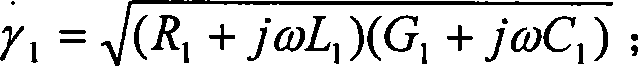Patents
Literature
940 results about "Residual voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The residual voltage is the voltage that remains in an output transistor while it is ON. For example, consider an NPN output with a power supply voltage of 24 V and a residual voltage of 2 V. ... A voltage of 22 V is applied to the load at this time. (Voltage across the load of 22 V = Power supply voltage of 24 V - Residual voltage of 2 V)
H-bridge with sensing circuit
InactiveUS6865417B2Interference with sensing is avoidedHeart defibrillatorsPulse therapyEnergy storage
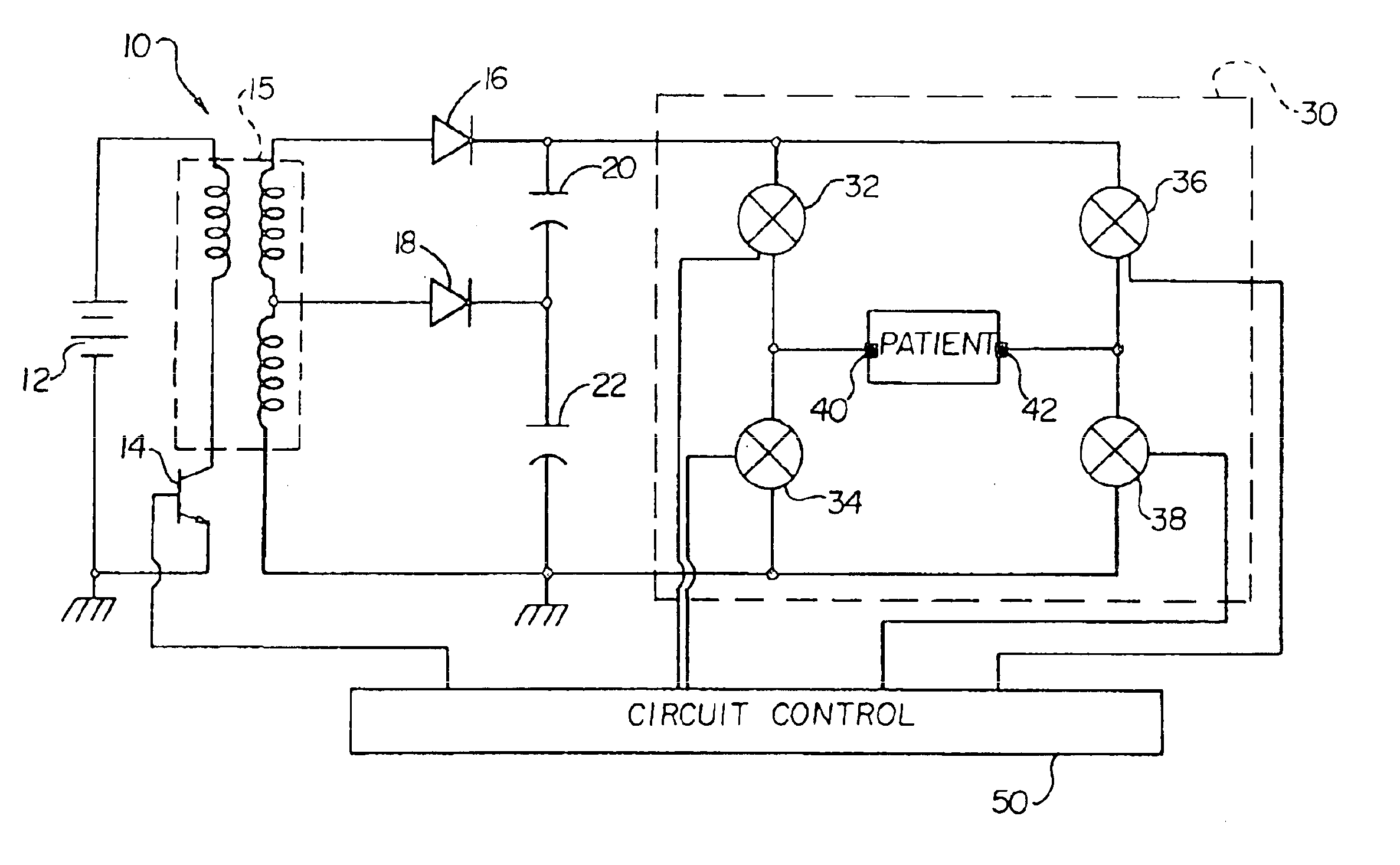
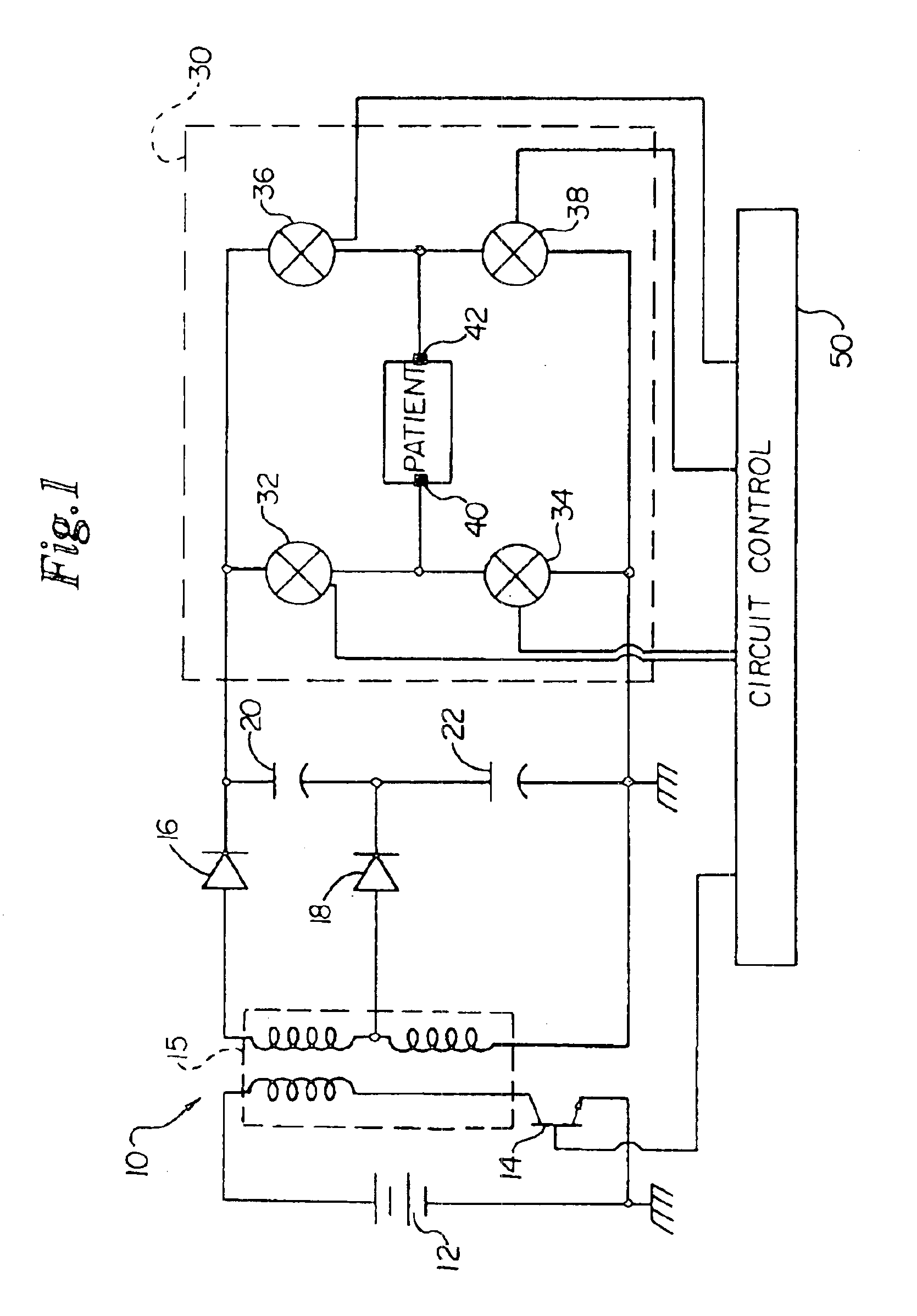
In a cardioverter / defibrillator system, an electrical circuit includes an energy storage device, an output circuit for controlling delivery of pulse therapy from the energy storage device to a patient, and a sensing circuit coupled across the patient to sense the patient's heart signal. The output circuit may be in the form of an H-bridge switching circuit wherein a pair of switches of the output circuit is simultaneously turned on to discharge residual voltage across the patient that remains after delivery of pulse therapy. Thus, interference with sensing of the patient's heart signal is avoided.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
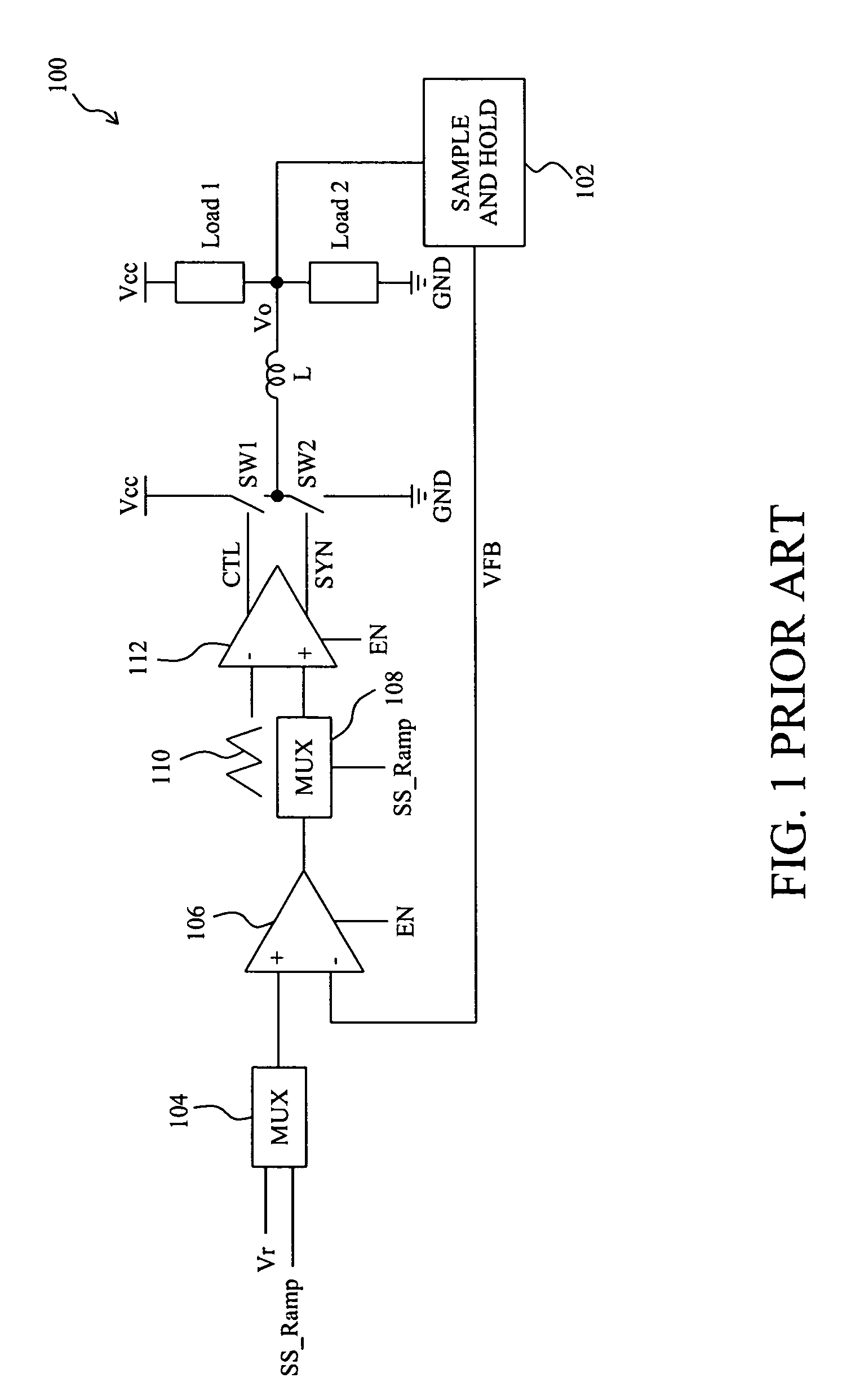
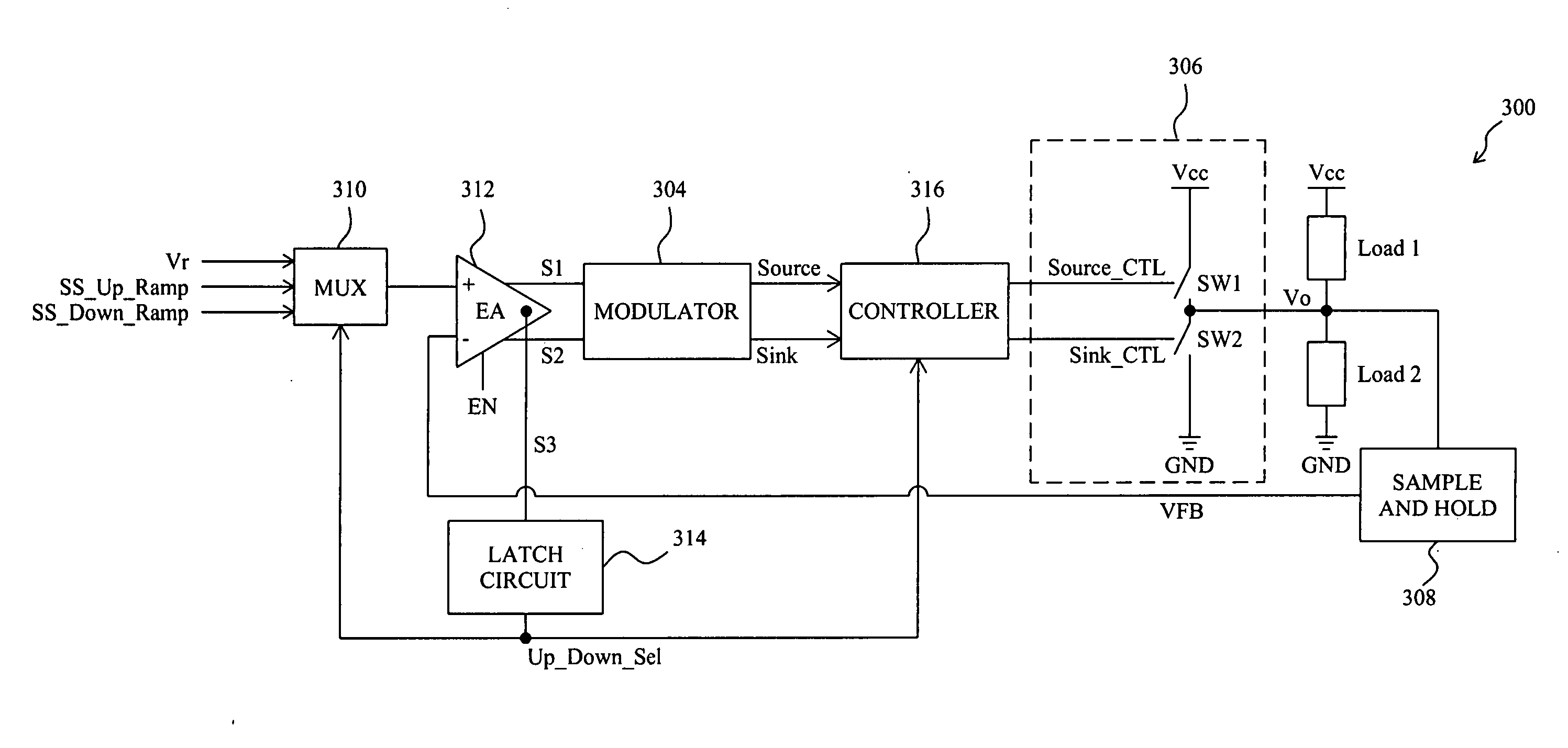
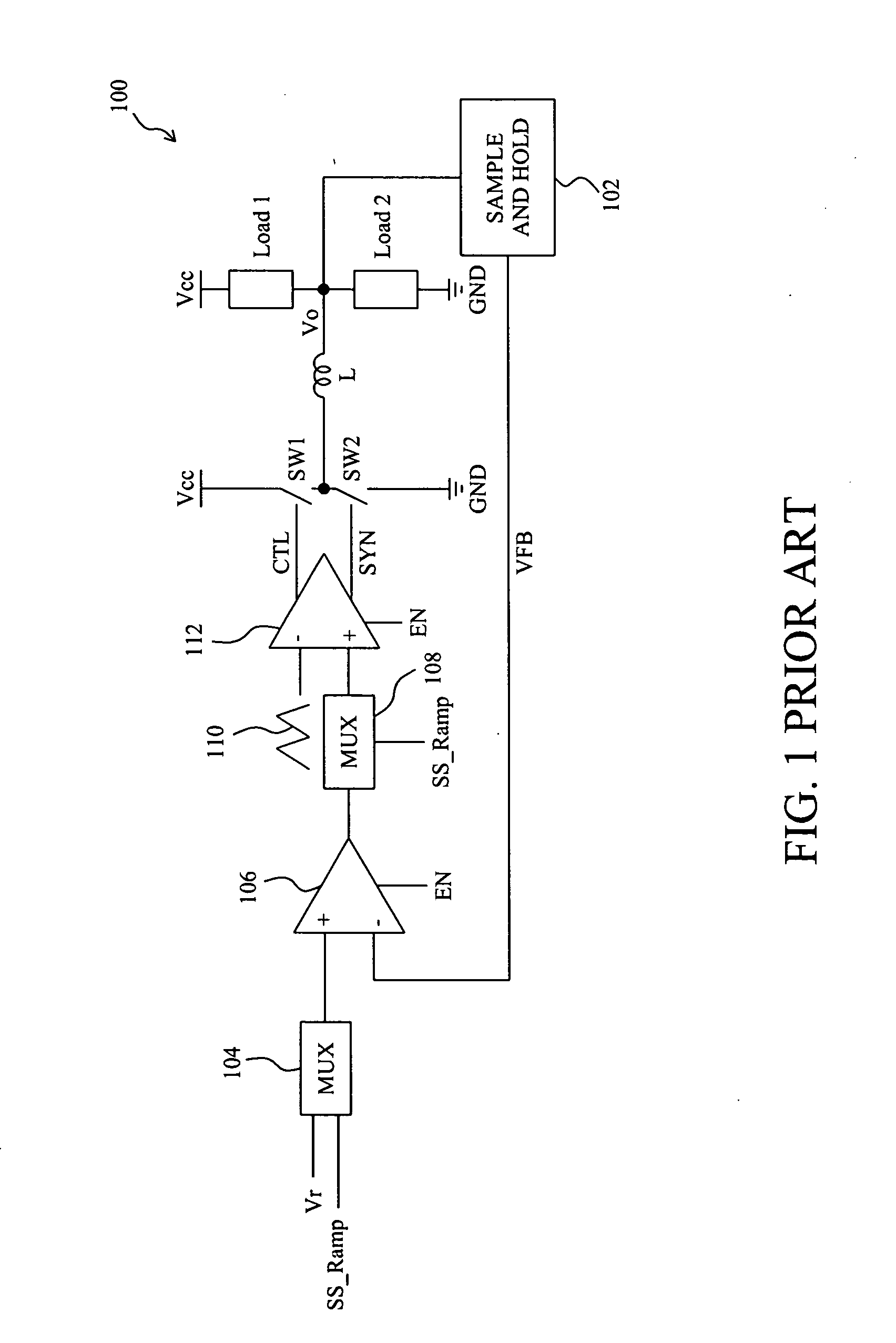
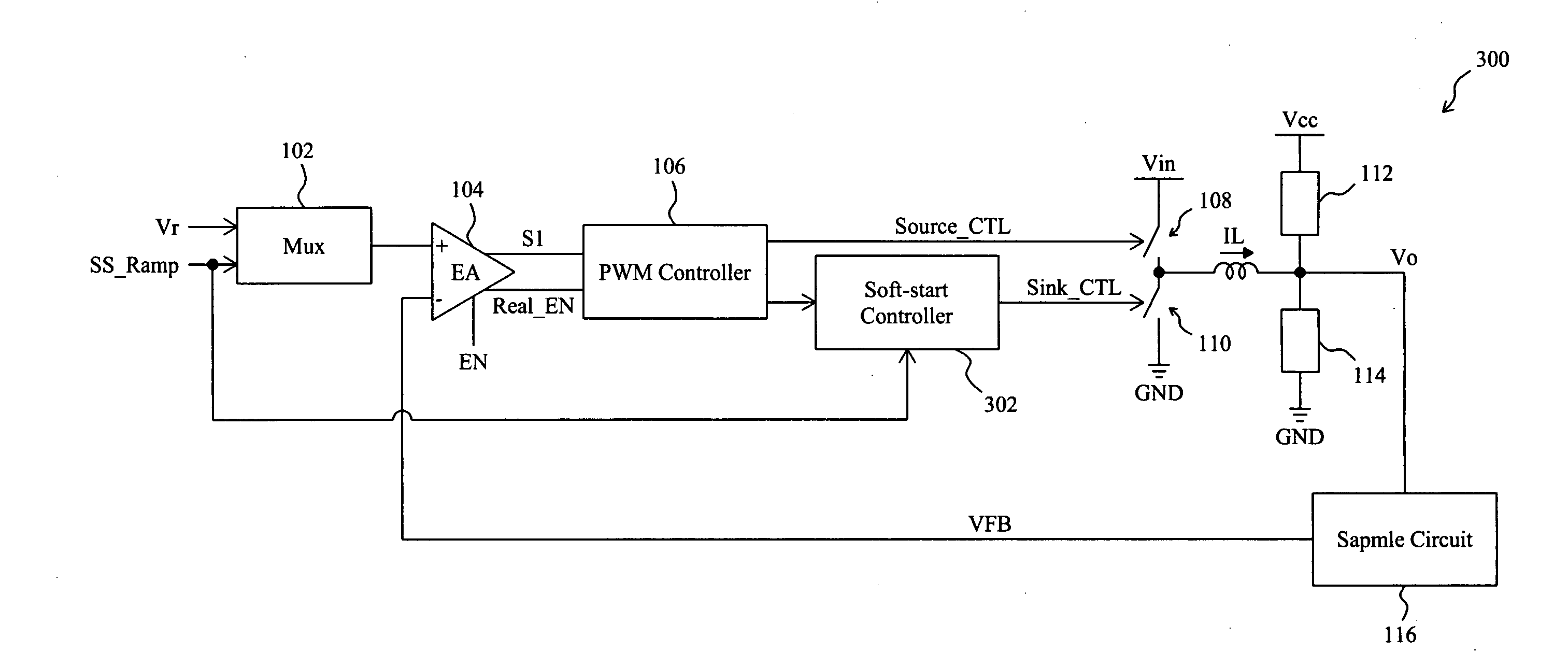
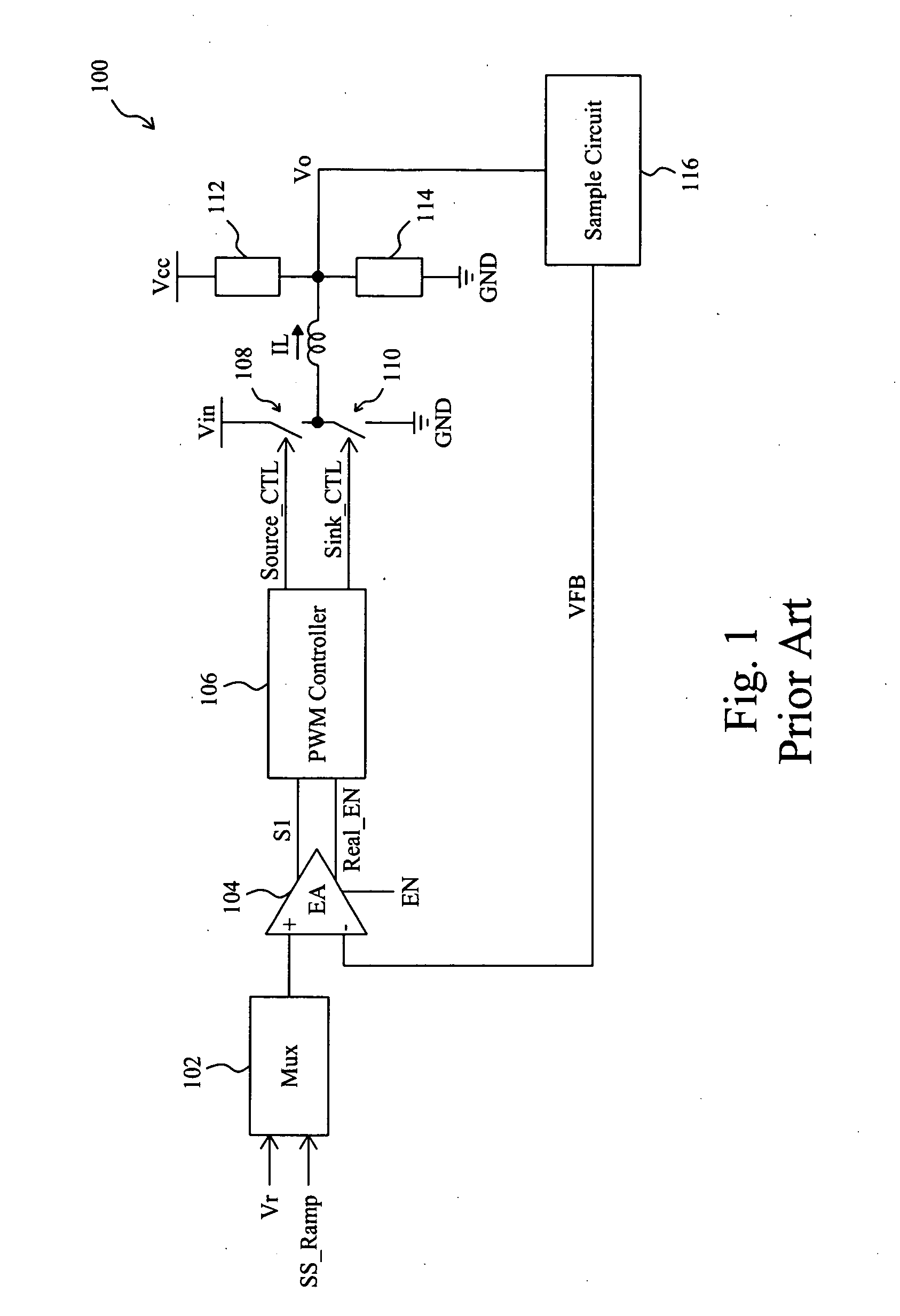
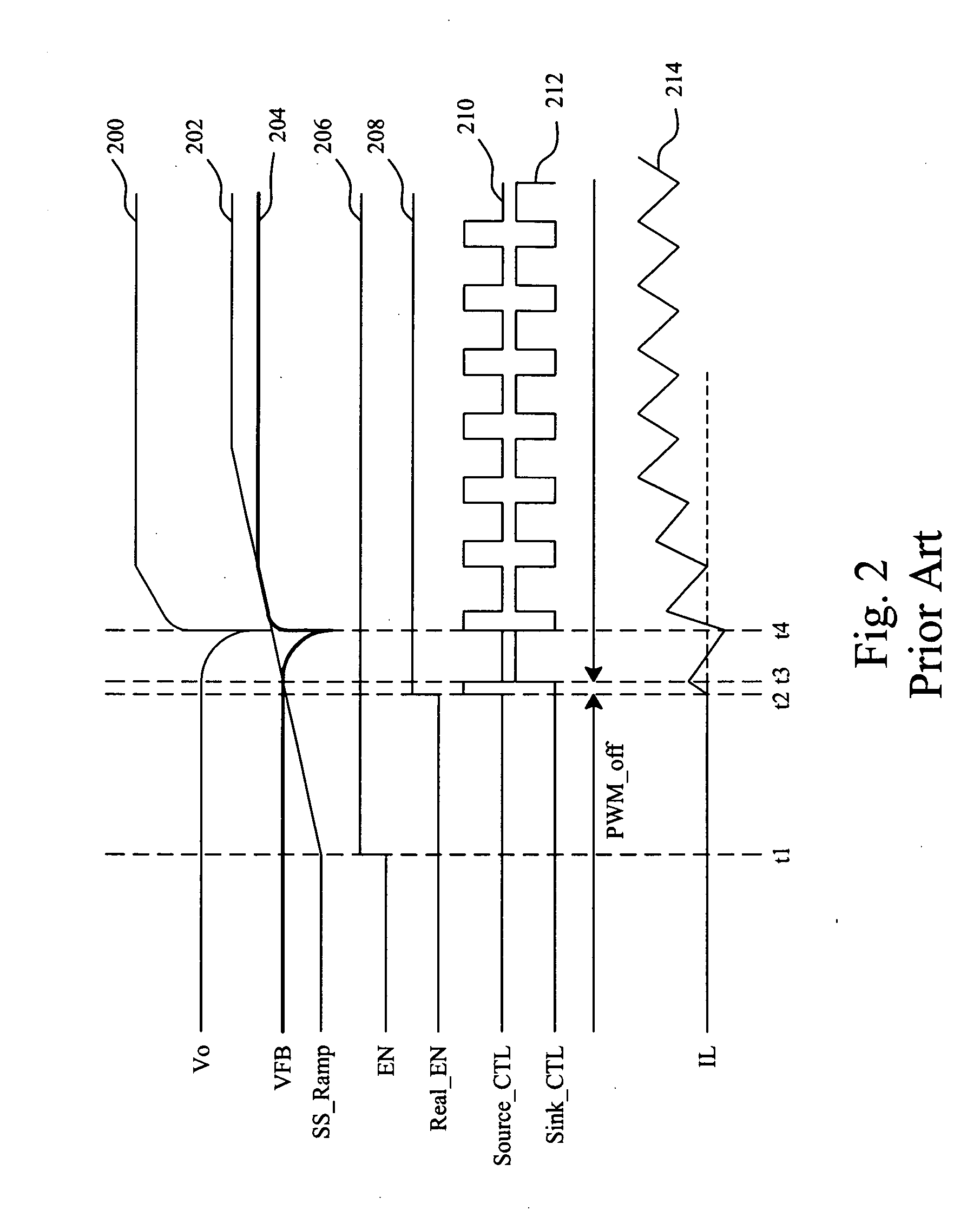
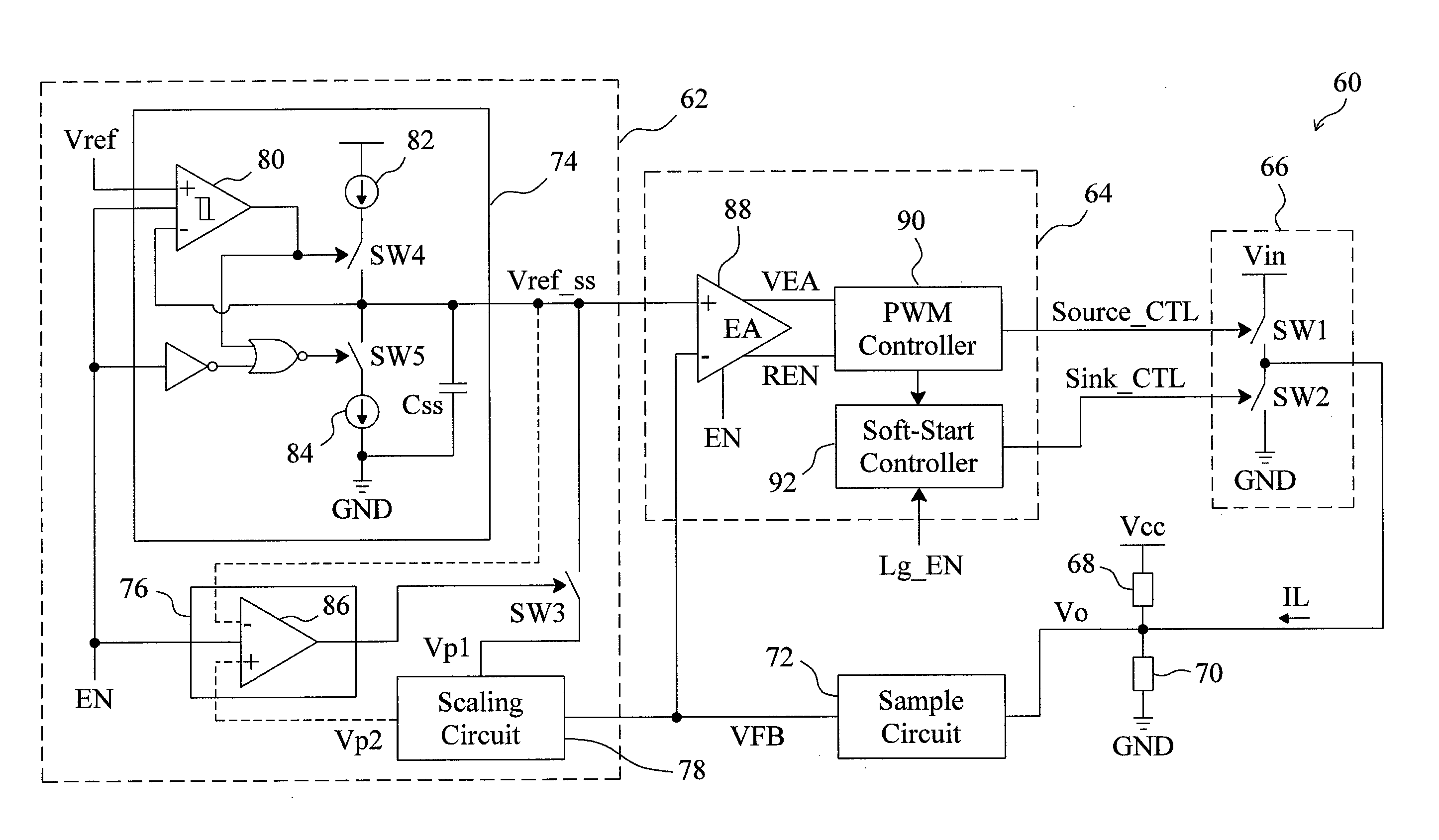
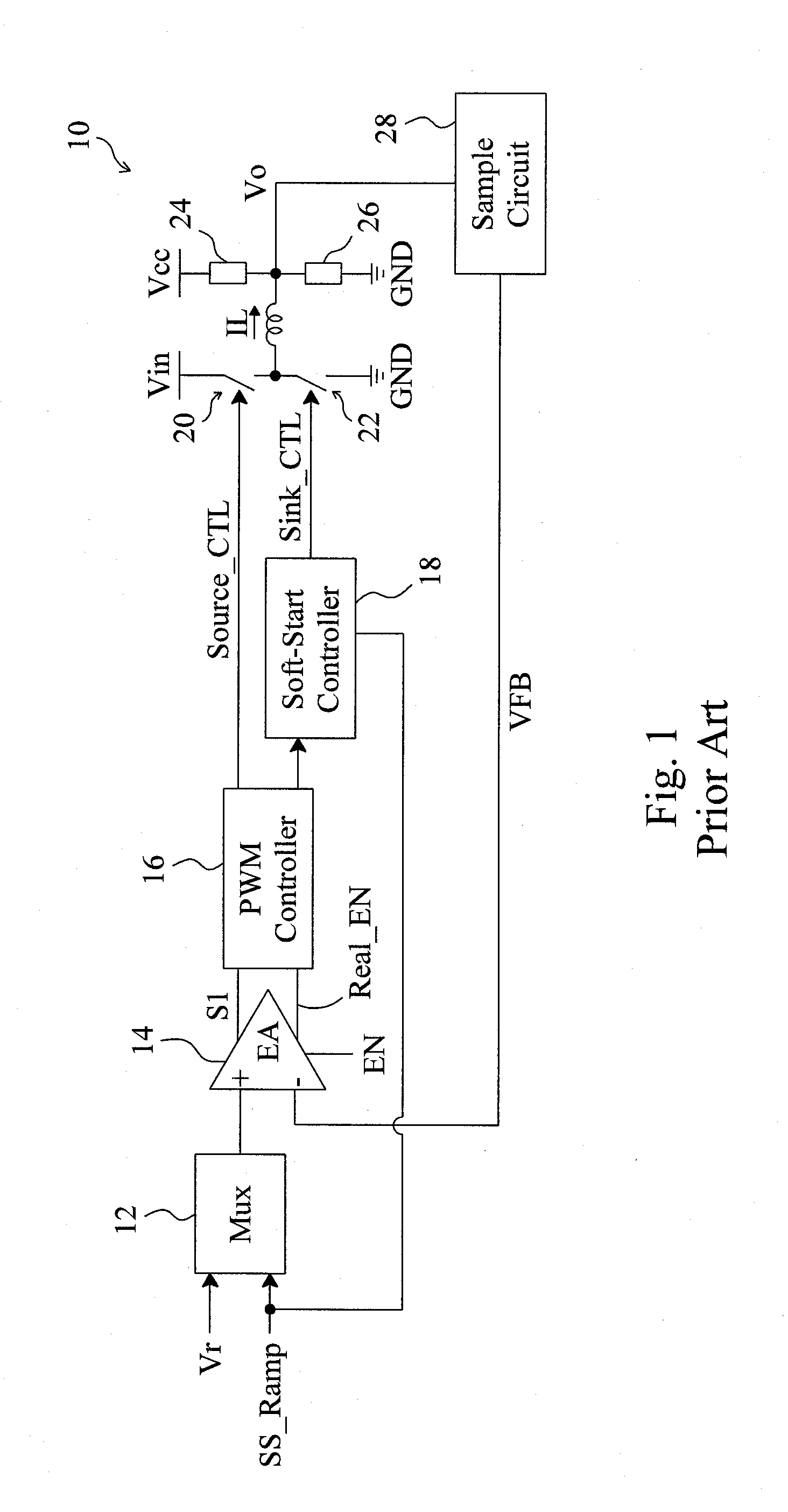
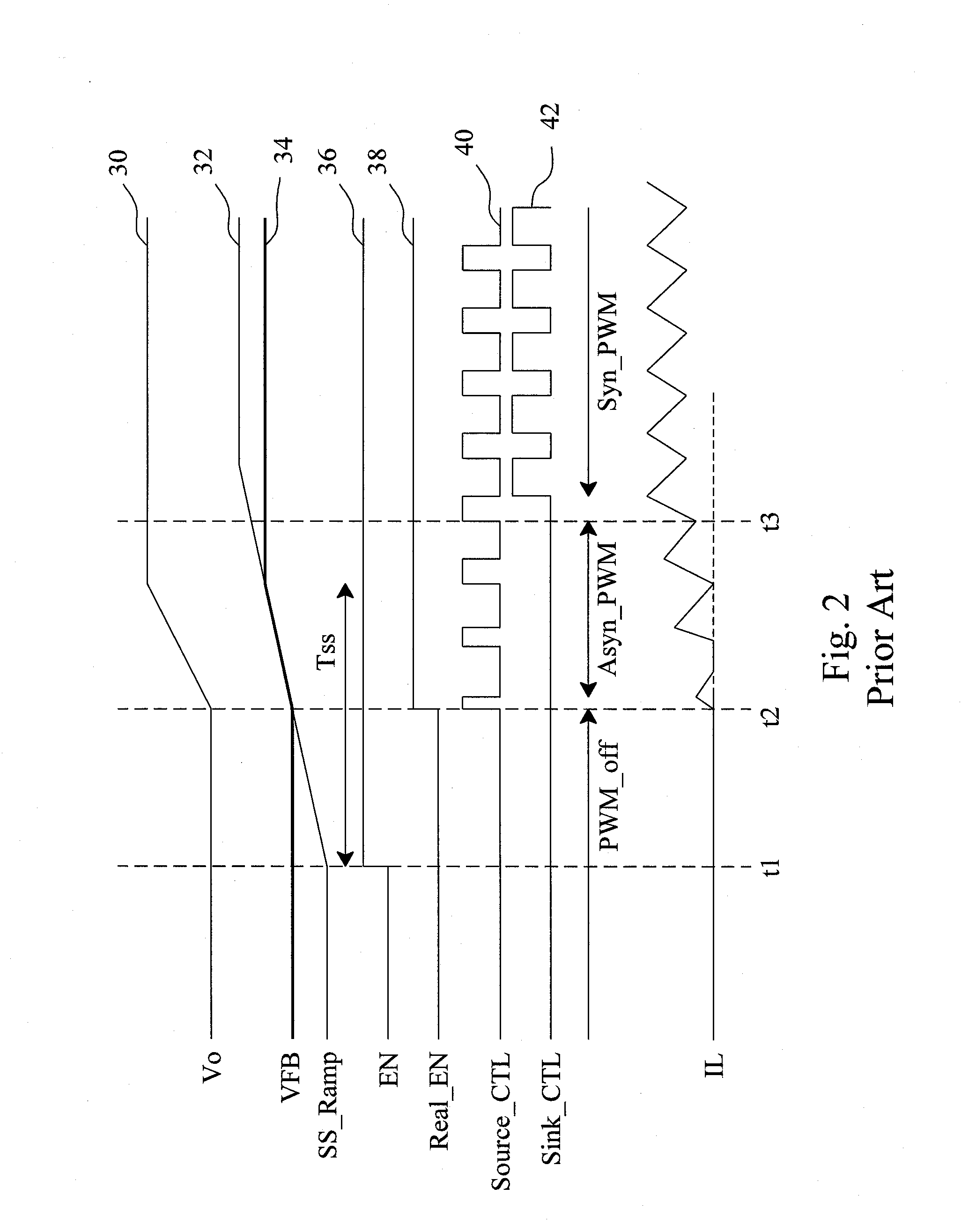
Circuit and method for soft start from a residual voltage
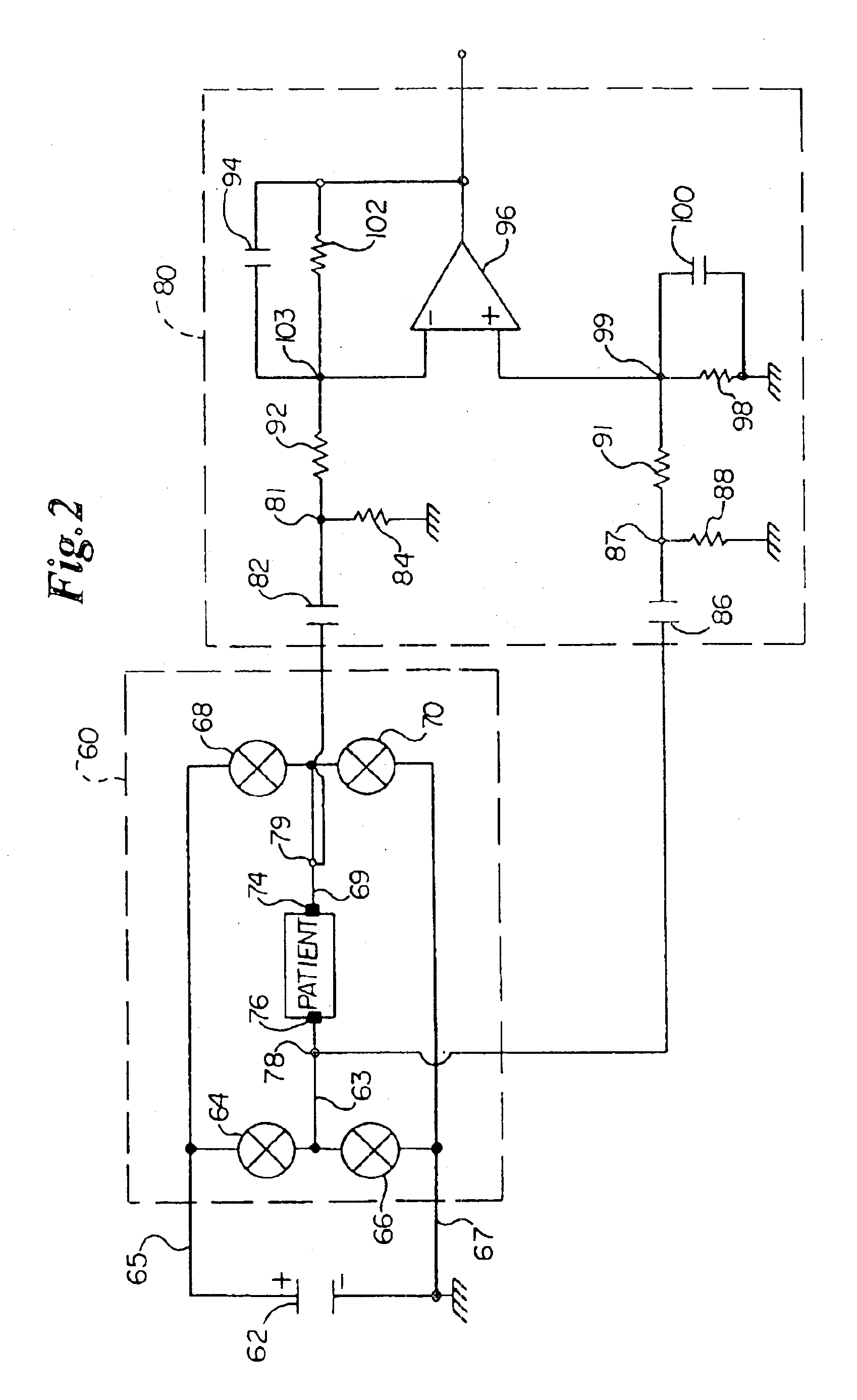
