Patents
Literature
264 results about "Current mode control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
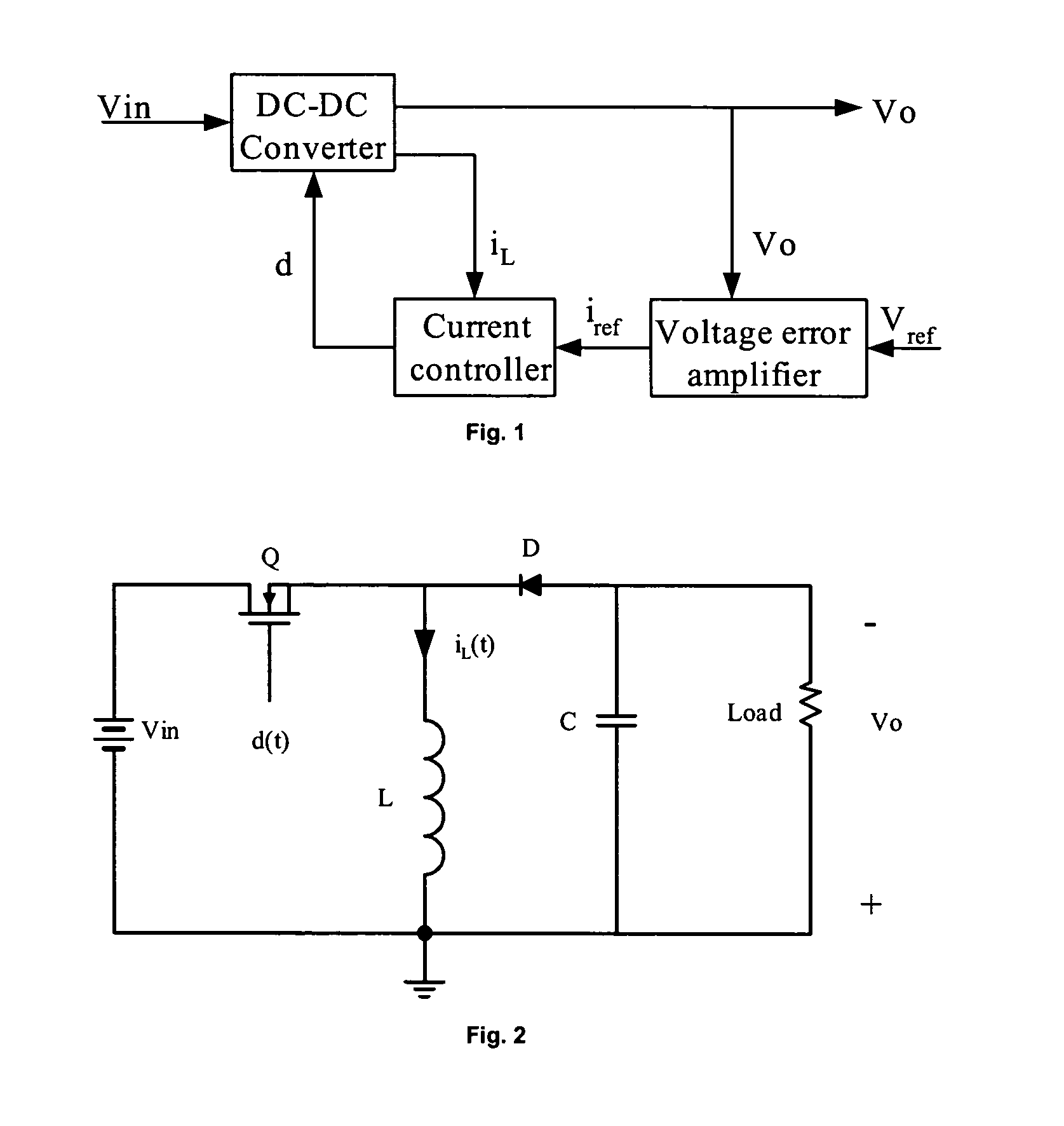
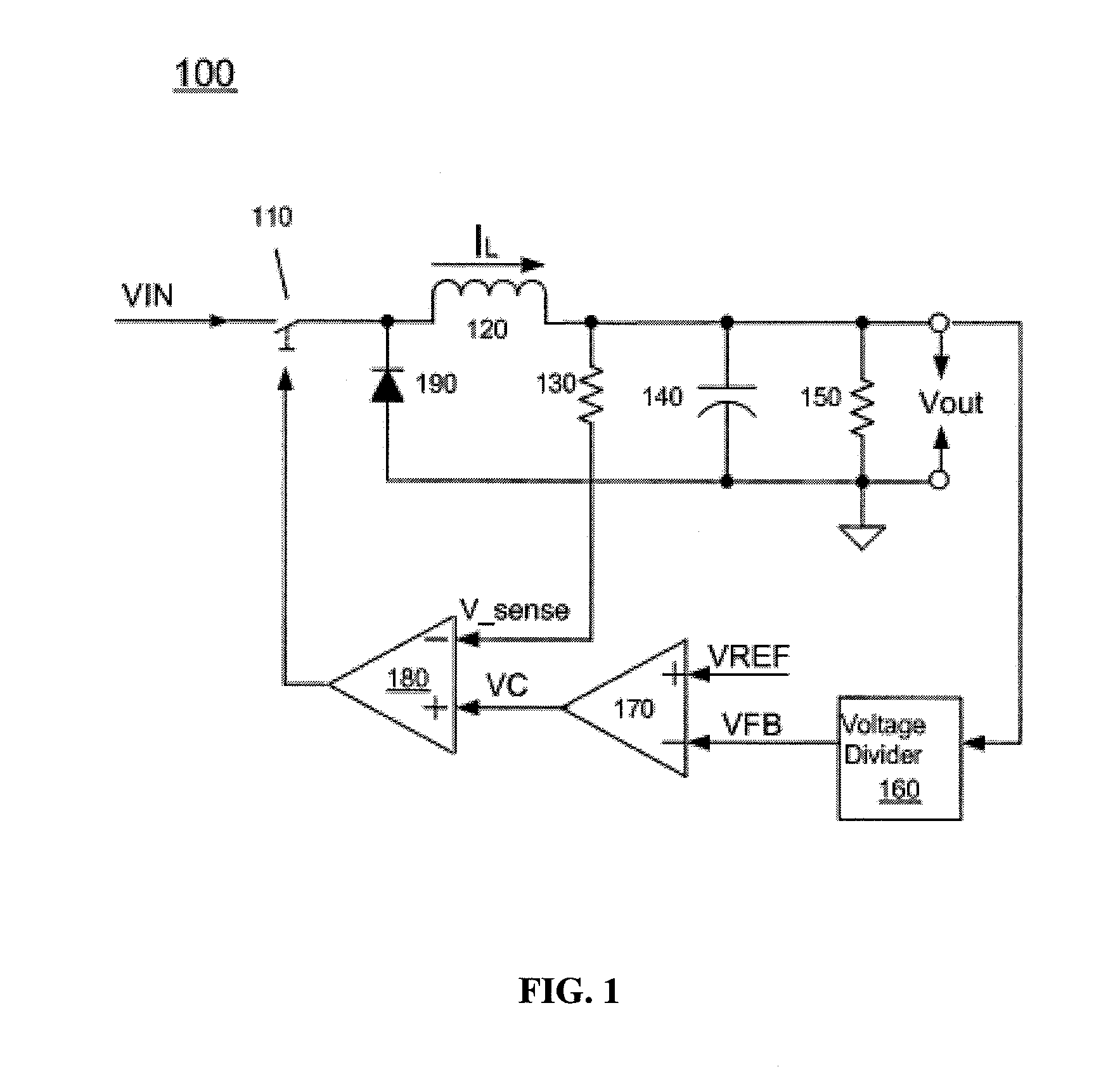
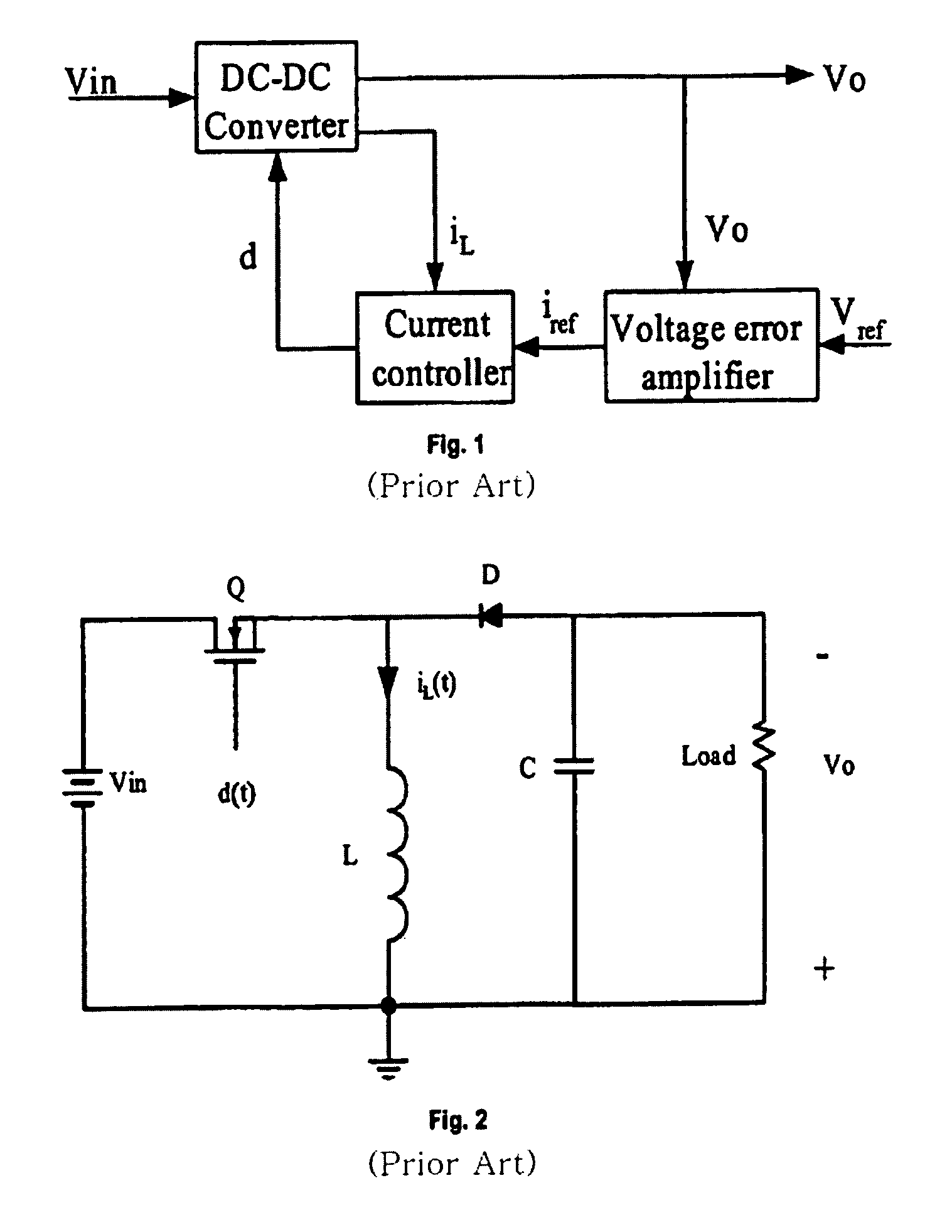
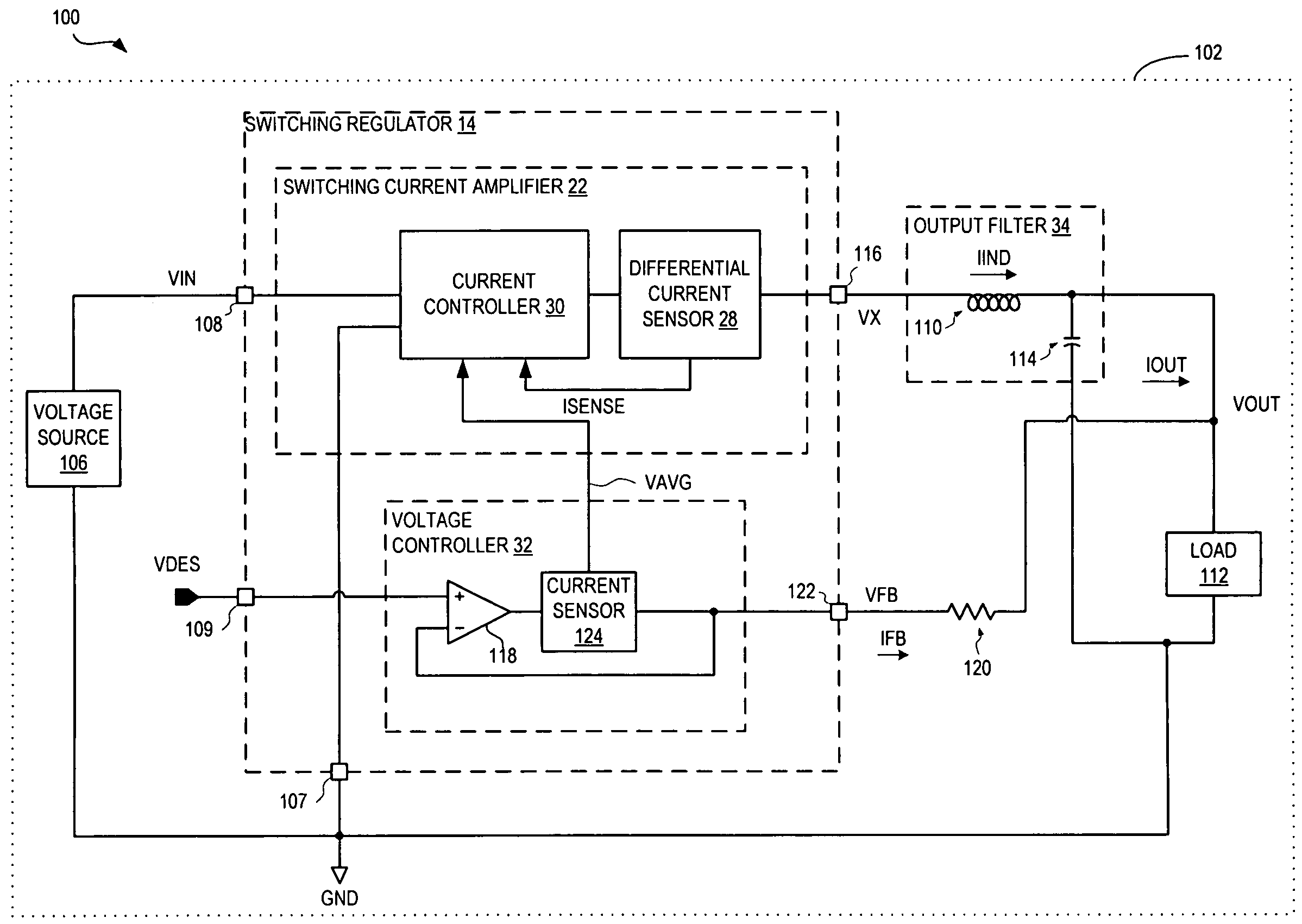
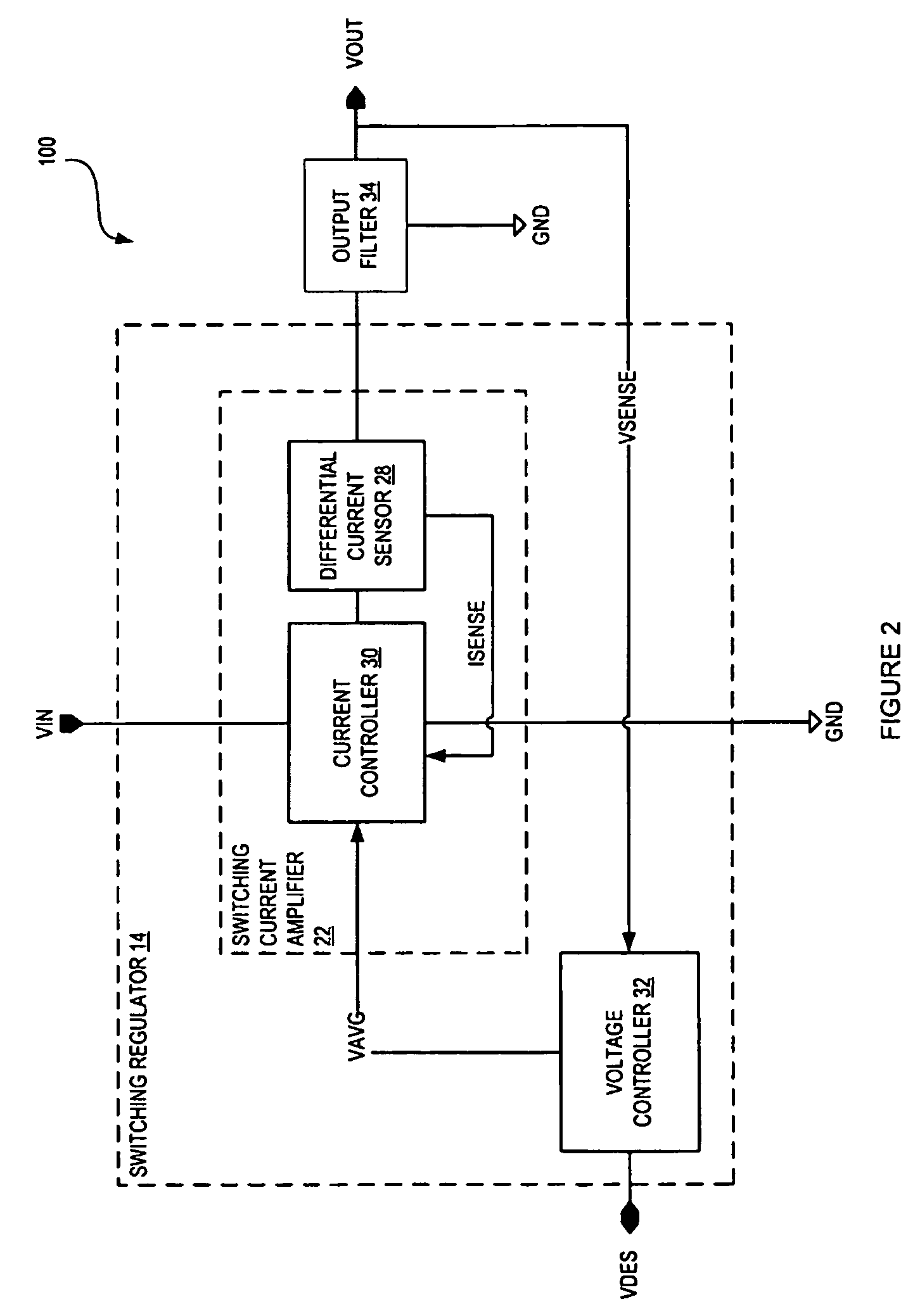
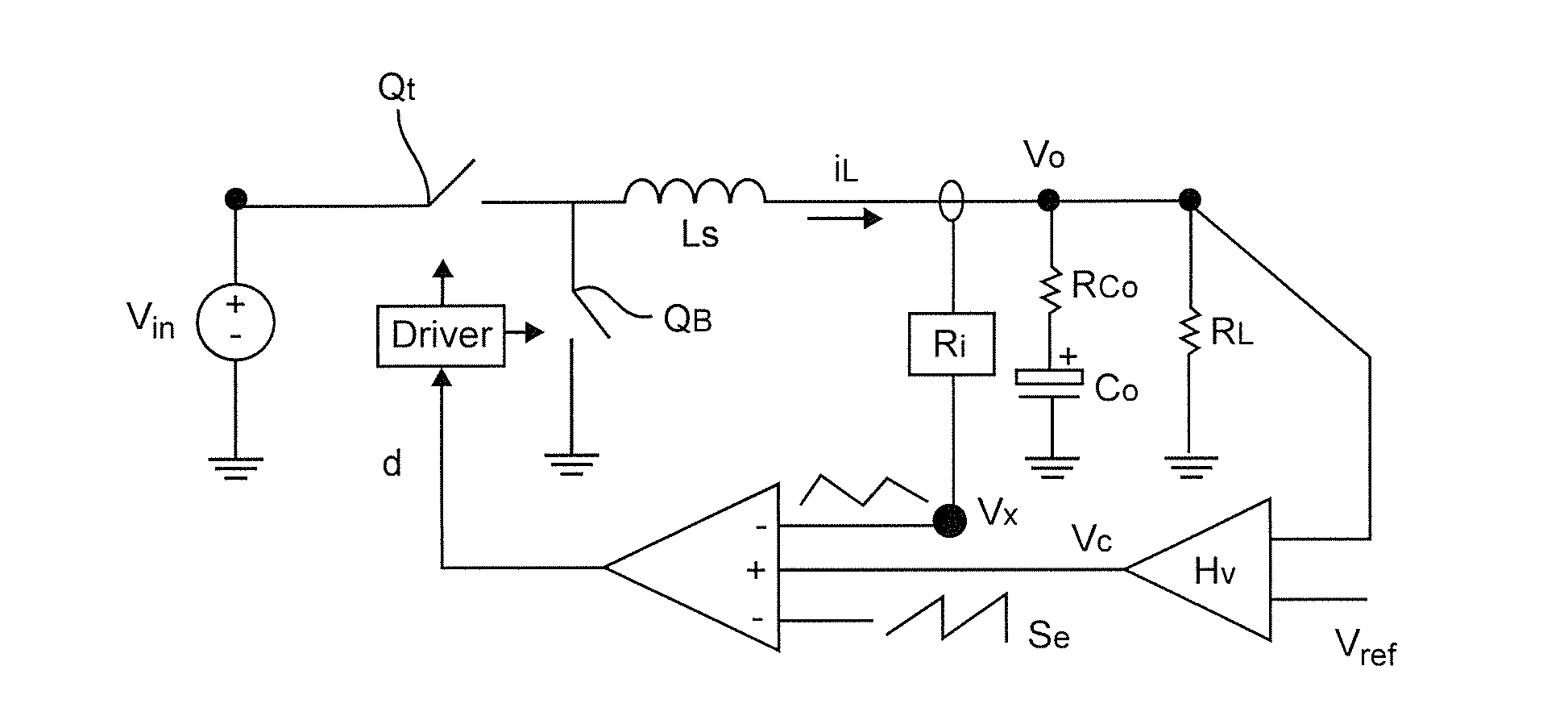
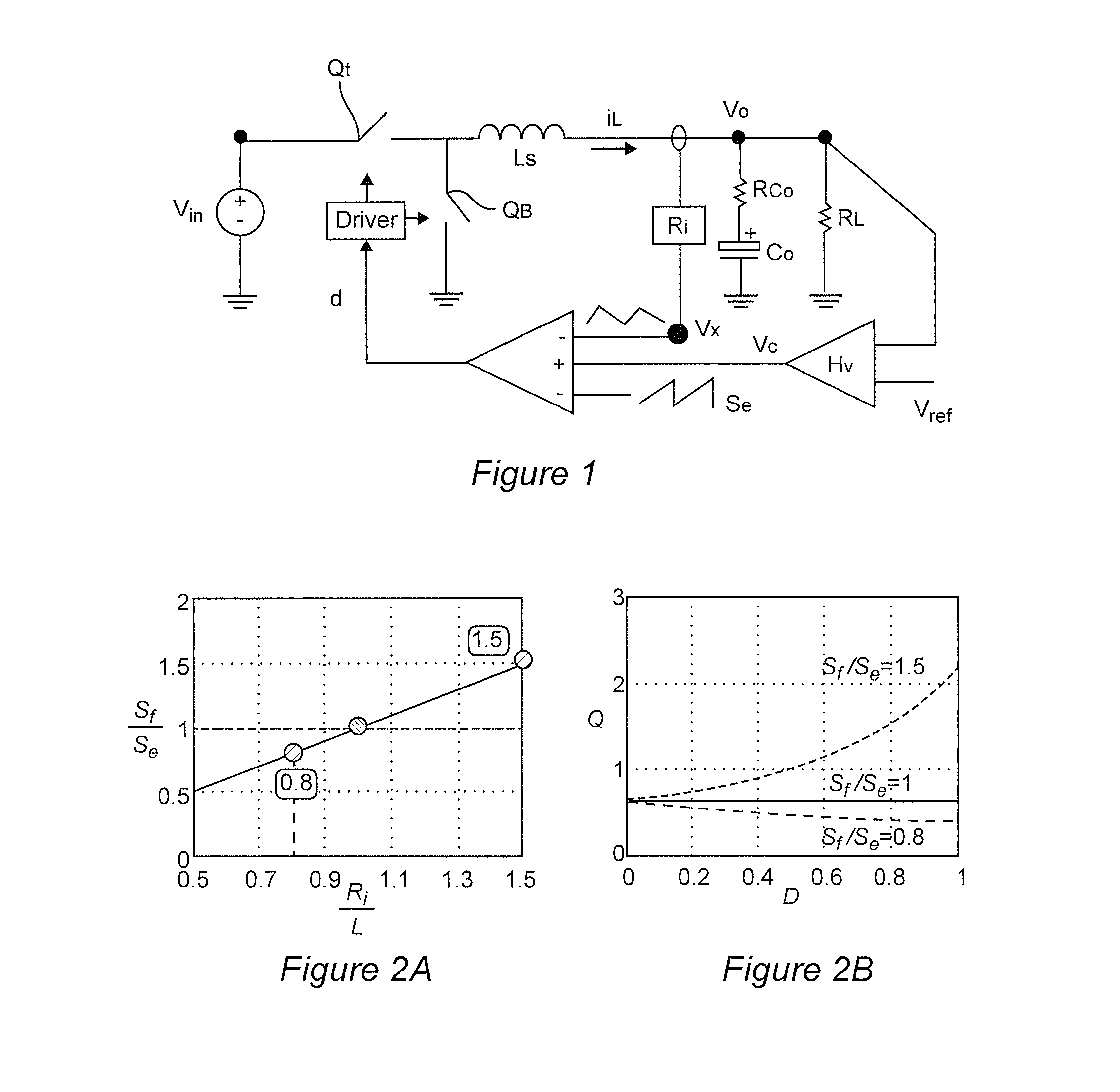
Called current-mode control, the technique derives the PWM ramp by adding a second loop feeding back the inductor current. This feedback signal comprises two parts: the AC-ripple current, and the DC or average value of the inductor current.
