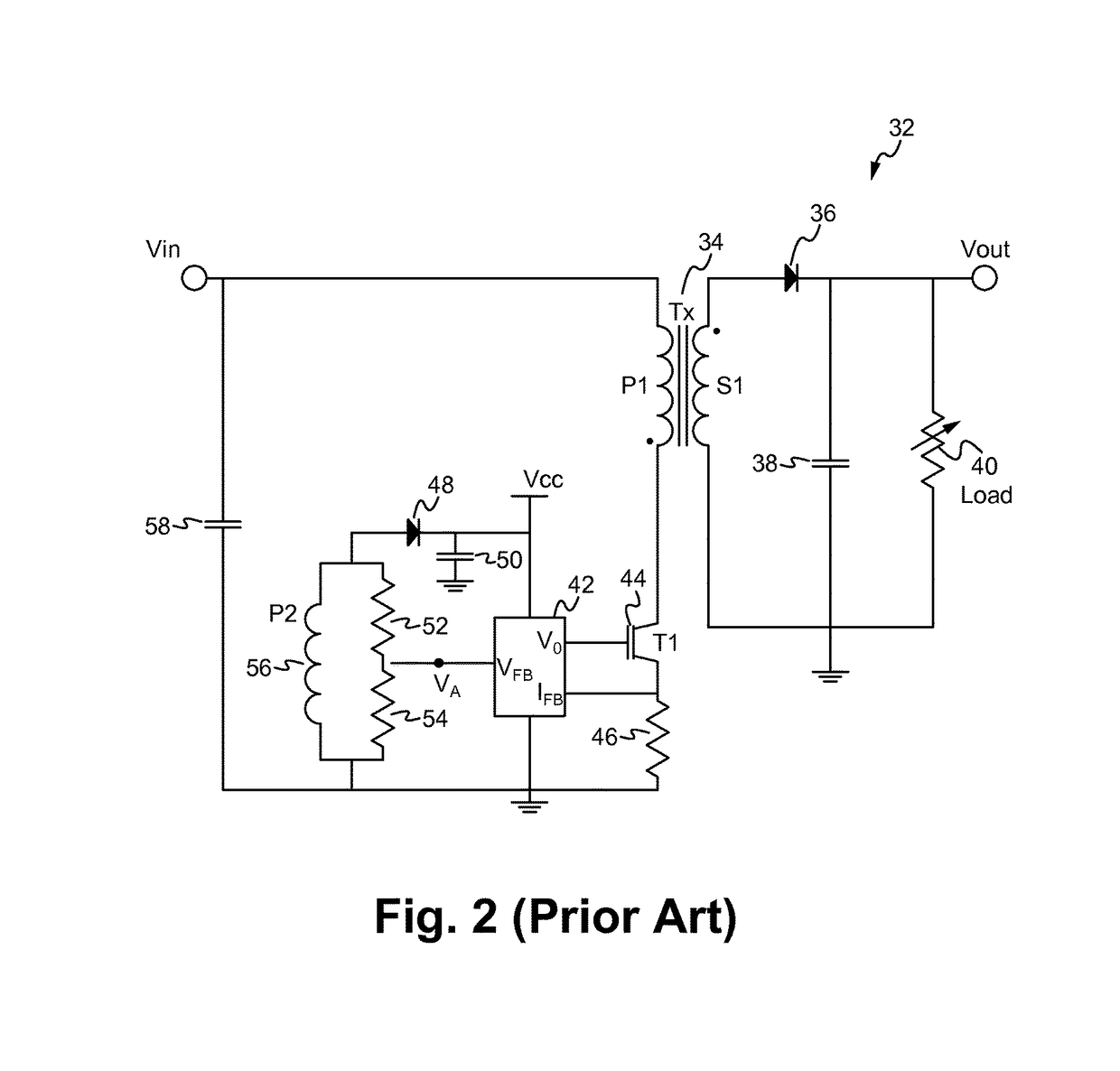
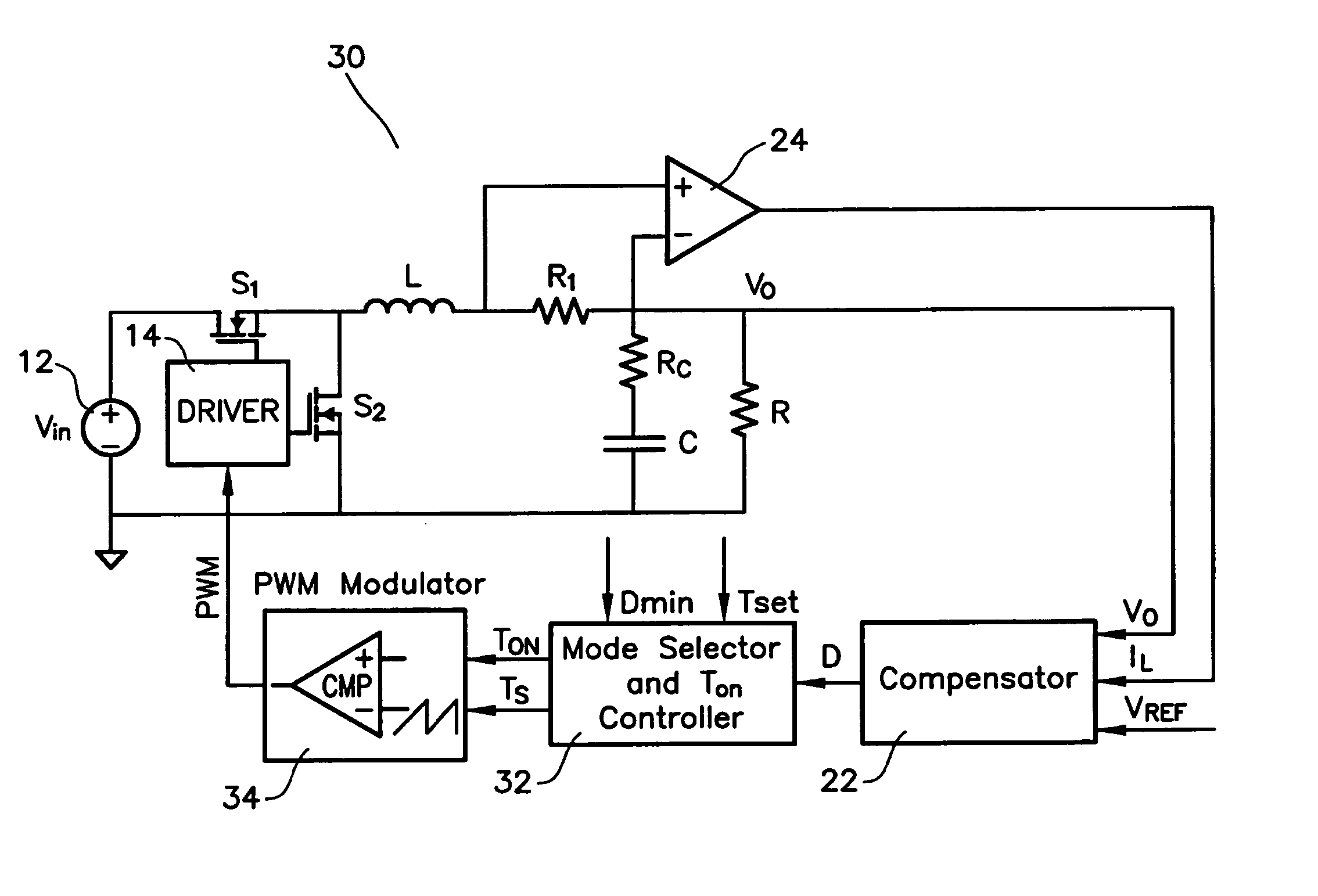
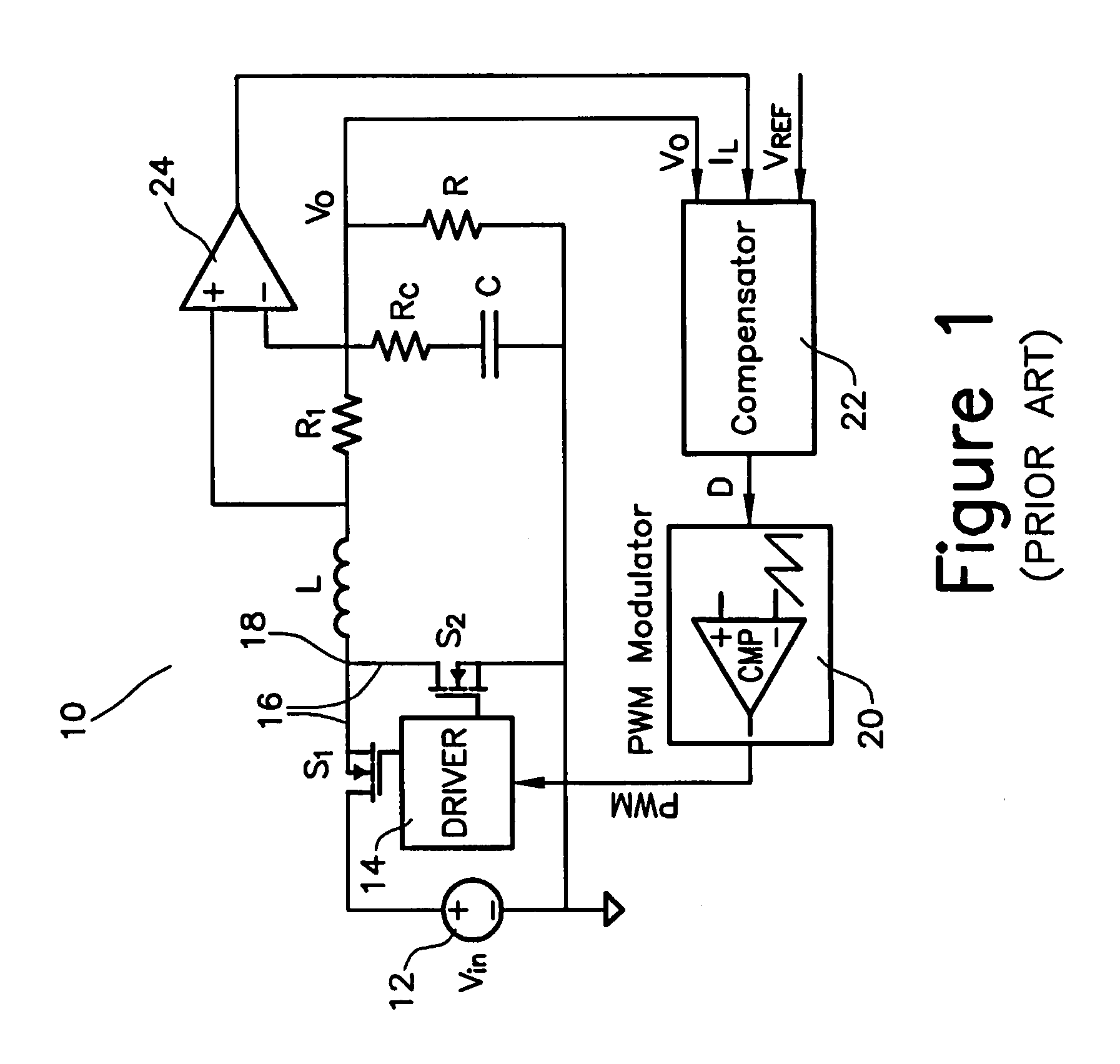
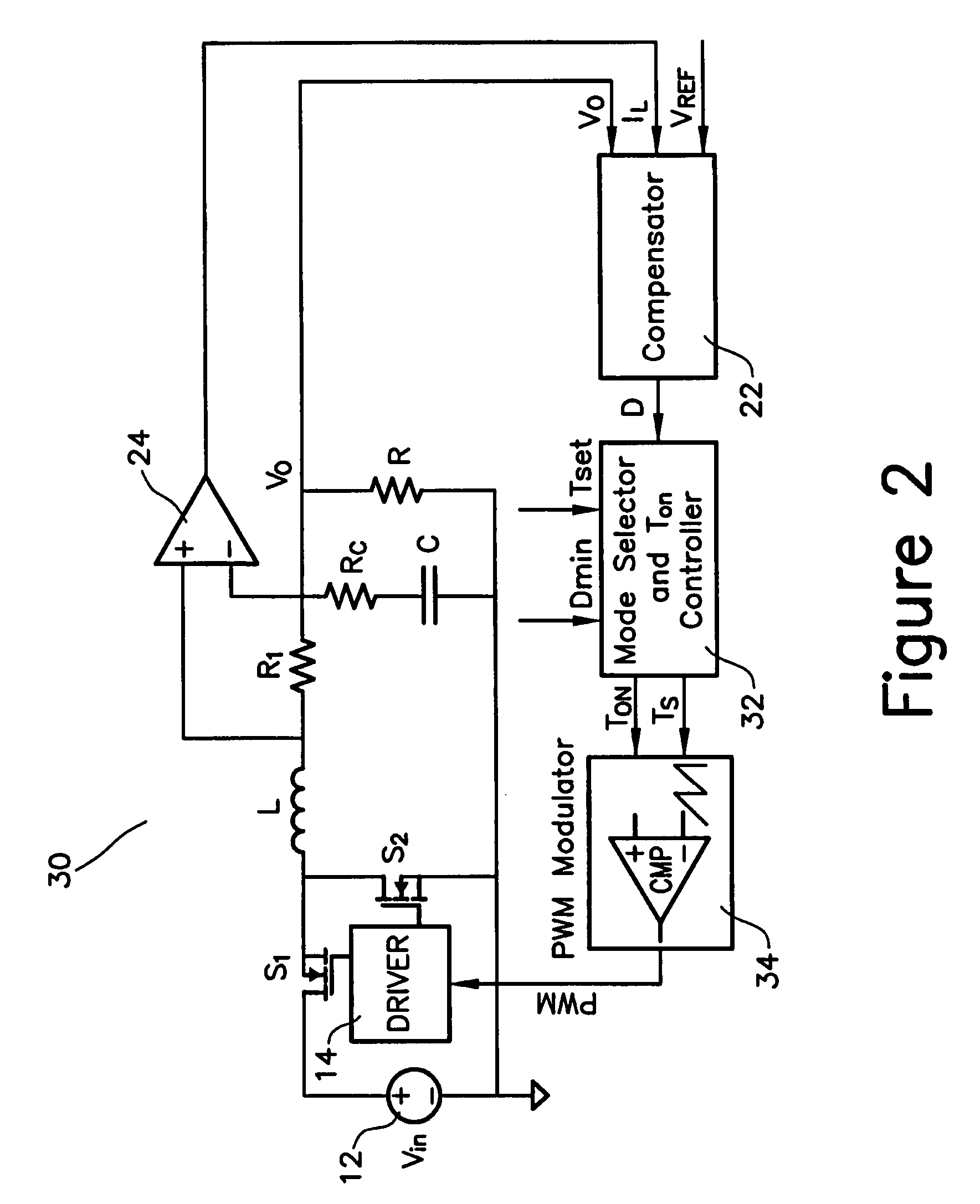
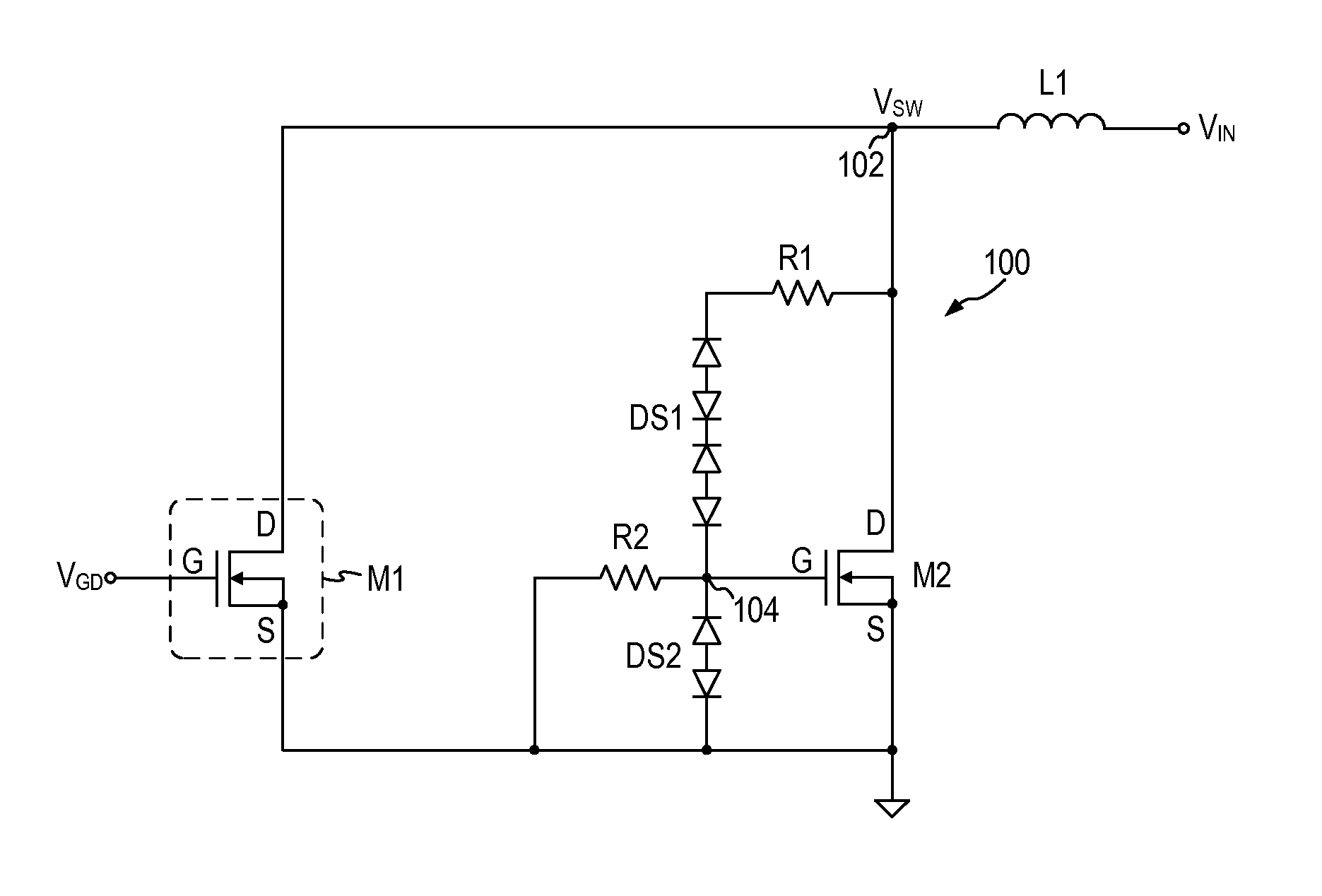
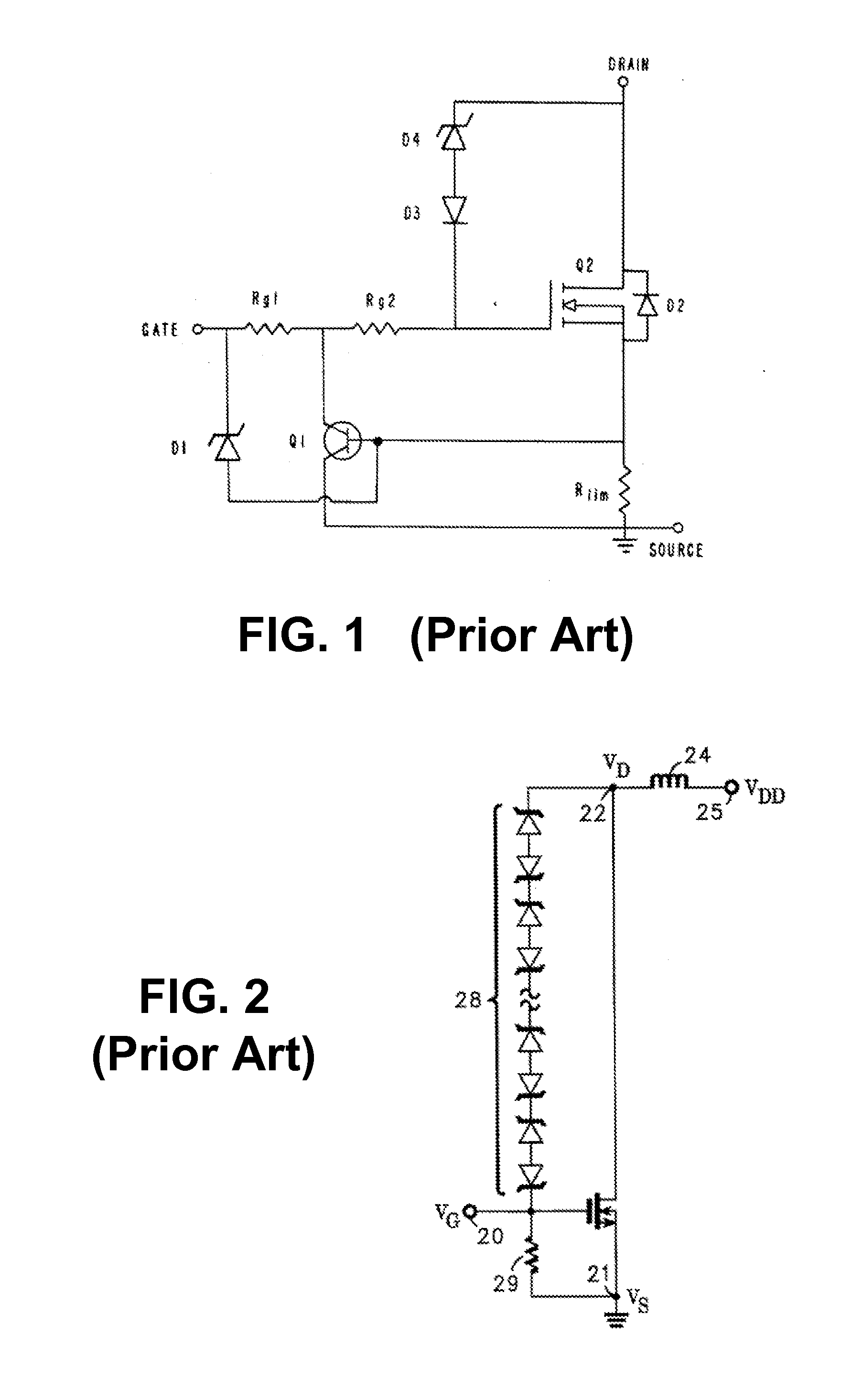
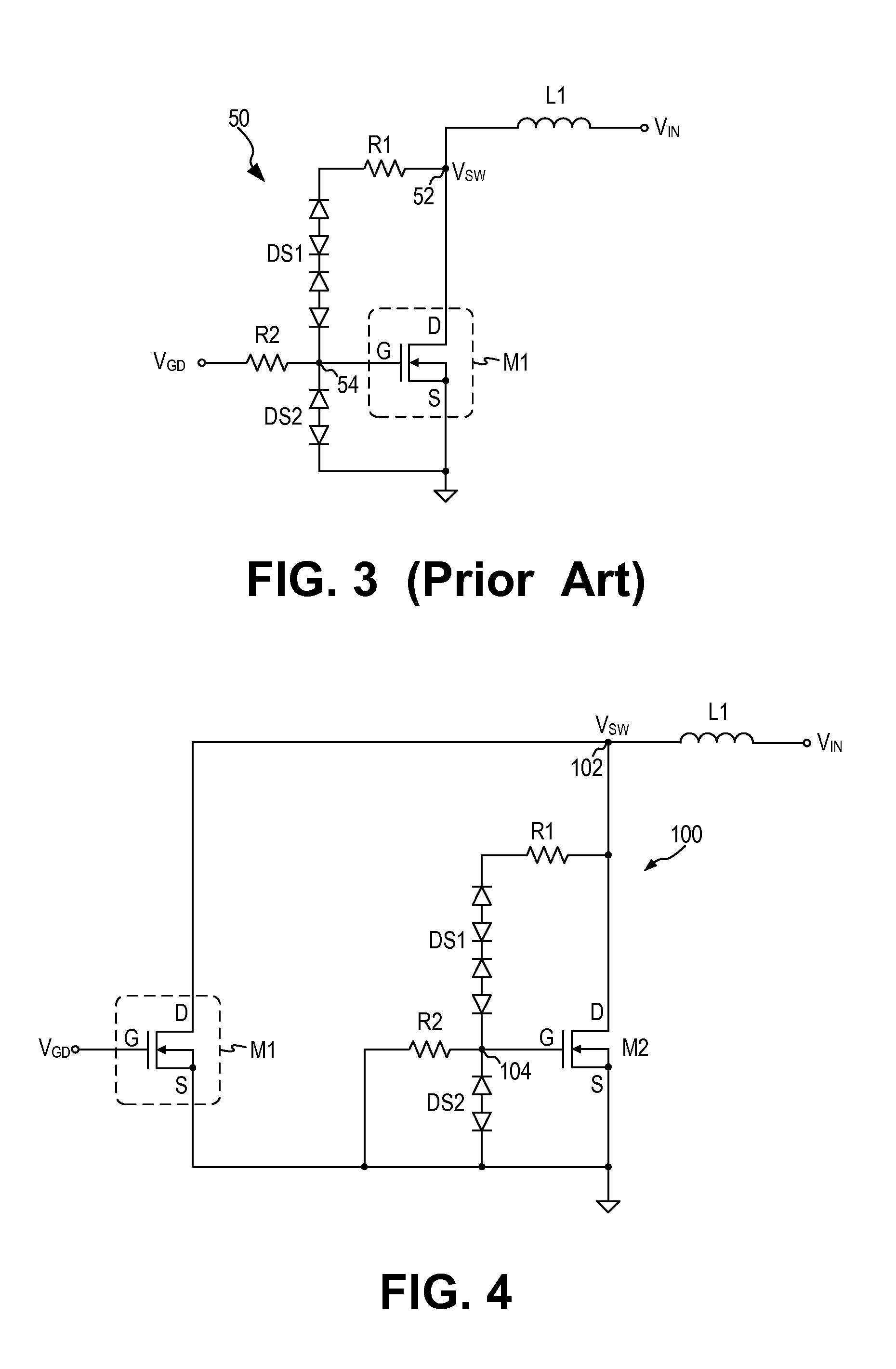
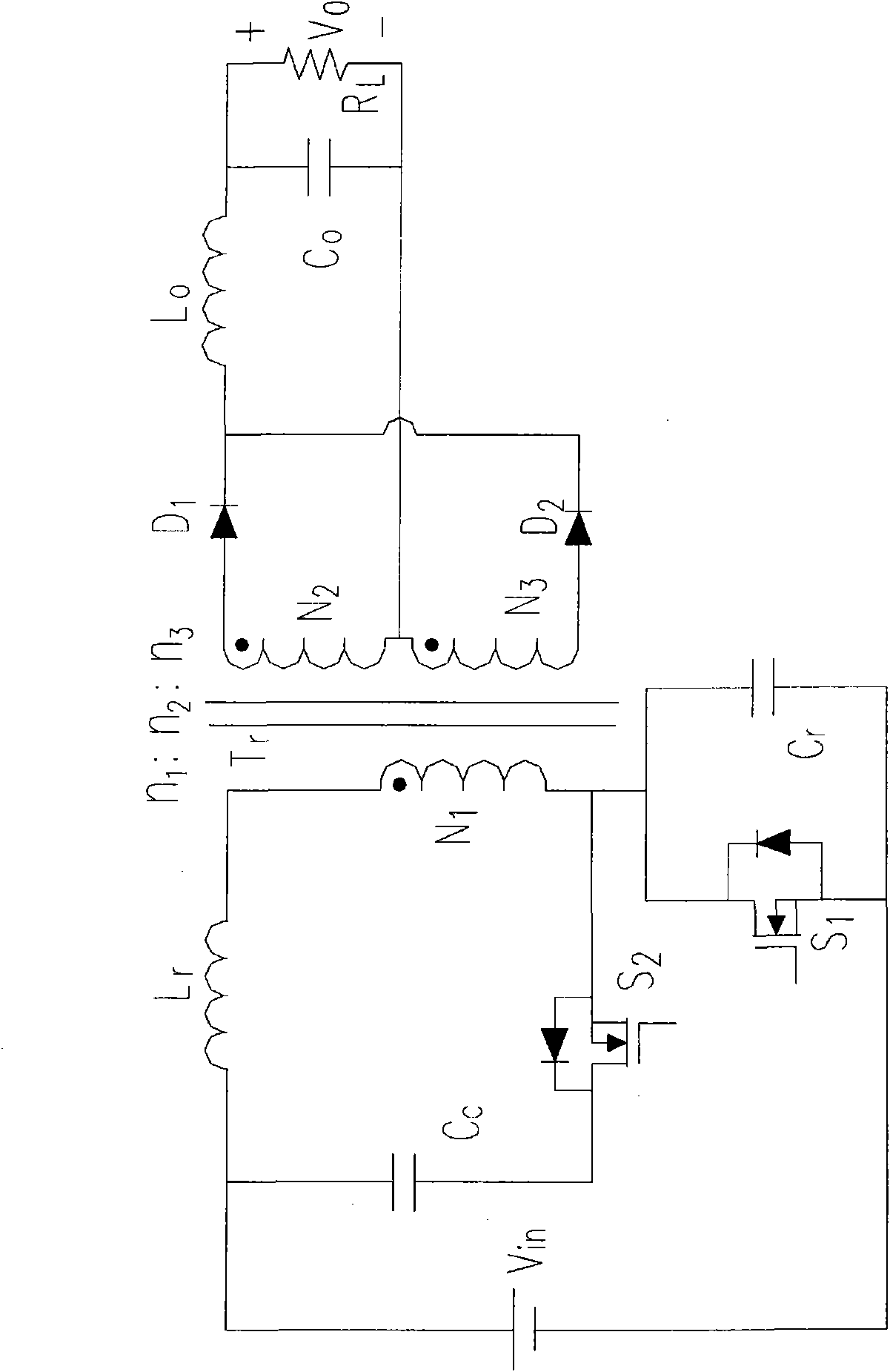
Patents
Literature
860 results about "Conduction mode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
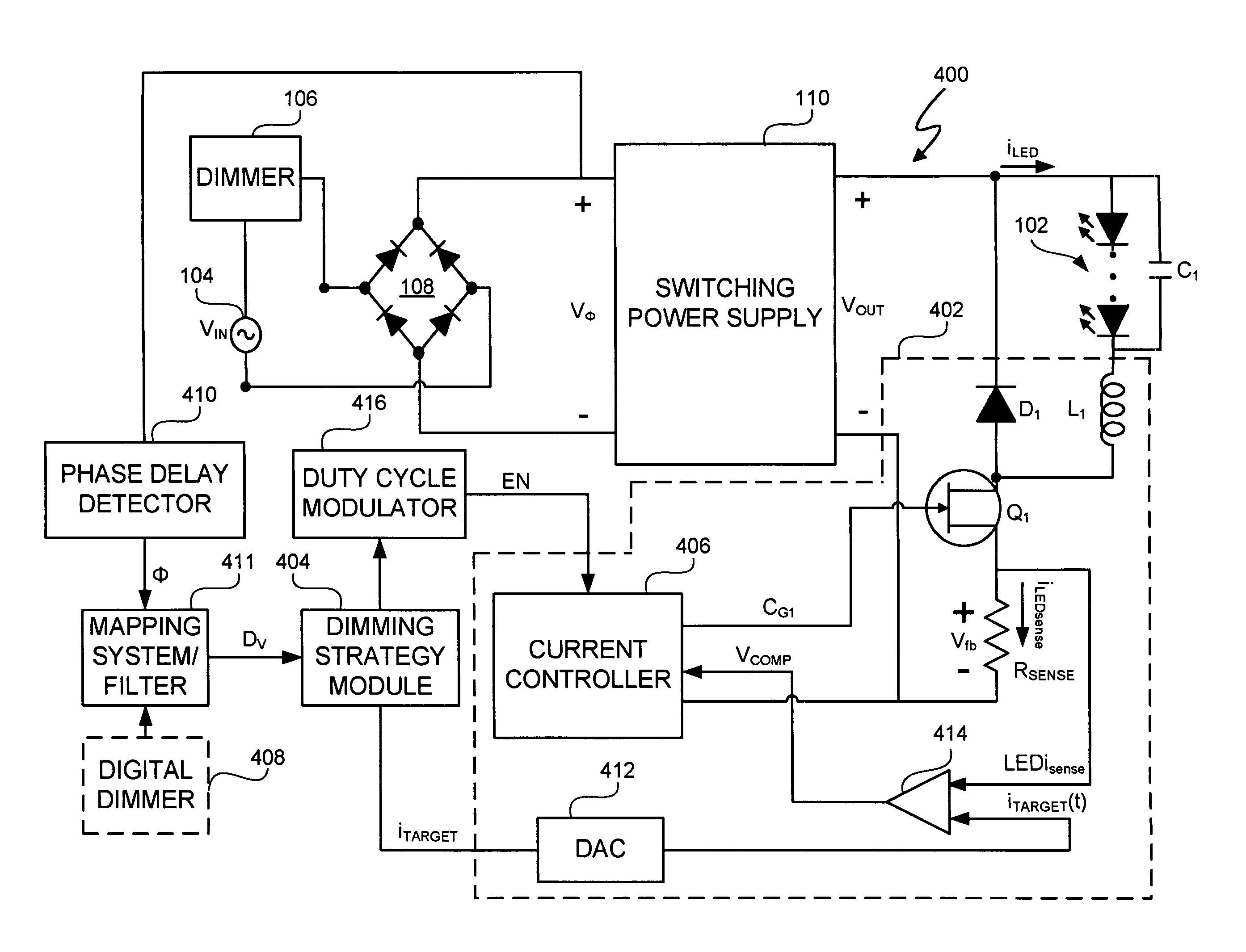
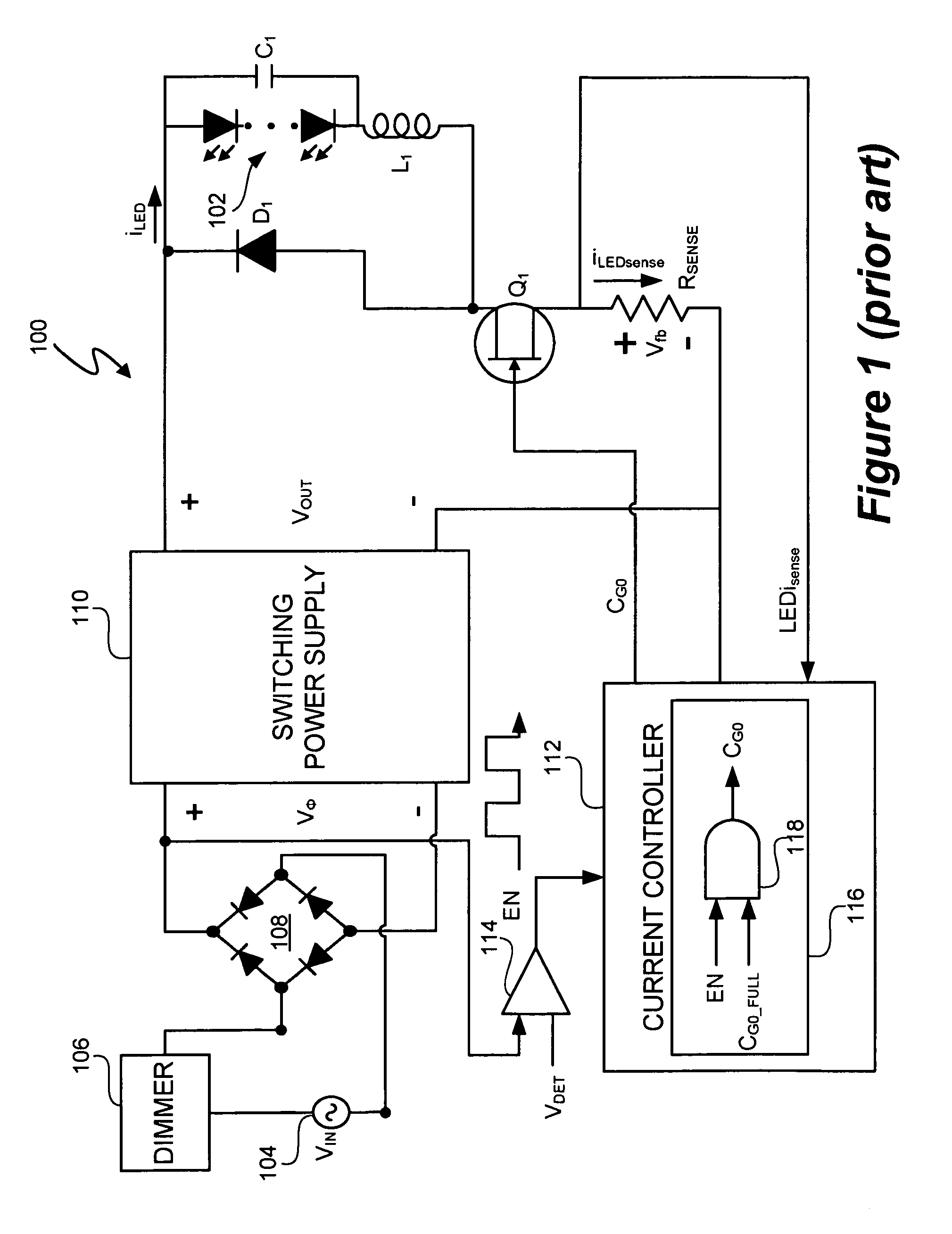
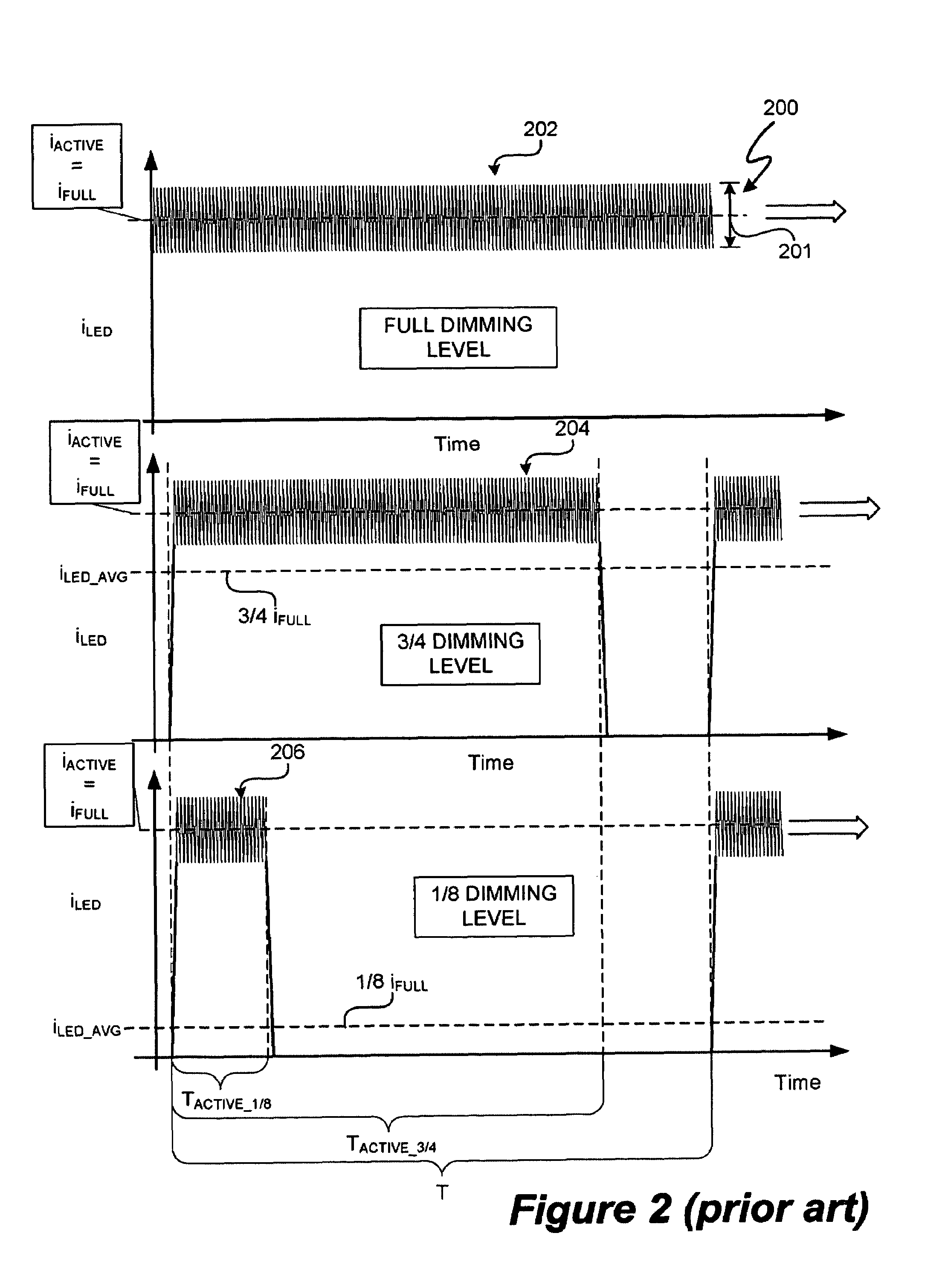
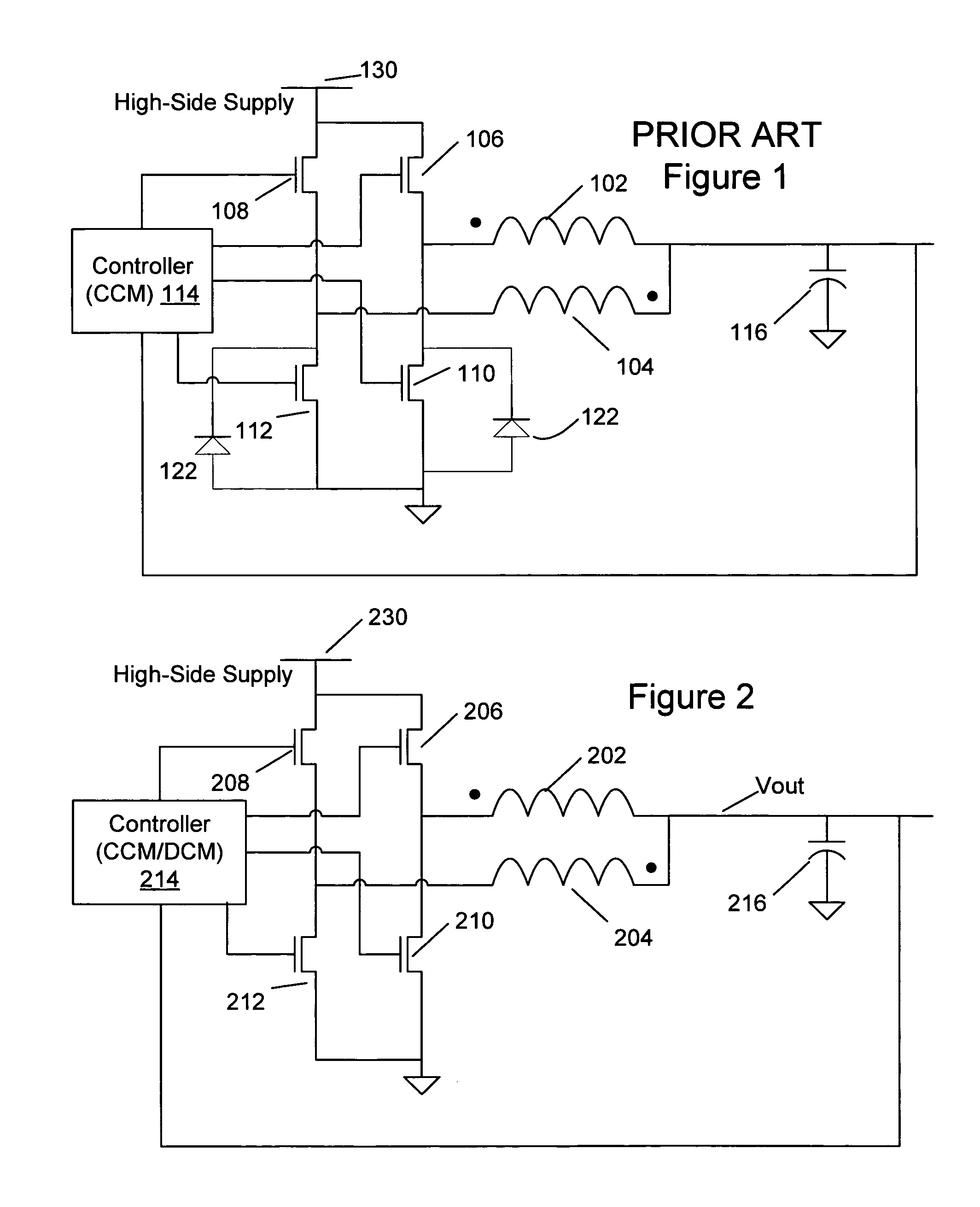
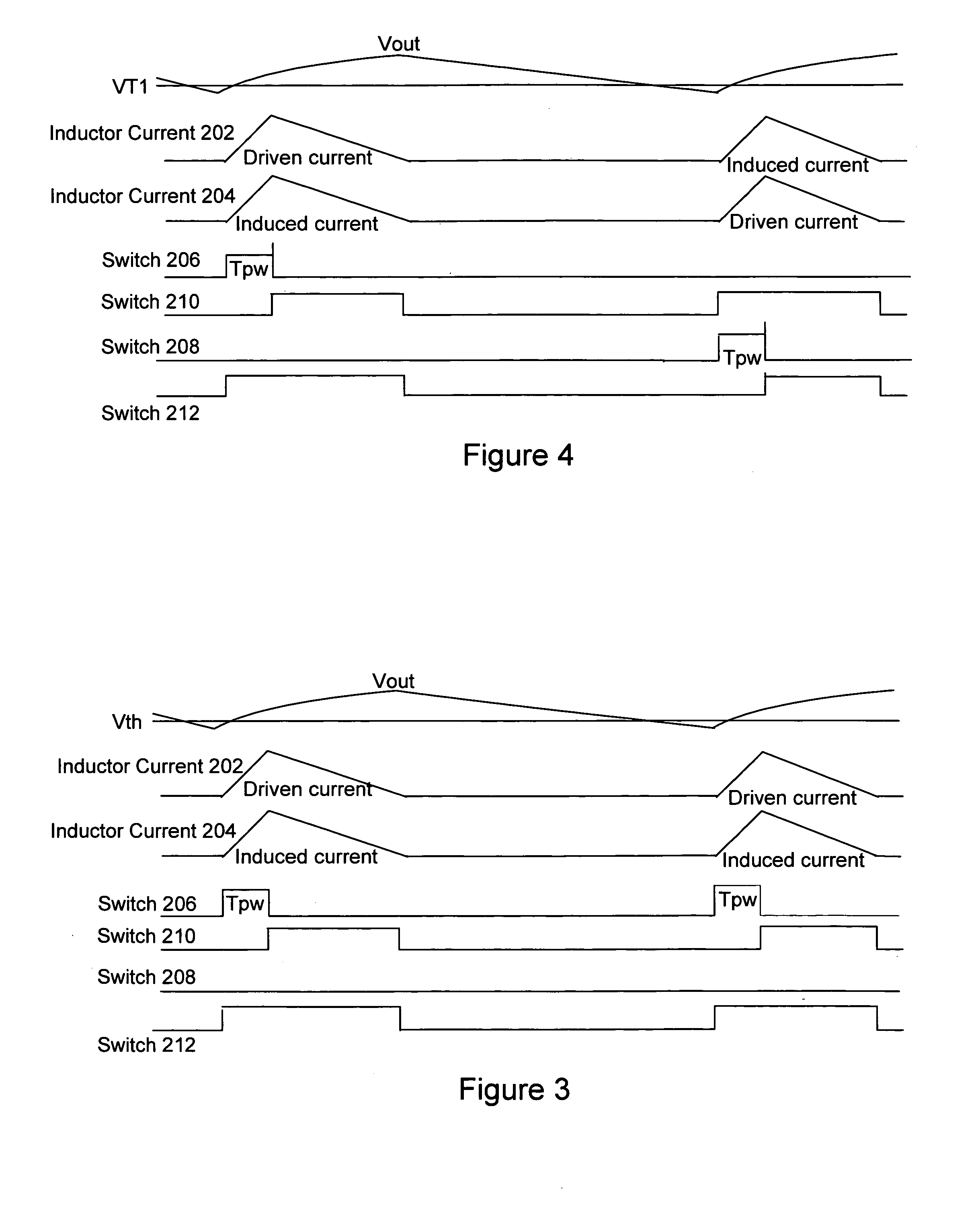
LED lighting system with a multiple mode current control dimming strategy
A light emitting diode (LED) lighting system includes a controller to control current in one or more LEDs in response to a dimming level input. The LED lighting system implements a dimming strategy having two modes of operation that allow the LED lighting system to dim the LEDs using an active value of an LED current less than a full value LED current while maintaining continuous conduction mode operation. In an active value varying mode of operation, the controller varies an active value of the LED current for a first set of dimming levels. In an active value, duty cycle modulation mode of operation, the controller duty cycle modulates an active value of the LED current for a second set of dimming levels. In at least one embodiment, the active value of the LED current varies from a full active value to an intermediate active value as dimming levels decrease.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
