Patents
Literature
32158results about "Decorative surface effects" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
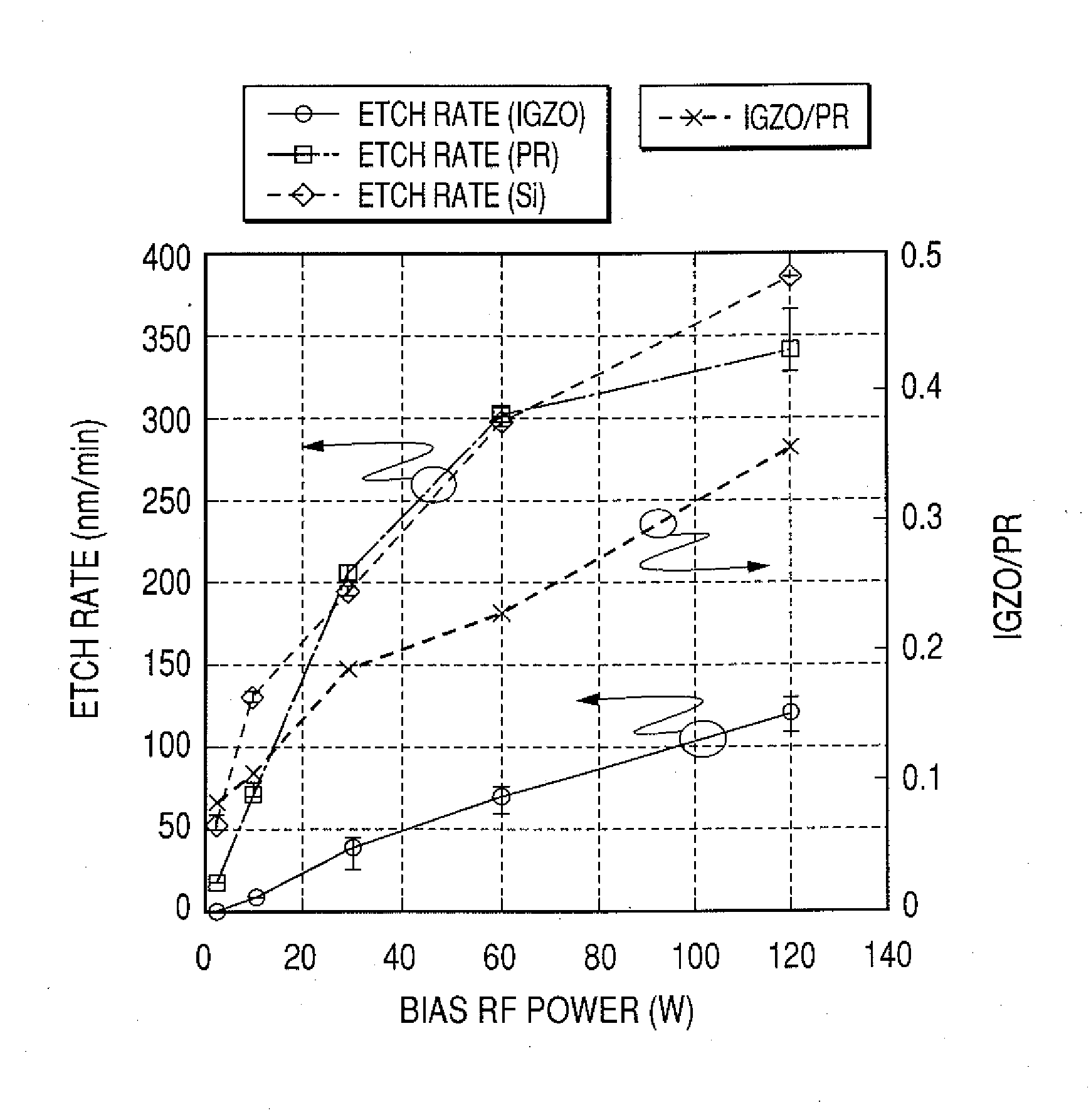
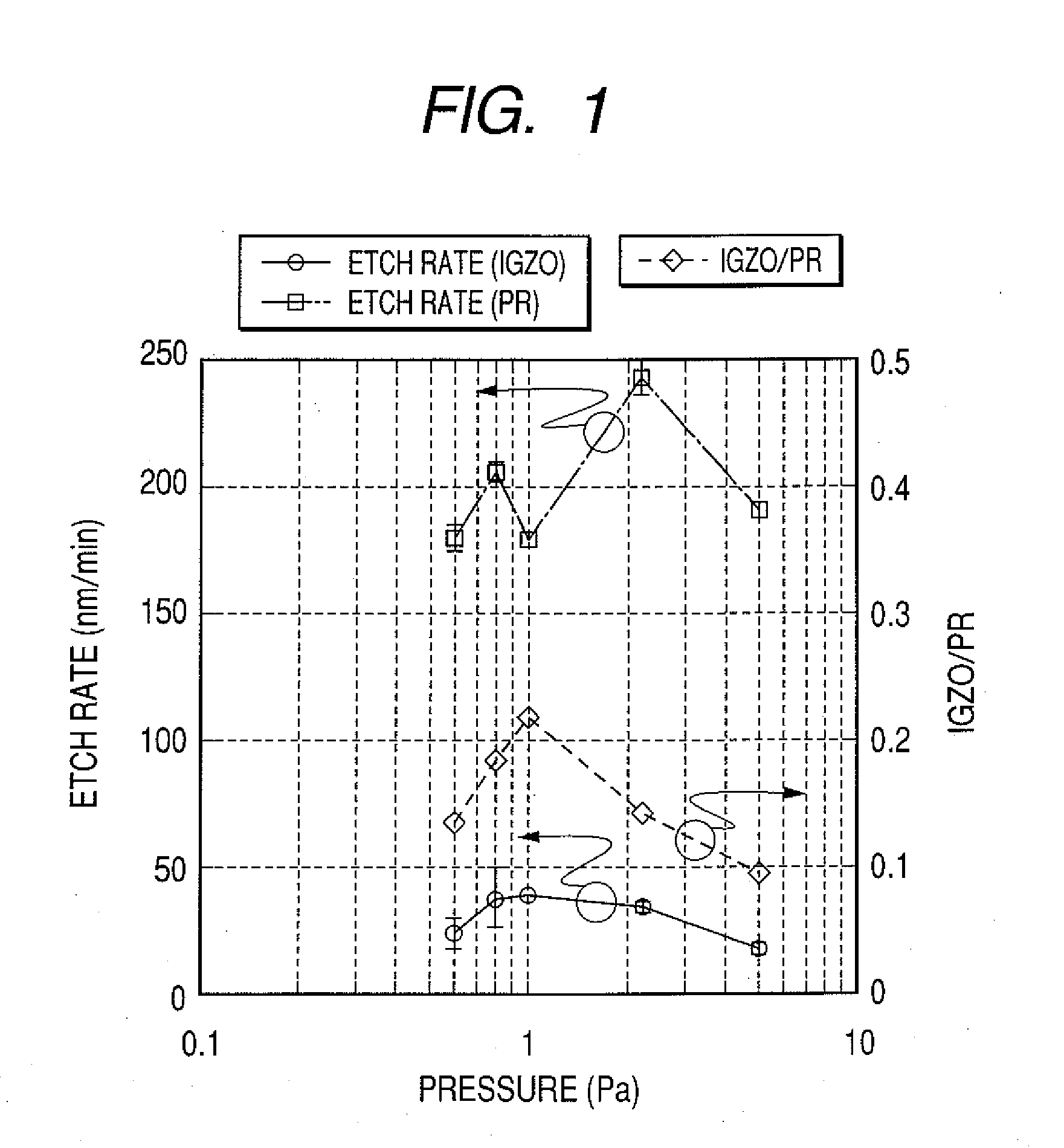
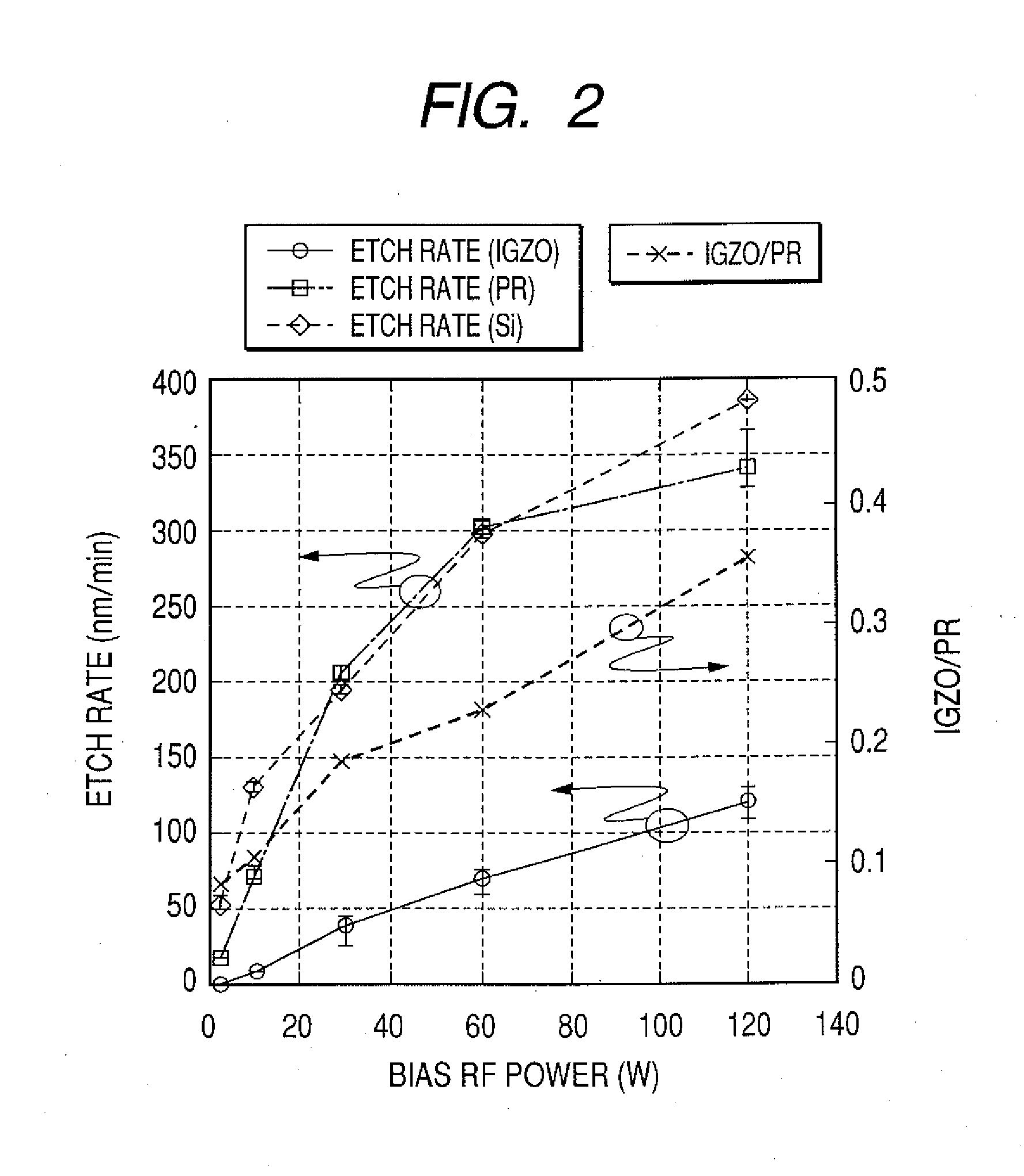
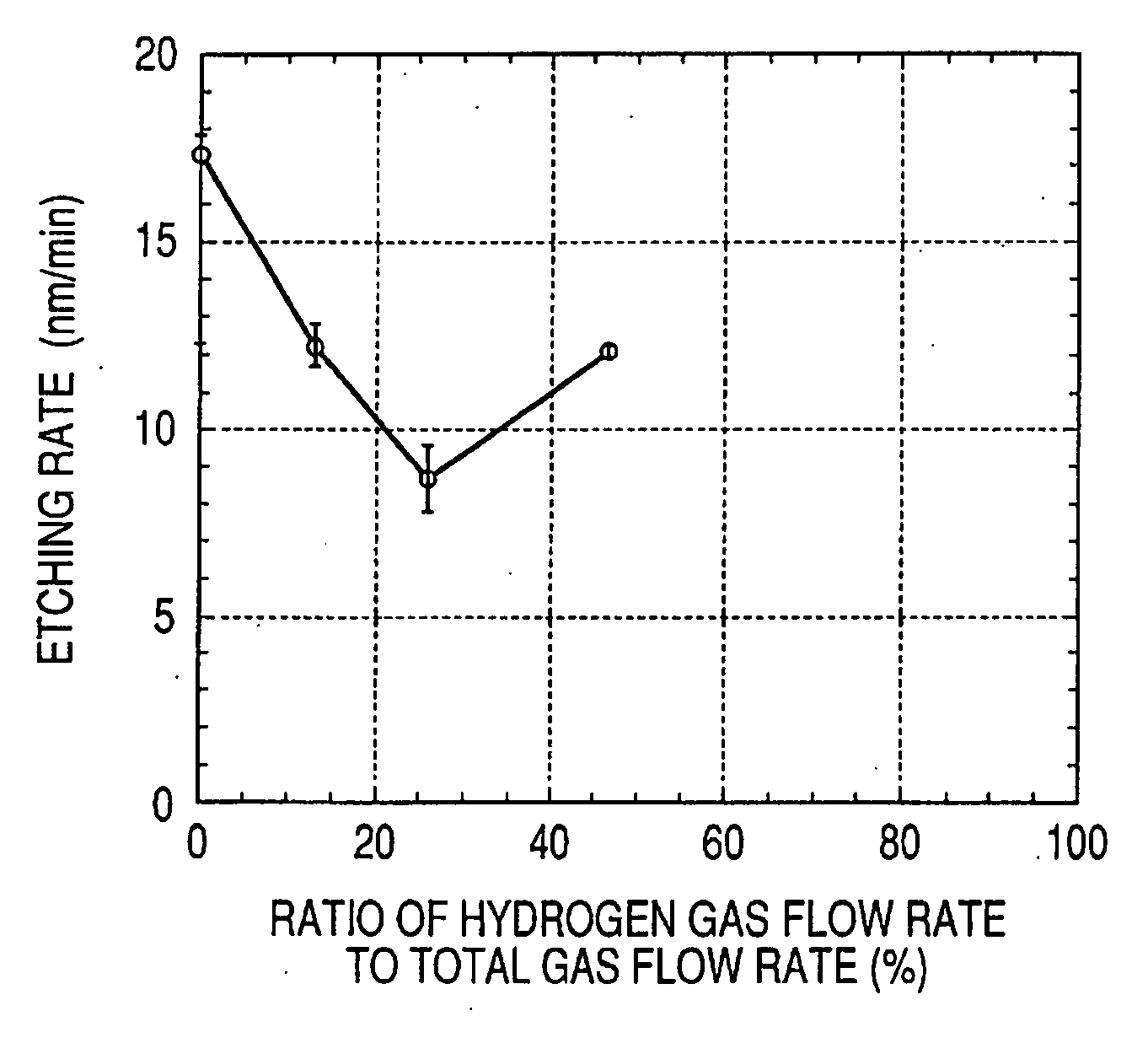
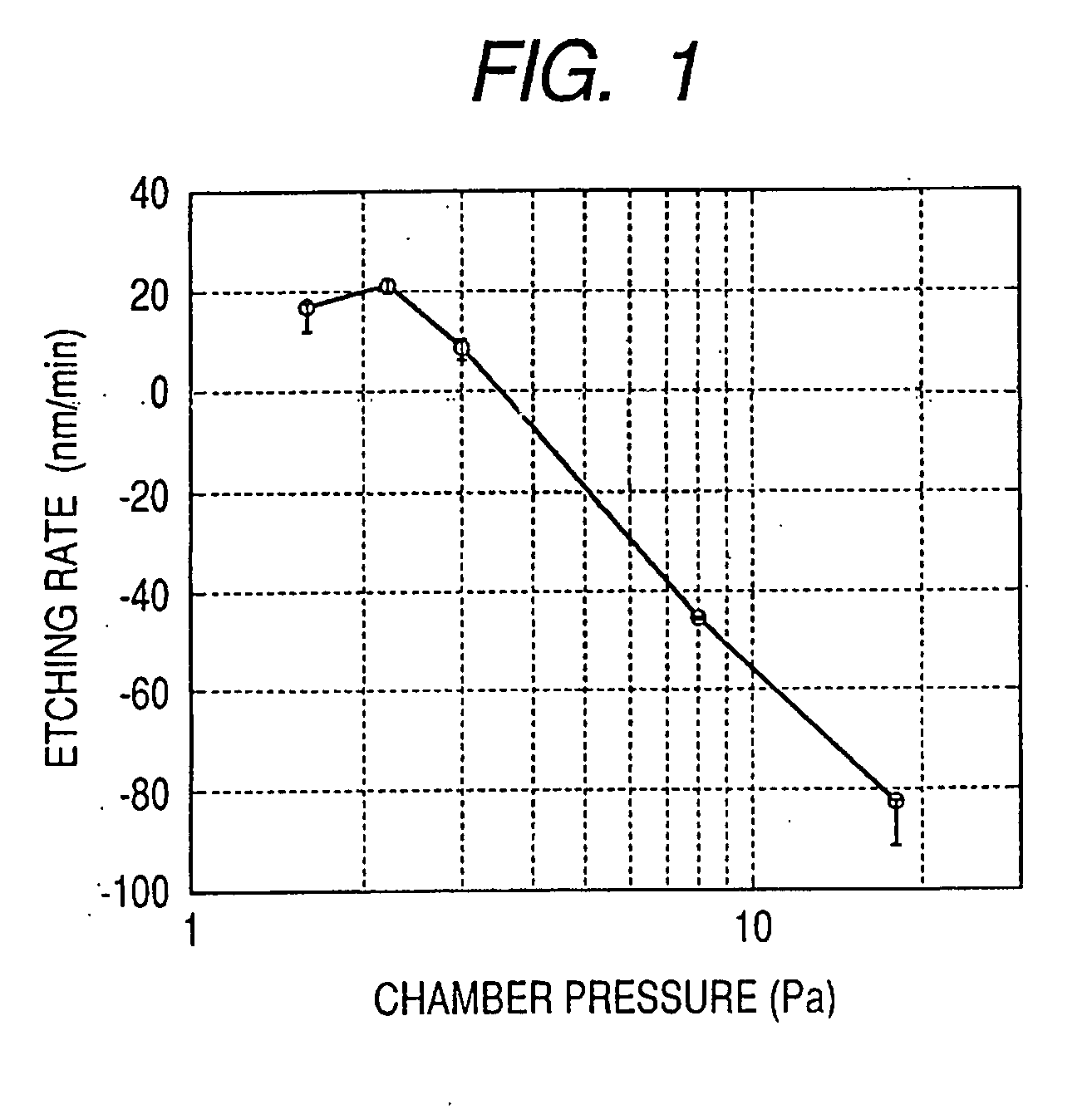
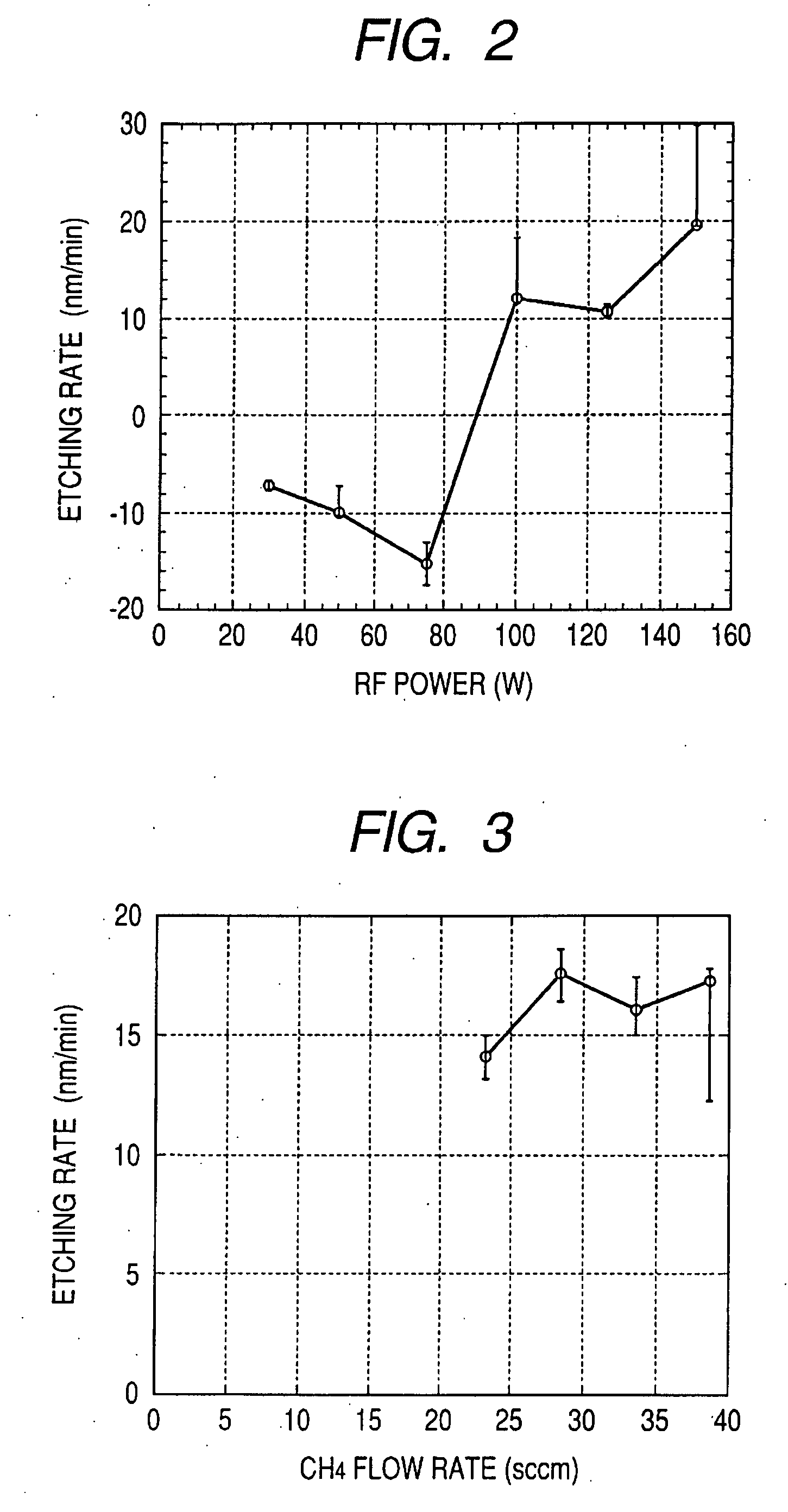
Method of dry etching oxide semiconductor film
InactiveUS20080038929A1Improve processing accuracyIncrease etch rateDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorDry etching
Provided is a dry etching method for an oxide semiconductor film containing at least In, Ga, and Zn, which includes etching an oxide semiconductor film in a gas atmosphere containing a halogen-based gas.
Owner:CANON KK
Dry etching method for oxide semiconductor film
InactiveUS20070287296A1Improve processing accuracyIncrease etch rateDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDry etchingSemiconductor
Provided is a dry etching method for an oxide semiconductor film made of In—Ga—Zn—O, in which an etching gas containing a hydrocarbon is used in a dry etching process for the oxide semiconductor film made of In—Ga—Zn—O formed on a substrate.