Parallel current mode control
InactiveUS20050270813A1Unity power factor for AC-DC converterLow costAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionCurrent mode controlMode control
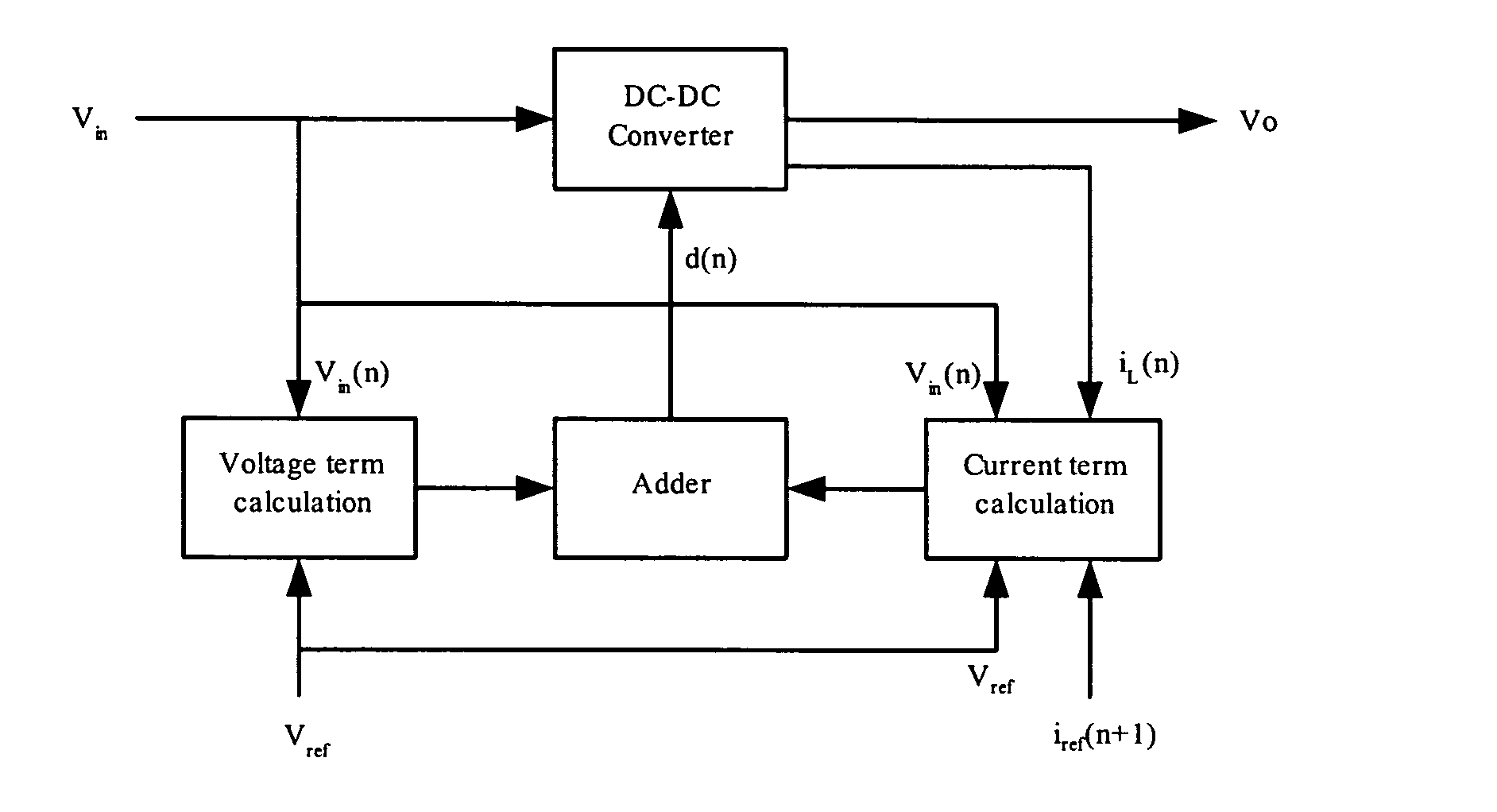
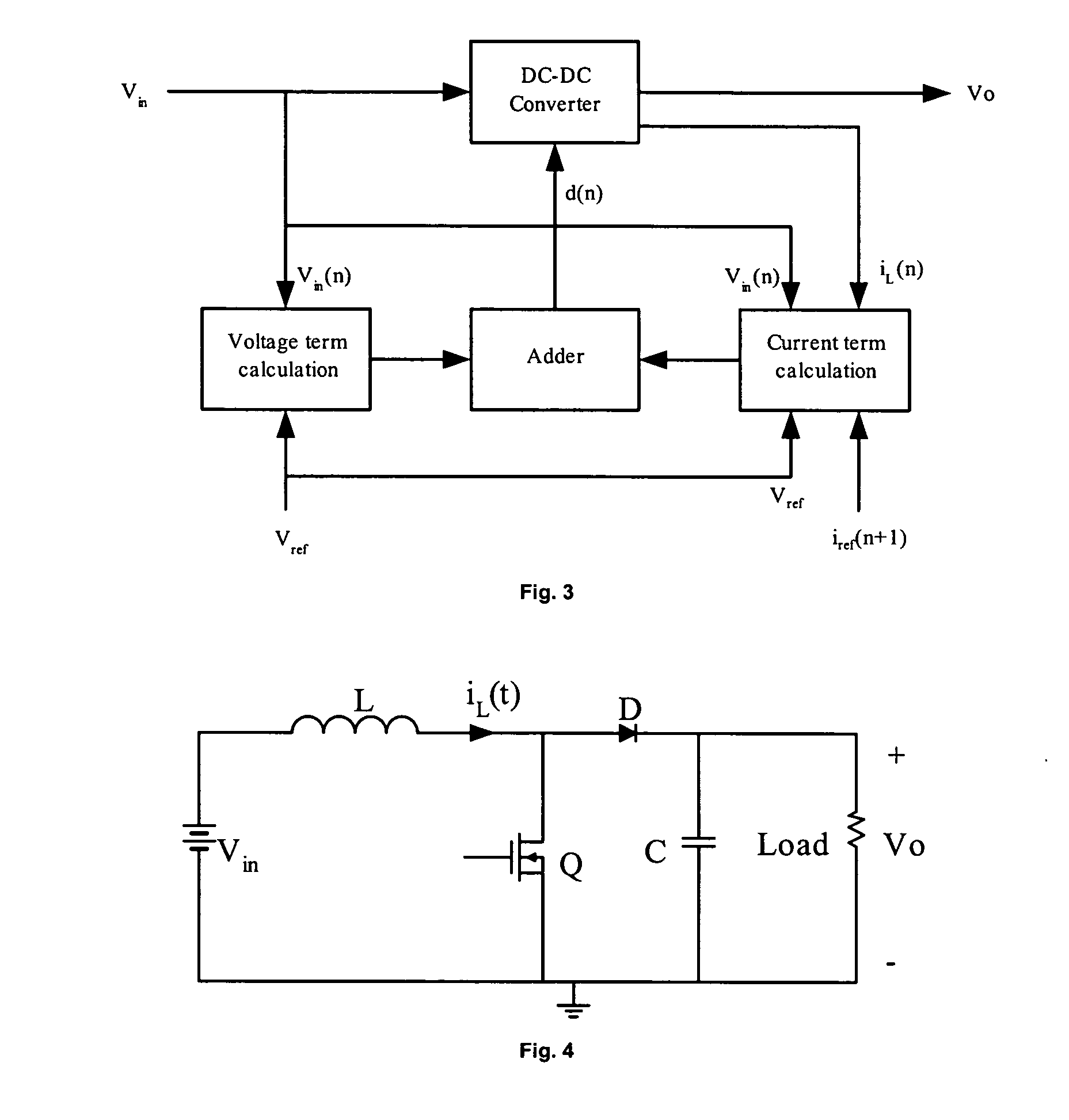
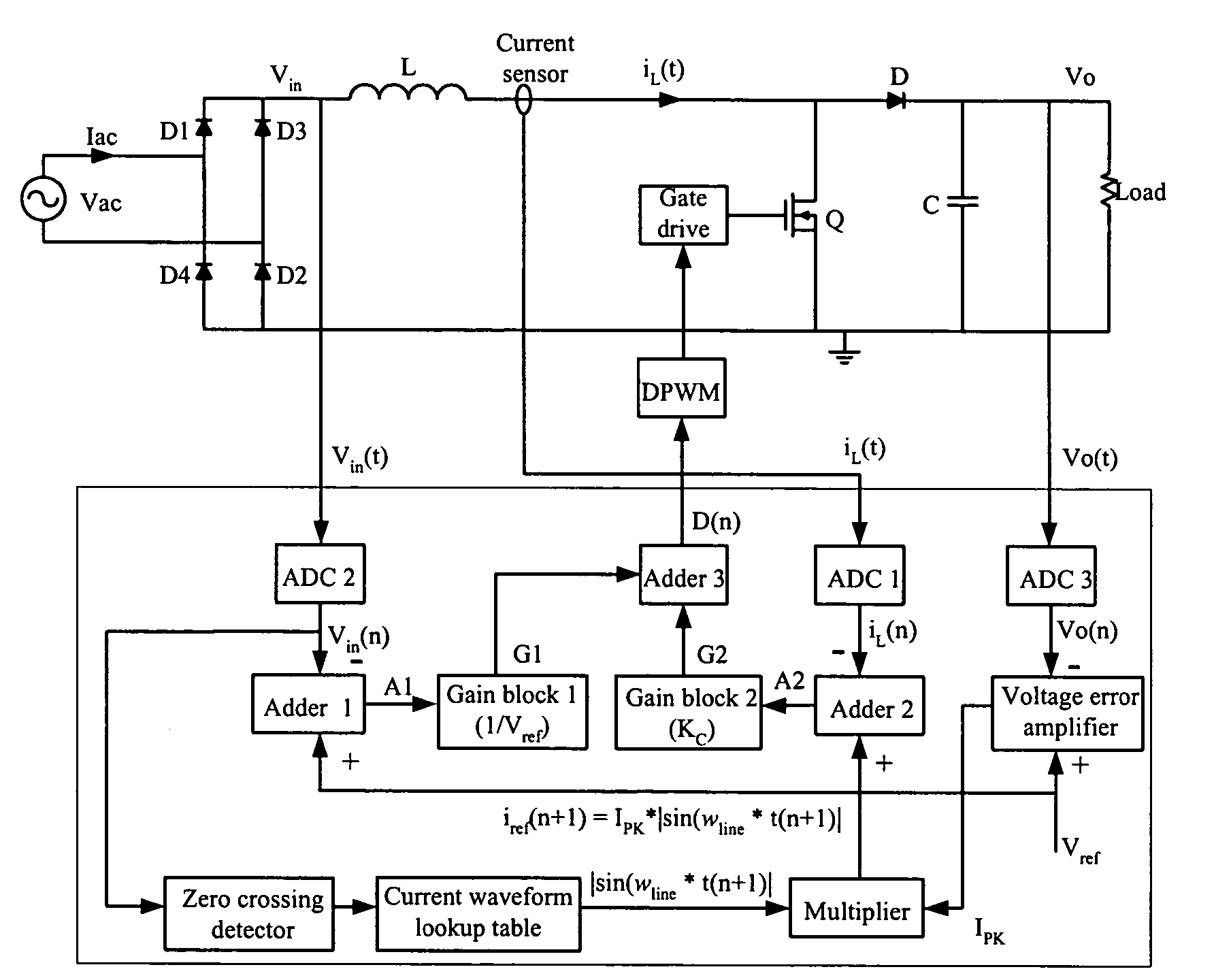
A method and apparatus to implement parallel current mode control that is suitable for digital and analog implementation. A duty cycle algorithm is composed of a voltage term and a parallel current term which depends on the inductor current change between the inductor current value at the beginning of a switching cycle and the reference inductor current value at the end of that switching cycle. Parallel current mode control can be applied to all DC-DC converters, including both non-isolated and isolated topologies. It can also be applied to AC-DC converters with power factor correction.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
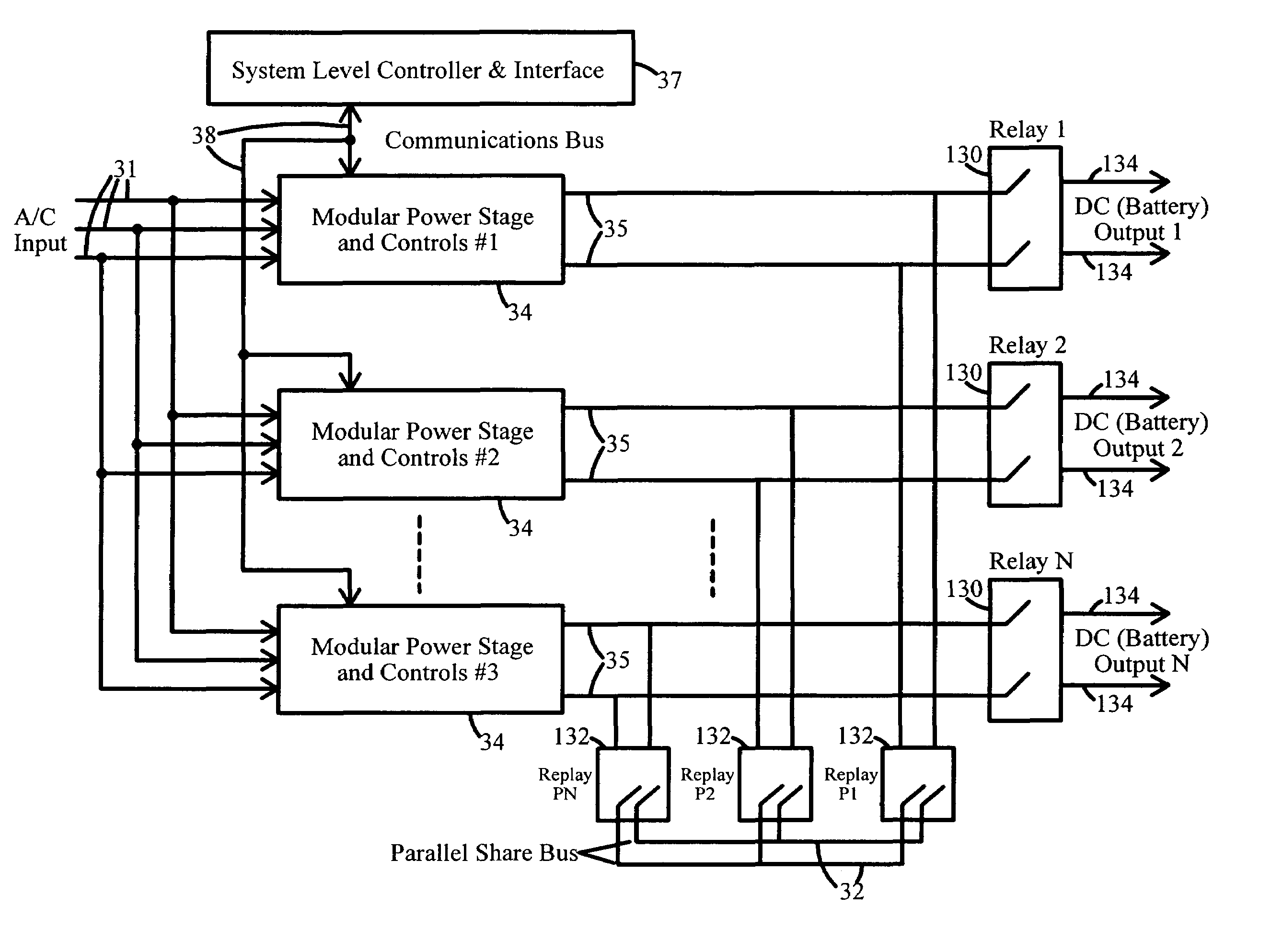
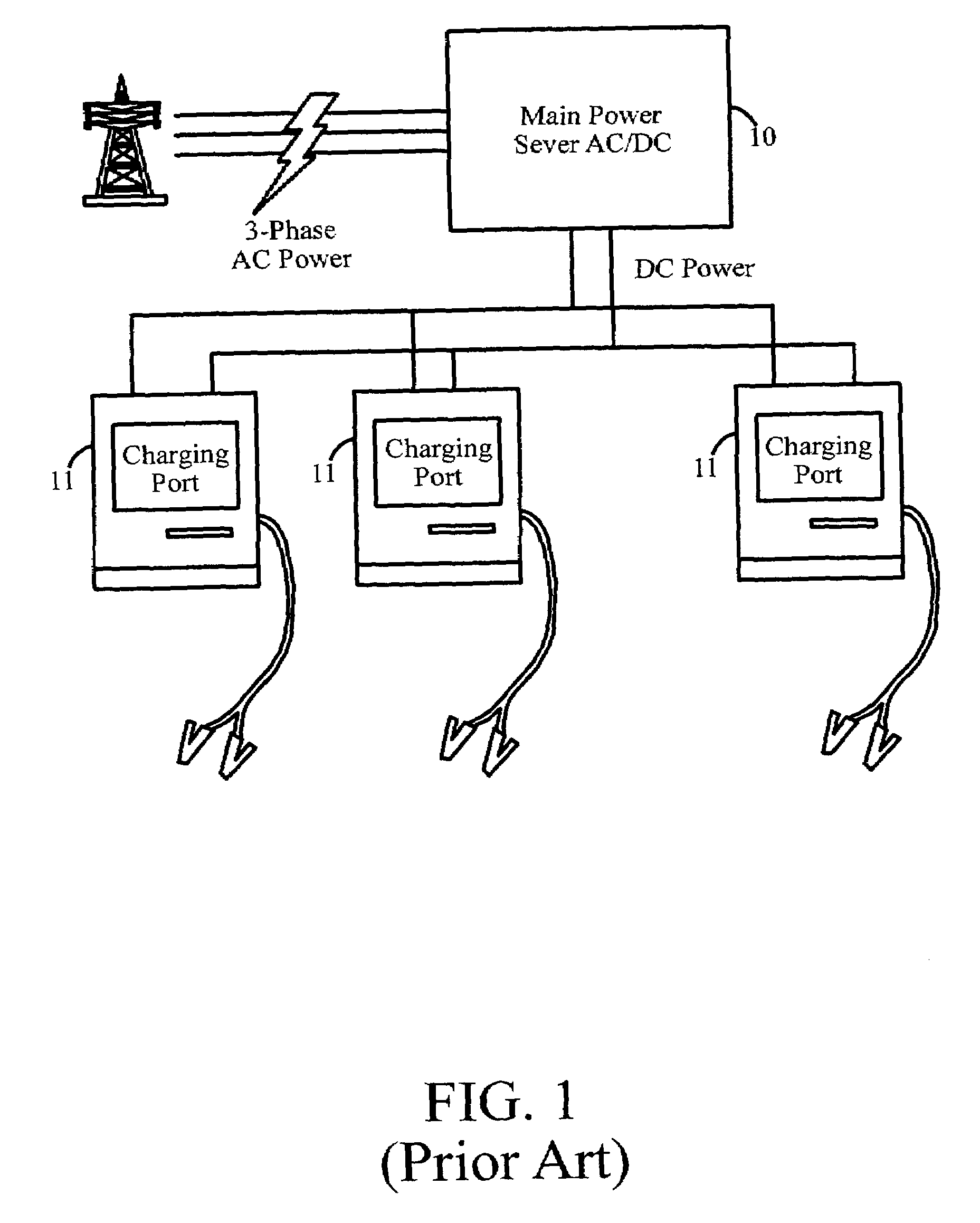
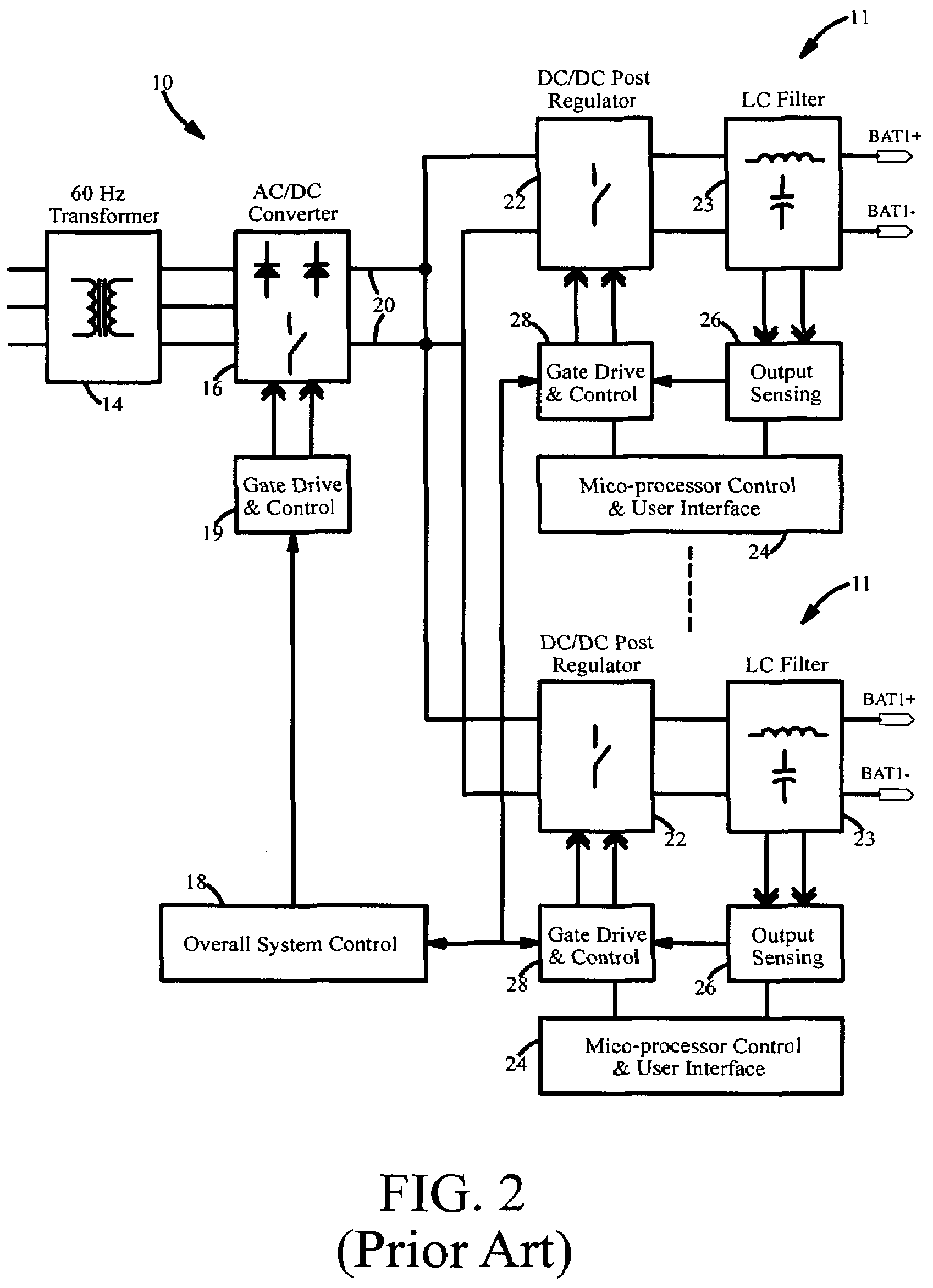
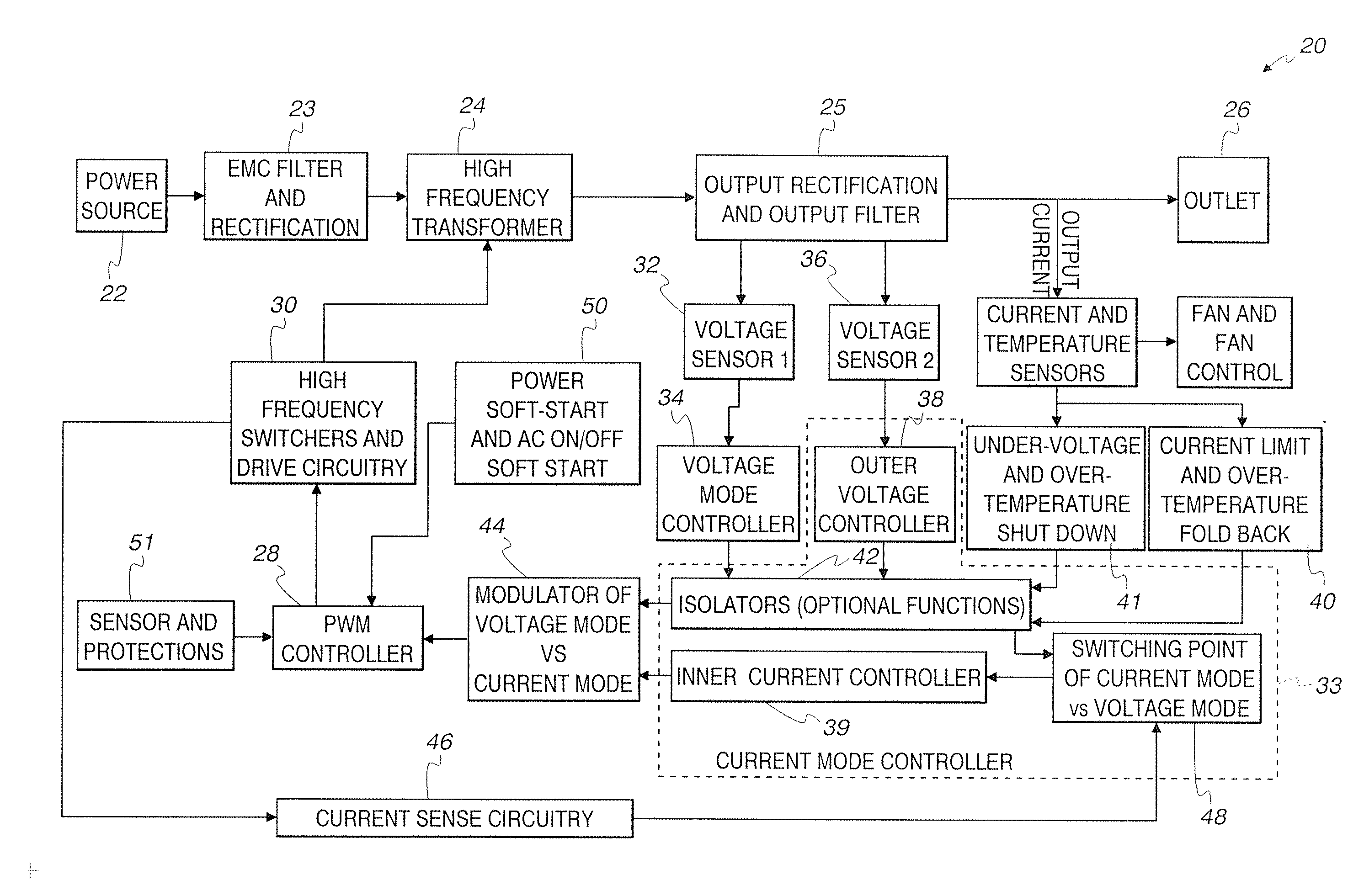
Modular and reconfigurable rapid battery charger
InactiveUS7135836B2Reduced charger complexityReduce installation costsBatteries circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionCurrent mode controlControl signal
The battery charger is modular and reconfigurable. It includes charging modular power stages that are configured to receive an alternating current (AC) input and provide a direct current (DC) output for charging a battery. These modular power stages include an inverter coupled to a rectifier circuit that outputs a battery charging current. The modular power stages can also each include a current mode controller coupled to the output of the rectifier circuit and configured to provide a current control signal for the modular power stage, a voltage mode controller coupled to the output of the rectifier circuit and configured to provide a voltage control signal for the modular power stage, and a droop sharing control and configured to ensure current sharing between a plurality of modular power stages under constant voltage operation. A system controller is configured to interface with the modular power stages.
