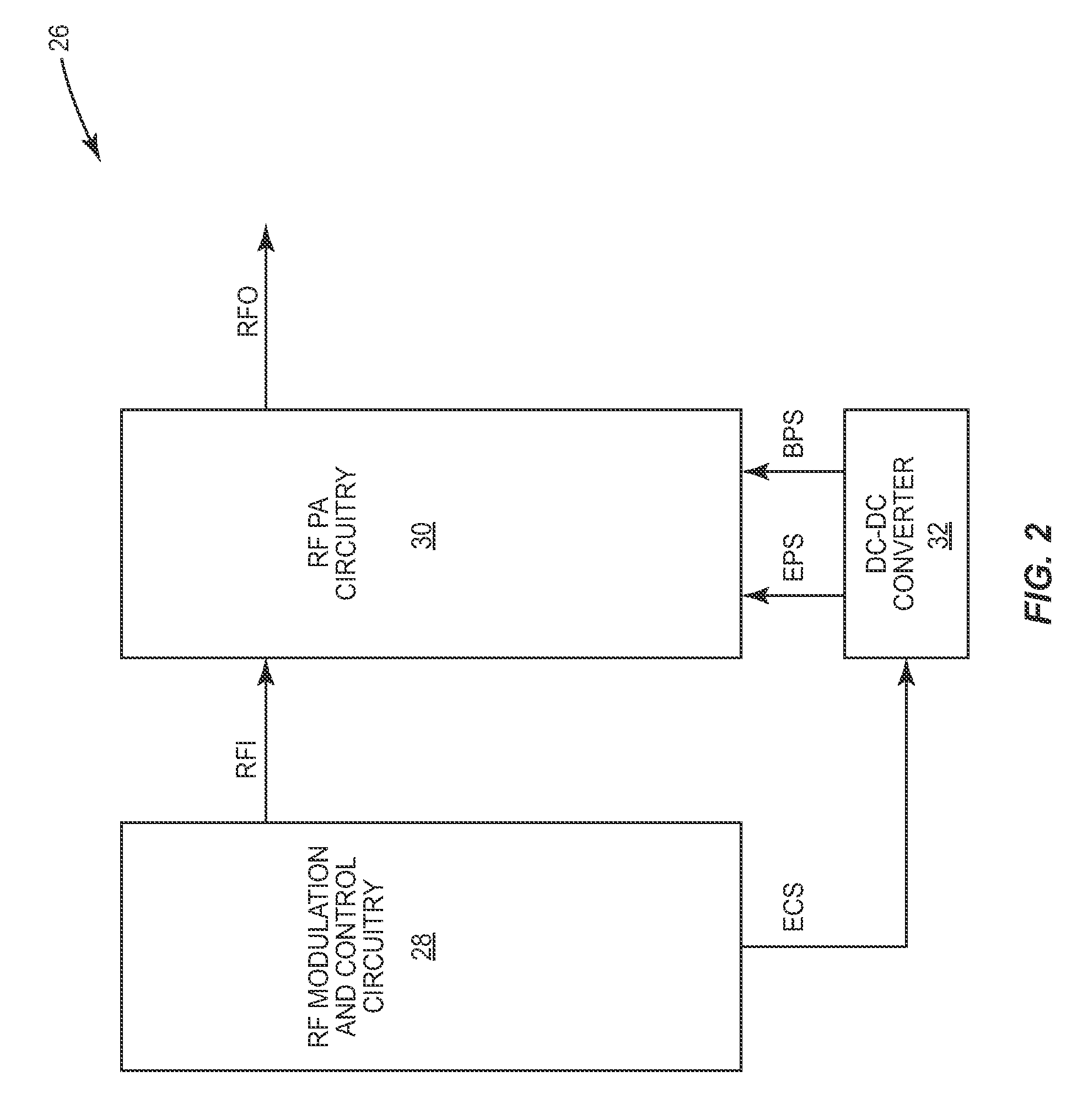
Patents
Literature
2526 results about "Buck converter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A buck converter (step-down converter) is a DC-to-DC power converter which steps down voltage (while stepping up current) from its input (supply) to its output (load). It is a class of switched-mode power supply (SMPS) typically containing at least two semiconductors (a diode and a transistor, although modern buck converters frequently replace the diode with a second transistor used for synchronous rectification) and at least one energy storage element, a capacitor, inductor, or the two in combination. To reduce voltage ripple, filters made of capacitors (sometimes in combination with inductors) are normally added to such a converter's output (load-side filter) and input (supply-side filter).
High efficiency power converter
InactiveUS7202653B2Improve efficiencyInhibit currentDc network circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionLinear regulatorReverse current
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Single inductor dual output buck converter with frequency and time varying offset control
ActiveUS7061214B2Convenient sourcePromote conversionDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationBuck converterTransverter
A single-inductor dual-output buck converter and control method that facilitates power conversion by converting a single DC power source / supply into two separate DC outputs, each of which can be configured to provide a selected / desired voltage by selection of respective duty cycles. The topology of the inverter includes a pair of diodes or switches that can selectively re-circulate inductor current. The converter is generally operated at a fixed frequency with four stages of operation. A first and third stage of operation provide power to a first and second output, respectively. A second and fourth stage of operation re-circulate inductor current and can partially recharge a battery type power source. The power output for each stage (voltage and current) can be selectively obtained by computing and employing appropriate time periods for the stages of operation that correspond to appropriate duty cycles.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
High-efficiency DC/DC voltage converter including down inductive switching pre-regulator and capacitive switching post-converter
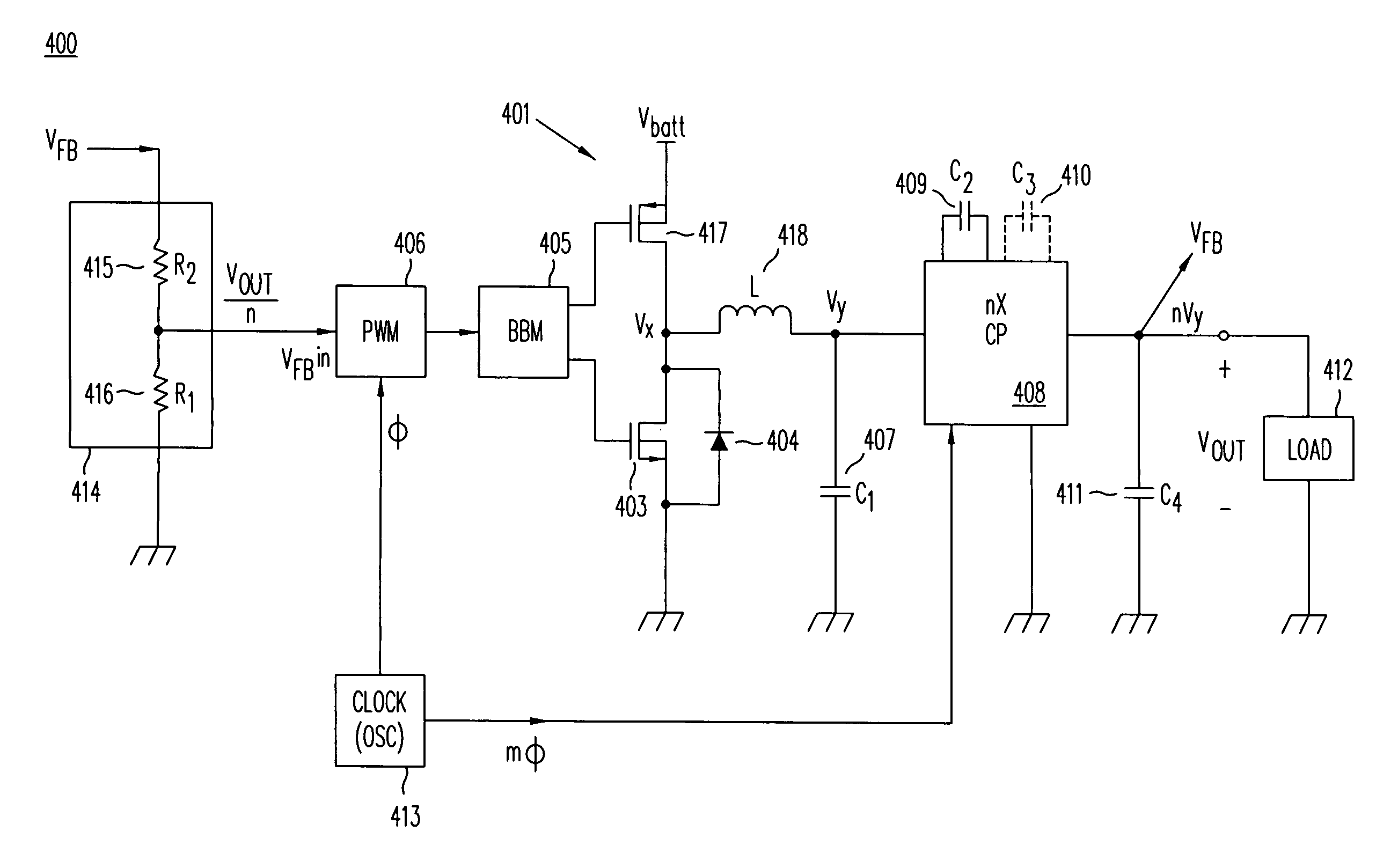
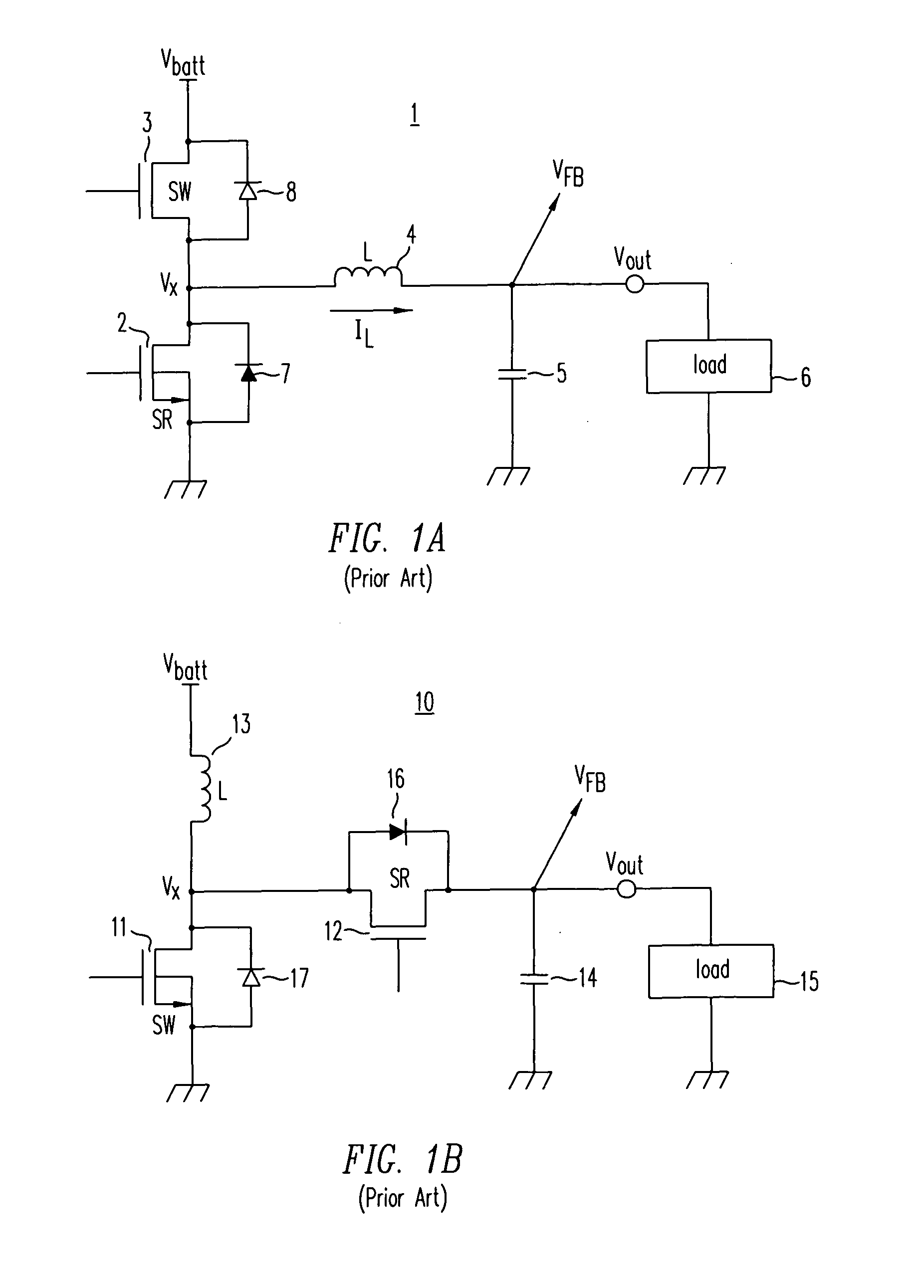
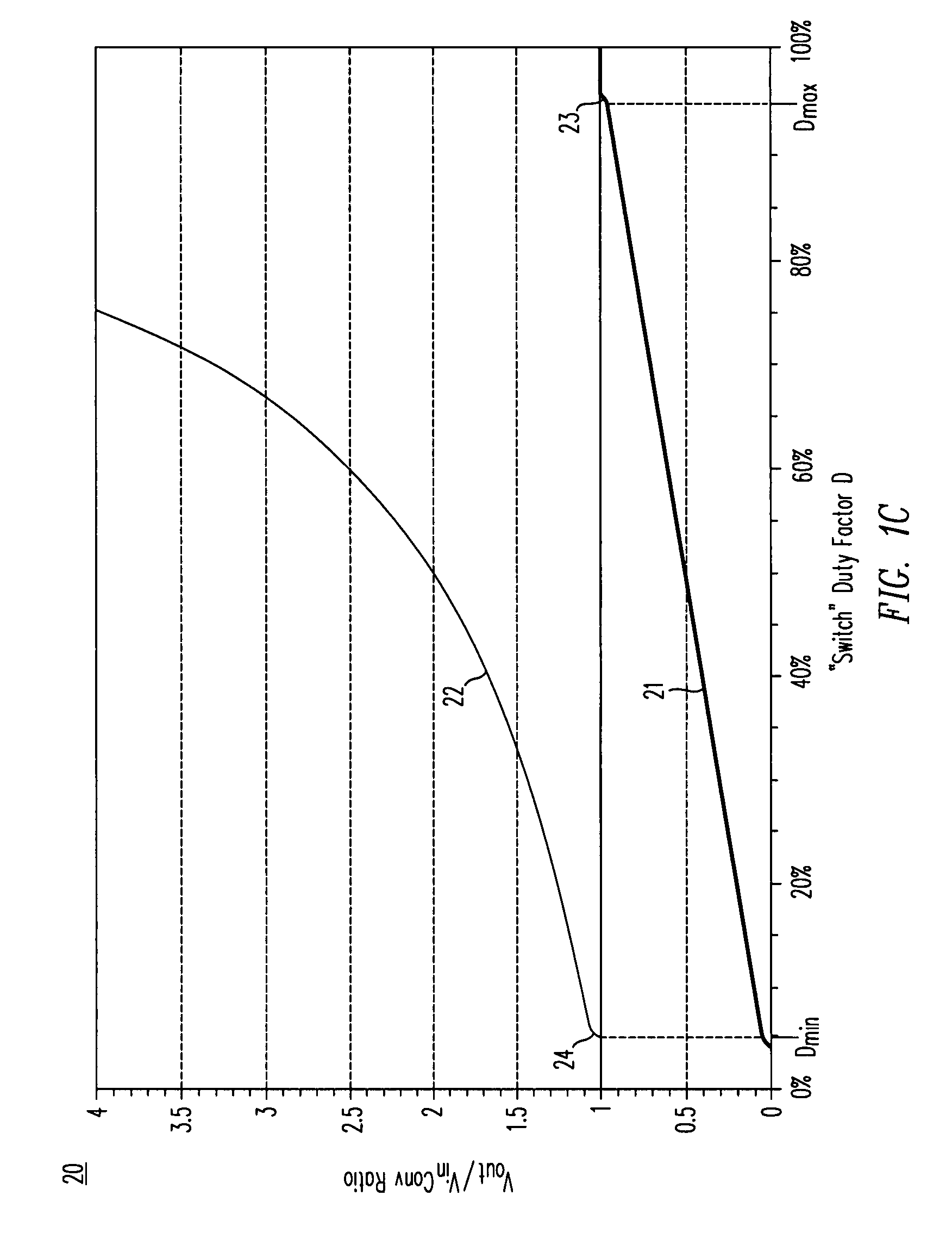
ActiveUS20080158915A1Poor regulationAvoid problemsEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceBuck converter
A DC / DC converter includes a pre-regulator stage, which may include a Buck converter, and a post-converter stage, which may include a charge pump. The duty factor of the pre-regulator stage is controlled by a feedback path that extends from the output terminal of the pre-regulator stage or the post-converter stage. The pre-regulator steps the input DC voltage down by a variable amount depending on the duty factor, and the post-converter steps the voltage at the output of the pre-regulator up or down by an positive or negative integral or fractional value. The converter overcomes the problems of noise glitches, poor regulation, and instability, even near unity input-to-output voltage conversion ratios.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Buck converter with inductor pre-energizing
ActiveUS7804282B2Simple control circuitDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationBuck converterĆuk converter
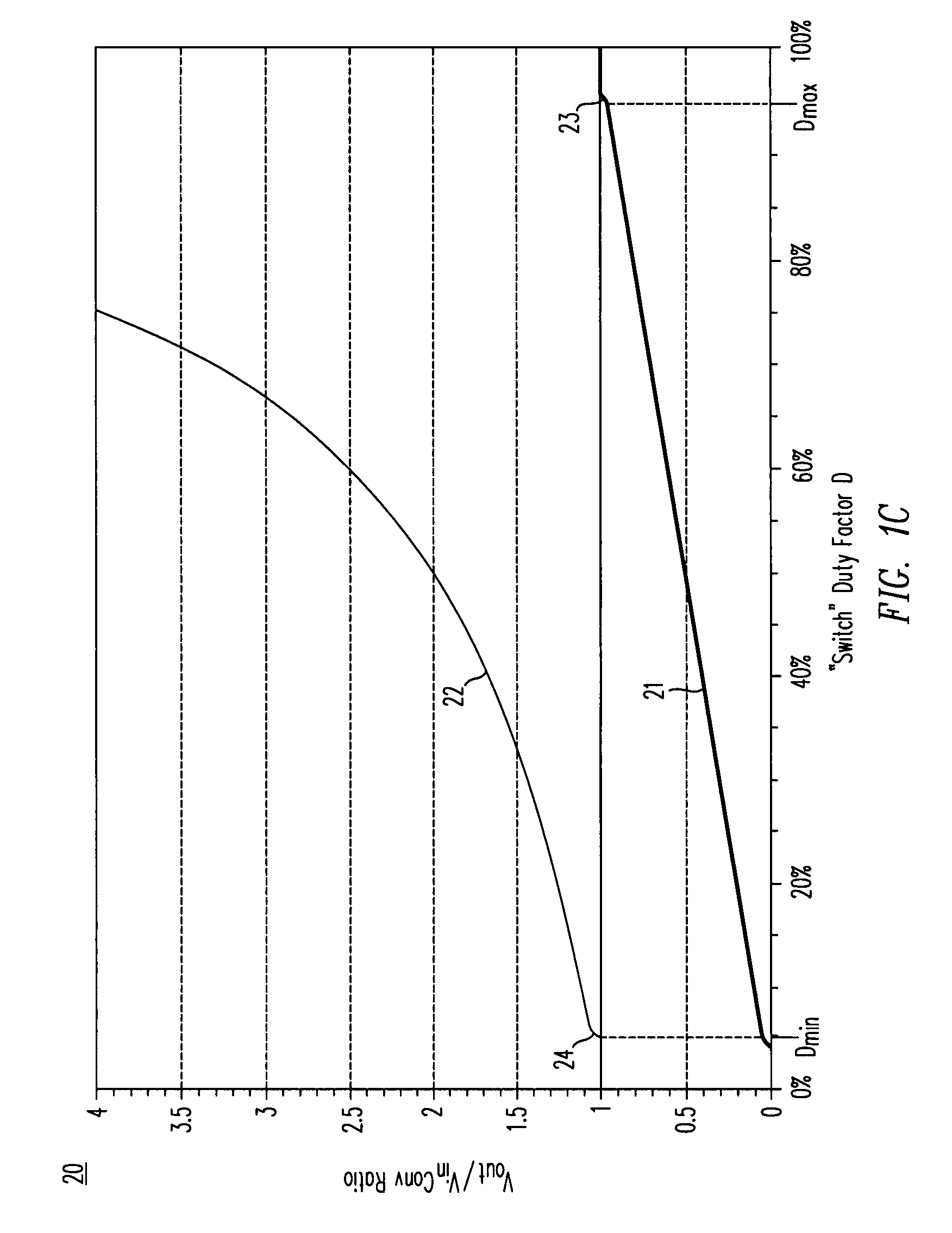
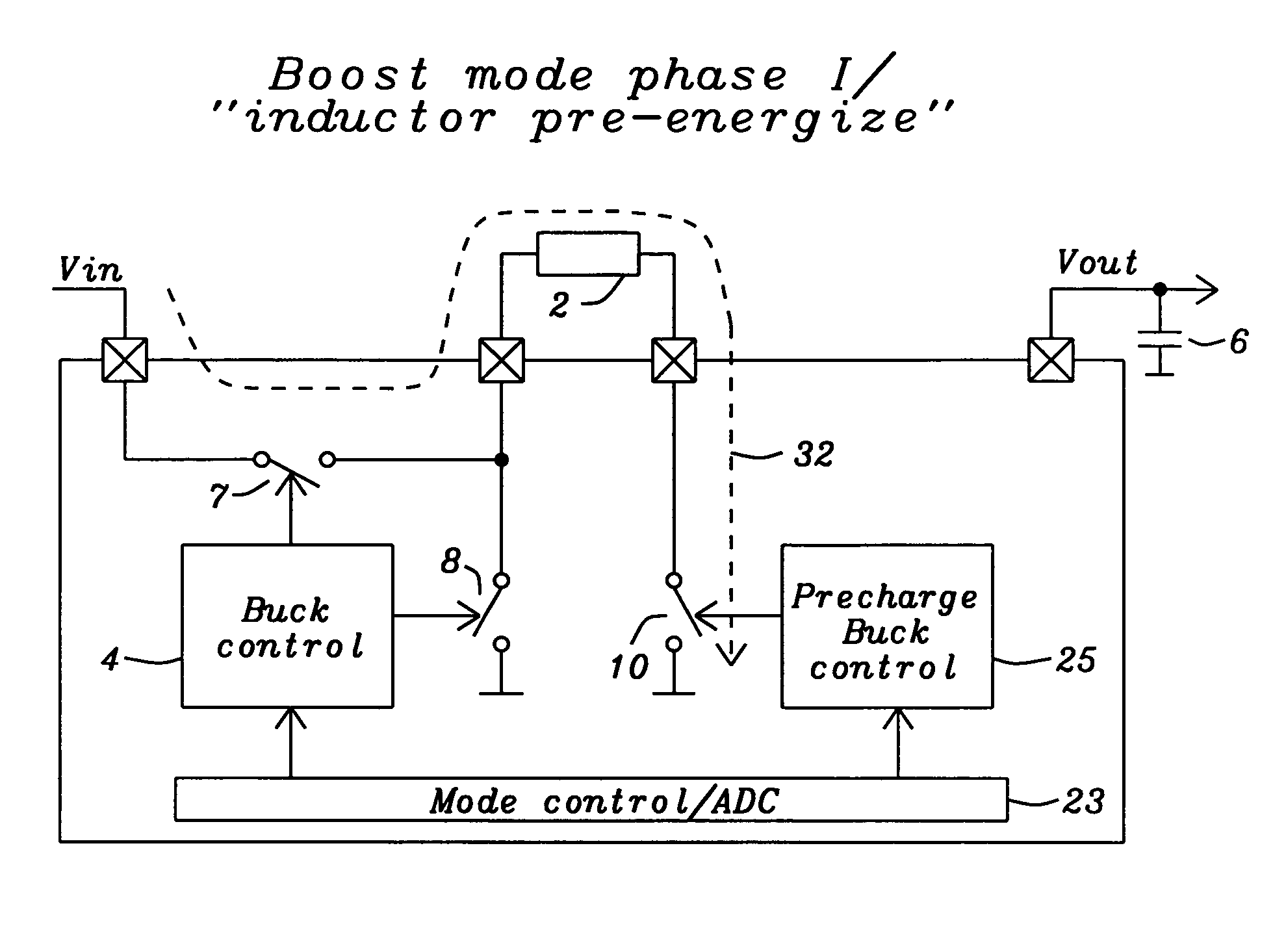
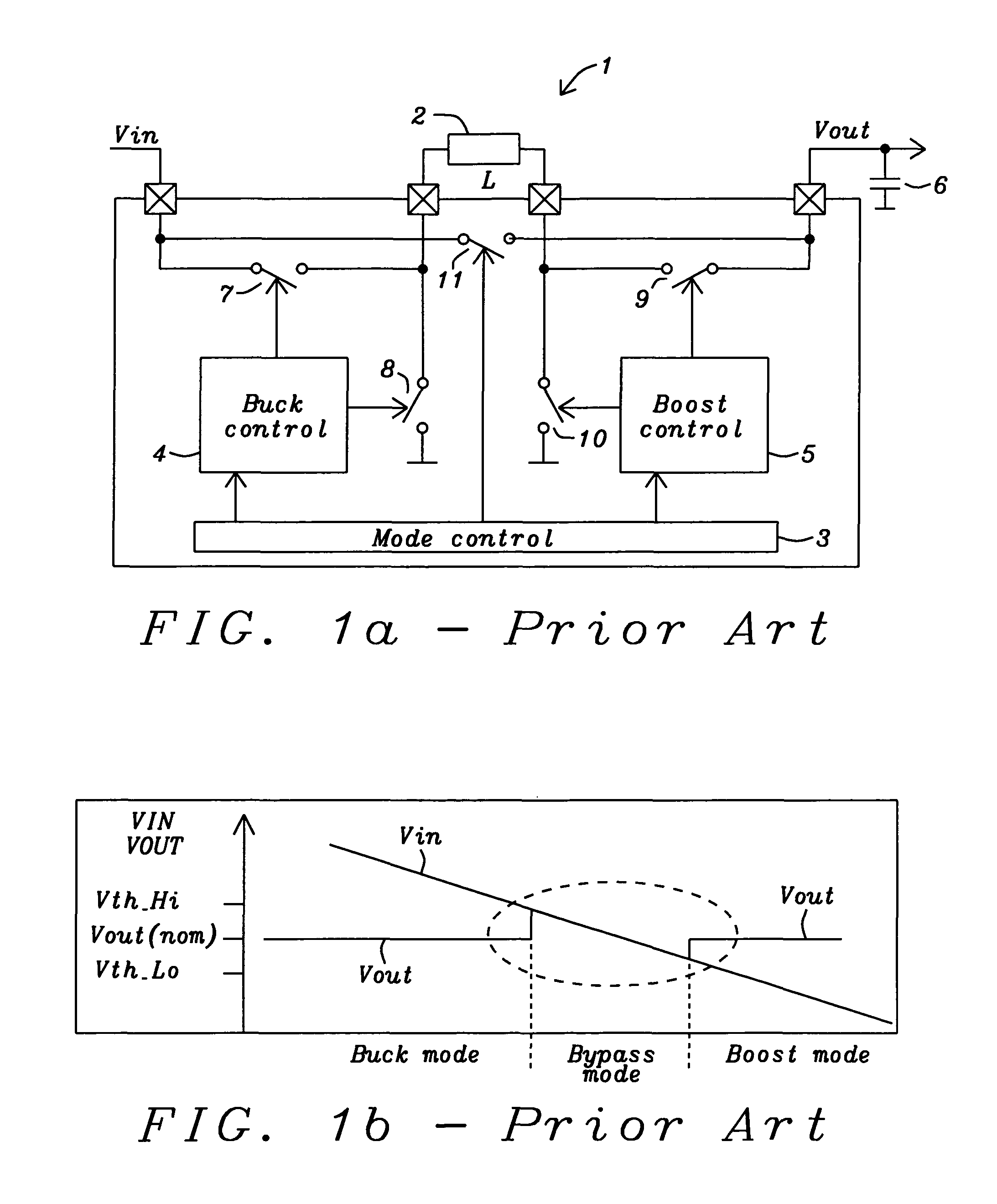
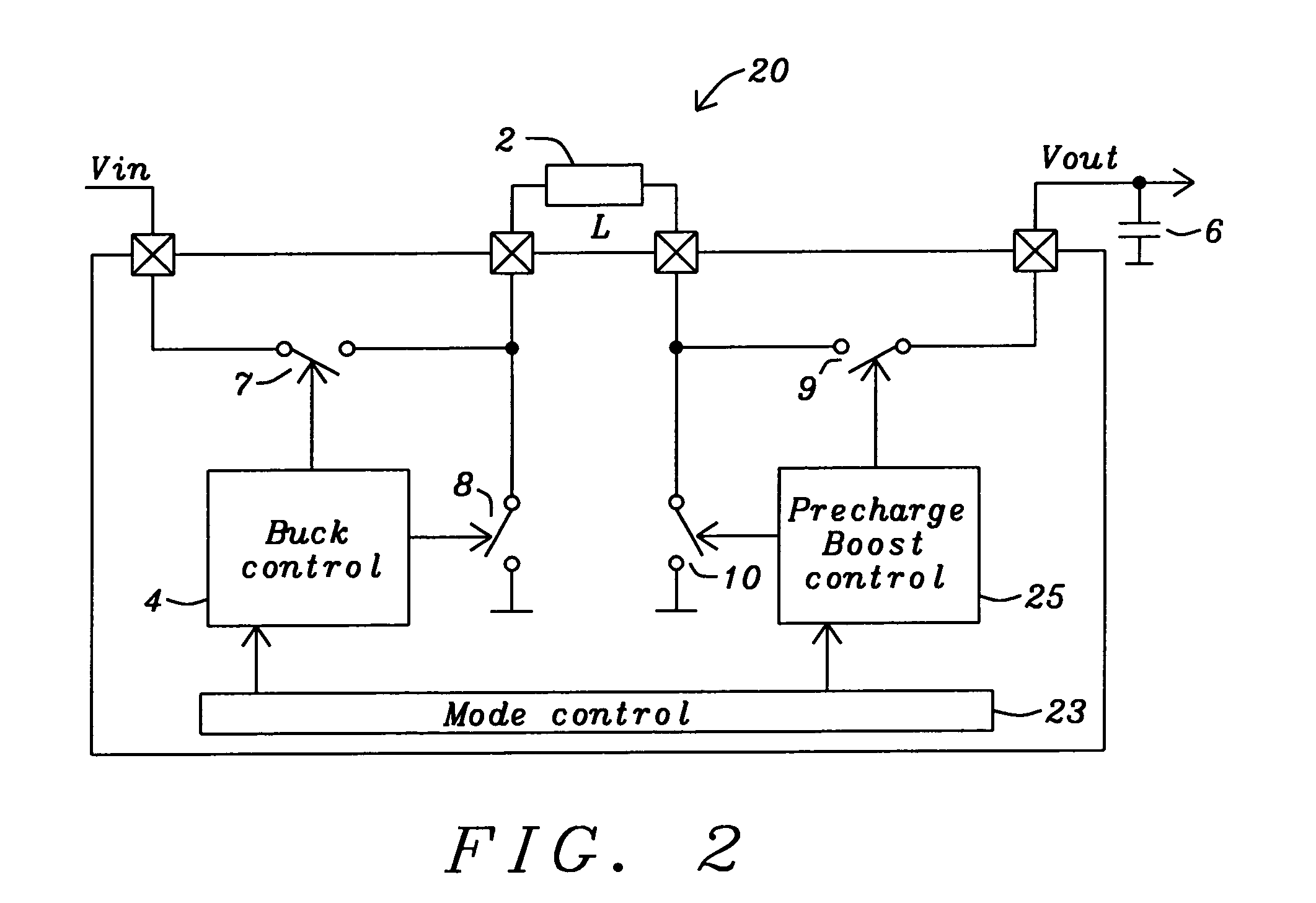
Circuits and methods to achieve a buck-boost converter, capable to achieve a constant output voltage by pre-charging of an inductor if the input voltage is close to the output voltage has been achieved. The prior art problem of output voltage variations occurring while the input voltage is close to the output voltage is avoided. In case the input voltage is lower than a defined threshold voltage or the duty cycle exceeds a defined maximum allowable level, the inductor of the converter is pre-charged followed by boosting of the energy of the inductor to the output of the converter. In both modes the control loops of the buck converter can be used for buck duty cycle control. The duration of the pre-charge depends upon the level of the input voltage, the lower the input level is the longer is the pre-charge performed.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
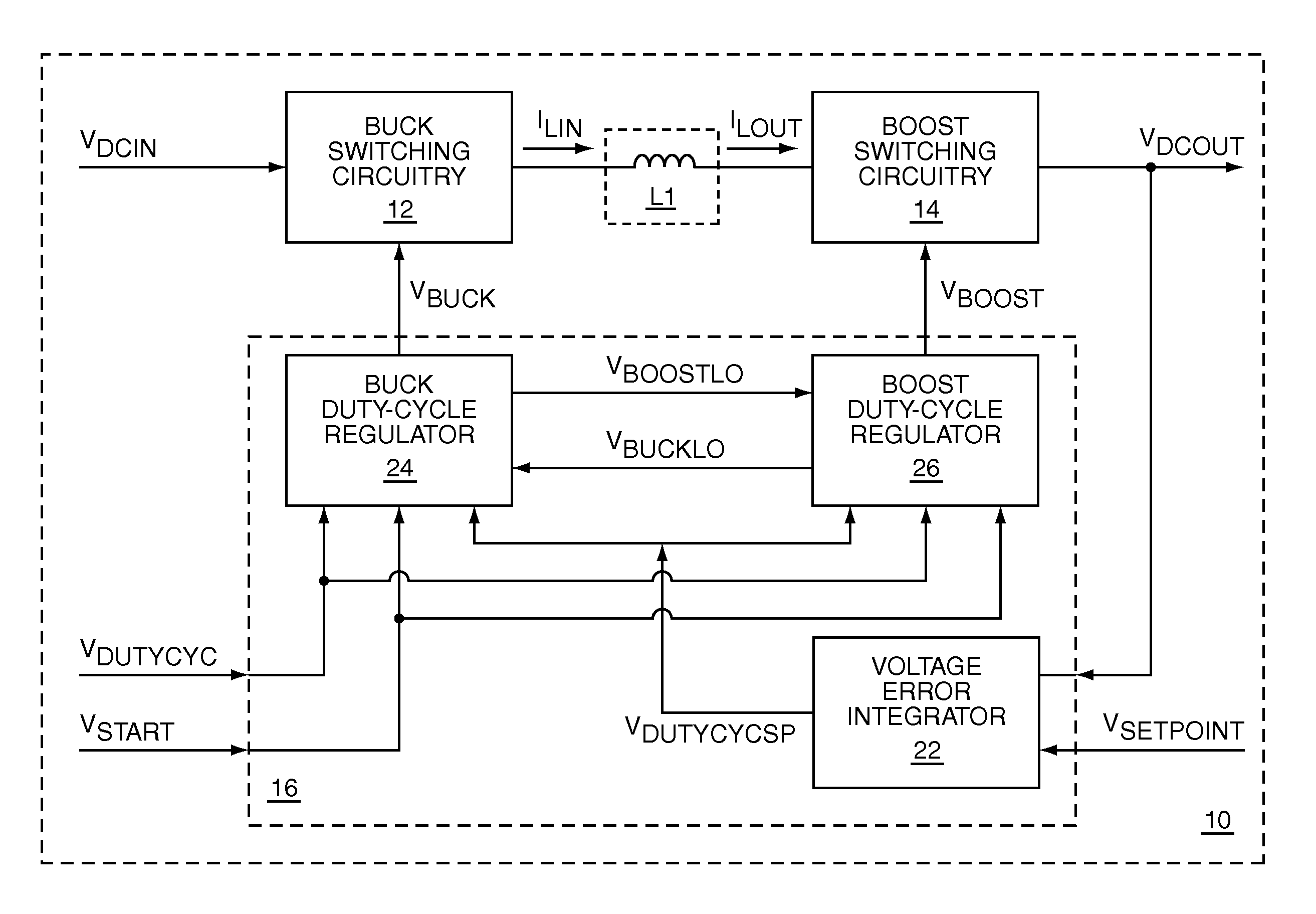
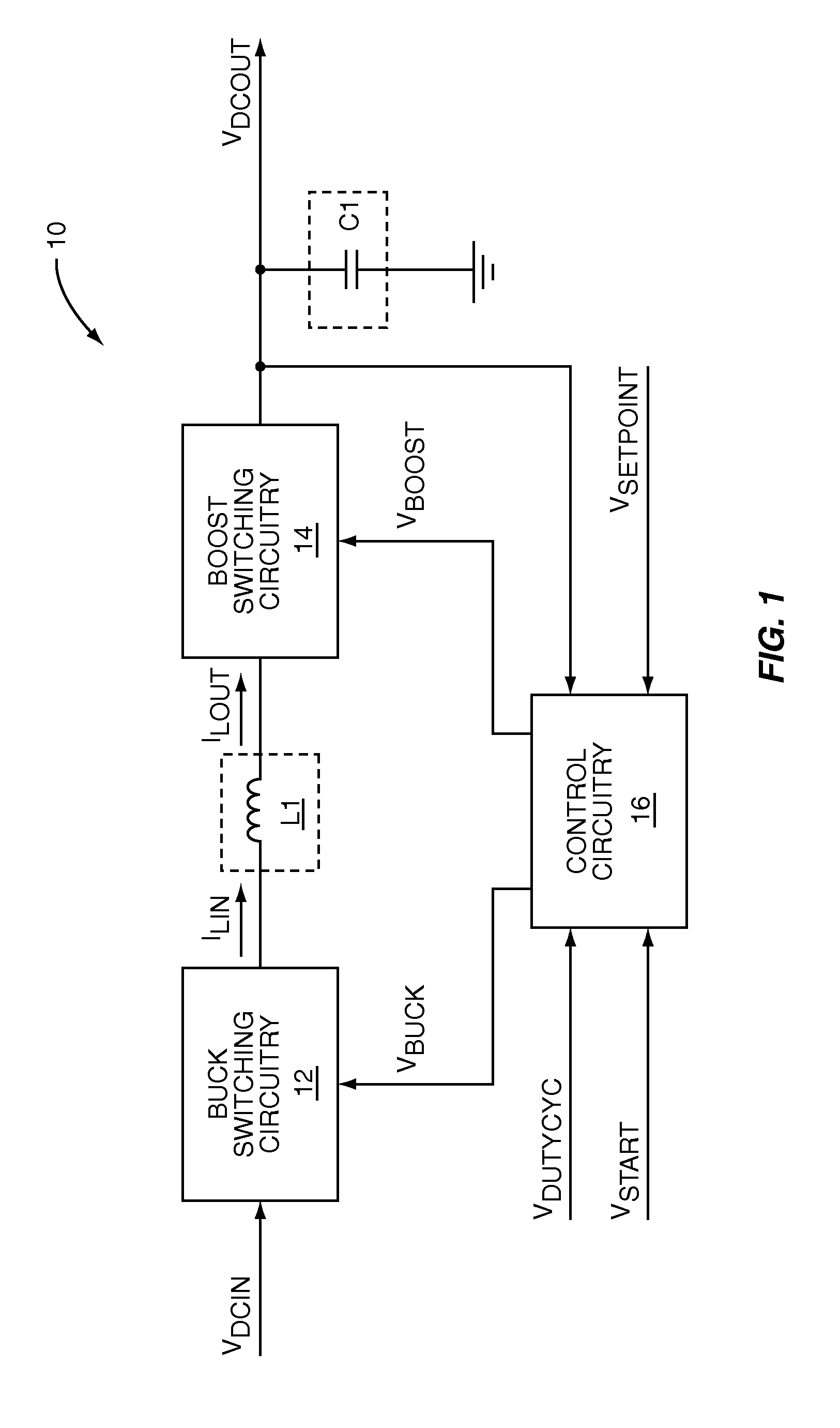
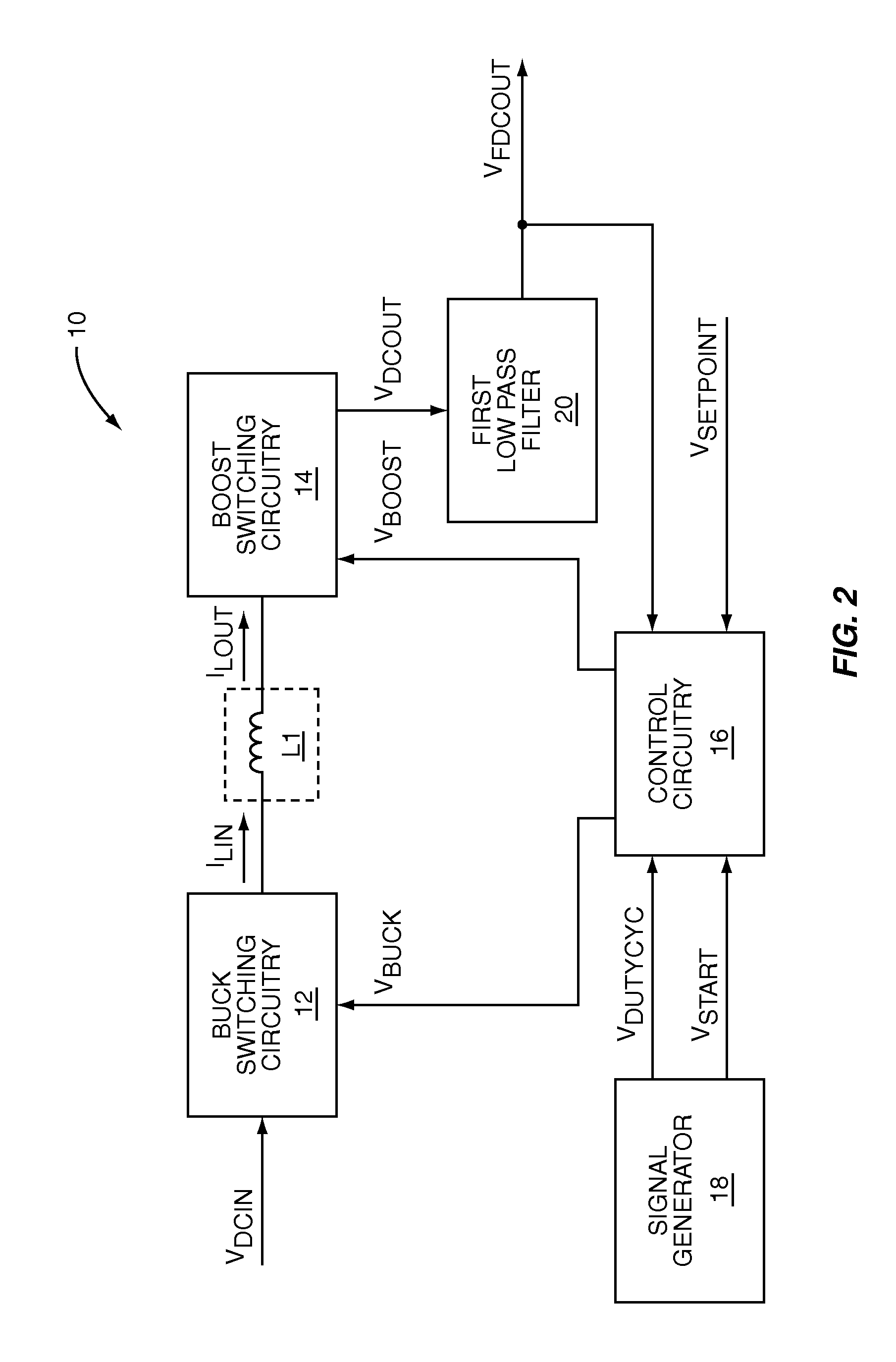
Switching power converter that supports both a boost mode of operation and a buck mode of operation using a common duty-cycle timing signal
ActiveUS7336056B1Remove overlapSmooth transitEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionIntegratorBuck converter
