Use of Si-rich oxide film as a chemical potential barrier for controlled oxidation
a technology of chemical potential barrier and silicide layer, which is applied in the direction of basic electric elements, electrical apparatus, and semiconductor devices, can solve the problems of so-called peeling of silicide layer and reciprocal lifting between layers, dislocation and defect, and short circuit between source and drain region
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
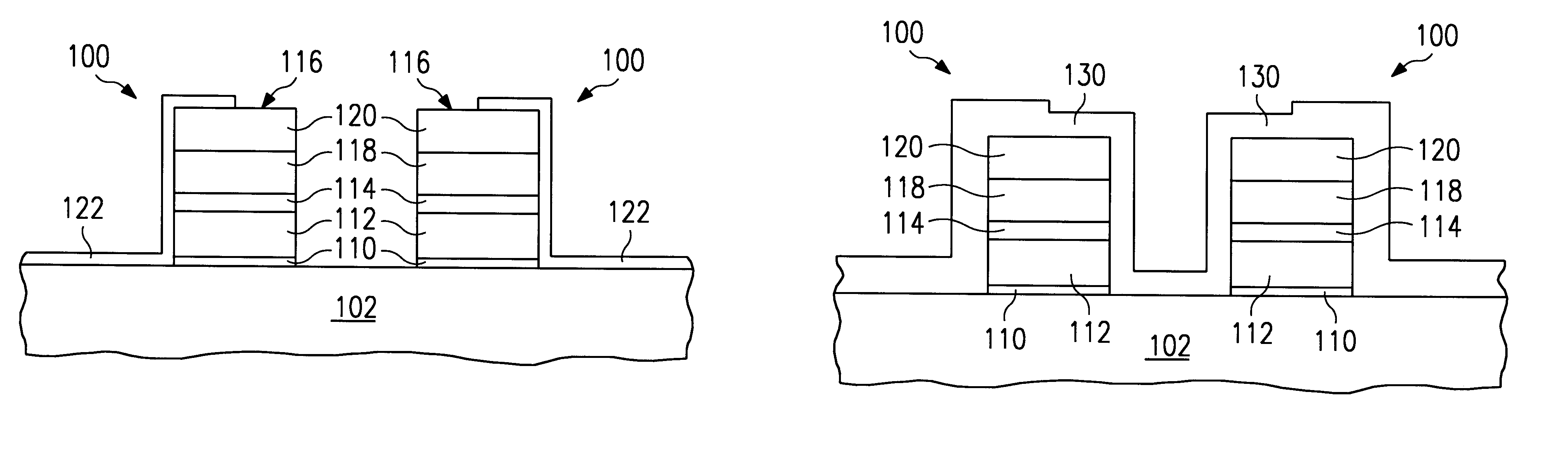
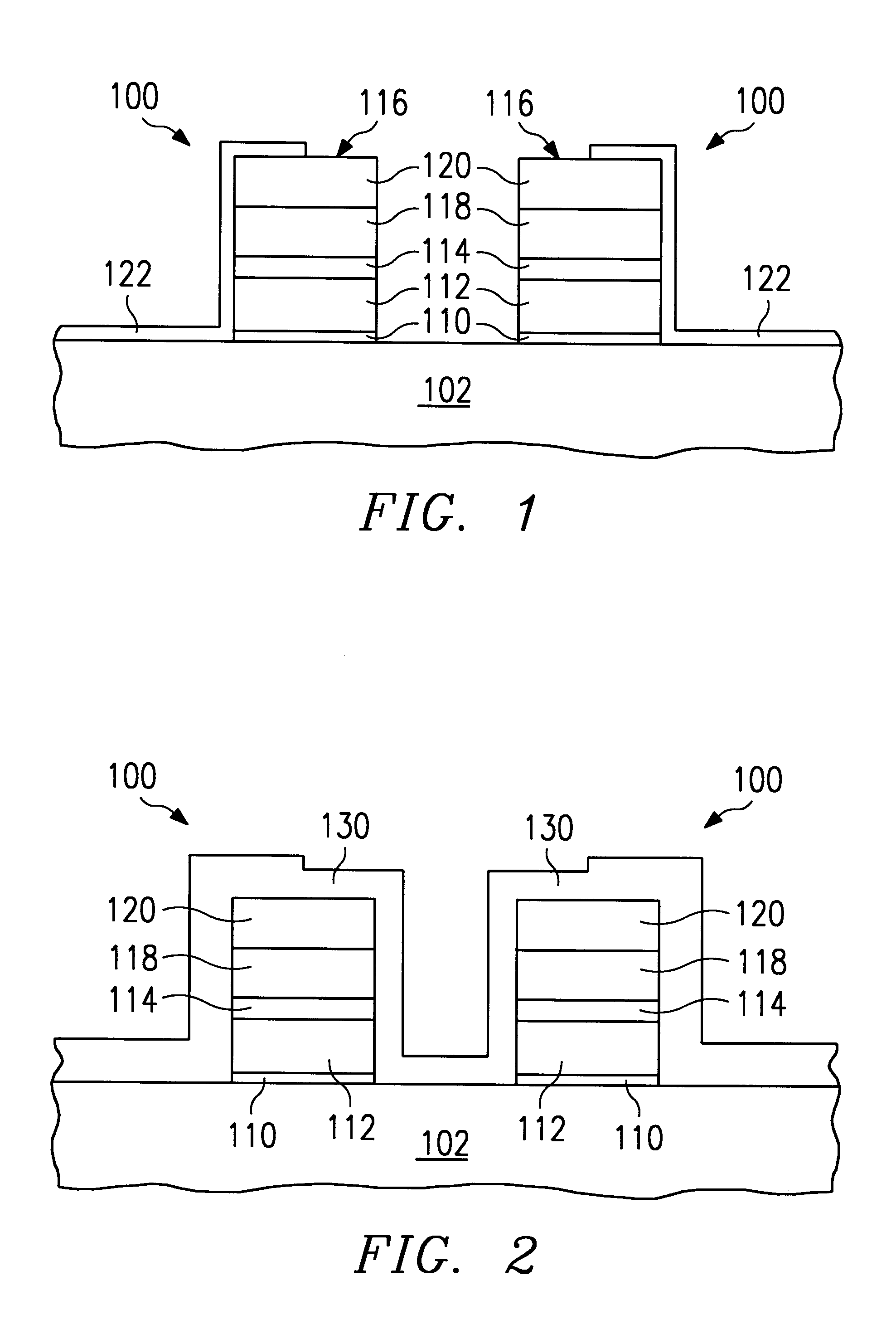
The invention will now be described in conjunction with forming a silicon-rich oxide barrier at the gate level of a FAMOS process. It will be apparent to those of ordinary skill in the art that the use of Si-rich oxide barrier, according to the invention, can be made any device process level where oxygen gettering is required in order to protect the underlying film or device structure while oxidation is required at the overlying structures. For example, the invention may be used as liner layers for controlling etch characteristics or as a means for controlling transistor VTs.