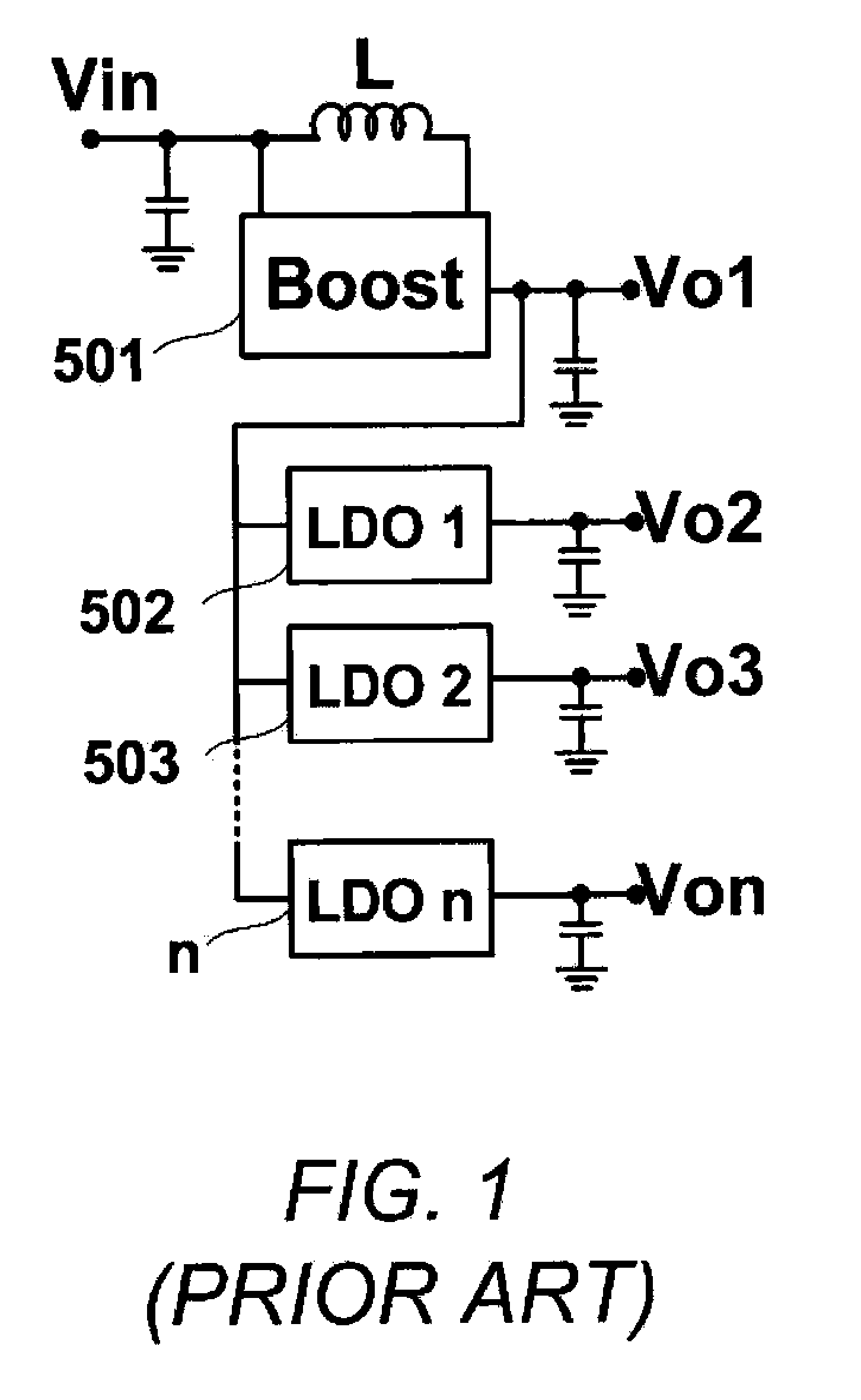
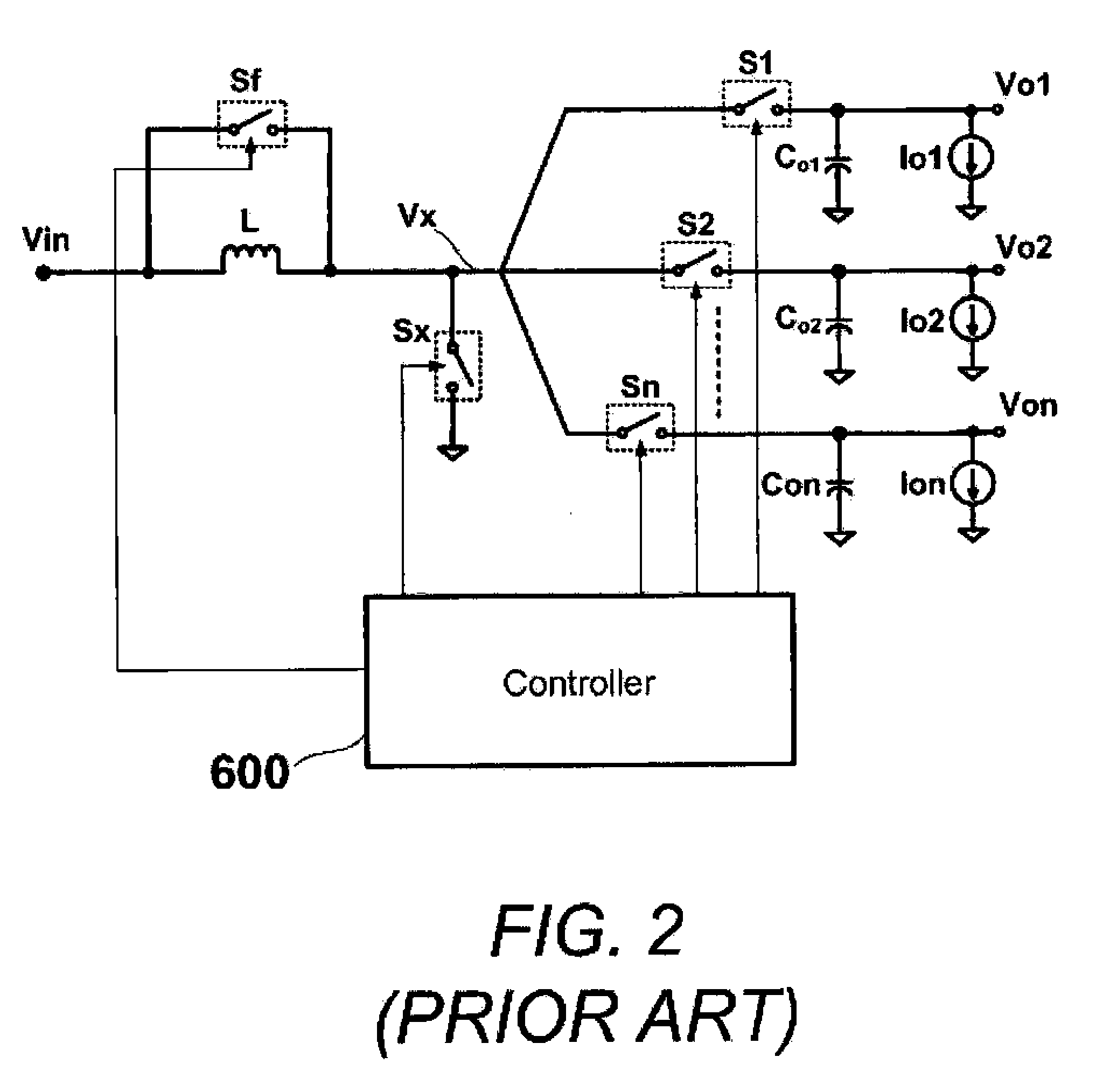
Multiple-Output DC-DC Converter
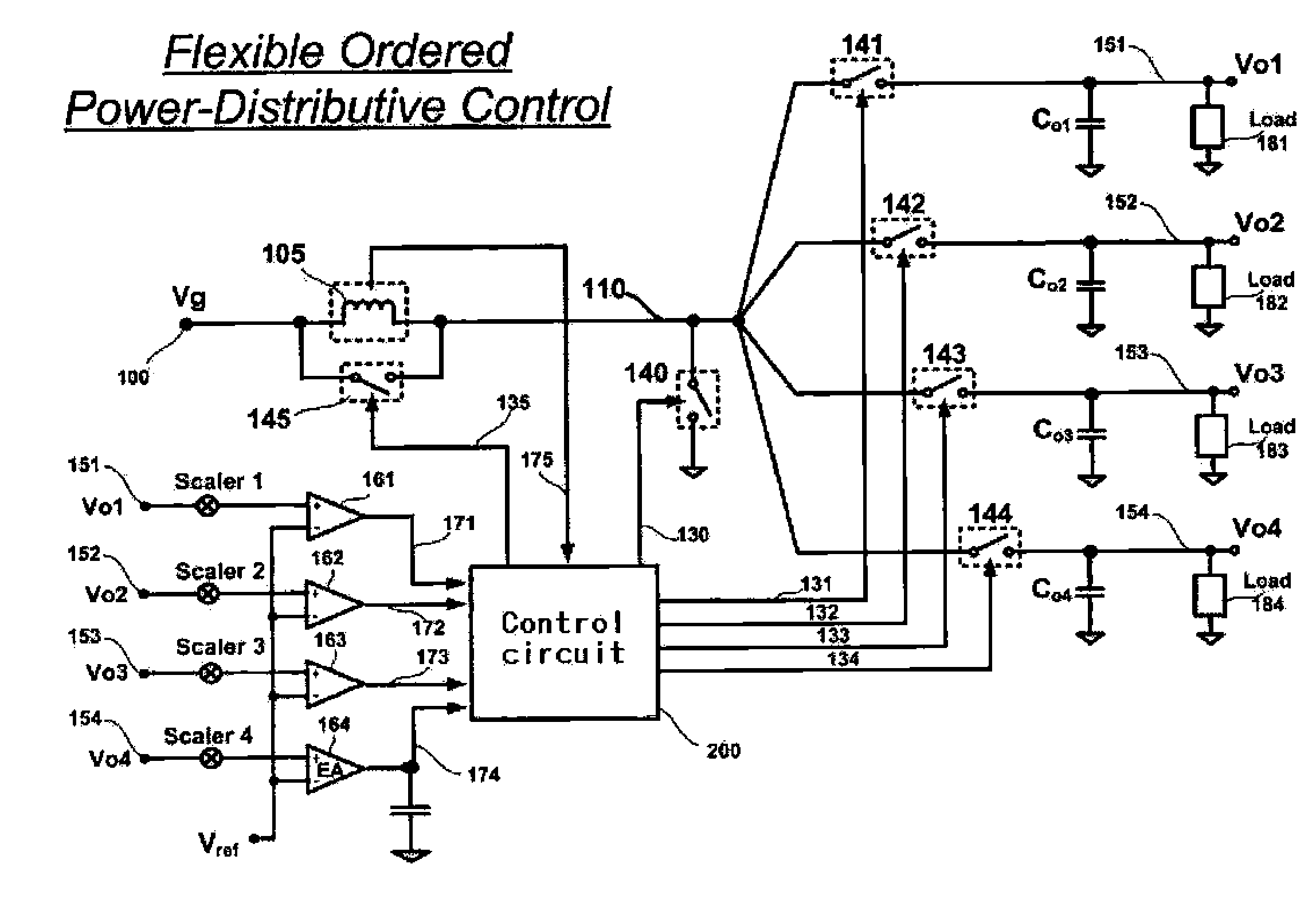
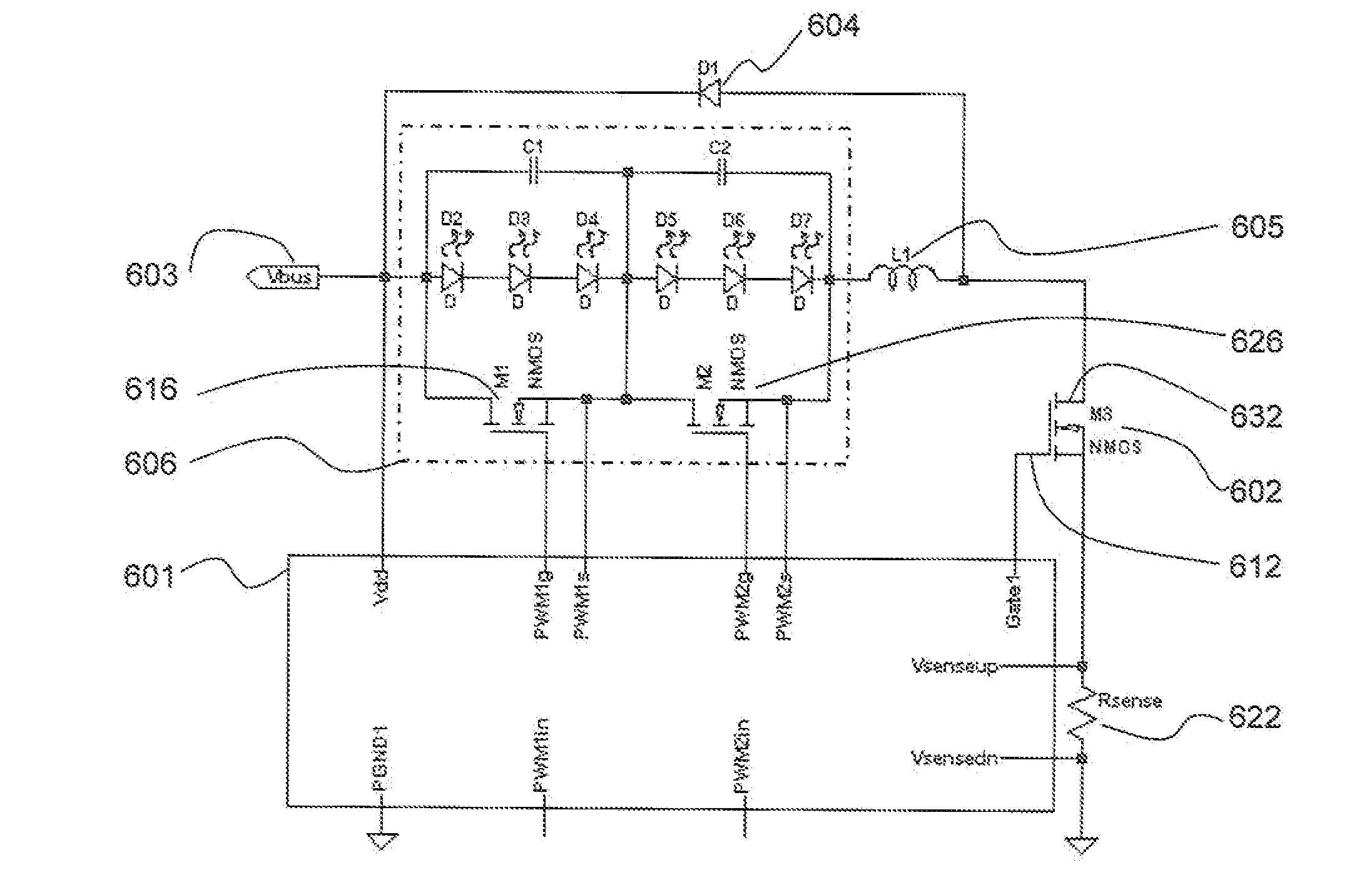
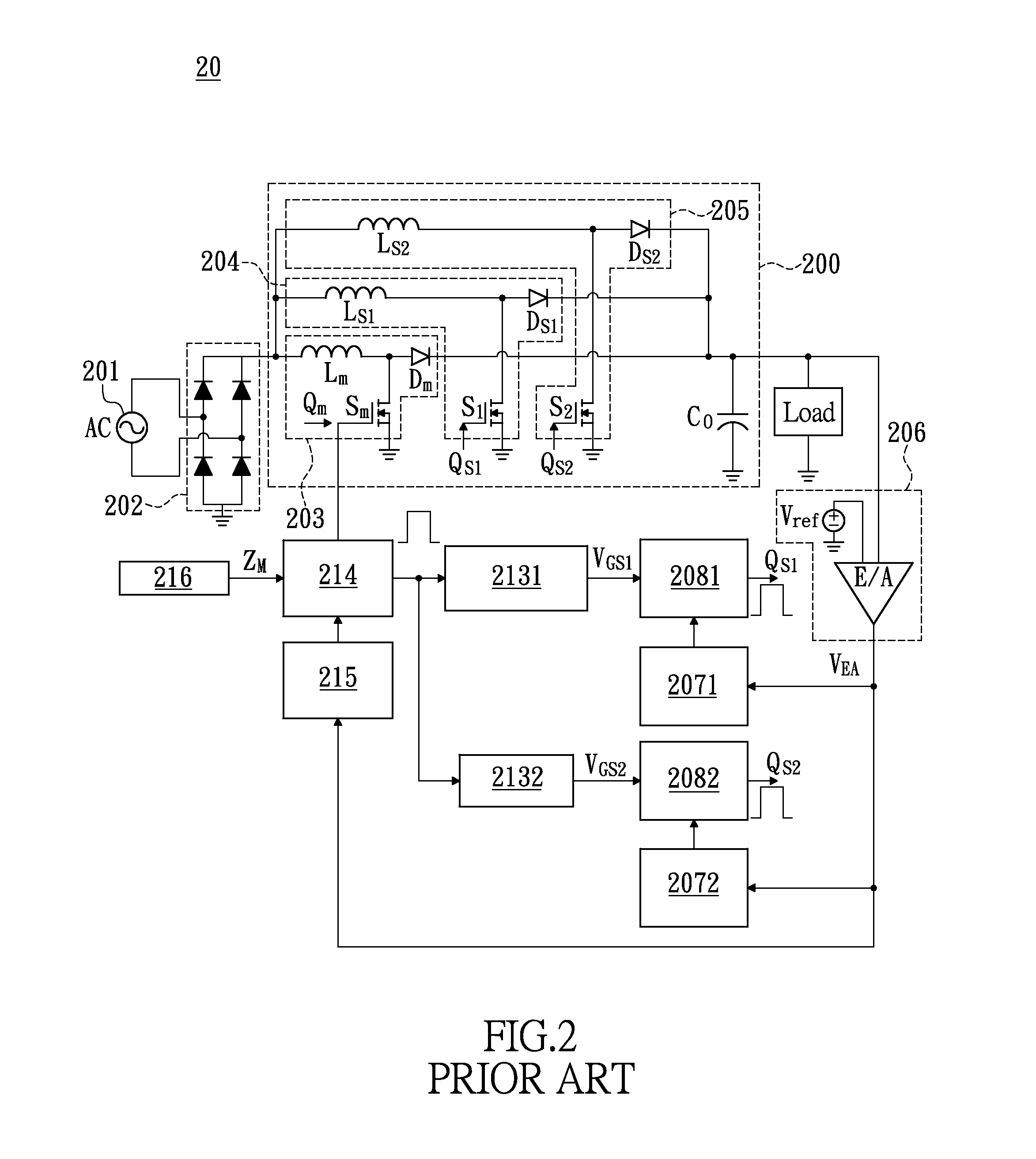
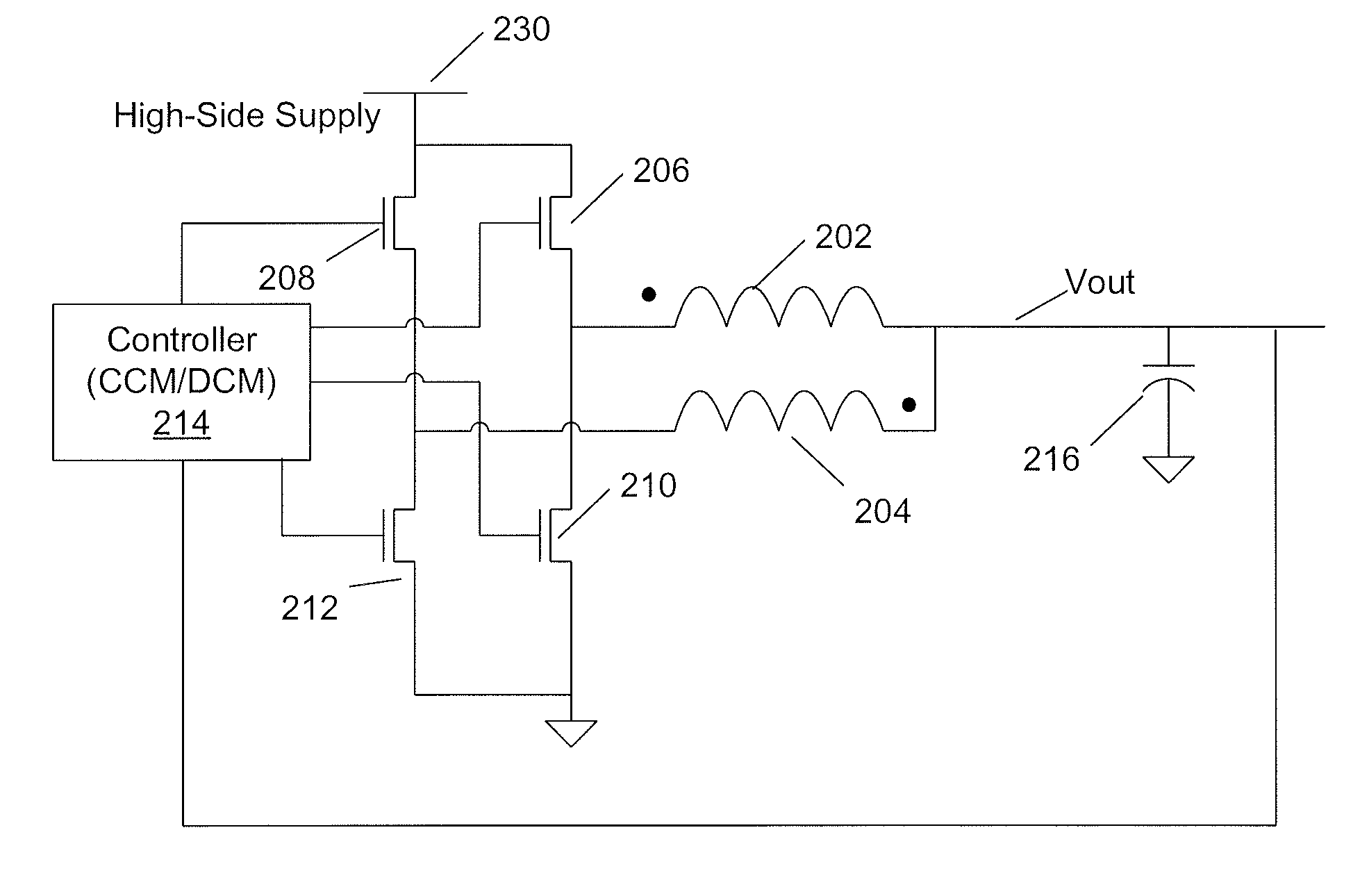
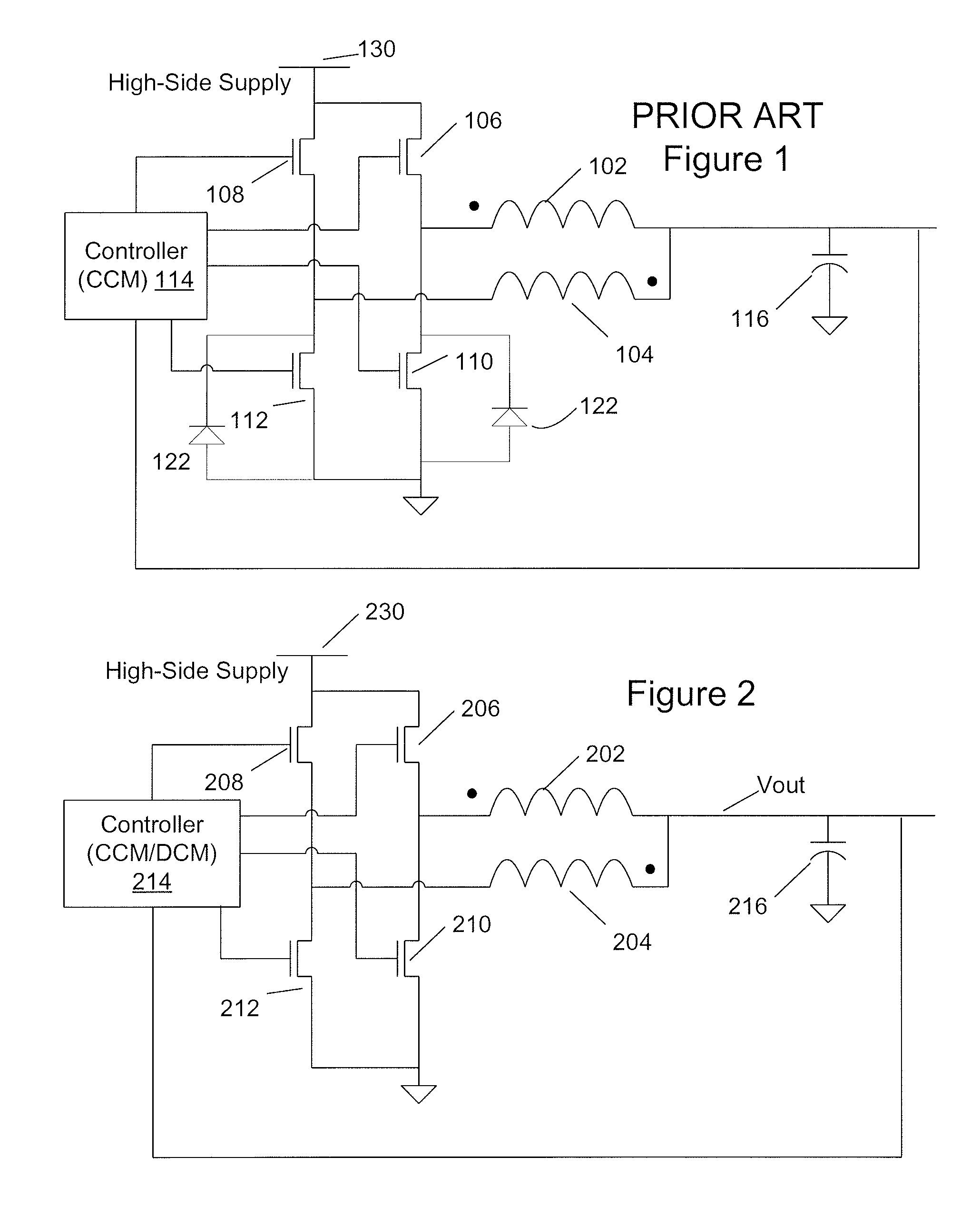
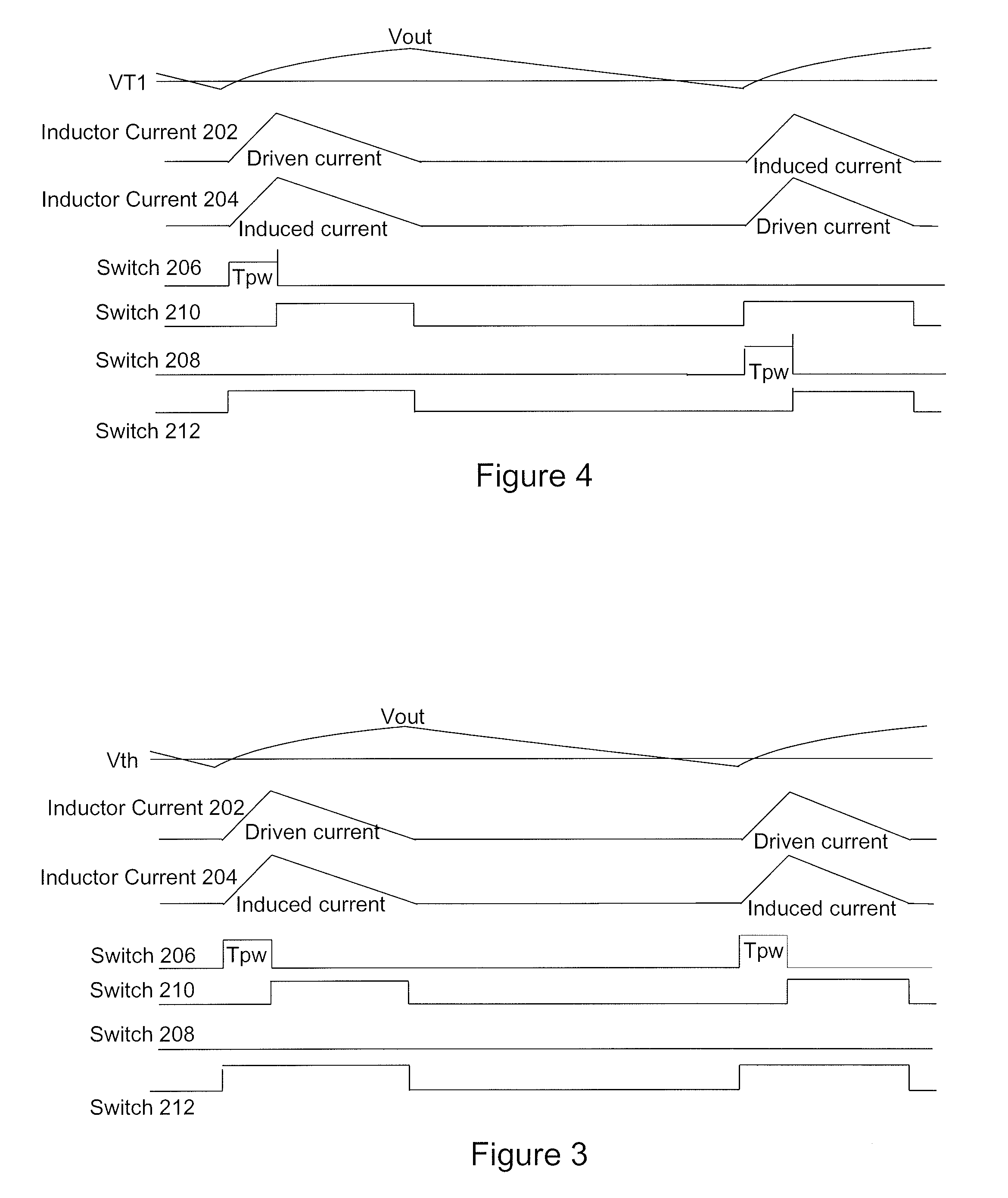
The invention relates to a DC / DC converter design. The converter requires only one single inductor to draw energy from one input source and distribute it to more than one outputs, employing Flexible-Order Power-Distributive Control (FOPDC). It include a single inductor, a number of power switches, comparators, only one error amplifier, a detecting circuit and a control block to regulate outputs. This converter can correctly regulate multiple outputs with fast transient response, low cross regulation, and effective switching frequency for each output. It can work in both discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) and continuous conduction mode (CCM). Moreover, with FOPDC, future output extension is simple, making a shorter time-to-market process for next versions of the converter. The design can be applied to different types of DC-DC converter.
Owner:JDA TECH
