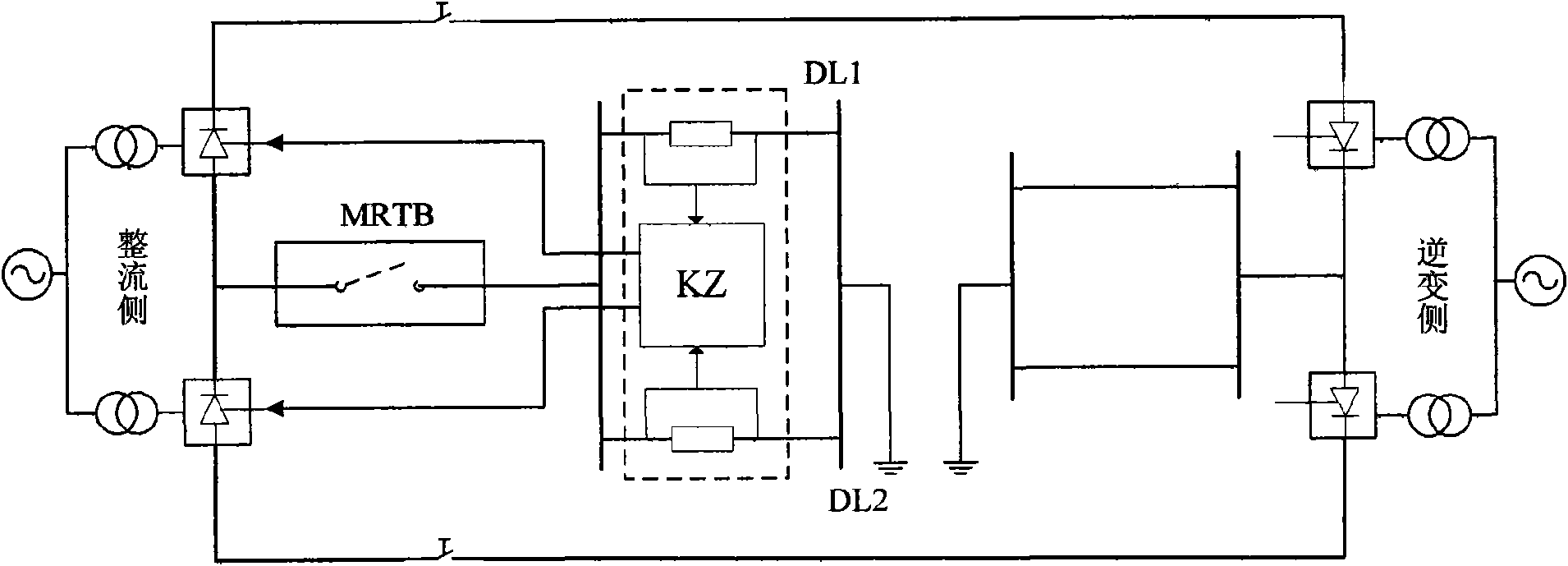
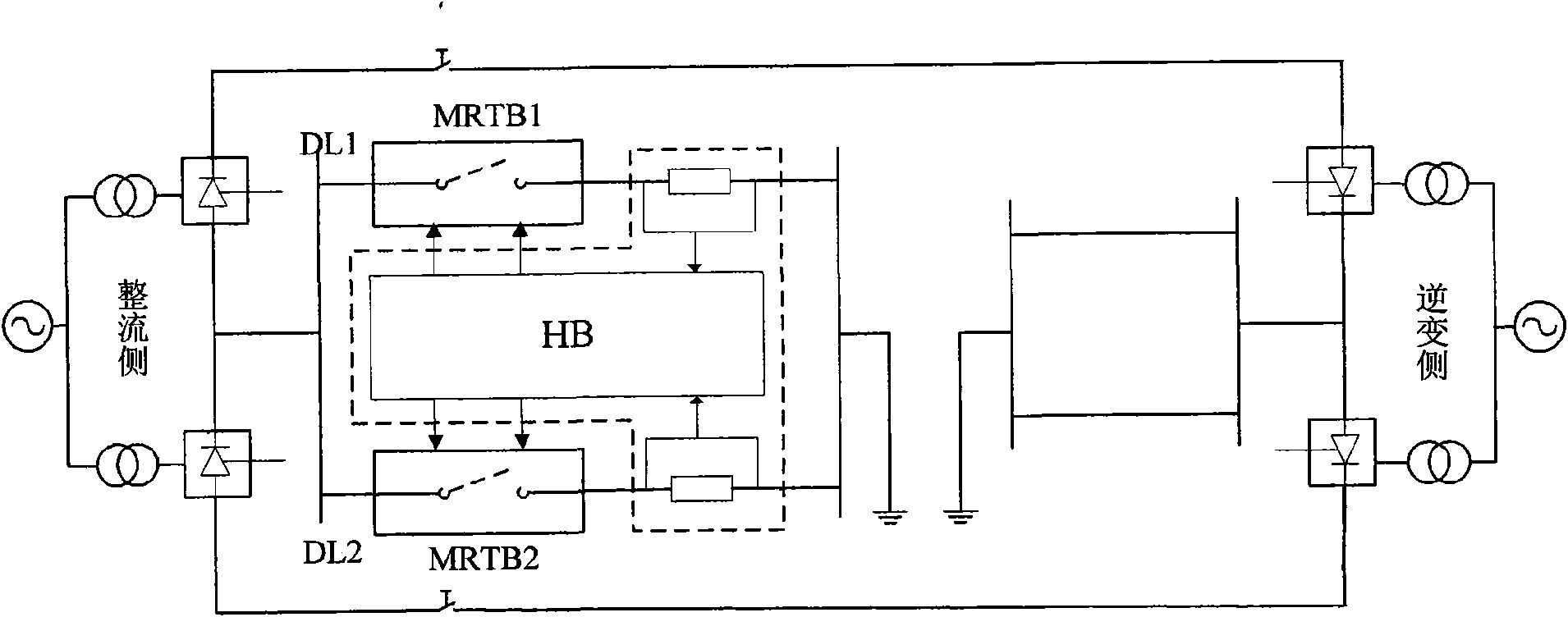
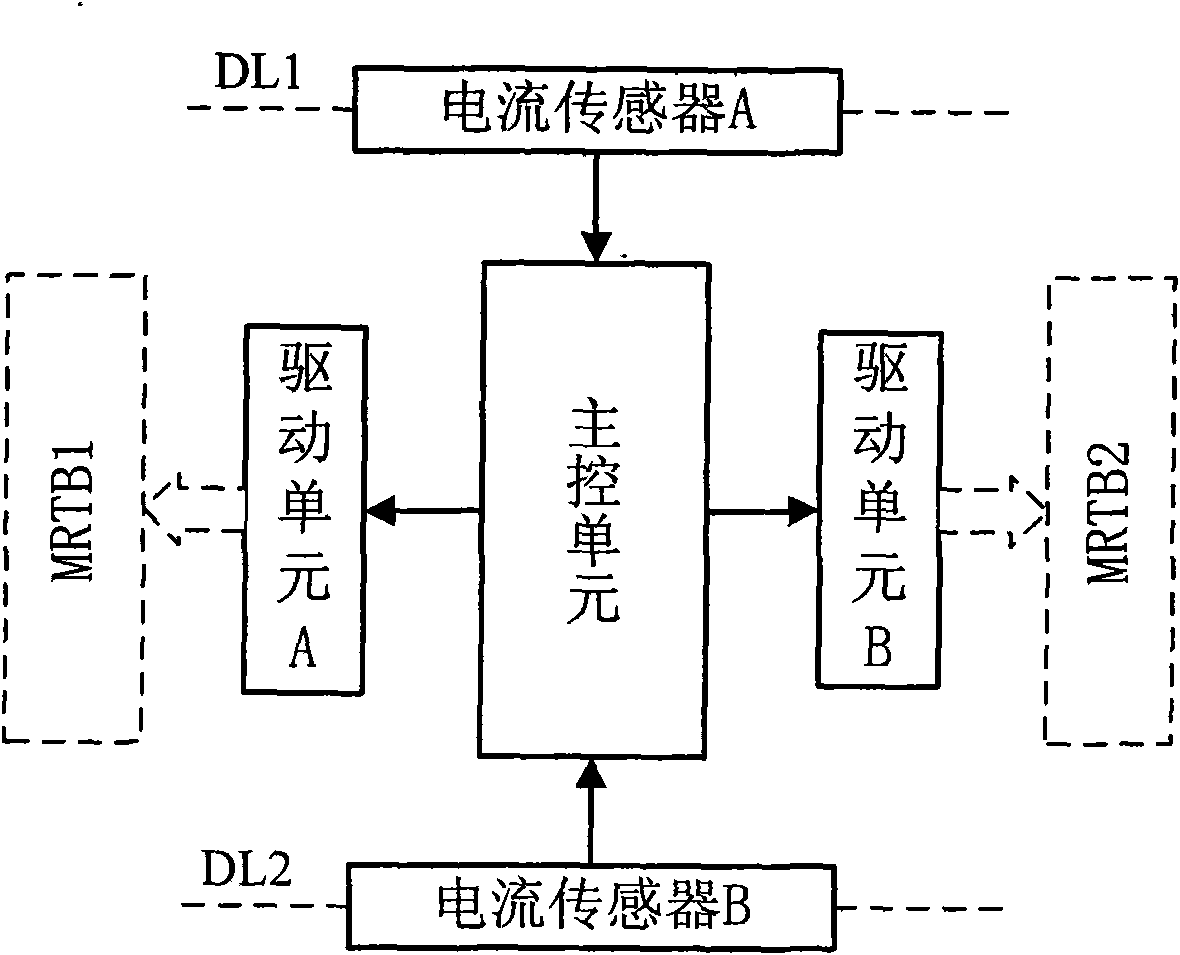
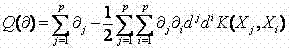Patents
Literature
1427 results about "Line current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
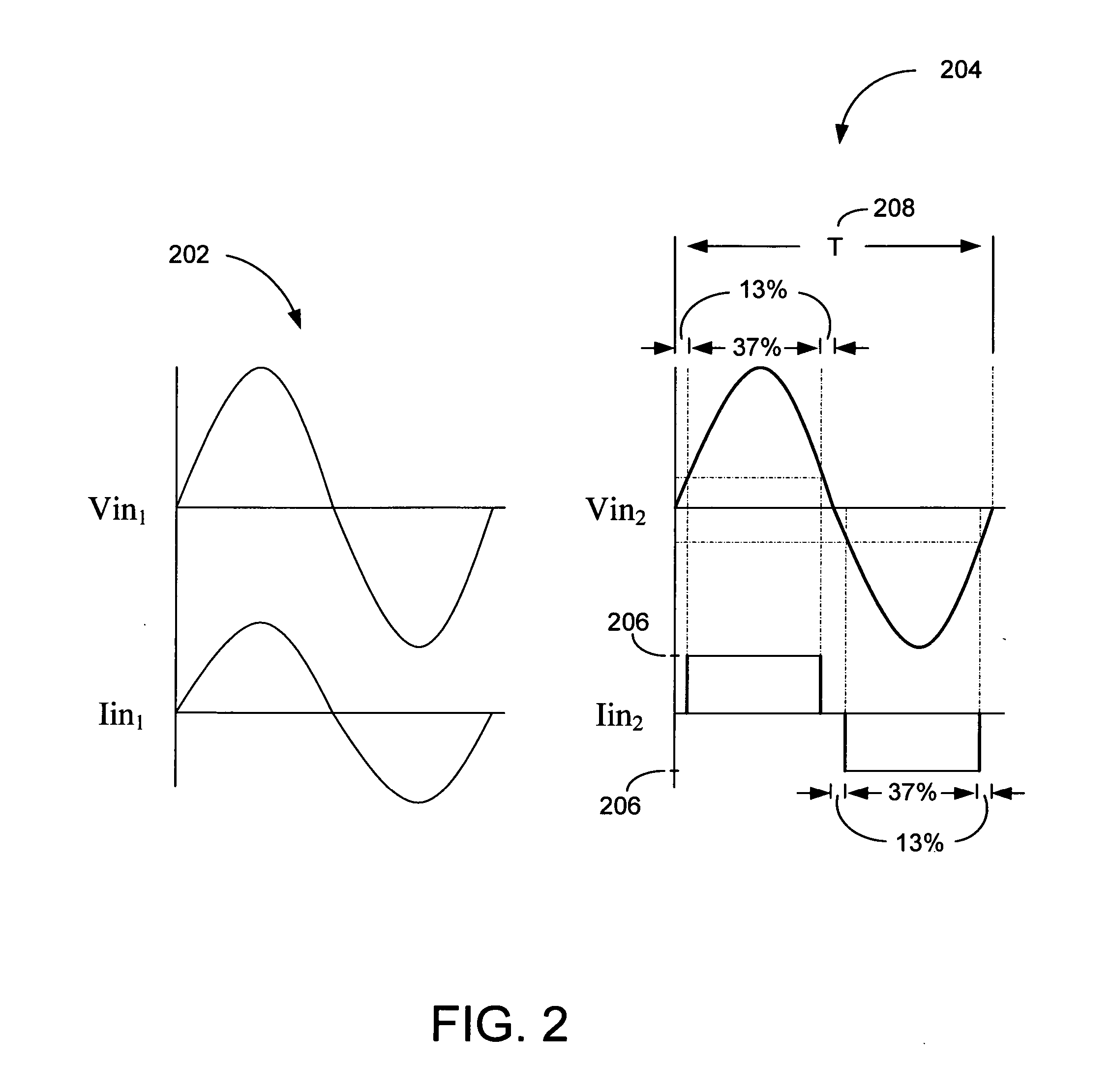
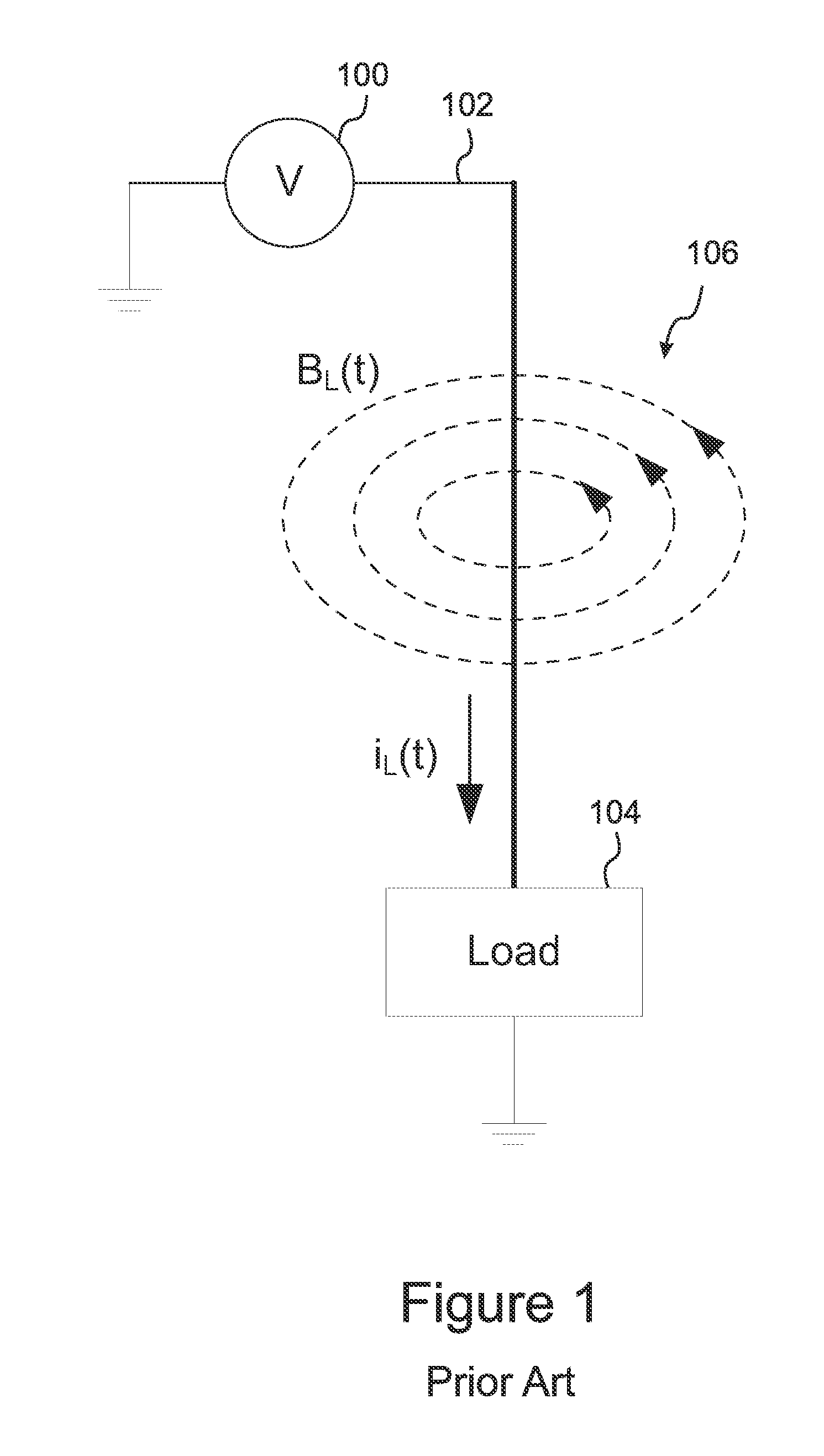
Phase voltage is the voltage measured across a single component in a three-phase source or load. Line current is the current through any one line between a three-phase source and load. Phase current is the current through any one component comprising a three-phase source or load.
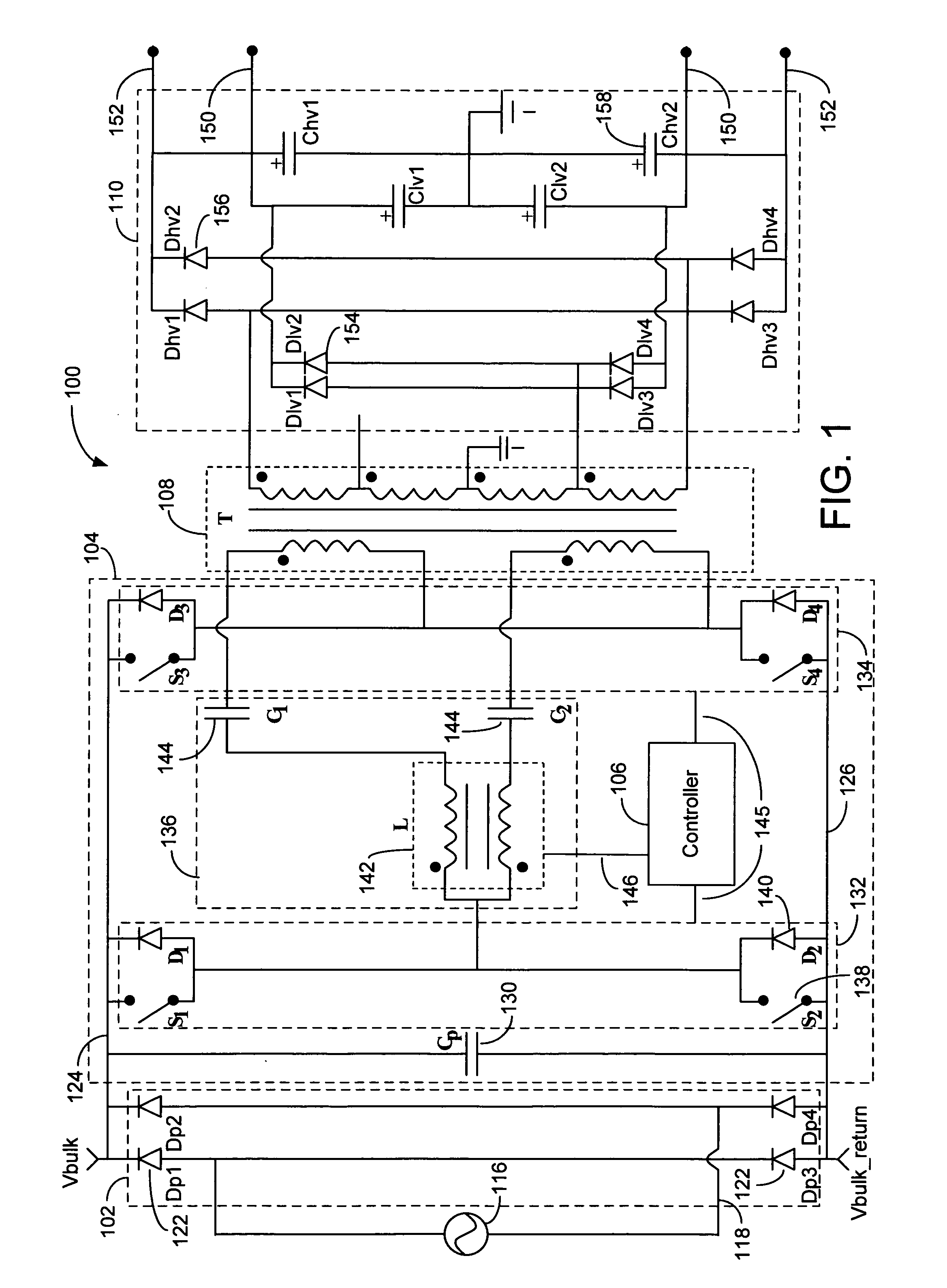
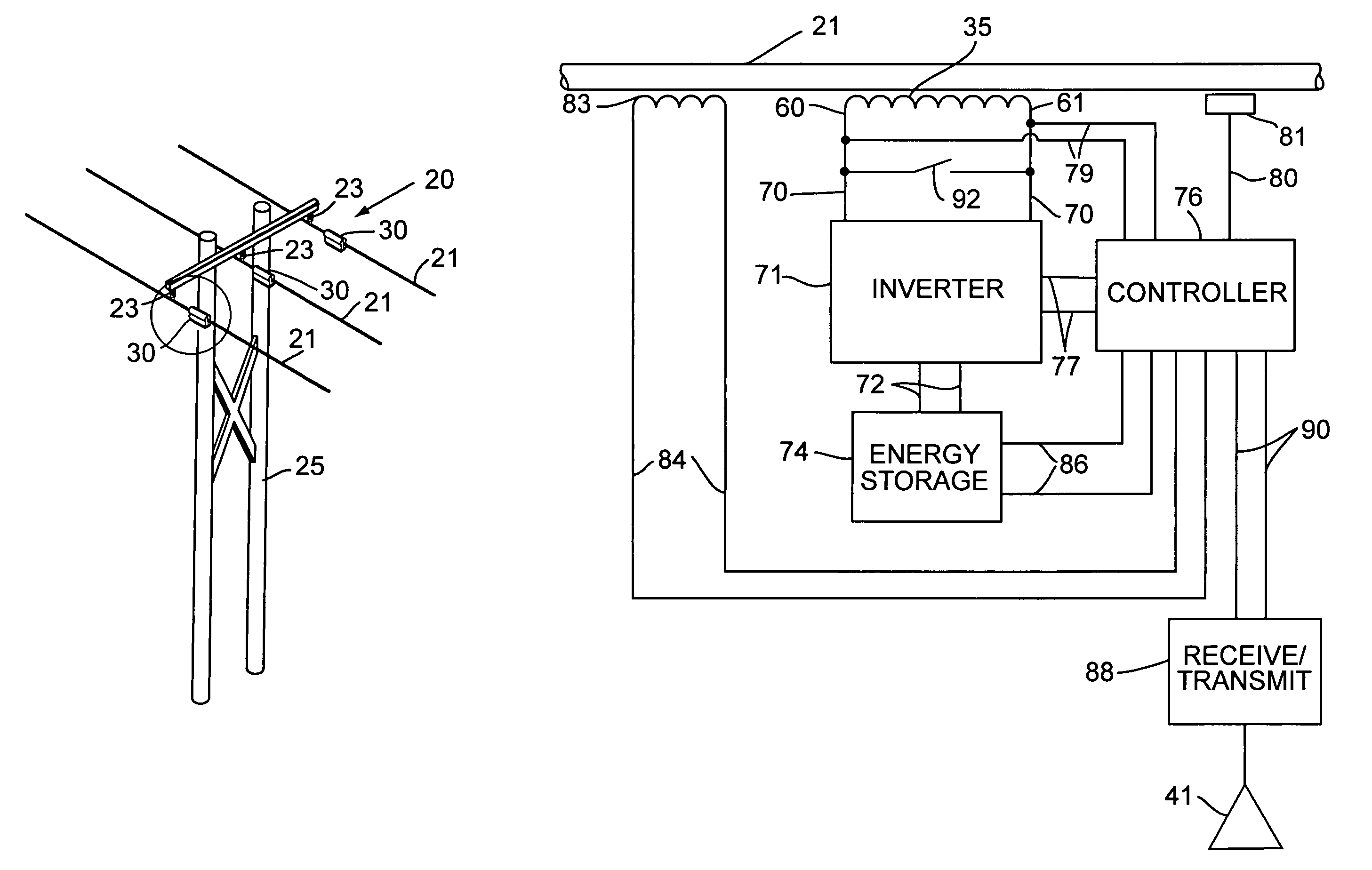
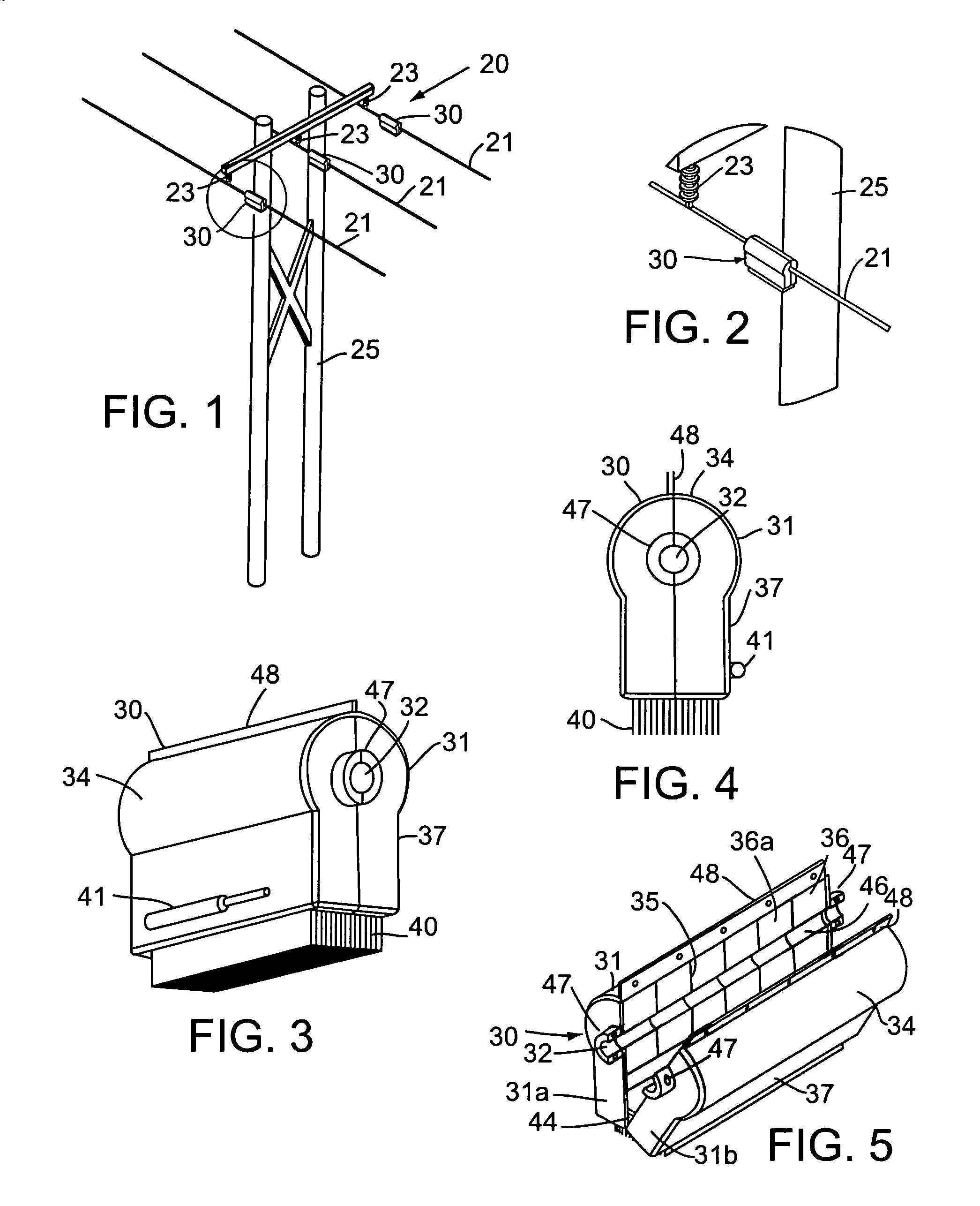
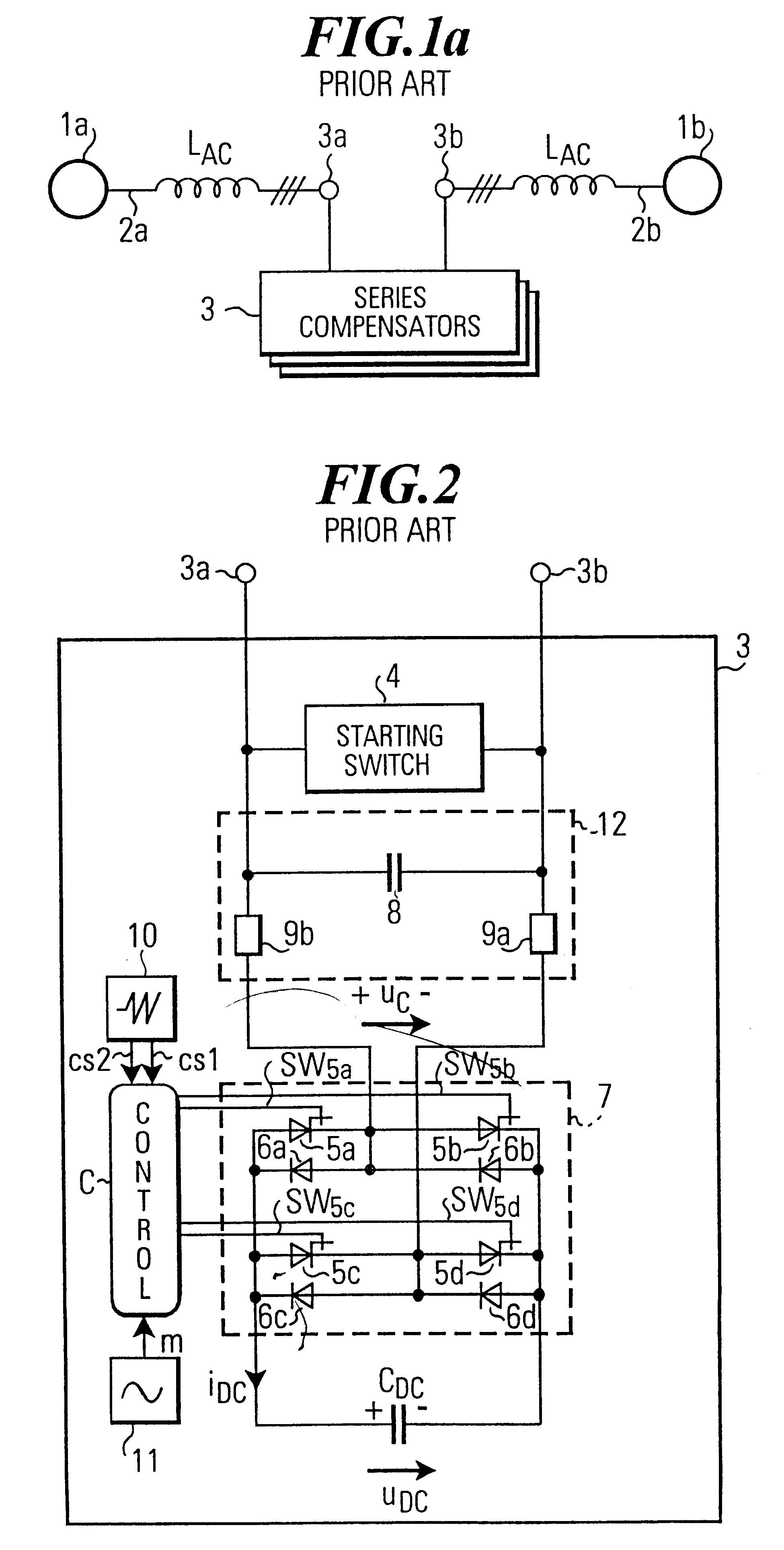
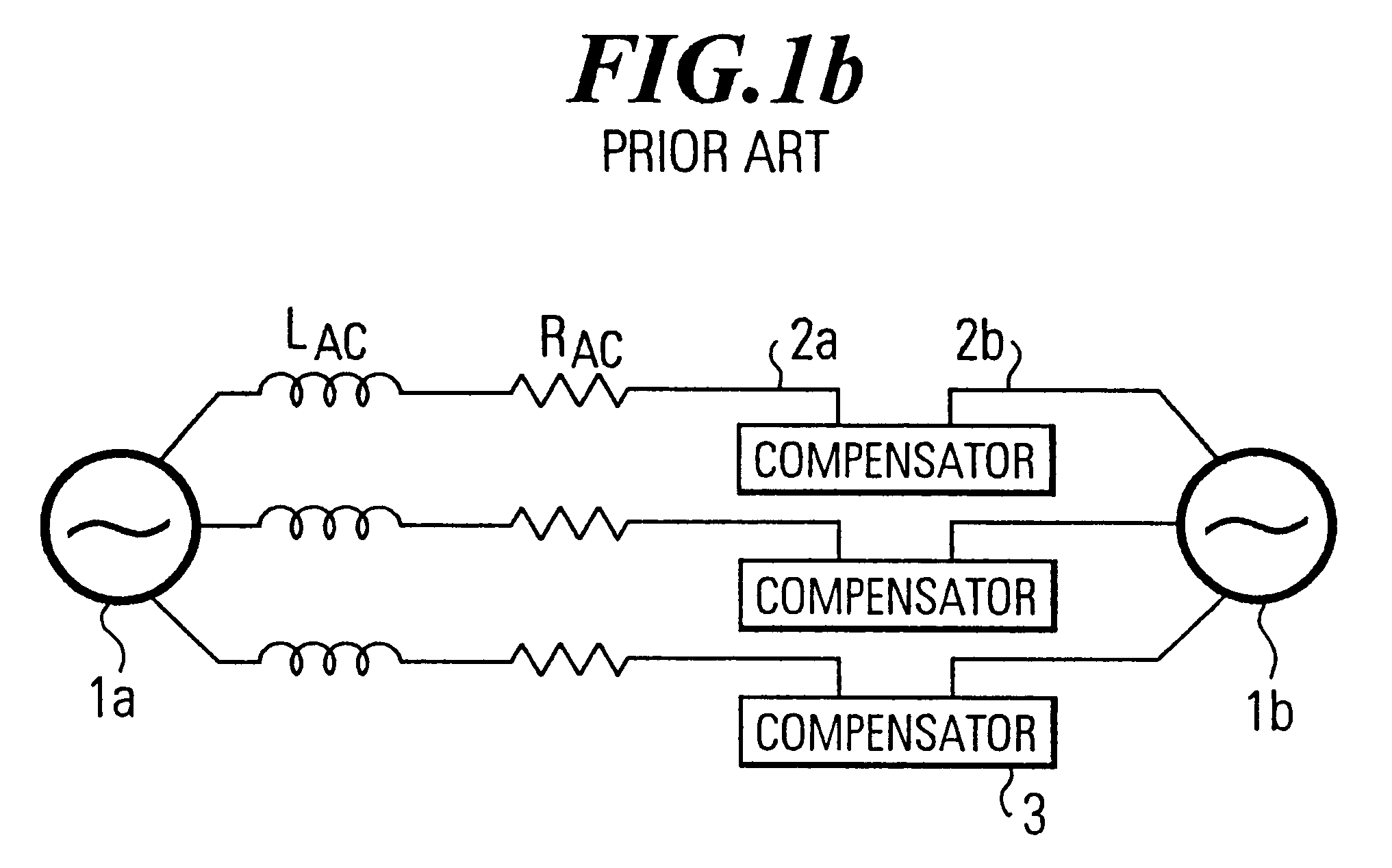
Systems and methods for distributed series compensation of power lines using passive devices
ActiveUS7835128B2Emergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentReactive power compensationElectrical conductorTransformer
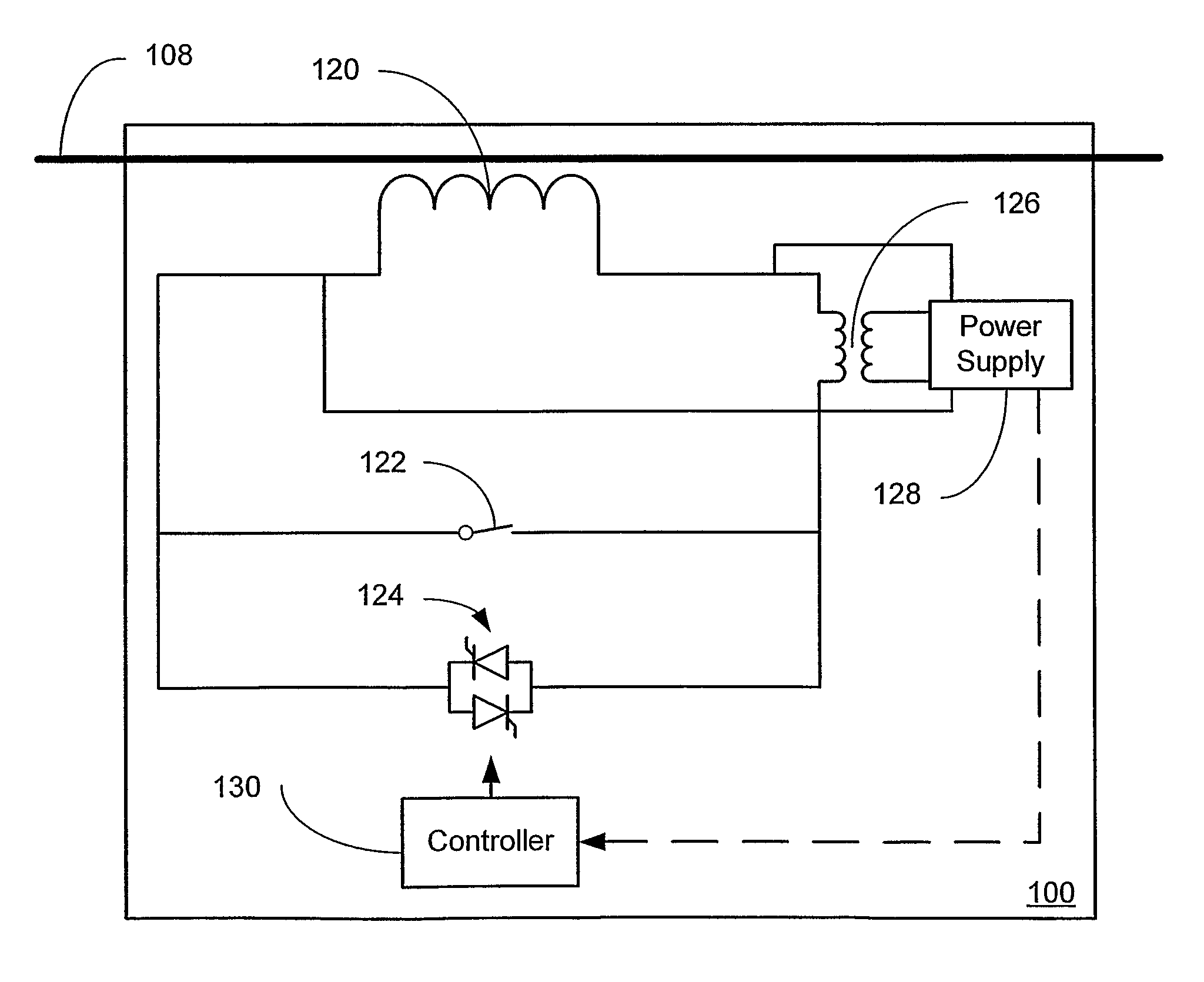
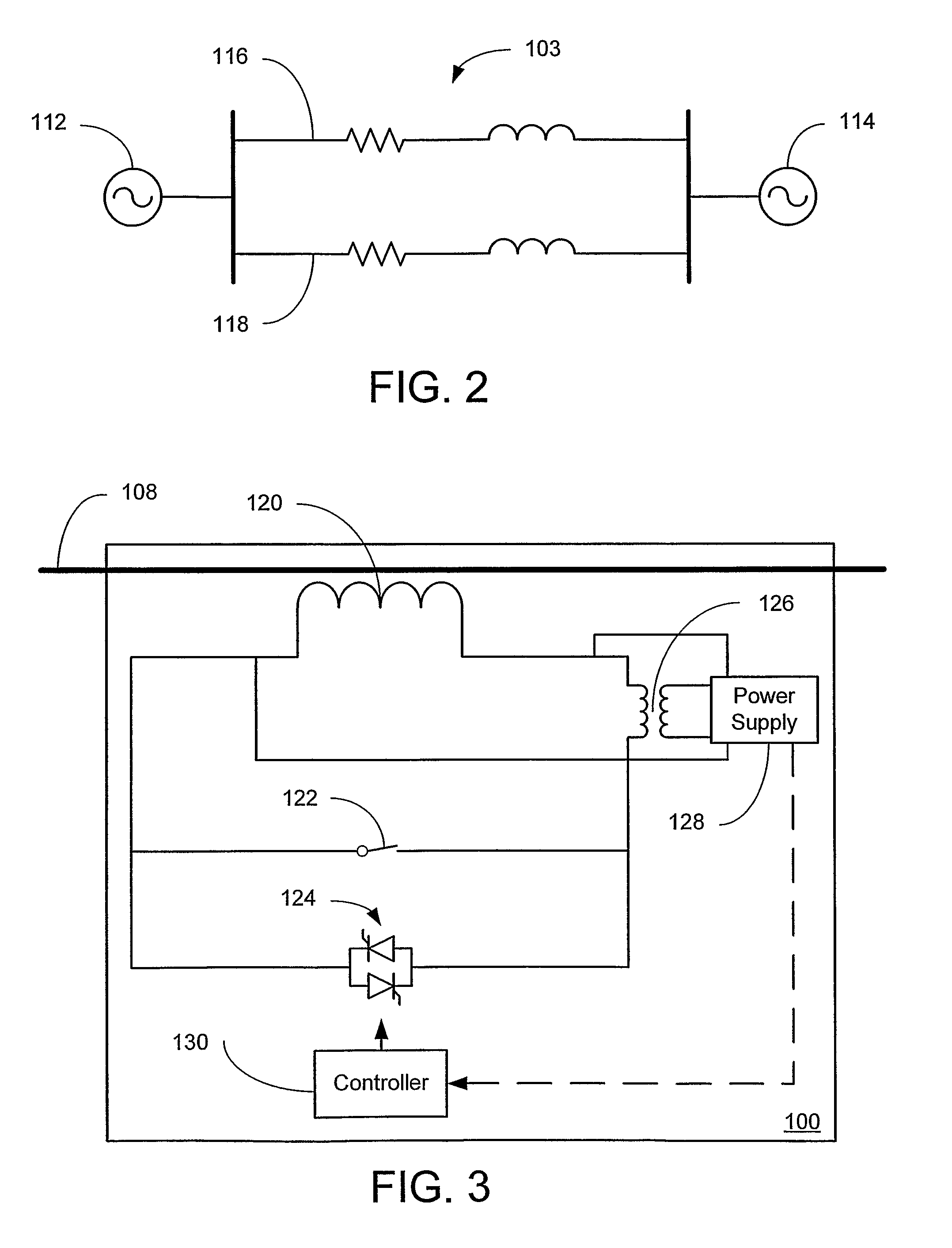
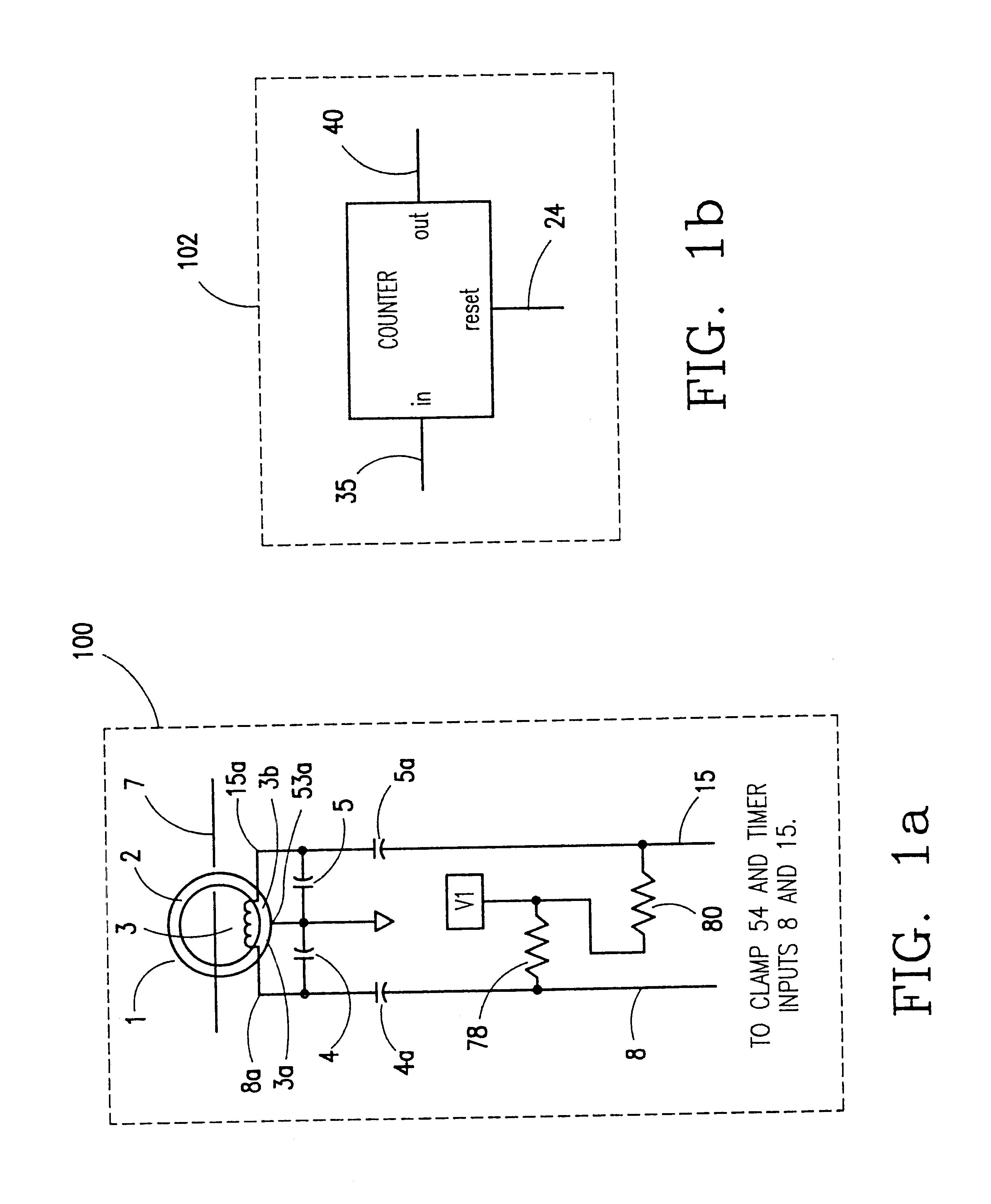
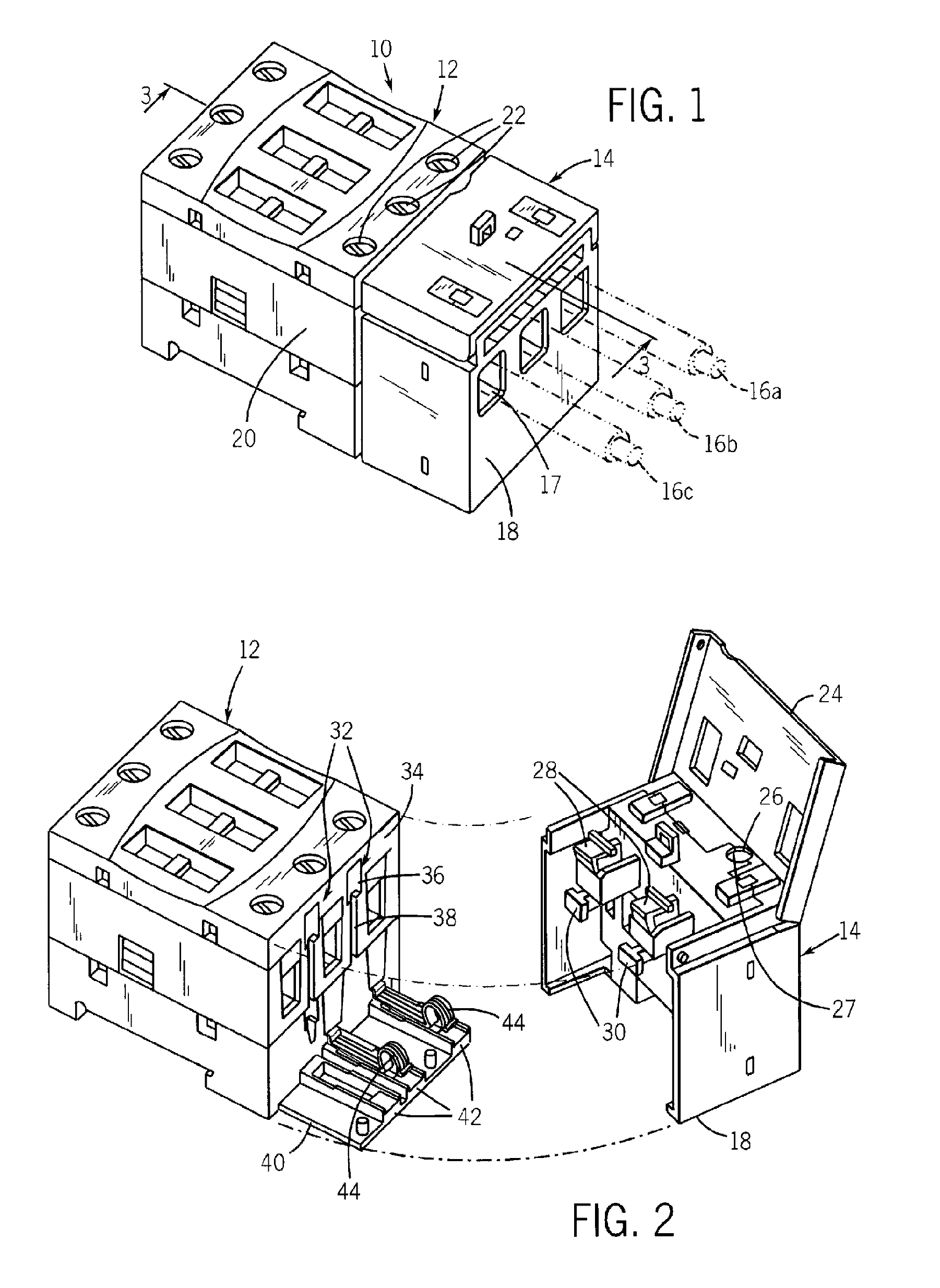
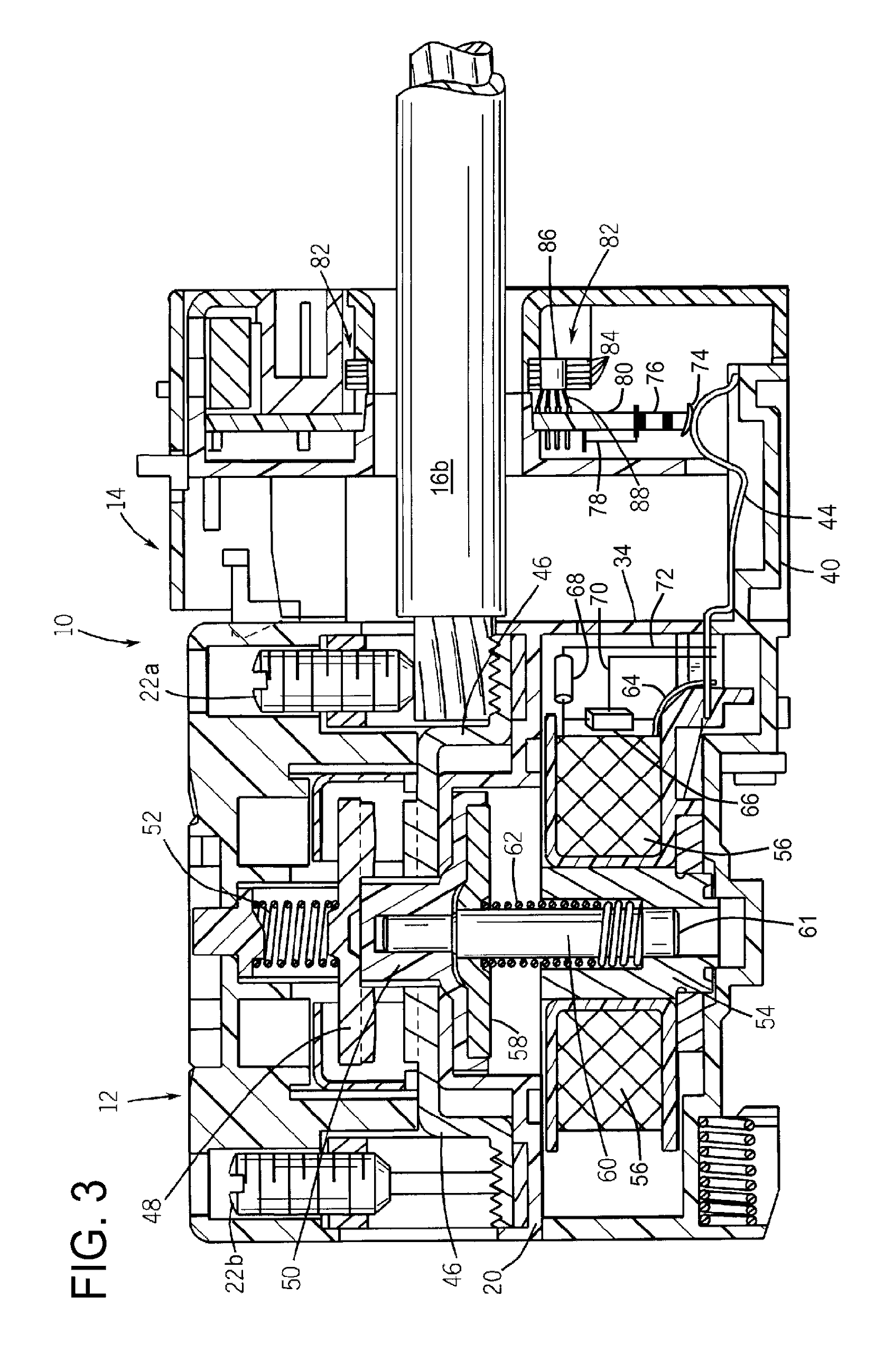
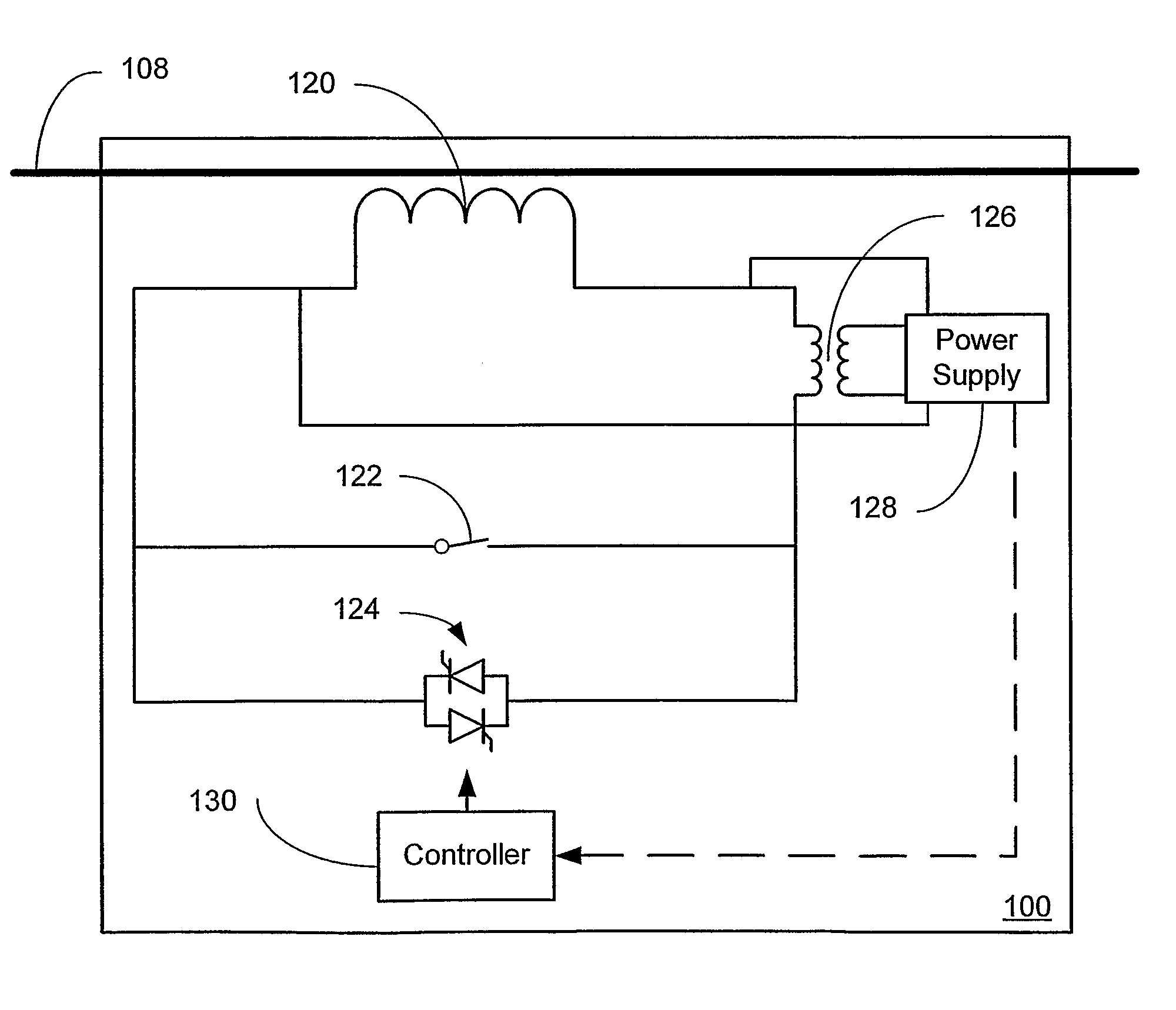
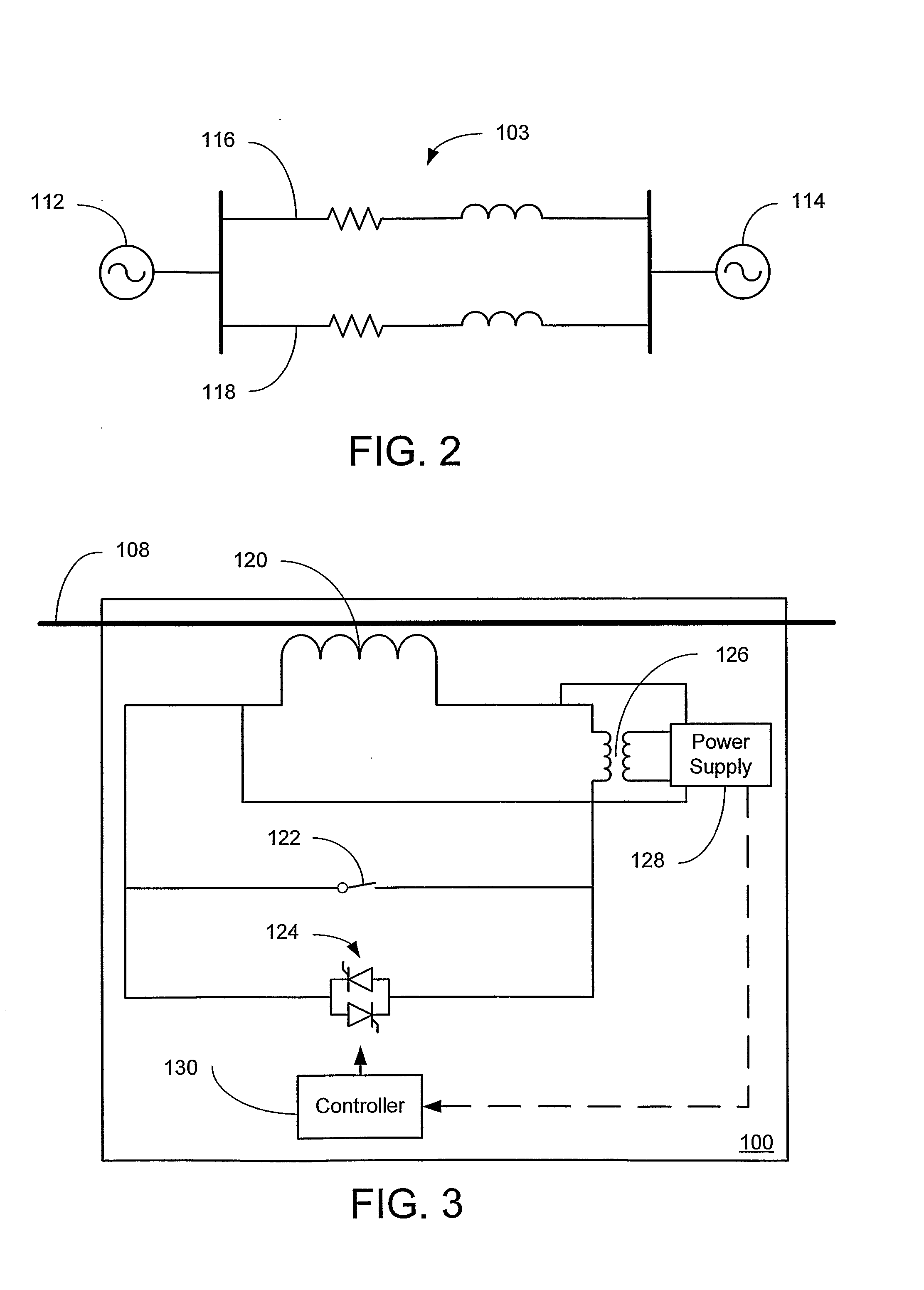
Systems and methods for implementing line overload control via providing distributed series impedance are disclosed. One system, amongst others, comprises at least one distributed series reactor (DSR). Each DSR comprises a single turn transformer (SST) comprising two split-core sections (132), a winding (120), and an air-gap (138), the air-gap designed such that a magnetizing inductance is produced when the two split-core sections (132) are clamped around a conductor (108). Each DSR further comprises a contact switch (122) that short circuits the winding when the contact switch (122) is in a closed condition, a power supply (128) that derives power from conductor line current, and a controller (130) configured to open the contact switch when the conductor line current reaches a predetermined value, thus causing insertion of the magnetizing inductance into the conductor. The controller (130) may be further configured to close the contact switch (122) when the conductor line current drops below the predetermined value.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Current controlled switch mode power supply
