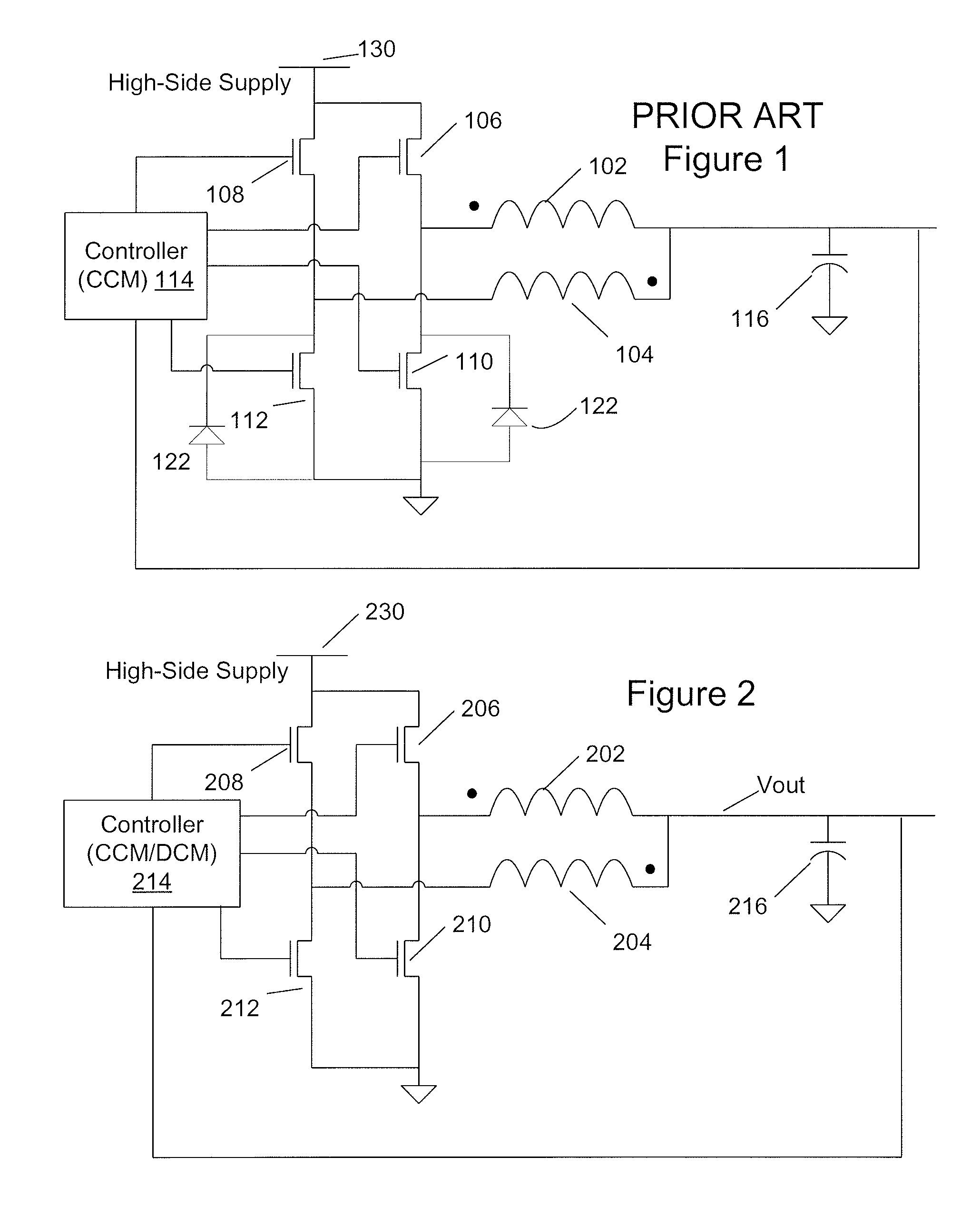
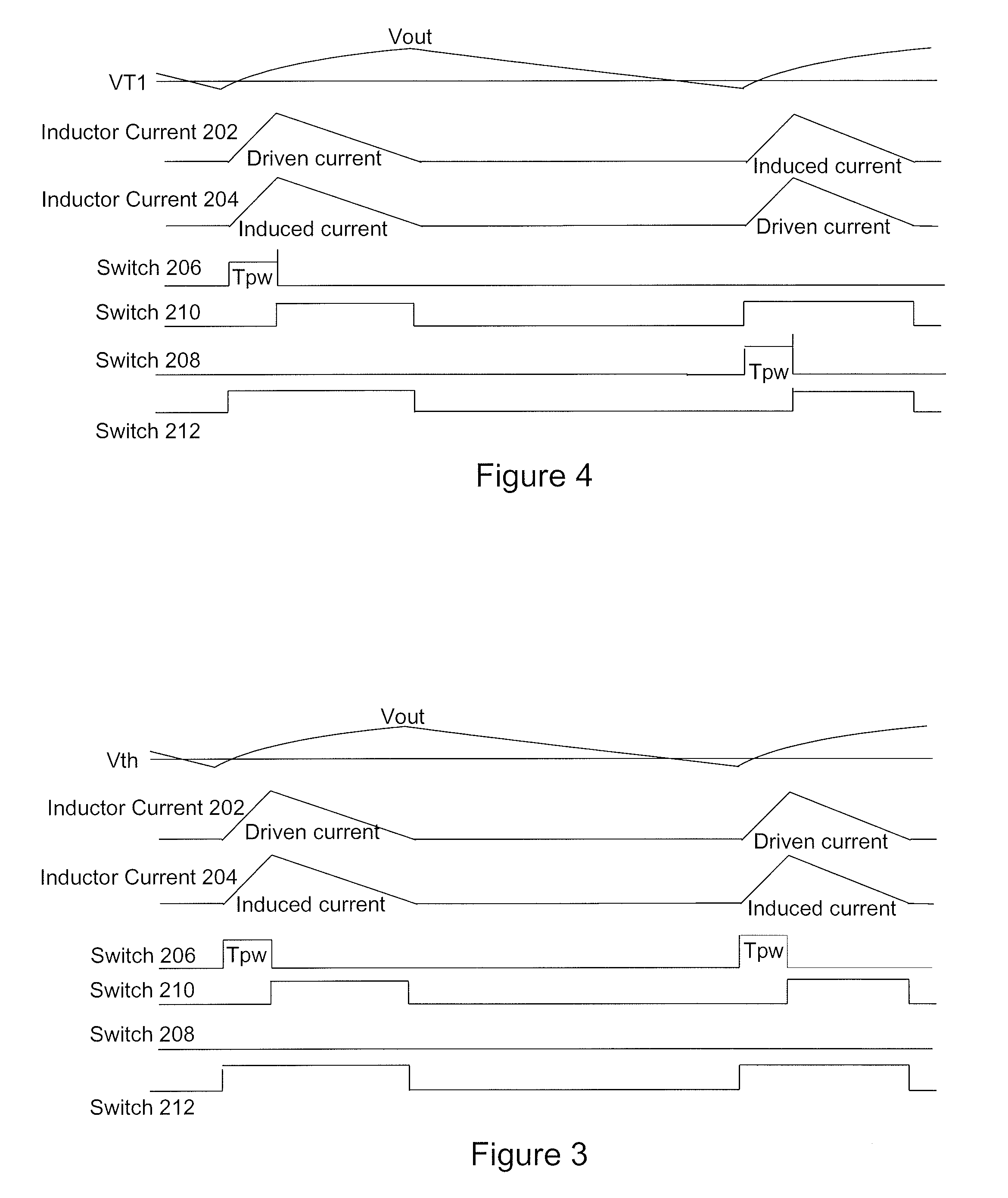
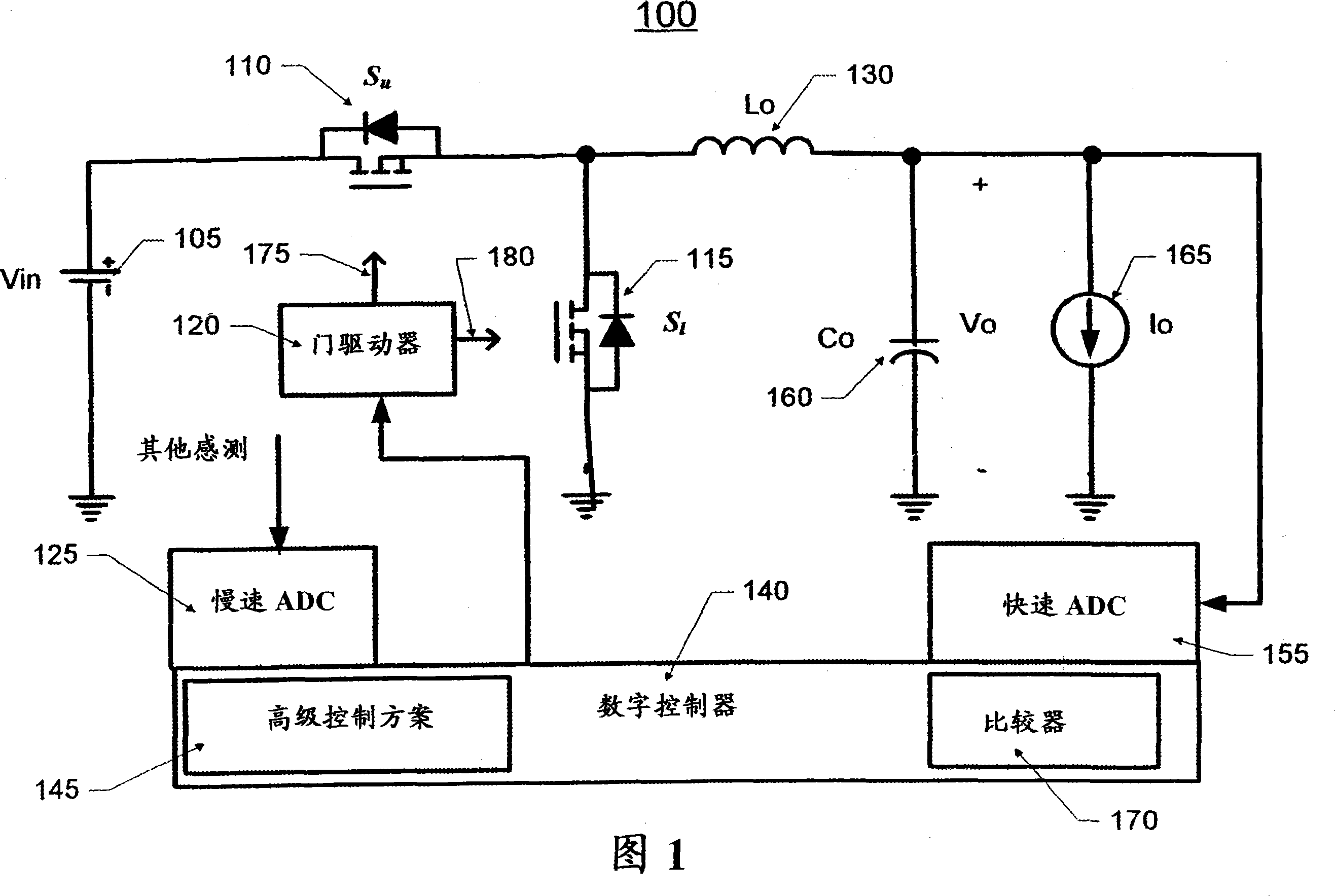
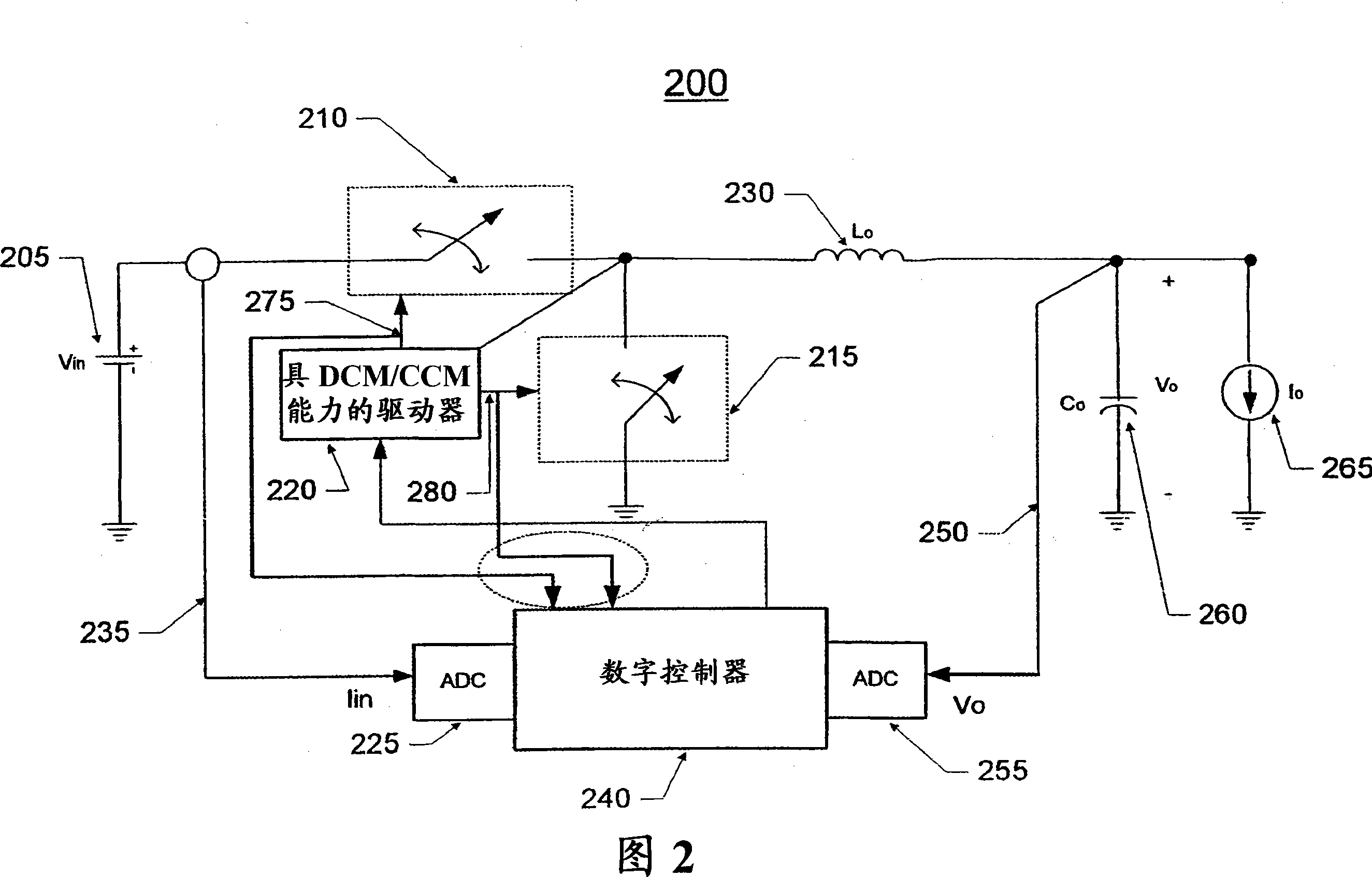
Patents
Literature
216 results about "Discontinuous conduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
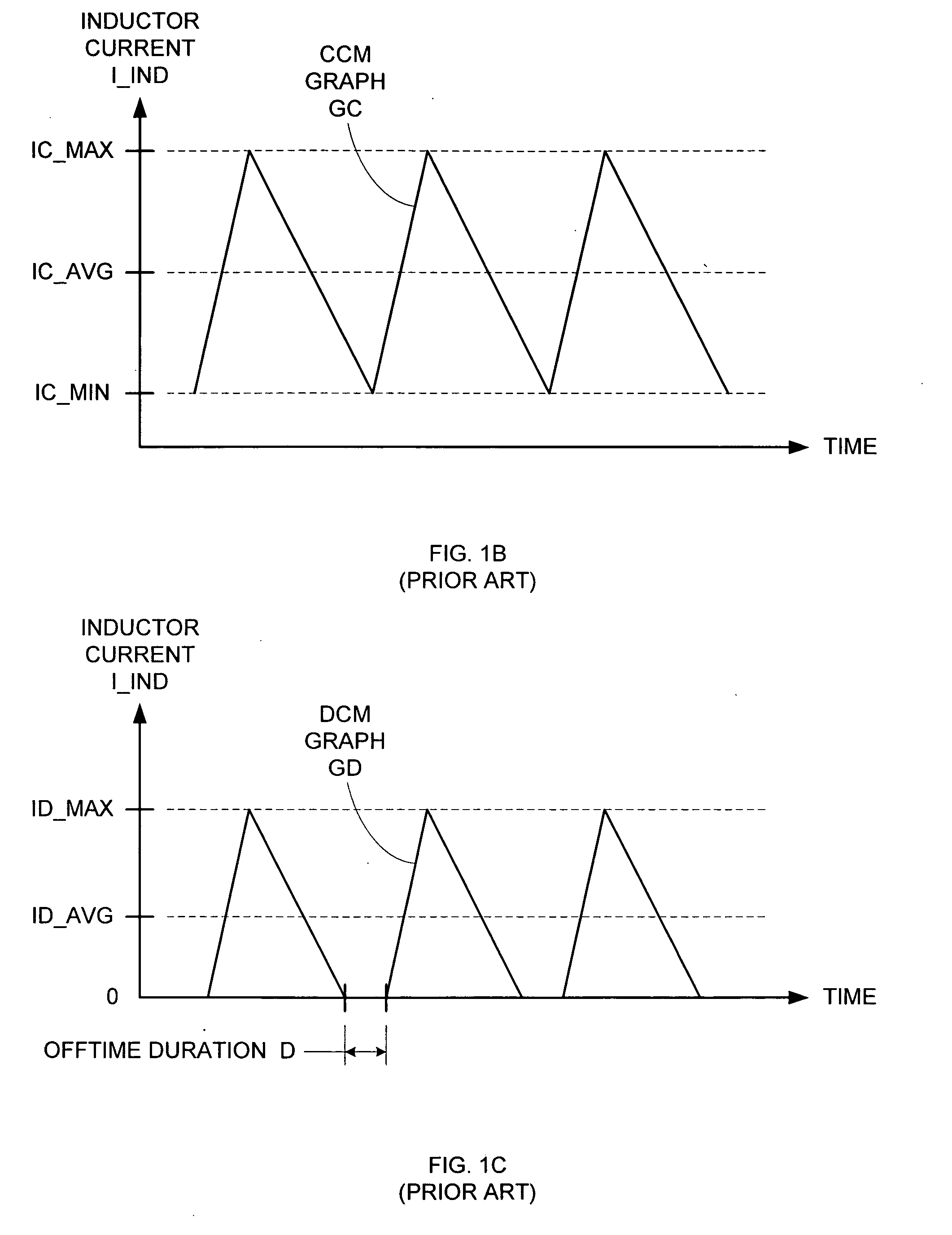
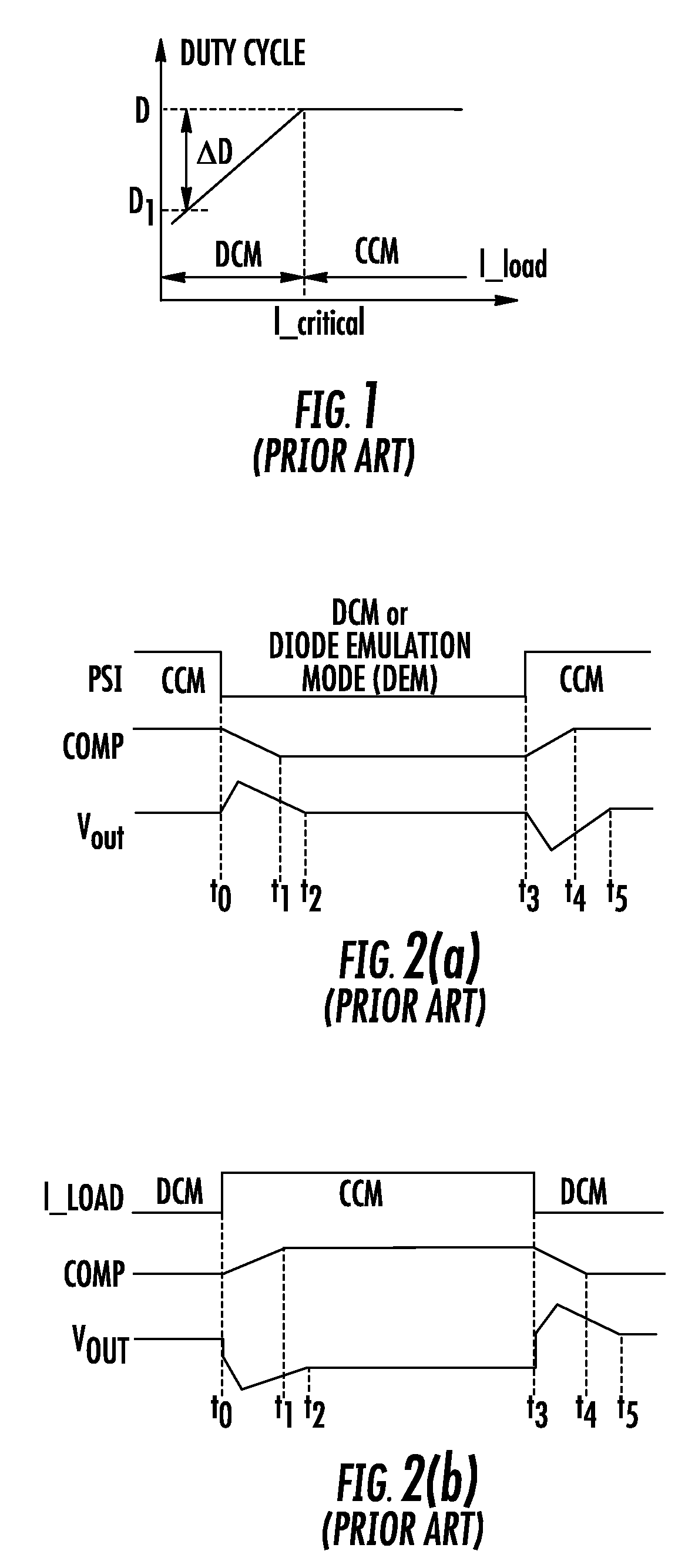
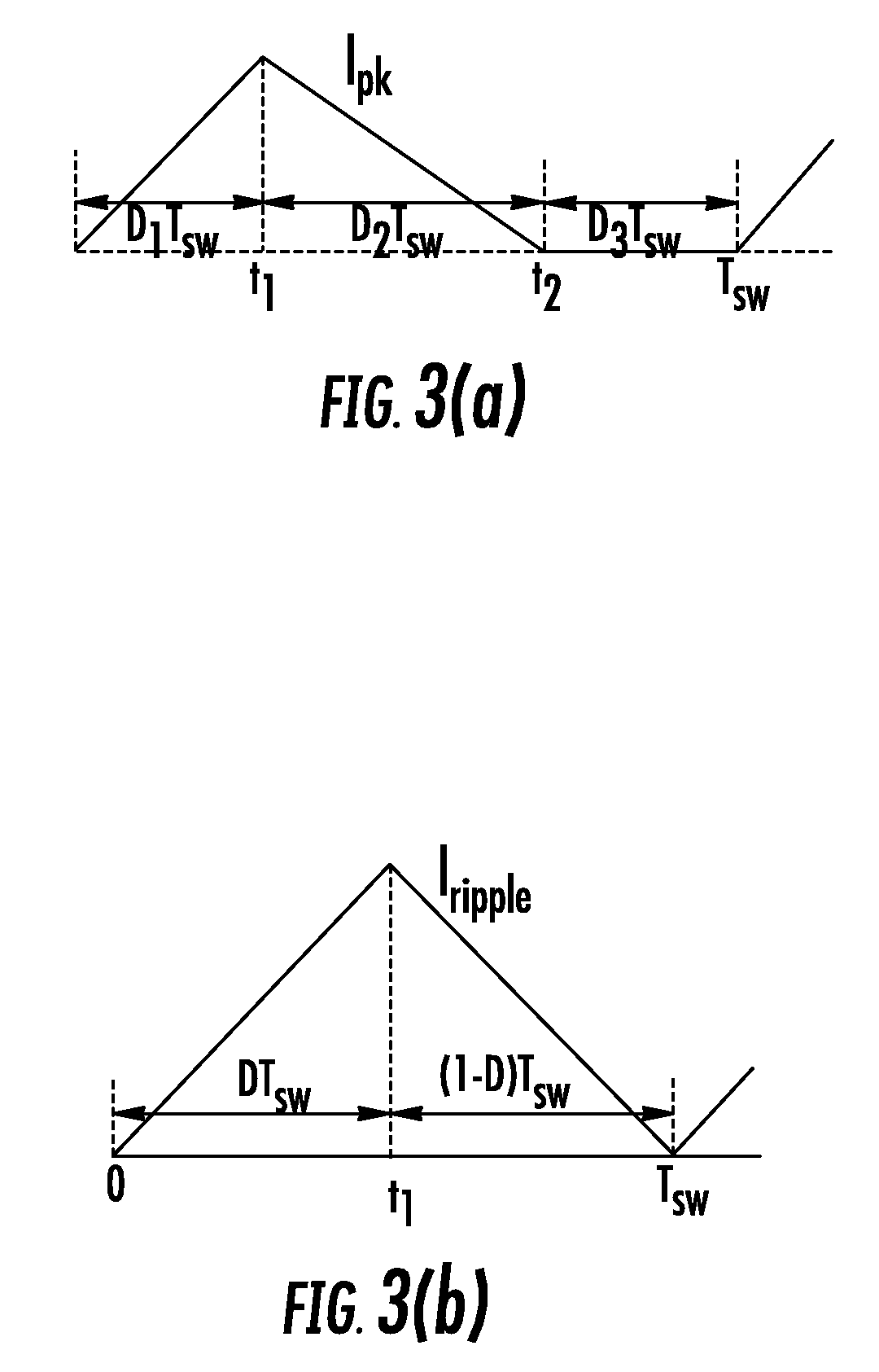
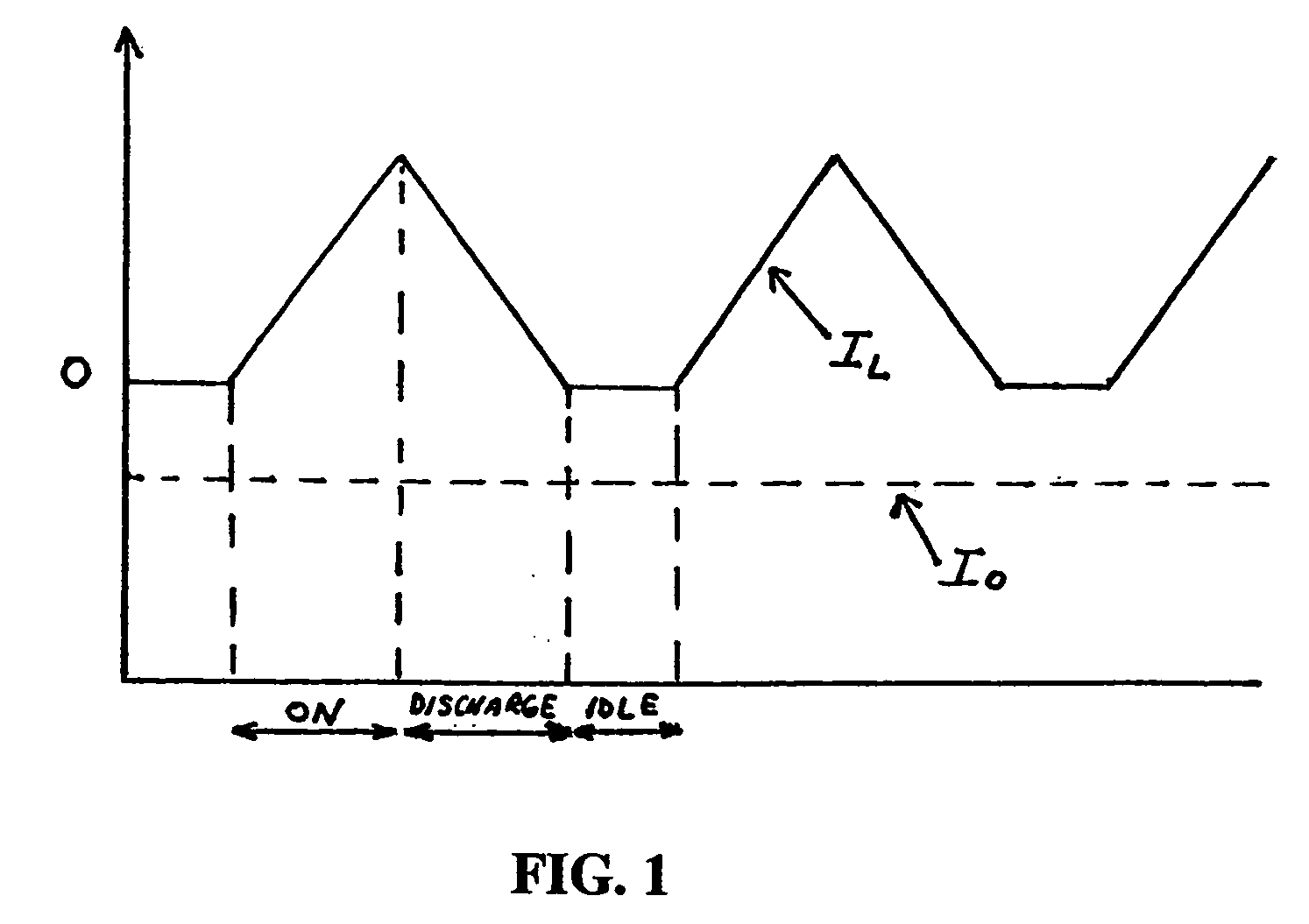
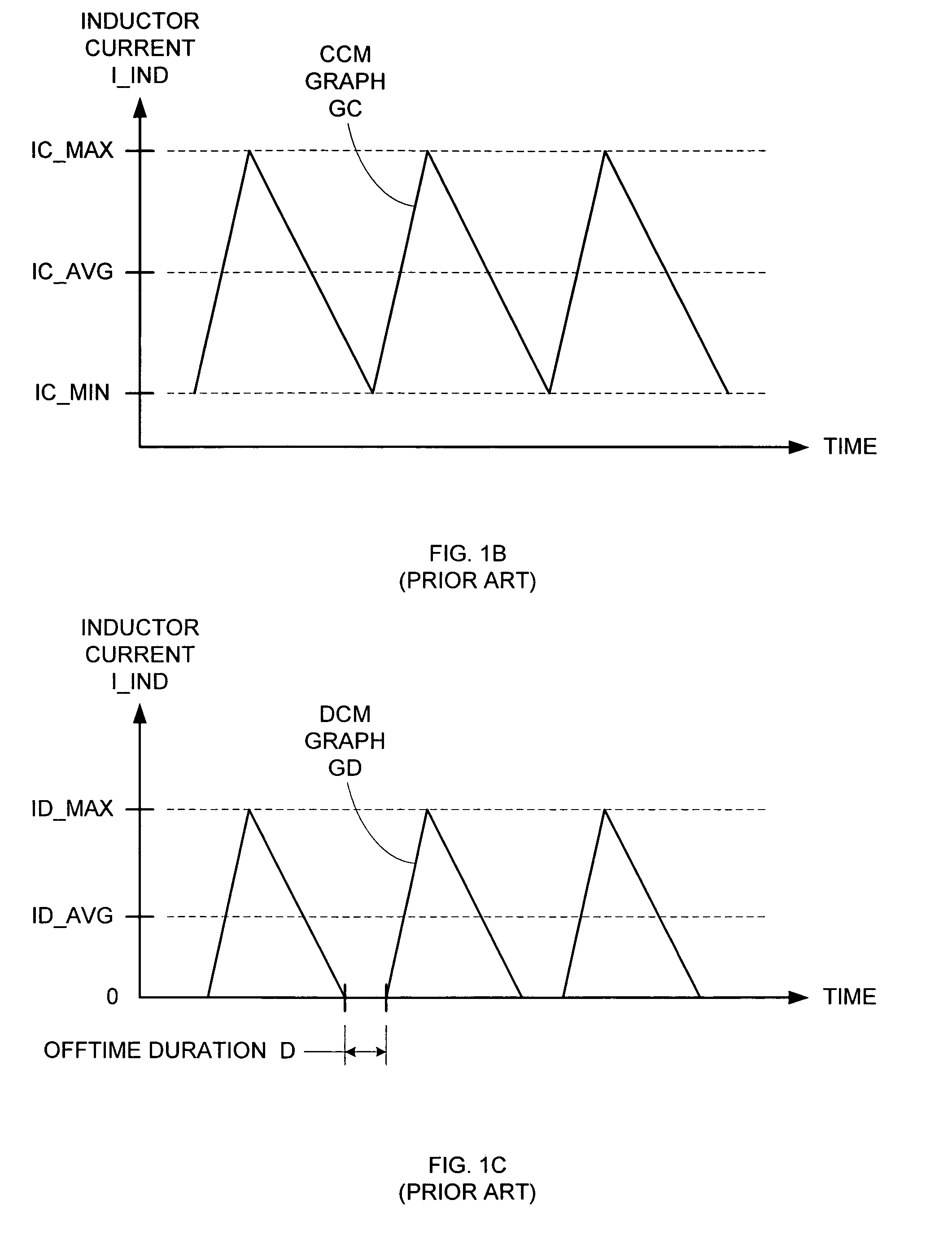
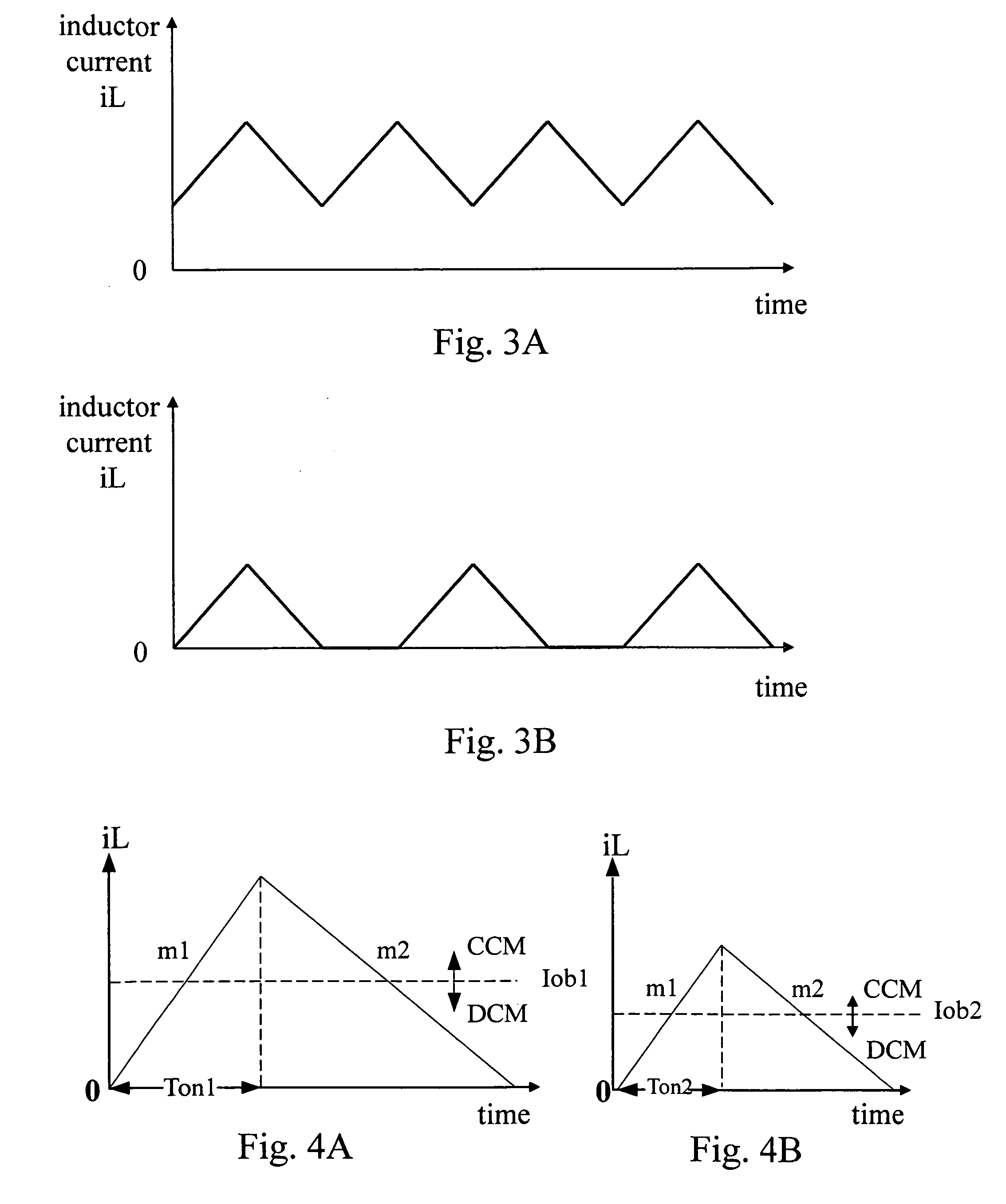
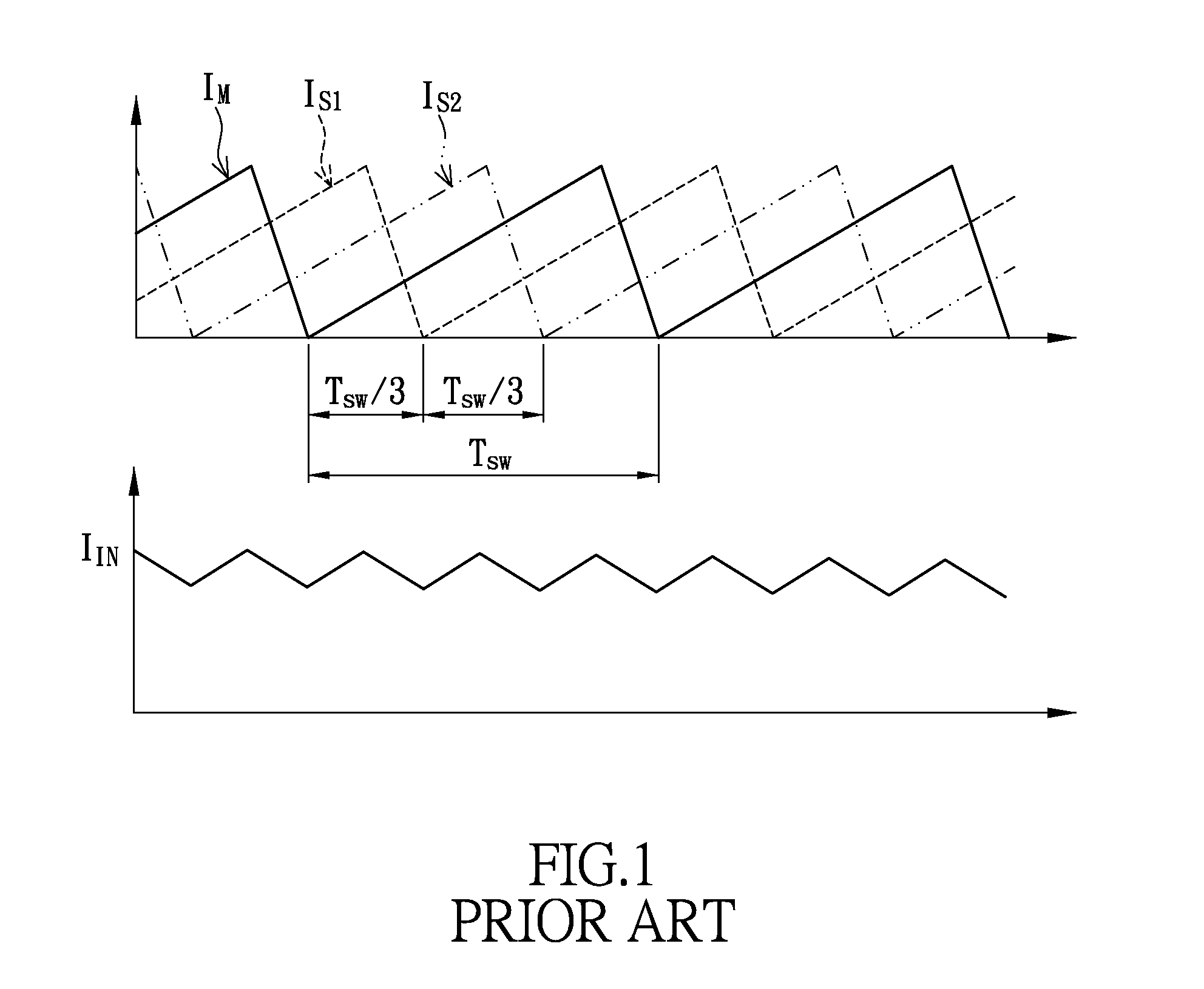
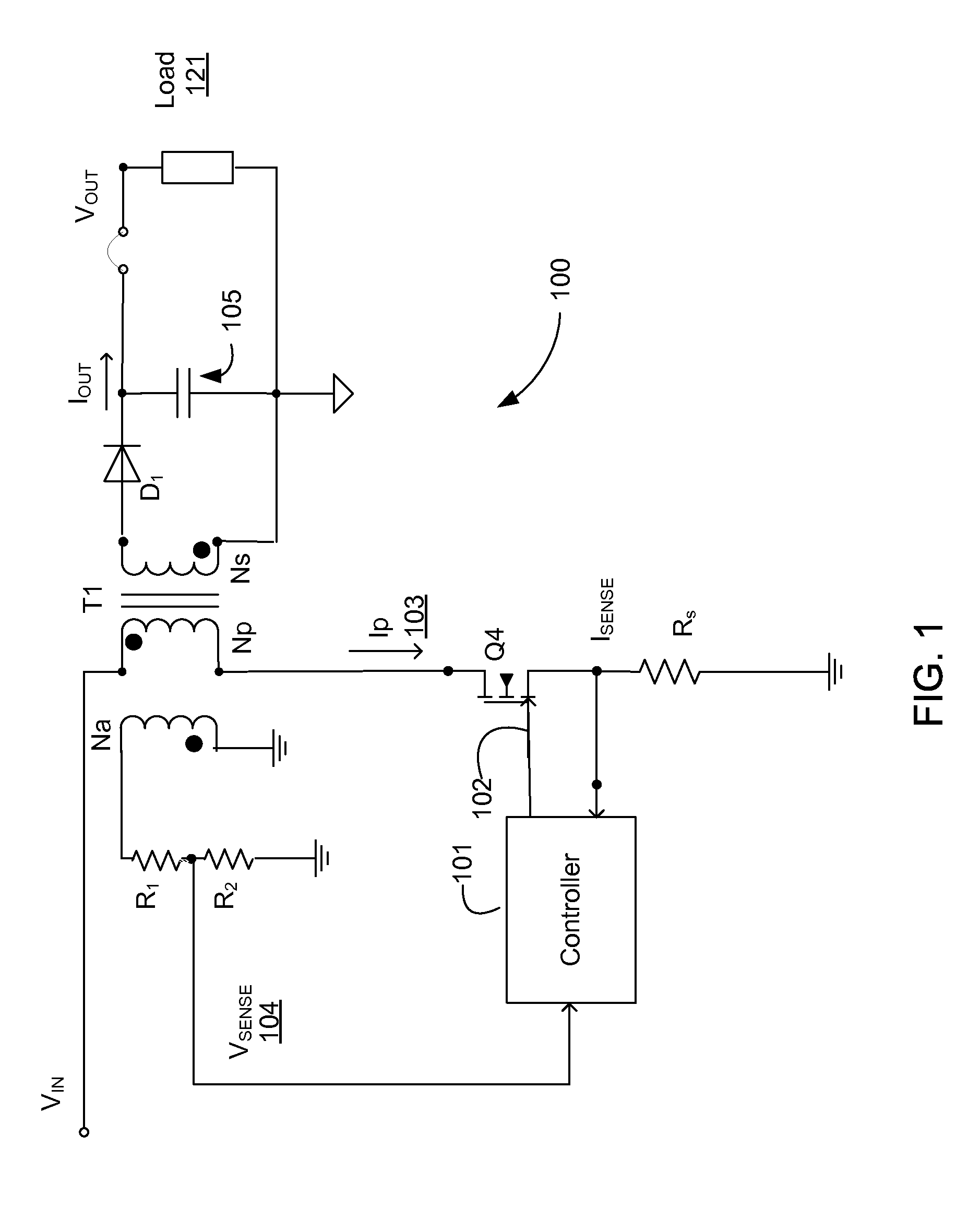
The discontinuous conduction mode arises when the switching ripple in an inductor current or capacitor voltage is large enough to cause the polarity of the applied switch current or voltage to reverse, such that the current- or voltage-unidirectional assumptions made in realizing the switch with semiconductor devices are violated.