Owner:CANON KK
Wound closure material
Articles are provided having no orientation or a multi-directional orientation. Such articles may be in the form of films, ribbons, sheets, and / or tapes and may be utilized as buttresses with a surgical stapling apparatus or as reinforcing means for suture lines. The articles may be produced with etchings on at least a part of a surface of the article.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Lithographic apparatus, device manufacturing method, and device manufactured thereby
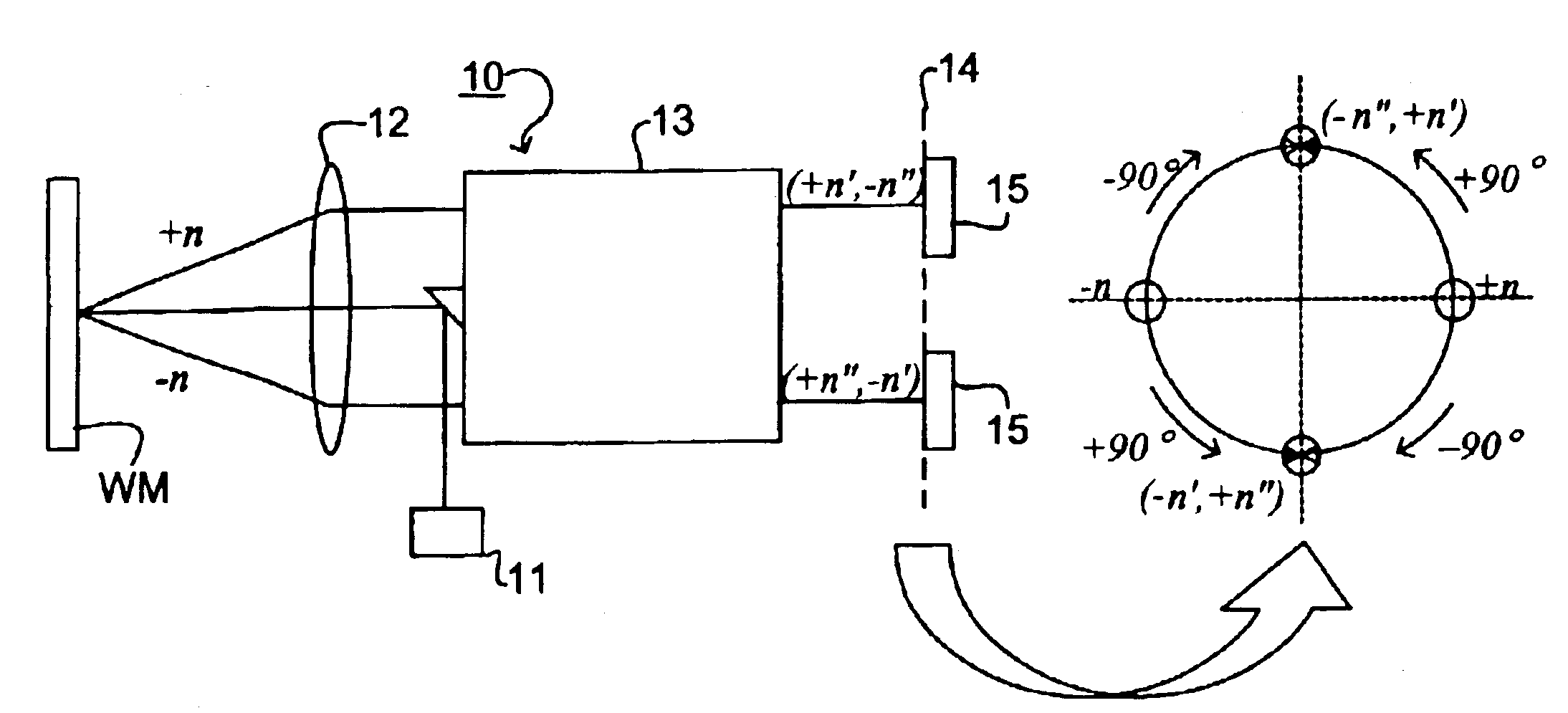
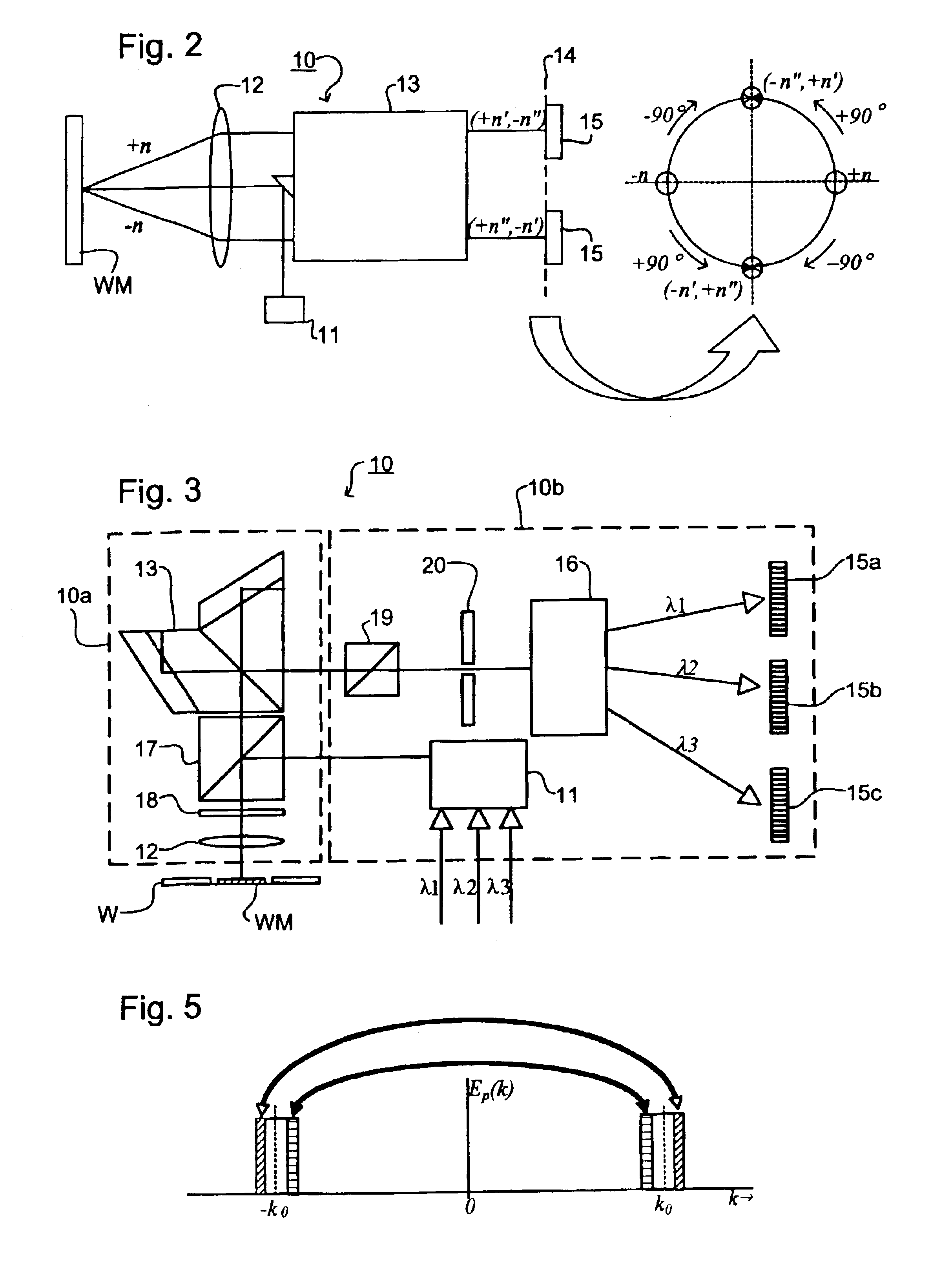
InactiveUS6961116B2Fine positioning informationLarge capture rangeDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsDiffraction orderPhase difference
An alignment system uses a self-referencing interferometer that produces two overlapping and relatively rotated images of an alignment markers. Detectors detect intensities in a pupil plane where Fourier transforms of the images are caused to interfere. The positional information is derived from the phase difference between diffraction orders of the two images which manifests as intensity variations in the interfered orders. Asymmetry can also be measured by measuring intensities at two positions either side of a diffraction order.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
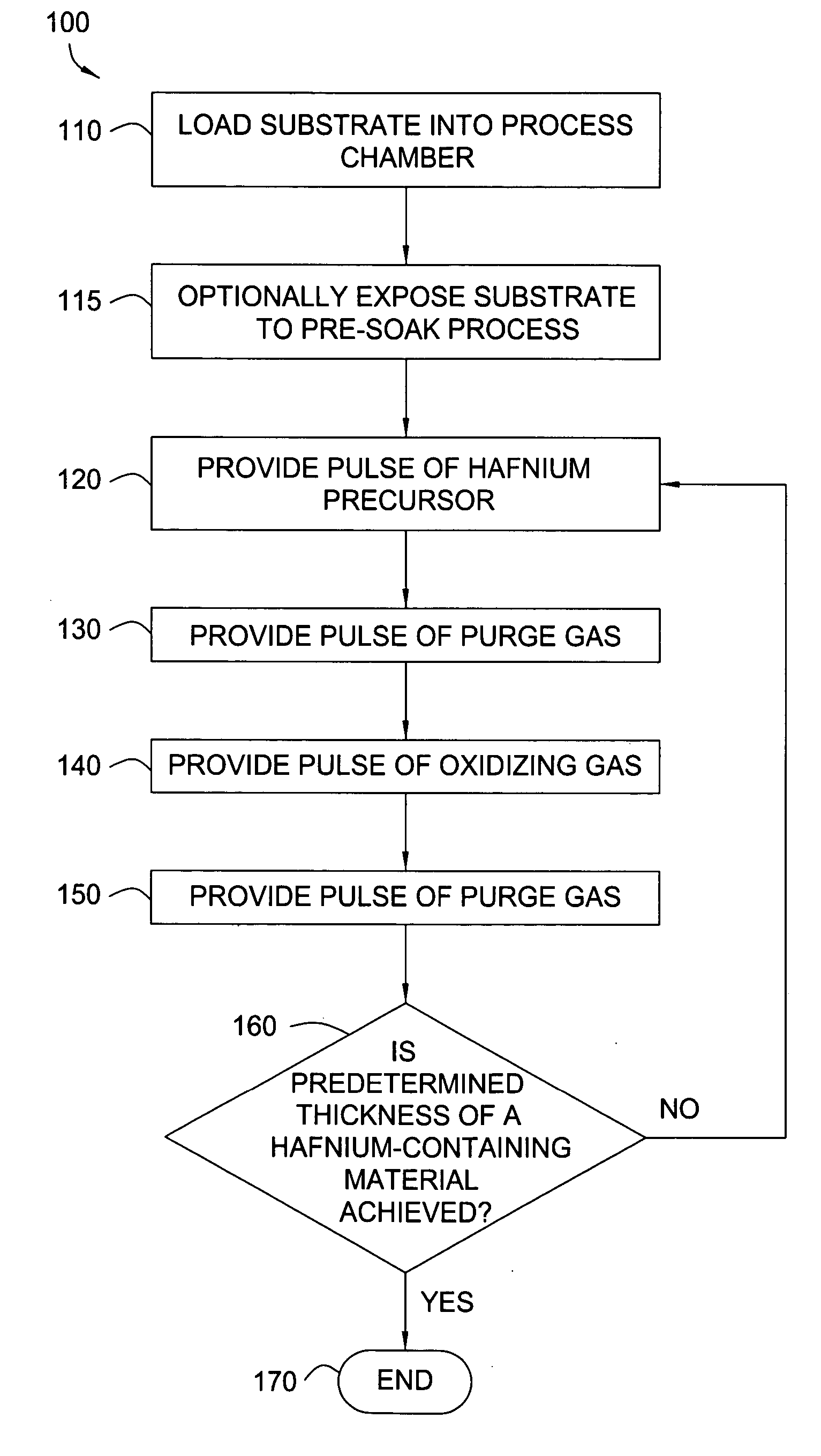
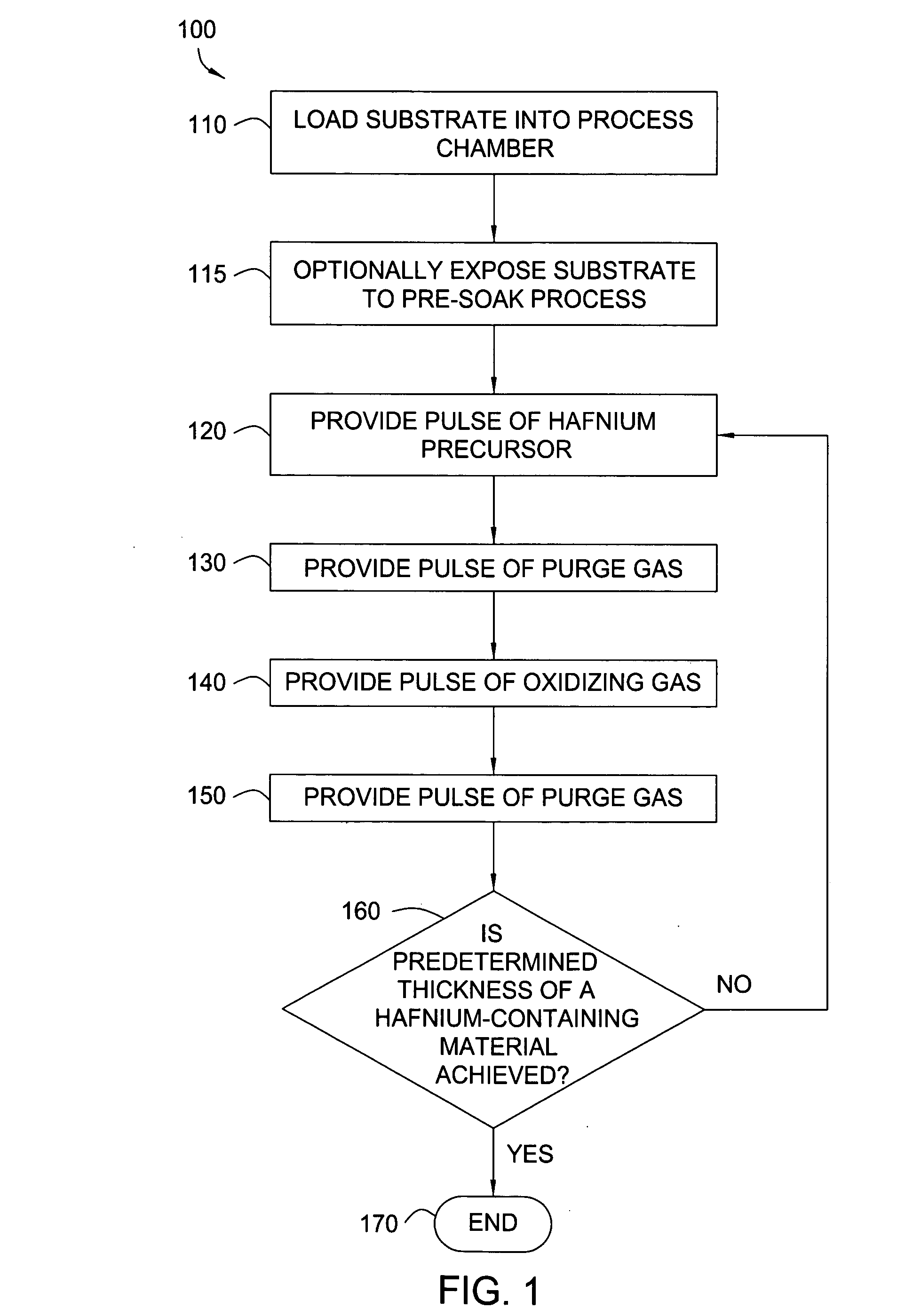
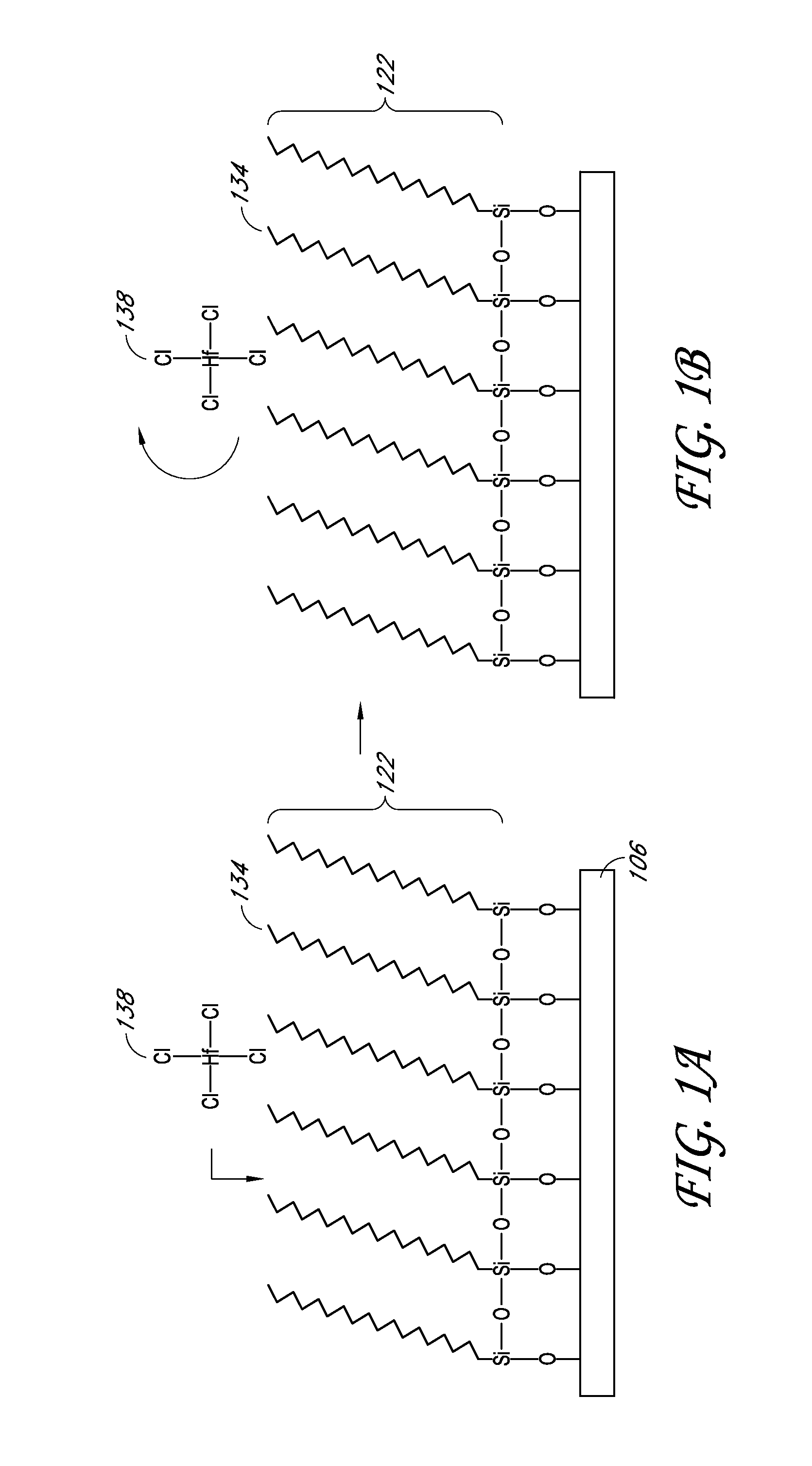
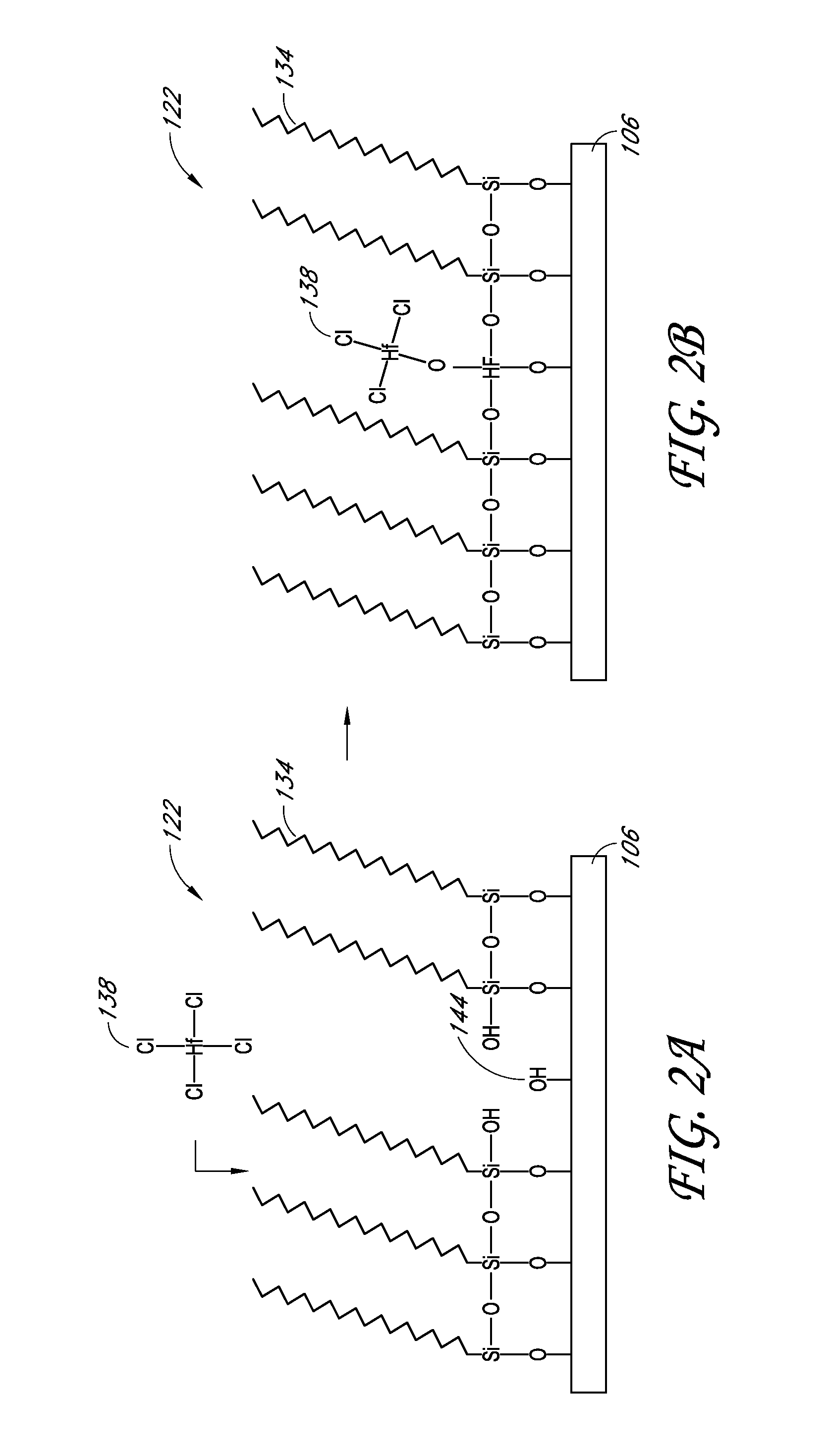
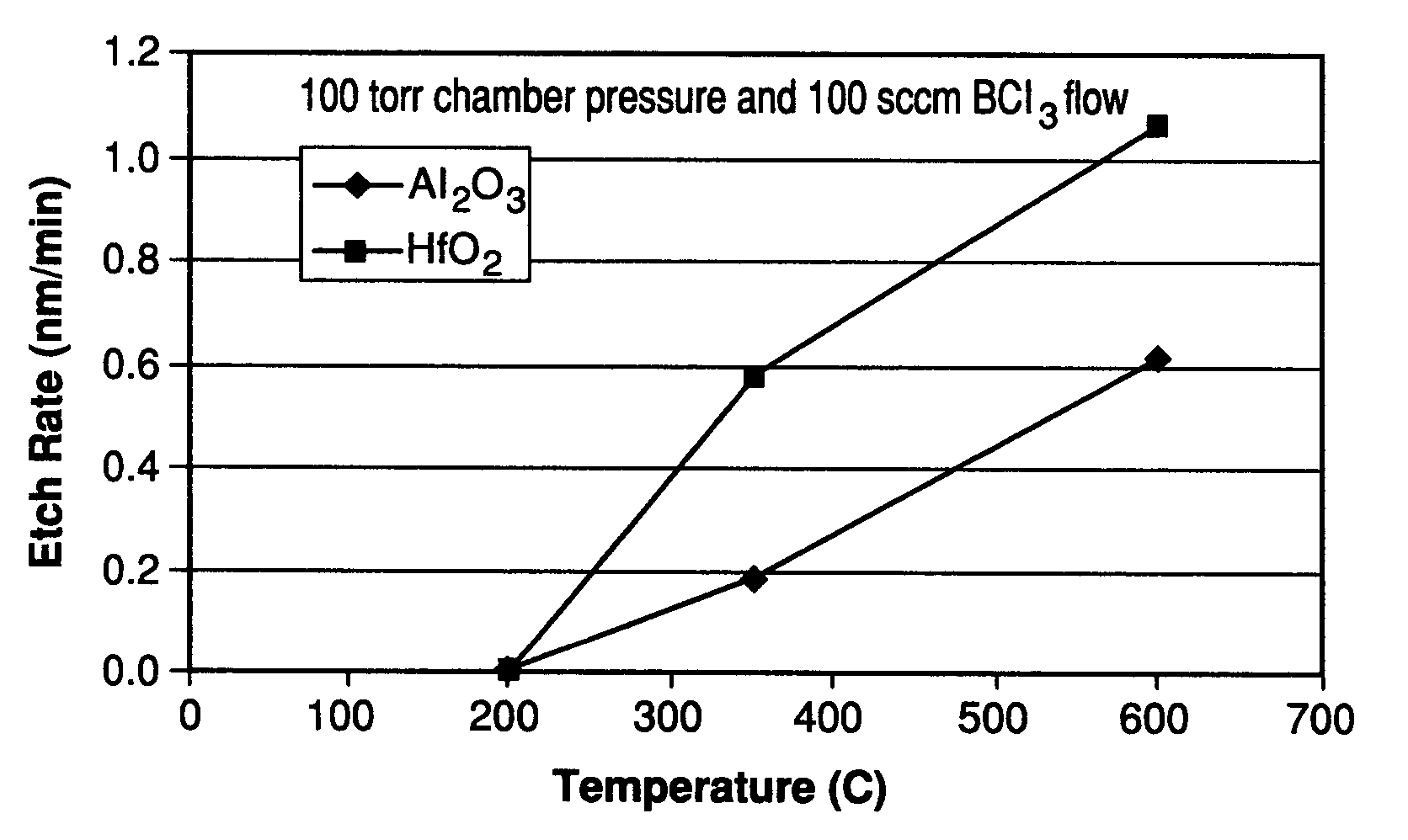
Apparatuses and methods for atomic layer deposition of hafnium-containing high-k dielectric materials
InactiveUS20050271813A1Steam generation heating methodsDecorative surface effectsGas phaseWater vapor
Embodiments of the invention provide methods for depositing dielectric materials on substrates during vapor deposition processes, such as atomic layer deposition (ALD). In one example, a method includes sequentially exposing a substrate to a hafnium precursor and an oxidizing gas to deposit a hafnium oxide material thereon. In another example, a hafnium silicate material is deposited by sequentially exposing a substrate to the oxidizing gas and a process gas containing a hafnium precursor and a silicon precursor. The oxidizing gas usually contains water vapor formed by flowing a hydrogen source gas and an oxygen source gas through a water vapor generator. In another example, a method includes sequentially exposing a substrate to the oxidizing gas and at least one precursor to deposit hafnium oxide, zirconium oxide, lanthanum oxide, tantalum oxide, titanium oxide, aluminum oxide, silicon oxide, aluminates thereof, silicates thereof, derivatives thereof or combinations thereof.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
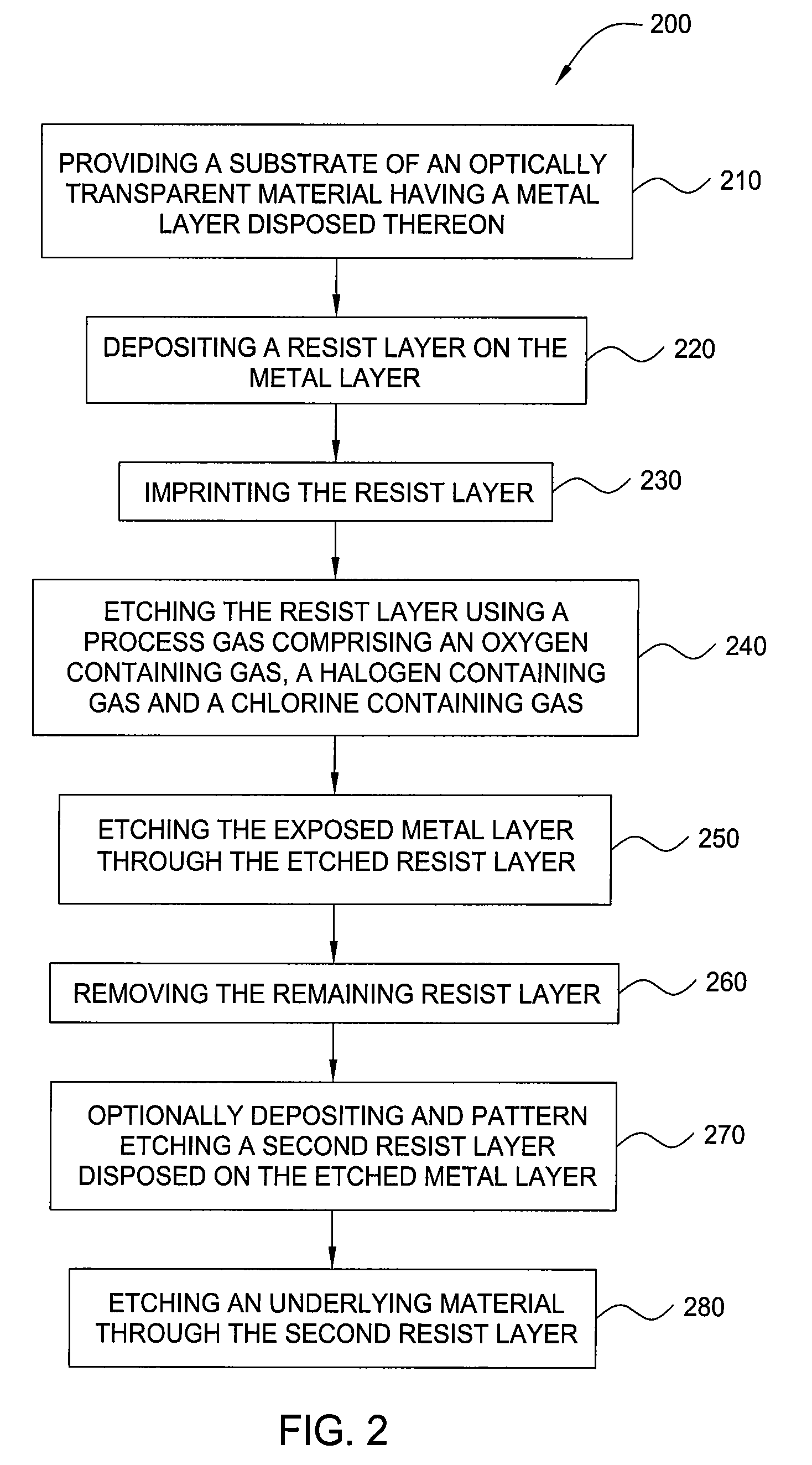
Methods of removing silicon oxide and gaseous mixtures for achieving same
ActiveUS20090275205A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical treatmentPartial oxidation
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method to improve the step coverage and pattern loading for dielectric films
InactiveUS20070232071A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingSilicon oxide
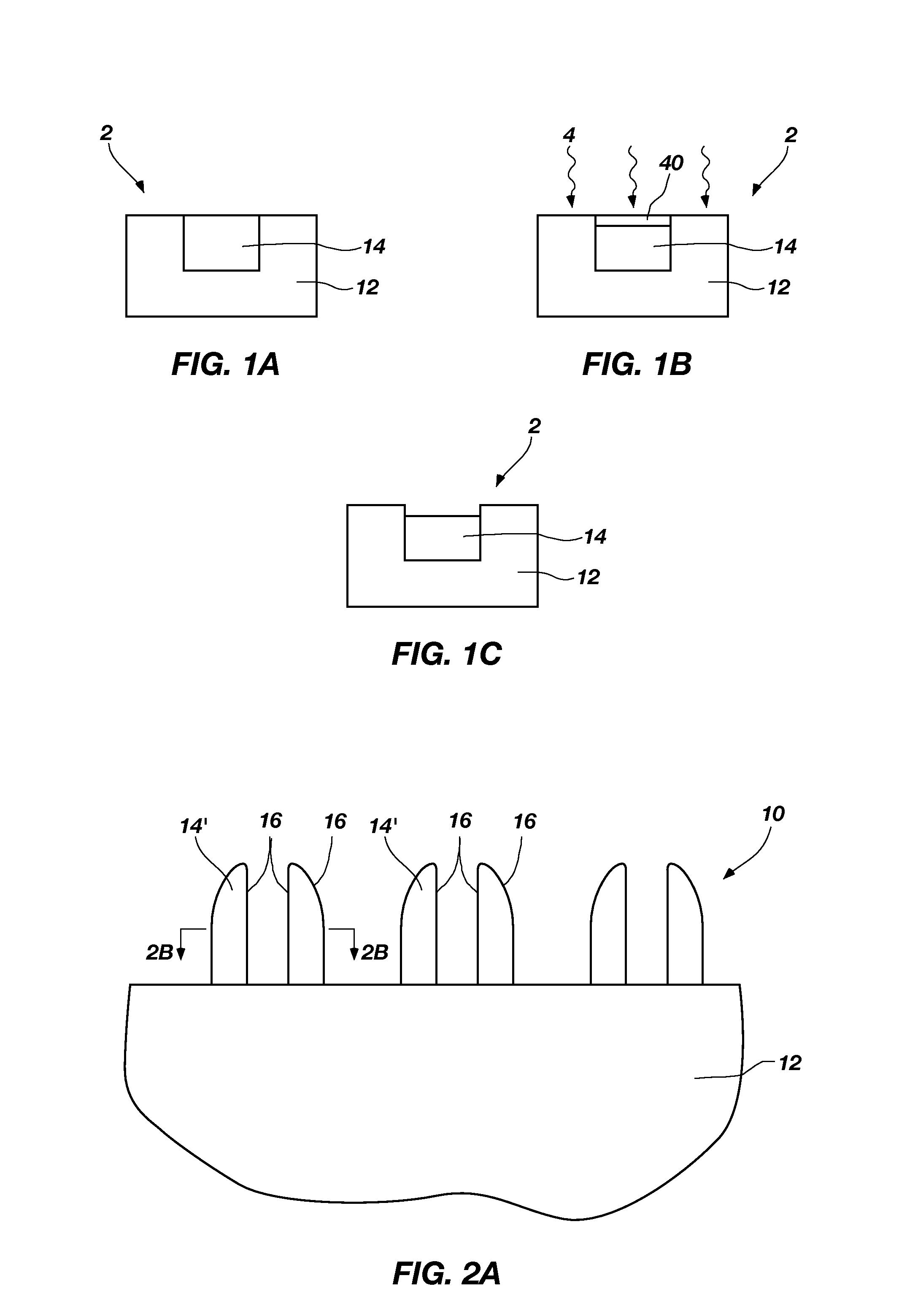
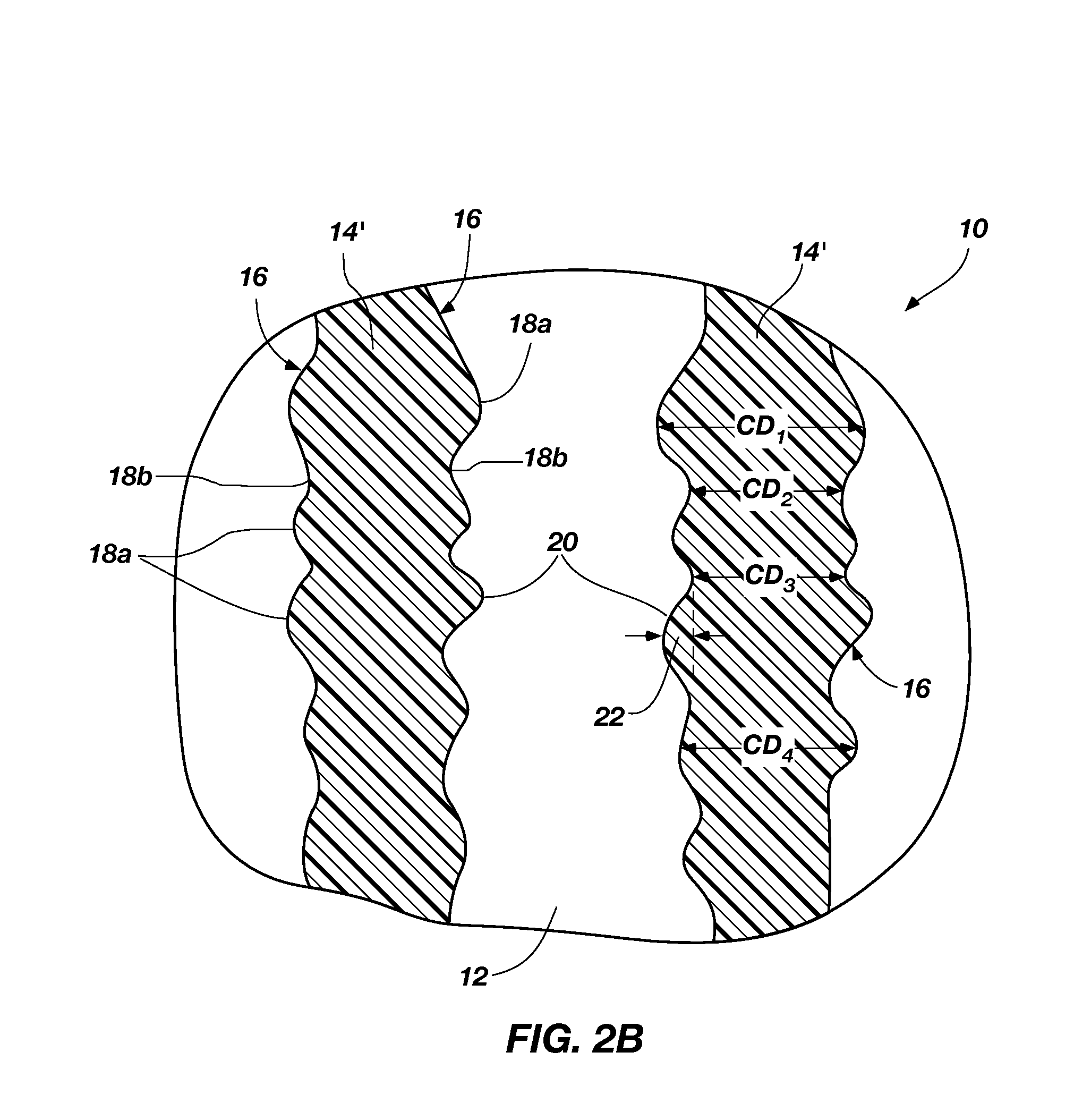
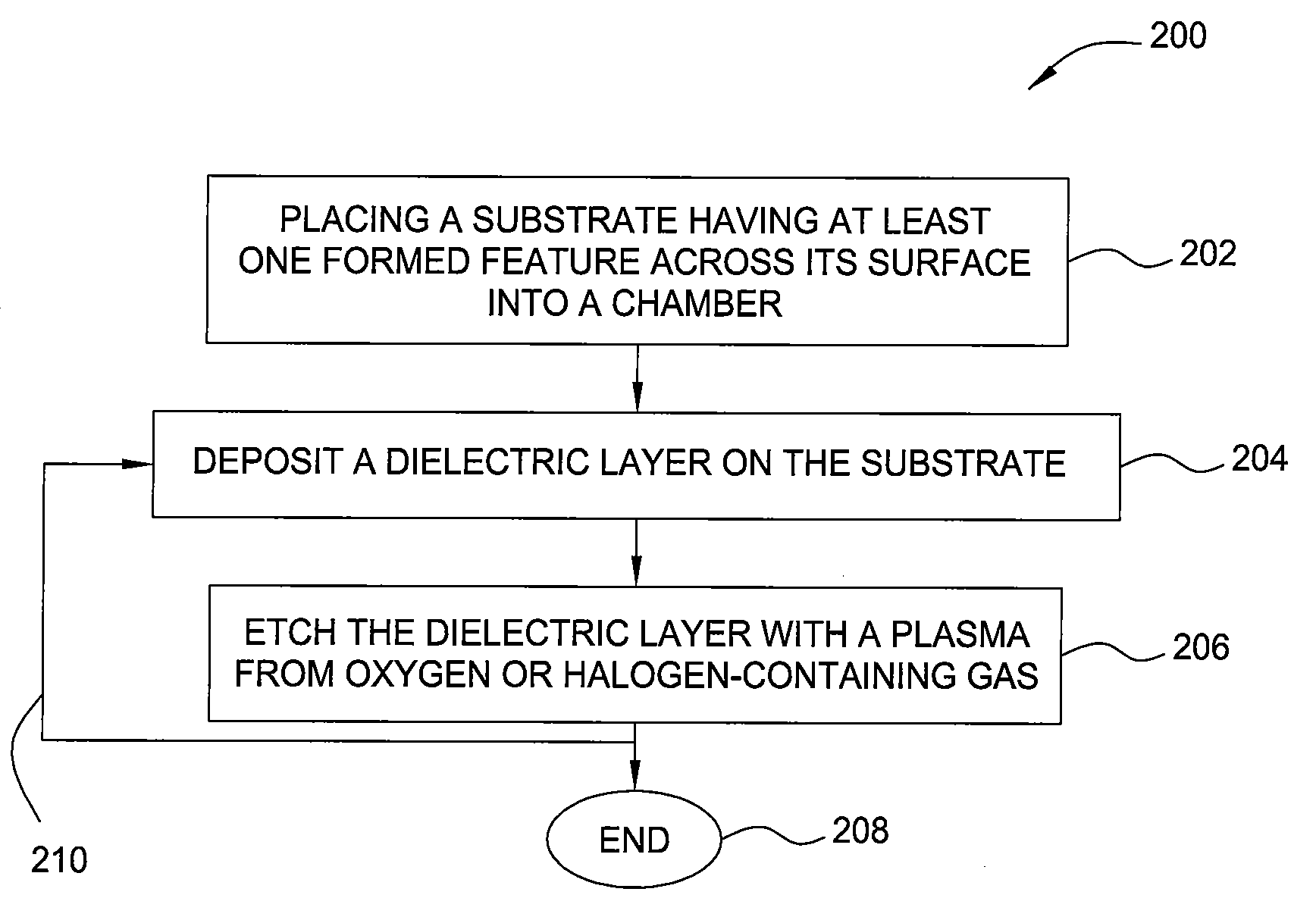
