Patents
Literature
1138 results about "Induction machine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition of induction machine 1 : an electric machine operating by electrostatic induction 2 : an alternating-current machine (as an induction motor or induction generator) in which primary and secondary windings rotate with respect to each other and in which energy is transferred from one circuit to the other circuit by electromagnetic induction
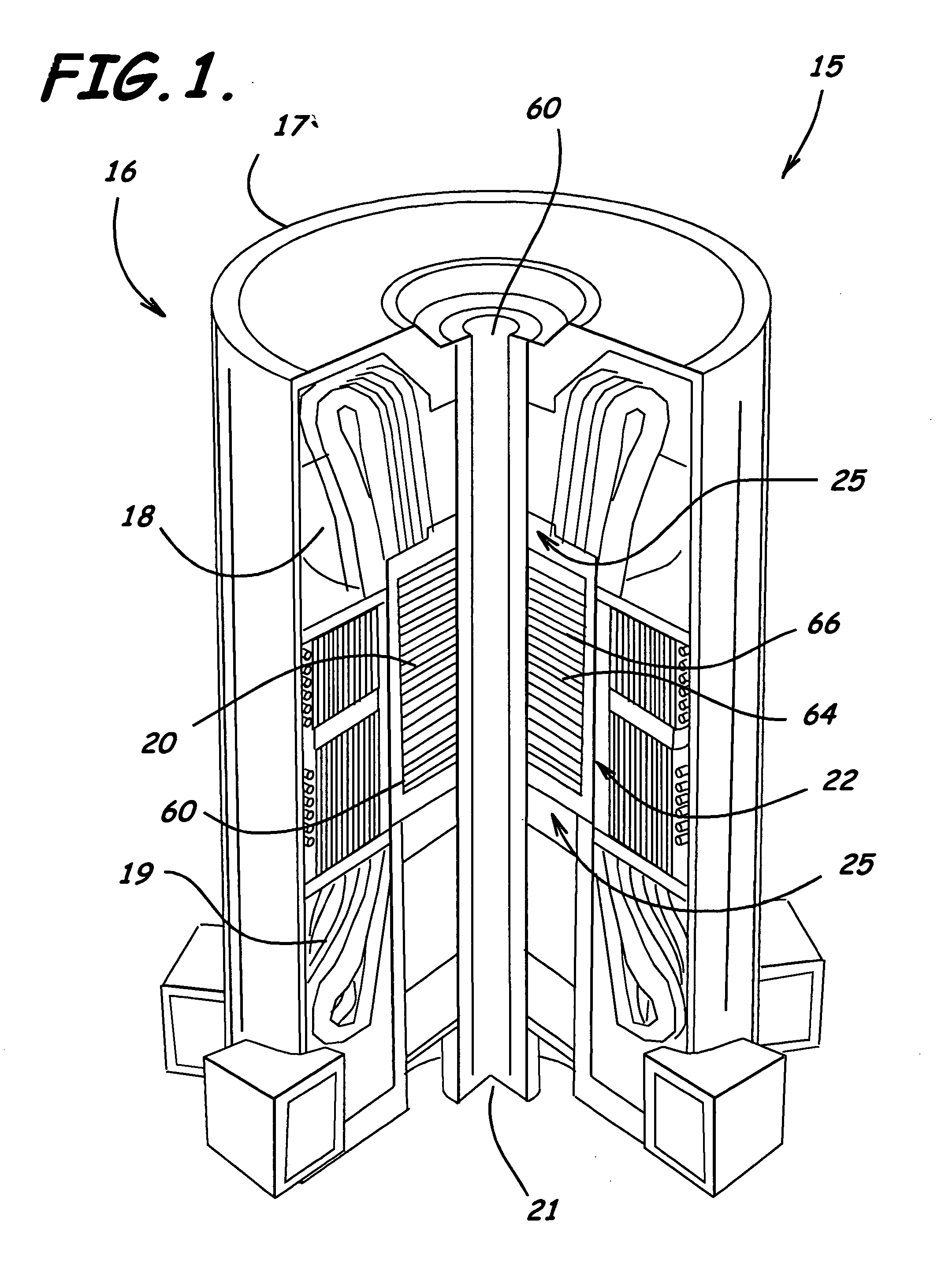
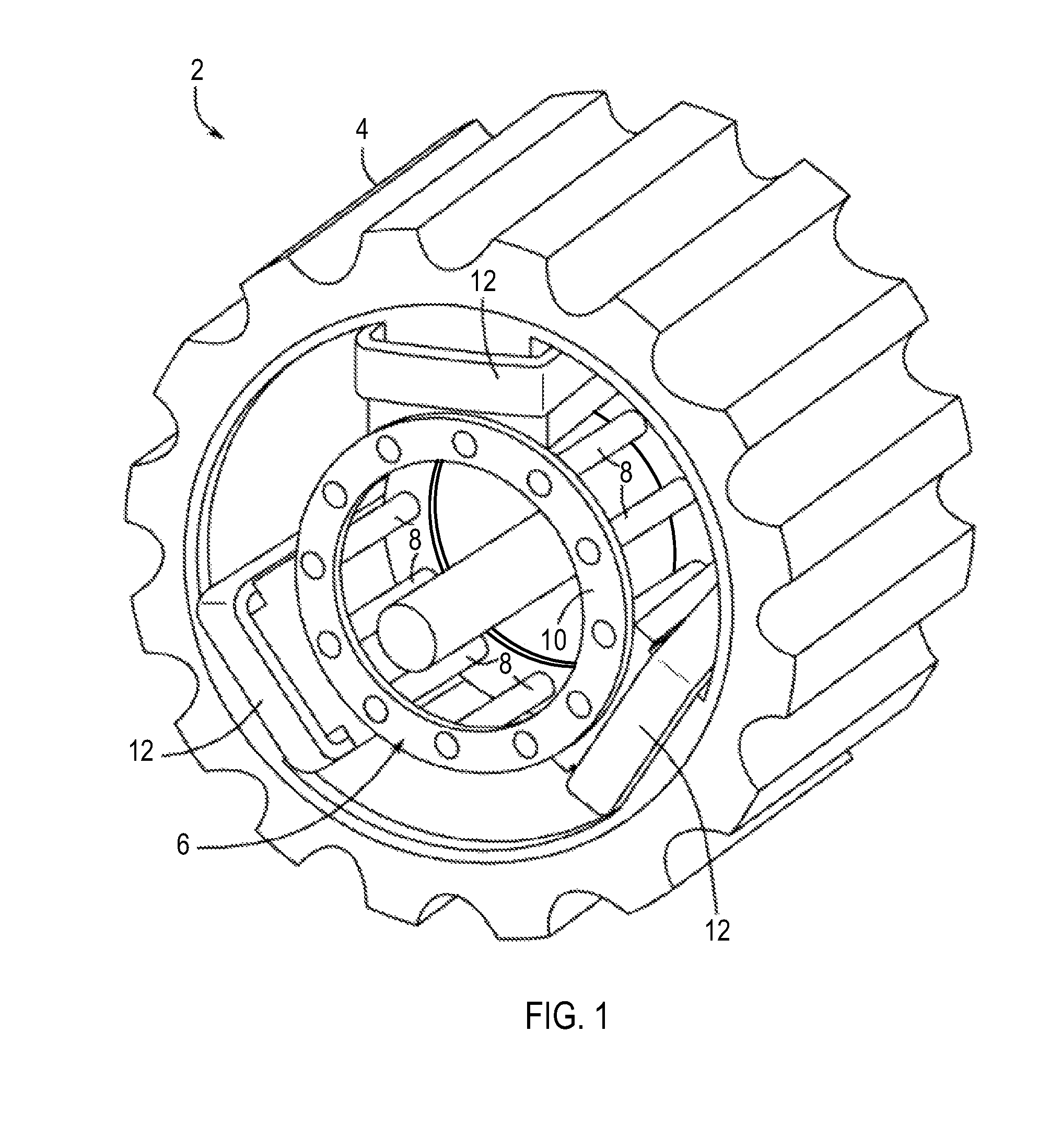
High strength induction machine, rotor, rotor cage end ring and bar joint, rotor end ring, and related methods
InactiveUS20060273683A1Relieve pressureAdvancement in operating speedSynchronous motorsAsynchronous induction motorsEngineeringHigh intensity
A high strength induction machine, rotor, rotor cage end ring and bar joint, rotor end ring, and related methods are provided. An embodiment of an end ring and bar joint includes a main body adapted to substantially surround a rotor shaft when mounted thereto, a plurality of slots extending inwardly in a radial direction from outer peripheries of the main body, a thicker end ring section extending outwardly from a medial portion of the main body, being thicker than the outer peripheries of the main body, and also being adapted to substantially surround the rotor shaft, and a plurality of bosses extending axially and outwardly from outer peripheral portions in a direction opposite to the thicker end ring section and each adapted to receive an end portion of a rotor bar therein.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
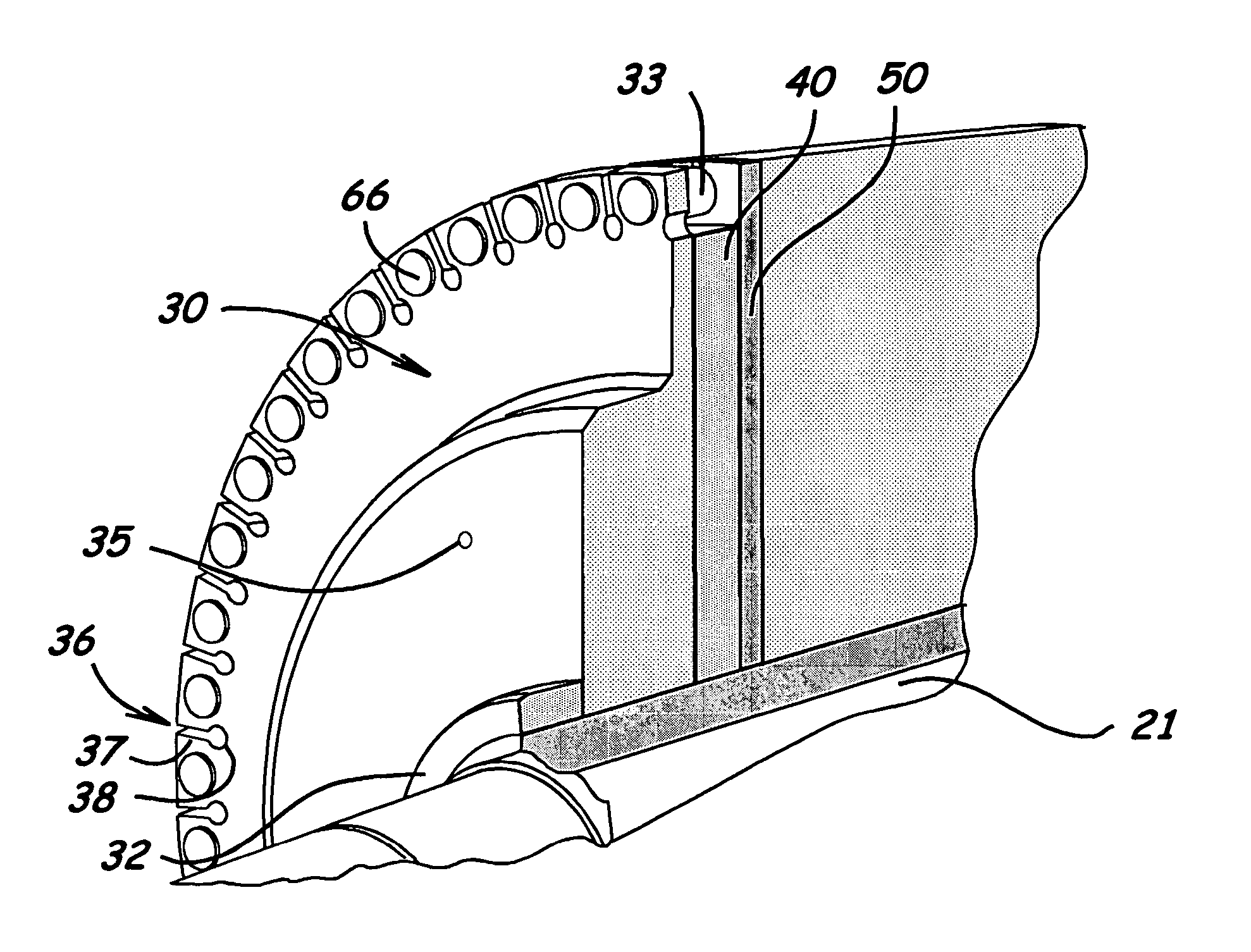
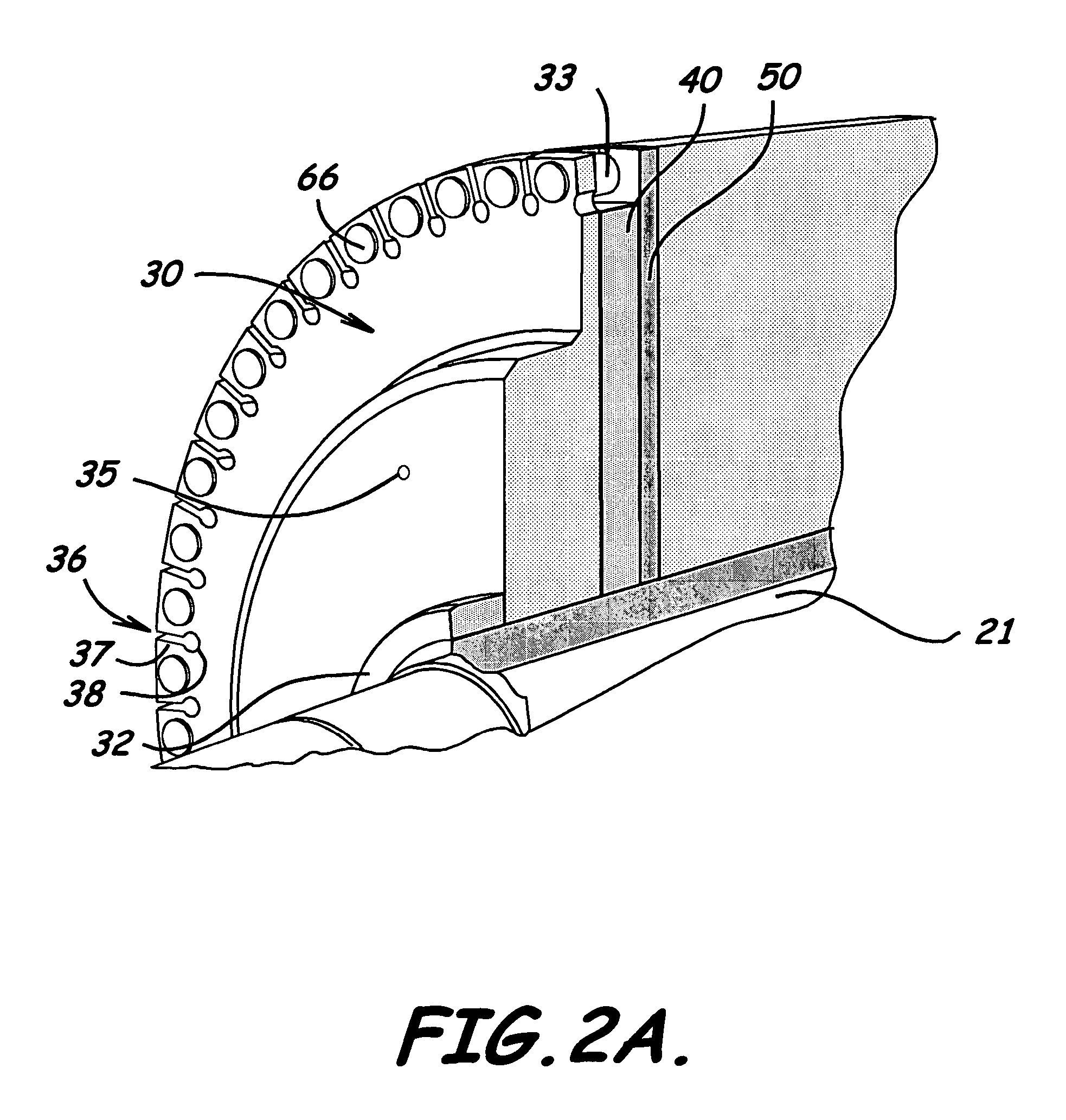
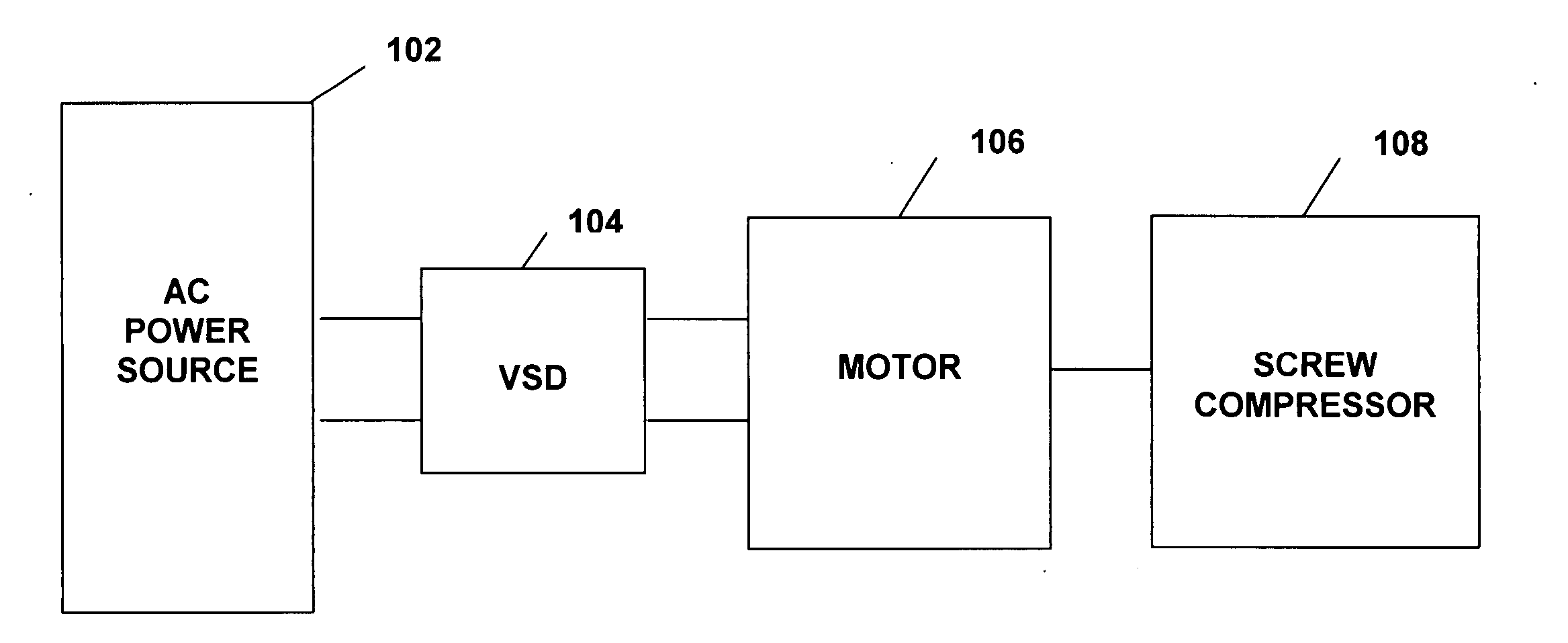
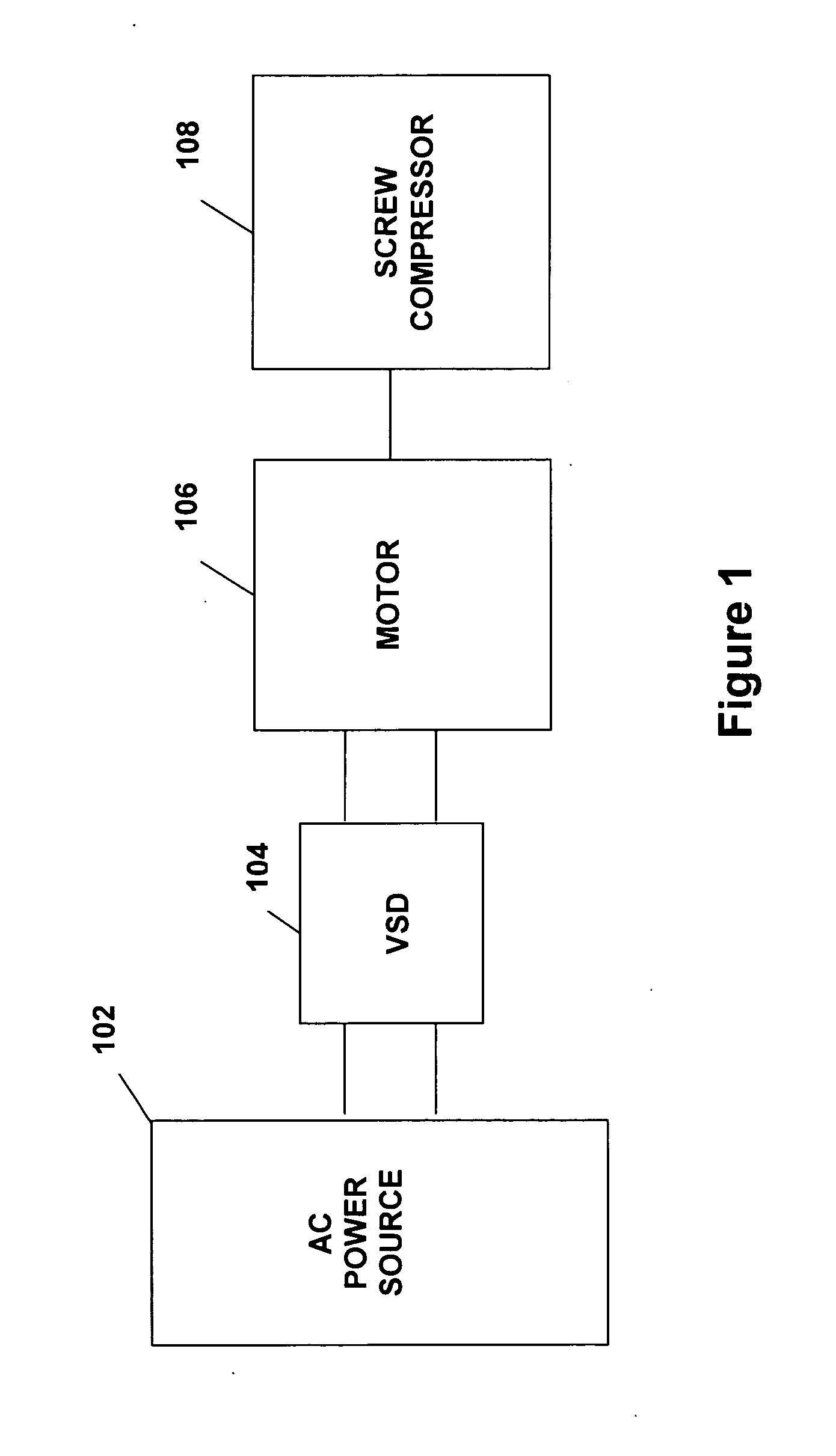
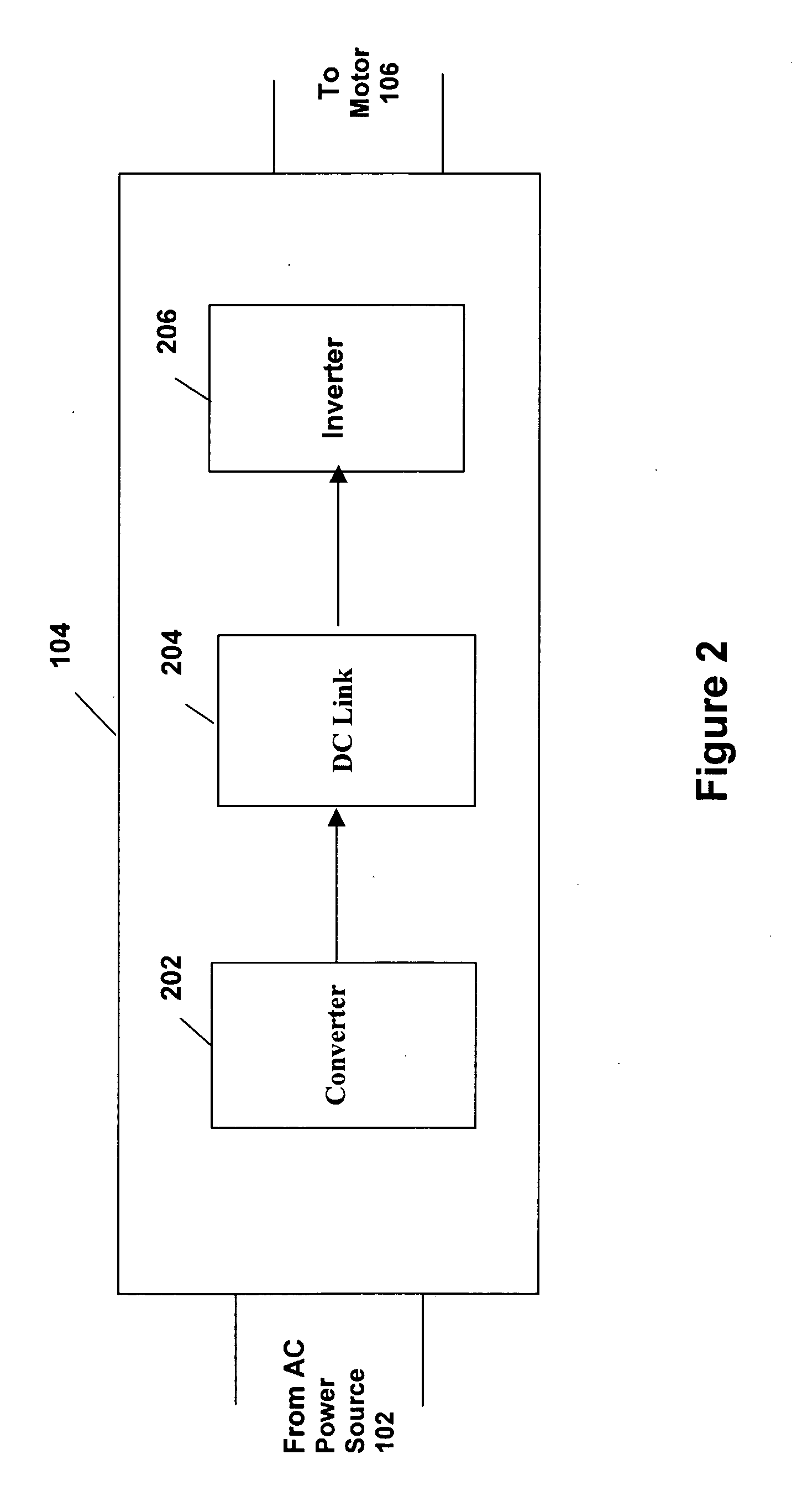
System and method for variable speed operation of a screw compressor
ActiveUS20050188708A1Efficient screw compressor operationReduce gas leakageAC motor controlRotary piston pumpsControl theoryOperating speed
A system and method are provided for variable speed operation of a screw compressor to obtain increased capacity and efficiency. The screw compressor is connected to an induction motor driven by a variable speed drive, wherein the screw compressor has a variable output capacity that is dependent on the output speed of the motor. To obtain increased capacity and efficiency, the screw compressor is operated at a speed greater than the screw compressor's rated speed and does not include a slide valve. The maximum operating speed of the screw compressor, which speed is greater than the rated speed, is related to the maximum operating speed of the motor when operated at a voltage and frequency provided by the variable speed drive that is greater than the motor's rated voltage and frequency in a constant flux or constant volts / Hz mode.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TYCO IP HLDG LLP
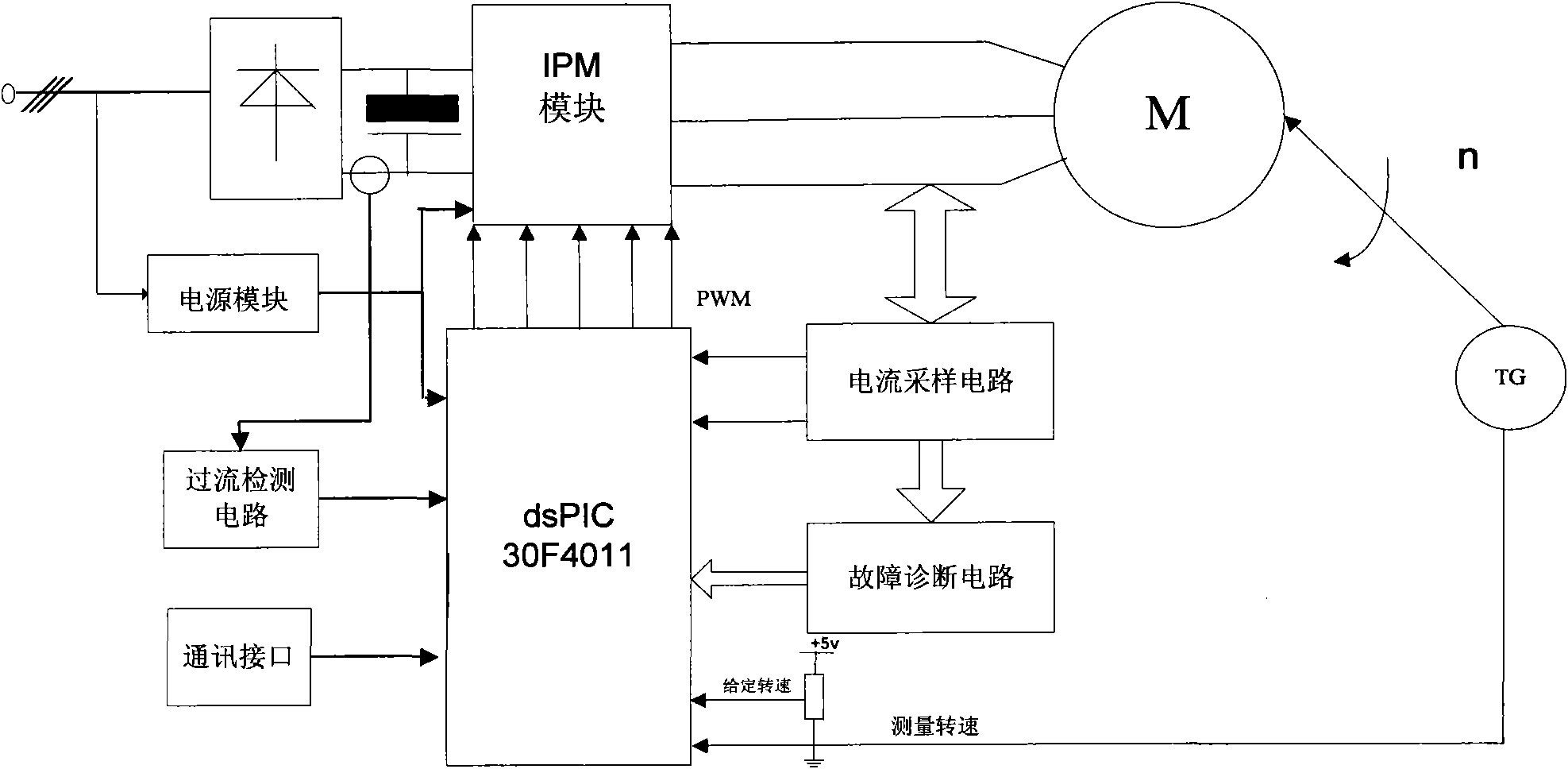
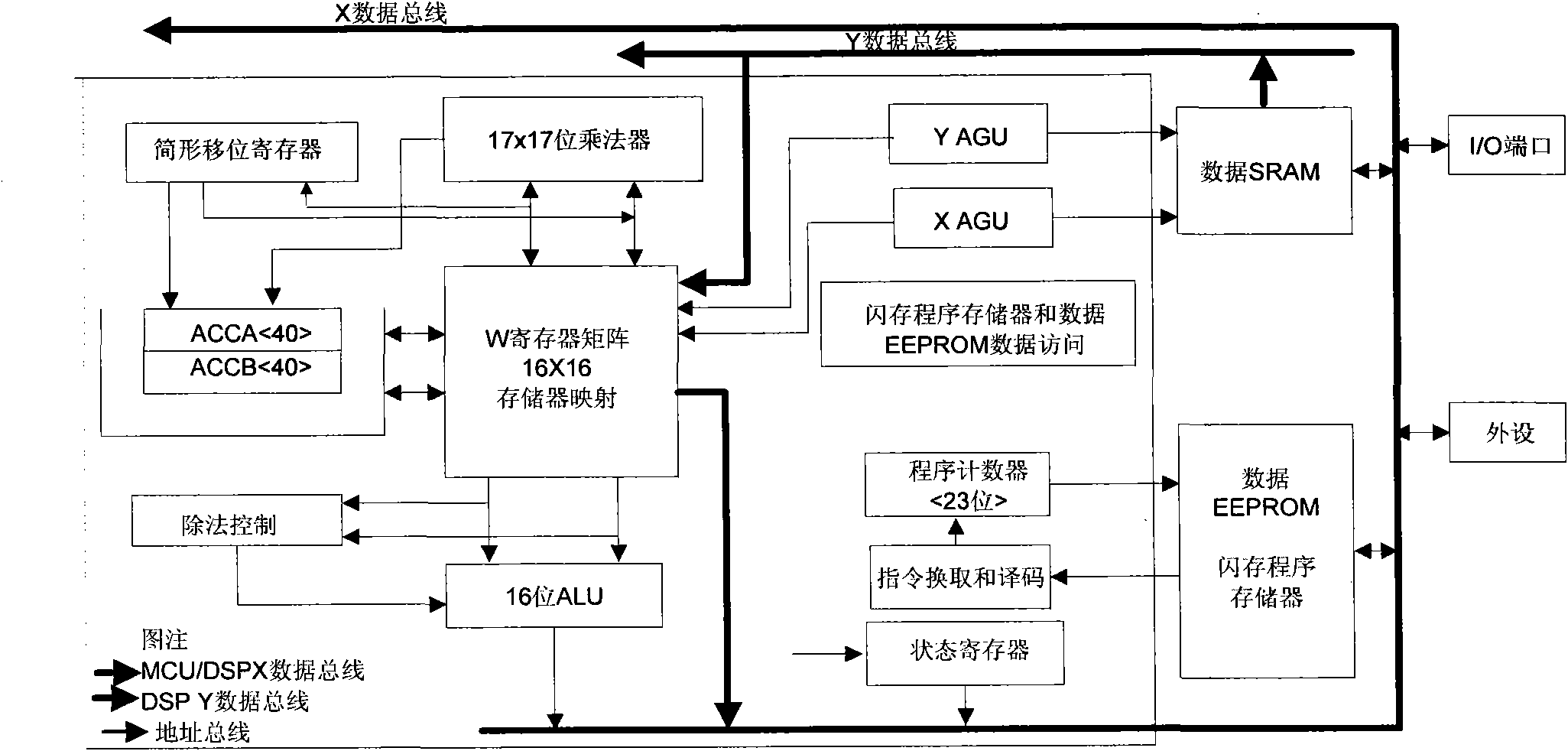
Singlechip-based induction motor variable frequency speed regulation control system
InactiveCN101977016AEfficient and rapid detectionDetect enoughAC motor controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsMicrocontrollerEngineering
The invention discloses a singlechip-based induction motor variable frequency speed regulation control system. The system comprises a main circuit, an auxiliary power circuit, an inverter circuit, a control part, an over-current protection circuit, a rotation speed detection circuit and other peripheral circuits. A 16-bit high-performance signal controller dsPIC30F4011 which is produced by the Microchip Company is used as a control core by the system to perform speed regulation based on vector control motor excitation. A digital signal controller dsPIC30F4011 of the America Microchip Technology Company is used as a chip special for motor control, a digital signal processor (DSP) inner core is embedded, and the chip has quick data processing capacity and is provided with abundant input and output equipment and interface circuits; an intelligent power module (IPM) IRAMSIOUP 60A of the IR Company is an inverter switching device, so that the variable frequency speed regulation control system of an asynchronous motor is constructed; and the system has the characteristics that the system is simple to drive and easy to realize.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
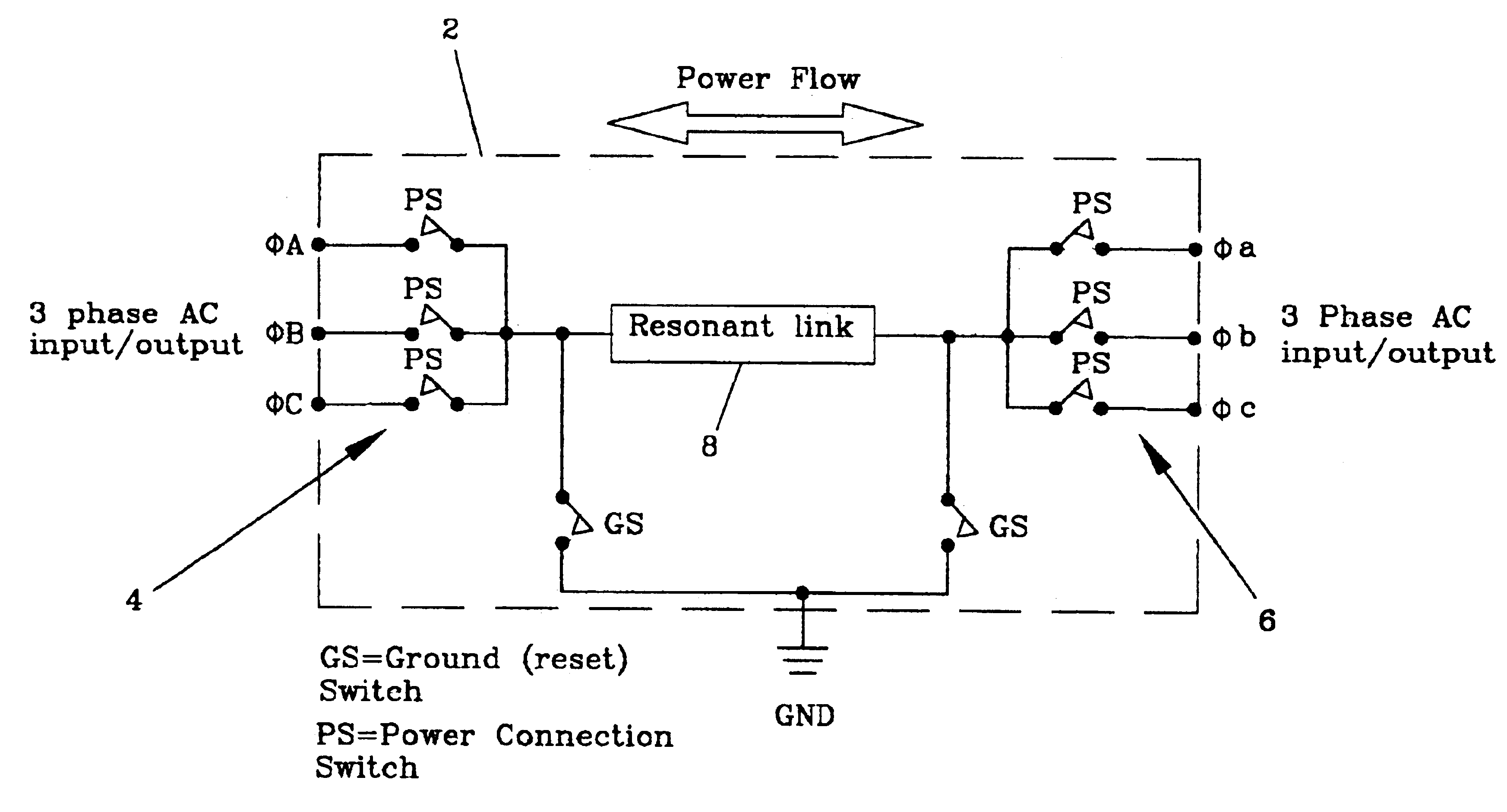
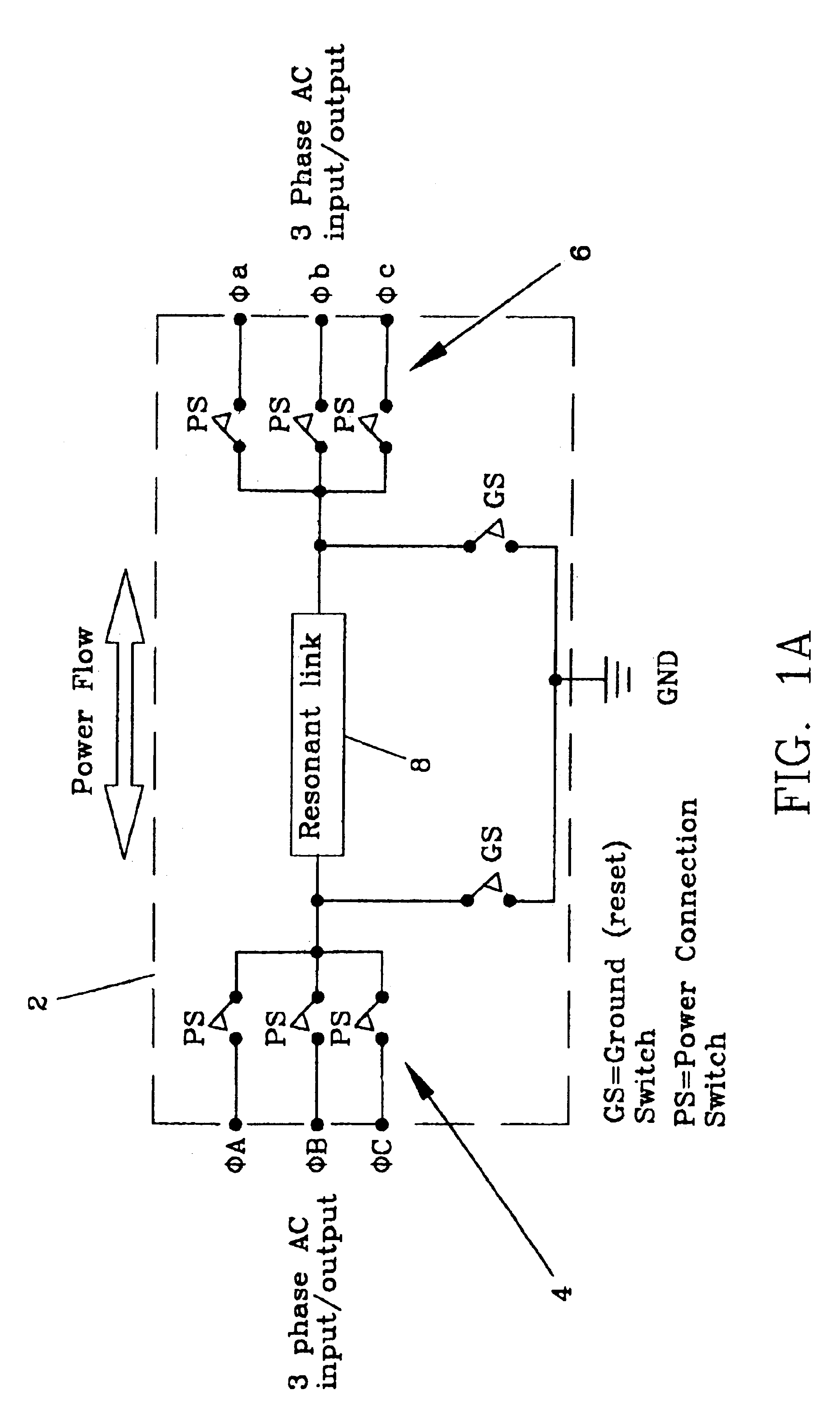
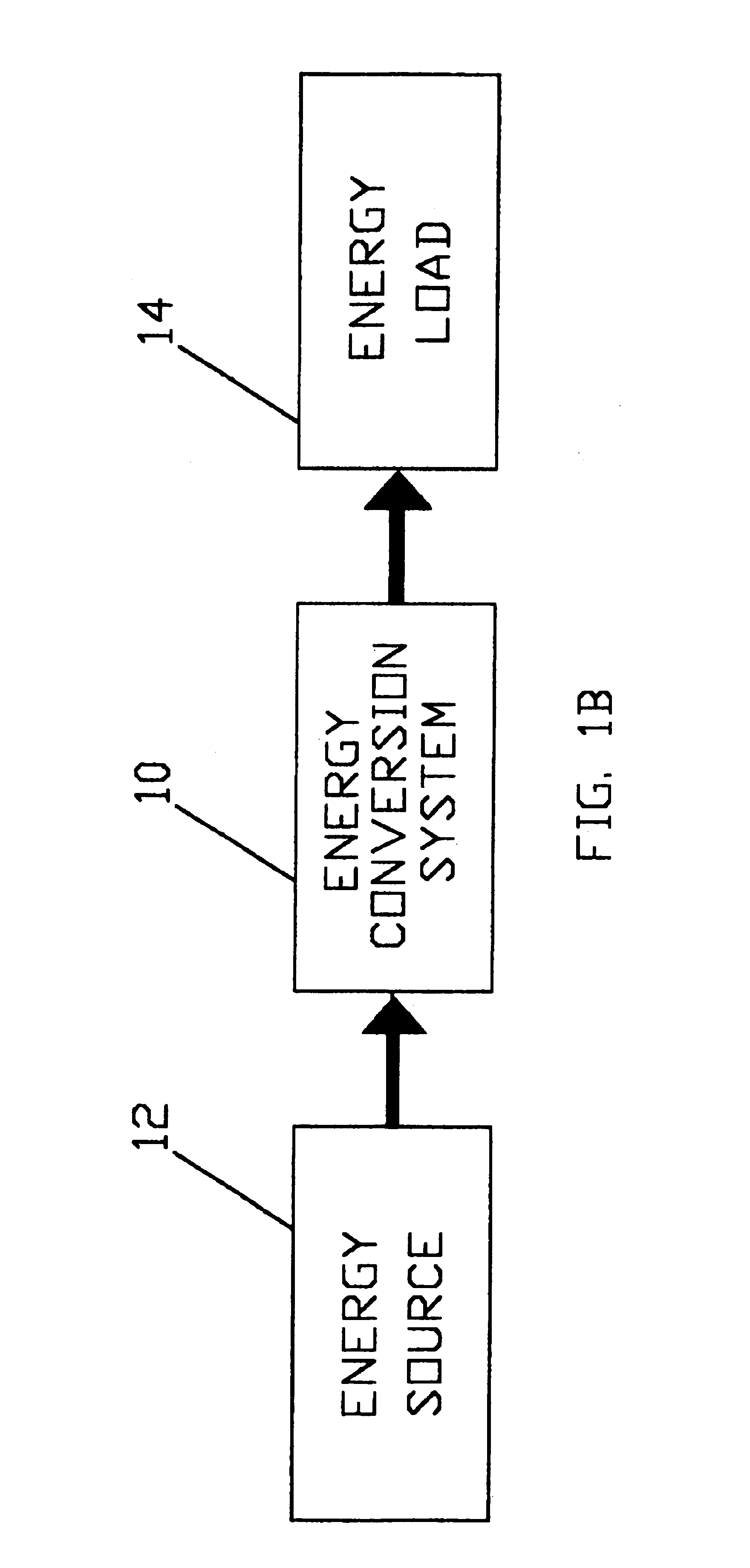
Electro-mechanical energy conversion system having a permanent magnet machine with stator, resonant transfer link and energy converter controls
ActiveUS6984897B2Raise the ratioImprove efficiencyAC motor controlWind motor controlEnergy transferMultiplexer