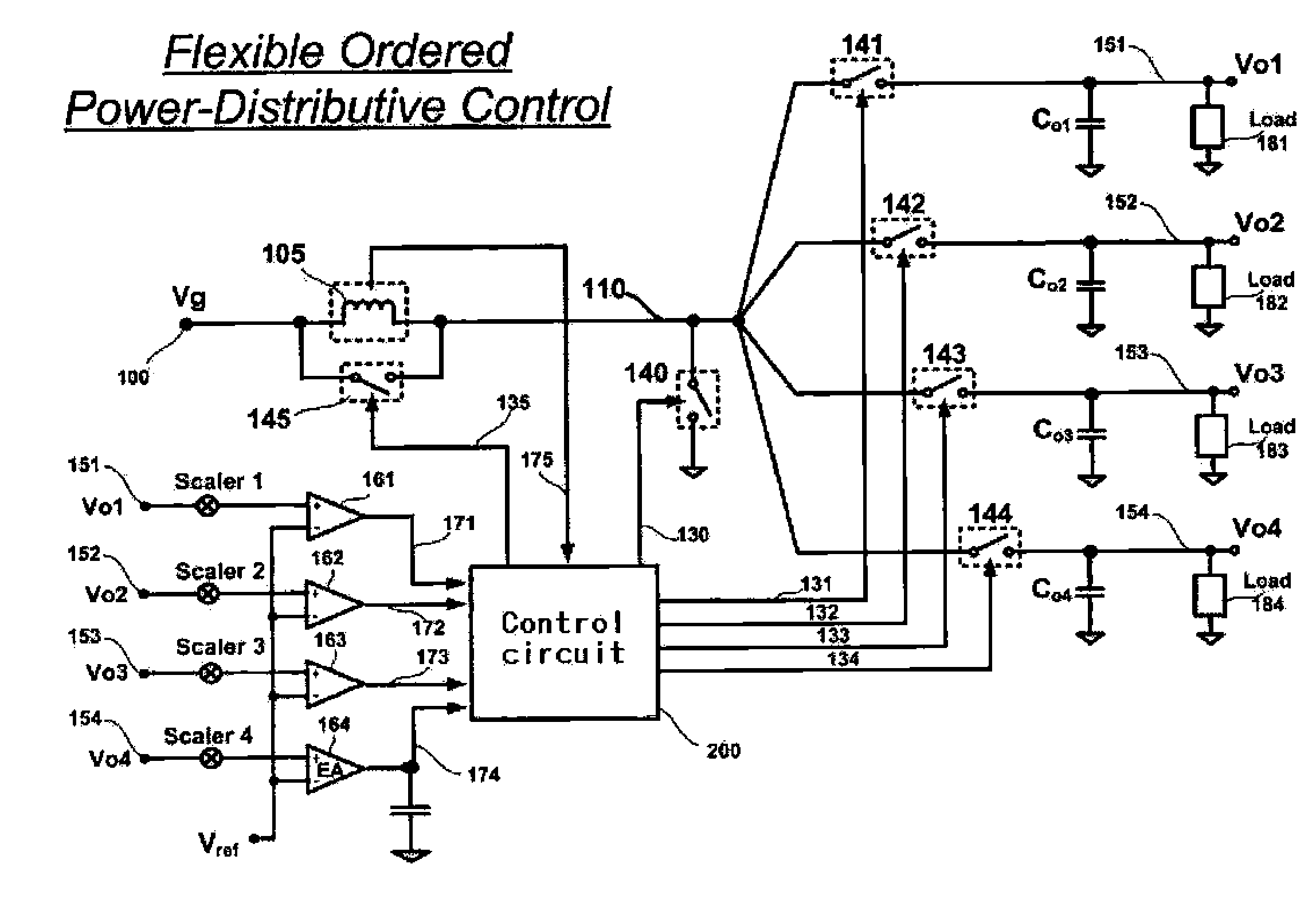
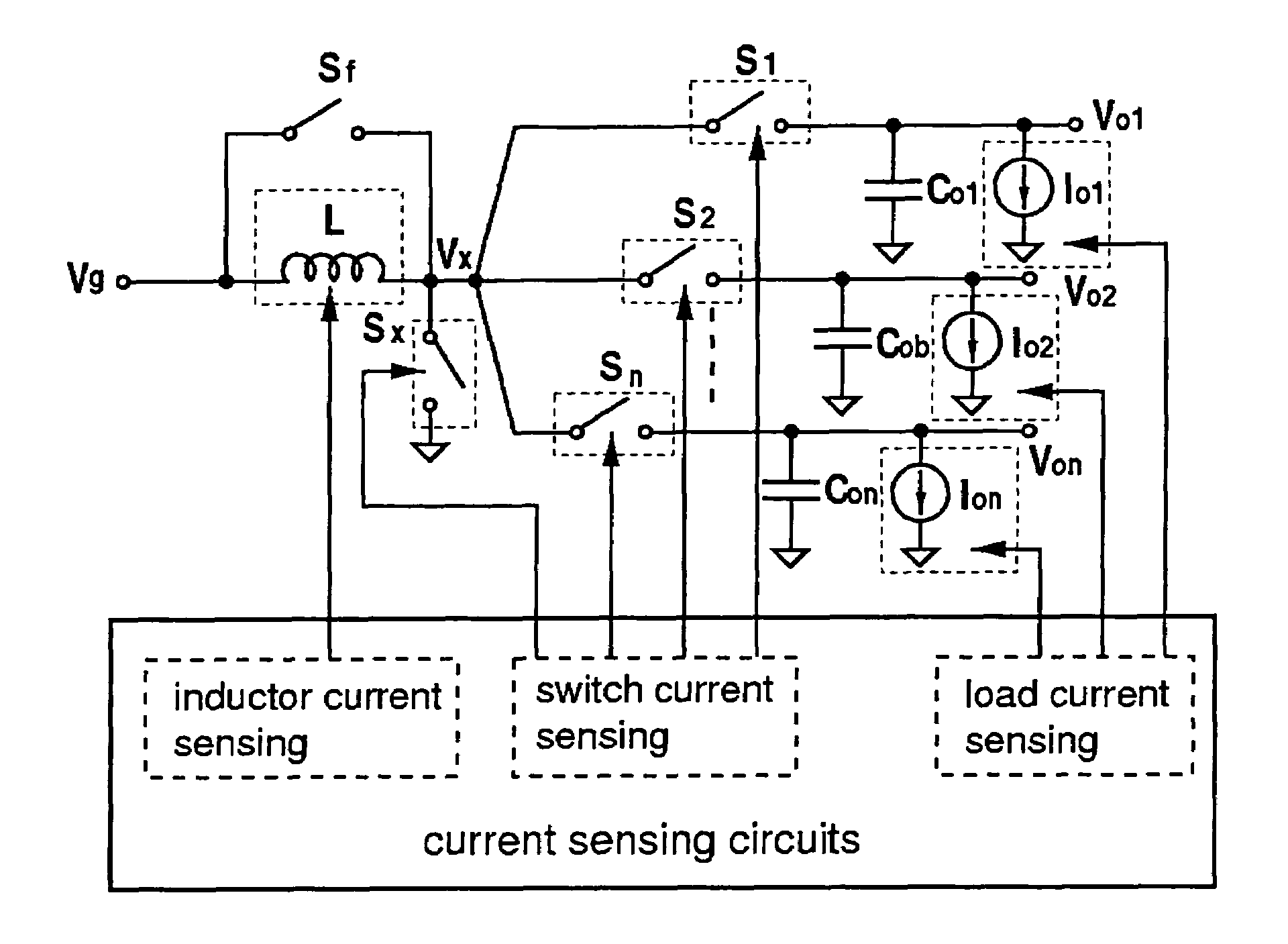
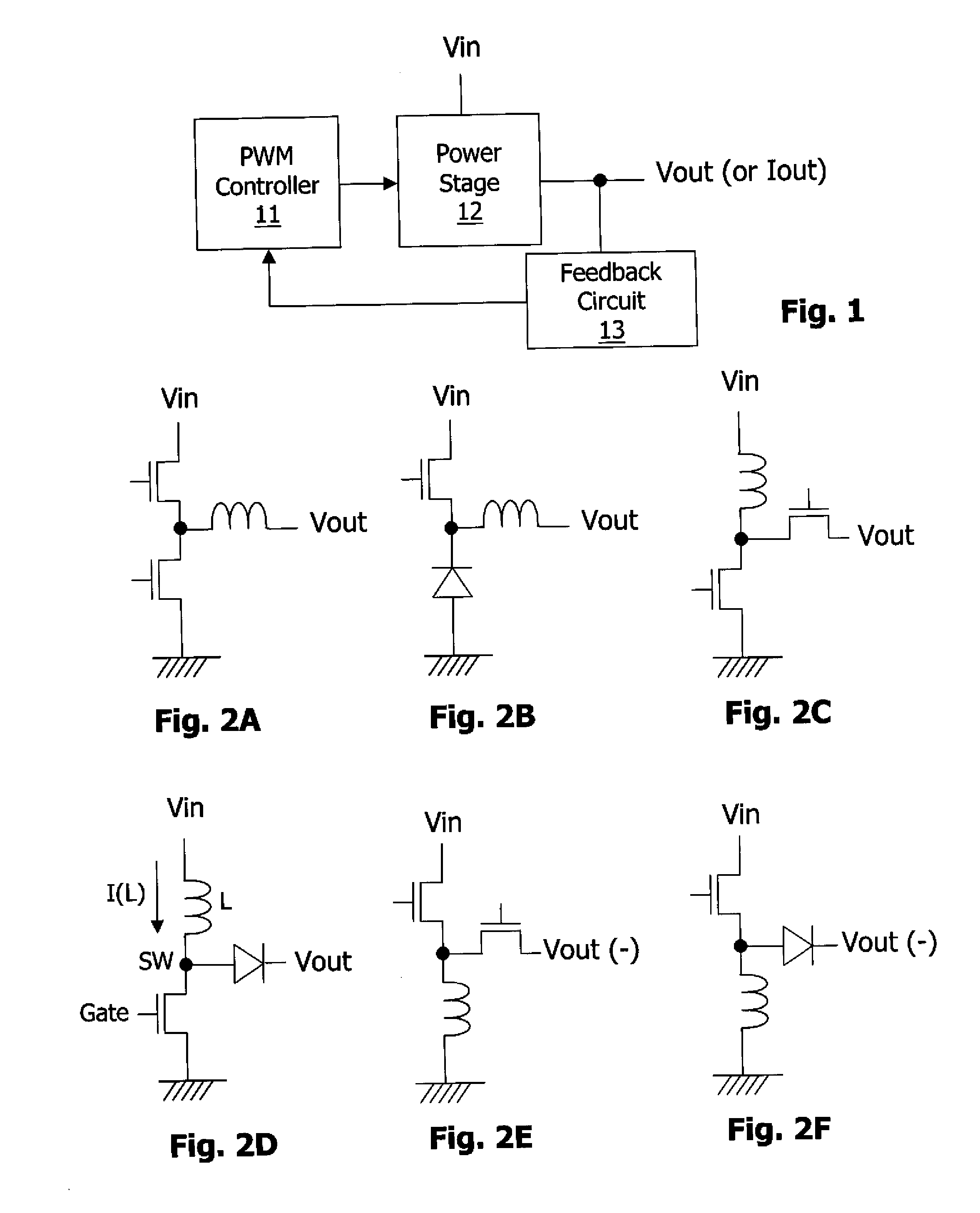
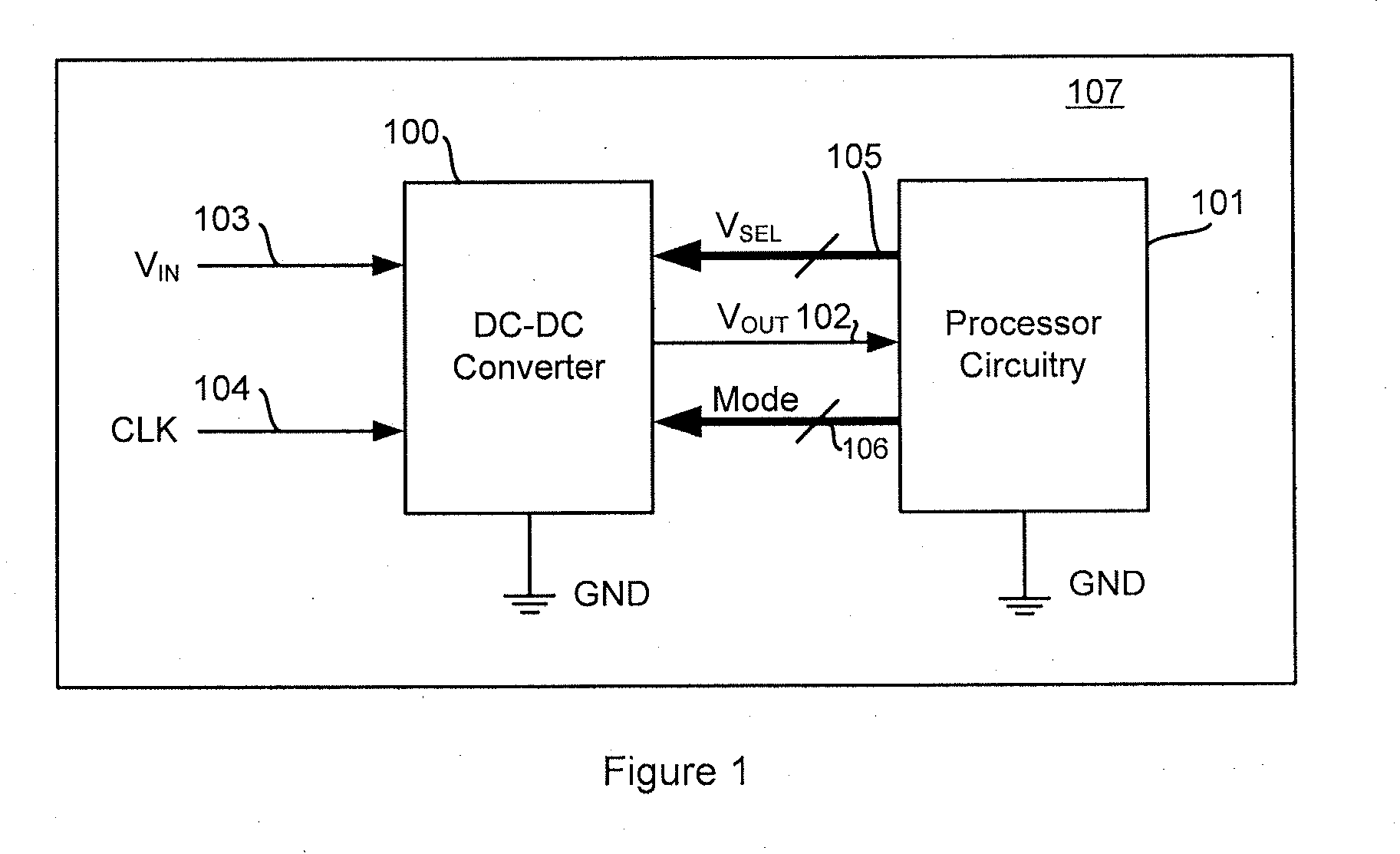
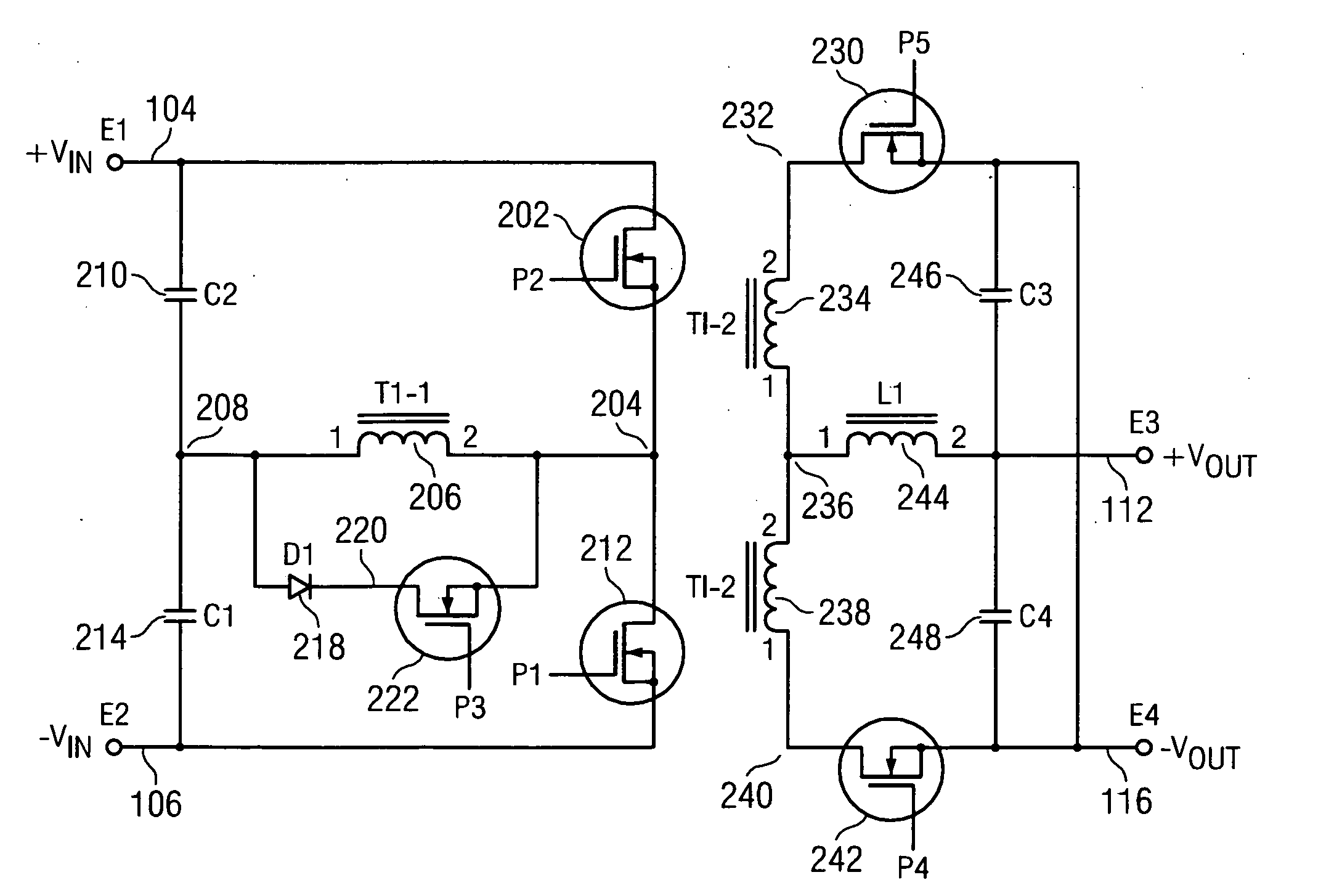
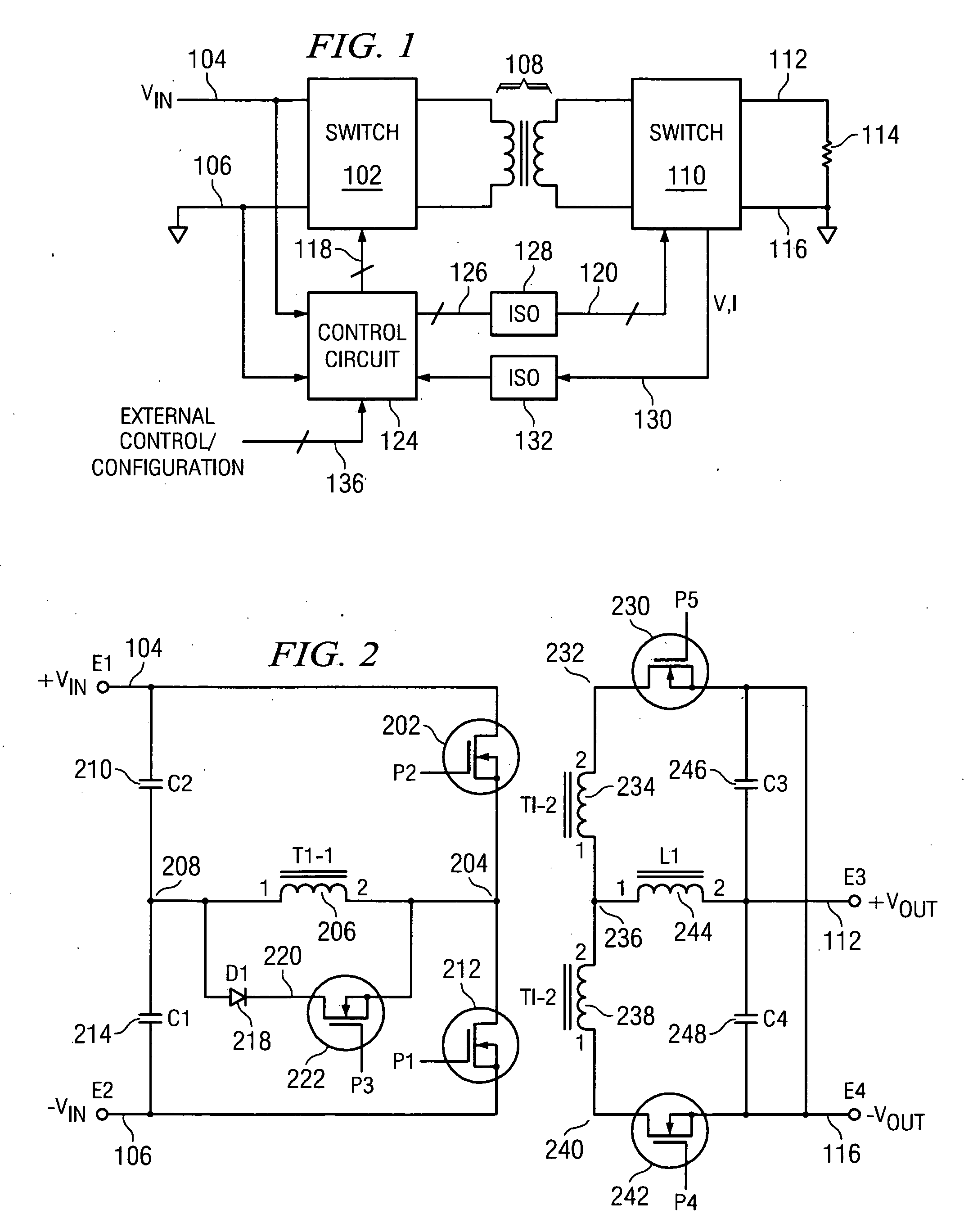
Multiple-Output DC-DC Converter
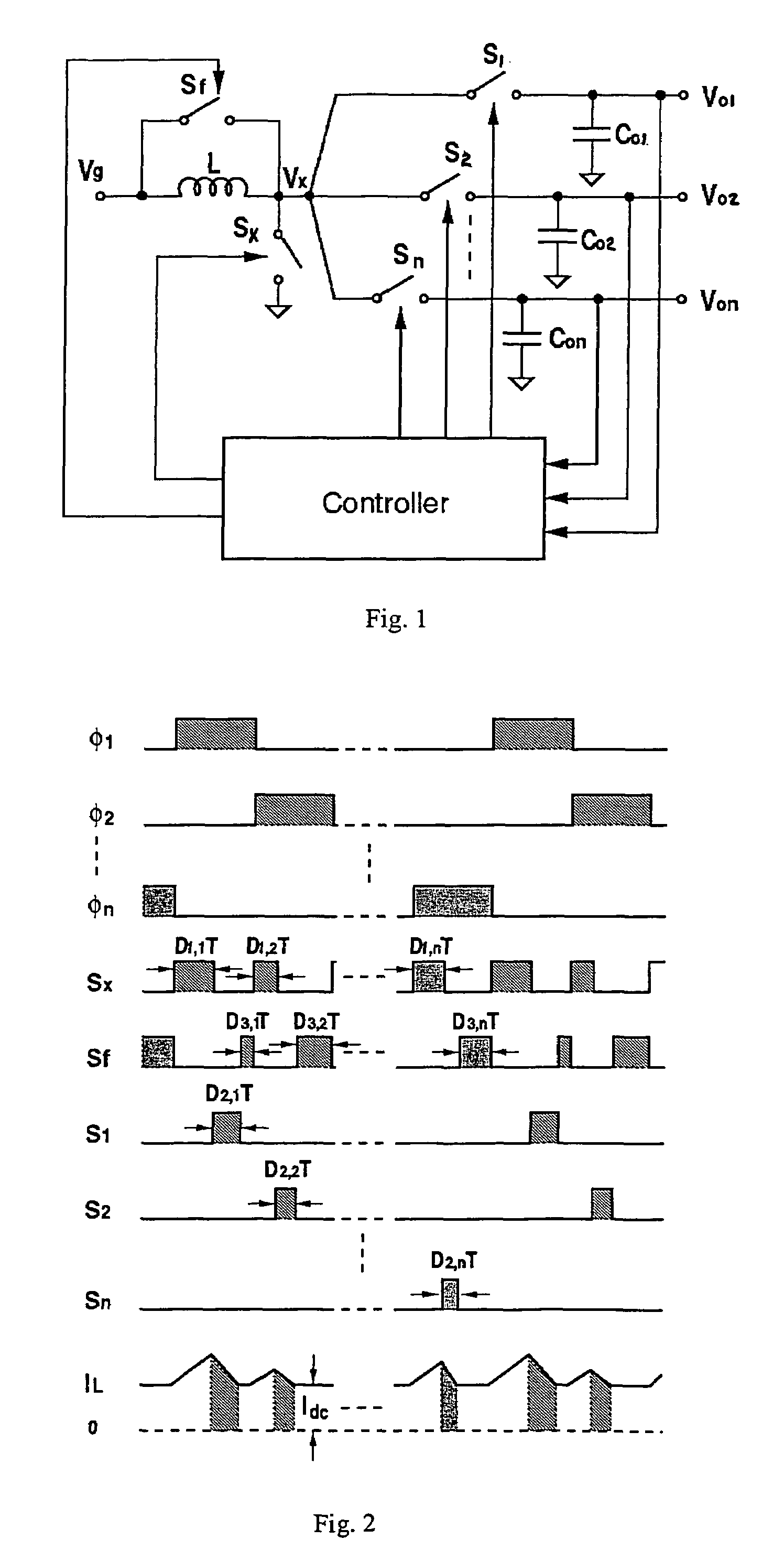
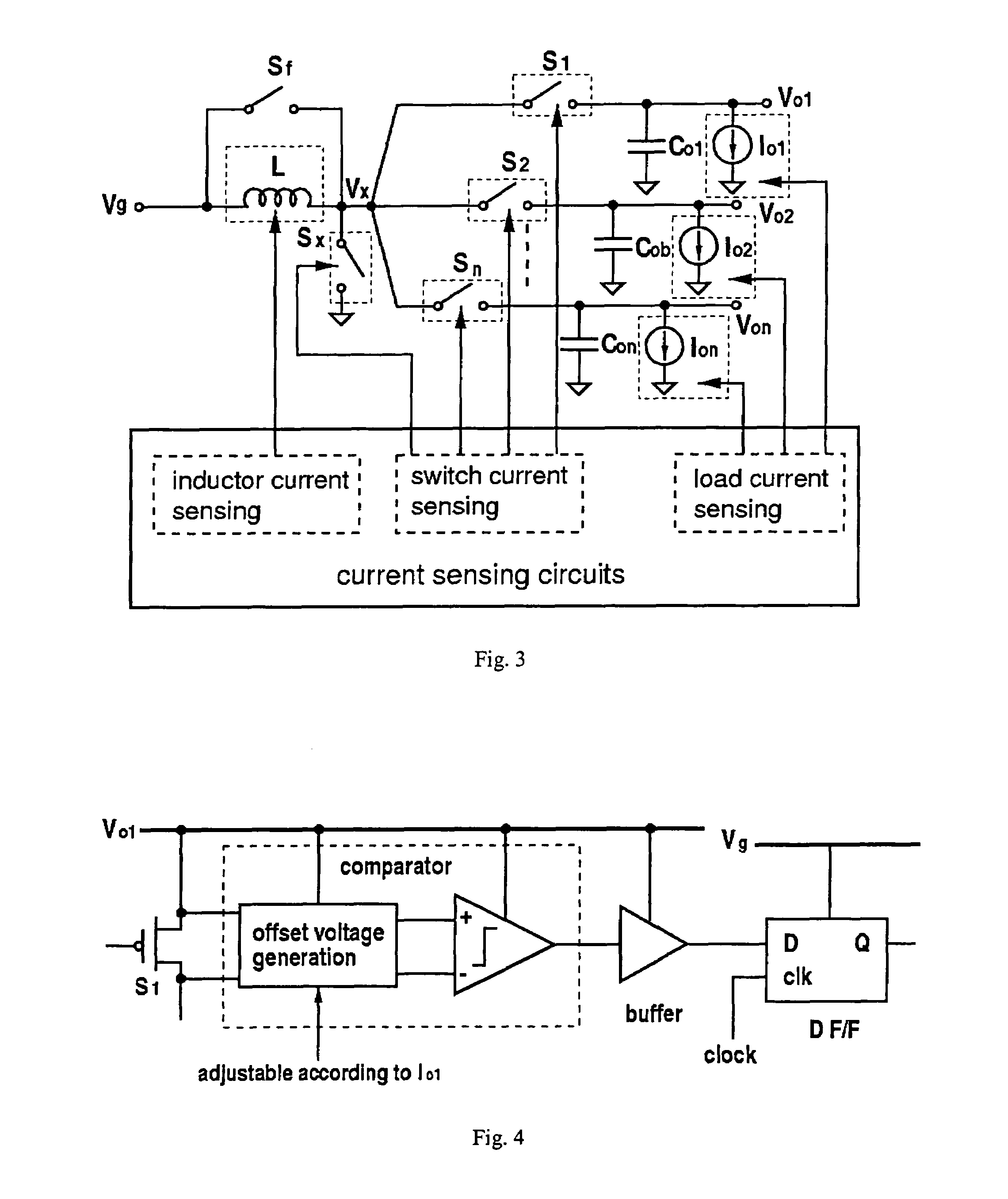
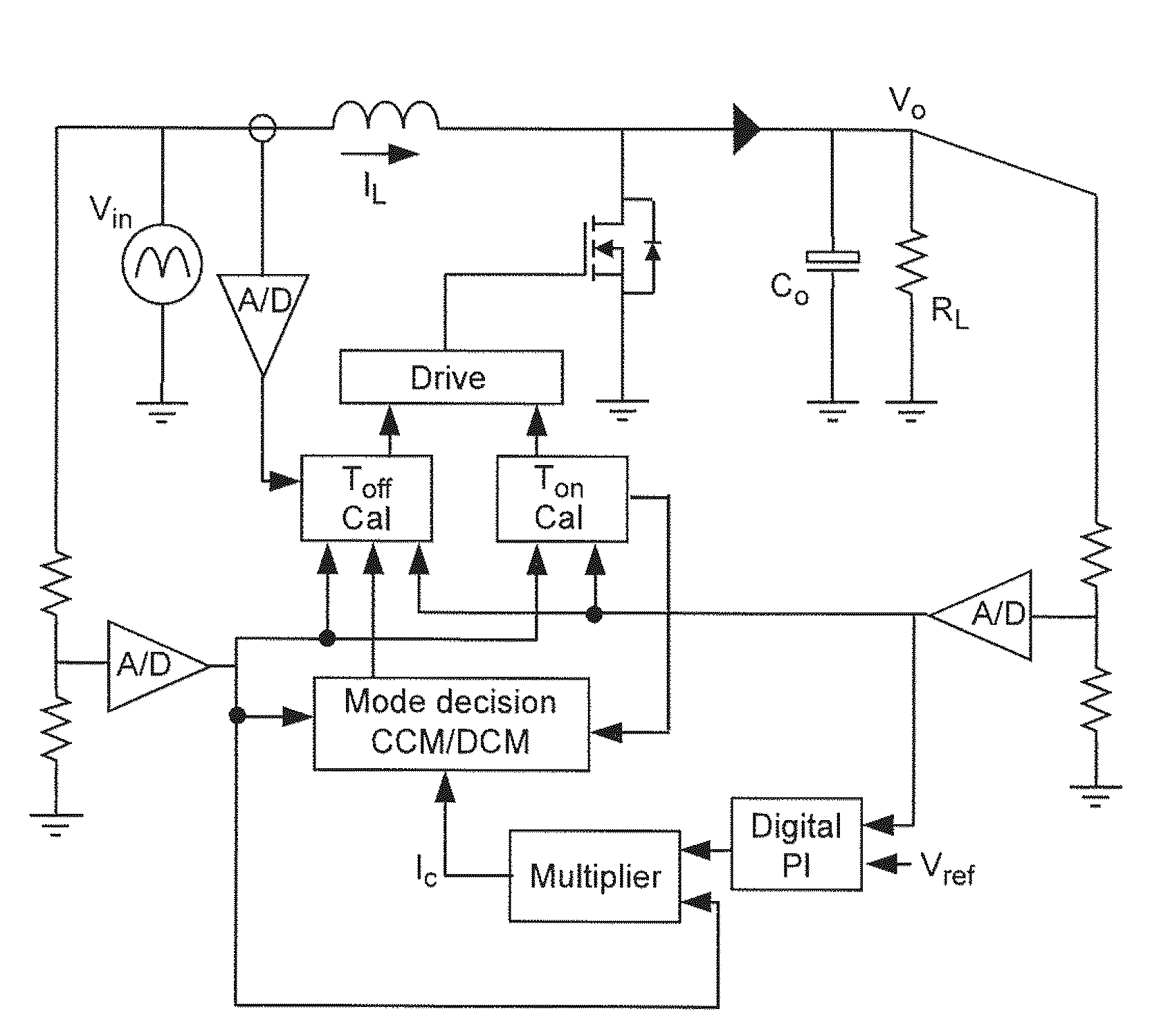
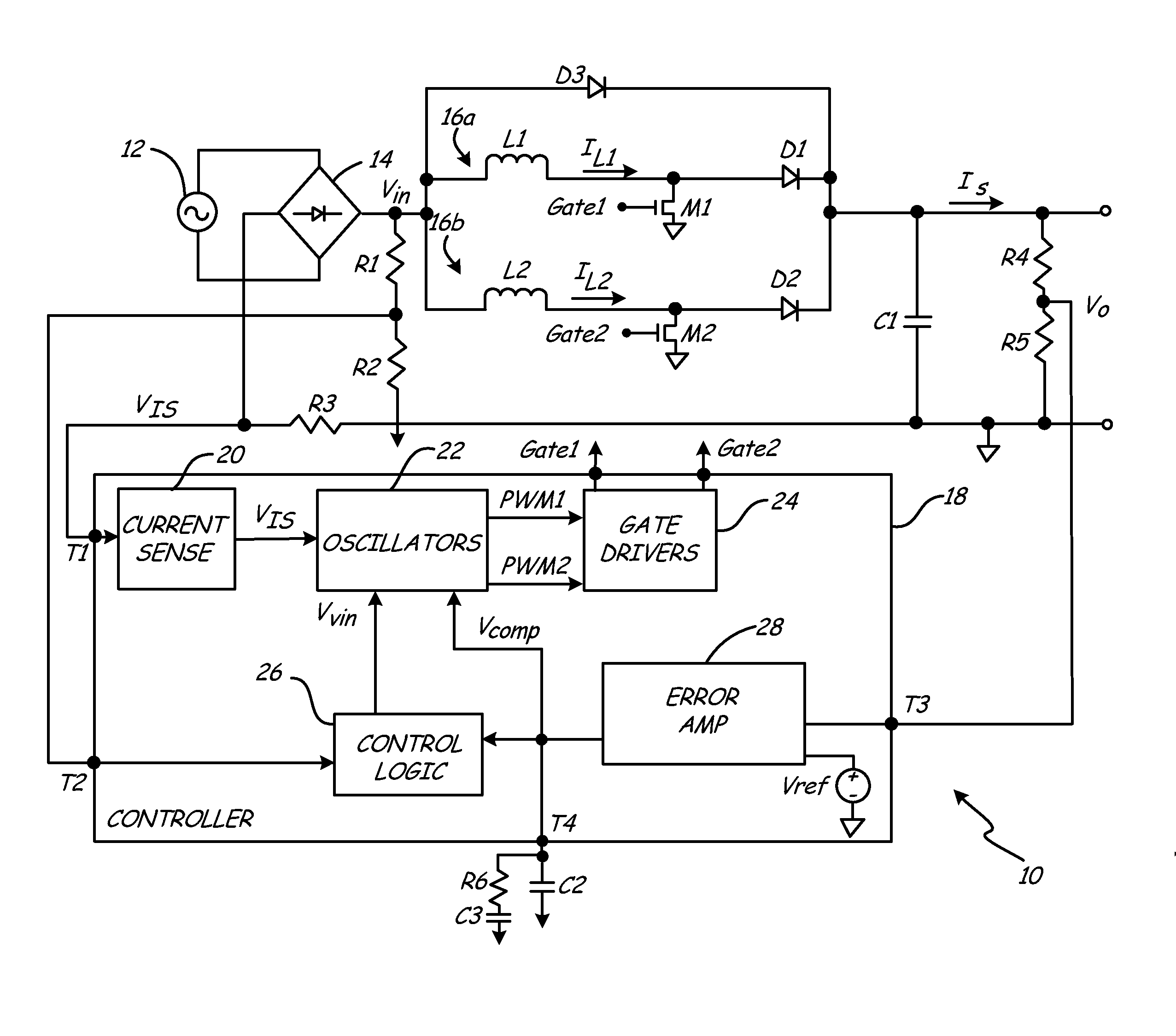
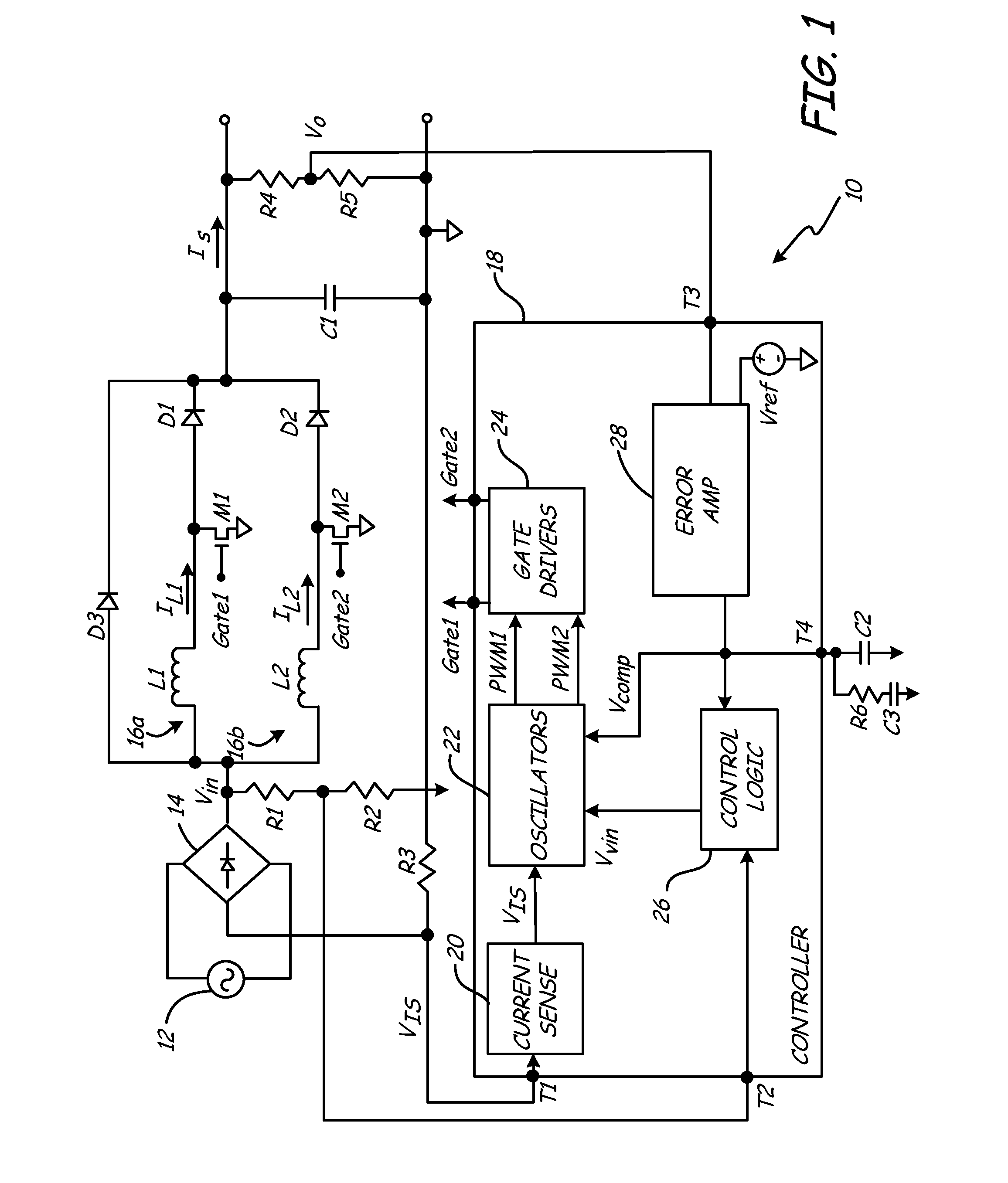
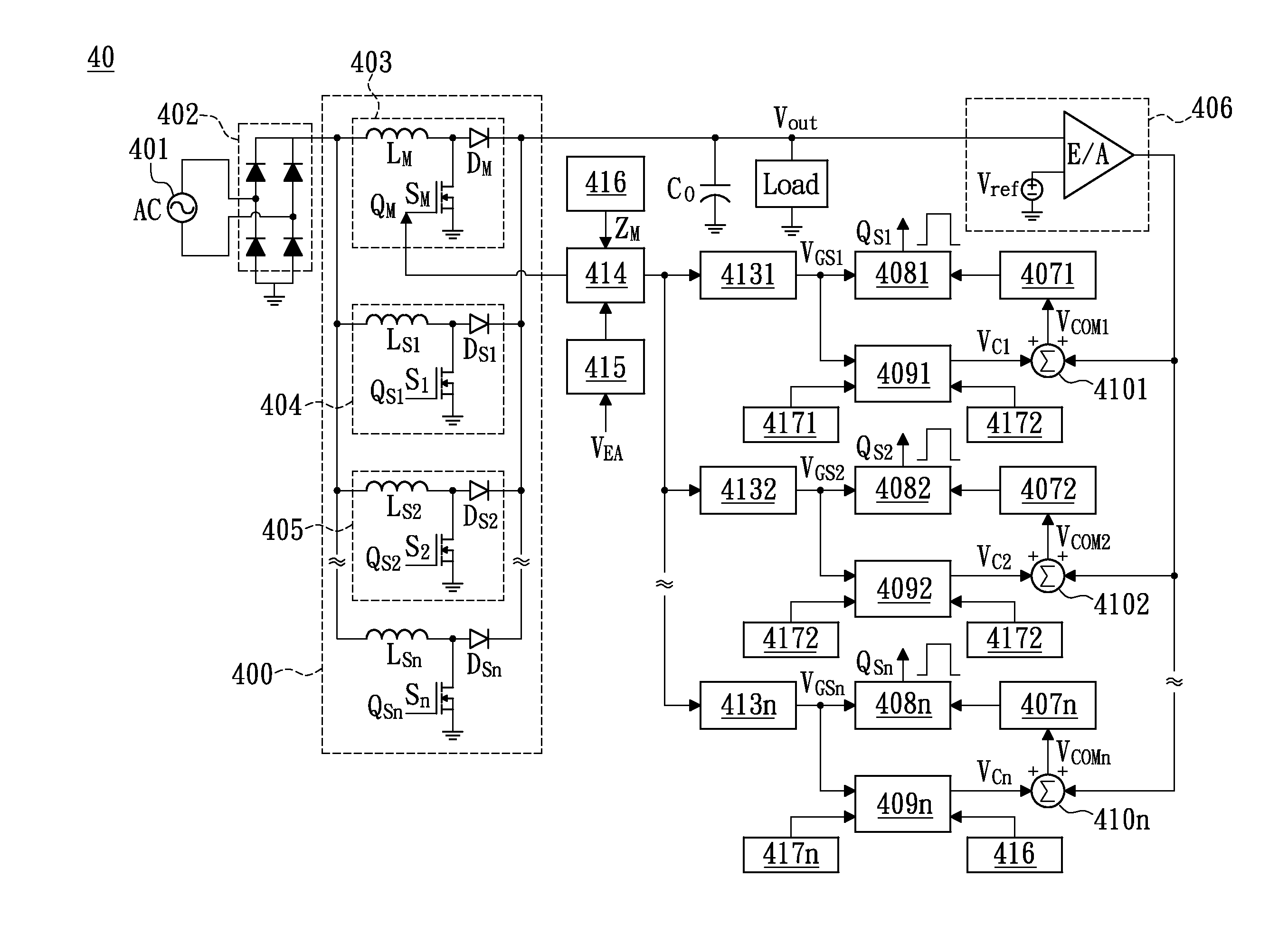
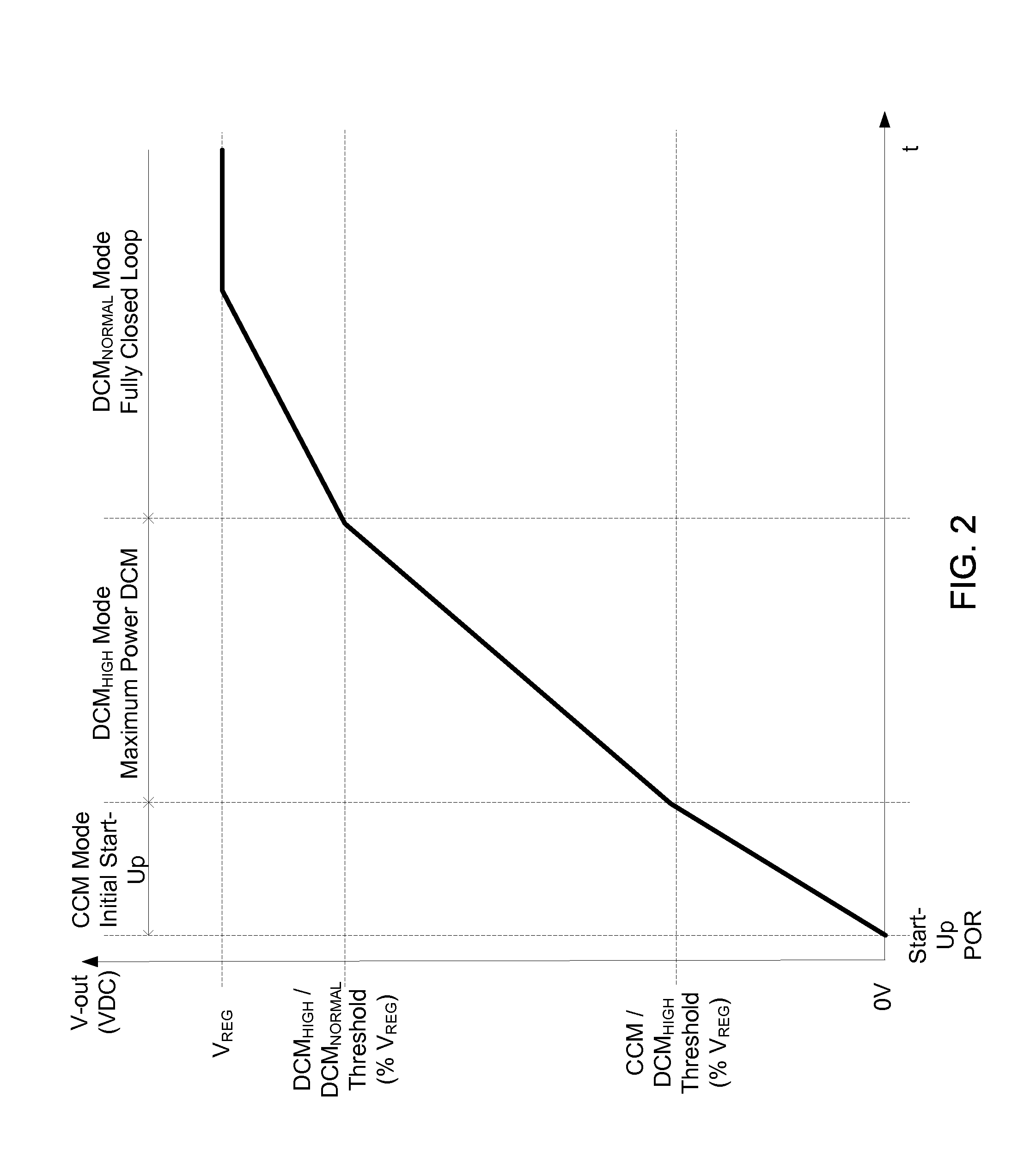
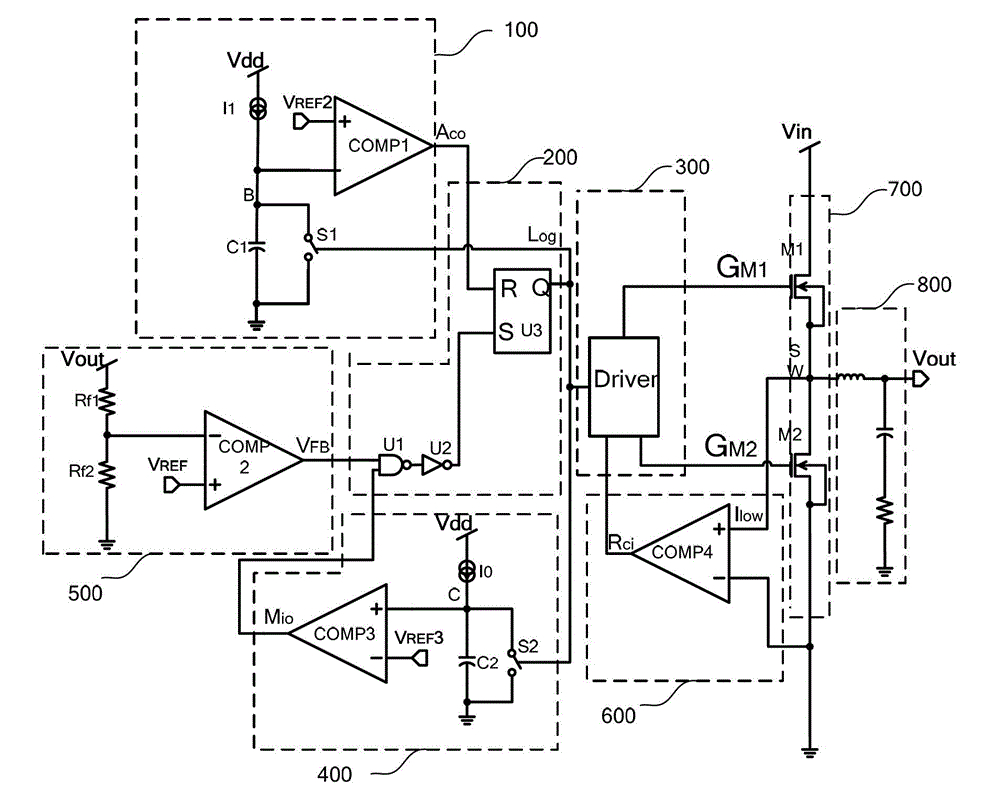
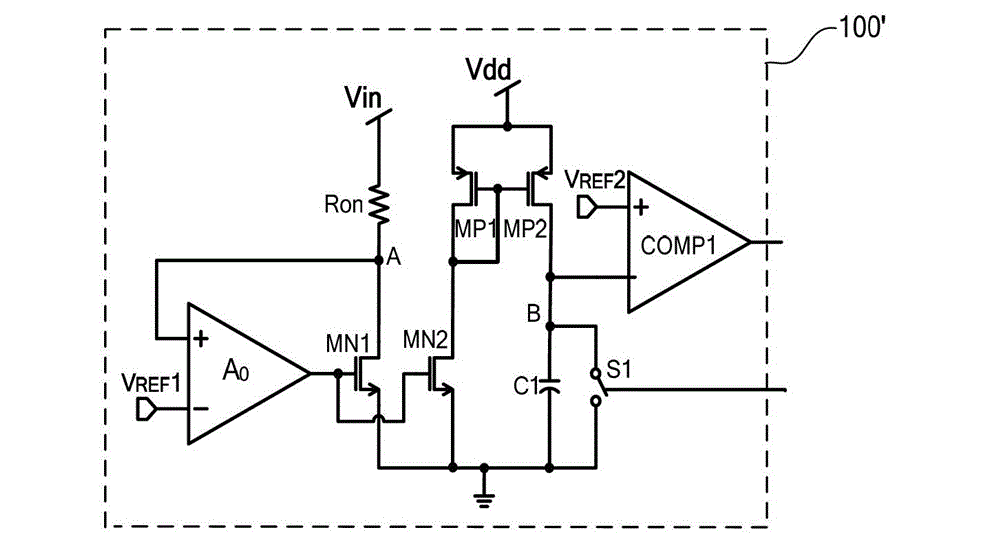
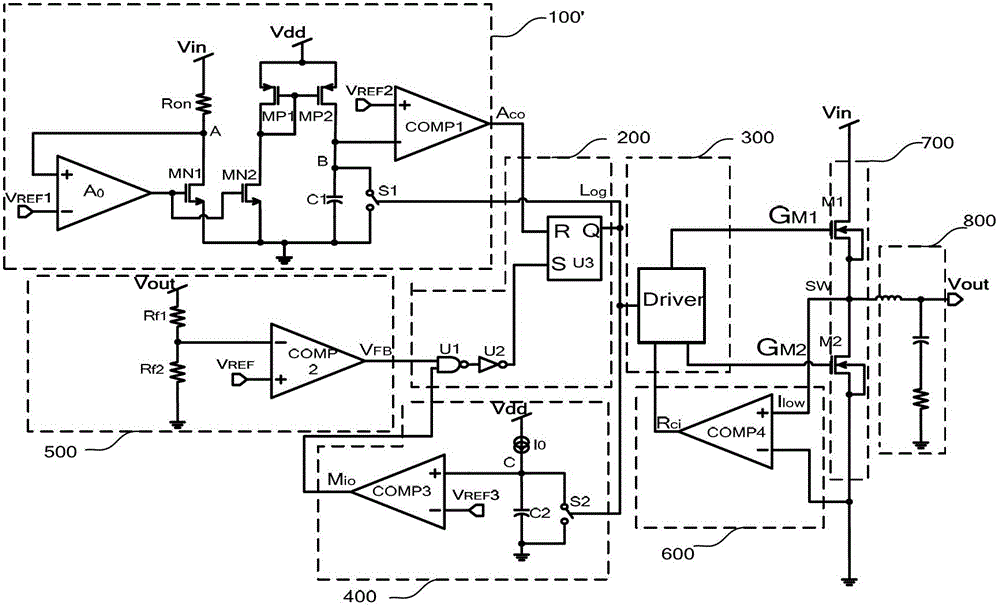
The invention relates to a DC / DC converter design. The converter requires only one single inductor to draw energy from one input source and distribute it to more than one outputs, employing Flexible-Order Power-Distributive Control (FOPDC). It include a single inductor, a number of power switches, comparators, only one error amplifier, a detecting circuit and a control block to regulate outputs. This converter can correctly regulate multiple outputs with fast transient response, low cross regulation, and effective switching frequency for each output. It can work in both discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) and continuous conduction mode (CCM). Moreover, with FOPDC, future output extension is simple, making a shorter time-to-market process for next versions of the converter. The design can be applied to different types of DC-DC converter.