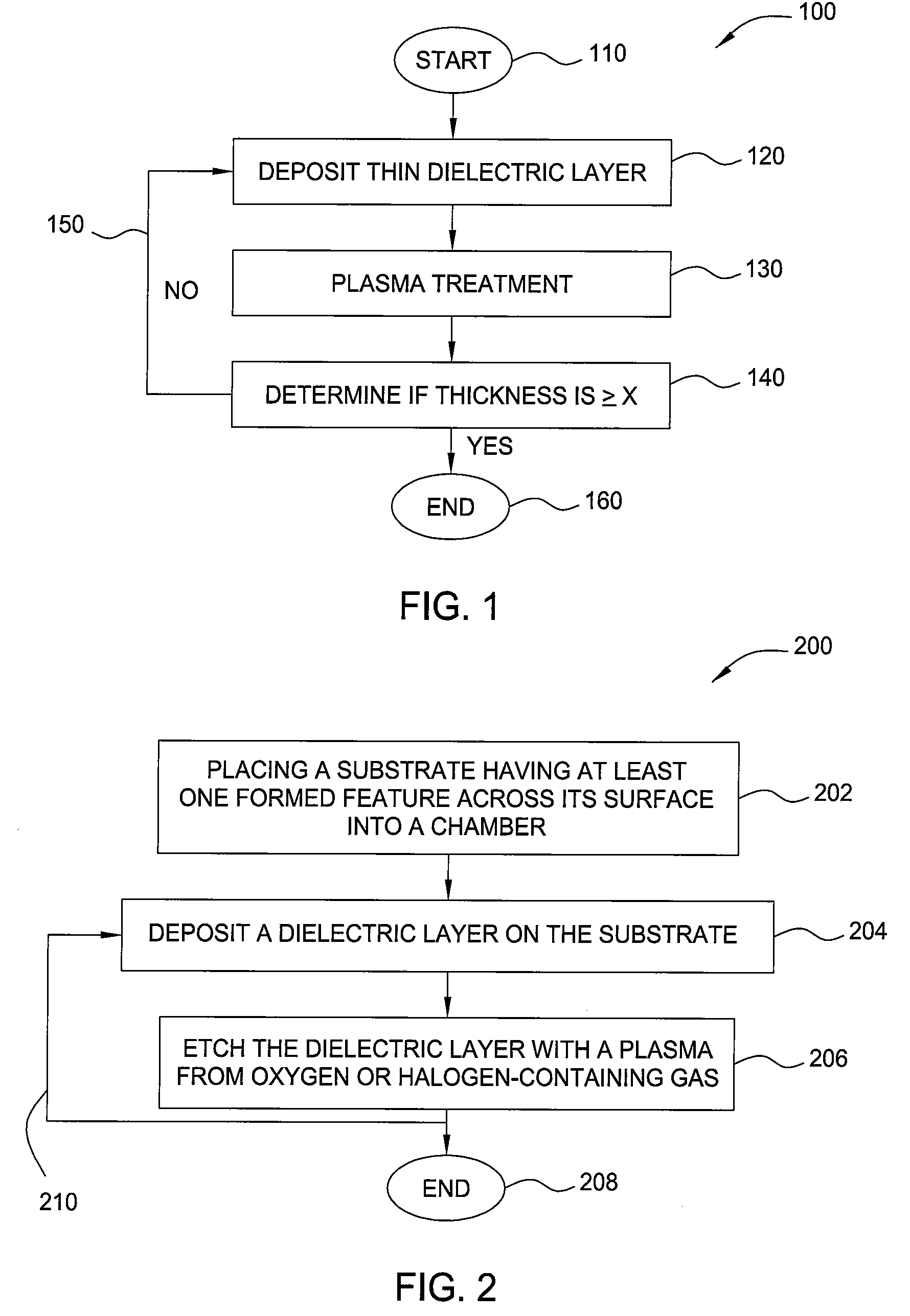
Methods of controlling the step coverage and pattern loading of a layer on a substrate are provided. The dielectric layer may be a silicon nitride, silicon oxide, or silicon oxynitride layer. The method comprises depositing a dielectric layer on a substrate having at least one formed feature across a surface of the substrate and etching the dielectric layer with a plasma from oxygen or a halogen-containing gas to provide a desired profile of the dielectric layer on the at least one formed feature. The deposition of the dielectric layer and the etching of the dielectric layer may be repeated for multiple cycles to provide the desired profile of the dielectric layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Atomic layer etching with pulsed plasmas
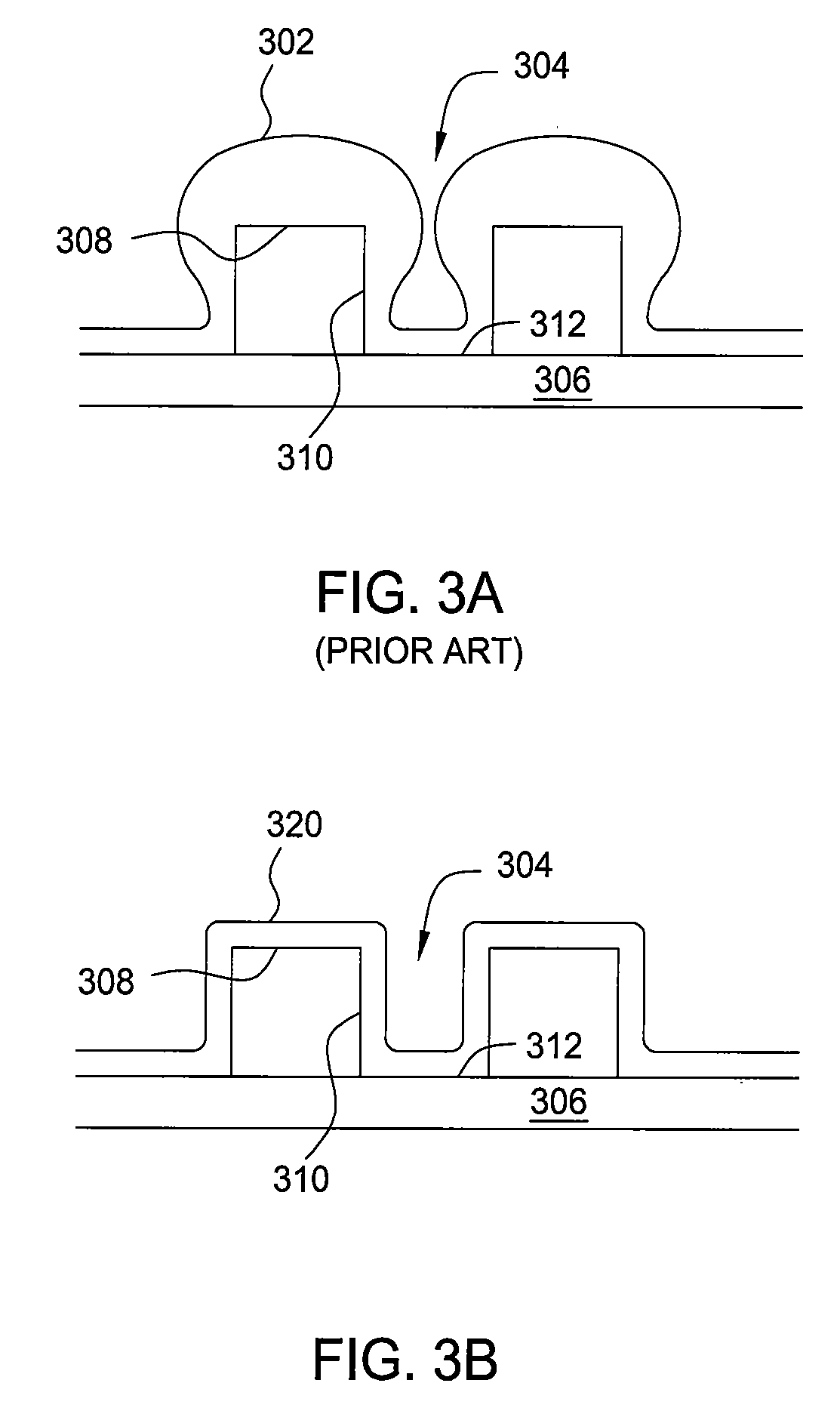
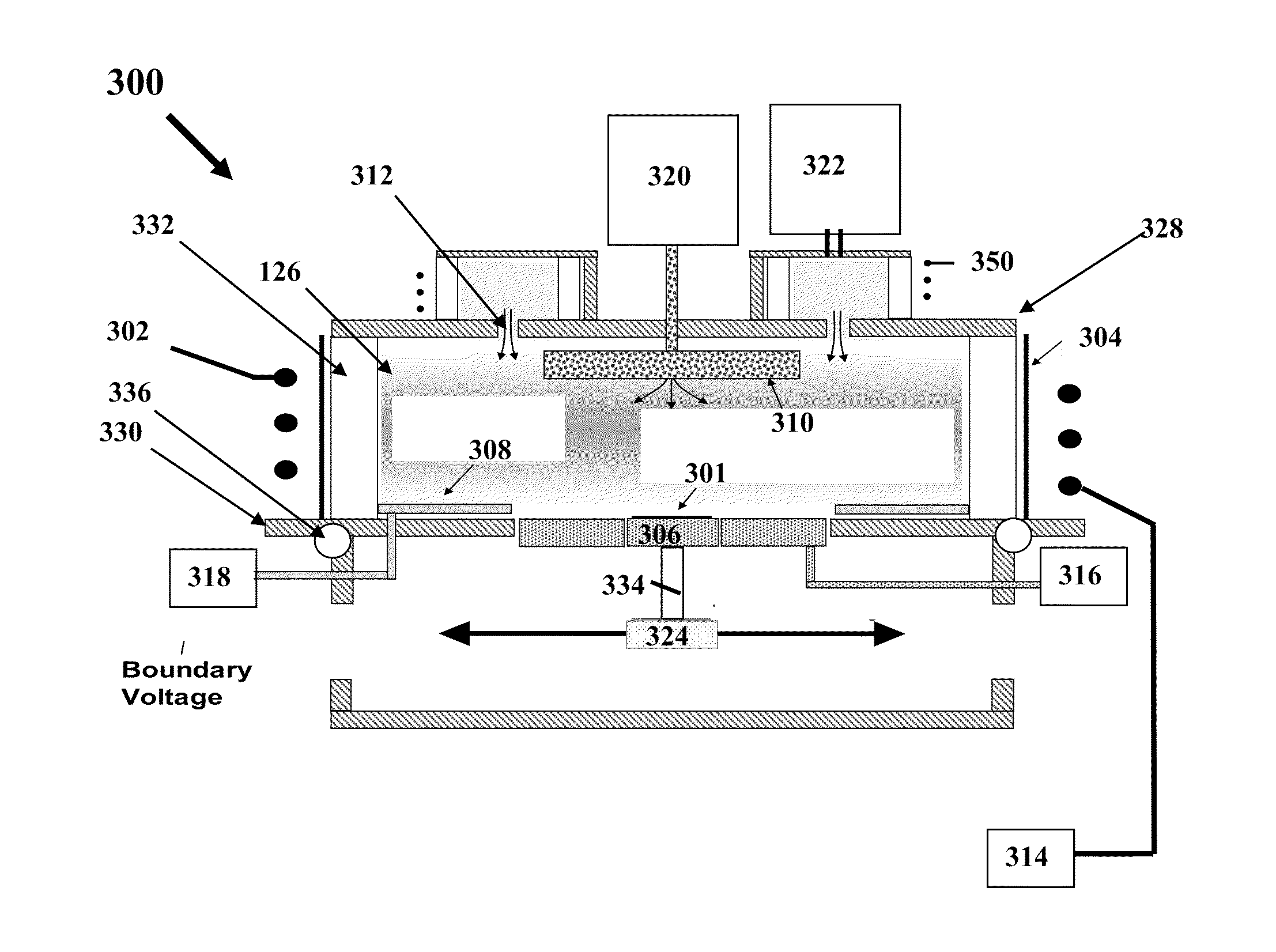
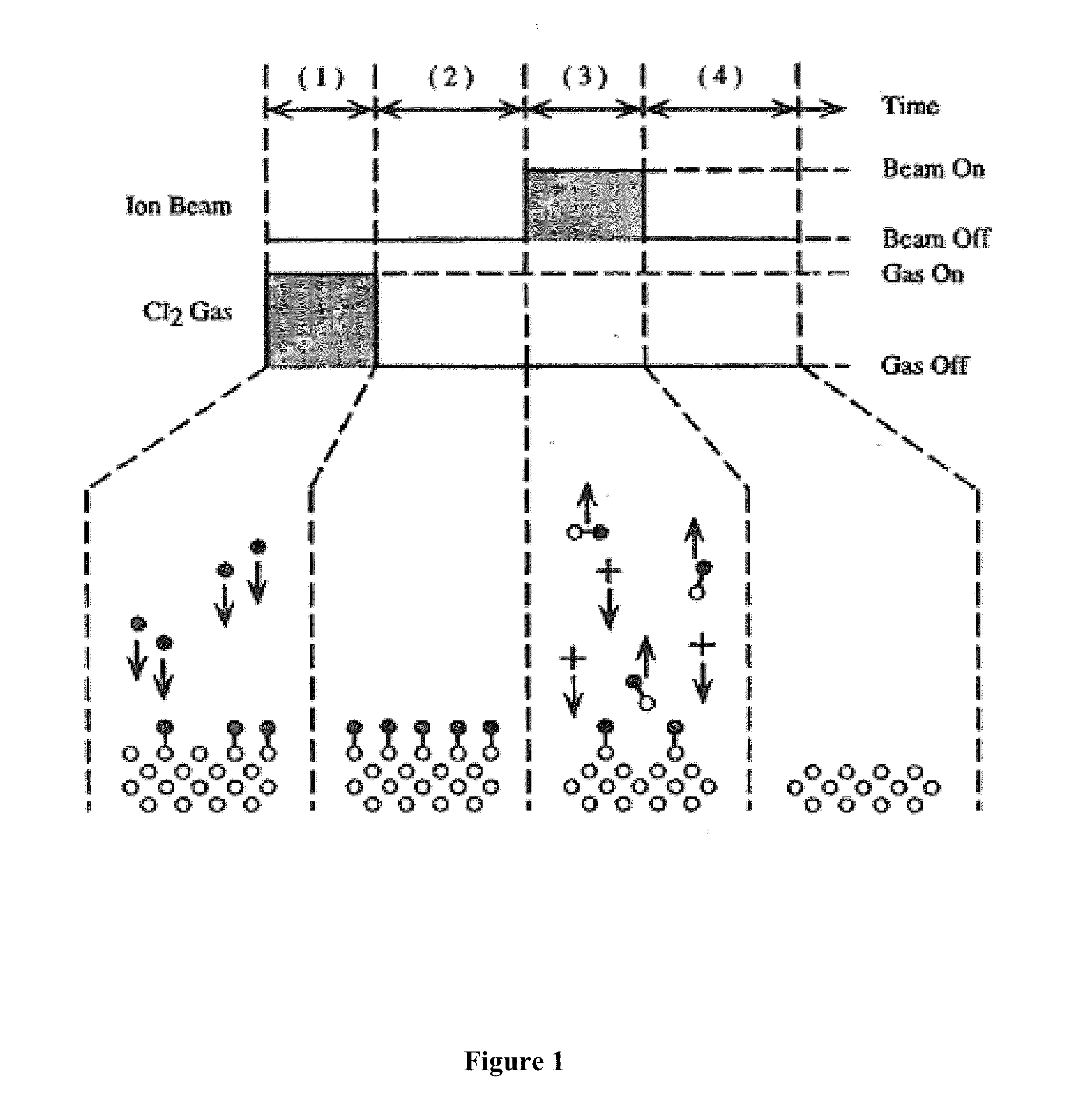
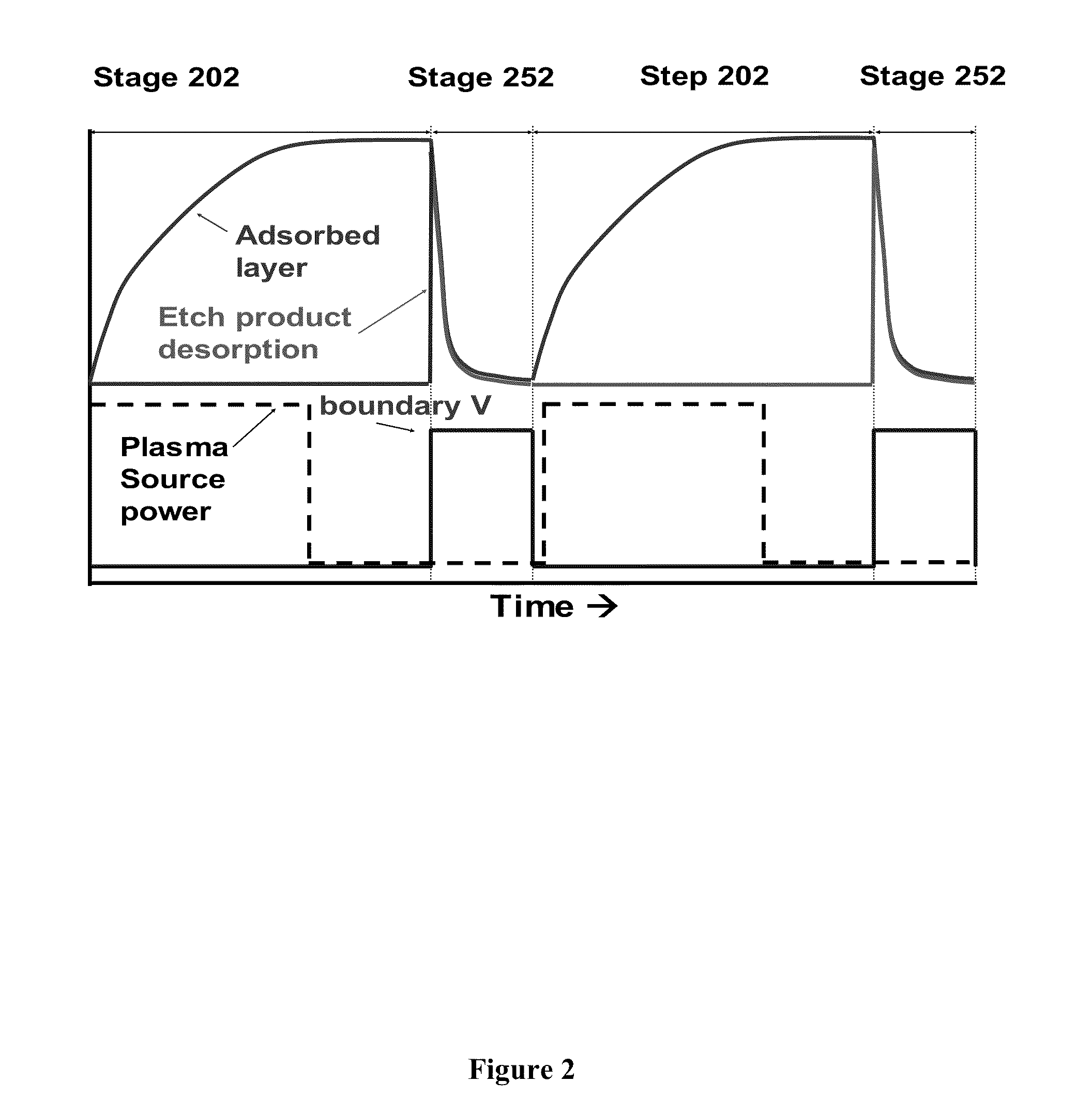
A system and method for rapid atomic layer etching (ALET) including a pulsed plasma source, with a spiral coil electrode, a cooled Faraday shield, a counter electrode disposed at the top of the tube, a gas inlet and a reaction chamber including a substrate support and a boundary electrode. The method includes positioning an etchable substrate in a plasma etching chamber, forming a product layer on the surface of the substrate, removing a portion of the product layer by pulsing a plasma source, then repeating the steps of forming a product layer and removing a portion of the product layer to form an etched substrate.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
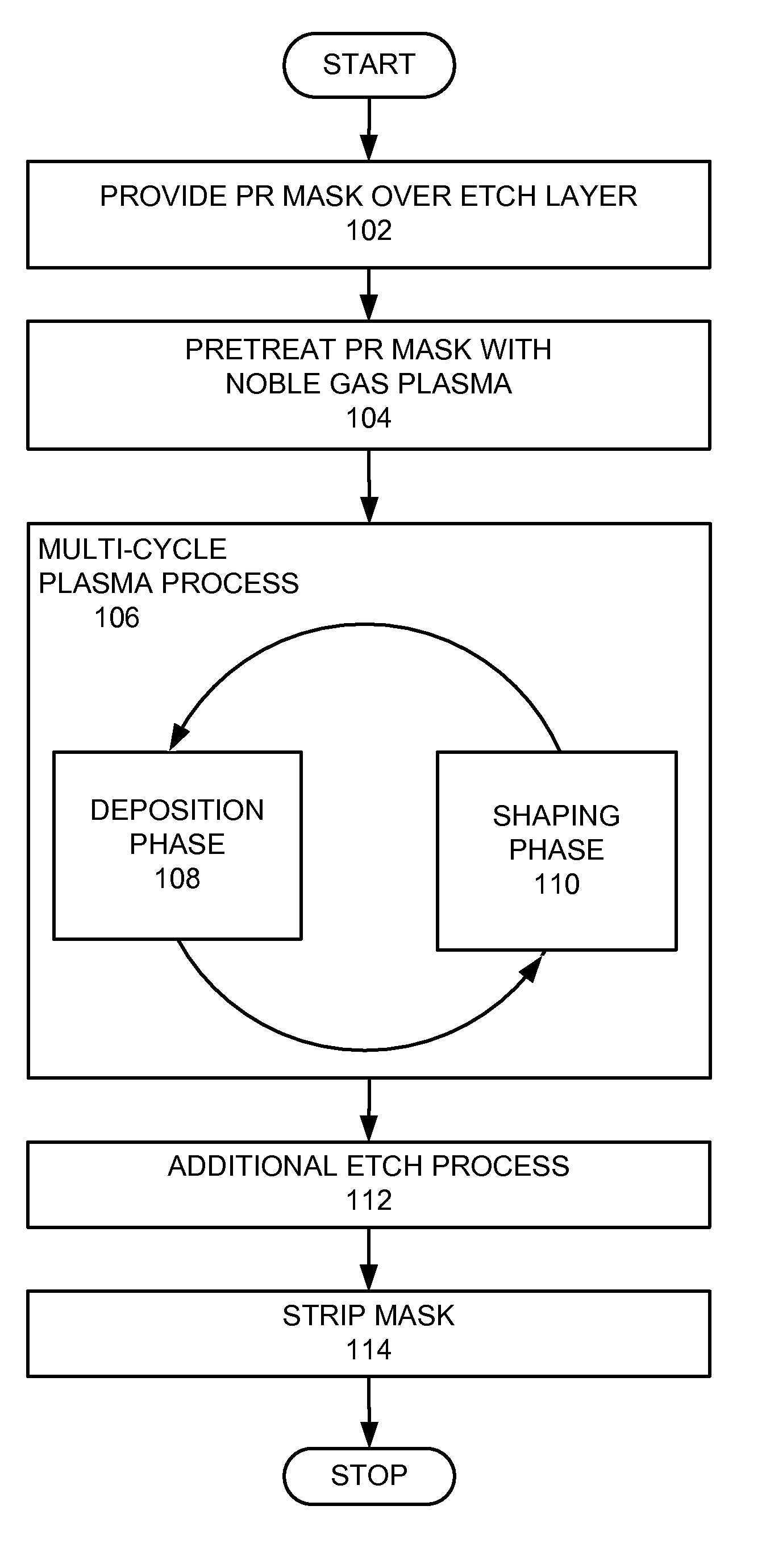
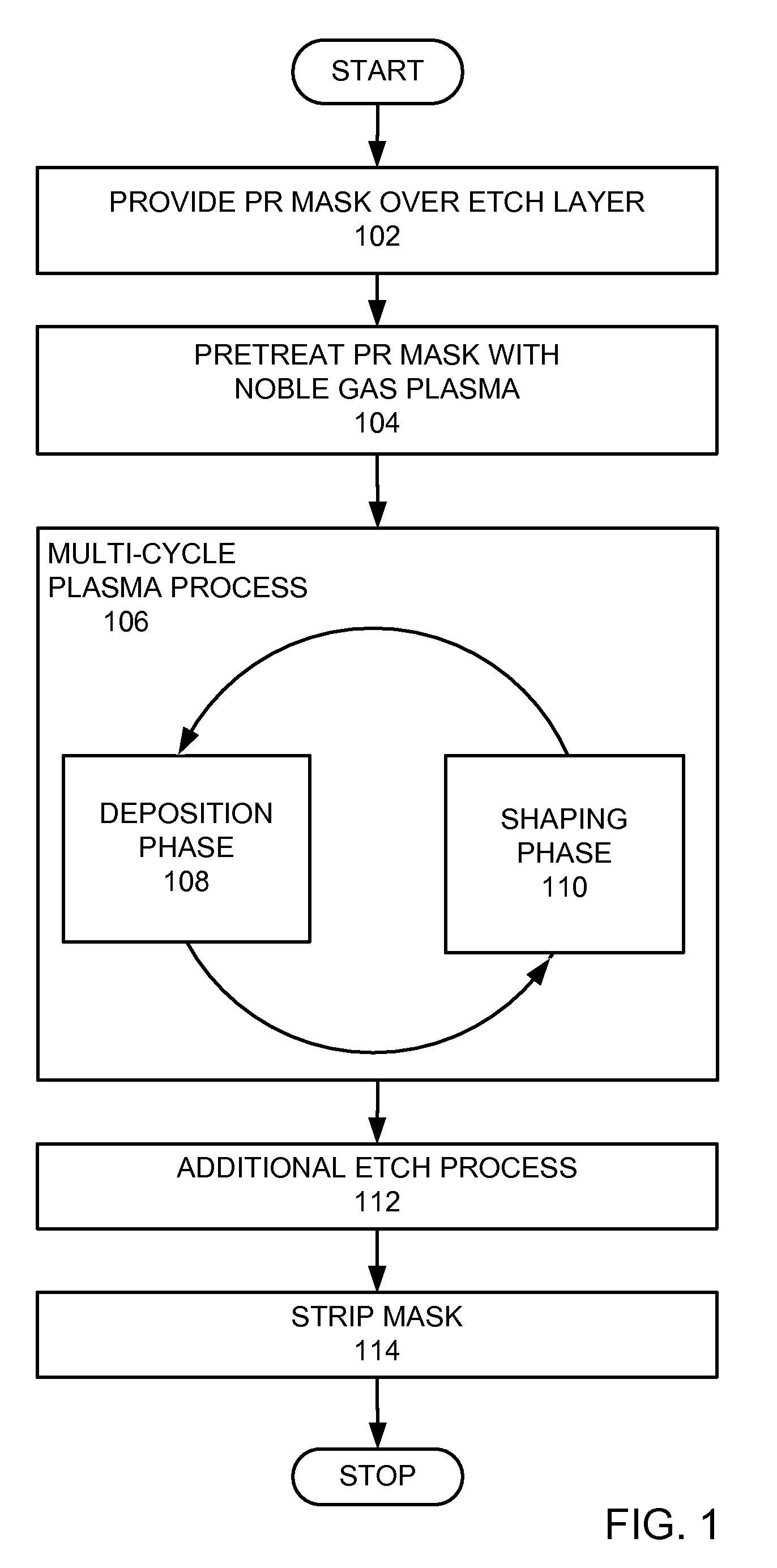
Plasma process with photoresist mask pretreatment
InactiveUS20090286400A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNoble gasLaser light
A method for etching features in a dielectric layer through a photoresist (PR) mask is provided. The PR mask is patterned using laser light having a wavelength not more than 193 nm. The PR mask is pre-treated with a noble gas plasma, and then a plurality of cycles of a plasma process is provided. Each cycle includes a deposition phase that deposits a deposition layer over the PR mask, the deposition layer covering a top and sidewalls of mask features of the PR mask, and a shaping phase that shapes the deposition layer deposited over the PR mask.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
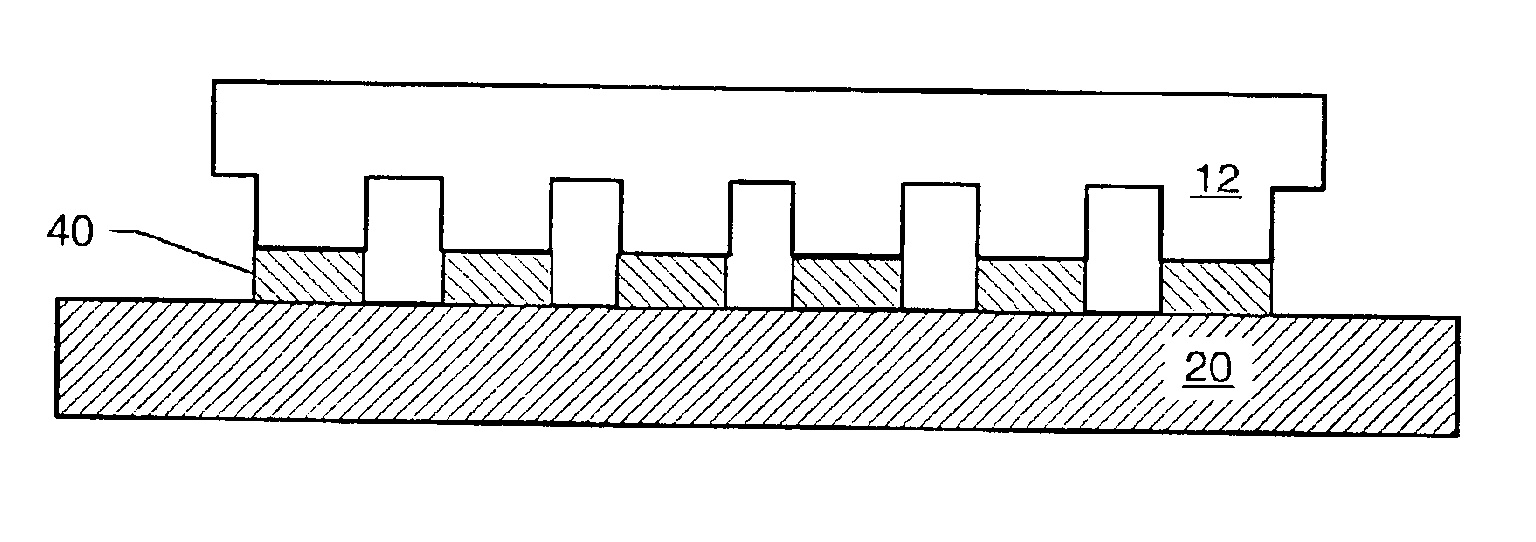
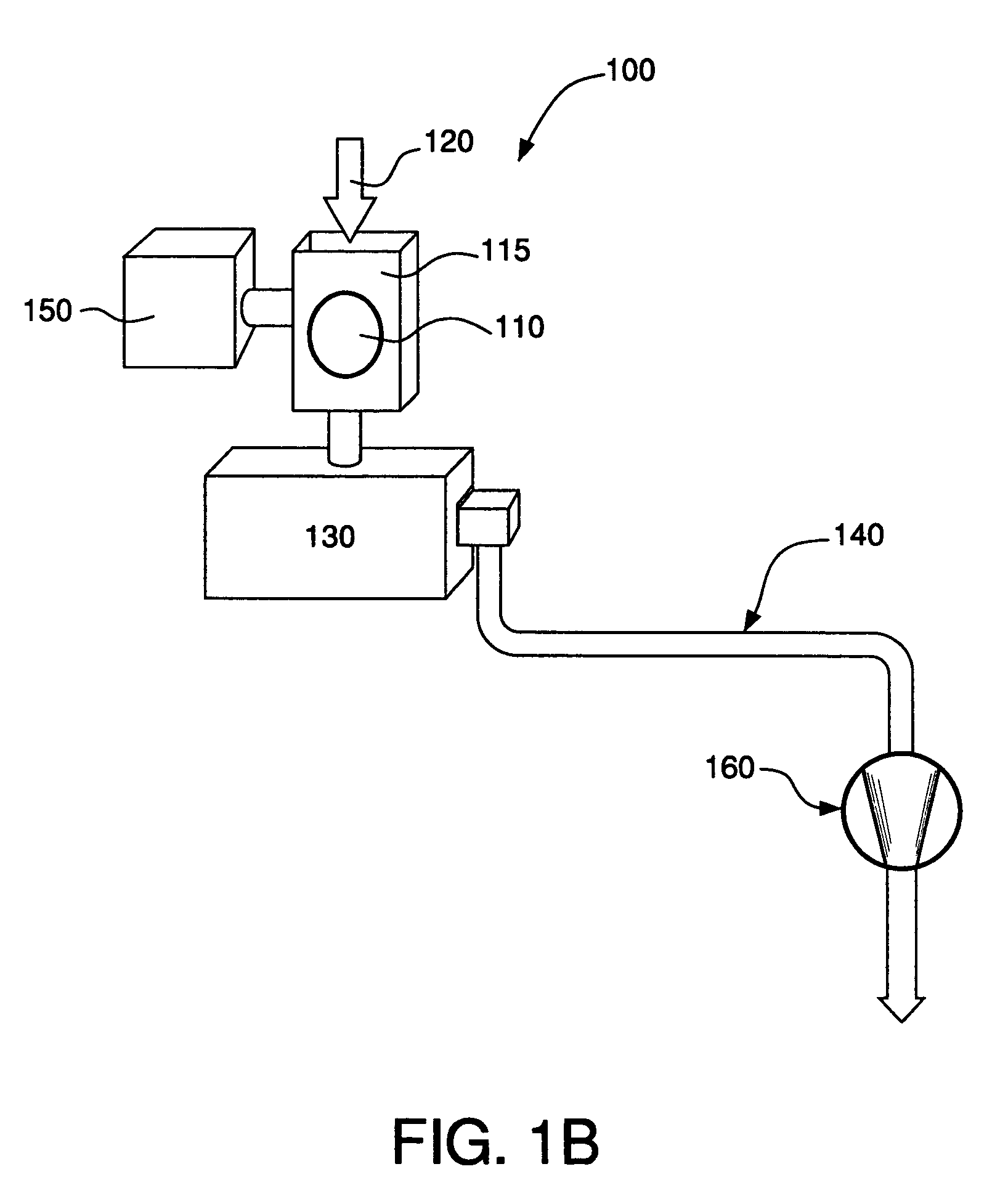
Conductor treating single-wafer type treating device and method for semi-conductor treating
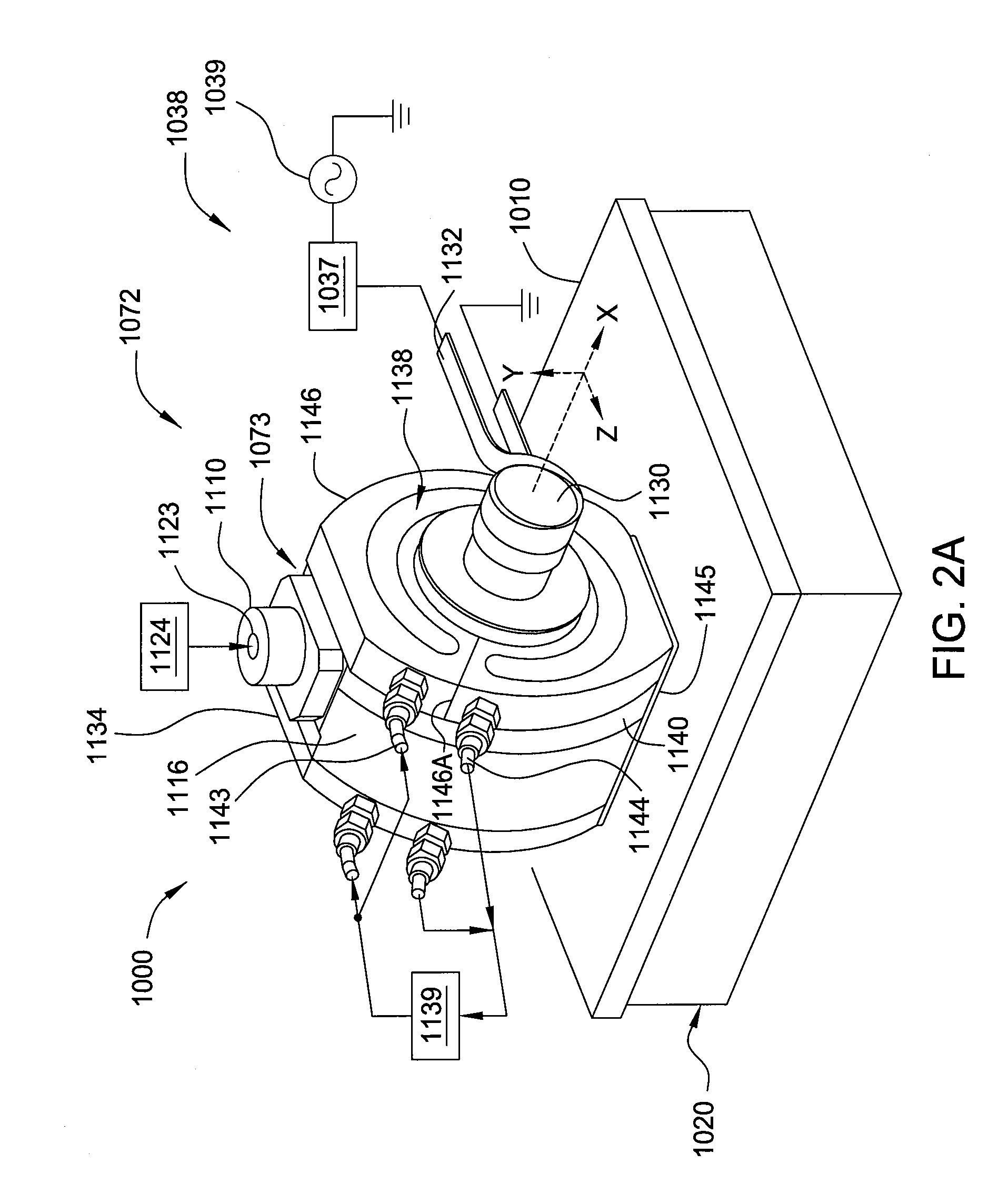
InactiveUS7235137B2High processing temperatureLiquid surface applicatorsDecorative surface effectsElectrical conductorEngineering
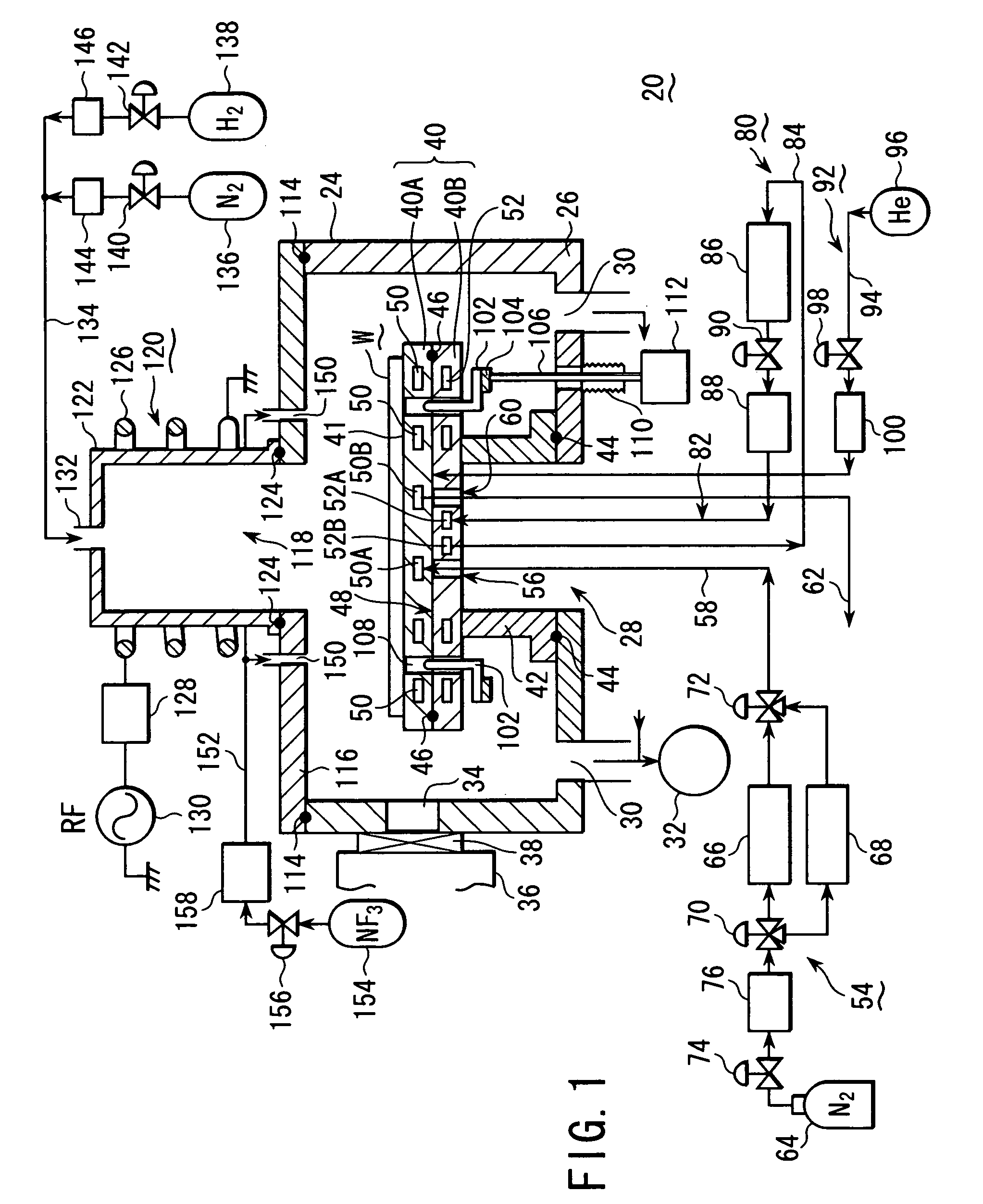
A single-substrate processing apparatus (20) has a worktable (40) disposed in a process chamber (24), which accommodates a target substrate (W). The worktable (40) has a thermally conductive mount surface (41) to place the target substrate (W) thereon. The worktable (40) is provided with a flow passage (50) formed therein, in which a thermal medium flows for adjusting temperature of the target substrate (W) through the mount surface (41). The flow passage (50) is connected to a thermal medium supply system (54), which selectively supplies a cooling medium and a heating medium.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Integrated low K dielectrics and etch stops