The present invention is a switching power converter that supports both a boost mode of operation and a buck mode of operation, uses one energy storage element, transitions smoothly between boosting and bucking, and avoids simultaneous boosting and bucking. The switching power converter uses a common duty-cycle timing signal and a common duty-cycle setpoint signal to provide a smooth transition between boosting and bucking, and to eliminate overlap between boosting and bucking. A voltage input error integrator is used to integrate out errors between an output voltage and a setpoint voltage to provide the common duty-cycle setpoint signal. Duty-cycle error integrators are used to integrate out errors between the common duty-cycle setpoint signal and the actual duty-cycle of either the buck converter or the boost converter. Non-overlapping boost operating and buck operating ranges are provided by the common duty-cycle setpoint signal.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Method and apparatus for welding with battery power
A method and apparatus provides welding-type power and preferably includes a removable battery or other energy storage device, a converter connected to the battery, and a controller. The controller may have a CV and / or a CSC and / or an AC weld control module, and / or an ac auxiliary control module. The converter is a boost converter, a buck converter, a cuk converter, a forward converter, an inverter, a bridge converter, and / or a resonant converter. The controller may include a battery charging control module, and may have one or more charging schedules, and / or data for stored charge, thermal information, expected life of the battery, maximum amp-hour charge for the battery, maximum charging current and / or feedback. The battery charging schedules may include at least 3 phases, such as a phase of increasing voltage and a phase of decreasing current, a substantially constant power phase. The controller can wirelessly provide data to a display or pda. A generator may provide power to the battery, charger, and / or the weld. It can include a vehicle and use its dc power system.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Multiphase clamp coupled-buck converter and magnetic integration
InactiveUS6784644B2Emergency protective circuit arrangementsApparatus without intermediate ac conversionVoltage regulator modulePush pull
Voltage regulation, transient response and efficiency of a voltage regulator module (VRM) is improved where short duty cycles are necessitated by large differentials of input and output voltage by including at least one clamping of a tap of an inductance in series with an output of each of a plurality of parallel branches or phases which are switched in a complementary fashion or providing coupling between inductors of respective phases. Such coupling between inductors is achieved in a small module with an integrated magnetic structure. Reduced component counts are achieved while deriving built-in input and output filters. Principals of the invention can be extended to isolation applications and push-pull forward converts, in particular. A lossless clamping circuit is also provided allowing spike currents to be suppressed while returning power to the output of the VRM.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
A/D converter having a dynamic encoder
InactiveUS6232908B1Increase speedReduce circuit sizeElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersBuck converterA d converter
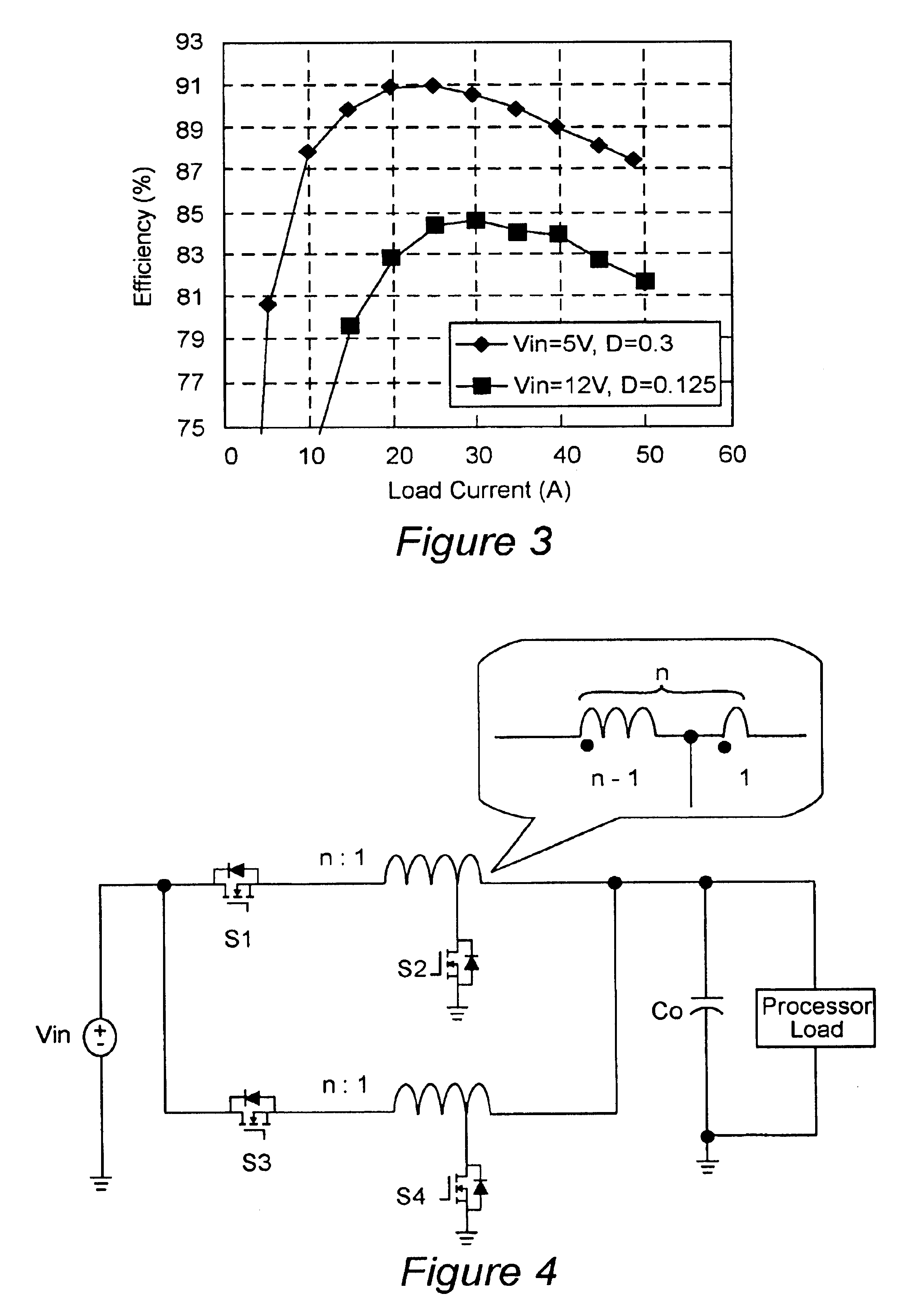
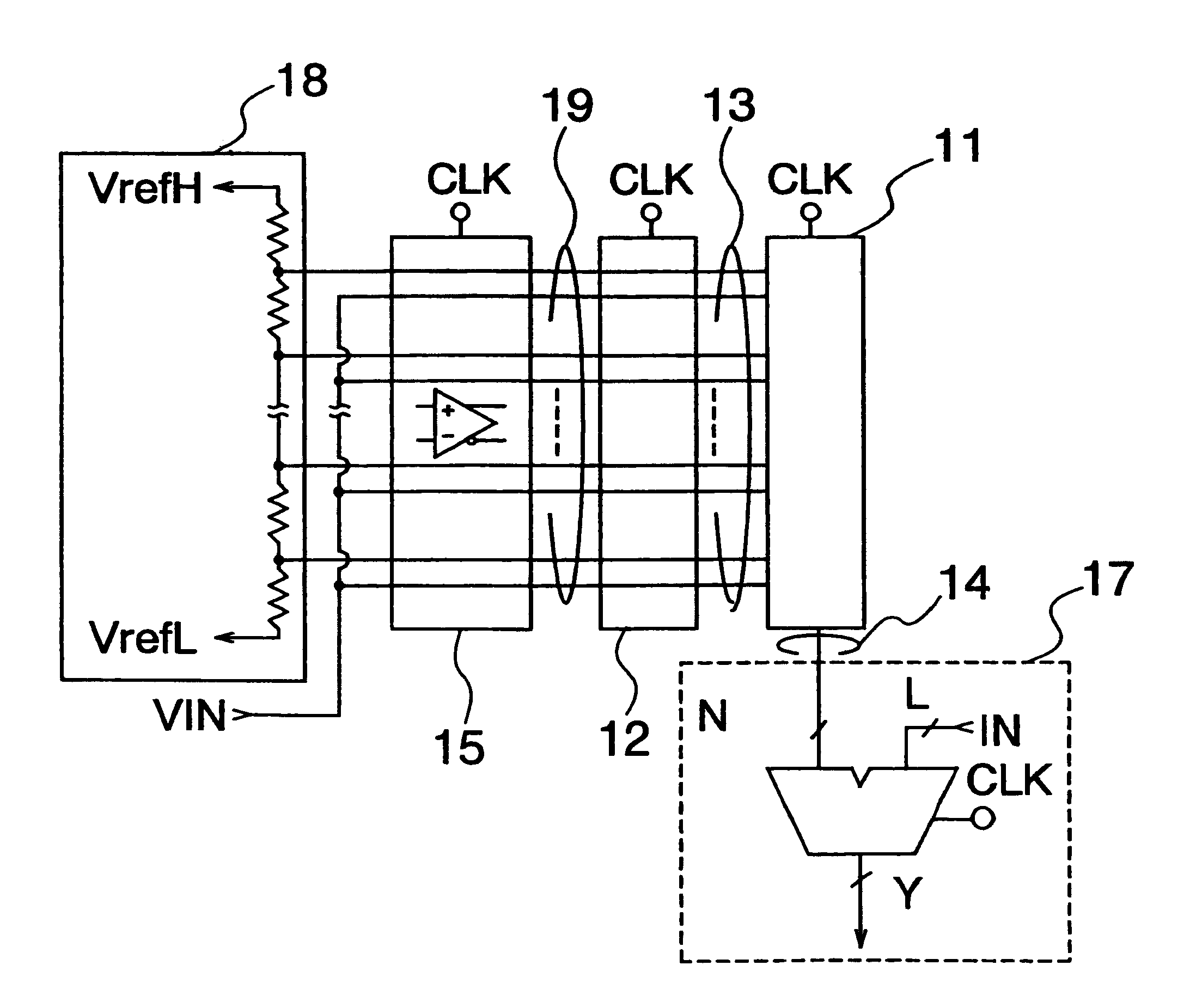
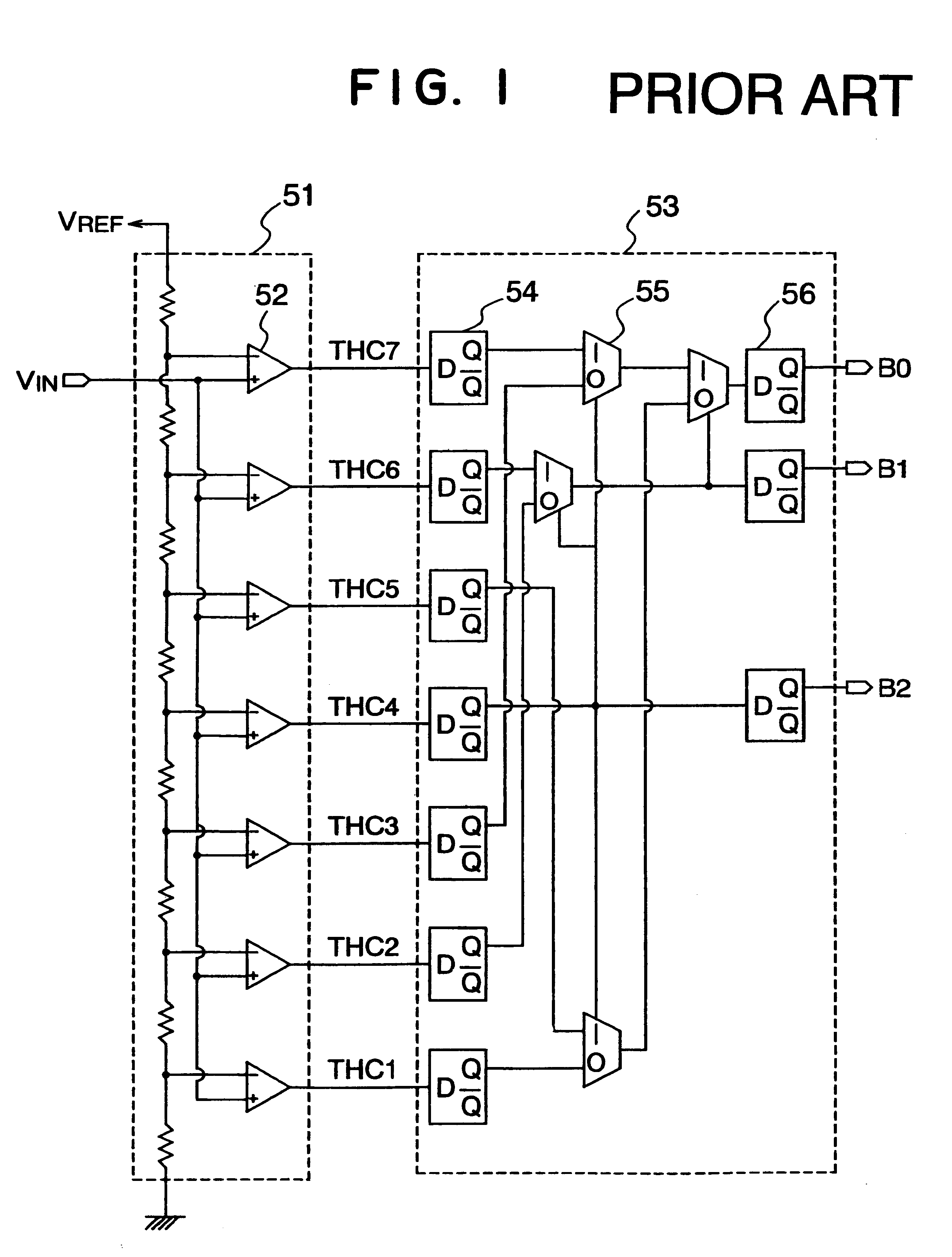
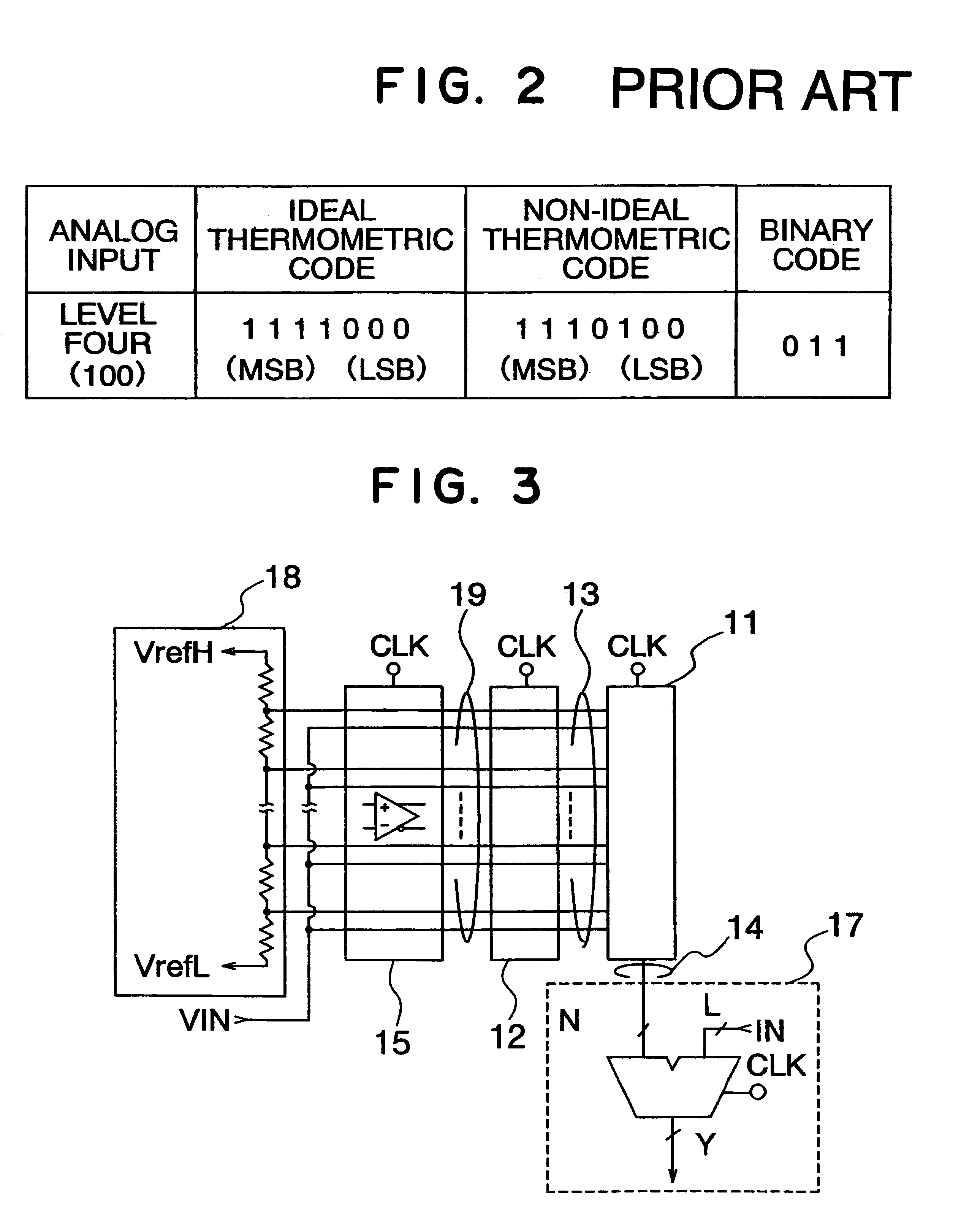
An A / D converter includes a resistor ladder for generating a plurality of reference potentials, a comparing section for comparing each of the reference potentials against an input analog signal to output a thermometric code, and a dynamic encoder composed of a combinational circuit to encode the thermometric code to a binary code by responding a clock signal. The A / D conversion is finished in a single clock cycle at a high speed, with a reduced number of elements and reduced power dissipation.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Photovoltaic module-mounted ac inverter
ActiveUS20080285317A1Total current dropIncrease the ripple frequencyConversion constructional detailsElectric power transfer ac networkEngineeringTransistor
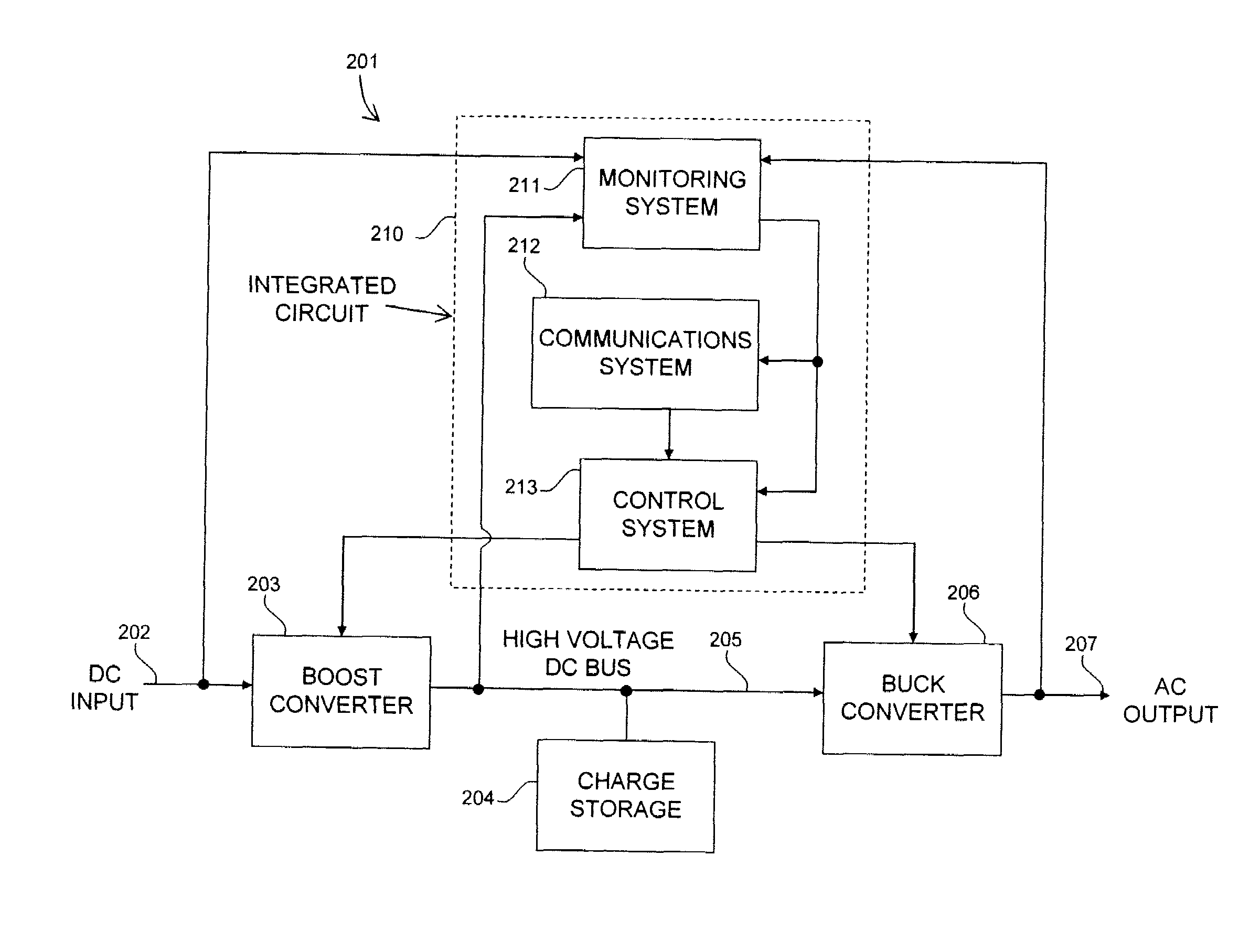
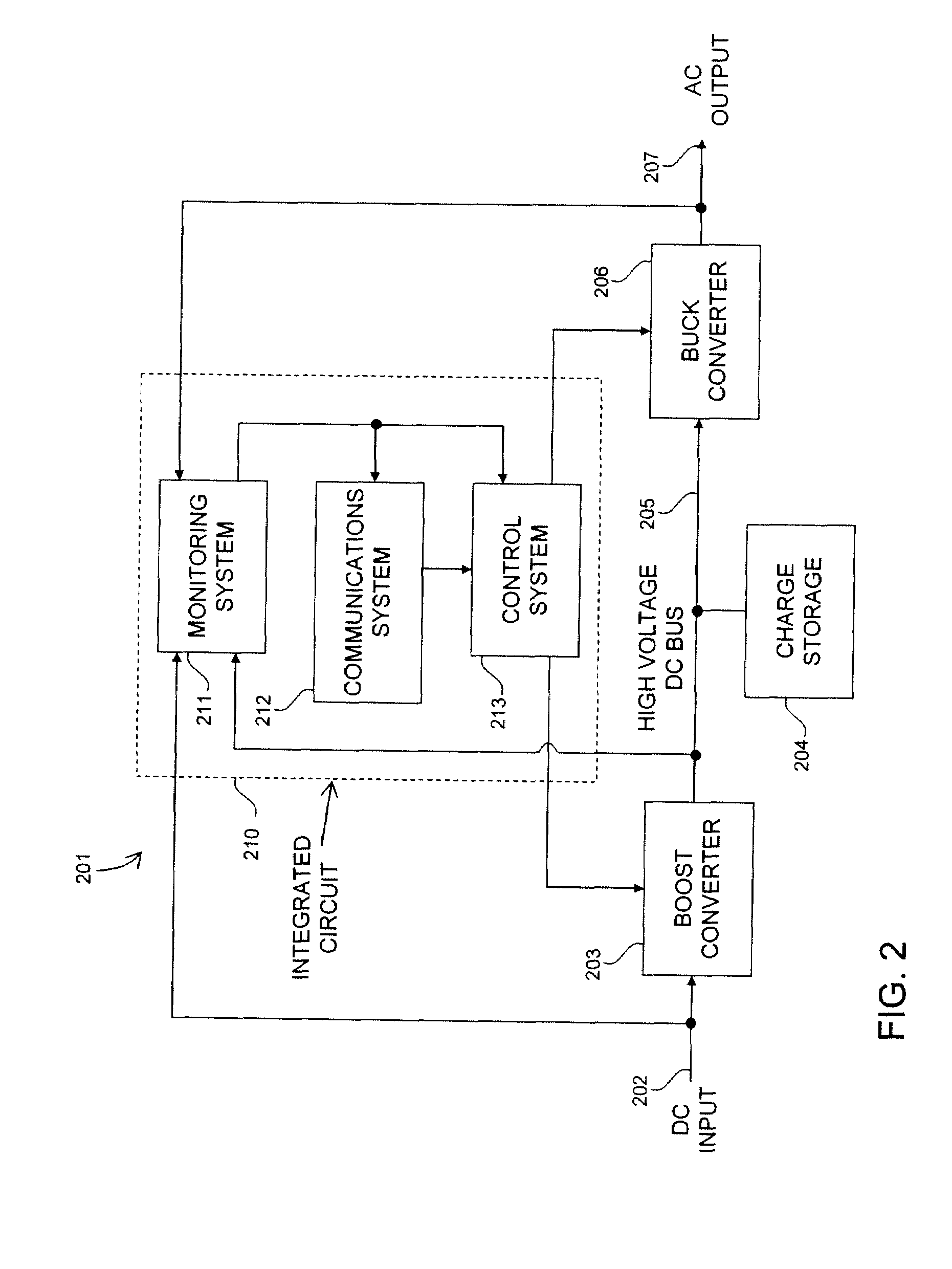
A photovoltaic module-mounted AC inverter circuit uses one or more integrated circuits, several power transistors configured as switches, several solid-dielectric capacitors for filtering and energy storage, several inductors for power conversion and ancillary components to support the above elements in operation. The integrated circuit includes all monitoring, control and communications circuitry needed to operate the inverter. The integrated circuit controls the activity of pulse-width modulated power handling transistors in both an input boost converter and a single-phase or multi-phase output buck converter. The integrated circuit also monitors all power processing voltages and currents of the inverter and can take appropriate action to limit power dissipation in the inverter, maximize the available power from the associated PV module and shut down the inverter output if the grid conditions so warrant. The integrated circuit implements power line communications by monitoring the AC wiring for signals and generating communications signals via the same pulse-width modulation system used to generate the AC power. Communications is used to report inverter and PV module status information, local identification code and to allow for remote control of inverter operation.