An electro-mechanical energy conversion system coupled between an energy source and an energy load comprising an energy converter device including a permanent magnet induction machine coupled between the energy source and the energy load to convert the energy from the energy source and to transfer the converted energy to the energy load and an energy transfer multiplexer to control the flow of power or energy through the permanent magnetic induction machine.
Owner:SPELLMAN HIGH VOLTAGE ELECTRONICS
High performance and energy-saving double-acting hydrostatic press driven by servo motor
InactiveCN101712207AImprove performanceOvercome a series of disadvantagesExtrusion control devicesForging press detailsClosed loopHydrostatic pressure
The invention relates to a high performance and energy-saving double-acting hydrostatic press driven by a servo motor. The invention retains the rapid liquid-filling and direction control circuits in the common hydrostatic press, but uses a controllable hydraulic source composed of an AC servo motor and a quantitative oil pump to replace an uncontrollable hydraulic source driven by a common induction motor and combine with various sensors, and realizes the energy-saving pressure, position and speed control of the system under the control and regulation of the electrical motor; displacement sensors are added in a main cylinder and an auxiliary cylinder, a pressure sensor is added in the oil inlet line of the main cylinder, thus realizing the closed-loop control of position, speed and pressure; and a proportional relief valve is added at the oil outlet of the auxiliary cylinder, thus realizing variable blank holder force floating blank-holding of the auxiliary cylinder, wherein the electrical motor is the high-power AC servo motor, the electrical motor is connected with a controller, and the flow control and the volume velocity-governing and pressure-regulating of the main oil line can be realized by controlling the speed of the electrical motor. The invention completely uses the advantages of the high-power AC servo motor such as high efficiency, controllable performance, adjustable performance and good reliability to realize the optimization of process parameters, improve the hydrostatic press performance and reduce the energy consumption.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
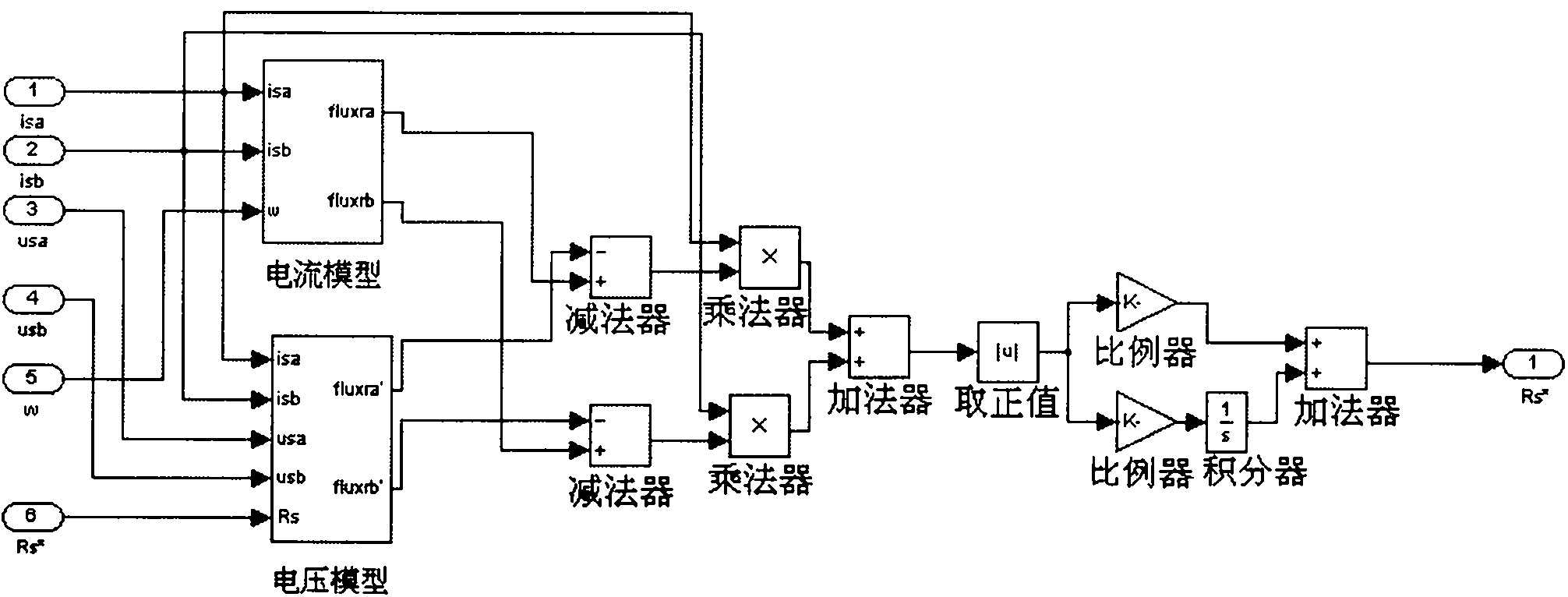
Induction motor stator resistance and temperature parameter identifying method
InactiveCN101783646AReduce usageEfficient identificationElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsReference modelConductor Coil
The invention relates to an induction motor stator resistance and temperature parameter identifying method. A control method based on model reference self-adaption is used for identifying the induction motor stator resistance and the stator winding temperature. According to the calculating method of an asynchronous motor rotor magnetic chain, the current magnetic chain calculating model is used as a reference model, a voltage magnetic chain calculating model is used as an adjusting model, and the output difference between the two models is used for continuously adjusting the stator resistance parameter in the voltage model through the self-adaption rate until the output difference of the two models is zero. The invention can effectively identify the stator resistance parameter and the stator winding temperature of the asynchronous motor in running, enhance the low-frequency property of the direct torque frequency-variable speed adjusting system of the asynchronous motor, eliminate the use of the temperature sensor, and save the cost of the speed adjusting system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
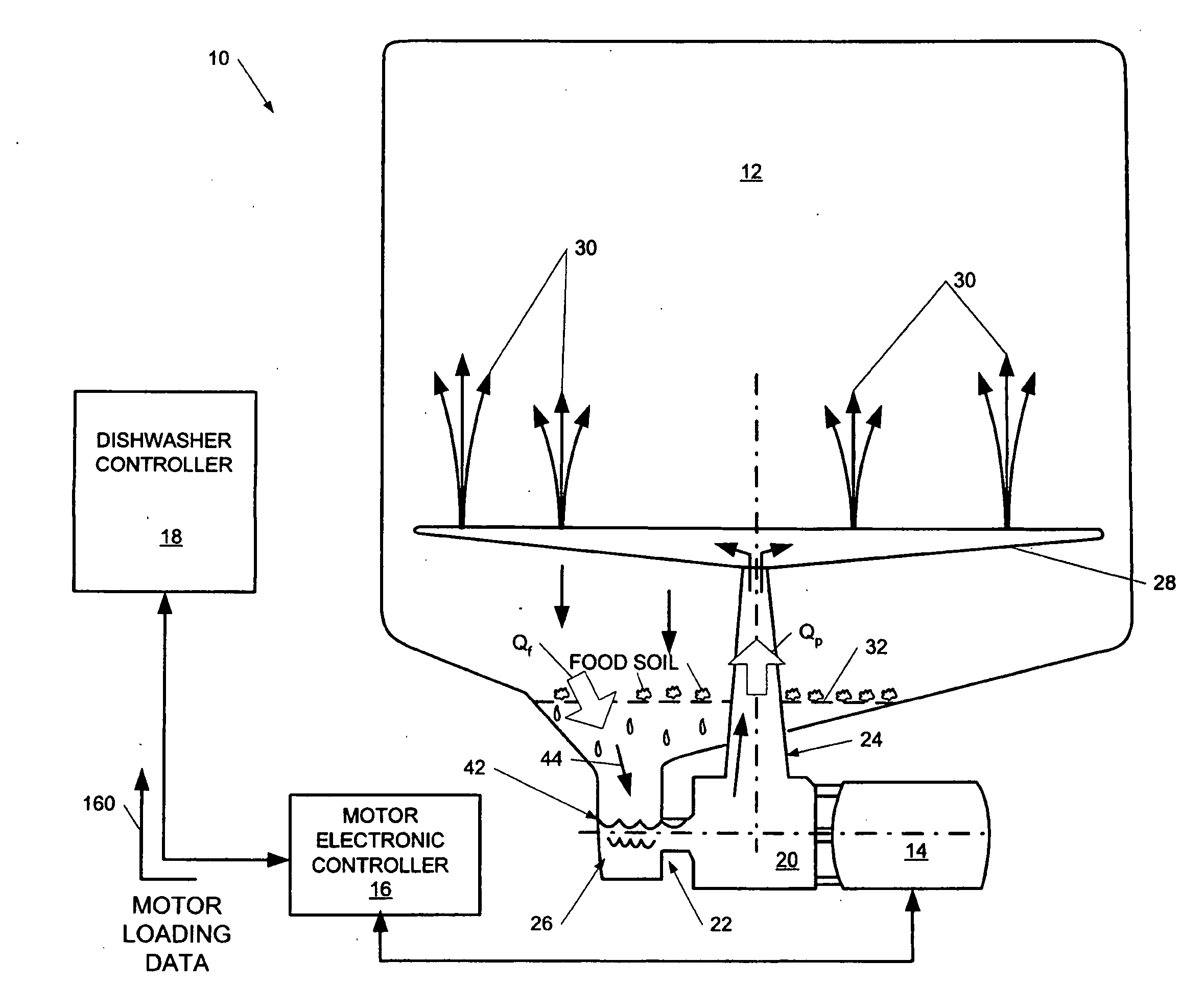
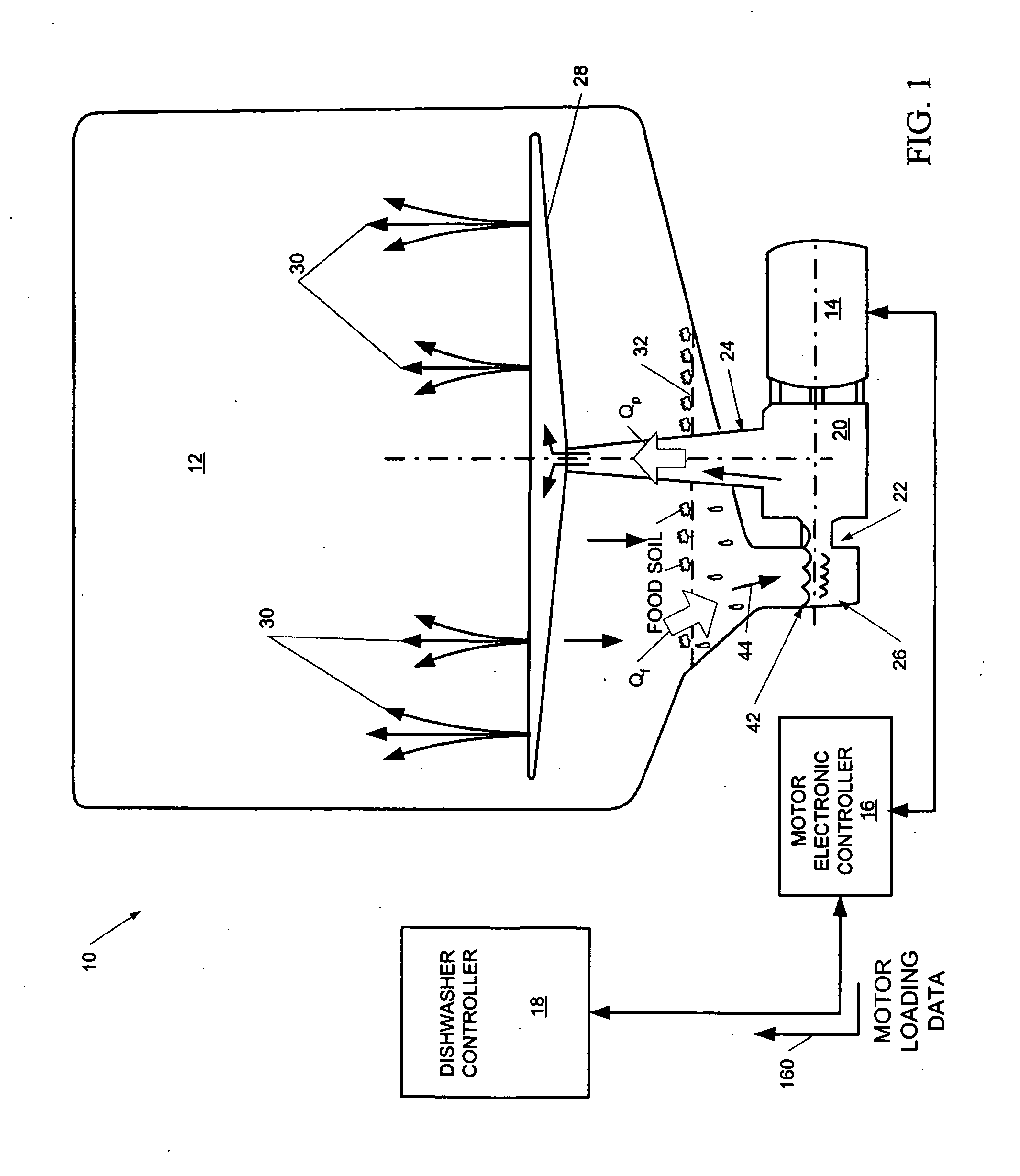
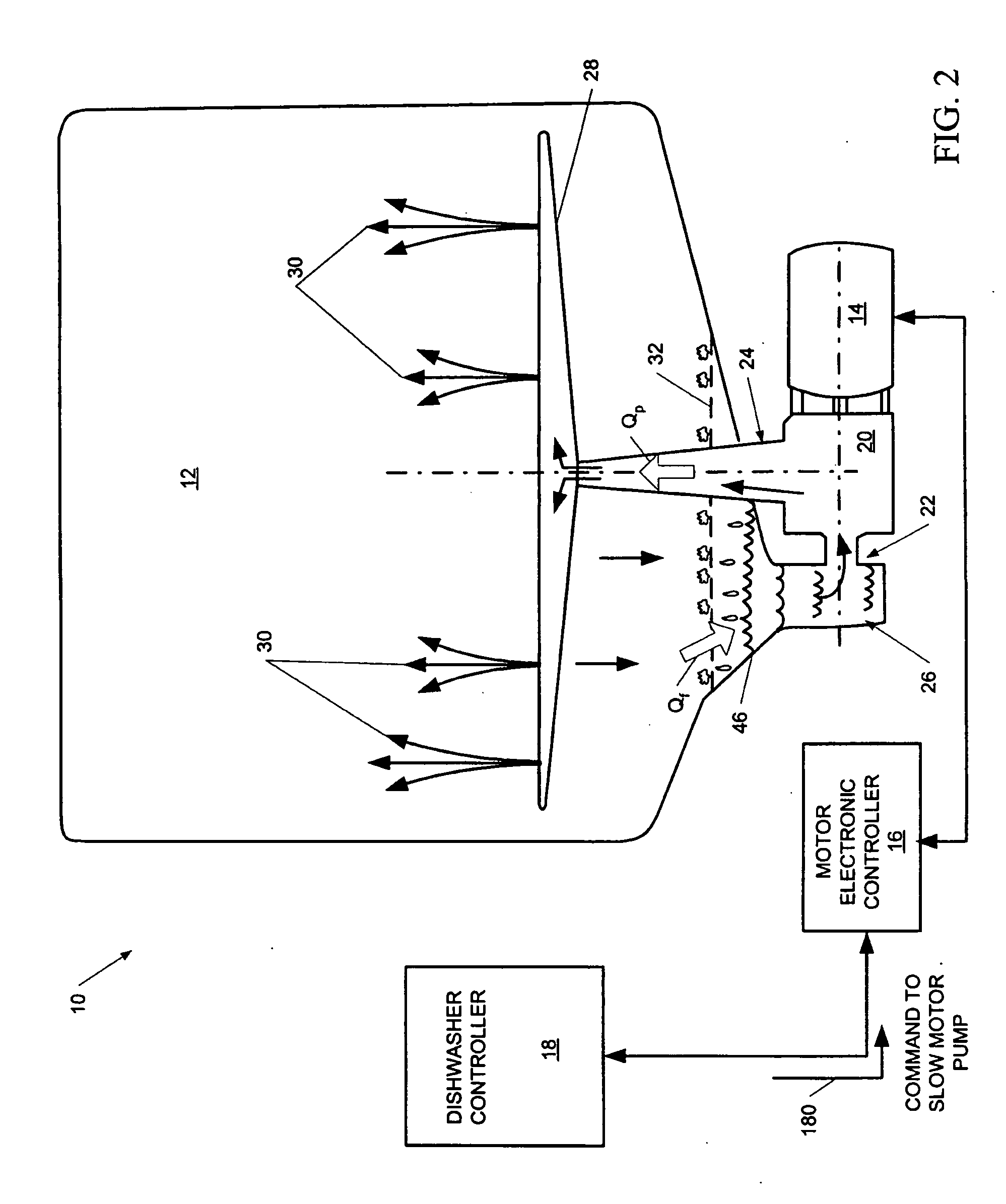
Dishwasher with controlled induction motor/pump
InactiveUS20060237044A1Easy to coverEasy to cleanAC motor controlAutomatic washing/rinsing machine detectionMotor speedMotor controller
A dishwasher having a speed-controlled induction motor coupled to a pump to drive the pump during dishwasher operation. A motor controller is connected to the induction motor to control the speed of operation of the induction motor. A dishwasher controller is connected to the motor controller for sending signals to, and receiving signals from, the motor controller during operation to control the motor speed. The flow rate of water through the pump discharge to a spray arm is controlled based on the phase of the wash cycle and the condition of the filter that blocks food debris from entering the sump. The motor speed is decreased to decrease the pump flow rate when the flow rate through the filter decreases in an early phase of the wash cycle. The motor speed is increased to increase the pump flow rate during later phases of the wash cycle. In steady state operation, the flow rate through the filter is matched to the flow rate through the pump discharge.
