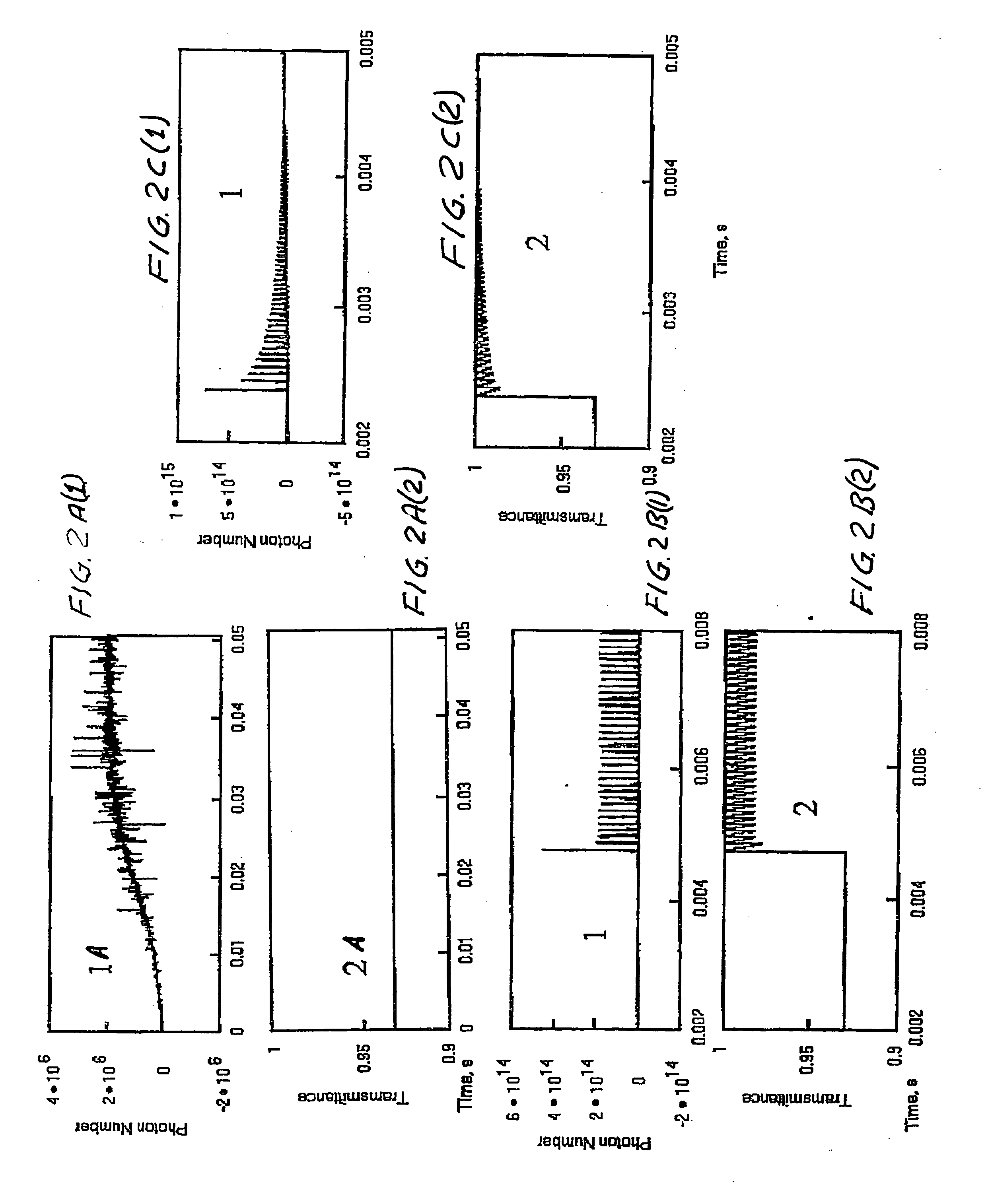
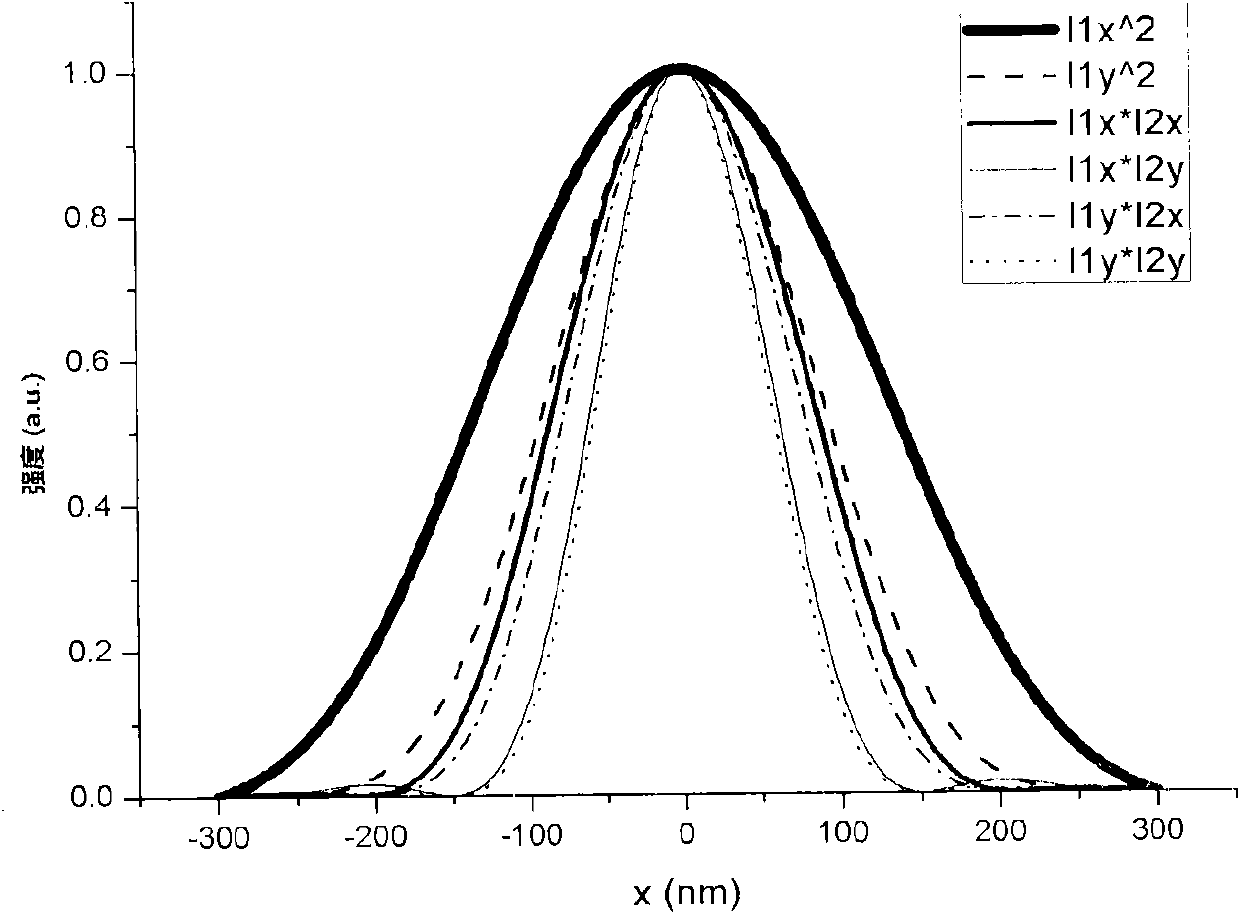
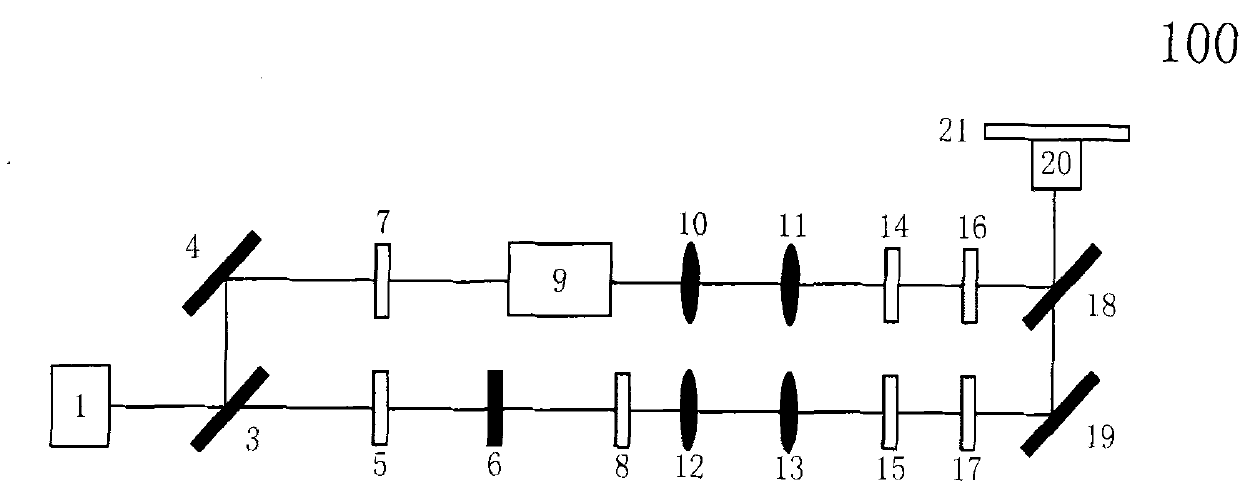
Patents
Literature
744 results about "Excited state" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
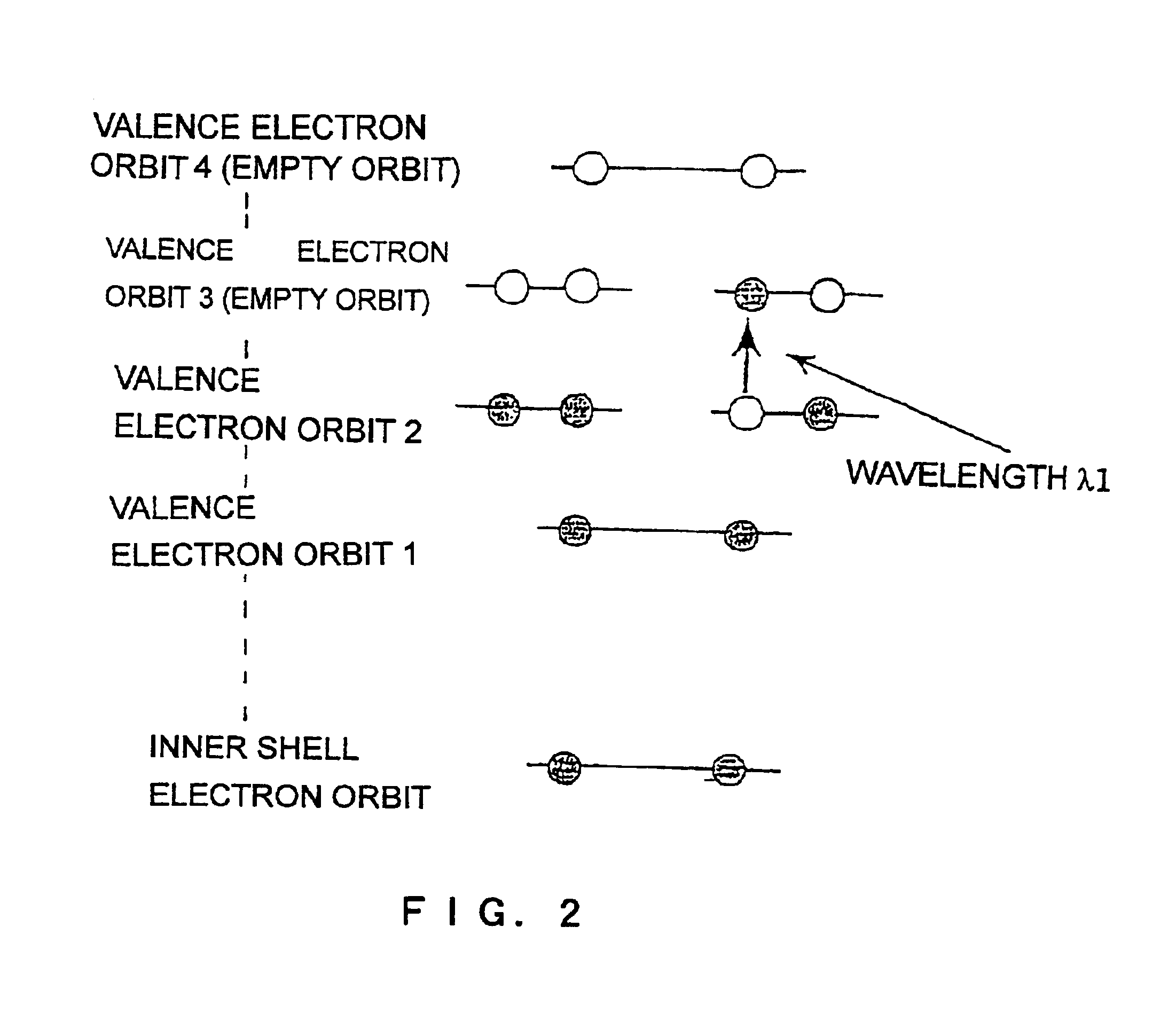
In quantum mechanics, an excited state of a system (such as an atom, molecule or nucleus) is any quantum state of the system that has a higher energy than the ground state (that is, more energy than the absolute minimum). Excitation is an elevation in energy level above an arbitrary baseline energy state. In physics there is a specific technical definition for energy level which is often associated with an atom being raised to an excited state. The temperature of a group of particles is indicative of the level of excitation (with the notable exception of systems that exhibit negative temperature).
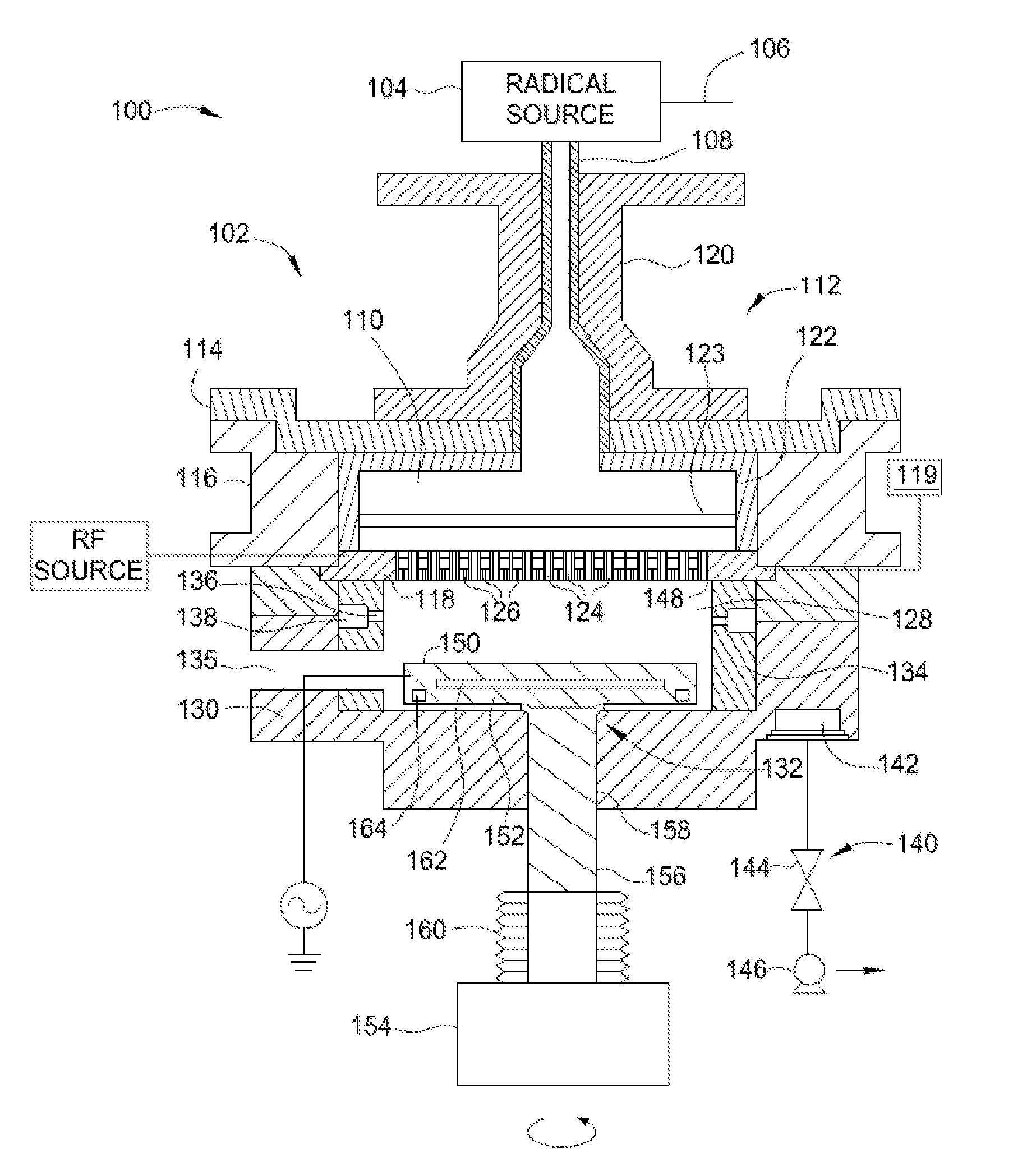
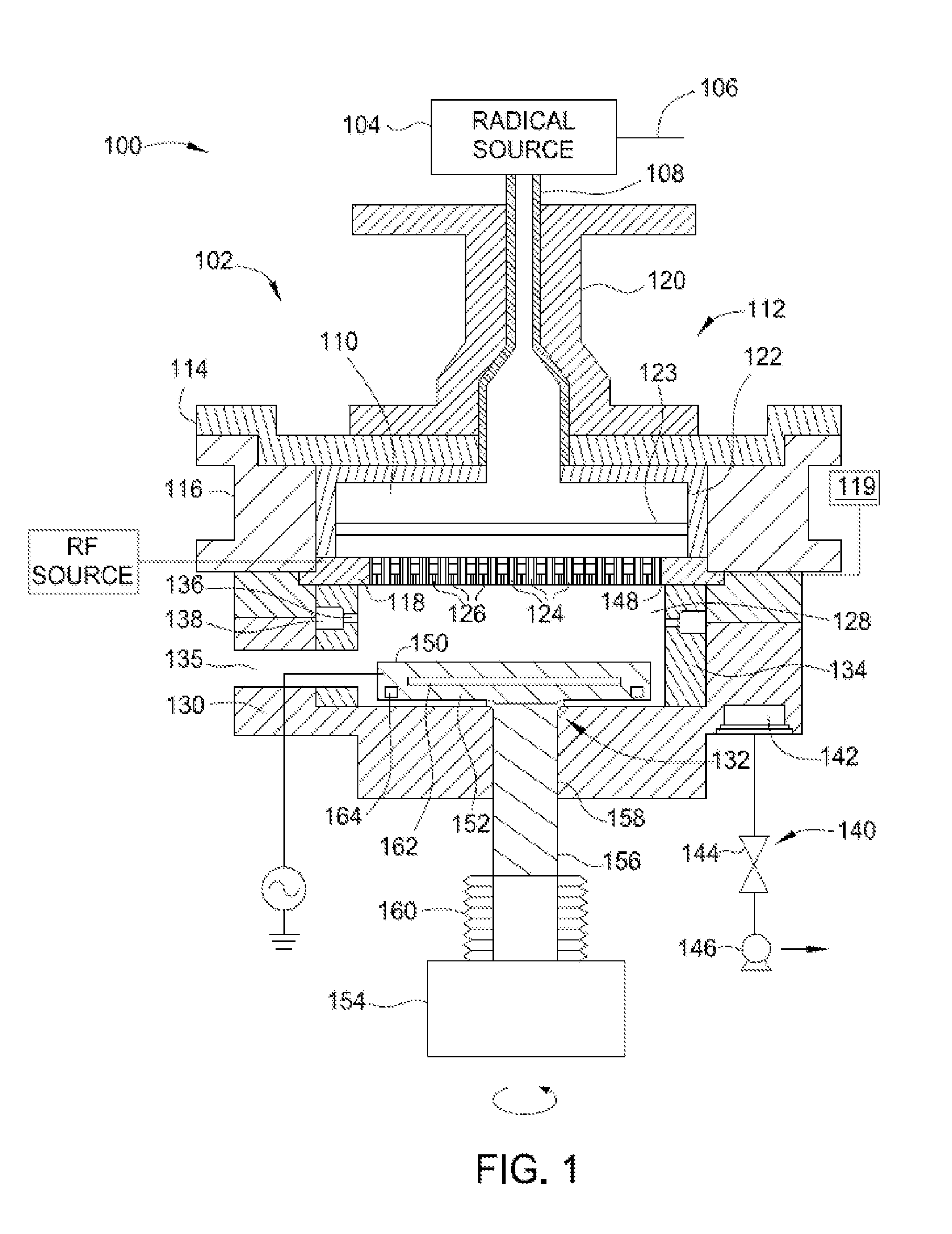
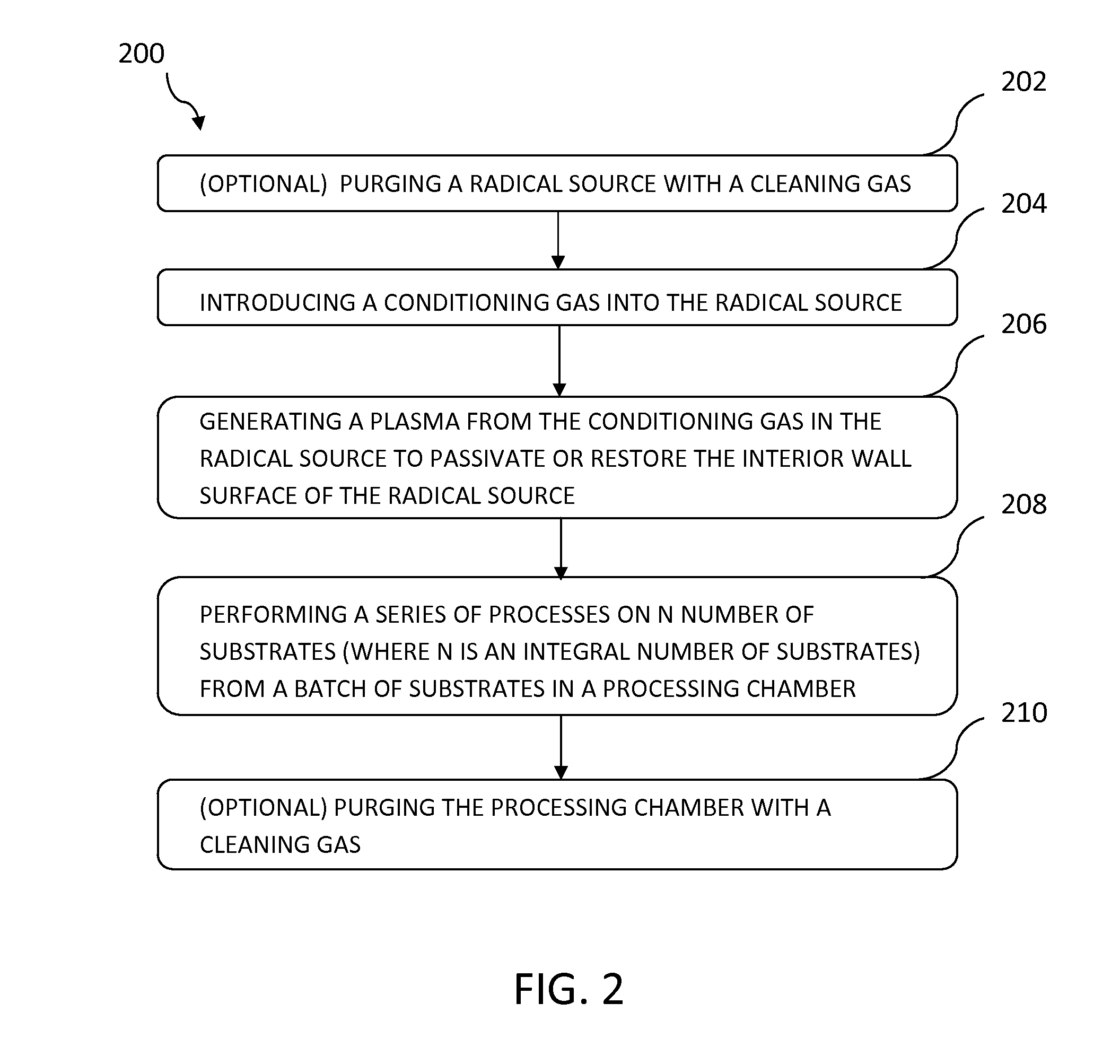
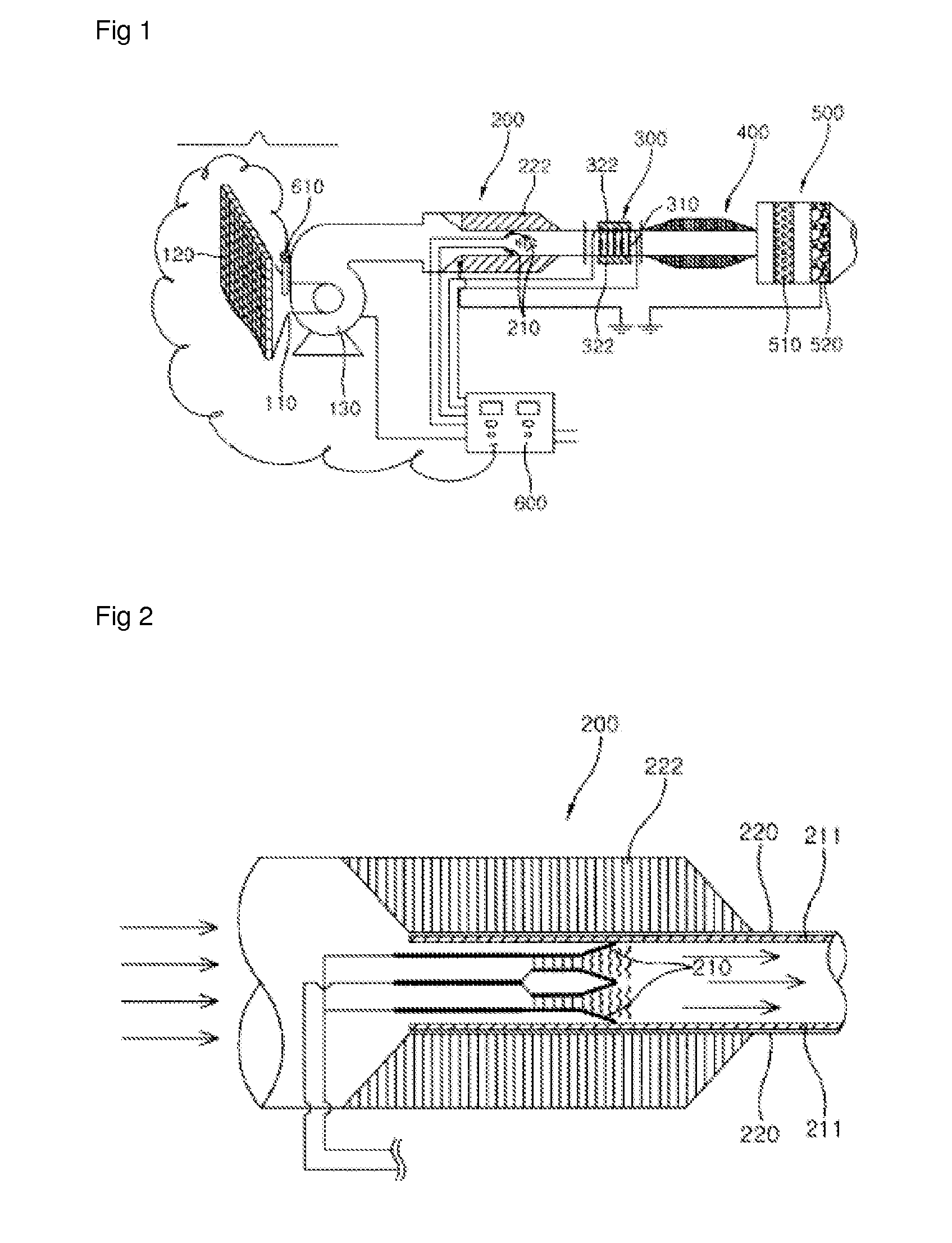
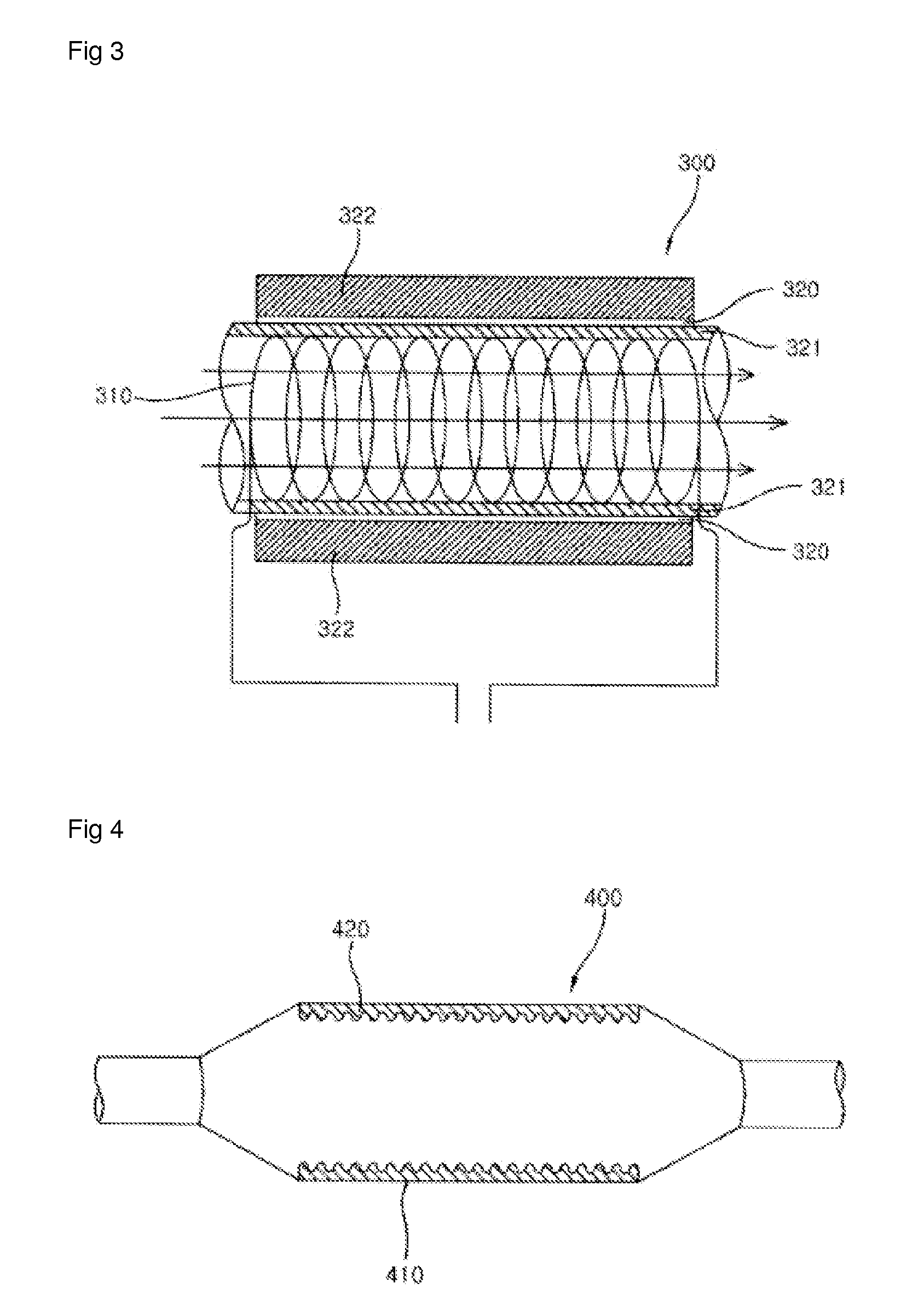
Conditioning remote plasma source for enhanced performance having repeatable etch and deposition rates
InactiveUS20160020071A1Electric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsPlasmonic couplingRemote plasma
Embodiments of the present disclosure generally relate to methods for conditioning an interior wall surface of a remote plasma generator. In one embodiment, a method for processing a substrate is provided. The method includes exposing an interior wall surface of a remote plasma source to a conditioning gas that is in excited state to passivate the interior wall surface of the remote plasma source, wherein the remote plasma source is coupled through