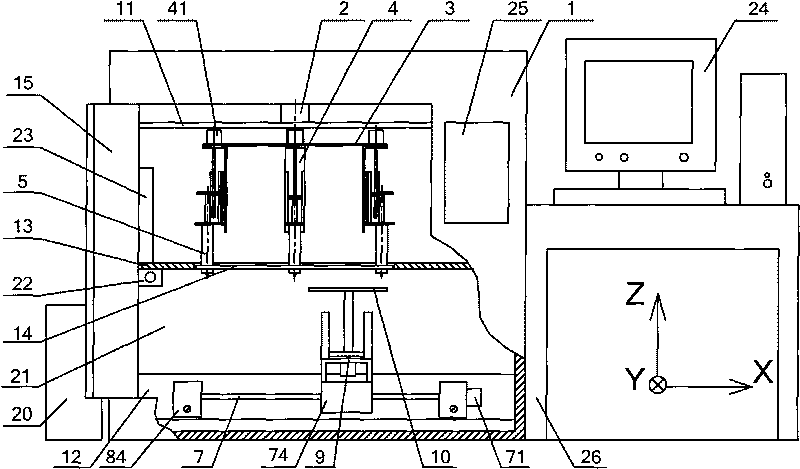
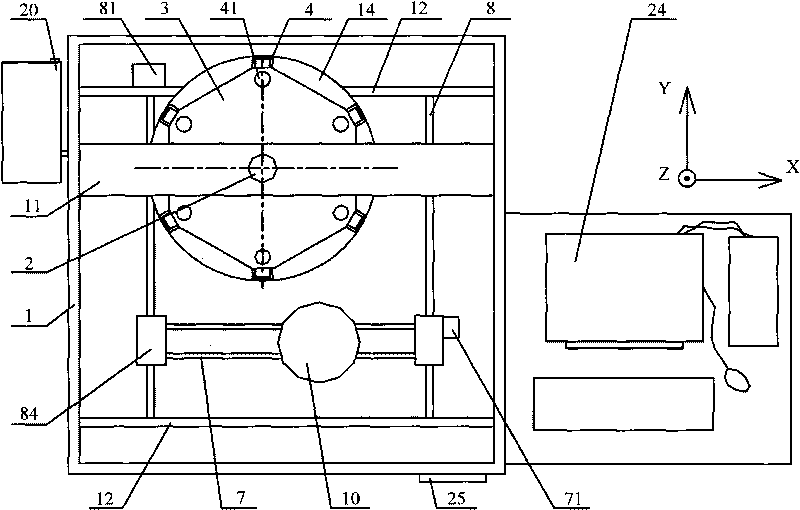
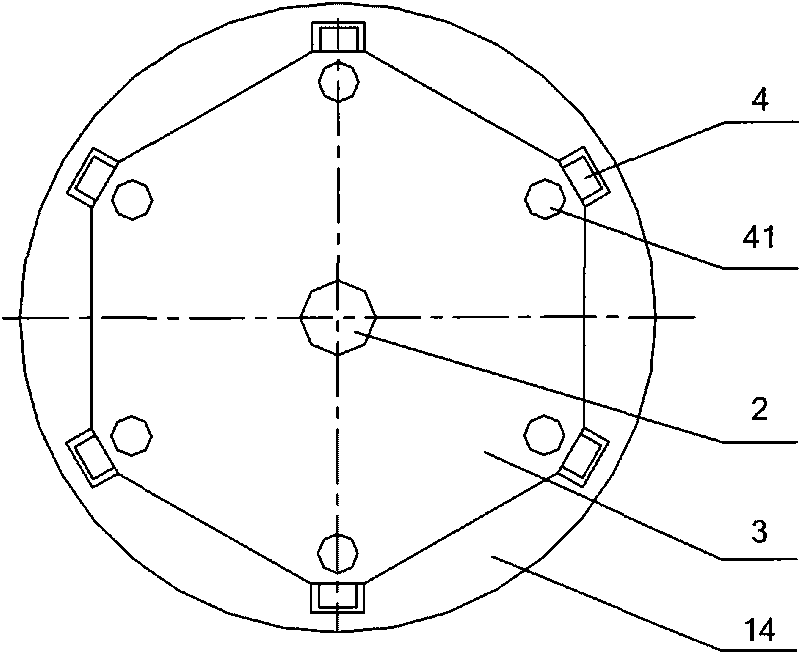
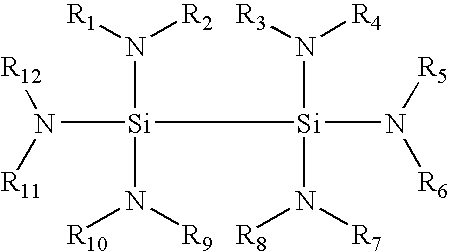
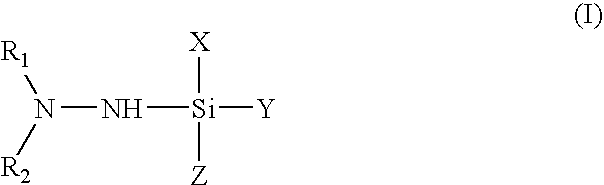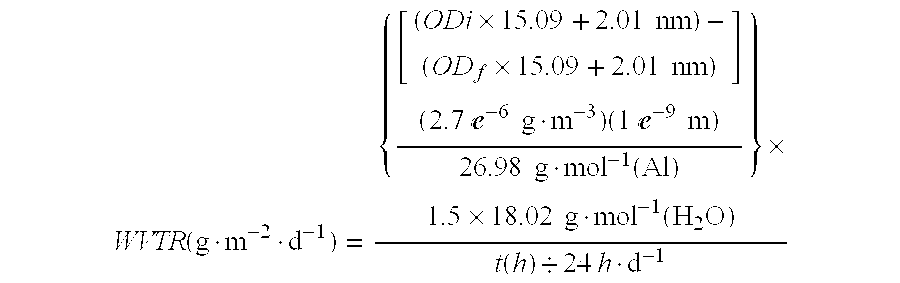Patents
Literature
255 results about "Low temperature deposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
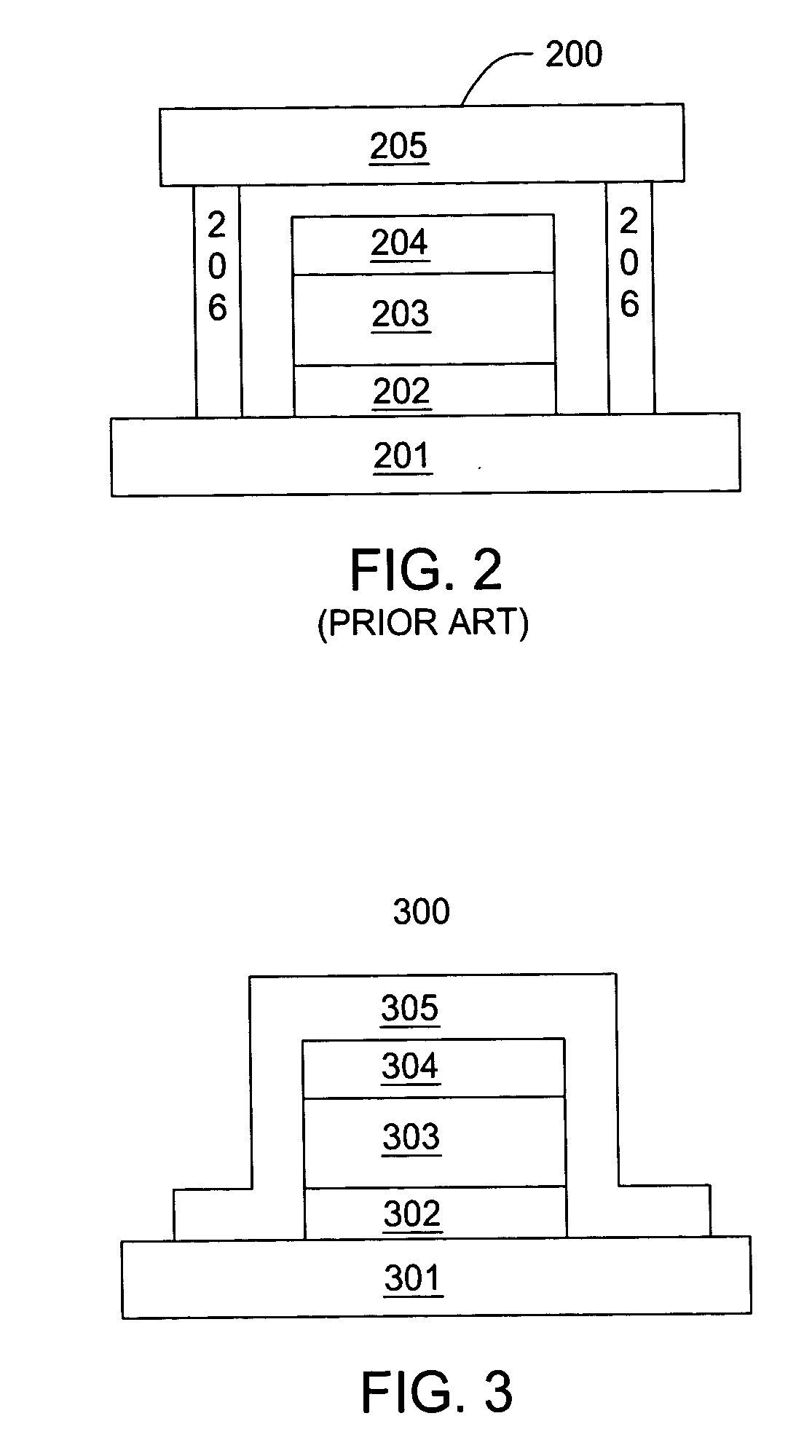
Low Temperature Arc Vapor Deposition. Low temperature arc vapor deposition takes place within a vacuum chamber. A low voltage within the chamber generates a high-current arc. Because it is in a vacuum, low voltage is achievable to generate the arc.
Low Temperature Deposition of Silicon-Containing Films
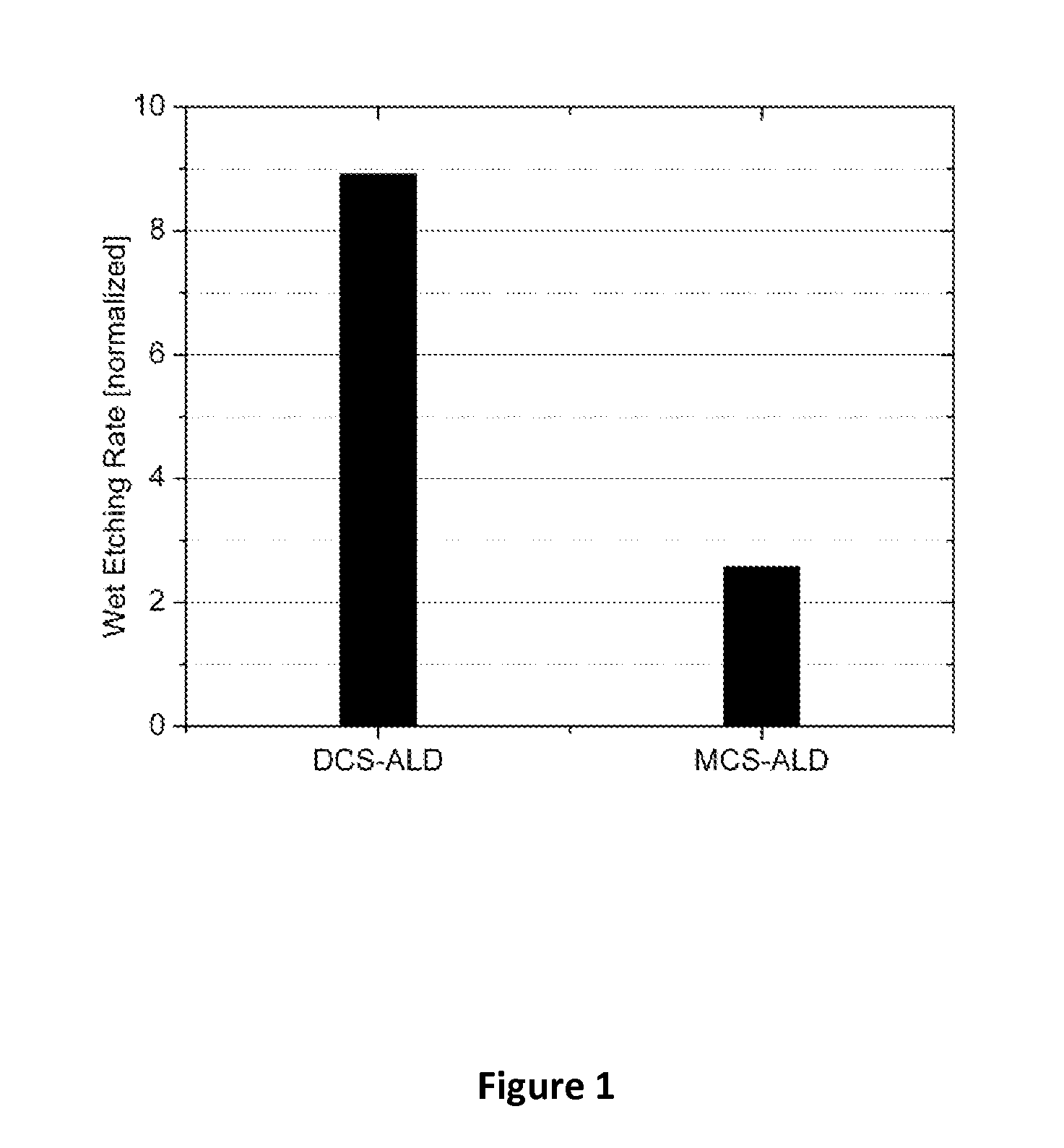
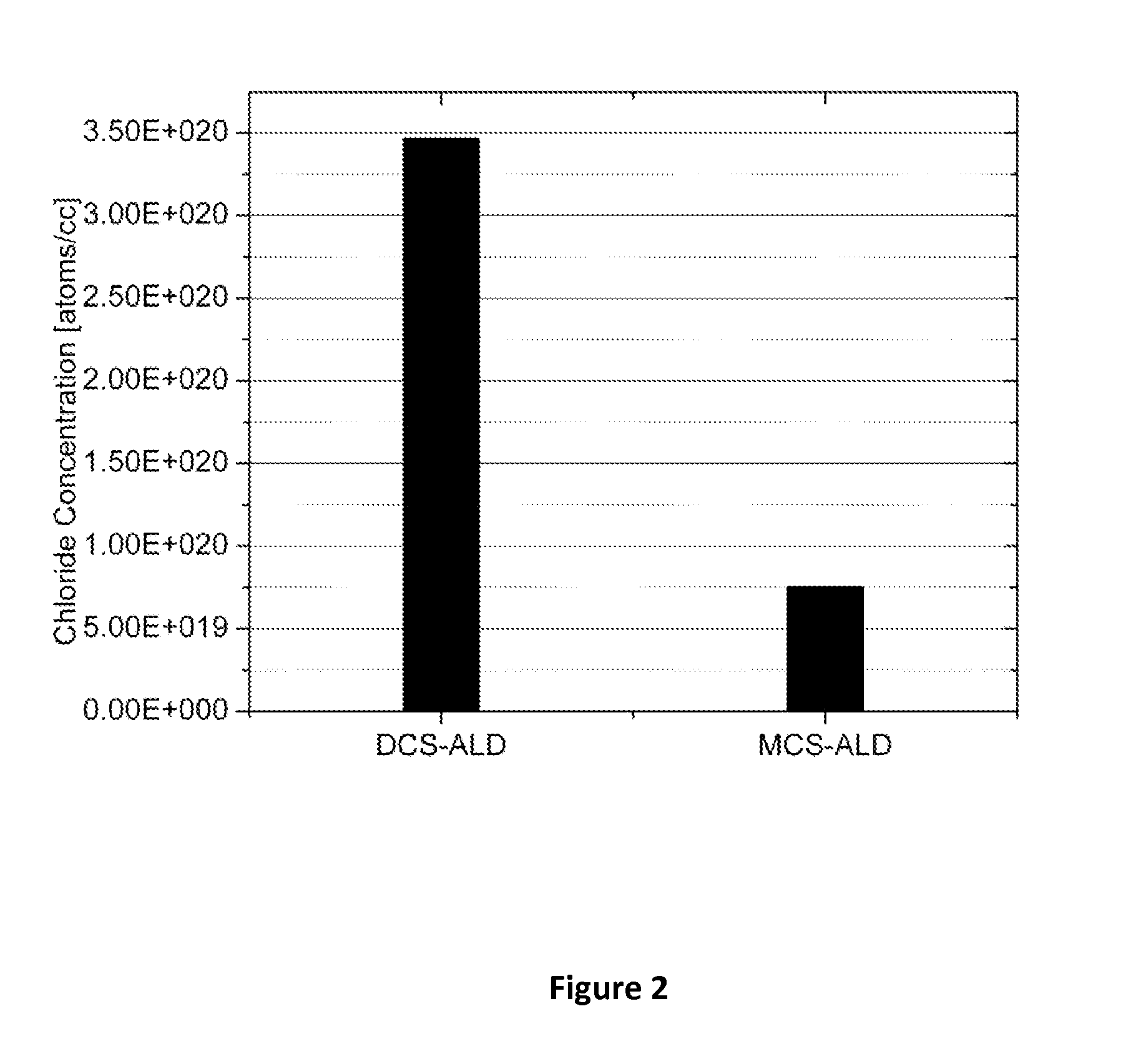
ActiveUS20100304047A1Low deposition temperatureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial surfacesLow temperature depositionDeposition temperature
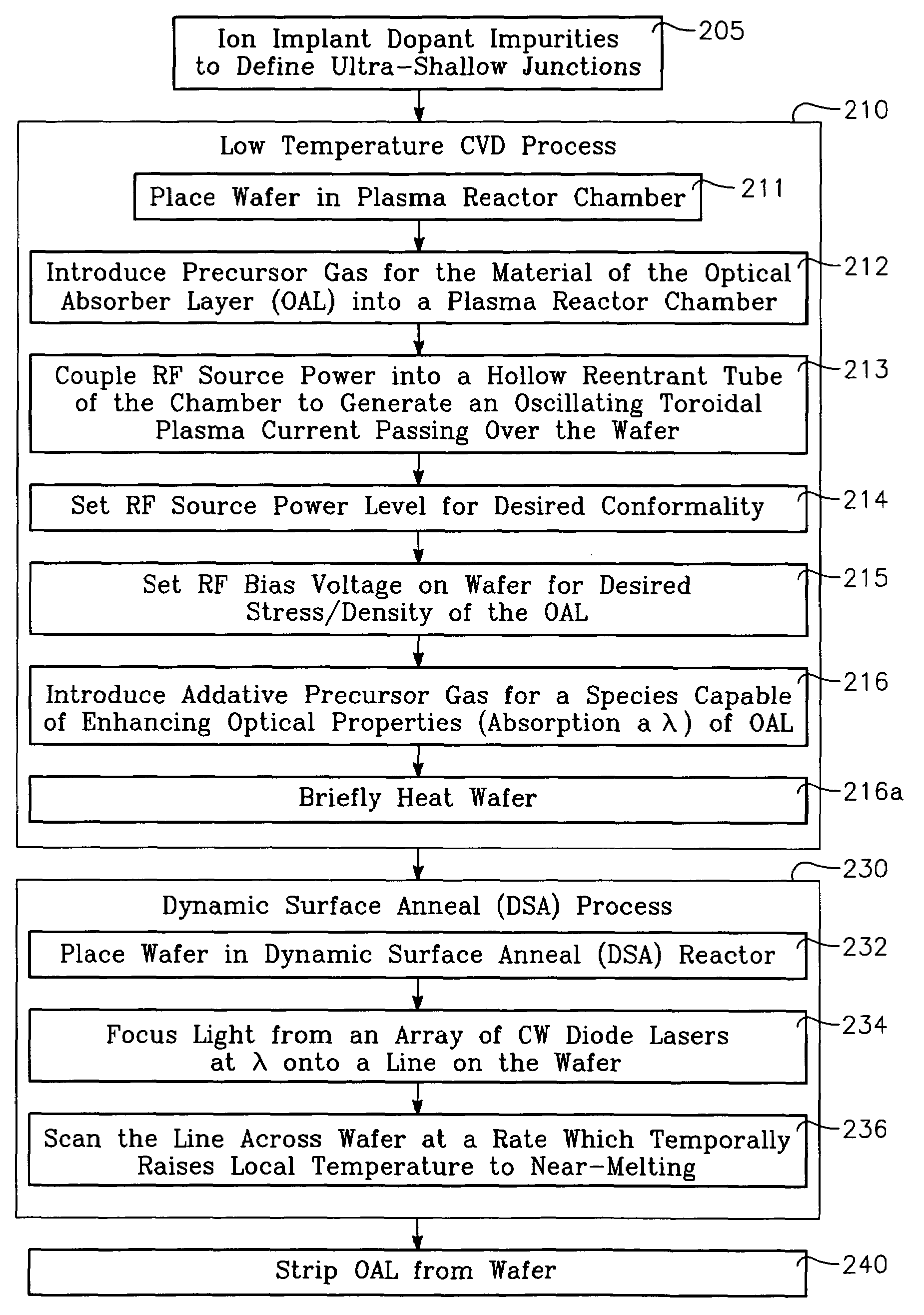
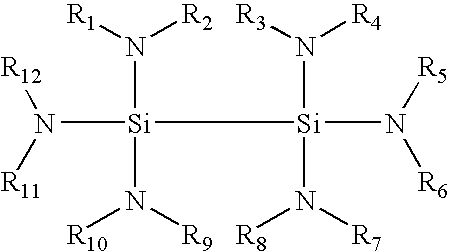
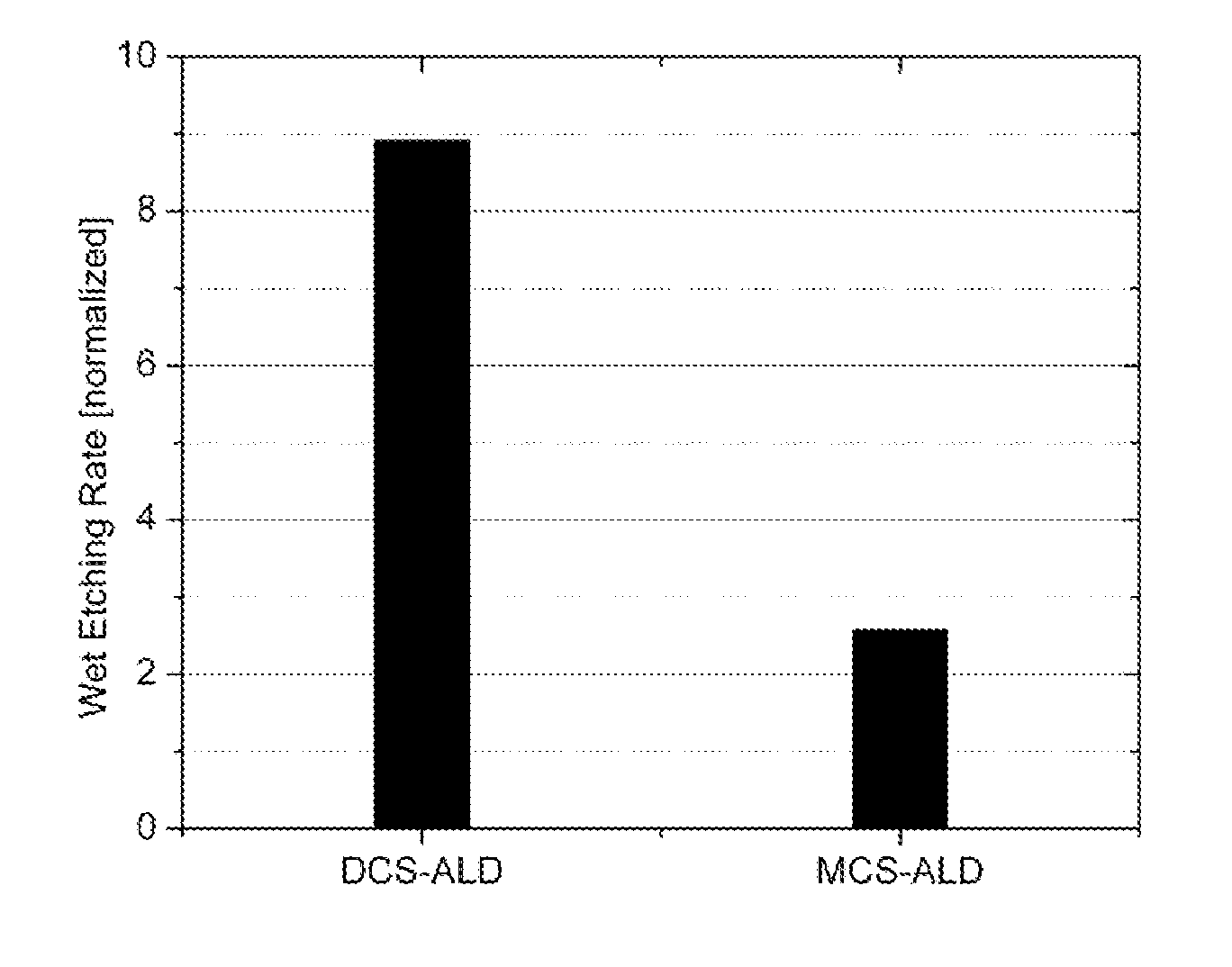
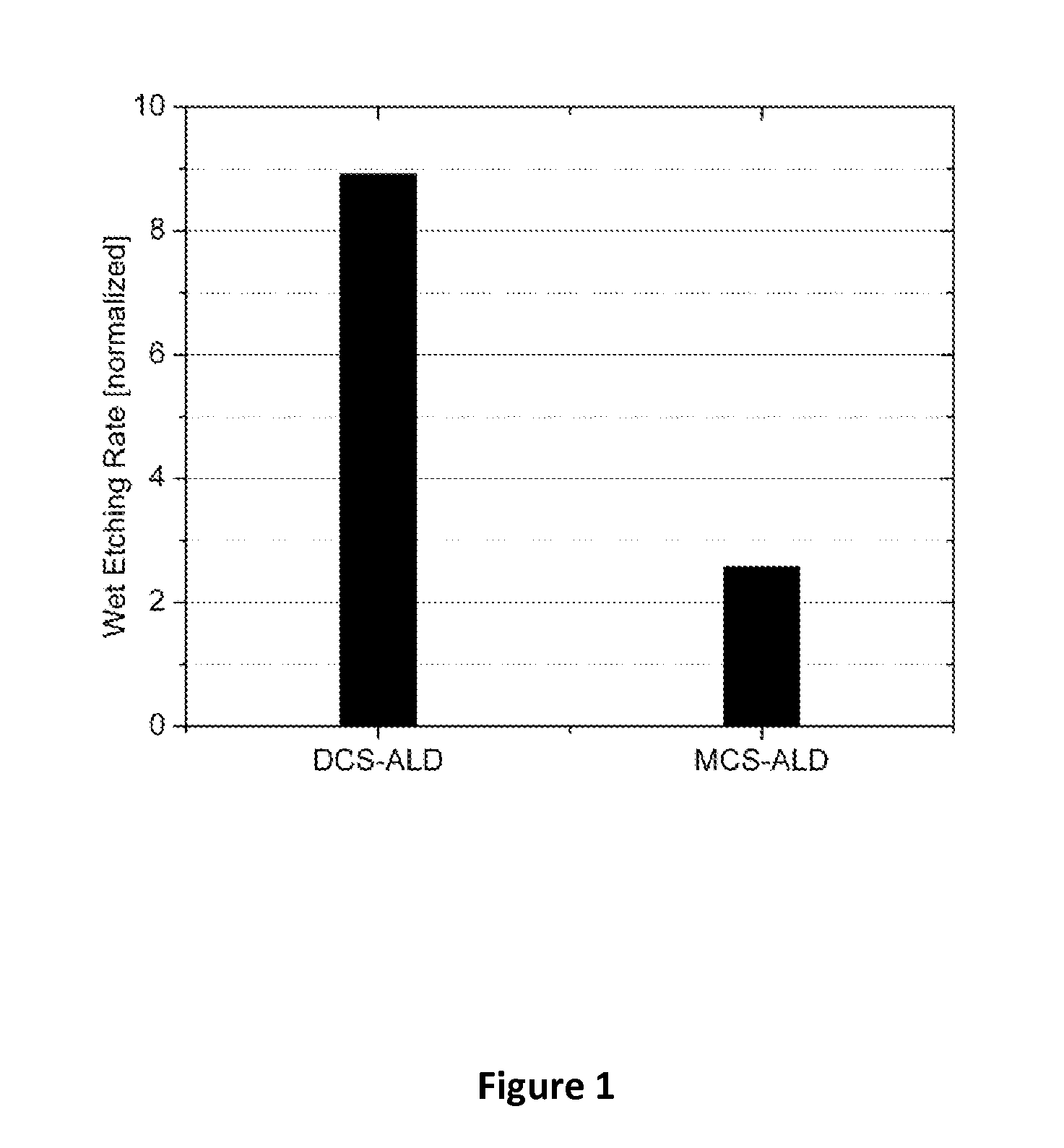
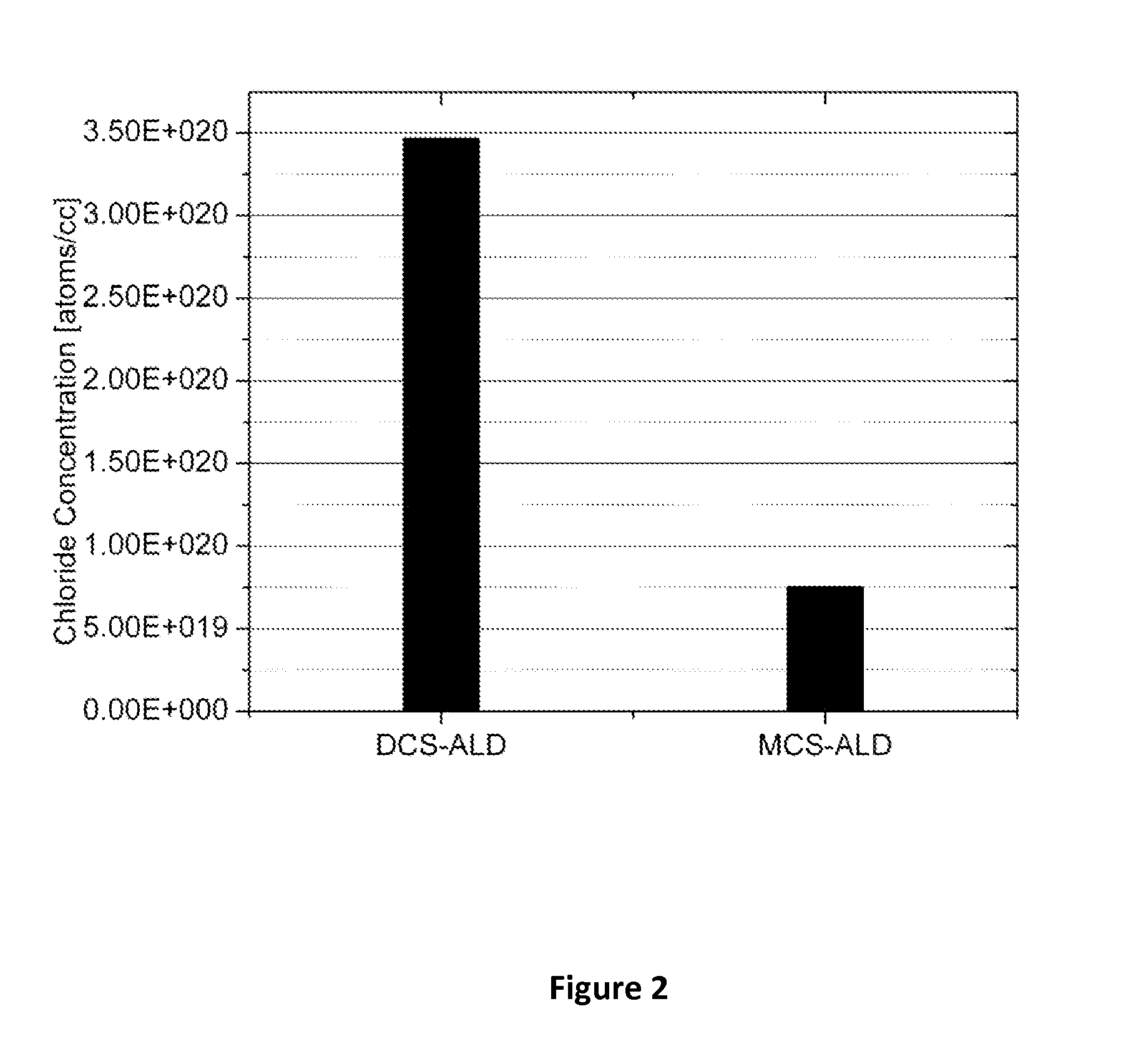
This invention discloses the method of forming silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, silicon oxide, carbon-doped silicon nitride, carbon-doped silicon oxide and carbon-doped oxynitride films at low deposition temperatures. The silicon containing precursors used for the deposition are monochlorosilane (MCS) and monochloroalkylsilanes. The method is preferably carried out by using plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition, plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition, and plasma enhanced cyclic chemical vapor deposition.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD +1
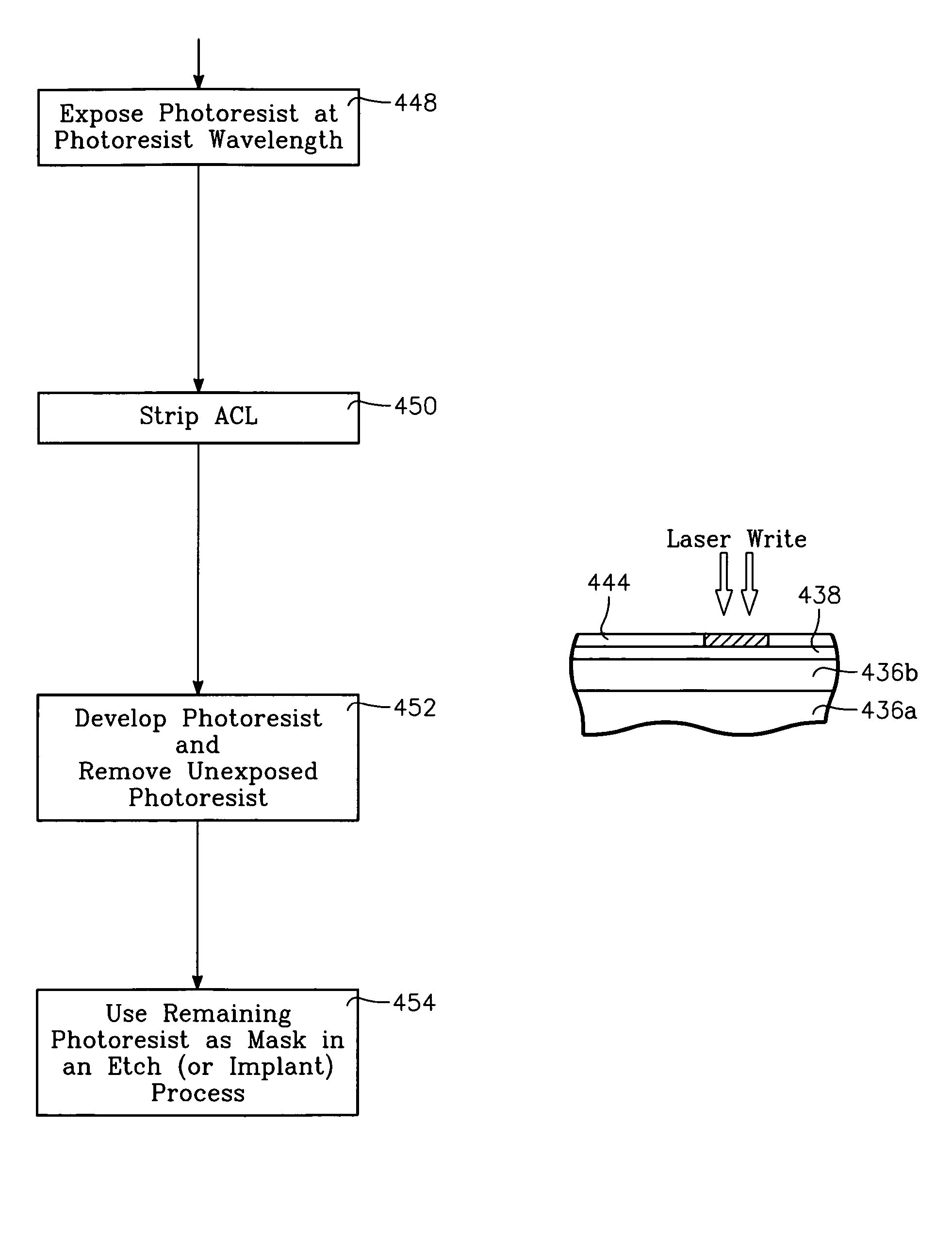
Semiconductor substrate process using a low temperature deposited carbon-containing hard mask
InactiveUS7323401B2Electric discharge tubesRadiation applicationsLow temperature depositionPlasma current
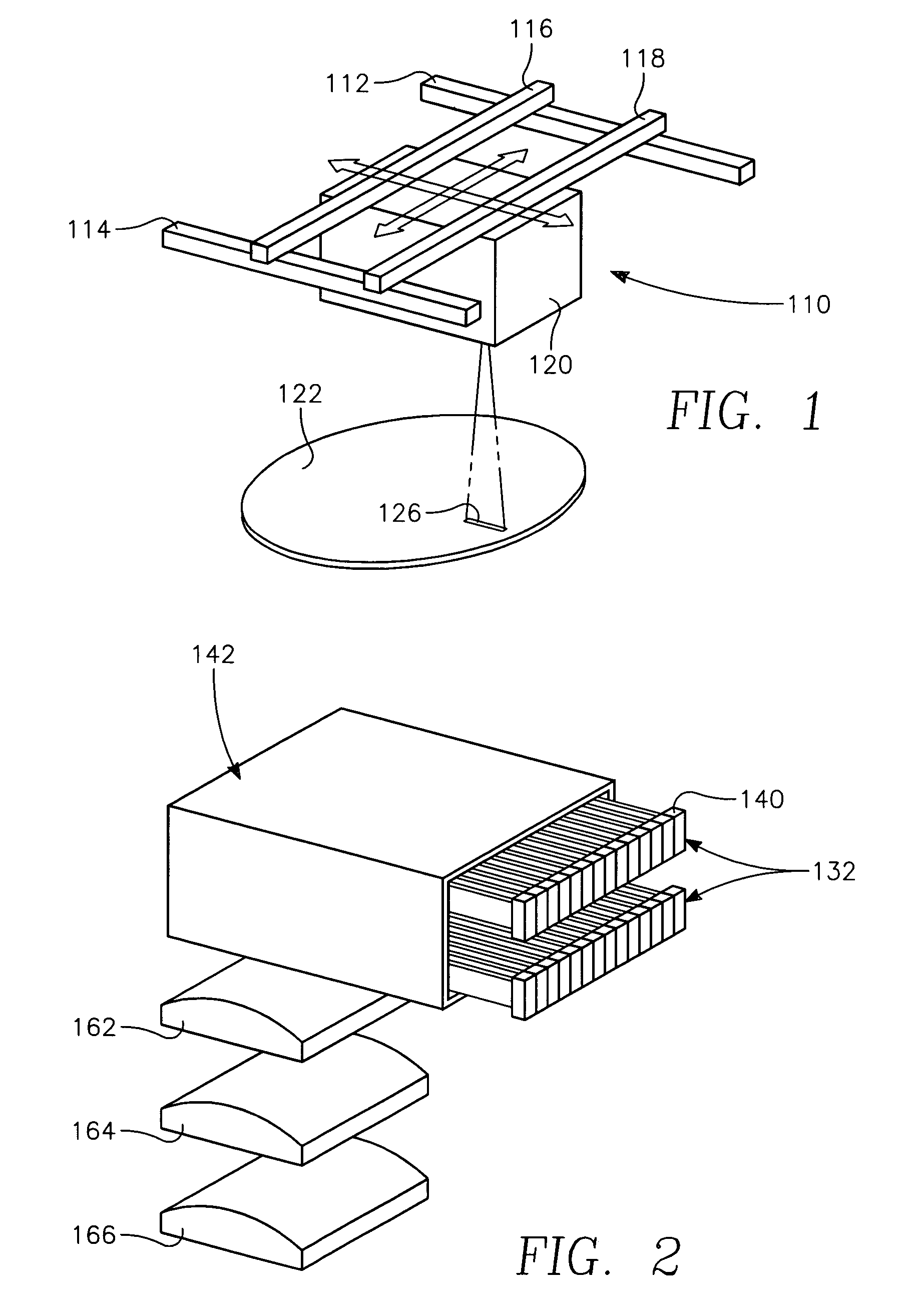
A method of processing a thin film structure on a semiconductor substrate using an optically writable mask includes placing the substrate in a reactor chamber, the substrate having on its surface a target layer to be etched in accordance with a predetermined pattern, and depositing a carbon-containing hard mask layer on the substrate by (a) introducing a carbon-containing process gas into the chamber, (b) generating a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by