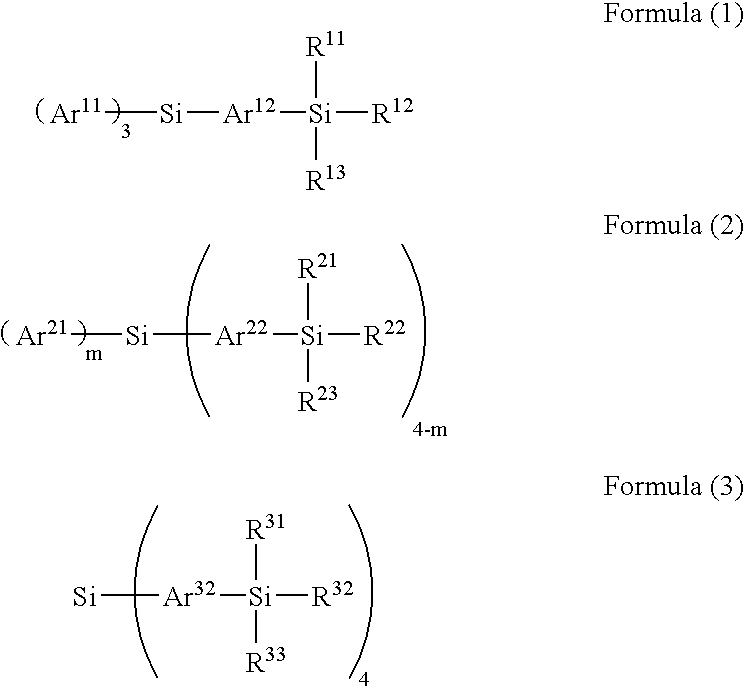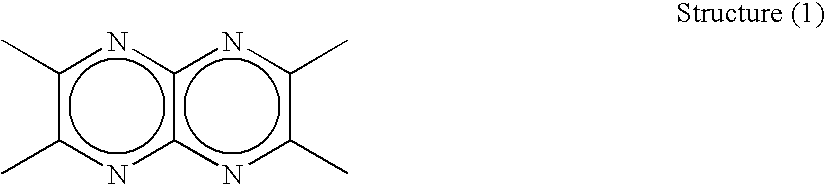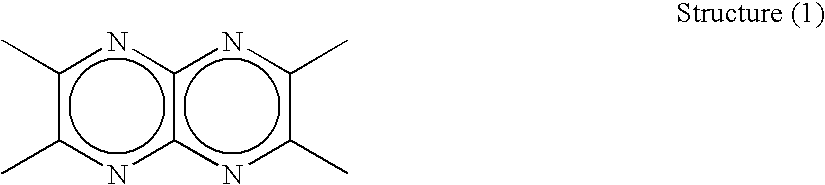Patents
Literature
15415 results about "Molecular physics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Molecular physics is the study of the physical properties of molecules, the chemical bonds between atoms as well as the molecular dynamics. Its most important experimental techniques are the various types of spectroscopy; scattering is also used. The field is closely related to atomic physics and overlaps greatly with theoretical chemistry, physical chemistry and chemical physics.
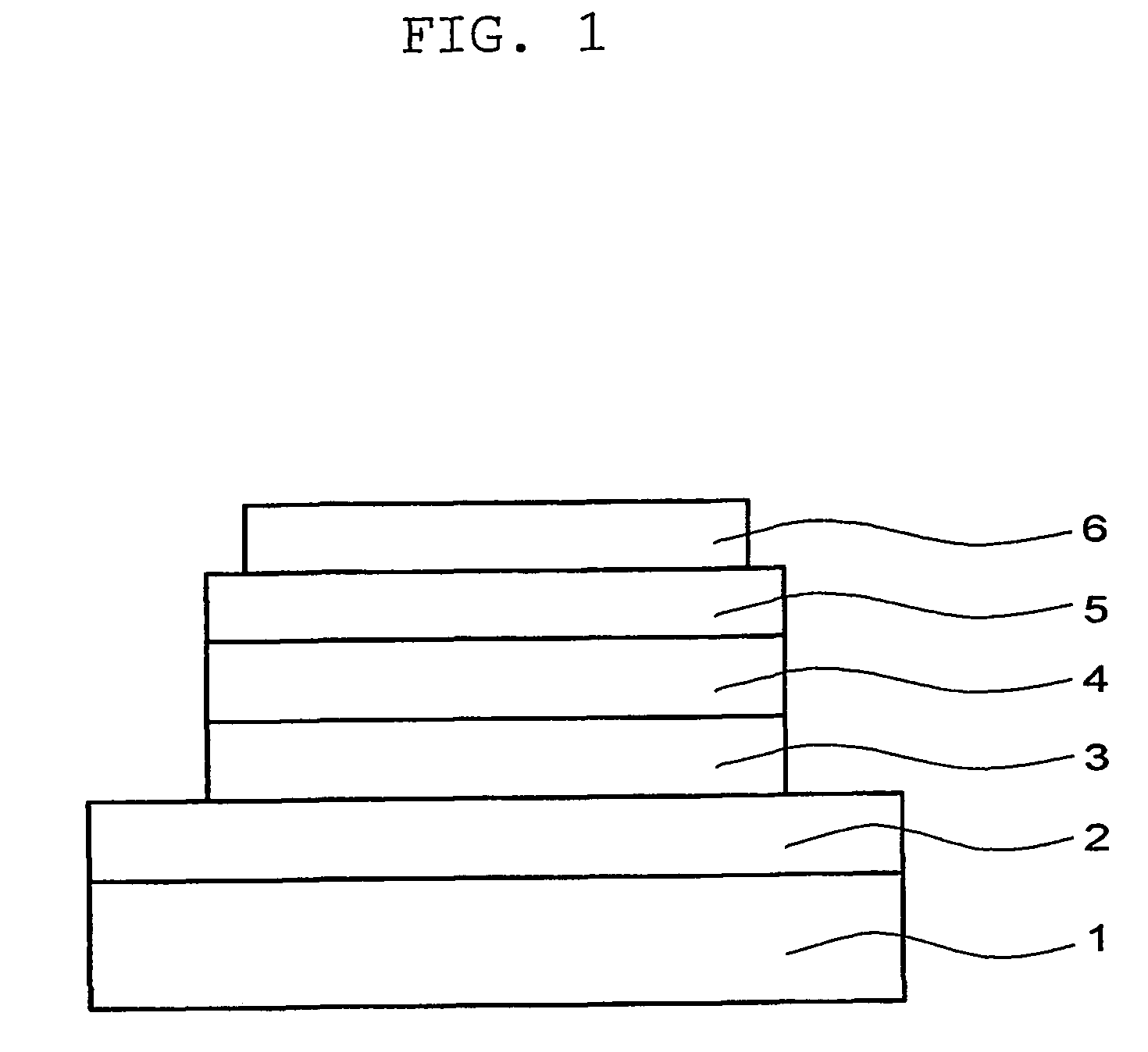
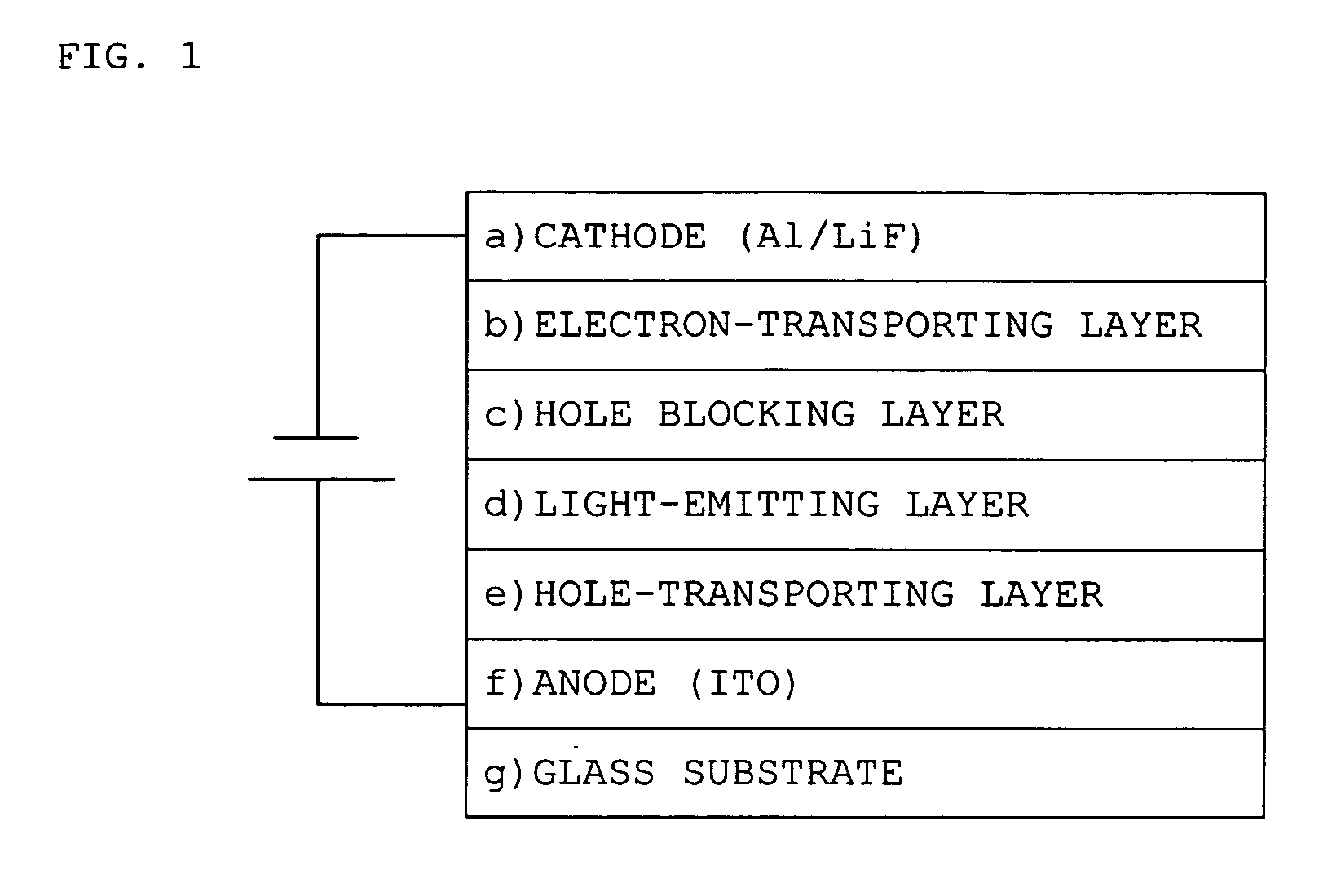
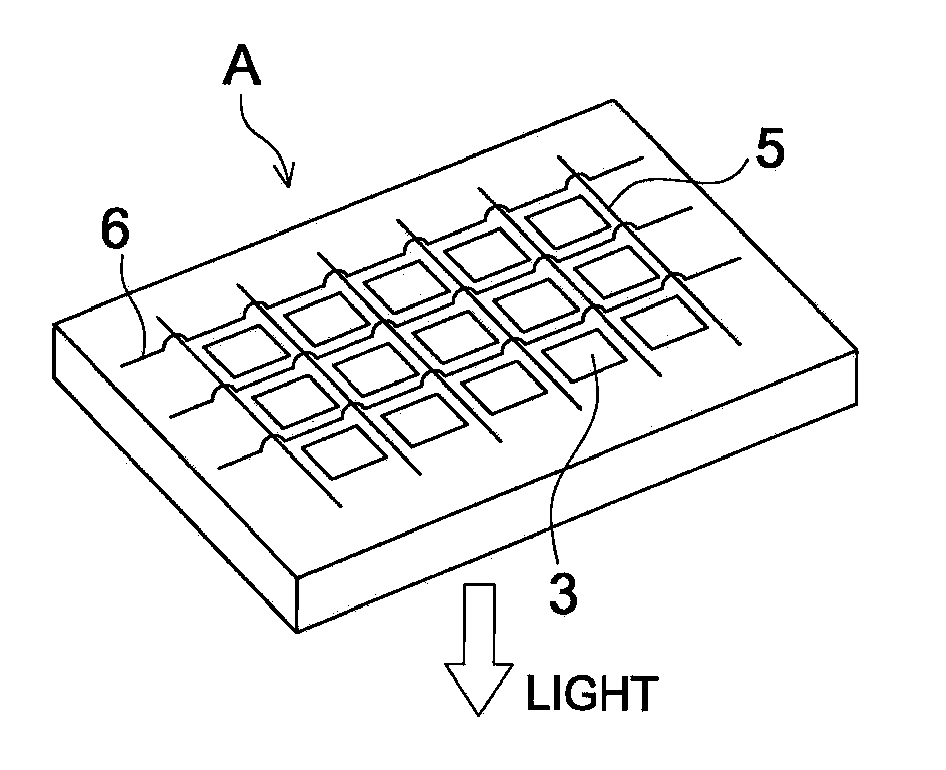
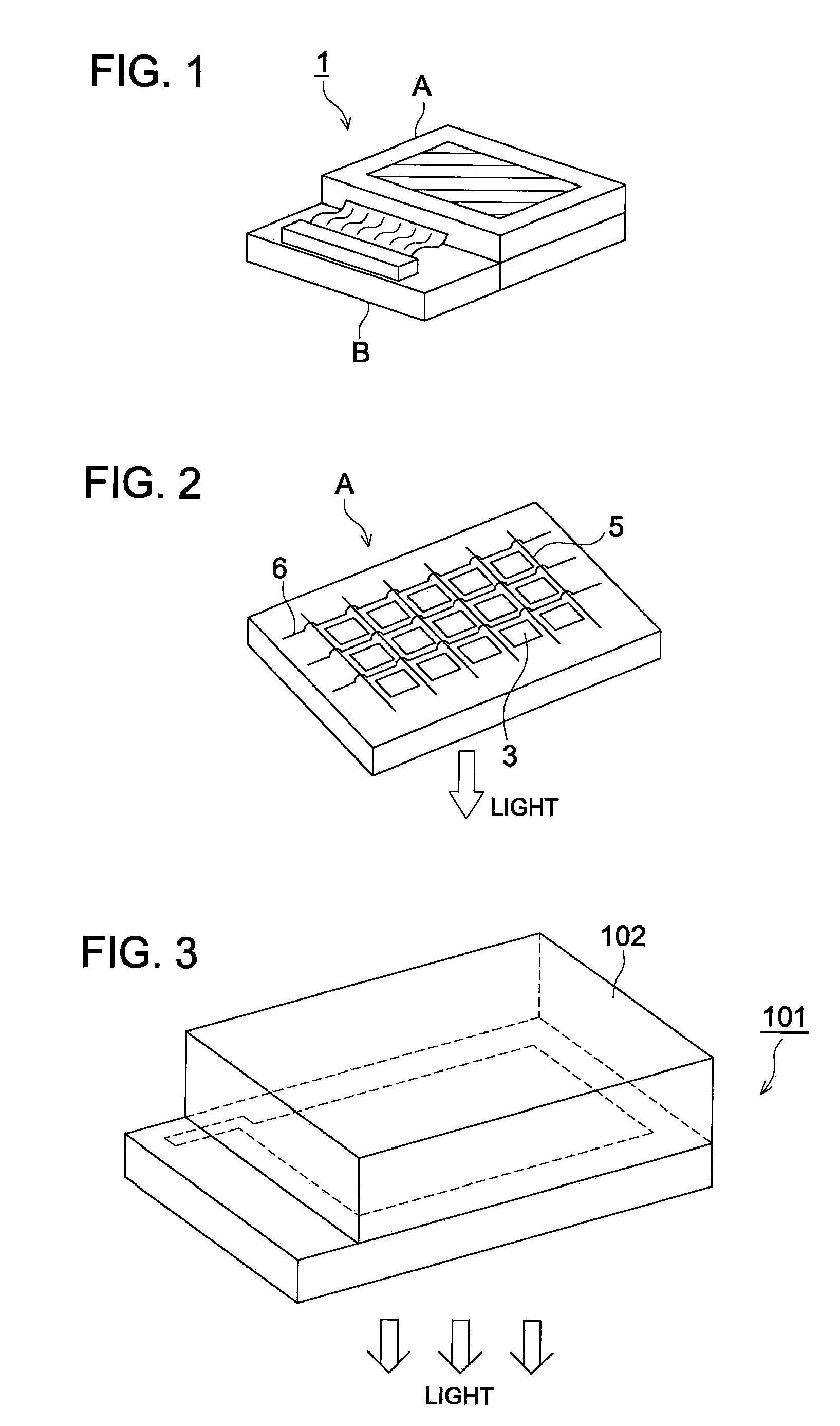
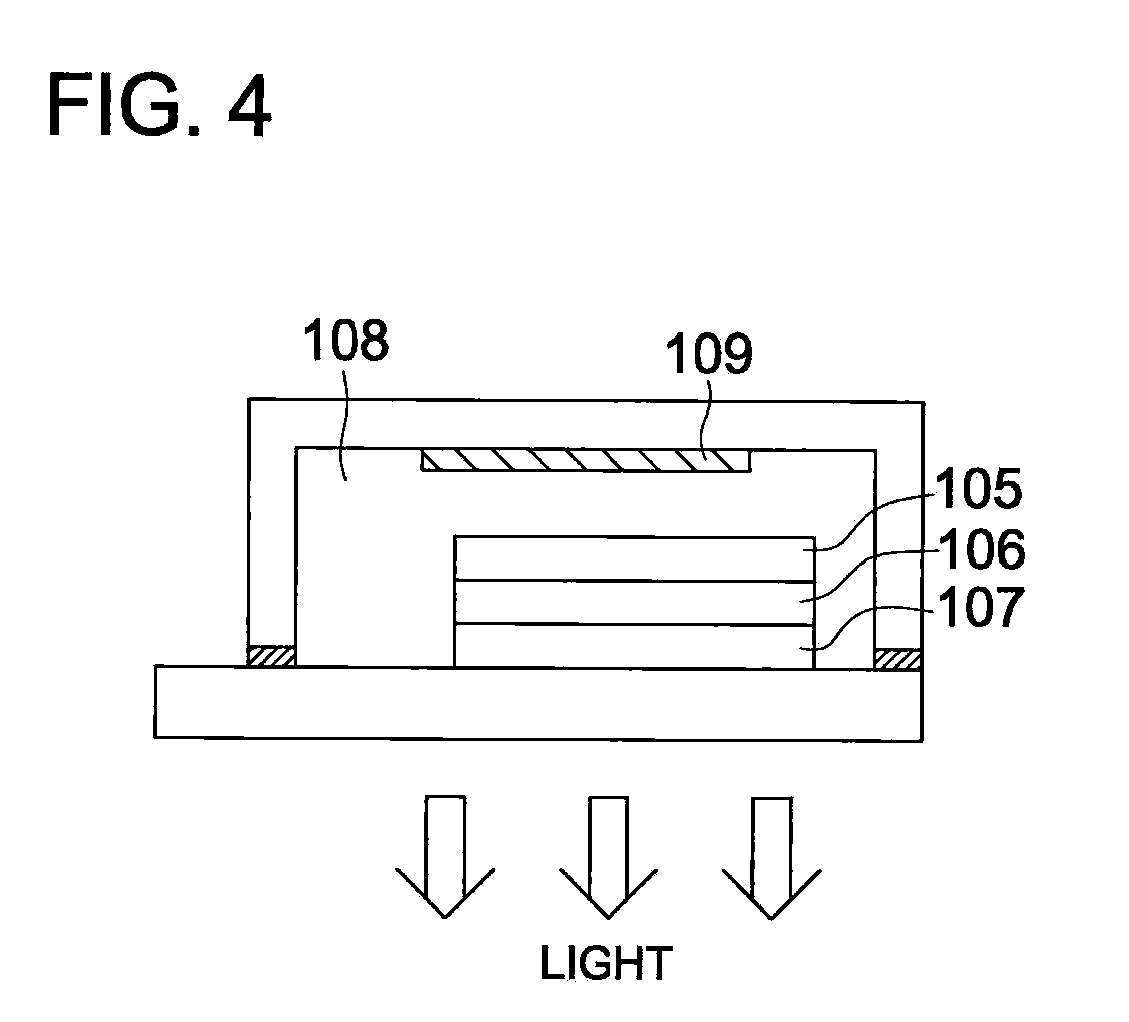
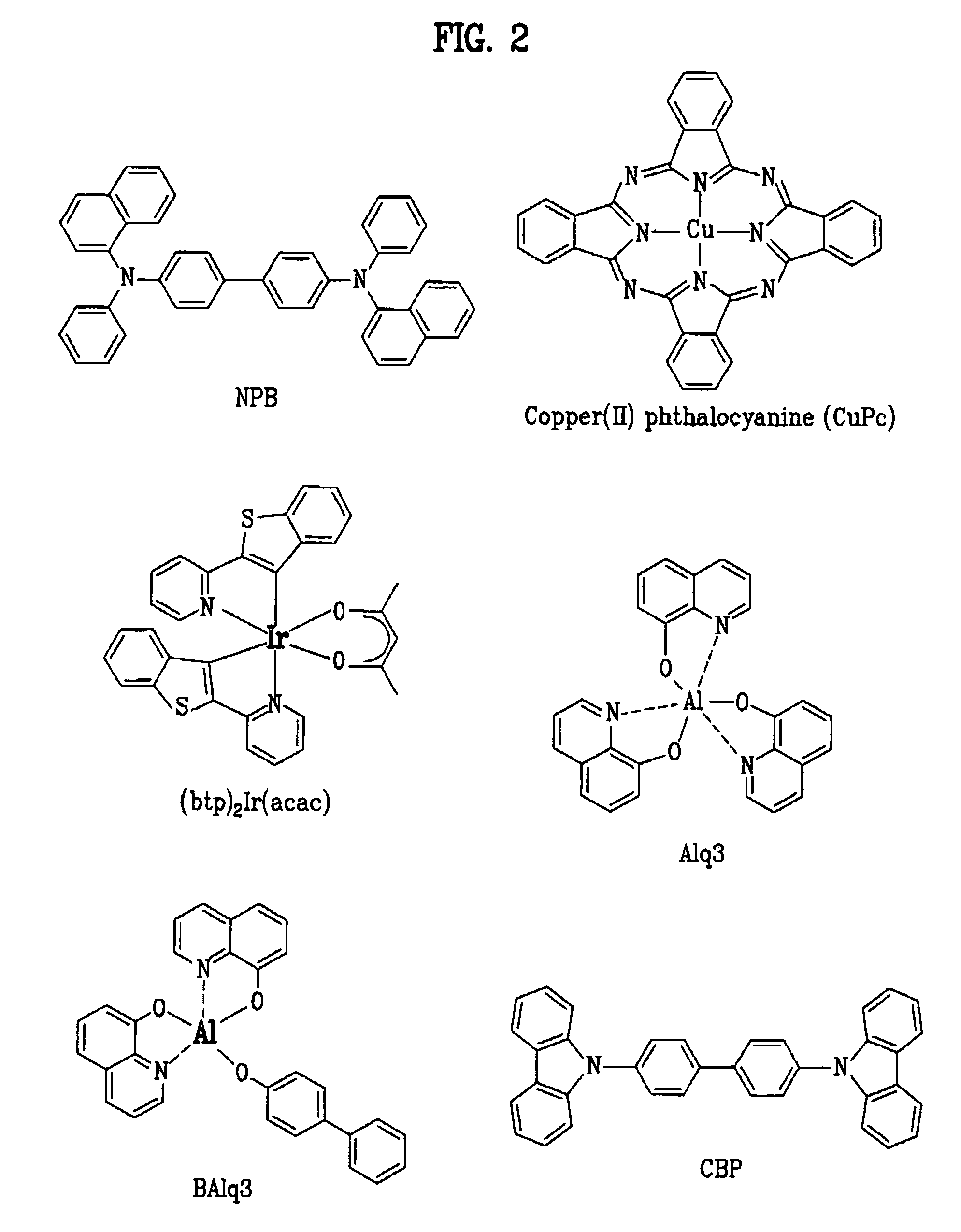
Light-emitting device
ActiveUS20060113549A1Desired characteristicTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesField-effect transistorActive layer
An object of the present invention is to provide a new light-emitting device with the use of an amorphous oxide. The light-emitting device has a light-emitting layer existing between first and second electrodes and a field effect transistor, of which the active layer is an amorphous.
Owner:CANON KK +2
Organic electroluminescent device
InactiveUS20050238919A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic layerCompound (substance)
An organic electroluminescent device including a pair of electrodes, and at least one organic layer including a luminescent layer between the pair of electrodes, in which the organic electroluminescent device includes at least one compound selected from the group consisting of the compounds represented by Formula (1), (2) and (3):
Owner:UDC IRELAND
Afinity domain for analyte sensor
InactiveUS20050176136A1Reduce impactBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteSorbent
Abstract of the DisclosureThe preferred embodiments provide a membrane system, particularly for use on an electrochemical sensor, wherein the membrane system includes an affinity domain that dampens the effects of target interferant(s) on the sensor. The affinity domain can be layer, surface, region, and / or portion of the membrane system formed using sorbents that have an affinity for the target interferant. The sorbents can be adapted to adsorb the interferants, for example using adsorbents such as chromatography packing materials. The sorbents can also be adapted to absorb the interferants by imprinting a molecular structure on the material that forms the affinity domain such that target interferants bind to the imprinted surfaces at the molecular level.
Owner:DEXCOM
Organic electroluminescent device
ActiveUS20060263635A1Group 5/15 element organic compoundsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsPlatinumNitrogen
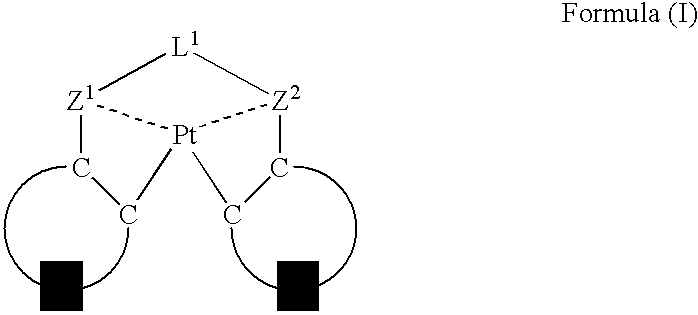
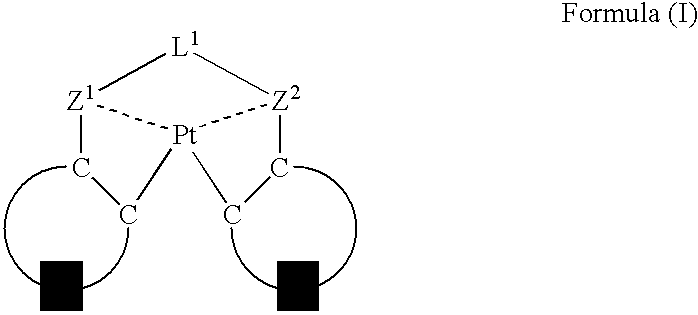
