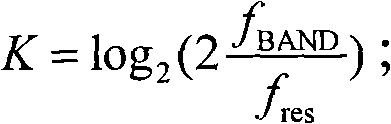Patents
Literature
683 results about "Self-tuning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In control theory a self-tuning system is capable of optimizing its own internal running parameters in order to maximize or minimize the fulfilment of an objective function; typically the maximization of efficiency or error minimization.
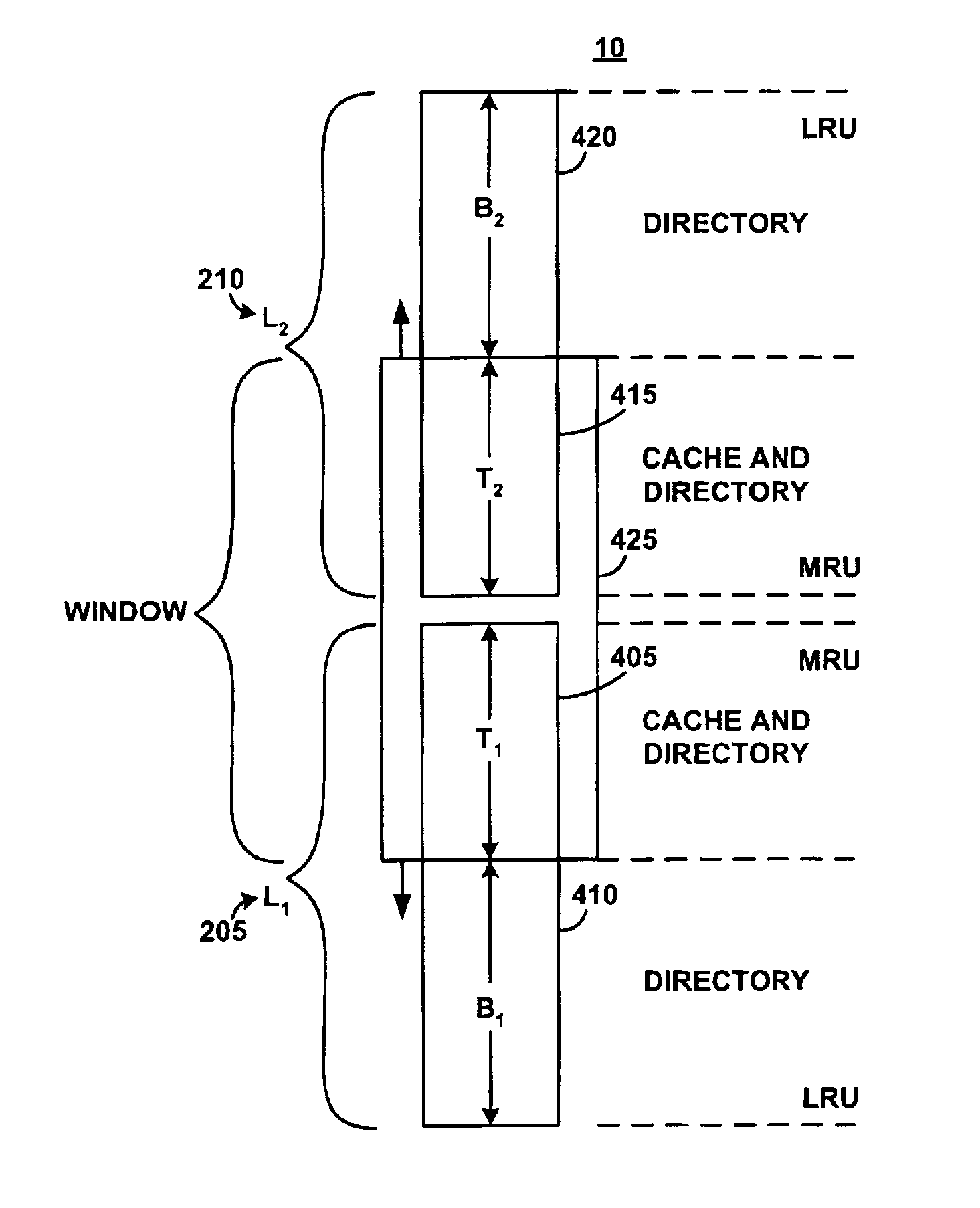
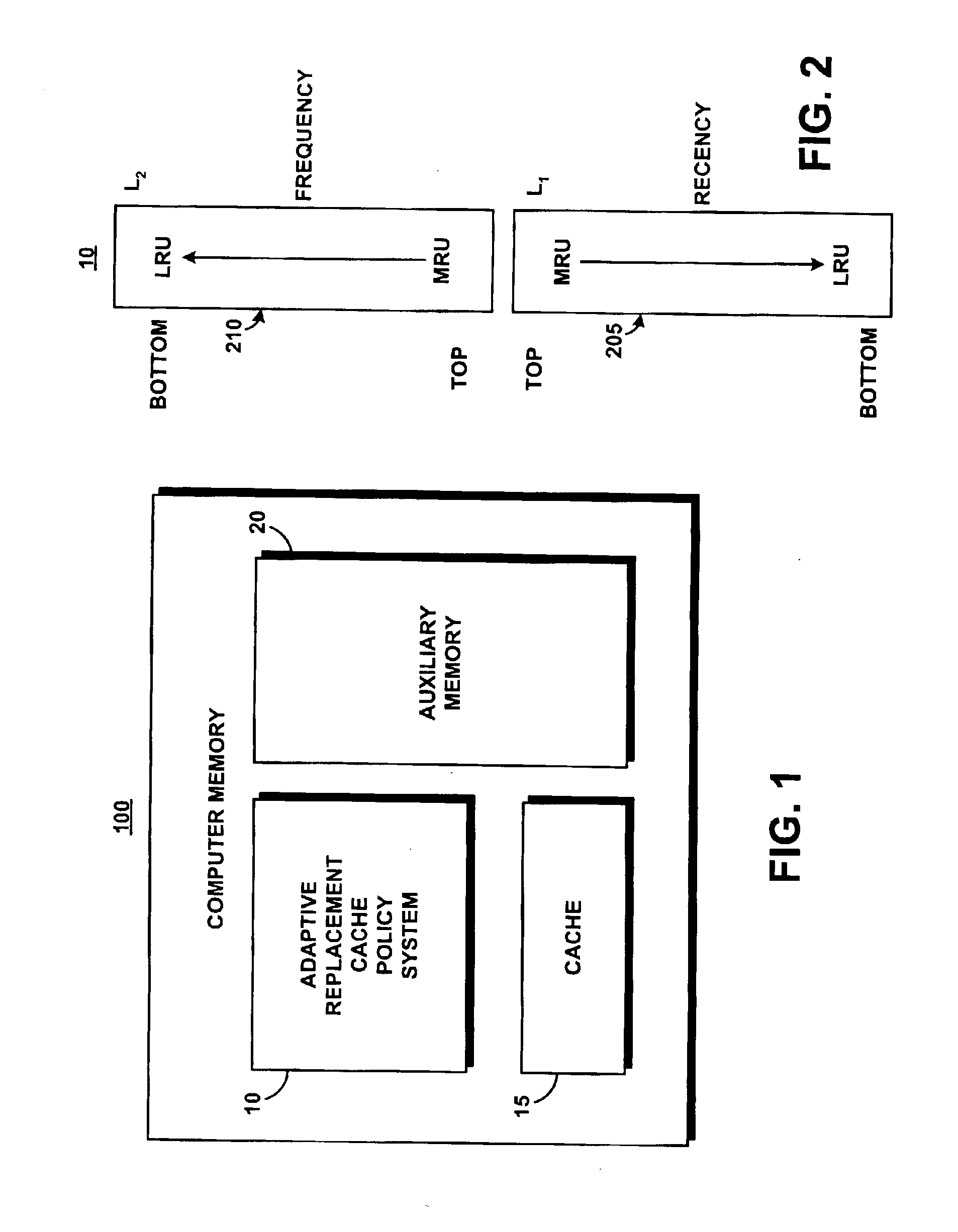
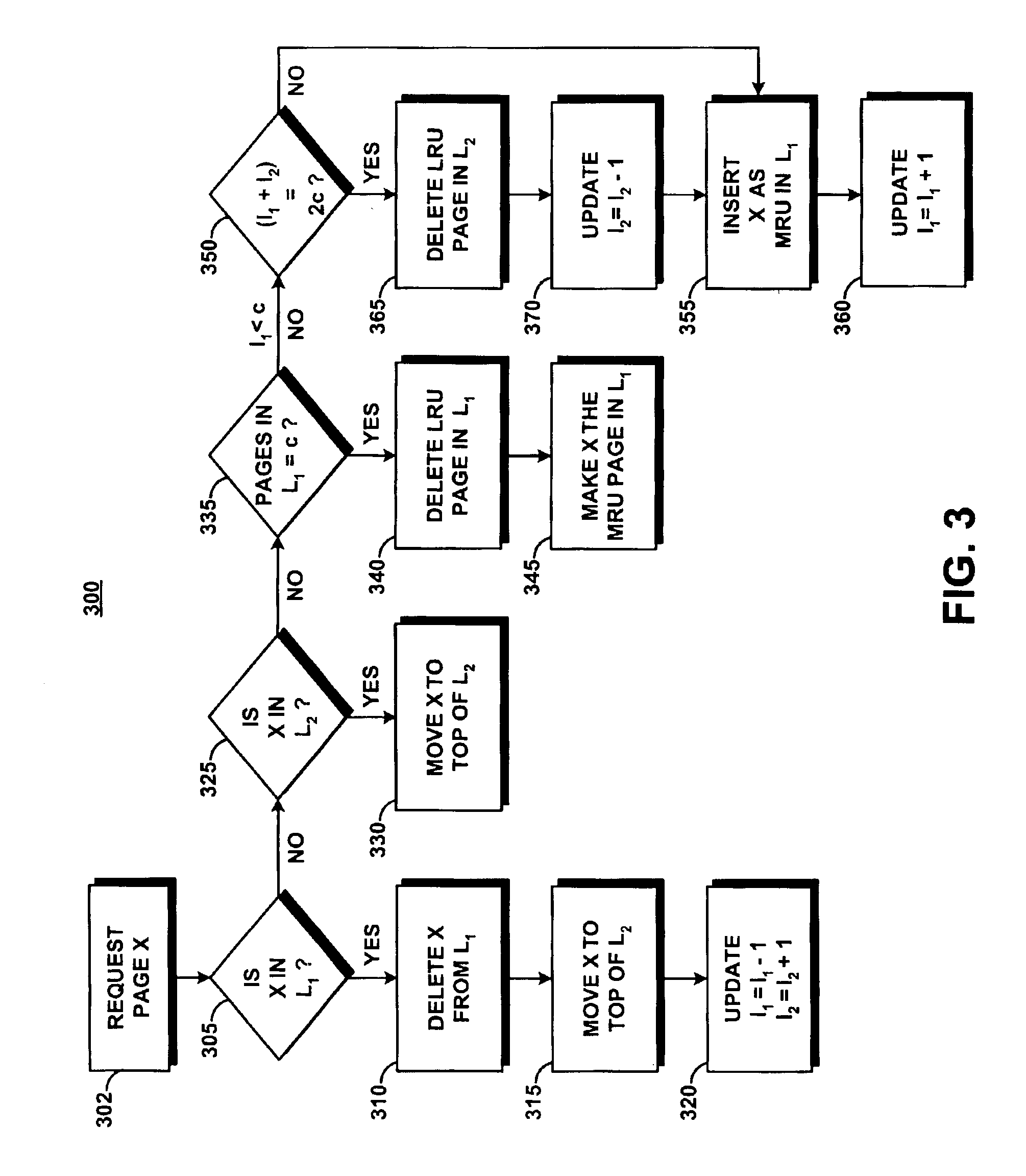
System and method for implementing an adaptive replacement cache policy
ActiveUS6996676B2Fast trackReduce overheadMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSelf-tuningHome page
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
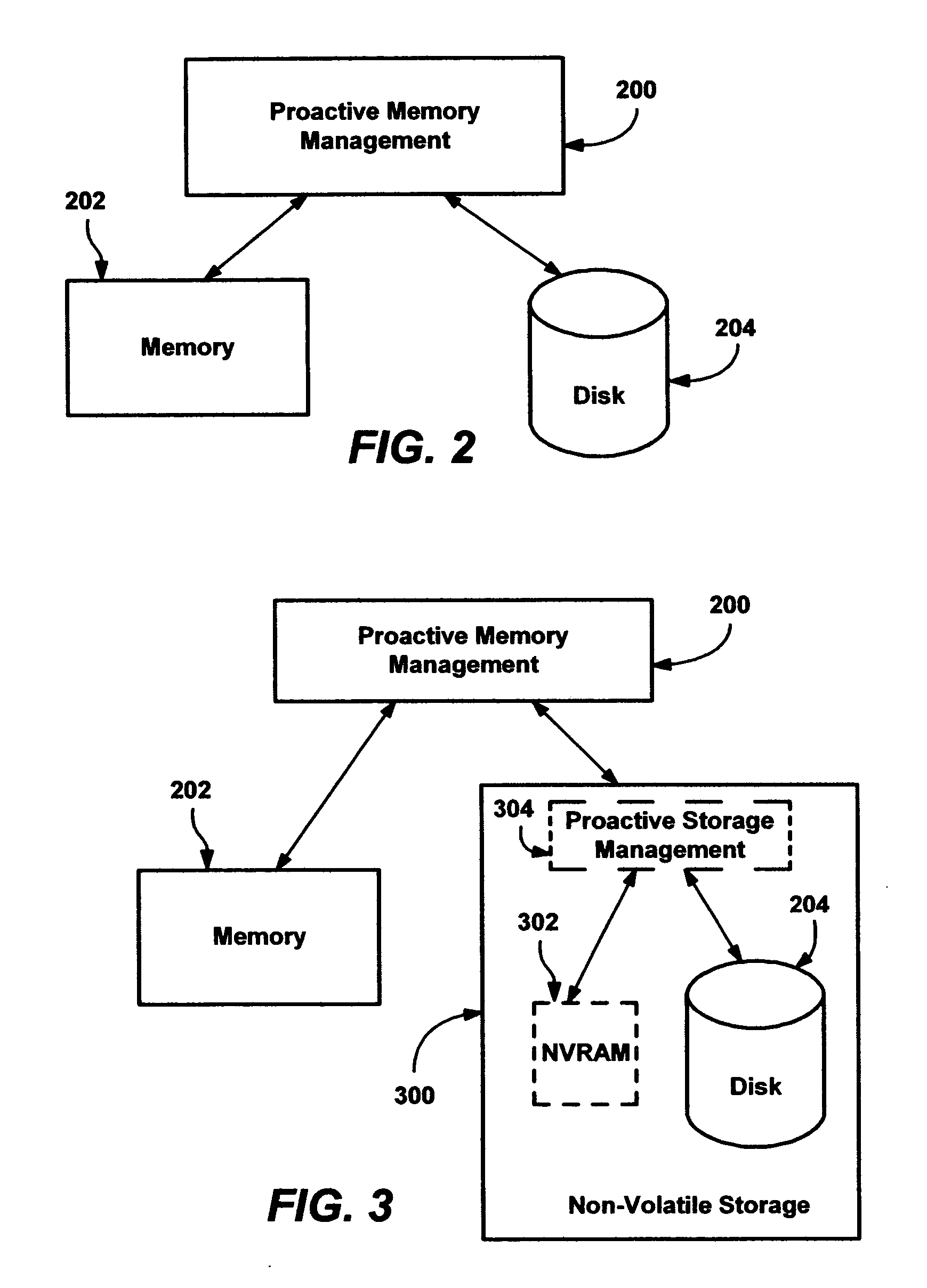
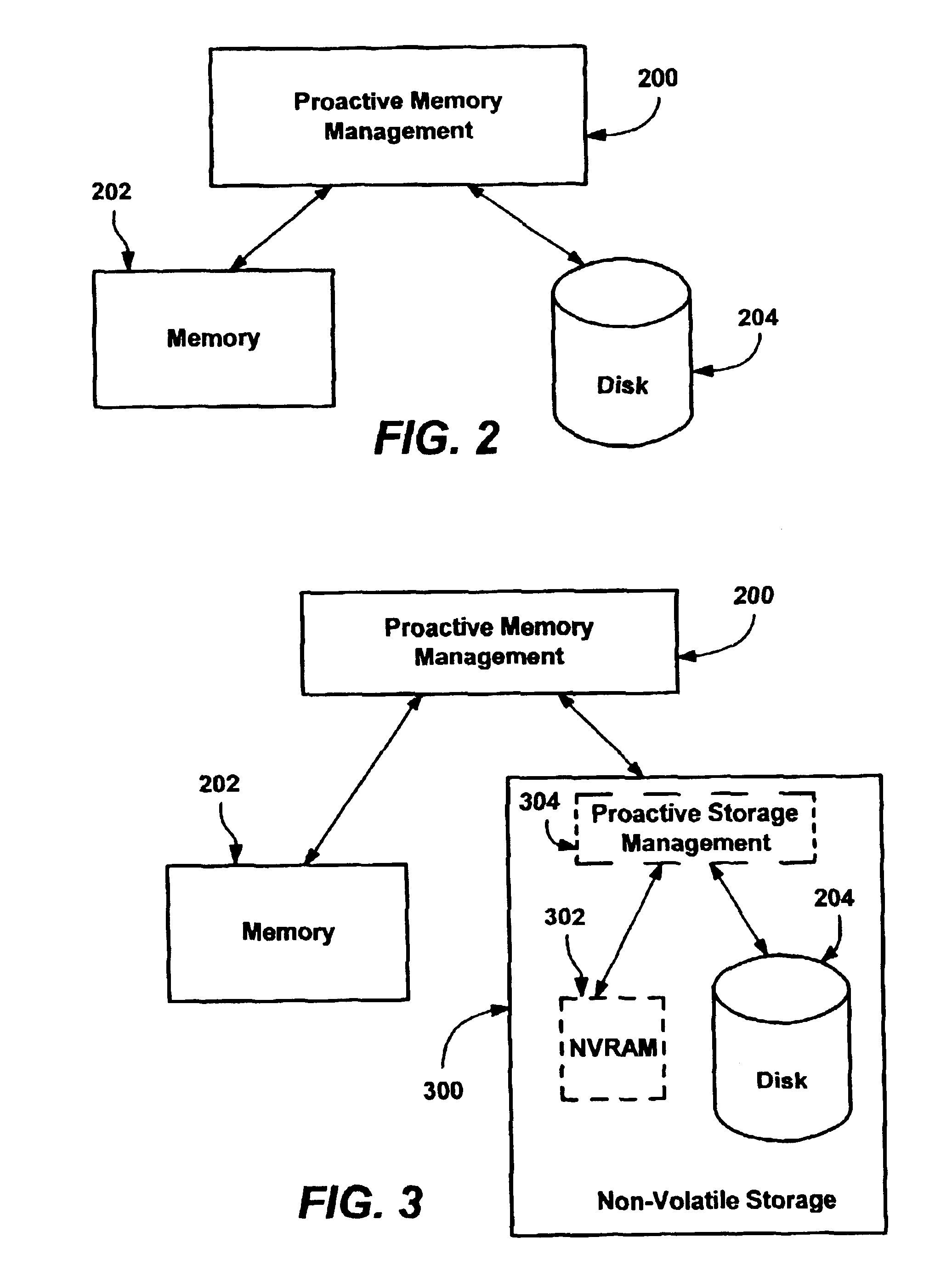
Methods and mechanisms for proactive memory management
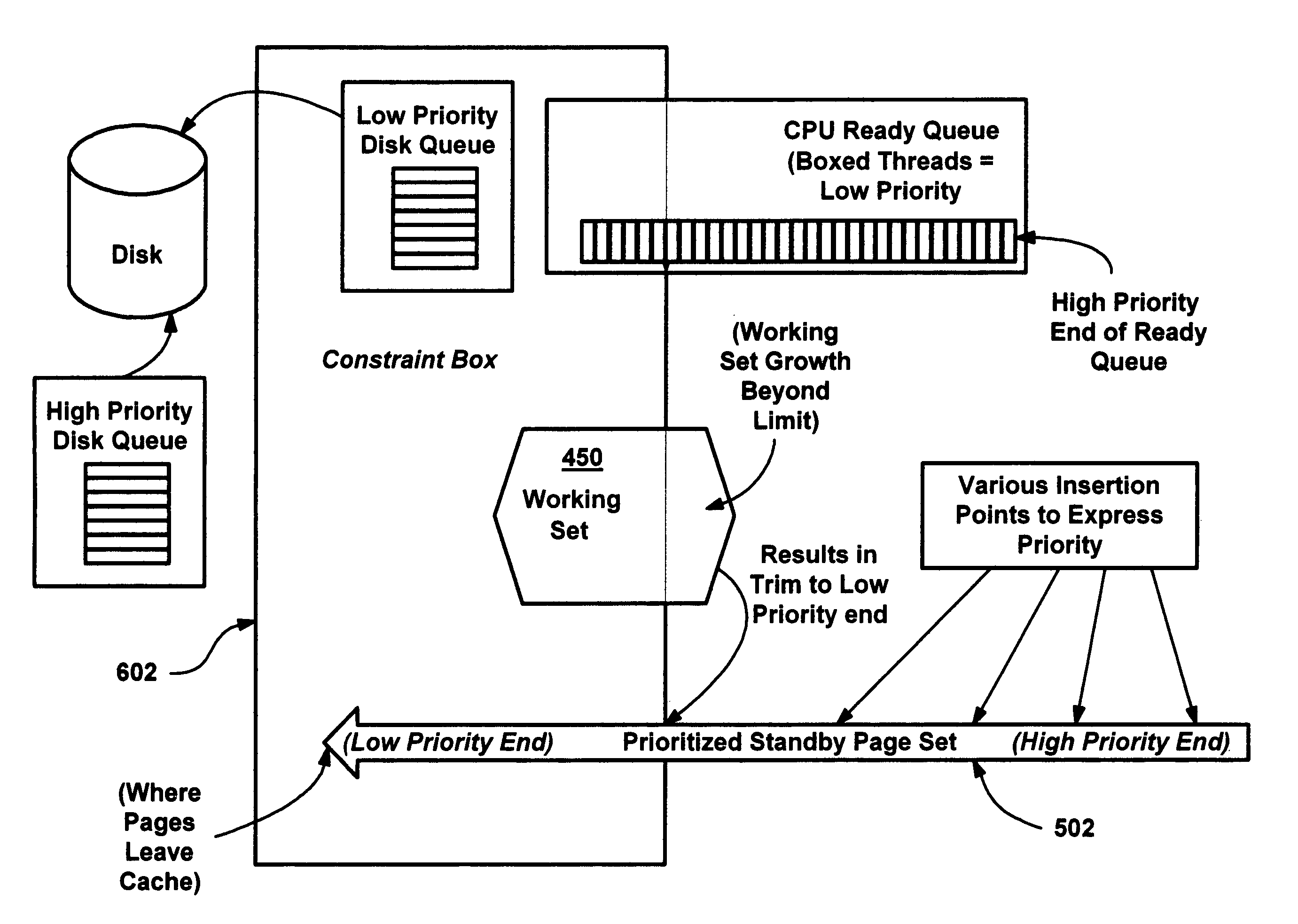
InactiveUS20050228964A1Reduces or eliminates on-demand disk transfer operationsReduces or eliminates I/O bottlenecksInput/output to record carriersFault responseSelf-tuningTerm memory
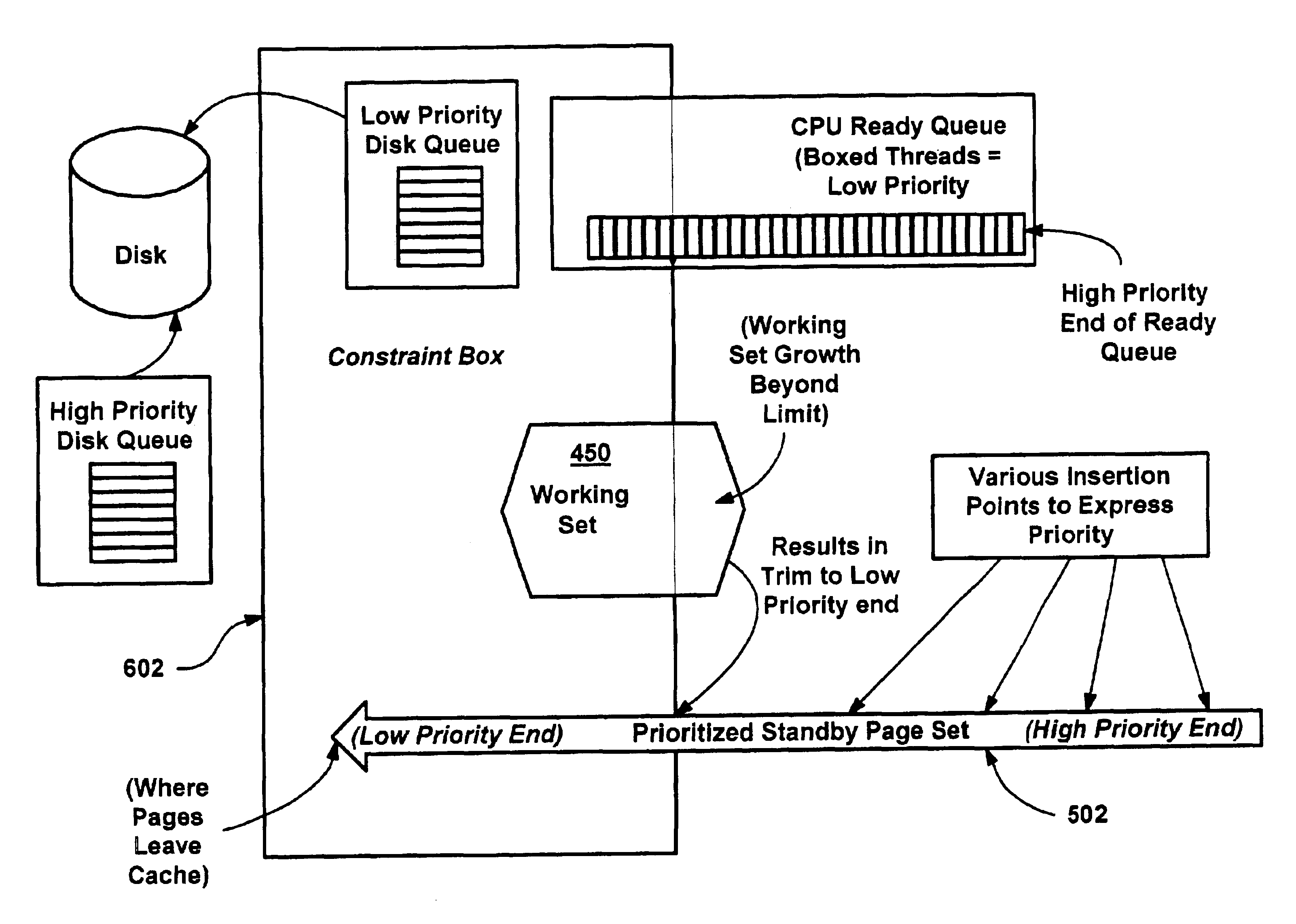
A proactive, resilient and self-tuning memory management system and method that result in actual and perceived performance improvements in memory management, by loading and maintaining data that is likely to be needed into memory, before the data is actually needed. The system includes mechanisms directed towards historical memory usage monitoring, memory usage analysis, refreshing memory with highly-valued (e.g., highly utilized) pages, I / O pre-fetching efficiency, and aggressive disk management. Based on the memory usage information, pages are prioritized with relative values, and mechanisms work to pre-fetch and / or maintain the more valuable pages in memory. Pages are pre-fetched and maintained in a prioritized standby page set that includes a number of subsets, by which more valuable pages remain in memory over less valuable pages. Valuable data that is paged out may be automatically brought back, in a resilient manner. Benefits include significantly reducing or even eliminating disk I / O due to memory page faults.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods and mechanisms for proactive memory management
InactiveUS6910106B2Raise priorityIncrease profitInput/output to record carriersFault responseSelf-tuningPaging
A proactive, resilient and self-tuning memory management system and method that result in actual and perceived performance improvements in memory management, by loading and maintaining data that is likely to be needed into memory, before the data is actually needed. The system includes mechanisms directed towards historical memory usage monitoring, memory usage analysis, refreshing memory with highly-valued (e.g., highly utilized) pages, I / O pre-fetching efficiency, and aggressive disk management. Based on the memory usage information, pages are prioritized with relative values, and mechanisms work to pre-fetch and / or maintain the more valuable pages in memory. Pages are pre-fetched and maintained in a prioritized standby page set that includes a number of subsets, by which more valuable pages remain in memory over less valuable pages. Valuable data that is paged out may be automatically brought back, in a resilient manner. Benefits include significantly reducing or even eliminating disk I / O due to memory page faults.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
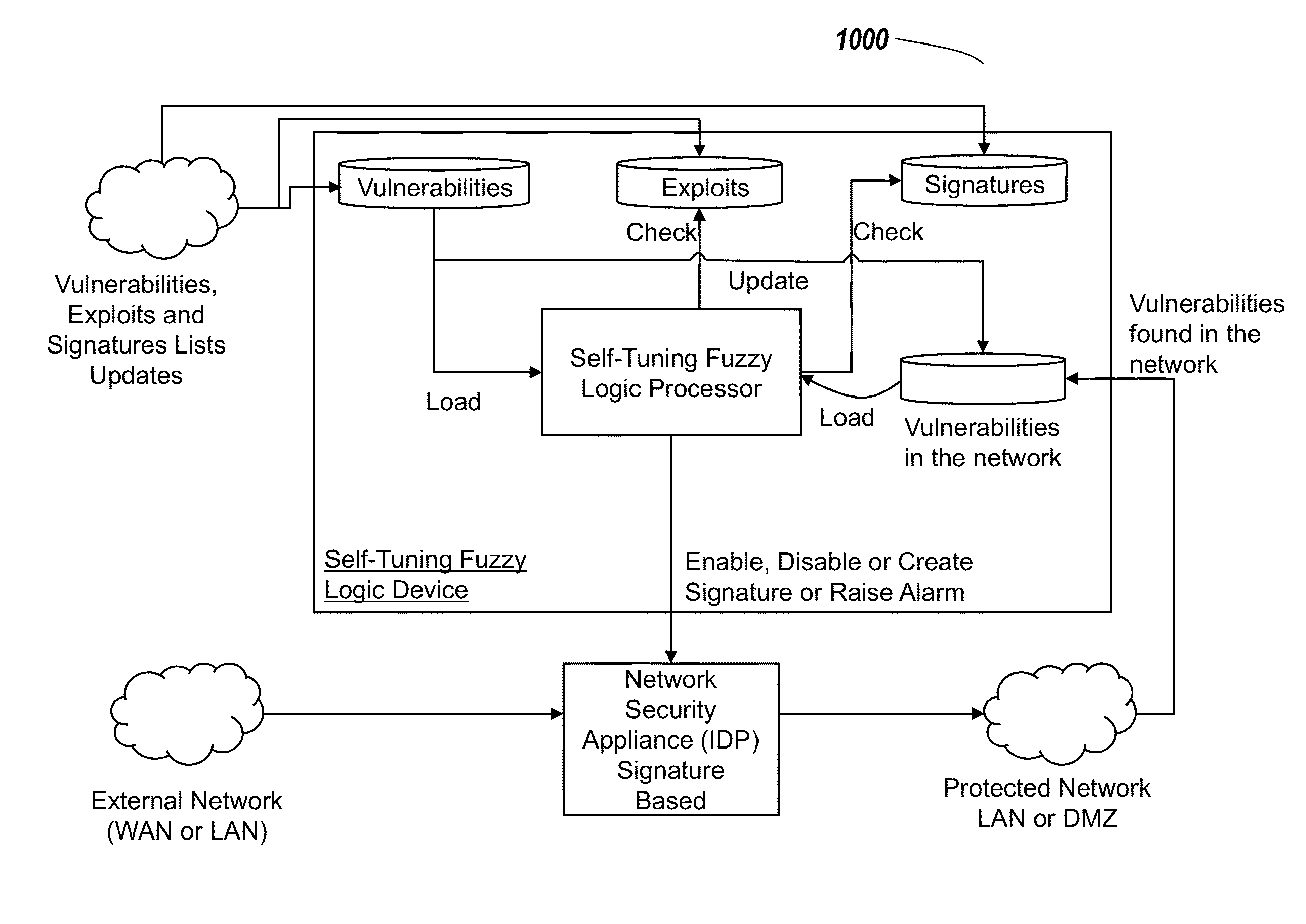
Systems and methods for self-tuning network intrusion detection and prevention
ActiveUS20150033340A1Improve efficiencyFast transferMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionSelf-tuningPrivate network
Systems and method of the present disclosure are directed to a network security tool. In some embodiments, the tool identifies a current vulnerability of a private network. The tool can determine a signature of an attack configured to exploit the current vulnerability. The tool can comparing the signature with active and inactive signatures stored in a signature repository. The tool can compare the signatures to identify an inactive signature corresponding to the signature of the attack configured to exploit the current vulnerability. The tool can automatically activate, responsive to the comparison, the identified inactive signature. The tool can use the activated signature to identify an exploit based on data packets received via the private network.
