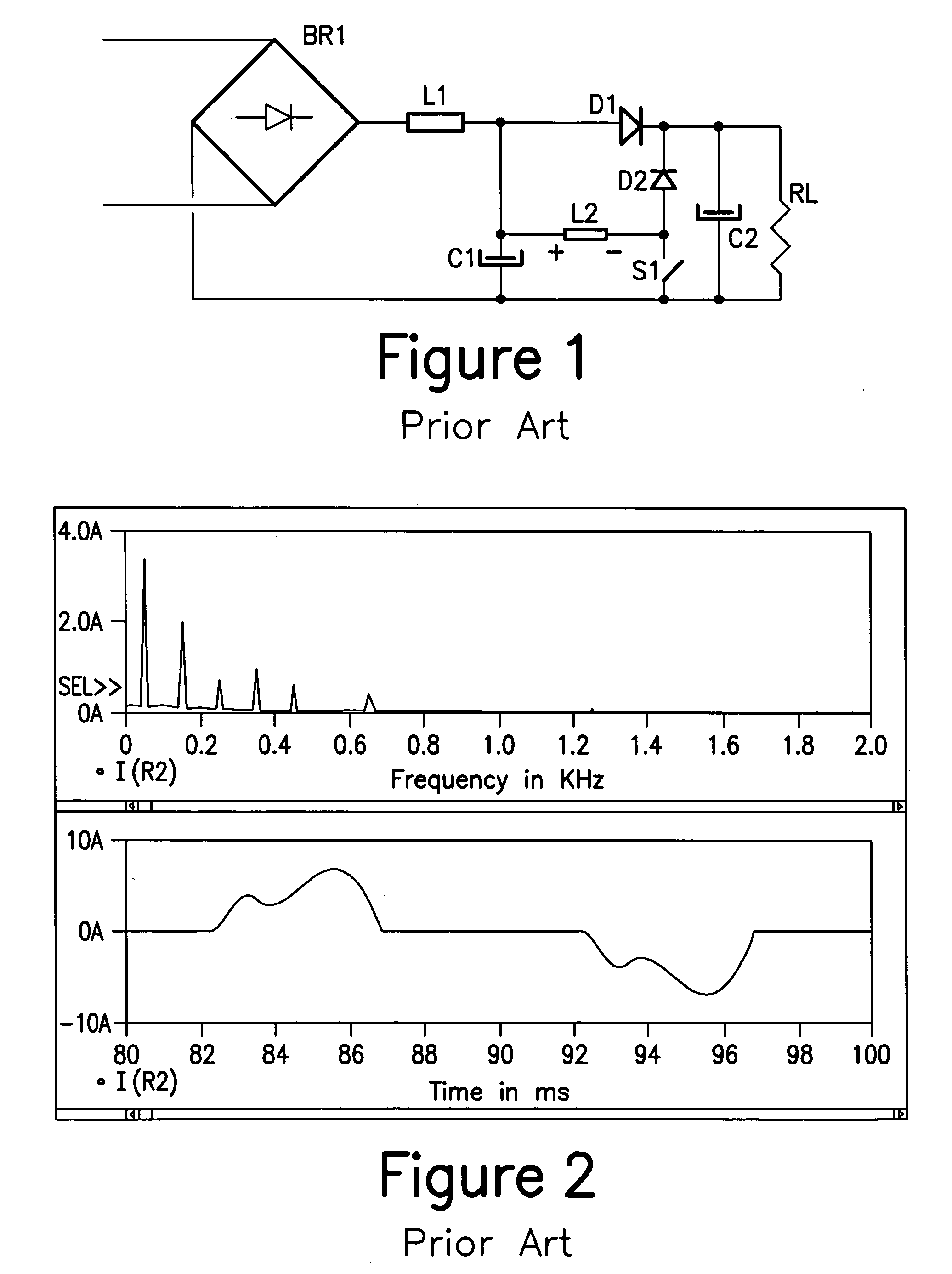
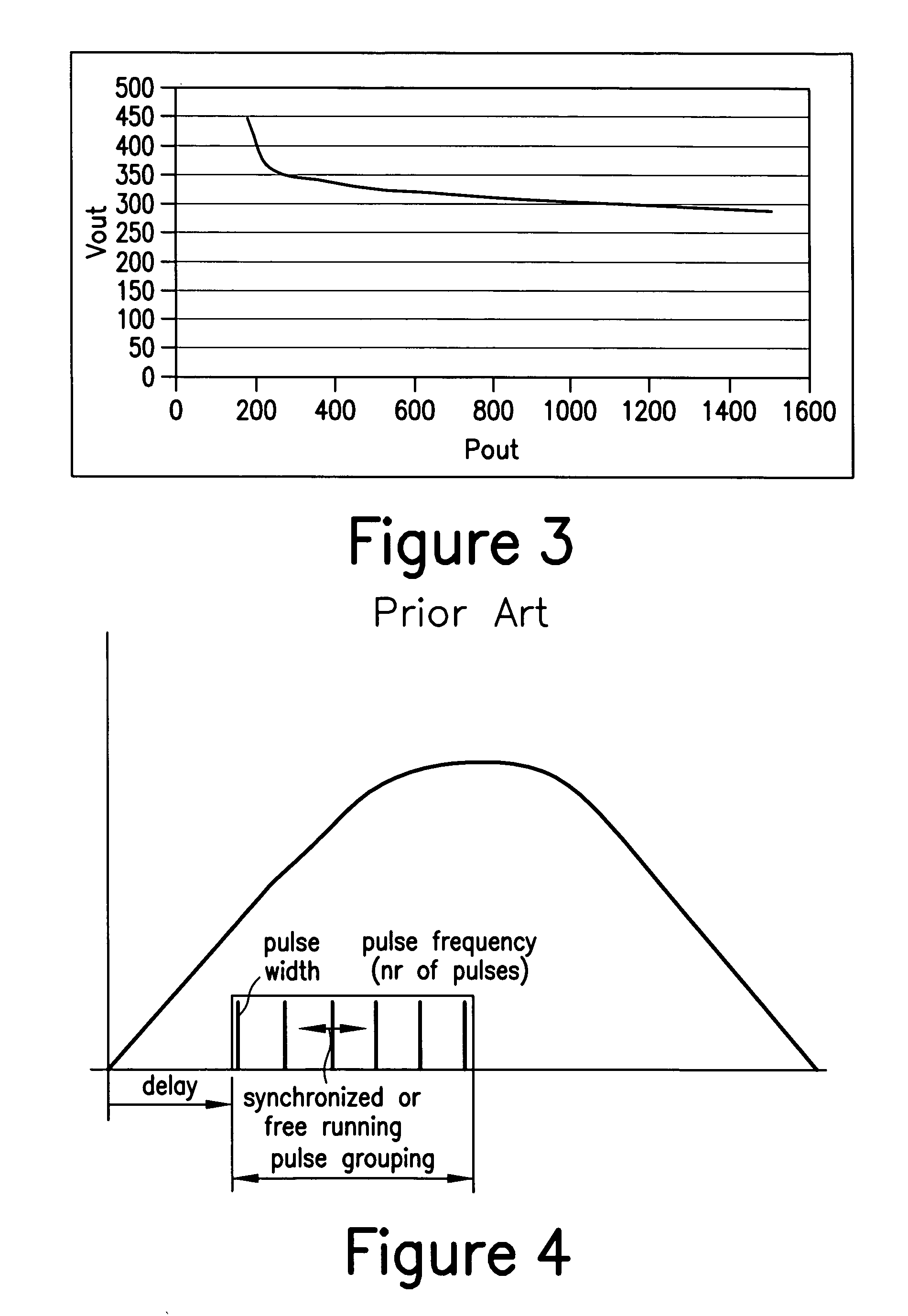
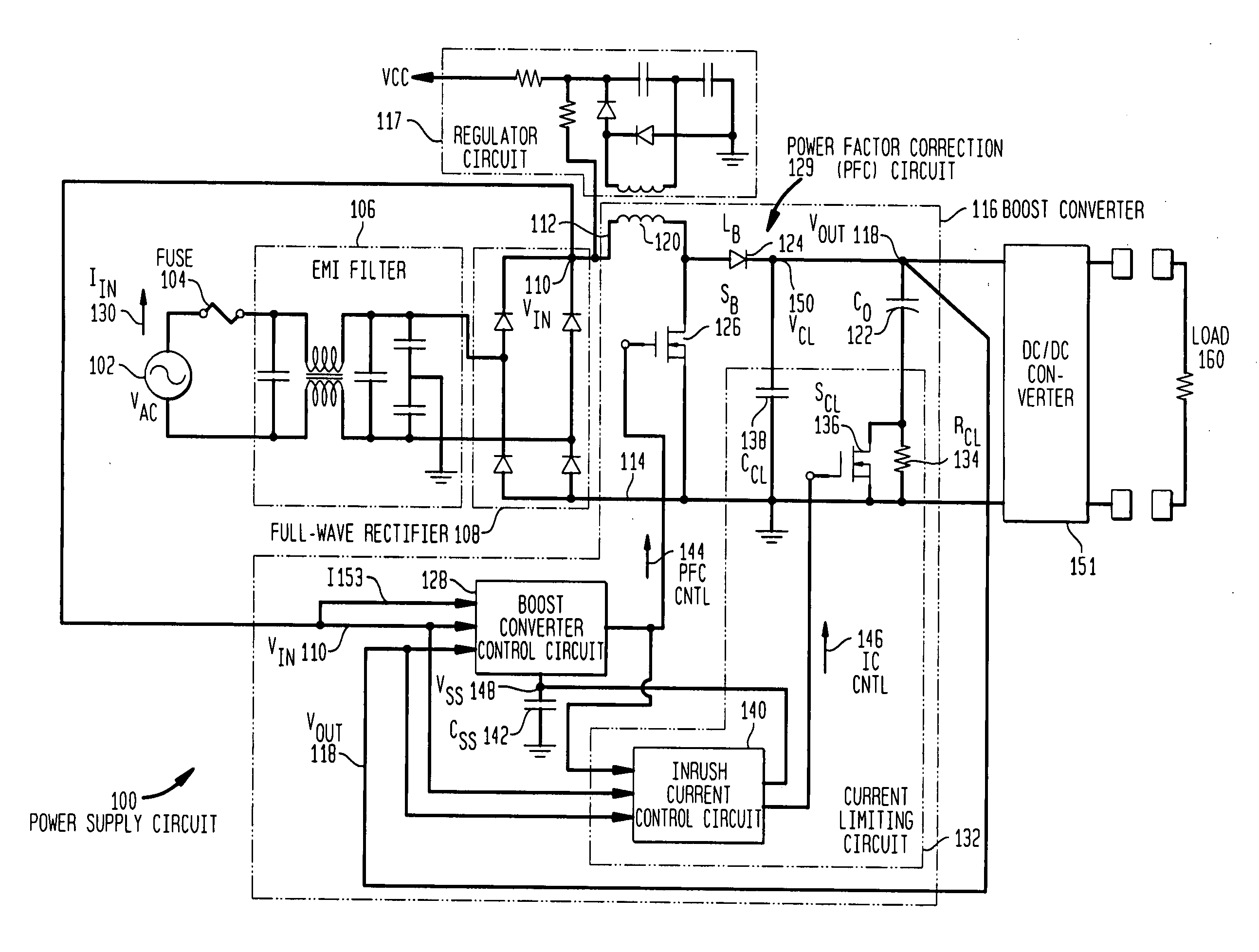
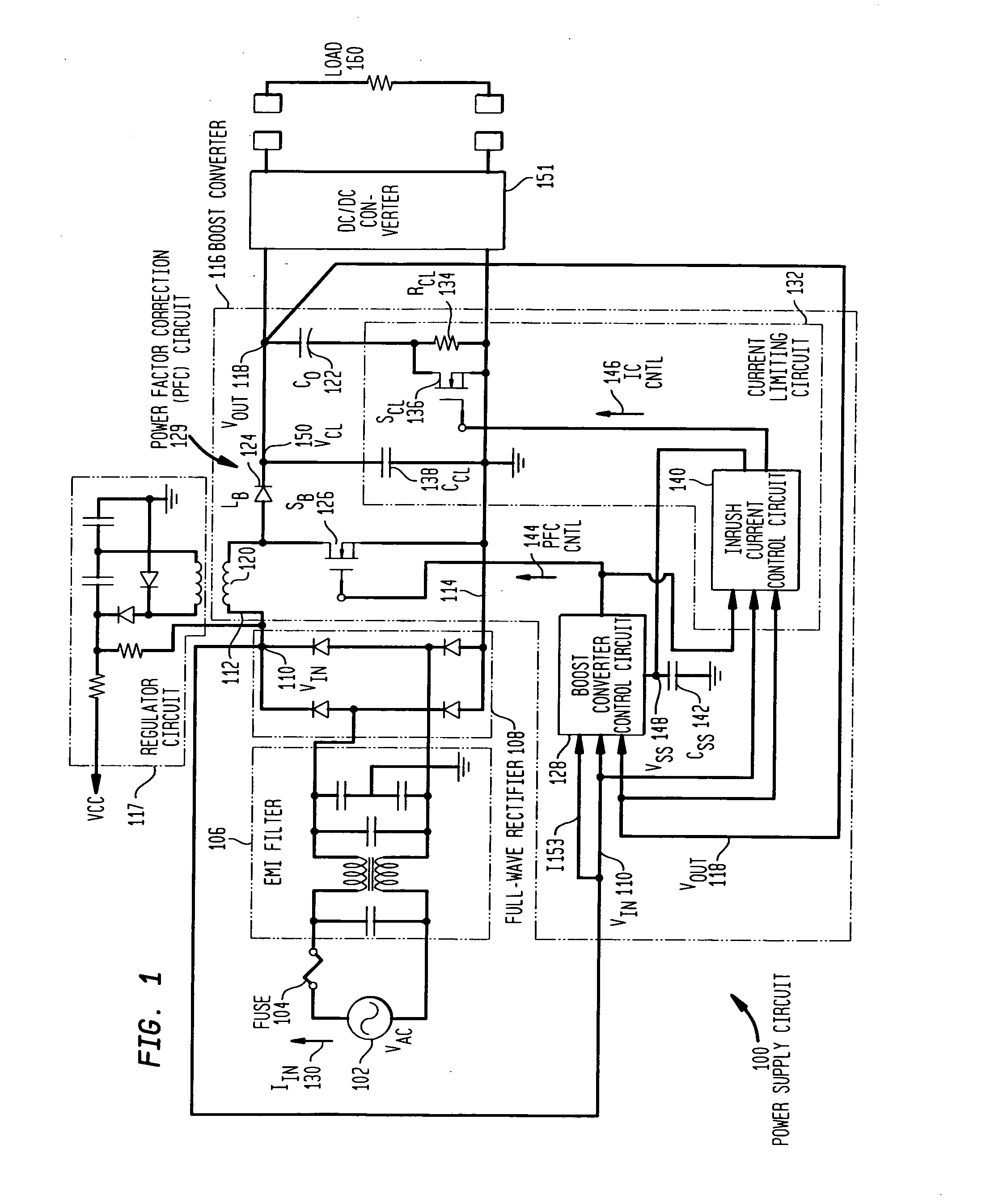
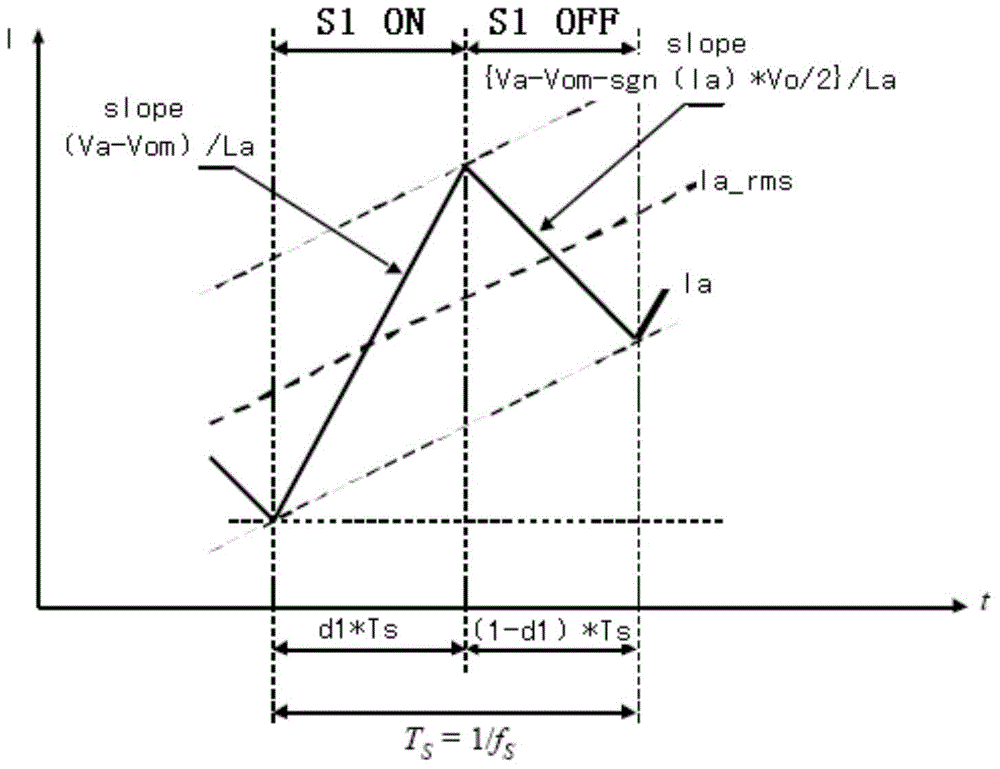
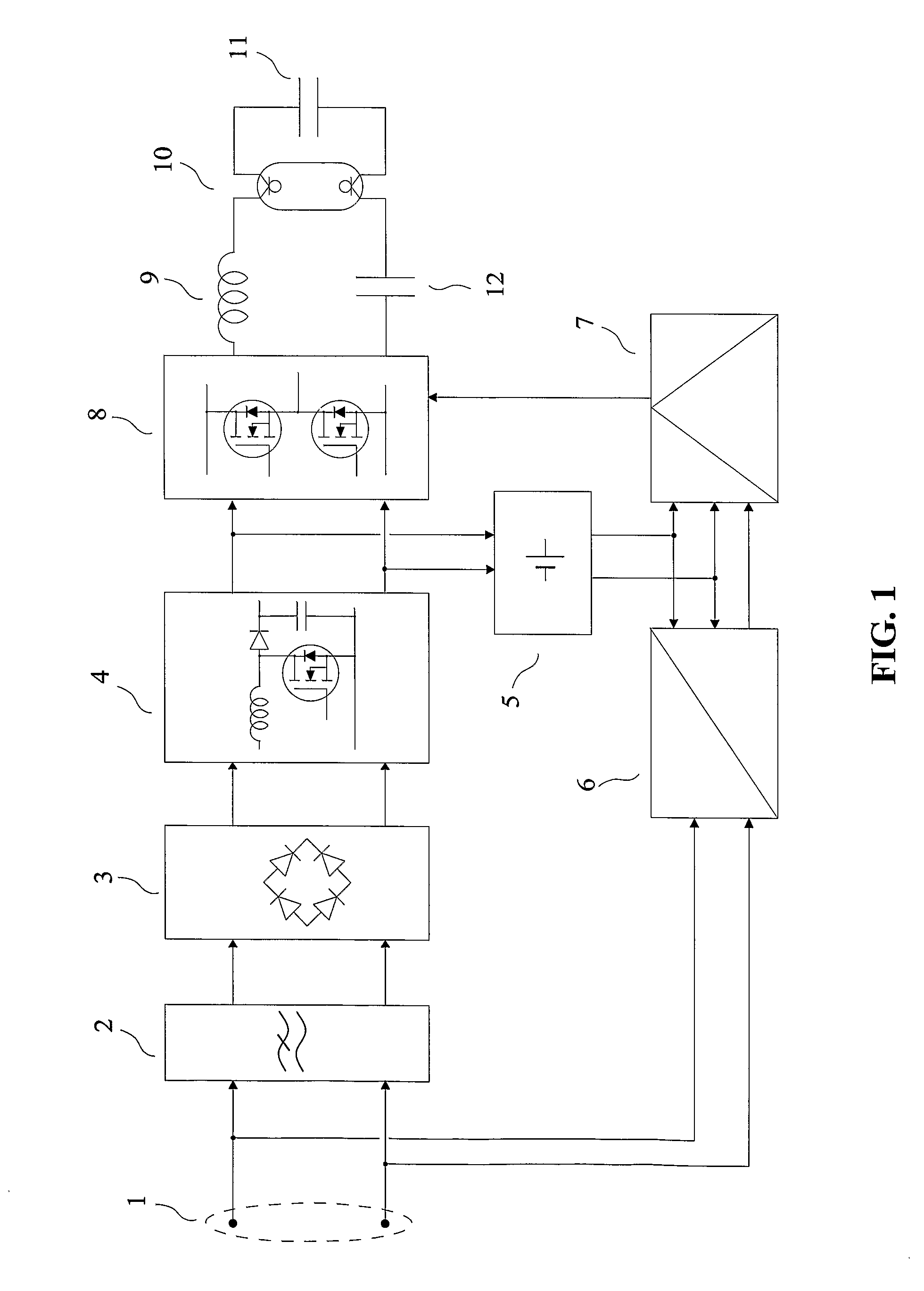
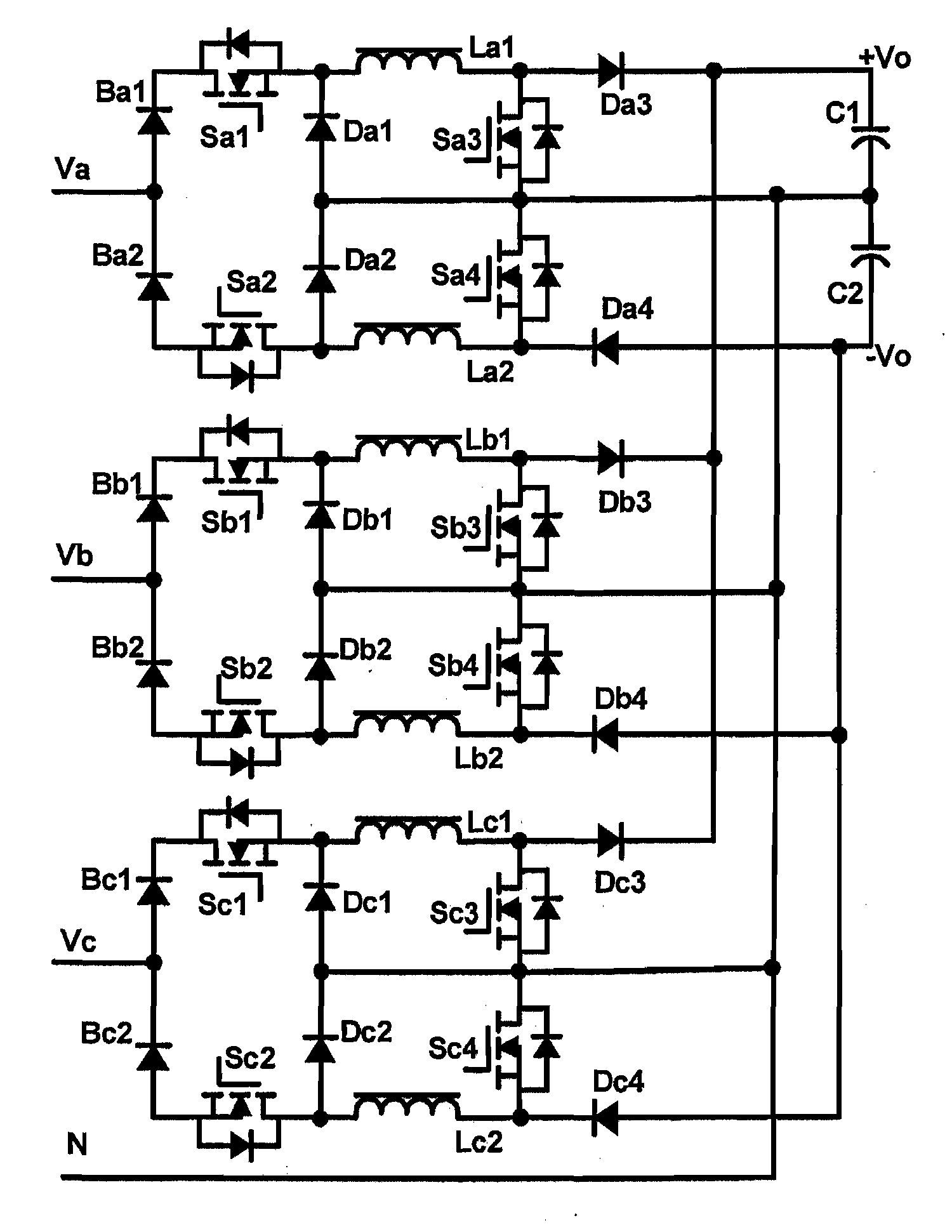