InactiveUS6340435B1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHydrogenFluorocarbon
A method of depositing and etching dielectric layers having low dielectric constants and etch rates that vary by at least 3:1 for formation of horizontal interconnects. The amount of carbon or hydrogen in the dielectric layer is varied by changes in deposition conditions to provide low k dielectric layers that can replace etch stop layers or conventional dielectric layers in damascene applications. A dual damascene structure having two or more dielectric layers with dielectric constants lower than about 4 can be deposited in a single reactor and then etched to form vertical and horizontal interconnects by varying the concentration of a carbon:oxygen gas such as carbon monoxide. The etch gases for forming vertical interconnects preferably comprises CO and a fluorocarbon, and CO is preferably excluded from etch gases for forming horizontal interconnects.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
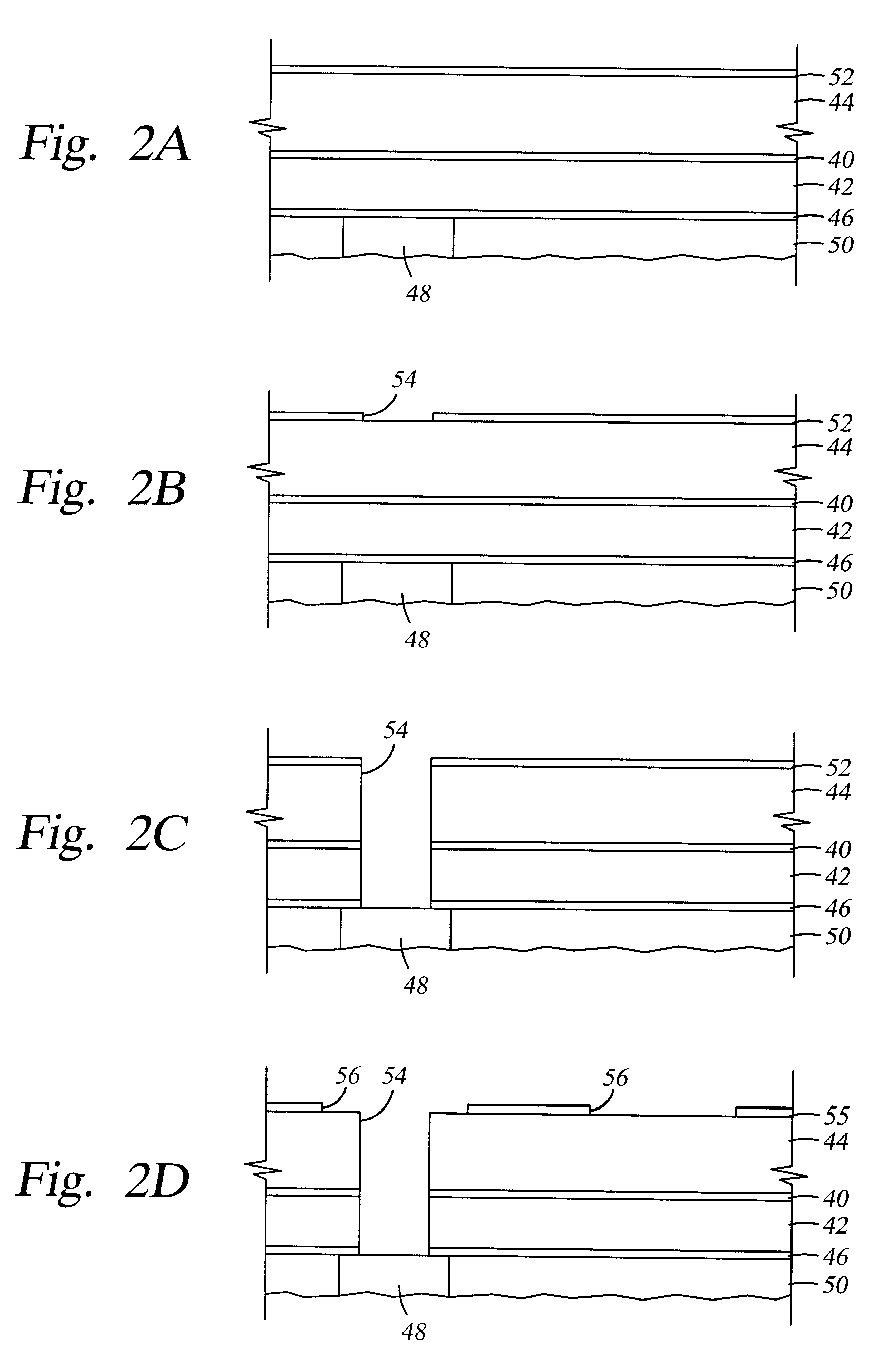
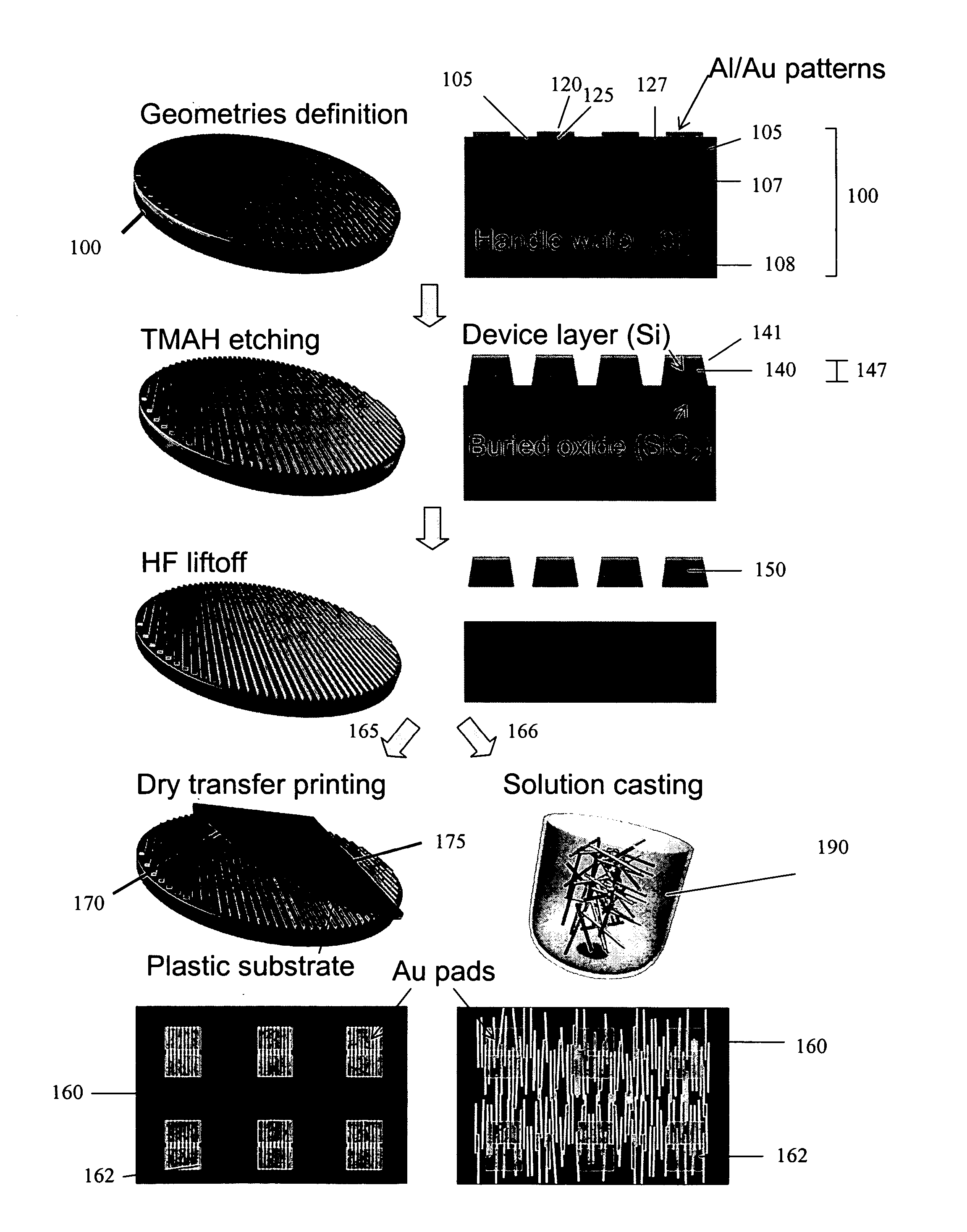
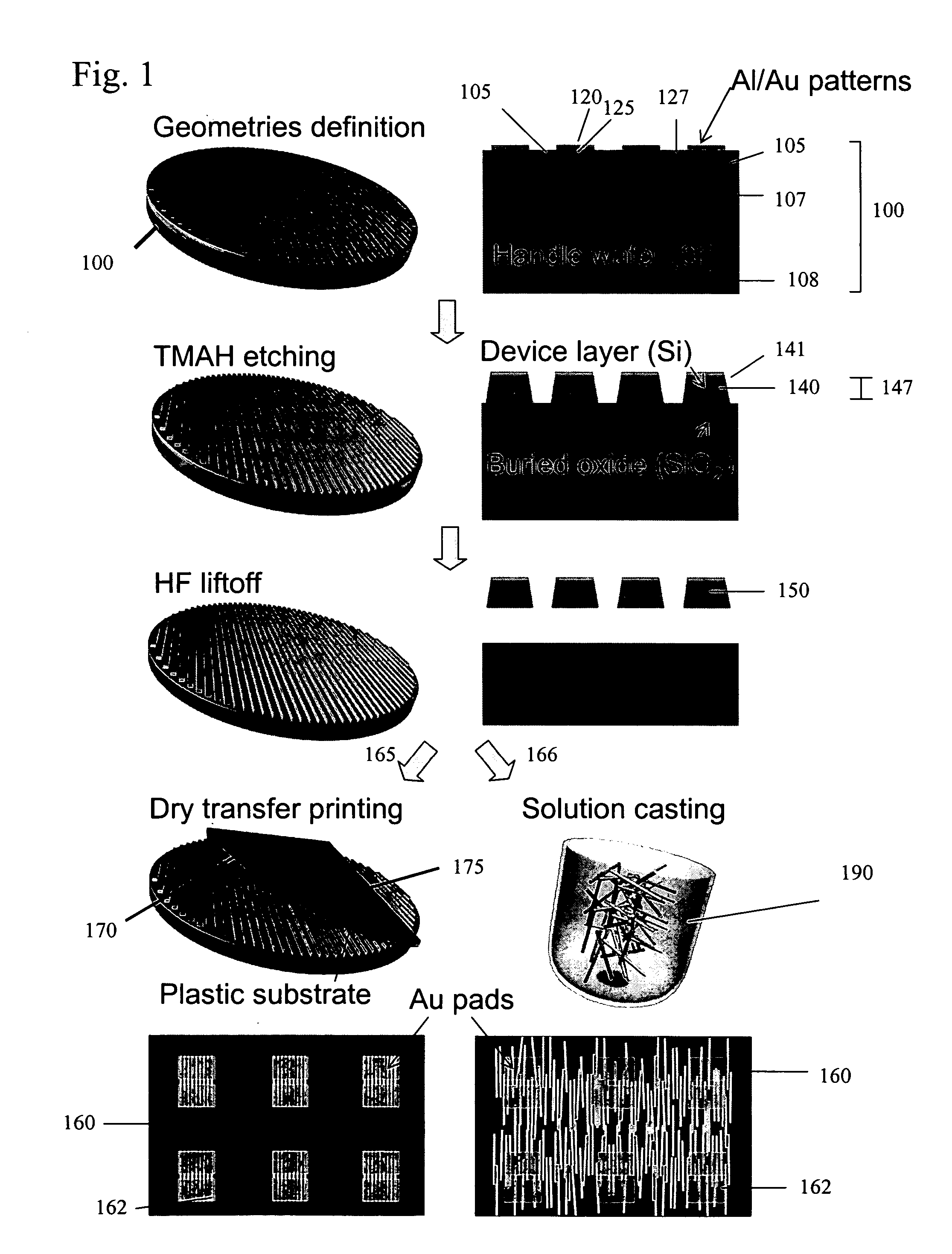
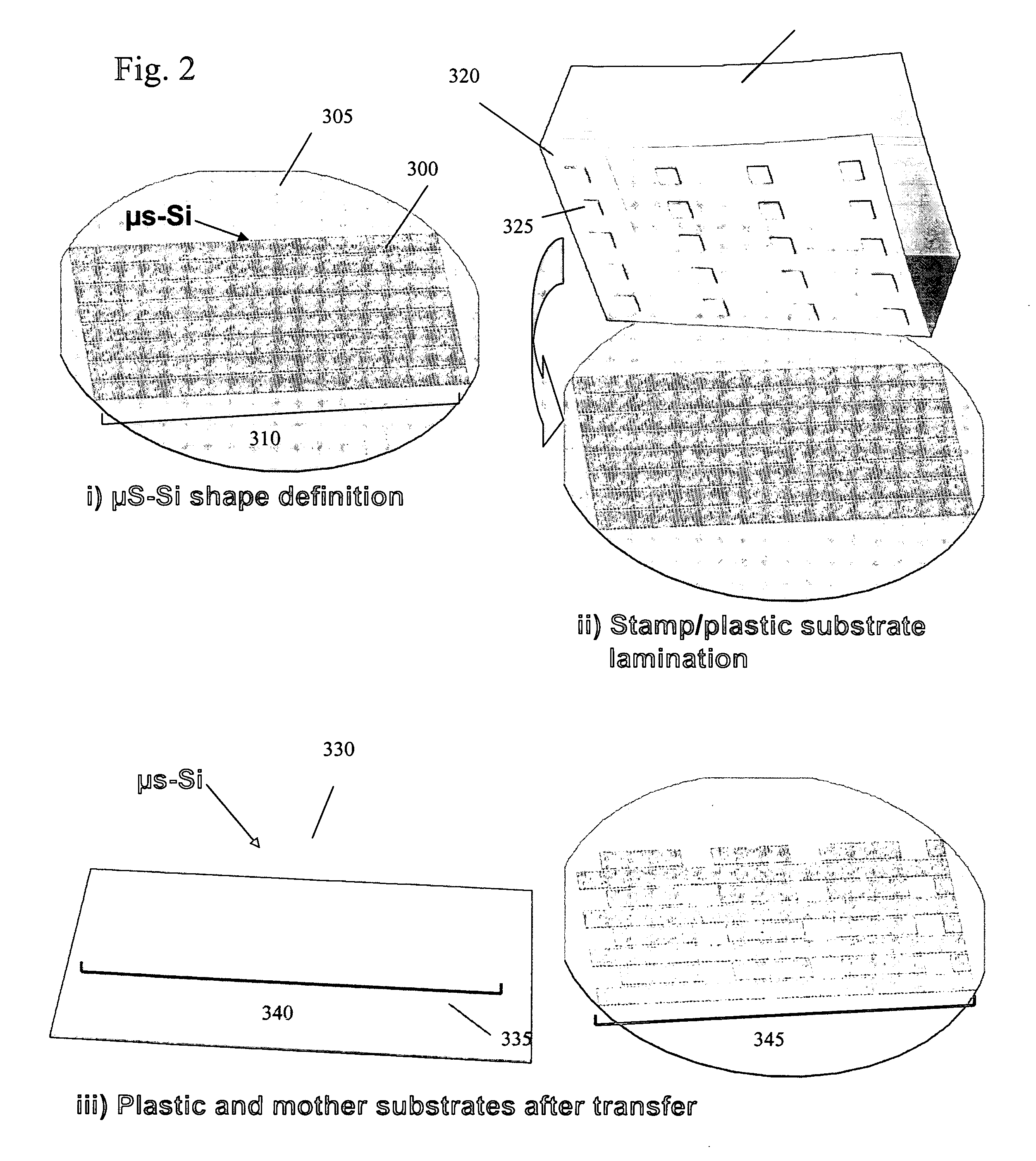
Stretchable semiconductor elements and stretchable electrical circuits
ActiveUS20060038182A1Complete release is preventedLow costTransistorDecorative surface effectsStretchable electronicsSemiconductor structure
The invention provides methods and devices for fabricating printable semiconductor elements and assembling printable semiconductor elements onto substrate surfaces. Methods, devices and device components of the present invention are capable of generating a wide range of flexible electronic and optoelectronic devices and arrays of devices on substrates comprising polymeric materials. The present invention also provides stretchable semiconductor structures and stretchable electronic devices capable of good performance in stretched configurations.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Nonwoven Having Durable Hydrophilic Coating
InactiveUS20110268932A1Promote migrationLamination ancillary operationsDecorative surface effectsHydrophilic coatingTrace Amounts
A nonwoven material coated with an amine-polyether silicone. The coating composition may include a wetting agent, an acid, and / or a defoamer. The nonwoven may be incorporated into a disposable absorbent article. The disposable absorbent article may include at least trace amounts of a mineral oil. The coating of the nonwoven may be durable even in the presence of mineral oil.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
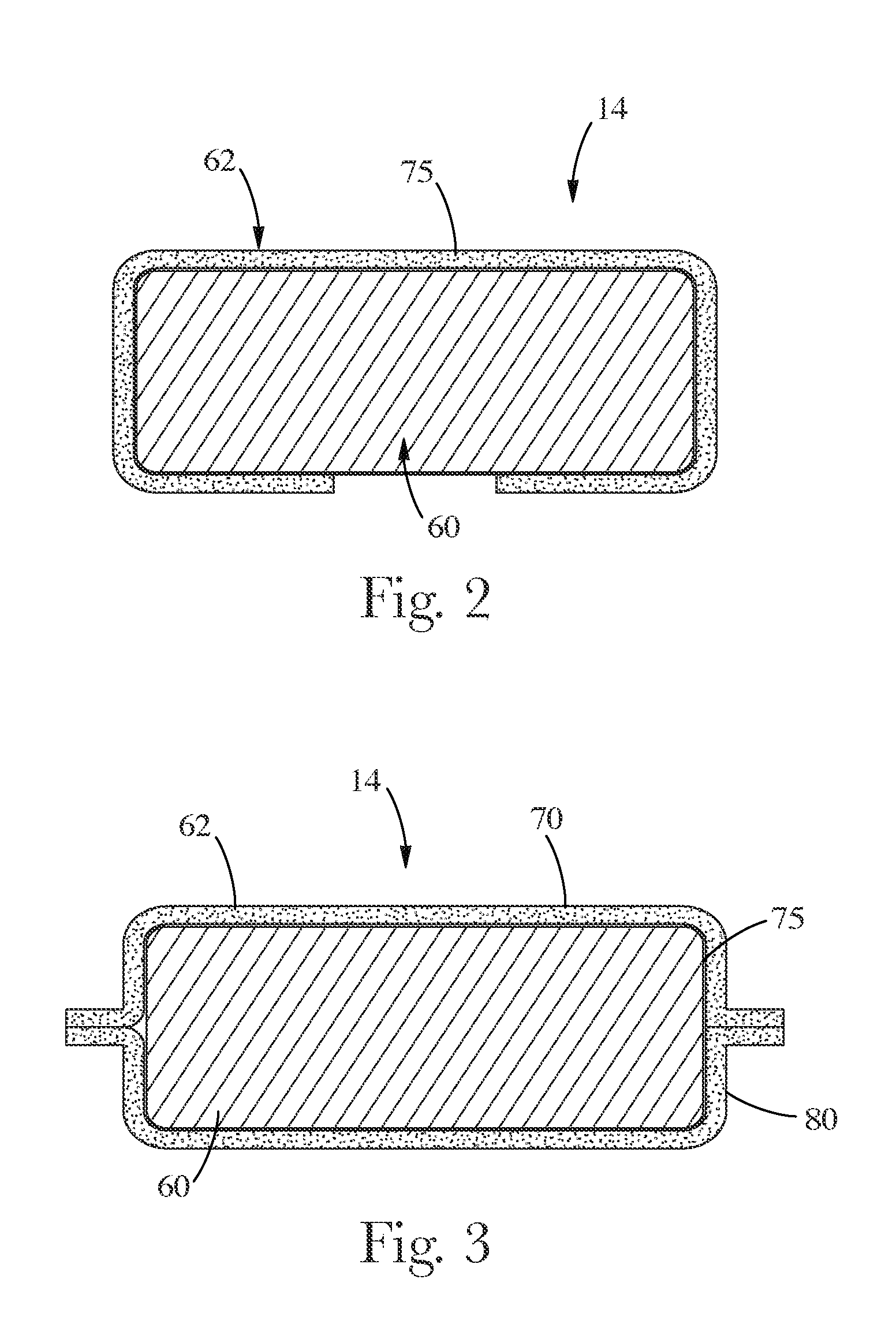
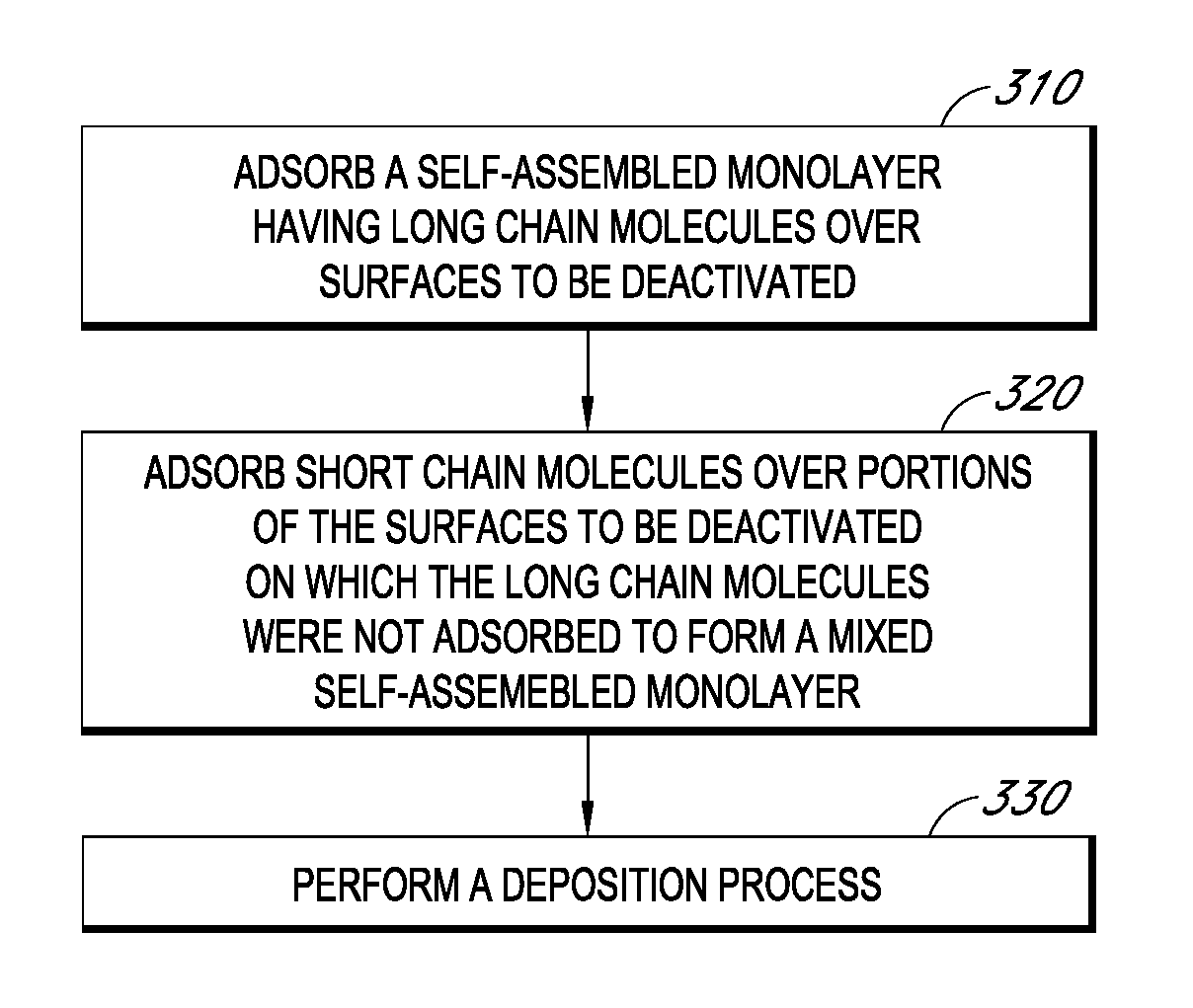
Reactive site deactivation against vapor deposition
Methods and structures relating to the formation of mixed SAMs for preventing undesirable growth or nucleation on exposed surfaces inside a reactor are described. A mixed SAM can be formed on surfaces for which nucleation is not desired by introducing a first SAM precursor having molecules of a first length and a second SAM precursor having molecules of a second length shorter than the first. Examples of exposed surfaces for which a mixed SAM can be provided over include reactor surfaces and select surfaces of integrated circuit structures, such as insulator and dielectric layers.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