Owner:CRYPTEIA NETWORKS
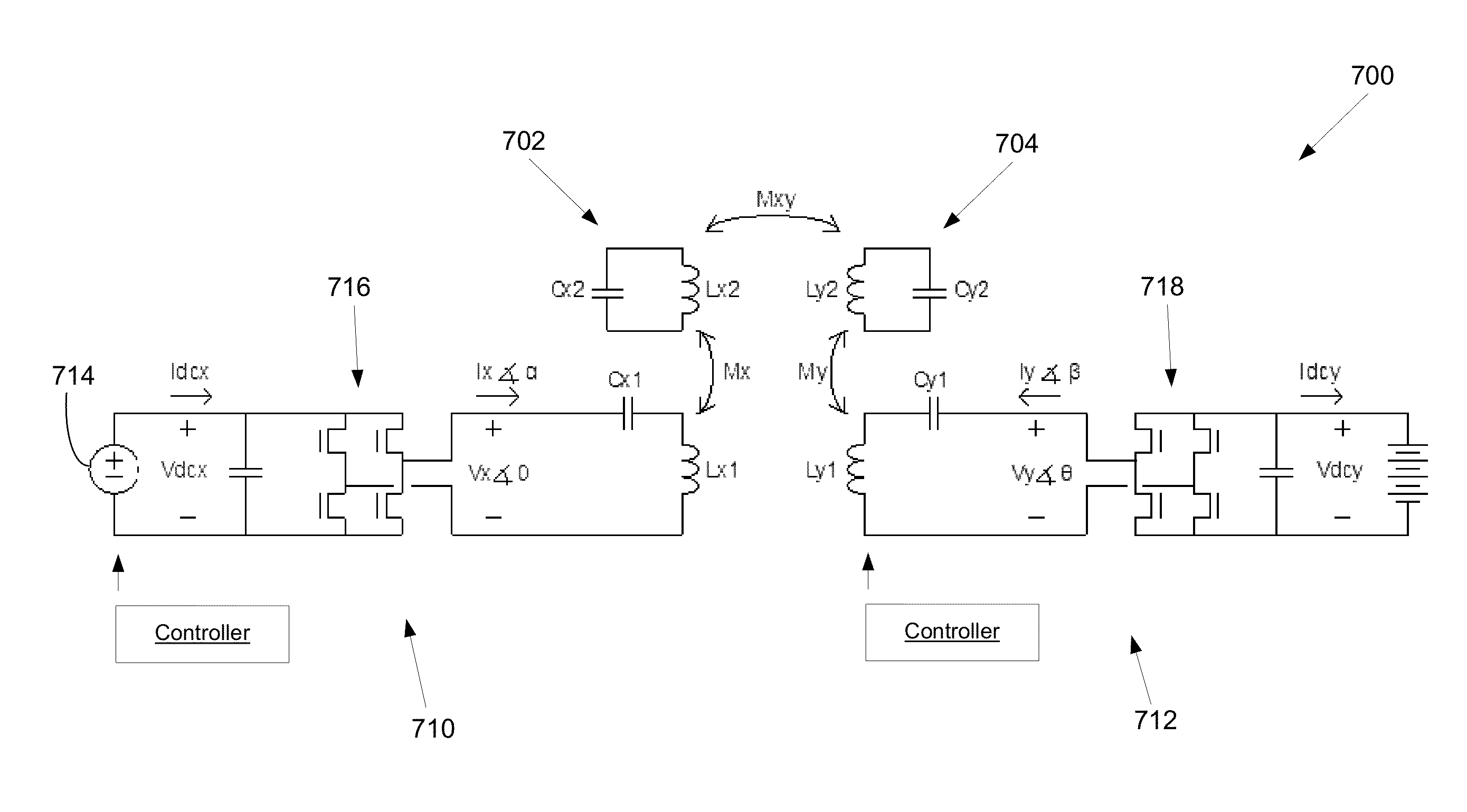
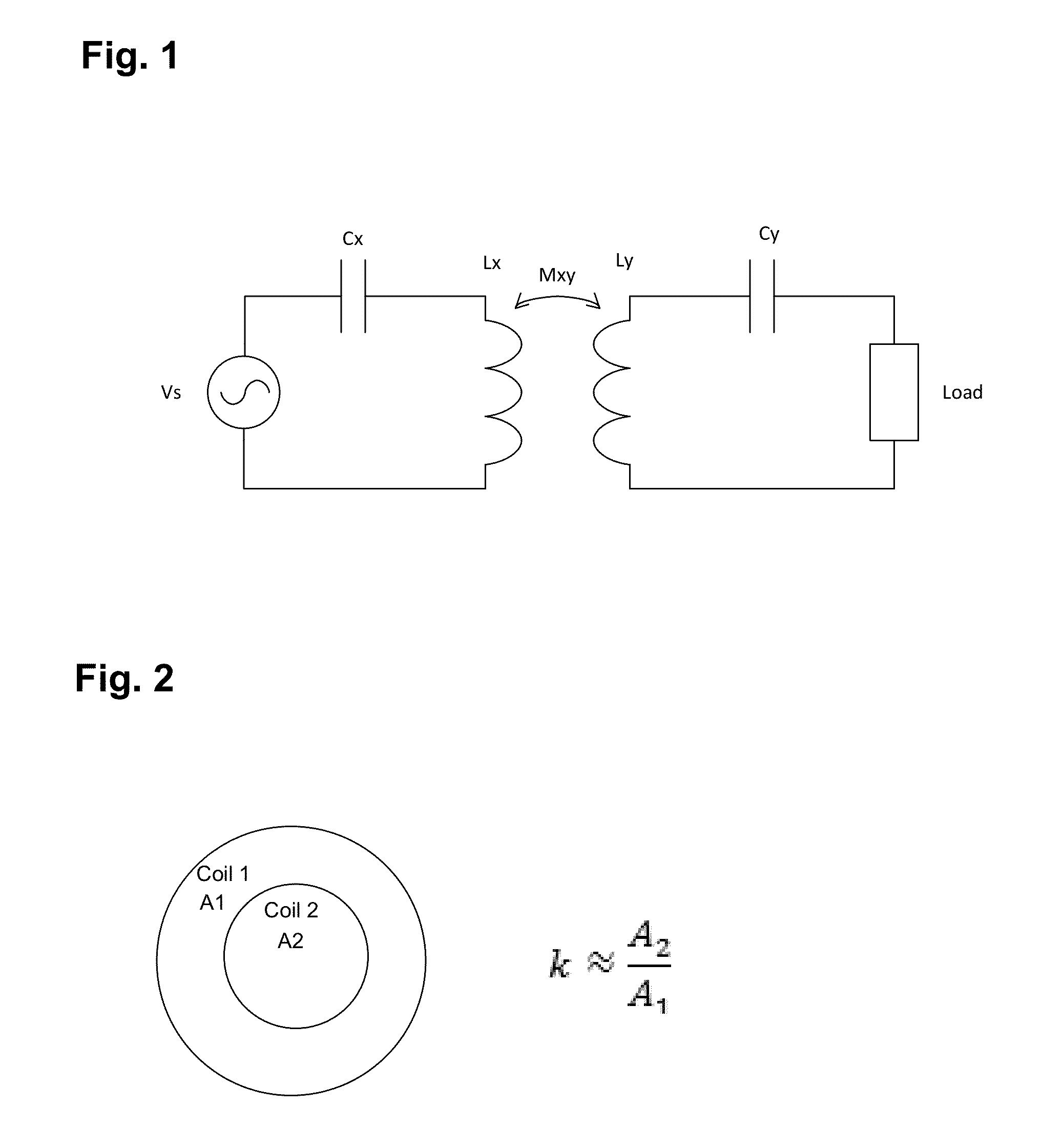
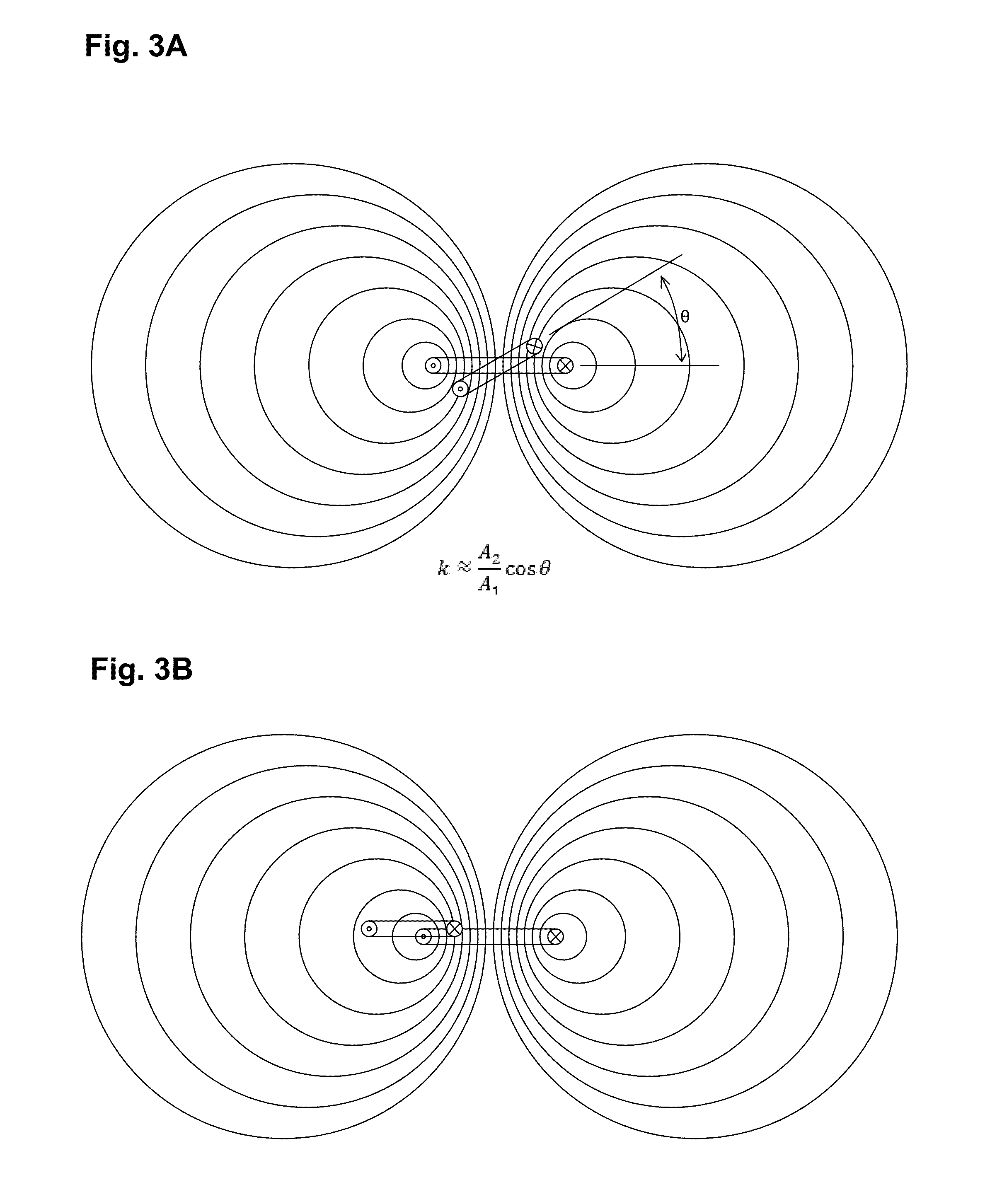
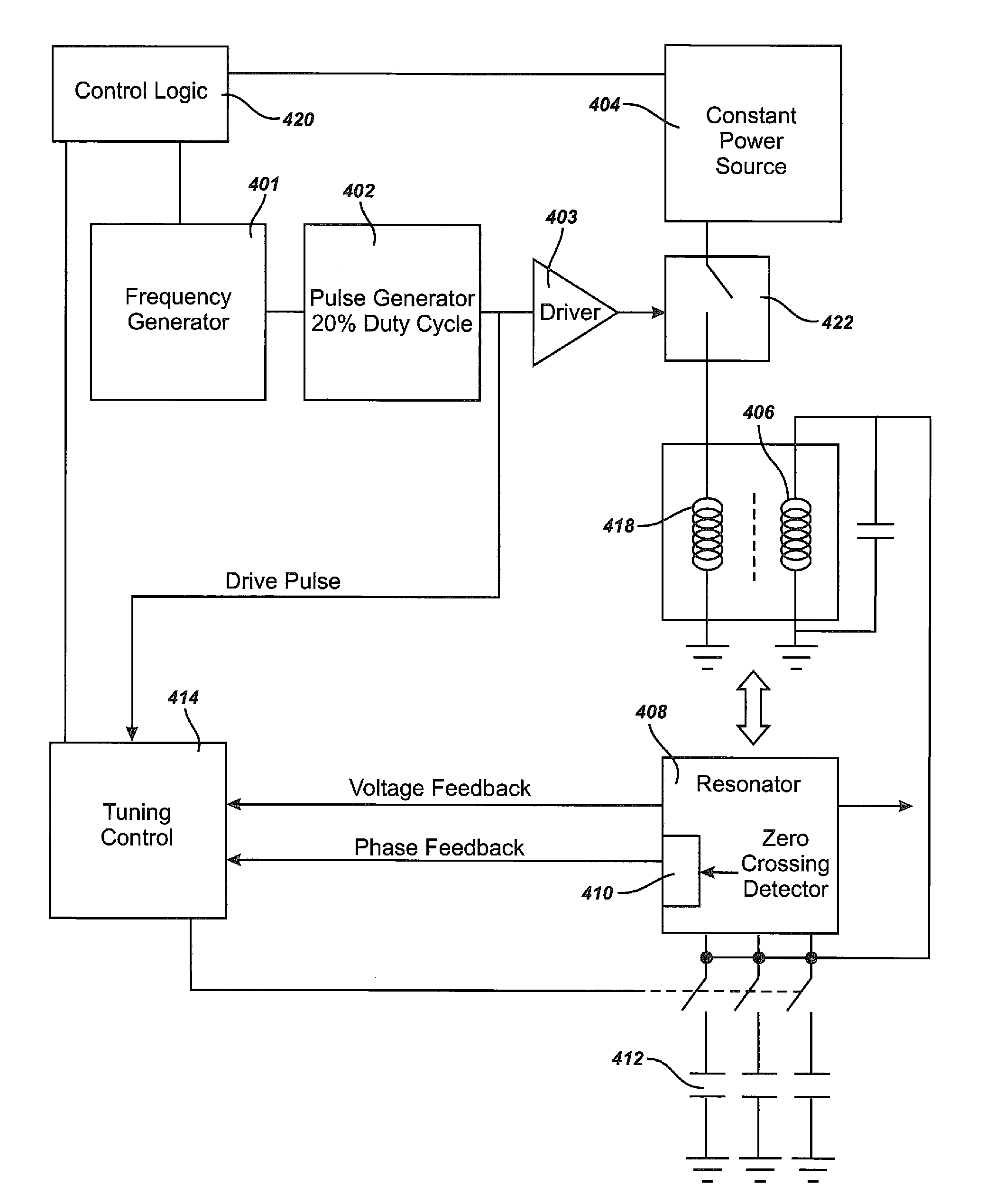
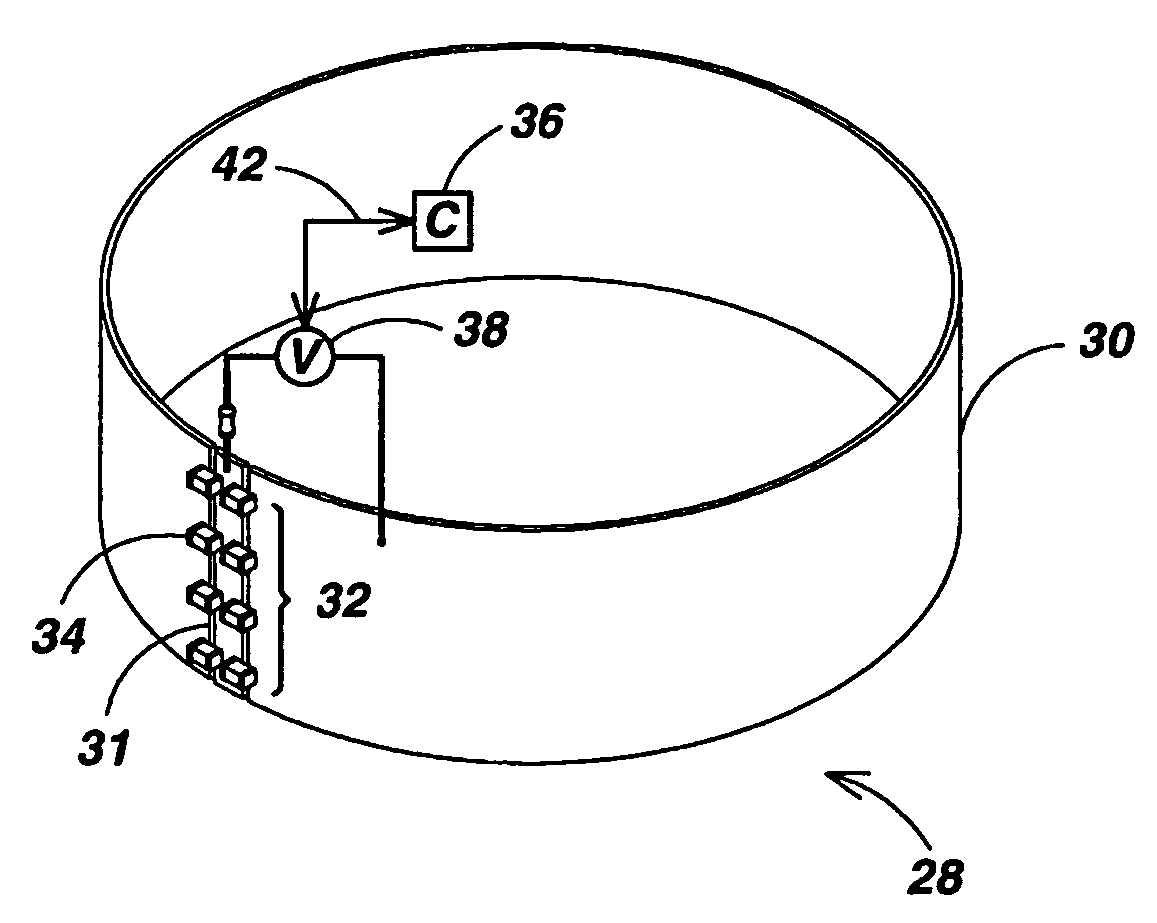
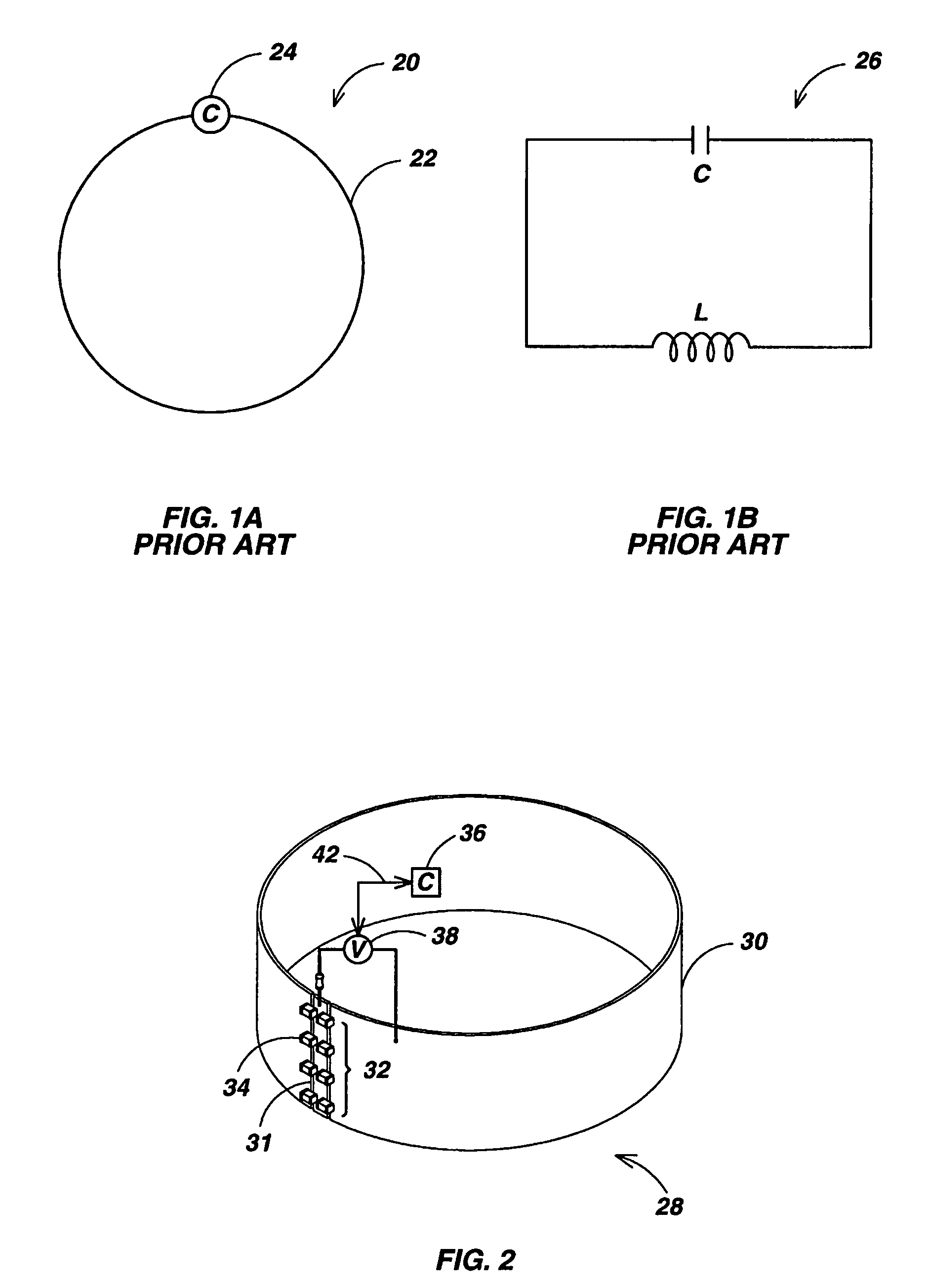
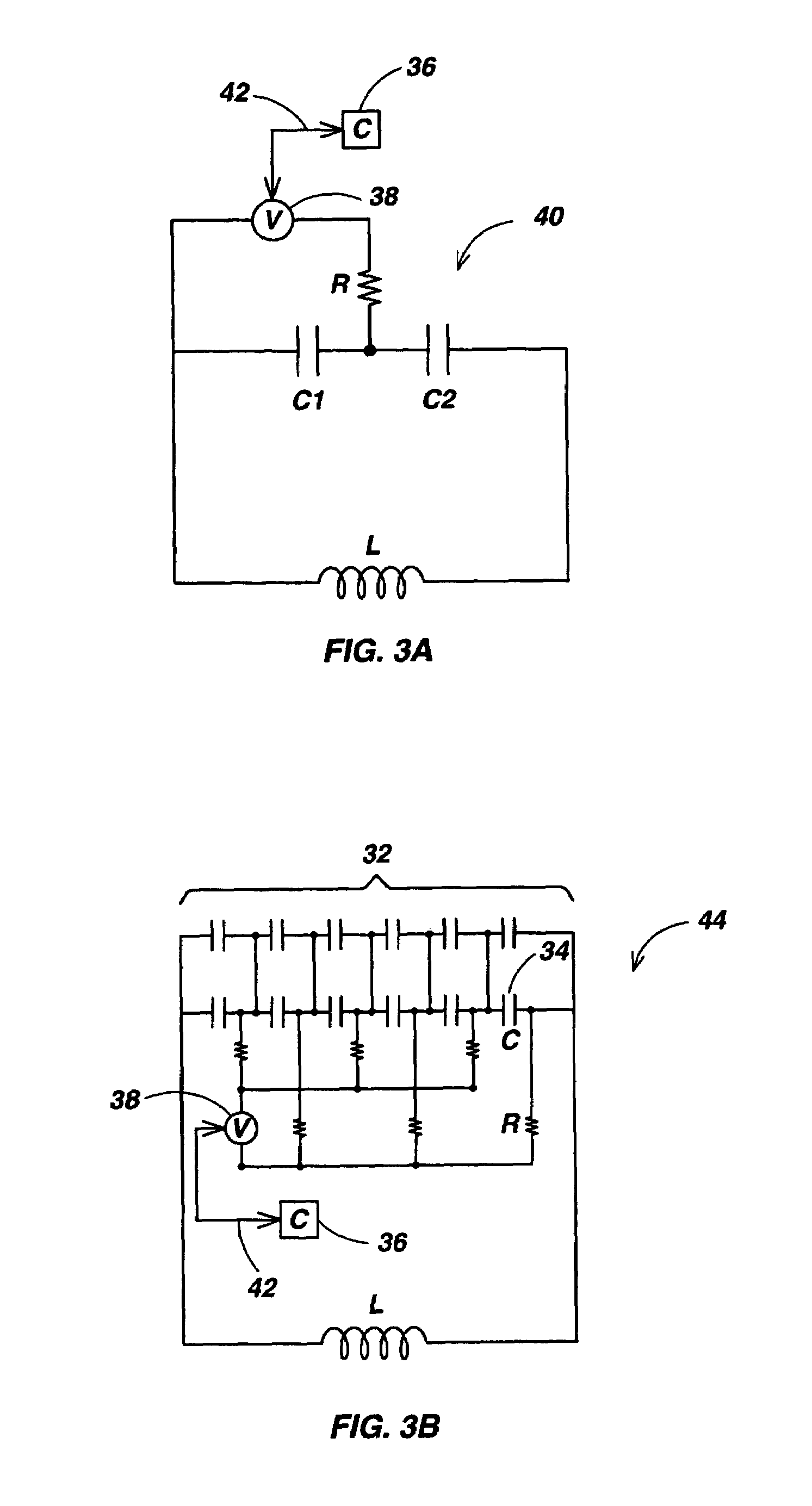
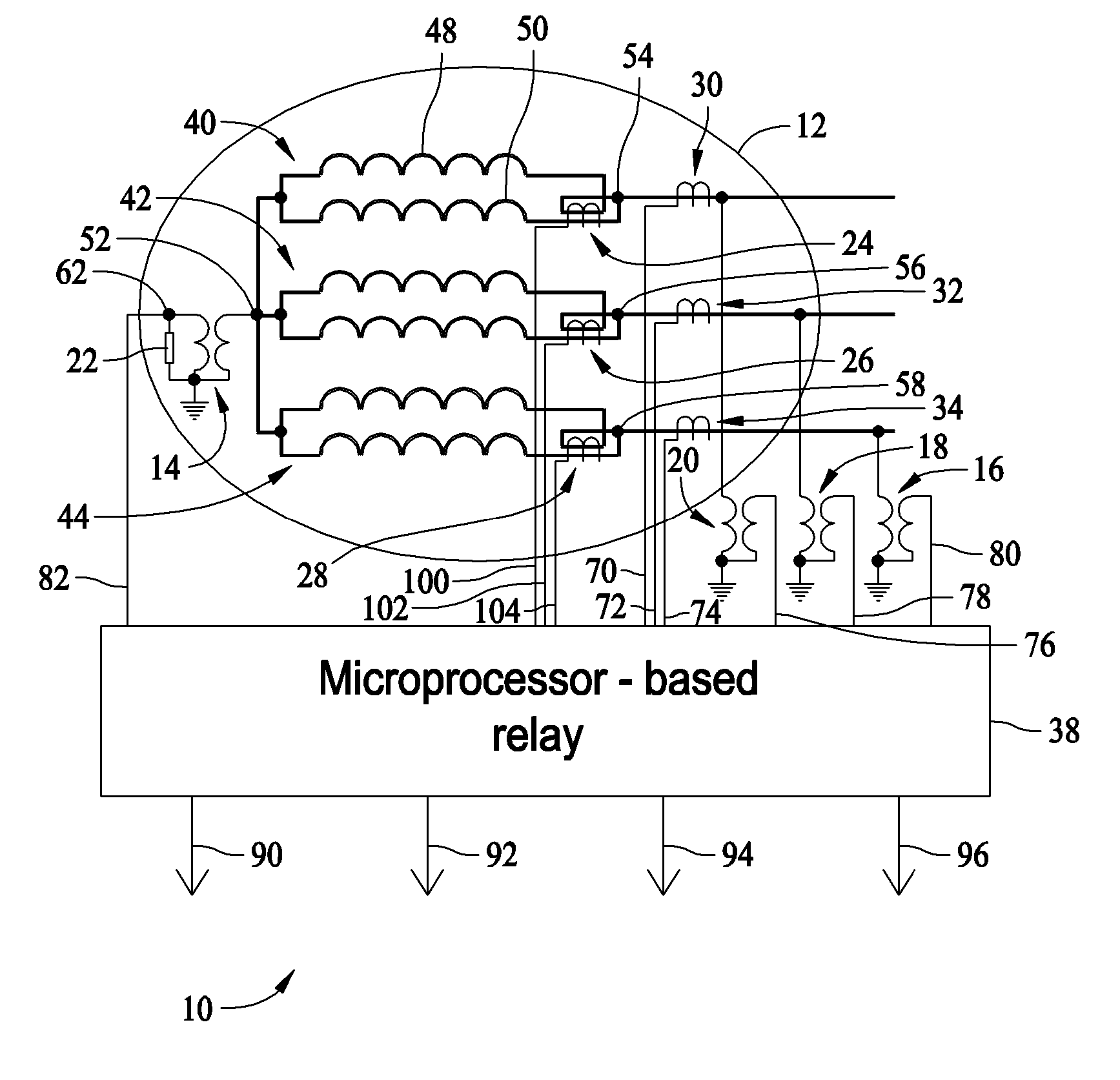
Self-tuning resonant power transfer systems
ActiveUS20140028110A1Small coefficientMaximize efficiencyTransformersCircuit arrangementsSelf-tuningTransfer system
Systems and designs for tuning a wireless power transfer system are provided, which may include any number of features. In one embodiment, a wireless power transfer system can be configured such that resonant frequencies of the system move towards an operating frequency of the system as a coupling coefficient between the transmit and receive resonators becomes smaller. In another embodiment, a receive controller can be configured to control a current delivered to a DC load by comparing an actual current at the DC load to a current requested by the DC load and adjusting an angle or a magnitude of a voltage at the DC load to match the requested current. In another embodiment, a rectifier circuit can act as a controlled voltage source and be configured to tune resonant frequencies between the transmit resonator and the receive resonator. Methods of use are also provided.
