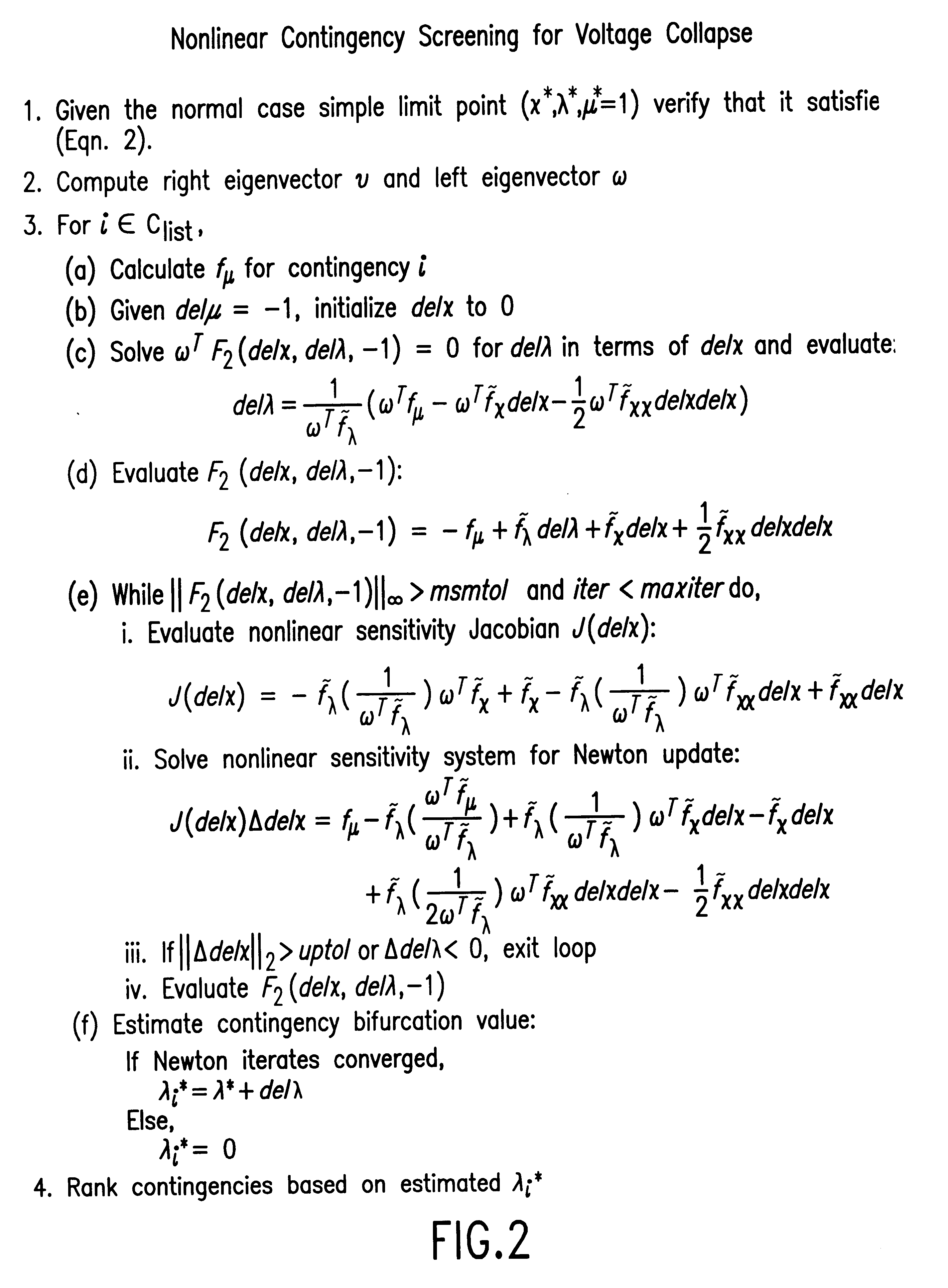Patents
Literature
918results about "Emergency protection data processing means" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
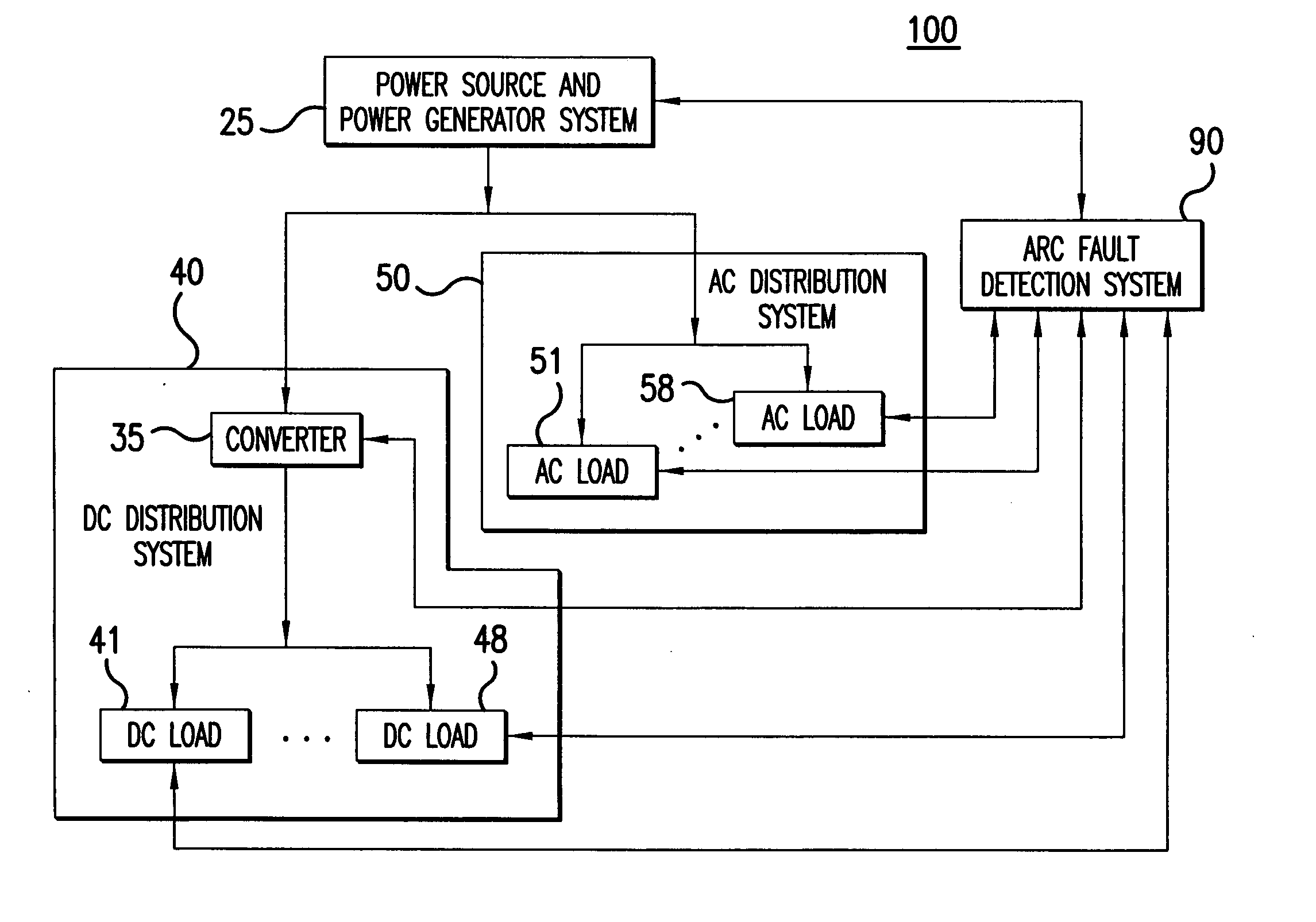
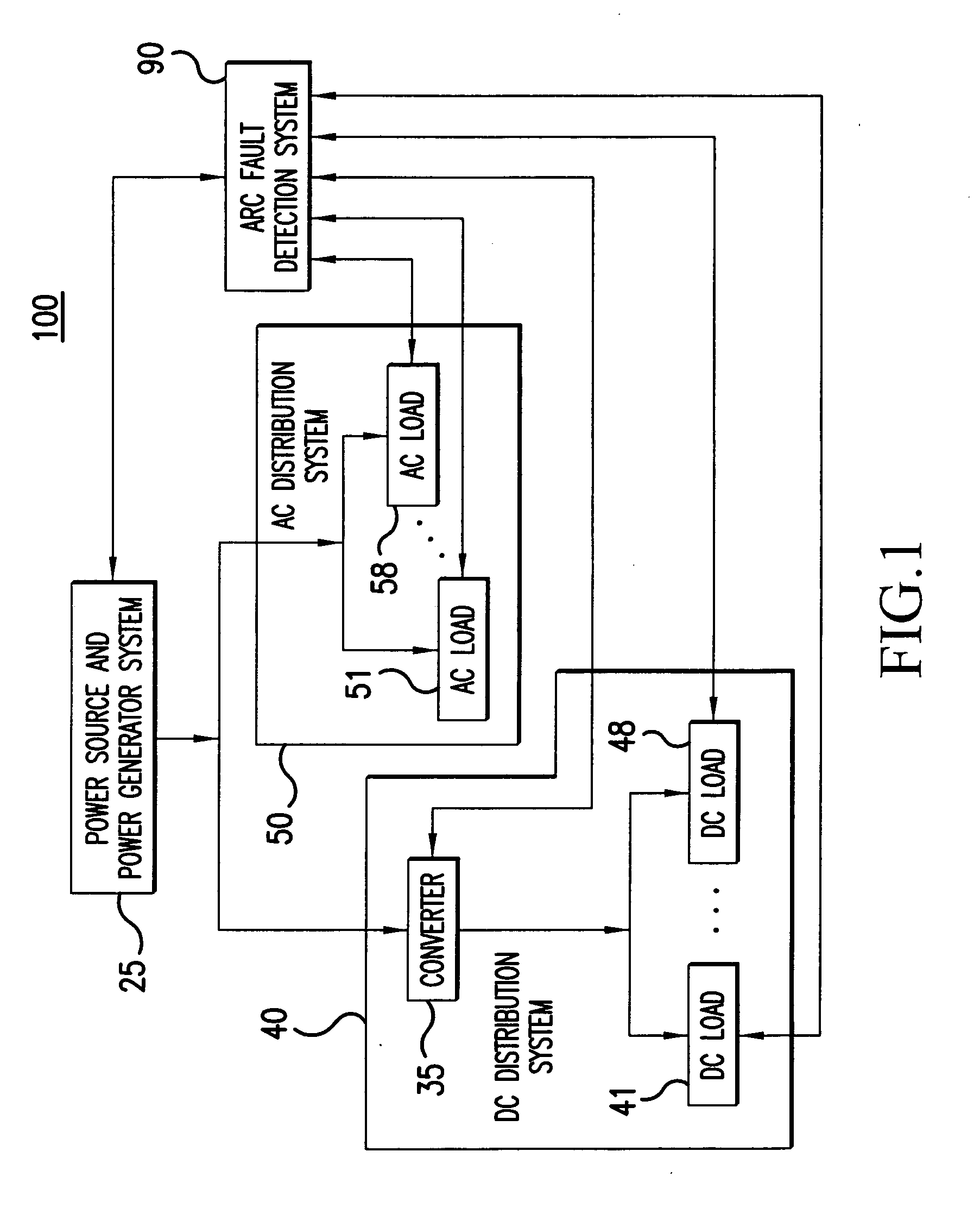
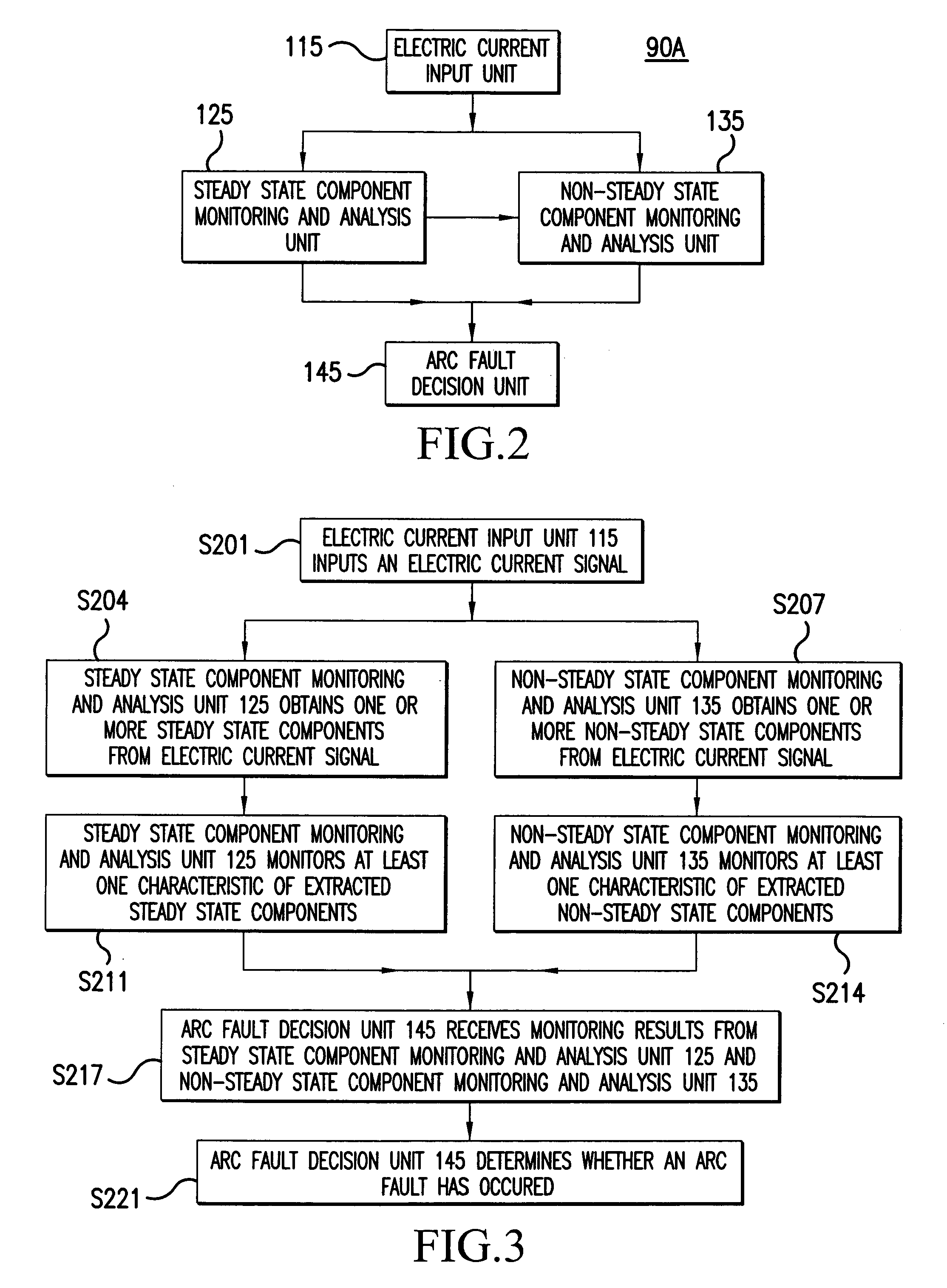
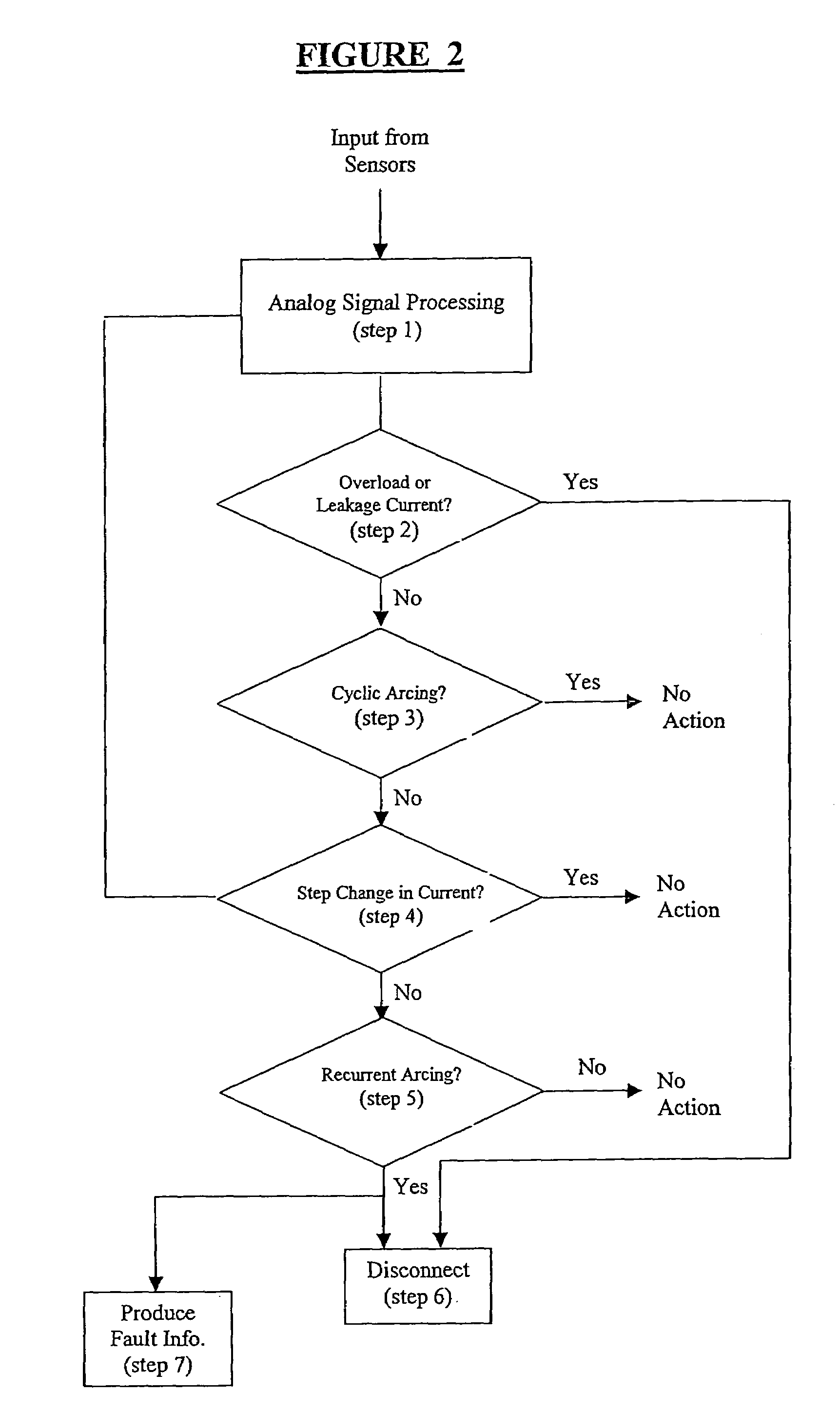
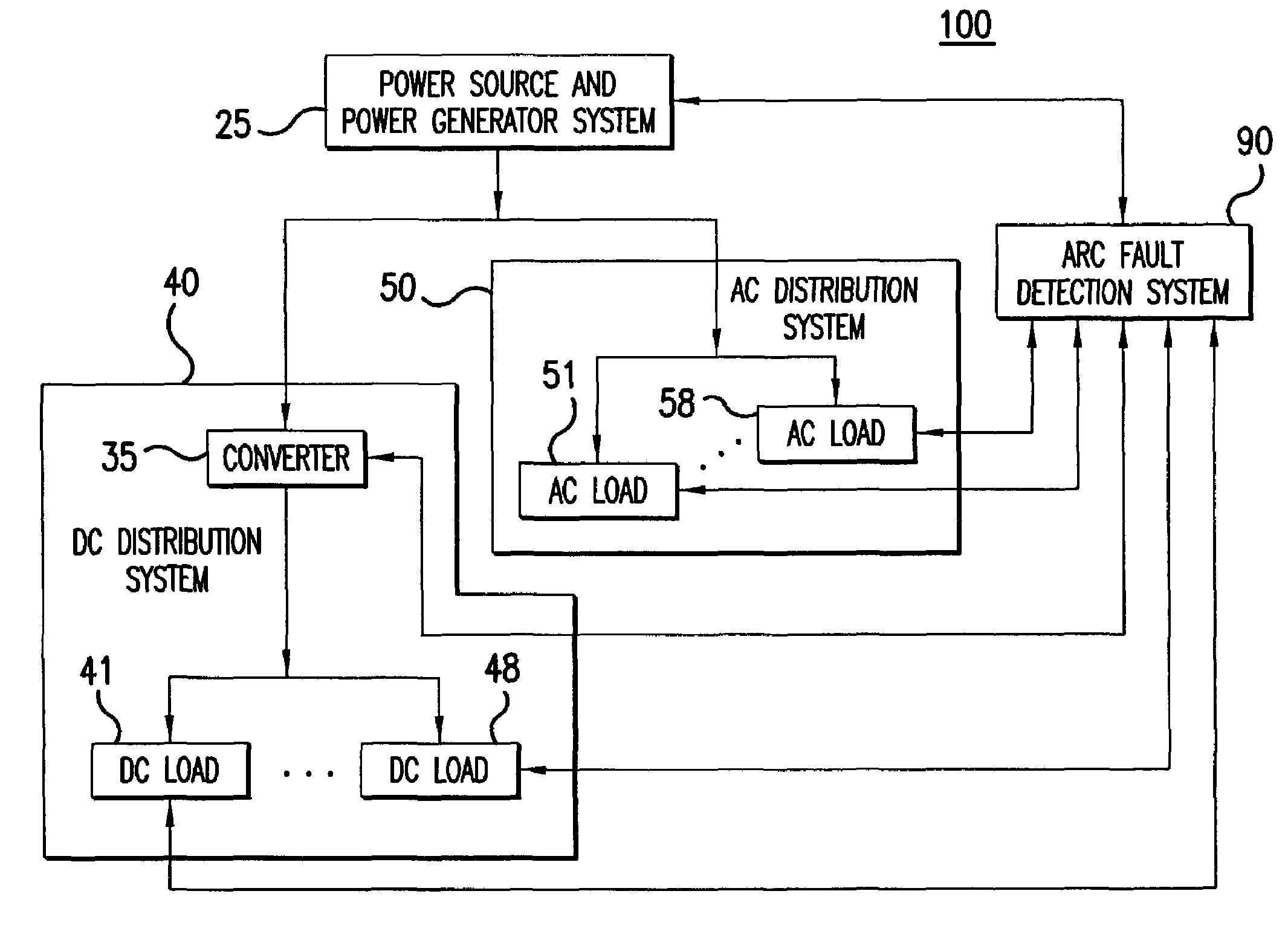
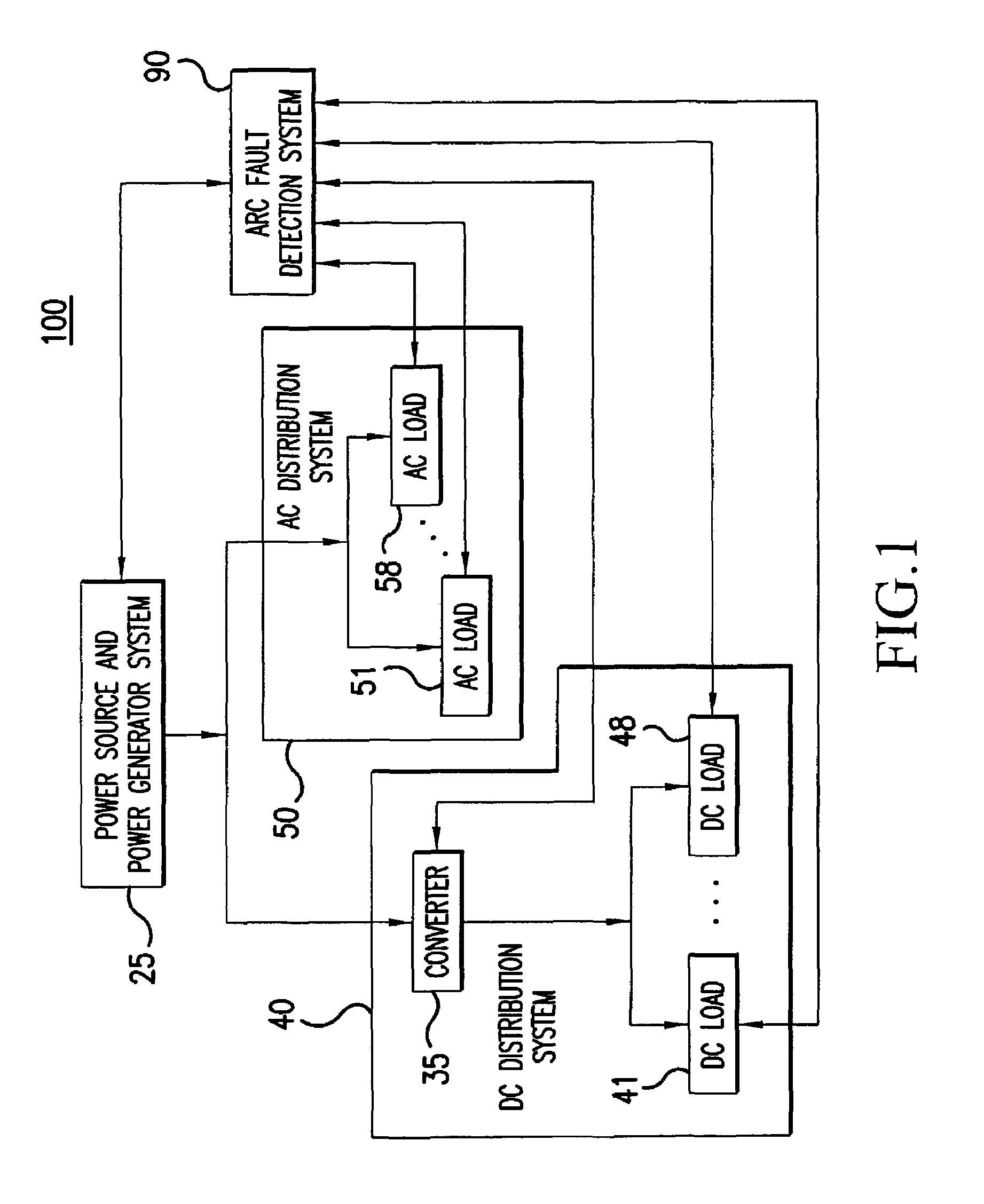
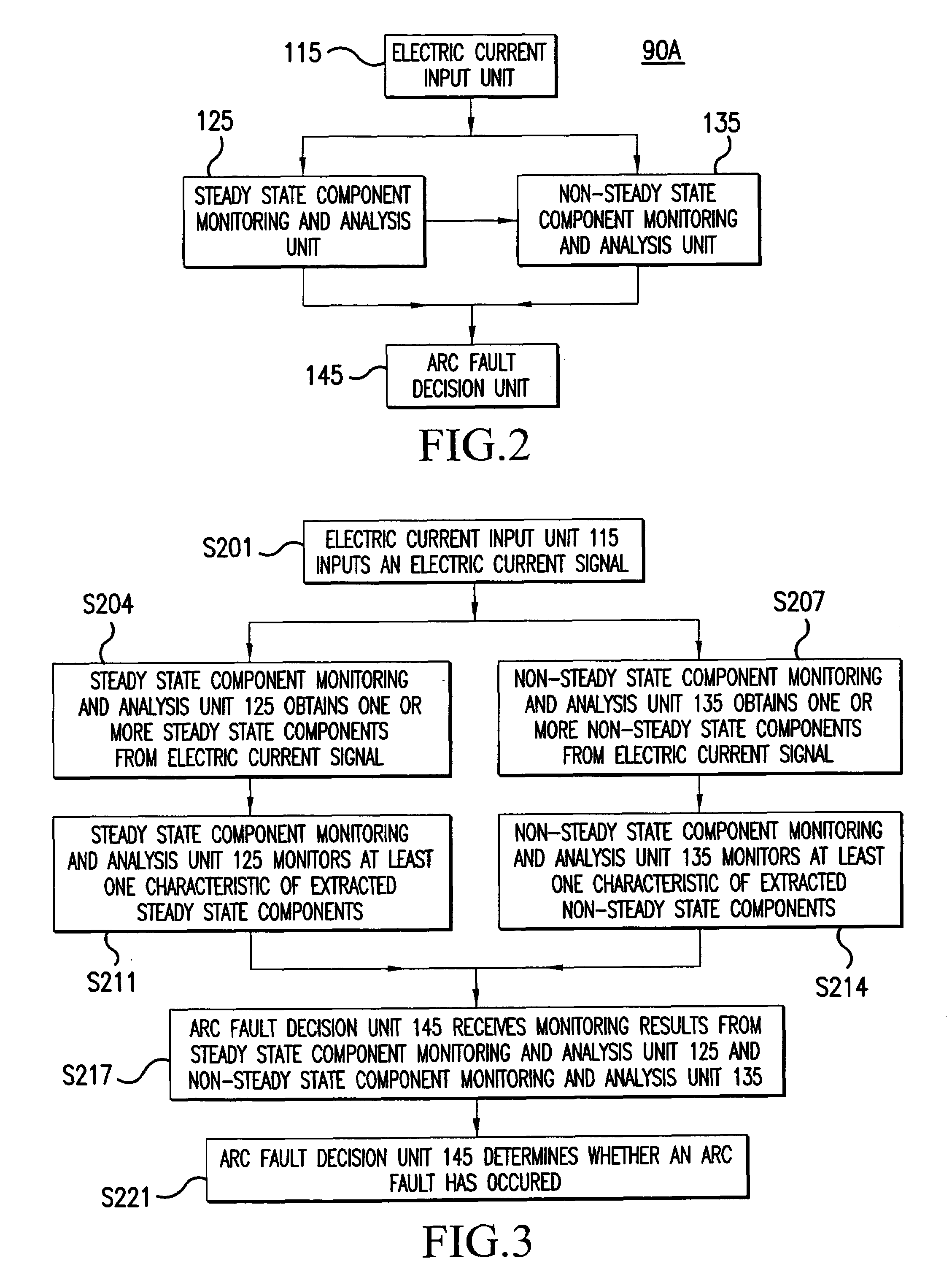
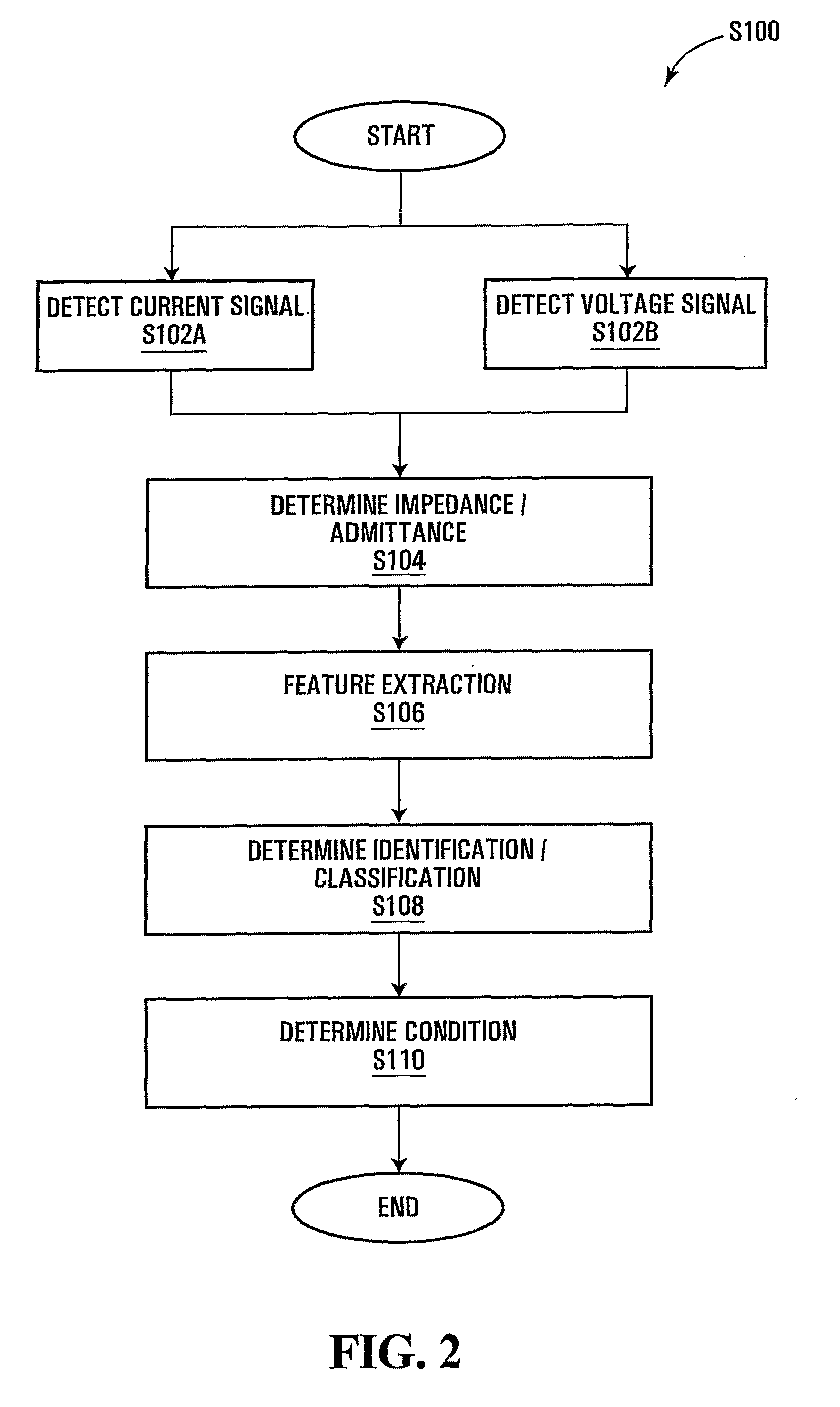
Method and apparatus for generalized arc fault detection
ActiveUS20060203401A1Electric switchesTesting electric installations on transportReliability engineeringAc current
A method and an apparatus detect series and / or parallel arc faults in AC and DC systems. The method according to one embodiment inputs an AC current signal; extracts a fundamental component of the AC current signal and monitoring an amplitude variation profile for the fundamental component, thereby generating a first arc fault detection measure; detects non-stationary changes in the AC current signal applying at least one measure of order higher than one, thereby generating a second arc fault detection measure; and determines whether an arc fault exists based on the first arc fault detection measure and the second arc fault detection measure.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC +1
Multifunctional Residential Circuit Breaker
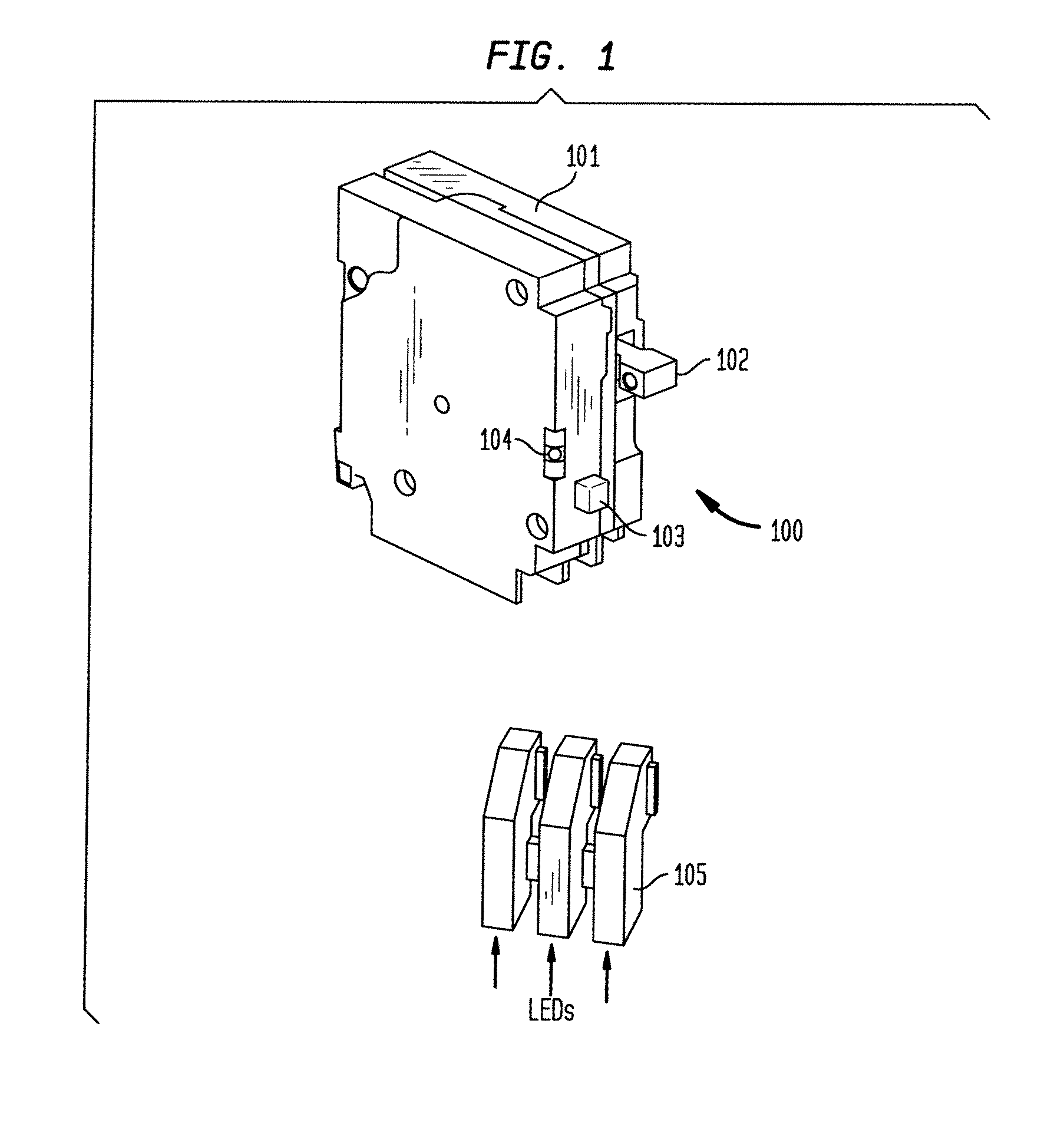
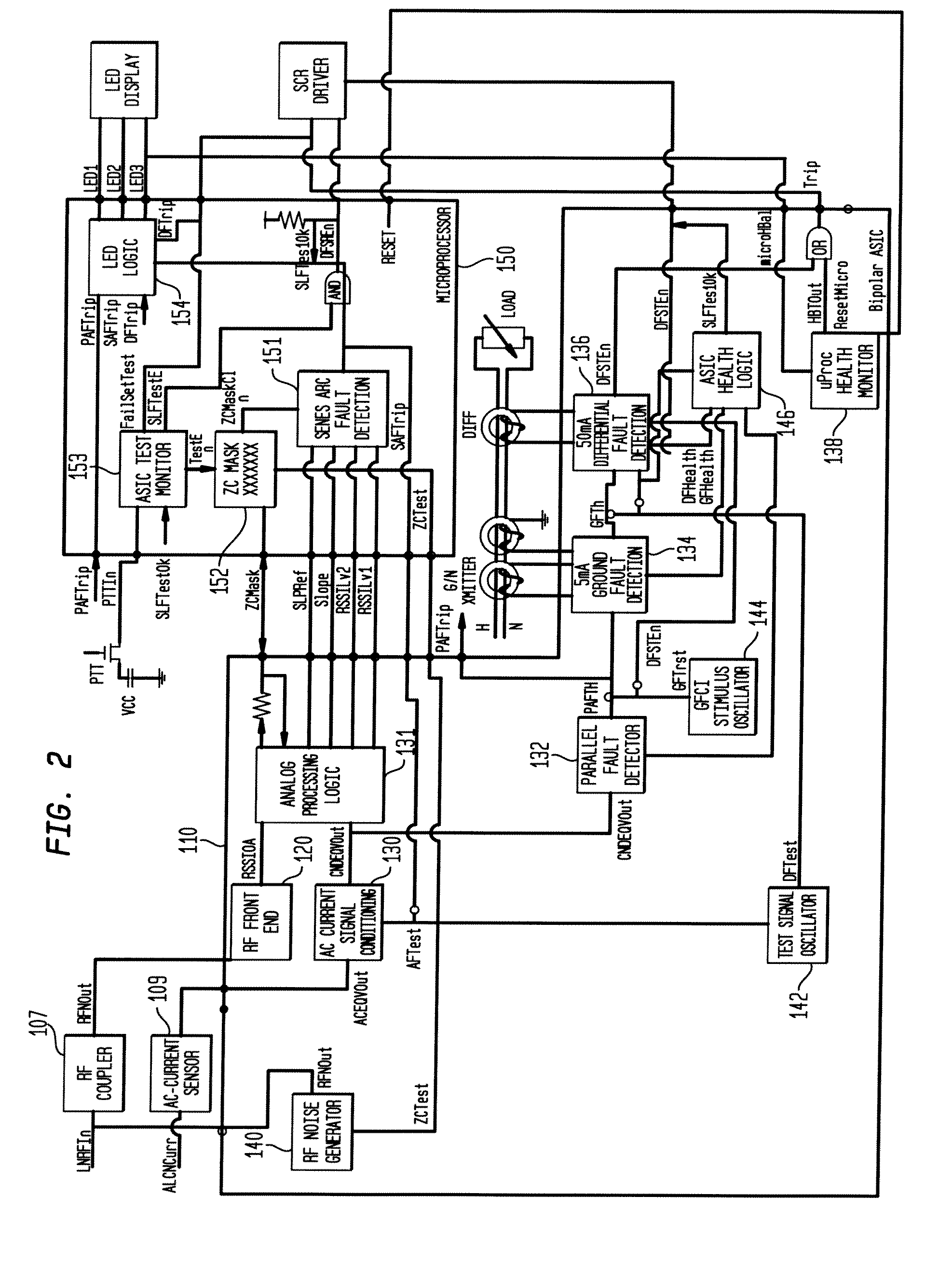
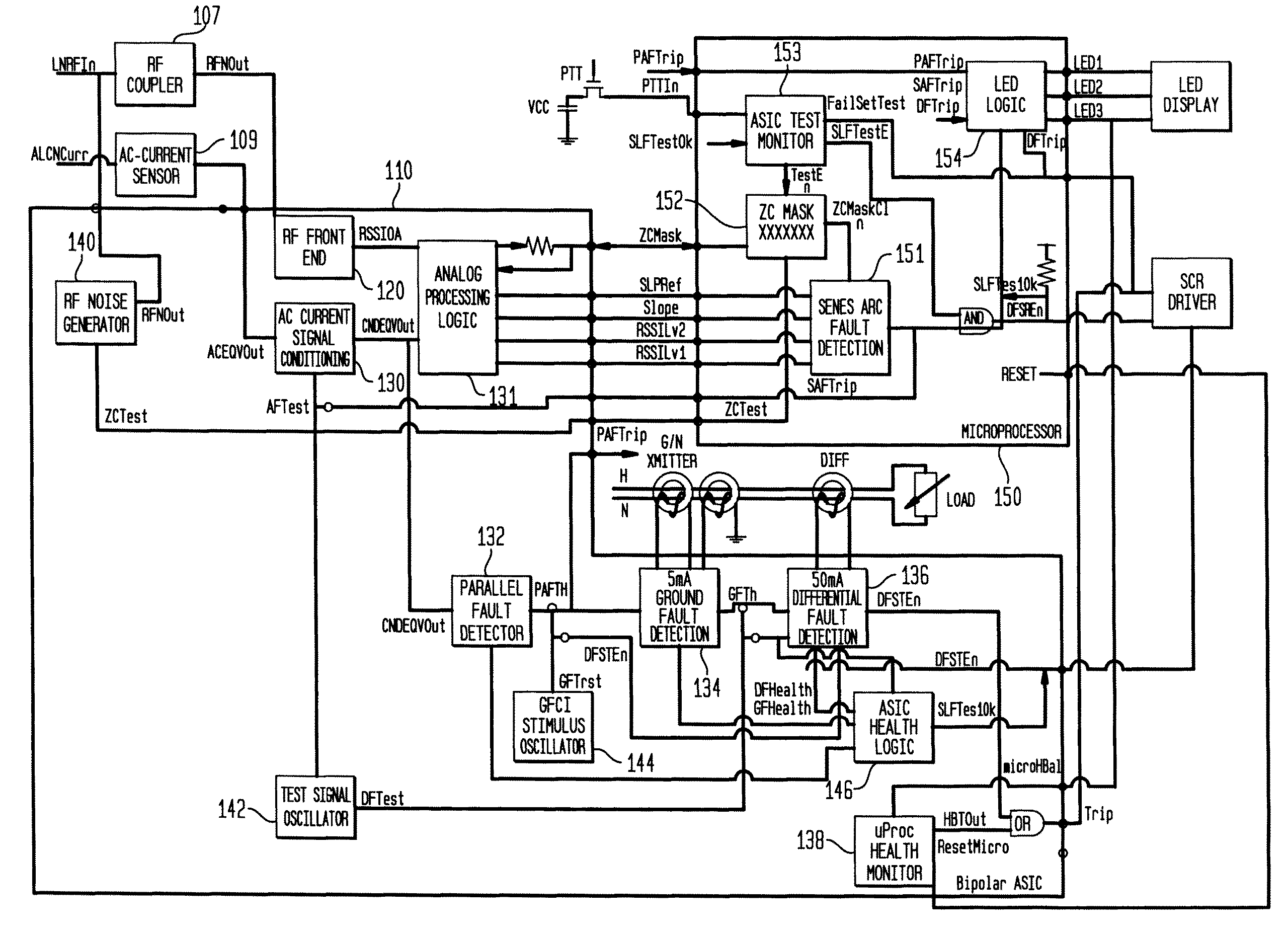
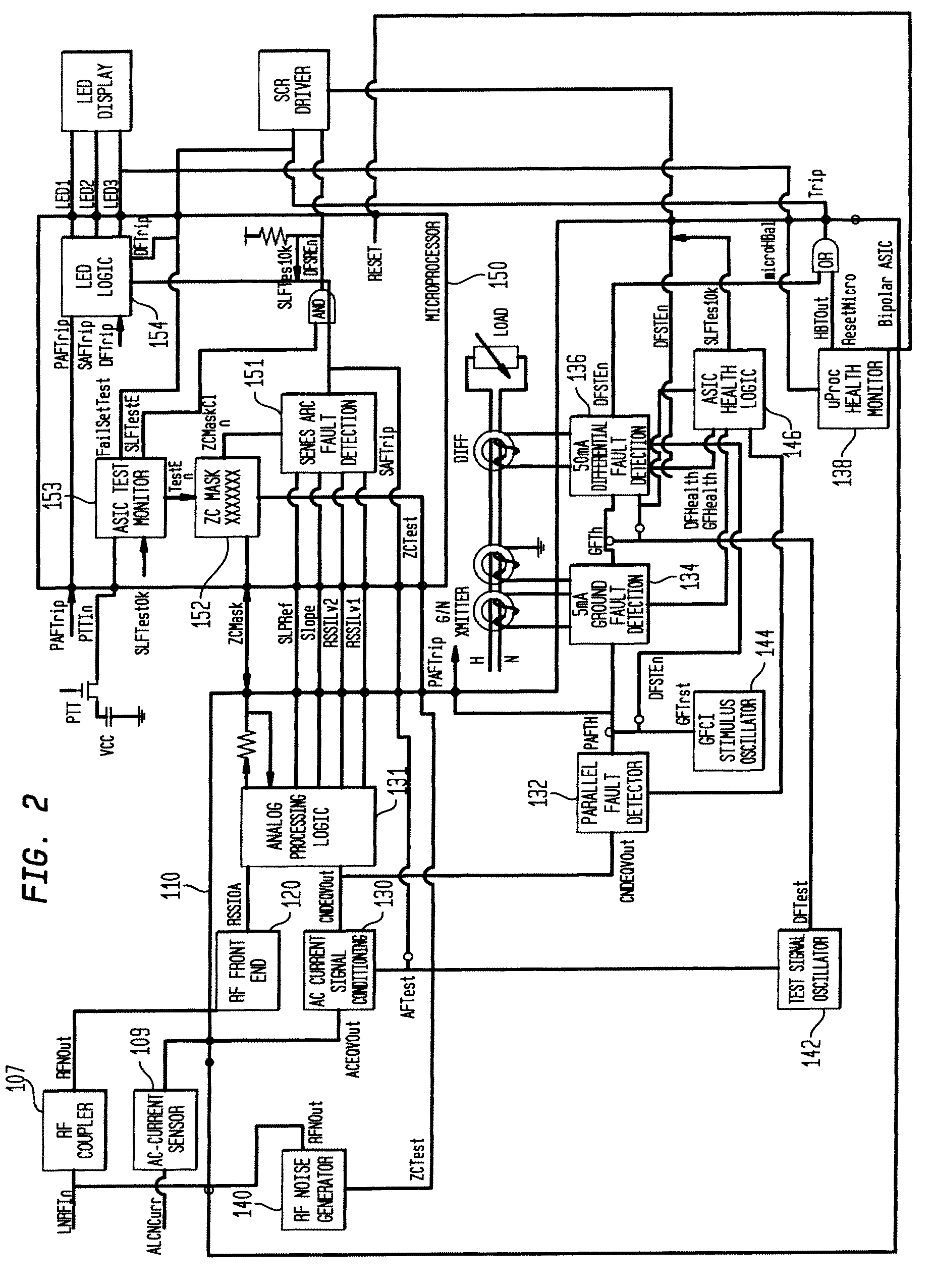
ActiveUS20090198459A1Quickly and effectively discriminateReduce impactElectrical testingEmergency protection data processing meansCurrent sensorEngineering
An electrical fault detection device for use in a branch of a power circuit that utilizes signals from an AC line current sensor coupled to an electrical distribution line having a primary and neutral lines, a line high-frequency sensor coupled to the electrical distribution line, a differential current sensor coupled to the primary and neutral lines, and a ground fault current sensor coupled to the primary and neutral lines. A signal conditioner receives the signals outputted by AC current line current sensor, the line high frequency sensor, the differential current sensor and the ground fault current sensor and generates a signal indicative of the load current associated with a branch of the power circuit. Output of the signal conditioner is sampled and processed by a processing resource. The processing resource has stored therein data representing a plurality of time-versus-current curves that define a plurality of regions in which tripping may or may not occur. One region has time data and current data that define a time-duration for a particular current magnitude for which no tripping will occur. Another region has time data and current data that define a time-duration of a particular current magnitude for which tripping will occur. Processing resource processes sampled signal to determine the region to which the processed time data and current data correspond, and generates a signal to initiate tripping if the sampled signal yields a time duration for a particular current magnitude that corresponds to a region for which tripping must occur.
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
System and method for control of power distribution
ActiveUS20090112375A1Level controlEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionModularityElectric distribution network
