selective laser powder processing
InactiveUS20090206065A1Quality improvementReduce spectral distortionAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyControl systemFeedback controller
The present invention relates to a method and a device to monitor and control the Selective Laser Powder Processing. A Selective Laser Powder Processing device comprising a feedback controller to improve the stability of the Selective Laser Powder Processing process is presented. A signal reflecting a geometric quantity of the melt zone is used in the feedback controller to adjust the scanning parameters (e.g. laser power, laser spot size, scanning velocity, . . . ) of the laser beam (4) in order to maintain the geometric quantity of the melt zone at a constant level. The signal reflecting the geometric quantity of the melt zone can also be displayed in order to monitor the Selective Laser Powder Processing process. The present invention allows for the production of three-dimensional objects from powder material and improves the state of the art by compensating variations of the border conditions (e.g. local heat conduction rate) by a feedback control system based on a geometric quantity of the melt zone resulting in e.g. a lower amount of dross material when overhang planes are scanned.
Owner:KRUTH JEAN PIERRE +1
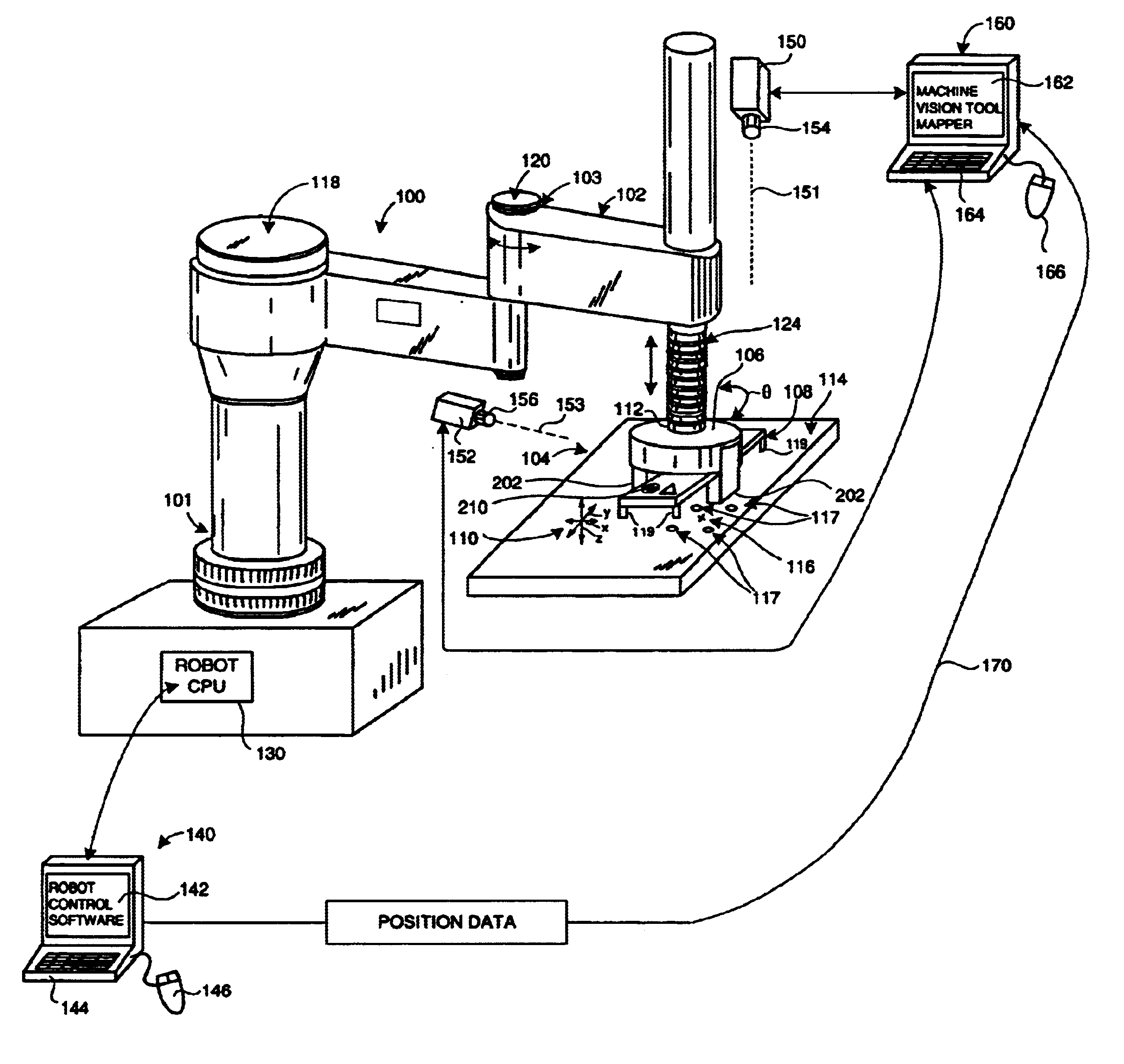
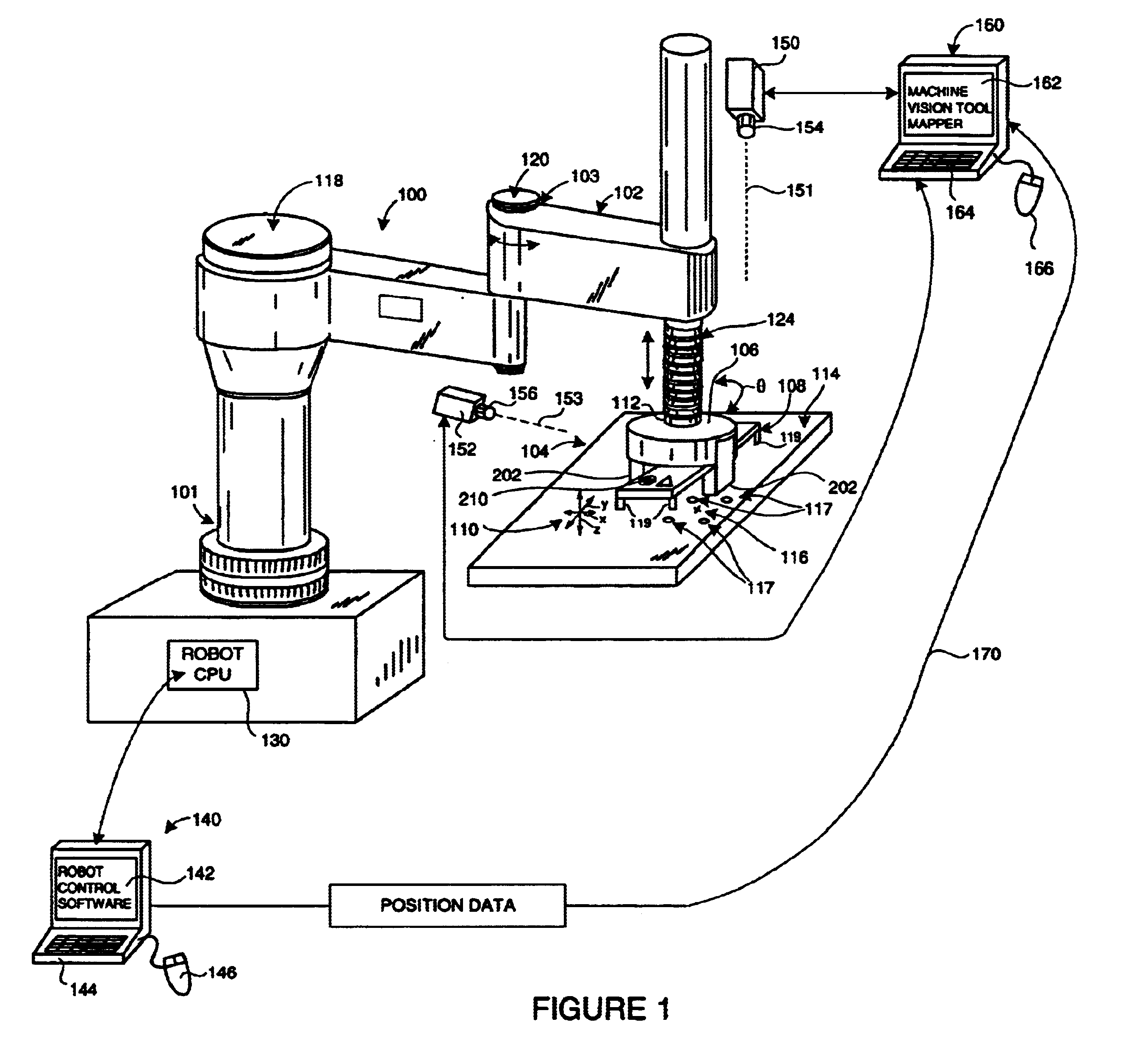
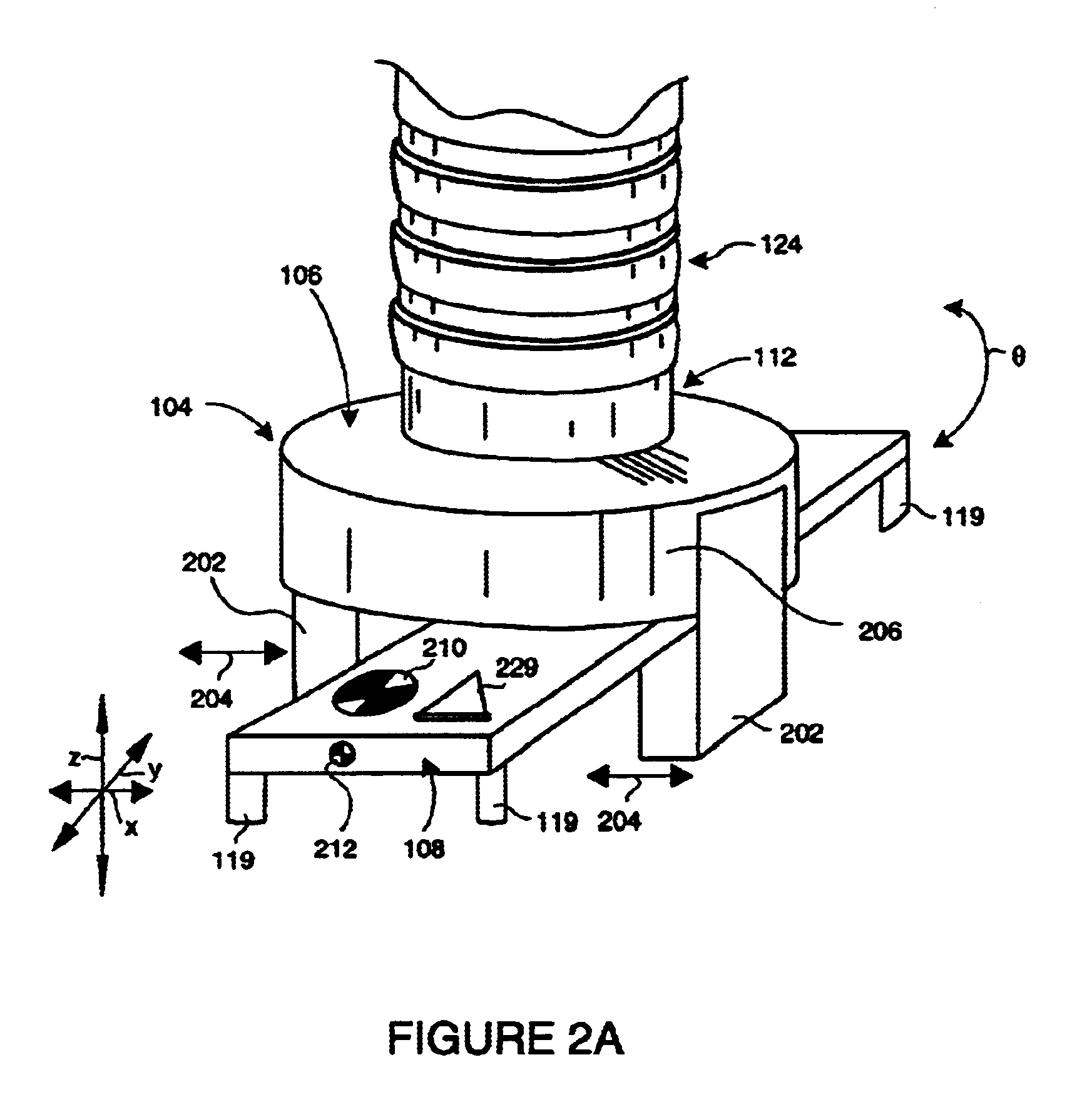
System and method for servoing robots based upon workpieces with fiducial marks using machine vision
InactiveUS6681151B1Sure easyLocated reliablyProgramme-controlled manipulatorPhotometry using reference valueEngineeringDegrees of freedom