A circuit and method for soft start of a system compare a feedback signal produced from an output voltage of the system with a ramp signal to generate a comparison signal, and enables the system once the comparison signal indicating the ramp signal reaches the feedback signal, such that the output voltage becomes active from a residual voltage toward a target level.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
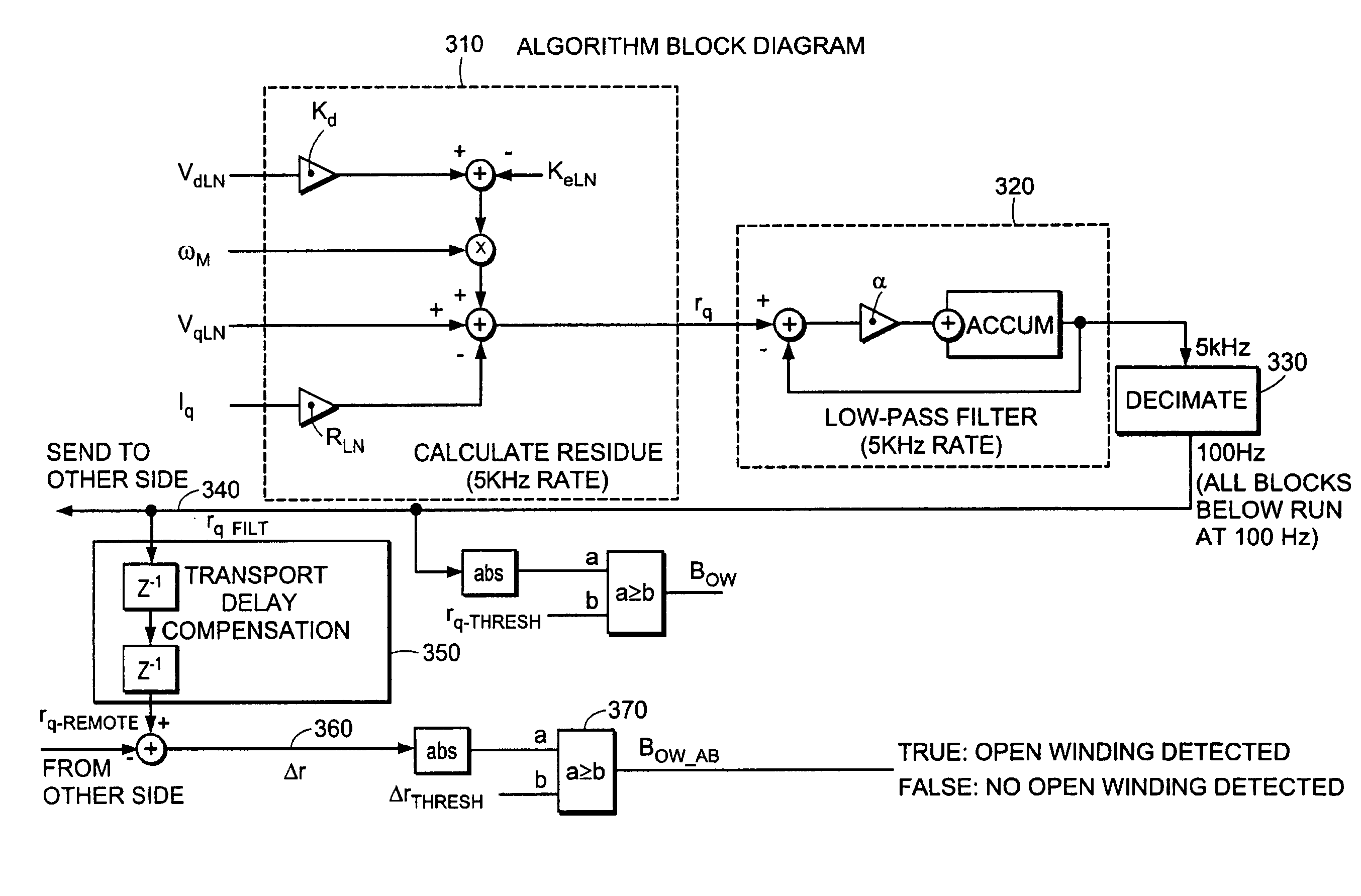
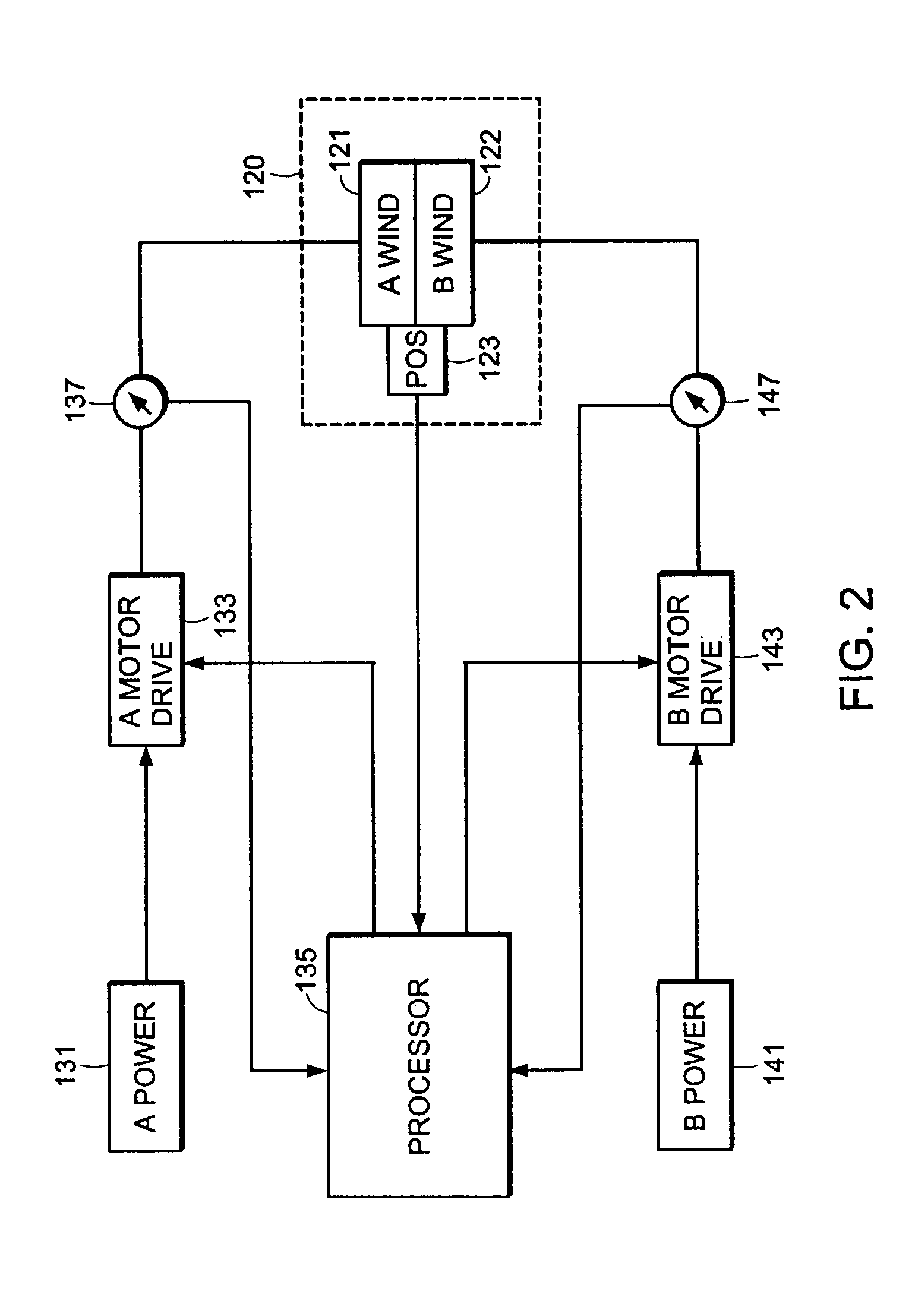
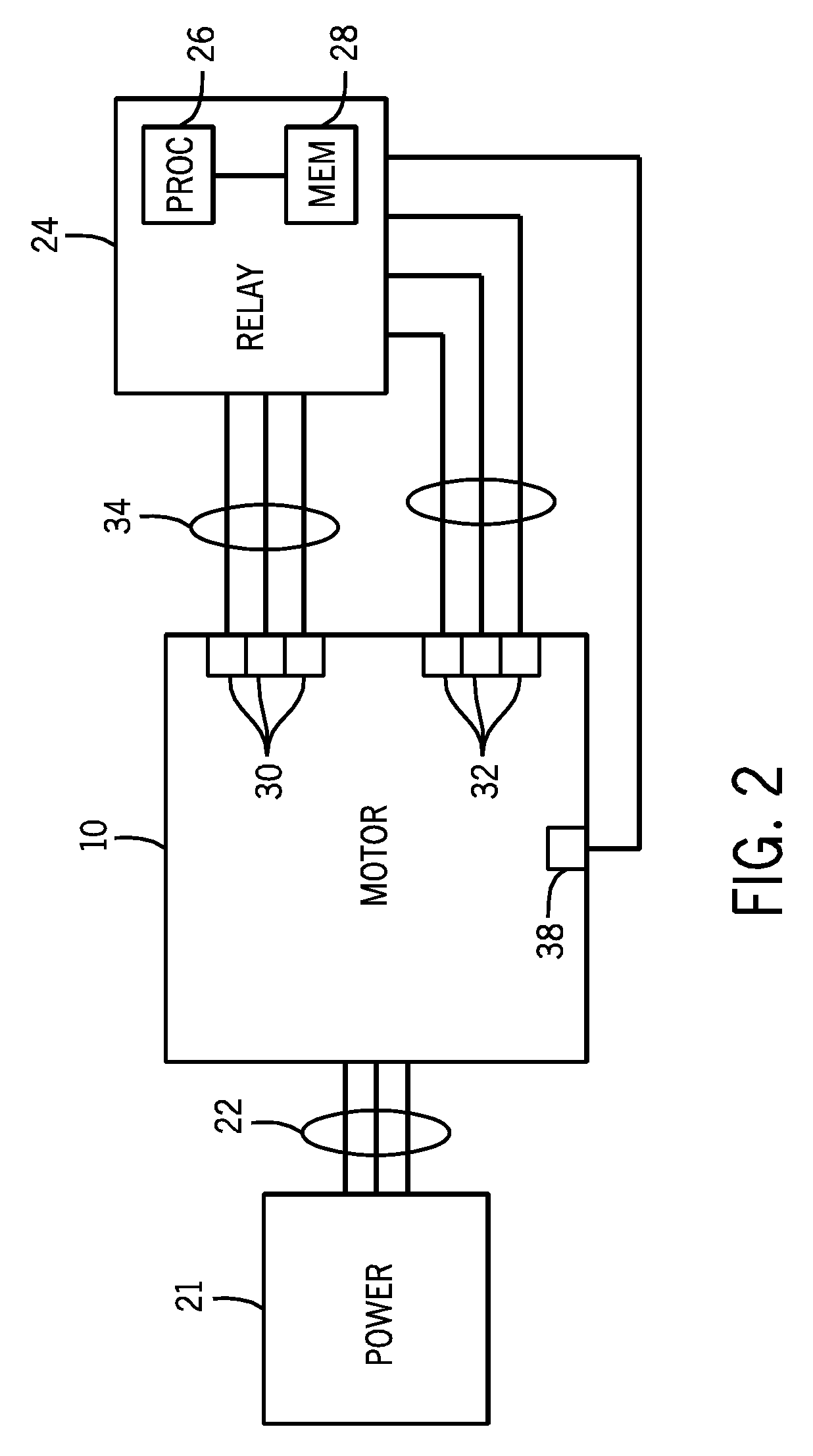
Model-based fault detection in a motor drive
A method for detecting an open winding in a motor. The method employs passive monitoring of the voltage, current and speed of the motor. A residue voltage is calculated that equals the difference between an idealized set of voltage drops across the motor load elements and the actual voltage drops. When the magnitude of the residue voltage equals or exceeds a threshold, an open winding condition may be declared and appropriate action may be taken.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
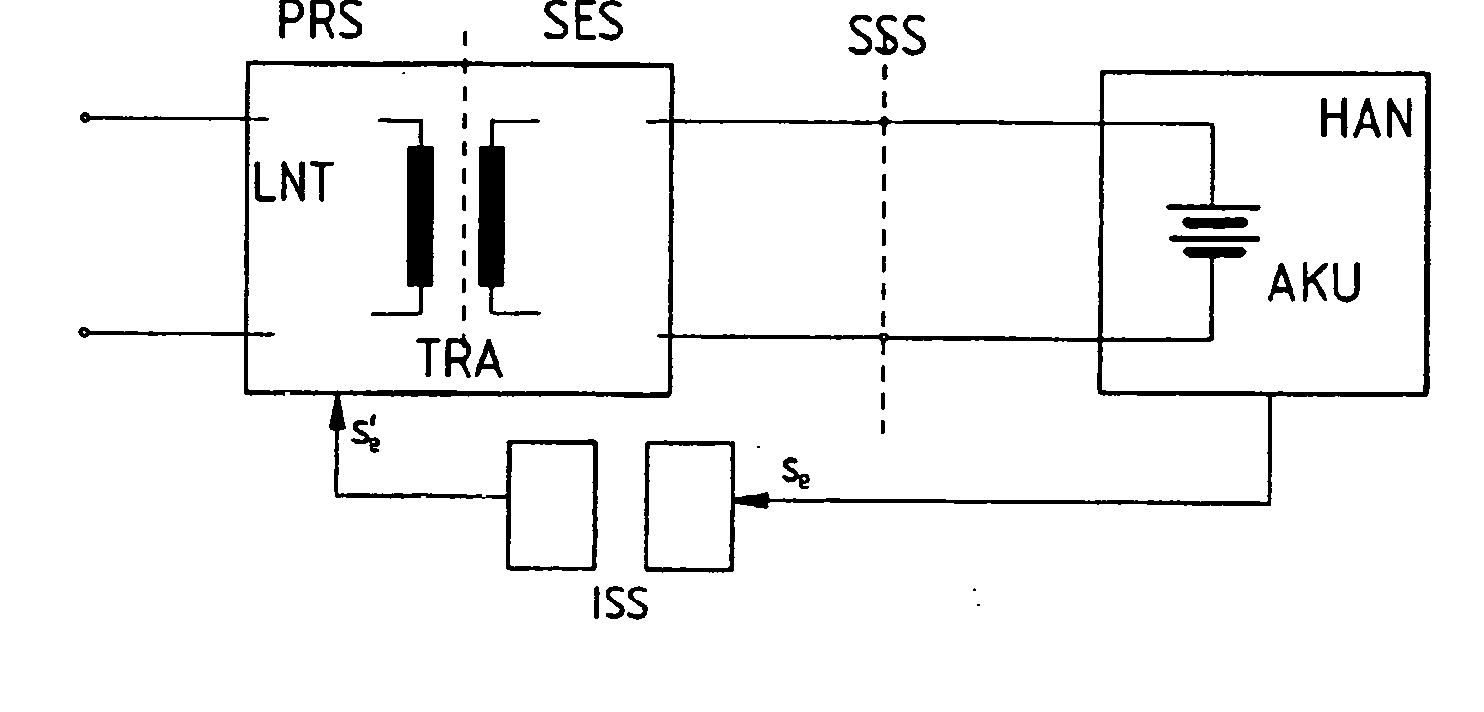
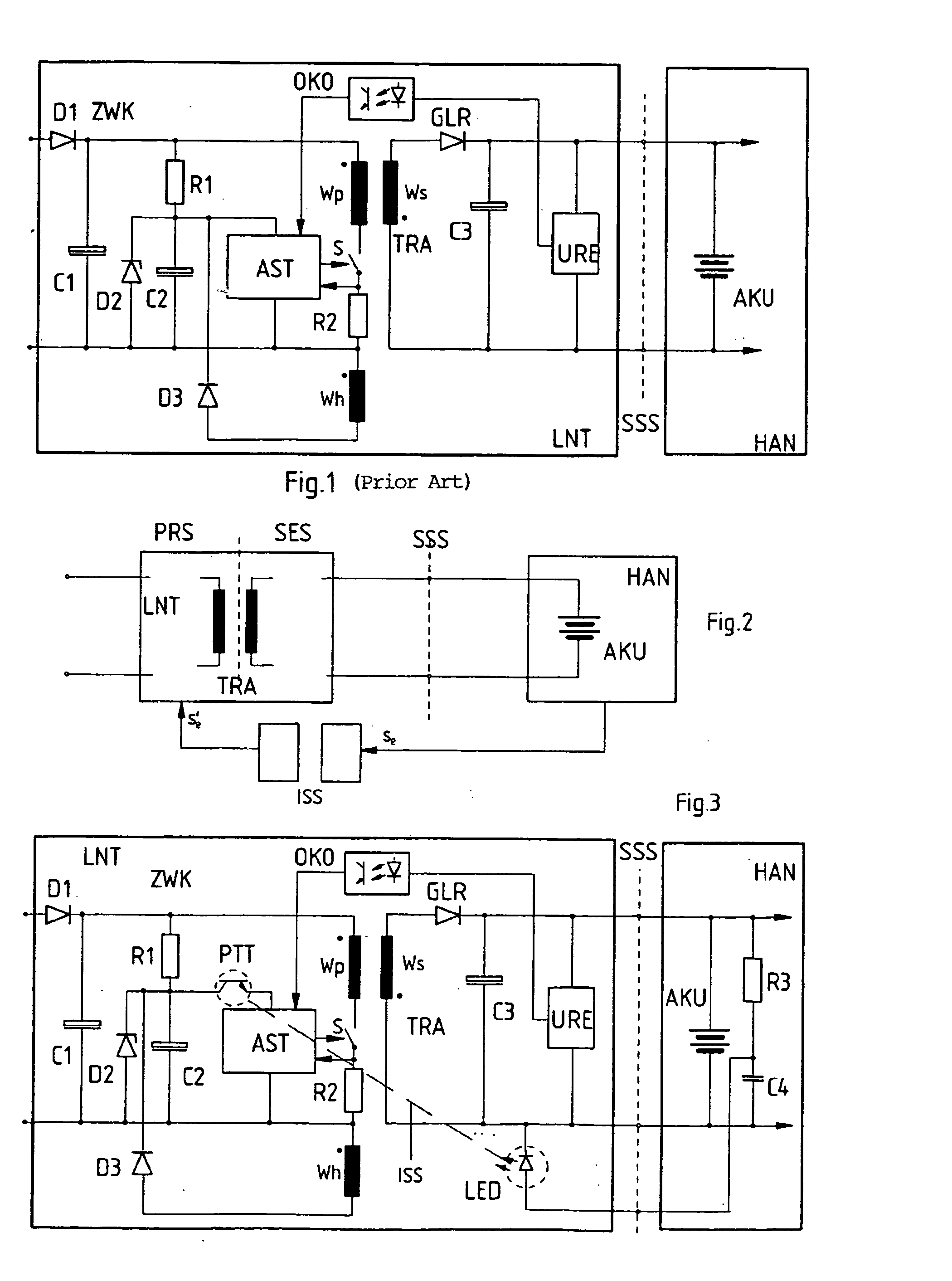
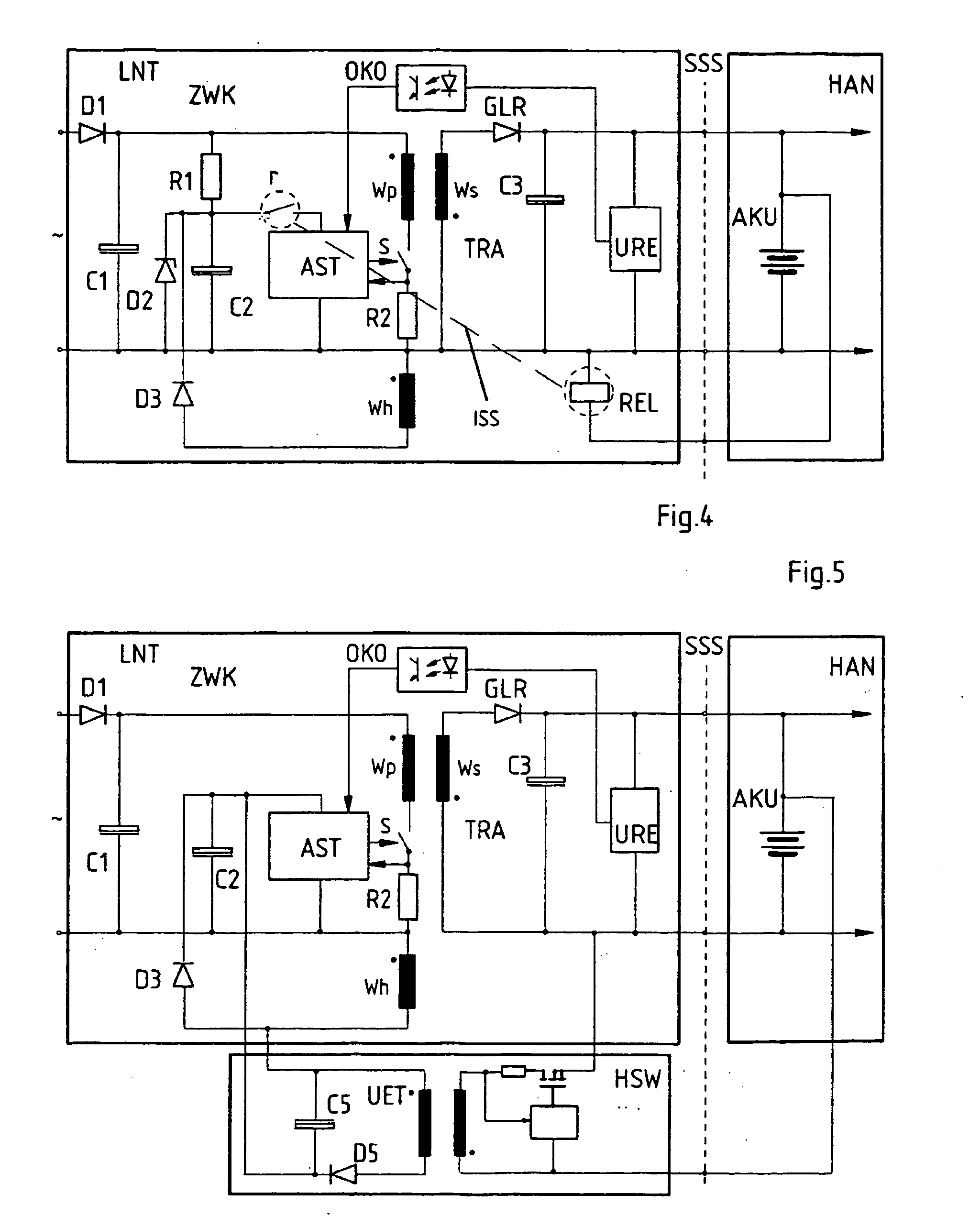
Power supply unit
InactiveUS20050168189A1Idle losses are sharply reduced or completely eliminatedLow costBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerEngineeringSecondary circuit
A charger (LNT) for a battery-fed electrical / electronic device (HAN), with an electrically isolating transformer (TRA), which can be fed at its primary circuit and of which the secondary circuit features a converter / rectifier (GLR) to supply a charge voltage for the battery (AKU) of the device, where charger and device can be connected via a plug-in electrical interface (SSS), and. when the connection is established to the plug-in interface (SSS) a switch-on signal (se) can be derived from the residual voltage of the battery (AKU), which can be forwarded via an isolating interface (ISS) from the secondary circuit (SES) to the primary circuit (PRS) to activate the charger (LNT).