Owner:TC1 LLC
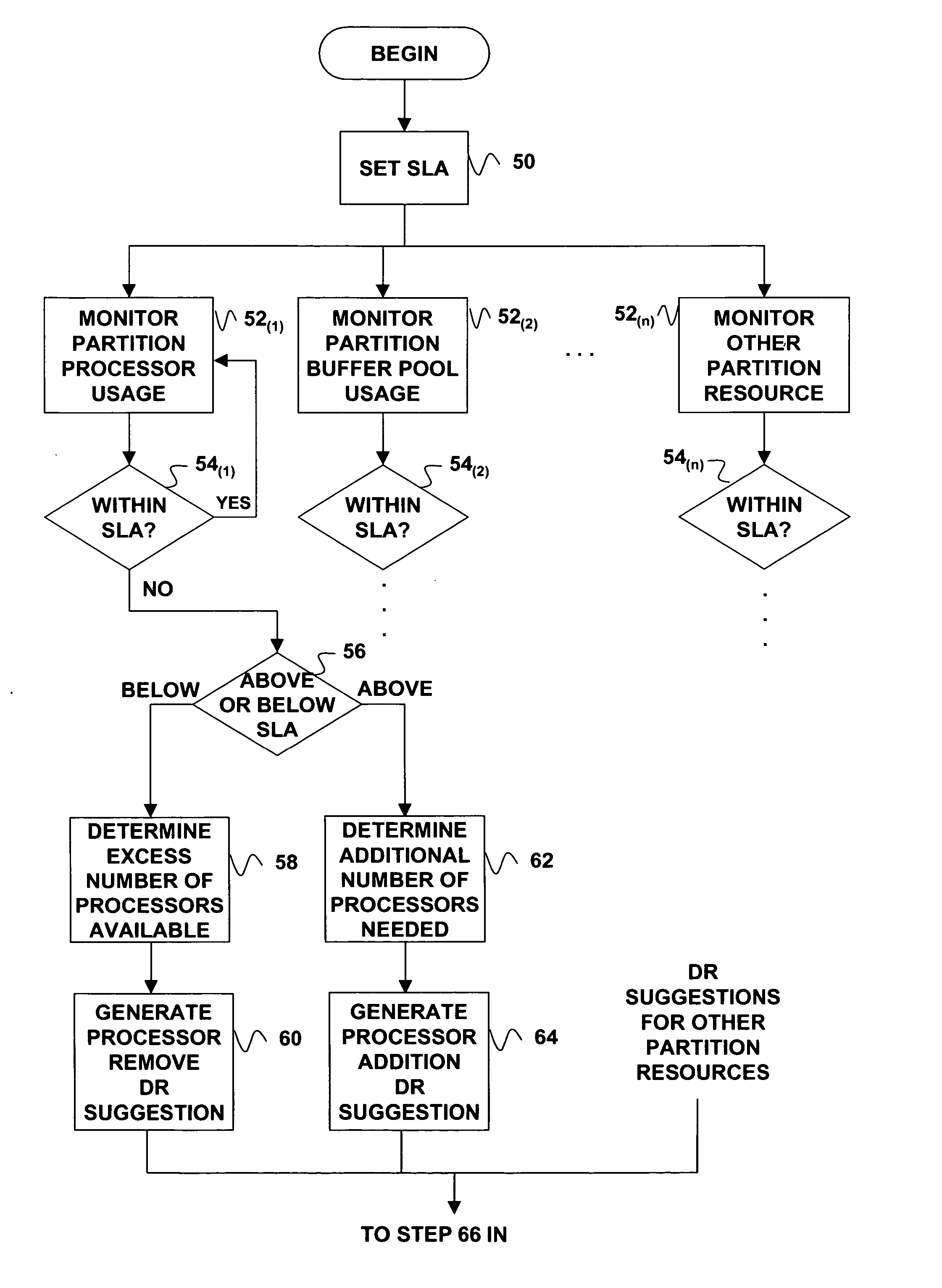
Autonomic self-tuning of database management system in dynamic logical partitioning environment
ActiveUS20060101224A1Improve artError detection/correctionProgram controlSelf-tuningDatabase application
Database partition monitoring and dynamic logical partition reconfiguration in support of an autonomic self-tunable database management system are provided by an automated monitor that monitors one or more resource parameters in a logical partition running a database application in a logically partitioned data processing host. The monitor initiates dynamic logical partition reconfiguration in the event that the parameters vary from predetermined parameter values. In particular, the monitor can initiate removal of resources if one of the resource parameters is being underutilized and initiate addition of resources if one of the resource parameters is being overutilized. The monitor can also calculate an amount of resources to be removed or added. The monitor can interact directly with a dynamic logical partition reconfiguration function of the data processing host or it can utilize an intelligent intermediary that listens for a partition reconfiguration suggestion from the monitor. In the latter configuration, the listener can determine where available resources are located and attempt to fully or partially satisfy the resource needs suggested by the monitor.
Owner:SAP AG
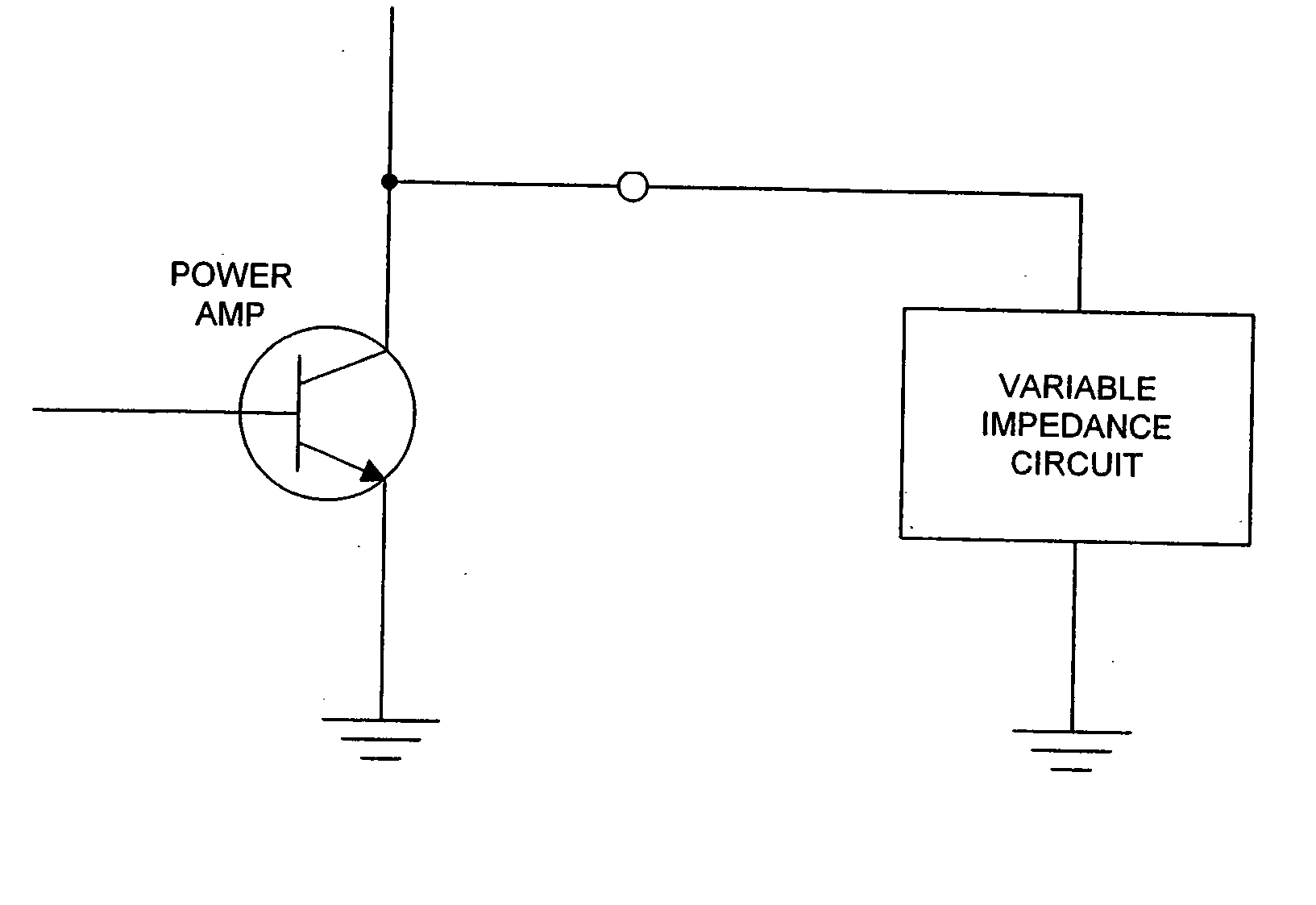
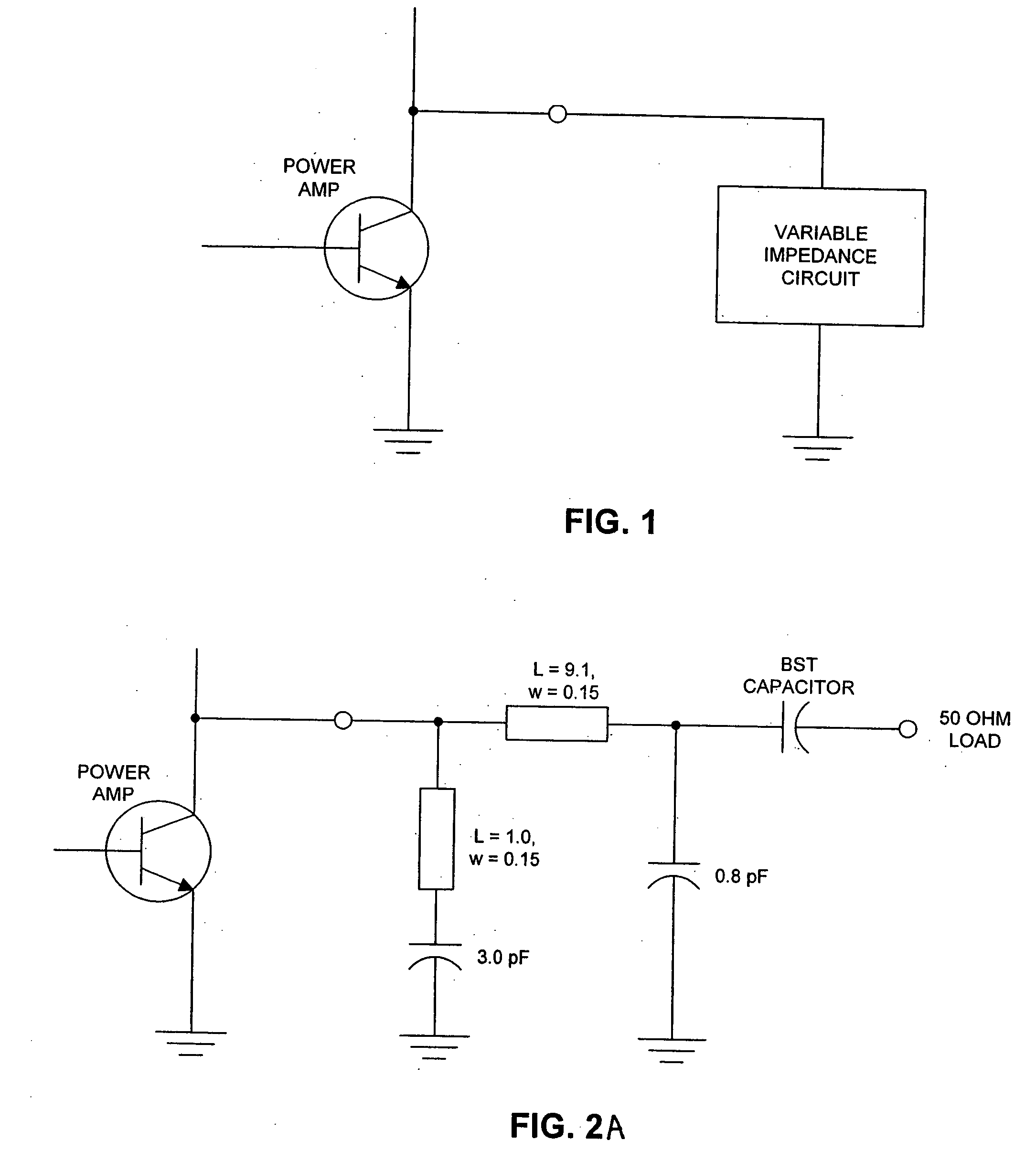
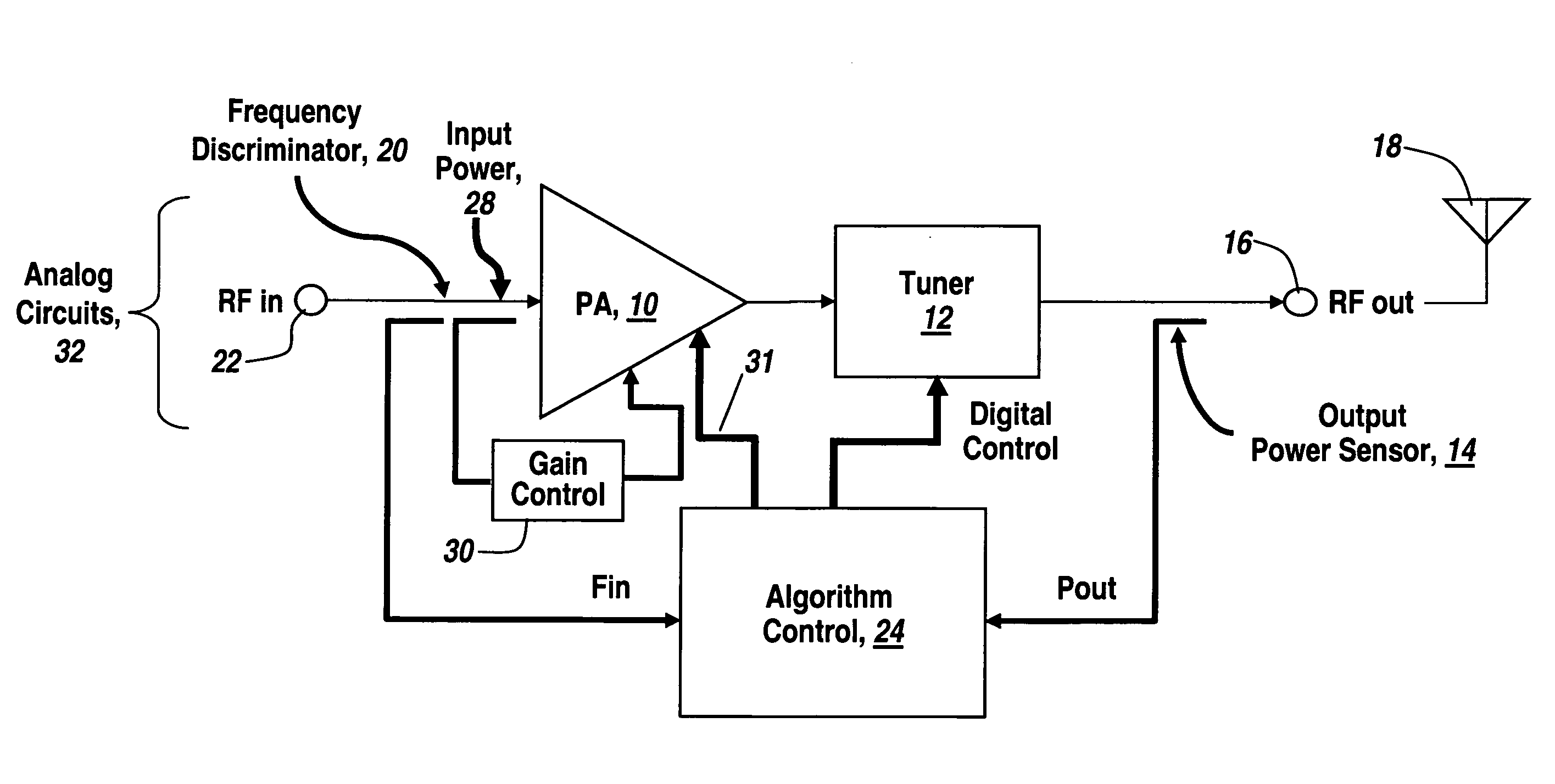
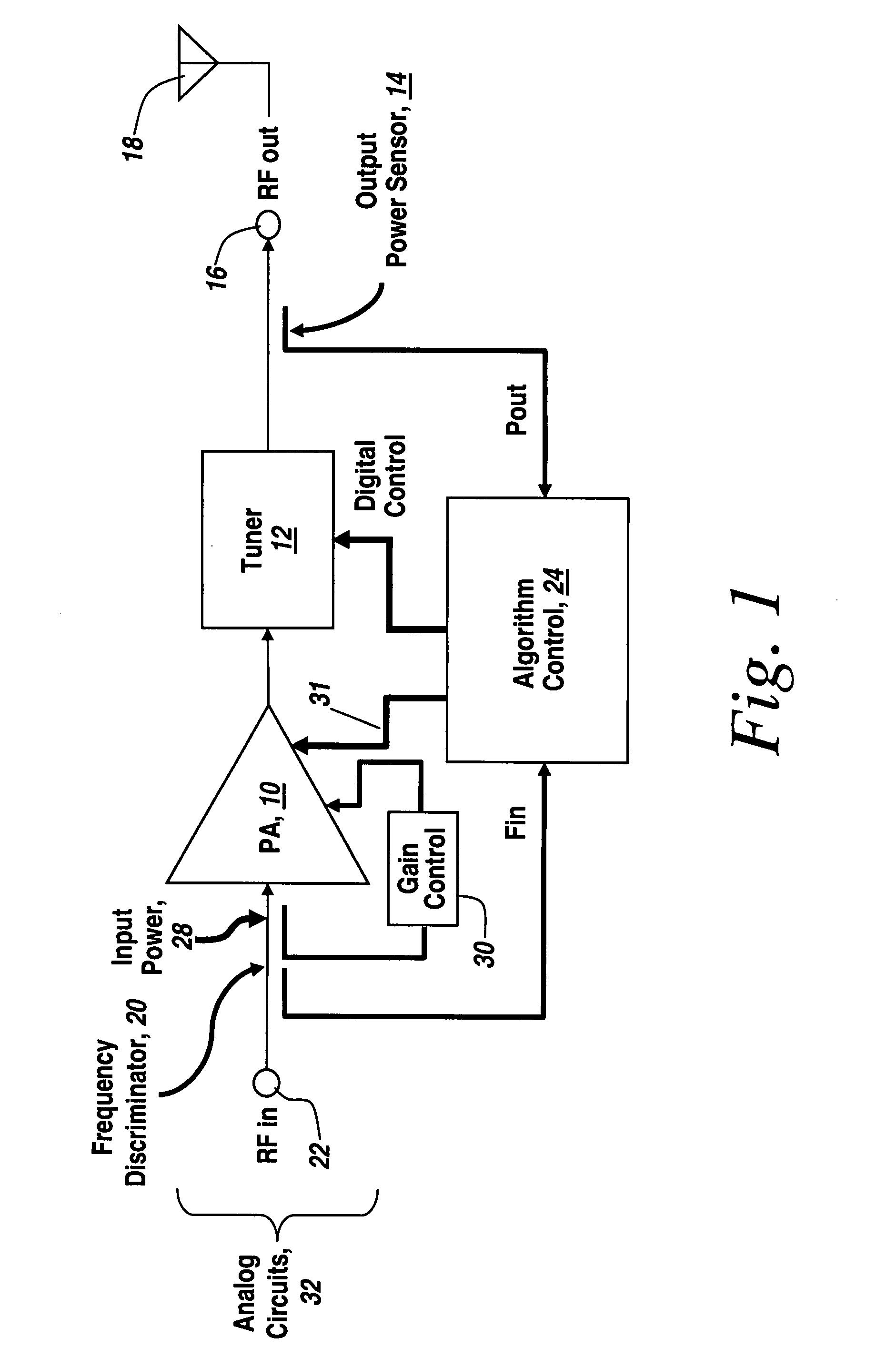
Self-tuning variable impedance circuit for impedance matching of power amplifiers
ActiveUS20050130608A1Improve power efficiencyImprove matchResonant long antennasAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAudio power amplifierSelf-tuning
A self-tuning variable impedance circuit provides improved performance. A variation in the power applied to the variable impedance circuit causes a corresponding change in the impedance of the circuit, resulting in improved performance. For example, the variable impedance circuit may be a matching circuit that “follows” the output power of a power amplifier, thereby increasing the power efficiency of the power amplifier.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Self-tuning link aggregation system
InactiveUS6498781B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData processing systemSelf-tuning
A data processing system and method in a computer network are disclosed for improving performance of a link aggregation system included in the network. Parameters are established which are utilized to determine performance criteria of the link aggregation system. A performance of the link aggregation system is determined by determining the performance criteria. The performance of the link aggregation system changes in response to a flow traffic burden on the link aggregation system changing. The link aggregation system dynamically modifies the parameters in response to the changing performance of the link aggregation system. The link aggregation system is self-tuning and capable of automatically adjusting to a changing flow traffic burden on the link aggregation system.
Owner:IBM CORP
High-Q self tuning locating transmitter
ActiveUS8013610B1Reduce AC-lossOptimize quality ( “ Q ” ) factorMagnetic property measurementsHaberdasherySelf-tuningElectrical conductor
A high-Q human-portable, battery-powered self-correcting tunable resonator in a transmitter apparatus for inducing alternating currents of high quality in buried conductors to facilitate their location. The transmitter apparatus employs an FET-driven capacitive tuning circuit and a coil design that achieves high precision, high-quality transmission signals, and which is equipped with a high-voltage booster for facilitating fault-localization applications.