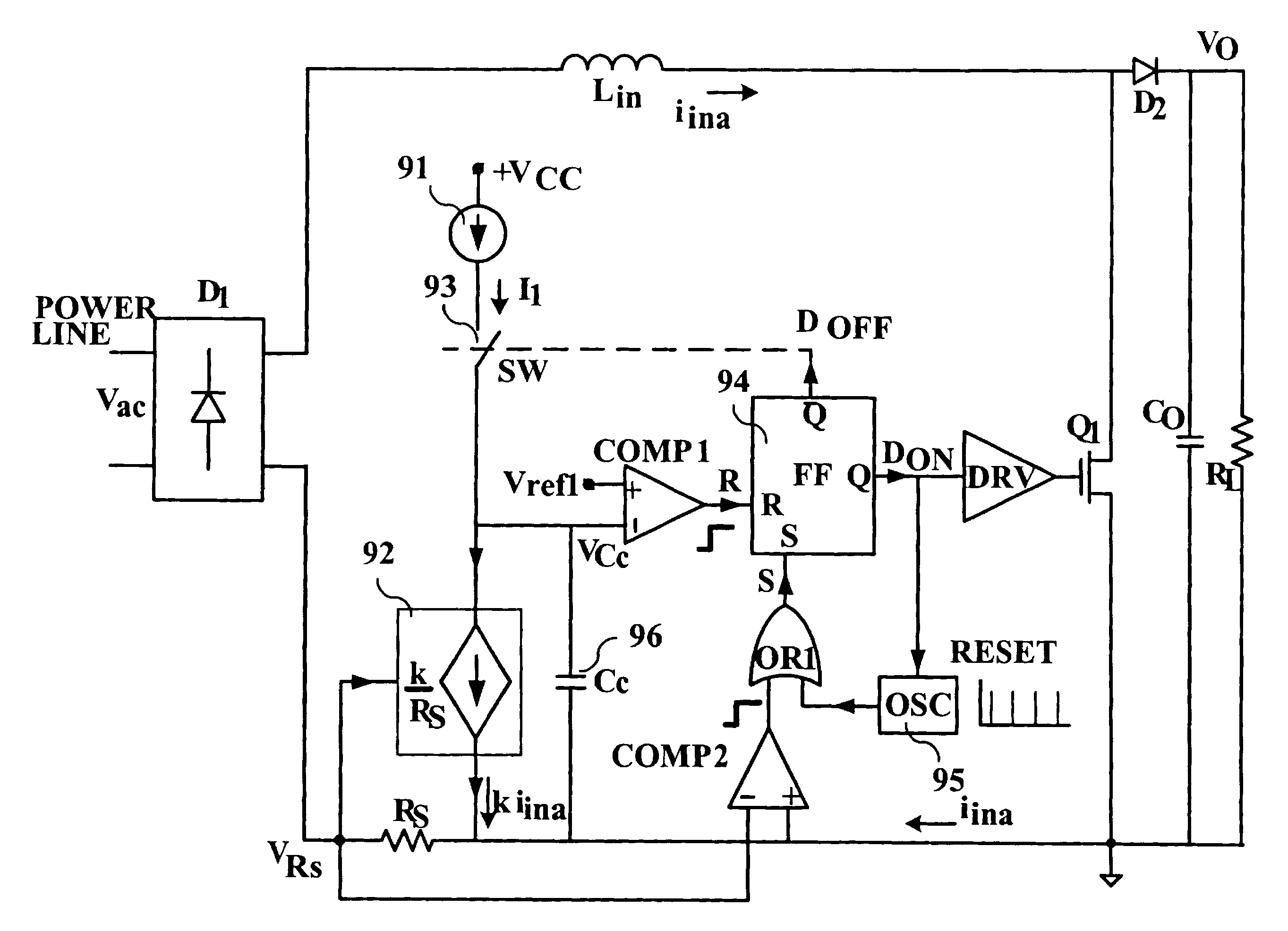
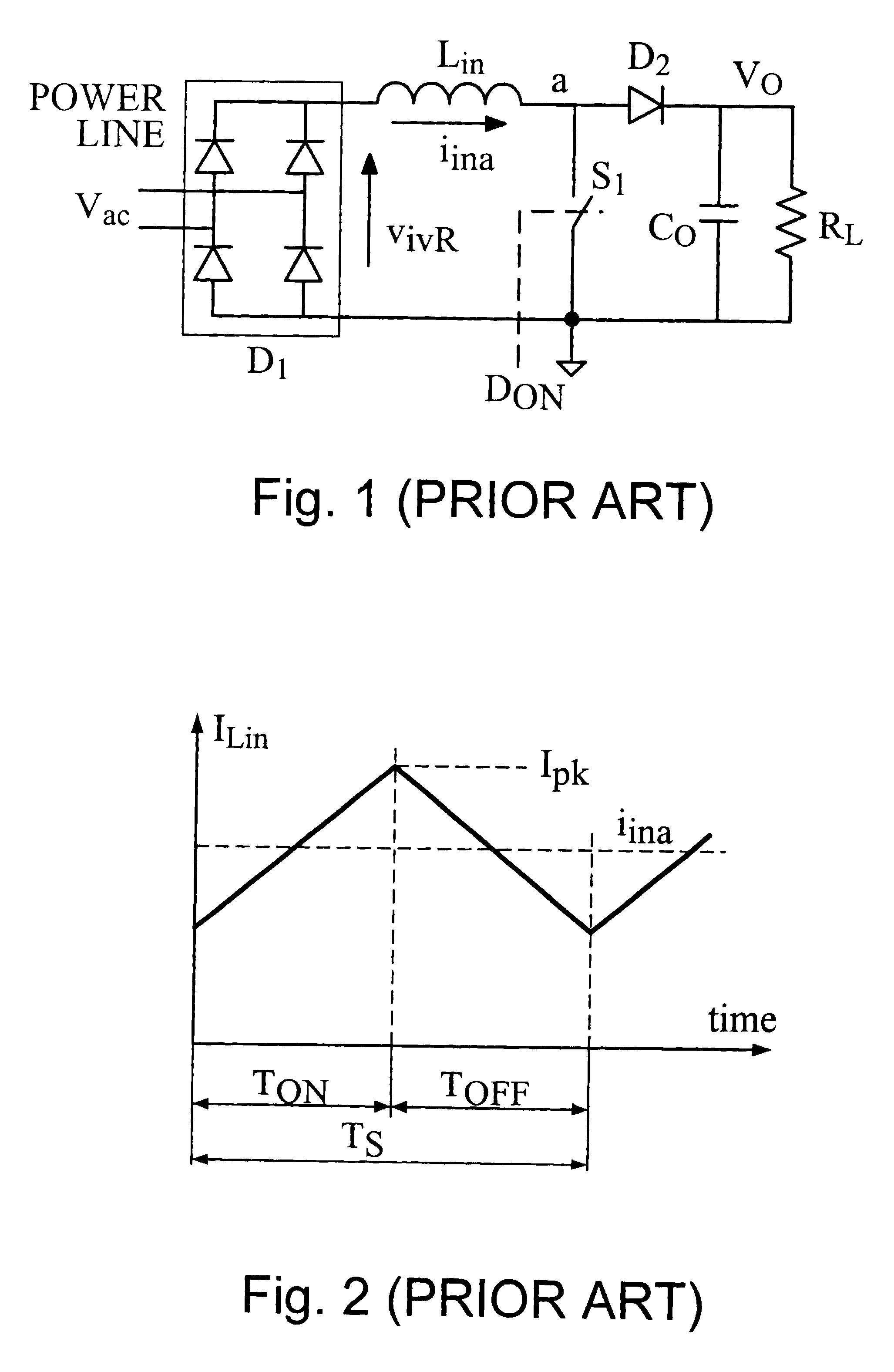
PFC apparatus for a converter operating in the borderline conduction mode
InactiveUS6469917B1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionHemt circuitsEngineering
Power factor correction apparatus, for a switching power supply fed by an array of rectifying diodes and consisting of at least an input inductor, a contact of which is connected in series with a contact of the array, and of a power switch connected between the other contact of the array and the other contact of the input inductor that comprises circuitry for identifying, in each cycle determined by the switching frequency of the power supply, whenever the instantaneous value of the current through the inductor reaches a minimal value; circuitry for switching the power switch to its conducting state in response to the minimal current through the inductor; circuitry for reflecting the current flowing through the inductor by a measurable or simulated parameter; and circuitry for providing indication, in each cycle, by using the parameter, the indication being related to the timing until the peak value of the current, that corresponds to a specific load, has been essentially reached, or to the time from the moment that the current reaches the minimal value until the timing, and for switching the power switch to its non-conducting state in response to the indication.