coupling plasma RF source power to an external portion of the reentrant path, and (c) coupling RF plasma bias power or bias voltage to the workpiece. The method further includes photolithographically defining the predetermined pattern in the carbon-containing hard mask layer, and etching the target layer in the presence of the hard mask layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
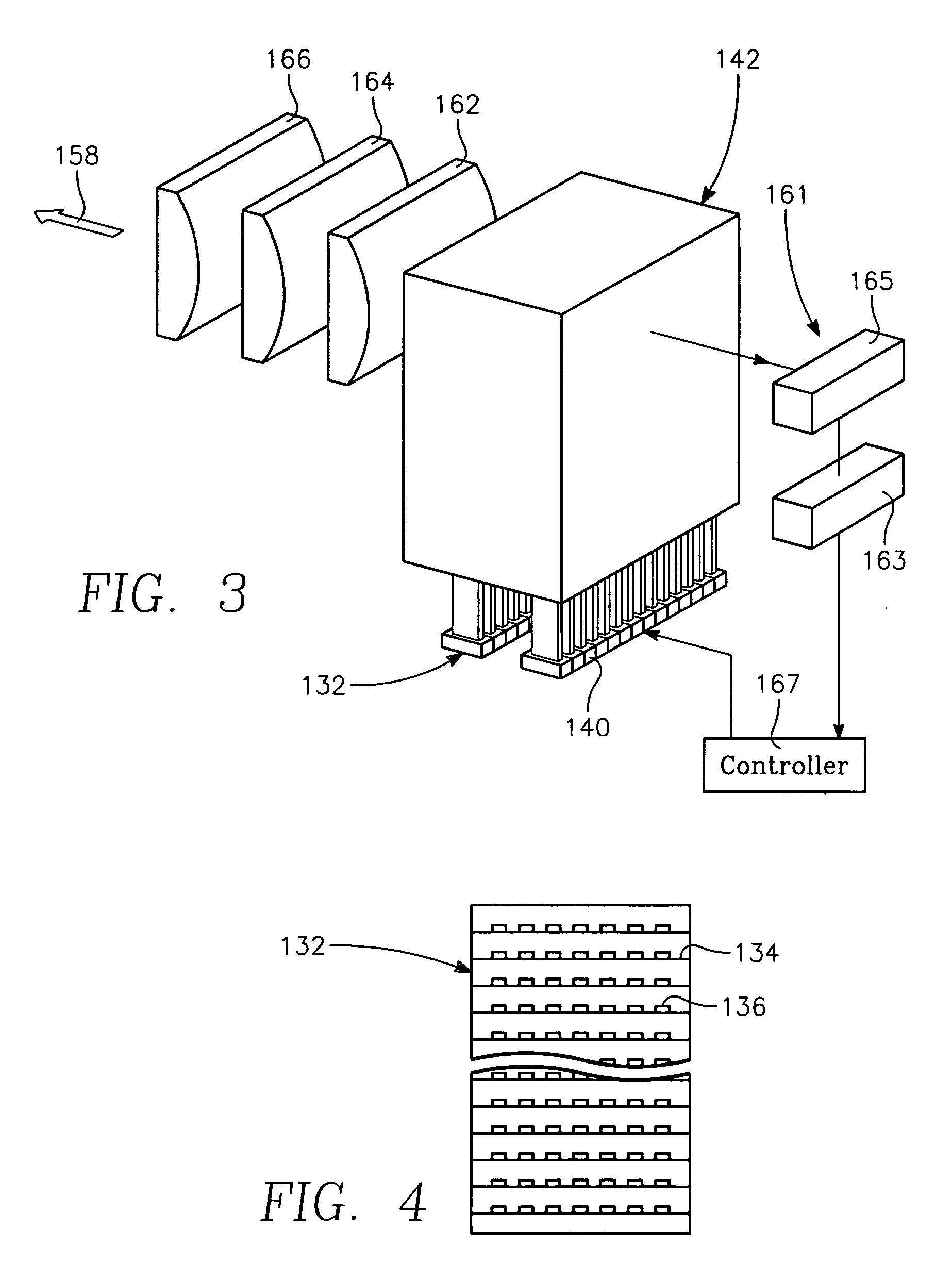
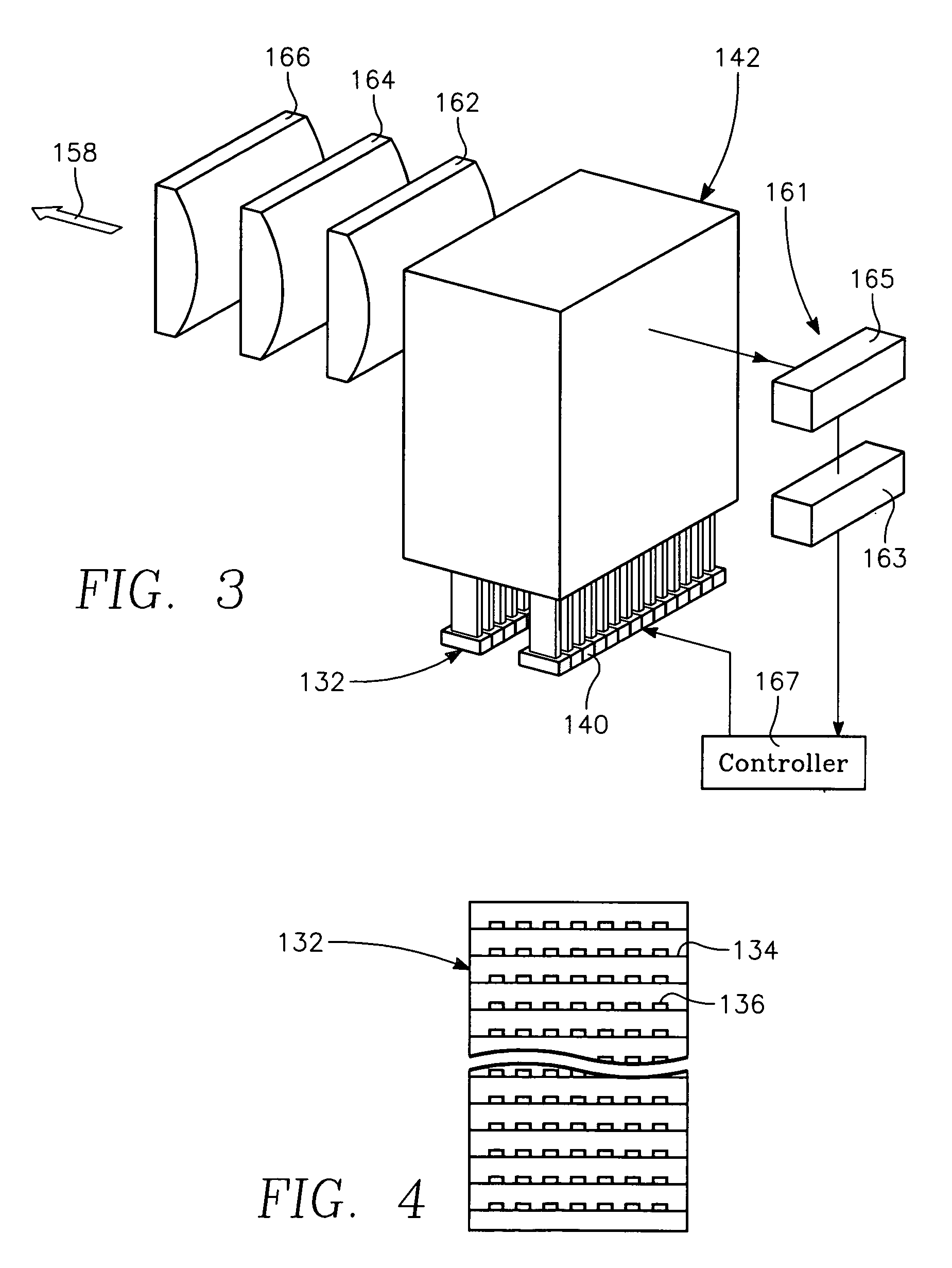
Copper conductor annealing process employing high speed optical annealing with a low temperature-deposited optical absorber layer
InactiveUS7335611B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesCopper conductorLow temperature deposition
A method of forming a conductor in a thin film structure on a semiconductor substrate includes forming high aspect ratio openings in a base layer having vertical side walls, depositing a dielectric barrier layer comprising a dielectric compound of a barrier metal on the surfaces of the high aspect ratio openings including the vertical side walls, depositing a metal barrier layer comprising the barrier metal on the first barrier layer, depositing a main conductor species seed layer on the metal barrier layer and depositing a main conductor layer. The method further includes annealing the main conductor layer by (a) directing light from an array of continuous wave lasers into a line of light extending at least partially across the thin film structure, and (b) translating the line of light relative to the thin film structure in a direction transverse to the line of light. The method of Claim 1 further comprising, prior to the annealing step, depositing an amorphous carbon optical absorber layer on the main conductor layer. The step of depositing an amorphous carbon optical absorber layer includes introducing a carbon-containing process gas into a reactor chamber containing the substrate in a process zone of the reactor, applying RF source power to an external reentrant conduit of the reactor to generate a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current passing through the process zone and applying a bias voltage to the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor substrate process using a low temperature deposited carbon-containing hard mask
InactiveUS20070032054A1Electric discharge tubesRadiation applicationsLow temperature depositionPlasma current