A system and method for servoing robot marks using fiducial marks and machine vision provides a machine vision system having a machine vision search tool that is adapted to register a pattern, namely a trained fiducial mark, that is transformed by at least two translational degrees and at least one mon-translational degree of freedom. The fiducial is provided to workpiece carried by an end effector of a robot operating within a work area. When the workpiece enters an area of interest within a field of view of a camera of the machine vision system, the fiducial is recognized by the tool based upon a previously trained and calibrated stored image within the tool. The location of the work-piece is derived by the machine vision system based upon the viewed location of the fiducial. The location of the found fiducial is compared with that of a desired location for the fiducial. The desired location can be based upon a standard or desired position of the workpiece. If a difference between location of the found fiducial and the desired location exists, the difference is calculated with respect to each of the translational axes and the rotation. The difference can then be further transformed into robot-based coordinates to the robot controller, and workpiece movement is adjusted based upon the difference. Fiducial location and adjustment continues until the workpiece is located the desired position with minimum error.
Owner:COGNEX TECH & INVESTMENT
Chevron film cooled wall
A wall in a gas turbine engine includes inner and outer surfaces having a row of compound chevron film cooling holes extending therethrough. The chevron holes diverge both longitudinally and laterally between an inlet at the wall inner surface and a chevron outlet at the wall outer surface.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method of making a biosensor