Owner:GREEN POWER TECH LTD
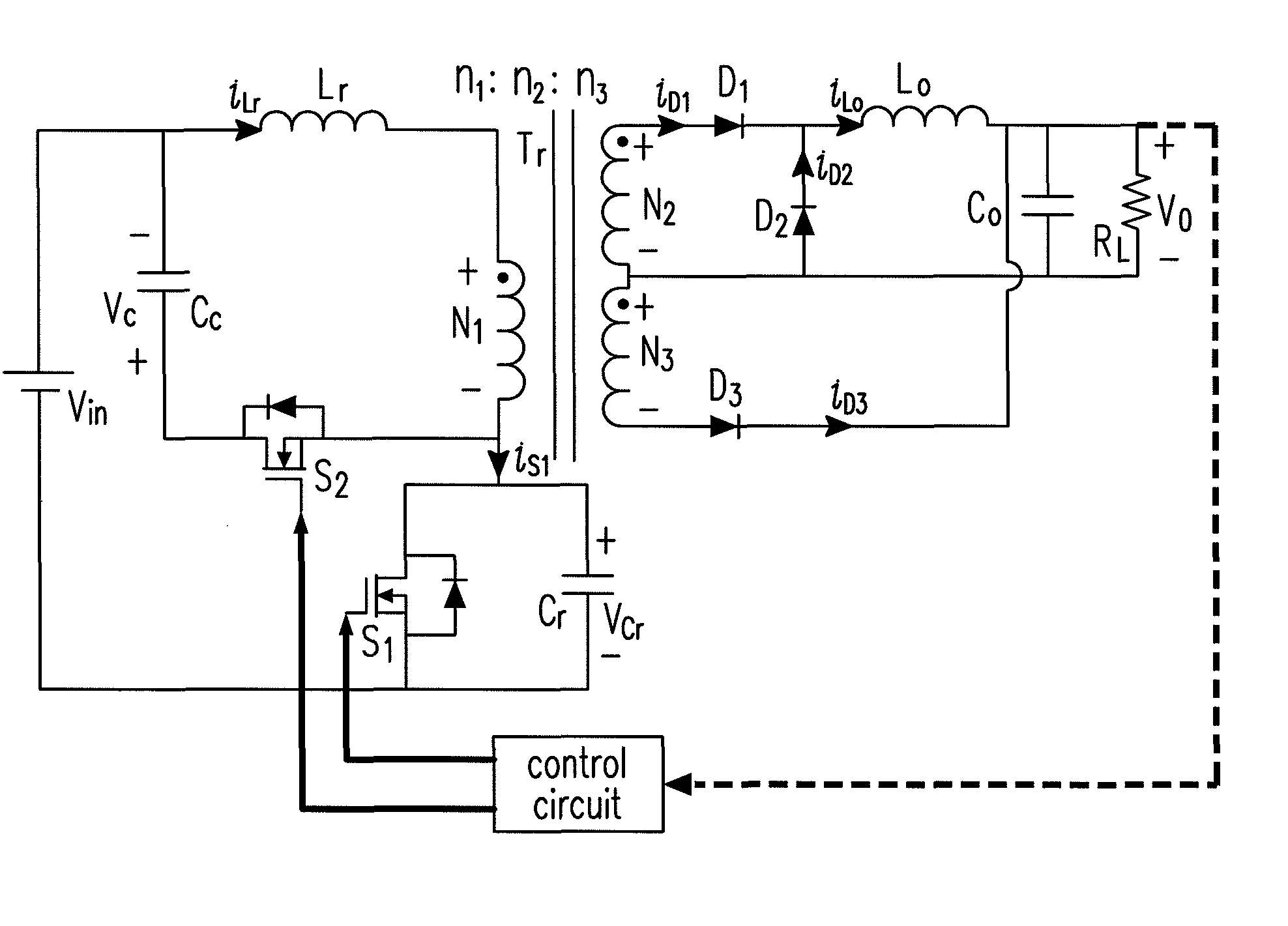
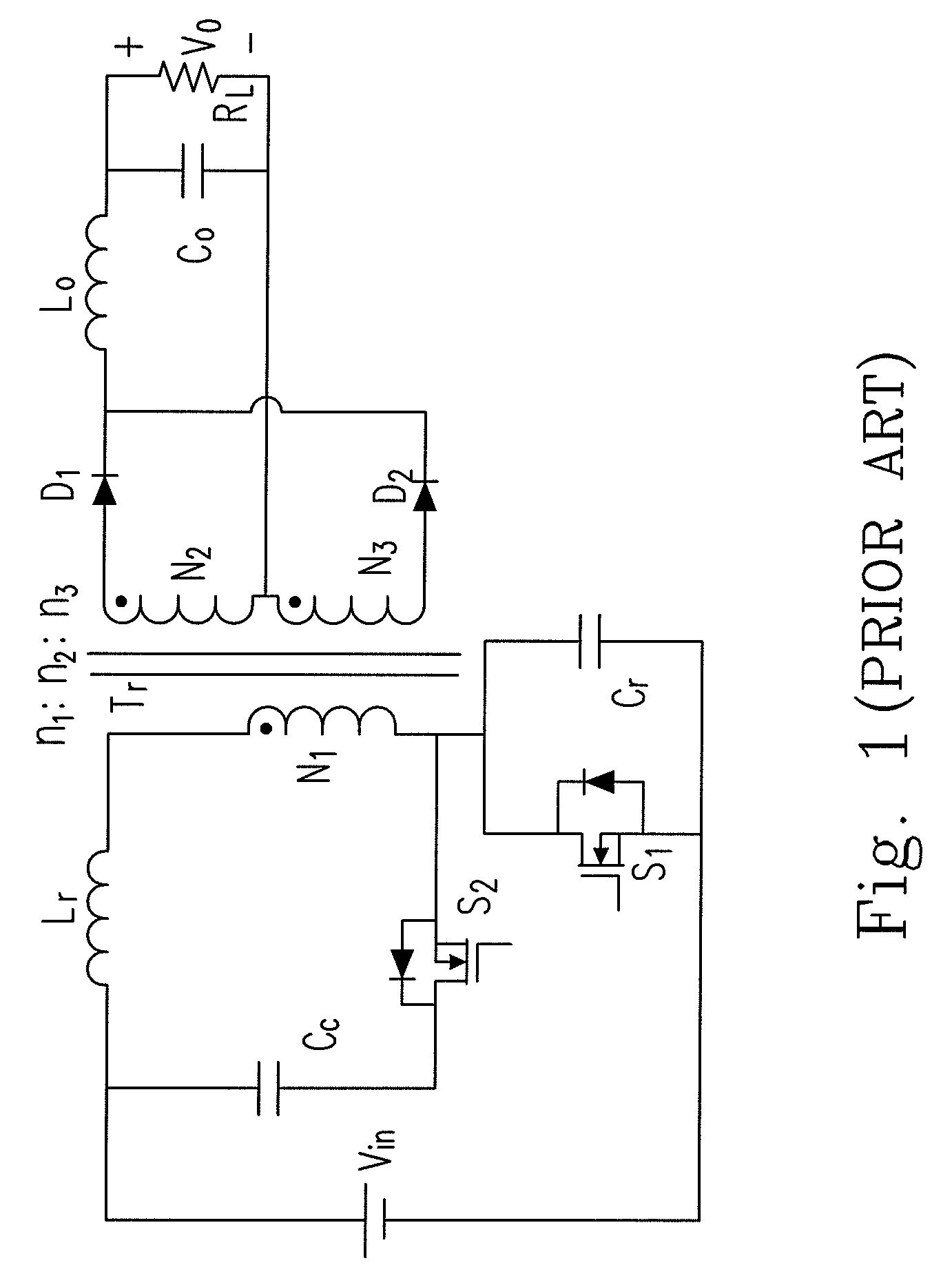
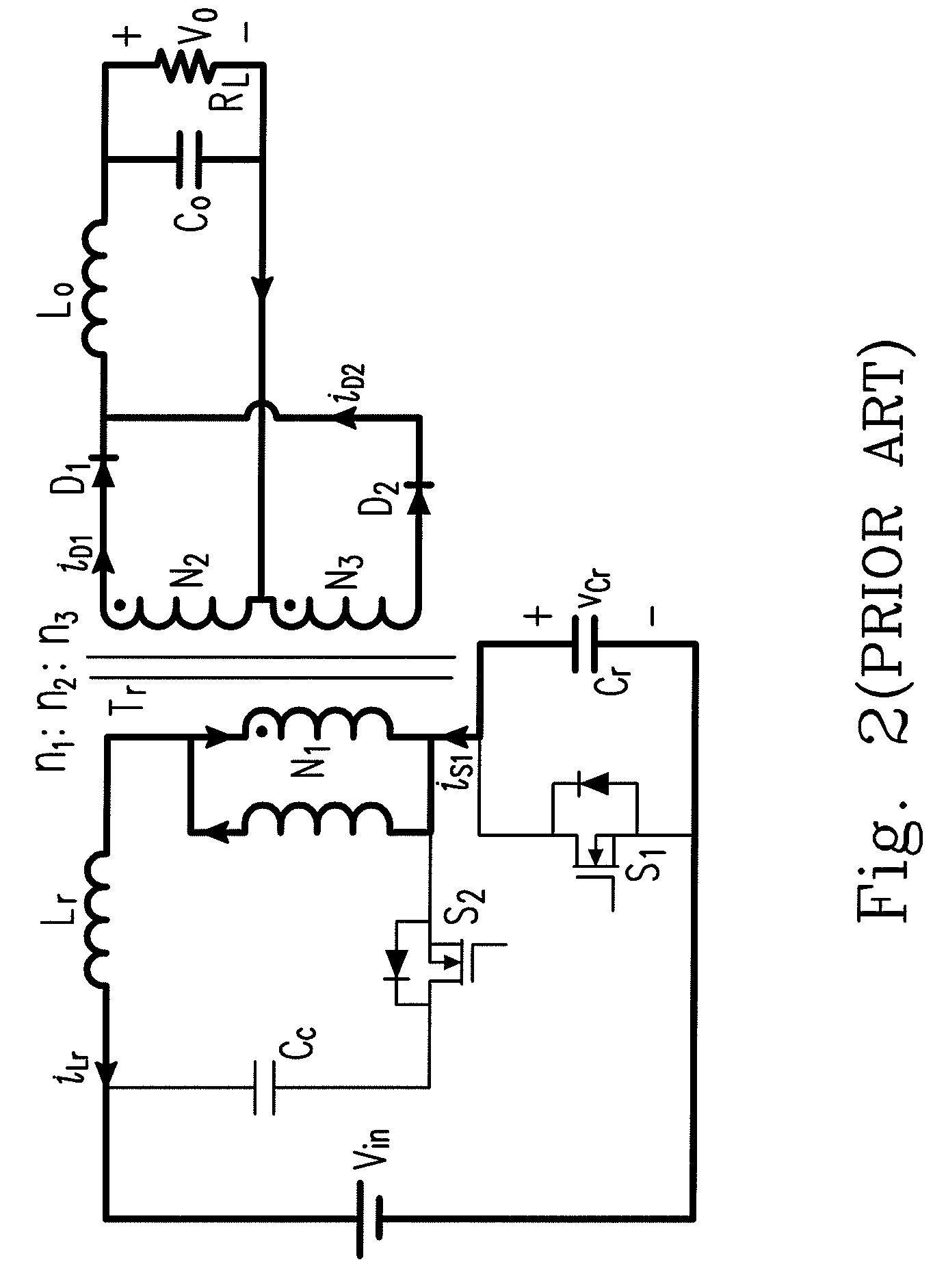
Forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit
ActiveUS20100067259A1Improve conversion efficiencyAdditional drawbackEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsHeavy loadCenter tap
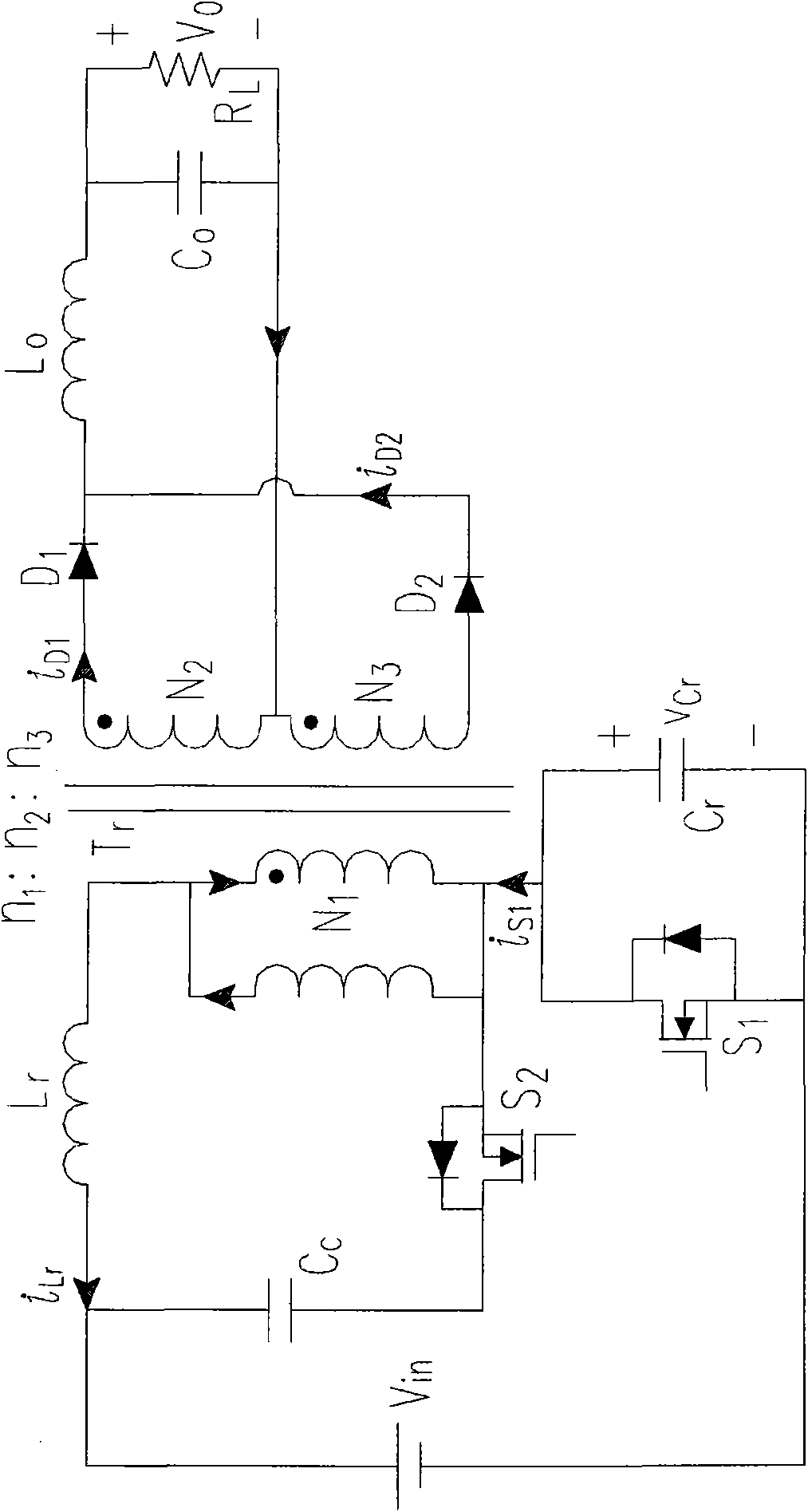
The present invention discloses a forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit. The secondary side of the proposed converter is of center-tapped configuration to integrate a forward circuit and a flyback circuit. The flyback sub-circuit operating continuous conduction mode is employed to directly transfer the reset energy of the transformer to the output load. The forward sub-circuit operating discontinuous conduction mode can correspondingly adjust the duty ratio with the output load change. Under the heavy load condition, the mechanism of active-clamp flyback sub-circuit can provide sufficient resonant current to facilitate the parasitic capacitance of the switches to be discharged to zero. Under the light load condition, the time interval in which the resonant current turns from negative into positive is prolonged to ensure zero voltage switching function. Meanwhile, the flyback sub-circuit wherein the rectifier diode is reverse biased is inactive in order to further reduce the power losses.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
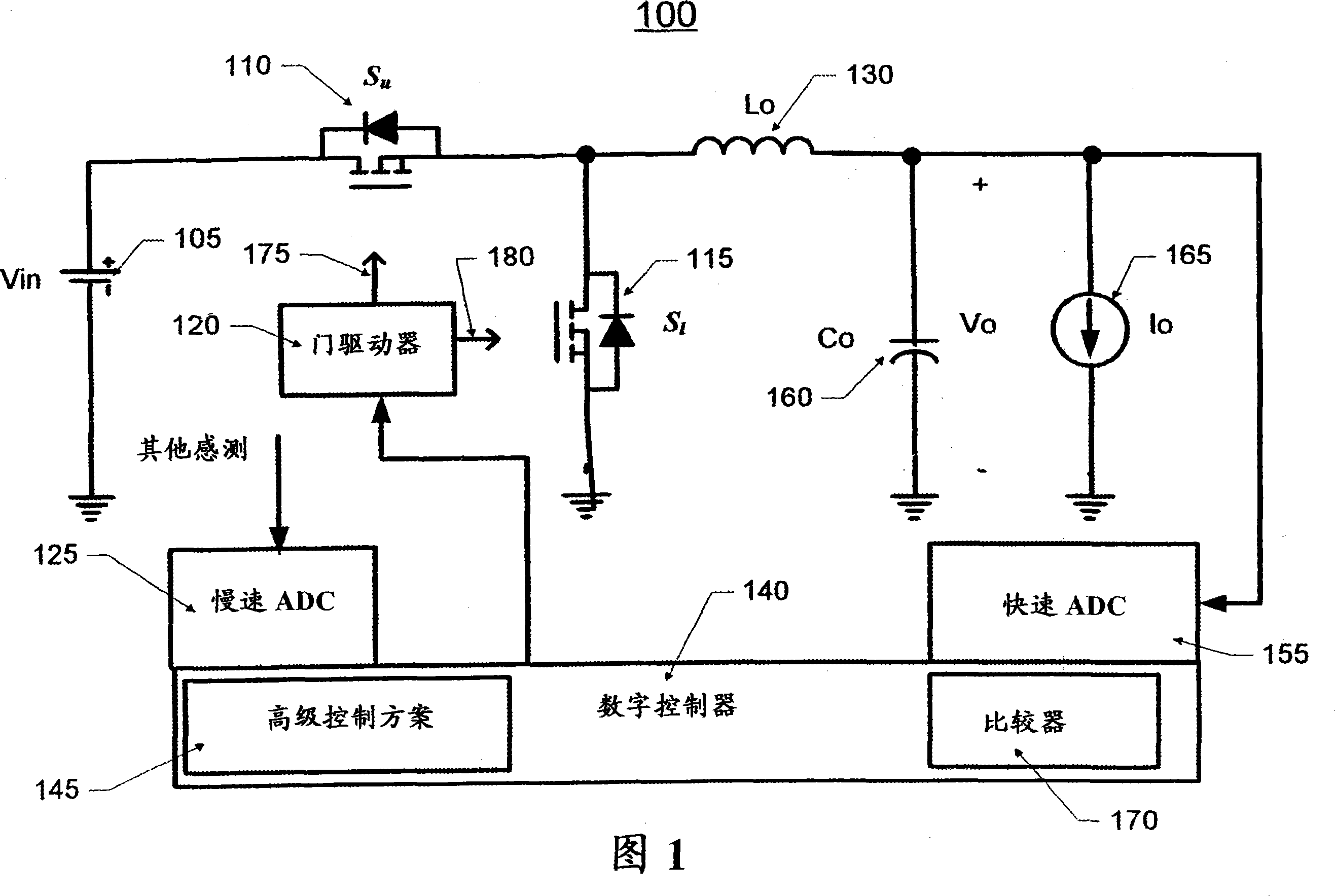
Switching power converter and method of controlling output voltage thereof using predictive sensing of magnetic flux
ActiveUS20050073862A1Improve immunityDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationIntegratorSwitching cycle
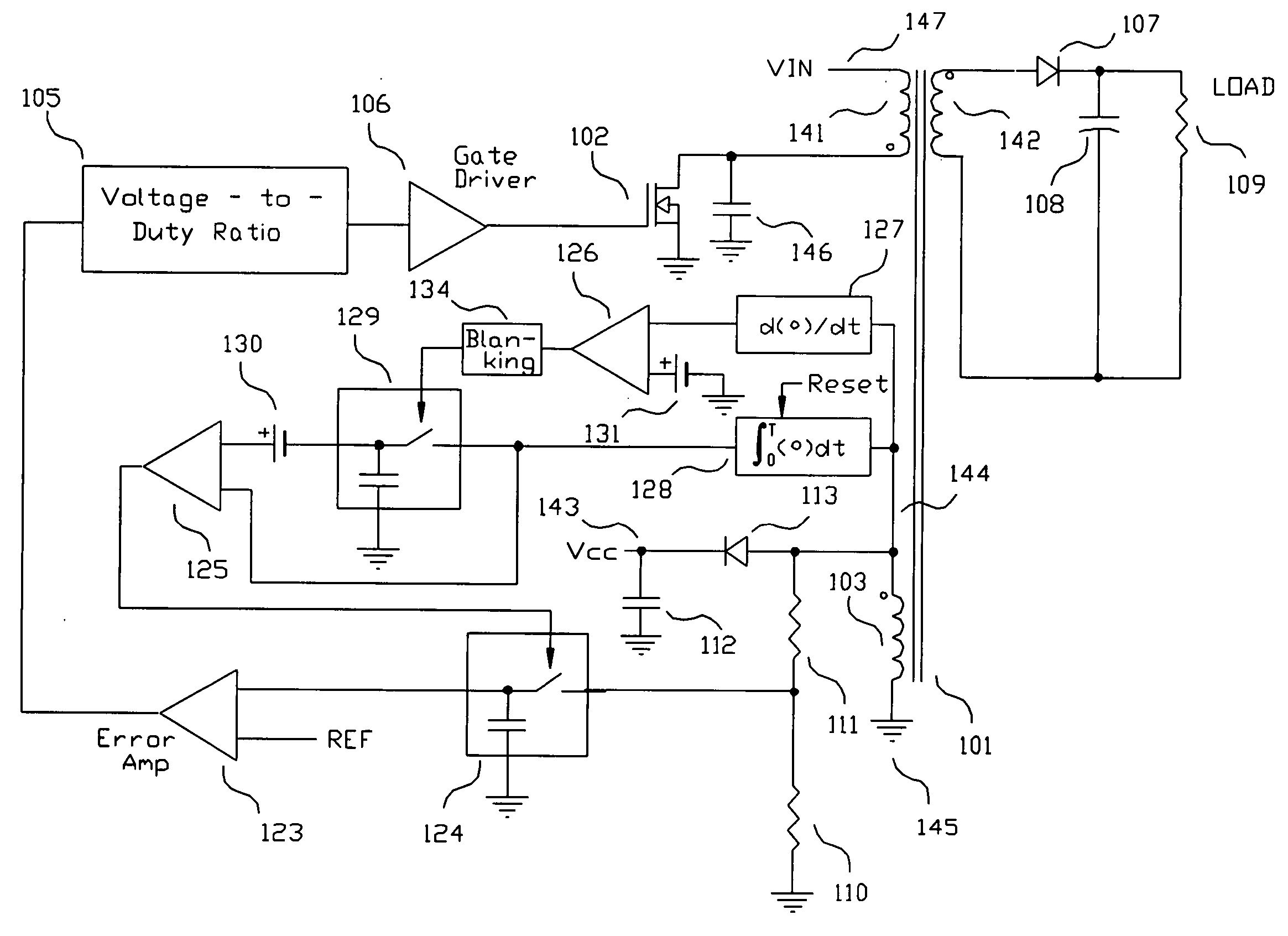
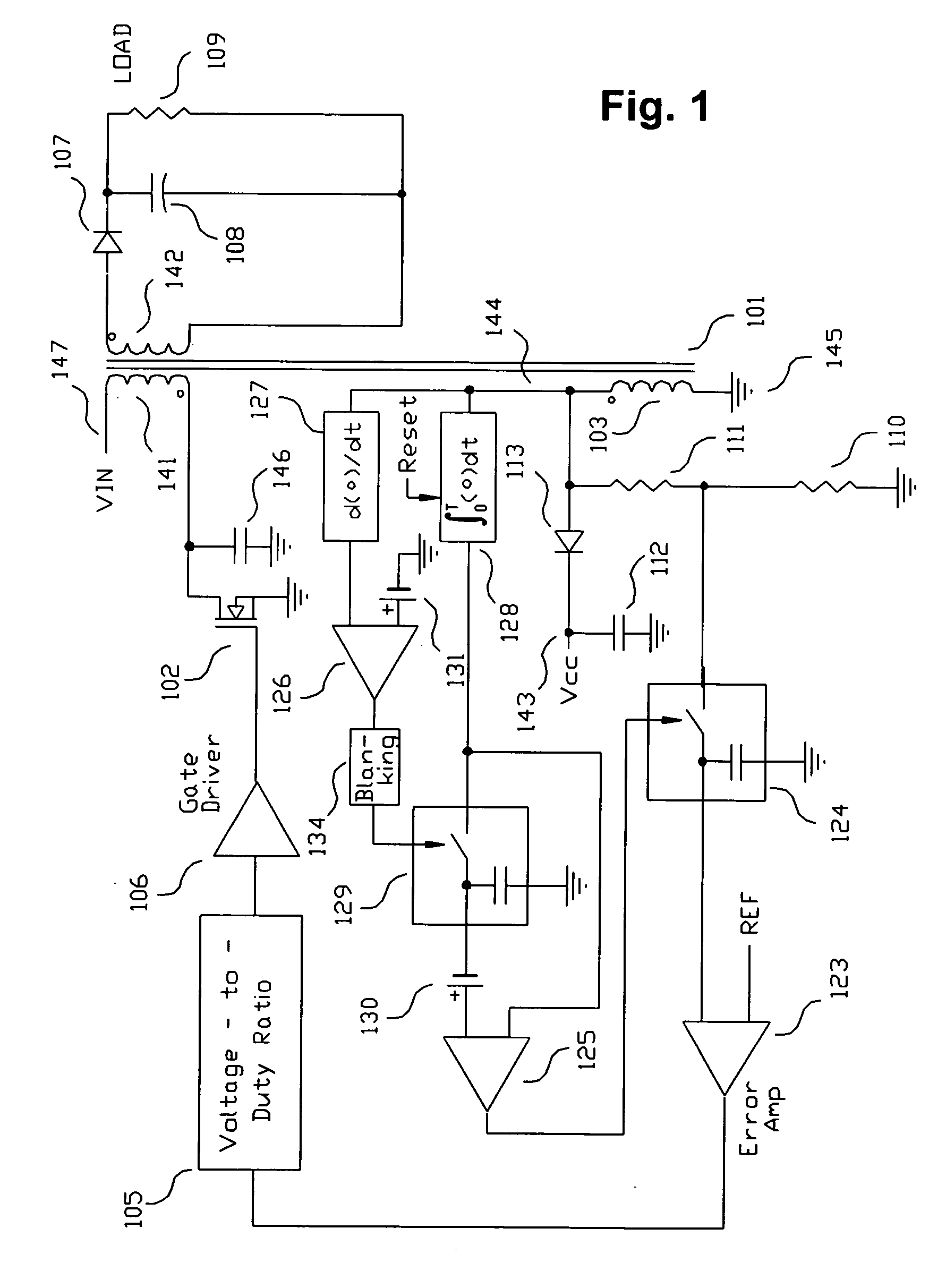
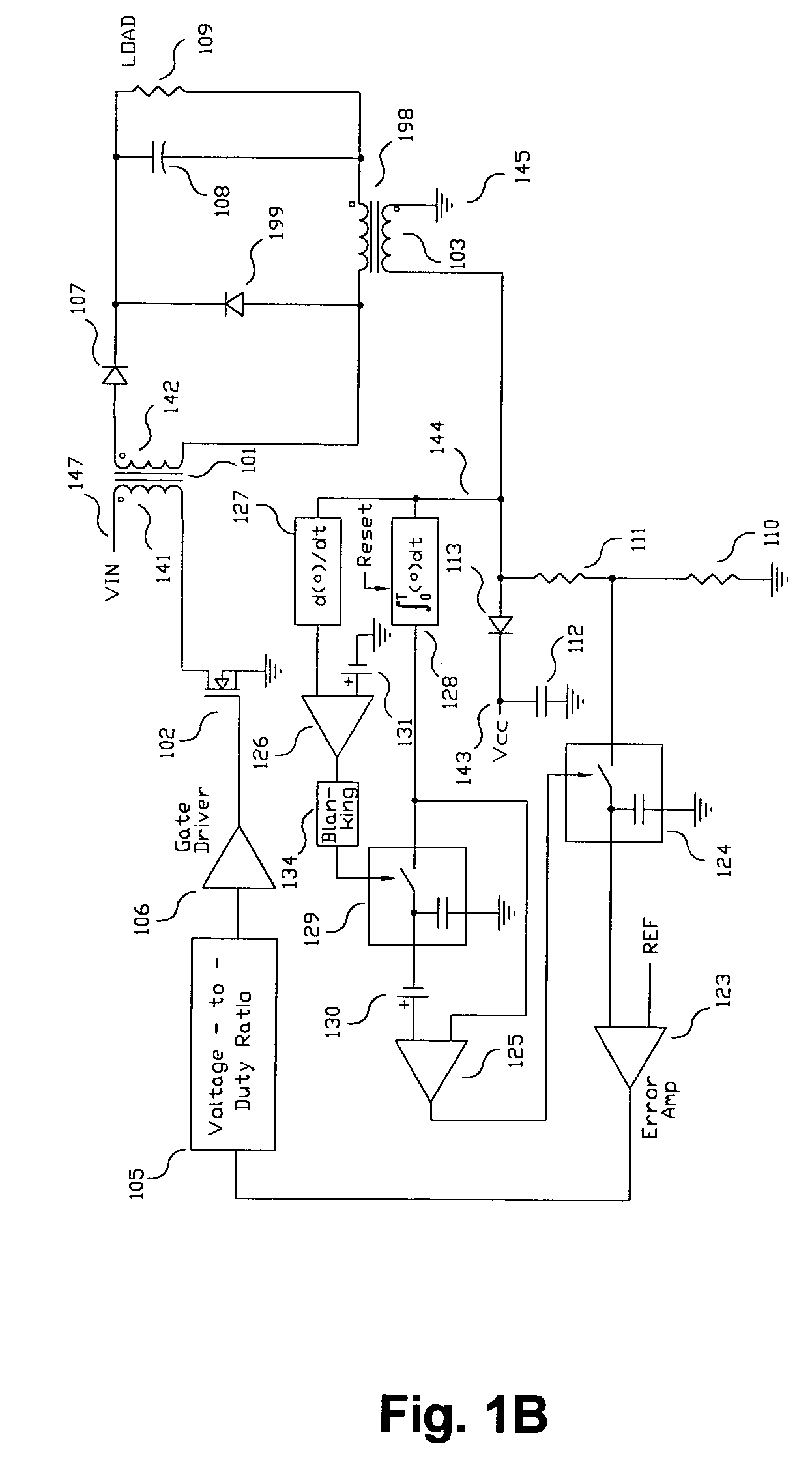
A switching power converter and method of controlling an output voltage thereof using predictive sensing of magnetic flux provides a low-cost switching power converter via primary-side control using a primary-side winding. The power converter has improved immunity to parasitic phenomena and other variations within the power converter components. An integrator is used to generate a voltage analog that represents magnetic flux within a power magnetic element via an integration of a voltage on a primary-side winding of the power magnetic element. A detection circuit detects the end of a half-cycle of post-conduction resonance that occurs in the power magnetic element subsequent to the energy level in the power magnetic element reaching zero. The voltage of the integrator is stored at the end of the post-conduction resonance half-cycle and is used to determine a sampling point prior to or equal to the start of post-conduction resonance in a subsequent switching cycle of the power converter (which is the predicted zero-energy storage point of the power magnetic element). The primary-side winding voltage is then sampled at the sampling point, providing an indication of the output voltage of the power converter. By predicting the zero-magnetic-energy storage point, the output voltage of a power converter operating in discontinuous or boundary conduction mode can be accurately controlled without being affected by parasitic phenomena or variations in circuit performance over time, input voltage and temperature.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
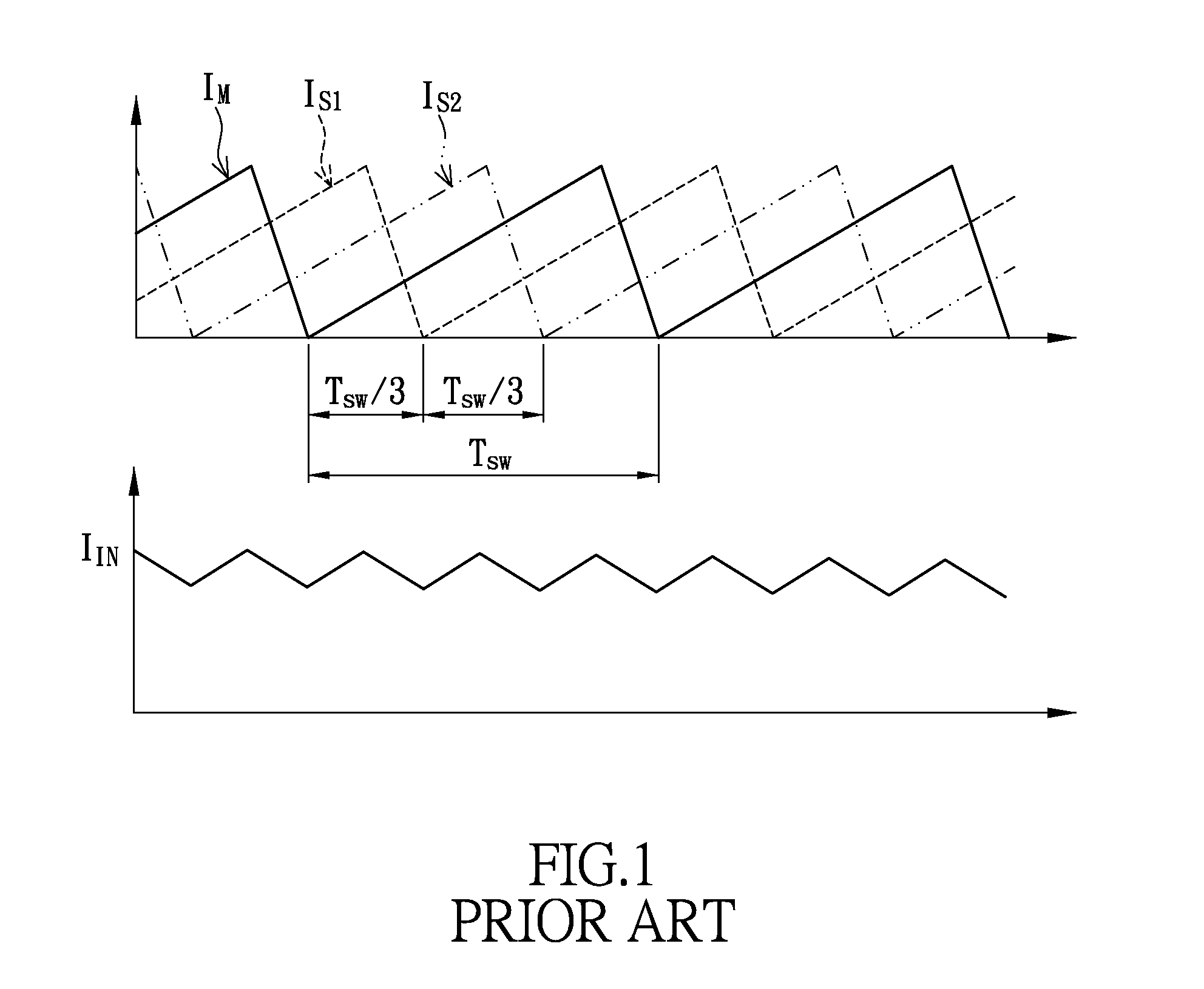
Method and apparatus for multi-phase DC-DC converters using coupled inductors in discontinuous conduction mode
ActiveUS7317305B1Improve efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationDc dc converterEngineering
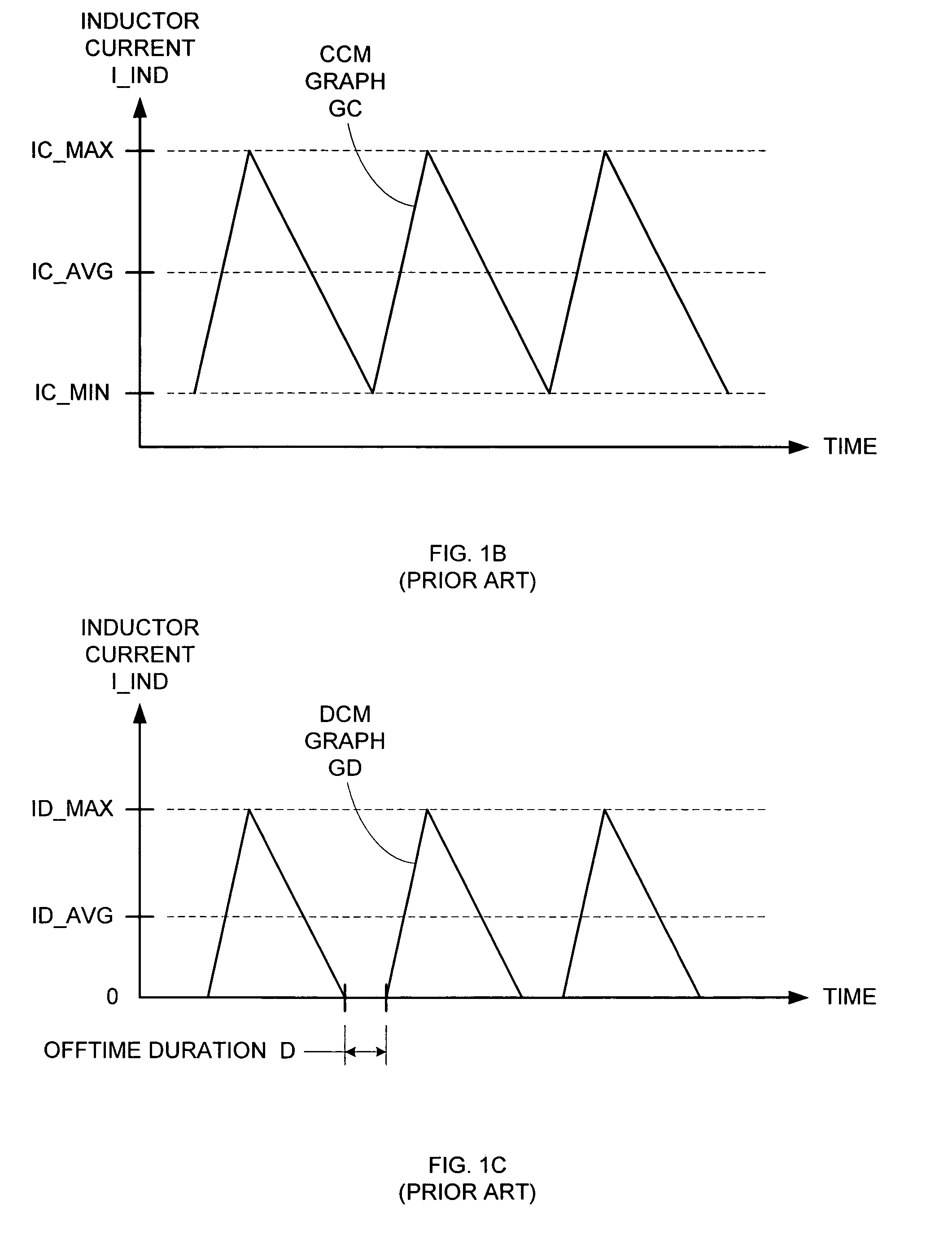
A multi-phase, coupled-inductor, DC-DC voltage converter operates in discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) when the system is operated at low output power demand. An embodiment of the converter switches to operating in continuous conduction mode (CCM) when the system is operated at high output power demand. Operation in single-drive and rotating phase DCM operation at low power are described. An alternative embodiment operates in a multiple-drive, rotating-phase, discontinuous conduction mode during at least one condition of output power demand.
Owner:VOLTERRA SEMICONDUCTOR
LED Illumination systems
InactiveUS20110309760A1Improve reliabilityLow costEfficient power electronics conversionElectroluminescent light sourcesBuck converterFlyback diode
An illumination system includes a power supply having a boost converter operating in the discontinuous conduction mode, a flyback converter operating in the critical conduction mode, and a switch coupled to the flyback converter. Several light emitting diodes receive power from the power supply. The boost converter may include a boost inductor (LB) and a boost diode (DB), constructed to perform the boost power factor correction (PFC) function. The flyback converter may includes a flyback inductor (LFB) and a flyback diode (DFB) and the power supply may be constructed to turn on the switch around the point where the current flowing in the flyback inductor reaches zero value.