Owner:JDA TECH
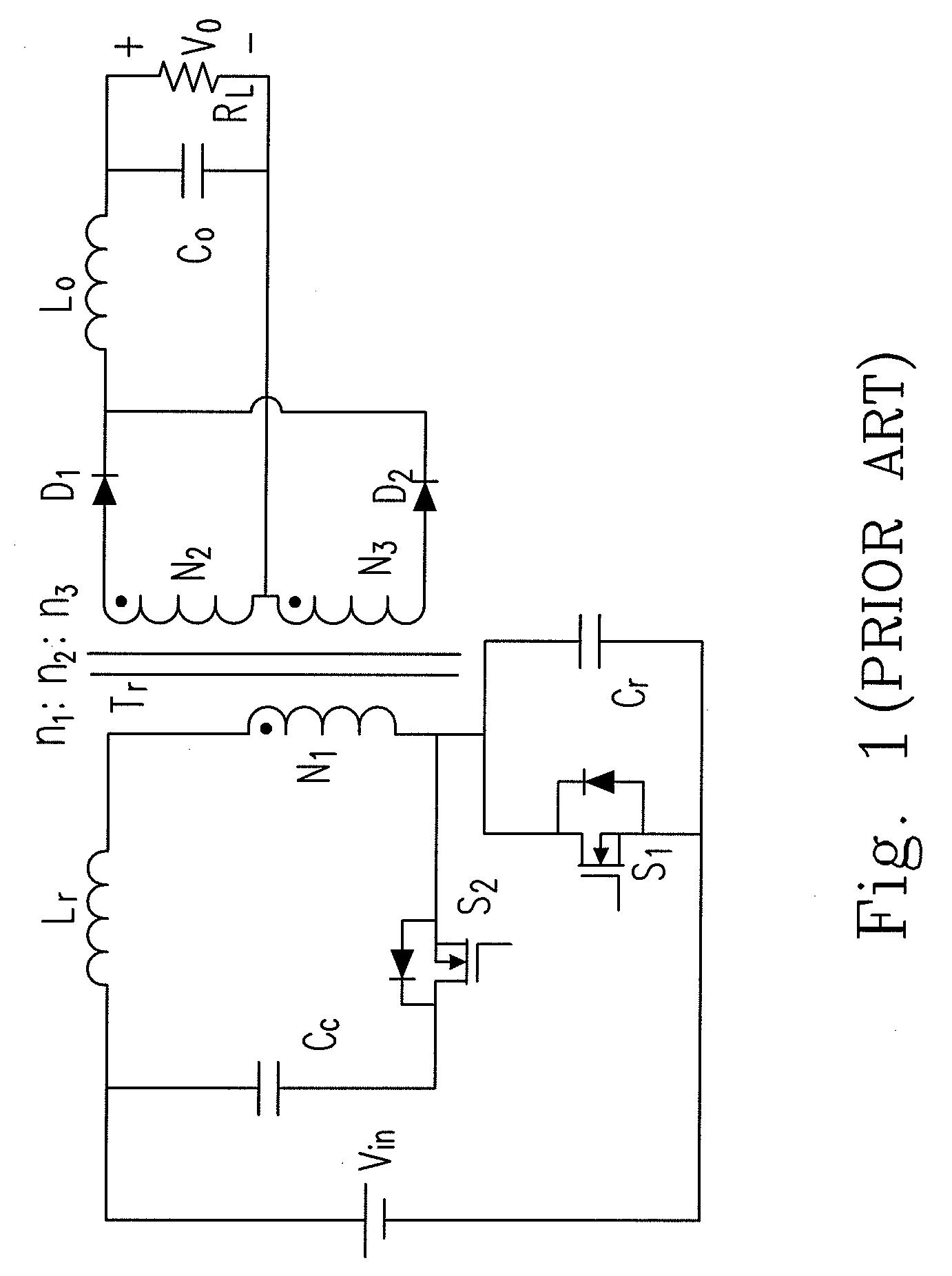
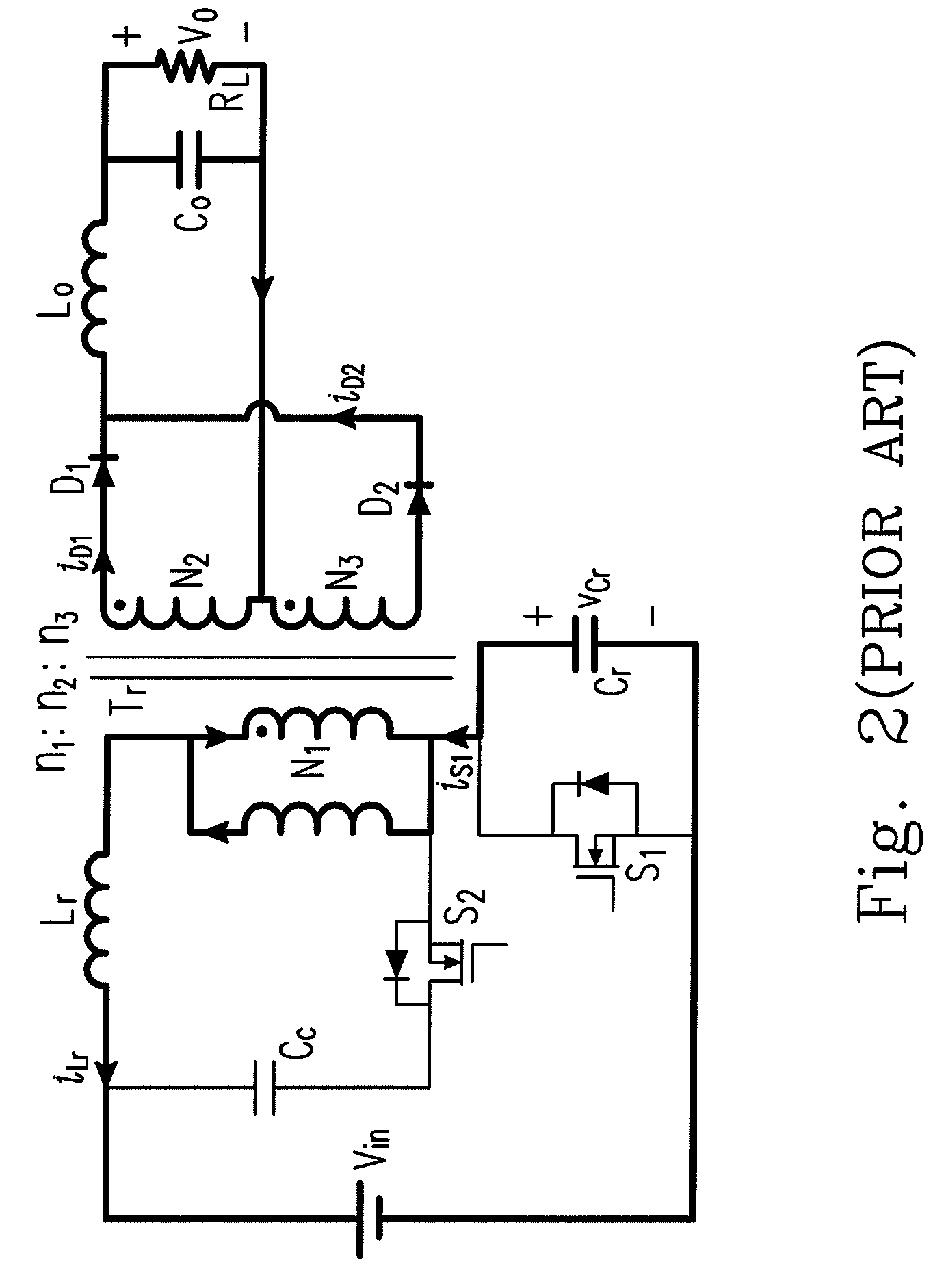
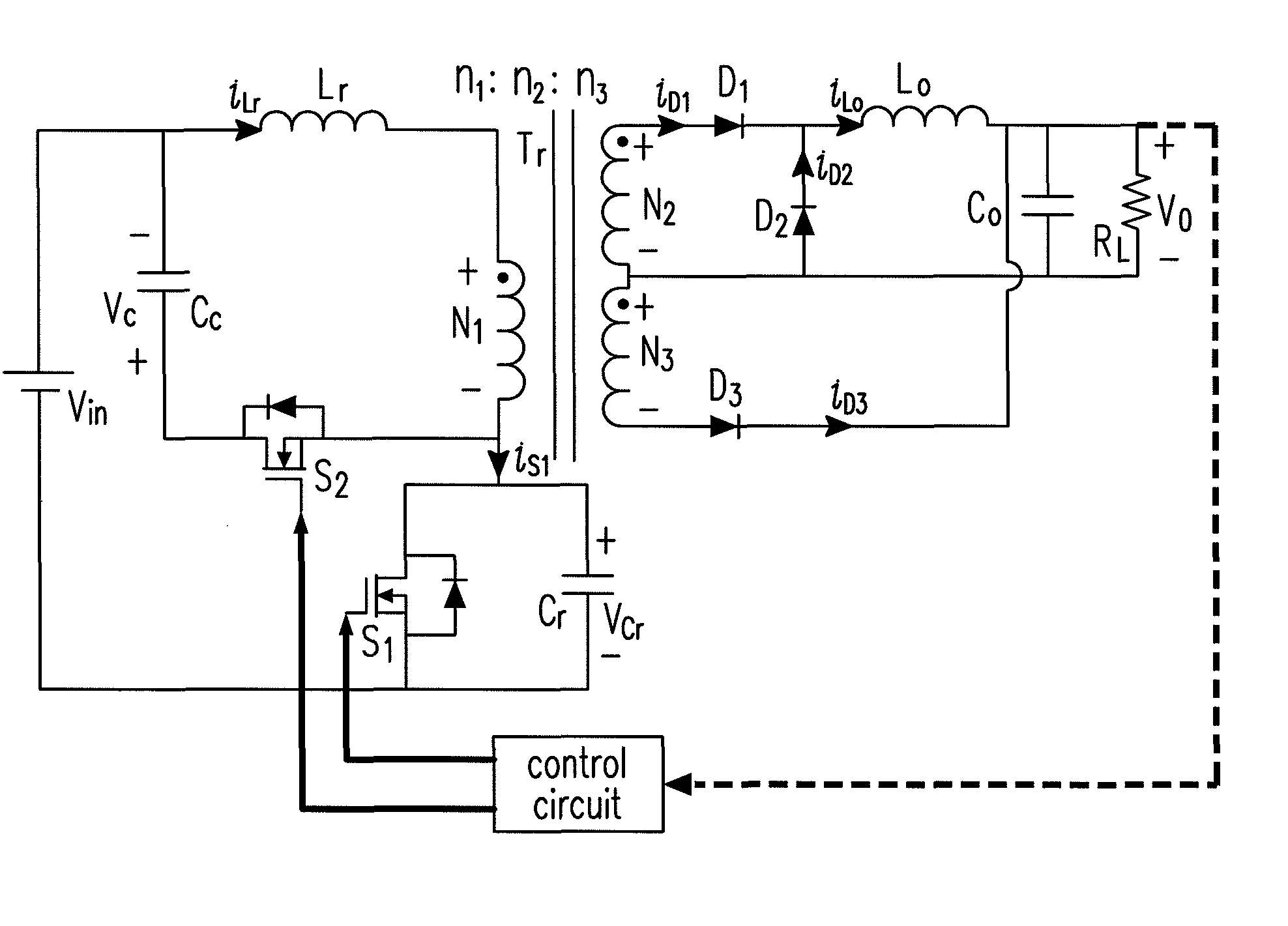
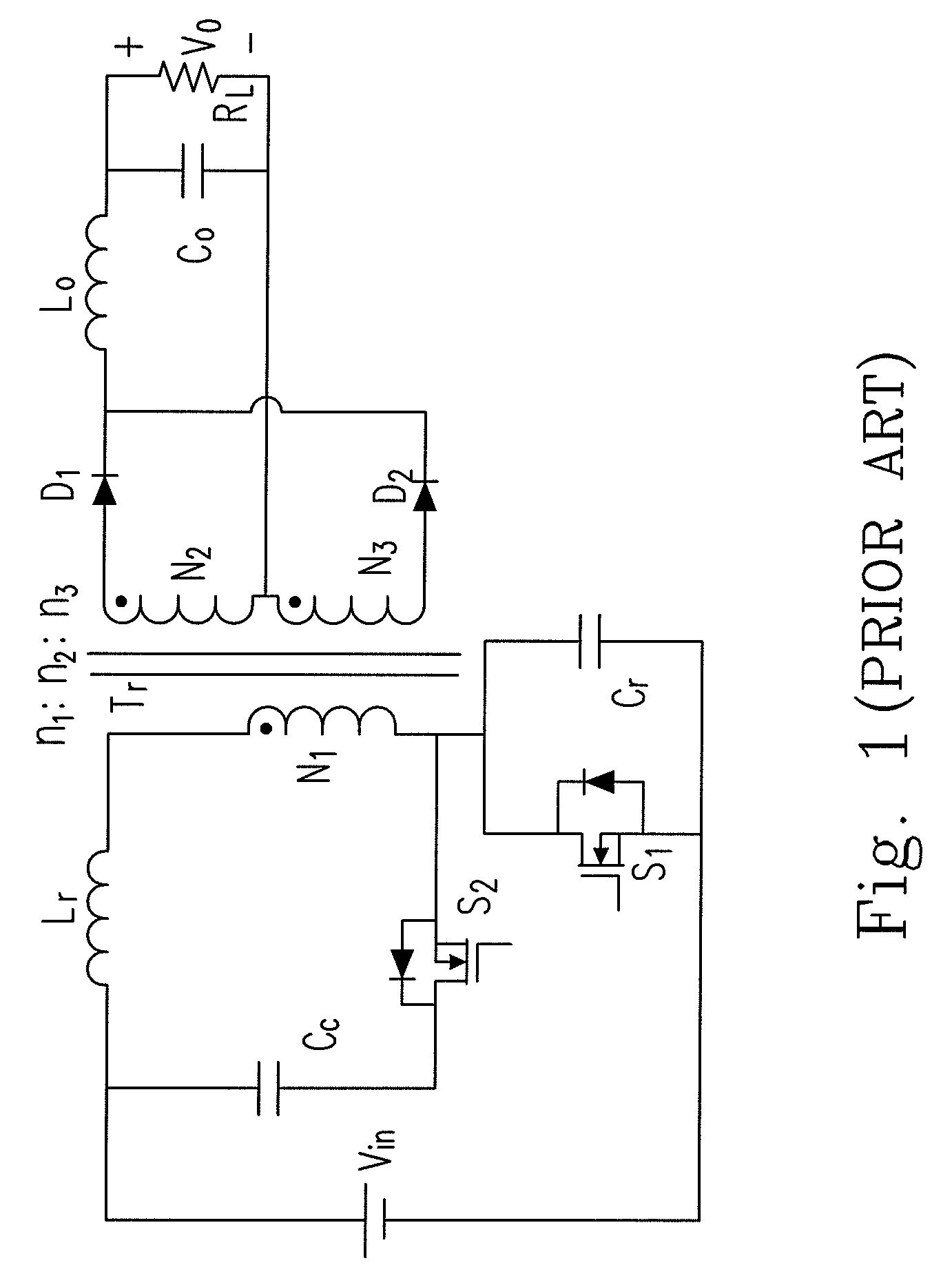
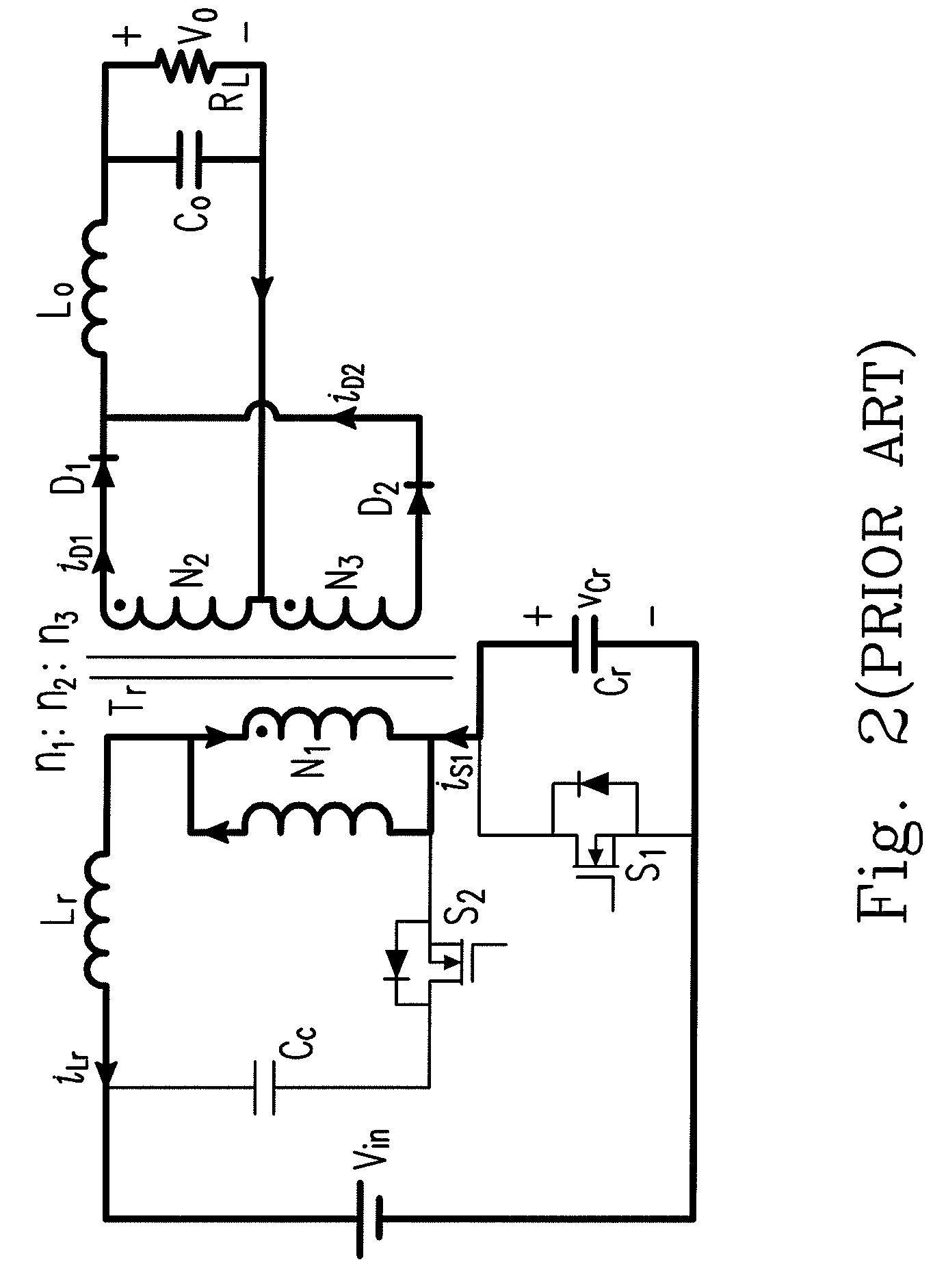
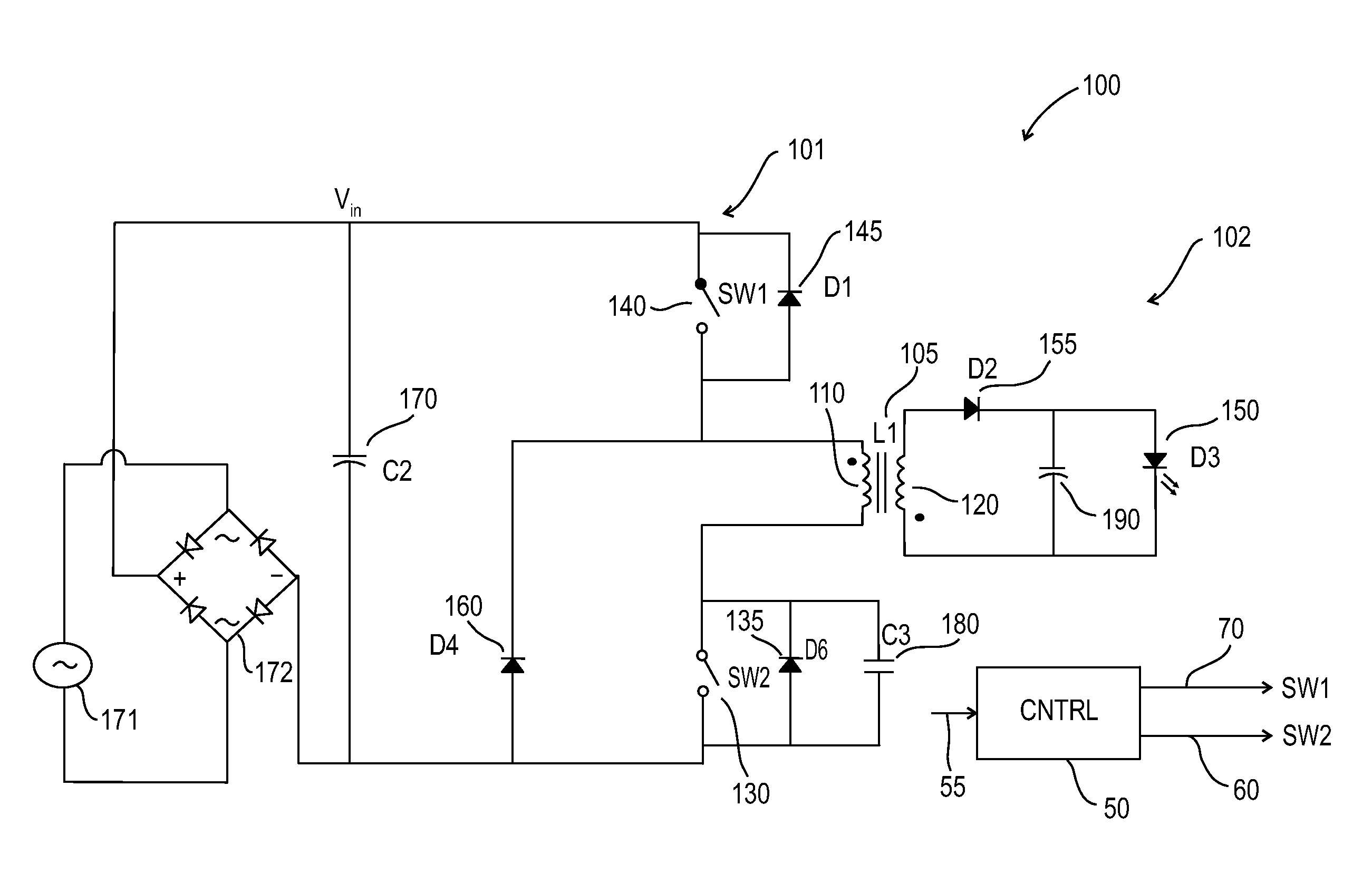
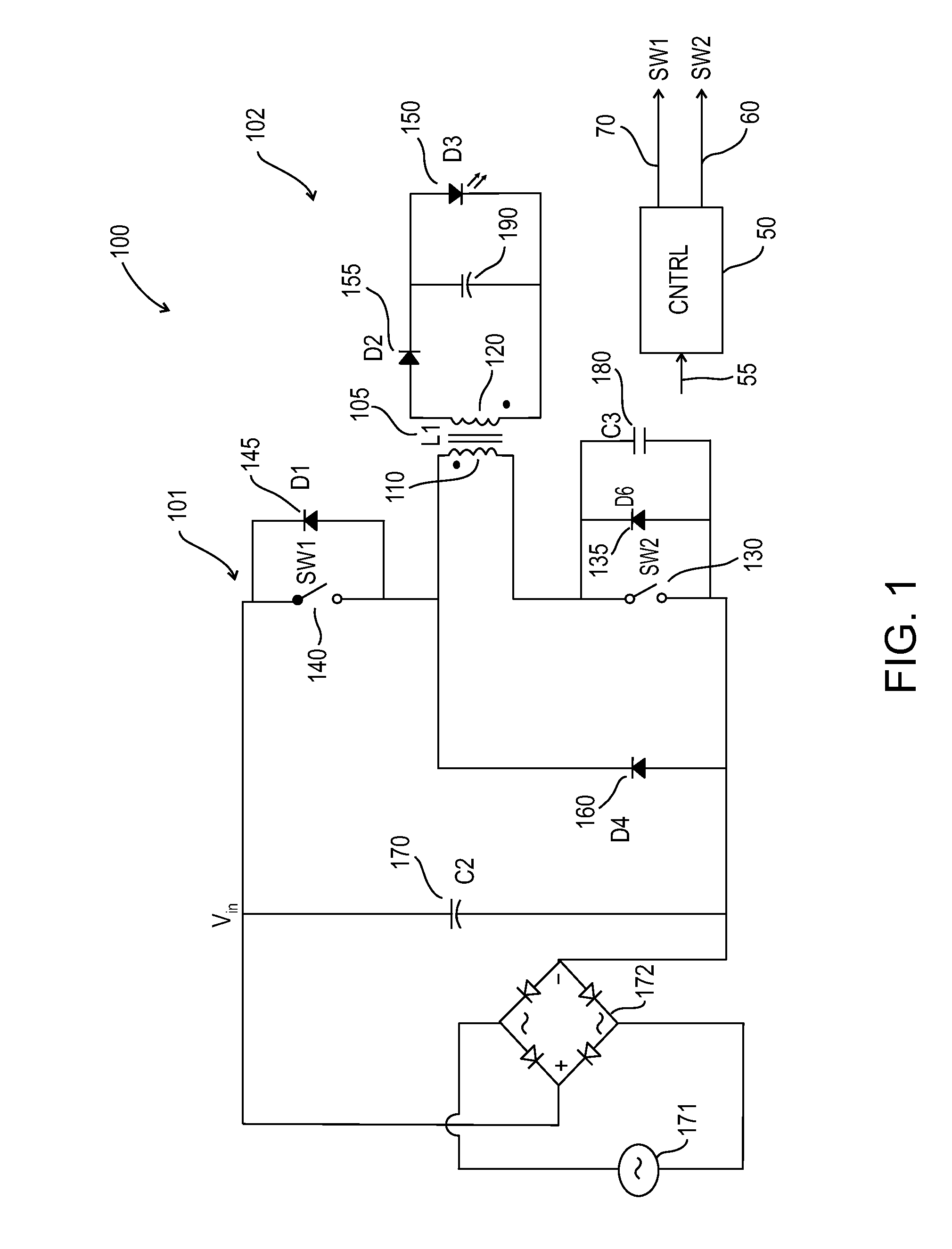
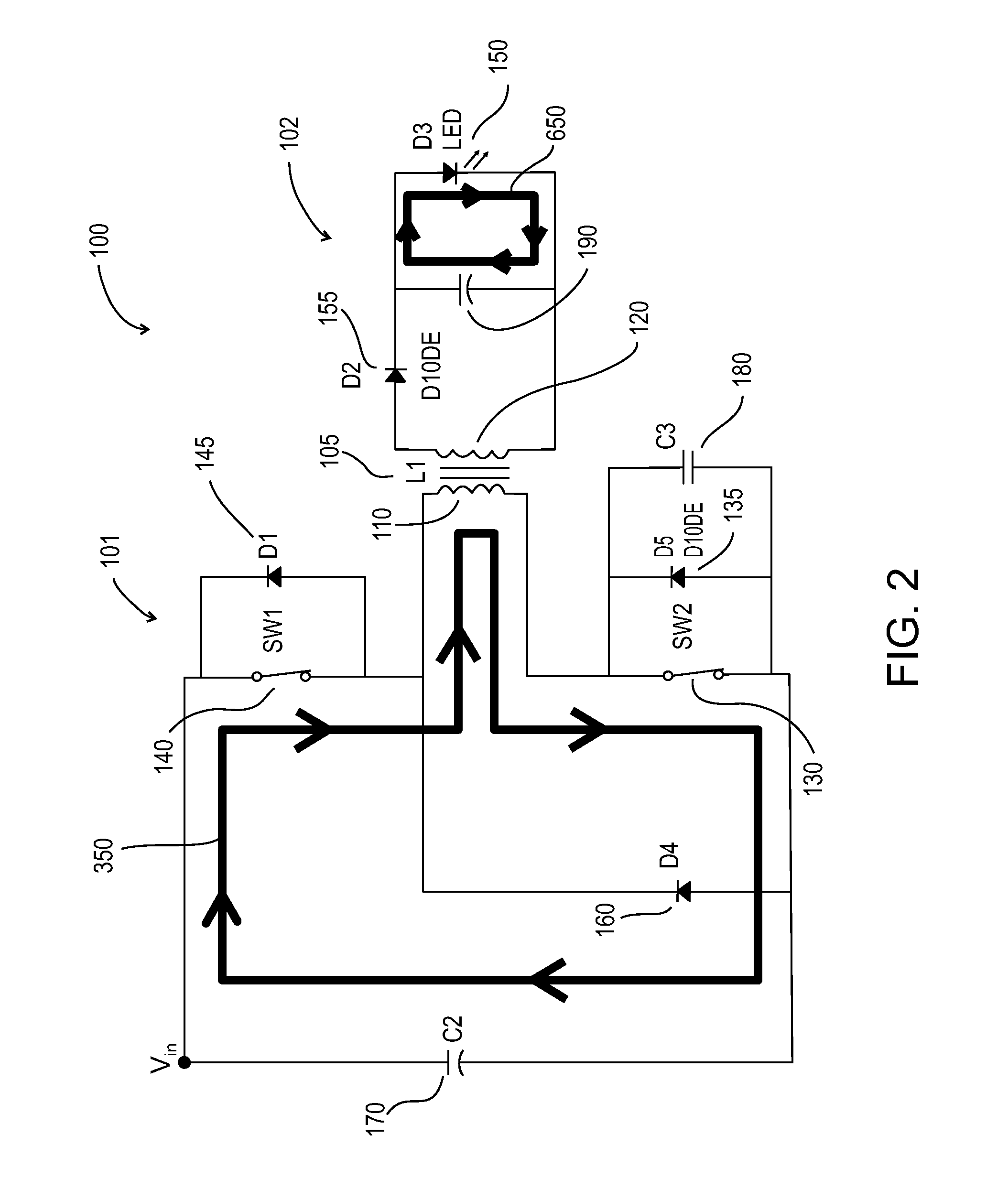
Forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit
ActiveUS20100067259A1Improve conversion efficiencyAdditional drawbackEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsHeavy loadCenter tap
The present invention discloses a forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit. The secondary side of the proposed converter is of center-tapped configuration to integrate a forward circuit and a flyback circuit. The flyback sub-circuit operating continuous conduction mode is employed to directly transfer the reset energy of the transformer to the output load. The forward sub-circuit operating discontinuous conduction mode can correspondingly adjust the duty ratio with the output load change. Under the heavy load condition, the mechanism of active-clamp flyback sub-circuit can provide sufficient resonant current to facilitate the parasitic capacitance of the switches to be discharged to zero. Under the light load condition, the time interval in which the resonant current turns from negative into positive is prolonged to ensure zero voltage switching function. Meanwhile, the flyback sub-circuit wherein the rectifier diode is reverse biased is inactive in order to further reduce the power losses.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Hysteretic CL power converter
ActiveUS20120170334A1Reduce the valueSmall sizeEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionĆuk converterSwitching frequency
A novel switching hysteretic power converter is presented. The power converter combines the function of a capacitive charge pump with the function of an inductive step down converter to obtain a switching boost converter with a much simpler control method with respect to conventional inductive boost power converters. The hysteretic control provides stable operation in all conditions with excellent load transient response. Furthermore the hysteretic control allows high frequency switching reducing the size and cost of the passive components. The Discontinuous Conduction Mode of operation provides very high efficiency even at light loads. The presented power converter can be operated as a boost converter or as a buck converter simply by changing the switching phase of one switch. In both types of operation the efficiency of the hysteretic power converter can be quite high even at high switching frequencies.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for multi-phase DC-DC converters using coupled inductors in discontinuous conduction mode
ActiveUS7317305B1Improve efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationDc dc converterEngineering
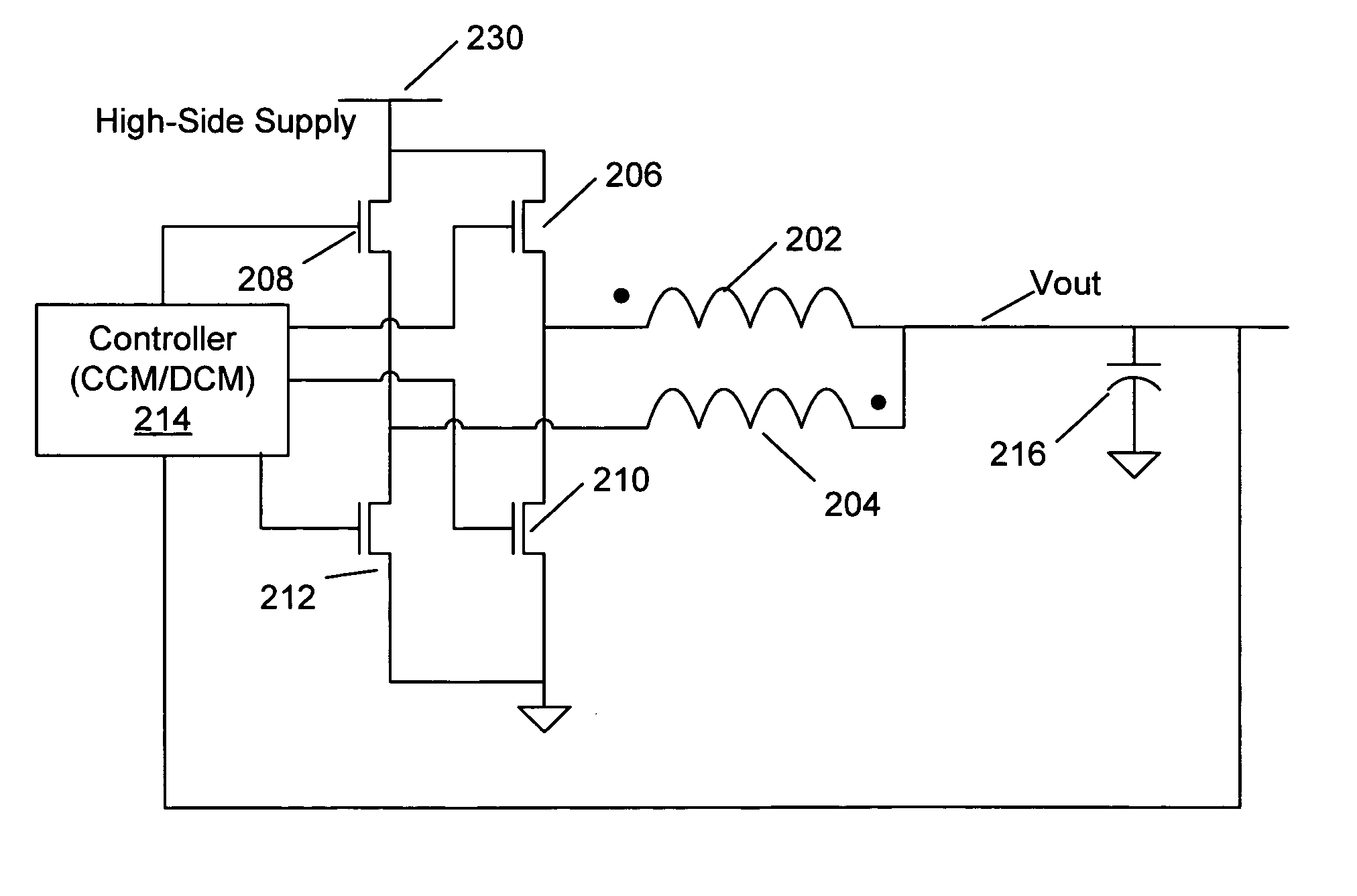
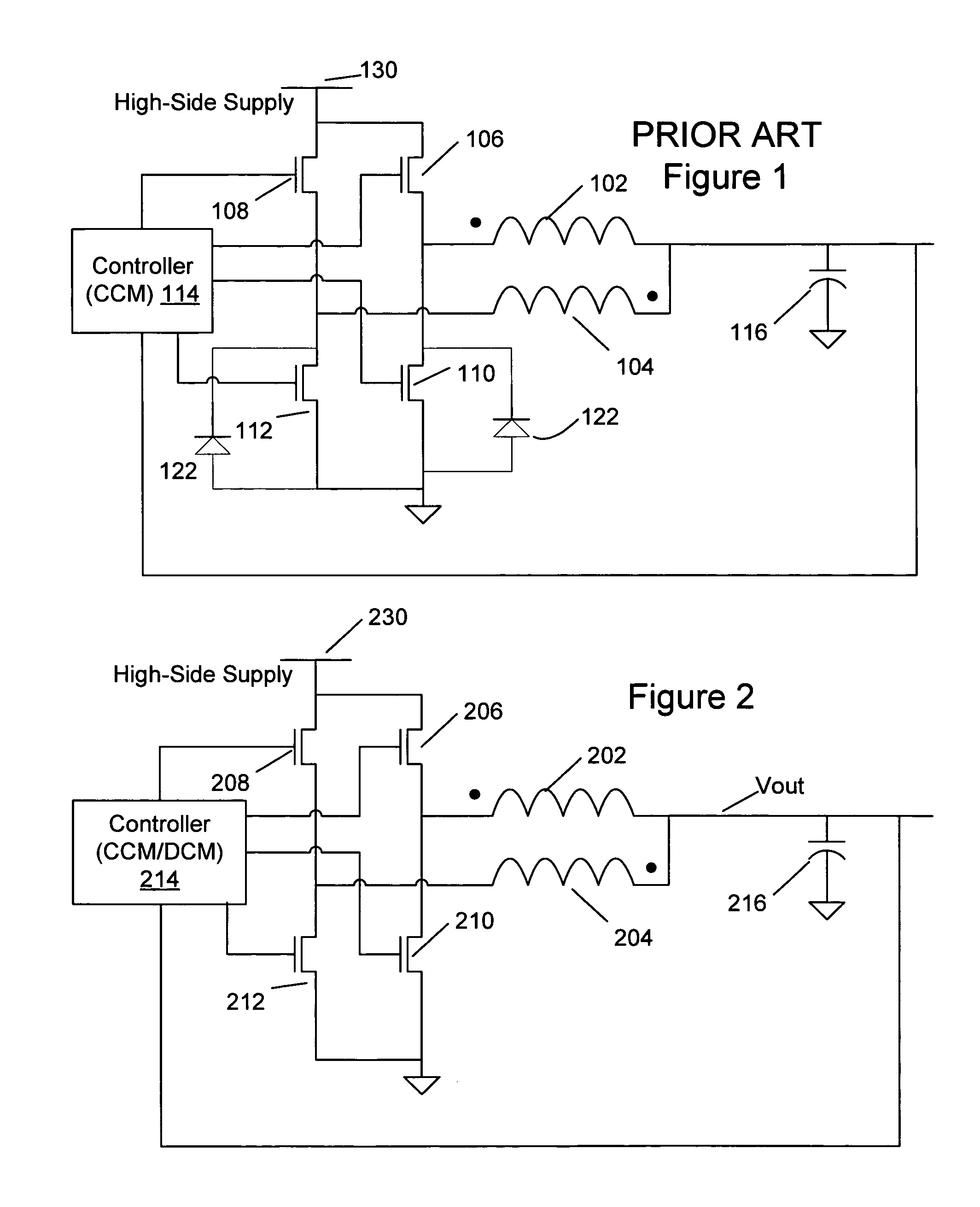
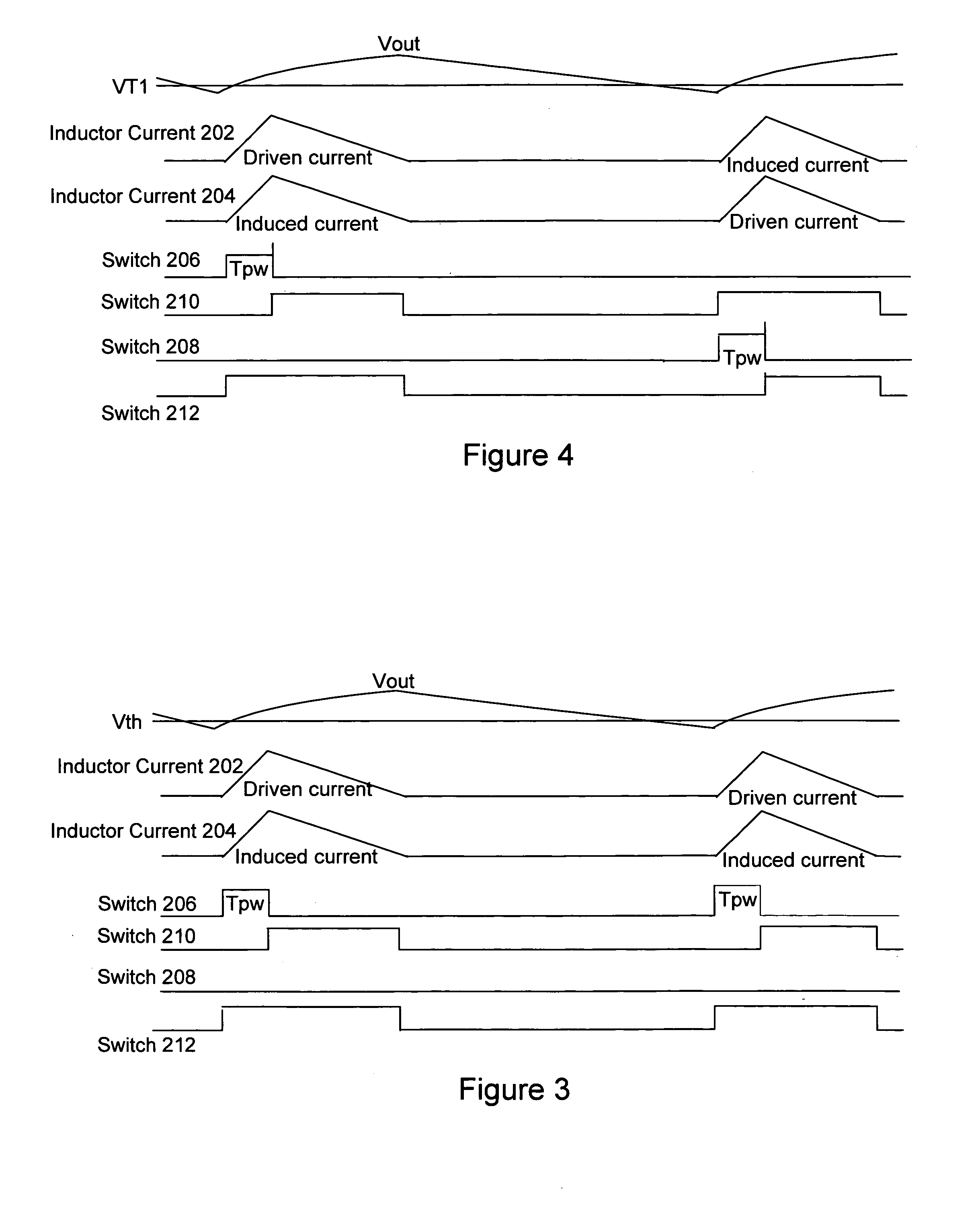
A multi-phase, coupled-inductor, DC-DC voltage converter operates in discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) when the system is operated at low output power demand. An embodiment of the converter switches to operating in continuous conduction mode (CCM) when the system is operated at high output power demand. Operation in single-drive and rotating phase DCM operation at low power are described. An alternative embodiment operates in a multiple-drive, rotating-phase, discontinuous conduction mode during at least one condition of output power demand.