A method of processing a thin film structure on a semiconductor substrate using an optically writable mask includes placing the substrate in a reactor chamber, the substrate having on its surface a target layer to be etched in accordance with a predetermined pattern, and depositing a carbon-containing hard mask layer on the substrate by (a) introducing a carbon-containing process gas into the chamber, (b) generating a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by coupling plasma RF source power to an external portion of the reentrant path, and (c) coupling RF plasma bias power or bias voltage to the workpiece. The method further includes photolithographically defining the predetermined pattern in the carbon-containing hard mask layer, and etching the target layer in the presence of the hard mask layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
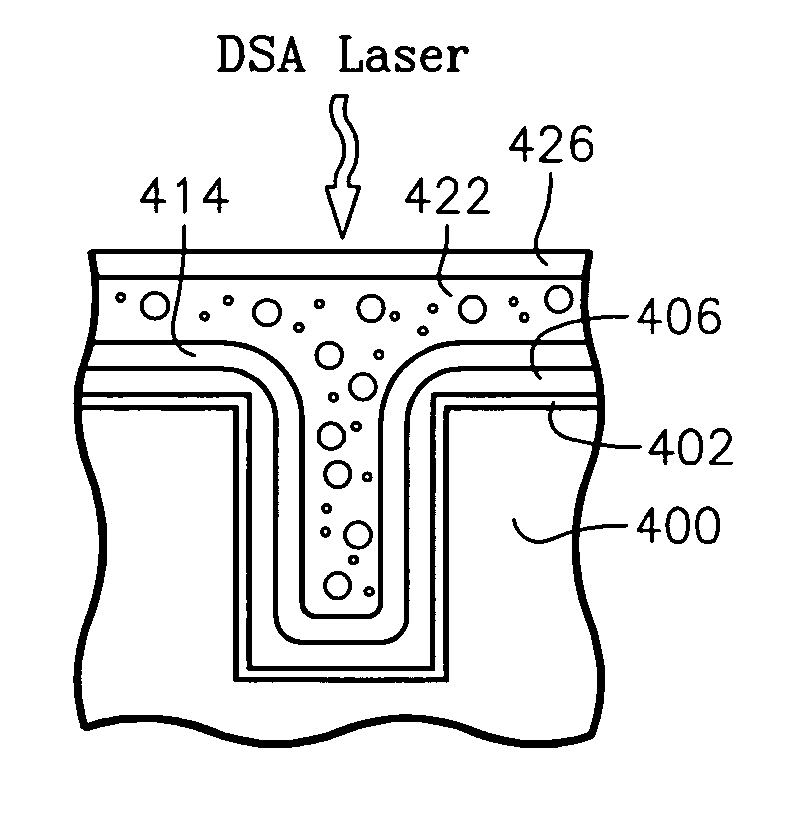
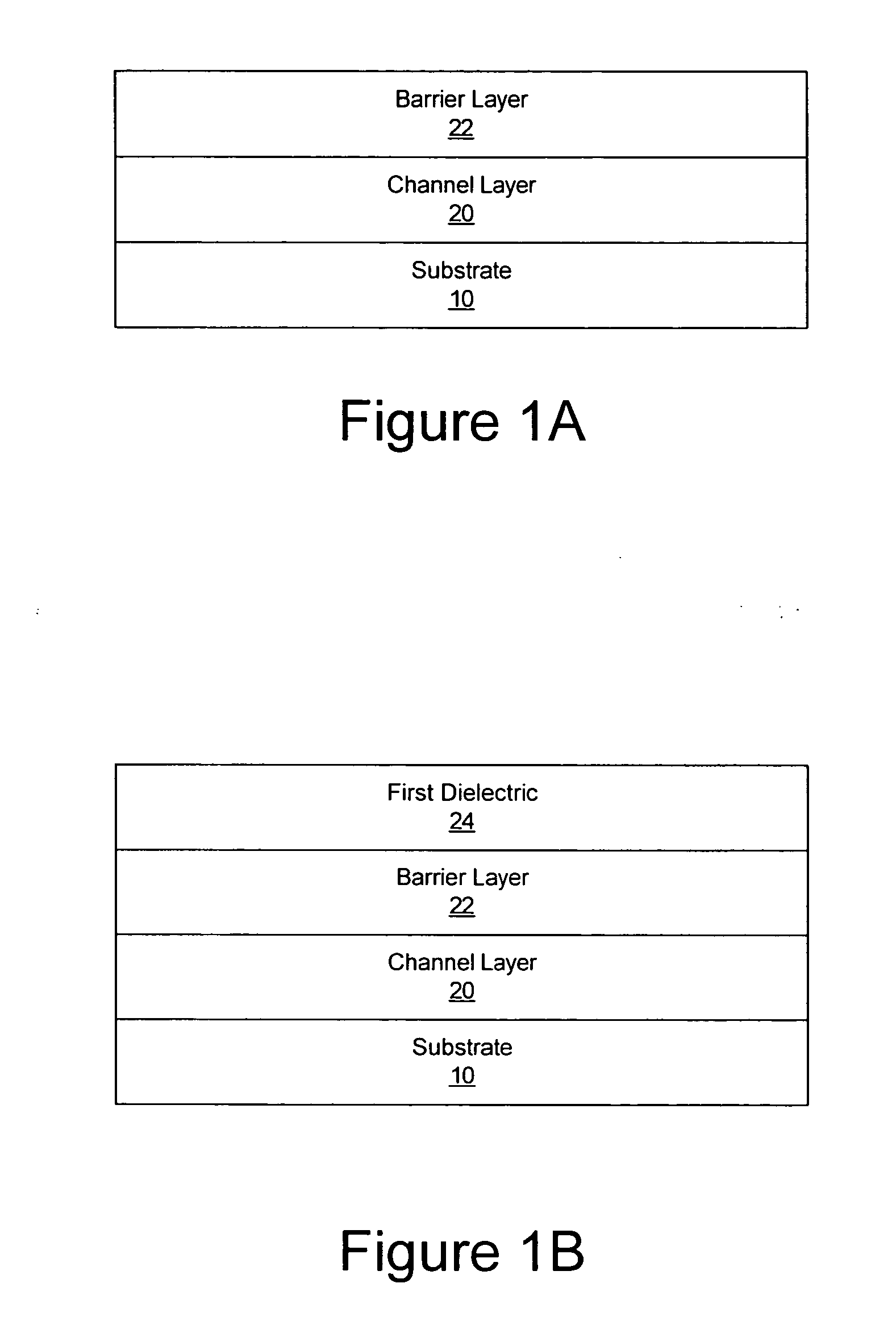
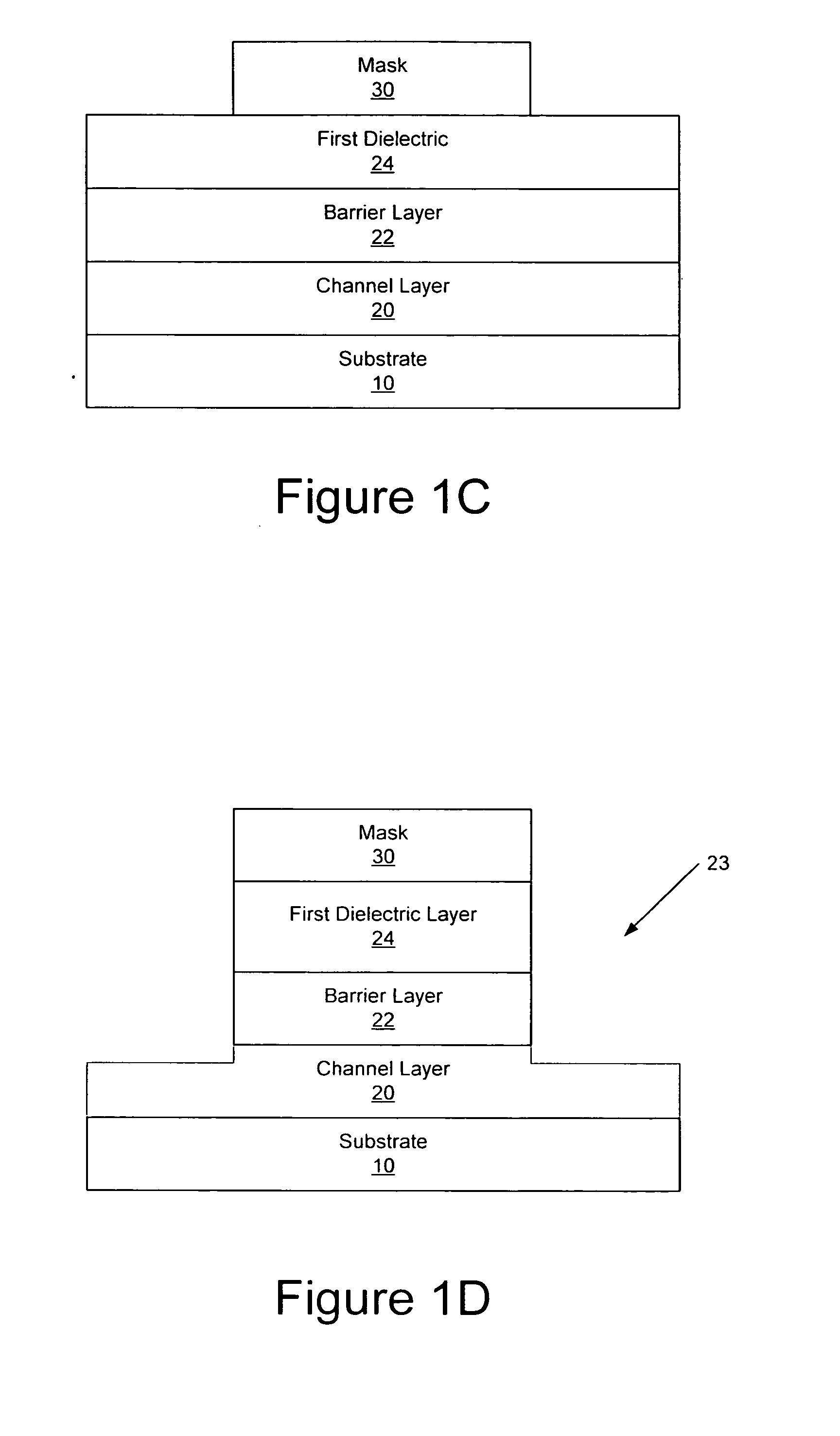
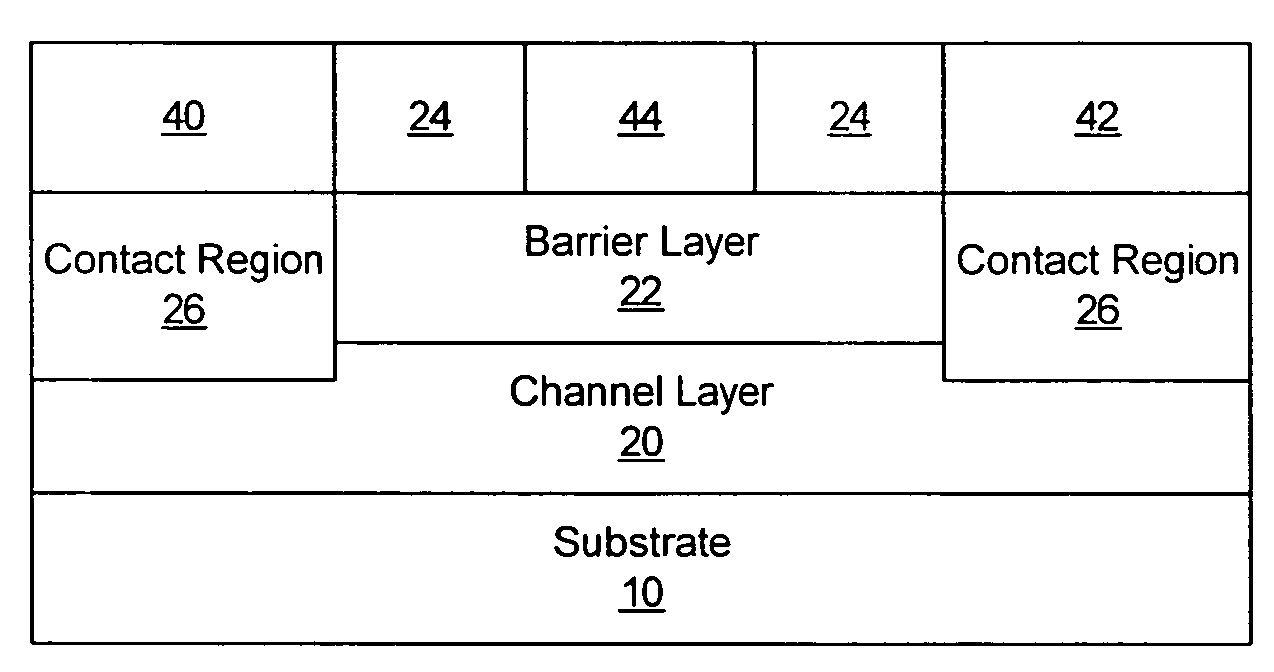
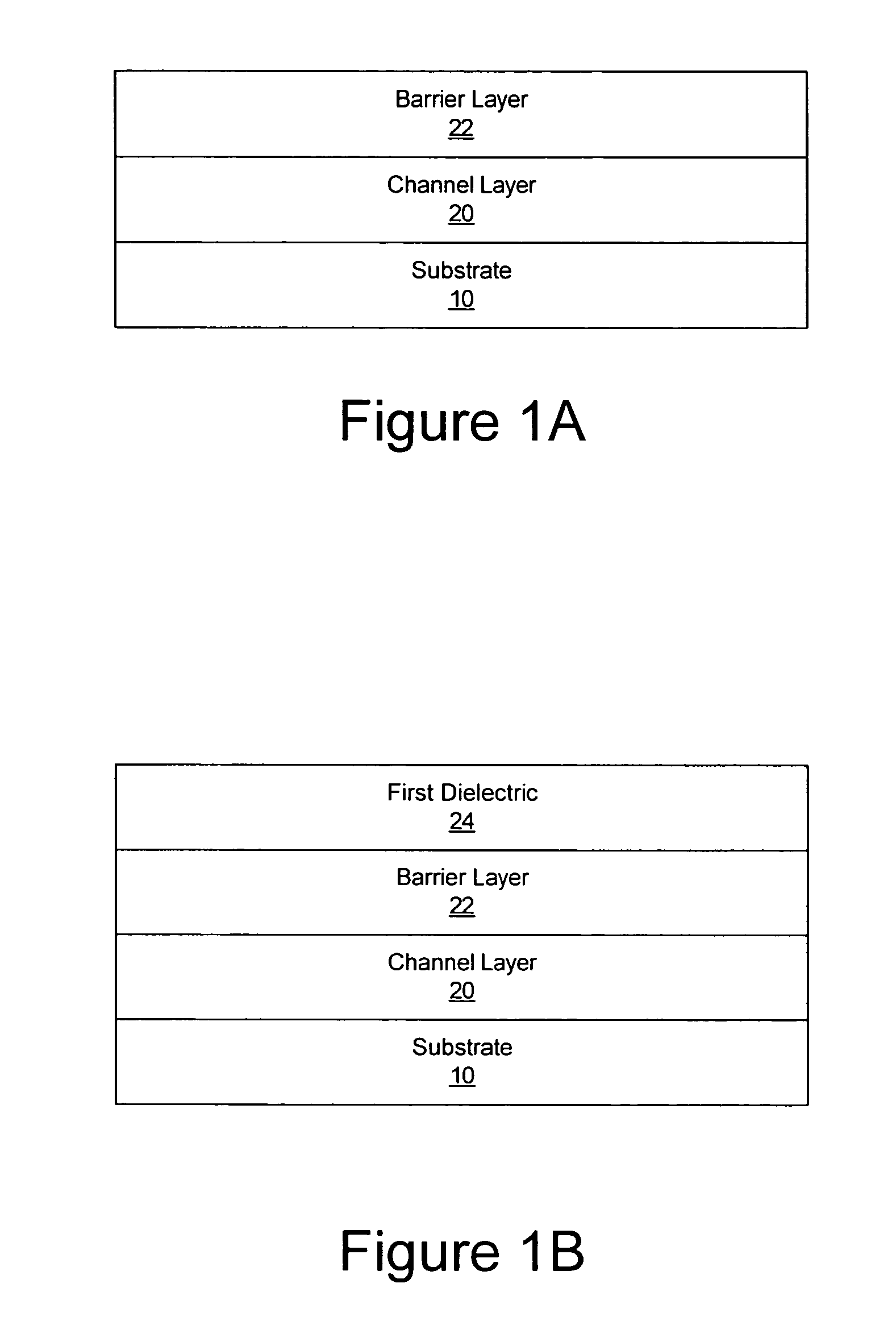
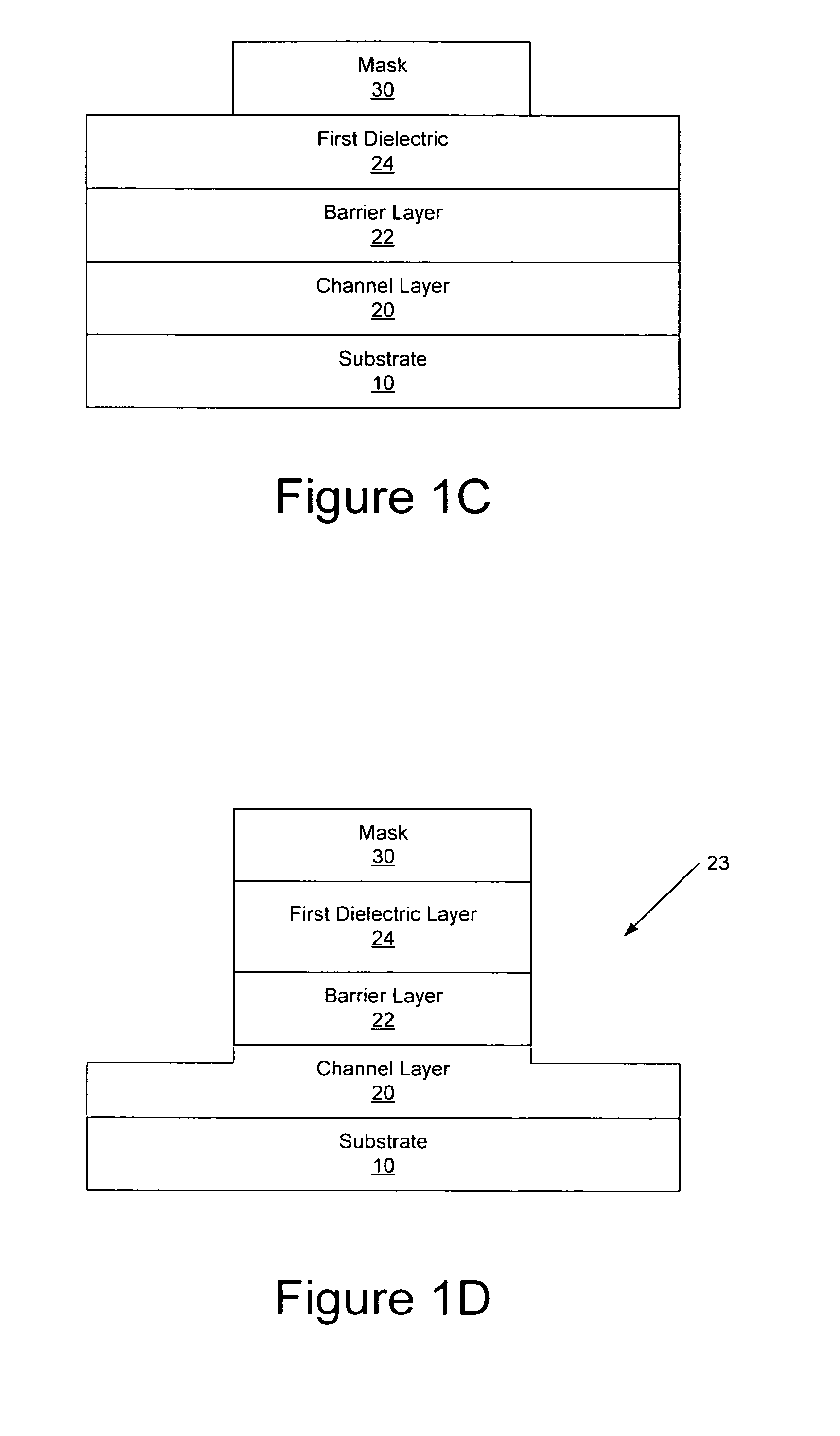
Methods of fabricating nitride-based transistors having regrown ohmic contact regions and nitride-based transistors having regrown ohmic contact regions
ActiveUS20050258451A1High electron mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLow temperature depositionSemiconductor materials
Transistor fabrication includes forming a nitride-based channel layer on a substrate, forming a barrier layer on the nitride-based channel layer, forming a contact recess in the barrier layer to expose a contact region of the nitride-based channel layer, forming a contact layer on the exposed contact region of the nitride-based channel layer, for example, using a low temperature deposition process, forming an ohmic contact on the contact layer and forming a gate contact disposed on the barrier layer adjacent the ohmic contact. A high electron mobility transistor (HEMT) and methods of fabricating a HEMT are also provided. The HEMT includes a nitride-based channel layer on a substrate, a barrier layer on the nitride-based channel layer, a contact recess in the barrier layer that extends into the channel layer, an n-type nitride-based semiconductor material contact region on the nitride-based channel layer in the contact recess, an ohmic contact on the nitride-based contact region and a gate contact disposed on the barrier layer adjacent the ohmic contact. The n-type nitride-based semiconductor material contact region and the nitride-based channel layer include a surface area enlargement structure.