Owner:EMD TECH
Single-inductor multiple-output switching converters in PCCM with freewheel switching
ActiveUS7432614B2Suppressing cross regulationSignificant stressDc network circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionFreewheelPeak value
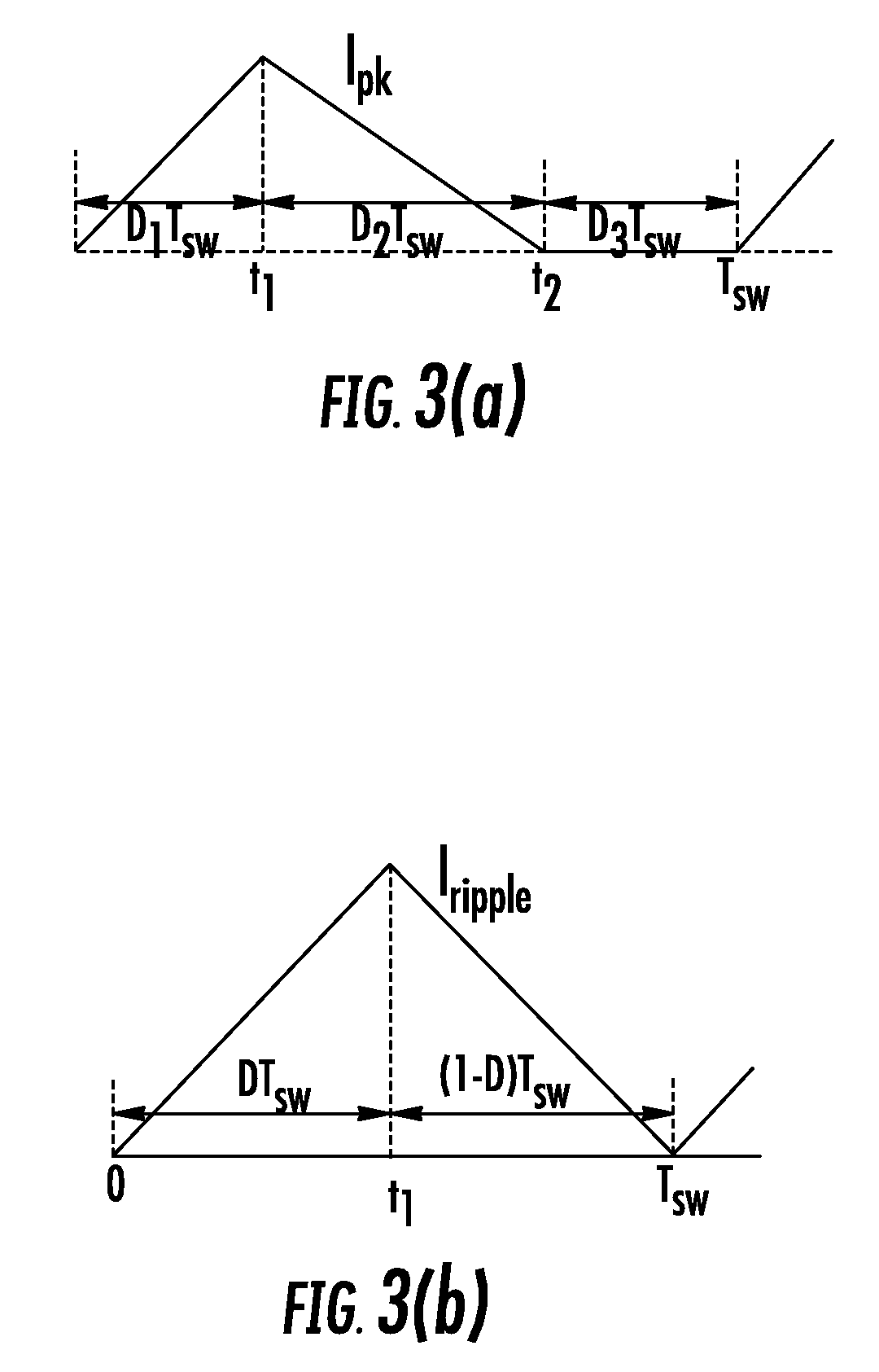
A method and apparatus are disclosed for single-inductor multiple-output switching converter design. With the proposed freewheel switching control, this converter operates in a pseudo-continuous conduction mode (PCCM) and is capable of handling large load currents with a much smaller current ripple and peak inductor current, while retaining low cross regulation. It can also work in discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) for high efficiency at light loads. This design can be applied to have single or multiple outputs and for different types of DC-DC conversions.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Power factor correction circuit and driving method thereof
ActiveUS20100110593A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionSwitched currentEngineering
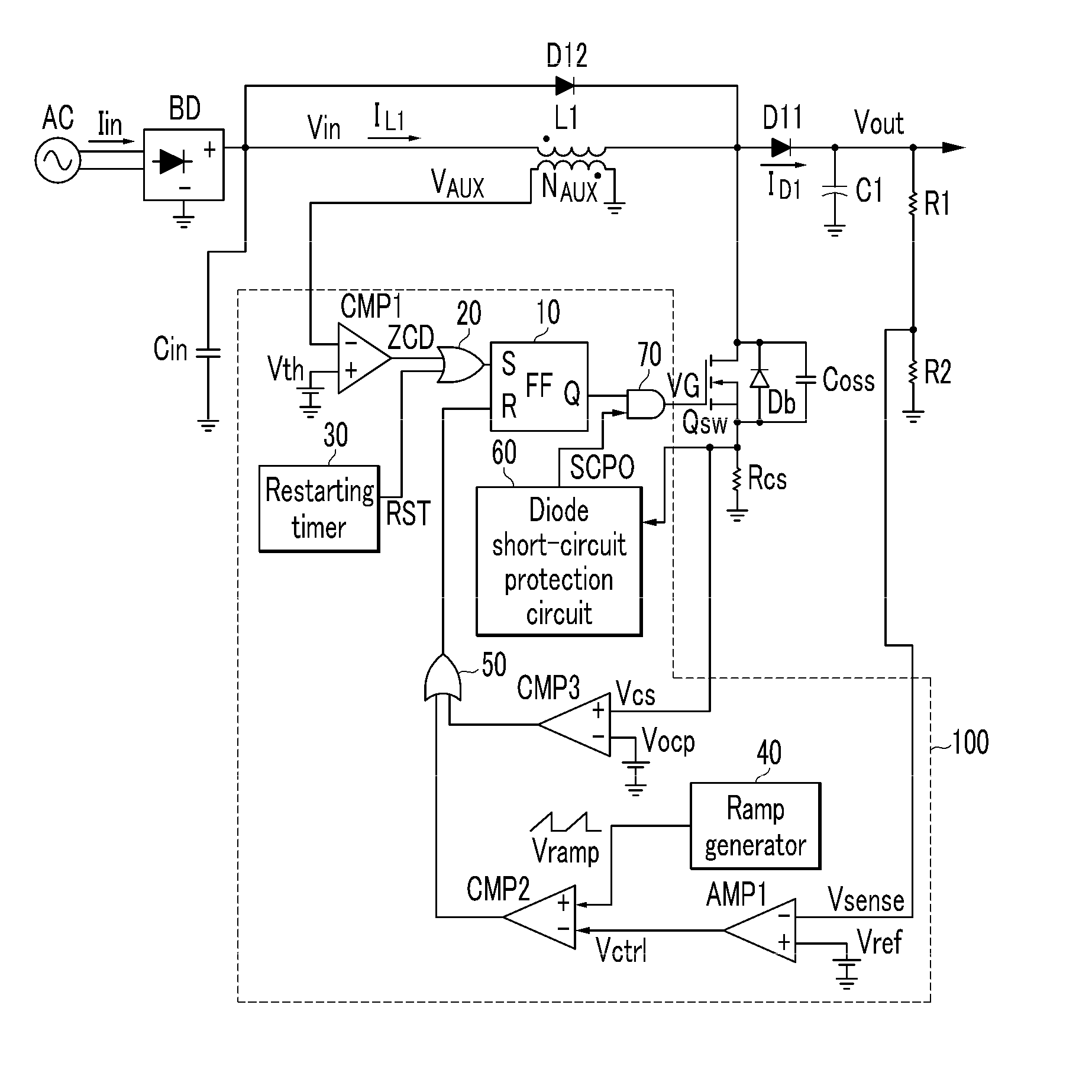
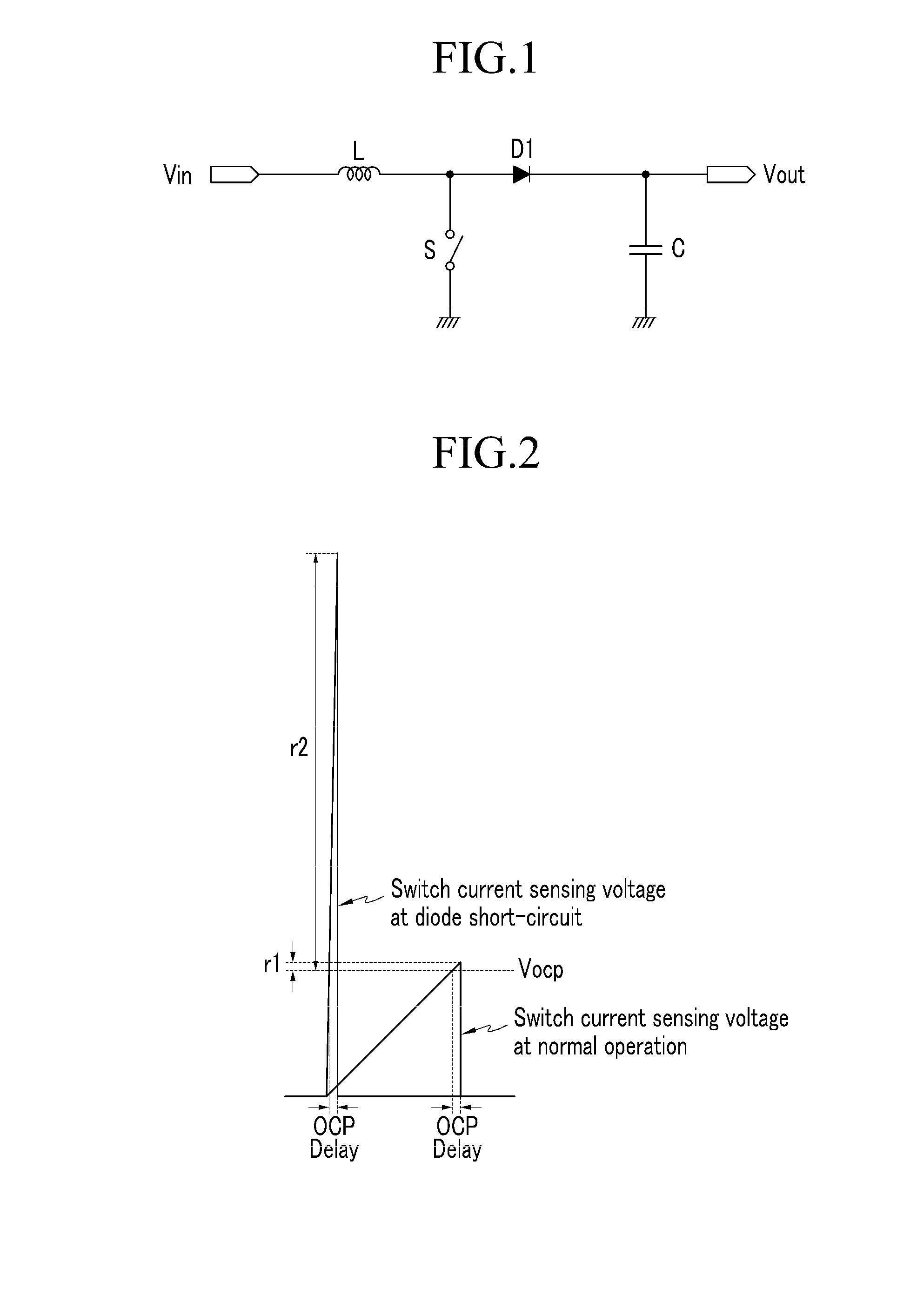
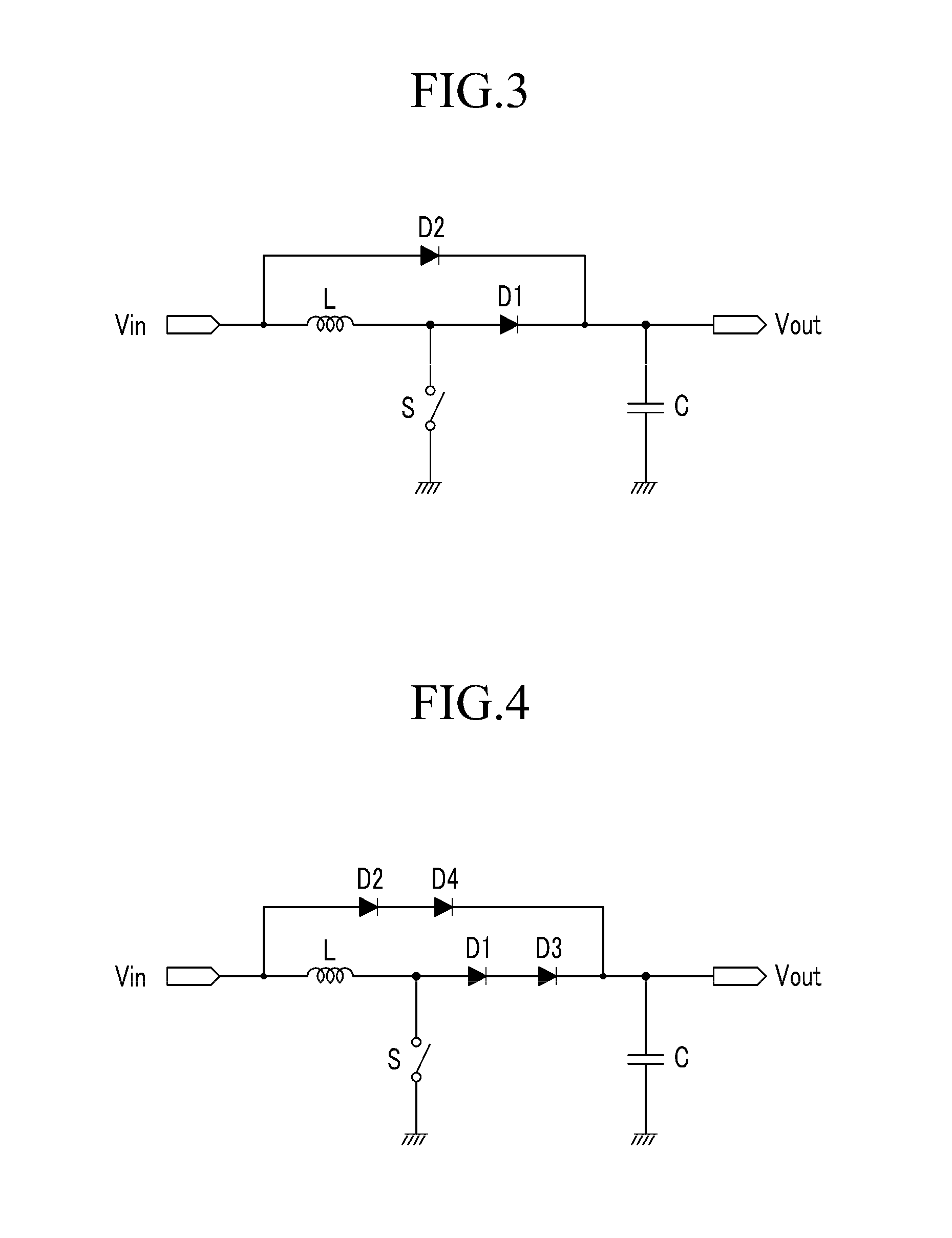
The present invention relates to a set protection circuit for when a diode short-circuit defect occurs in a power factor correction circuit of a critical conduction mode. In a conventional power factor correction circuit, an excessive amount of current flows to a switch if a diode is short-circuited so that the switch is damaged. In order to prevent damage to the switch, the present invention provides a method for stopping turn-on of the switch when a switch current is excessive.
Owner:SILICON MITUS
LED current bias control using a step down regulator
ActiveUS20060238174A1Simplified configuration requirementsPrediction is simpleElectroluminescent light sourcesElectric variable regulationMode controlPwm signals
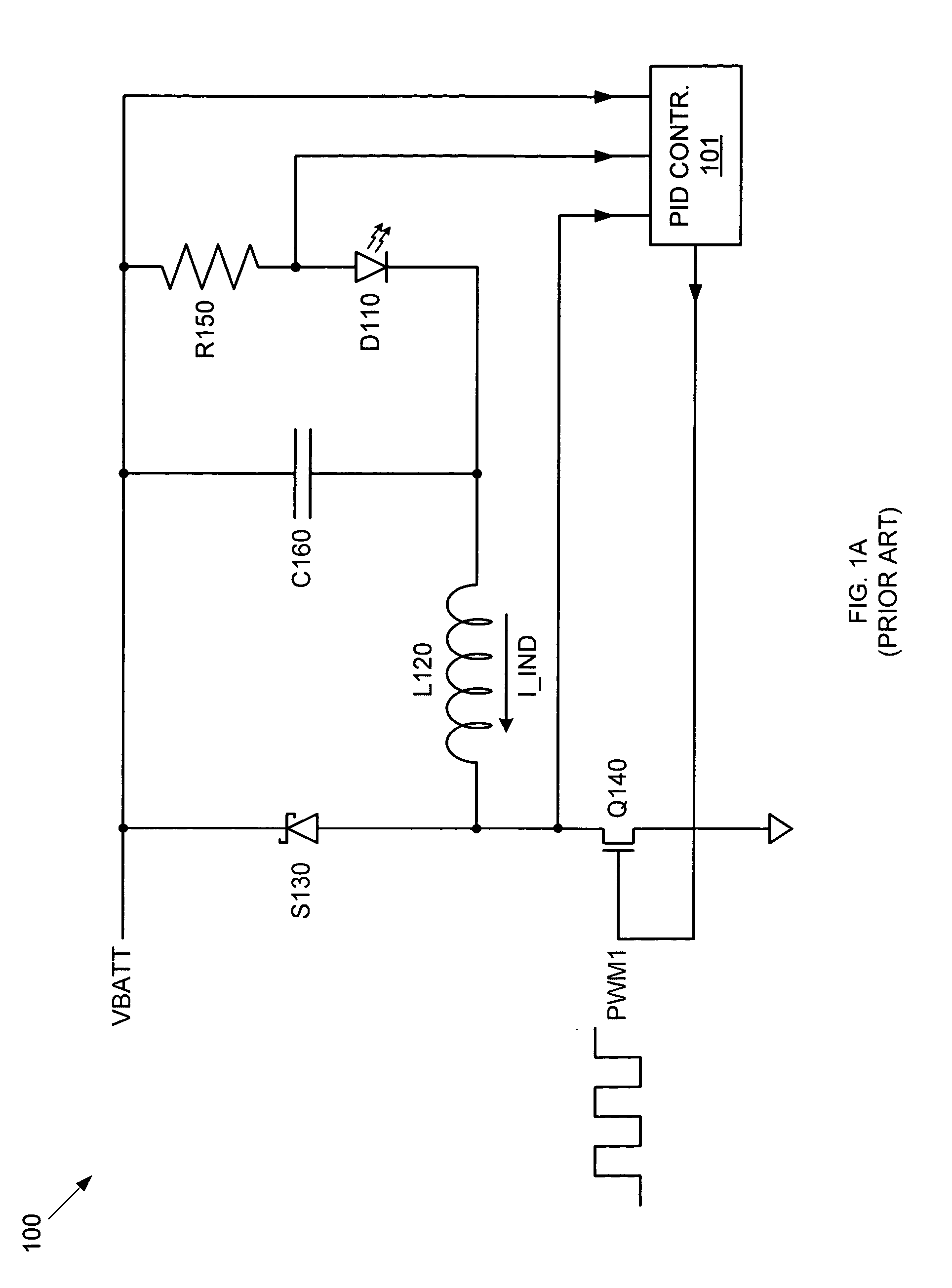
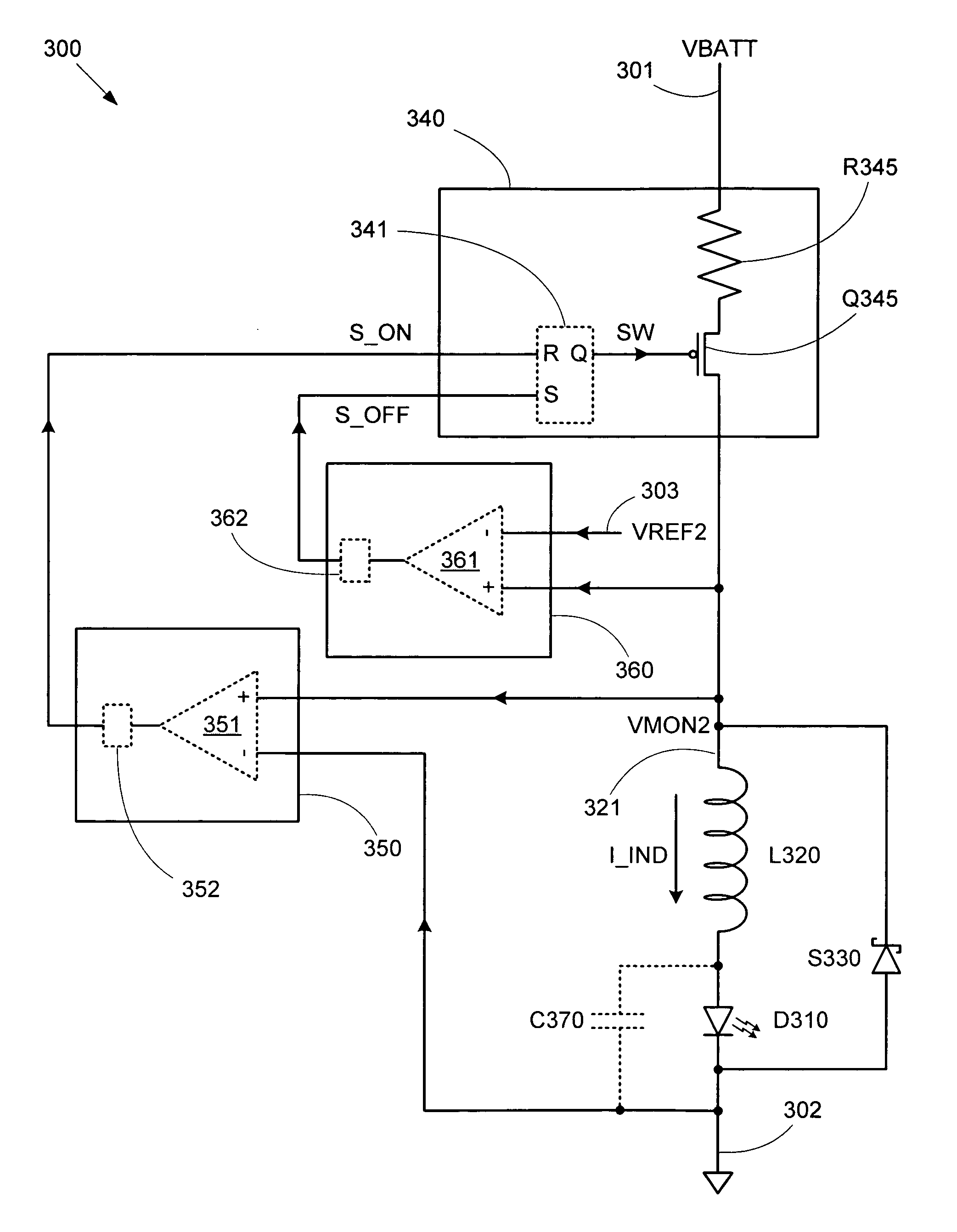
A step down switching regulator circuit that is particularly well-suited to drive high power LEDs includes a crossover conduction mode (XCM) control circuit that maintains operation at the crossover point between continuous conduction mode (CCM) and discontinuous conduction mode (DCM). This XCM operation provides an inductor current waveform that ramps up and down between zero and a desired maximum current. One or more comparators in the XCM control circuit can be used to control switching between the inductor current ramp up and ramp down phases. In this manner, complex feedback loop logic and PID controlled PWM signal generation logic can be avoided, and the need for external sense resistors and associated interface pins can be eliminated.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
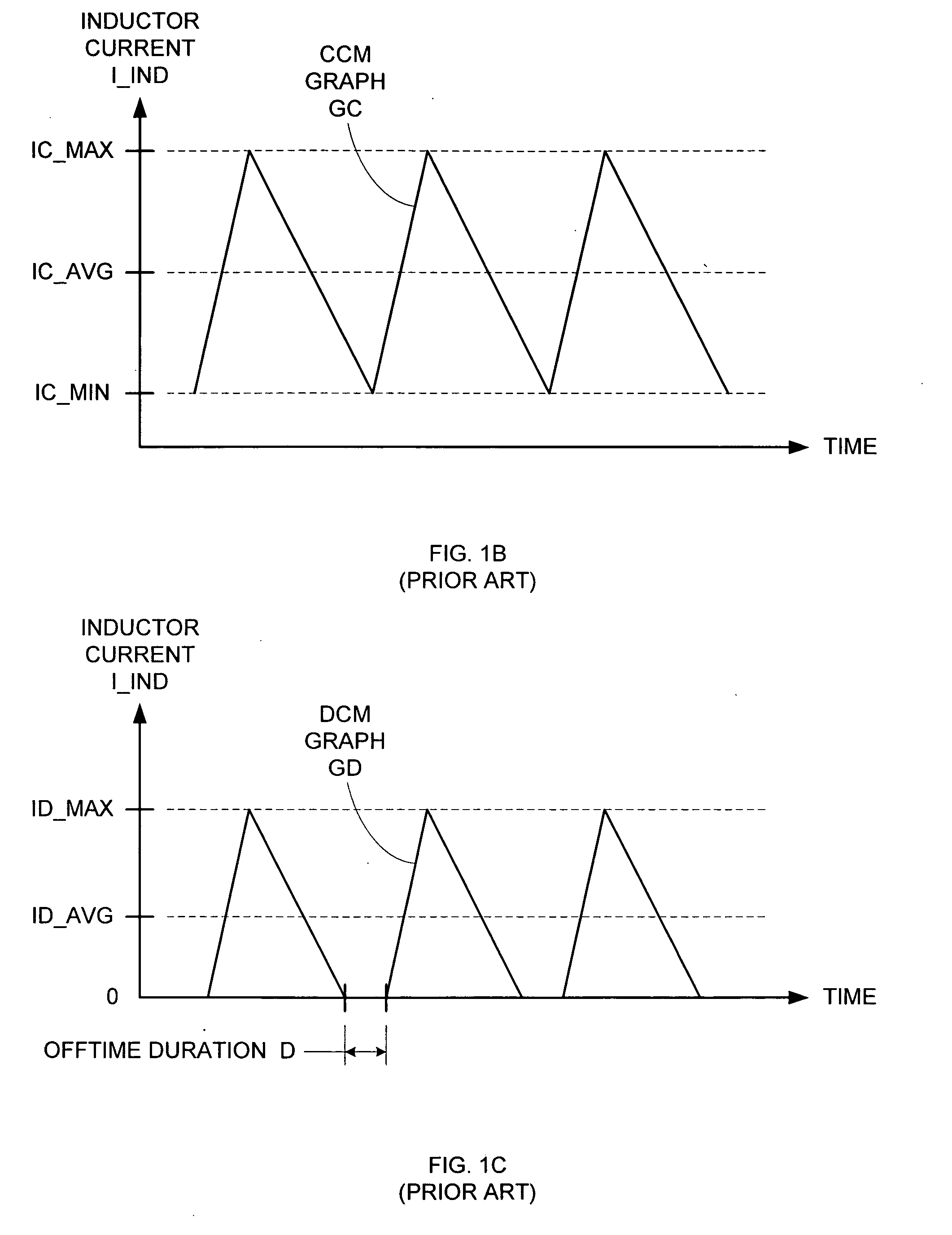
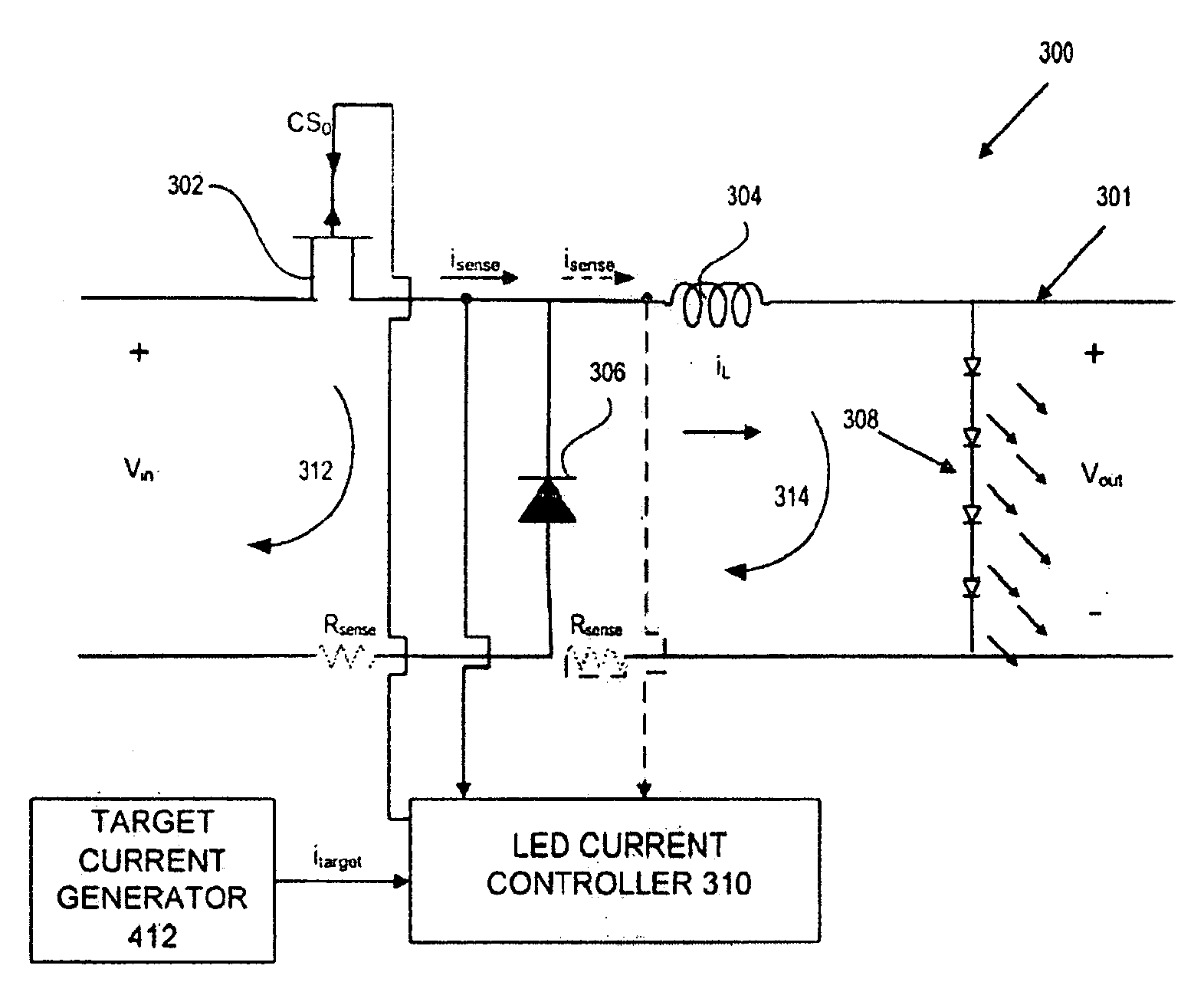
Adjustable Constant Current Source with Continuous Conduction Mode ("CCM") and Discontinuous Conduction Mode ("DCM") Operation
A converter system and method of operating a converter system are disclosed. The converter system comprises a converter power stage that can operate in a Discontinuous Conduction Mode (DCM) in a range of output currents and a Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM) in another range of output currents. The converter power stage includes at least an inductor with an inductor value and a control switch. The converter power stage provides an average current. A current controller is coupled to the converter power stage. When the converter power stage operates in DCM, the converter power stage provides the average current and the current controller is configured to measure the inductor value of the inductor. Furthermore, the current controller can also be configured to measure an input-to-output conversion ratio from the converter power stage.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Adaptive on-time control for power factor correction stage light load efficiency
ActiveUS20120014148A1Total current dropImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionHigher order harmonicsSwitching frequency
Light load efficiency of a power factor correction circuit is improved by adaptive on-time control and providing for selection between a continuous conduction mode and a discontinuous conduction mode wherein the discontinuous conduction mode increases time between switching pulses controlling connection of a cyclically varying voltage to a filter / inductor that delivers a desired DC voltage and thus can greatly reduce the switching frequency at light loads where switching frequency related losses dominate efficiency. The mode for controlling switching is preferably selected for each switching pulse within a half cycle of the cyclically varying input voltage. A multi-phase embodiment allows cancellation of EMI noise at harmonics of the switching frequency and adaptive change of phase angle allows for cancellation of dominant higher order harmonics as switching frequency is reduced.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Drive system of synchronous motor
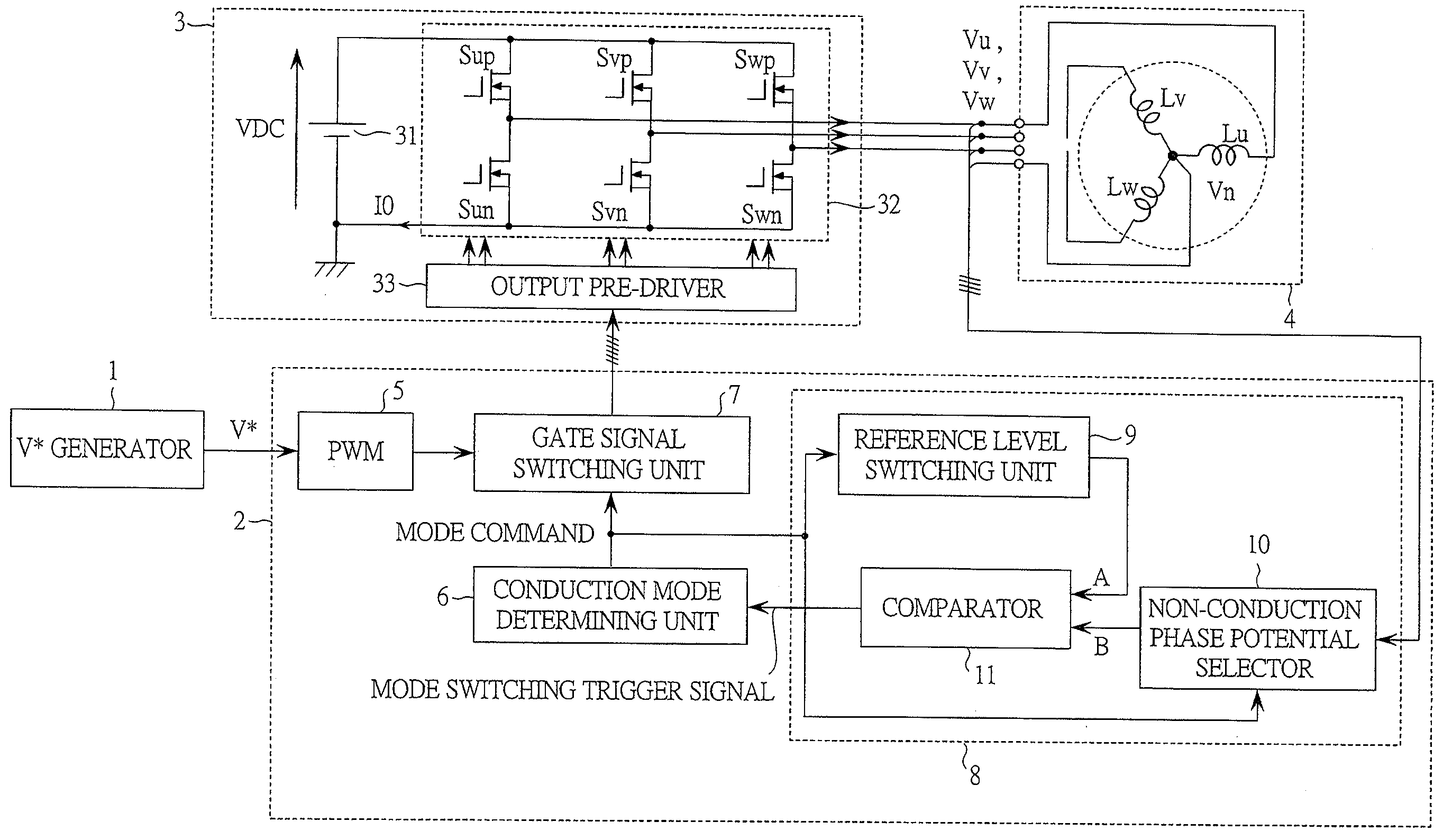
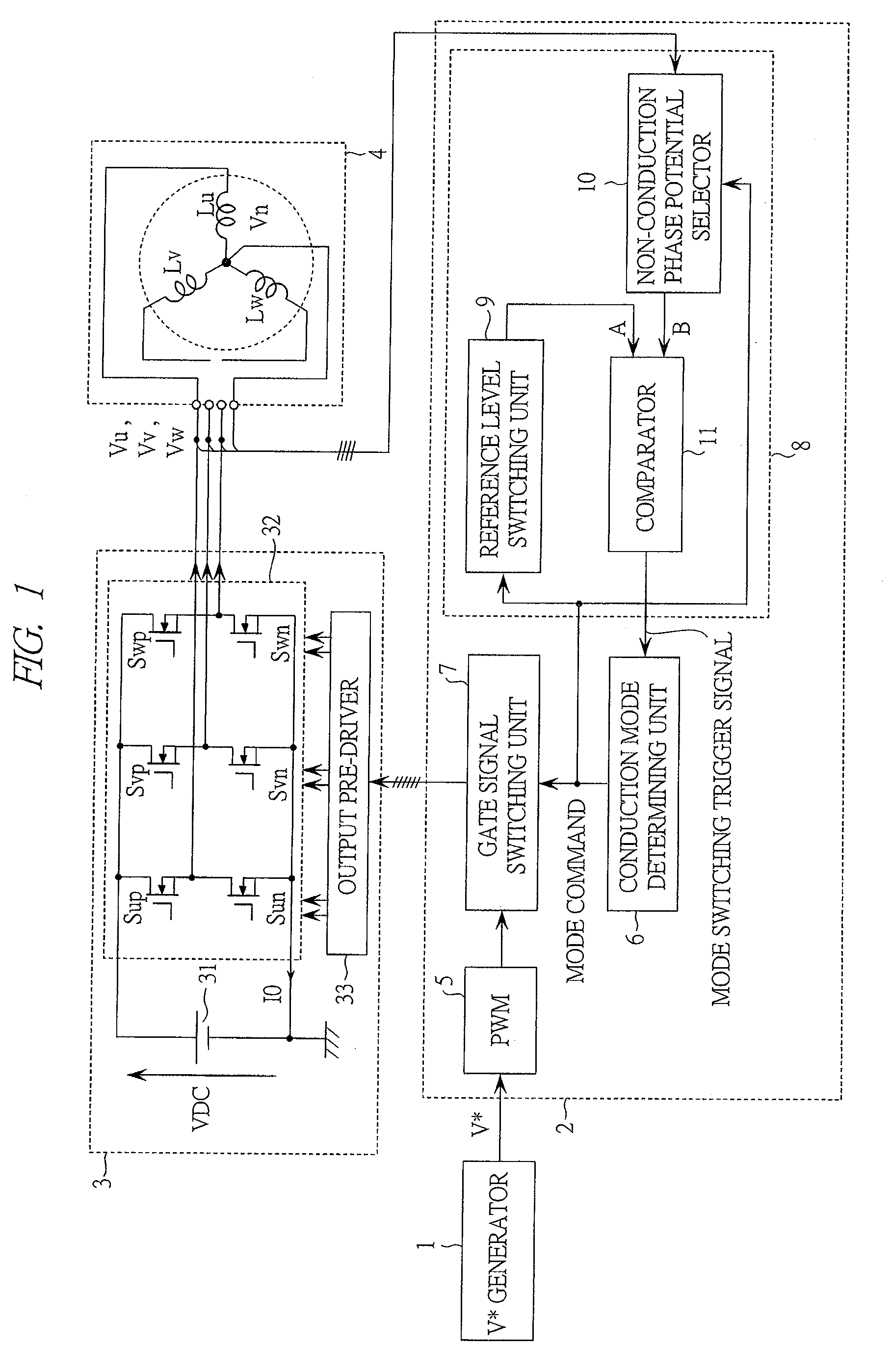
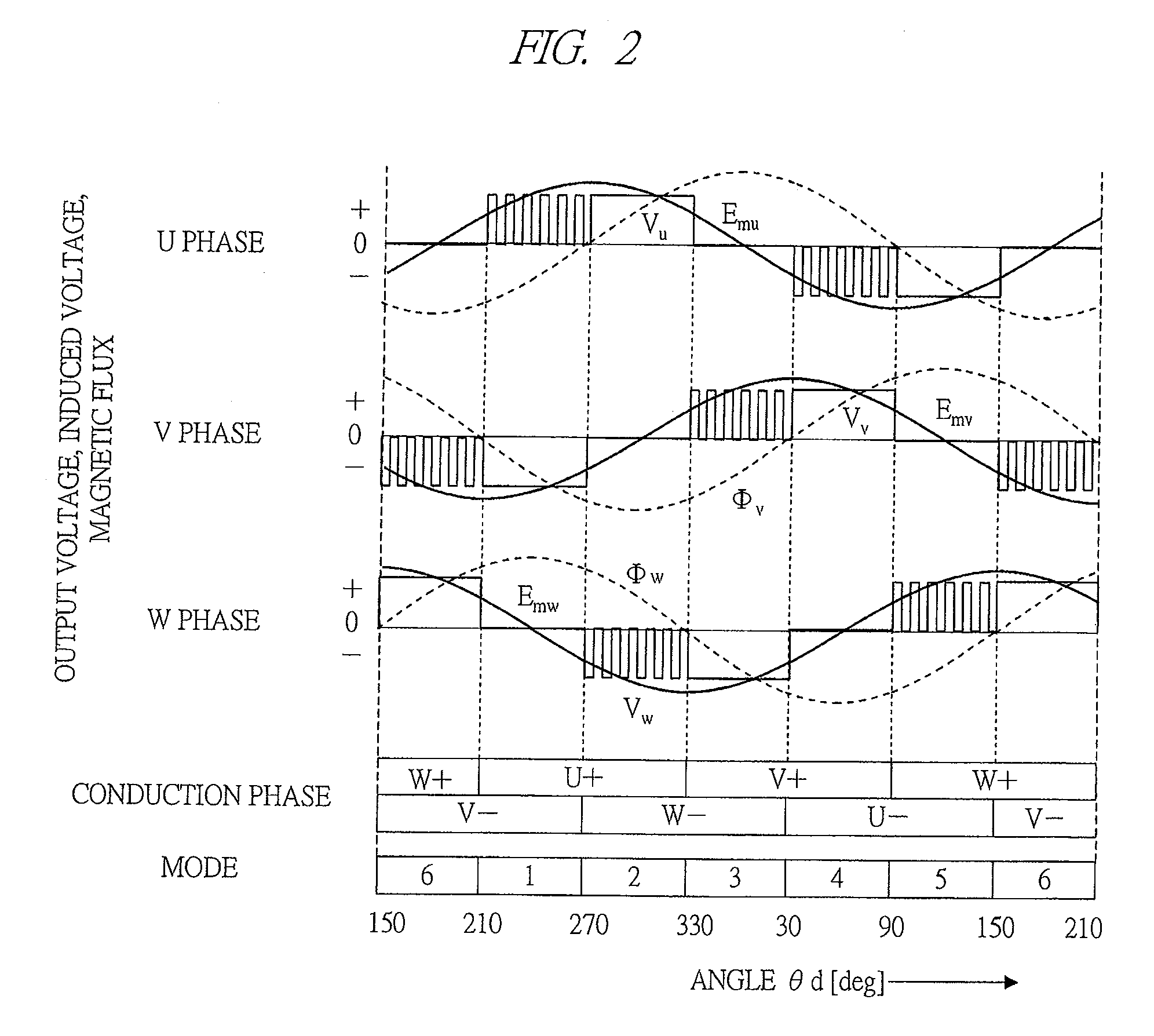
InactiveUS20090200971A1Acceleration time shortenedEfficiently formedMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersSynchronous motorPermanent magnet motor
