High-voltage direct-current transmission line high-resistance grounding fault identification method based on distributed parameters
A high-resistance ground fault, high-voltage DC technology, applied in fault locations, emergency protection circuit devices, electrical components, etc. Problems such as fault information and description, to achieve the effect of short action time, meet rapidity requirements, and improve sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
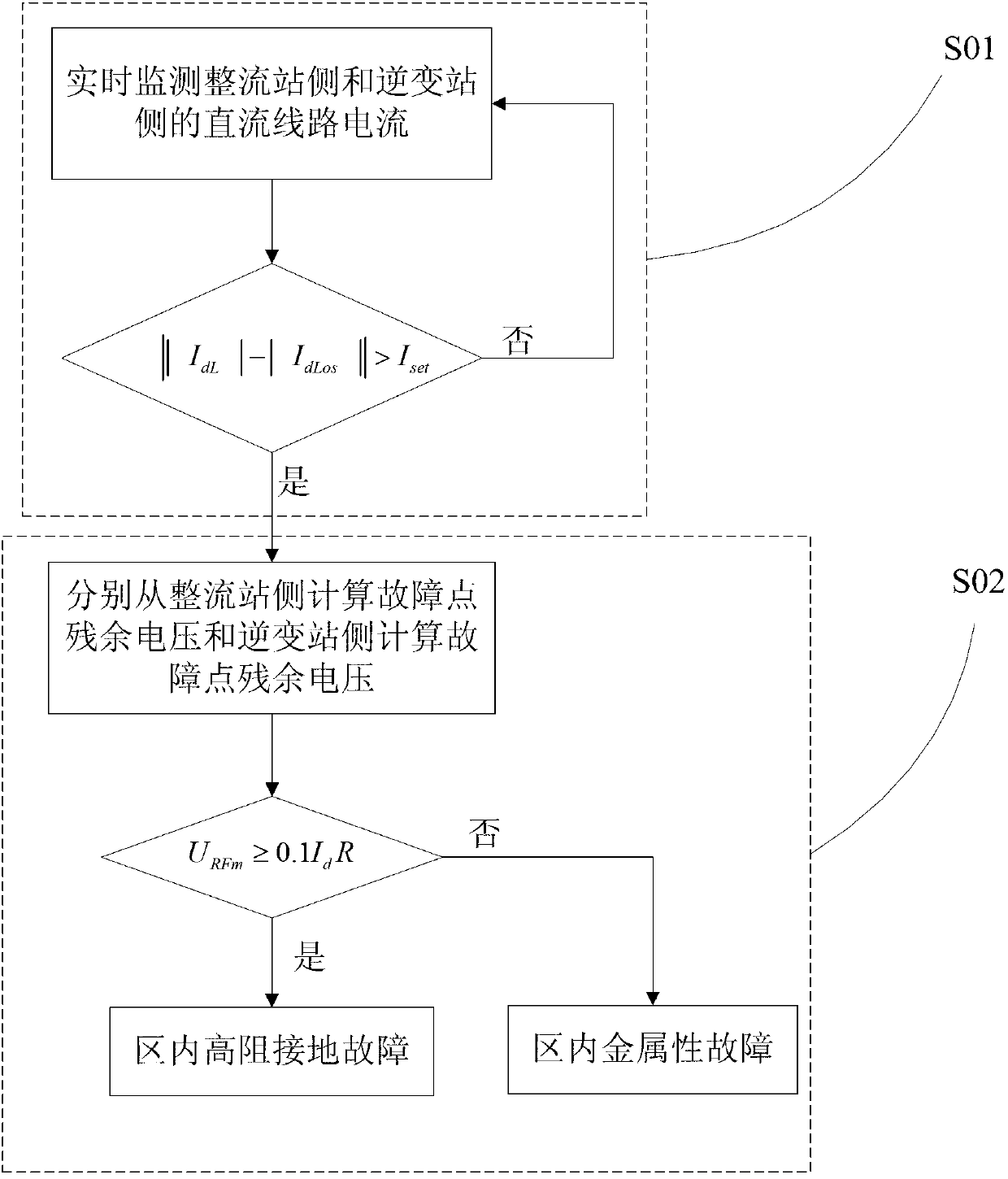
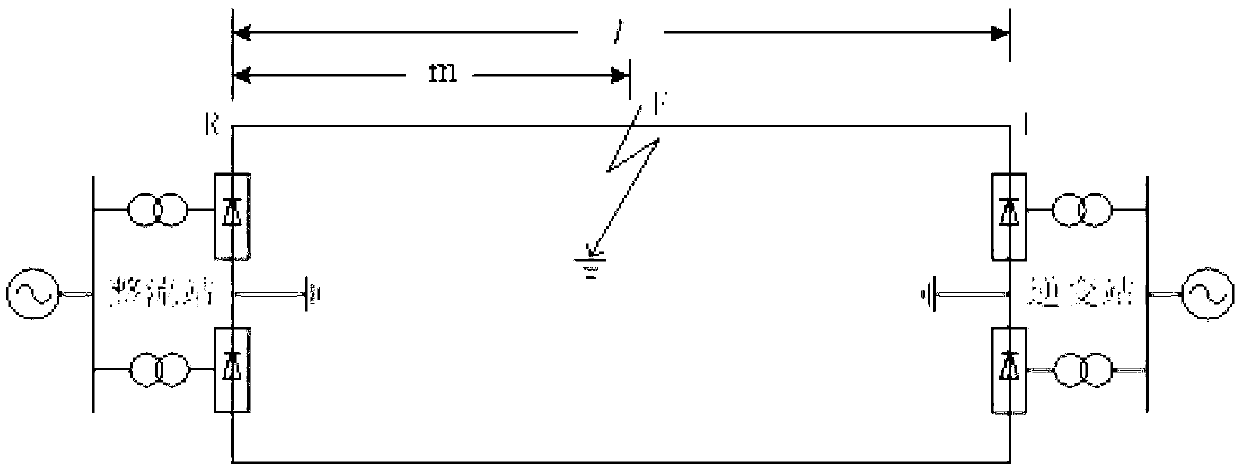
[0041] Please refer to figure 1 shown, combined with figure 2 A model diagram of the HVDC transmission line shown. A method for identifying a high-resistance ground fault of a high-voltage direct current transmission line with distributed parameters, comprising the following steps:
[0042] S01. Real-time monitoring of the DC line current on the side of the rectifier station and the side of the inverter station. If formula (1) is satisfied within 3ms, it is judged that there is a fault point in the high-voltage DC transmission line, and S02 is executed; otherwise, continue monitoring DC line current at rectifier station side and inverter station side;
[0043] ||I R |-|I I ||>I set (1)
[0044] Formula (1) is the entrance of the invention for protecting the HVDC transmission line. Among them, I R is the DC line current at the rectifier station side, I I is the DC line current at the inverter side, I set is the set value, I set =max{1.6I co ,0.05I n}, I co is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com