ActiveUS20060152947A1Improve power factorReduce equipment stressEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcSingle stageAudio power amplifier
A single stage switch mode power converter receives a supply line voltage and a supply line current from a power supply line, and provides one or more regulated output voltages for a load, such as an amplifier. The power converter is operable to regulate the output voltage(s) using a controller that includes a voltage controlled current loop. The controller can enable substantially constant supply line current to be drawn from the power supply line by selectively allowing conduction of the supply line current through the power converter. A power factor of the supply line voltage and the supply line current may be optimized by the controller at medium to high power levels thereby maximizing the power provided to the switch mode power converter from the power supply line. Due to the adaptive nature of the controller, the power converter can operate over a wide range of supply line voltage.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Arc fault circuit interrupter
InactiveUS6373257B1Emergency protective arrangement detailsElectric switchesElectric power systemEngineering
An arc fault detector for detecting electric power lines includes a sensor for sensing the derivative of the current on the electric power line, a converter circuit for converting the derivative of the line current into first and second signals, the first signal responsive to positive step transitions of arc fault current, and the second signal responsive to negative step transitions of arc current, and a temporal detector for signaling the presence of an arc fault when one of the first and second signals follows the other within a predetermined time, or window, and in which a sequence of one of the signals following the other signal occurs in a second predetermined interval of time.
