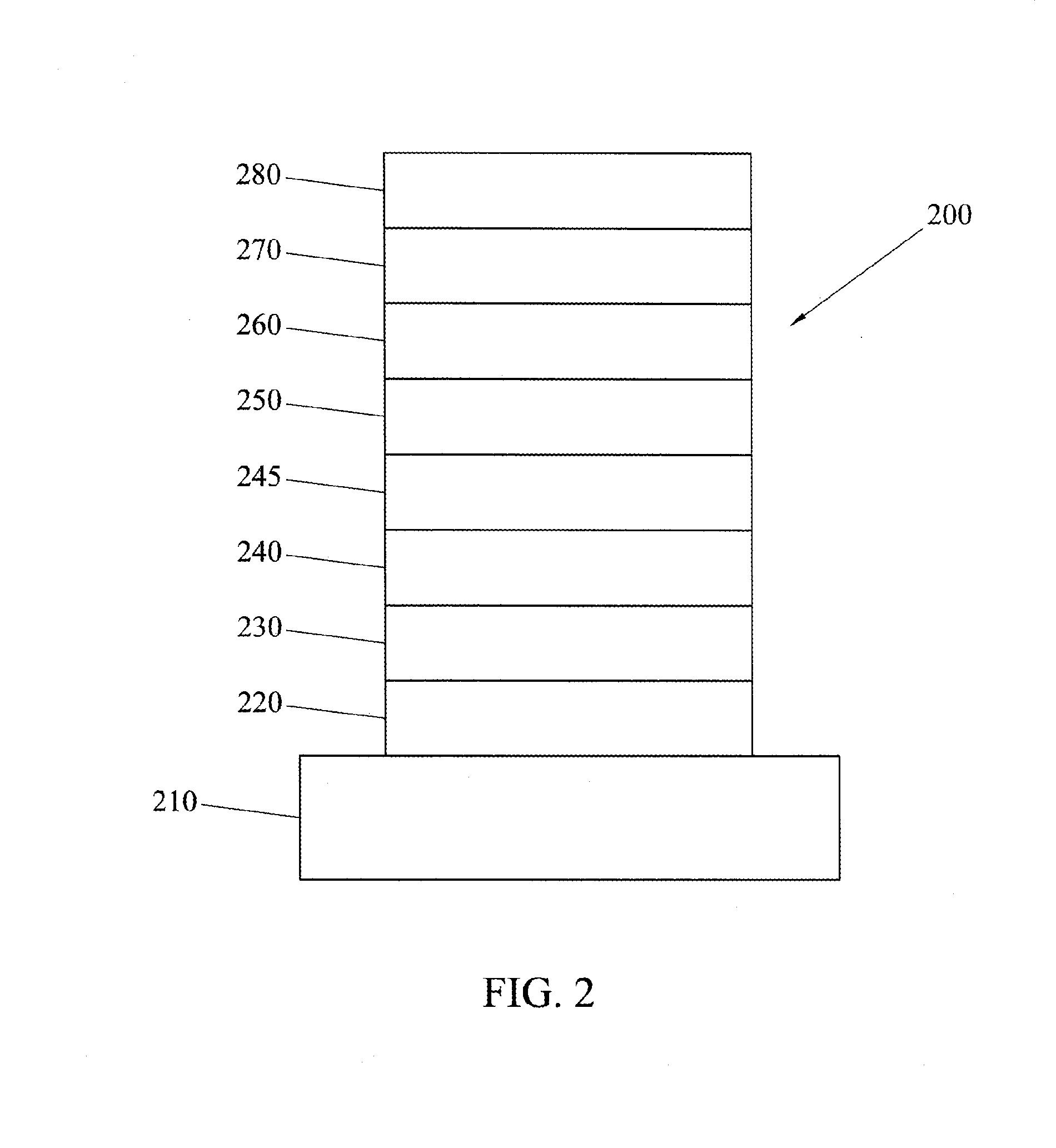
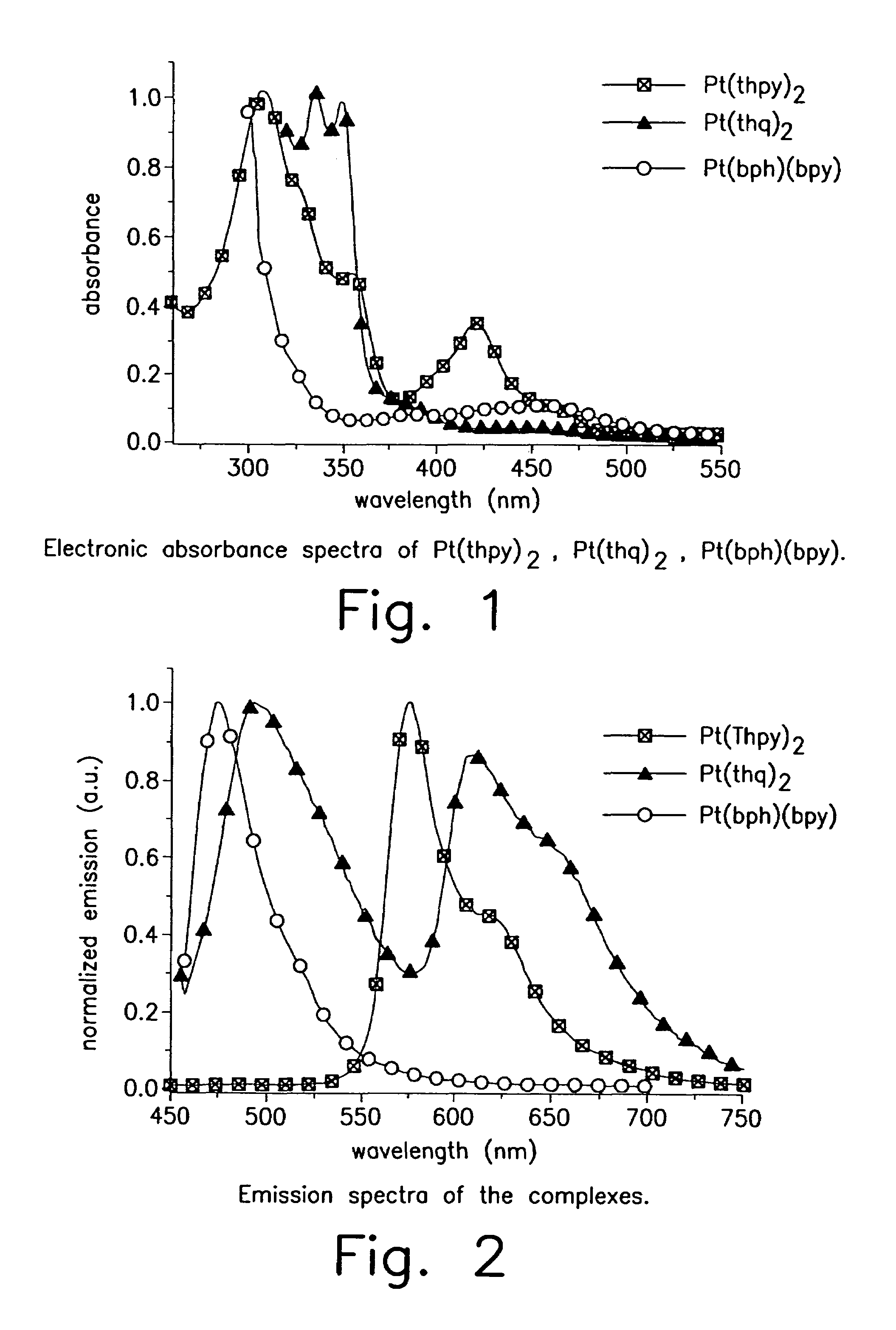
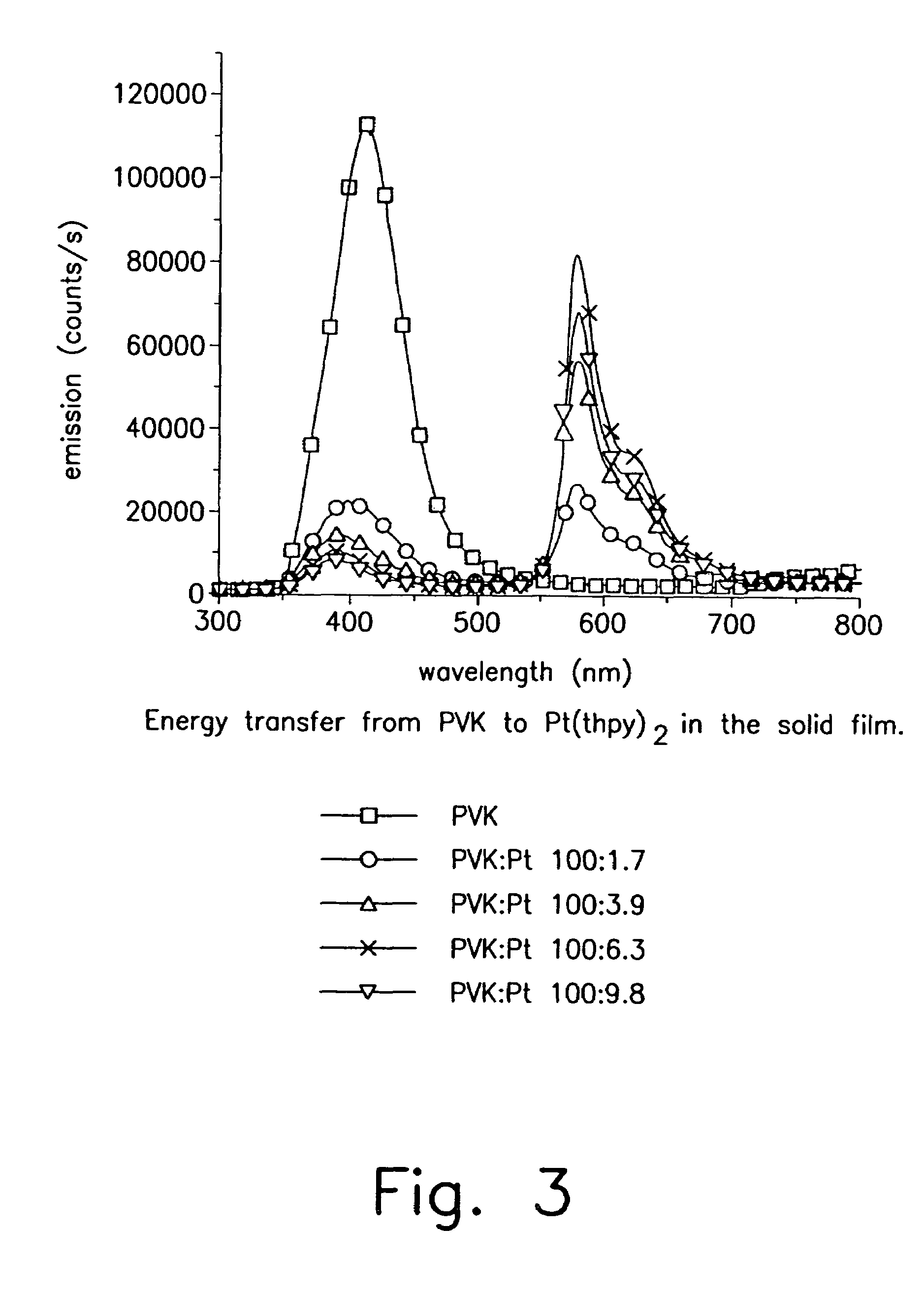
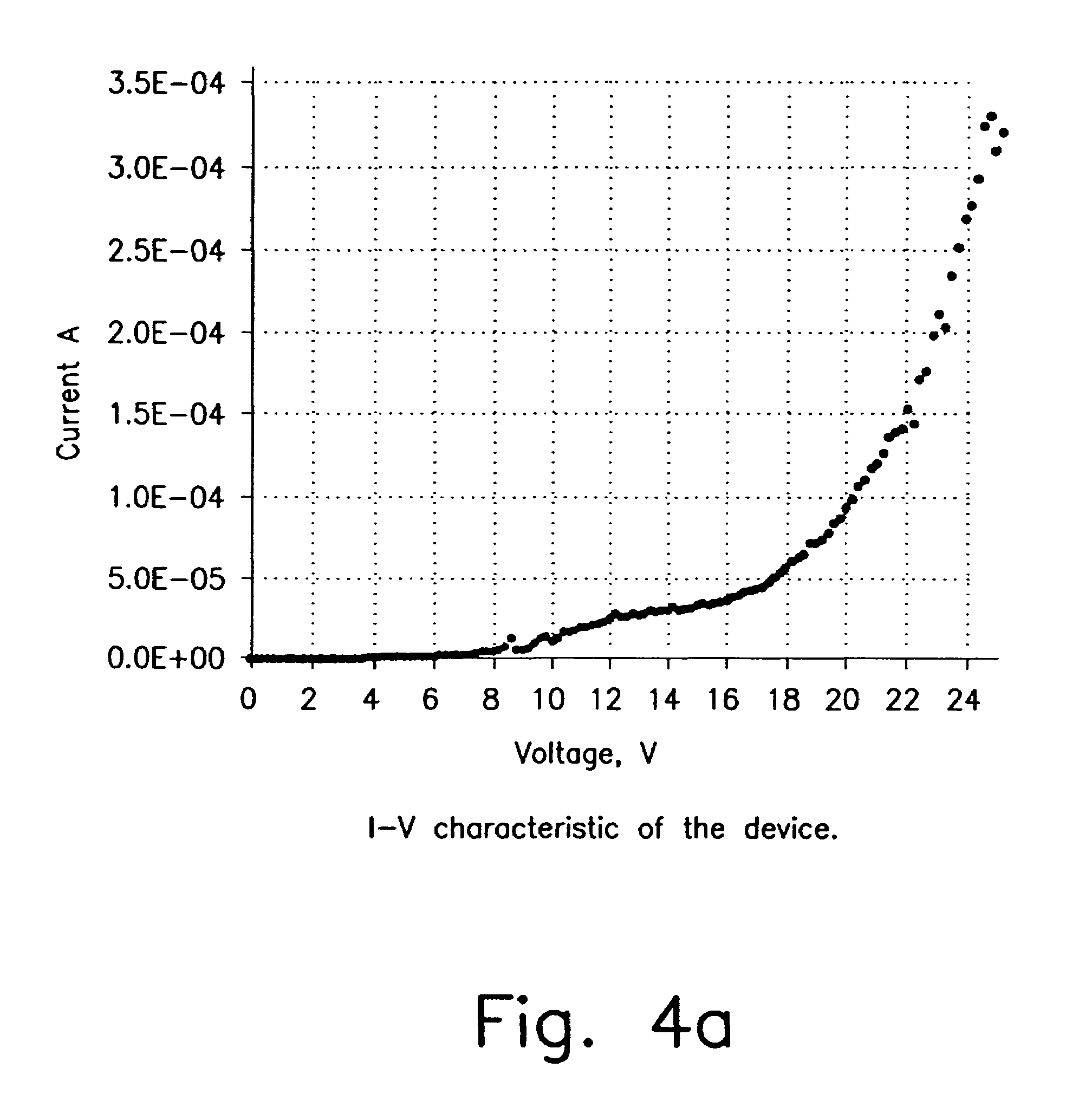
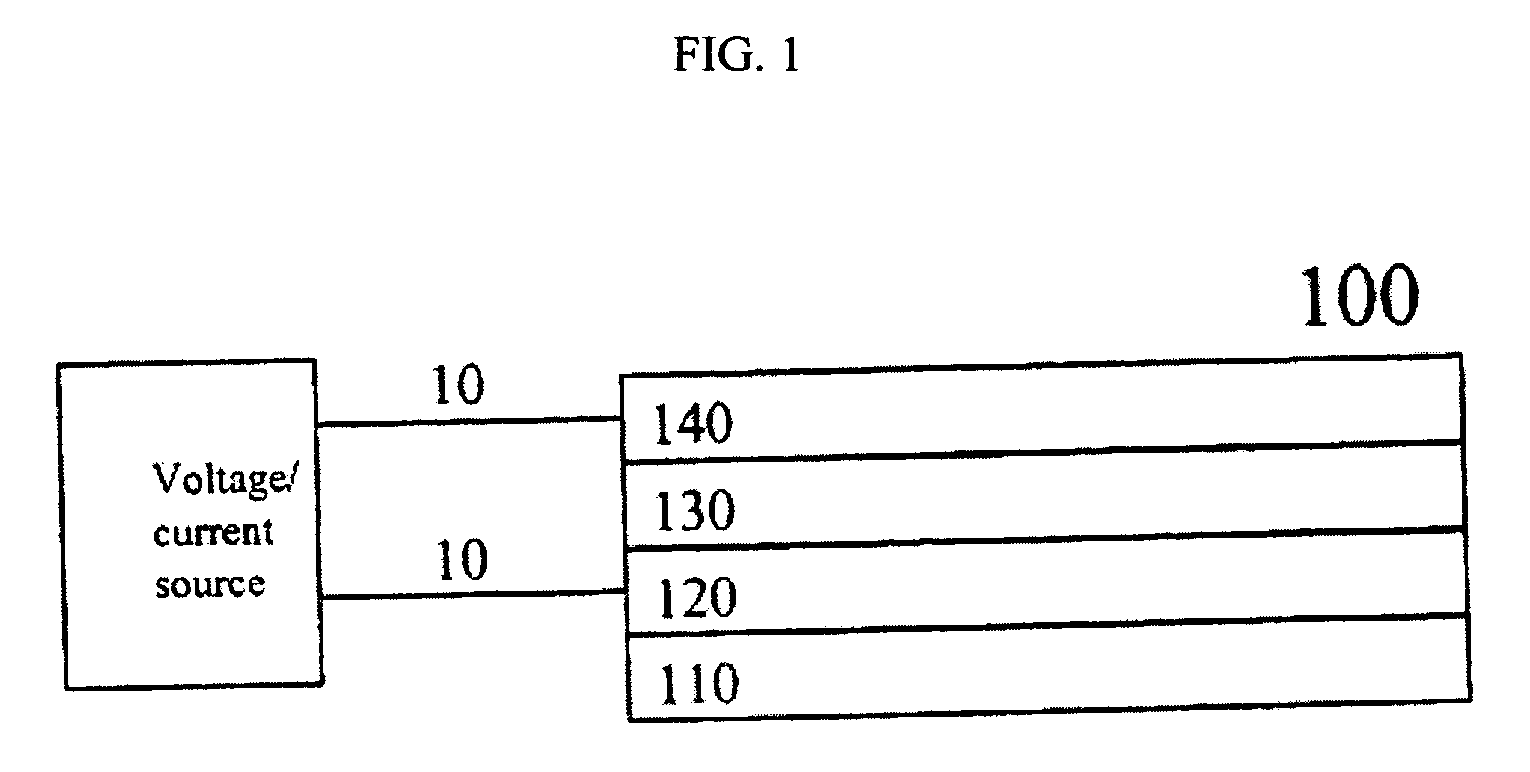
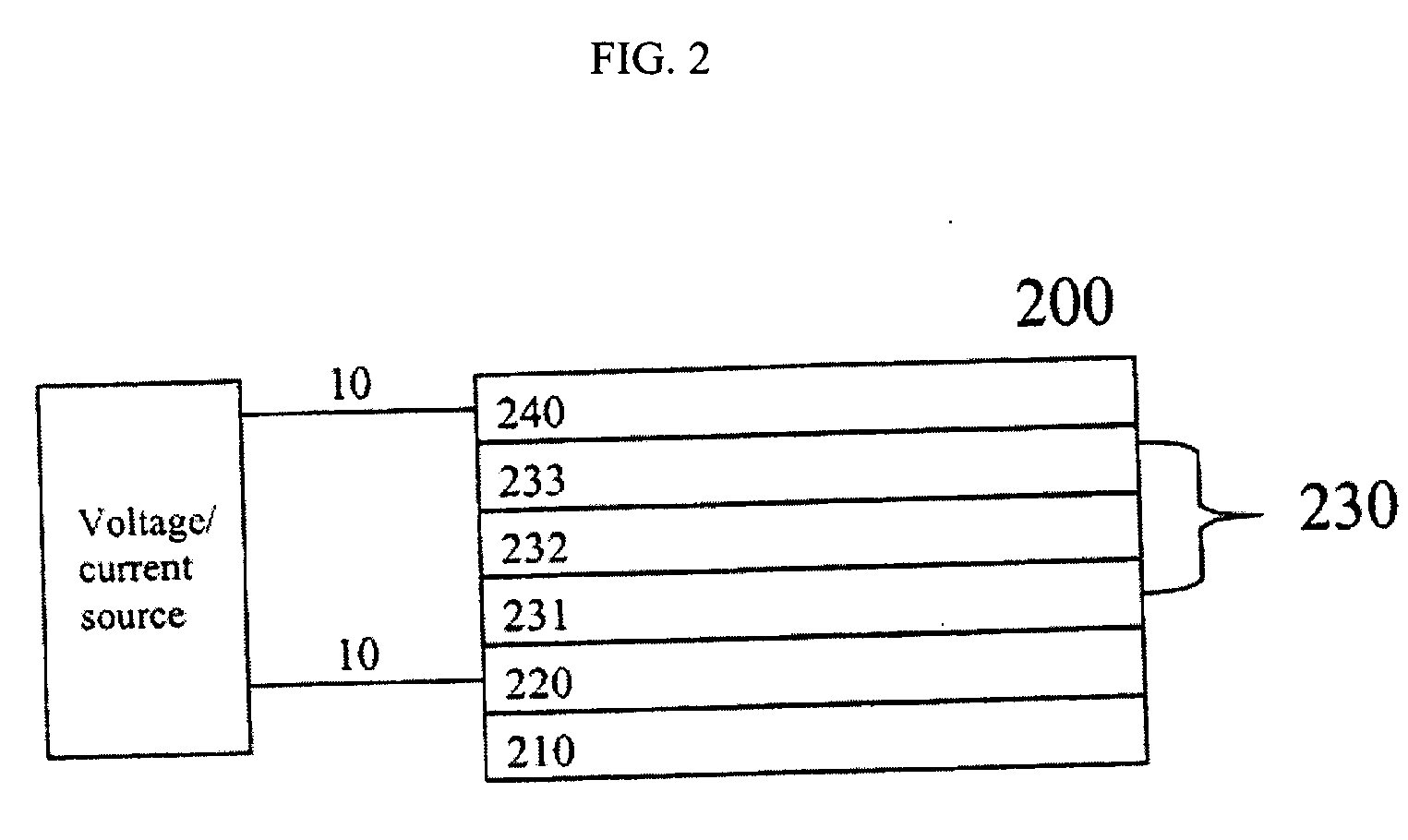
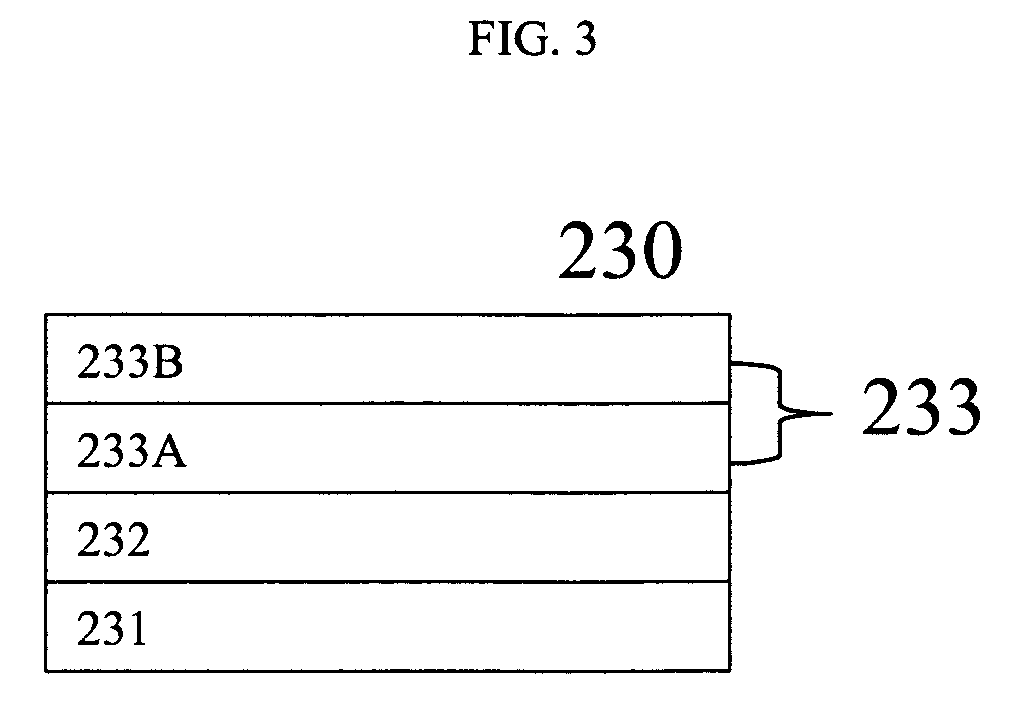
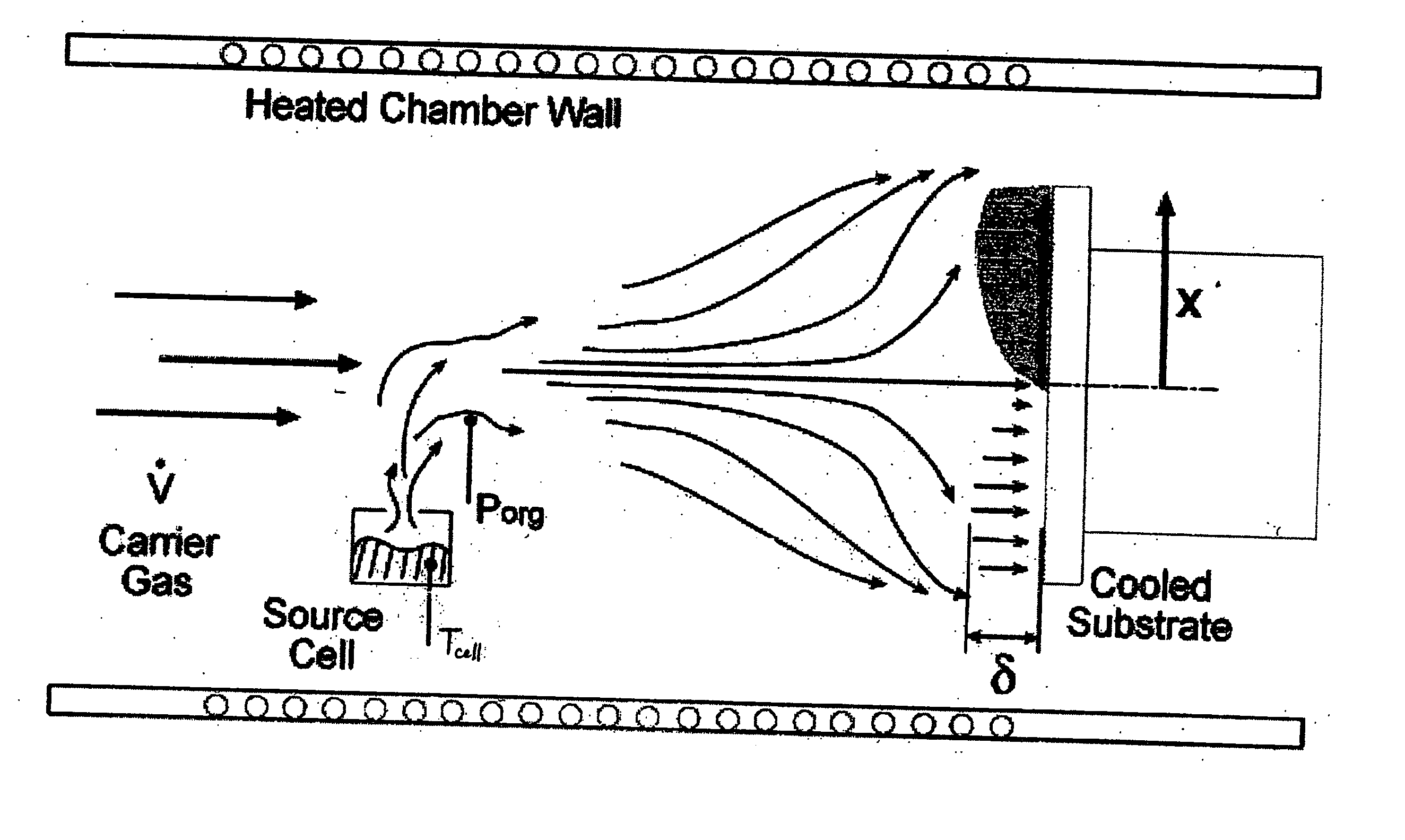
Patents
Literature
1436 results about "Exciton" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
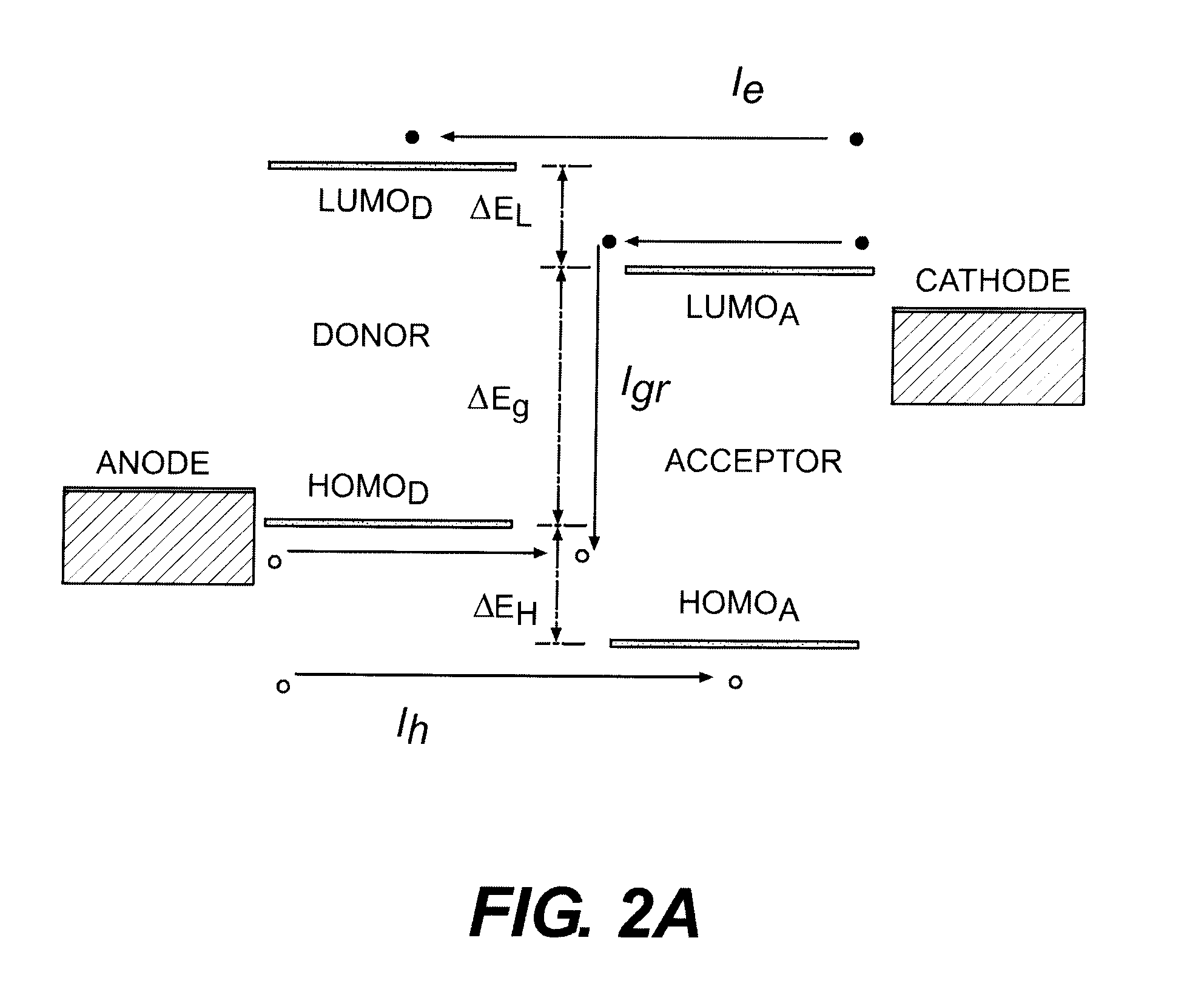
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and an electron hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids. The exciton is regarded as an elementary excitation of condensed matter that can transport energy without transporting net electric charge.