InactiveUS7073246B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsConductive materialsEngineering
A method of making a biosensor is provided. The biosensor includes an electrically conductive material on a base and electrode patterns formed on the base, the patterns having different feature sizes. The conductive material is partially removed from the base using broad field laser ablation so that less than 90% of the conductive material remains on the base and that the electrode pattern has an edge extending between two points. A standard deviation of the edge from a line extending between two points is less than about 6 μm.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC +1
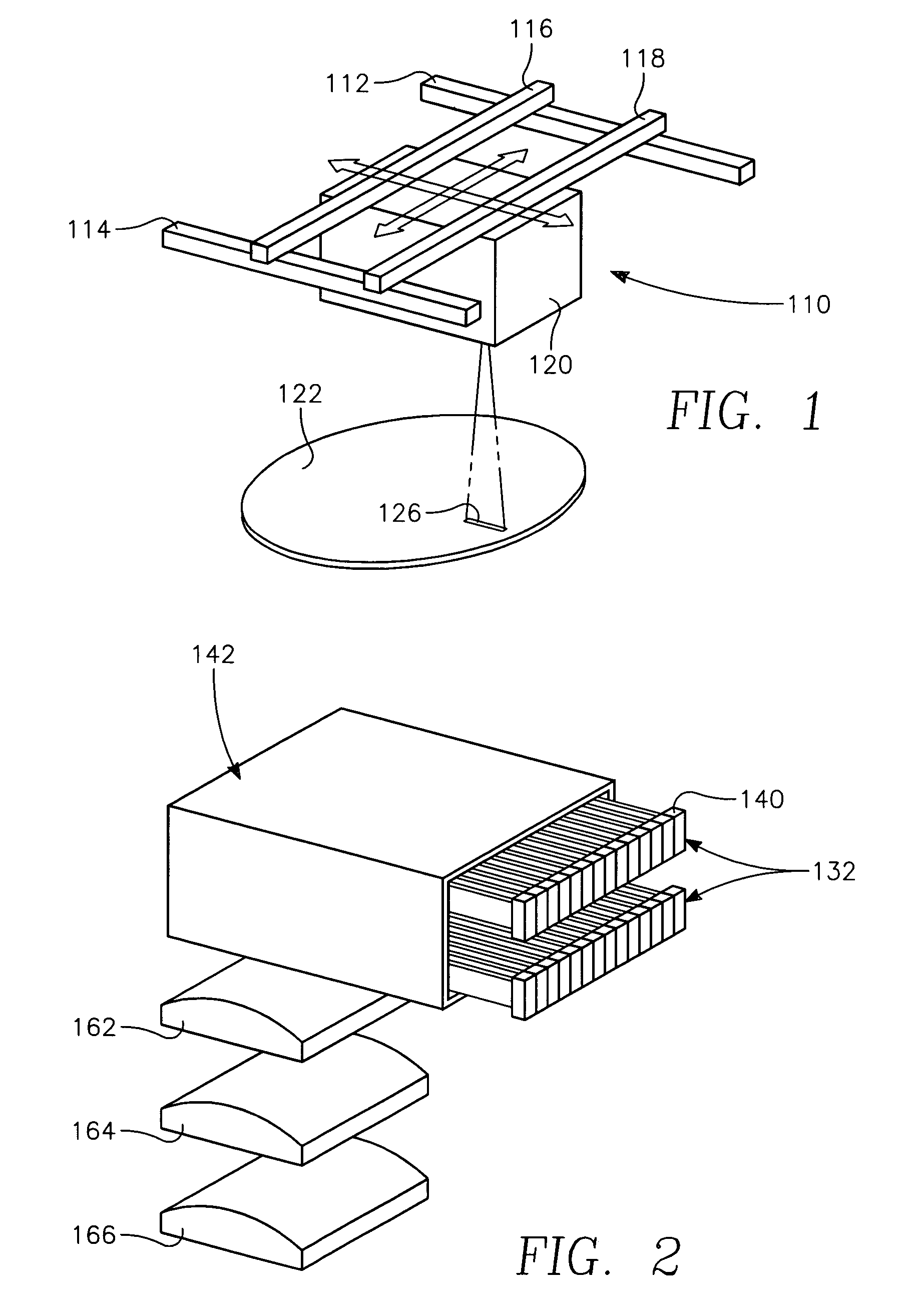
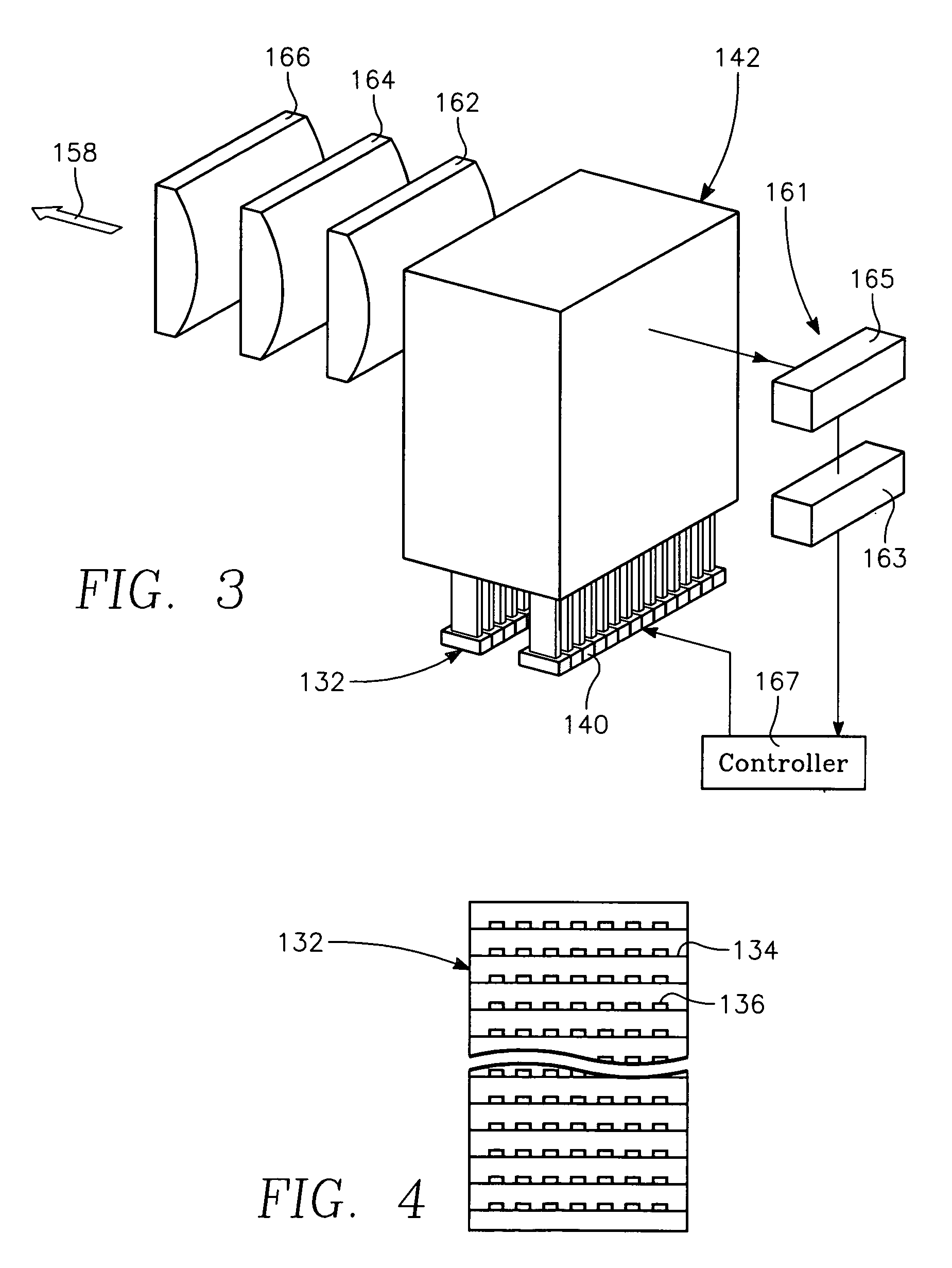
Dynamic surface annealing using addressable laser array with pyrometry feedback
Apparatus for dynamic surface annealing of a semiconductor wafer includes a source of laser radiation emitting at a laser wavelength and comprising an array of lasers arranged in rows and columns, the optical power of each the laser being individual adjustable and optics for focusing the radiation from the array of lasers into a narrow line beam in a workpiece plane corresponding to a workpiece surface, whereby the optics images respective columns of the laser array onto respective sections of the narrow line beam. A pyrometer sensor is provided that is sensitive to a pyrometer wavelength. An optical element in an optical path of the optics is tuned to divert radiation emanating from the workpiece plane to the pyrometry