Owner:SIEMENS AG OESTERR
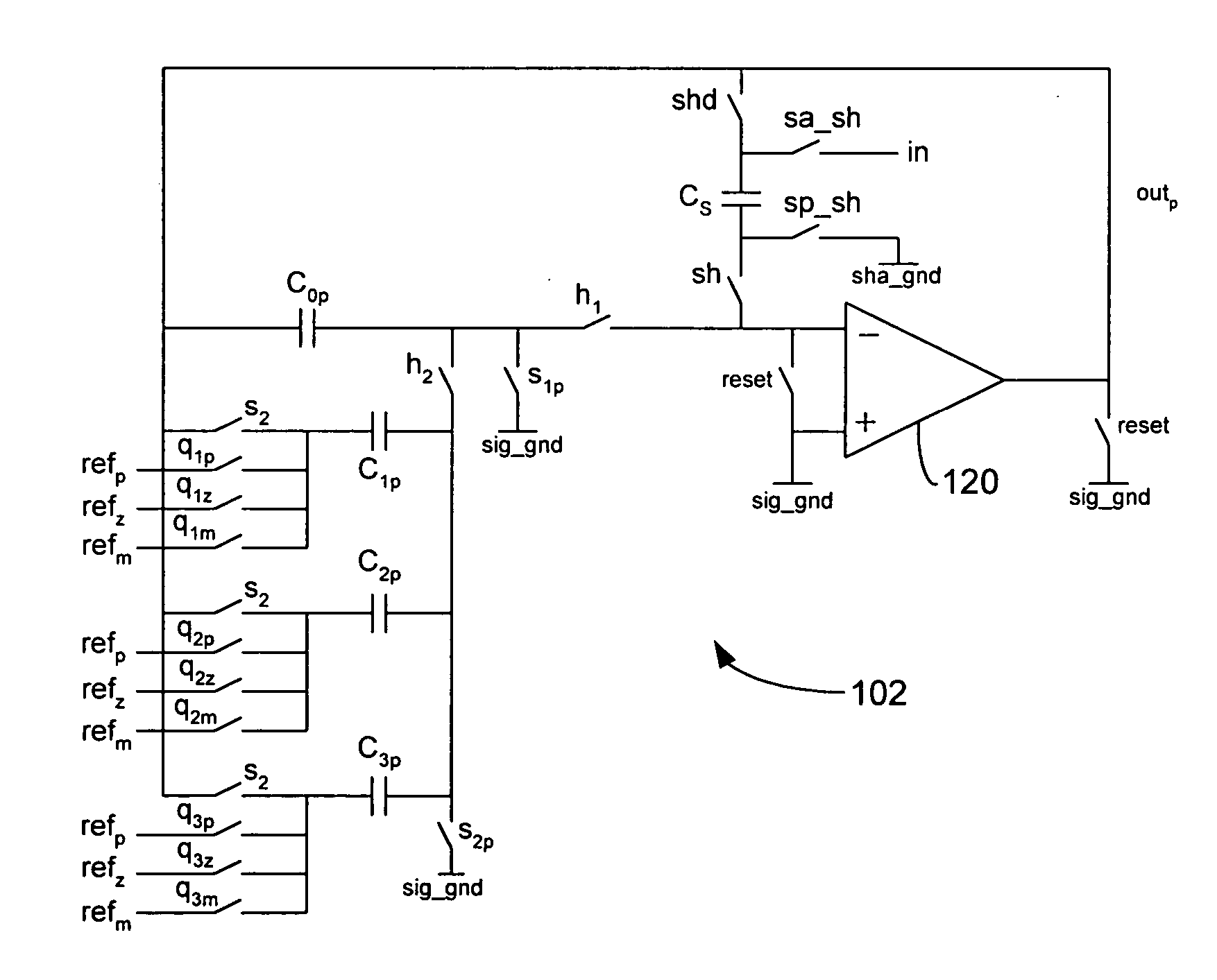
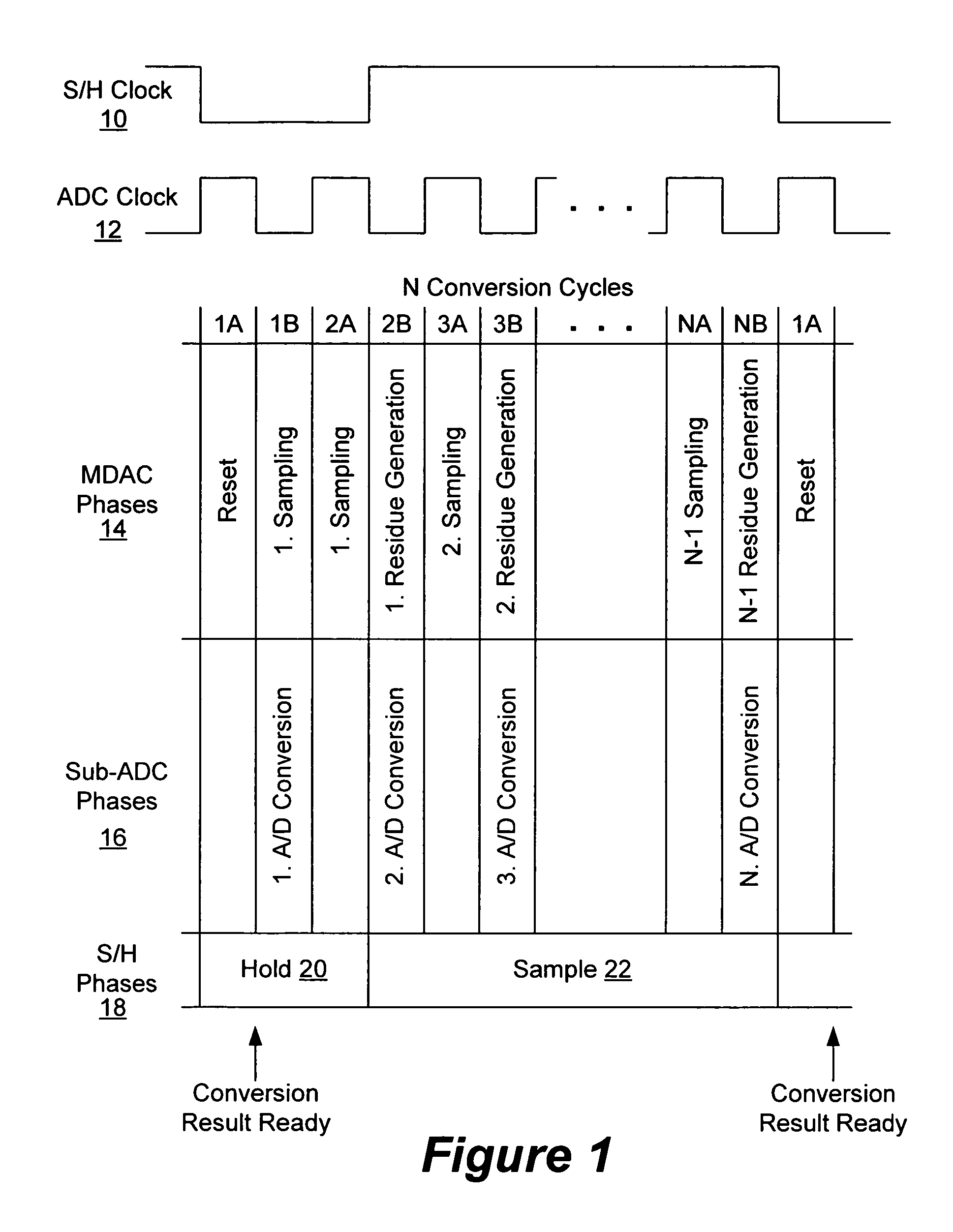
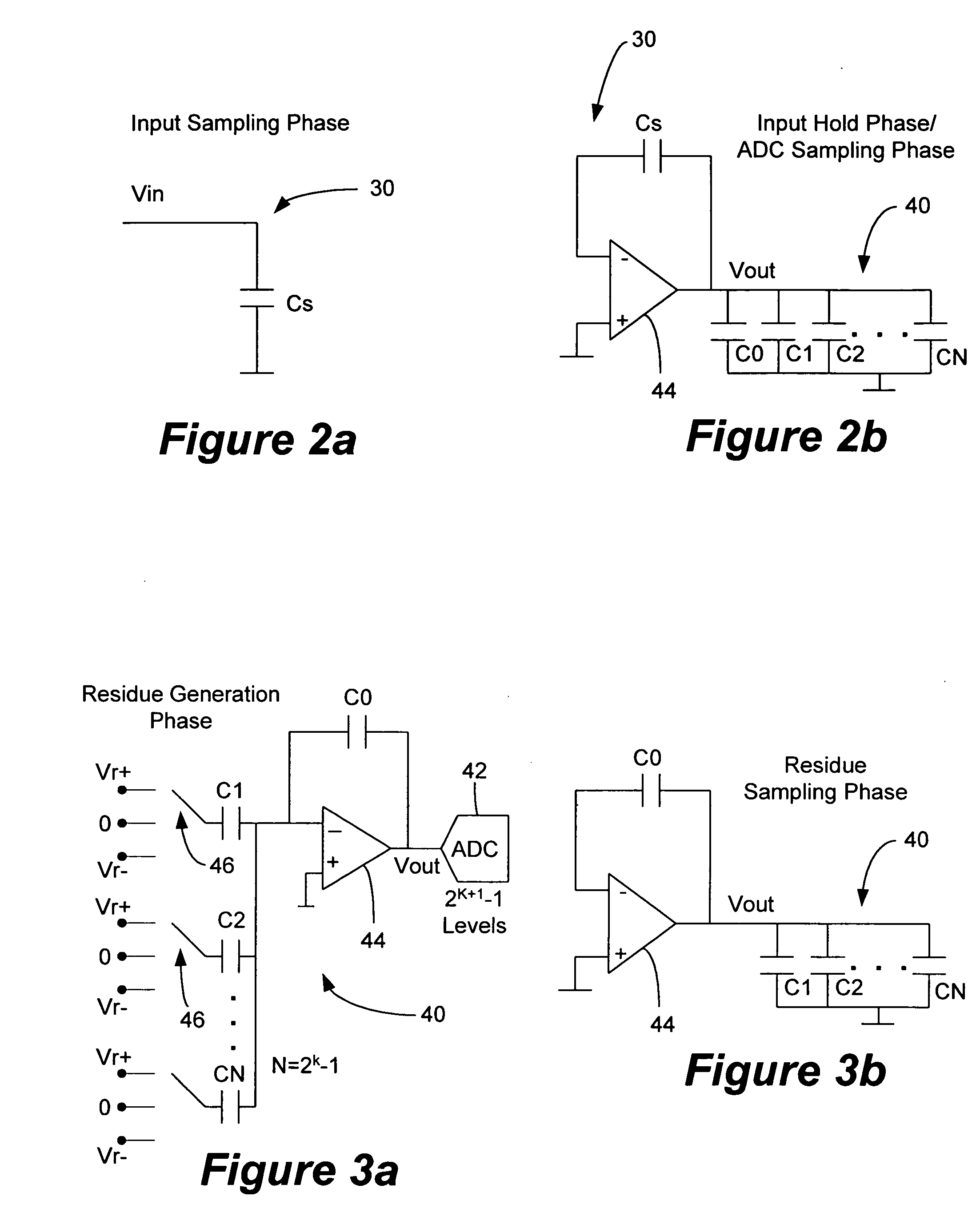
Architecture for an algorithmic analog-to-digital converter
ActiveUS20050140537A1Improve area efficiencyHighly suitableElectric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlAudio power amplifierControl signal
An algorithmic analog-to-digital converter (ADC) includes a sample-and-hold circuit and an ADC processing unit operating in parallel and sharing a single operational amplifier. The ADC processing unit includes an MDAC with a switched capacitor topology and a sub-ADC. The ADC processing unit is clocked by an internal clock that is N times faster than the sample-and-hold clock. Each cycle is further sub-divided into two phases. During one phase the capacitors are coupled to a residue or sampled voltage provided by the MDAC, and during another phase the capacitor are coupled to a reference voltage determined by the switch control signals generated by the sub-ADC. A set of data bits is generated by the ADC processing unit during each ADC clock cycle. The N sets of data bits are added to generate the digital output stream.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
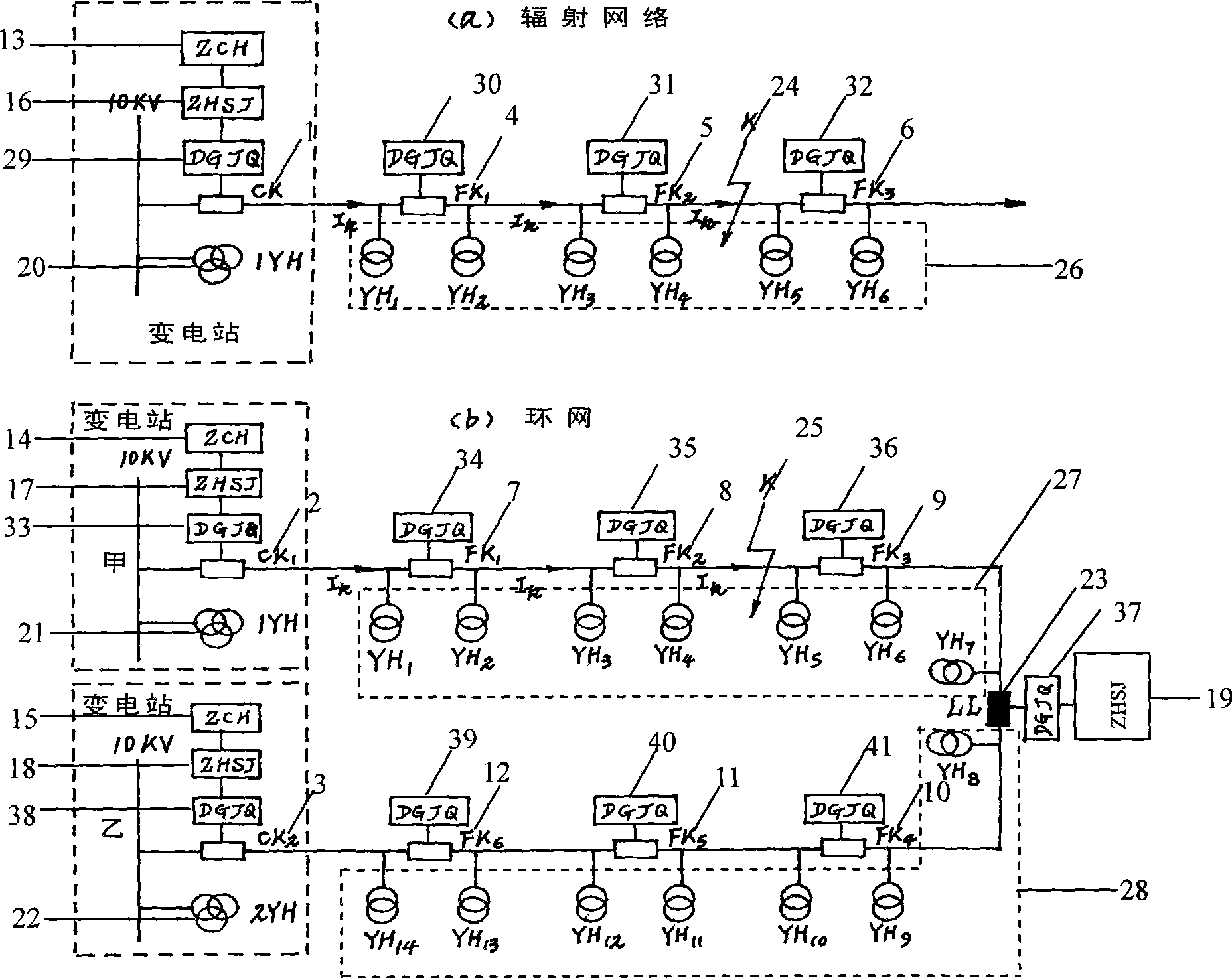
Method for detecting distribution network short circuit fault and restoring power supply in non-broken-down section
InactiveCN101534001AQuickly restore powerRestoration of power ensuresEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionFault locationElectricityThree-phase
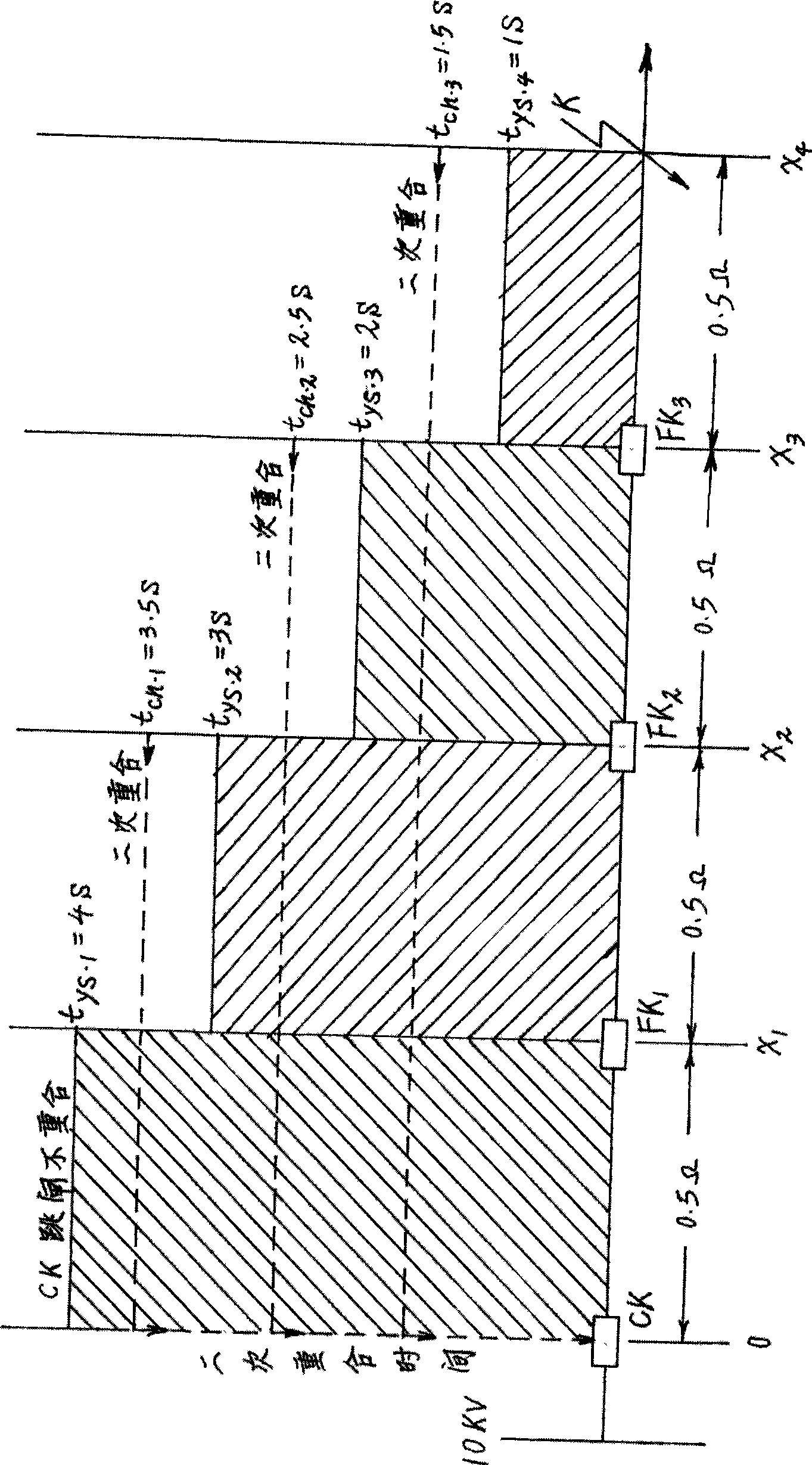
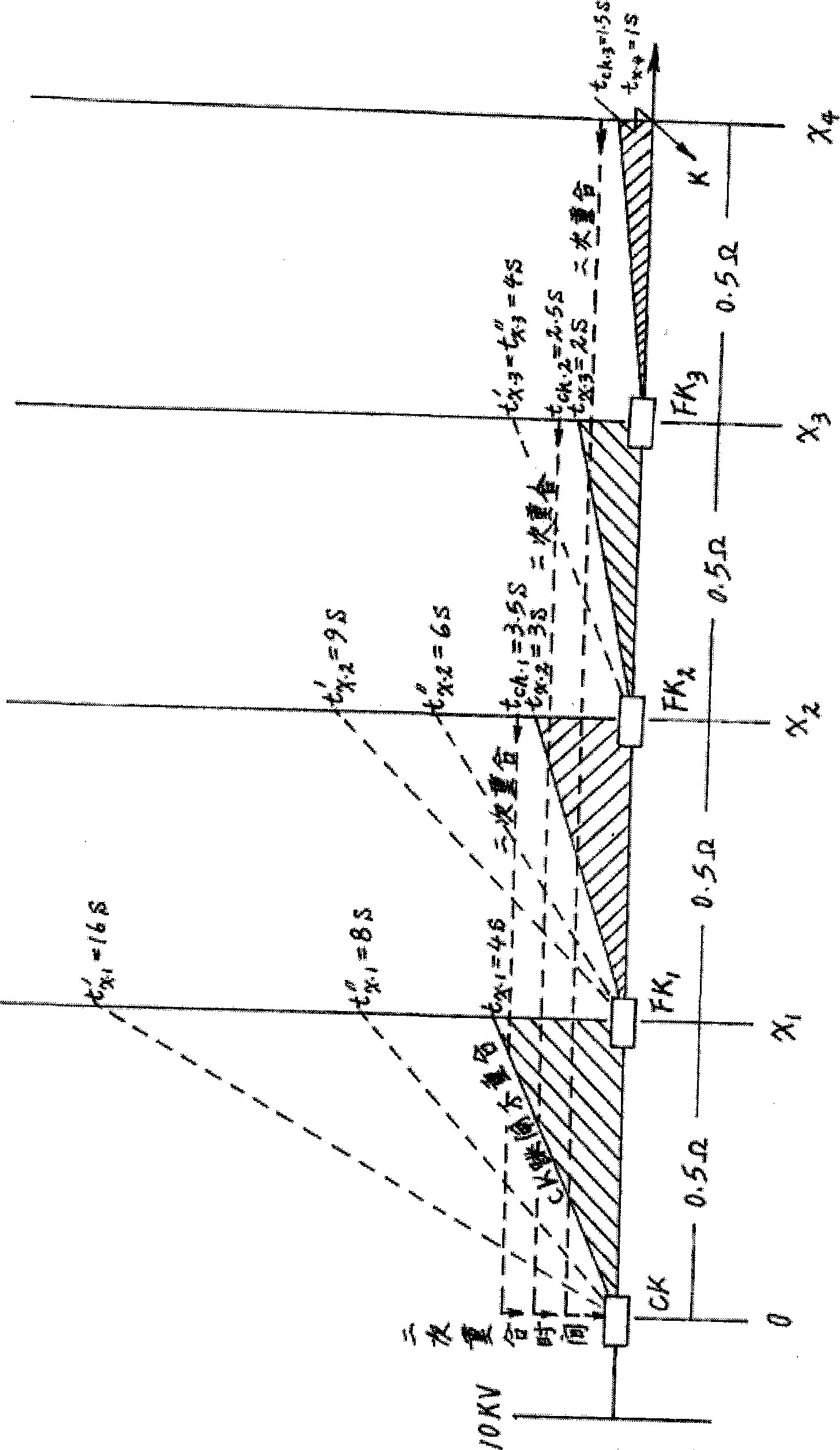
The invention relates to a processing method for distribution network short circuit fault, in particular to a method for detecting the distribution network short circuit fault and restoring power supply in a non-broken-down section, and capable of achieving feeder line automatic local control. Short circuit fault detectors A (29) to M (41) are utilized for detecting the short circuit fault, and then reclosing time selection devices A (16), B (17), C (18) and D (19) are utilized for restoring power supply in the non-broken-down section. When short circuit happens, outlet switch A (1) or B (2) and C (2) protect the tripping in a relay way, and during permanent short circuit, the outlet switch A (1) or B (2) and C (3) protect the tripping of a second time in the relay way, a short circuit fault switch is pressed to achieve zero current tripping closedown, and a non-fault switch detects residual voltage cut-off and closedown for the second time. The outlet switch A (1) or B (2) and C (3) are coincided for the second time, so that the fault section is separated, the operation time limit of the non-fault switch is longer than the second reclosing time, three-phase normal voltage can be obtained, and the tripping no longer happens. As for the condition that the power is supplied by round network, one side of an interconnection switch (23) is deprived of electricity, non-fault switch for switching-on and tripping is delayed, and the voltage switching-on is detected in sequence.