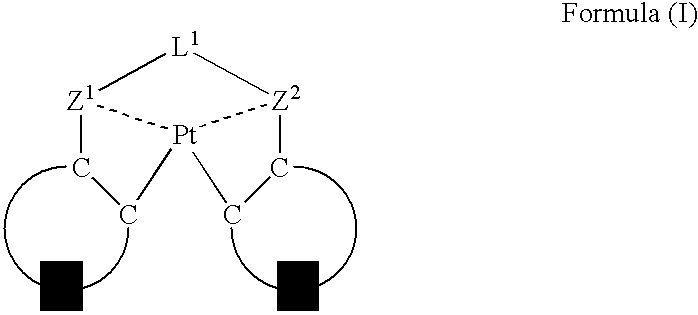
An organic electroluminescent device having a pair of electrodes and at least one organic layer interposed between the pair of electrodes, in which the at least one organic layer contains at least one compound represented by formula (I): wherein, Z1 and Z2 each independently represent a nitrogen-containing aromatic six-membered ring coordinated to the platinum through a nitrogen atom; Q1 represents a group of atoms necessary for forming, together with the —C—C—, a nitrogen-containing aromatic five-membered ring; L1 represents a single bond or a divalent linking group; and n is 0 or 1.
Owner:UDC IRELAND +1
Light emitting material and organic light-emitting device
InactiveUS7396598B2High efficiency of light emissionKeep energy smallDischarge tube luminescnet screensGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsFluorescenceTriplet state
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multi-array, multi-specific electrochemiluminescence testing
InactiveUS6066448AMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProviding materialElectrochemiluminescence
Materials and methods are provided for producing patterned multi-array, multi-specific surfaces which are electronically excited for use in electrochemiluminescence based tests. Materials and methods are provided for the chemical and / or physical control of conducting domains and reagent deposition for use in flat panel displays and multiply specific testing procedures.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
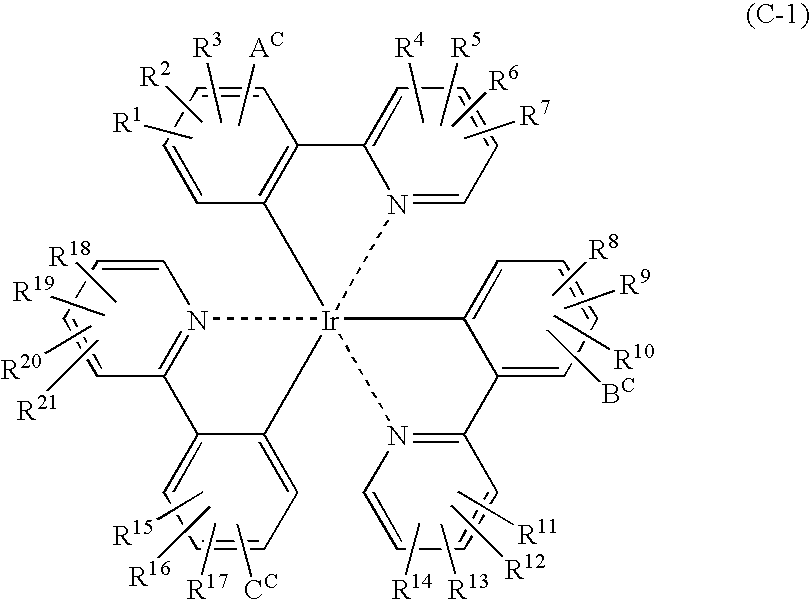
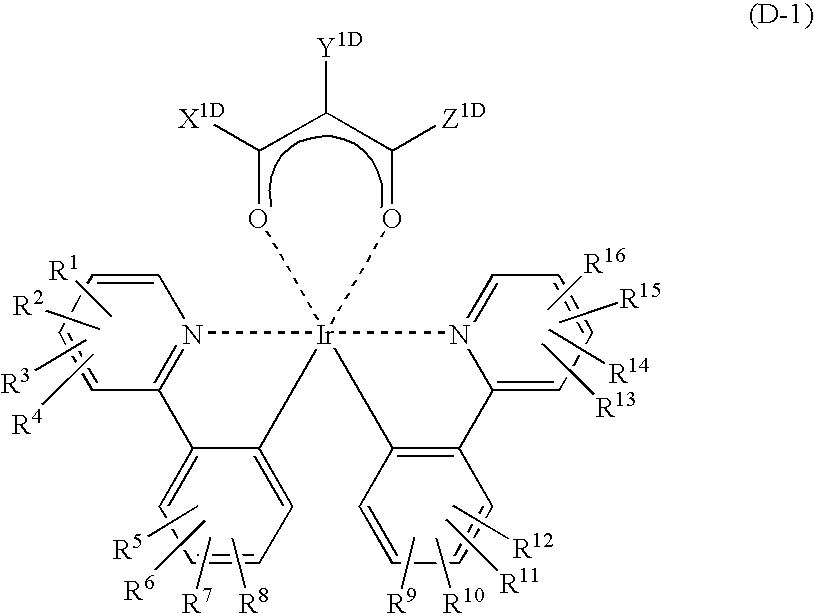
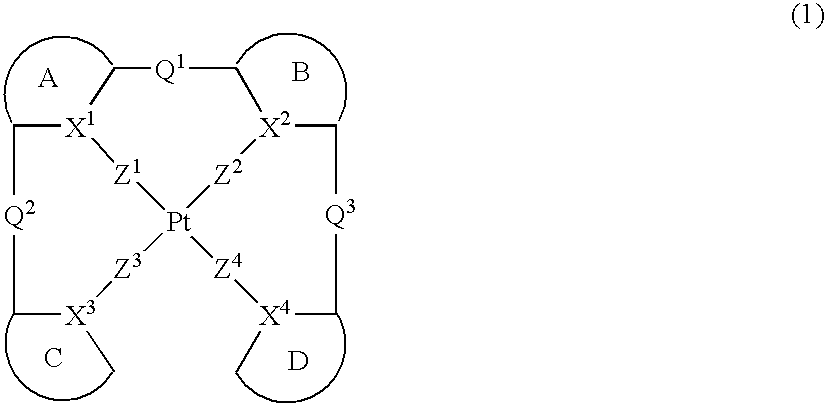
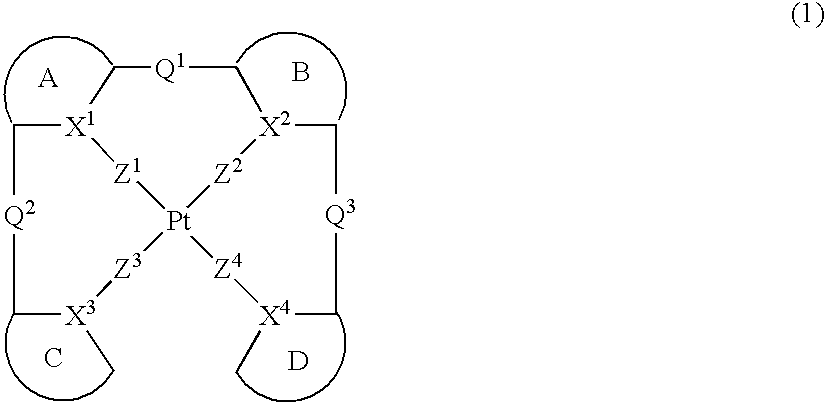
Platinum complex and light emitting device
ActiveUS20070103060A1Enhanced glowSolve low luminous efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOxygenLight emission
Provision of a novel platinum complex which is useful as a material for a light-emitting device of good light emission characteristic and light emission efficiency, and a novel light-emitting material that may be utilized in various fields. A platinum complex represented by the following general formula (1): (in which two rings of ring A, ring B, ring C, and ring D represent nitrogen-containing heterocyclic rings which may have a substituent and the remaining two rings of them represent aryl rings or hetero aryl rings which may have a substituent, the ring A and the ring B, the ring A and the ring C or / and the ring B and the rind D may form condensed rings. Two of X1, X2, X3, and X4 represent nitrogen atoms coordination bonded to a platinum atom and the remaining two of them represent carbon atoms or nitrogen atoms. Q1, Q2, and Q3 each represents a bond, oxygen atom, sulfur atom or bivalent group, two of Z1, Z2, Z3, and Z4 represent coordination bonds, and the remaining two of them represent covalent bonds, oxygen atoms or sulfur atoms), and a light-emitting device containing the platinum complex.