sensor. As a result, the optics images each of the respective section of the narrow line beam onto a corresponding portion of the pyrometer sensor. The apparatus further includes a controller responsive to the pyrometry sensor and coupled to adjust individual optical outputs of respective columns of the laser array in accordance with outputs of corresponding portions of the pyrometry sensor.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
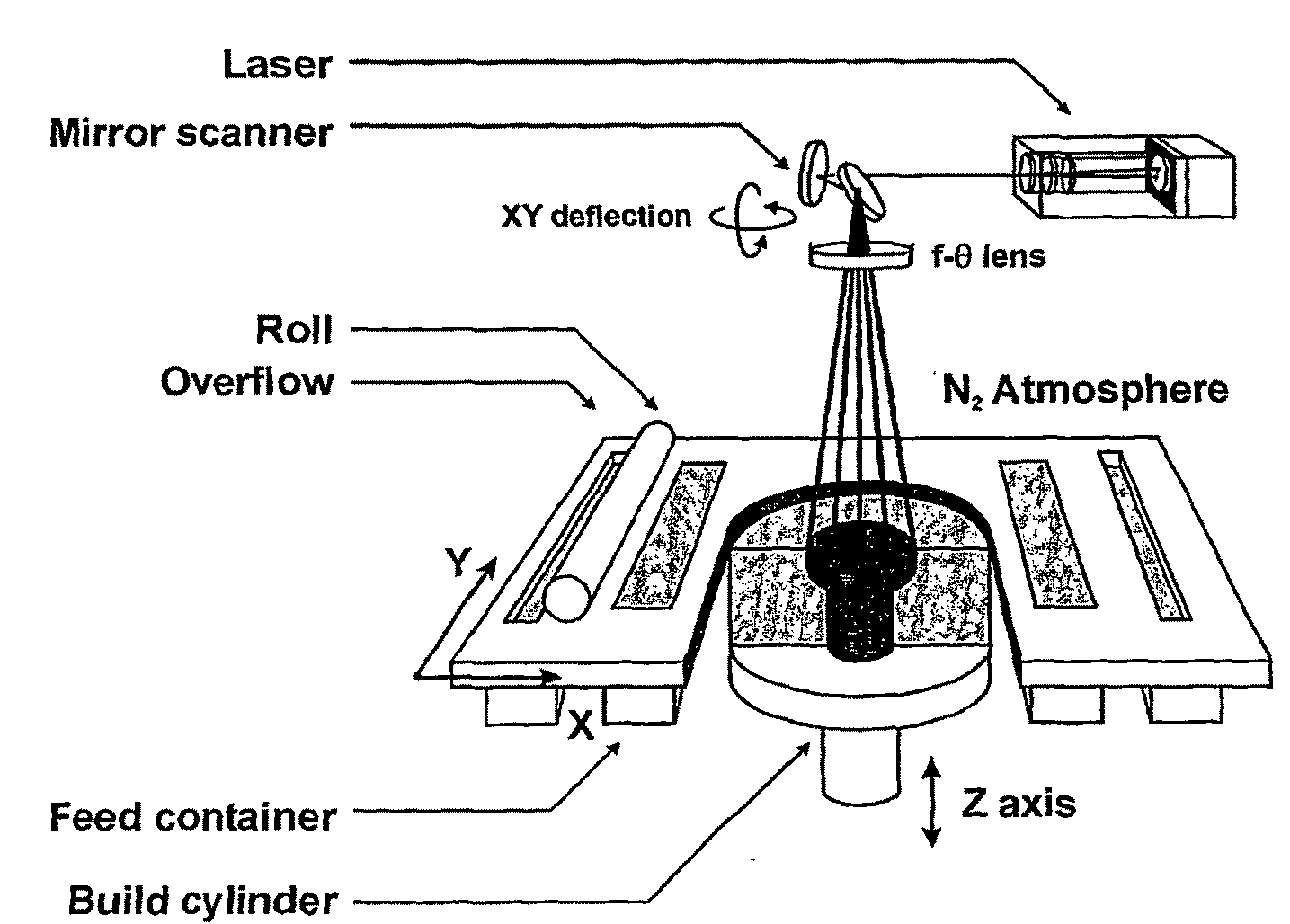
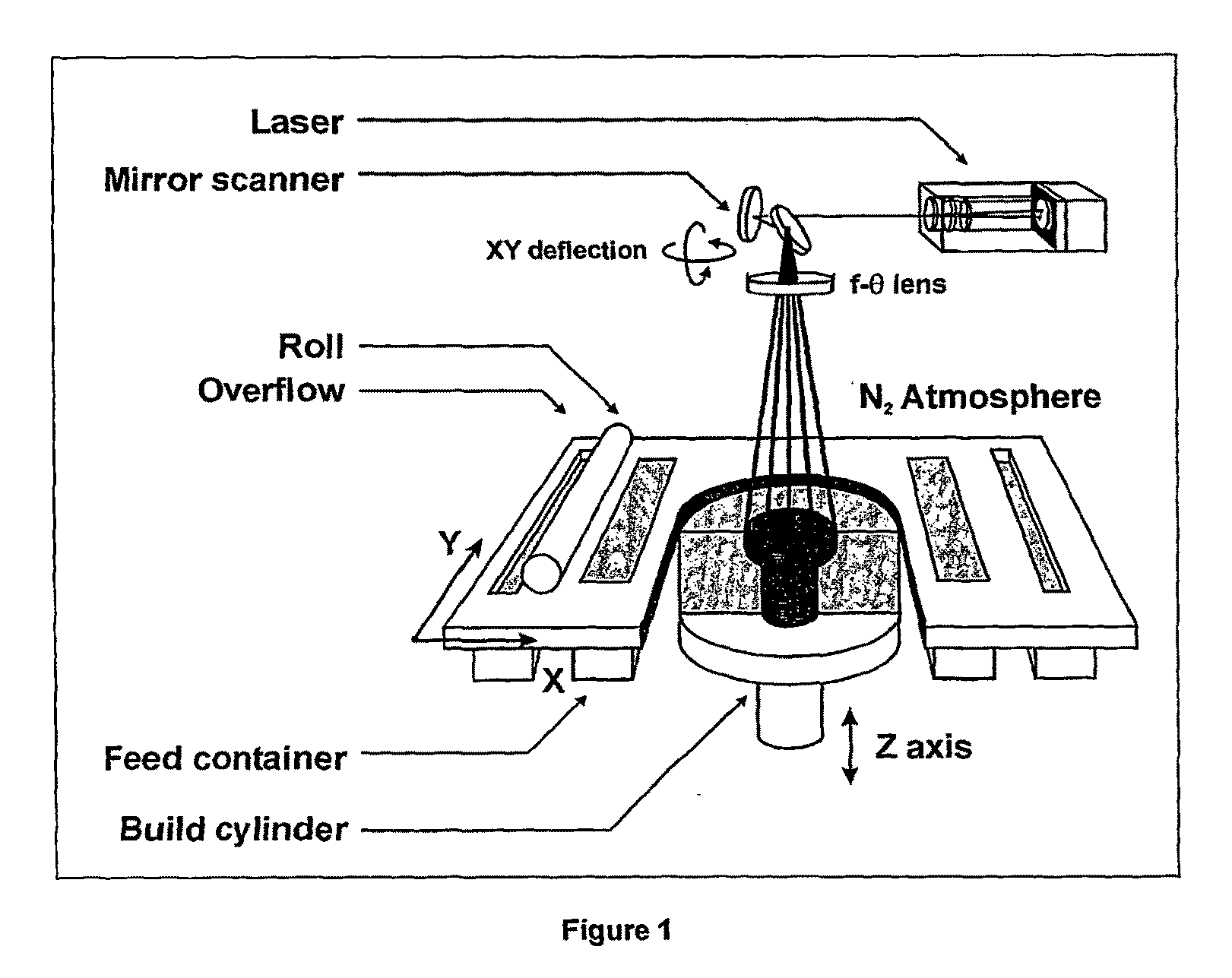
Method for producing a three-dimensional object
InactiveUS6042774AShorten production timeAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresIrradiationMaterials science
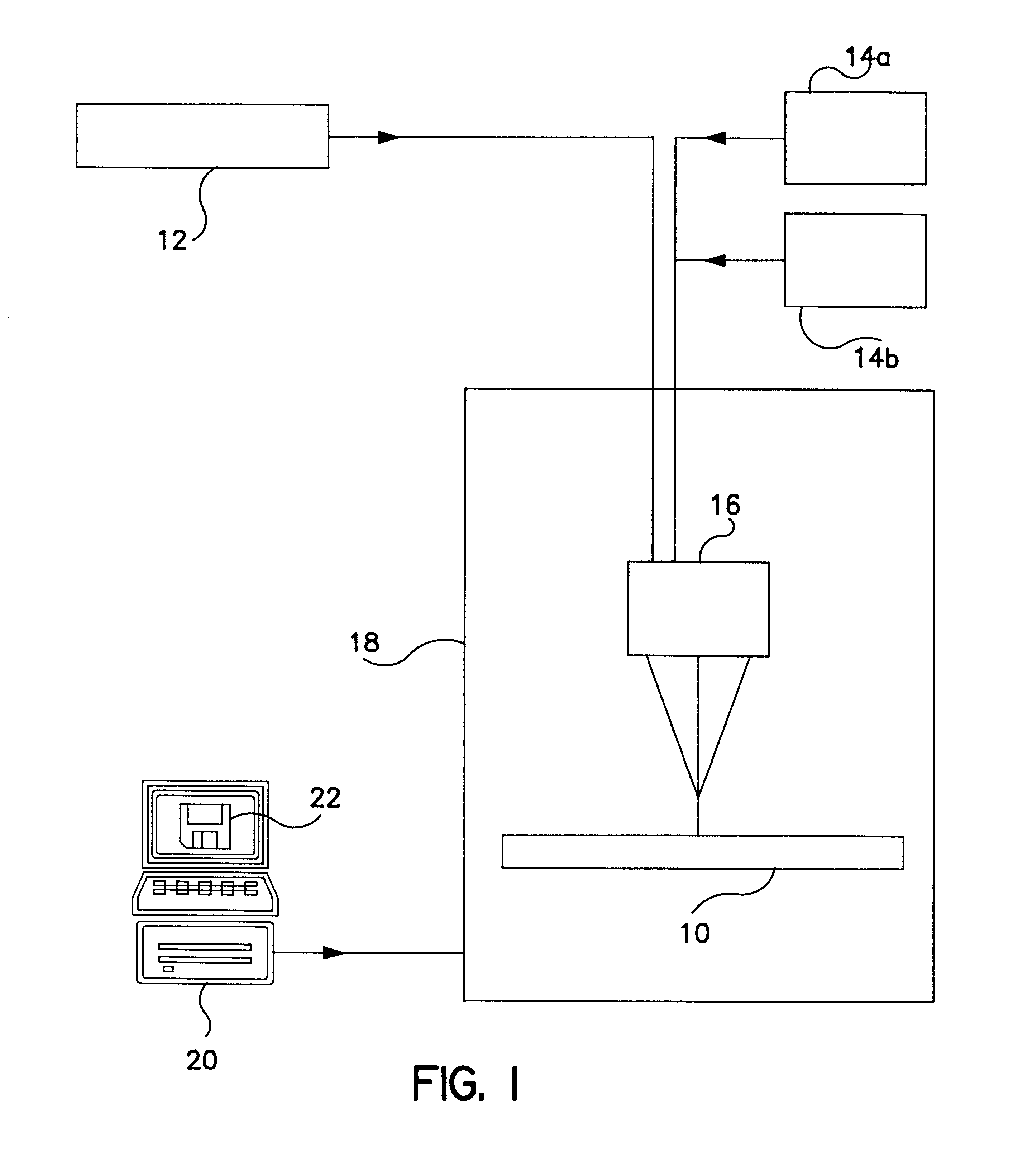
A method of producing an object by successive solidification of layers of a powder material is disclosed. The method provides a preformed base plate having a metal plate with a solidified layer of a powder material formed thereon. Then, successive layers of said powder material are applied and solidified on the solidified layer of the base plate to form the object. In further detail, the method for produces a three-dimensional by providing a support and a preformed base plate having an upper surface for supporting the object. The base plate is removably attached to the support. Means are provided for adjusting the elevation of said upper surface. A layer of the powder material is applied to the upper surface of the base plate. The powder material is solidified at points corresponding to a cross-section of the object by irradiation with electromagnetic or particle radiation. Then, the applying and solidifying steps are repeated for completing the object.