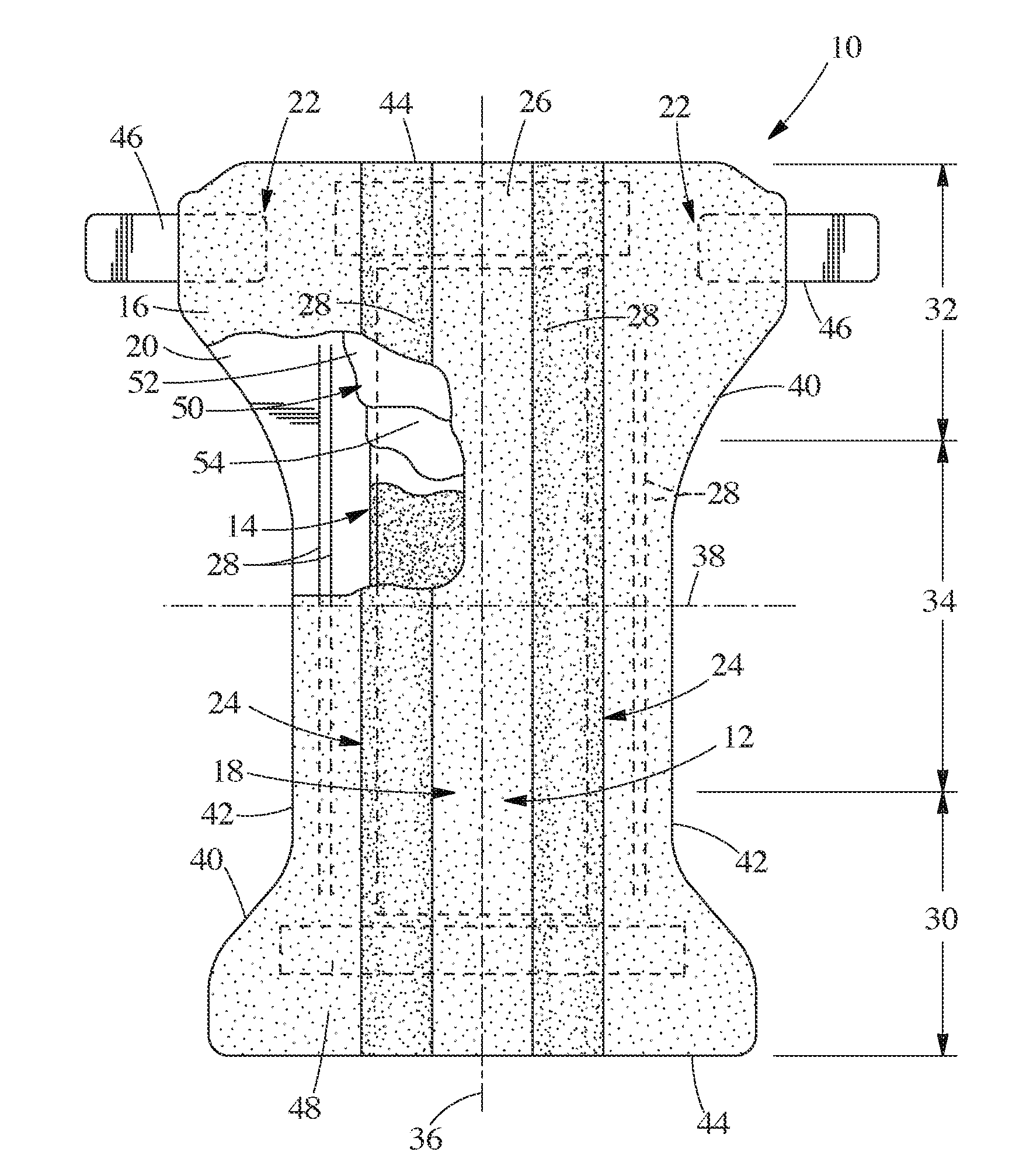
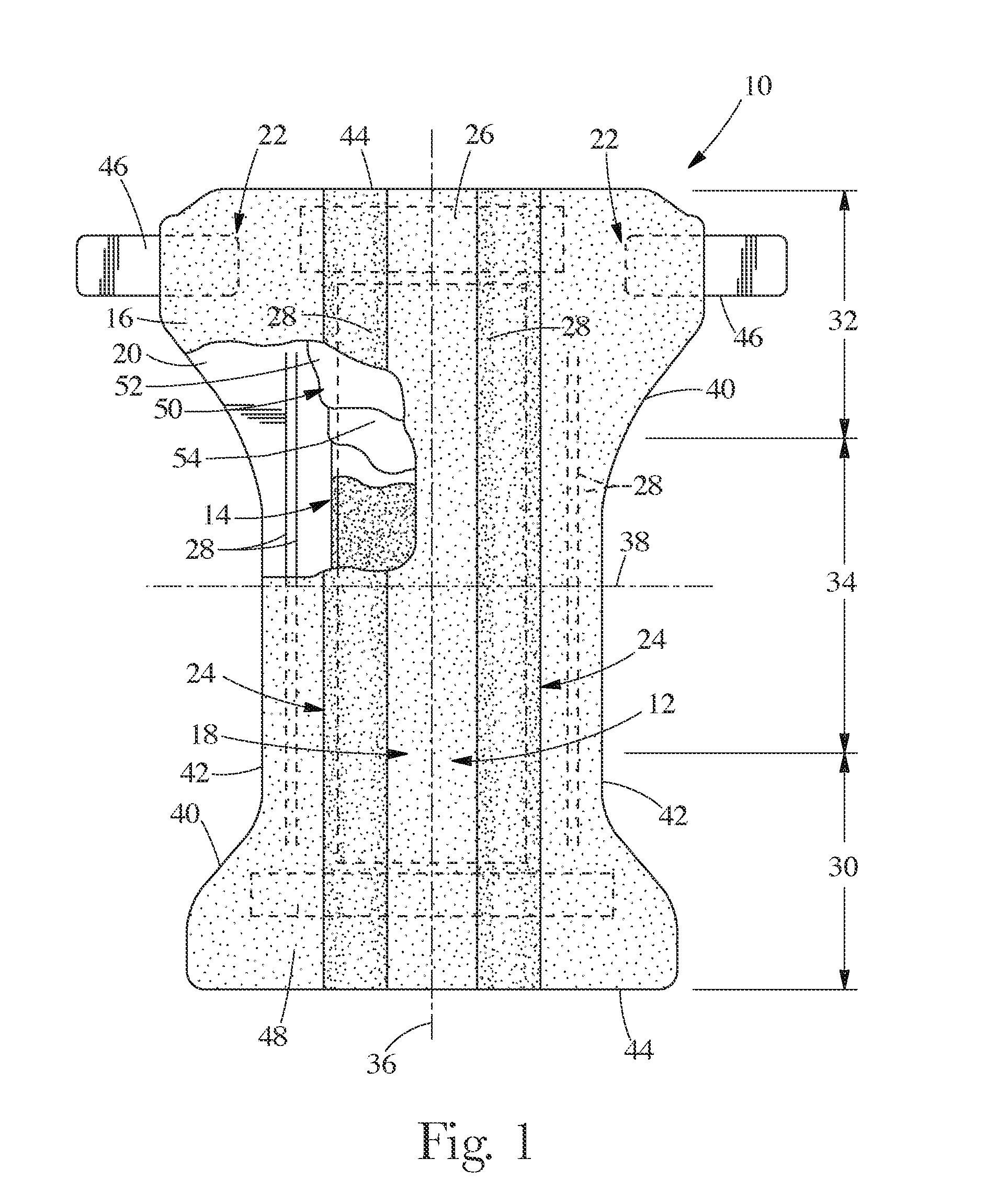
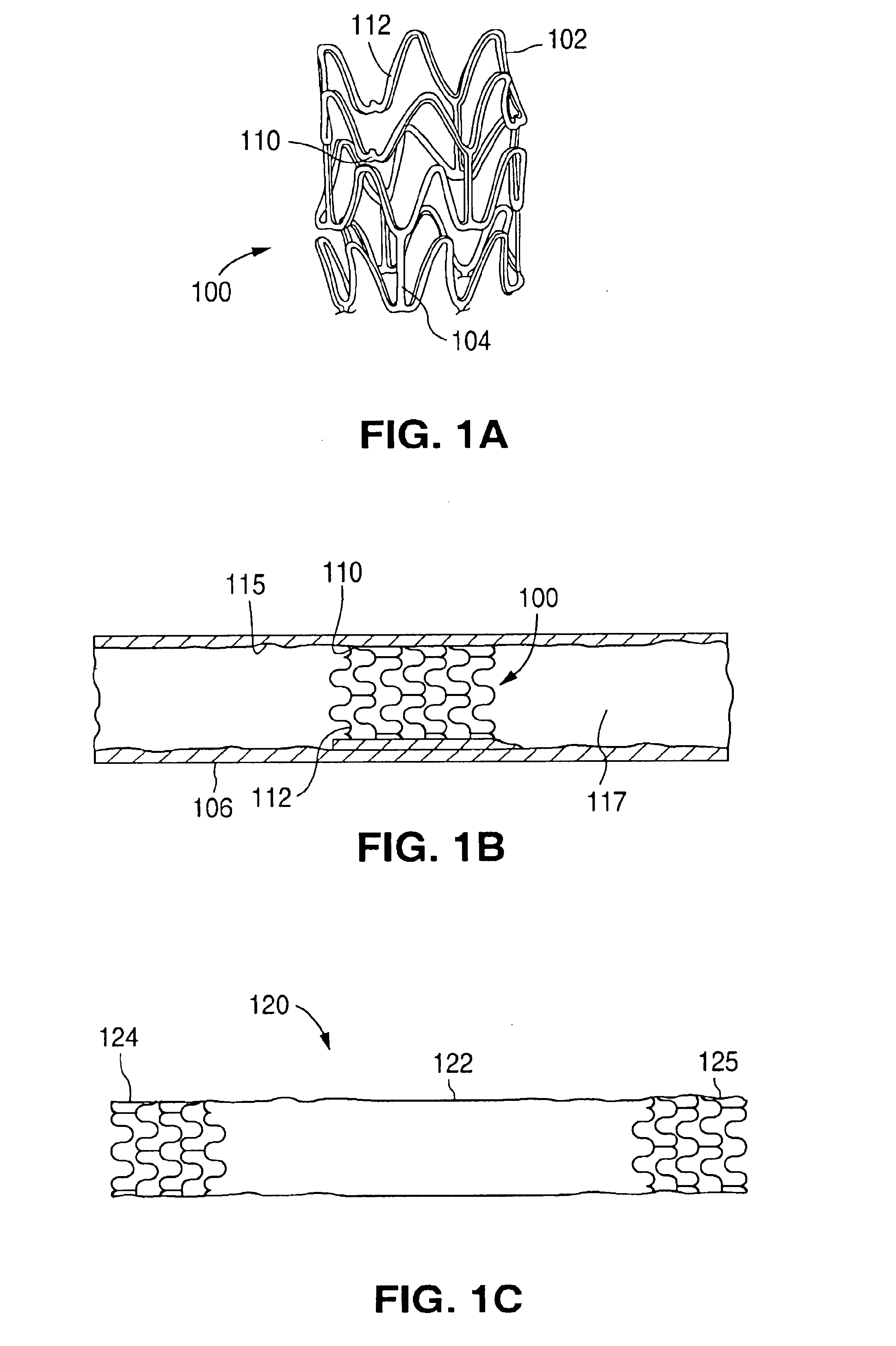
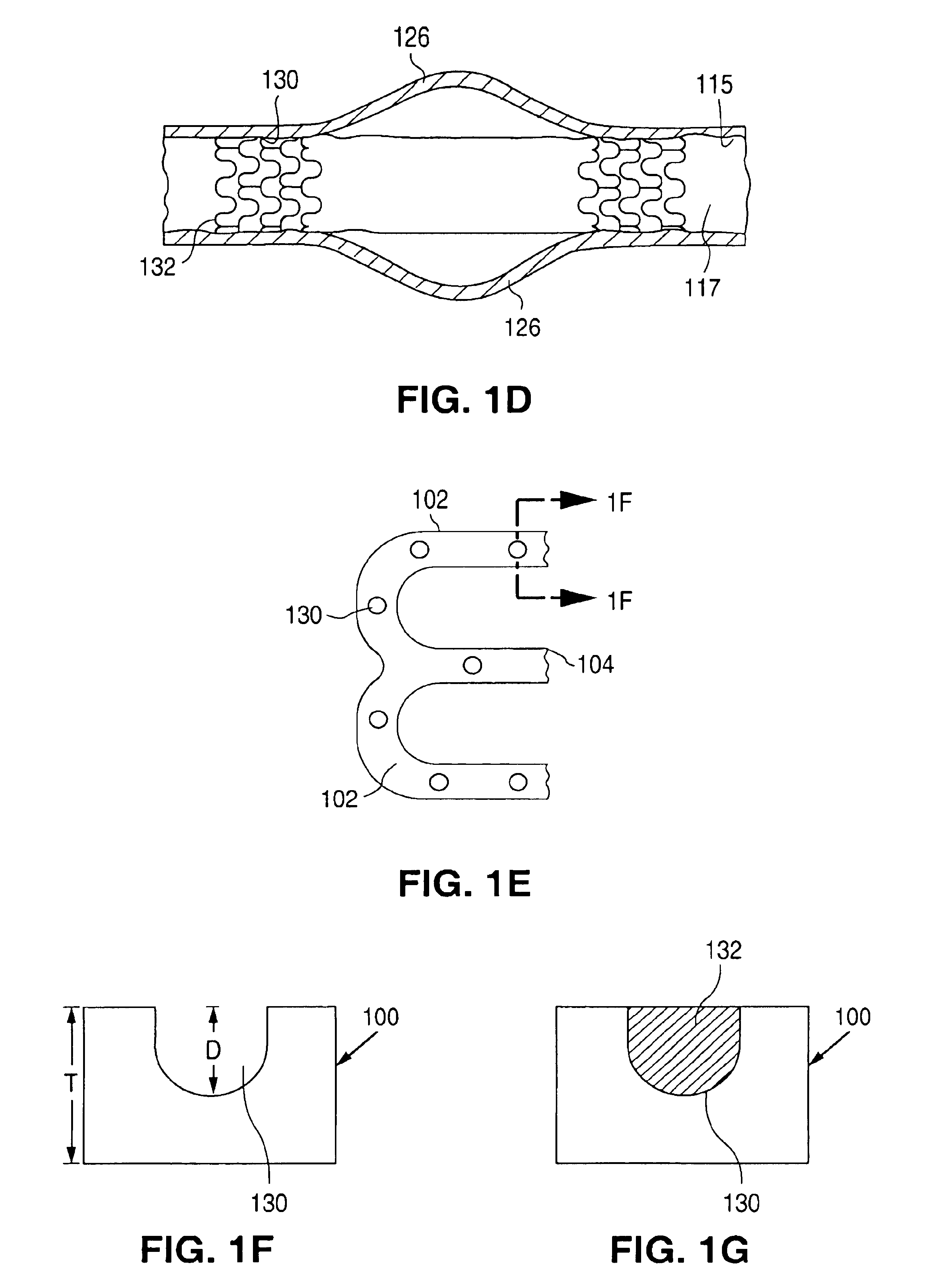
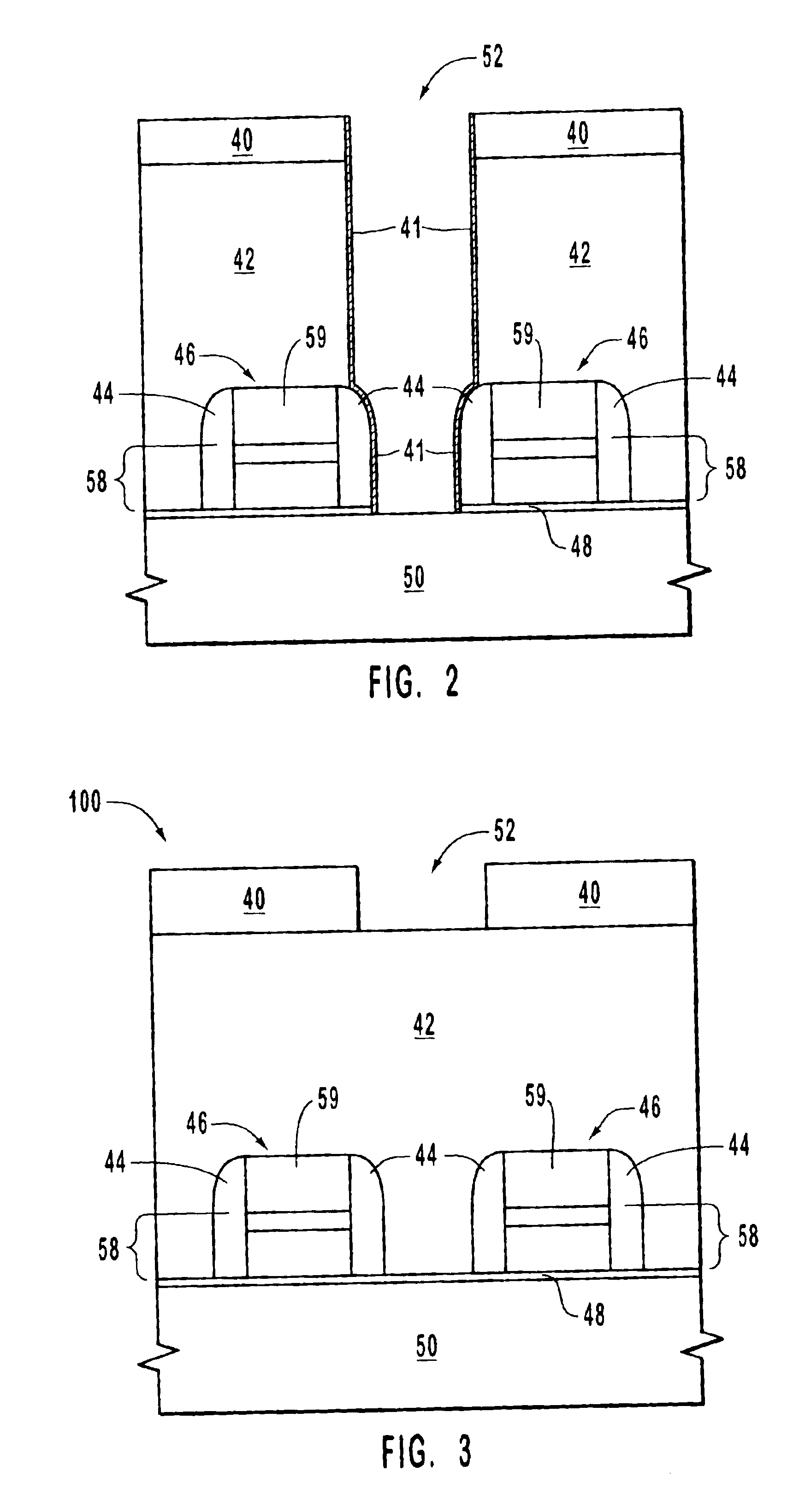
Surface features of an implantable medical device
An implantable medical device, such as a stent or graft, having asperities on a designated region of its outer surface is disclosed. The asperities can serve to improve retention of one or more layers of a coating on the device and to increase the amount of coating that can be carried by the device. The asperities can be formed by using a stream of pressurized grit to roughen the surface. The asperities can also be formed by removing material from the outer surface, for example, by chemical etching with or without a patterned mask. Alternatively, the asperities can be formed by adding material to the outer surface, for example, by welding powder particles to the outer surface or sputtering.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Formation of discontinuous films during an imprint lithography process
ActiveUS6932934B2Low viscosityMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsLithography processLithographic artist
The present invention is directed to methods for patterning a substrate by imprint lithography. An imprint lithography method includes placing a curable liquid on a substrate. A template may be contacted with the curable liquid. Surface forces at the interface of the curable liquid and the template cause the curable liquid to gather in an area defined by a lower surface of the template. Alternately, the curable liquid may fill one or more relatively shallow recesses in the template and the area under the template lower surface. Activating light is applied to the curable liquid to form a patterned layer on the substrate.
Owner:CANON KK
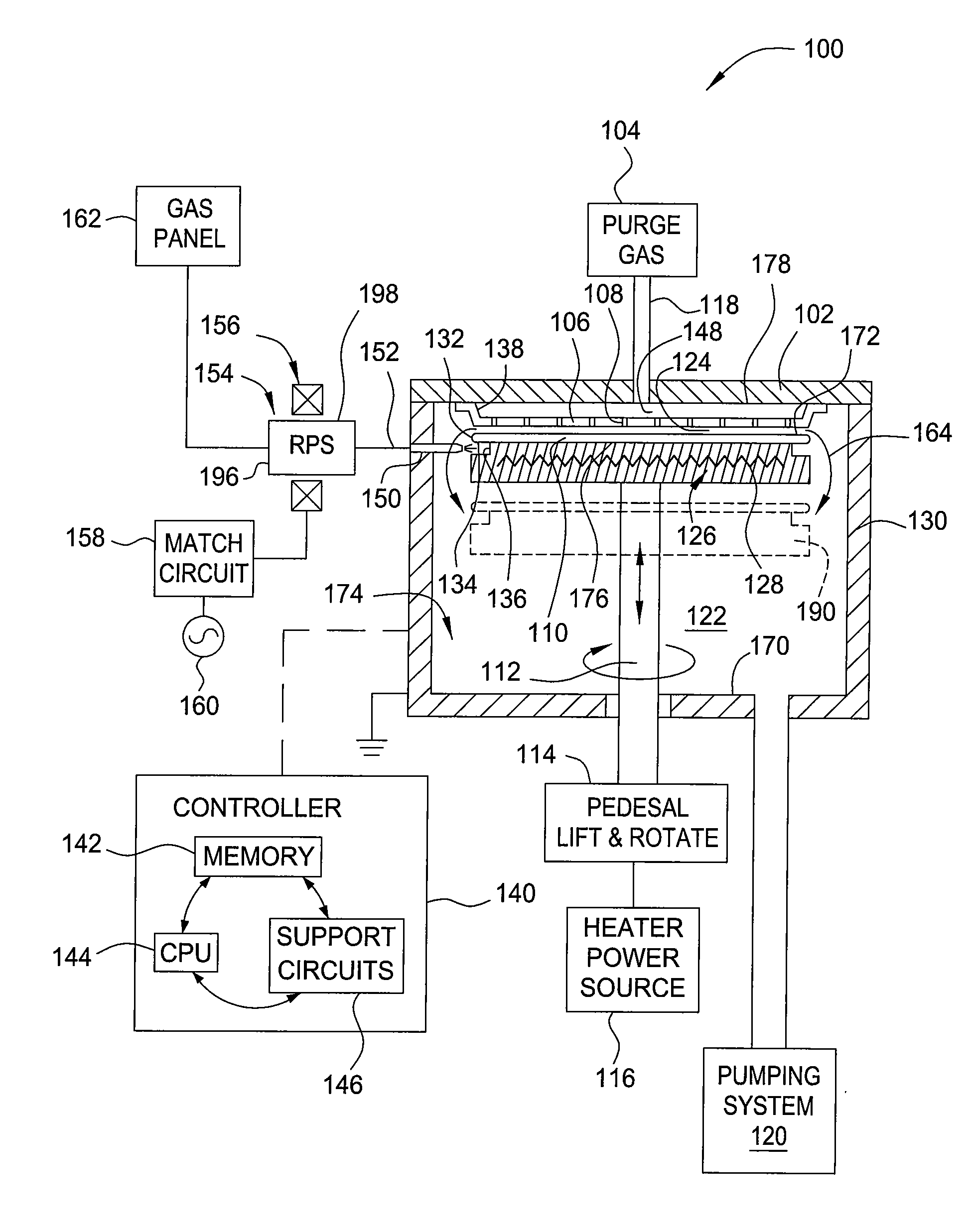
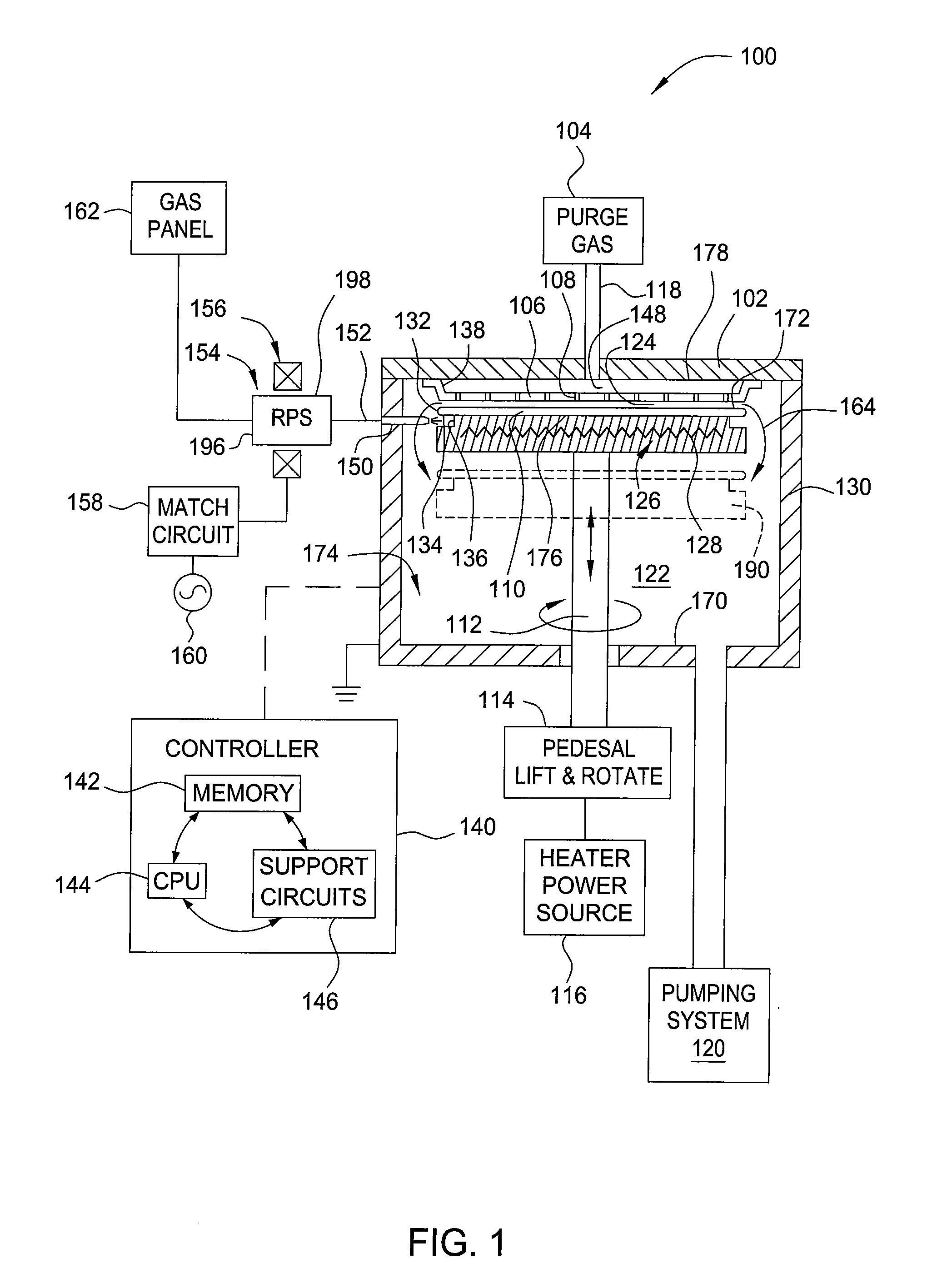
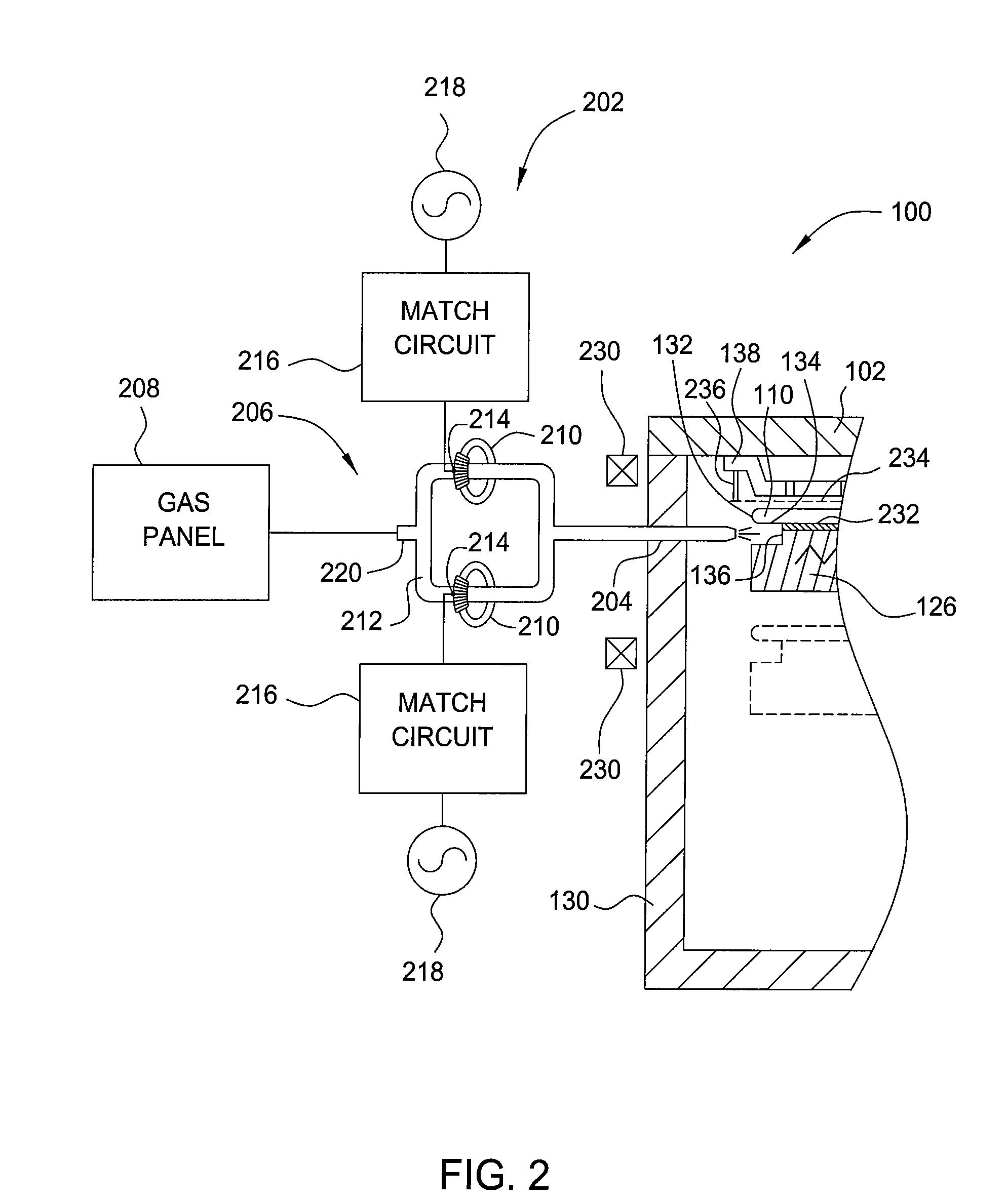
Method and apparatus for removing polymer from a substrate
InactiveUS20090277874A1Reduce in quantityElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsRemote plasmaEngineering
A method and an apparatus for removing polymer from a substrate are provided. In one embodiment, an apparatus utilized to remove polymer from a substrate includes a processing chamber having a chamber wall and a chamber lid defining a process volume, a substrate support assembly disposed in the processing chamber, a remote plasma source coupled to the processing chamber through an outlet port formed through the processing chamber, the outlet port having an opening pointing toward an periphery region of a substrate disposed on the substrate support assembly, and a substrate supporting surface of the substrate support assembly that substantially electrically floats the substrate disposed thereon relative to the substrate support assembly.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
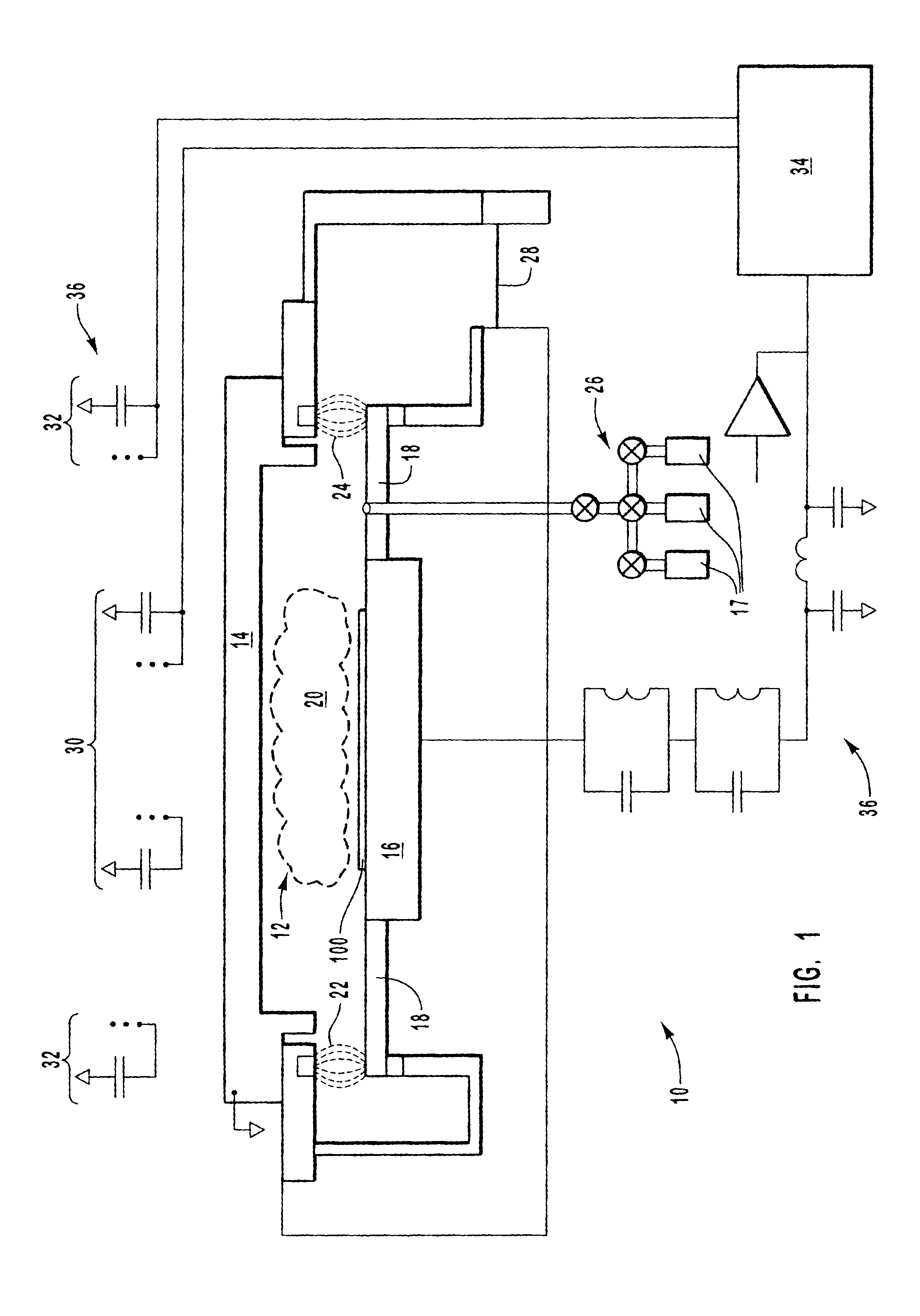
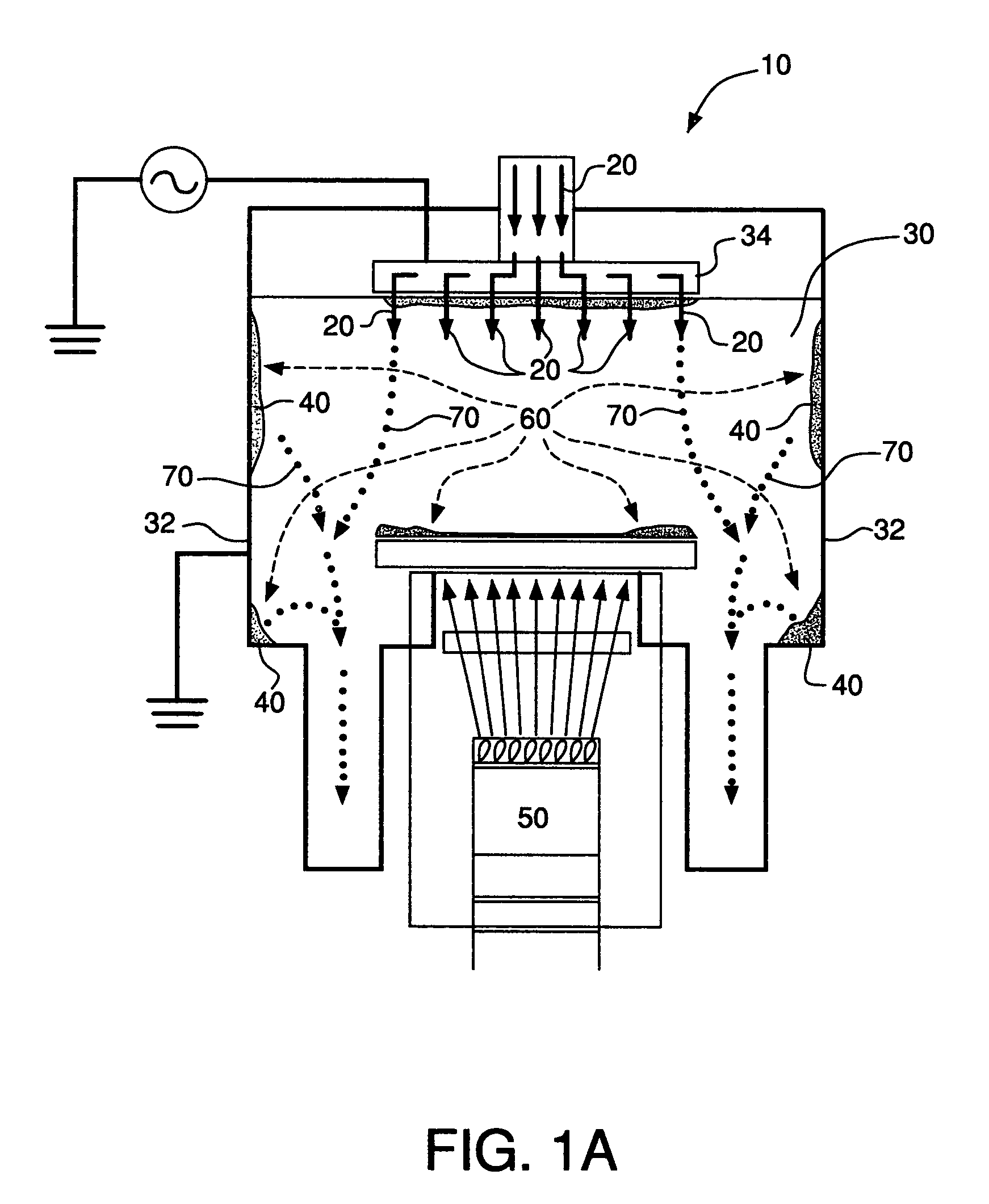
Plasma reactor apparatus with multiple gas injection zones having time-changing separate configurable gas compositions for each zone