Owner:VOLTERRA SEMICONDUCTOR
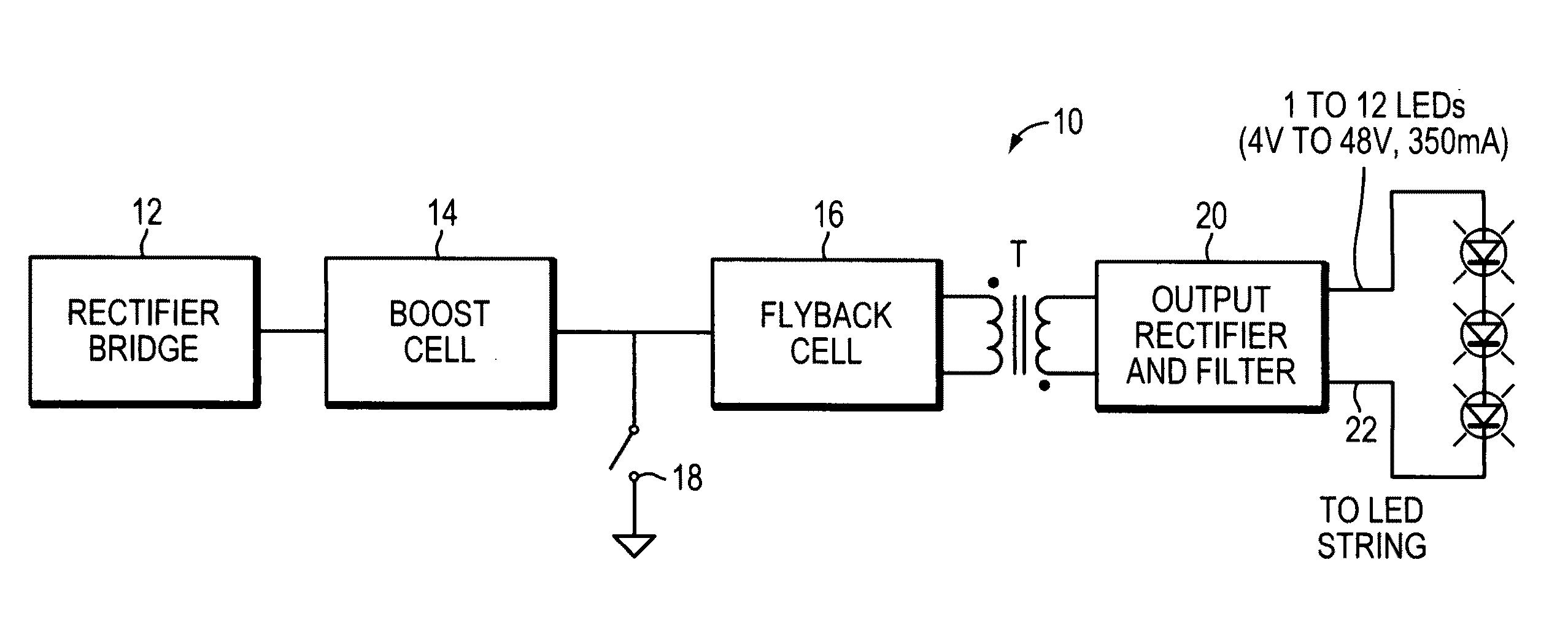
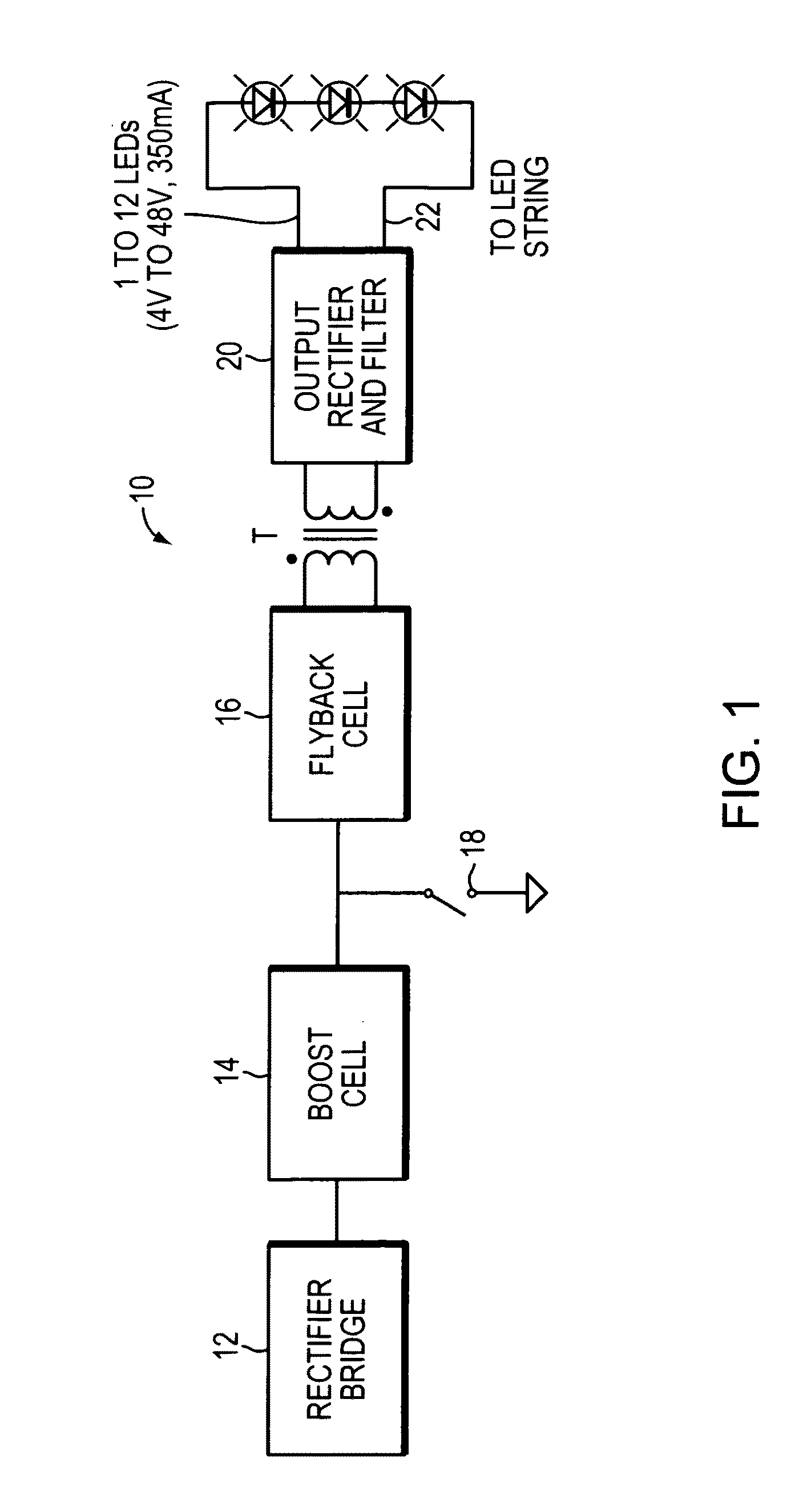
LED Illumination systems
InactiveUS20110309760A1Improve reliabilityLow costEfficient power electronics conversionElectroluminescent light sourcesBuck converterFlyback diode
An illumination system includes a power supply having a boost converter operating in the discontinuous conduction mode, a flyback converter operating in the critical conduction mode, and a switch coupled to the flyback converter. Several light emitting diodes receive power from the power supply. The boost converter may include a boost inductor (LB) and a boost diode (DB), constructed to perform the boost power factor correction (PFC) function. The flyback converter may includes a flyback inductor (LFB) and a flyback diode (DFB) and the power supply may be constructed to turn on the switch around the point where the current flowing in the flyback inductor reaches zero value.
Owner:EMD TECH
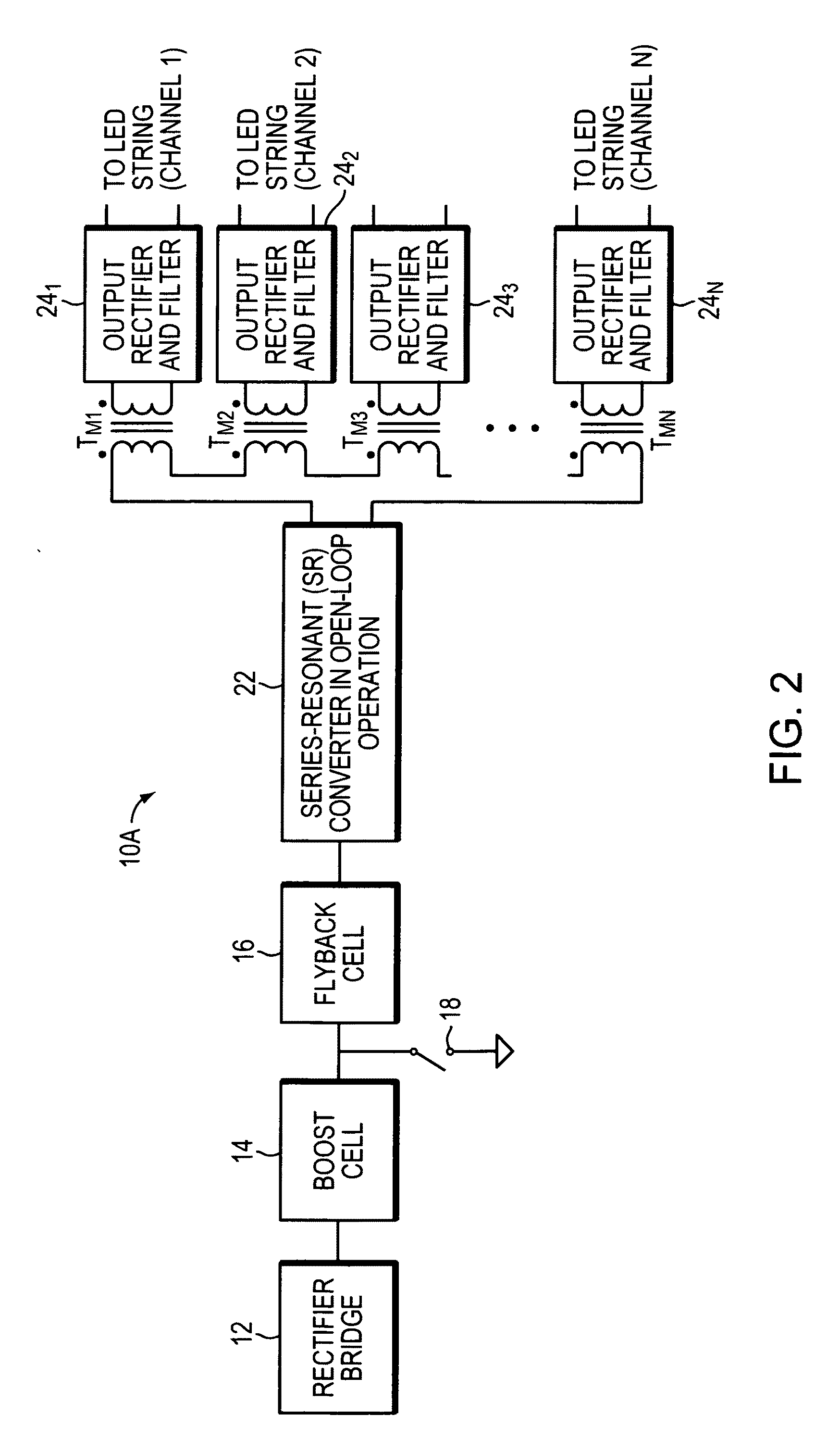
Single-inductor multiple-output switching converters in PCCM with freewheel switching
ActiveUS7432614B2Suppressing cross regulationSignificant stressDc network circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionFreewheelPeak value
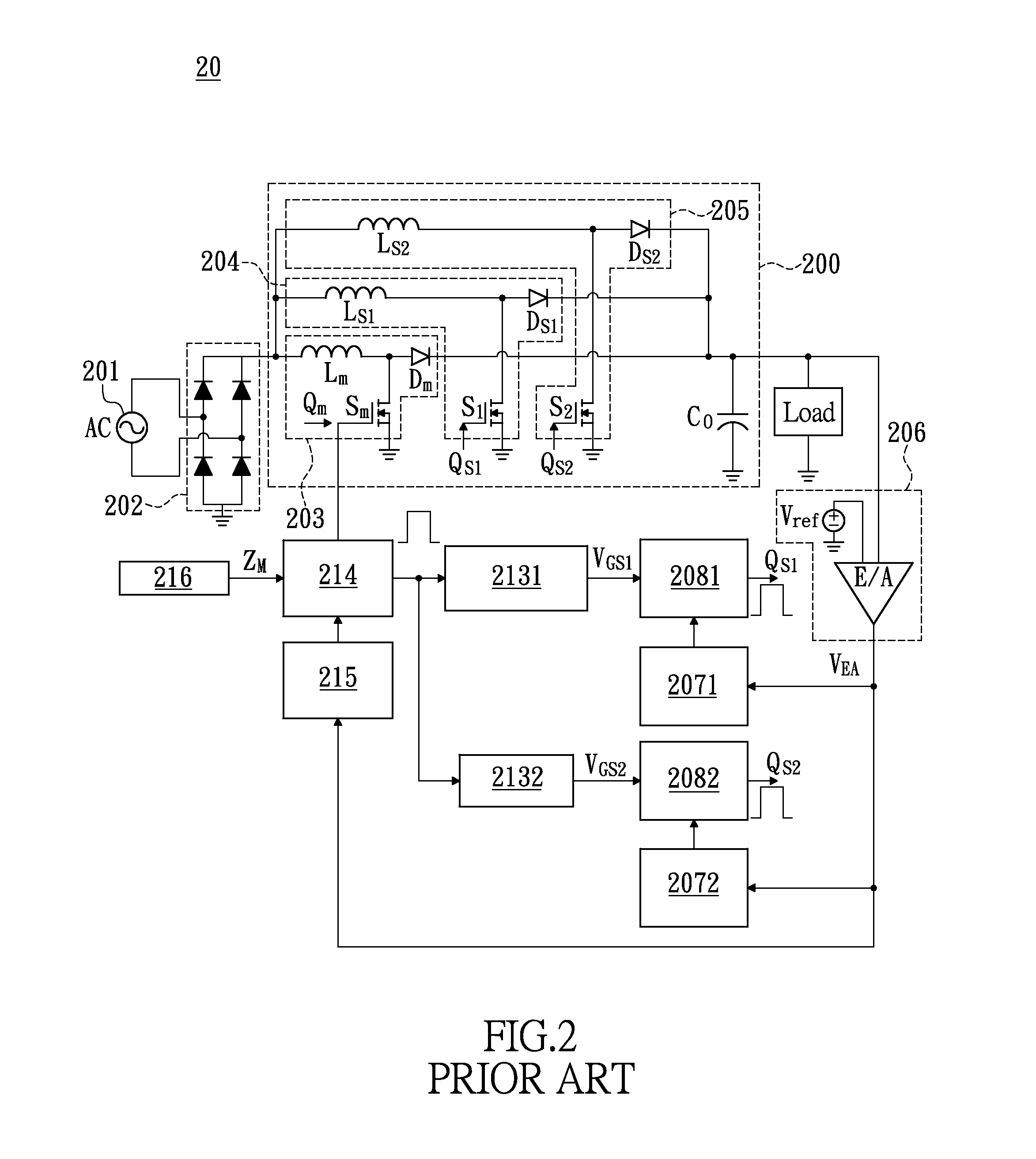
A method and apparatus are disclosed for single-inductor multiple-output switching converter design. With the proposed freewheel switching control, this converter operates in a pseudo-continuous conduction mode (PCCM) and is capable of handling large load currents with a much smaller current ripple and peak inductor current, while retaining low cross regulation. It can also work in discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) for high efficiency at light loads. This design can be applied to have single or multiple outputs and for different types of DC-DC conversions.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
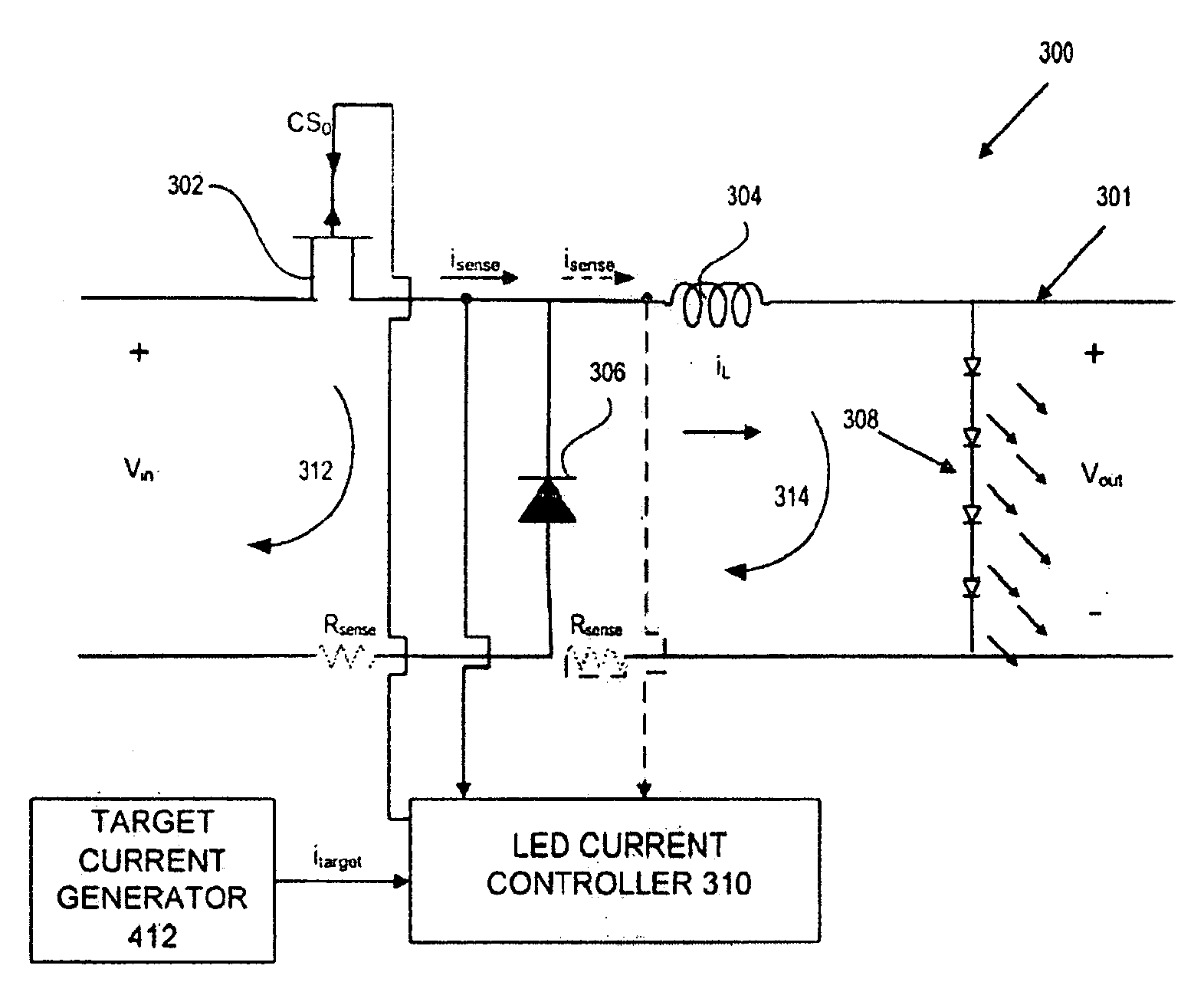
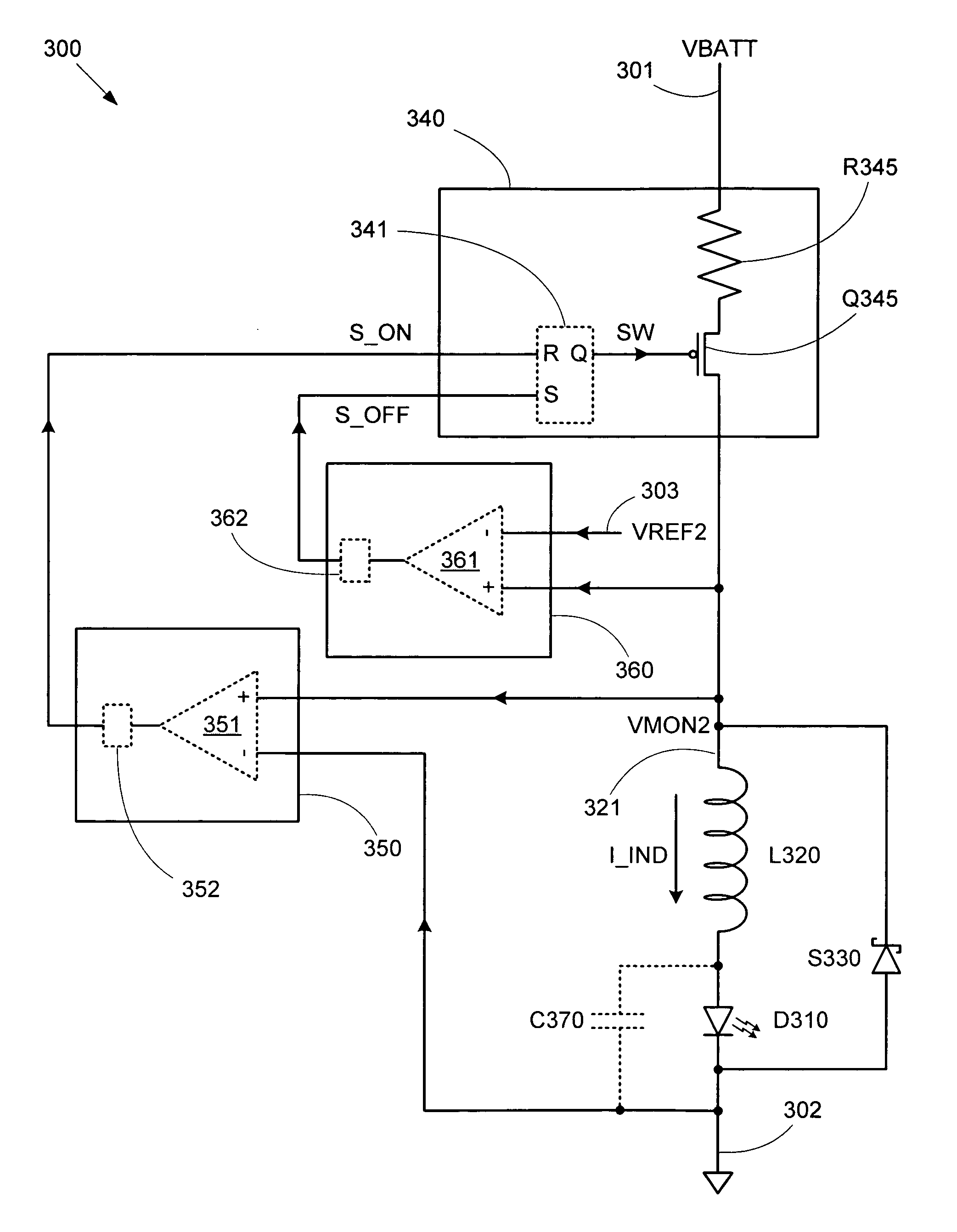
LED current bias control using a step down regulator
ActiveUS20060238174A1Simplified configuration requirementsPrediction is simpleElectroluminescent light sourcesElectric variable regulationMode controlPwm signals
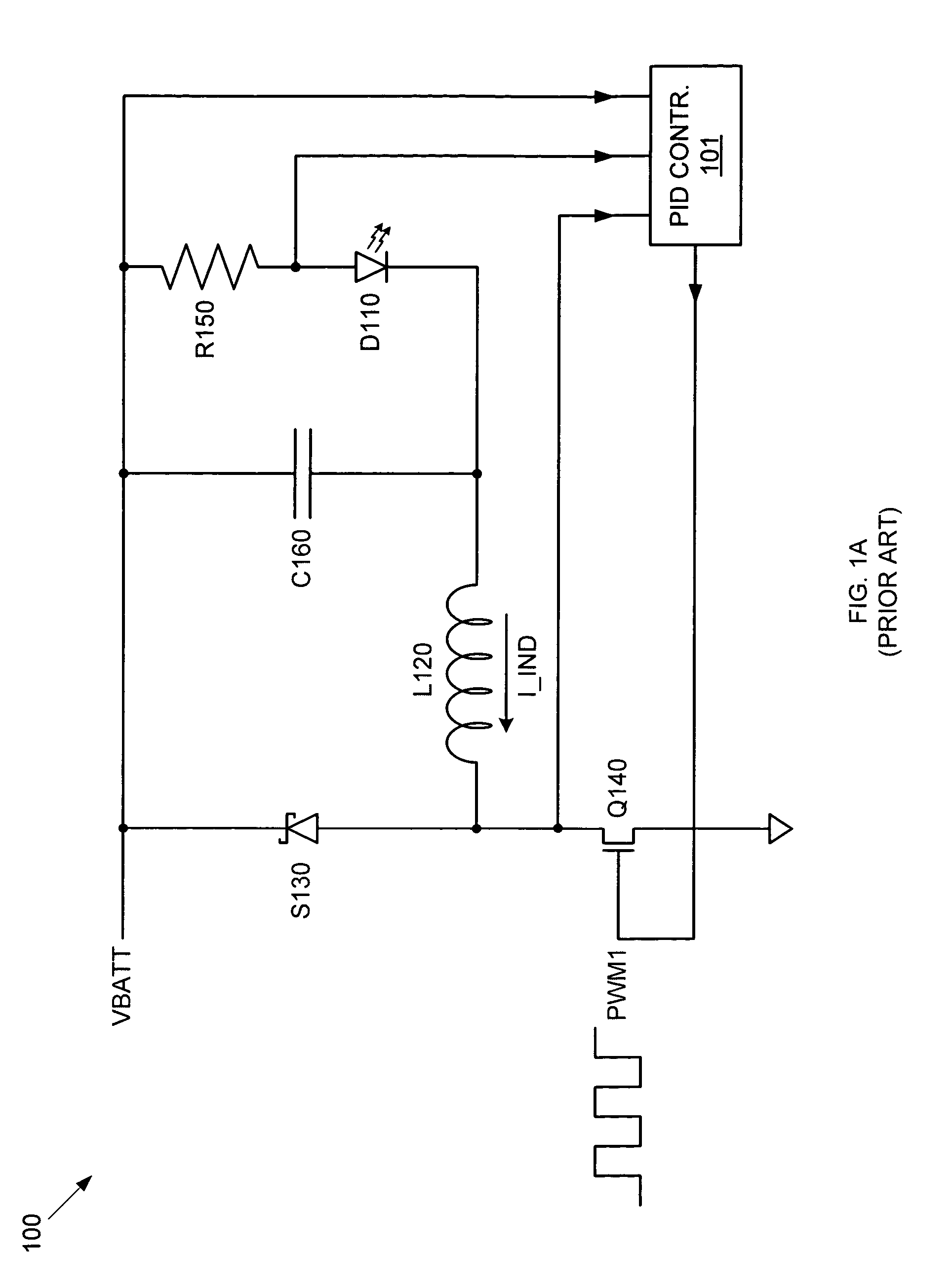
A step down switching regulator circuit that is particularly well-suited to drive high power LEDs includes a crossover conduction mode (XCM) control circuit that maintains operation at the crossover point between continuous conduction mode (CCM) and discontinuous conduction mode (DCM). This XCM operation provides an inductor current waveform that ramps up and down between zero and a desired maximum current. One or more comparators in the XCM control circuit can be used to control switching between the inductor current ramp up and ramp down phases. In this manner, complex feedback loop logic and PID controlled PWM signal generation logic can be avoided, and the need for external sense resistors and associated interface pins can be eliminated.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
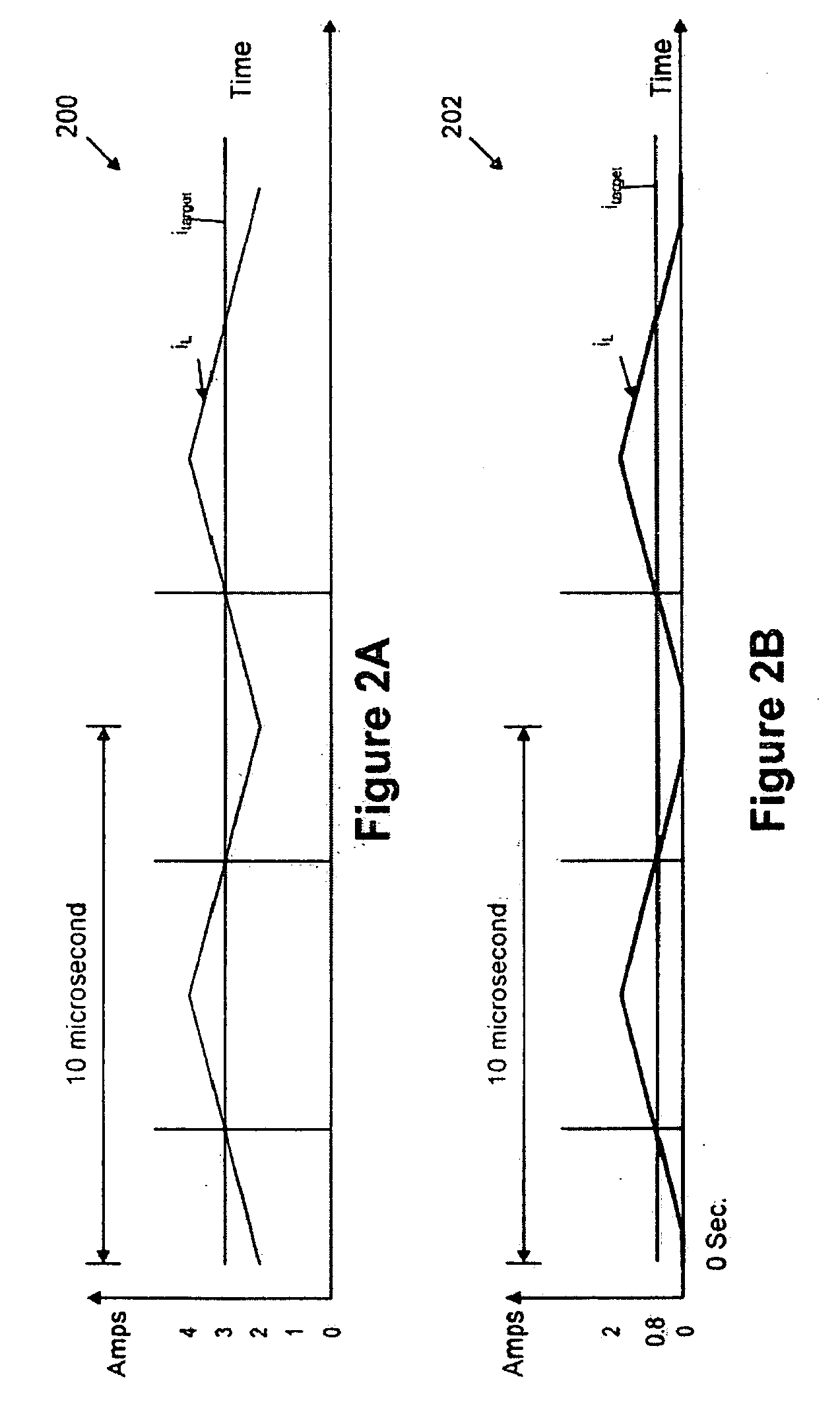
Adjustable Constant Current Source with Continuous Conduction Mode ("CCM") and Discontinuous Conduction Mode ("DCM") Operation
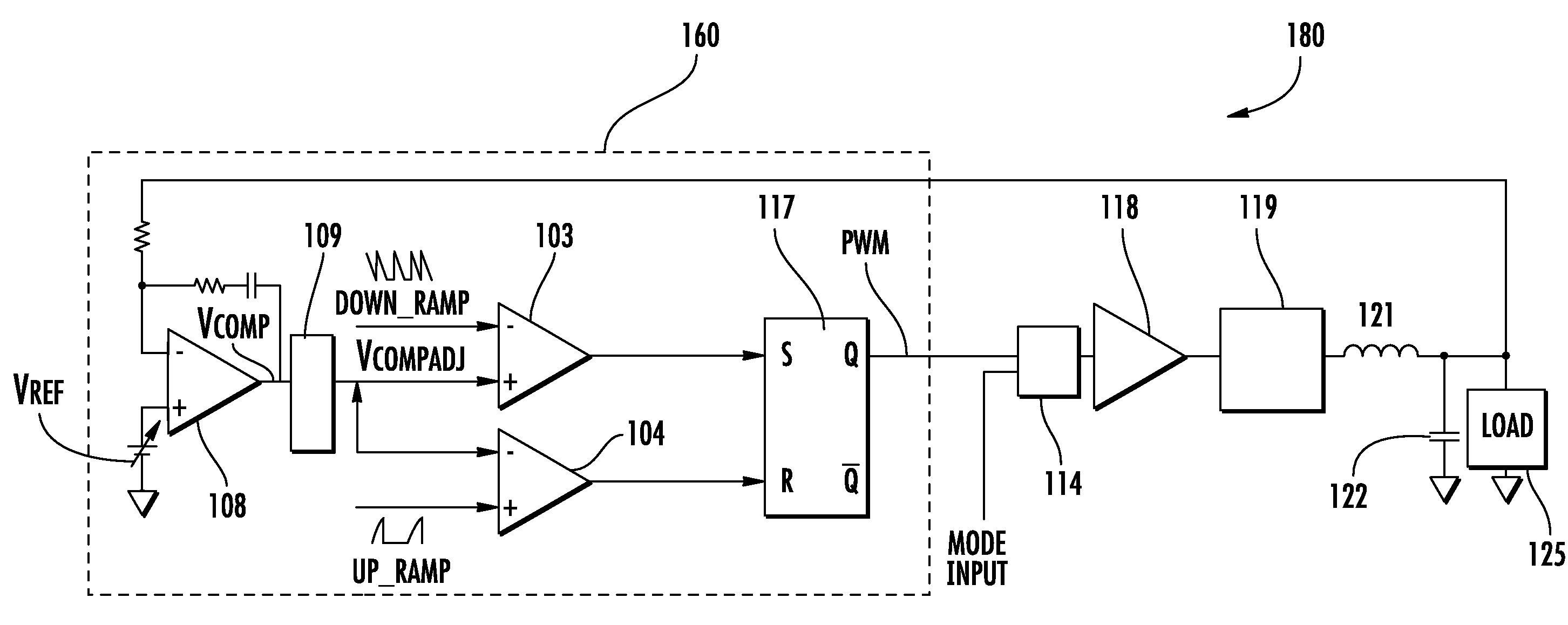
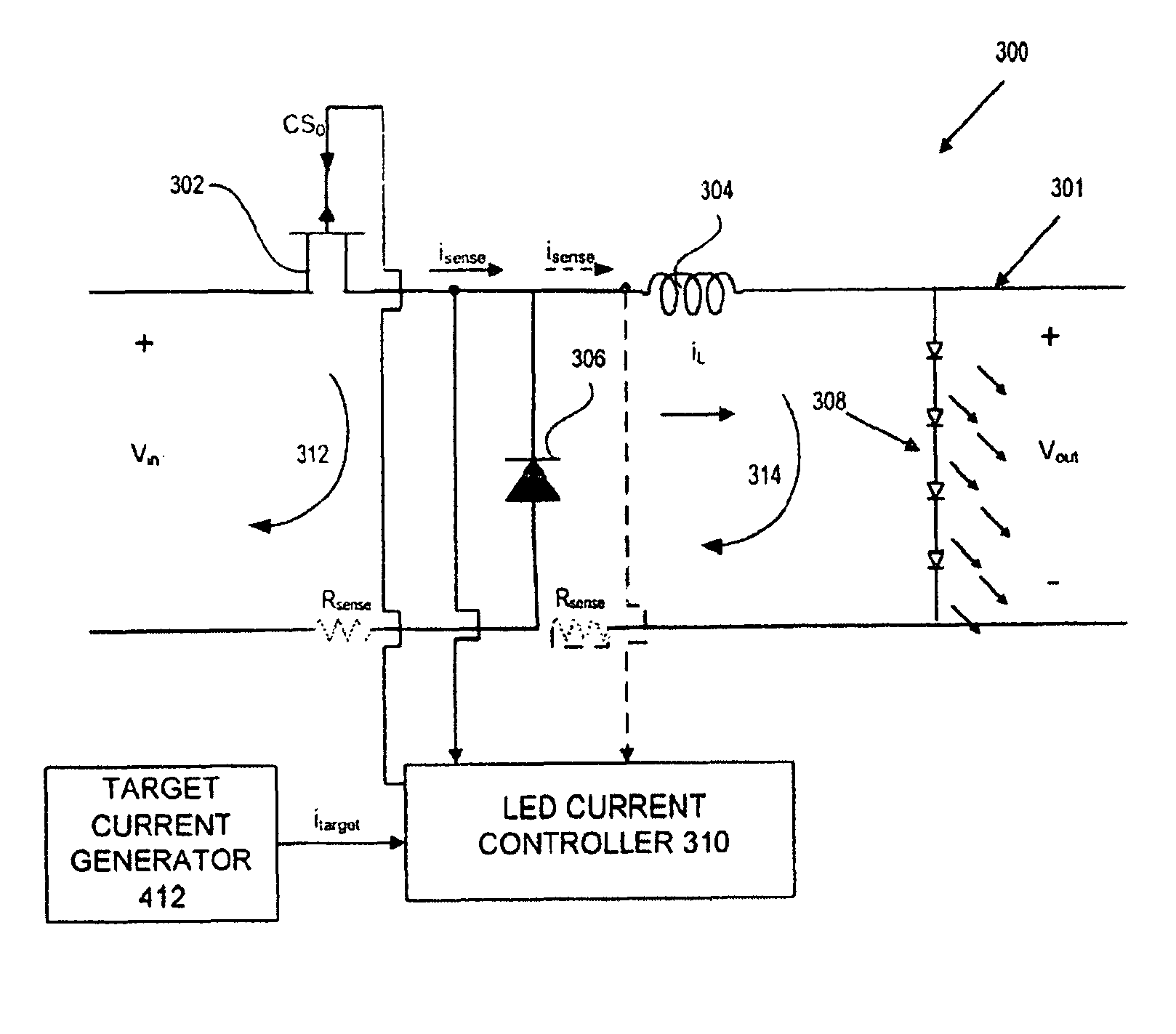
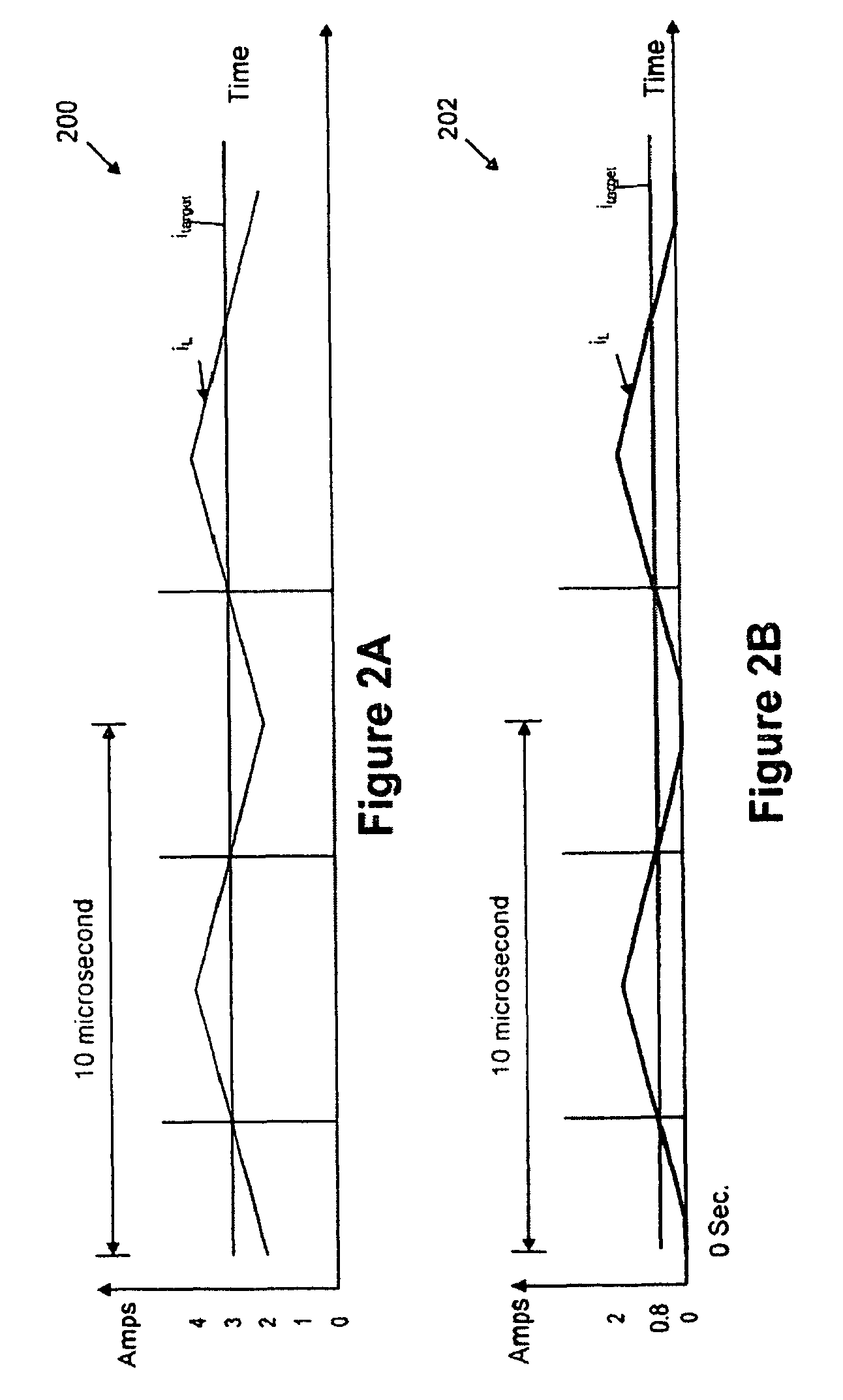
A converter system and method of operating a converter system are disclosed. The converter system comprises a converter power stage that can operate in a Discontinuous Conduction Mode (DCM) in a range of output currents and a Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM) in another range of output currents. The converter power stage includes at least an inductor with an inductor value and a control switch. The converter power stage provides an average current. A current controller is coupled to the converter power stage. When the converter power stage operates in DCM, the converter power stage provides the average current and the current controller is configured to measure the inductor value of the inductor. Furthermore, the current controller can also be configured to measure an input-to-output conversion ratio from the converter power stage.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Adaptive on-time control for power factor correction stage light load efficiency
ActiveUS20120014148A1Total current dropImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionHigher order harmonicsSwitching frequency
Light load efficiency of a power factor correction circuit is improved by adaptive on-time control and providing for selection between a continuous conduction mode and a discontinuous conduction mode wherein the discontinuous conduction mode increases time between switching pulses controlling connection of a cyclically varying voltage to a filter / inductor that delivers a desired DC voltage and thus can greatly reduce the switching frequency at light loads where switching frequency related losses dominate efficiency. The mode for controlling switching is preferably selected for each switching pulse within a half cycle of the cyclically varying input voltage. A multi-phase embodiment allows cancellation of EMI noise at harmonics of the switching frequency and adaptive change of phase angle allows for cancellation of dominant higher order harmonics as switching frequency is reduced.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Controller having comp node voltage shift cancellation for improved discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) regulator performance and related methods
ActiveUS20080284398A1Improve performanceReduce variationDc network circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionVoltage shiftEngineering