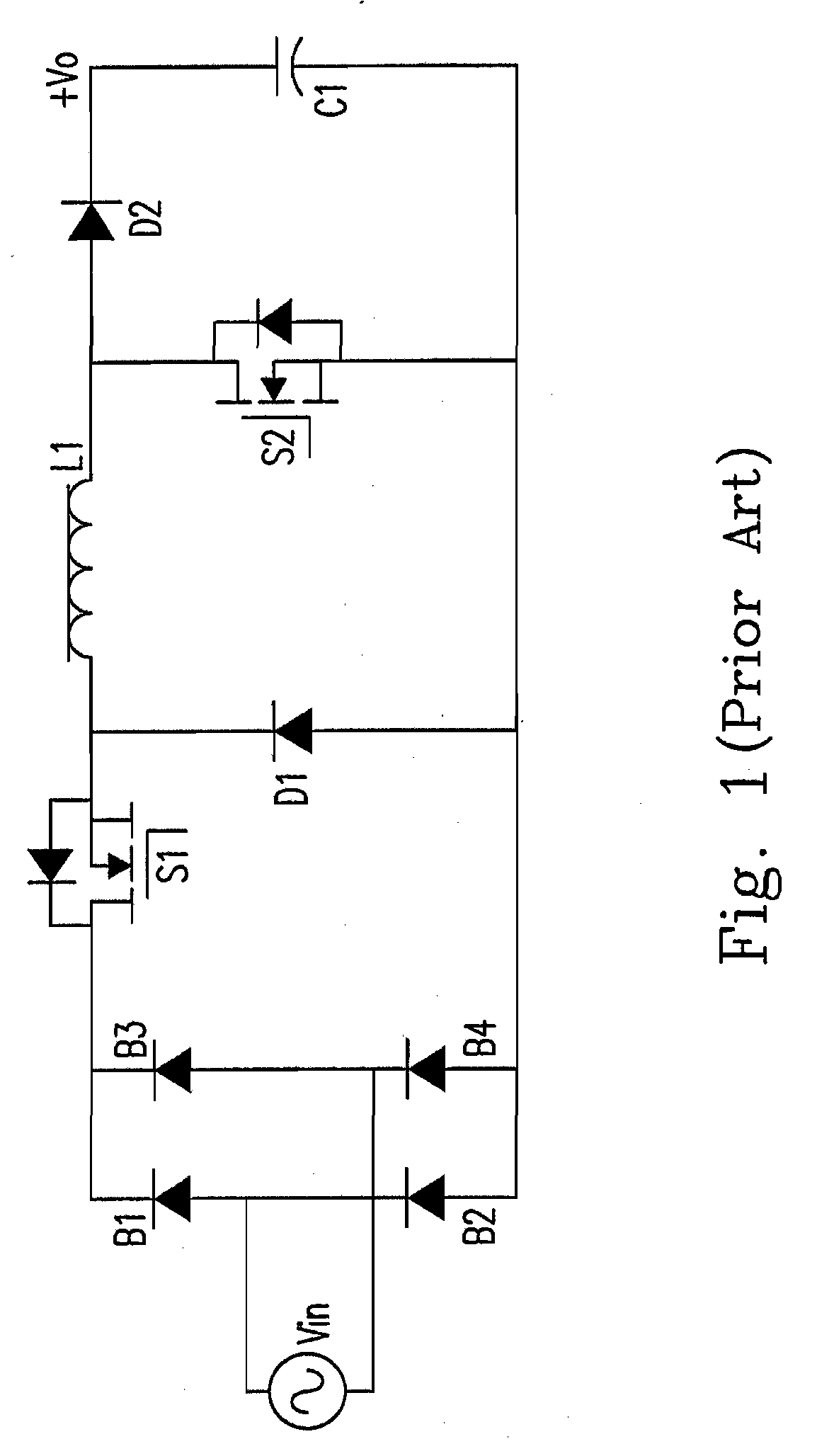
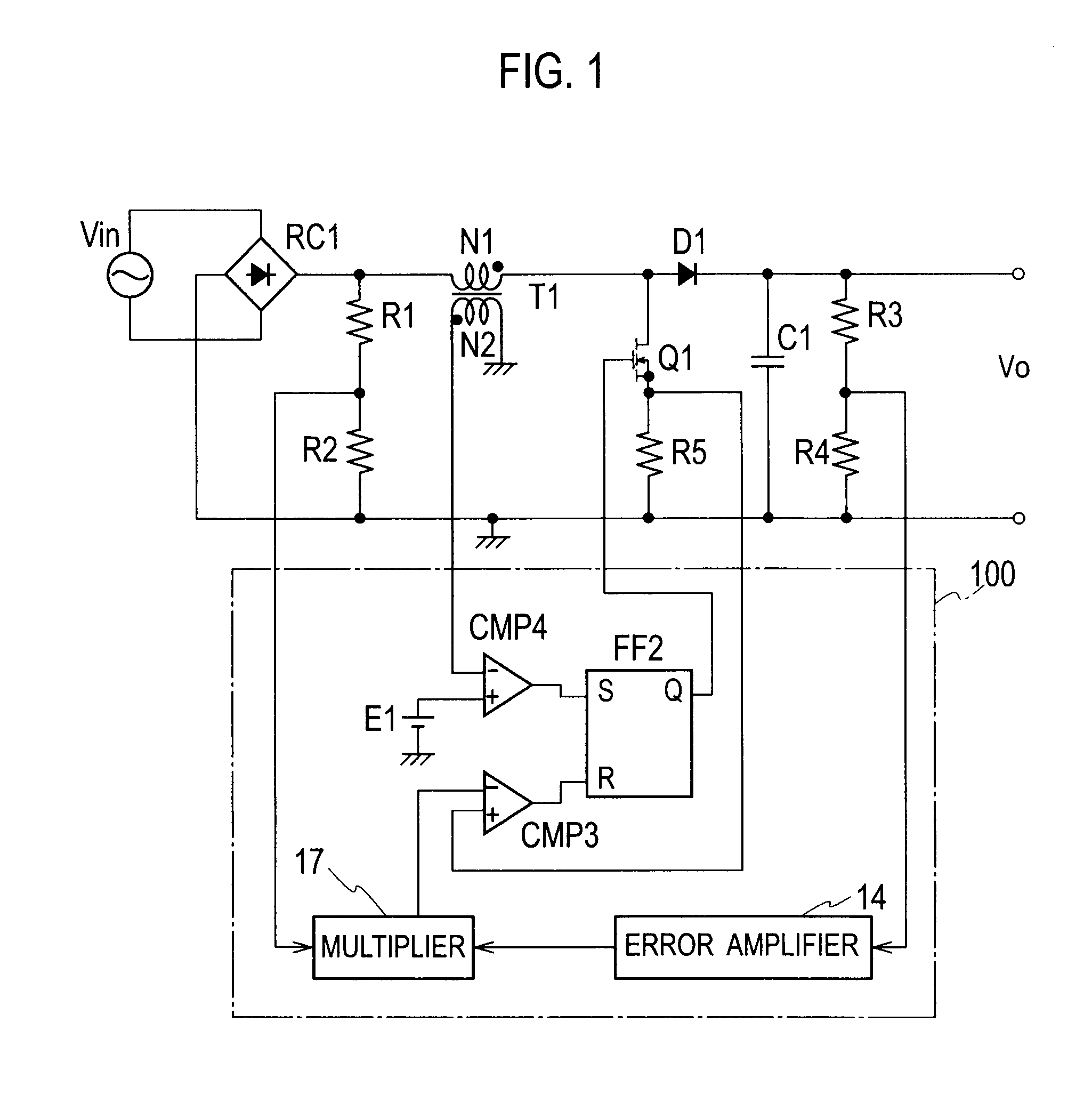
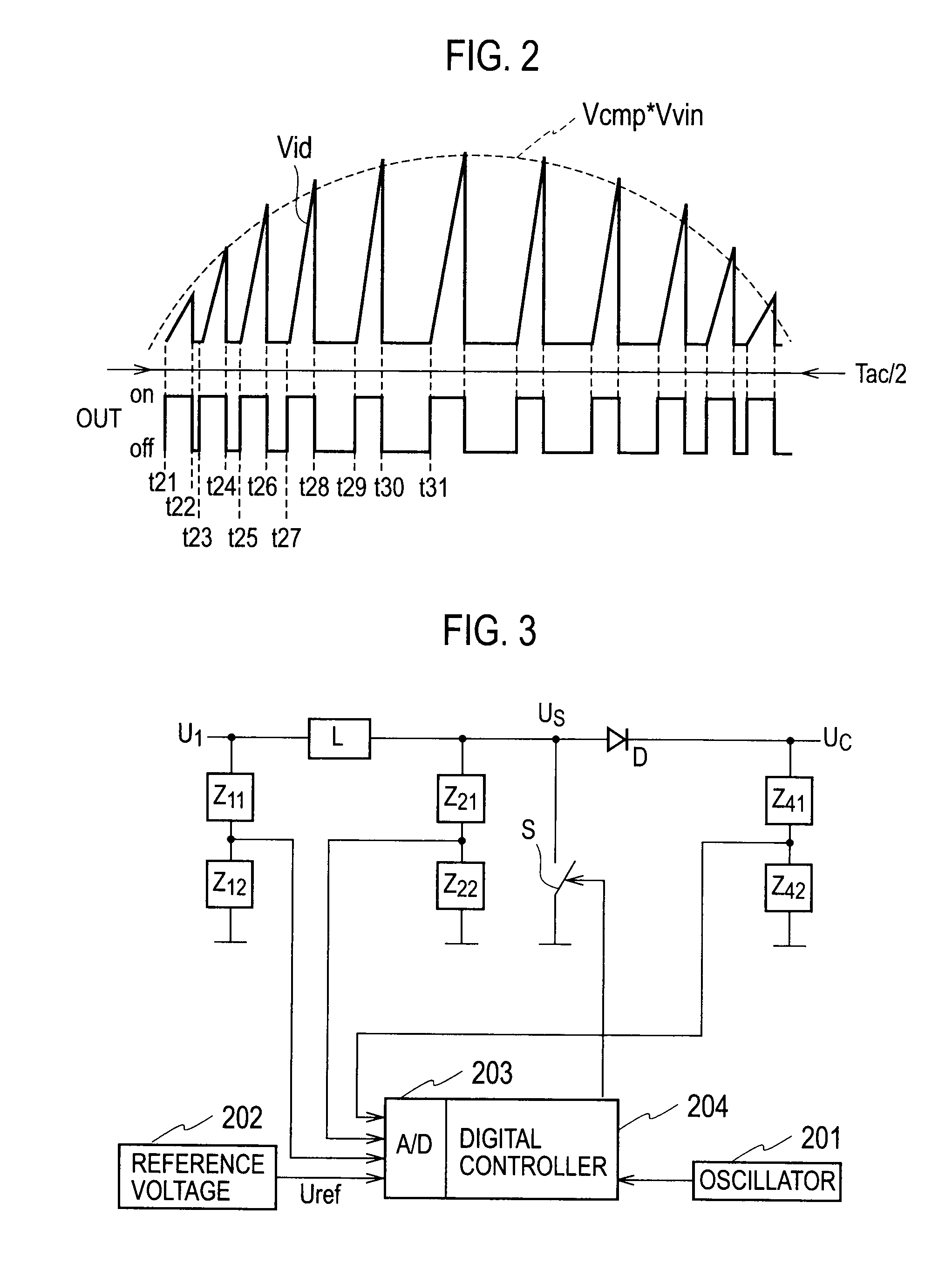
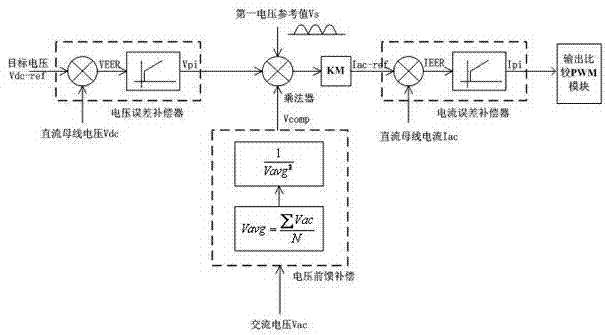
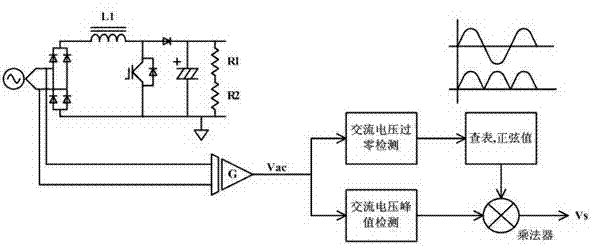
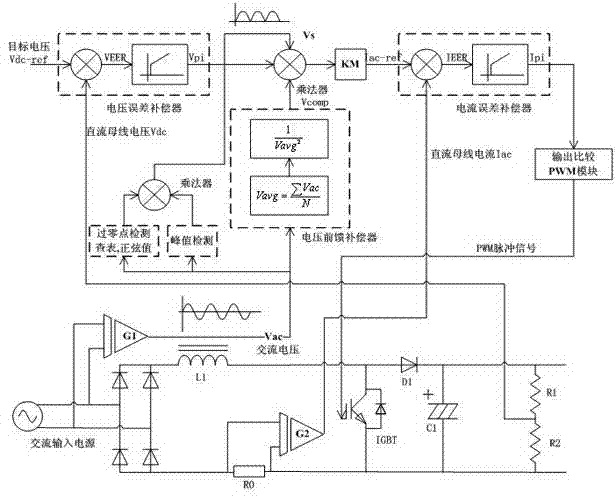
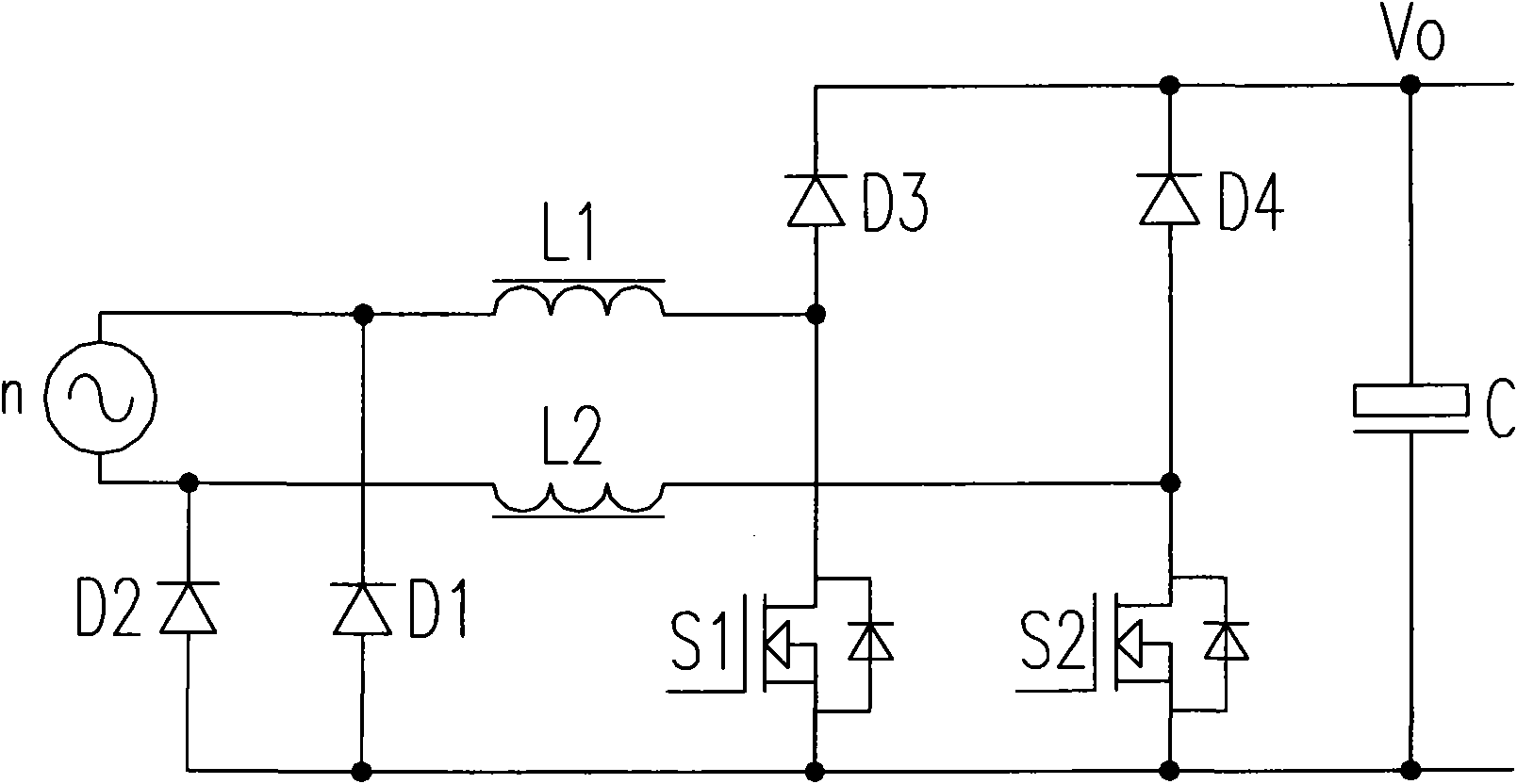