Owner:VIKING RANGE
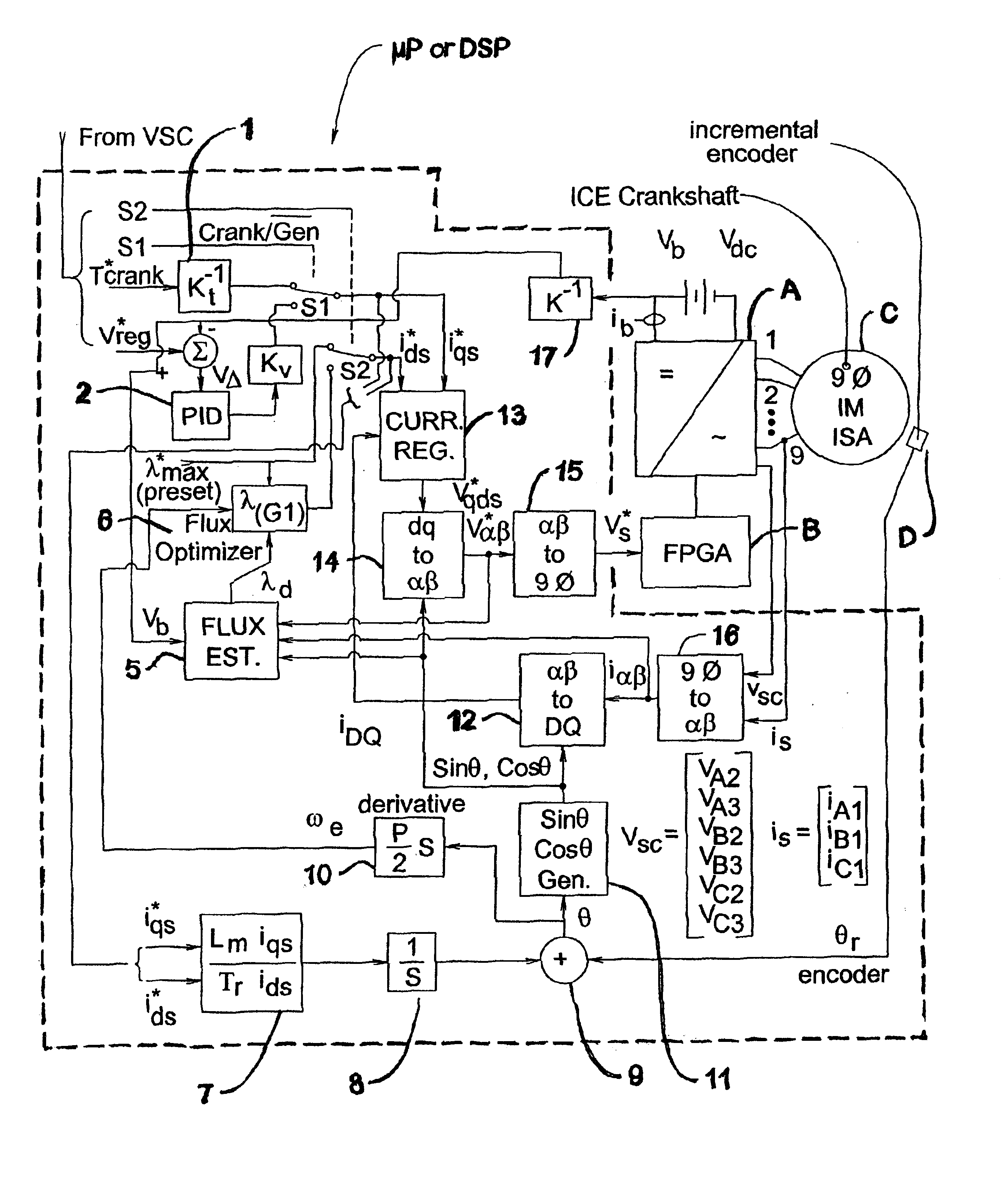
Variable speed power generator having two induction generators on a common shaft
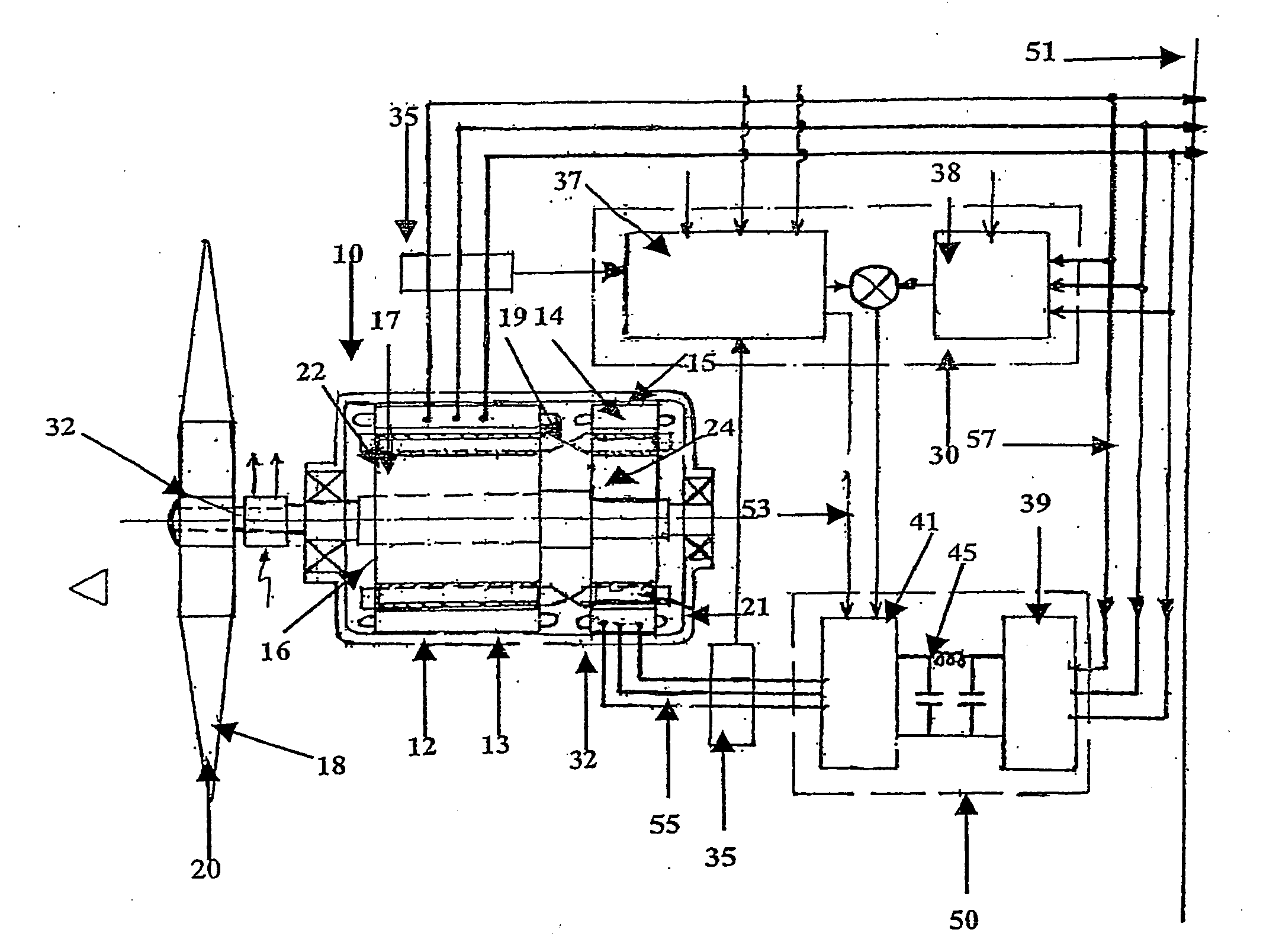
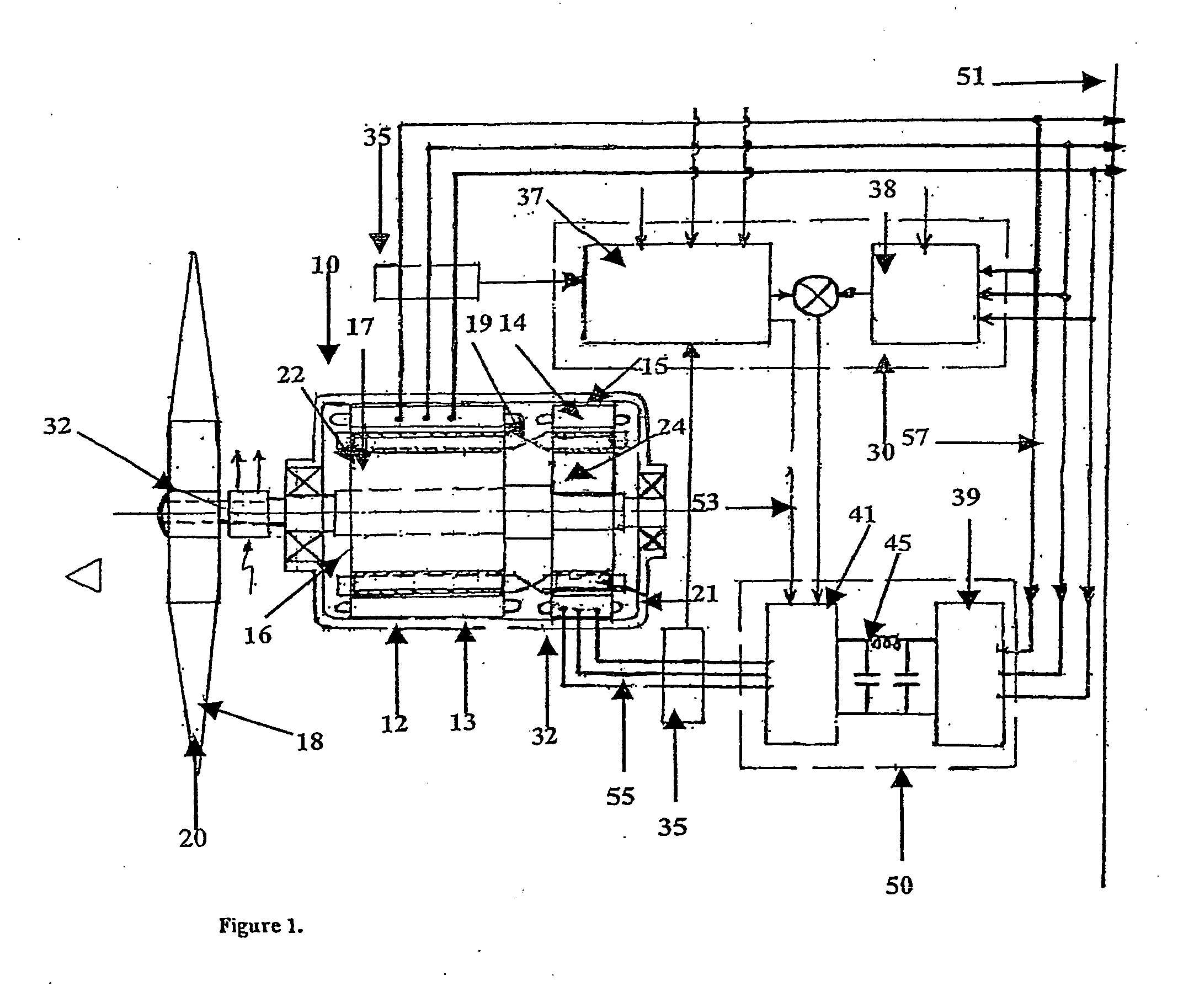
A variable speed power generator system, includes a primary power induction generator (12), a secondary control induction (14), each of the induction generators having a rotor (22, 24) mounted so as to be rotated by a common shaft (16) of a variable speed prime mover (20), an inverter (50) connected to the stator (15) of the secondary control induction generator, a controller (30) connected to the inverter controls the output of the inverter, output of the primary induction generator is connected to the grid (51), controller provides output signal to the inverter based on selected inputs to the controller so that the output of the primary induction generator matches the active and reactive power requirements of the grid. An induction machine which includes a rotor having laminations and insulated cage bars, the bars being electrically isolated from on another as well as electrically insulated from the laminations.
Owner:VARISPEED ELECTRIC MOTORS
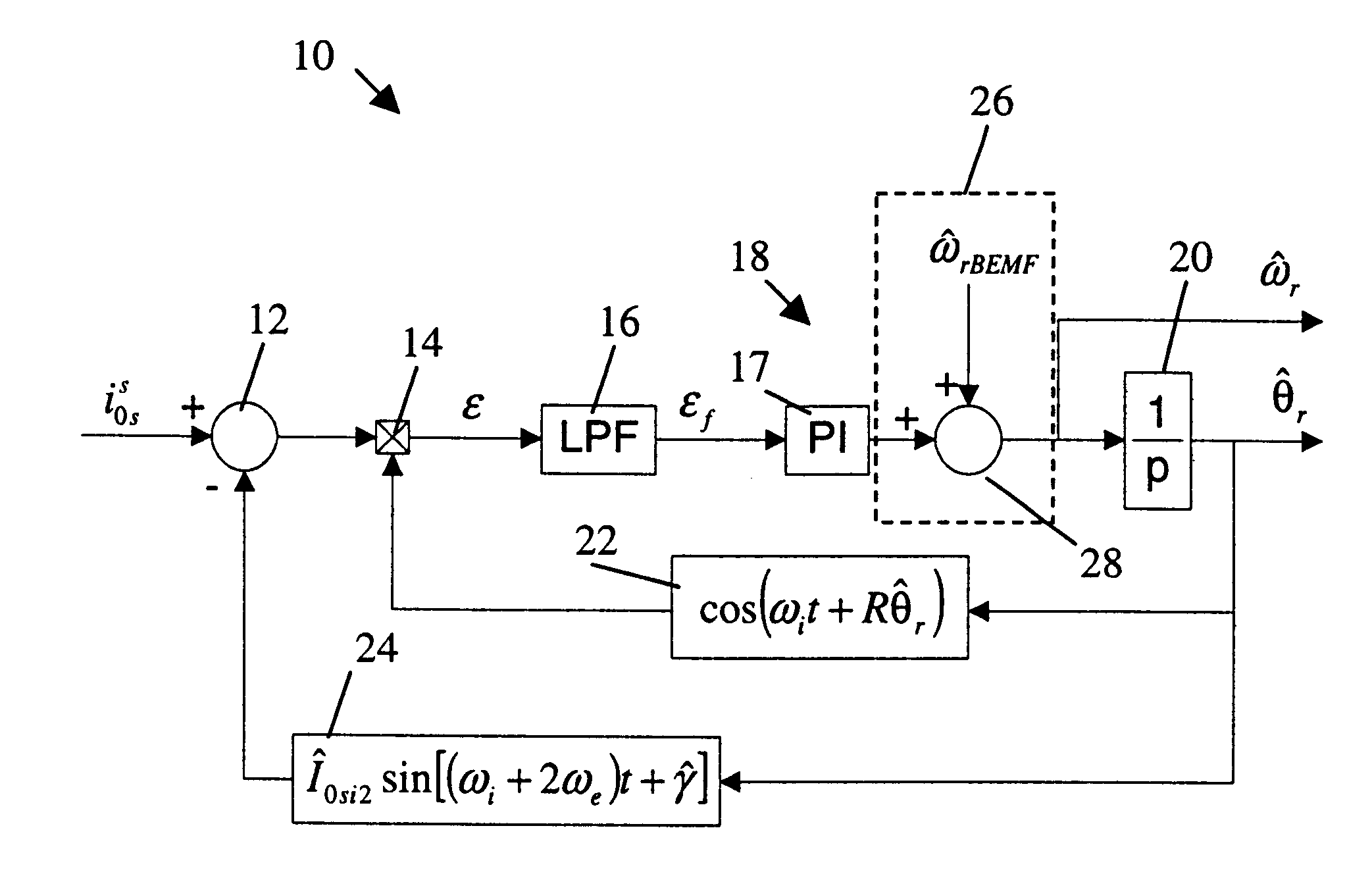
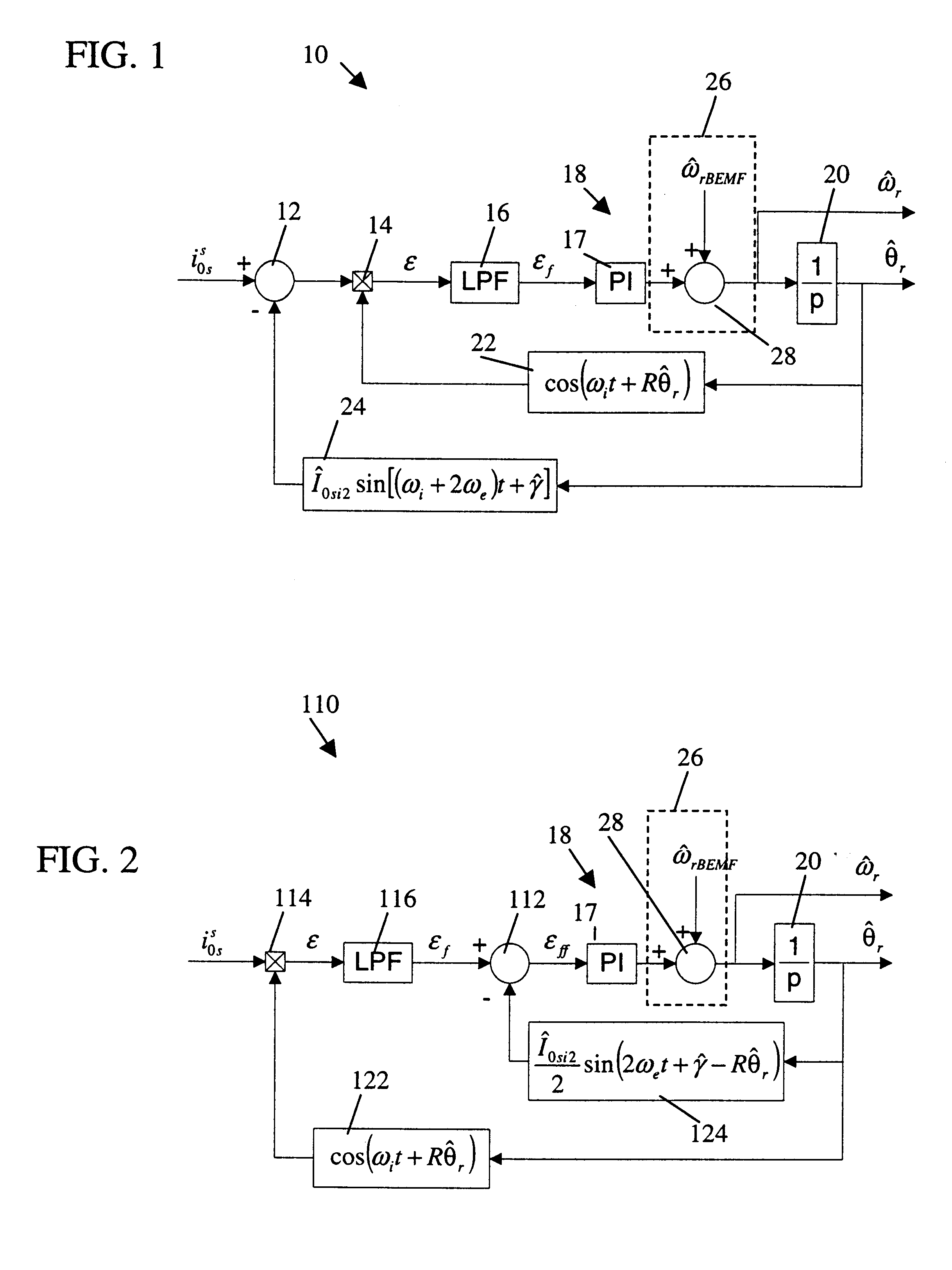
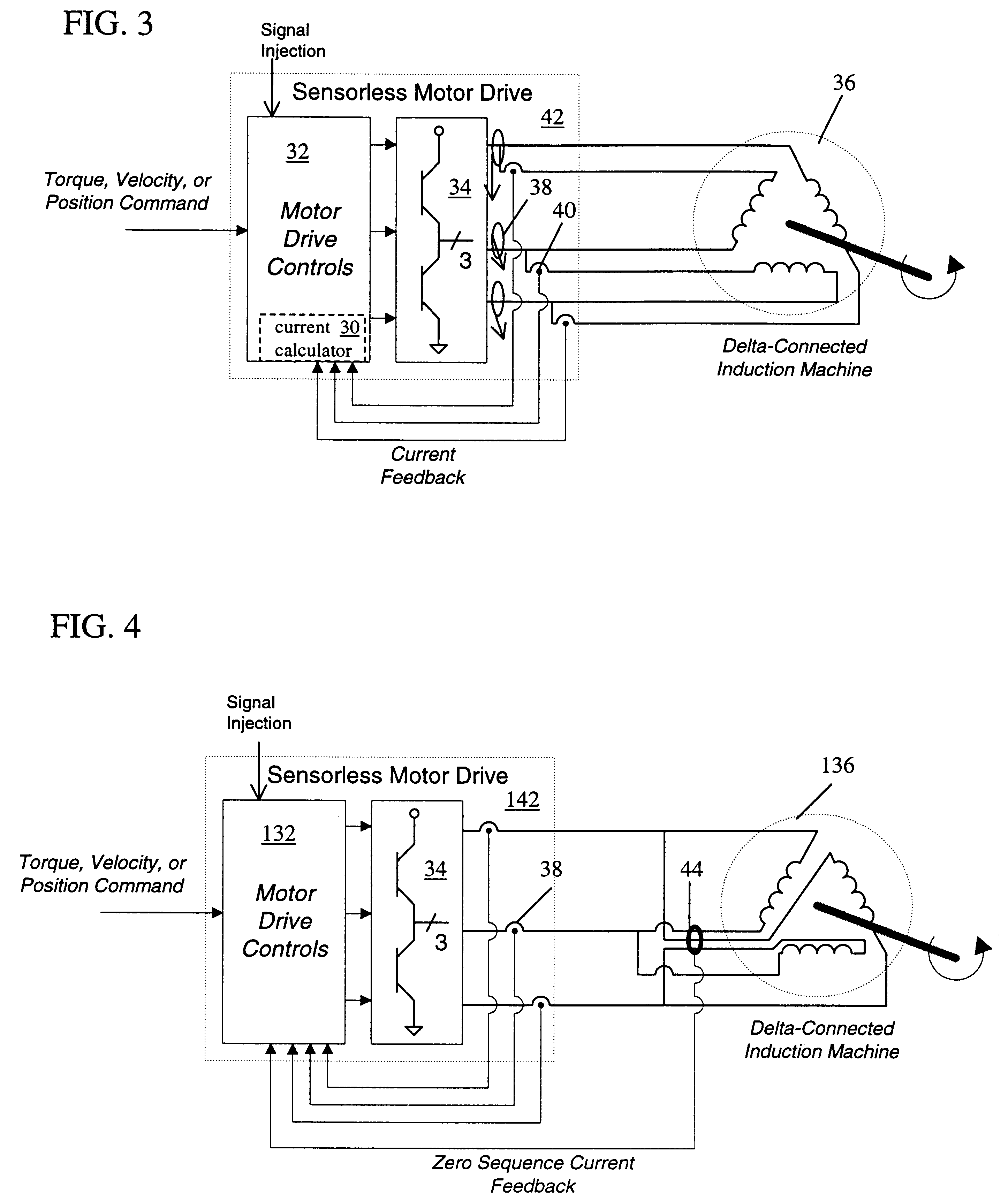
System and method for sensorless rotor tracking of induction machines
InactiveUS6388420B1Electronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlSequence signalFundamental frequency
A drive system comprises a rotor position and velocity tracker adapted to decouple fundamental frequency effects of a zero sequence signal of an induction machine from the zero sequence signal and to use a resulting error signal to estimate a position and a velocity of a rotor of the induction machine.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE AIR BRAKE TECH CORP
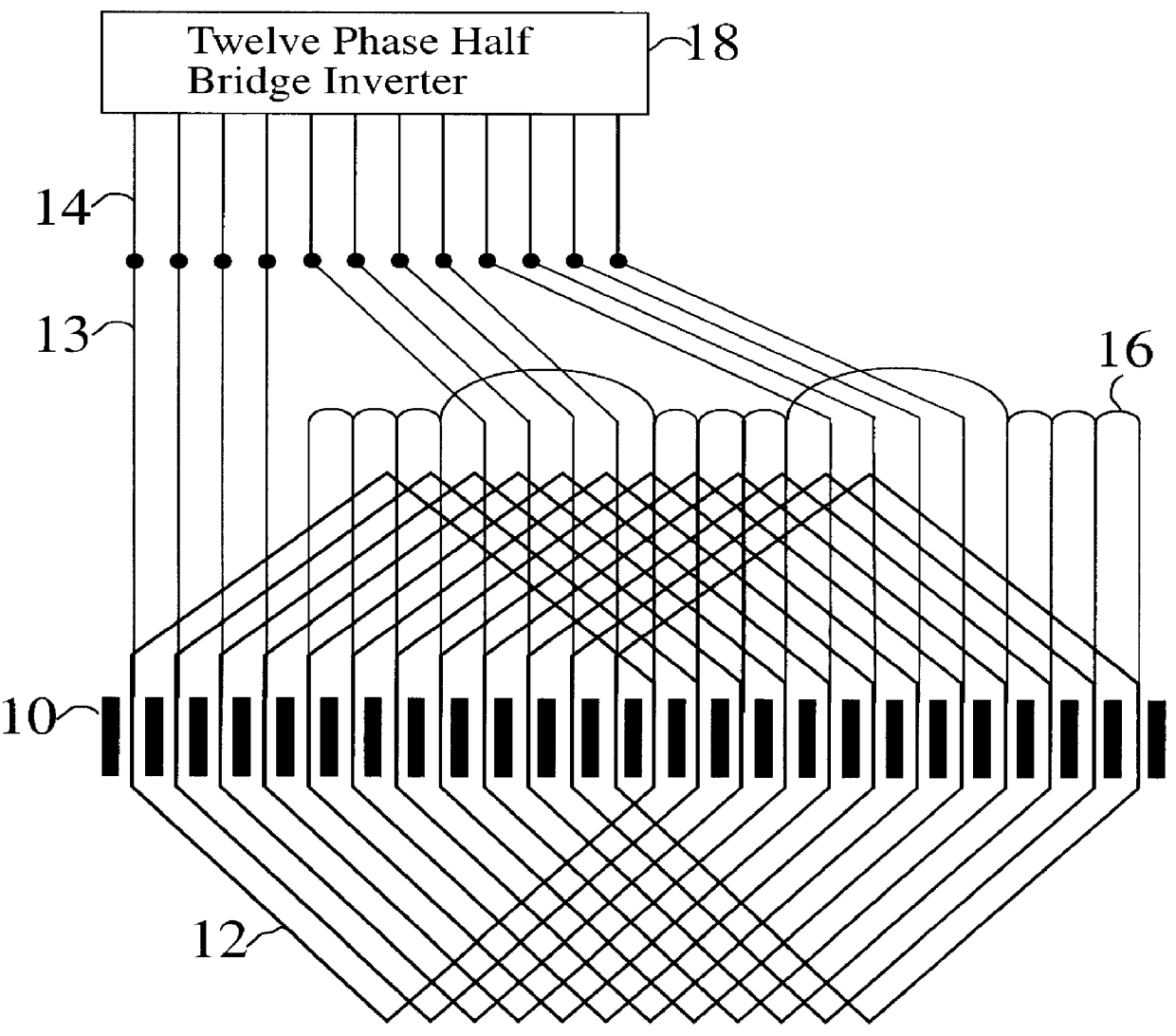
Polyphase induction electrical rotating machine
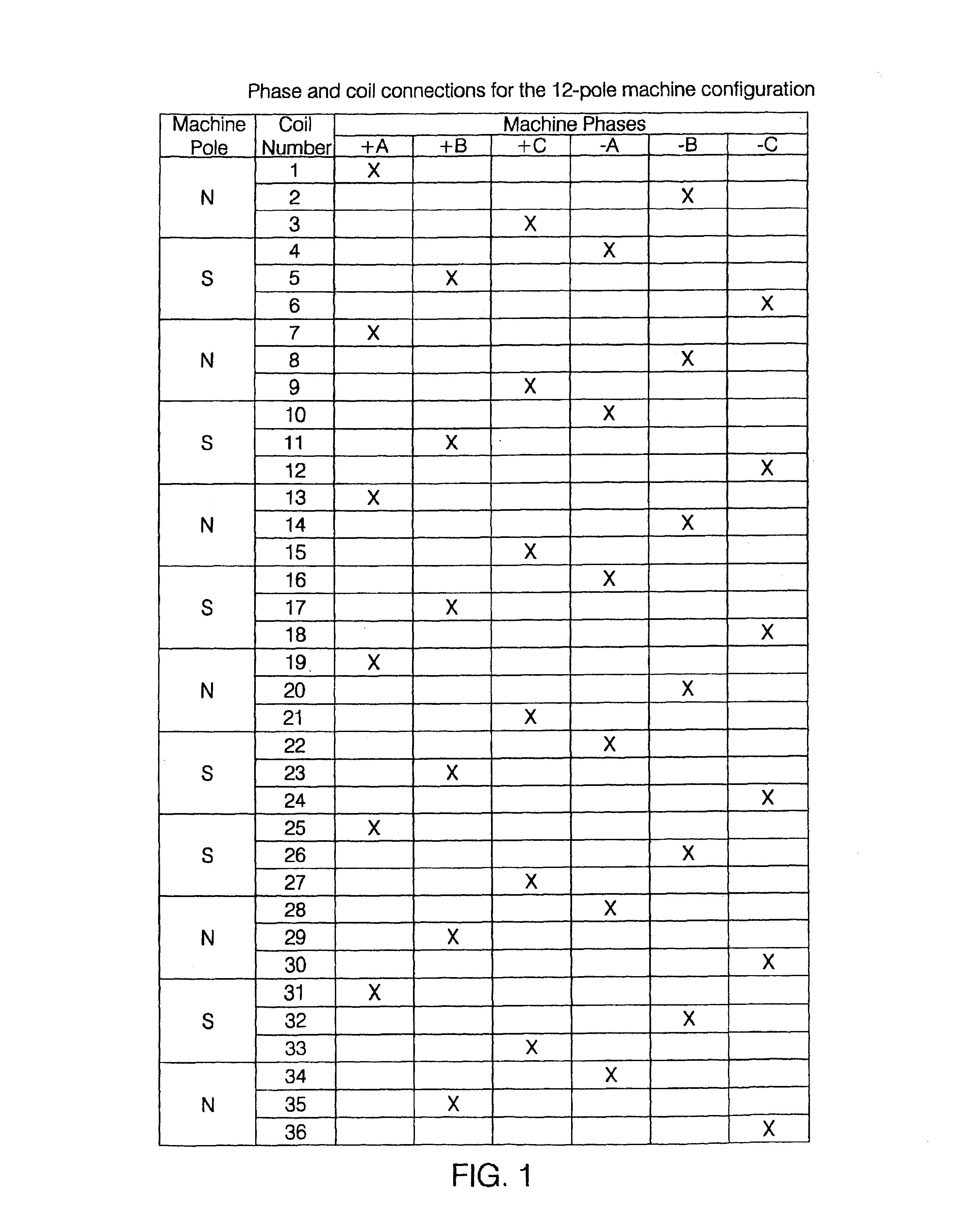
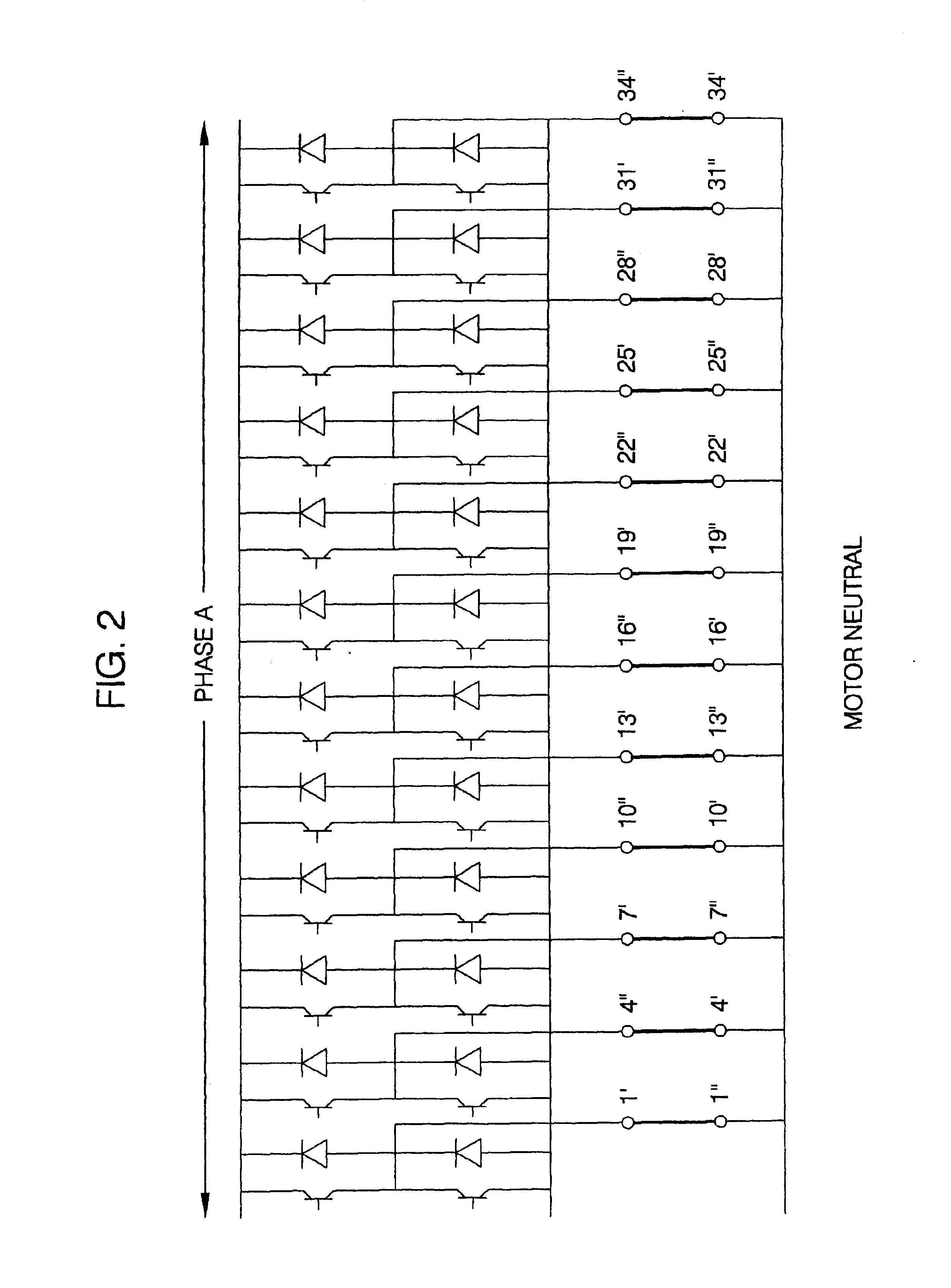
A polyphase induction machine operated by an inverter drive system. The machine is constructed with concentrated full span windings. Twelve or more phases are used to sufficiently cover the airgap region, in contrast to the conventional three phases using distributed and chorded windings. Substantial efficiency and starting torque benefits are thereby obtained.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