Owner:EOS ELECTRO OPTICAL SYST
Formation of heteroepitaxial layers with rapid thermal processing to remove lattice dislocations
InactiveUS20160155629A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesReaction temperatureGallium nitride
Method and devices are disclosed for device manufacture of gallium nitride devices by growing a gallium nitride layer on a silicon substrate using Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) followed by rapid thermal annealing. Gallium nitride is grown directly on silicon or on a barrier layer of aluminum nitride grown on the silicon substrate. One or both layers are thermally processed by rapid thermal annealing. Preferably the ALD process use a reaction temperature below 550° C. and preferable below 350° C. The rapid thermal annealing step raises the temperature of the coating surface to a temperature ranging from 550 to 1500° C. for less than 12 msec.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
Transparent material processing with an ultrashort pulse laser
InactiveUS20100025387A1Reduce quality problemsPoor precisionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFine working devicesLight beamOptoelectronics
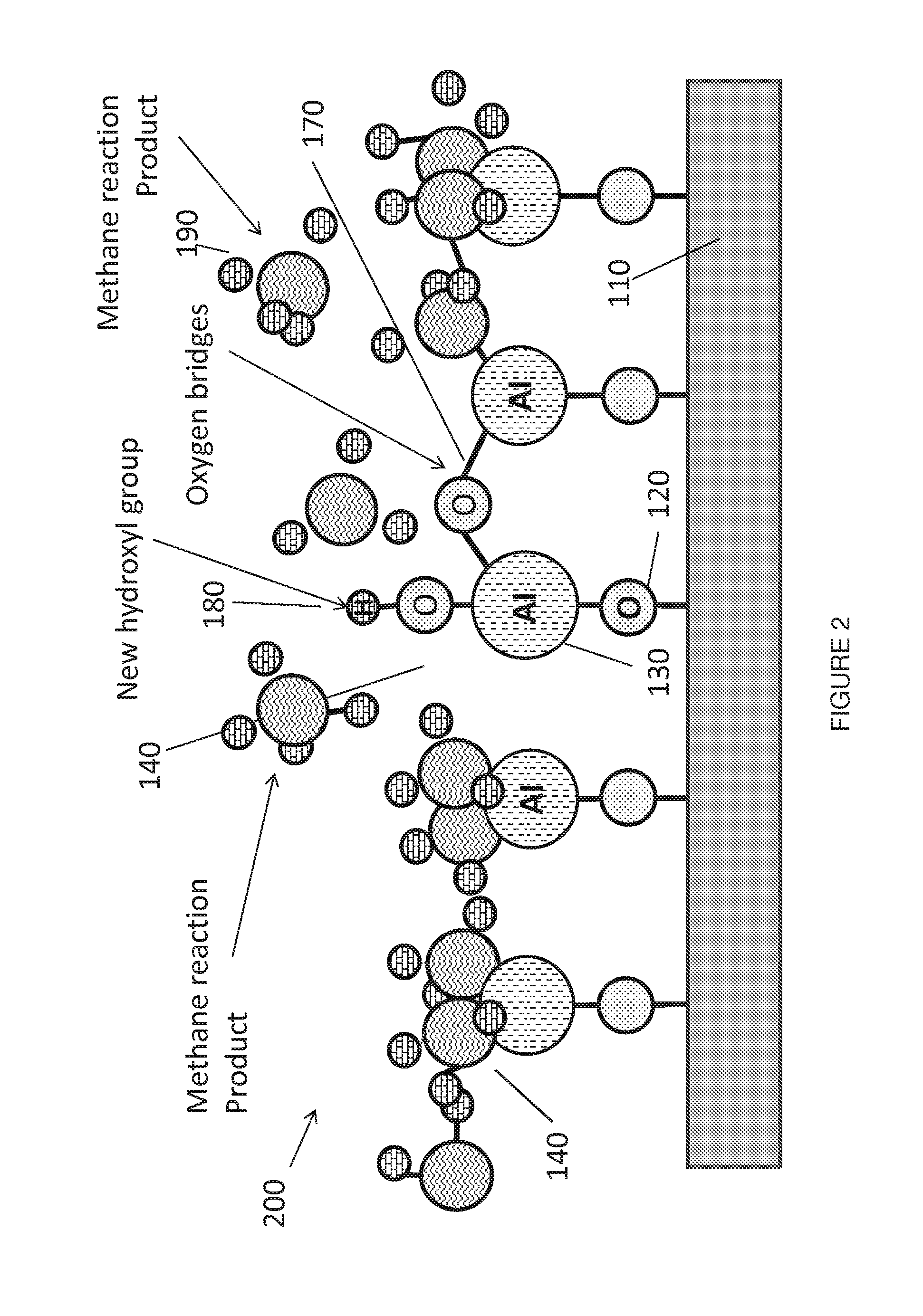
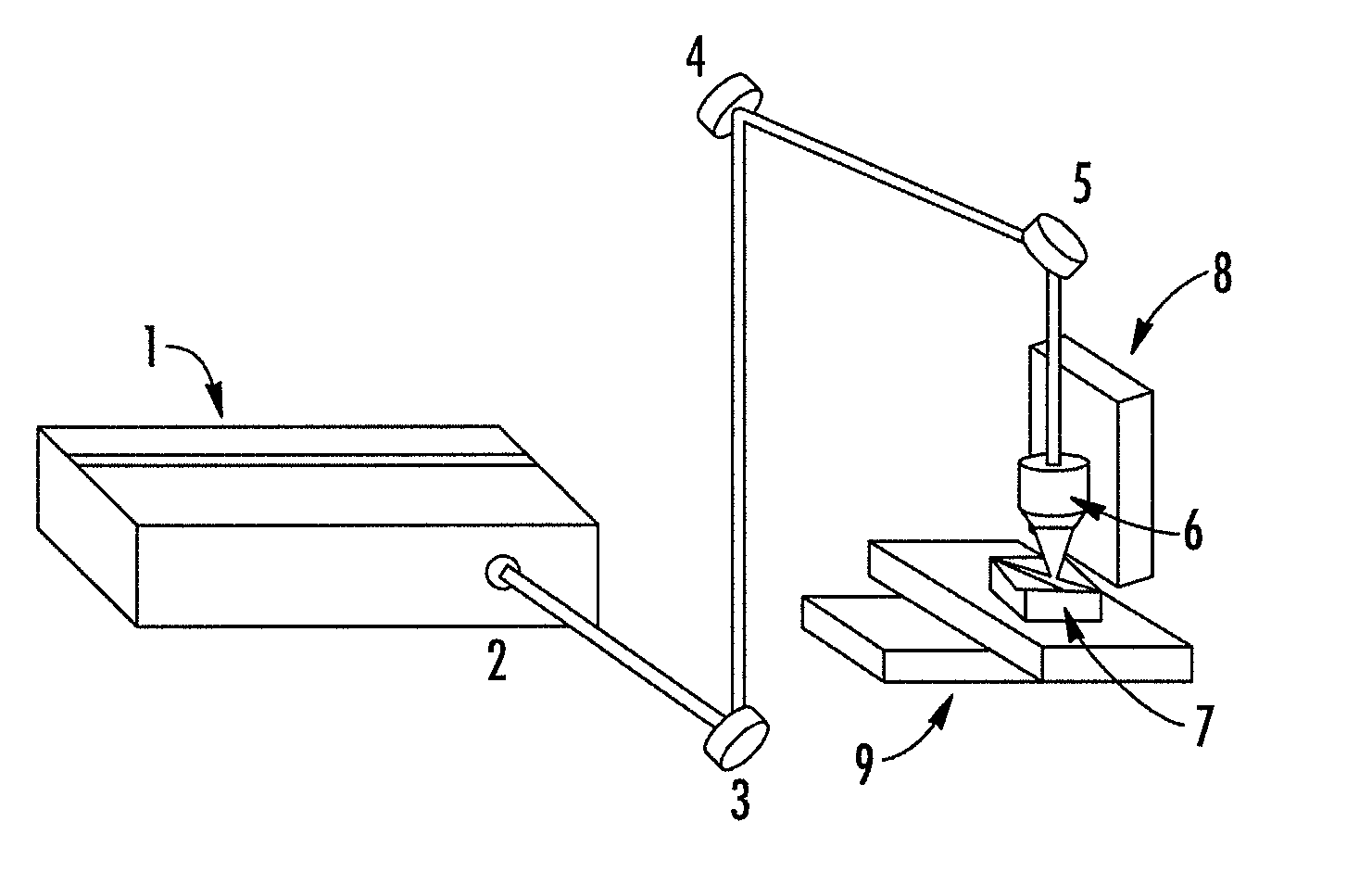
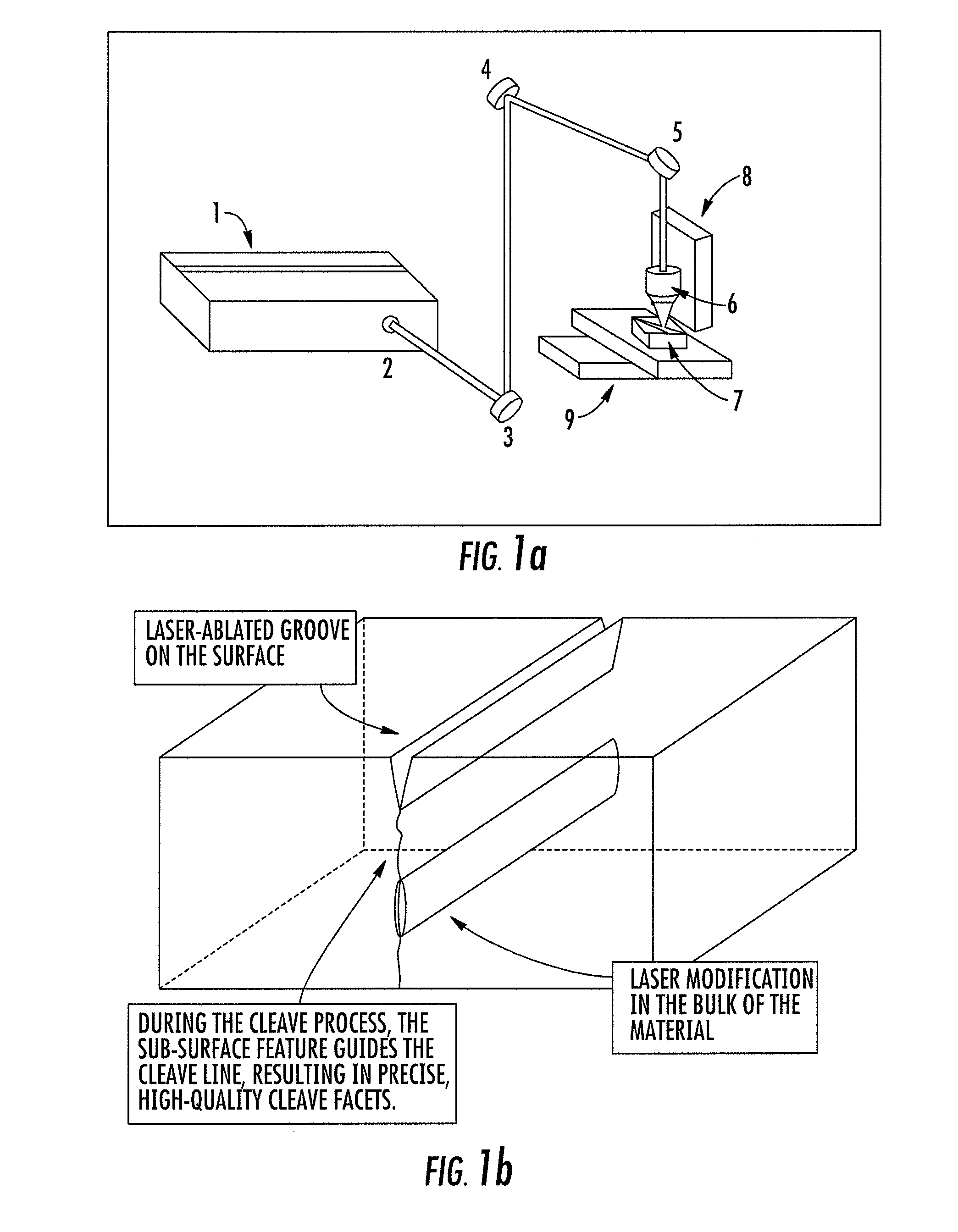