A modulation controller includes an error amplifier which receives a reference voltage and an output voltage (VOUT) from a switching regulator being controlled by the controller at its inputs and provides a VCOMP signal at its output, and at least one comparator, wherein a first input of the comparator is coupled to an output of the error amplifier and a second input coupled to receive a ramp signal. A VCOMP shift cancellation circuit is interposed between the first or second input of the comparator, wherein the VCOMP shift cancellation circuit improves diode conduction mode performance (DCM) of the regulator by reducing a variation in average VCOMP.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Time-limiting mode (TLM) for an interleaved power factor correction (PFC) converter
InactiveUS20110110132A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionActive power factor correctionTime limit
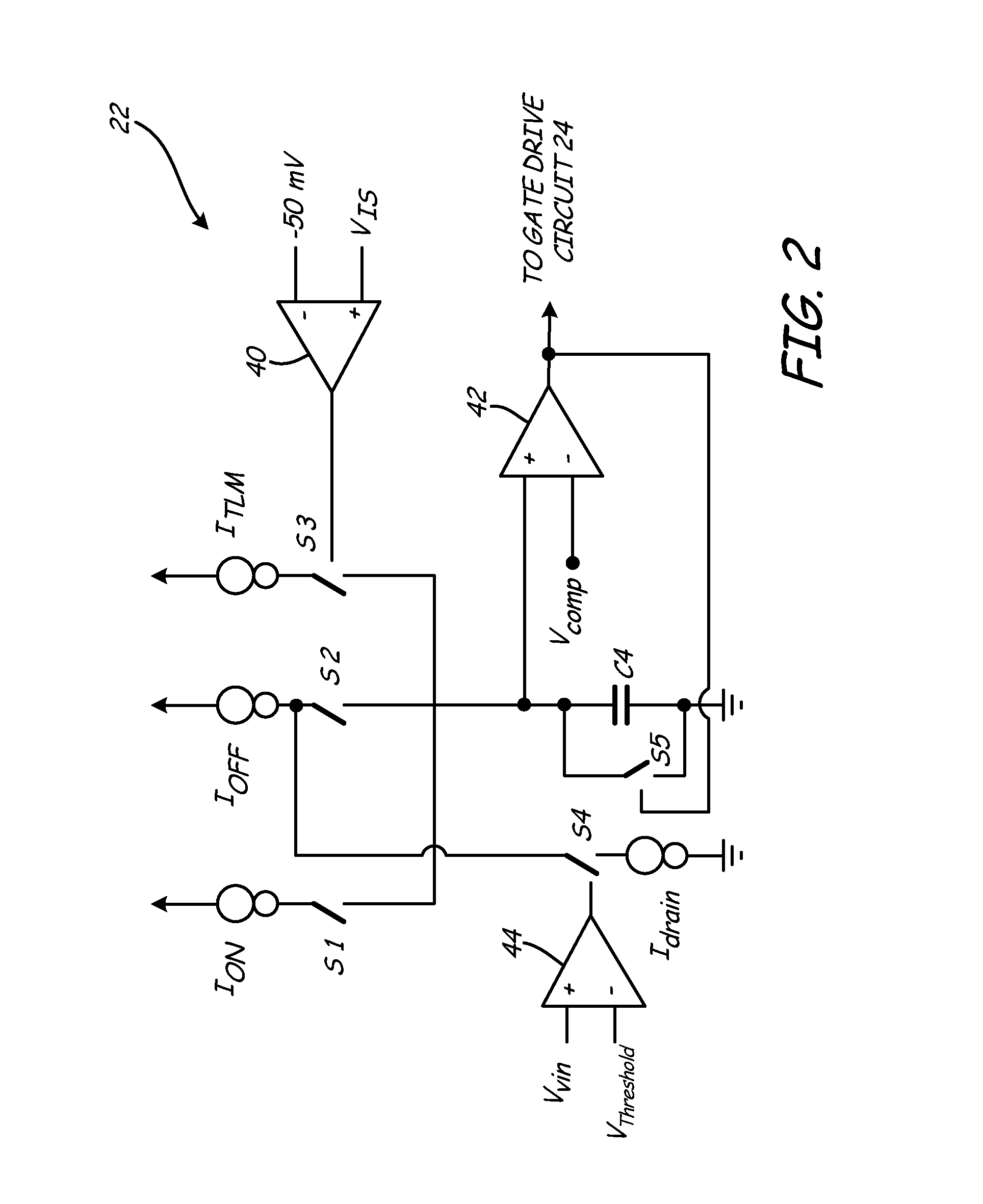
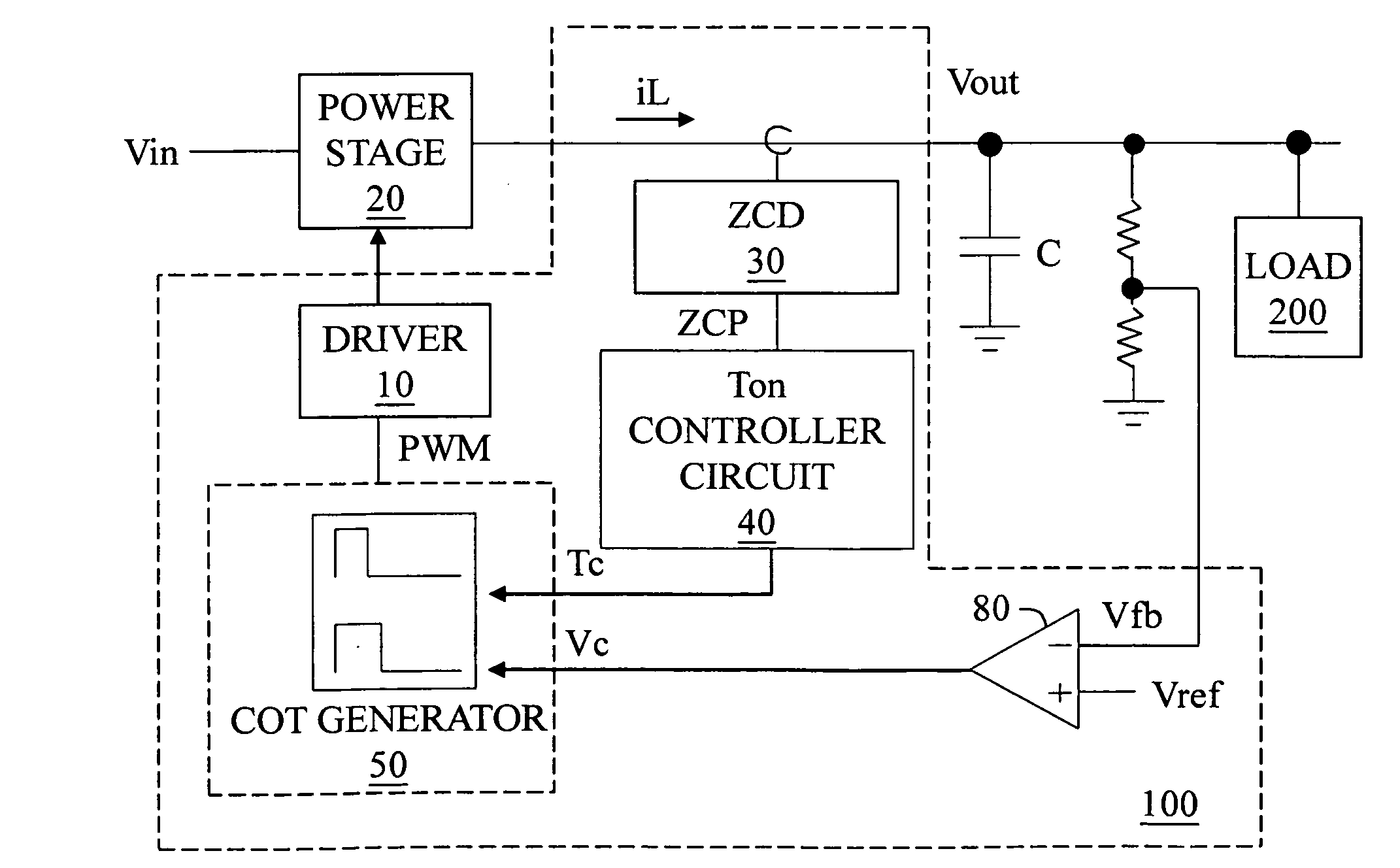
The present invention provides a method of controlling an interleaved power factor correction (PFC) circuit operating in a discontinuous conduction mode (DCM). The controller employs a normal mode of operation in which inductor currents in each PFC sub-circuit are estimated based on the monitored input voltage and monitored output voltage, and switching devices associated with each PFC sub-circuit are controlled to ensure DCM operation. As the input voltage increases, the OFF times of each PFC sub-circuit increase such that the inductor currents no longer overlap. In response, the controller activates a time-limiting mode (TLM) in which OFF time durations for each sub-circuit are based on the monitored sum of load currents as opposed to the monitored input voltage and monitored output voltage.
Owner:POLAR SEMICON
Regulated open-loop constant-power power supply
InactiveUS20050151518A1Reduce weightLow costElectroluminescent light sourcesDc-dc conversionConstant powerMeasuring output
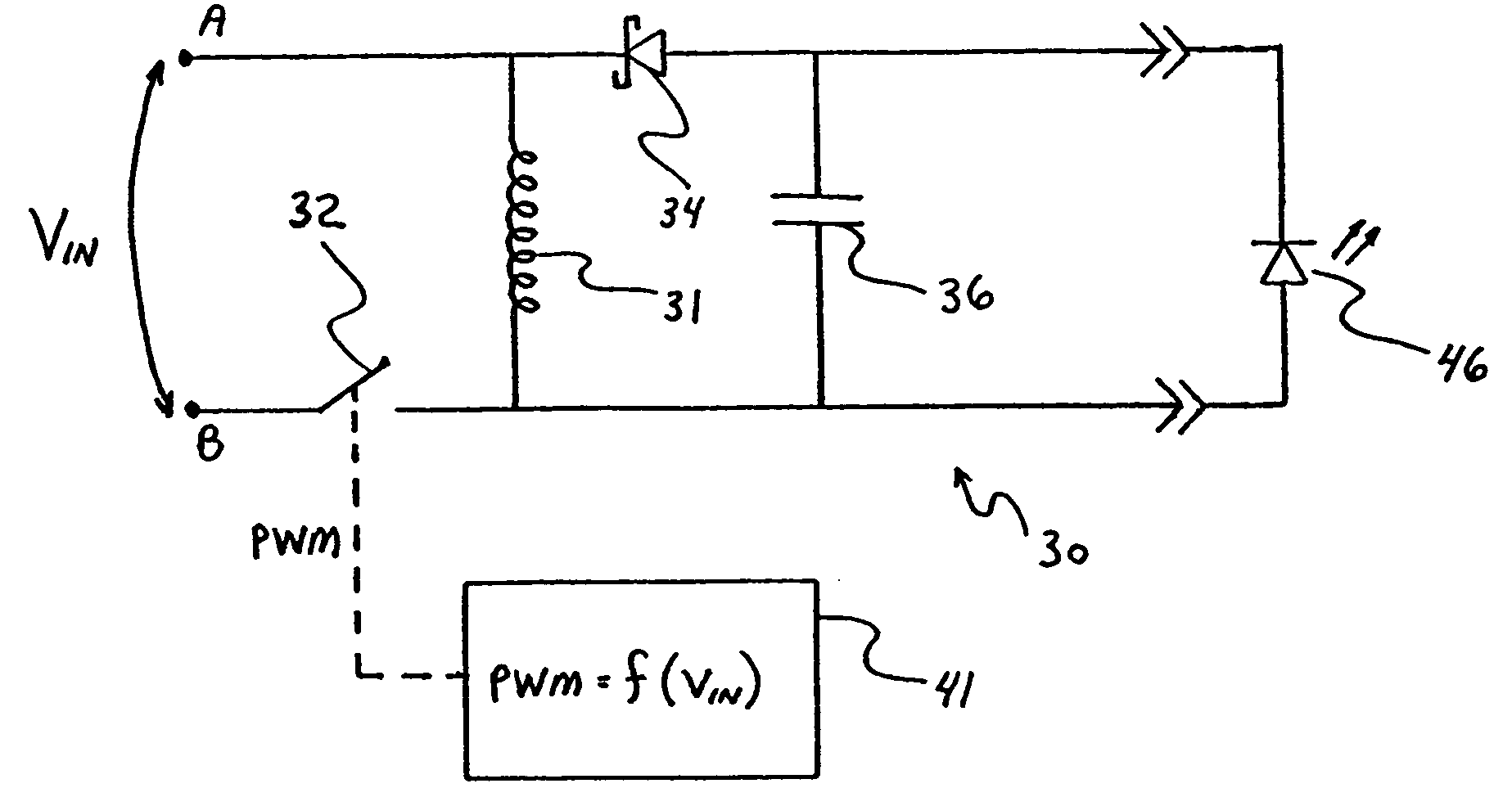
A constant-power switching power supply has an inductor with an inductor current that remains in discontinuous conduction mode (DCM), where the power supply supplies and maintains constant output power to a load without measuring output parameters, by regulating charge-up time of the inductor. A method of maintaining a constant output power for a power supply being run in discontinuous conduction mode (DCM), having an inductor, includes obtaining a measured input voltage for voltage being input to the power supply, obtaining from a memory a set of values based on the measured input voltage, and driving a pulse width modulation (PWM) generator based on the set of values, the driving of the PWM generator thereby regulating a charge-up time of the inductor to correspond to the measured input voltage, whereby the regulating of the charge-up time of the inductor maintains an essentially constant power for a load.
Owner:SCHNEIKER HENRY D +1
Forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit
ActiveUS8009448B2Improve conversion efficiencyAdditional drawbackEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsEngineeringHeavy load
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
LED current bias control using a step down regulator
ActiveUS7323828B2Simple requirementsPrediction is simpleElectroluminescent light sourcesElectric light circuit arrangementEngineeringControl circuit
A step down switching regulator circuit that is particularly well-suited to drive high power LEDs includes a crossover conduction mode (XCM) control circuit that maintains operation at the crossover point between continuous conduction mode (CCM) and discontinuous conduction mode (DCM). This XCM operation provides an inductor current waveform that ramps up and down between zero and a desired maximum current. One or more comparators in the XCM control circuit can be used to control switching between the inductor current ramp up and ramp down phases. In this manner, complex feedback loop logic and PID controlled PWM signal generation logic can be avoided, and the need for external sense resistors and associated interface pins can be eliminated.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Control circuit and method for reducing output ripple in constant on-time switching regulator
InactiveUS20120019225A1Reduce output rippleReduce outputDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationTime switchingControl circuit
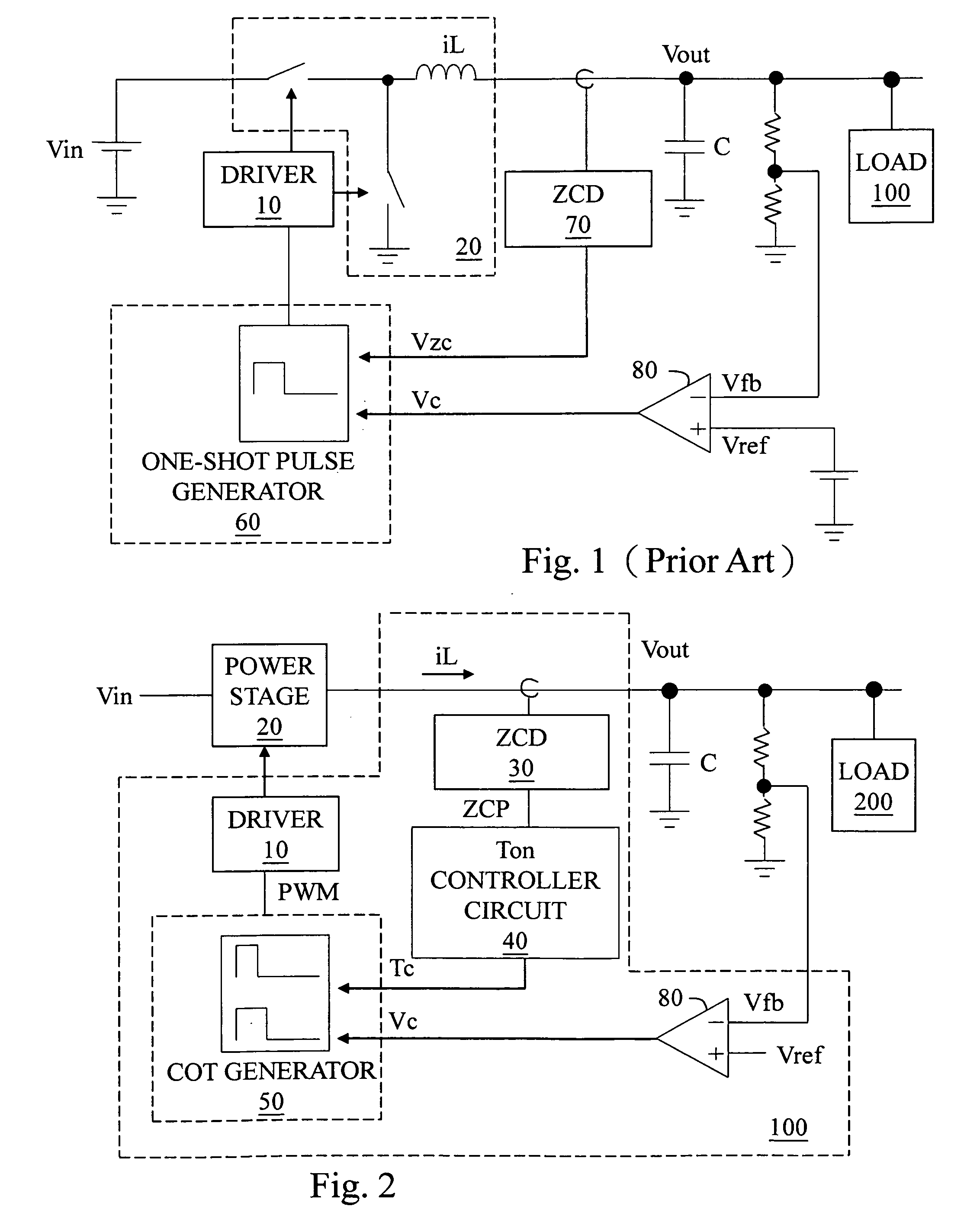
The present invention discloses a control circuit for reducing output ripple in a constant on-time switching regulator and a method thereof, for controlling a power stage. The control circuit determines whether a zero current period wherein an output current is zero is longer than a threshold period, and switches the on-time period to a shorter period if it is longer, whereby the power stage operates according to the shorter period while still in the discontinuous conduction mode (DCM).
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
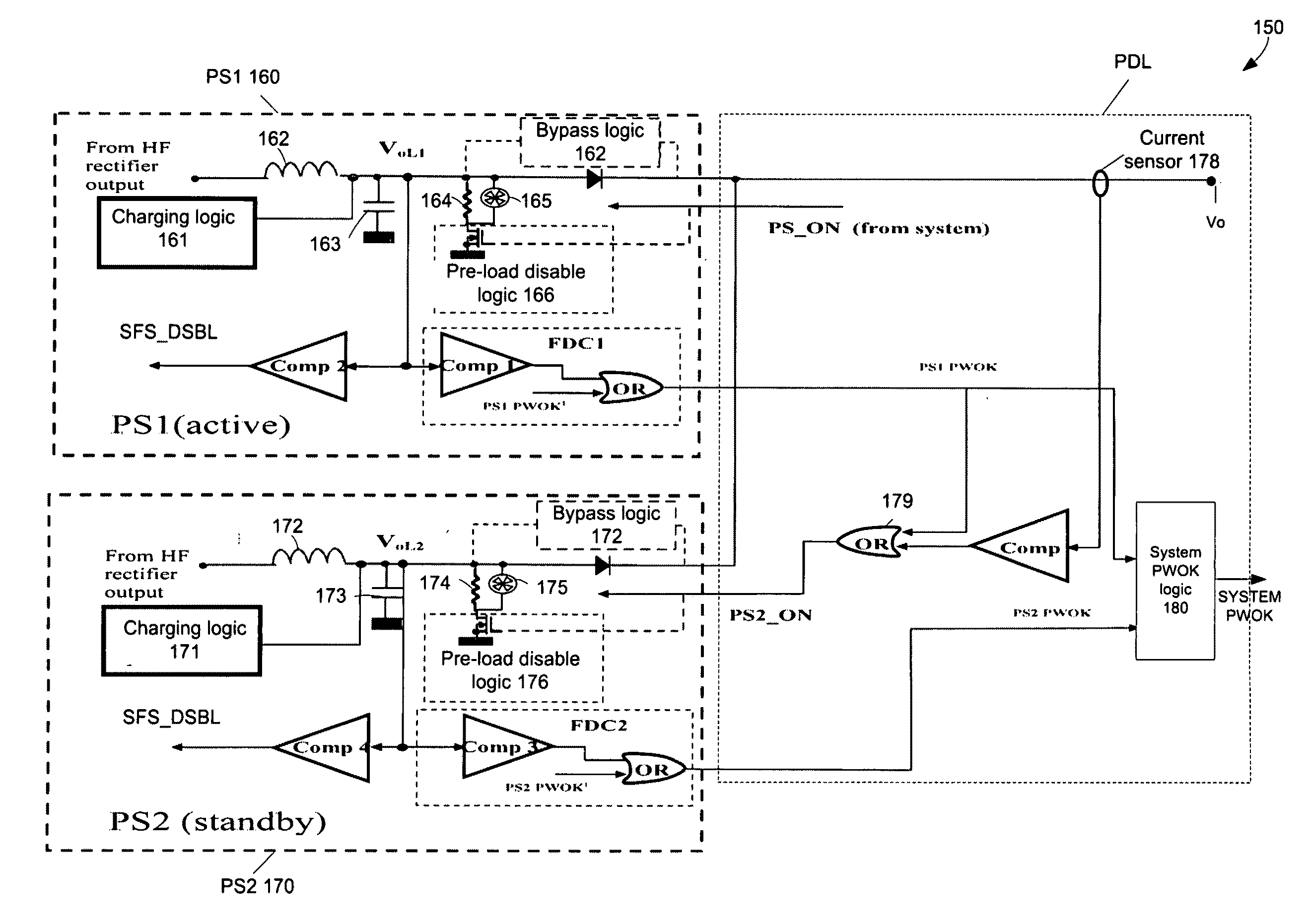
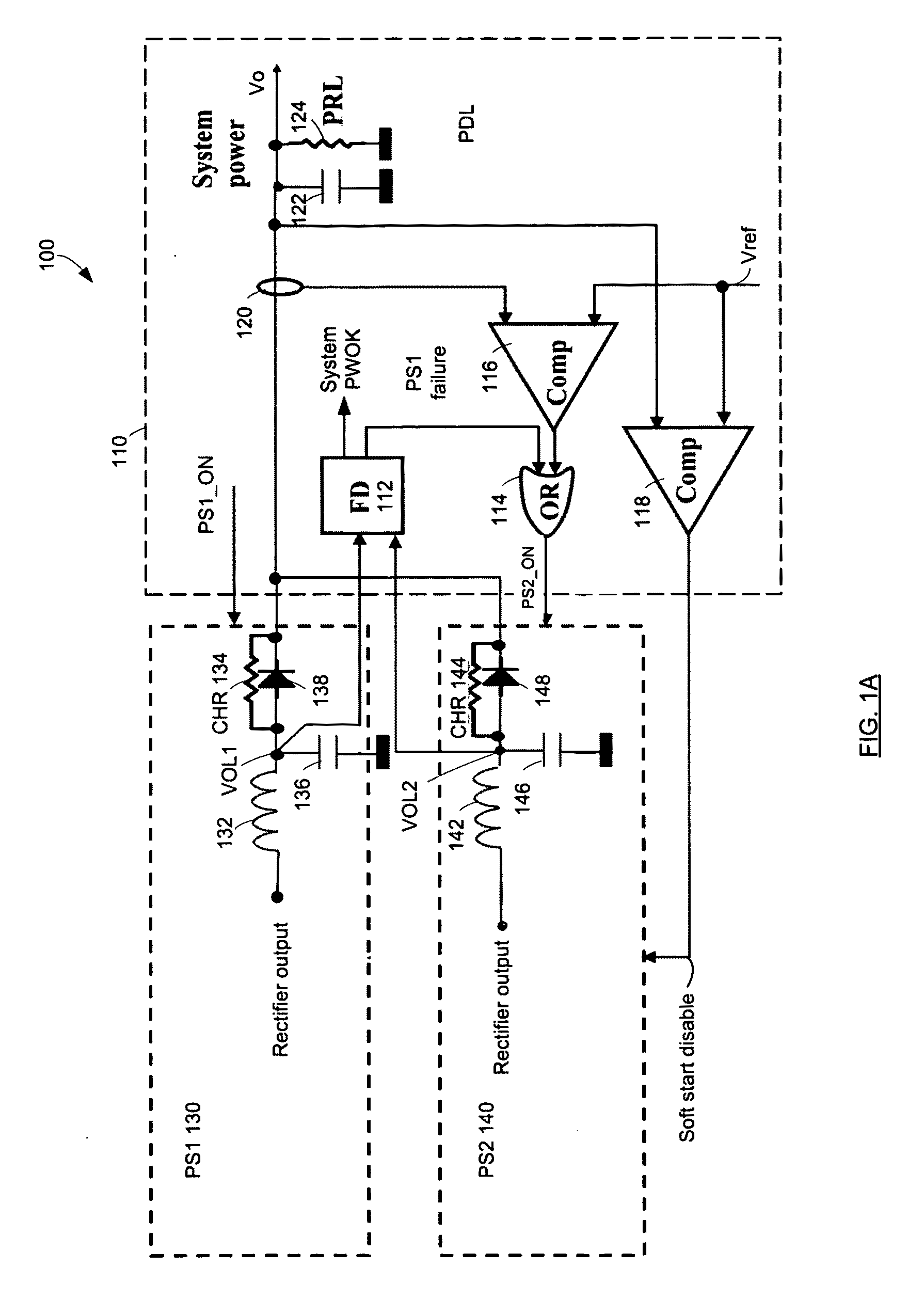
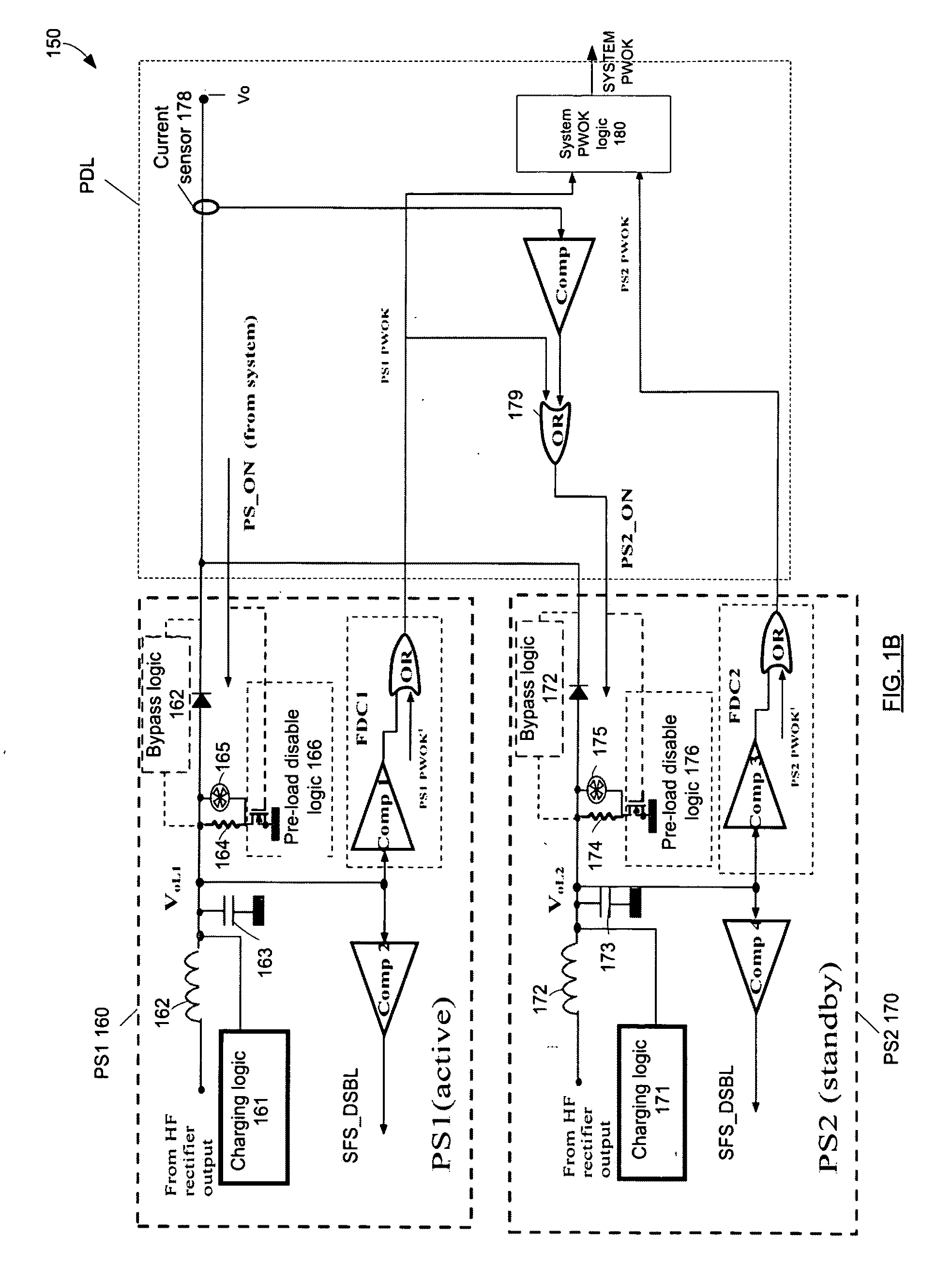
Reducing power losses in a redundant power supply system
InactiveUS20100332857A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalPower network operation systems integrationStandby powerEngineering
A power supply system includes at least a first power supply module and at least one redundant power supply module. The at least one power supply module supplies power to an output terminal. The at least one redundant power supply module operates in a first state and in a second state. In the first state the second power supply module supplies power to the output terminal. In the second state the second power supply module provides standby power and operates in a burst mode (for example, such as a discontinuous conduction mode).