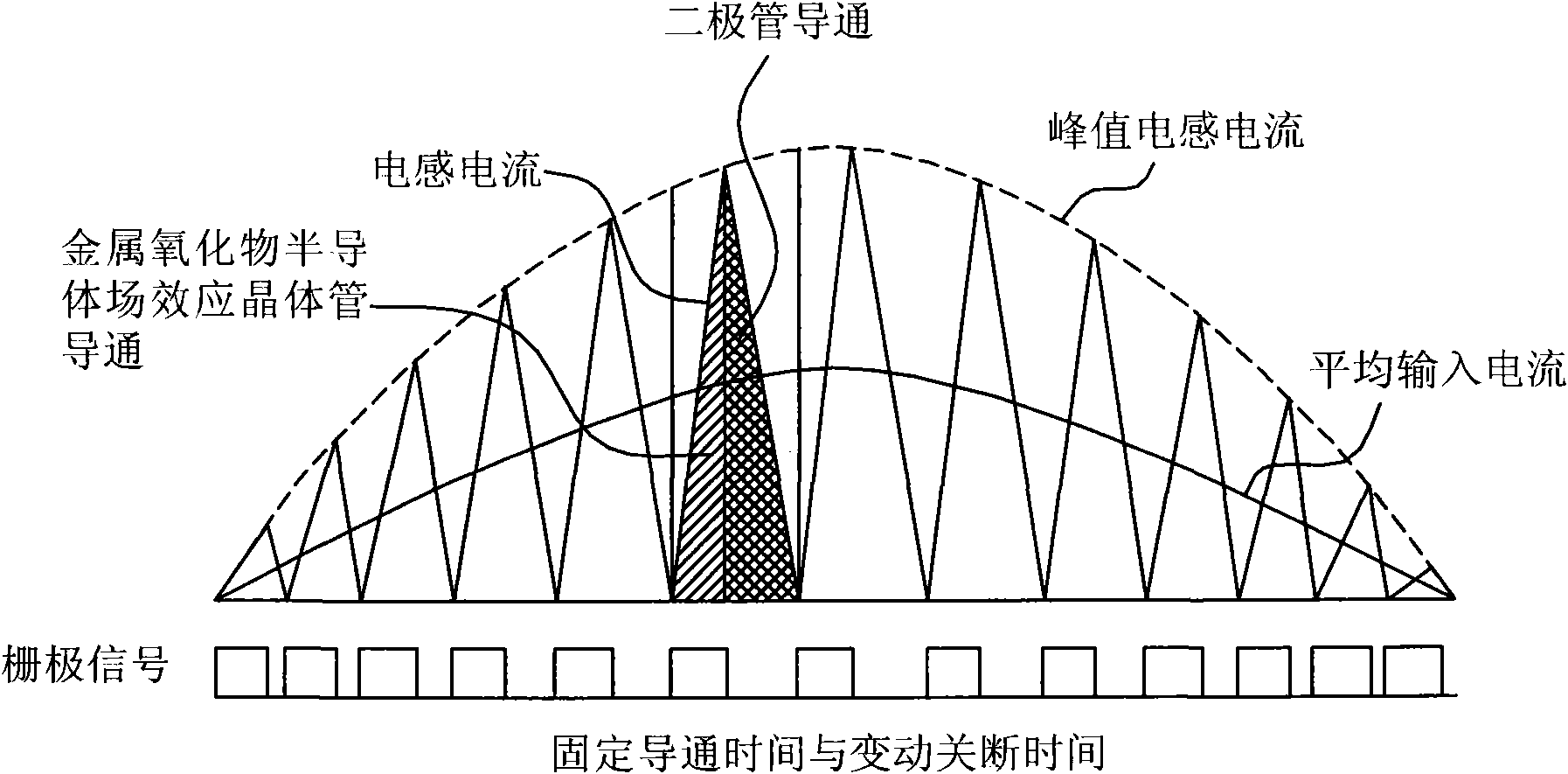
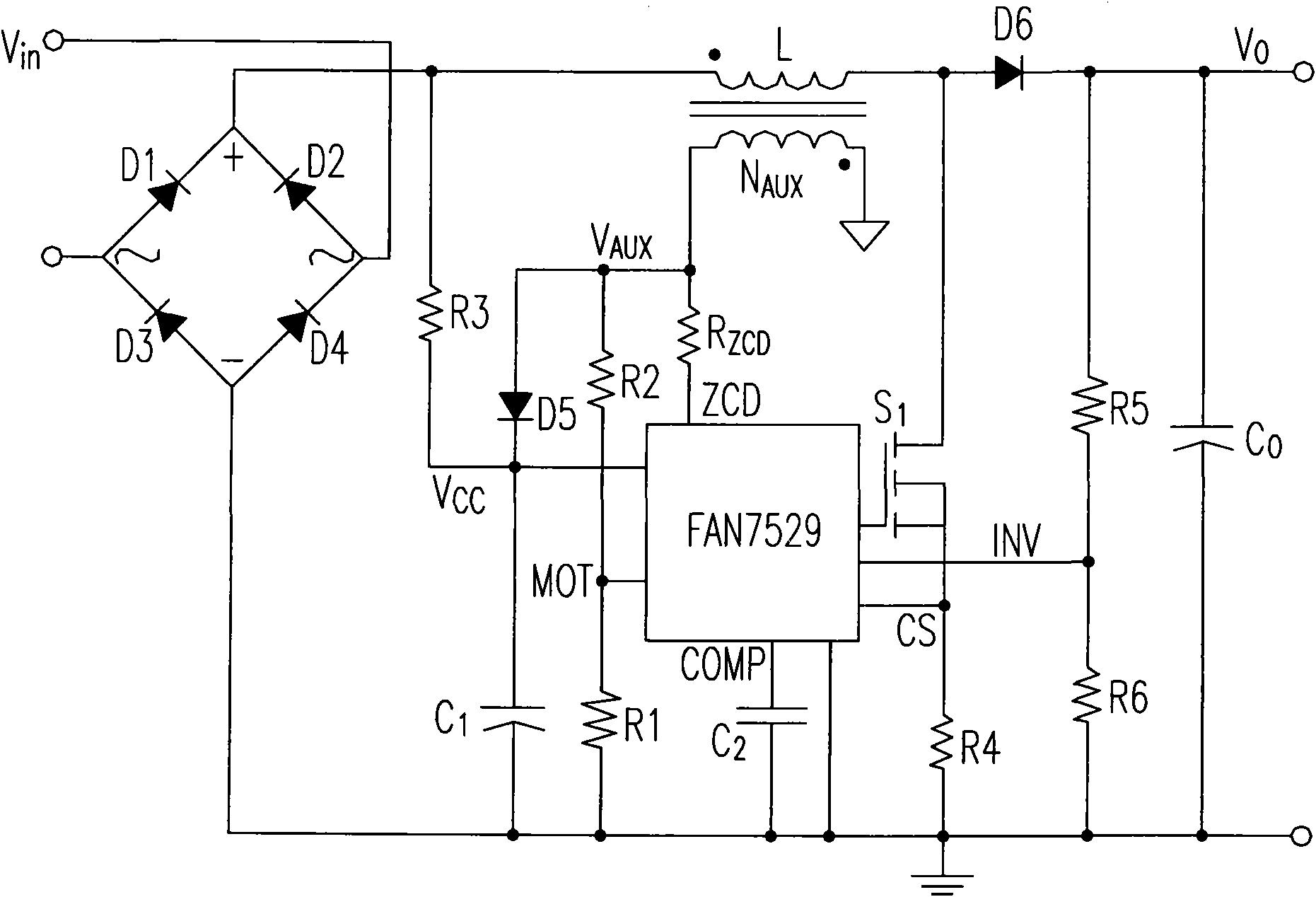
Patents
Literature
1448 results about "Power factor correction circuits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
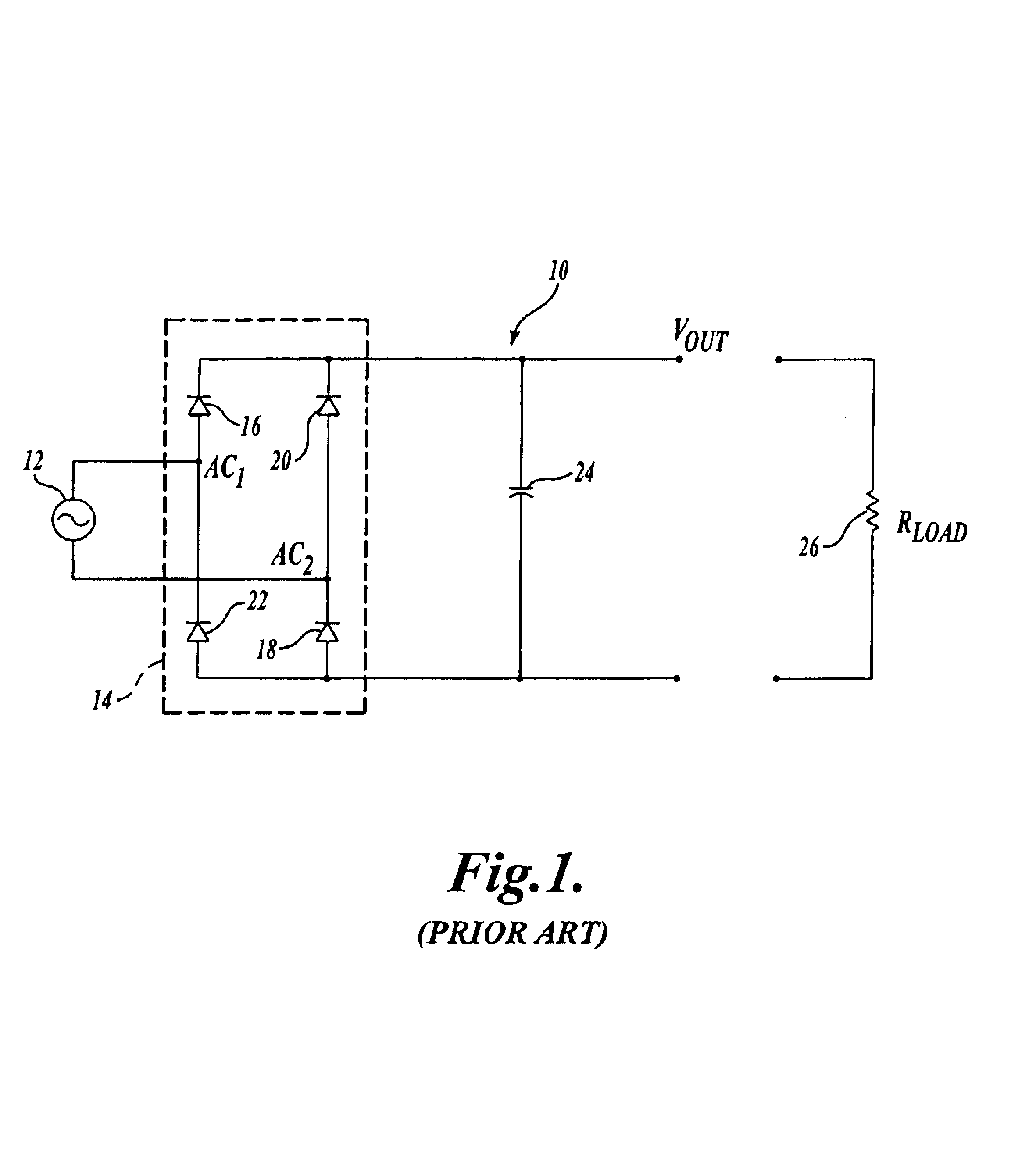
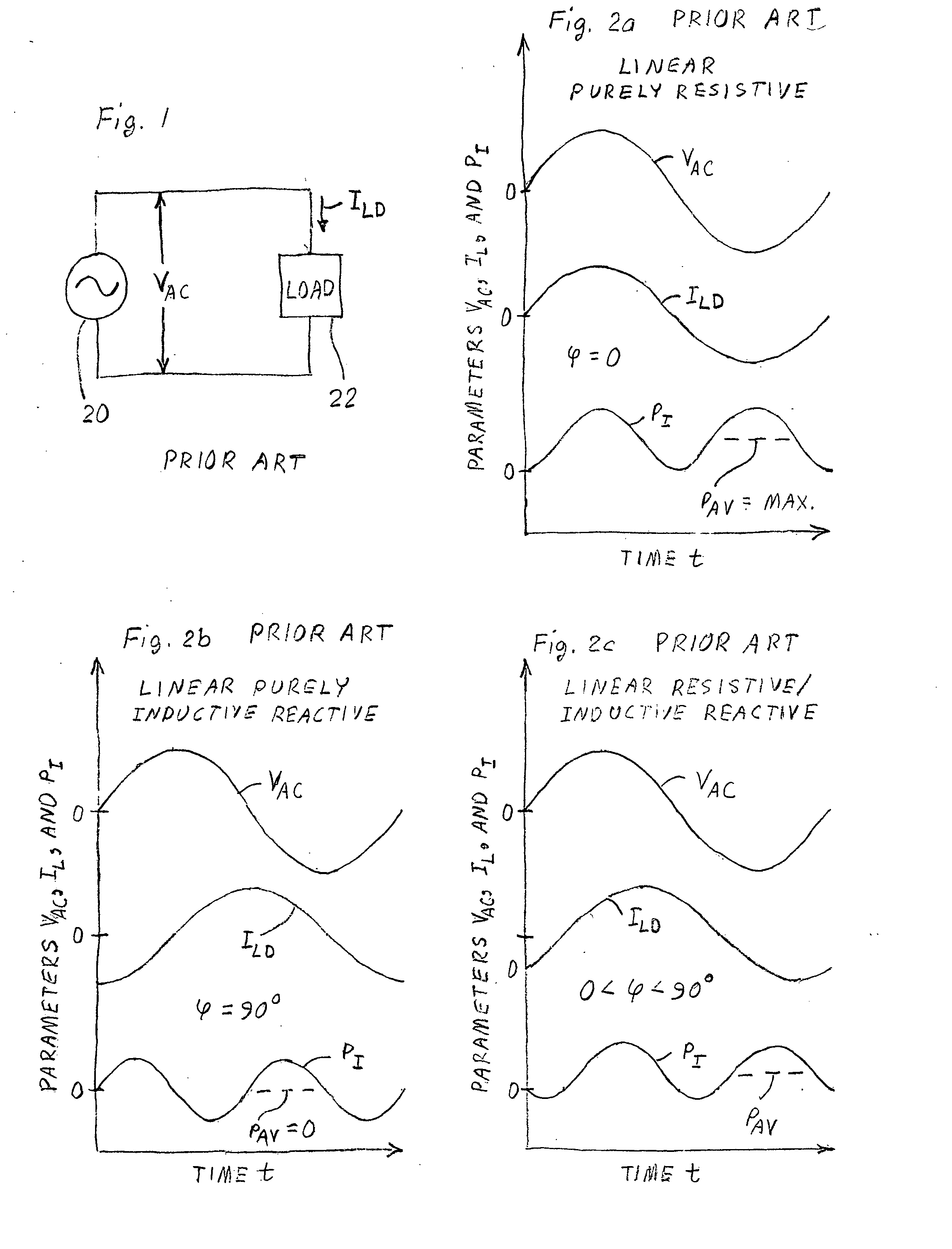