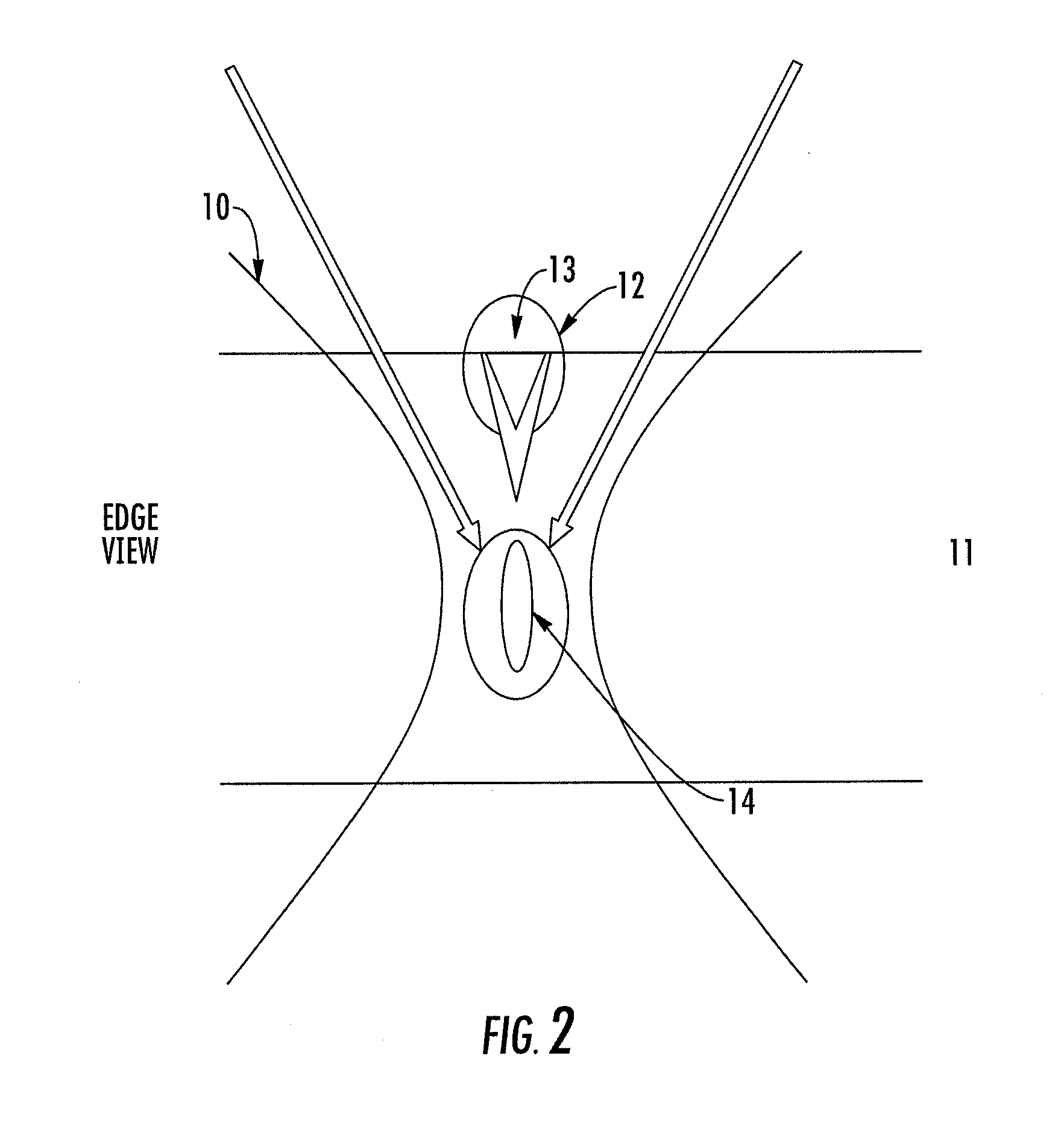
Methods, devices, and systems for ultrashort pulse laser processing of optically transparent materials are disclosed, with example applications in scribing, marking, welding, and joining. For example, ultrashort laser pulses create scribe features with one pass of the laser beam across the material, with at least one of the scribe features being formed below the surface of the material. Slightly modifying the ultrashort pulse laser processing conditions produces sub-surface marks. When properly arranged, these marks are clearly visible with correctly aligned illumination. Reflective marks may also be formed with control of laser parameters. A transparent material other than glass may be utilized. A method for welding transparent materials uses ultrashort laser pulses to create a bond through localized heating. In some embodiments of transparent material processing, a multifocus beam generator simultaneously forms multiple beam waists spaced depthwise relative to the transparent material, thereby increasing processing speed.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
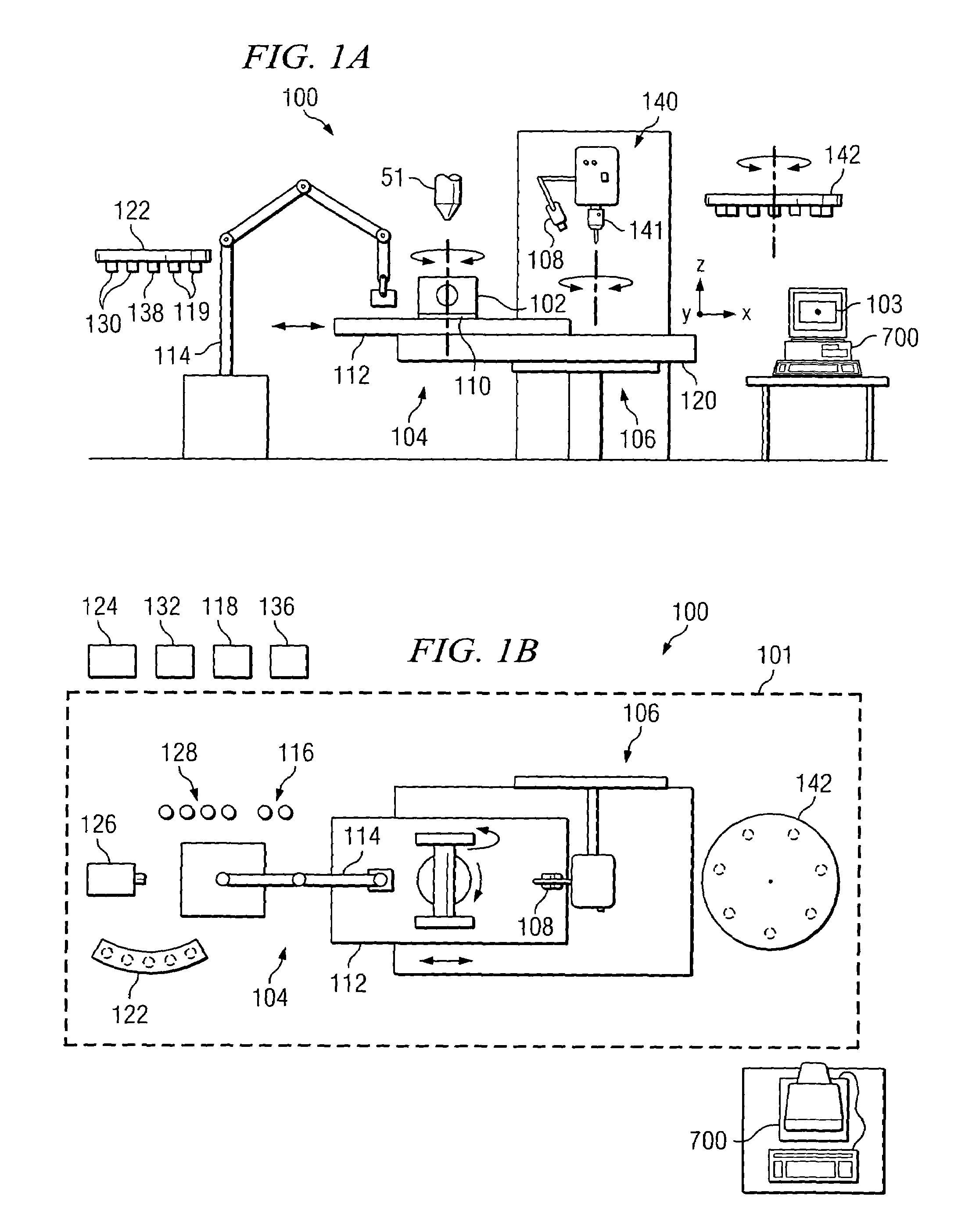
System and method for fabricating or repairing a part
InactiveUS7020539B1Improve accuracyHigh geometric accuracyAdditive manufacturing apparatusTool changing apparatusMulti axisMachining