Owner:ENPHASE ENERGY
Multiphase voltage regulator having coupled inductors with reduced winding resistance
InactiveUS7649434B2Transformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsDc-dc conversionBuck converterCoupling
A multiple phase buck converter or boost converter, or buck-boost converter has an inductor in each phase. The inductors are inversely coupled. In a first embodiment, the converter includes a toroidal magnetic core with inductors extending under and over opposite sides of the toroidal magnetic core. The coupled inductors are thereby inversely coupled and have a relatively low ohmic resistance. In a second embodiment, the converter comprises a ladder-shaped magnetic core (i.e. having parallel sides, and connecting rungs). In this case, the inductors extend under the sides, and over the rungs. Each inductor is disposed over a separate rung. The ladder-shaped magnetic core is preferably disposed flat on a circuit board. Inverse coupling and low ohmic resistance are also provided in the second embodiment having the ladder structure.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Methods and apparatus for power supply load dump compensation
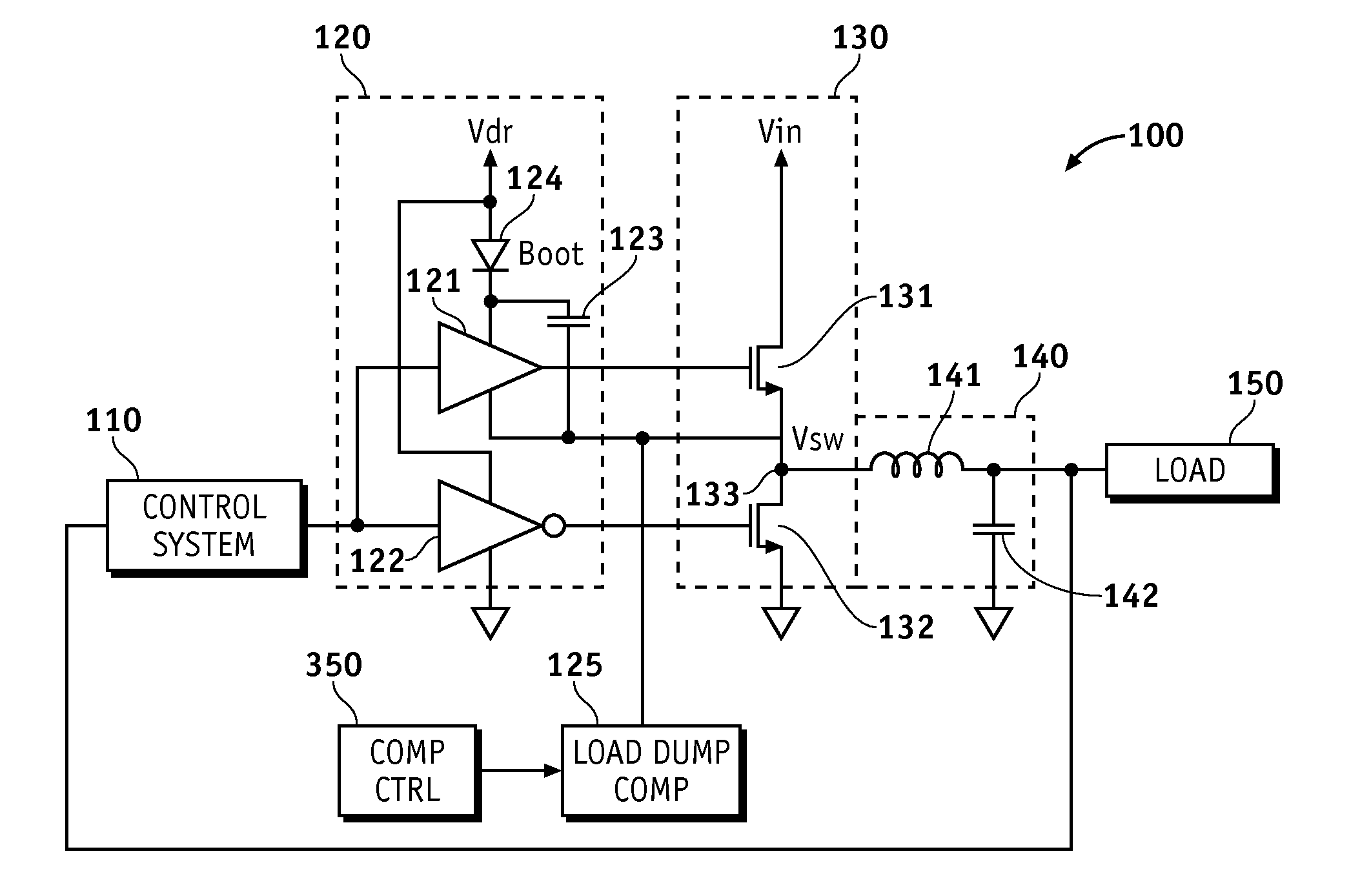
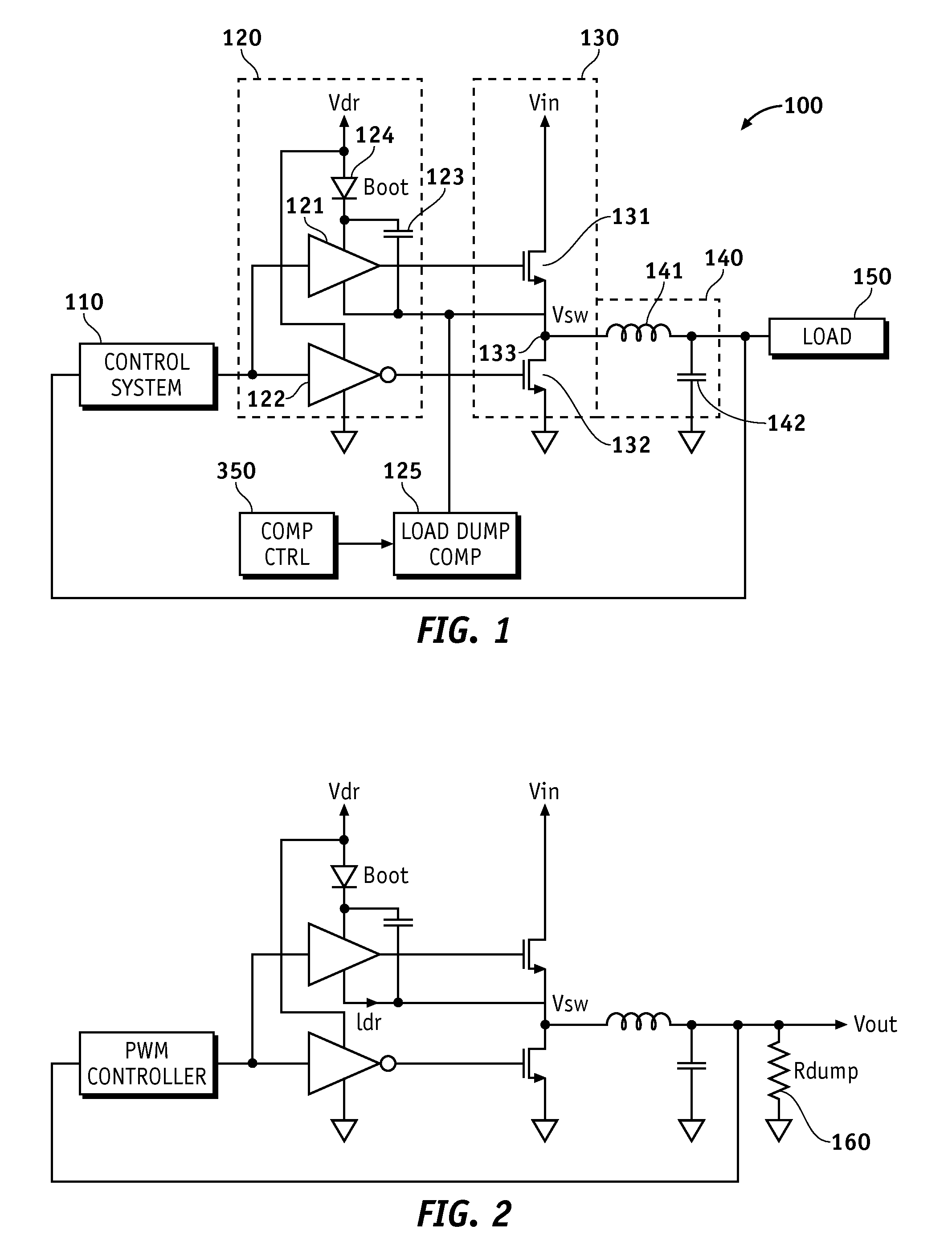
Methods and apparatus for power supply load dump compensation according to various aspects of the present invention may operate in conjunction with a power stage system, such as a power stage system comprising a bootstrapped driver circuit and a power stage responsive to the driver circuit. The power stage system may further include a load dump compensation circuit connected to the driver circuit, wherein the load dump compensation circuit is configured to remove a bias current generated by the bootstrapped driver circuit. Various aspects of the present invention may be implemented in conjunction with any appropriate power supply, such as a switching regulator, for example a buck converter.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
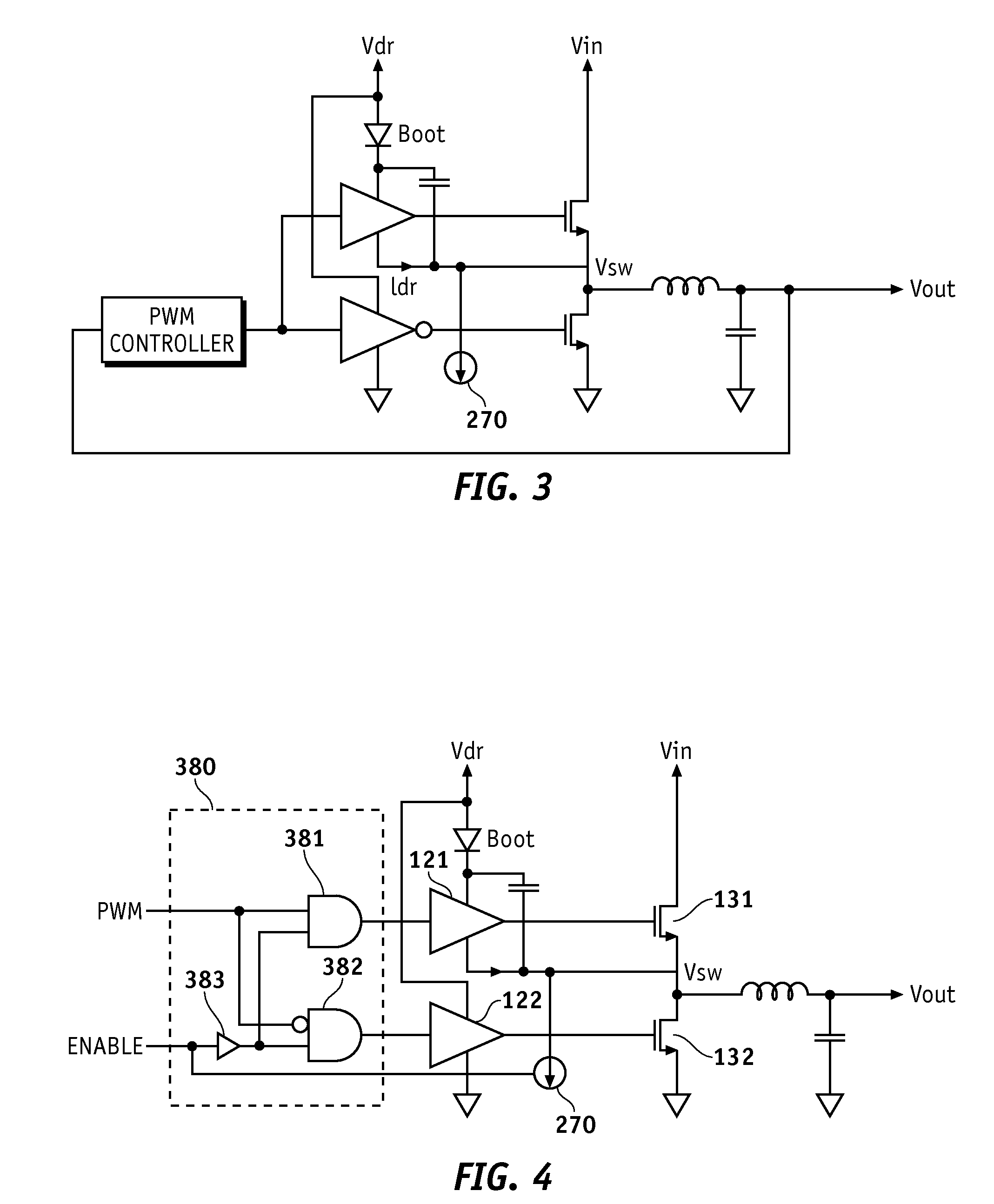
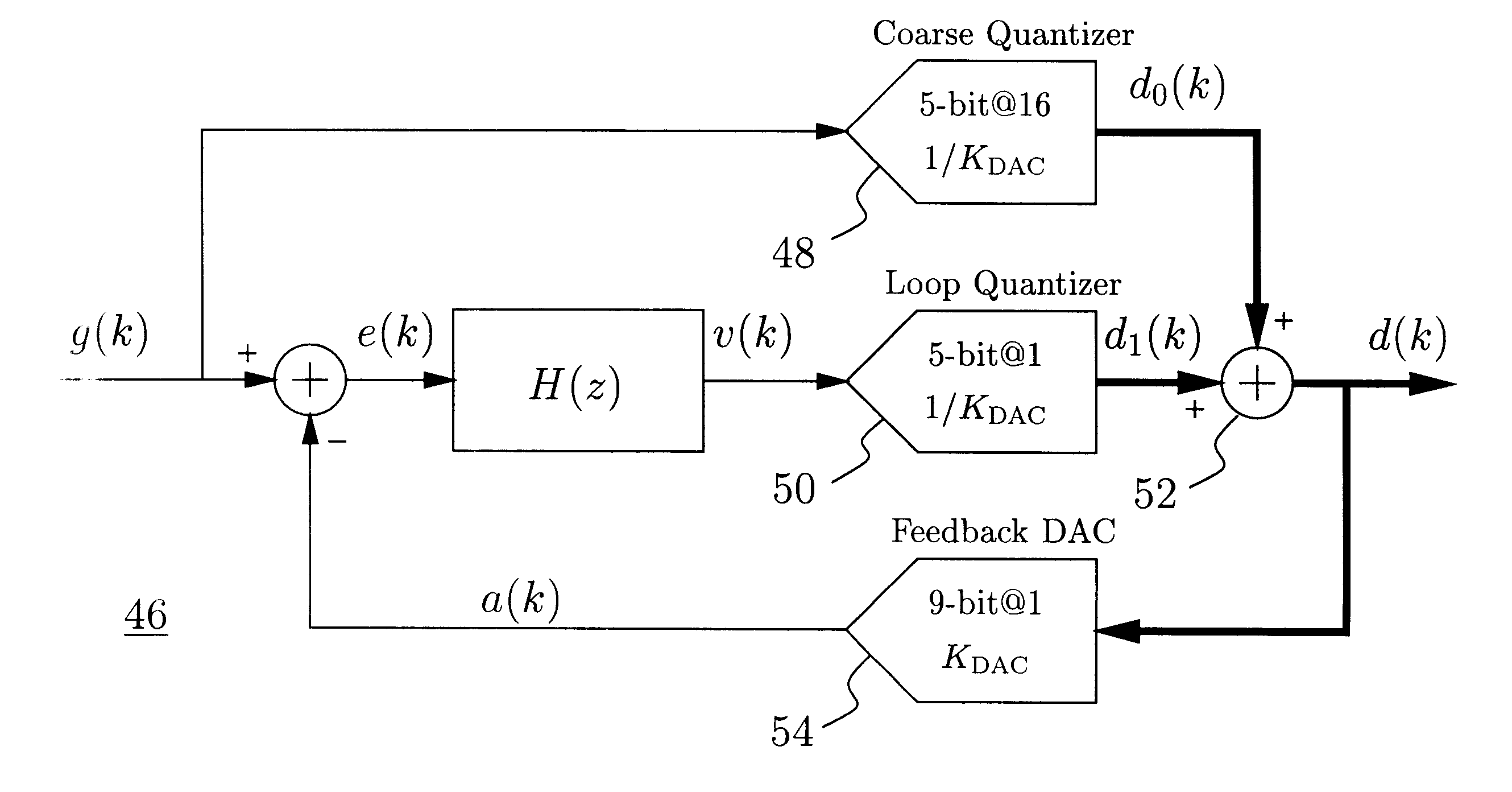
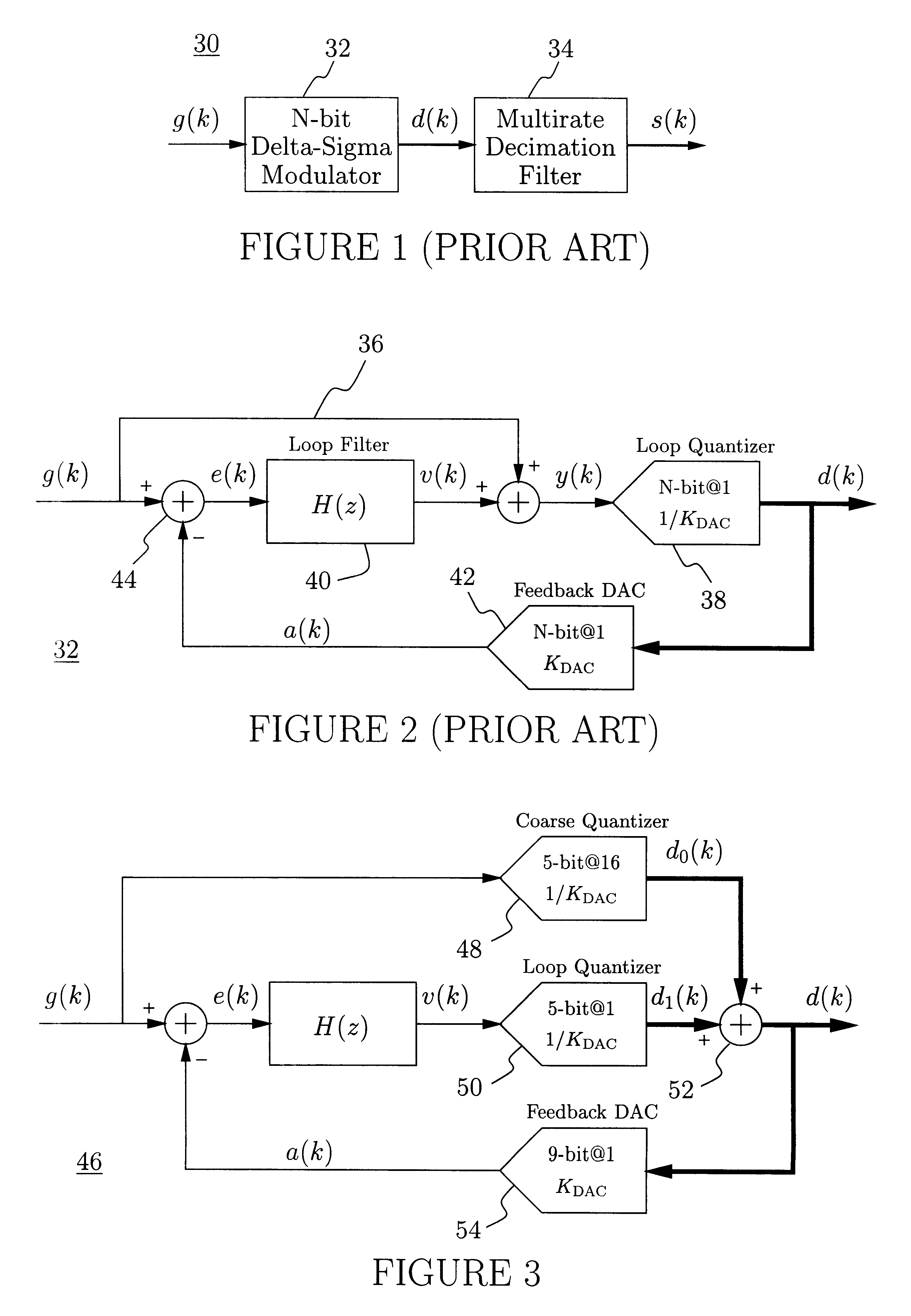
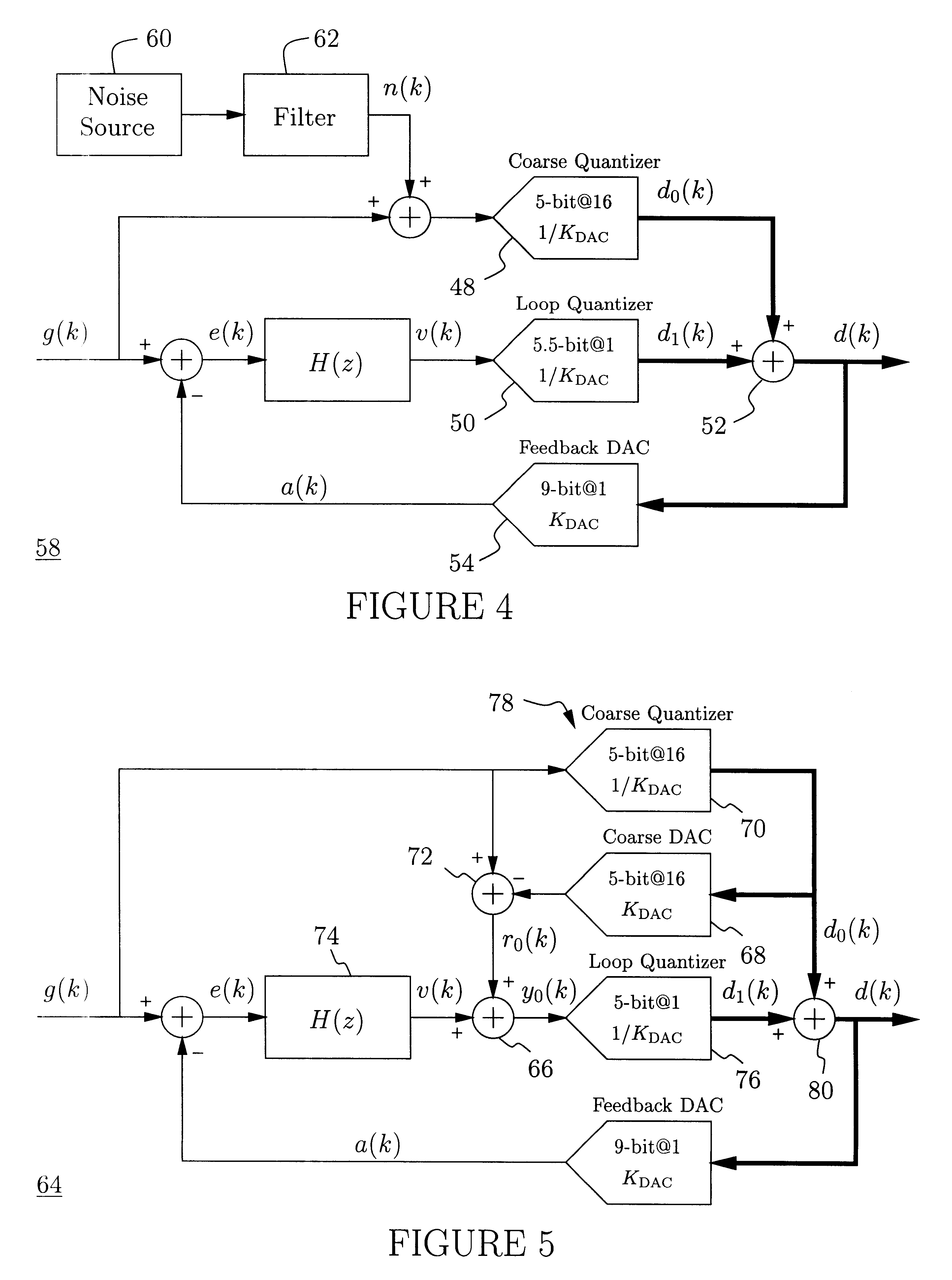
Delta-sigma A/D converter
InactiveUS6271782B1Without compromising the modulator's stabilityTo overcome the large delayElectric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationLoop filterAnalog feedback
A delta-sigma modulator comprising a first quantizer providing a first digital signal d0(k) representing the input signal g(t); a loop filter with input signal paths; a loop quantizer providing a corrective digital signal d1(k) representing the loop filter's output signal y(t); an array of feedback DACs D / A converting the sum d(k)=df(k)=d0(k)+d1(k) of the first and the corrective digital signals and injecting feedback signals into the loop filter.The loop filter's input node is applied the difference of the input signal g(t) and the global analog feedback signal a3(t). The global feedback signal a3(t) is delayed several clock cycles with respect to the digital output signal d(k). The delay is used to carry out mismatch-shaping and deglitching algorithms in the feedback DACs. The feedback DACs' different delays and gain coefficients are designed such that the modulator is stable. The filter's input signal paths and the compensating DAC are designed such that the gain from the input signal g(t) to the loop quantizer is small, ideally zero. Thus, the loop quantizer's resolving range can be a fraction of the first quantizer's resolving range, whereby the output signal's d(k) resolution can be much higher than the individual resolutions of d0(k) and d1(k).The delta-sigma modulator is well suited for the implementation of high-resolution wide-bandwidth A / D converters. Important applications include digital communication systems.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES BV
High-efficiency DC/DC voltage converter including down inductive switching pre-regulator and capacitive switching post-converter
ActiveUS7782027B2Poor regulationIncrease heightEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionCapacitanceBuck converter