Owner:CREE INC
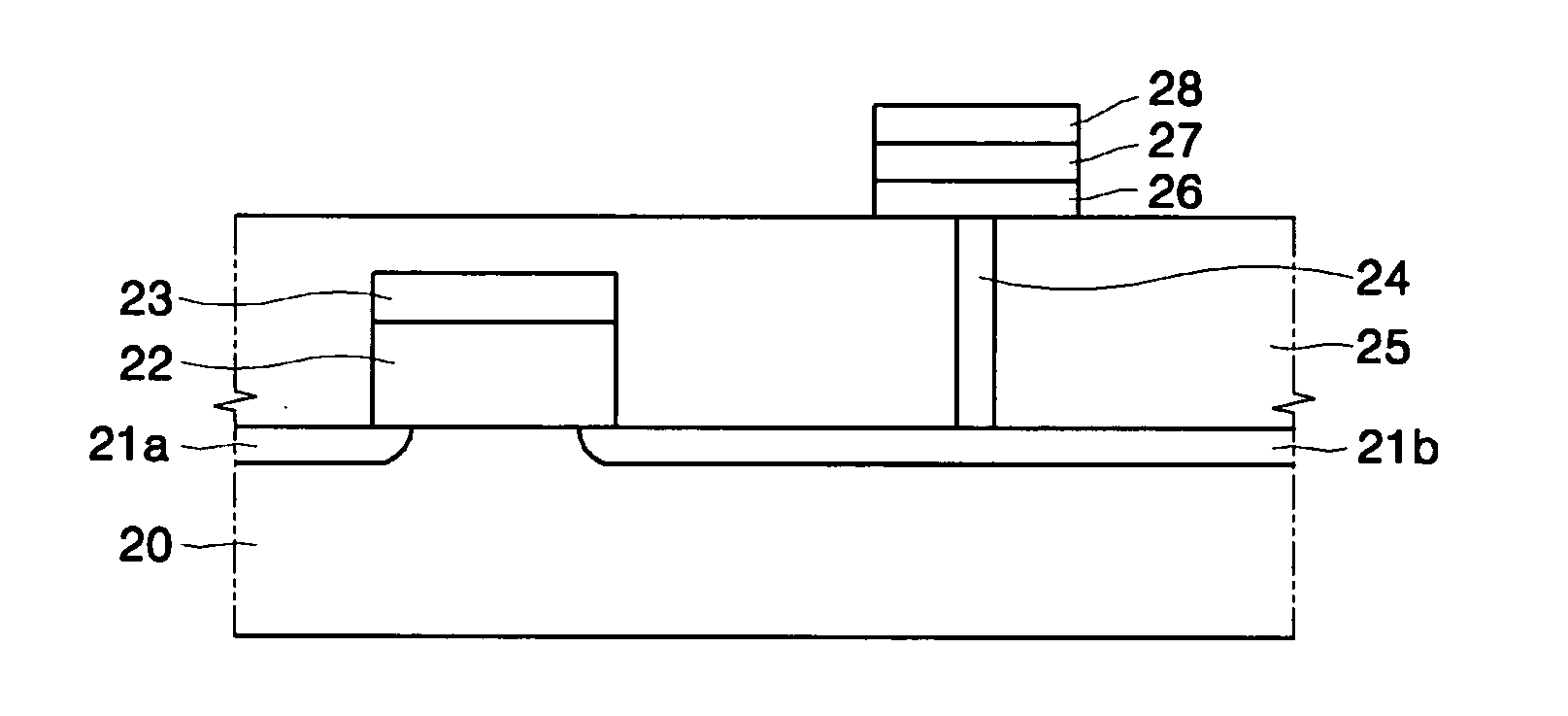
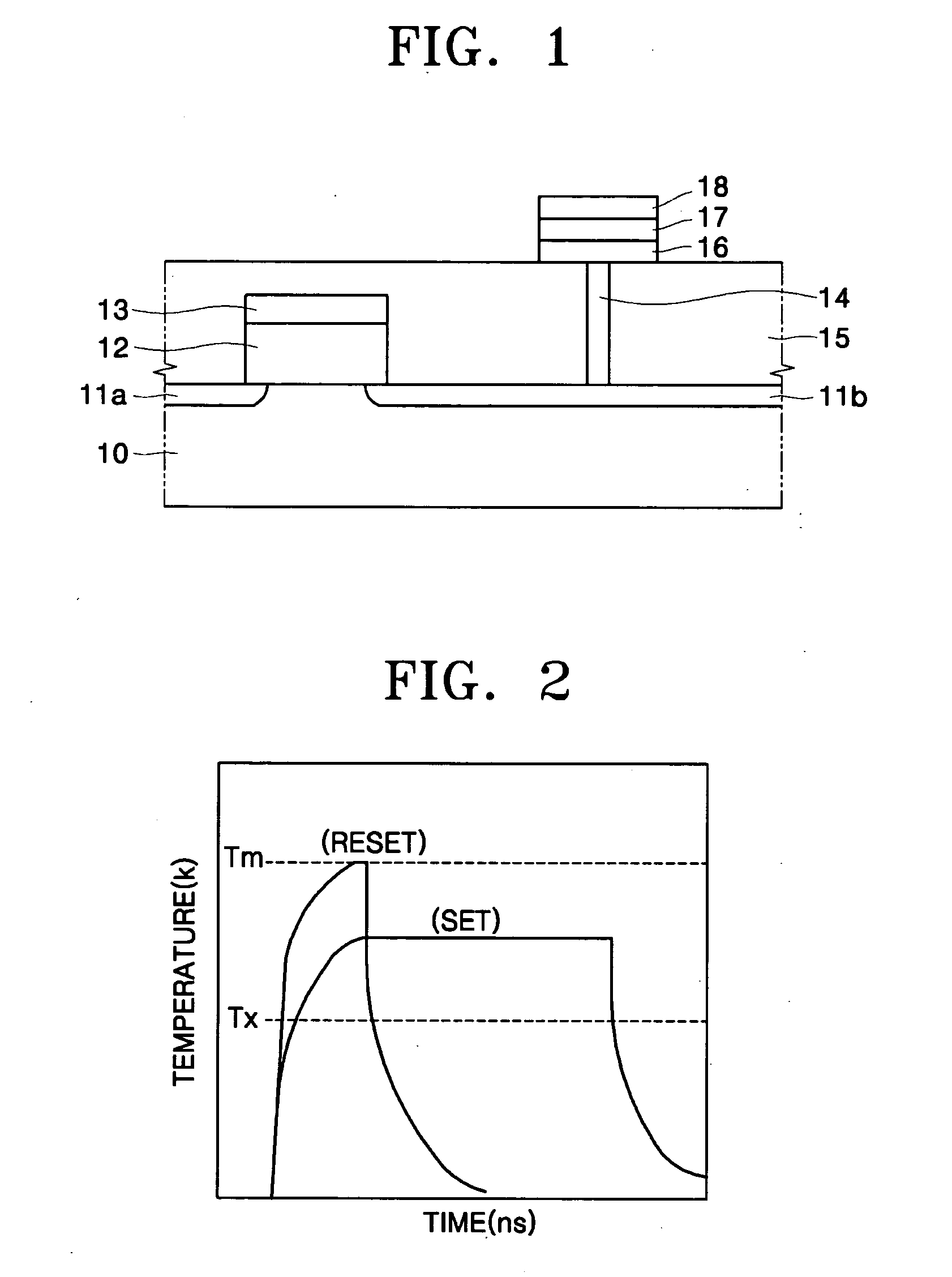
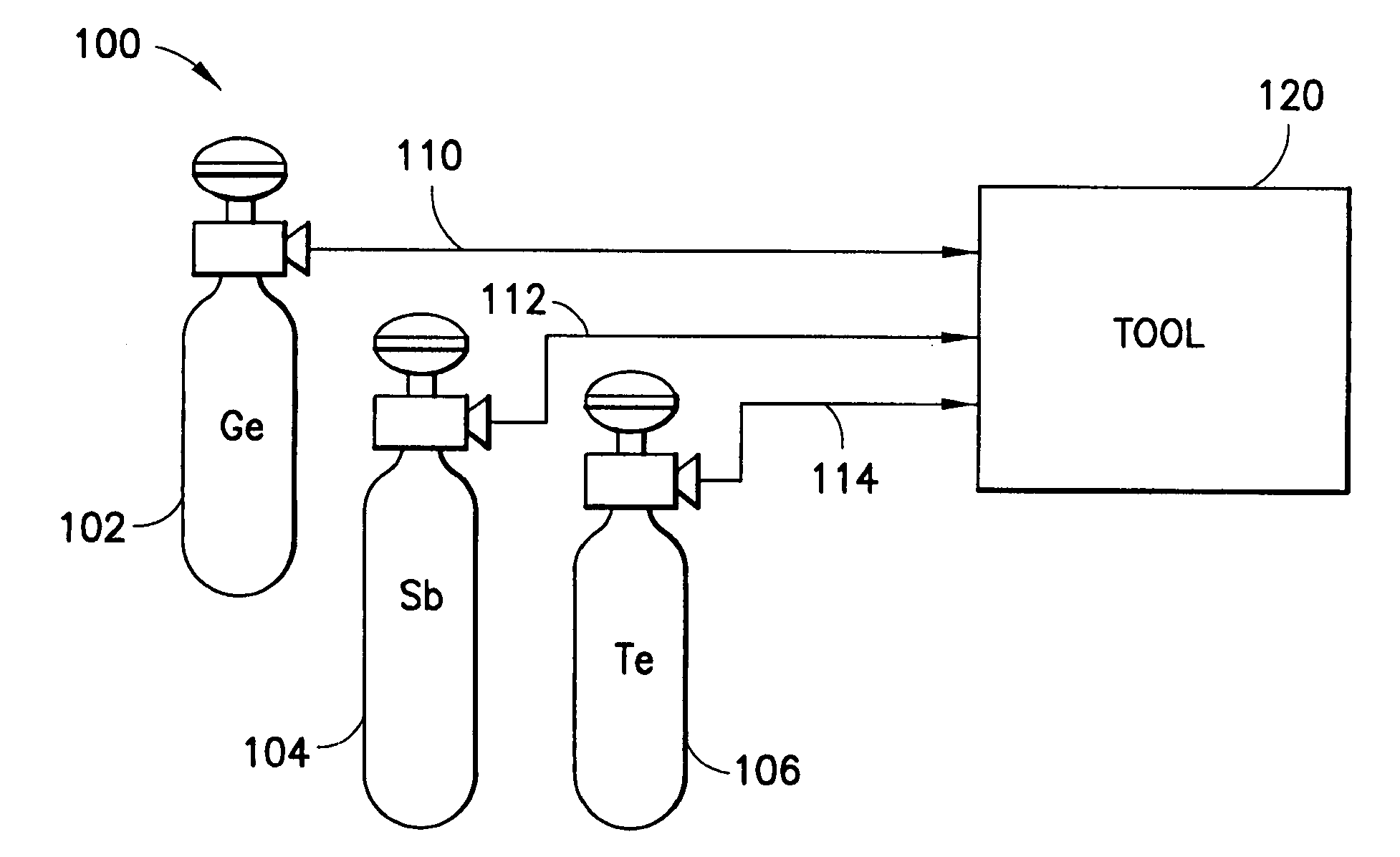
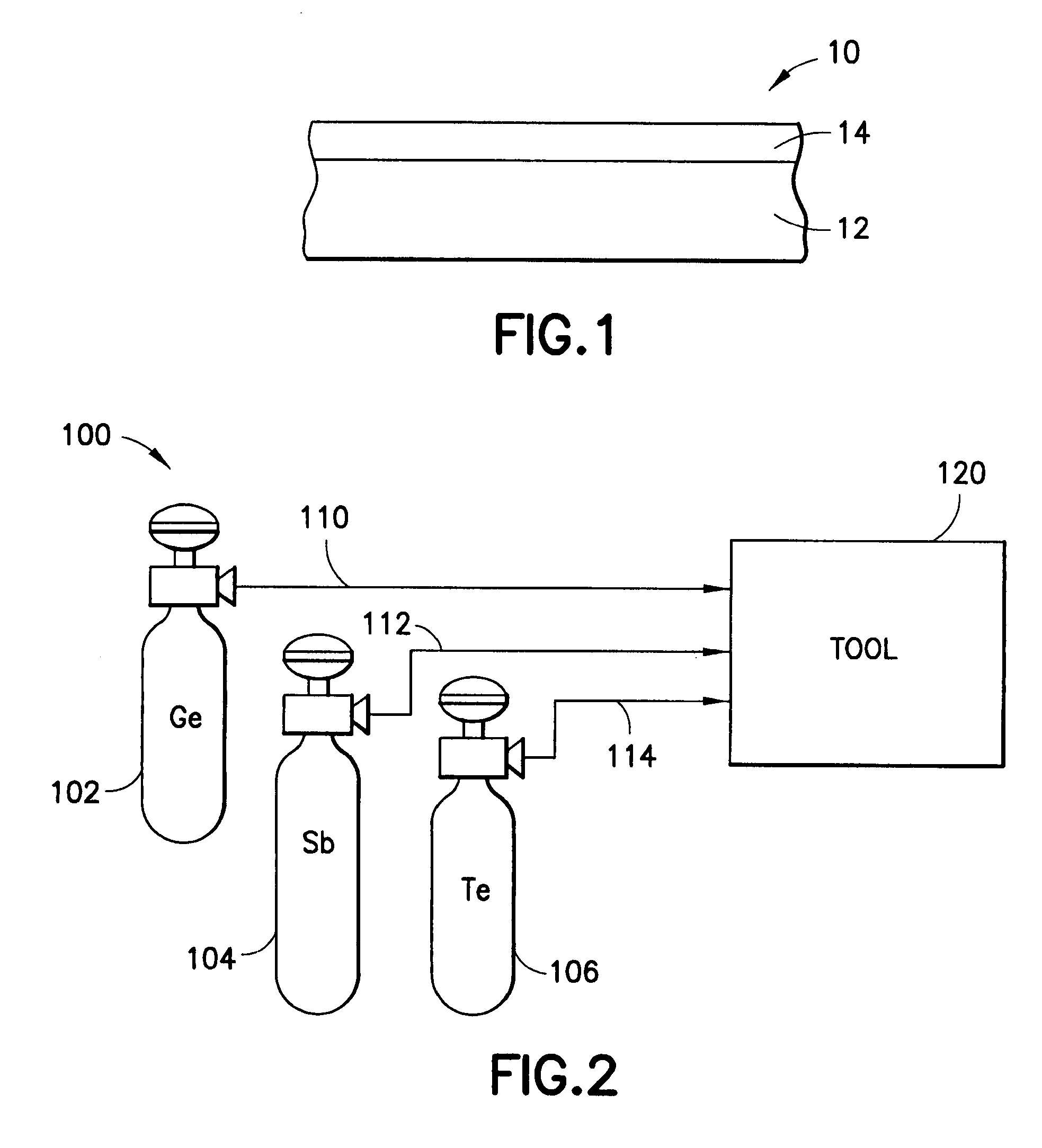
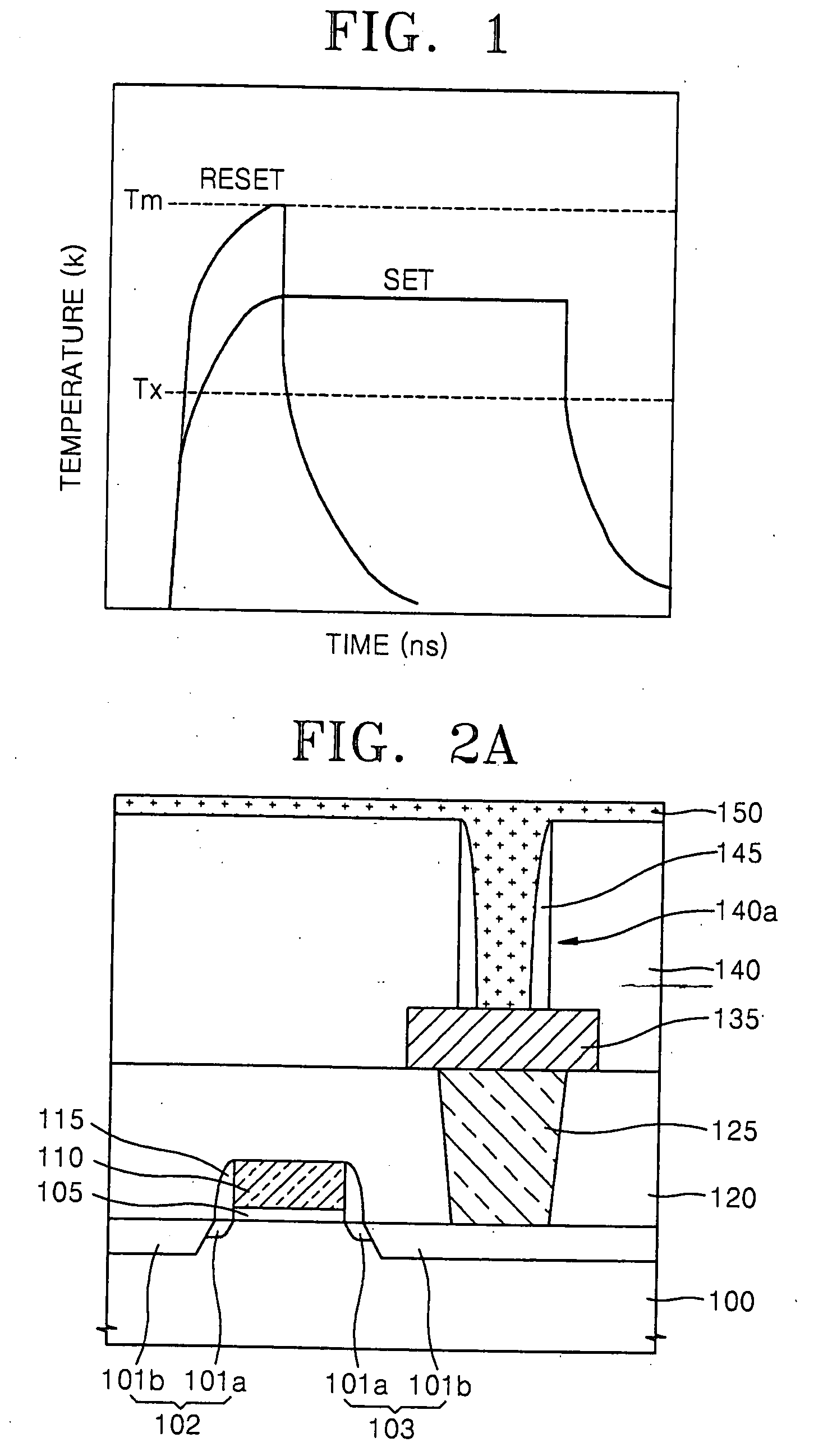
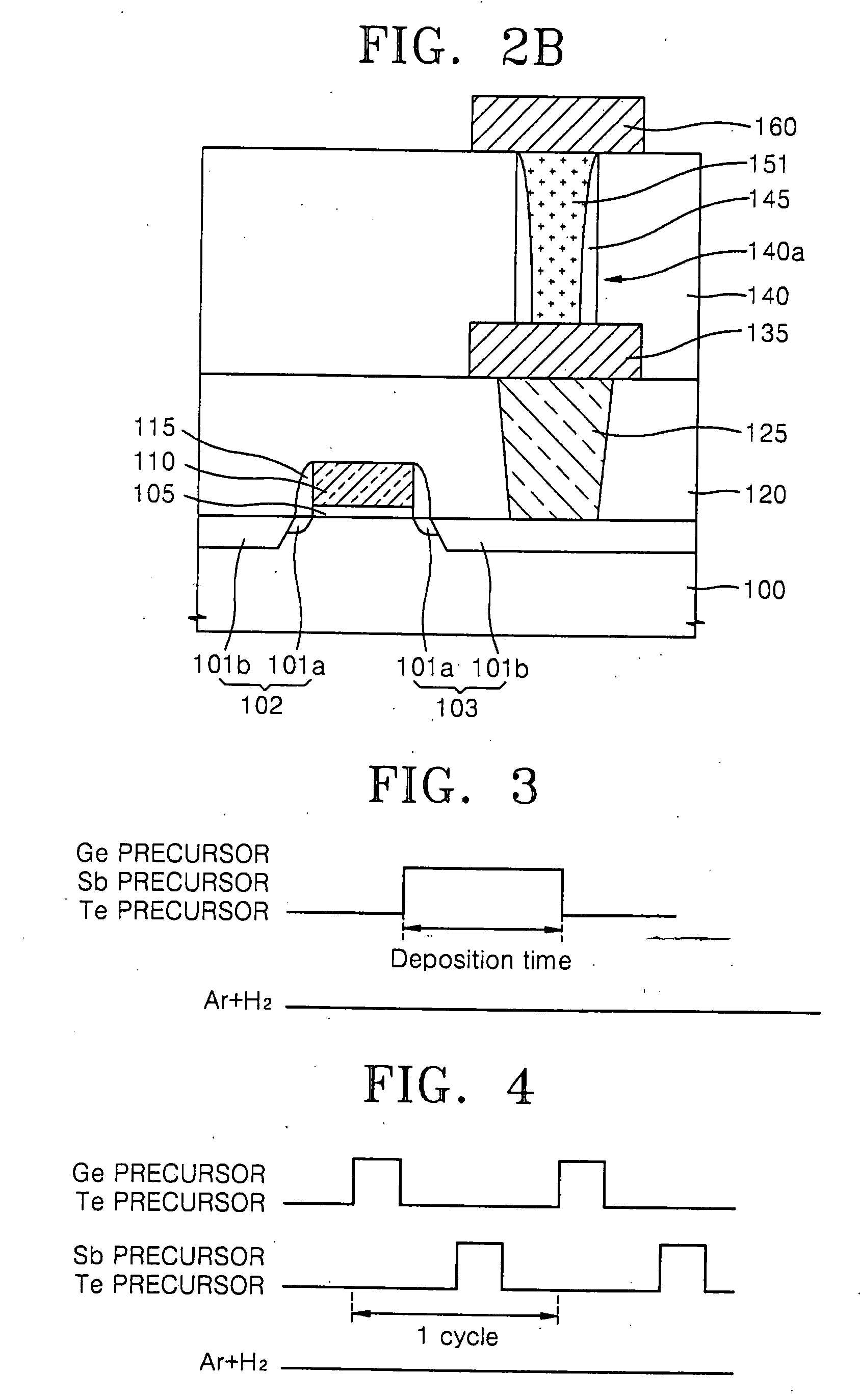
Ge precursor, GST thin layer formed using the same, phase-change memory device including the GST thin layer, and method of manufacturing the GST thin layer
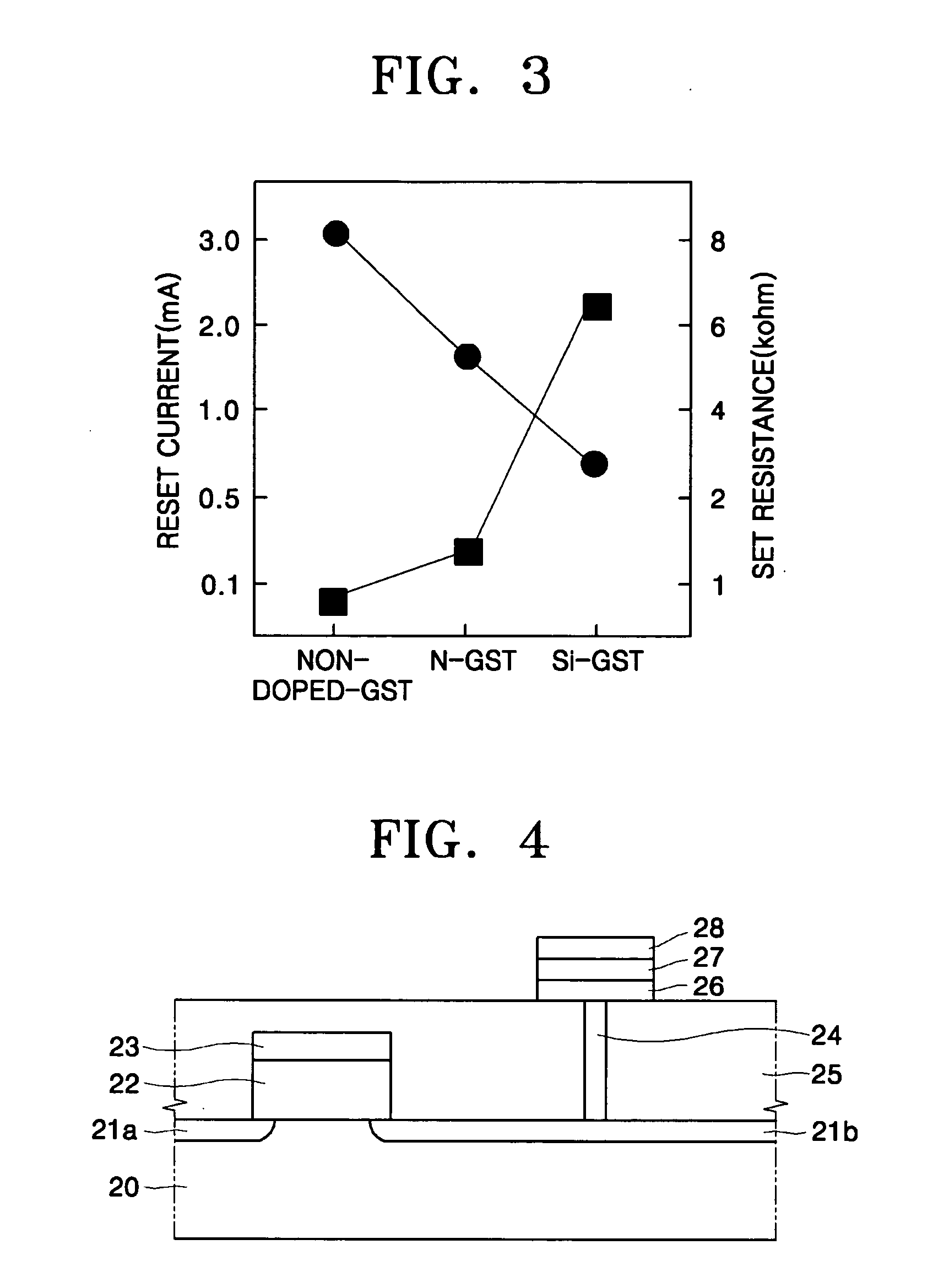
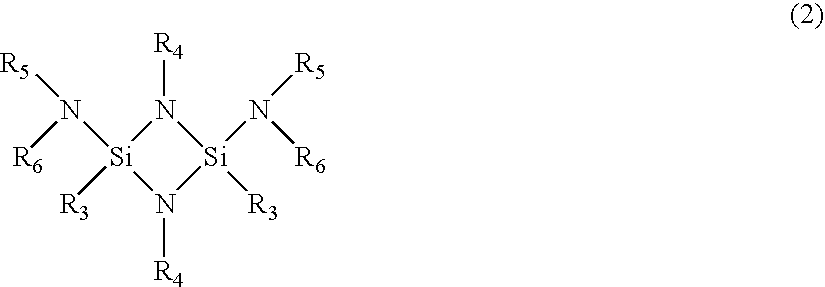
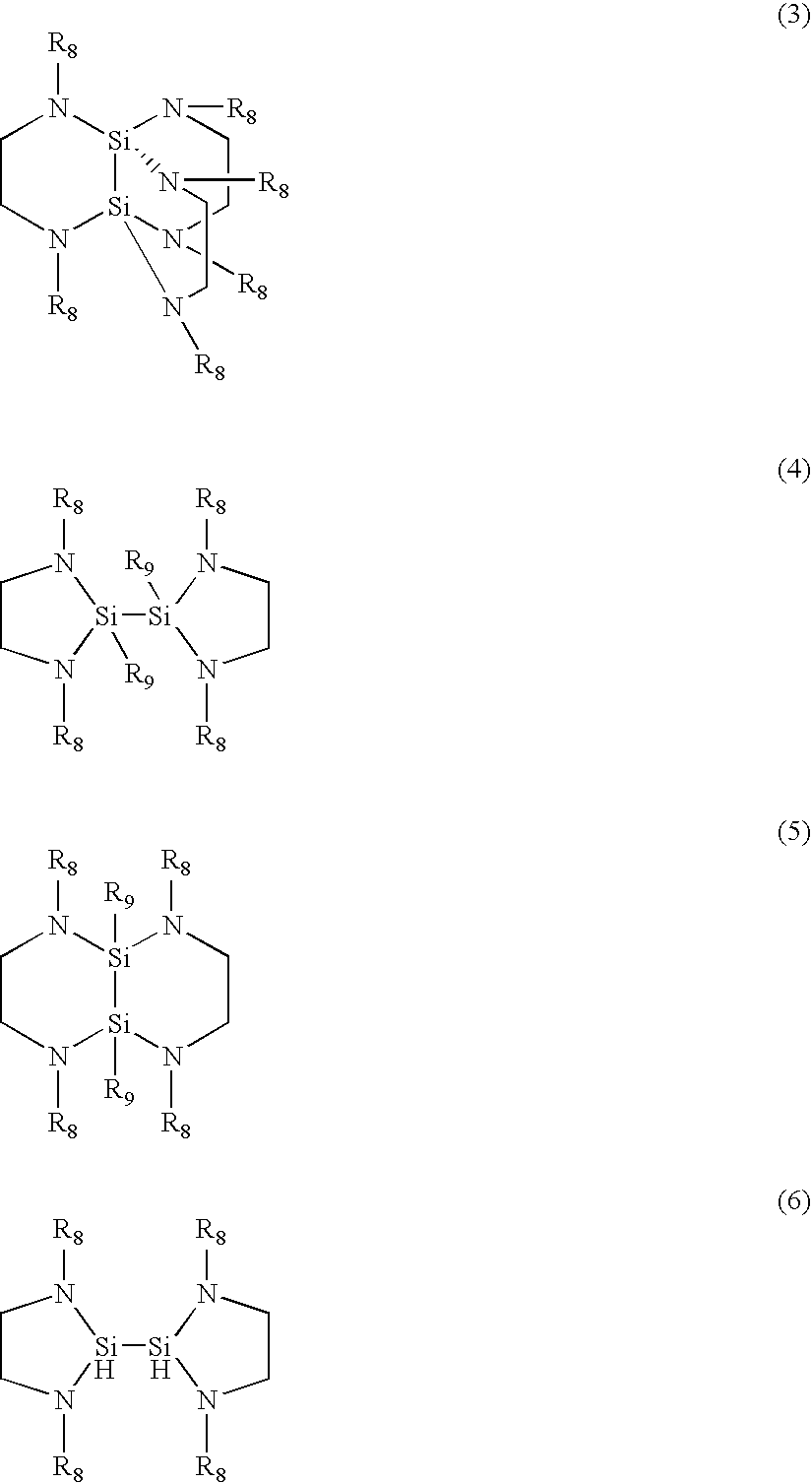
ActiveUS20060138393A1Uniform thicknessImproved performance characteristicsSolid-state devicesGermanium organic compoundsLow temperature depositionPhase-change memory
Provided are a Ge precursor for low temperature deposition containing Ge, N, and Si, a GST thin layer doped with N and Si formed using the same, a memory device including the GST thin layer doped with N and Si, and a method of manufacturing the GST thin layer. The Ge precursor for low temperature deposition contains N and Si such that the temperature at which the Ge precursor is deposited to form a thin layer, particularly, the GST thin layer doped with N and Si, can be low. In addition, during the low temperature deposition, H2 plasma can be used. The GST phase-change layer doped with N and Si formed from the Ge precursor for low temperature deposition has a low reset current. Therefore, a memory device including the GST phase-change layer doped with N and Si can be highly integrated, have a high capacity, and can be operated at a high speed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
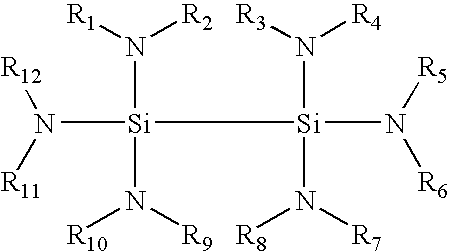
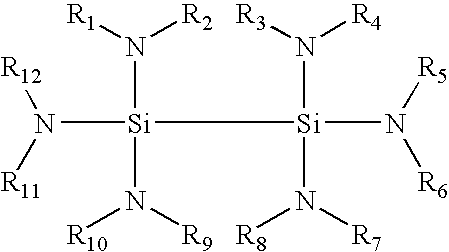
Composition and method for low temperature deposition of silicon-containing films such as films including silicon nitride, silicon dioxide and/or silicon-oxynitride
ActiveUS20040096582A1Silicon organic compoundsPolycrystalline material growthLow temperature depositionGas phase
Silicon precursors for forming silicon-containing films in the manufacture of semiconductor devices, such as low dielectric constant (k) thin films, high k gate silicates, low temperature silicon epitaxial films, and films containing silicon nitride (Si3N4), siliconoxynitride (SiOxNy) and / or silicon dioxide (SiO2). The precursors of the invention are amenable to use in low temperature (e.g., <500° C.) chemical vapor deposition processes, for fabrication of ULSI devices and device structures.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Methods of fabricating nitride-based transistors having regrown ohmic contact regions
ActiveUS7432142B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLow temperature depositionSemiconductor materials
Transistor fabrication includes forming a nitride-based channel layer on a substrate, forming a barrier layer on the nitride-based channel layer, forming a contact recess in the barrier layer to expose a contact region of the nitride-based channel layer, forming a contact layer on the exposed contact region of the nitride-based channel layer, for example, using a low temperature deposition process, forming an ohmic contact on the contact layer and forming a gate contact disposed on the barrier layer adjacent the ohmic contact. A high electron mobility transistor (HEMT) and methods of fabricating a HEMT are also provided. The HEMT includes a nitride-based channel layer on a substrate, a barrier layer on the nitride-based channel layer, a contact recess in the barrier layer that extends into the channel layer, an n-type nitride-based semiconductor material contact region on the nitride-based channel layer in the contact recess, an ohmic contact on the nitride-based contact region and a gate contact disposed on the barrier layer adjacent the ohmic contact. The n-type nitride-based semiconductor material contact region and the nitride-based channel layer include a surface area enlargement structure.
Owner:CREE INC
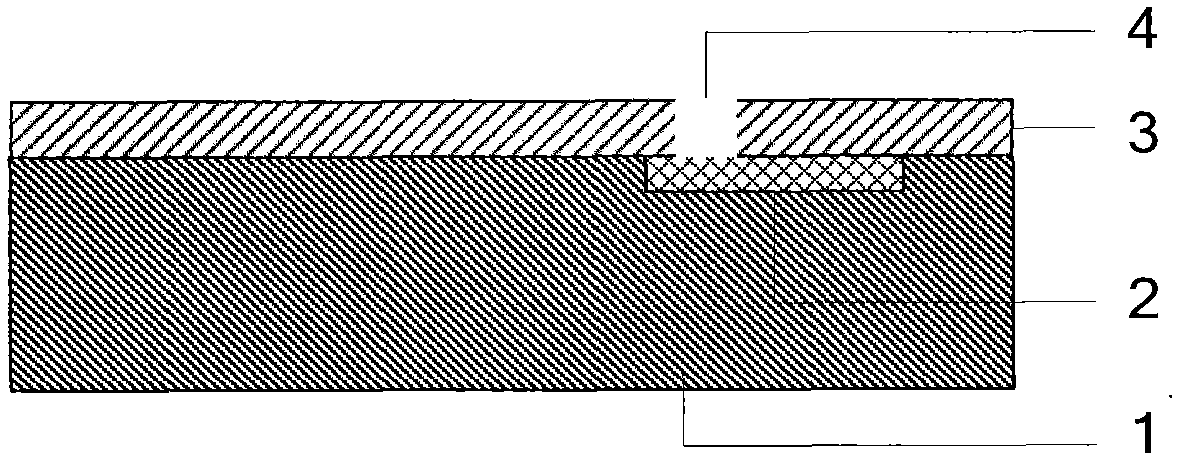
Water-barrier performance of an encapsulating film
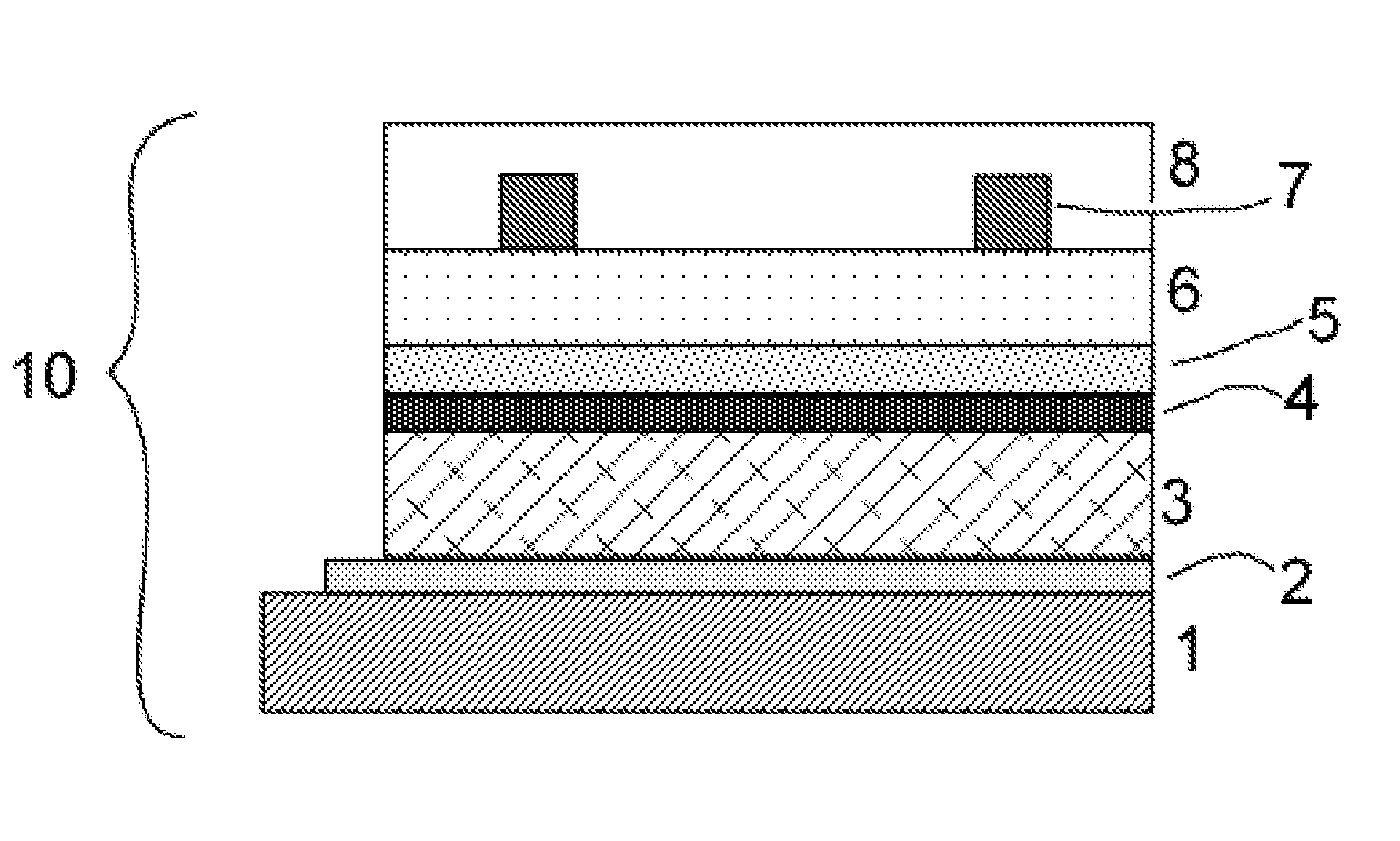
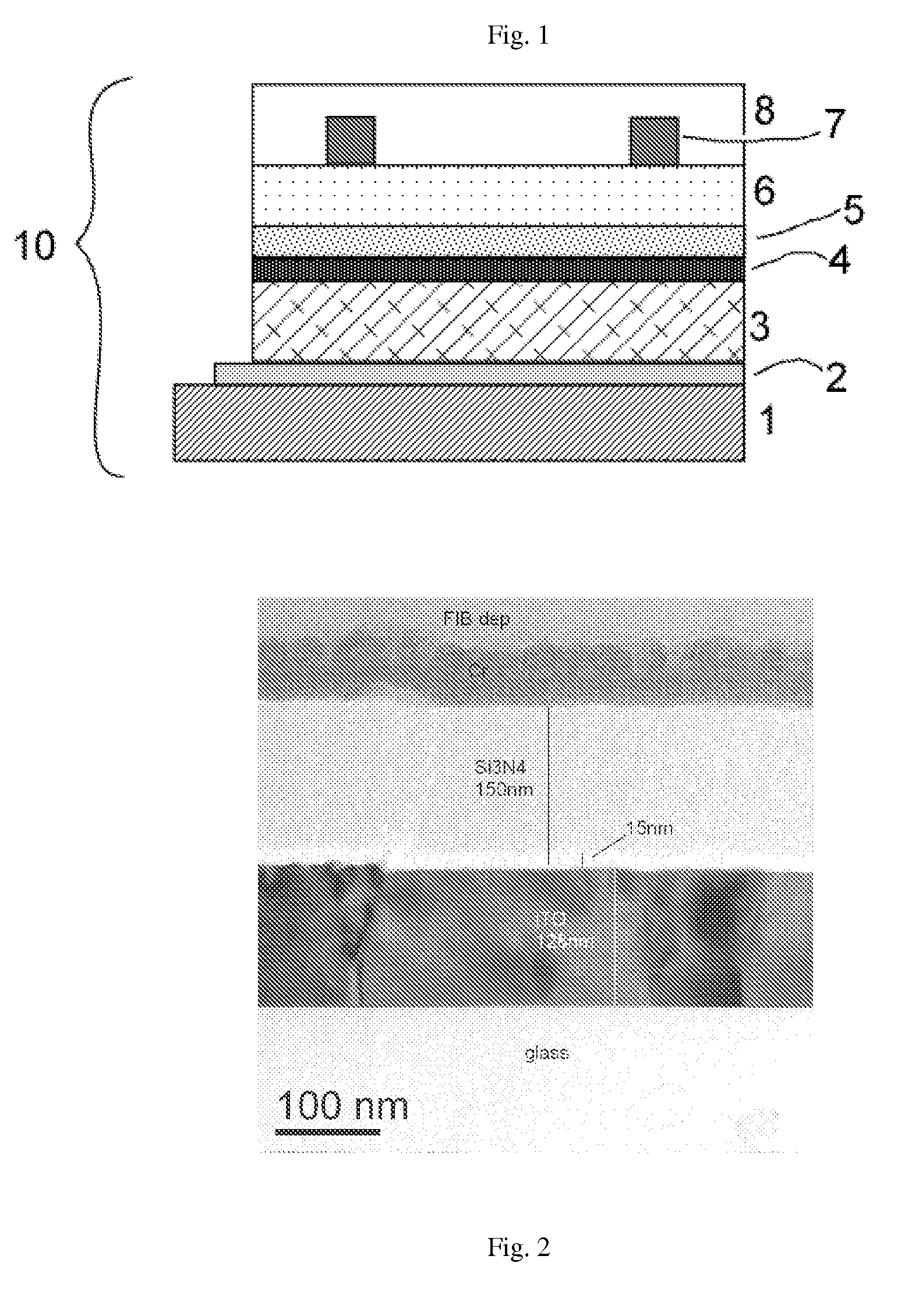
ActiveUS20050287688A1Improve waterproof performanceGood film uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolid state diffusion coatingLow temperature depositionSubstrate type
A method and apparatus for depositing a material layer onto a substrate is described. The method includes delivering a mixture of precursors for the material layer into a process chamber and depositing the material layer on the substrate at low temperature. The material layer can be used as an encapsulating layer for various display applications which require low temperature deposition process due to thermal instability of underlying materials used. In one aspect, the encapsulating layer includes one or more material layers (multilayer) having one or more barrier layer materials and one or more low-dielectric constant materials. The encapsulating layer thus deposited provides reduced surface roughness, improved water-barrier performance, reduce thermal stress, good step coverage, and can be applied to many substrate types and many substrate sizes. Accordingly, the encapsulating layer thus deposited provides good device lifetime for various display devices, such as OLED devices. In another aspect, a method of depositing an amorphous carbon material on a substrate at low temperature is provided. The amorphous carbon material can be used to reduce thermal stress and prevent the deposited thin film from peeling off the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Low temperature deposition of phase change memory materials