A system for controlling a multi-feed power distribution network is described herein. The network includes a first network sector that includes a first plurality of devices connected to a first power source and a second network sector that includes a second plurality of devices connected to a second power source. The system includes a first controller and a second controller. The first controller is configured to control operation of the first network sector and exchange data with the second controller. The second controller is configured to control operation of the second network sector and exchange data with the first controller. The system is modular and it can be expanded to include additional controllers as necessary. Methods and a computer program product for controlling a multi-feed power distribution network are also described.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for control of an electric power distribution system in response to circuit abnormalities
InactiveUS20050251296A1Efficiently and flexibly respondImprove reconfigurabilityMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlReconfigurabilityDistribution power system
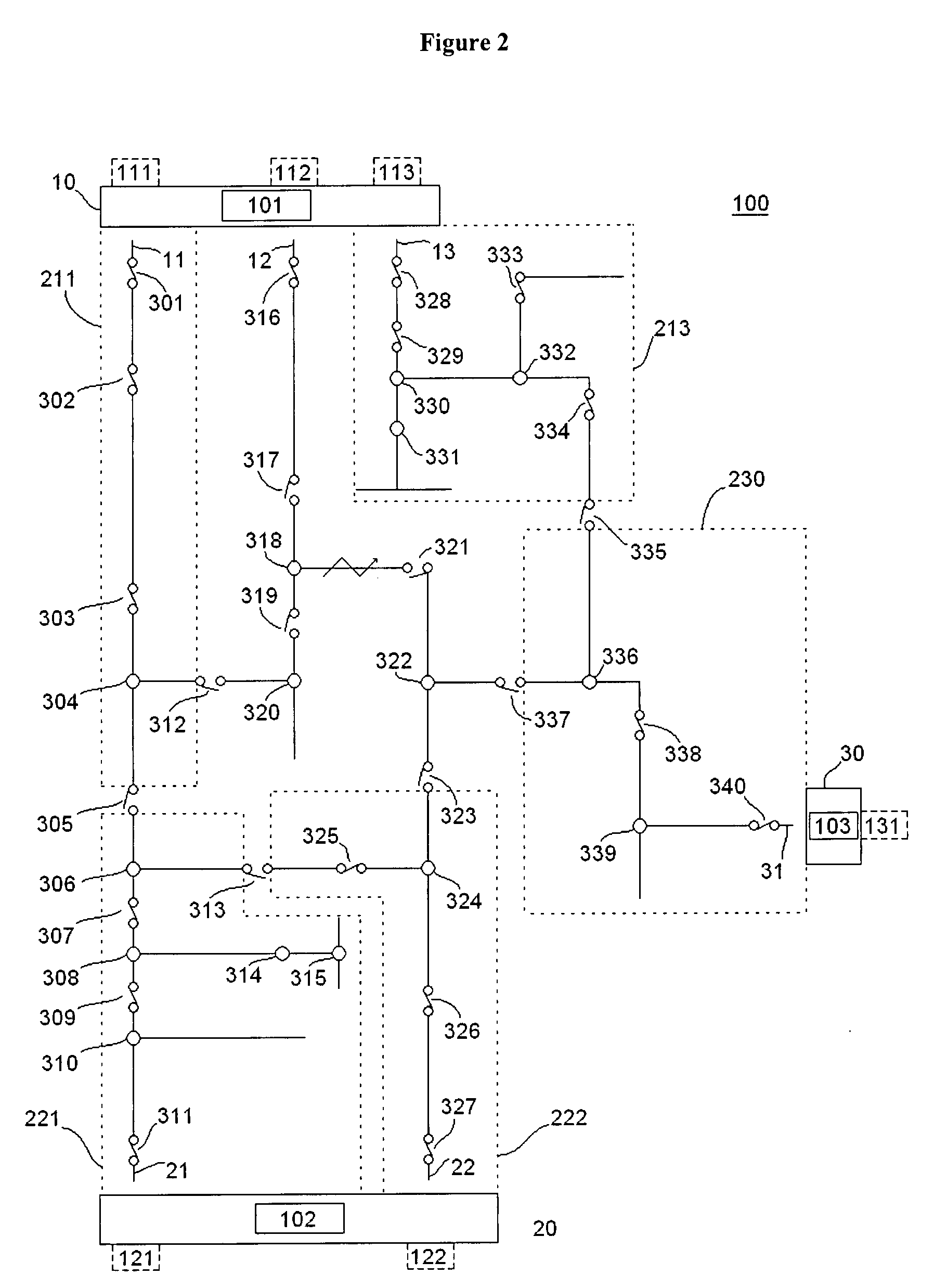
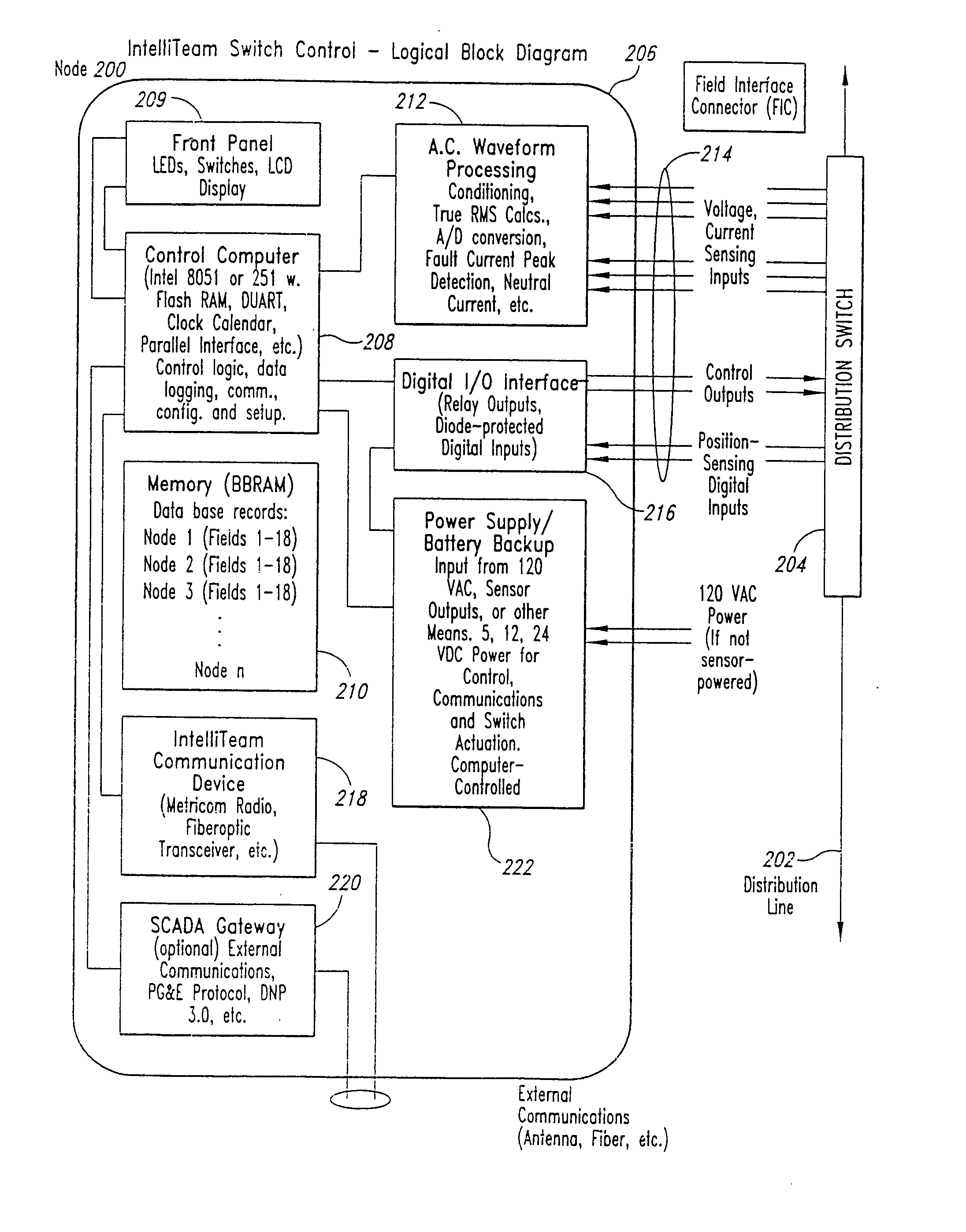
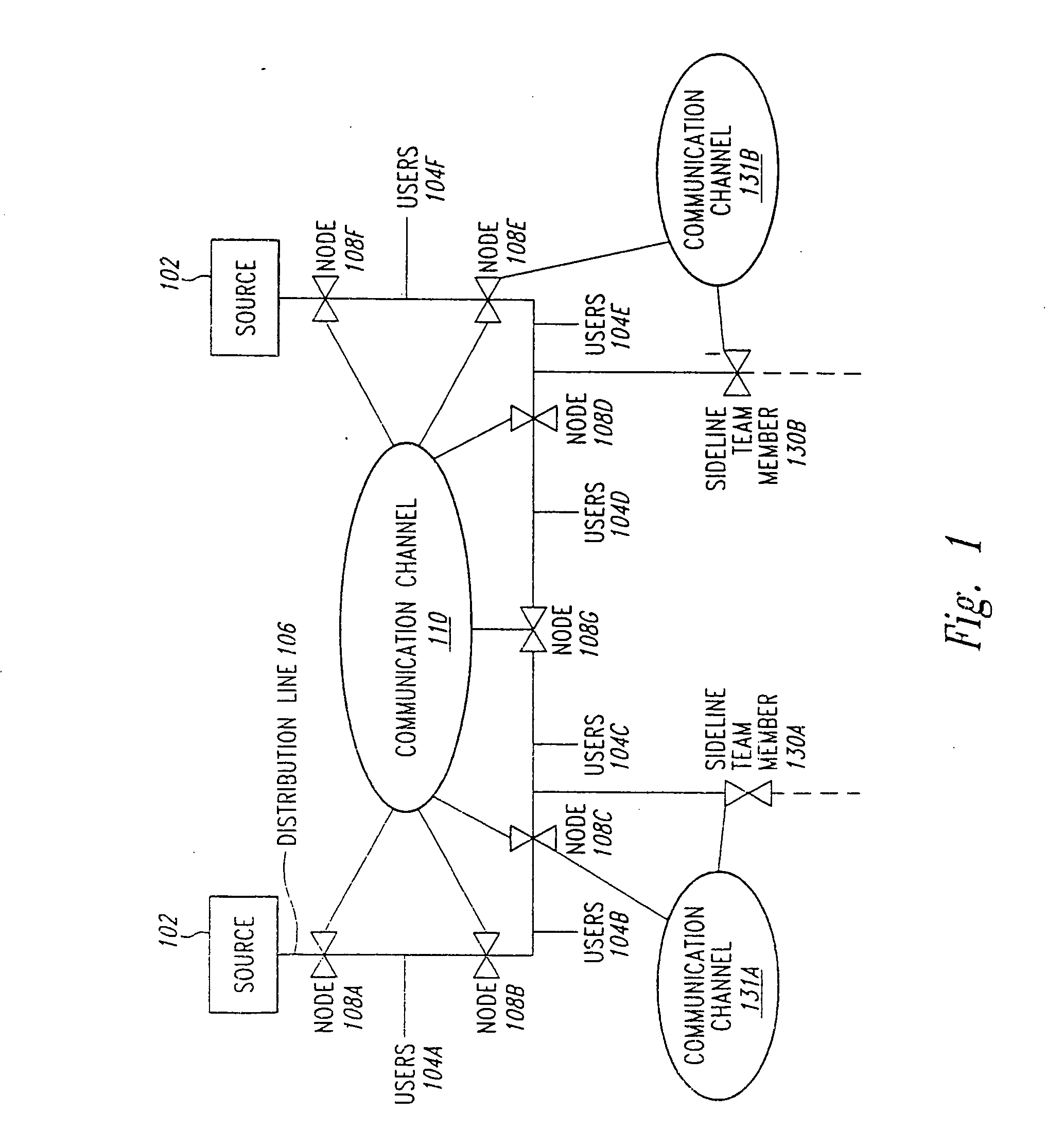
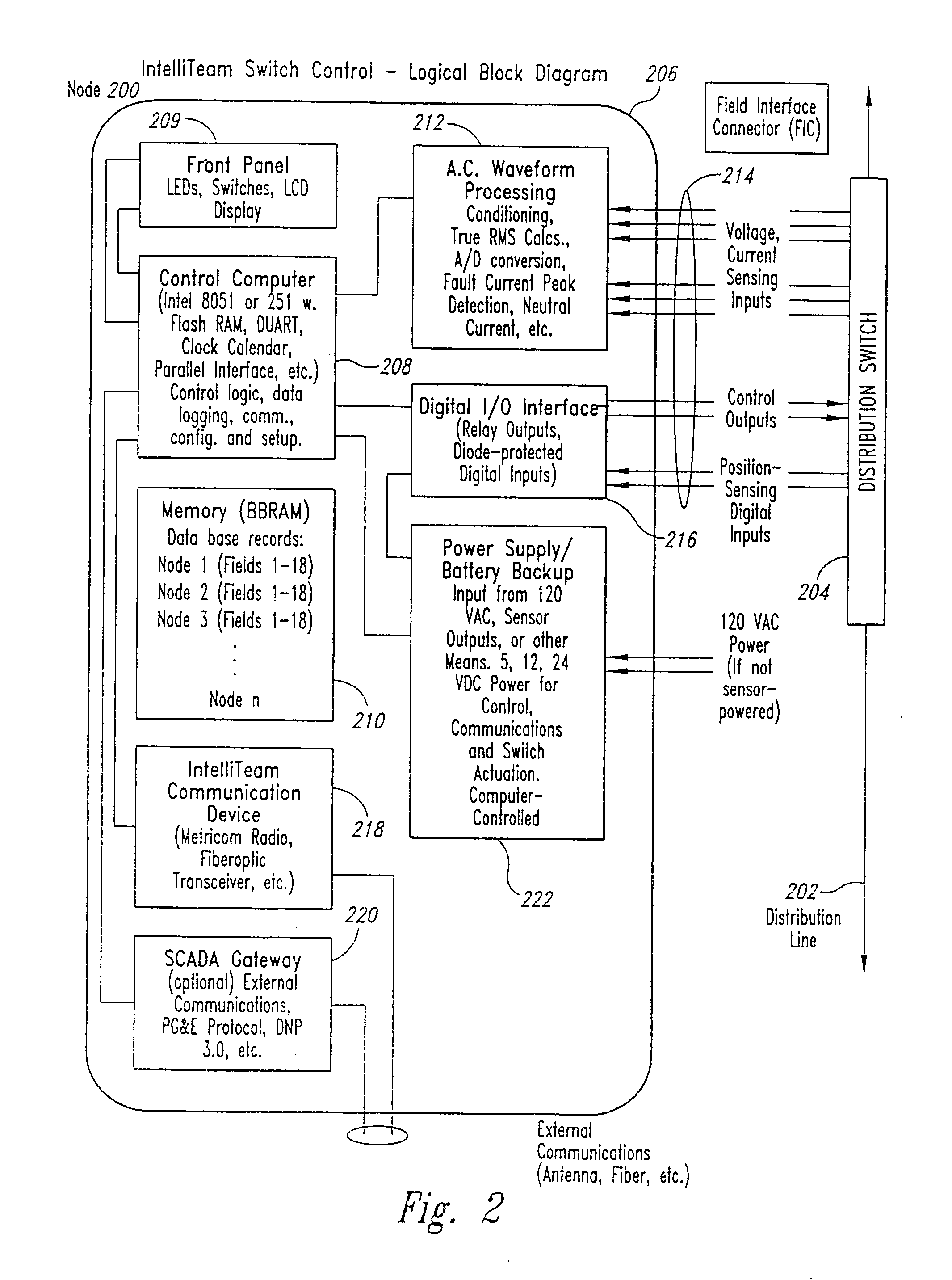
A methodology and related system apparatus is provided for using and coordinating the use of information conveyed over communications to most efficiently and flexibly respond to abnormalities to reconfigure and restore service to end customers in commodity distribution systems in a manner to enhance the reconfigurability of the distribution system, e.g. circuit reconfiguration in an electrical power distribution system. Methodology is also provided to appropriately allocate system resources of the distribution system when so desired, e.g. to prevent the potential overloading of electrical power sources. In one illustrative arrangement, the methodology is characterized by resources at each node and communications of source allocation data or messages to other nodes to request and establish an appropriate allocation of system resources. In a preferred arrangement and especially useful for larger distribution systems, “teams” of nodes are defined in the distribution system having associated switching controls with the various teams communicating amongst each other to “negotiate” or work out the most efficient and expeditious reconfiguration of the system in response to fault conditions and other circuit abnormalities.
Owner:TRACY NELSON WILLIAM CHRISTIAN +3
Method and apparatus for control of an electric power distribution system in response to circuit abnormalities
InactiveUS20070005193A1Improve reconfigurabilityMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlReconfigurabilityDistribution power system
A methodology and related system apparatus is provided for using and coordinating the use of information conveyed over communications to most efficiently and flexibly respond to abnormalities to reconfigure and restore service to end customers in commodity distribution systems in a manner to enhance the reconfigurability of the distribution system, e.g. circuit reconfiguration in an electrical power distribution system. Methodology is also provided to appropriately allocate system resources of the distribution system when so desired, e.g. to prevent the potential overloading of electrical power sources. In one illustrative arrangement, the methodology is characterized by resources at each node and communications of source allocation data or messages to other nodes to request and establish an appropriate allocation of system resources. In a preferred arrangement and especially useful for larger distribution systems, “teams” of nodes are defined in the distribution system having associated switching controls with the various teams communicating amongst each other to “negotiate” or work out the most efficient and expeditious reconfiguration of the system in response to fault conditions and other circuit abnormalities.