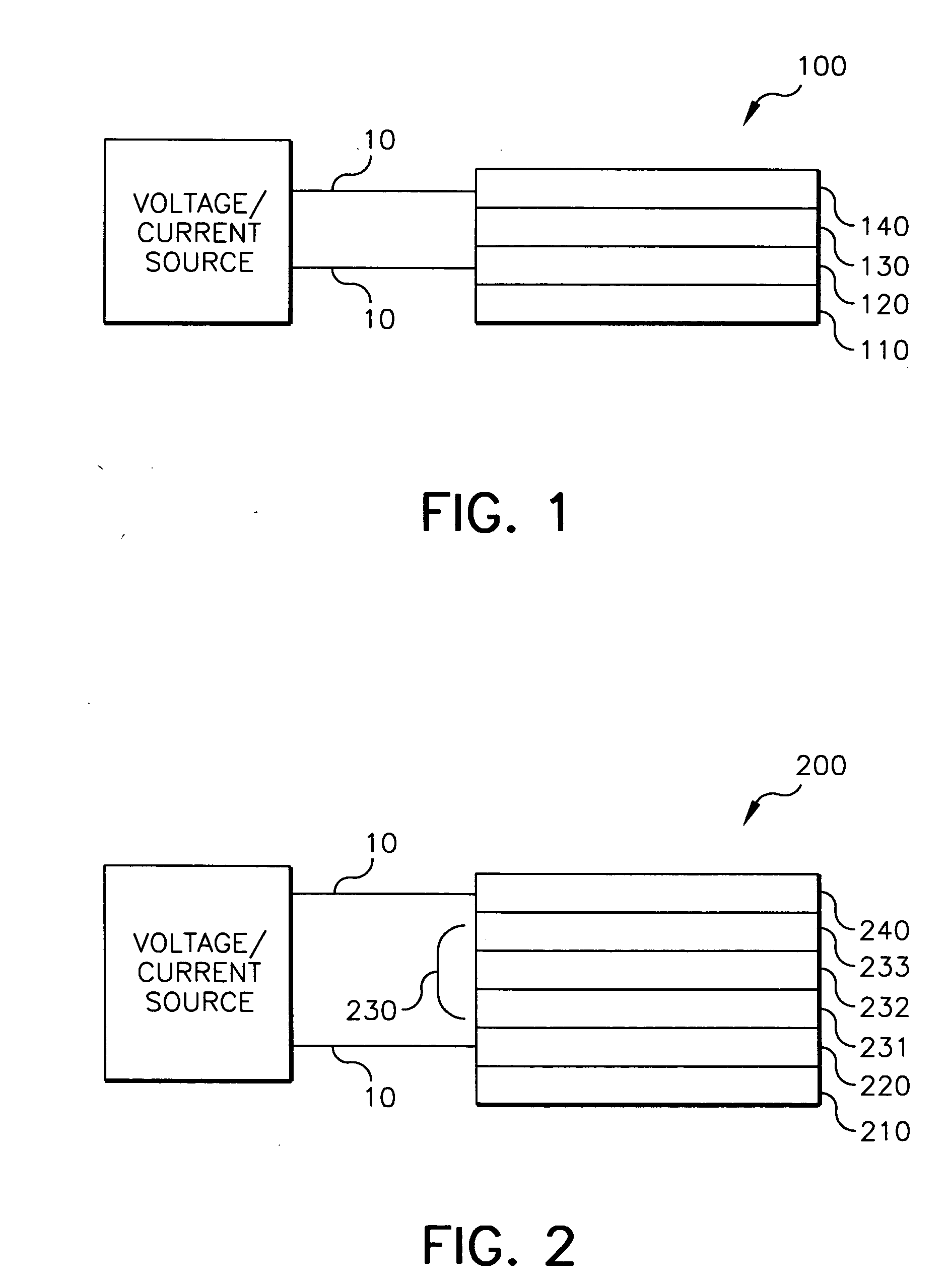
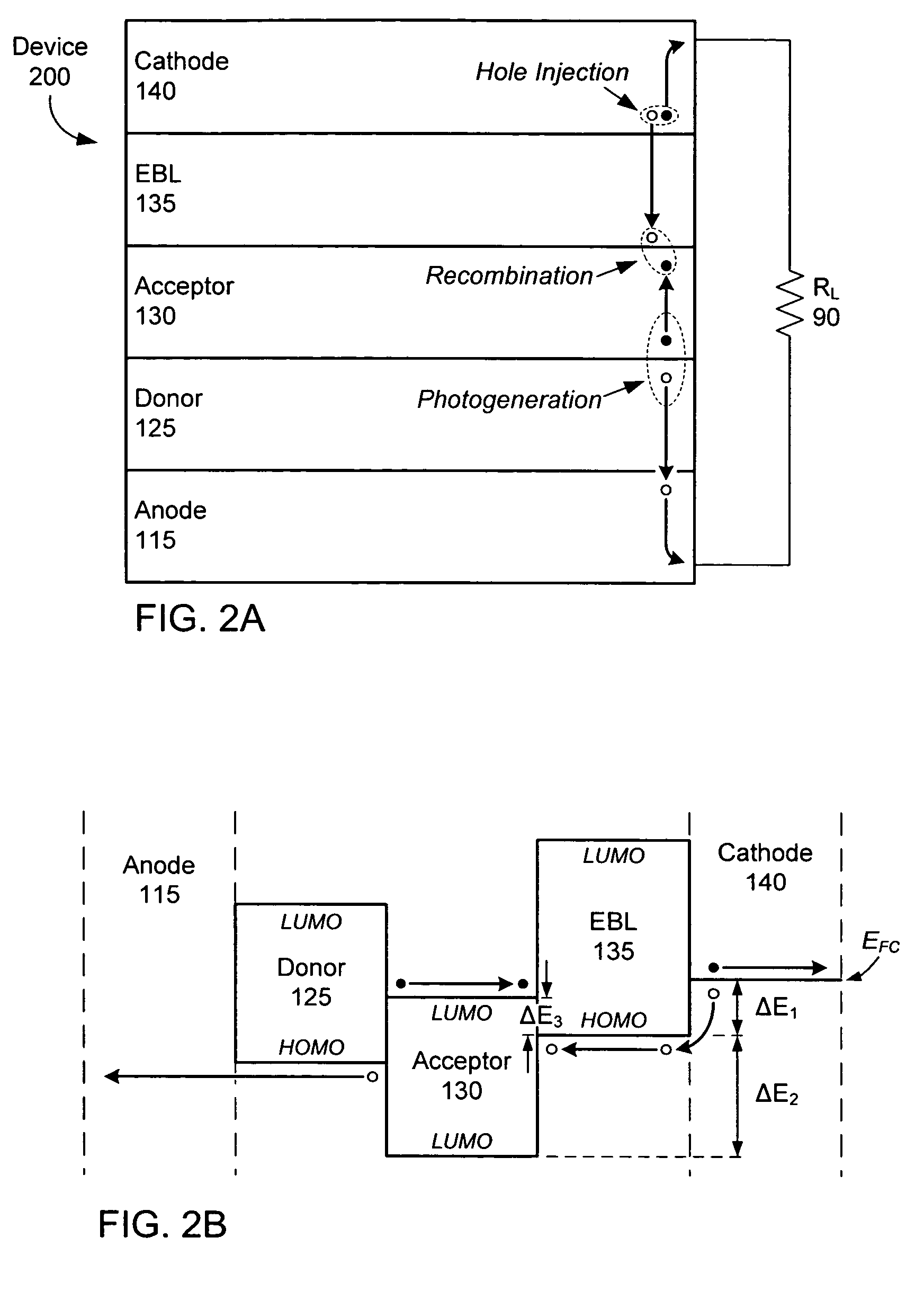
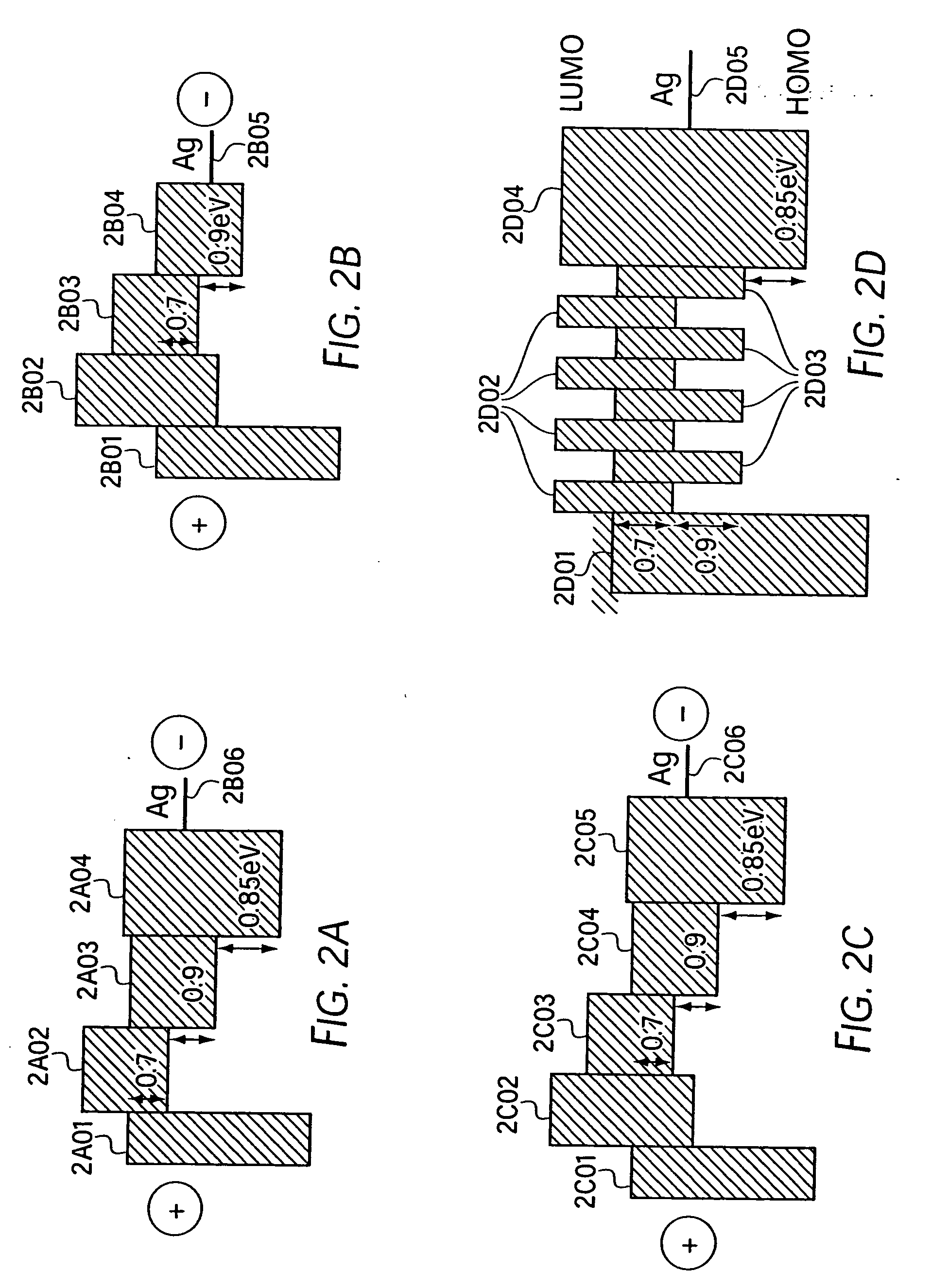
Intersystem crossing agents for efficient utilization of excitons in organic light emitting devices
InactiveUS6310360B1Improve efficiencyElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesOrganic light emitting deviceHost material
Organic light emitting devices are described wherein the emissive layer comprises a host material containing a fluorescent or phosphorescent emissive molecule, which molecule is adapted to luminesce when a voltage is applied across the heterostructure, wherein an intersystem crossing molecule of optical absorption spectrum matched to the emission spectrum of the emissive molecule enhances emission efficiency.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV +1
Solar cells using fullerenes
InactiveUS6580027B2Improve efficiencyIncrease the electric field strengthPV power plantsNanoinformaticsSolar cellFullerene
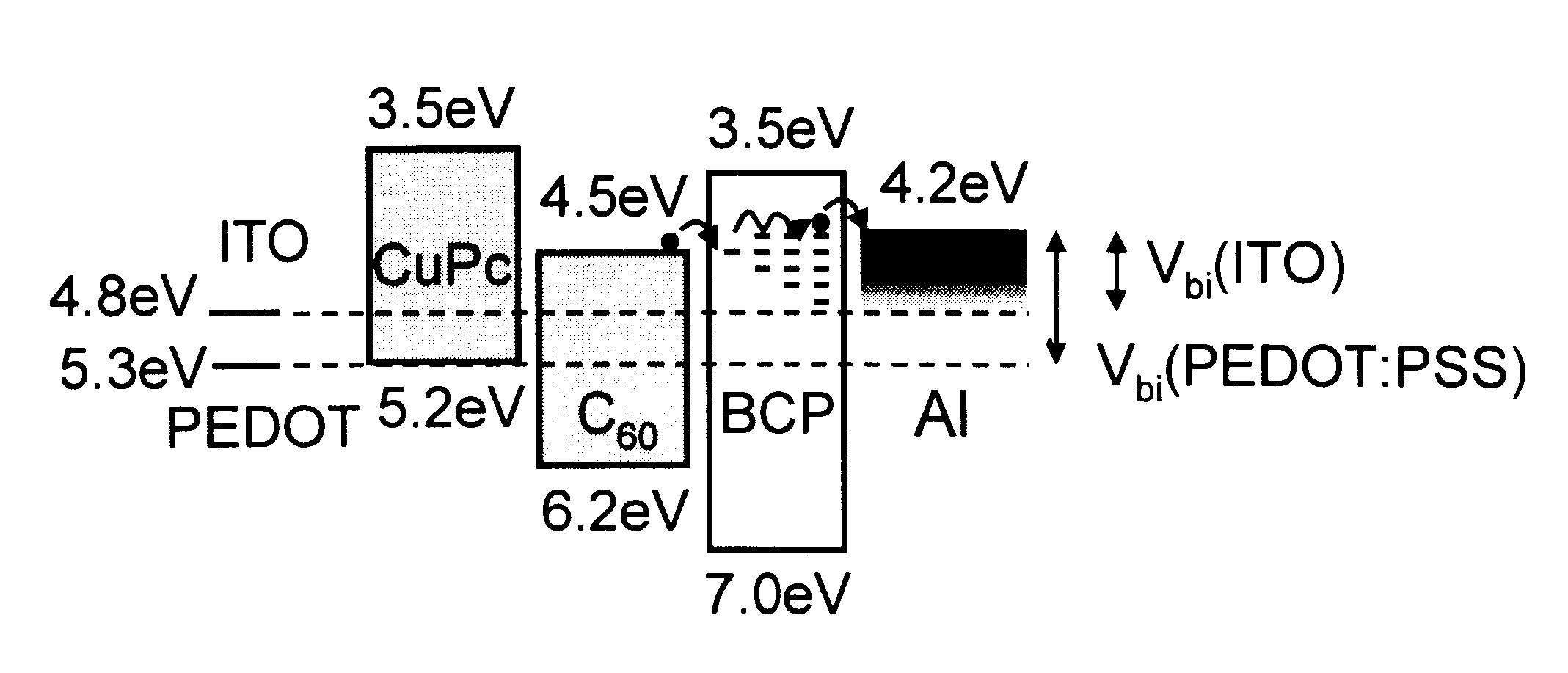
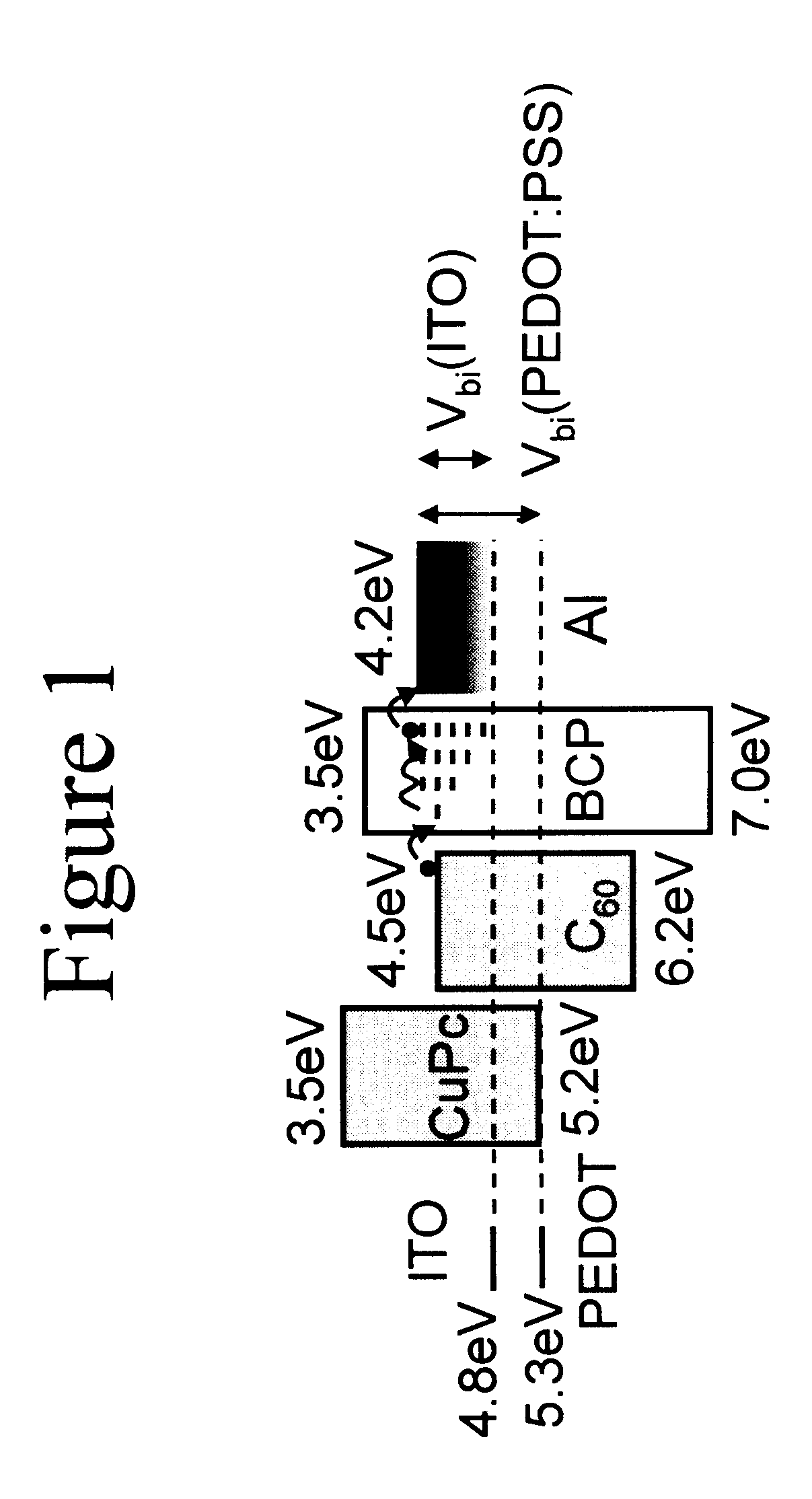
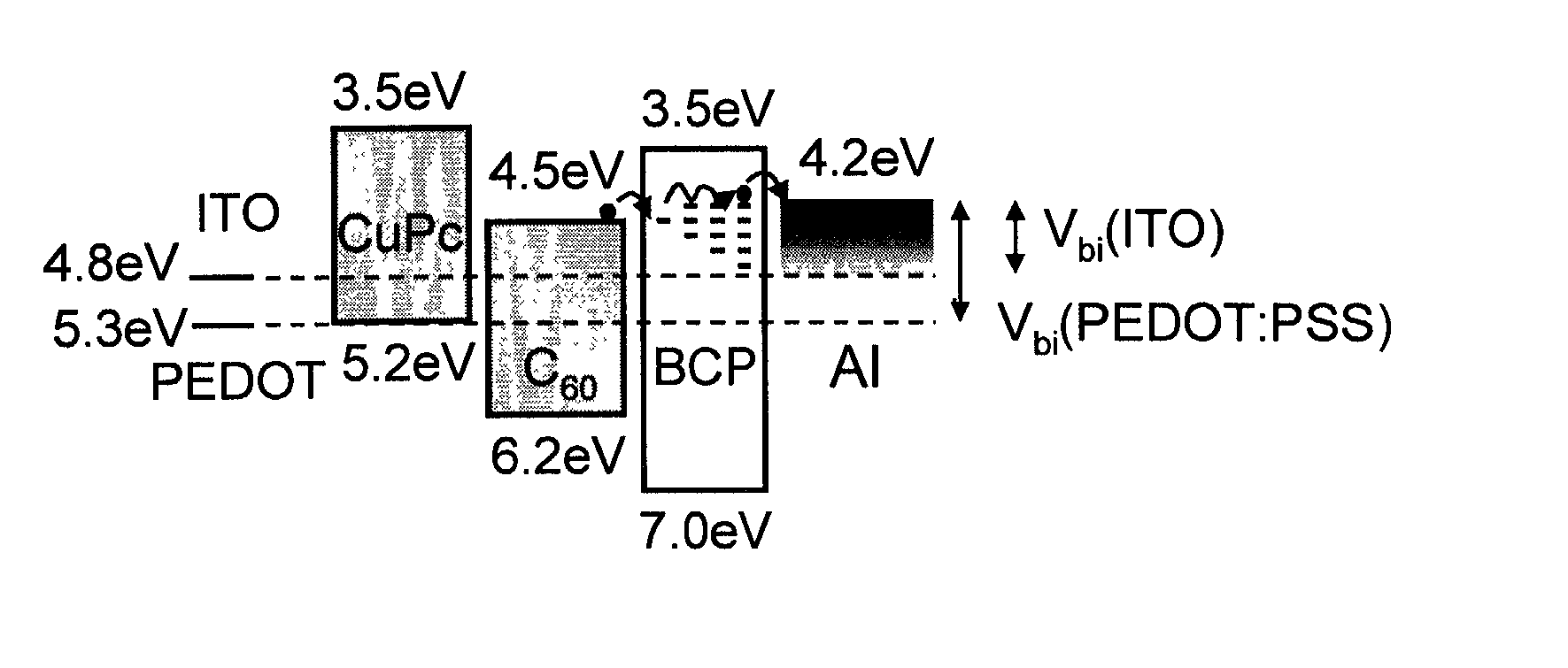
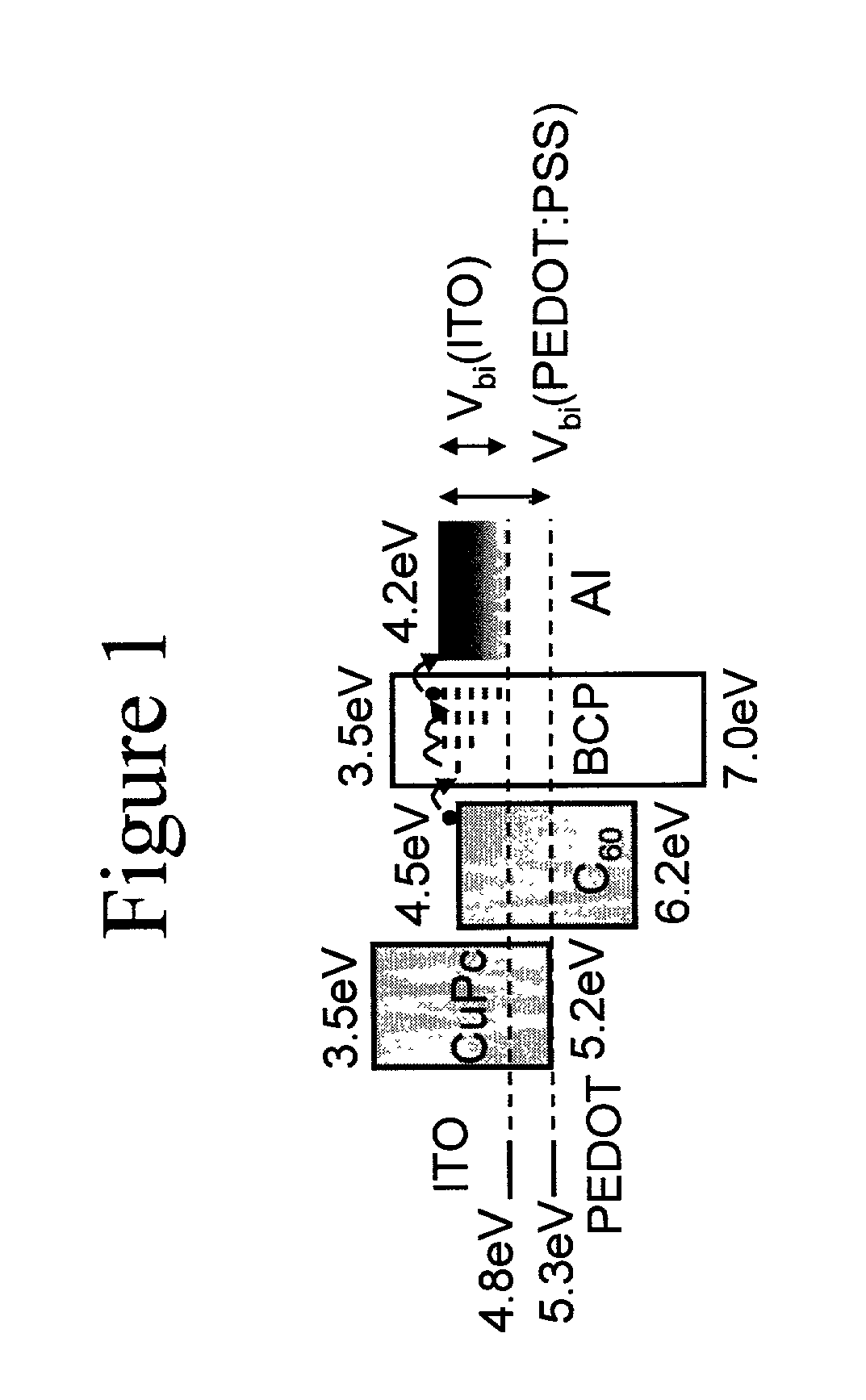
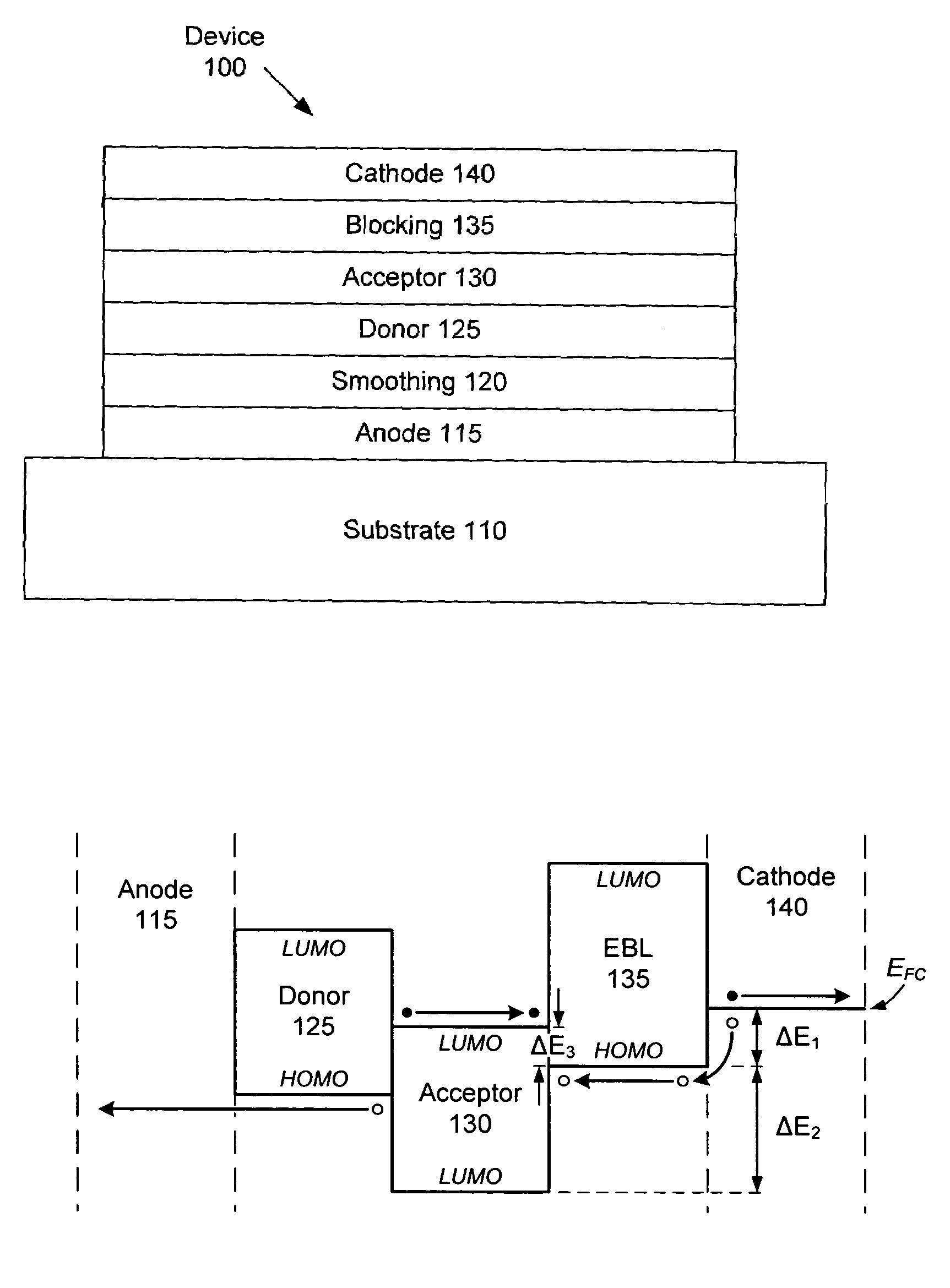
Organic photosensitive optoelectronic devices are disclosed. The devises comprise photoconductive organic thin films in a heterostructure, which include an exciton blocking layer to enhance device efficiency. The use of fullerenes in the electron conducting layer has lead to devices with high efficiency. Single heterostructure, stacked and wave-guide type embodiments are disclosed. Devices having multilayer structures and an exciton blocking layer are also disclosed. Guidelines for selection of exciton blocking layers are provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Electron transporting compounds and organic electroluminescent devices using the same
InactiveUS20140284580A1Prolonged lifetime stabilityLow working voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic transmissionPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
Disclosed is a novel compound of Formula 1 and an organic electroluminescent device using the same. In Formula 1, X and Y independently represents a hydrogen, an aromatic or a hetero aromatic hydrocarbon having C5 to C10 carbons; X and Y may be the same or different; Ar1 to Ar2 each represent a hydrogen, an unsubstituted or substituted aromatic hydrocarbon having C4 to C12 carbons, or an unsubstituted or substituted condensed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon having C4 to C12 carbons; Ar1 to Ar2 can form a fused aromatic ring system with the adjacent aromatic hydrocarbons. The compound of Formula 1 is present in the electron injection or a transport material, or an exciton blocking layer in the organic light emitting device, and thereby improving the device stability, lowering the operational voltage.