A DC / DC converter includes a pre-regulator stage, which may include a Buck converter, and a post-converter stage, which may include a charge pump. The duty factor of the pre-regulator stage is controlled by a feedback path that extends from the output terminal of the pre-regulator stage or the post-converter stage. The pre-regulator steps the input DC voltage down by a variable amount depending on the duty factor, and the post-converter steps the voltage at the output of the pre-regulator up or down by an positive or negative integral or fractional value. The converter overcomes the problems of noise glitches, poor regulation, and instability, even near unity input-to-output voltage conversion ratios.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
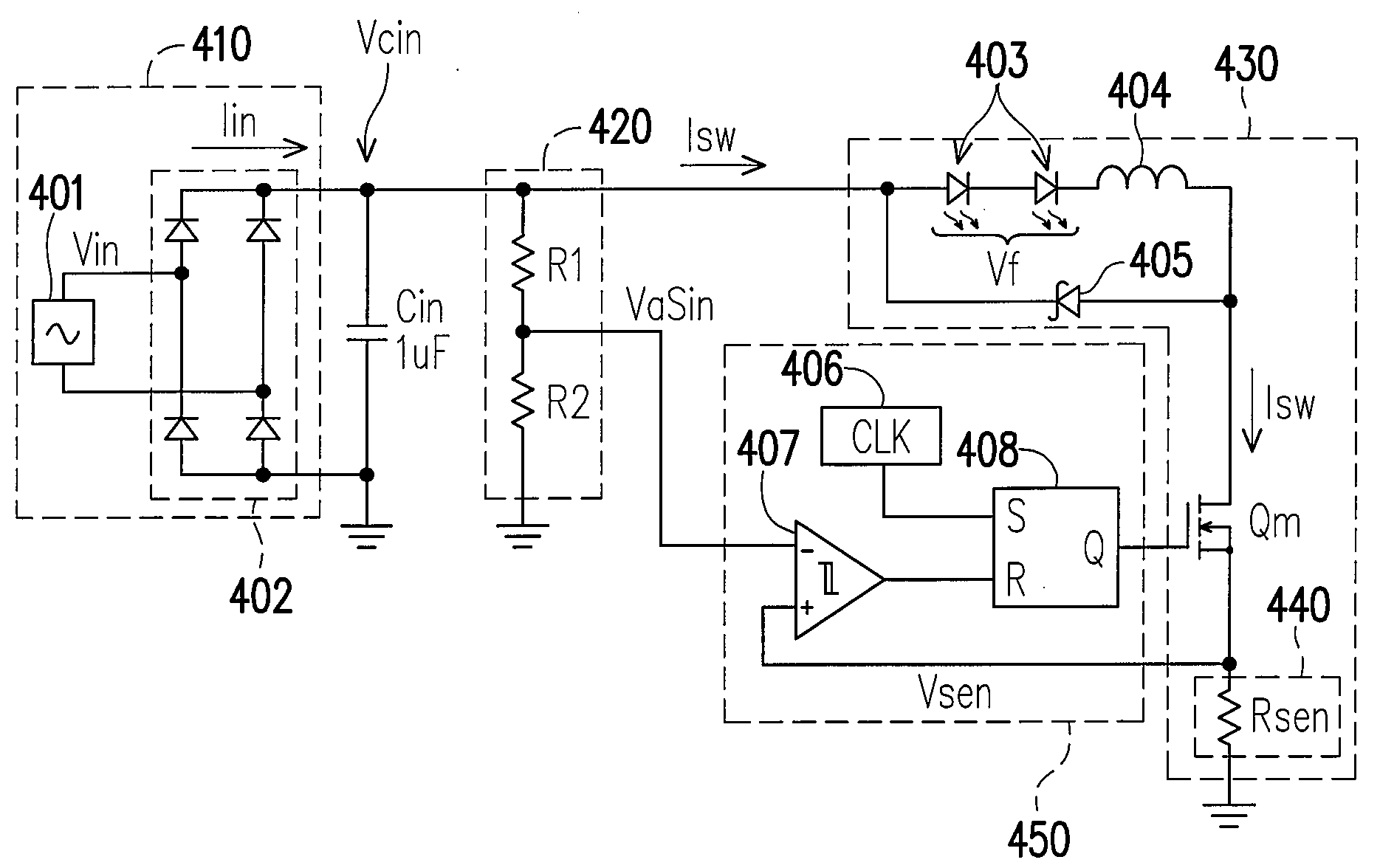
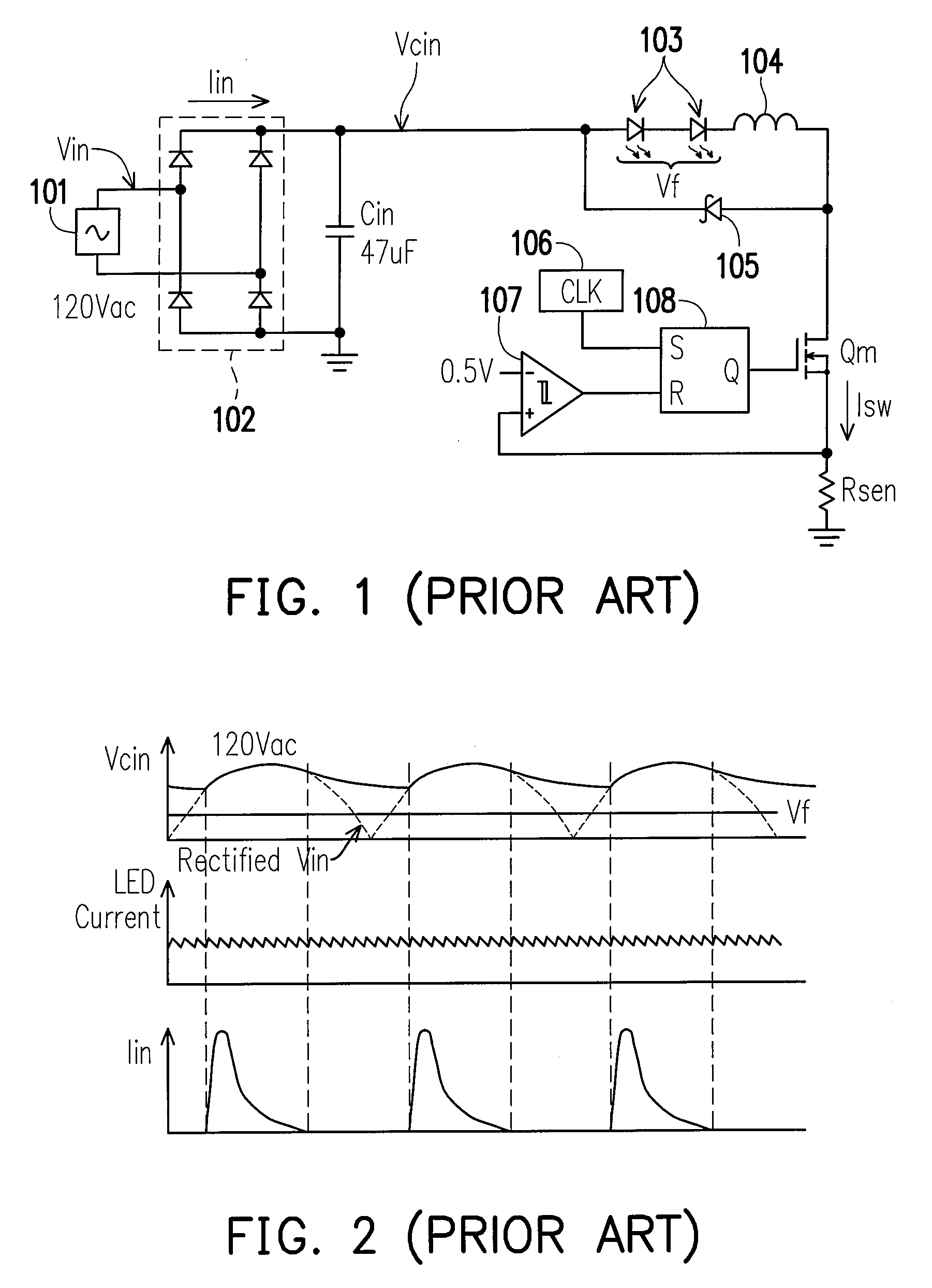
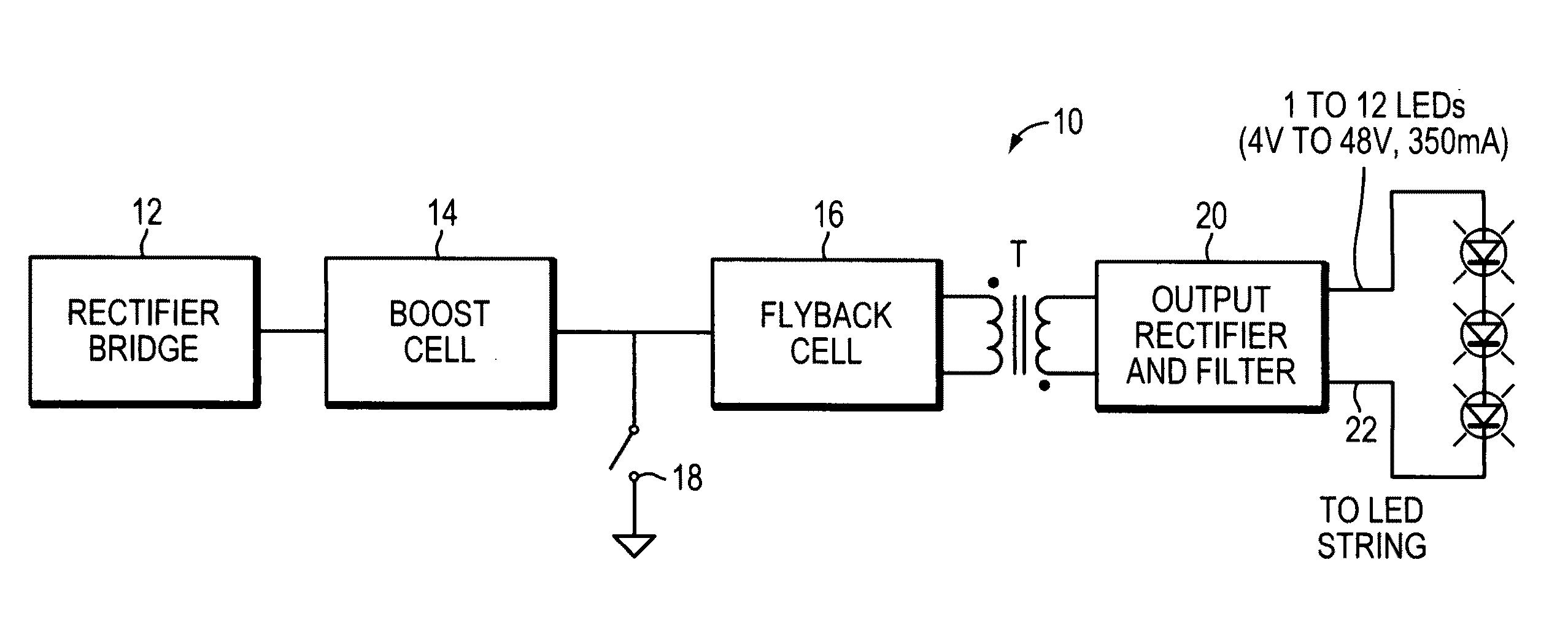
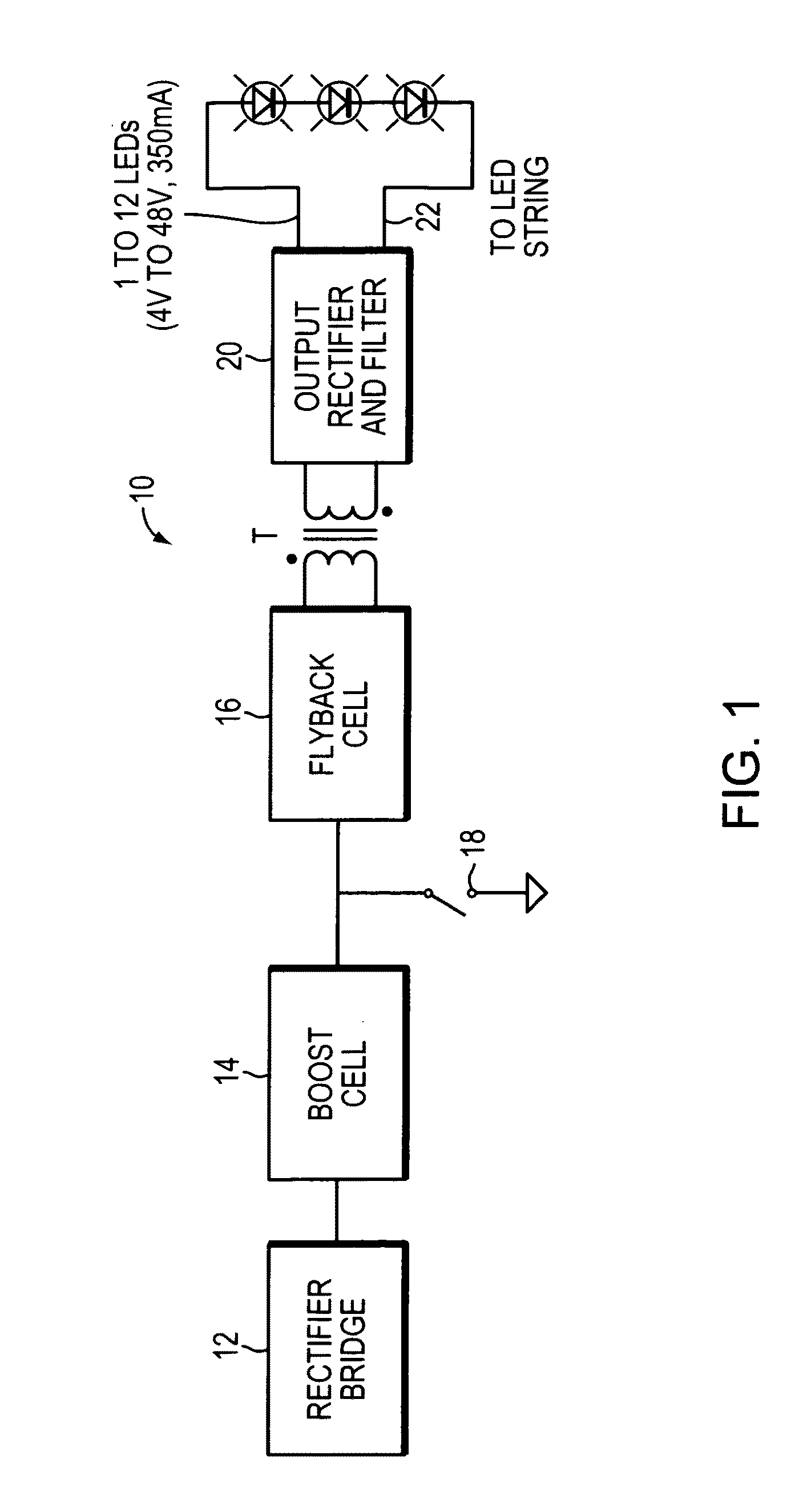
Buck converter LED driver circuit
InactiveUS20080316781A1Simple designHigh input power factorElectroluminescent light sourcesDc-dc conversionDriver circuitBuck converter
A buck converter LED driver circuit is provided. The driver circuit includes a buck power stage, a rectified AC voltage source, a voltage waveform sampler, and a control circuit. The buck power stage includes at least one LED and provides a first signal directly proportional to the current through the LED. The rectified AC voltage source is coupled to the buck power stage for driving the buck power stage. The voltage waveform sampler is coupled to the rectified AC voltage source for providing a second signal directly proportional to the voltage provided by the rectified AC voltage source. The control circuit is coupled to the voltage waveform sampler and the buck power stage for turning on and turning off the buck power stage according to a comparison between the first signal and the second signal.
Owner:GREEN MARK TECH
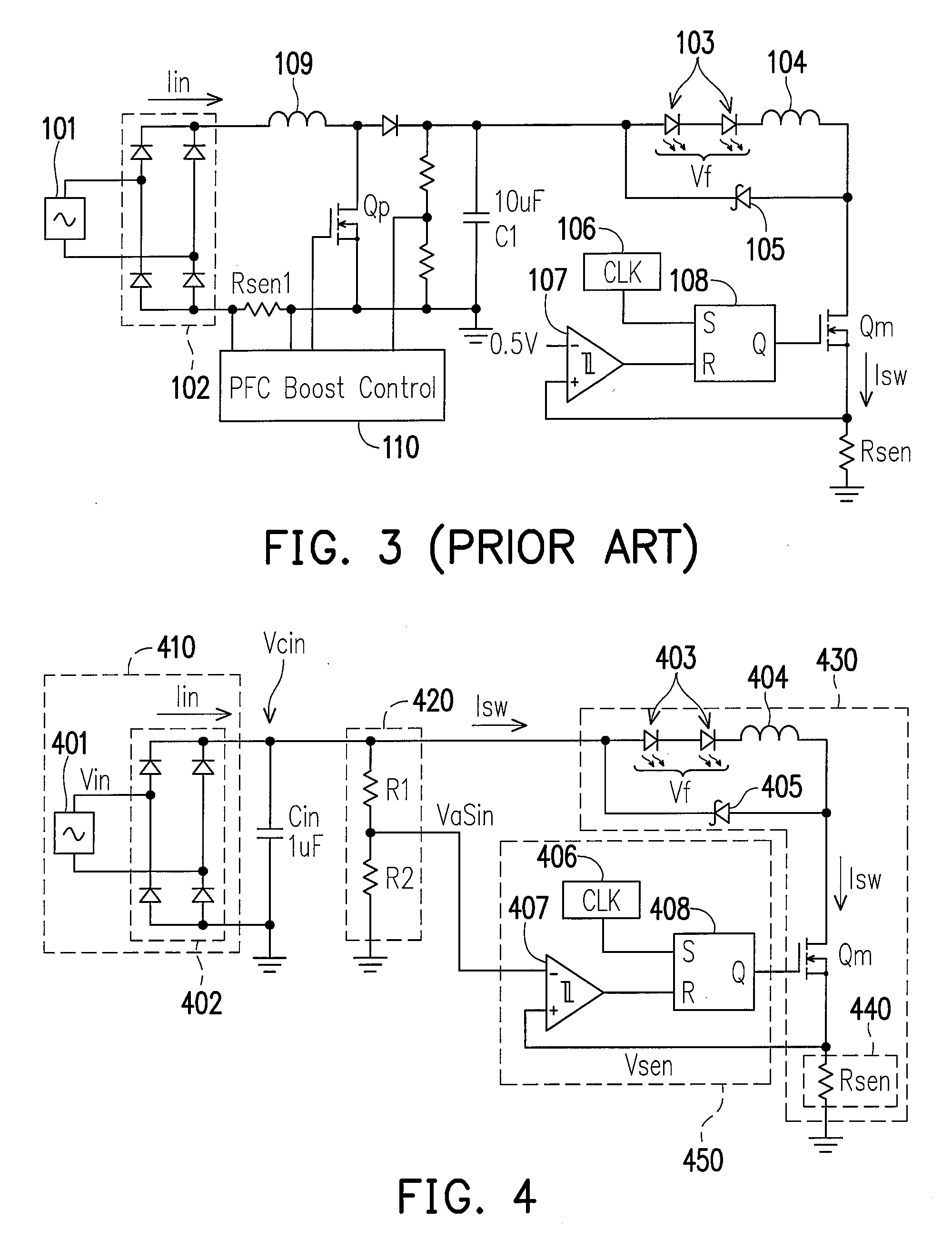
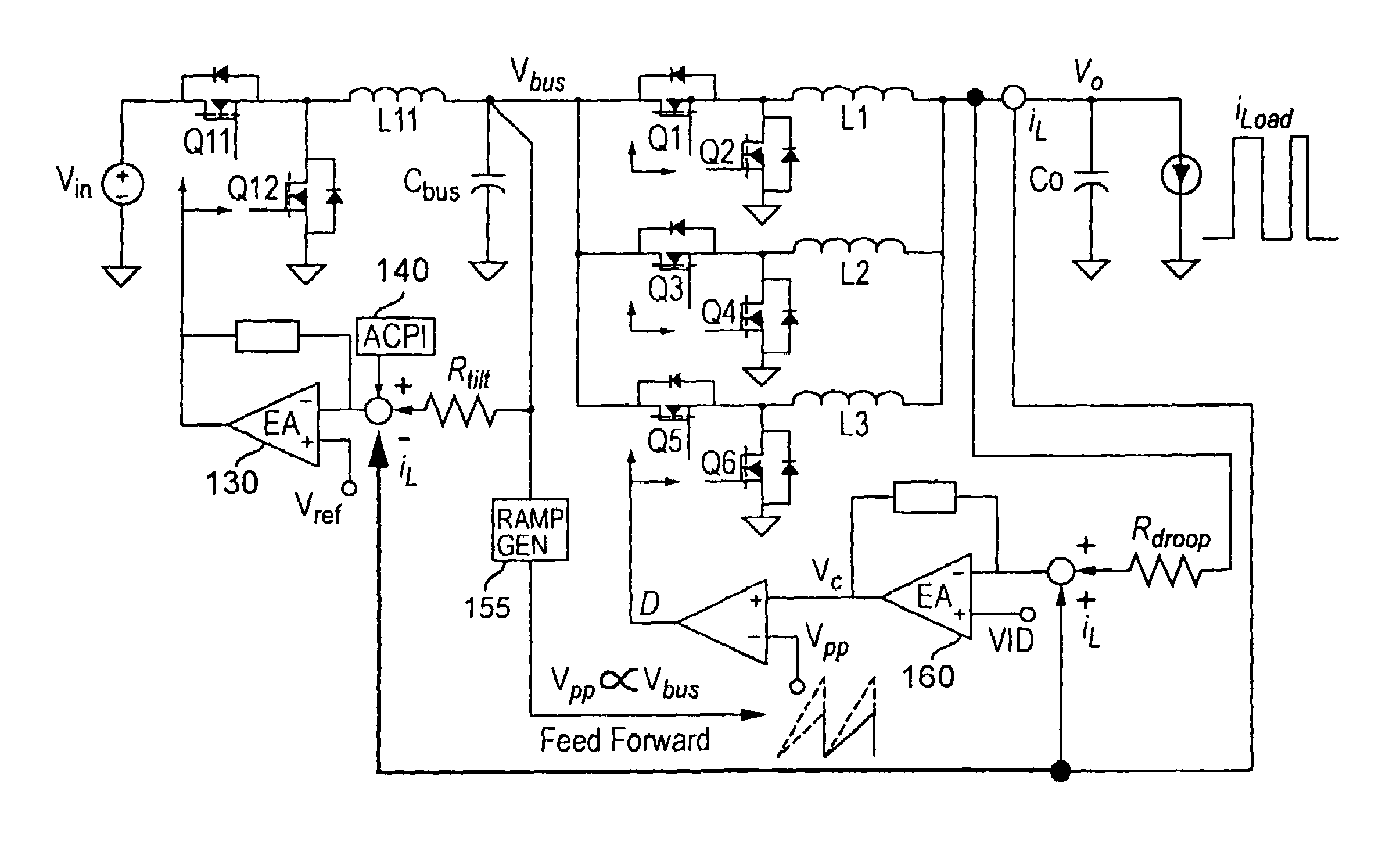
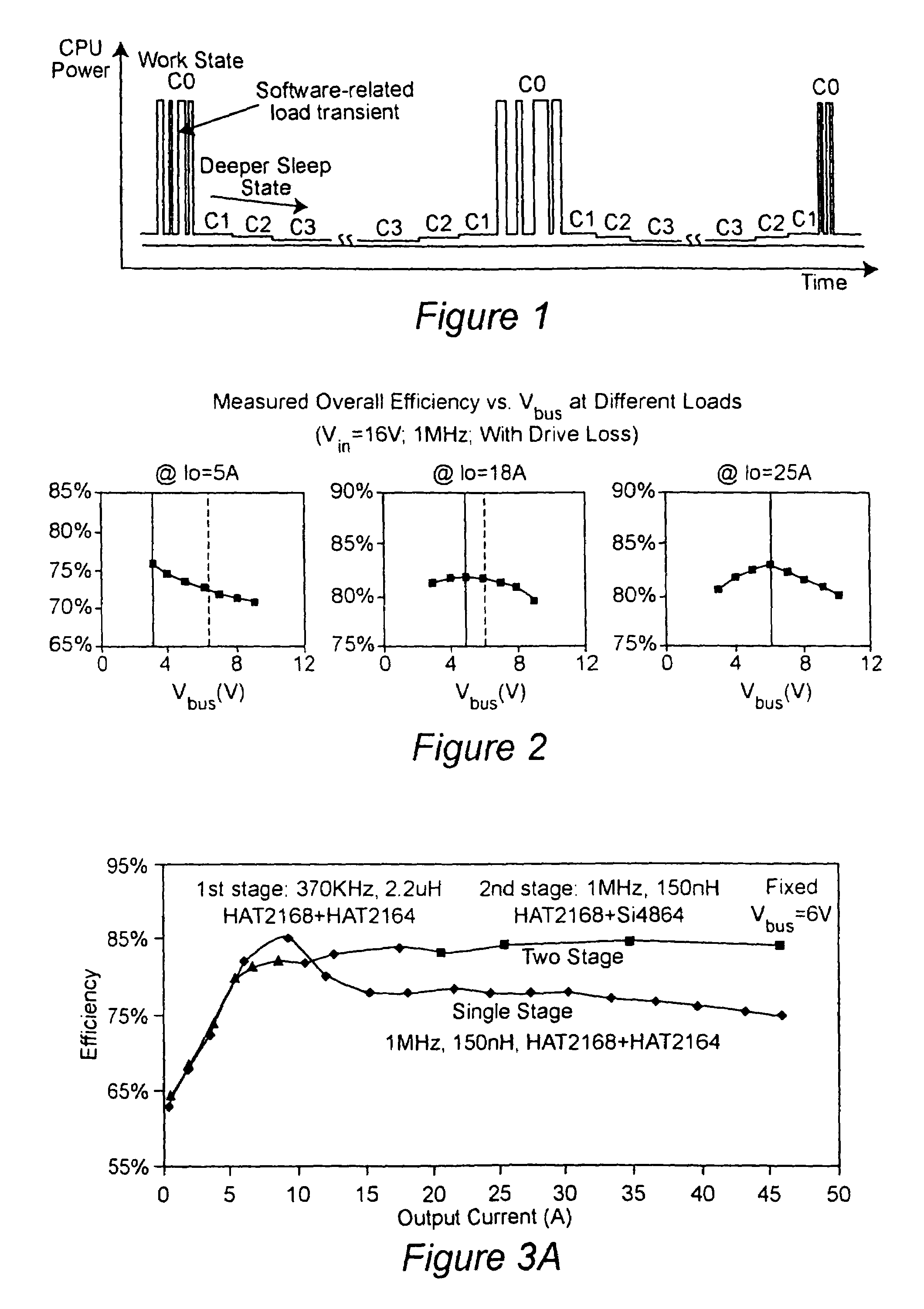
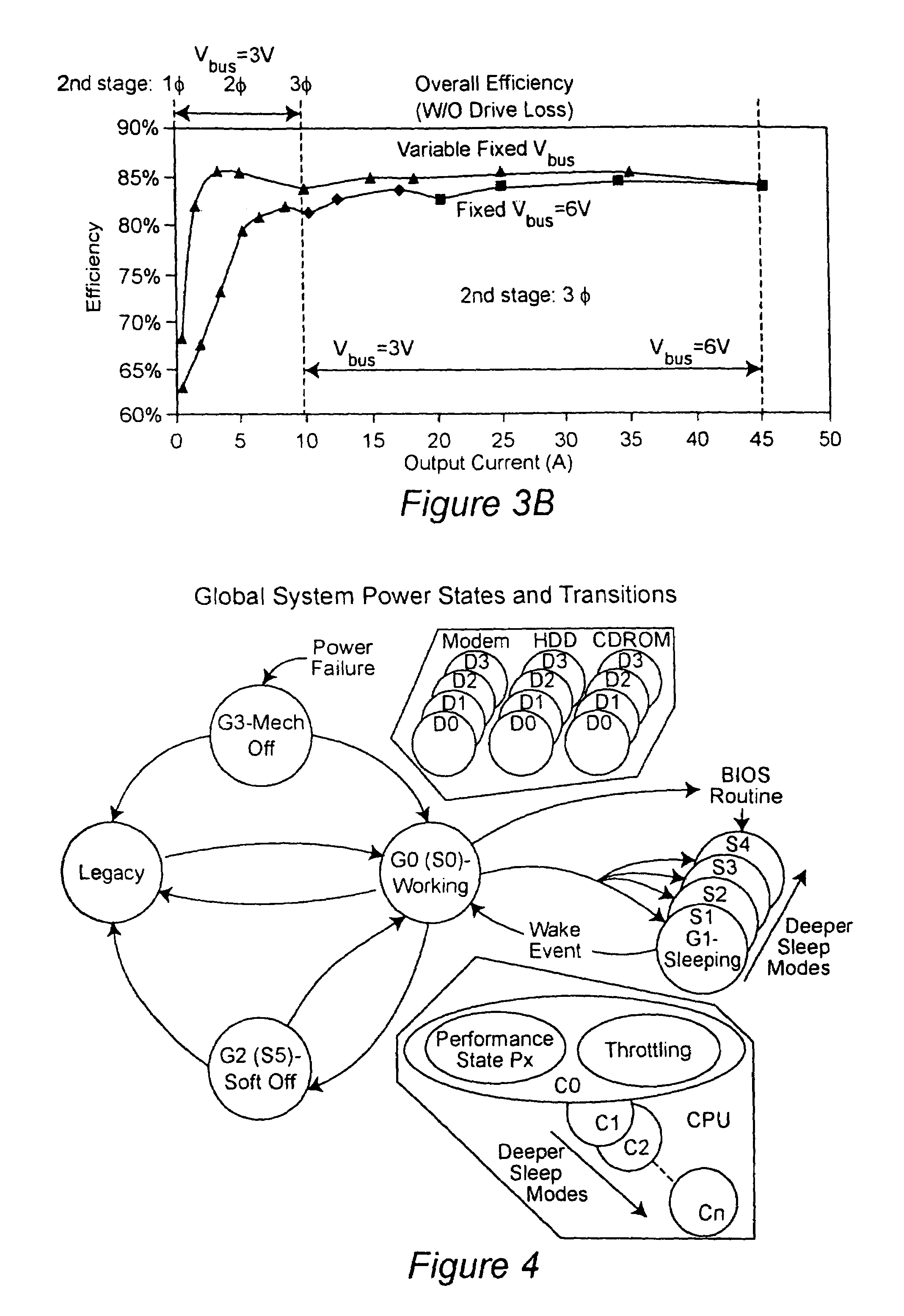
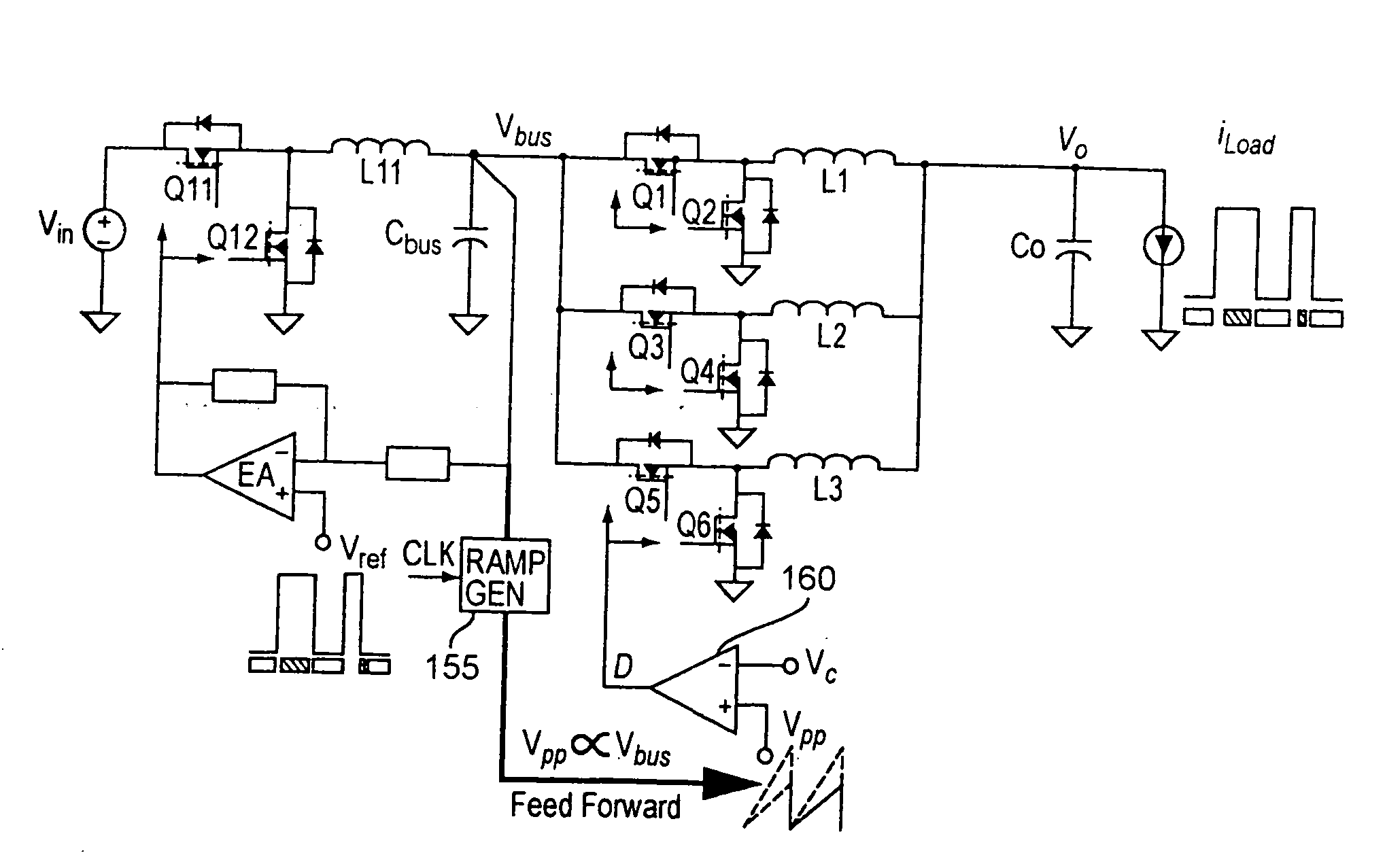
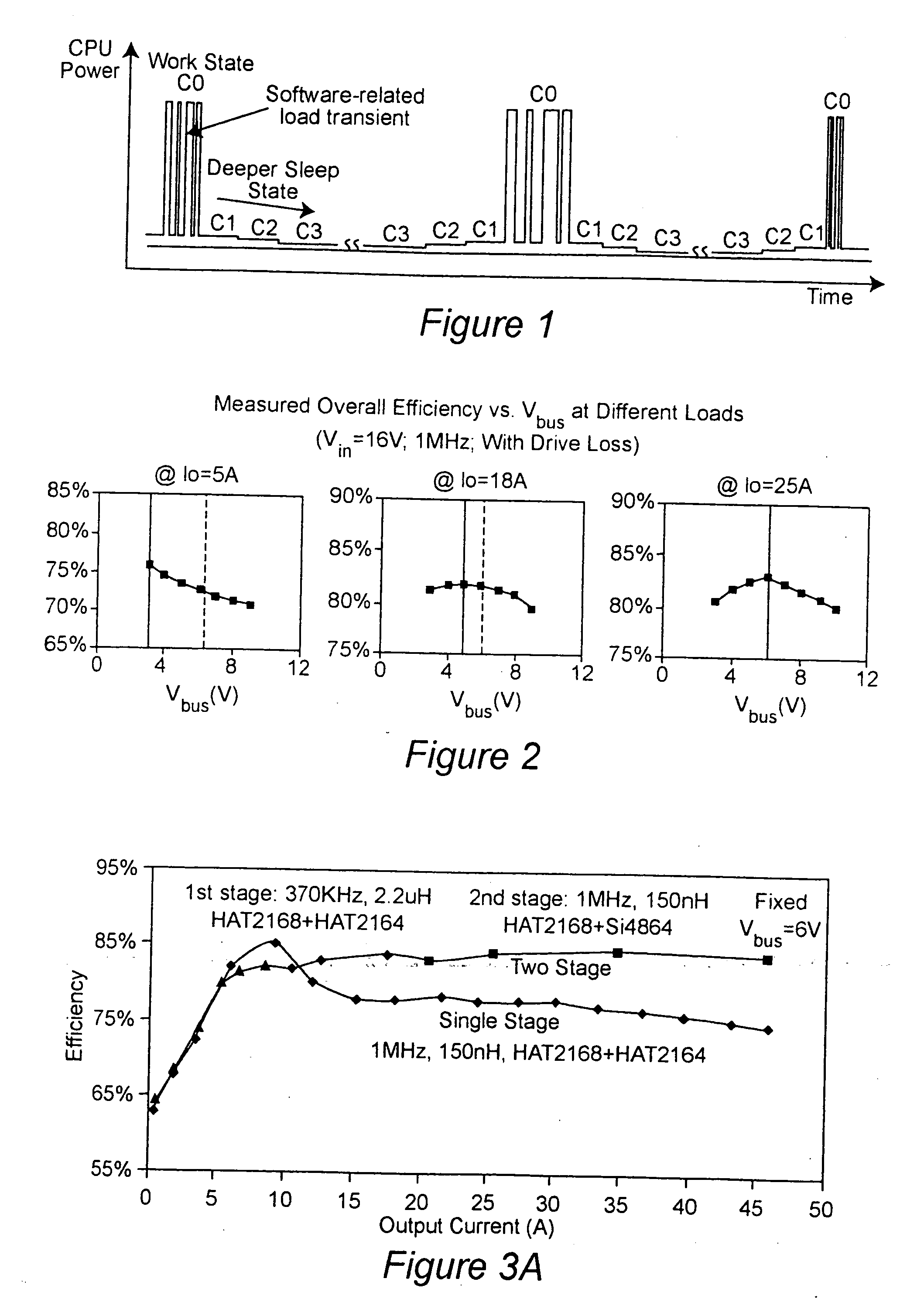
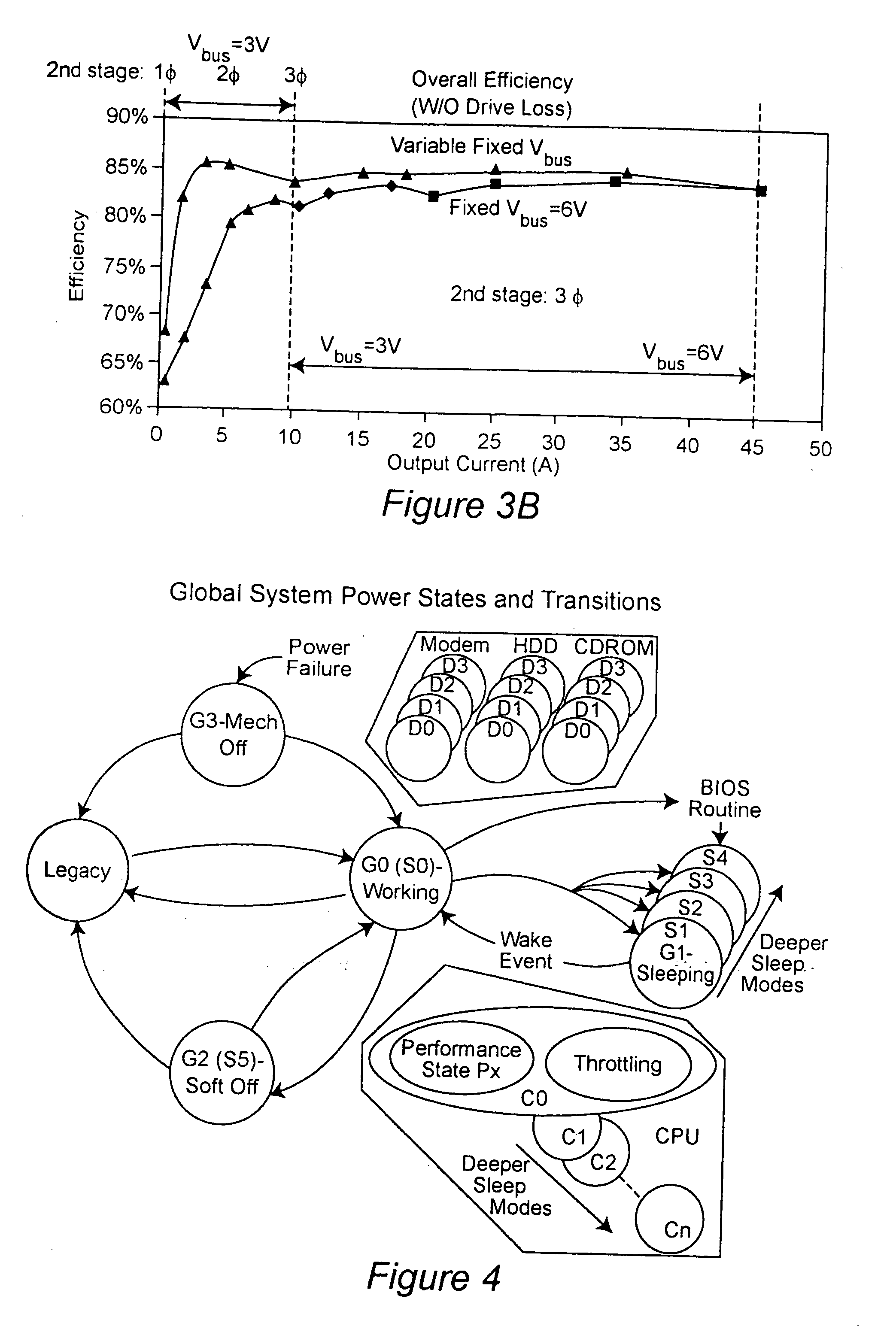
Two-stage voltage regulators with adjustable intermediate bus voltage, adjustable switching frequency, and adjustable number of active phases
InactiveUS7071660B2Improve efficiencyWide variationEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionBuck converterSwitching frequency
A two-stage power converter that dynamically adjusts to output current requirements includes a first stage regulator that provides power to a second stage regulator. The first stage can be a buck converter, and the second stage can be a multiple-phase buck converter. The output voltage of the first stage (intermediate bus voltage Vbus) is varied according to the load current to optimize conversion efficiency. To provide maximum efficiency, the Vbus voltage is increased as load current increases. The Vbus voltage provided by the first stage can be varied by duty cycle or operating frequency control. In another embodiment, the switching frequency of the second stage is varied as output current changes so that output current ripple is held constant. In an embodiment employing a multiple-phase buck converter in the second stage, the number of operating phases are varied as output current changes.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
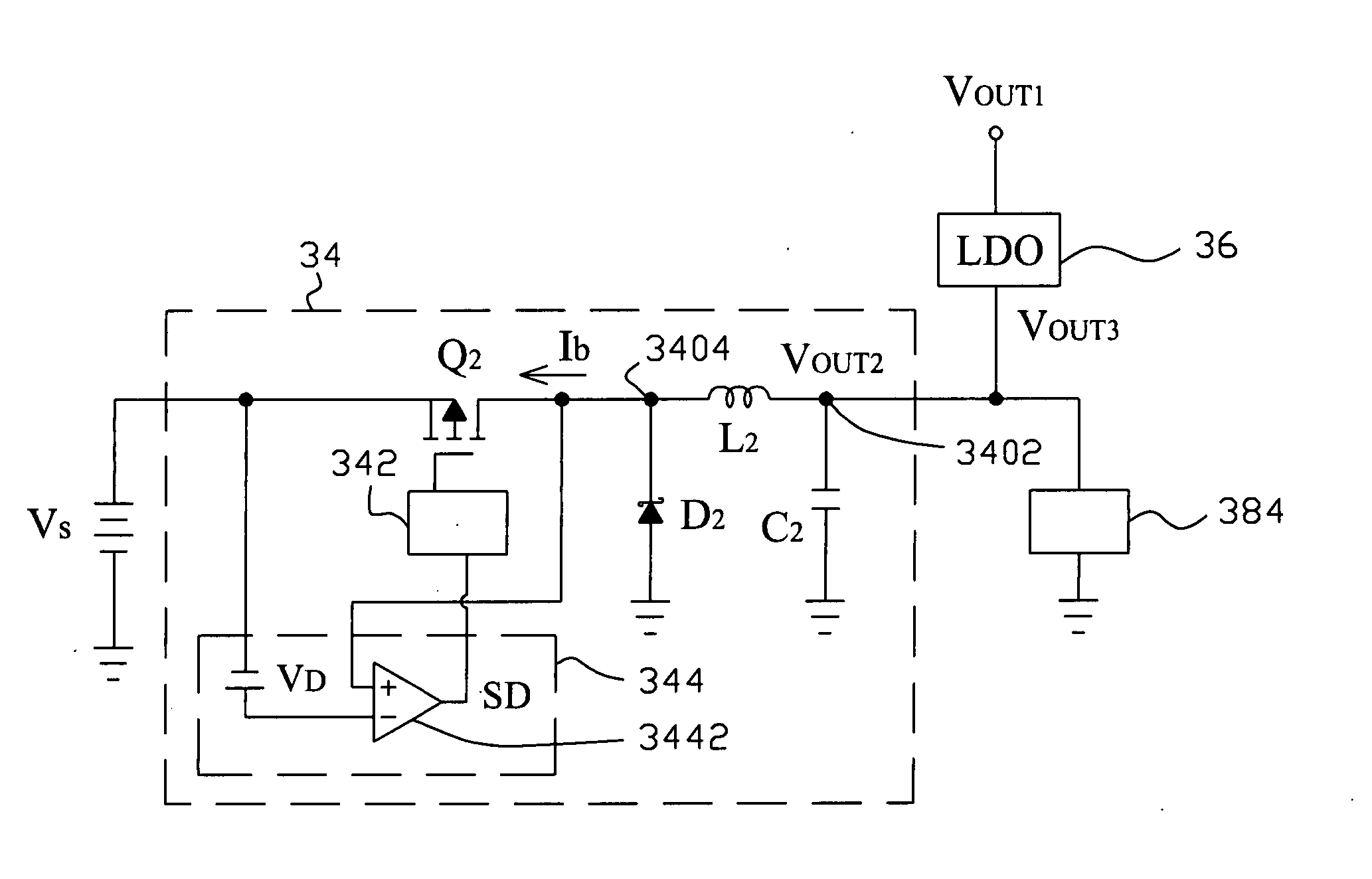
Efficiency improved voltage converter
InactiveUS20050017701A1Improve efficiencyAvoid flowElectric variable regulationVoltage converterBuck converter
A voltage converter improves the efficiency thereof by connecting a boost converter and an LDO regulator with a buck converter in parallel. The boost converter boosts up a supply voltage to generate a first output voltage at a first output, and the buck converter bucks down the supply voltage to generate a second output voltage at a second output. When the second output voltage is lower than a threshold, the LDO regulator converts the first output voltage to a third voltage at said second output.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit
ActiveUS20100067259A1Improve conversion efficiencyAdditional drawbackEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsHeavy loadCenter tap
The present invention discloses a forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit. The secondary side of the proposed converter is of center-tapped configuration to integrate a forward circuit and a flyback circuit. The flyback sub-circuit operating continuous conduction mode is employed to directly transfer the reset energy of the transformer to the output load. The forward sub-circuit operating discontinuous conduction mode can correspondingly adjust the duty ratio with the output load change. Under the heavy load condition, the mechanism of active-clamp flyback sub-circuit can provide sufficient resonant current to facilitate the parasitic capacitance of the switches to be discharged to zero. Under the light load condition, the time interval in which the resonant current turns from negative into positive is prolonged to ensure zero voltage switching function. Meanwhile, the flyback sub-circuit wherein the rectifier diode is reverse biased is inactive in order to further reduce the power losses.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
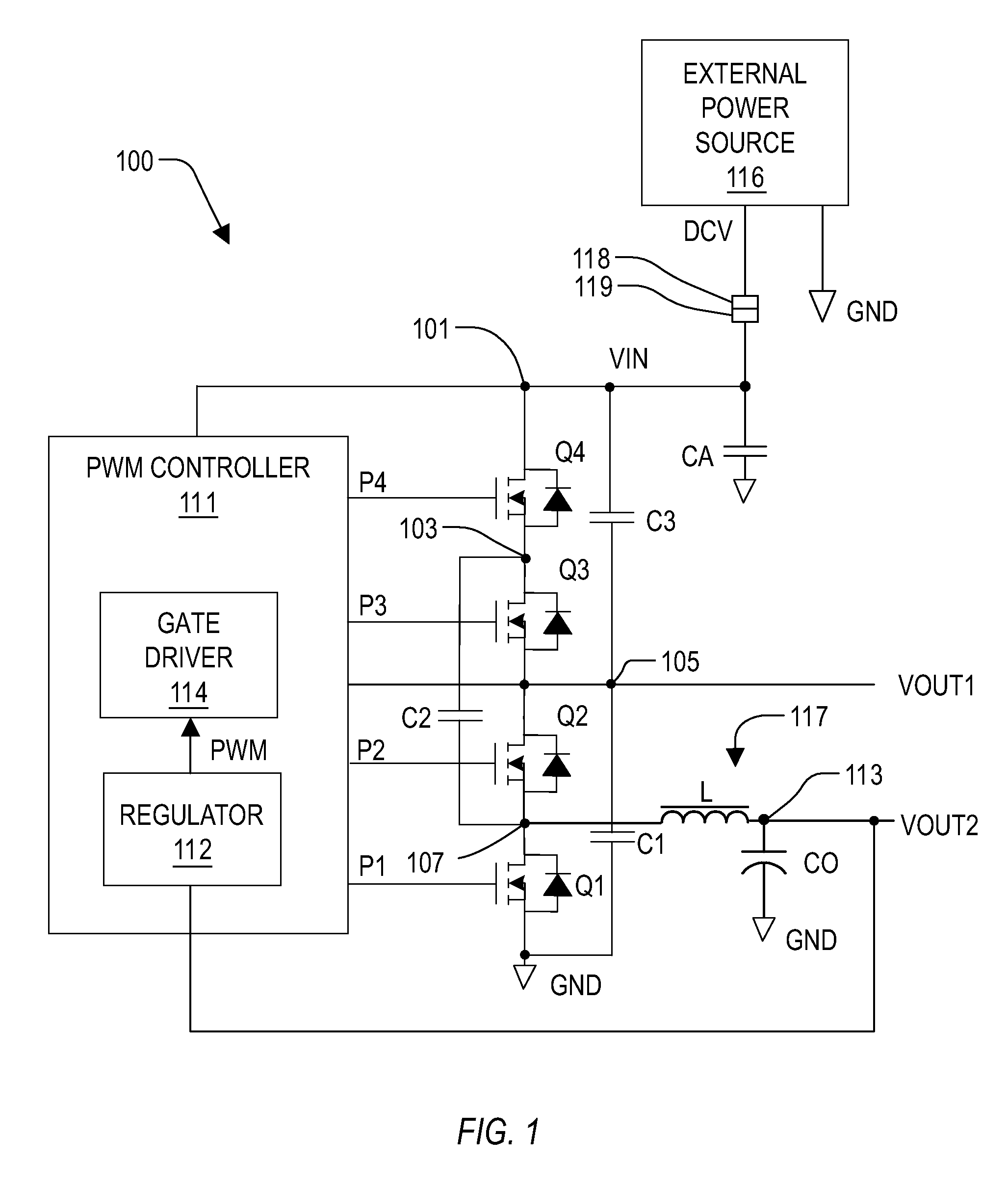
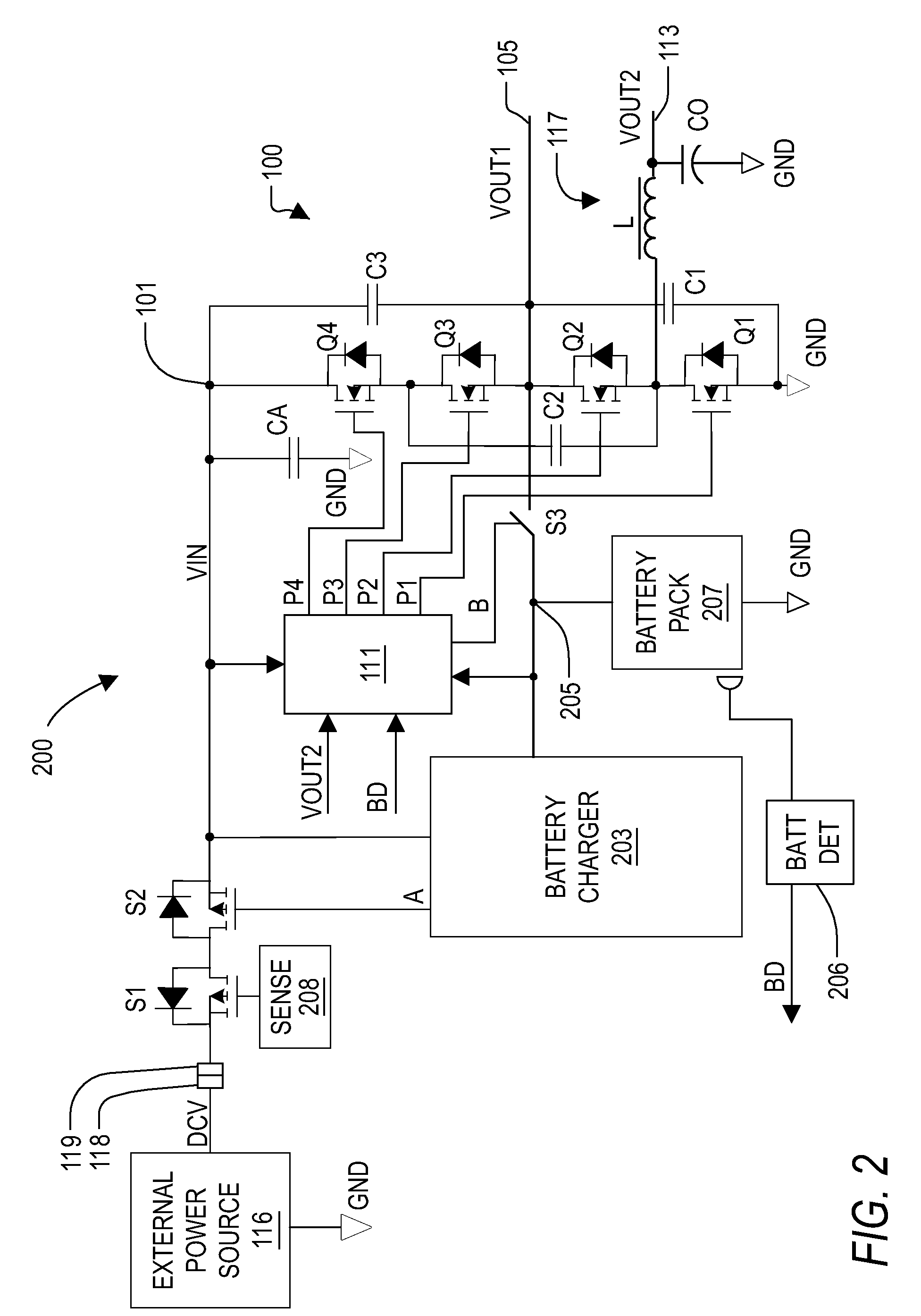
Voltage converter with combined capacitive voltage divider, buck converter and battery charger
InactiveUS20090033293A1Batteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionĆuk converterCapacitive voltage divider
A voltage converter including a capacitive voltage divider combined with a buck converter and battery charger. The converter includes four capacitors, a switch circuit, an inductor and a controller. The capacitors form a capacitor loop between an input node and a reference node and include a fly capacitor controlled by the switch circuit, which is controlled by a PWM signal to half the input voltage to provide a first output voltage on a first output node, and to convert the first output voltage to the second output voltage via the inductor. The controller controls the PWM signal to regulate the second output voltage, and provides a voltage control signal to control the input voltage to maintain the first output node between a predetermined minimum and maximum battery voltage levels. A battery charge path is coupled to the reference node and battery charge mode depends upon the battery voltage.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Residue-compensating A/D converter
InactiveUS6556158B2Low-cost highly-linearSuitable for useElectric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationModem deviceFrequency spectrum
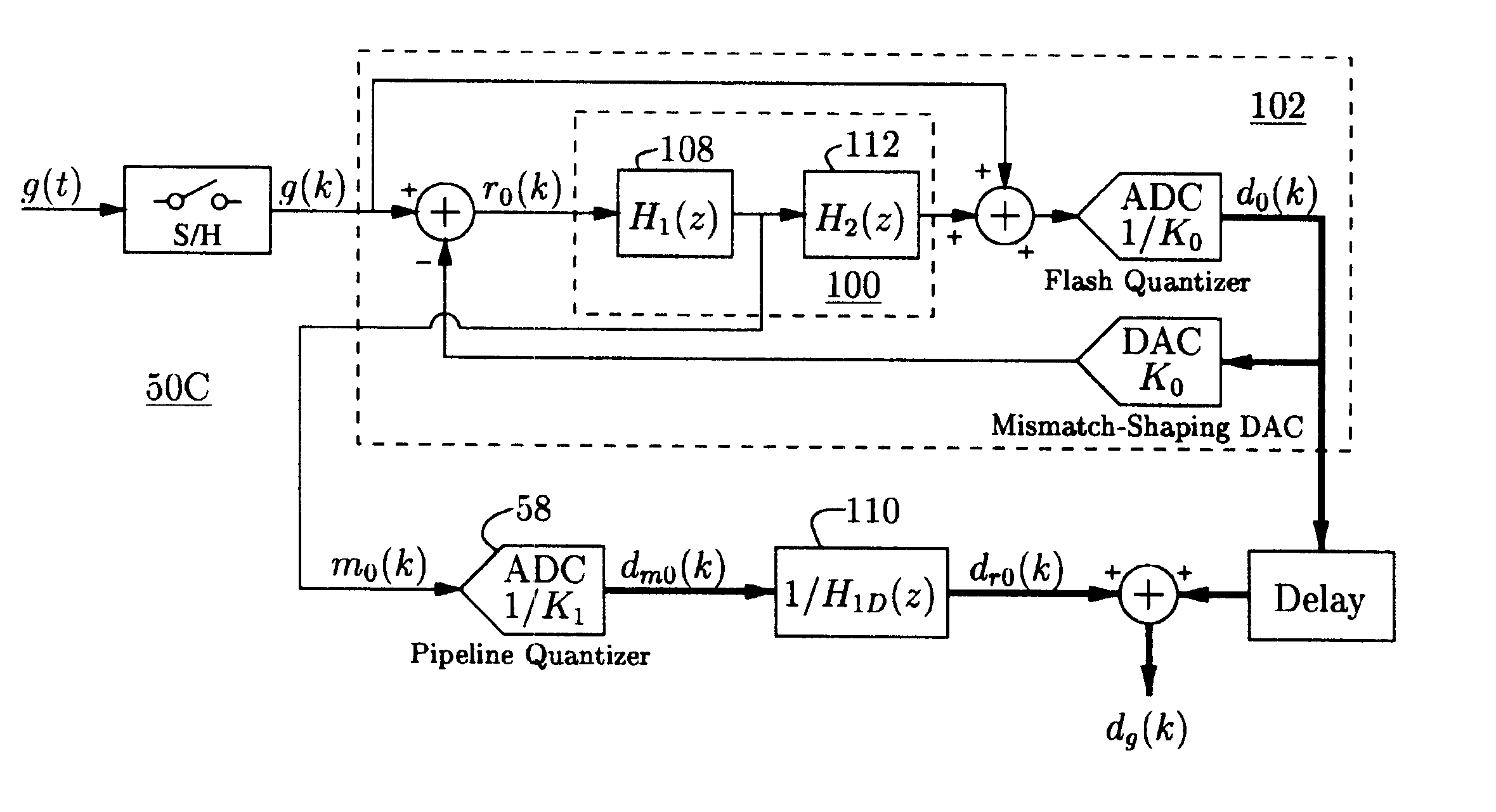
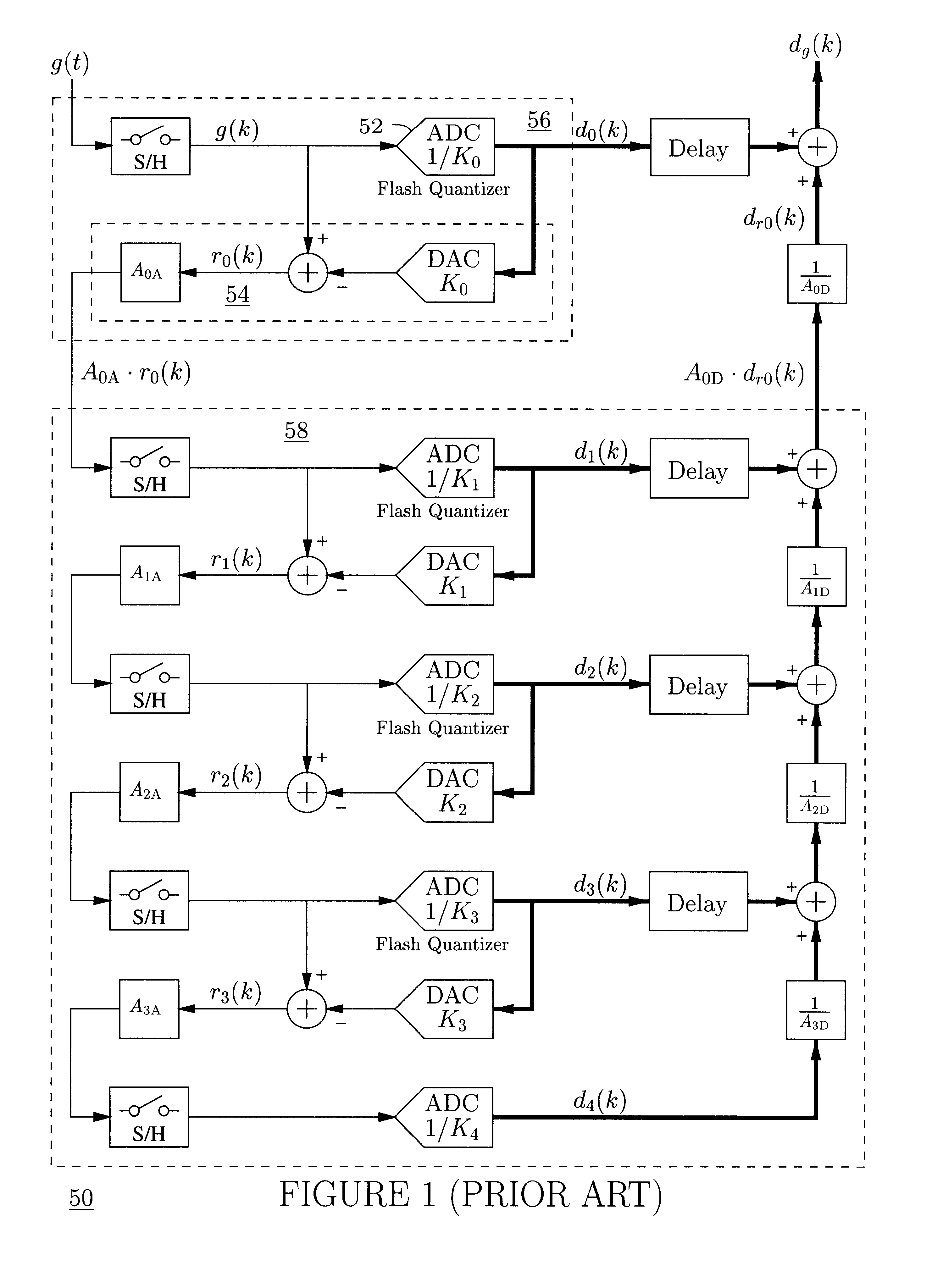
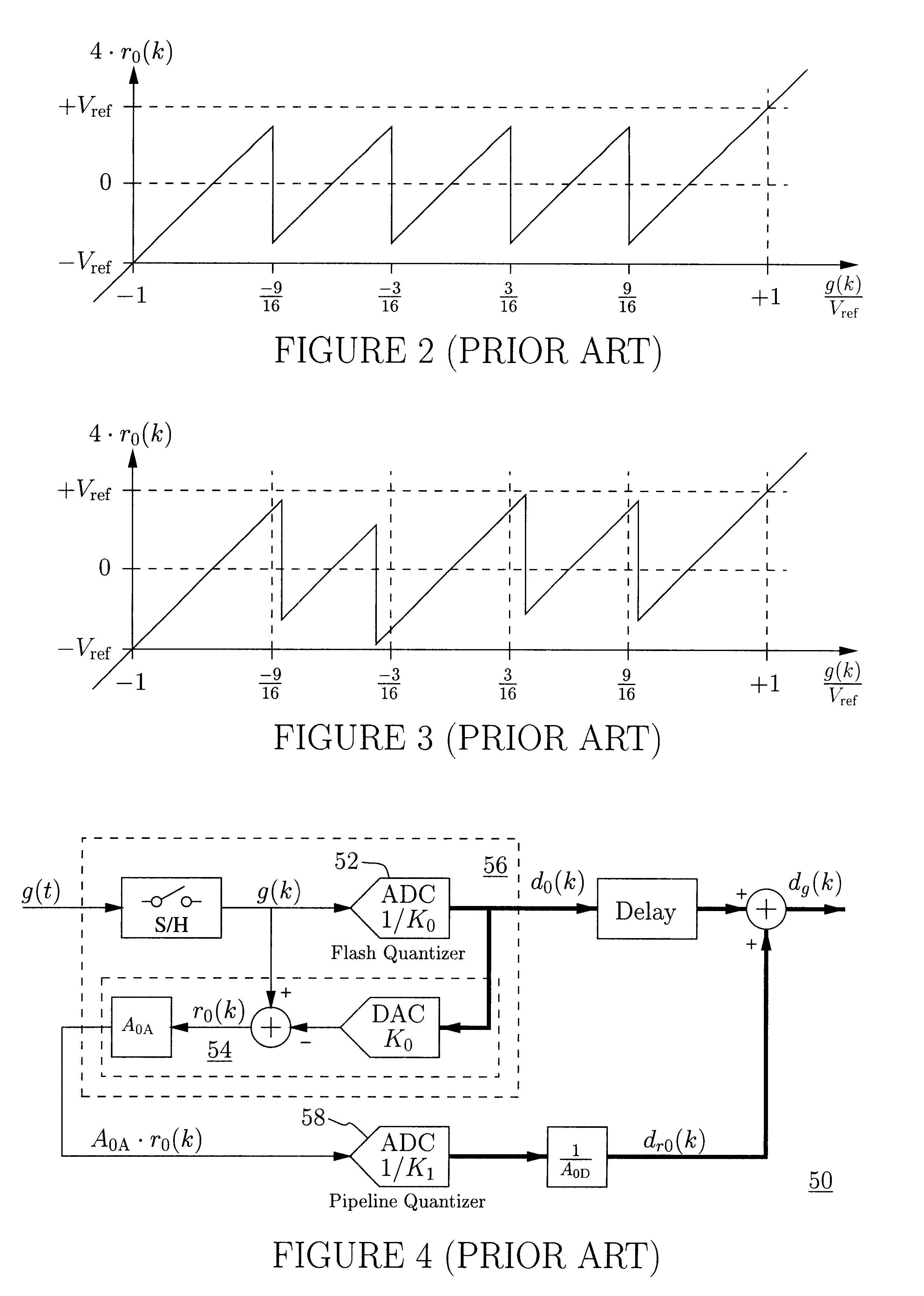
An analog-to-digital converter system [50D] processing an input signal, g, which can be either a discrete-time or a continuous-time signal. A first quantizer [154] generates a first digital signal, d0(k), representing the sum of the input signal, g, and a dithering signal, y0. A digital-to-analog converter [156] generates an analog feedback signal, alpha, representing accurately the first digital signal, d0(k). The DAC [156] may be linearized by the use of mismatch-shaping techniques. A filter [158] generates the dithering signal, y0, by selectively amplifying in the signal band the residue signal, r0, defined as the difference of the input signal, g, and the analog feedback signal, alpha. Optional signal paths [166][168] are used to minimize the closed-loop signal transfer function from g to y0, which ideally will be zero. An analog compensation signal, m0, which is described by a well-controlled relationship to the residue signal, r0, is extracted from the filter [158]. Ideally, the closed-loop signal transfer function from g to m0 will be zero, or at least small in the signal band. A second quantizer [160] converts the analog compensation signal, m0, into a second digital signal, dm0(k). The two digital signals, d0(k) and dm0(k), are filtered individually and then added to form the overall output signal, dg(k). The