Owner:S&C ELECTRIC
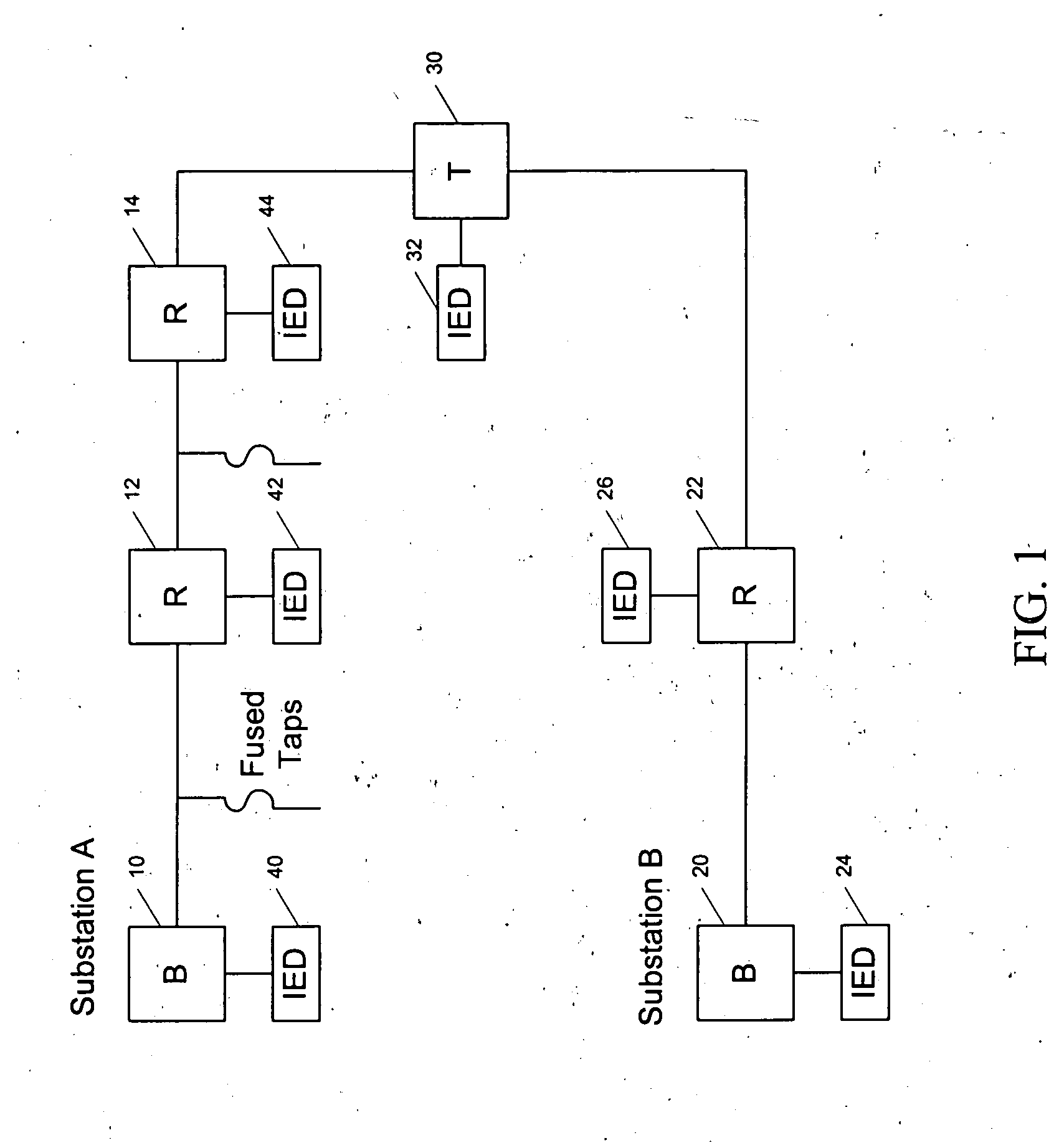
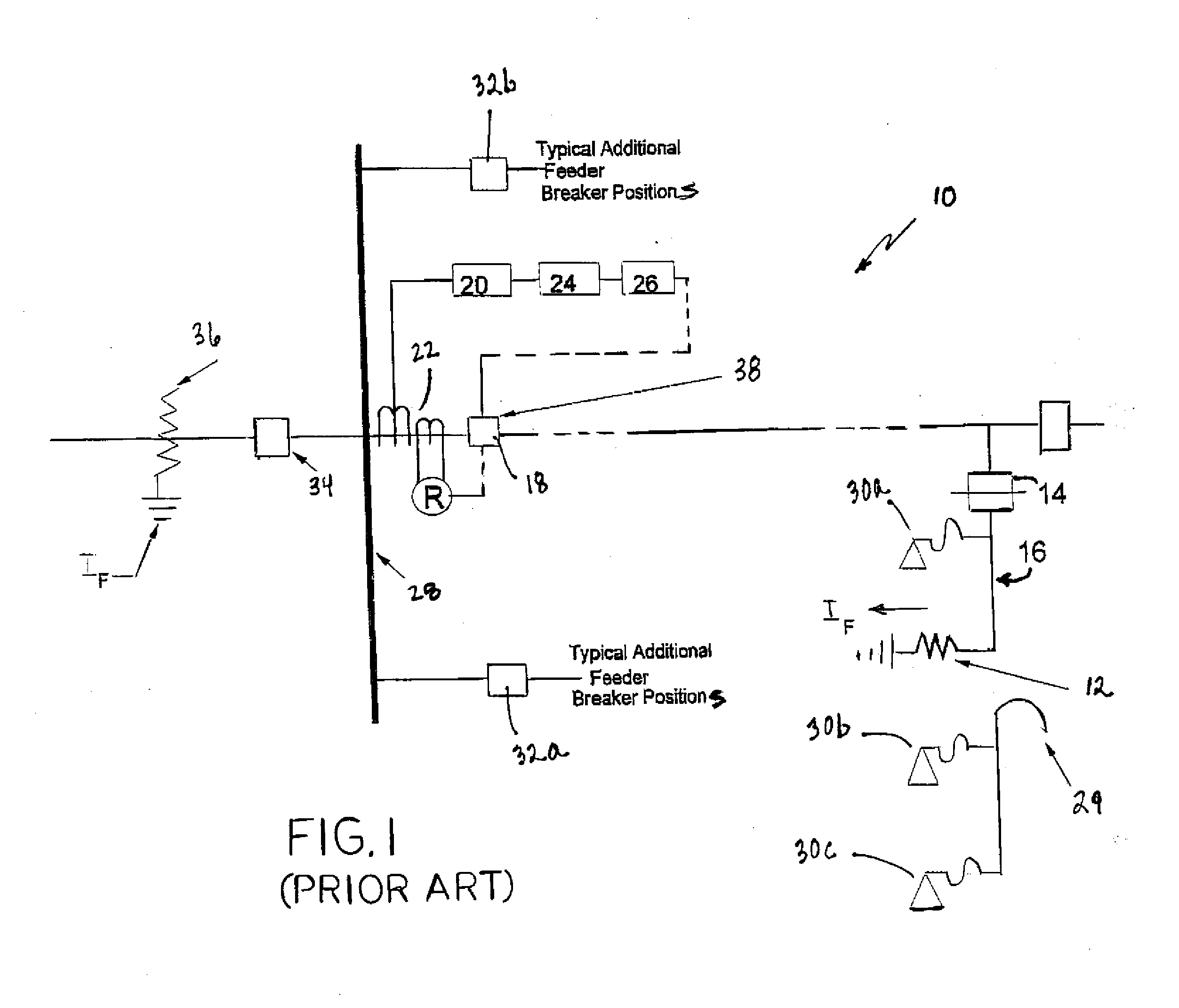
Method and system for programming and implementing automated fault isolation and restoration using sequential logic
ActiveUS20120265360A1Avoid excessive impactIncrease the number ofMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlCommunications systemDistribution power system
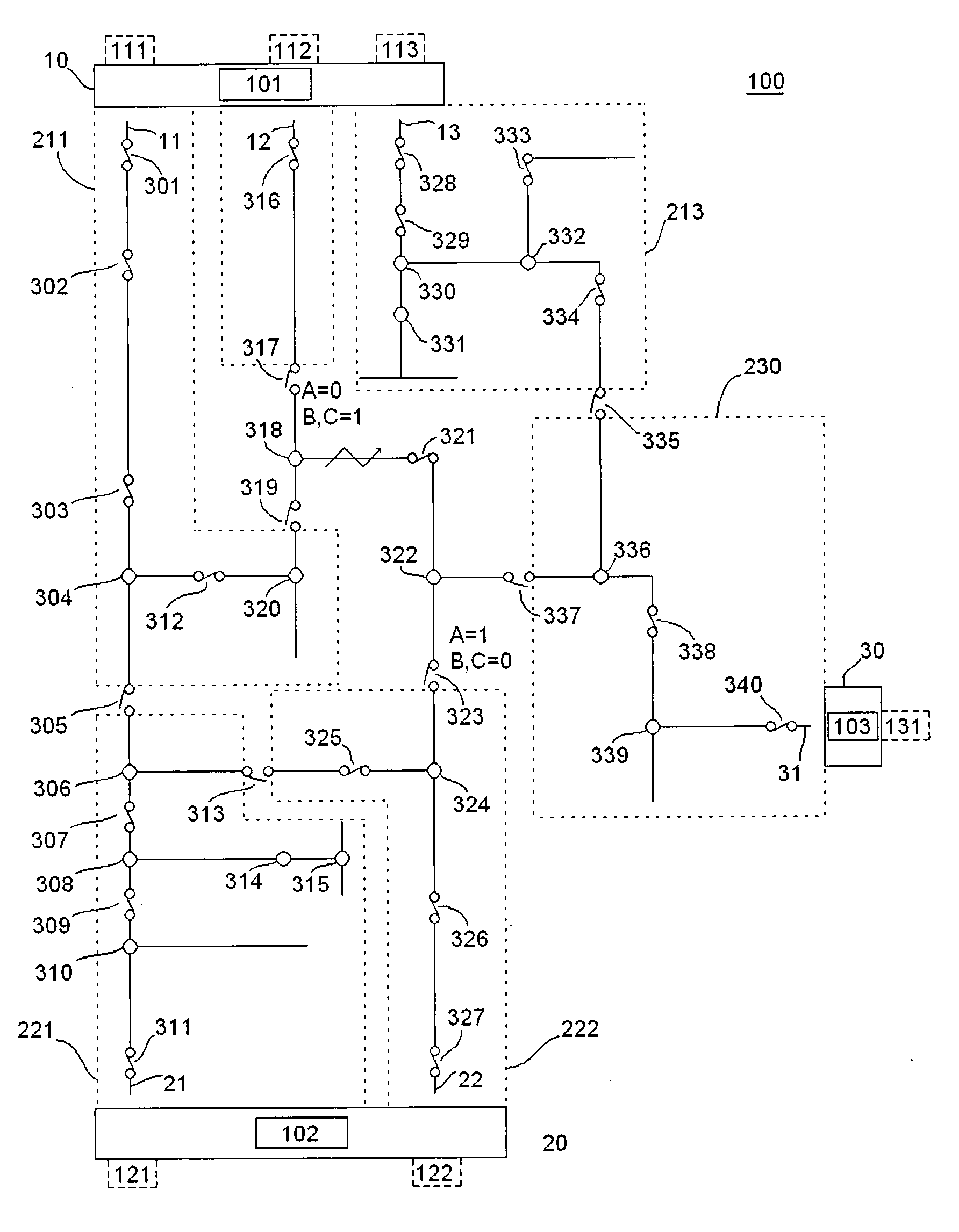
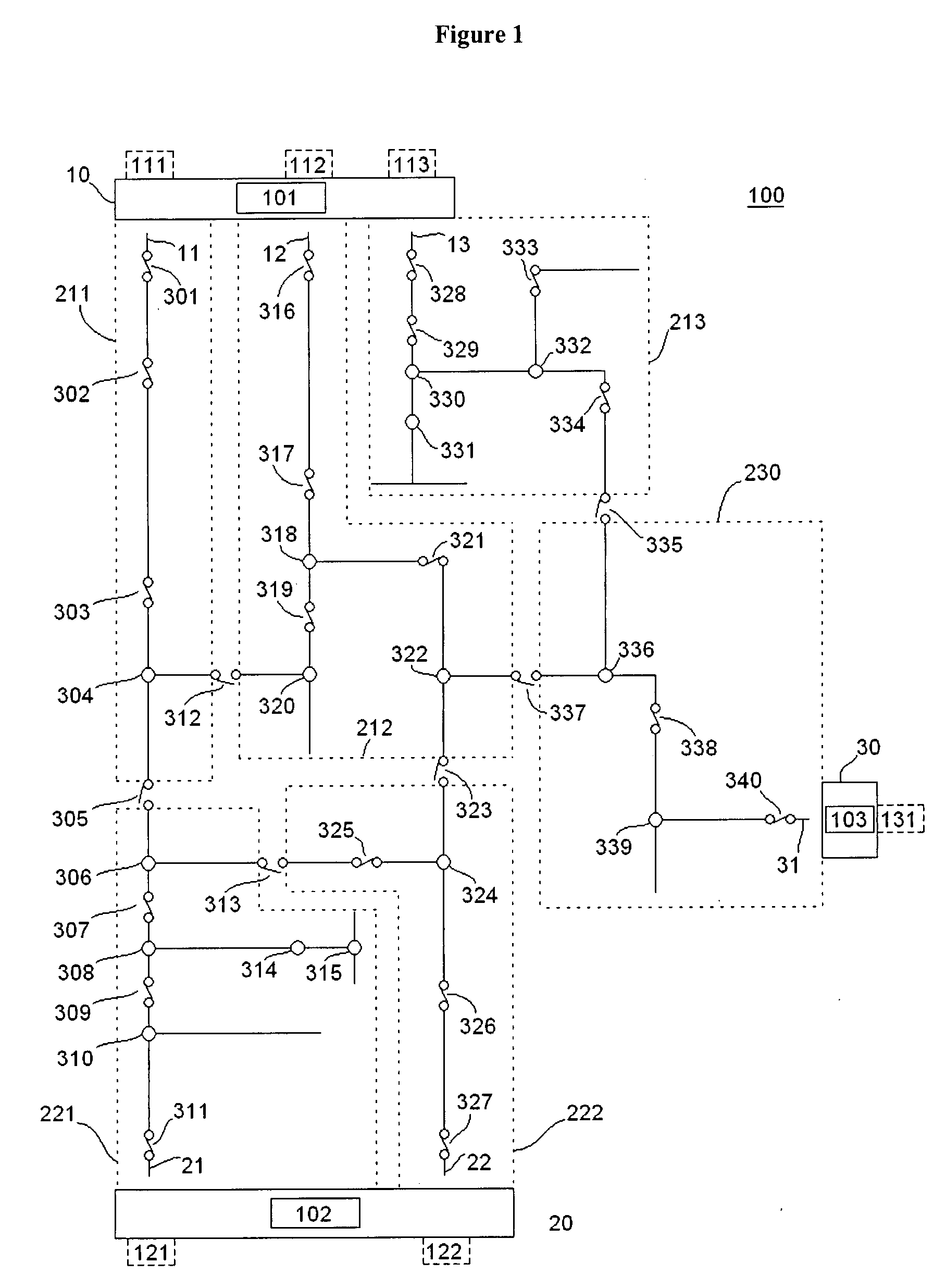
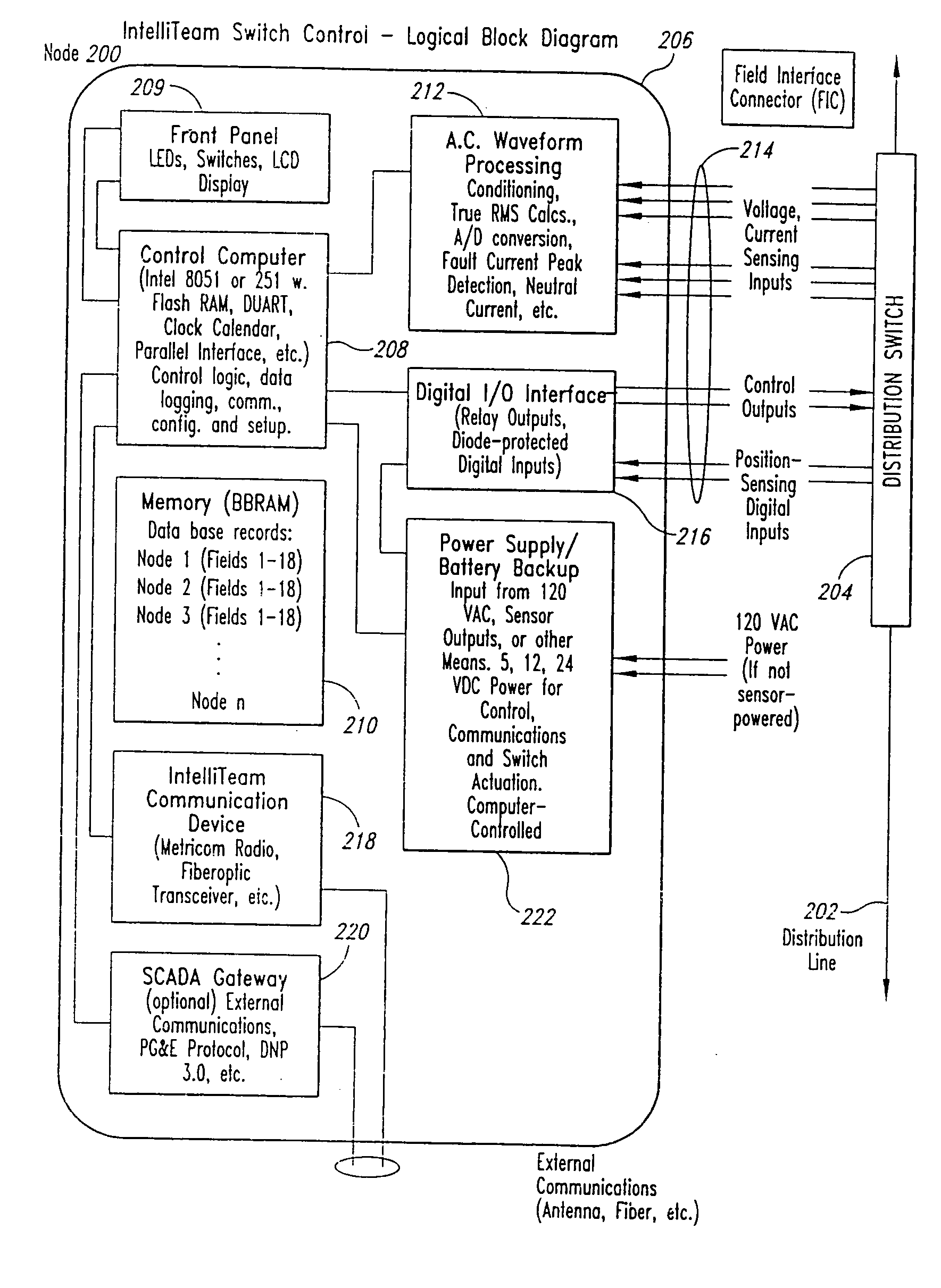
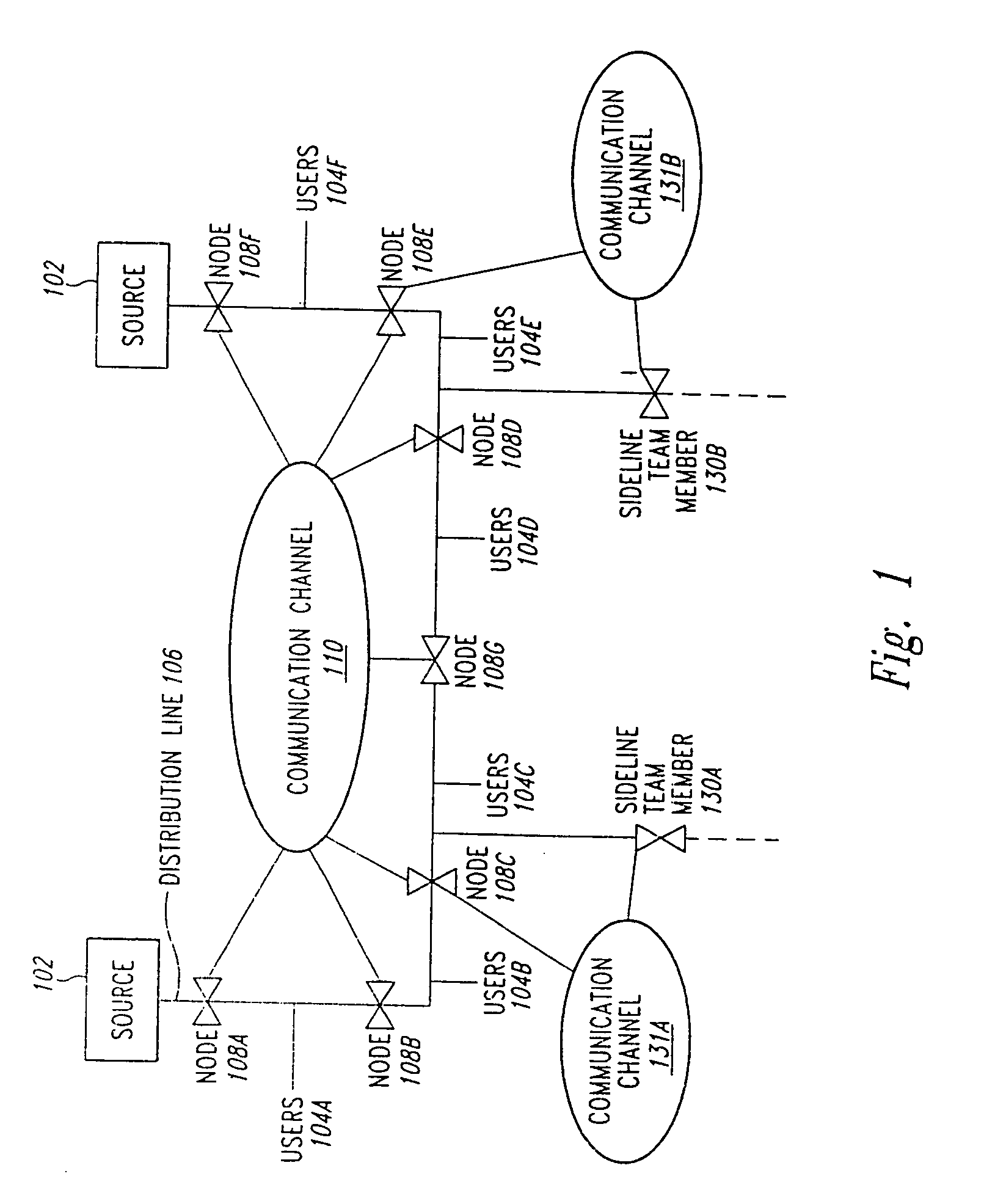
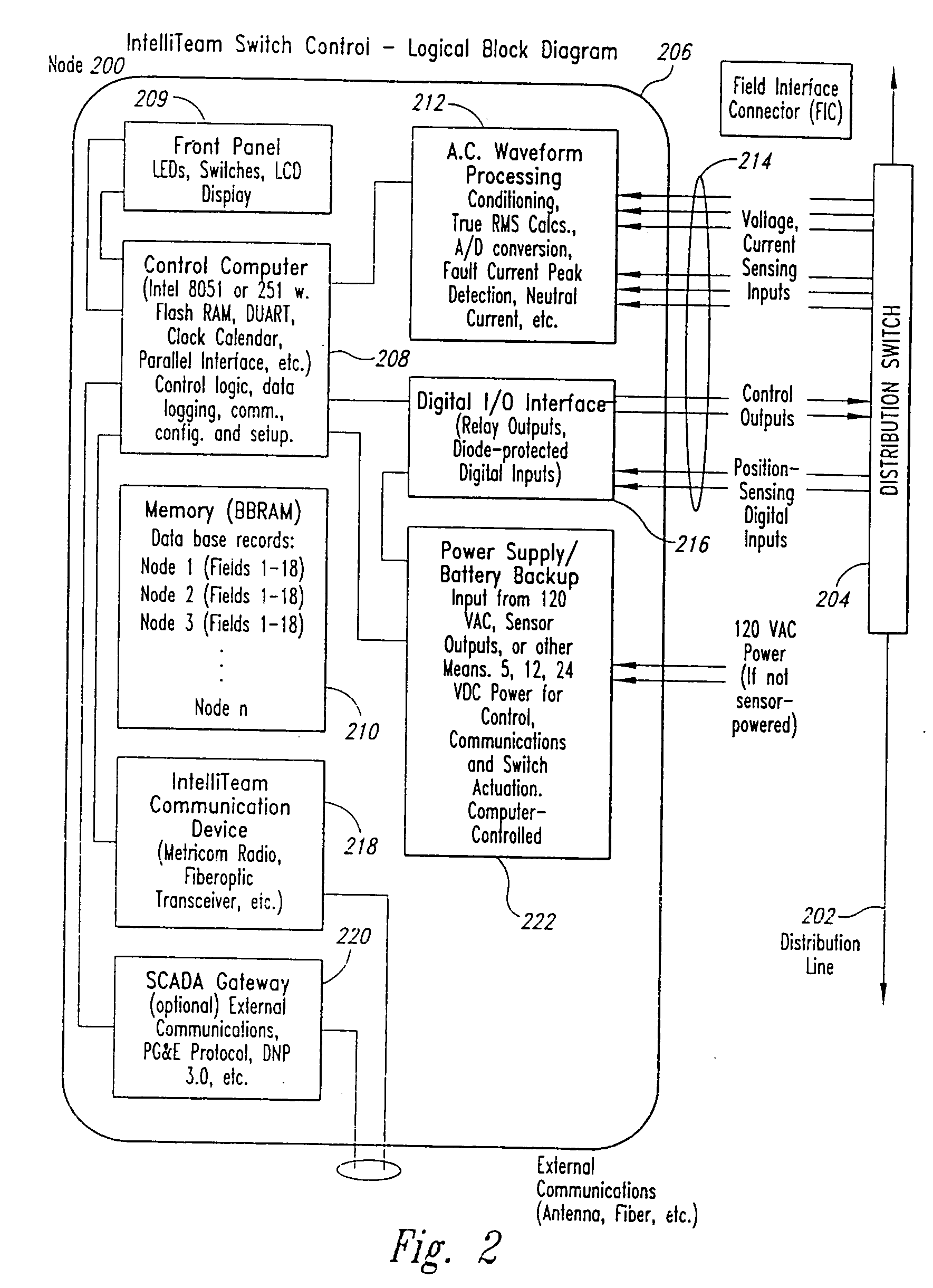
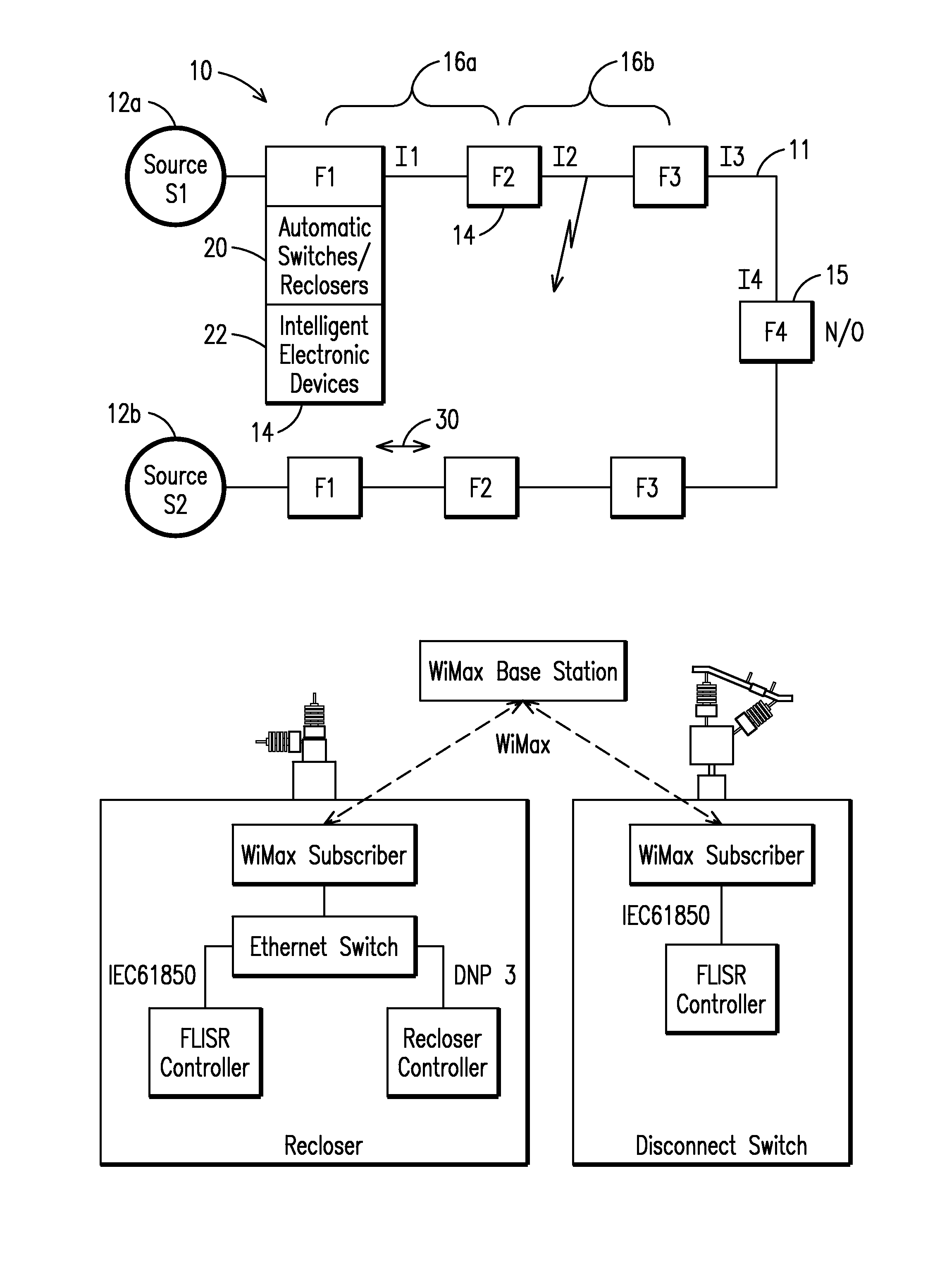
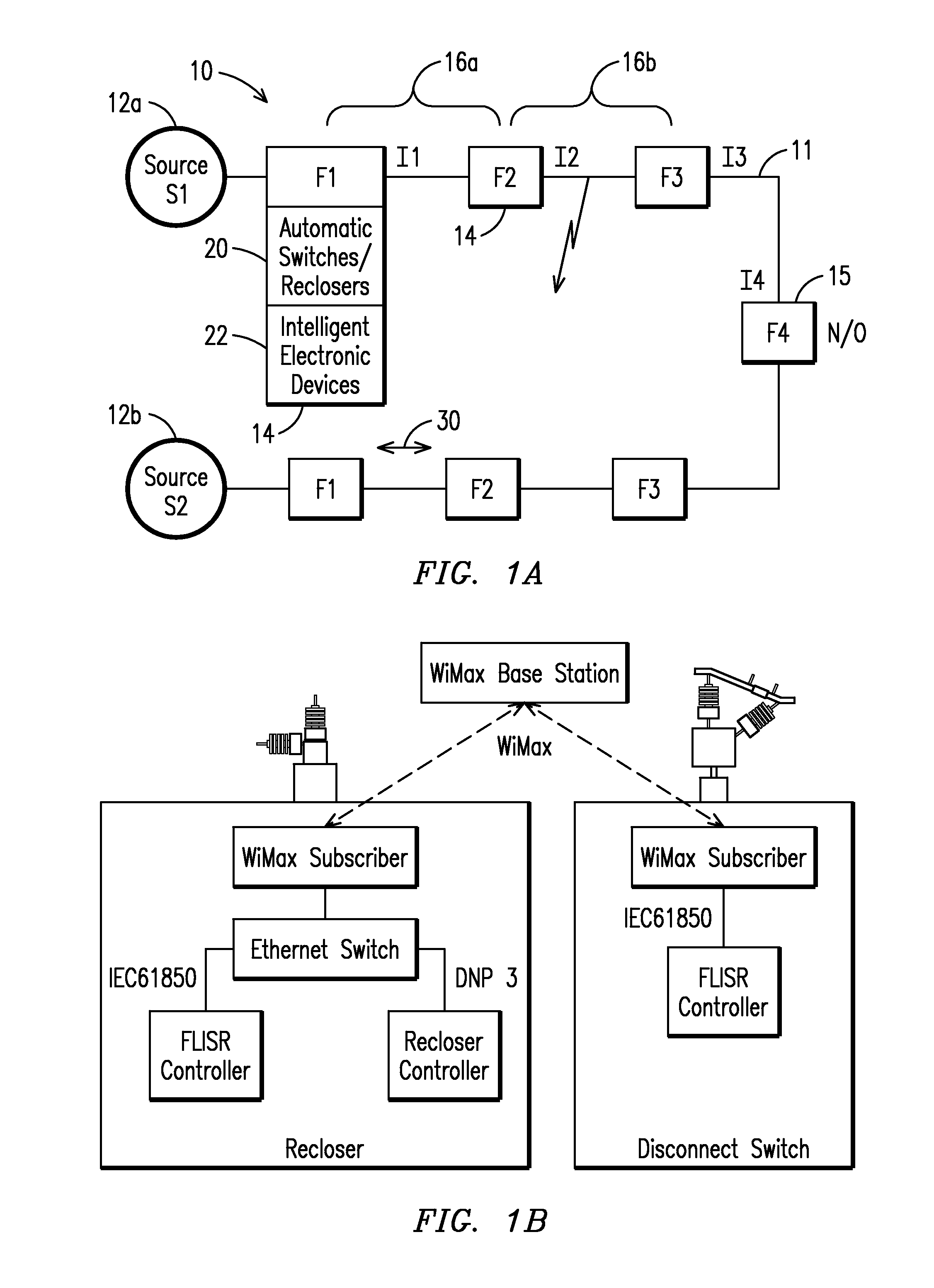
A method and system for programming and implementing automated fault isolation and restoration of high-speed fault detection of circuits in power distribution networks using sequential logic and peer-to-peer communication is provided. High-speed fault detection of circuits in power distribution networks uses protective relay devices (14) segmenting a distribution line (11) having Intelligent Electronic Devices (IED) (22) associated with switching devices (20) communicating peer-to-peer via a communication system (30) to provide fast and accurate fault location information in distribution systems with sequential logic.
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
Computerized electricity system having an arc fault detecting sub-system
InactiveUS7282924B1Neutralize effectMechanical power/torque controlTesting dielectric strengthElectric power systemCurrent sensor
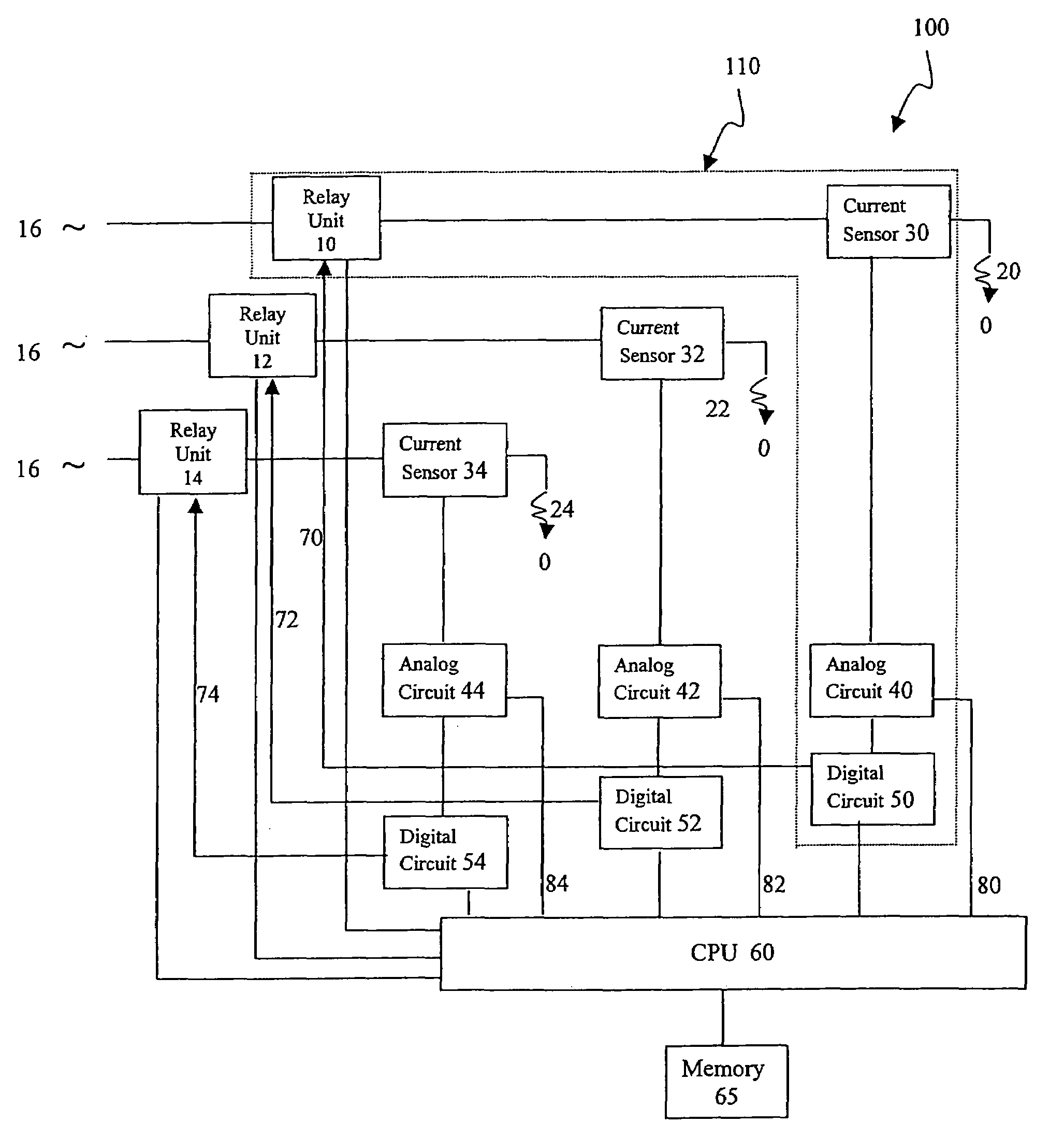
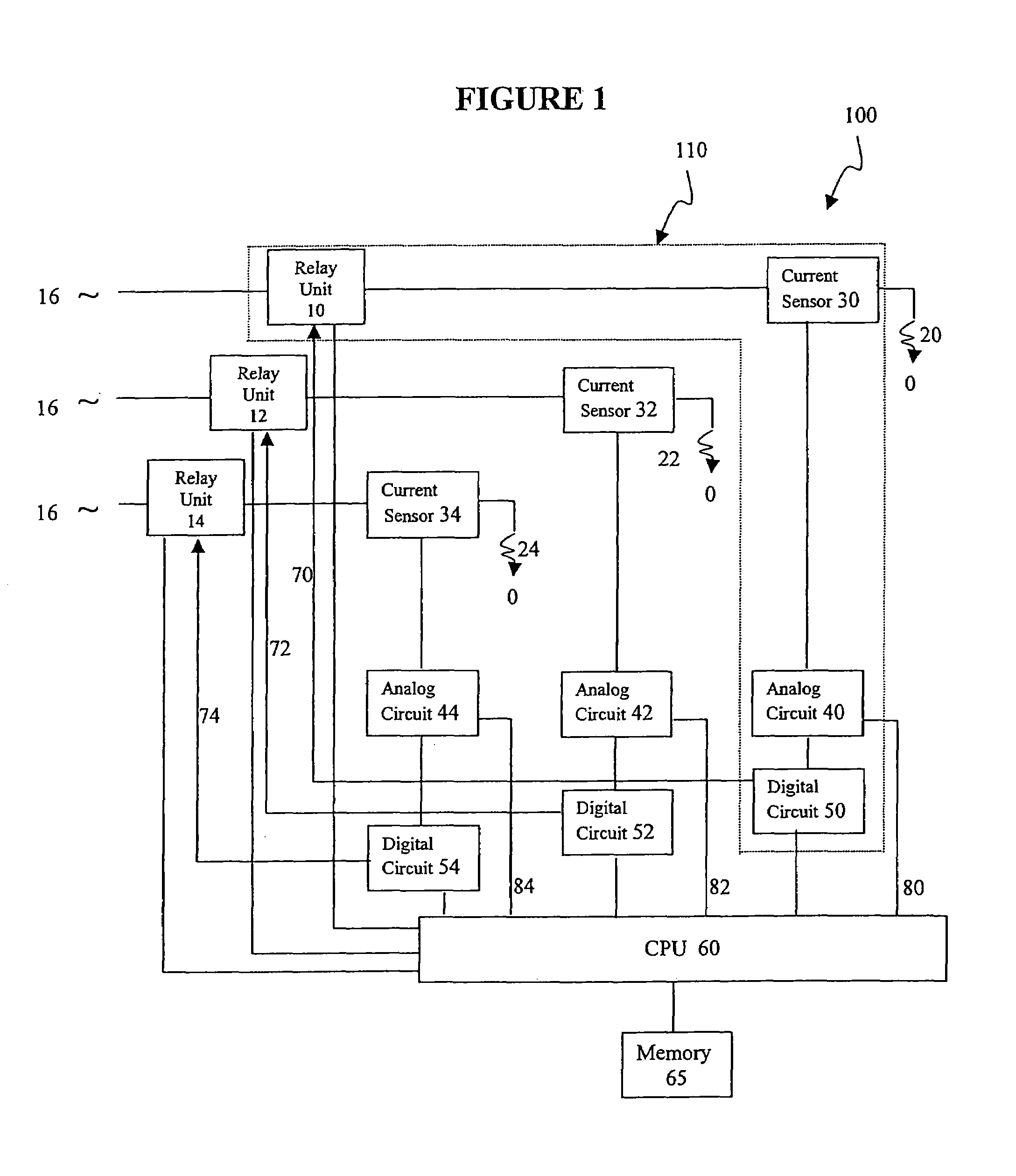
A computerized electricity system for connecting loads to a power source, including: (a) an arc fault detecting sub-system having at least one module including: (i) a relay unit, electrically associated with a particular load, for connecting and disconnecting to a power source; (ii) a current source for measuring a current being delivered from the power source to the load, to produce a current measurement; (iii) an analog circuit for receiving the current measurement from the current sensor, and for producing an analog signal based on the current measurement, and a second signal for indicating a potential arc fault event, and (iv) a digital circuit for receiving the second signal from the analog circuit and producing data, and (b) a processing unit connected to each module, so as to receive data corresponding to the analog signal, and the data from the digital circuit, the processing unit for identifying the arc faults, and wherein the processing unit is configured to command the relay unit to disconnect the current in response to identifying the arc faults, and wherein the processing unit is configured to provide this command only if several pre-determined conditions are met, (I) after detection of the potential arc fault event, the current measurement remains substantially unchanged, and (II) after a detection of at least one addition potential arc fault event, the arc fault events are found to be acyclic.