InactiveUS20090124039A1Silicon organic compoundsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsLow temperature depositionPhase-change memory
A system and method for forming a phase change memory material on a substrate, in which the substrate is contacted with precursors for a phase change memory chalcogenide alloy under conditions producing deposition of the chalcogenide alloy on the substrate, at temperature below 350° C. with the contacting being carried out via chemical vapor deposition or atomic layer deposition. Various tellurium, germanium and germanium-tellurium precursors are described, which are useful for forming GST phase change memory films on substrates.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Composition and method for low temperature deposition of silicon-containing films such as films including silicon nitride, silicon dioxide and/or silicon-oxynitride
ActiveUS7531679B2Silicon organic compoundsPolycrystalline material growthLow temperature depositionDevice material
Silicon precursors for forming silicon-containing films in the manufacture of semiconductor devices, such as low dielectric constant (k) thin films, high k gate silicates, low temperature silicon epitaxial films, and films containing silicon nitride (Si3N4), siliconoxynitride (SiOxNy) and / or silicon dioxide (SiO2). The precursors of the invention are amenable to use in low temperature (e.g., <500° C.) chemical vapor deposition processes, for fabrication of ULSI devices and device structures.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Water-barrier performance of an encapsulating film
ActiveUS7183197B2Improve waterproof performanceGood film uniformityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLow temperature depositionSubstrate type
A method and apparatus for depositing a material layer onto a substrate is described. The method includes delivering a mixture of precursors for the material layer into a process chamber and depositing the material layer on the substrate at low temperature. The material layer can be used as an encapsulating layer for various display applications which require low temperature deposition process due to thermal instability of underlying materials used. In one aspect, the encapsulating layer includes one or more material layers (multilayer) having one or more barrier layer materials and one or more low-dielectric constant materials. The encapsulating layer thus deposited provides reduced surface roughness, improved water-barrier performance, reduce thermal stress, good step coverage, and can be applied to many substrate types and many substrate sizes. Accordingly, the encapsulating layer thus deposited provides good device lifetime for various display devices, such as OLED devices. In another aspect, a method of depositing an amorphous carbon material on a substrate at low temperature is provided. The amorphous carbon material can be used to reduce thermal stress and prevent the deposited thin film from peeling off the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
MEMS fabrication on a laminated substrate
ActiveUS20050062653A1Increasing energy of plasmaEnhanced vapor depositionSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsLow temperature depositionEngineering
Systems and methods are provided that facilitate the formation of micro-mechanical structures and related systems on a laminated substrate. More particularly, a micro-mechanical device and a three-dimensional multiple frequency antenna are provided for in which the micro-mechanical device and antenna, as well as additional components, can be fabricated together concurrently on the same laminated substrate. The fabrication process includes a low temperature deposition process allowing for deposition of an insulator material at a temperature below the maximum operating temperature of the laminated substrate, as well as a planarization process allowing for the molding and planarizing of a polymer layer to be used as a form for a micro-mechanical device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Diffusion barriers formed by low temperature deposition
InactiveUS20050110142A1Inhibited DiffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLow temperature depositionDiffusion barrier
A solid state device includes a first material and a second material. A barrier layer is formed between the first material and the second material to prevent diffusion between the first material and the second material. The barrier layer includes a metal form of at least one of Ru and Re. The barrier layer is preferably formed using a low temperature deposition process, where the substrate is less than 400 degrees C.