ActiveUS8231799B2Electric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsGas compositionEngineering
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Plasma source design
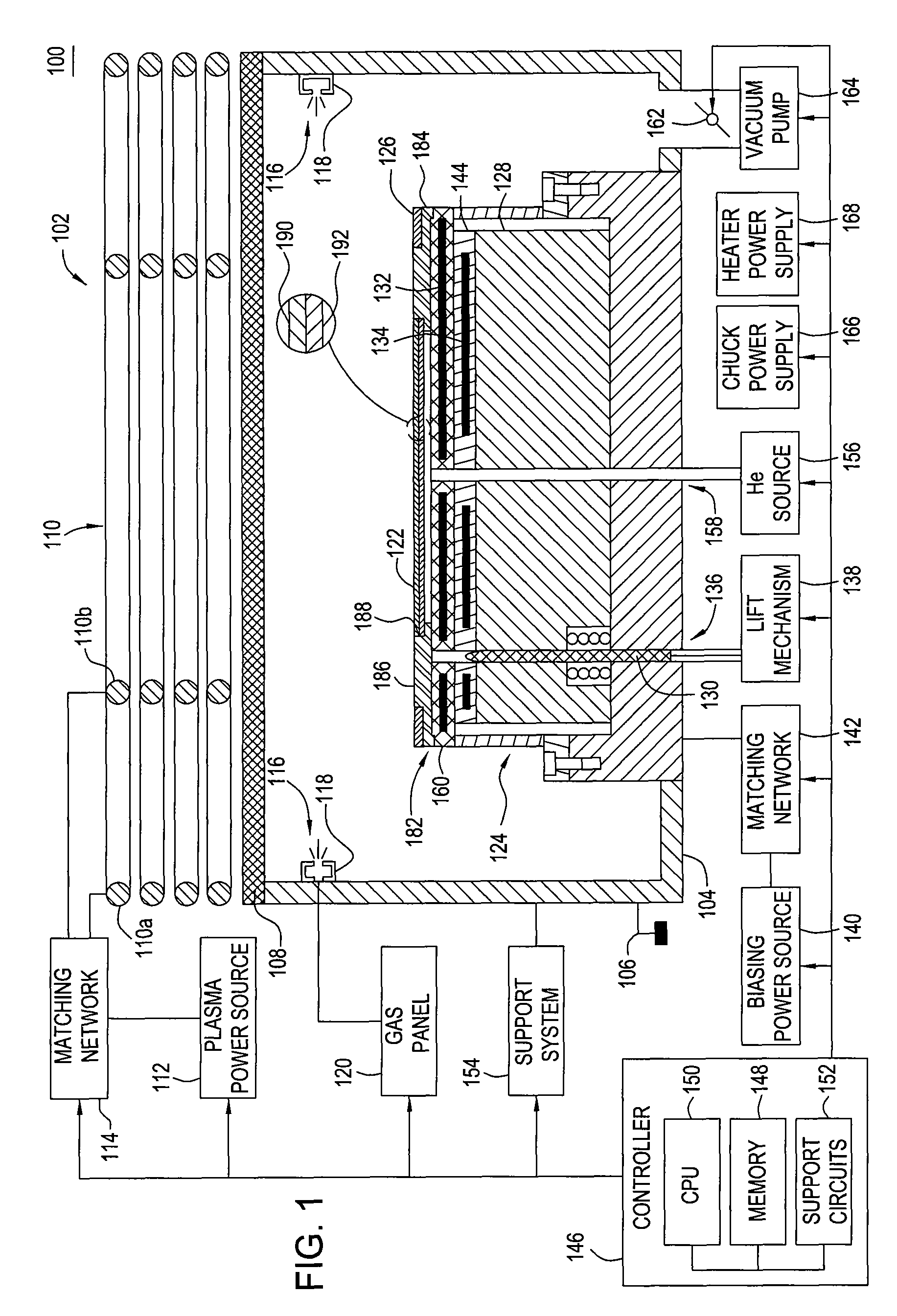
Embodiments of the present invention generally provide a plasma source apparatus, and method of using the same, that is able to generate radicals and / or gas ions in a plasma generation region that is symmetrically positioned around a magnetic core element by use of an electromagnetic energy source. In general, the orientation and shape of the plasma generation region and magnetic core allows for the effective and uniform coupling of the delivered electromagnetic energy to a gas disposed in the plasma generation region. In general, the improved characteristics of the plasma formed in the plasma generation region is able to improve deposition, etching and / or cleaning processes performed on a substrate or a portion of a processing chamber that is disposed downstream of the plasma generation region.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
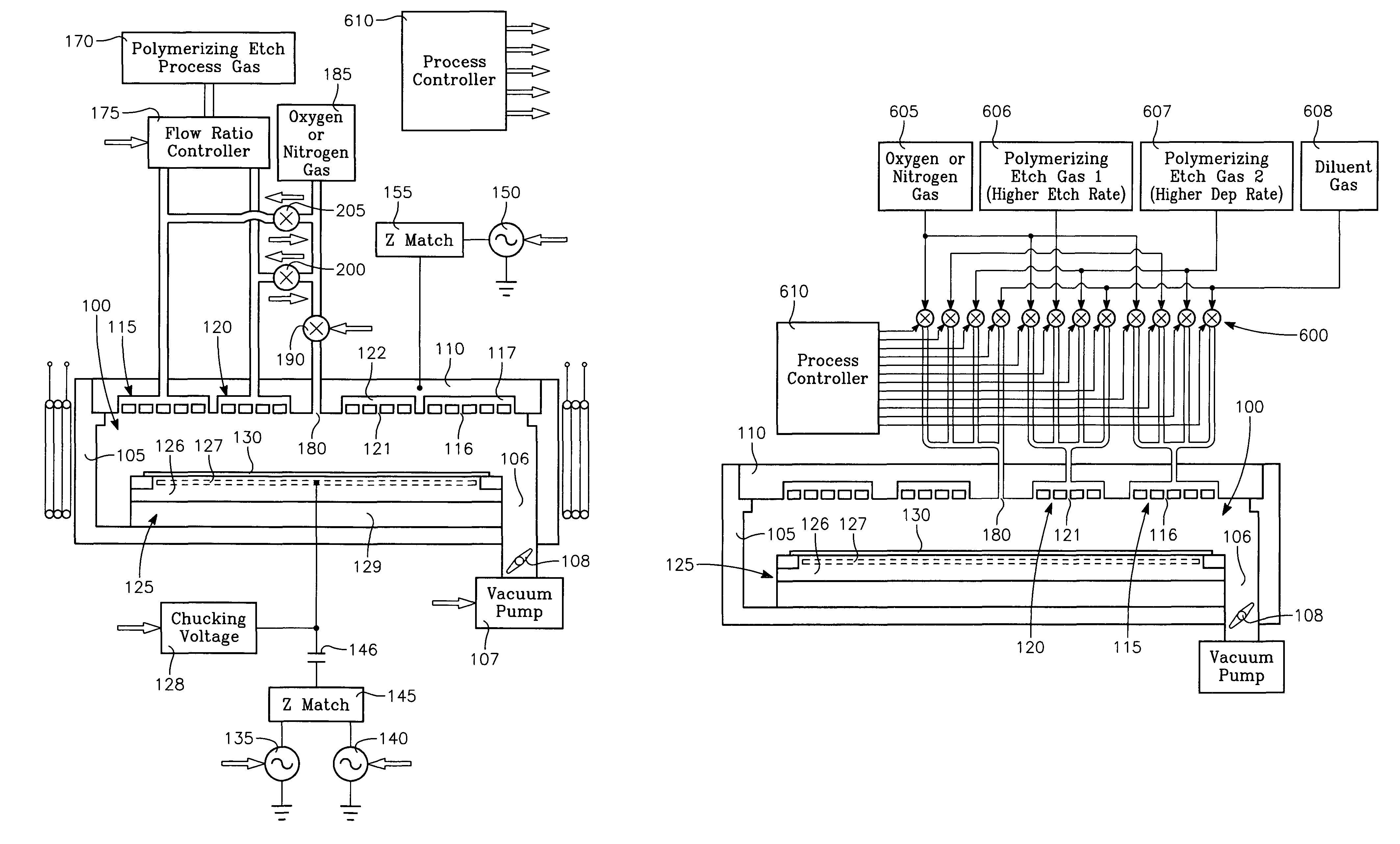
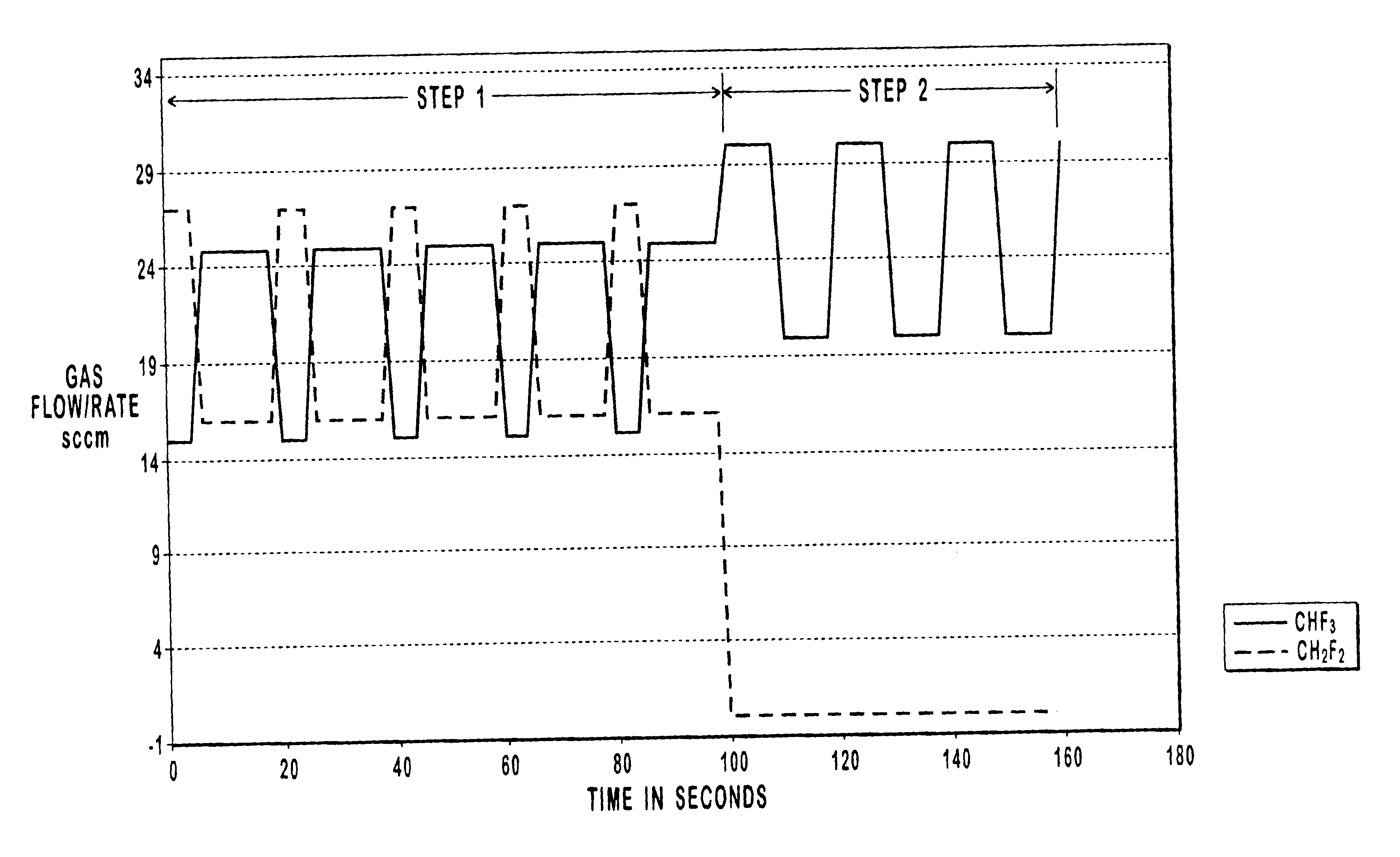
Gas pulsing for etch profile control
InactiveUS6784108B1Increase flow rateReduce flow rateElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsEngineeringAnisotropic etching
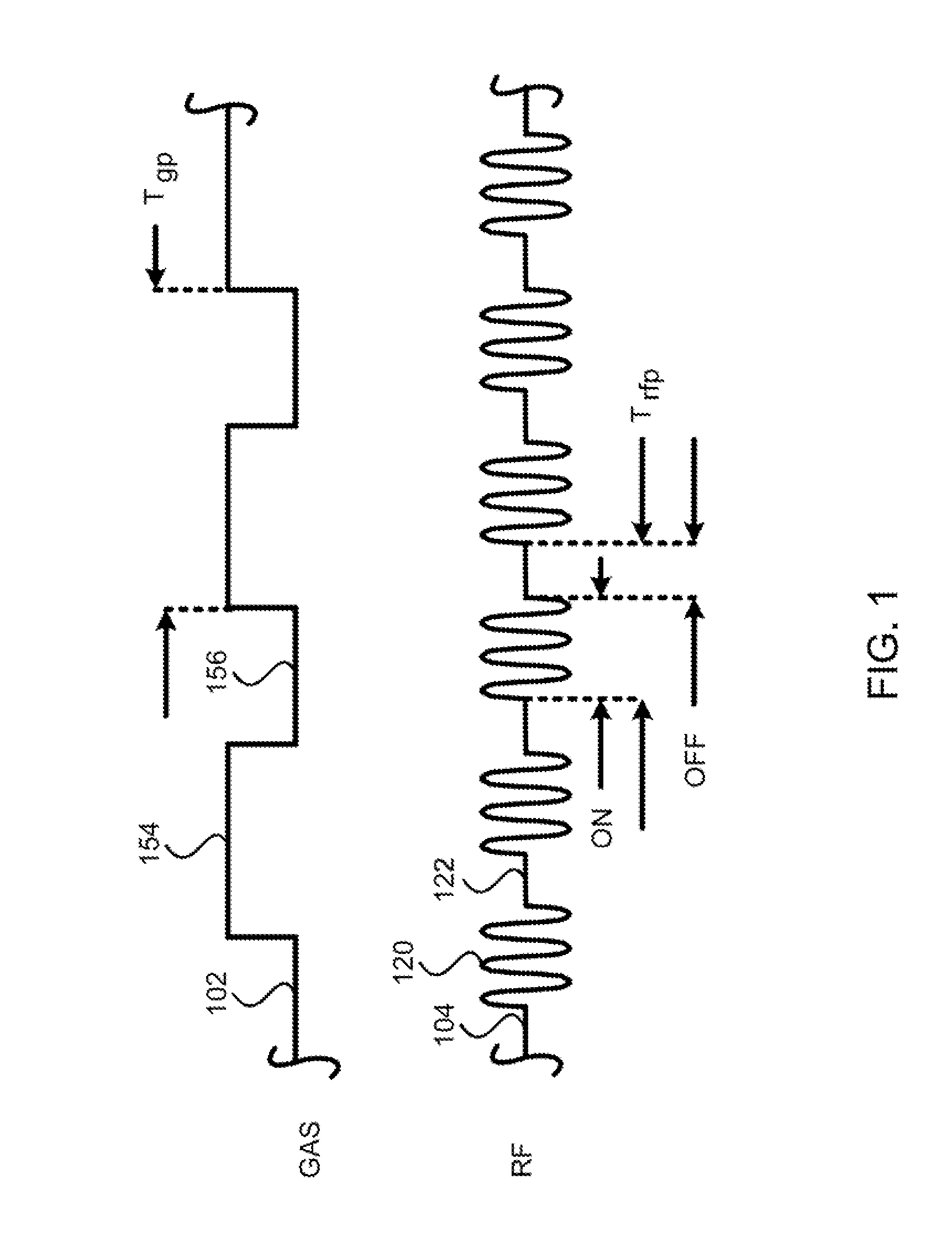
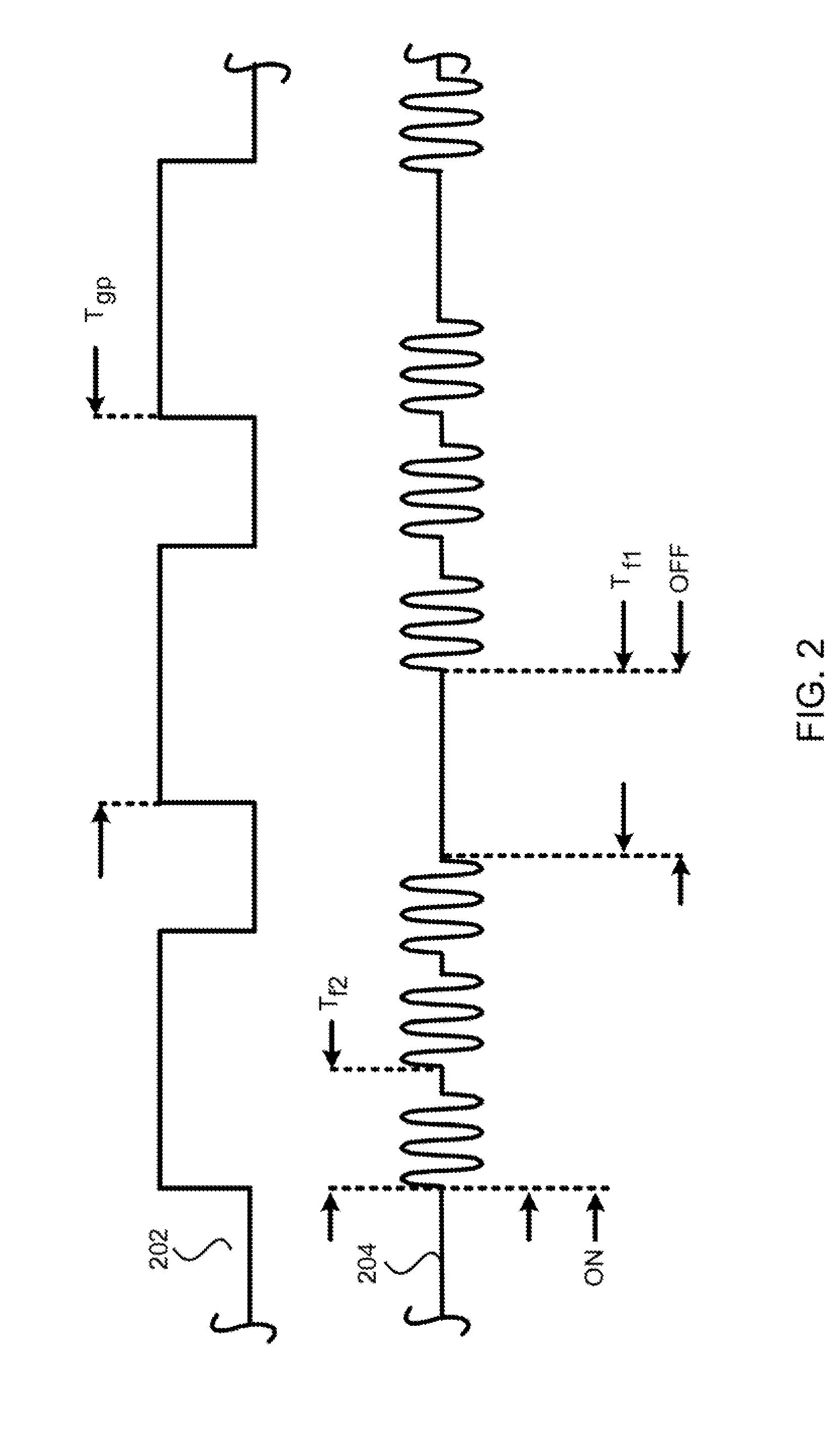
Etch profile control with pulsed gas flow and its applications to etching such as anisotropic etching of high aspect ratio features and etching of self-aligned contact structures in various processes. Pulsing can be applied according to this invention to the flow rate of a gas such as an etchant gas, a gas that leads to the deposition of a protective layer, a gas that modifies the deposition of a protective layer, and a gas that modifies etching.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Gate linewidth tailoring and critical dimension control for sub-100 nm devices using plasma etching
InactiveUS6864041B2Tight tolerance variationMinimal variationVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsDecorative surface effectsImage resolutionLine width
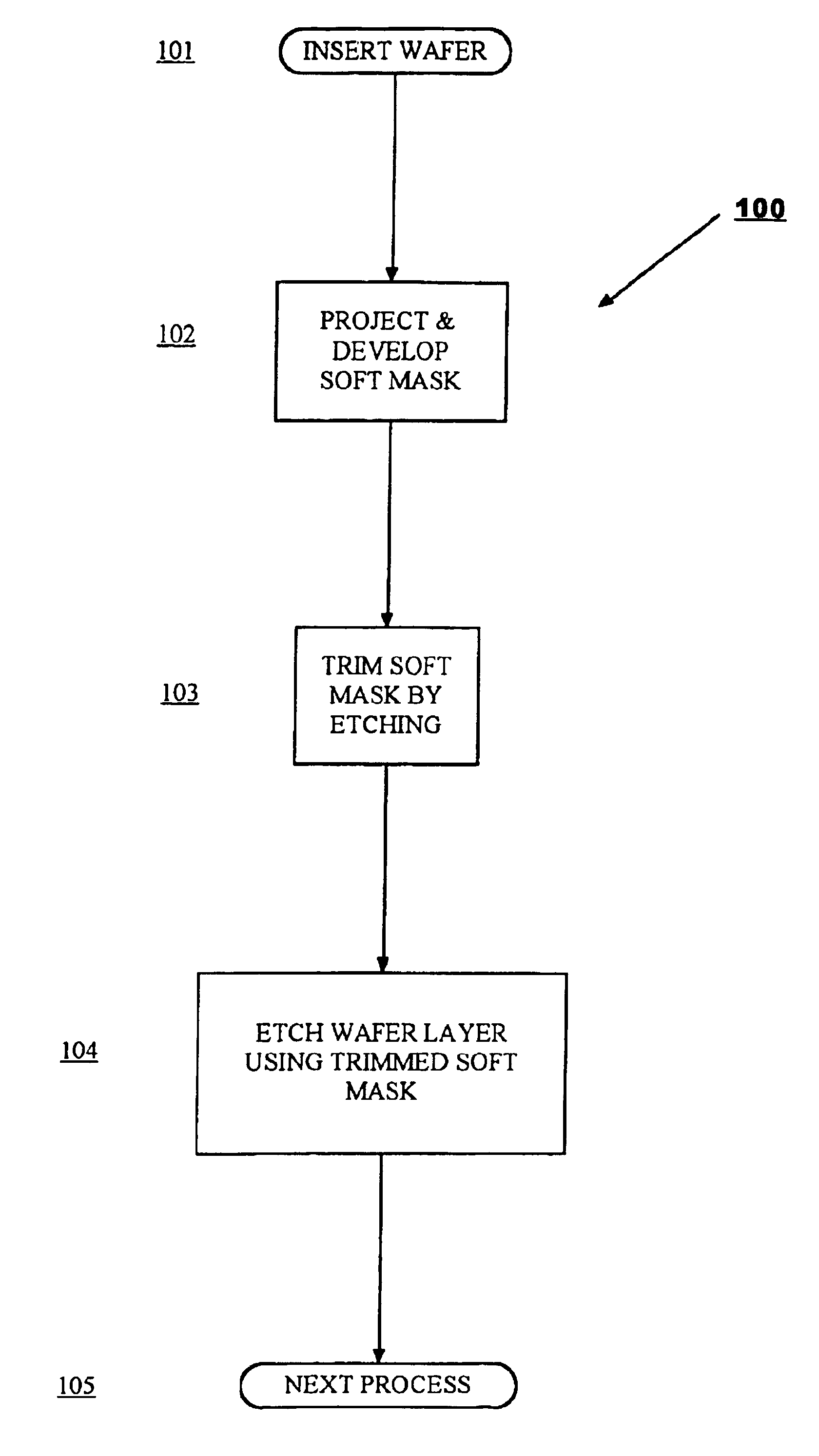
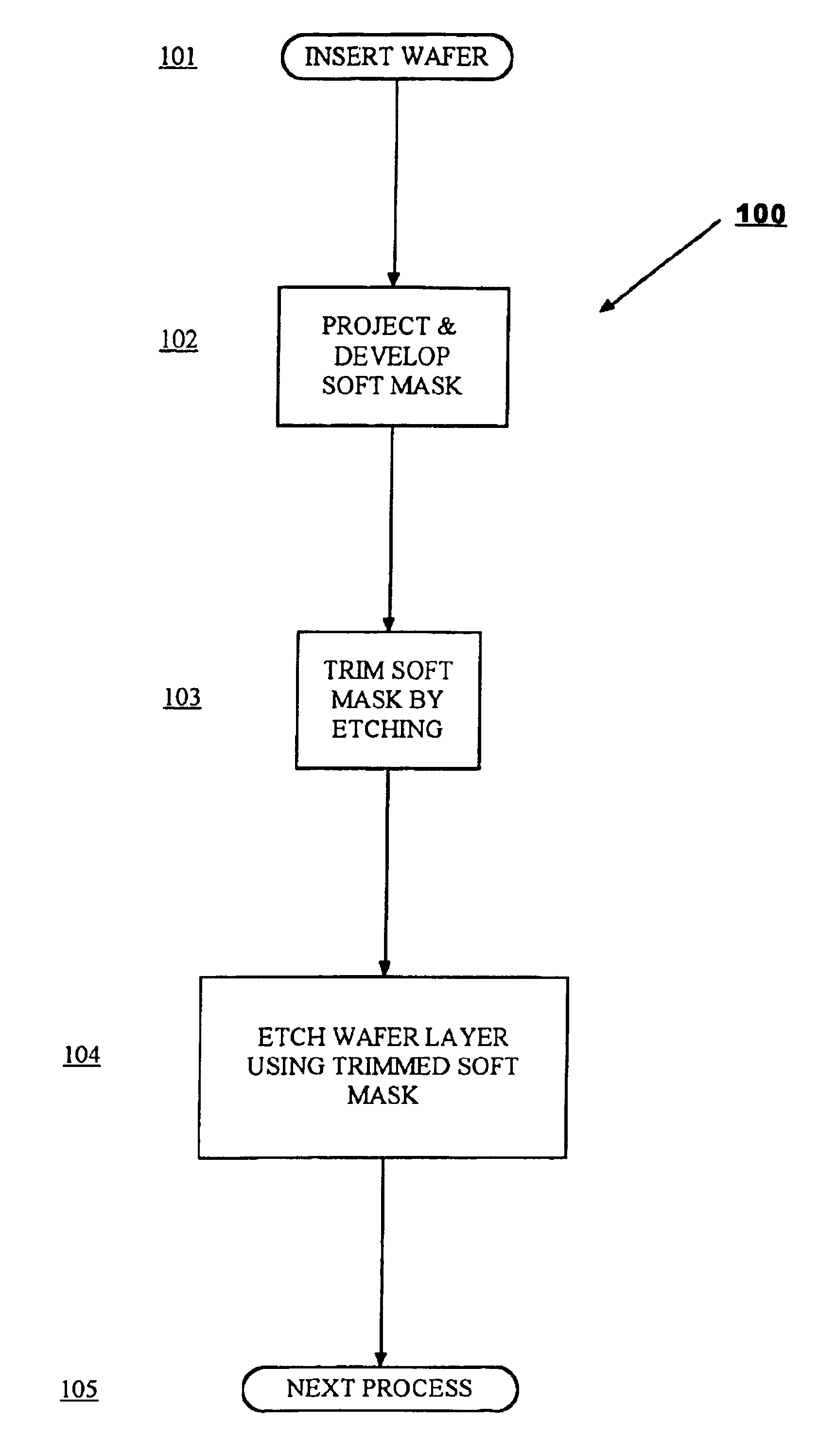
A method of fabricating an electronic chip on a wafer in which a first mask at a predetermined lower resolution is developed on the wafer and then etched under a first set of conditions for a predetermined period to achieve a mask that is below the resolution limit of current lithography. The etched mask is then used as a hard mask for etching material on a lower layer.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Mixed mode pulsing etching in plasma processing systems
A method for processing substrate in a chamber, which has at least one plasma generating source, a reactive gas source for providing reactive gas into the interior region of the chamber, and a non-reactive gas source for providing non-reactive gas into the interior region, is provided. The method includes performing a mixed-mode pulsing (MMP) preparation phase, including flowing reactive gas into the interior region and forming a first plasma to process the substrate that is disposed on a work piece holder. The method further includes performing a MMP reactive phase, including flowing at least non-reactive gas into the interior region, and forming a second plasma to process the substrate, the second plasma is formed with a reactive gas flow during the MMP reactive phase that is less than a reactive gas flow during the MMP preparation phase. Perform the method steps a plurality of times.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Polymer solution for nanoimprint lithography to reduce imprint temperature and pressure