Owner:TARGET HI TECH ELECTRONICS
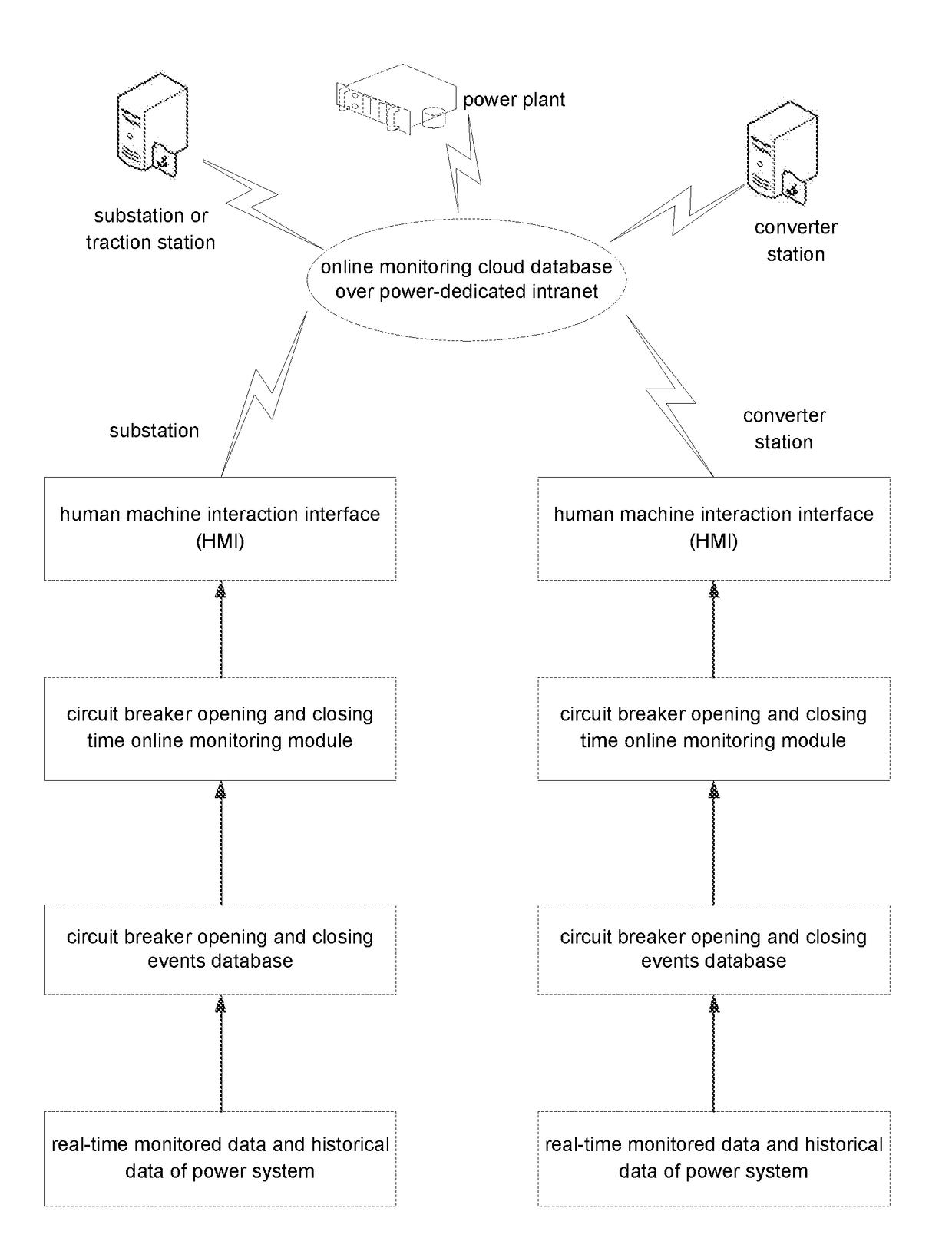
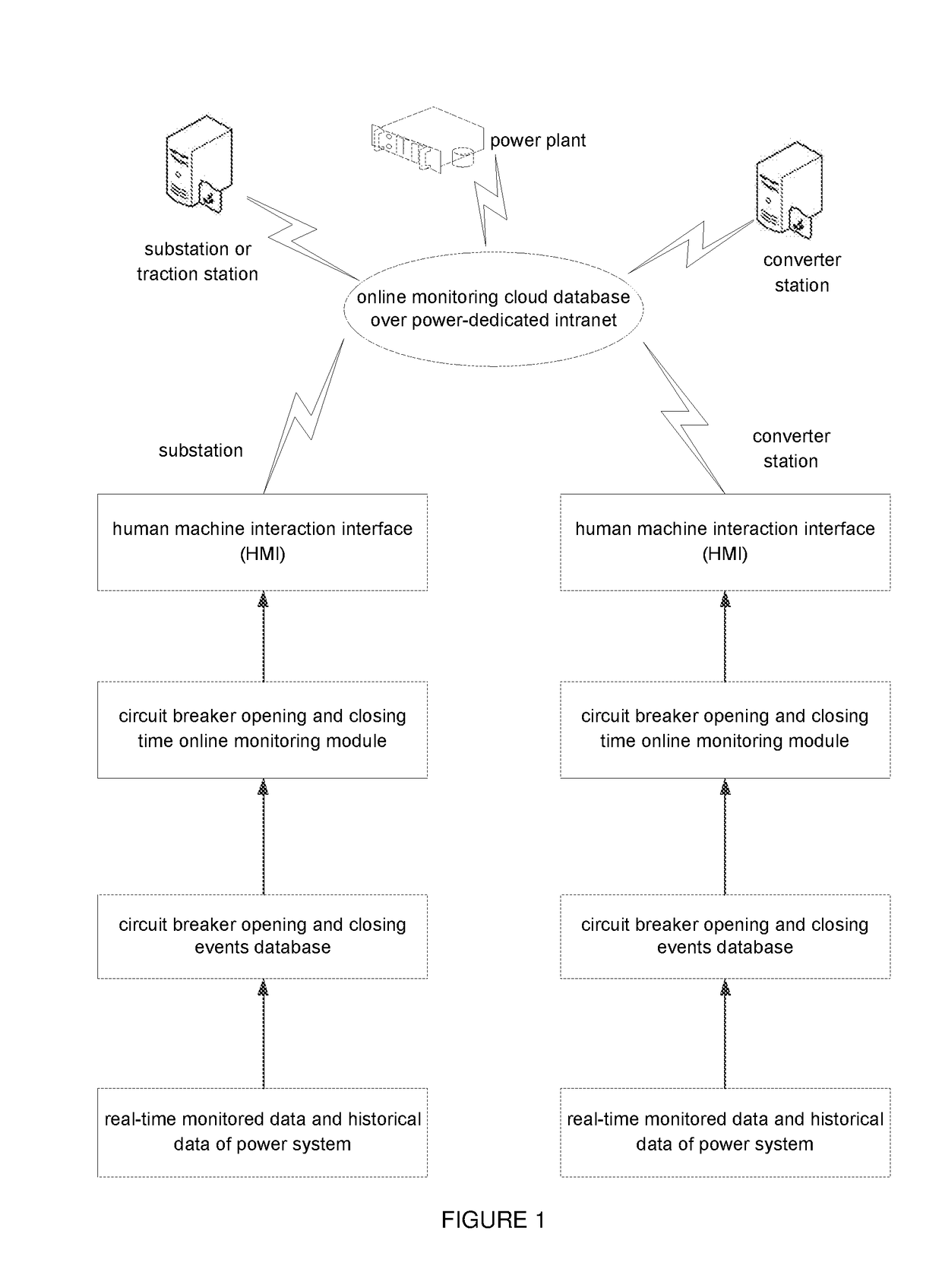
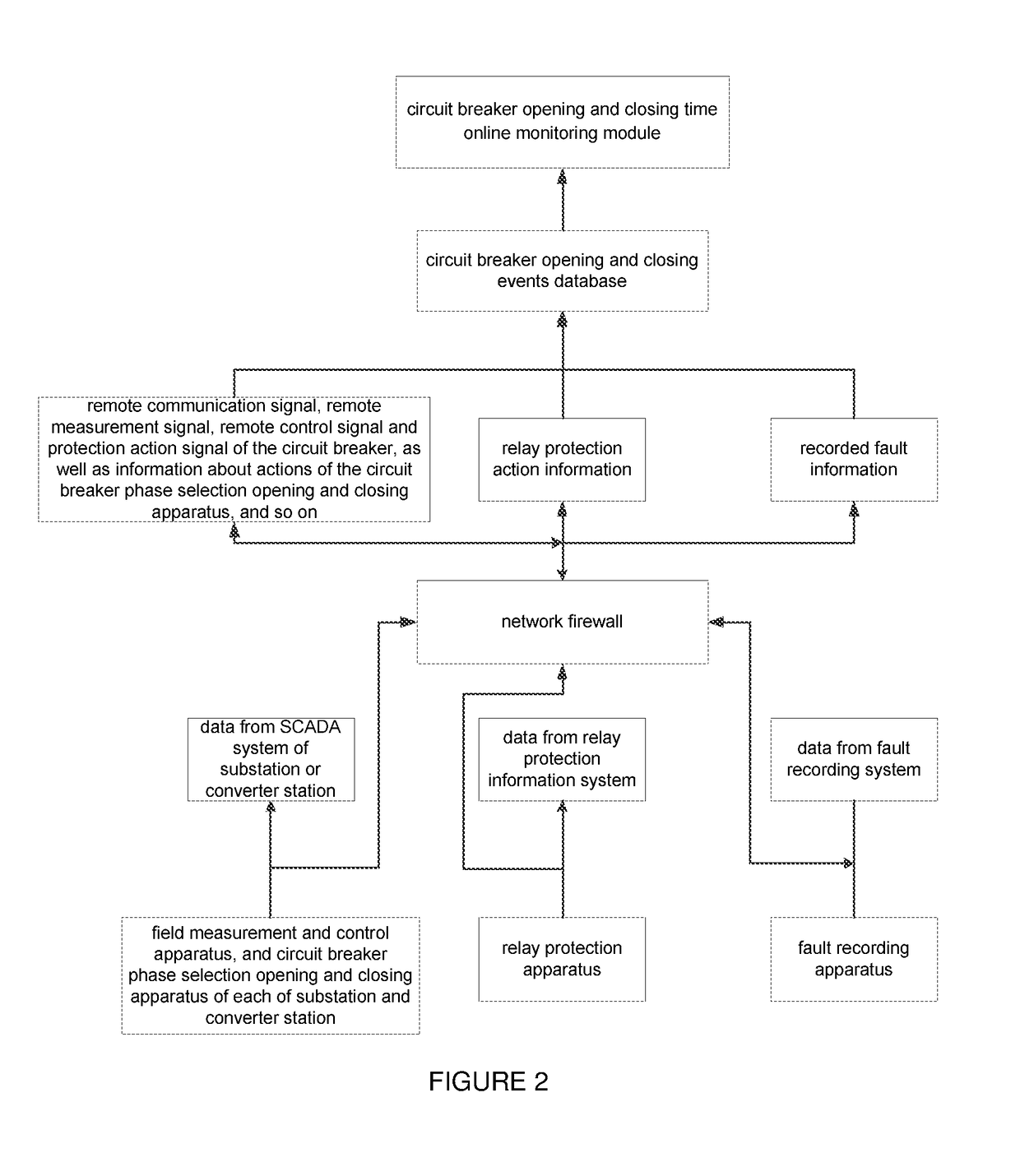
High-voltage circuit breaker opening and closing time online monitoring apparatus, smart multi-dimensional big data analyzing expert system for high-voltage circuit breaker in power grid and method therefor
ActiveUS20180059186A1Electric switchesEmergency protection data processing meansEngineeringMulti dimensional
Provided are a high-voltage circuit breaker opening and closing time online monitoring apparatus, a smart multi-dimensional big data analyzing expert system for a high-voltage circuit breaker in a power grid, and methods therefor. The opening and closing time online monitoring apparatus includes a circuit breaker opening and closing events database, a circuit breaker opening and closing time online monitoring module, and a human machine interaction interface. Data in the circuit breaker opening and closing events database is derived from a SCADA and a measurement and control apparatus thereof, a circuit breaker phase selection opening and closing apparatus, a relay protection apparatus and a relay protection information system, and a fault recording apparatus and a fault recording system of each of a substation and a converter station. The circuit breaker opening and closing time online monitoring module includes various modules, and cloud databases for such online monitoring are created.
Owner:YANG QIBEI
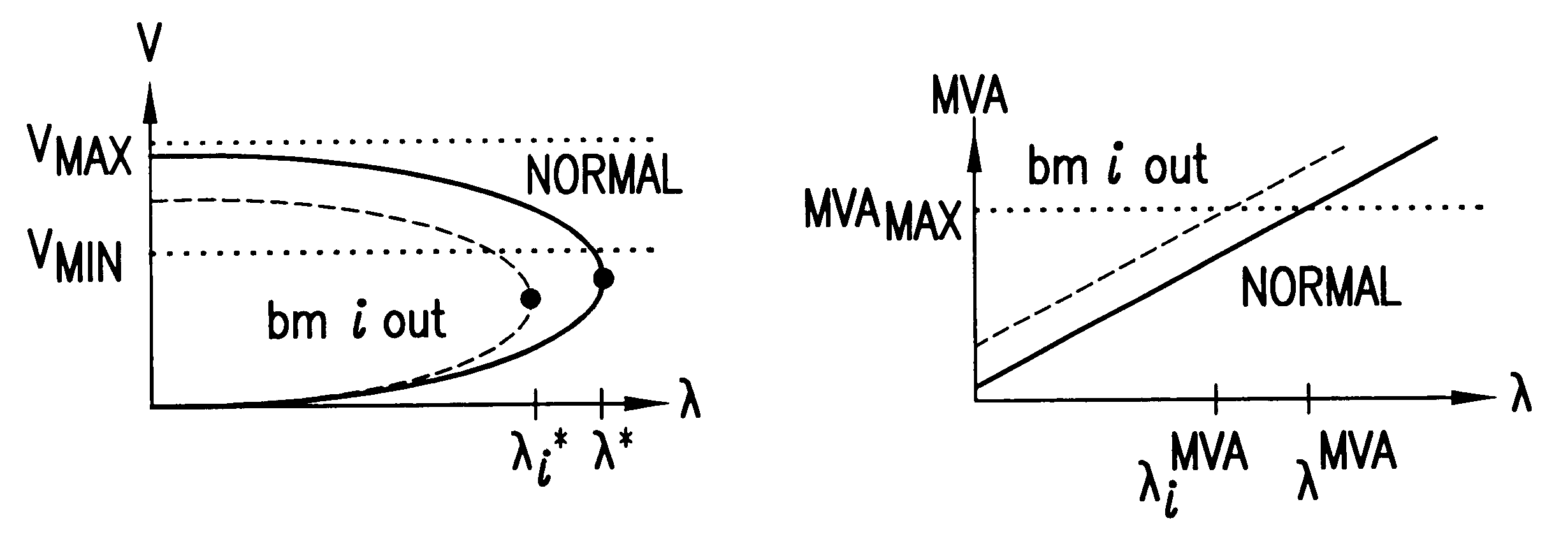
Nonlinear contingency screening for voltage collapse
InactiveUS6496757B1Screening contingencies fasterMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlSaddle-node bifurcationElectric power system
A method for estimating the severity of generator unit outage and multi-terminal branch outage contingencies with respect to voltage collapse in large-scale electric power systems which includes the steps of estimating a post-contingency saddle-node bifurcation induced voltage collapse point of an electric power system following a set of generator unit outages and / or a set of branch outages and calculating a distance to collapse of said power system. The post-contingency voltage collapse point is determined by application of a nonlinear contingency screening method.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Generator protection methods and systems self-tuning to a plurality of characteristics of a machine
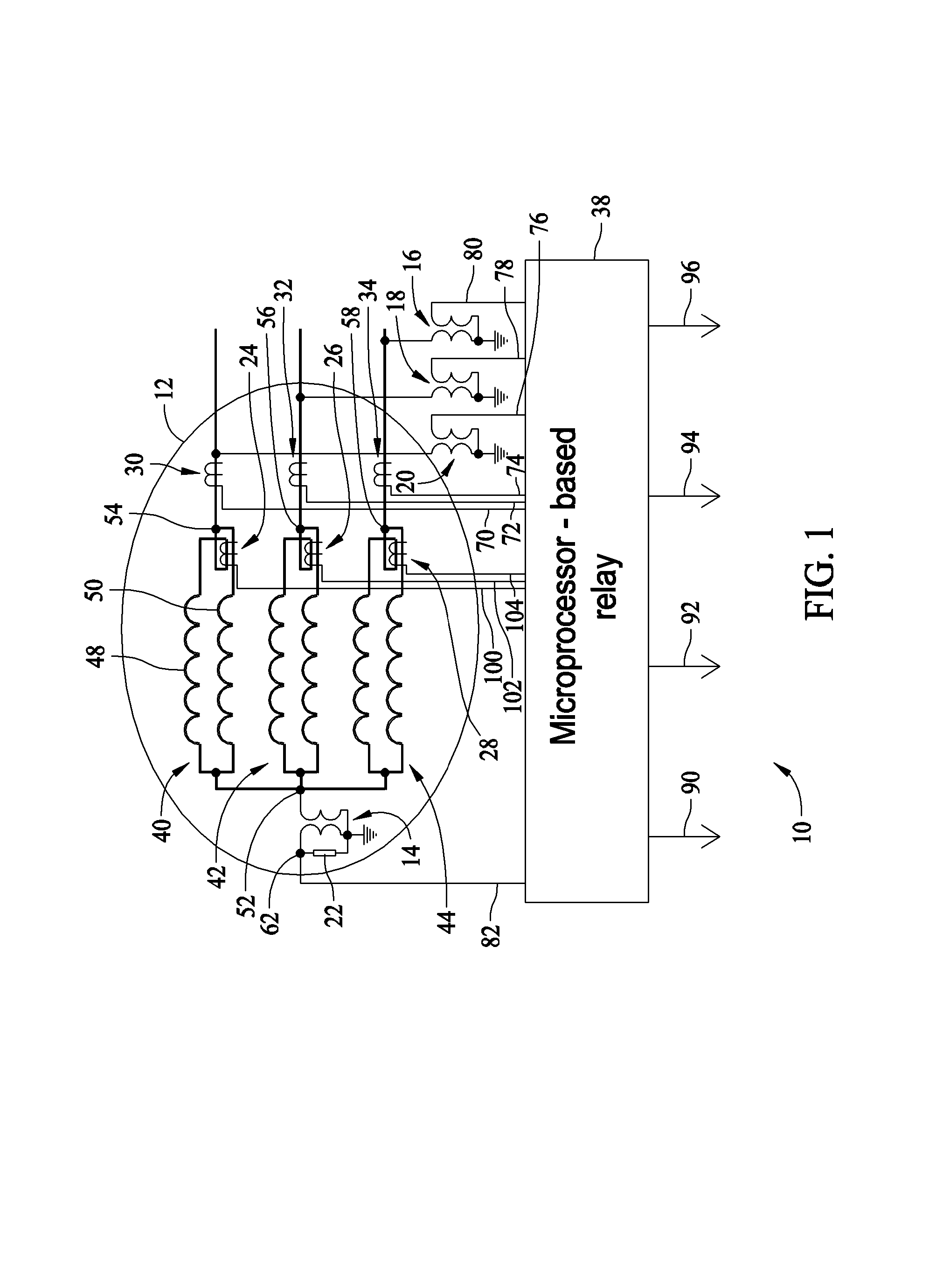
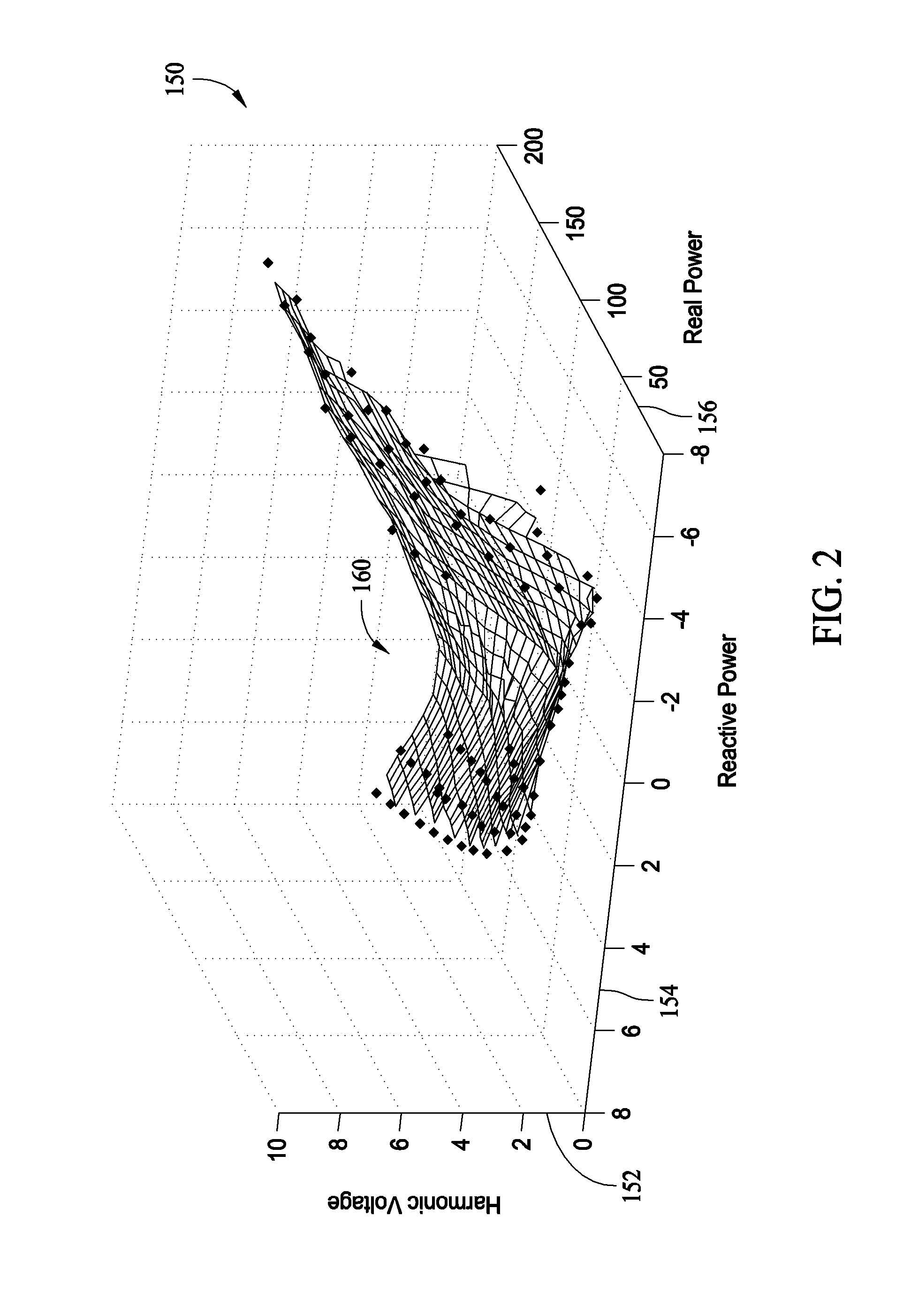
ActiveUS7253634B1Spectral/fourier analysisEmergency protection data processing meansSelf-tuningHarmonic
A method for detecting stator ground faults in a generator is described. The method includes receiving a neutral voltage signal from a neutral point of a stator, receiving a plurality of terminal voltage and current signals from the stator, deriving a magnitude of a harmonic component from the neutral voltage signal, deriving a total complex power from the terminal voltage and current signals, calculating an expected value of a harmonic based on the complex power at a first time and a plurality of values of the complex power, where the values of the complex power are measured at times before the first time, and comparing the expected value and a measured value of the harmonic.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Three-phase power signal processor
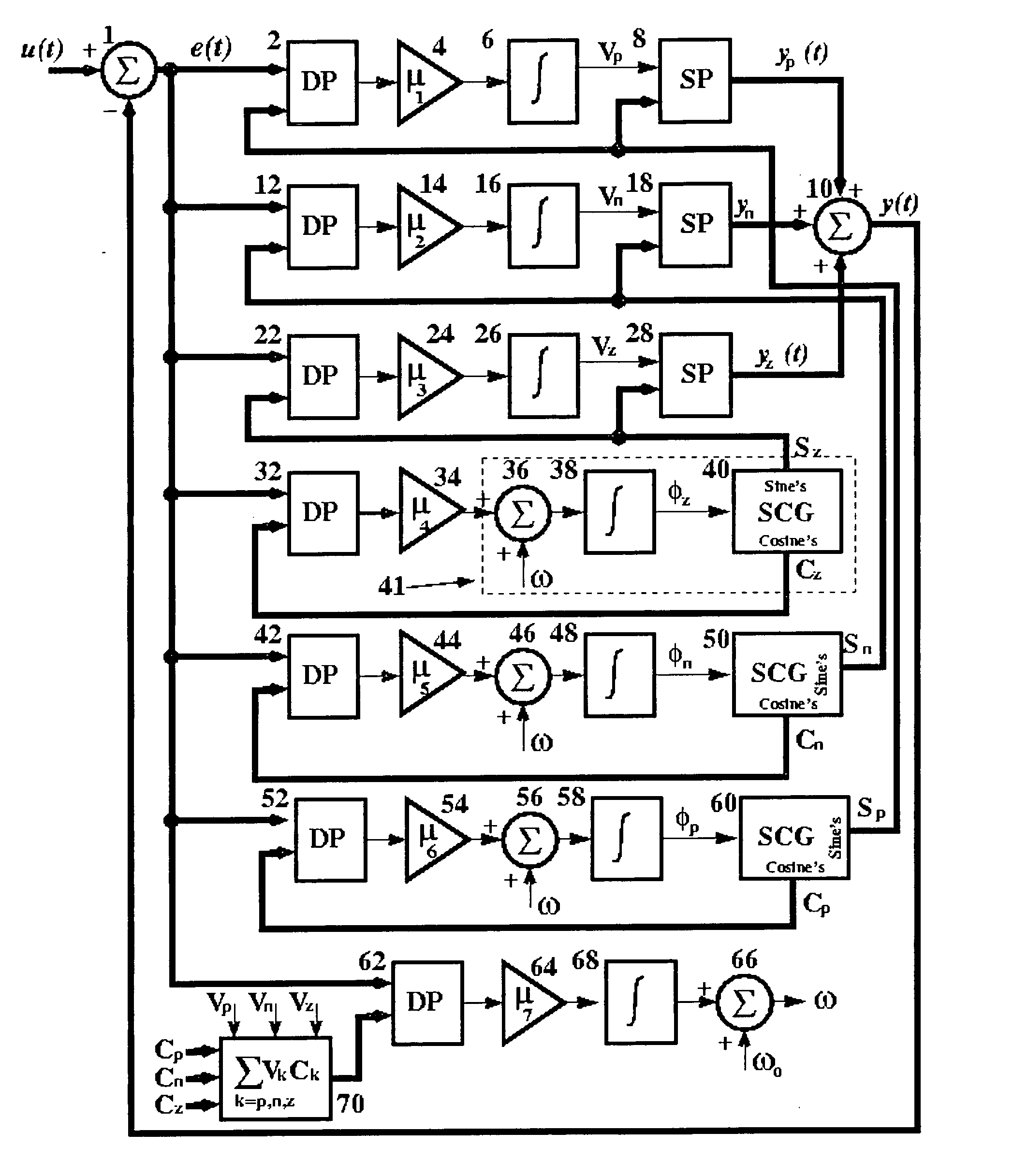
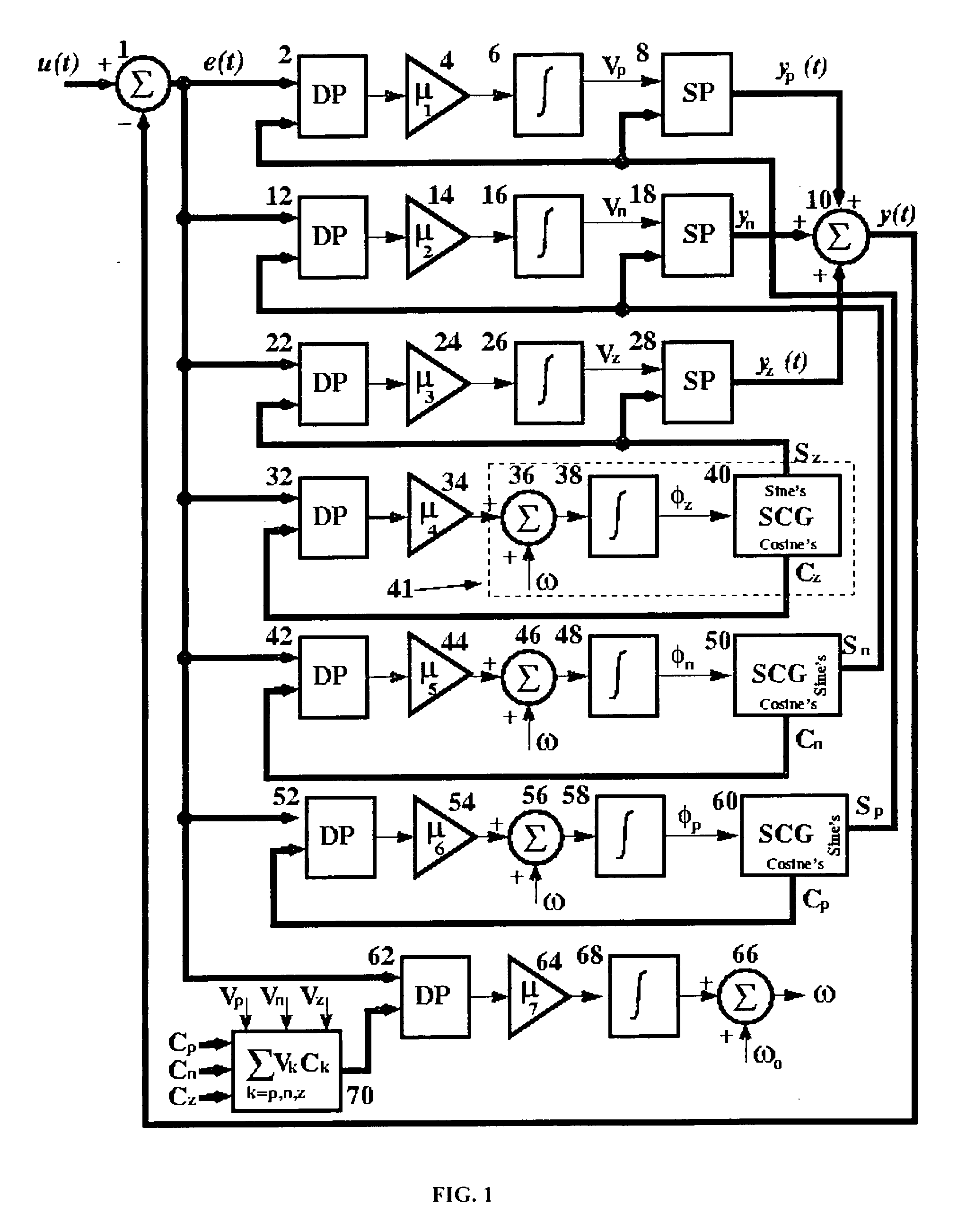
InactiveUS20050231871A1Improve accuracyEasy to implementElectric devicesPulse automatic controlPower qualityAdaptive filter
A Three-phase Power Signal Processor (TPSP) is disclosed for general three-phase power system applications. The TPSP is developed based on the concepts from adaptive filter and dynamical systems theories. The structure of the TPSP is unified as it provides a multiplicity of the signals and pieces of information without the need to change, modify, or enhance the structure or to impose excessive computational time or resource requirements. The presented TPSP receives a set of three-phase measured signals, which can be voltage, current, magnetic flux, etc, and provides (1) the instantaneous and steady-state symmetrical components, (2) the fundamental components, (3) the peak values (magnitudes) of the symmetrical components, (4) the frequency and its rate of change, (5) the synchronization signal(s) and zero-crossing instants, (6) the phase-angles of the symmetrical components, and (7) the disturbance signatures. Two or more TPSP units, when properly augmented, further provide (8) the individual harmonic components, (9) the inter-harmonics, (10) the instantaneous real and reactive current components, (11) the total harmonic distortion, dc-offset, and power factor. The TPSP can serve as the building block for various signal processing requirements encountered in the context of power system applications including power systems control, protection, monitoring, and power quality.