Owner:IBM CORP
High-density plasma oxidation for enhanced gate oxide performance
InactiveUS7381595B2Improve bulk and interfacial qualityPromote efficient oxidationTransistorSolid-state devicesLow temperature depositionHigh density
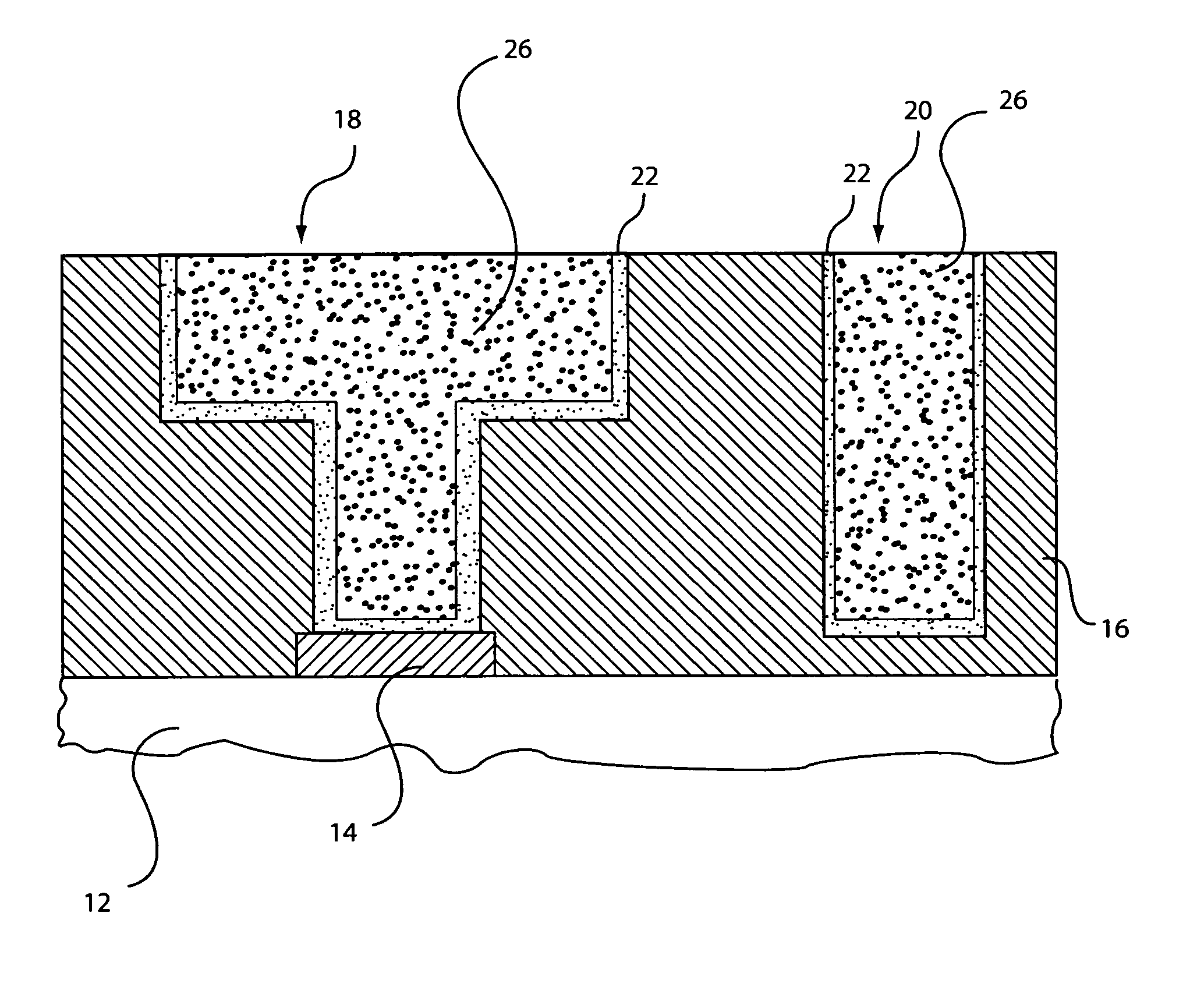
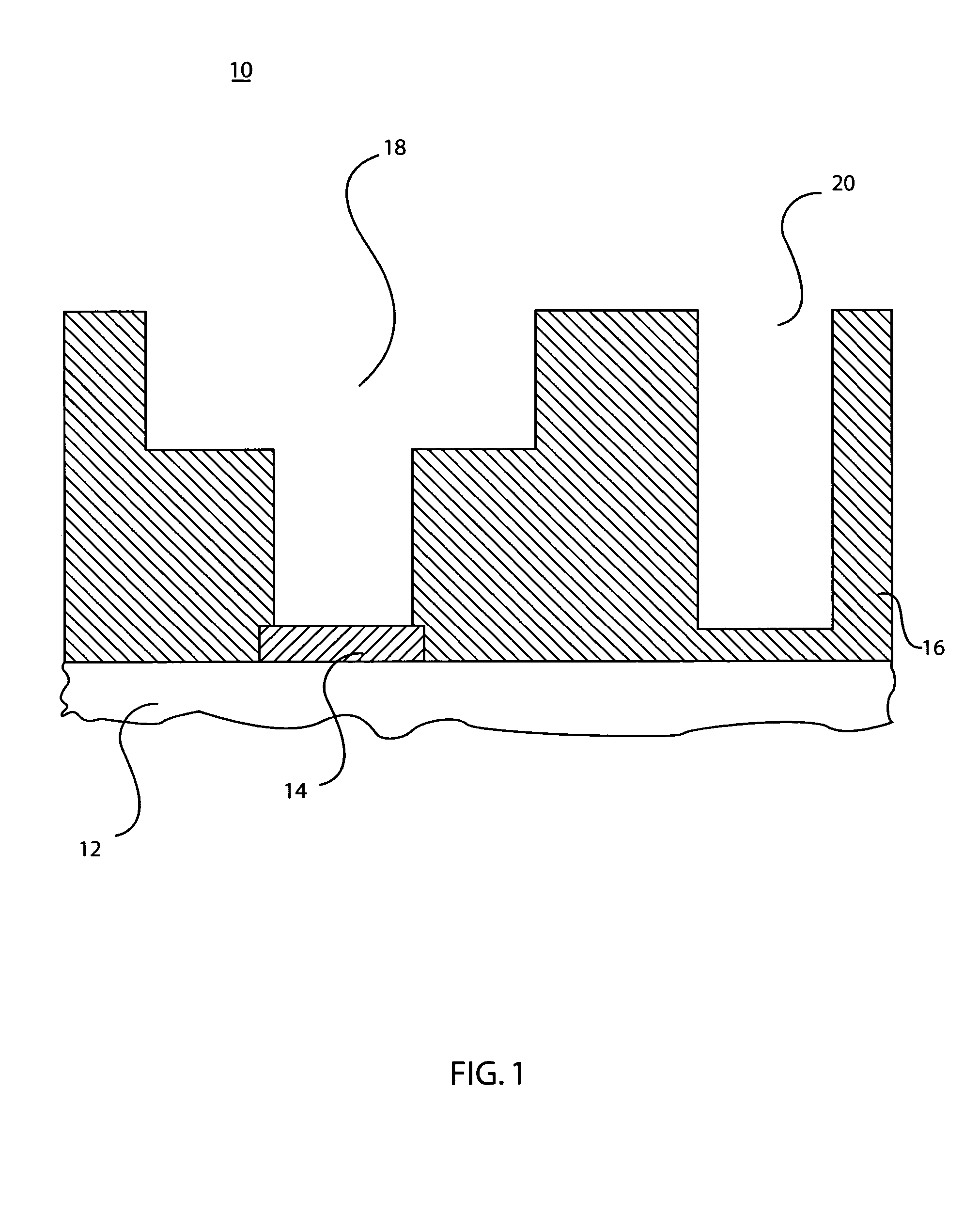
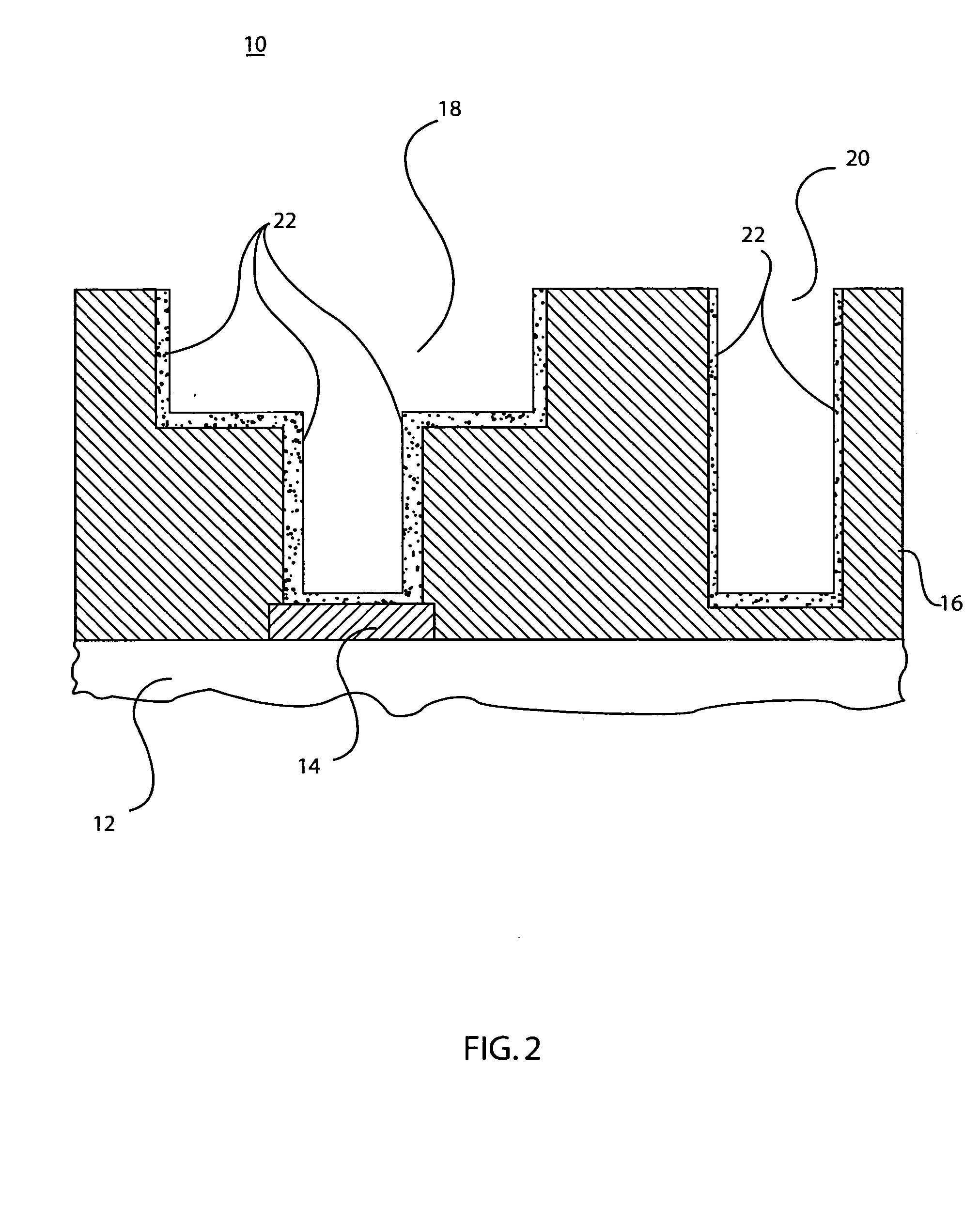
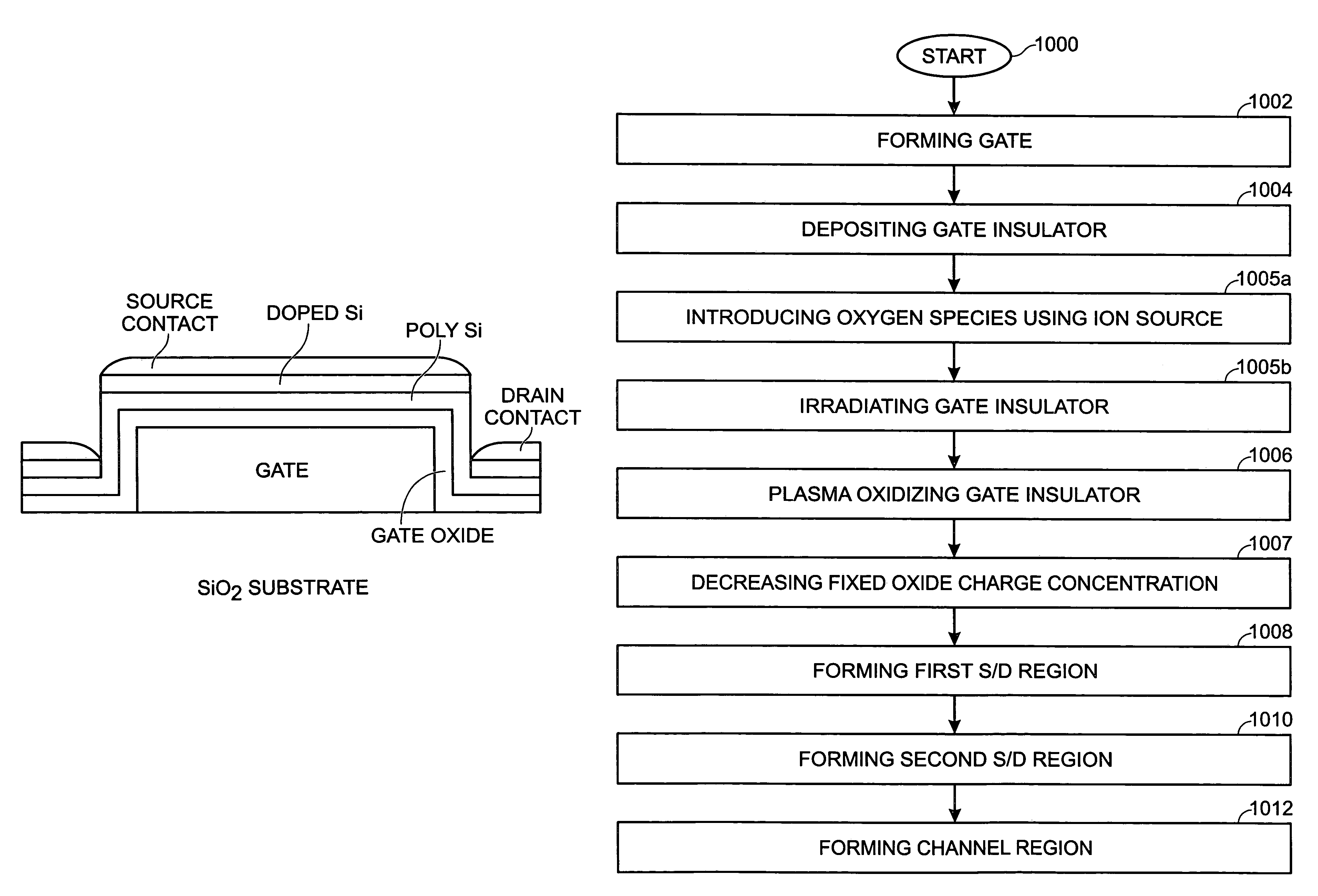
A method is provided for forming a low-temperature vertical gate insulator in a vertical thin-film transistor (V-TFT) fabrication process. The method comprises: forming a gate, having vertical sidewalls and a top surface, overlying a substrate insulation layer; depositing a silicon oxide thin-film gate insulator overlying the gate; plasma oxidizing the gate insulator at a temperature of less than 400° C., using a high-density plasma source; forming a first source / drain region overlying the gate top surface; forming a second source / drain region overlying the substrate insulation layer, adjacent a first gate sidewall; and, forming a channel region overlying the first gate sidewall, in the gate insulator interposed between the first and second source / drain regions. When the silicon oxide thin-film gate insulator is deposited overlying the gate a Si oxide layer, a low temperature deposition process can be used, so that a step-coverage of greater than 65% can be obtained.
Owner:SHARP KK
Composition and method for low temperature deposition of silicon-containing films
ActiveUS7446217B2Silicon organic compoundsPolycrystalline material growthLow temperature depositionSilanes
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Low temperature deposition of silicon-containing films
ActiveUS8298628B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingLow temperature depositionDeposition temperature
This invention discloses the method of forming silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, silicon oxide, carbon-doped silicon nitride, carbon-doped silicon oxide and carbon-doped oxynitride films at low deposition temperatures. The silicon containing precursors used for the deposition are monochlorosilane (MCS) and monochloroalkylsilanes. The method is preferably carried out by using plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition, plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition, and plasma enhanced cyclic chemical vapor deposition.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD +1
Low Temperature Wafer Level Processing for MEMS Devices
ActiveUS20110027930A1Impedence networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLow temperature depositionEngineering
Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) are small integrated devices or systems that combine electrical and mechanical components. It would be beneficial for such MEMS devices to be integrated with silicon CMOS electronics and packaged in controlled environments and support industry standard mounting interconnections such as solder bump through the provisioning of through-wafer via-based electrical interconnections. However, the fragile nature of the MEMS devices, the requirement for vacuum, hermetic sealing, and stresses placed on metallization membranes are not present in packaging conventional CMOS electronics. Accordingly there is provided a means of reinforcing the through-wafer vias for such integrated MEMS-CMOS circuits by in filling a predetermined portion of the through-wafer electrical vias with low temperature deposited ceramic materials which are deposited at temperatures below 350° C., and potentially to below 250° C., thereby allowing the re-inforcing ceramic to be deposited after fabrication of the CMOS electronics.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
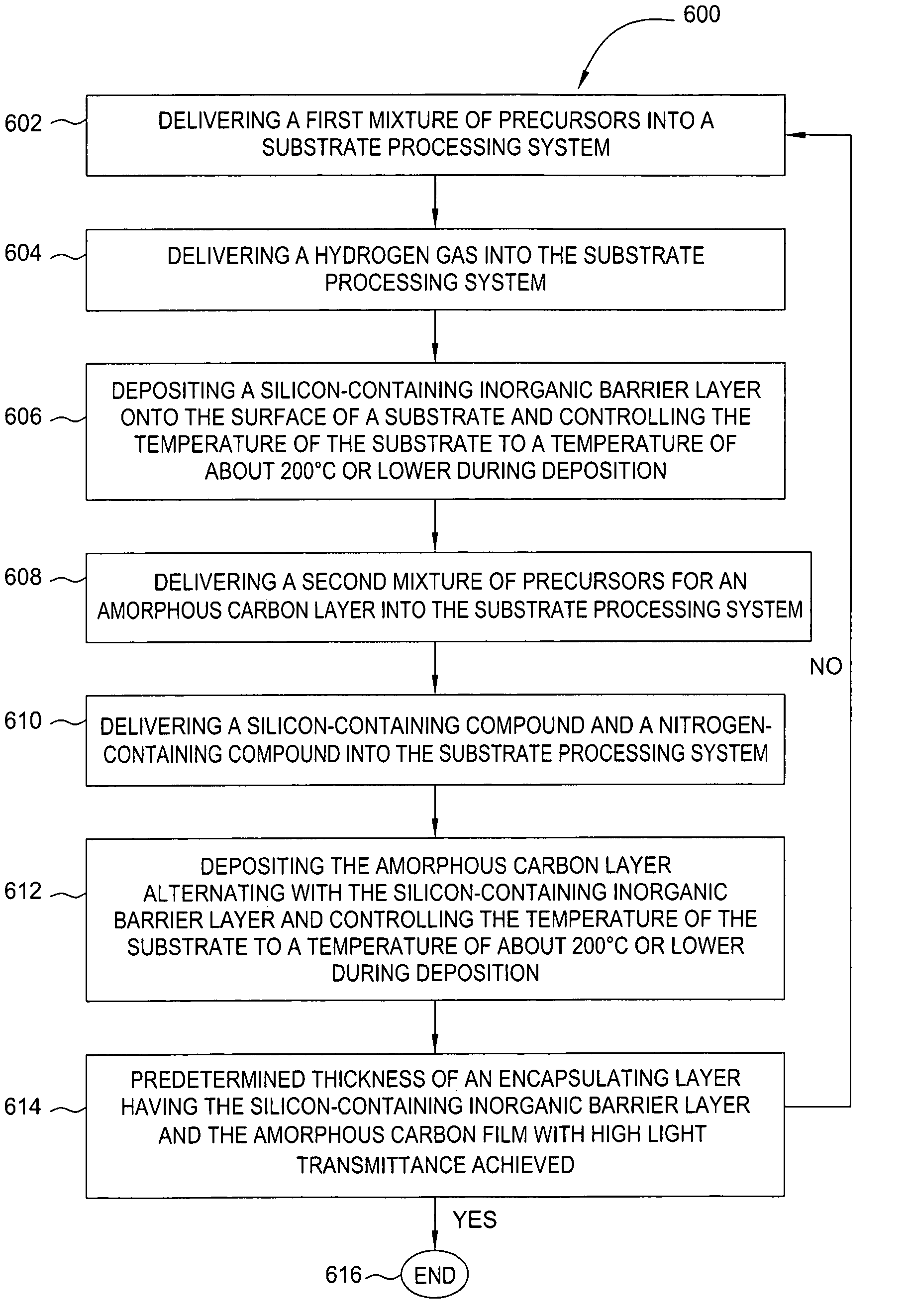
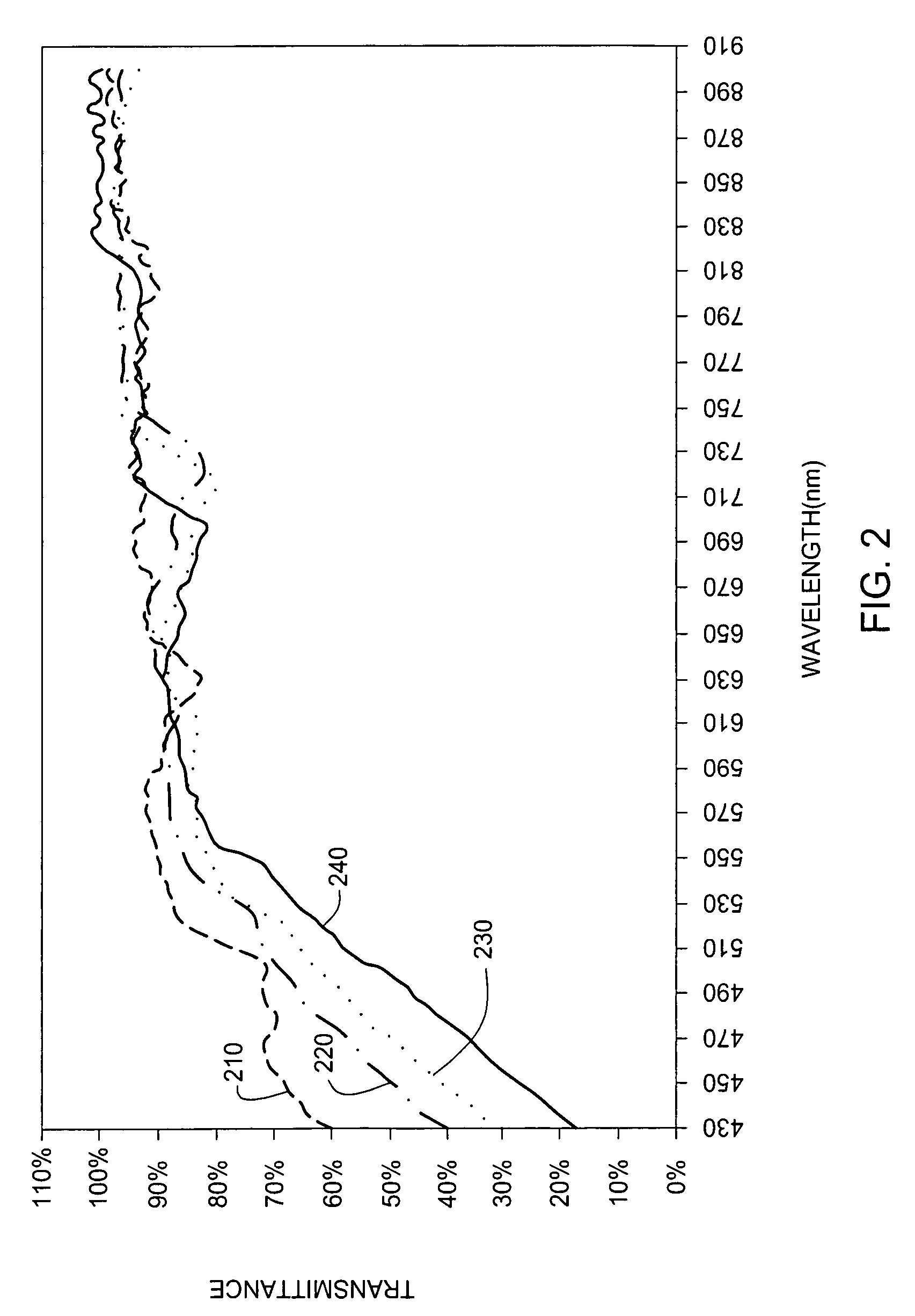
Method to improve transmittance of an encapsulating film
ActiveUS20060078677A1Good film uniformityHigh light transmittanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLow temperature depositionThermal instability
A method for depositing a carbon-containing material layer onto a substrate includes delivering a mixture of precursors for the carbon-containing material layer into a process chamber, doping the carbon-containing material layer with silicon, and depositing the carbon-containing material layer at low temperature. In one aspect, improved light transmittance of the carbon-containing material layer at all wavelengths of a visible light spectrum is obtained. In addition, a method for depositing an encapsulating layer is provided for various display applications which require low temperature deposition process due to thermal instability of underlying materials used. The encapsulating layer may include one or more barrier layer material layers and one or more amorphous carbon material layers. The amorphous carbon material can be used to reduce thermal stress and prevent the deposited thin film from peeling off the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Monosilane or disilane derivatives and method for low temperature deposition of silicon-containing films using the same
This invention relates to silicon precursor compositions for forming silicon-containing films by low temperature (e.g., <550° C.) chemical vapor deposition processes for fabrication of ULSI devices and device structures. Such silicon precursor compositions comprise at least a silane or disilane derivative that is substituted with at least one alkylhydrazine functional groups and is free of halogen substitutes.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