Owner:PASS SEYMOUR
Distributed floating series active impedances for power transmission systems
ActiveUS20050073200A1Reduce congestionGuaranteed normal transmissionFlexible AC transmissionBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionElectric power system
Floating electrically isolated active impedance modules are formed to attach to power transmission lines without breaking the lines such that the power line forms a secondary of the main transformer of the module. Each module includes an electrical energy storage device and a switching circuit, such as a single phase inverter, connected to the storage device and to the main transformer primary winding. The inverter can be controlled to couple a selected voltage to the transmission line through the main transformer primary winding which can provide effective positive impedance, negative impedance, or a voltage at or near phase quadrature with the line current. Many active impedance modules may be distributed over a power system grid to allow control of the impedance of the power lines in the grid and to steer power through the grid, with each module electrically isolated from ground and from other phase lines of the transmission system.
Owner:SOFT SWITCHING TECH
Wireless Branch Circuit Energy Monitoring System
ActiveUS20130329331A1Increase laborSimple materialElectric switchesEmergency protection for supplying operative powerElectrical conductorTransceiver
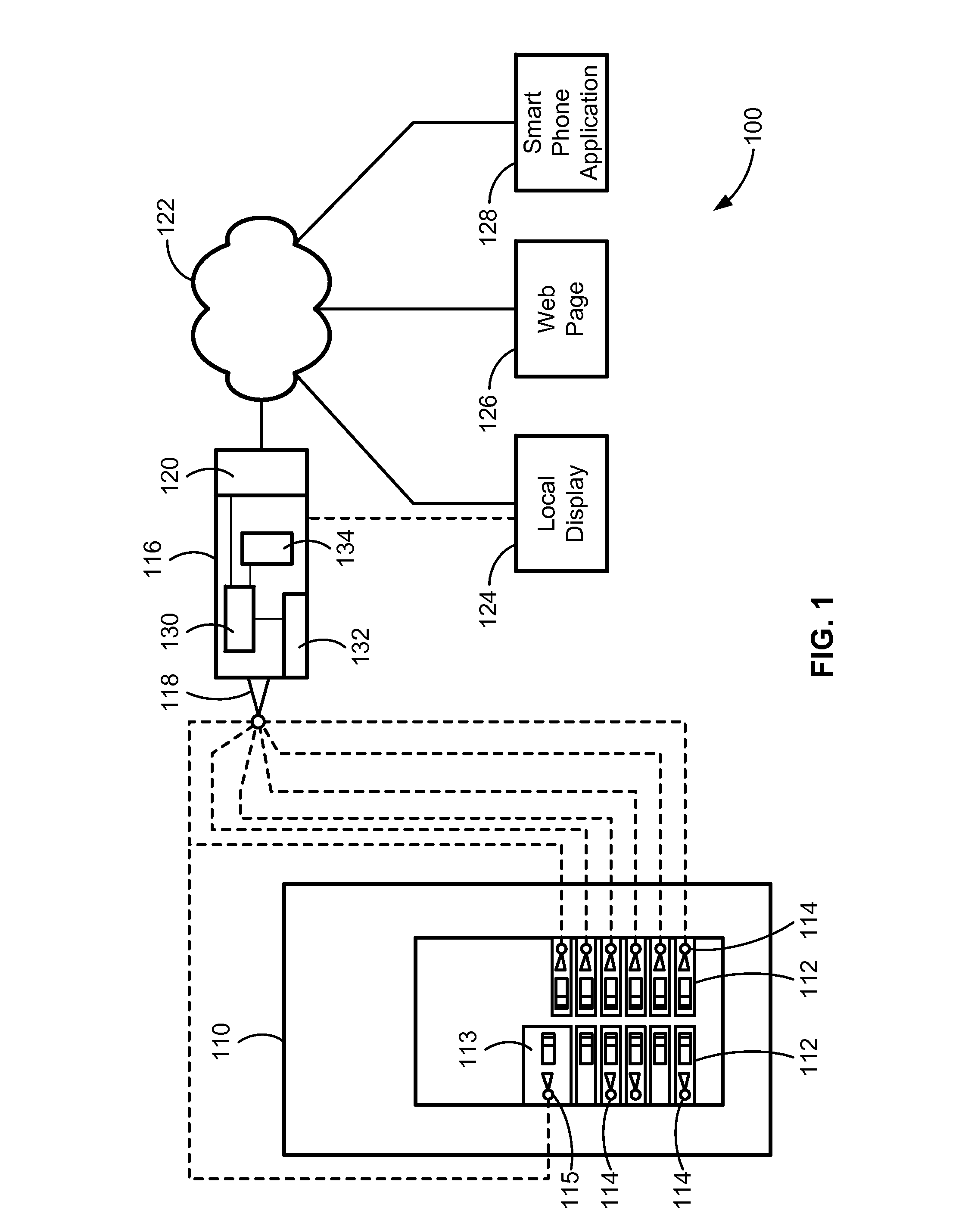
A circuit breaker (such as a miniature circuit breaker) that wirelessly communicates state and fault information to a main energy monitoring module. The wireless circuit breaker includes a transceiver and a power supply that harvests energy inductively from the line current conductor without the need for a connection to a neutral conductor. The wireless circuit breaker can be implemented in the same package as existing circuit breakers, eliminating the need to replace the panel when upgrading to a system that employs a main energy monitoring module. The wireless circuit breaker can also include an energy storage device for supplying power to the circuit breaker after it has tripped, allowing the circuit breaker to transmit information after a trip. The main energy monitoring module includes a processor and a gateway for evaluating and transmitting information received from the circuit breaker to other applications, such as webpages and smartphones.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC USA INC
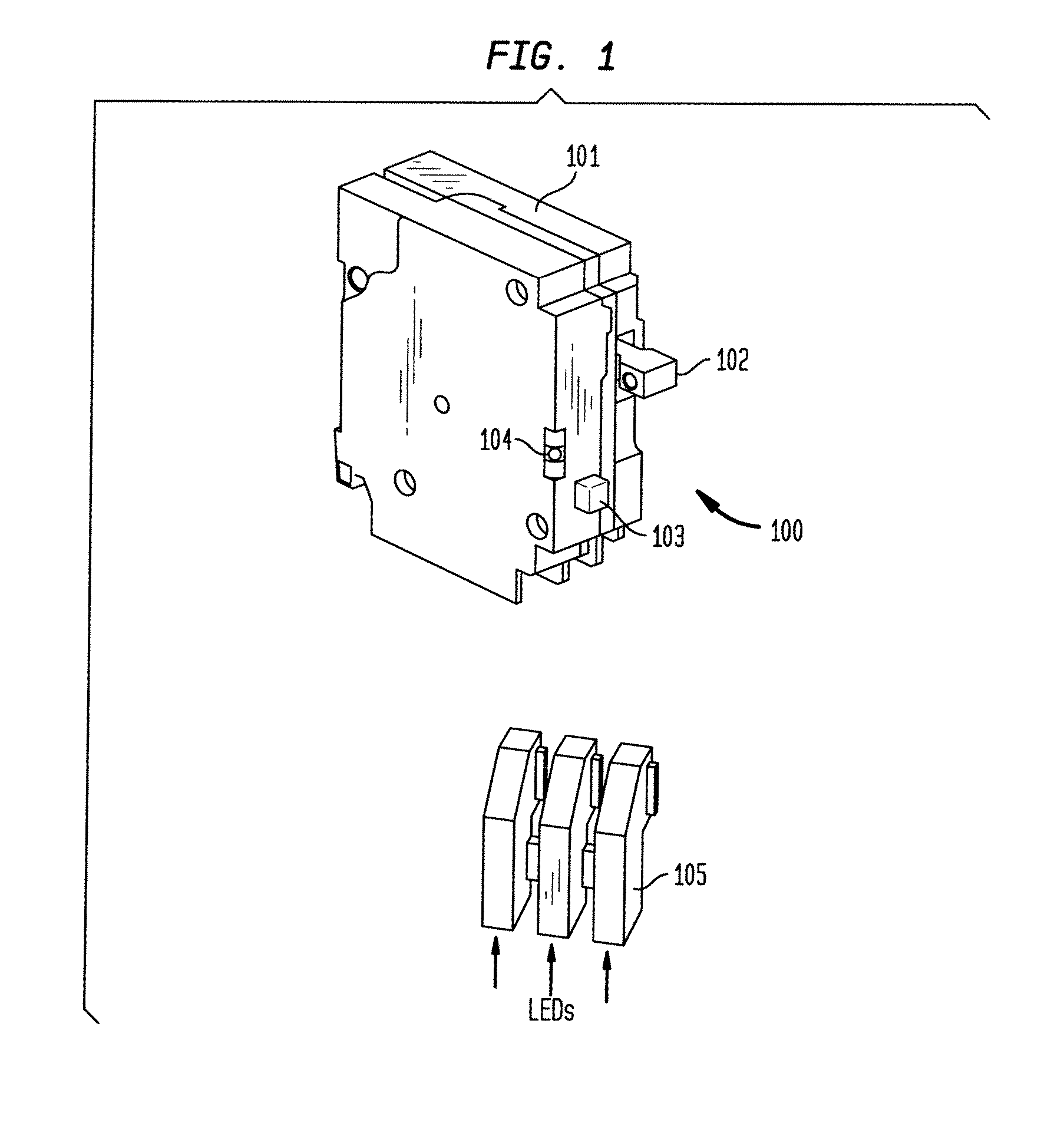
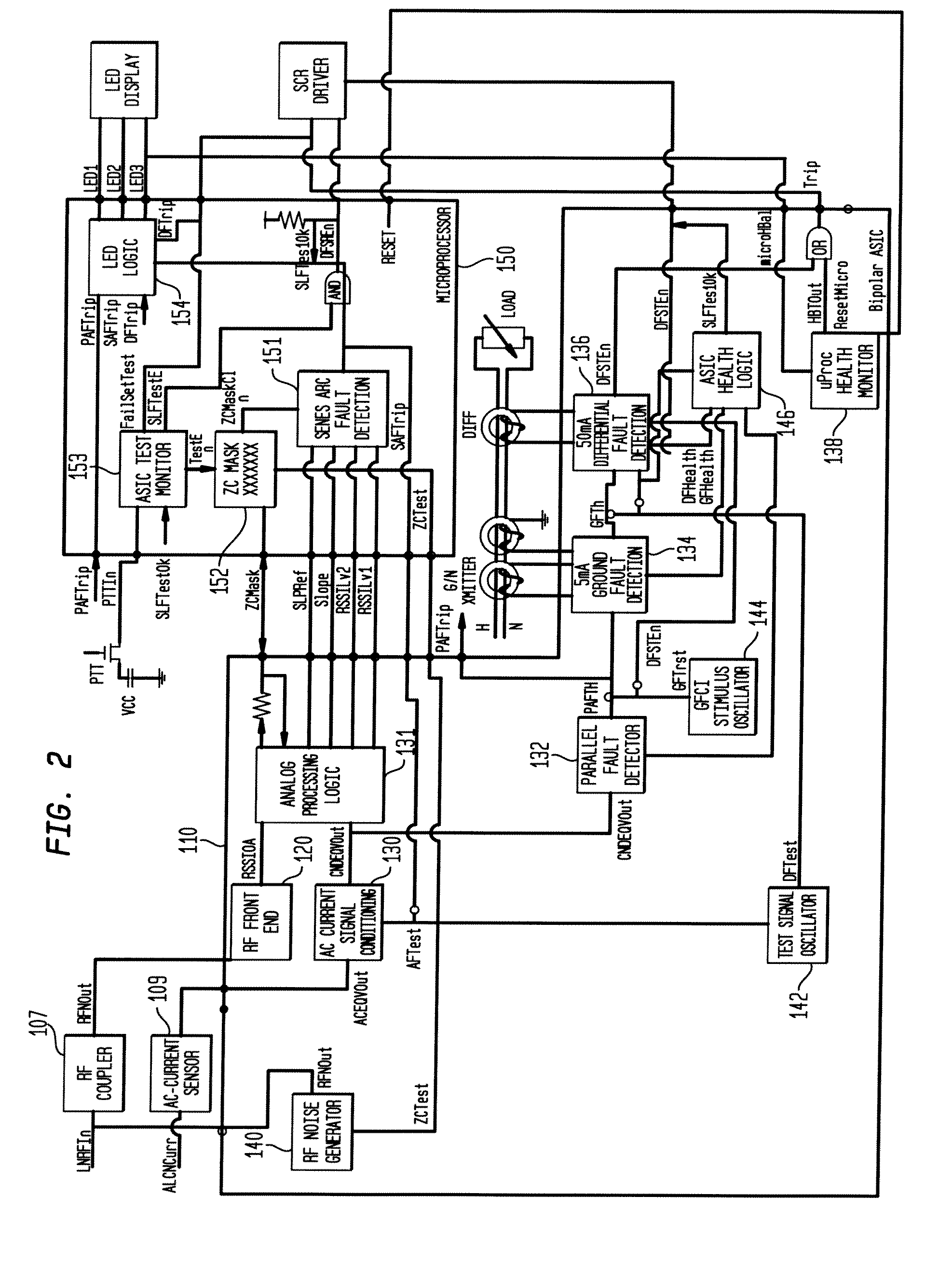
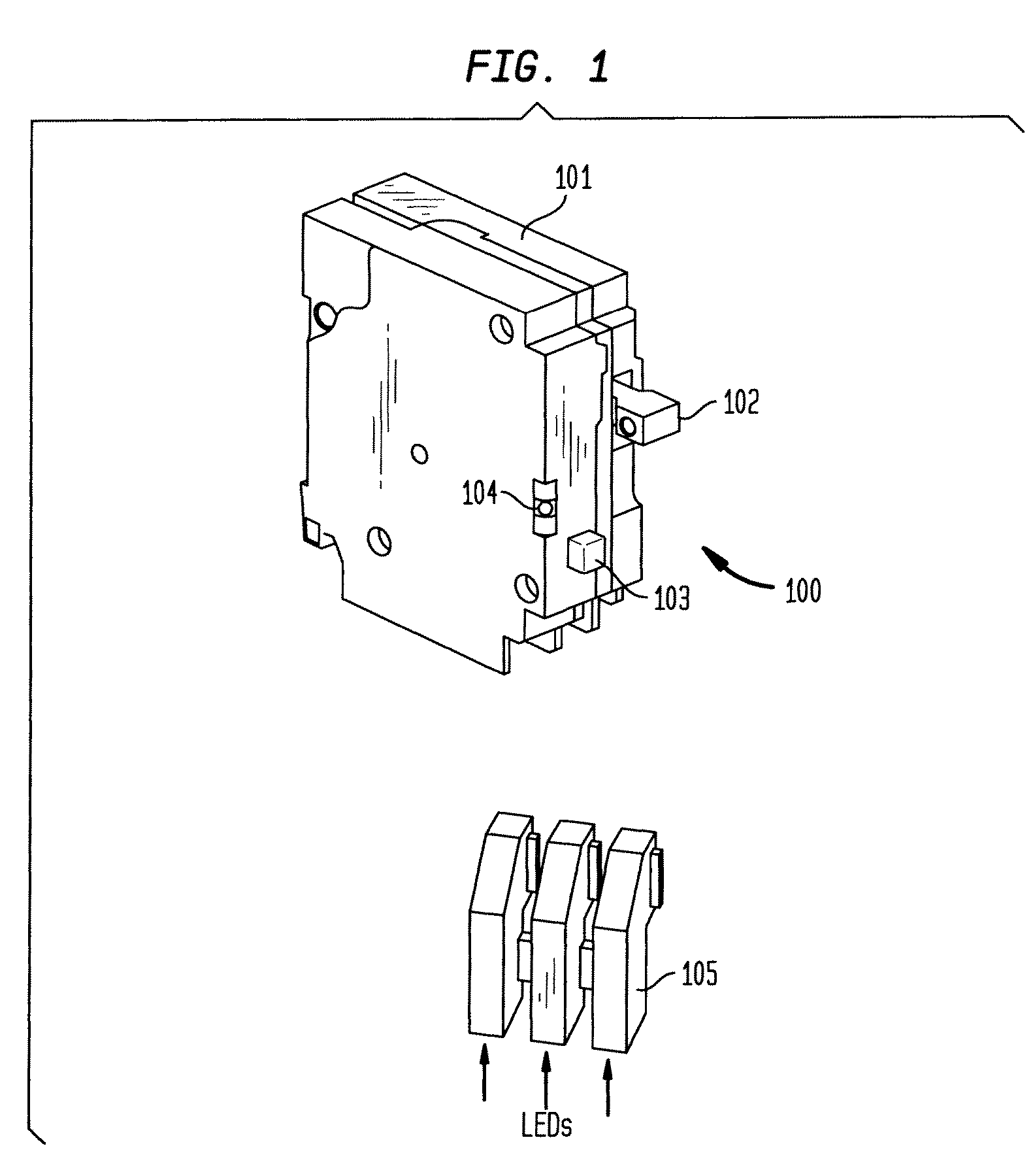
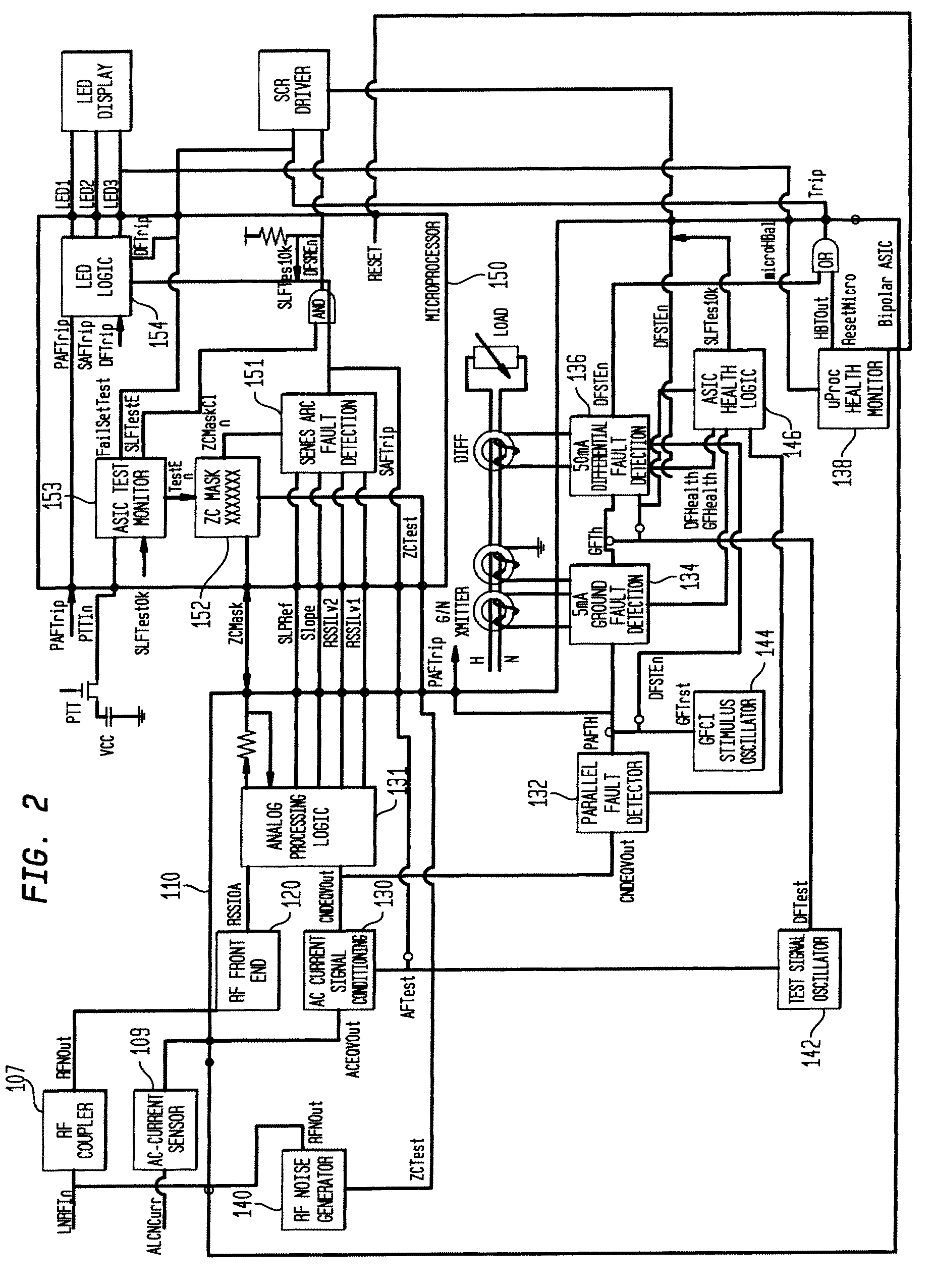
Multifunctional Residential Circuit Breaker
ActiveUS20090198459A1Quickly and effectively discriminateReduce impactElectrical testingEmergency protection data processing meansCurrent sensorEngineering
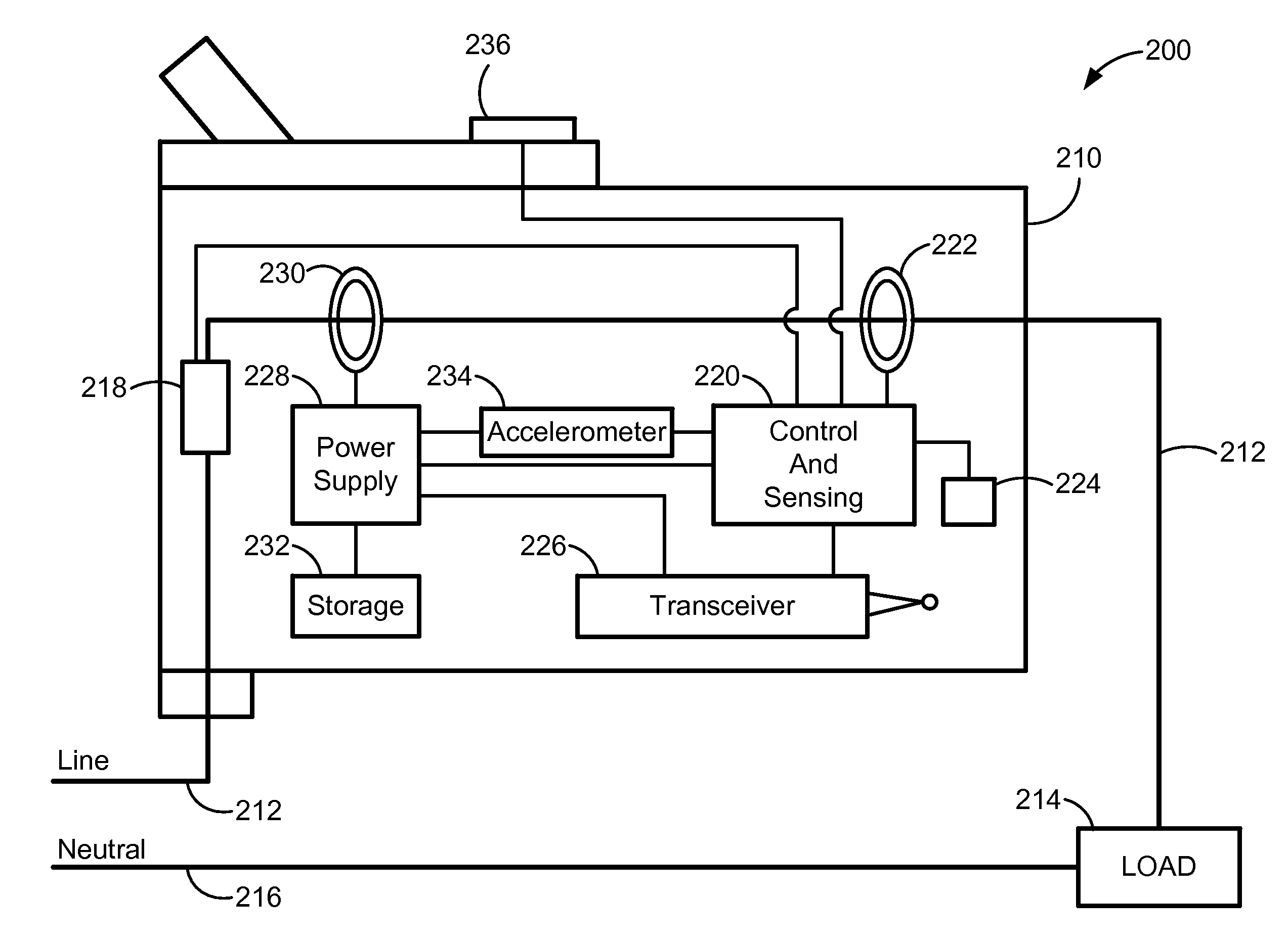
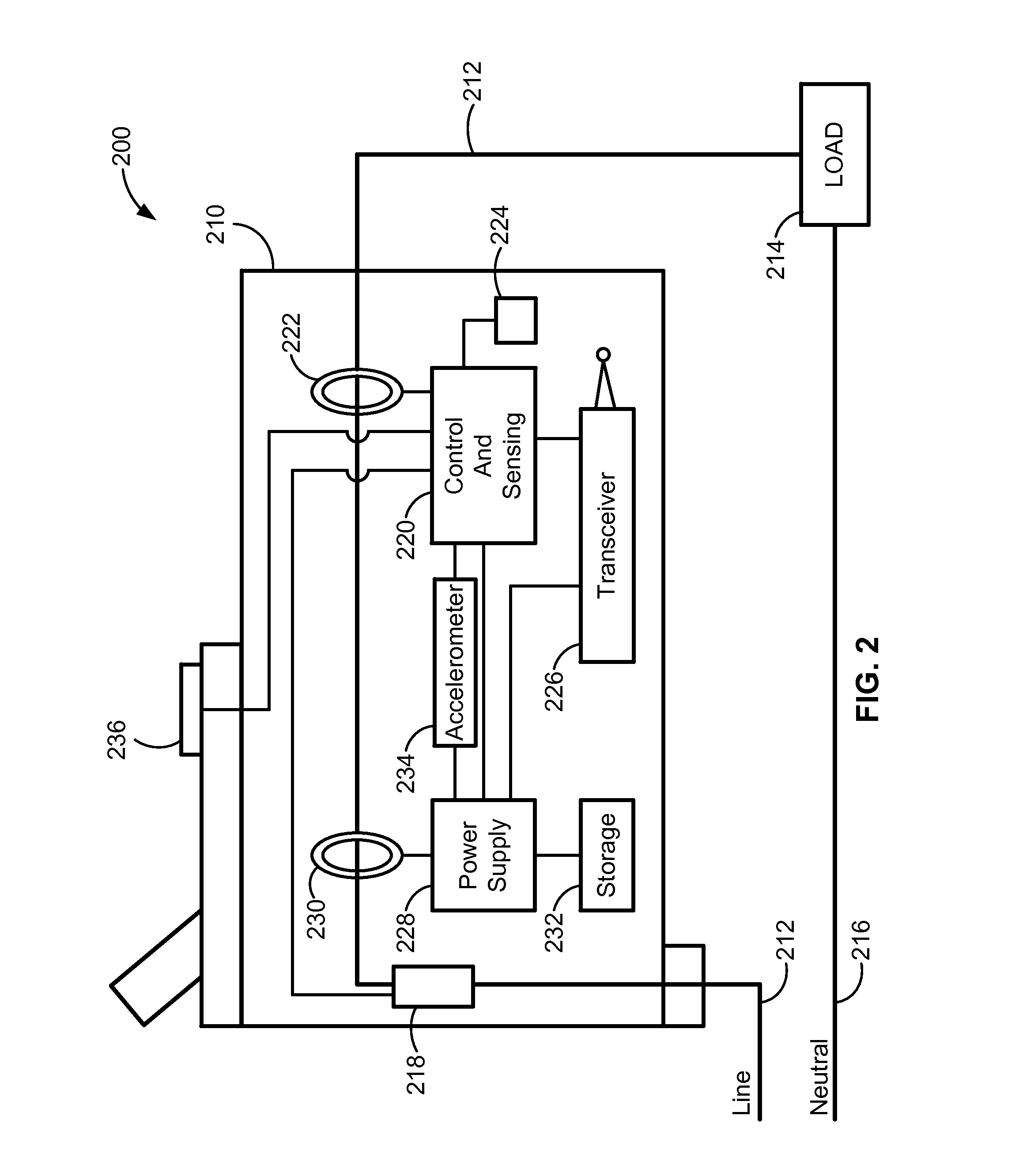
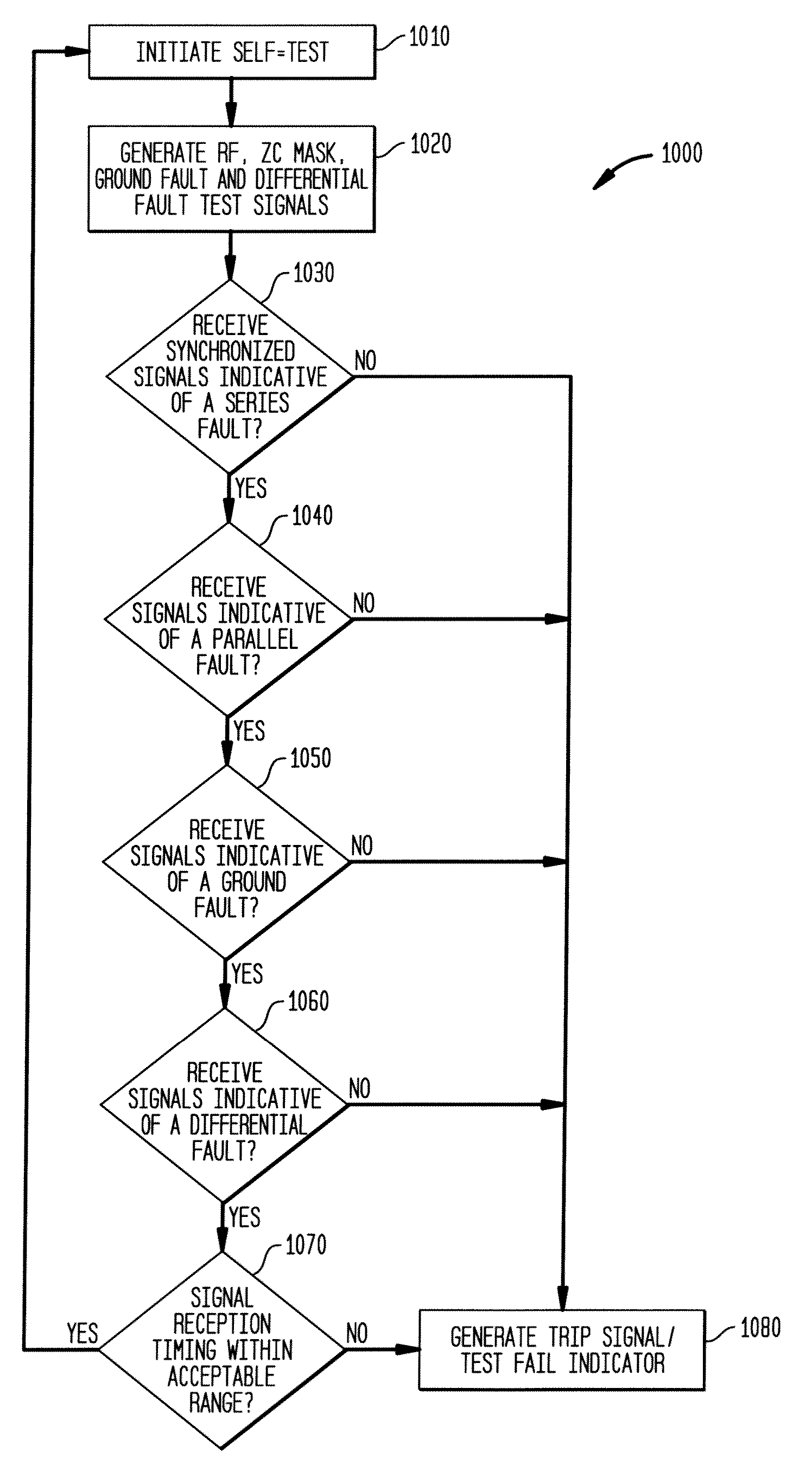
An electrical fault detection device for use in a branch of a power circuit that utilizes signals from an AC line current sensor coupled to an electrical distribution line having a primary and neutral lines, a line high-frequency sensor coupled to the electrical distribution line, a differential current sensor coupled to the primary and neutral lines, and a ground fault current sensor coupled to the primary and neutral lines. A signal conditioner receives the signals outputted by AC current line current sensor, the line high frequency sensor, the differential current sensor and the ground fault current sensor and generates a signal indicative of the load current associated with a branch of the power circuit. Output of the signal conditioner is sampled and processed by a processing resource. The processing resource has stored therein data representing a plurality of time-versus-current curves that define a plurality of regions in which tripping may or may not occur. One region has time data and current data that define a time-duration for a particular current magnitude for which no tripping will occur. Another region has time data and current data that define a time-duration of a particular current magnitude for which tripping will occur. Processing resource processes sampled signal to determine the region to which the processed time data and current data correspond, and generates a signal to initiate tripping if the sampled signal yields a time duration for a particular current magnitude that corresponds to a region for which tripping must occur.