Owner:E RAY OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
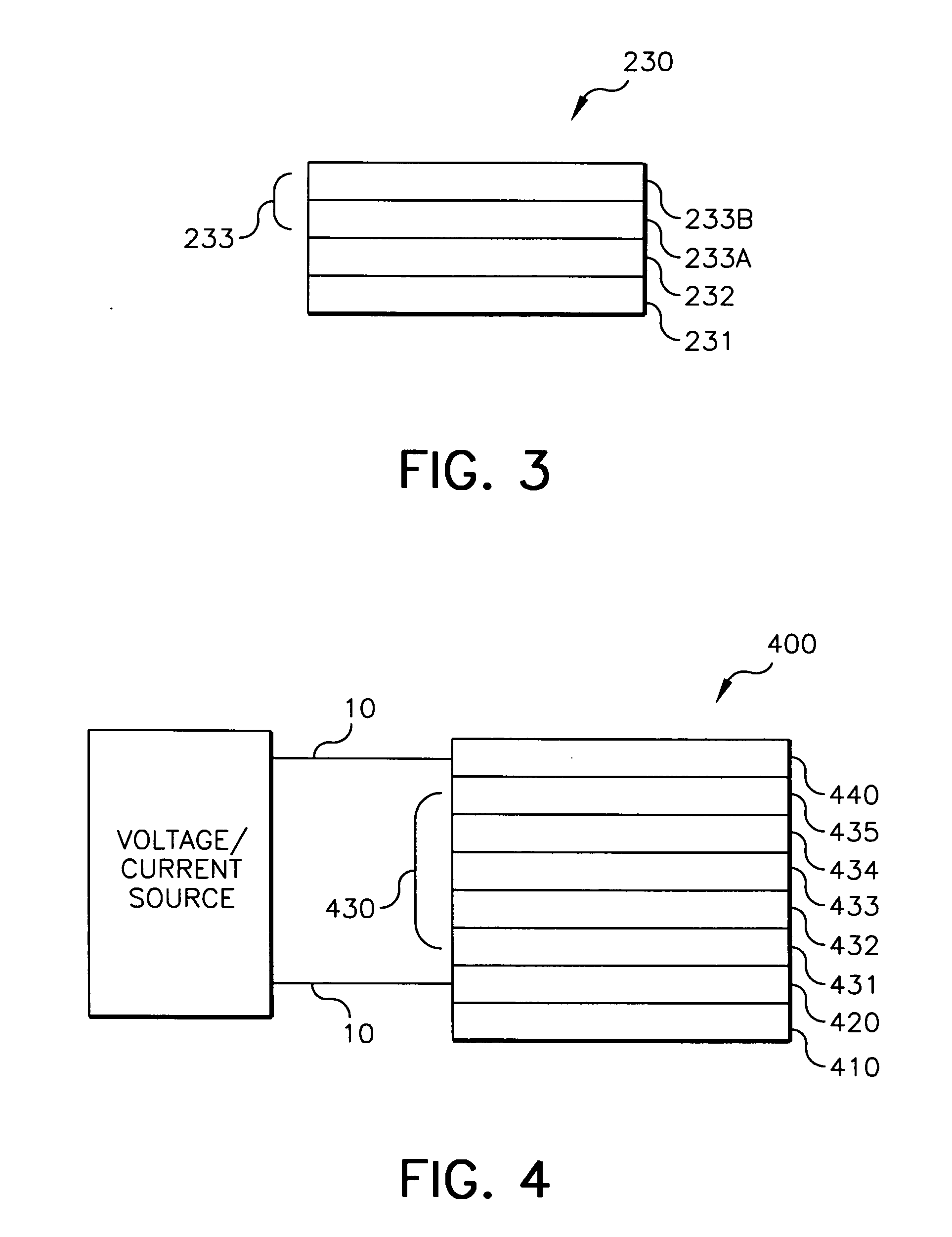
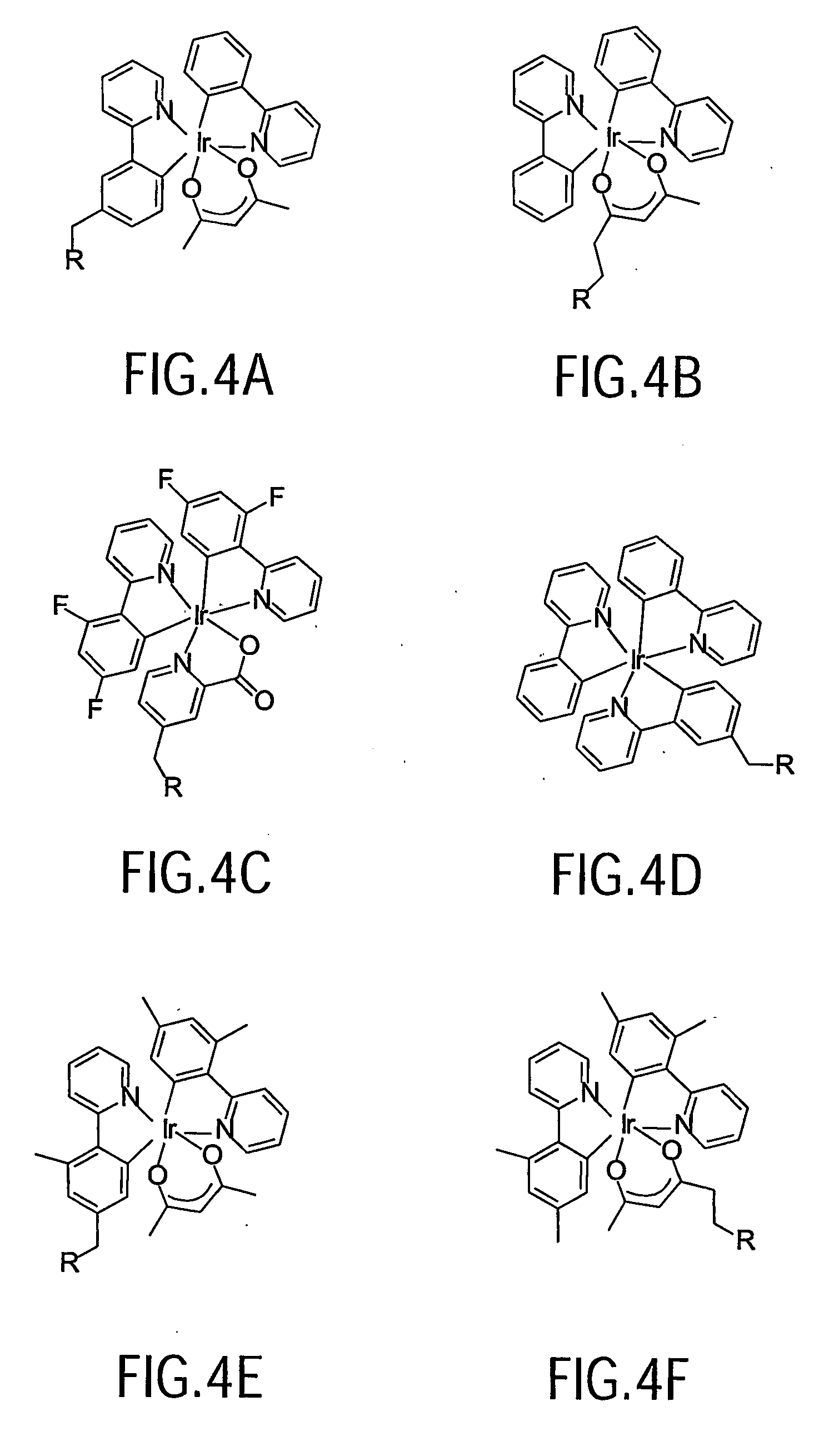
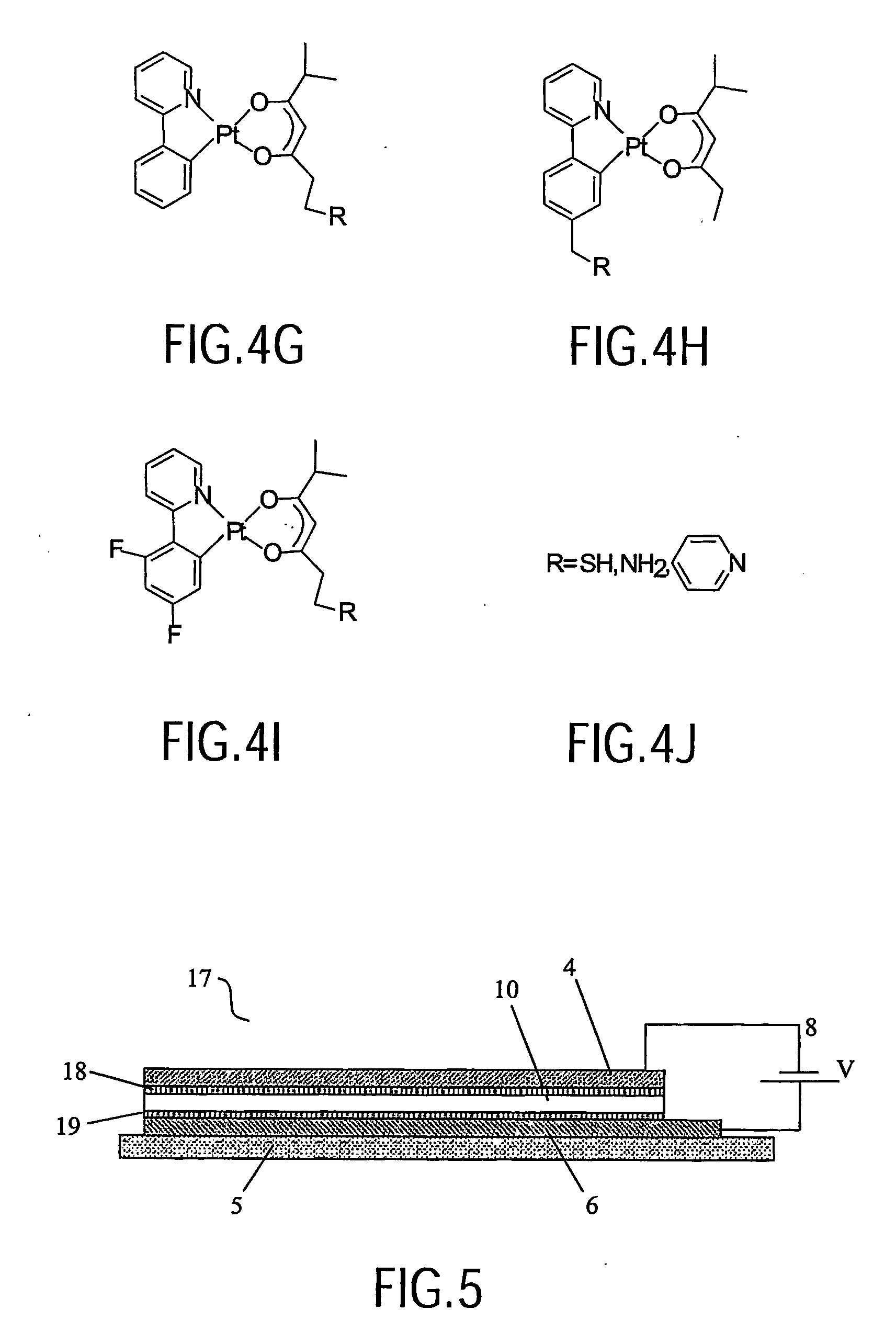
Organometallic complexes as phosphorescent emitters in organic LEDs
InactiveUS7001536B2Easy to combineDeterioration in emission qualityGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsElectroluminescent light sourcesIridiumPt element
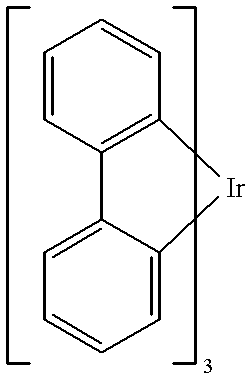
Organic light emitting devices are described wherein the emissive layer comprises a host material containing an emissive molecule, which molecule is adapted to luminesce when a voltage is applied across the heterostructure, and the emissive molecule is selected from the group of phosphorescent organometallic complexes, including cyclometallated platinum, iridium and osmium complexes. The organic light emitting devices optionally contain an exciton blocking layer. Furthermore, improved electroluminescent efficiency in organic light emitting devices is obtained with an emitter layer comprising organometallic complexes of transition metals of formula L2MX, wherein L and X are distinct bidentate ligands. Compounds of this formula can be synthesized more facilely than in previous approaches and synthetic options allow insertion of fluorescent molecules into a phosphorescent complex, ligands to fine tune the color of emission, and ligands to trap carriers.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV +1
Phosphorescent oleds with exciton blocking layer
ActiveUS20060134460A1Improve efficiencyReduce the driving voltageDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesElectron holePhosphorescent oleds
An electroluminescent device comprises a cathode and an anode; and, located therebetween, a light-emitting layer (LEL) comprising at least one hole transporting co-host and at least one electron transporting co-host, together with at least one phosphorescent emitter, and wherein the triplet energy of each of the co-host materials is greater than the triplet energy of the phosphorescent emitter, and further containing an exciton blocking layer comprising a hole transporting material with triplet energy greater or equal to 2.5 eV adjacent the emitting layer on the anode side. The invention provides devices that emit light with high luminous efficiency at low voltage.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Molding technique for fabrication of optoelectronic devices
InactiveUS7253017B1Large scaleMaterial nanotechnologyPV power plantsSemiconductor materialsNanostructure
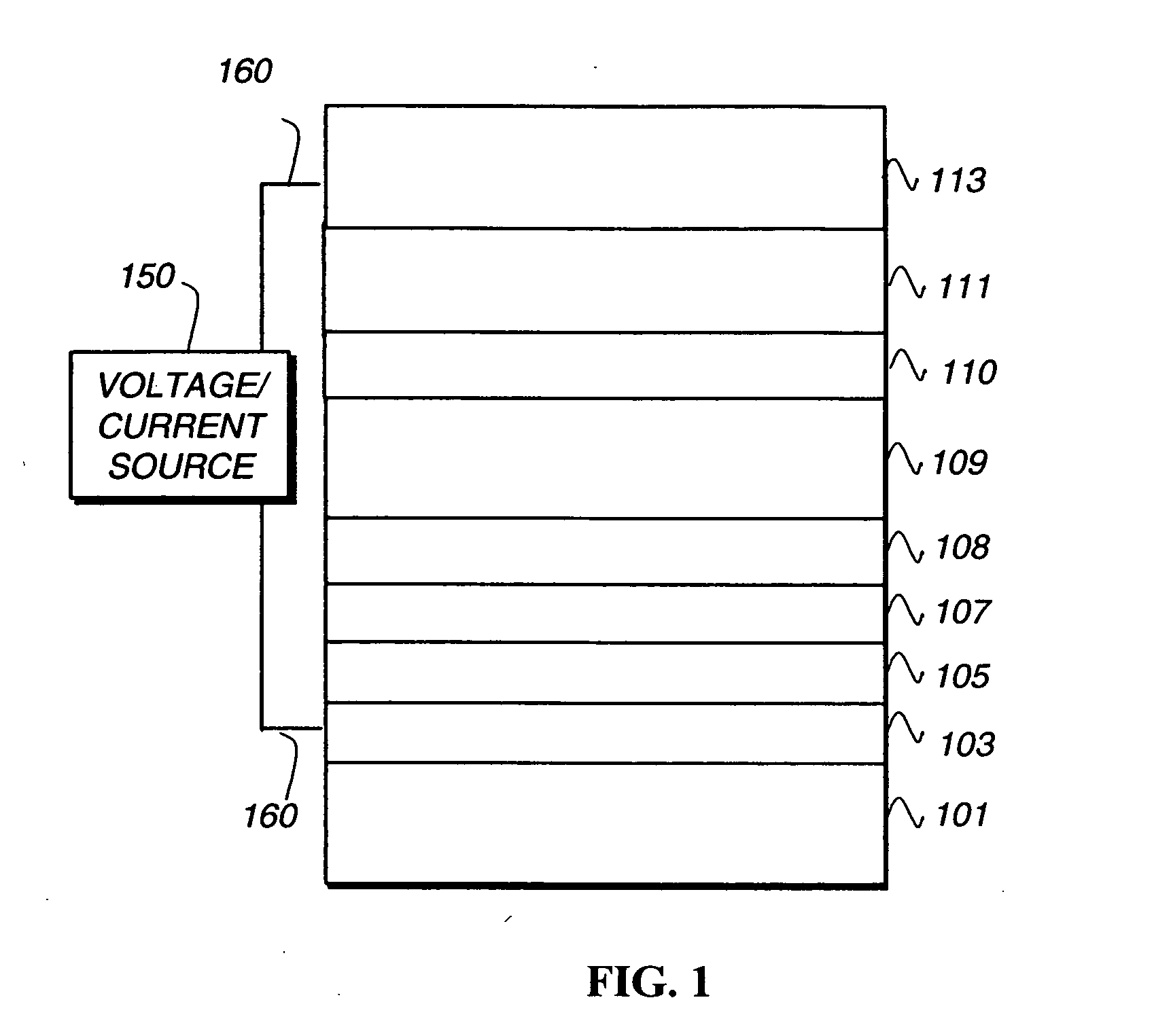
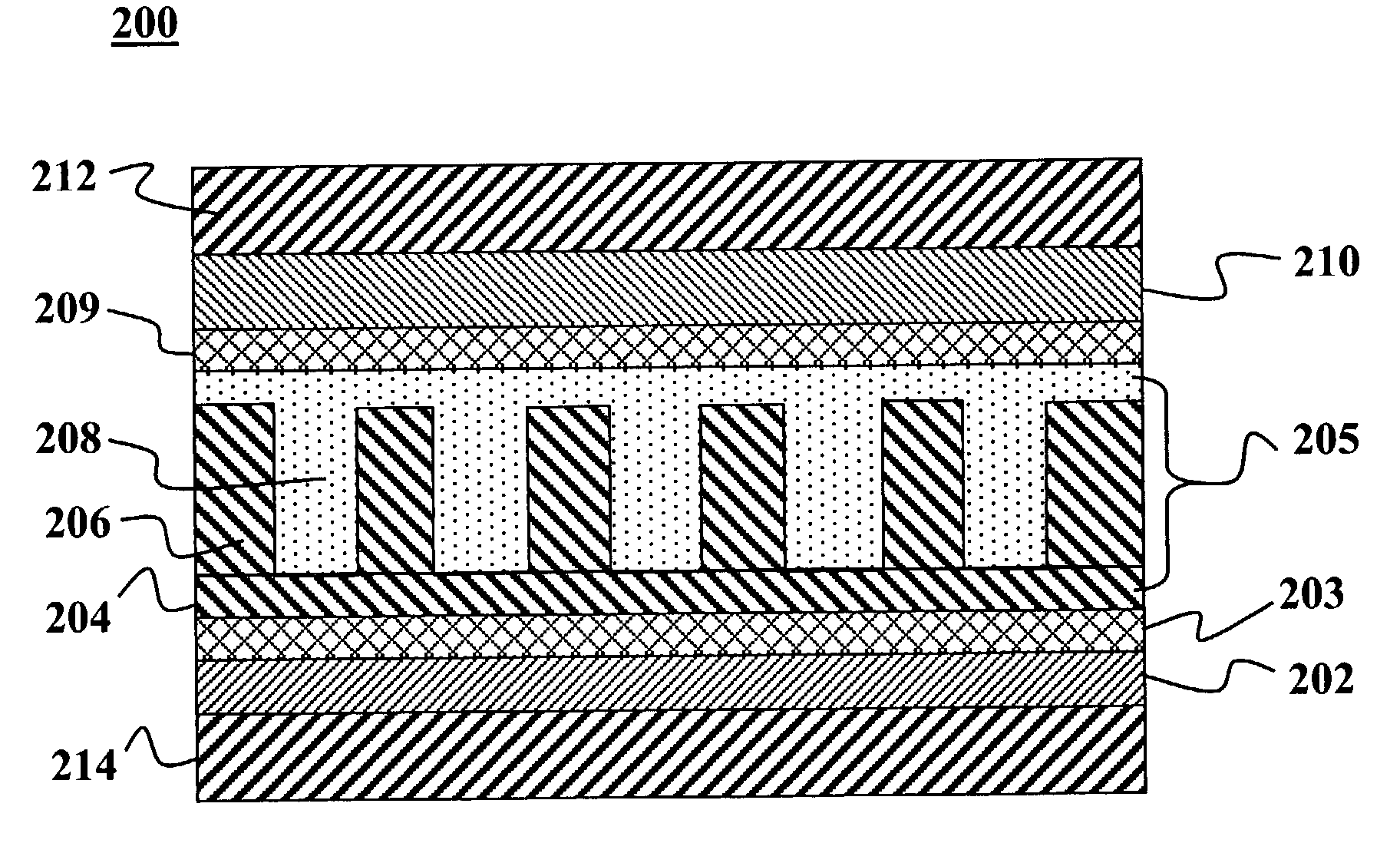
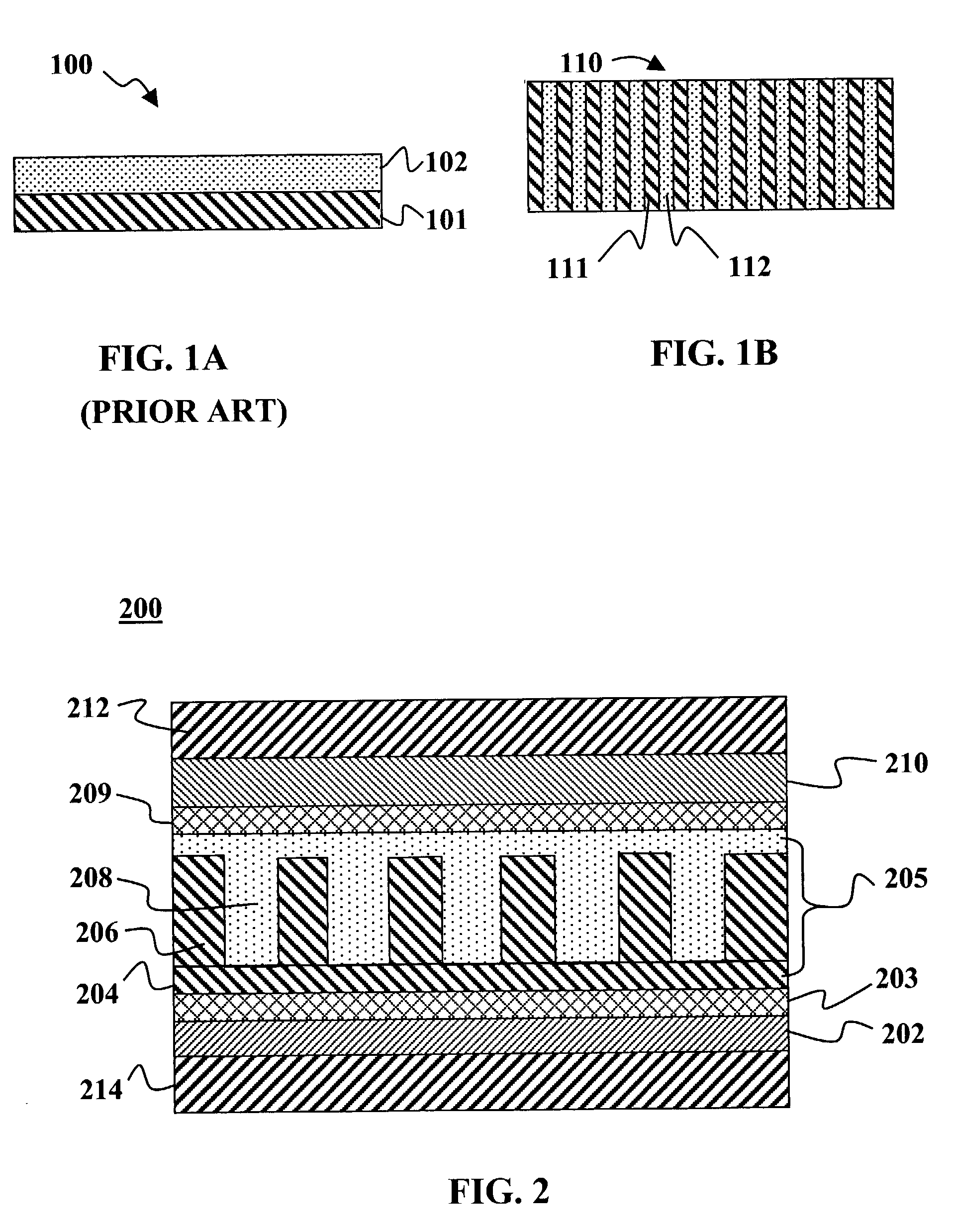
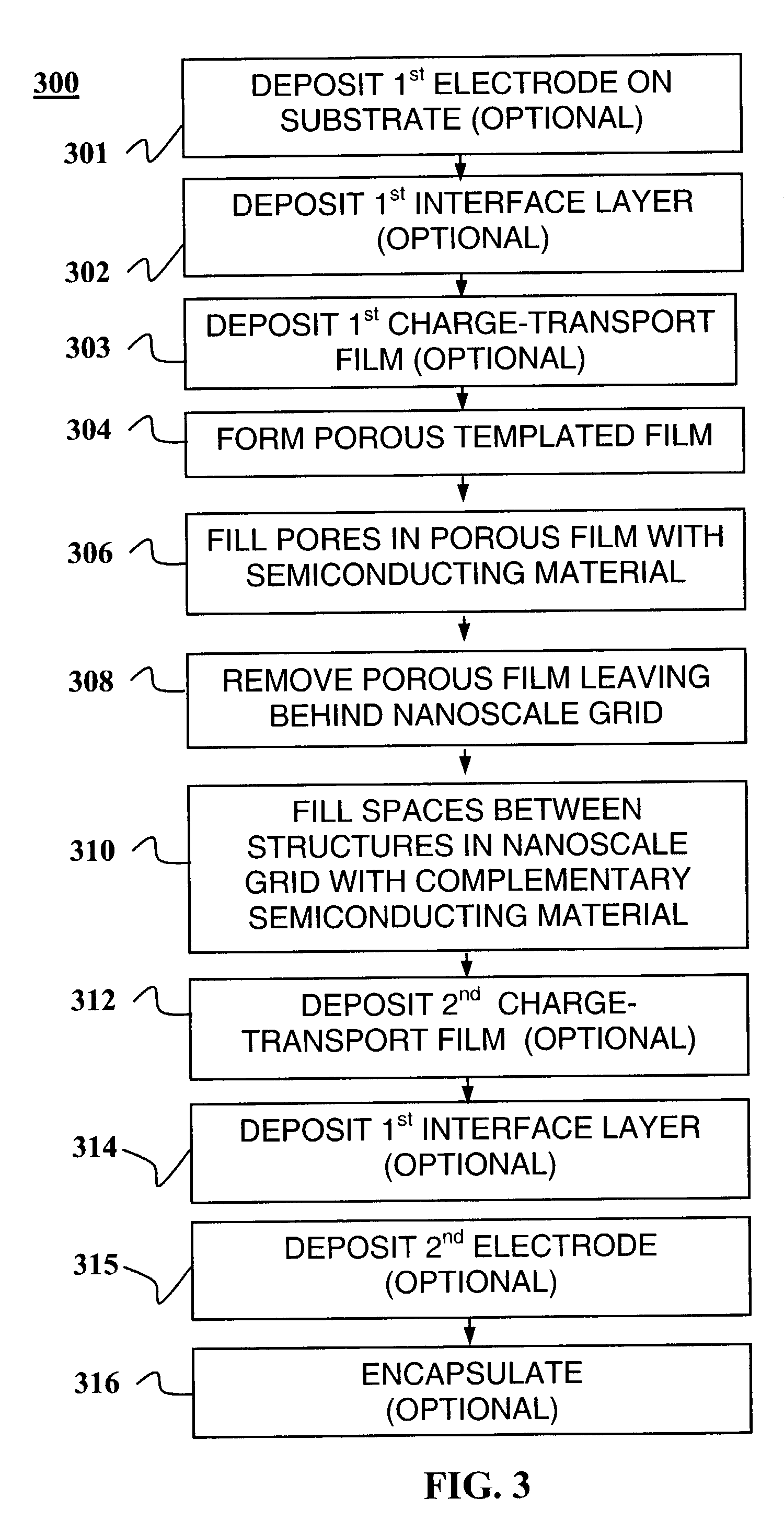
Charge splitting networks for optoelectronic devices may be fabricated using a nanostructured porous film, e.g., of SiO2, as a template. The porous film may be fabricated using surfactant temptation techniques. Any of a variety of semiconducting materials including semiconducting metals and metal oxides (such as TiO2, CdSe, CdS, CdTe, or CuO) may be deposited into the pores of the porous template film. After deposition, the template film may be removed by controlled exposure to acid or base without disrupting the semiconducting material leaving behind a nanoscale network grid. Spaces in the network grid can then be filled with complementary semiconducting material, e.g., a semiconducting polymer or dye to create a exciton-splitting and charge transporting network with superior optoelectronic properties for an optoelectronic devices, particularly photovoltaic devices.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Solar cells using fullerenes
InactiveUS20020189666A1Improve efficiencyImprove photovoltaic performanceNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesSolar cellFullerene
Organic photosensitive optoelectronic devices are disclosed. The devises comprise photoconductive organic thin films in a heterostructure, which include an exciton blocking layer to enhance device efficiency. The use of fullerenes in the electron conducting layer has lead to devices with high efficiency. Single heterostructure, stacked and wave-guide type embodiments are disclosed. Devices having multilayer structures and an exciton blocking layer are also disclosed. Guidelines for selection of exciton blocking layers are provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Phosphorescent OLEDs with exciton blocking layer
ActiveUS7597967B2Improve efficiencyReduce the driving voltageDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsPhosphorescent oledsLow voltage
An electroluminescent device comprises a cathode and an anode; and, located therebetween, a light-emitting layer (LEL) comprising at least one hole transporting co-host and at least one electron transporting co-host, together with at least one phosphorescent emitter, and wherein the triplet energy of each of the co-host materials is greater than the triplet energy of the phosphorescent emitter, and further containing an exciton blocking layer comprising a hole transporting material with triplet energy greater or equal to 2.5 eV adjacent the emitting layer on the anode side. The invention provides devices that emit light with high luminous efficiency at low voltage.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