Owner:KARIMI GHARTEMANI MASOUD M K
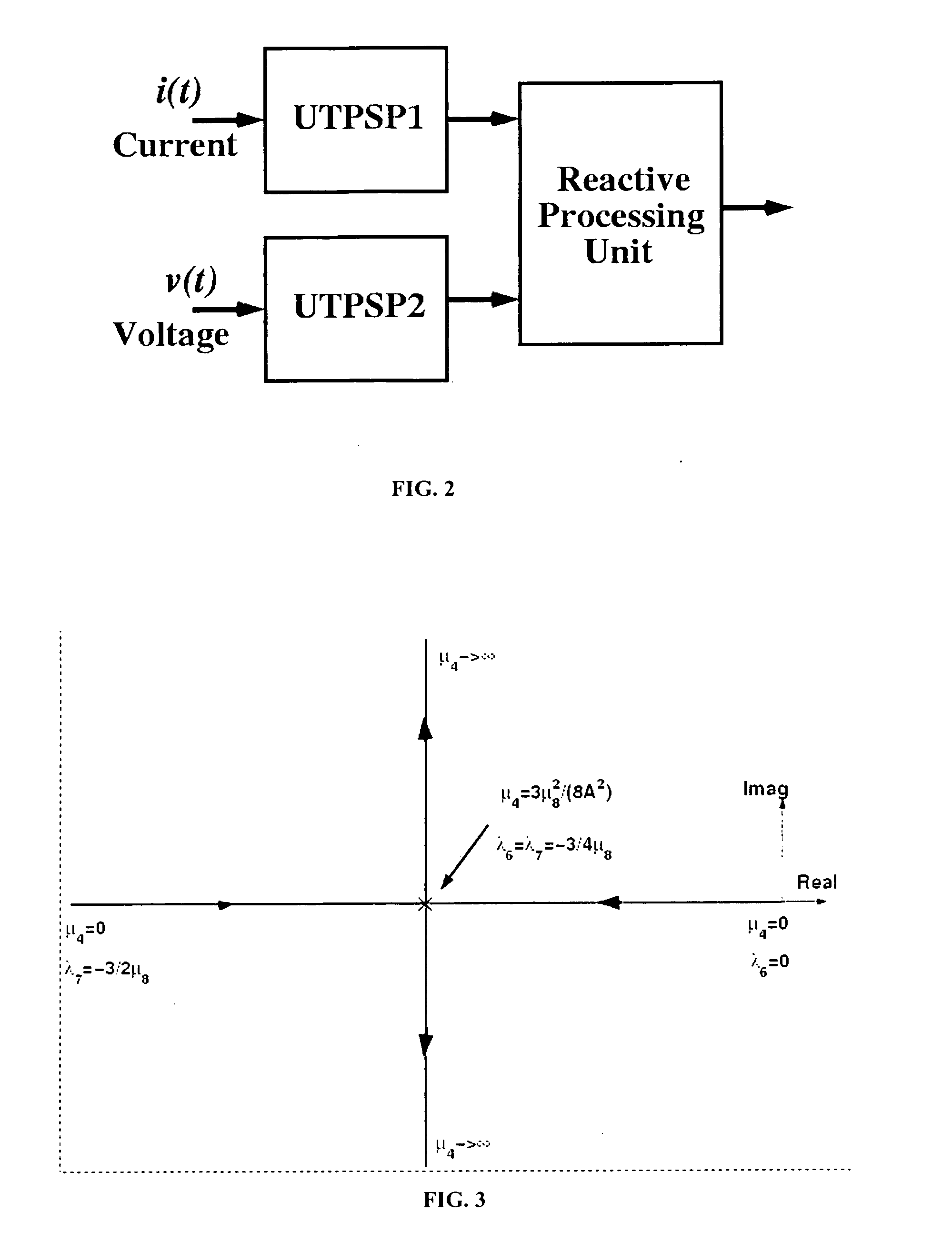
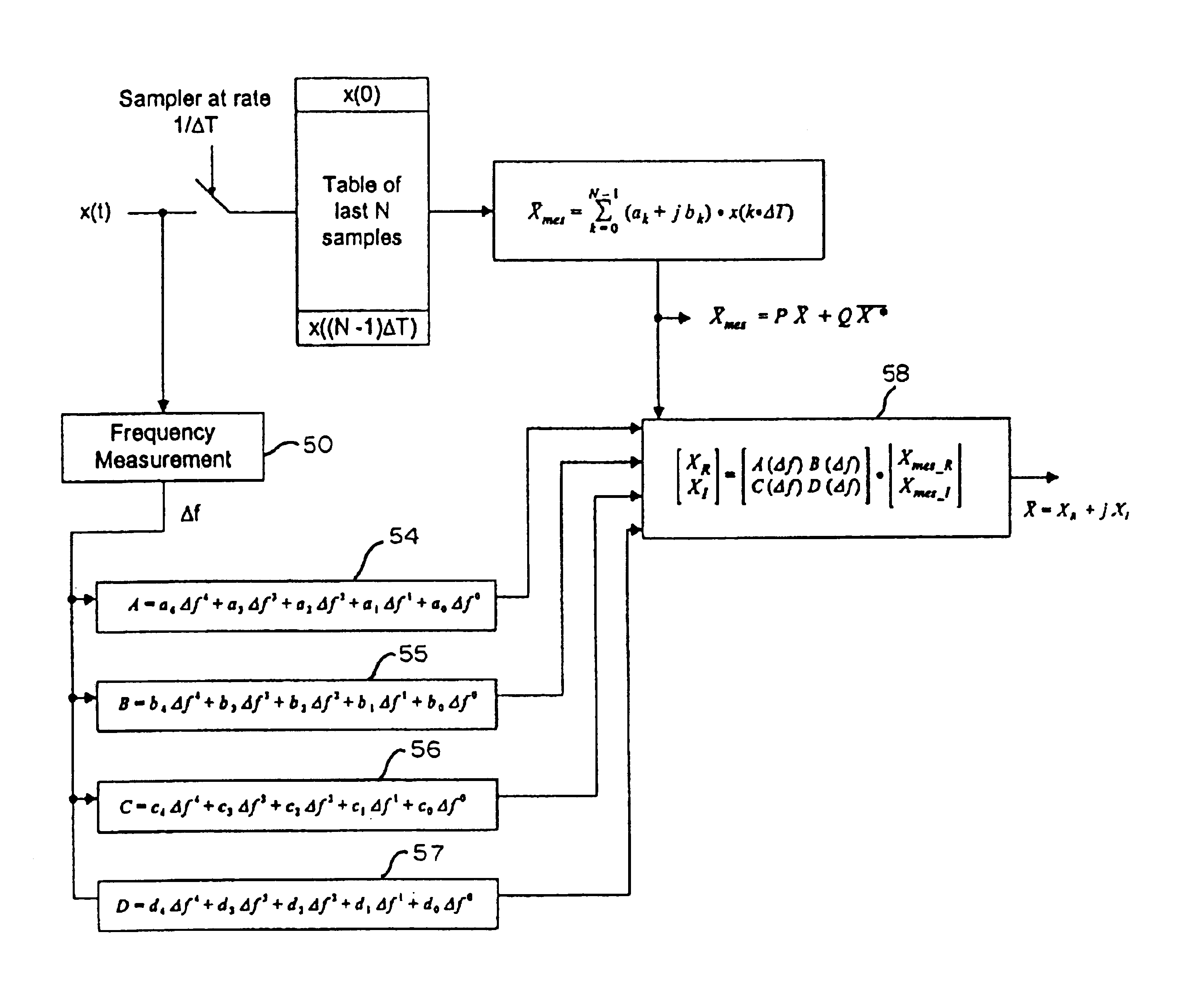
System and method for exact compensation of fundamental phasors
InactiveUS6934654B2Emergency protection data processing meansTransmission monitoringWave shapeEngineering
A measured phasor representing a sinusoidal power signal waveform is produced by orthogonal FIR filters, one of which produces the real part of the phasor and the other of which produces the imaginary part. The frequency difference between the rated frequency of the signal waveform in the power system and the actual frequency of the waveform at any selected point in time is determined and the elements (A, B, C, D) of a compensation matrix is determined. The compensation matrix is then used to perform a linear transformation to produce an exact phasor for the waveform.
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
Multifunctional residential circuit breaker
ActiveUS8023235B2Quickly and effectively discriminateReduce impactElectrical testingEmergency protection data processing meansCurrent sensorEngineering
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
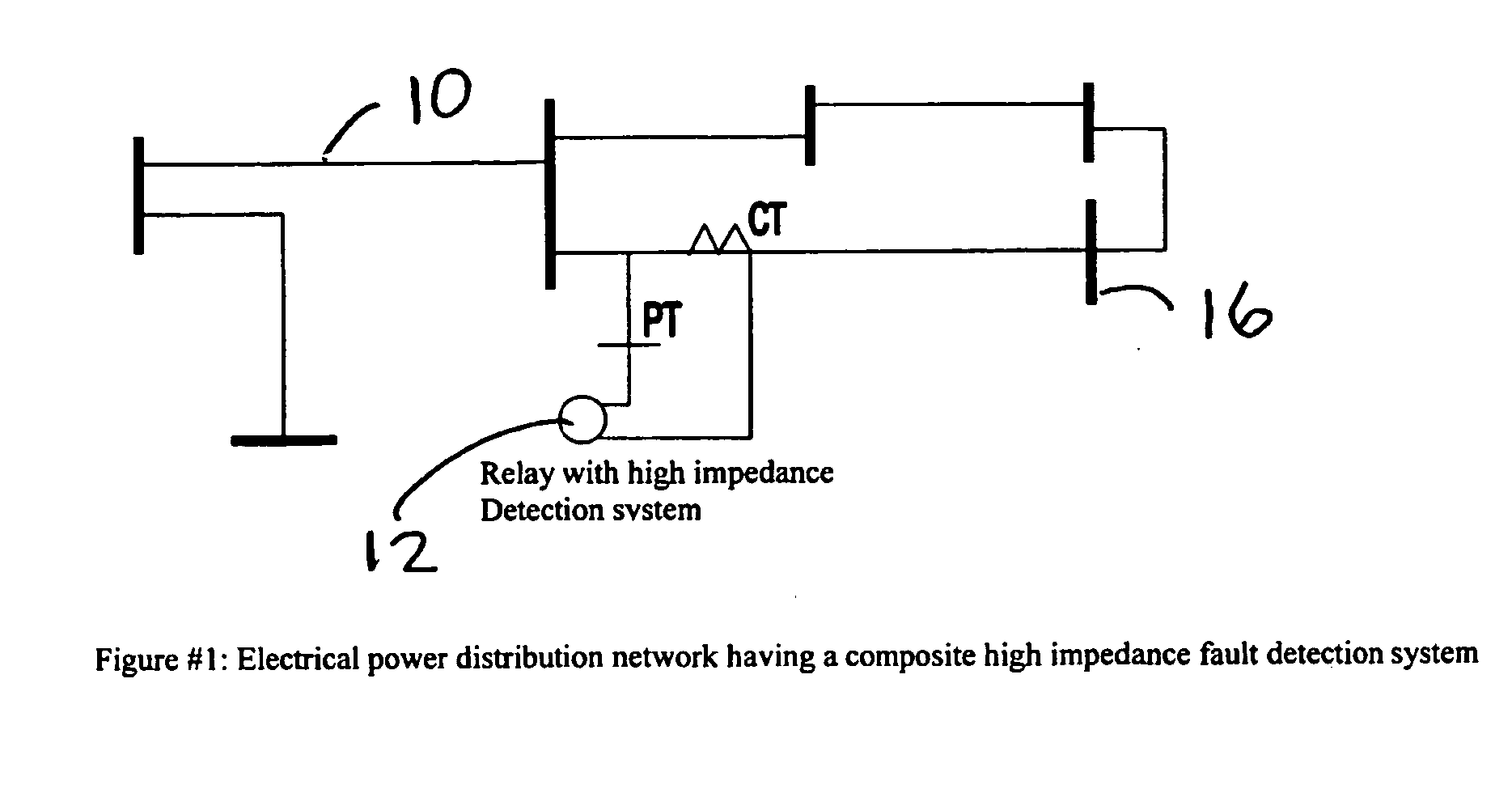
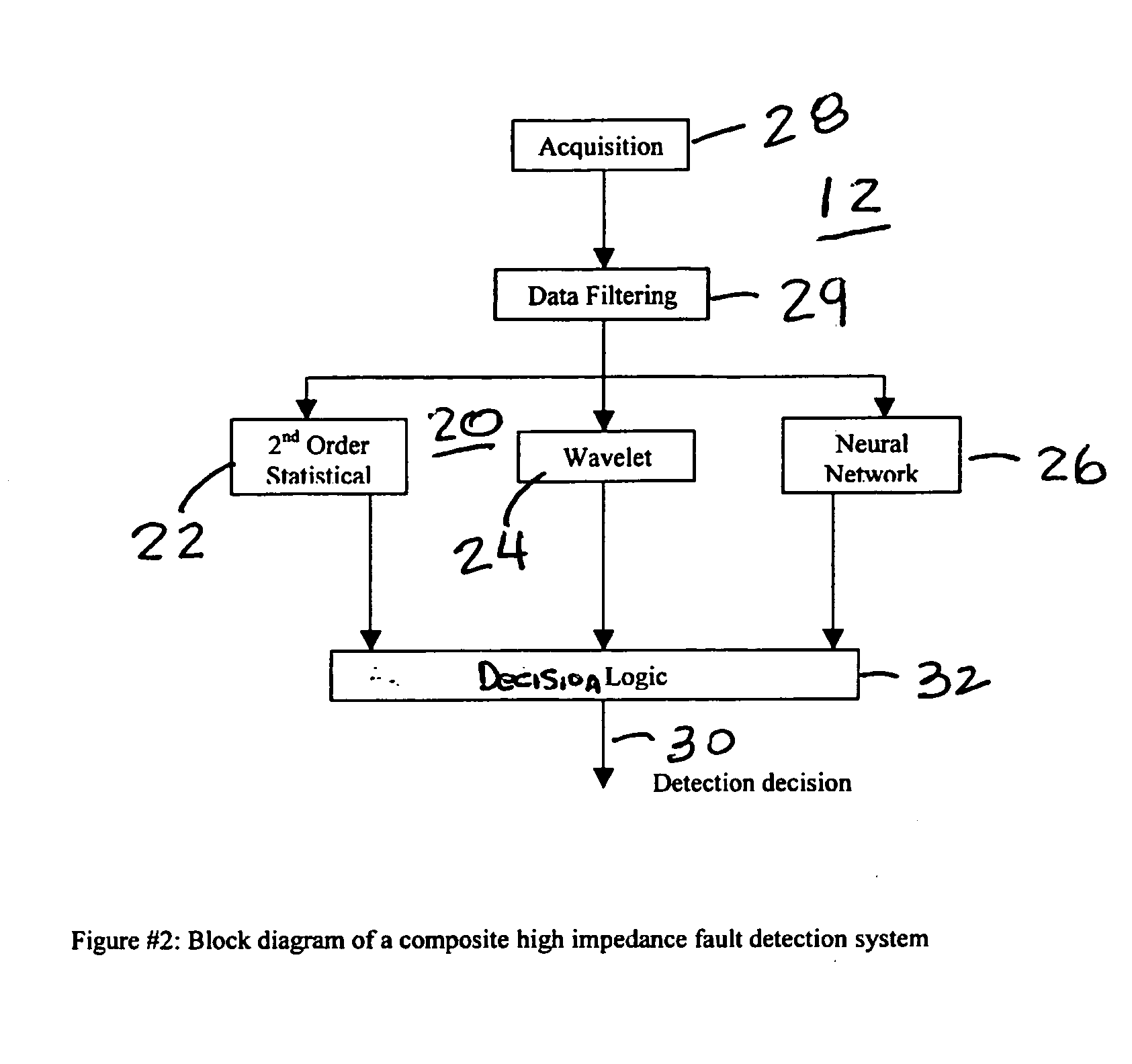
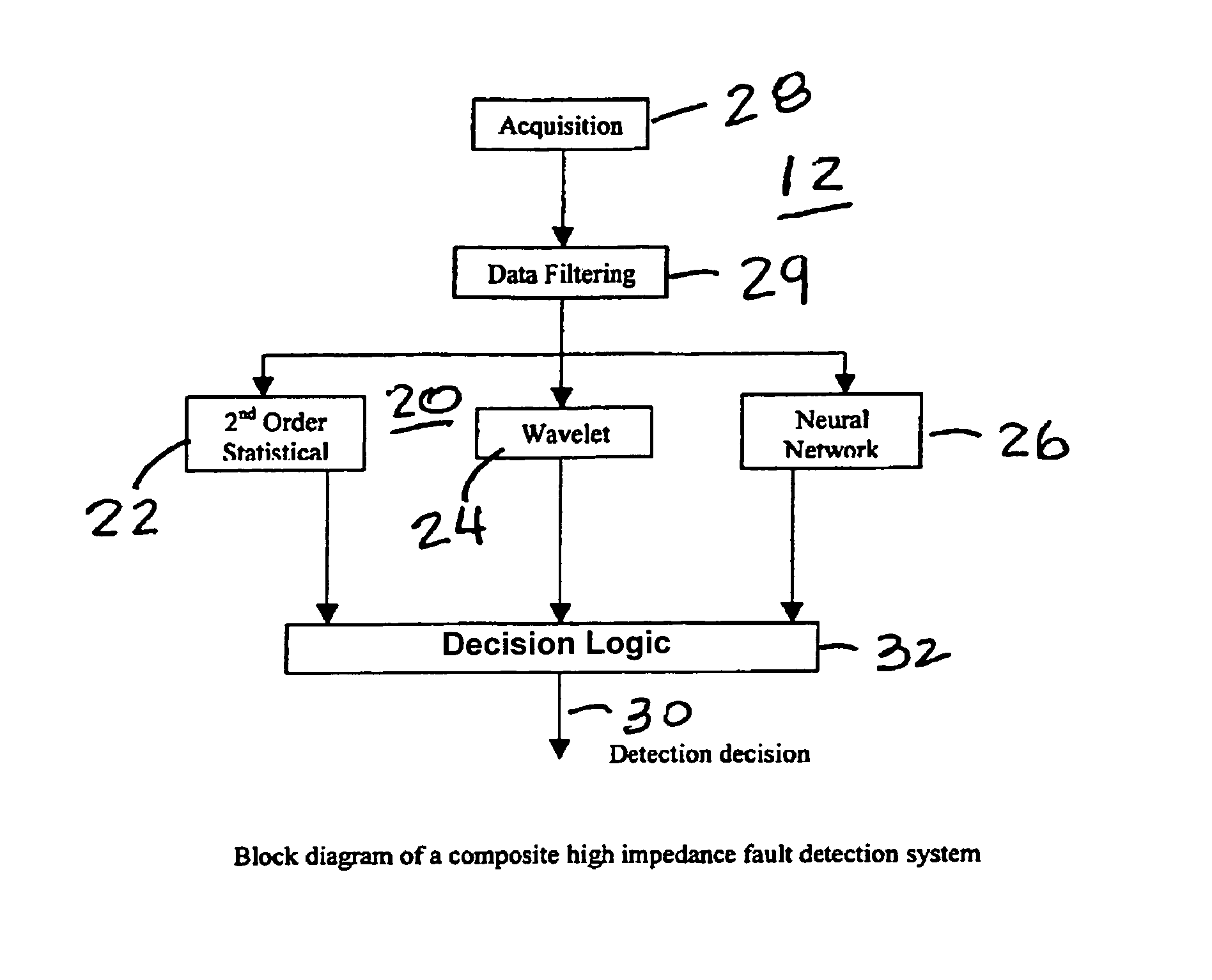
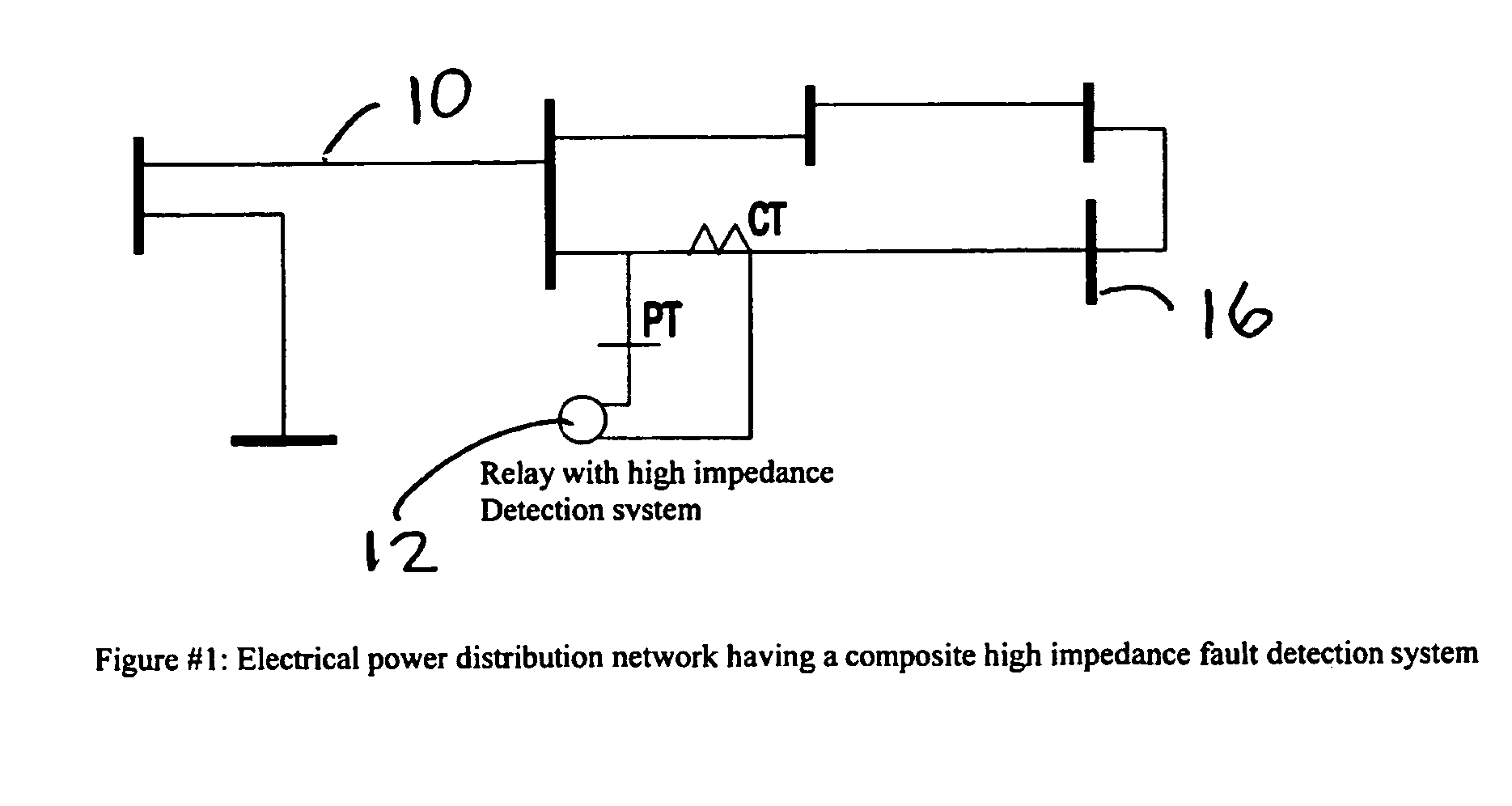
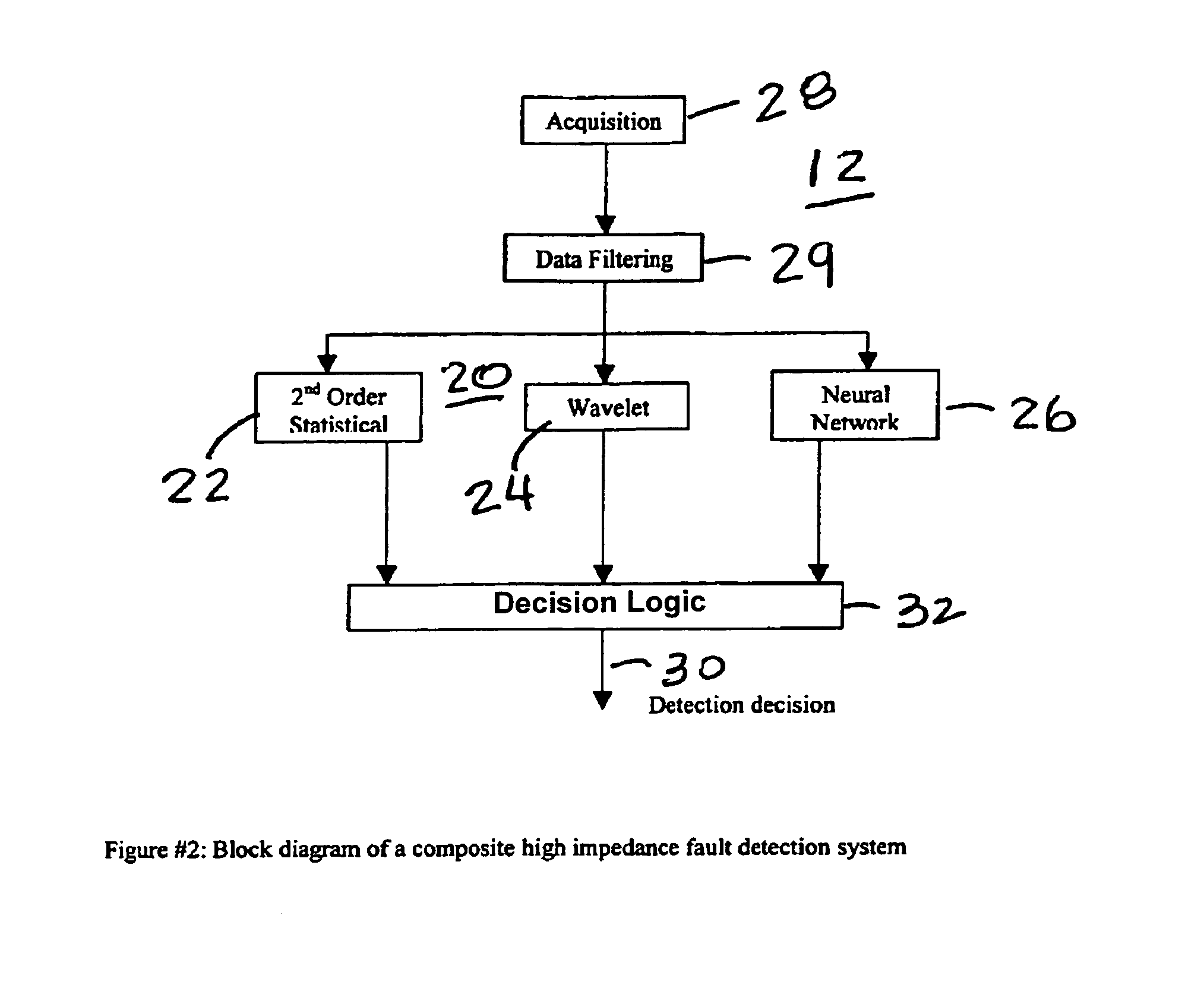
High impedance fault detection
ActiveUS20050171647A1Mechanical power/torque controlLevel controlElectric forceHigher-order statistics
An apparatus, system, and method for detecting high impedance faults in electrical power lines using a composite high impedance fault detection system having a voter logic that samples the logical outputs from a plurality of independent high impedance detection systems and determines a high impedance fault if any two of the plurality of independent high impedance detection systems indicates a high impedance fault. Preferably, the plurality of high impedance detection systems include a wavelet based high impedance fault detection system having a first logical output, a higher order statistics based high impedance fault detection system having a second logical output, and a neural net based high impedance fault detection system having a third logical output. Preferably, each of the plurality of high impedance fault detection systems includes an independent high impedance fault detection application that independently detects a high impedance fault on the electrical power line.