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
Apparatus for calibrated non-invasive measurement of electrical current
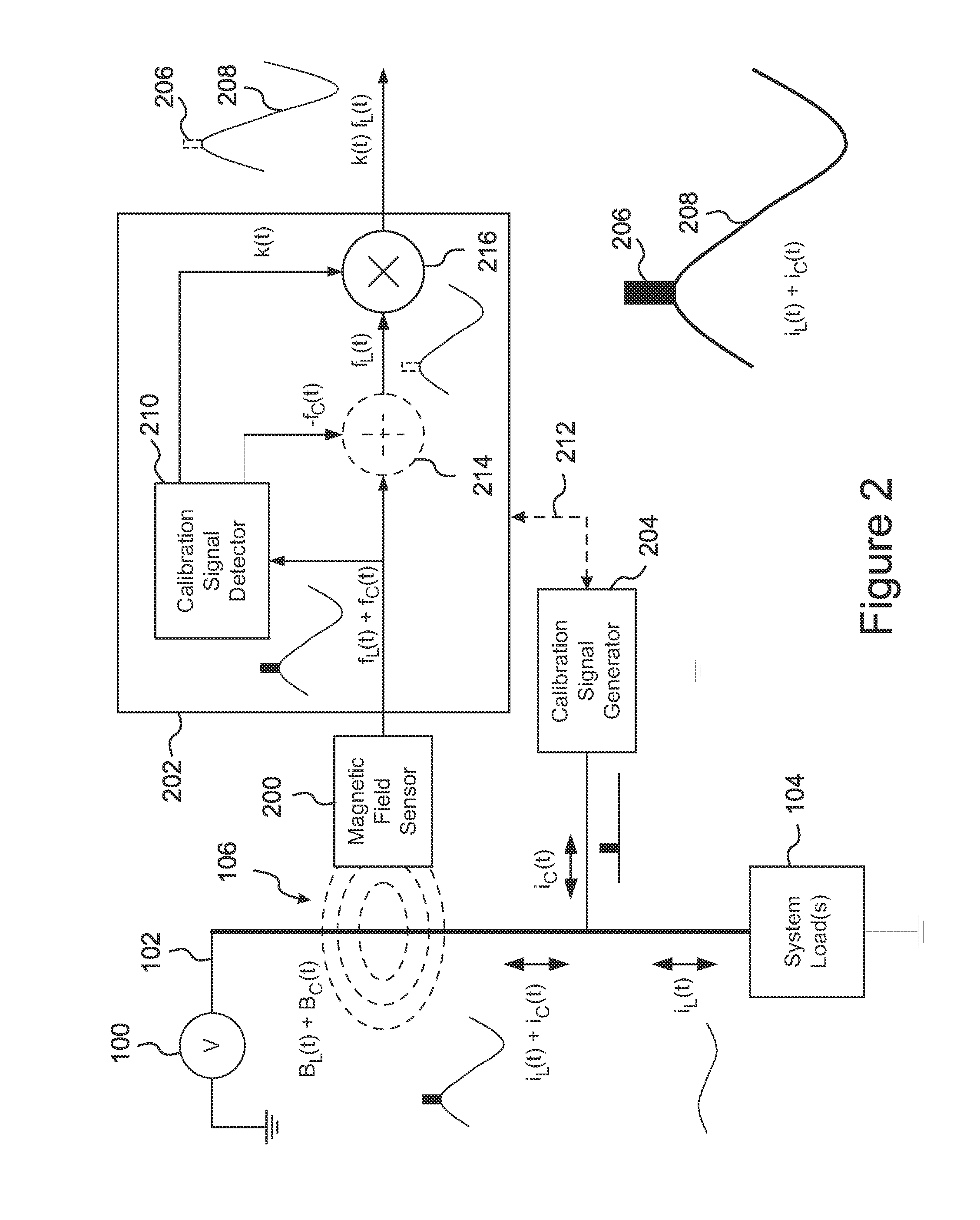
ActiveUS20120001617A1Improve dynamic rangeStrong signalDynamo-electric motor metersVoltage/current isolationElectrical conductorData center
A system for accurate measurement and monitoring of AC or DC electrical current flowing through electrical conductors includes one or more current sensors, a receiver, and one or more calibration signal generators (“CSG's”) that can be plugged into outlets or otherwise coupled to the conductors so as to add automated, time-varying calibration signals to the conductors, such as current pulses or pulse patterns. The sensors are placed on a circuit breaker panel, around a cable, or otherwise near the conductors. The receiver distinguishes the calibration signals by their timing, pulse patterns, frequencies, or other time-varying features, uses their known amplitudes to calibrate the sensitivity of each sensor to each conductor, and determines the current flowing in each conductor. Among other applications, the invention can monitor building current usage, CO and data center power usage and distribution, and power line current leakage, and can calibrate invasive and / or non-invasive current sensors.
Owner:REYNOLDS BRETT S
Distributed floating series active impedances for power transmission systems
ActiveUS7105952B2Reduce congestionEfficient powerFlexible AC transmissionBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionTransformer
Floating electrically isolated active impedance modules are formed to attach to power transmission lines without breaking the lines such that the power line forms a secondary of the main transformer of the module. Each module includes an electrical energy storage device and a switching circuit, such as a single phase inverter, connected to the storage device and to the main transformer primary winding. The inverter can be controlled to couple a selected voltage to the transmission line through the main transformer primary winding which can provide effective positive impedance, negative impedance, or a voltage at or near phase quadrature with the line current. Many active impedance modules may be distributed over a power system grid to allow control of the impedance of the power lines in the grid and to steer power through the grid, with each module electrically isolated from ground and from other phase lines of the transmission system.
Owner:SOFT SWITCHING TECH
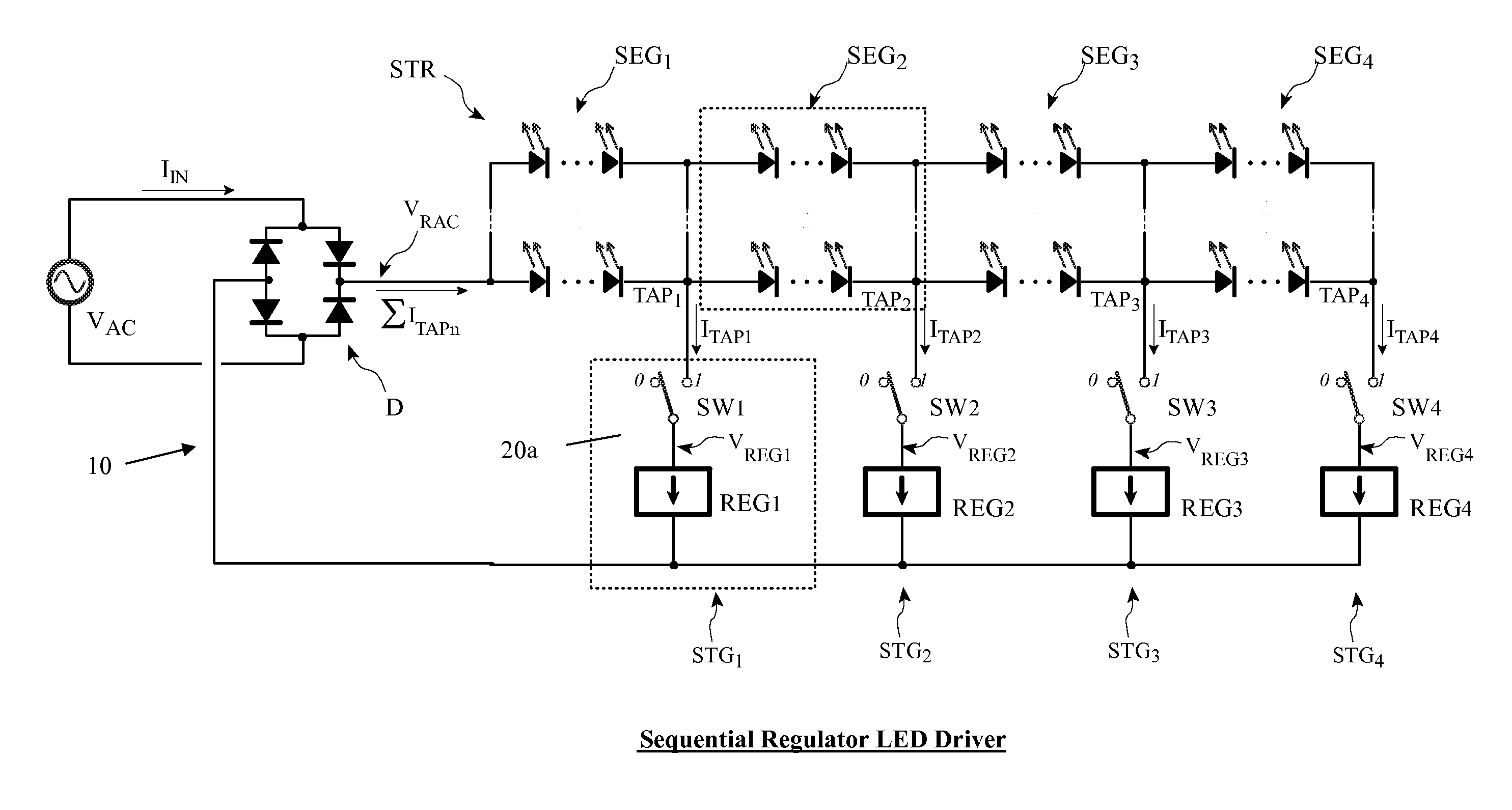
Multiple stage sequential current regulator
ActiveUS20120262075A1Eliminate needDc network circuit arrangementsElectroluminescent light sourcesPower factorEngineering
An LED driver circuit operating from the AC power line providing high efficiency, good line and load regulation, high power factor, low line current harmonics, low conducted EMI, high LED utilization, and lamp dimming compatibility, while consisting of a minimal number of components. No inductors, nor capacitors (including electrolytics), nor high current switching transistors are employed. The top of a string of series connected LED segments is connected to the output of a rectifier, which in turn is connected to an AC sine wave power source. The string is tapped at various locations, including the bottom of the string. Each segment can consists of any number of serial or parallel connected LEDs. Current control elements or regulators sink current at each tap and are sequentially turned on and off one at a time, tracking the rectified sine wave voltage. Voltage across each regulator and current when conducting is individually controllable. Power loss in the regulators is minimized by keeping regulator voltage to a minimum. The regulators may control current in a multitude of ways, including a constant current, or a current dependent on voltage across the regulators including a resistor, or a combination. The driver is self-commutating, with the sequencing of the current control elements an inherent feature closely integrated with the current control elements and providing optimal performance over variable operating conditions. Given the large number of design variables, the driver circuit can be optimized for various performance criteria including input voltage range, line / load regulation, output power / current, efficiency, power factor, line current harmonics, dimmer compatibility, and LED utilization.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