OLEDs with improved operational lifetime
InactiveUS20060141287A1Adversely reducing purity of colorImprove efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSimple Organic CompoundsDopant
An organic light-emitting device includes a substrate, an anode and a cathode disposed over the substrate, and a light-emitting layer disposed between the anode and the cathode wherein the light-emitting layer includes a host and at least one dopant. The host of the light-emitting layer is selected to include a solid organic material including a mixture of at least two components wherein the first host component is an organic compound capable of transporting electrical charges and also forms an aggregate, and the second component of the mixture is an organic compound capable, of transporting electrical charges and, upon mixing with the first host component, is capable of forming a continuous and substantially pin-hole-free layer. The dopant of the light-emitting layer is selected to collect excitons and produce colored light, and an electron-transporting layer is disposed between the light-emitting layer and the cathode for providing improved electron injection and transport.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
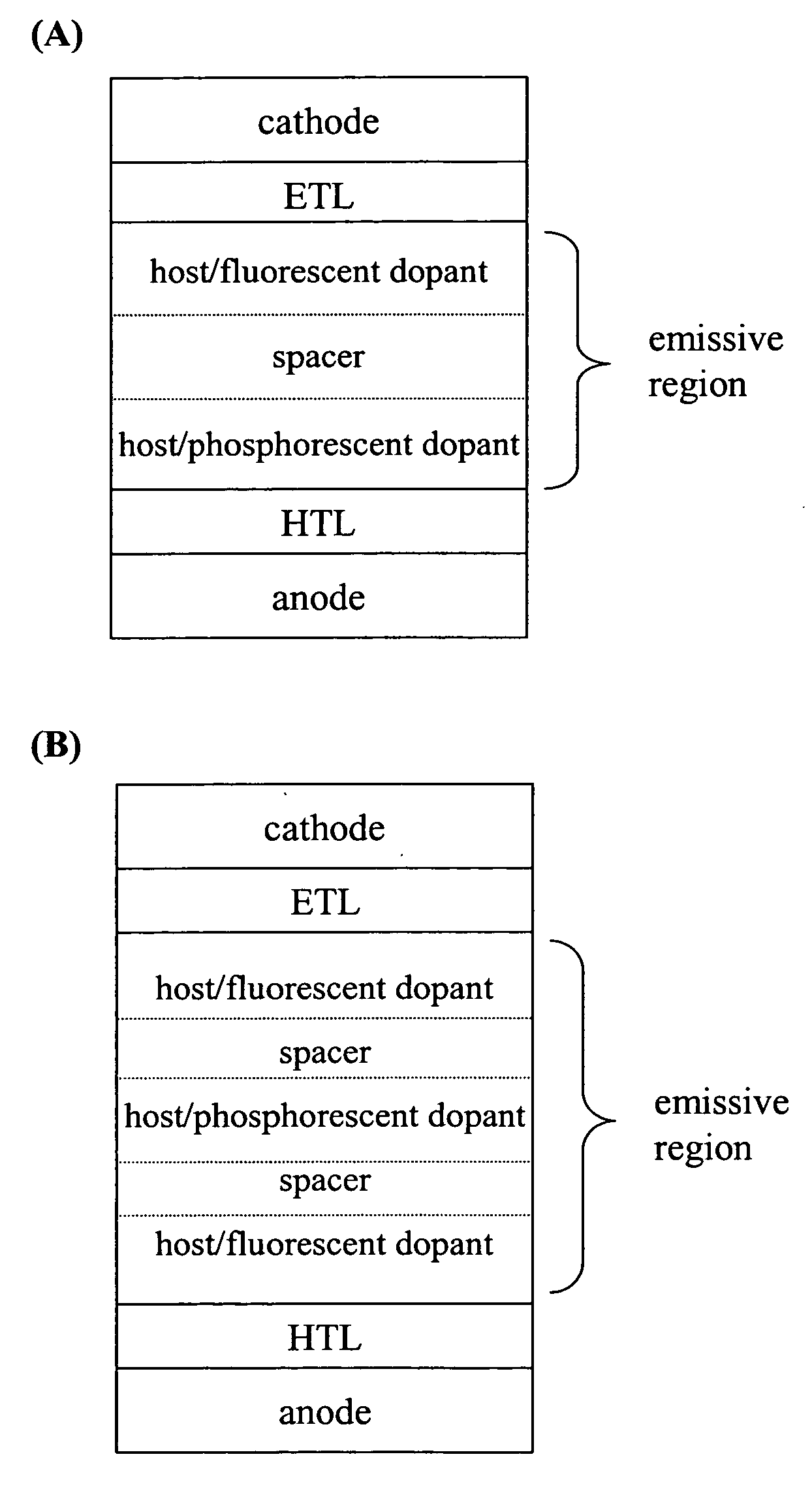
Fluorescent filtered electrophosphorescence
ActiveUS20060279203A1Stable color balanceImprove stabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic light emitting devicePhosphorescence
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
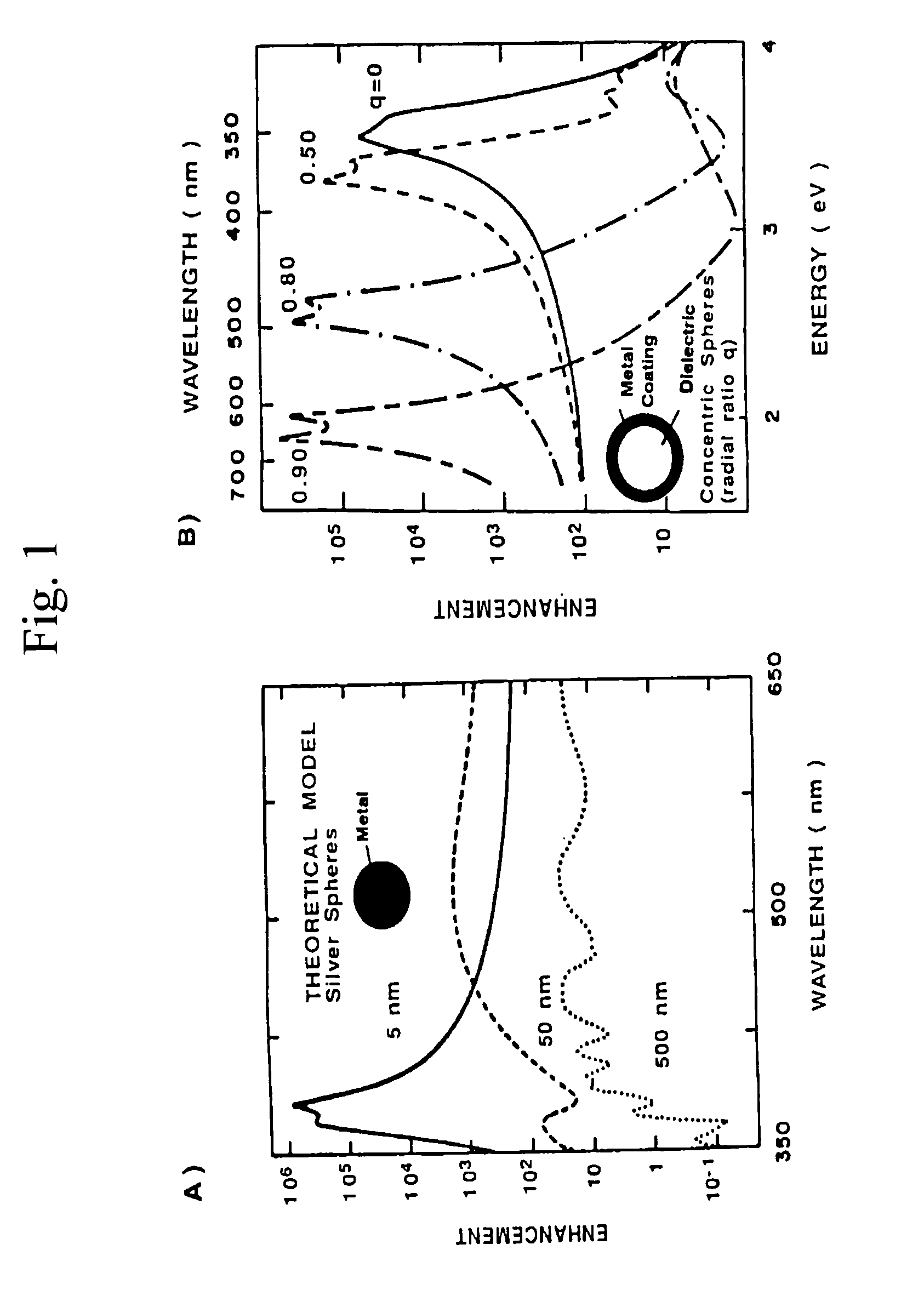
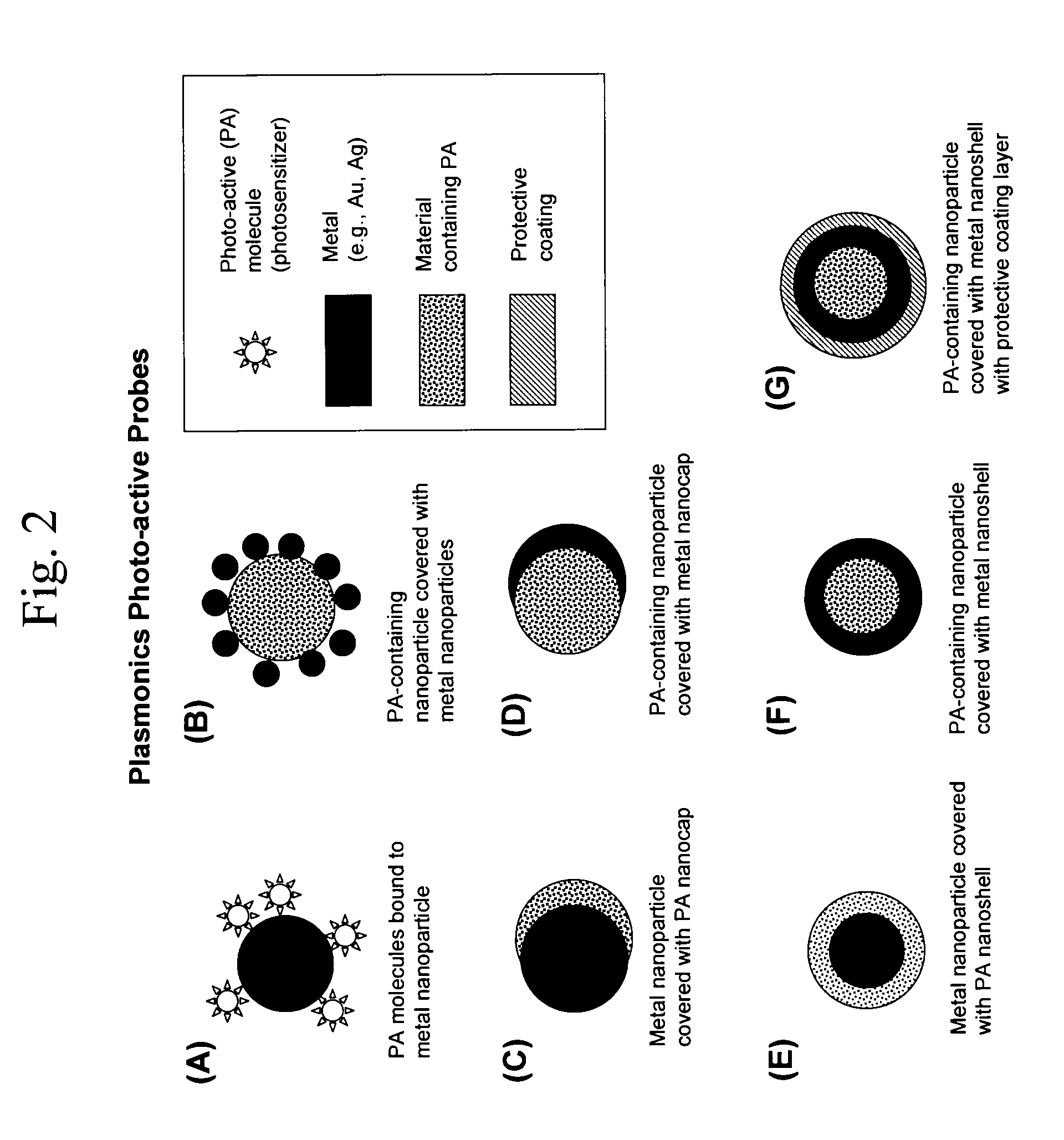
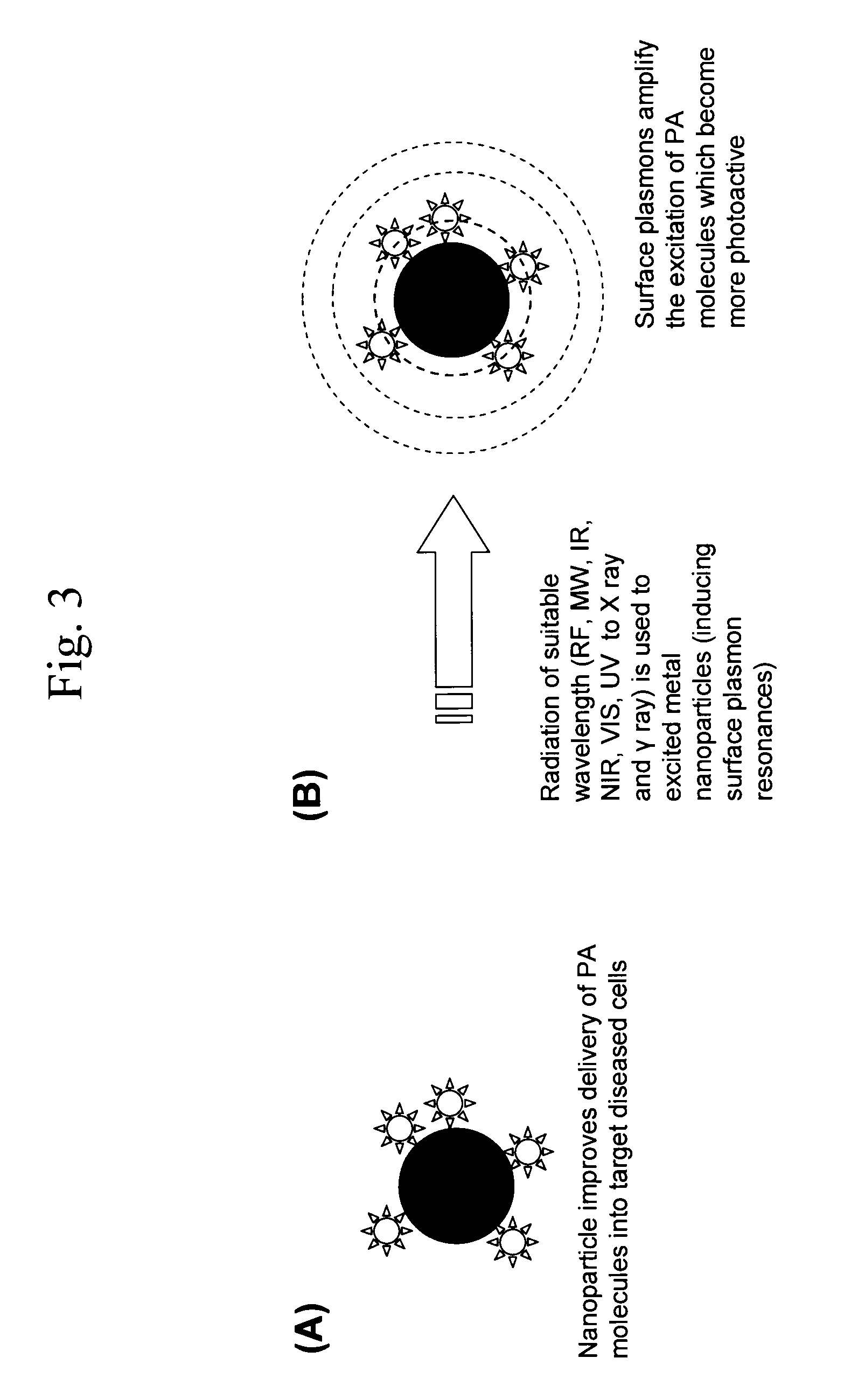
Methods and systems for treating cell proliferation disorders using plasmonics enhanced photospectral therapy (PEPST) and exciton-plasmon enhanced phototherapy (EPEP)
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Fluorescent filtered electrophosphorescence
ActiveUS20060273714A1Stable color balanceImprove stabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesLuminophoreTriboluminescence
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
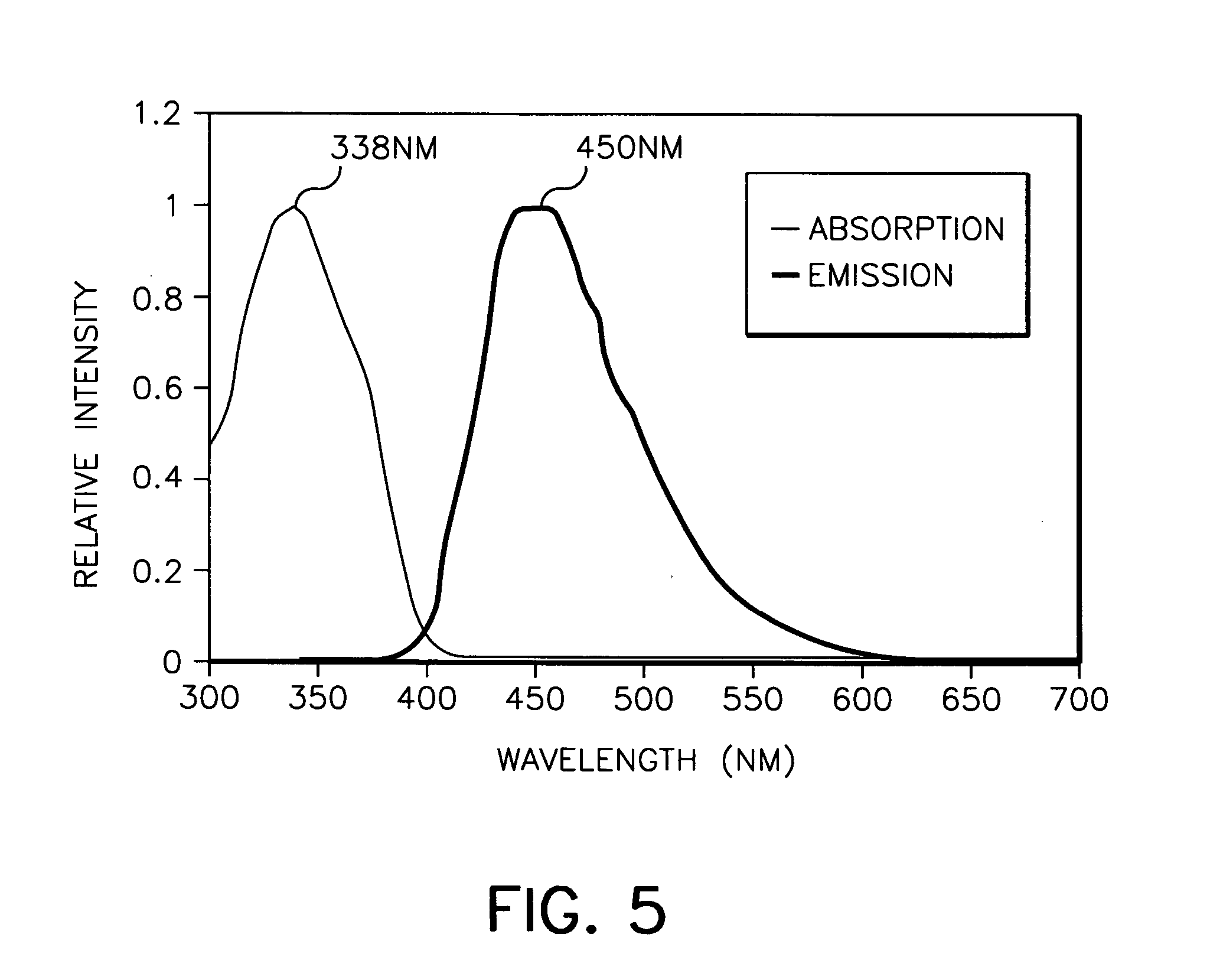
Organometallic complexes as phosphorescent emitters in organic LEDS
InactiveUS7291406B2Easy to combineDeterioration in emission qualityOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensIridiumPt element
Organic light emitting devices are described wherein the emissive layer comprises a host material containing an emissive molecule, which molecule is adapted to luminesce when a voltage is applied across the heterostructure, and the emissive molecule is selected from the group of phosphorescent organometallic complexes, including cyclometallated platinum, iridium and osmium complexes. The organic light emitting devices optionally contain an exciton blocking layer. Furthermore, improved electroluminescent efficiency in organic light emitting devices is obtained with an emitter layer comprising organometallic complexes of transition metals of formula L2MX, wherein L and X are distinct bidentate ligands. Compounds of this formula can be synthesized more facilely than in previous approaches and synthetic options allow insertion of fluorescent molecules into a phosphorescent complex, ligands to fine tune the color of emission, and ligands to trap carriers.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF PRINCETON UNIV +1
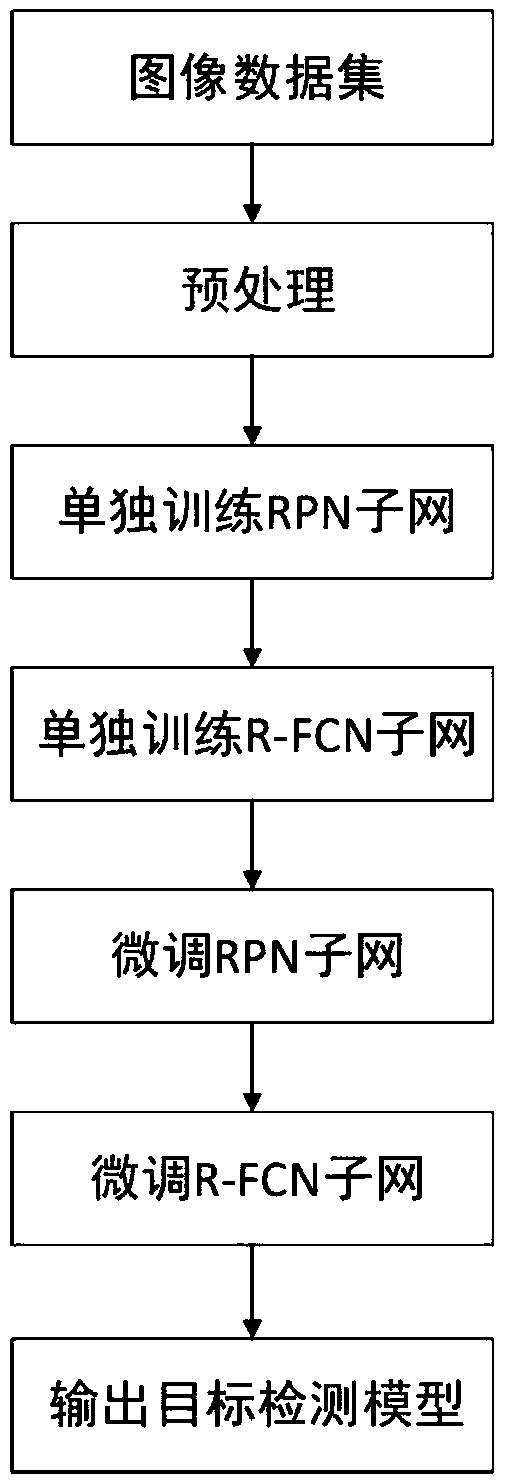
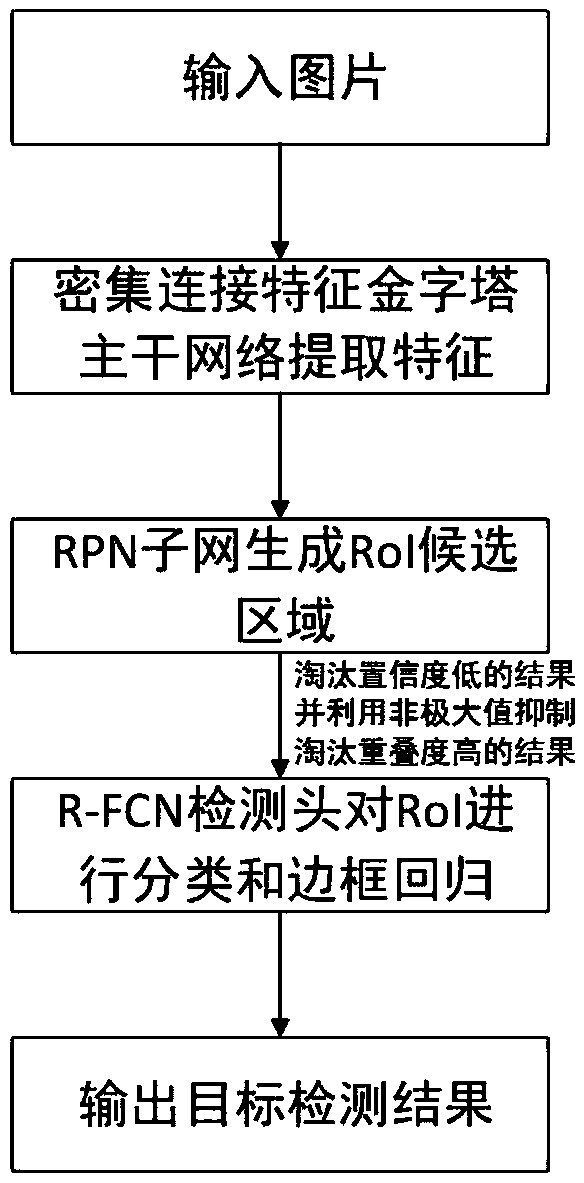
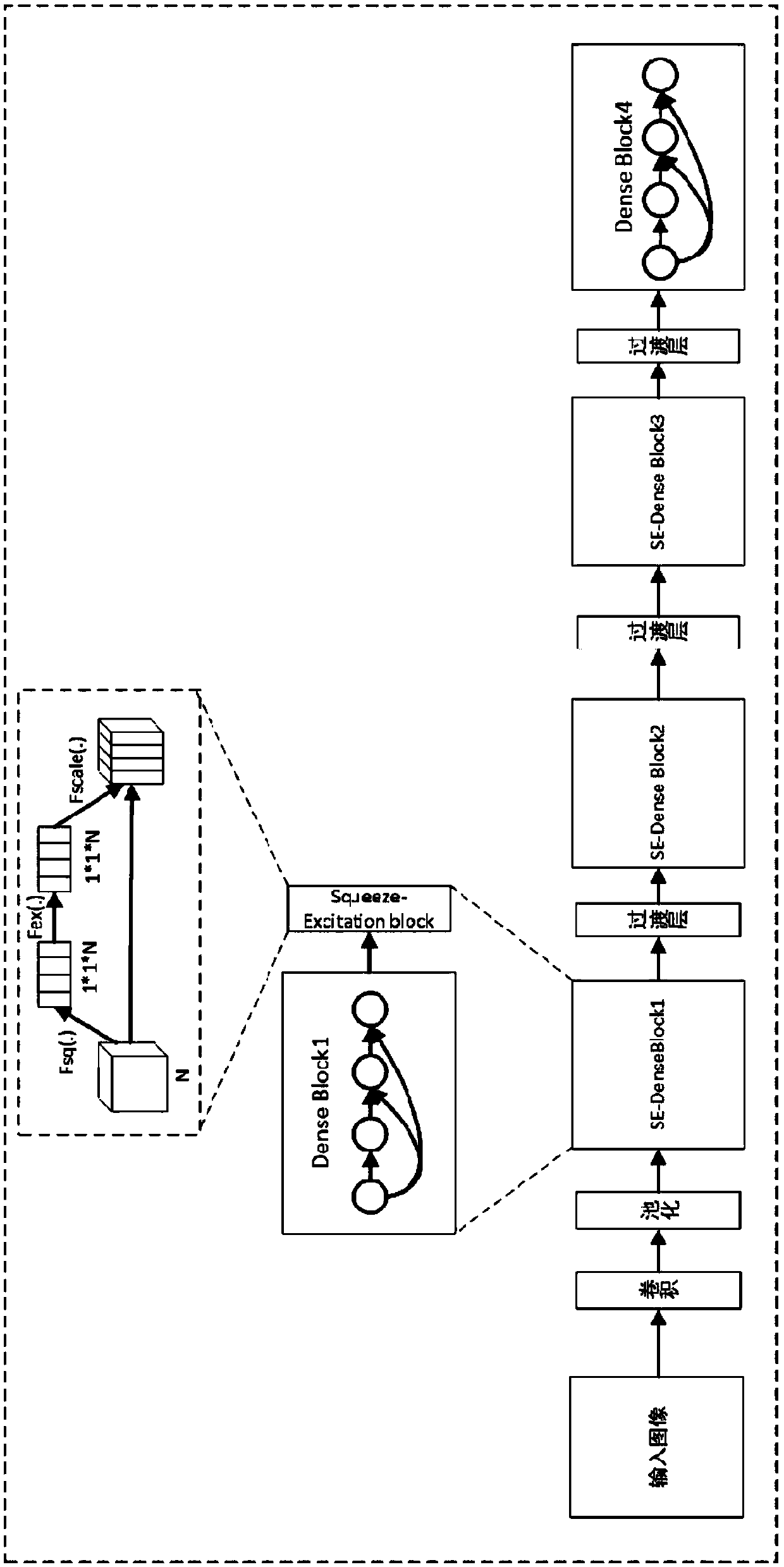
Target detection method based on a dense connection characteristic pyramid network
ActiveCN109614985AEnhanced Representational CapabilitiesImprove adaptabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setImaging processing
The invention discloses a target detection method based on a dense connection characteristic pyramid network, and relates to the image processing and computer vision technology. The method comprises the steps of collecting an image data set labeled with a target bounding box and category information; constructing a dense connection feature pyramid network containing a Squeeze-Exciton structure capable of learning a dependency relationship between feature channels as a feature extraction backbone network; alternately training the RPN subnet and the R-FCN subnet to obtain a target detection model; and detecting a specific target in the image by using the model. The squeeze-Exciton structure and a dense connection structure are introduced into a feature extraction trunk network, characterization capability of the model is enhanced, adaptability of the model to targets of different sizes is enhanced through the feature pyramid structure, calculation sharing of the whole network model is achieved to the maximum degree through the R-FCN detection head, calculation resources are saved, and performance of the whole target detection model is improved. .