Owner:POWER DESIGNERS USA
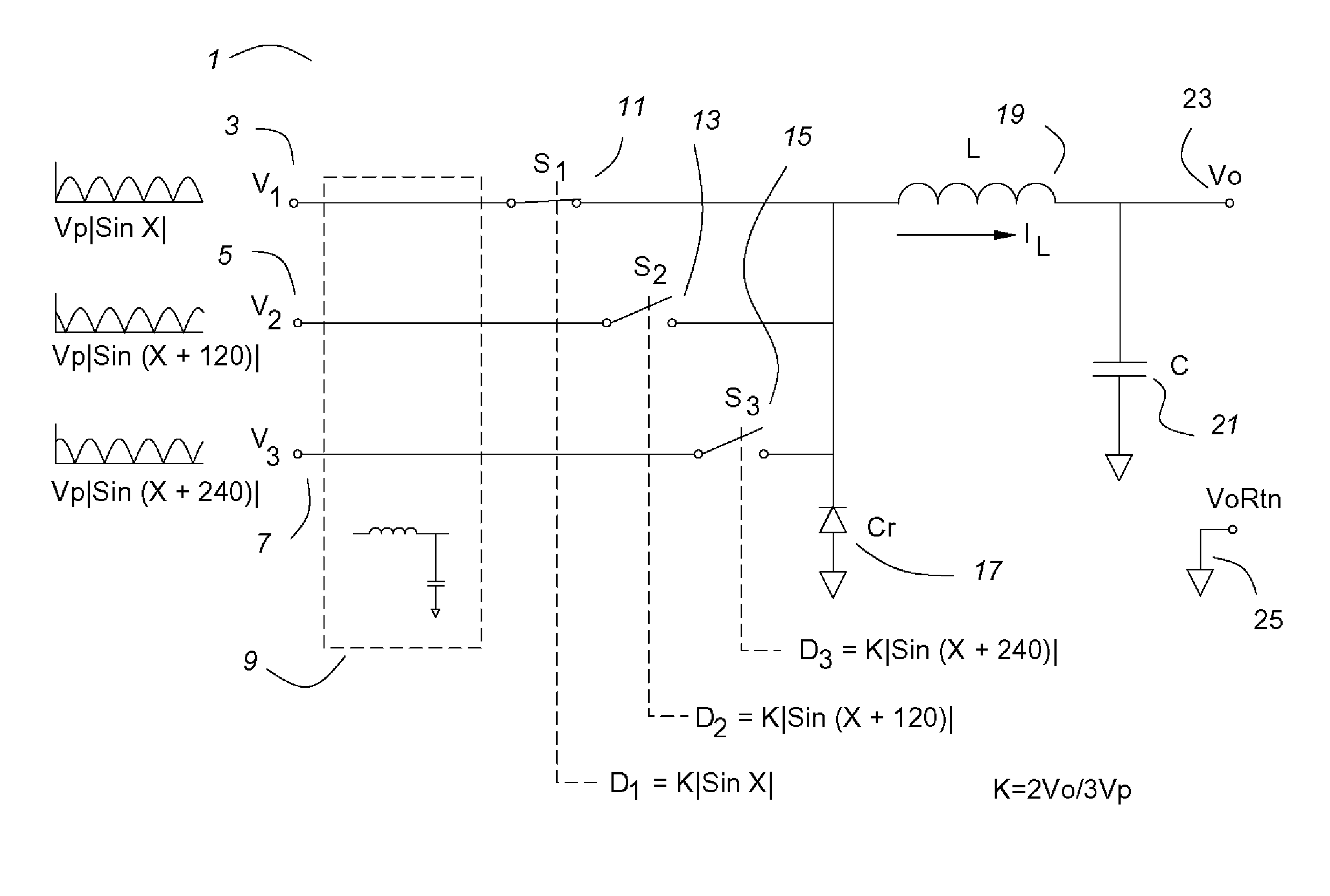
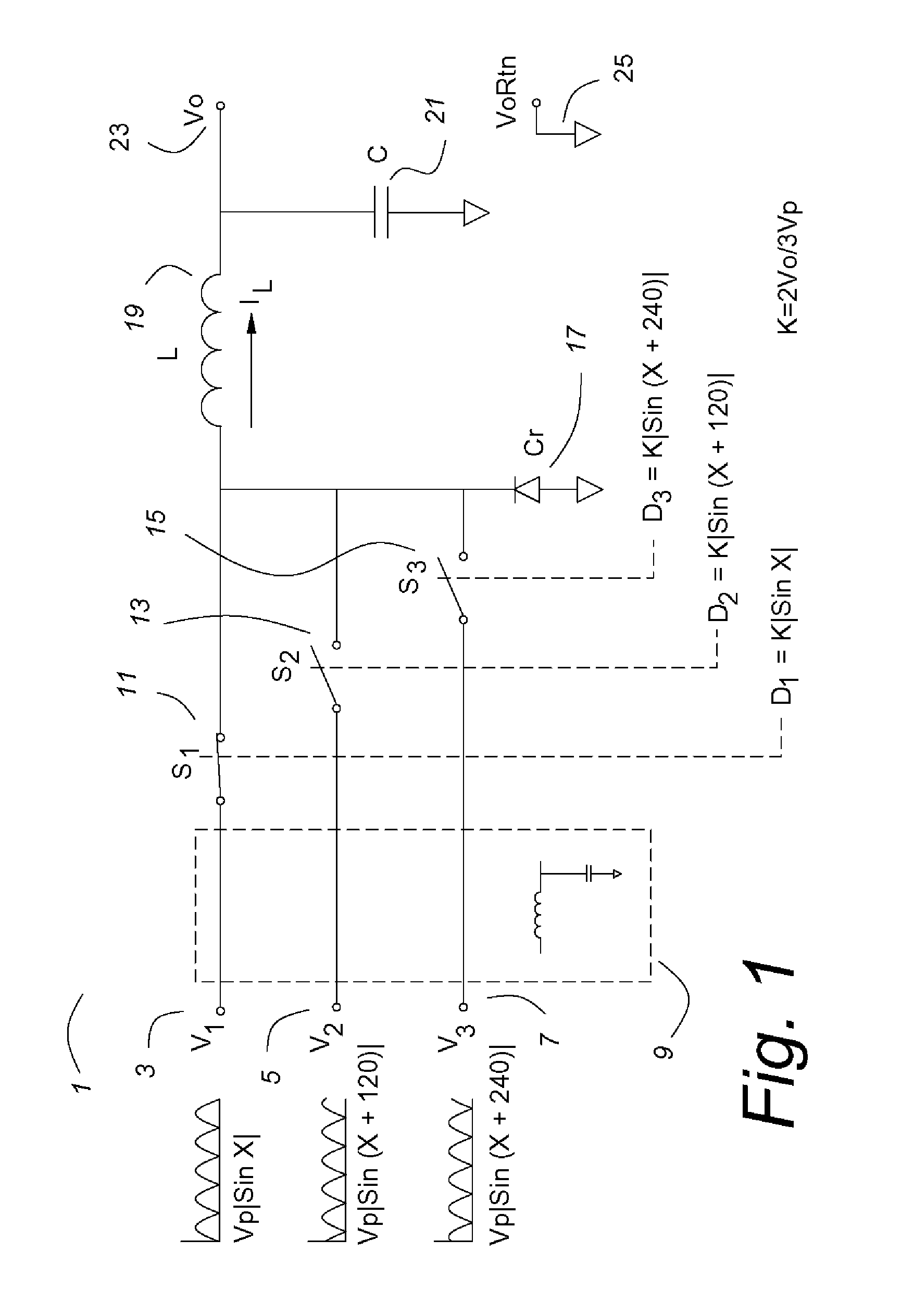
Three phase buck power converters having input current control
InactiveUS7139180B1Efficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionCurrent mode controlPower factor
A three phase buck power converter having input power control is described. The power converter uses a three input buck converter comprising switches for each phase, a catch rectifier, an inductor and an output capacitor. The duty cycle of the three switches is constrained to have a sine function relationship that may be derived from the input voltage wave form or from a reference oscillator. When so constrained, the input currents have high power factor. The output is a precise, high quality dc voltage, comparable to the output of a dc—dc buck converter, and the dynamic response is comparable. Voltage mode and current mode controls are shown, as is a precise line regulation feed forward for the voltage mode embodiment. The three phase buck power converter may be operated in reverse as a three phase boost converter, as they are reciprocal. A three phase ac—ac converter may have a three phase buck converter as its input and a three phase boost converter as its output.
Owner:HERBERT EDWARD
Non-isolated current-mode-controlled switching voltage regulator
InactiveUS20090322299A1Dc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCurrent mode controlControl signal
A novel voltage regulator includes an indictor, a switching transistor, a rectifier, an error amplifier circuit, a first voltage comparator circuit, a second voltage comparator circuit, an oscillator circuit, and a driver circuit. The first voltage comparator circuit outputs a modulation signal. The second voltage comparator circuit activates an enable signal when the error voltage exceeds the second reference voltage. The oscillator circuit outputs a clock signal with a fixed frequency according to the enable signal. The oscillator circuit enters a first state when the enable signal is activated and deactivated within a period of time shorter than a threshold time, and enters a second state when the enable signal remains activated during a period of time longer than the threshold time. The driver circuit generates the switching control signal based on the clock signal and the modulation signal.
Owner:RICOH ELECTRONIC DEVICES CO LTD
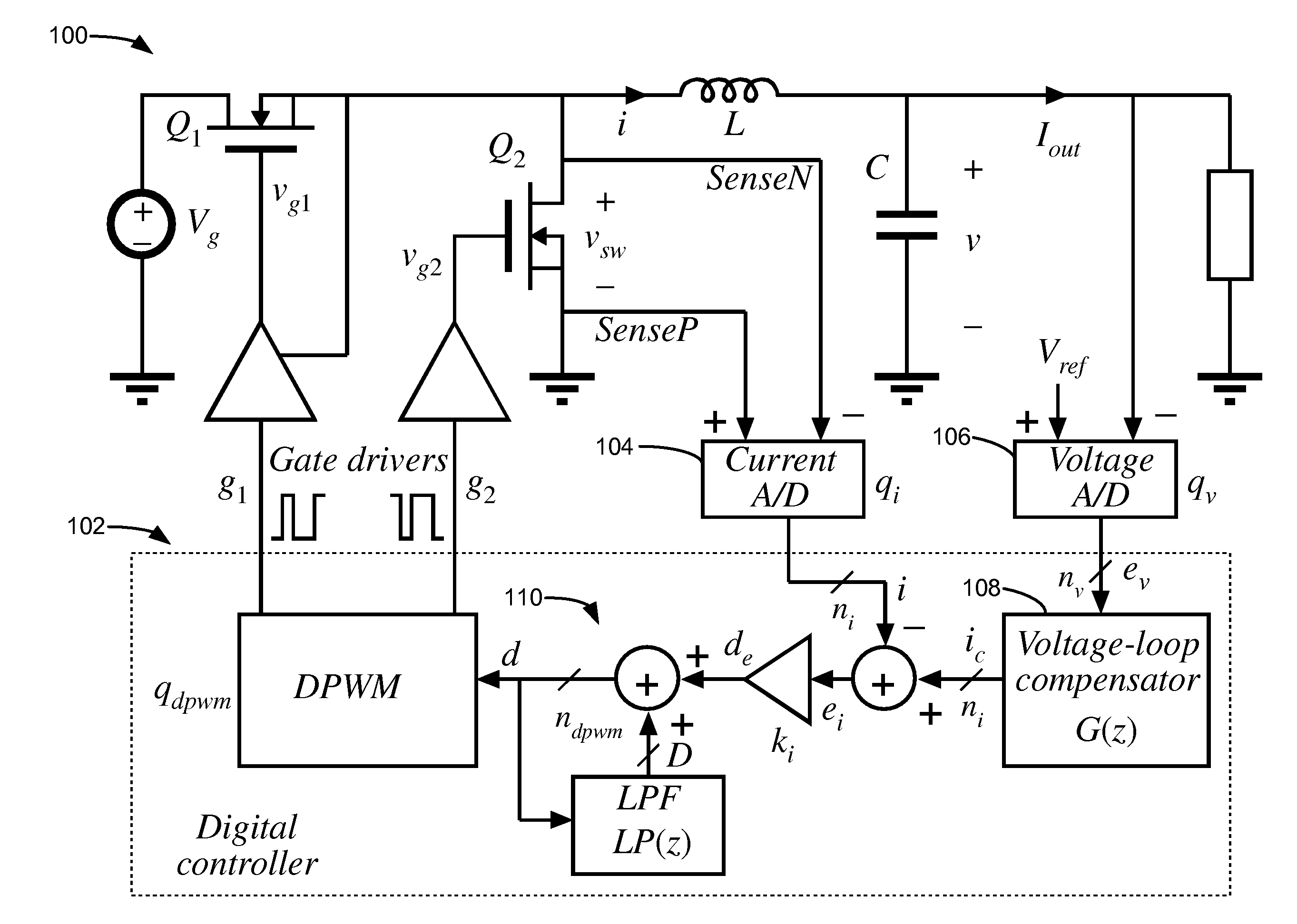
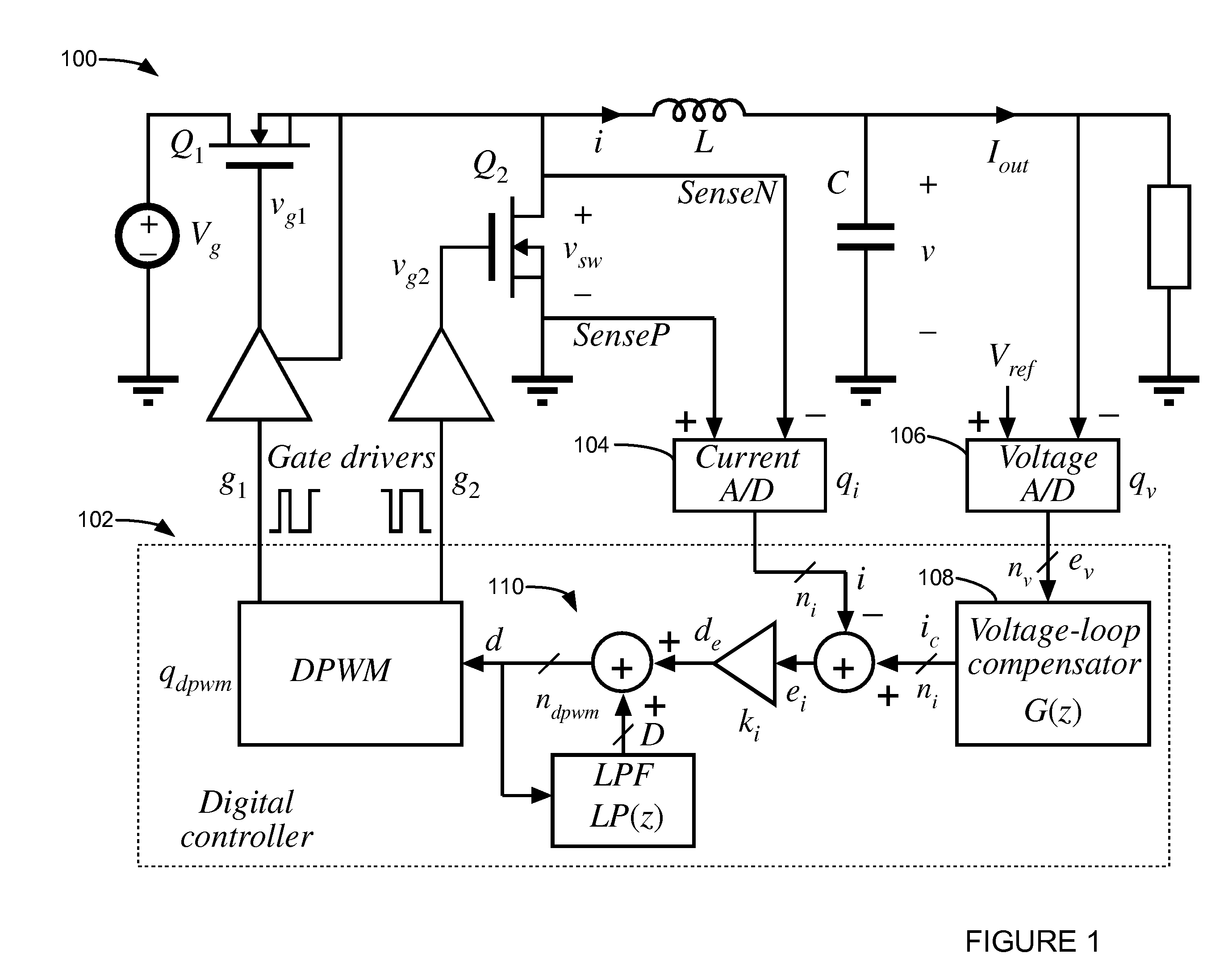
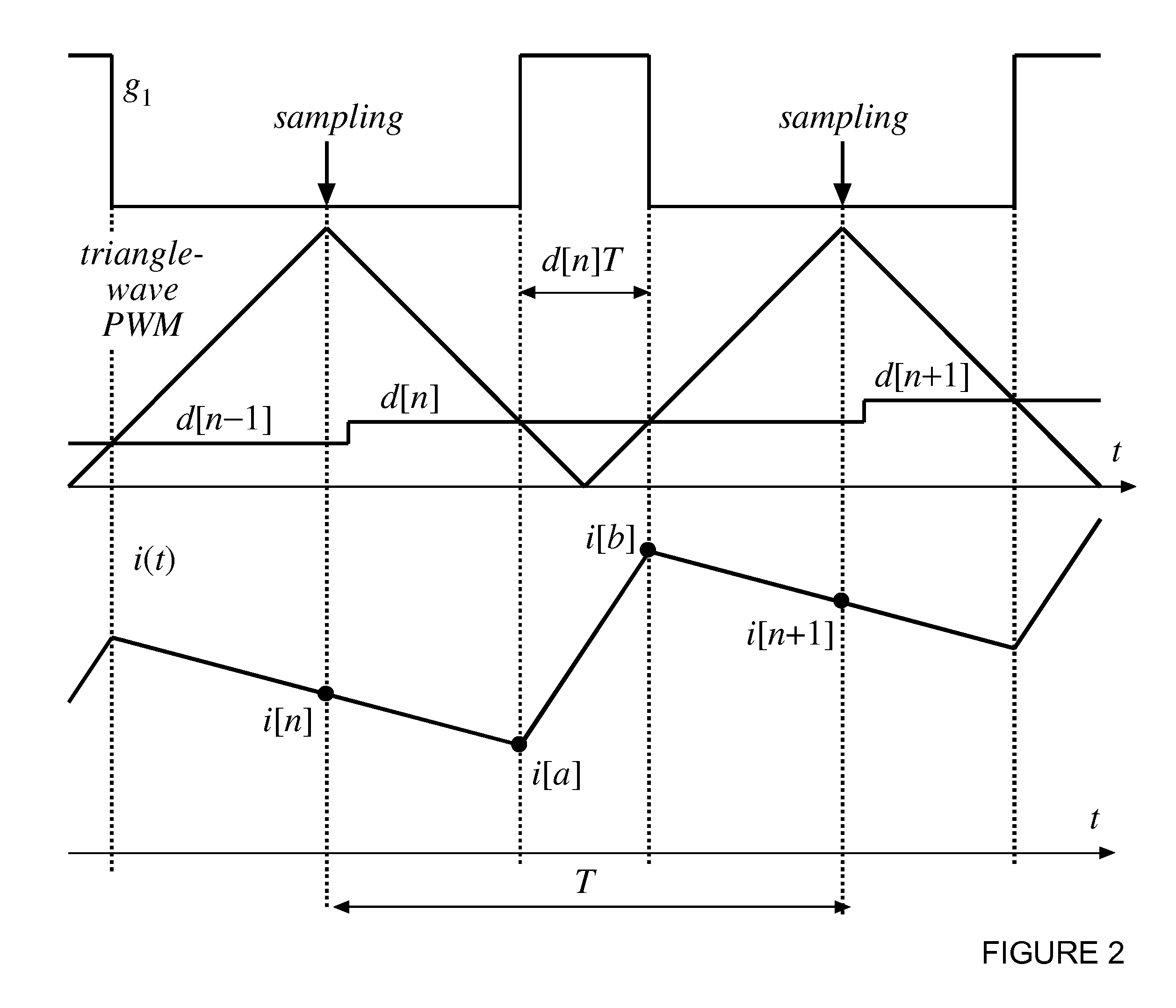
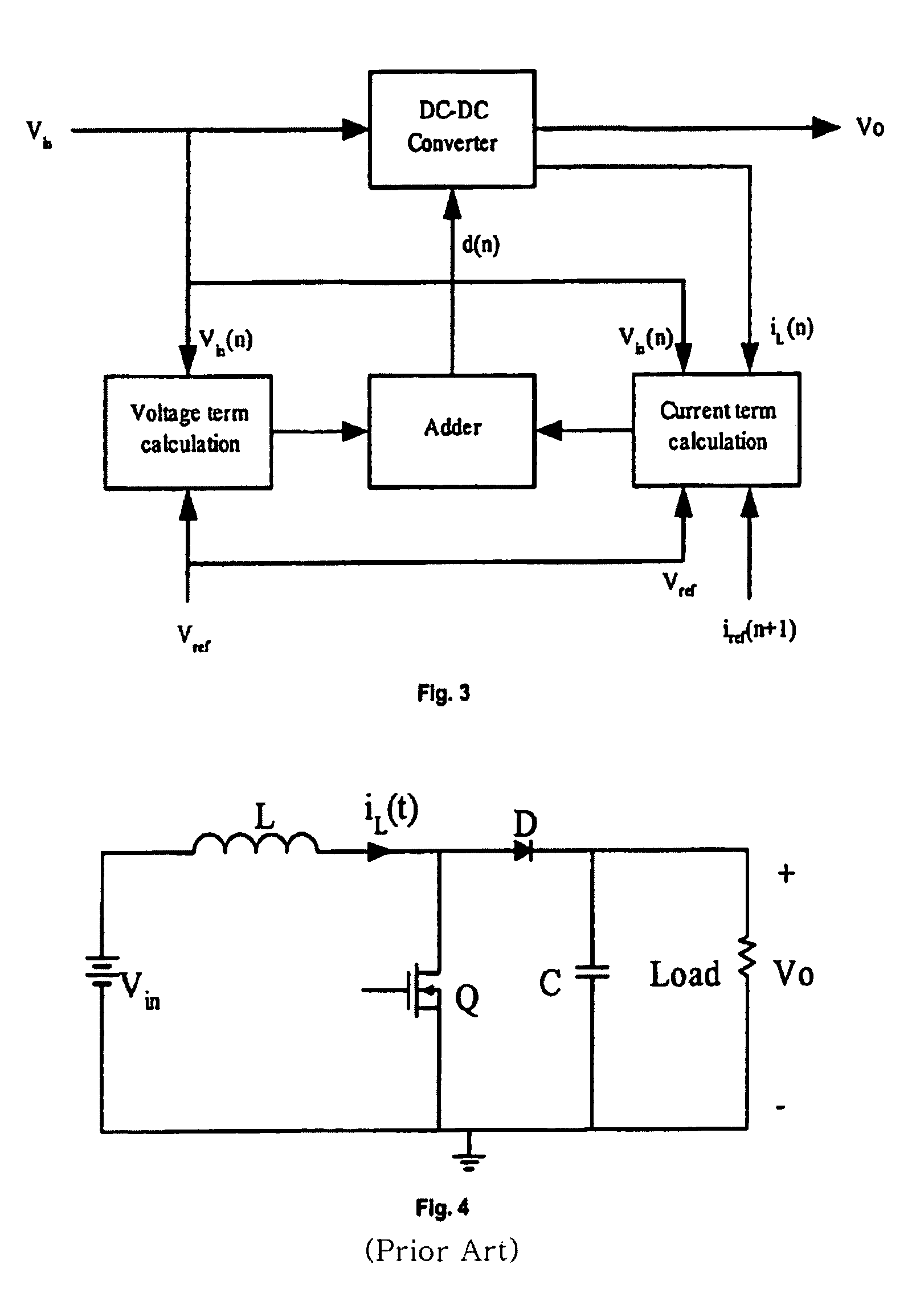
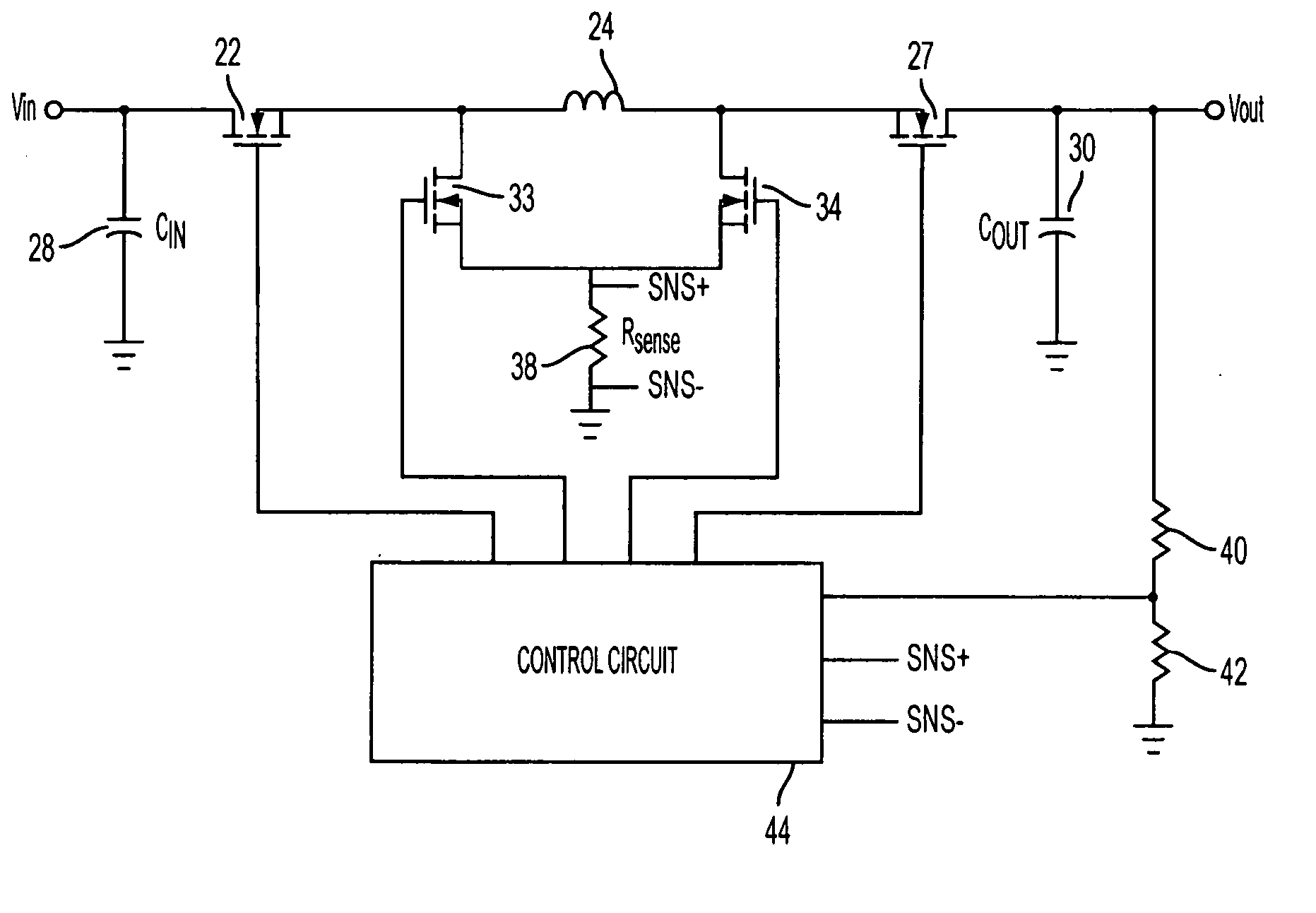
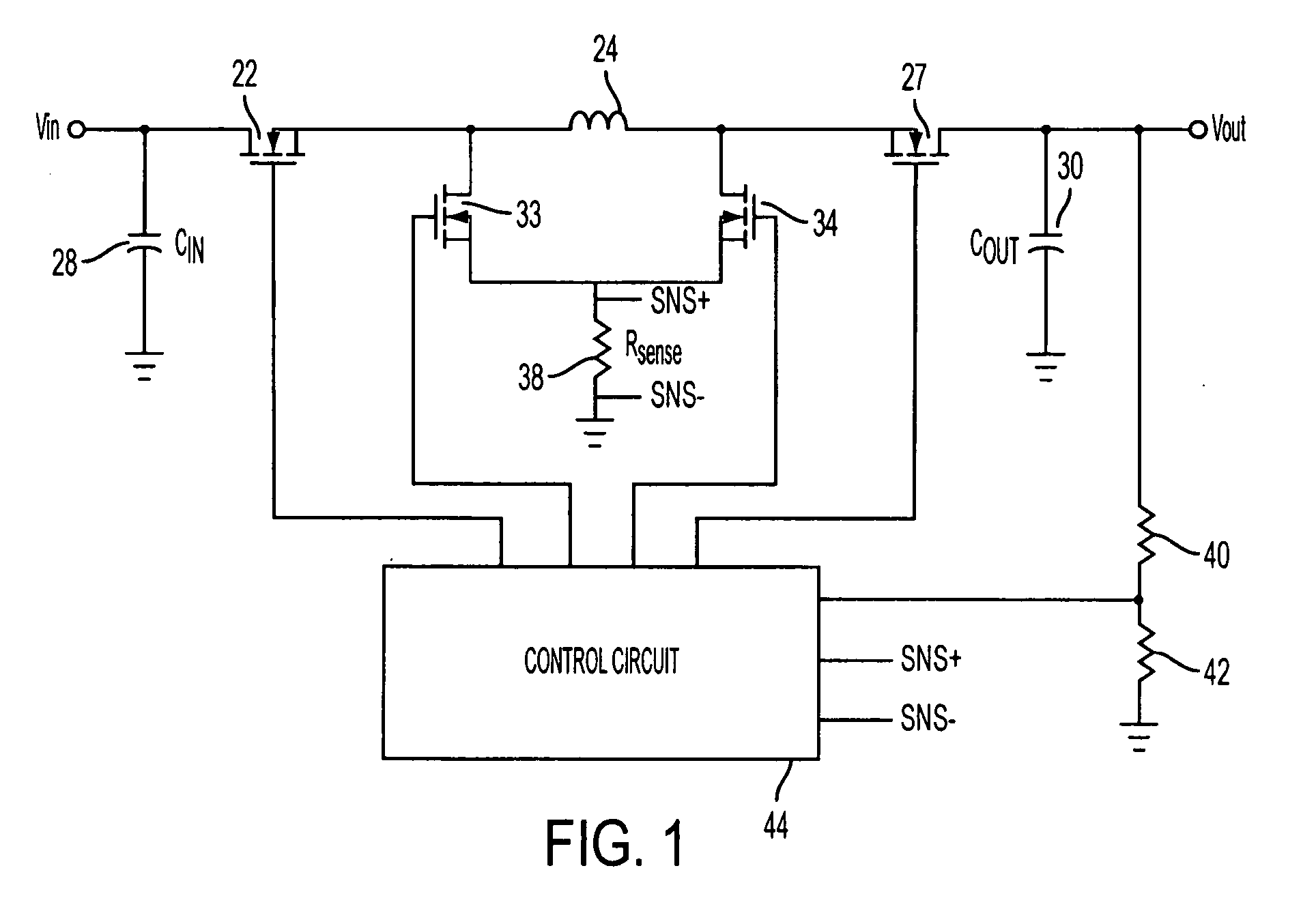
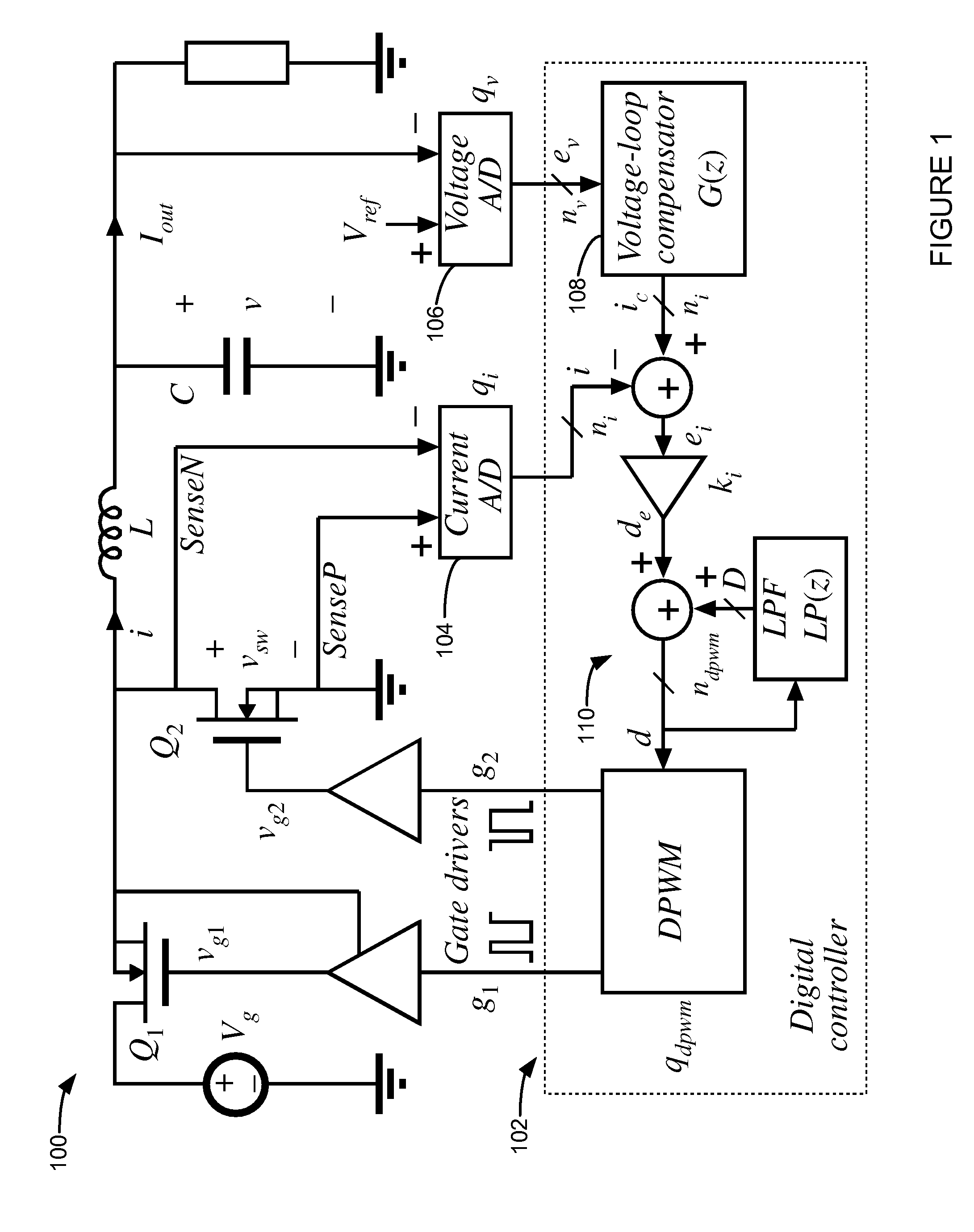
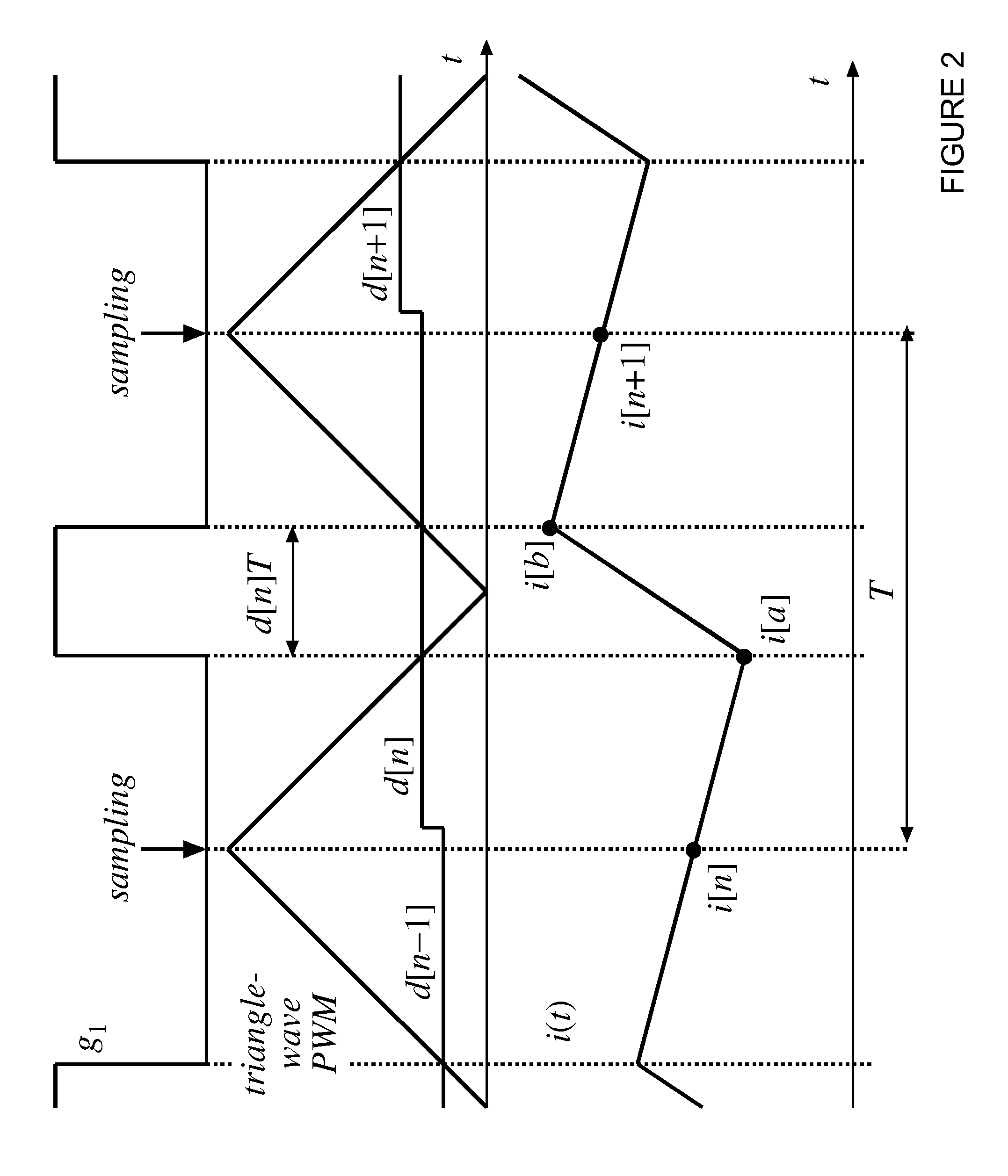
Digital Current Mode Controller
A digital current-mode controller for a DC-DC converter is disclosed. The controller comprises a digital current reference; and a current loop compensator adapted to receive a digital current error signal derived from a digital current sample sensed from the DC-DC converter and the digital current reference and to generate a duty-cycle command, wherein the current loop compensator comprises a low-pass filter that is used in generating the duty-cycle command. A DC-DC regulator comprising a digital current-mode controller and a method of controlling a DC-DC converter are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Self-adaptive current-mode-control circuit for a switching regulator
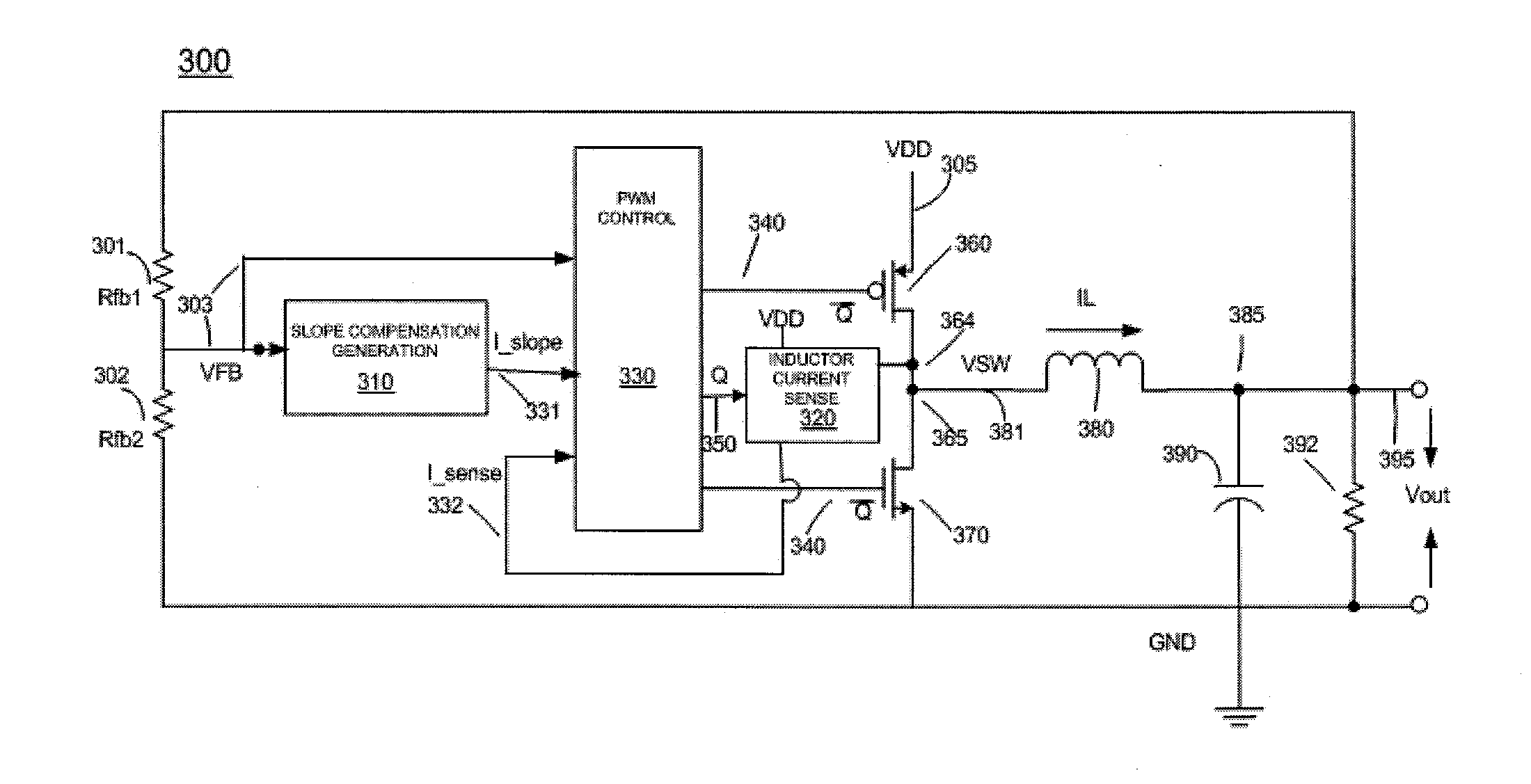
ActiveUS20120119718A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionCurrent mode controlMode control