Owner:ABB INC
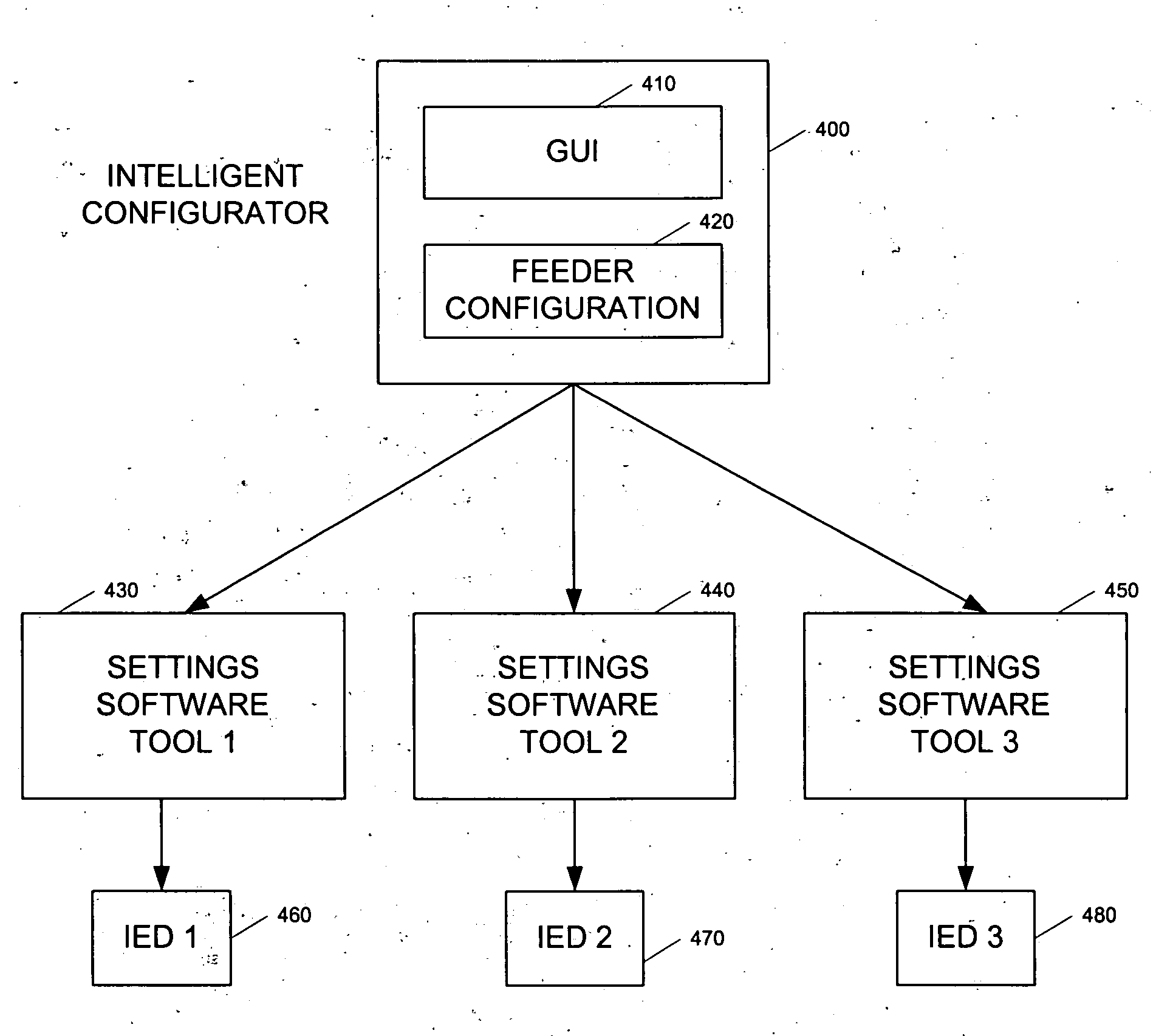
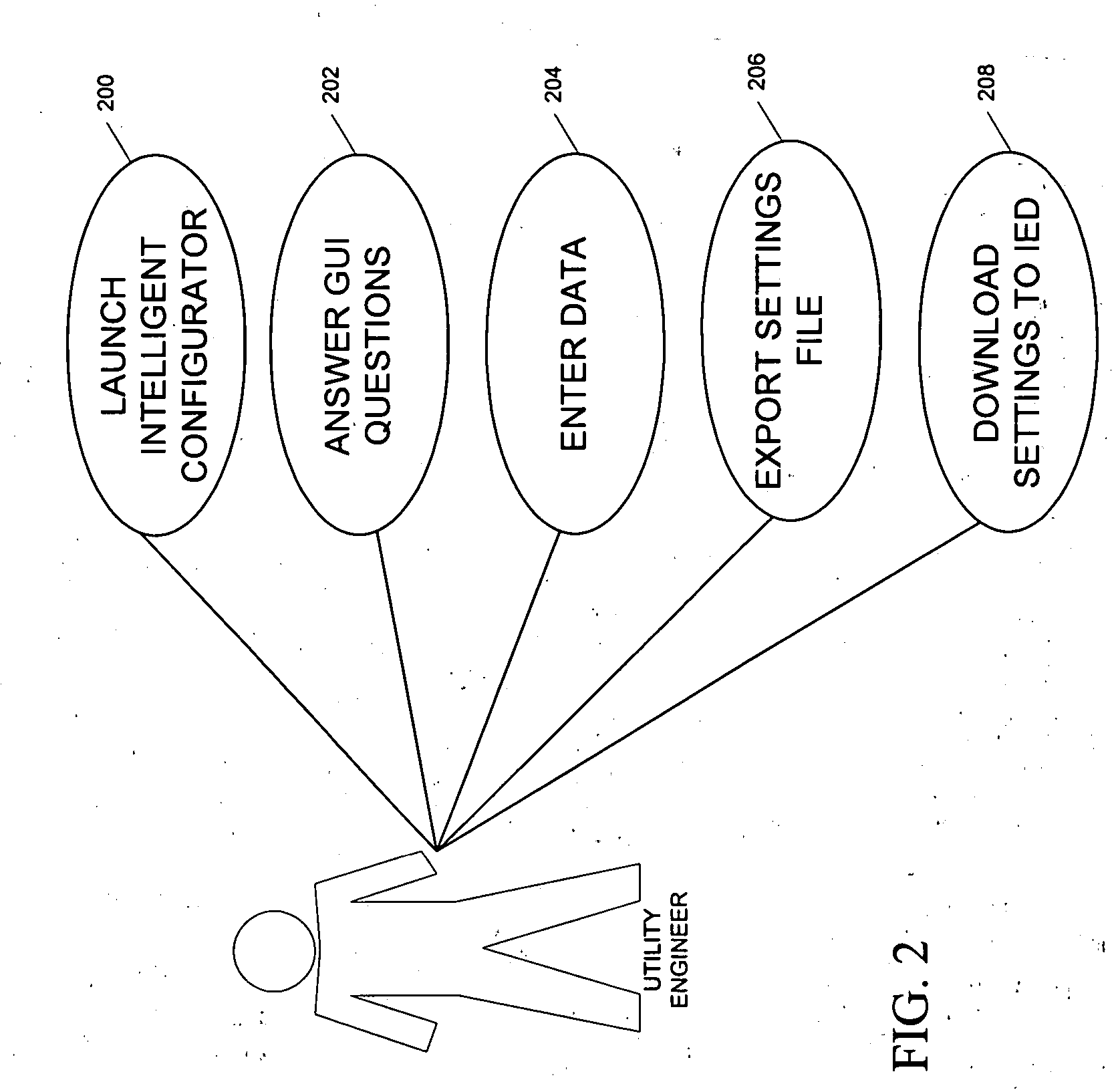
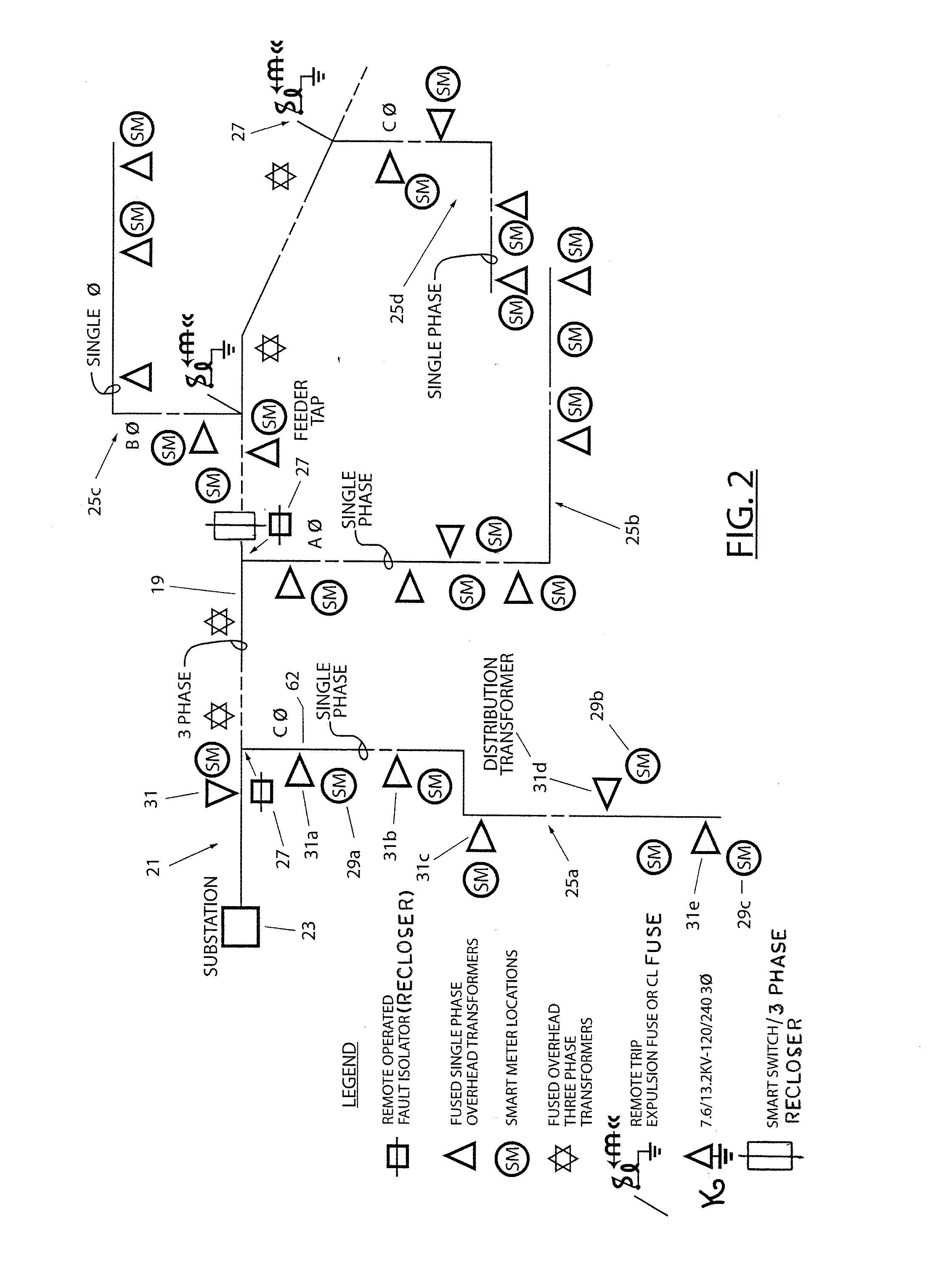
Automated intelligent configuration tool for power system protection and control and monitoring devices
InactiveUS20050097373A1Parameter calibration/settingComputer controlElectric power transmissionPower-system protection
An automatic configuration tool for use with power protection and restoration devices such as reclosers and switches in power transmission and distribution systems. An automatic configuration application provides a plurality of menus to a user on a graphical user interface to enable the user to select a plurality of options that are processed by various calculation engines to determine the configuration settings for a specific power protection and restoration device. The configuration settings that are generated are downloaded directly into the power protection and restoration device to provide protection, control and monitoring.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
Method and apparatus for generalized arc fault detection
ActiveUS7391218B2Electric switchesEmergency protection data processing meansElectrical currentReliability engineering
A method and an apparatus detect series and / or parallel arc faults in AC and DC systems. The method according to one embodiment inputs an AC current signal; extracts a fundamental component of the AC current signal and monitoring an amplitude variation profile for the fundamental component, thereby generating a first arc fault detection measure; detects non-stationary changes in the AC current signal applying at least one measure of order higher than one, thereby generating a second arc fault detection measure; and determines whether an arc fault exists based on the first arc fault detection measure and the second arc fault detection measure.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC +1
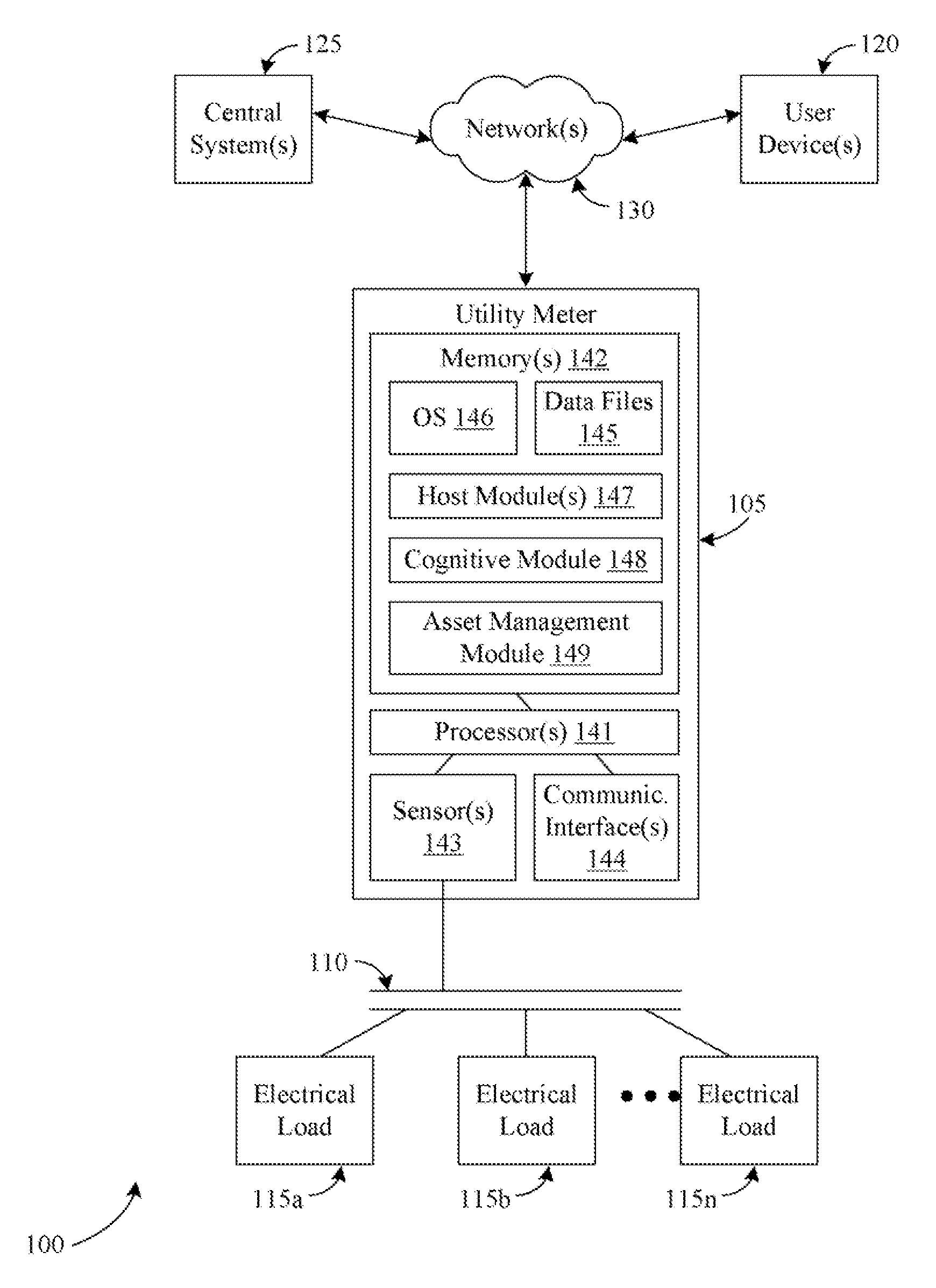
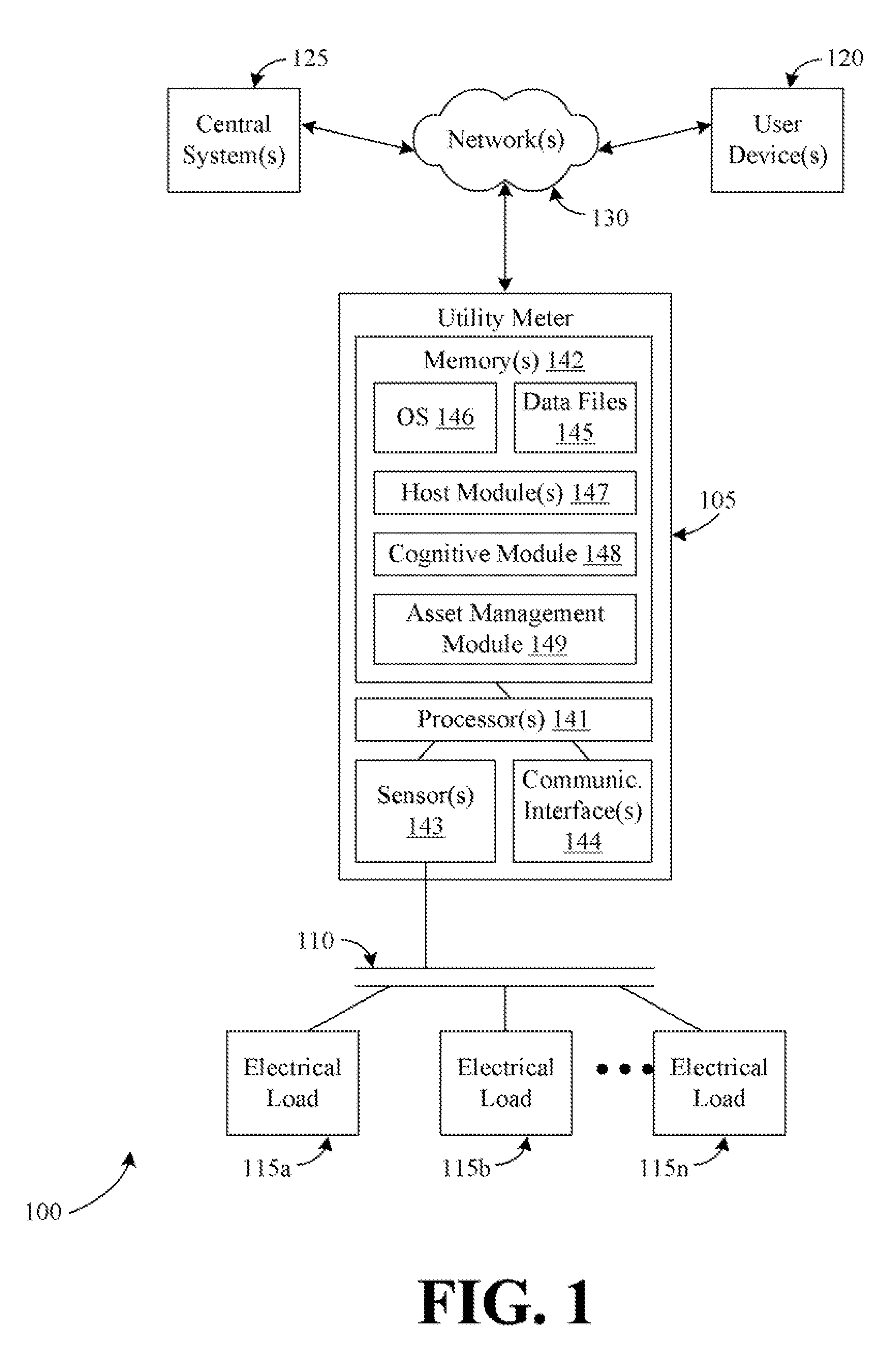
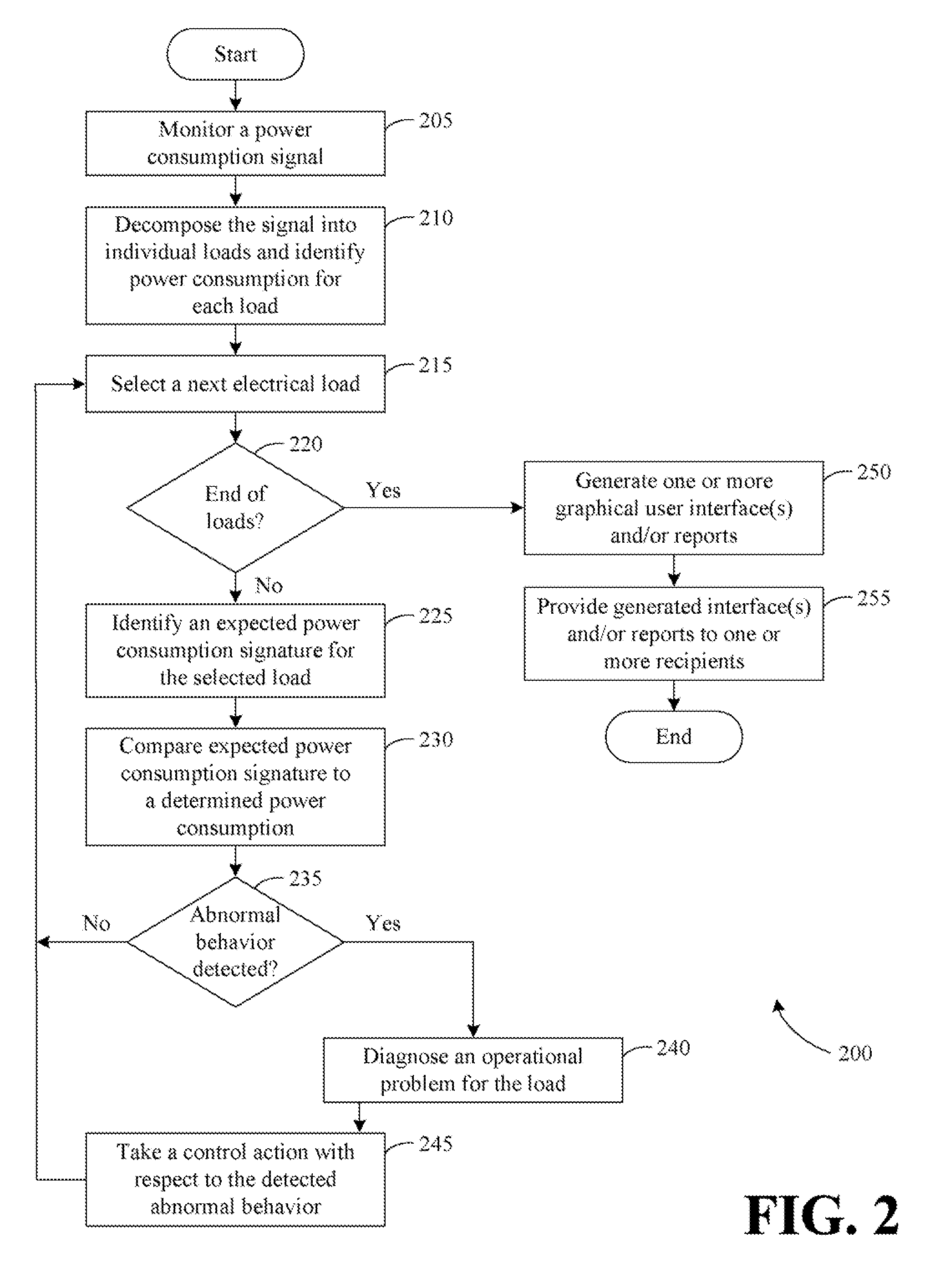
Systems, methods, and apparatus for evaluating load power consumption utilizing a power meter
InactiveUS20120323510A1Load forecast in ac networkDynamo-electric motor metersControl engineeringComputer science
Systems, methods, and apparatus for evaluating load power consumption utilizing a power meter are provided. A power line signal for a structure associated with a power meter may be measured by the power meter. The power line signal may be decomposed by the power meter into respective power consumption data for a plurality of individual loads powered by the power line signal. The power consumption data for a load included in the plurality of individual loads may be compared by the power meter to expected power consumption data for the load. Based at least in part upon the comparison, the power meter may determine whether the load is operating within one or more desired parameters.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
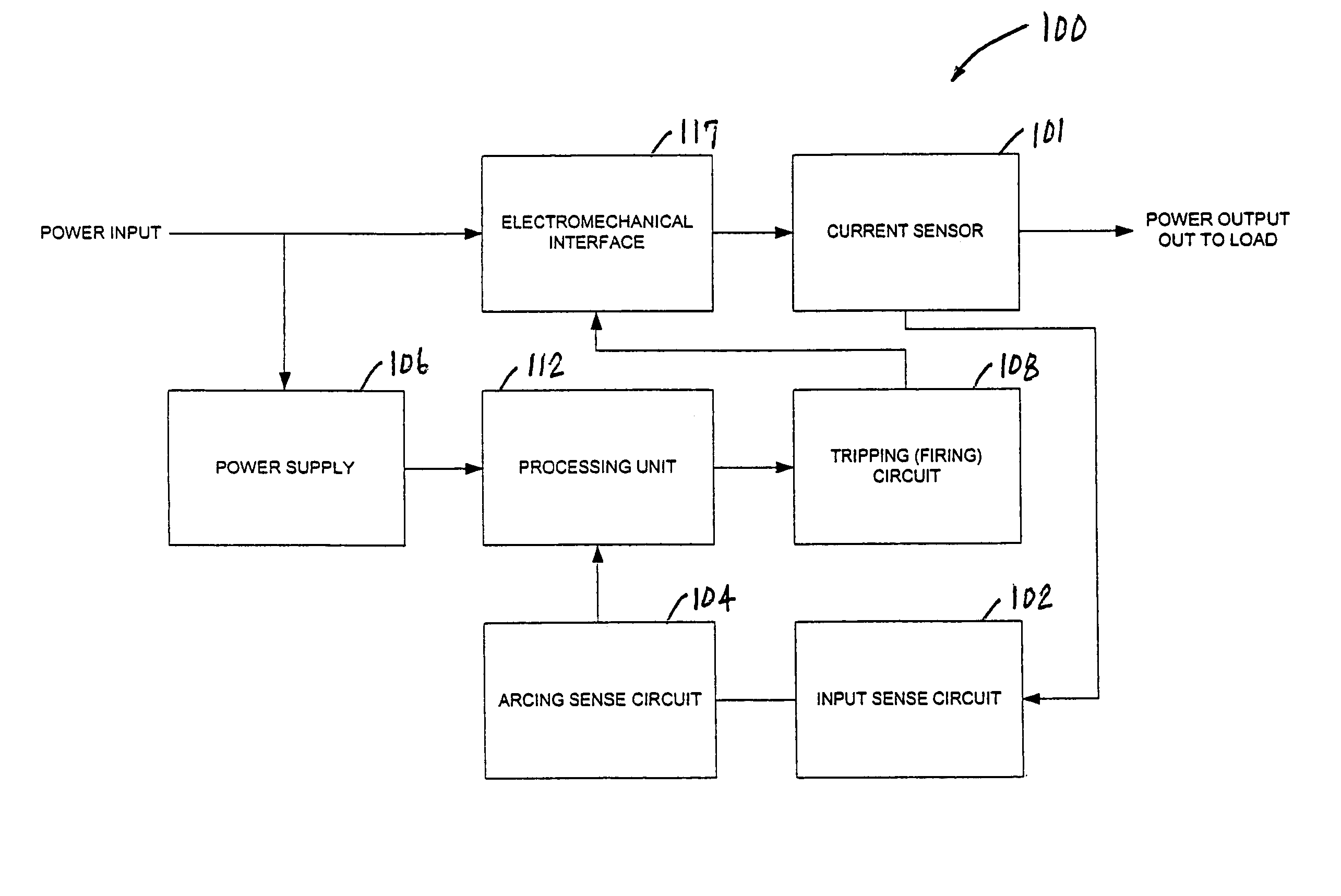
Method for detecting arc faults
InactiveUS7190562B2Improve reliabilityReduce sensitivityEmergency protection data processing meansEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionCurrent sensorElectric power
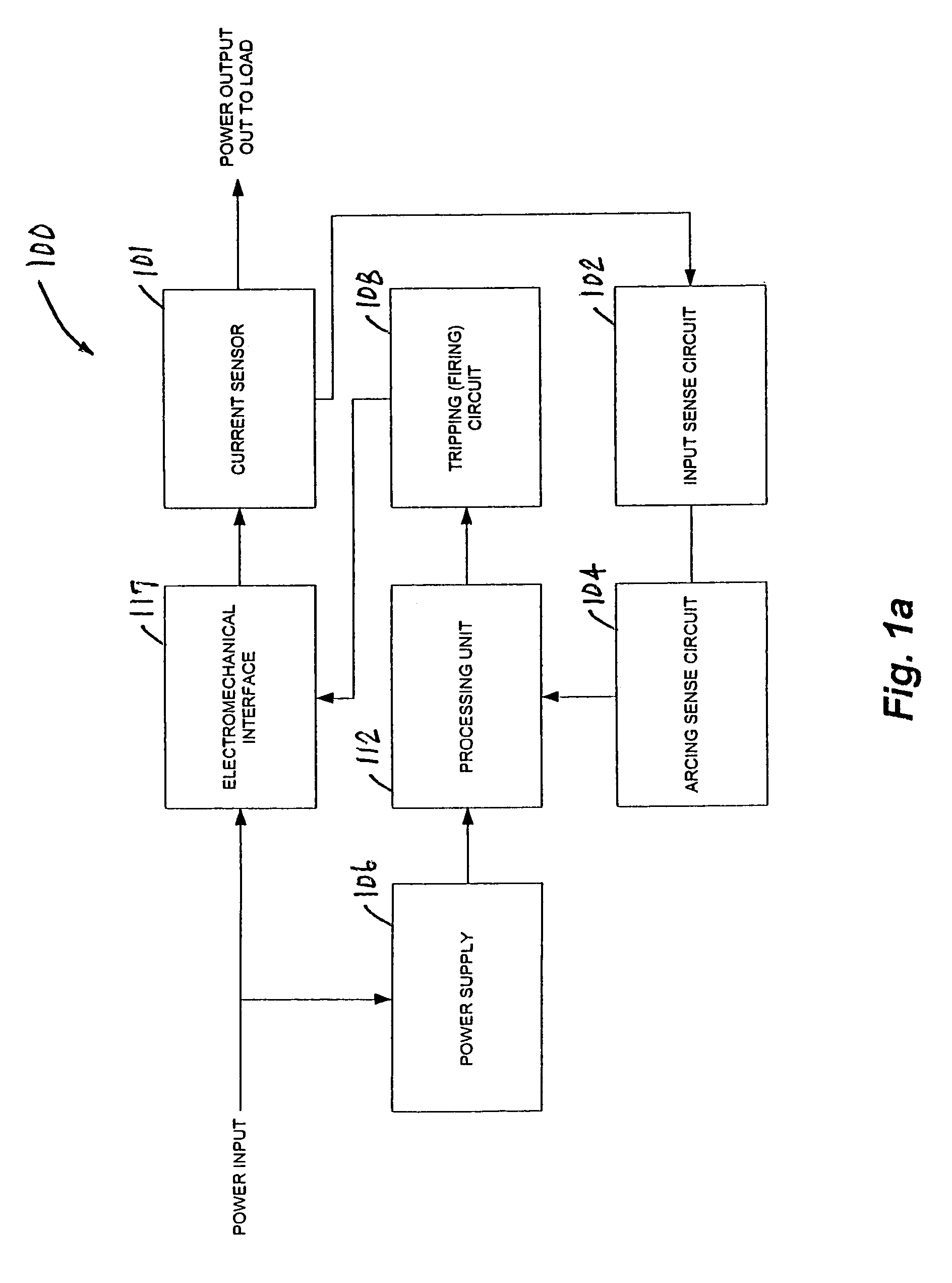
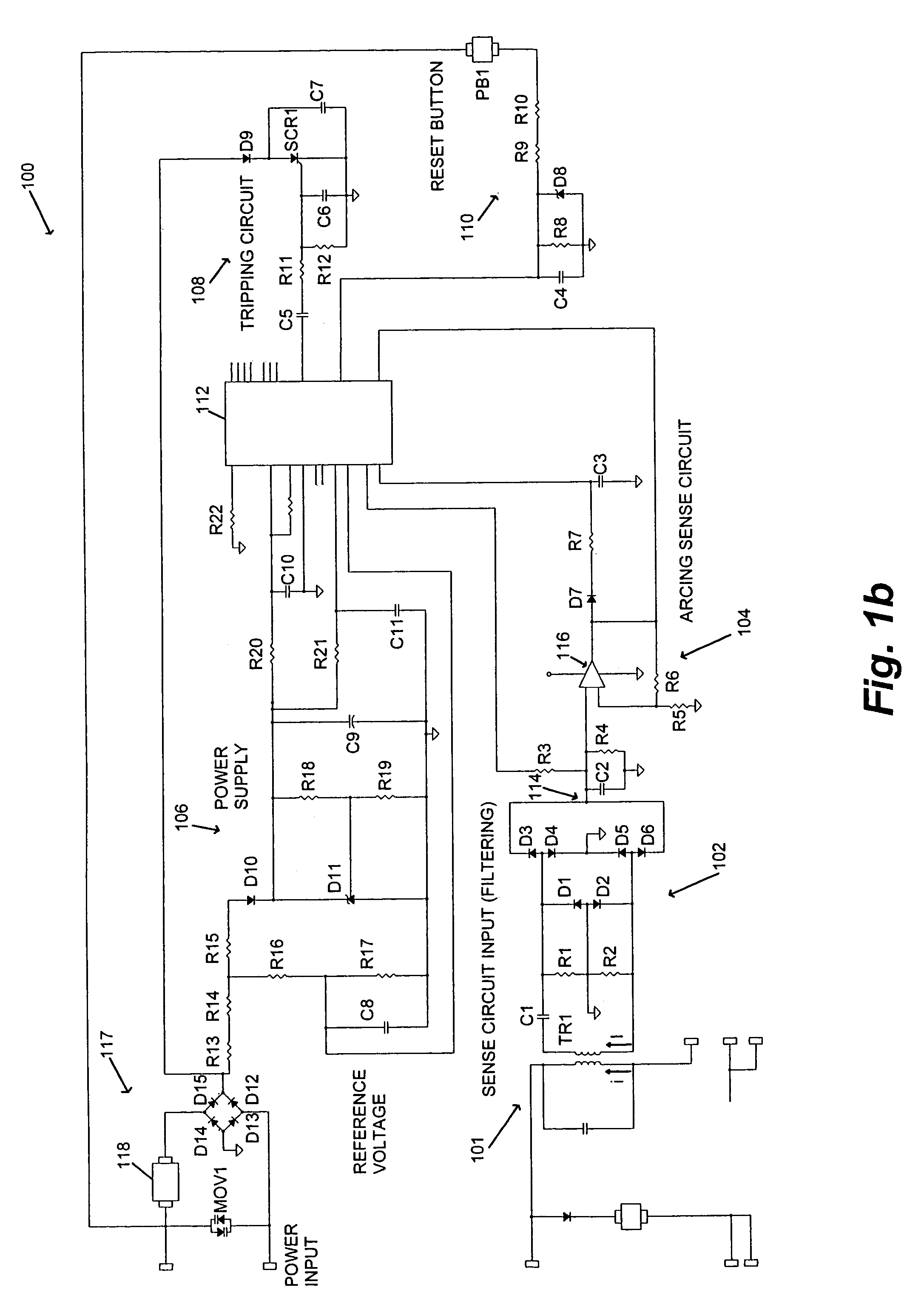
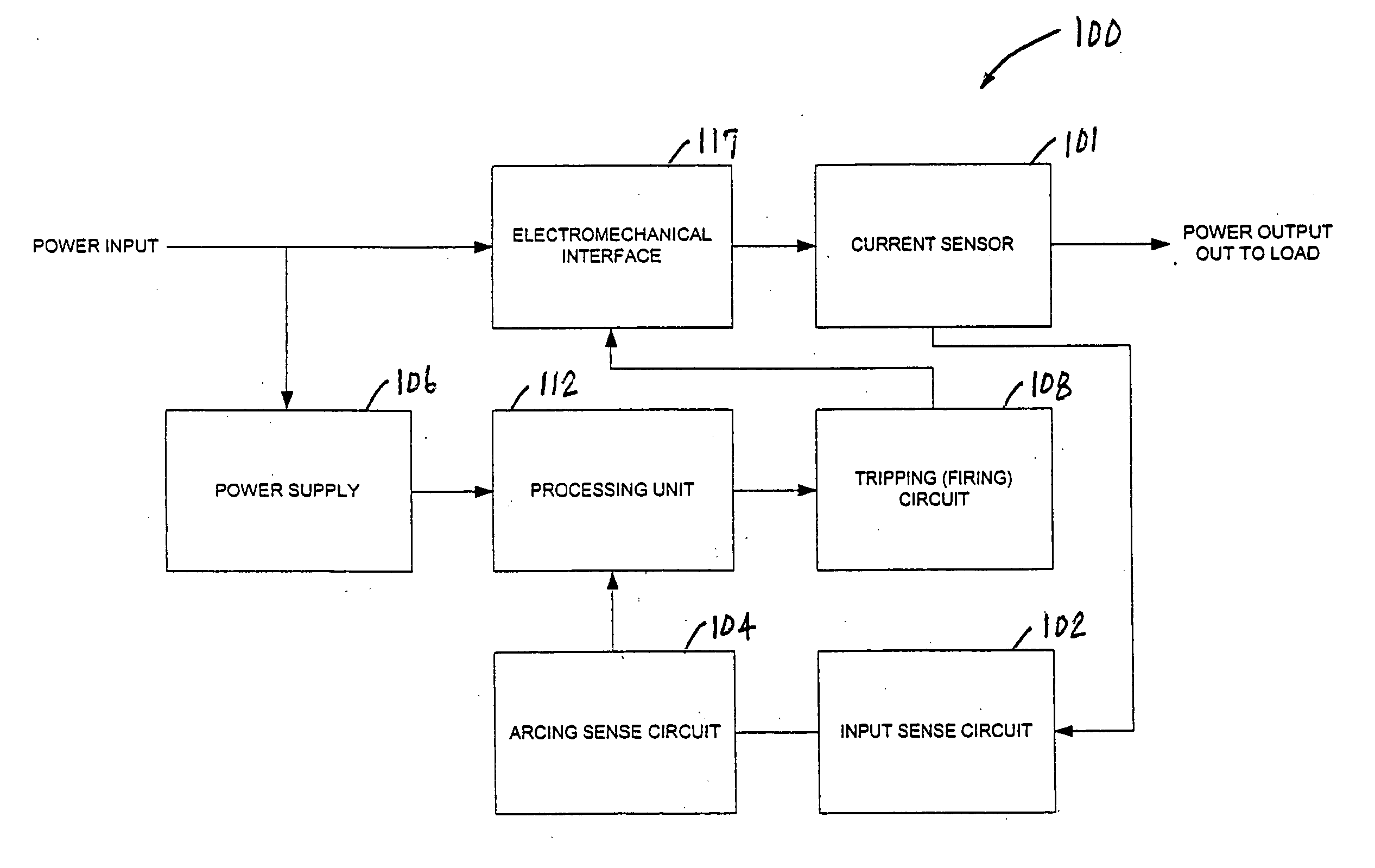
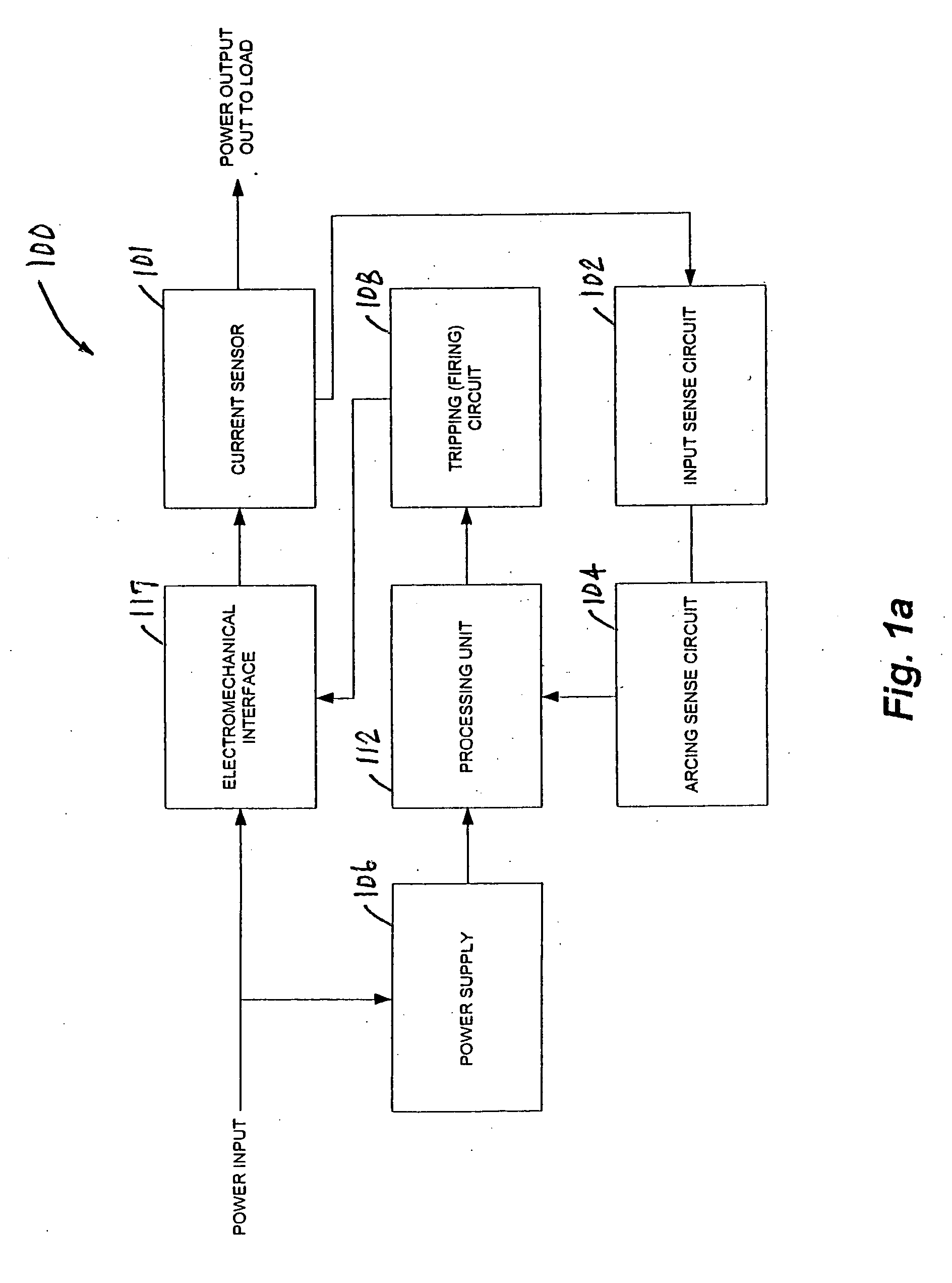
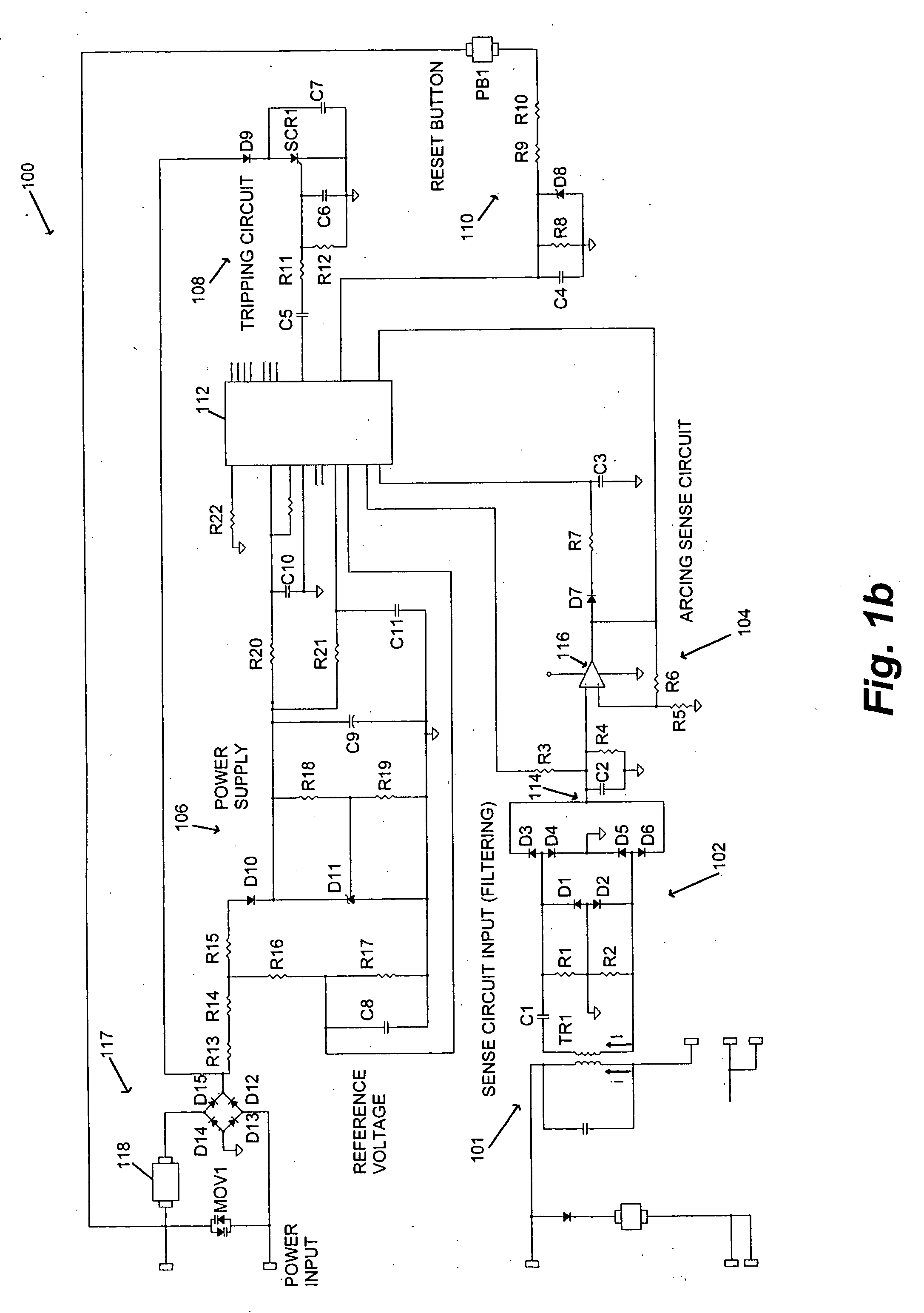
An apparatus and method for detecting arc faults that have reduced susceptibility to nuisance tripping. The apparatus includes a current sensor, an input sense circuit, an arcing sense circuit, a power supply, a tripping (firing) circuit, a processor, and an electromechanical interface. The current sensor monitors a power input comprising an AC current, and provides high frequency components of the. AC current to the input sense circuit. The input sense circuit filters and rectifies the AC signal, and provides the rectified signal to the arcing sense circuit. The arcing sense circuit provides a voltage level accumulated over a predetermined time period, and digital signals indicative of possible electrical arcing occurring during the sampling period, to the processor. The processor measures the voltage level, stores information relating to measured voltages and the digital signals, and processes the stored information using one or more algorithms, thereby determining whether the signals resulted from an arc fault or a nuisance load. In the event the signals resulted from an arc fault, the processor activates the firing circuit to trip the electromechanical interface, thereby interrupting the power output to the load.