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
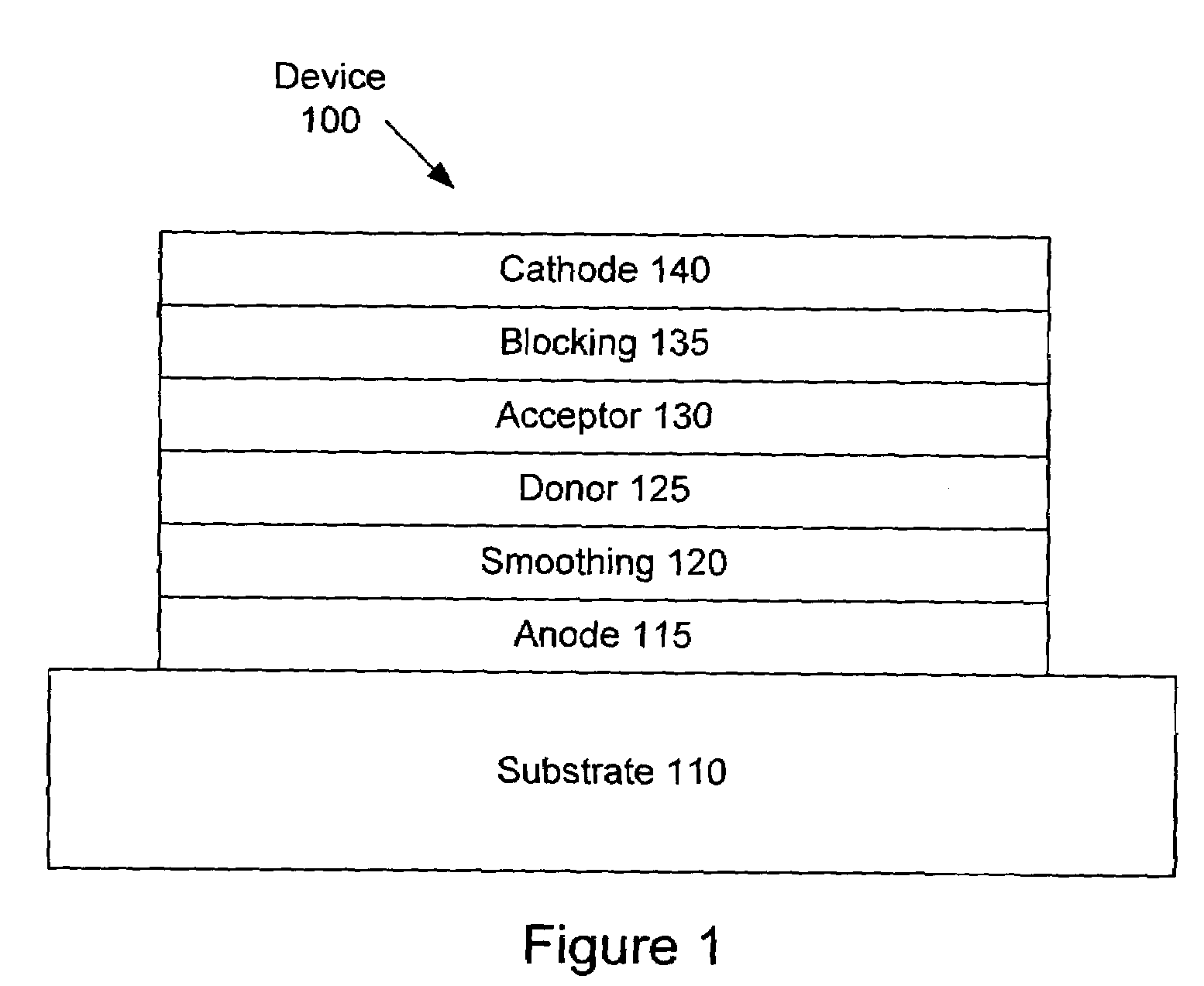
Method of fabricating an organic photosensitive optoelectronic device with an exciton blocking layer
InactiveUS6844025B2Increase the electric field strengthEasy to separateLayered productsNanoinformaticsPhotodetectorBlocking layer
Organic photosensitive optoelectronic devices (“OPODs”) are disclosed which include an exciton blocking layer to enhance device efficiency. Single heterostructure, stacked and wave-guide type embodiments are disclosed. Photodetector OPODs having multilayer structures and an exciton blocking layer are also disclosed. Guidelines for selection of exciton blocking layers are provided.
Owner:PRINCETON UNIV
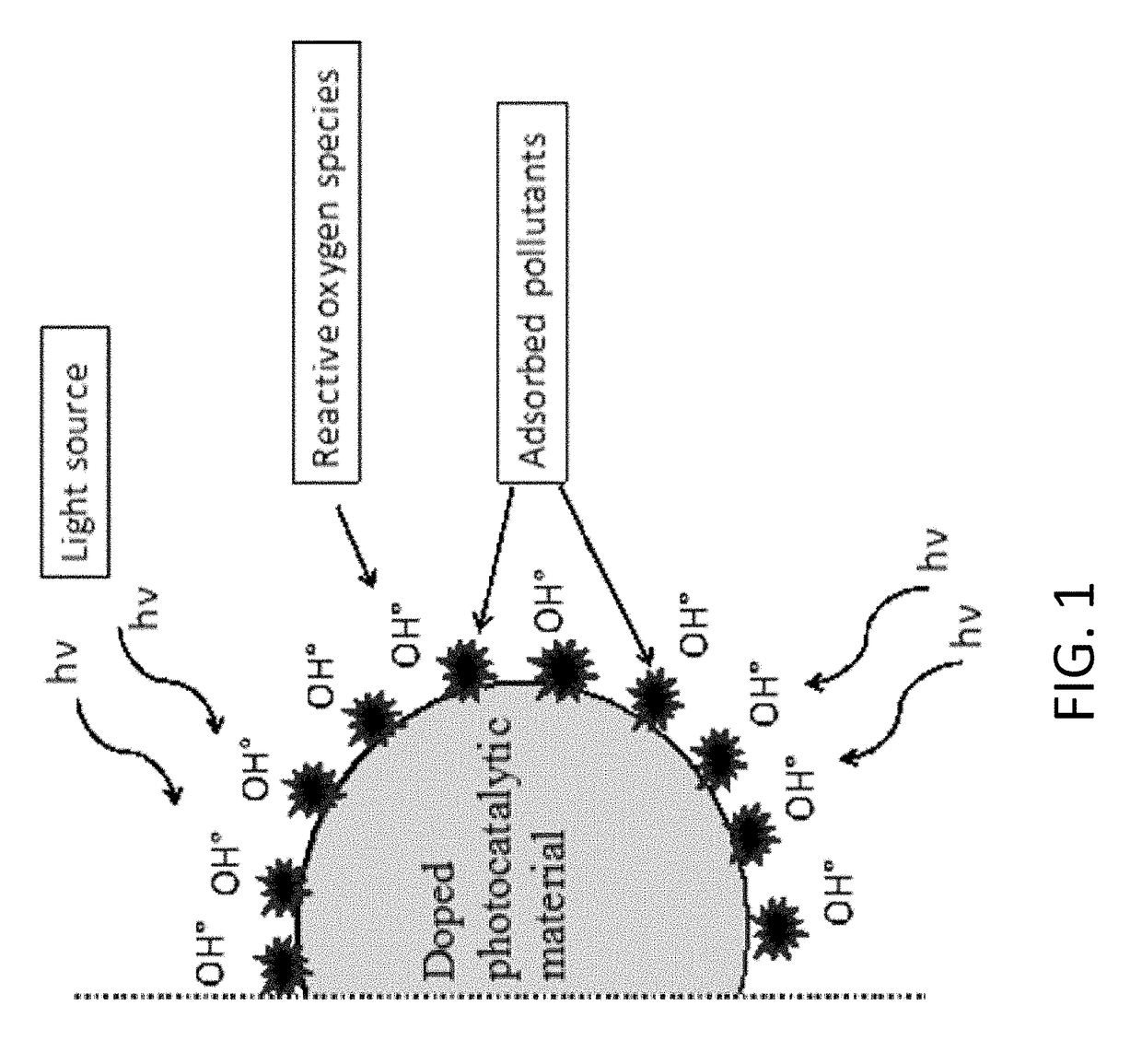
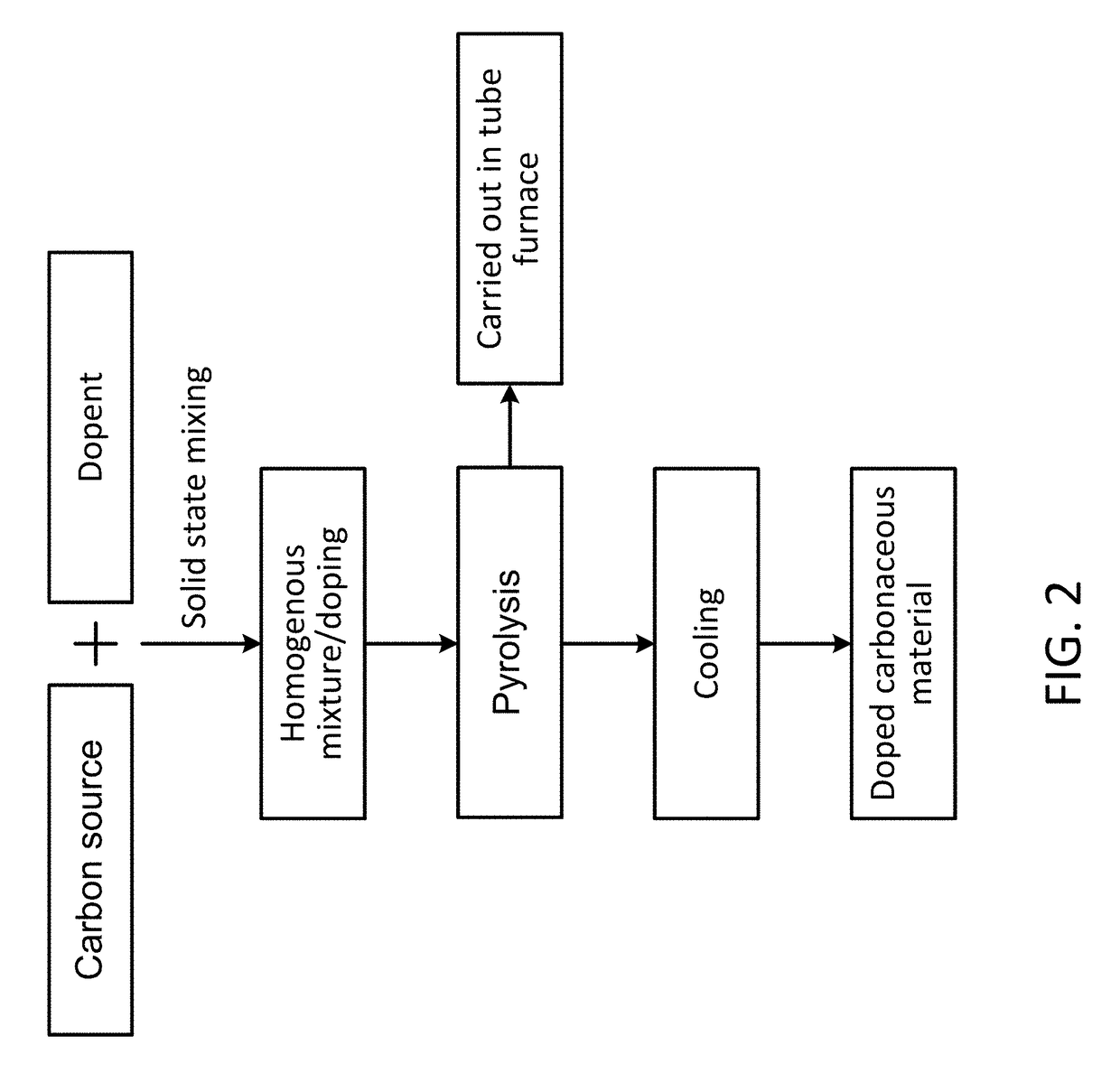
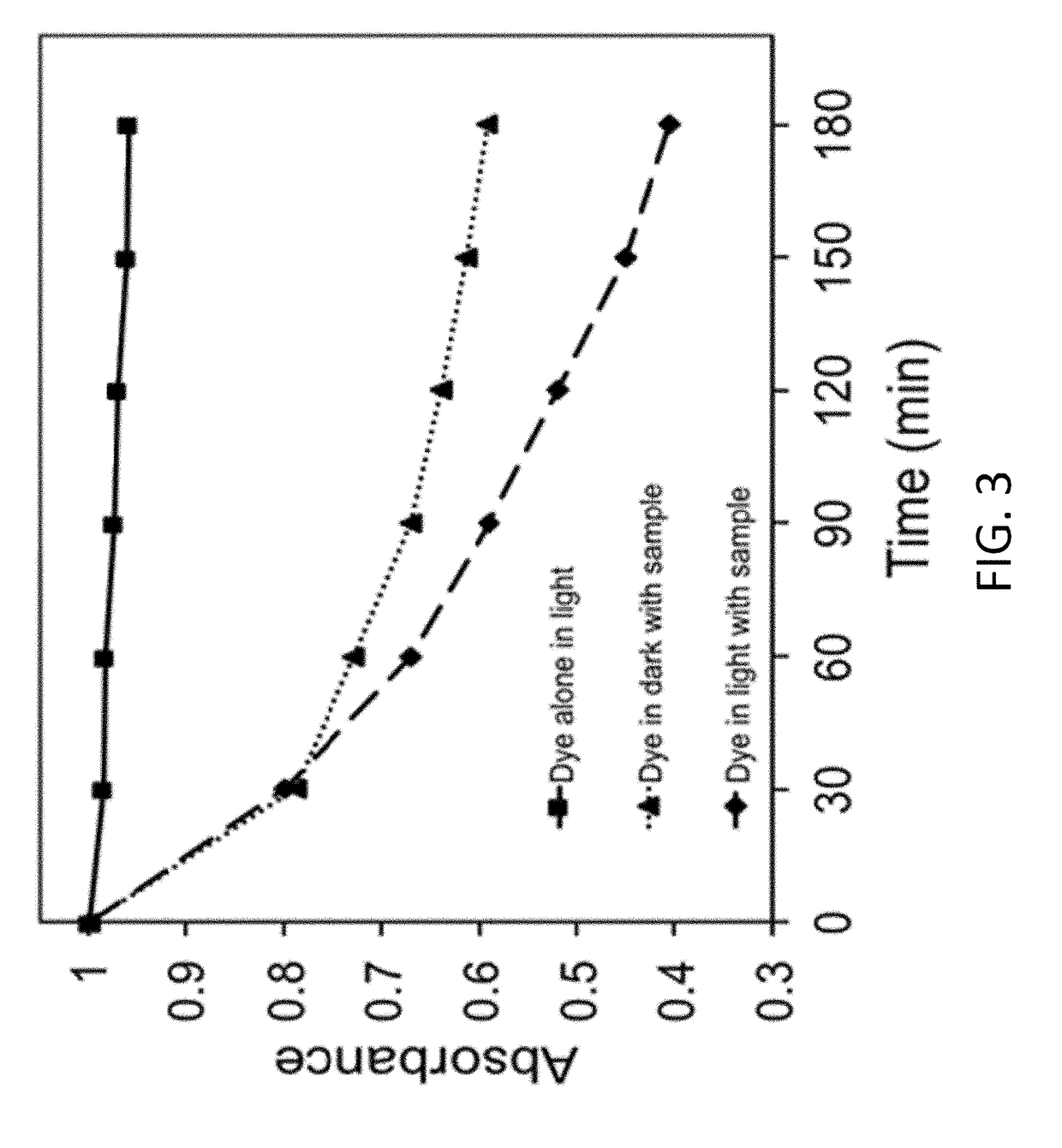
Doped carbonaceous materials for photocatalytic removal of pollutants under visible light, making methods and applications of same
ActiveUS20190015818A1Efficient removalWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsSuperoxide radicalSinglet oxygen
A method of synthesizing a doped carbonaceous material includes mixing a carbon precursor material with at least one dopant to form a homogeneous / heterogeneous mixture; and subjecting the mixture to pyrolysis in an inert atmosphere to obtain the doped carbonaceous material. A method of purifying water includes providing an amount of the doped carbonaceous material in the water as a photocatalyst; and illuminating the water containing the doped carbonaceous material with visible light such that under visible light illumination, the doped carbonaceous material generates excitons (electron-hole pairs) and has high electron affinity, which react with oxygen and water adsorbed on its surface forming reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as hydroxyl radicals and superoxide radicals, singlet oxygen, hydrogen peroxide, that, in turn, decompose pollutants and micropollutants.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
OLEDs with improved operational lifetime
InactiveUS20060040131A1Adversely reducing purity of colorImprove efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSimple Organic CompoundsDopant
An organic light-emitting device includes a substrate, an anode and a cathode disposed over the substrate, and a light-emitting layer disposed between the anode and the cathode wherein the light-emitting layer includes a host and at least one dopant. The host of the light-emitting layer is selected to include a solid organic material including a mixture of at least two components wherein the first host component is an organic compound capable of transporting electrical charges and also forms an aggregate, and the second component of the mixture is an organic compound capable of transporting electrical charges and, upon mixing with the first host component, is capable of forming a continuous and substantially pin-hole-free layer. The dopant of the light-emitting layer is selected to collect excitons and produce colored light, and an electron-transporting layer is disposed between the light-emitting layer and the cathode for providing improved electron injection and transport.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Method of fabricating an optoelectronic device having a bulk heterojunction
ActiveUS20050227390A1Acceptable power conversion efficiencyAcceptable quantum yieldMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureHeterojunctionMolecular materials
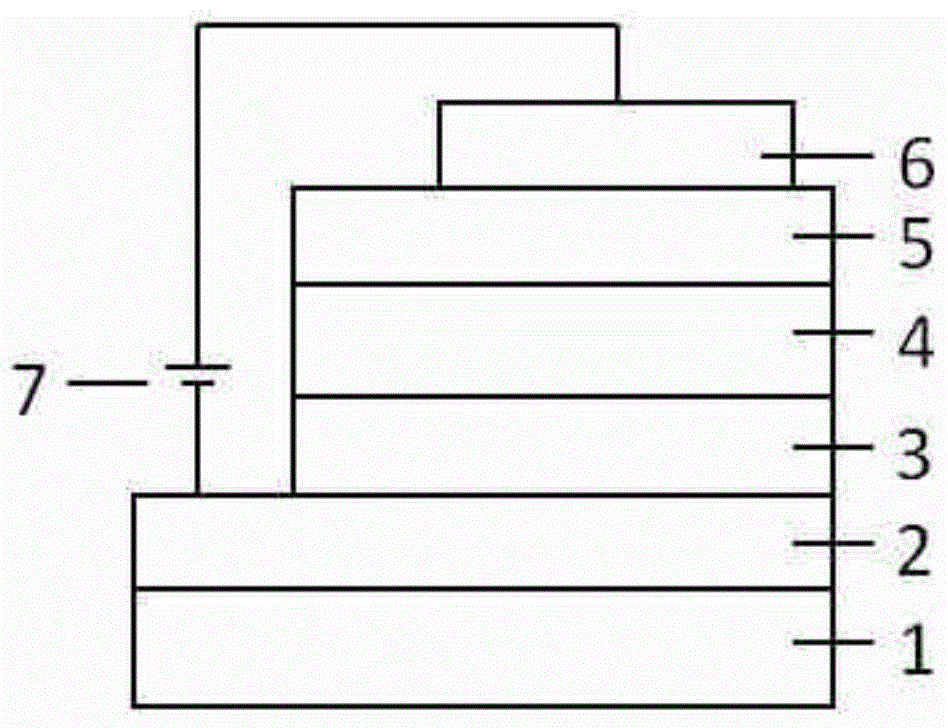
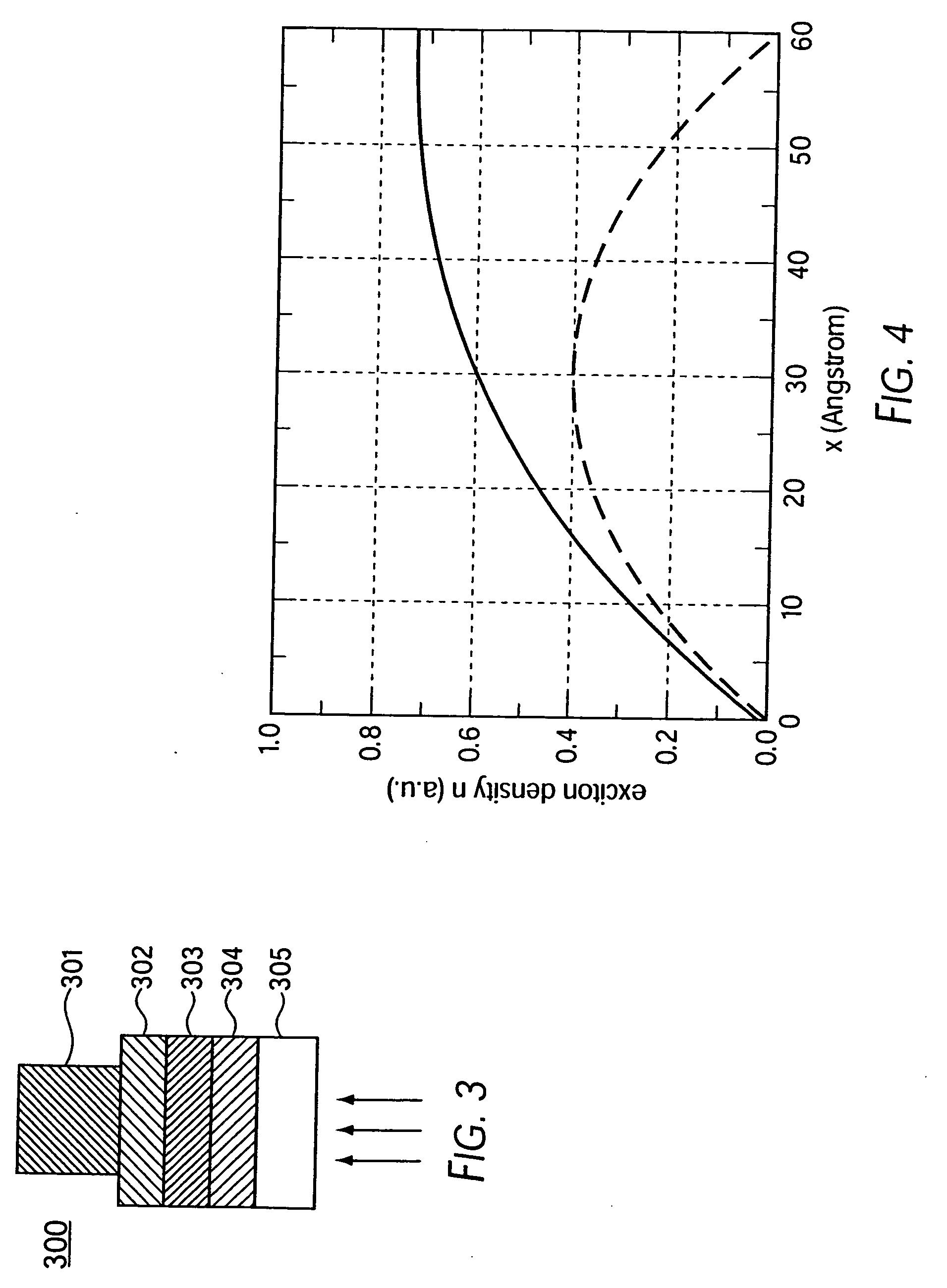
A method of fabricating an optoelectronic device comprises: depositing a first layer having protrusions over a first electrode, in which the first layer comprises a first organic small molecule material; depositing a second layer on the first layer such that the second layer is in physical contact with the first layer; in which the smallest lateral dimension of the protrusions are between 1 to 5 times the exciton diffusion length of the first organic small molecule material; and depositing a second electrode over the second layer to form the optoelectronic device. A method of fabricating an organic optoelectronic device having a bulk heterojunction is also provided and comprises: depositing a first layer with protrusions over an electrode by organic vapor phase deposition; depositing a second layer on the first layer where the interface of the first and second layers forms a bulk heterojunction; and depositing another electrode over the second layer.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Enhancement of organic photovoltaic cell open circuit voltage using electron/hole blocking exciton blocking layers
InactiveUS20110012091A1Improve power conversion efficiencyReduce decreaseNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesElectron blocking layerBlocking layer