Owner:江苏汉天星配电自动化科技有限公司
Stator turn fault detection apparatus and method for induction machine
A system and method are provided for correction of parameters used in determination of stator turn faults of an induction motor. An embodiment may include determining a residual impedance and / or a residual voltage of the motor, and correcting a normalized cross-coupled impedance based on the residual impedance and residual voltage. Additional embodiments may include measuring an operating temperature of the motor and determining a negative sequence impedance of the motor based on the temperature. Another embodiment may include measuring voltages and currents of the motor and determining phasors for the voltages and currents using compensation for variations from a nominal frequency of the motor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
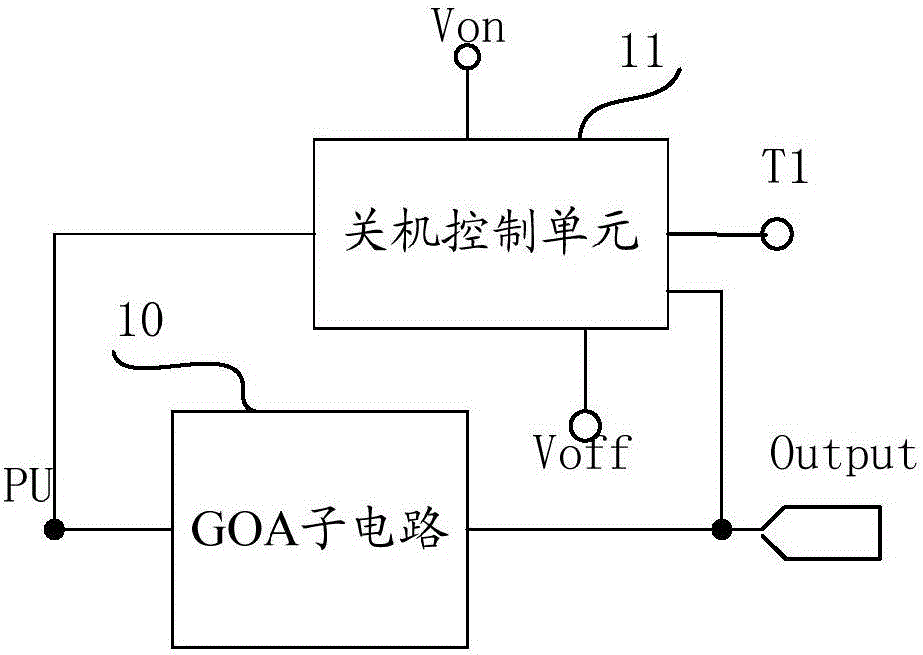
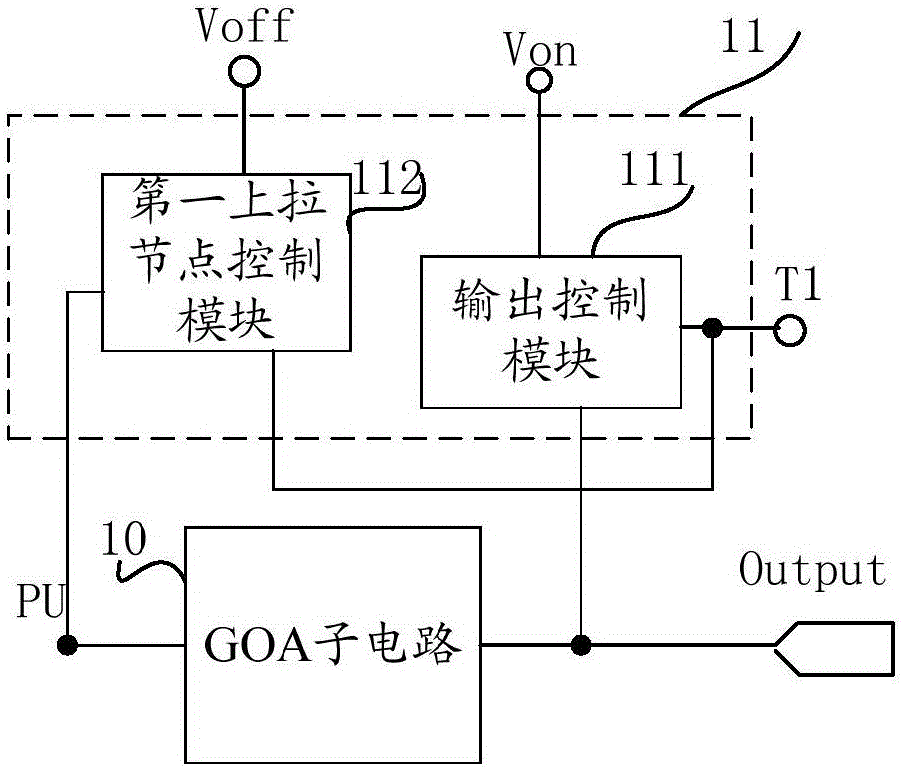
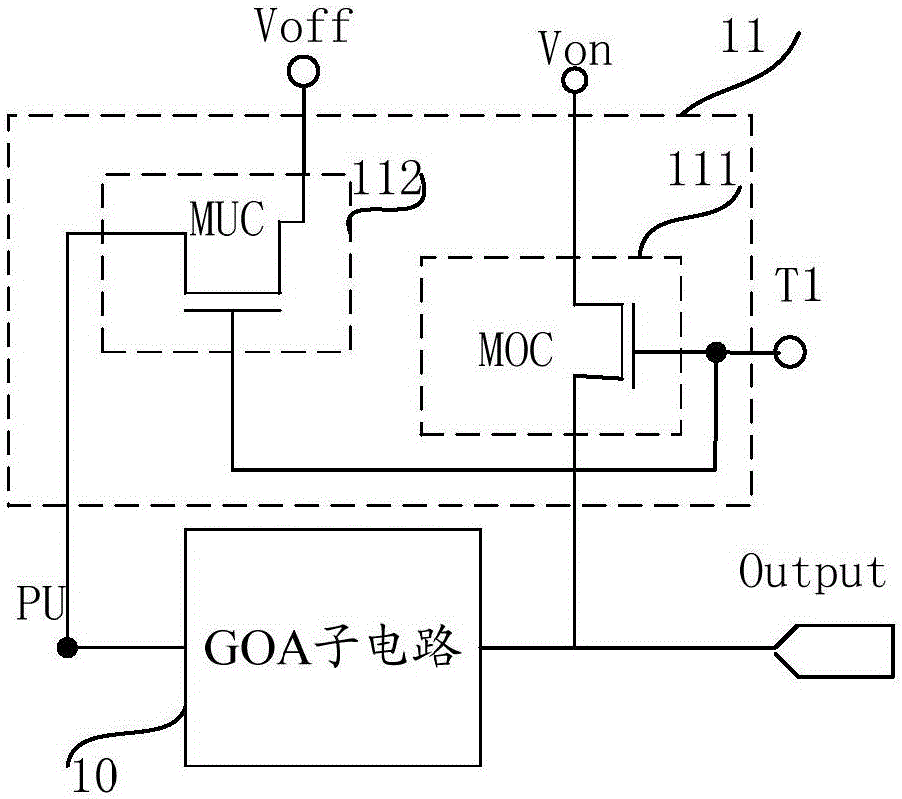
Shift register circuit, driving method, GOA circuit and display device
InactiveCN106486085APrevent feature driftEliminate shutdown afterimageStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerControl signal
The invention provides a shift register circuit, a driving method, a gate-on-array (GOA) circuit and a display device. The shift register circuit comprises a GOA sub circuit including a pull-up node. Besides, the shift register circuit also includes a shutdown control unit that is used for controlling a cut-in voltage output line to apply a cut-in voltage to a gate driving signal output terminal when a shutdown control signal of a display panel is received and controlling the pull-up node to connect a turn-off voltage output line. According to the invention, the shutdown ghost can be eliminated by using the shutdown control unit; and the characteristic drift of the transistor controlled by the pull-up node due to the residual voltage of the pull-up node after shutdown can be prevented, so that an adverse phenomenon can be prevented to a certain extent.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Circuit and method for soft start from a residual voltage
A circuit and method for soft start of a system compare a feedback signal produced from an output voltage of the system with a ramp signal to generate a comparison signal, and enables the system once the comparison signal indicating the ramp signal reaches the feedback signal, such that the output voltage becomes active from a residual voltage toward a target level.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
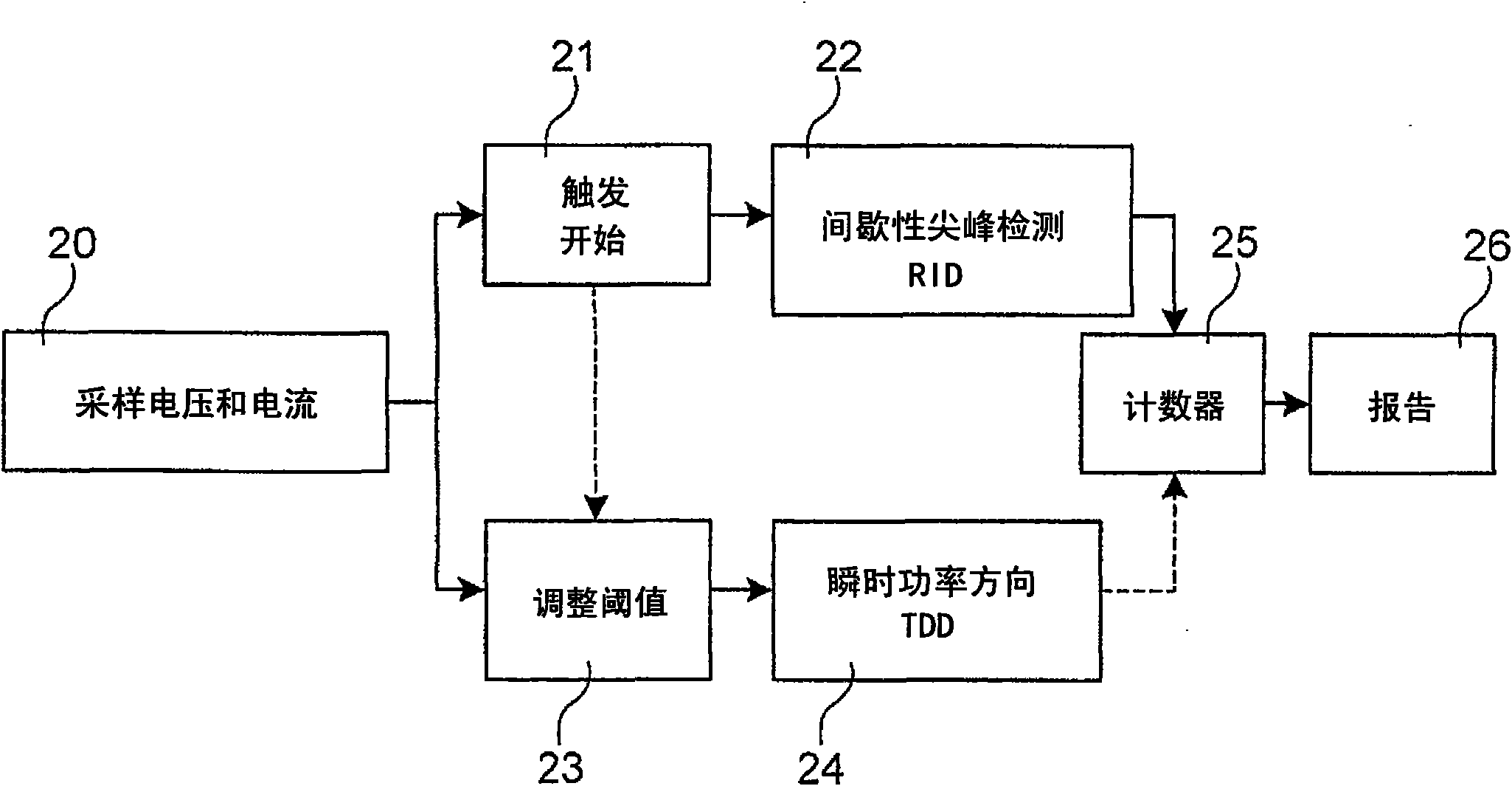
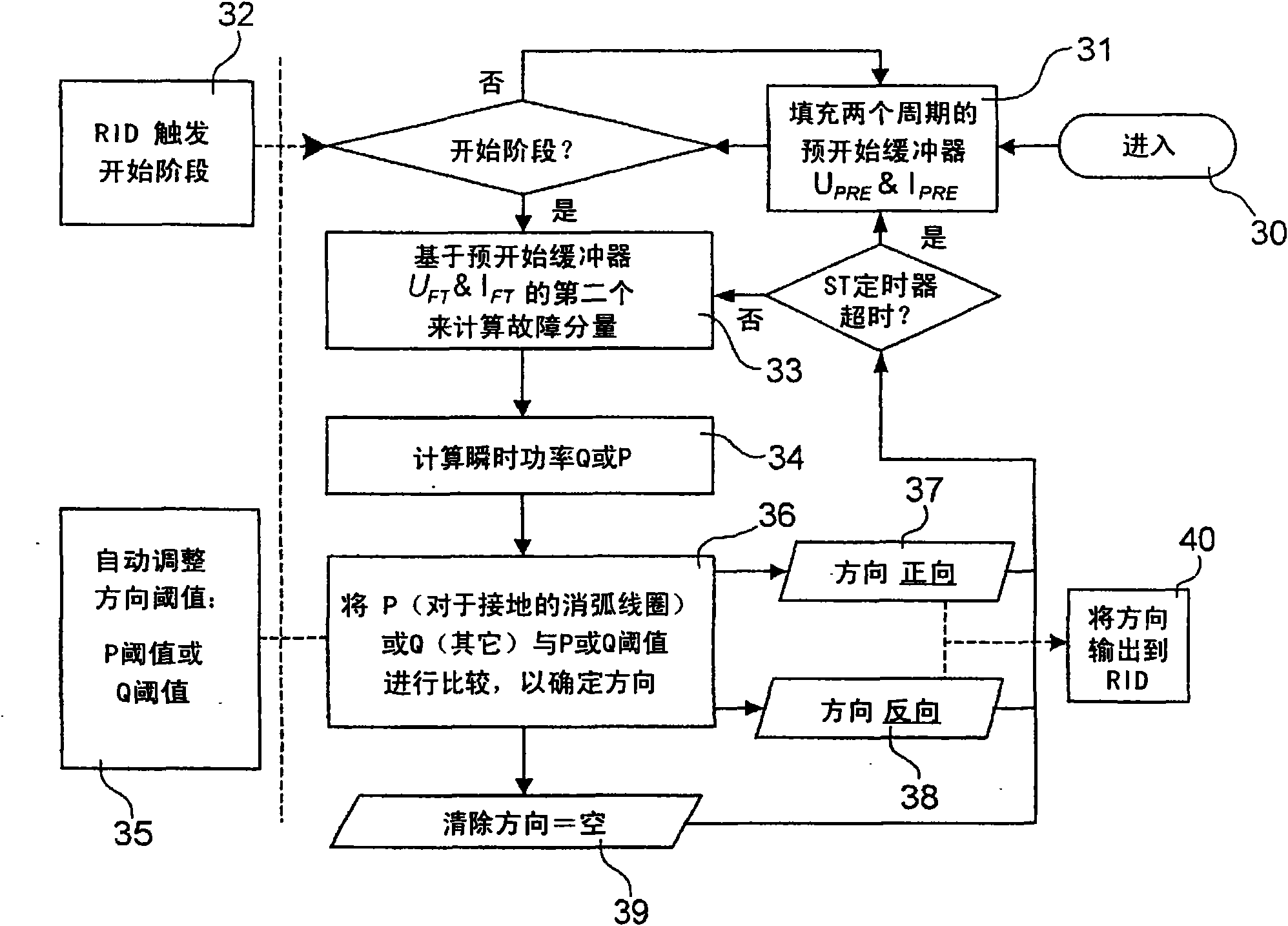
Method and system for carrying out transient and intermittent earth fault detection and direction determination in three-phase medium-voltage distribution system
InactiveCN101858948ASuitable for analysisEasy to useEmergency protective arrangement detailsFault location by conductor typesTransient stateDistribution system
The invention relates to a method and a system for carrying out transient and intermittent earth fault detection and direction determination in a three-phase medium-voltage distribution system comprising a plurality of circuits. The system comprises a sampling unit for sampling residual currents and residual voltages on the circuits, a transient direction detection unit based on the instantaneous power, a random intermittent detection unit based on the intermittent change of the magnitude of the residual current, an integrated transient direction detection and random intermittent detection unit, and an alarm unit for indicating the inspection of the status of a circuit.
Owner:AREVA T& D UK +1
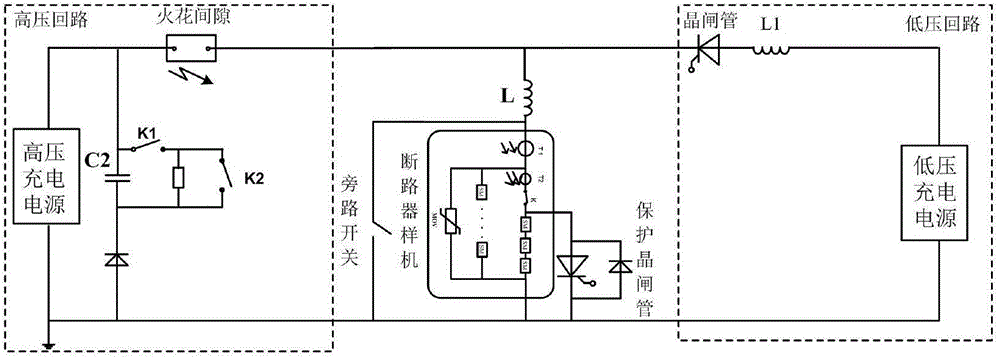
Breaking test device and test method for high-voltage direct current breaker
The invention relates to a breaking test device and test method for a high-voltage direct current breaker. A reactor L of the device is connected in series with the high-voltage direct current breaker and then separately connected in parallel with a high-voltage circuit and a low-voltage circuit; a bypass switch is connected in parallel to two ends of the high-voltage direct current breaker; and a protection thyristor is connected in parallel to two ends of a full-bridge module in a mechanical switch-full-bridge module branch. In the test method, rated current from a low-voltage high-current source is injected to the breaker via a thyristor isolating valve; a capacitor is charged by a high-voltage low-current source, initial test voltage is established, the high-voltage circuit is discontinuously triggered by spark, the test current is adjusted by the reactor and then injected into the breaker, the thyristor isolating valve is switched off, breaking is accomplished when the expected breaking current or the maximum breaking time arrives, and the breaker tolerates transient recovery overvoltage and residual voltage of the capacitor in the high-voltage circuit. The device and the method can reproduce current, voltage and thermal stress of the high-voltage direct current breaker in practical operation, are high in test equivalence, and have the capability of reliably detecting the breaking performance of the breaker.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
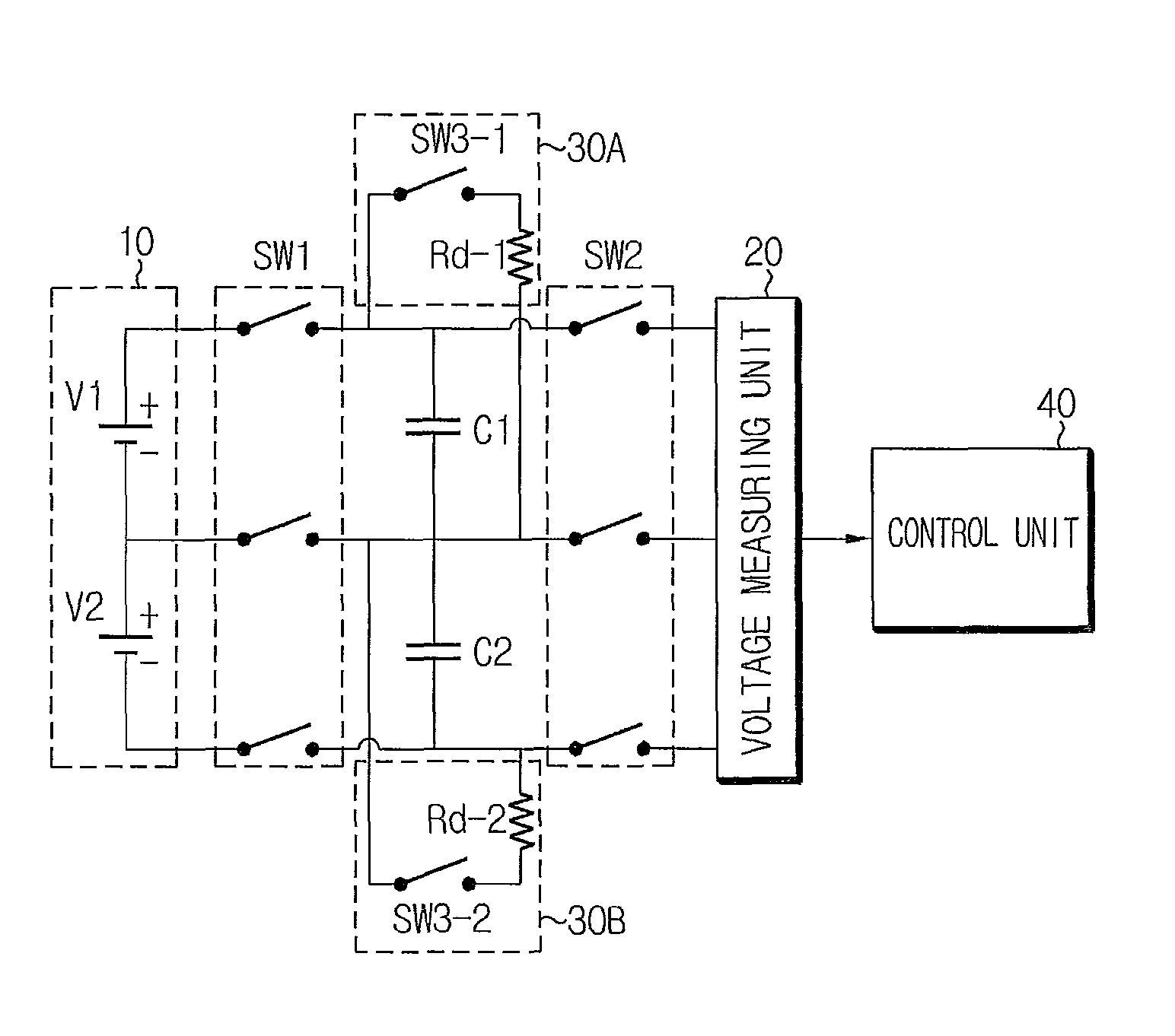
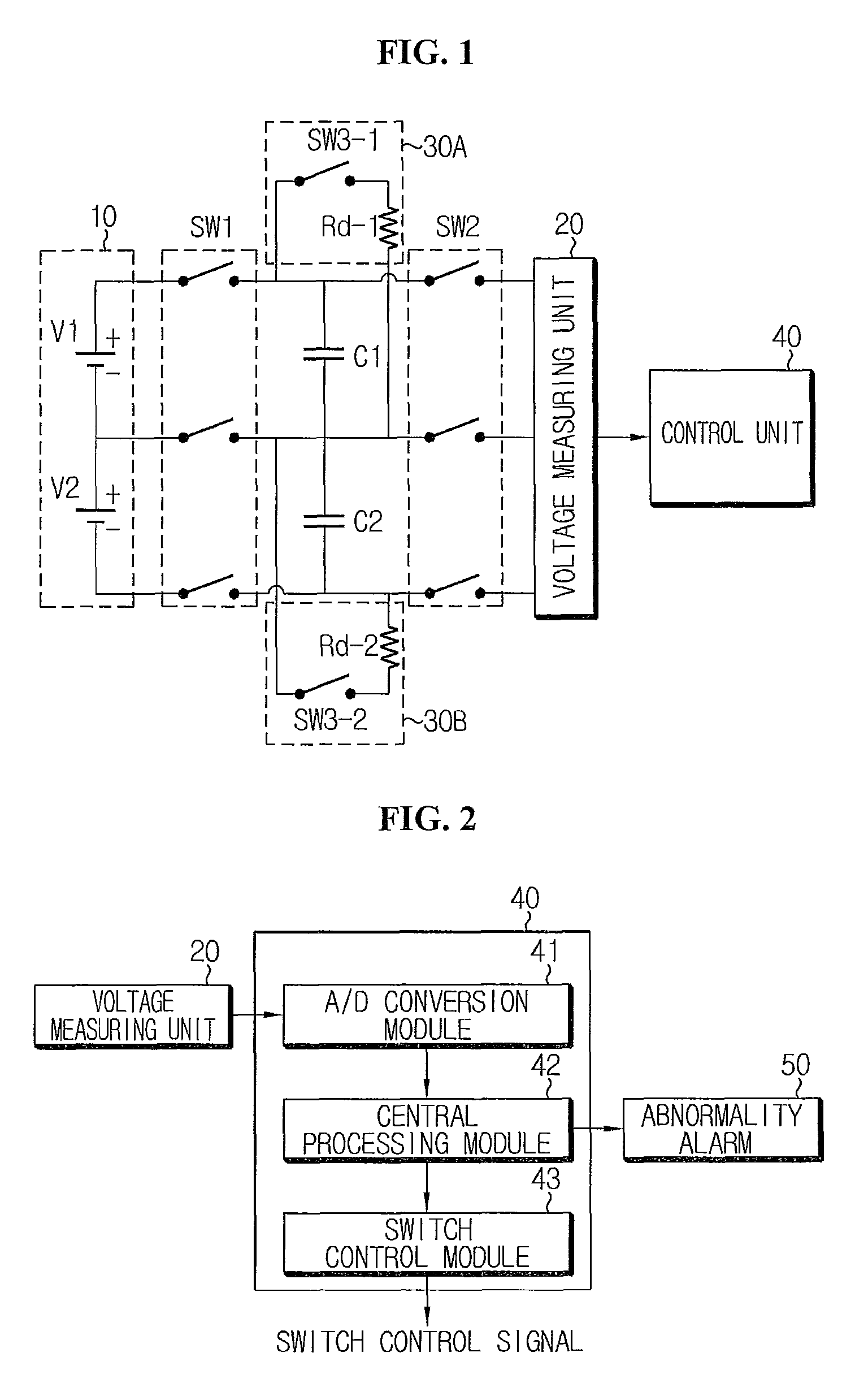
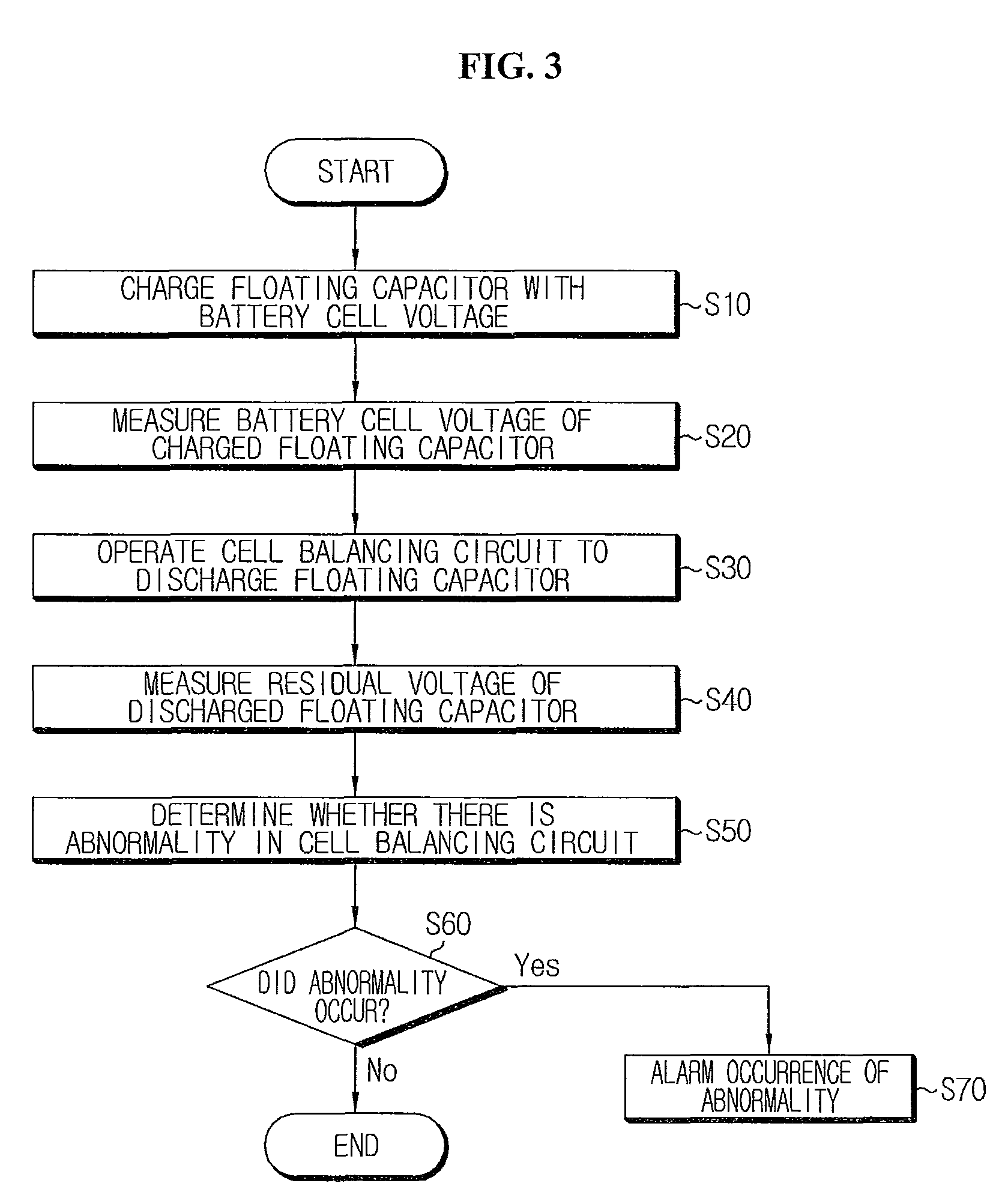
Apparatus and method for diagnosing abnormality in cell balancing circuit
Provided are an apparatus and a method for diagnosing an abnormality in a cell balancing circuit. The apparatus may include a floating capacitor charged with voltage of a battery cell, a cell balancing circuit for discharging the floating capacitor, a voltage measuring unit for measuring the battery cell voltage of the charged floating capacitor and a residual voltage of the discharged floating capacitor, and a control unit for determining an abnormality in the cell balancing circuit based on the residual voltage of the discharged floating capacitor.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Permanent magnet synchronous motor field failure diagnosis method based on residual voltage after ac dump