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Intersystem crossing agents for efficient utilization of excitons in organic light emitting devices
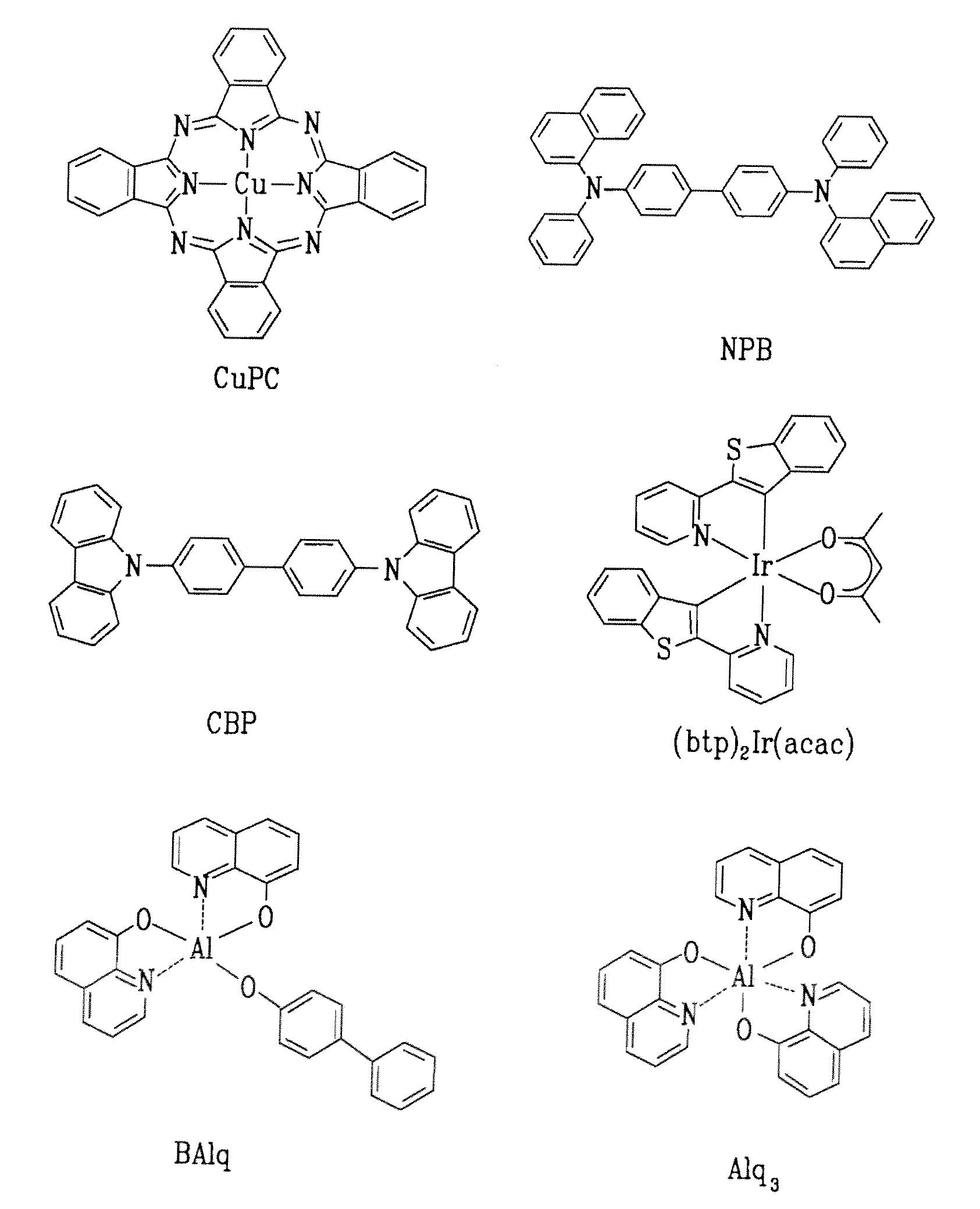
InactiveUS6310360B1Improve efficiencyElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesOrganic light emitting deviceHost material
Organic light emitting devices are described wherein the emissive layer comprises a host material containing a fluorescent or phosphorescent emissive molecule, which molecule is adapted to luminesce when a voltage is applied across the heterostructure, wherein an intersystem crossing molecule of optical absorption spectrum matched to the emission spectrum of the emissive molecule enhances emission efficiency.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV +1
Current-induced magnetic switching device and memory including the same
InactiveUS6256223B1High bulk densitySimpler driving circuitsNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsNanoparticleConduction band
A magnetic switching device, includes a first electrode, a second electrode, and a nanoparticle having a magnetic moment and being disposed between the first and second electrodes. At least one of the first electrode and the second electrode includes a magnetic material which has a net spin polarization in its conduction band for injecting, into the nanoparticle, an electrical current including a net spin polarization for overcoming the magnetic moment of the nanoparticle upon selection of a predetermined magnitude for the electrical current.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Organo luminescent semiconductor nanocrystal probes for biological applications and process for making and using such probes
A semiconductor nanocrystal compound is described capable of linking to an affinity molecule. The compound comprises (1) a semiconductor nanocrystal capable of emitting electromagnetic radiation and / or absorbing energy, and / or scattering or diffracting electromagnetic radiation-when excited by an electromagnetic radiation source or a particle beam; and (2) at least one linking agent, having a first portion linked to the semiconductor nanocrystal and a second portion capable of linking to an affity molecule. The compound is linked to an affinity molecule to form a semiconductor nanocrystal probe capable of bonding with a detectable substance. Subsequent exposure to excitation energy will excite the semiconductor nanocrystal in he probe, causing the emission of electromagnetic radiation. Further described are processes for respectively: making the semiconductor nanocrystal compound; making the semiconductor nanocrystal probe; and using the probe to determine the presence of a detectable substance in a material.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
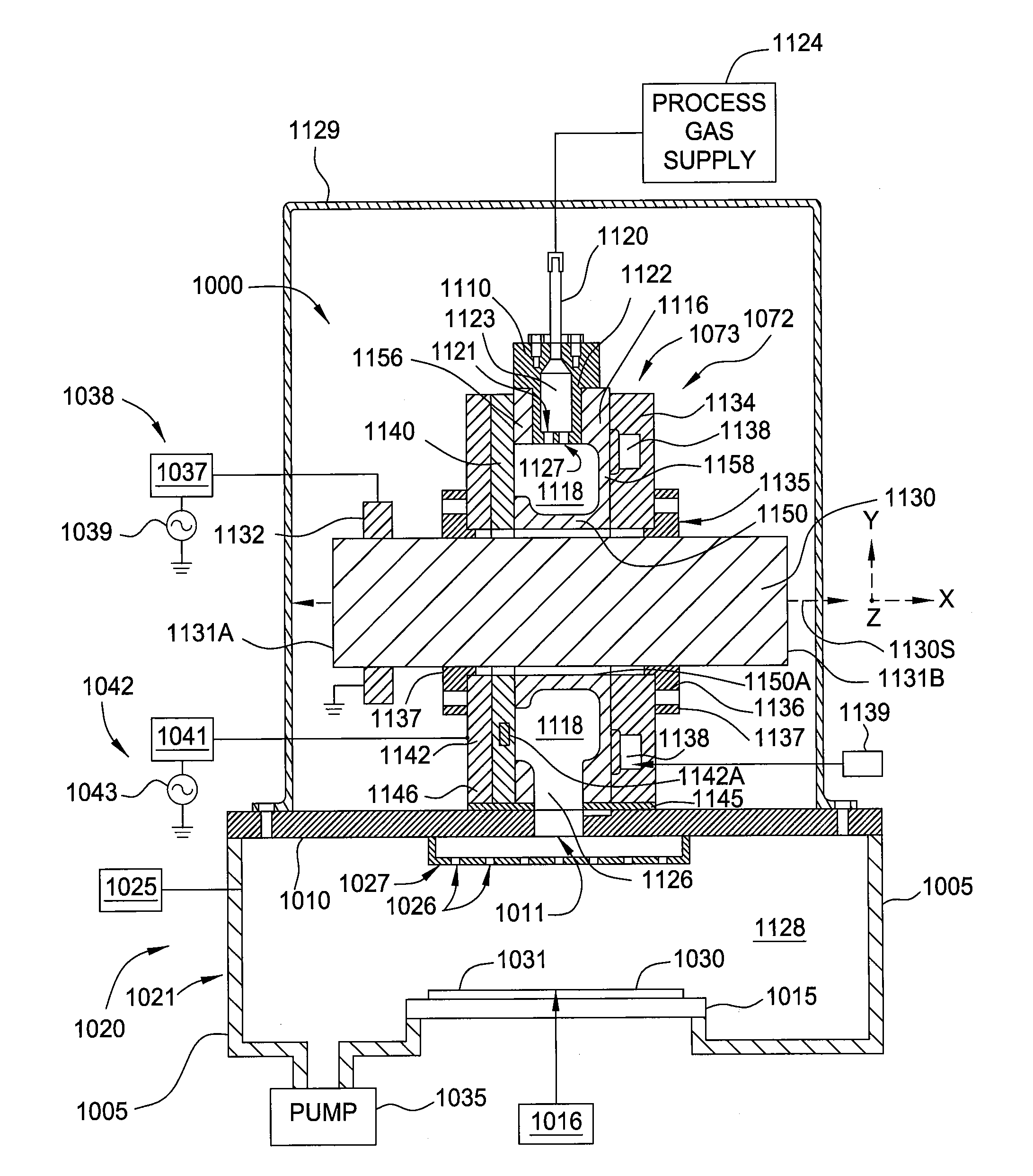
Semiconductor processing system and methods using capacitively coupled plasma
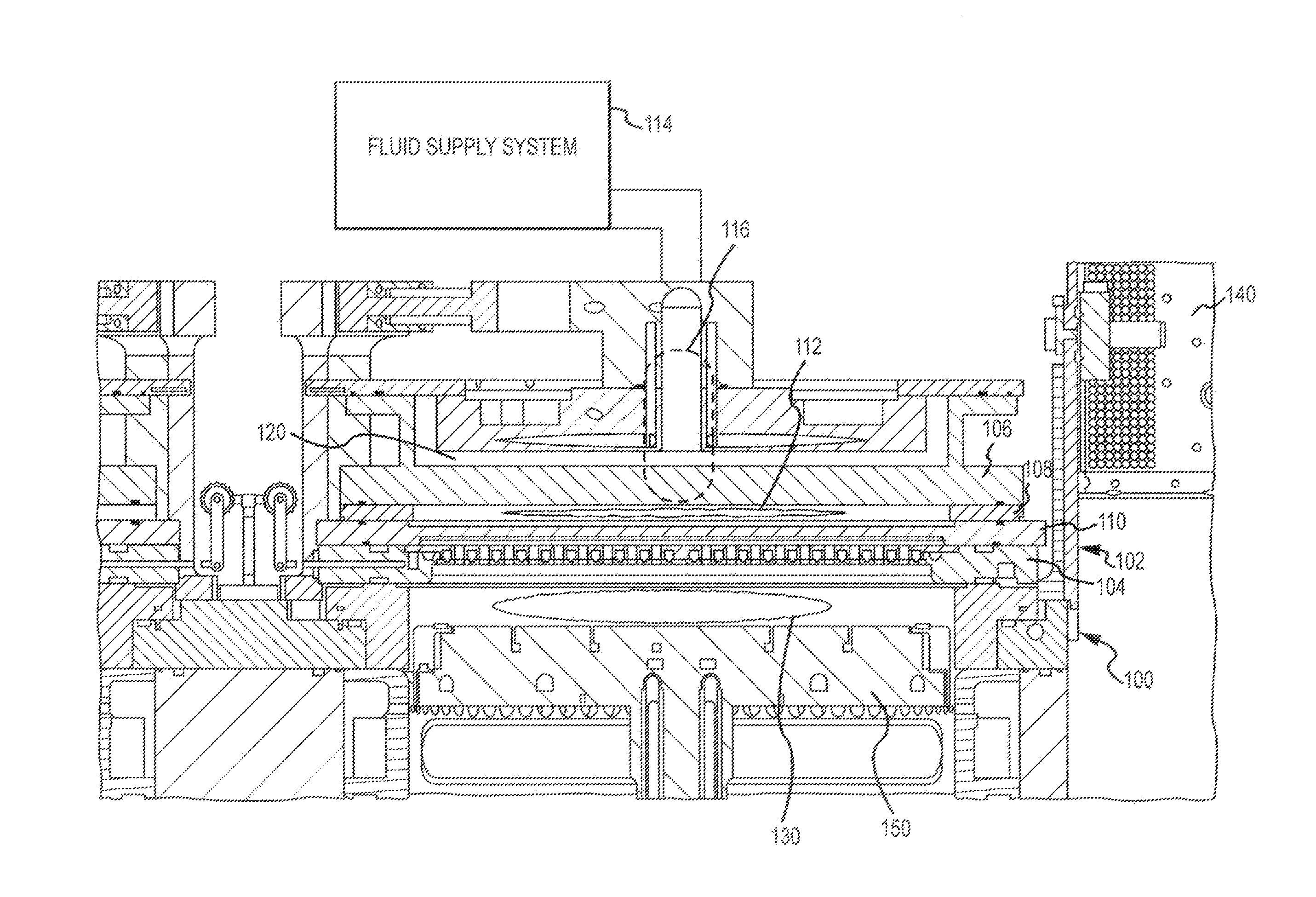
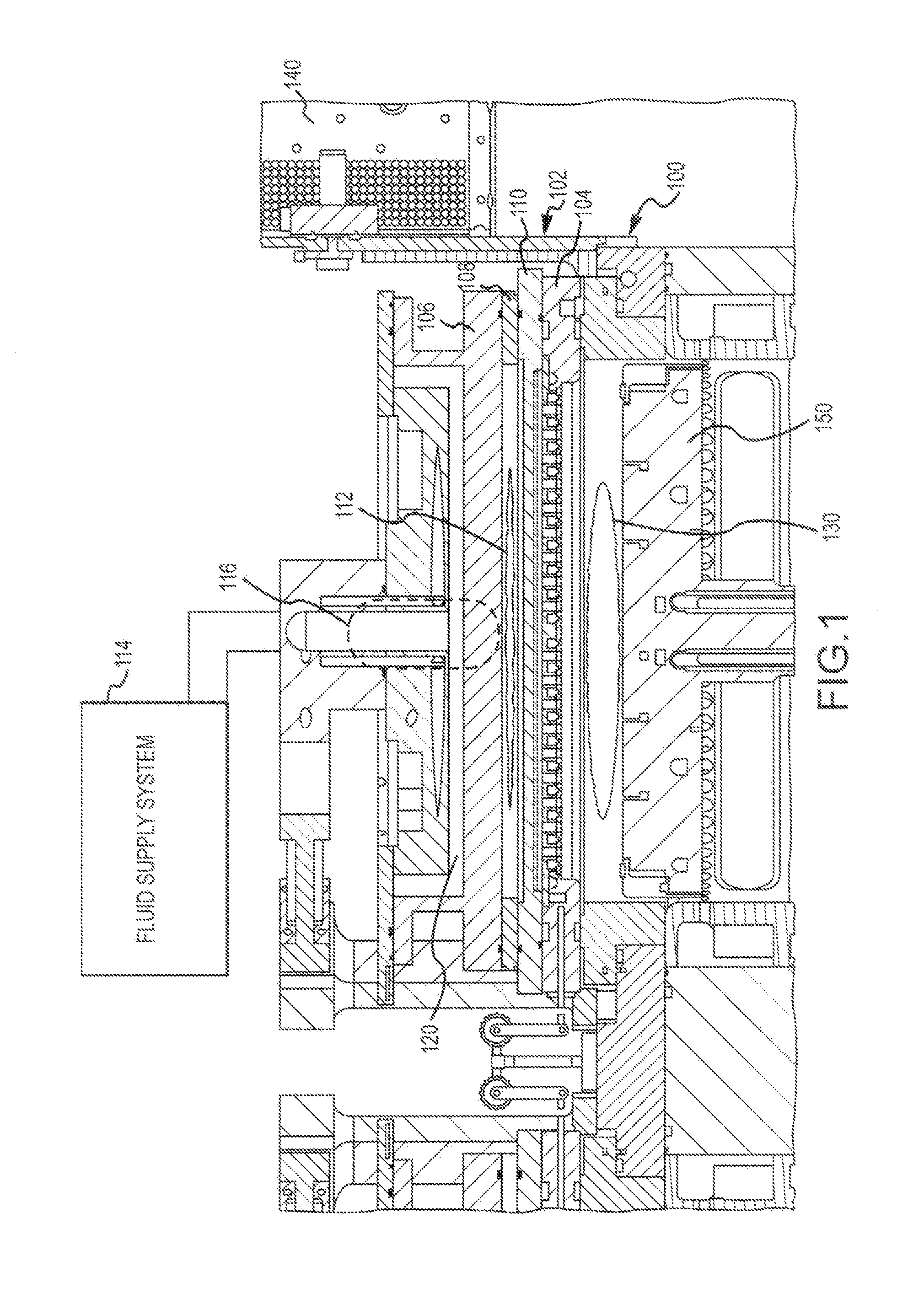
InactiveUS20120180954A1Conducive to environmental controlEliminate and reduce numberElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceSemiconductor
Substrate processing systems are described that have a capacitively coupled plasma (CCP) unit positioned inside a process chamber. The CCP unit may include a plasma excitation region formed between a first electrode and a second electrode. The first electrode may include a first plurality of openings to permit a first gas to enter the plasma excitation region, and the second electrode may include a second plurality of openings to permit an activated gas to exit the plasma excitation region. The system may further include a gas inlet for supplying the first gas to the first electrode of the CCP unit, and a pedestal that is operable to support a substrate. The pedestal is positioned below a gas reaction region into which the activated gas travels from the CCP unit.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Coupled electrochromic compounds with photostable dication oxidation states
InactiveUS6249369B1High photochemical stabilityTenebresent compositionsNon-linear opticsAction spectrumElectronic communication
Coupling of anodic electrochromic compounds by a covalent bond or a bridge link which provides for electronic communication between the coupled electrochromic compounds results in coupled electrochromic compounds which exhibit greater stability as well as electrochromic activity that differs from the monomeric electrochromic compounds. Extension of the absorption spectrum into the near-infrared region of the spectrum is frequently observed. The coupled electrochromic compounds are highly suitable for use in electrochromic media used to produce electrochromic devices.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Organic electroluminescent element, display device and lighting device
ActiveUS20100084966A1Improve emission efficiencyLong life-timeOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensDisplay deviceHost material
Disclosed is an organic electroluminescent device having long life, while exhibiting high luminous efficiency. Also disclosed are an illuminating device and a display, each using such an organic electroluminescent device. In the organic electroluminescent device, a compound represented by the general formula (A) which is suitable as a host material for a phosphorescent metal complex is used at least in one sublayer of a light-emitting layer.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Methods of analyzing polymers using a spatial network of fluorophores and fluorescence resonance energy transfer
InactiveUS6263286B1Easy to analyze and useMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresEnergy transferResonance
The present invention relates to methods and apparatuses for analyzing molecules, particularly polymers, and molecular complexes with extended or rod-like conformations. In particular, the methods and apparatuses are used to identify repetitive information in molecules or molecular ensembles, which is interpreted using an autocorrelation function in order to determine structural information about the molecules. The methods and apparatuses of the invention are used for, inter alia, determining the sequence of a nucleic acid, determining the degree of identity of two polymers, determining the spatial separation of specific sites within a polymer, determining the length of a polymer, and determining the velocity with which a molecule penetrates a biological membrane.