a conduit to a processing chamber in which a substrate is disposed, and the conditioning gas comprises an oxygen-containing gas, a nitrogen-containing gas, or a combination thereof. The method has been observed to be able to improve dissociation / recombination rate and plasma coupling efficiency in the processing chamber, and therefore provides repeatable and stable plasma source performance from wafer to wafer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
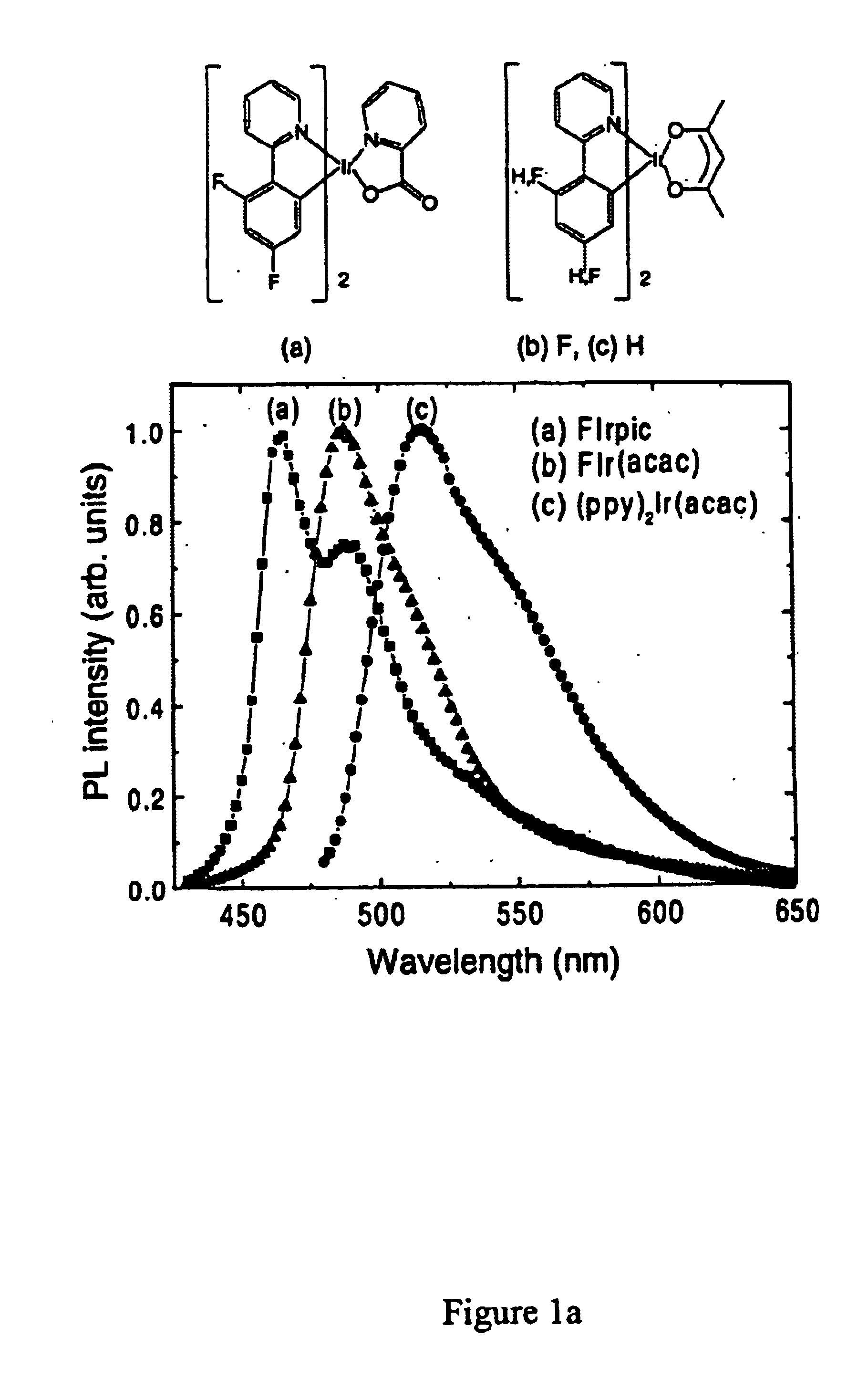
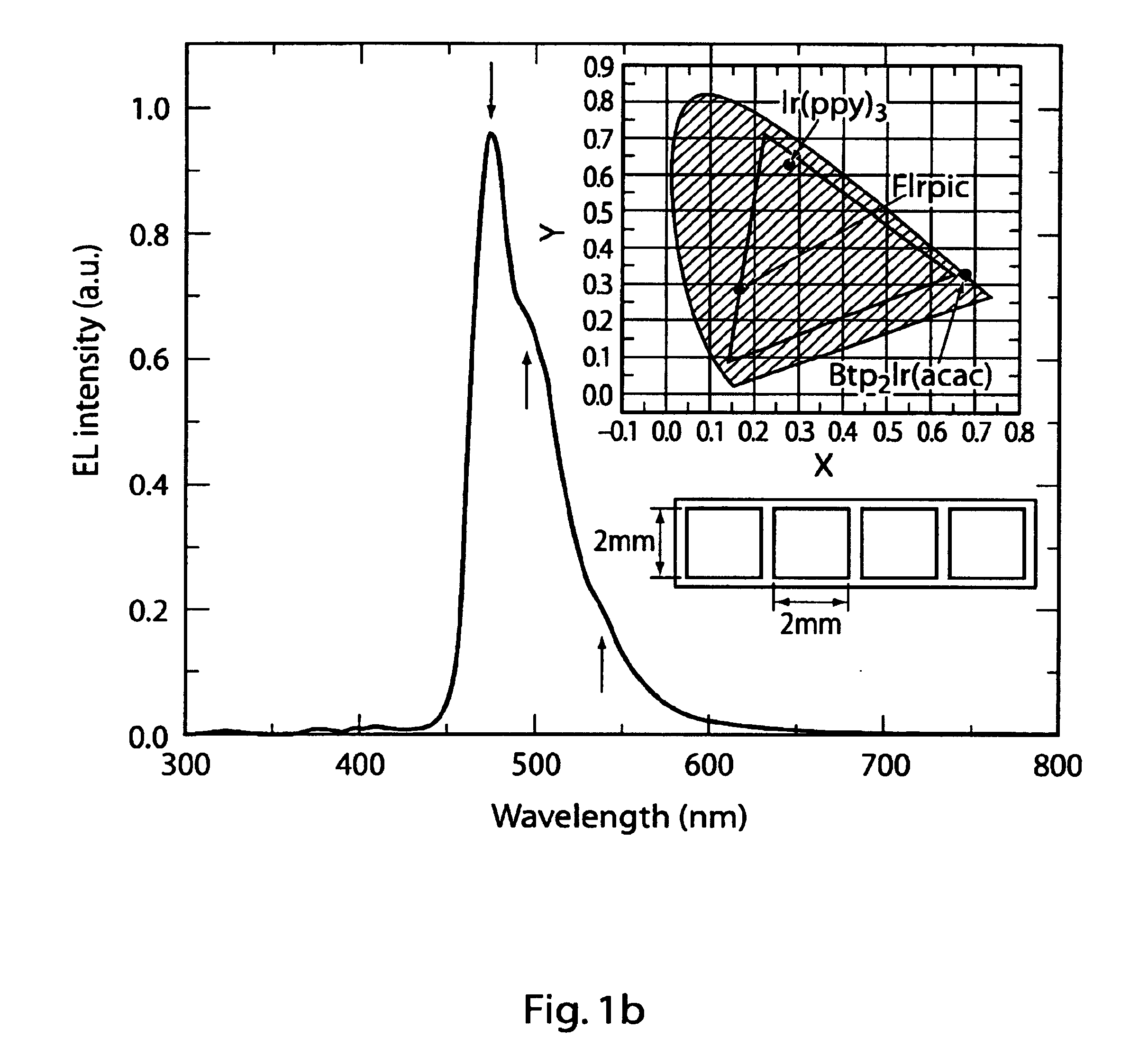
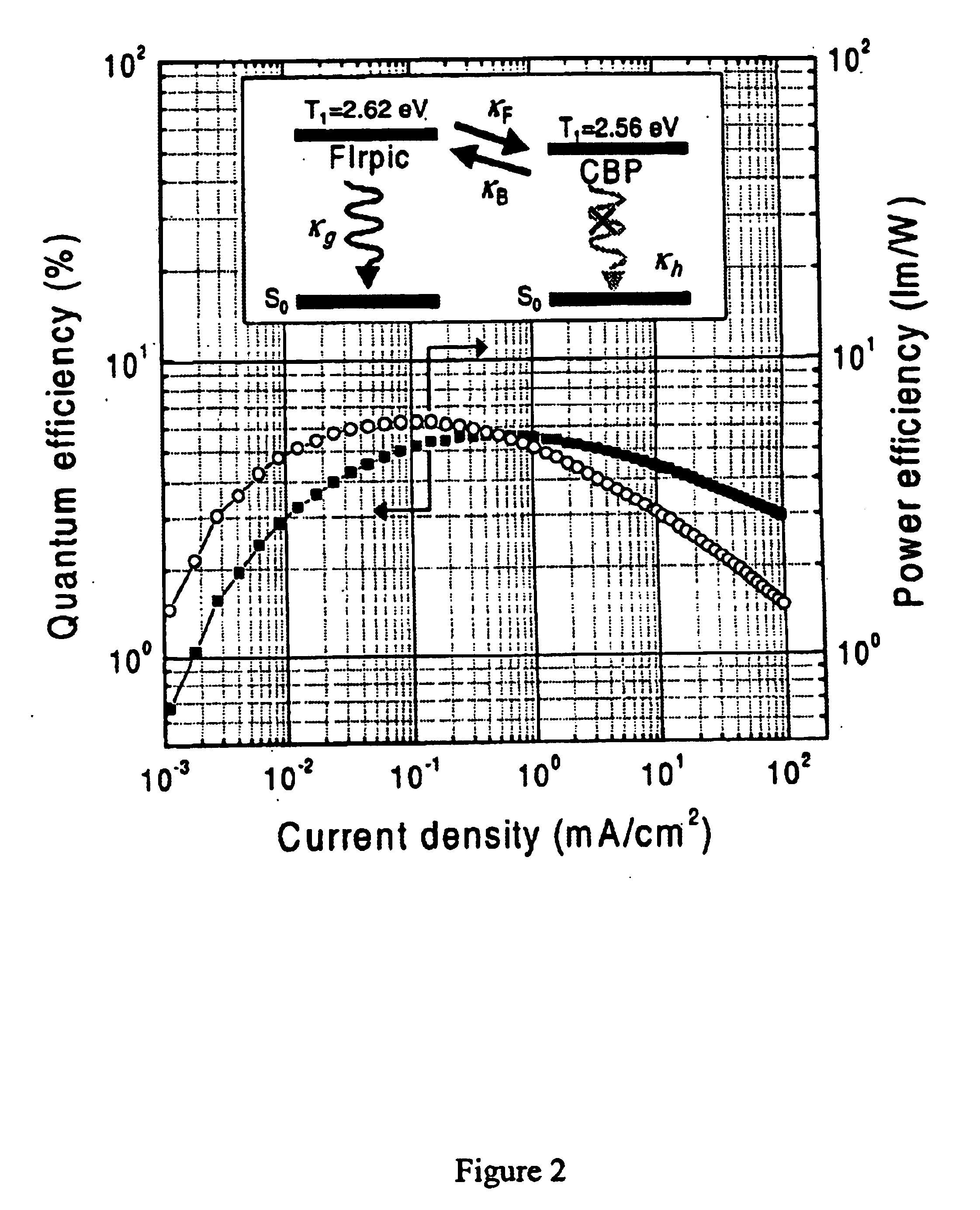
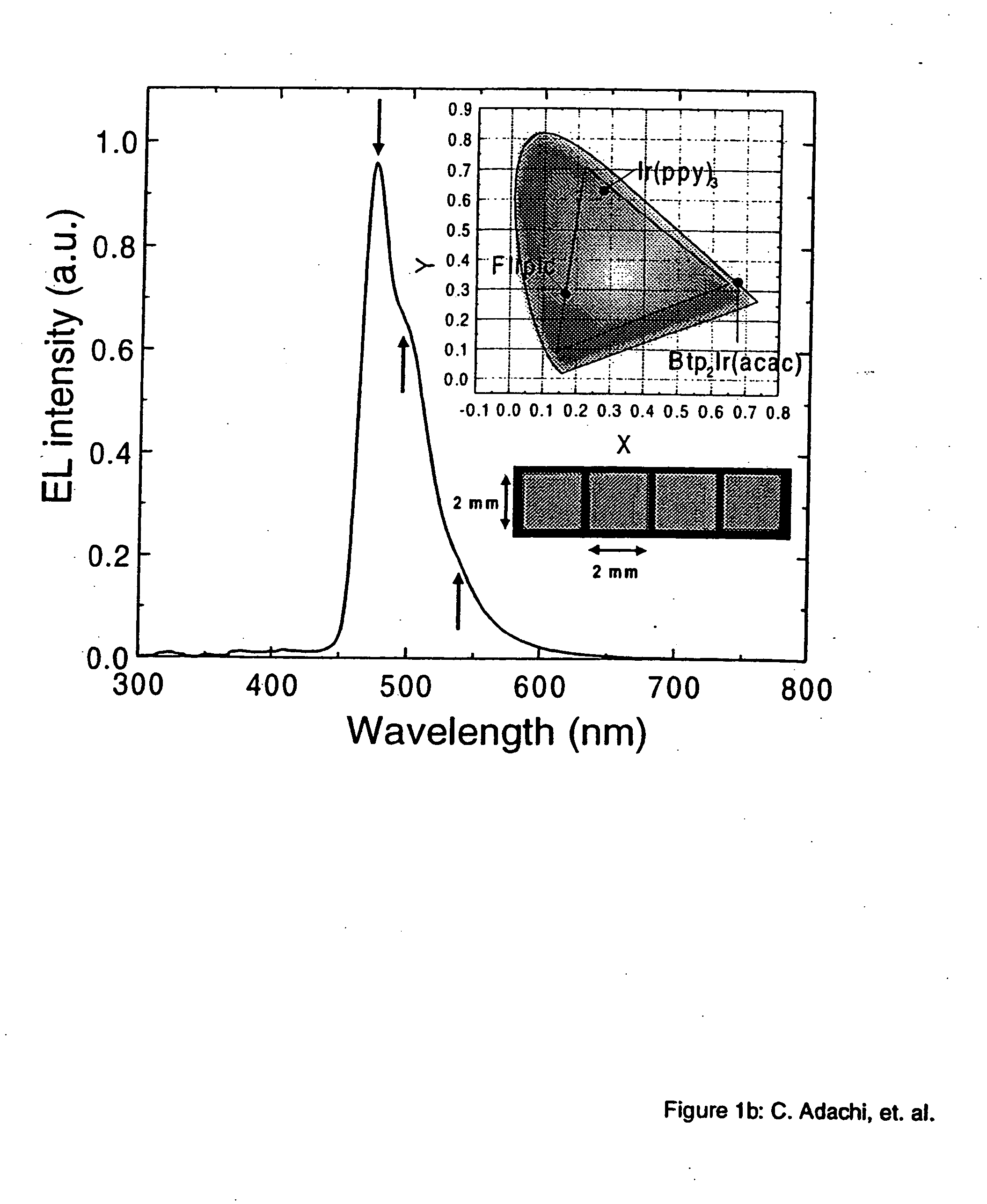
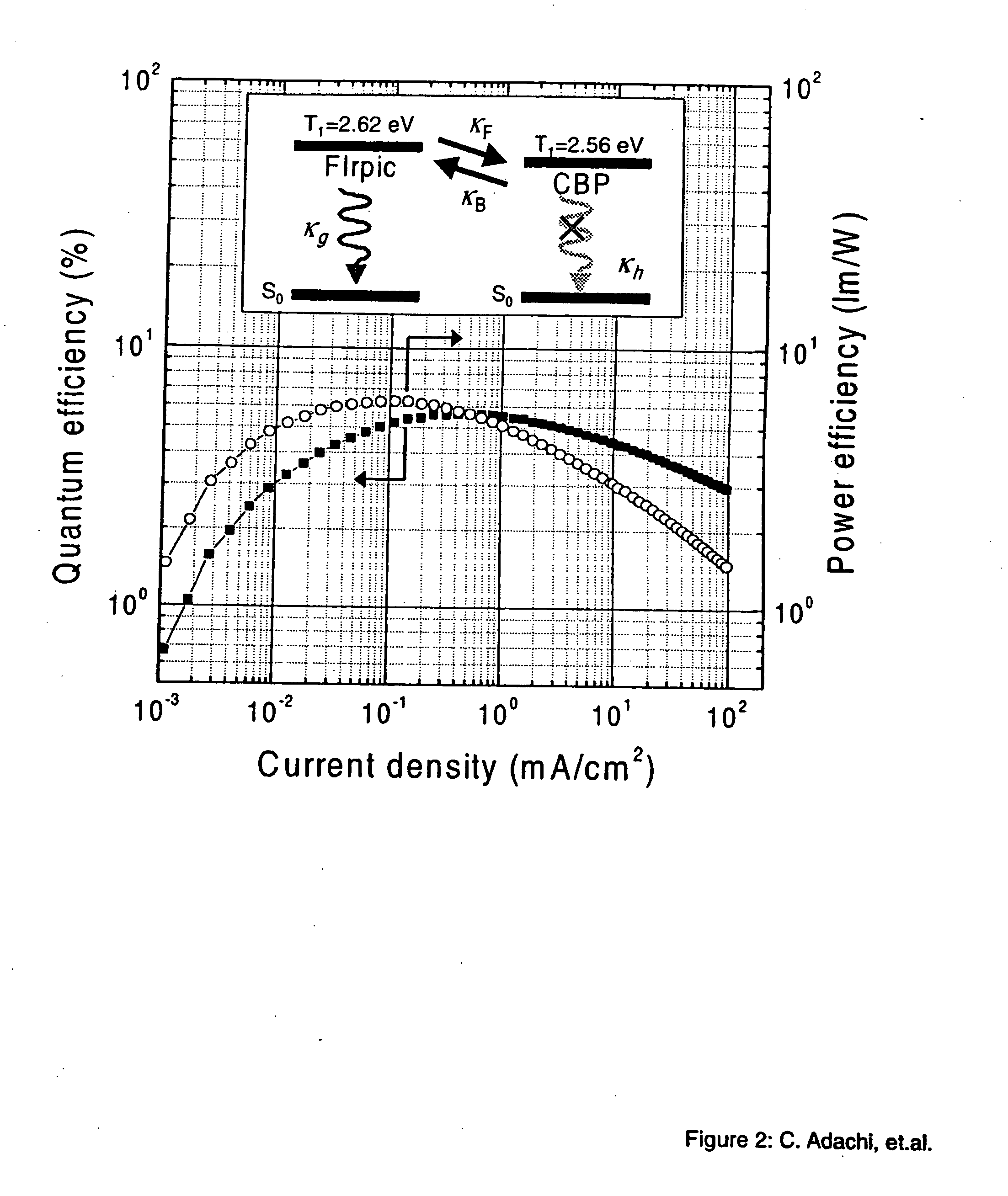
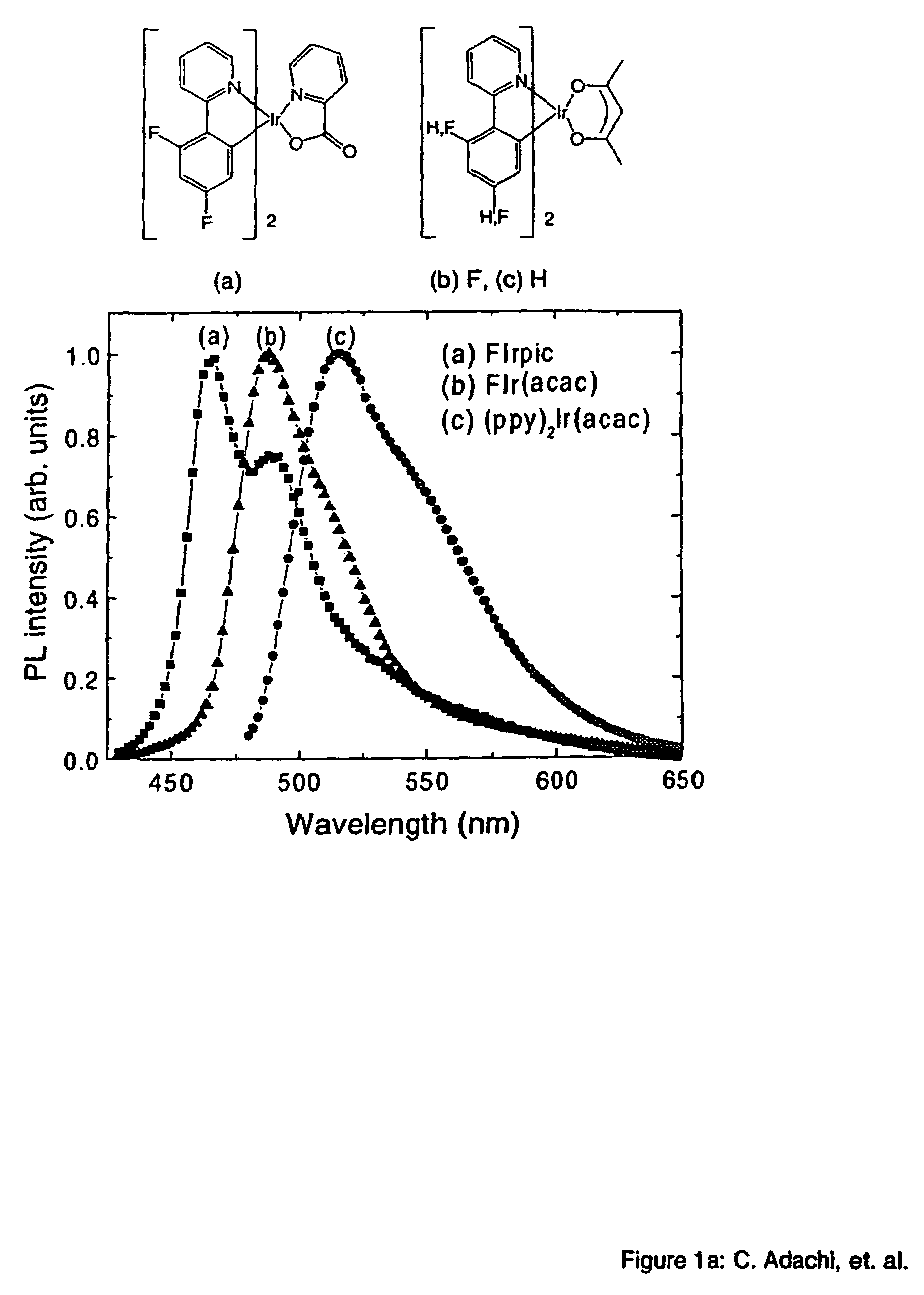
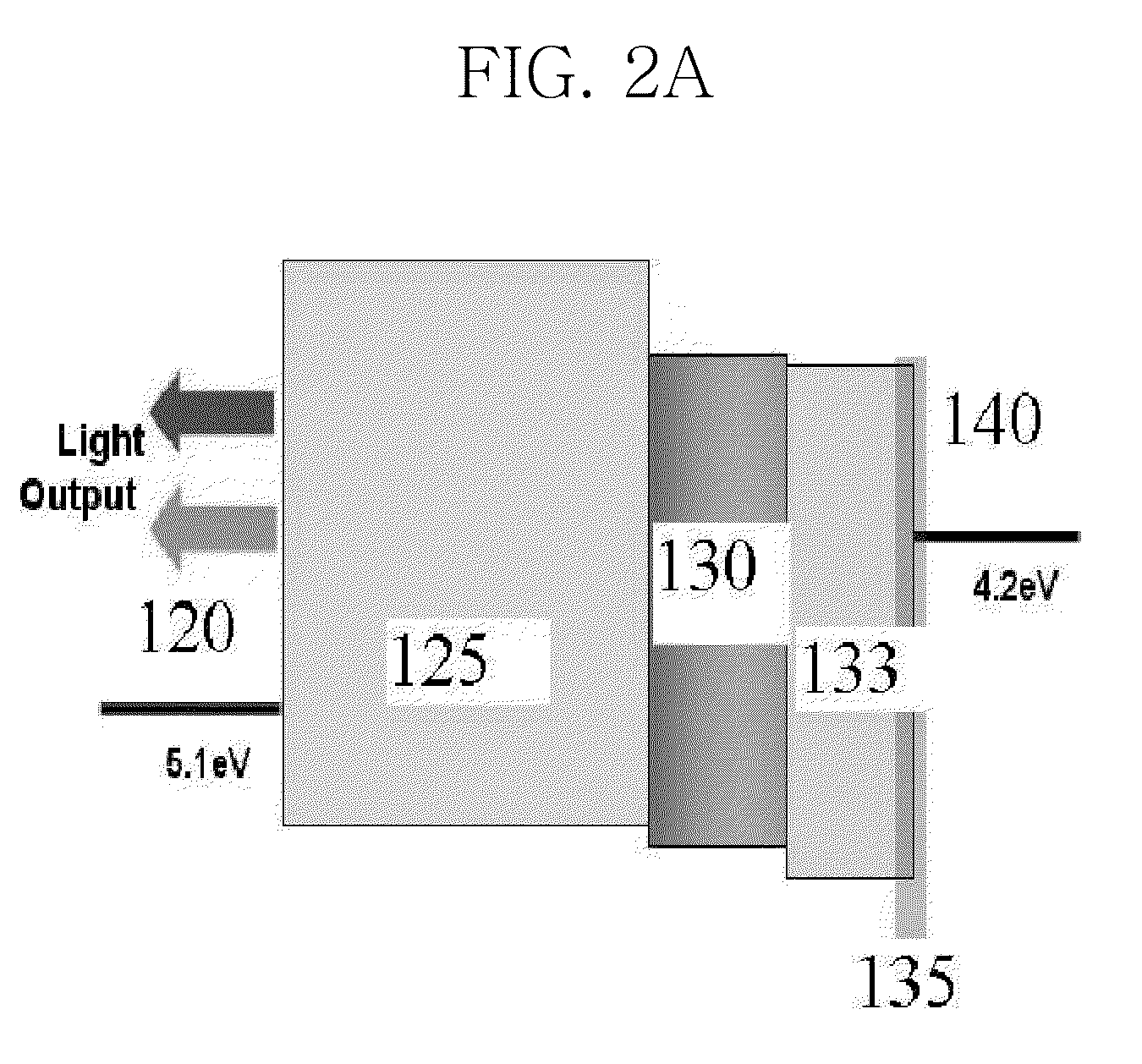
Organometallic compounds and emission-shifting organic electrophosphorescence
InactiveUS6939624B2Improved electrophosphorescenceIndium organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensExcited stateOrganic light emitting device
Emissive phosphorescent organometallic compounds are described that produce improved electroluminescence, particularly in the blue region of the visible spectrum. Organic light emitting devices employing such emissive phosphorescent organometallic compounds are also described. Also described is an organic light emitting layer including a host material having a lowest triplet excited state having a decay rate of less than about 1 per second; a guest material dispersed in the host material, the guest material having a lowest triplet excited state having a radiative decay rate of greater than about 1×105 or about 1×106 per second and wherein the energy level of the lowest triplet excited state of the host material is lower than the energy level of the lowest triplet excited state of the guest material.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +3