A drive system of a permanent magnet motor is constituted of a mode switching trigger generator which monitors a state of a permanent magnet motor and issues a mode switching trigger, a conduction mode determining unit which receives the mode switching trigger and switches the mode of the permanent magnet motor, and a PWM generator which outputs a PWM signal to an inverter in accordance with the output of the conduction mode determining unit. The mode switching trigger is generated on condition that the speed electromotive force of the permanent magnet motor exceeds a constant or variable threshold value.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Controller having comp node voltage shift cancellation for improved discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) regulator performance and related methods
ActiveUS20080284398A1Improve performanceReduce variationDc network circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionVoltage shiftEngineering
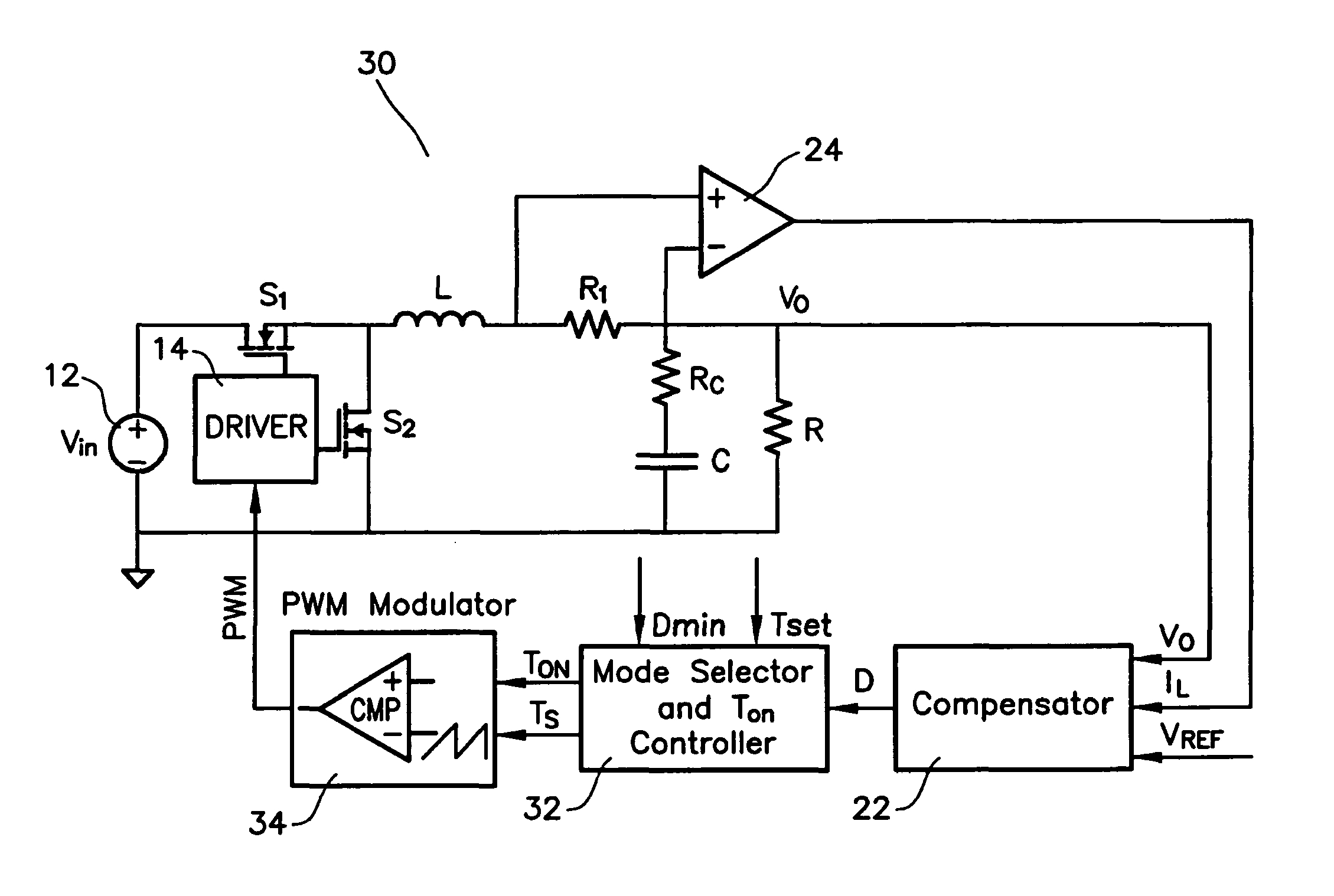
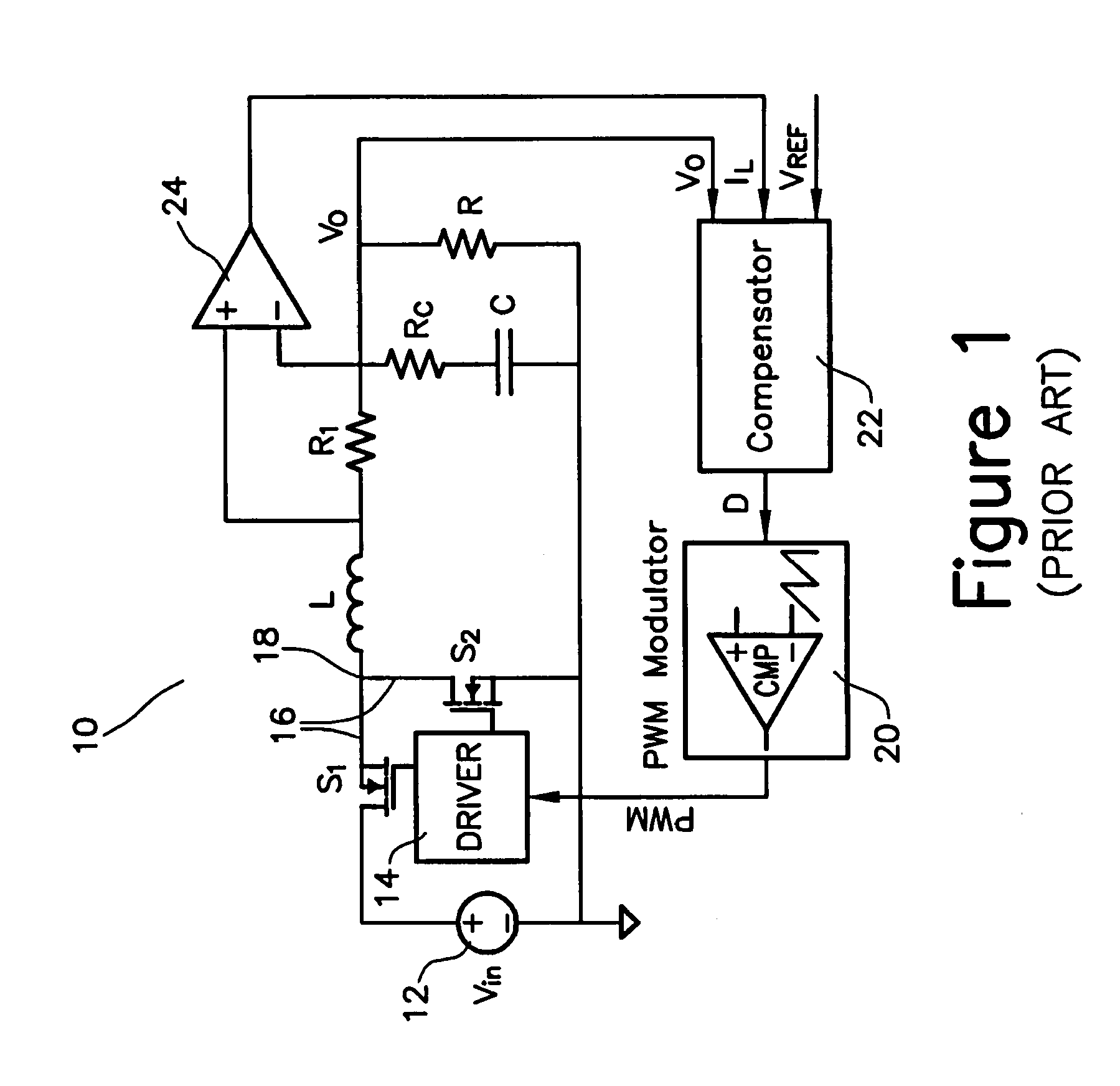
A modulation controller includes an error amplifier which receives a reference voltage and an output voltage (VOUT) from a switching regulator being controlled by the controller at its inputs and provides a VCOMP signal at its output, and at least one comparator, wherein a first input of the comparator is coupled to an output of the error amplifier and a second input coupled to receive a ramp signal. A VCOMP shift cancellation circuit is interposed between the first or second input of the comparator, wherein the VCOMP shift cancellation circuit improves diode conduction mode performance (DCM) of the regulator by reducing a variation in average VCOMP.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
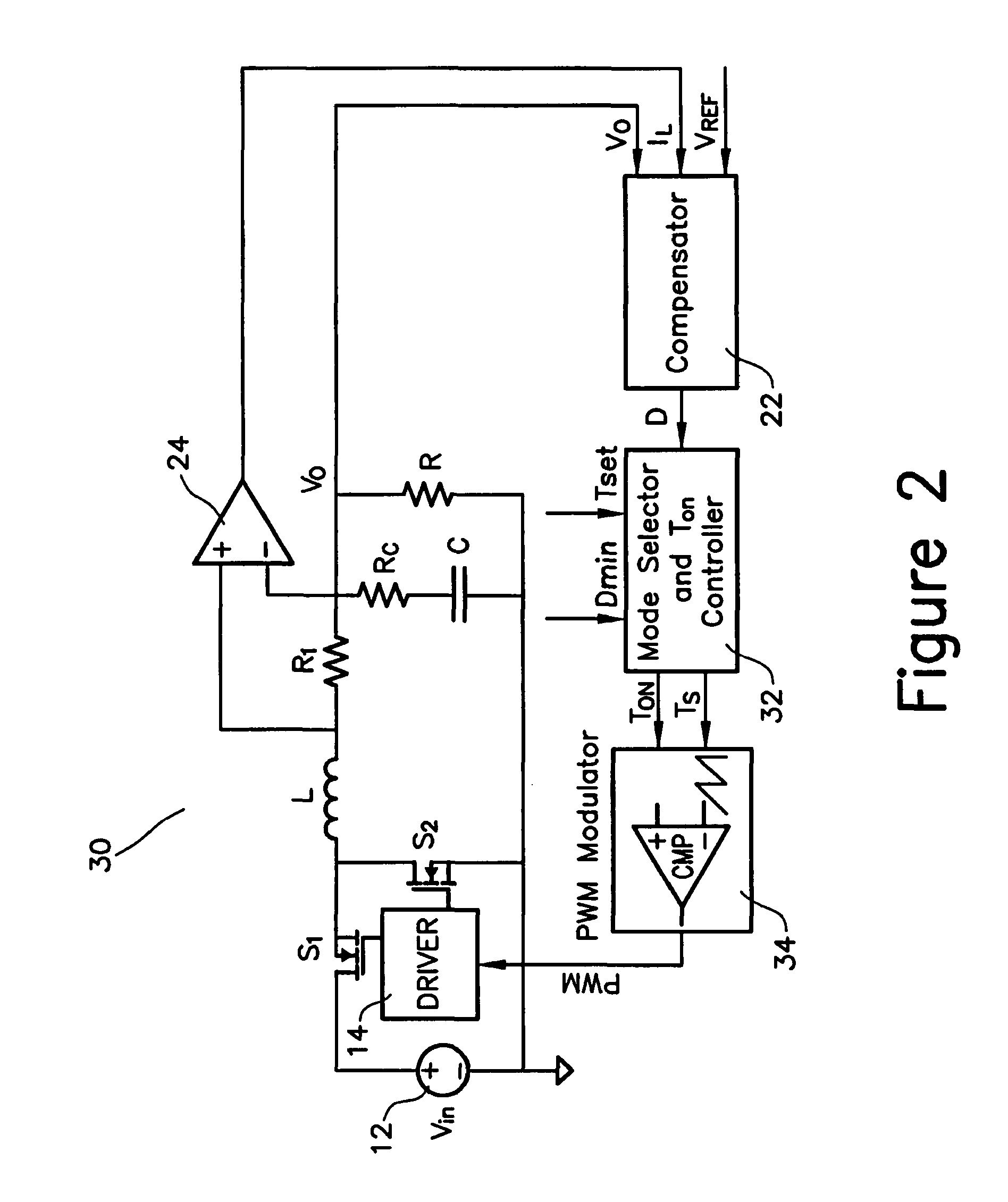
Multi-mode switching control circuit and method for improving light load efficiency in switching power supplies
ActiveUS7755342B2Improve performanceEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionConstant frequencySwitching frequency
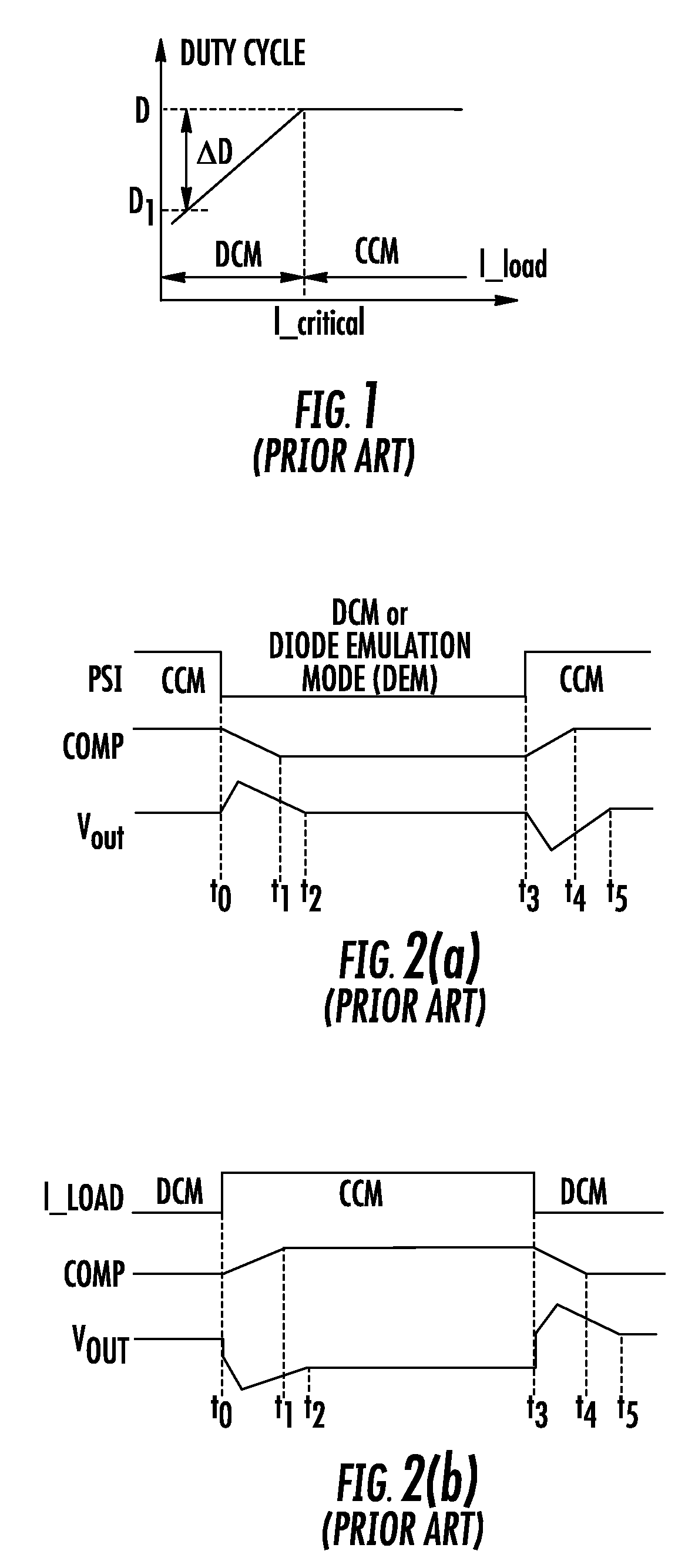
A circuit for transitioning between a discontinuous and a fixed frequency continuous conduction mode (DCM) and (CCM) of a power converter having a driver receiving PWM signals and controlling a switching stage comprises a control switch and a sync switch connected at a common switching node for driving a load. The circuit including a PWM modulator for providing PWM signals; and a mode selector for receiving a duty cycle value, a preset switching period, and a duty cycle at a critical conduction point having a switching frequency equal to the preset switching period and providing an on-time of the control switch and a switching period to the PWM modulator, wherein if the duty cycle value is greater than the duty cycle at a critical conduction point, the PWM modulator will drive will provide the PWM signals to operate the switching stage in the CCM with constant-frequency duty cycle control, and if the duty cycle value is less than duty cycle at a critical conduction point, the PWM modulator will drive will provide the PWM signals to operate the switching stage in the DCM by turning off the sync switch when a load current becomes negative.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Forward-flyback converter with active-clamp circuit
ActiveUS8009448B2Improve conversion efficiencyAdditional drawbackEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsEngineeringHeavy load
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
LED current bias control using a step down regulator
ActiveUS7323828B2Simple requirementsPrediction is simpleElectroluminescent light sourcesElectric light circuit arrangementEngineeringControl circuit
A step down switching regulator circuit that is particularly well-suited to drive high power LEDs includes a crossover conduction mode (XCM) control circuit that maintains operation at the crossover point between continuous conduction mode (CCM) and discontinuous conduction mode (DCM). This XCM operation provides an inductor current waveform that ramps up and down between zero and a desired maximum current. One or more comparators in the XCM control circuit can be used to control switching between the inductor current ramp up and ramp down phases. In this manner, complex feedback loop logic and PID controlled PWM signal generation logic can be avoided, and the need for external sense resistors and associated interface pins can be eliminated.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Switched mode power converter and method of operating the same
InactiveUS20110109247A1Reduce output rippleHigh operating requirementsElectroluminescent light sourcesElectronic switchingEngineeringConduction mode
A switched mode power converter is disclosed, together with a method for operating the same. The power converter is adapted to be operable in the boundary conduction mode, and operation is interruptible in the absence of any load requirement.
Owner:NXP BV
High-speed PWM control apparatus for power converters with adaptive voltage position and its driving signal generating method
InactiveUS7109692B1Prevent overshootLower component costsDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationHigh speed controlSwitching frequency
A high-speed PWM control apparatus with adaptive voltage position and a driving signal generating method thereof is provided. The present invention automatically detects a change in the loading and adjusts the voltage position instantaneously for stabilizing the voltage and reducing the loading output power consumption. The present invention does not require a clock signal to generate a driving signal and does not require an error amplifier to control the modulation. Therefore, the present invention has a fast transient response that responds to the change of the loading instantaneously and has a stabilizing effect. When the apparatus is on a continuous conduction mode (CCM), the switching frequency of the controller is still fixed even though the input voltage Vin and the output voltage Vout are changed. The electrical-magnetic noise disturbance is improved.