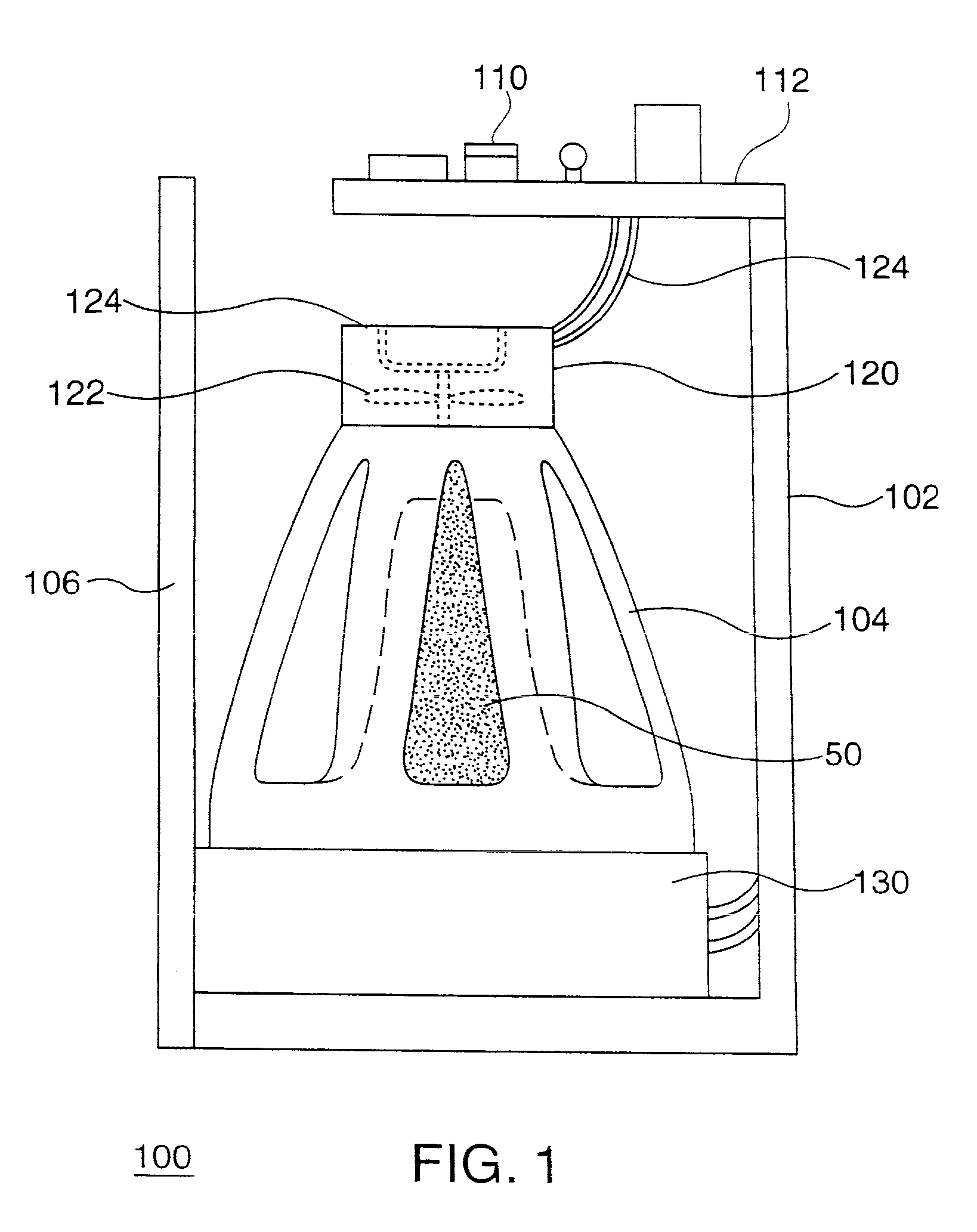
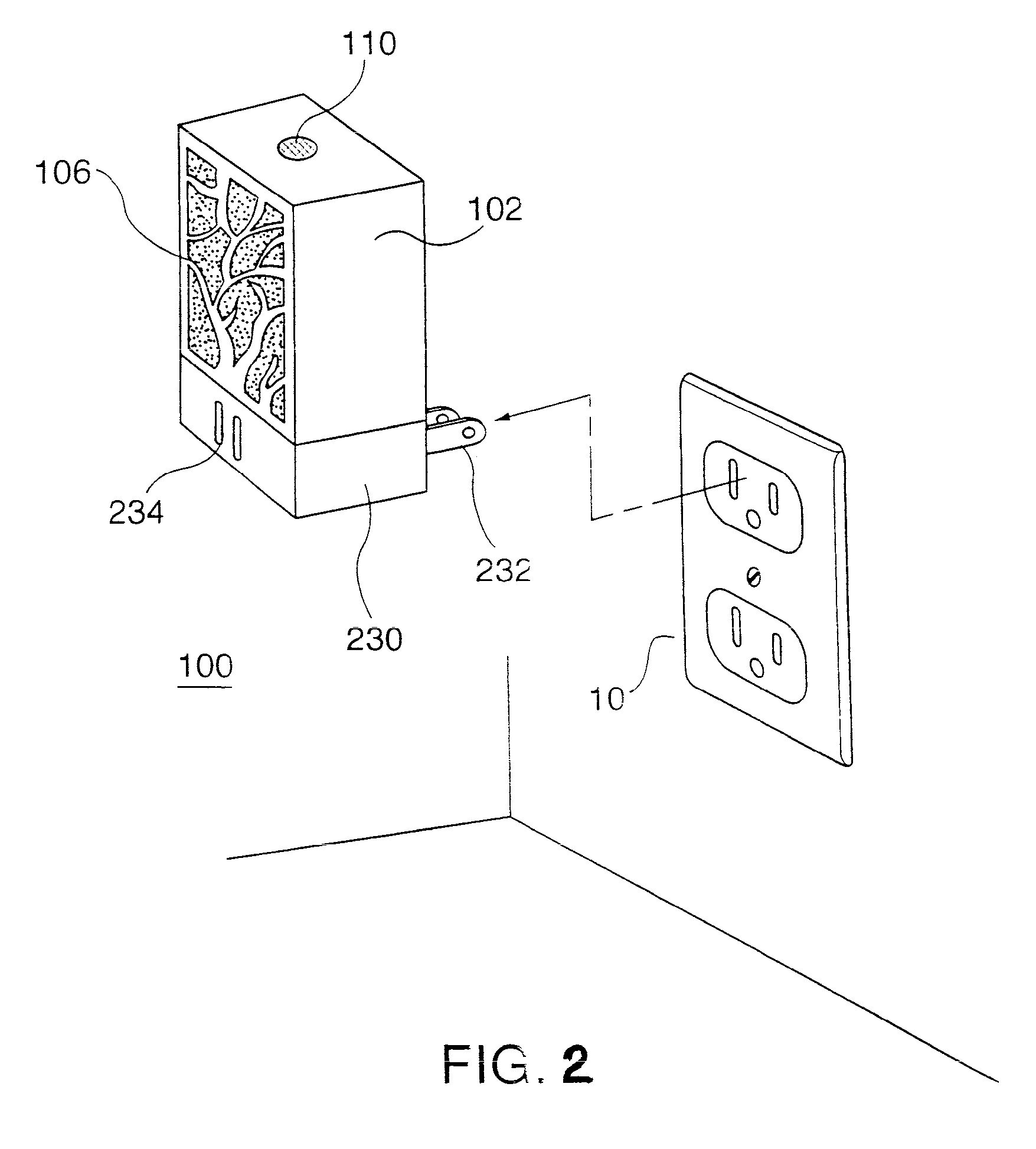
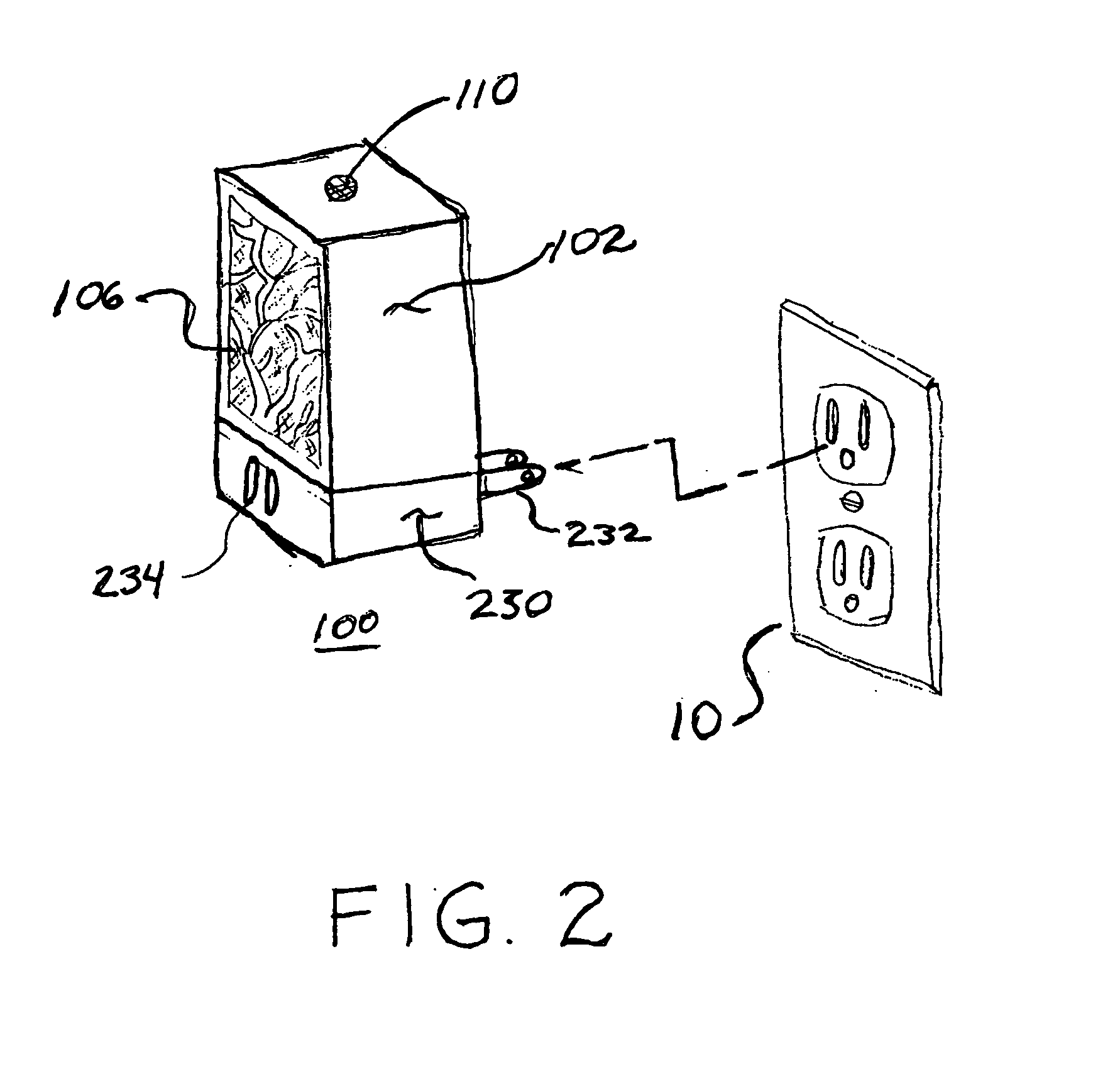
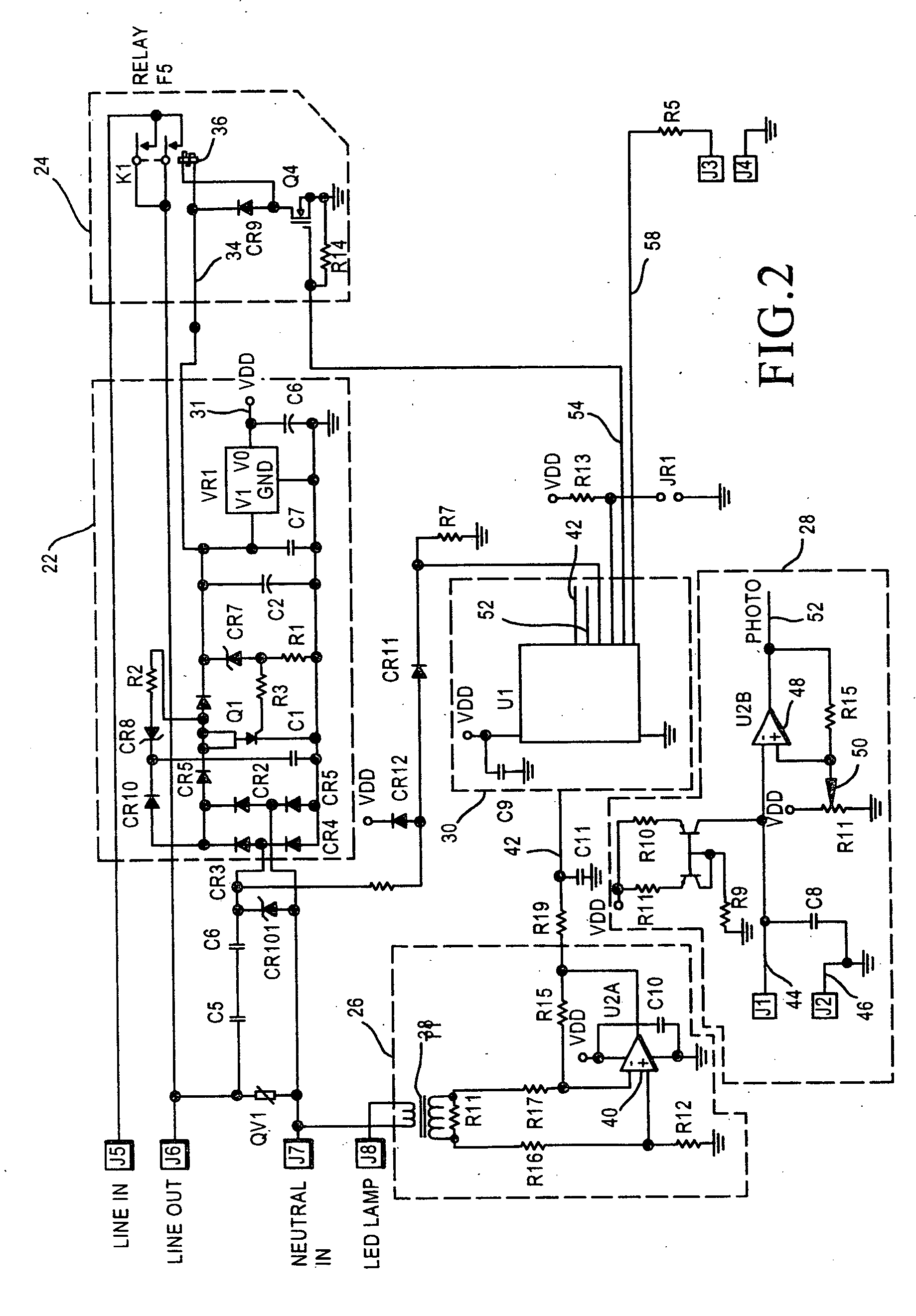
Fan-Driven Air Freshener
The present invention combines an air freshener that has a source of air freshening chemical with a fan that is controlled either by an optical device that senses light or a motion detector. When a light is turned on or motion is detected, the fan will be activated for a predetermined time period. In certain embodiments, the fan will stop turning after a predetermined time. Alternatively, the fan can continue to be powered until the light source is turned off (or all motion ceases), and only then either immediately shut down, or shut down after a predetermined time period. In certain preferred embodiments the source of air freshening chemical is disposed beneath the fan and allows fragrance to be delivered over time without the fan. The additional airflow provided by the fan causes more volatile fragrance chemicals to be removed from the source of air freshening chemical and admitted into the environment. The fan motor of the present invention is driven by a power source, such as batteries, AC line current or alternate sources such as solar cells. Preferably, a microprocessor controls the fan so that a “burst mode” is created by controlling the frequency and intensity of the pulses of air freshener that are emitted.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES
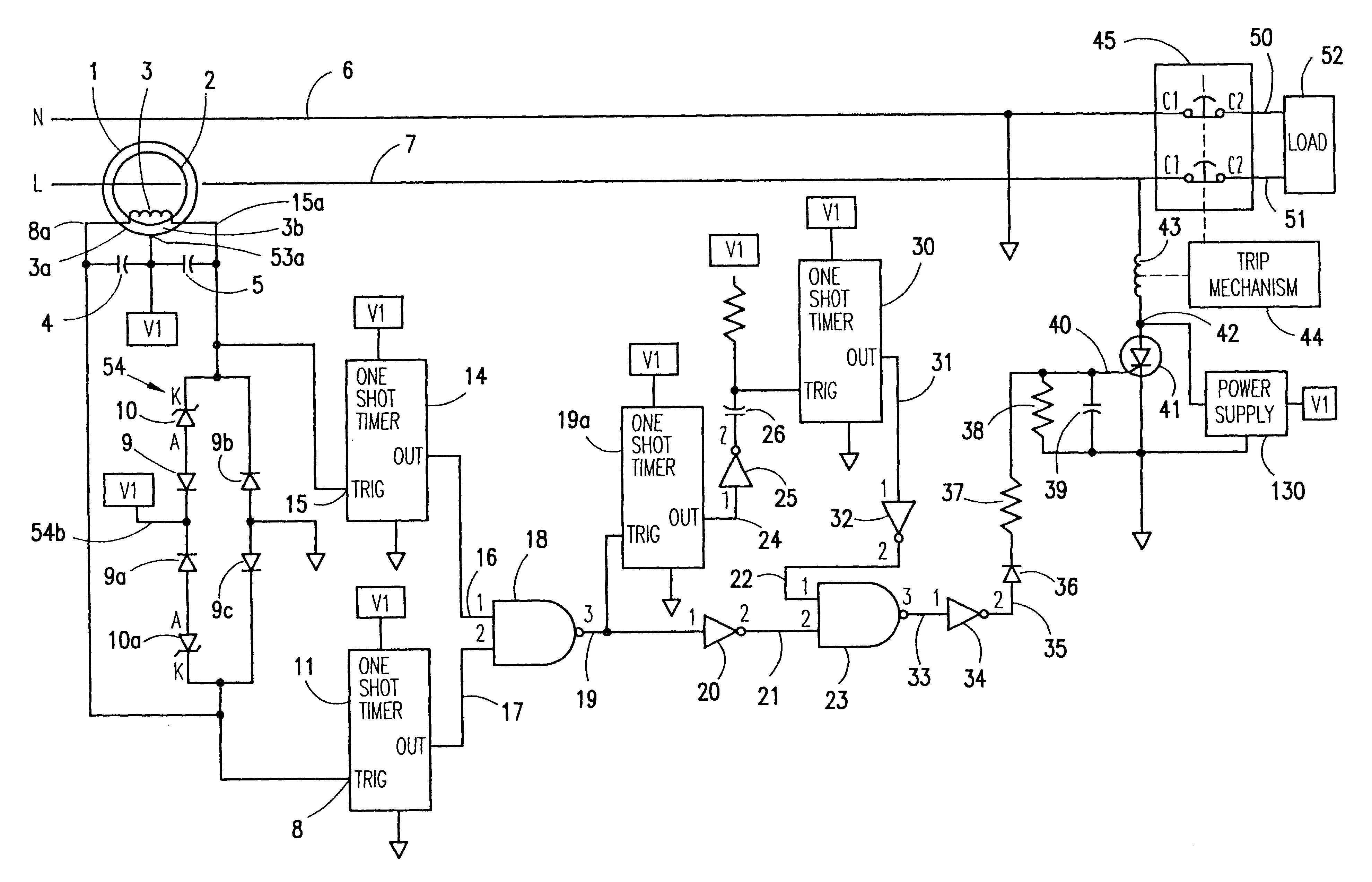
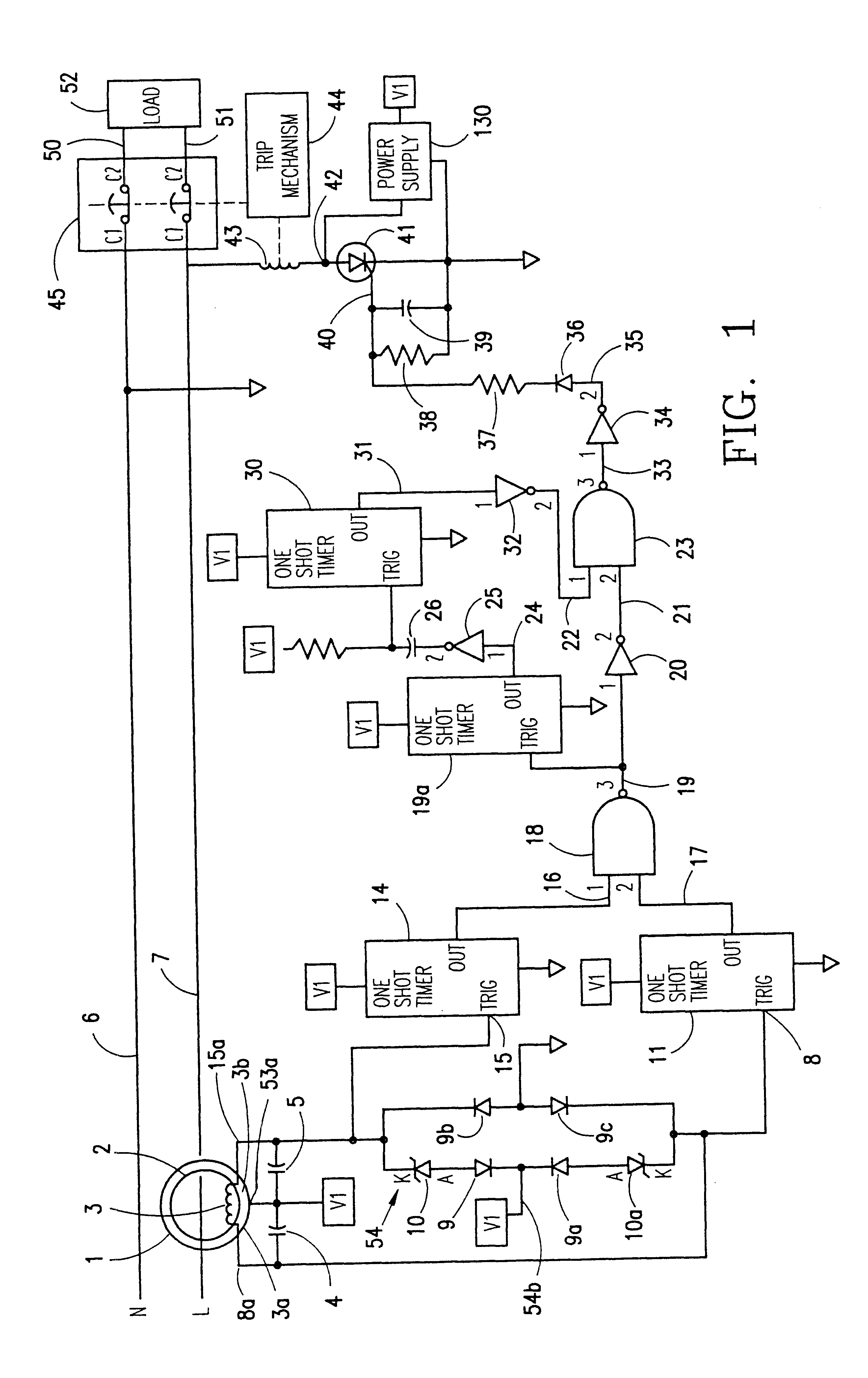
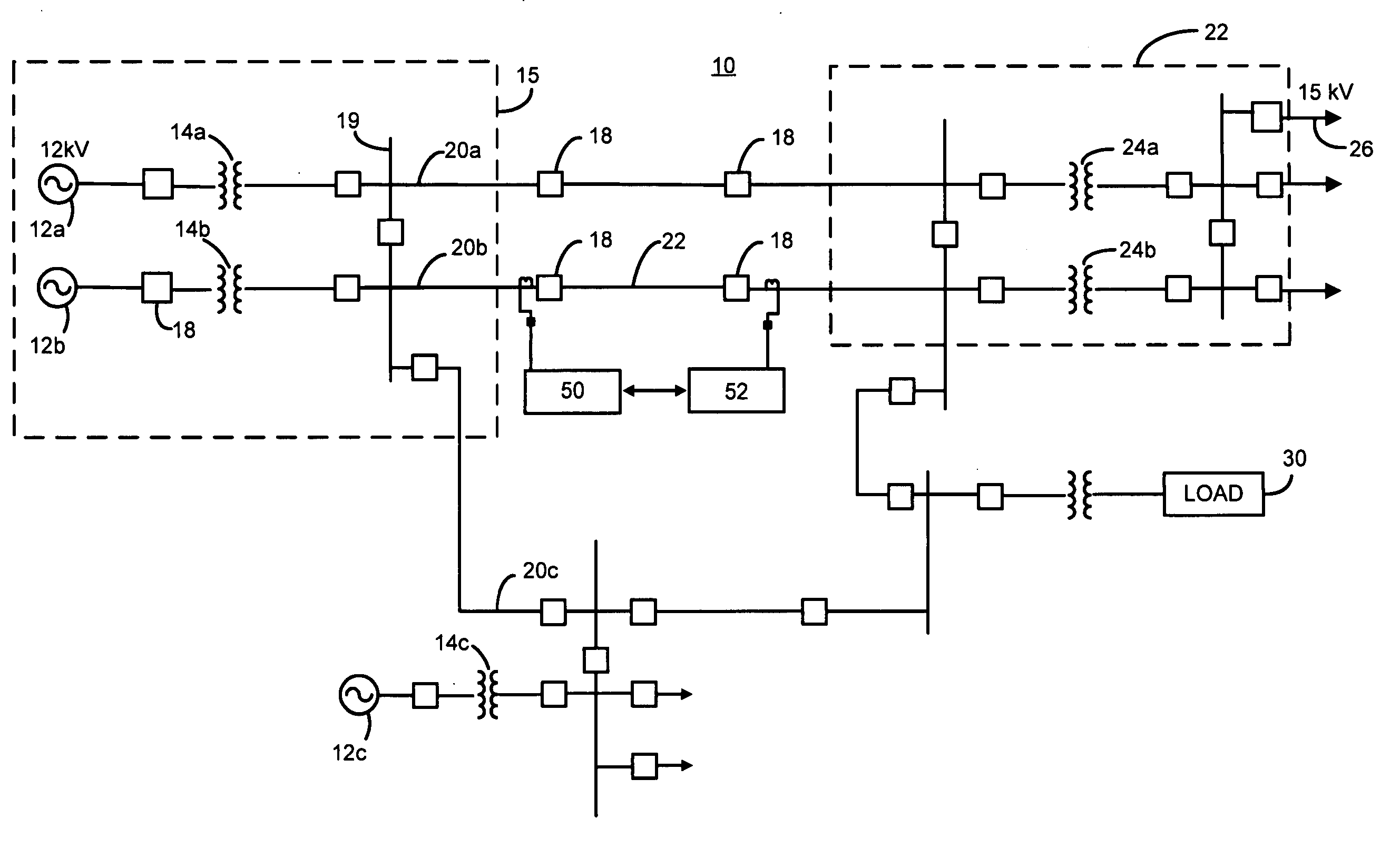
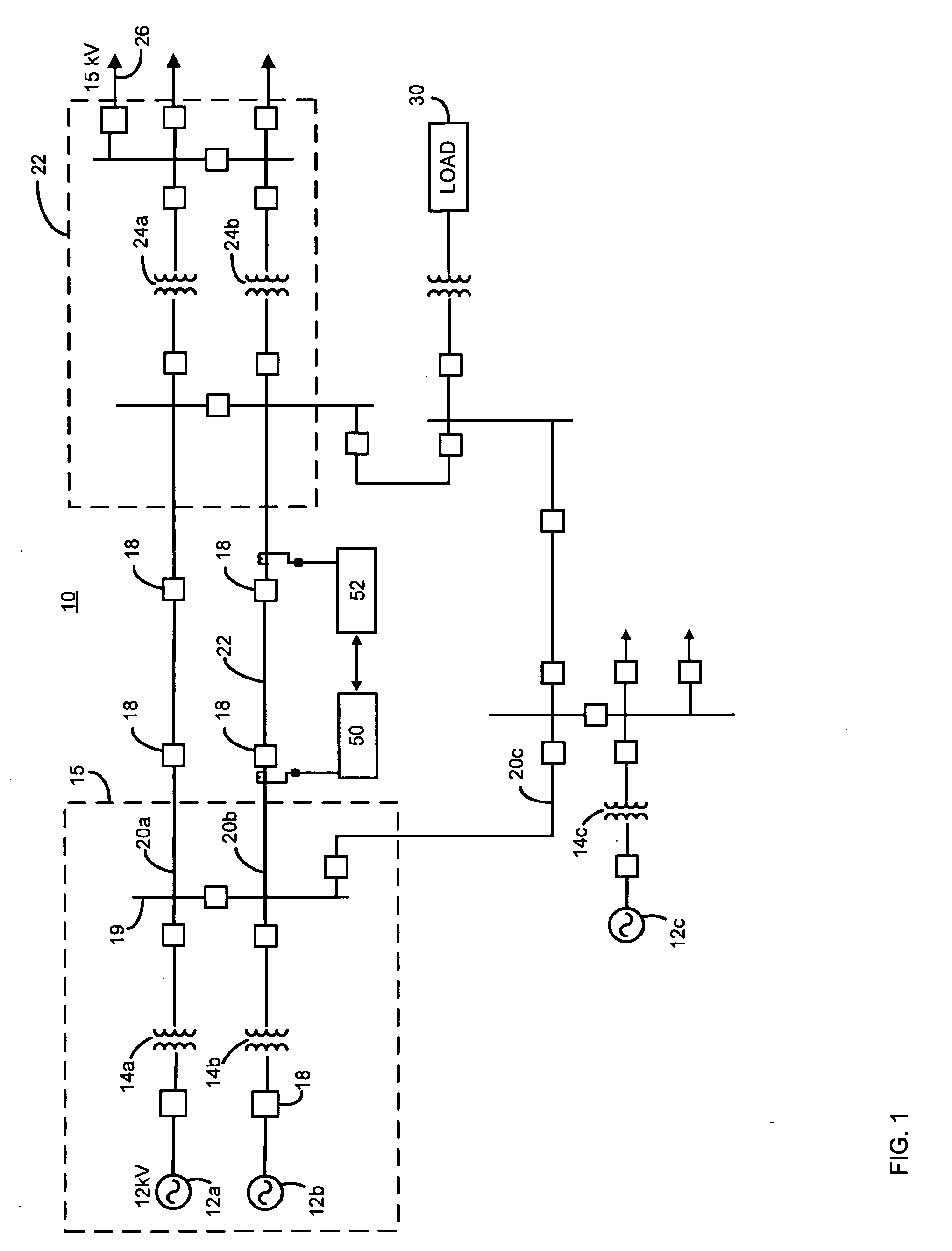
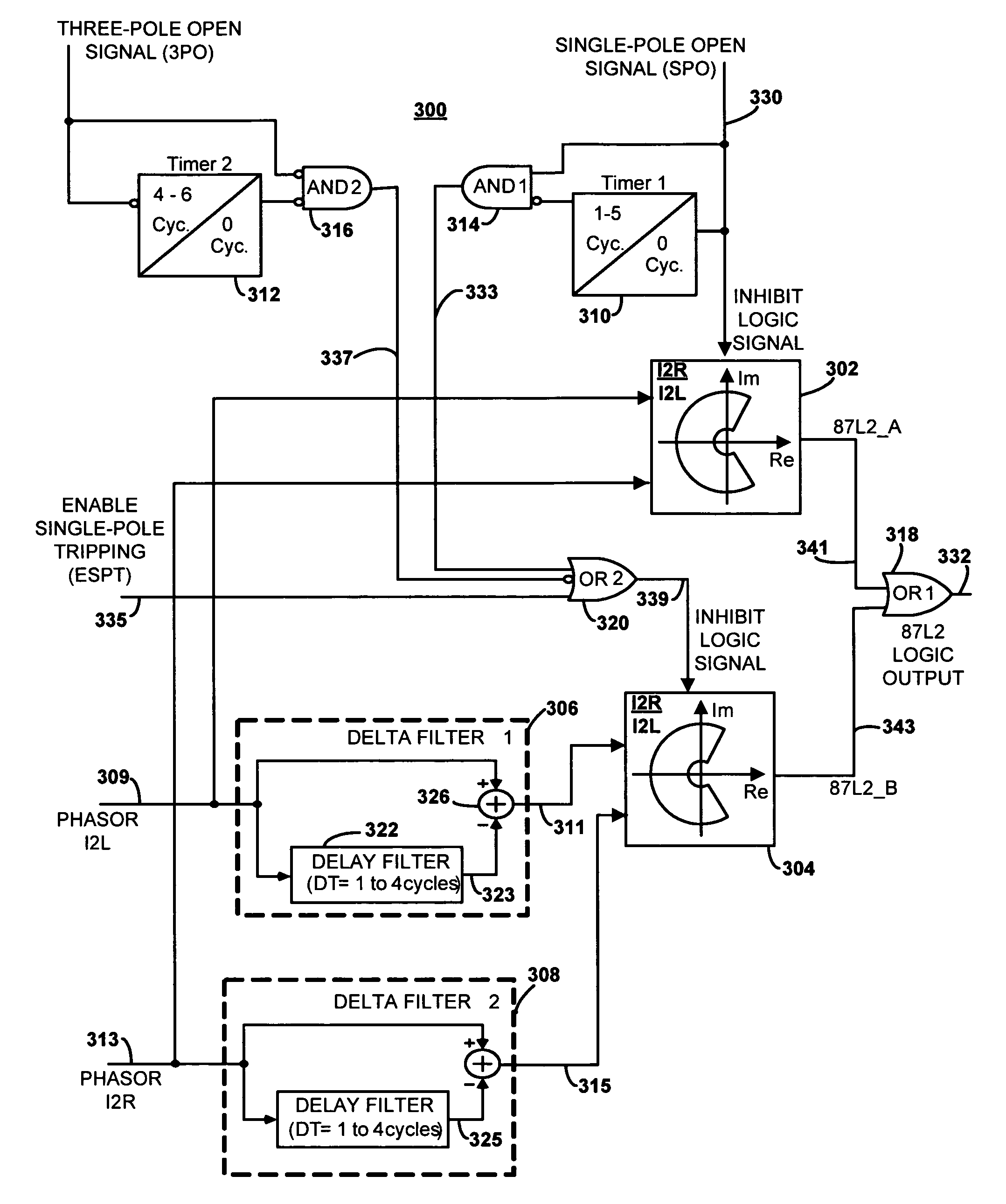
System, apparatus and method for compensating the sensitivity of a sequence element in a line current differential relay in a power system
ActiveUS20070070565A1Emergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEngineeringLine current
An apparatus and method compensate for the sensitivity of at least one line current differential element of a first current differential relay providing differential protection for a transmission line of a power system during a single-phase pole-open condition. The apparatus includes a first delta filter configured to remove a first pre-fault current from a first fault current of the transmission line to derive a compensated first current phasor. The apparatus also includes a second delta filter configured to remove a second pre-fault current from a second fault current of the transmission line to derive a compensated second current phasor. The compensated first and second current phasors are provided to the at least one line current differential element to compensate the sensitivity of the at least one line current differential element.
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
Methods and apparatus for dimming light sources
Methods and apparatus for dimming light sources are described herein. In certain embodiments, a bias circuit selectively biases a solid state switch during a portion of half-cycle of a line voltage after a settable delay. In some embodiments, the delay of the bias circuit is adjustable by a user, which varies the amount of energy provided to a light source, and the light generated there from. A charge circuit biases the switch for a period of time in the event the bias circuit experiences an operating condition (a ringing current) that may cause the switch to become open during the half-cycle of the line current. As a result of the charge circuit, the light source coupled to the line current does not experience substantial flickering and is compatible with low power compact fluorescent lights. The dimmer can be combined with other components to form a light harvesting system.
Owner:PURESPECTRUM
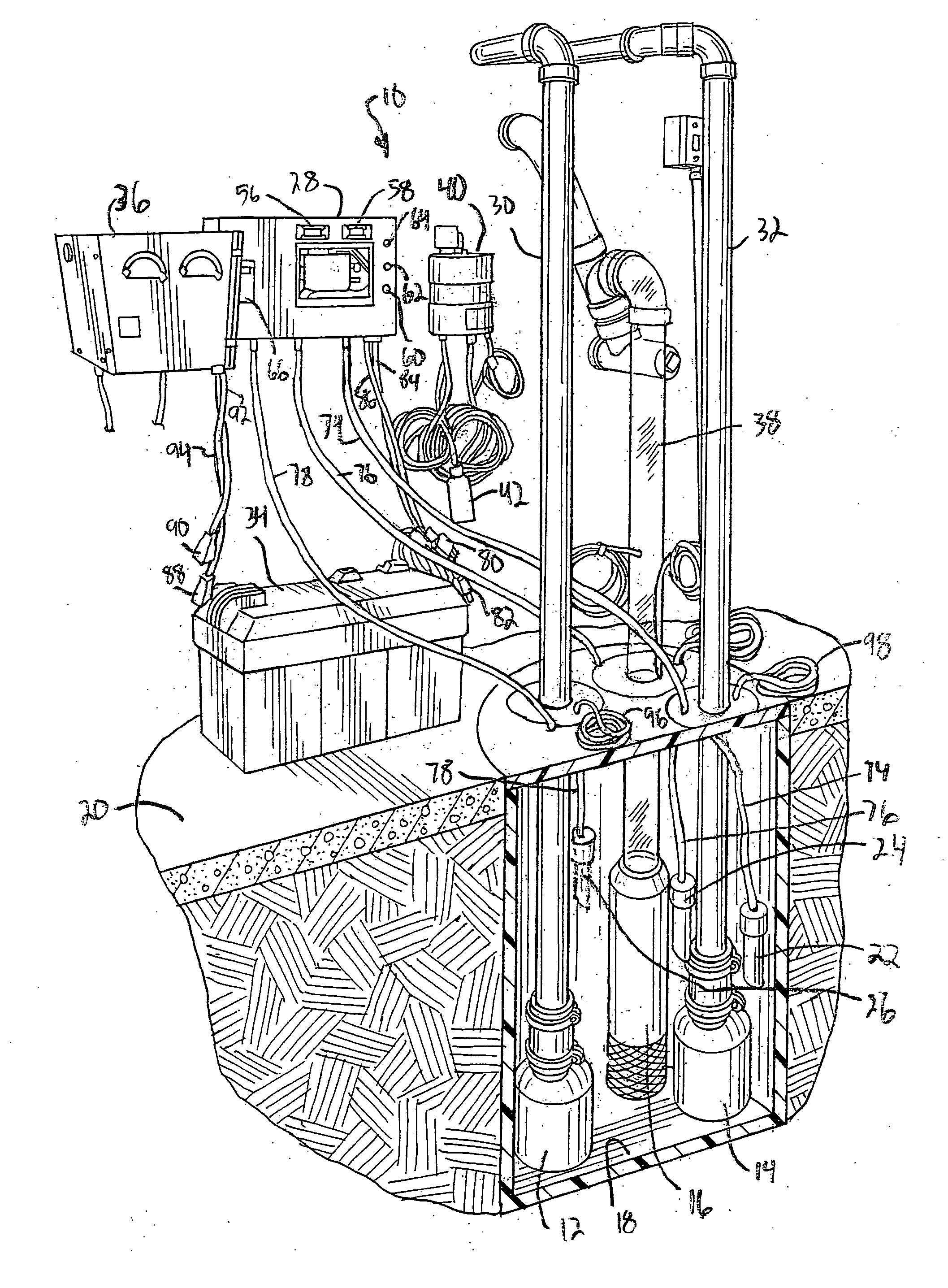
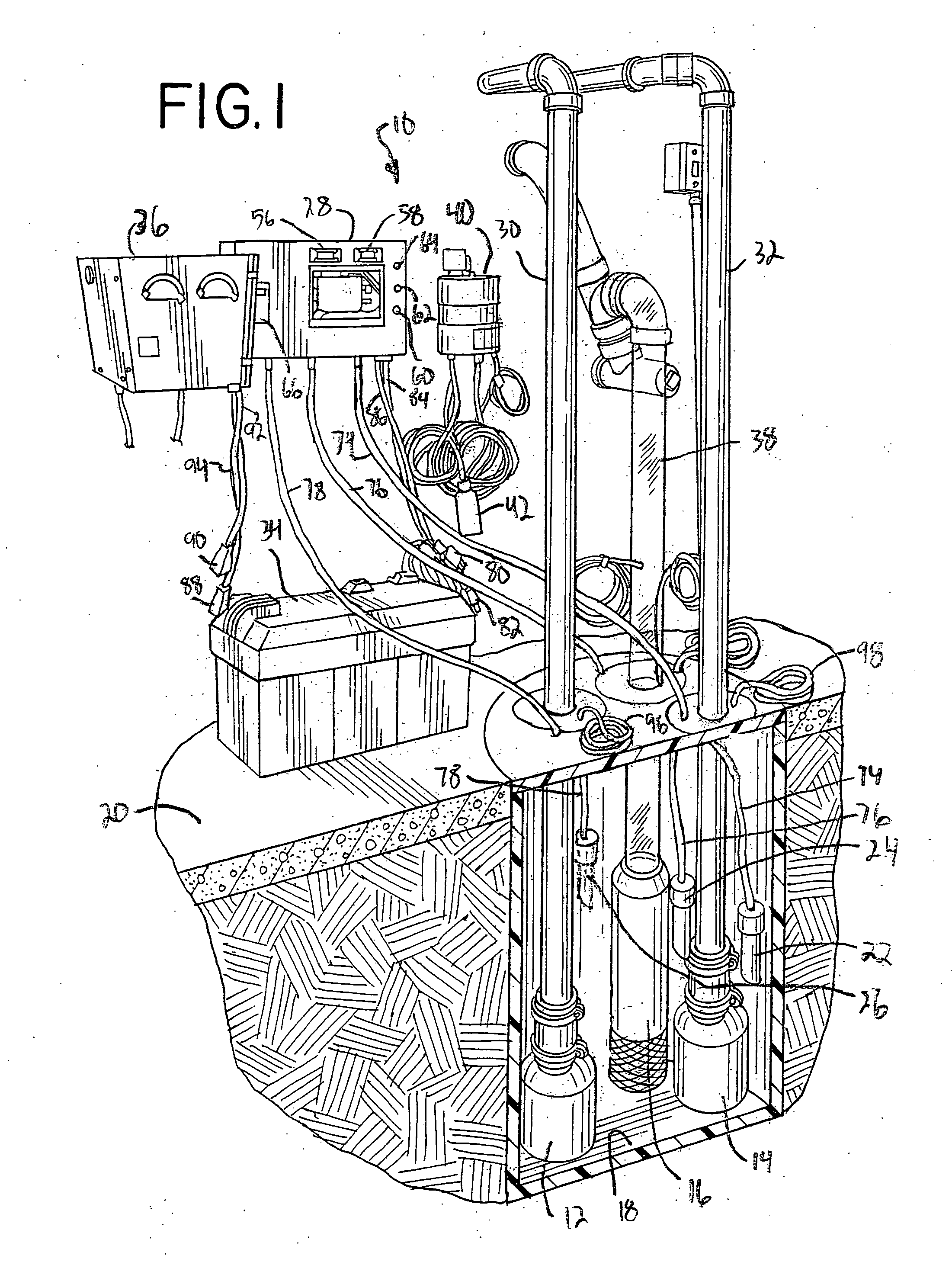
Basement flood control system
A basement flood control system for use in a structure having a basement floor located below ground level and having a sump pit or other collection basin for gathering subterranean water. The system has two primary pump units operated with line current, a battery-operated back-up pump unit, and a sensor arrangement for sensing water level in the collection basin. A controller is connected to the sensor arrangement and the pump units for variously activating the pump units singly or in any combination responsive to the water level detected by the sensor arrangement.