Light-Emitting Device
ActiveUS20120217487A1External quantum efficiencyIncrease ratingsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingExcited stateLight emitting device
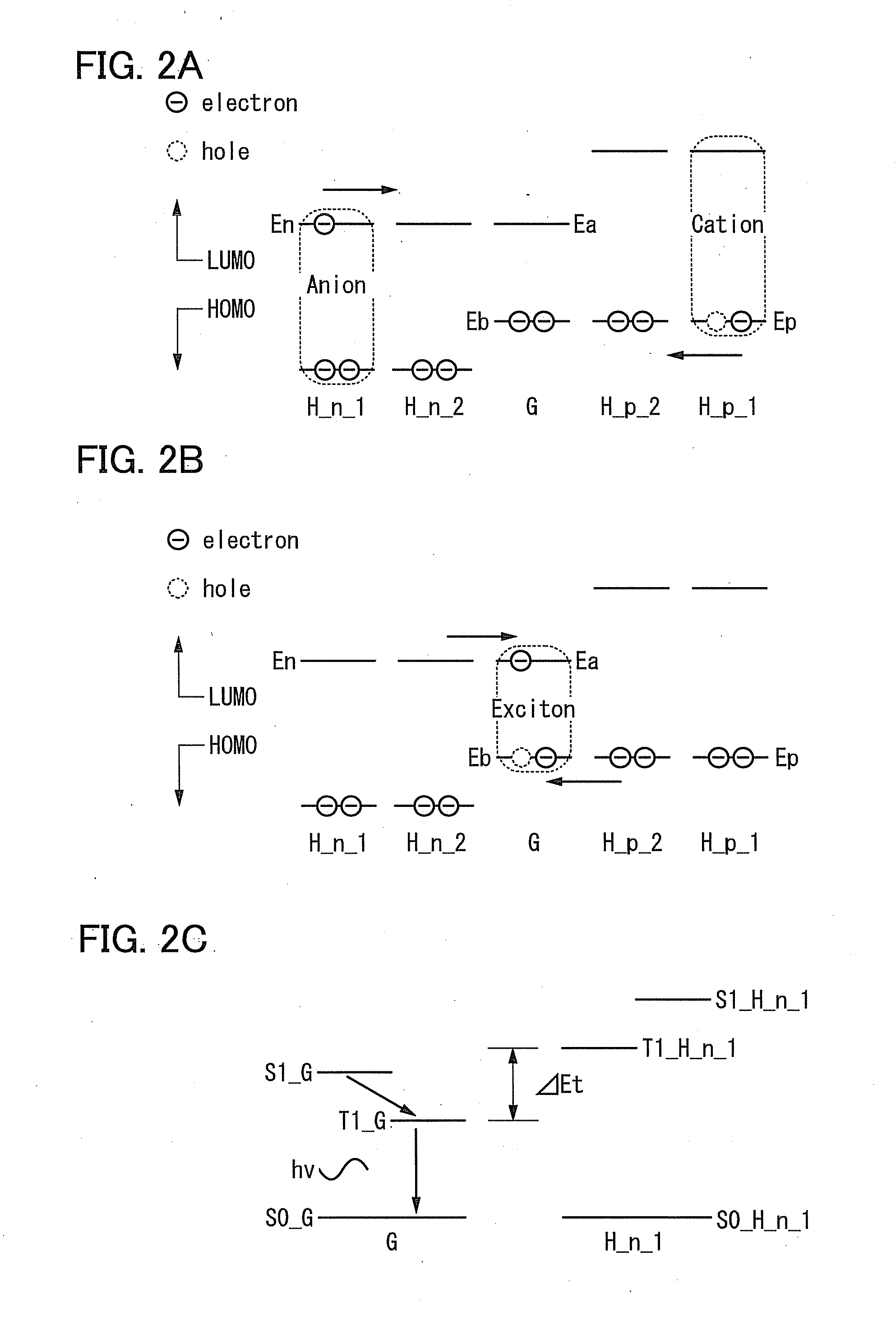
A light-emitting element includes a light-emitting layer including a guest, an n-type host and a p-type host between a pair of electrodes, where the difference between the energy difference between a triplet excited state and a ground state of the n-type host (or p-type host) and the energy difference between a triplet excited state and a ground state of the guest is 0.15 eV or more. Alternatively, in such a light-emitting element, the LUMO level of the n-type host is higher than the LUMO level of the guest by 0.1 eV or more, or the HOMO level of the p-type host is lower than the HOMO level of the guest by 0.1 eV or more.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Organic electroluminescent devices
InactiveUS20050106419A1Low resistivityReduced stabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSimple Organic CompoundsElectron injection
An organic electroluminescent device includes an anode electrode layer, a cathode electrode layer opposed to the anode electrode layer, and a luminous layer containing an organic compound disposed between the anode electrode layer and the cathode electrode layer. An excitation state of the organic compound in the luminous layer is created upon a hole injection from the anode electrode layer, and an electron injection from the cathode electrode layer, thereby causing light emission in the organic electroluminescent device. An electron-accepting material is provided