Owner:NIKO SEMICON +1
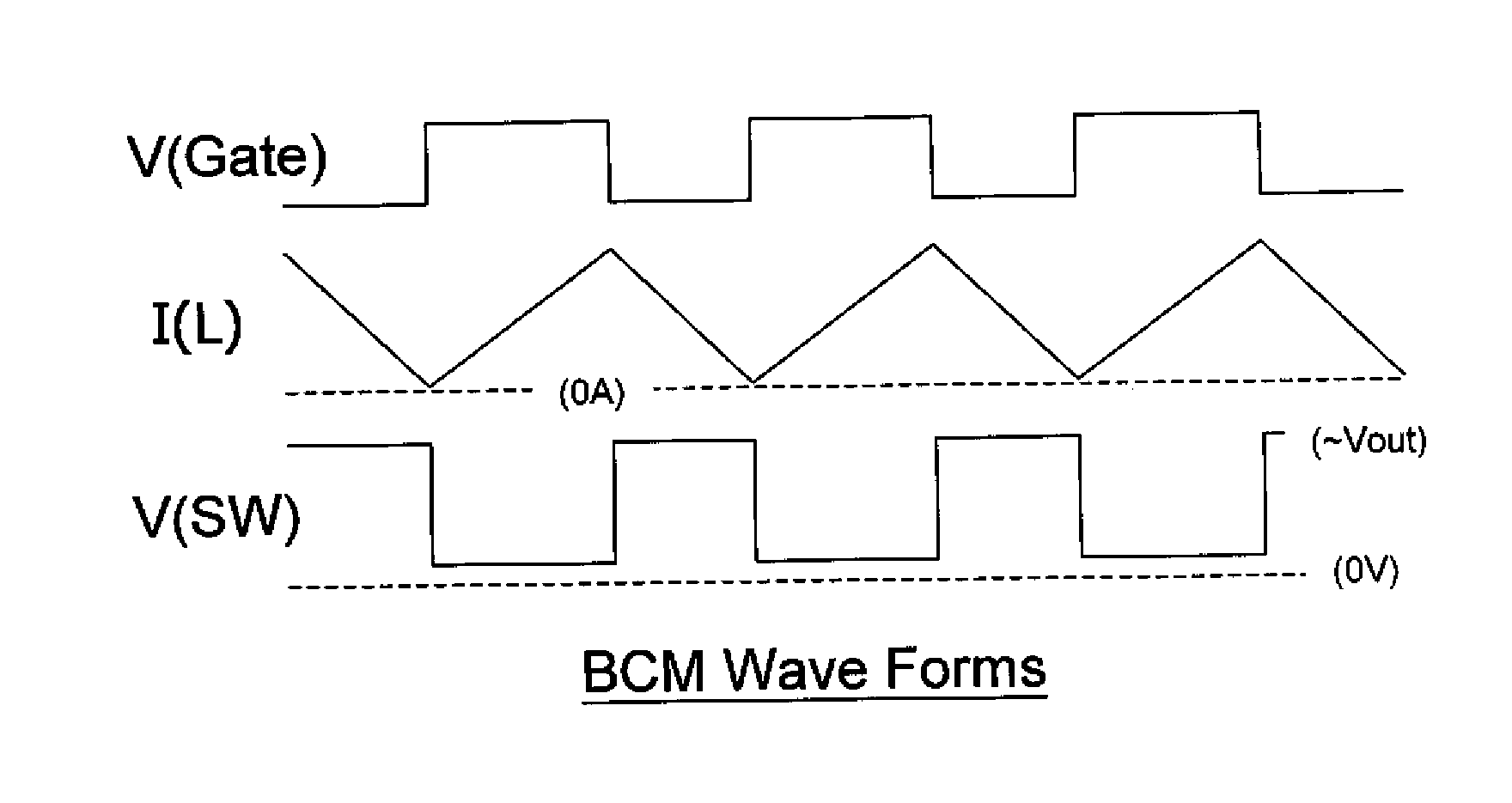
Boundary conduction mode switching regulator and driver circuit and control method thereof
The present invention discloses a boundary conduction mode (BCM) switching regulator, and a driver circuit and a control method of the switching regulator, for controlling a power stage to convert an input voltage to an output voltage or output current. The BCM switching regulator detects whether it is operating in continuous conduction mode (CCM) or discontinuous conduction mode (DCM), and adjusts the On-time, Off-time, or frequency of the power stage accordingly, so that the switching regulator operates in or near BCM.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Dc-dc converters
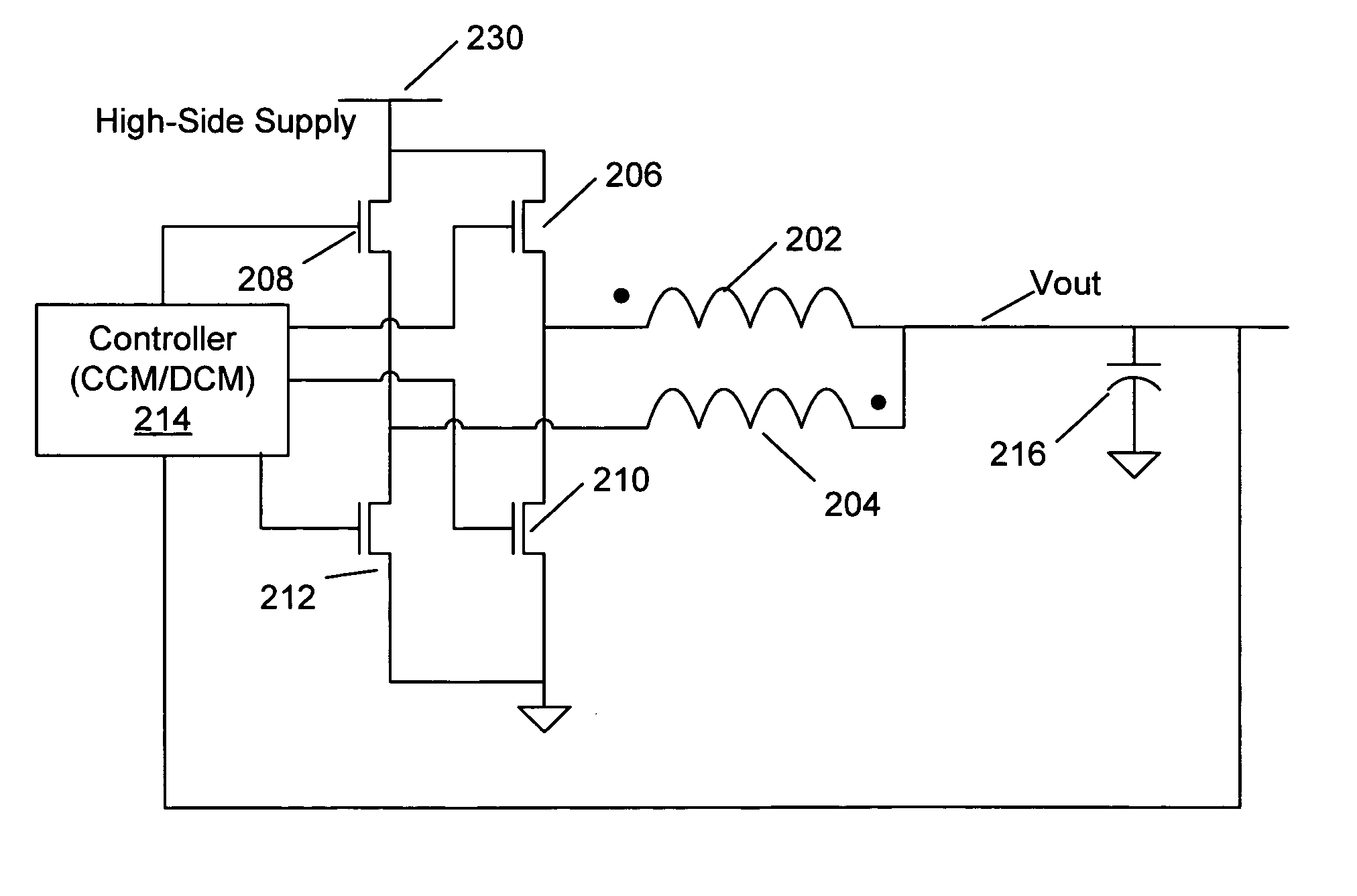
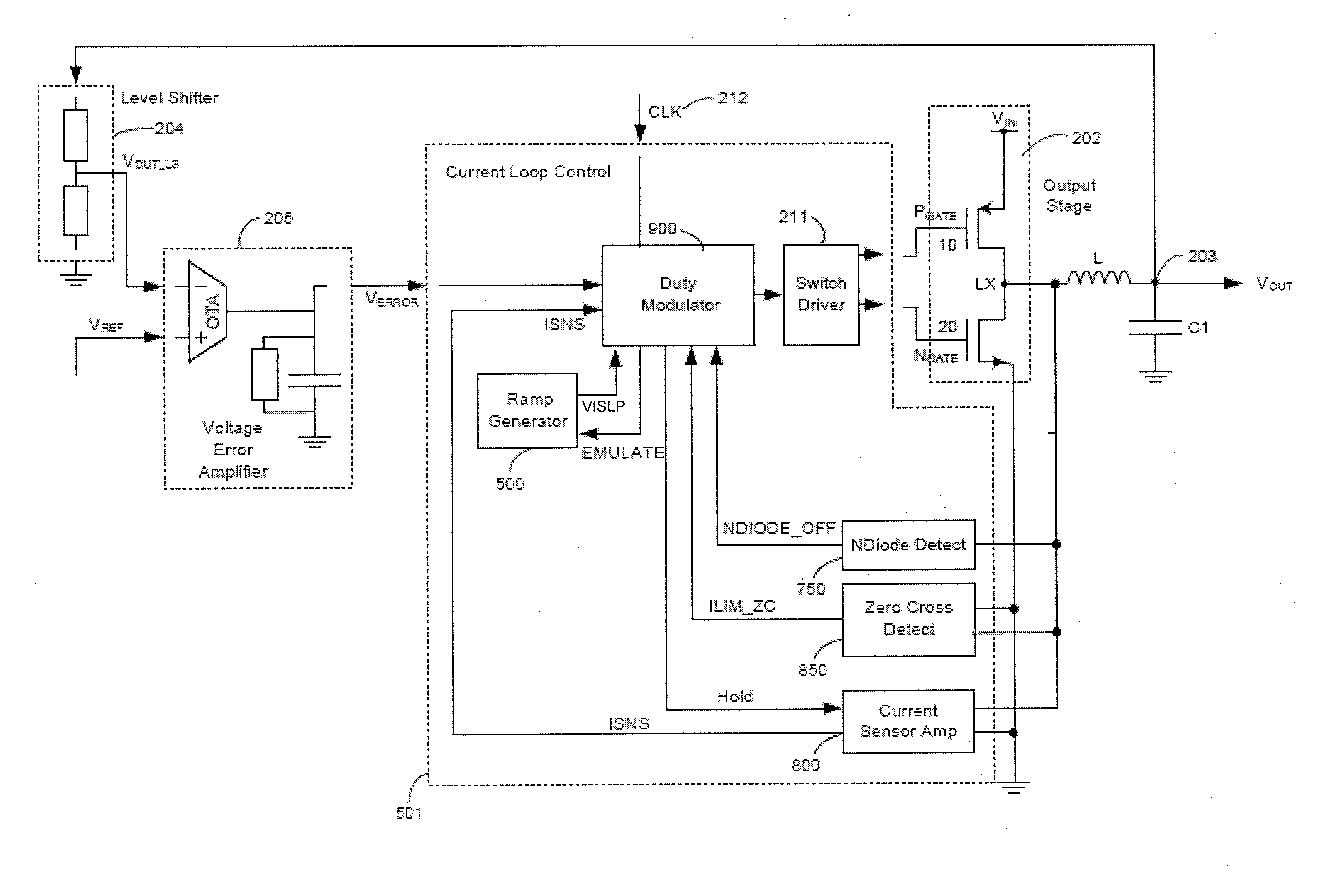
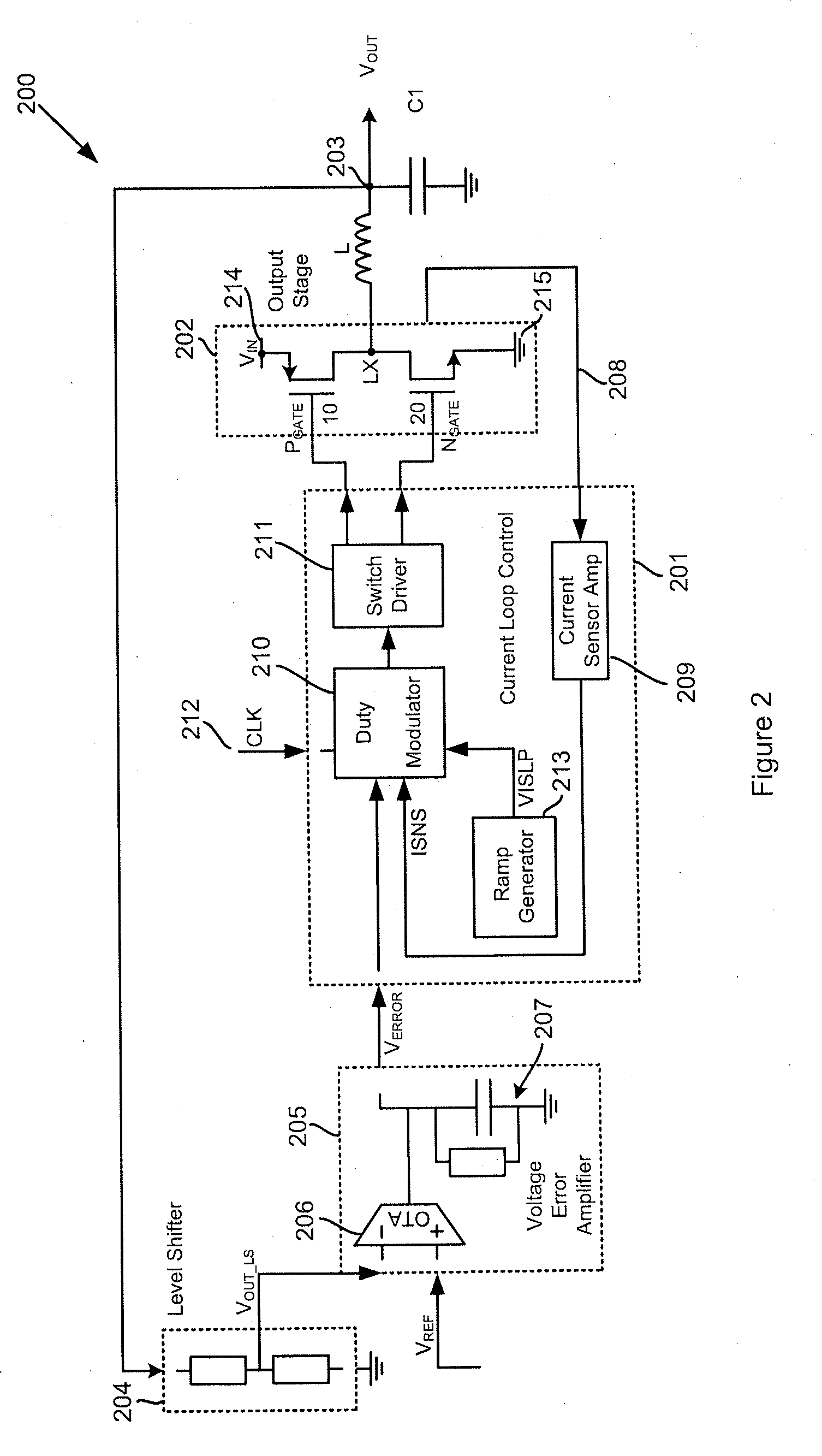
ActiveUS20110050185A1Easy to controlTransistorEfficient power electronics conversionCurrent loadCurrent loop control
Methods and apparatus for control of DC-DC converters, especially in valley current mode. The DC-DC converter is operable so that a low side supply switch may be turned off, before the high side supply switch is turned on. During the period when both switches are off the current loop control remains active and the change in inductor (L) current is emulated. One embodiment uses a current sensor for lossless current sensing and emulates the change in inductor current by holding the value of the output of the current sensor (ISNS) at the time that the low side switch turns off and adding an emulated ramp signal (VISLP) until the inductor current reaches zero. Embodiment employing a pulse-skip mode of operation based on a minimum conduction time are also disclosed. The invention enables a seamless transition from Continuous Conduction Mode the Discontinuous Conduction Mode and Pulse Skipping and provide converters that are efficient at low current loads.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
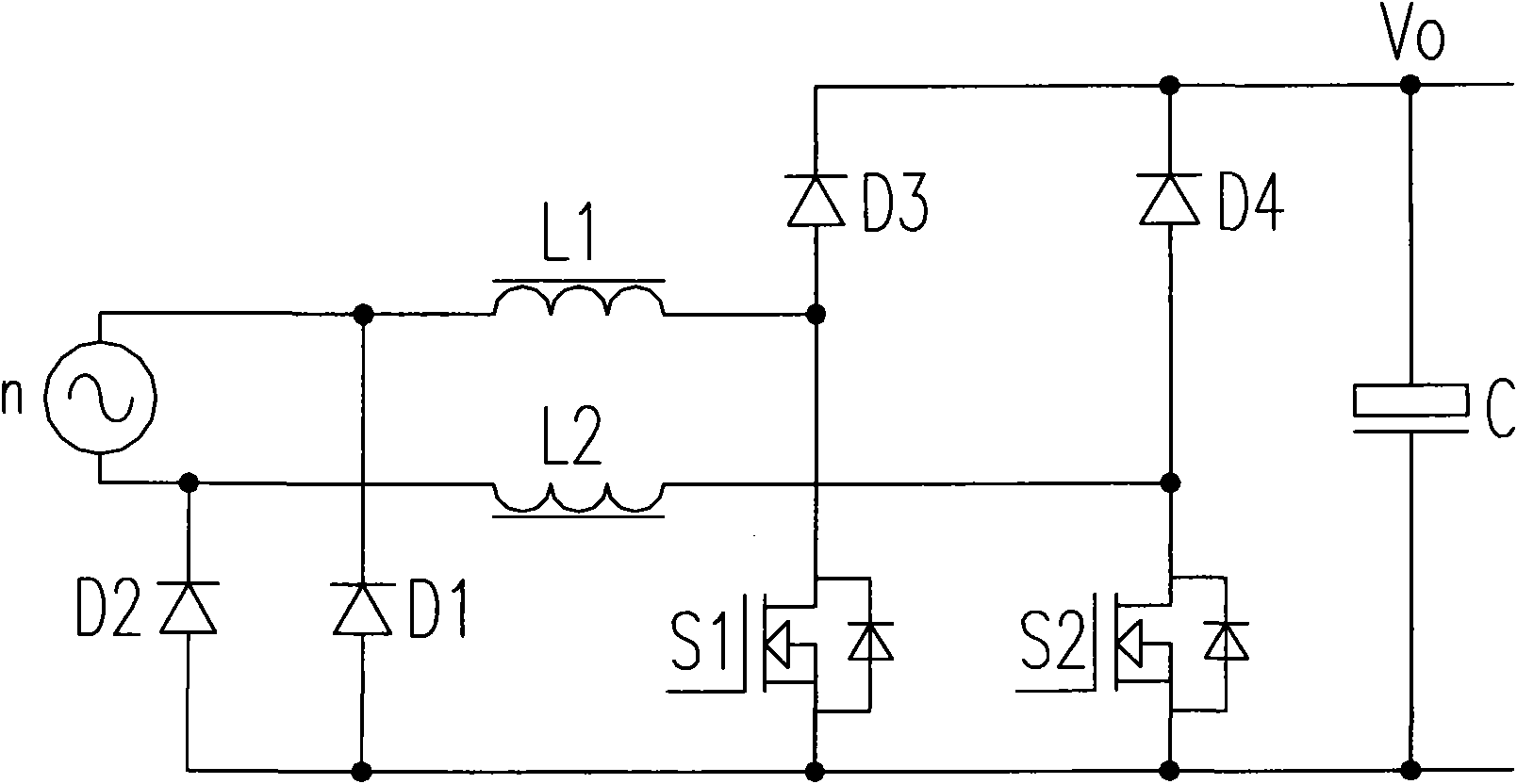
Bridgeless power factor circuit correcting circuit system used for critical conduction mode and control method thereof
ActiveCN101552546AEfficient power electronics conversionEnergy industryPower factor correction circuitsConductor Coil
The invention discloses a bridgeless power factor circuit correcting circuit system used for critical conduction mode and a control method thereof. The bridgeless power factor circuit correcting circuit system comprises a bridgeless power factor correcting circuit, a first auxiliary winding and a second auxiliary winding, wherein the bridgeless power factor correcting circuit comprises a first switch, a first inductance and a second inductance; the first auxiliary winding is coupled to the first inductance and produces a first sensing signal; the second auxiliary winding is coupled to the second inductance and produces a second sensing signal, the first sensing signal and the second sensing signal are used for producing an inductance current detection signal; meanwhile, when the value of the inductance current detection signal is zero, the first switch is connected.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC +1
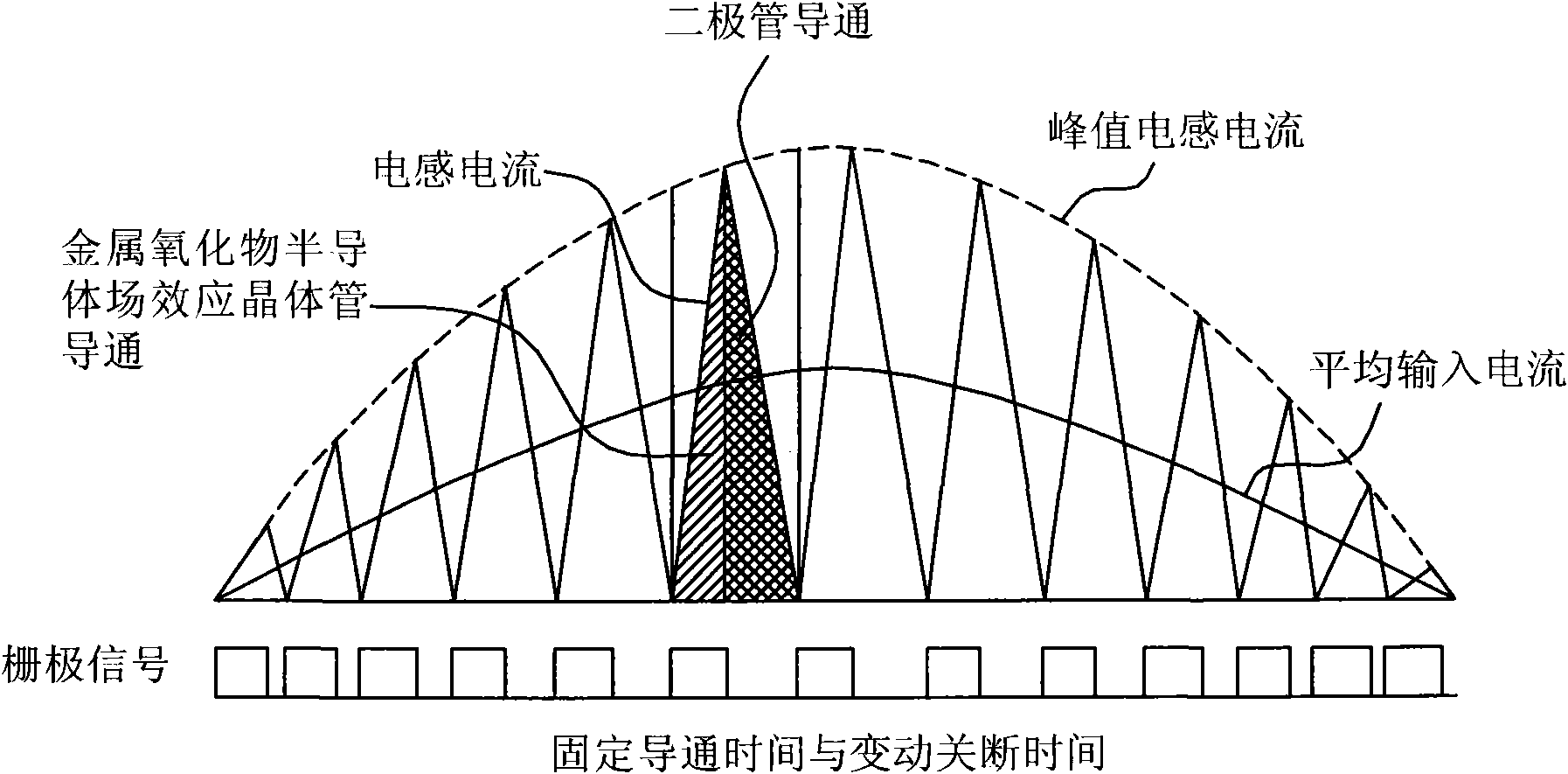
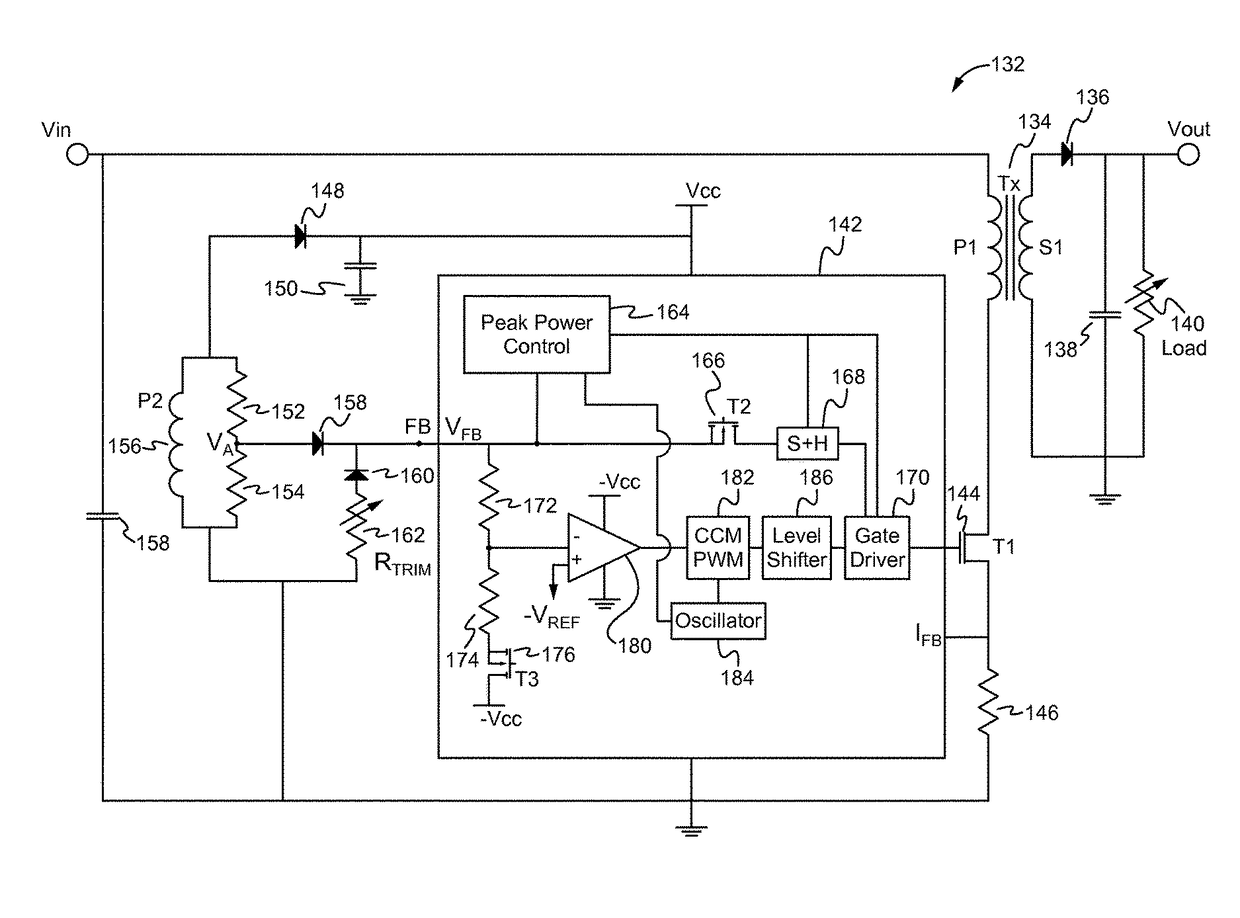
Peak power control technique for primary side controller operation in continuous conduction mode
A power converter includes a primary side controller configured to operate the power converter in the discontinuous conduction mode during low to mid-power requirements and to operate the power converter in the continuous conduction mode during high or peak power requirements. The power converter includes a primary side auxiliary winding that provides a feedback signal to the primary side controller, and an adjusted resistor and diode circuit which is coupled to a multi-function feedback (FB) pin of the primary side controller. The primary side controller monitors for a peak power demand, upon detection of which a negative supply rail is enabled, which is used to compensate for voltage losses due to non-zero current while operating in the CCM, thereby enabling output voltage regulation while operating in the CCM during peak power demand.