Owner:U S GENOMICS INC
Water-soluble fluorescent nanocrystals
InactiveUS6444143B2High quantum yieldHigh spectral purityMaterial nanotechnologyNanosensorsQuantum yieldOrganic layer
A water soluble semiconductor nanocrystal capable of light emission is provided, including a quantum dot having a selected band gap energy, a layer overcoating the quantum dot, the overcoating layer comprised of a material having a band gap energy greater than that of the quantum dot, and an organic outer layer, the organic layer comprising a compound having a least one linking group for attachment of the compound to the overcoating layer and at least one hydrophilic group space apart from the linking group by a hydrophobic region sufficient to prevent electron charge transfer across the hydrophobic region. The particle size of the nanocrystal core is in the range of about 12.ANG. to about 150.ANG., with a deviation of less than 10% in the core. The coated nanocrystal exhibits photoluminescende having quantum yield of greater than 10% in water.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Technique for strain engineering in si-based transistors by using embedded semiconductor layers including atoms with high covalent radius
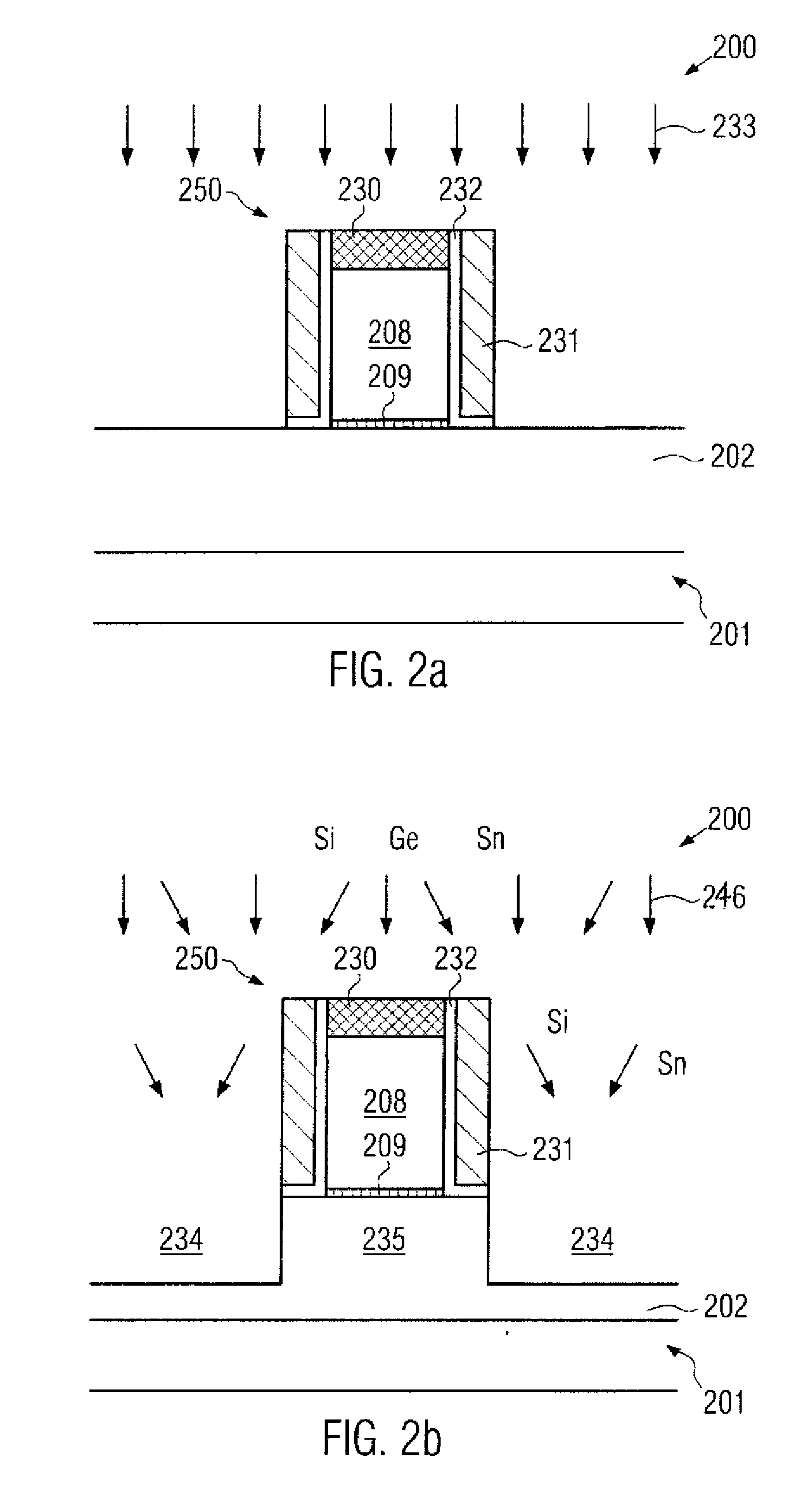
By incorporating an atomic species of increased covalent radius, which may at least partially substitute germanium, a highly efficient strain mechanism may be provided, in which the risk of stress relief due to germanium conglomeration and lattice defects may be reduced. The atomic species of increased radius, such as tin, may be readily incorporated by epitaxial growth techniques on the basis of tin hydride.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Solar cells using fullerenes
InactiveUS6580027B2Improve efficiencyIncrease the electric field strengthPV power plantsNanoinformaticsSolar cellFullerene
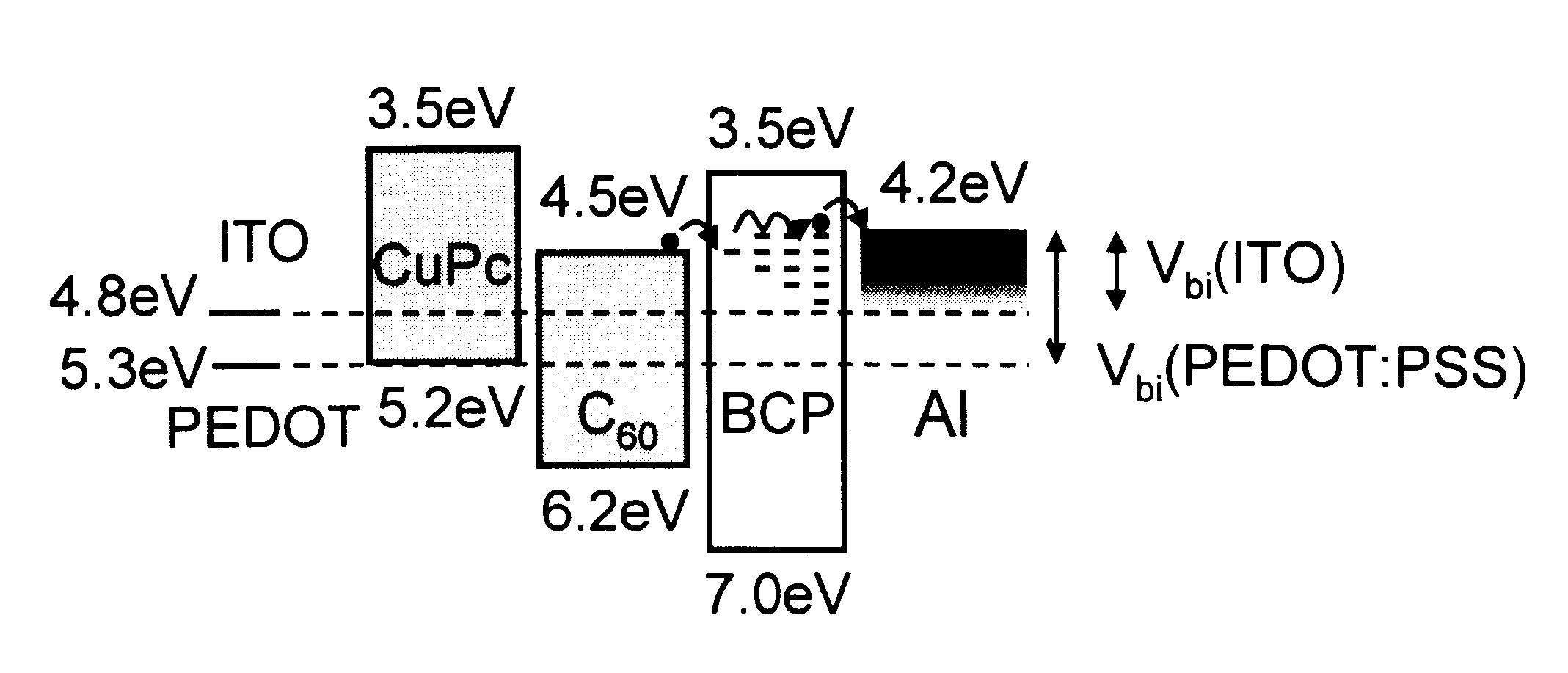
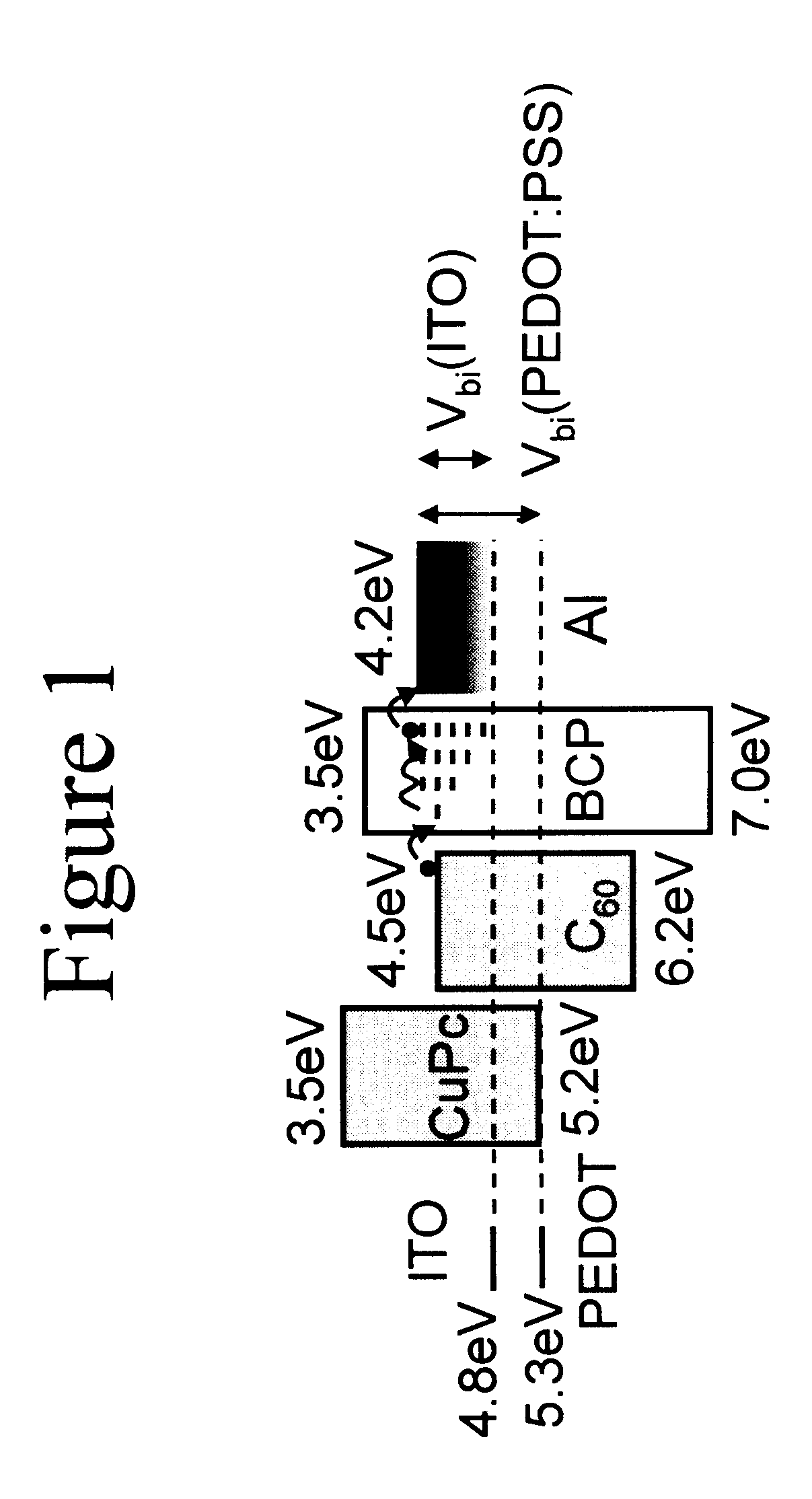
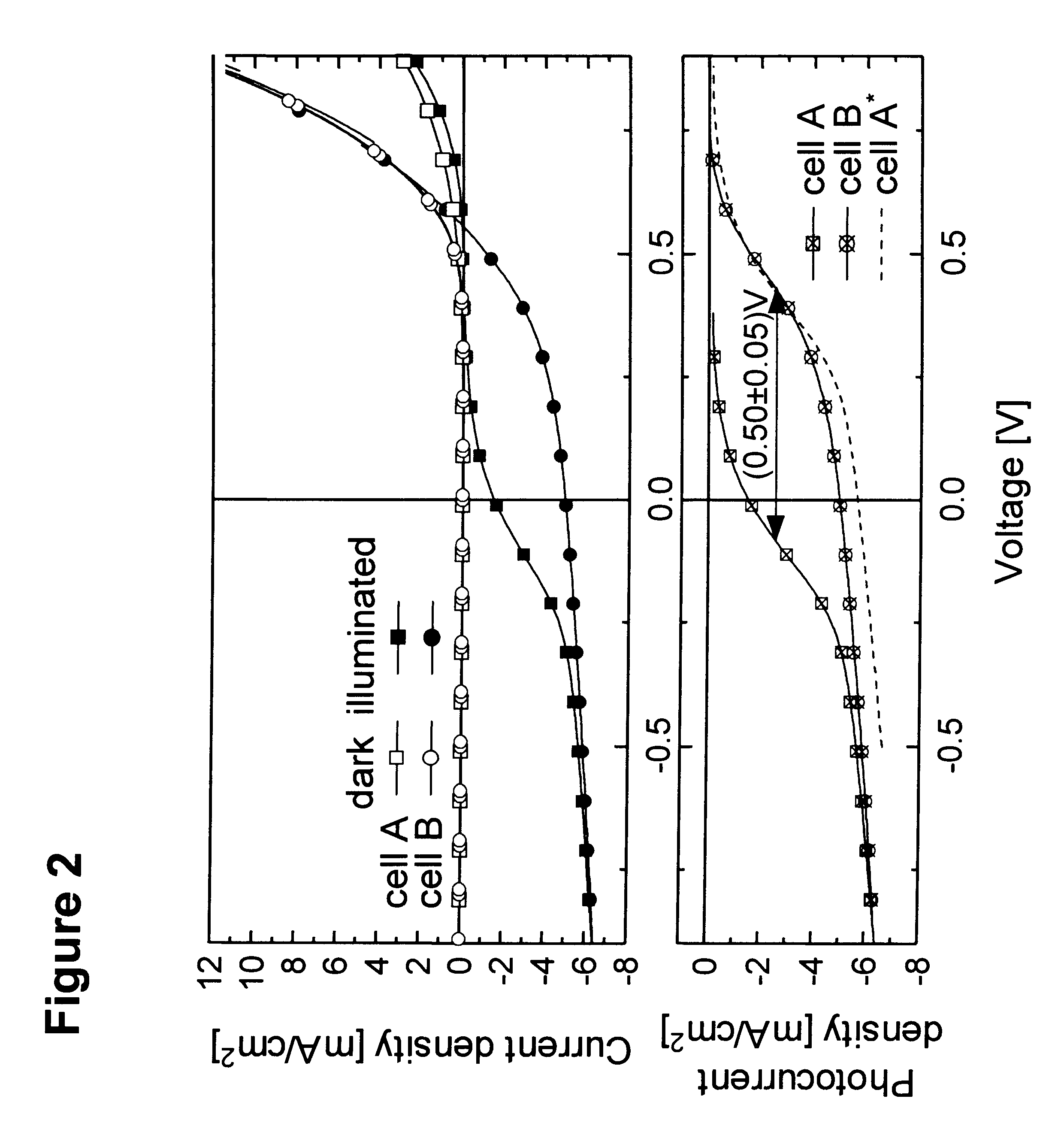
Organic photosensitive optoelectronic devices are disclosed. The devises comprise photoconductive organic thin films in a heterostructure, which include an exciton blocking layer to enhance device efficiency. The use of fullerenes in the electron conducting layer has lead to devices with high efficiency. Single heterostructure, stacked and wave-guide type embodiments are disclosed. Devices having multilayer structures and an exciton blocking layer are also disclosed. Guidelines for selection of exciton blocking layers are provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Sequential gas flow oxide deposition technique
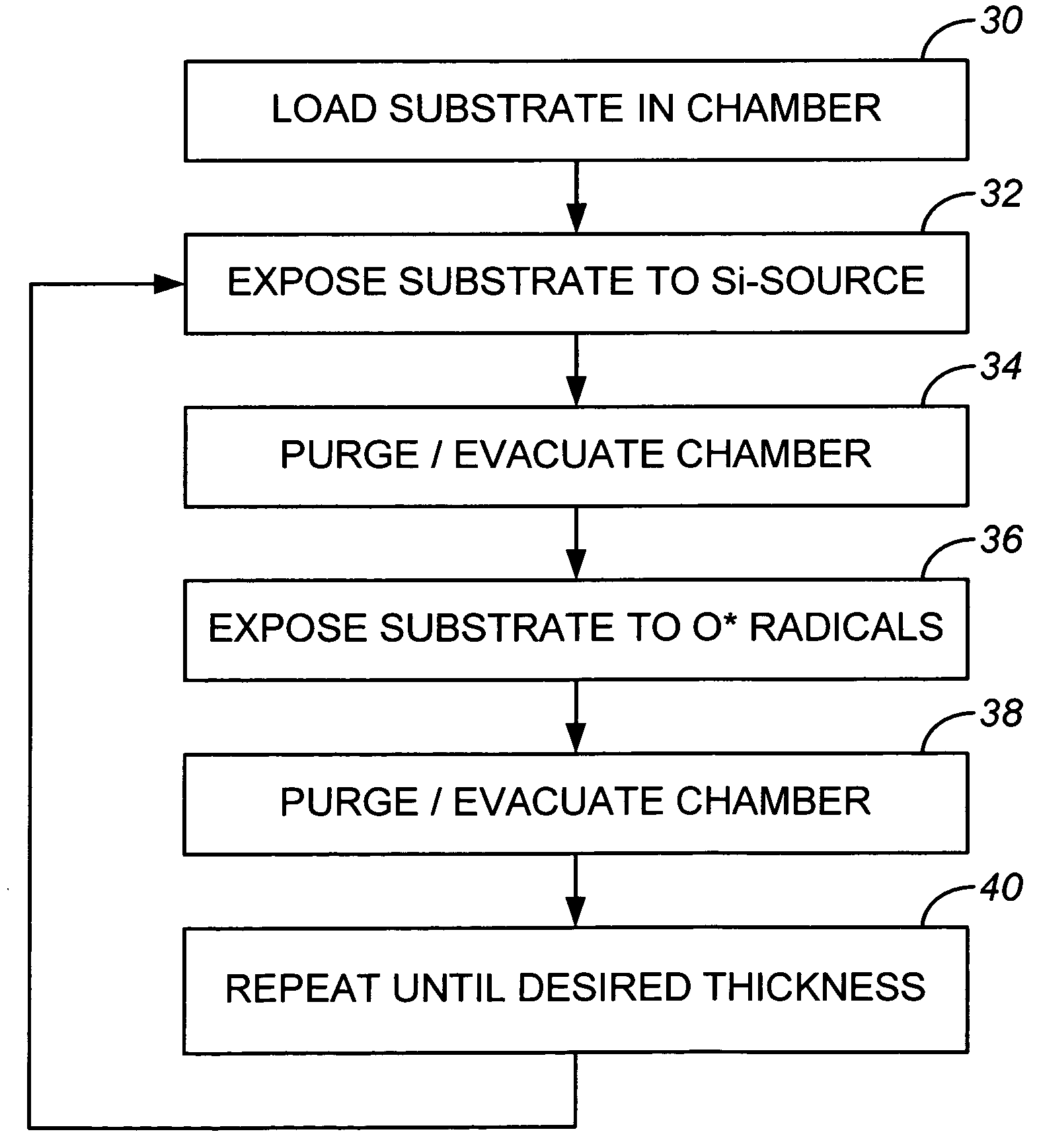
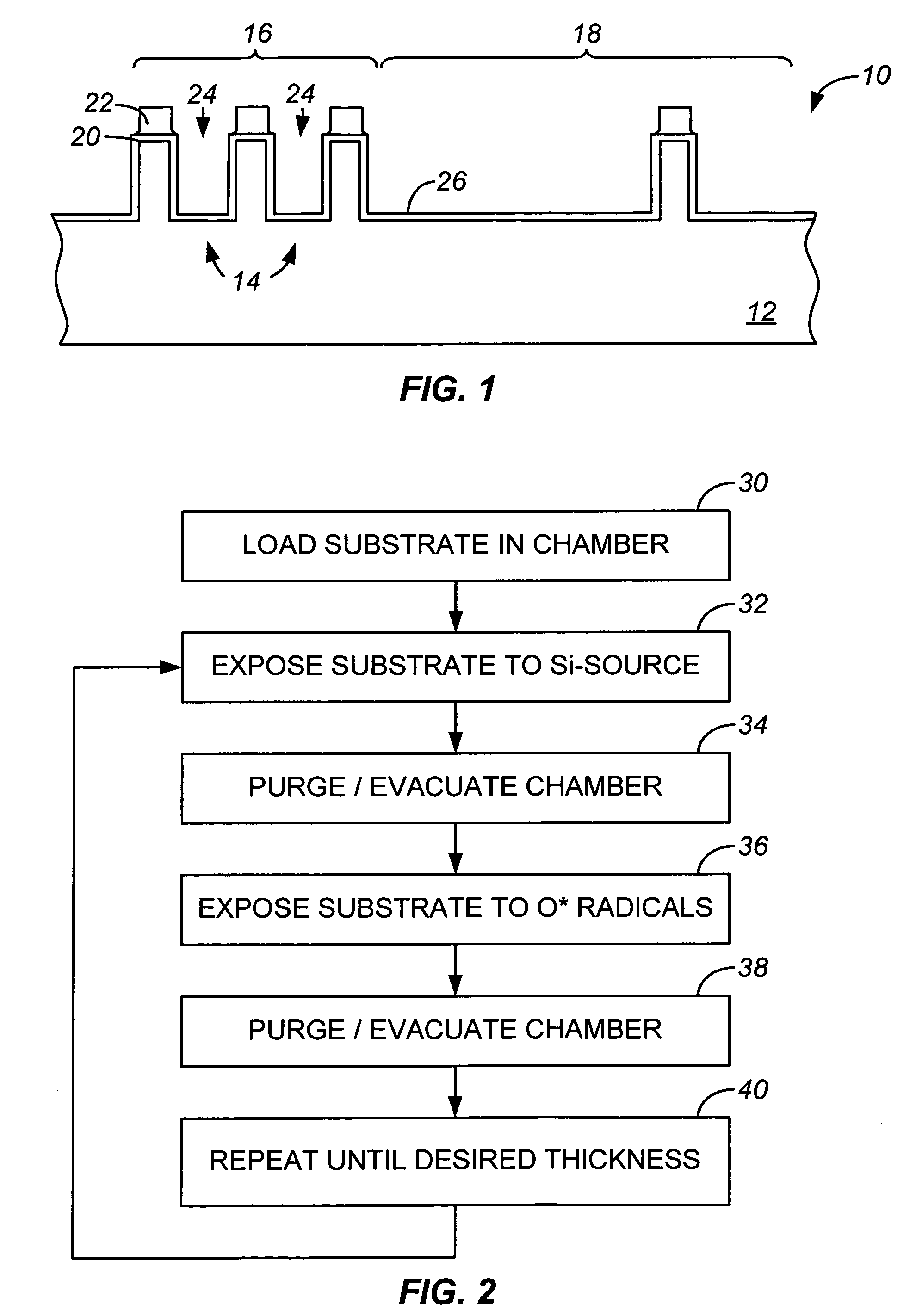
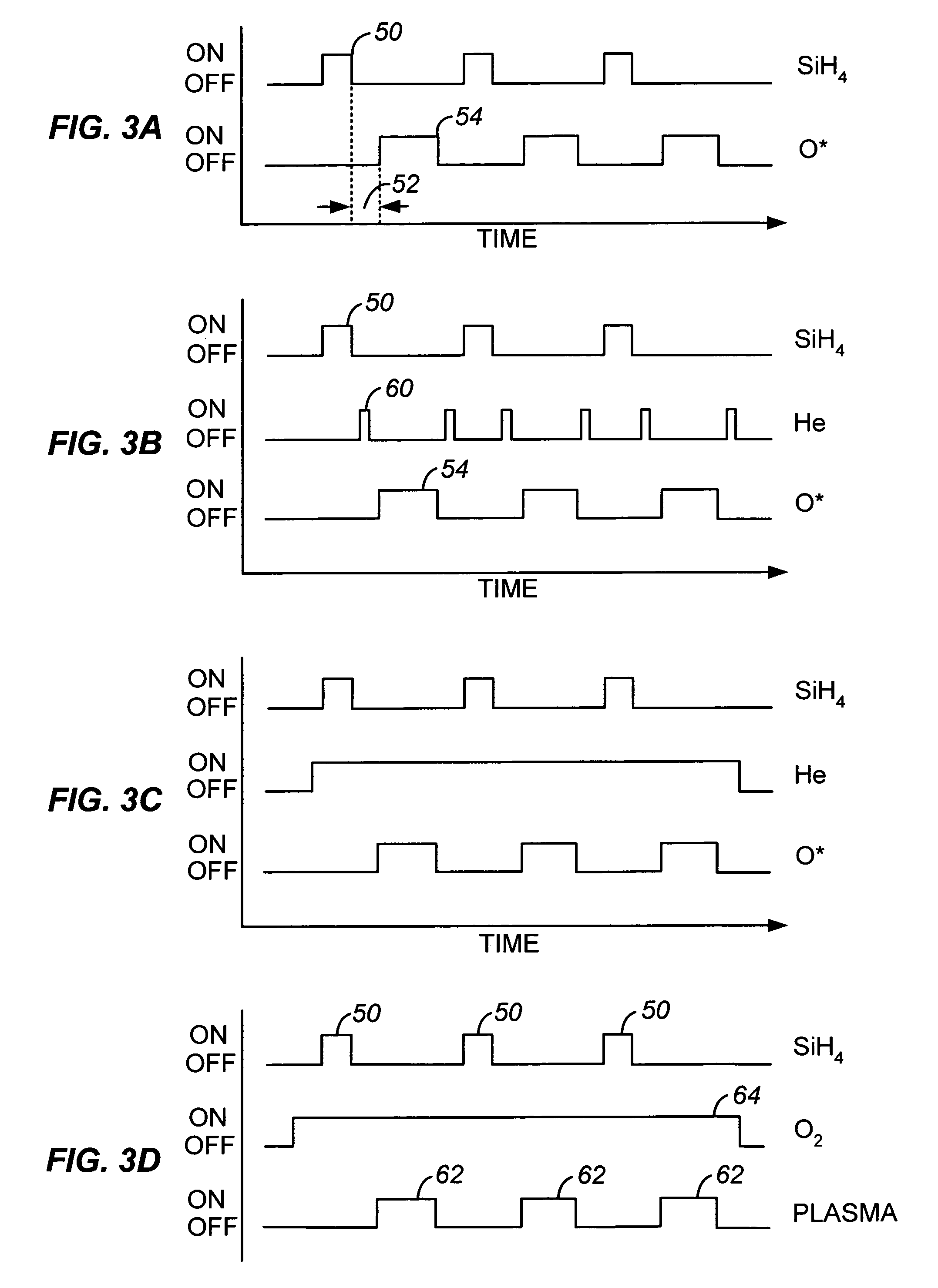
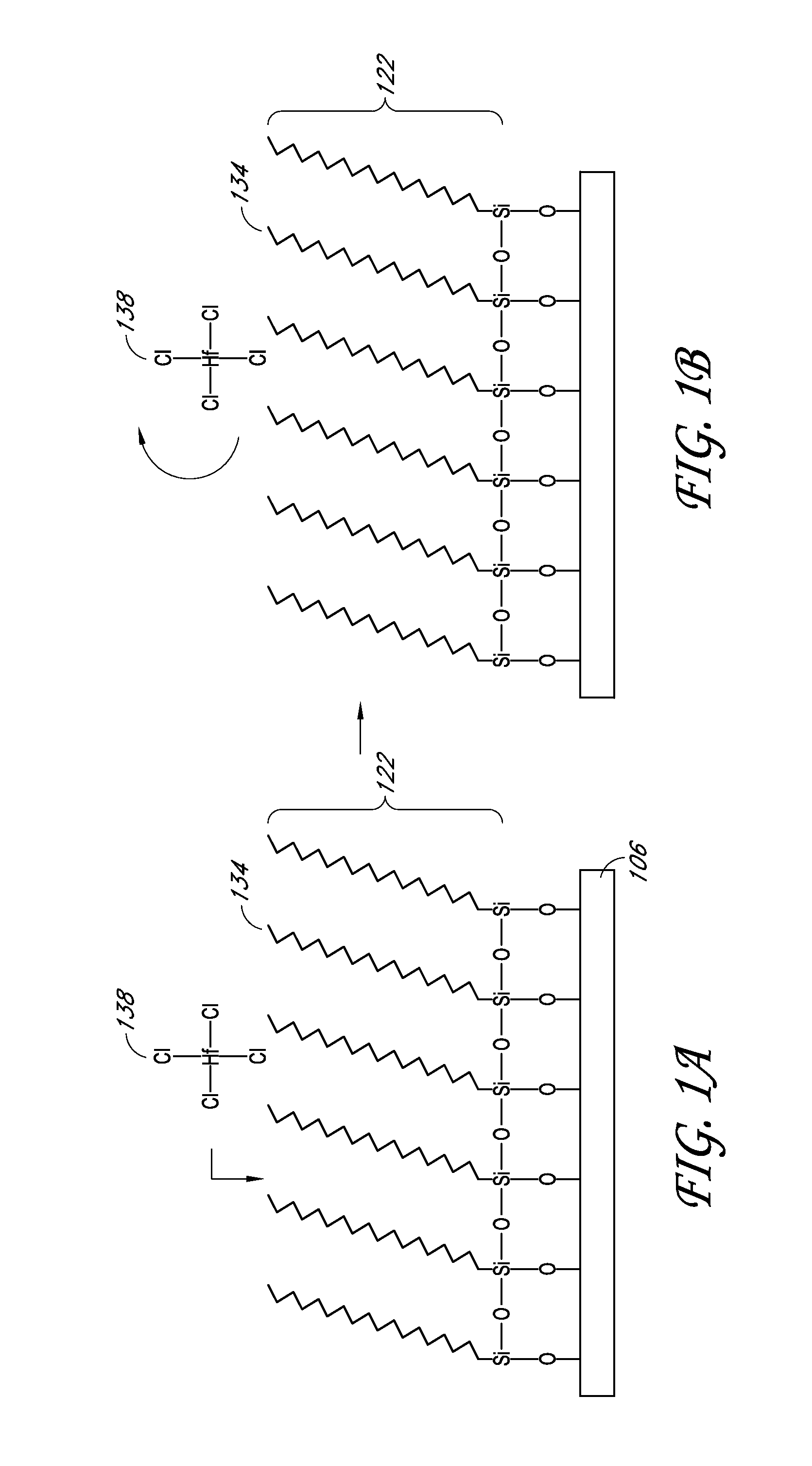
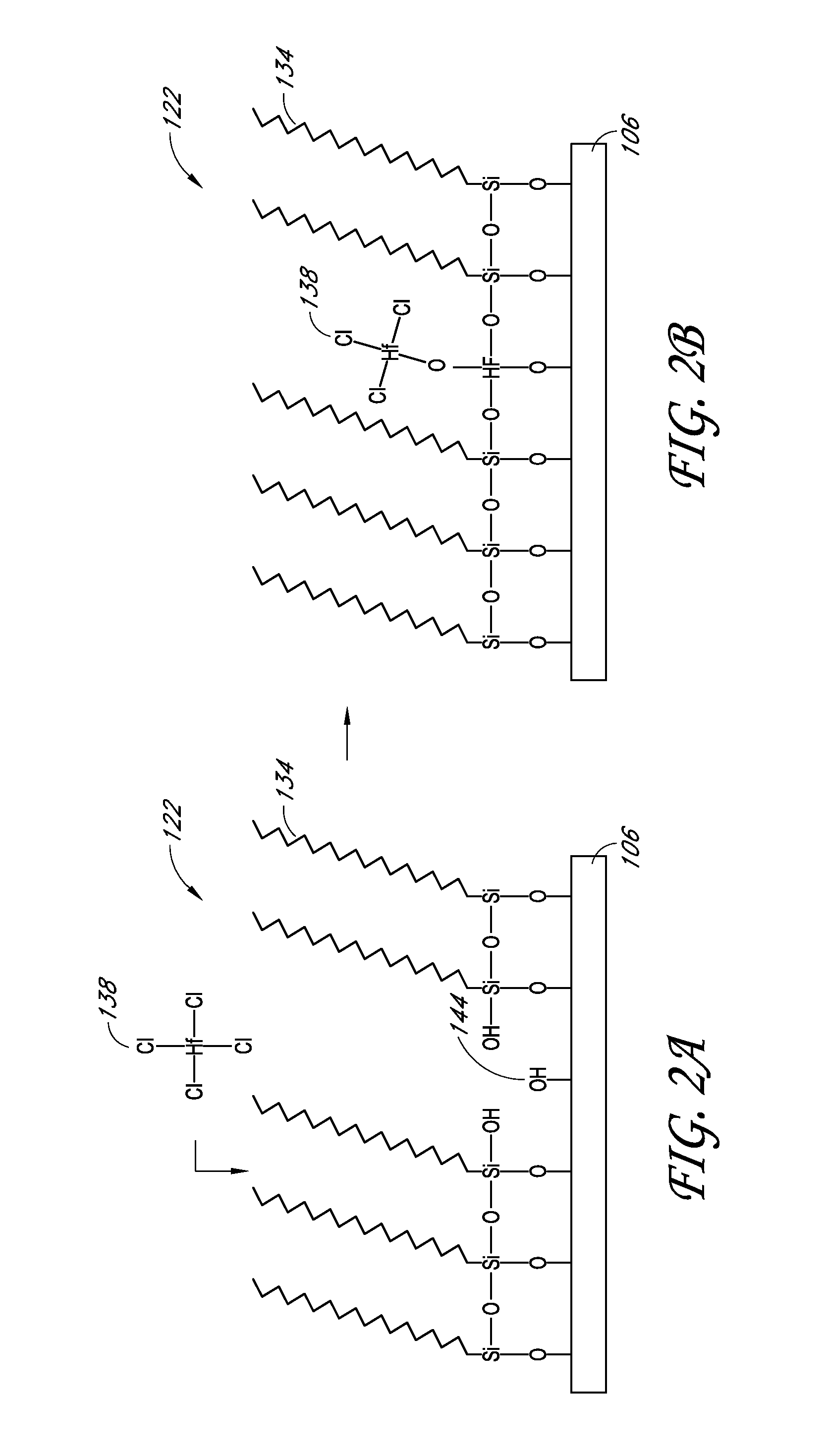