Rotating electrical machine and hybrid drive unit provided with the same
InactiveUS20070090707A1Loss can be reducedReduce lossesDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesAsynchronous induction motorsConductor CoilMagnet
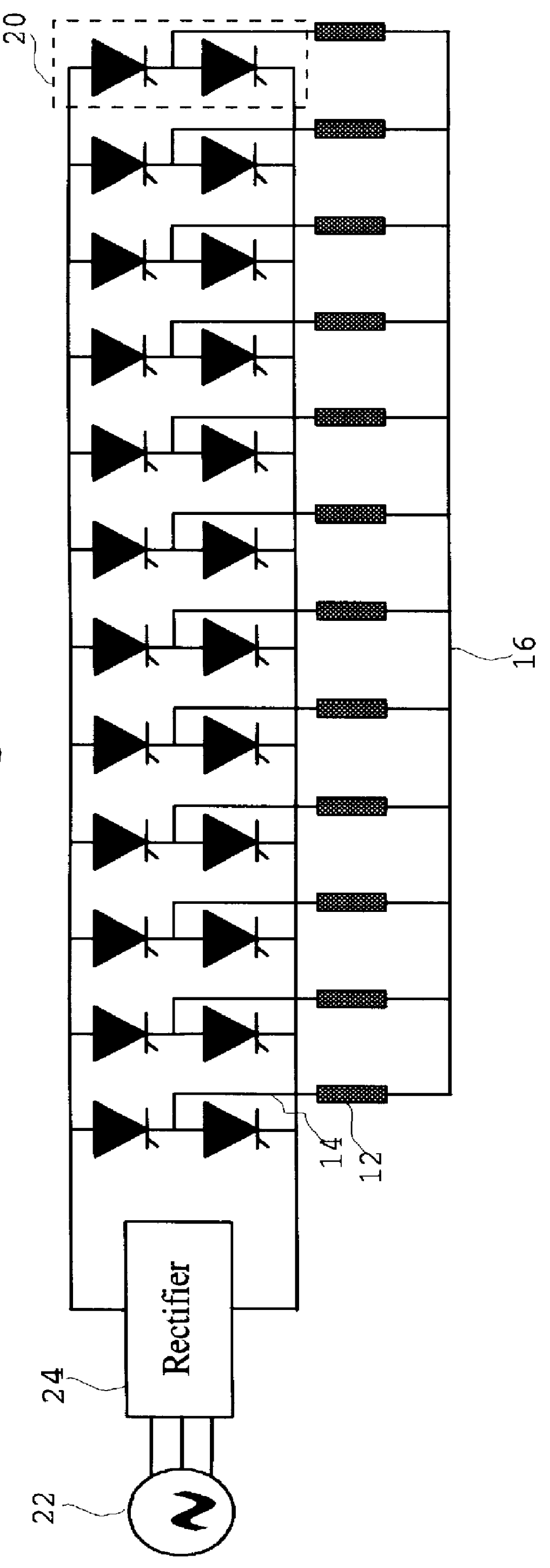
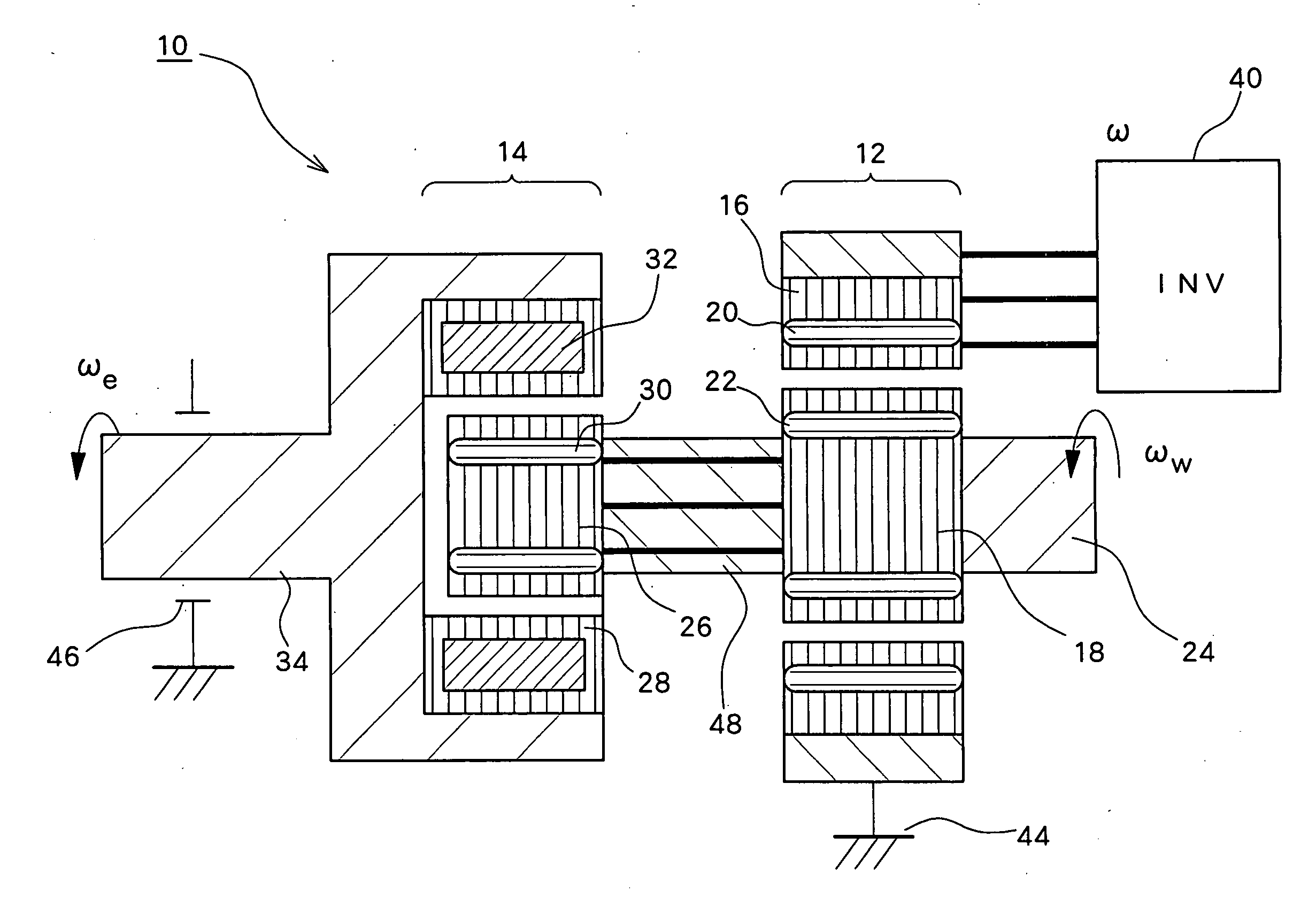
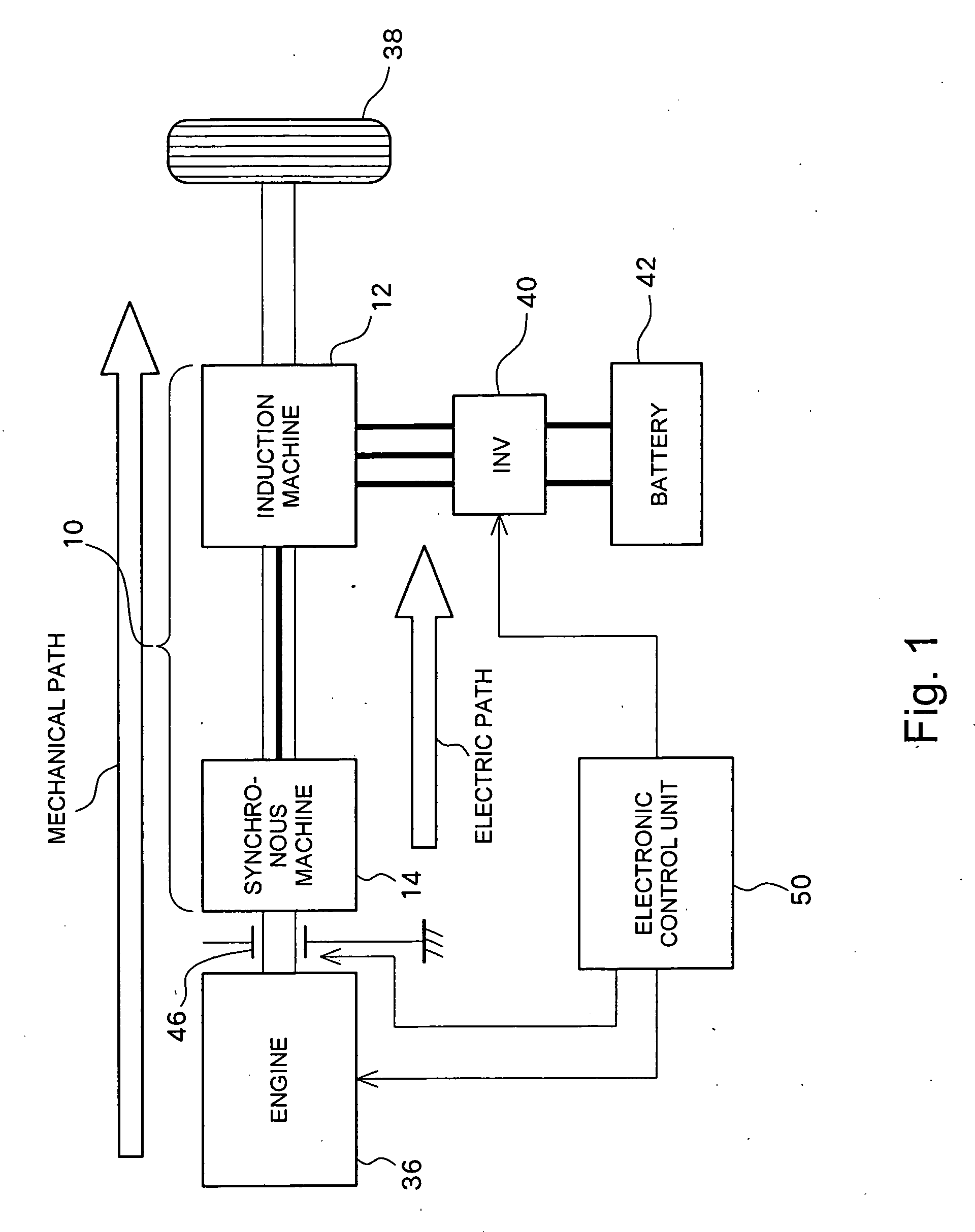
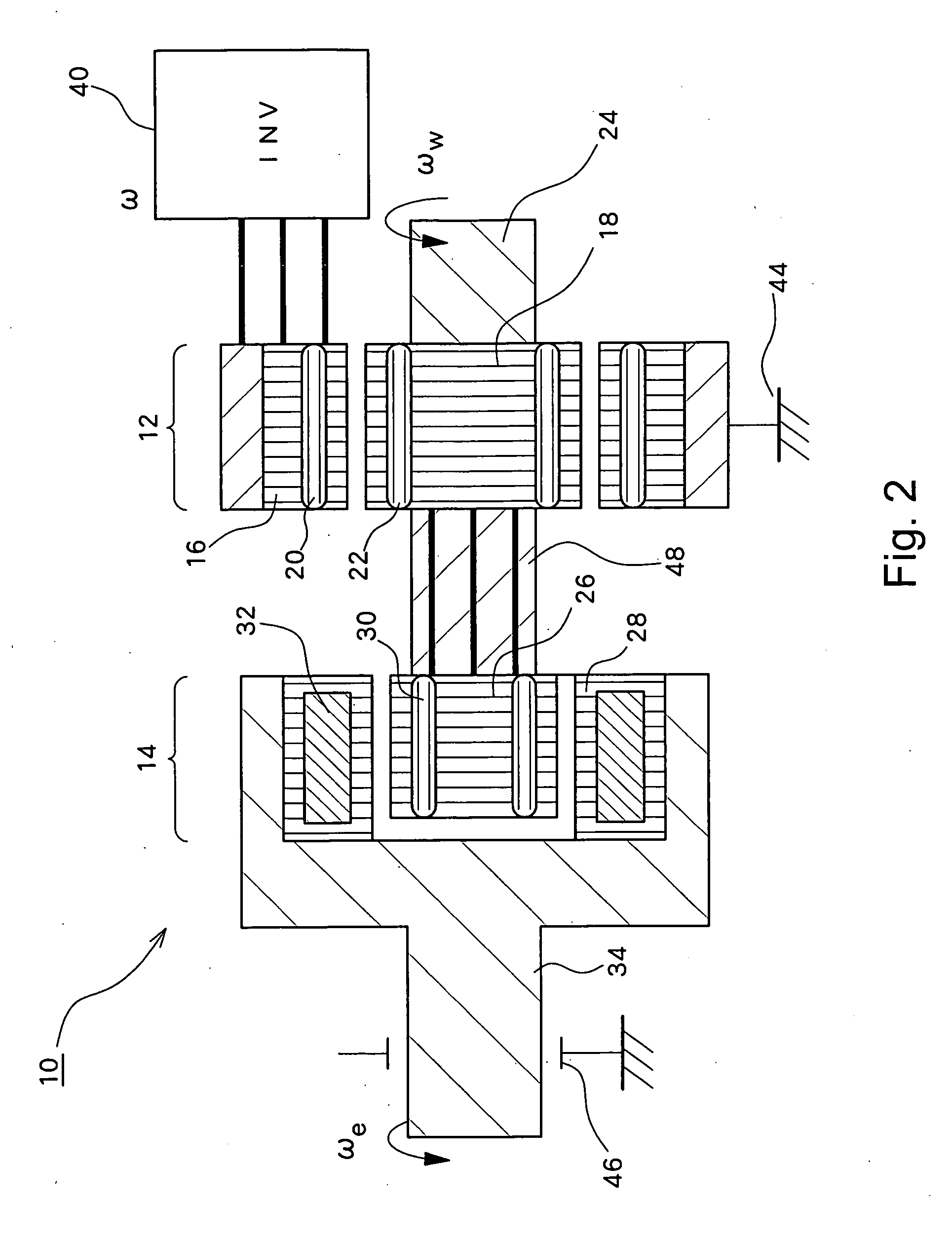
An induction machine includes a stator provided with stator windings and a first rotor provided with first rotor windings, and generates an induction current in one of the stator windings and the first rotor windings by a rotating magnetic field generated in the other of the stator windings and the first rotor windings. A synchronous machine includes a second rotor which is provided with second rotor windings connected to the first rotor windings and coupled to the first rotor, and a third rotor which is provided with permanent magnets and rotatable independent of the second rotor, and a torque acts between the second rotor and the third rotor due to the interaction between the rotating magnetic field generated in the second rotor windings and the field flux generated in the permanent magnets.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
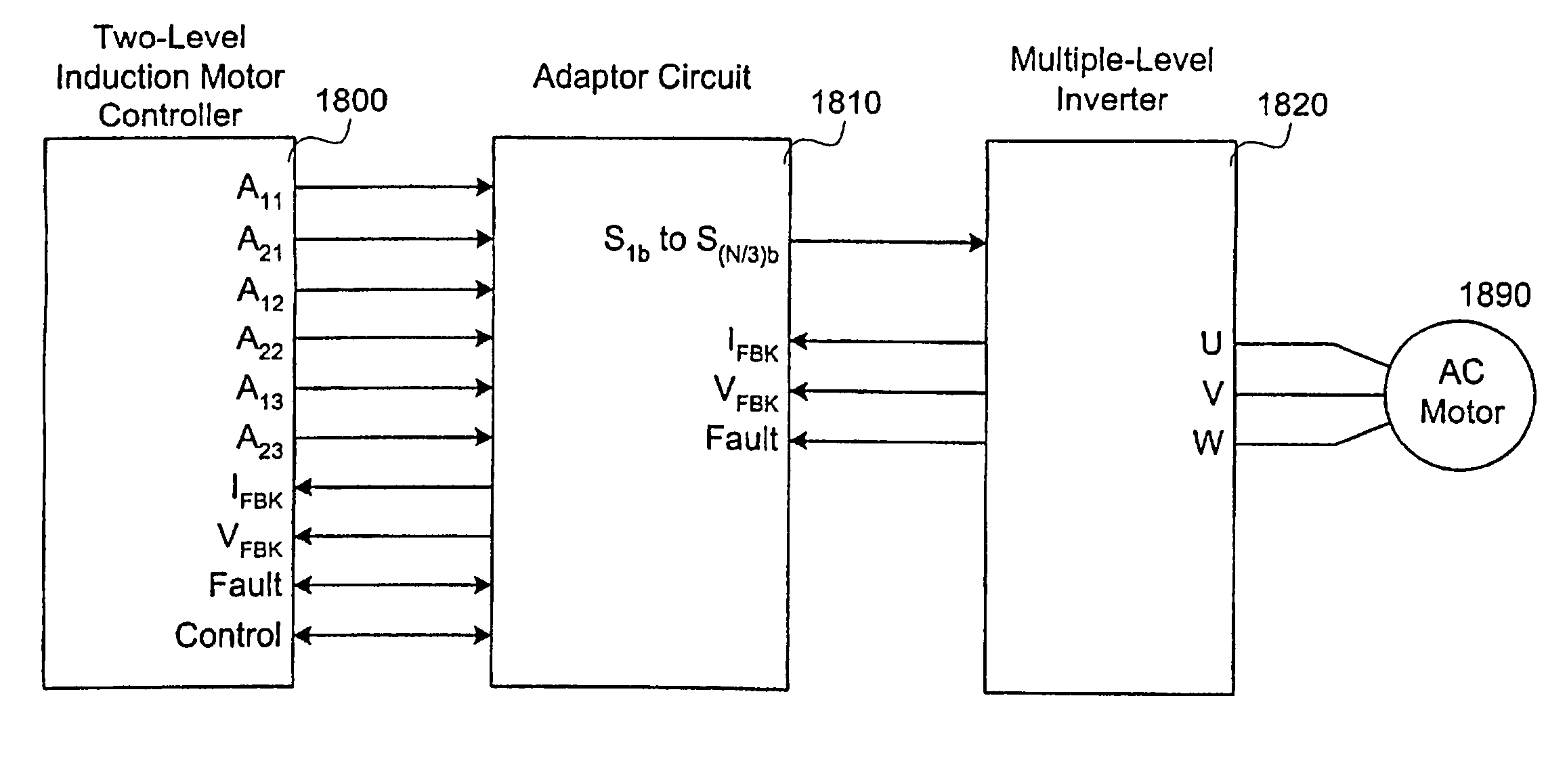
Low voltage, two-level, six-pulse induction motor controller driving a medium-to-high voltage, three-or-more-level AC drive inverter bridge
A method and circuit enabling off-the-shelf controllers designed for use with a two-level AC drive inverter bridge (1920) to drive inverter bridges with three-or-more levels. Signals from an ordinary induction motor controller or a two-level induction motor controller (2200) are used to drive the twelve-or-more switches of a three-or-more level inverter bridge (1920), as are used in medium-and-high voltage applications. The proper sequence and timing of switching for the three-or-more-level inverter bridge is based in-part upon either the output of the six pulse-width modulators, or the output of the flux and torque control device, or the voltage control device (2210), of the two-level controller (2200).