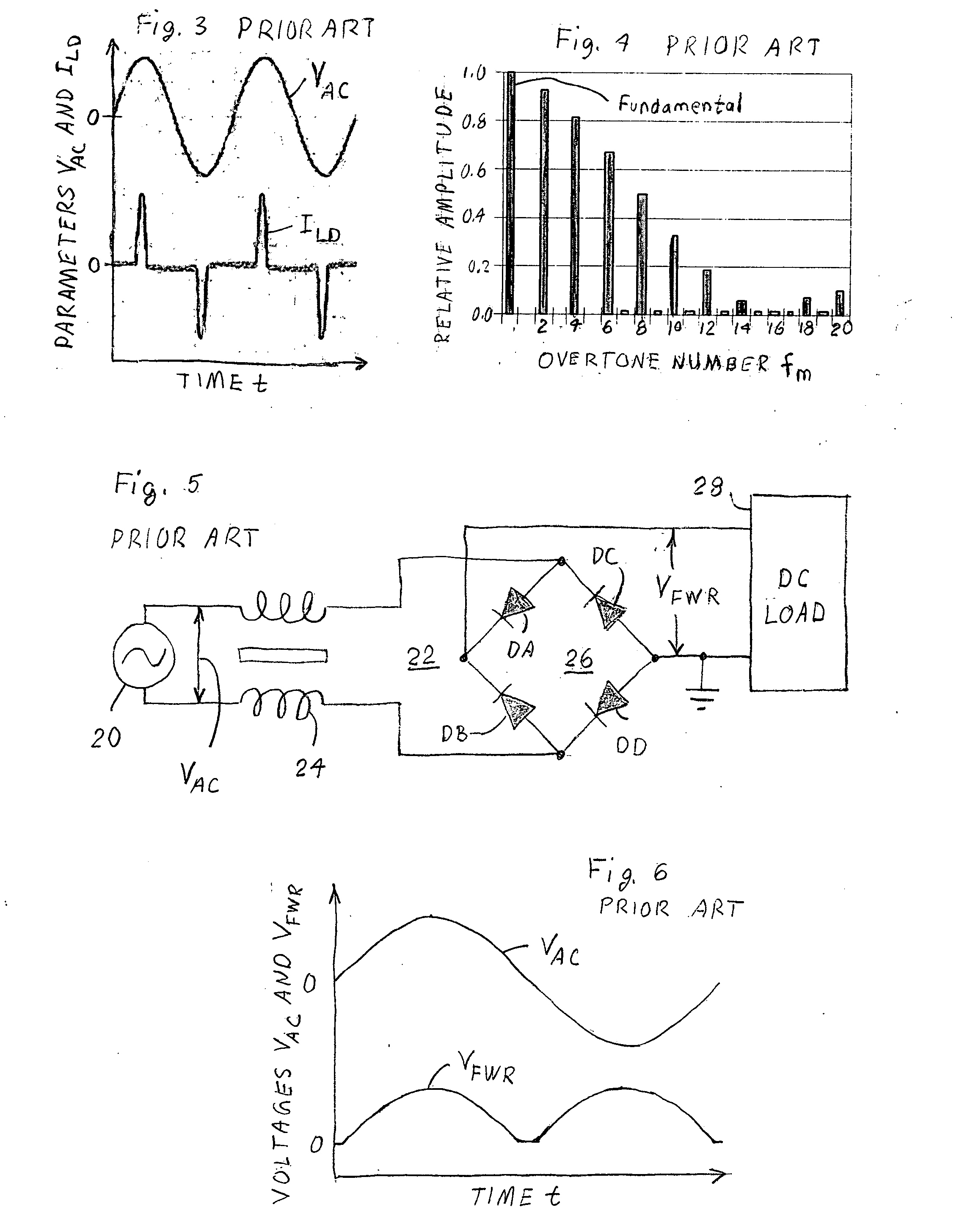
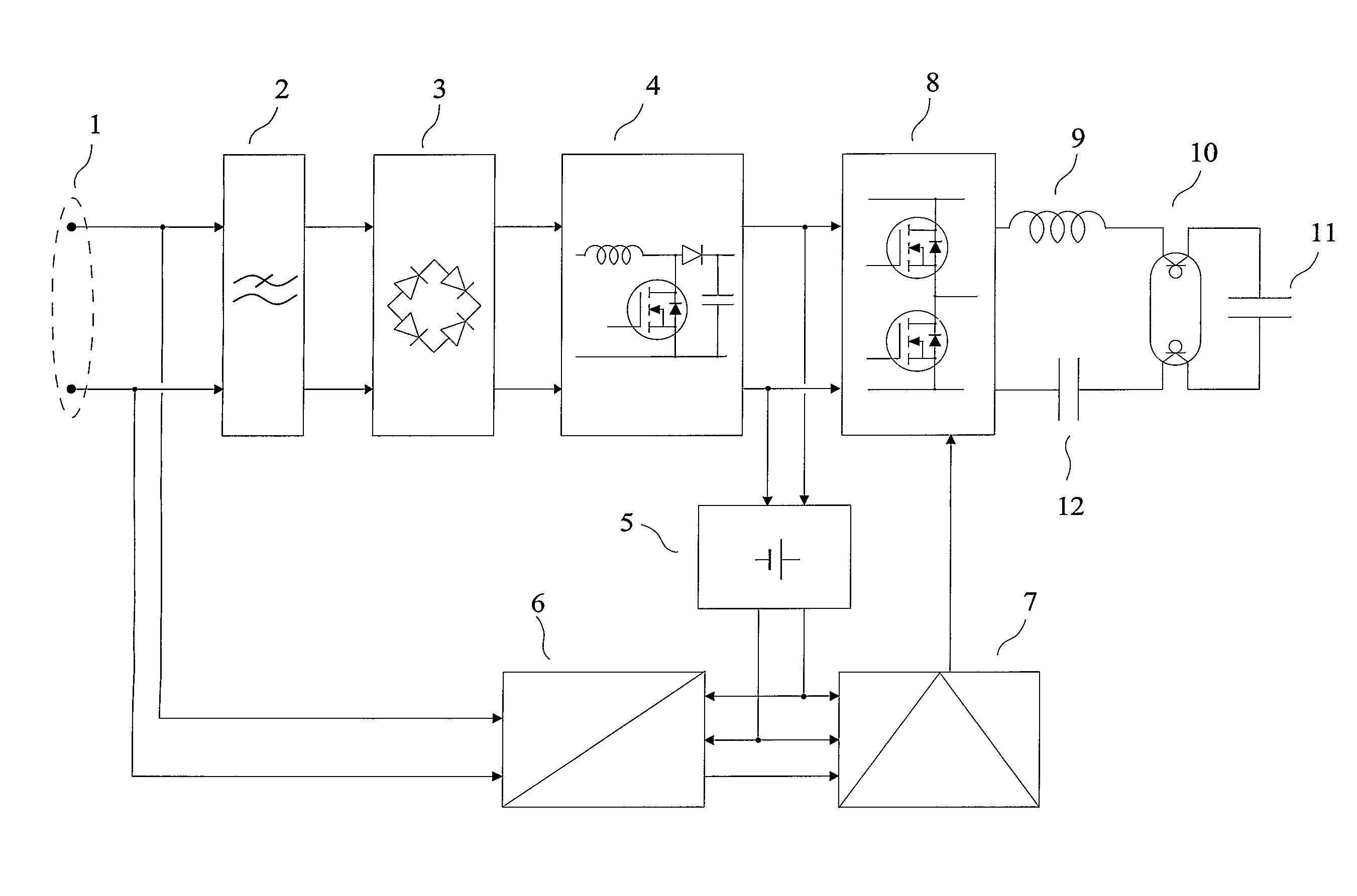
Power Factor Correction. Definition: The power factor correction means bringing the power factor of an AC circuit nearer to one by using the equipment which absorbs or supply the reactive power to the circuit.