second digital filter [164] has a low signal-band gain, which implies that the sensitivity to signal-band errors caused by the second quantizer [160] will be low. The output signal, dg(k), is a highly-accurate high-resolution representation of the input signal, g. Circuit imperfections, such as mismatch, gain errors, and nonlinearities, will cause only noise-like errors having a very low spectral power density in the signal band.The invention facilitates the implementation of uncalibrated highly-linear high-resolution wide-bandwidth A / D converters [50D], e.g., for use in digital communication systems, such as xDSL modems and other demanding consumer-market products for which low cost is of the essence.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES BV
Electric ARC welder and plasma cutter
InactiveUS6023037AReduce Harmonic DistortionImprove power factorAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcFull waveTransformer coupling
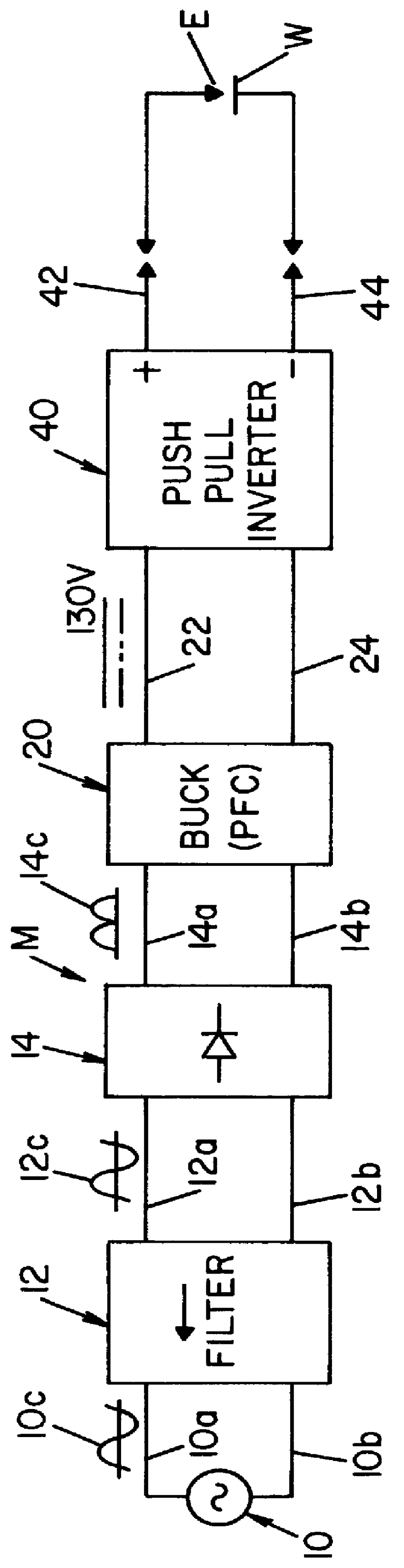
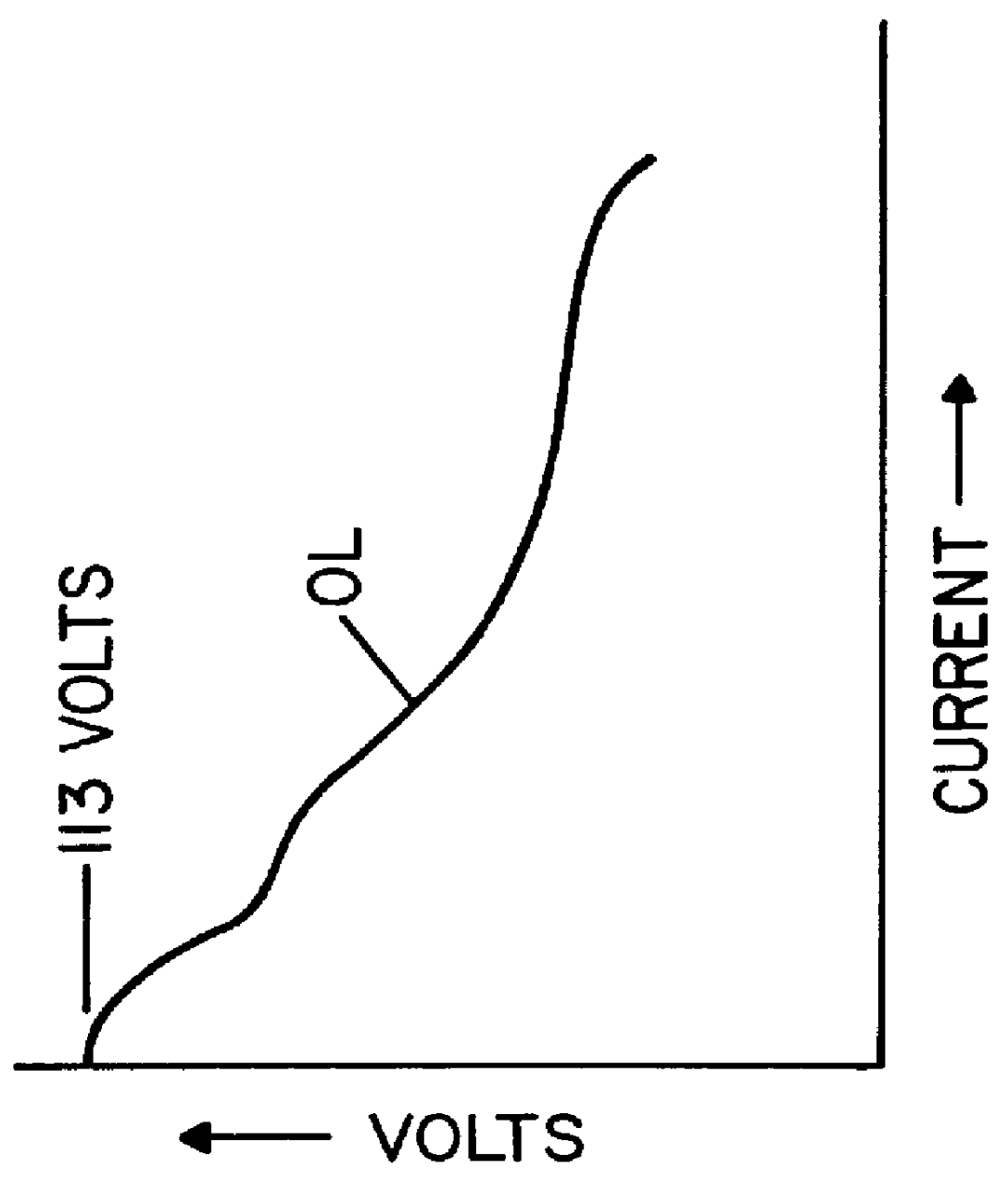
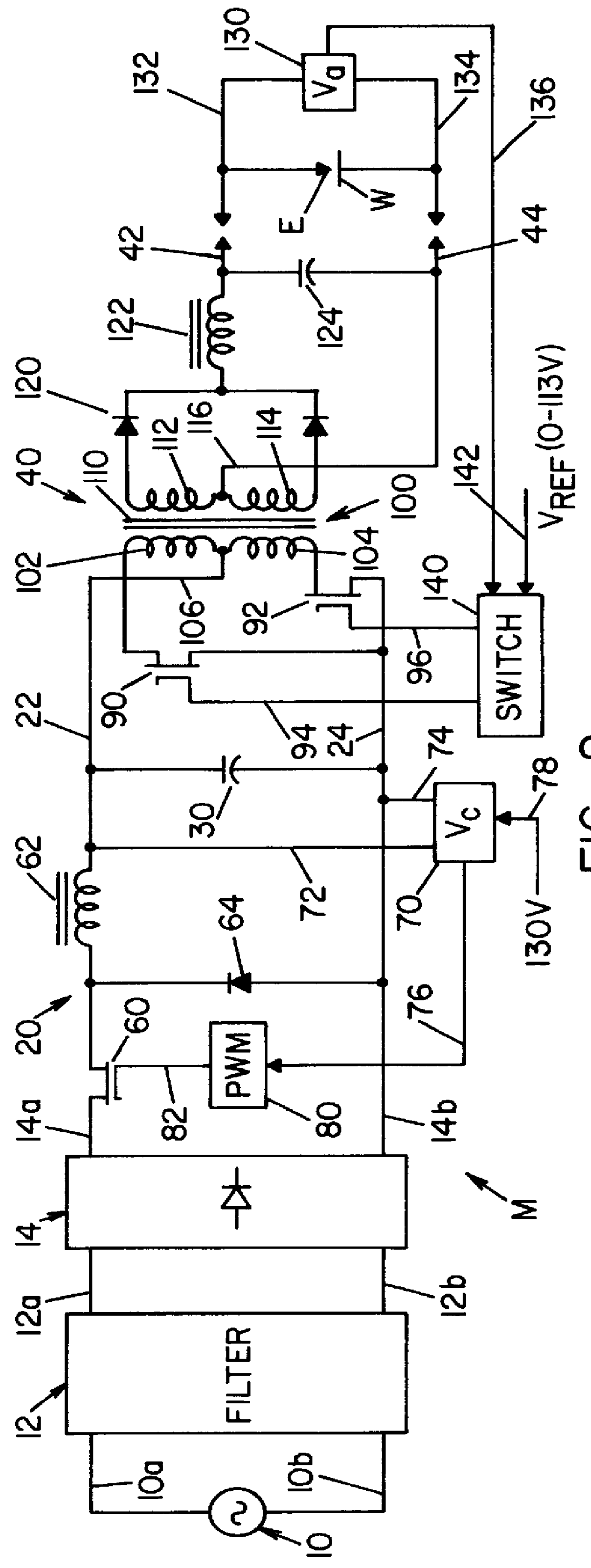
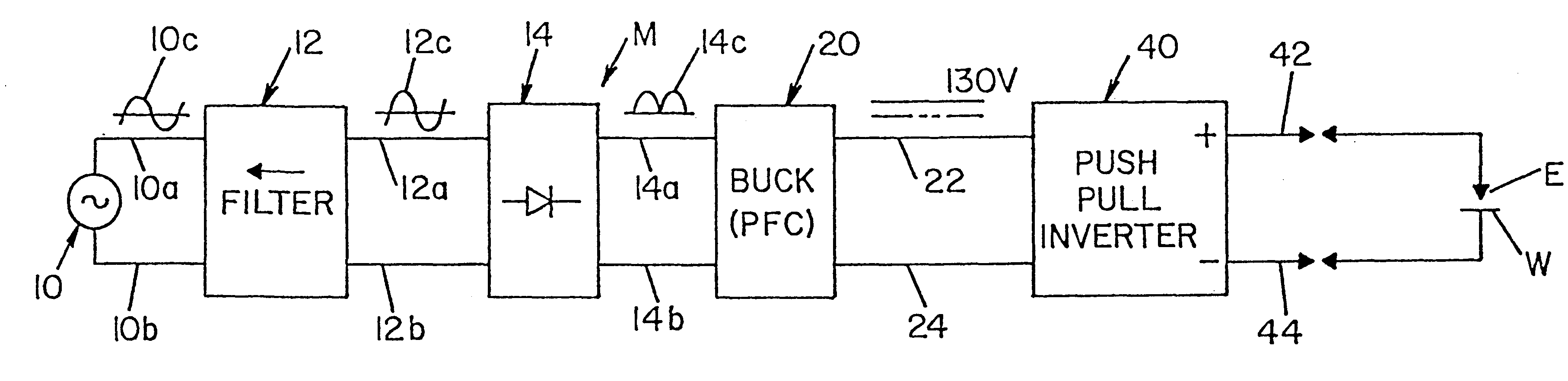
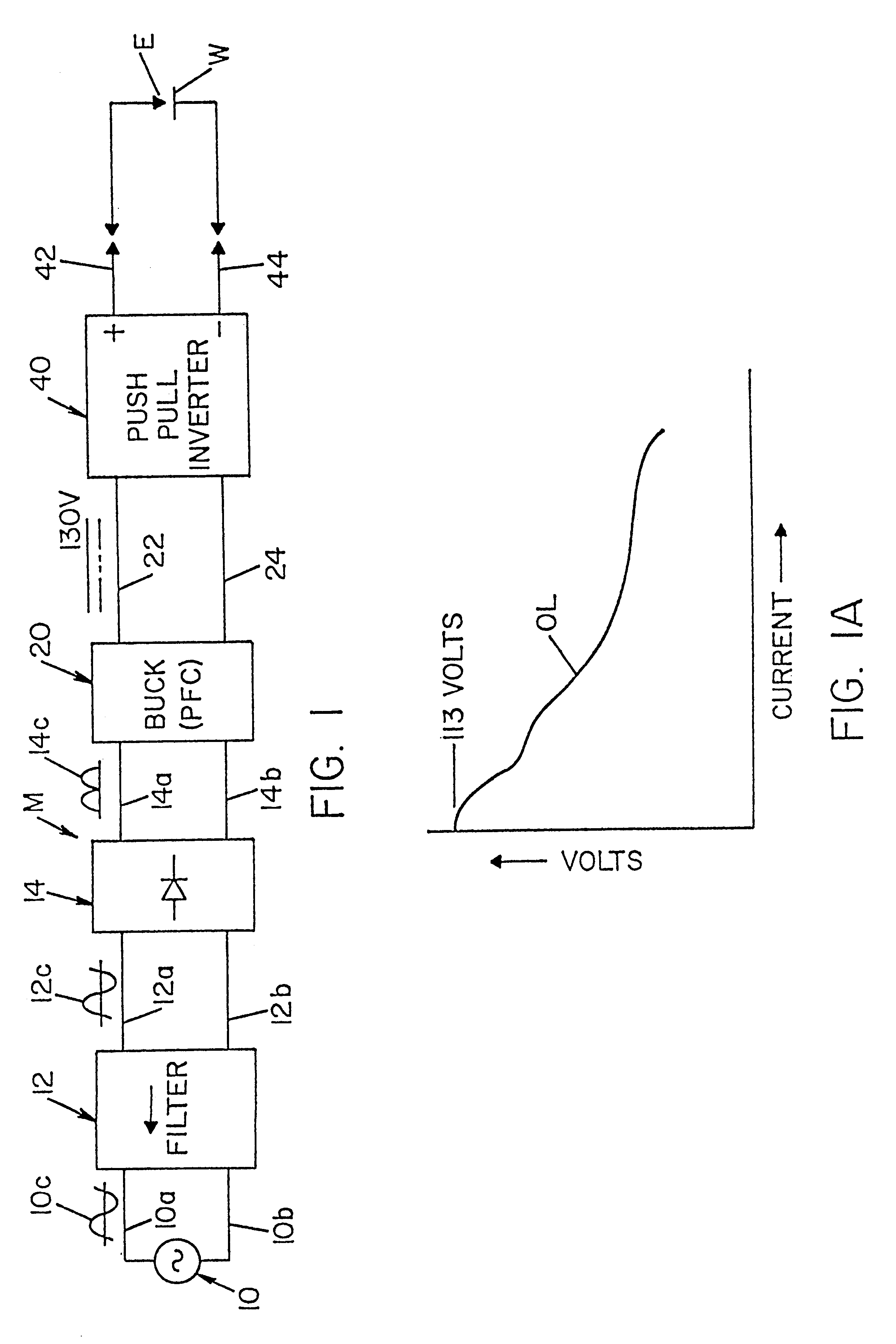
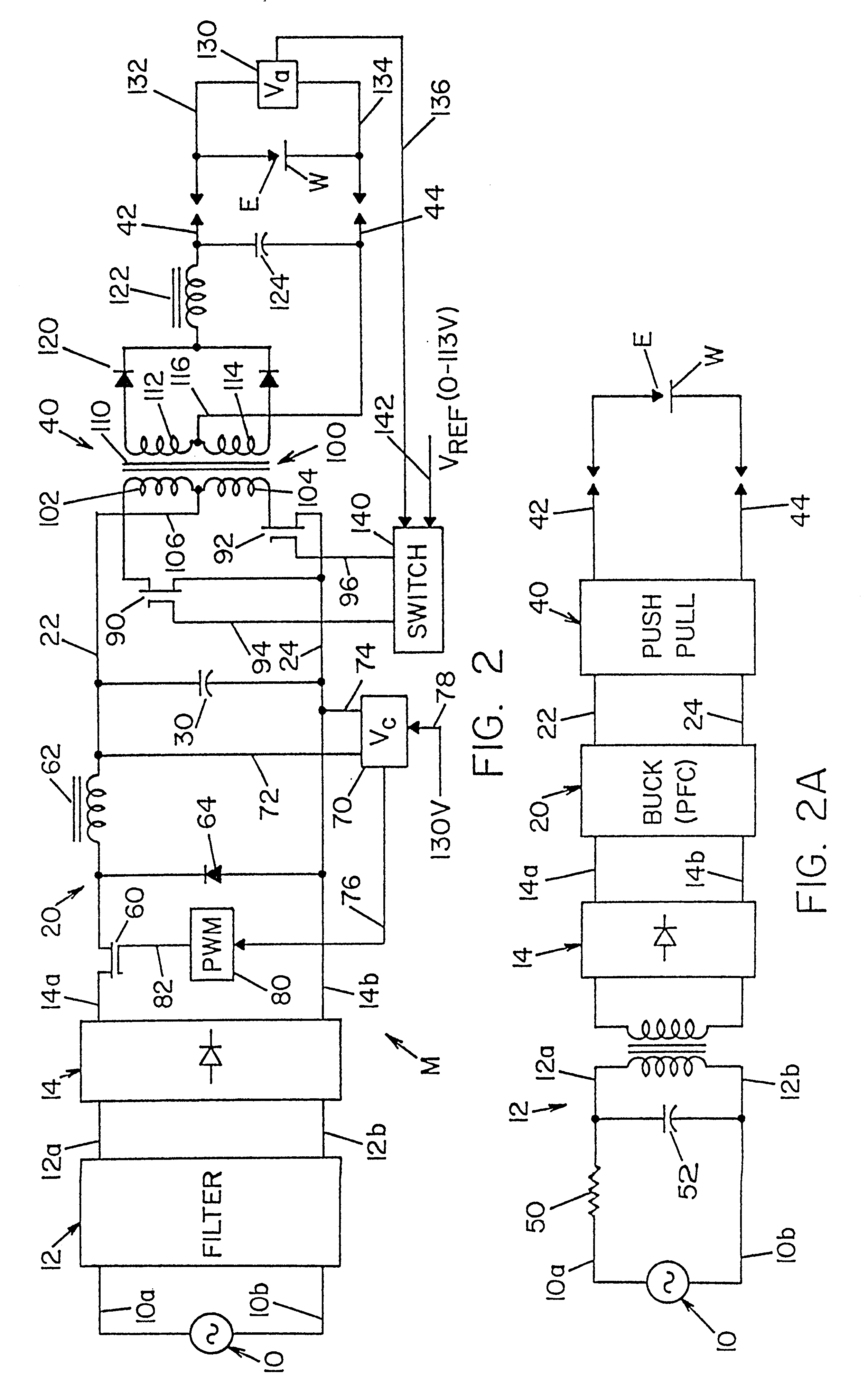
A single phase power supply module for electric arc welders and plasma arc cutters comprising: a single phase input stage; positive and negative output terminals; a full wave rectifier connected to the input stage for rectifying the single phase voltage at the input stage; a buck converter type power factor correcting circuit for controlling current flow from the input stage to the rectifier, which buck converter has an output capacitor regulated to an intermediate voltage in the range of 100-150 volts; and, a high speed DC to DC converter having an internal transformer coupling applying voltage across the output terminals and means for regulating the applied voltage to an output voltage in the range of 0-113 volts. The module is universal and several can be connected in parallel, in series or to switch networks to construct several welders or cutters.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
Ballast circuit for high intensity discharge lamps
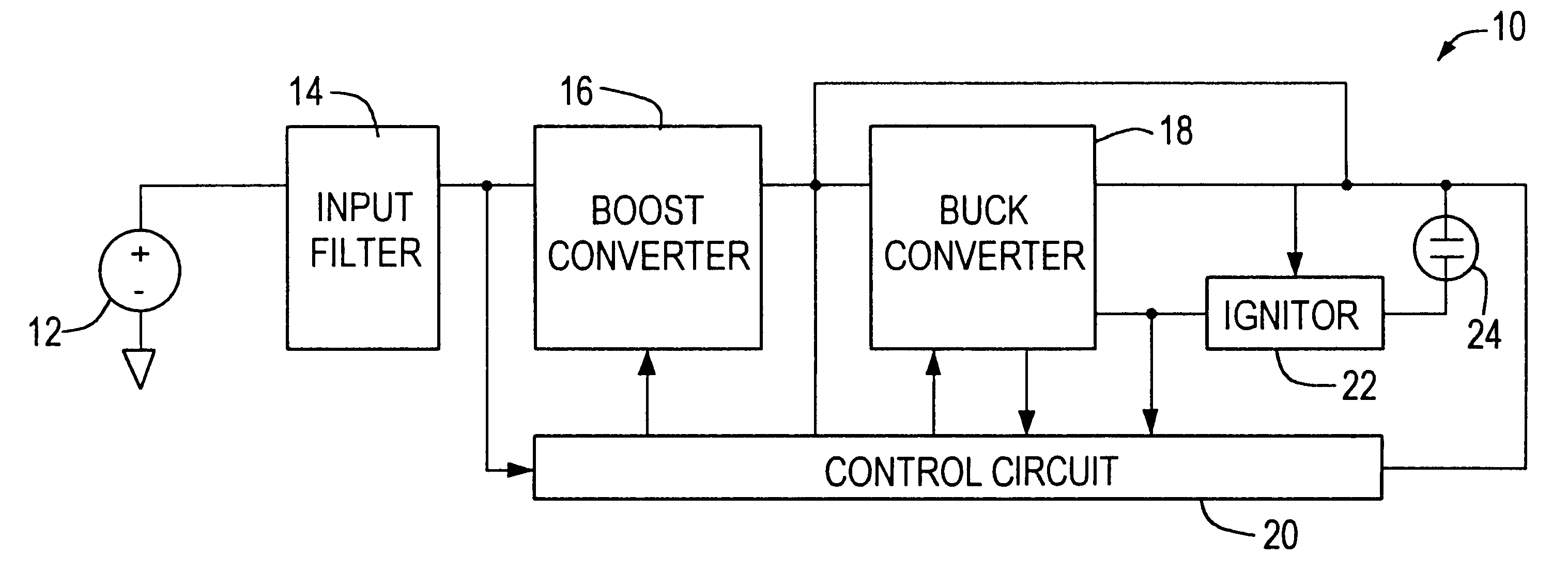
InactiveUS6181084B1Eliminate flickeringMinimises levelAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcBuck converterBoost controller
A ballast circuit for a high intensity discharge lamp includes a boost converter, responsive to a dc input voltage, for providing a boosted dc output voltage; a boost controller, responsive to the boosted dc output voltage, for driving the boost converter to maintain the boosted output voltage at a predetermined level; a buck converter, responsive to the boosted dc output voltage, for providing a reduced dc output voltage; and a buck controller, responsive to the reduced output voltage, for driving the buck converter to operate the discharge lamp in a transition mode and maintaining the reduced dc output voltage at a preselected level for operating the discharge lamp in a steady state mode.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Complementary power supply system of wind and photovoltaic power generation based on super capacitor power storage
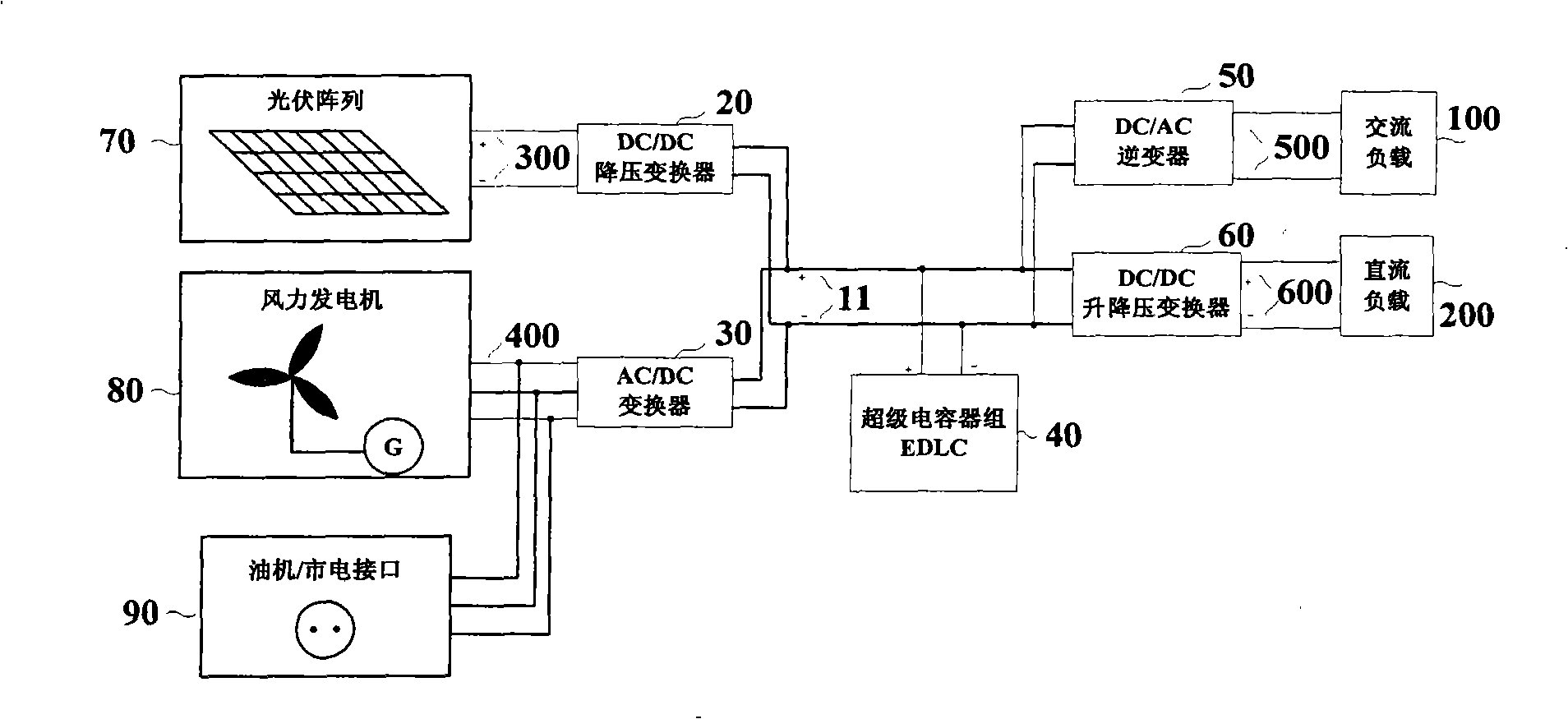
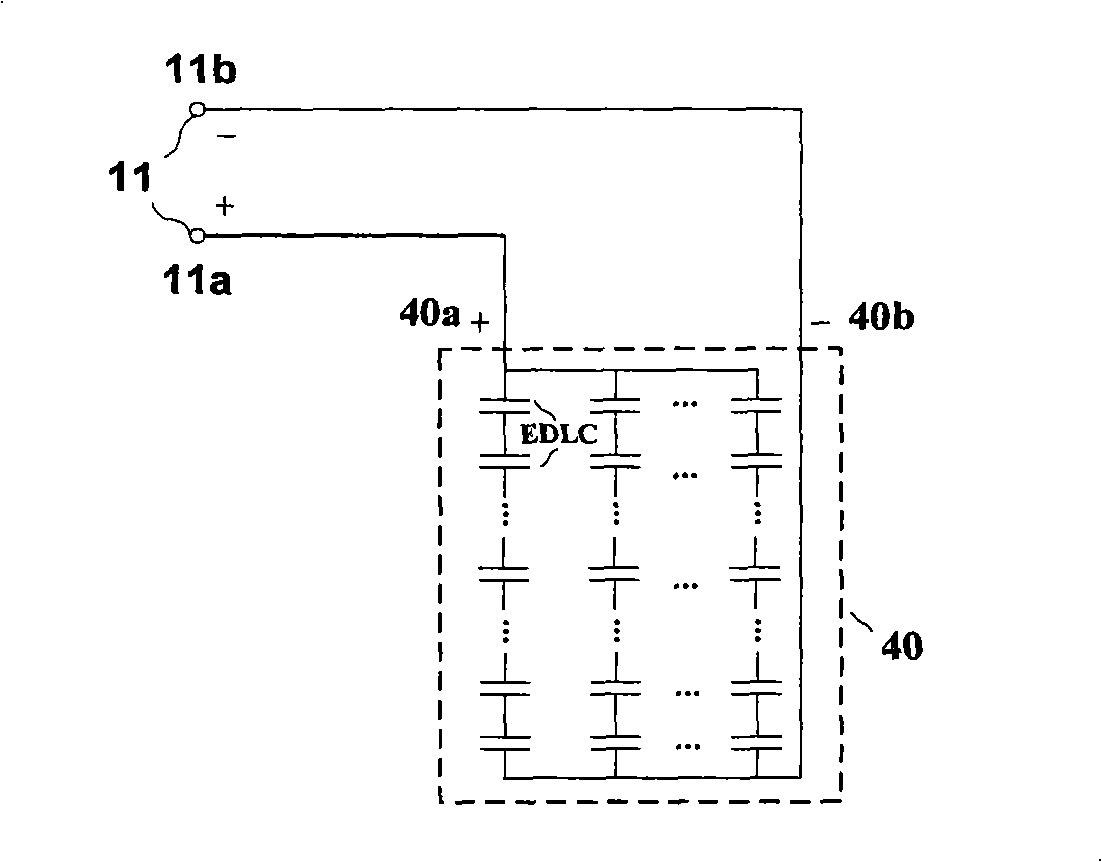
InactiveCN101286655AImprove securityImprove stabilityElectrical storage systemDc network circuit arrangementsLight energyEngineering
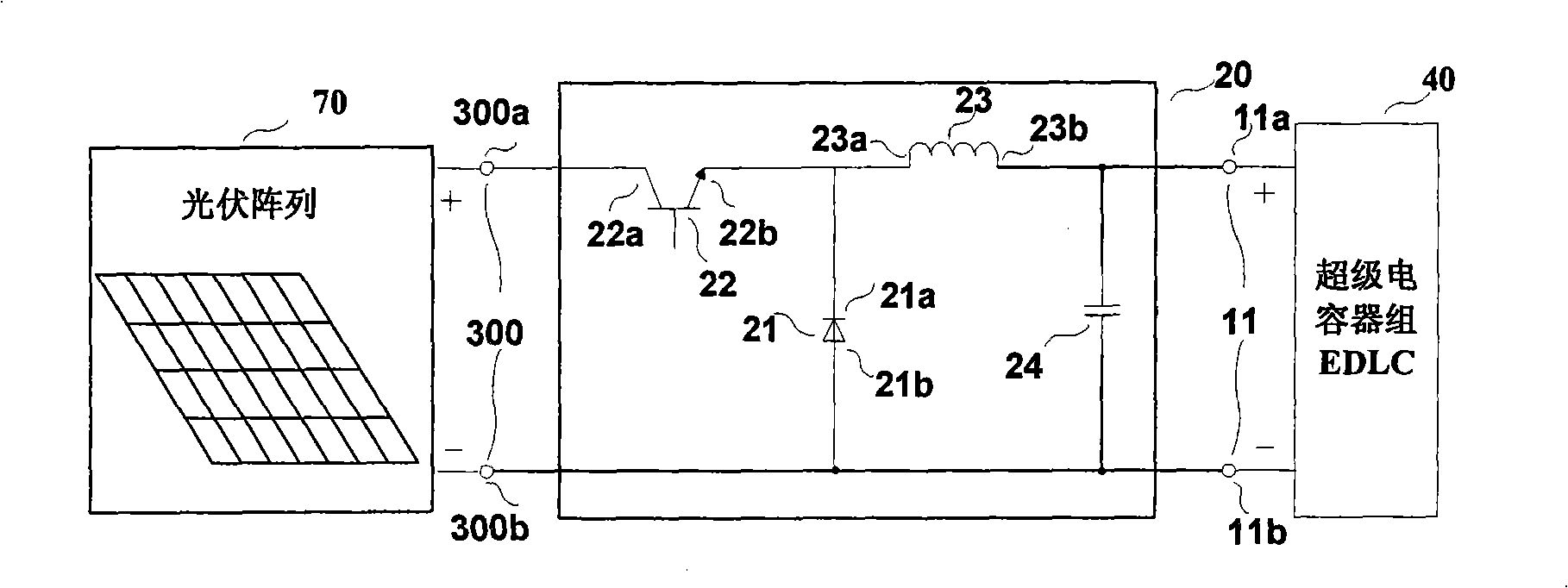
The invention relates to a wind energy and light energy complementary power supply system based on the energy storage of a super-capacitor, which comprises a DC / DC buck converter (20), an AC / DC converter (30), a super-capacitor unit (40), a DC / AC inverter (50), a DC / DC boost-buck converter (60), a photovoltaic array (70), a wind mill generator (80), an oil engine / commercial power interface (90), an AC load (100) and a DC load (200). The photovoltaic array (70) is connected with the super-capacitor unit (40) by the DC / DC buck converter (20). The wind mill generator (80) and the oil engine / commercial power interface (90) are connected with the super-capacitor unit (40) by the AC / DC converter (30). The super-capacitor unit (40) supplies power to the AC load (100) by the DC / Ac inverter (50) and the DC load (200) by the DC / DC boost-buck converter (60). The invention provides a super-capacitor energy storage device used for the wind energy and light energy complementary power supply system, which can continuously provide power for the communication systems and the residents in remote areas where a distribution network cannot reach.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ethernet to phase shift key converter