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD +1
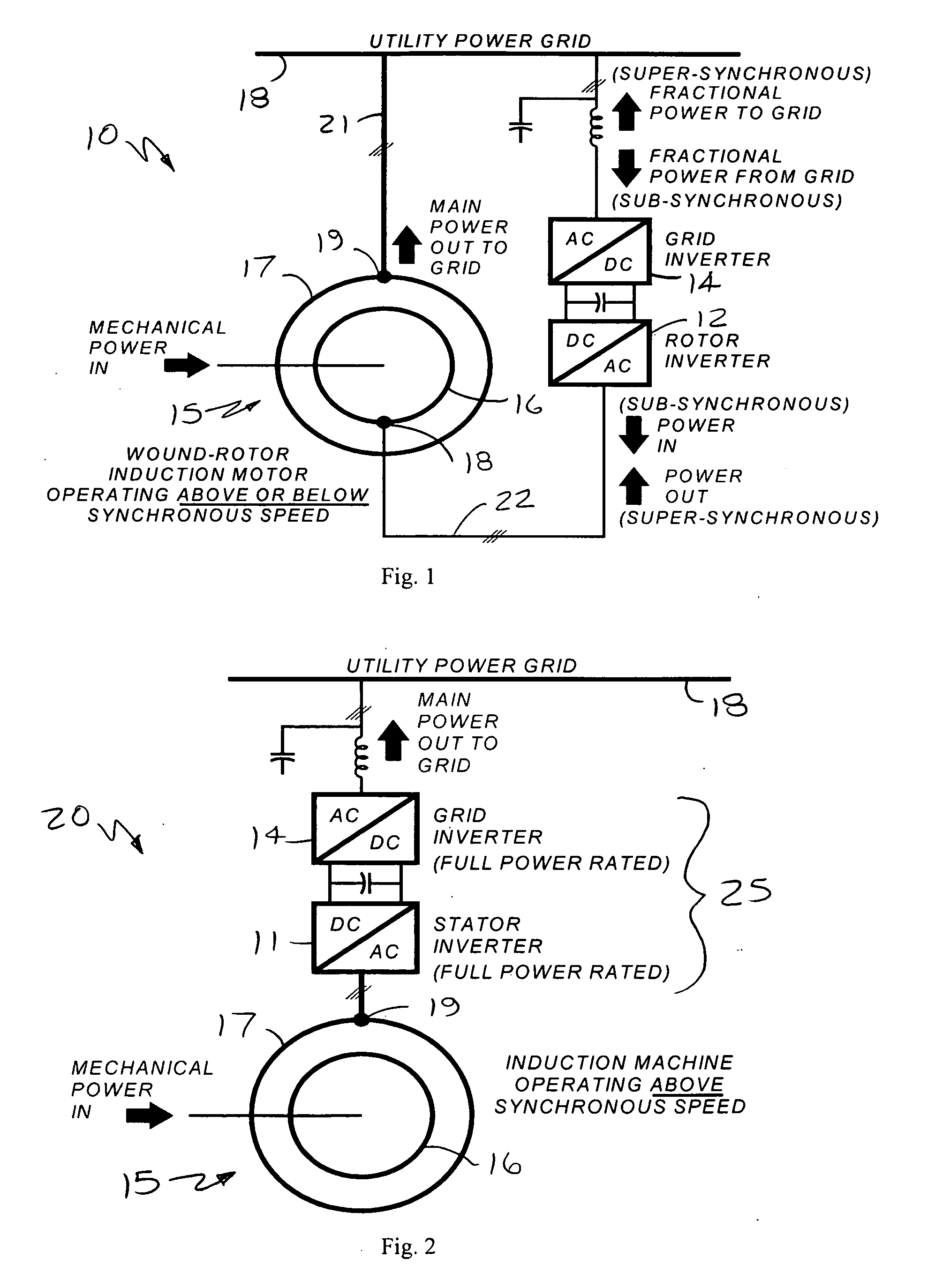
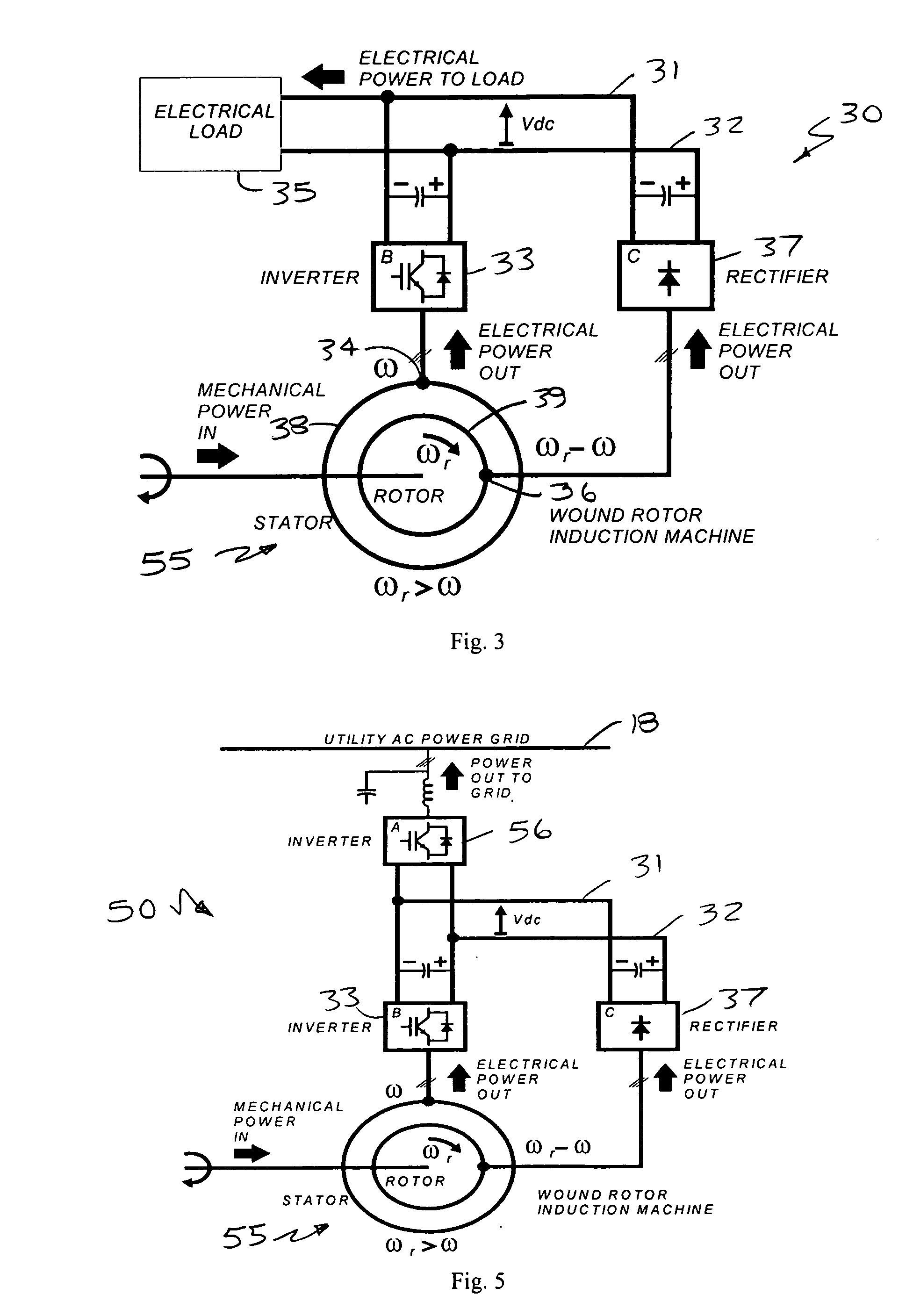
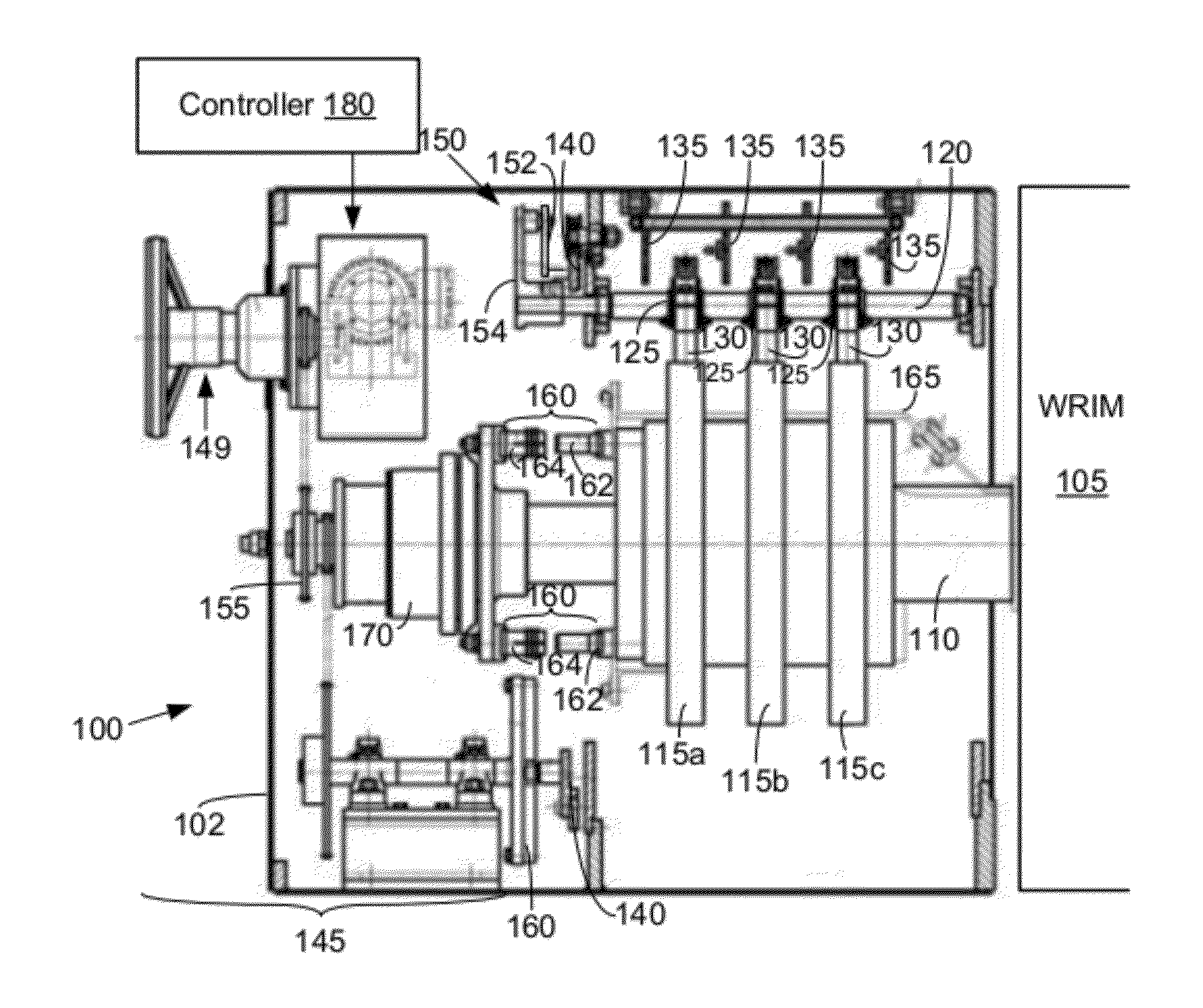
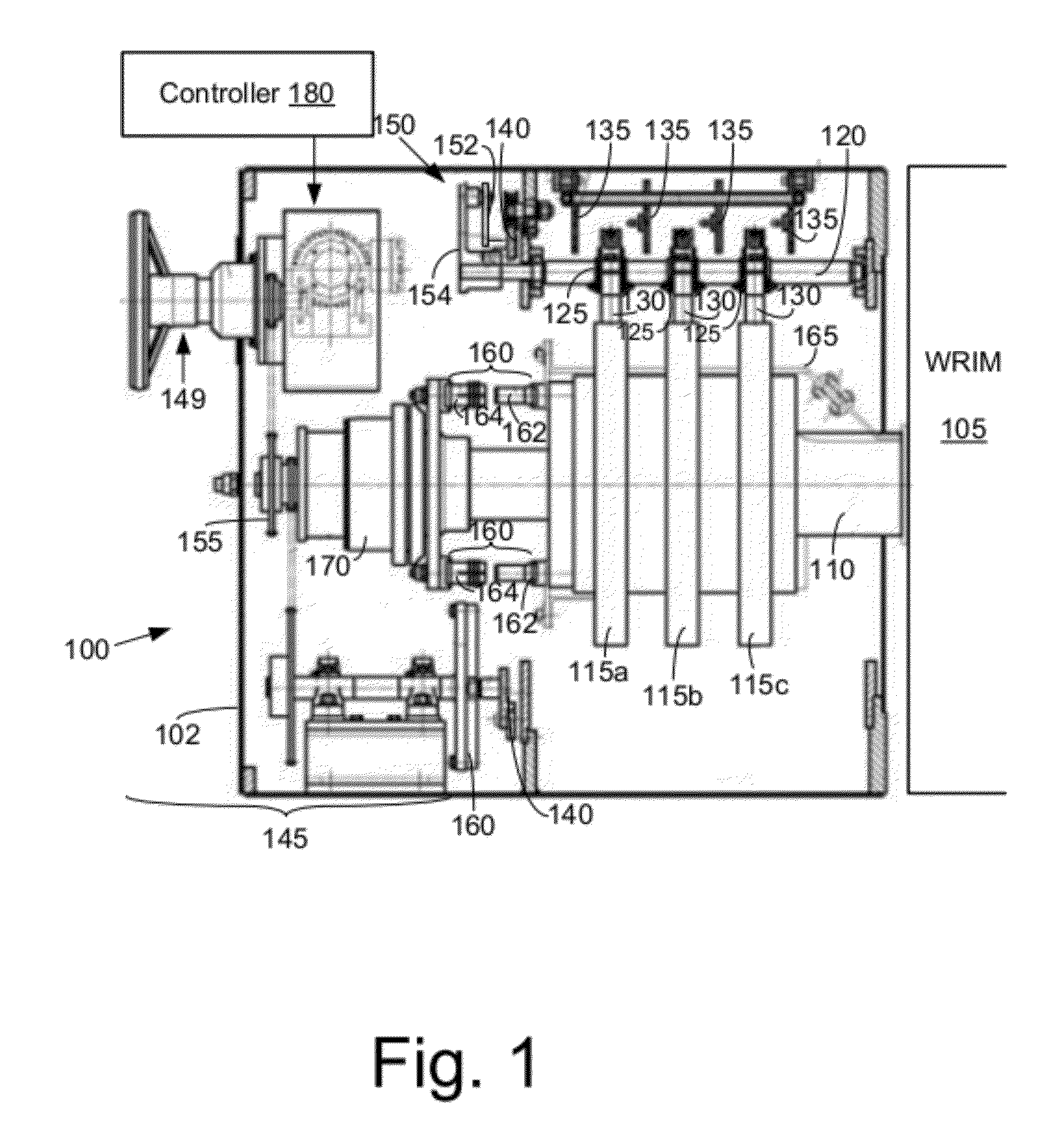
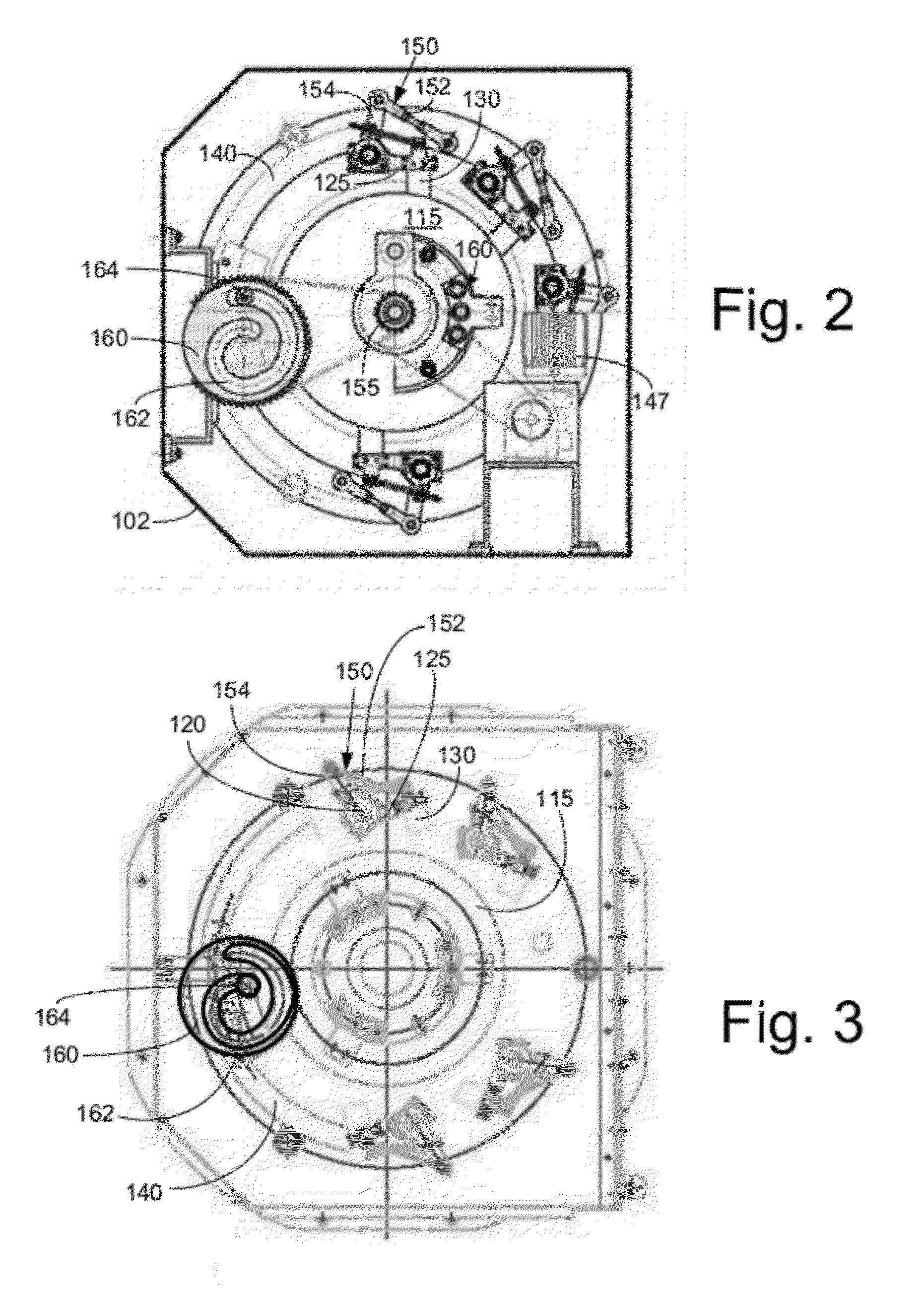
Slip-controlled, wound-rotor induction machine for wind turbine and other applications
InactiveUS20070063677A1Emergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlConstant frequencyEngineering
A system and method for providing constant-frequency electrical power from variable-speed mechanical power are disclosed. The system includes a wound-rotor induction machine generator (WRIMG), a first power converter, e.g., an inverter or a bridge rectifier, that provides power from the stator assembly of the WRIMG to the load, and a second power converter, e.g., an inverter or a bridge rectifier, that provides power from the rotor assembly of the WRIMG to the load. A controller controls the output stator-current based on comparisons between measured DC load bus data and a reference DC load bus voltage value, measured machine shaft angular position and reference rotor frequency data, and measured stator-current data that is fed-back to the stator-current controller by the power converter device(s).
Owner:PERFECT GALAXY INT
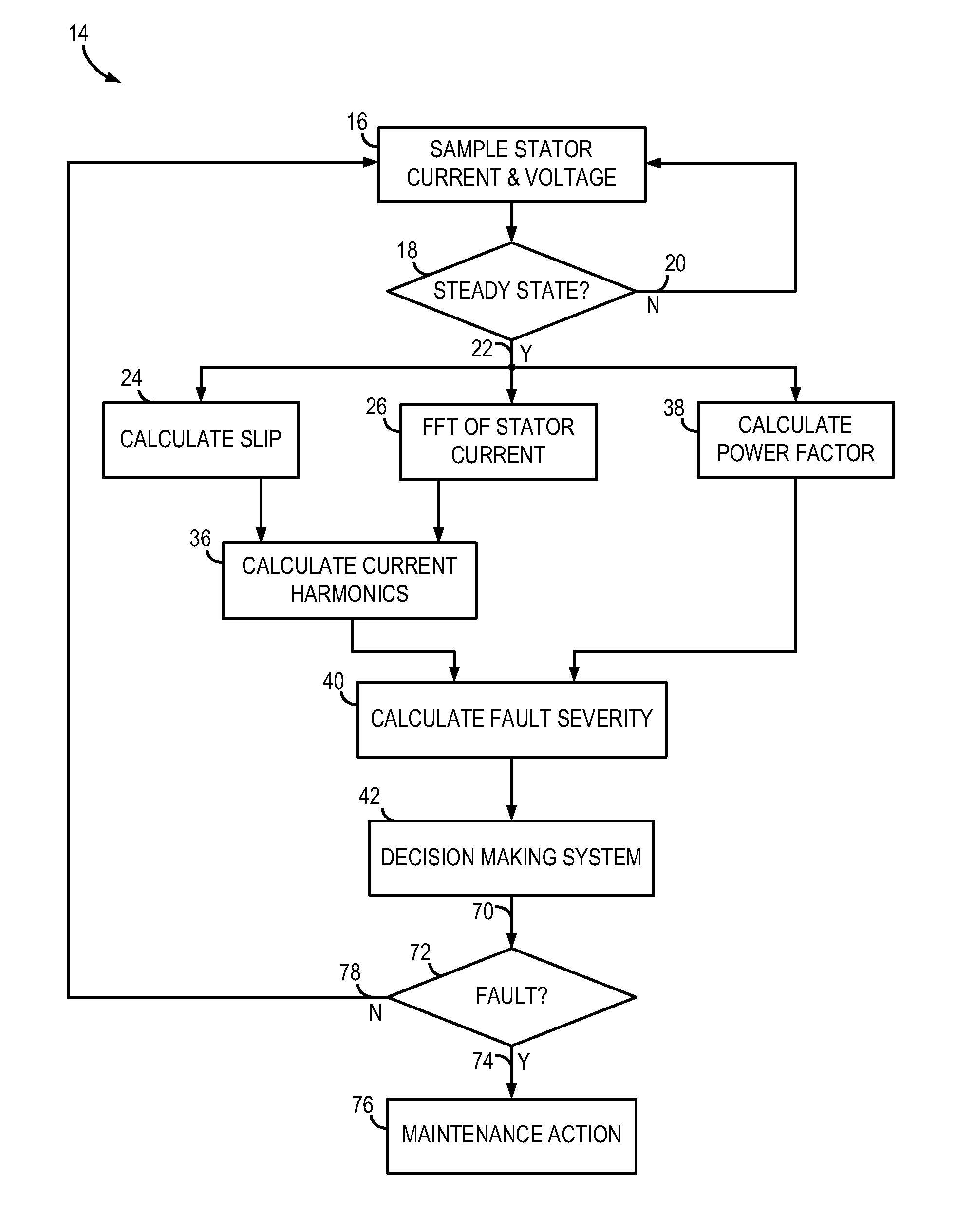
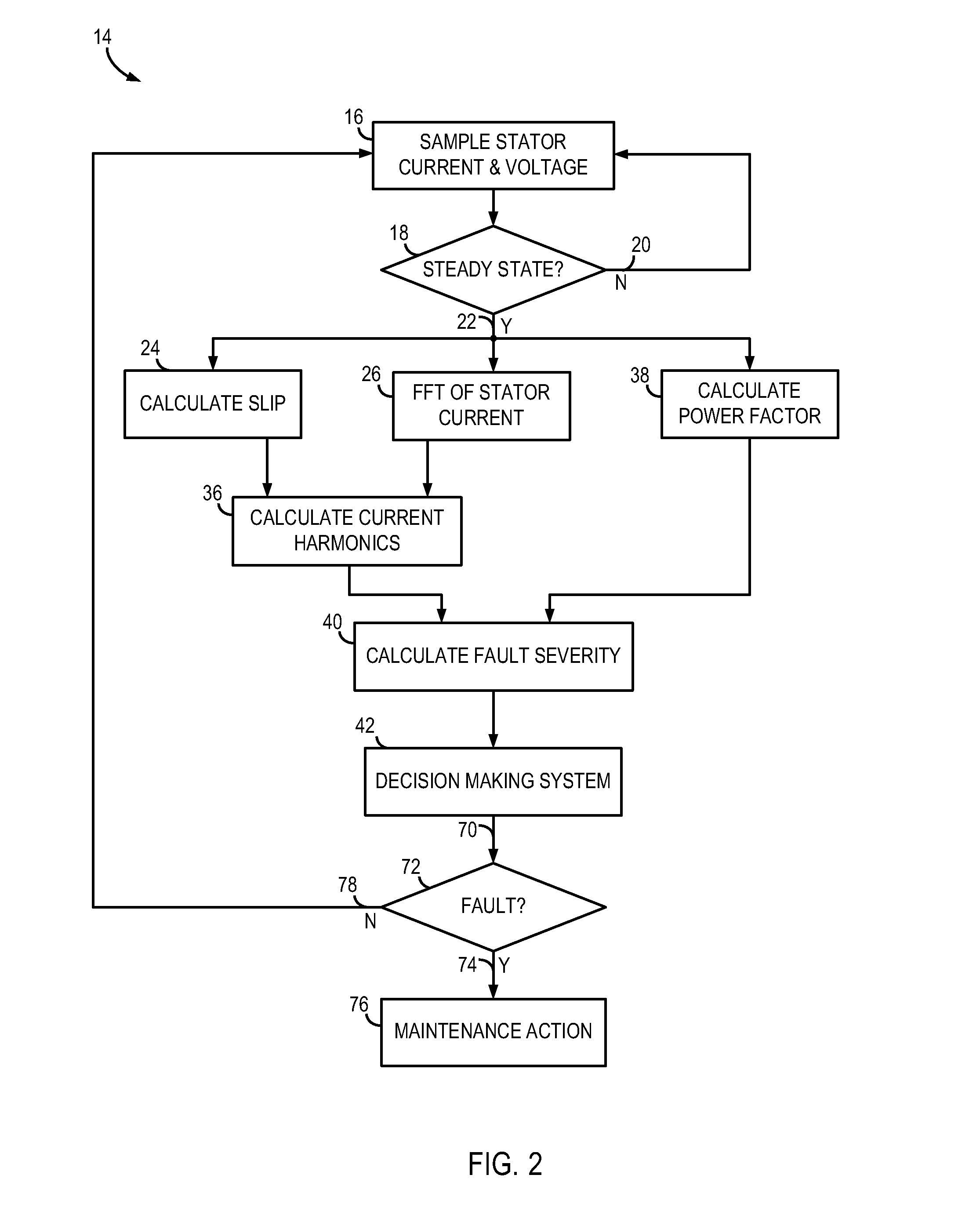
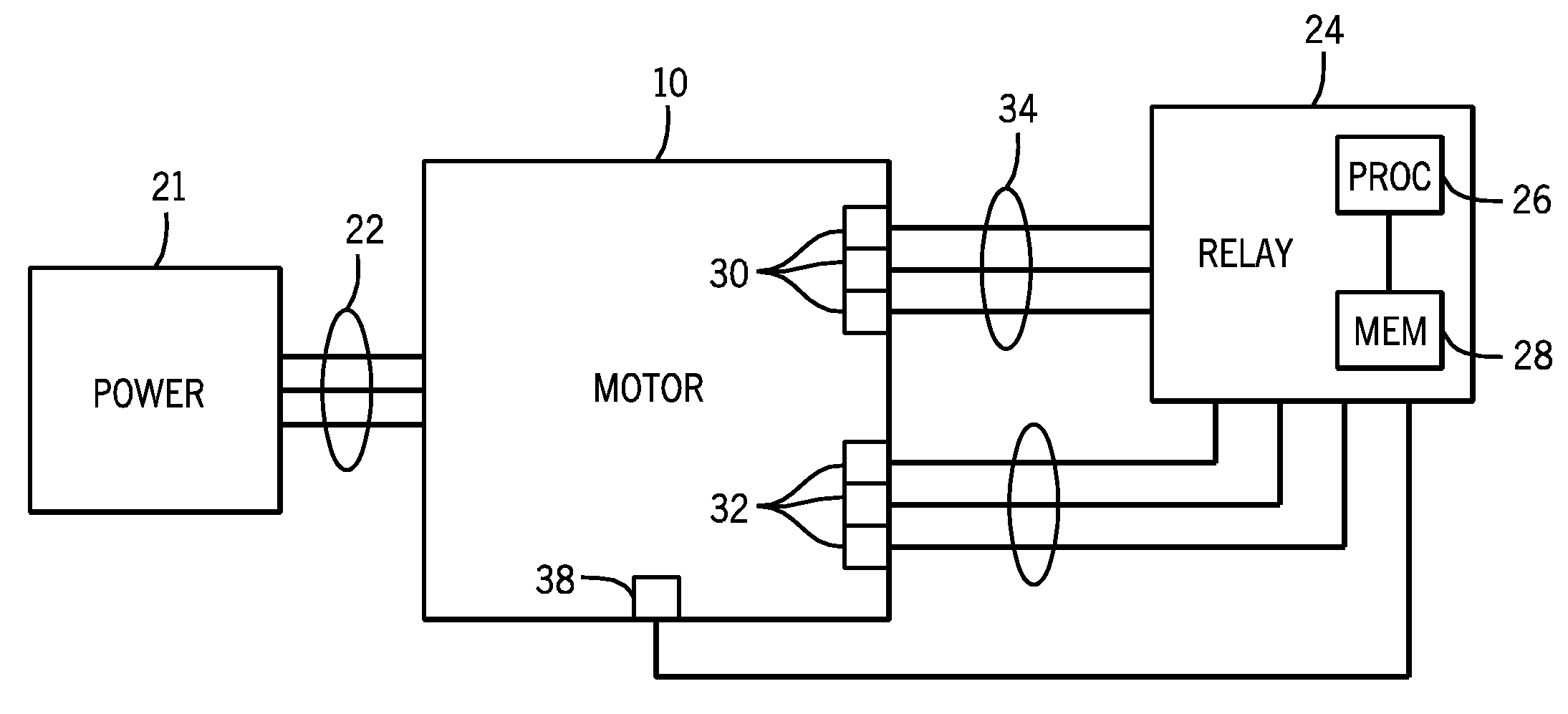
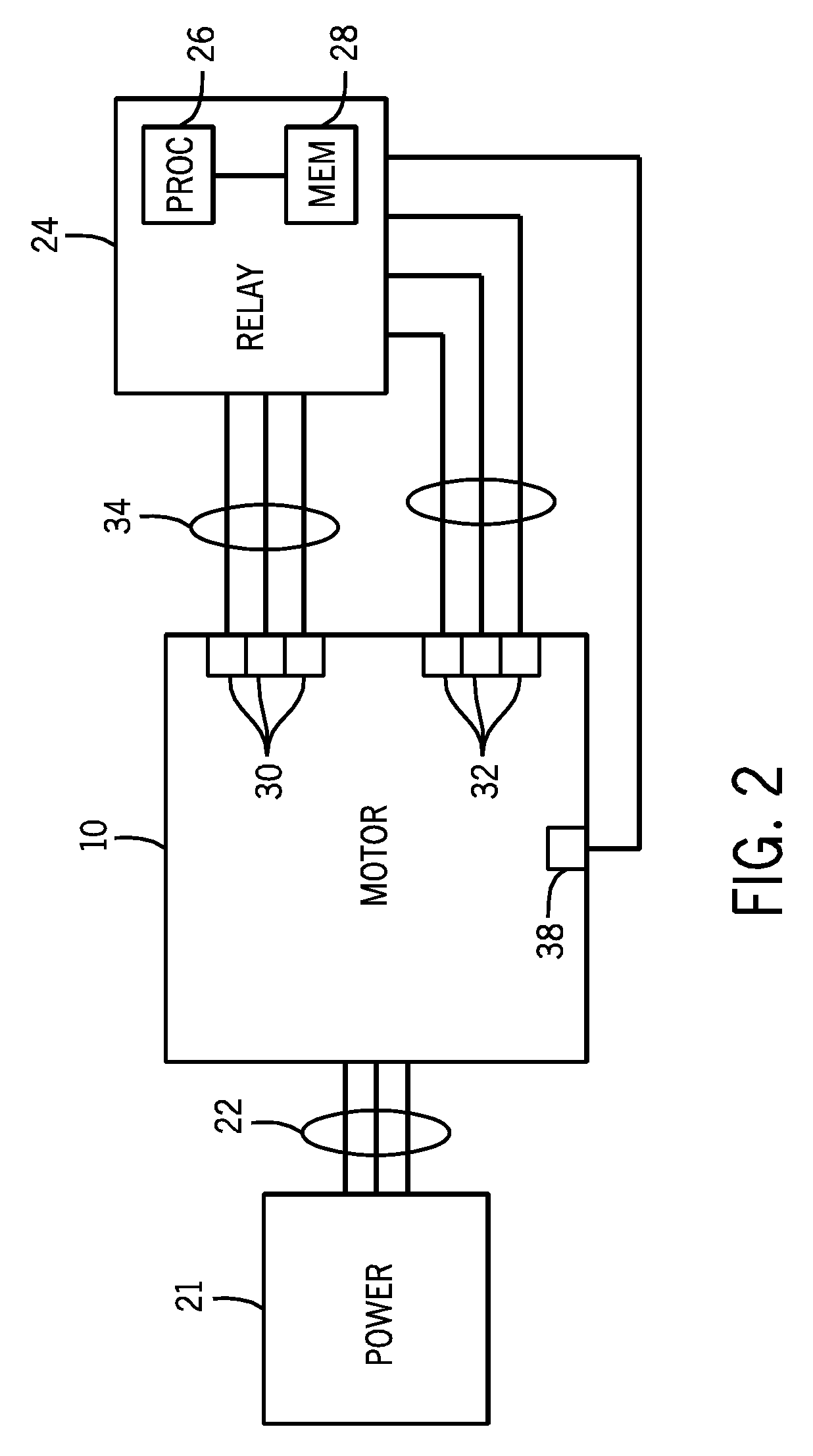
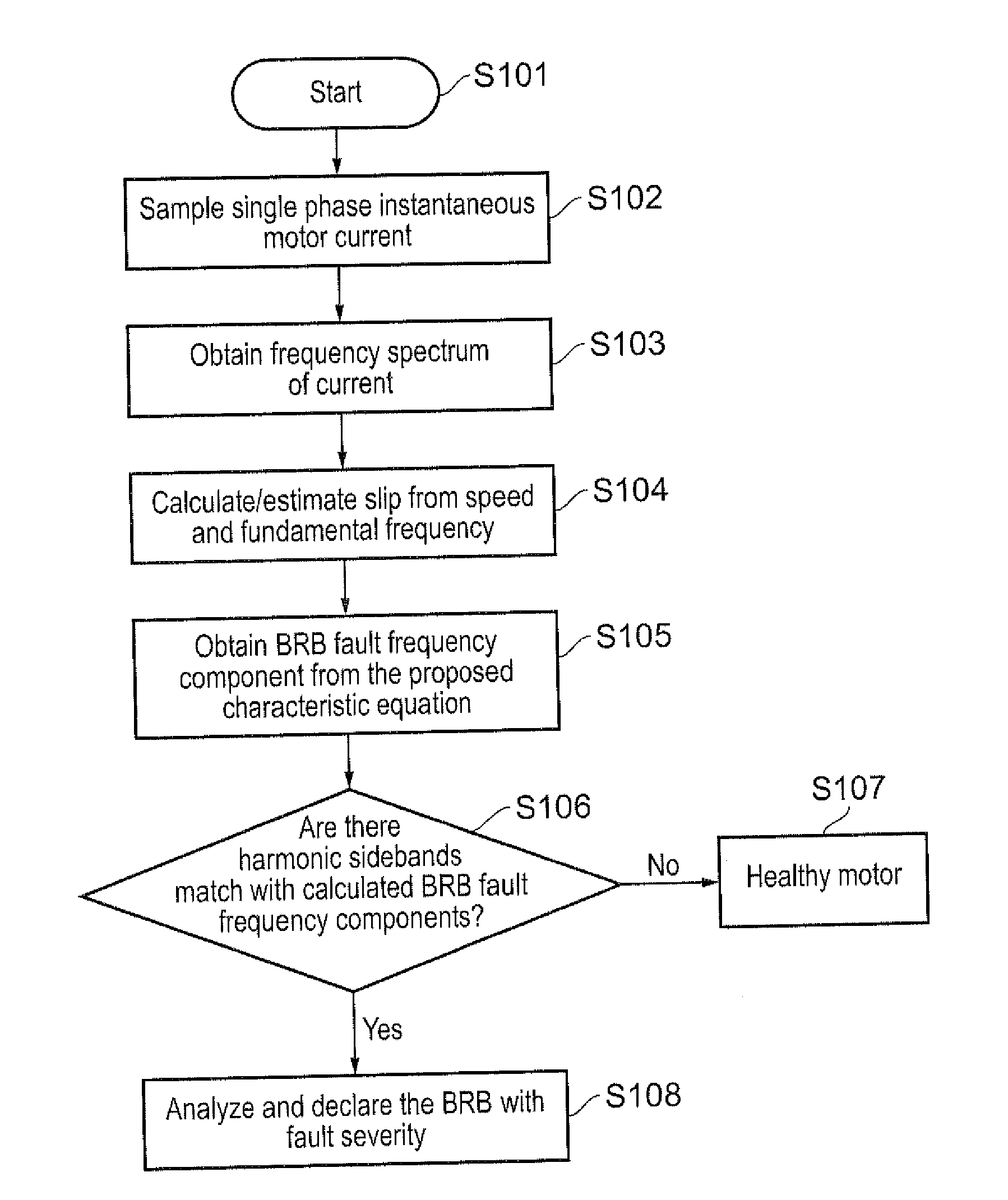
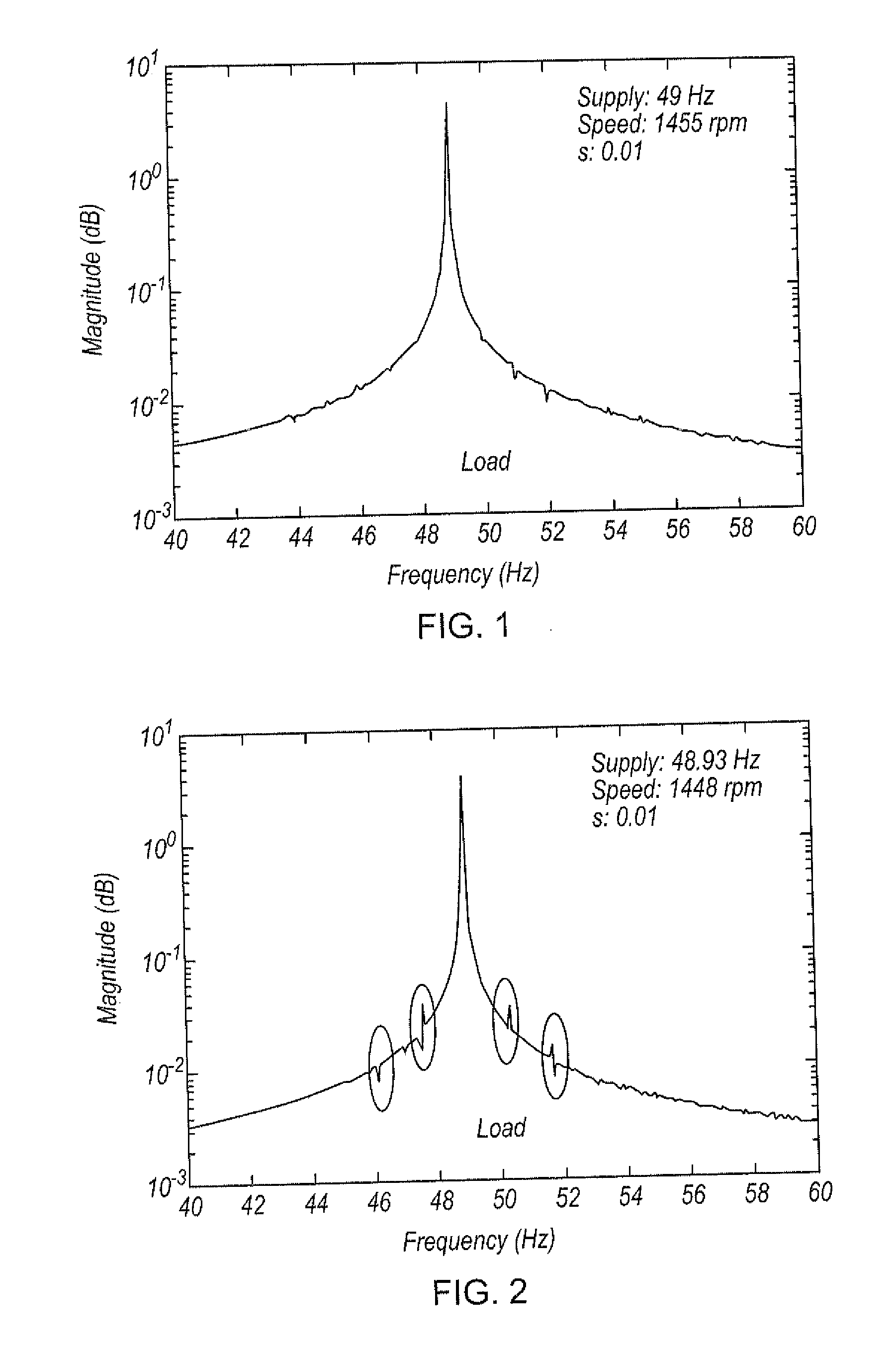
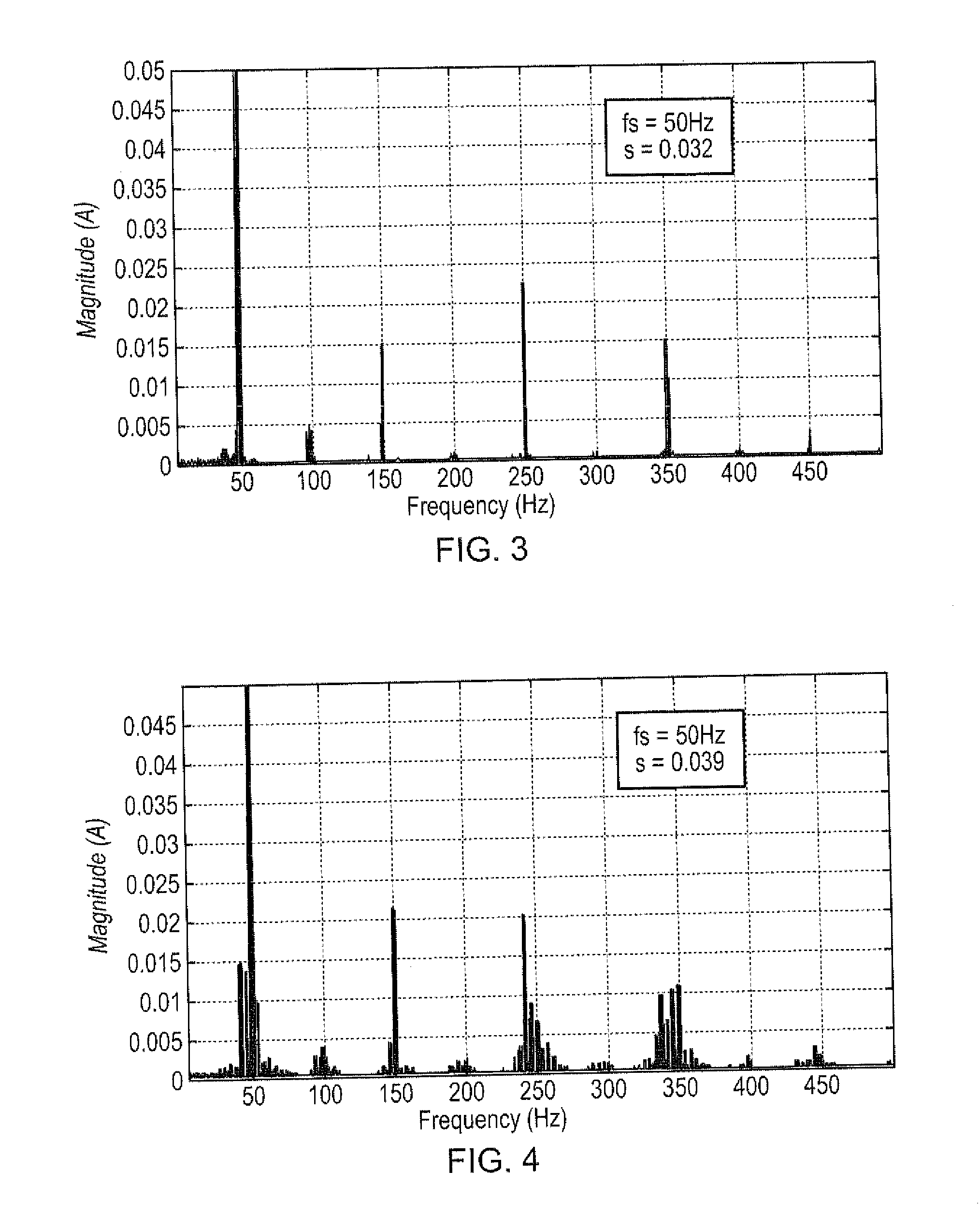
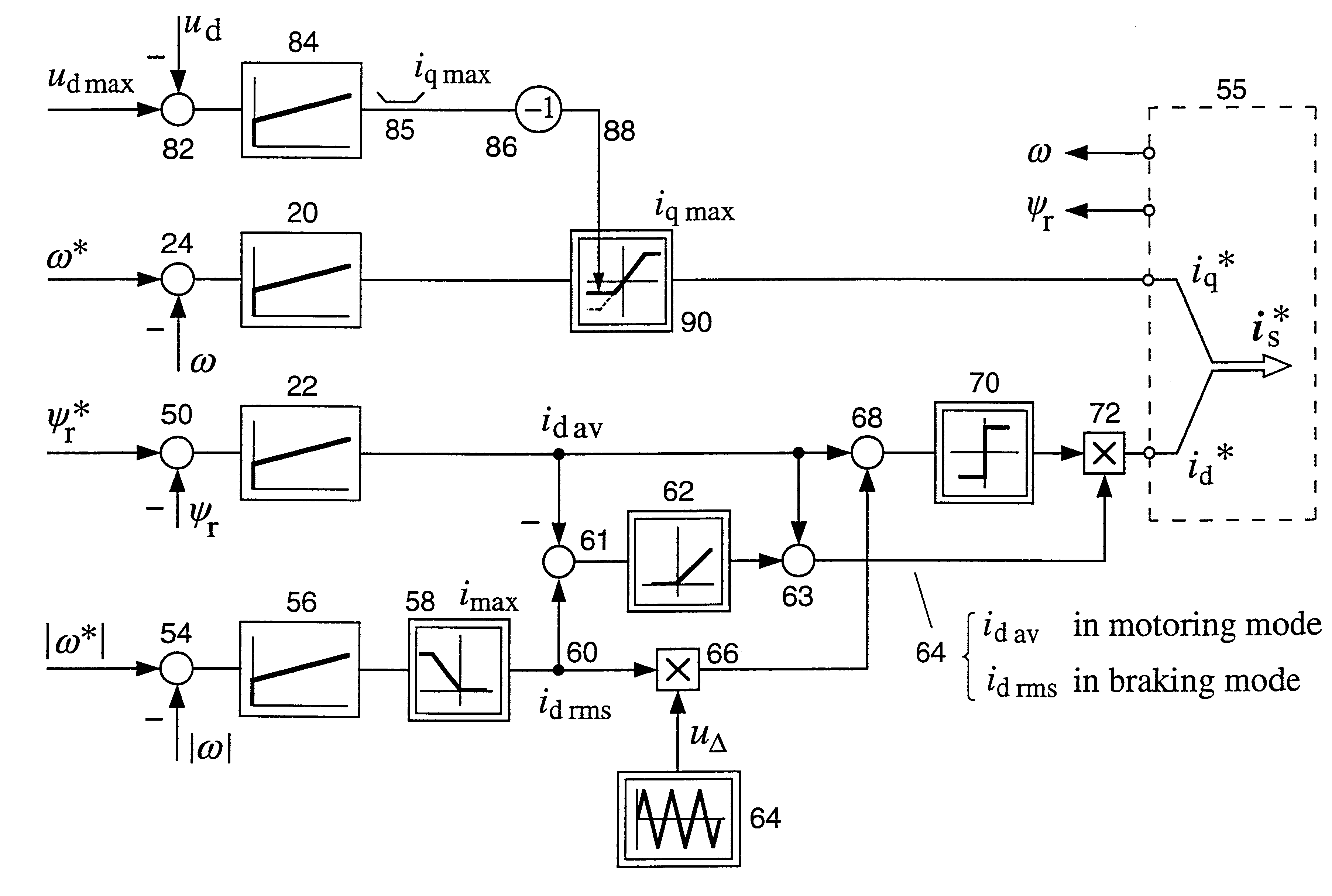
System and method for detecting fault in an AC machine
A system and method for detecting a rotor fault condition in an AC induction machine is disclosed. The system includes a processor programmed to receive voltage and current data from an AC induction machine, generate a current frequency spectrum from the current data, and identify rotor-fault related harmonics in the current frequency spectrum. The processor is also programmed to calculate a fault severity indicator using the voltage and current data, identified rotor-fault related harmonics, and motor specifications, analyze the fault severity indicator to determine a possibility of rotor fault. The processor generates an alert based on the possibility of rotor fault.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
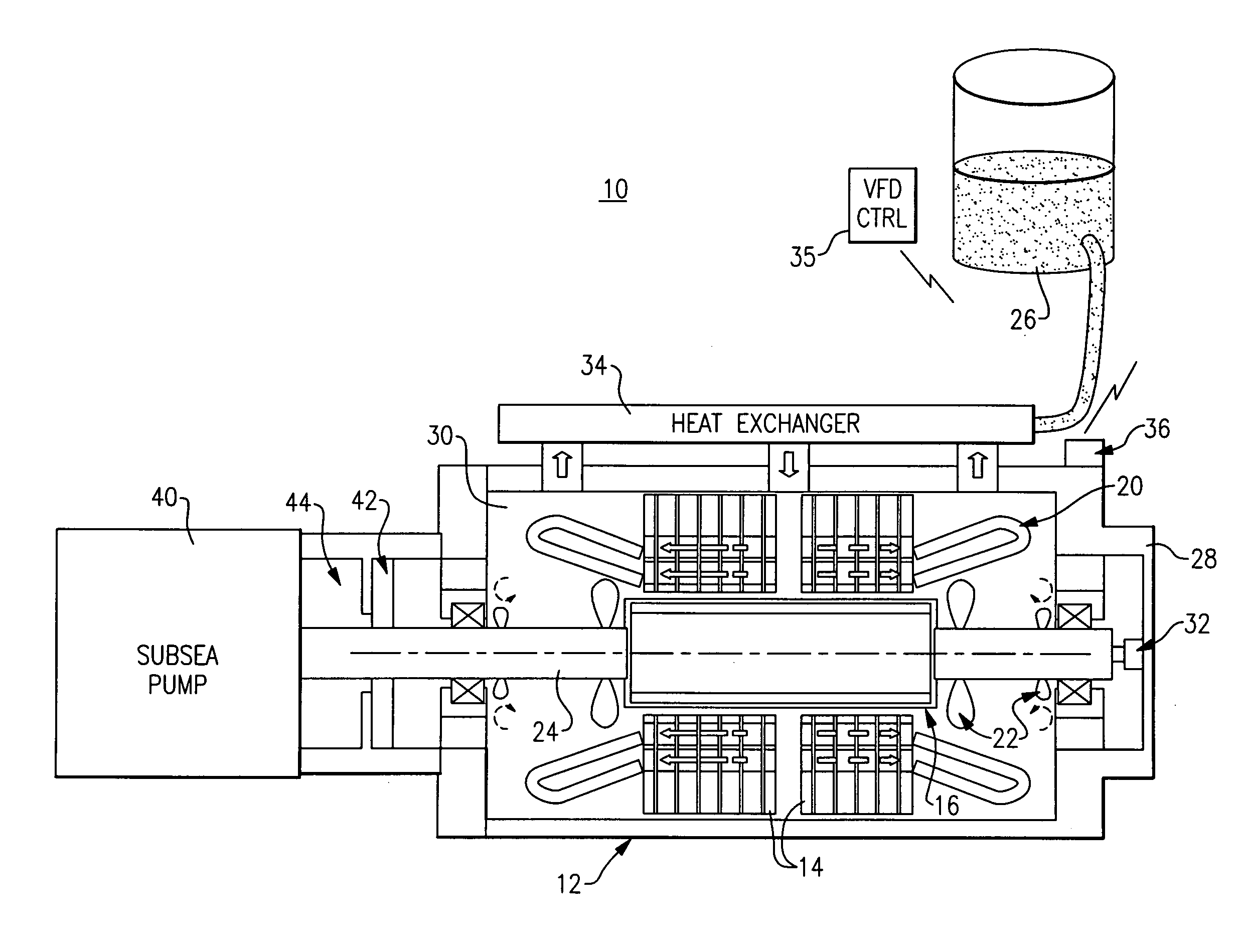
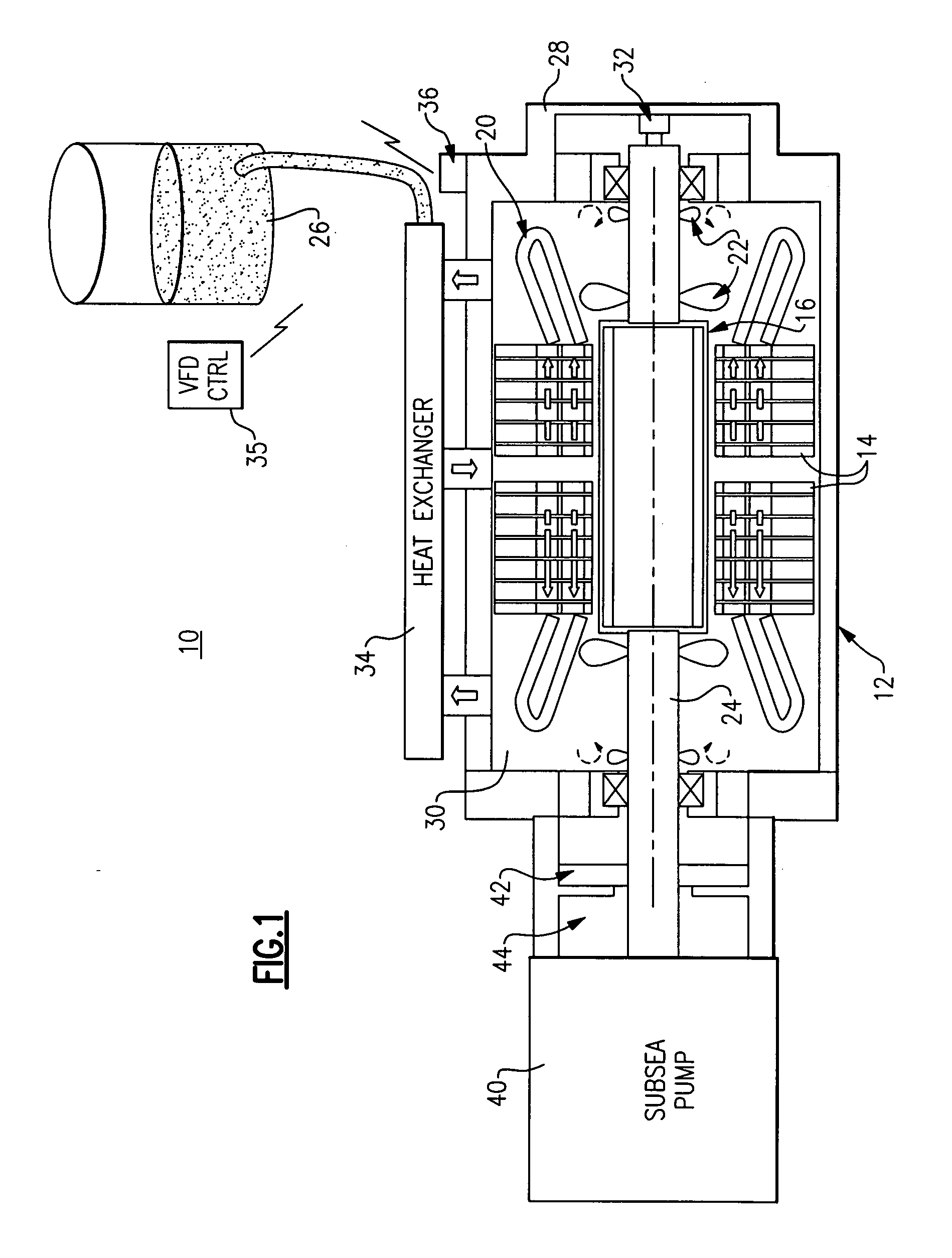
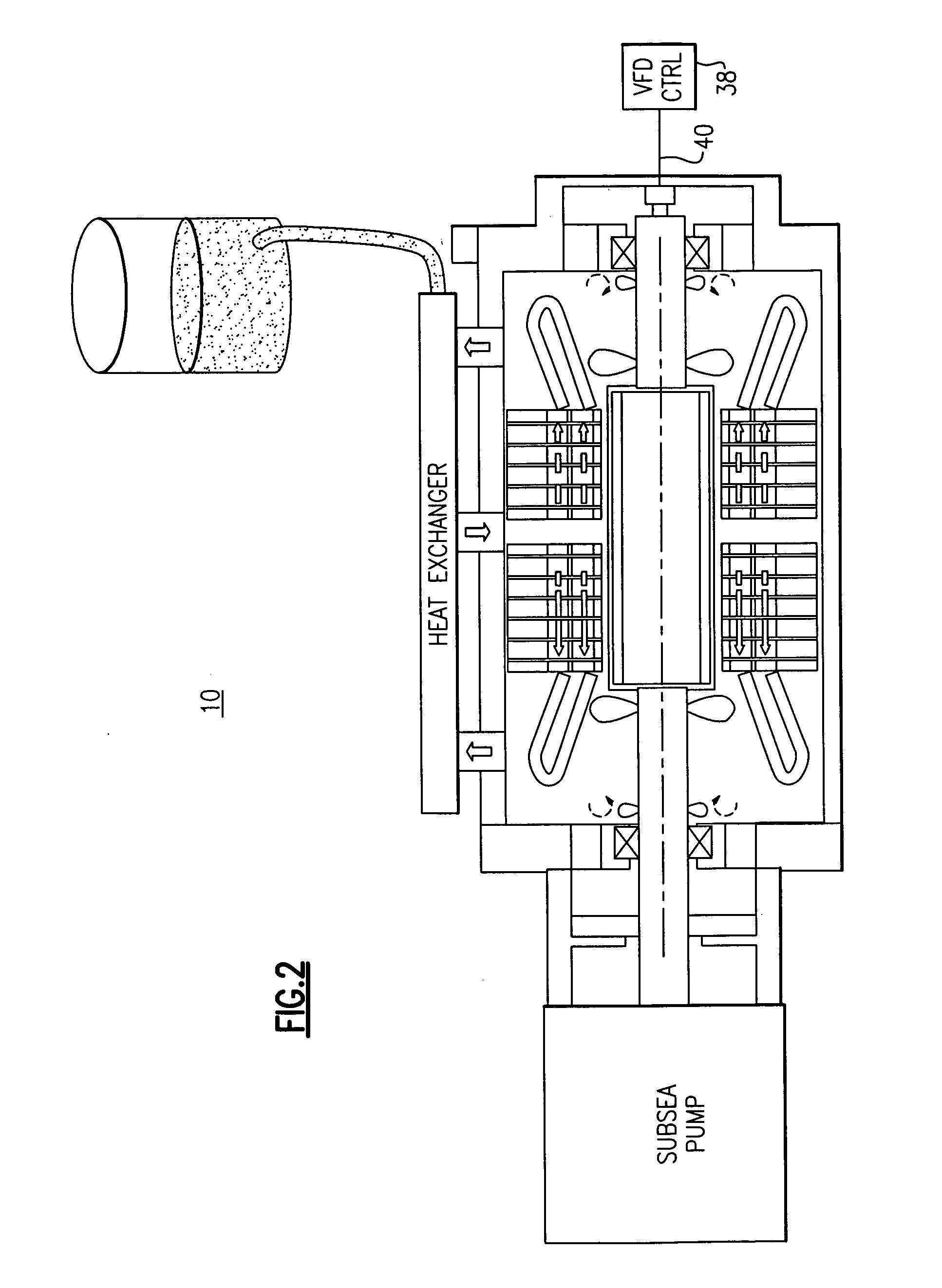
Permanent magnet motor for subsea pump drive
InactiveUS20090232664A1Avoid corrosionPositive displacement pump componentsPump controlPermanent magnet motorInconel
A subsea pump drive employs a permanent magnet (PM) motor to drive a subsea pump. The PM motor rotor in one embodiment is canned with a non-magnetic material such as inconel that can provide a desired level of corrosion protection. The PM motor provides a subsea pump drive that is smaller and more efficient, having a high power factor than a subsea pump drive utilizing a conventional induction motor. The PM motor subsea pump drive eliminates the necessity for a topside storage tank and associated fluid transfer lines when the motor rotor is cooled with processed fluid.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Stator turn fault detection apparatus and method for induction machine