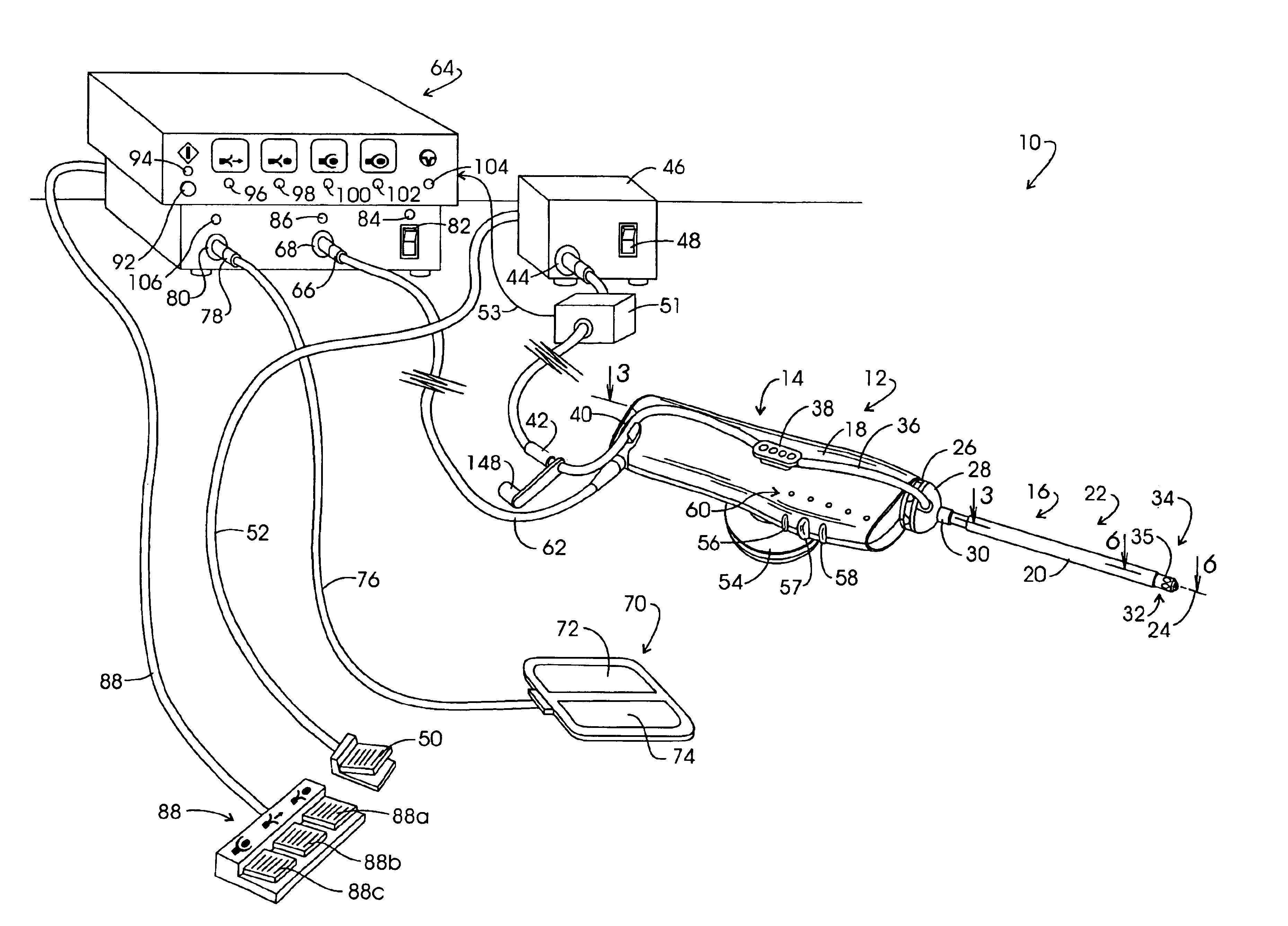
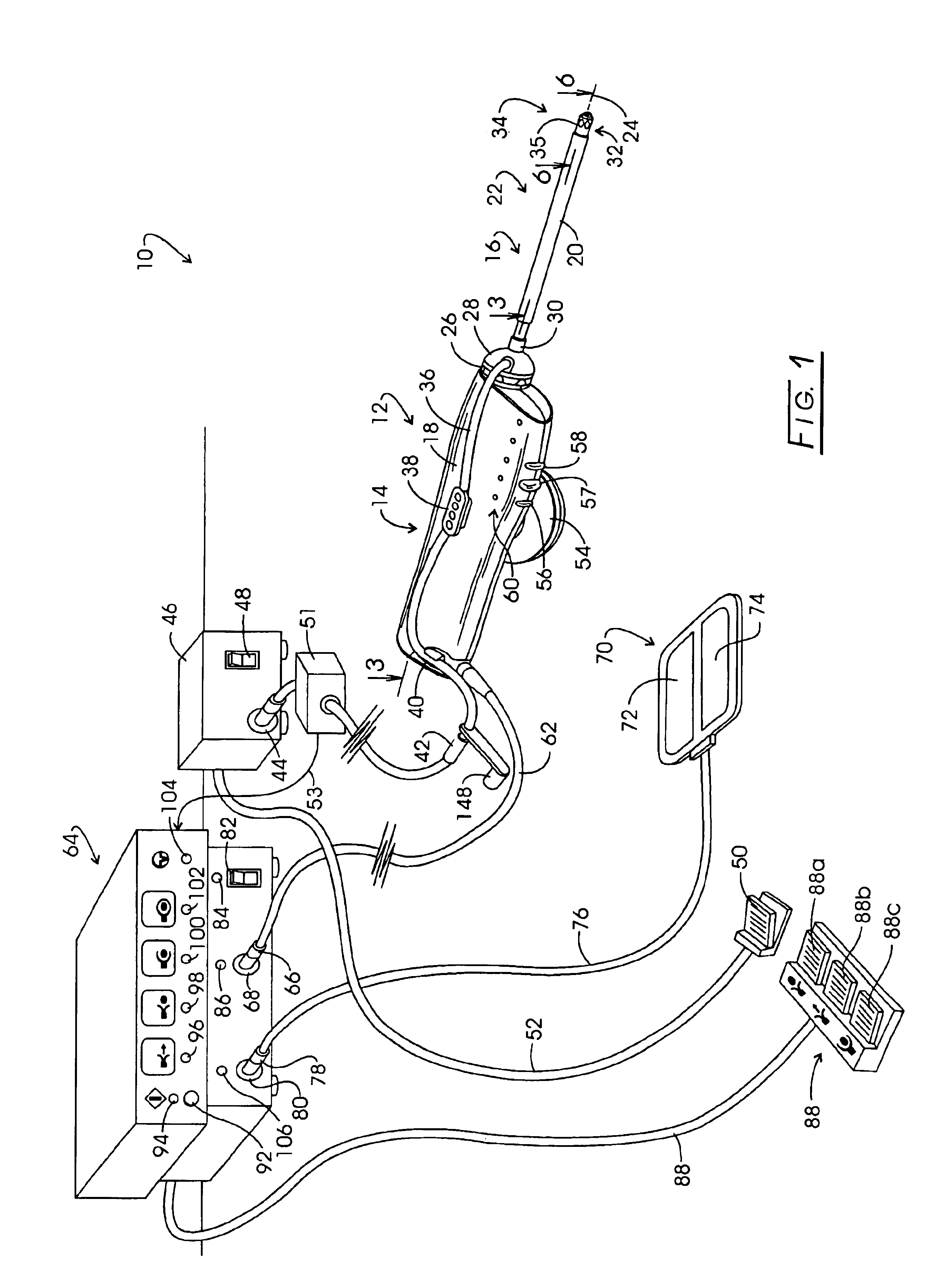
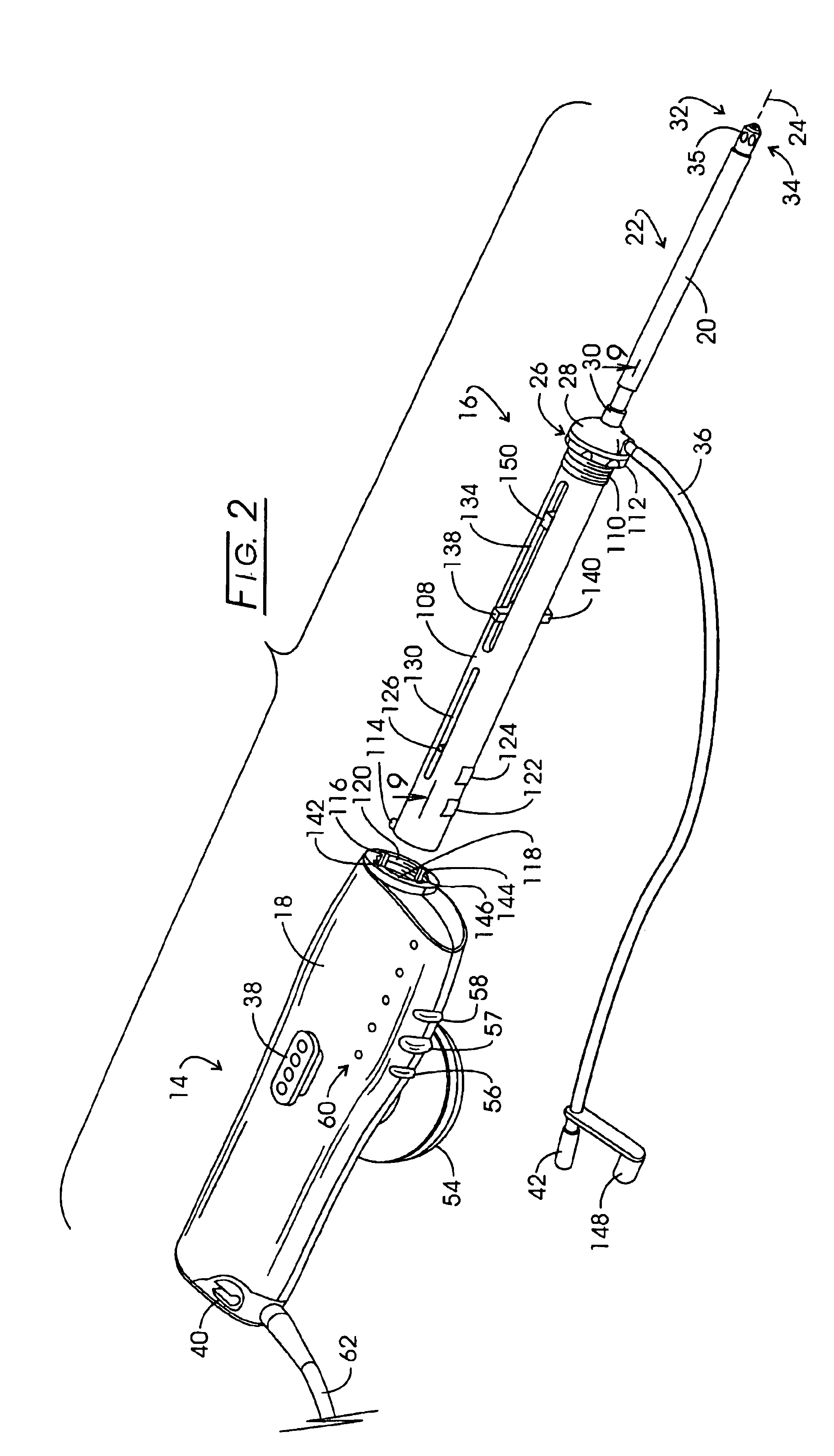
Electrosurgical generator
InactiveUS6923804B2Improving impedanceIncrease resistanceSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesResonant inverterConstant power
An electrosurgical generator which provides a constant power output particularly suited for cutting arc formation at an active electrode which exhibits a dynamic active surface area of varying geometry. Essentially constant power-based control is achieved through the utilization of a d.c. link voltage the level of which functions to establish the amplitude of the output of an RF resonant inverter. A dual loop feedback control is described wherein output power based control signals are slowly introduced at low gain, while link voltage based controls are comparatively rapidly applied. Enhanced development of a controlling d.c. link voltage is achieved through the utilization of an input network incorporating a power factor correction stage.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
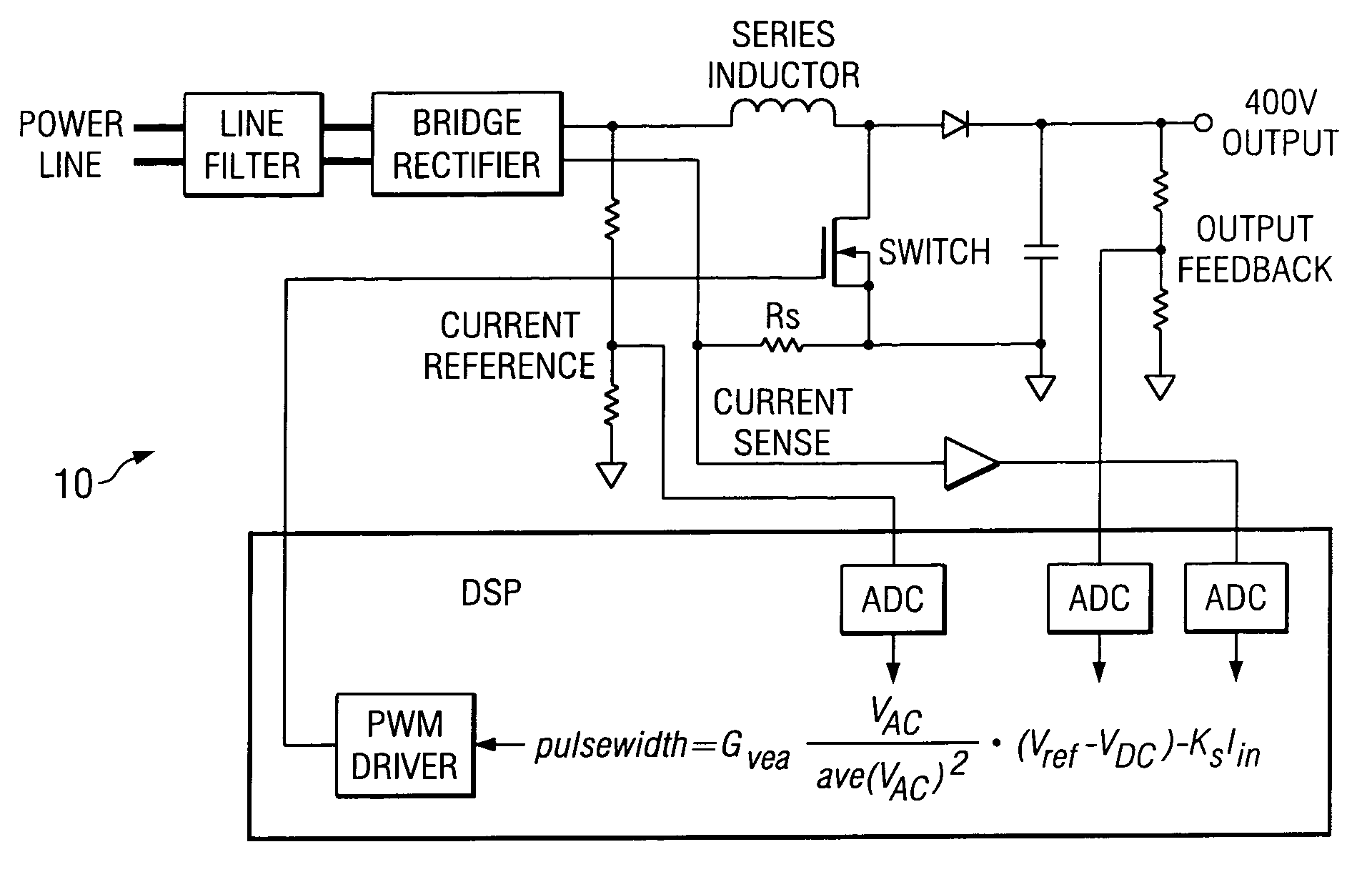
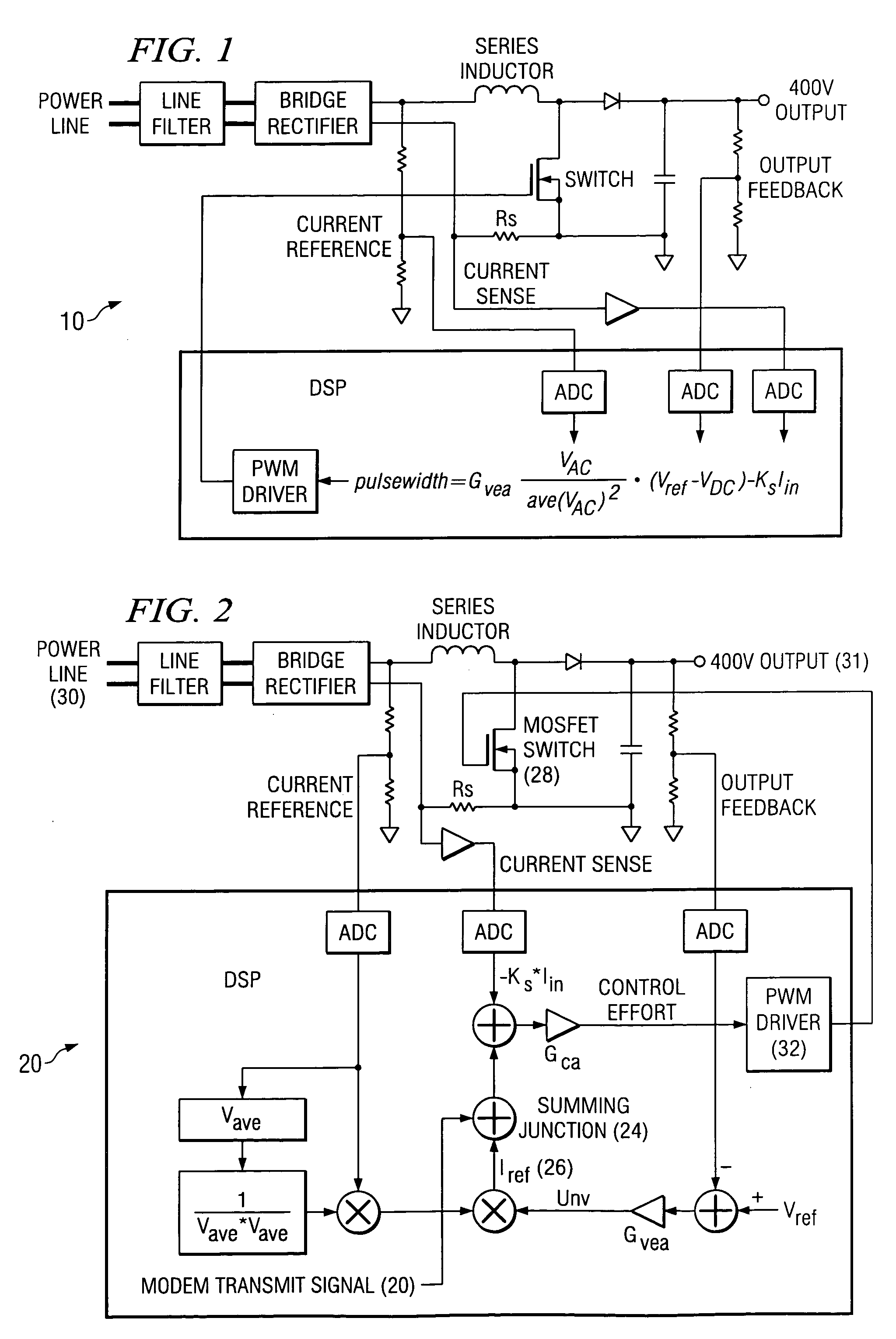
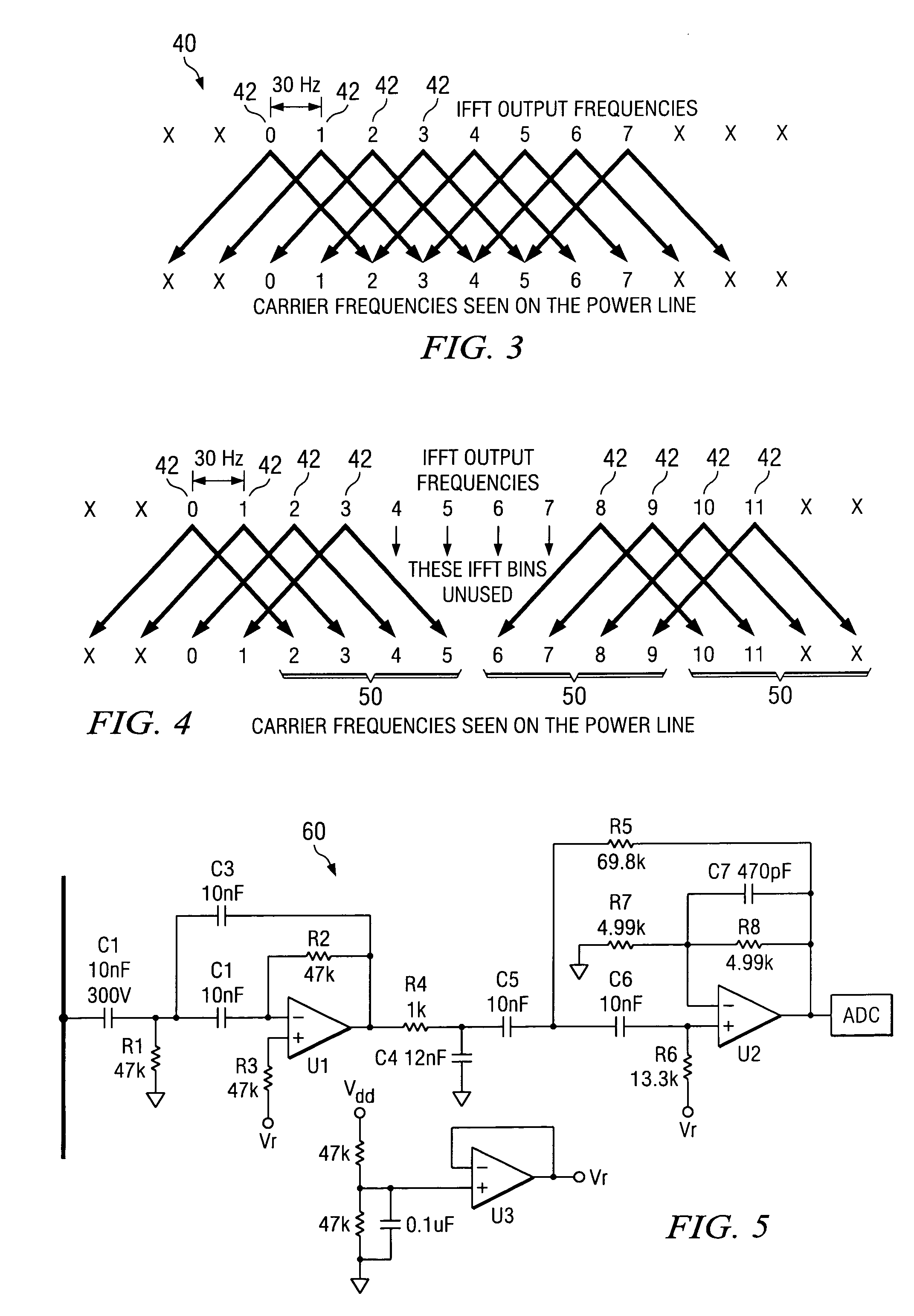
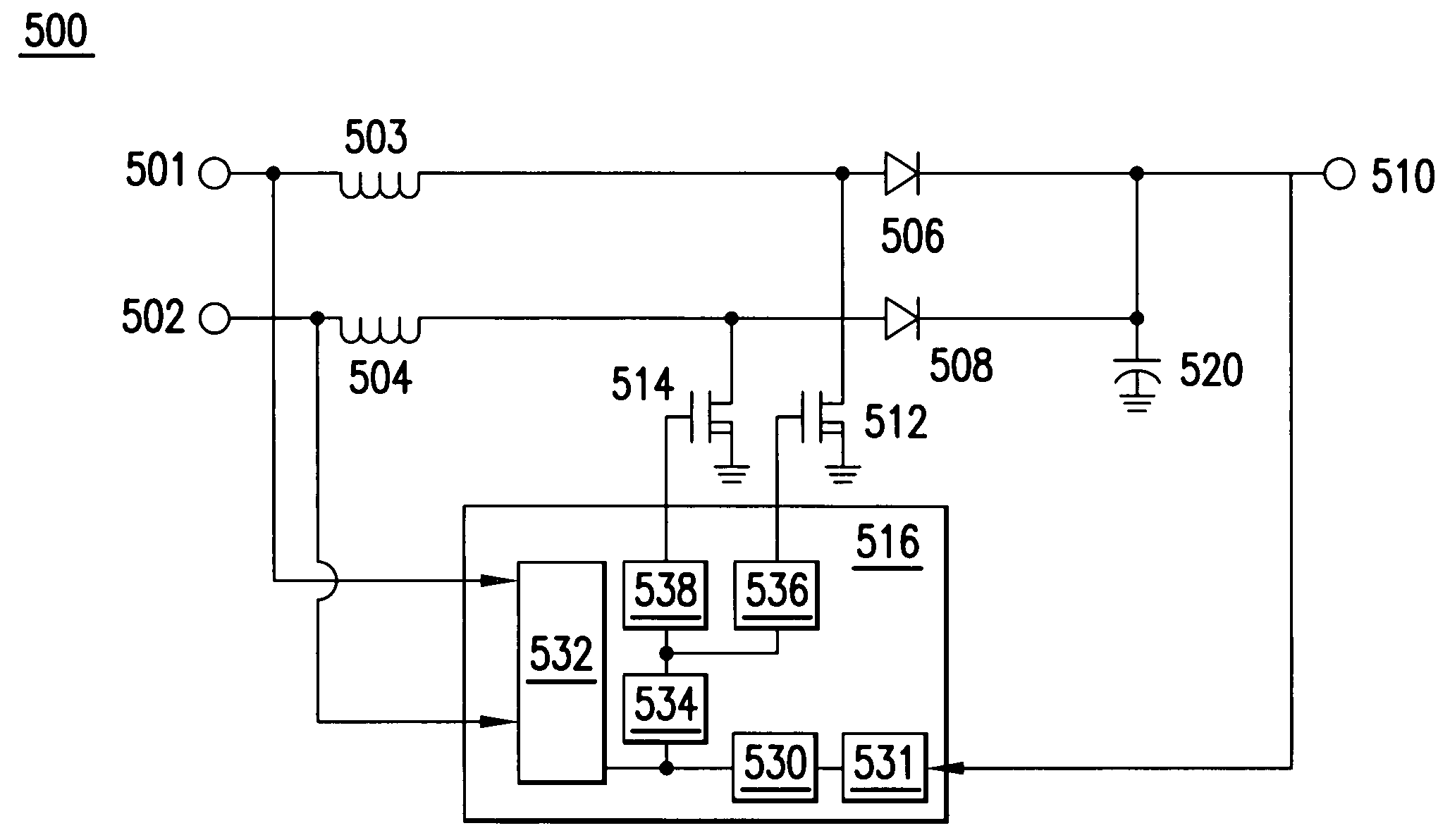
Power line communication using power factor correction circuits
ActiveUS7205749B2Systems using filtering and bypassingAc-dc conversion without reversalElectronic systemsPower MOSFET
A PFC circuit modulating a power line using pulse width modulation (PWM) to drive a power MOSFET and series inductor across the power line. Since many modern electronic systems include a power factor correction circuit (PFC) that already includes a series inductor and power MOSFET, a PLC is incorporated into a controller to inject a PLC transmit signal into a control loop for the PFC circuit. This can be done using either an analog PFC controller, such as the UCC28517, the UCC2819A, or a digital PFC controller such as based on a TMS320C24xx DSP.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Electric ARC welder and plasma cutter
InactiveUS6023037AReduce Harmonic DistortionImprove power factorAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcFull waveTransformer coupling
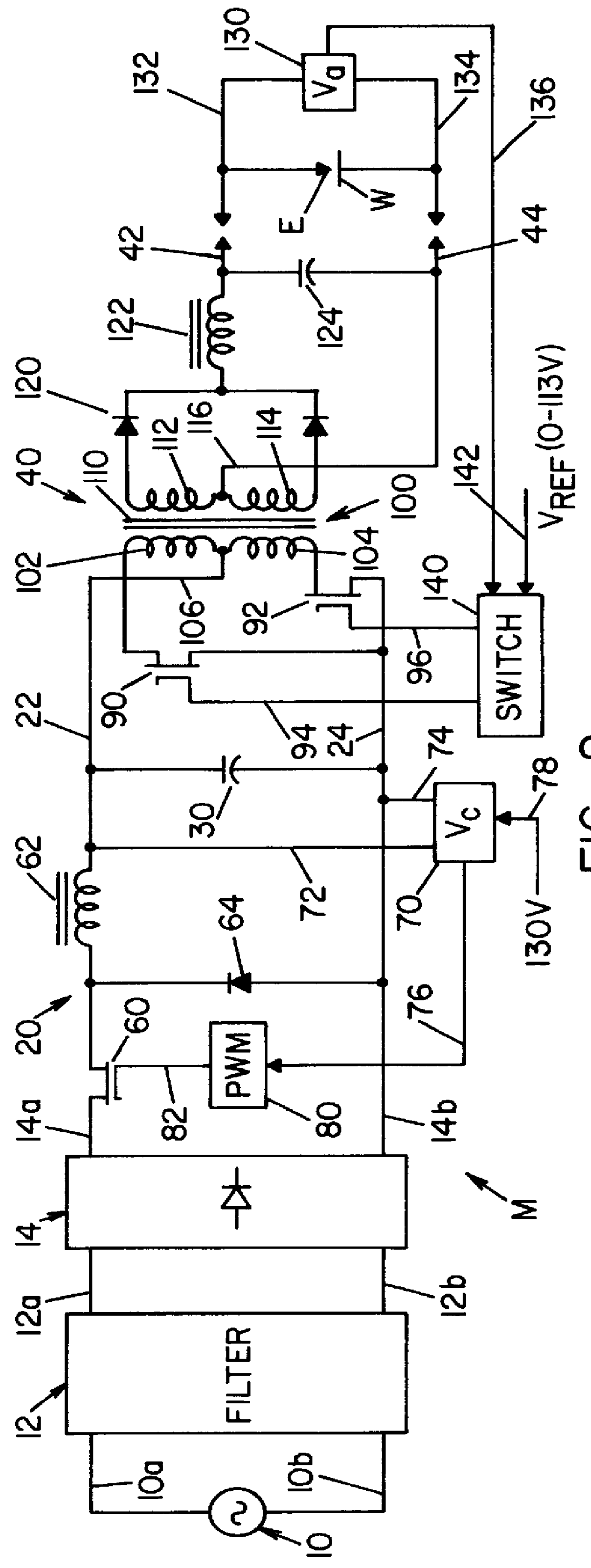
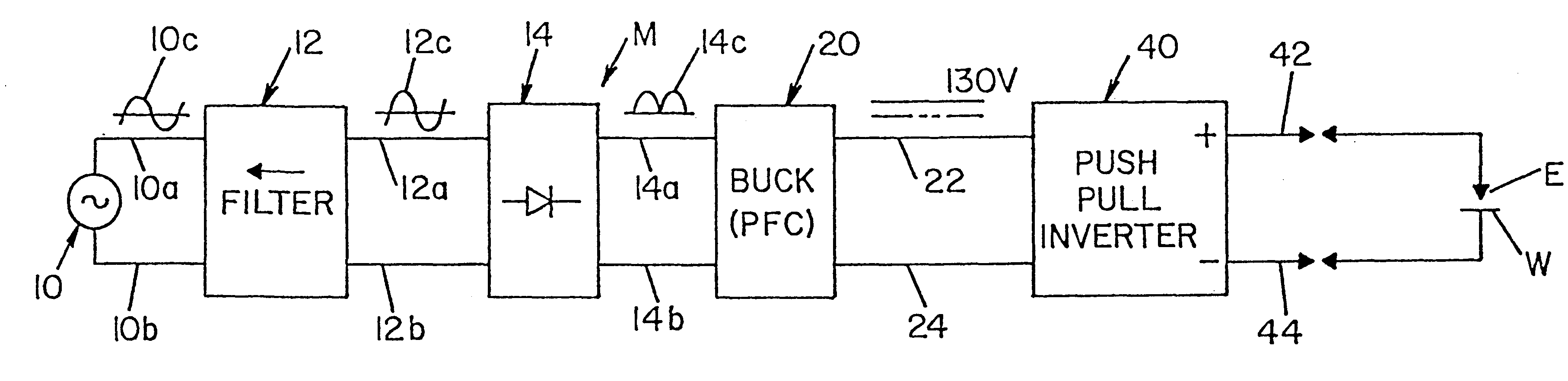
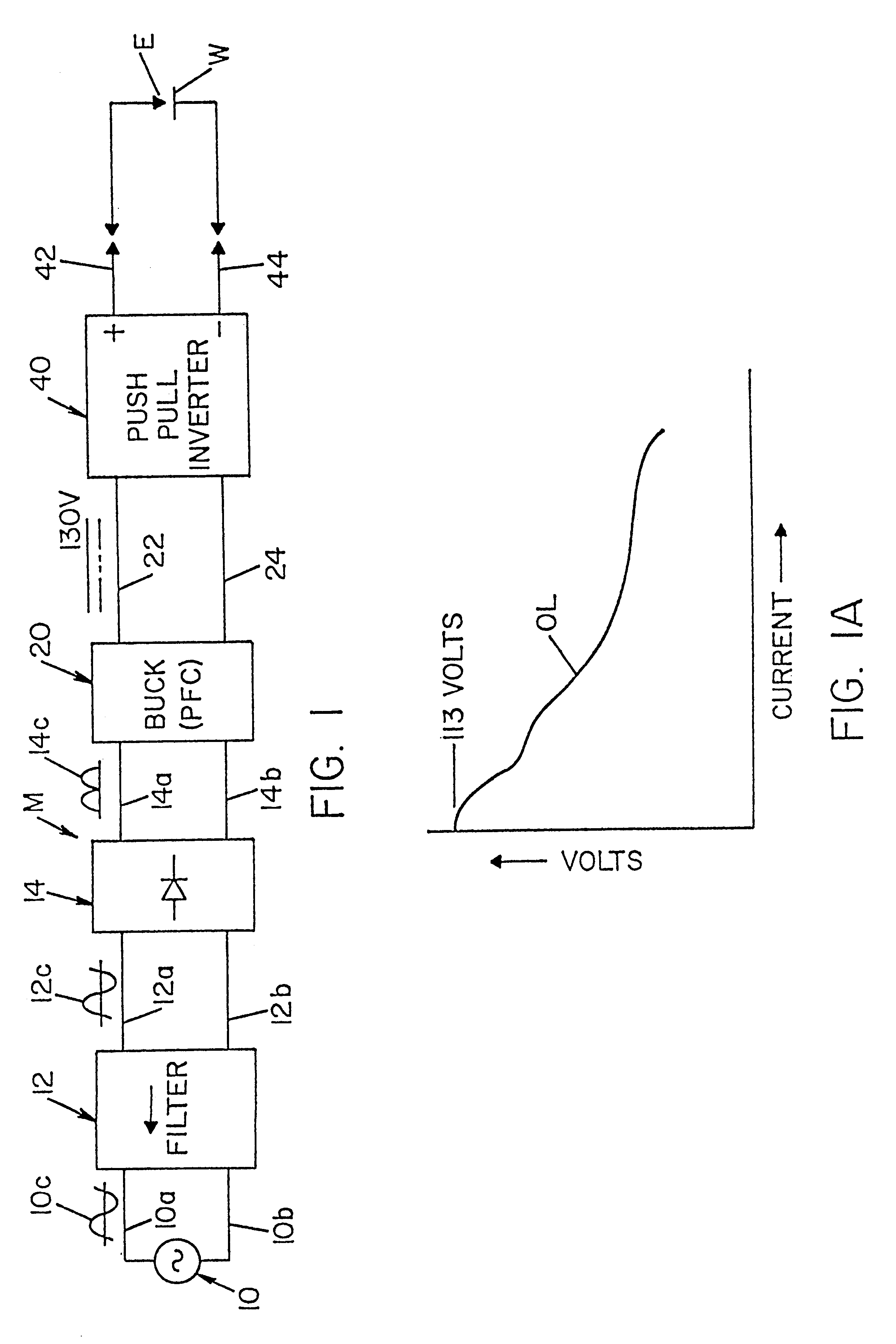
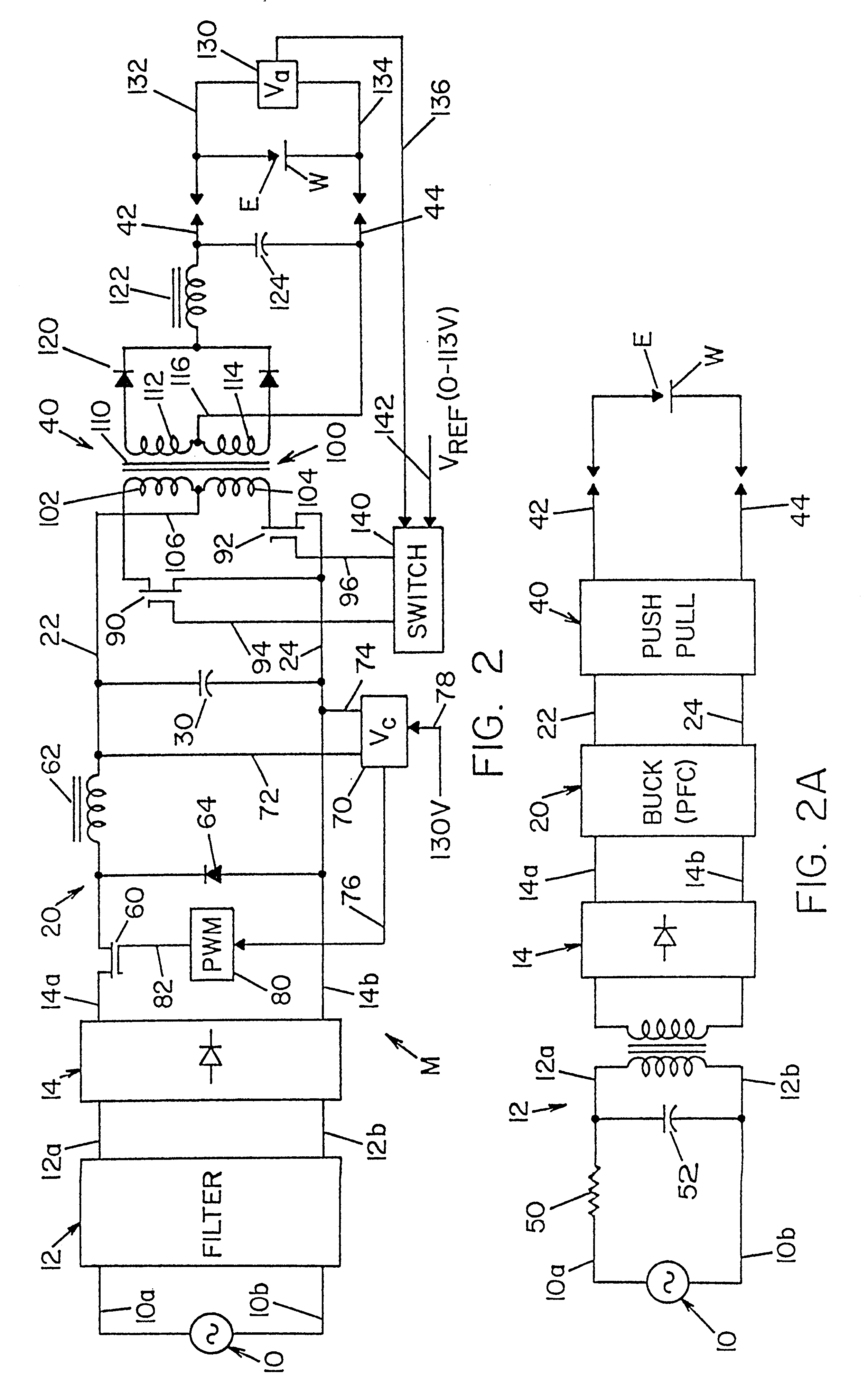