Owner:INTEL CORP
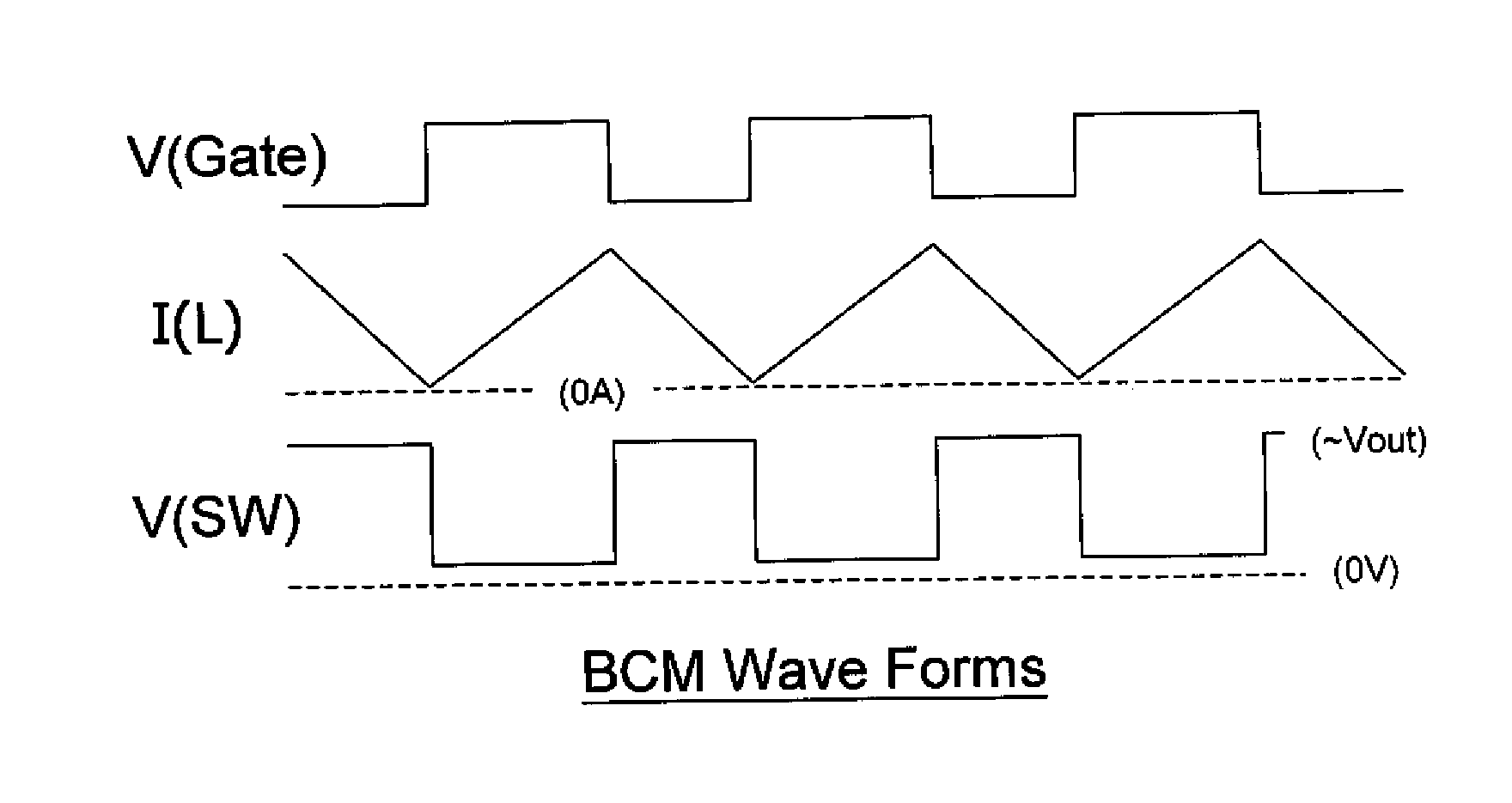
Boundary conduction mode switching regulator and driver circuit and control method thereof
The present invention discloses a boundary conduction mode (BCM) switching regulator, and a driver circuit and a control method of the switching regulator, for controlling a power stage to convert an input voltage to an output voltage or output current. The BCM switching regulator detects whether it is operating in continuous conduction mode (CCM) or discontinuous conduction mode (DCM), and adjusts the On-time, Off-time, or frequency of the power stage accordingly, so that the switching regulator operates in or near BCM.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
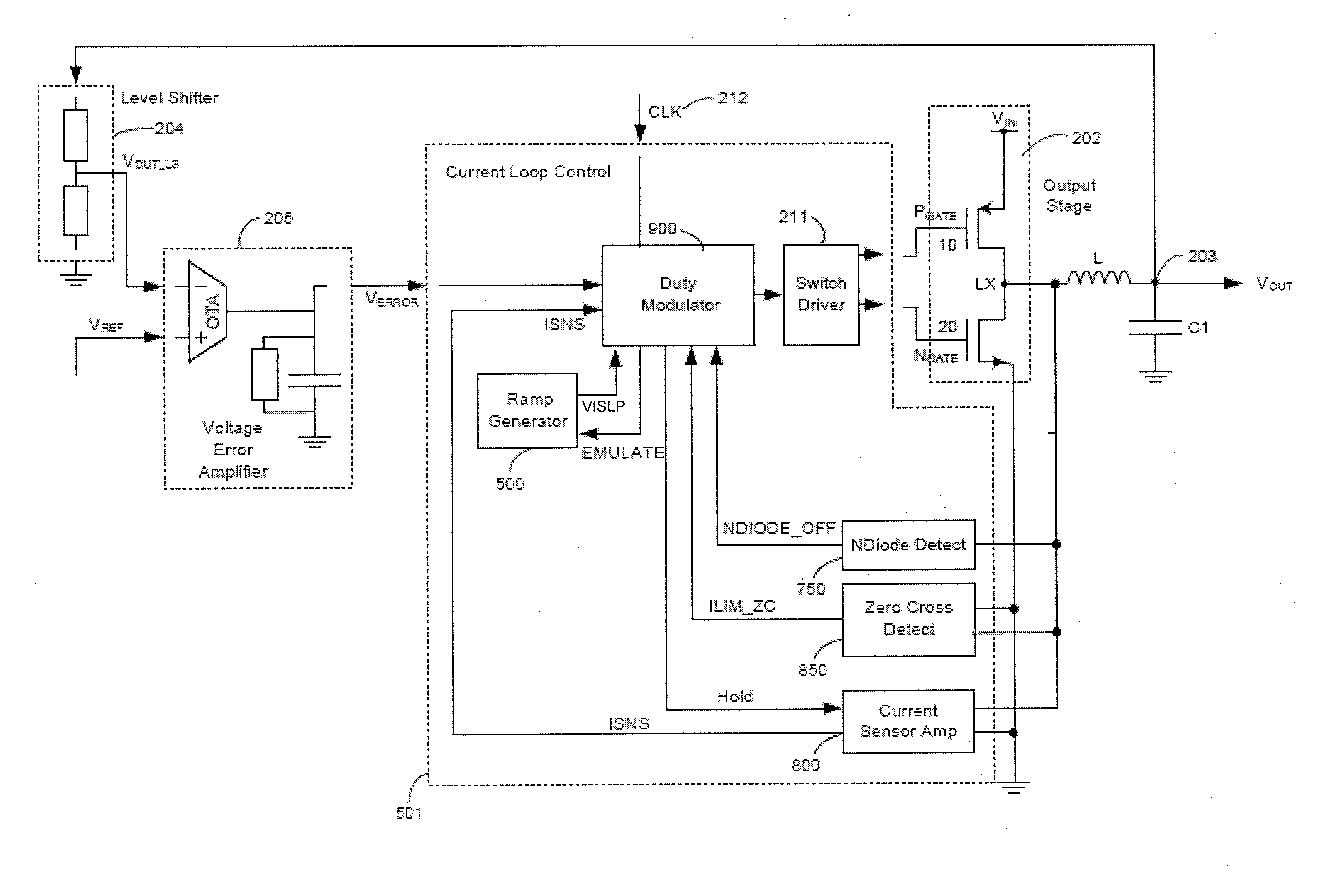
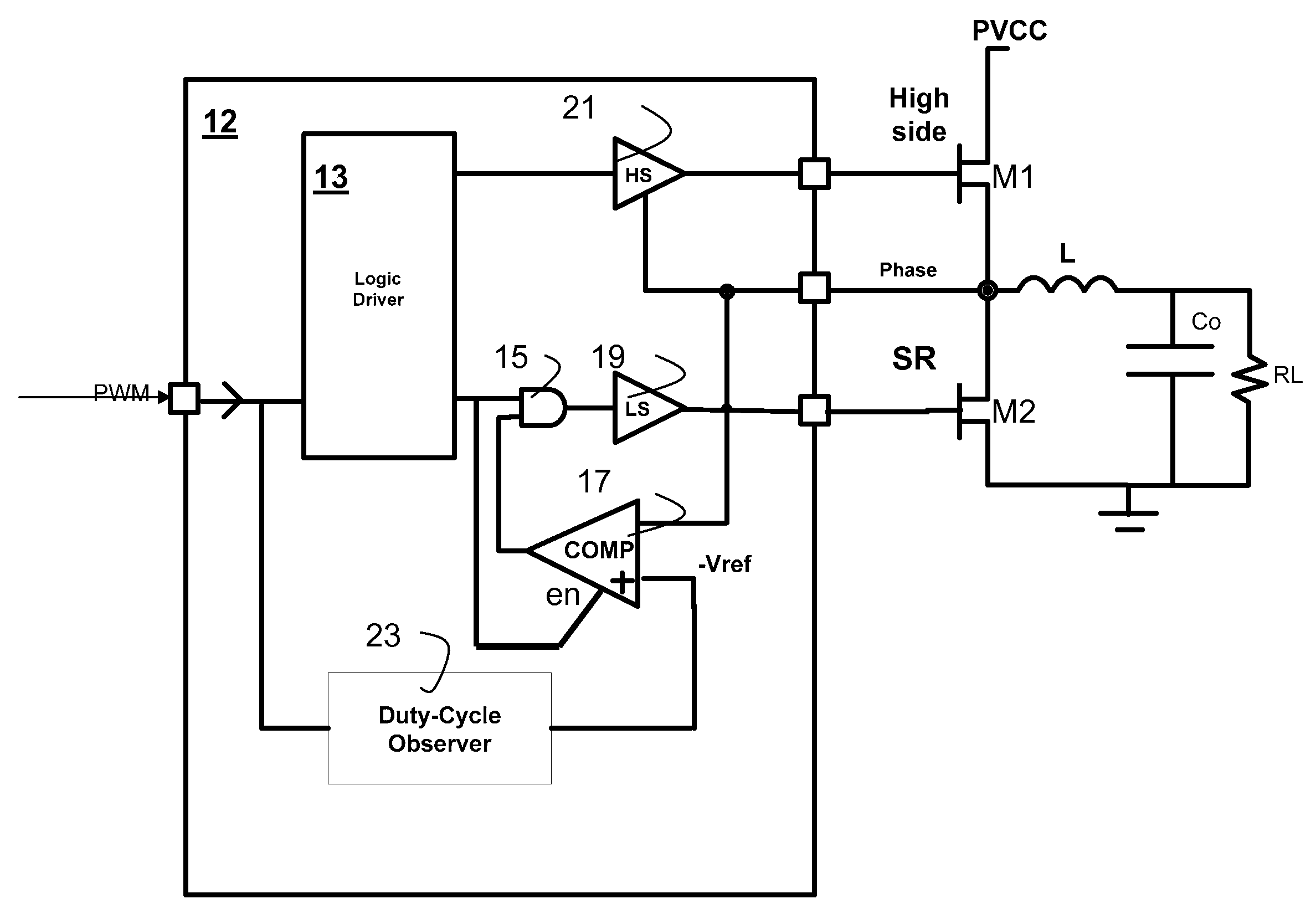
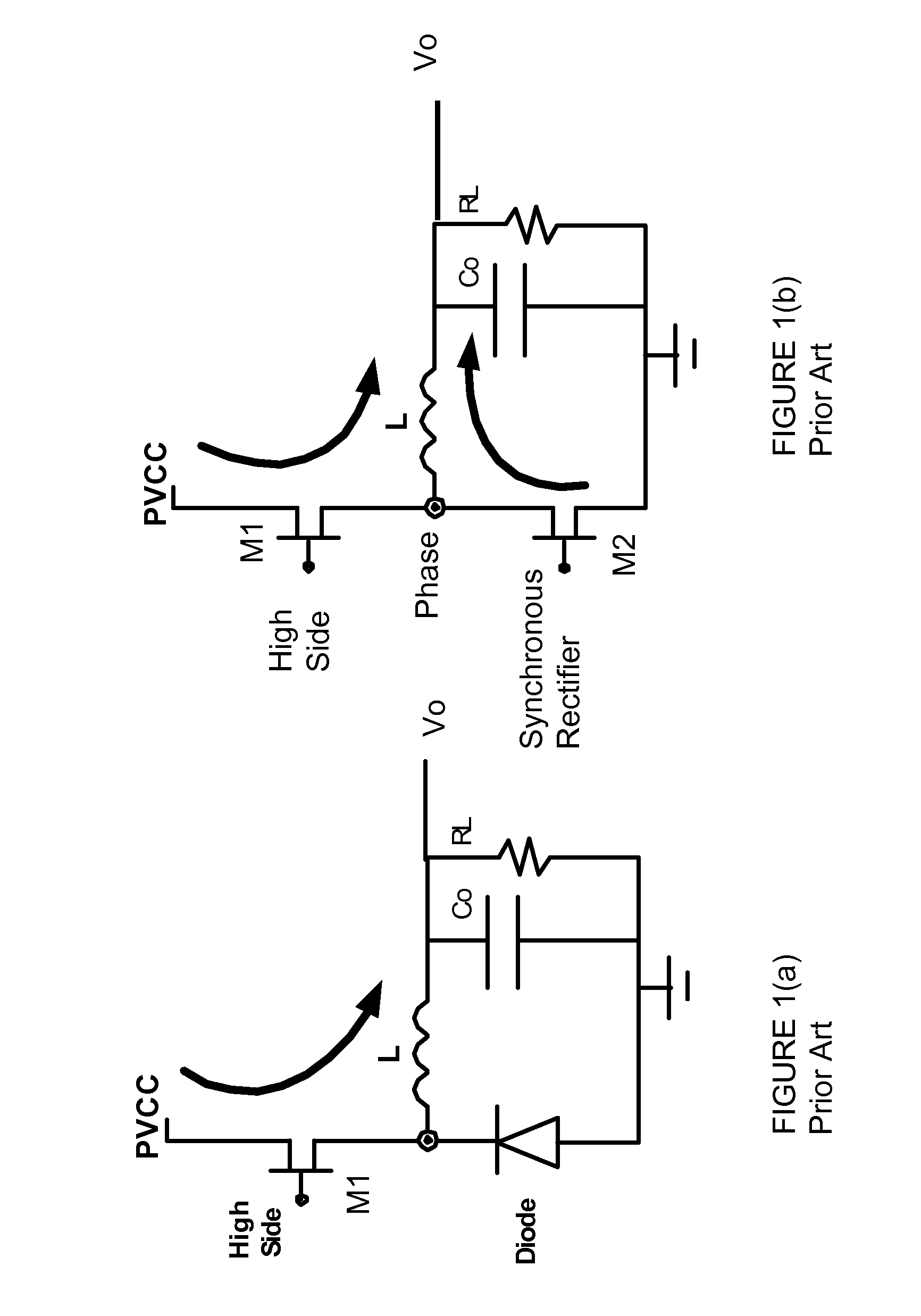
Dc-dc converters
ActiveUS20110050185A1Easy to controlTransistorEfficient power electronics conversionCurrent loadCurrent loop control
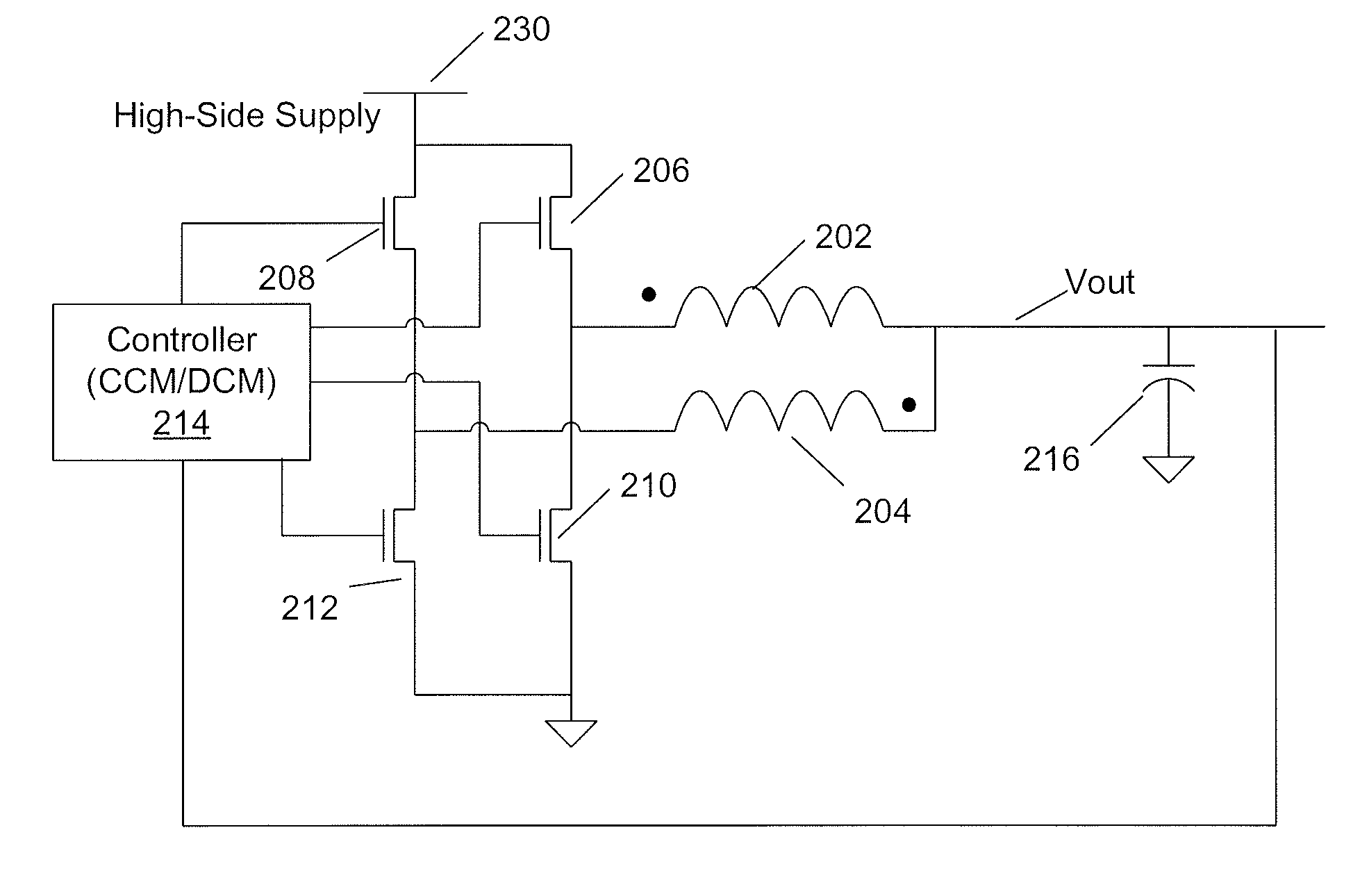
Methods and apparatus for control of DC-DC converters, especially in valley current mode. The DC-DC converter is operable so that a low side supply switch may be turned off, before the high side supply switch is turned on. During the period when both switches are off the current loop control remains active and the change in inductor (L) current is emulated. One embodiment uses a current sensor for lossless current sensing and emulates the change in inductor current by holding the value of the output of the current sensor (ISNS) at the time that the low side switch turns off and adding an emulated ramp signal (VISLP) until the inductor current reaches zero. Embodiment employing a pulse-skip mode of operation based on a minimum conduction time are also disclosed. The invention enables a seamless transition from Continuous Conduction Mode the Discontinuous Conduction Mode and Pulse Skipping and provide converters that are efficient at low current loads.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
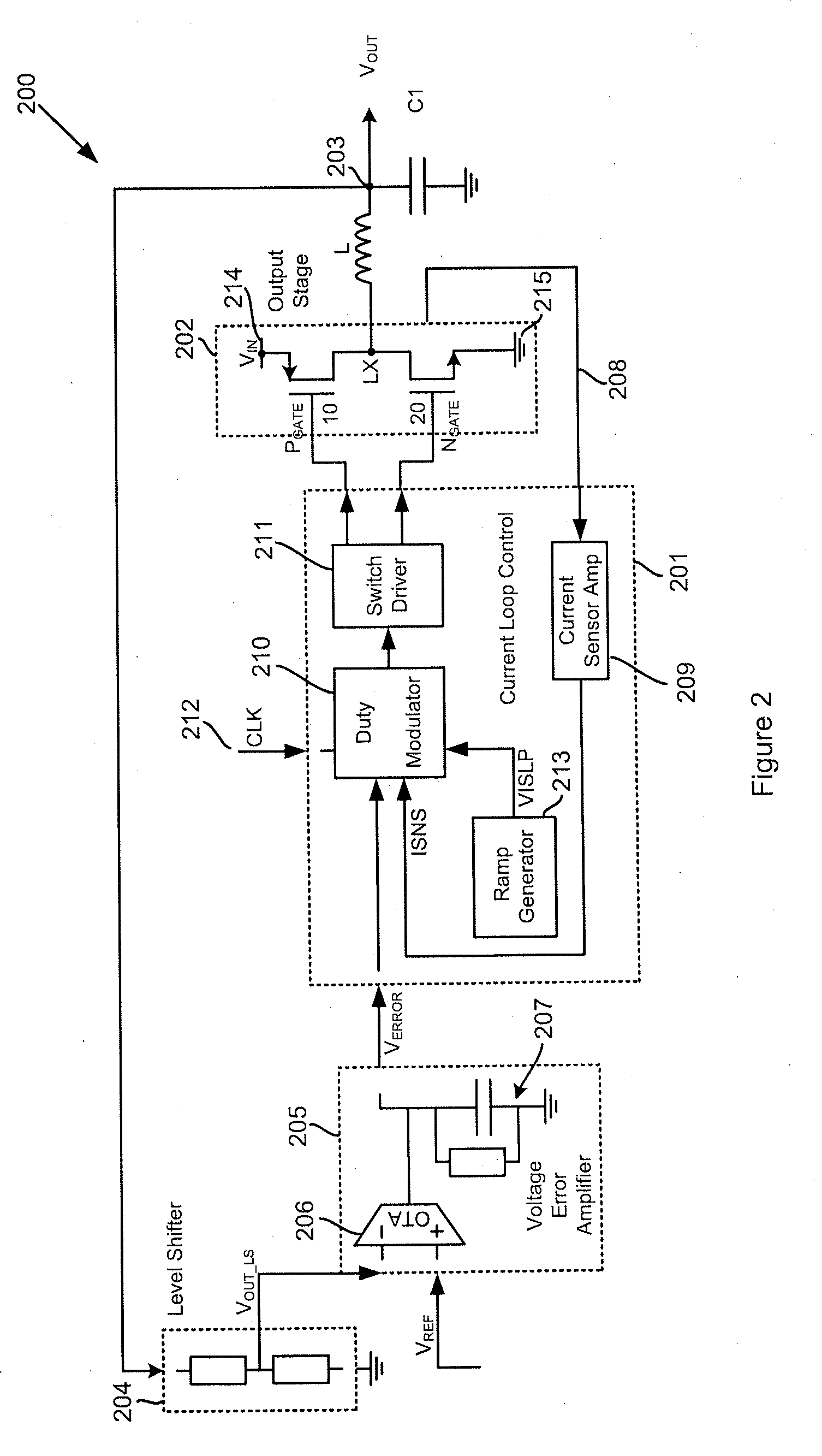
Discontinuous Conduction Mode Control Circuit and Method for Synchronous Converter
ActiveUS20090323375A1Improve efficiencyEfficient and reliableDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationMode controlControl signal
Circuit and method for controlling a synchronous power converter in discontinuous conduction mode with increased efficiency is disclosed. Circuitry is provided outputting gating signals to a high side driver and a synchronous rectifier responsive to a pulse width modulated input signal, an inhibit circuit for inhibiting the gating signal to the synchronous rectifier upon detection of a zero crossing condition; a comparator receiving a measured circuit value from the synchronous converter and a reference value and outputting a zero crossing condition; and a duty cycle observer circuit for determining the average duty cycle of the pulse width modulated input signal and for varying the reference value. A method is disclosed determining if the average duty cycle in the pulse width modulated input signal is increasing in response to varying a reference value, and inhibiting a synchronous rectifier control signal when the comparator indicates a zero crossing condition.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
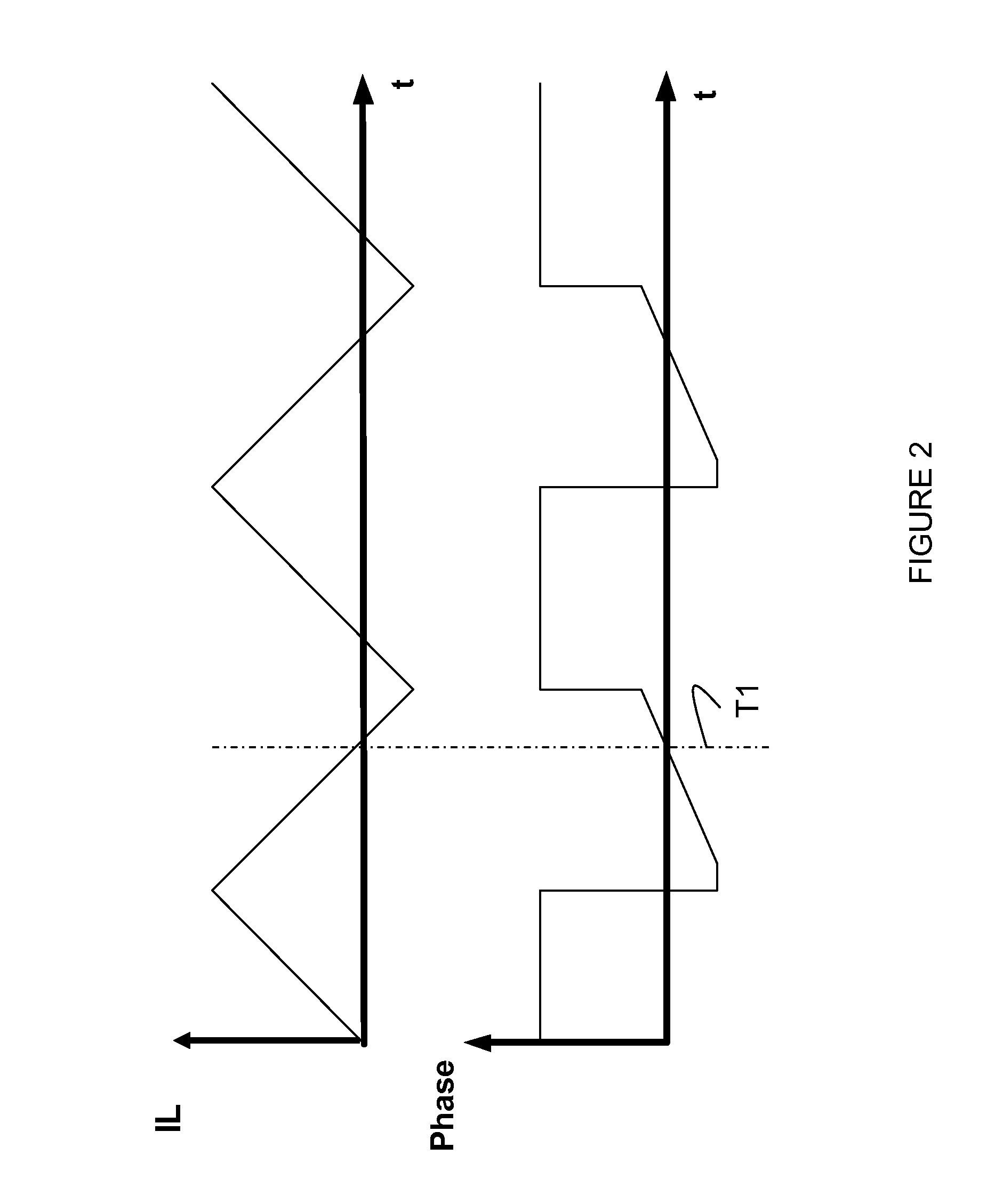
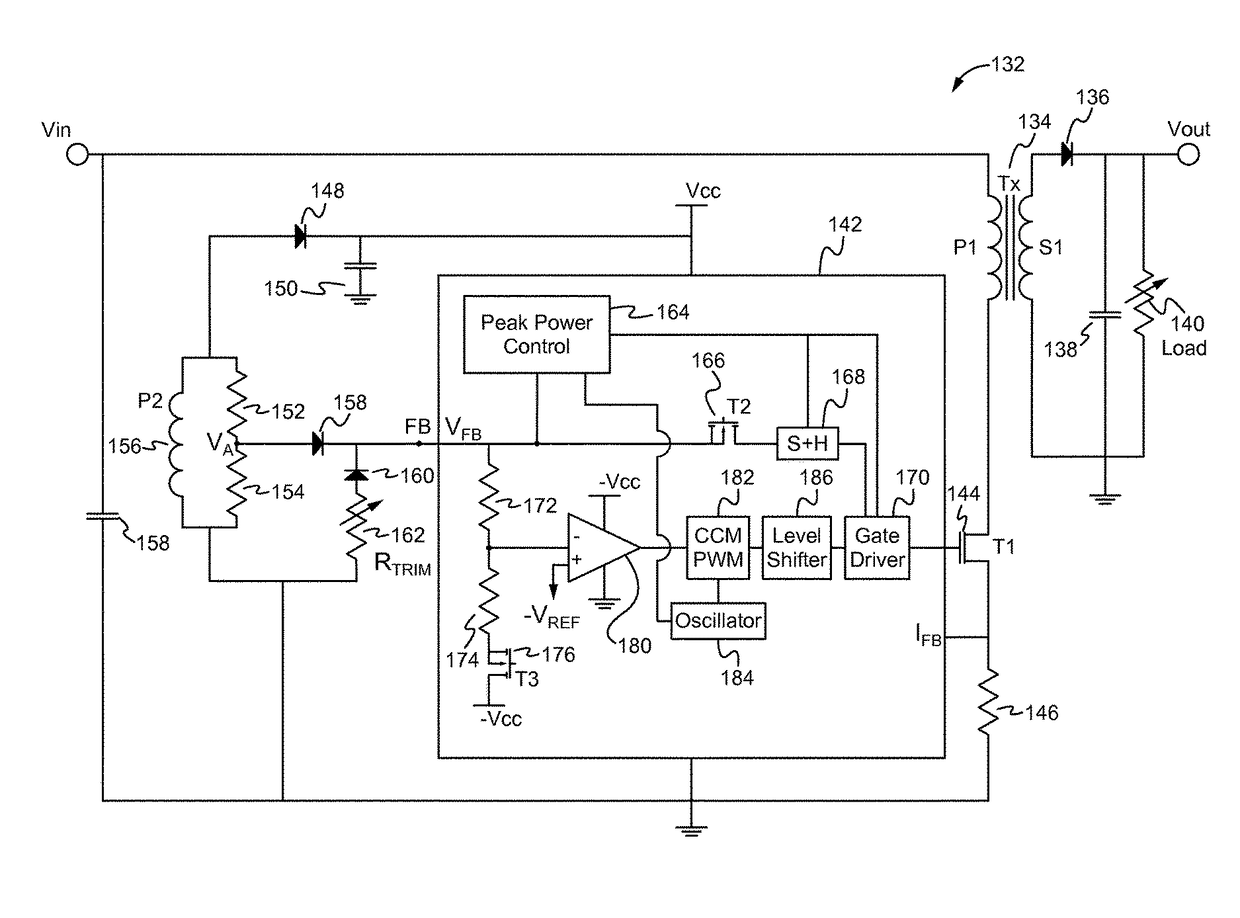
Peak power control technique for primary side controller operation in continuous conduction mode
A power converter includes a primary side controller configured to operate the power converter in the discontinuous conduction mode during low to mid-power requirements and to operate the power converter in the continuous conduction mode during high or peak power requirements. The power converter includes a primary side auxiliary winding that provides a feedback signal to the primary side controller, and an adjusted resistor and diode circuit which is coupled to a multi-function feedback (FB) pin of the primary side controller. The primary side controller monitors for a peak power demand, upon detection of which a negative supply rail is enabled, which is used to compensate for voltage losses due to non-zero current while operating in the CCM, thereby enabling output voltage regulation while operating in the CCM during peak power demand.