A current-mode-control circuit for a switching regulator is provided. The circuit includes a first transistor coupled to a power supply voltage, a second transistor, and an inductor. The circuit further includes a slope compensation generation circuit coupled to the output of the current control circuit through a feedback loop, the slope compensation generation circuit generating a slope compensation current related to the output voltage, an inductor current sensing circuit coupled to the first transistor and the second transistor, and configured to calculate a current through the inductor and output a inductor sense current, and a pulse-width modulation control circuit coupled to the slope generation circuit and the inductor current sense circuit, the pulse-width modulation control circuit receiving the output of the current control circuit, the slope compensation current and the inductor sense current as inputs.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Current-mode control for switched step up-step down regulators
ActiveUS7394231B2Short transition timeSave powerDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceConstant frequency
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Current-mode control for switched step up-step down regulators
ActiveUS20060176038A1Short transition timeSave powerDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationConstant frequencyCurrent mode control
A switched regulator circuit provides step-up and step-down operation in which the level of the input voltage can be greater, equal to, or less than a preset controlled output voltage. A four switch arrangement or two switch arrangement provides buck, boost, and buck-boost regulation under constant frequency valley-peak current mode control. A single sense resistor may be utilized for sensing inductor current during only a short period during each duty cycle. As an alternative to the sense resistor, the switches themselves can be used to sense current during operation.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Switching voltage regulators with hysteretic control for enhanced mode-transition speed and stability
ActiveUS20120161728A1Multiple input and output pulse circuitsInstant pulse delivery arrangementsCurrent mode controlMode control
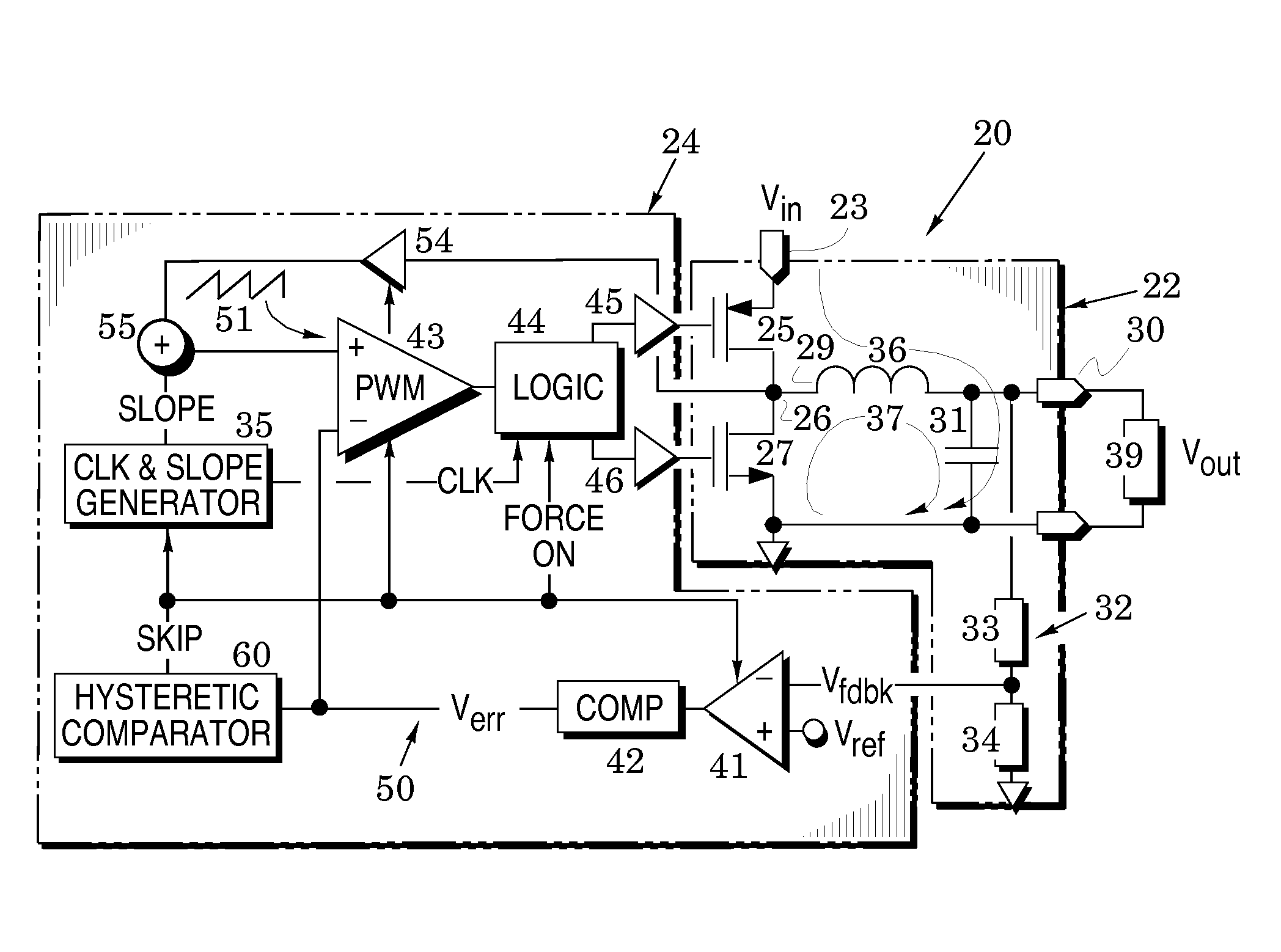
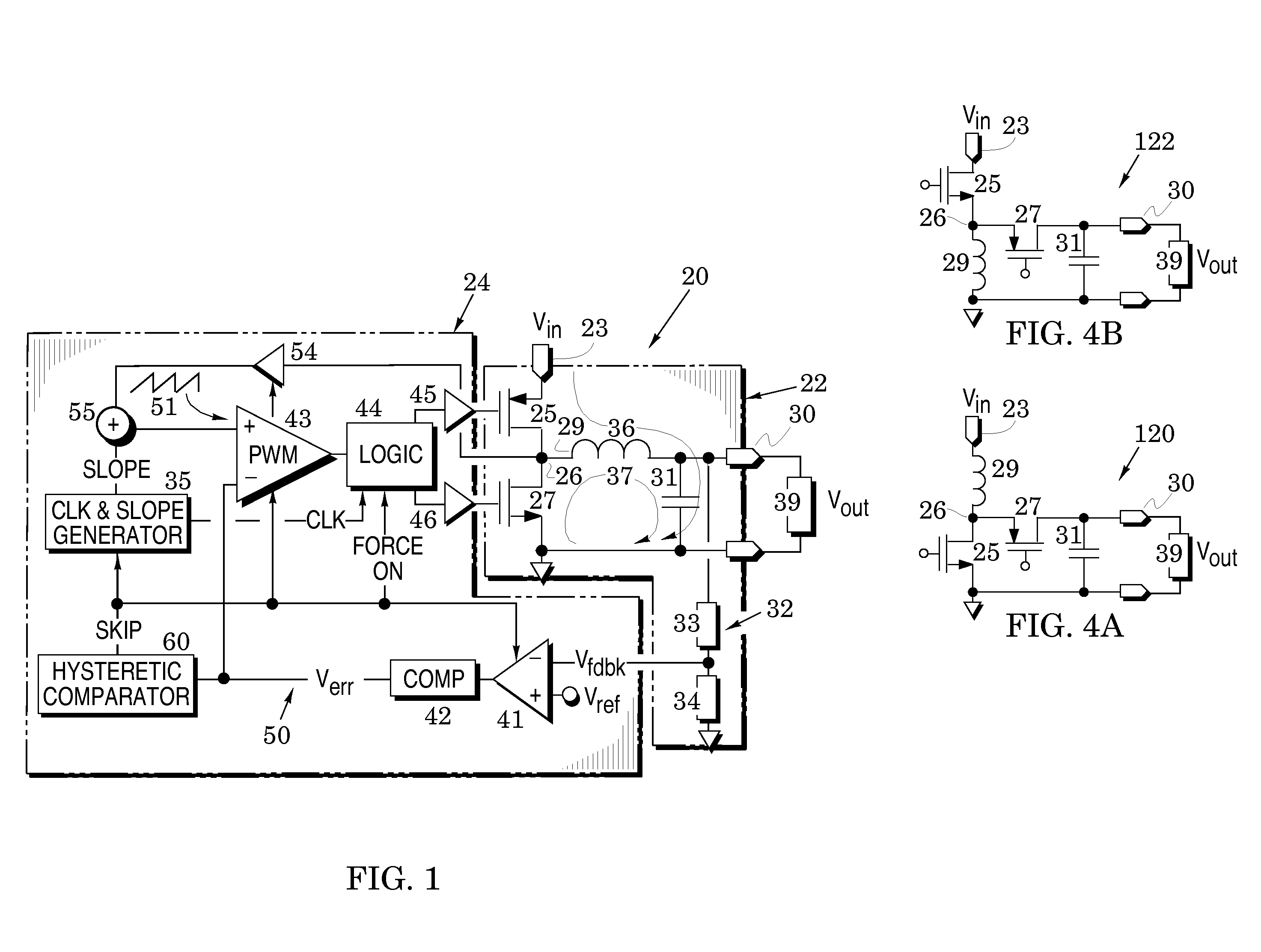
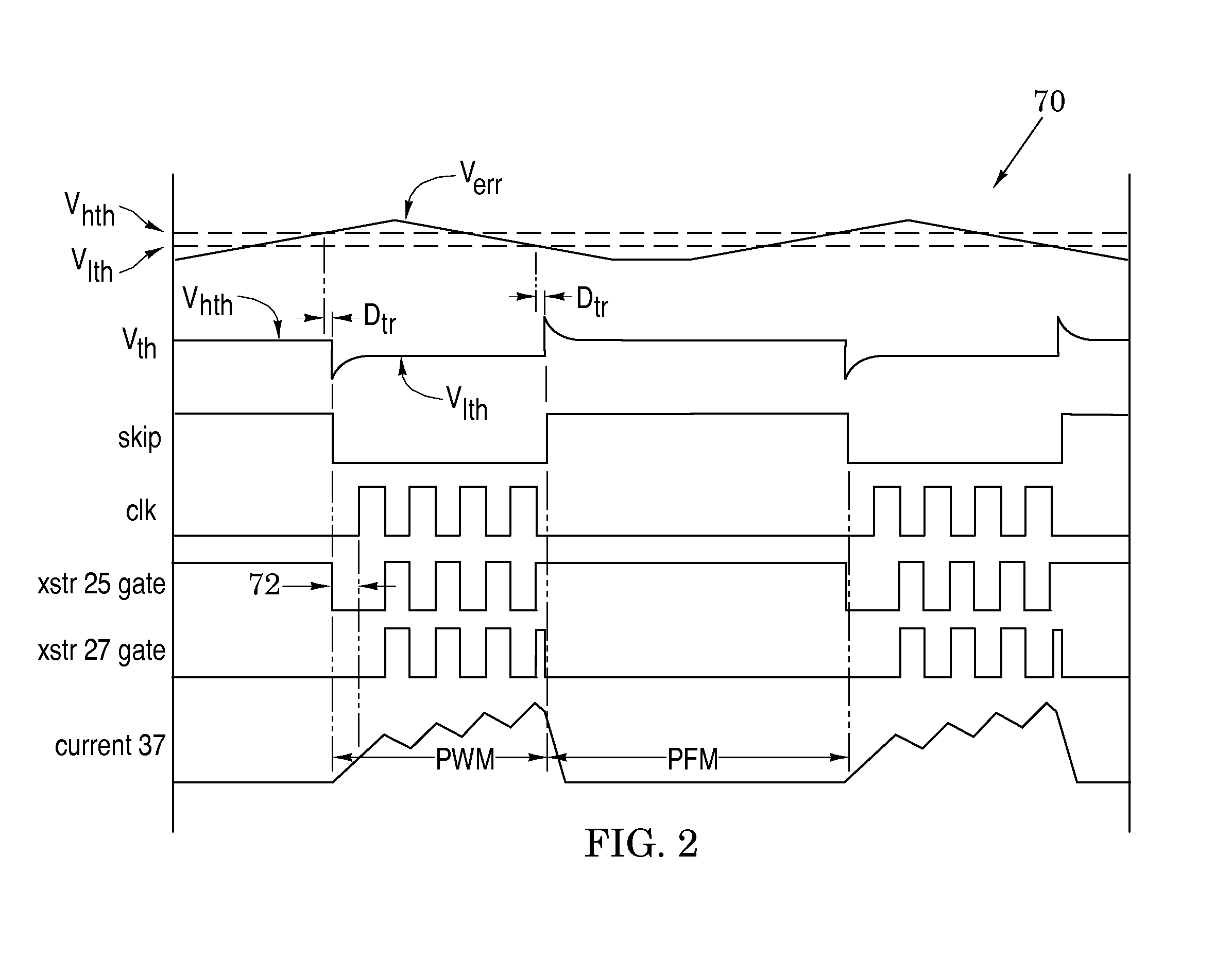
Switching voltage regulator embodiments are provided with hysteretic control to thereby switch between pulse-width modulation and pulse-frequency modulation operational modes. The switching is in response to different levels of an error voltage Verr in the feedback loop of voltage regulators. The hysteretic control is configured to provide a dc hysteretic response to changes in the error voltage Verr and also an ac hysteretic response to these changes. These two responses can be independently set to thereby enhance operational speed of the voltage regulators and also enhance immunity to transient noise signals that are generated by the mode switching. The voltage regulator embodiments facilitate instant return from the pulse-frequency modulation operational mode to the pulse-width modulation operational mode so that the stability of the feedback control of the regulator is enhanced. This feature is especially useful when the feedback loop is configured to include current-mode control as it minimizes the time duration in which the feedback loop operates in a voltage-mode control. The instant return insures that the feedback loop is immediately returned to the greater stability of the current-mode control.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
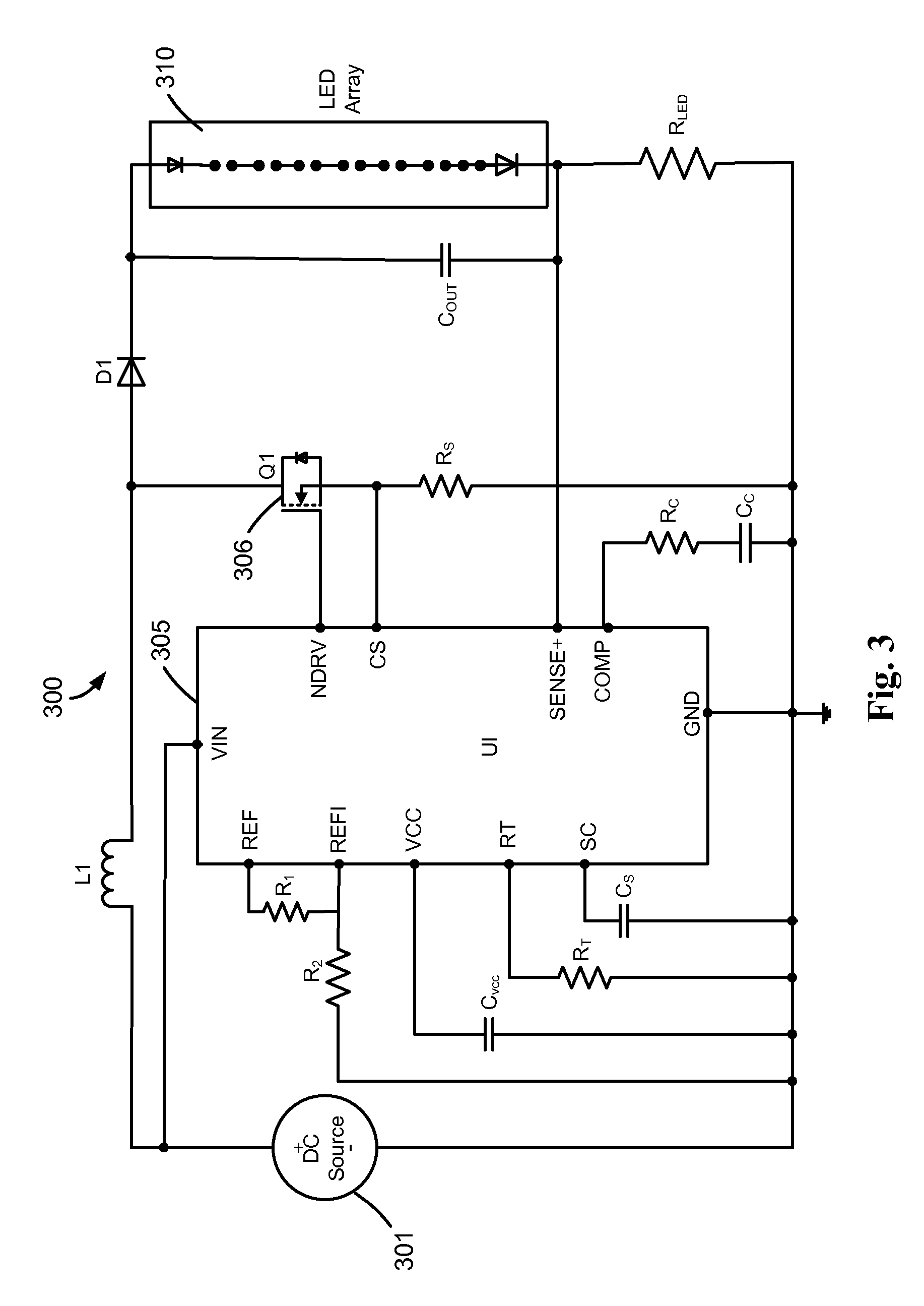
Power Factor Correction in and Dimming of Solid State Lighting Devices
ActiveUS20100045210A1Large capacitanceElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesCurrent mode controlAverage current
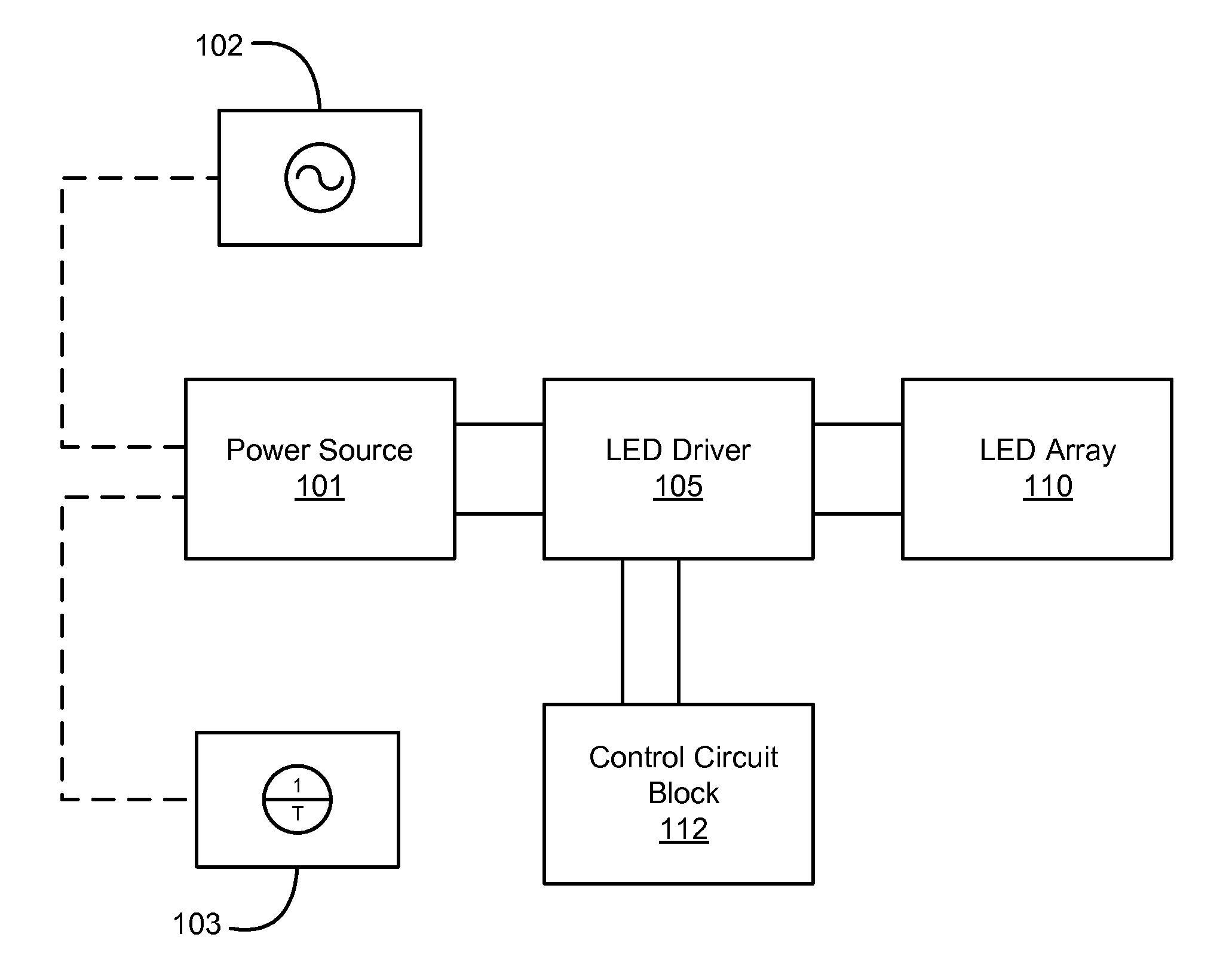
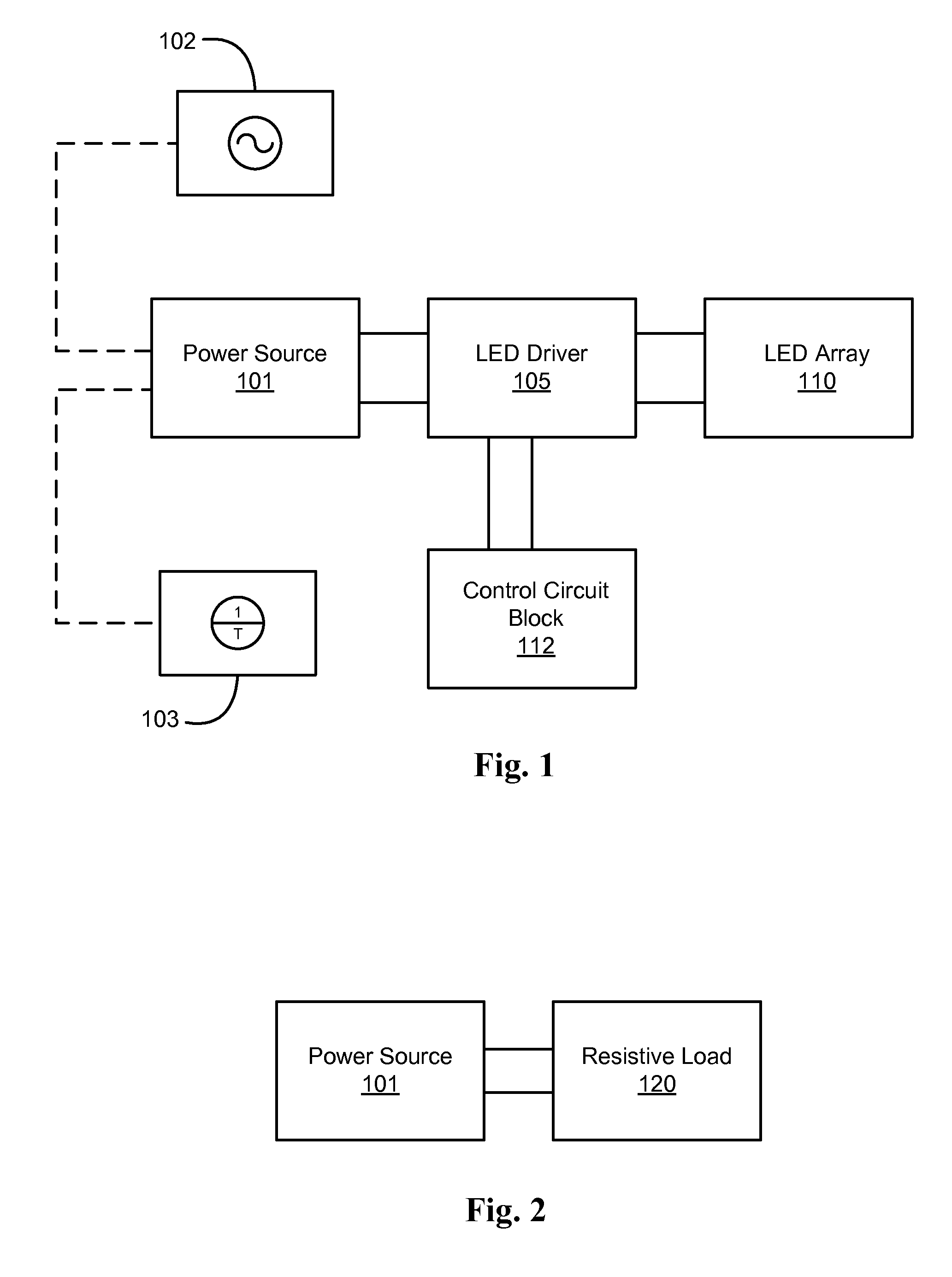