InactiveCN103454585AEasy to operateOvercoming diagnostic deficienciesDynamo-electric machine testingMotor speedFrequency changer
The invention discloses a permanent magnet synchronous motor field failure diagnosis method based on residual voltage after ac dump and belongs to the field of electric automobile motor failure diagnosis. The method includes the steps of collecting a voltage momentary signal of any phase of a stator end at the alternating current dumping moment, capturing the waveform of the residual voltage after ac dump since the alternating current dumping moment from the voltage momentary signal, initially judging the probability of the field failure, conducting frequency spectrum conversion on the captured residual voltage after ac dump, determining a fundamental component amplitude, determining the ratio of the fundamental component amplitude to the motor speed as a failure feature, setting a failure pre-warning threshold value, determining the ratio of the failure feature to the failure pre-warning threshold value as a failure factor, and judging whether the field failure exists or not according to the failure factor. The method is not influenced by the converter supply, a permanent magnet synchronous motor is detected without being influenced by the load, the defect that the traditional diagnosis is conducted through the stator current is effectively overcome, and the field failure of the electric automobile permanent magnet synchronous motor can be quite flexibly and quite reliably diagnosed.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
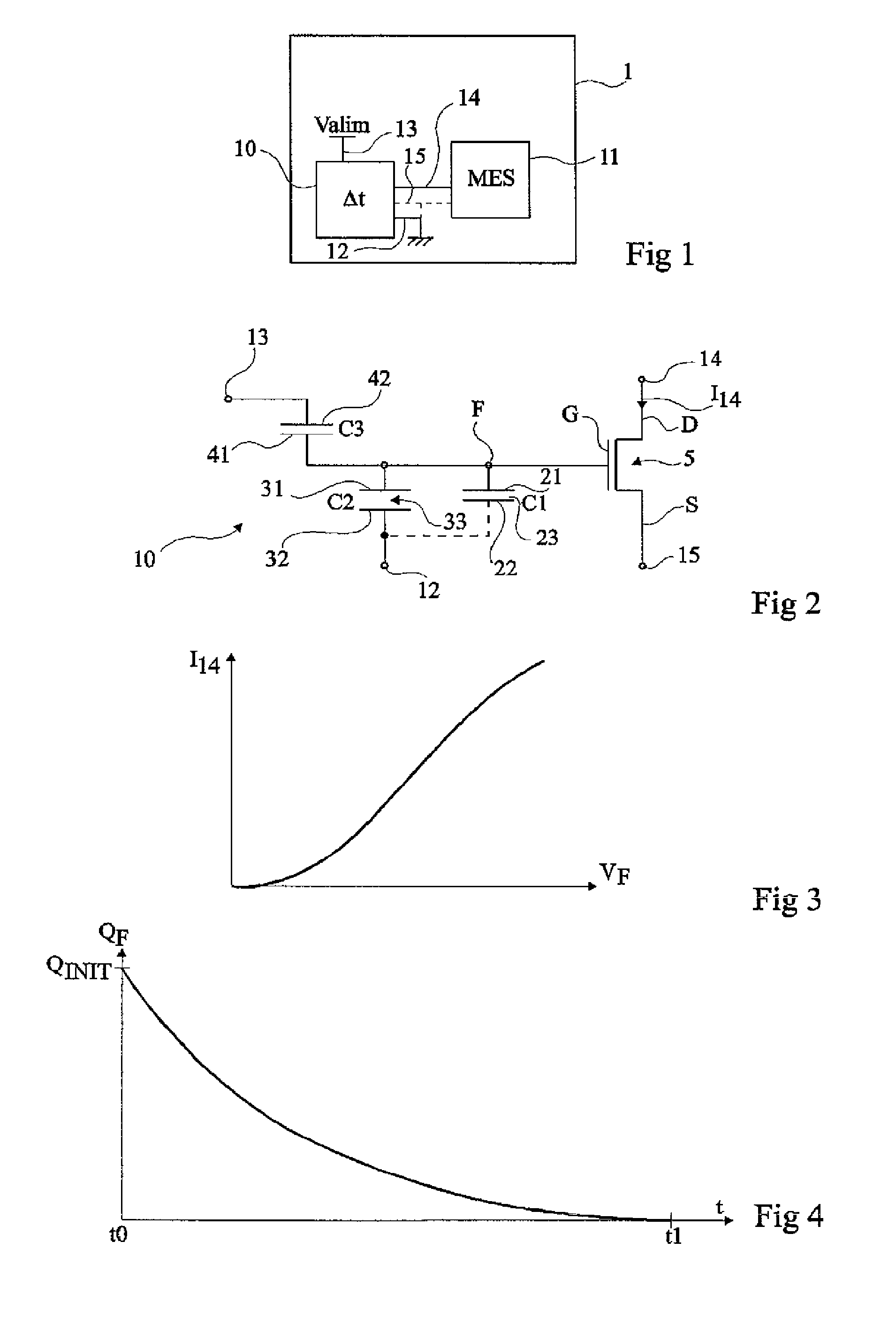
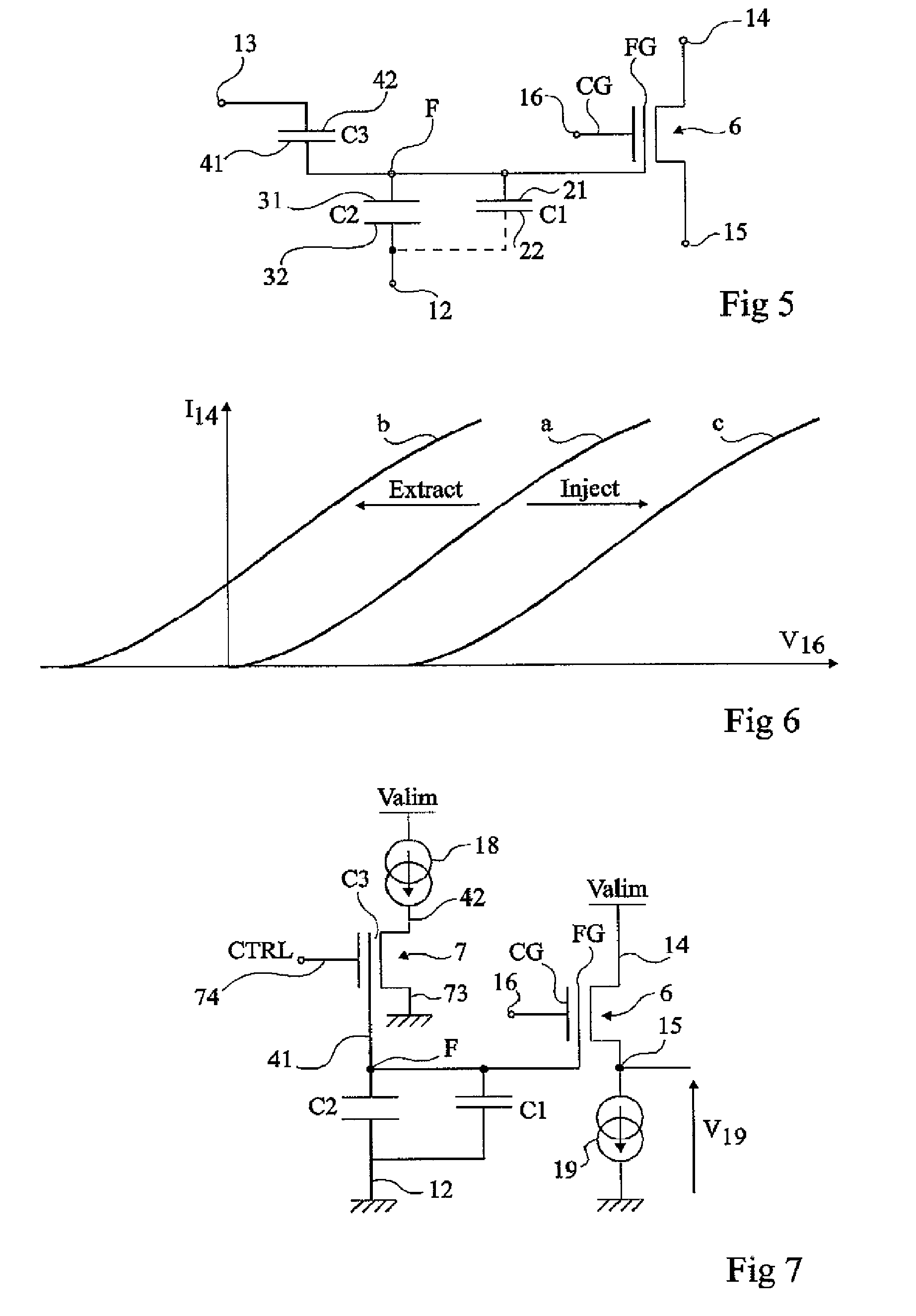
Circuit for reading a charge retention element for a time measurement
ActiveUS8036020B2Fast programmingDigital storageMeasurement by measuring electric/magnetic quantity changeCapacitanceCharge retention
A method and a circuit for reading an electronic charge retention element for a temporal measurement, of the type including at least one capacitive element whose dielectric exhibits a leakage and a transistor with insulated control terminal for reading the residual charges, the reading circuit including; two parallel branches between two supply terminals, each branch including at least one transistor of a first type and one transistor of a second type, the transistor of the second type of one of the branches consisting of that of the element to be read and the transistor of the second type of the other branch receiving, on its control terminal, a staircase signal, the respective drains of the transistors of the first type being connected to the respective inputs of a comparator whose output provides an indication of the residual voltage in the charge retention element.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
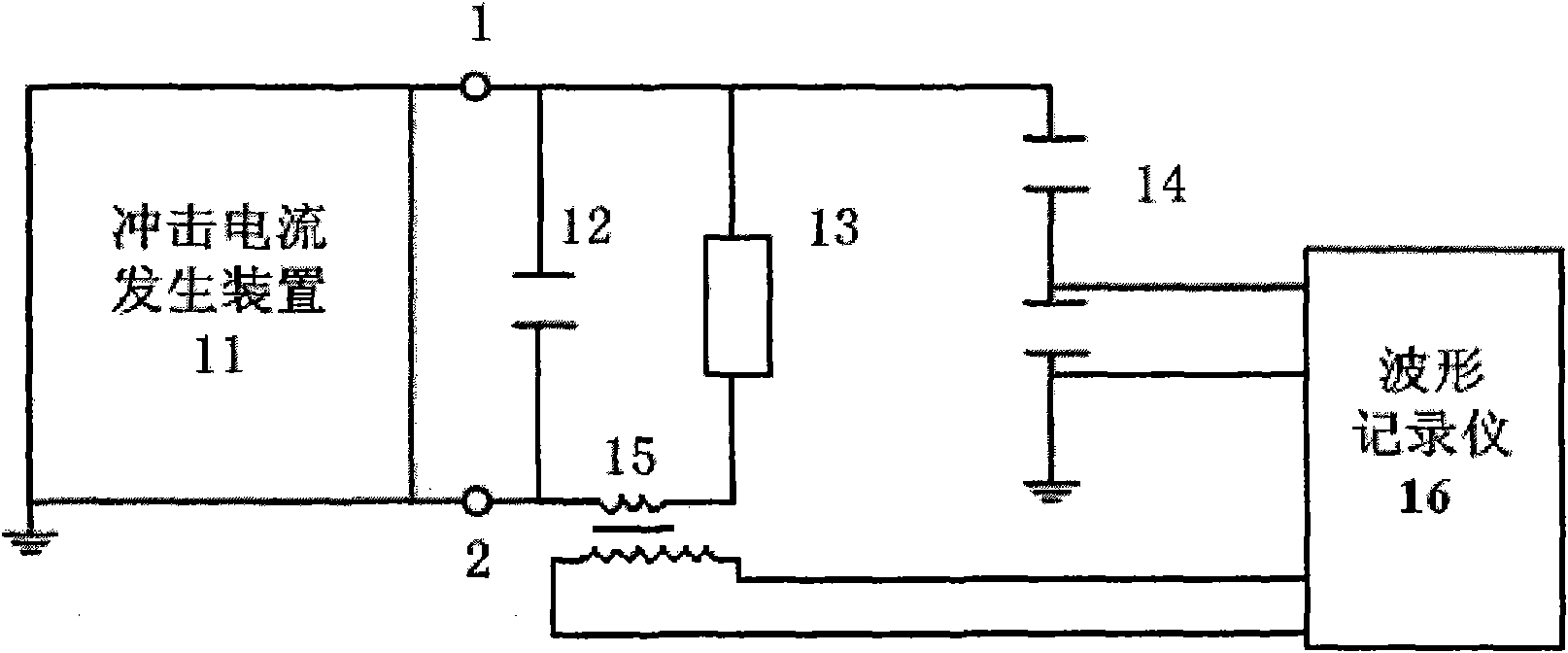
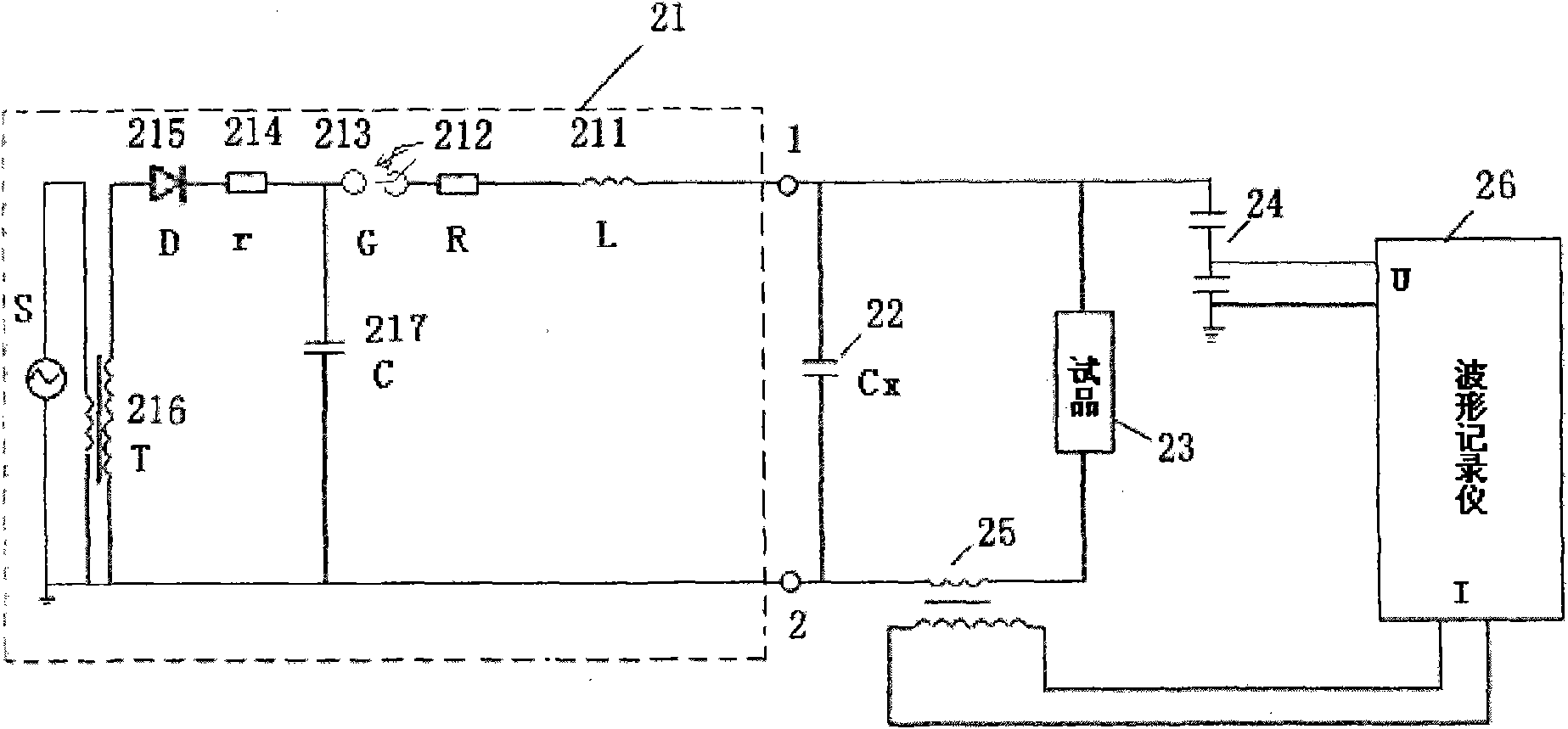
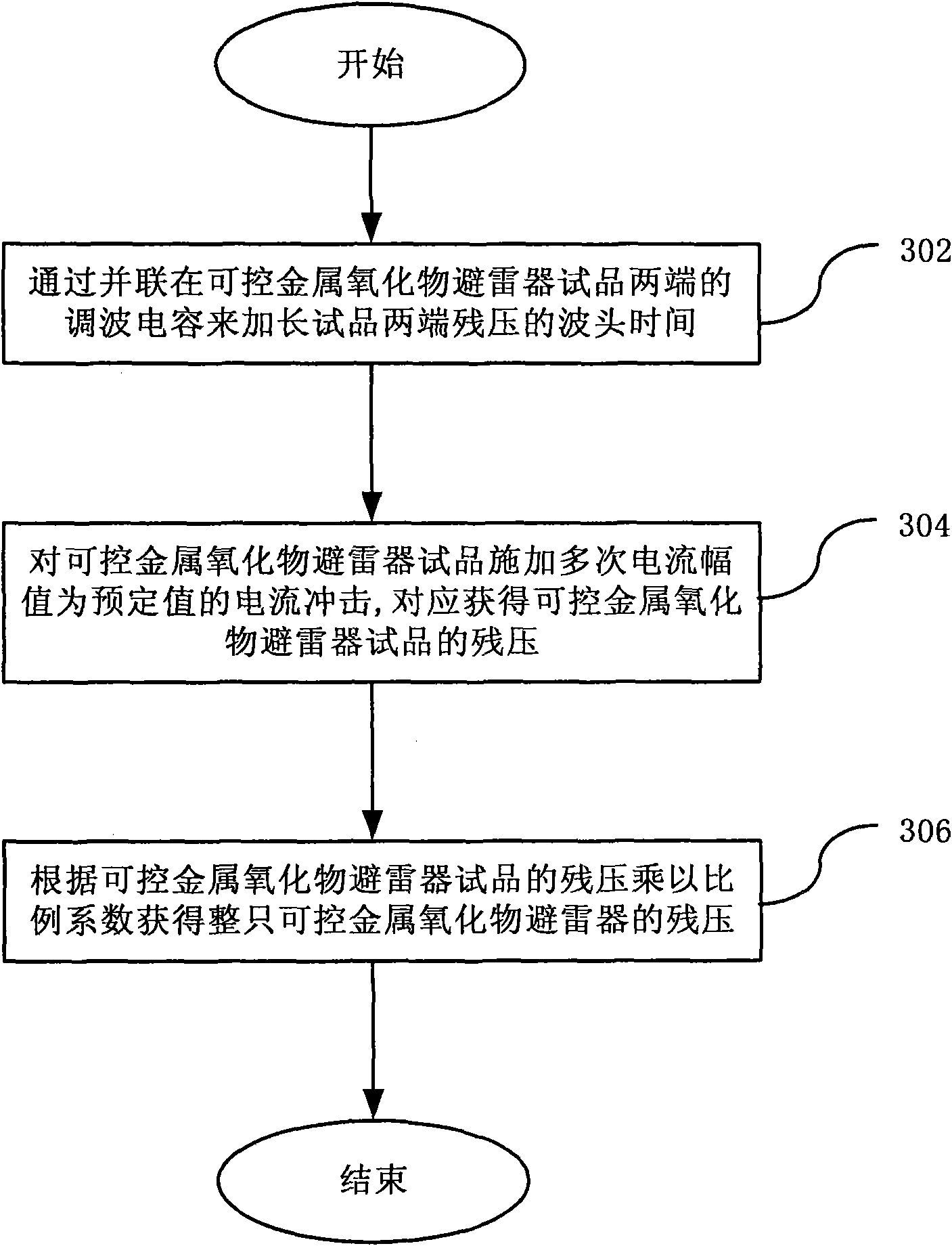
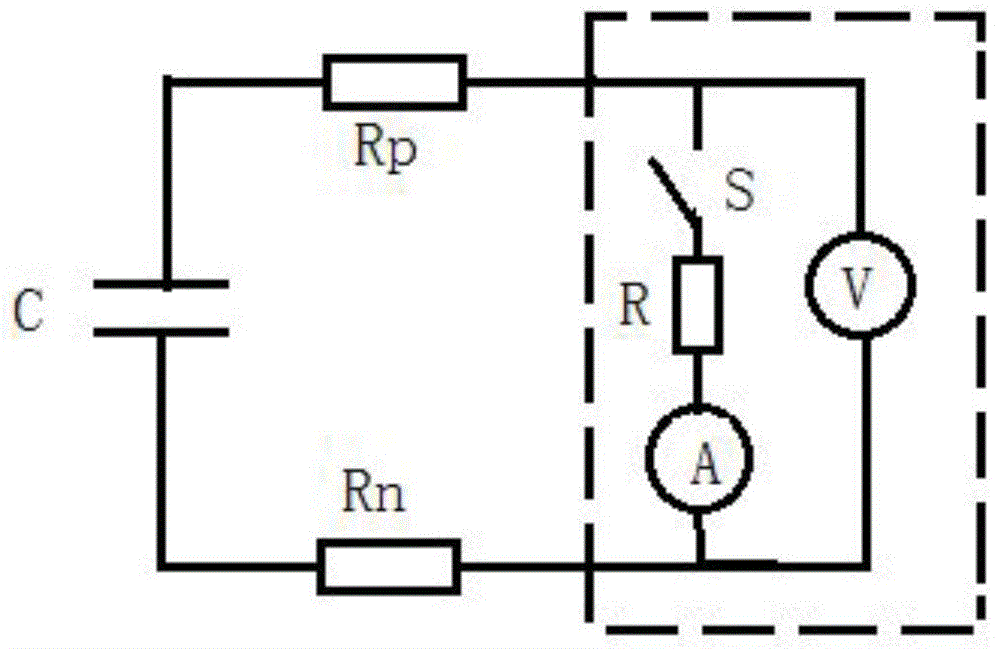
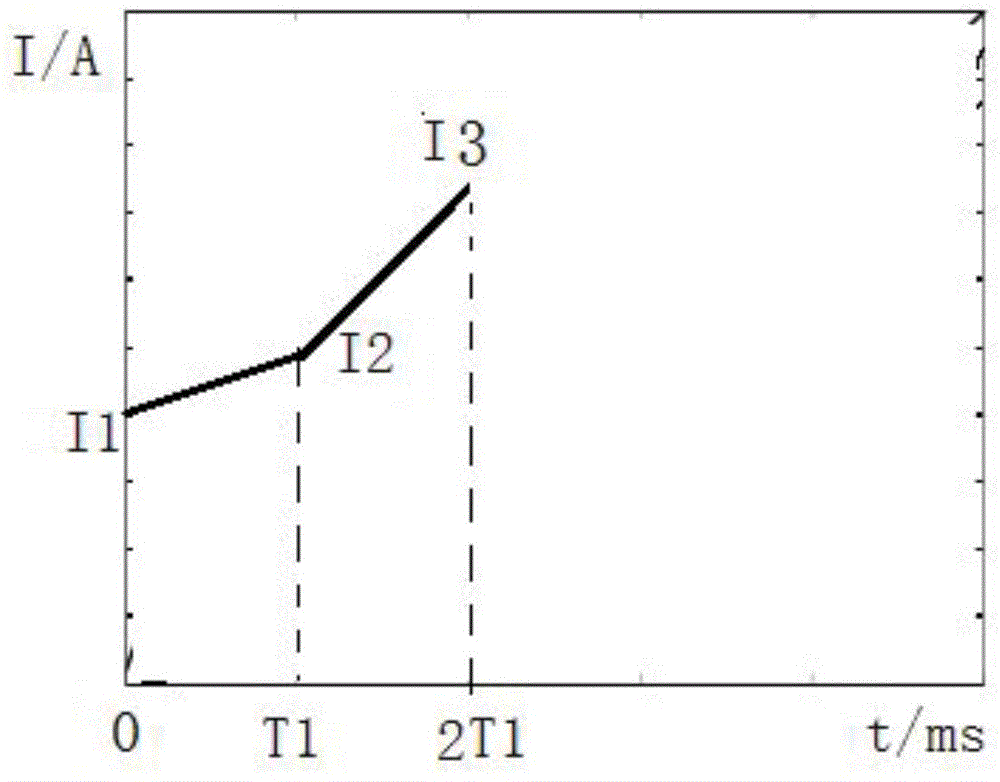
Residual voltage test circuit of controllable metal oxide arrester and method thereof
The invention discloses a residual voltage test circuit of a controllable metal oxide arrester and a method thereof. The test circuit comprises an impulse current generation device, an impulse modulation capacitor, a voltage divider, a Rogowski coil and a wave form recorder; wherein the impulse current generation device generates operation impulse current and / or lightning impulse current, and is provided with a high voltage output end and a low voltage output end; the impulse modulation capacitor is connected in parallel with a controllable arrester sample between the high voltage output end and the low voltage output end; one end of the voltage divider is connected with the high voltage output end of the impulse current generation device, while the other end is earthed; the Rogowski coil is directly sleeved on a conductor on a branch circuit of the controllable arrester sample; the wave form recorder is connected with the voltage divider and the output end of the Rogowski coil respectively, and is used for recording voltage and current wave form of the controllable arrester sample. The residual voltage test circuit for the controllable arrester and the method thereof prolong wave head time of the residual voltage on the controllable arrester sample by using the impulse modulation capacitor without changing parameters of the test circuit or the wave form of the lightning impulse current, so that tests have better system equivalence.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Method for detecting electric quantity of lithium ion battery for electric vehicle
The invention provides a method for detecting the electric quantity of a lithium ion battery for an electric vehicle. The method comprises obtaining a function expression of an OCV-SOC (Open Circuit Voltage and State Of Charge) curve by an interpolation method in the case of constant discharge current and setting the road conditions during usage to select a minimum error of curve reference table; measuring the OCV of the lithium ion battery under the fully-charged state and a current value under external loads, obtaining the internal resistance of the lithium ion battery through a loop current value, the load size, the load voltage and the OCV and meanwhile recording the total number of charging and discharging of the battery; collecting the working loop current of the lithium ion battery and the voltage of each end of the battery every T1 time when the lithium ion battery works, obtaining the voltage of the equivalent capacitance through the conversion according to the internal resistance, performing the difference operation on the voltage, performing the integral operation on the time through the current, calculating the ratio of the voltage and the current and obtaining the residual voltage through the comparison on a newly proposed reference curve.