A method of depositing a silica glass insulating film over a substrate. In one embodiment the method comprises exposing the substrate to a silicon-containing reactant introduced into a chamber in which the substrate is disposed such that one or more layers of the silicon-containing reactant are adsorbed onto the substrate; purging or evacuating the chamber of the silicon-containing reactant; converting the silicon-containing reactant into a silica glass insulating compound by exposing the substrate to oxygen radicals formed from a second reactant while biasing the substrate to promote a sputtering effect, wherein an average atomic mass of all atomic constituents in the second reactant is less than or equal to an average atomic mass of oxygen; and repeating the exposing, purging / evacuating and exposing sequence a plurality of times until a desired film thickness is reached.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Reactive site deactivation against vapor deposition
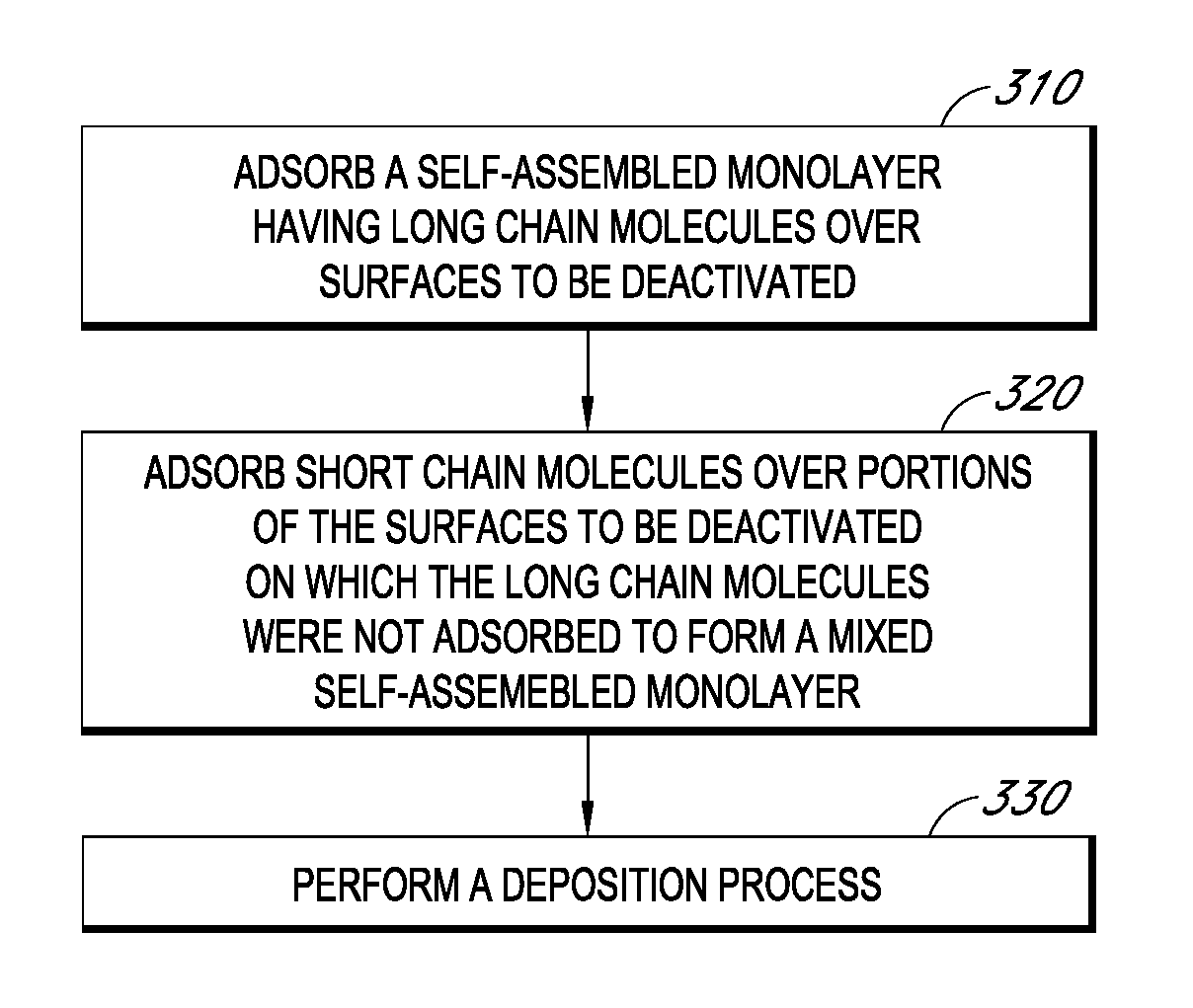
Methods and structures relating to the formation of mixed SAMs for preventing undesirable growth or nucleation on exposed surfaces inside a reactor are described. A mixed SAM can be formed on surfaces for which nucleation is not desired by introducing a first SAM precursor having molecules of a first length and a second SAM precursor having molecules of a second length shorter than the first. Examples of exposed surfaces for which a mixed SAM can be provided over include reactor surfaces and select surfaces of integrated circuit structures, such as insulator and dielectric layers.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
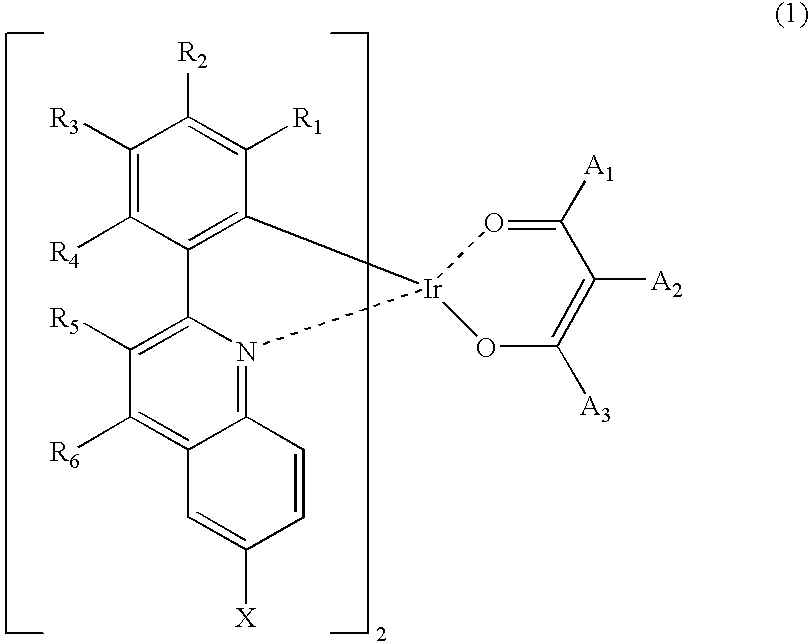
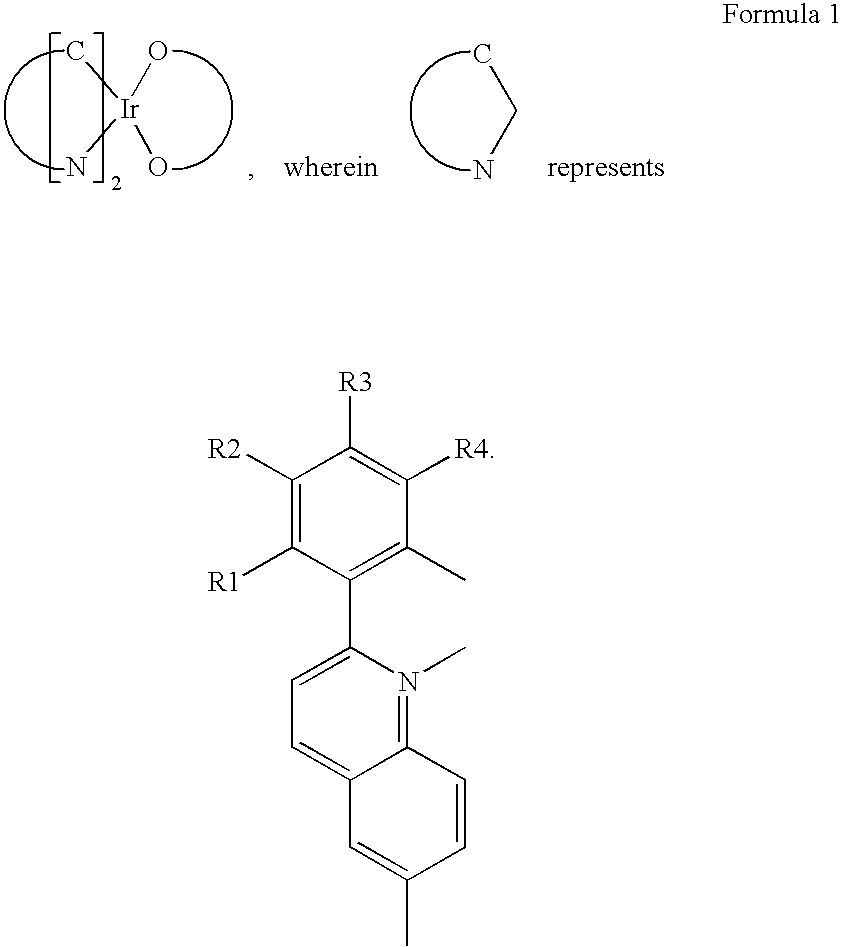
Red phosphorescent compounds and organic electroluminescent devices using the same
ActiveUS20090104472A1Good red color puritySolve low luminous efficiencyIndium organic compoundsElectroluminescent light sourcesQuantum efficiencyOrganic electroluminescence
Provided are red phosphorescent compounds represented by Formula 1:Organic electroluminescent devices using the red phosphorescent compounds are further provided. The organic electroluminescent devices exhibit good red color purity, high quantum efficiency, high power efficiency, high luminance, and long lifetime.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
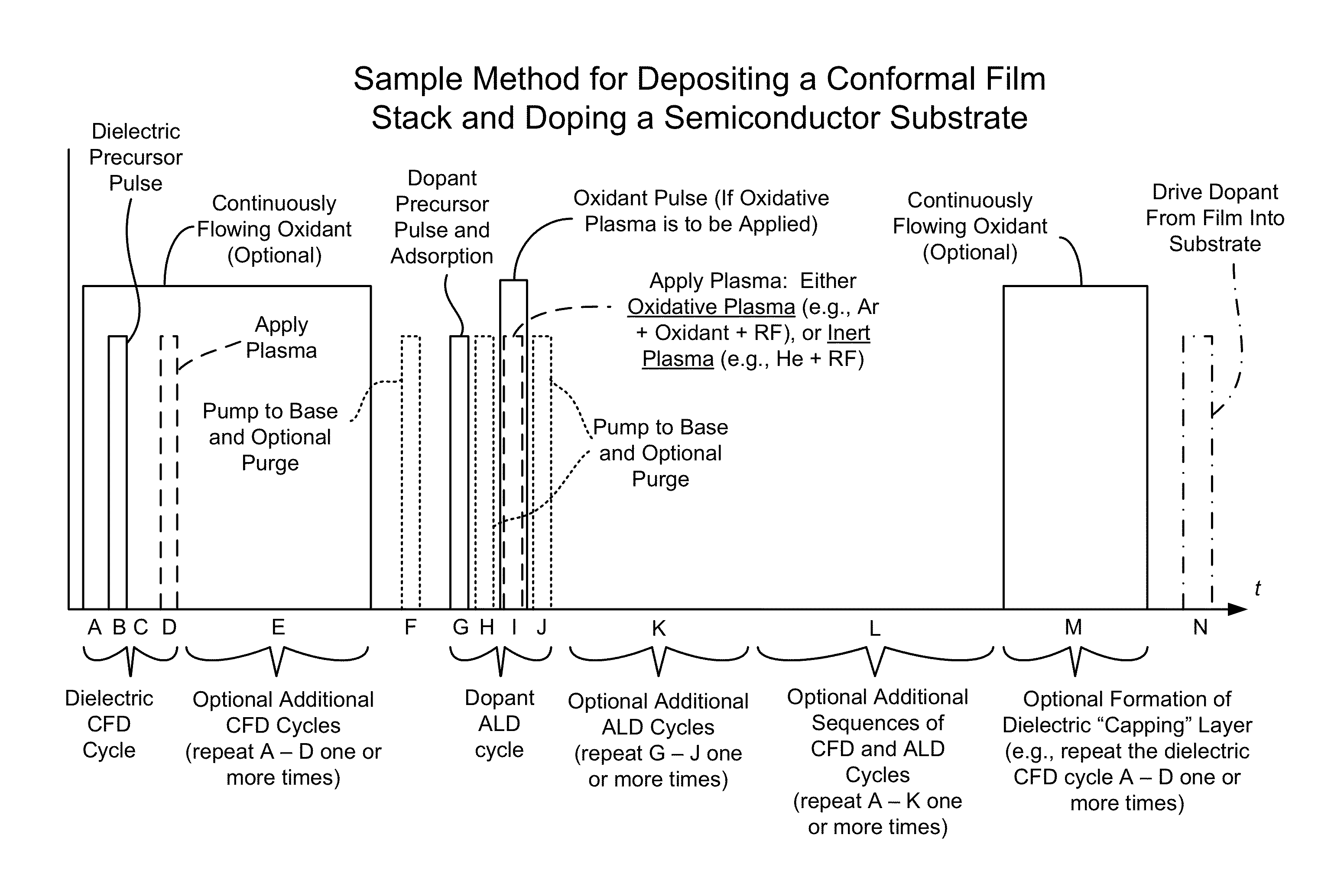
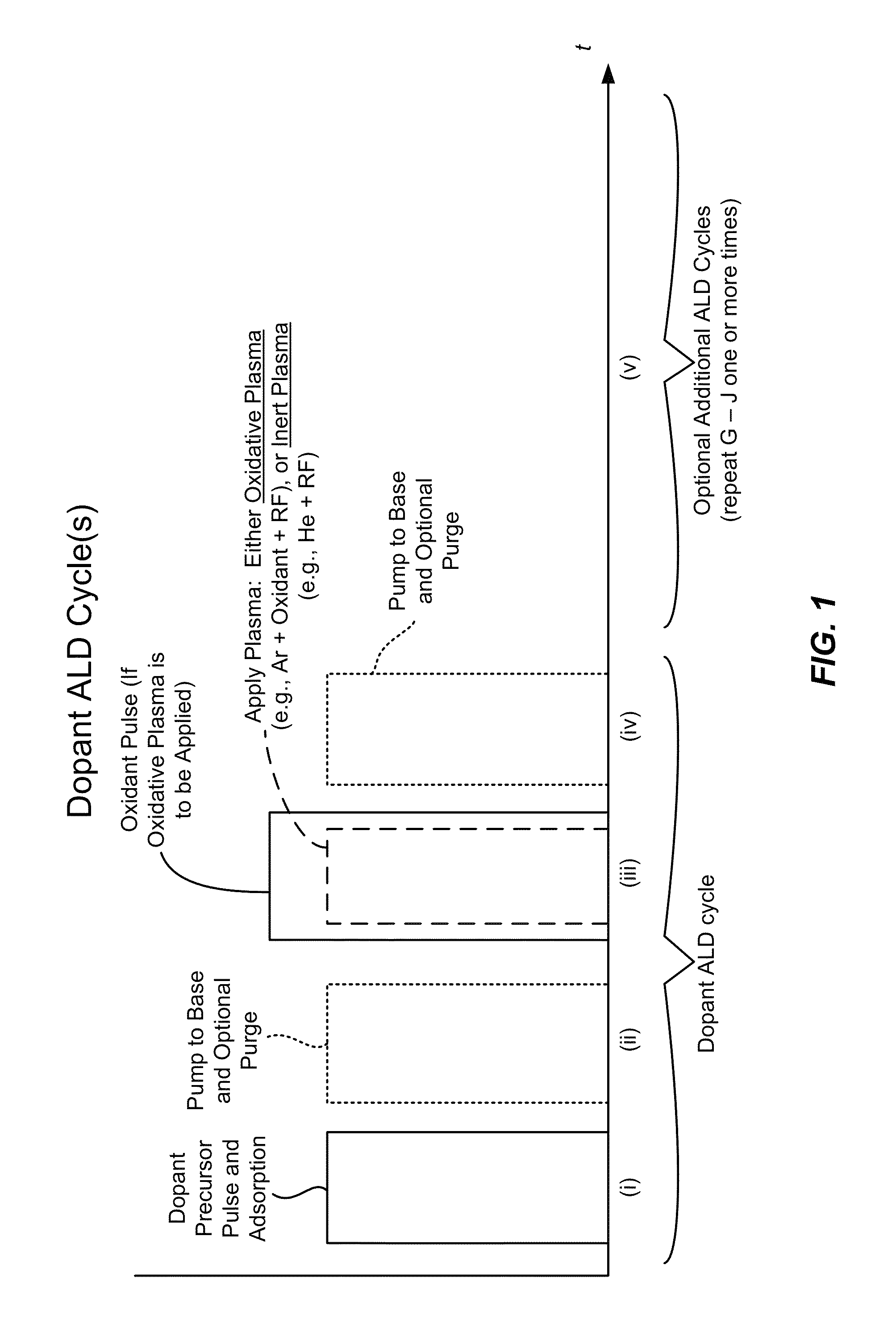
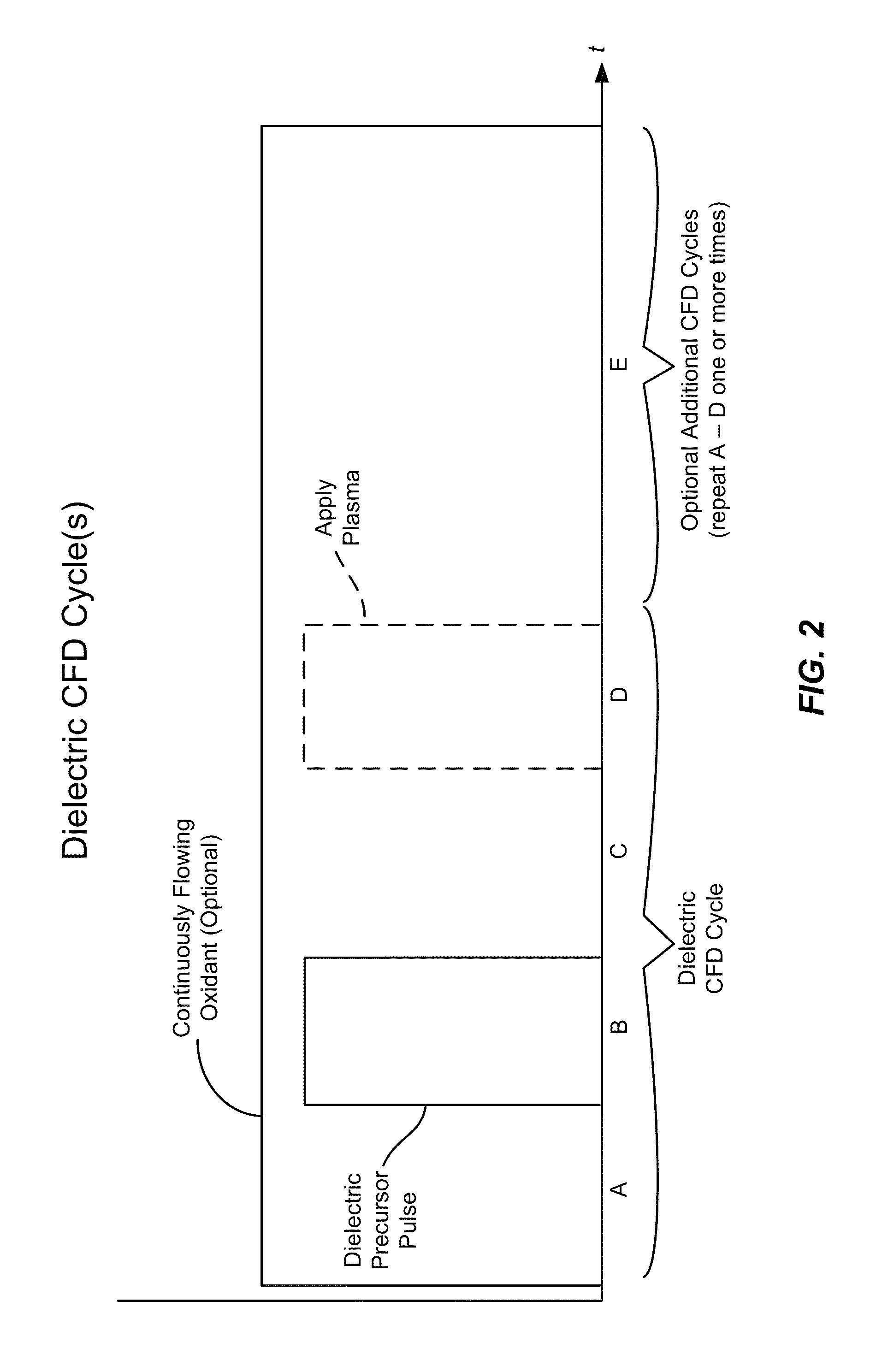
Conformal doping via plasma activated atomic layer deposition and conformal film deposition
ActiveUS8956983B2Liquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantPatterned substrate