An apparatus and method provides a driver circuit that provides for power factor correction (PFC) to a load, such as a solid-state lighting (SSL) device, such as, for example, a light emitting diode (LED) or an array or cluster of LEDs. A programmable reference is provided in the circuit to operate in a fixed frequency peak current mode control (FFPCMC) or in a fixed frequency average current mode control (FFACMC). A driver circuit is employed to operate the SSL device using power derived from a main power source which may be DC or AC. In a FFPCMC embodiment, a programmable power reference is programmed to be a fixed DC voltage. In a FFACMC embodiment, source input current to the circuit can be programmed to be proportional to the rectified AC voltage after a bridge rectifier.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
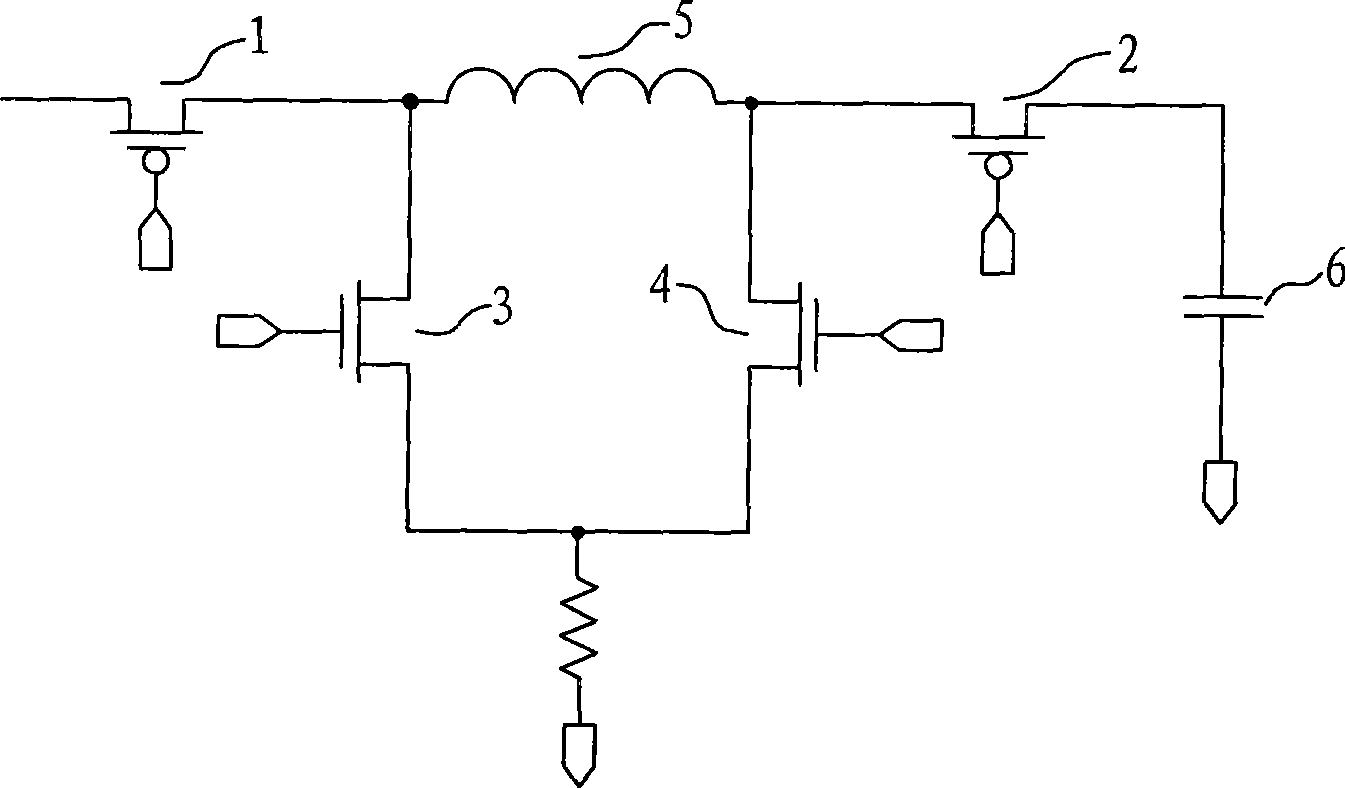
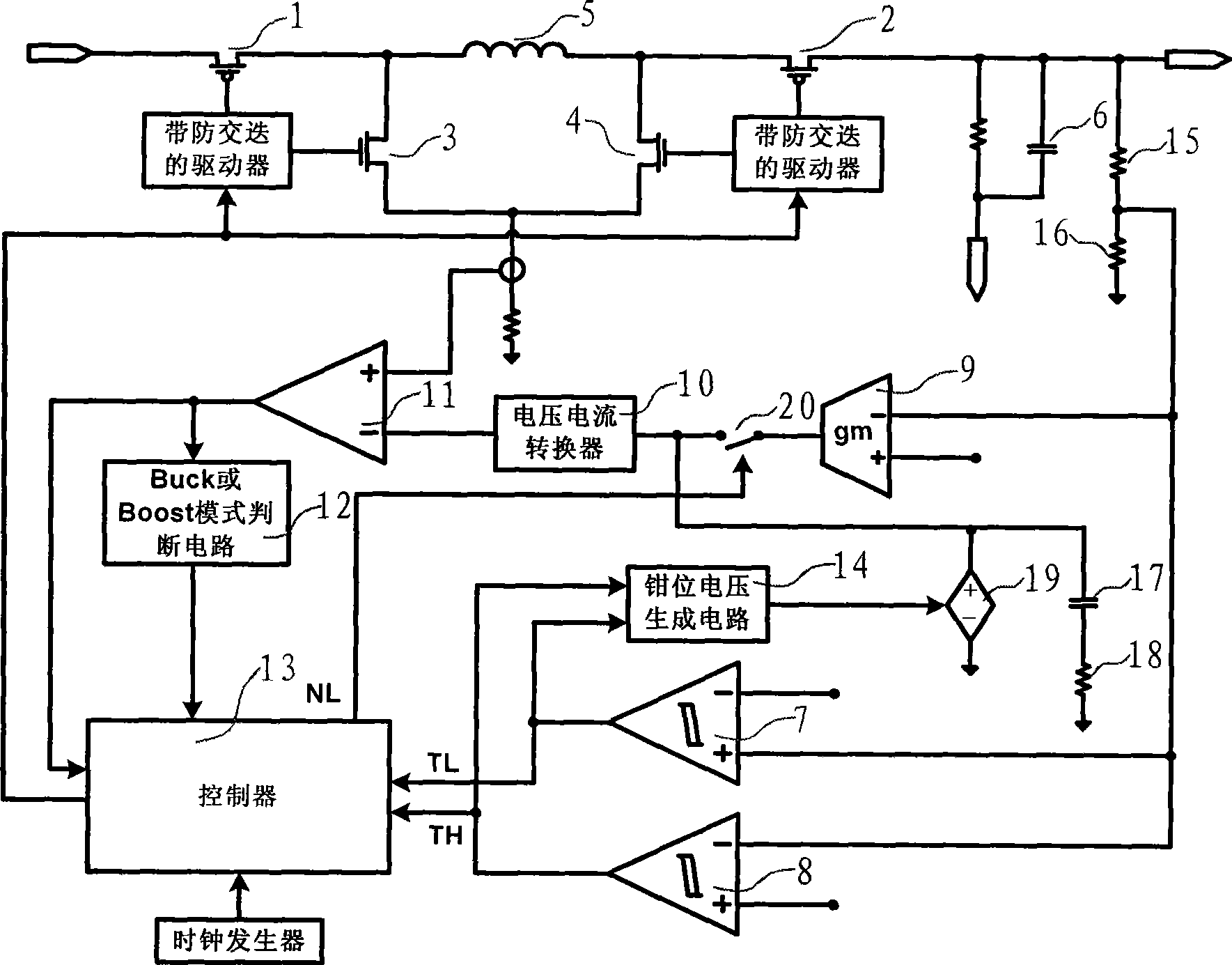
Controlling method and apparatus for four switch step-up step-down DC-DC converter
InactiveCN101499717AQuick responseSolve the technical problem of oscillationApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceLinear control
The invention discloses a method for controlling a four-switch buck-boost DC-DC converter. The method integrates the advantages of the linear control and the nonlinear control, adopts the control of a current mode during the steady state and carries out the voltage sampling at a voltage output terminal; the sampling voltage and the benchmark voltage are input in an error amplifier; the output signal of the error amplifier is used as the benchmark input of a current comparator; the output terminal of the error amplifier is also connected with a compensation network which consists of resistances and capacitors; when the loaded jumps, the nonlinear control is carried out. The invention also discloses a device used for implementing the method. The invention realizes the application of the nonlinear control on the four-switch buck-boost topology, simultaneously solves the technical problem that the oscillation occurs when the load jumps during the nonlinear control process, thereby leading the output voltage to reach the stable value quickly, and improving the response speed of the buck-boost converter.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Variable frequency current-mode control for switched step up-step down regulators
ActiveUS7466112B2Short transition timeSave powerDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCurrent mode controlMode control
A switched regulator circuit provides step-up and step-down operation in which the level of the input voltage can be greater, equal to, or less than a preset controlled output voltage. A four switch arrangement or two switch arrangement provides buck, boost, and buck-boost regulation under variable frequency valley-peak current mode control. A single sense resistor may be utilized for sensing inductor current during each duty cycle.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
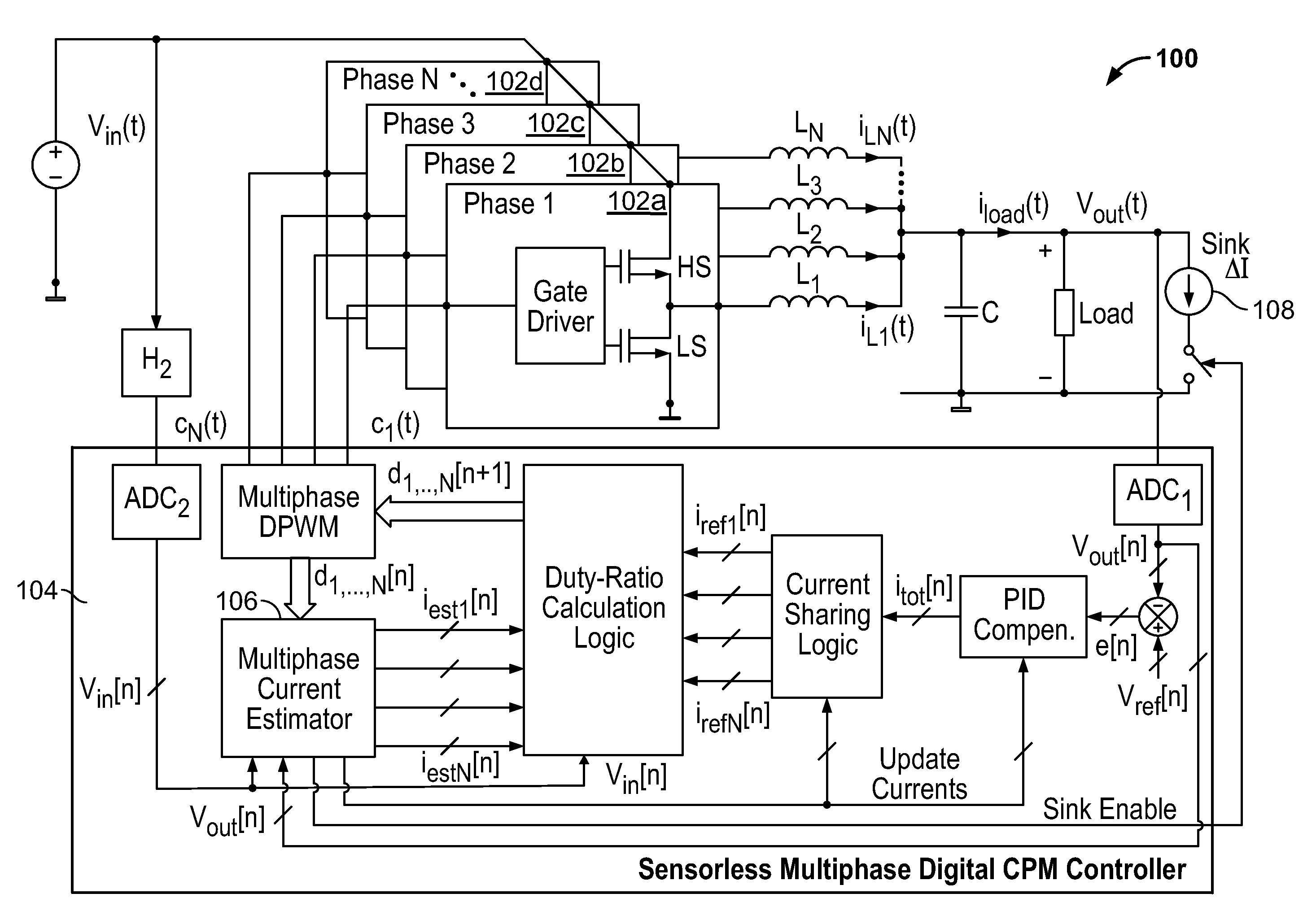
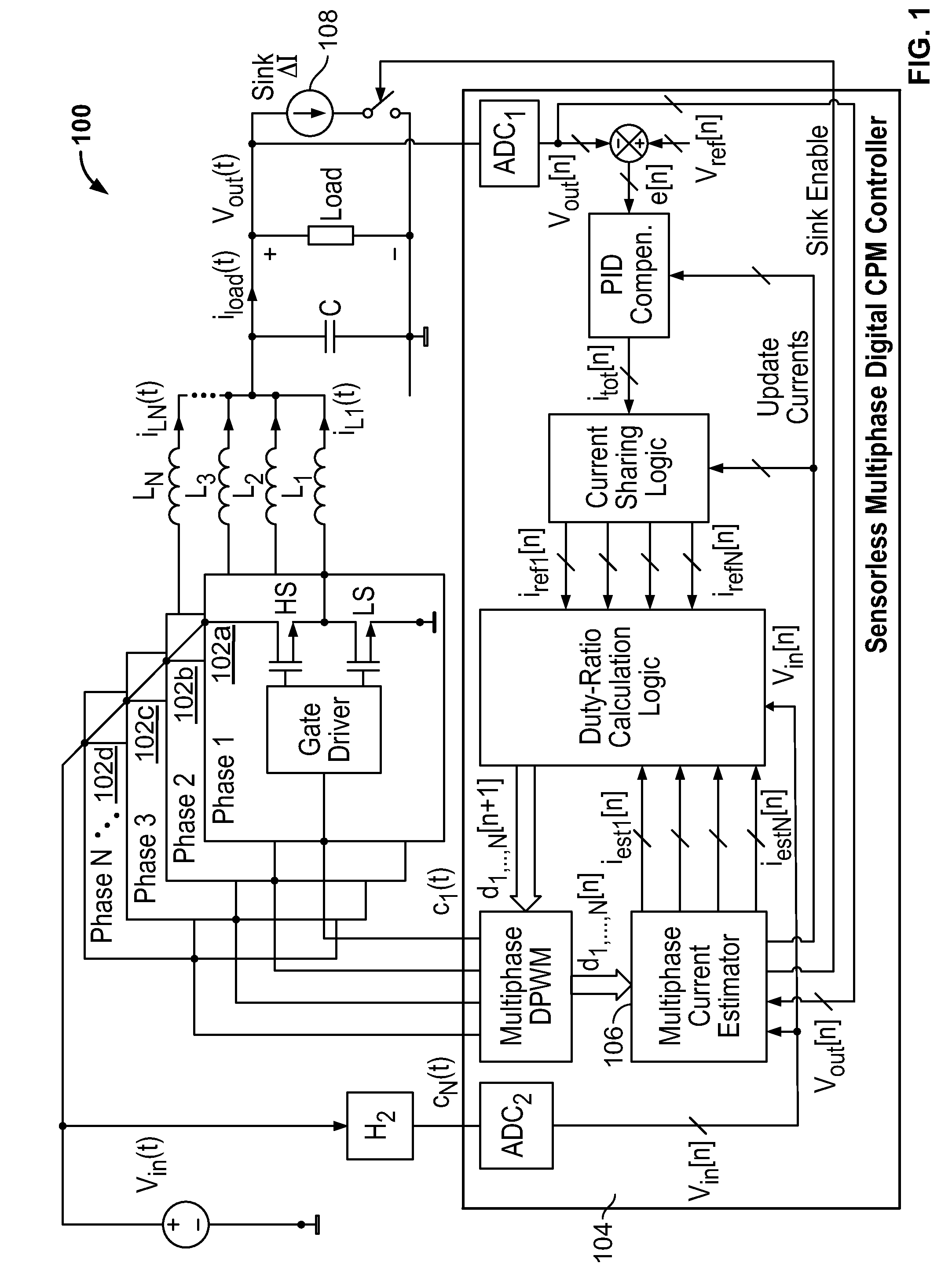
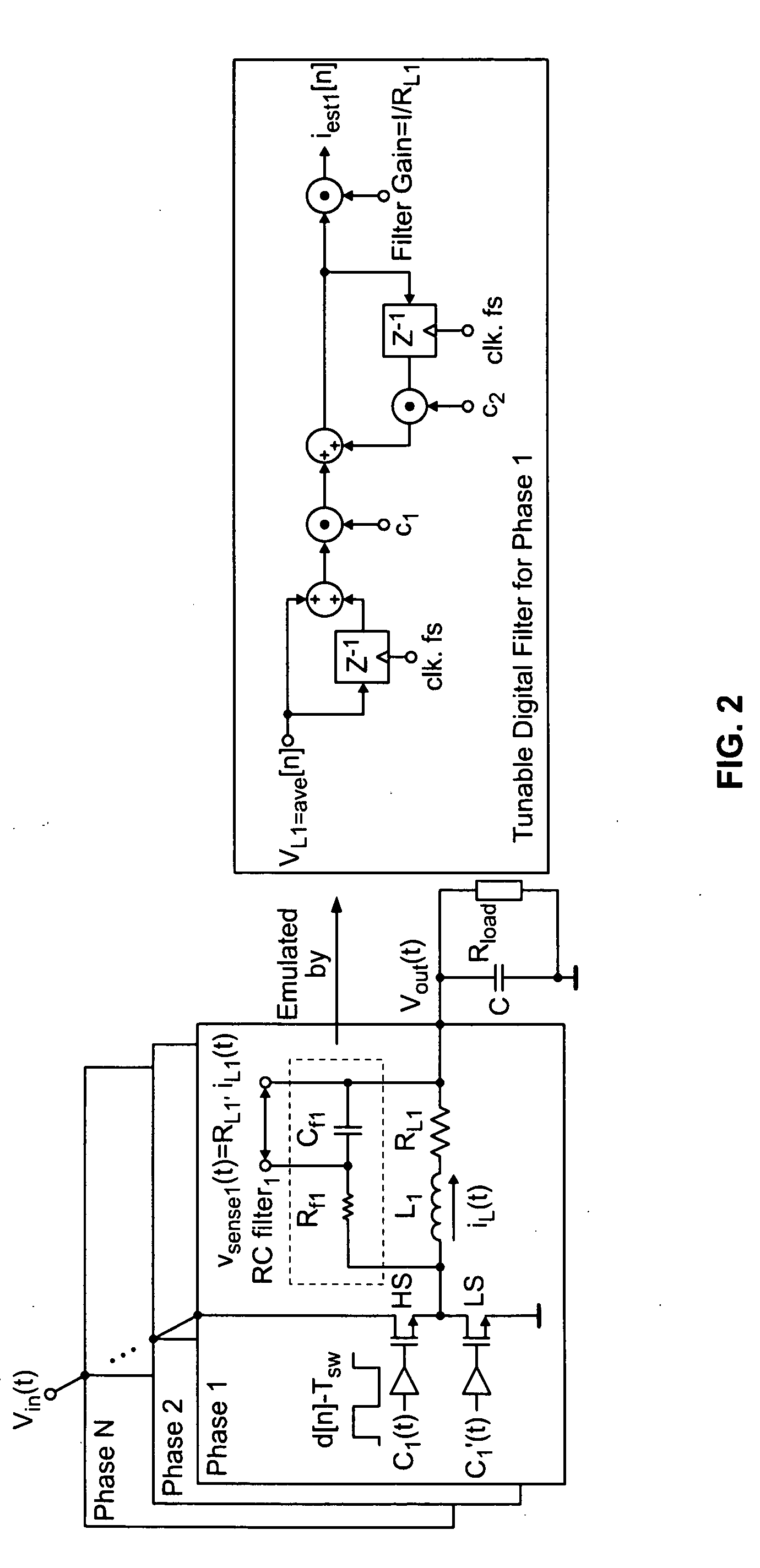
Self-tuning sensorless digital current-mode controller with accurate current sharing for multiphase dc-dc converters
Owner:EXAR CORP
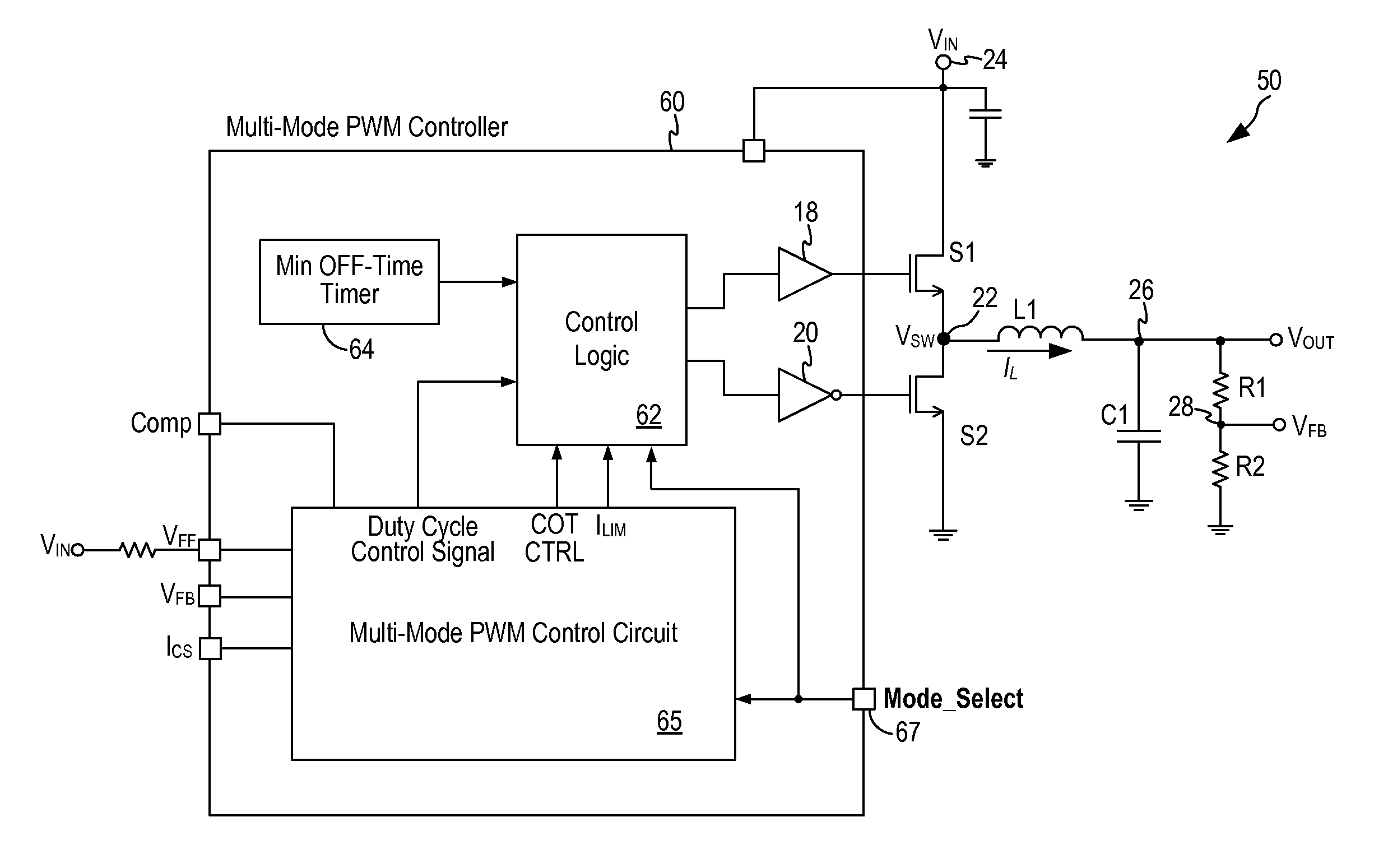
Configurable multi-mode pwm controller
InactiveUS20130249511A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionCurrent mode controlPower flow
A multi-mode pulse width modulation (PWM) controller for a buck switching regulator includes a multi-mode PWM control circuit where the PWM control circuit is configured to operate in one of multiple control schemes selectable by a mode select signal. In one embodiment, the multi-mode PWM control circuit incorporates a peak current mode control scheme, a voltage mode control scheme, and a valley current mode control scheme. In another embodiment, the multi-mode PWM control circuit further incorporates a constant ON-time control scheme.