Owner:YUYAO YIWEI ELECTRONICS TECH
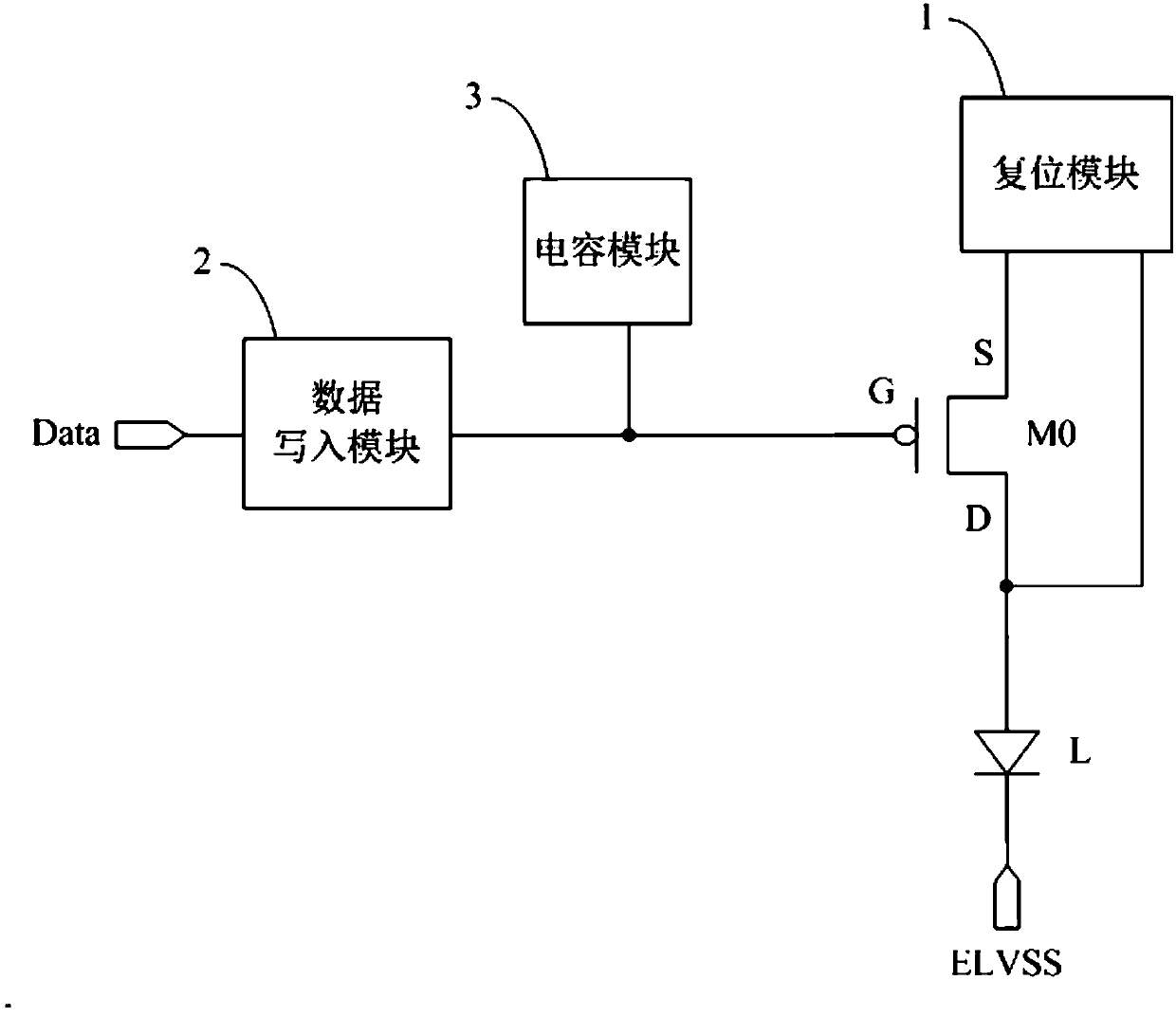
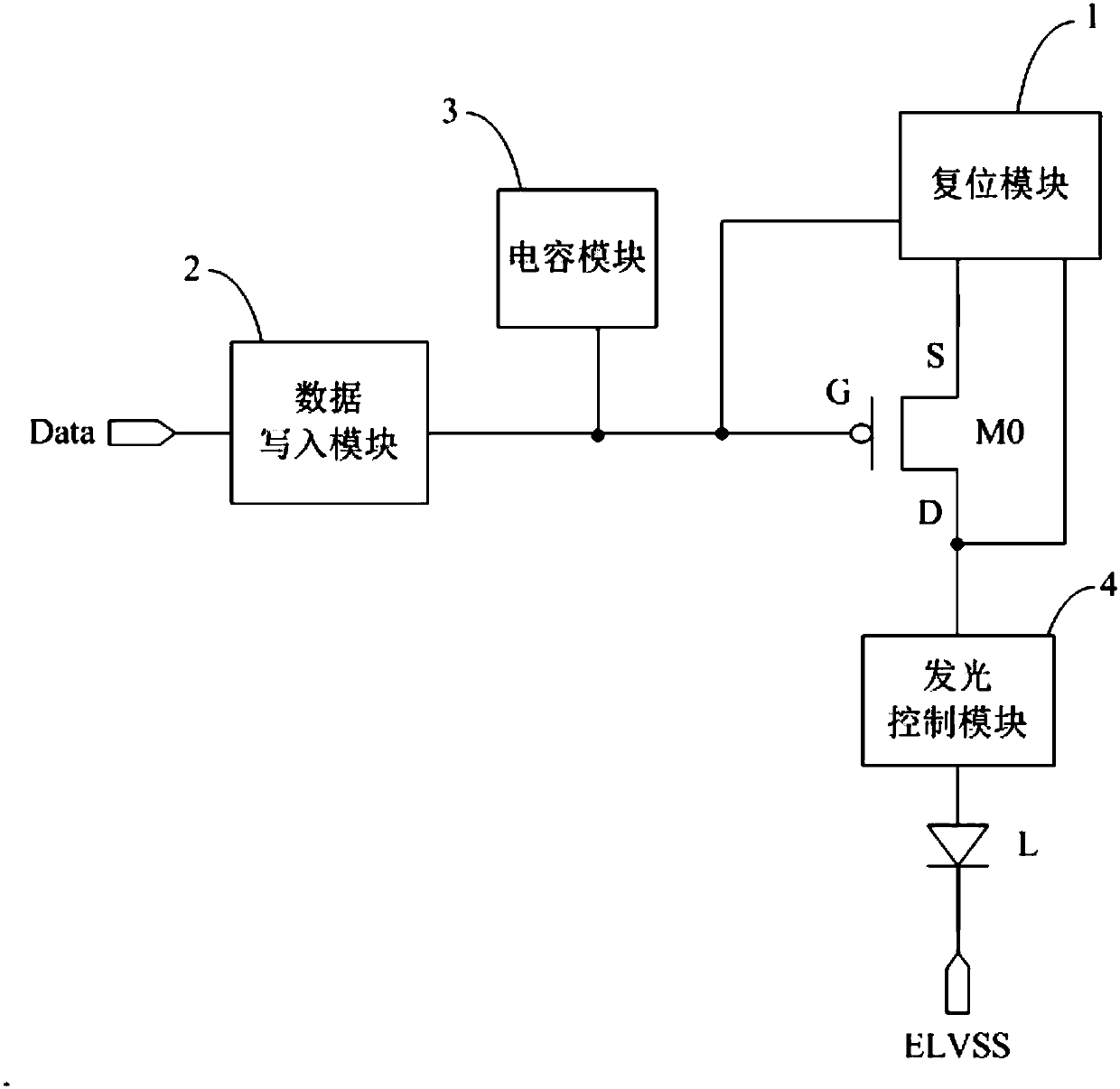
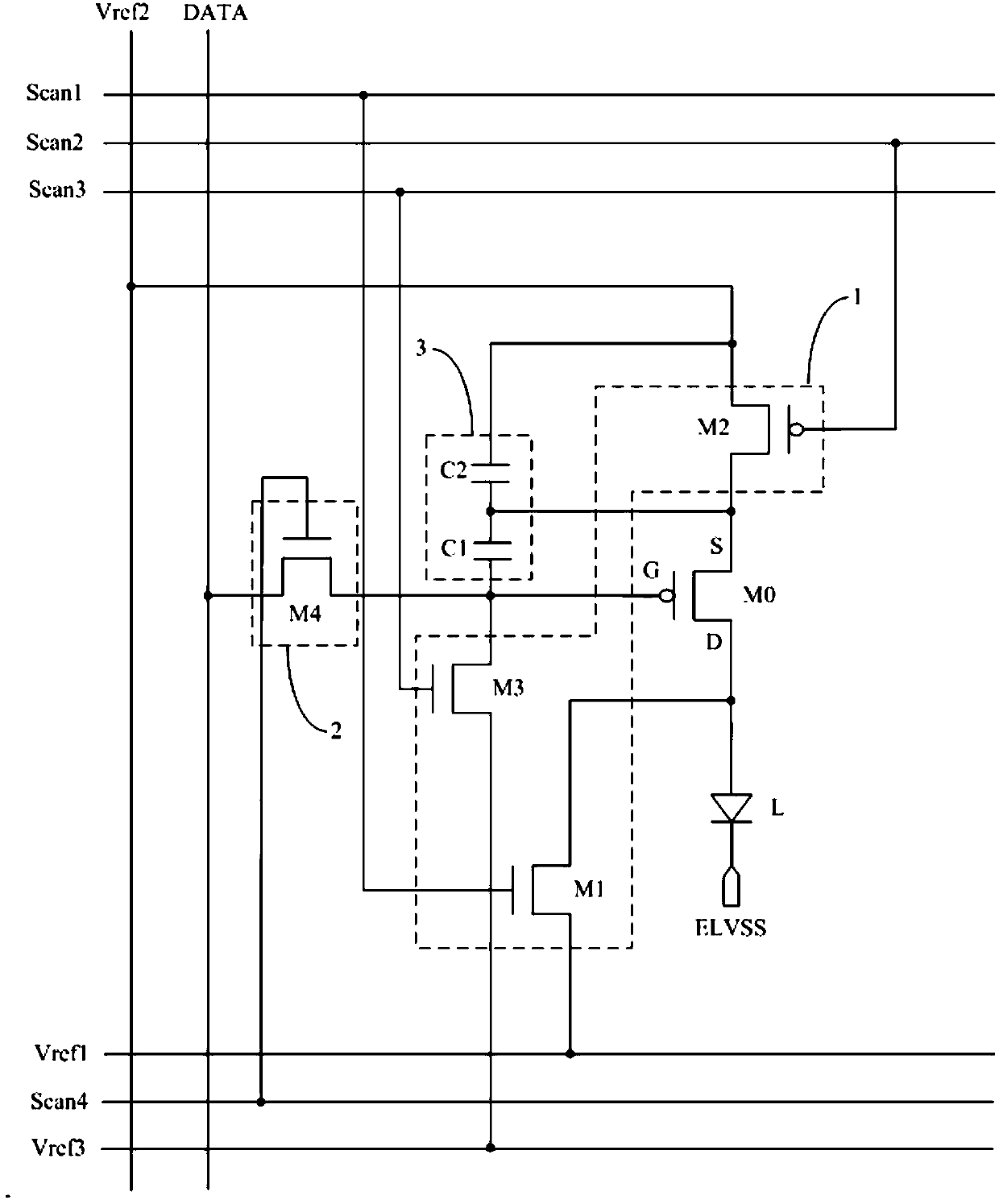
Pixel circuit, driving method, electroluminescent display panel and display device
ActiveCN108206008AImprove uniformity of light emissionAvoid the effects of lightStatic indicating devicesDriving currentElectricity
The invention discloses a pixel circuit, a driving method, an electroluminescent display panel and a display device. A first pole and a second pole of a driving transistor can be reset in the reset phase by a reset module, and then data signals are written by a data writing module into a grid of the driving transistor, and a driving current is generated by the driving transistor to drive a light emitting device to emit light. In this way, the voltage of the first pole of the driving transistor can be set to a fixed voltage and the voltage of the second pole of the driving transistor can be setto a fixed voltage before each writing of the data signals, so that the influence of the residual voltage of a previous frame on the light emission of the frame can be avoided, and the uniformity oflight emission of the display panel can be improved.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
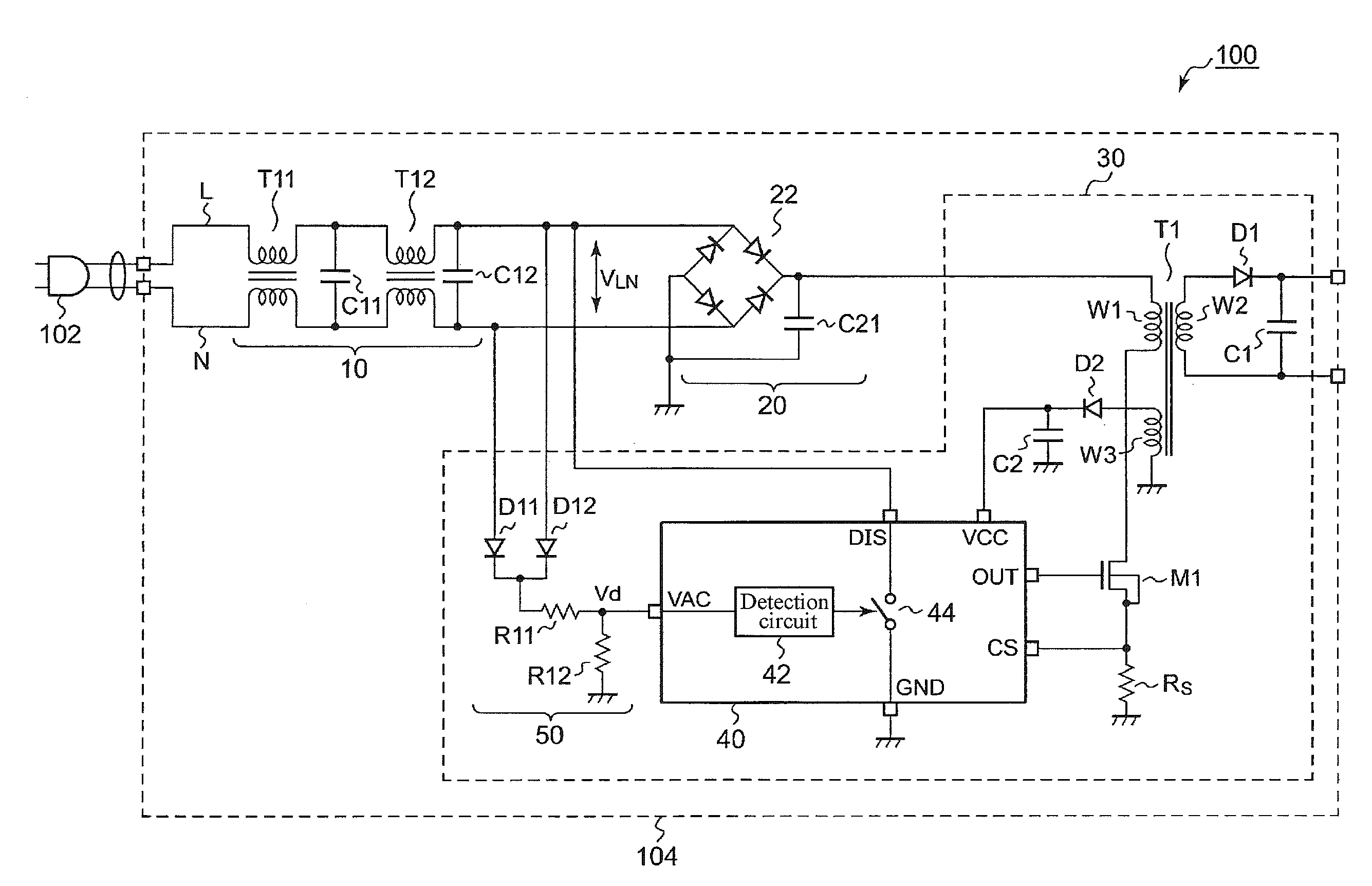
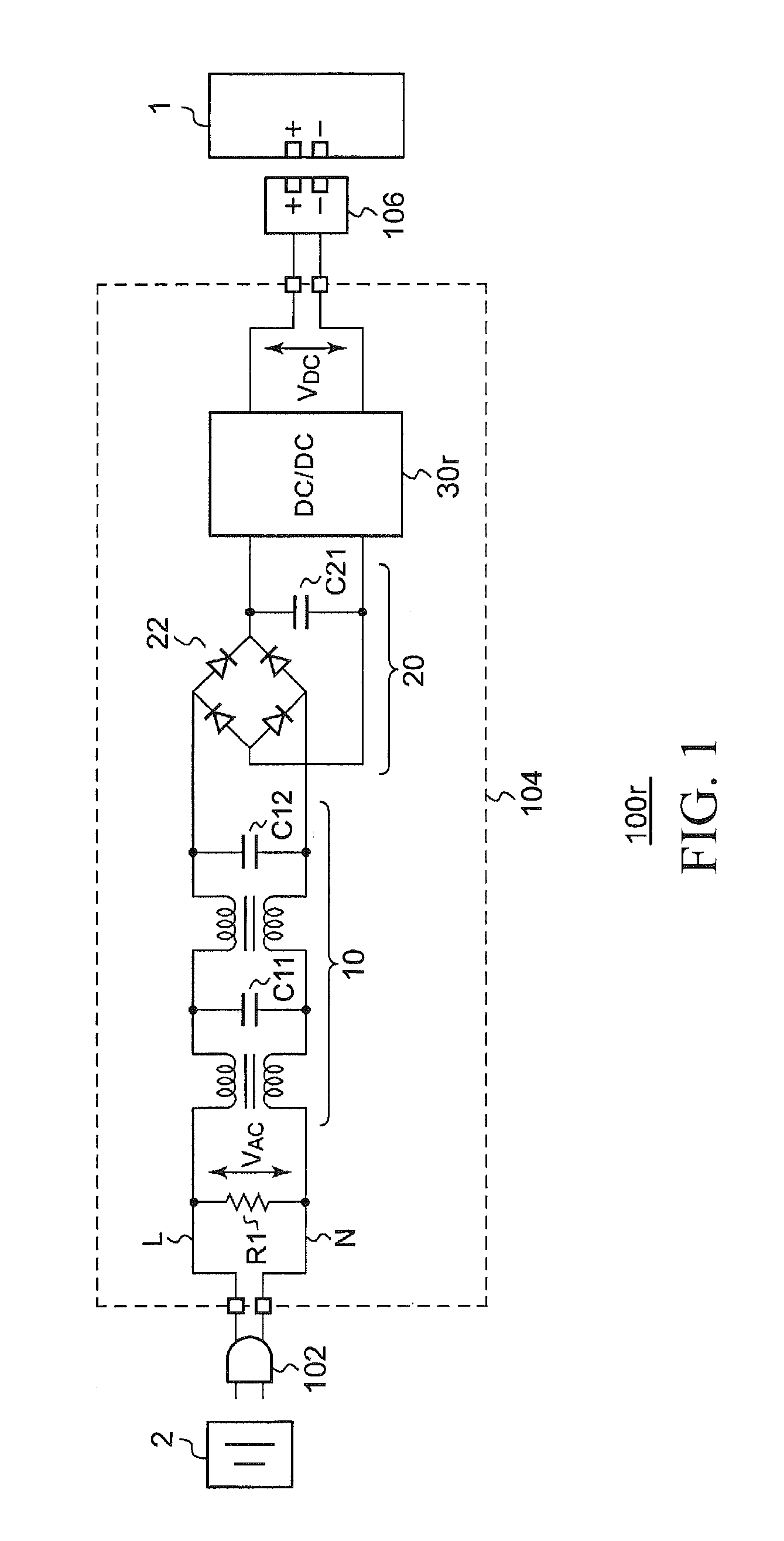
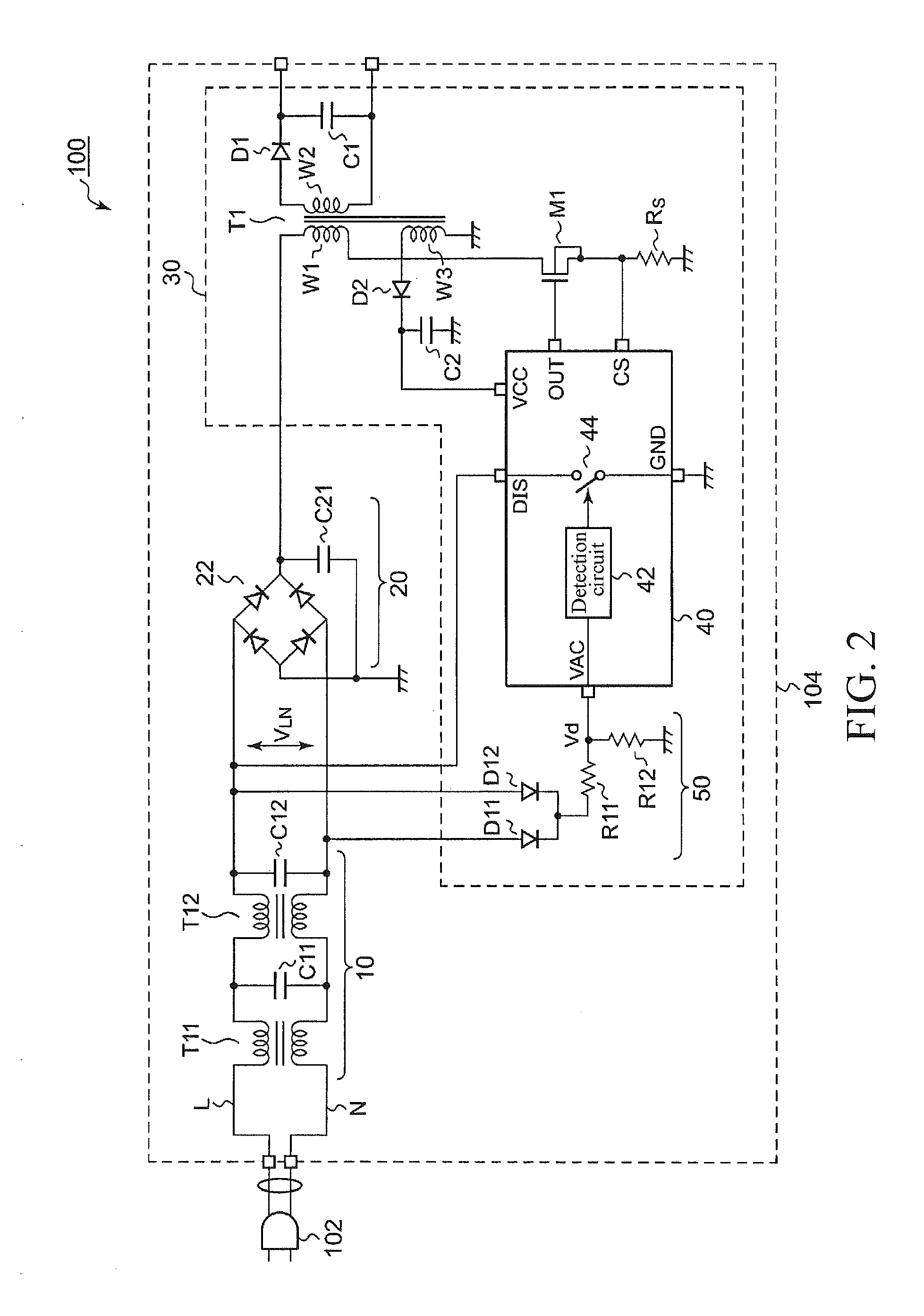
Ac/dc converter, and ac power adapter and electronic apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20130027983A1Reduce power consumptionDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationWave detectionAC - Alternating current
The present invention provides an Alternating Current / Direct Current (AC / DC) converter employing measures not only against residual voltage but also to reduce power consumption. The AC / DC converter receives an Alternating Current (AC) voltage through a concentric plug and converts the AC voltage into a Direct Current (DC) voltage. A discharge path is disposed on a path from a discharge terminal to a ground terminal. A detection circuit compares a wave detection voltage with a predetermined threshold voltage, and enables the discharge path to be turned on when the wave detection voltage is continuously lower than the threshold voltage for a predetermined detection time.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
A single phase grounding failure relay protection method based on negative electrical impedance relay
ActiveCN101106047AIncreased sensitivitySwitch operated by earth fault currentsPhase currentsTransformer
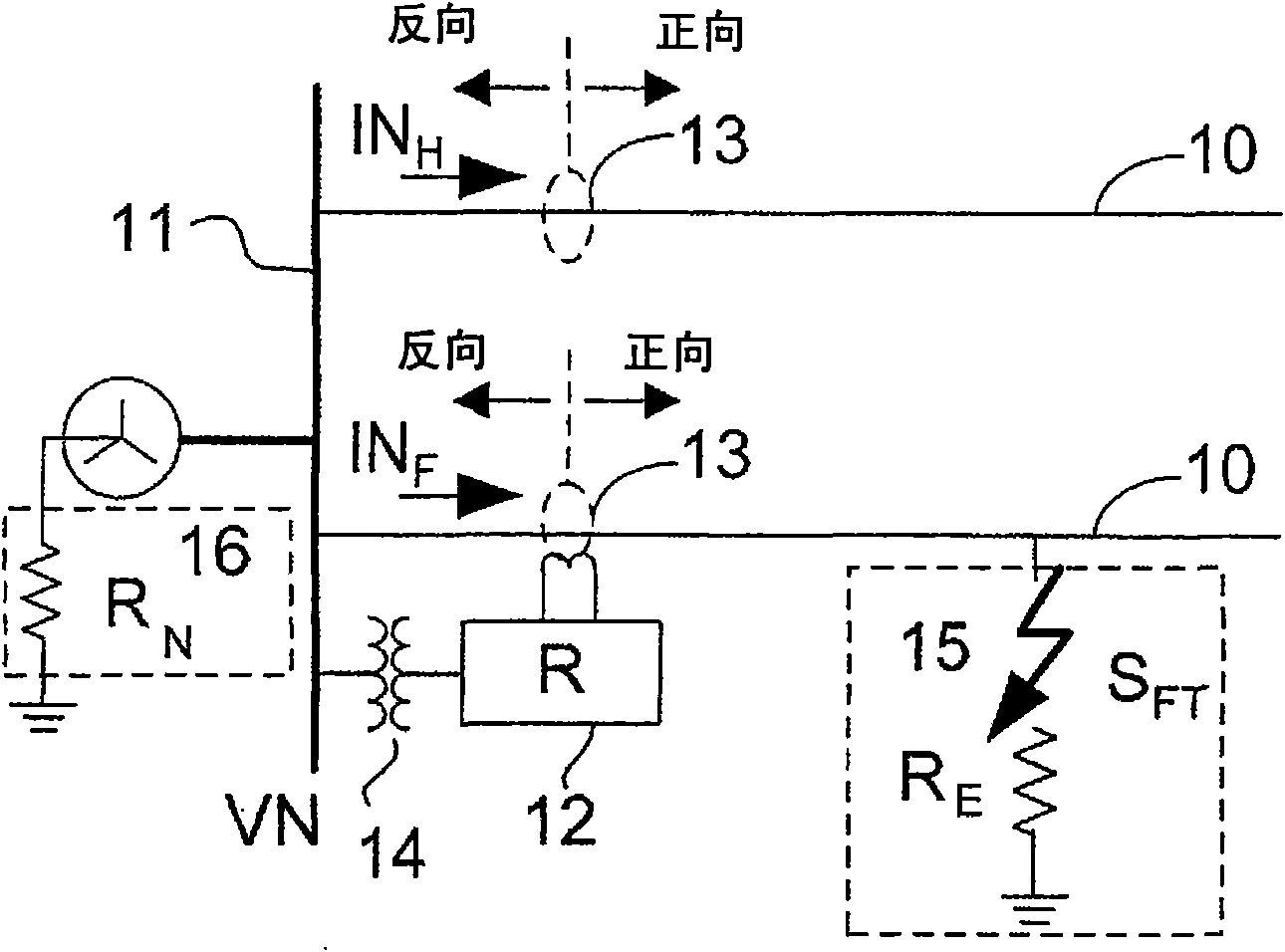
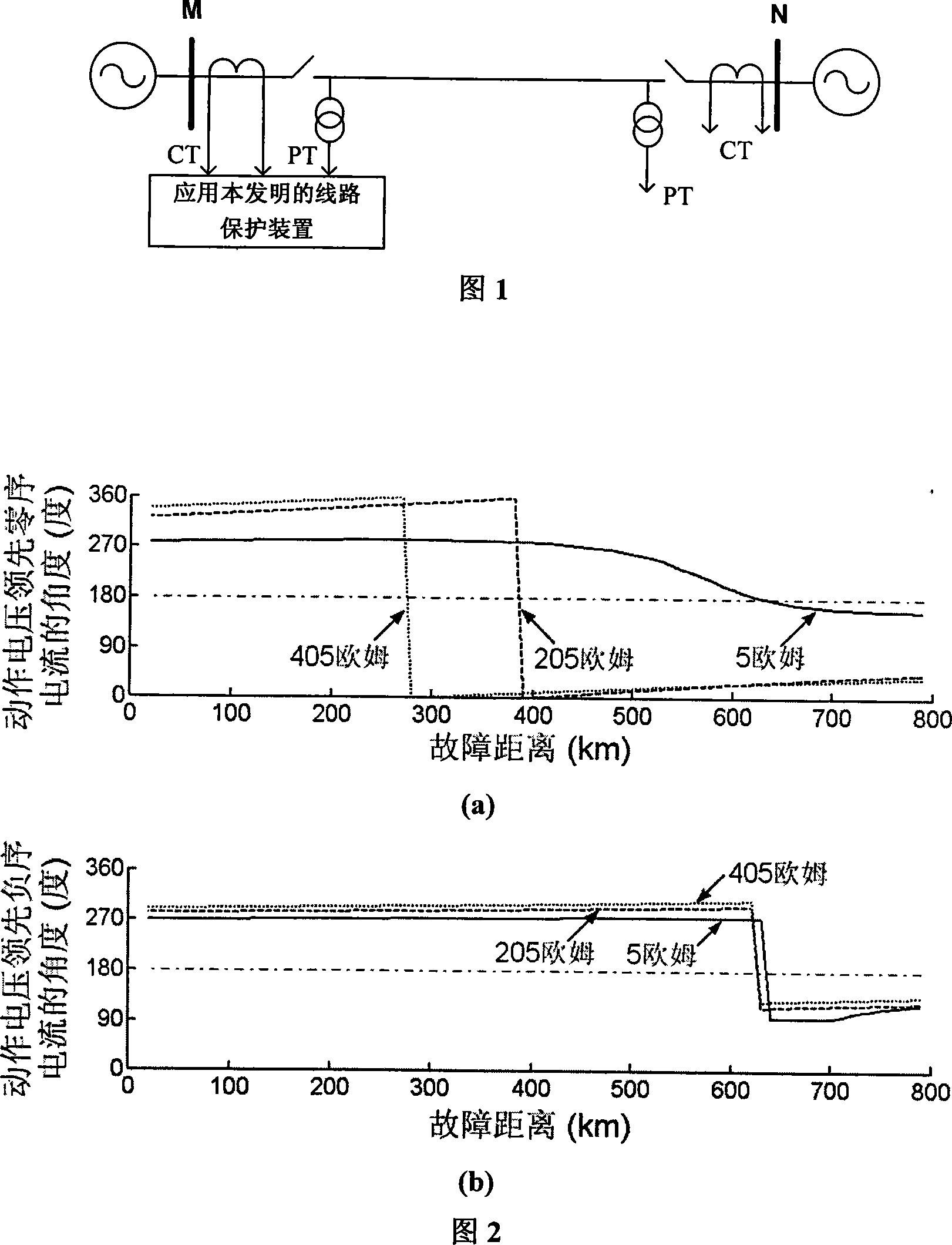
The invention belongs to electric power system field, in particular to a single-phase grounding failure relay protection method based on a negative sequence reactance relay. The method includes: Measure the circuit's failure phase voltage Uphi, phase current Iphi, zero sequence voltage U0, zero sequence current I0, and negative sequence current I2 at the installation place of transformer station as the input values; calculate the residual voltage phasor of the failure point through measuring voltage, measuring current, negative sequence current at the place of protection installation, and circuit impedance angle; constitute the action voltage phasor Uop through measuring voltage, measuring current, residual voltage phasor of failure point, and impedance value within the scope of circuit protection; calculate the angle that the action voltage phasor Uop leads the negative sequence current iU2. If the angle is within the range of [180 DEG, 360 DEG], the protection action sends a signal of tripping operation; contrarily, the protection will not take any action. The method is suitable for the electricity transmission side of ultra / super high voltage electric circuit, particularly ultra / super high voltage heavy load electric circuit. The invention can meet requirements for selection, reliability, sensitivity, and speediness of relay protection.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
First-stage circuit structure of pipelined analog-to-digital converter
InactiveCN102983863AGuaranteed accuracyReduce design pressureAnalogue-digital convertersCapacitanceDigital down converter
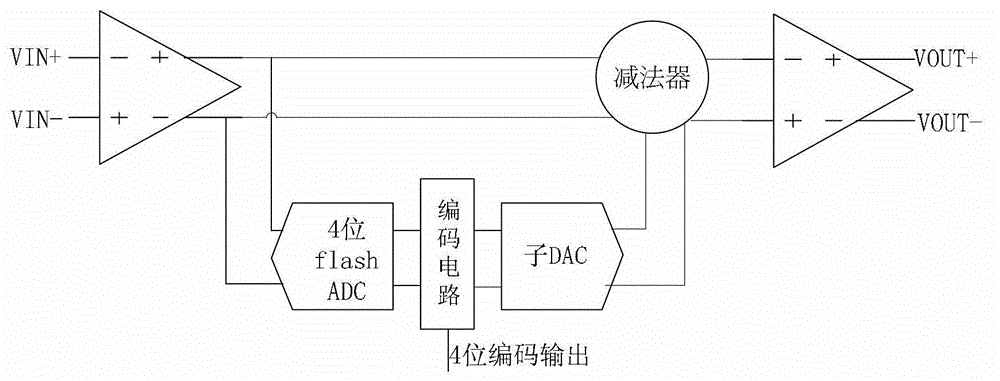
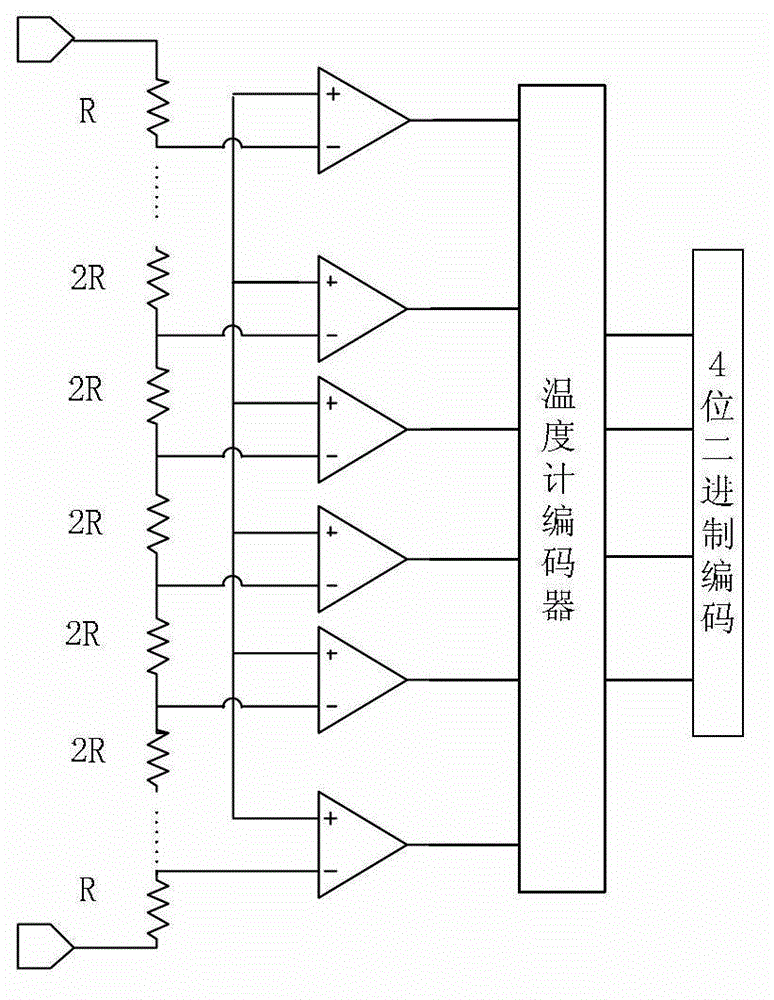
The invention discloses a first-stage circuit structure of a pipelined analog-to-digital converter, which comprises a 4-digit fully parallel analog-to-digital converter, a code circuit and a residue gain analog-to-digital converter. A two-phase non-overlapping clock is adopted, a sampling phase samples input voltage, and a maintaining phase amplifies residual voltage. The residue gain analog-to-digital converter consists of a sub analog-to-digital converter, a subtracter and a residue amplifier. During sampling, the 4-digit fully parallel analog-to-digital converter conducts comparison and quantification on the input voltage and generates a 16-digit thermometer code which is converted to a 4-digit binary output code by the encoder. A lower pole plate of a sampling capacitor array is connected with the input voltage, and an upper pole plate thereof is connected with a common mode level for sampling an input. During maintaining, the sub analog-to-digital converter outputs different voltages to the sampling capacitor array according to a control of the thermometer code; subtraction from the input voltage is accomplished according to twice charge conservation; and a feedback capacitor is in bridge connection with the two ends of the residue amplifier to amplify the residual voltage by 8 times for use by a backward-stage circuit.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
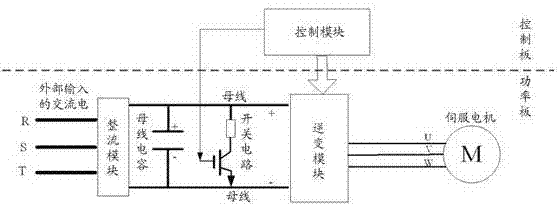
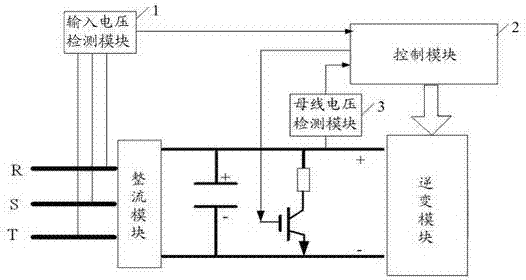
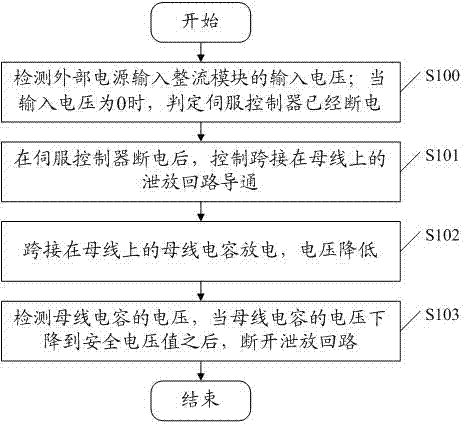
Method and device for discharging residual voltage of bus of servo controller
ActiveCN102545193AAvoid electric shockReduce voltageEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentCapacitanceElectricity
An embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a device for discharging residual voltage of a bus of a servo controller. The method includes: detecting input voltage input into a rectifying module of the servo controller by an external power supply; judging that the servo controller is powered off when the input voltage is zero; controlling a discharging loop bridged on the bus to be connected when the servo controller is powered off and discharging electricity for a bus capacitor bridged on the bus; and detecting voltage of the bus capacitor and disconnecting the discharging loop after voltage of the bus capacitor is reduced to a safe voltage value. By adopting the method and the device for discharging residual voltage of the bus of the servo controller provided by the embodiment, after the servo controller is powered off by accidents, electric energy stored on the bus capacitor can be discharged fast, and voltage on the bus capacitor can be fast reduced to be below the safe voltage value, so that operators are prevented from suffering from electric shock and safety hazards are avoided.