Disclosed herein are methods of doping a patterned substrate in a reaction chamber. The methods may include forming a first conformal film layer which has a dopant source including a dopant, and driving some of the dopant into the substrate to form a conformal doping profile. In some embodiments, forming the first film layer may include introducing a dopant precursor into the reaction chamber, adsorbing the dopant precursor under conditions whereby it forms an adsorption-limited layer, and reacting the adsorbed dopant precursor to form the dopant source. Also disclosed herein are apparatuses for doping a substrate which may include a reaction chamber, a gas inlet, and a controller having machine readable code including instructions for operating the gas inlet to introduce dopant precursor into the reaction chamber so that it is adsorbed, and instructions for reacting the adsorbed dopant precursor to form a film layer containing a dopant source.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Thin-film transistor, method of producing the same, and devices provided with the same
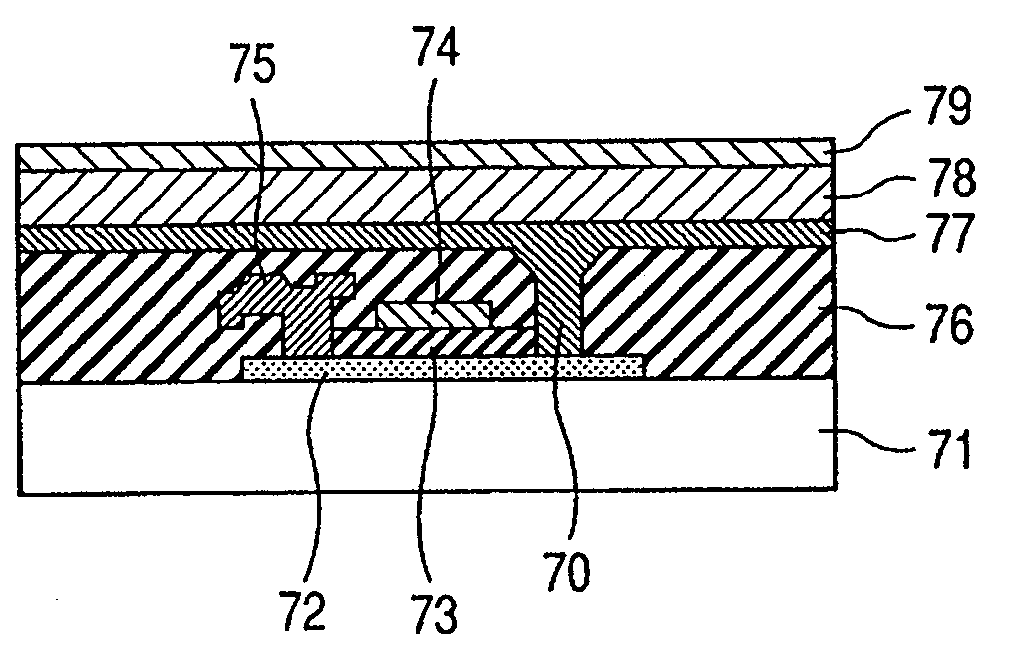
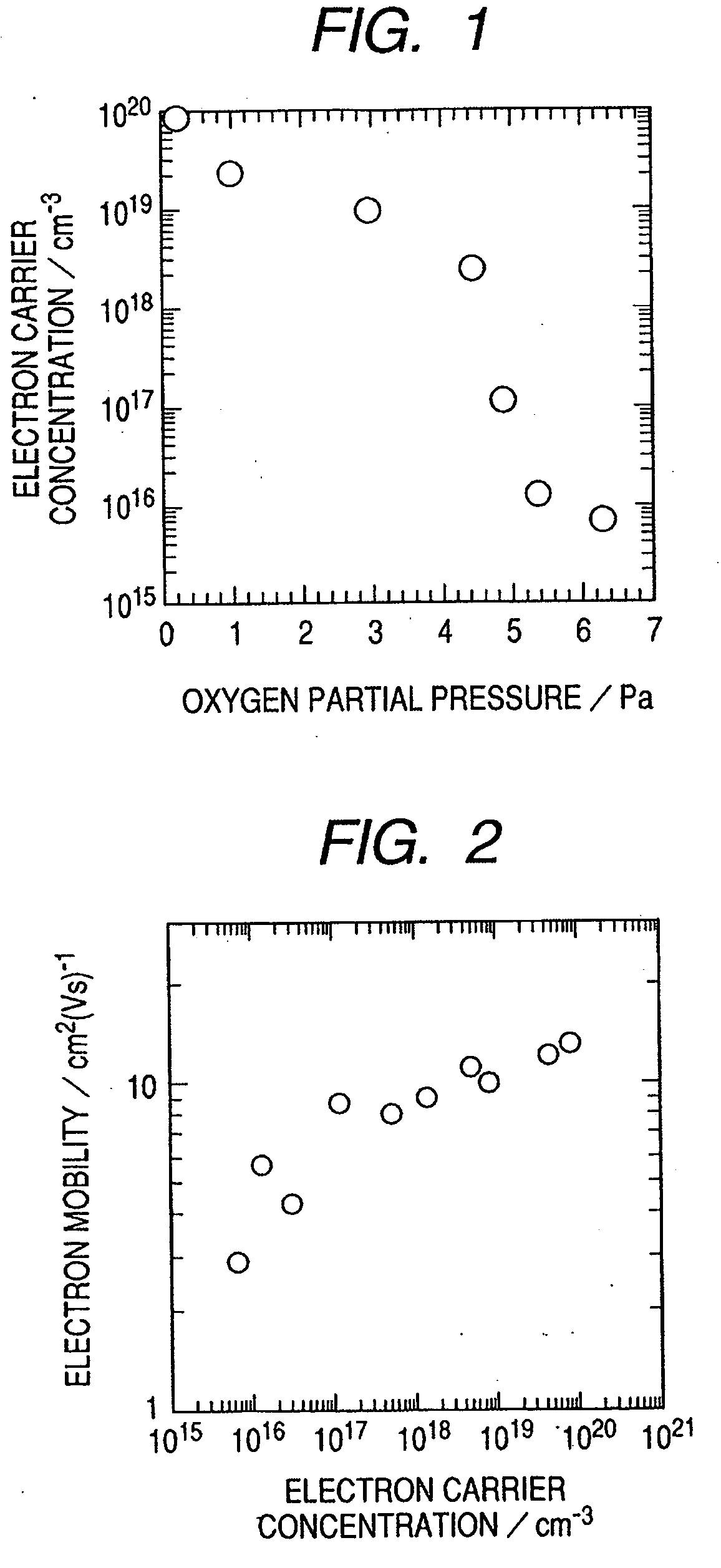
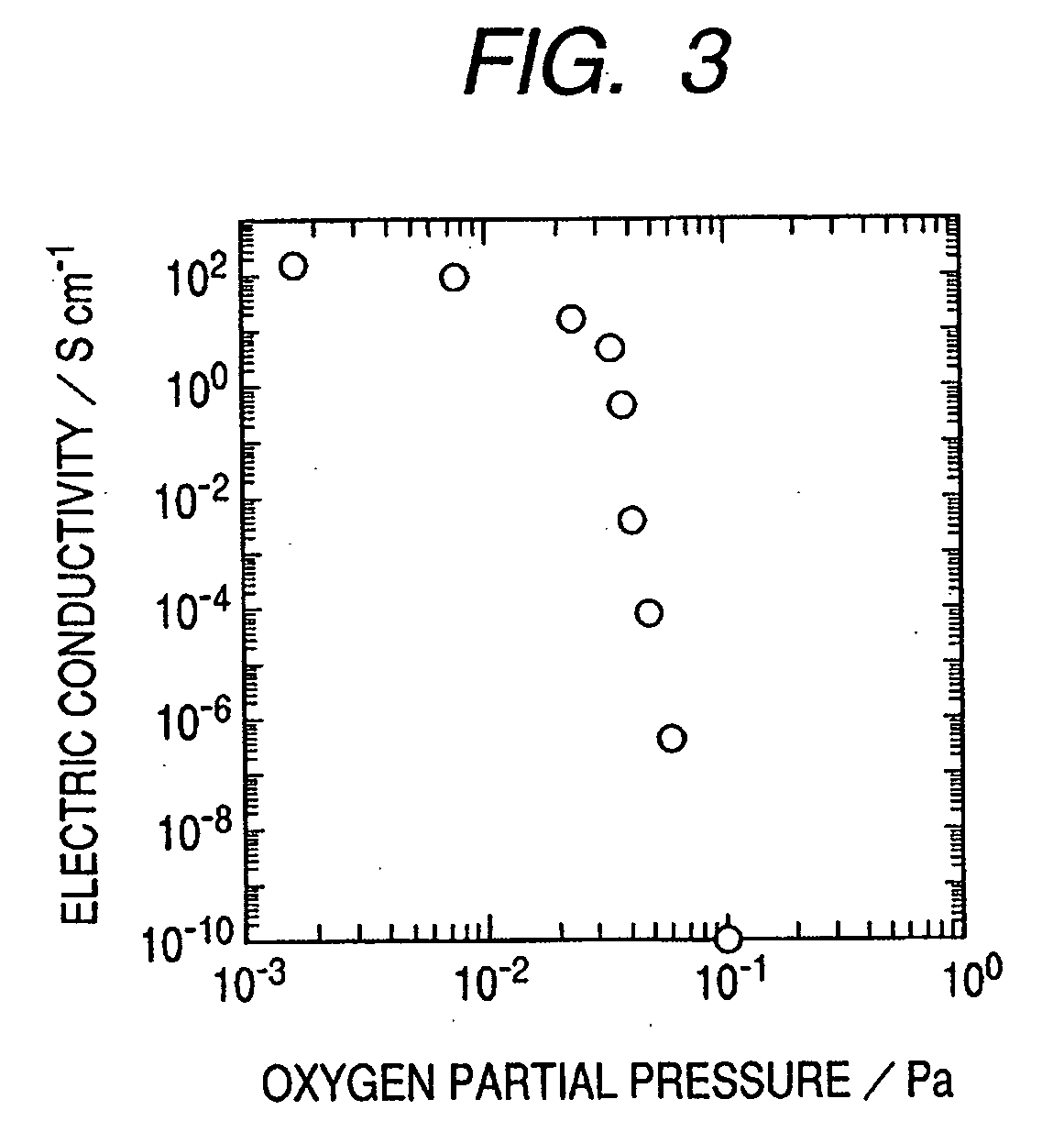
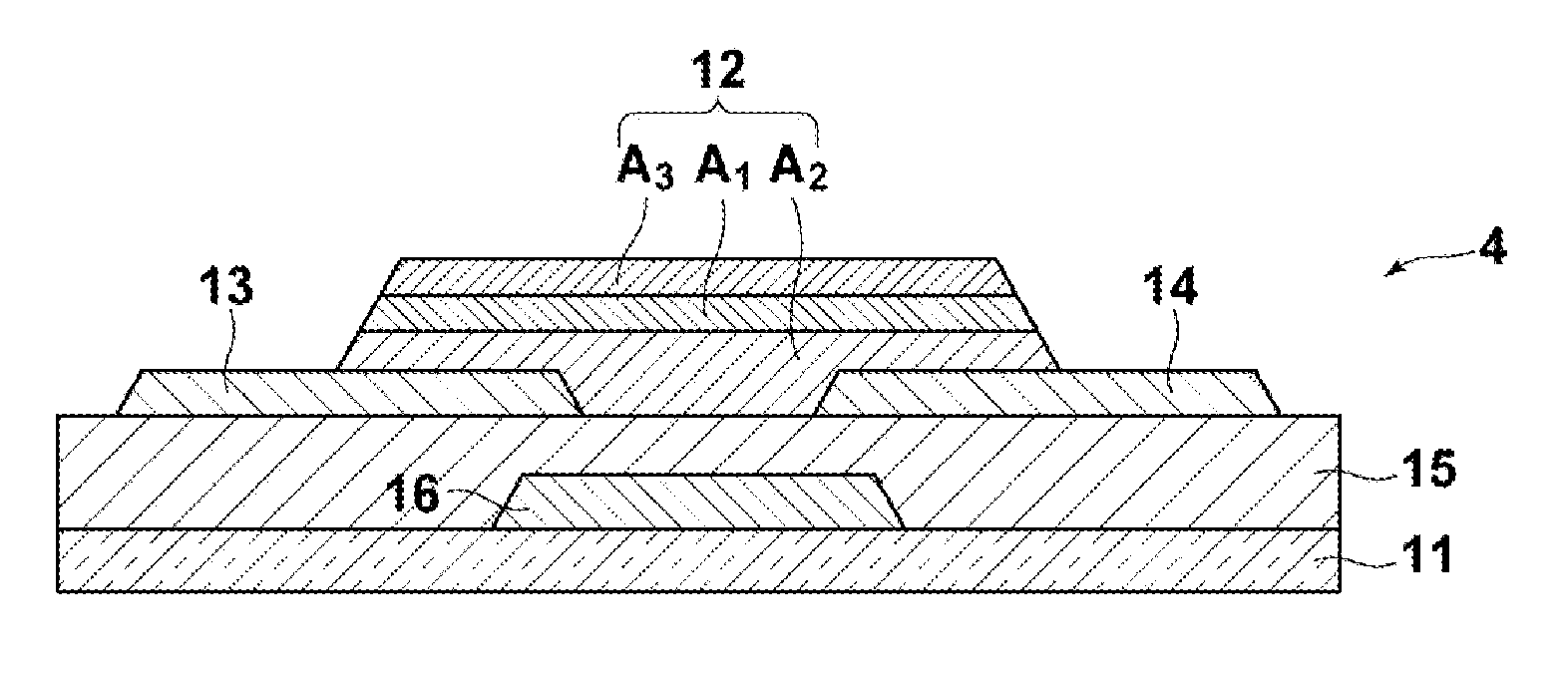
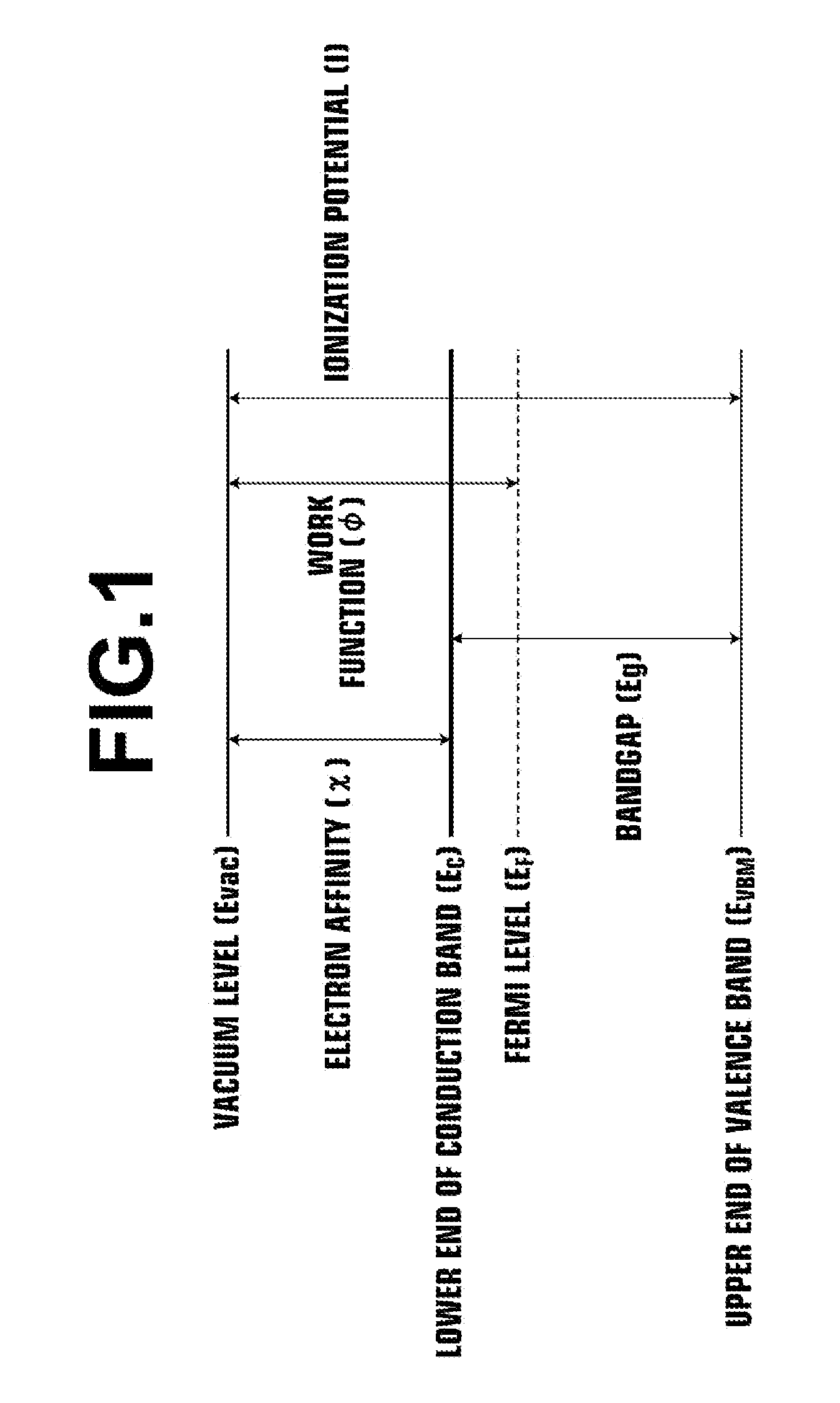
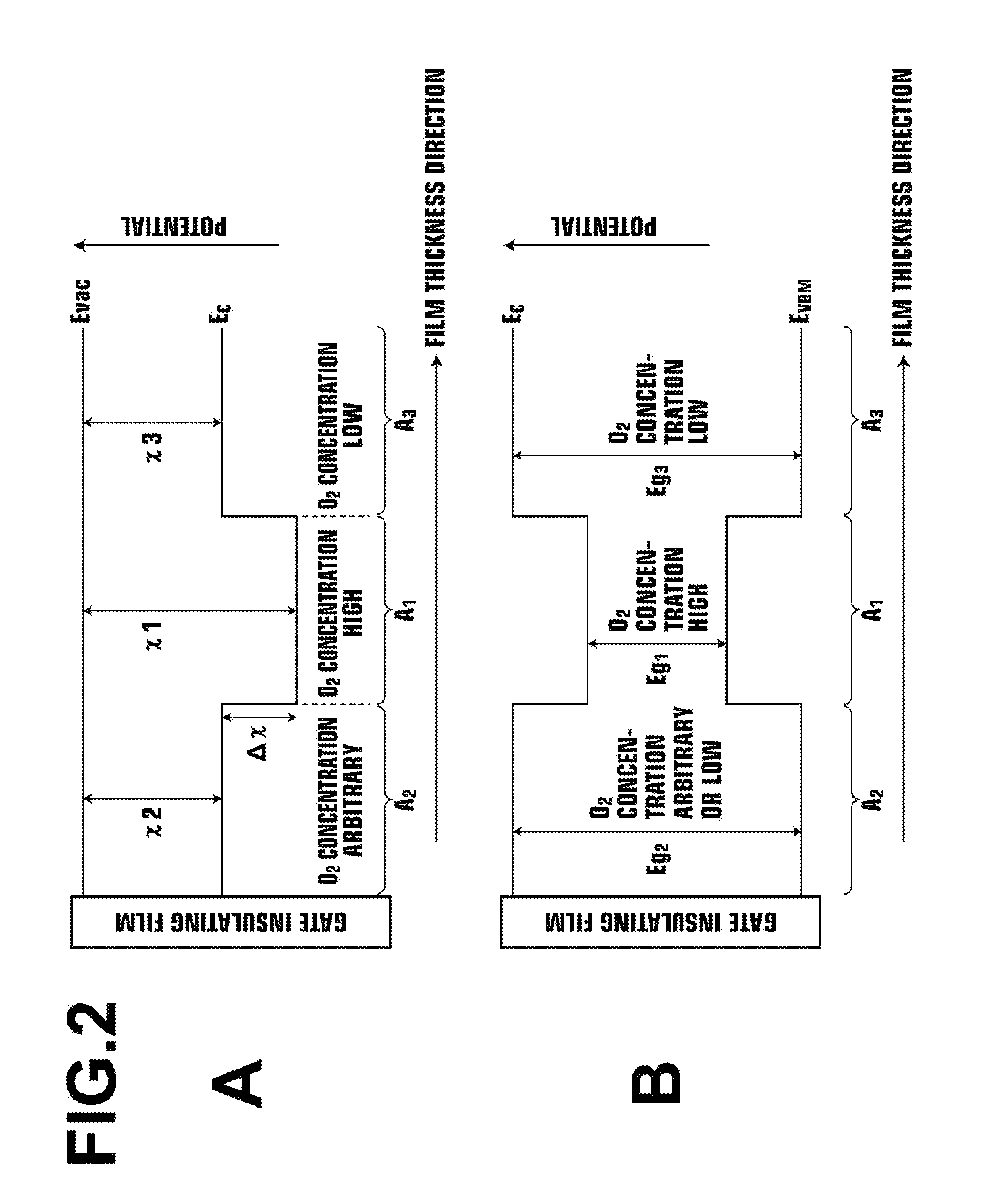
ActiveUS20110140100A1Low mobilityIncrease carrier densityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygenSemiconductor
A thin-film transistor including an oxide semiconductor layer is disclosed. The oxide semiconductor layer includes a first area, a second area and a third area forming a well-type potential in the film-thickness direction. The first area forms a well of the well-type potential and has a first electron affinity. The second area is disposed nearer to the gate electrode than the first area and has a second electron affinity smaller than the first electron affinity. The third area is disposed farther from the gate electrode than the first area and has a third electron affinity smaller than the first electron affinity. At least an oxygen concentration at the third area is lower than an oxygen concentration at the first area.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Red phosphorescent compound and organic electroluminescent device using the same
ActiveUS20090085476A1Solve low luminous efficiencyLong luminescence lifetimeIndium organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic electroluminescenceMolecular physics
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Plasma source design
Embodiments of the present invention generally provide a plasma source apparatus, and method of using the same, that is able to generate radicals and / or gas ions in a plasma generation region that is symmetrically positioned around a magnetic core element by use of an electromagnetic energy source. In general, the orientation and shape of the plasma generation region and magnetic core allows for the effective and uniform coupling of the delivered electromagnetic energy to a gas disposed in the plasma generation region. In general, the improved characteristics of the plasma formed in the plasma generation region is able to improve deposition, etching and / or cleaning processes performed on a substrate or a portion of a processing chamber that is disposed downstream of the plasma generation region.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Red phosphorescent compound and organic electroluminescent device using the same