Owner:NIEDERMEYER KARL
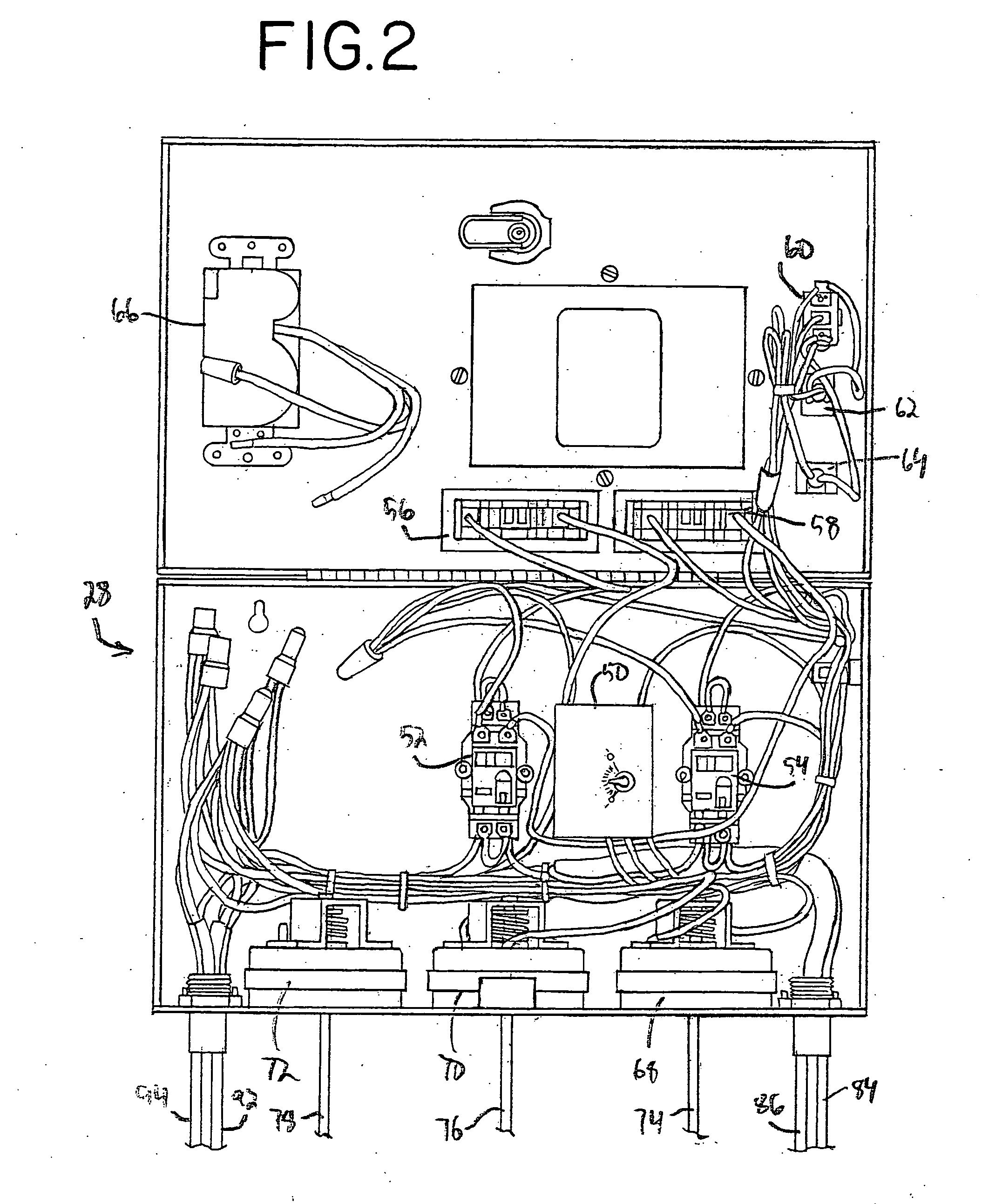
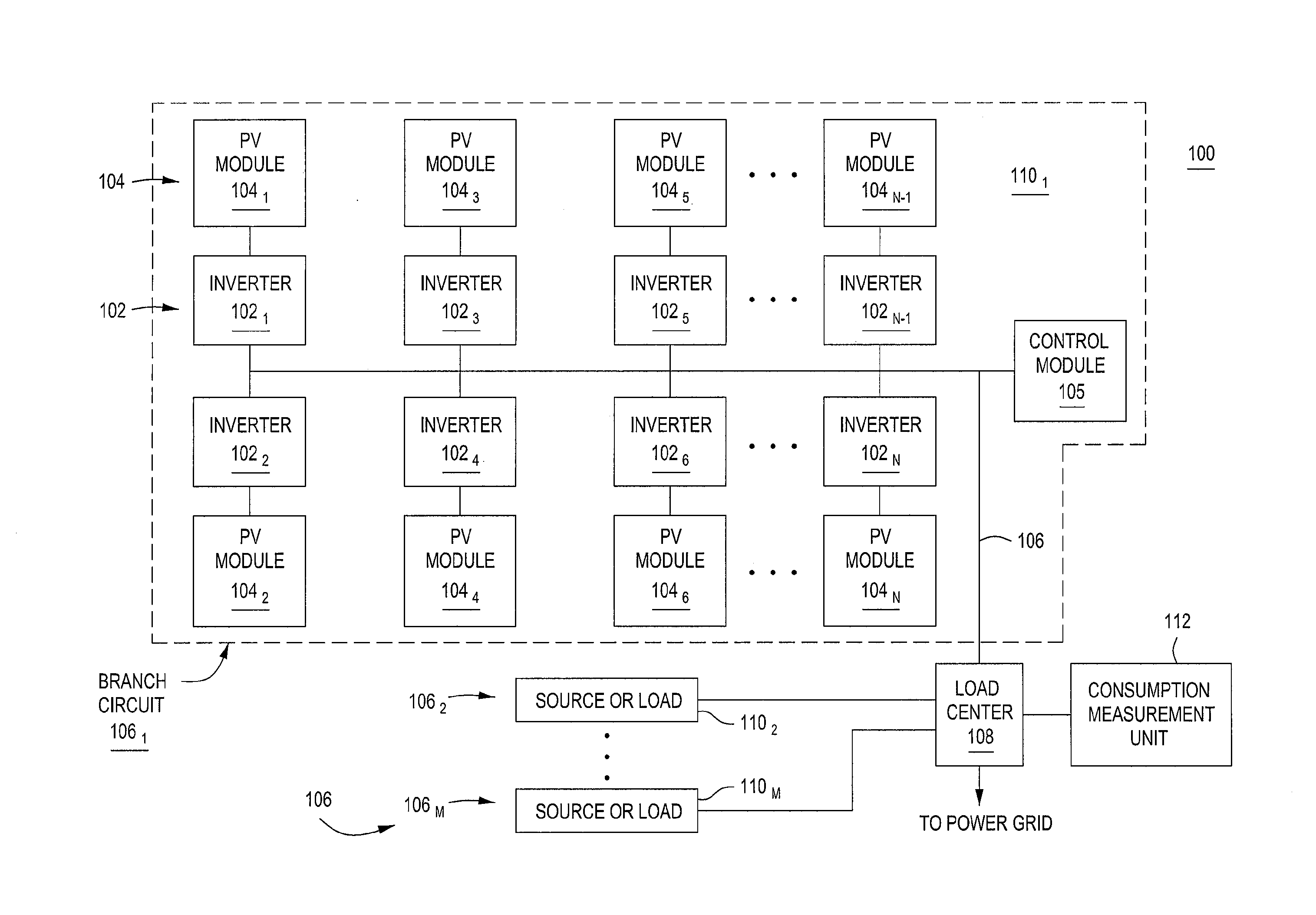
Method and apparatus for characterizing a circuit coupled to an AC line
ActiveUS20100181830A1Batteries circuit arrangementsCurrent/voltage measurementCurrent sampleElectrical polarity
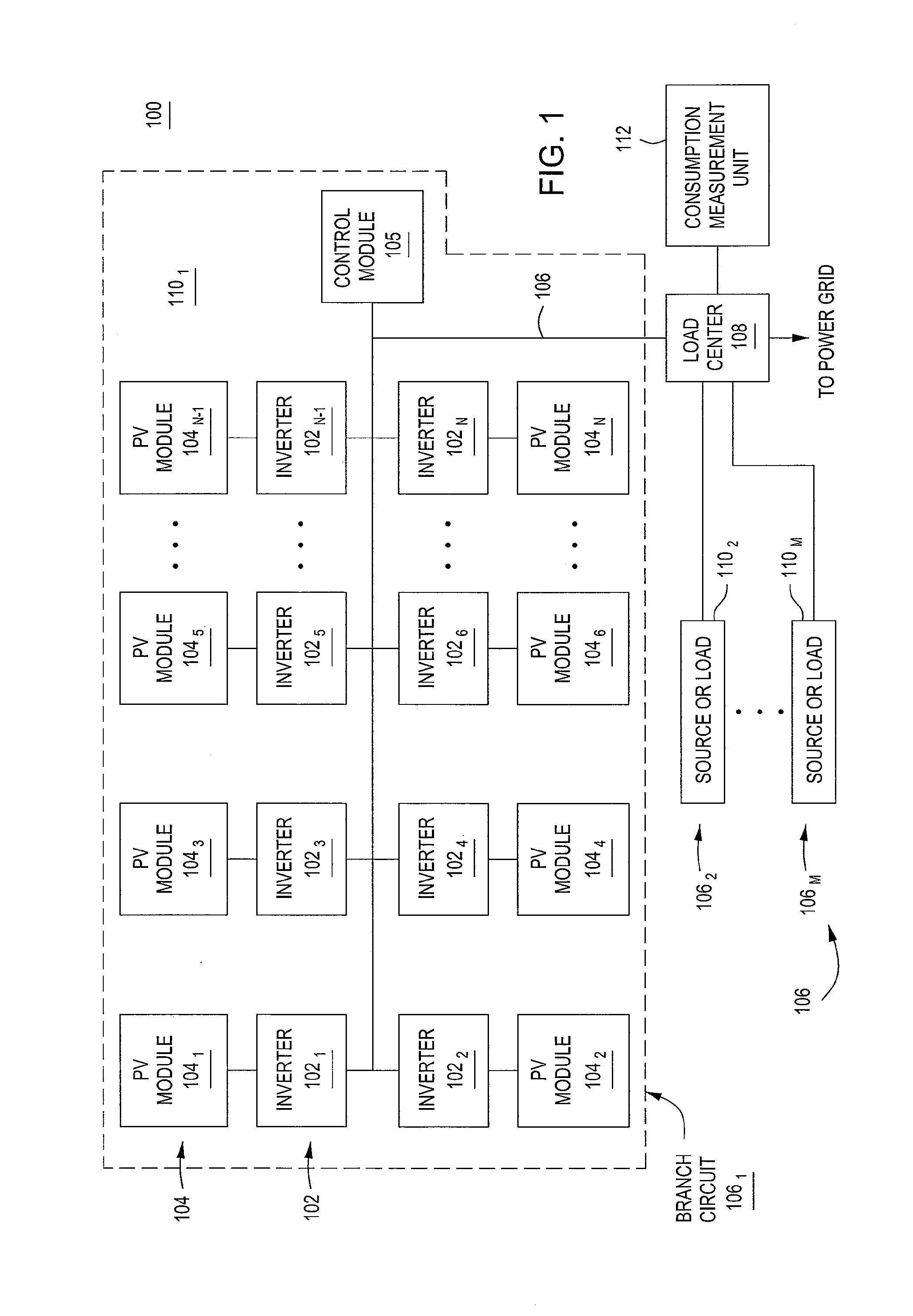
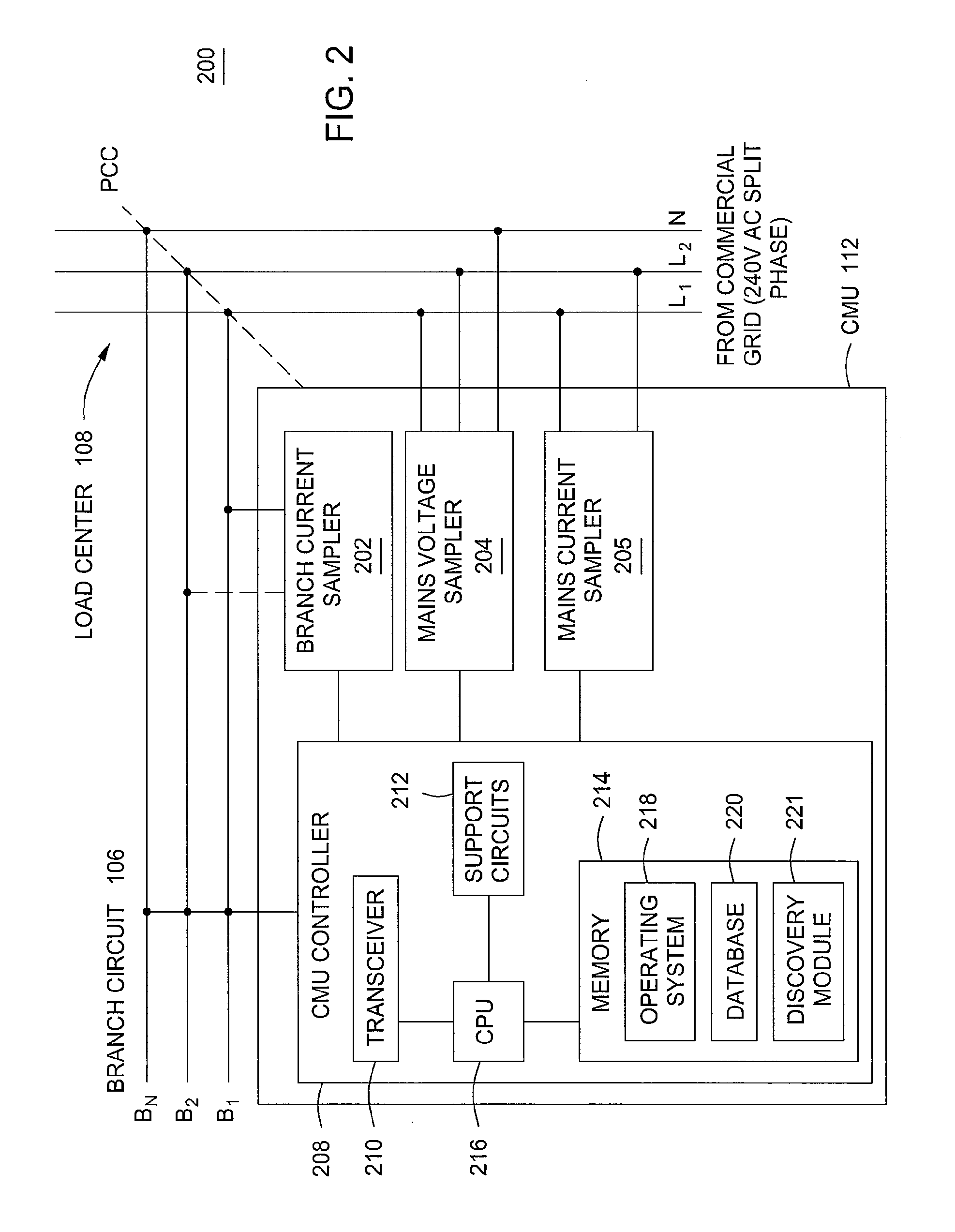
A method and apparatus for characterizing a circuit coupled to an AC line. The apparatus comprises a consumption measurement unit (CMU), adapted for coupling, independent of voltage and current polarity, to the AC line and the circuit. The CMU comprises a discovery module adapted for (i) generating a circuit current signature based on current samples representative of current on a phase of the circuit, (ii) generating at least one AC line current signature based on AC line current samples representative of current on each phase of the AC line, and (iii) determining, based on the circuit current signature, the at least one AC line current signature, and at least one of a source profile or a load profile, at least one of a type or a voltage characteristic for the circuit.
Owner:ENPHASE ENERGY
Multi-terminal flexible DC grid DC line quick protection method and system based on single-terminal voltage
ActiveCN109119977AEfficient identificationThe result of the protection judgment has no effectEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault location by conductor typesSize differenceTerminal voltage
The invention discloses a multi-terminal flexible DC grid DC line quick protection method and system based on single-terminal voltage. The method comprises the following steps: collecting the voltagesignals on the two sides of DC positive and negative line current limiting reactors in real time; forming a low voltage starting criterion; performing wavelet transform on the calculated line mode voltage on the current limiting reactors and calculating the wavelet transform modulus maximum; performing the data validity test and recording the size and the symbol of the first wavelet transform modulus maximum meeting the data validity condition; establishing the fault identification criterion to identify the fault based on the symbol and amplitude difference of the single-terminal voltage traveling wave wavelet transform modulus maximum; and constructing the fault pole identification criterion to identify the fault pole based on the size difference of the voltage traveling wave transient energy. According to the line protection method, the fault direction can be reliably and quickly identified under various initial fault conditions, and the transition resistance, the fault location andthe fault of the AC system and other factors have little influence on the protection criterion so as to have high reliability and sensitivity.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +2
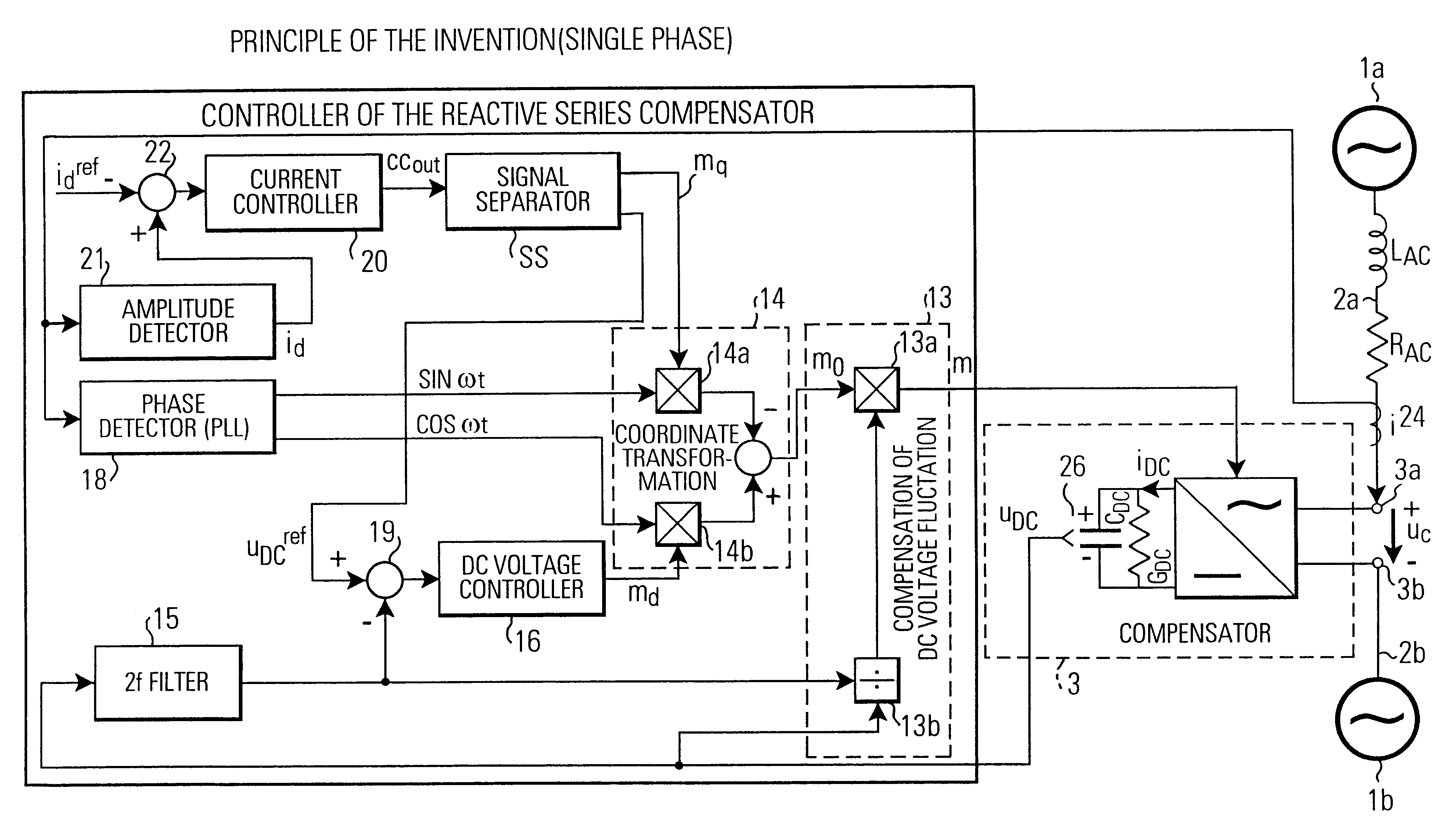
Controller of adjustable DC voltage for a transformerless reactive series compensator
InactiveUS6242895B1Avoids zero voltageHarmonics are still reducedReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationElectric variable regulationTransformerEngineering
A controller for controlling a reactive series compensator serially inserted at compensator terminals into a power transmission line for controlling the line current. The controller includes a current control loop and a voltage control loop. A current controller outputs a control voltage (cc.sub.out) indicating a desired compensator terminal output voltage (u.sub.c). A control method selector means generates, in a low output voltage region, a constant reference voltage (u.sub.DC.sup.ref) for the voltage control loop and a variable modulation index mq of a modulation signal m=m.sub.d cos (.omega.t) -m.sub.q sin (.omega.t). In a high output voltage range, the control method selector outputs a constant modulation index m.sub.q and a variable reference voltage (u.sub.DC.sup.ref). The voltage controller outputs the modulation index m.sub.d of the modulation signal m. Furthermore, the control method selector can include a rate limiter for limiting the change rate of the reference voltage (u.sub.DC.sup.ref). In connection with the control method selection and / or the rate limiter, a decoupling control for making the voltage and current control loops independent from each other can be used. The controllers find particular application in transformerless reactive series compensators for single-phase or three-phase control.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
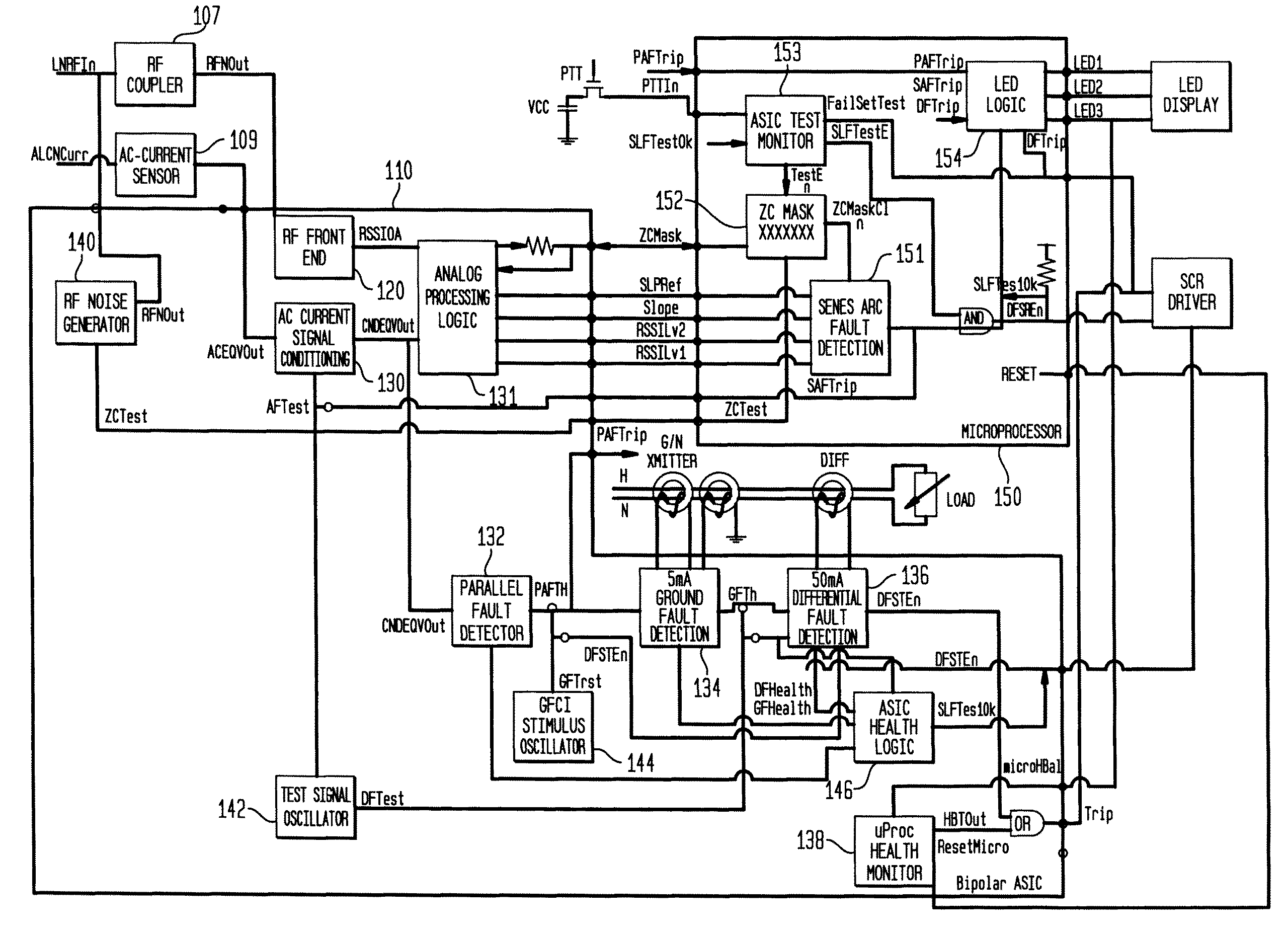
Arc fault detection technique
InactiveUS20070058304A1Improve reliabilityReduce sensitivityEmergency protective arrangement detailsArrangements responsive to excess currentInformation processingWave shape
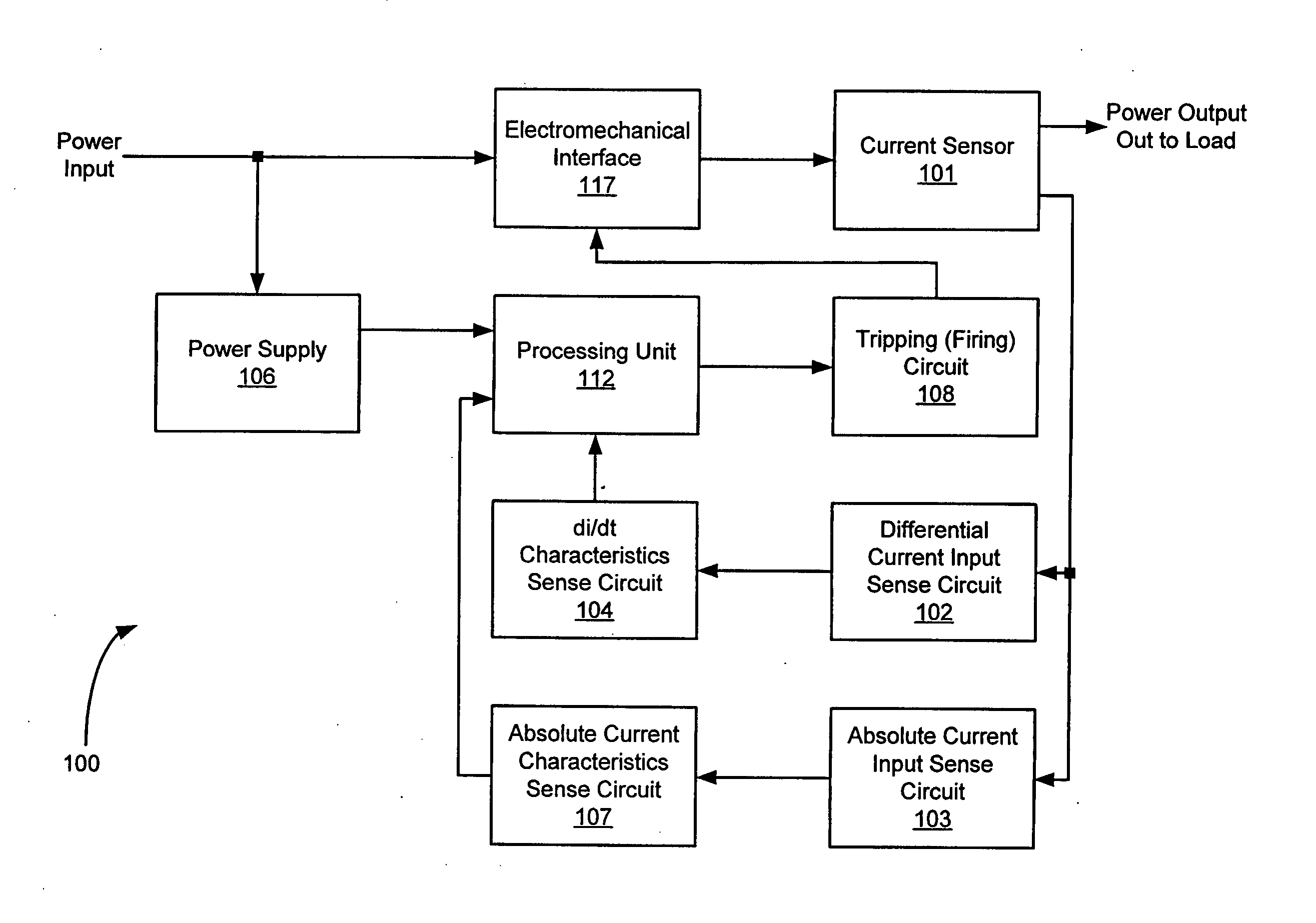
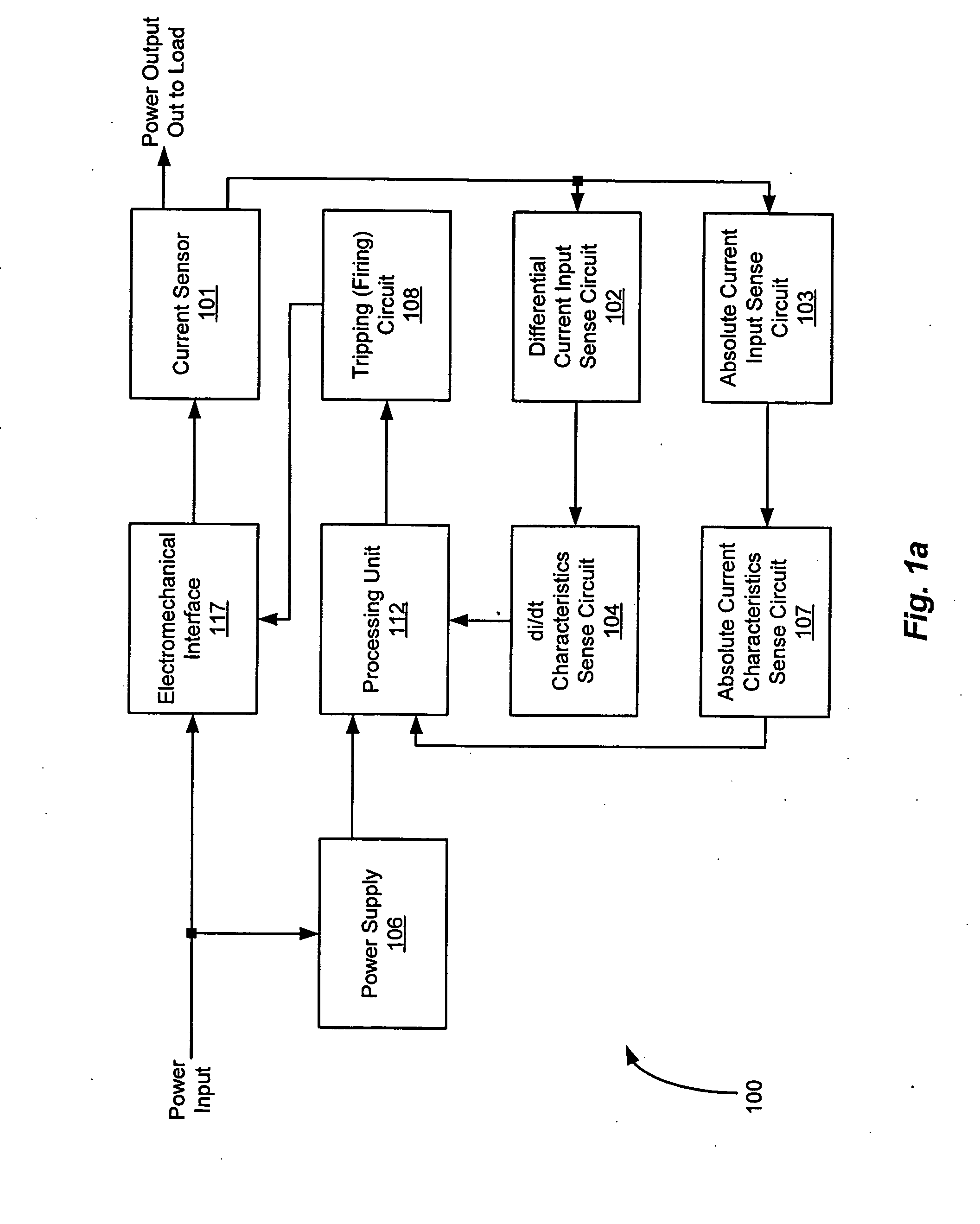
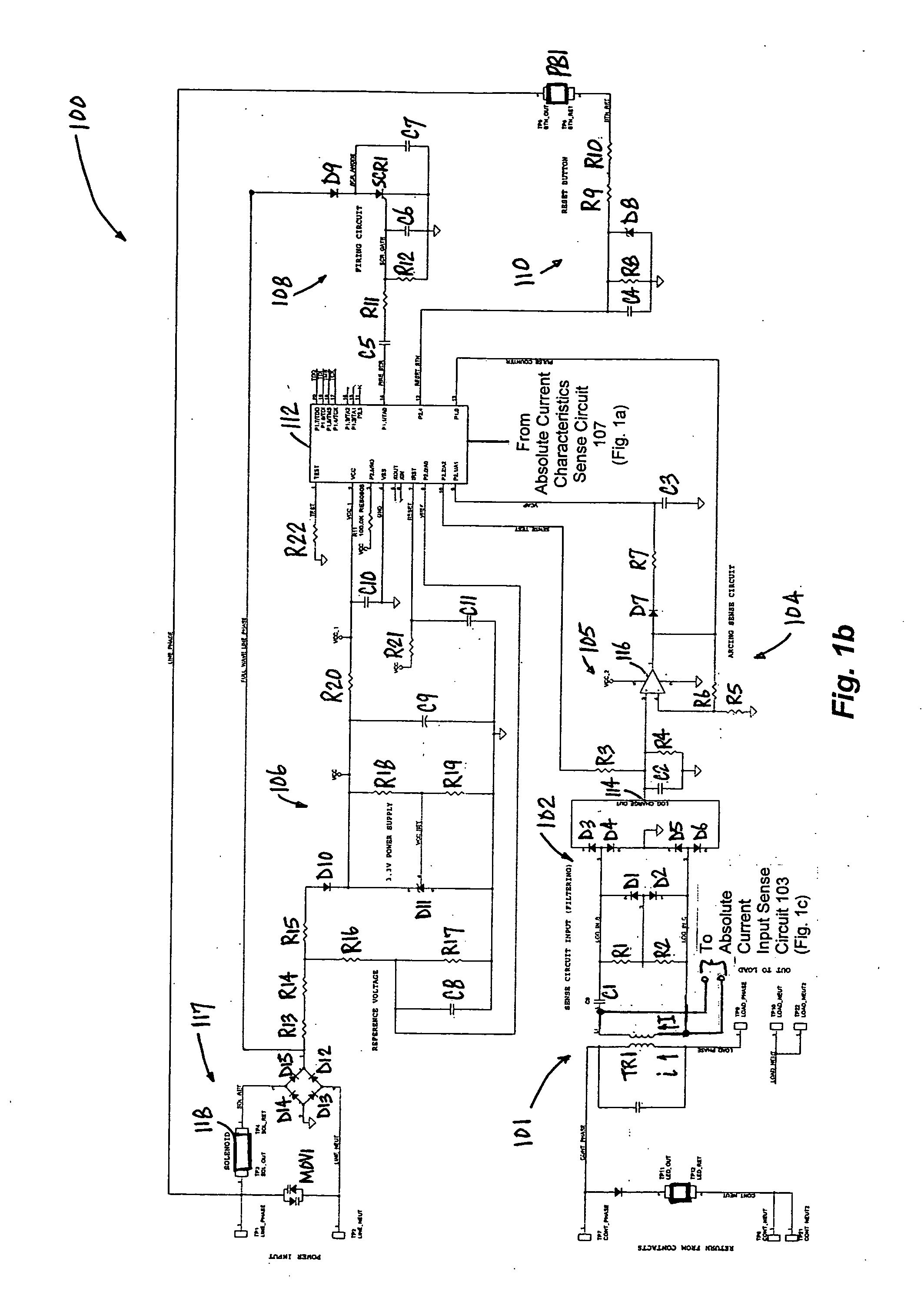
An apparatus and a method of detecting arc faults that have reduced susceptibility to nuisance tripping. The apparatus includes a current sensor, a differential current input sense circuit, a differential current (di / dt) characteristics sense circuit, an absolute current input sense circuit, an absolute current characteristics sense circuit, a power supply, a tripping circuit, a processing unit, and an electromechanical interface. The di / dt characteristics sense circuit provides information relating to the characteristic di / dt signature of a power line current. The absolute current characteristics sense circuit provides information relating to the absolute current waveform characteristics of the power line current. The processing unit correlates the di / dt characteristics to the absolute current characteristics to distinguish between electrical arc faults and nuisance loads, thereby reducing the susceptibility of the apparatus to nuisance tripping.