Owner:MICREL
Dynamic current sharing dc-dc switching power supply
ActiveUS20050286277A1Batteries circuit arrangementsDc source parallel operationCurrent mode controlSwitching power
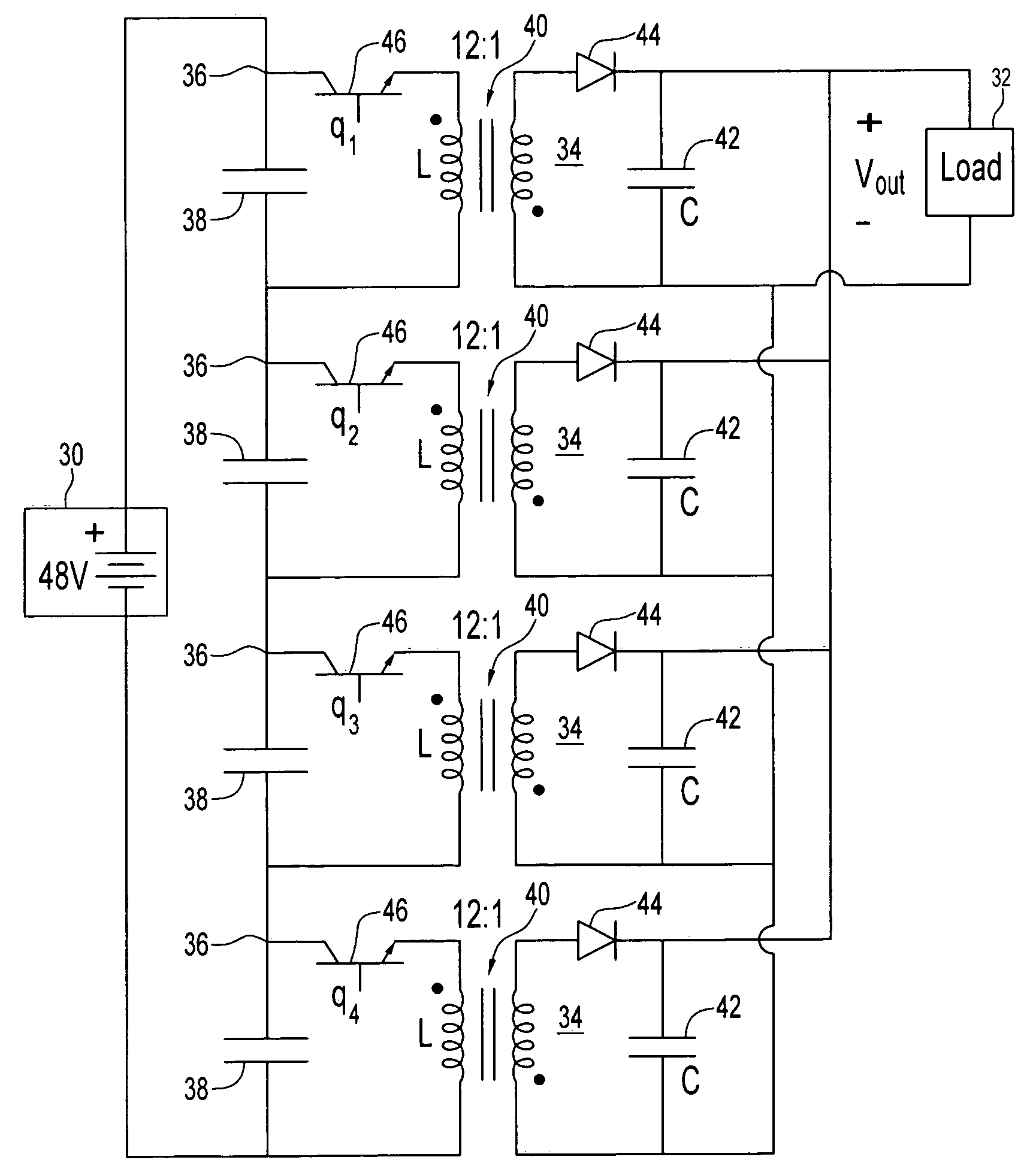
A power supply in an embodiment of the invention includes a plurality of dc-dc switching power converters, each of which has its input isolated from its output. The power converters are arranged with their respective inputs being series connected and their respective outputs being parallel connected in an embodiment of the invention. In another embodiment of the inputs are parallel connected and the outputs series connected. Each power converter includes an input filter in each of said dc-dc switching power converters and an output filter. Each power converter includes a sensorless current mode control circuit controlling its switching duty ratio.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
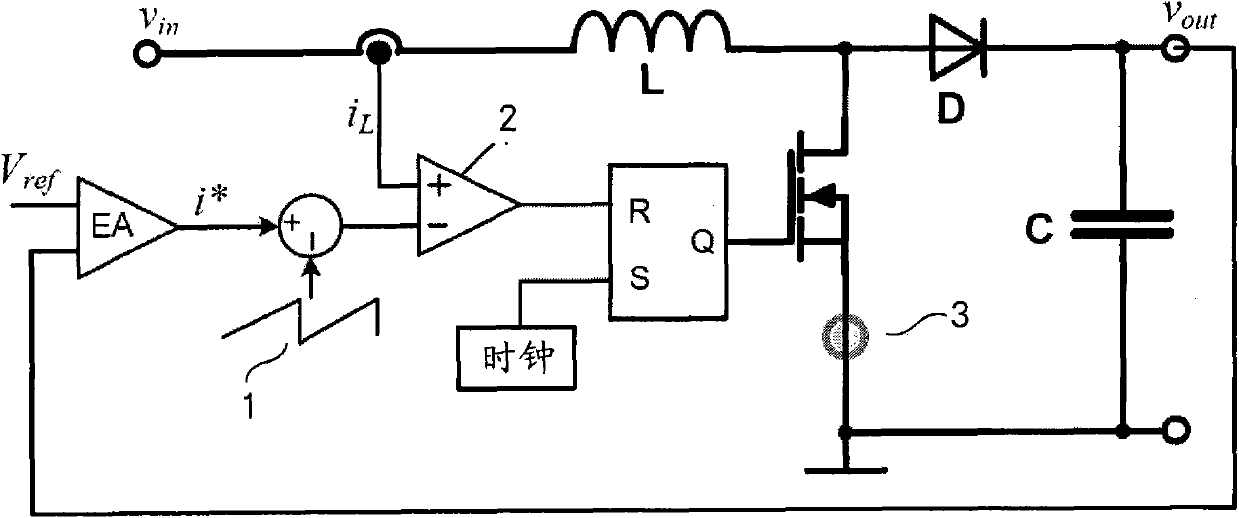
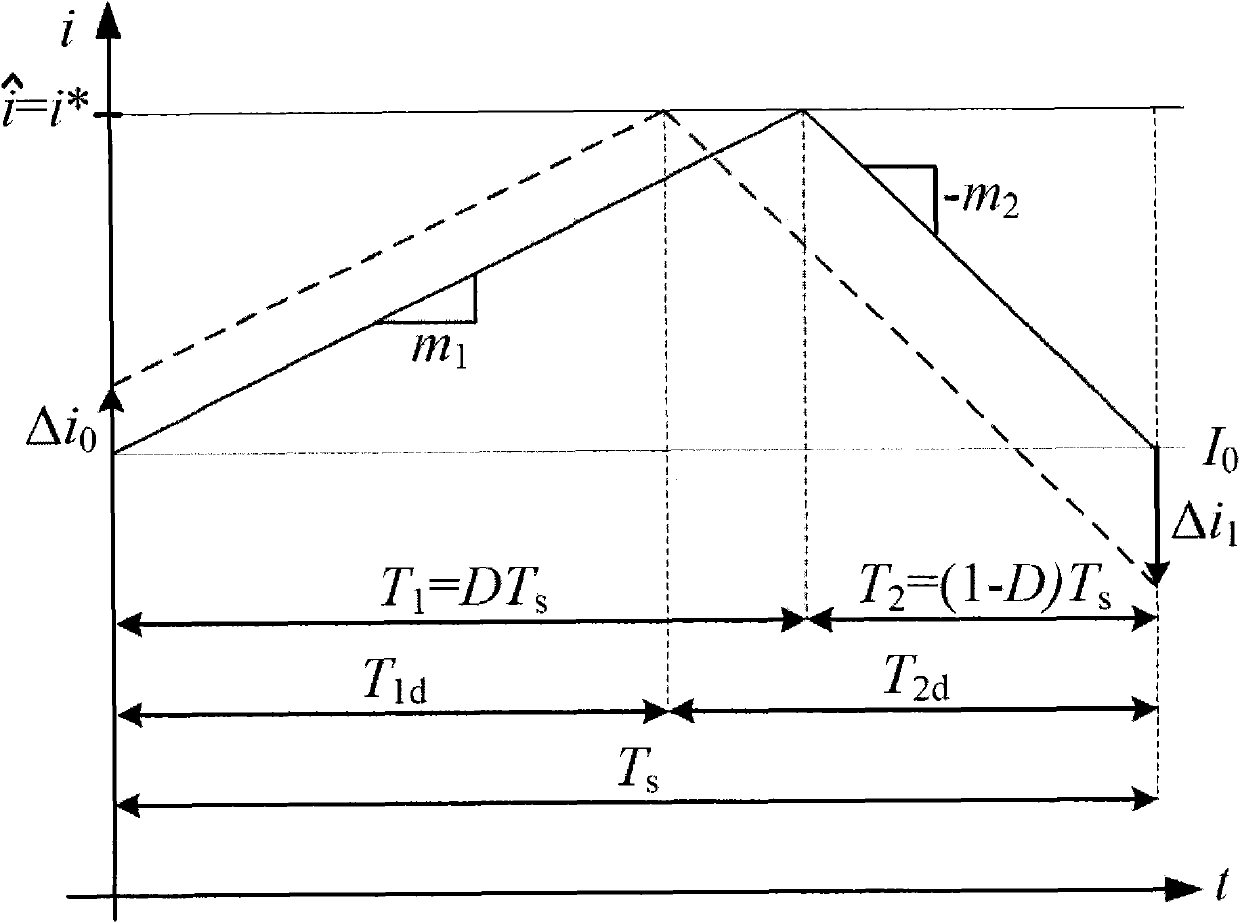
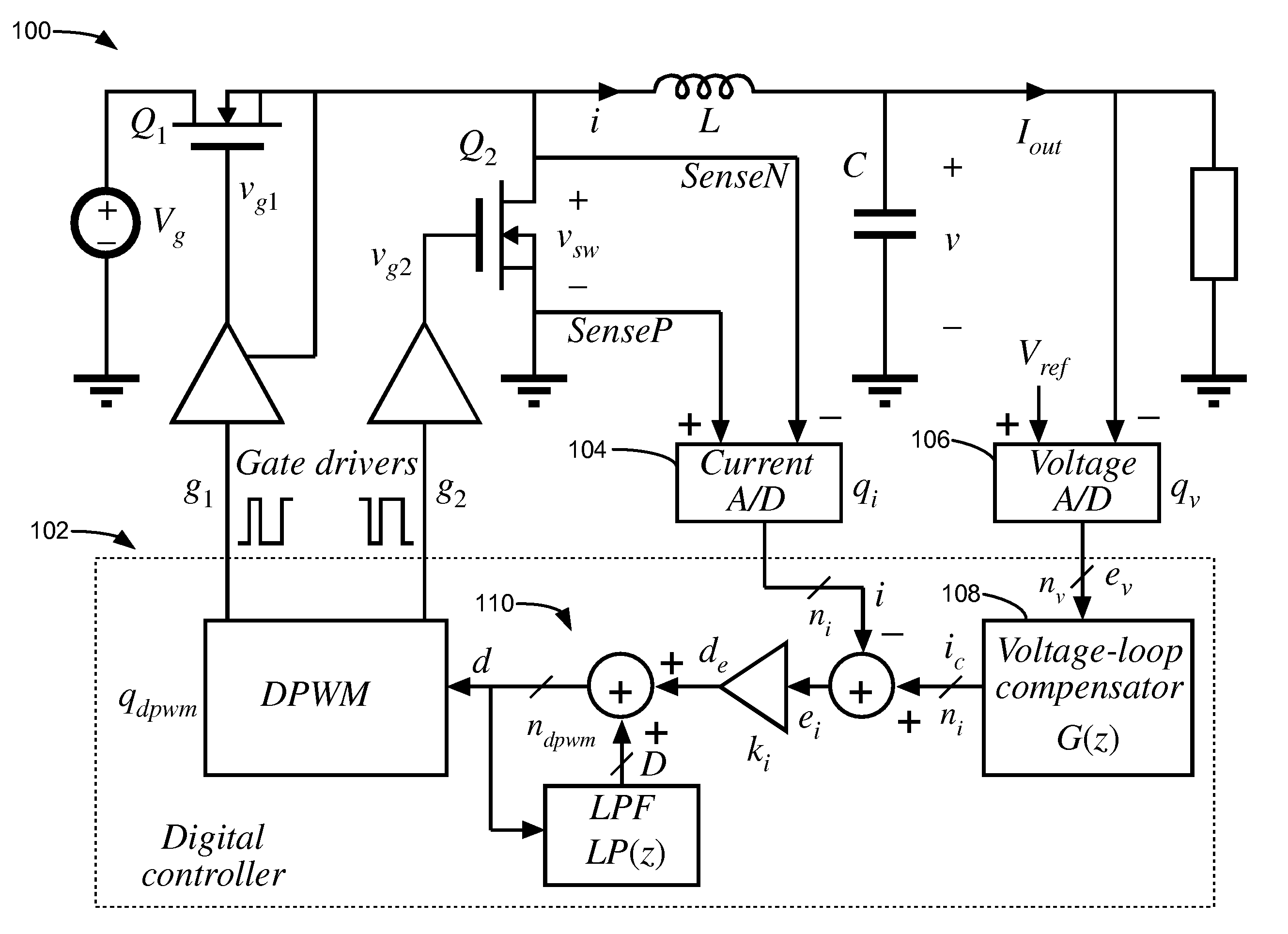
Digital slope compensation for current mode control
ActiveCN102025274AReduce the numberDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCurrent mode controlDigital analog converter
A digital slope compensation apparatus and method for a switched-mode power supply use a sensor for sensing and generating an analog inductor current ( i L ) of the switched-mode power supply, a comparator (2) for generating a trigger signal according to a comparison of an analog current threshold level and the analog inductor current ( i L ), and a pulse width modulator (PWM) for controlling the operation of a switched-mode power supply, wherein the pulse width modulator (PWM) is arranged to be triggered by the trigger signal of the comparator. A first analog to digital converter is arranged for converting an analog output voltage ( V out ) of the switched-mode power supply into a digital output voltage, means are arranged for transforming the digital output voltage into a digital current threshold level ( i cmp ), and a digital to analog converter is arranged for generating the analog current threshold level according to the digital current threshold level ( i cmp ).
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) PUBLIC CO LTD
Parallel current mode control using a direct duty cycle algorithm with low computational requirements to perform power factor correction
InactiveUS7317625B2Unity power factor for AC-DC converterLow costAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionCurrent mode controlSwitching cycle
A method and apparatus to implement parallel current mode control that is suitable for digital and analog implementation. A duty cycle algorithm is composed of a voltage term and a parallel current term which depends on the inductor current change between the inductor current value at the beginning of a switching cycle and the reference inductor current value at the end of that switching cycle. Parallel current mode control can be applied to all DC-DC converters, including both non-isolated and isolated topologies. It can also be applied to AC-DC converters with power factor correction.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
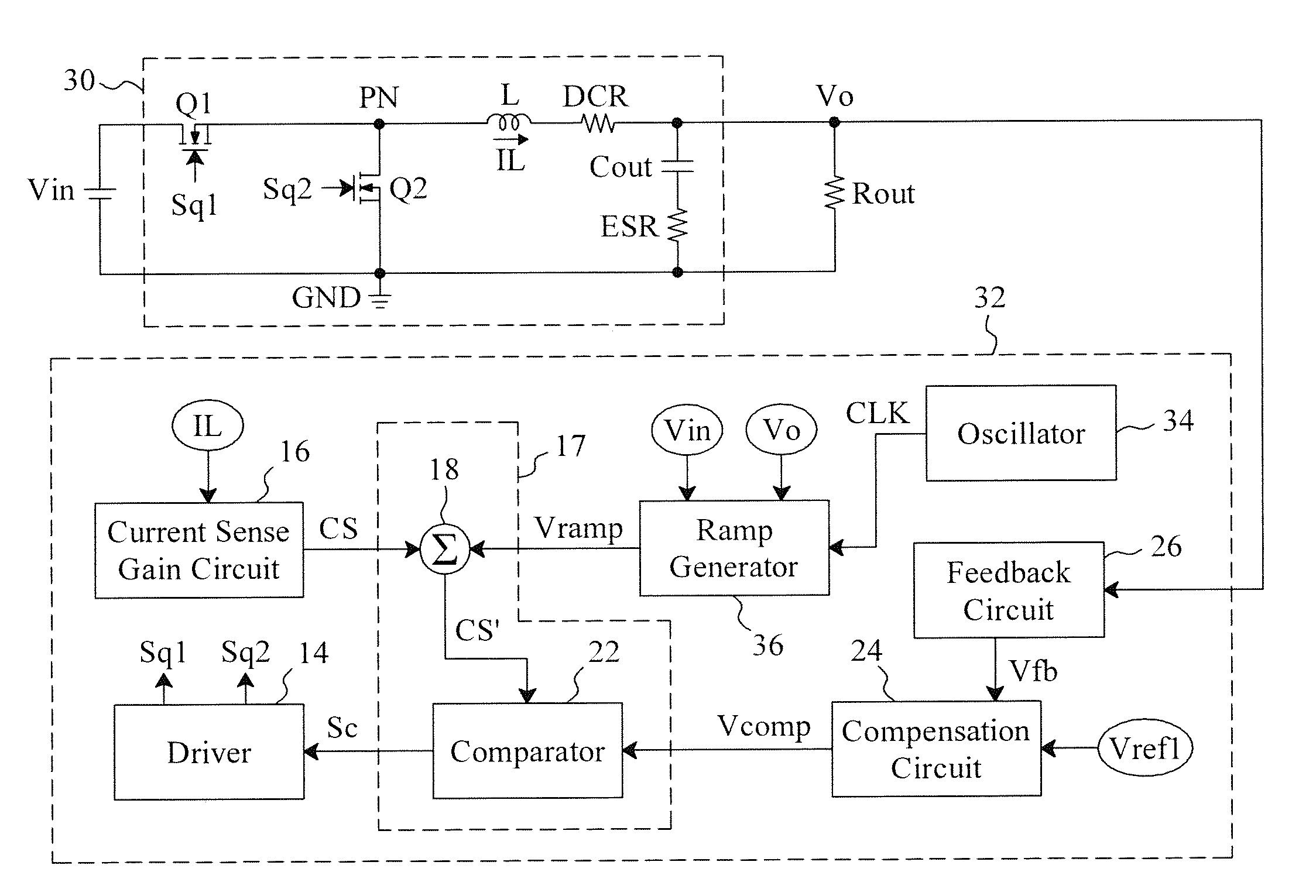
Control circuit and method for a current mode controlled power converter
InactiveUS20120105030A1Improve stabilityDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCurrent mode controlEngineering
A control circuit and method for a current mode controlled power converter to convert an input voltage into an output voltage, dynamically adjust the peak or the valley of a ramp signal depending on either or both of the input voltage and the output voltage. Under different conditions of the input voltage and the output voltage, the current mode controlled power converter can generate stable output voltages with an invariant inductor and an invariant compensation circuit, without sub-harmonic which otherwise may happen.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
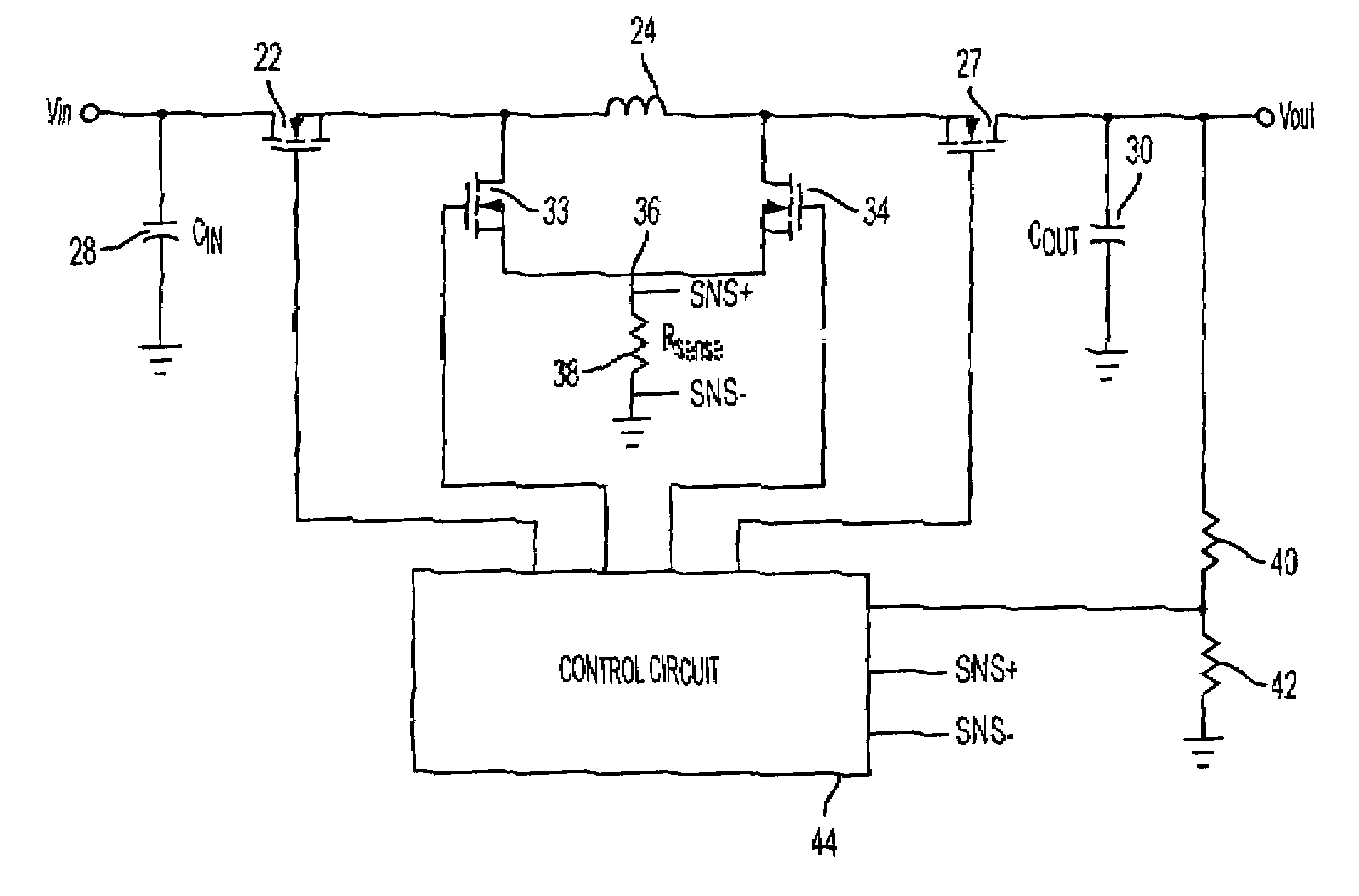
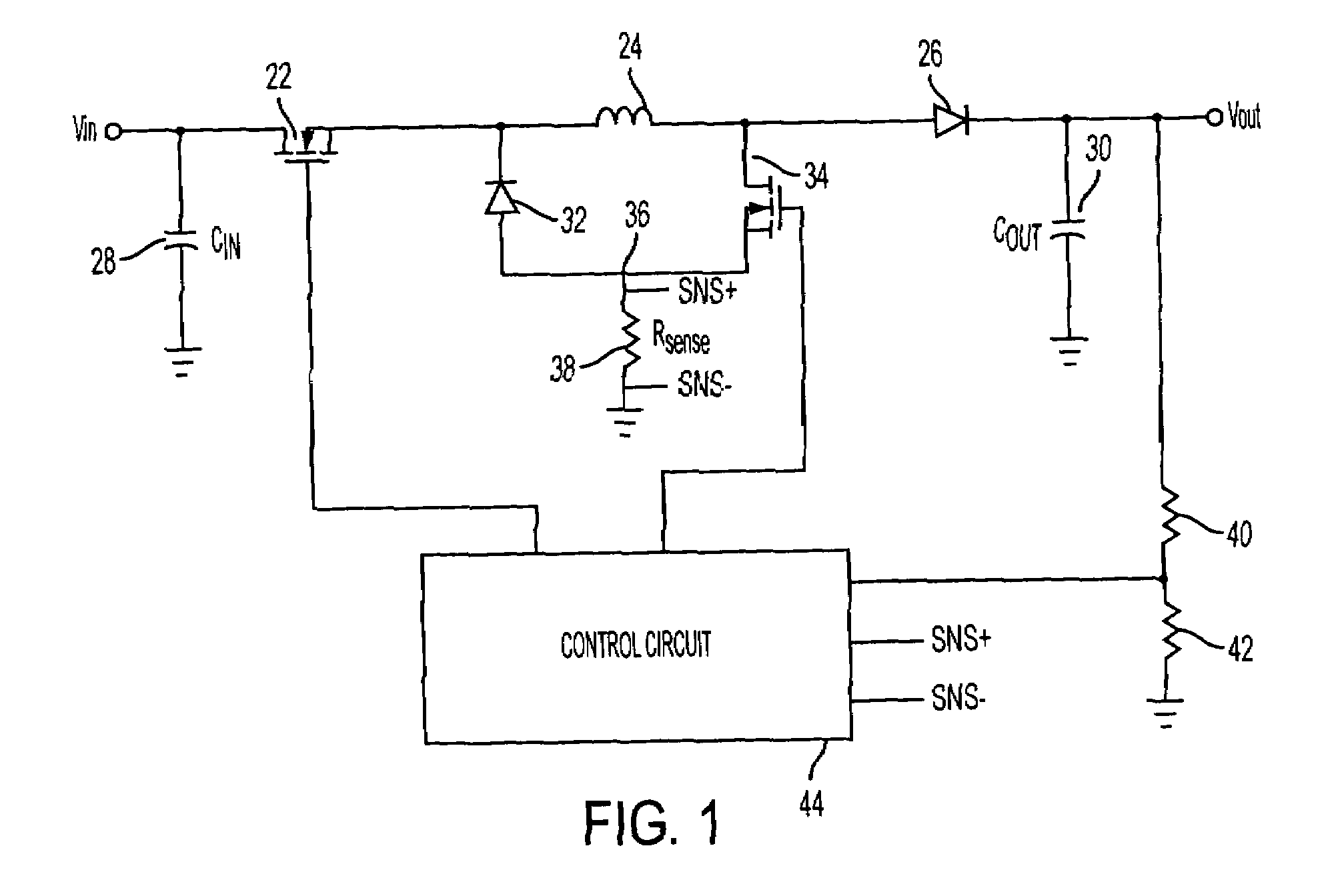
Method and apparatus for improved current mode control for large conversion ratio synchronous buck converter with lossless current sense
InactiveUS7508182B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioEasy to monitorEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionCurrent mode controlSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Methods and apparatuses are provided for monitoring an inductor output current delivered to a load by a power converter. For example, there is provided an apparatus comprising: at least one power switch operatively coupled to an input voltage source; an output inductor operatively coupled to the at least one power switch and to the load; and a current sensor operatively coupled to the output inductor, the current sensor providing a current sense signal corresponding to the inductor output current delivered to the load. In one embodiment, the current sensor comprises: a filter comprising a first resistor coupled in series with a first capacitor; and a second capacitor coupled in parallel with the first resistor, the first and second capacitors forming an AC voltage divider to increase the signal-to-noise ratio of the current sense signal.