Owner:深圳市合信自动化技术有限公司
Circuit and method for soft start of a switching regulator from a residual voltage
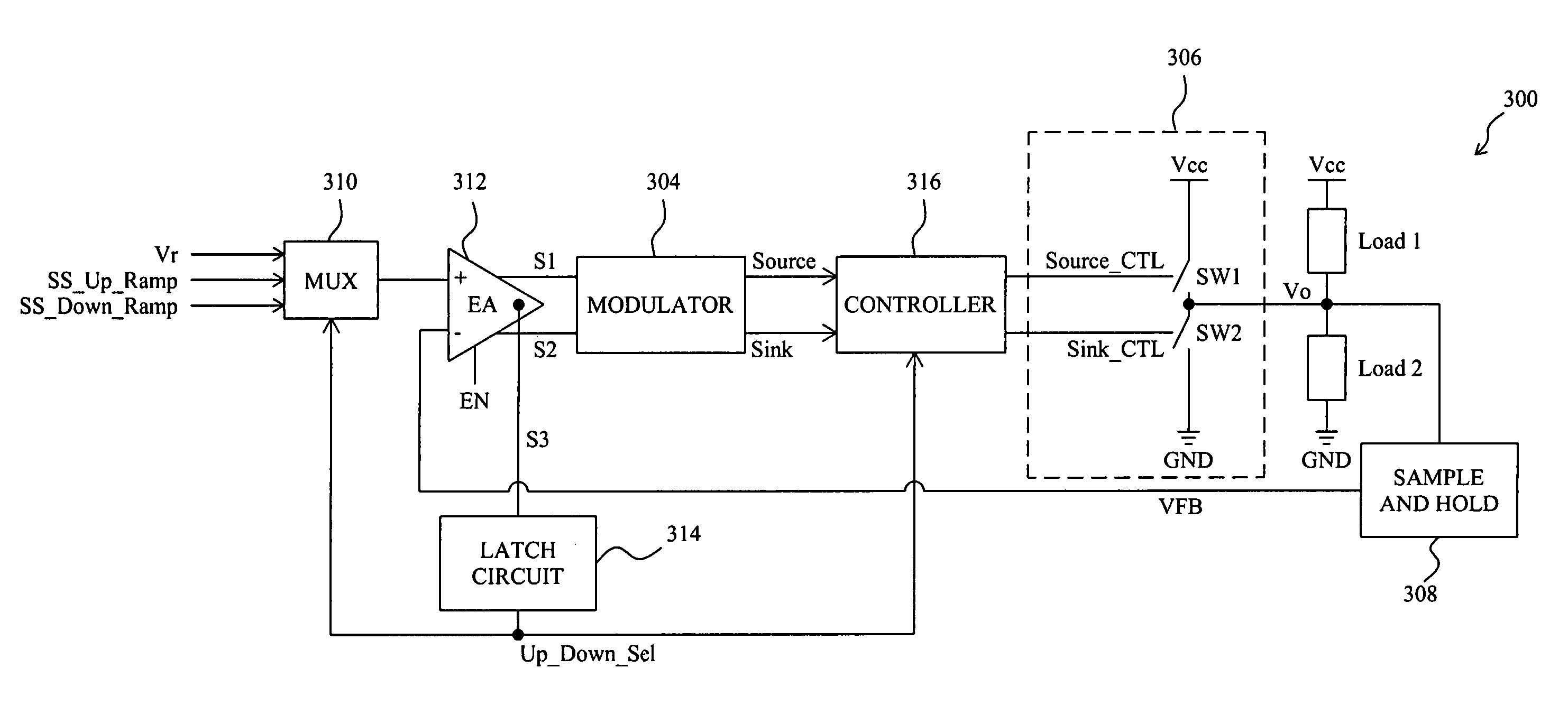
ActiveUS20080238397A1Inhibit currentEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionReverse currentControl theory
For soft start of a switching regulator, the output voltage of the switching regulator is fed back to be compared with a ramp signal, in order to trigger a comparison signal when the ramp signal rises up to reach the feedback signal, to enable the switching regulator such that the output voltage changes from a residual voltage toward a target value. The low side switch of the switching regulator is kept off for a period of time after the switching regulator is enabled, so as to prevent a reverse current during the soft start period.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
High-voltage direct-current transmission line high-resistance grounding fault identification method based on distributed parameters
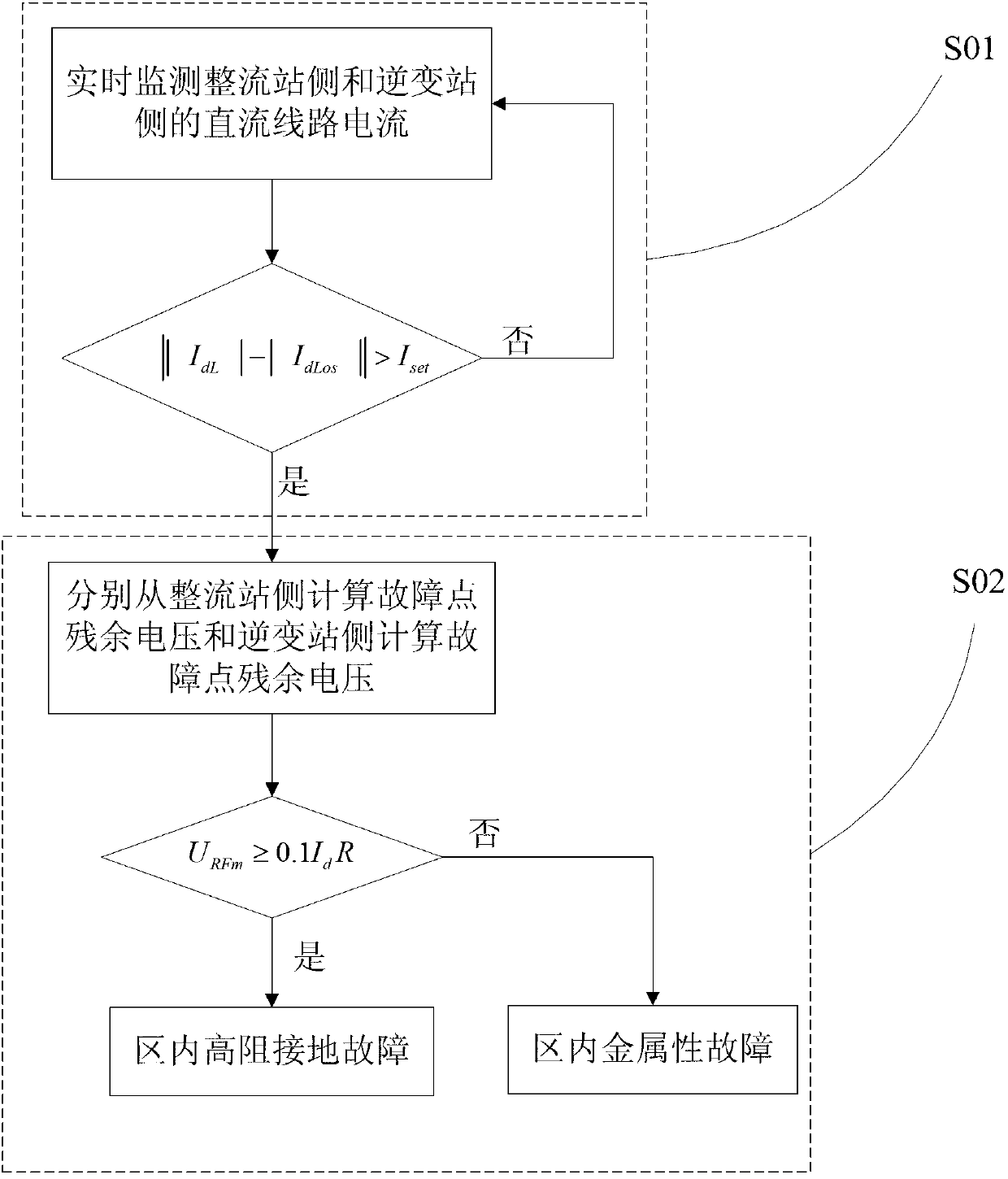
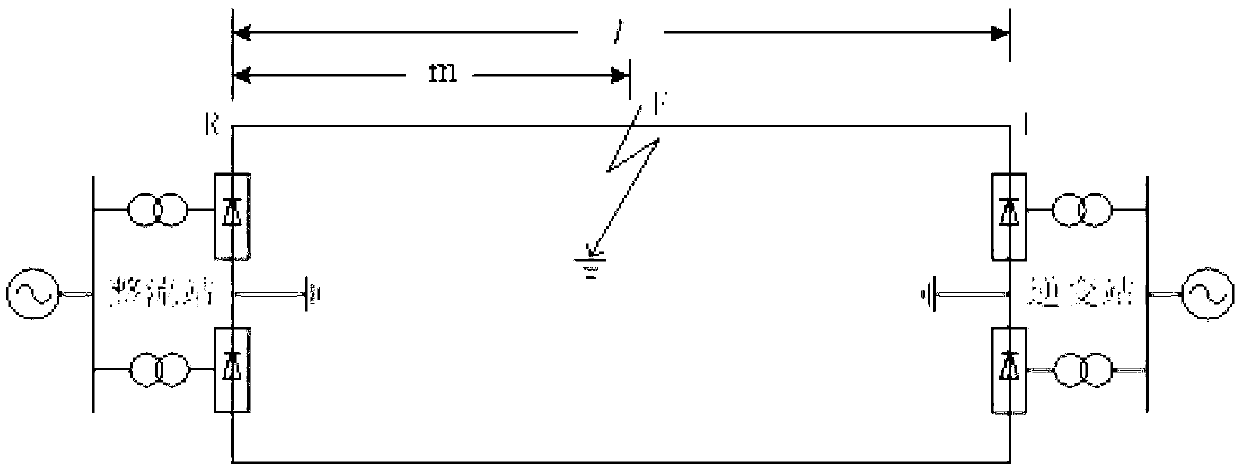
ActiveCN103346542AIncreased sensitivityMake up for the lack of long delay (about 1 second)Emergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationElectrical resistance and conductanceHigh resistance
The invention discloses a high-voltage direct-current transmission line high-resistance grounding fault identification method based on distributed parameters. The method comprises the following steps that step 1, direct-current line current at a rectification station side and direct-current line current at an inversion station side are monitored in real time, if the condition (||IR|-|II||) I set is satisfied in continuous 3ms, the existence of a fault point in a high-voltage direct-current transmission line is judged, and then a step 2 is conducted; step 2, fault point residual voltage URFm is calculated at the rectification station side and fault point residual voltage UIFm at the inversion station side is calculated respectively, and if URFM>=0.1IdR, an in-zone high-resistance grounding fault is judged, and a protecting outlet t1 is delayed; if URFm< 0.1IdR, an in-zone metal fault is judged, and a protecting outlet t2 is delayed. According to the high-voltage direct-current transmission line high-resistance grounding fault identification method based on the distributed parameters, the fault point residual voltage when the high-voltage direct-current transmission line grounding fault occurs is compared with initial stable voltage when high-resistance grounding fault occurs, whether the high-resistance grounding fault occurs or not is judged, so that the protecting outlet is started, the protecting outlet is not influenced by transition resistance, the shortage of protection of motion rejection when the high-resistance grounding fault occurs in a current direct-current line is compensated, and the flexibility of protection motion is improved.
Owner:EXAMING & EXPERIMENTAL CENT OF ULTRAHIGH VOLTAGE POWER TRANSMISSION COMPANY CHINA SOUTHEN POWER GRID
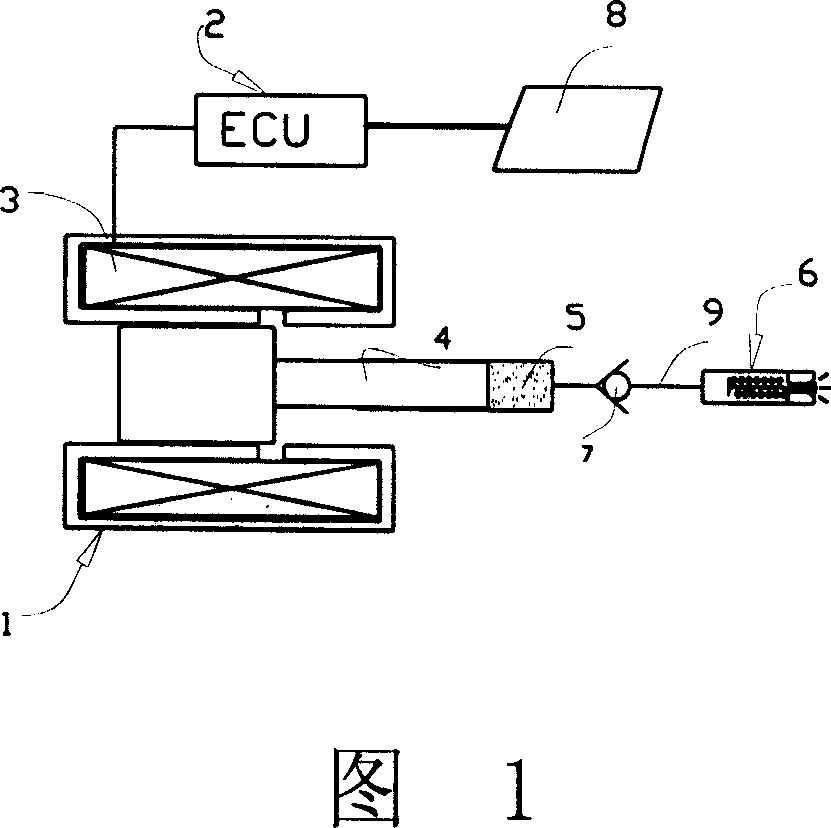
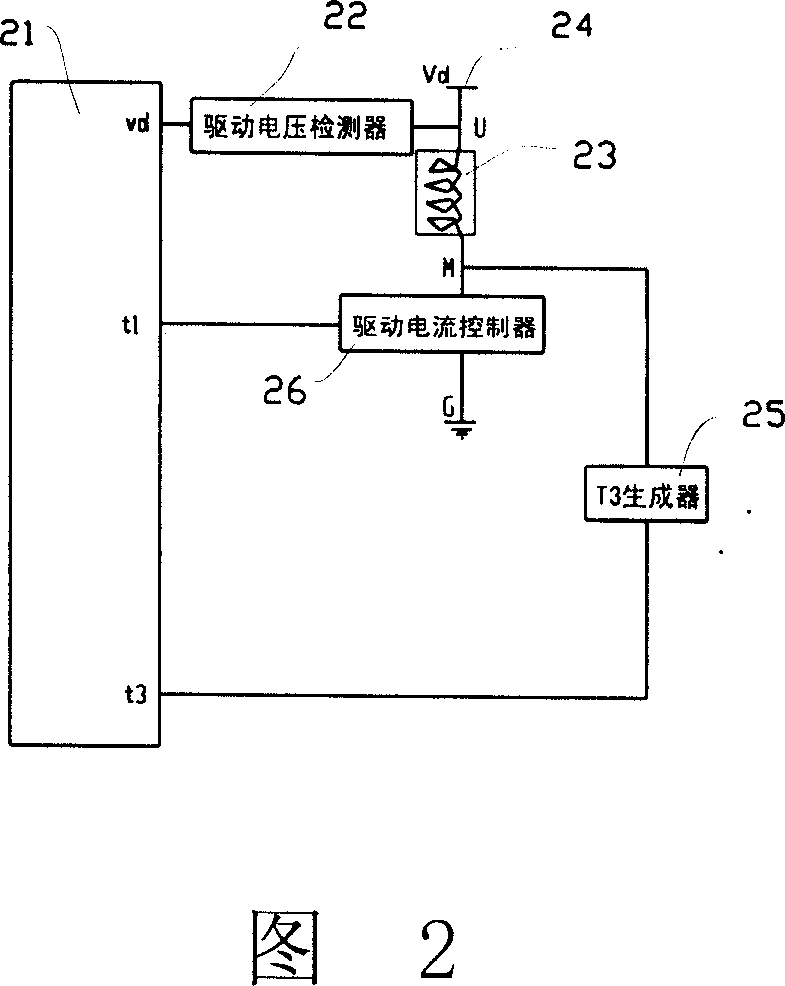
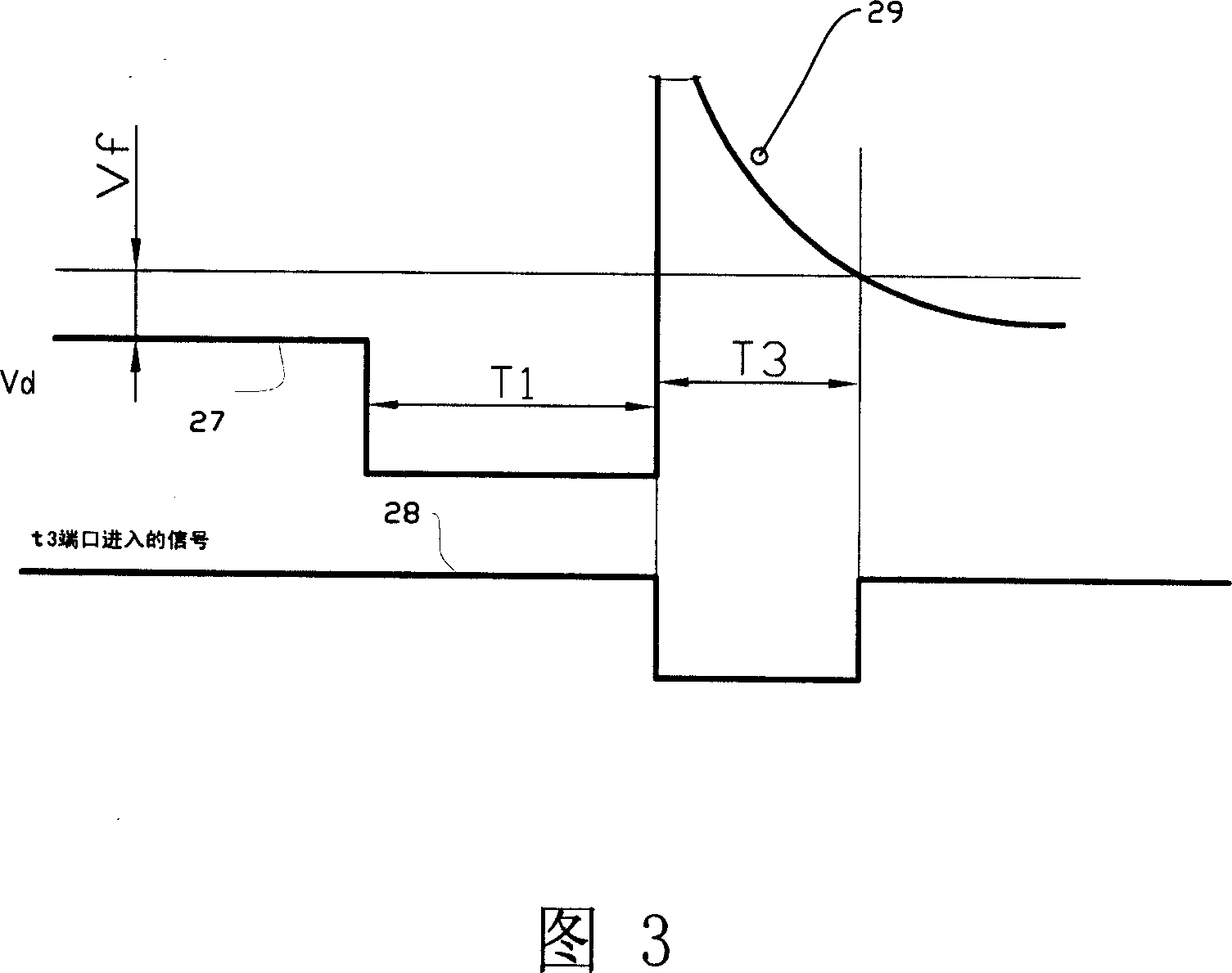
Electromagnetic fuel pump nozzle drive control method and its device
A drive control method and drive control device for an electromagnetism fuel pump spray nozzle, an aiming feedback signal is obtained by a plunger displacement signal, especially characteristic parameters of the residual voltage curve, based on the aiming feedback signal a driving pulse width is predicted, the aiming oil quantity reached by each oil injection is controlled by the predicted driving pulse width, thereby realizing close loop control for the electromagnetism fuel oil pump nozzle device to improve precision supplied for the engine fuel, and avoid and reduce change of jet flow caused by factors such as mechanical wear, change of backspring force, change of nozzle opening pressure, change of fuel channel resistance, change of nozzle flow coefficient, change of friction force brought by the change of liquid viscidity and fuel impurity, change of driving voltage, in the meanwhile, the invention can realize real time monitoring for the working of the electromagnetism fuel injection pump nozzle by the ECU unit, and perform abnormal condition and fault diagnosis.