Owner:SEEKTECH
Fuzzy logic control of an RF power amplifier for automatic self-tuning
InactiveUS20080090539A1Life of batteryMinimize powerMultiple-port networksResonant long antennasSelf-tuningEngineering
Fuzzy logic is utilized to control an RF amplifier and associated tuner for continuous self-optimization and automatic load matching to at least double the battery life of a battery-powered transmitter.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
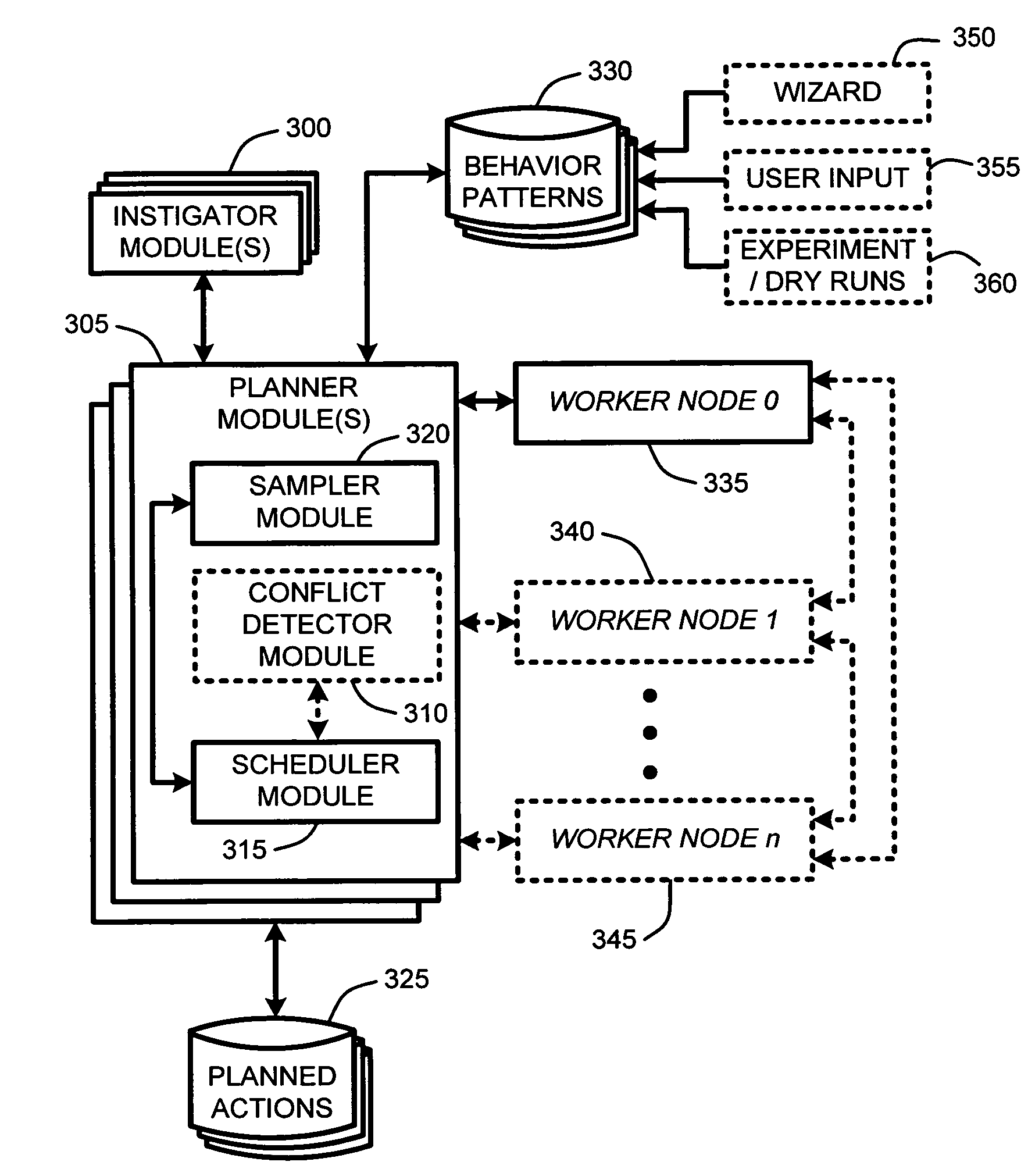
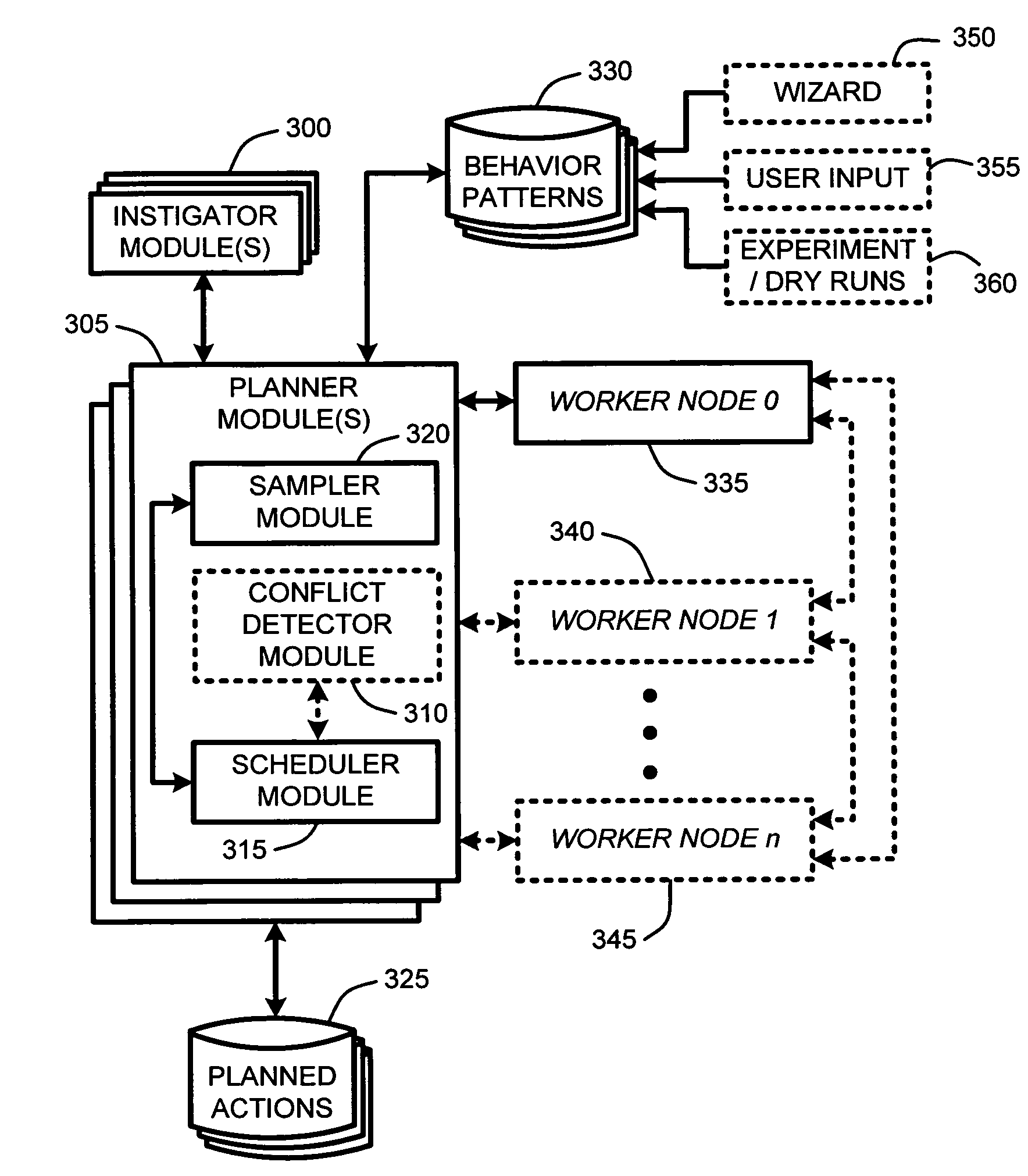
Real-time self tuning of planned actions in a distributed environment
ActiveUS20070011683A1Maximize use of resourcesResource allocationDigital computer detailsEffect lightAutomatic programming
Automatic programming, scheduling, and control of planned activities at “worker nodes” in a distributed environment are provided by a “real-time self tuner” (RTST). The RTST provides self-tuning of controlled interoperation among an interconnected set of distributed components (i.e., worker nodes) including, for example, home appliances, security systems, lighting, sensor networks, medical electronic devices, wearable computers, robotics, industrial controls, wireless communication systems, audio nets, distributed computers, toys, games, etc. The RTST acts as a centralized “planner” that is either one of the nodes or a dedicated computing device. A set of protocols allow applications to communicate with the nodes, and allow one or more nodes to communicate with each other. Self-tuning of the interoperation and scheduling of tasks to be performed at each node uses an on-line sampling driven statistical model and predefined node “behavior patterns” to predict and manage resource requirements needed by each node for completing assigned tasks.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
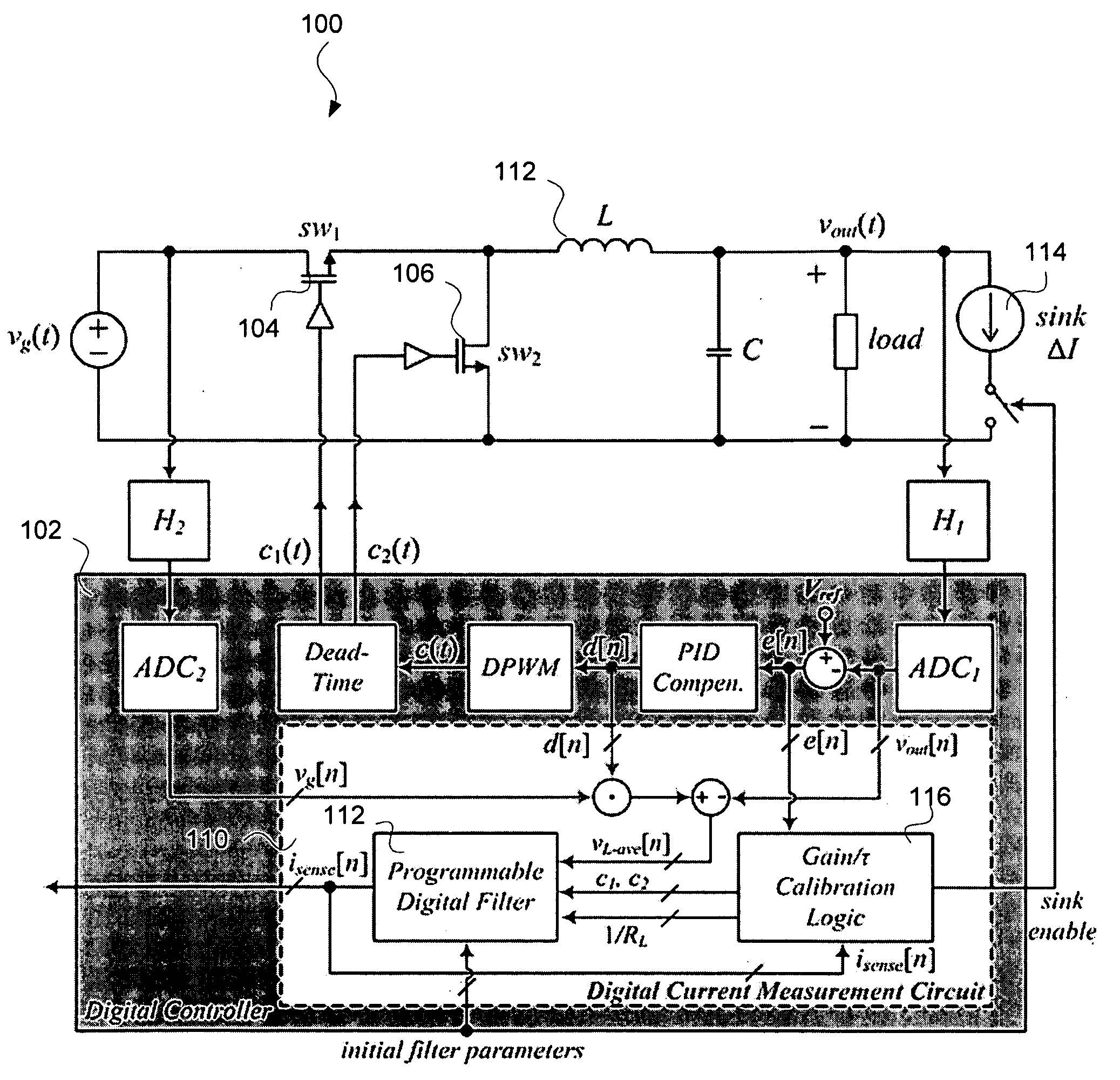
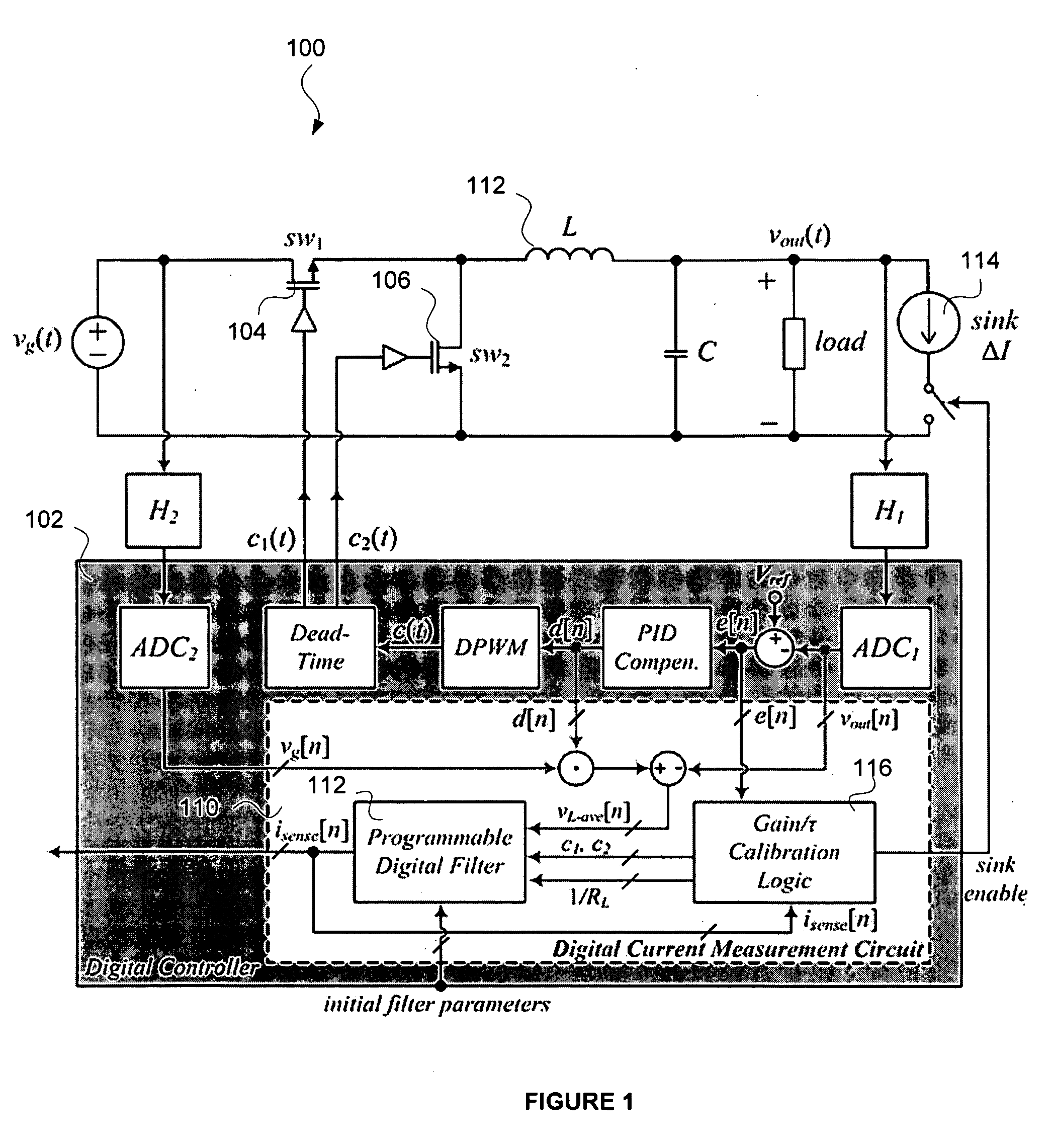
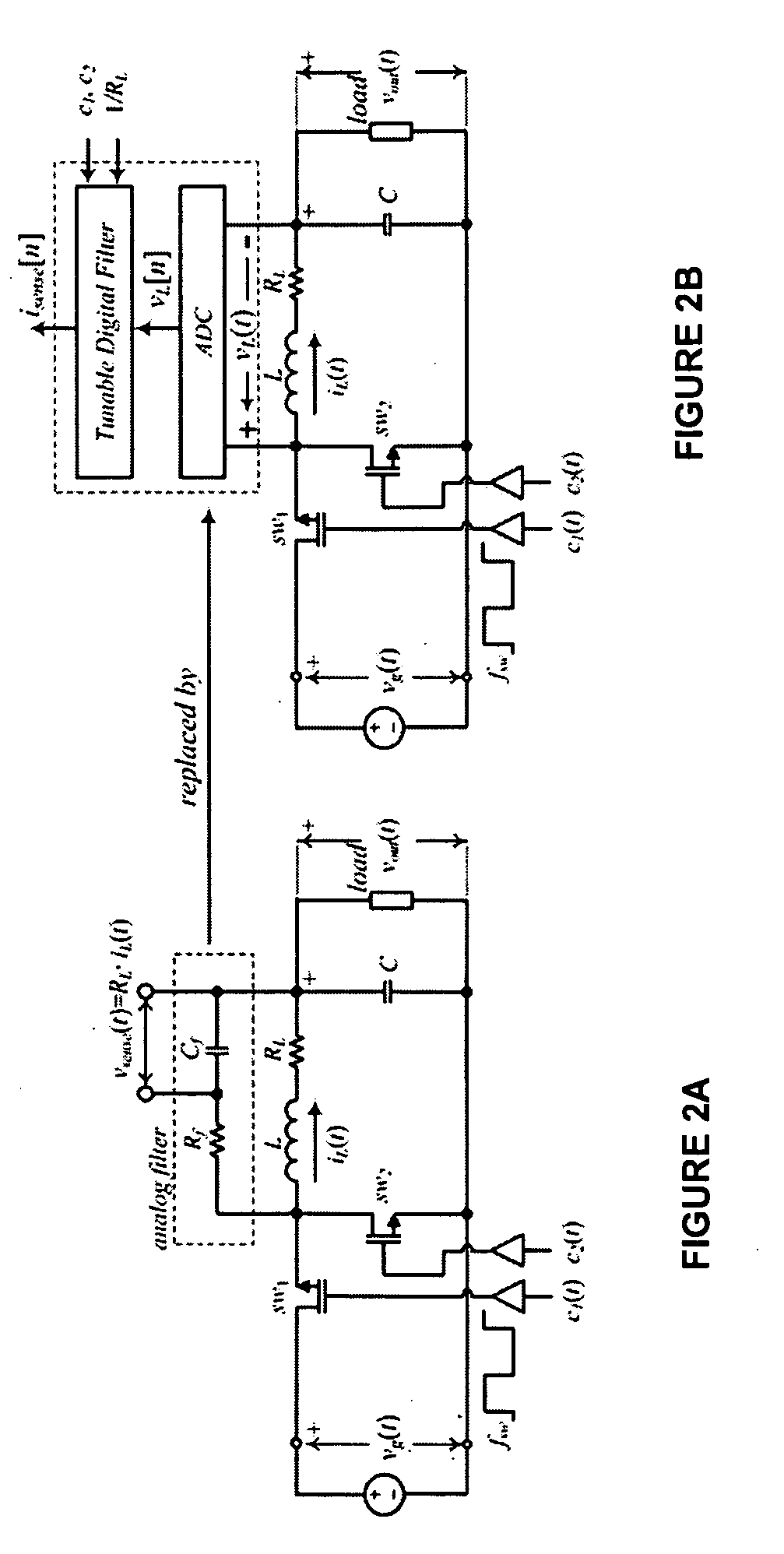
Self-tuning digital current estimator for low-power switching converters
ActiveUS20090267582A1Fast and Accurate EstimationElectrical measurement instrument detailsDc-dc conversionSelf-tuningPower switching
A switched mode power can use a digital controller to control the switching of the at least one switch of the switched mode power supply. The current through the power inductor can be estimated using a self-tuning digital current estimator.
Owner:EXAR CORP
Phase-locked loop and automatic frequency calibration circuit thereof and phase-locked loop self-tuning locking method
InactiveCN101951259ASpeed up lock timeGuaranteed robustnessPulse automatic controlSelf-tuningLock time
The invention discloses a phase-locked loop and an automatic frequency calibration circuit thereof. The phase-locked loop comprises a phase / frequency detector, a charge pump, a filter, a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) and a first frequency divider which are connected in sequence, wherein the phase-locked loop further comprises the automatic frequency calibration circuit; the automatic frequency calibration circuit reduces the oscillation frequency CKV of the VCO when the oscillation frequency CKV of the VCO after undergoing frequency division by the first frequency divider is higher than the reference frequency CKR, and increases the oscillation frequency CKV of the VCO when the oscillation frequency CKV of the VCO is lower than the reference frequency CKR; and a precharging circuit A0 is connected at the input end of the filter and carries out precharging when AFC carries out searching. The phase-locked loop has the rapid self-tuning locking function and ensures the VCO to carry out coarse tuning automatically to approach the final tuning coil, thus reducing the locking time of the phase-locked loop.
Owner:SHANGHAI NATLINEAR ELECTRONICS CO LTD
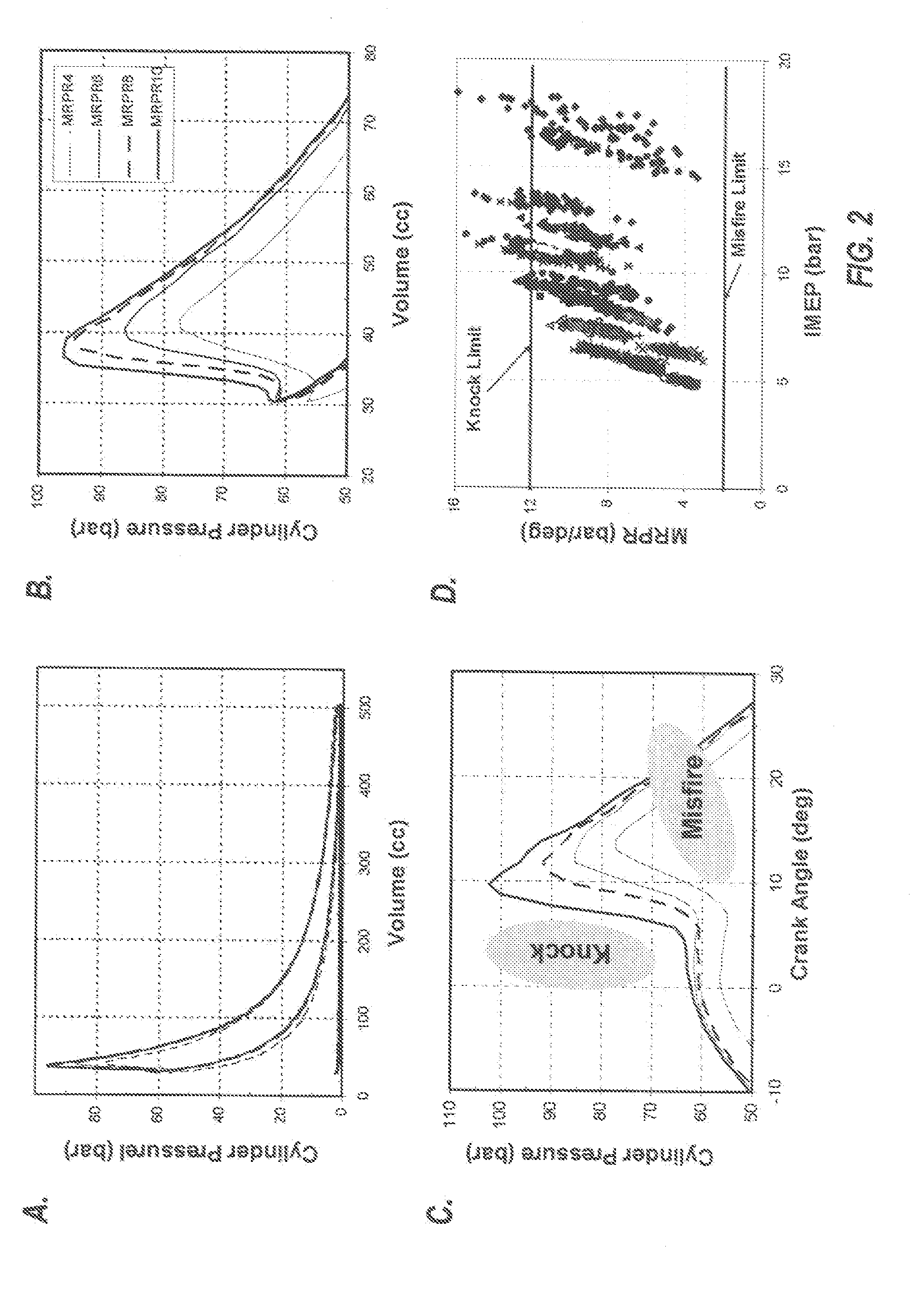
Method and system of transient control for homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) engines
InactiveUS20100031924A1Reduce computing loadRobust engine controlElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesApplying knowledgeHcci combustion
A HCCI engine with a model reference adaptive feedback control system maintains stable HCCI combustion during speed / load transitions by: (1) estimating the maximum rate of pressure rise (MRPR), for each cycle, from an extra-cylinder sensor metric, such as a crankshaft dynamics or knock sensor metric, via statistical vector-to-vector correlation; (2) periodically self-tuning the vector-to-vector correlation; (3) applying knowledge base models to guide cycle-to-cycle adjustments of fuel quantity and other engine parameters, to maintain a target MRPR value.
Owner:U S ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE
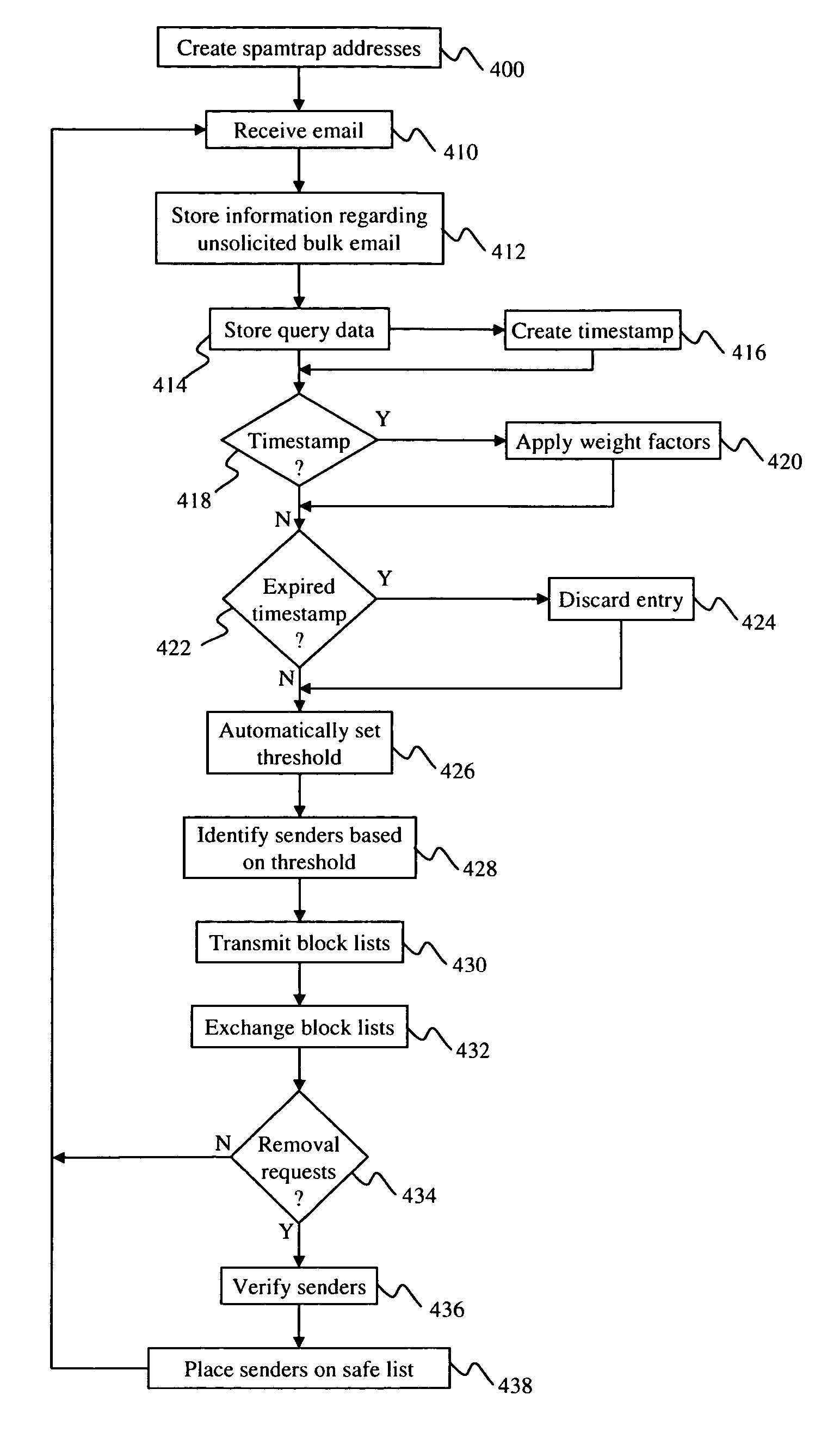
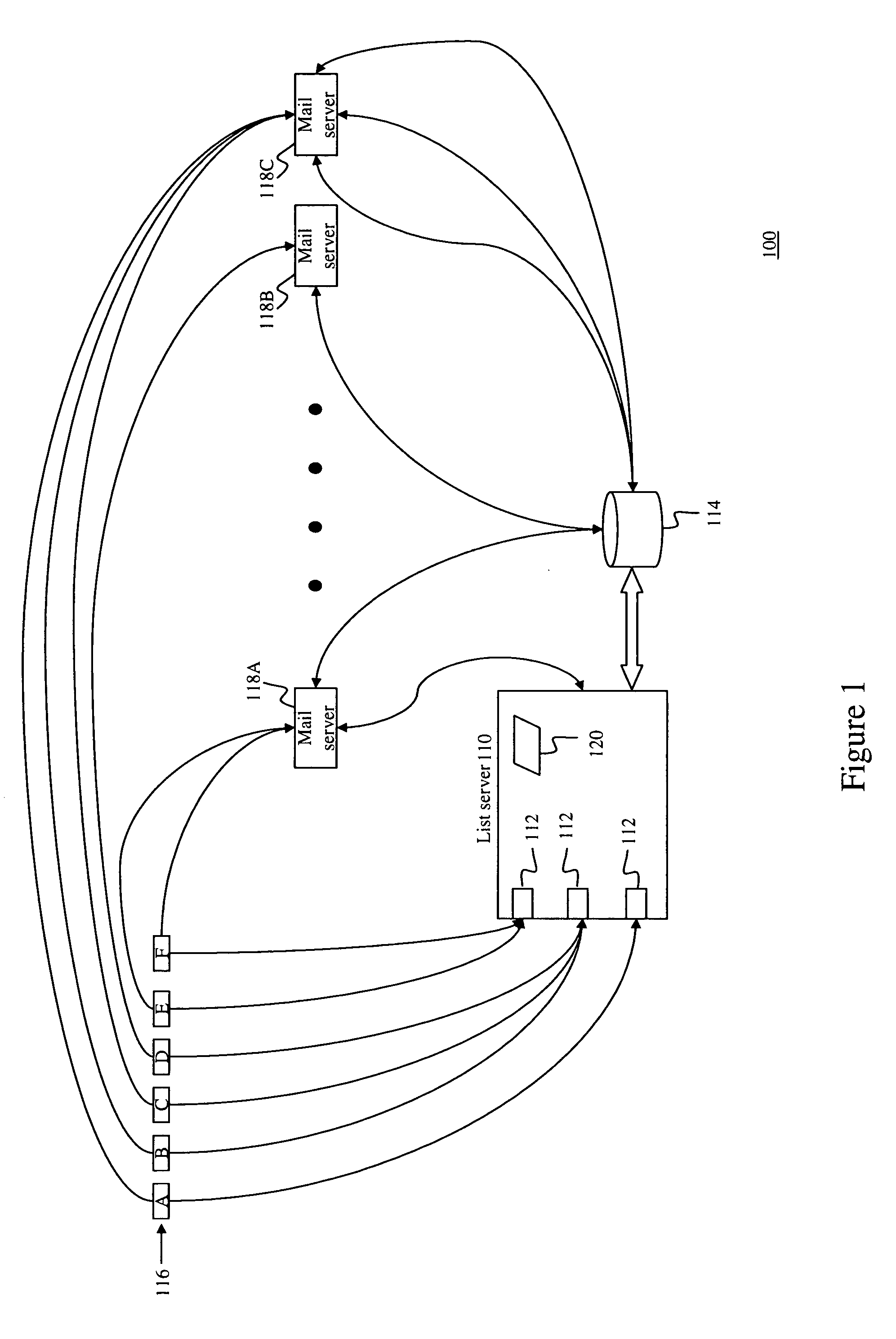
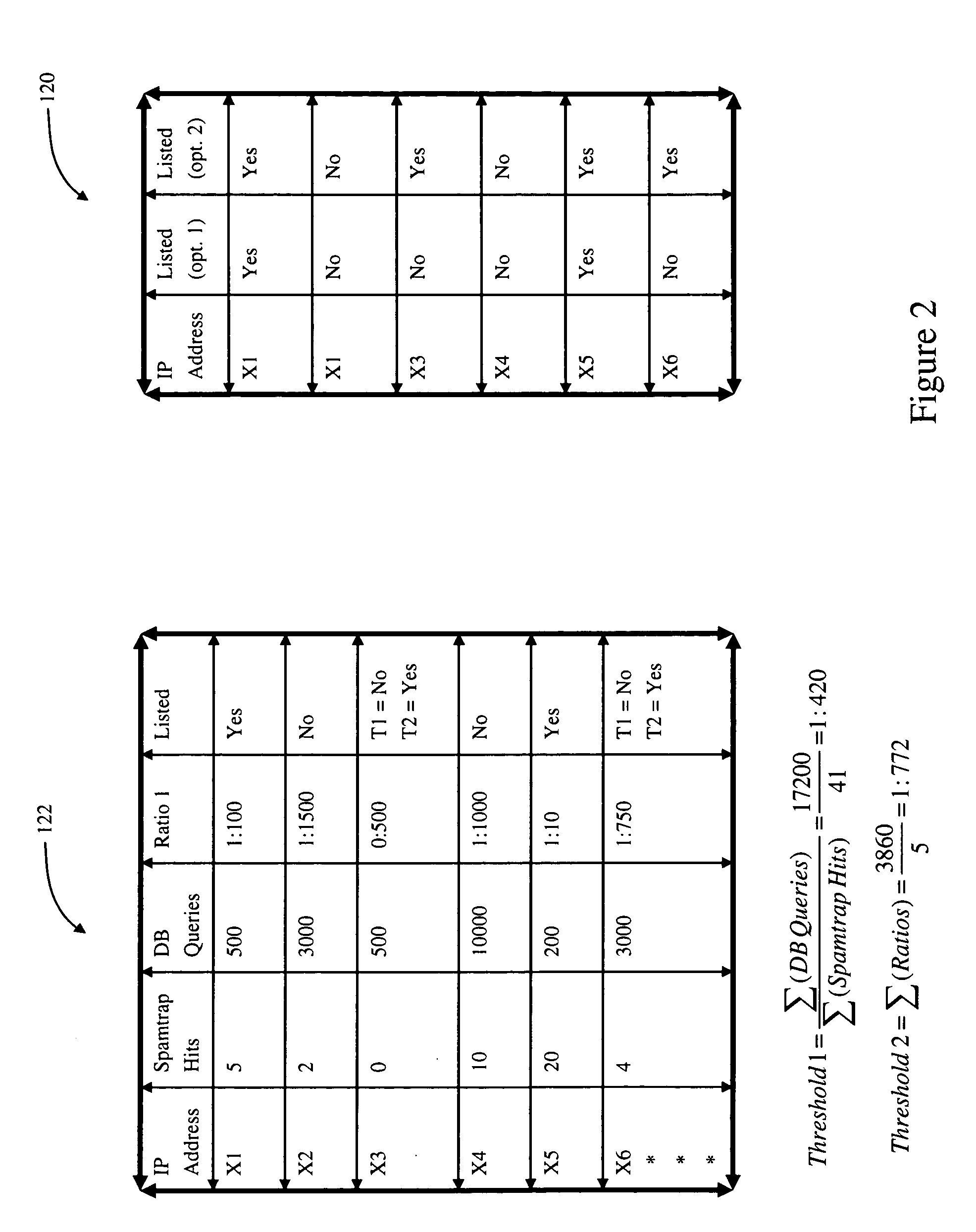
Self-tuning statistical method and system for blocking spam
ActiveUS20060075030A1Save precious resourcesSave resourcesMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksSelf-tuningSpamming
A system is provided for detecting unsolicited bulk email (spam). A list server receives email from various senders as well as queries regarding the senders. A database is used for storing information corresponding to the amount of unsolicited bulk email received at the spamtrap addresses. The list server dynamically makes a determination as to which senders are transmitting a disproportionate amount of email and should be labeled as spammers. The determinations made by the list server are based on the amount of unsolicited bulk email received from senders relative to the total amount of email transmitted by senders.
Owner:RED HAT
Compact self-tuned electrical resonator for buried object locator applications
ActiveUS7276910B2Improved efficiency and induced output powerLower equivalent series resistanceDetection of traffic movementResonatorsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A self-tuning resonator for use in a transmitter apparatus for inducing alternating currents in a buried conductor. The resonator is dynamically tuned at frequencies below 500 kHz by exploiting the inherent voltage-variability of net capacitance in multilayer ceramic capacitors. The transmitter apparatus provides improved efficiency and induced output power suitable for use in a man-portable locator system, providing a very high magnetic field output from a physically small battery-powered resonator at frequencies under 500 kHz. The resonator exhibits a very low equivalent series resistance (ESR) and is adaptively returned to a predetermined resonant frequency responsive to any changes in resonance arising from phenomena such as component heating, thereby supporting very high tank circuit currents from battery-powered source to produce very high magnetic flux output.