InactiveUS6556581B1Modulated-carrier systemsRepeater/relay circuitsBandpass filteringDifferential signaling
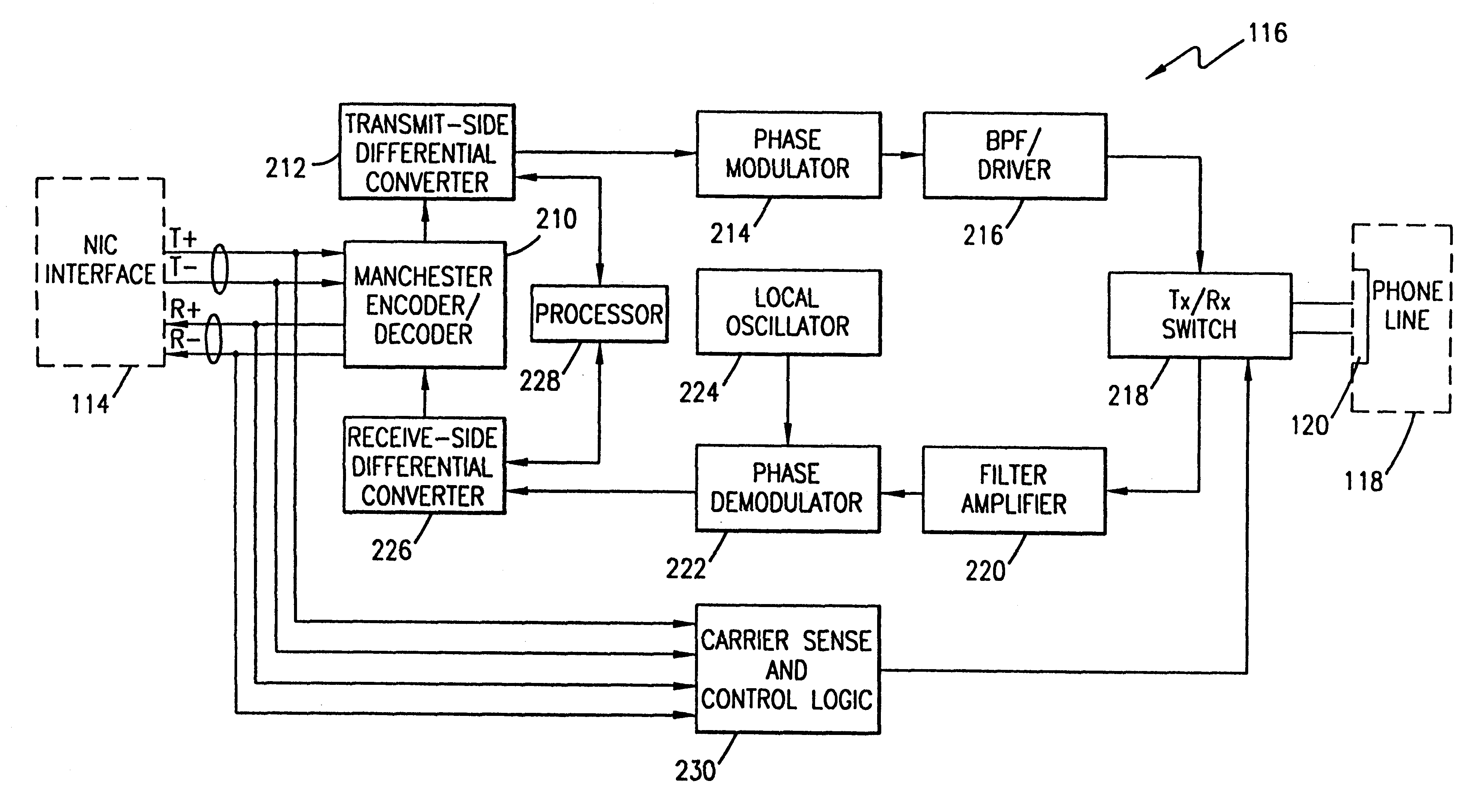
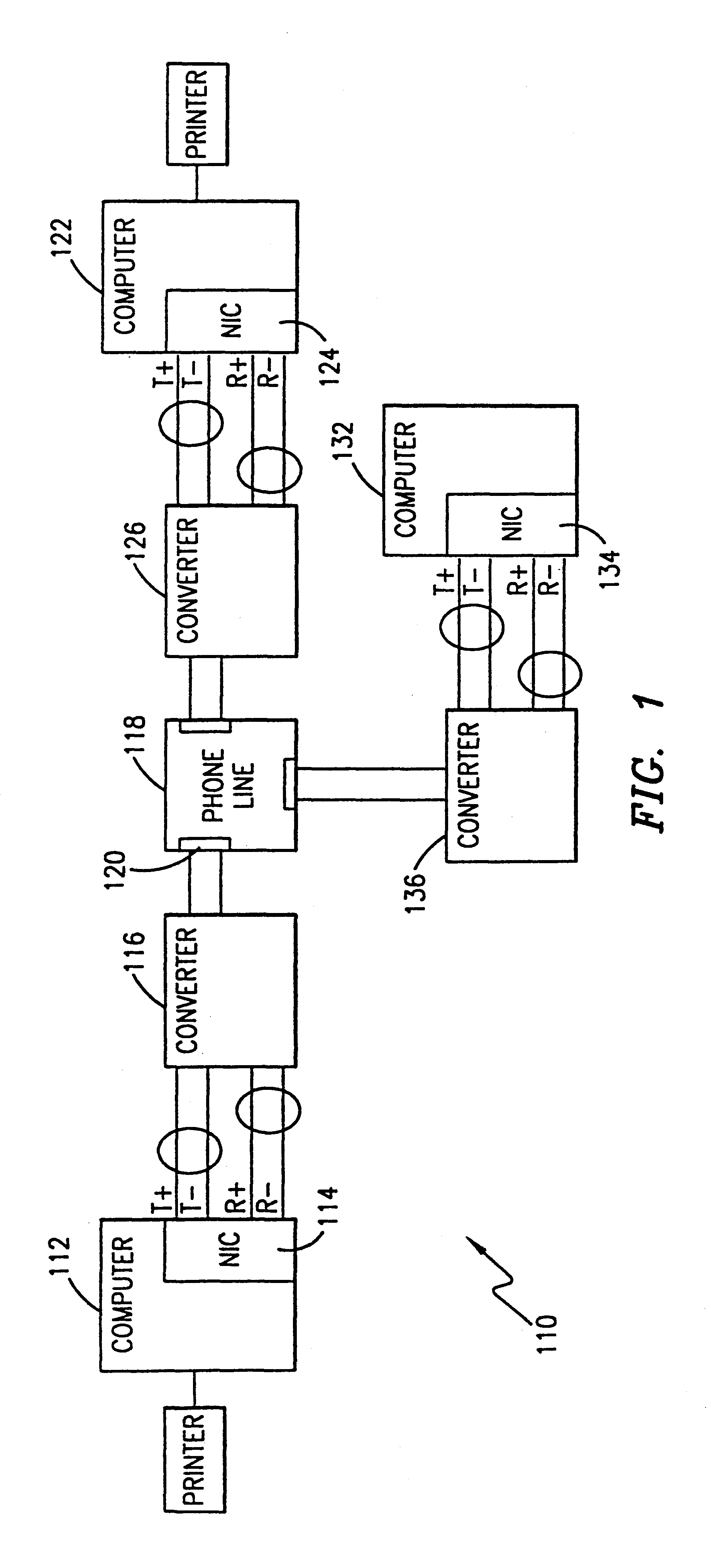
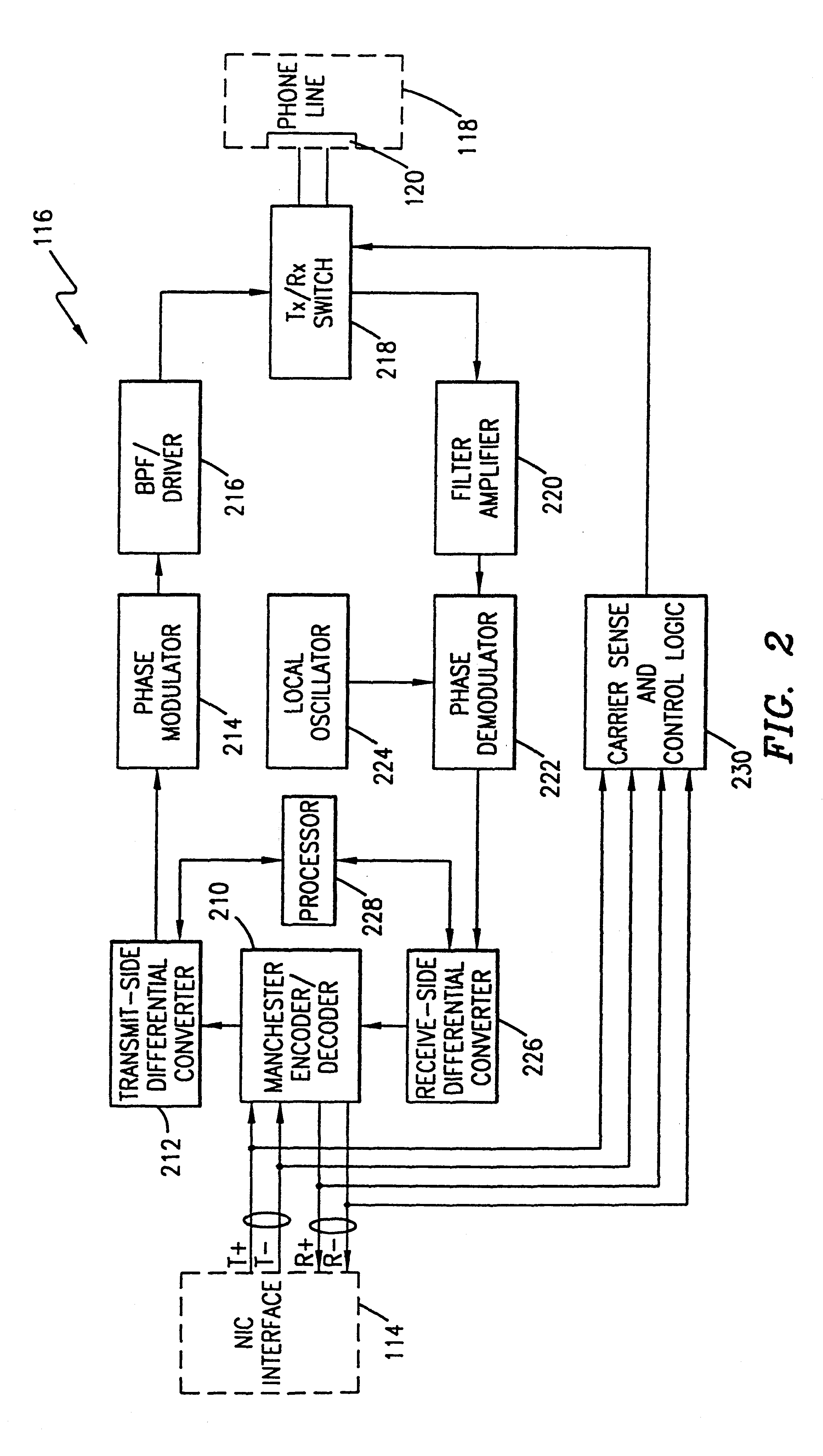
A device for seamlessly providing 10BASE-T compatible data communications over an ordinary single twisted-pair home phone line between multiple computers and / or peripherals is disclosed. Each component that is to communicate over a home phone line needs a 10BASE-T compatible network interface card (NIC) for interfacing with the device. A transmit / receive switch is used to switch the device between a transmit mode and a receive mode. When a signal is being transmitted from a component, a Manchester decoder converts the signals received from the NIC into a raw data stream. A differential converter converts the raw data signal received from the NIC to a differential signal. A modulator is used to modulate the signal to a RF signal using a PSK, QPSK, QAM, MCM or similar modulation schemes. A filter is used to limit the bandwidth of the modulated signal and a driver is used to amplify the signal to match the impedance of the phone line. When the device receives a signal over the phone line, the signal is filtered using a bandpass filter and then amplified. The signal is then demodulated using an appropriate demodulation scheme before being differentially encoded. A Manchester encoder encodes the received signal for compatible operation with a receiving NIC.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
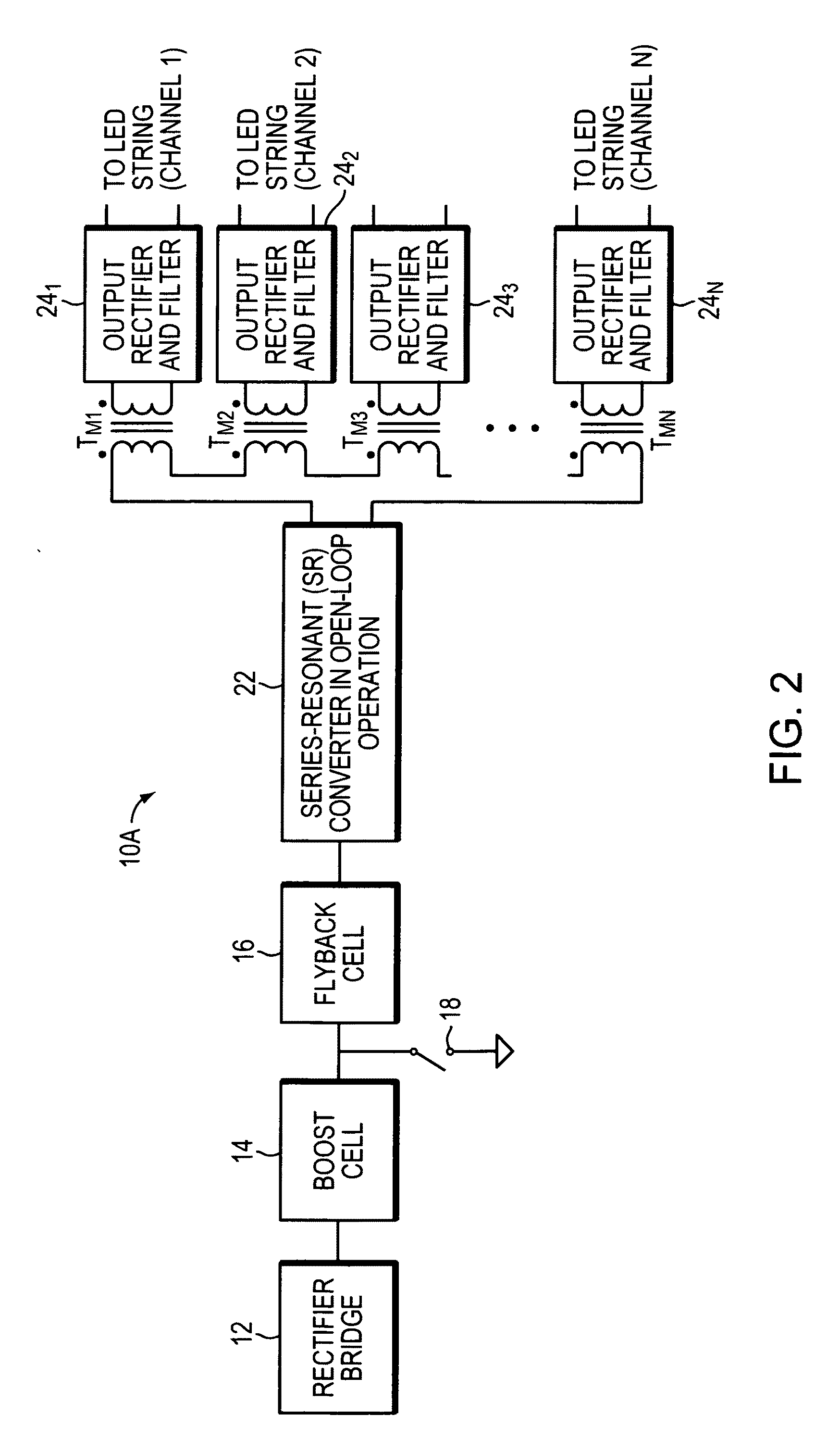
Multi Channel LED Driver
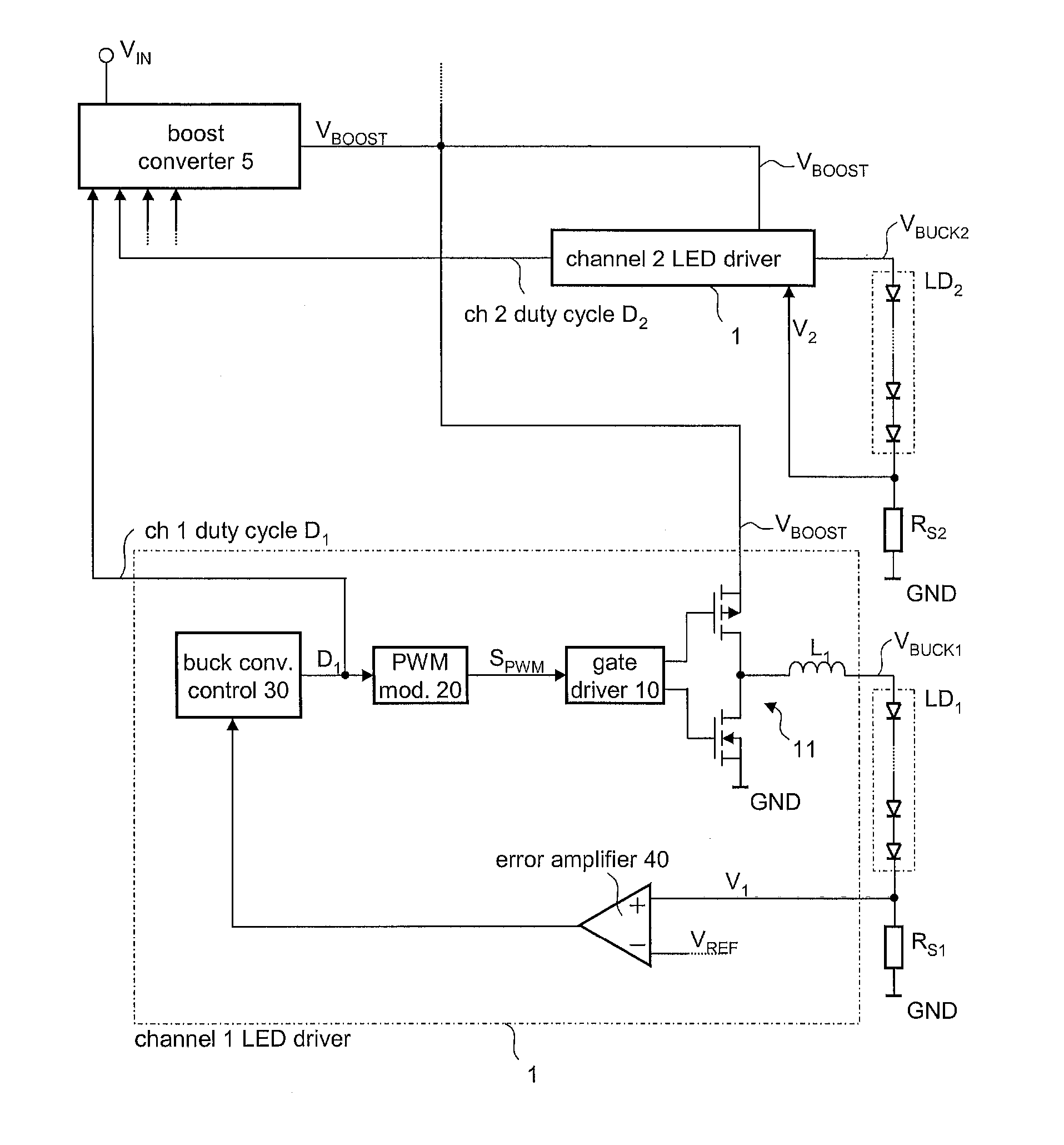
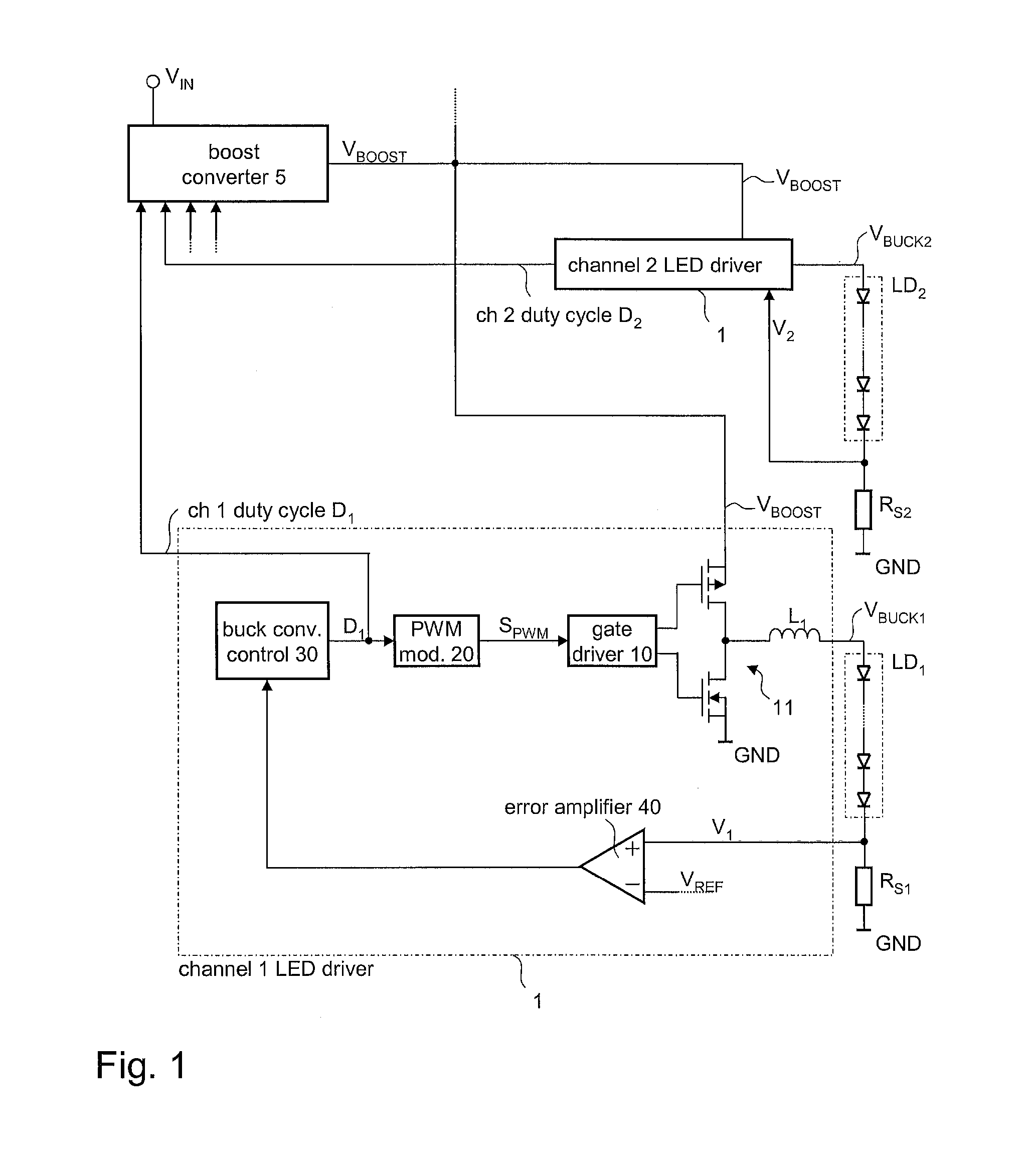
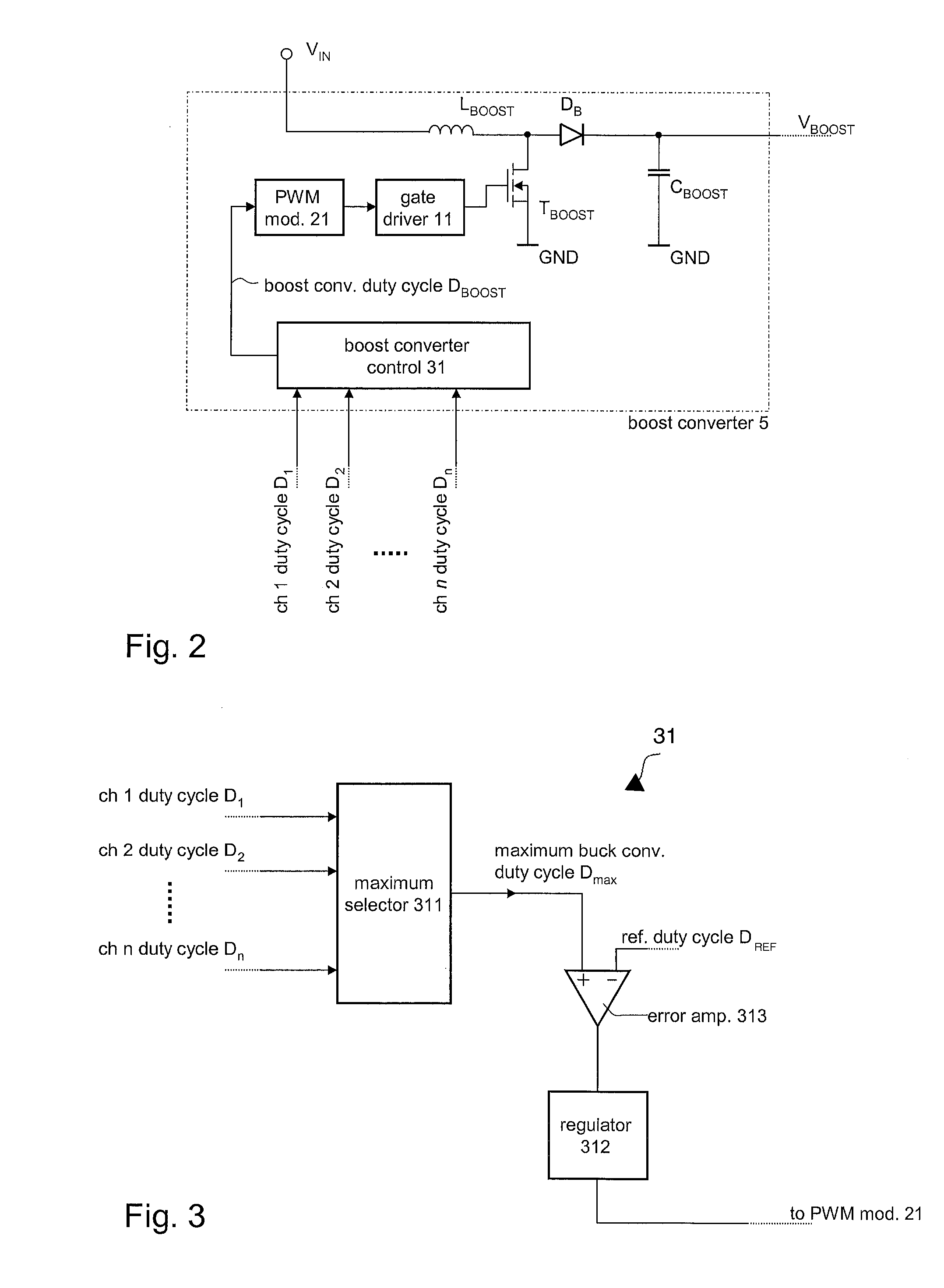
A driver circuit includes a buck converter associated with each LED chain for supplying a load current thereto. The buck converter receives an input voltage and is configured to provide a supply voltage to the associated LED chain such that the resulting load current of the LED chain matches at least approximately a predefined reference current value. The driver circuit further includes a switching converter that receives a driver supply voltage from a power supply and provides, as an output voltage, the input voltage for the buck converters. The switching converter is configured to provide an input voltage to the buck converters such that the maximum of the ratios between the input voltage and the supply voltages provided to the LED chains matches a predefined tolerance reference ratio.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Electric arc welder and plasma cutter
InactiveUS6177645B1Reduce Harmonic DistortionImprove power factorAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcFull waveEngineering
A single phase power supply module for electric arc welders and plasma arc cutters comprising: a single phase input stage; positive and negative output terminals; a full wave rectifier connected to the input stage for rectifying the single phase voltage at the input stage; a buck converter type power factor correcting circuit for controlling current flow from the input stage to the rectifier, which buck converter has an output capacitor regulated to an intermediate voltage in the range of 100-150 volts; and, a high speed DC to DC converter having an internal transformer coupling applying voltage across the output terminals and means for regulating the applied voltage to an output voltage in the range of 0-113 volts. The module is universal and several can be connected in parallel, in series or to switch networks to construct several welders or cutters.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