Owner:SENSATA TECH MASSACHUSETTS INC
Built-in instrumentation integrating power measurement, distribution and management, power safety, and automation control
PendingUS20200328586A1Power distribution line transmissionCoupling device detailsControl engineeringInstrumentation
Built-in instrumentation for power measurement integrating power monitoring, delivery and management, power safety, and automation control.
Owner:BRAINWAVE RES CORP
Solid-state line disturbance circuit interrupter
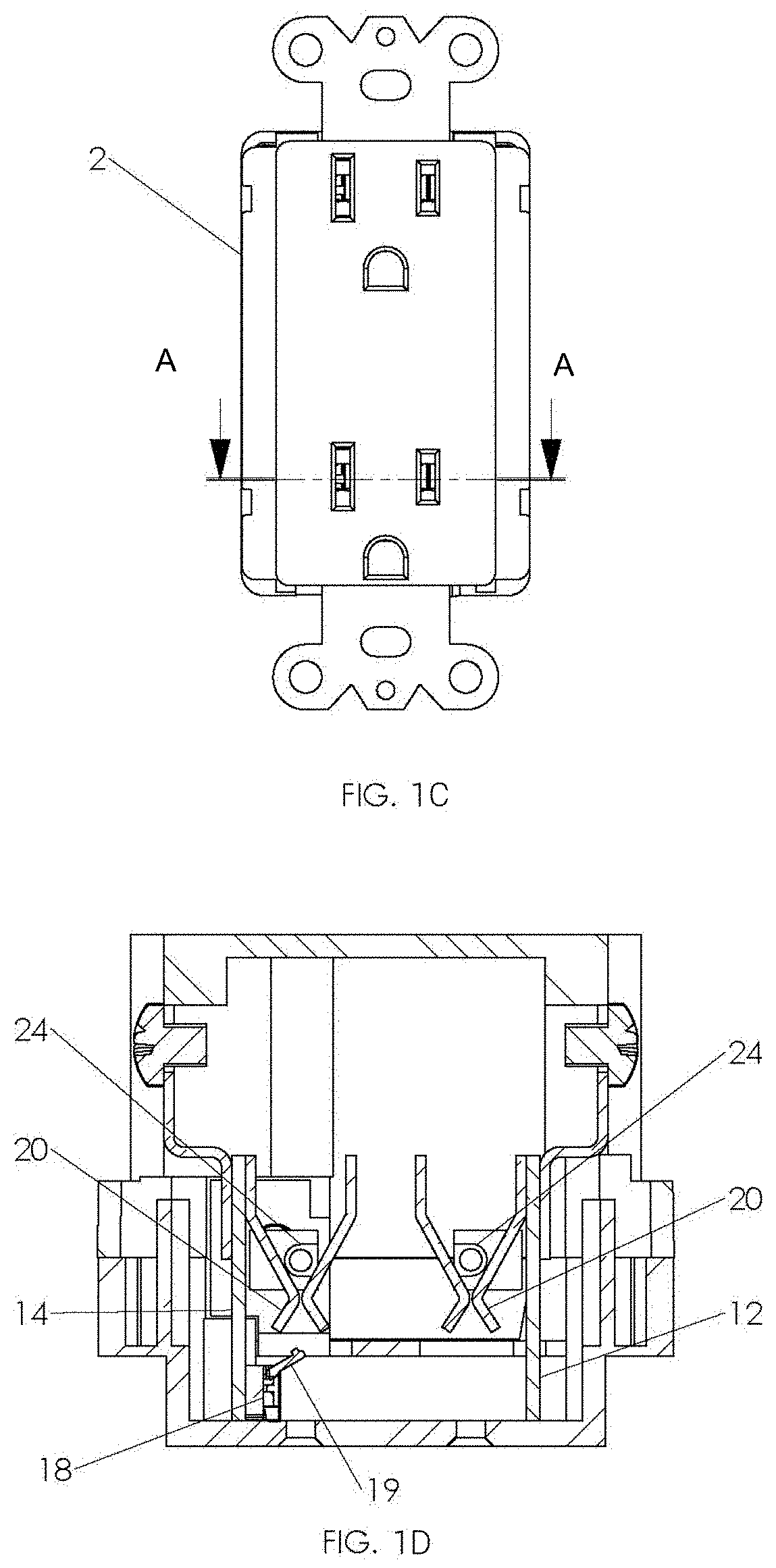
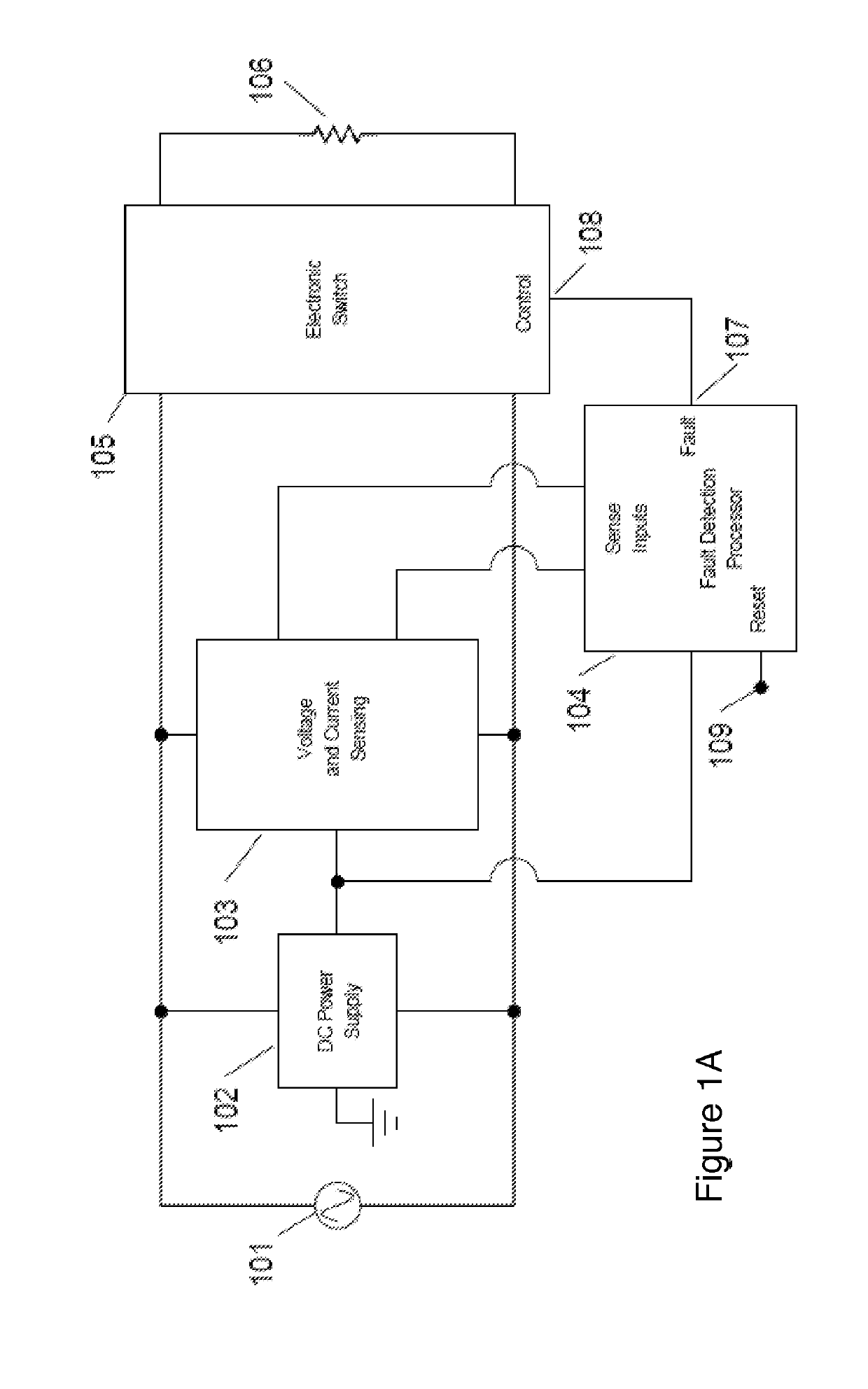
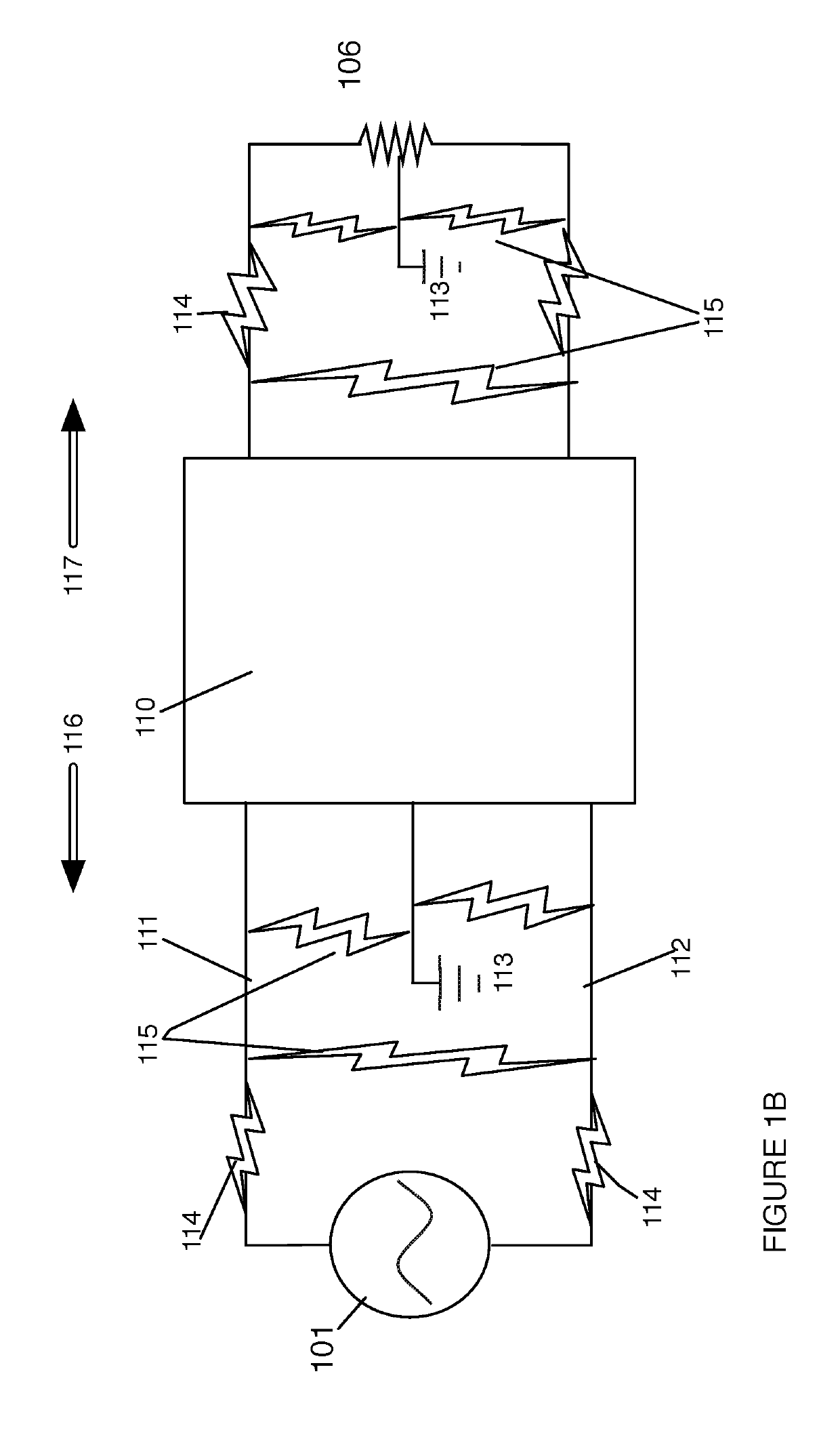
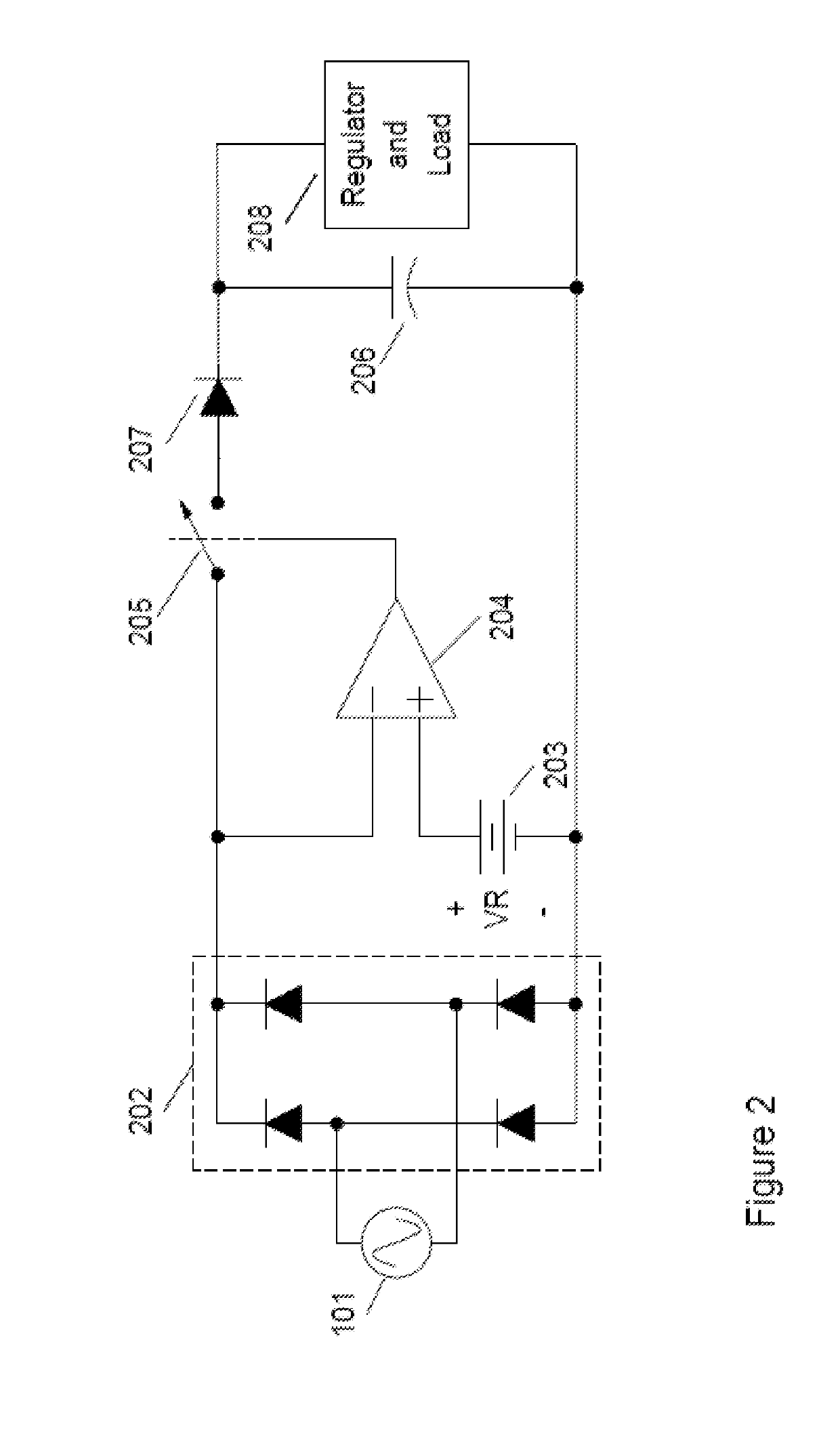
ActiveUS20190207375A1Reduce power consumptionLow costAc-dc conversion without reversalEmergency protection detectionLow voltageHigh pressure
The invention relates to a novel approach for the protection of electrical circuits from ground faults and parallel and series arc faults in a fully solid-state circuit configuration. Solid-state circuits and methods of use are described that provide the key functions of low-voltage DC power supply, mains voltage and current sensing, fault detection processing and high voltage electronic switching.
Owner:INTELESOL LLC
Arc fault circuit interrupter and method providing improved nuisance trip rejection
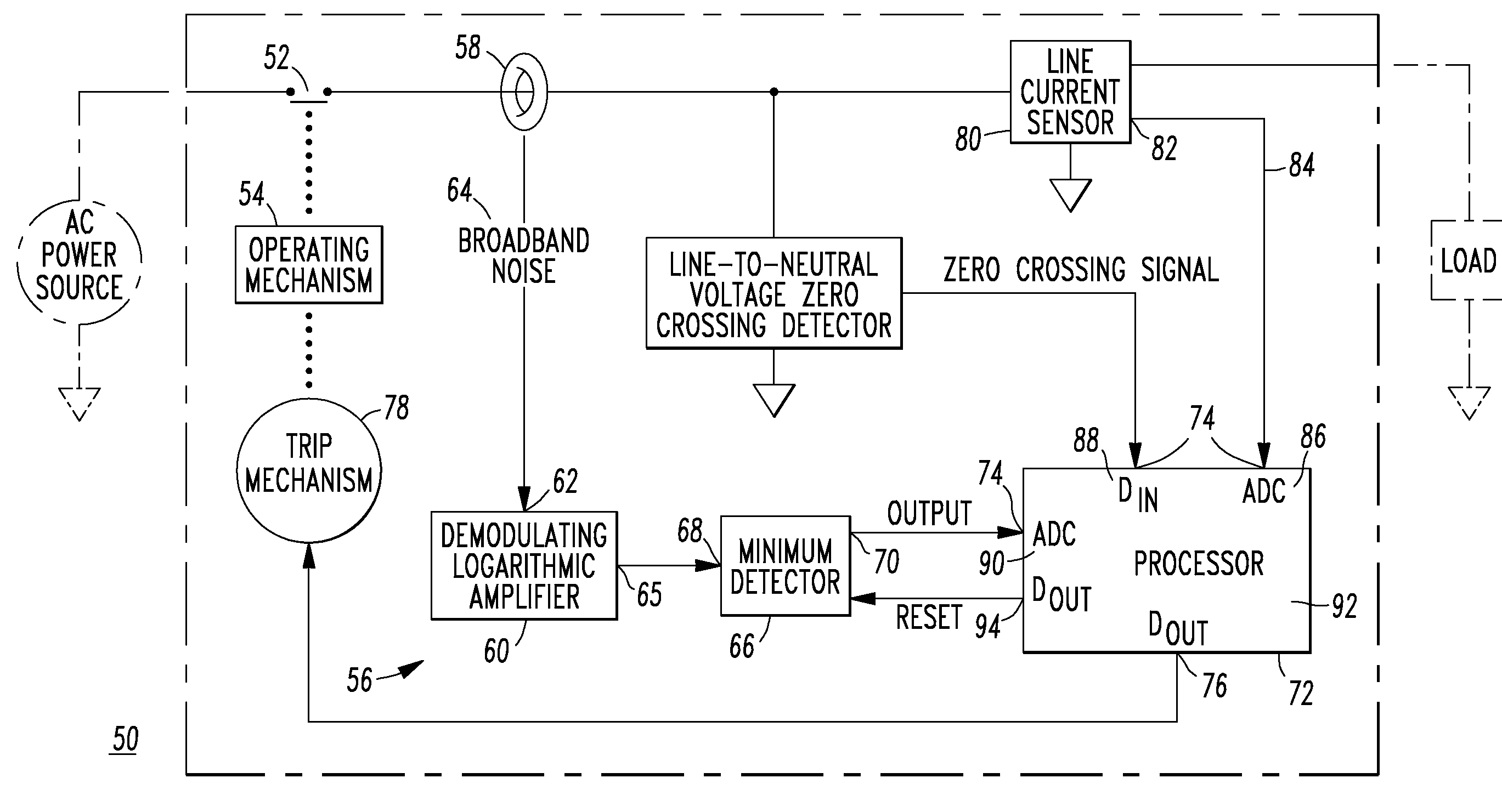
ActiveUS20100157486A1Improve abilitiesEmergency protection data processing meansEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionBroadband noiseCurrent sensor
An arc fault circuit interrupter includes separable contacts, an operating mechanism and an arc fault detector structured to detect an arc fault condition operatively associated with the contacts. The arc fault detector includes a tuned current sensor structured to sense broadband noise of a current flowing through the contacts, a compression circuit including an input of the sensed broadband noise and an output. The compression circuit compresses the dynamic range of the sensed broadband noise. A minimum detector includes an input of the compression circuit output and an output of the minimum value of the minimum detector input. A processor includes a number of inputs and an output. One of the inputs is the output of the minimum value of the minimum detector. A trip mechanism cooperates with the output of the processor and the operating mechanism to trip open the contacts responsive to the detected arc fault condition.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
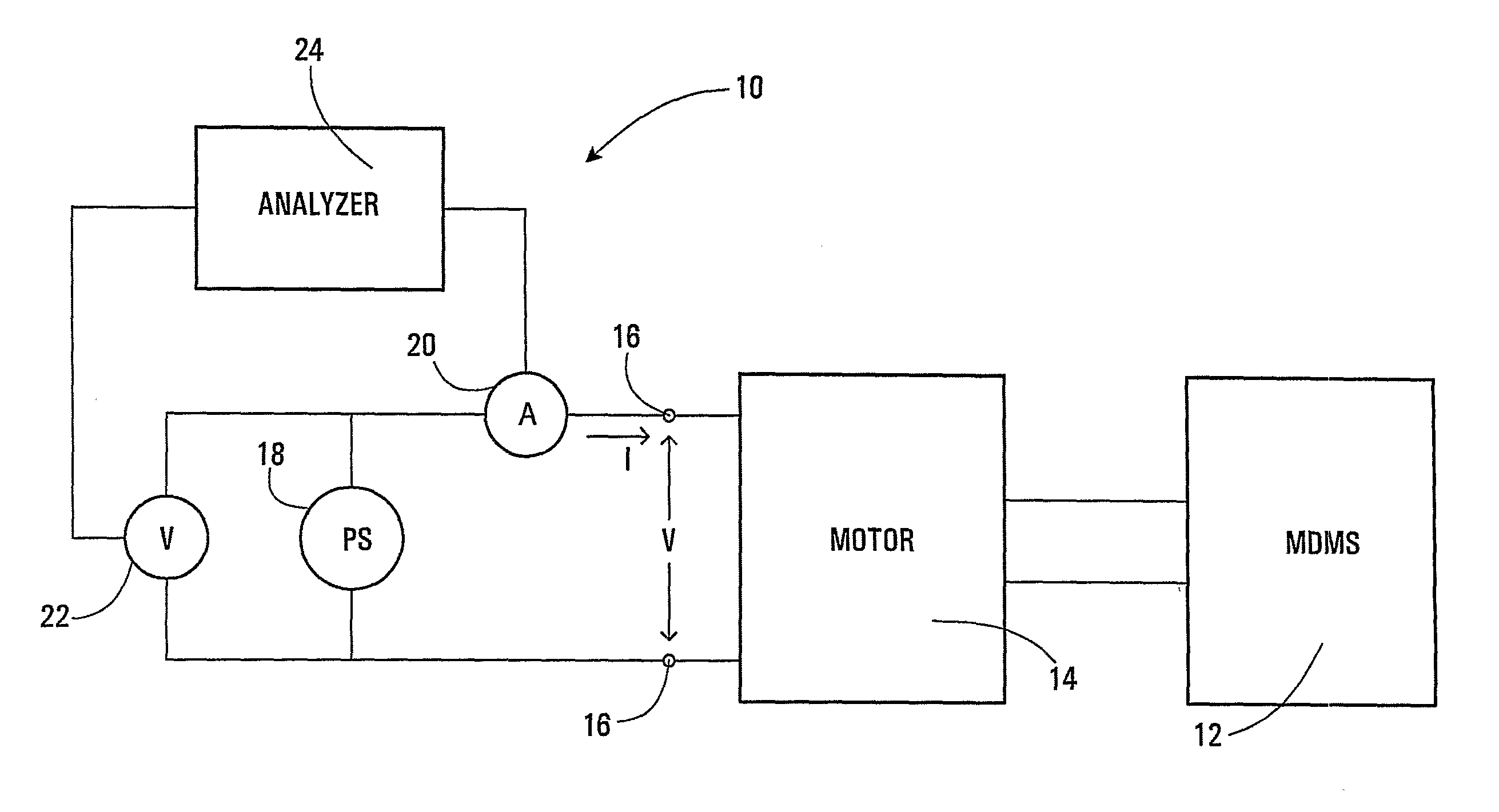
Method and Apparatus for Assessing Condition of Motor-Driven Mechanical System
InactiveUS20070282548A1Reliable indicatorMachine gearing/transmission testingMachine bearings testingMotor driveAdmittance
Conditions of a mechanical system driven (12) by a motor (14) can be assessed by monitoring an admittance or impedance at an input to the motor (14) over a period of time. The admittance or impedance may be determined by measuring the input voltage (22) and current (20). Variations in admittance or impedance are associated with known conditions including faults. An analyser (24) processes the admittance or impedance and provides a warning signal if a known fault condition is determined. The processing may be done using a neural processor.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
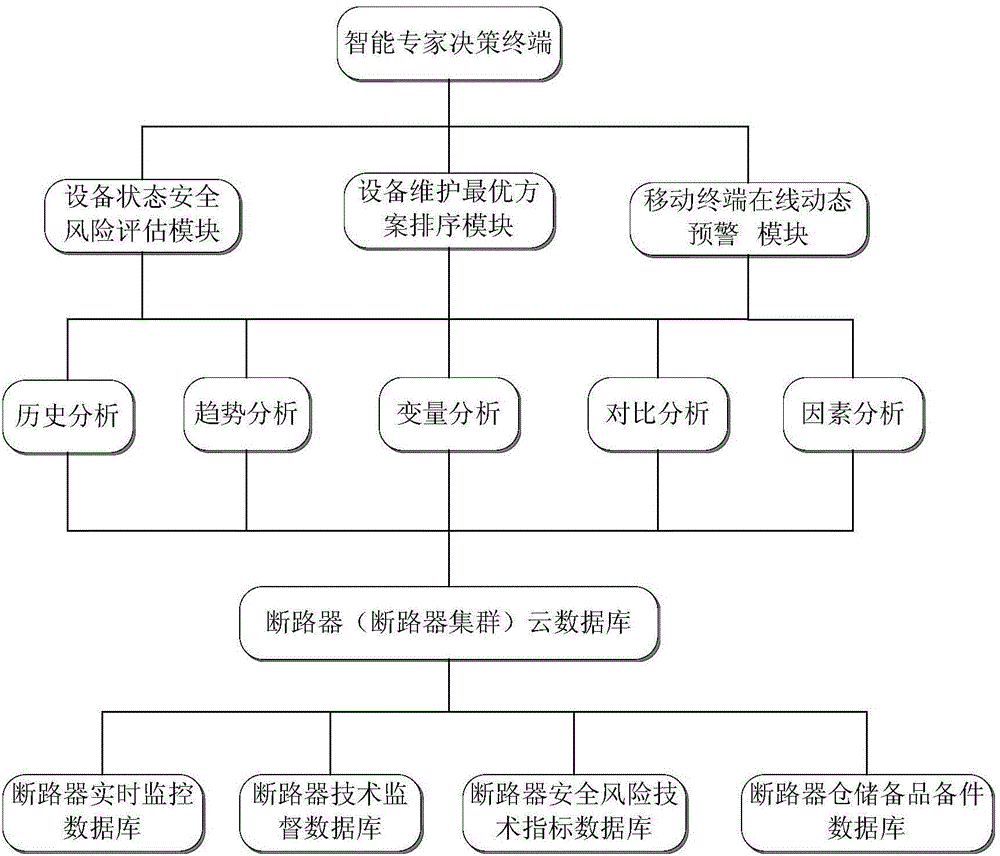
Intelligent multidimensional big-data analyzing expert system for high-voltage circuit breakers of power grid
ActiveCN104810926AIntelligent Monitoring ClusterImprove reliabilityCurrent/voltage measurementTesting/monitoring control systemsPower gridOnline and offline
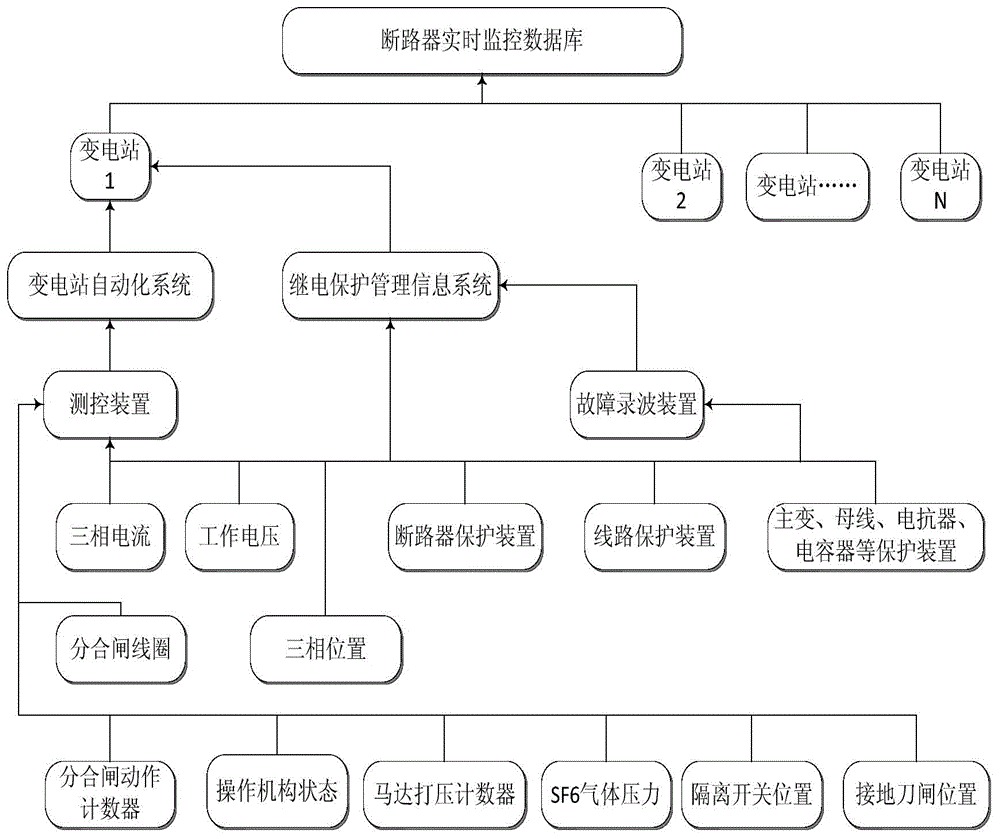
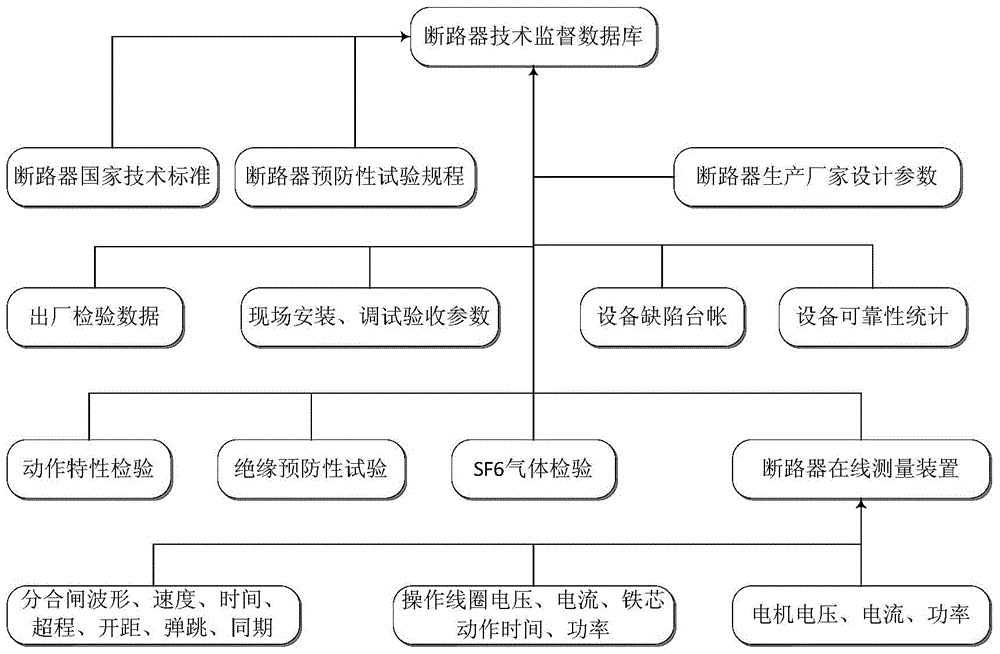
The invention discloses an intelligent multidimensional big-data analyzing expert system for high-voltage circuit breakers of a power grid. The intelligent multidimensional big-data analyzing expert system is composed of a high-voltage circuit breaker cloud database or a high-voltage circuit breaker cluster (hereafter called circuit breaker) cloud database and an intelligent expert deciding terminal with a multidimensional analyzing function. The intelligent multidimensional big-data analyzing expert system has the advantages that on the basis of a big-data analysis technology, the intelligent multidimensional big-data analyzing expert system performs multidimensional analysis on huge amount of online and offline cloud data, so that unified real-time monitoring and management for the circuit breakers is achieved, functions of circuit breaker state security risk assessment, optimal equipment maintenance scheme ordering, online mobile terminal dynamic warning and the like are provided, security and economic levels in running maintenance of high-voltage circuit breaker equipment are promoted, and the high-voltage circuit breaker can be managed better in an equipment overall lifecycle.
Owner:杨启蓓
High impedance fault detection
An apparatus, system, and method for detecting high impedance faults in electrical power lines using a composite high impedance fault detection system having a voter logic that samples the logical outputs from a plurality of independent high impedance detection systems and determines a high impedance fault if any two of the plurality of independent high impedance detection systems indicates a high impedance fault. Preferably, the plurality of high impedance detection systems include a wavelet based high impedance fault detection system having a first logical output, a higher order statistics based high impedance fault detection system having a second logical output, and a neural net based high impedance fault detection system having a third logical output. Preferably, each of the plurality of high impedance fault detection systems includes an independent high impedance fault detection application that independently detects a high impedance fault on the electrical power line.