Owner:SEEK TECH
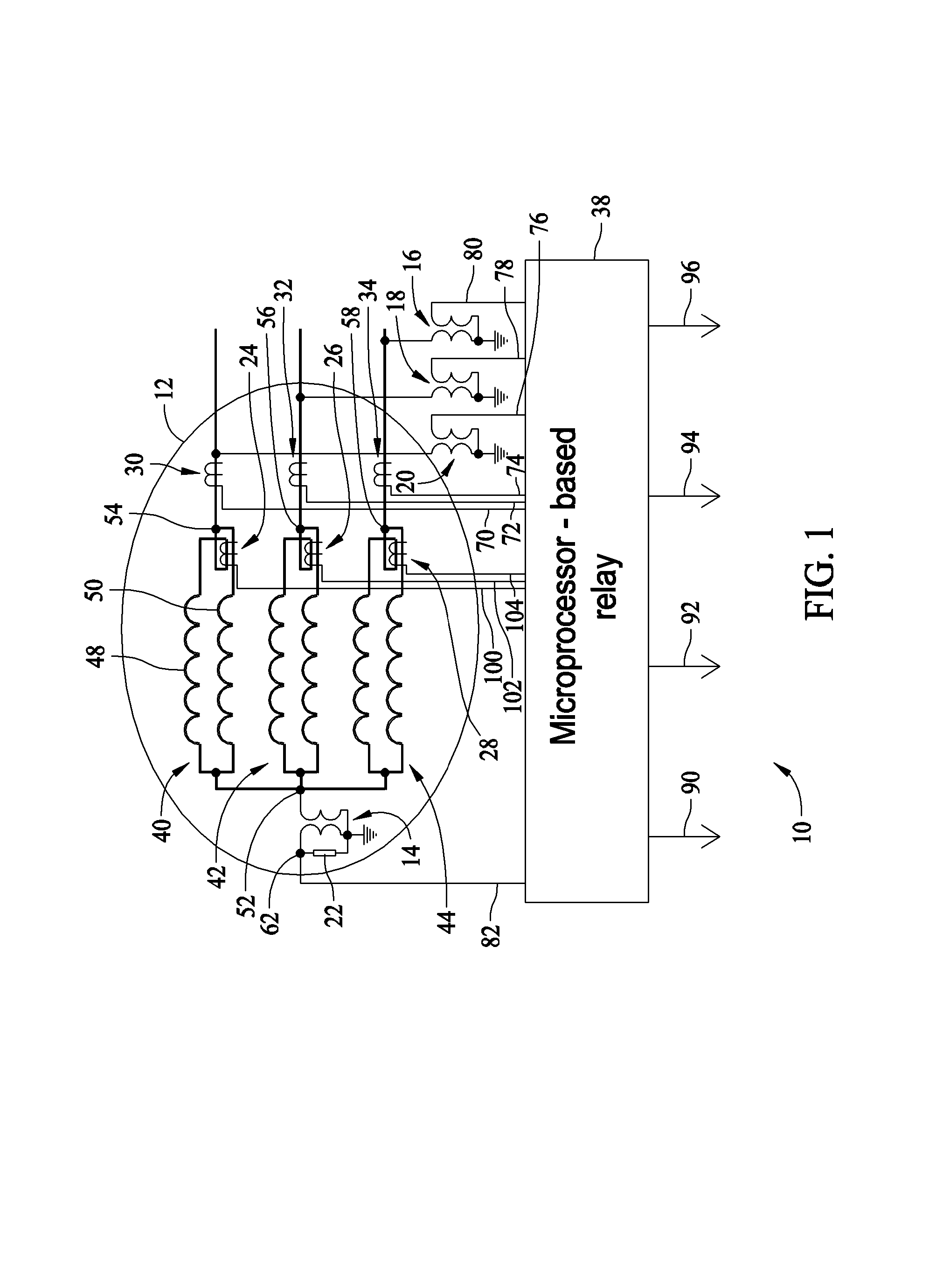
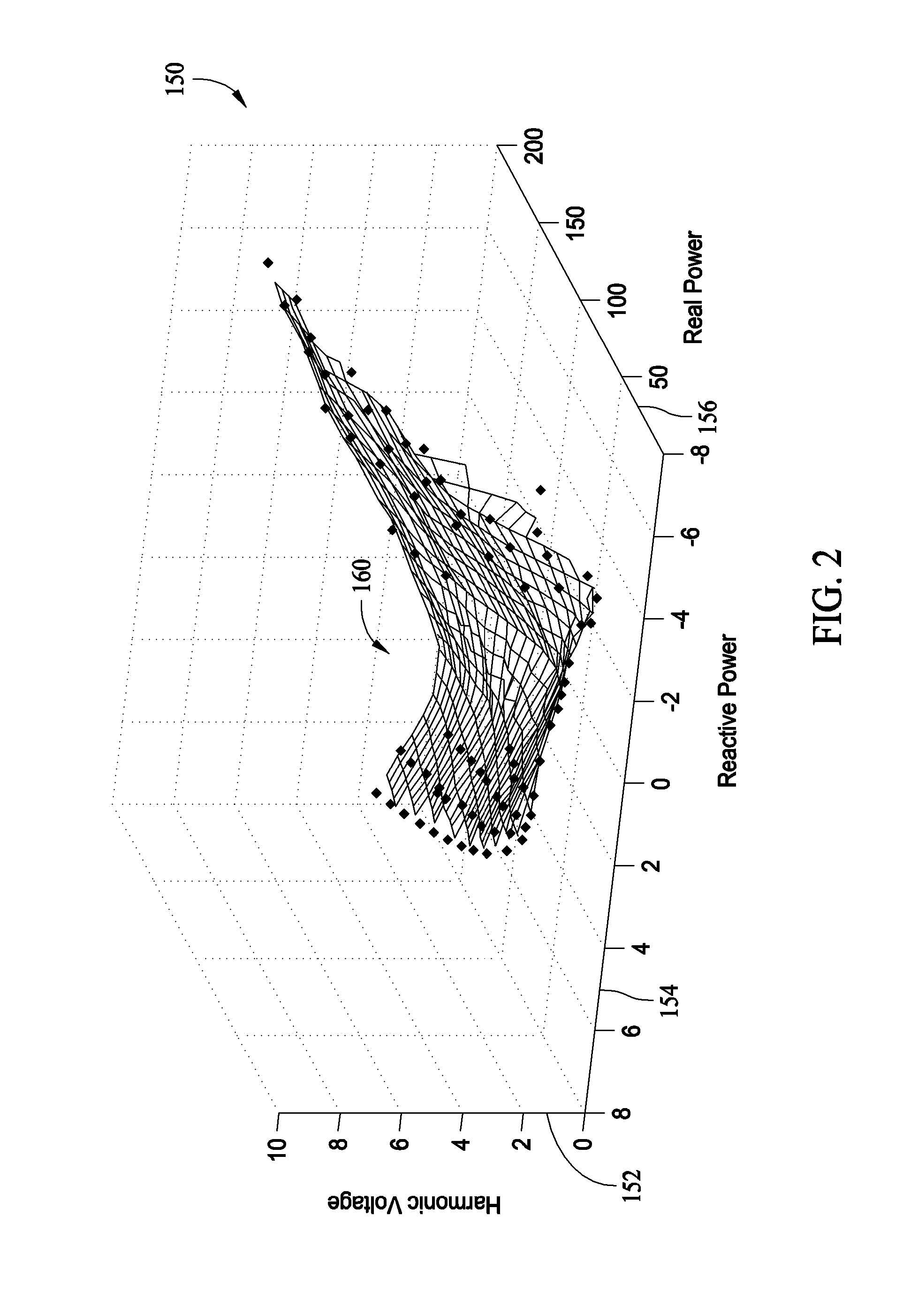
Generator protection methods and systems self-tuning to a plurality of characteristics of a machine
ActiveUS7253634B1Spectral/fourier analysisEmergency protection data processing meansSelf-tuningHarmonic
A method for detecting stator ground faults in a generator is described. The method includes receiving a neutral voltage signal from a neutral point of a stator, receiving a plurality of terminal voltage and current signals from the stator, deriving a magnitude of a harmonic component from the neutral voltage signal, deriving a total complex power from the terminal voltage and current signals, calculating an expected value of a harmonic based on the complex power at a first time and a plurality of values of the complex power, where the values of the complex power are measured at times before the first time, and comparing the expected value and a measured value of the harmonic.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
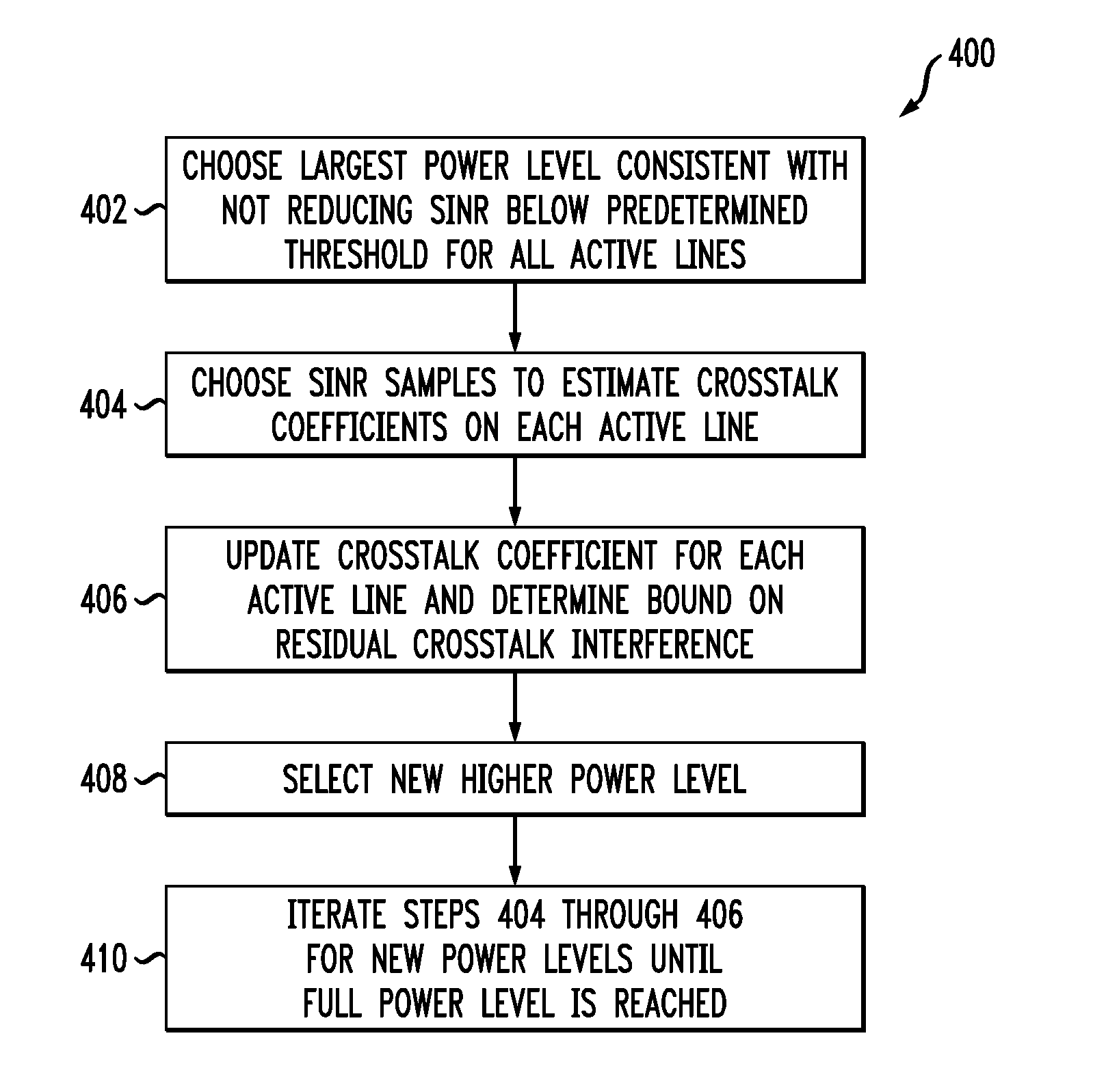
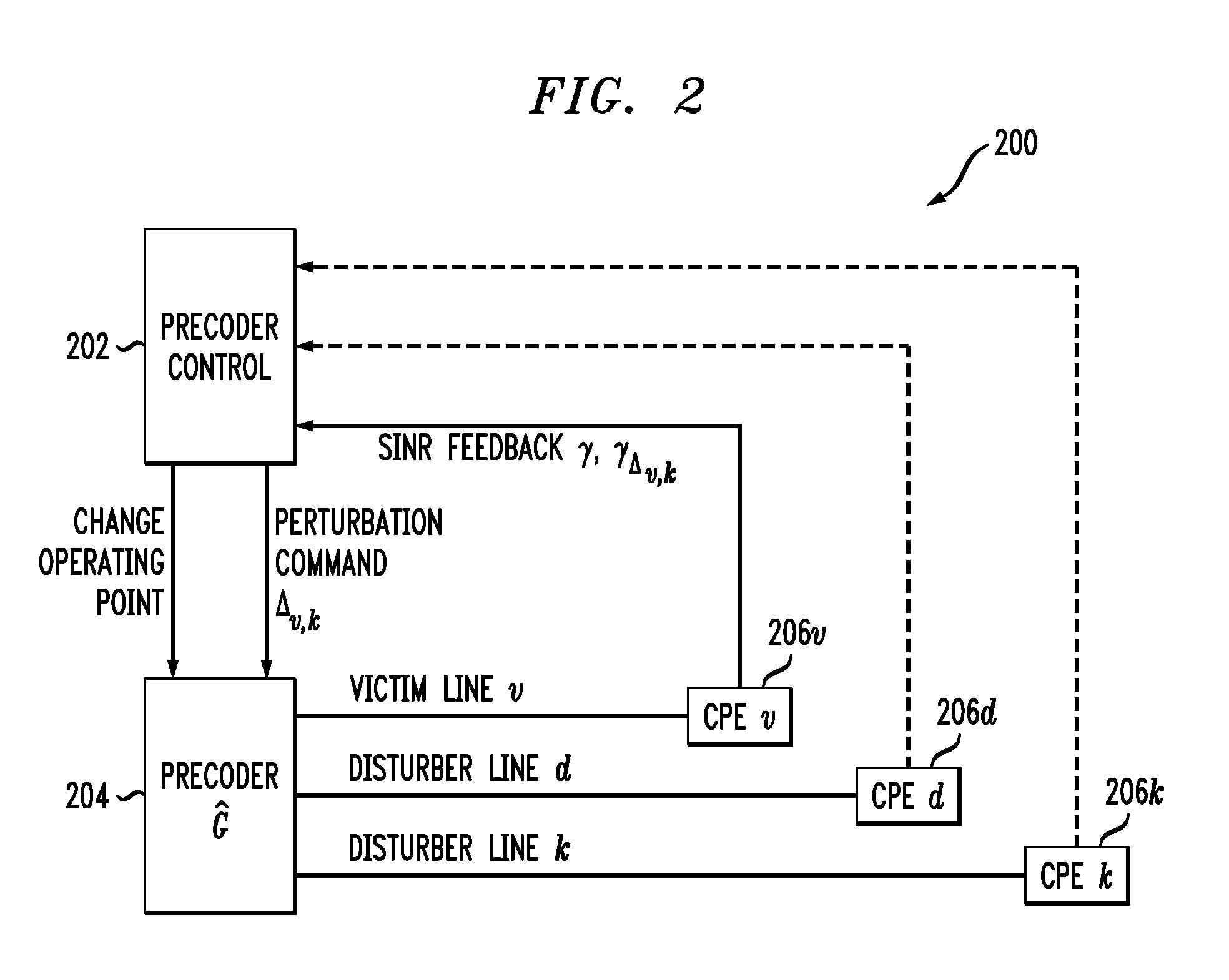
Method and apparatus for self-tuning precoder
ActiveUS20090059780A1Reduce errorsFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexCommunications systemCrosstalk measurement
Techniques are disclosed for compensating for crosstalk using adaptation of data signals transmitted over respective channels of a communication system. For example, a method includes the following steps. A first set of estimated measures of crosstalk is obtained for at least a selected portion of a plurality of communication channels over which data signals are to be transmitted from a transmitter to at least a selected portion of a plurality of receivers. A first set of data signals based on the first set of estimated measures of crosstalk is adapted to generate a first set of adjusted data signals. The first set of adjusted data signals is transmitted to corresponding ones of the plurality of receivers. A second set of estimated measures of crosstalk is obtained for the selected portion of the plurality of communication channels. A second set of data signals for transmission based on the second set of estimated measures of crosstalk is adapted to generate a second set of adjusted data signals. Iteration of the obtaining, adjusting and transmitting steps is performed so as to reduce an error between subsequent estimated measures of crosstalk and actual measures of crosstalk for the plurality of communication channels.
Owner:RPX CORP
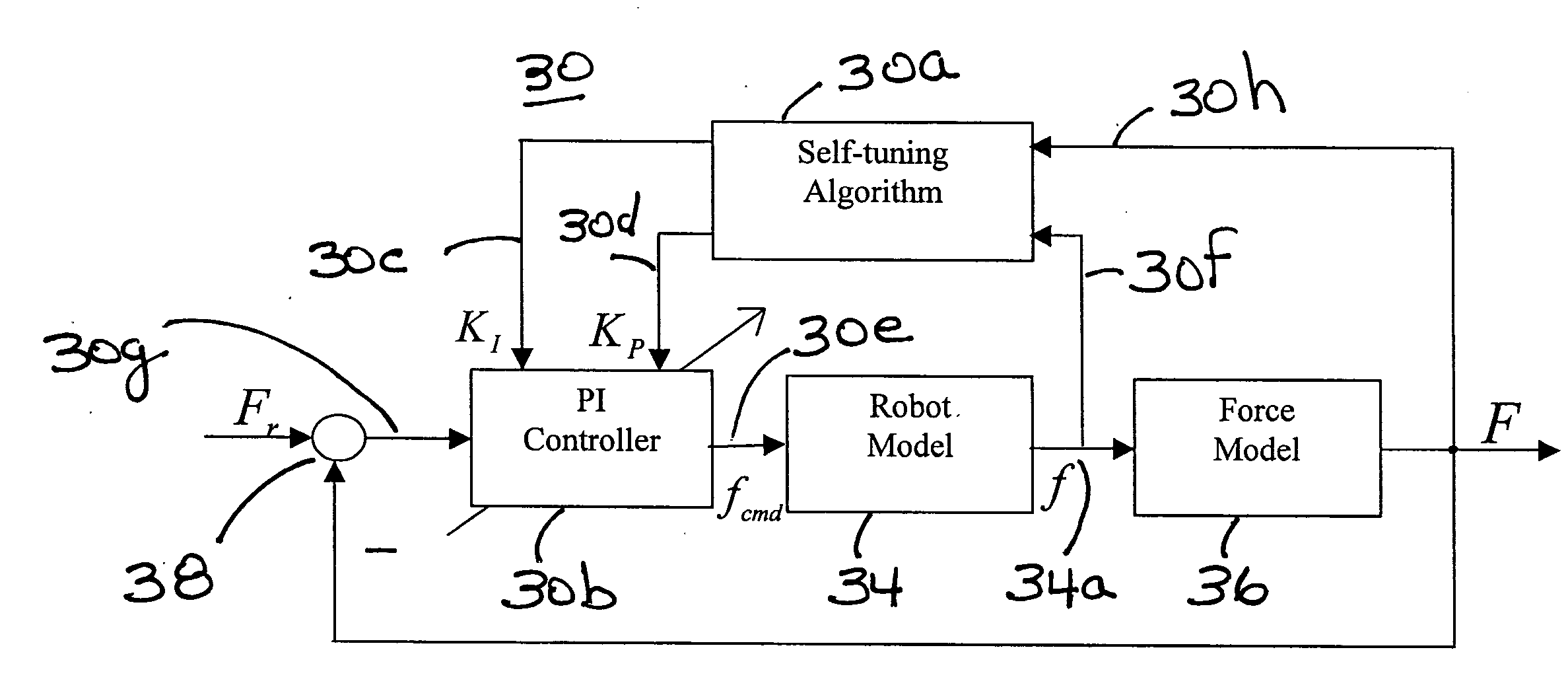
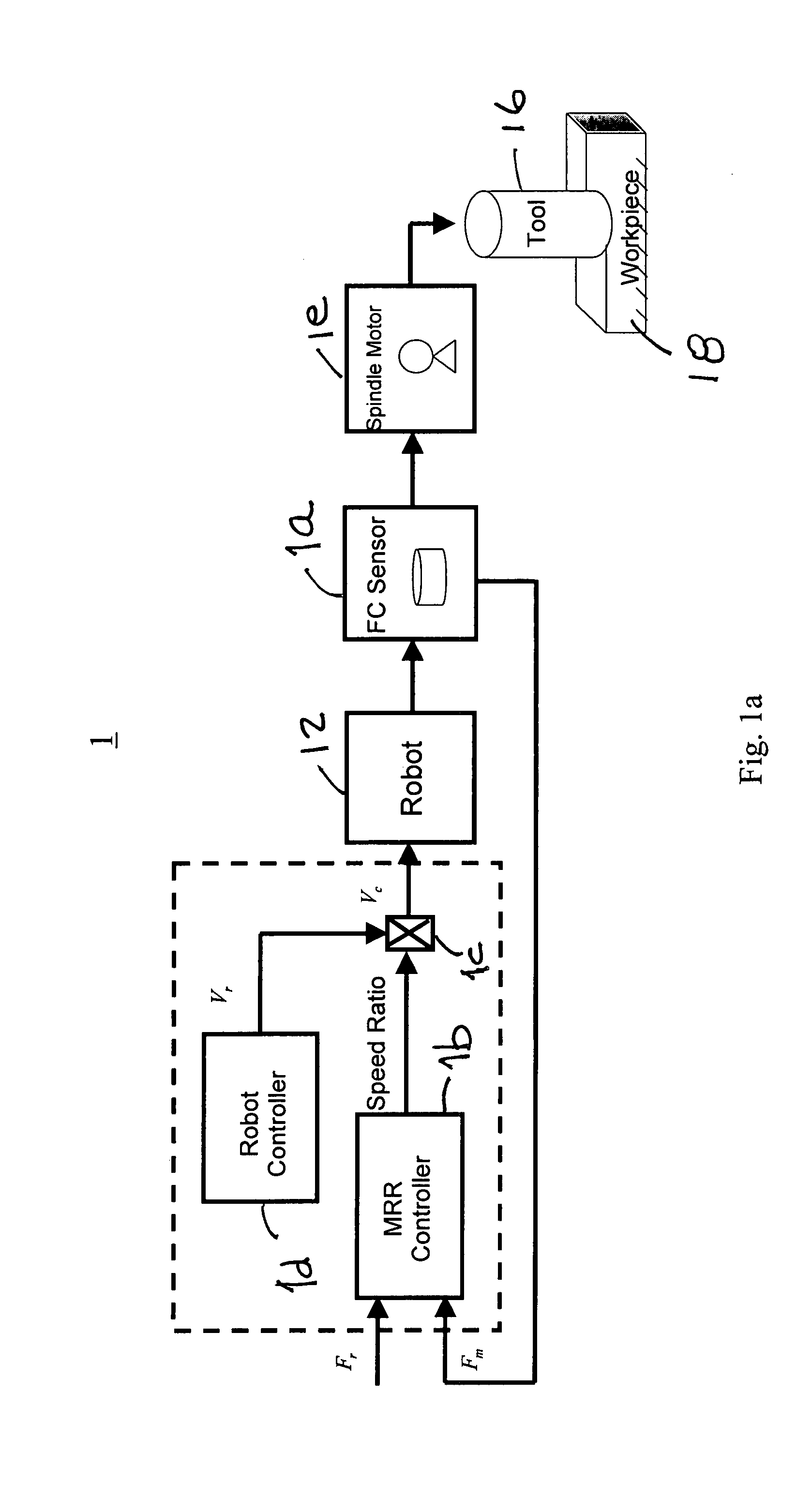
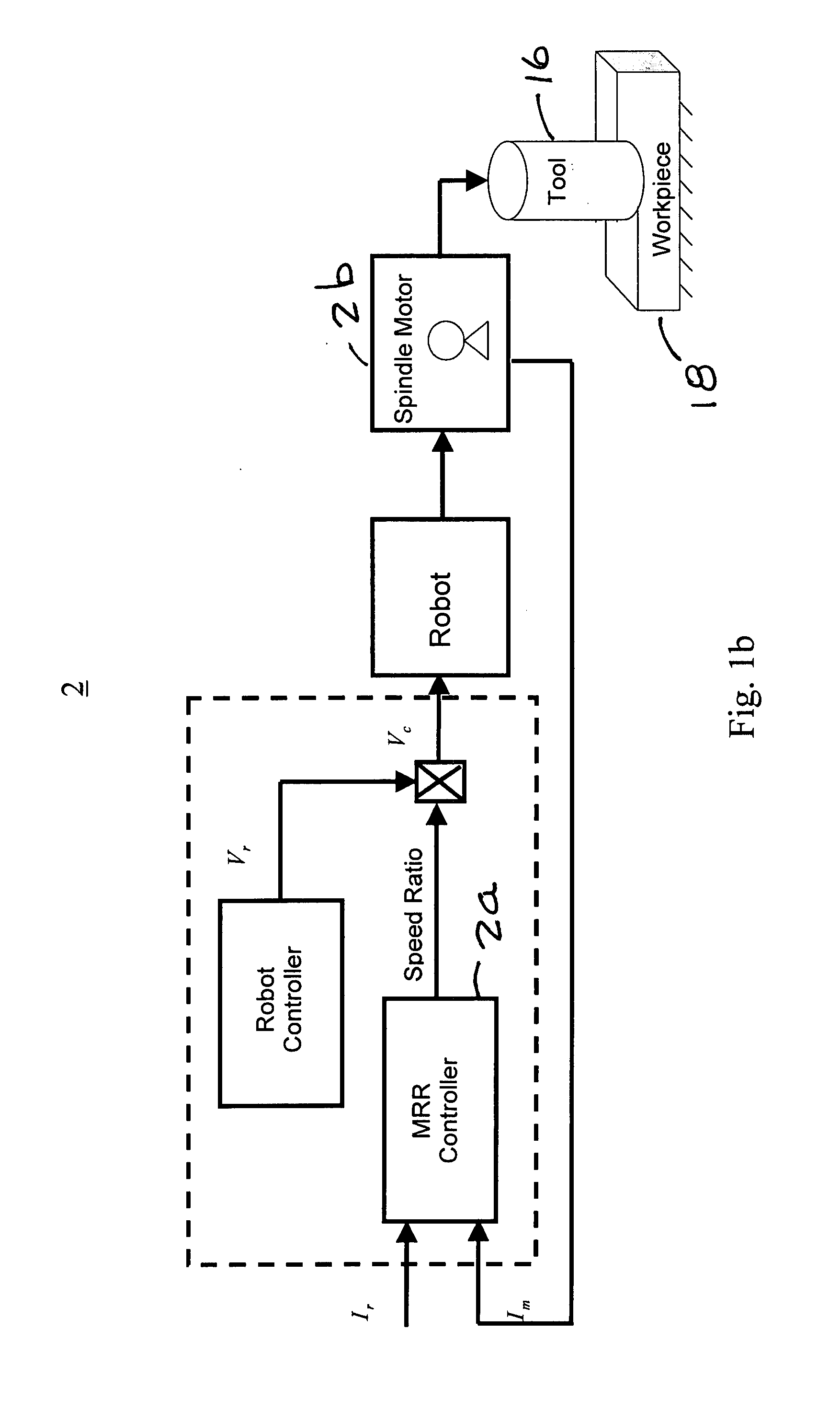
Controlled material removal rate (CMRR) and self-tuning force control in robotic machining process
InactiveUS20080065257A1Programme-controlled manipulatorMeasurement/indication equipmentsSelf-tuningMaterial removal
A method and apparatus for a robotic machining process that gives a controlled removal rate of material from a workpiece when an object, tool or workpiece, held by a robot is brought into contact with a stationary object, workpiece or tool. A signal indicative of the force applied by the held object t the stationary object is used to control the rate at which the robot moves the held object in relation to the stationary object. Associated with the robot is a controller that has tunable proportional and integral gains. The controller determines a command for the feed rate of the tool when the tool engages the workpiece. In response to that command, the proportional and integral gains are tuned to obtain a cutting force to be applied to the workpiece when the tool engages the workpiece that is substantially the same as a desired cutting force.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
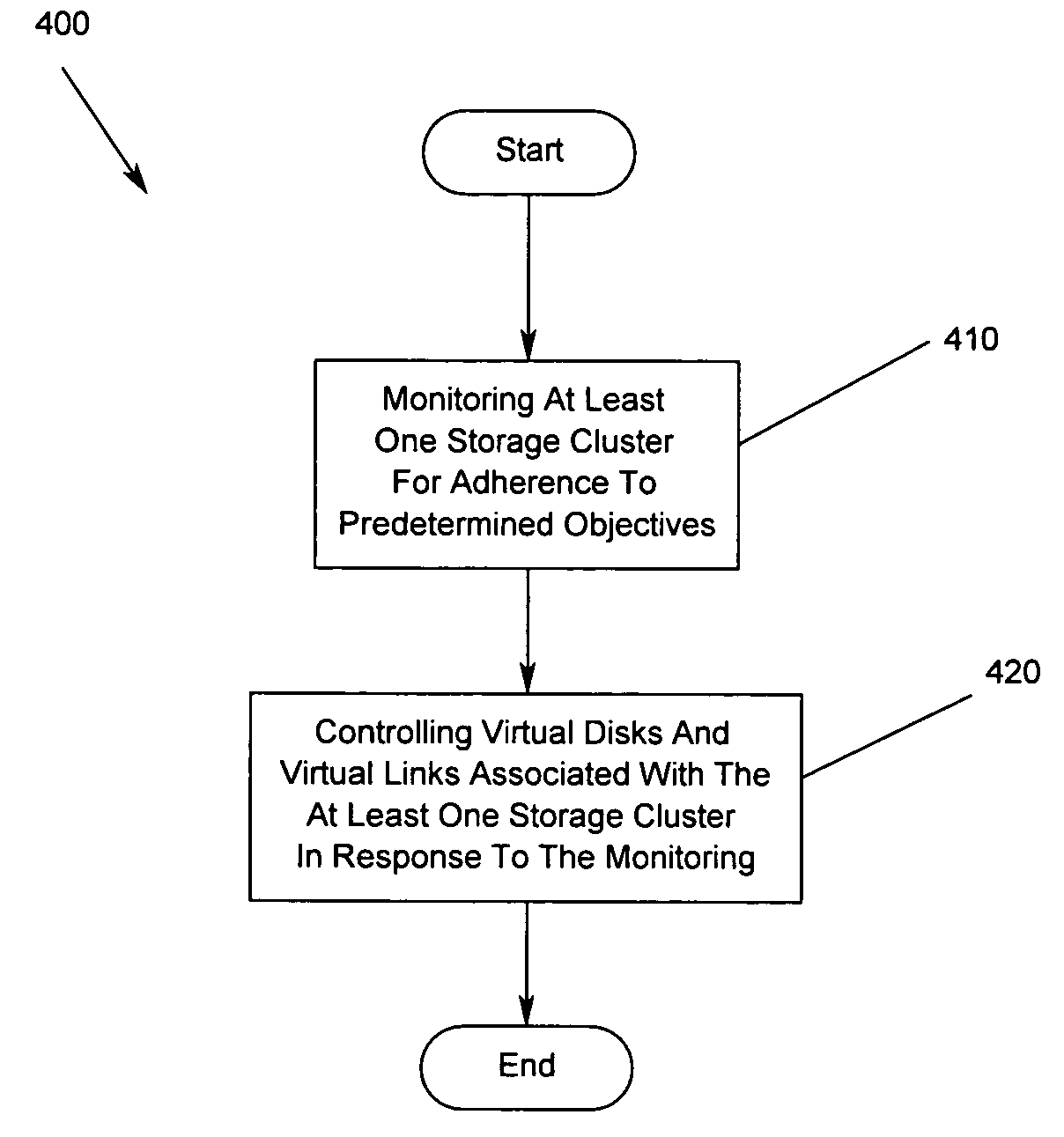
Method, apparatus and program storage device for providing adaptive, attribute driven, closed-loop storage management configuration and control
InactiveUS20060161752A1Less user complexityImprove performanceTransmissionMemory systemsSelf-tuningClosed loop
A method, apparatus and program storage device for providing adaptive, attribute driven, closed-loop storage management configuration and control is disclosed. The closed loop control mechanism provides not only continuous self-tuning to the storage system, but also allows the system to perform the initial configuration better.