A system and method are provided for correction of parameters used in determination of stator turn faults of an induction motor. An embodiment may include determining a residual impedance and / or a residual voltage of the motor, and correcting a normalized cross-coupled impedance based on the residual impedance and residual voltage. Additional embodiments may include measuring an operating temperature of the motor and determining a negative sequence impedance of the motor based on the temperature. Another embodiment may include measuring voltages and currents of the motor and determining phasors for the voltages and currents using compensation for variations from a nominal frequency of the motor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Fault detection in induction machines
ActiveUS20150260794A1Provide reliablyEasy to identifyFrequency measurement arrangementSpecial data processing applicationsPower flowElectric machine
A method of detecting a fault in an induction machine having one or more windings arranged to draw current at a supply frequency, the method including: performing a process of judging whether a respective sideband of one or more selected harmonics of the supply frequency exists at a predetermined fault frequency in a signal in the one or more windings; and determining that a fault has occurred if the judgement is positive; wherein in the judging process each of the selected harmonics of the supply frequency is a harmonic frequency of the supply frequency other than the supply frequency itself.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
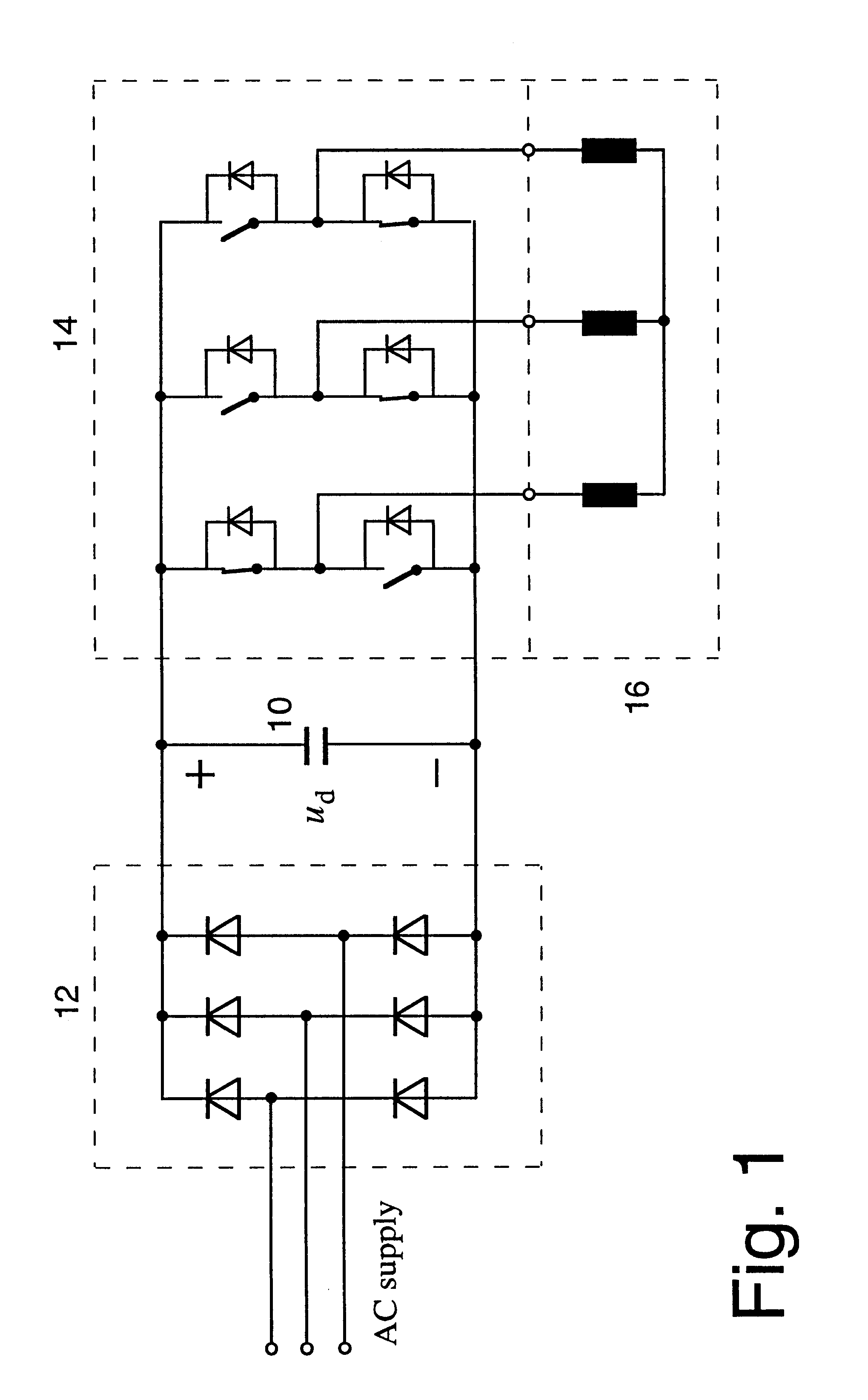
Method of braking a vector controlled induction machine, control device for carrying out the method and storage medium
InactiveUS6326762B1Improves field oriented controlMaximum braking abilityElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersControl vectorEngineering
A method and a control device for braking a variable speed vector controlled induction machine are driven by a pulse width modulation (PWM) inverter, in which the q-current component and the d-current component of the stator current are controlled independently from one another in accordance with a first reference signal (iq*) and a second reference signal (id*), respectively. For braking, high frequency components are superimposed on the second reference signal (id*), and the root-mean-square (rms) value (id rms) and the average value (id av) of the resultant second reference signal are controlled independently from one another such that the field requirements are met by the average value and high machine losses are produced by the rms value.
Owner:WEG AUTOMACAO
Motor parameter detection method and motor parameter detection device
The invention discloses a motor parameter detection method and a motor parameter detection device. The motor parameter detection method comprises the following steps: opening the circuit of one of phase windings of a motor; detecting stator leakage inductance and rotor leakage inductance; applying rated voltage with higher frequency than rated power between the other two phases of the motor; and detecting the stator leakage inductance and the rotor leakage inductance according to the computational formula of the stator leakage inductance and the rotor leakage inductance. The invention provides the off-line motor parameter detection method and the motor parameter detection device under the static condition of the rotor of an induction motor, which achieve high accuracy of motor parameter detection through reducing the influences of voltage errors and a skin effect as long as current or voltage with different frequencies is applied between the two phases of the motor in sequence.