Owner:ABB INC
Distributing line fault detection system based on cloud server
ActiveCN107994539AShorten the timeReliable design principleEmergency protection data processing meansData switching networksPower flowComputer module
The invention relates to a distributing line fault detection system based on a cloud server. The distributing line fault detection system comprises the cloud server and data management subsystems arranged on all area line monitoring points of a power distribution network respectively; voltage and current signals of power supply lines are collected, and the voltage and current signals of the powersupply lines are weak electric signals obtained in the mode that all the voltage and current signals of the power supply lines are converted by a voltage current transformer respectively; switch datacollecting modules are used for collecting action characteristics of switches and signals of the temperatures of contactors; the line monitoring points are subjected to forecast judgment of fault types according to data matched in an overhauling log base; the monitoring points subjected to forecast judgment of fault types according to judging modules are further subjected to fault warning identification reminding, and forecast fault position information of the corresponding monitoring points is further sent to mobile terminals of area maintenance persons of faults.
Owner:STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER CO BINZHOU CITY BINCHENG DISTRICT POWER SUPPLY CO
Surge arrestor condition monitoring
InactiveUS20120239321A1Easily evaluate and identifyImprove convenienceElectrical testingEmergency protection data processing meansEngineeringDrain current
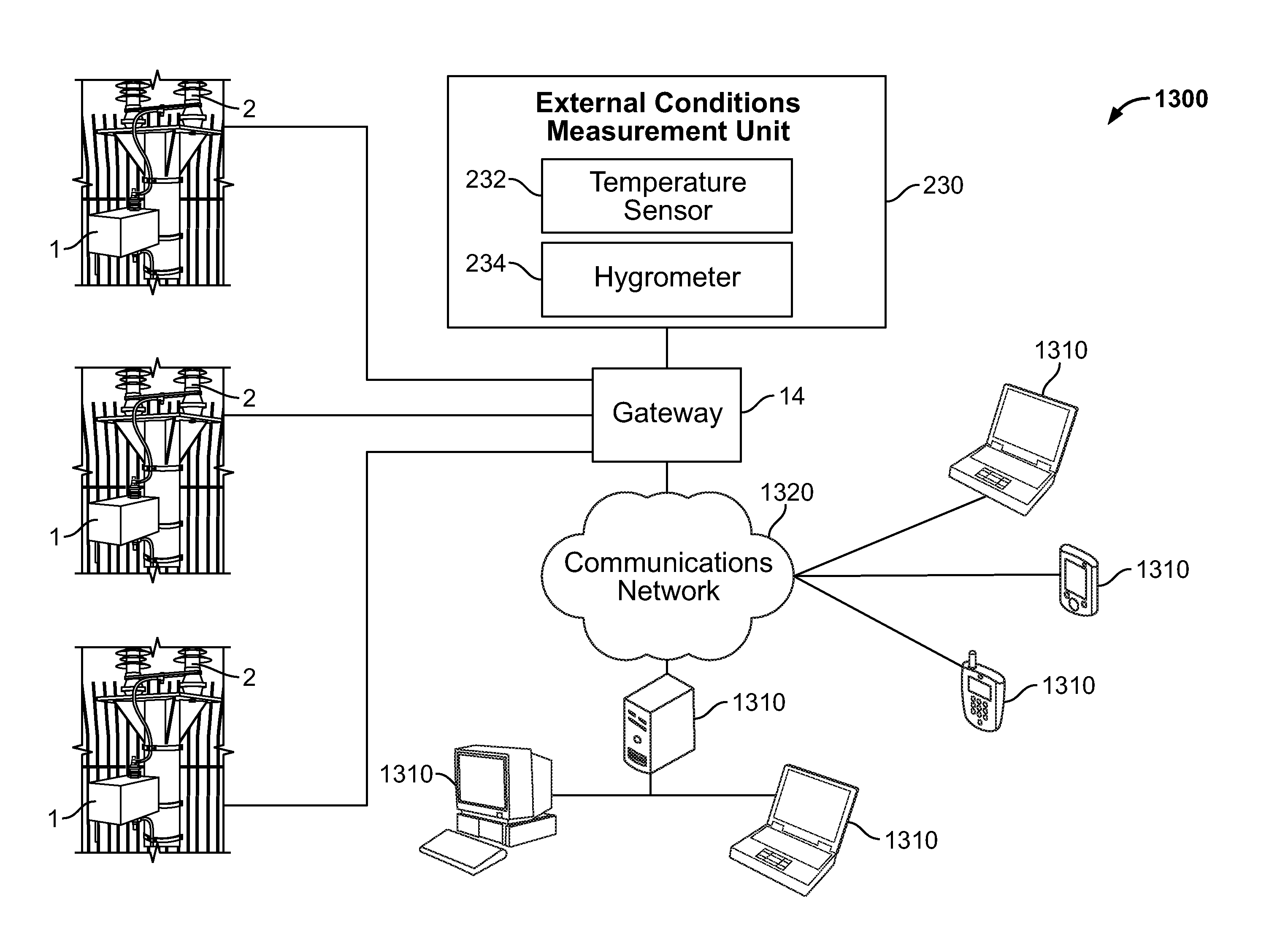
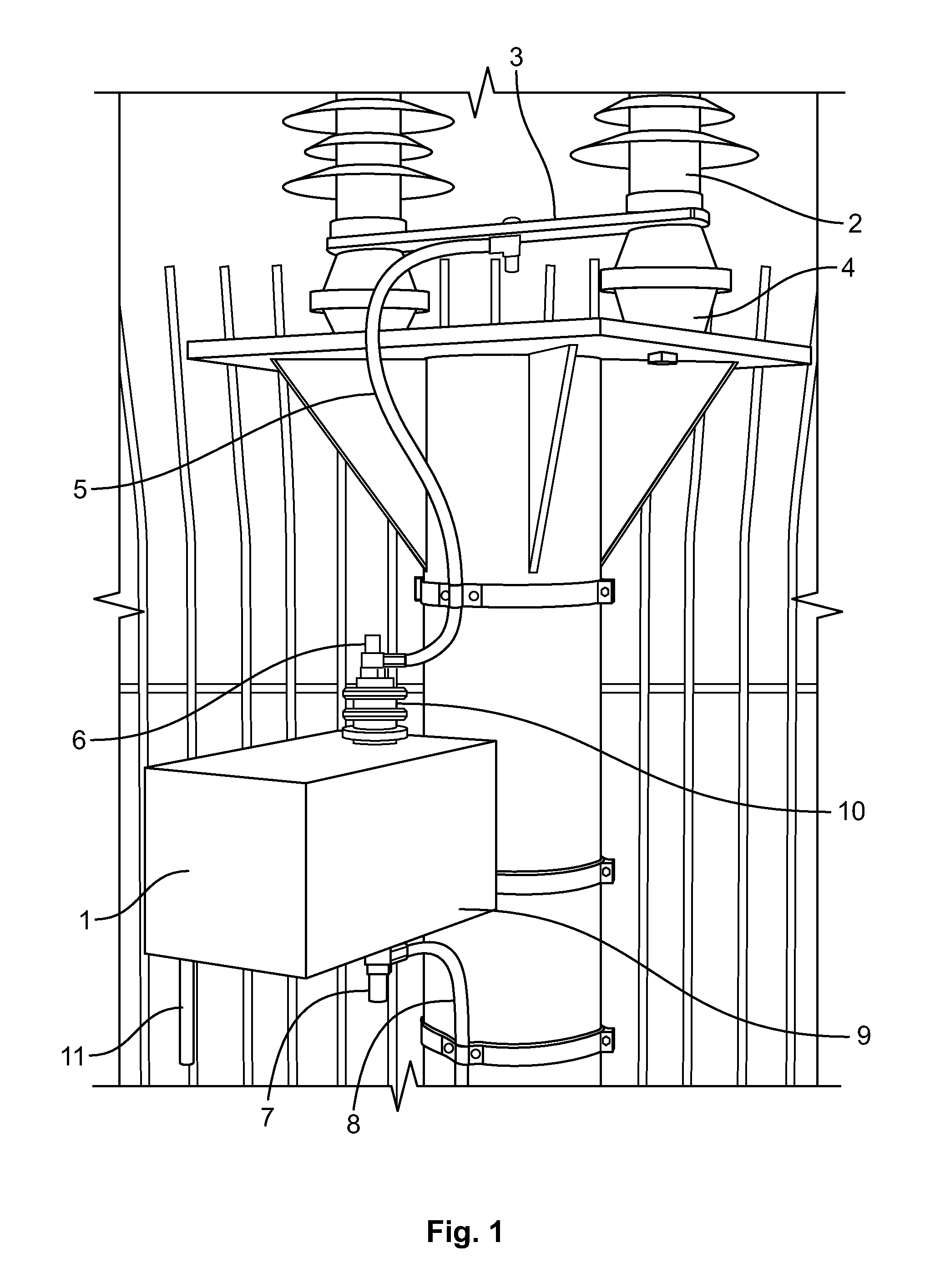
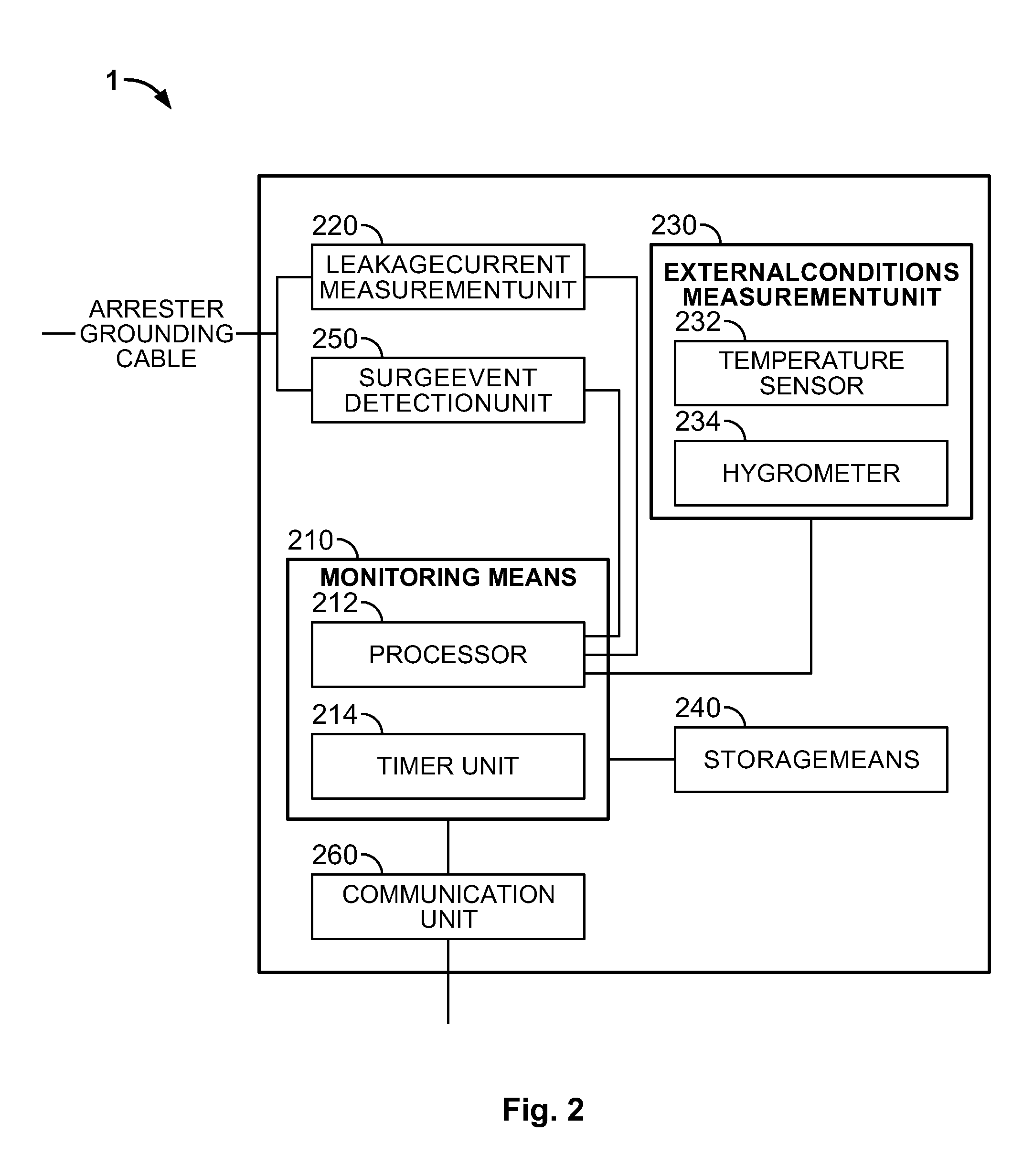
A monitoring device (1) for monitoring a condition of a surge arrester comprises monitoring means (210) adapted to monitor a leakage current recovery of the surge arrester after an occurrence of a surge over a recovery monitoring period following the surge event. The monitoring of recovery of surge arrester leakage current following the surge event in the arrester is used to estimate the time to recovery of the leakage currents and to identify a deterioration in the condition of the arrester by comparing the evolution of the time to recovery over time.
Owner:RAYCHEM INT IRISH BRANCH
Method for detecting arc faults
InactiveUS20060050450A1Improve reliabilityReduce sensitivityEmergency protection data processing meansEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionCurrent sensorDigital signal
An apparatus and method for detecting arc faults that have reduced susceptibility to nuisance tripping. The apparatus includes a current sensor, an input sense circuit, an arcing sense circuit, a power supply, a tripping (firing) circuit, a processor, and an electromechanical interface. The current sensor monitors a power input comprising an AC current, and provides high frequency components of the. AC current to the input sense circuit. The input sense circuit filters and rectifies the AC signal, and provides the rectified signal to the arcing sense circuit. The arcing sense circuit provides a voltage level accumulated over a predetermined time period, and digital signals indicative of possible electrical arcing occurring during the sampling period, to the processor. The processor measures the voltage level, stores information relating to measured voltages and the digital signals, and processes the stored information using one or more algorithms, thereby determining whether the signals resulted from an arc fault or a nuisance load. In the event the signals resulted from an arc fault, the processor activates the firing circuit to trip the electromechanical interface, thereby interrupting the power output to the load.
Owner:SENSATA TECH MASSACHUSETTS INC
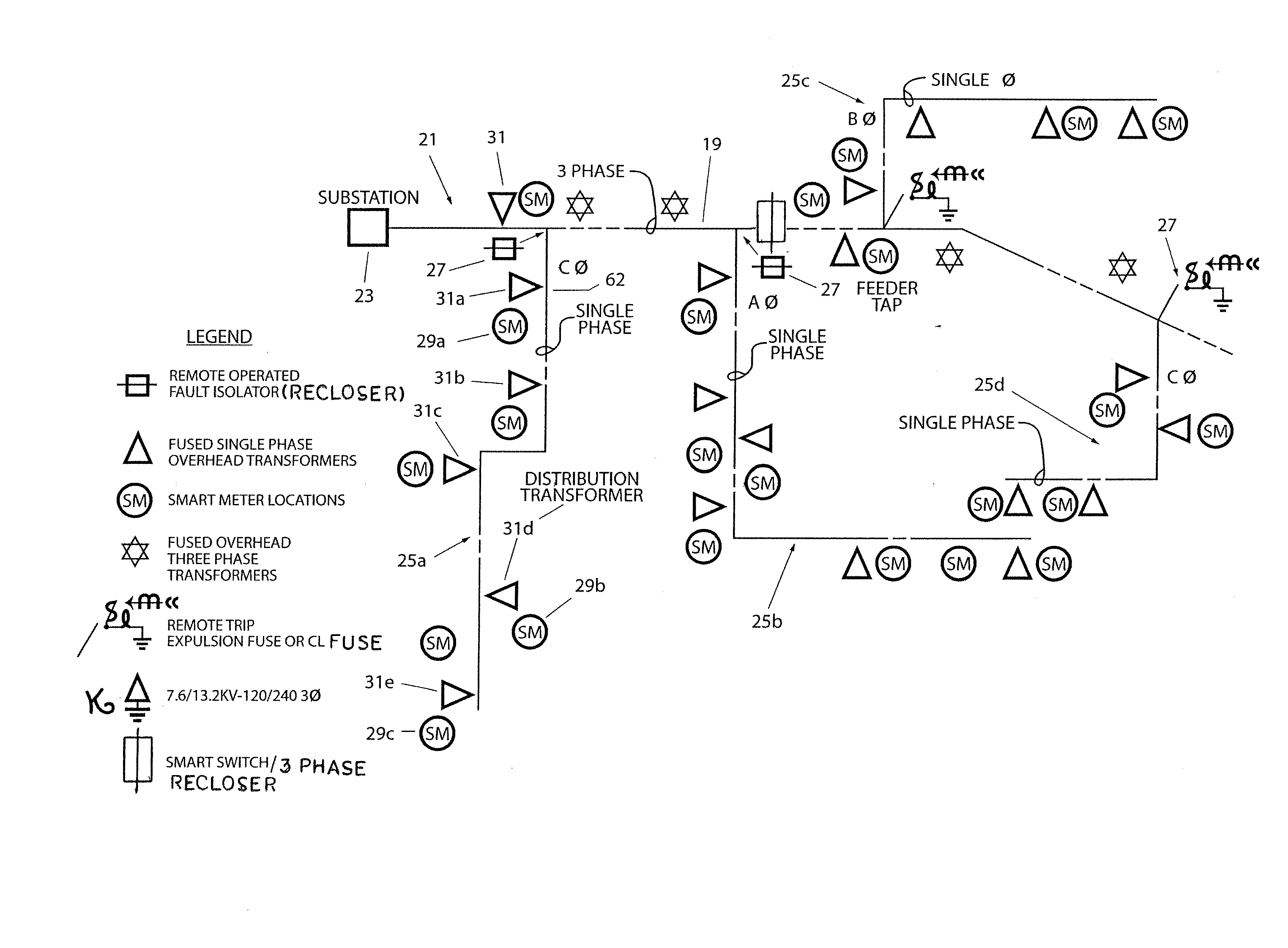
Low fault current isolator system
ActiveUS20140362486A1Low costQuicker and saferProtective switch detailsCoupling contact membersDistribution transformerElectrical conductor
A low fault current isolation arrangement senses a loss of voltage and automatically isolates and de-energizes a down live primary wire if overcurrent protection devices have not cleared the high impedance fault in an electric power distribution network. Incorporating an operator selectable time delay response, the low fault current isolation arrangement permits overcurrent protection devices to attempt to detect and shut down the affected conductor, and then isolates and shuts down the low current fault if the overcurrent devices are not successful. The isolation arrangement continuously monitors AC voltage as remotely provided by smart meters even after a fault location is de-energized, and serves as a back up, and not as a replacement, for existing overcurrent protection schemes. A host computer operates in conjunction with plural smart meters each coupled to an associated customer distribution transformer in conjunction with the fault isolator to detect and shut down high impedance faults.
Owner:ELECTRICAL MATERIALS
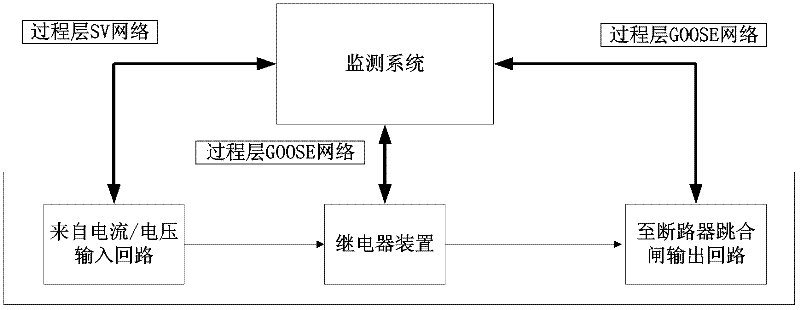
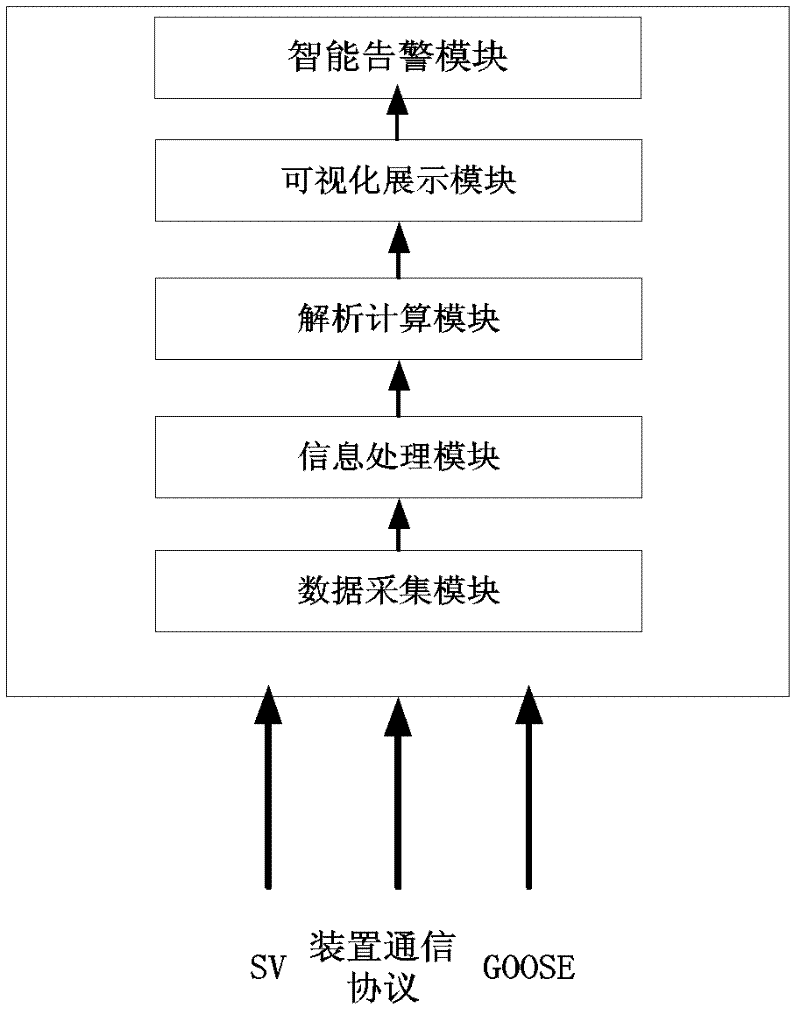
System for visually dynamically monitoring running state of relay protector
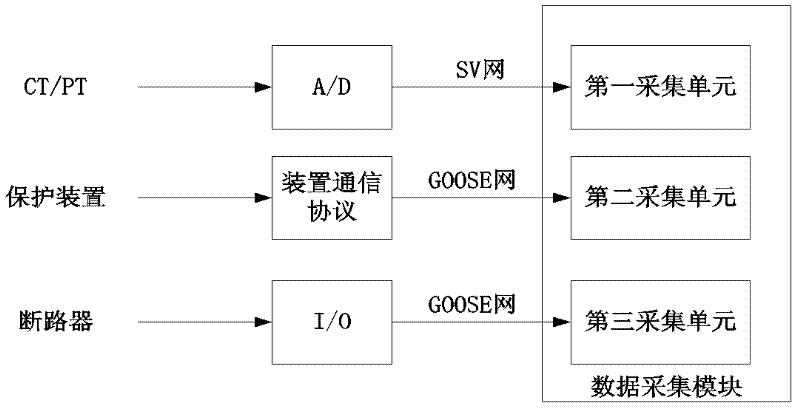
ActiveCN102647026AReduce chance of protection flawsEmergency protection data processing meansInformation processingData acquisition
The invention relates to a system for visually dynamically monitoring running state of a relay protector, belonging to the technical field of power supply distribution. The system comprises a data acquisition module, an information processing module, an analysis calculation module, a visual display module, and an intelligent alarm module, wherein the data acquisition module is used for respectively acquiring an SV (signature version) message, a protection device communication protocol message, and a GOOSE (generic object oriented substation event) message, and outputting the messages to the information processing module. According to the invention, the technician can visually observe the real-time running and action state of a protection device so as to determine the accordance degree between the action response property of the relay protector and the protection design requirement.
Owner:SHANGHAI YIHAO AUTOMATION CO LTD
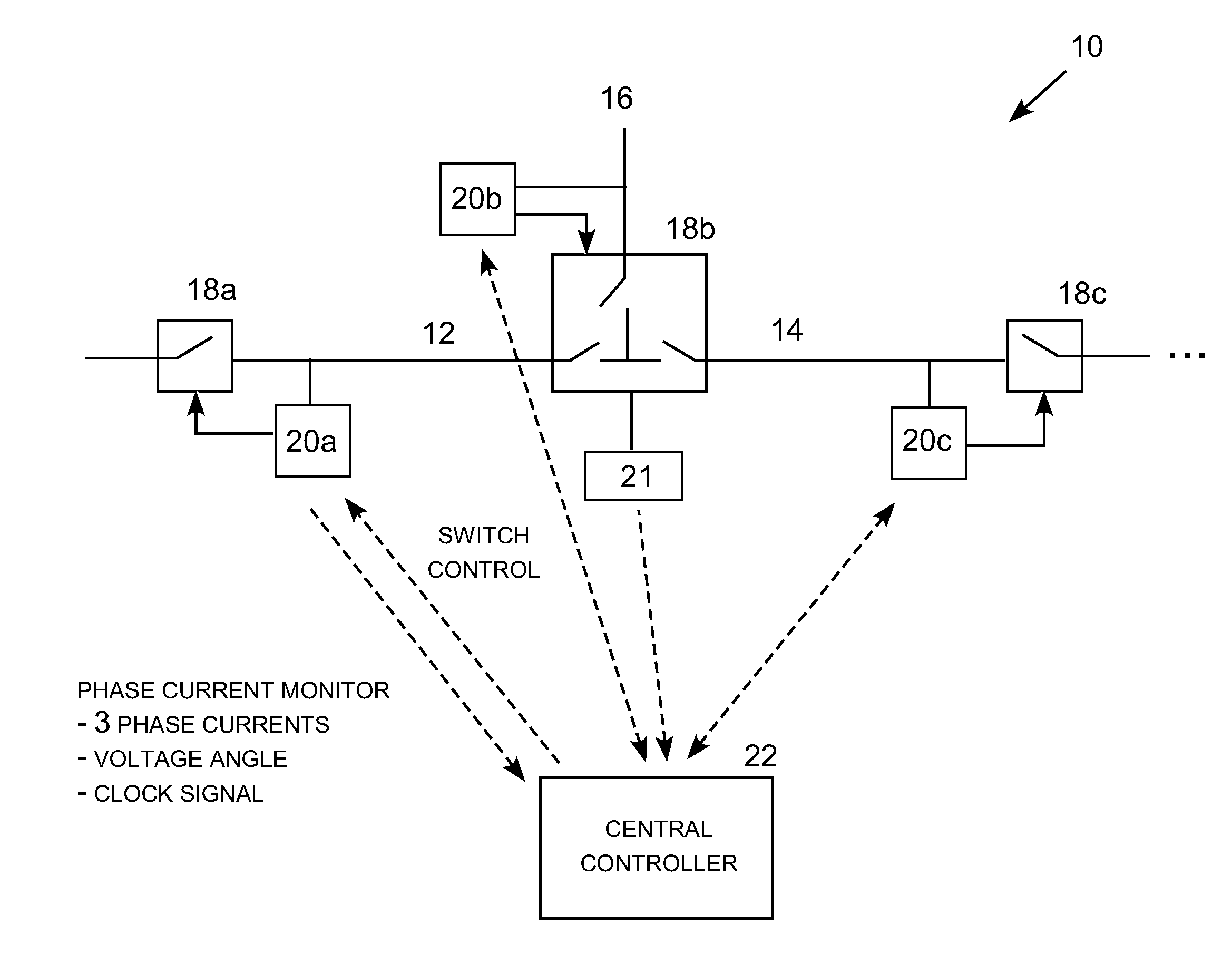
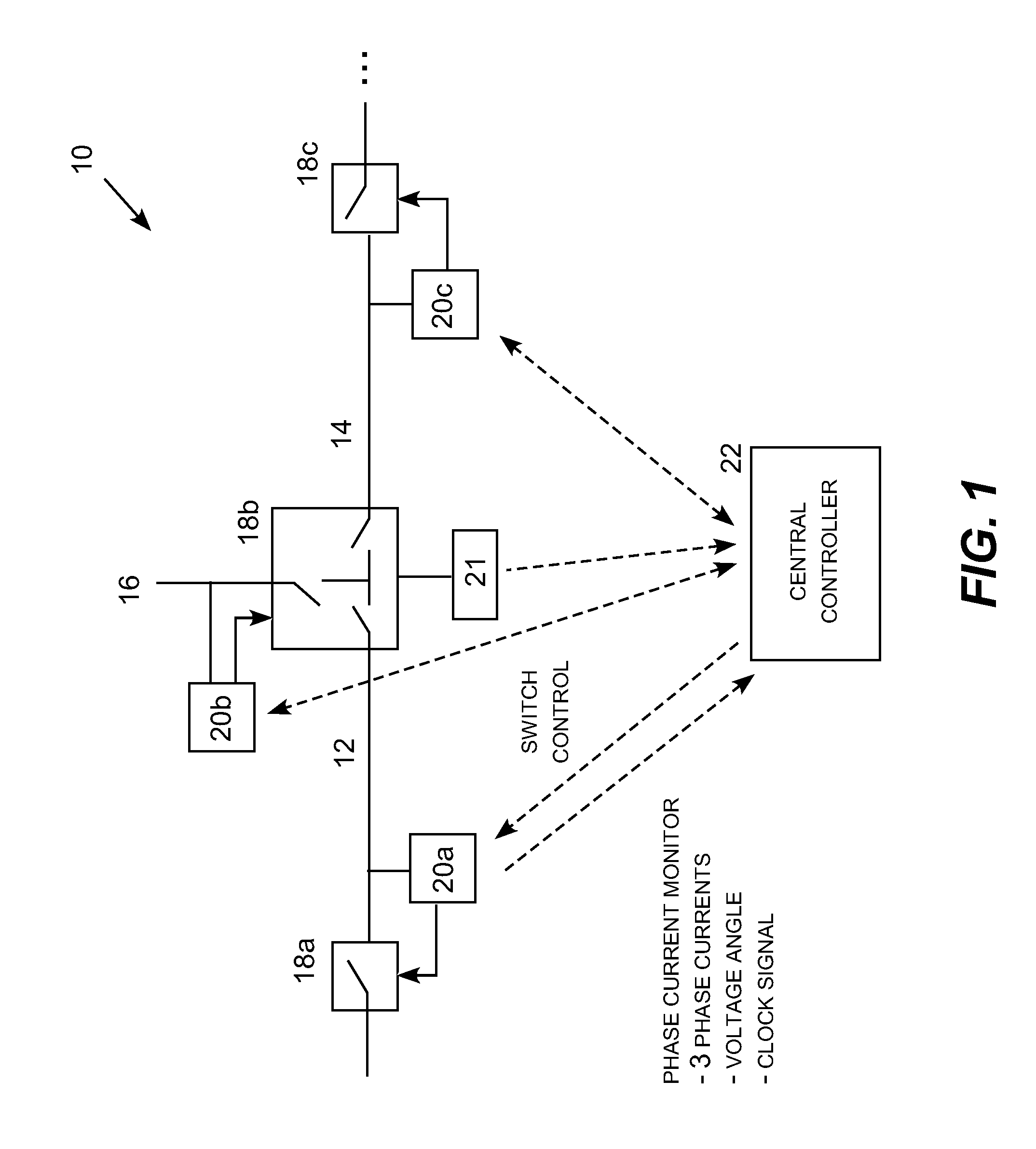
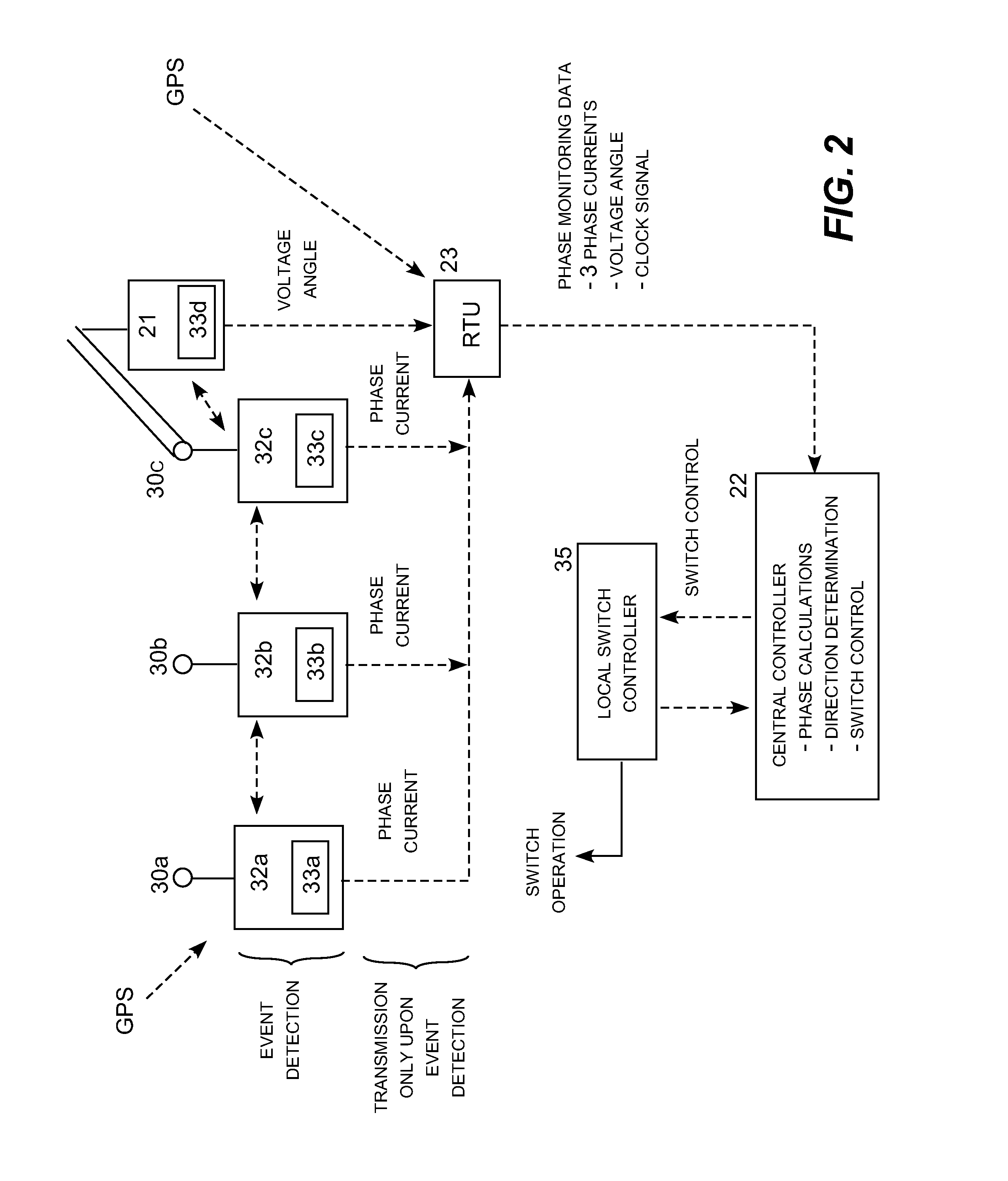
Fault detection and isolation using a common reference clock
A fault detection and isolation system for distribution electric power lines utilizing a remote reference voltage signal, multiple three-phase current monitors producing asynchronous event data, and a common reference clock. A voltage measurement obtained for a power line at a substation may be synchronized with multiple current phase measurements taken at a power monitoring location along that particular power line. The same voltage measurement may be similarly synchronized with current measurements taken at multiple current monitoring locations along the power line. As a result, the same voltage measurement may be synchronized with current measurements taken multiple tap points along the power allowing a fault on a tapped line segment to be identified, located and isolated. An alternative embodiment utilizes differential current analysis utilizing current measurements from adjacent current monitoring locations correlated to a common reference clock to locate faults and therefore does not require a voltage measurement.
Owner:SOUTHERN STATES
Popular searches
Fault location Testing circuits Emergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/current Arrangements responsive to excess current Special data processing applications Resources Material dimension control Dc network circuit arrangements Control using feedback Systems intergating technologies
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com