A single phase power supply module for electric arc welders and plasma arc cutters comprising: a single phase input stage; positive and negative output terminals; a full wave rectifier connected to the input stage for rectifying the single phase voltage at the input stage; a buck converter type power factor correcting circuit for controlling current flow from the input stage to the rectifier, which buck converter has an output capacitor regulated to an intermediate voltage in the range of 100-150 volts; and, a high speed DC to DC converter having an internal transformer coupling applying voltage across the output terminals and means for regulating the applied voltage to an output voltage in the range of 0-113 volts. The module is universal and several can be connected in parallel, in series or to switch networks to construct several welders or cutters.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
Power supply controller for exercise equipment drive motor
InactiveUS6906503B2Improve power factorRaise transfer toAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionPower controllerDrive motor
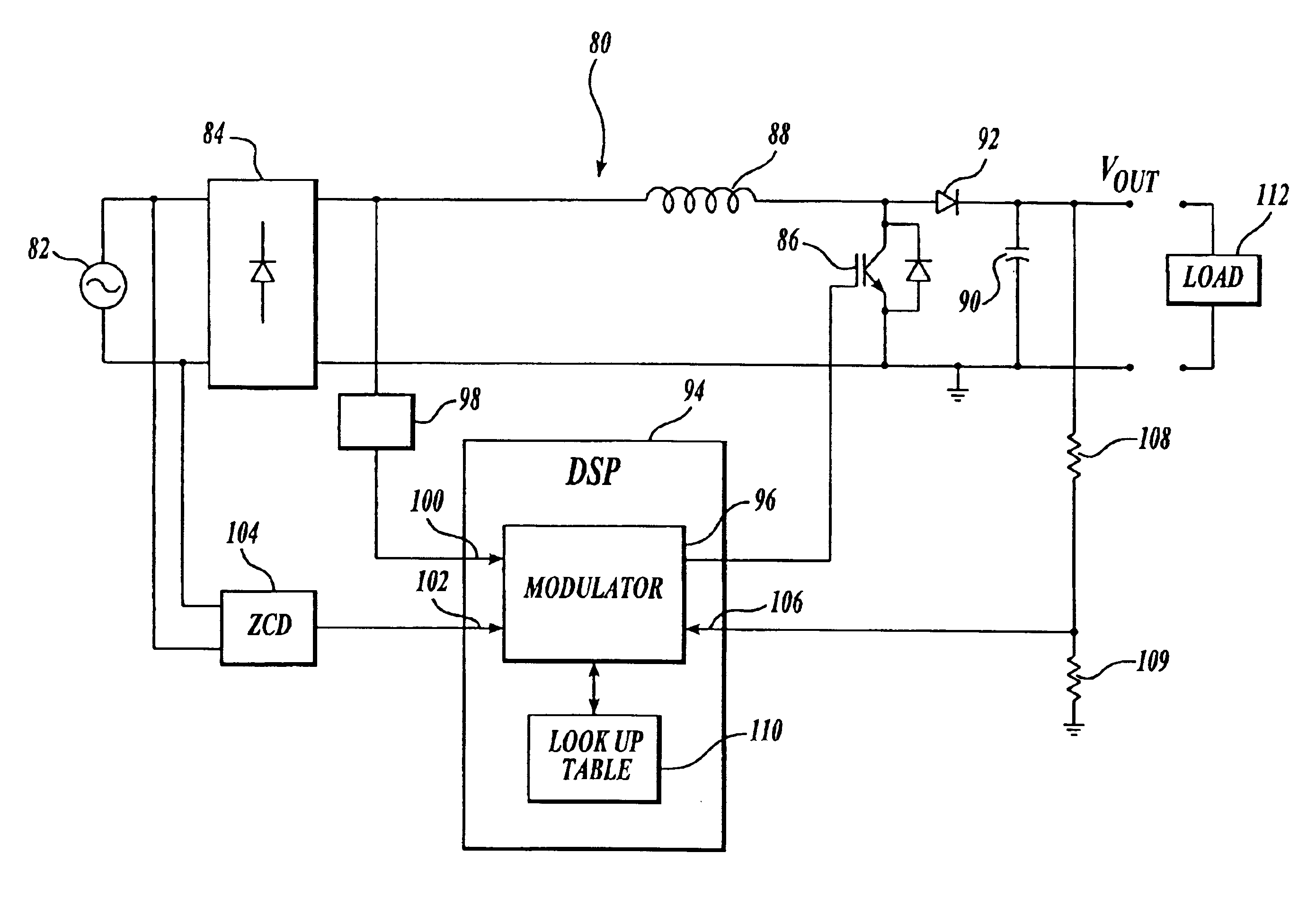
A combined power supply and driver control module includes rectifier circuitry, switching circuitry, and driver circuitry for providing output power to a load. Rectified output from an input power source is used to produce a DC power. The switching circuitry receives the DC power and modulates the input current drawn from the power source. An intelligent control module includes control circuitry, such as a digital processor, for controlling the switching circuitry. Power factor is improved by modulating the input current to be closer in phase with the voltage of the power source. Also disclosed is a power factor correction circuit in which a digital processor reads waveform values from a lookup table and modulates the input current waveform based on the values. A zero crossing detector connected to the input power source may direct the digital processor when to commence reading values from the lookup table.
Owner:PRECOR
Electric arc welder and plasma cutter
InactiveUS6177645B1Reduce Harmonic DistortionImprove power factorAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcFull waveEngineering
A single phase power supply module for electric arc welders and plasma arc cutters comprising: a single phase input stage; positive and negative output terminals; a full wave rectifier connected to the input stage for rectifying the single phase voltage at the input stage; a buck converter type power factor correcting circuit for controlling current flow from the input stage to the rectifier, which buck converter has an output capacitor regulated to an intermediate voltage in the range of 100-150 volts; and, a high speed DC to DC converter having an internal transformer coupling applying voltage across the output terminals and means for regulating the applied voltage to an output voltage in the range of 0-113 volts. The module is universal and several can be connected in parallel, in series or to switch networks to construct several welders or cutters.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