ActiveUS20070104979A1High color purityLong life-timeIndium organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensDopantHydrogen
Disclosed herein is a red phosphorescent compound of the following Formula 1: wherein is R1 is a C1-C4 alkoxy group, R2, R3, R4 and R5 are independently selected from hydrogen, C1-C4 alkyl groups and C1-C4 alkoxy groups, and is selected from 2,4-pentanedione, 2,2,6,6,-tetramethylheptane-3,5-dione, 1,3-propanedione, 1,3-butanedione, 3,5-heptanedione, 1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentanedione, 1,1,1,5,5,5-hexafluoro-2,4-pentanedione, and 2,2-dimethyl-3,5-hexanedione. Further disclosed herein is an organic electroluminescent (EL) device comprising an anode, a hole injecting layer, a hole transport layer, a light-emitting layer, an electron transport layer, an electron injecting layer, and a cathode laminated in this order wherein one of the red phosphorescent compounds is used as a dopant of the light-emitting layer.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Organic electroluminescent device and material for organic electroluminescent device
ActiveUS20090167167A1Improve performanceHigh electron-accepting propertyOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic electroluminescenceMolecular physics
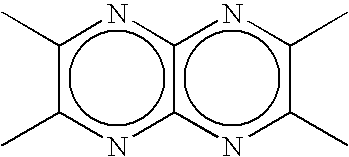
Disclosed is a novel compound useful as a constituent of an organic EL device. Also disclosed is a practical organic EL device using this compound. This organic EL device has low driving voltage, long life, and reduced leakage current. Specifically disclosed is a compound characterized by having at least one structure (1) shown below in a molecule. Structure (1)
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD +1
Red phosphorescence compounds and organic electroluminescence device using the same
ActiveUS7740957B2High color purityLong durabilityIndium organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensDopantOrganic electroluminescence
Red phosphorescence compounds and organic electro-luminescence device using the same are disclosed. In an organic electroluminescence device including an anode, a hole injecting layer, a hole transport layer, a light emitting layer, an electron transport layer, an electron injecting layer, and a cathode serially deposited on one another, the organic electroluminescence device may use a compound as a dopant of the light emitting layer.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Plasma source design