Owner:SEMTECH CORP
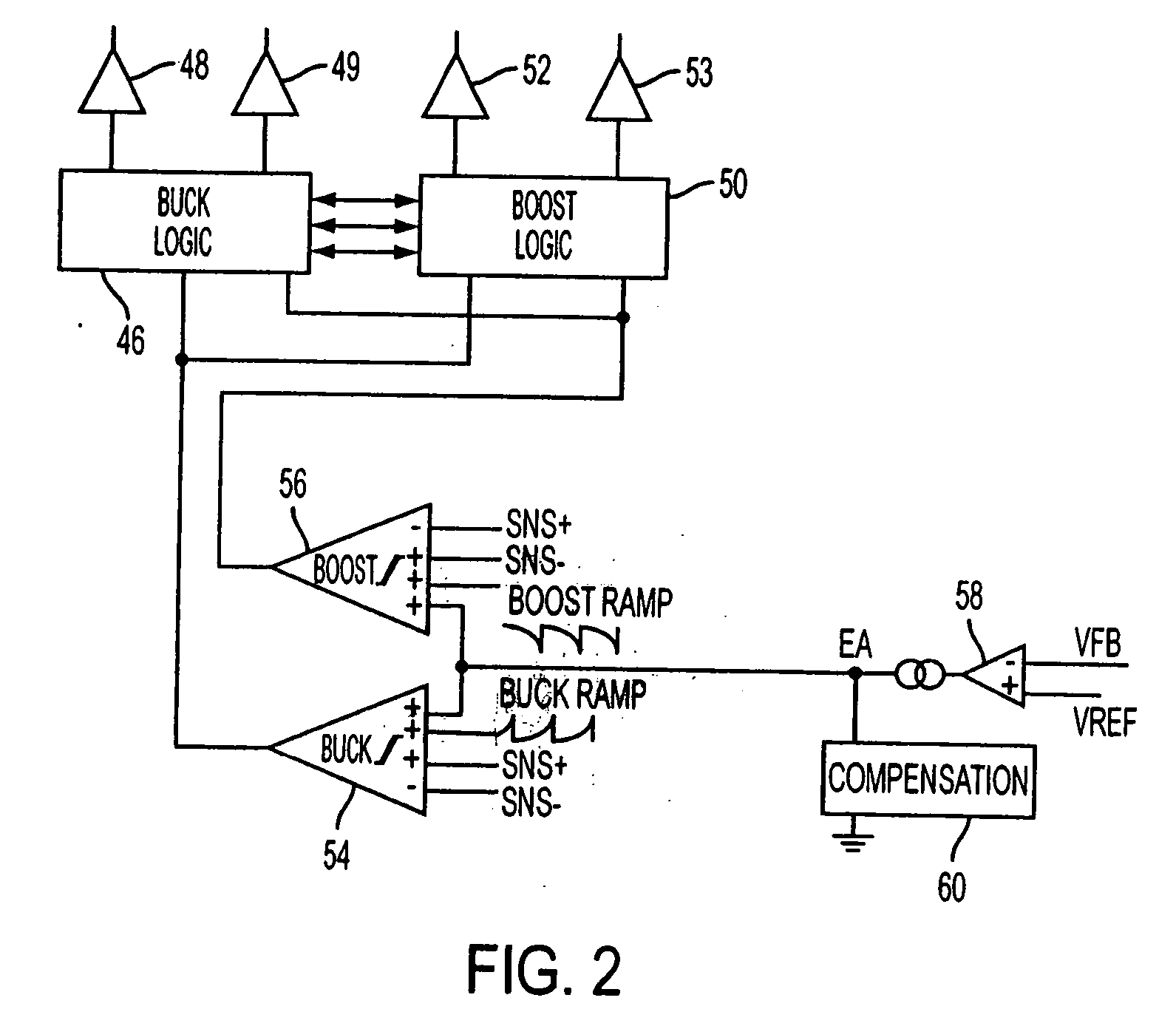
Switching scheme for step up-step down converters using fixed frequency current-mode control
ActiveUS20110279098A1Inhibition transitionDc-dc conversionAc network voltage adjustmentCurrent mode controlMode control
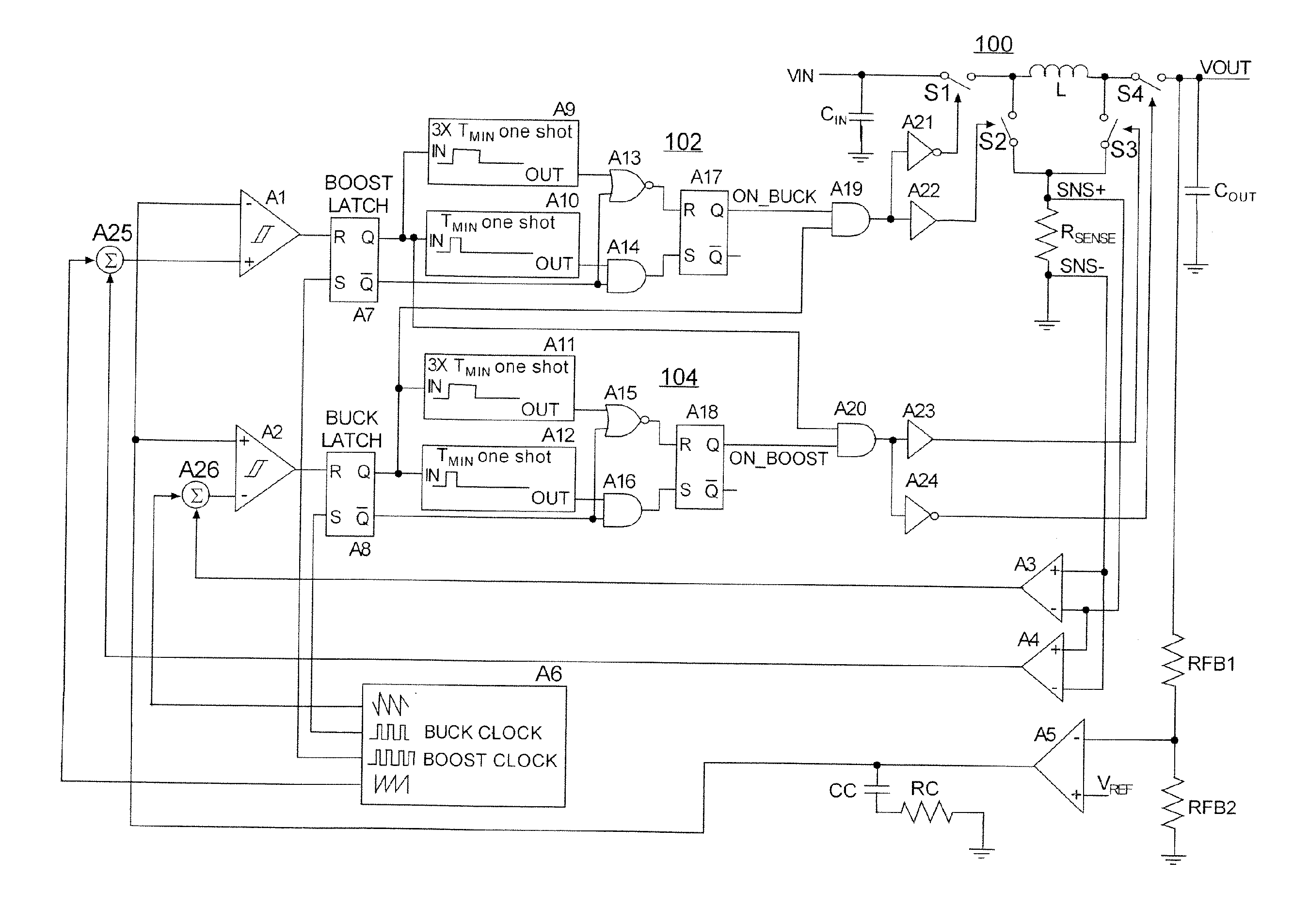
Novel circuitry and methodology for controlling a step up-step down switching regulator that produces a regulated output signal at an output node in response to an input signal at an input node, and has an inductive device, a plurality of switching circuits for providing connection of the inductive device to the input and output nodes and a ground node, and a switch control circuit for driving the switching devices so as to enable the power supply system to operate in a boost mode to increase the input signal, in a buck mode to decrease the input signal, and in a buck-boost mode when a difference between the input signal and the output signal is within a predetermined range. Buck-boost latch circuitry is provided for latching a transition between the buck mode and the buck-boost mode, or between the boost mode and the buck-boost mode based on a predetermined condition.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Switching regulator with average current mode control
A system and method control an output voltage across a load using current mode control to control current through an output filter connected to the load. The output voltage across the load is compared with a reference voltage to generate a reference current signal indicative of a desired average current through the load. A control signal is generated to indicate when an output current is greater than the desired output current. The output filter is alternately coupled to a first supply rail and to a second supply rail in response to the control signal to generate an average current through the load.
Owner:VOLTERRA SEMICONDUCTOR
External Ramp Autotuning for Current Mode Control of Switching Converter
ActiveUS20140306680A1Stable and high system bandwidthDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCurrent mode controlMode control
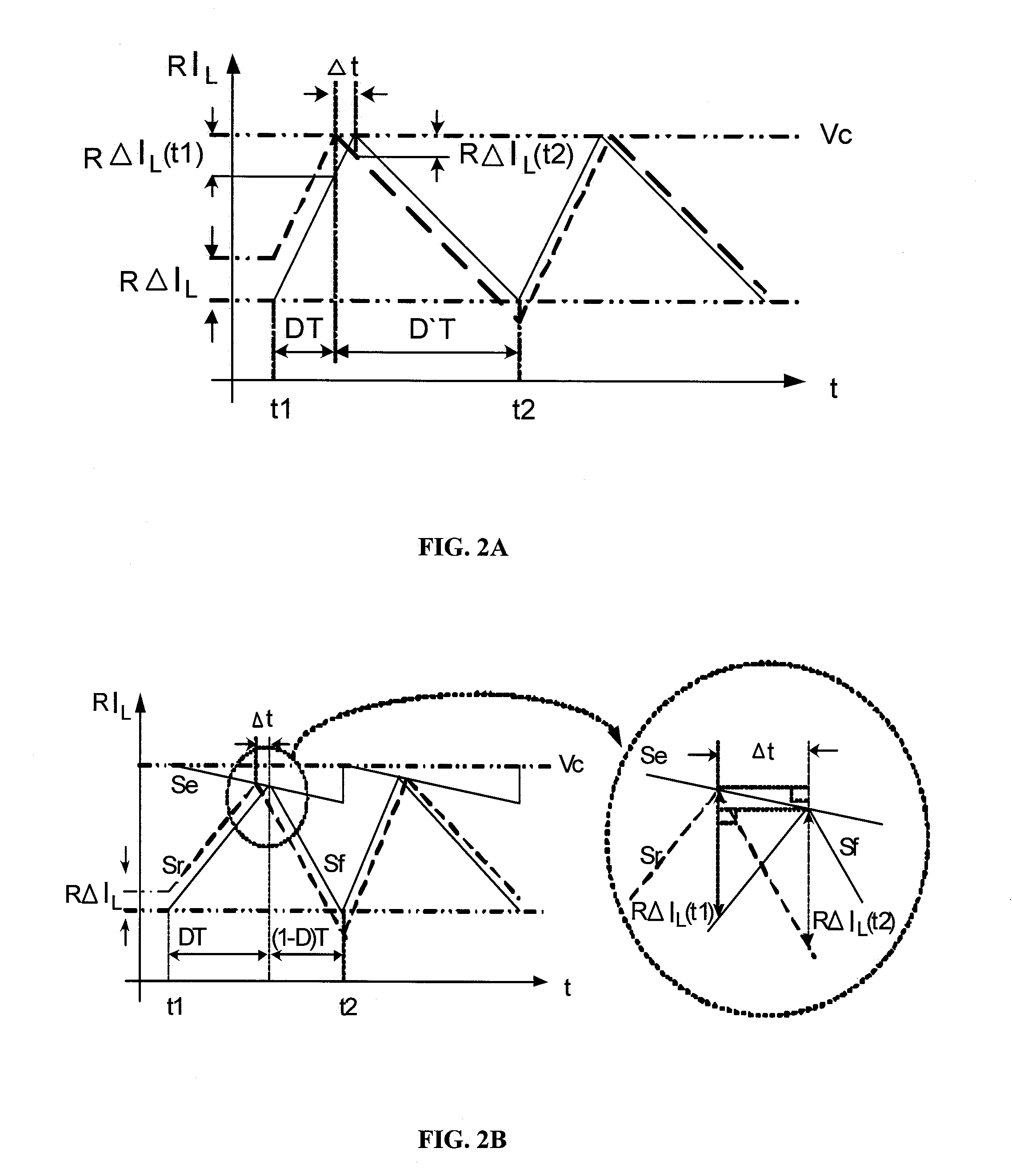
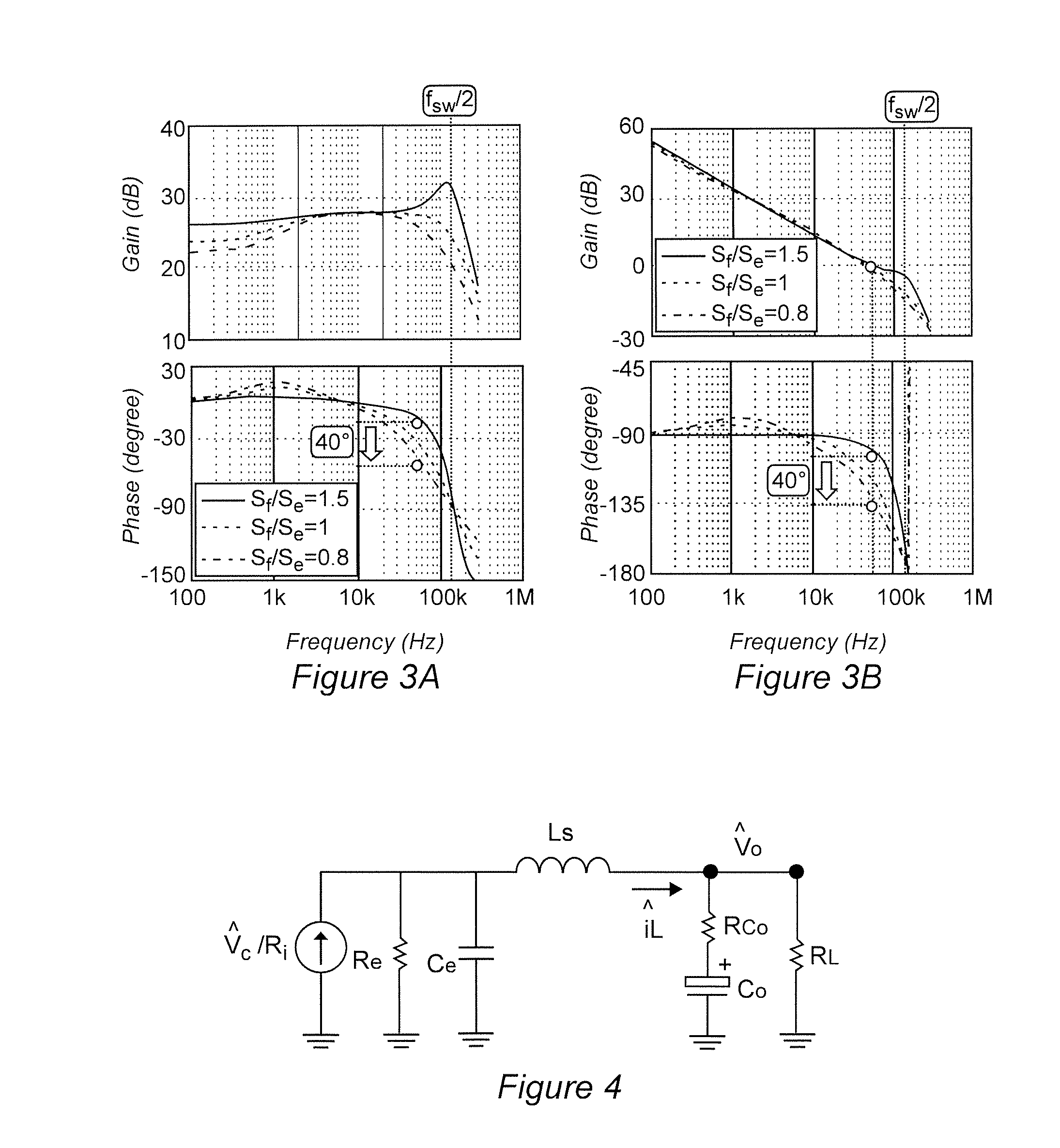
Peak current, valley current or average current mode controlled power converters in either digital or analog implementations obtain a stabilized feedback loop and allow high system bandwidth design by use of an external ramp generator using a slope computation equation or design parameters based on fixing the quality factor of a double pole at one-half of the switching frequency at a desired value The slope of the external ramp waveform is tuned automatically with knowledge of the slope change in the waveform of inductor current of a power converter derived by differentiating a waveform in the current feedback loop. This autotuning of the external ramp generator provides immunity of quality factor change under variations of duty cycle, component values of topological change of the power converter.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Dynamic current sharing dc-dc switching power supply
ActiveUS7030512B2Batteries circuit arrangementsDc source parallel operationCurrent mode controlSwitching power
A power supply in an embodiment of the invention includes a plurality of dc—dc switching power converters, each of which has its input isolated from its output. The power converters are arranged with their respective inputs being series connected and their respective outputs being parallel connected in an embodiment of the invention. In another embodiment of the inputs are parallel connected and the outputs series connected. Each power converter includes an input filter in each of said dc—dc switching power converters and an output filter. Each power converter includes a sensorless current mode control circuit controlling its switching duty ratio.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
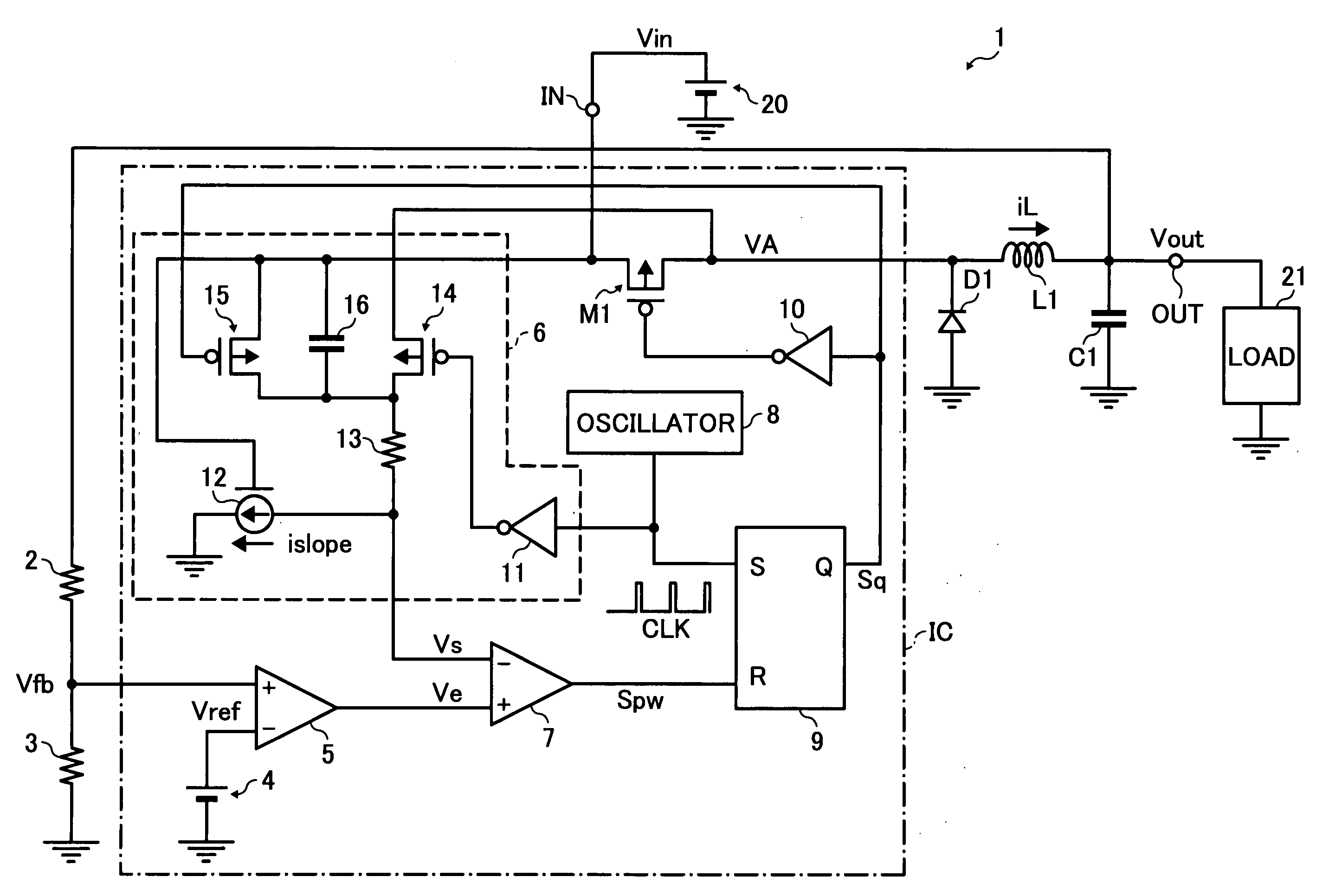
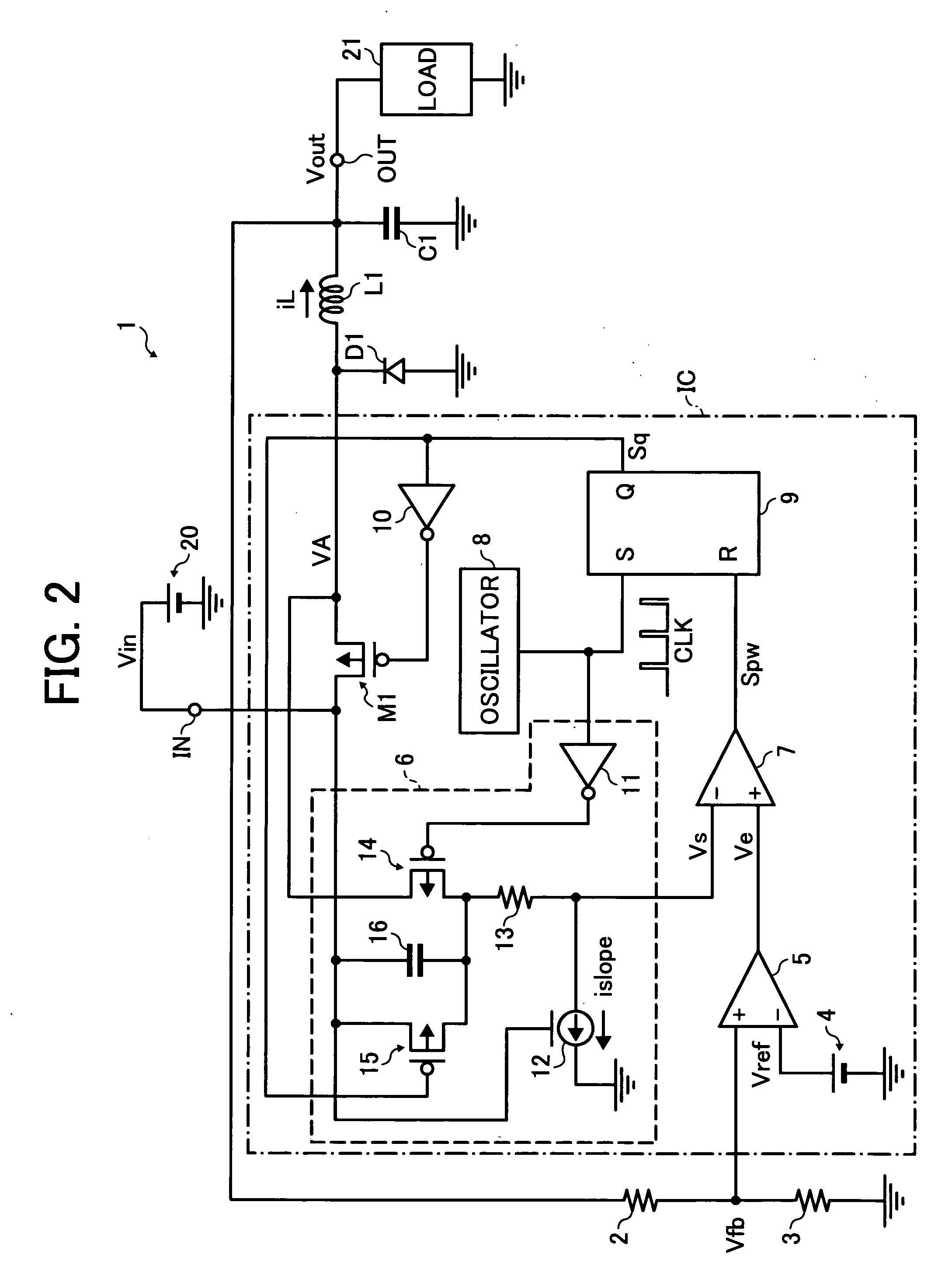
Current-mode controlled switching regulator and control method therefor
InactiveUS20080150508A1Simple circuitAvoid oscillationDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationVoltage generatorCurrent mode control
A current-mode controlled switching regulator and control method therefor. The switching regulator includes input and output terminals, a switching device to switch in accordance with a control signal, an inductor to store charge from an input voltage at the input terminal based on the switching device, a rectifying device to discharge the charge stored in the inductor, an error amplifier to amplify a voltage difference between a divided voltage generated by dividing an output voltage at the output terminal and a predetermined reference voltage, a slope voltage generator to generate and output a slope voltage having a slope angle corresponding to the input voltage, and a switching controller to compare a voltage output from the error amplifier with the slope voltage, generate a pulse signal with a duty cycle corresponding to a comparison result, and control the switching of the switching device according to the pulse signal.