Owner:XIOTECH CORP
Self-tuning ultrasonic meter
InactiveUS20050055171A1Correction errorWide applicabilityVolume/mass flow measurementElectrical measurementsSelf-tuningTemperature stratification
A method and related ultrasonic meter identify and correct for transit time errors such as peak switch errors. The method includes calculating values for a set of diagnostics from measurements of the fluid flow, including transit time measurements. Based on the values for the diagnostics, and whether and how they fall outside of their respective ranges, the meter can identify a variety of problems with the meter or fluid flow, such as whether there has been an intermittent peak switch, a permanent peak switch, or the presence of noise, velocity pulsation in the fluid flow, temperature stratification, or other problem. In the event there is a problem with the meter, the meter self-tunes in order to minimize the chances of the problem happening again.
Owner:MICRO MOTION INC
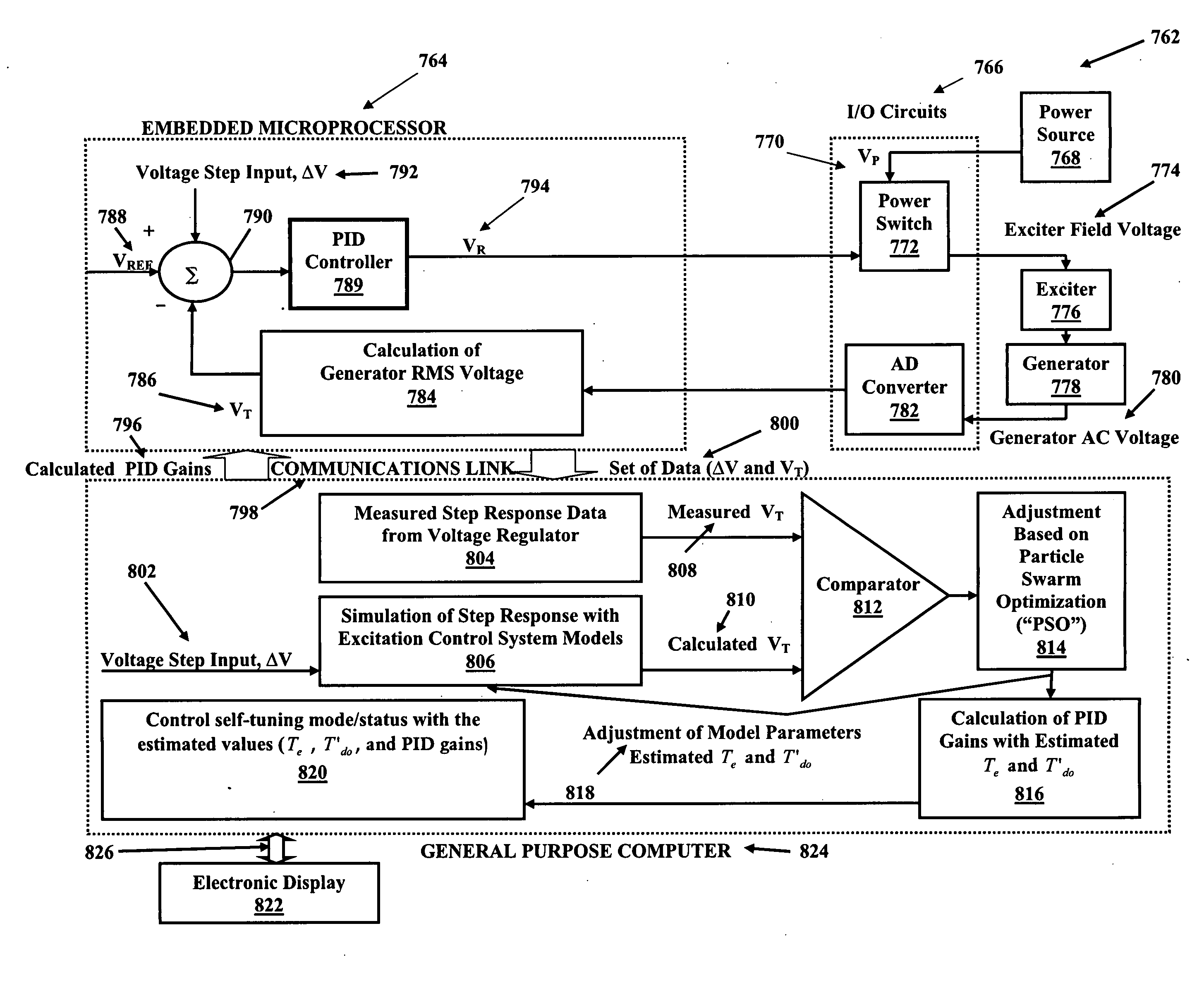
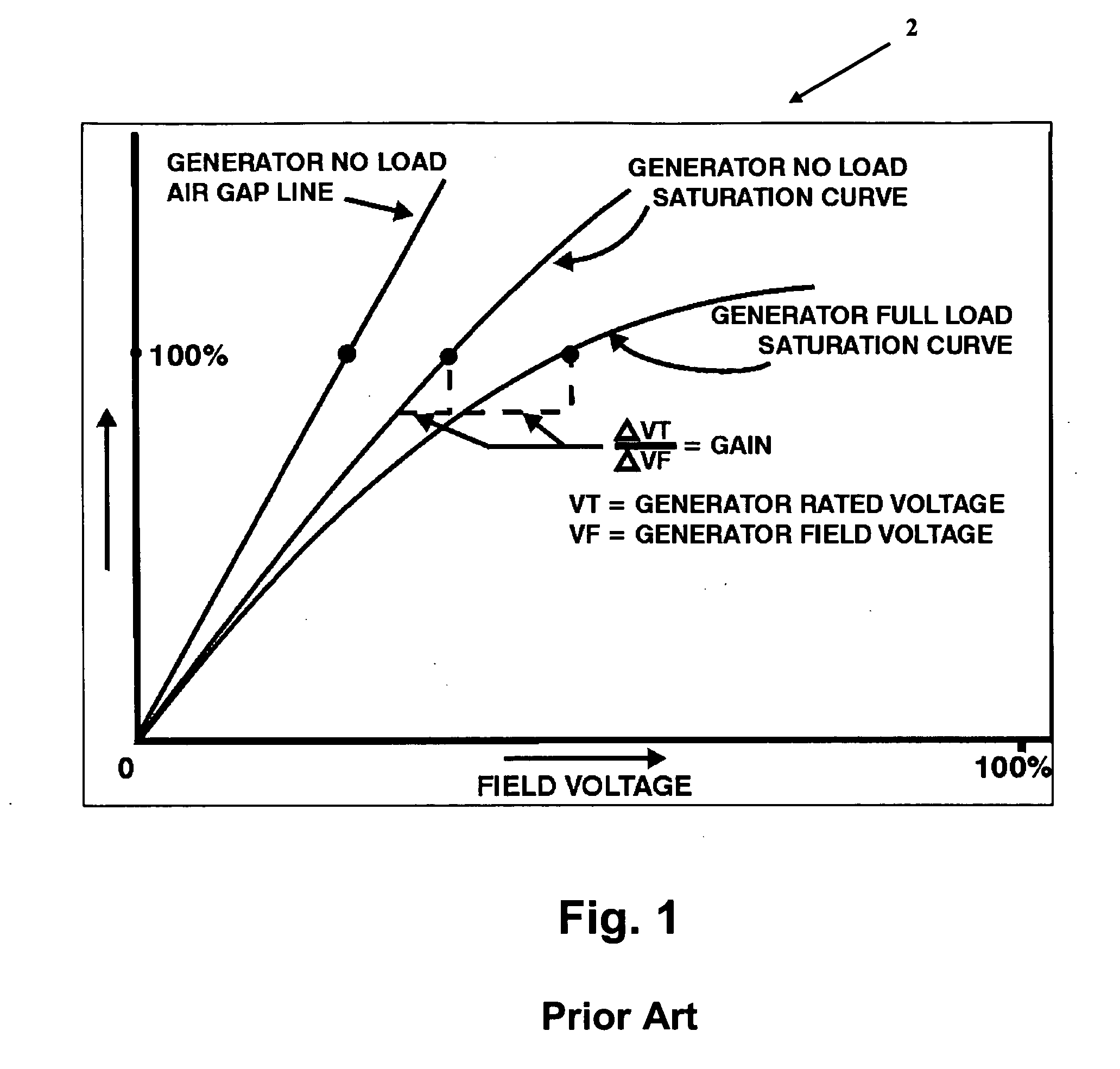
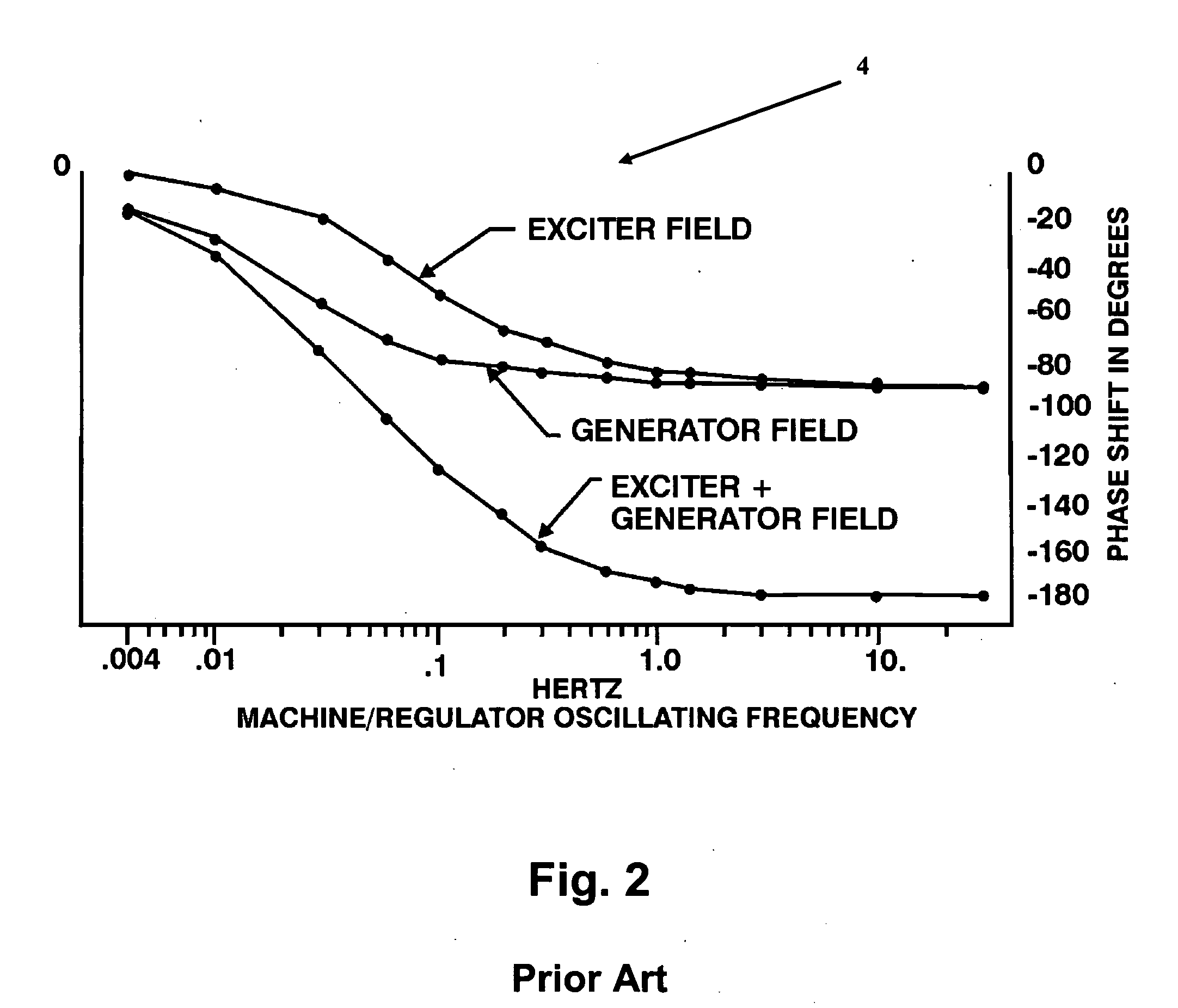
Digital Excitation Control System Utilizing Swarm Intelligence and An Associated Method of Use
A system and method of use for self-tuning a PID controller utilized with an exciter and generator is disclosed. The system includes a power source, an exciter electrically connected to the power source, a generator that is electrically energized by the exciter, and a processor that provides a PID controller that calculates an estimated exciter time constant and an estimated generator time constant using particle swarm optimization (“PSO”) to control exciter field voltage. The particle swarm optimization (“PSO”) technique includes increasing the voltage reference by a predetermined percentage over a predetermined time period, initializing each particle position of exciter time constant and generator time constant, calculating generator voltage, performing a fitness evaluation and then obtaining and updating best values. This is followed by repeating the steps of determining the generator voltage, the fitness evaluation, and the best values over a predetermined number of iterations.
Owner:BASLER ELECTRIC
Real-time self tuning of planned actions in a distributed environment
ActiveUS8156500B2Maximize use of resourcesResource allocationDigital computer detailsApplication softwareWearable computer
Automatic programming, scheduling, and control of planned activities at “worker nodes” in a distributed environment are provided by a “real-time self tuner” (RTST). The RTST provides self-tuning of controlled interoperation among an interconnected set of distributed components (i.e., worker nodes) including, for example, home appliances, security systems, lighting, sensor networks, medical electronic devices, wearable computers, robotics, industrial controls, wireless communication systems, audio nets, distributed computers, toys, games, etc. The RTST acts as a centralized “planner” that is either one of the nodes or a dedicated computing device. A set of protocols allow applications to communicate with the nodes, and allow one or more nodes to communicate with each other. Self-tuning of the interoperation and scheduling of tasks to be performed at each node uses an on-line sampling driven statistical model and predefined node “behavior patterns” to predict and manage resource requirements needed by each node for completing assigned tasks.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
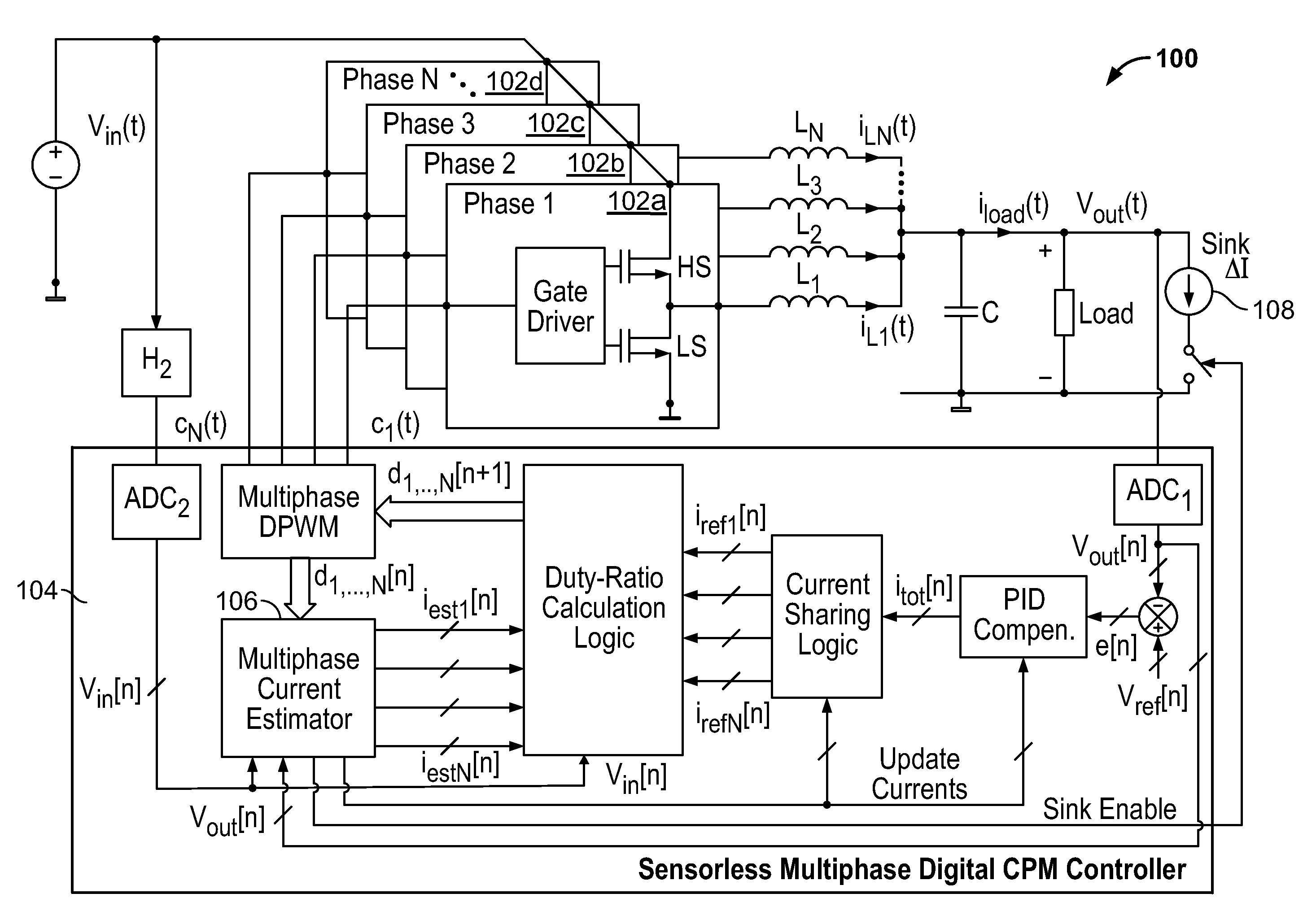
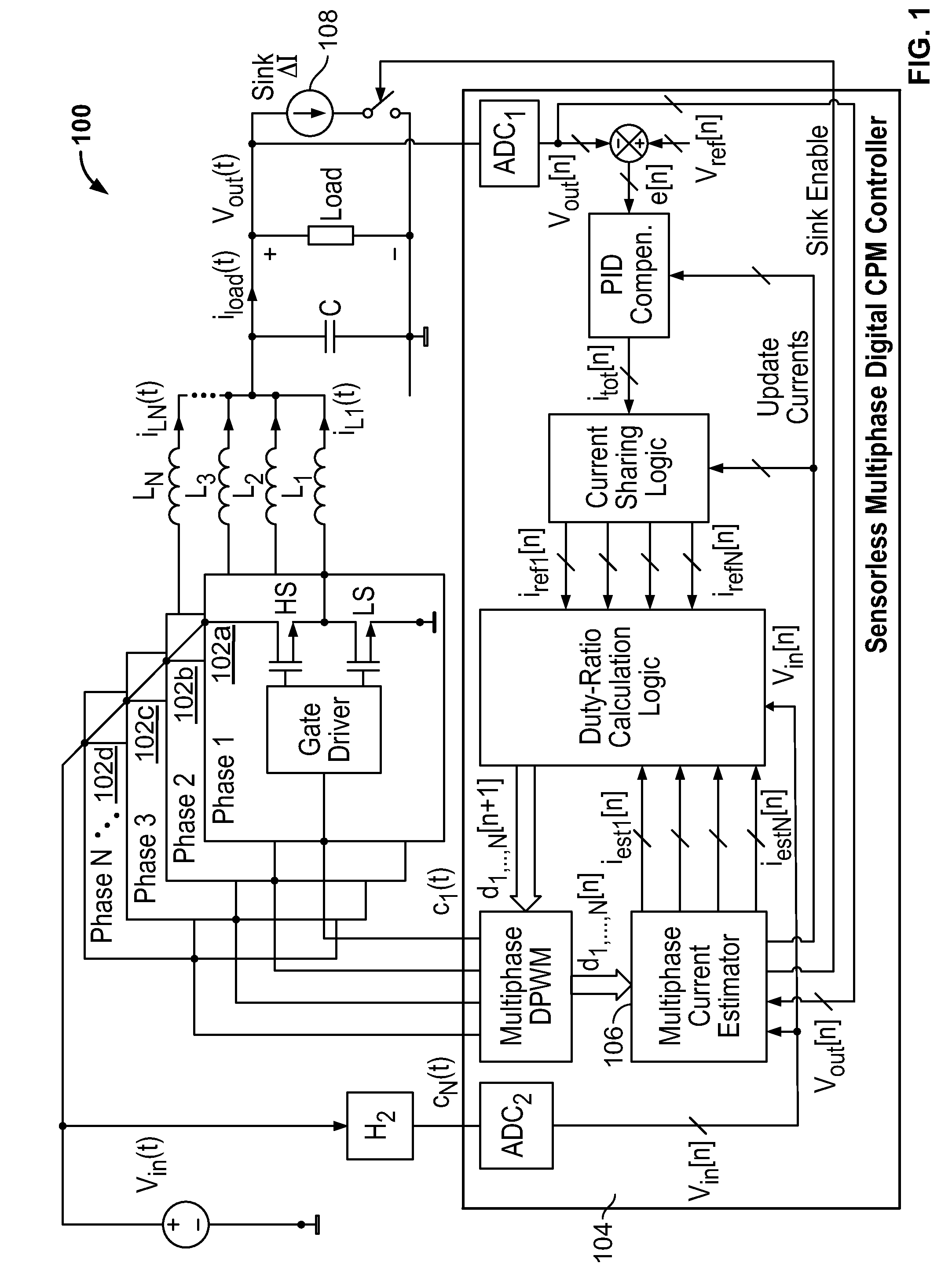
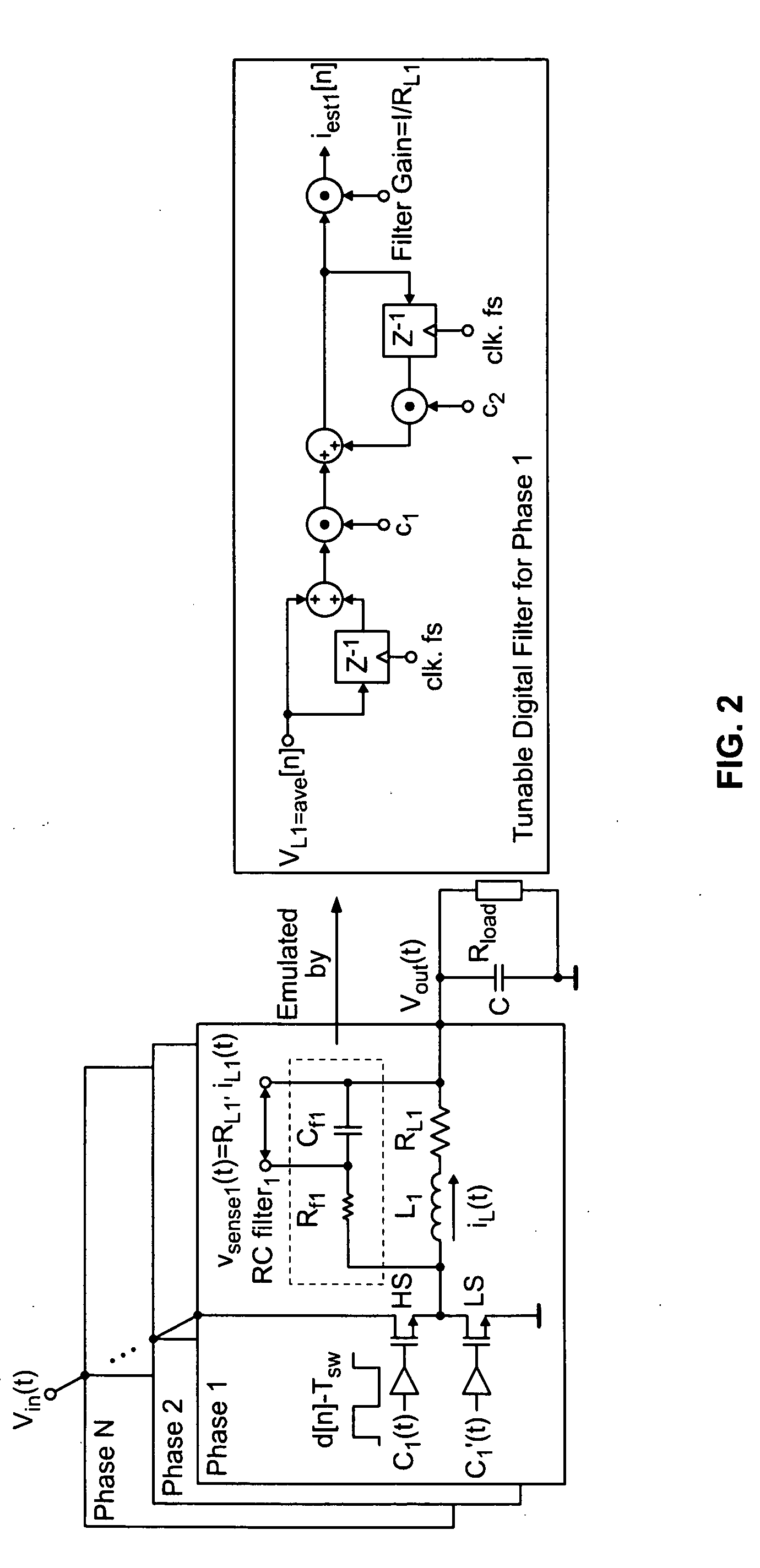
Self-tuning sensorless digital current-mode controller with accurate current sharing for multiphase dc-dc converters
Owner:EXAR CORP
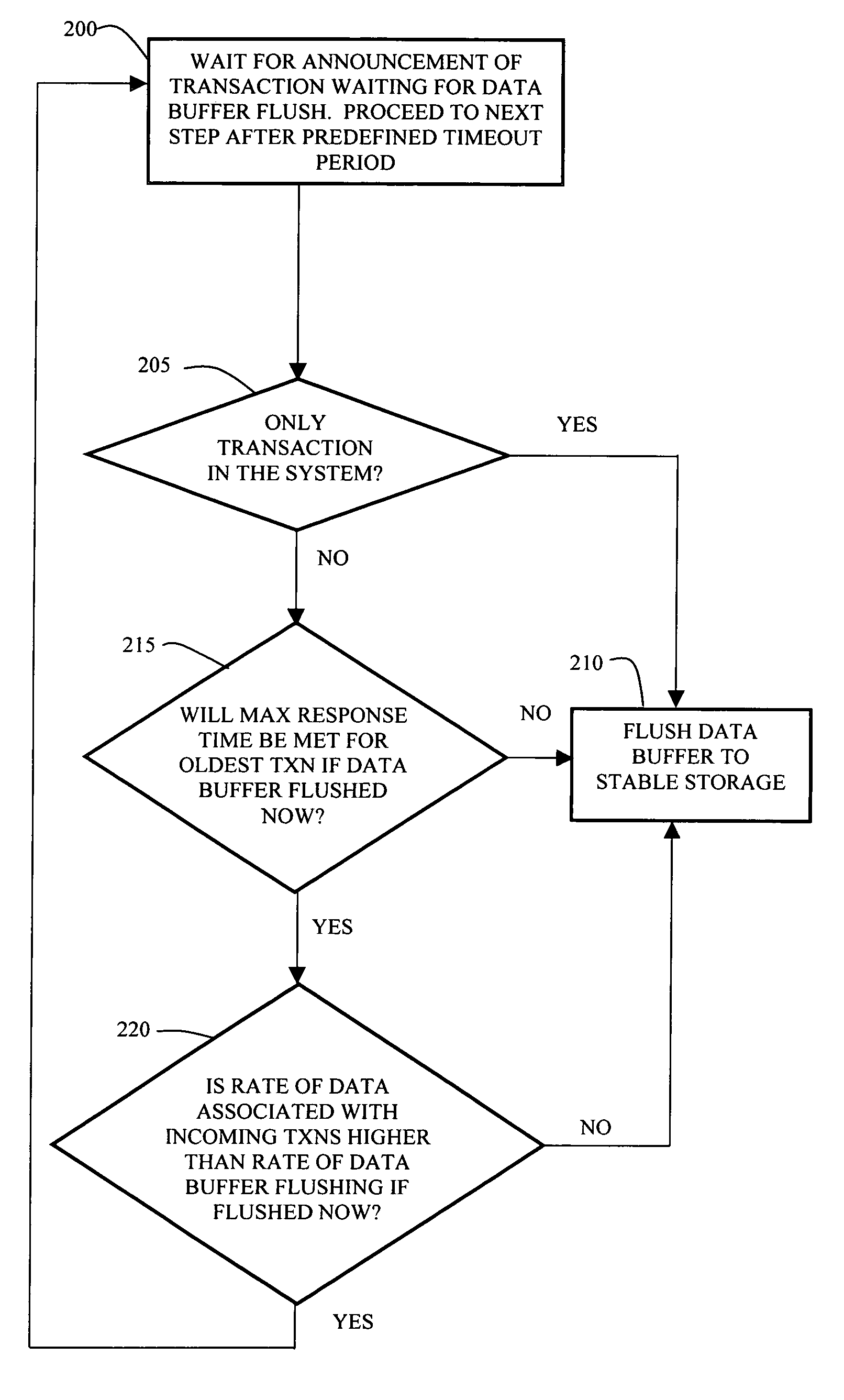
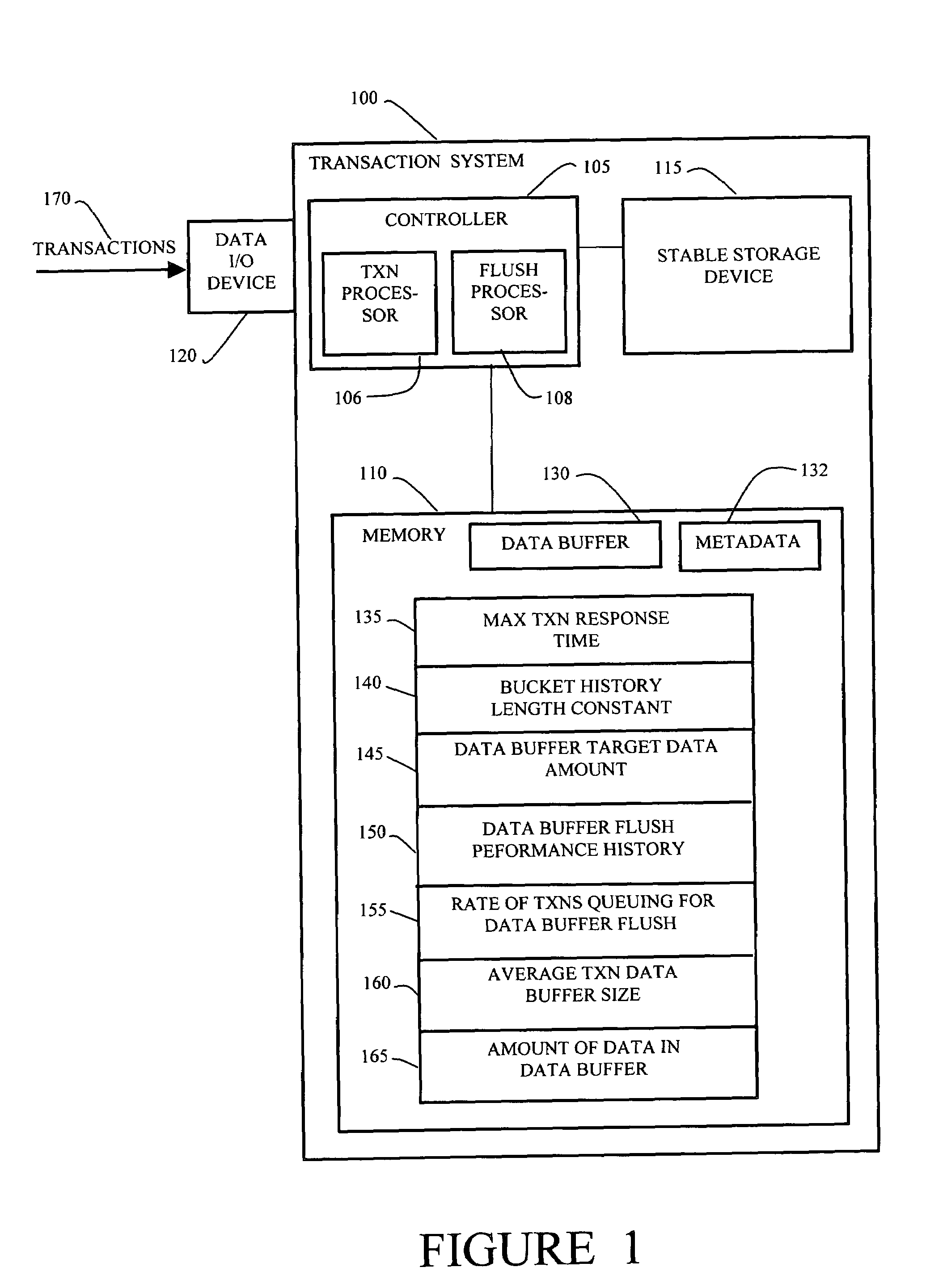
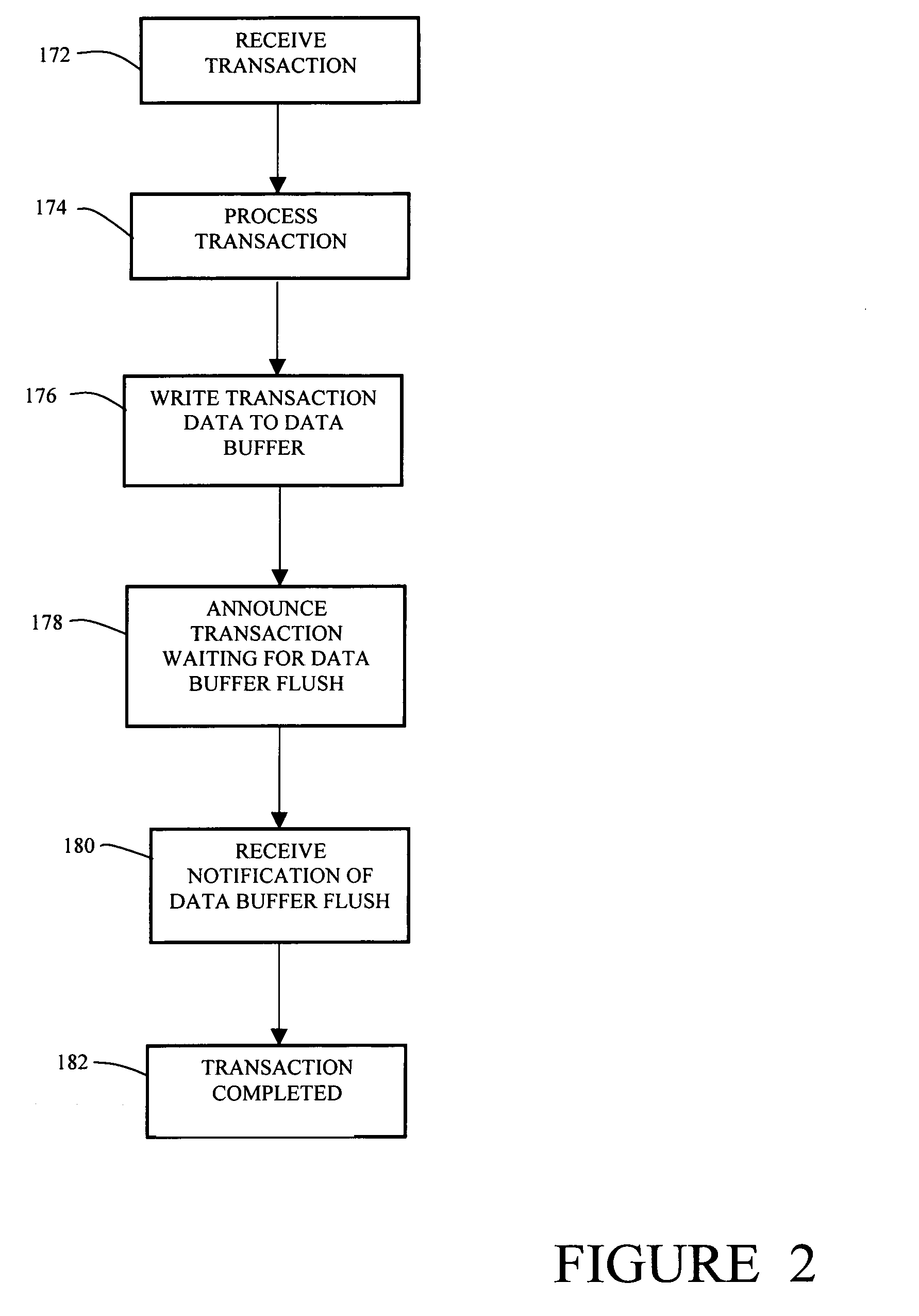
Method and apparatus for self-tuning transaction batching
InactiveUS7165129B1Improve responseImprove throughputMemory architecture accessing/allocationSpecial data processing applicationsSelf-tuningPeak value
In a transaction system, a dynamic batching process enables efficient flushing of data in a data buffer to a stable storage device. The transaction system uses constant values and dynamic values and a system performance history to adjust the rate of flushing data and also to adjust the amount of data flushed in each flush operation. The transaction system is able to respond to both spikes in rate of received transactions as well as more gradual changes in the rate of received transactions and to automatically adapt to stable storage device performance variations.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