Owner:FLEXTRONICS AP LLC
Method and apparatus for improving light load efficiency in switching power supplies
ActiveUS20080042709A1Improve performanceEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionConstant frequencySwitching frequency
A circuit for transitioning between a discontinuous and a fixed frequency continuous conduction mode (DCM) and (CCM) of a power converter having a driver receiving PWM signals and controlling a switching stage comprises a control switch and a sync switch connected at a common switching node for driving a load. The circuit including a PWM modulator for providing PWM signals; and a mode selector for receiving a duty cycle value, a preset switching period, and a duty cycle at a critical conduction point having a switching frequency equal to the preset switching period and providing an on-time of the control switch and a switching period to the PWM modulator, wherein if the duty cycle value is greater than the duty cycle at a critical conduction point, the PWM modulator will drive will provide the PWM signals to operate the switching stage in the CCM with constant-frequency duty cycle control, and if the duty cycle value is less than duty cycle at a critical conduction point, the PWM modulator will drive will provide the PWM signals to operate the switching stage in the DCM by turning off the sync switch when a load current becomes negative.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Active Clamp Protection Circuit For Power Semiconductor Device For High Frequency Switching
A protection circuit for a power transistor includes a first transistor connected in parallel with the power transistor and having a control terminal connected to a first power supply voltage through a first resistive element; and a first set of diodes connected between a first terminal and a control terminal of the first transistor. In operation, the voltage at the first terminal of the first transistor is clamped to a clamp voltage and the first transistor is turned on to conduct current in a forward conduction mode when an over-voltage condition occurs at a first terminal of the power transistor.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
Forward-flyback converter with active clamping circuit
ActiveCN101686015AImprove the shortcomingsReduce power lossEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionBuck converterResonance
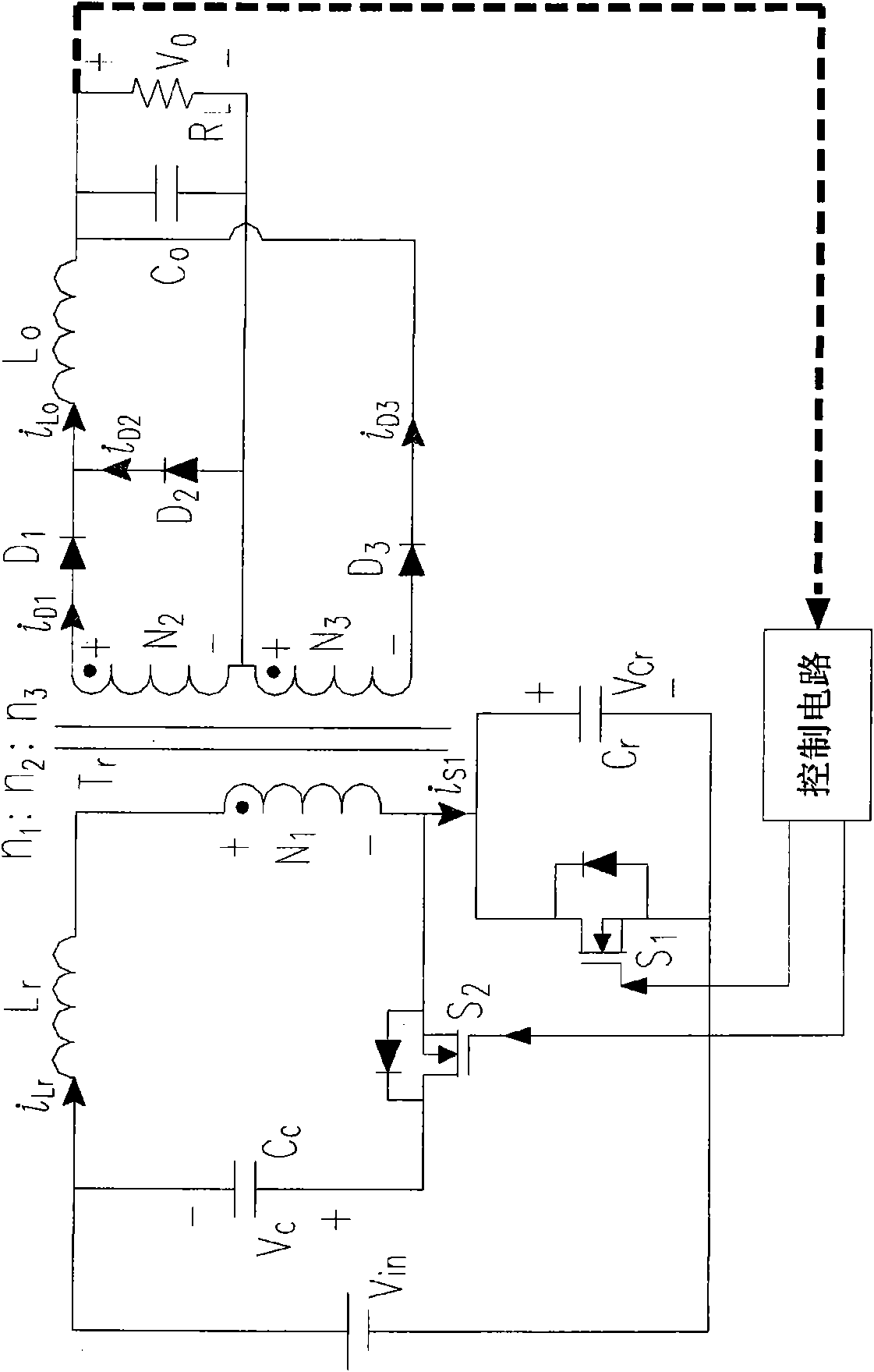
The invention discloses a forward-flyback converter with an active clamping circuit. The secondary side output of the converter comprises a flyback sub-circuit operating in a continuous conduction mode and a forward sub-circuit operating in a non-continuous conduction mode. Under over-load output, the converter uses a zero voltage switching mechanism of an active clamping flyback sub-circuit to provide sufficient resonance current; and under light-load output, the converter prolongs the time that the resonance current is converted from negative current into positive current to ensure that a switch realizes zero voltage switching, and reversal of biasing of a diode of the flyback sub-circuit is designed, so that the sub-circuit can not continue to work and unnecessary element power loss canbe reduced. Thus, the converter can simultaneously take account of the conversion efficiencies of over-load output and light-load output under a wide load fluctuation range.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
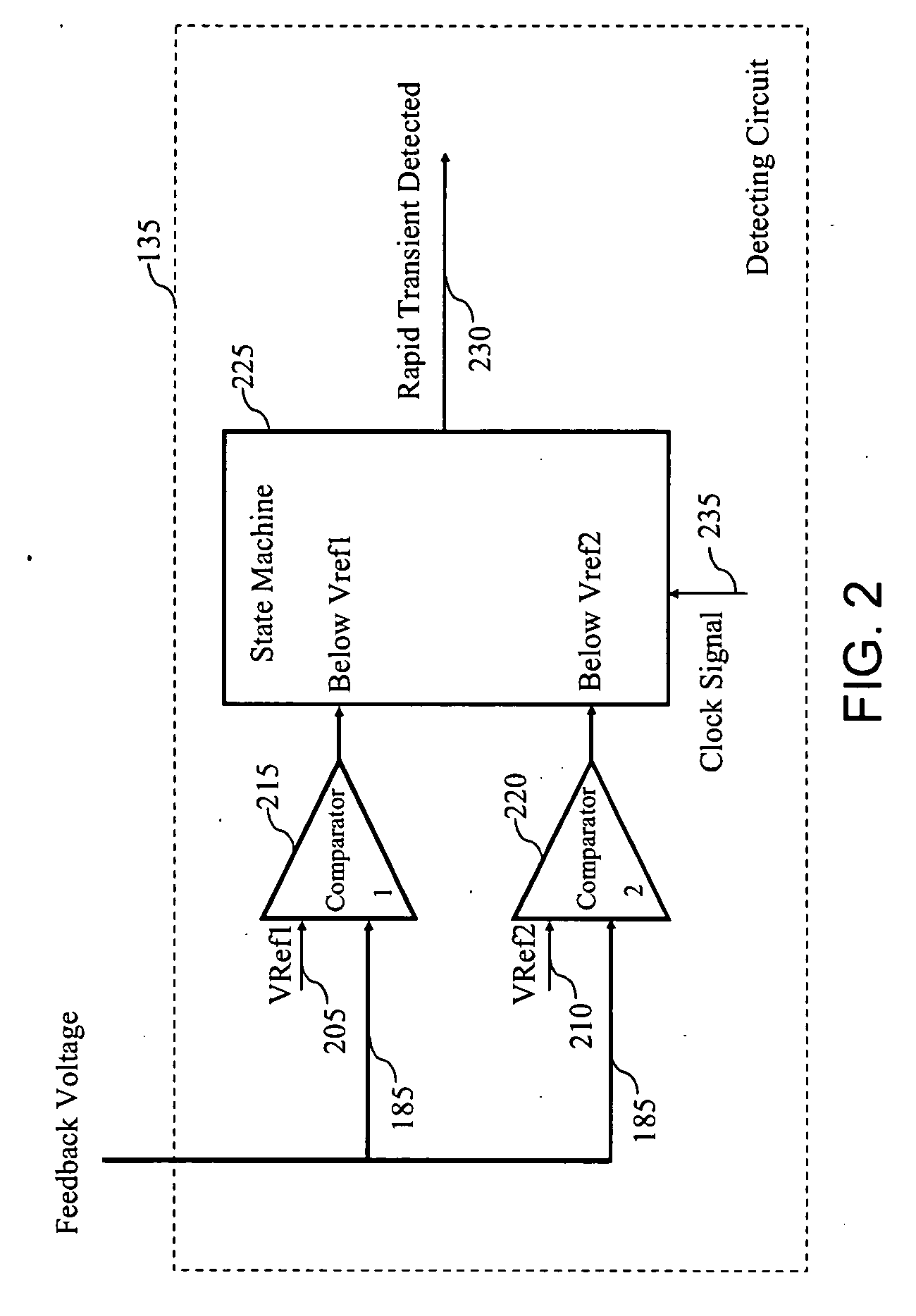
Transient recovery circuit for switching devices
InactiveUS20090278516A1Promote recoveryEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionOperating pointVoltage
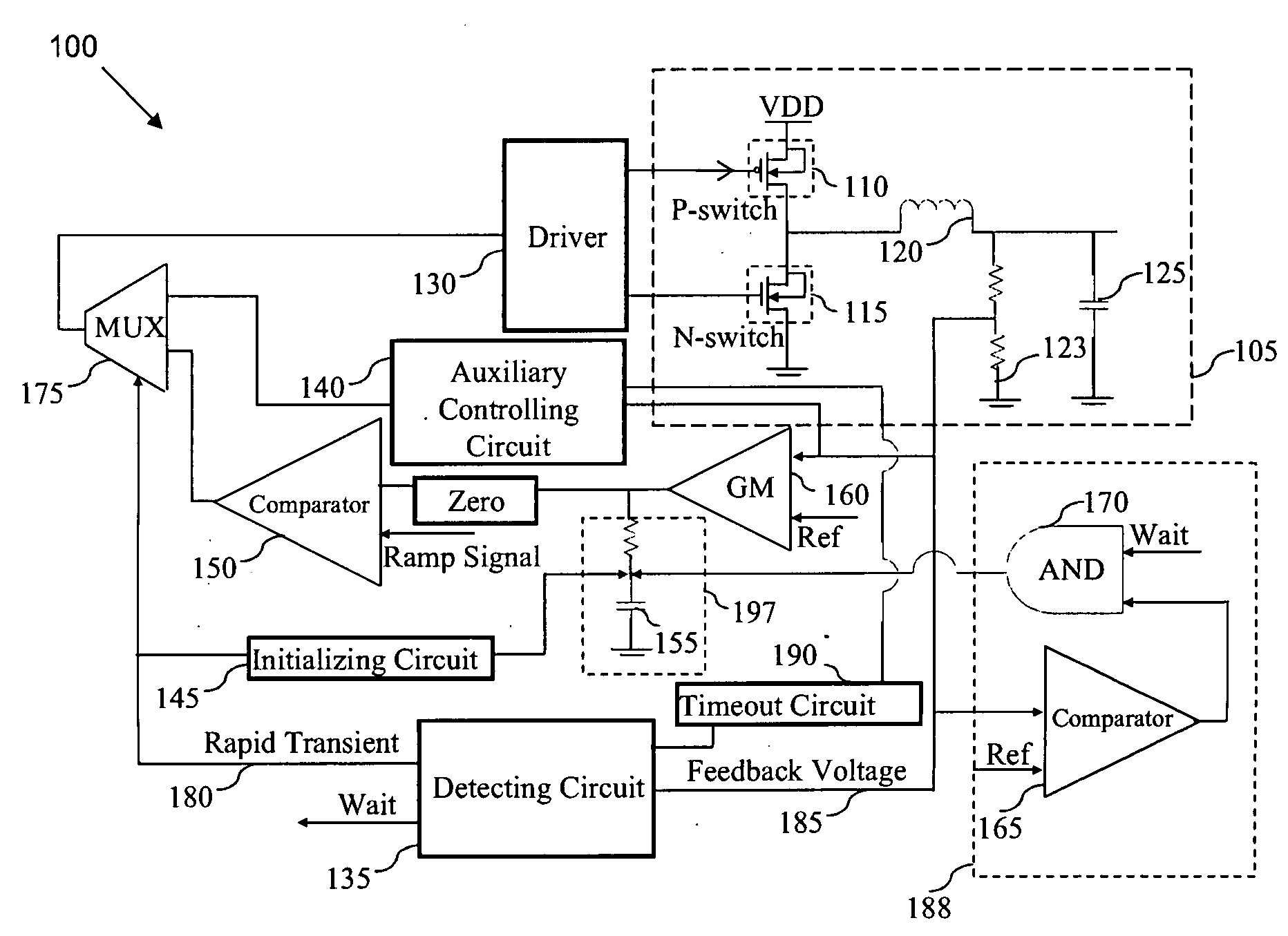
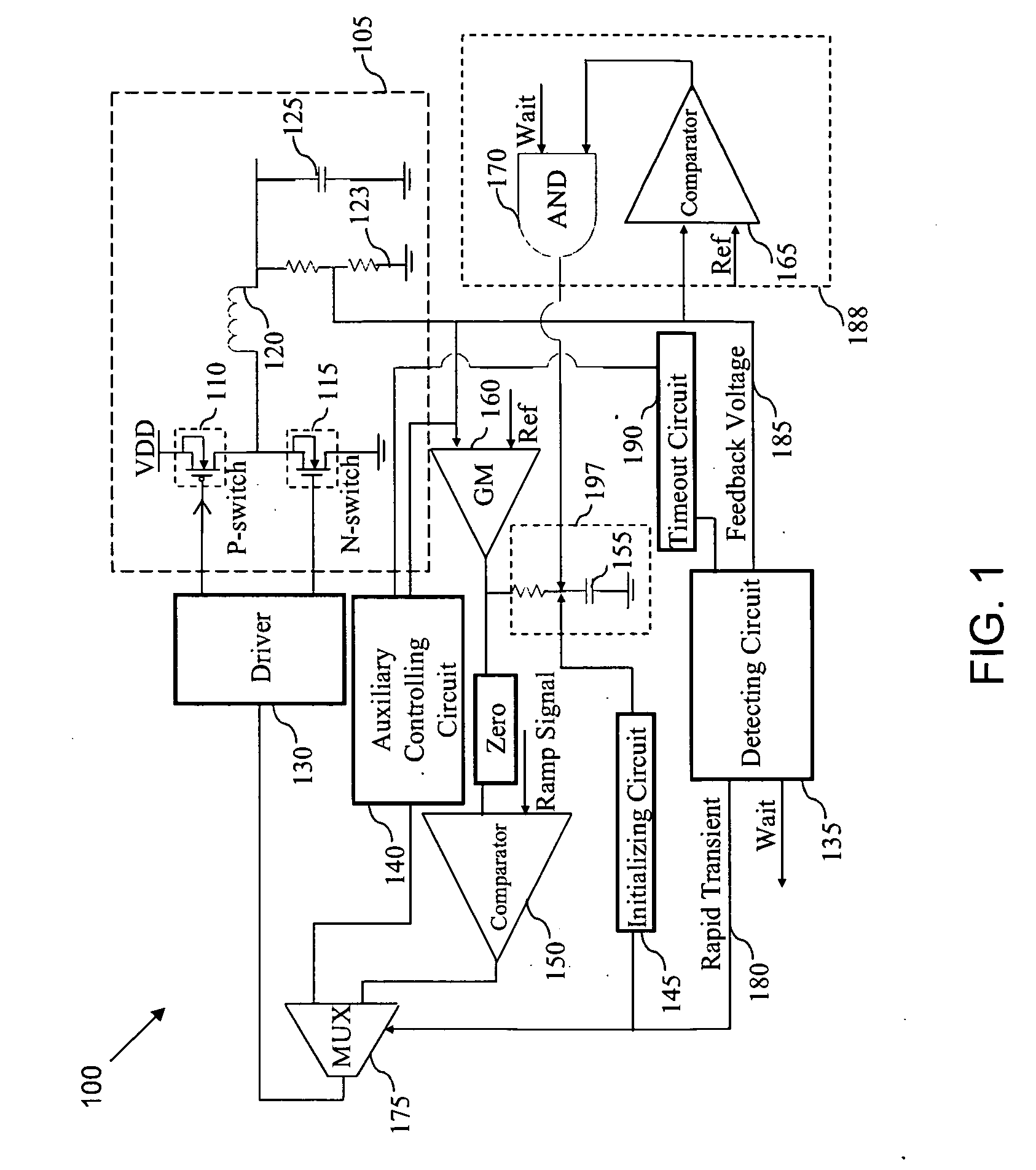
A transient recovery circuit for switching devices. The transient recovery circuit includes a detecting circuit for detecting a rapid transient in an output voltage of a switching device by detecting a rate of the output voltage transient; an auxiliary controlling circuit in a feedback loop of the switching device for correcting the output voltage by changing a bandwidth of the feedback loop if the rapid transient is detected; and an initializing circuit for initializing the feedback loop to expected operating points in a continuous conduction mode after correcting the output voltage.
Owner:COSMIC CIRCUITS PRIVATE LIMITED
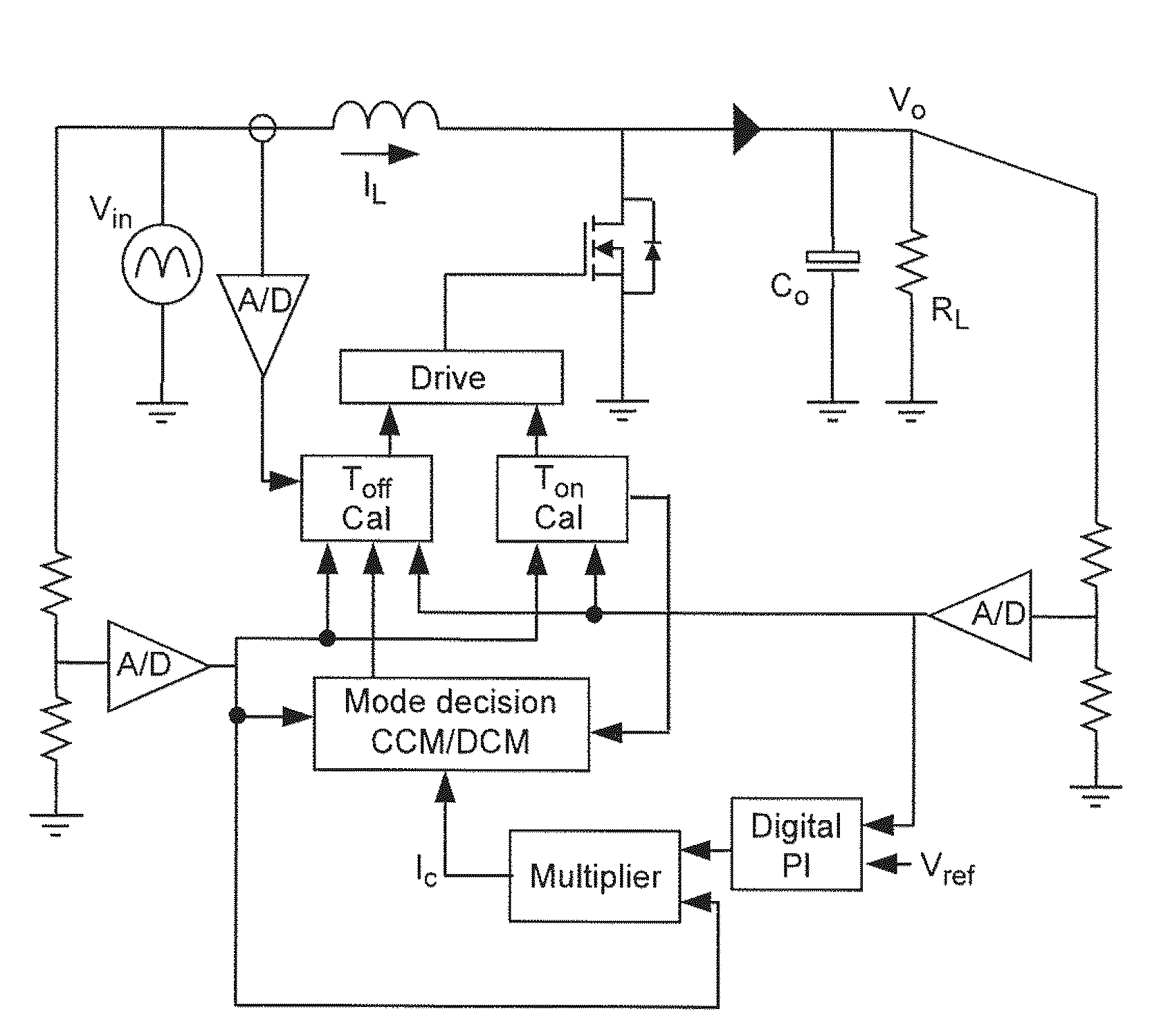
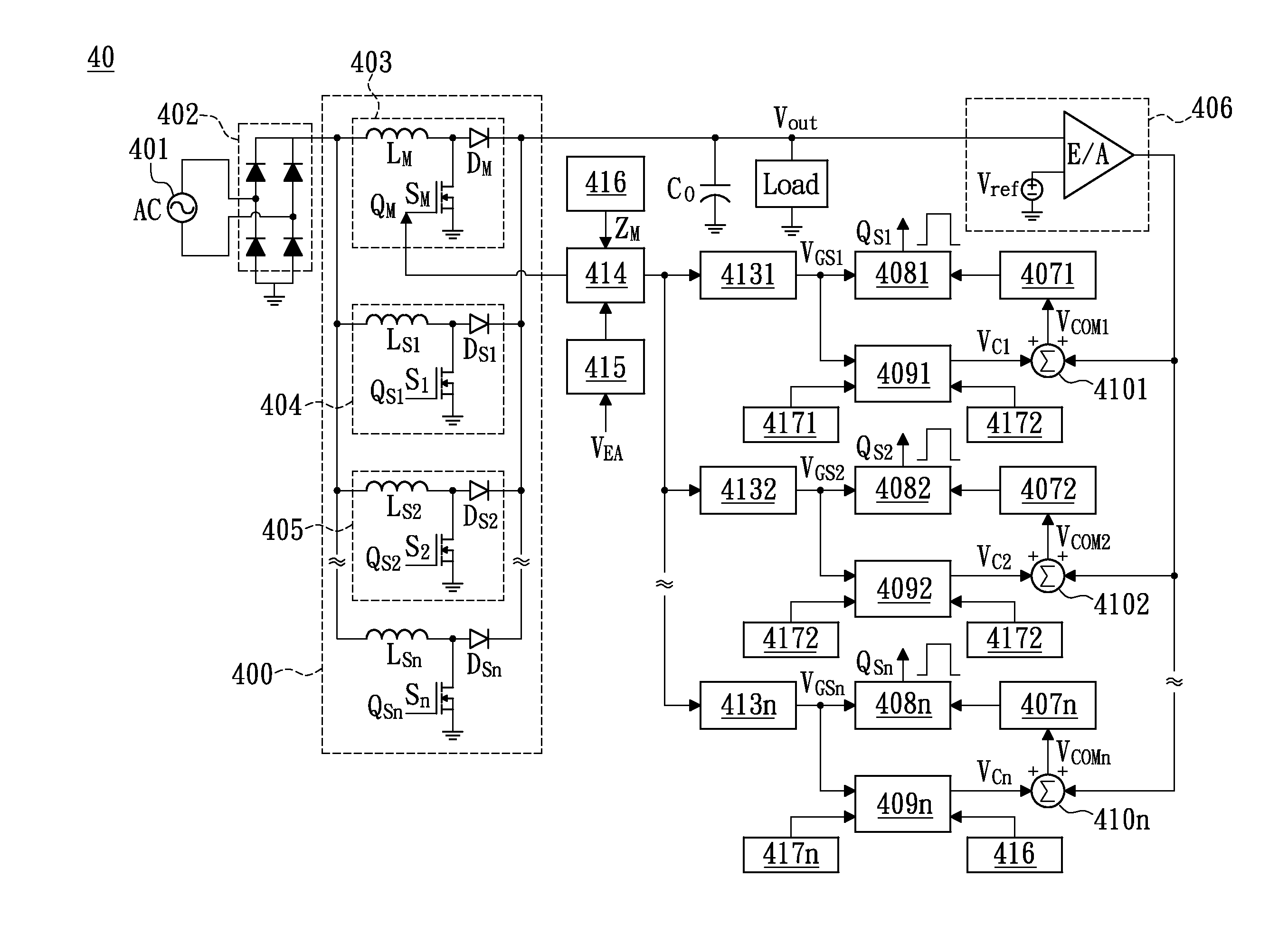
Control device for multiphase interleaved dc-dc converter and control method thereof
ActiveUS20140334196A1Improve power factorEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDc dc converterPhase difference
This instant disclosure provides a control method for interleaved multiphase Boost PFC converter. The interleaved multiphase Boost PFC converter has a master phase and a plurality of slave phases, the master phase operates in the critical conduction mode, the master of each slave phase has an inductor and a power switch. The control method comprises, configuring the phase difference between each slave phase and the master phase; setting up each slave phase to operate in the critical conduction mode; monitoring the operating mode of each slave phase is in the continuous conducting mode, the discontinuous conducting mode, or the critical conduction mode when the system is disturbed; and adjusting the power switch on time of the slave phase according to the operating mode of the slave phase so as to make the slave phase return to operate in critical conduction mode.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for multi-phase DC-DC converters using coupled inductors in discontinuous conduction mode
ActiveUS7548046B1Improve efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationDc dc converterCoupling inductor
Owner:VOLTERRA SEMICONDUCTOR
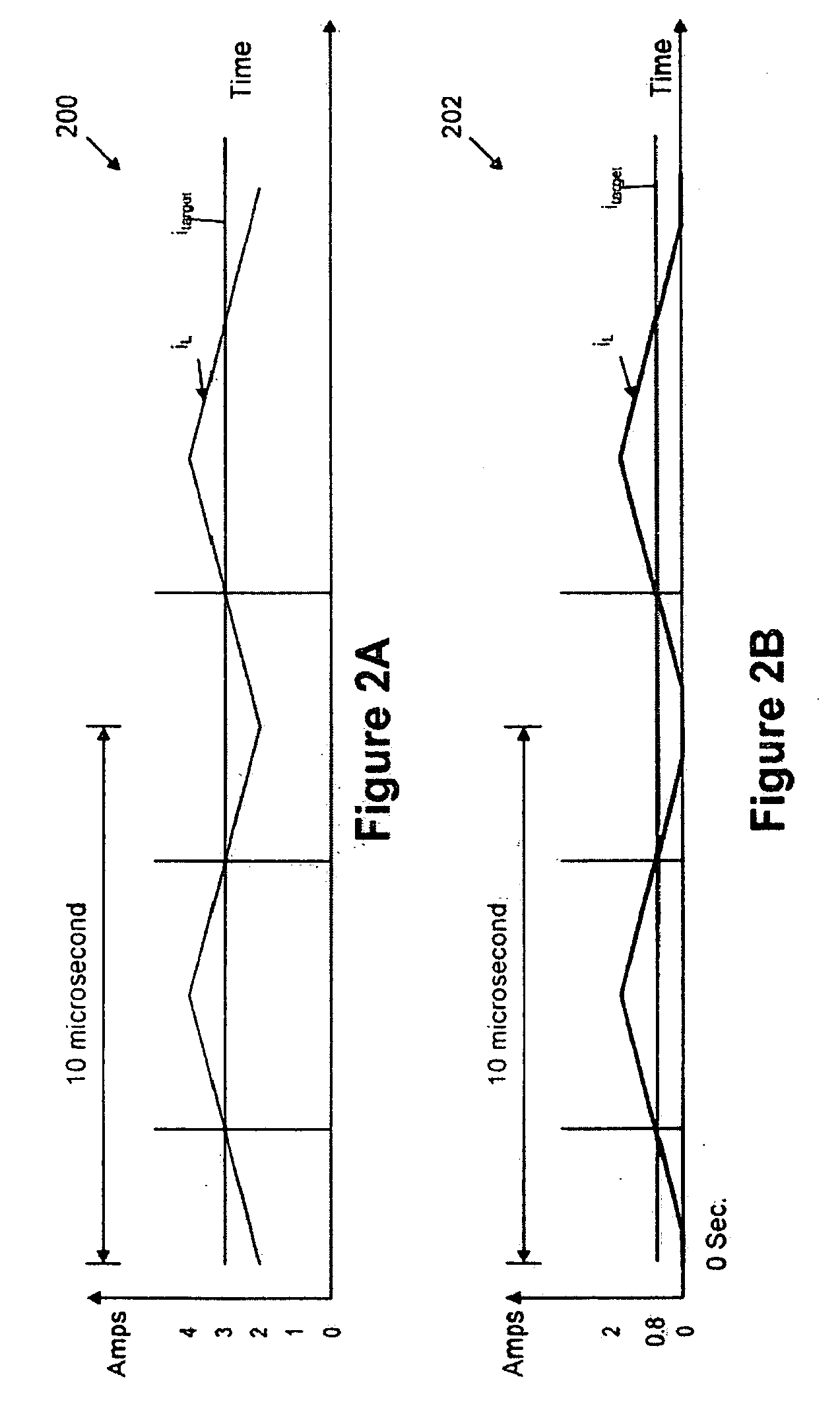
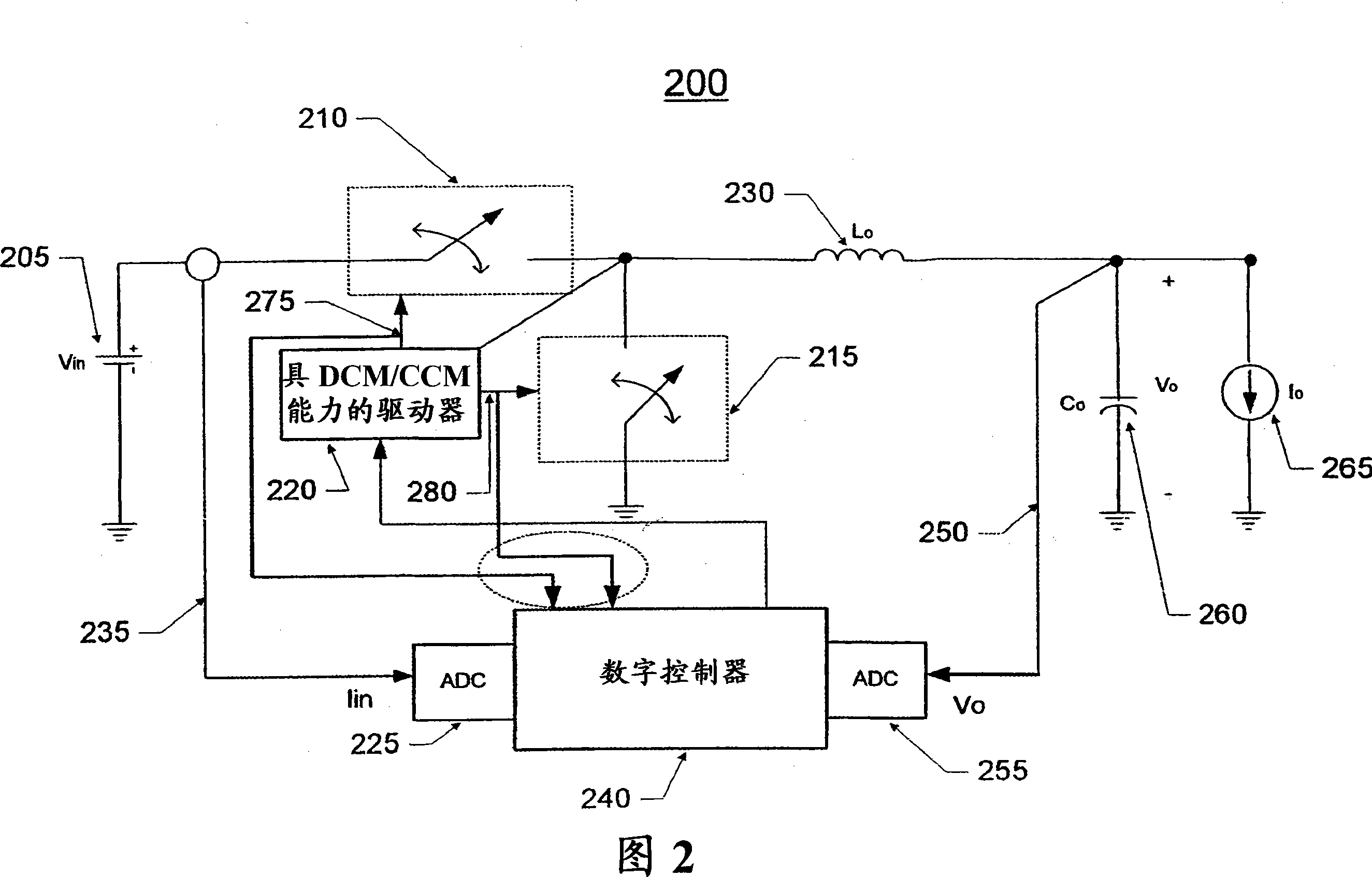
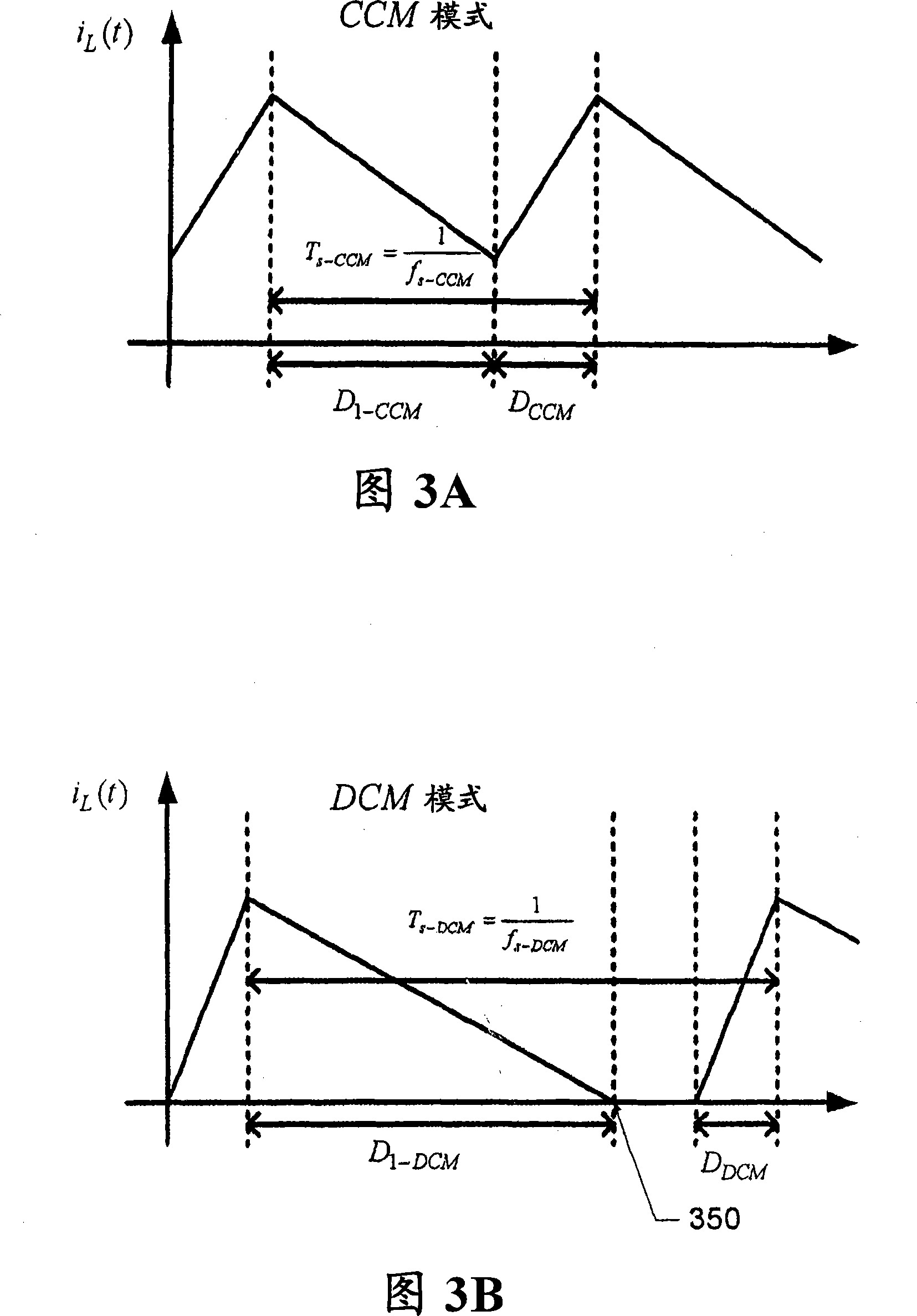
Adaptive controller with mode tracking and parametric estimation for digital power converters
InactiveCN101252311AApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationTransverterPeak value
A controller for a power stage may adaptively control power switches to improve the efficiency of power consumption by the power stage and detect continuous conduction mode (''CCM'') and discontinuous conduction mode (''DCM'') operations of the power stage without instantaneous or cycle by cycle sensing and sampling of the output inductor current. Additionally, the controller may be used to facilitate the estimation of output inductor value, the peak inductor current value, and other information on converter operations.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com