Owner:FLEXTRONICS AP LLC
Control device for multiphase interleaved dc-dc converter and control method thereof
ActiveUS20140334196A1Improve power factorEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDc dc converterPhase difference
This instant disclosure provides a control method for interleaved multiphase Boost PFC converter. The interleaved multiphase Boost PFC converter has a master phase and a plurality of slave phases, the master phase operates in the critical conduction mode, the master of each slave phase has an inductor and a power switch. The control method comprises, configuring the phase difference between each slave phase and the master phase; setting up each slave phase to operate in the critical conduction mode; monitoring the operating mode of each slave phase is in the continuous conducting mode, the discontinuous conducting mode, or the critical conduction mode when the system is disturbed; and adjusting the power switch on time of the slave phase according to the operating mode of the slave phase so as to make the slave phase return to operate in critical conduction mode.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for multi-phase DC-DC converters using coupled inductors in discontinuous conduction mode
ActiveUS7548046B1Improve efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationDc dc converterCoupling inductor
Owner:VOLTERRA SEMICONDUCTOR
Adaptive controller with mode tracking and parametric estimation for digital power converters
InactiveCN101252311AApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationTransverterPeak value
A controller for a power stage may adaptively control power switches to improve the efficiency of power consumption by the power stage and detect continuous conduction mode (''CCM'') and discontinuous conduction mode (''DCM'') operations of the power stage without instantaneous or cycle by cycle sensing and sampling of the output inductor current. Additionally, the controller may be used to facilitate the estimation of output inductor value, the peak inductor current value, and other information on converter operations.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Switching Parameter Based Discontinuous Mode-Critical Conduction Mode Transition
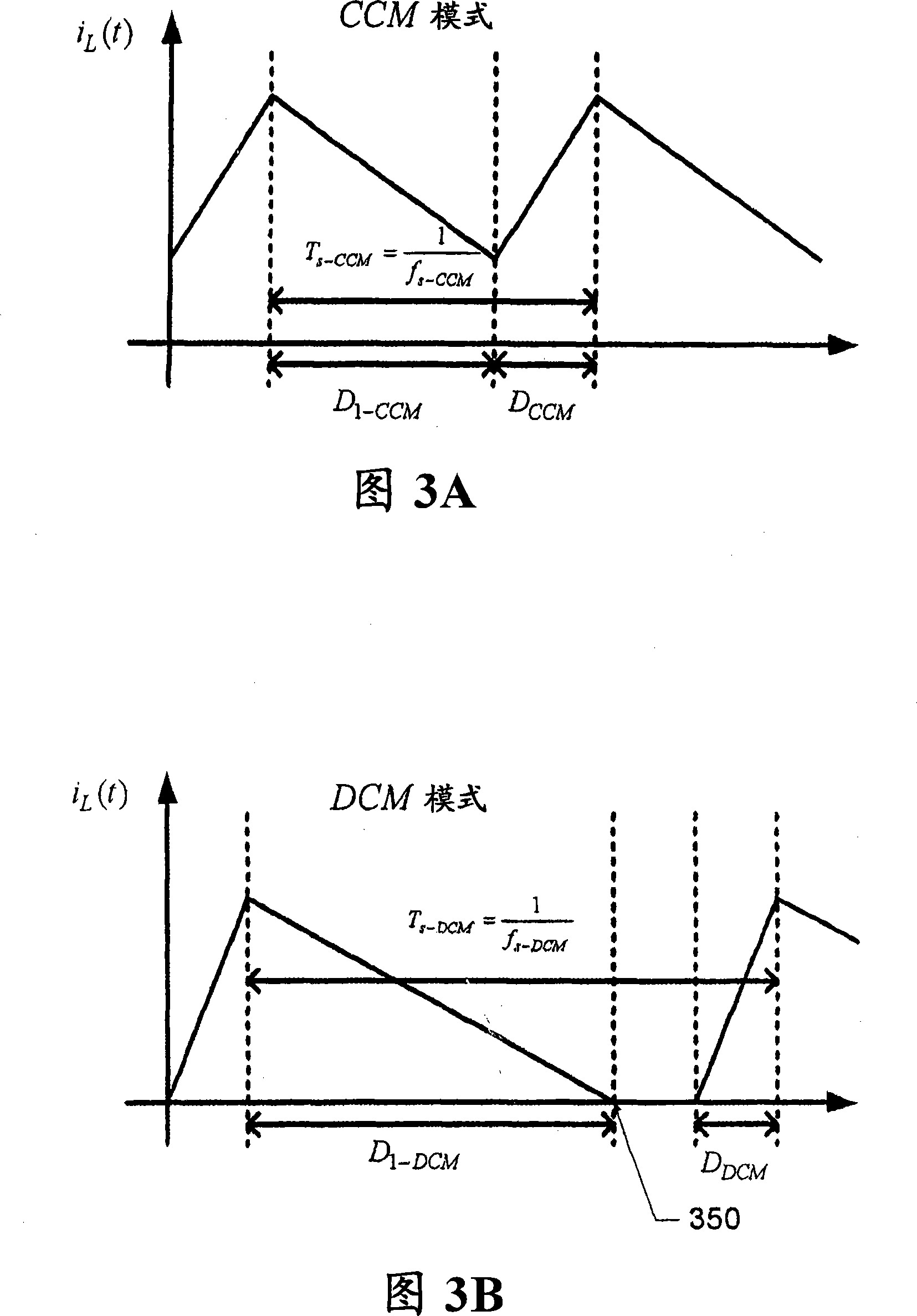
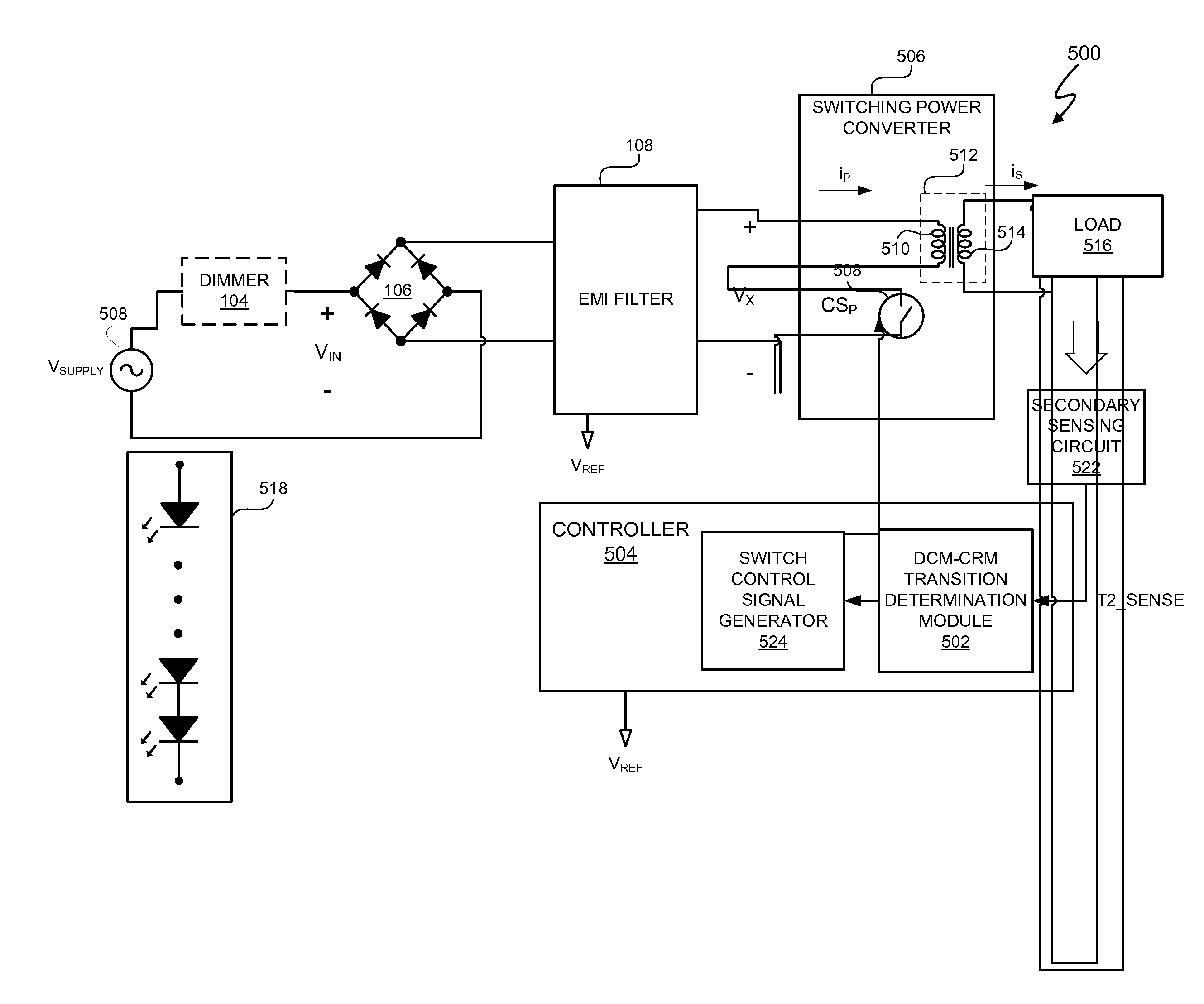
An electronic system includes a controller to provide at least dual-mode conduction control of a switching power converter. In at least one embodiment, the controller is capable to control transitions between discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) and critical conduction mode (CRM) of the switching power converter using a measured switching time parameter having a value corresponding with an approximately peak voltage of a time-varying supply voltage supplied to the switching power converter. In at least one embodiment, the controller dynamically compensates for changing parameters of the electronic system by dynamically determining a minimum non-conductive time of the control switch of the switching power converter using the measured switching time parameter value at approximately the peak of the supply voltage of the supply voltage.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Resonant fly-back power converter and LED lighting unit powered therefrom
InactiveUS20120299503A1Reduce power lossZero voltage switchingEfficient power electronics conversionConversion constructional detailsTime extensionElectricity
A method for controlling powering with a resonant fly-back power converter includes powering an output circuit including a load, with a inductor of a resonant fly-back power converter including a primary winding electrically connected to an input circuit of the fly-back converter and secondary winding electrically connected to the output circuit of the fly-back converter, operating the converter in a discontinuous conduction mode. Charging and discharging of the primary winding is controlled with a first and second switching element and a capacitor connected across the second switching element selected for resonating with the primary winding. Both first and second switching elements are operative to connect primary winding to an input voltage source over a defined on-time. The pulsing of the first and second switching elements is synchronized and the on-time of the second switching element is extended with respect to the on-time of the first switching element.
Owner:NAHORLED
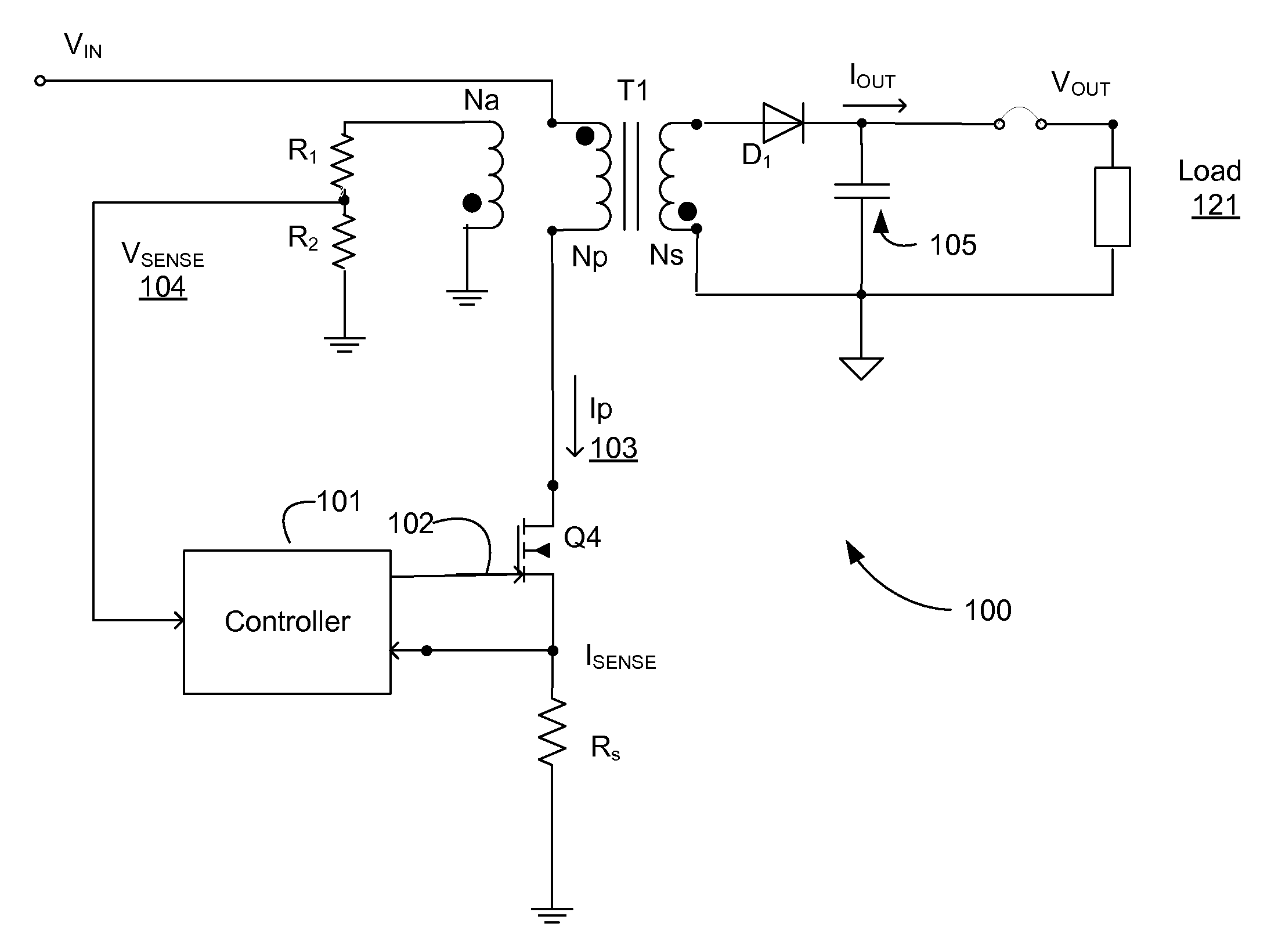
Adaptively controlled soft start-up scheme for switching power converters
ActiveUS20120176819A1Increase the output voltageMinimize overshootConversion with intermediate conversion to dcApparatus with intermediate ac conversionTransformerControl signal
A switching power converter provides regulated voltage to a load according to a desired regulation voltage. The switching power converter includes a transformer coupled to a switch and a switch controller for generating a control signal to control switching. The switch controller monitors a sensed voltage representing the output voltage of the switching power converter. The switch controller controls switching of the switch to operate the switching power converter in a continuous conduction mode while the sensed output voltage indicates that the output voltage is less than a first threshold voltage. The switch controller controls switching of the switch to operate the switching power converter in a discontinuous conduction mode while the sensed output voltage is above the first threshold voltage.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Self-adaptive constant-on-time control circuit
InactiveCN102751874AReduce switching actionImprove efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationEngineeringOperating frequency
The invention discloses a self-adaptive constant-on-time control circuit, which comprises a first transistor, a second transistor, a third transistor, a fourth transistor, a first operational amplifier, a first comparator, a first capacitive reactance unit, a first resistance unit and a switch unit. Due to the adoption of the self-adaptive constant-on-time control circuit, the problem of a traditional constant-on-time (Cot) control circuit that the working frequency is changed along with the input voltage can be solved, the quasi-steady working frequency under continuous conduction mode (CCM) status is realized, the on-off action of a power tube is reduced by reducing the working frequency under the discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) status, the on-off loss is reduced, the efficiency of a converter under a light load is improved, and the high efficiency of a full load section can be realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Adjustable constant current source with continuous conduction mode (“CCM”) and discontinuous conduction mode (“DCM”) operation
A converter system and method of operating a converter system are disclosed. The converter system comprises a converter power stage that can operate in a Discontinuous Conduction Mode (DCM) in a range of output currents and a Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM) in another range of output currents. The converter power stage includes at least an inductor with an inductor value and a control switch. The converter power stage provides an average current. A current controller is coupled to the converter power stage. When the converter power stage operates in DCM, the converter power stage provides the average current and the current controller is configured to measure the inductor value of the inductor. Furthermore, the current controller can also be configured to measure an input-to-output conversion ratio from the converter power stage.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
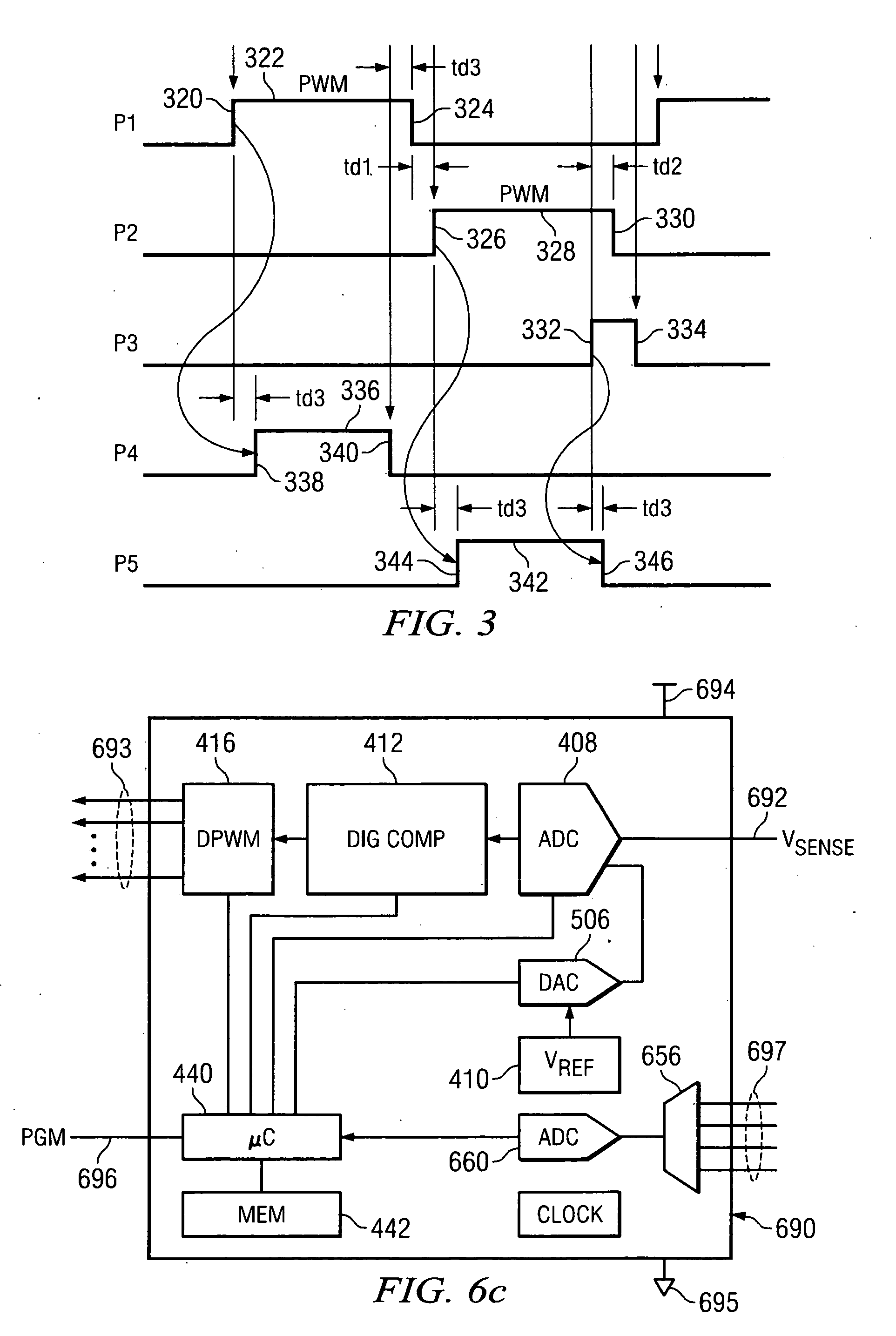
MCU/driver point of load digital controller with optimized voltage
ActiveUS20070139973A1Improve power efficiencyMaximize power efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionPoint of loadControl signal
A system for optimizing the power efficiency of a switching power converter operating at a switching frequency includes a digital controller for receiving an analog signal representing an output DC voltage of the switching power converter for comparison to a desired output voltage level and generating switching control signals to control the operation of the power supply to regulate the output DC voltage to said desired output voltage level. At least two of the switching control signals have a dead time between a first edge of a first control signal and a second edge of a second control signal. The dead time is programmable to control a power efficiency of the switching power converter. The switching control signals additionally switch the power supply between a continuous conduction mode and a discontinuous conduction mode responsive to a mode control signal. The operation of the digital controller is parameterized by a set of operating parameters. A driver circuit is connected to an output of the digital controller to drive the switching control signals and further includes an input for a regulated voltage. The voltage regulator selects the regulated voltage to the driver circuit responsive to a voltage control signal. A micro controller determines the parameters used by said digital controller, establishes the programmable dead time between the control signals to substantially maximize power efficiency of the switching power converter, generates a voltage control signal to substantially maximize the power efficiency of the switching power converter and generates the mode control signal responsive to a current signal from the switching power converter. The micro controller operates independently of the operation of the digital controller.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
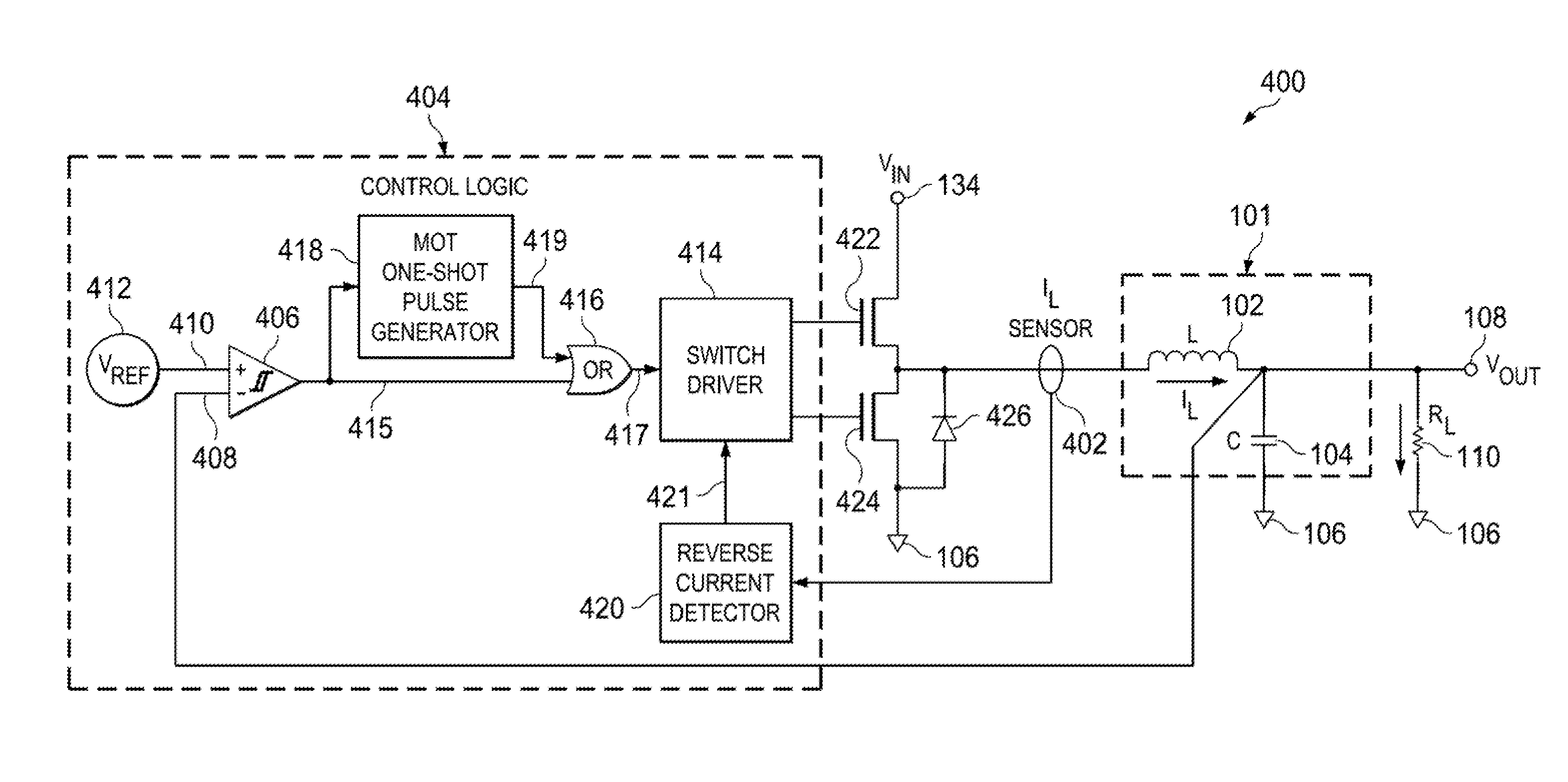
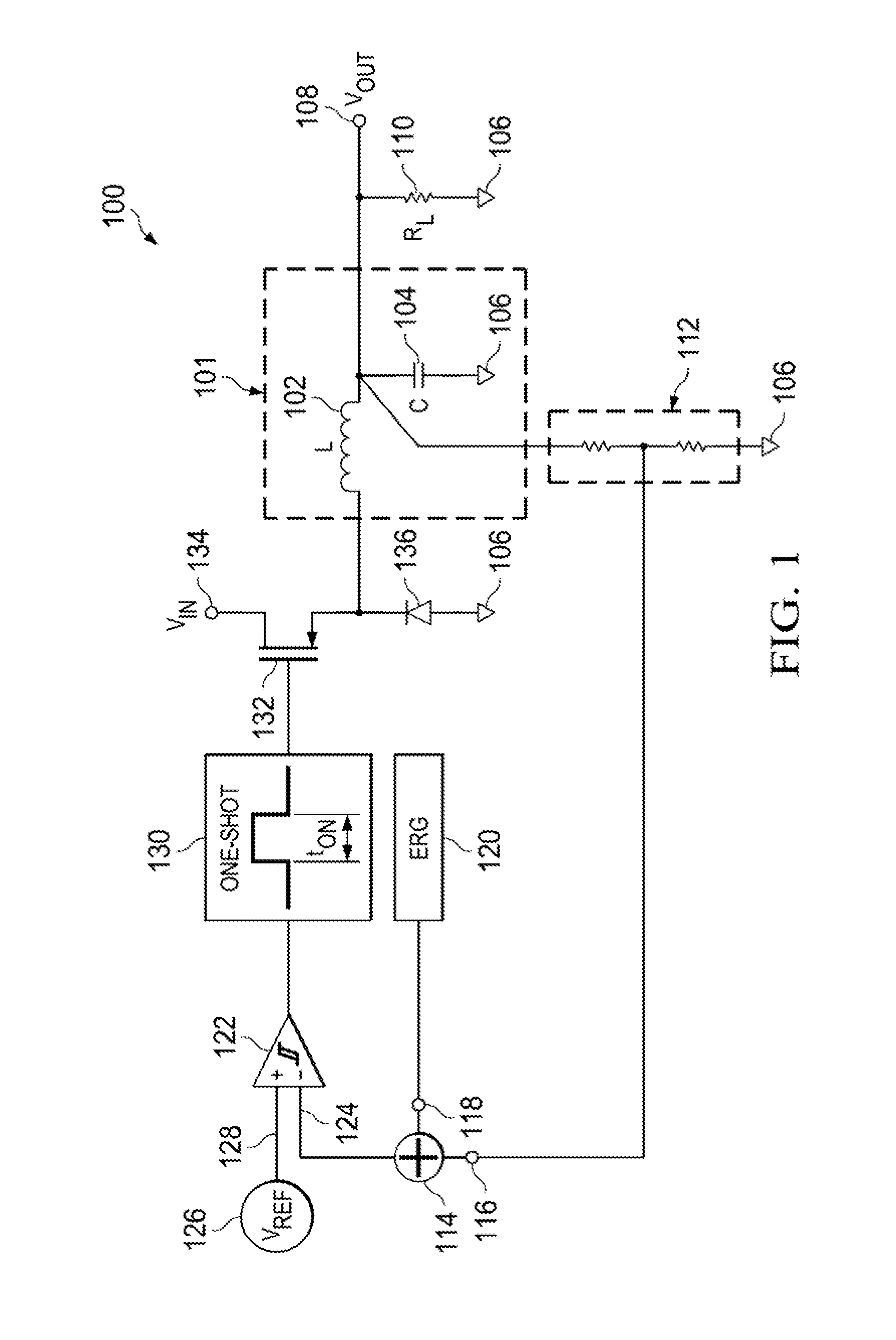
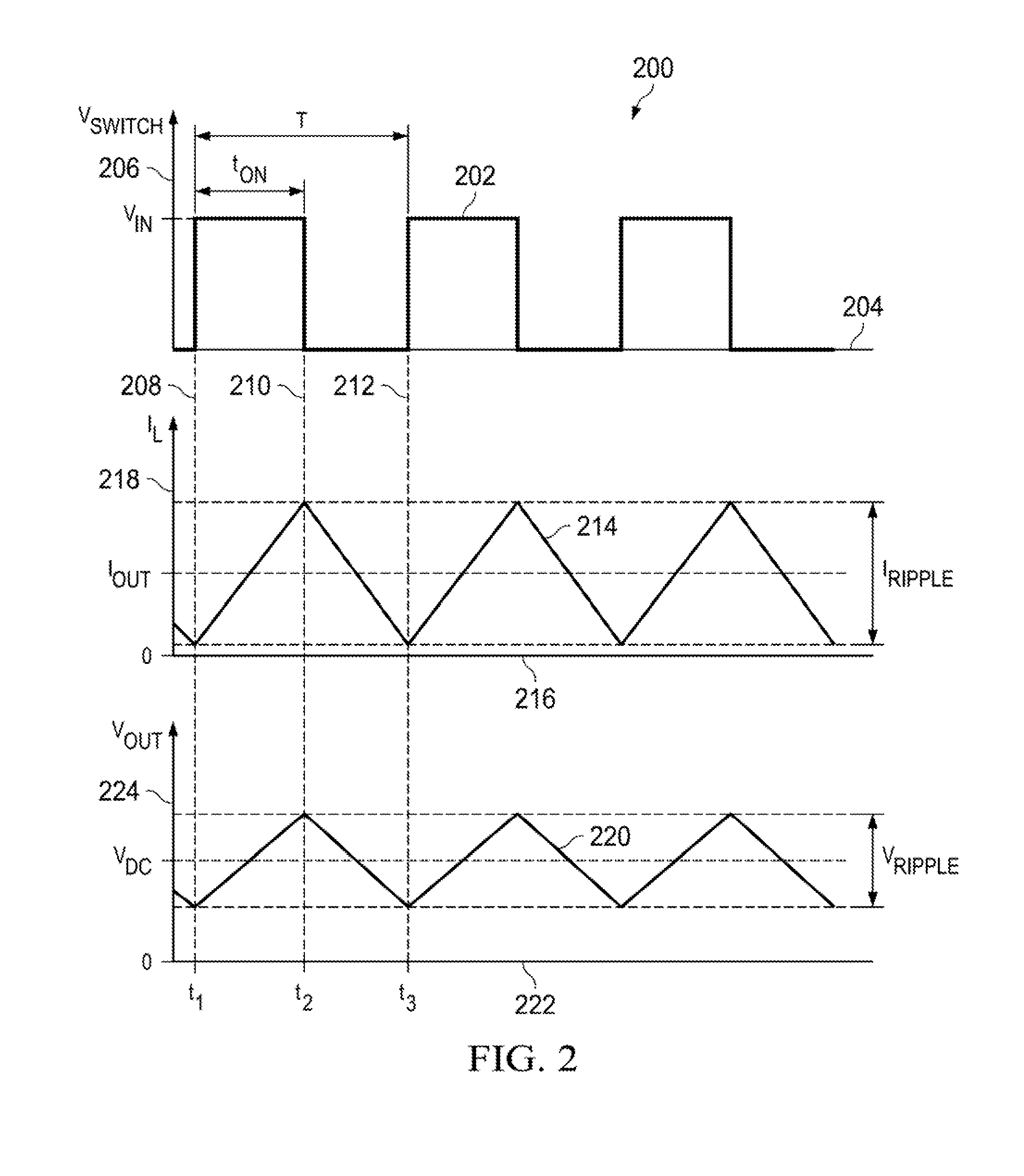
Minimum on-time control for low load dc/dc converter
ActiveUS20150326102A1Alleviate stability issuesReduce loadEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionElectricityPower flow
Aspects of the present invention provide a DC / DC converter for use with a supply voltage and operable to drive a load, wherein the DC / DC converter includes a VIN node, a VOUT node, a switching component, a filter, a comparator, a current detecting component and a control component. The VIN node can receive the supply voltage and the VOUT node can provide an output voltage to drive the load. The filter electrically connects the switching component with the VOUT node. The comparator can generate a comparison signal based on the output voltage. The current detecting component can detect when a current in a direction from the filter toward the VOUT node decreases to zero. The control component can control the switching component so as to provide the output voltage at the VOUT node in a discontinuous conduction mode to drive the load.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com