InactiveUS20040110856A1Reduce pressureReduce the temperatureNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsCross-linkVitrification
A method of forming features on substrates by imprinting is provided. The method comprises: (a) forming a polymer solution comprising at least one polymer dissolved in at least one polymerizable monomer; and (b) depositing the polymer solution on a substrate to form a liquid film thereon; and then either: (c) curing the liquid film by causing the monomer(s) to polymerize and optionally cross-linking the polymer(s) to thereby form a polymer film, the polymer film having a glass transition temperature (Tg); and imprinting the polymer film with a mold having a desired pattern to form a corresponding negative pattern in the polymer film, or (d) imprinting the liquid film with the mold and curing it to form the polymer film. The temperature of imprinting is as little as 10° C. above the Tg, or even less if the film is in the liquid state. The pressure of the imprinting can be within the range of 100 to 500 psi.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
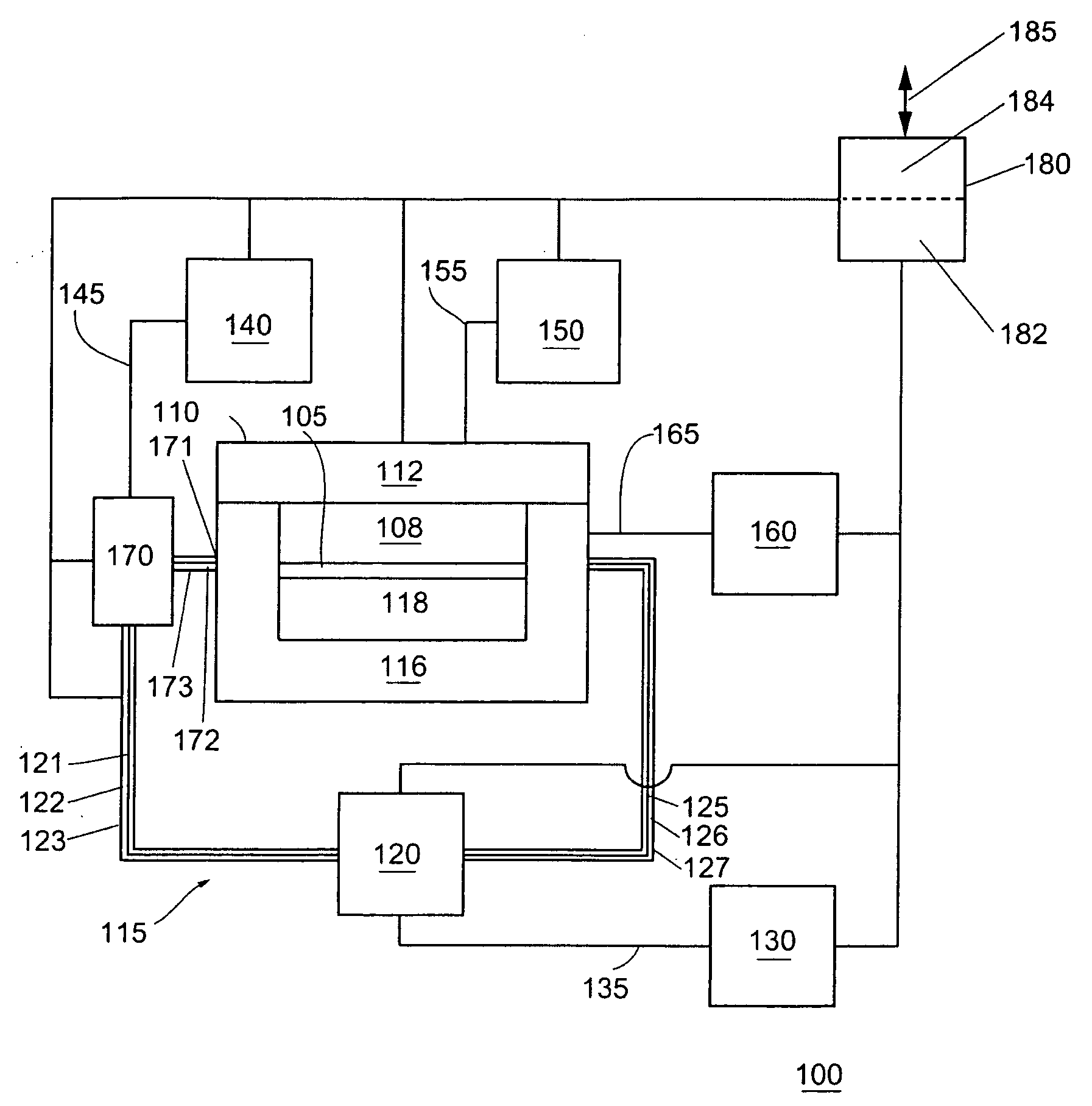
Method for etching high dielectric constant materials and for cleaning deposition chambers for high dielectric constant materials
A process for the removal of a substance from a substrate for etching and / or cleaning applications is disclosed herein. In one embodiment, there is provided a process for removing a substance having a dielectric constant greater than silicon dioxide from a substrate by reacting the substance with a reactive agent that comprises at least one member from the group consisting a halogen-containing compound, a boron-containing compound, a hydrogen-containing compound, nitrogen-containing compound, a chelating compound, a carbon-containing compound, a chlorosilane, a hydrochlorosilane, or an organochlorosilane to form a volatile product and removing the volatile product from the substrate to thereby remove the substance from the substrate.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Phase change based heating element system and method
InactiveUS20060226117A1Avoid overall overheatingVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsDecorative surface effectsTemperature controlProcess engineering
A method of and apparatus for regulating carbon dioxide using a pre-injection assembly coupled to a processing chamber operating at a supercritical state is disclosed. The method and apparatus utilize a source for providing supercritical carbon dioxide to the pre-injection assembly and a temperature control element for maintaining the pre-injection region at a supercritical temperature and pressure.
Owner:SUPERCRITICAL SYSEMS
Method of fabrication of a microstructure having an internal cavity
InactiveUS6297072B1Easy to manufactureImprove air tightnessAcceleration measurement using interia forcesDecorative surface effectsInternal cavityMicrostructure