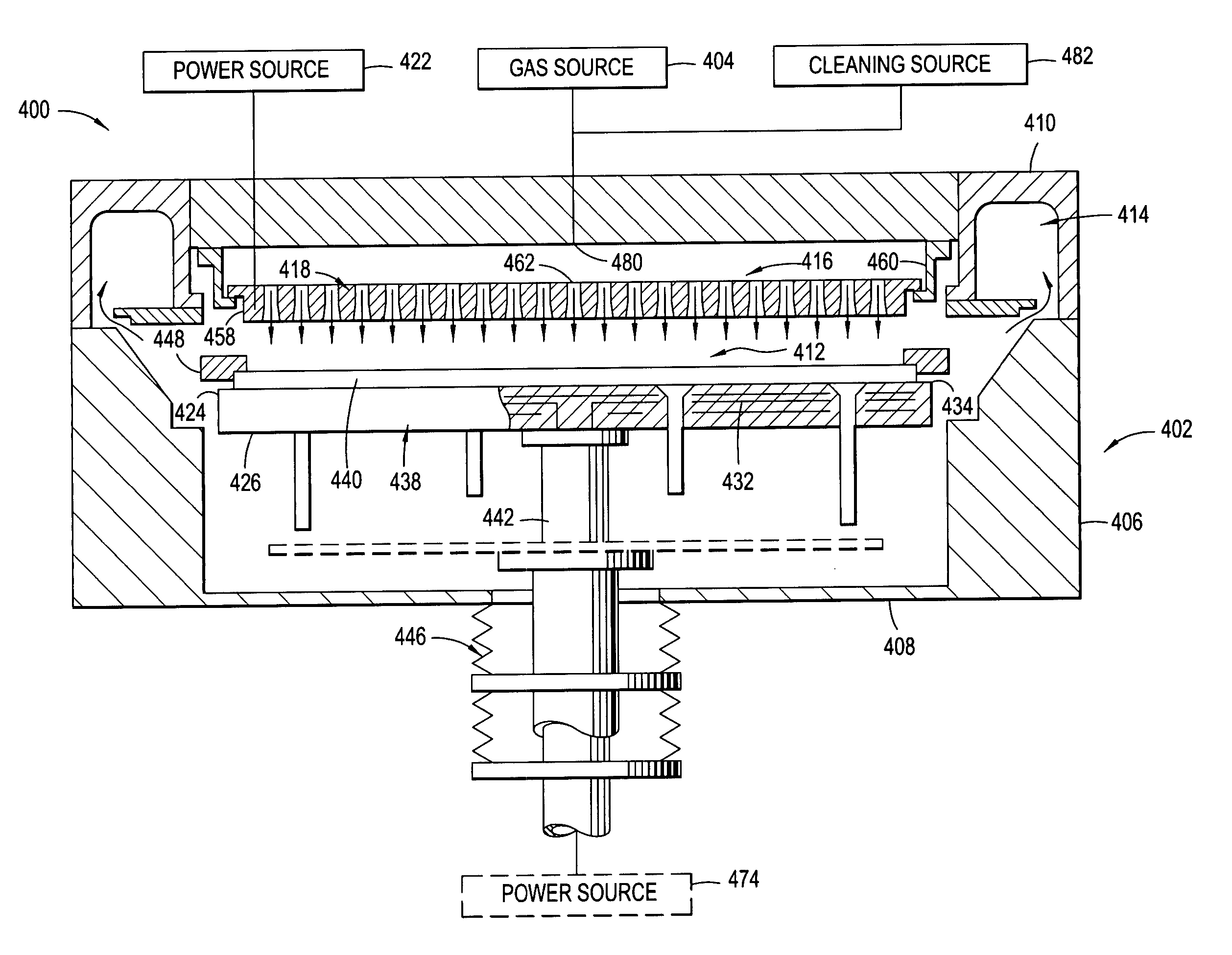
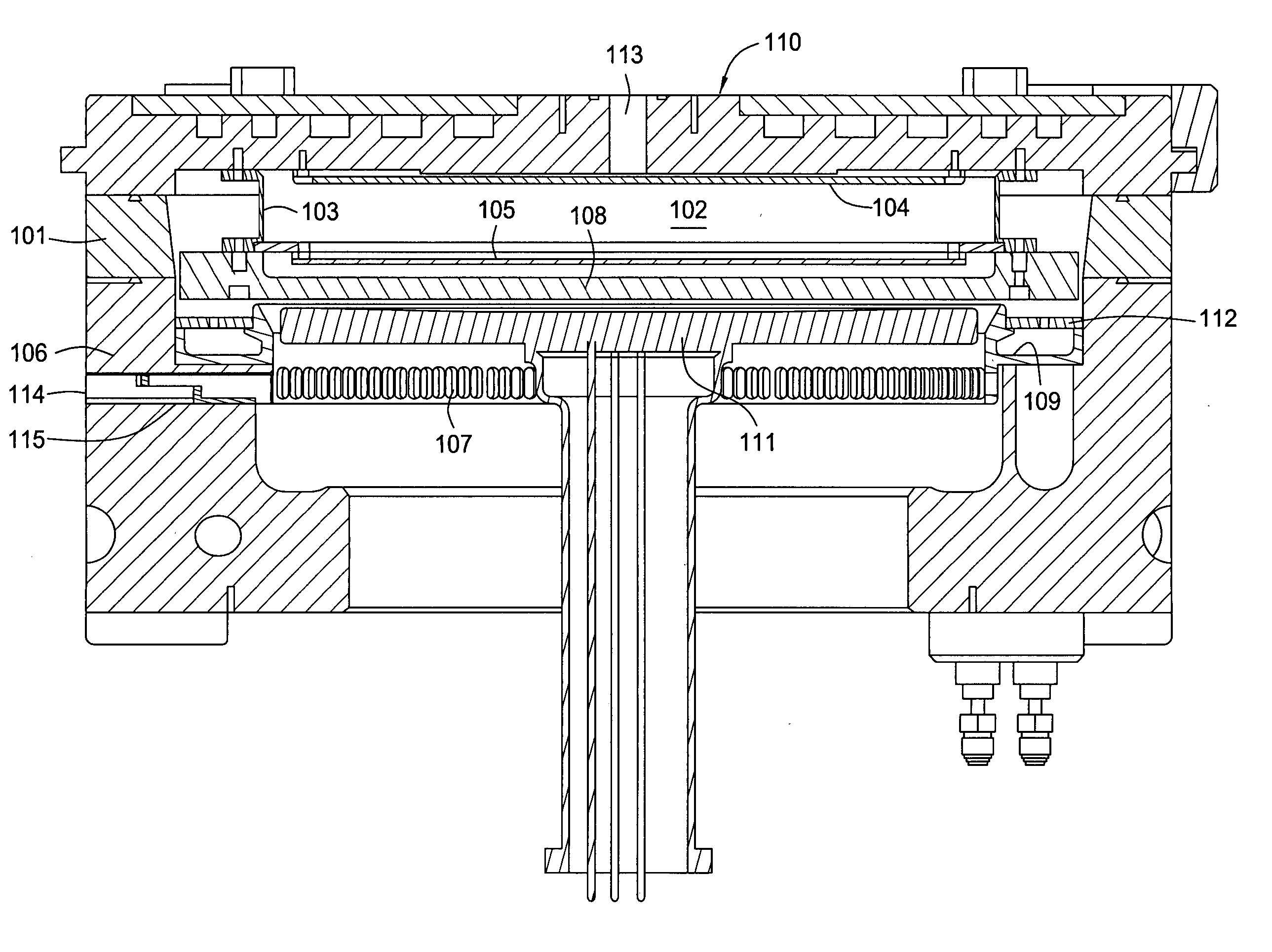
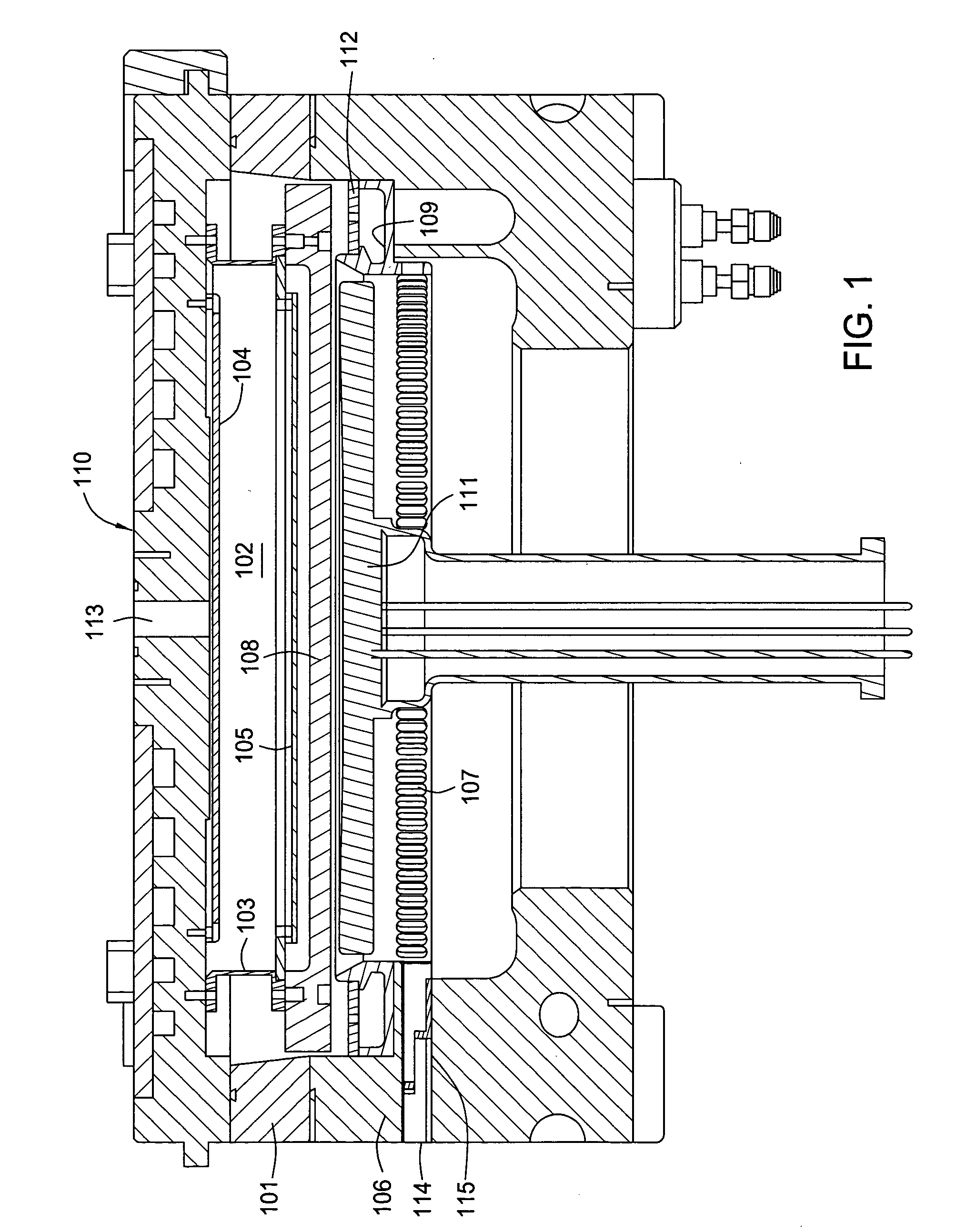
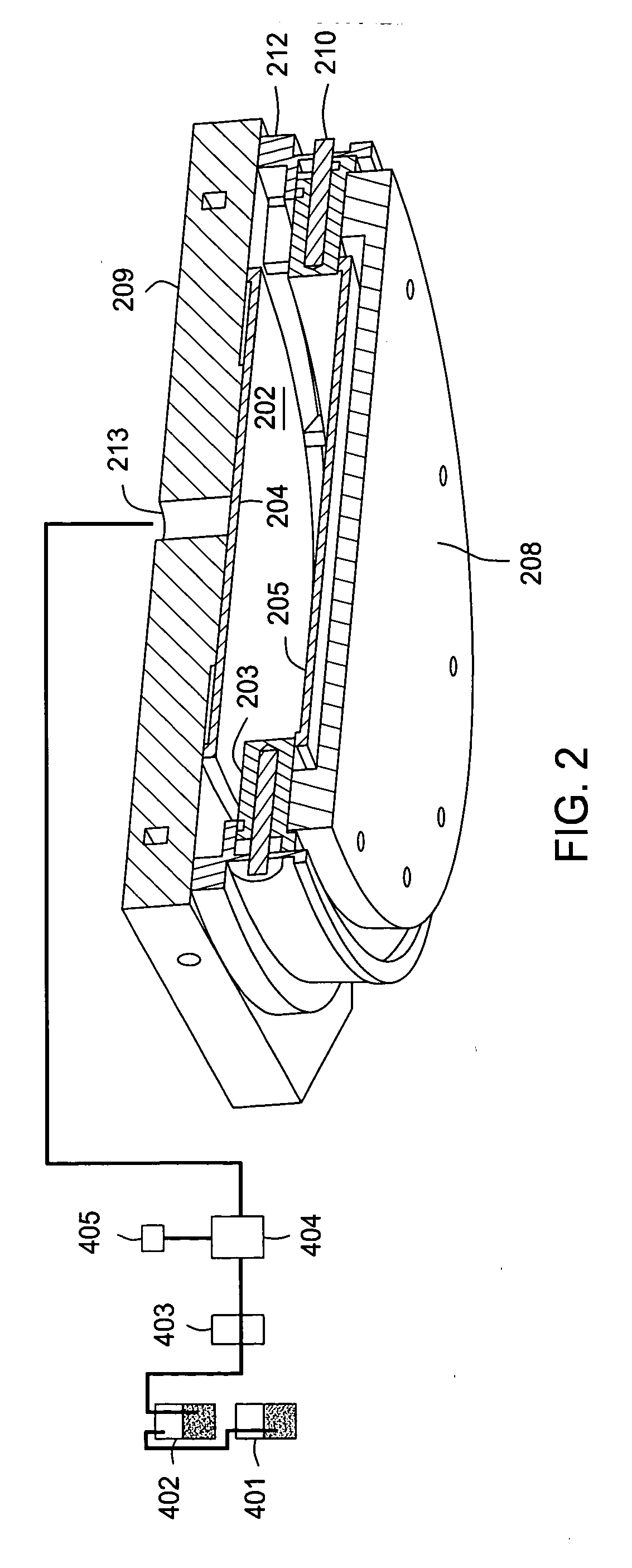
Method and apparatus for the low temperature deposition of doped silicon nitride films
InactiveUS20070082507A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingLow temperature depositionHydrogen
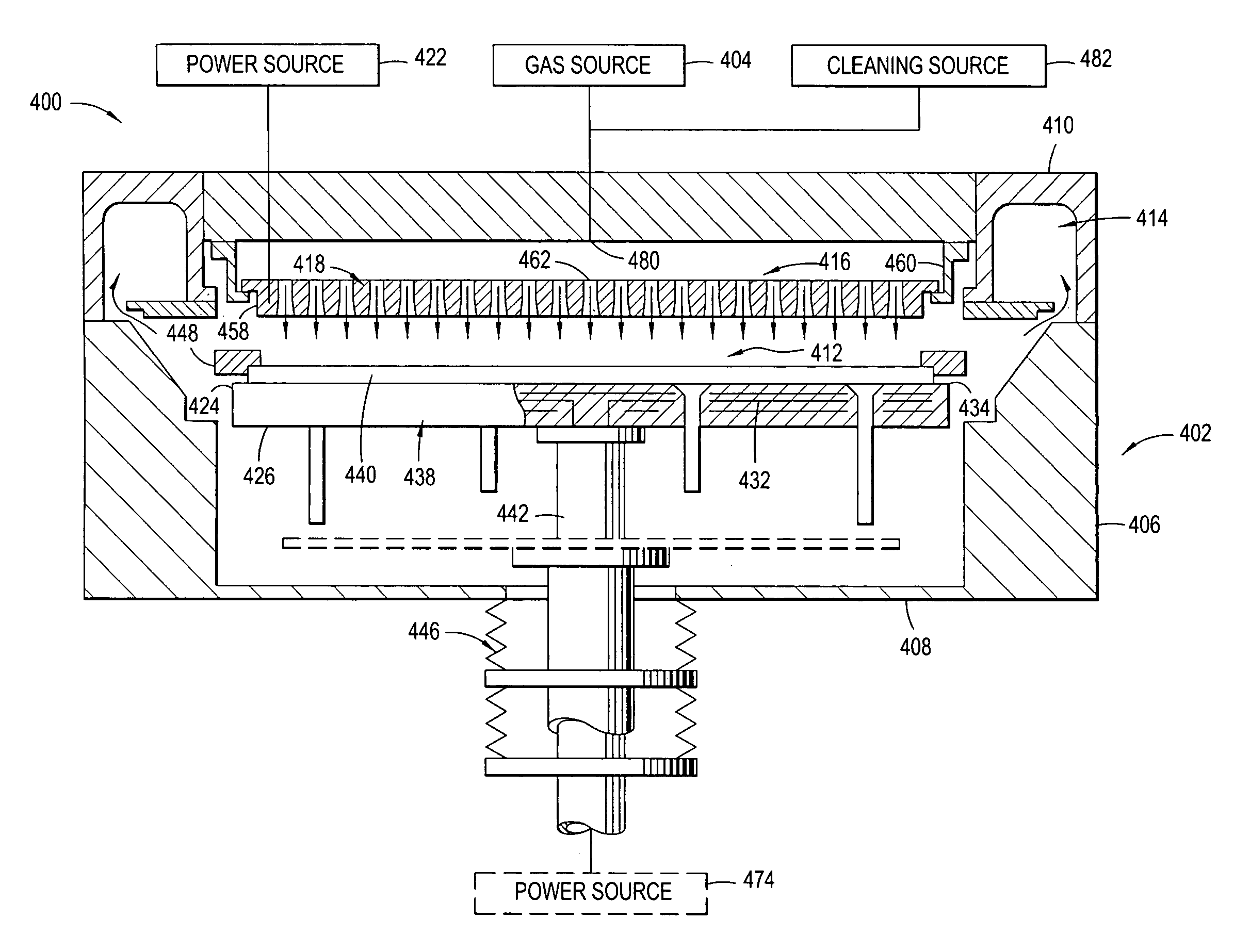
A method and apparatus for low temperature deposition of doped silicon nitride films is disclosed. The improvements include a mechanical design for a CVD chamber that provides uniform heat distribution for low temperature processing and uniform distribution of process chemicals, and methods for depositing at least one layer comprising silicon and nitrogen on a substrate by heating a substrate, flowing a silicon containing precursor into a processing chamber having a mixing region defined by an adaptor ring and one or more blocker plates and an exhaust system heating the adapter ring and a portion of the exhaust system, flowing one or more of a hydrogen, germanium, boron, or carbon containing precursor into the processing chamber, and optionally flowing a nitrogen containing precursor into the processing chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Organic Light Emitting Display Having Touch Sensor and Method of Fabricating the Same
ActiveUS20180061898A1Avoid introducingReliable contactSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing cost reductionLow temperature deposition
Disclosed are an organic light emitting display having touch sensors, which may achieve process simplification and cost reduction, and a method of fabricating the same. The organic light emitting display includes a plurality of touch electrodes disposed on an encapsulation unit disposed so as to cover light emitting elements, the touch electrodes are formed through a low-temperature deposition process and may thus have amorphous characteristics so as to prevent damage to an organic light emitting layer during formation of the touch electrodes, and the touch electrodes are disposed on the encapsulation unit without a separate attachment process and may thus simplify the overall process and reduce manufacturing costs.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Metal precursors for low temperature deposition and methods of forming a metal thin layer and manufacturing a phase-change memory device using the metal precursors
ActiveUS20080108174A1Solid-state devicesGermanium organic compoundsLow temperature depositionPhase-change memory
The present invention provides metal precursors for low temperature deposition. The metal precursors include a metal ring compound including at least one metal as one of a plurality of elements forming a ring. Methods of forming a metal thin layer and manufacturing a phase change memory device including use of the metal precursors is also provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Monolithic integrated SiC MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) pressure sensor and production method thereof
InactiveCN102062662AImprove reliabilityImprove yieldDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceCMOS
The invention discloses a monolithic integrated SiC MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) pressure sensor and a production method thereof. The pressure sensor comprises a first substrate in which a CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) processing circuit is inlayed, a second substrate provided with a pressure cavity and a capacitor induction thin film arranged between the two substrates. The thin film is formed sandwiching an electrode between two layers of PECVD SiC thin films and is suspended on the pressure cavity; a lower electrode covers the surface of the pressure cavity; part of the first substrate above the pressure cavity is provided with a deep groove for exposing the PECVD SiC thin film on the upper layer; the CMOS processing circuit is located beside the deep groove and is communicated with the upper electrode. The sensor uses SiC of low-temperature deposition as the induction thin film, has good performance and is suitable for corrosive environment. Besides, the invention realizes integration between the sensor and the processing circuit by using a post-CMOS method so as to improve the integral precision and stability of the device.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method to improve transmittance of an encapsulating film
ActiveUS7214600B2Good film uniformityHigh light transmittanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLow temperature depositionThermal instability
A method for depositing a carbon-containing material layer onto a substrate includes delivering a mixture of precursors for the carbon-containing material layer into a process chamber, doping the carbon-containing material layer with silicon, and depositing the carbon-containing material layer at low temperature. In one aspect, improved light transmittance of the carbon-containing material layer at all wavelengths of a visible light spectrum is obtained. In addition, a method for depositing an encapsulating layer is provided for various display applications which require low temperature deposition process due to thermal instability of underlying materials used. The encapsulating layer may include one or more barrier layer material layers and one or more amorphous carbon material layers. The amorphous carbon material can be used to reduce thermal stress and prevent the deposited thin film from peeling off the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