According to one embodiment of the invention, a system for fabricating a part includes a computer operable to control the fabrication of a three-dimensional part using a solid CAD model, a deposition station operable to deposit successive two-dimensional layers of material to fabricate the three-dimensional part, and a machining station operable to remove at least a portion of one or more of the deposited two-dimensional layers of material. The deposition station includes a substrate on which to fabricate the three-dimensional part, a welding-based deposition system having a welding torch, a laser-based deposition system having a laser head, a plasma powder cladding system having a plasma torch, and a multi-axis robot operable to, when directed by the computer, utilize one of the welding-based deposition system, laser-based deposition system, and plasma powder cladding system to deposit any of the two-dimensional layers of material. The machining station includes a multi-axis milling machine and an automatic tool changer. The milling machine is operable to, when directed by the computer, select from a plurality of machining tools associated with the automatic tool changer for use in the milling machine.
Owner:SOUTHERN METHODIST UNIVERSITY
Method of and apparatus in a filter tipping machine for manipulating a web
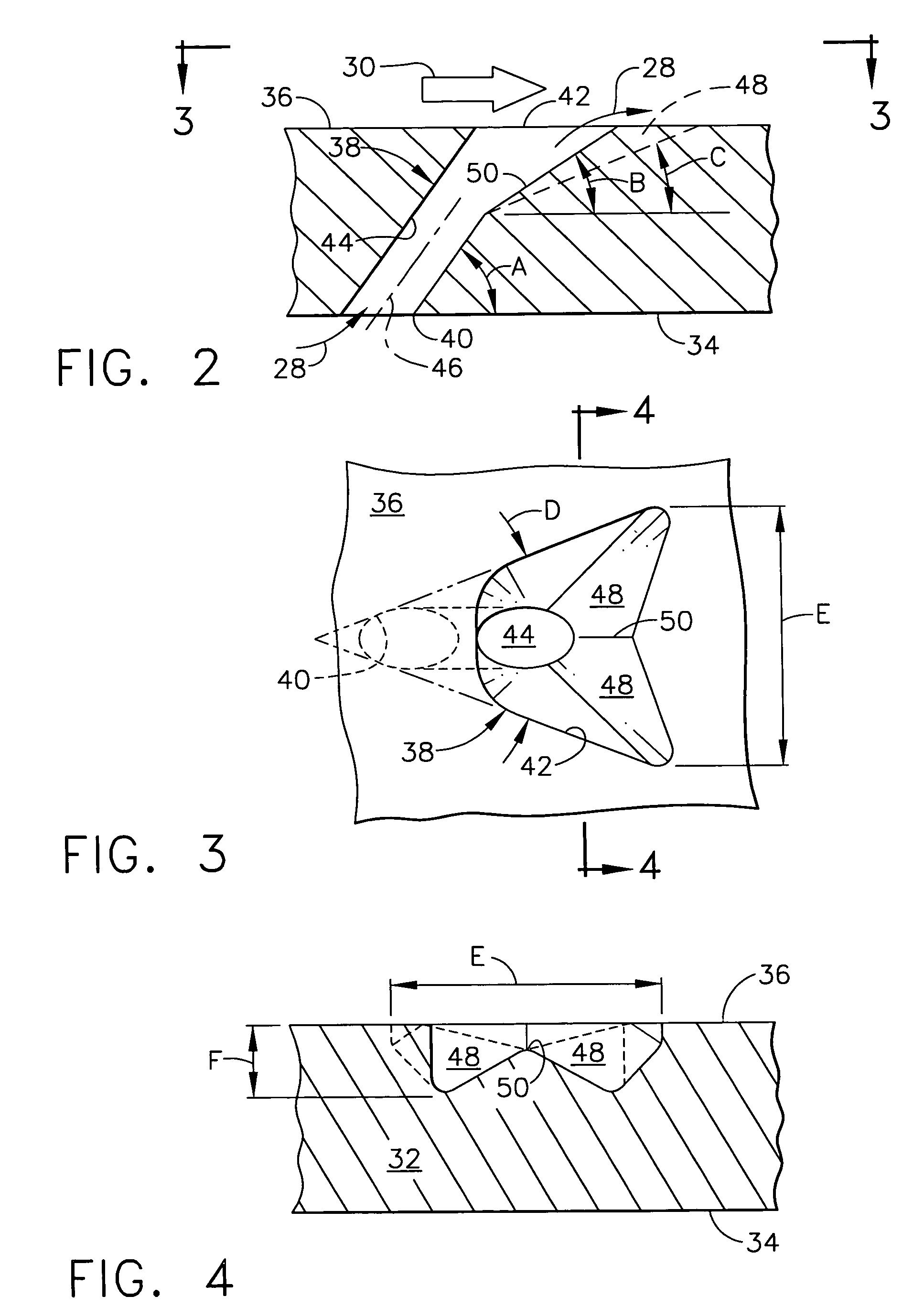
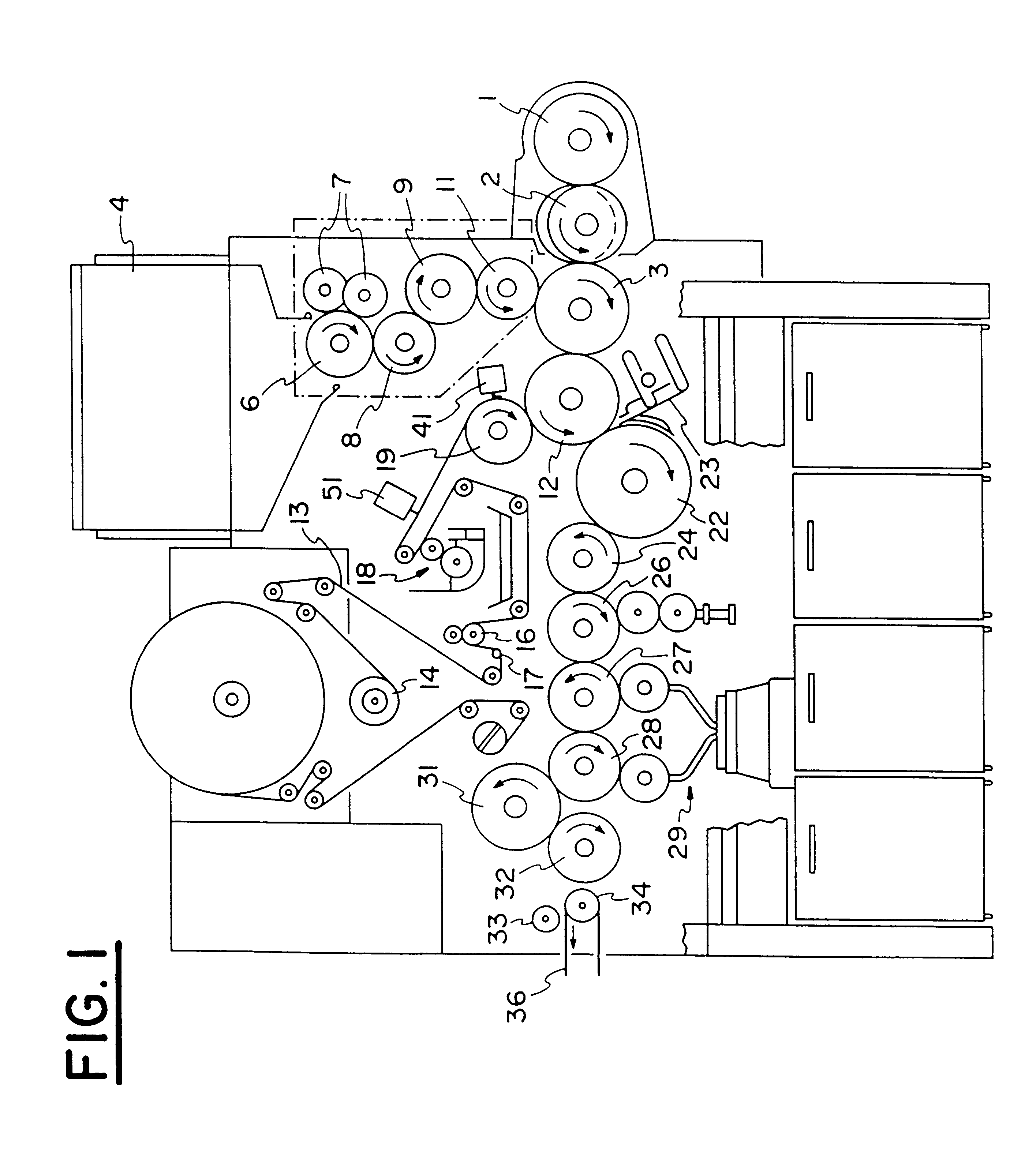
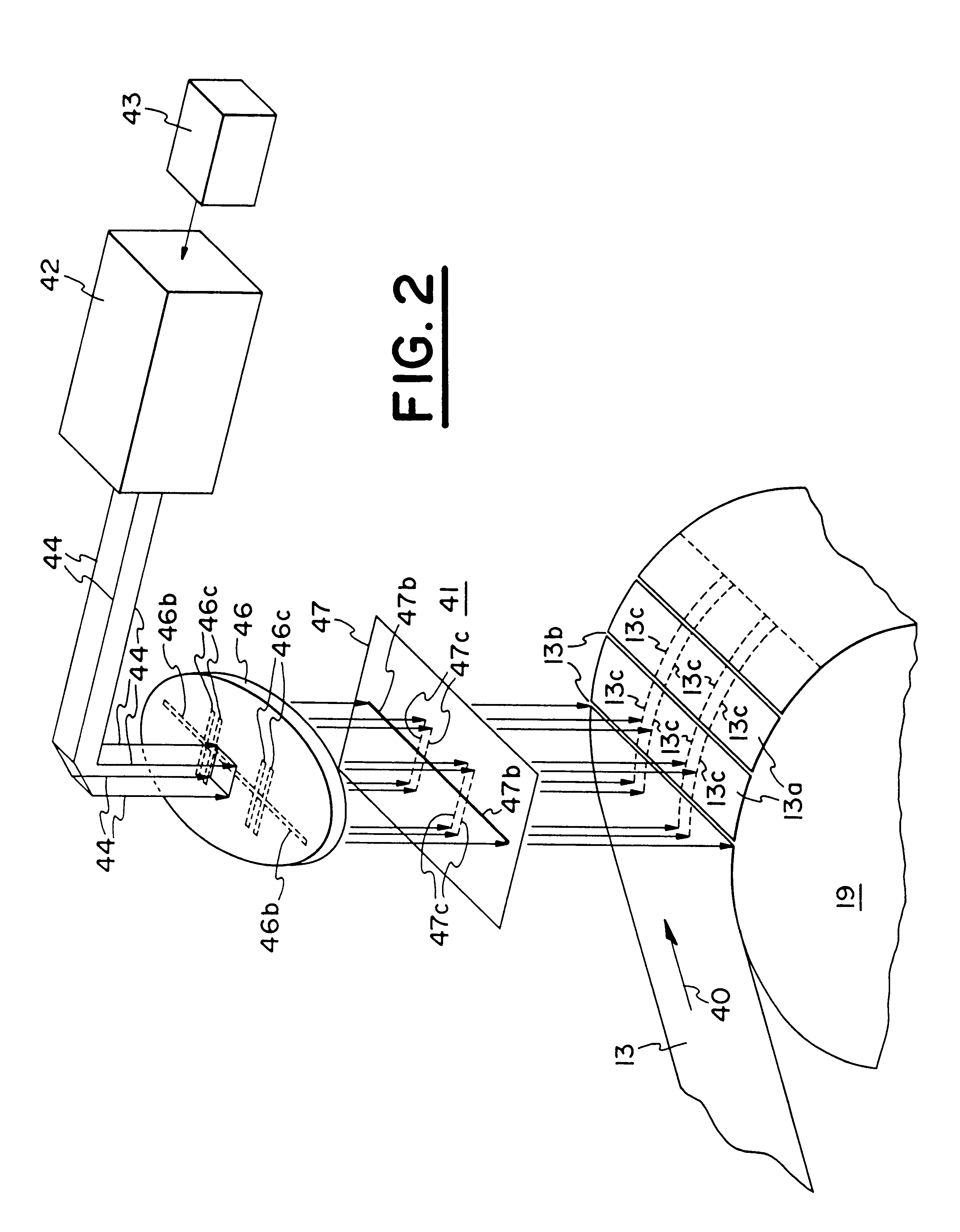
InactiveUS6229115B1More reliableLess expensiveCigarette manufactureLaser beam welding apparatusFiberAdhesive
A running web of tipping paper (one side of which is coated with a film of adhesive) in a filter cigarette making machine is subdivided into discrete uniting bands and / or is perforated by resorting to a single source or to two discrete sources of coherent radiation. Each source is associated with a control unit which initiates the emission of short-lasting flashes of coherent radiation. Such radiation is caused to impinge upon a diffractive focusing lens which focuses coherent radiation upon one or more masks having openings for coherent radiation which is to sever the web along transversely extending linear zones and / or to provide the web with desired arrays of perforations. The perforations permit atmospheric air to enter the column of tobacco smoke in a filter cigarette wherein the tobacco-containing portion and the filter mouthpiece are united by a perforated adhesive-coated uniting band.
Owner:HAUNI MASCHINENBAU AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com