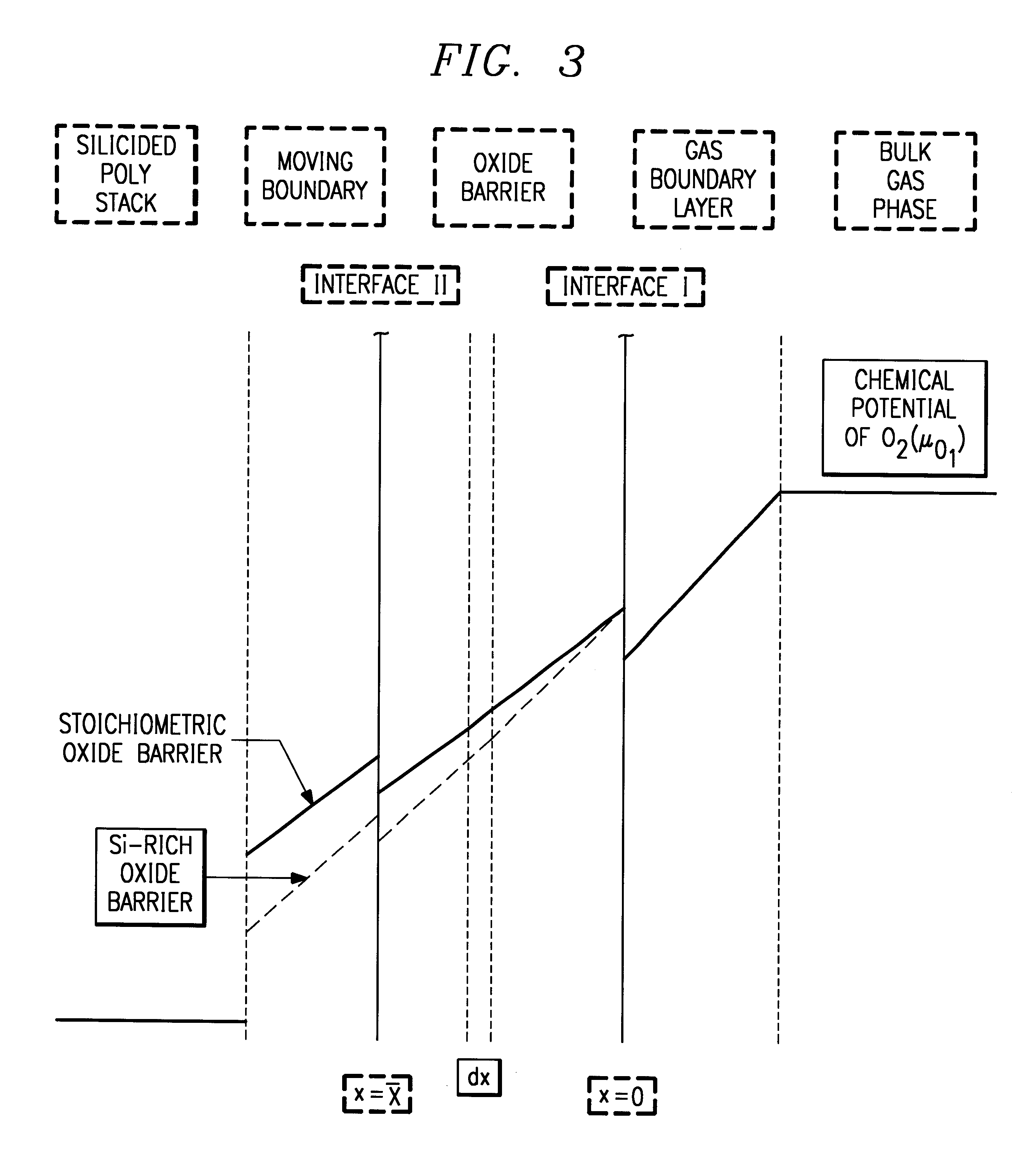
The invention is a two-step oxidation process that provides a preliminary, fast, uniform, and low temperature deposition of a layer of silicon-enriched oxide followed by a reoxidation. The term silicon enriched oxide is used to refer to a silicon oxide layer having an excess of silicon atoms. The silicon-enriched oxide is stable and its composition SiO.sub.x, can be accurately controlled during deposition. The p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com