in at least one hole transportation layer capable of transporting holes injected from the anode electrode layer disposed between the anode electrode layer and the cathode electrode layer, and the electron-accepting material is positioned at a site which is not adjacent to the anode electrode layer.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
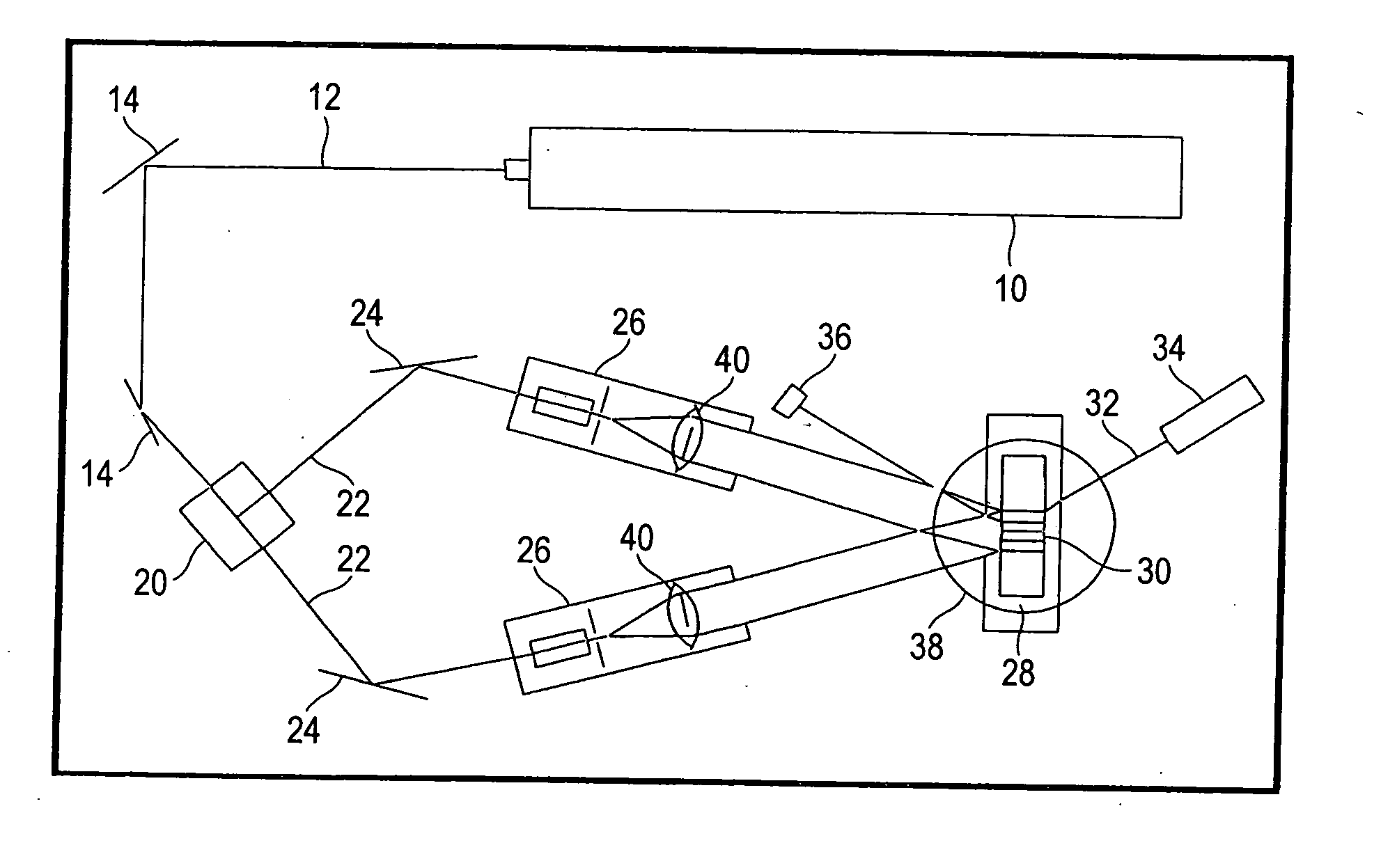
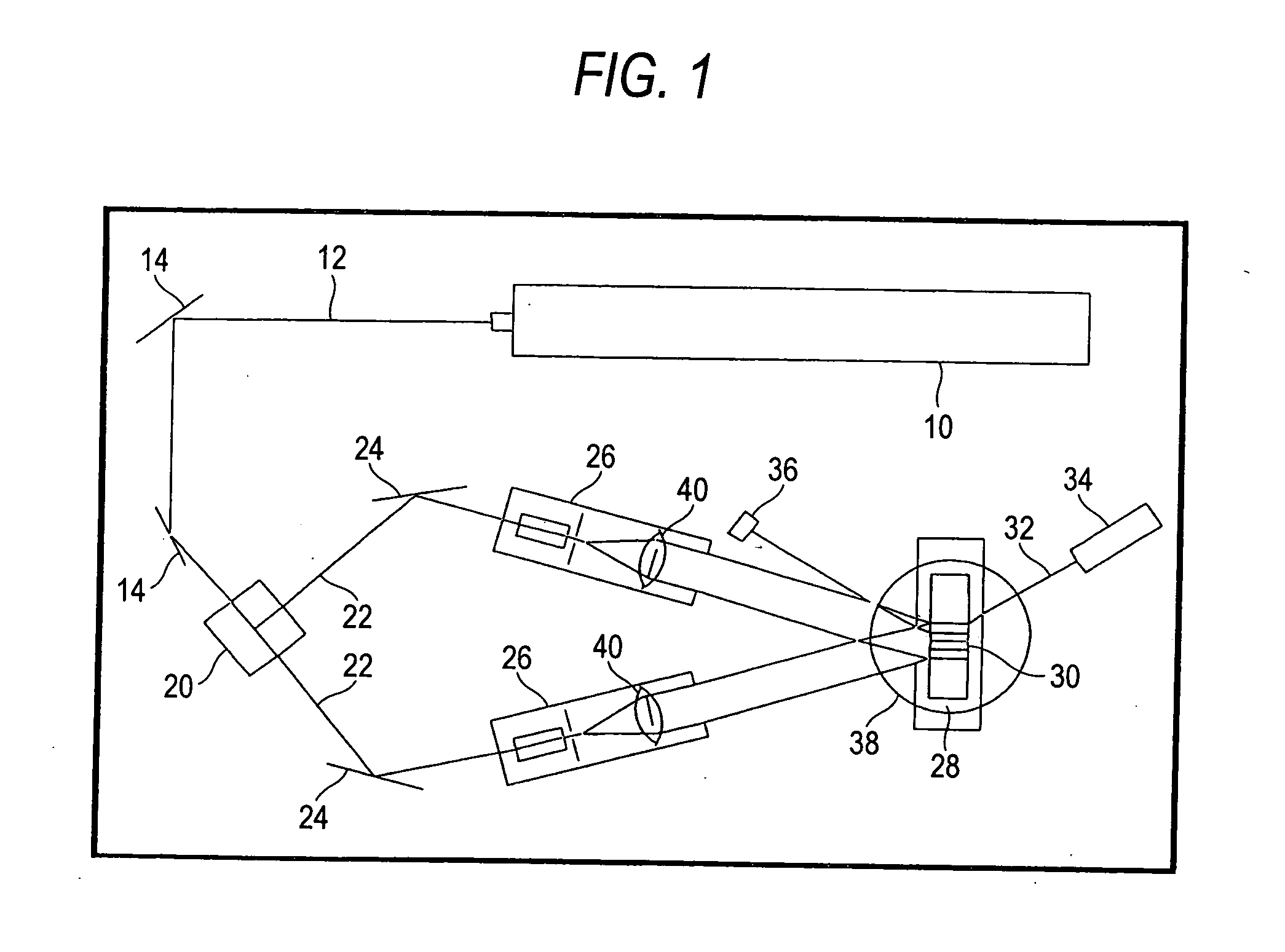
Super-resolution microscope system and method for illumination
InactiveUS6667830B1High resolutionReducing diffractive limitPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersElectronic statesExcited state
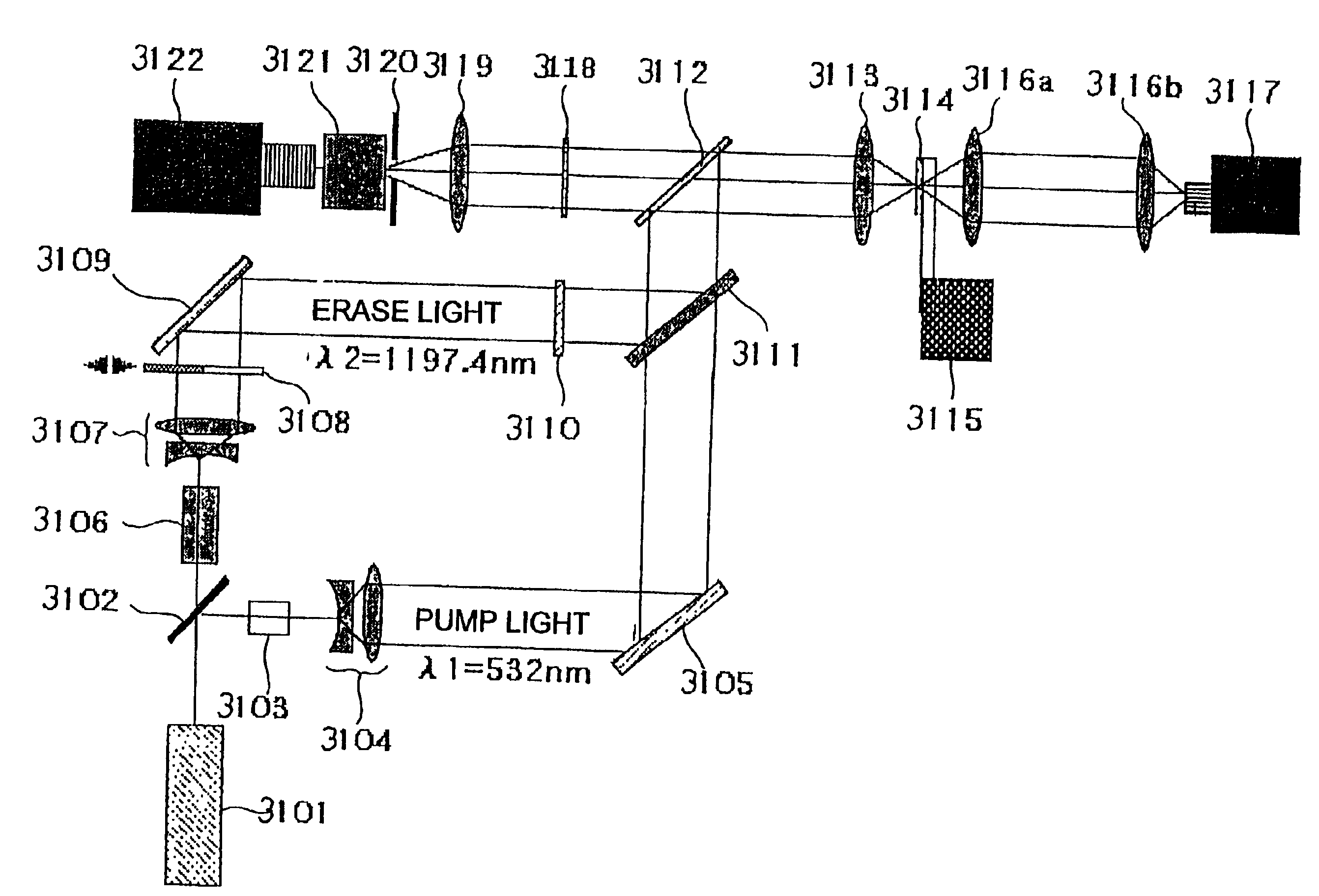
A microscope system comprising an adjusted specimen and a microscope body, wherein the adjusted specimen is dyed with molecule which has three electronic states including at least a ground state and in which an excited wavelength band from the first electron excited state to the second electron excited state overlaps a fluorescent wavelength band upon deexcitation through a fluorescence process from the first electron excited state to a vibrational level in the ground state. There is provided a novel microscope system which is enabled to condense an erase light for exciting a molecule in the first electron excited state to the second electron excited state in an excellent beam profile by using a simple, compact optical system and which has high stability and operability and an excellent super-resolution.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Organometallic compounds and emission-shifting organic electrophosphorescence
InactiveUS20050214576A1Indium organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensExcited stateOrganic light emitting device