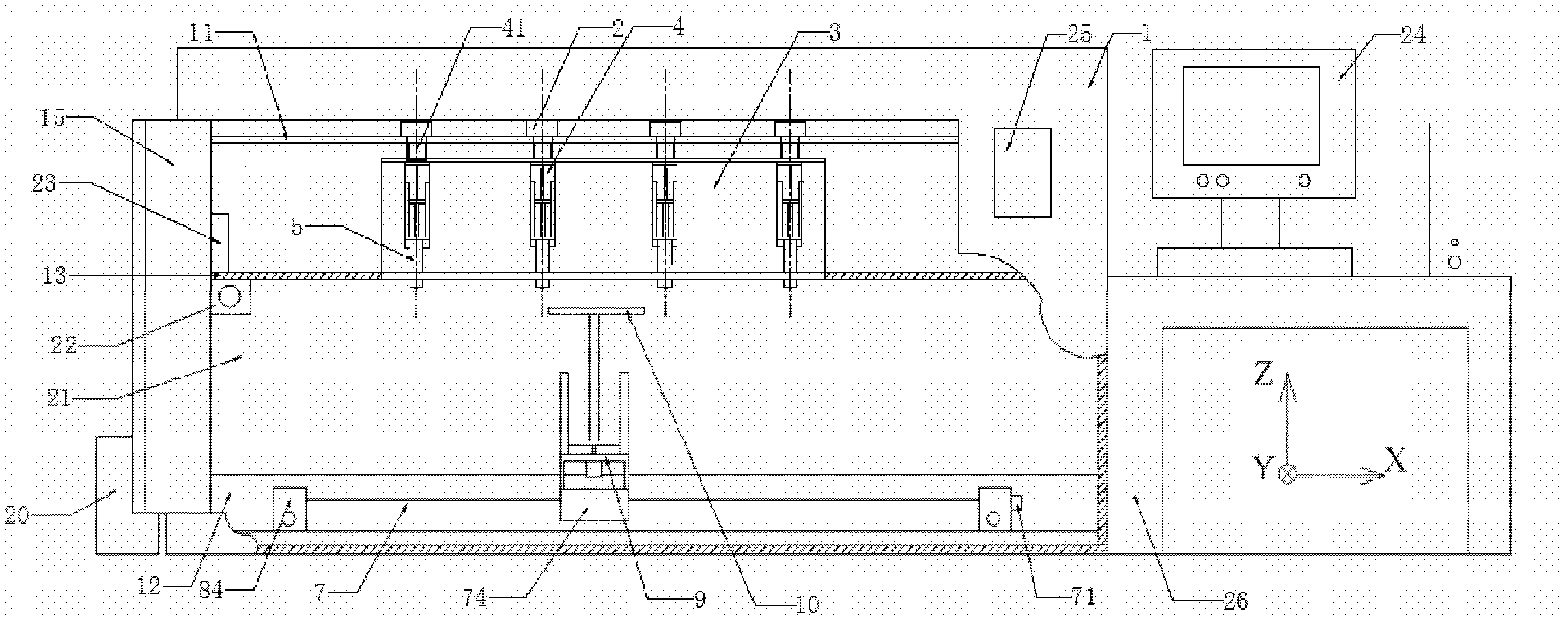
Rotating disc type multi-nozzle three-dimensional controlled forming system for complex organ precursor
InactiveCN101692987ARealize free switchingHigh degree of automationStentsProsthesisLow temperature depositionData processing system
The invention relates to a rotating disc type multi-nozzle three-dimensional controlled forming system for a complex organ precursor, belonging to the technical field of tissue engineering. The system mainly comprises a box body, a bracket, a rotating disc type multi-nozzle jetting device, a forming chamber, a forming table, a three-dimensional moving mechanism, a refrigerating device, a control system and a data processing system, wherein the rotating disc type multi-nozzle jetting device comprises a rotating disc and nozzle assemblies, and the nozzle assemblies are uniformly and circumferentially distributed on the rotating disc. When a precursor of a complex organ, such as liver, heart, kidney and the like, is formed, by utilizing a low-temperature deposition manufacturing process theory, the forming chamber is firstly cooled, the motions of the three-dimensional moving mechanism and the rotation and the material jetting of the rotating disc type multi-nozzle jetting device are controlled by the control system, and the forming table does three-dimensional motions; different nozzle assemblies can be changed by the rotation of the rotating disc so as to extrude to form and accumulate matrix materials with different tissue scaffolds and cells on the forming table. The device adopts a rotating disc type multi-nozzle interactive forming mode and can realize the precise forming of various non-homogeneous materials with complex three-dimensional structures.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Composition and method for low temperature deposition of silicon-containing films
ActiveUS20040138489A1Silicon organic compoundsPolycrystalline material growthLow temperature depositionGas phase
This invention relates to silicon precursor compositions for forming silicon-containing films by low temperature (e.g., <300° C.) chemical vapor deposition processes for fabrication of ULSI devices and device structures. Such silicon precursor compositions comprise at least one disilane derivative compound that is fully substituted with alkylamino and / or dialkylamino functional groups.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
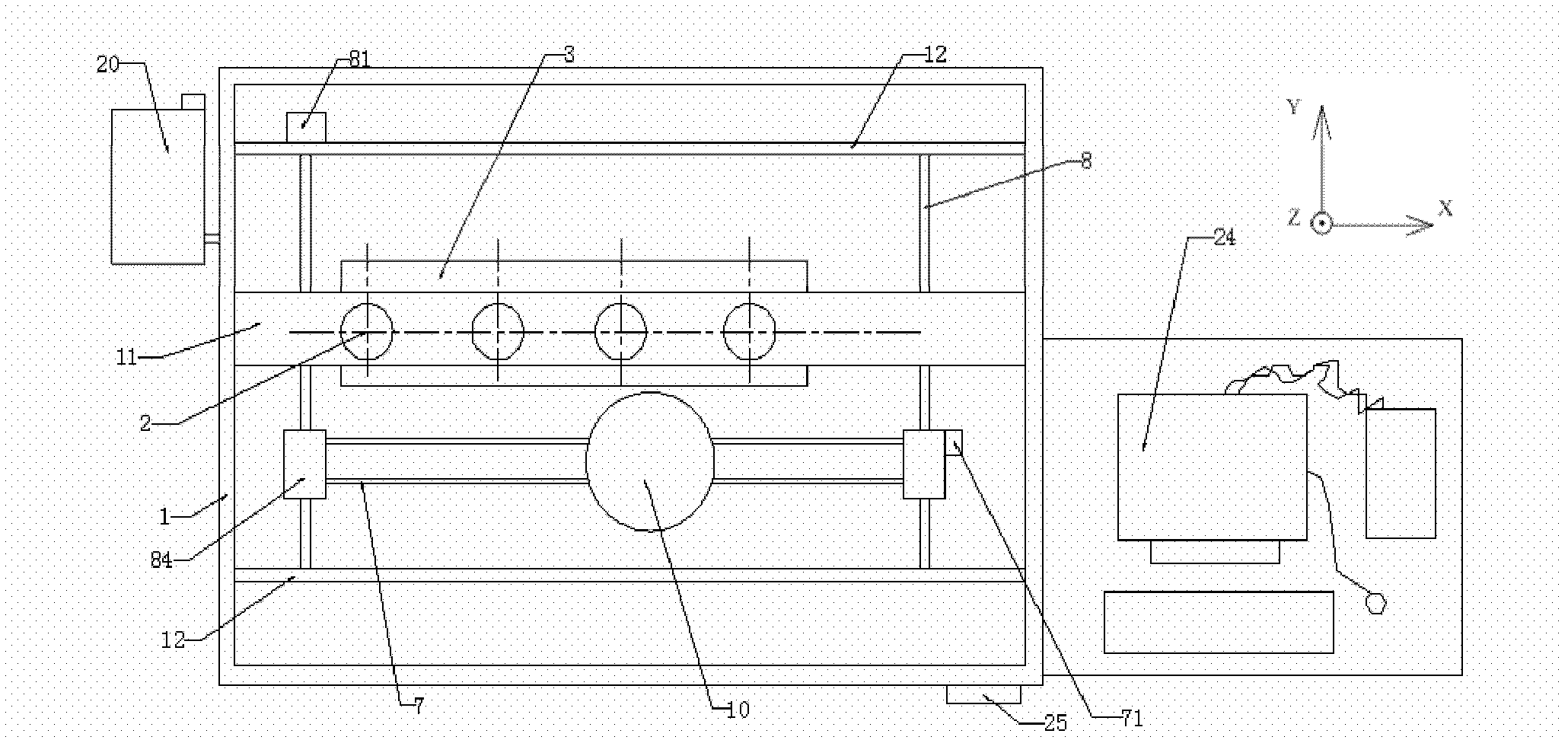
Fixed multi-nozzle complex organ precursor three-dimensional controlled forming system
InactiveCN102319126ASimple structureEasy to controlProsthesisLow temperature depositionData processing system
The invention provides a fixed multi-nozzle complex organ precursor three-dimensional controlled forming system, and belongs to the technical field of tissue engineering. The system mainly comprises a case body, a bracket, a fixed multi-nozzle injection device, a forming chamber, a forming table, a three-dimensional motion mechanism, a refrigeration device and a control and data processing system, wherein the fixed multi-nozzle injection device comprises a fixed nozzle scaffold and nozzle components; and the nozzle components are uniformly distributed on the fixed nozzle scaffold in a parallel or array way. When the precursor of a complex organ, such as liver, heart, kidney and the like, is formed, the forming chamber is cooled by utilizing a low-temperature deposition process principle, and a control system controls motion of the forming table and three-dimensional motion mechanism, as well as injection of the fixed multi-nozzle injection device, so that different tissue scaffold materials and cell / matrix composite materials can be deposited and formed on the forming table. According to the device, accurate formation of a plurality of heterogeneous materials with complex three-dimensional structures can be realized by adopting a fixed multi-nozzle interactive forming mode.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Use of Si-rich oxide film as a chemical potential barrier for controlled oxidation
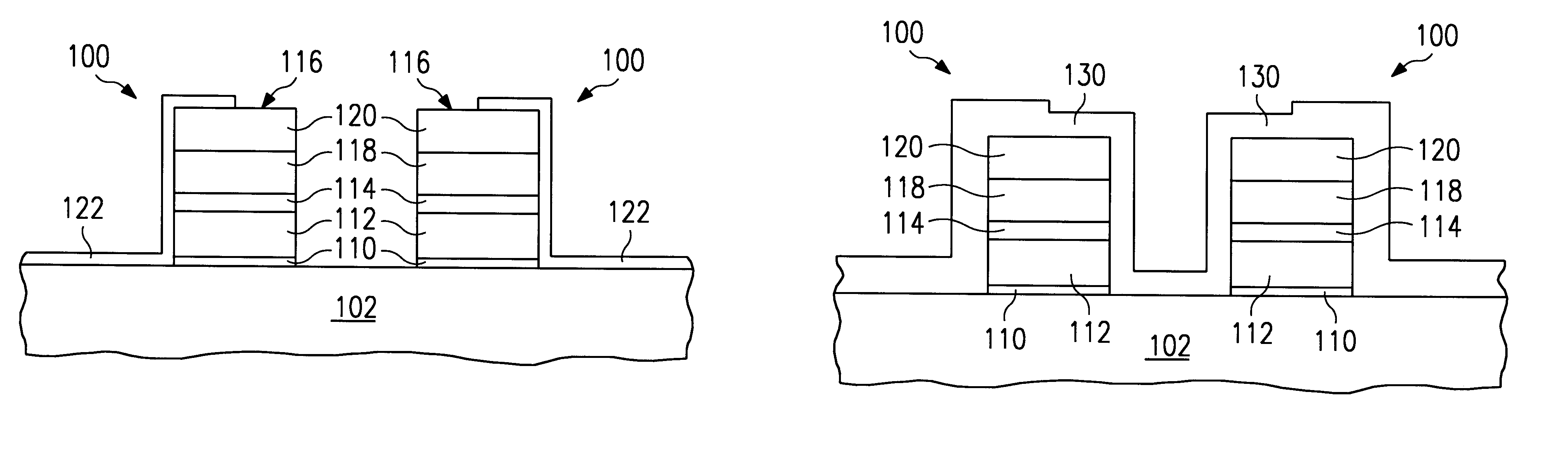
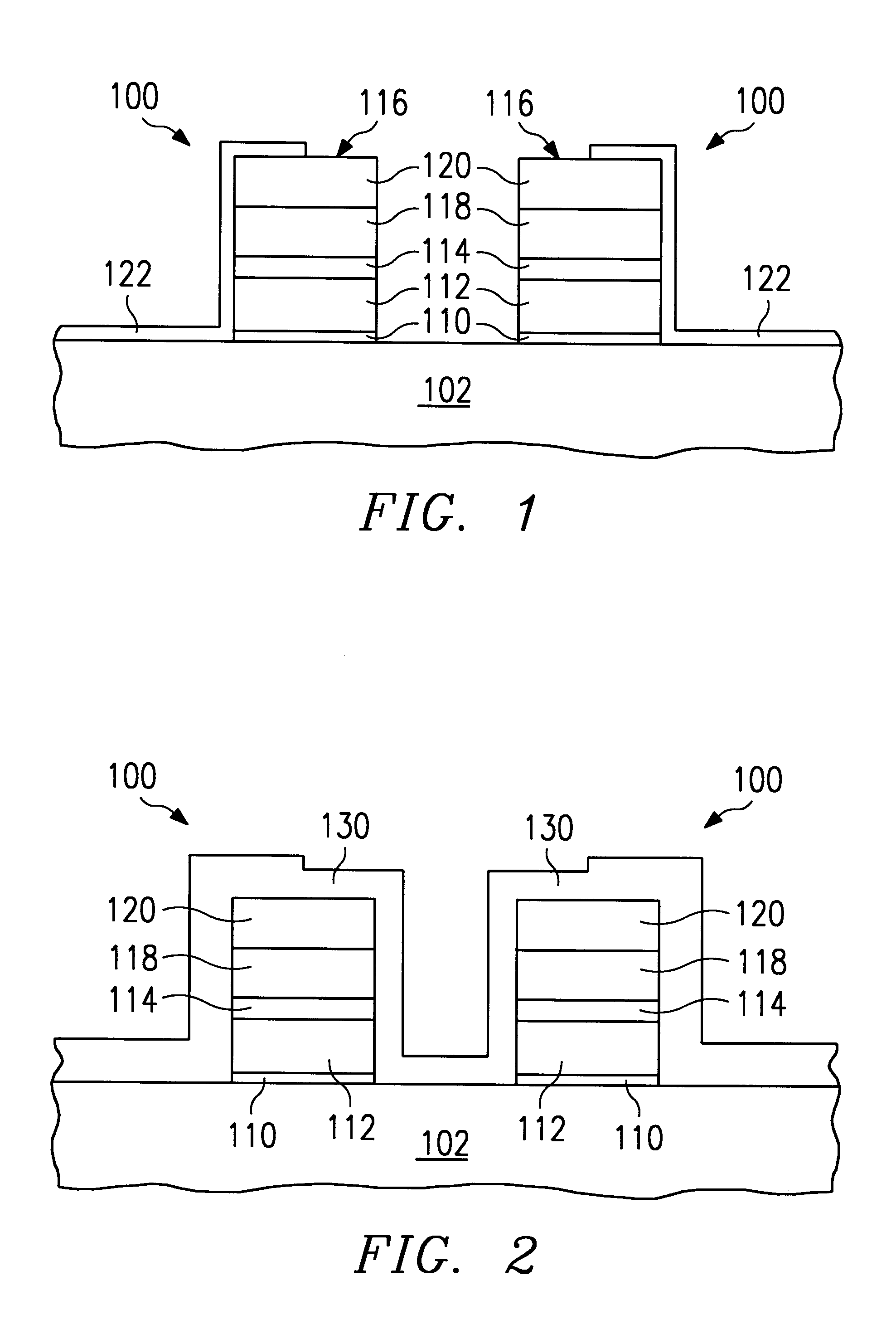
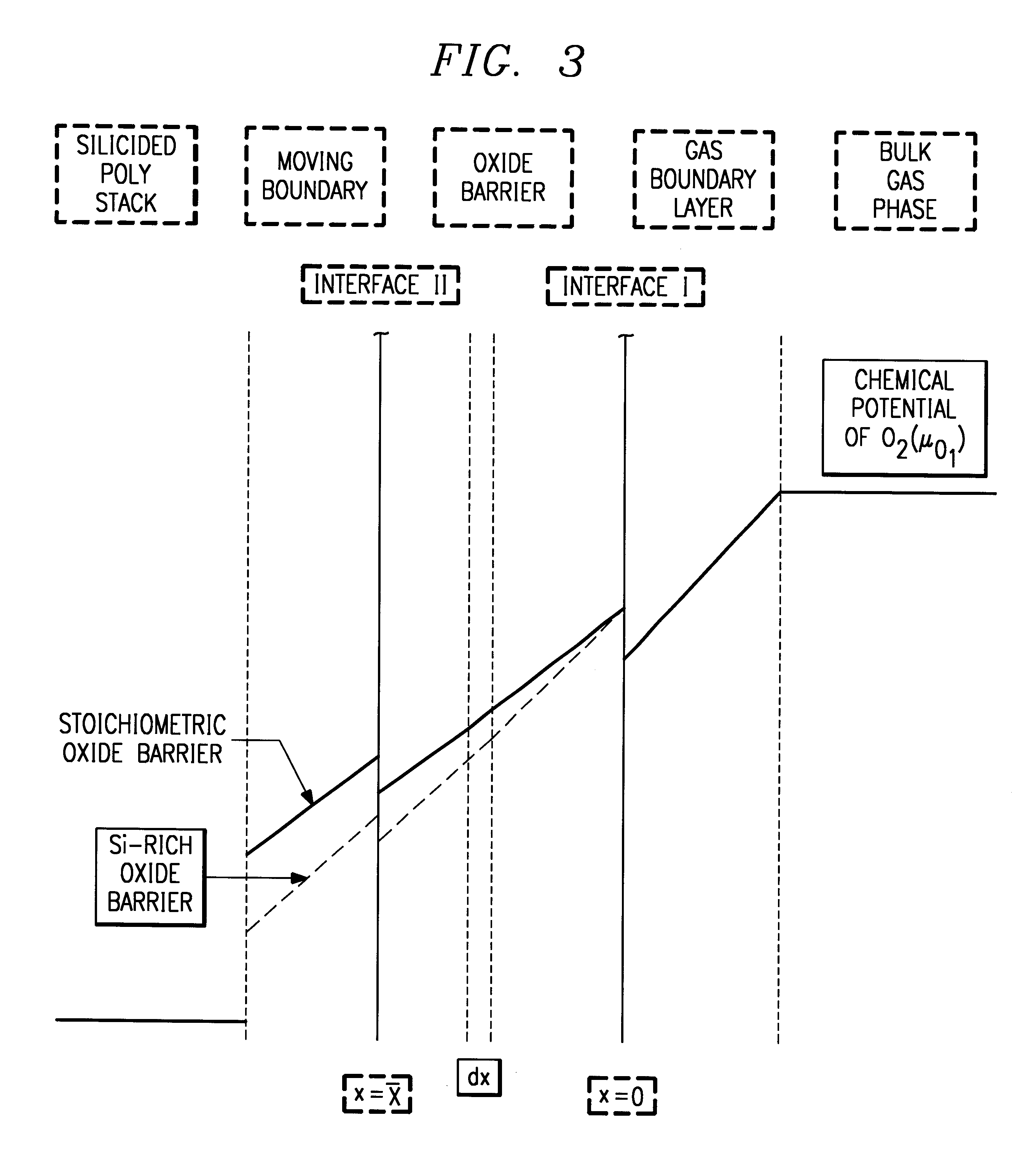
InactiveUS6274429B1Easy to controlSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLow temperature depositionSilicon oxide
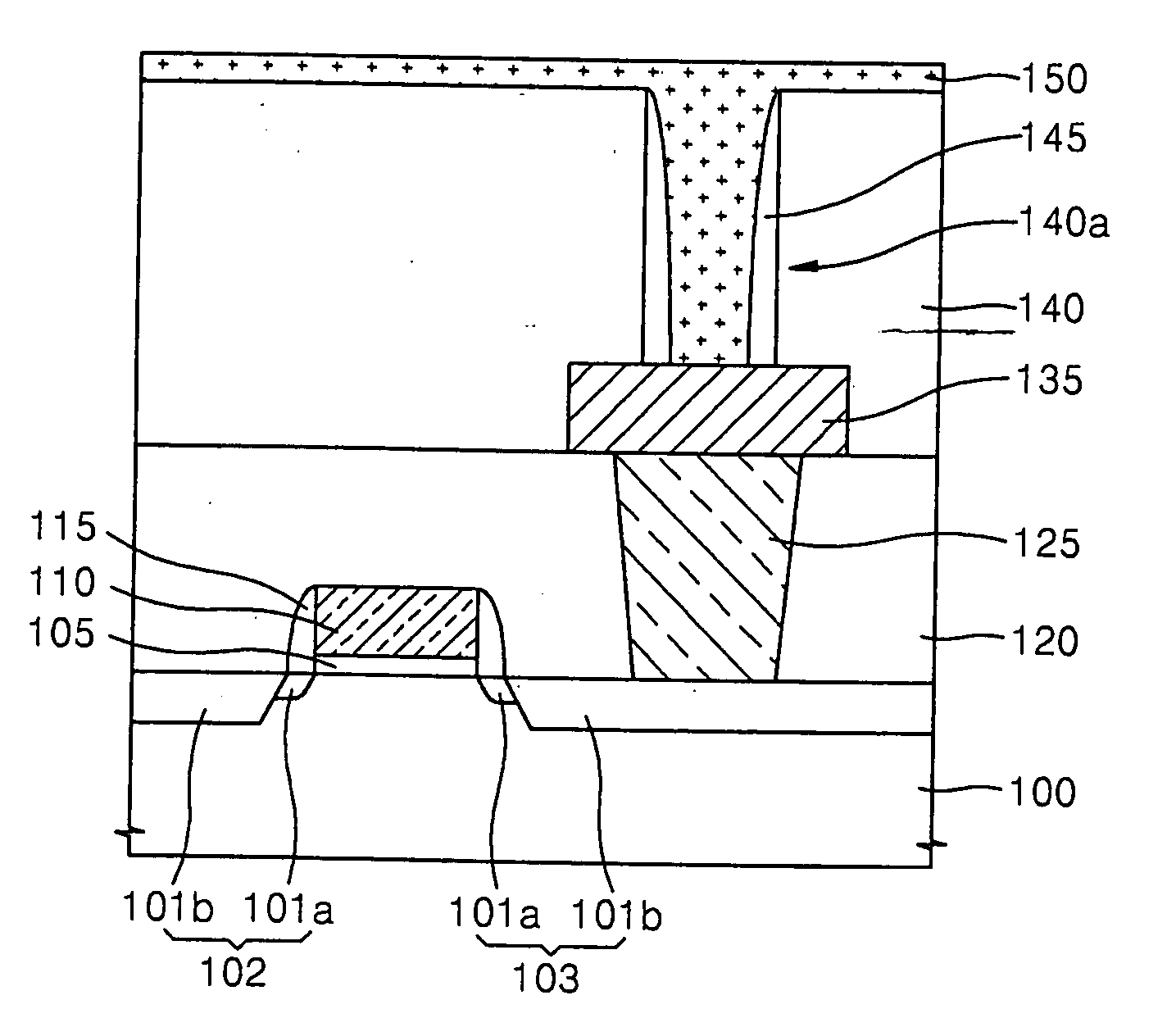
An oxidation process for reducing the data retention loss (DRL) in a FAMOS device comprising the steps of (1) low temperature deposition of a silicon-enriched silicon oxide (130) over a FAMOS transistor gate stack (116) and (2) annealing said silicon-enriched oxide (130) at a high temperature in oxygen atmosphere to convert said silicon-enriched oxide (130) to a thermal oxide. The silicon enriched oxide (130) acts as both an oxygen getter and diffusion barrier during the annealing step.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method of forming a protective layer on thin-film photovoltaic articles and articles made with such a layer
InactiveUS20100243046A1Improve barrier propertiesImprove the immunitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationSputteringLow temperature deposition
Chalcogenide based photovoltaic devices cells with good resistance to environmental elements can be formed by direct low temperature deposition of inorganic barrier layers onto the film. A unique multilayer barrier can be formed in a single step when reactive sputtering of the silicon nitride onto an inorganic oxide top layer of the PV device.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com