Controller for a power factor corrector and method of regulating the power factor corrector
InactiveUS7012413B1Efficient power electronics conversionElectric variable regulationPower switchingEngineering
Owner:LINEAGE POWER
Burst mode resonant power converter with high conversion efficiency
InactiveUS20110085354A1Improve conversion efficiencyLowering maximum switch frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTransformerResonant power converters
A burst mode resonant power converter with high conversion efficiency has a rectifier, a power factor correction circuit, a resonant circuit, a controller, and a burst mode triggering unit. The maximum frequency switching end of the controller is connected to a maximum frequency variable circuit. When the load is medium or heavy, the maximum frequency variable circuit increases the maximum switch frequency of the controller. When the load is in the no-load or the light conditions, it reduces the maximum switch frequency thereof. Therefore, the controller reduces the number of times that the resonant circuit switches the bridge switch circuit. The conduction cycle of the 50% pulse signal output to the bridge switch circuit becomes longer. Larger energy can be transmitted at a time to the secondary coil of the transformer. This increases the overall efficiency.
Owner:ACBEL POLYTECH INC
Instant start electronic ballast with universal AC input voltage
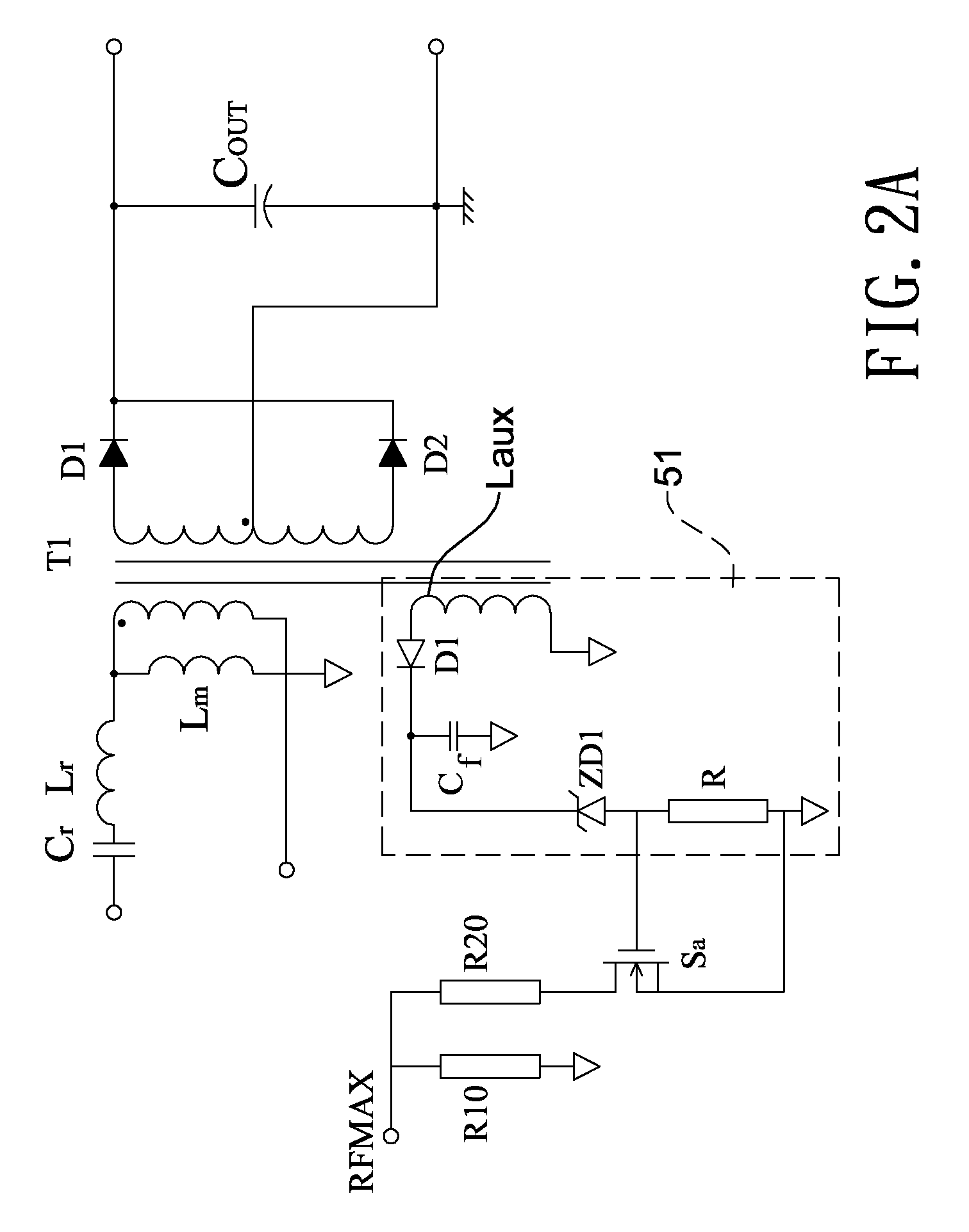
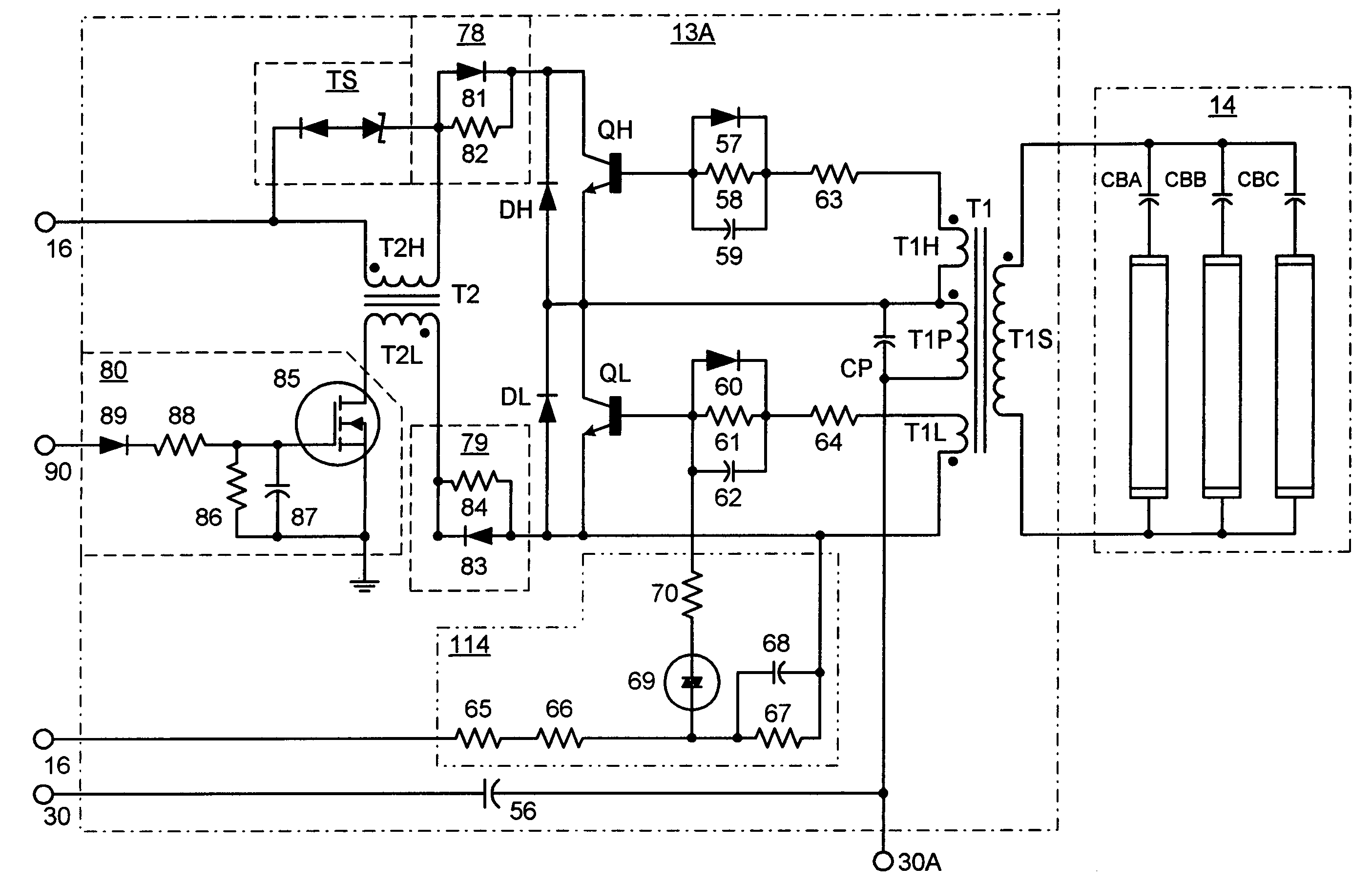
InactiveUS7061188B1Improve unit efficiencyLimit power lossElectric heatingElectric light circuit arrangementZener diodeEngineering
The present invention relates to an electronic ballast that energizes fluorescent lamps connected in a parallel configuration. The ballast employs a power factor correcting boost converter that can be used over a wide range of AC line voltages to provide regulated power to a self-oscillating sine wave inverter that drives the fluorescent lighting load at high frequencies. The inverter employs special networks that limit a certain type of shoot-through current, and thus improve the efficiency of the unit. Also included is a restart circuit that limits power losses during the zero lamp condition, by periodically interrupting the inverter operation when the zero lamp state is detected. To improve operation of the power factor correcting circuitry over the wide range of AC line voltages, a DC offset is added to the sampled AC voltage at the higher AC line voltages by Zener diode based coupling circuit.