Emissive phosphorescent organometallic compounds are described that produce improved electroluminescence, particularly in the blue region of the visible spectrum. Organic light emitting devices employing such emissive phosphorescent organometallic compounds are also described. Also described is an organic light emitting layer including a host material having a lowest triplet excited state having a decay rate of less than about 1 per second; a guest material dispersed in the host material, the guest material having a lowest triplet excited state having a radiative decay rate of greater than about 1×105 or about 1×106 per second and wherein the energy level of the lowest triplet excited state of the host material is lower than the energy level of the lowest triplet excited state of the guest material.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +2
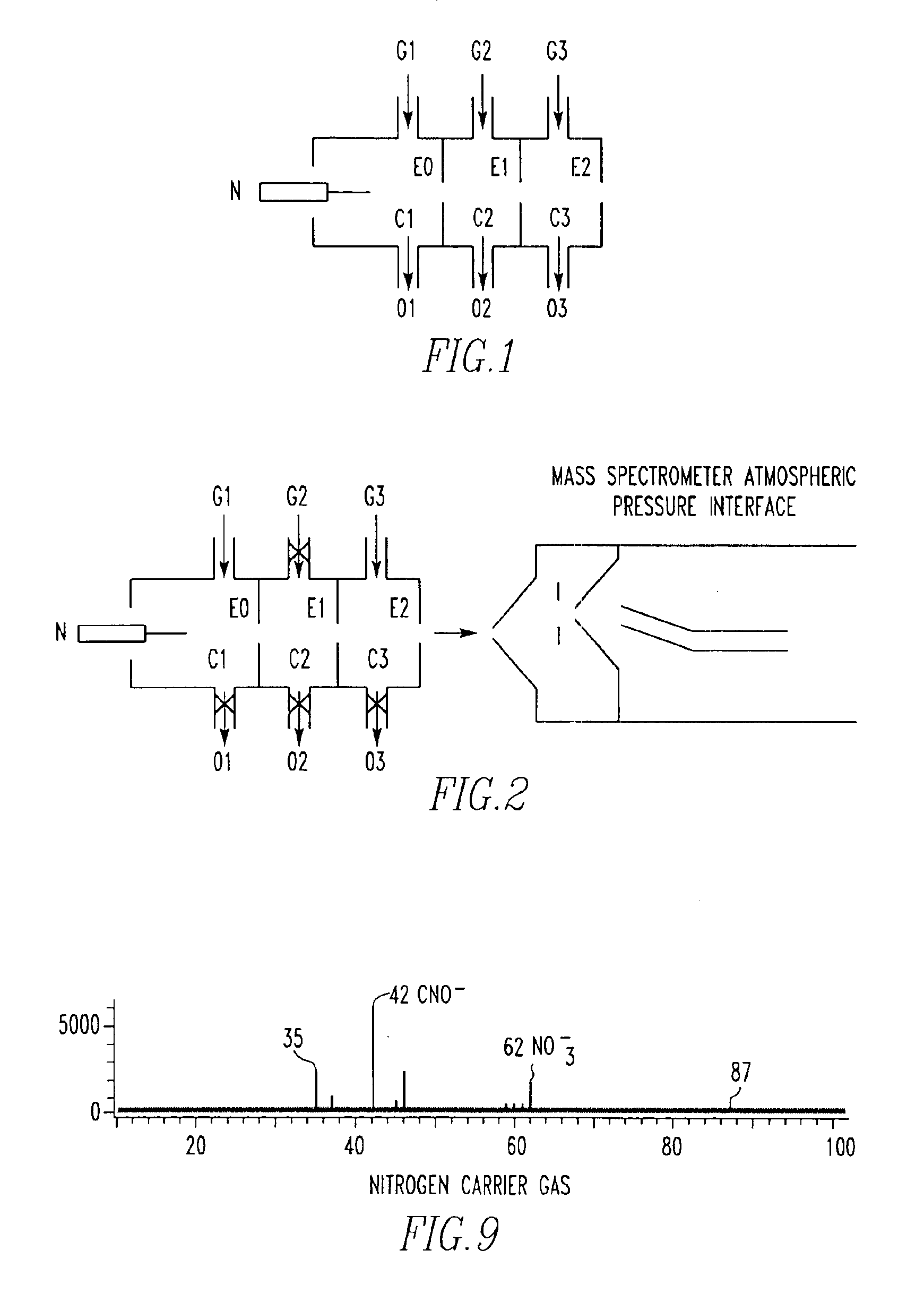
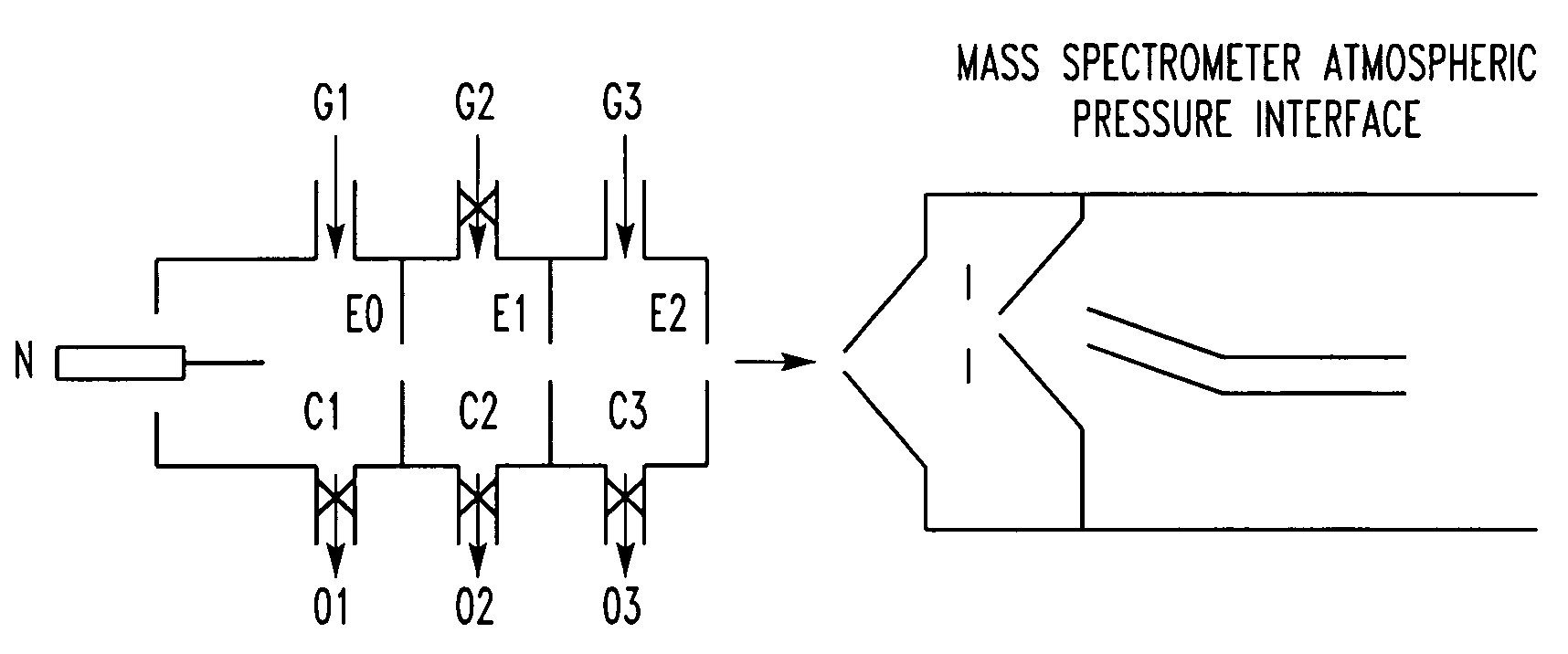
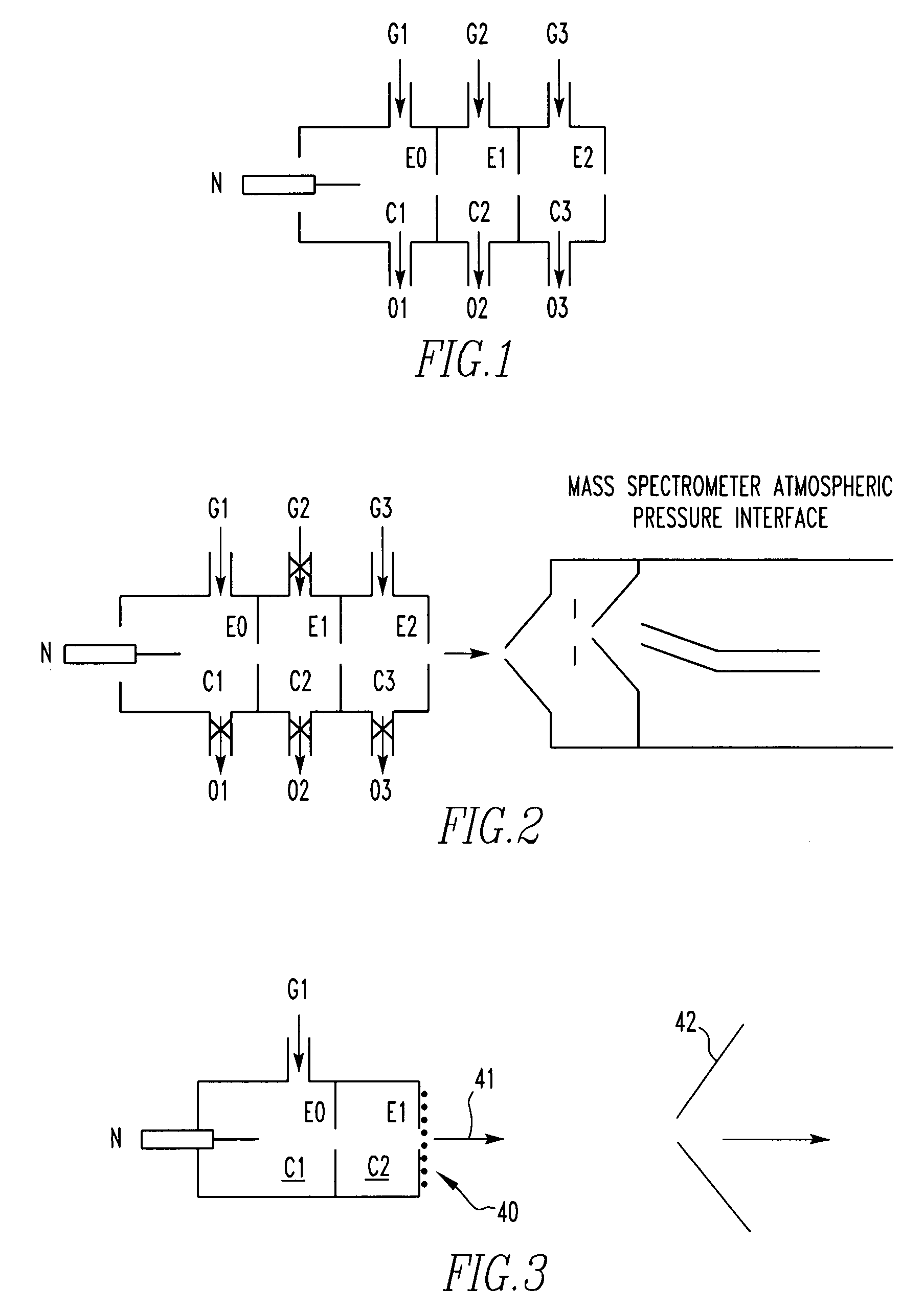
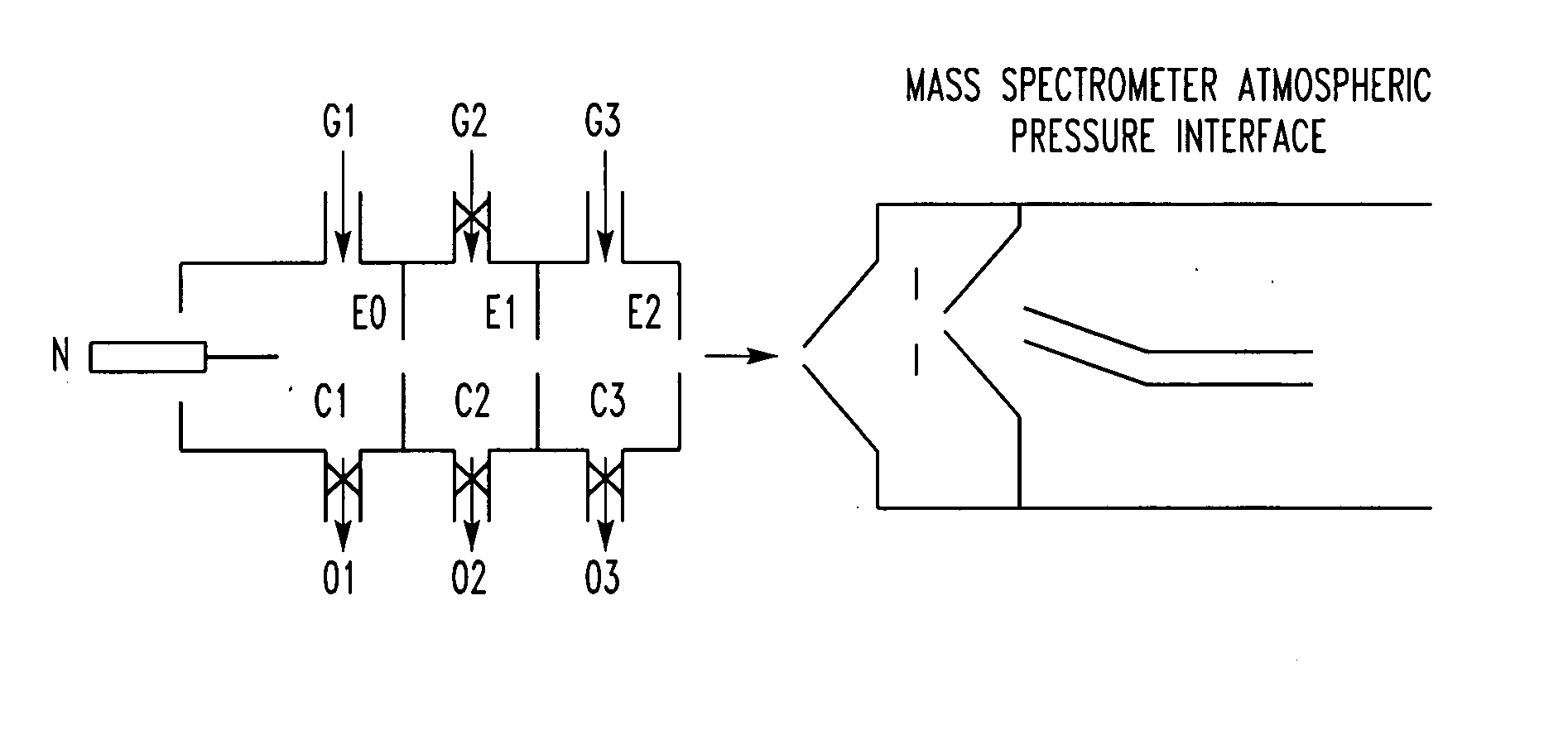
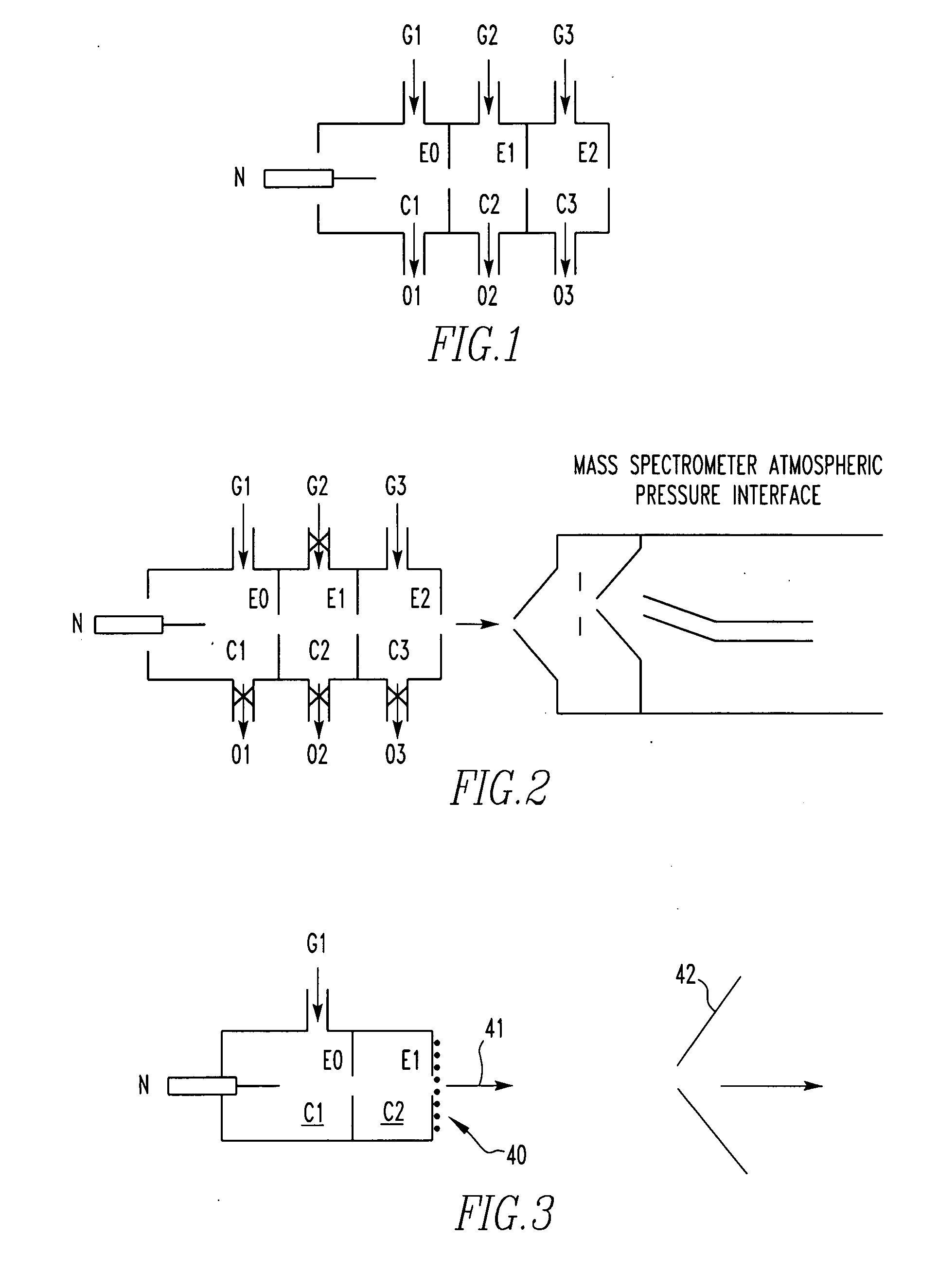
Atmospheric pressure ion source
A non-radioactive atmospheric pressure device for ionization of analytes comprises an atmospheric pressure chamber having an inlet for carrier gas, a first electrode at one end, and a counter-electrode at the other end of the chamber for creating an electrical discharge in the carrier gas thus creating metastable neutral excited-state species. Optionally, a grid is provided to generate electrons or ions by contact with the excited-state species. The carrier gas containing the excited-state species or the electrons generated therefrom is directed at an analyte at atmospheric pressure near ground potential to form analyte ions.