Two-stage voltage regulators with adjustable intermediate bus voltage, adjustable switching frequency, and adjustable number of active phases
InactiveUS20050184713A1Improve efficiencyWide variationEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionBuck converterEngineering
A two-stage power converter that dynamically adjusts to output current requirements includes a first stage regulator that provides power to a second stage regulator. The first stage can be a buck converter, and the second stage can be a multiple-phase buck converter. The output voltage of the first stage (intermediate bus voltage Vbus) is varied according to the load current to optimize conversion efficiency. To provide maximum efficiency, the Vbus voltage is increased as load current increases. The Vbus voltage provided by the first stage can be varied by duty cycle or operating frequency control. In another embodiment, the switching frequency of the second stage is varied as output current changes so that output current ripple is held constant. In an embodiment employing a multiple-phase buck converter in the second stage, the number of operating phases are varied as output current changes.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Low power A/D converter
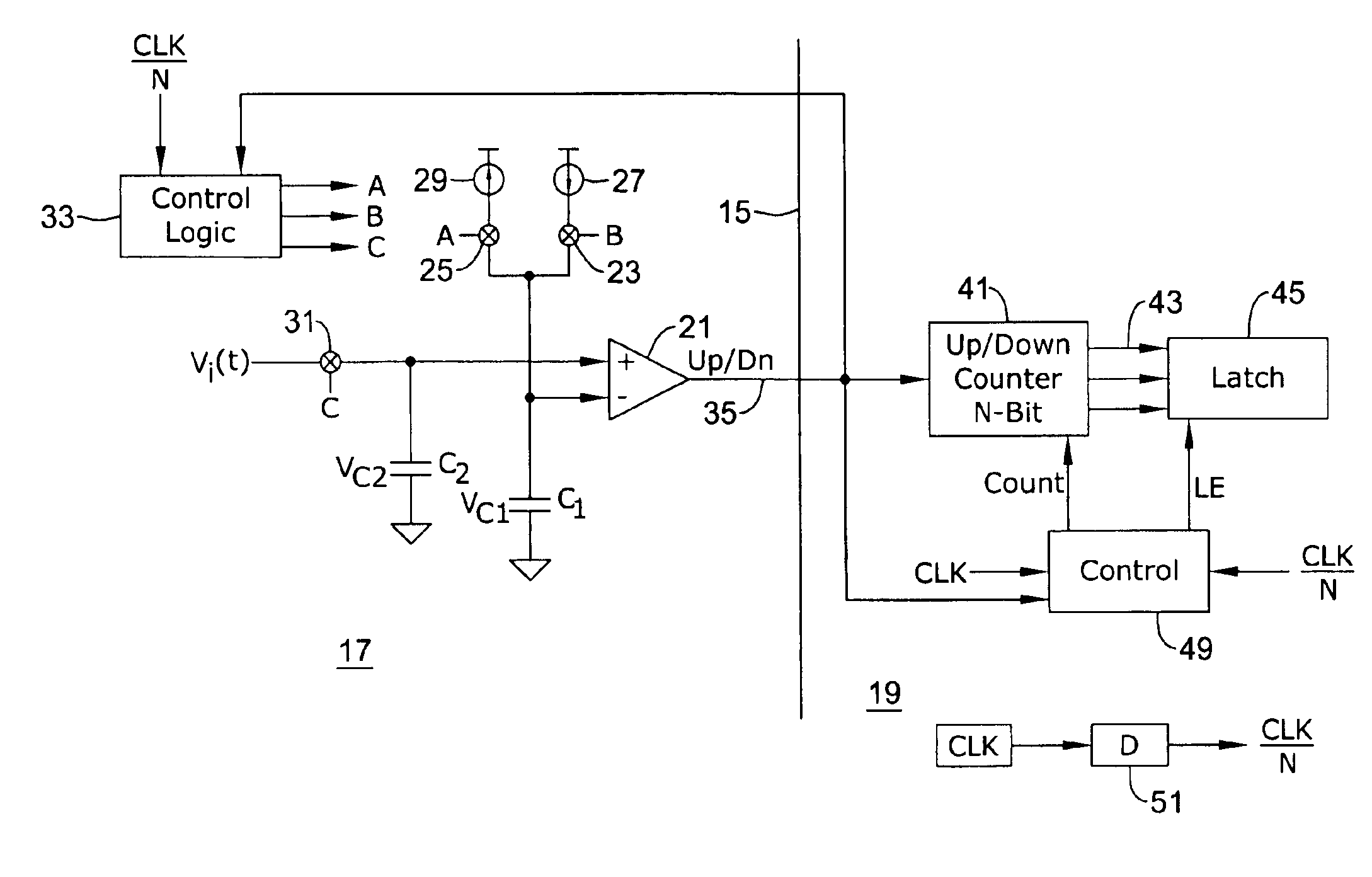
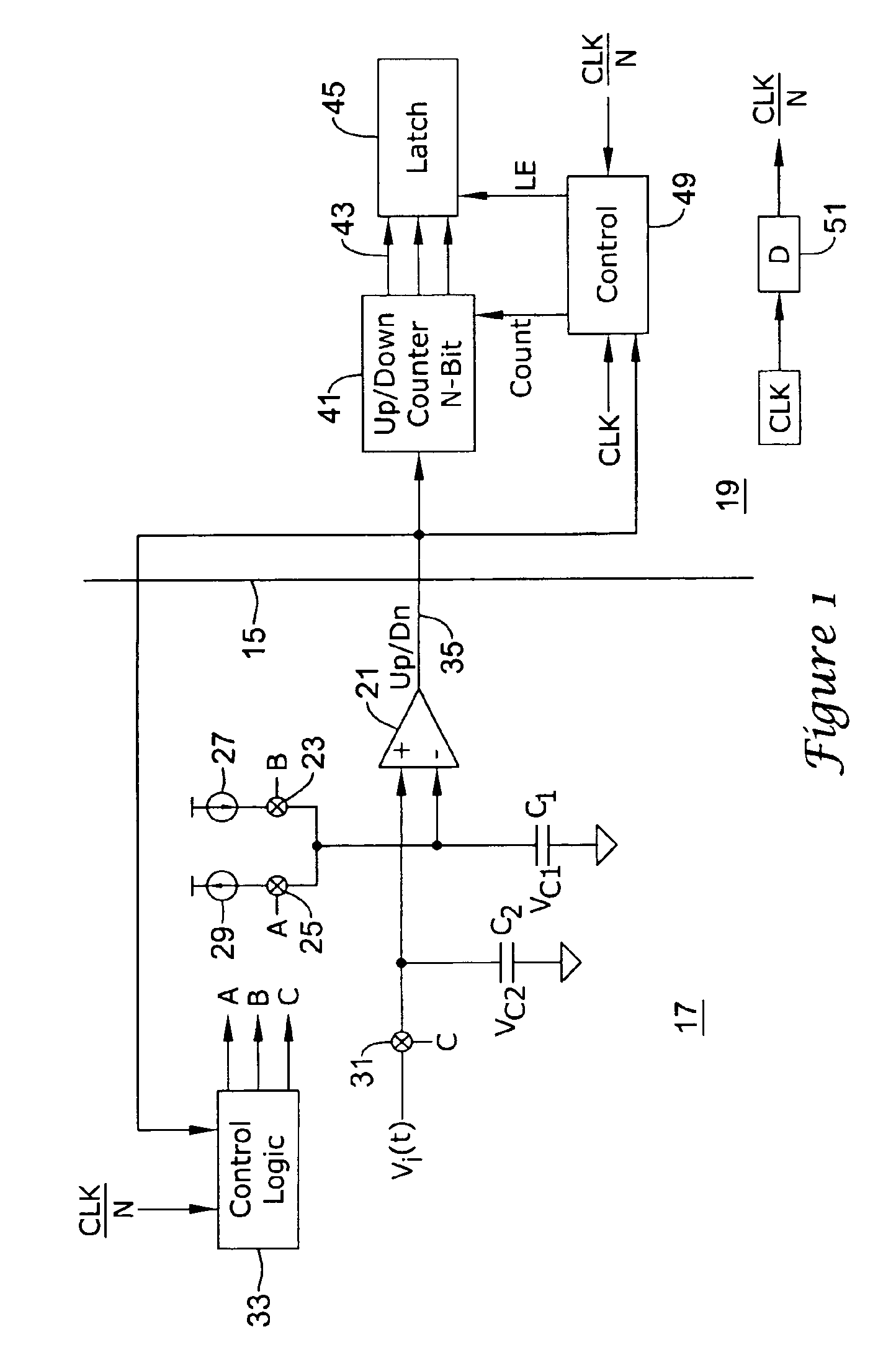
InactiveUS6927721B2Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsBuck converterĆuk converter
A comparator is arranged to compare a series of analog voltage signal samples on a first capacitor with a voltage on a second capacitor which is linearly increased or decreased to equal the sample value. The comparator's single output freezes the count of the counter at counts which are proportional to the voltage of the respective samples. In this manner, analog to digital conversion can be accomplished using a single line between the analog and digital sides of a circuit, thereby reducing parasitic capacitance.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
LED Illumination systems
InactiveUS20110309760A1Improve reliabilityLow costEfficient power electronics conversionElectroluminescent light sourcesBuck converterFlyback diode
An illumination system includes a power supply having a boost converter operating in the discontinuous conduction mode, a flyback converter operating in the critical conduction mode, and a switch coupled to the flyback converter. Several light emitting diodes receive power from the power supply. The boost converter may include a boost inductor (LB) and a boost diode (DB), constructed to perform the boost power factor correction (PFC) function. The flyback converter may includes a flyback inductor (LFB) and a flyback diode (DFB) and the power supply may be constructed to turn on the switch around the point where the current flowing in the flyback inductor reaches zero value.
Owner:EMD TECH
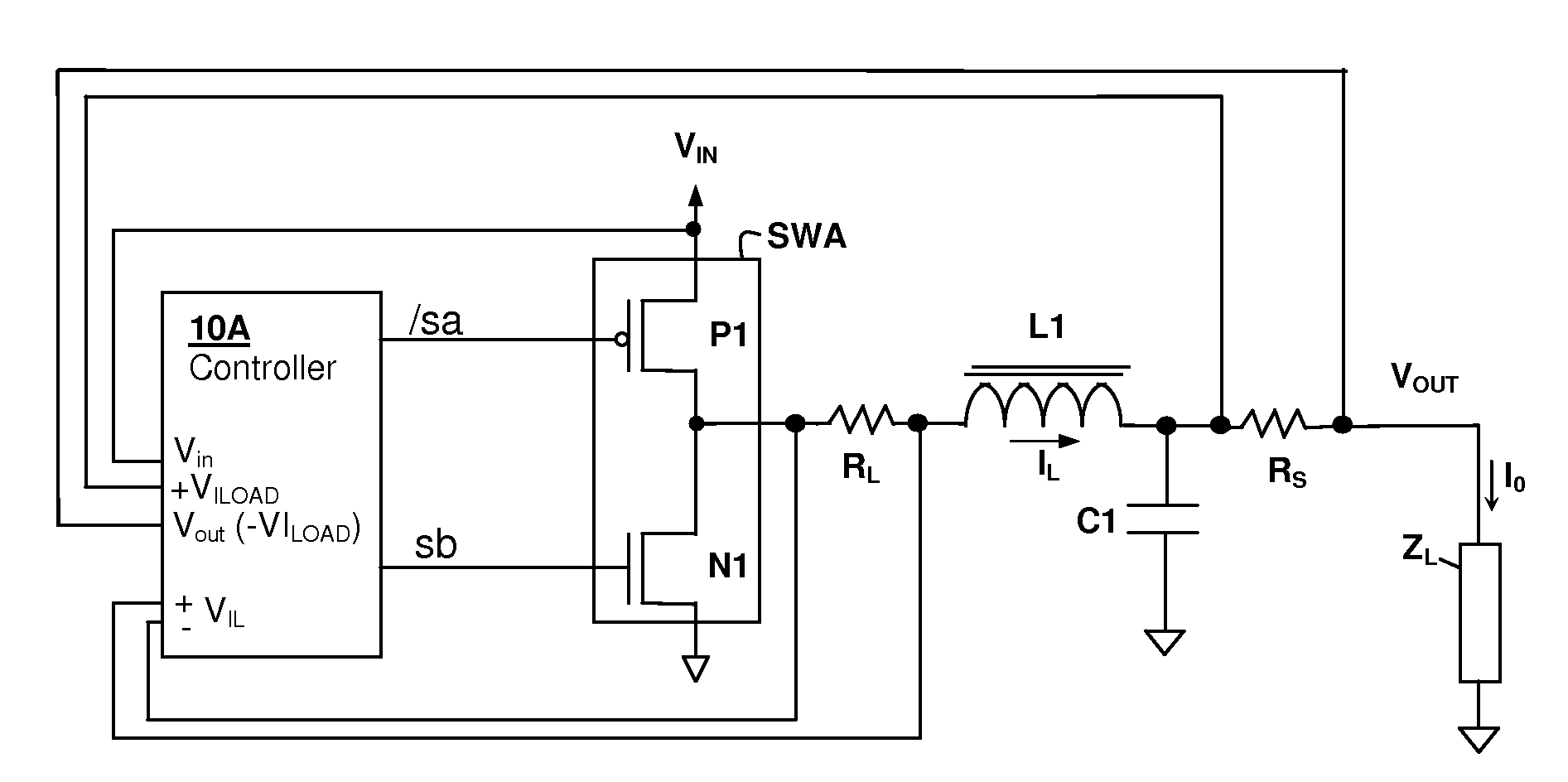
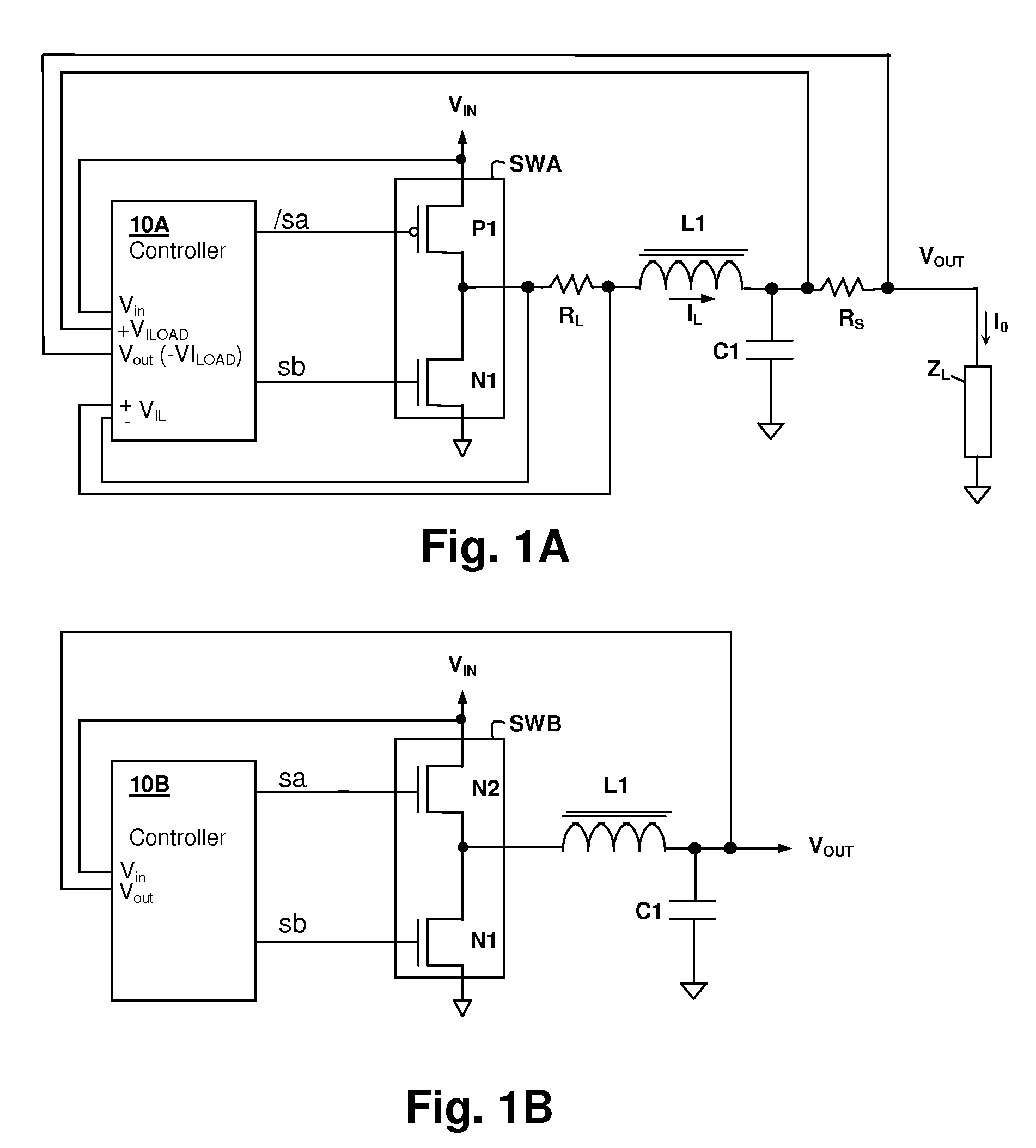
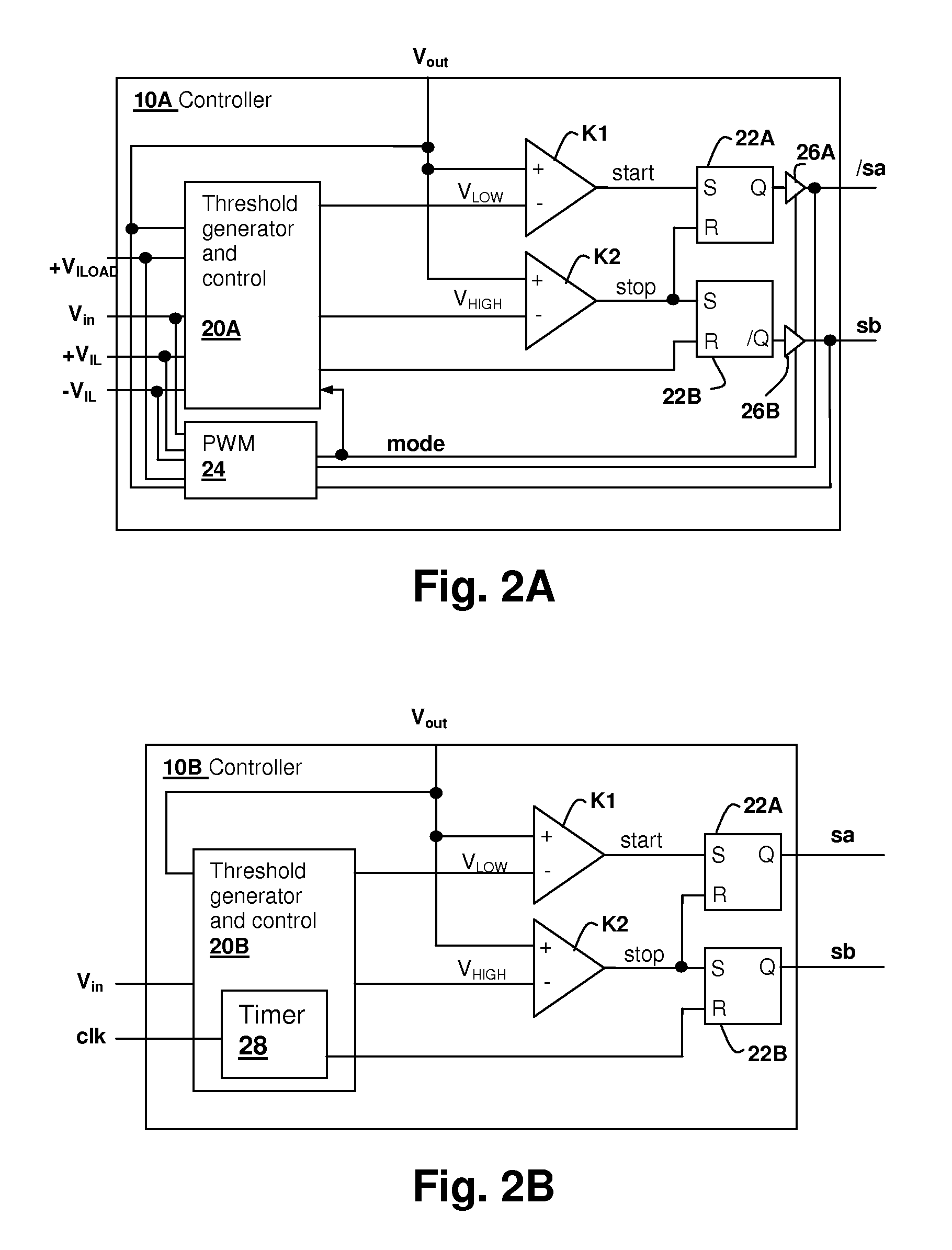
Hysteretic buck converter having dynamic thresholds
ActiveUS20090322300A1Improved ripple controlEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsBuck converterĆuk converter
A hysteretic buck converter provides improved regulation control, in particular for buck converter standby operation. A comparison circuit compares the output voltage of the buck converter to a waveform that is generated from an indication of the output current of the converter, so that the turn-on time of the converter is advanced as the output current demand increases. The resulting action anticipates a reduction in output voltage due to the increased current, preventing an excursion of the output voltage below the ripple voltage minimum. The turn-off time of the converter is controlled by an upper threshold that limits the ripple voltage maximum. The output current indication may be a measurement of output current, or may be a dynamic value calculated from the input voltage and the output voltage waveform.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com