Owner:塞尔福(厦门)工业有限公司
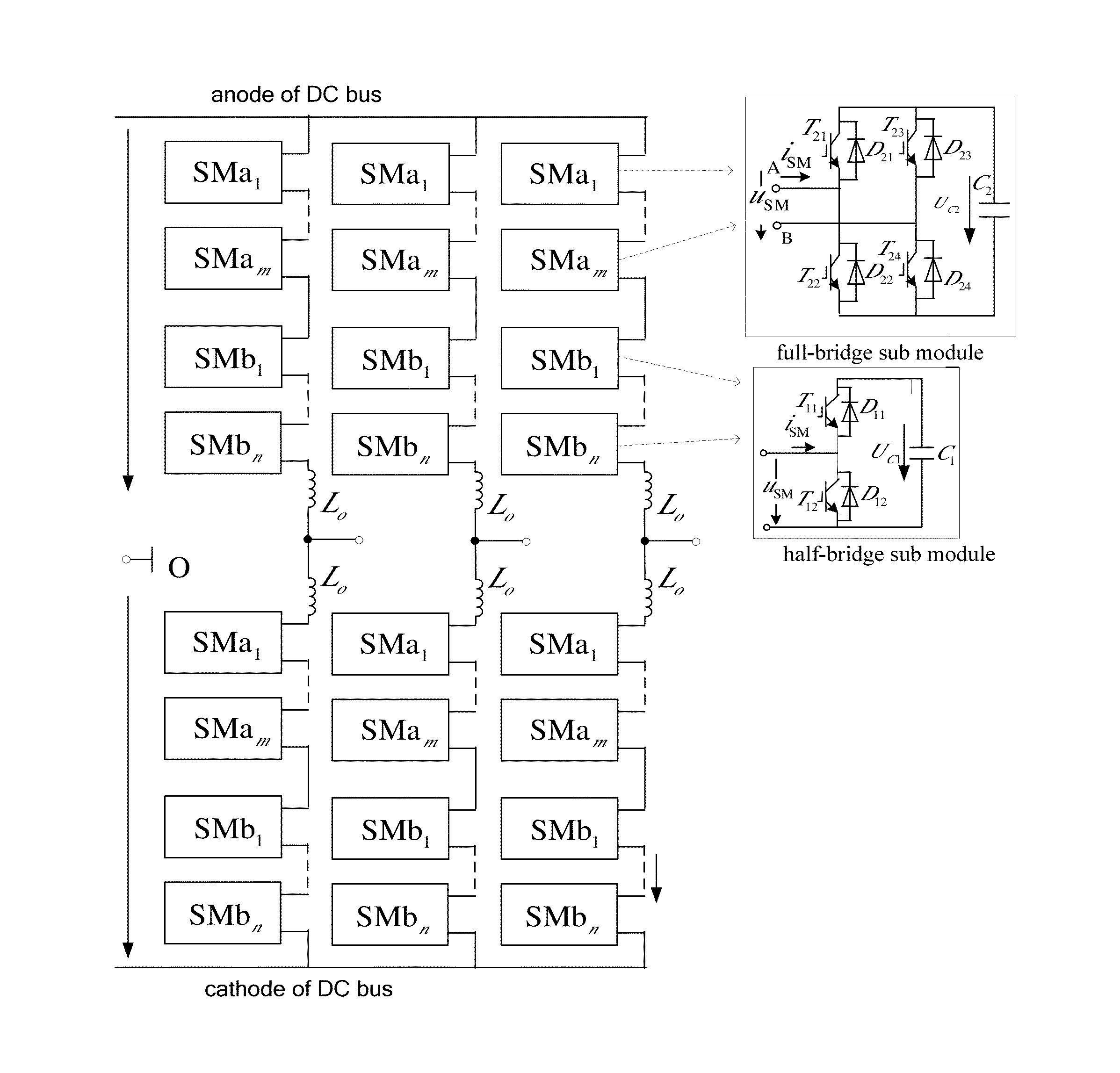
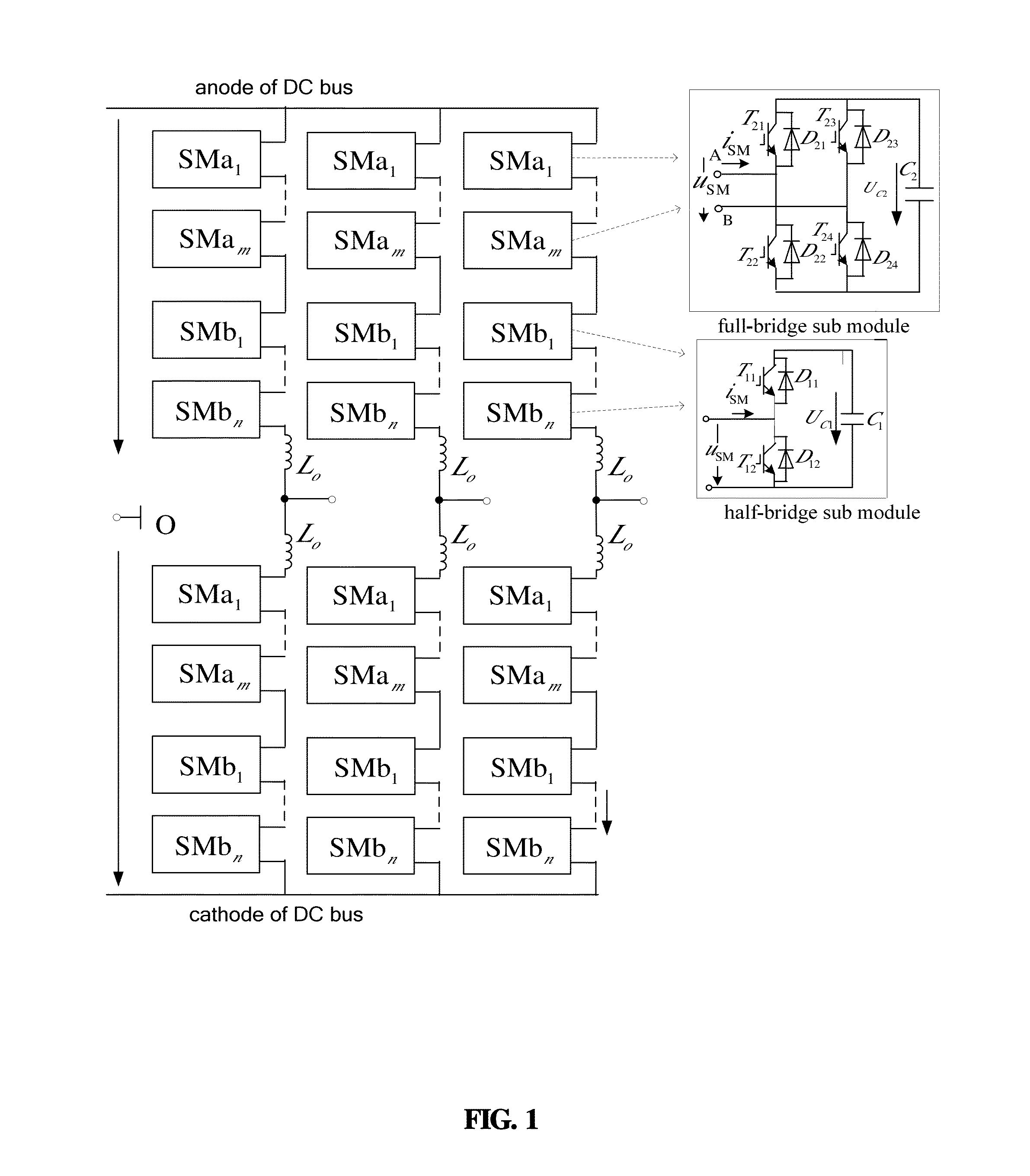
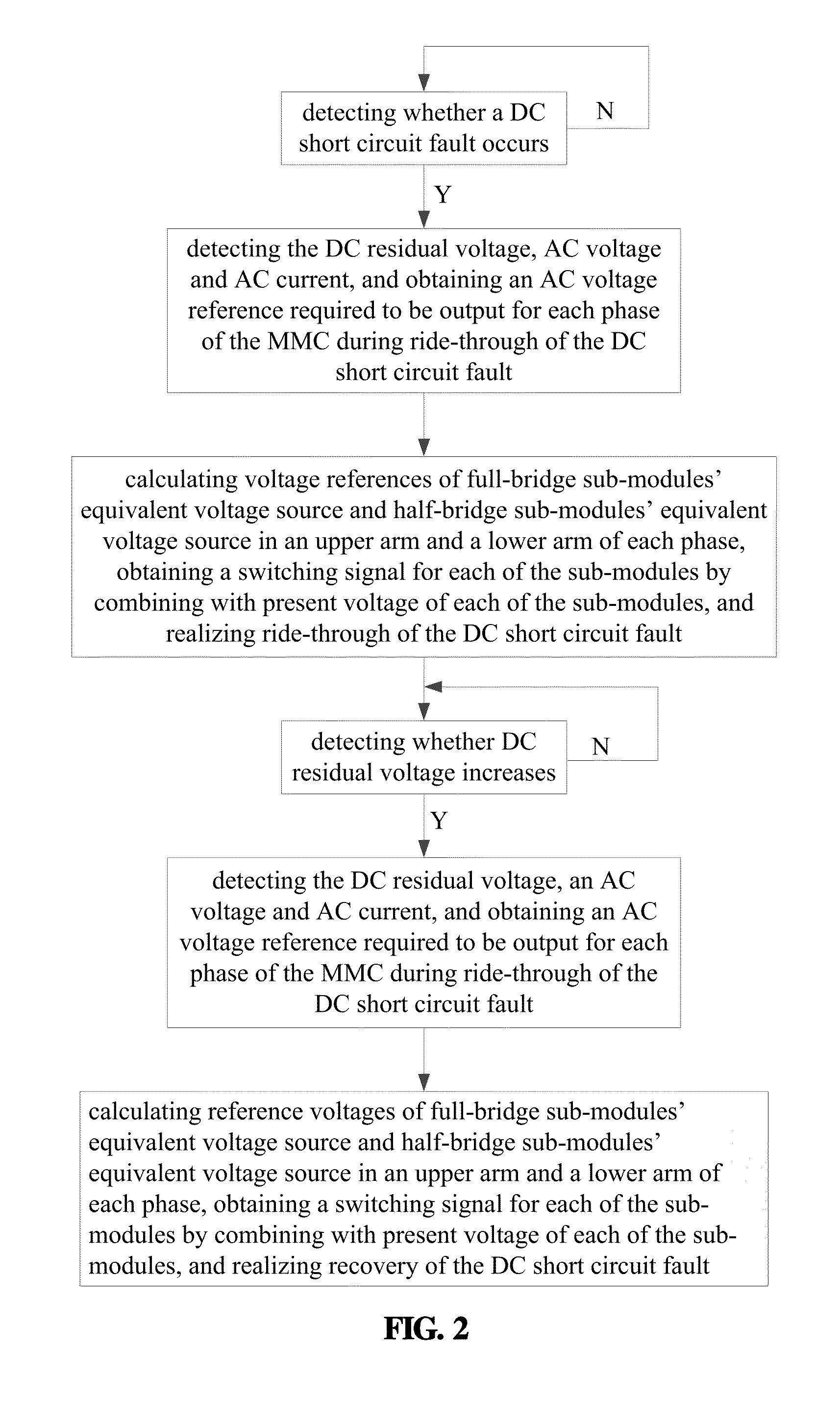
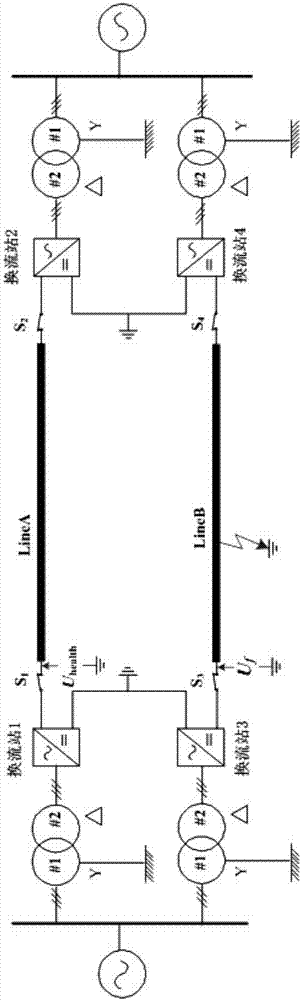
Ride-through and recovery method for DC short circuit faults of hybrid mmc-based HVDC system
ActiveUS20160094117A1Fast response to faultsPromote recoveryAc-dc conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsRecovery methodFull bridge
A ride-through and recovery method for DC short circuit faults of a hybrid modular multilevel converter based high-voltage direct current transmission (MMC-HVDC) system, the hybrid MMC including multiple full-bridge sub-modules and half-bridge sub-modules, and the method including: 1) detecting whether a DC short circuit fault occurs, and proceeding to step (2) if yes and continuing detecting if no; 2) realizing ride-through of the DC short circuit fault; 3) detecting whether a DC residual voltage increases, and proceeding to step (4) if yes and continuing detecting if no; and 4) realizing DC short circuit fault recovery.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Small current earthing wire-selecting method
InactiveCN101068078AImprove the accuracy of judgmentEffective detection functionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationObservational errorEngineering
This invention relates to an earth line selection method including a computer, a communication network, an integrated test device and a protection test device characterizing that when a single-phase earth fault happens to the system, residual voltage is generated at the hatch triangle place of a bus voltage mutual inductor, theoretically, zero-sequence current of the faulty circuit should be the maximum, yet actual value may be not, so three circuits with the greatest current amplitude are selected as the faulty earth circuits, then the breaker of a circuit with not important load is selected to trip then to compare the residual voltage, zero-sequence current and power direction with those after the trip so as to determine which one in the three is the earth faulty circuit.
Owner:BEIHAI YINHE HI TECH INDAL
Soft-start circuit and method for a switching regulator
InactiveUS20110006746A1Reduce soft-start timeShorten the switching timeElectric variable regulationPower conversion systemsStart timeEngineering
A soft-start circuit for a switching regulator includes a signal generator and a scaling circuit coupled to the signal generator. During soft-start, the signal generator provides a ramp signal for the switching regulator such that the output voltage of the switching regulator changes from a residual voltage toward a target level. When soft-start is triggered, the scaling circuit provides a scaling voltage depending on the residual voltage, to shift the level of the ramp signal and consequently shorten the soft-start time of the switching regulator.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
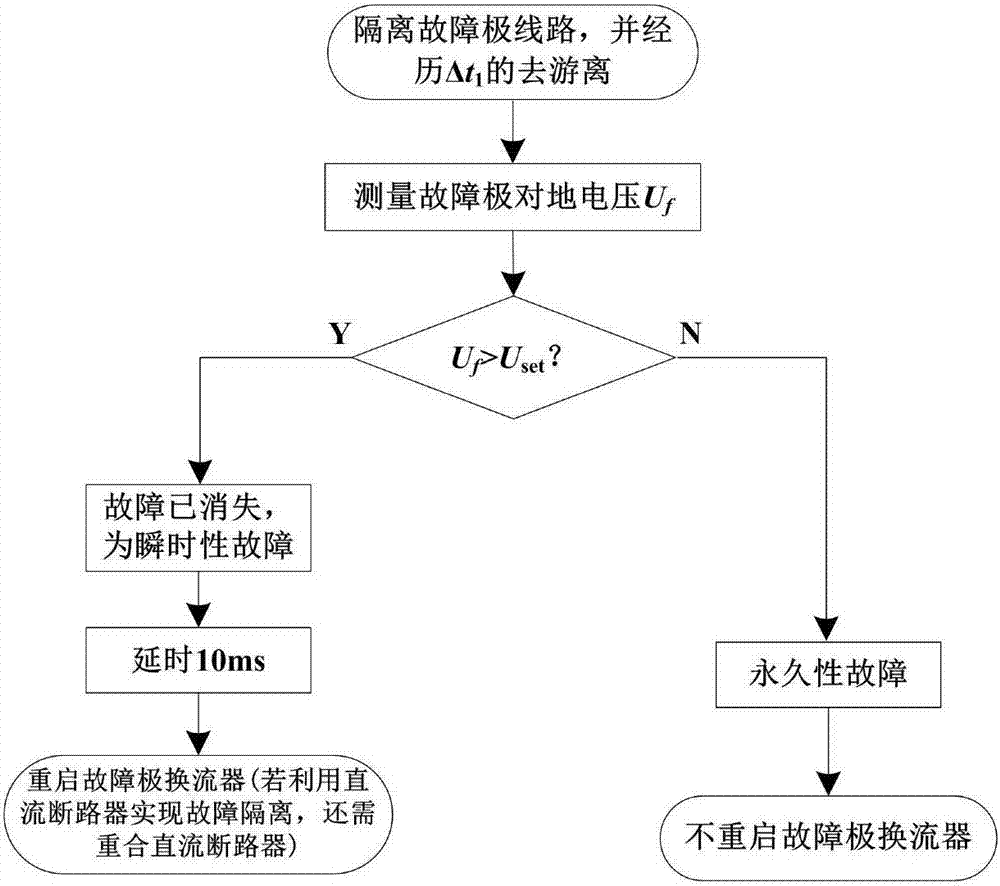
Adaptive reclosure method for monopolar grounding fault of true bipolar MMC-HVDC power transmission system
ActiveCN107359588AAvoid secondary overcurrent impactElectric power transfer ac networkEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionTime delaysDc circuit breaker
The present invention discloses an adaptive reclosure method for the novel monopolar grounding fault of a true bipolar MMC-HVDC power transmission system. According to the invention, after the occurrence of a monopolar grounding fault and the isolation of a faulty electrode circuit, the grounding voltage Uf of the faulty electrode circuit is measured after the experience of a certain period of dissociation process. According to the principle of electrostatic induction between power transmission circuits, if Uf is larger than Uset, the residual voltage occurs to the circuit. A fault point has disappeared, and the fault is determined as a transient fault. After the time delay of delta t2, a faulty electrode converter is restarted. If the fault isolation is achieved by a DC circuit breaker, the DC circuit breaker needs to be re-switched on. If Uf is smaller than Uset, little residual voltage occurs to the circuit. The fault point still exists, and the fault is determined as a permanent fault. The faulty electrode converter is not restarted. By adopting the above method, the pre-judgment of a fault type can be realized without unlocking the converter, so that the secondary damage of the system is avoided. Compared with existing reclosure methods for the true bipolar MMC-HVDC power transmission system, the secondary overcurrent impact caused by the reclosure of a permanent monopolar grounding fault is effectively avoided.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
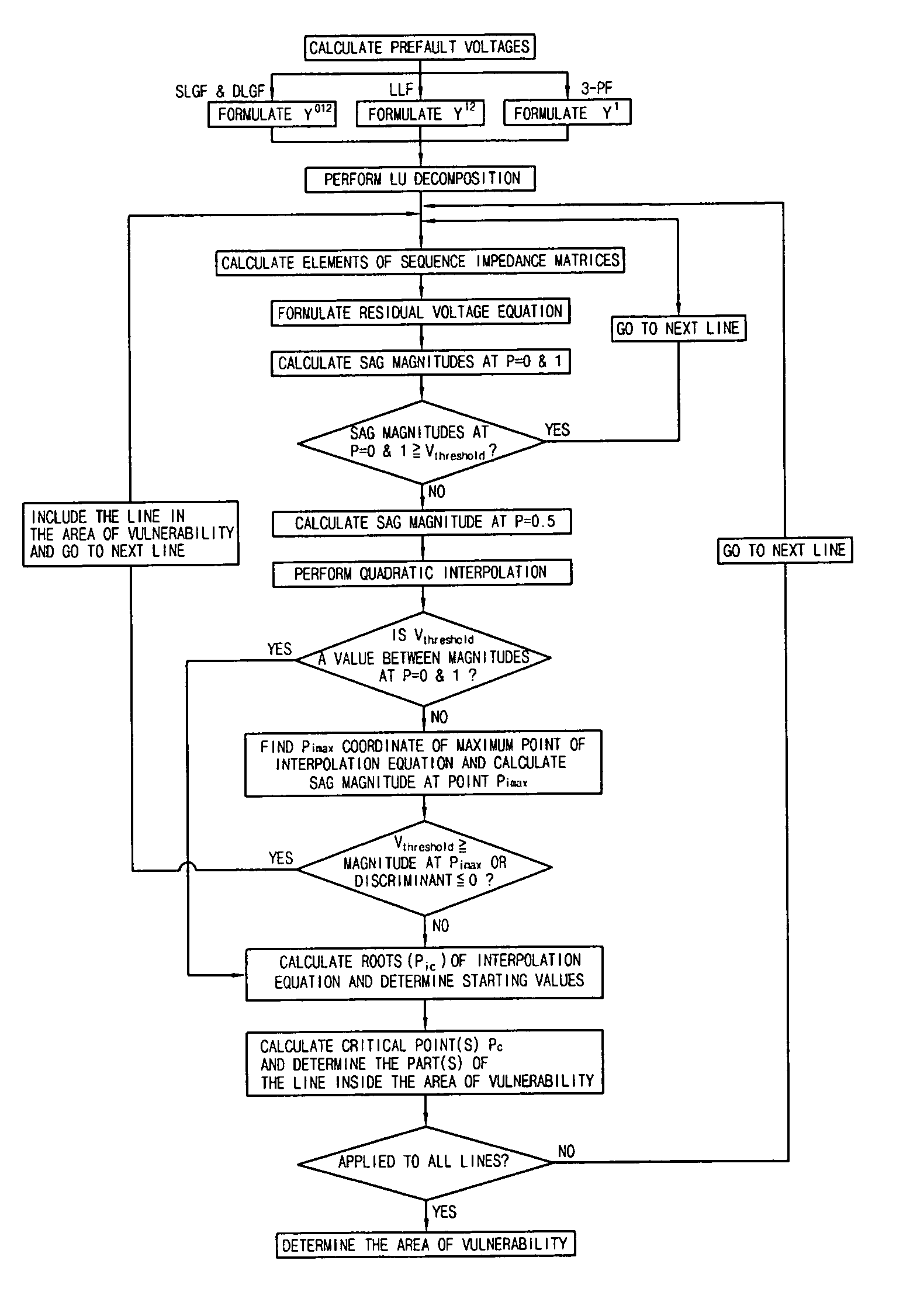
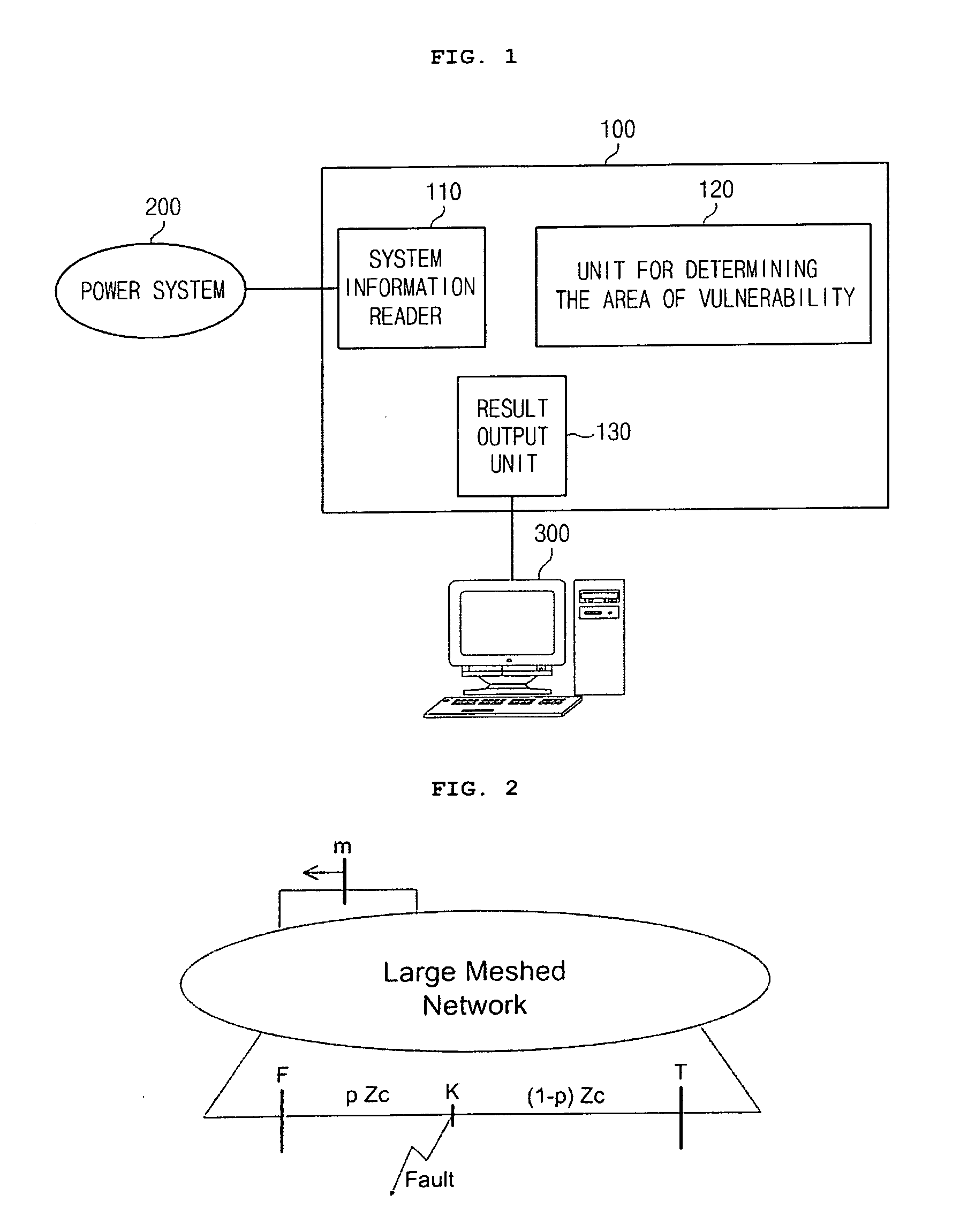
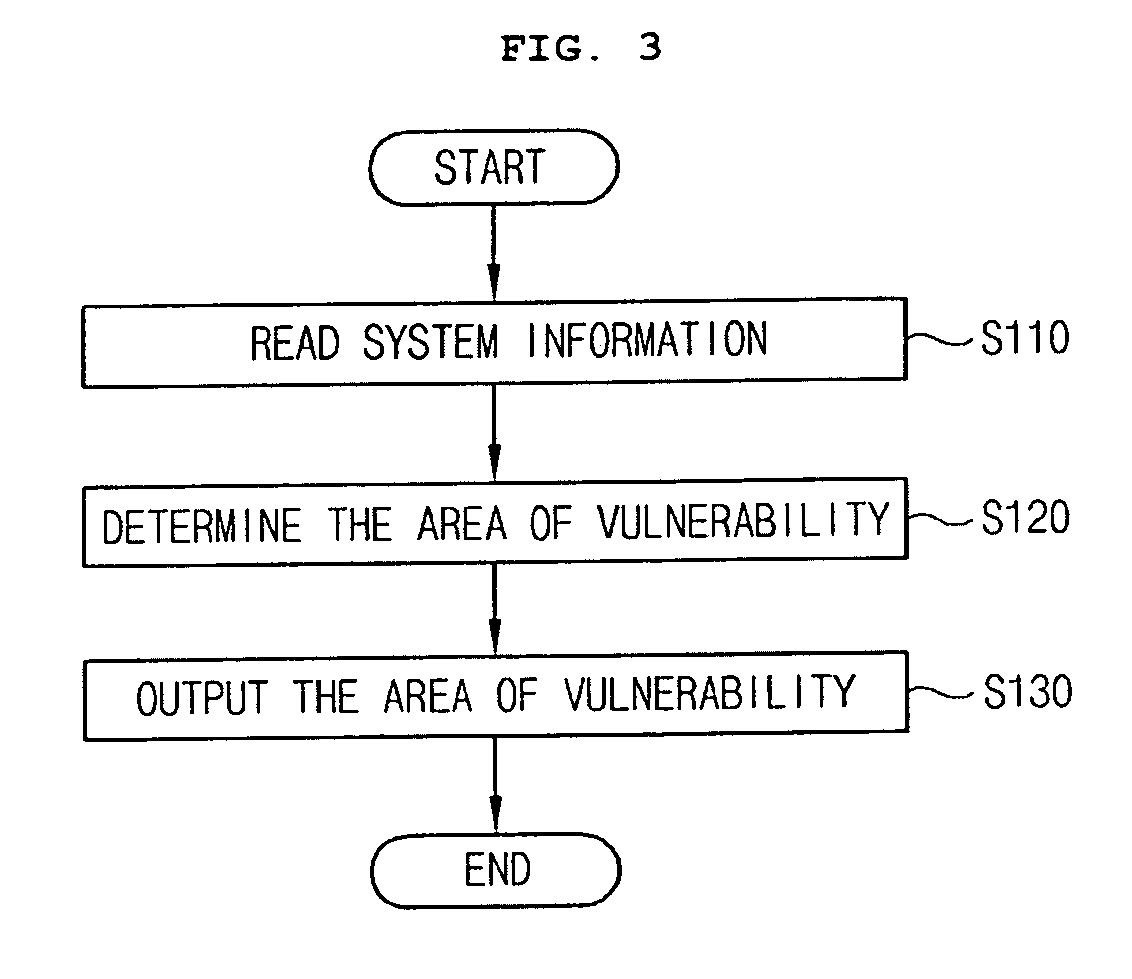
System and method of determining the area of vulnerability for estimation of voltage sags and computer-readable medium having embodied thereon computer program for the method
InactiveUS20090030623A1Quick calculationRapid and accurate calculationCurrent/voltage measurementEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionElectric power systemEngineering
Provided is a system for determining the area of vulnerability for estimation of voltage sages including: a system information reader reading information on a power system; a unit for determining the area of vulnerability calculating a voltages at a target bus corresponding to ends of a fault line by using the system information and a first residual voltage equation that is a voltage relationship between points in the fault line in the power system where a fault is simulated and the target bus where a voltage change due to the fault occurs, calculating a voltage at the target bus corresponding to a point between the ends when the voltages at the target bus corresponding to the ends are not higher than a predetermined voltage threshold, deriving a second residual voltage equation that is an approximate quadratic interpolation equation for the first residual voltage equation by using the voltages at the target bus corresponding to the ends and the point between the ends of the fault line, calculating the voltage of the target bus corresponding to the point of the fault line by using the second residual voltage equation, and determining the point of the fault line corresponding to a voltage of the target bus equal to or lower than the predetermined voltage threshold as the area of vulnerability; and a result output unit outputting results of the determination of the area of vulnerability.
Owner:KOREA UNIV IND & ACAD COLLABORATION FOUNDATION
Contrable metal oxide arrester in use for transmission system in supervoltage, extra high voltage
ActiveCN101093742AReduce charge rateImprove operational reliabilityVaristor coresOvervoltage protection resistorsMetal oxide surge arresterHigh pressure
The controllable arrester in metal oxide includes control part and fixed part connected in series. In normal operation of system, the control part and the fixed part together bear system voltage. When amplitude value of system over voltage exceeds prearranged threshold value, the fixed part bears system over voltage. Combining power electronic device in large power with arrester in metal oxide (MO), the invention puts forward concept and designing idea of controllable arrester for aiming at issue of over voltage protection for transmission system in super voltage, extra high voltage. Based on condition of maintaining invariable performance parameters of MO resistance piece, the invention reduces residual voltage of arrester effectively by using characteristics: quick response speed of power electronic device, steady operation, and flexible adjustment so as to raise protection level for arrester.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com