Owner:JEOL USA
Light-emitting layer and light-emitting element
ActiveUS20120217486A1Increase energy levelInhibition transitionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIridiumExcited state
To provide a highly efficient organic light-emitting element. An extremely thin layer (a monomolecular film or the like) containing an organic light-emitting material such as an iridium complex is provided between a layer of an n-type organic material (an organic material having a high electron-transport property) and a layer of a p-type organic material (an organic material having a high hole-transport property). In a structure described above, in a layer of the organic light-emitting material, electrons are injected from the LUMO of the n-type organic material to the LUMO of the organic light-emitting material, and holes are injected from the HOMO of the p-type organic material to the HOMO of the organic light-emitting material, whereby the organic light-emitting material is brought into an excited state and emits light.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for atmospheric pressure analyte ionization
ActiveUS7112785B2Time-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansExcited stateAnalyte
Owner:JEOL USA
Organometallic compounds and emission-shifting organic electrophosphorescence
InactiveUS7381479B2Group 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesExcited stateOrganic light emitting device
Emissive phosphorescent organometallic compounds are described that produce improved electroluminescence, particularly in the blue region of the visible spectrum. Organic light emitting devices employing such emissive phosphorescent organometallic compounds are also described. Also described is an organic light emitting layer including a host material having a lowest triplet excited state having a decay rate of less than about 1 per second; a guest material dispersed in the host material, the guest material having a lowest triplet excited state having a radiative decay rate of greater than about 1×105 or about 1×106 per second and wherein the energy level of the lowest triplet excited state of the host material is lower than the energy level of the lowest triplet excited state of the guest material.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +2
Light-emitting element, light-emitting device, display device, electronic device, and lighting device
ActiveUS20130306945A1Improve emission efficiencyReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFluorescenceDisplay device
An object is to provide a light-emitting element which includes an exciplex being used as an energy donor capable of efficiently transferring energy to a substance exhibiting thermally activated delayed fluorescence. The exciplex comprises two kinds of substances and its singlet and triplet excited states are close to each other. Thus, by making light emission of the exciplex overlap with an absorption band on the longest wavelength side which corresponds to absorption by the substance exhibiting thermally activated delayed fluorescence, i.e., an energy acceptor, in a singlet excited state, it becomes possible to achieve efficient energy transfer from a singlet excited state of the exciplex to a singlet excited state of the substance exhibiting thermally activated delayed fluorescence, and it also becomes possible to achieve efficient energy transfer from a triplet excited state of the exciplex to a triplet excited state of the substance exhibiting thermally activated delayed fluorescence.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method and spectral/imaging device for optochemical sensing with plasmon-modified polarization
InactiveUS20050186565A1Low fluorescence quantum yieldHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiberFluorescence
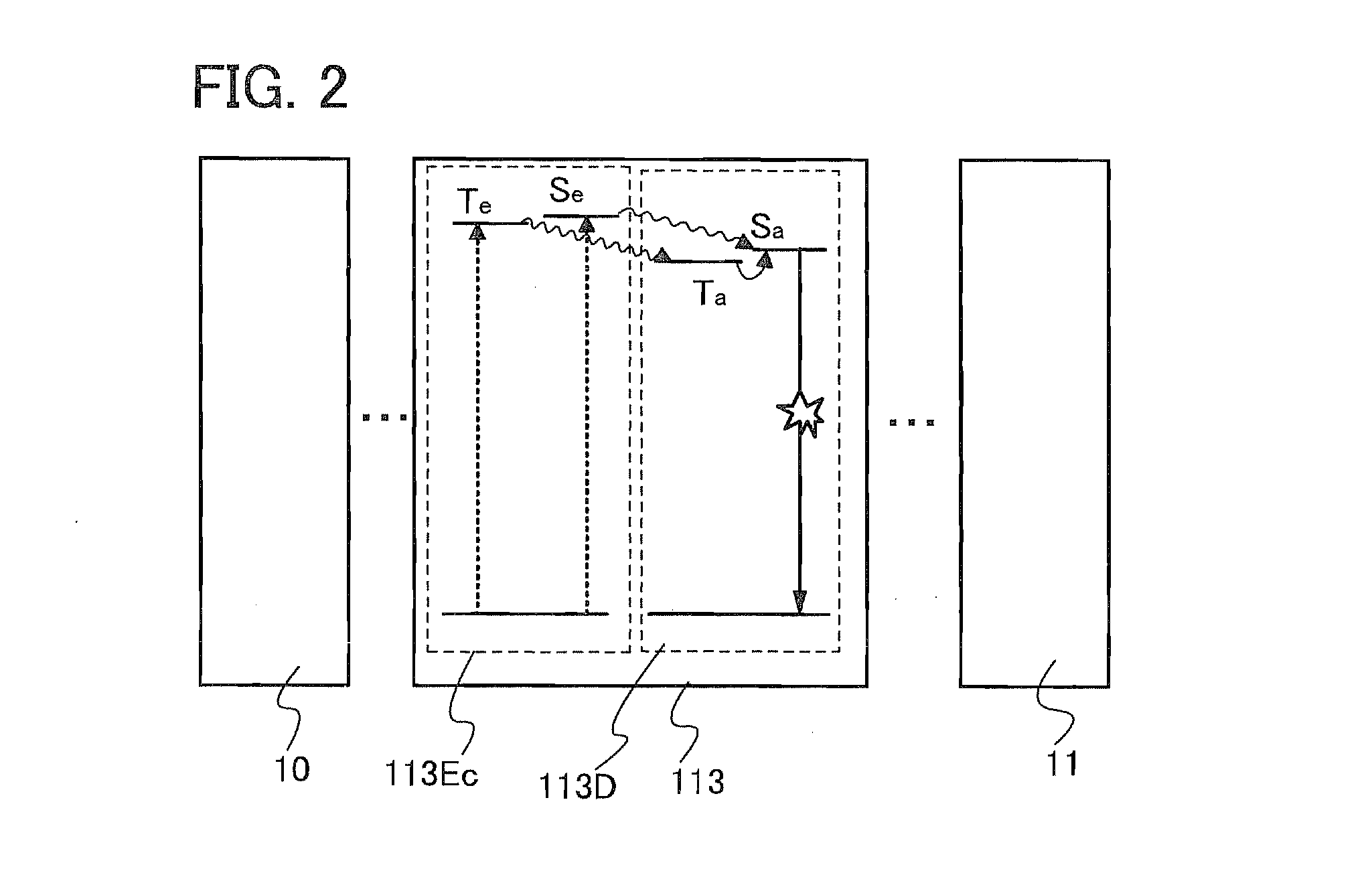
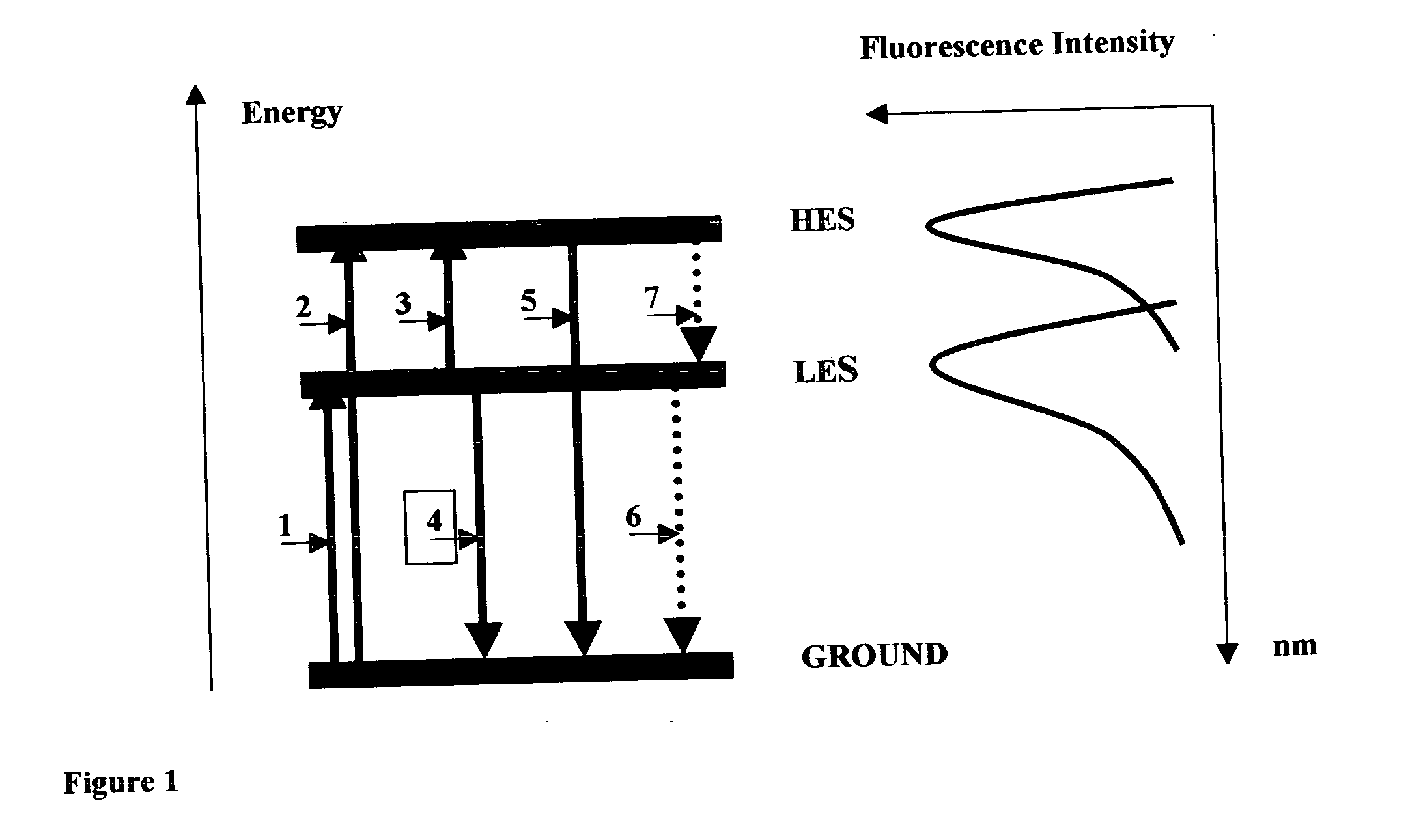
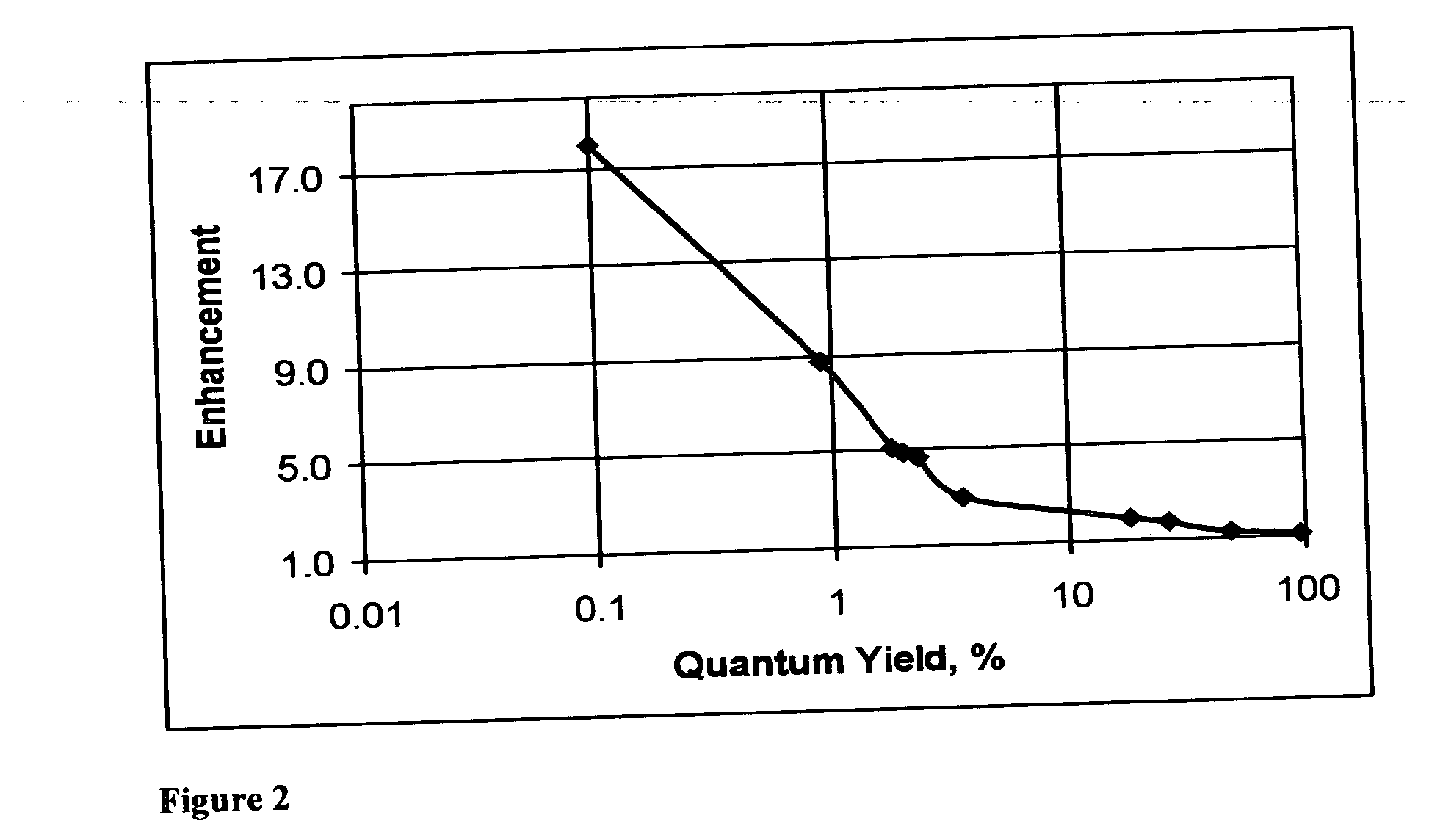
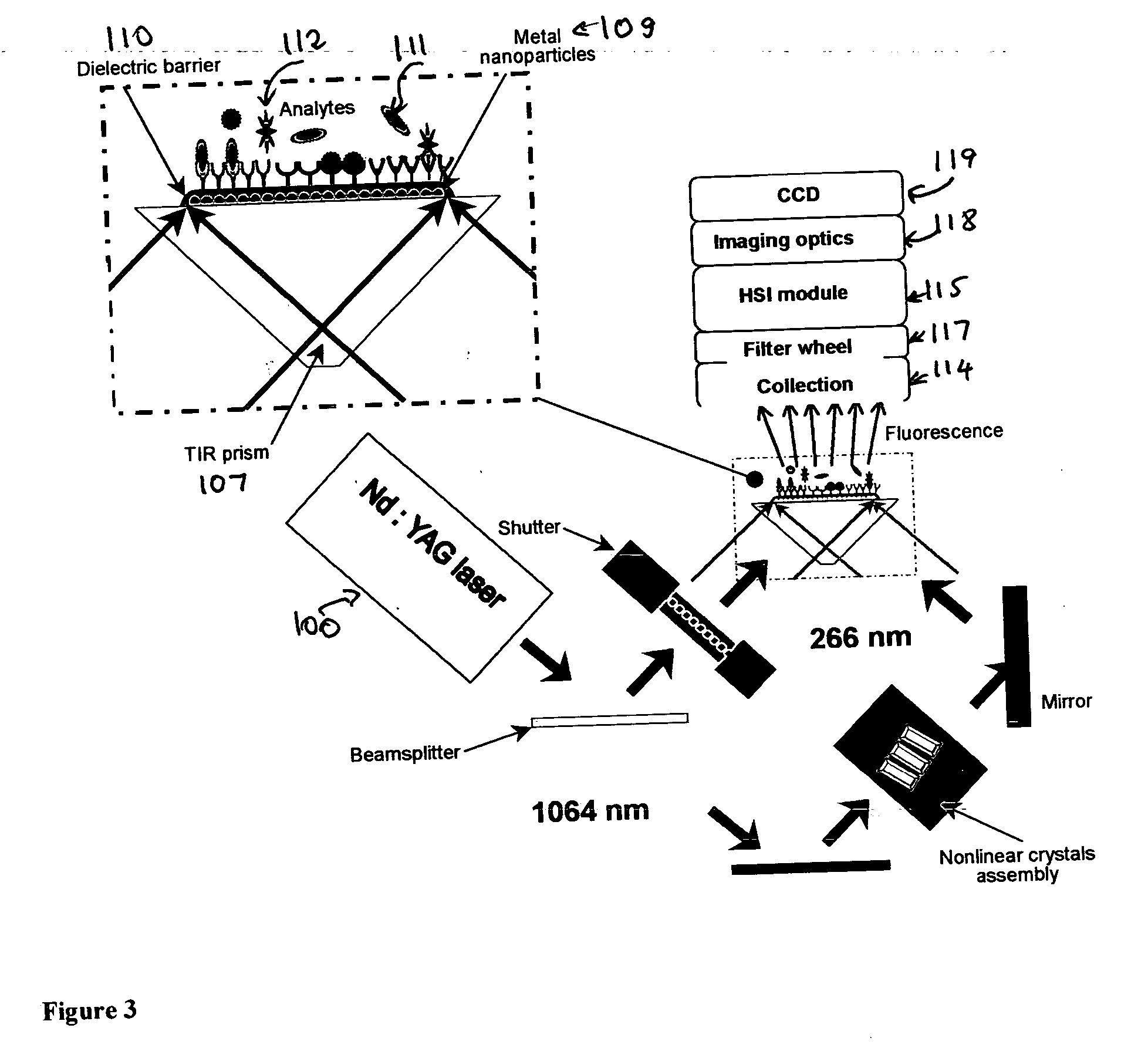
The invention discloses a method and spectral-imaging device for optochemical sensing with plasmon-modified multiband fluorescence polarization and with plasmon-modified polarization phase shift changes of a light beam reflected and / or passed through a total internal reflection conducting structure. The optochemical sensing is performed for molecules placed nearby the conducting structure and being excited by surface plasmon resonance (SPR) to lower excited state (LES) and / or to higher excited states (HES). The invention also describes the spectral imaging device with an improved sensitivity of several orders of magnitude. The disclosed method and imaging device may find applications in clinical diagnostics, pharmaceutical screening, biomedical research, biochemical-warfare detection and other diagnostic techniques. The device can be used in bio-chip and micro-array technologies, flowcytometer, fiber optic and other types of diagnostic devices.
Owner:AMERICAN ENVIRONMENTAL SYST
Hologram recording material, hologram recording method and optical recording medium
InactiveUS7572555B2Low shrinkageImprove recording densityPhotomechanical apparatusPhotosensitive material auxillary/base layersEnergy transferExcited state
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Dark quenchers for donor-acceptor energy transfer
InactiveUS7019129B1Minimize fluorescenceEnhanced interactionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEnergy transferExcited state
Owner:HSBC TRUSTEE COMPANY UK LIMITED AS SECURITY AGENT
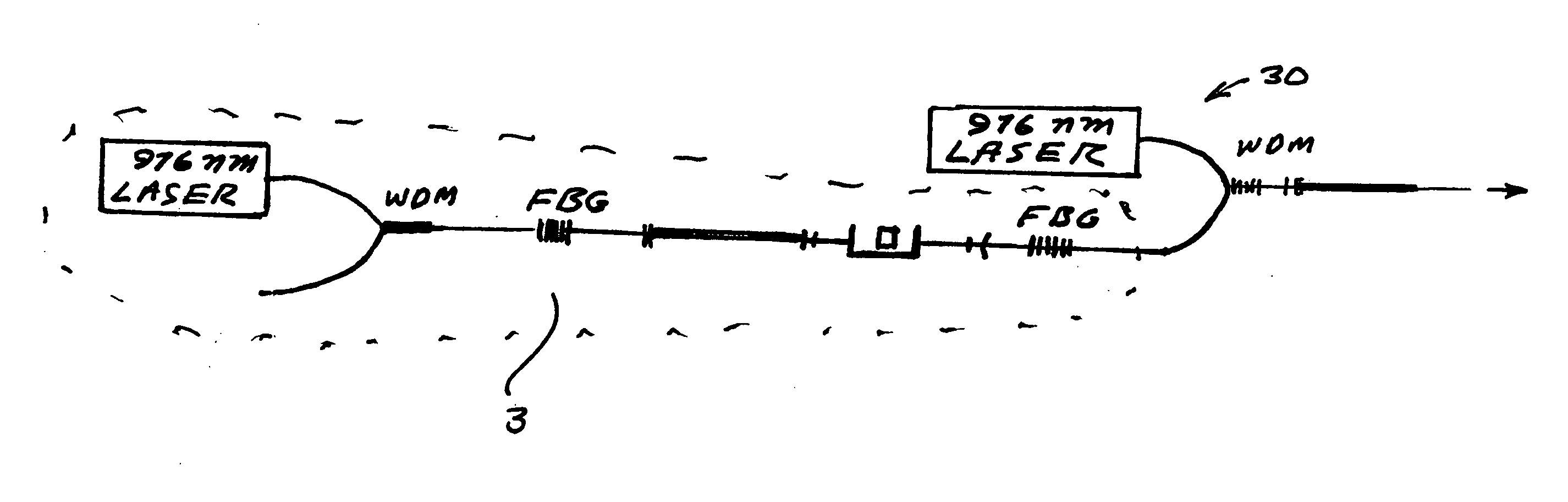
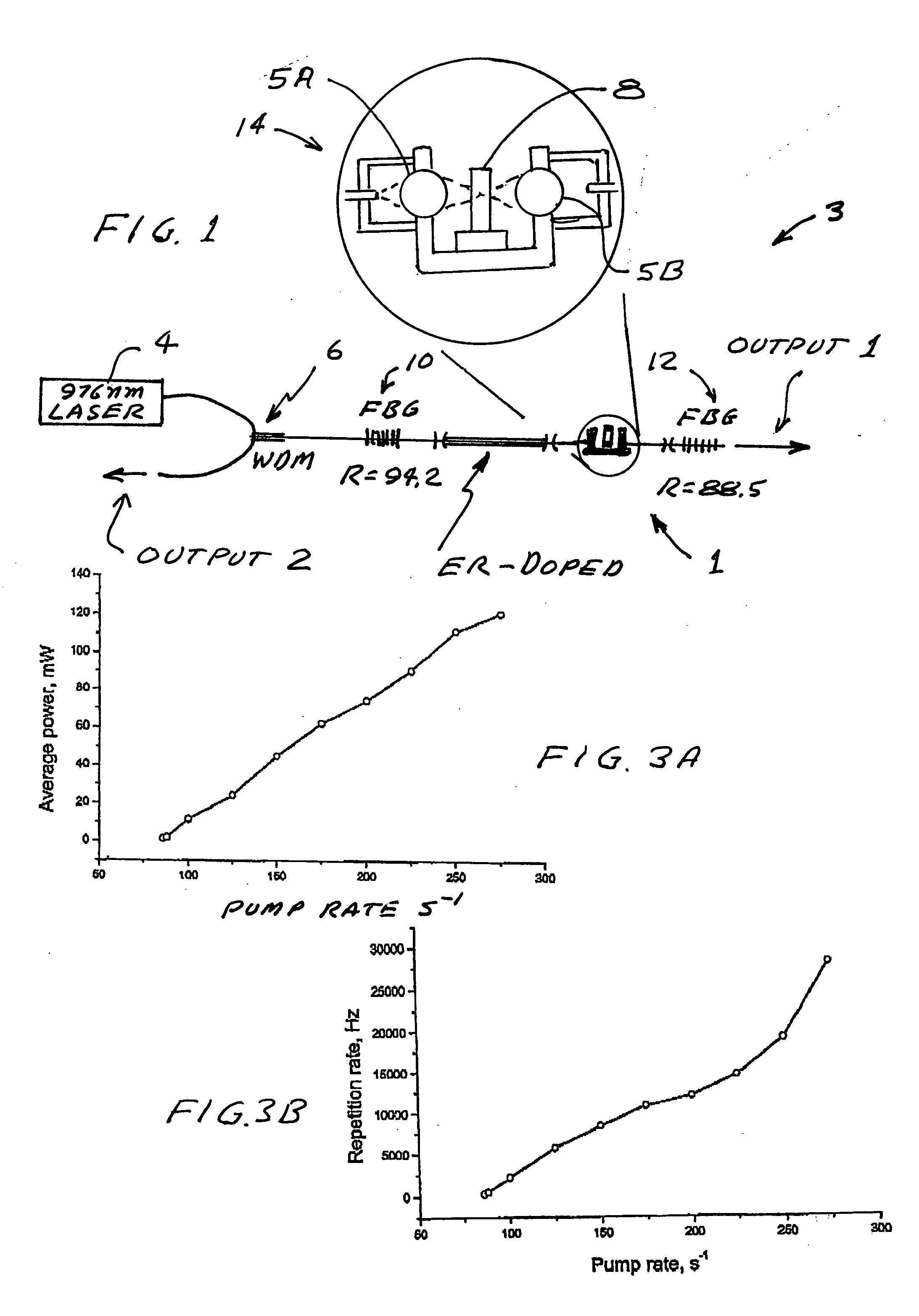
Passive Q-switch modulated fiber laser
InactiveUS20060007965A1High average and peak power pulseLow costLaser using scattering effectsSurgical instrument detailsExcited stateOptoelectronics
An all-fiber erbium laser oscillating in a passive Q switched mode. The laser includes a crystal saturable absorber that may be Co2+:ZnSe or Cr2+:ZnSe. In preferred embodiments continuous pumping or short pulse pumping may be utilized. The laser is characterized by low threshold high-power, short-pulse generation. In preferred embodiments the threshold is only about 20 mW. The crystals are bleached at extremely low intensity, of about 0.8 kW / cm2 and provide moderate relaxation time of the excited state (290 μs) within a spectral range of about 1400-1800 nm. The simplicity of the design and low cost of that laser 2000).