Owner:BEIJING A&E TECH
Mitigation of harmonic currents and conservation of power in non-linear load systems
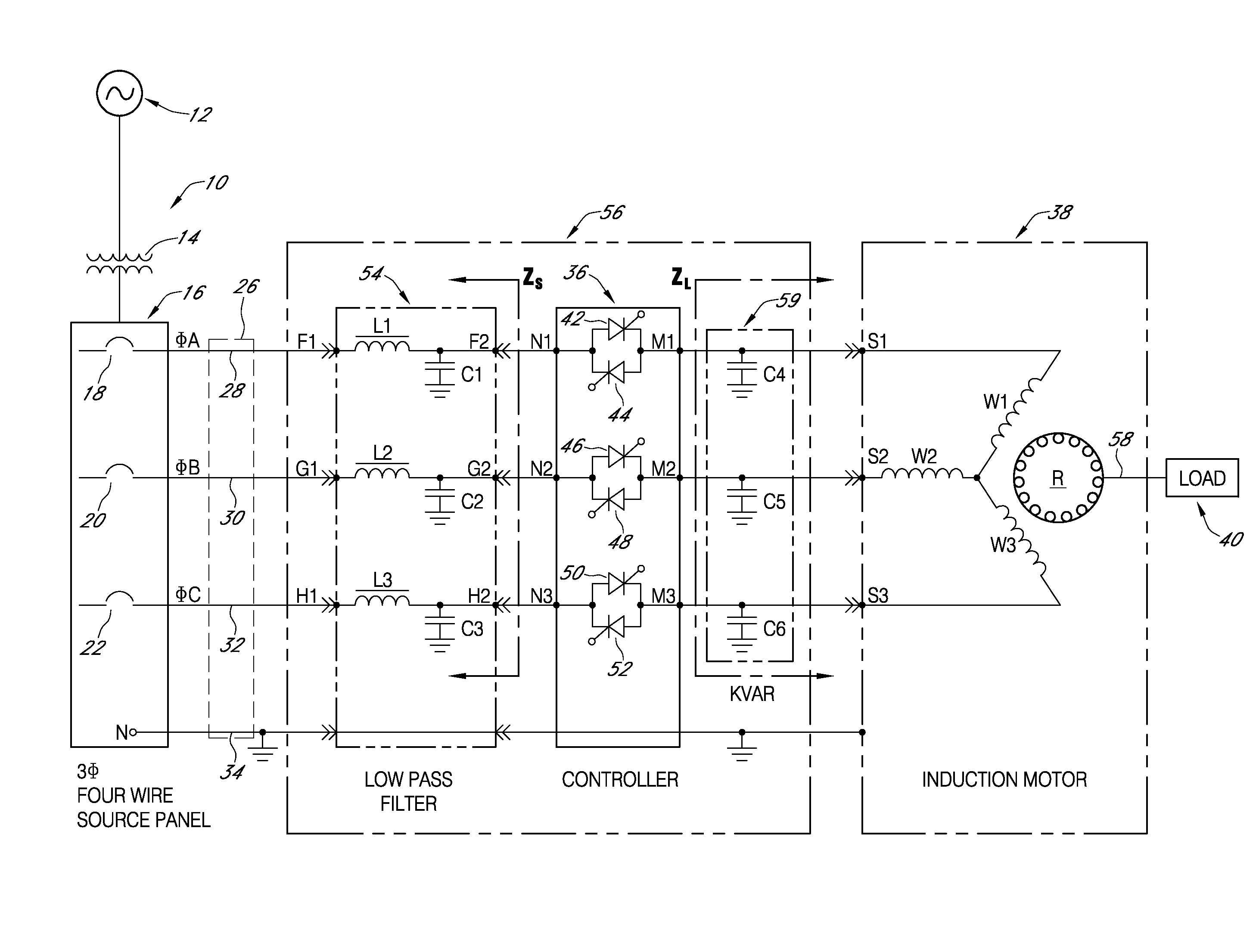
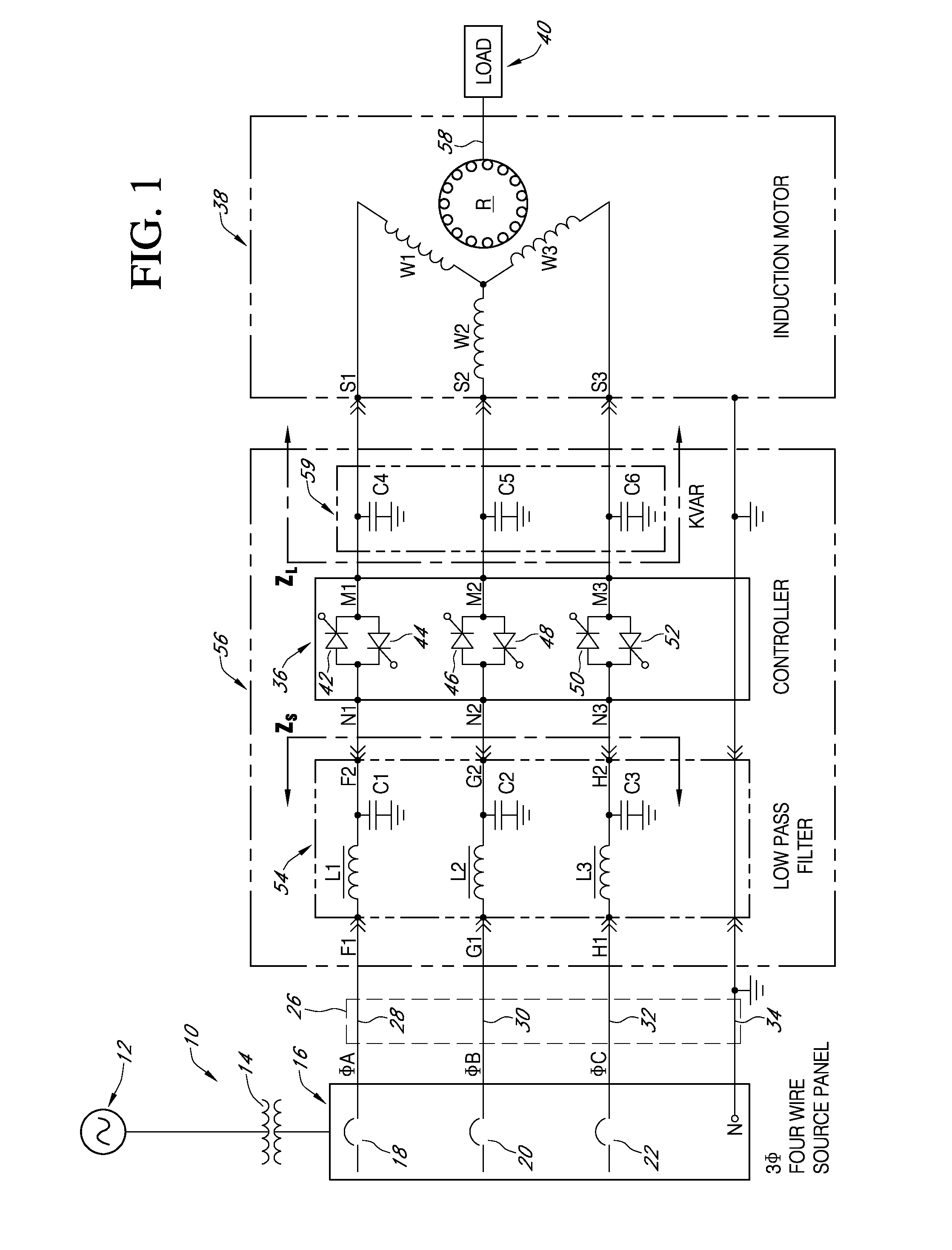
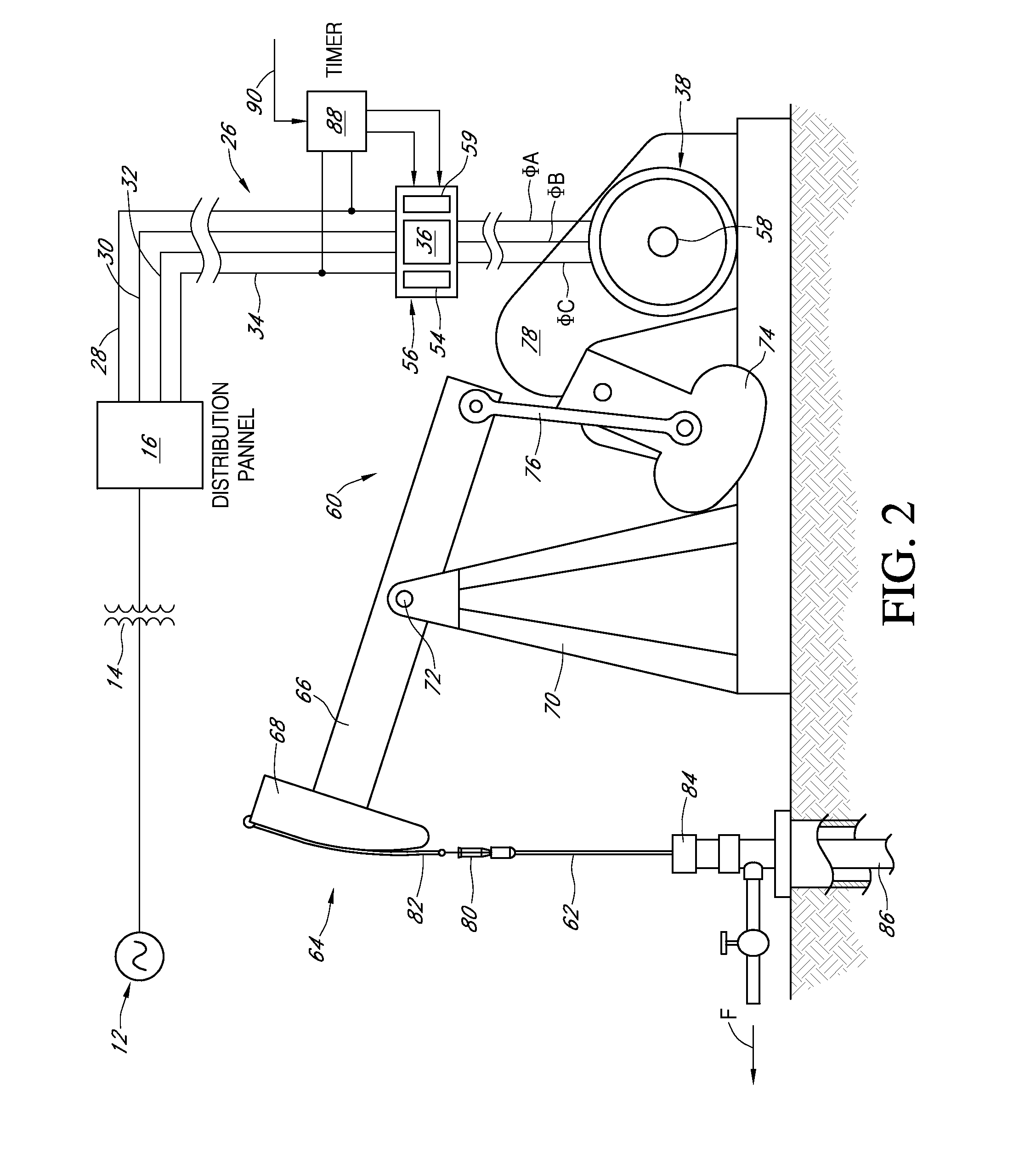
InactiveUS7309973B2Increasing operating efficiency and performanceIncrease powerSingle-phase induction motor startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersLow-pass filterPower control
An AC power controller system applies three-phase AC operating power to an induction motor that drives a non-linear mechanical load. A primary low pass filter is connected in series between branch phase conductors and a power controller of the type that uses gate-controlled switching thyristors for controlling power to the motor. KVAR capacitors connected between the power controller and the induction motor phase windings form a secondary low pass filter across the controller output terminals. The primary and secondary low pass filters isolate the power controller and induction motor with respect to spurious noise and harmonics generated by local as well as remote sources, and also improve real power transfer efficiency from the power generating source to the induction motor by transforming the effective impedance of the power source and the induction motor load.
Owner:POWER CONSERVATION LTD
Method for observing rotary speed of induction motor of Kalman filter with index fading factor
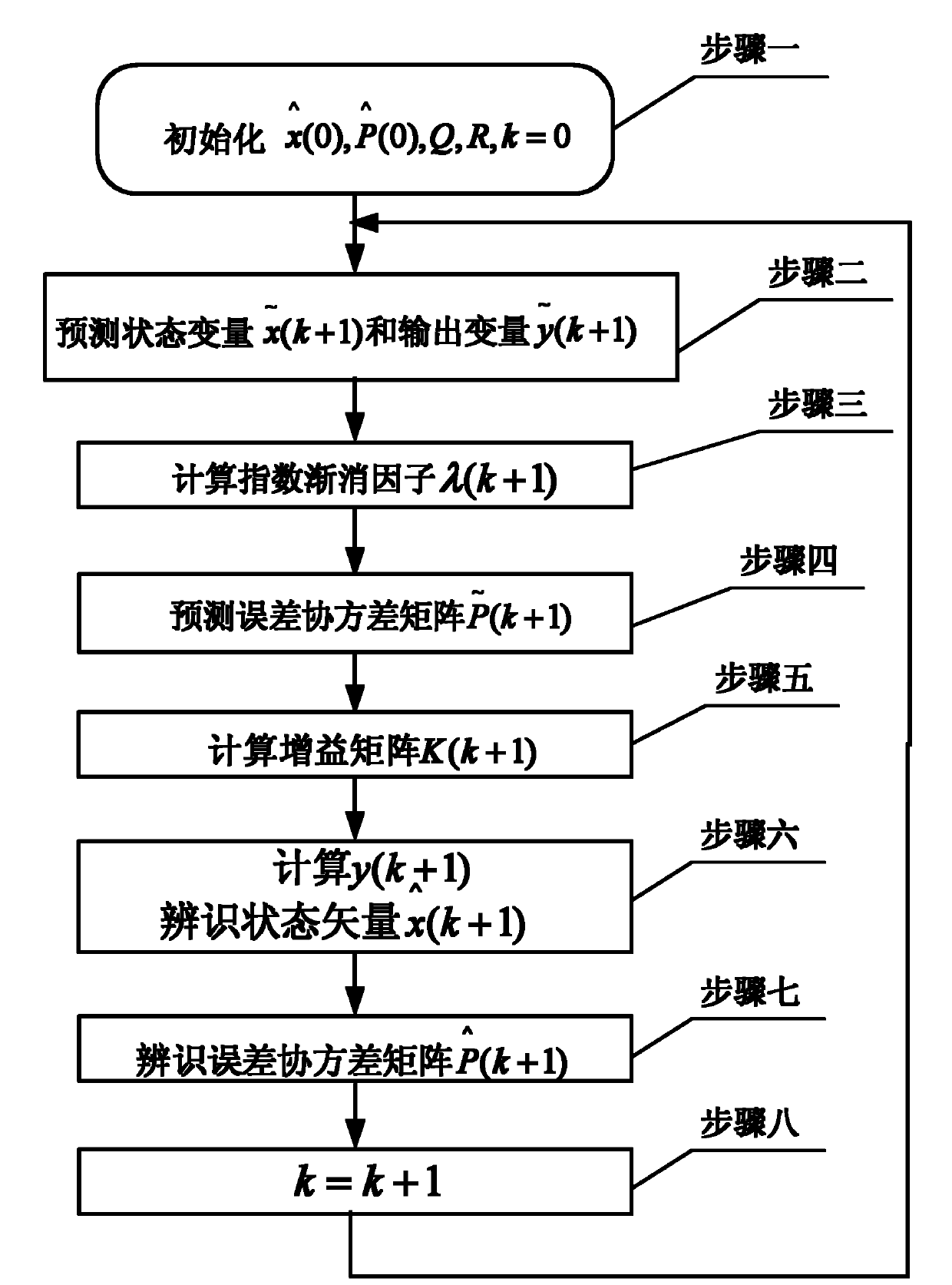
InactiveCN102176653AReduce mistakesReduce distractionsElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsKaiman filterState variable
The invention provides a method for observing a rotary speed of am induction motor of a Kalman filter with index fading factor, belonging to the field of drive control of motors. The method solves the problem that the observing result of state variable is influenced because the matrix error of the noise covariance is great in the standard Kalman filter EKF (Extended Kalman Filter) algorithm which is used for observing the rotary speed of the induction motor in the prior art. In the invention, the method realizes the rotary speed observation on the basis of a rotary speed observer and the Kalman filter is utilized in the rotary speed observer to carrying out error predication; the index fading factor lambda (K+1) is introduced into an error covariance matrix predictive equation of the Kalman filter in the process of realizing the rotary speed observation by operating the rotary speed observer; and the error covariance matrix predictive equation is shown in the specification. The method provided by the invention is suitable for observing the rotary speed of the induction motor.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
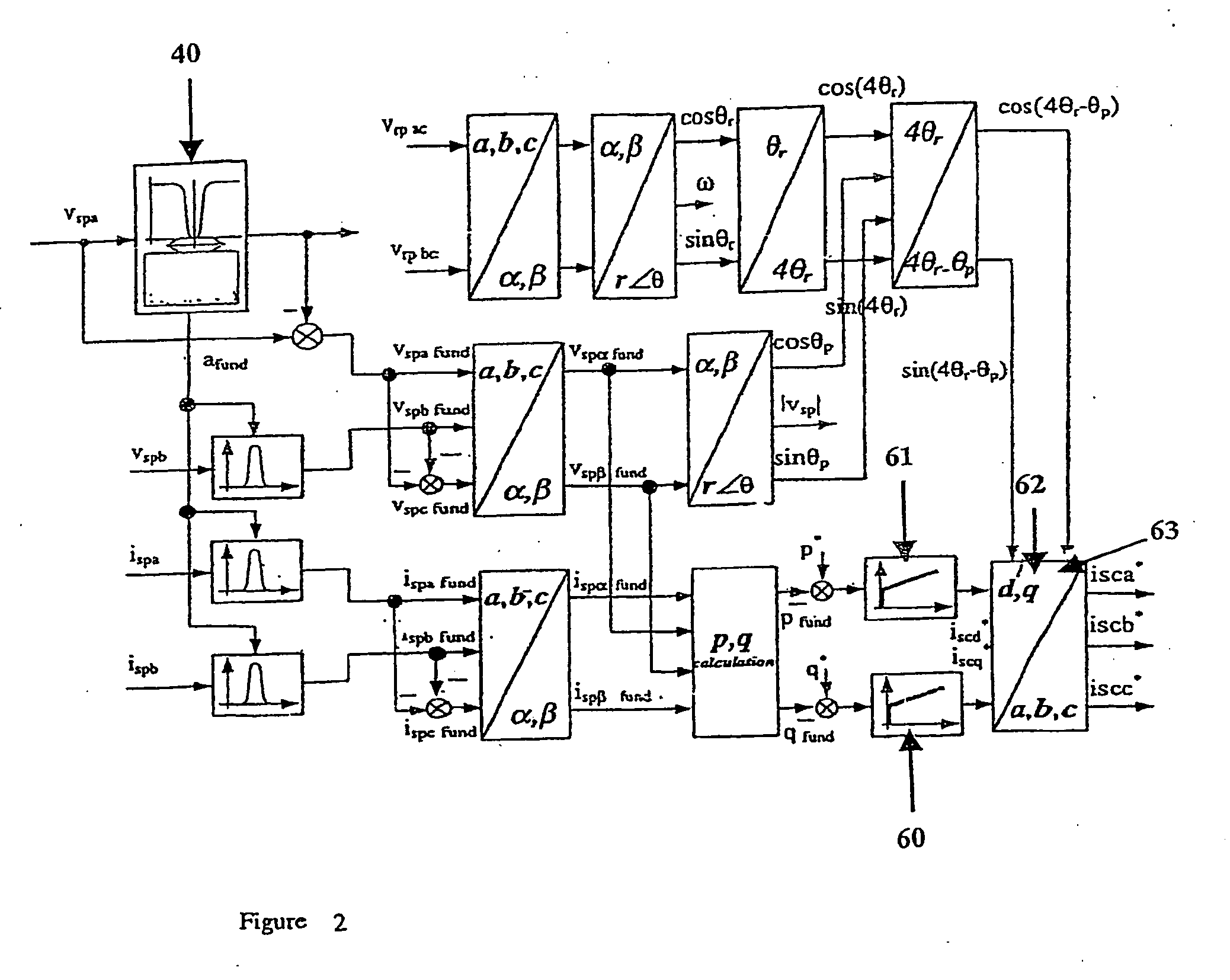
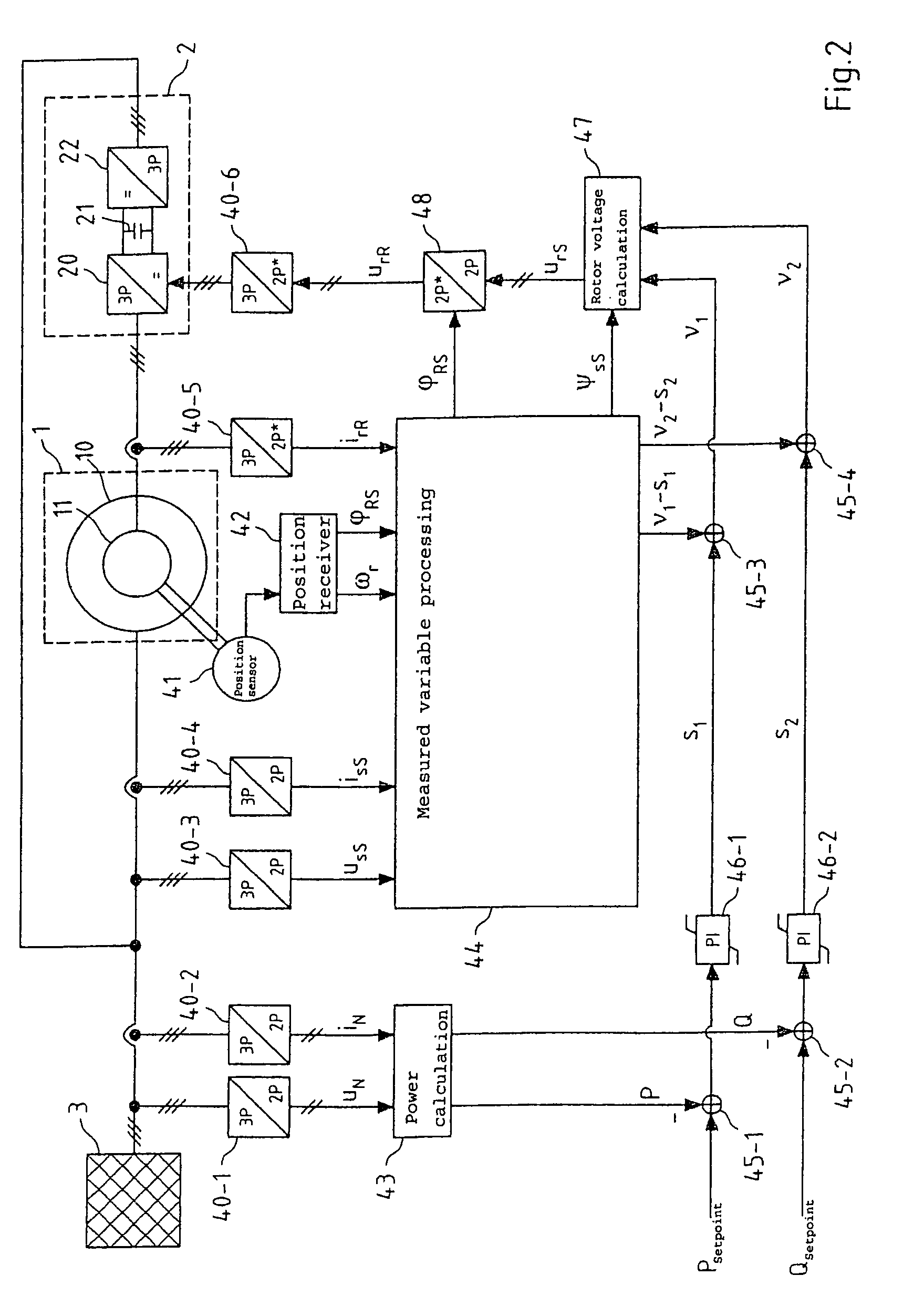
Power control of an induction machine
ActiveUS7423406B2Simple simultaneously stable regulationSimple processGenerator control circuitsIgnition automatic controlElectric machineConductor Coil
Regulation of the active and reactive power of an induction machine in a coordinate system fixed on the winding, wherein a first regulator output variable is generated using a first regulator as a function of a setpoint variable deviation of the active power and a second regulator output variable is generated using a second regulator as a function of a setpoint variable deviation of the reactive power, feedback variables are added to each of the first and second regulator output variables, which are functions of at least one chronologically changing system variable of the induction machine, and a voltage or a current of the induction machine is determined as a manipulated variable without further regulation at least from the first and second regulator output variables added to the feedback variables. The feedback variables may linearize the regulation path and then allow restriction to only two simple regulators, e.g., two PI regulators. The regulation may be used in double-fed asynchronous machines.