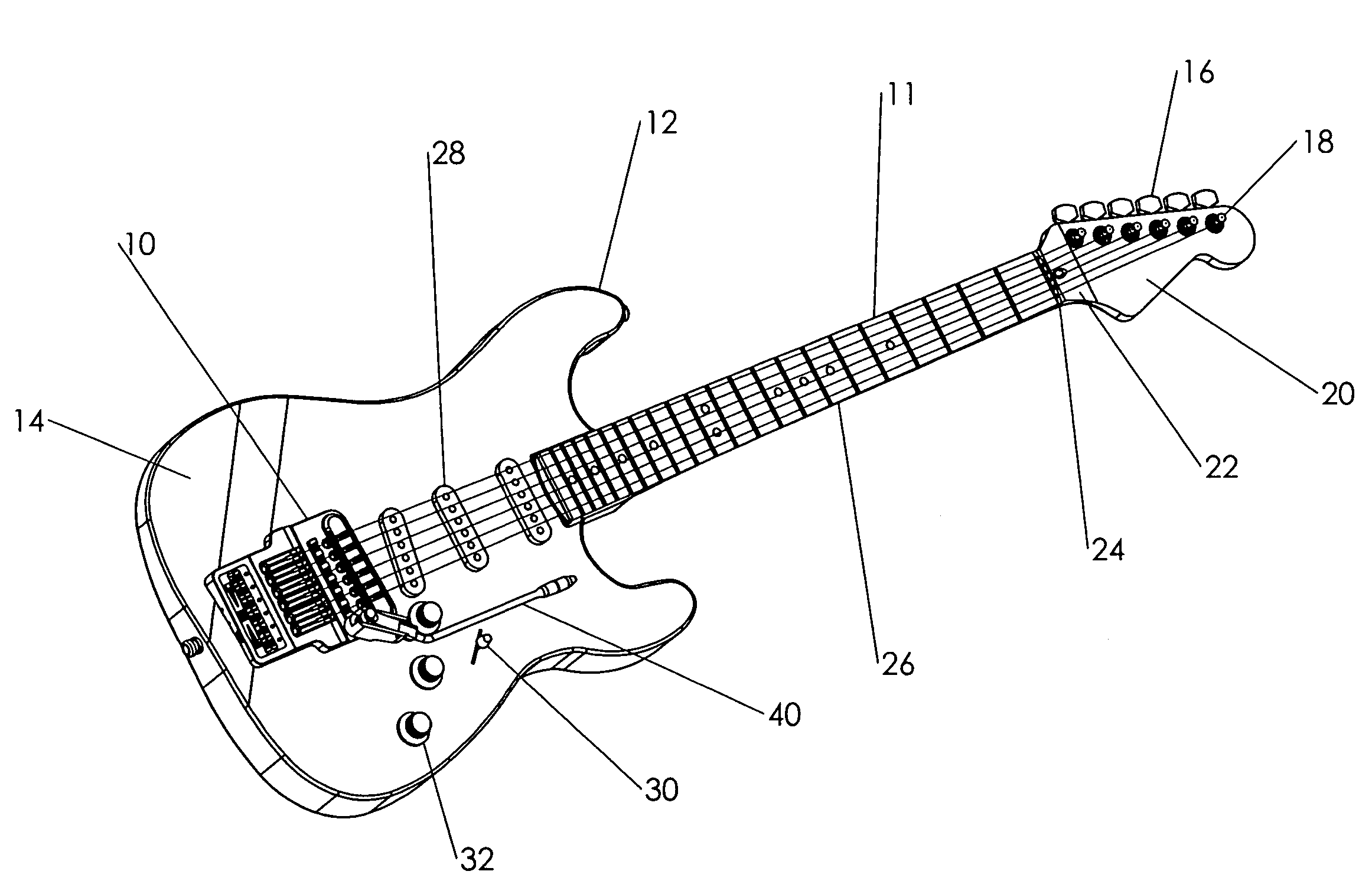
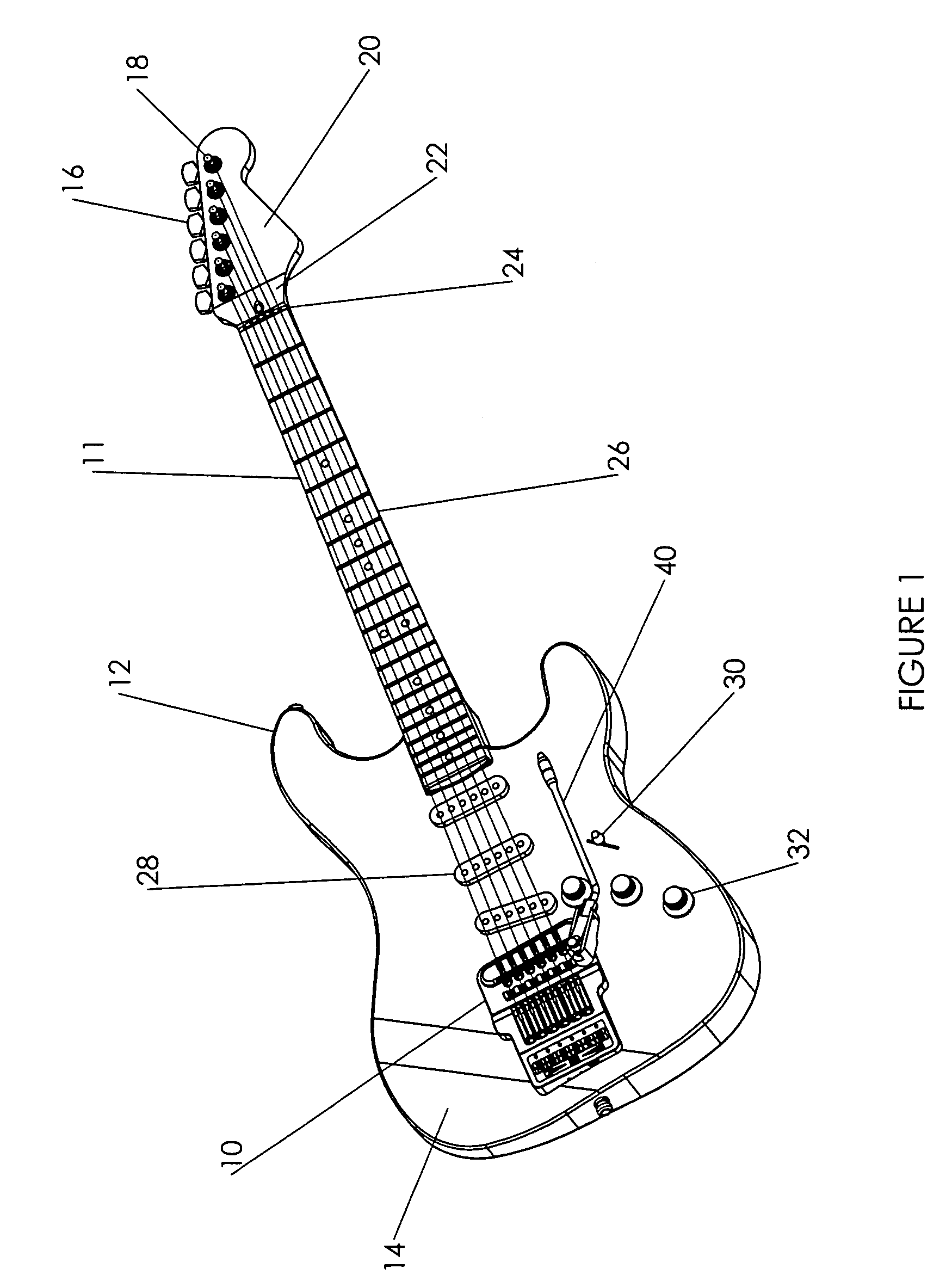
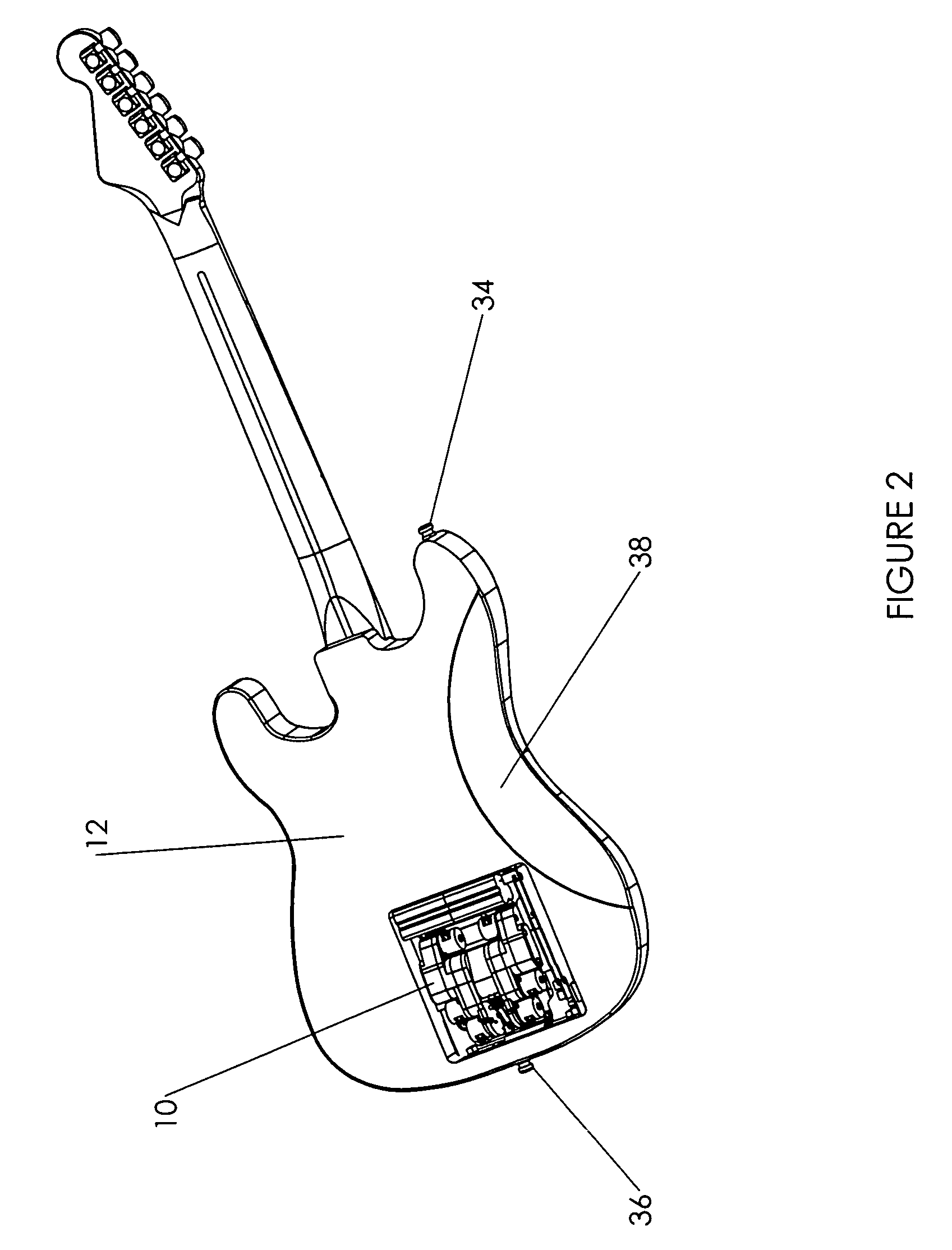
Apparatus and method for self-tuning stringed musical instruments with an accompanying vibrato mechanism
An automatic tuning system for a stringed instrument is provided having a string adjustment assembly comprising a motor and gear assembly, wherein the motor and gear assembly is pivotable on a housing for the tuning system. The system can also include a vibrato arm in contact with the motor and gear assembly, and a vibrato return spring in contact with both the motor and gear assembly and the instrument, which is capable of reversibly changing the position of a string contact surface in the string adjustment assembly with respect to the string, thereby lowering the pitch of the string and then raising it to its original pitch. The system can also include an option board for wireless communication with remote components such as a remote footswitch or other type of control panel. Other remote devices may also be wirelessly connected to the tuning system, including other instruments, audio devices for receiving sound, and the like. The system comprises a processor that can be preprogrammed with generic instructions for motor movement to achieve specific pitch changes and can also be programmed to store the motor instructions required to achieve specific pitch changes each time the system performs an automatic tuning correction, and to utilize these instructions the next time the system is tuned. The system is capable of performing fine tuning corrections as well as of prompting a user to perform coarse-tuning corrections. It also allows a user to change tunings while playing.
Owner:AXCENT TUNING SYST
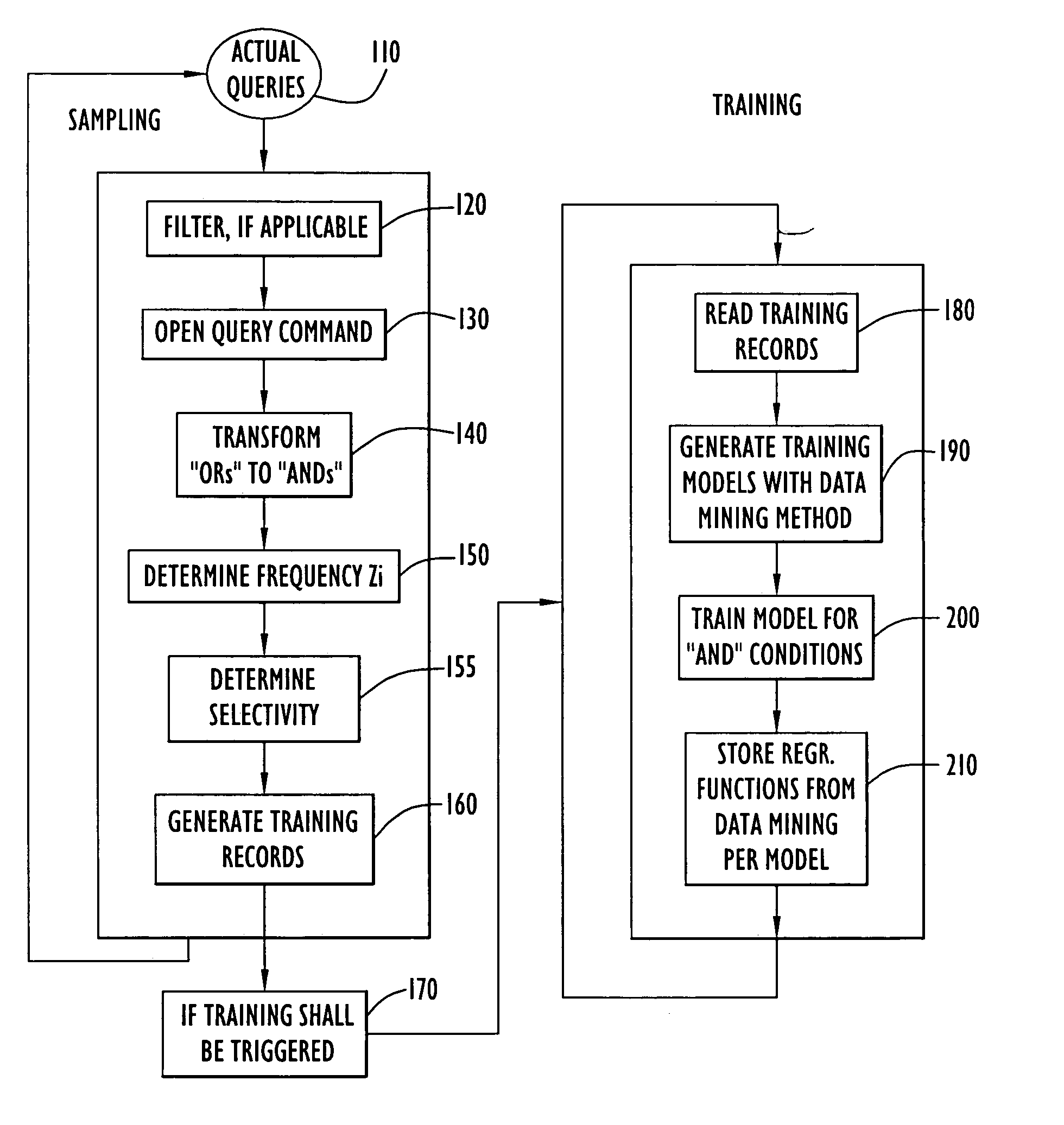
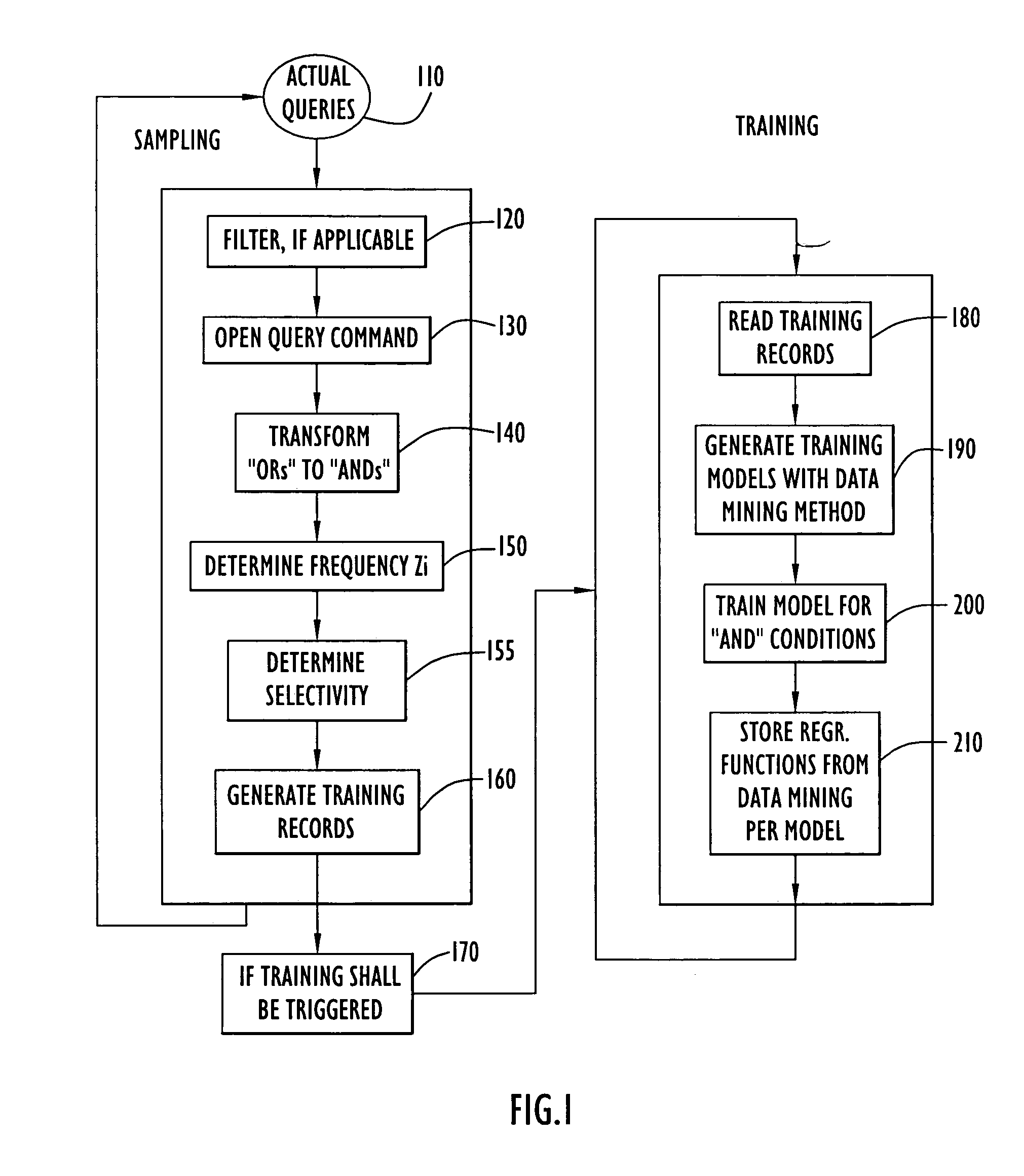
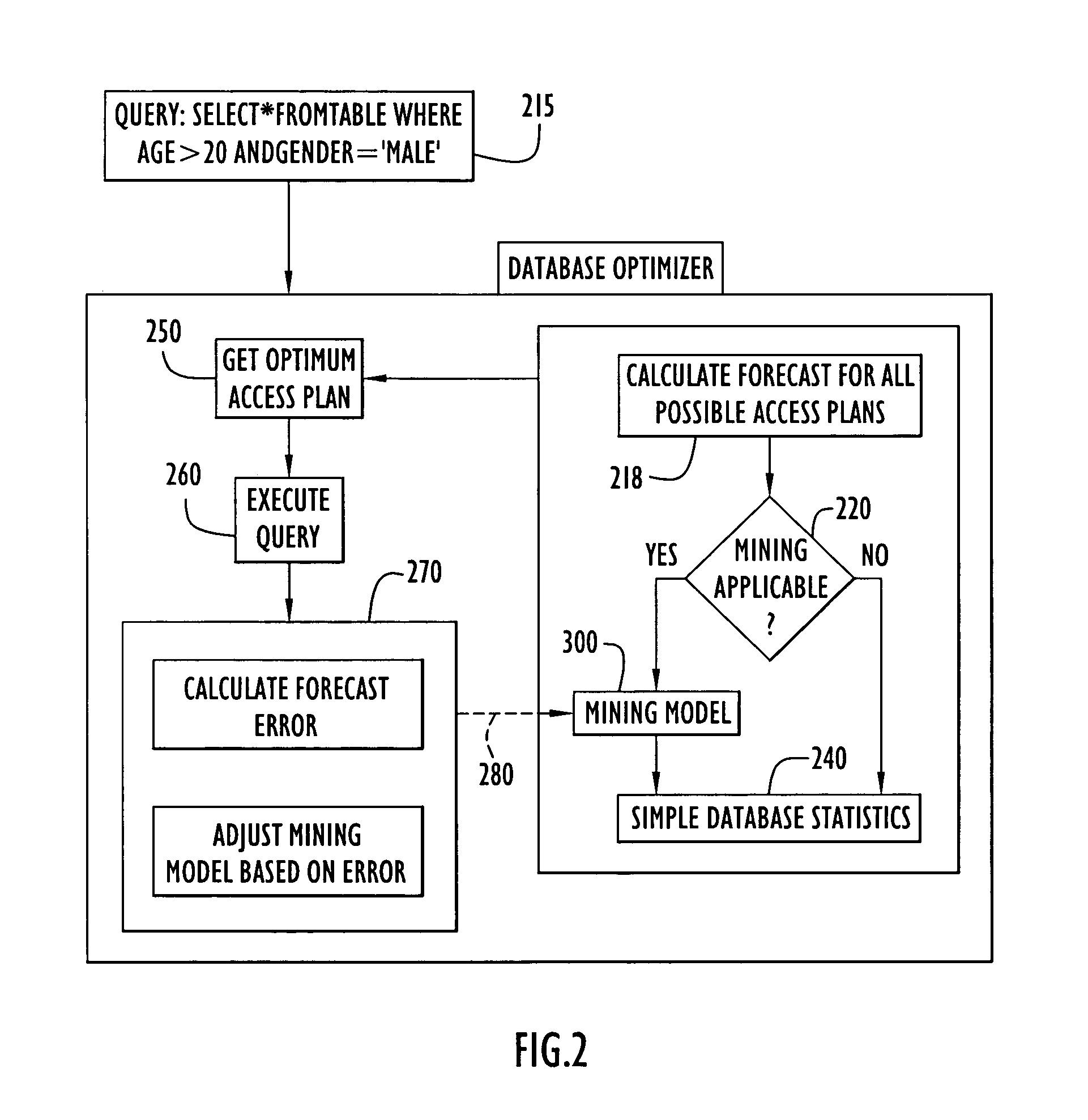
Self tuning database retrieval optimization using regression functions
InactiveUS7136850B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData setSelf-tuning
A system and method for accessing a relational database and estimating the selectivity of a query (e.g., an SQL query) in order to better predict the number of qualifying records for simple and complex queries. A dataset is created based upon queries applied against the database by the user community. The dataset is populated with information related to query conditions and their respective combinations. A regression function reflecting correlations between query conditions is generated and used as a data mining model to calculate table-specific estimates for the cardinality of subsequent queries. An appropriate access method is then selected from a set of available access methods based upon the number of estimated query-qualifying records. By periodically updating the regression model with FIFO managed queries, a self-tuning mechanism is achieved resulting in better selectivity / result size estimates for use in selecting access methods used in compiling subsequent SQL queries applied against the database.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Piezoelectric touch probe
InactiveUS6708420B1Mechanical measuring arrangementsPoint coordinate measurementsAccelerometerDigital control
The instant invention is a dynamic piezoelectric touch probe for use with coordinate measurement machines. The touch probe is characterized by five subsystems; (1) piezoelectric vibrator controlled by a self-tuning drive circuit that adjusts operating frequency and amplitude, (2) a high sensitivity, resonant accelerometer unit coupled to the piezoelectric vibrator, (3) a flexible suspension / stylus with transverse resonant frequencies tuned to the operating frequency band of the piezoelectric vibrator, (4) a digital control circuit that automatically sweeps the operating band of the piezoelectric vibrator to (a) detect the resonant frequency of the stylus / suspension, (b) set the drive signal frequency at the resonance of the stylus / suspension and (c) control the drive signal amplitude, and (5) a triaxial load cell system that is useful for detecting excessive low frequency suspension / stylus vibration, and excessive impact force during a touch event.