Owner:PHARMALASE
Organic mixture, composite containing organic mixture, organic electronic device and application
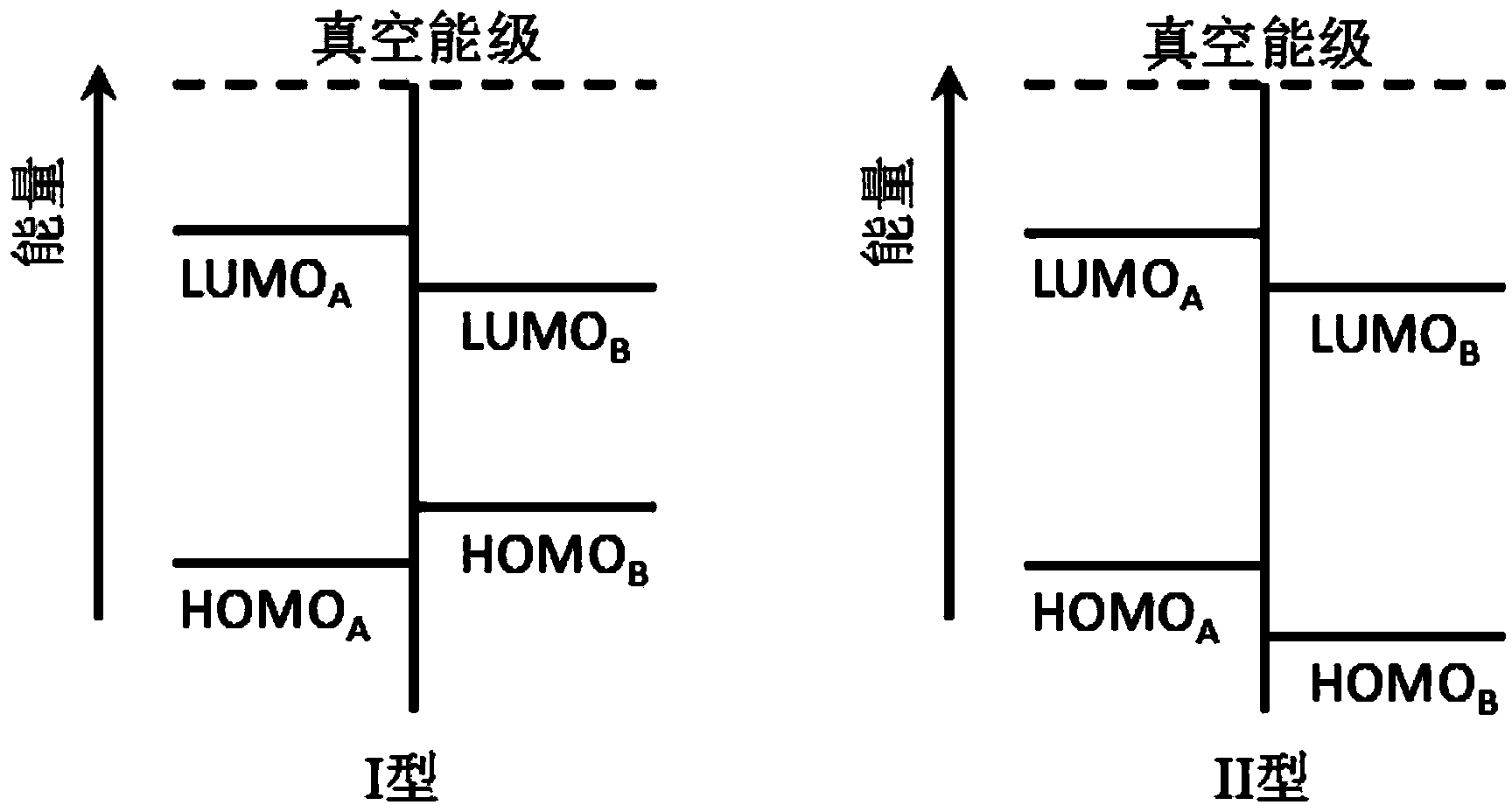
ActiveCN103985822ALong efficiencySolution to short lifeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTriboluminescenceExcited state
The invention discloses an organic mixture, a composite containing the organic mixture, an organic electronic device and application. The organic mixture comprises a first main material H1, a second main material H2 and an organic fluorescence radiation material E1, wherein the second main material H2 and the first main material H1 form a composite excited state material. The first main material H1 and the second main material H2 have II-type heterogeneous structures, and the radiation wavelength of the organic fluorescence radiation material E1 is larger than or equal to the radiation wavelength of the composite excited state material formed by the first main material H1 and the second main material H2. According to the solution, a radiation device is low in manufacturing cost, high in efficiency, long in service life and low in roll-off.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CHINARAY OPTOELECTRONICS MATERIALS
Non-invasive method of determining oxygen concentration in a sealed package
InactiveUS20070212789A1Improve accuracyImprove temperature measurement accuracyChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceInvestigating time/temperature historyExcited stateLuminous intensity
The invention is a method of measuring oxygen concentration in a package having an oxygen sensitive product disposed therein. The method includes exposing a luminescent compound that is disposed in an interior of the package to light having a wavelength that is absorbed by the luminescent compound so that the luminescent compound is promoted into an excited state. When the exposure of the light is terminated, the excited luminescent compound emits light that is detectable by a detector positioned outside of the package. The intensity of the emitted light is inversely proportional to the oxygen concentration and is used in conjunction with mathematical function that describes the luminescent intensity of the luminescent compound as a function of oxygen concentration and temperature to calculate the oxygen concentration. The method may be used to verify and track the oxygen concentration of a package as it moves through a distribution system.
Owner:CRYOVAC ILLC
Laser micro/nano processing system and method
ActiveCN102000912AHigh processing resolutionPrecise Control of ResolutionNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsLaser lightMobile station
The invention provides a laser micro / nano processing system and a laser micro / nano processing method. The system of the invention comprises a laser light source, an optical retardation component, an optical focusing component and a computer-controlled micro mobile station, wherein the laser light source is used for providing a first laser beam having a first wavelength and a second laser beam having a second wavelength, the pulse widths of the first laser beam and the second laser beam range from femtosecond to nanosecond and the first wavelength is different from the second wavelength; the optical retardation component is used for regulating the optical path of the first laser beam or the second laser beam so that the difference between the arrival times of the first laser beam and the second laser beam at a focus is not greater than the level life time for a photochromic material to be processed to be excited to an excited state; the optical focusing component is used for focusing the first laser beam and the second laser beam onto the same focus; and the computer-controlled micro mobile station is used for regulating a photochromic material on the computer-controlled micro mobile station to the focus.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
White organic light emitting device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100133522A1Improve luminous efficiencyColor shiftElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesHole transport layerLight emitting device
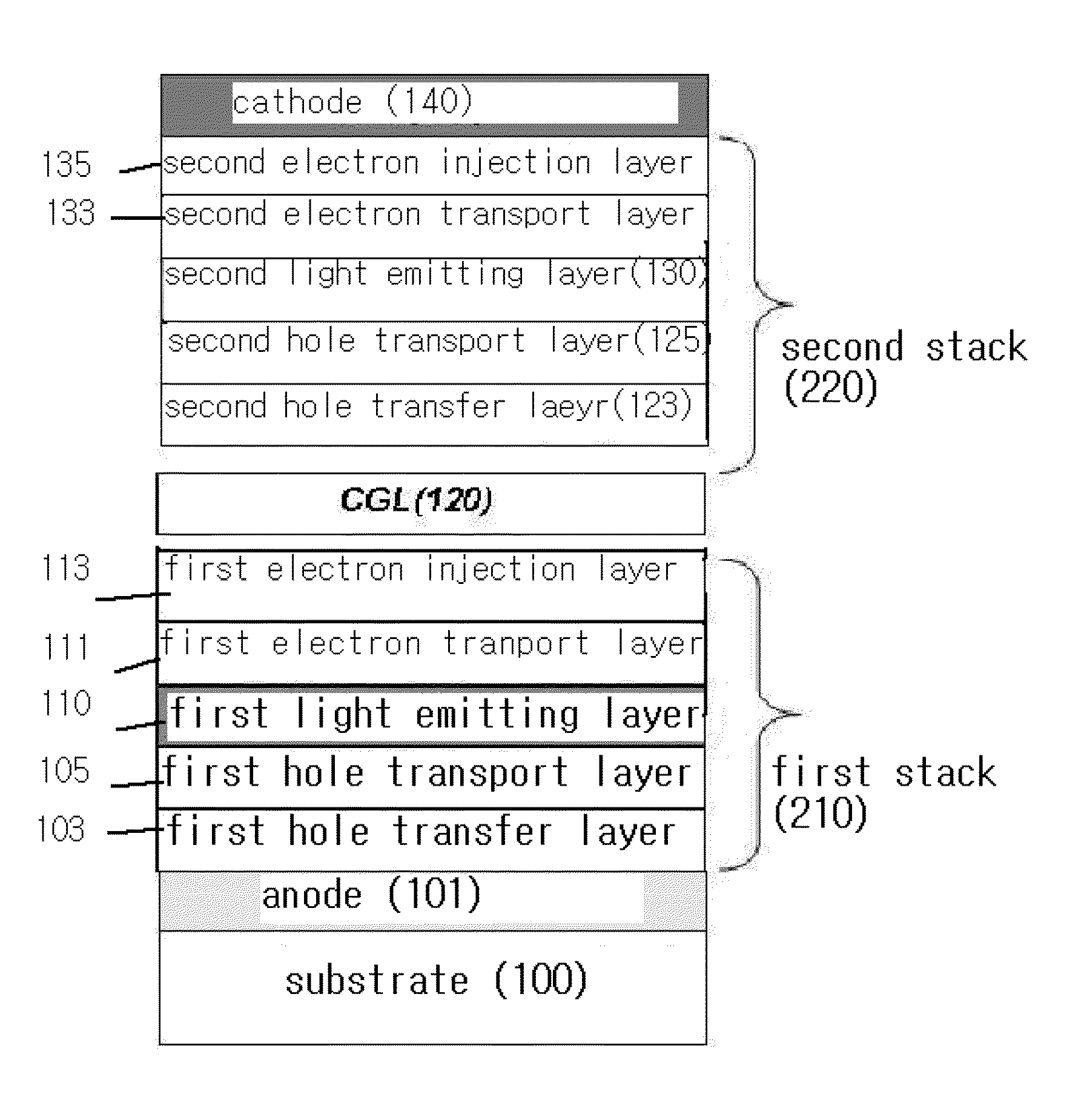
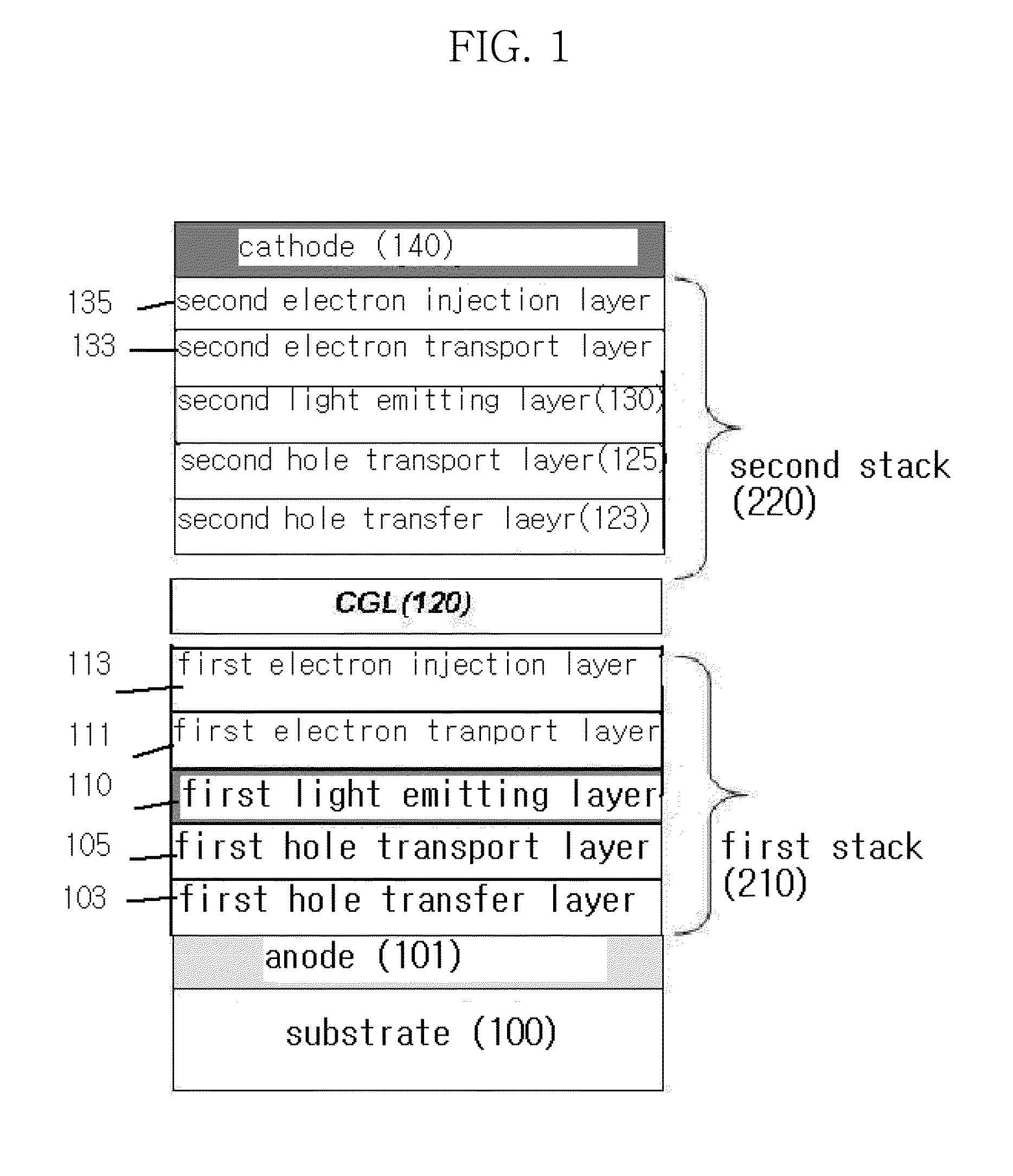
The present invention relates to a white organic light emitting device and a method for manufacturing the same, in which a hole transport layer is made to have an energy level higher than an energy level of an excited state of a phosphorescent light emitting layer adjacent thereto for enhancing light emitting efficiency of the hole transport layer without an additional exciton blocking layer, and a dopant content in the phosphorescent light emitting layer is adjusted for preventing color shift from taking place.The white organic light emitting device includes an anode and a cathode placed on a substrate opposite to each other, a charge generation layer formed between the anode and the cathode, a first stack of a first hole transport layer, a first light emitting layer for emitting a blue light, and a first electron transport layer between the anode and the charge generation layer, and a second stack of a second hole transport layer, a second light emitting layer having a host doped with phosphorescence red and green together, and a second electron transport layer between the charge generation layer and the cathode, wherein the second hole transport layer has an energy level set higher than a triplet excited state energy level of the second light emitting layer.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Dark quenchers for donor-acceptor energy transfer
InactiveUS20050272088A1Minimize fluorescenceEnhanced interactionAnthraquinone-azo dyesMonoazo dyesEnergy transferExcited state
The present invention provides a family of dark quenchers, termed Black Hole Quenchers (“BHQs”), that are efficient quenchers of excited state energy but which are themselves substantially non-fluorescent. Also provided are methods of using the BHQs, probes incorporating the BHQs and methods of using the probes.
Owner:HSBC TRUSTEE COMPANY UK LIMITED AS SECURITY AGENT
Double-resonance-absorption microscope
InactiveUS6844963B2Easy to operateImprove maintainabilityEmission spectroscopyRaman/scattering spectroscopyExcited stateResonance
The present invention provides various embodiments of a double-resonance-absorption microscope which realizes a super-resolution by using double resonance absorption. In particular, a double-resonance-absorption microscope includes a light source for a pump light of a wavelength λ1 which excites a sample molecule to a first electronic excited state from a ground state, a light source for an erase light of a wavelength λ2 which excites the sample molecule to a second electronic excited state or a higher excited state from the first electronic excited state, and an overlap component for partially overlapping irradiating areas of the pump light and the erase light with each other. An emission area upon deexcitation of the sample molecule to the ground state from the first electronic excited state is partially inhibited by irradiating the pump light and the erase light through the overlap means. On an optical path of the erase light, a spatial filter is provided which has a condenser lens, a collimate lens, and a pinhole therebetween, and performs condensing of the erase light onto the pinhole by the condenser lens and collimating of the erase light passed through the pinhole into a parallel beam by the collimate lens.
Owner:NIPON ROPER KK +1
Electrical excitation of label substances at insulating film-coated conductors
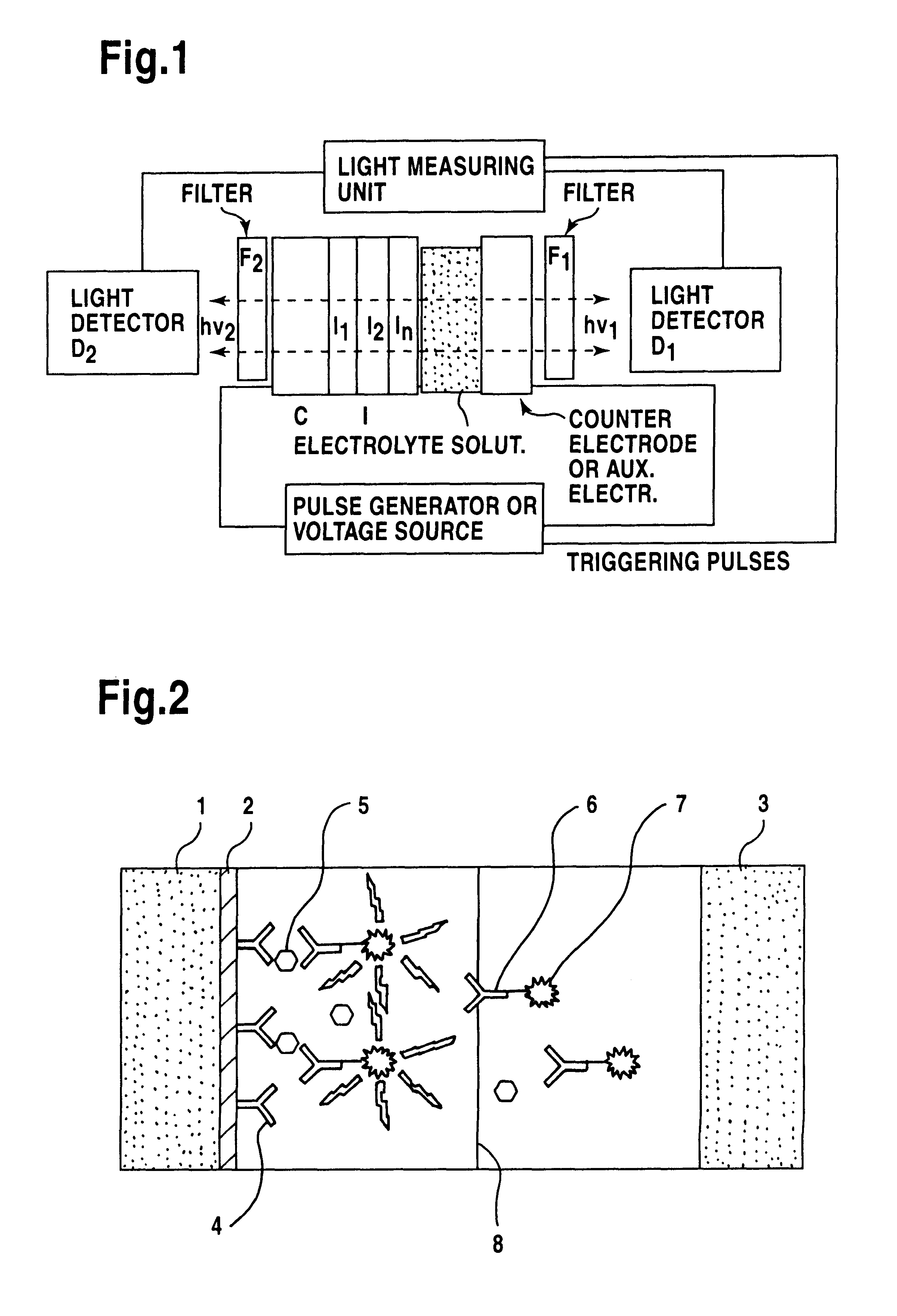
InactiveUS6251690B1Microbiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceElectricityExcited state
The excitation of label molecules usable in chemical and biochemical analysis by electrical pulses at electrodes covered with a thin insulating film, and the use of such electrodes in chemical, clinical and biochemical analysis. The electrodes include a conducting base material that has been coated with an organic or inorganic insulating film or multiple layers of such films, so that either one or several label compounds can be excited to an excited state which is deexcited by emission of ultraviolet, visible or infrared light, in aqueous solution providing the basis for reproducible analytical applications in bioaffinity assays such as immunoassays and DNA-probing assays.