Embodiments of the present invention generally provide a plasma source apparatus, and method of using the same, that is able to generate radicals and / or gas ions in a plasma generation region that is symmetrically positioned around a magnetic core element by use of an electromagnetic energy source. In general, the orientation and shape of the plasma generation region and magnetic core allows for the effective and uniform coupling of the delivered electromagnetic energy to a gas disposed in the plasma generation region. In general, the improved characteristics of the plasma formed in the plasma generation region is able to improve deposition, etching and / or cleaning processes performed on a substrate or a portion of a processing chamber that is disposed downstream of the plasma generation region.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method For Depositing an Amorphous Carbon Film with Improved Density and Step Coverage
ActiveUS20080003824A1High densityLower thermal budgetPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarbon layerKrypton
A method for depositing an amorphous carbon layer on a substrate includes the steps of positioning a substrate in a chamber, introducing a hydrocarbon source into the processing chamber, introducing a heavy noble gas into the processing chamber, and generating a plasma in the processing chamber. The heavy noble gas is selected from the group consisting of argon, krypton, xenon, and combinations thereof and the molar flow rate of the noble gas is greater than the molar flow rate of the hydrocarbon source. A post-deposition termination step may be included, wherein the flow of the hydrocarbon source and the noble gas is stopped and a plasma is maintained in the chamber for a period of time to remove particles therefrom.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
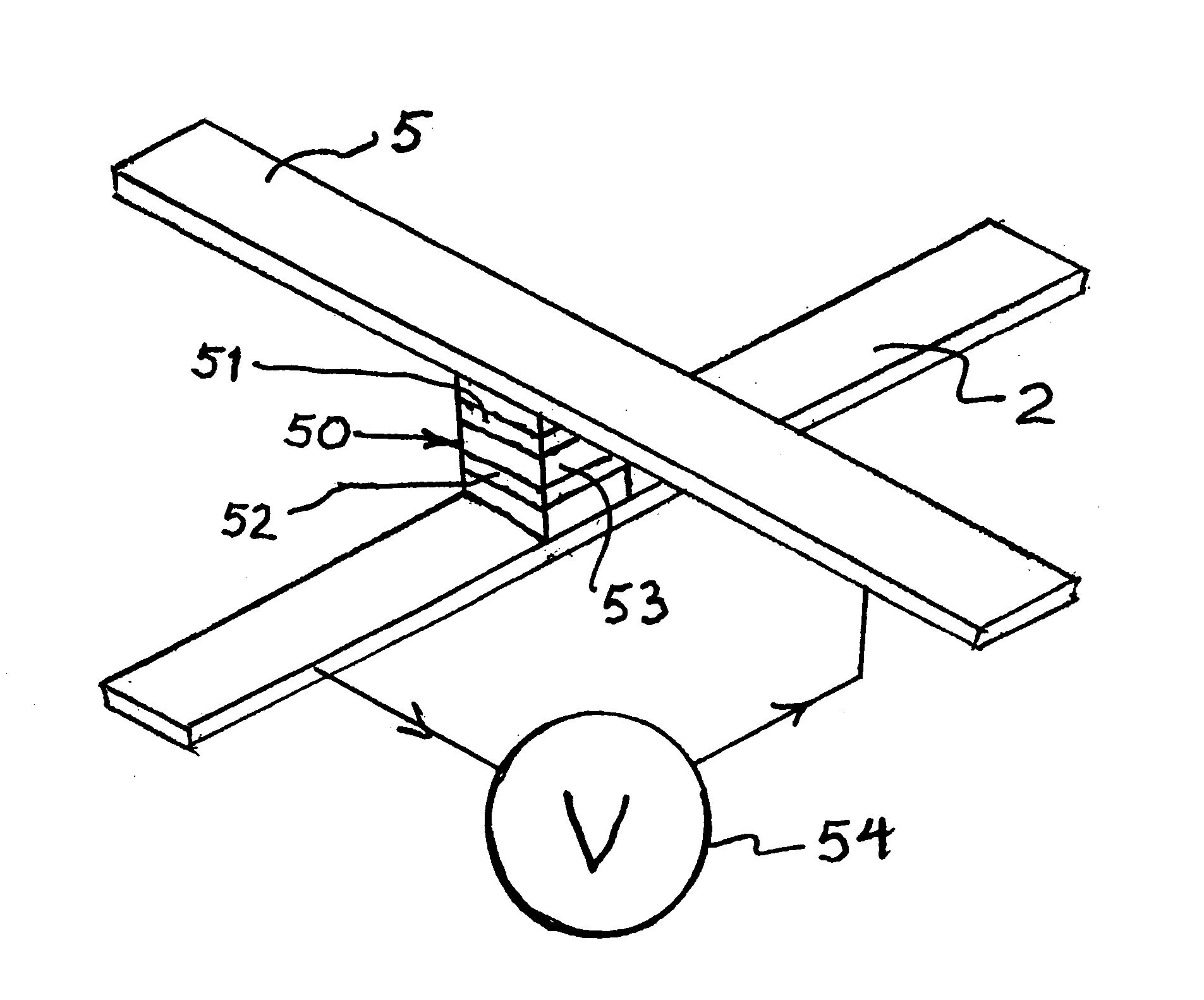
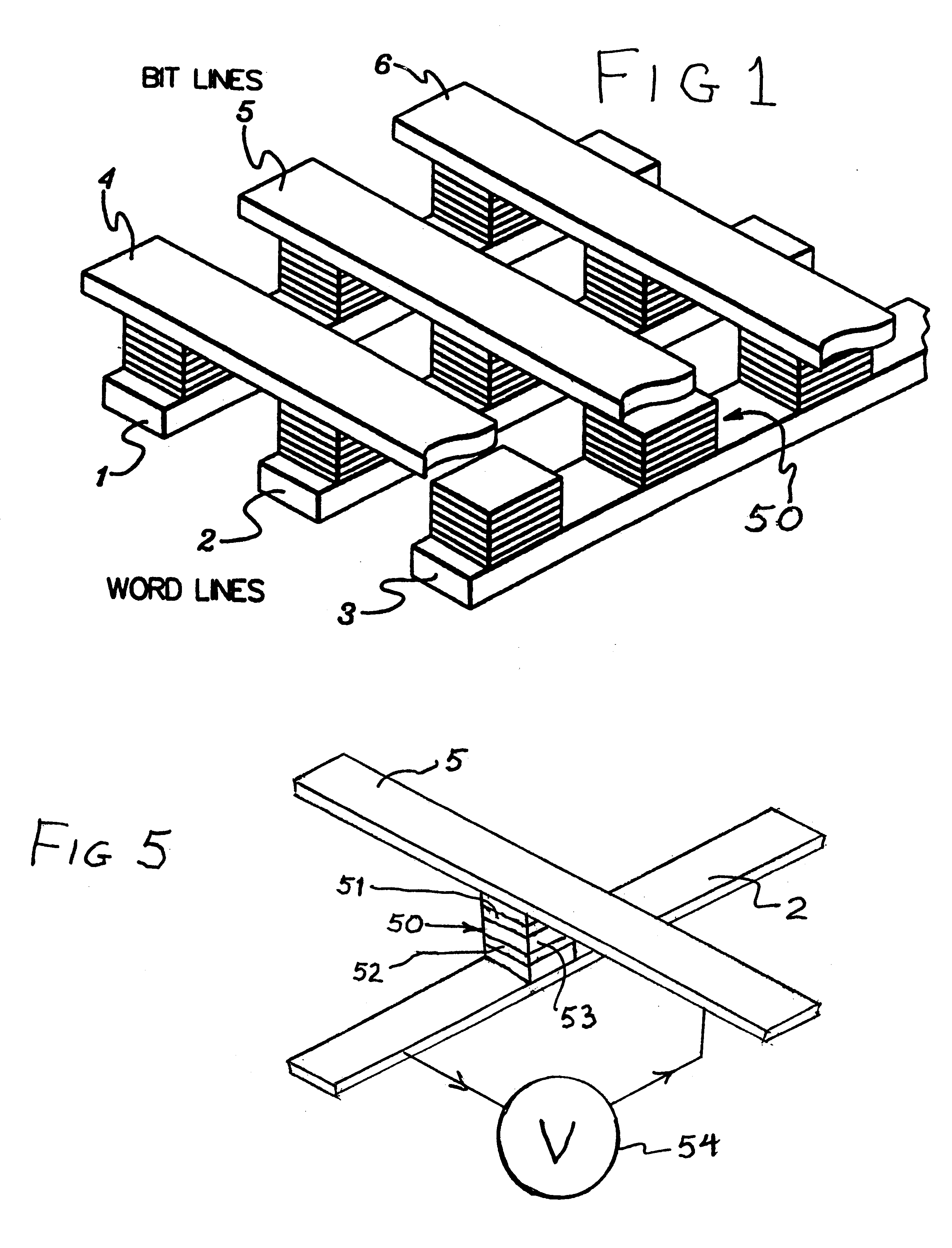
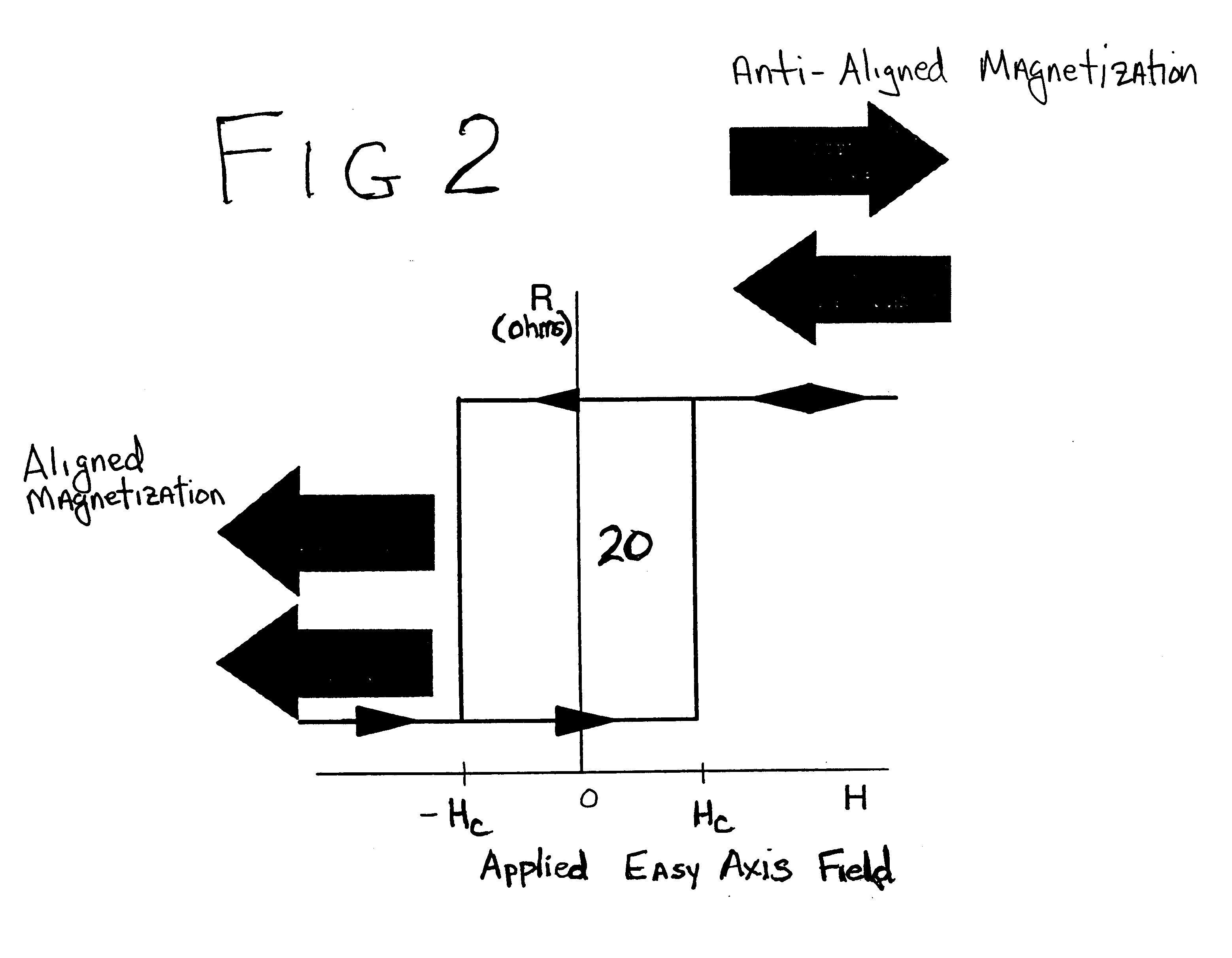
Thermally-assisted magnetic random access memory (MRAM)
It is important to ensure good selectivity of a single magnetic tunnel junction storage cell within a memory array without affecting nearby storage cells. For this purpose, this memory array of storage cells preferably comprises a) an array of electrically conducting bit lines and electrically conducting word lines which form intersections therebetween, b) a storage cell disposed at each of said intersections, each storage cell comprising at least one reversible magnetic region or layer characterized by a magnetization state which can be reversed by applying thereto a selected external magnetic field, said reversible magnetic layer comprising a material whose magnetization state is more easily reversed upon a change in the temperature thereof, and c) a temperature change generator for changing the temperature of said reversible magnetic layer of only a selected one of said array of storage cells at any moment. To select a cell, it is preferable to select a cell by using a brief pulse of tunnelling current between the intersecting bit and word lines at that cell in order to provide sufficient Joule heating to facilitate a change in the magnetization state of its reversible magnetic layer, which preferably comprises a ferrimagnetic material.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com