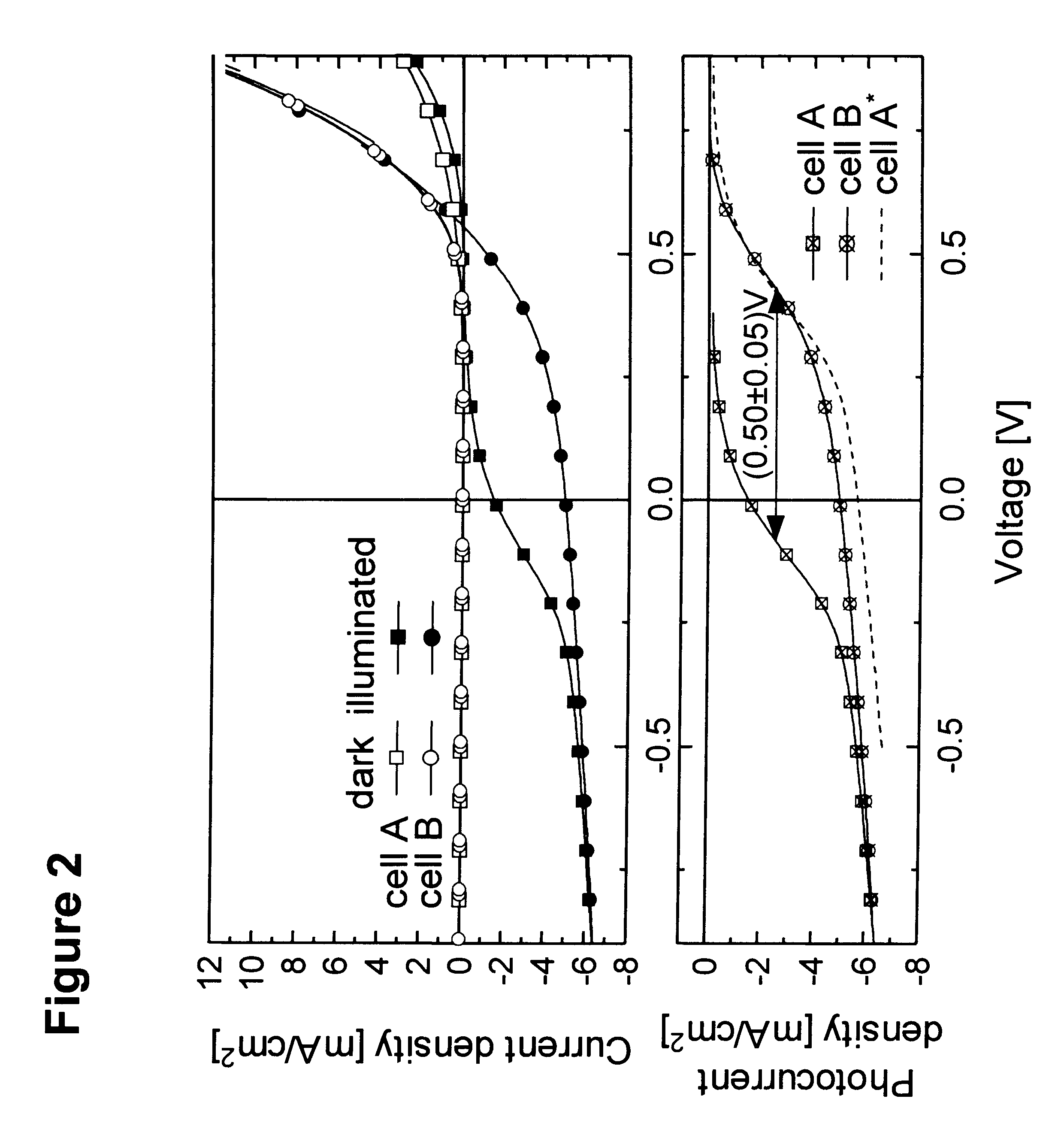
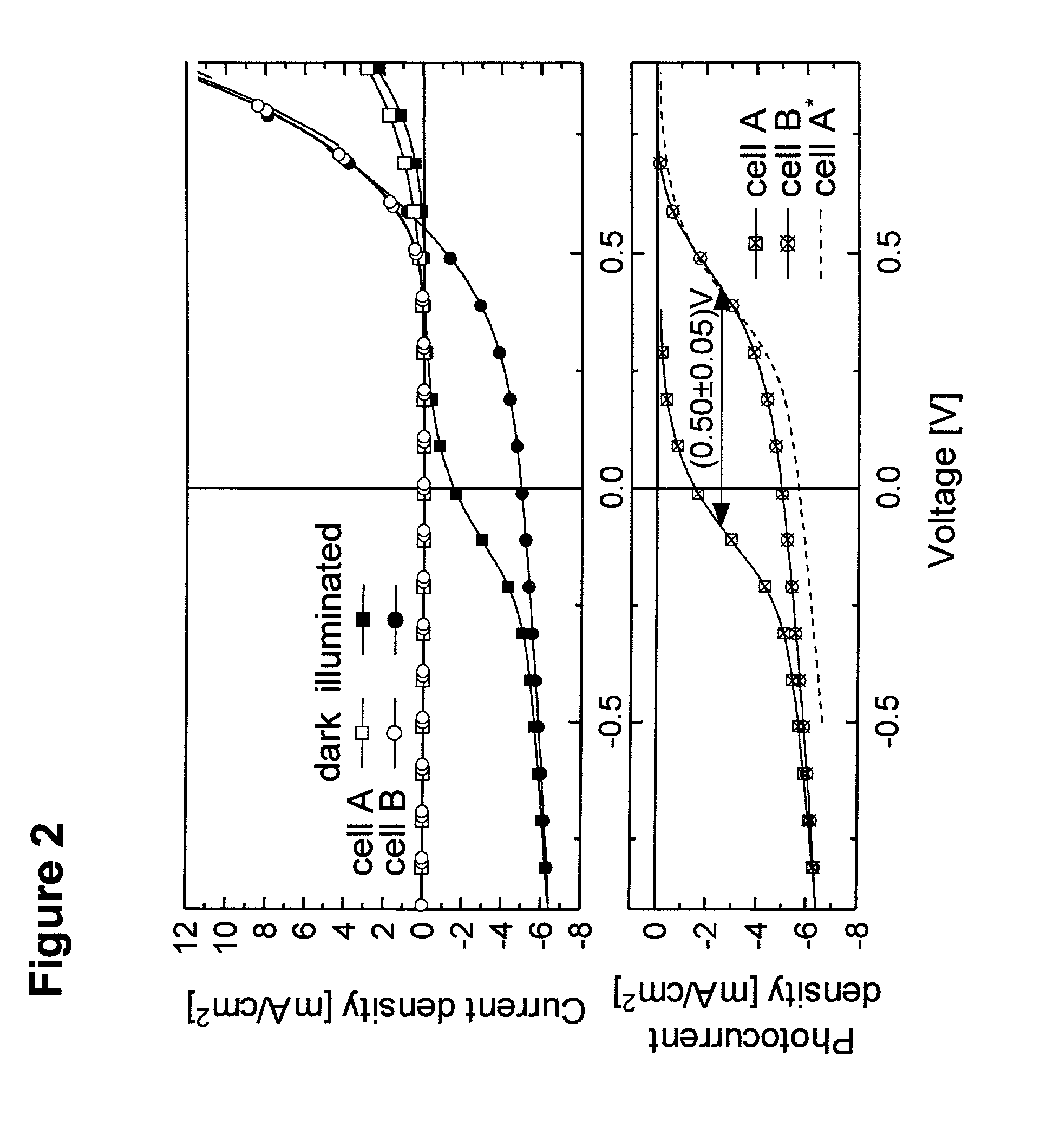
The present disclosure relates to photosensitive optoelectronic devices comprising at least one of an electron blocking or hole blocking layer. Further disclosed are methods of increasing power conversion efficiency in photosensitive optoelectronic devices using at least one of an electron blocking or hole blocking layer. The electron blocking and hole blocking layers presently disclosed may reduce electron leakage current by reducing the dark current components of photovoltaic cells. This work demonstrates the importance of reducing dark current to improve power conversion efficiency of photovoltaic cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
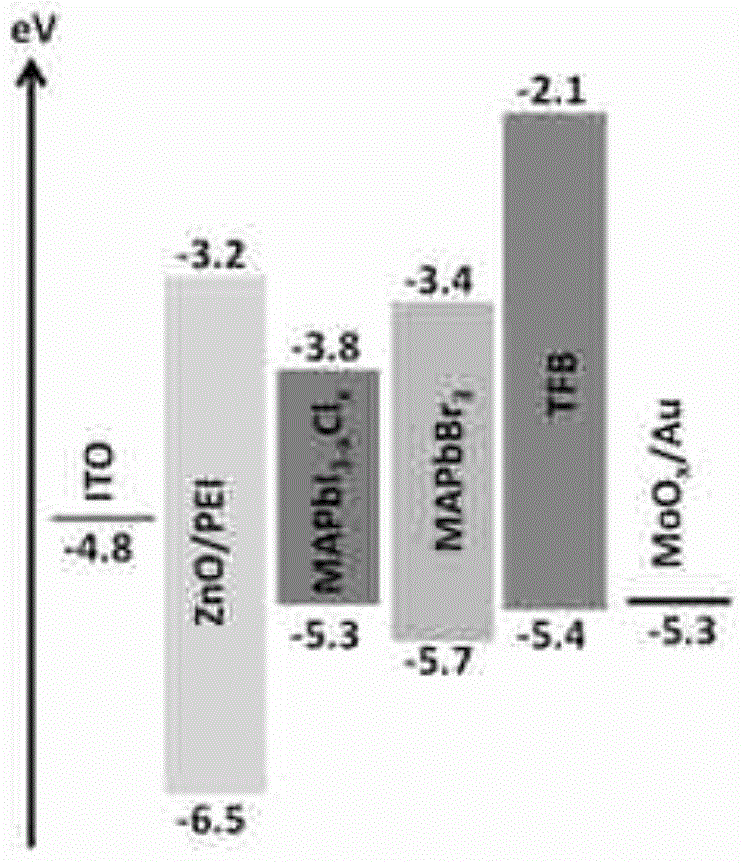
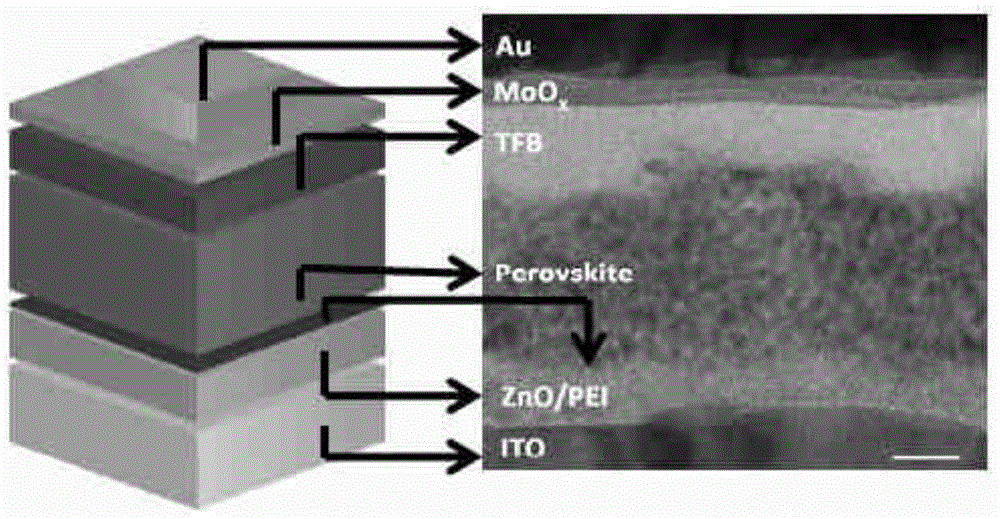
Perovskite type electroluminescence device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104681731AIncrease brightnessEasy to filmSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic transmissionBlocking layer
The invention discloses a perovskite type electroluminescence device. The device comprises a substrate, a cathode, an electronic transmission-hole blocking layer, a luminescent layer, a hole transmission-electron blocking layer and an anode, wherein the luminescent layer is made of a material of a perovskite structure; the structure of the device can effectively promote injection and transmission of the charge carriers, restrict the sufficient recombination luminescence of the charge carriers / excitons, and adjust the emission color from the near ultraviolet light band, the visible light band to the near-infrared band by means of changing the components of the luminescent material. The electroluminescence device provided by the invention is high in efficiency, low in turn-on voltage, excellent in color saturation and stable in spectrum changed along with the voltage, meanwhile, the perovskite type electroluminescence device is simple in process, low in cost and is suitable for being widely used in the products of the display and illumination field, in particular suitable for the large-sized industrial production of the high-performance electroluminescence devices with low cost and flexible substrate.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Thermal activation delayed fluorescent material and organic electroluminescent device
ActiveCN105503766AShort lifeImprove efficiencyOrganic chemistryBenzene azine dyesAcridineTriplet state
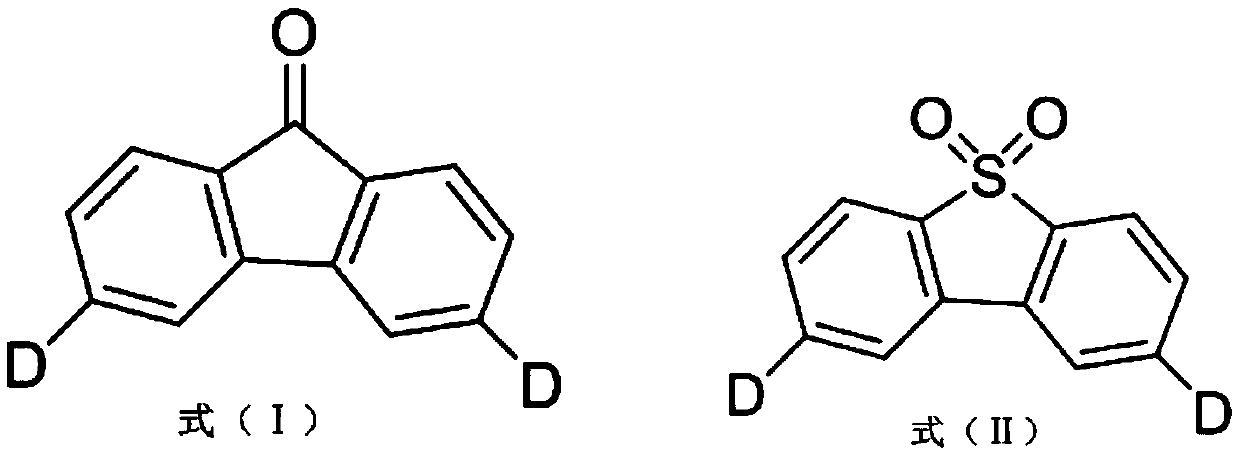
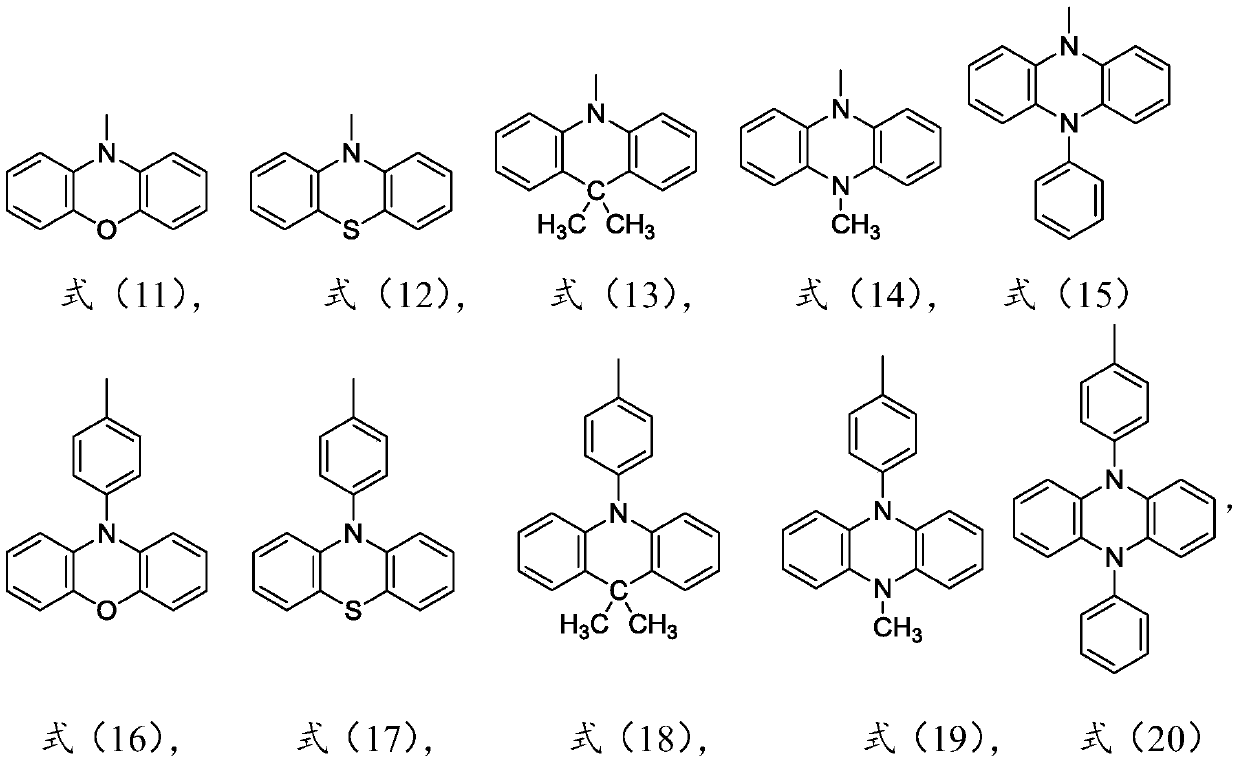
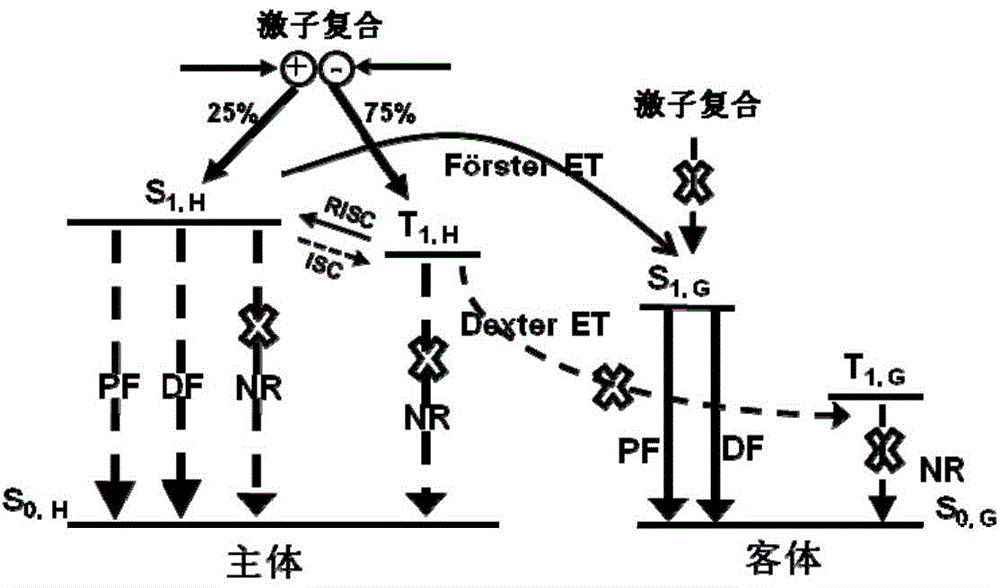
The invention relates to a thermal activation delayed fluorescent material with a general formula of the structure shown as the formula (I) or the formula (II). D is one of phenoxazinyl, phenothizainyl, 9,9-dimethyl acridine, 9-methyl phenazinyl, 9-phenyl phenazinyl, 4-phenoxazinyl-1-phenyl, 4-phenothizainyl-1-phenyl, 4-(9,9-dimethyl)acridinyl-1-phenyl, 4-(9-methyl)-phenazinyl-1-phenyl, 4-(9-phenyl)phenazinyl-1-phenyl and 3,5-bis-carbazolyl-1-phenyl. The invention further relates to an organic electroluminescent device which comprises a light-emitting layer, and luminescent dye of the light-emitting layer is the thermal activation delayed fluorescent material. The singlet state-triplet state energy gap (delta EST) of the thermal activation delayed fluorescent material is very small, triplet state excitors can be converted into singlet state excitors through inverse intersystem crossing (RIST) to emit light, and the efficiency and stability of an OLED device can be improved. The formula is shown in the description.
Owner:KUNSHAN GO VISIONOX OPTO ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
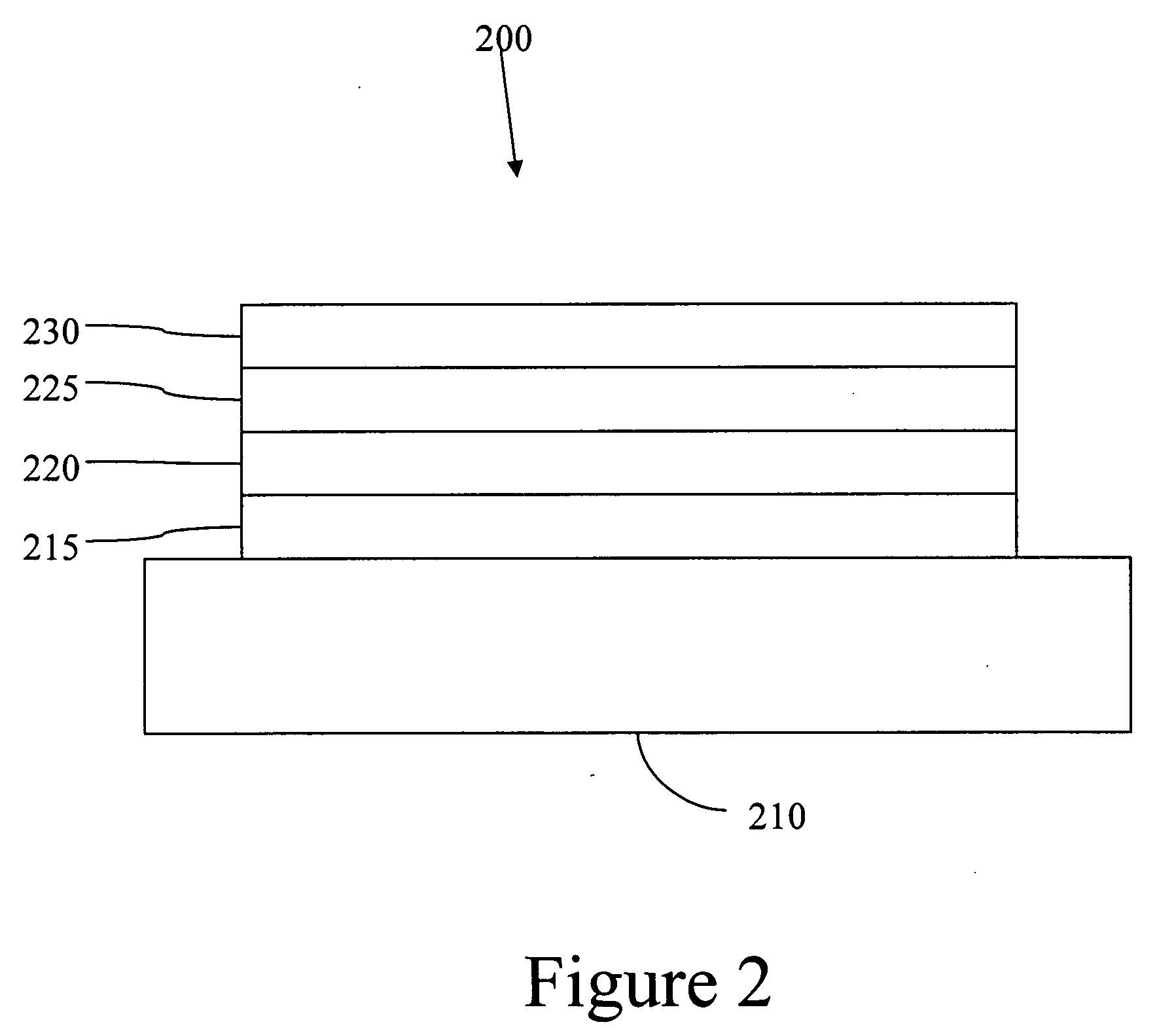
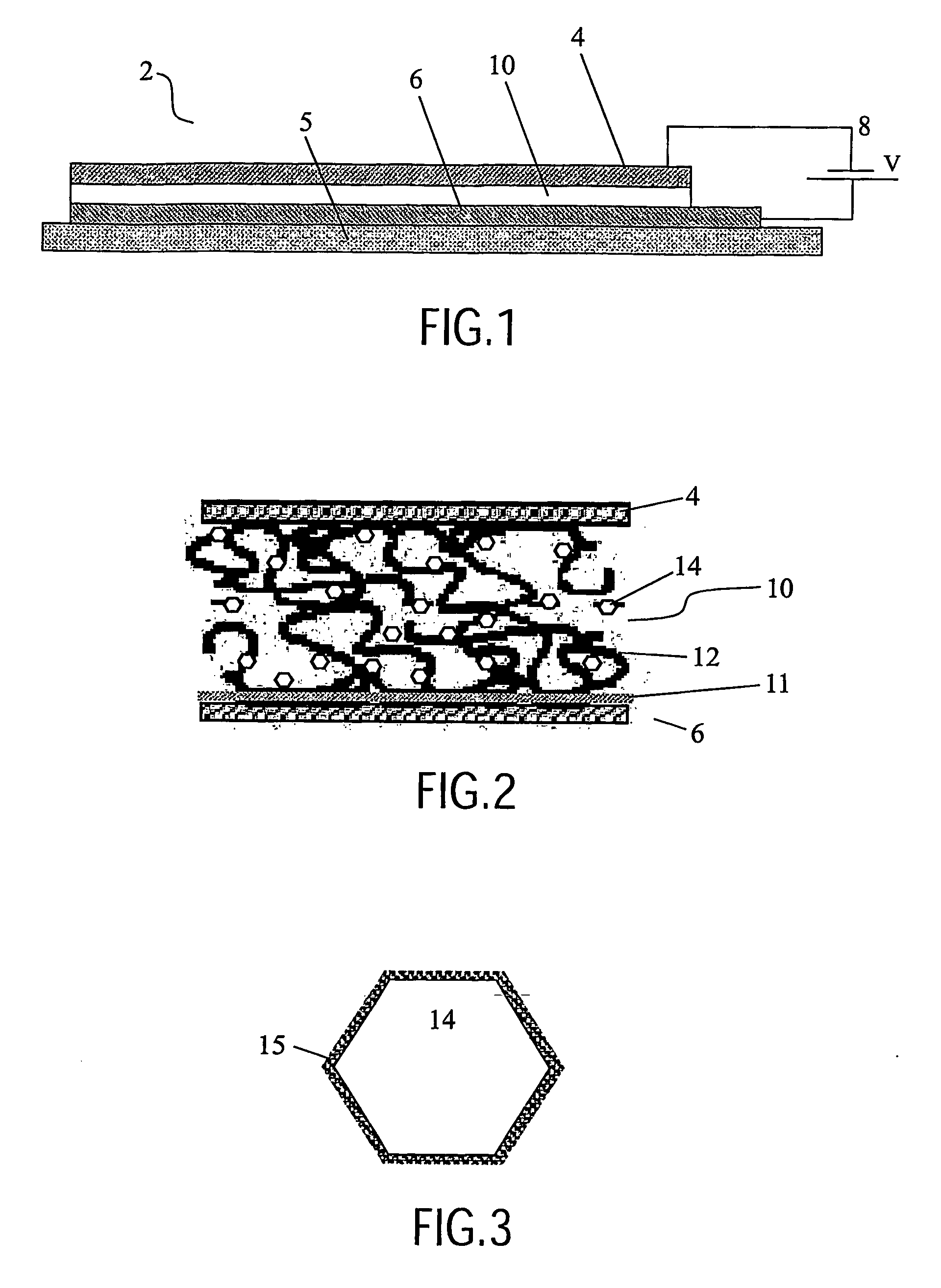
Organic photosensitive cells having a reciprocal-carrier exciton blocking layer
ActiveUS7230269B2Easy injectionRecombination loss is minimizedDischarge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsBlocking layerBlock layer
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
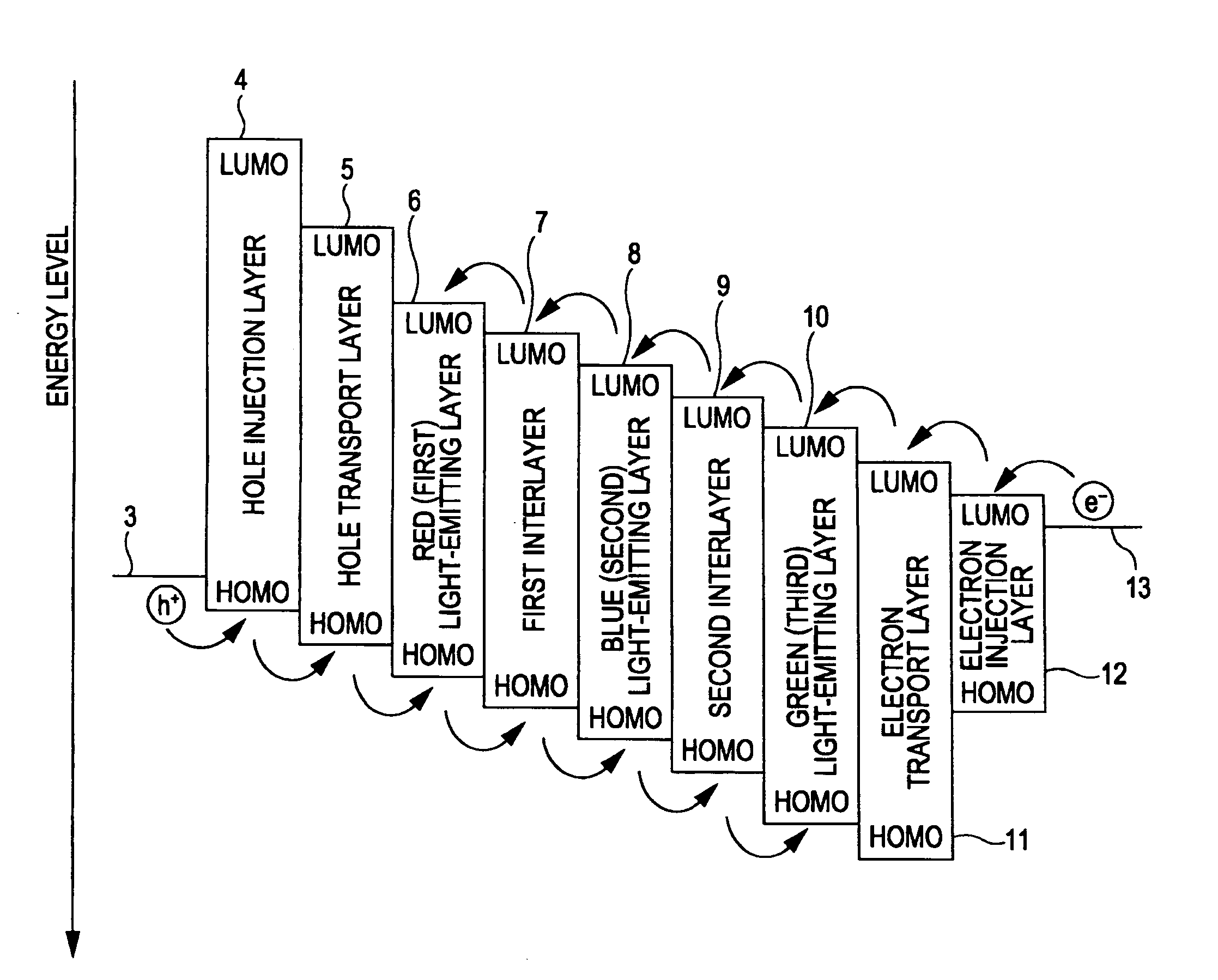
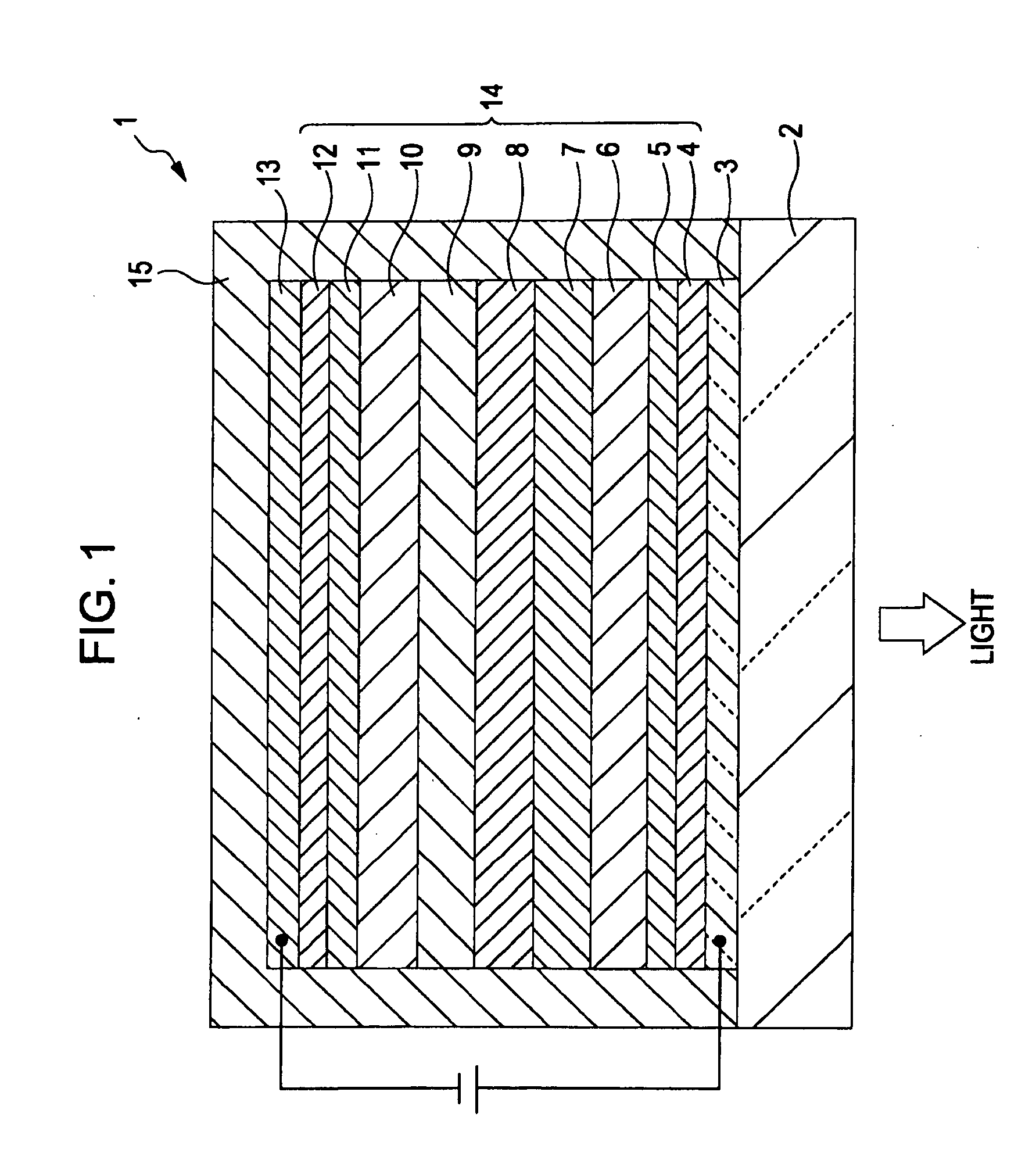
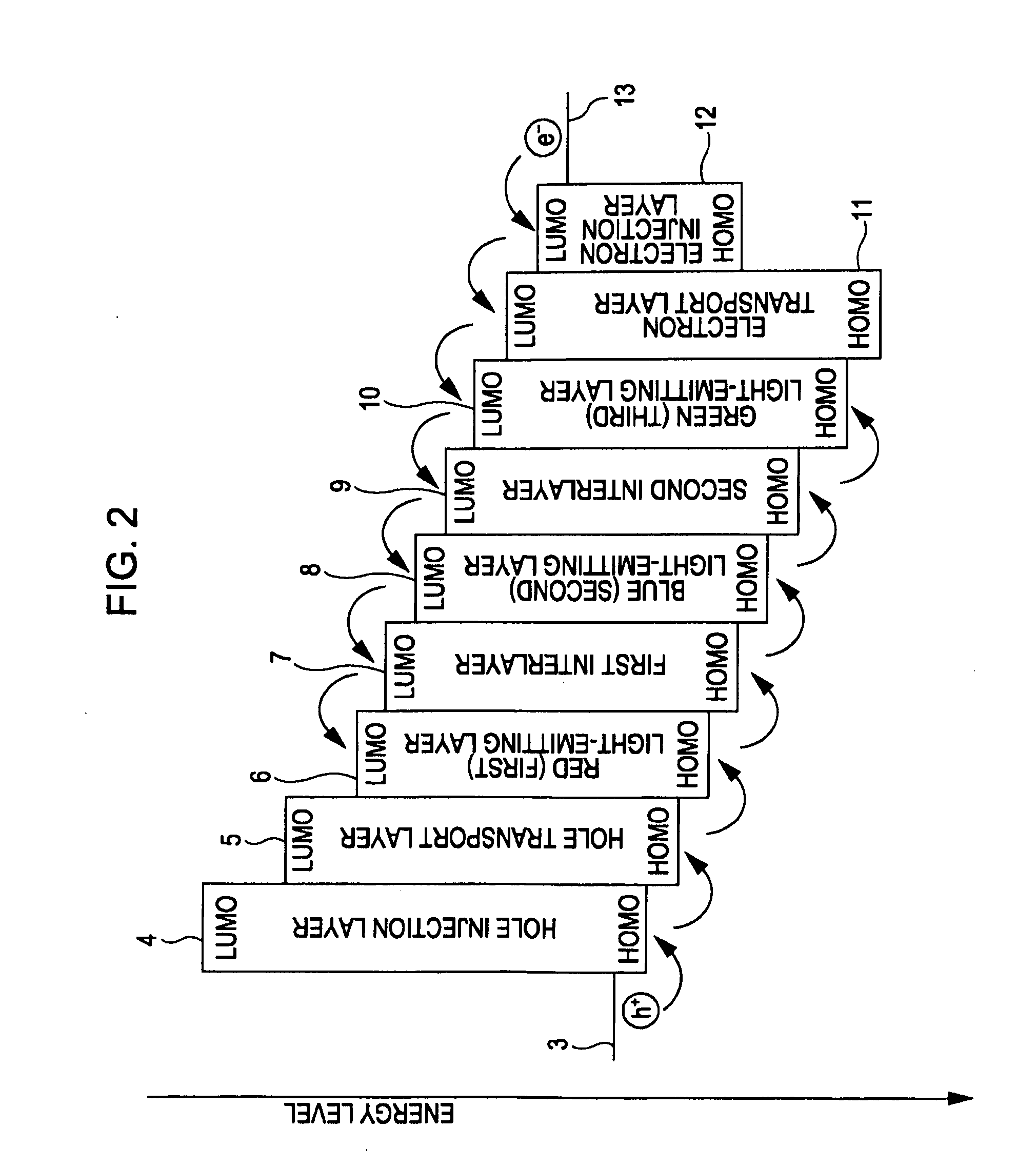
Light-emitting element, display device, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20090261360A1Excellent durability and luminous efficiencyImprove balanceElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesEnergy transferDisplay device
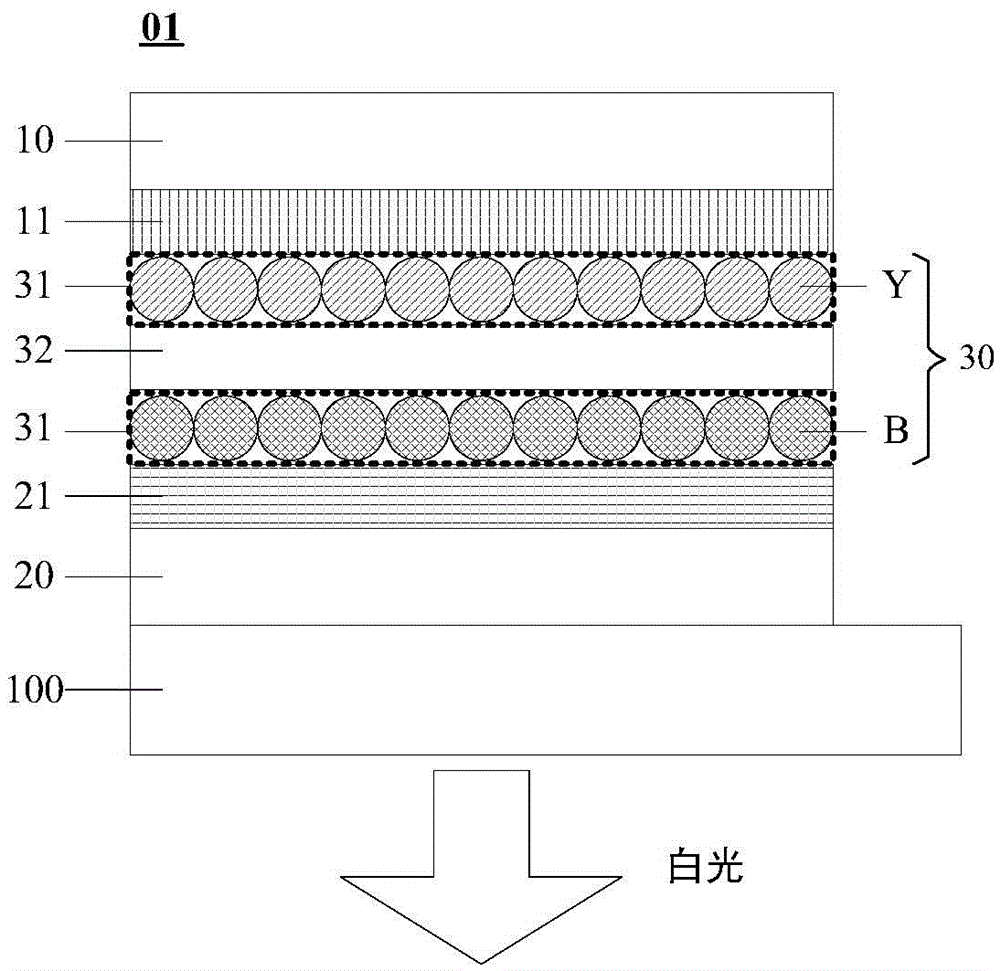
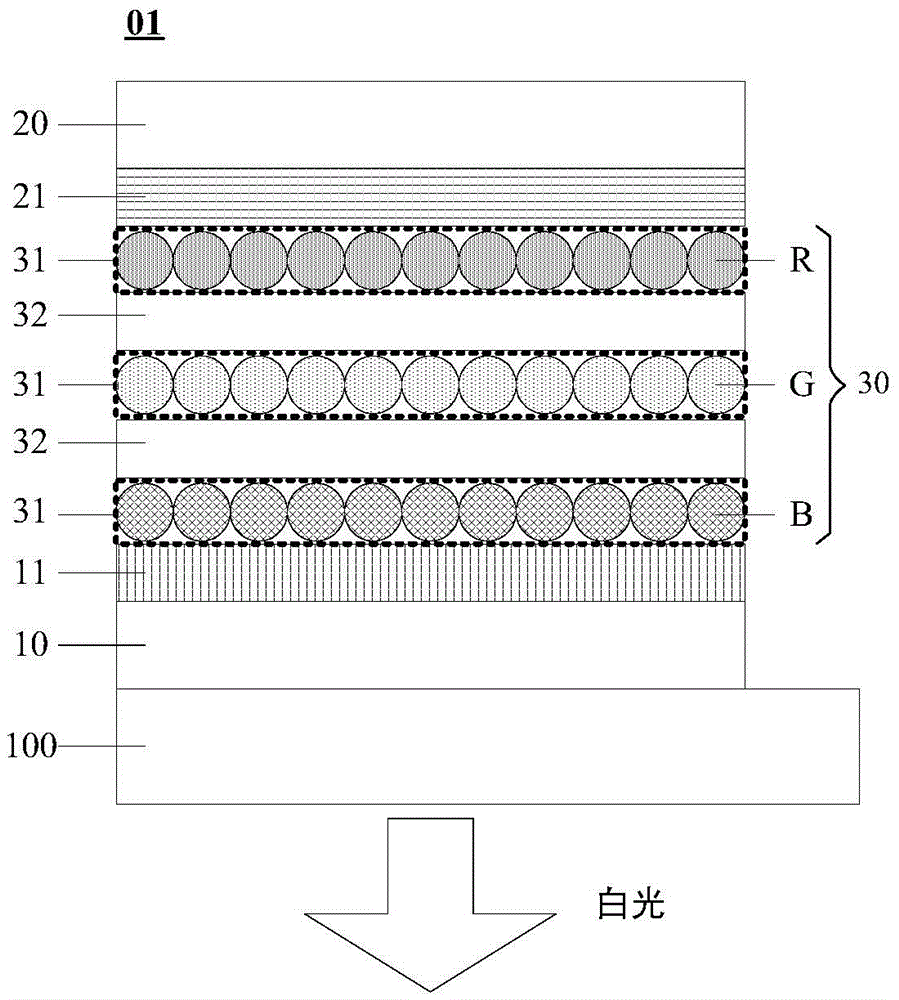