Owner:LABMASTER
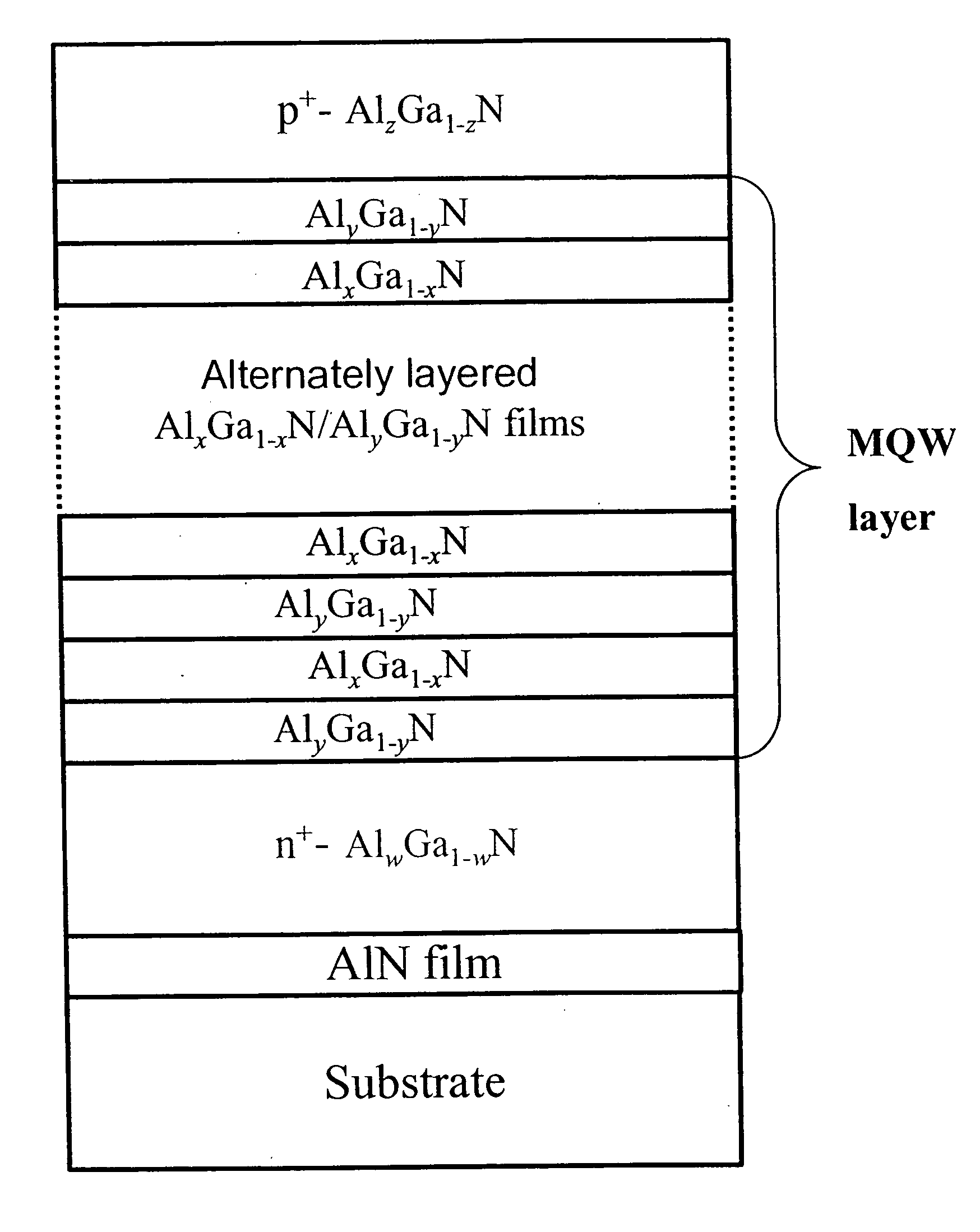
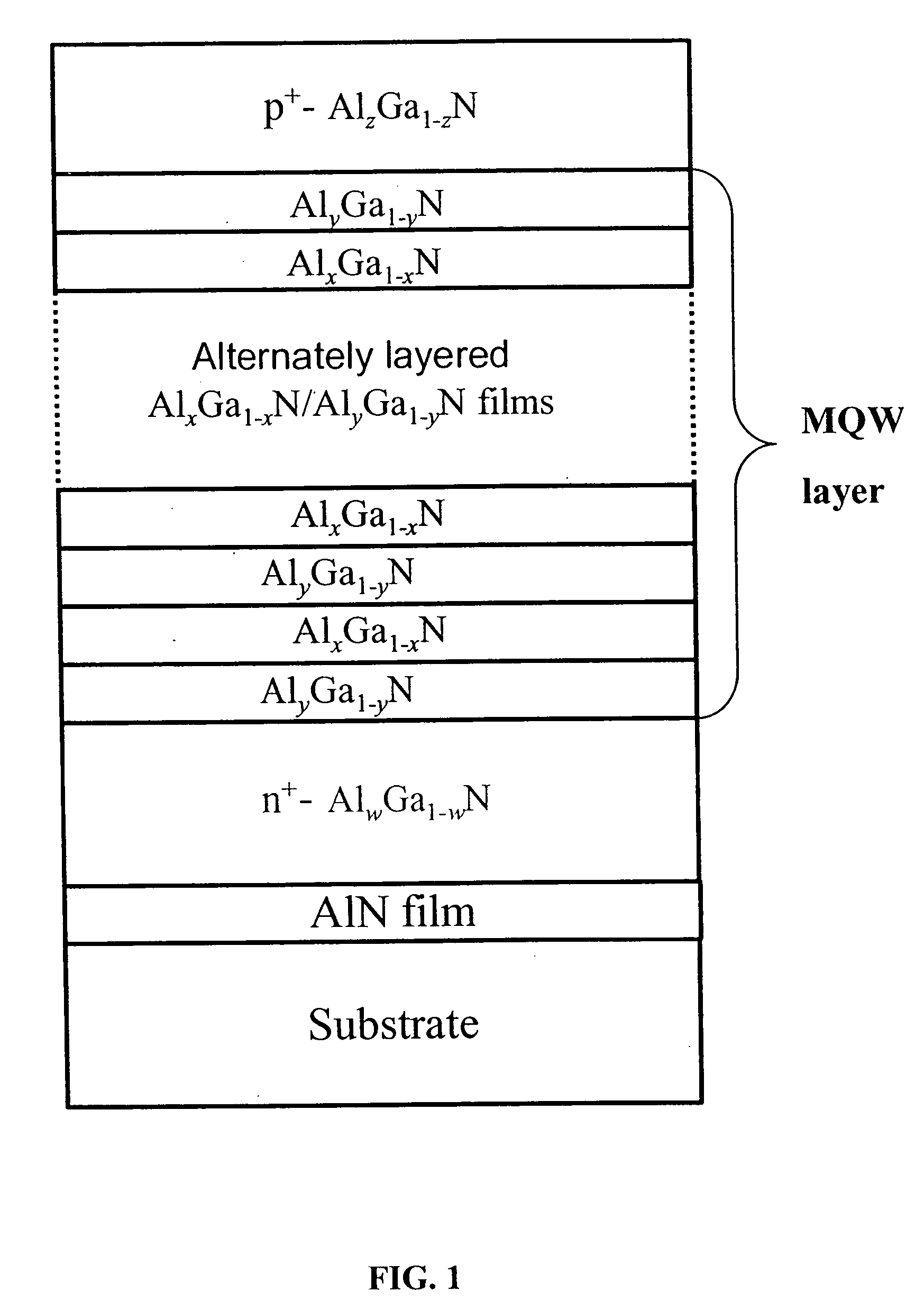
Photodetectors and optically pumped emitters based on III-nitride multiple-quantum-well structures
The design and operation of a p-i-n device, operating in a sequential resonant tunneling condition for use as a photodetector and an optically pumped emitter, is disclosed. The device contains III-nitride multiple-quantum-well (MQW) layers grown between a III-nitride p-n junction. Transparent ohmic contacts are made on both p and n sides. The device operates under a certain electrical bias that makes the energy level of the first excitation state in each well layer correspond with the energy level of the ground state in the adjoining well layer. The device works as a high-efficiency and high-speed photodetector with photo-generated carriers transported through the active MQW region by sequential resonant tunneling. In a sequential resonant tunneling condition, the device also works as an optically pumped infrared emitter that emits infrared photons with energy equal to the energy difference between the first excitation state and the ground state in the MQWs.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Pinch valve
ActiveUS8622365B2Quick switchLight weightDiaphragm valvesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesExcited statePinch valve
Owner:SMC CORP
Method for atmospheric pressure analyte ionization
ActiveUS20050196871A1High affinityTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansExcited stateAnalyte
Owner:JEOL USA
Biological retarder anti-cancer technology
In order to solve the high-speed cancer excited state problem, a biological retarder is needed. Cancer energy is converted into intramolecular transfer or other vibrational state transfer through collision. By means of the nucleus retarder principle, a neutron and a retarder atomic nucleus are subjected to collision so that the speed can be decreased, and the retarder which does not absorb neutrons and does not react with neutrons is selected. An important task of the cancer biology and even the natural science is that which material can bear a cancer nuclear fission biological retarder. According to repeated experiments, various safety factors are synthesized, and finally a biological moderator is correctly selected through a successful experiment. Bifidobacterium is free of toxicity and harm to a body, and the biological retarder can be ideal for treating a cancer. In the future, more microorganism retarders will be produced, the biological retarder is used for decelerating tumors, a proper amount of deceleration molecular nuclear energy can be used as senile cell addition nuclear energy, and the biological retarder gives power to biological science and will play an indispensable critical role.
Device for indoor air purification and sterilization
ActiveUS20120207647A1Improve purification effectImprove the bactericidal effectLighting and heating apparatusExhaust apparatusExcited stateContact time
The present invention relates to a device for indoor air purification and sterilization which excites indoor air by arc discharge to decompose bad odor and sterilize air, wherein an excited state is maintained by applying a magnetic field and the contact time between molecules activated by arc and pollutants is extended, thereby improving air purification and sterilization effects, and the noise generated by arc discharge is reduced by a silencer and ozone and static electricity are removed by a filter which removes ozone and a metal filter for removing static electricity, respectively, thereby enabling very suitable configuration for indoor air purification and sterilization.
Owner:KIM BU YEOL
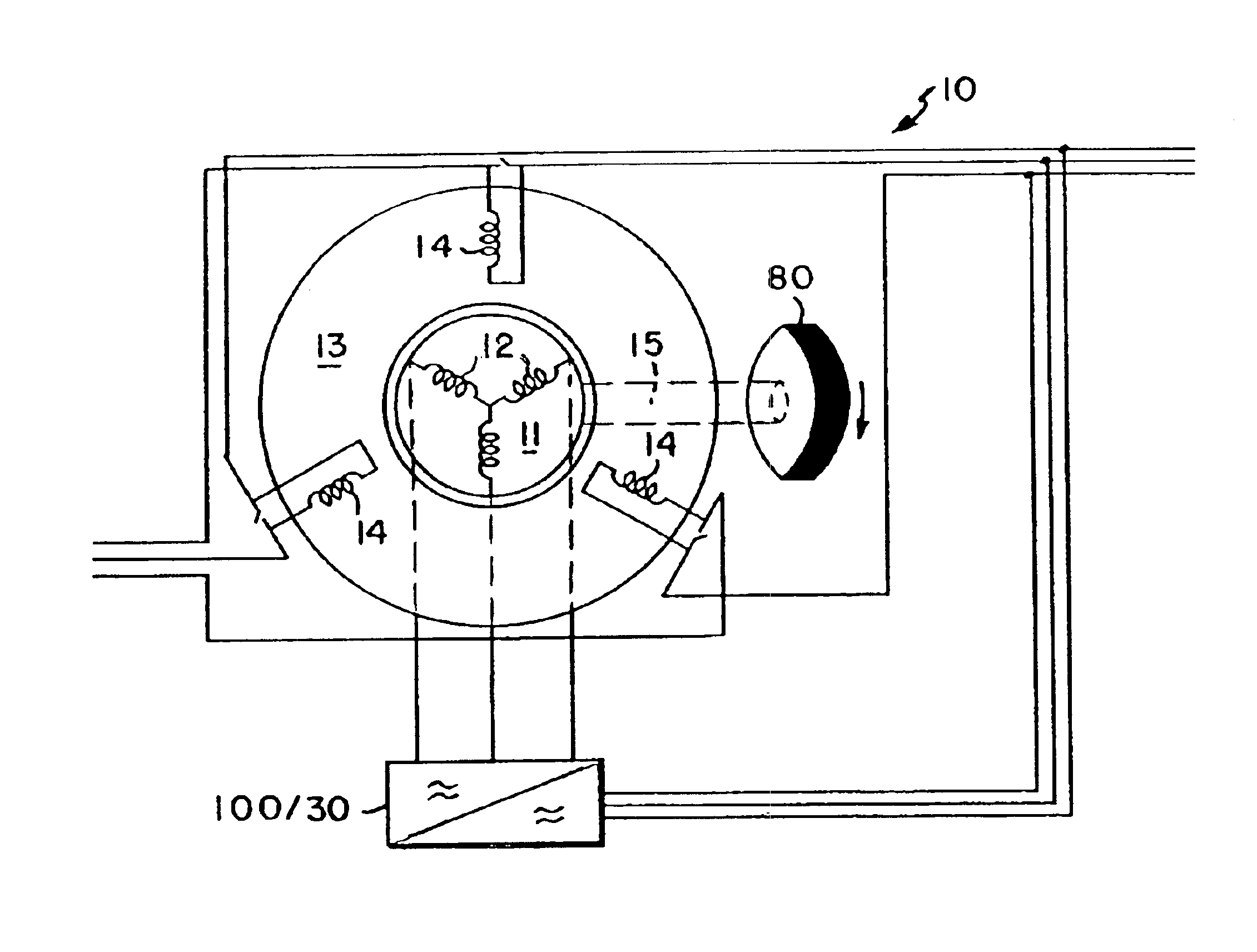
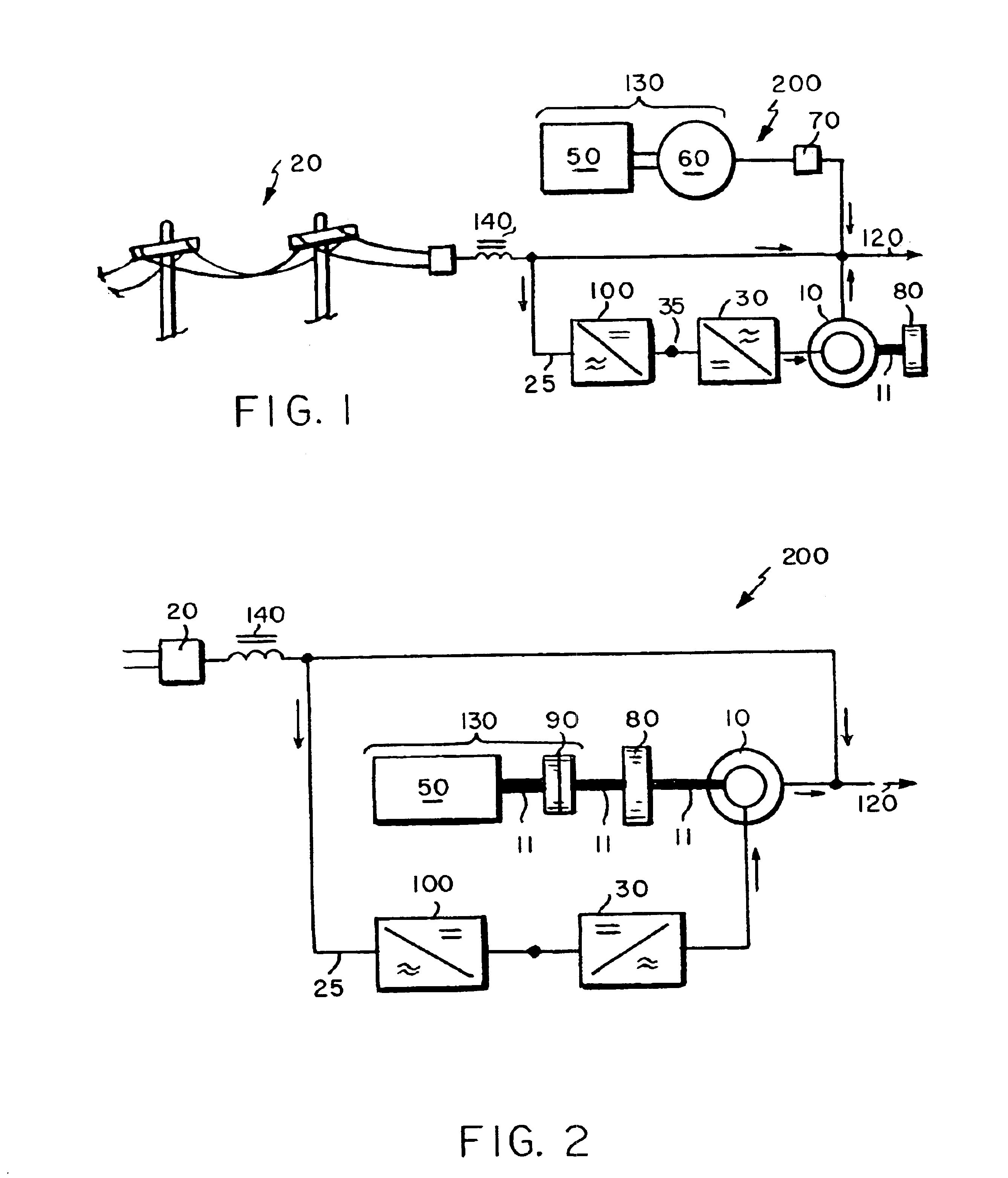
Uninterruptible power supply system using a slip-ring, wound-rotor-type induction machine and a method for flywheel energy storage
InactiveUS7071581B2Low costBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerFlywheel energy storageThermal energy storage
Several embodiments of an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) system, which system provides highly reliable output power to a load using a slip-ring induction machine and a flywheel combination, are disclosed as well as methods relating thereto. In a preferred embodiment, the UPS system comprises a back-up power source, e.g., an engine and generator, and a slip-ring, or wound-rotor, induction motor and flywheel combination, which are in parallel to a primary power source, e.g., a utility grid. During normal operation of the UPS, the primary power source supplies alternating current and voltage to the load and the UPS compensates for voltage drop across the isolating inductor. Moreover, the primary power source keeps the slip-ring induction machine and flywheel in an excited state, i.e., the rotor of the slip-ring induction machine, the shaft of which is shared by the flywheel, is excited above normal synchronous speed. When the primary power source fails, the flywheel, which is rotating at super-synchronous speed and storing kinetic energy, drives the rotor of the slip-ring induction machine and generates, i.e., induces current in the stator. Accordingly, the flywheel and slip-ring induction machine combination provides instantaneous, short term power to the load until the back-up power source has powered up and been brought on line.
Owner:PERFECT GALAXY INT
Laser capable of simultaneously outputting nanosecond pulses and pico-second pulses
ActiveCN102709801AImprove utilization efficiencyAvoid complexityLaser detailsChemical reactionHigh energy
The invention discloses a laser capable of simultaneously outputting nanosecond pulses and pico-second pulses. The laser comprises a signal source, a signal isolation system and an amplifier. According to the invention, with an electric light control technology of combining an extra-cavity Pockels cell and intra-cavity Pockels cell, a regenerative amplification process is realized in case of signal light importing so as to obtain high-energy pico-second laser output, and cavity empty process is also realized in case of no signal light importing so as to obtain nanosecond pulse output; and thefree combination of the two processes can be realized according to practical application demand, and as a result, free combination of numbers of the nanosecond pulses and the pico-second pulses in a single laser is realized and is output in an alternative way. The laser provided by the invention has an important application in high-precision high-efficiency fine processing field, as well as basicresearch fields such as plasma excitation, excited state control, chemical reaction control, special radiation excitation and the like.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Hologram recording material composition, hologram recording material and hologram recording method
InactiveUS20050046915A1High sensitivityHigh refractive indexPhotomechanical apparatusRecord information storageChemical reactionVolumetric Mass Density
To provide a composition for a hologram recording material, a hologram recording material and a hologram recording method applicable to a high density optical recording medium, a three-dimensional display, a holographic optical element etc. and capable of attaining a high sensitivity, a high diffraction efficiency, a satisfactory storage property, a low shrinkage rate, a dry process, a multiplex recording property and a high recording density. An unrewritable hologram recording method including a step in which a sensitizing dye absorbs light by an exposure to form an excited state, a chemical reaction step including a color forming reaction involving an electron transfer or an energy transfer from such excited state, and a hologram-forming step by such chemical reaction.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com