A method of fabricating a microstructure having an inside cavity. The method includes depositing a first layer or a first stack of layers in a substantially closed geometric configuration on a first substrate. Then, performing an indent on the first layer or on the top layer of said first stack of layers. Then, depositing a second layer or a second stack of layers substantially with said substantially closed geometric configuration on a second substrate. Then, aligning and bonding said first substrate on said second substrate such that a microstructure having a cavity is formed according to said closed geometry configuration.
Owner:CP CLARE +1
Method of forming MEMS device
InactiveUS6861277B1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive materialsOptoelectronics
A method of forming a MEMS device includes depositing a conductive material on a substructure, forming a first sacrificial layer over the conductive material, including forming a substantially planar surface of the first sacrificial layer, and forming a first element over the substantially planar surface of the first sacrificial layer, including communicating the first element with the conductive material through the first sacrificial layer. In addition, the method includes forming a second sacrificial layer over the first element, including forming a substantially planar surface of the second sacrificial layer, forming a support through the second sacrificial layer to the first element after forming the second sacrificial layer, including filling the support, and forming a second element over the support and the substantially planar surface of the second sacrificial layer. As such, the method further includes substantially removing the first sacrificial layer and the second sacrificial layer, thereby supporting the second element relative to the first element with the support.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
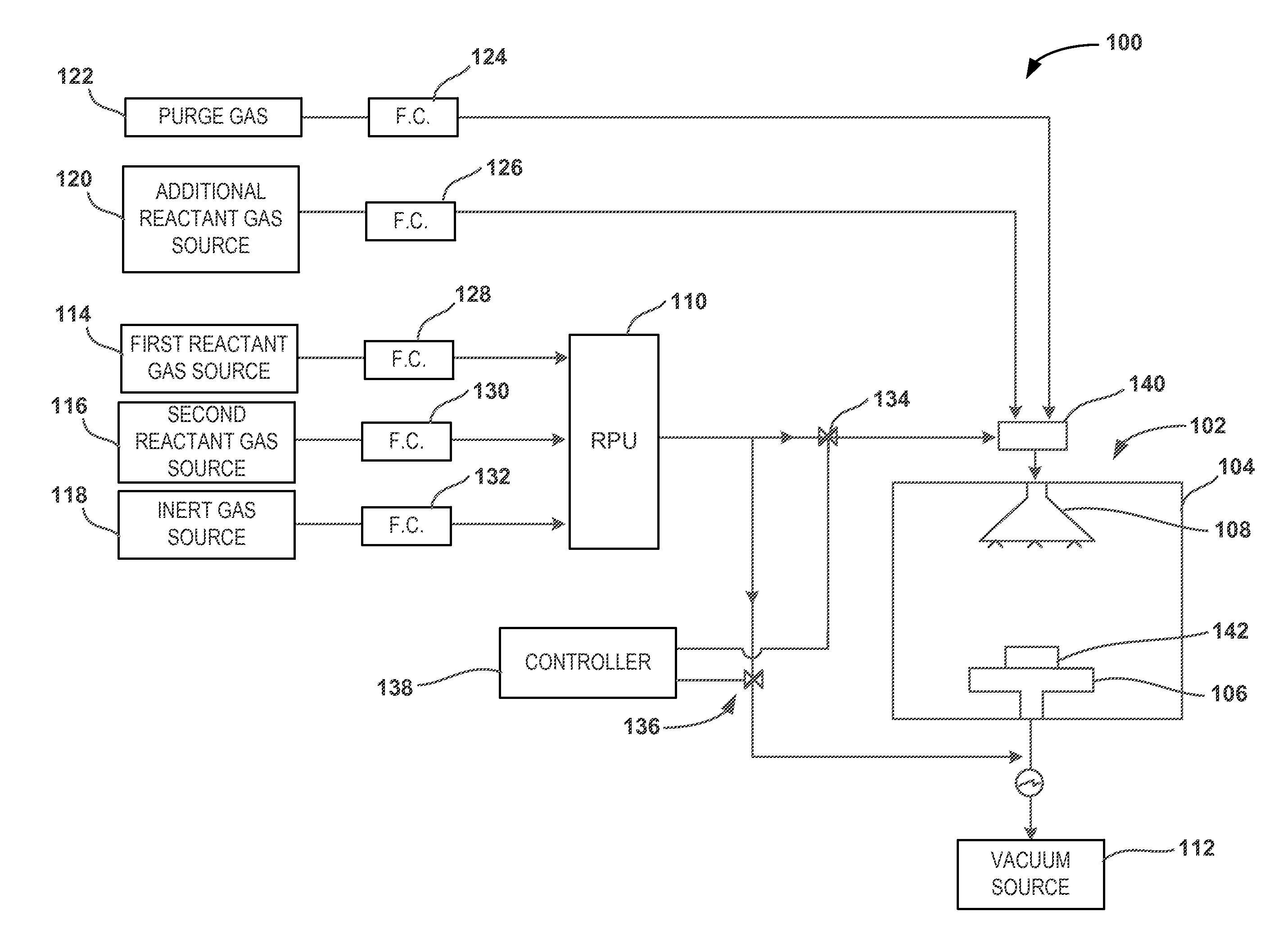
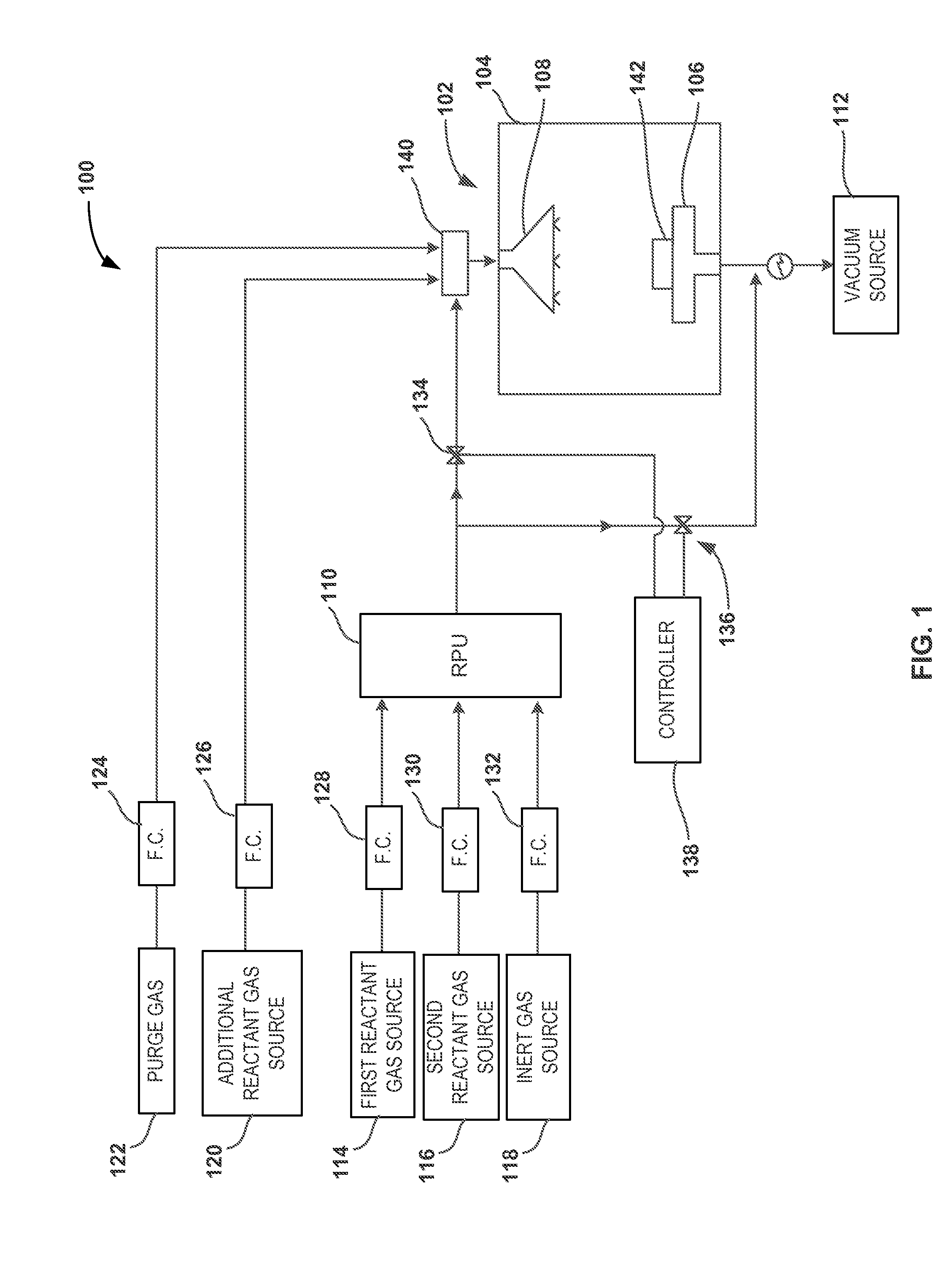
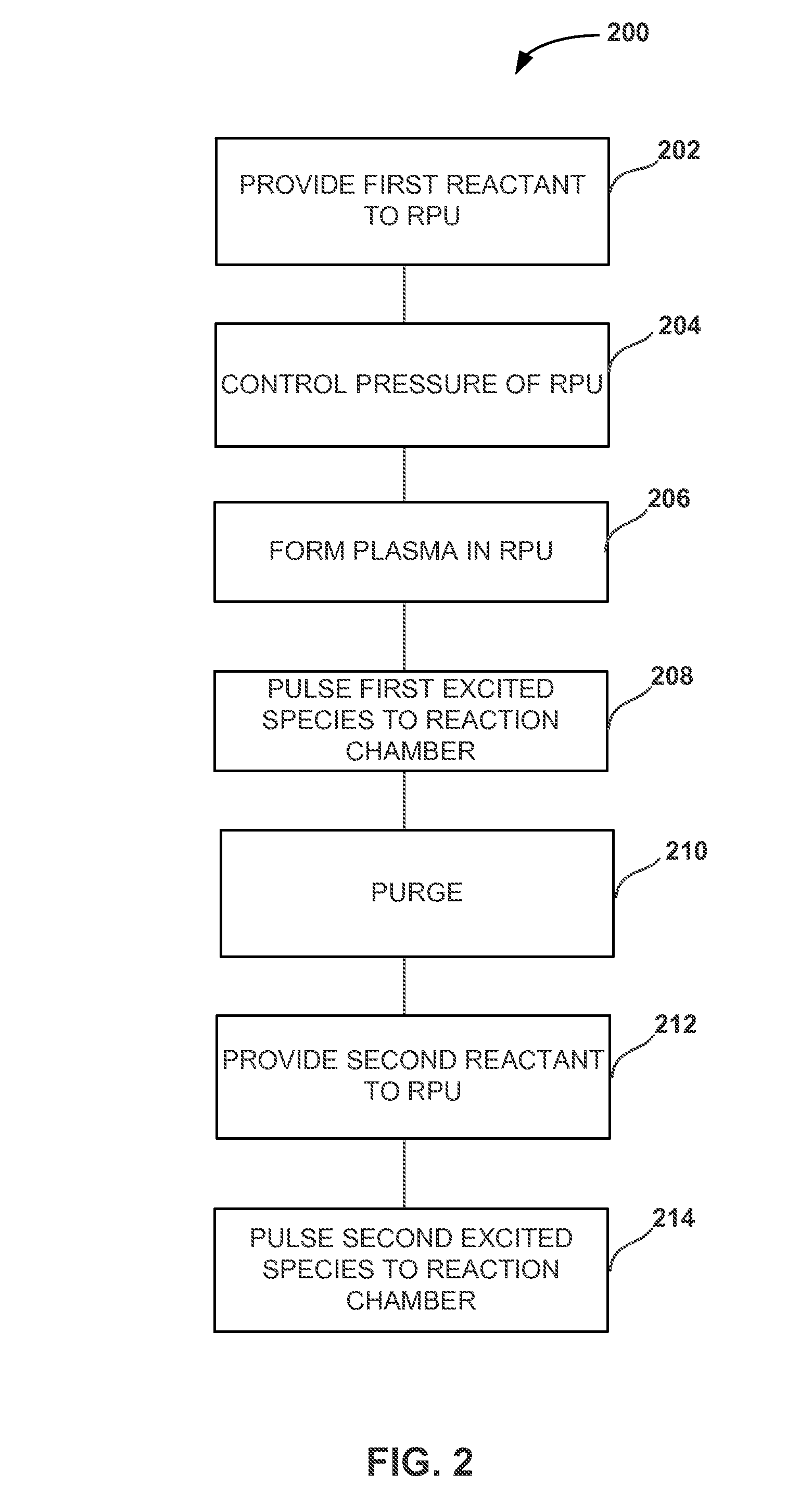
Pulsed remote plasma method and system
ActiveUS20140251954A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaEngineering
A system and method for providing pulsed excited species from a remote plasma unit to a reaction chamber are disclosed. The system includes a pressure control device to control a pressure at the remote plasma unit as reactive species from the remote plasma unit are pulsed to the reaction chamber.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Step and repeat imprint lithography processes
The present invention is directed to methods for patterning a substrate by imprint lithography. Imprint lithography is a process in which a liquid is dispensed onto a substrate. A template is brought into contact with the liquid and the liquid is cured. The cured liquid includes an imprint of any patterns formed in the template. In one embodiment, the imprint process is designed to imprint only a portion of the substrate. The remainder of the substrate is imprinted by moving the template to a different portion of the template and repeating the imprint lithography process.
Owner:CANON KK
Etching of nano-imprint templates using an etch reactor
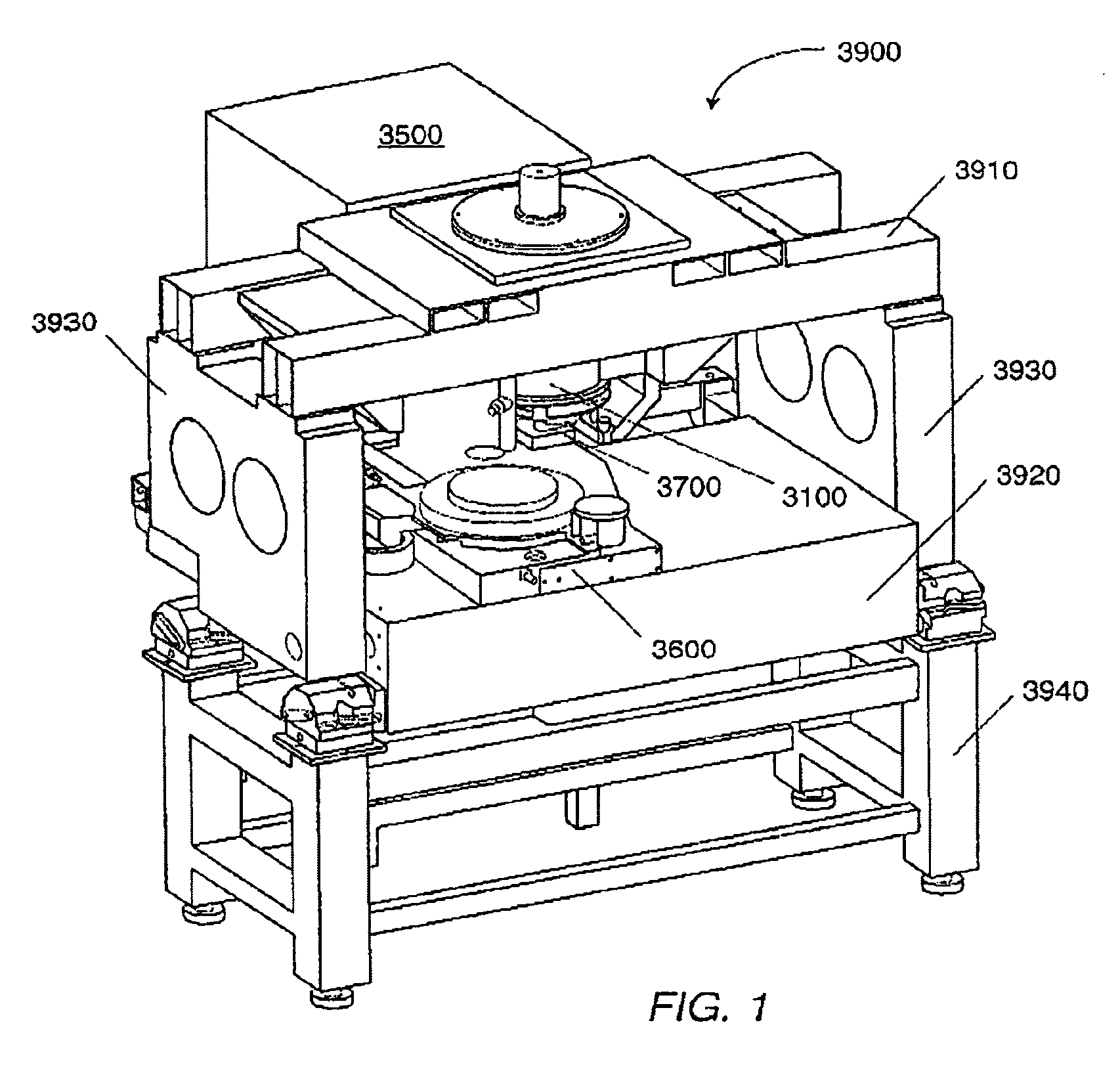
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com