Owner:K B ELECTRONICS INC
Induction machine
InactiveUS20140252910A1Improve power factorImprove efficiencySynchronous motorsAsynchronous induction motorsElectric machineMechanical engineering
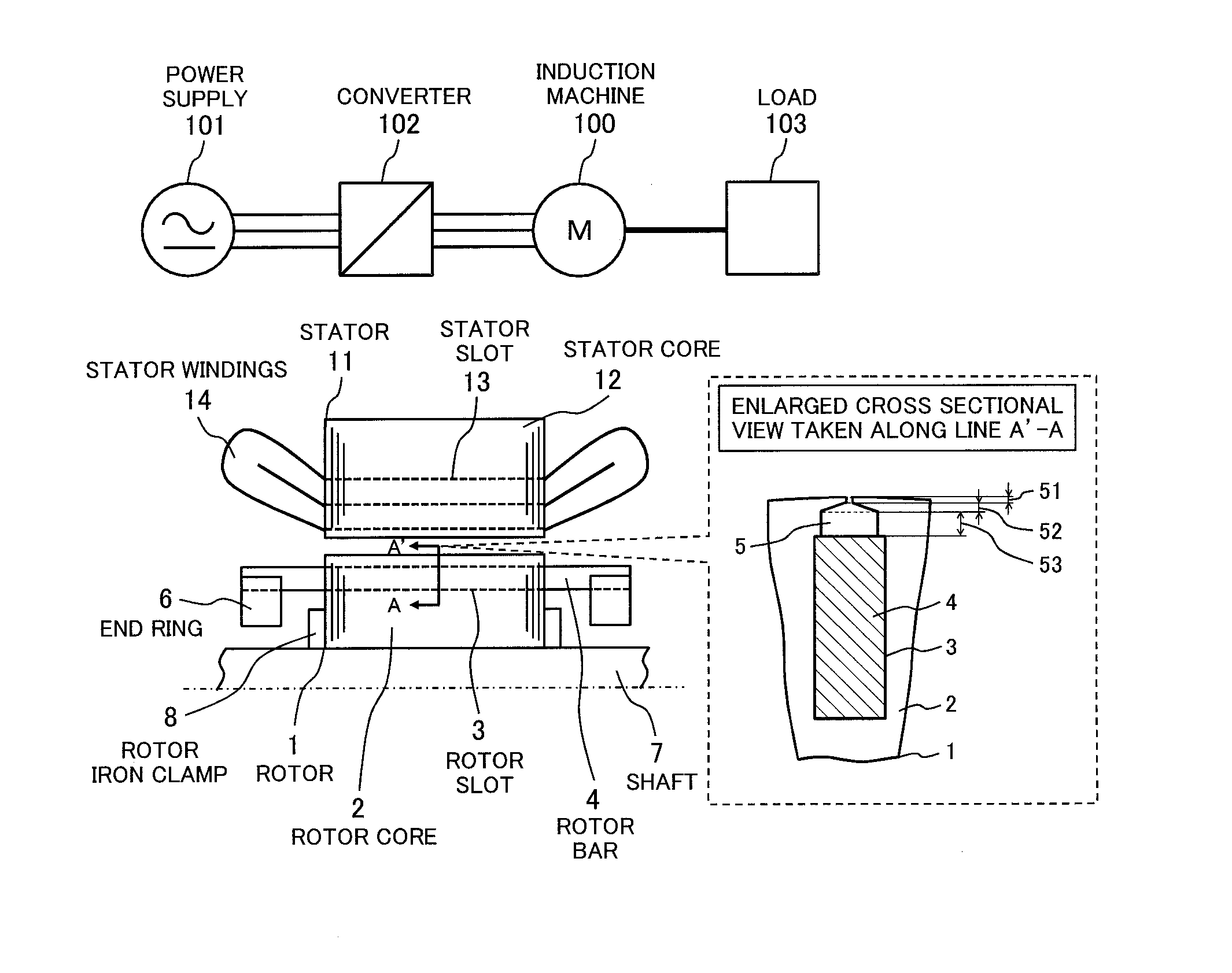
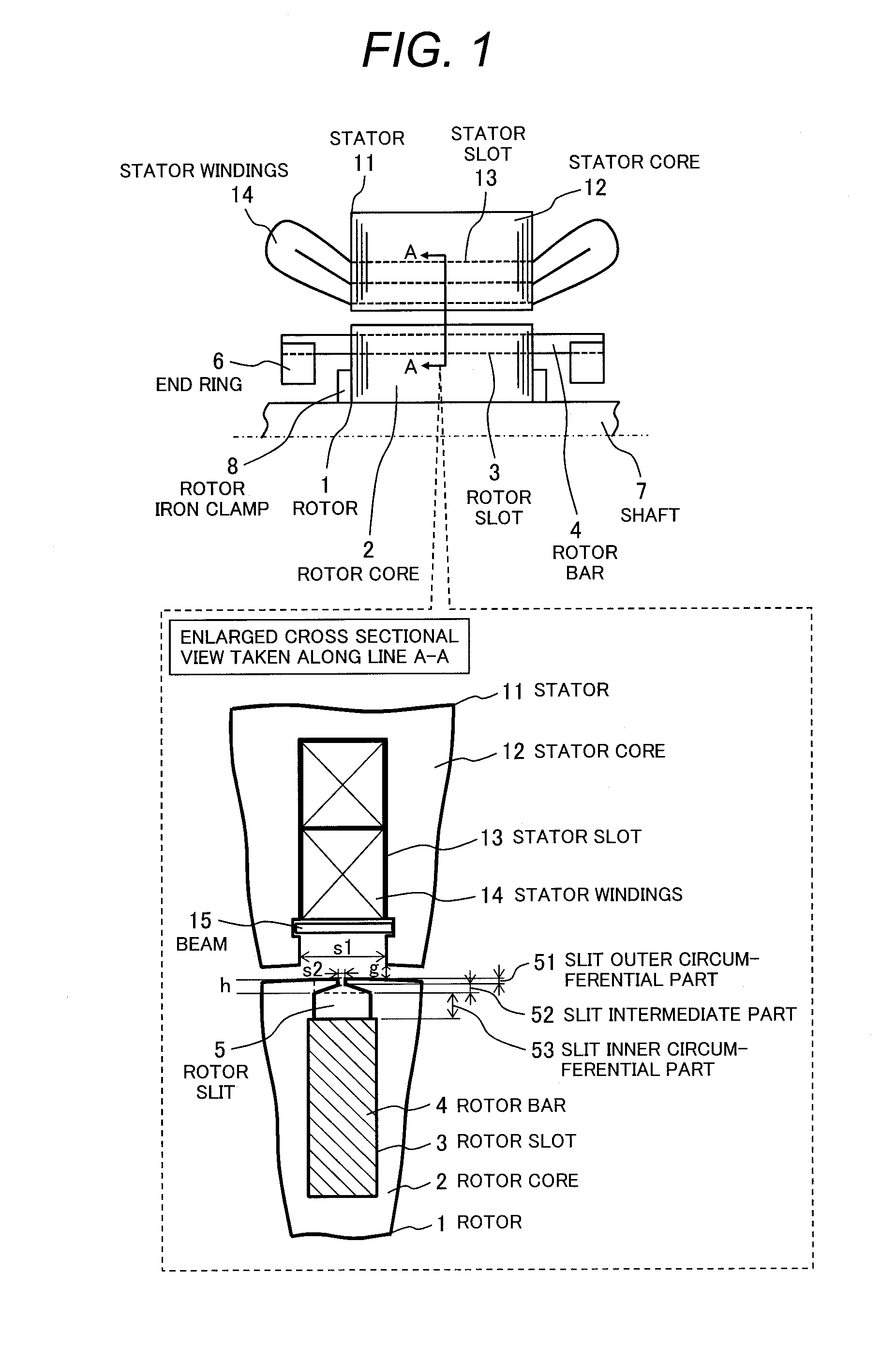
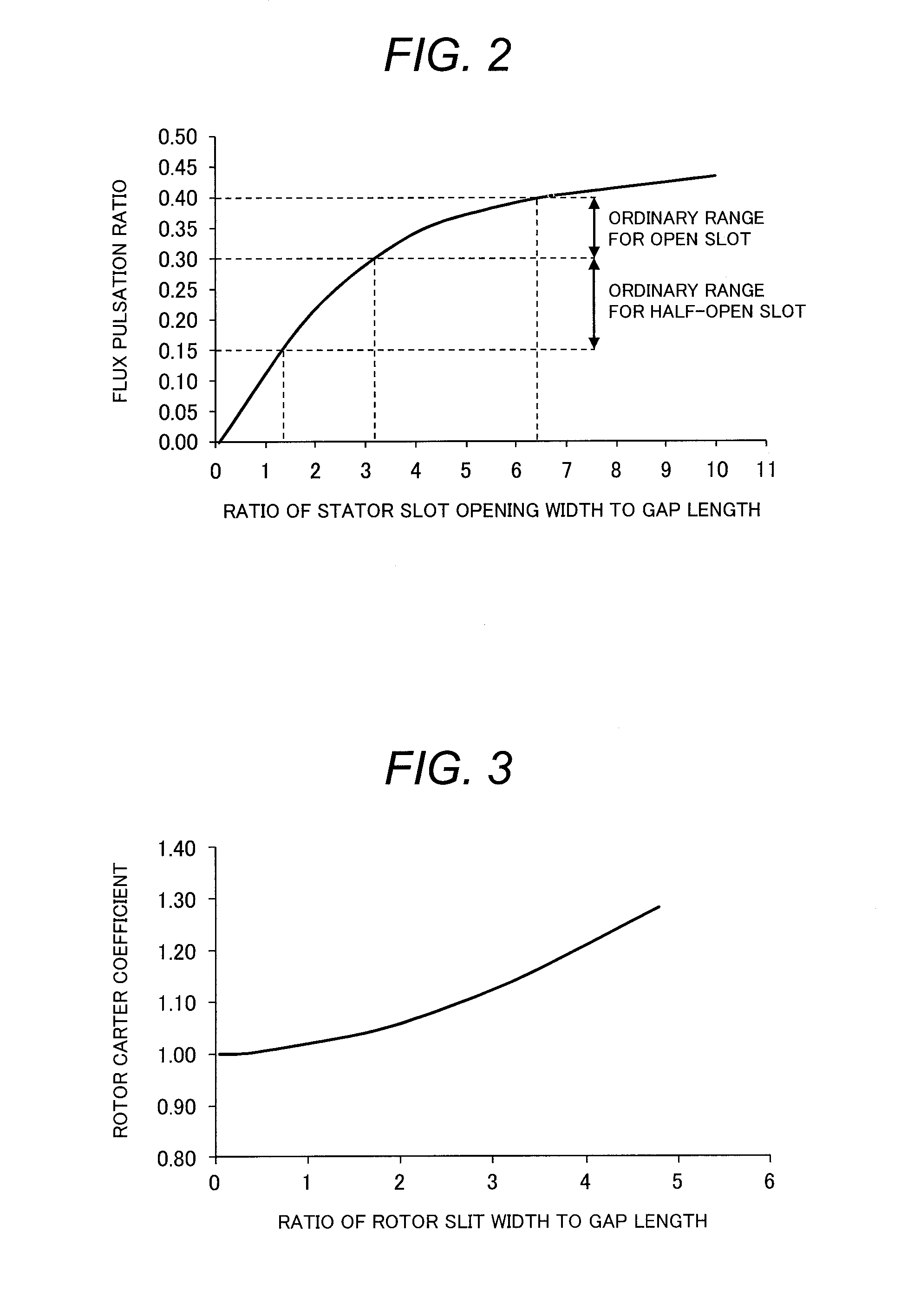
There is provided an induction machine having a squirrel-cage rotor, the rotor including: a rotor core; a plurality of rotor slots formed on the rotor core and aligned circumferentially at a predetermined interval; a plurality of rotor bars inserted into one of the plurality of rotor slots; and a plurality of rotor slits formed adjacent to the plurality of rotor slots on an outer circumferential side of the rotor core. The each rotor slit is formed as a hollow such that a cross sectional shape thereof is distinguished into three parts of a slit outer circumferential part, a slit intermediate part, and a slit inner circumferential part. A circumferential width of the each rotor slit on an innermost circumferential side is larger than that on an outermost circumferential side. A circumferential width of the slit intermediate part increases from an outer circumferential side toward an inner circumferential side.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
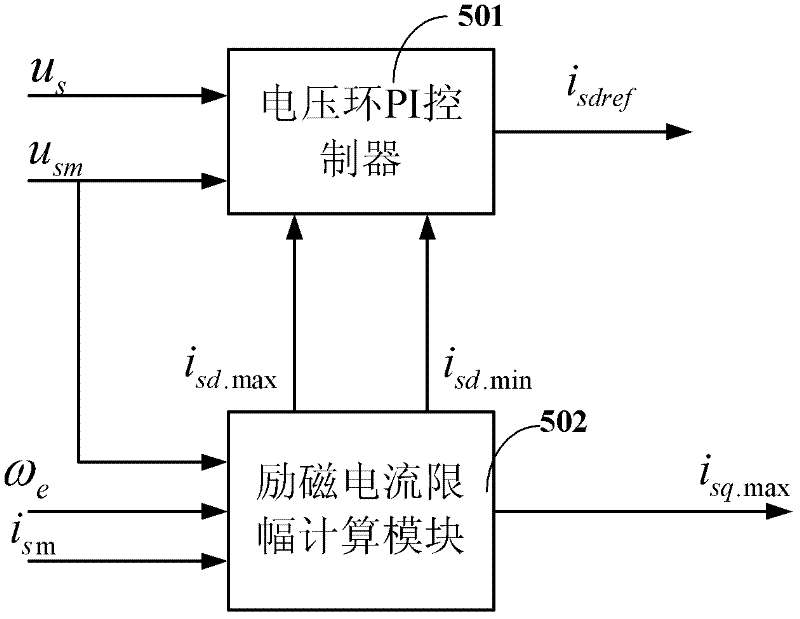
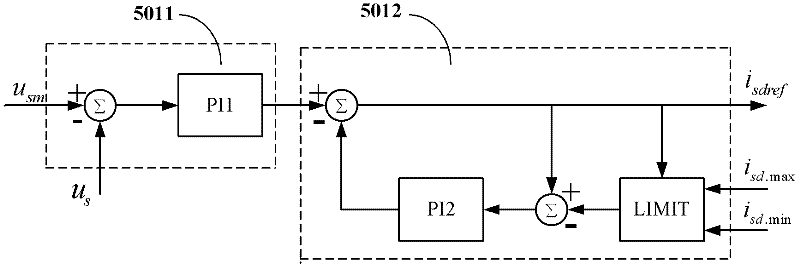
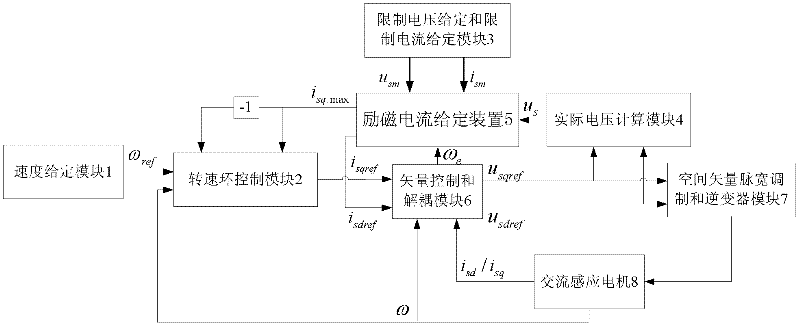
Exciting current given device of induction motor of electric vehicle
InactiveCN102403950AReduce back EMFReduce jitterElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsConstant powerVoltage vector
The invention discloses an exciting current given device for an induction motor of an electric vehicle. On the basis of the prior art, the exciting current given device is additionally provided with an exciting current limiting calculation module and a limiting PI (proportional integral) control module. When the induction motor normally runs, the calculated amplitude limiting maximum value (isd.Max) of the exciting current decreases along with the increase of the real synchronous speed omega e. The exciting current isdref of a voltage loop PI controller decreases under the condition of invariable maximum voltage vector (usm). Due to the decrease of the exciting current (isdref), the counter electromotive force of the induction machine decreases, therefore, under the condition of invariable busbar voltage uDC, the induction motor can rise to a higher rotating speed. In addition, according to the exciting current given device of the induction motor of the electric vehicle, the calculation of switching points among a constant torque area, a constant power area and a constant voltage area is eliminated, so that the level jump of output exciting currents caused by the inaccurate calculation of switching points can be effectively prevented, the given value of the exiting currents can vary stably, the joggling of the induction motor control caused by the level jump of the given valueof the exciting currents is reduced, and the safety of the induction motor control is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
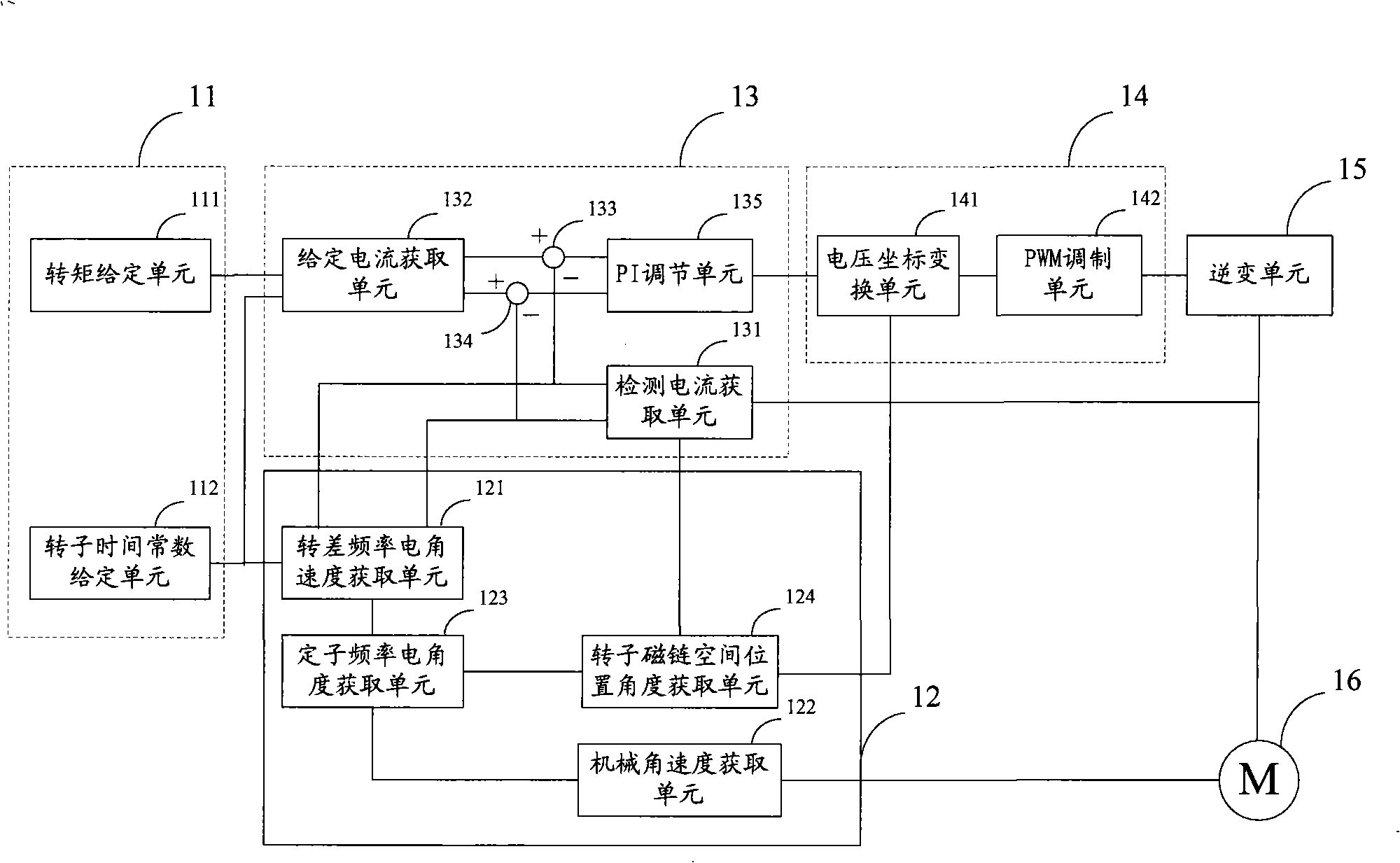
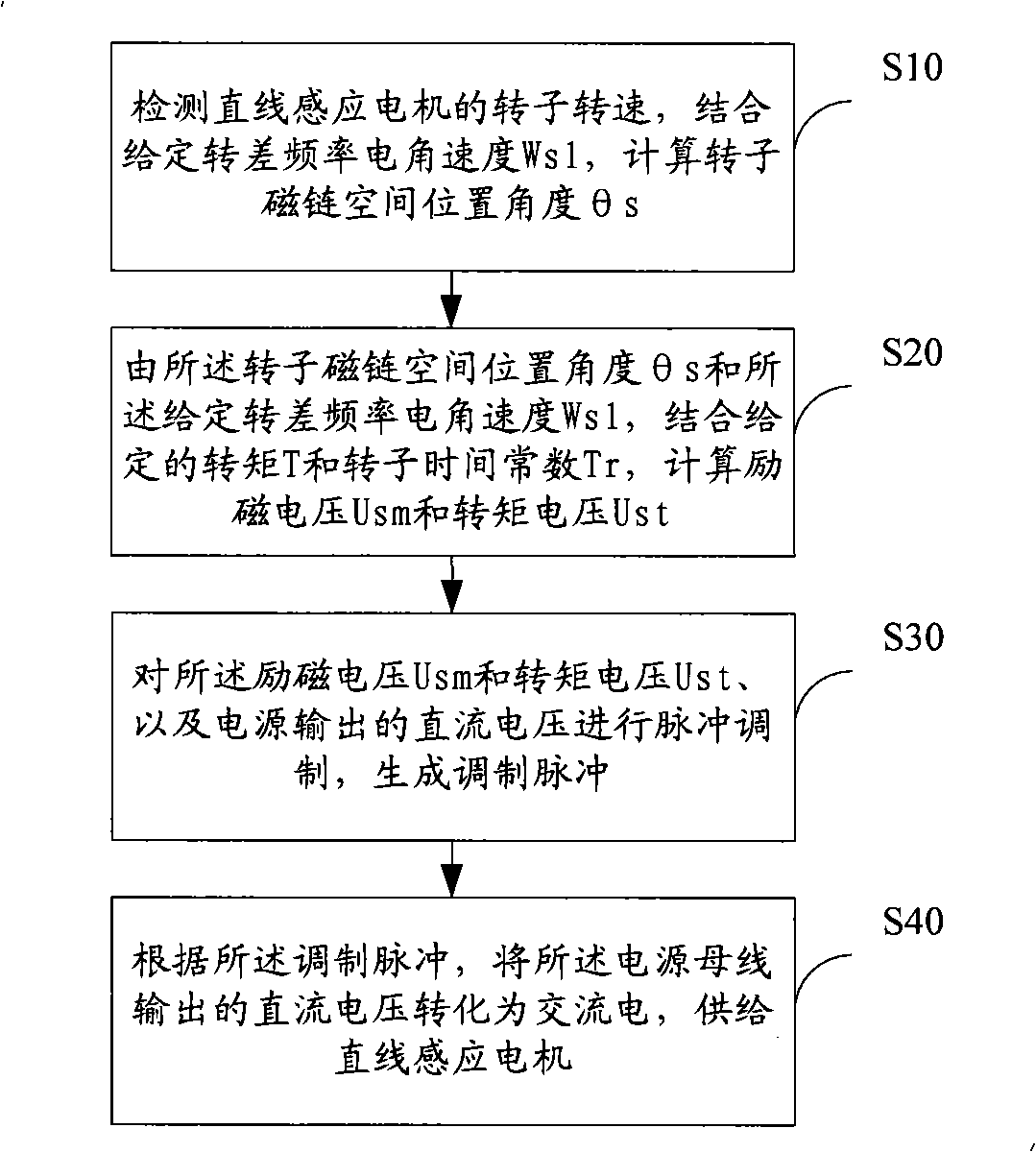
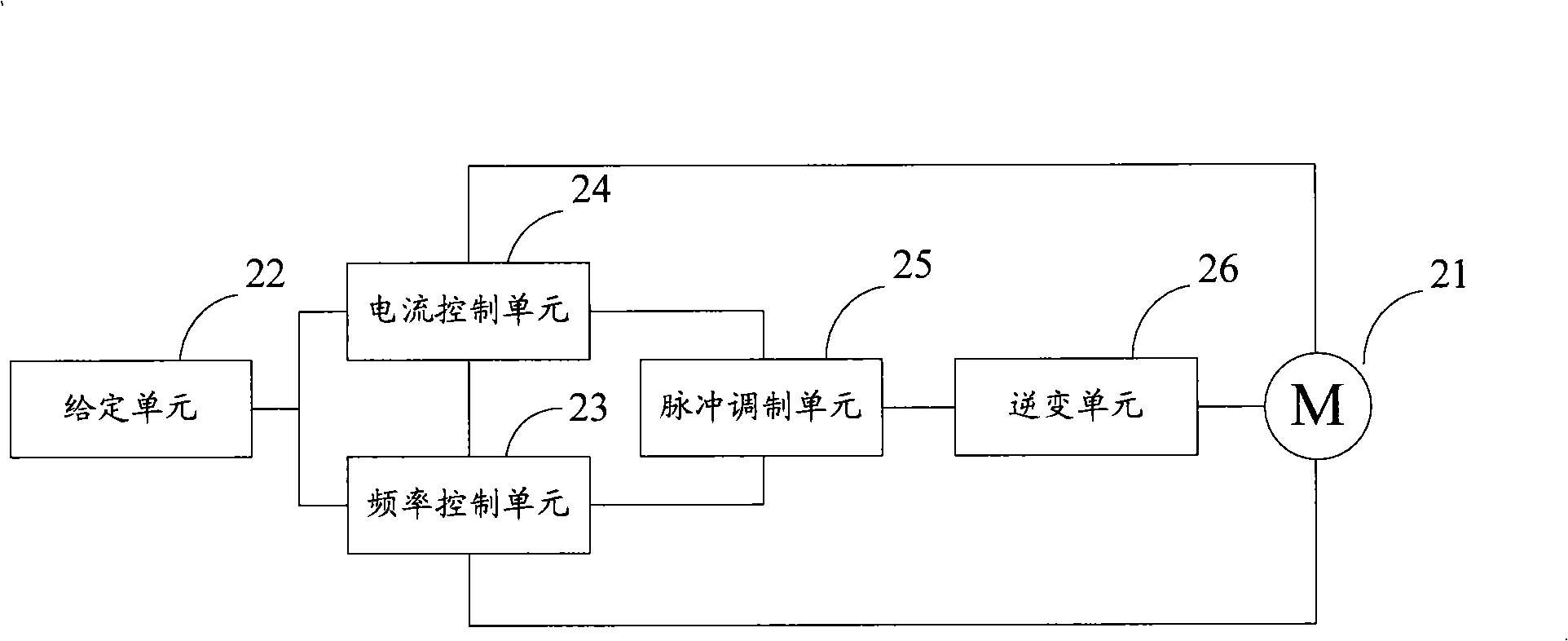
Constant slip frequency vector control method and system for linear induction motor
ActiveCN101316093AExcellent slip frequency electrical angular velocitySmooth orientation angleElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPosition angleAngular velocity
The invention discloses a linear induction motor constant slip frequency vector control method. The method comprises the steps as follows: detecting the rotation speed of a rotor of a linear induction motor, calculating the magnetic chain space position angle Theta<s> of the rotor according to the given slip frequency electric angular velocity Wsl; calculating the excitation voltage Usm and torque voltage Ust according to the magnetic chain space position angle Theta<s> and the given slip frequency electric angular velocity Wsl and combining a given torque T and a rotor time constant Tr; generating modulation pulses by pulse-modulating the excitation voltage Usm and the torque voltage Ust and the DC voltage output by the power supply; converting the DC voltage output by the power supply into the AC electricity so as to be supplied to the linear induction motor according to the modulation pulse. The invention also discloses a linear induction motor constant slip frequency vector control system. The linear induction motor constant slip frequency vector control method and system of the invention can realize the constant slip frequency vector control of the linear induction motor.
Owner:ZHUZHOU CSR TIMES ELECTRIC CO LTD
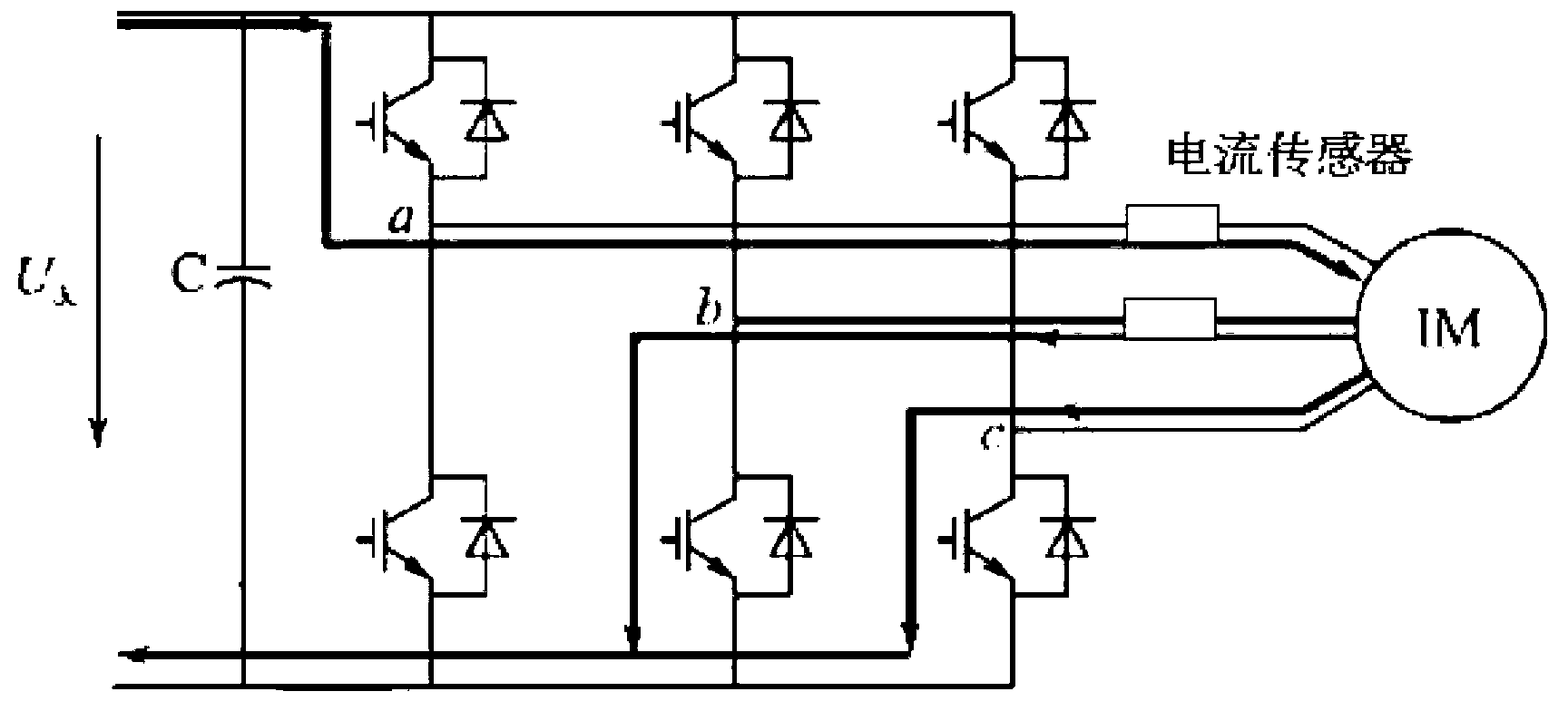
Three-phase current reconstruction method using single sampling resistance
ActiveCN103199791ALow costImprove accuracyMotor parameters estimation/adaptationFrequency changerVoltage vector
The invention provides a three-phase current reconstruction method using single sampling resistance. The method includes the following steps: A, sampling direct-current bus current of a frequency converter; B, estimating three-phase current and counter electromotive force of an induction motor by using a state observer; C, judging whether current reconstruction is needed according to action time of effective vectors, if yes, carrying out a step D, and if not, skipping to a step G; D, observing motor current in an abnormal sampling area of the three-phase current by using the state observer; E, carrying out error control on the observed motor current; F, carrying out amplitude limiting processing on the variable quantity of the observed motor current; G, generating space vector pulse width modulation (SVPWM) signals; and H, setting time for the next time of direct-current bus current sampling, interrupting the process, and returning to the step A. According to the three-phase current reconstruction method using the single sampling resistance, accuracy and generality of current estimation are improved, the wide-range current reconstruction with various SVPWM models is precisely achieved, SVPWM voltage basic vectors are not changed, and voltage vector total harmonic distortion (THD) values are significantly reduced.
Owner:SINO WEALTH ELECTRONICS
Voltage orienting frequency conversion controller for open loop non-speed sensor
InactiveCN101425777ASolve the problem of light load oscillationGuaranteed uptimeElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlLow speedCurrent sensor
The invention relates to a voltage orientation frequency-vary controller of an opening-ring no-speed sensor, and a controlling technology of a sensing motor, which overcomes the problems of the poor loaded capacity and the light loaded oscillation of a motor caused by the influences of the factors of the voltage decrease of a stator resistor, rotating difference frequencies, dead areas, and the like in the low-speed running of the traditional constant-voltage frequency-ratio control. The voltage orientation frequency-vary controller is composed of the following units, i.e. a current sensor, a vector coordinate changing unit, a PI adjustor, a calculating unit of voltage boosting amount, a sliding-frequency calculating unit, a frequency adder, a first operation unit, a second operation unit, a third operation unit, a fourth operation unit, a fifth operation unit, a sixth operation unit and a SVPWM unit. The PI adjustor is used for controlling the no-power current, and the problem of the light-loaded oscillation of the sensing motor is effectively inhibited. The product of the power current and the motor stator resistance is used as the voltage boosting in loading, the loaded capacity of the motor is obviously improved, and the low-speed performance of the motor is greatly improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Systems, Methods, and Apparatus for Lifting Brushes of an Induction Motor
Systems, methods, and apparatus associated for lifting brushes and shorting slip rings are provided. One embodiment may include an actuating mechanism in operable communication with multiple brushes and a plurality of electrical contacts. Each of the brushes may be adapted for selective contact with a respective slip ring of an induction motor. The electrical contacts may be in electrical communication with respective terminals of rotor windings of the induction motor. When the actuating mechanism is actuated, at least a portion of the electrical contacts create electrical shorts between at least a portion of the slip rings and the rotor windings of the induction motor. When the actuating mechanism is actuated, at least a portion of the brushes are lifted from contacting the plurality of slip rings.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Toroidally wound induction motor-generator with selectable number of poles and vector control
InactiveUS6876176B2Increase torqueReduce speedElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersEngineeringMotor–generator
A system including an induction machine with a toroidally wound stator and a squirrel cage rotor is presented. The toroidally wound stator has a plurality of phase windings. A position sensor may be operatively connected to the induction machine for providing a position indication that is indicative of a relative position of the rotor and the stator. The system also includes an inverter having a plurality of solid-state switches and a control system. The inverter has the same number of phases as the toroidal induction machine. The inverter is connected to selectively energize the phase windings. A programmable microprocessor, such as a digital signal processor, is operatively connected to the induction machine and includes a program to implement vector control of the induction machine. The microprocessor can also control the inverter so that the induction machine operates with a predetermined number of poles using pole phase modulation.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
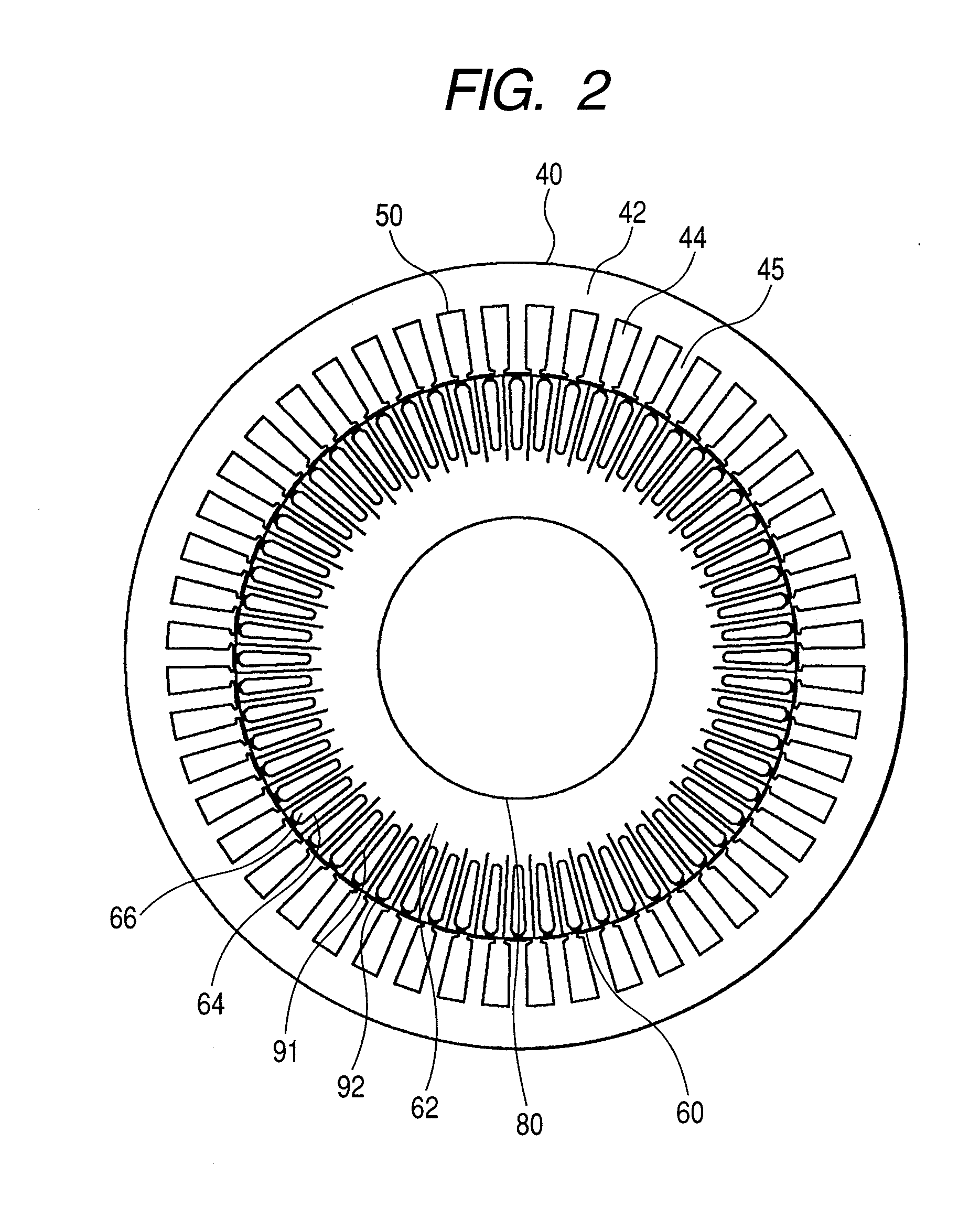
Induction machine
InactiveUS20080238237A1Reduce iron lossImprove efficiencyWindingsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectrical conductorConductor Coil
An induction machine has a stator and rotor. The stator comprises teeth and slots and stator winding disposed in the slots. The rotor comprises a rotor core having teeth and slots and a rotor-conductor disposed in the rotor slots. Both of the stator core and rotor core are made of laminated steel sheets, and the teeth and slots made of steel sheets are formed by etching.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com