A light-emitting element includes a cathode, an anode, a first light-emitting layer that is disposed between the cathode and the anode and that emits light of a first color, a second light-emitting layer that is disposed between the first light-emitting layer and the cathode and that emits light of a second color different from the first color, a third light-emitting layer that is disposed between the second light-emitting layer and the cathode and that emits light of a third color different from the first color and the second color, a first interlayer that is disposed between the first light-emitting layer and the second light-emitting layer so as to be in contact with the first and second light-emitting layers and that has a function of preventing energy transfer of an exciton between the first light-emitting layer and the second light-emitting layer, and a second interlayer that is disposed between the second light-emitting layer and the third light-emitting layer so as to be in contact with the second and third light-emitting layers and that has a function of preventing energy transfer of an exciton between the second light-emitting layer and the third light-emitting layer, wherein the first interlayer has a hole-transporting property higher than that of the second interlayer, and the second interlayer has an electron-transporting property higher than that of the first interlayer.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL KEYSTONE TECH LLC
Electroluminescent device
InactiveUS20070077594A1Improve performanceImprove power efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyPreparing sample for investigationQuantum dotLight emitting device
The invention relates to a matrix of electroluminescent organic material having quantum dots embedded therein. Electrodes provide electrons and holes to the matrix forming excitons to be transferred to the quantum dots. The invention provides transfer molecules on the quantum dots facilitating the transfer of excitons from the electroluminescent organic material to the quantum dots, by first transferring them to the transfer molecules. The transfer molecules are chosen to make a transfer rate of excitons from the organic material to the transfer molecules larger than a decay rate of excitons in the organic material. More specifically, the organic matrix forms a light emitting layer in a light emitting device (LED). Also, the electroluminescent organic material is preferably an electroluminescent polymer.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
White organic light emitting device and method for manufacturing the same
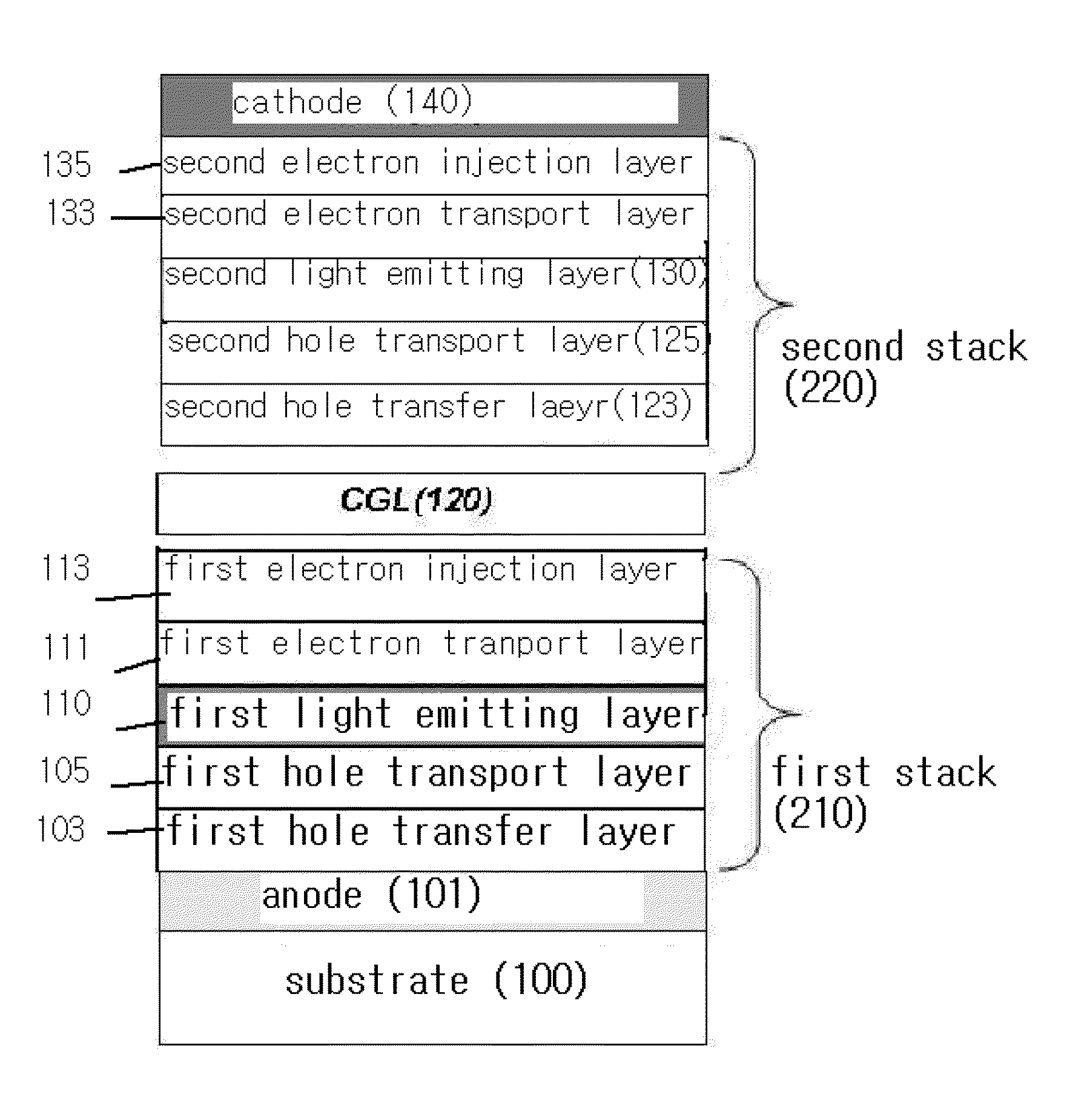
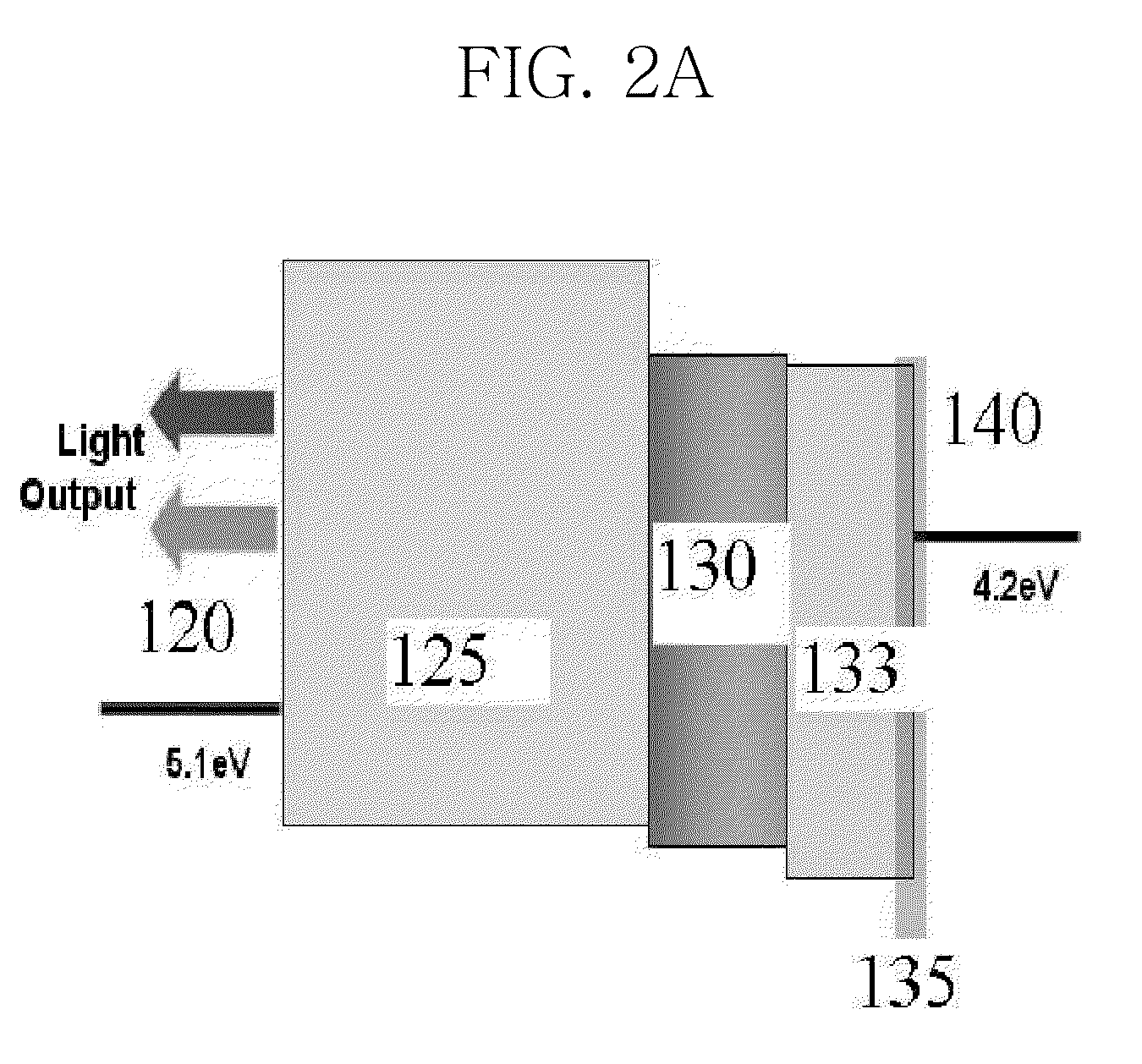
ActiveUS20100133522A1Improve luminous efficiencyColor shiftElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesHole transport layerLight emitting device
The present invention relates to a white organic light emitting device and a method for manufacturing the same, in which a hole transport layer is made to have an energy level higher than an energy level of an excited state of a phosphorescent light emitting layer adjacent thereto for enhancing light emitting efficiency of the hole transport layer without an additional exciton blocking layer, and a dopant content in the phosphorescent light emitting layer is adjusted for preventing color shift from taking place.The white organic light emitting device includes an anode and a cathode placed on a substrate opposite to each other, a charge generation layer formed between the anode and the cathode, a first stack of a first hole transport layer, a first light emitting layer for emitting a blue light, and a first electron transport layer between the anode and the charge generation layer, and a second stack of a second hole transport layer, a second light emitting layer having a host doped with phosphorescence red and green together, and a second electron transport layer between the charge generation layer and the cathode, wherein the second hole transport layer has an energy level set higher than a triplet excited state energy level of the second light emitting layer.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Organic photovoltaic cell incorporating electron conducting exciton blocking layers
ActiveUS20120235125A1Improve power conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureNanoinformaticsFill factorWide gap
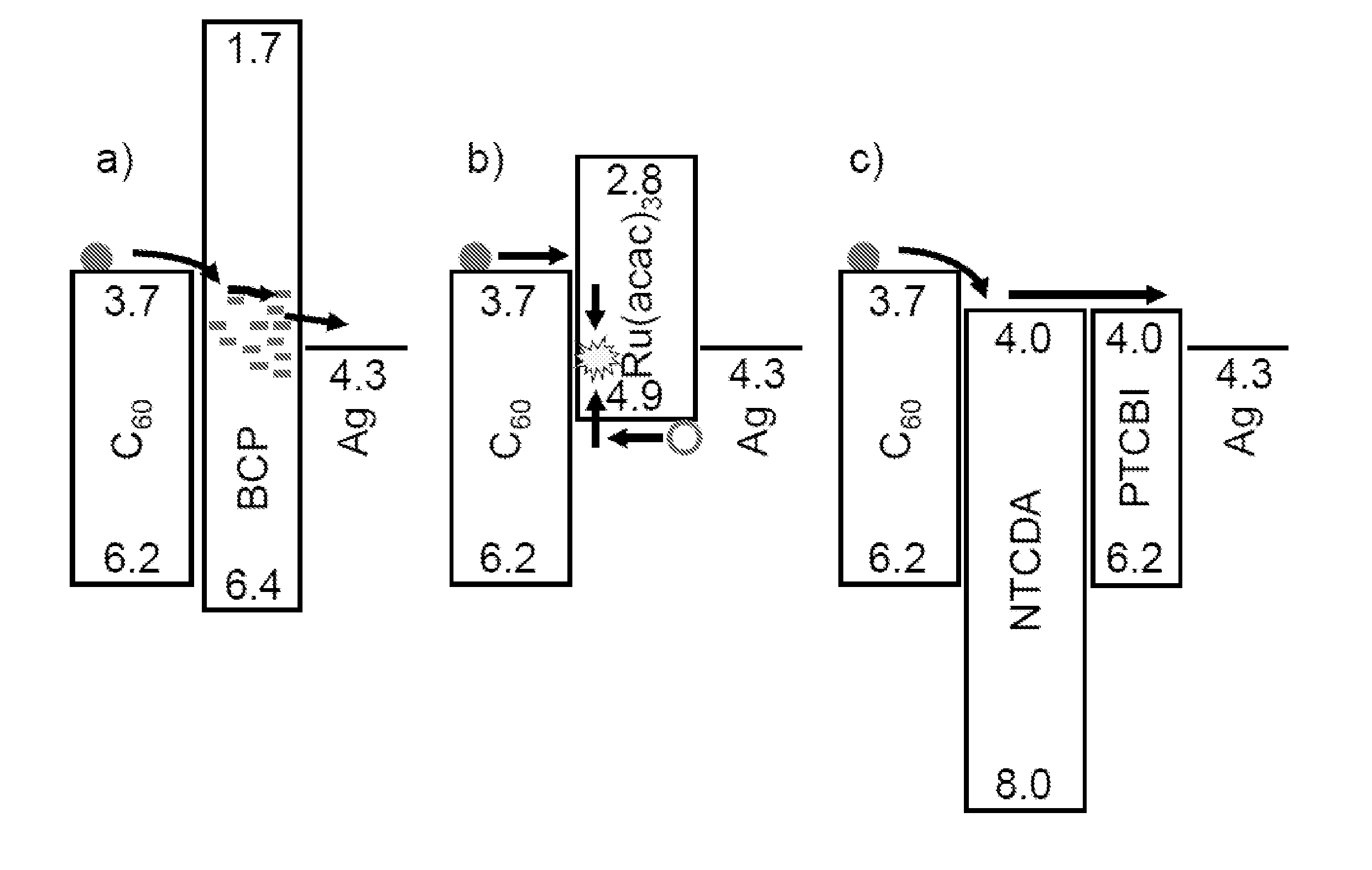
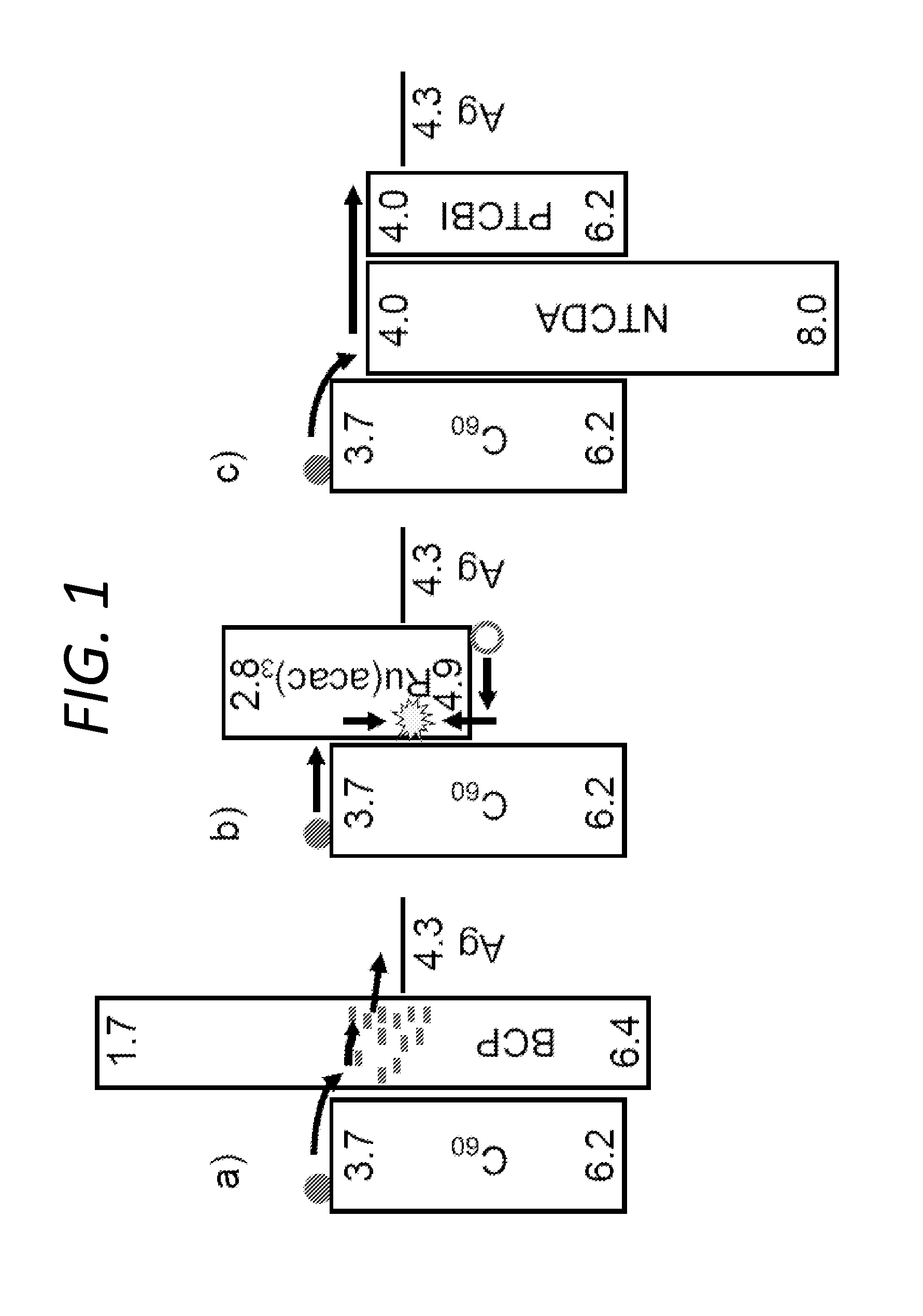
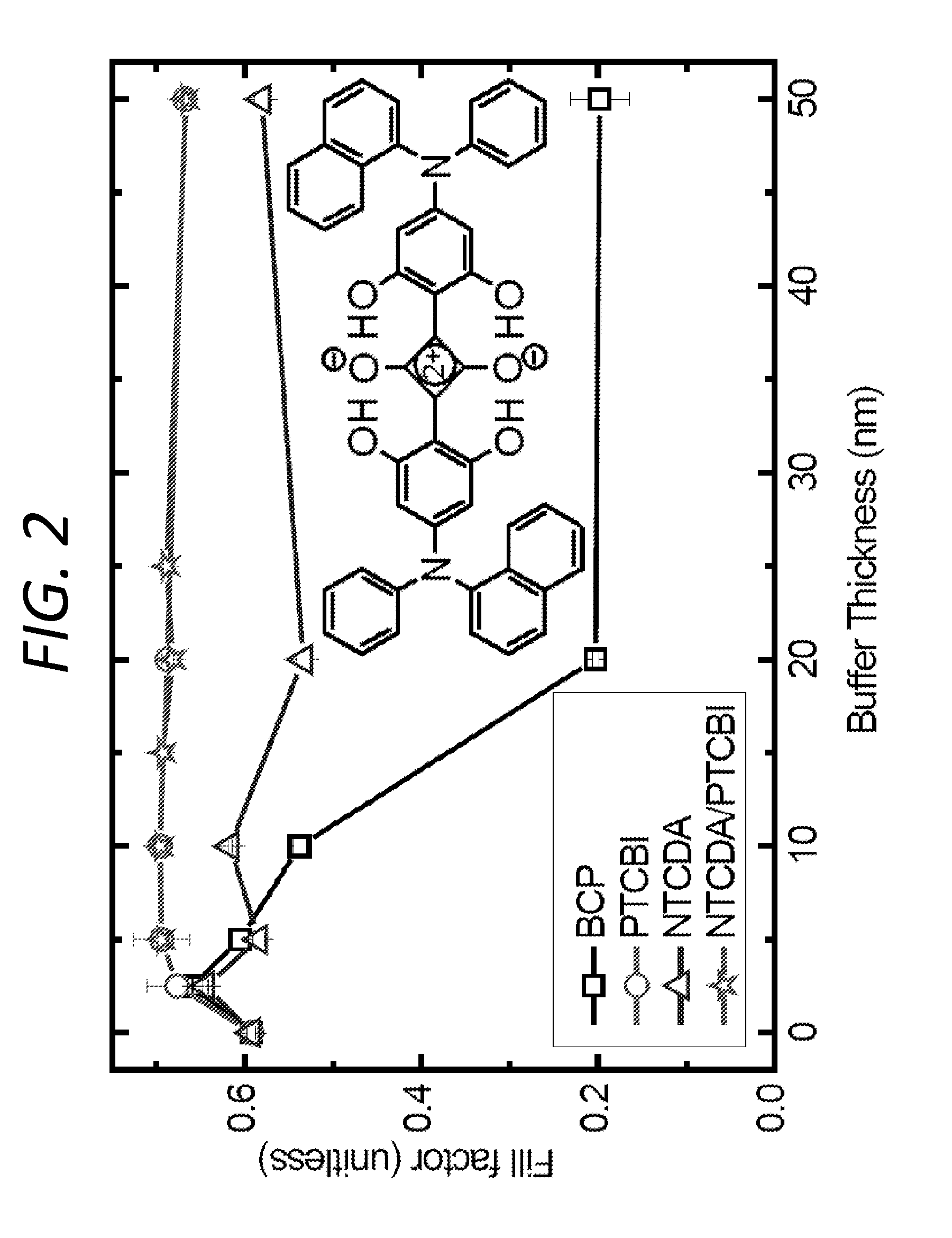
The present disclosure relates to photosensitive optoelectronic devices comprising a compound blocking layer located between an acceptor material and a cathode, the compound blocking layer comprising: at least one electron conducting material, and at least one wide-gap electron conducting exciton blocking layer. For example, 3,4,9,10 perylenetetracarboxylic bisbenzimidazole (PTCBI) and 1,4,5,8-napthalene-tetracarboxylic-dianhydride (NTCDA) function as electron conducting and exciton blocking layers when interposed between the acceptor layer and cathode. Both materials serve as efficient electron conductors, leading to a fill factor as high as 0.70. By using an NTCDA / PTCBI compound blocking layer structure increased power conversion efficiency is achieved, compared to an analogous device using a conventional blocking layers shown to conduct electrons via damage-induced midgap states.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