Owner:RICOH ELECTRONIC DEVICES CO LTD
Protection for switched step up/step down regulators
ActiveUS20060176037A1Timely controlDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationVoltage converterCurrent mode control
A four switch voltage converter is regulated for buck mode and boost mode under constant frequency valley-peak current mode control. Protection circuits are responsive to output voltage and regulator current to prevent excessive current that otherwise might result from abnormally low output voltage short circuit, or spurious switching abnormalities during low duty cycle operation. The regulator control circuit is responsive to the protection circuits to automatically connect a regulator inductor between a common potential and the output to limit current.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Digital current mode controller
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
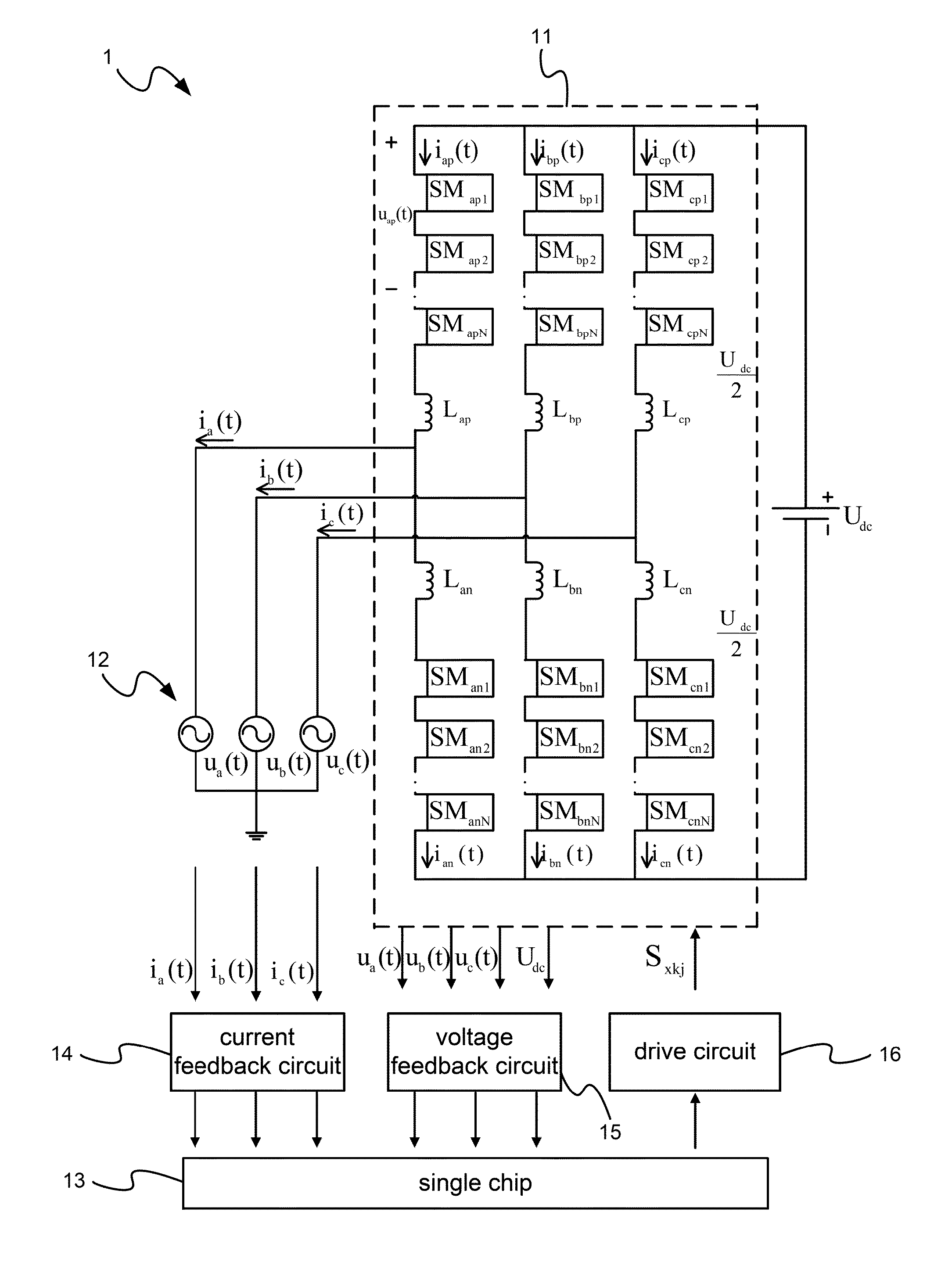
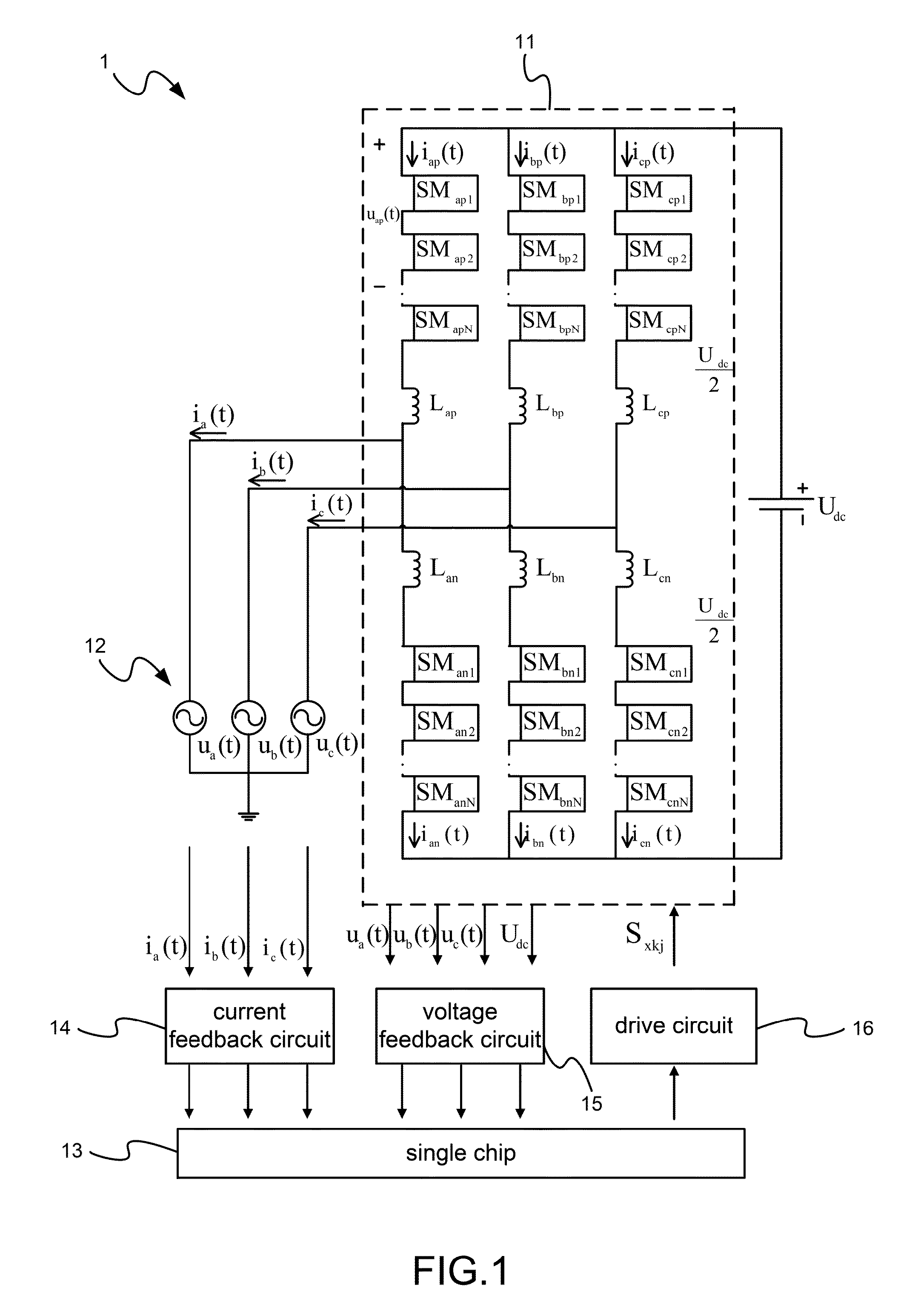
Method of current control of three-phase modular multilevel converter with inductance changes allowed
ActiveUS9413260B1Easy to adjustSimple processAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion constructional detailsCurrent mode controlReference current
Current of a three-phase multilevel modular converter (MMC) is controlled. The control is a division-summation (D-Σ) method yet uses integration to replace the two steps of division and summation. Common D-Σ characteristic equations are used for all areas. Inductance changes are considered in the characteristic equations. Current source is used to control converter. Therefore, the current of the converter can be traced to sinusoidal reference current even when the inductance changes become big. The modulation method and the capacitor-voltage balancing method are submodule unified pulse width modulation (SUPWM) and sorted voltage-balancing method, respectively. The current control directly obtains a law of the current change on each conducting module of an arm. It does not need complex sector judgments and table look-ups. Thus, the amount of computation and memory for a processor can be relatively reduced.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Time-based current control in switching regulators
InactiveUS6987380B1Low rippleEfficient voltage regulationDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCurrent mode controlCurrent limiting
Control circuits that employ time-based current control methods for switching voltage regulators are provided. The control circuit includes a current estimation circuit and optionally, a transfer function circuit. The current estimation circuit generates estimates of regulator output current as function of switch period for use as a threshold indicative of peak current limit. This arrangement eliminates the need for error amplifiers to provide effective current mode control. The absence of error amplifiers allows fabrication of switching regulators on smaller die areas and provides switching regulators with reduced power consumption.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Controller and control method for DC-DC converter
ActiveUS20070057658A1Improve efficiencyLow efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLinear regulatorDc dc converter
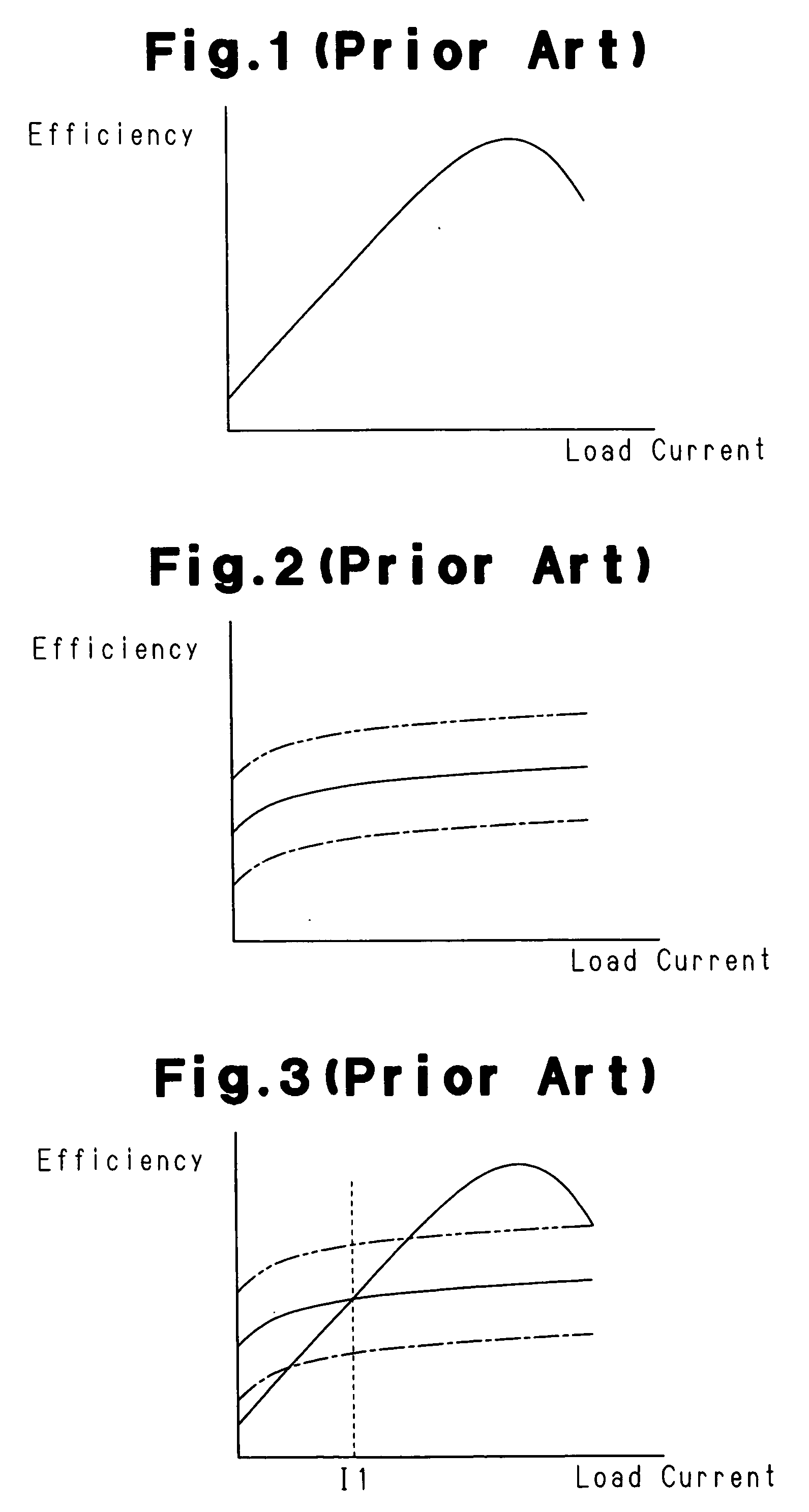
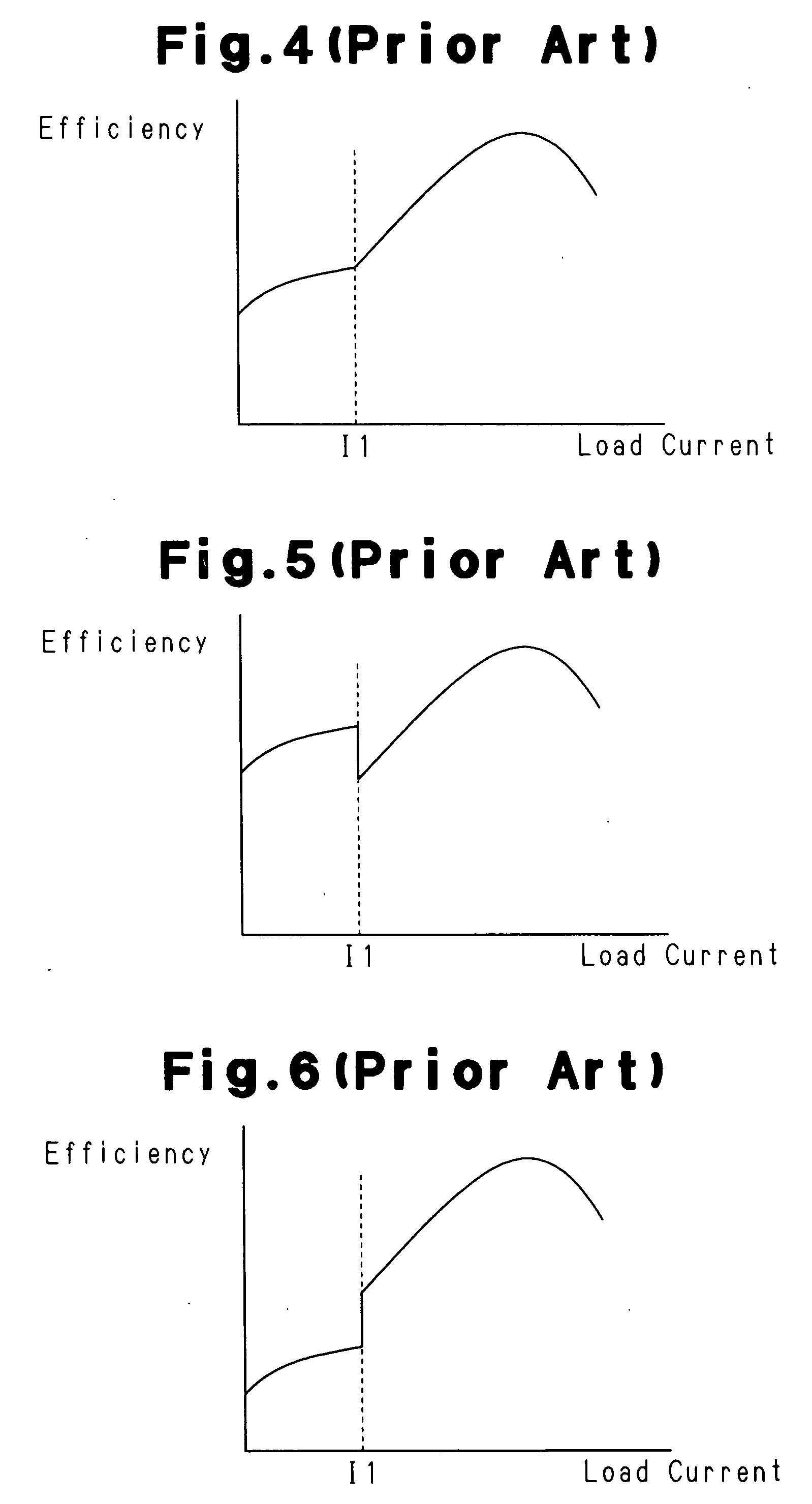
A DC-DC converter having conversion efficiency that is not lowered by input voltage change. A mode control circuit of the DC-DC converter monitors the input voltage, output voltage generated from the input voltage, and output current. The output current changes in accordance with the output voltage. Based on the input voltage, output voltage, and consumption current of a controller of the DC-DC converter, the mode control circuit generates a signal that is in accordance with load current in which efficiency of a switching regulator and efficiency of a linear regulator are substantially the same. The mode control circuit further compares a signal corresponding to the output current and the signal that is in accordance with the load current to generate a mode control signal. The controller operates the DC-DC converter as the switching regulator or the linear regulator in accordance with the mode control signal.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
RV converter with current mode and voltage mode switching
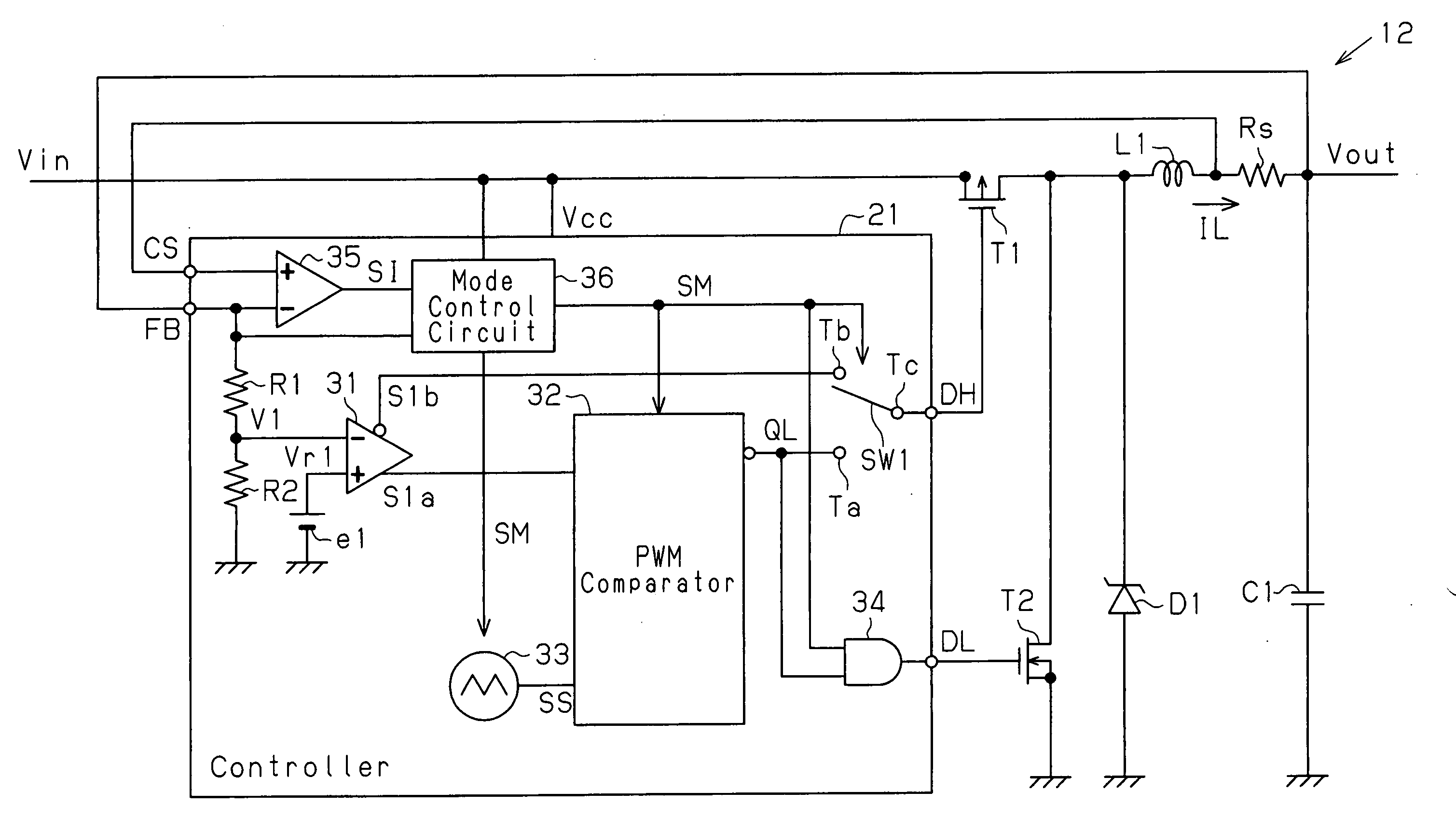
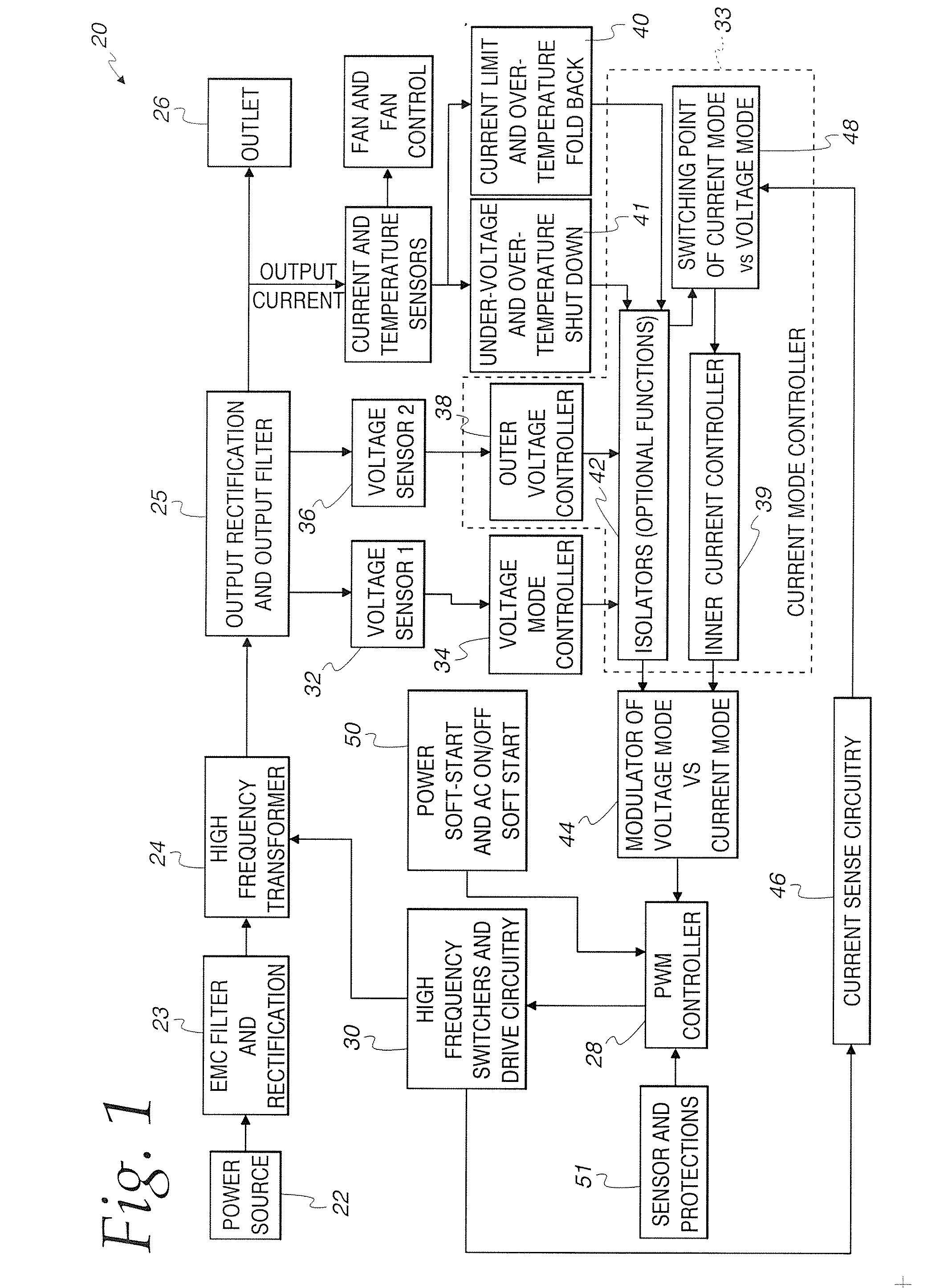
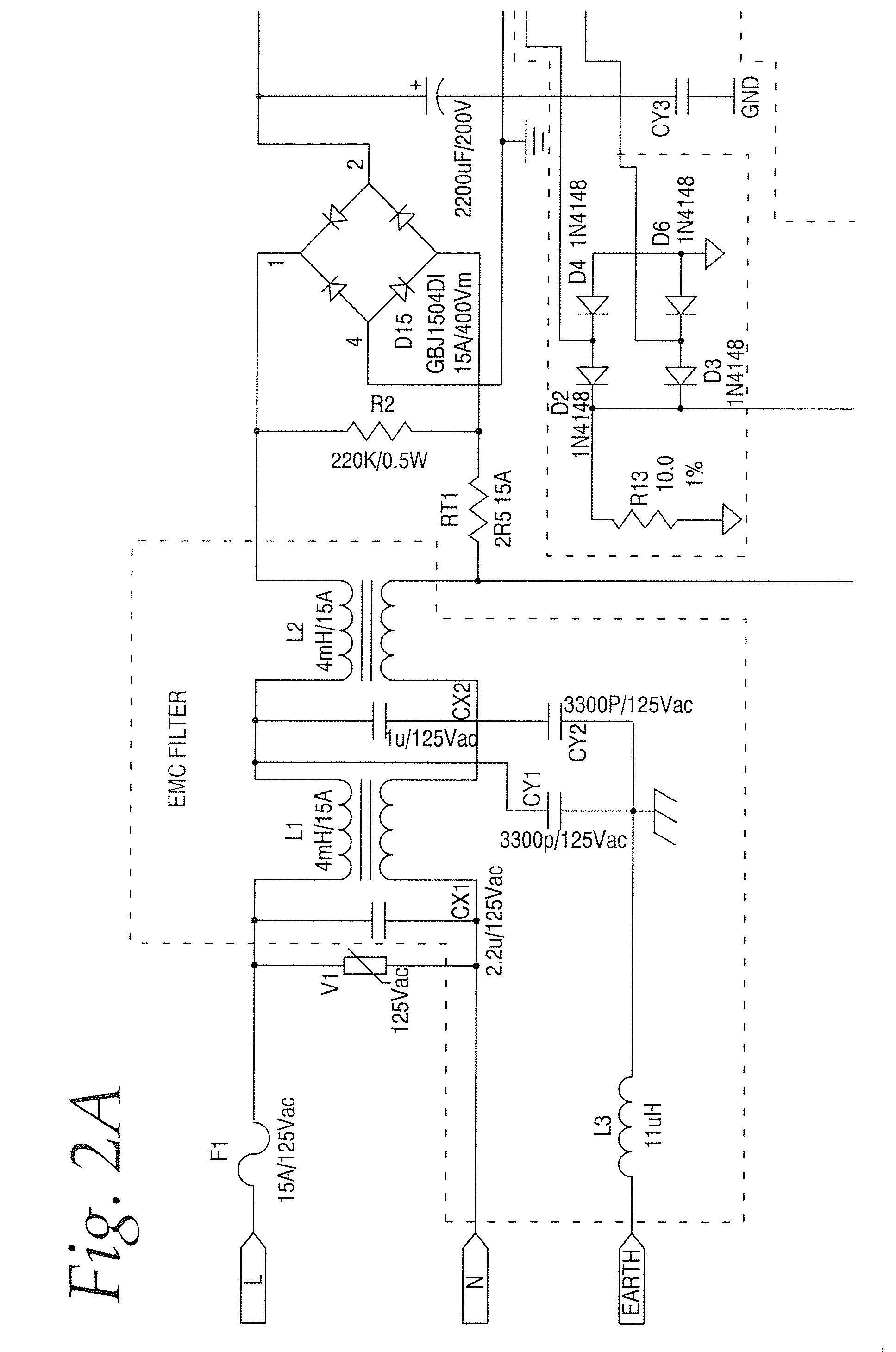
ActiveUS20070176584A1Fast transient responseAvoid noiseEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcCurrent mode controlHemt circuits
A switched mode converter is disclosed that includes both voltage mode and current mode control. The switched mode converter also includes mode logic for switching between a voltage mode and a current mode. The converter includes current sensing circuitry for sensing the switcher current on the primary side of the transformer and the load current on the secondary side as well as voltage sensing circuitry for sensing the converter output voltage. When the load current is less than a predetermined value, the converter operates in a voltage mode. During the voltage mode, the output voltage of the voltage mode controller is used to control the duty cycle of a pulse width modulation (PWM) controller. When the load current is greater than a predetermined value, the converter operates in a current mode. In a current mode, the primary switcher current is used to control the PWM controller. As such, during a light load in which the converter is voltage controlled, there is no need for a minimum load to stabilize the control loop. In a current-mode, the control loop will have a relatively faster transient response and avoid flux imbalance in push-pull topology. As such, the converter provides the advantages of both known voltage controlled and current controlled switched mode converters. In addition, by the careful arrangement of the locations of a EMC filter, a primary heat sink, a secondary heat sink, a power transformer T1 and other power devices as well as a cooling fan, a smaller EMC filter can be used due to the primary heat sink performing a dual function of thermal management and additionally providing EMC shielding to prevent the noise, for example, the noise generated by the transformer, from reaching the filter. In addition, the primary heat sink is configured to face the air flow while the secondary heat sink is placed close to the fan with its fin direction the same as the direction of the air flow. As such, both the primary and the secondary heat sink get maximum air flow, allowing smaller heat sinks to be used in order to provide a reliable and cost-effective switched mode converter.
Owner:SCHUMACHER ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com