Owner:QUALITY VISION INT
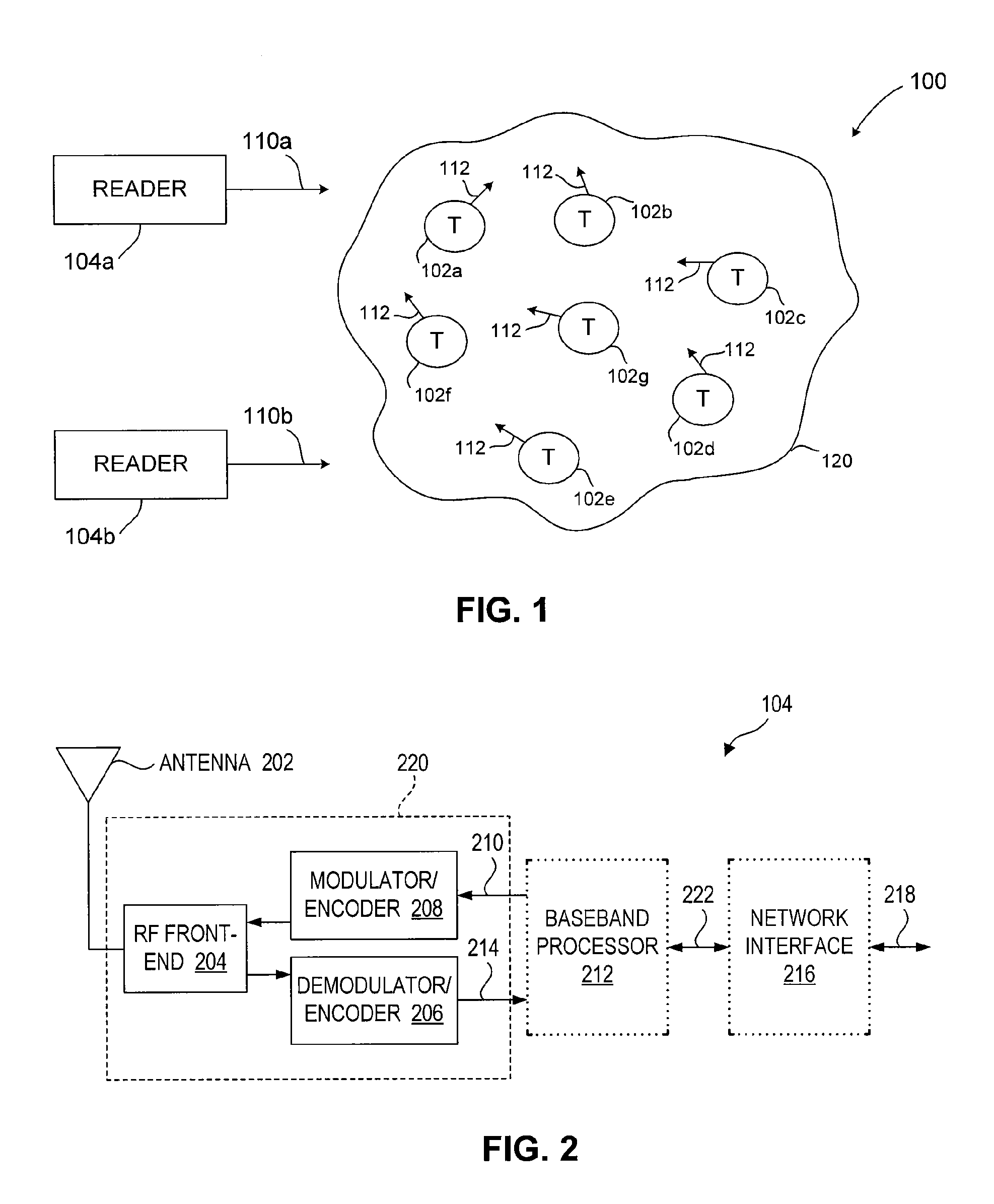
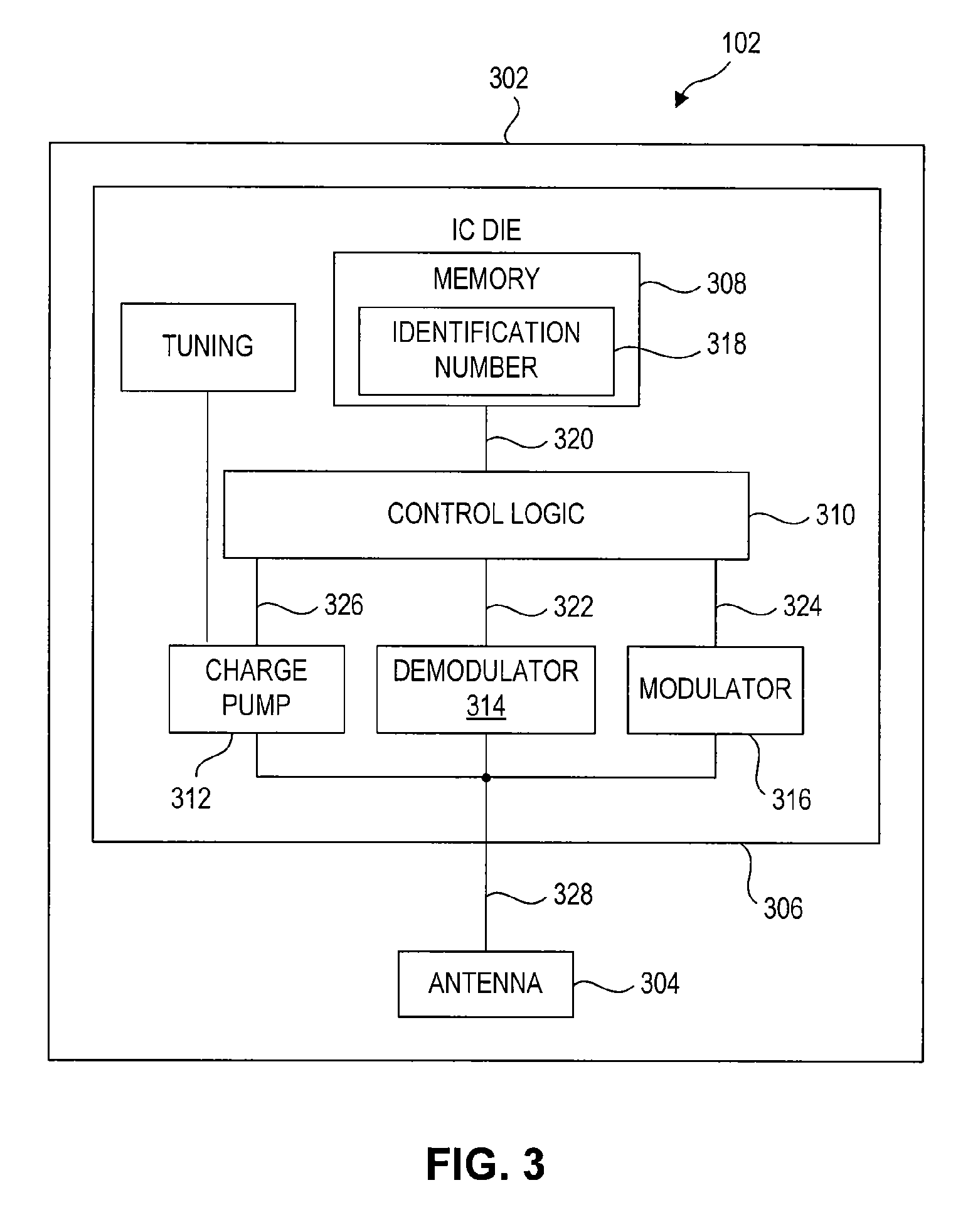
Self Tuning RFID
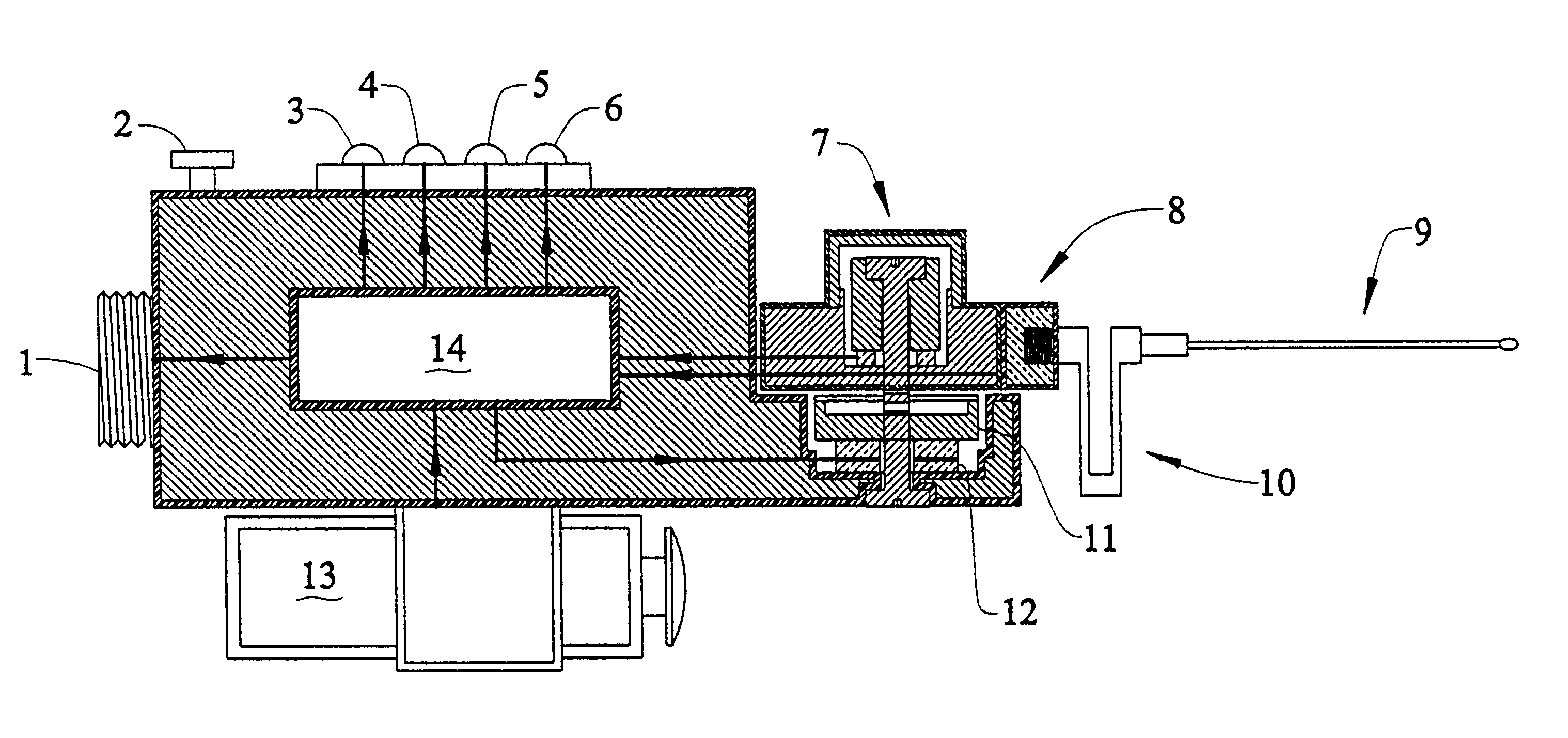
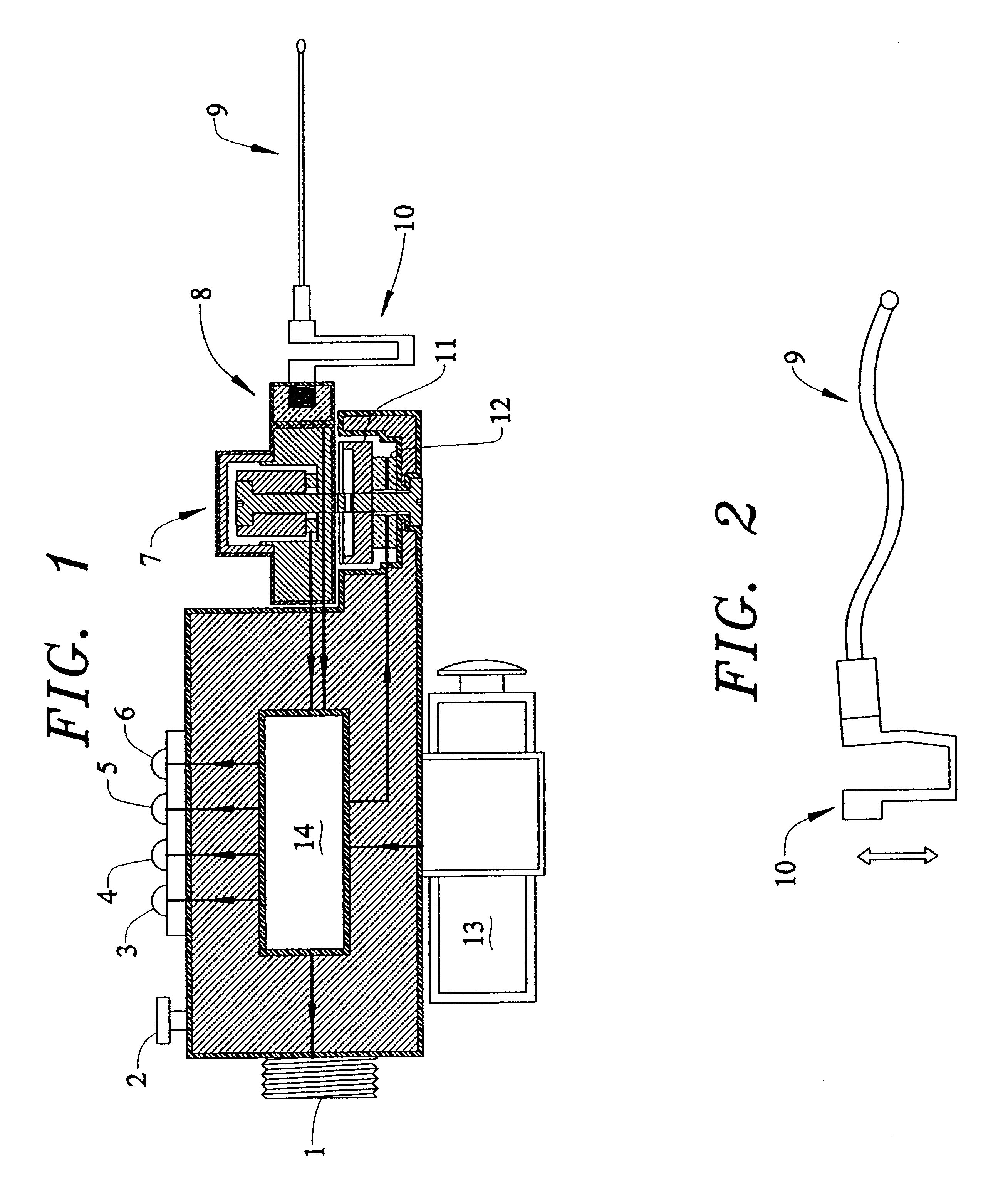
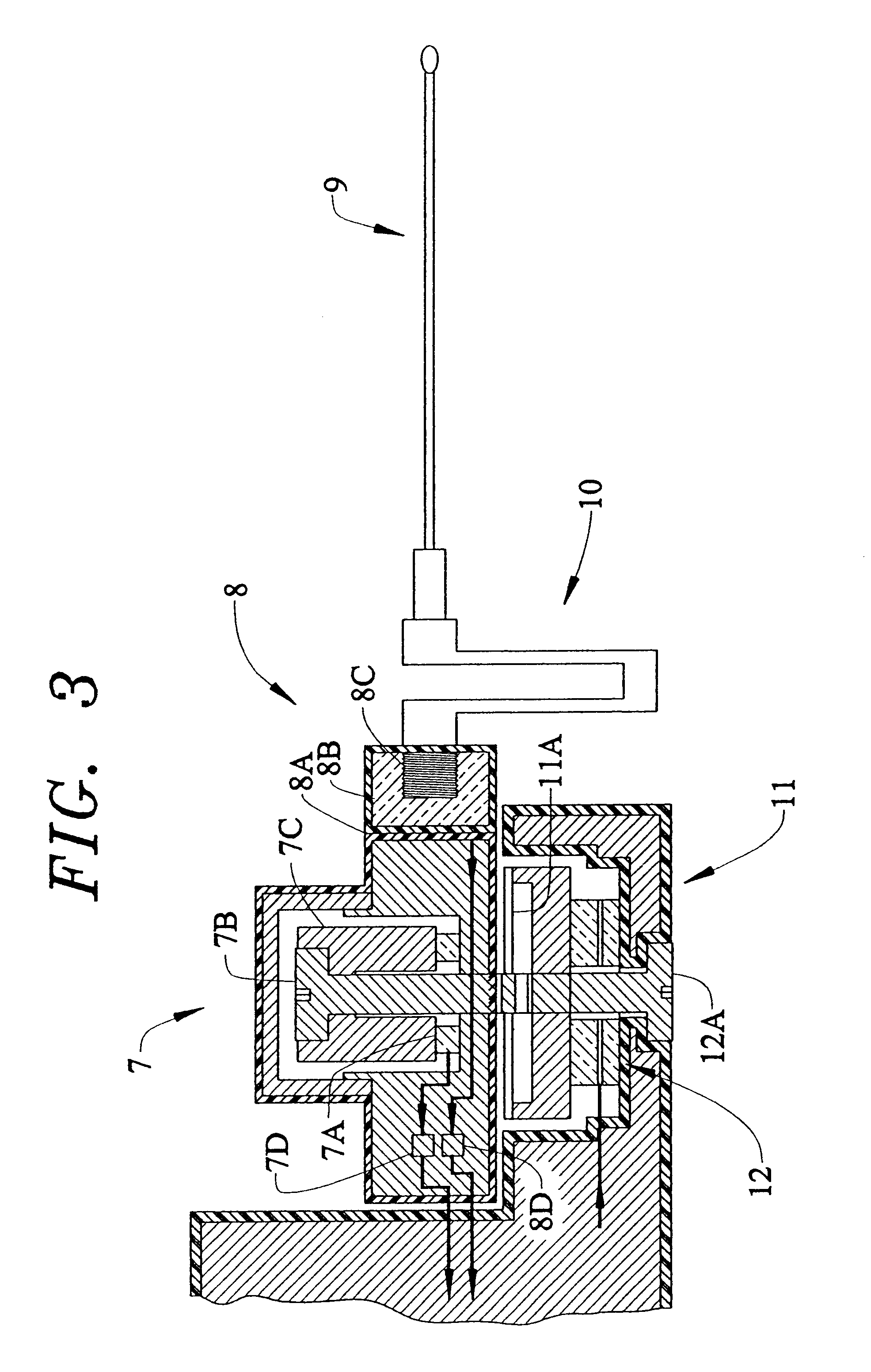
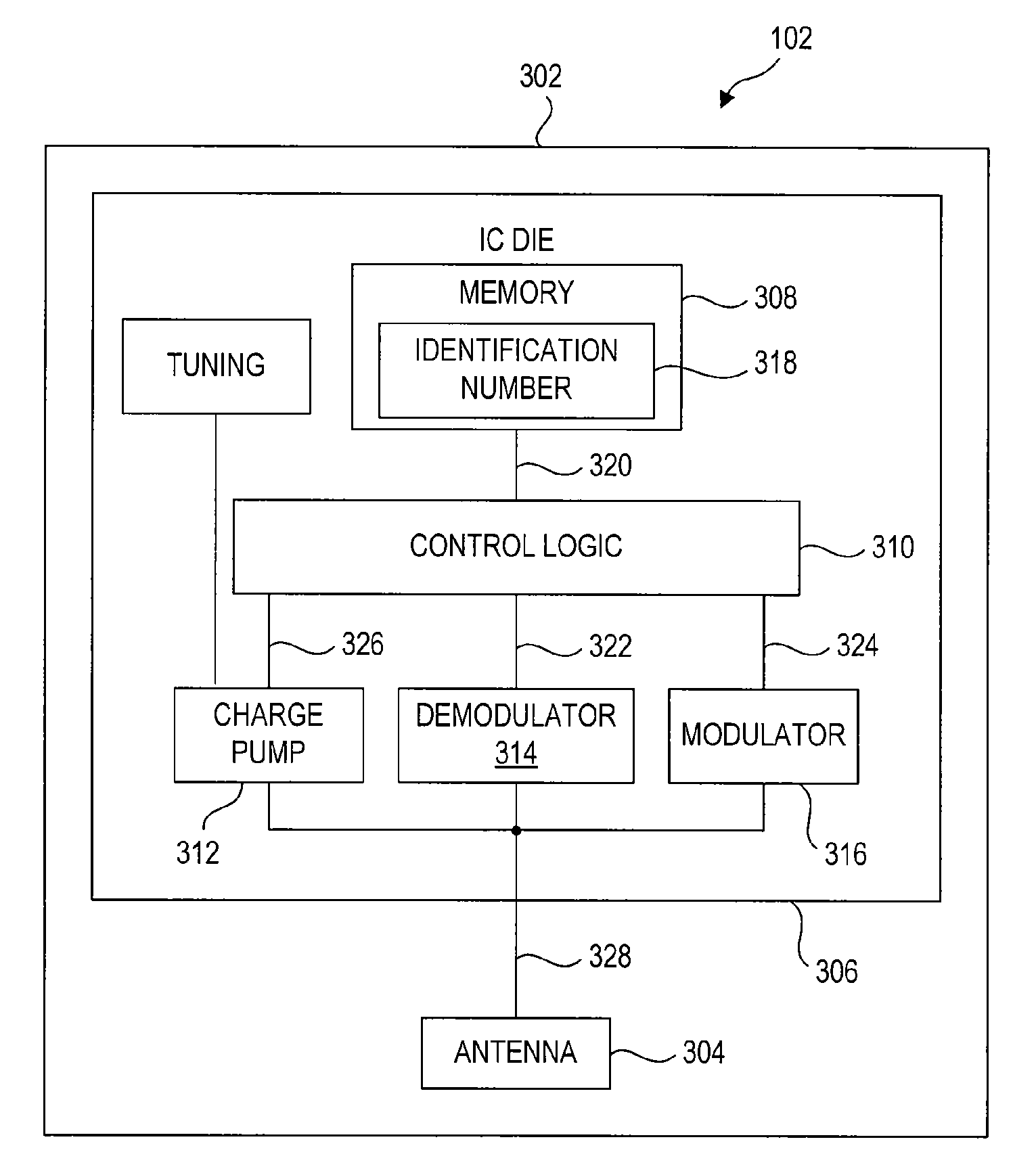
ActiveUS20100019907A1Avoid obscuring purposeMemory record carrier reading problemsRecord carriers used with machinesElectrical resistance and conductanceSelf-tuning
The antenna of an RFID tag is automatically tuned by controlling both the real and imaginary components impedance “seen” by the antenna. The real component (resistive) is controlled by controlling a tap of a charge pump circuit of the tag. The imaginary (reactive) component is controlled by connecting one or more reactive elements of an antenna tuning circuit to the antenna. The real component is controlled by a first digital control loop that automatically activates successive taps on a charge pump of the RFID tag which effectively controls the resistance seen by the antenna. A second digital control loop controls the connection of the various reactive components.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
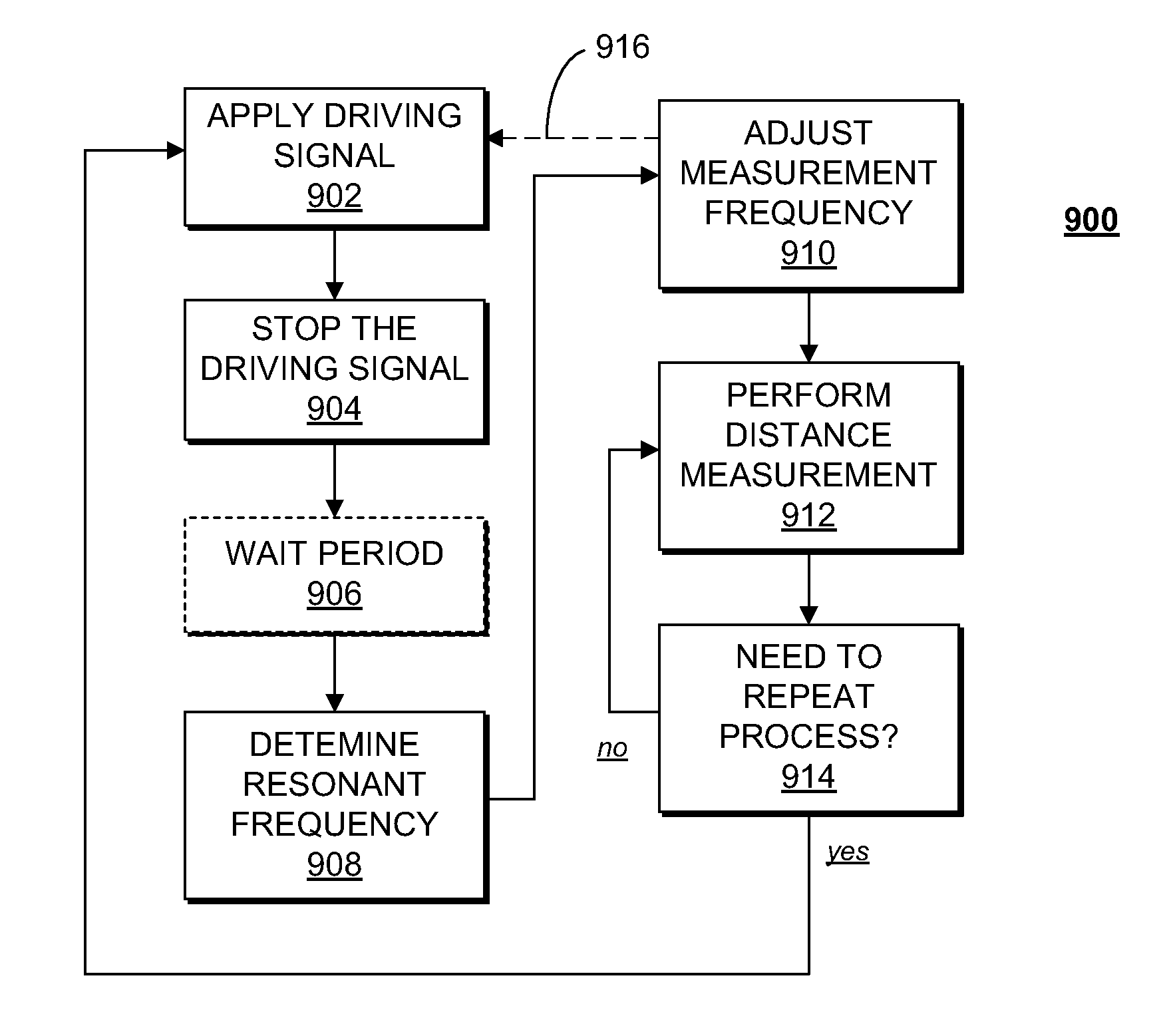
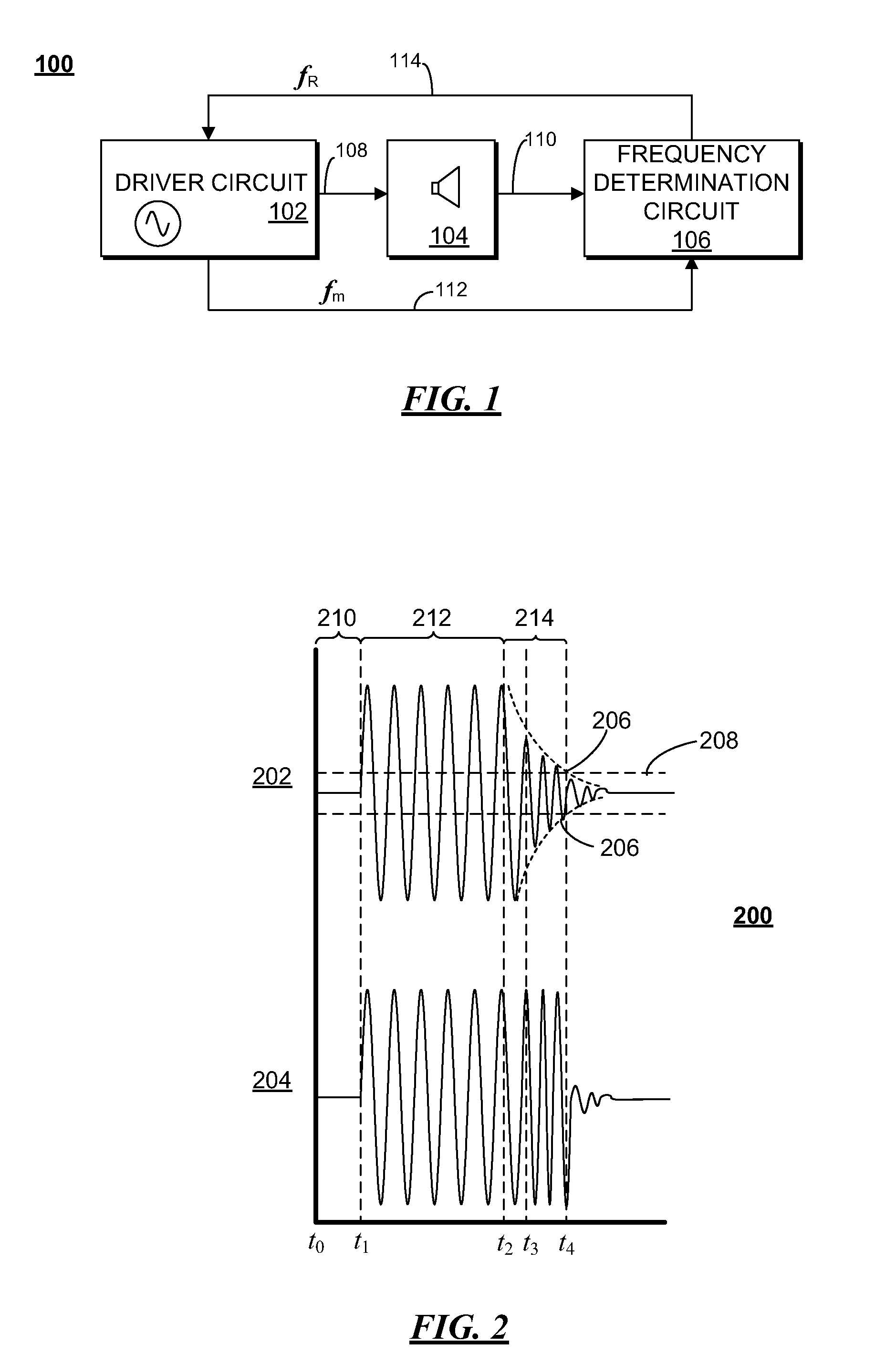
Self-tuning acoustic measurement system
ActiveUS20110261652A1Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSelf-tuningTransducer
In one embodiment, an acoustic distance measurement system can dynamically adjust its measurement frequency to a frequency that is within a preselected bandwidth of the resonant frequency of an acoustic transducer used in making acoustic distance measurements.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com