Owner:SENSATA TECH MASSACHUSETTS INC
Multifunctional residential circuit breaker
ActiveUS8023235B2Quickly and effectively discriminateReduce impactElectrical testingEmergency protection data processing meansCurrent sensorEngineering
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
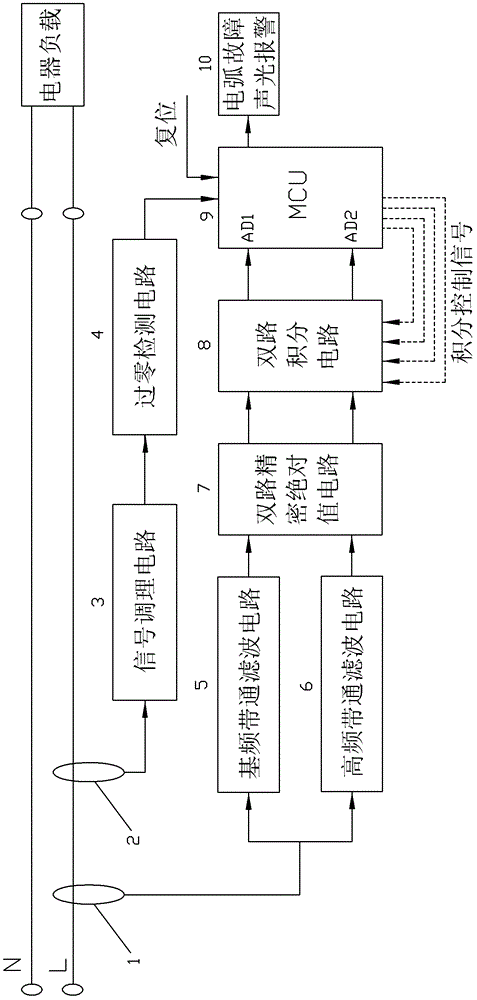
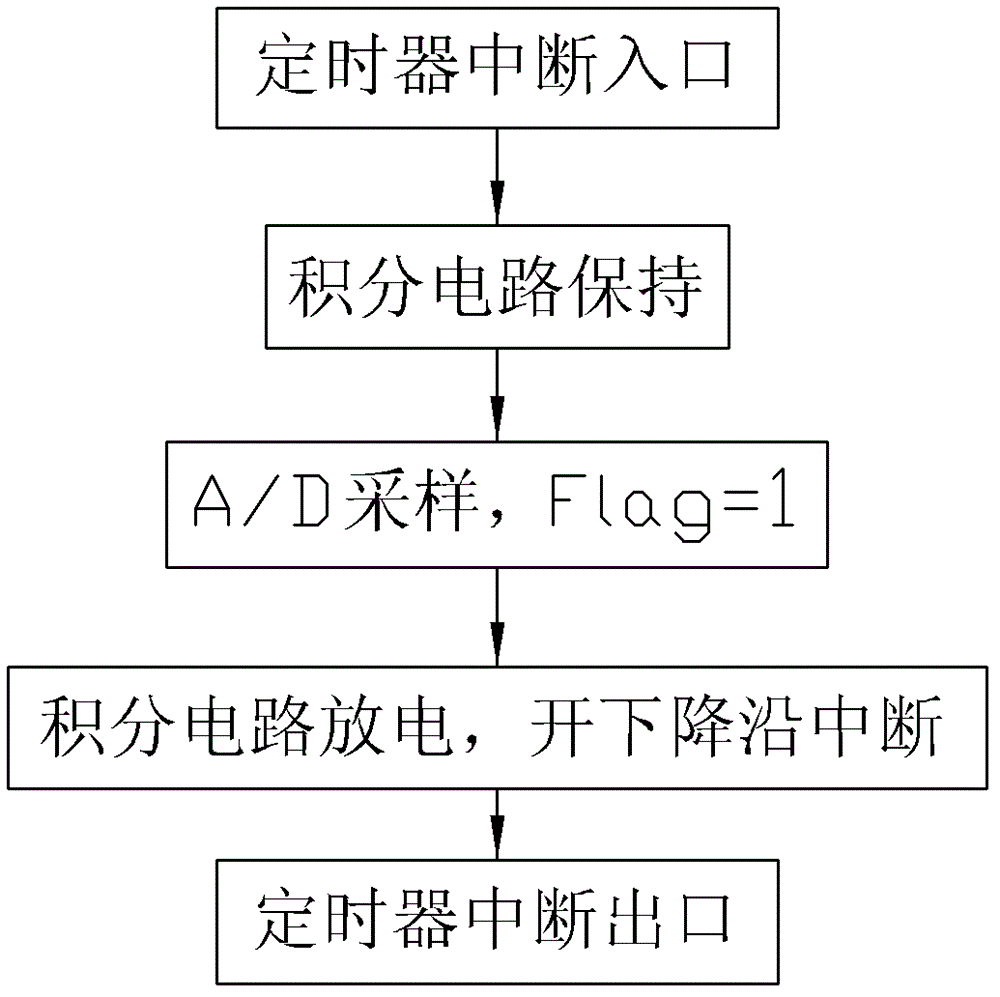
Low-voltage arc fault detection method
InactiveCN102749533AImprove reliabilityAvoid misuseCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical testingLow voltageCurrent sensor
A low-voltage arc fault detection method comprises collecting current signals in a loop through a current sensor, obtaining fundamental frequency analog signals and high frequency analog signals, achieving accumulating calculation of the fundamental frequency analog signals and high frequency analog signals of power frequency cycle through an integrating circuit, an interrupt trigger and a timer, and further obtaining higher harmonic occupancy. According to the method, whether arc faults occur is judged by real-time monitoring of change characteristics of the line current higher harmonic occupancy and calculation of over-limit times of the higher harmonic occupancy, normal arc and fault arc which are generated by some special electric appliance loads and normal on-off action are distinguished by judging whether higher harmonic occupancy changes caused by the arc faults are periodic and judging occurring frequency, occurrence of the arc faults can be detected in real time, the method is not limited by an installing position, malfunction caused by disturbance of operating arc generated by normal circuit opening and closing and loads such as a switch power and a dust collector can be avoided well, and the reliability is high.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
System, apparatus and method for compensating the sensitivity of a sequence element in a line current differential relay in a power system
An apparatus and method compensate for the sensitivity of at least one line current differential element of a first current differential relay providing differential protection for a transmission line of a power system during a single-phase pole-open condition. The apparatus includes a first delta filter configured to remove a first pre-fault current from a first fault current of the transmission line to derive a compensated first current phasor. The apparatus also includes a second delta filter configured to remove a second pre-fault current from a second fault current of the transmission line to derive a compensated second current phasor. The compensated first and second current phasors are provided to the at least one line current differential element to compensate the sensitivity of the at least one line current differential element.
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
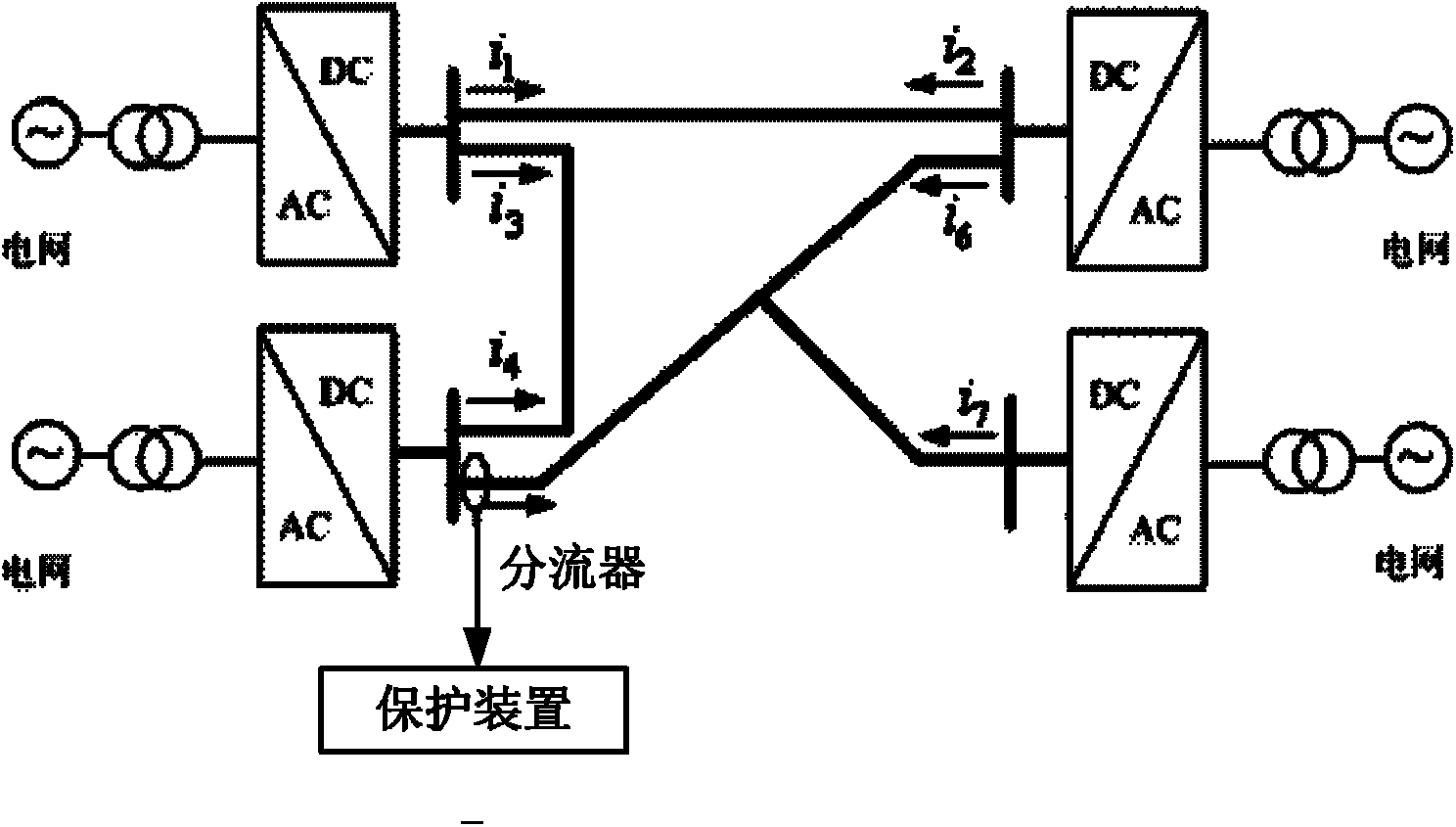
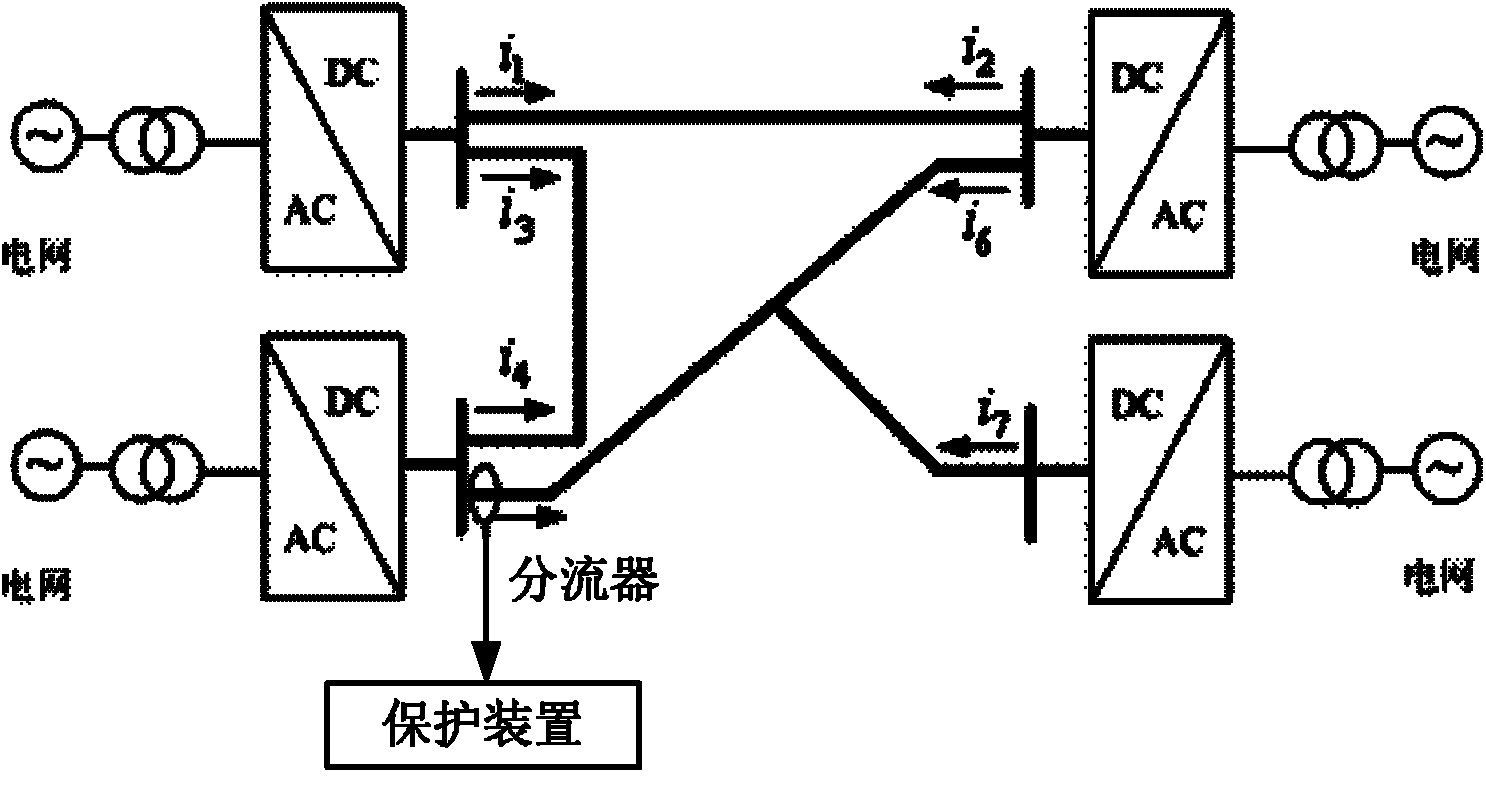
Ground electrode circuit protective system and device of high-voltage DC transmission system
ActiveCN101540501APrevent lockoutElectric power transfer ac networkEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDc circuit breakerEngineering
Owner:CSG EHV POWER TRANSMISSION
Magnetic random access memory array with free layer locking mechanism
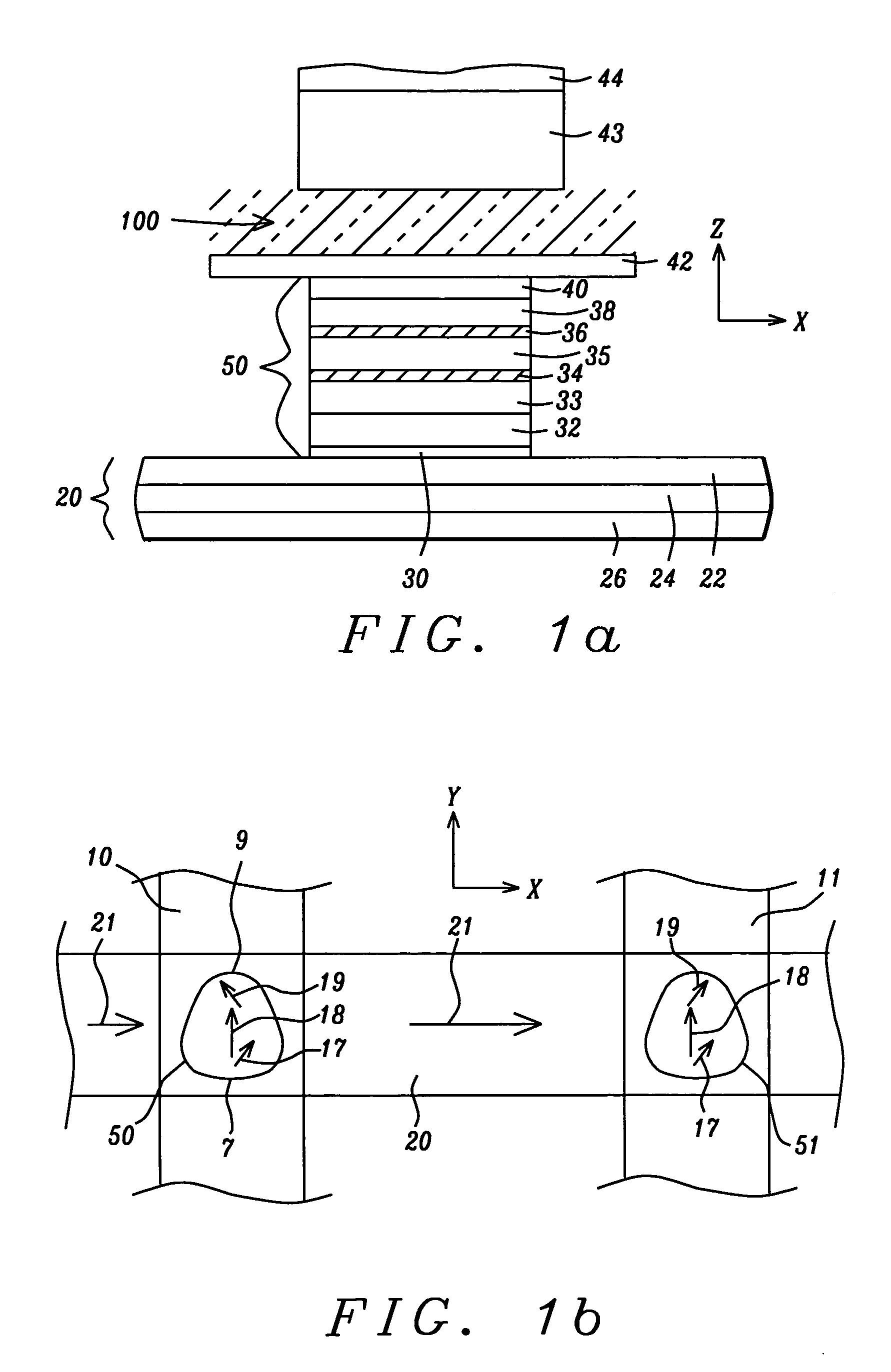
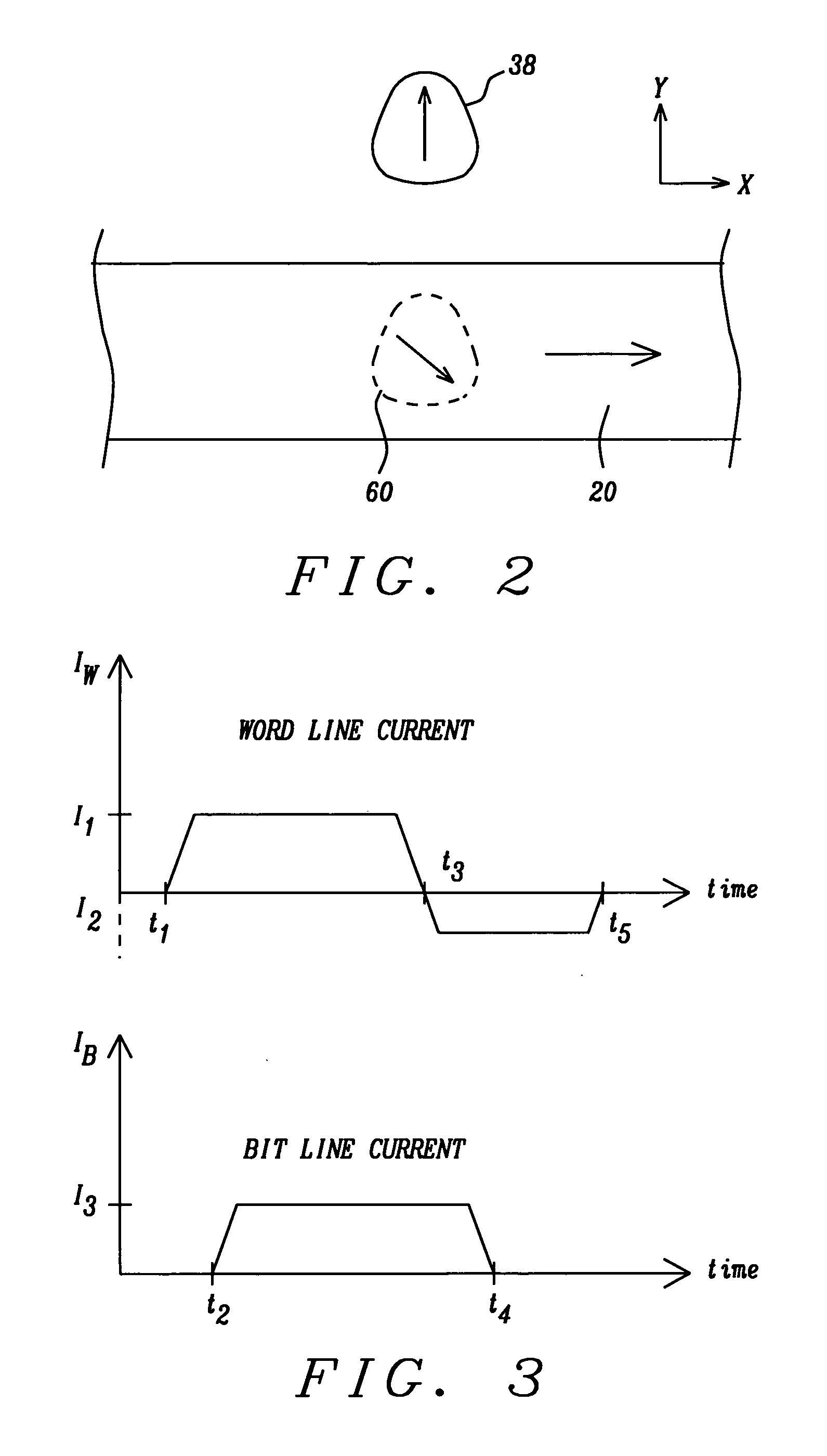
InactiveUS7211874B2Data efficientSmall sizeMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesStable stateBit line
An MTJ MRAM cell element, whose free layer has a shape induced magnetic anisotropy, is formed between orthogonal word and bit lines. The bit line is a composite line which includes a high conductivity current carrying layer and a soft adjacent magnetic layer (SAL). During operation, the soft magnetic layer concentrates the magnetic field of the current and, due to its proximity to the free layer, it magnetically couples with the free layer to produce two magnetization states of greater and lesser stability. During switching, the layer is first placed in the less stable state by a word line current, so that a small bit line current can switch its magnetization direction. After switching, the state reverts to its more stable form as a result of magnetostatic interaction with the SAL, which prevents it from being accidentally rewritten when it is not actually selected and also provides stability against thermal agitation.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Pilot protection method for direct current line current abrupt change of multi-terminal direct current transmission system
InactiveCN102510050AReduce trafficDownsamplingEmergency protective circuit arrangementsTransient statePower flow
The invention provides a pilot protection method for the direct current line current abrupt change of a multi-terminal direct current transmission system. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, acquiring fault transient state current amperage; 2, calculating the current abrupt change in one period of time by using the acquired fault transient state current amperage, comparing the current abrupt change with a setting value according to the value of the current abrupt change and judging the direction of faults; and 3, distinguishing inside-area and outside-area faults by the cooperation of the current abrupt change directional elements at the terminals of a line; and if the directional element at each terminal is judged to have a forward directional fault, the fault is judged as the inside-area fault, and if at least one directional element is judged to have a reverse directional fault, the fault is judged as the outside-area fault. The method has the advantages that only current data is used, the required sampling rate is low, the current abrupt change is easy to calculate, the communication amount is small, and line faults can be rapidly detected; all energy information but a high frequency signal in a fault transient state is used, the signal energy is strong, and the protection is safety and reliable; and the method is applied to a parallel, a serial and a hybrid multi-terminal direct current system.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
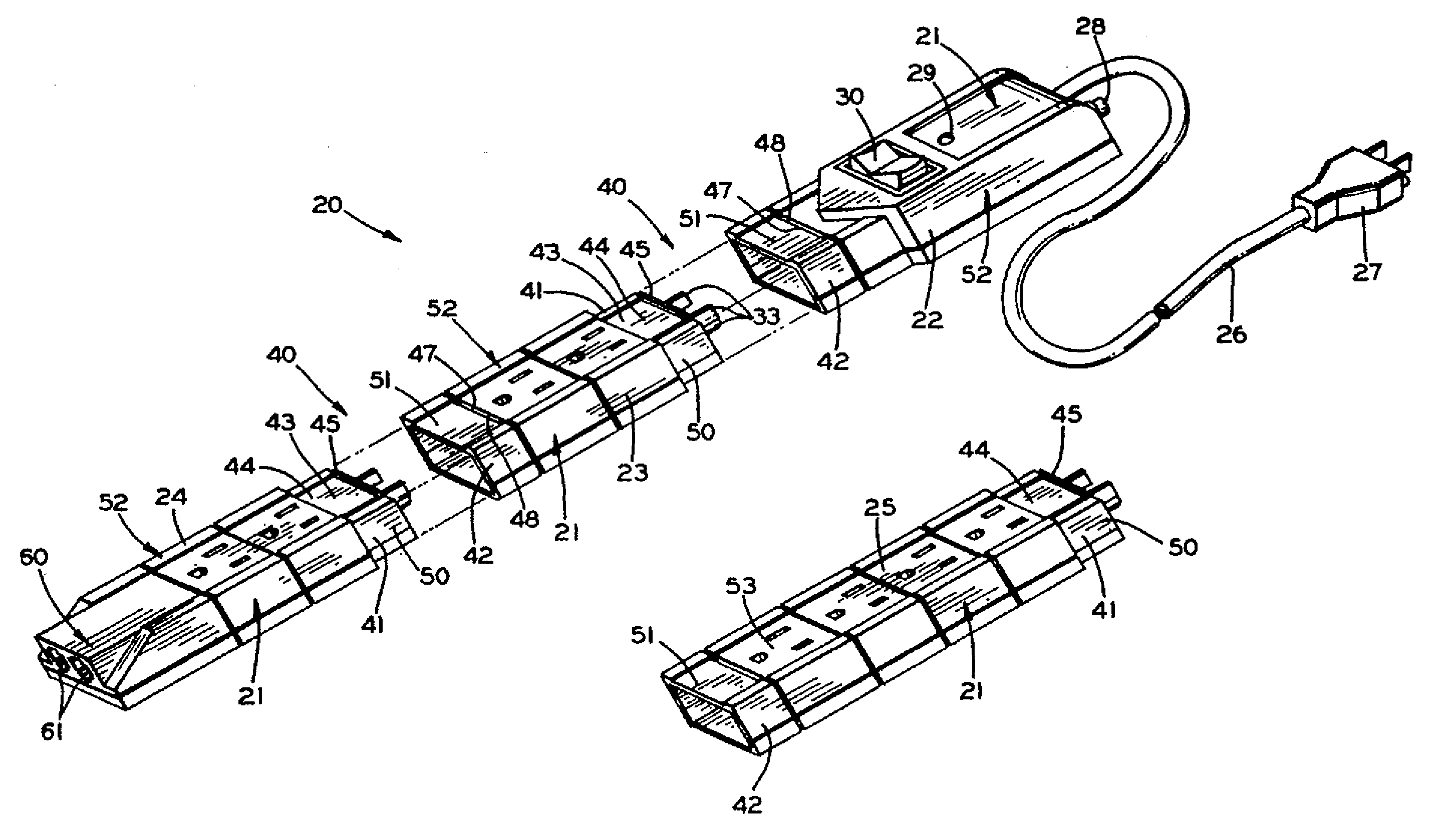
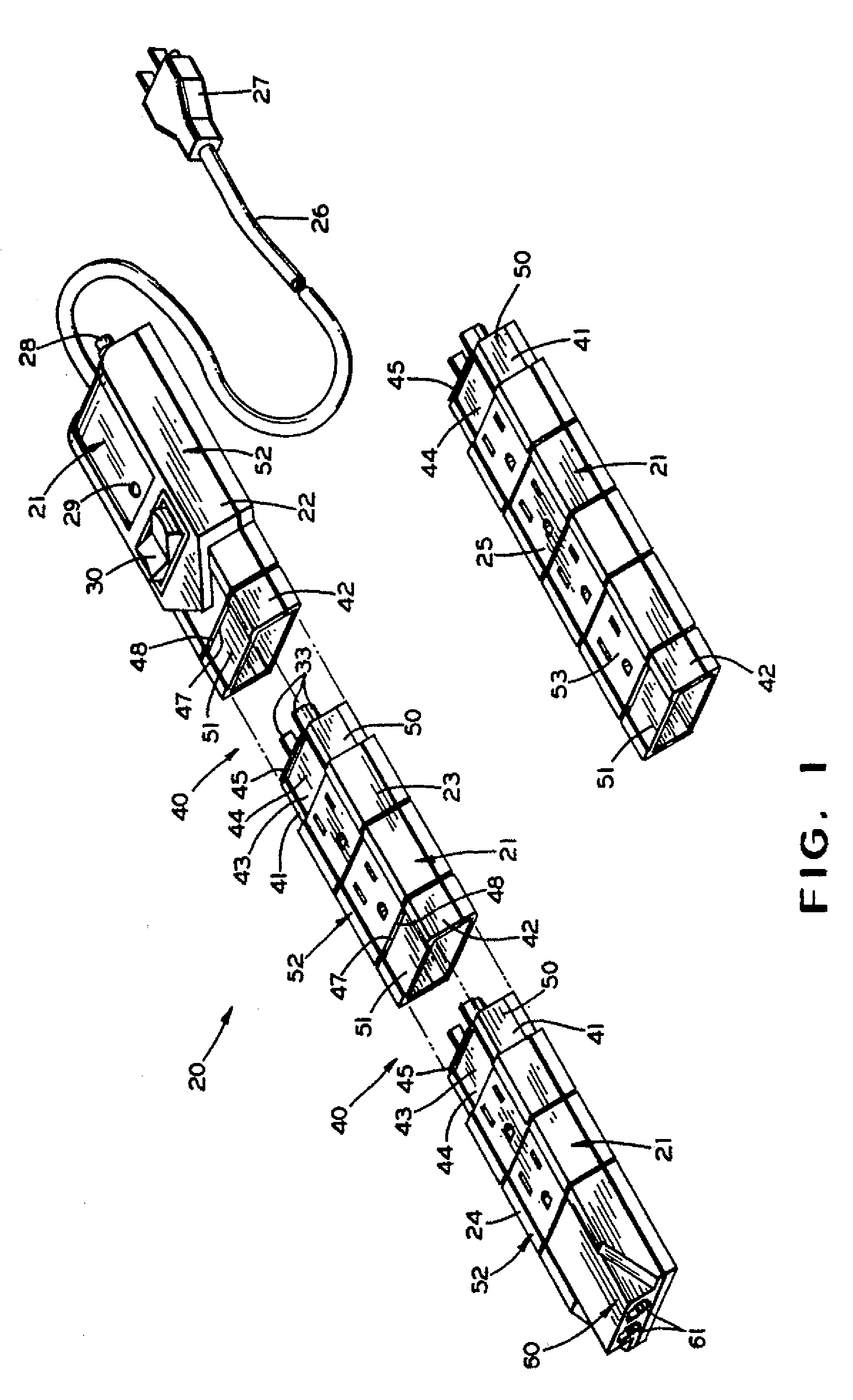
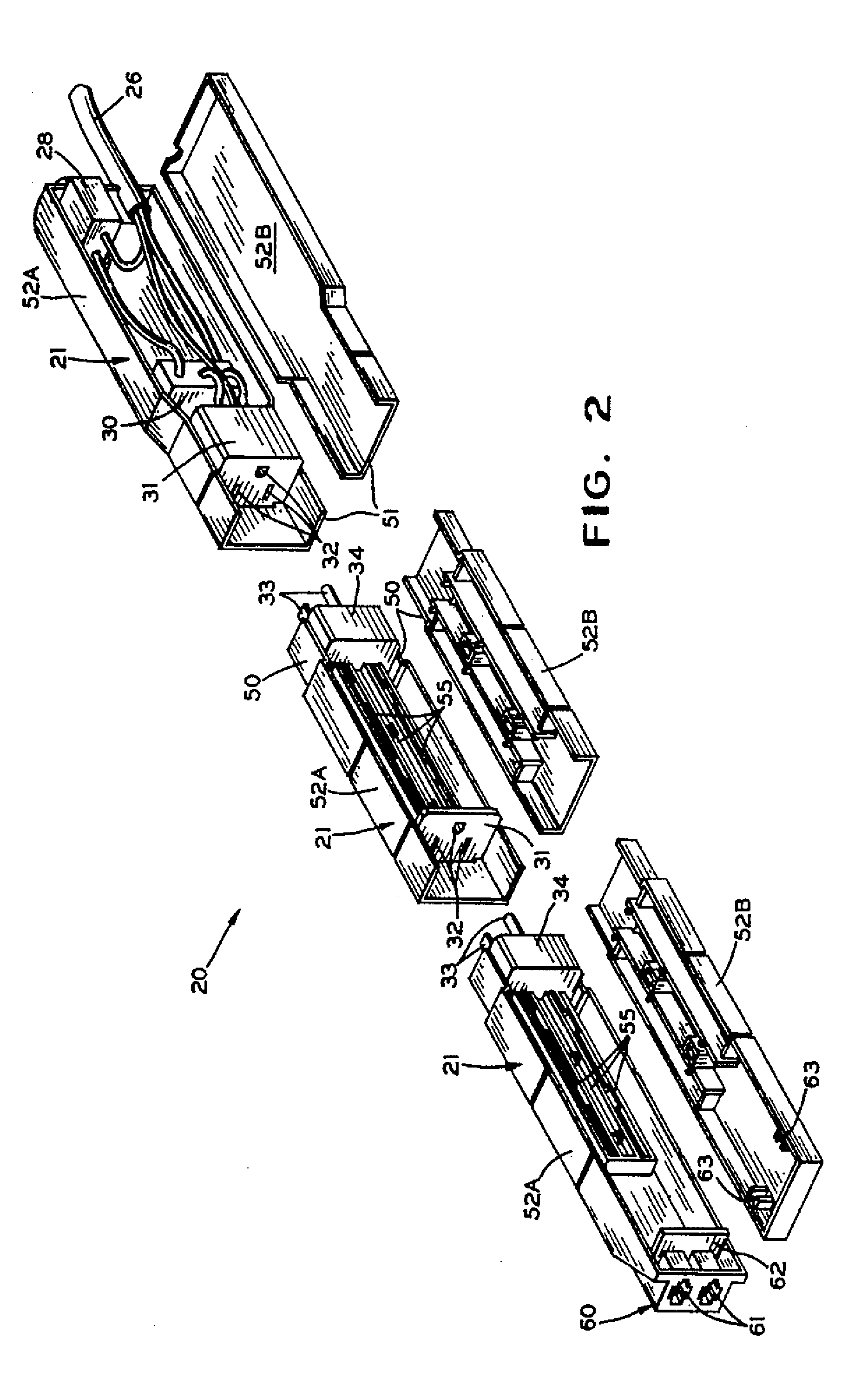
Modular Outlet Strip
InactiveUS20070109710A1Easy to manufactureLow costElectrically conductive connectionsCoupling device detailsModem deviceModularity
A modular surge protector is provided where only the number and types of modules needed are purchased and connected together by a fixed line current or a removable power supply outlet. Generally, the modular surge protector includes a power distribution module, which is connected to a source of line current and one or more power supply modules, which may be connected via an additional line current or may be attached by the use of a power supply outlet. Each of the power supply modules will have at least one power supply outlet and may also have a modem surge protector.