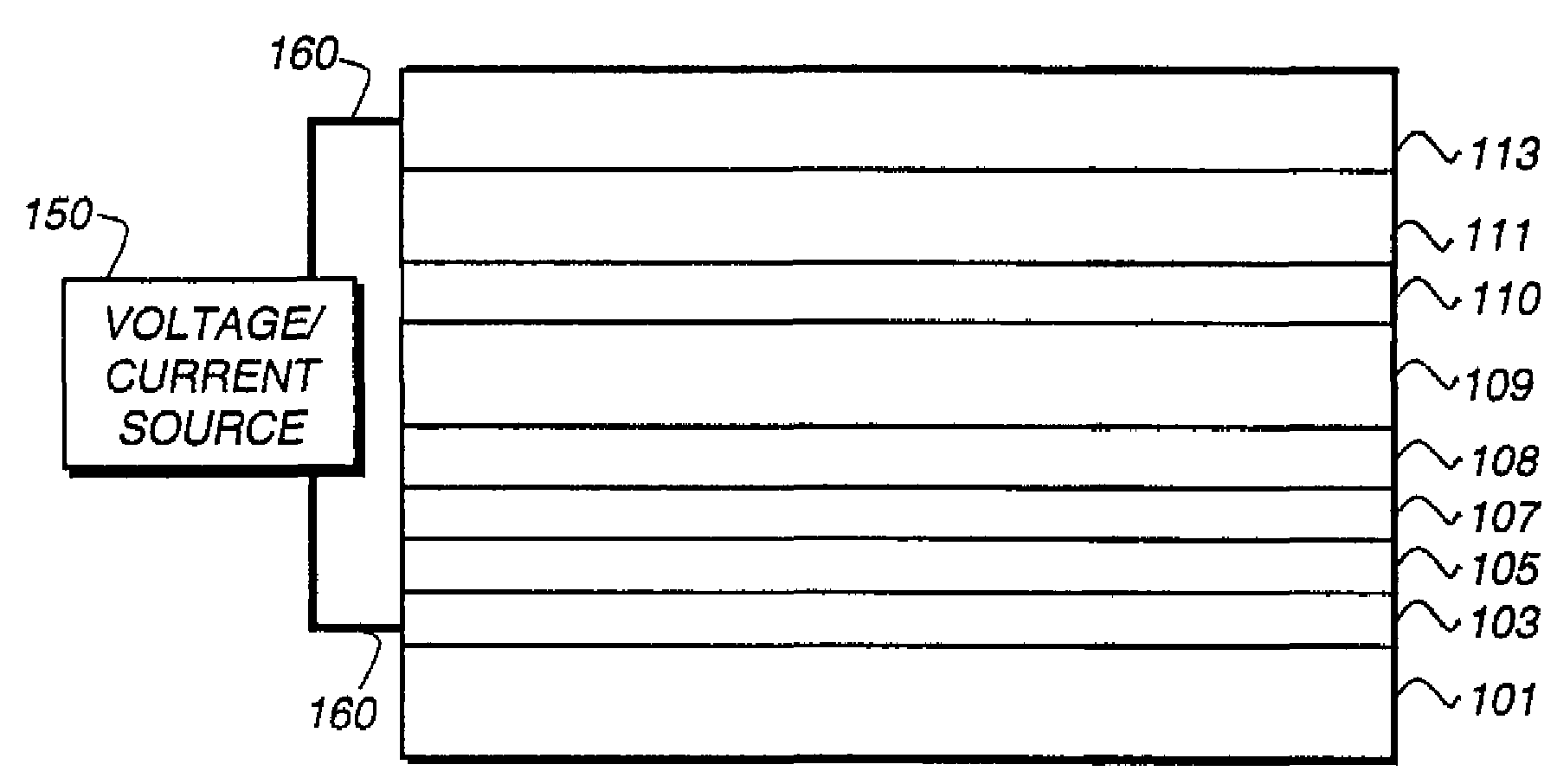
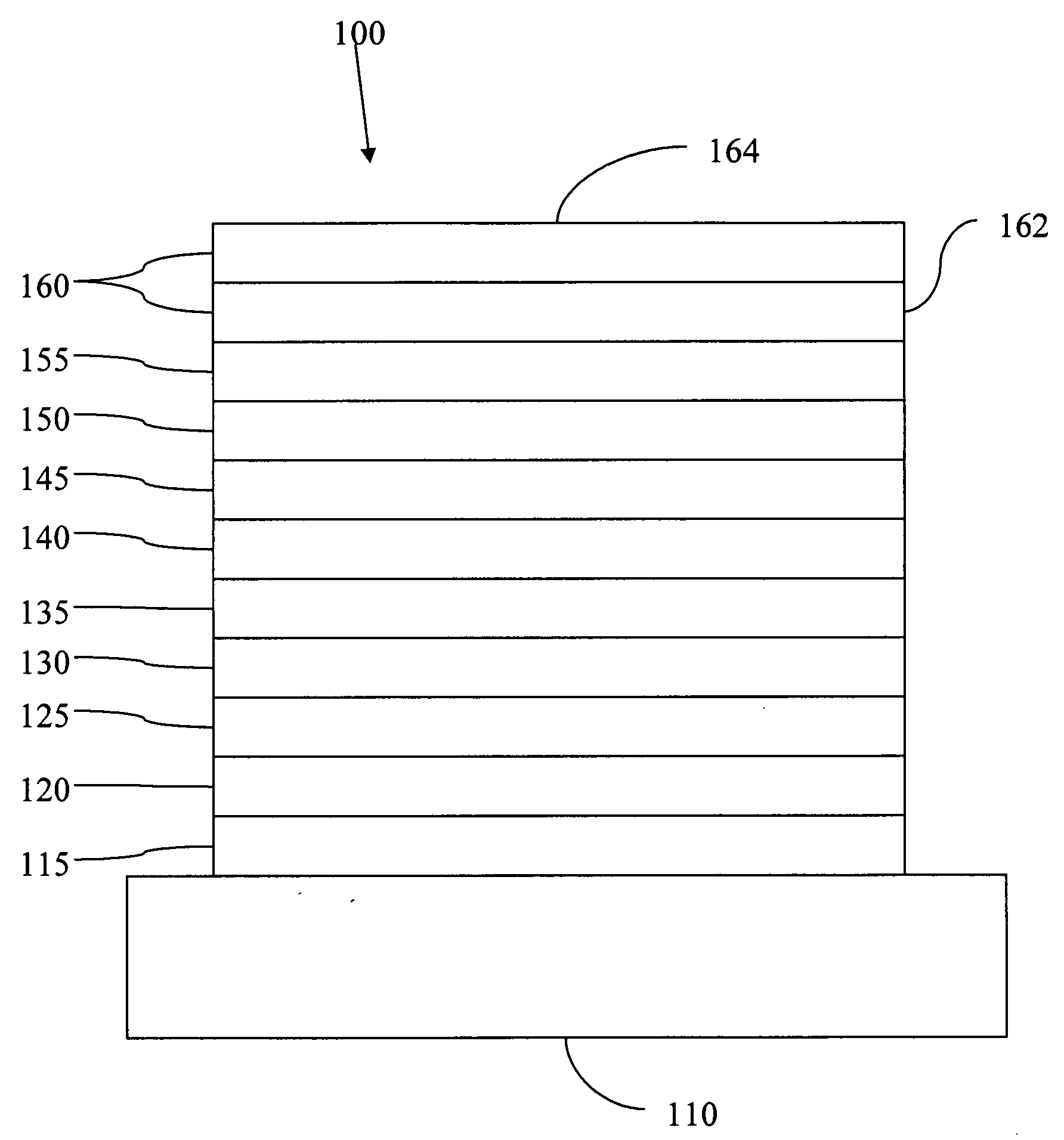
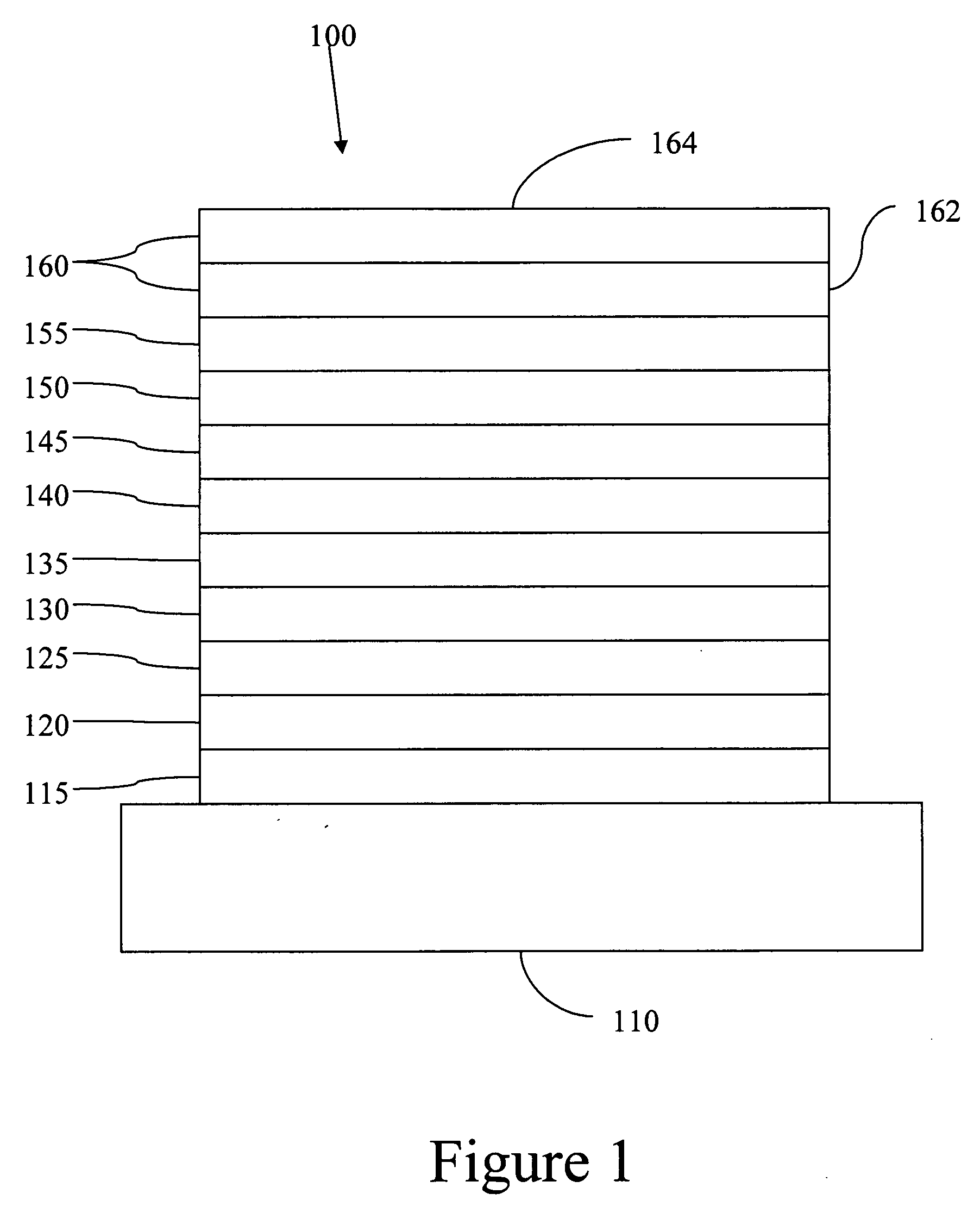
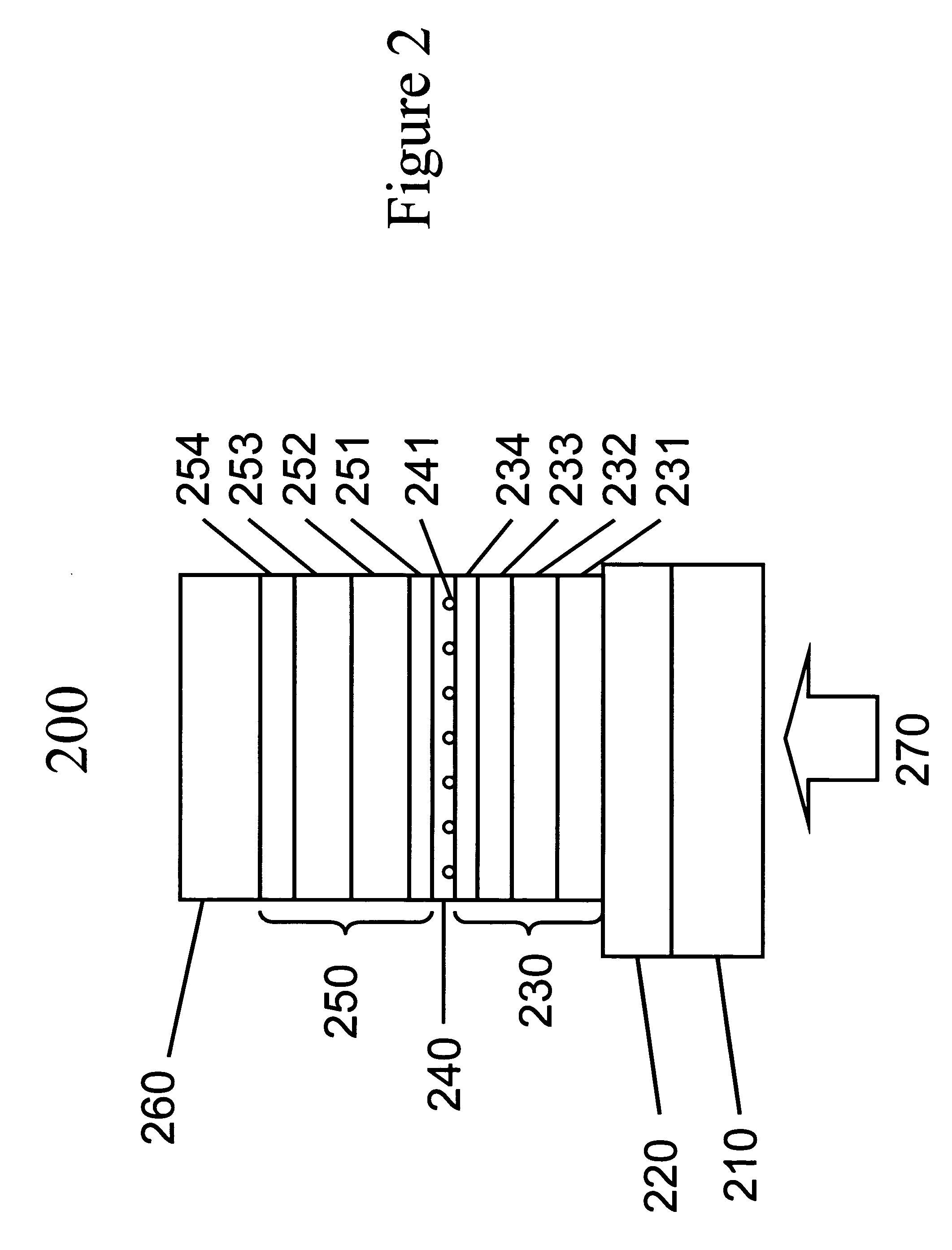
Stacked organic photosensitive devices
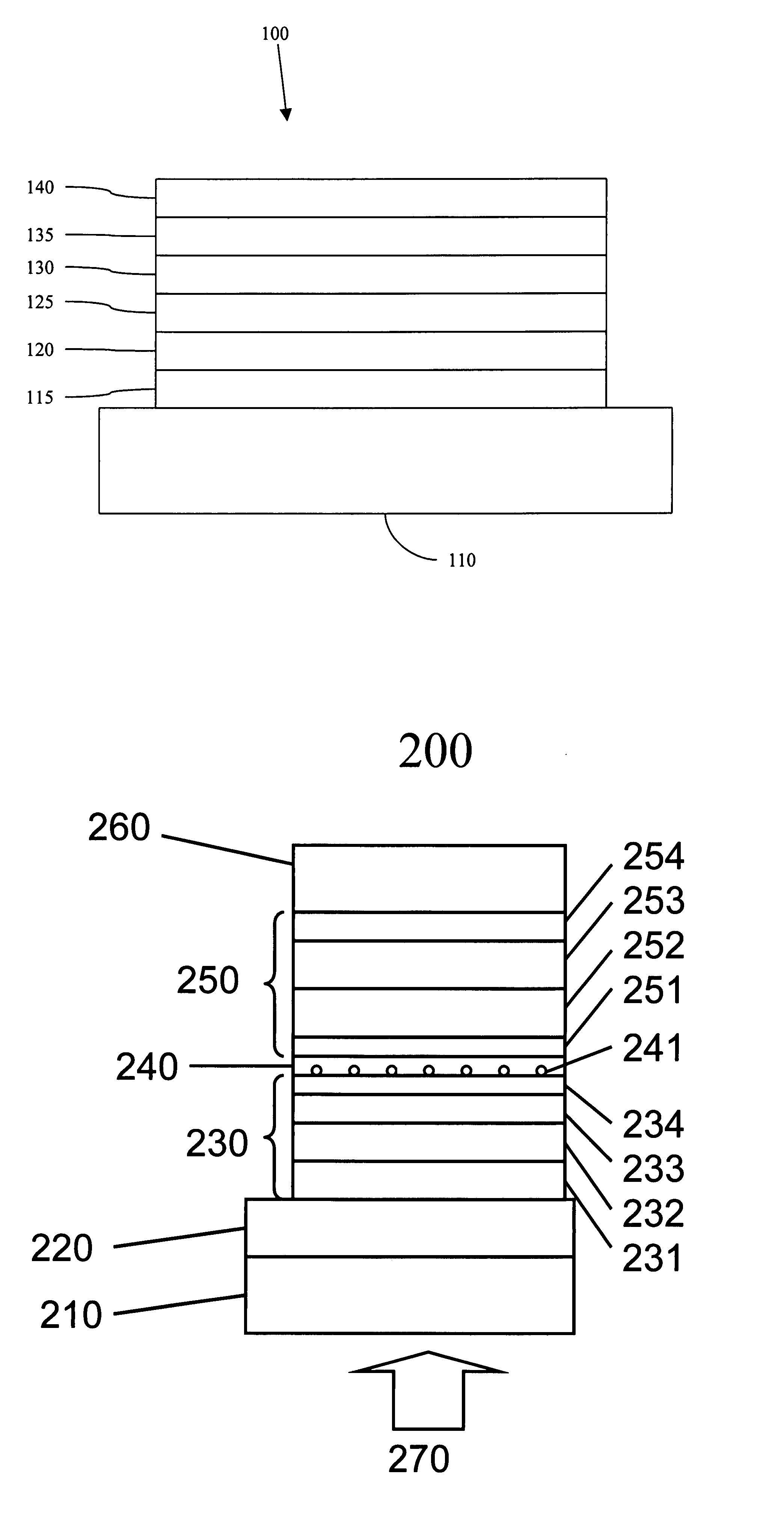
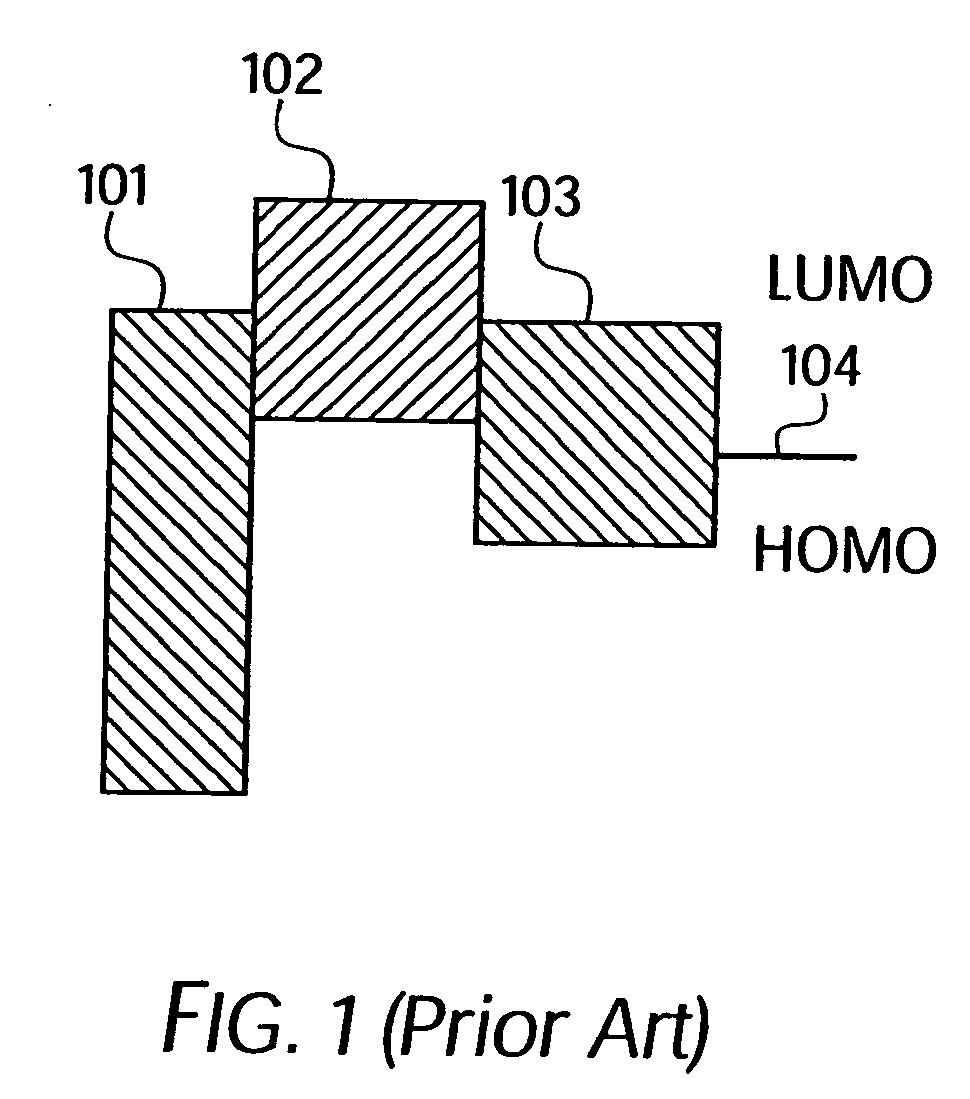
A device is provided having a first electrode, a second electrode, a first photoactive region having a characteristic absorption wavelength λ1 and a second photoactive region having a characteristic absorption wavelength λ2. The photoactive regions are disposed between the first and second electrodes, and further positioned on the same side of a reflective layer, such that the first photoactive region is closer to the reflective layer than the second photoactive region. The materials comprising the photoactive regions may be selected such that λ1 is at least about 10% different from λ2. The device may further comprise an exciton blocking layer disposed adjacent to and in direct contact with the organic acceptor material of each photoactive region, wherein the LUMO of each exciton blocking layer other than that closest to the cathode is not more than about 0.3 eV greater than the LUMO of the acceptor material.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Highly-efficient organic electroluminescent device based on fluorescence doped luminescent layer
ActiveCN104835916AImprove luminous efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic transmissionLuminescence
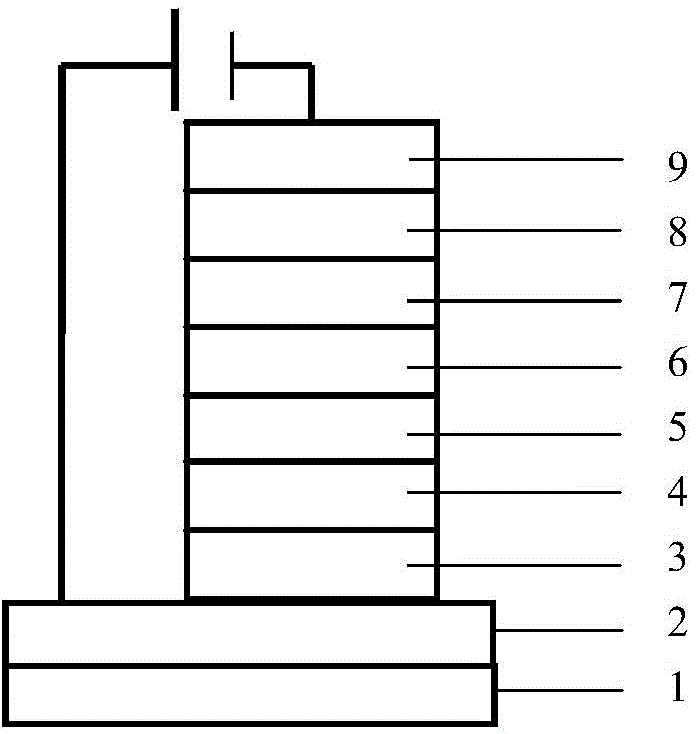
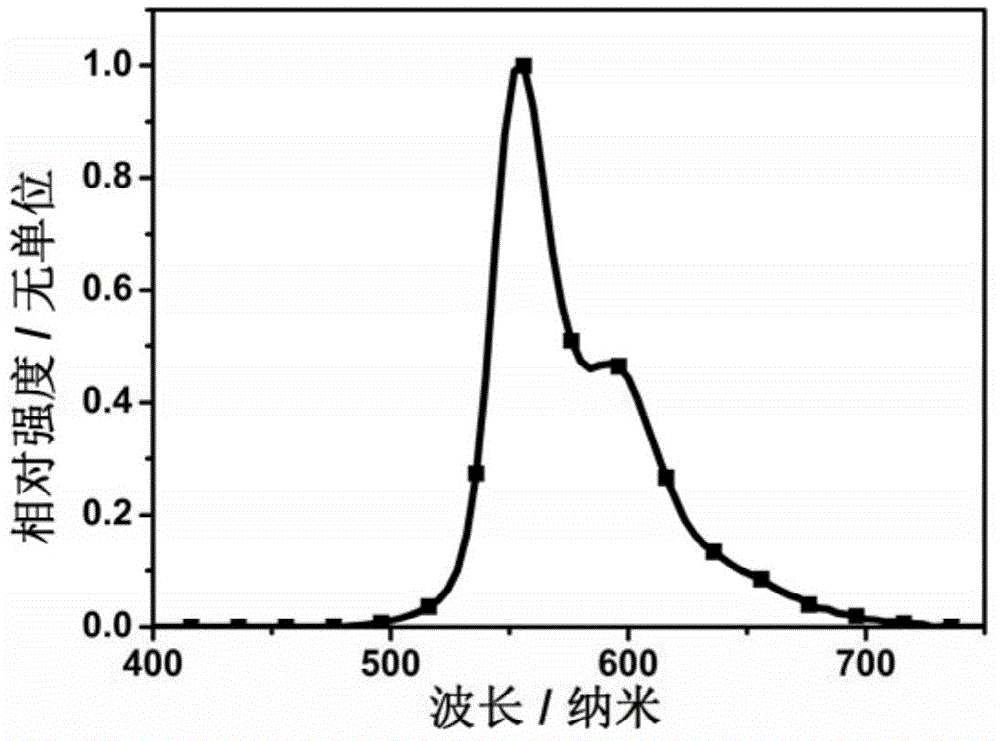
The invention relates to a device structure of an organic light-emitting diode (OLED), and especially relates to a highly-efficient organic electroluminescent device based on a fluorescence doped luminescent layer. The organic electroluminescent device comprises a transparent substrate, a transparent anode, a cavity transmission layer, a first exciton barrier layer, a luminescent layer, a second exciton barrier layer, an electronic transmission layer, an electronic injecting layer and a metal cathode. The luminescent layer is formed by mixing a main body and a guest body. The main body material is organic small molecules whose energy difference between a first kind single heavy excitation state and a triplet excitation state is quite small. The guest body material is dye molecules with high fluorescence efficiency, like quinacridone derivatives. The highly-efficient organic electroluminescent device based on a fluorescence doped luminescent layer is advantageous in that the external quantum efficiency exceeds 5% of theoretic limit efficiency of a conventional fluorescence device, and the luminescence efficiency of a fluorescent OLED device can be effectively improved; the luminescent device of the invention is high in brightness, low in starting voltage, high in efficiency, and low in efficiency roll-off.
Owner:JILIN YUANHE ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CO LTD
Light-emitting device and preparation method thereof as well as display device
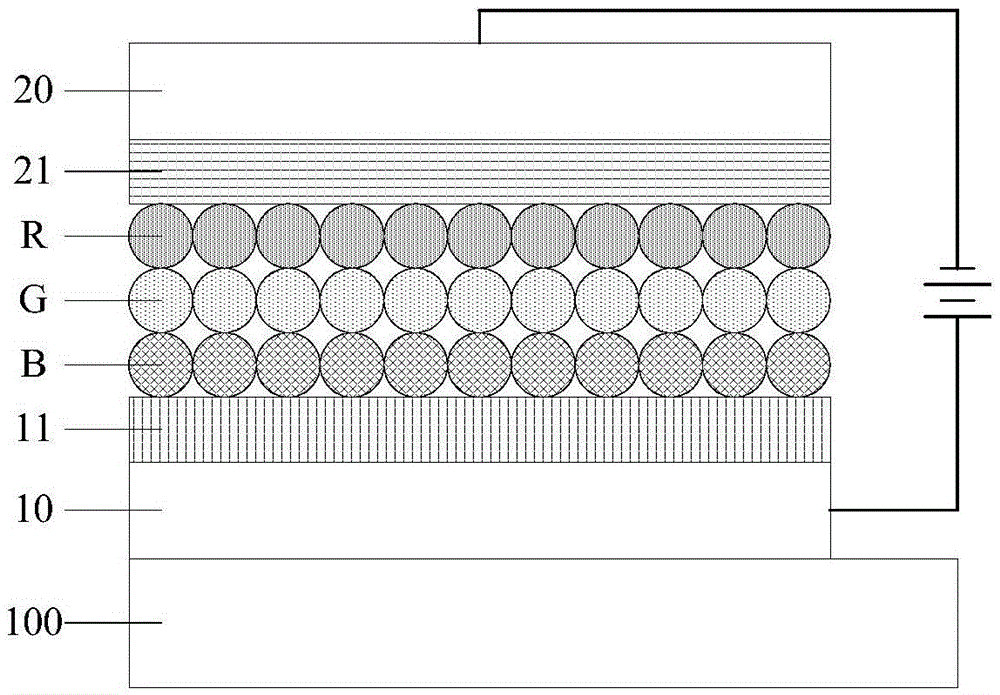
ActiveCN105552244AThe luminous effect does not diminishImprove luminosityNanotechElectroluminescent light sourcesHigh energyDisplay device
Embodiments of the invention provide a light-emitting device and a preparation method thereof as well as a display device, relating to the field of display technologies and solving a problem of light-emitting color cast due to high-energy exciton transfer in the light-emitting device while reducing the energy consumption of the device. The light-emitting device comprises an anode and a cathode which are opposite, a hole transfer layer close to the anode, an electron transfer layer close to the cathode and a light-emitting function layer arranged between the hole transfer layer and the electron transfer layer, wherein the light-emitting function layer comprises at least two layers of quantum dot light-emitting layers capable of emitting different colors of light and a transparent insulating layer arranged between any two adjacent layers of quantum dot light-emitting layers. The method is used for preparing the light-emitting device and the display device comprising the light-emitting device.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Organic photosensitive optoelectronic device with an exciton blocking layer
InactiveUS20050136232A1Increase the electric field strengthEasy to separateLayered productsNanoinformaticsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com