Owner:MILAN HENRY
Method and apparatus for monitoring wellness of contactors and starters
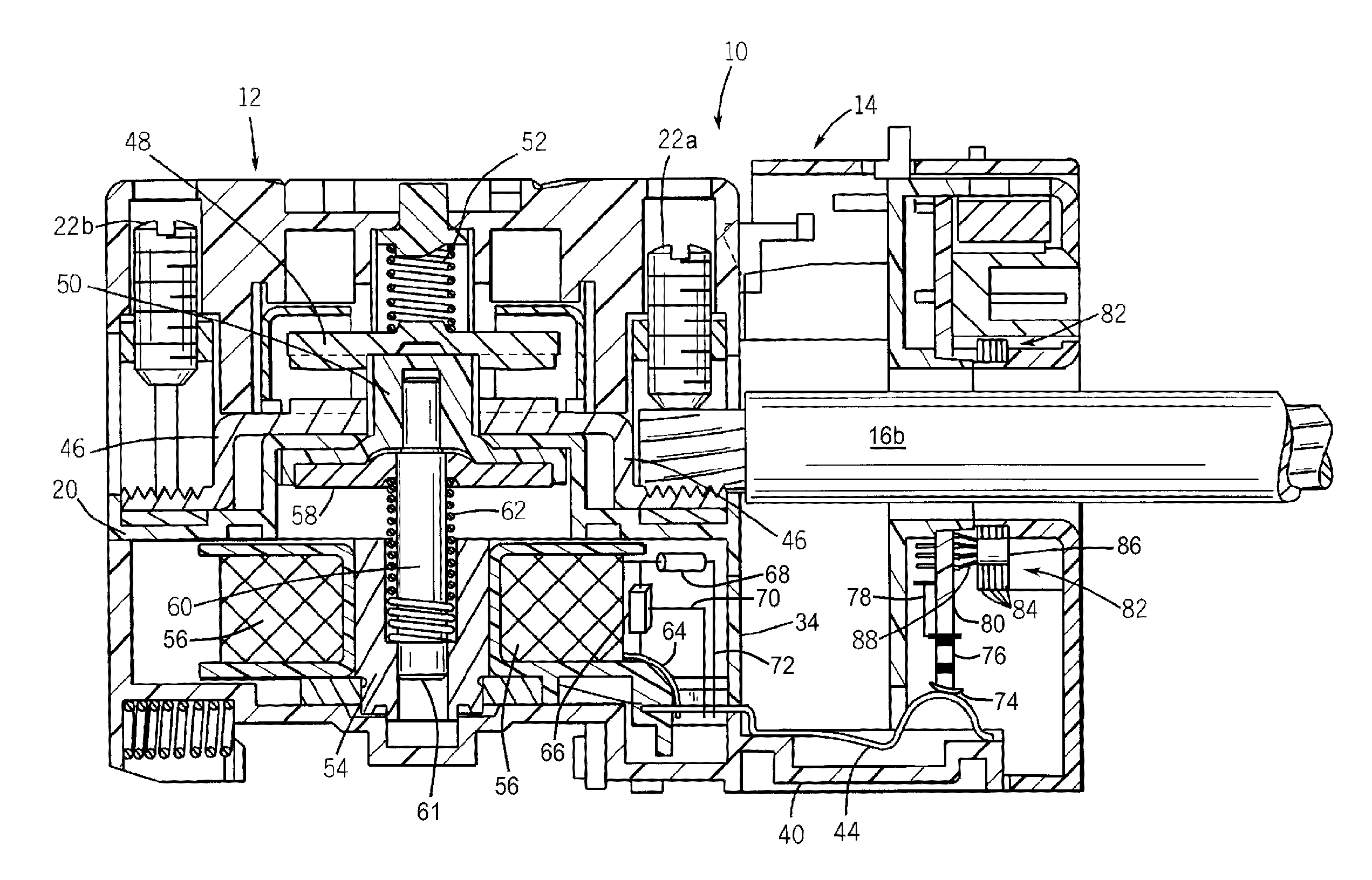
InactiveUS7705601B2Overcomes shortcomingAccurately indicatedContact testing/inspectionElectromagnetic relay detailsSafety InterlockLine current
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Fan-driven air freshener
InactiveUS20050079113A1Overcome problemsSamplingExhaust apparatusMotion detectorCompound (substance)
The present invention combines an air freshener that has a source of air freshening chemical with a fan that is controlled either by an optical device that senses light or a motion detector. When a light is turned on or motion is detected, the fan will be activated for a predetermined time period. In certain embodiments, the fan will stop turning after a predetermined time. Alternatively, the fan can continue to be powered until the light source is turned off, or all motion ceases, and only then either immediately shut down, or shut down after a predetermined time period. In certain preferred embodiments the source of air freshening chemical is disposed beneath the fan and allows fragrance to be delivered over time without the fan. The additional airflow provided by the fan causes more volatile fragrance chemicals to be removed from the source of air freshening chemical and admitted into the environment. The fan motor of the present invention is driven by a power source, such as batteries, AC line current or alternate sources such as solar cells. Preferably, a microprocessor controls the fan so that a “burst mode” is created by controlling the frequency and intensity of the pulses of air freshener that are emitted.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES
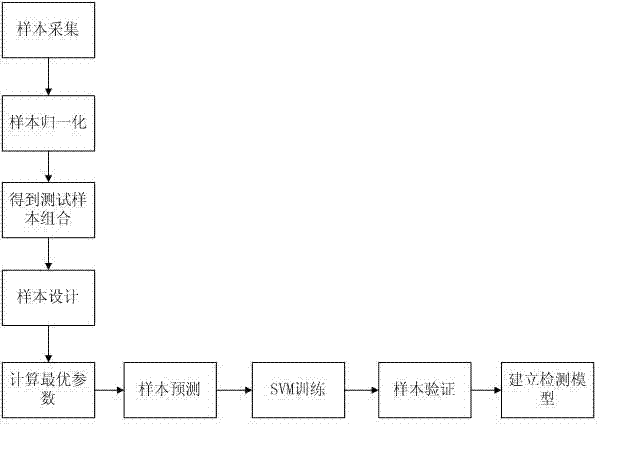
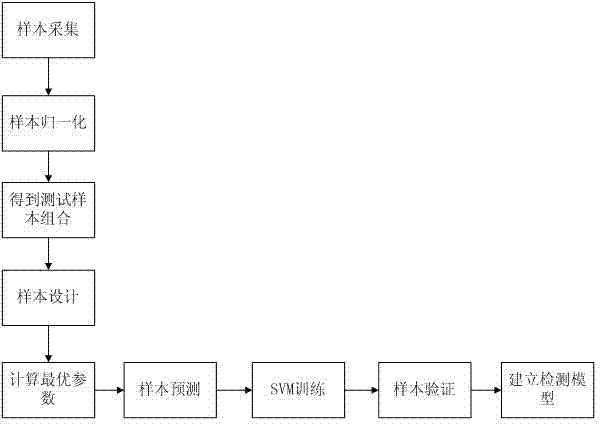
Support vector machine based fault electric arc detection method
InactiveCN102331543AImprove recognitionImprove accuracyCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical testingSupport vector machineCurrent sample
The invention provides a support vector machine based fault electric arc detection method, relating to the technical field of electric arc protection and solving the technical problem of improving fault electric arc identifying and judging accuracy. The method provided by the invention comprises the following concrete steps of: 1) acquiring current samples of circuits to be detected under different loads and working conditions; 2) normalizing the waveform of each current sample; 3) obtaining a test sample combination according to the normalized current samples; 4) dividing the test sample combination into a train set and a verification set; 5) calculating a kernel function parameter and a punishment parameter which have the highest prediction accuracy rate; 6) predicting each sample in the verification set; 7) training by utilizing different sample sets to obtain a weight matrix; 8) verifying the samples in the verification set by utilizing the weight matrix, and creating a detection model according to the verification result; and 9) identifying and judging the fault electric arc by utilizing the detection model. By applying the method provided by the invention, false operation of fault electric arc detection equipment under the action of an interference load can be effectively avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF WORK SAFETY SCI +1
Systems and Methods for Distributed Series Compensation of Power Lines Using Passive Devices
ActiveUS20080310069A1Emergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentReactive power compensationElectrical conductorTransformer
Systems and methods for implementing line overload control via providing distributed series impedance are disclosed. One system, amongst others, comprises at least one distributed series reactor (DSR). Each DSR comprises a single turn transformer (SST) comprising two split-core sections (132), a winding (120), and an air-gap (138), the air-gap designed such that a magnetizing inductance is produced when the two split-core sections (132) are clamped around a conductor (108). Each DSR further comprises a contact switch (122) that short circuits the winding when the contact switch (122) is in a closed condition, a power supply (128) that derives power from conductor line current, and a controller (130) configured to open the contact switch when the conductor line current reaches a predetermined value, thus causing insertion of the magnetizing inductance into the conductor. The controller (130) may be further configured to close the contact switch (122) when the conductor line current drops below the predetermined value.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Method for achieving single-phase earth fault line selection of small current grounding system
InactiveCN103592571AHigh sensitivityGuaranteed reliabilityFault locationHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
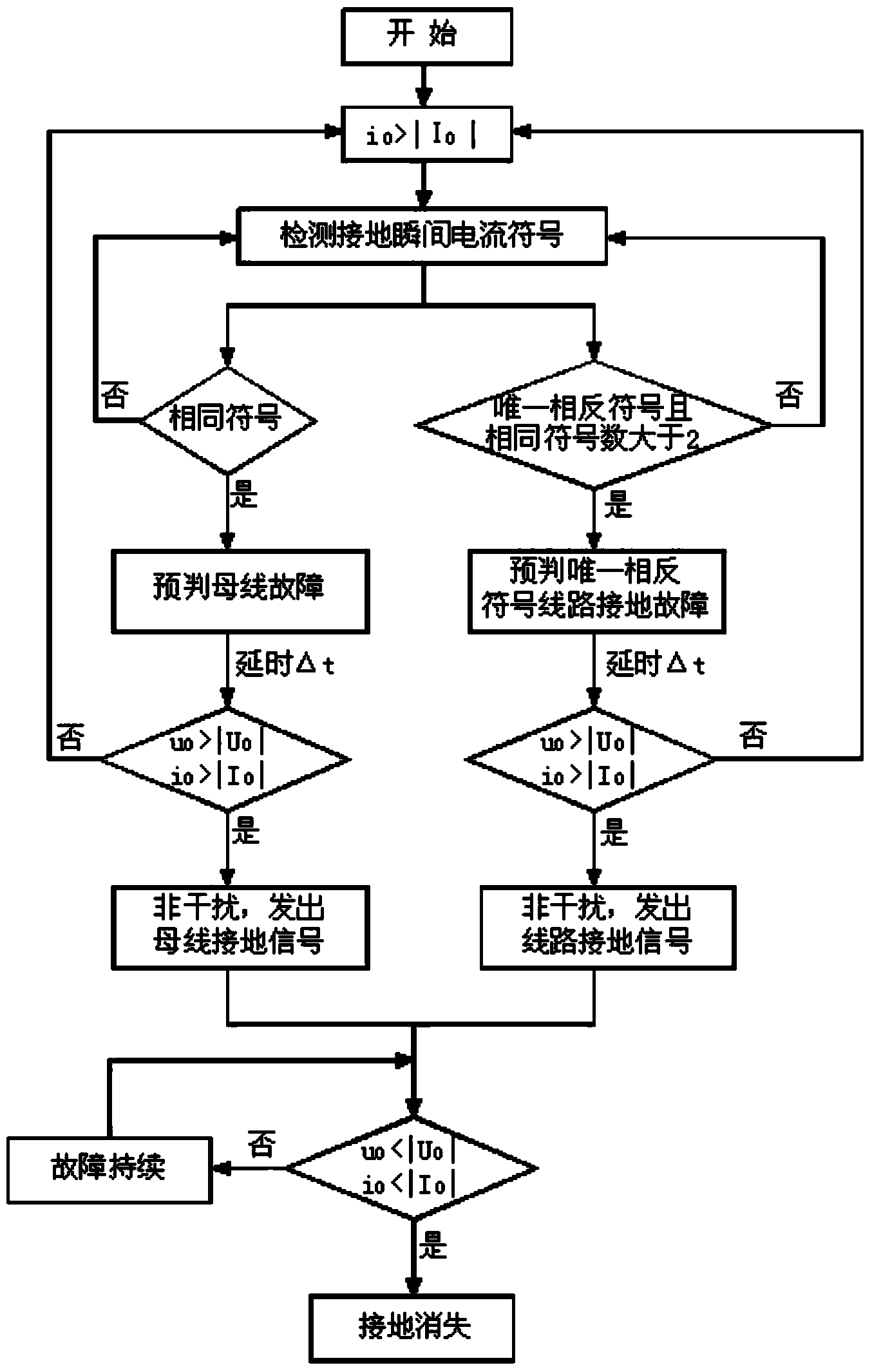
A method for achieving single-phase earth fault line selection of a small current grounding system is characterized in that a high-precision zero-sequence current transformer is adopted by each feeder line; a single-phase earth fault of the system is confirmed when the instantaneous value of the zero-sequence current i0 of any one feeder line exceeds a set threshold / I0 / ; comparison is conducted on symbols of all loop circuits at the moment of threshold triggering, and data after the triggering do not participate in judgment; the symbol of a faulty line current is unique and opposite to the symbols of non-faulty line currents, and the number of non-faulty lines is larger than or equal to 2; when the symbols of all the currents are identical, a bus earth fault is confirmed. The method for achieving single-phase earth fault line selection of the small current grounding system is adaptable to three grounding modes, namely neutral non-grounding, arc suppression coil grounding and neutral point high resistance grounding, of the small current grounding system and is not affected by a grounding moment phase angle, system unreal grounding and TV disconnection, and correction operation can still be achieved when the zero-sequence voltage of a bus is reduced to be 10% of a phase voltage by a transition resistor.
Owner:珠海威瀚科技发展有限公司
Anti-cycling control system for luminaires
InactiveUS20050035720A1Relieve pressureElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementControl systemEngineering
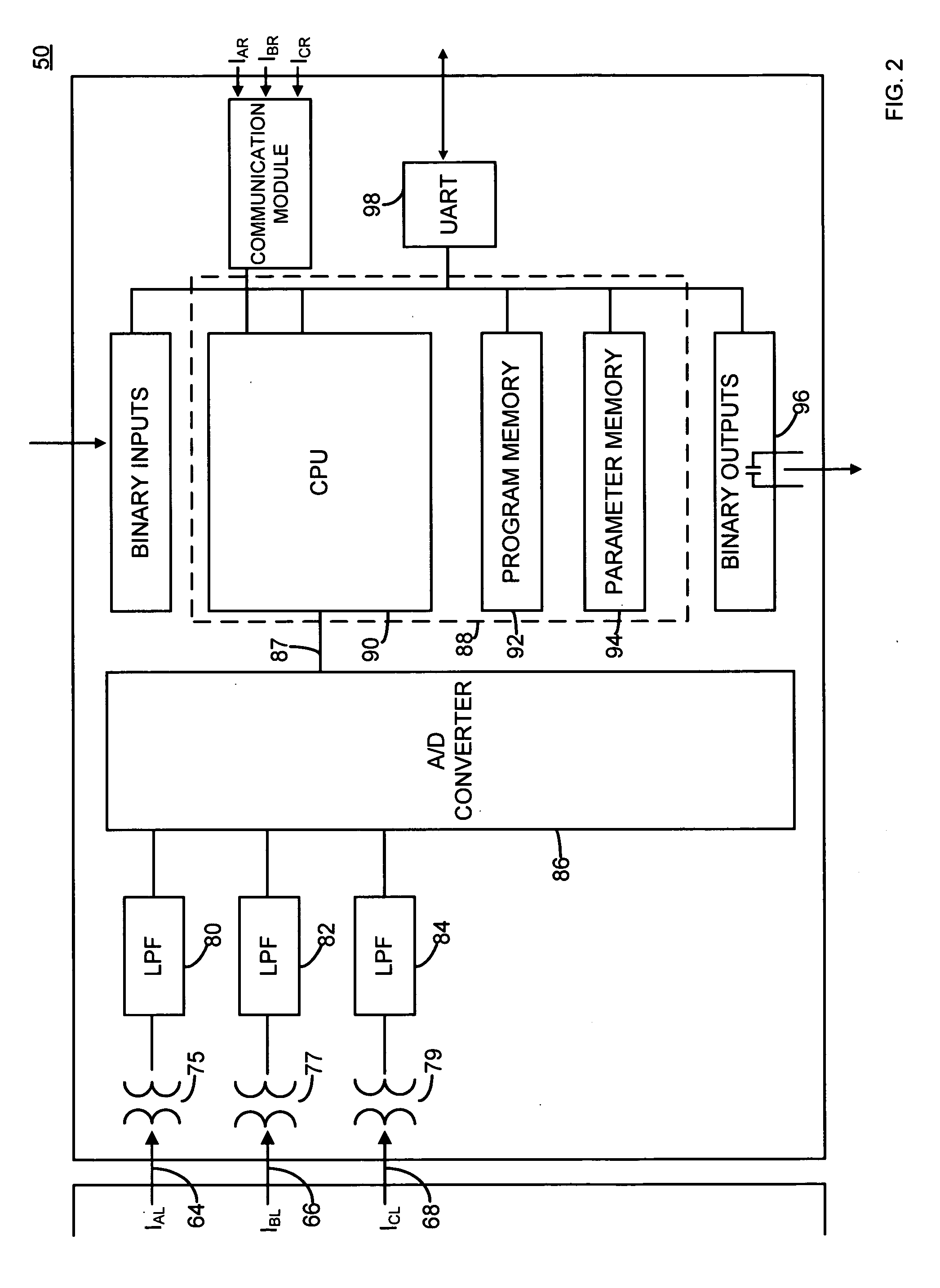
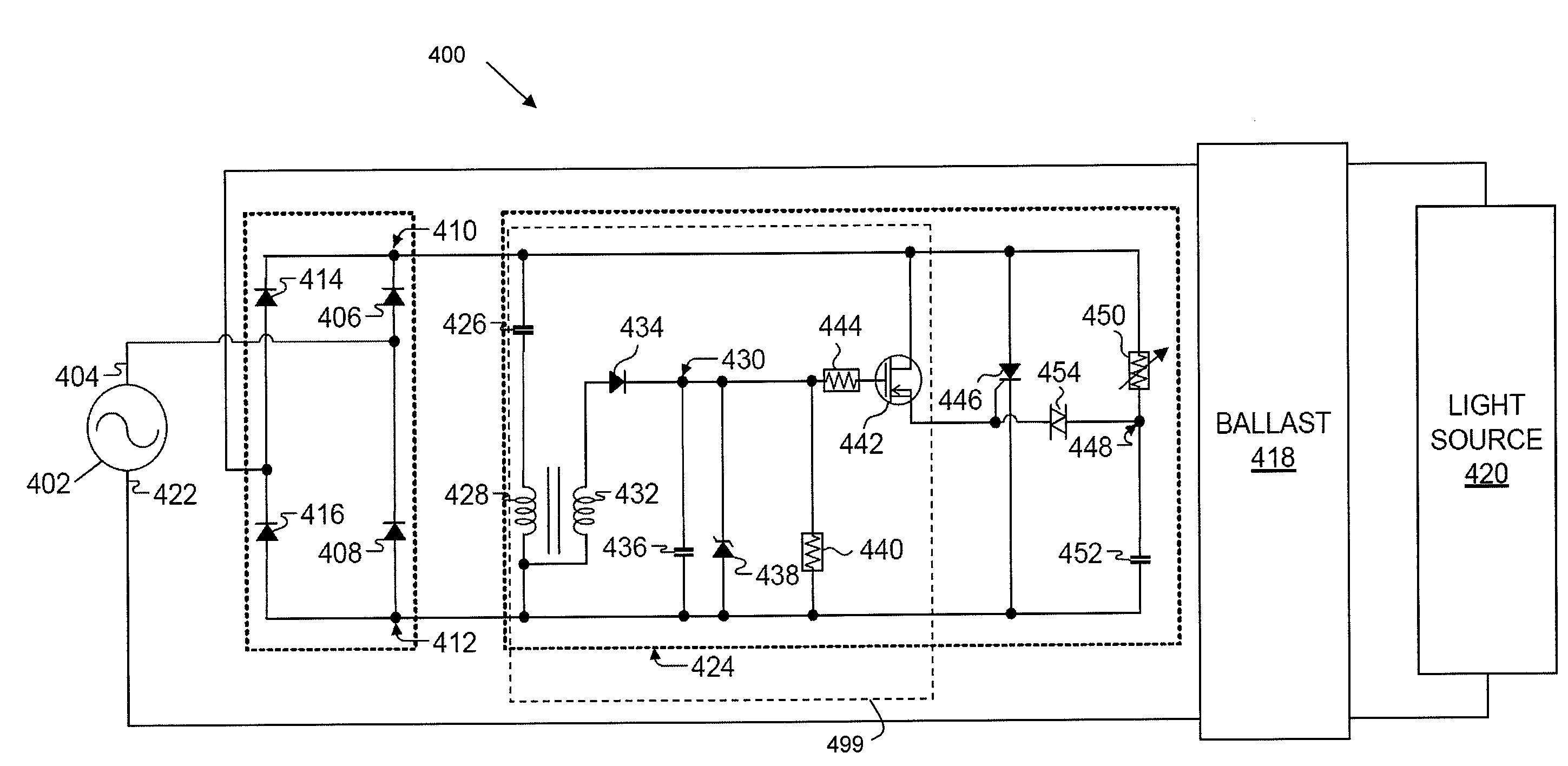
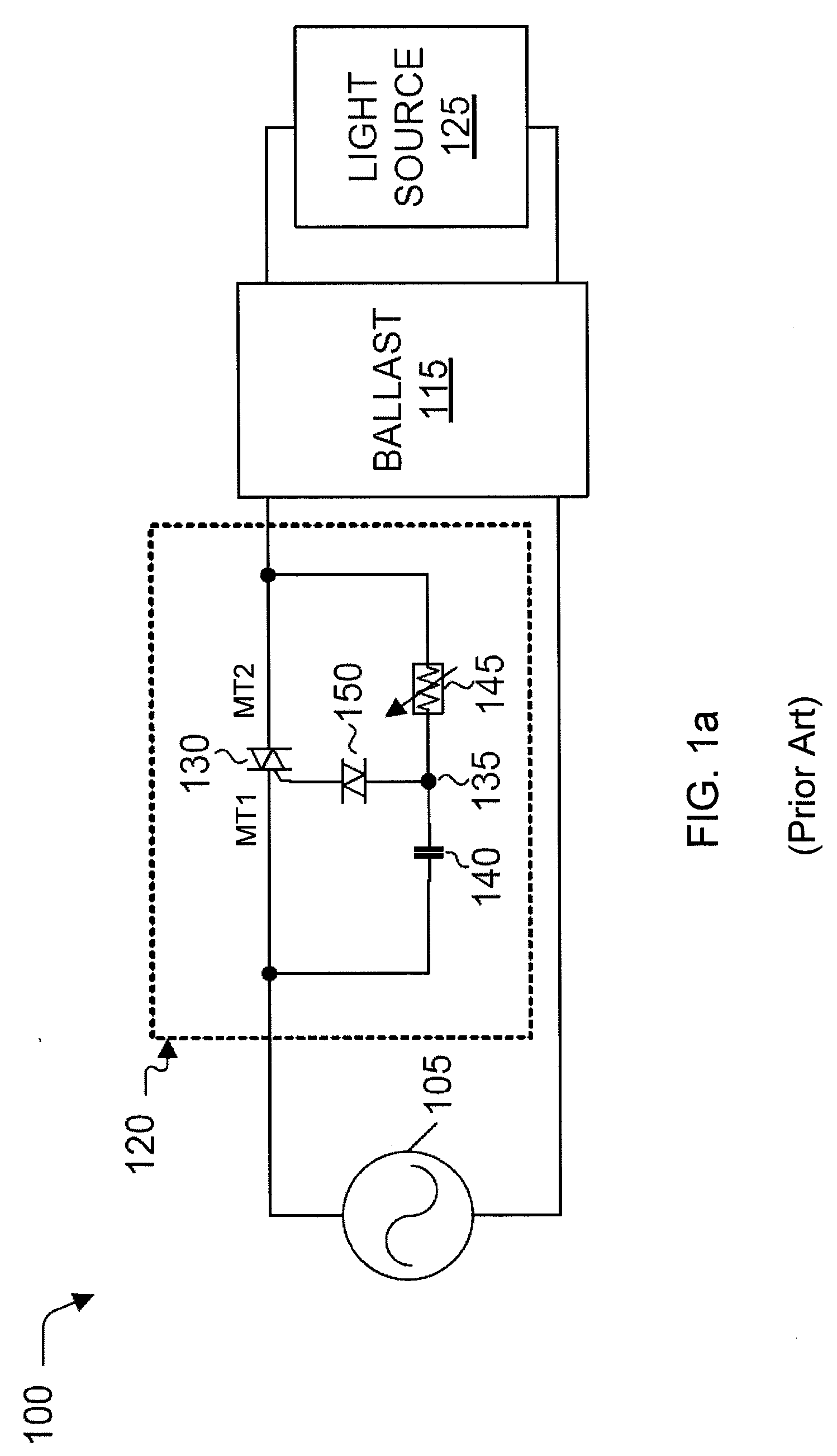
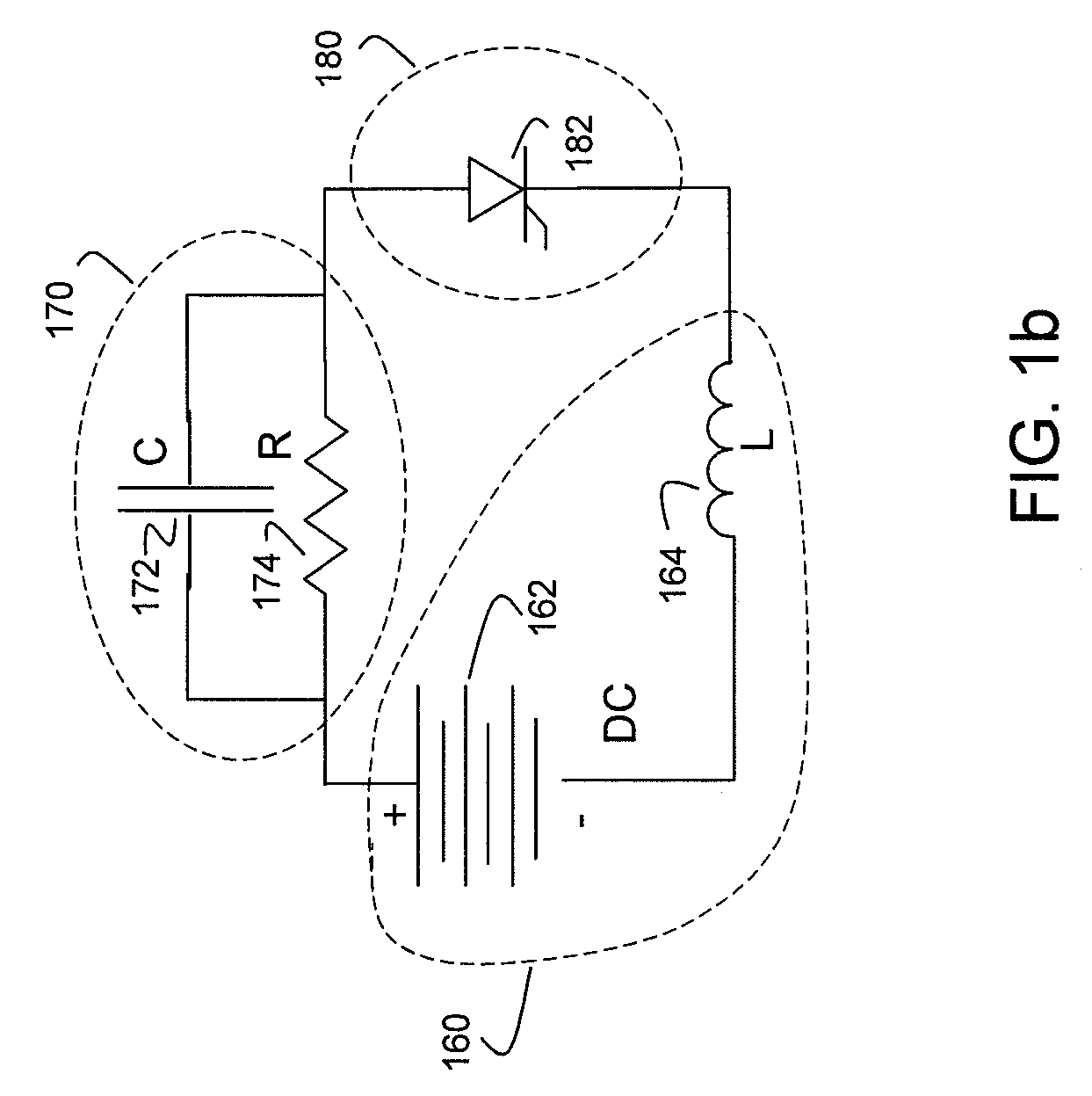
An anti-cycling luminaire control system may detect repeated lamp-off conditions and interrupt power to the lamp and provide an indication of lamp cycling after a predetermined number of lamp-off conditions has been detected. The control system also provides a cool-off period after a lamp-off cycling event is detected during which time restarting of the lamp is inhibited. If the lamp does not restart after multiple restart attempts and cool-off periods, the system determines that a fault condition exists, and may provide a fault alert. The system may provide for shut-off or dimming of the lamp during the night after a portion of the night has passed. This delayed turn-off may be varied according to the length of the night. Starting and dimming the lamp at a zero voltage crossing of the line current can reduce stress on luminaire and control system components and reduce maintenance.
Owner:BLAKE FREDERICK H
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com