Owner:TECHN CONSUMER PRODS
Electronic power supply device
InactiveUS6219263B1Efficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionOvervoltageElectronic switch
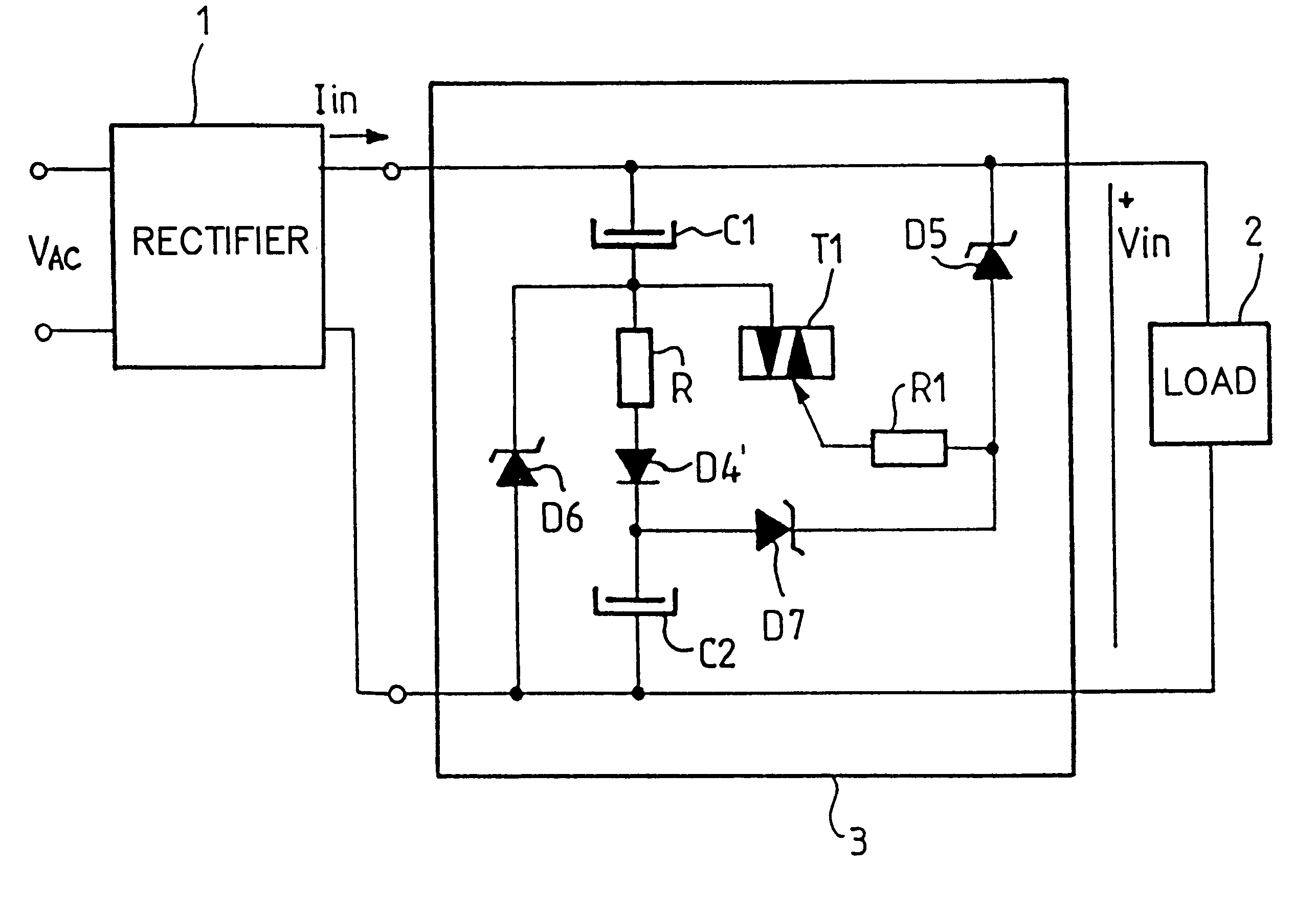
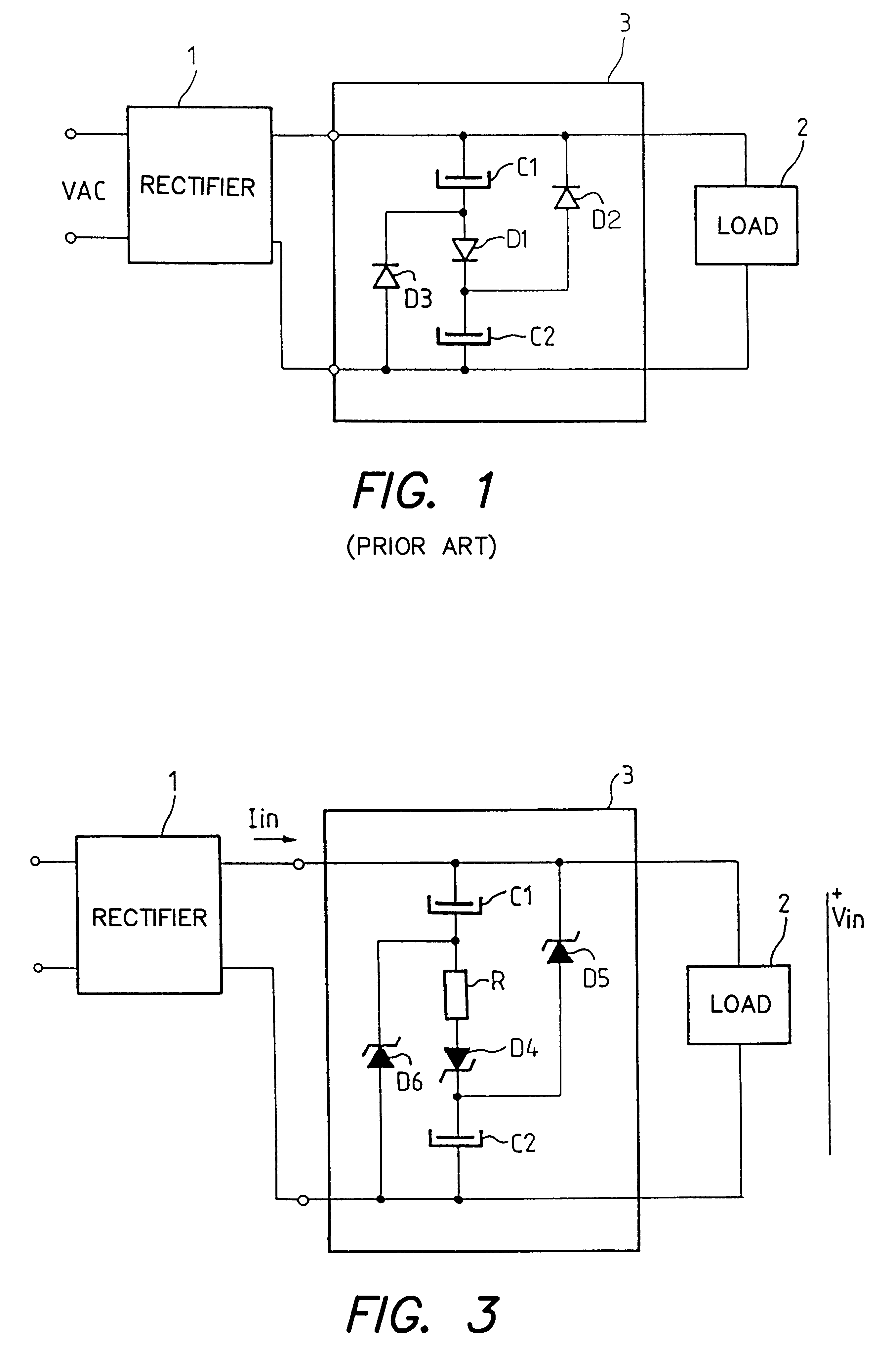
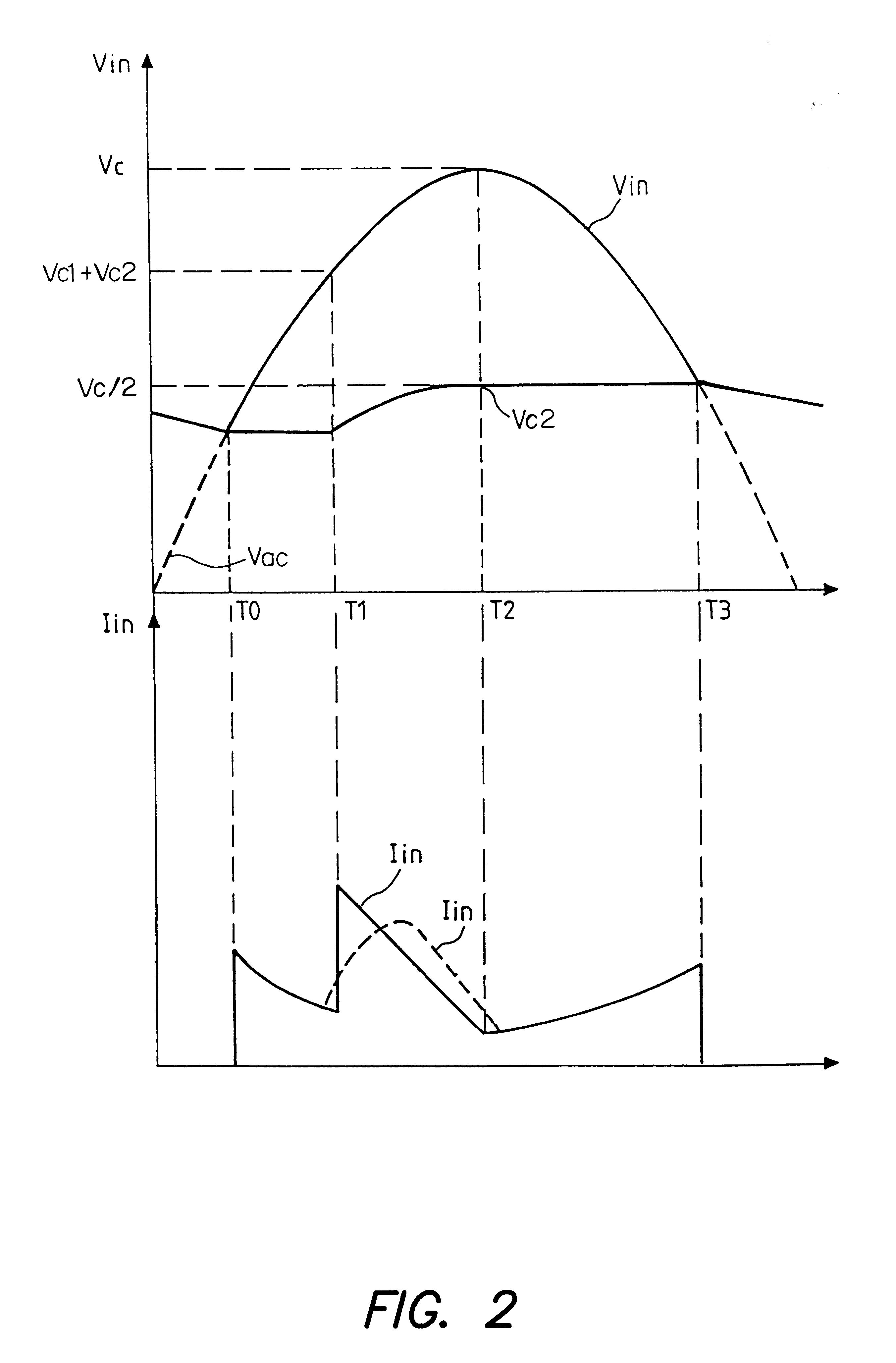
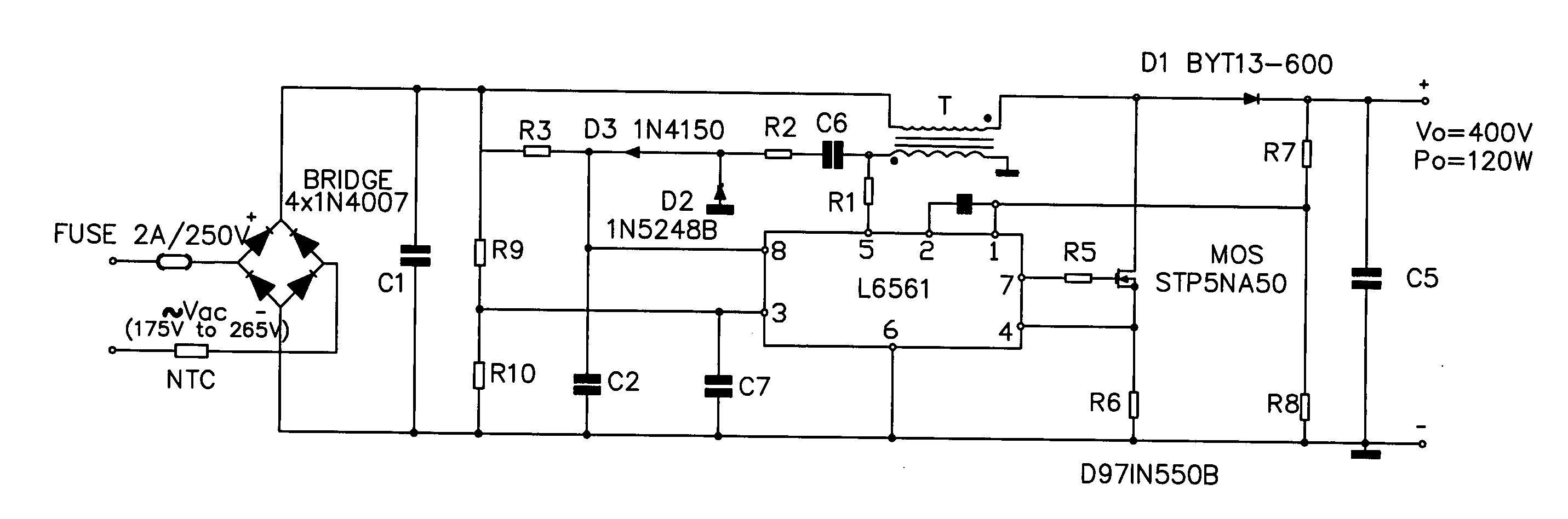
A power factor correction circuit using a first rectifier diode to control the series charging of two capacitors and two rectifier diodes to control the parallel discharging of the two capacitors. The power factor correction circuit further includes a resistor that is series-connected with the first diode to improve the power factor and to reduce the current drawn when the voltage is turned on. The rectifier diodes are advantageously voltage limiting diodes to protect the downline circuitry against overvoltages. In one improvement, a current-controlled electronic switch is used for protection against overvoltages that are just above the peak value of the line voltage.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Power factor correction circuit and driving method thereof
ActiveUS20100110593A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionSwitched currentEngineering
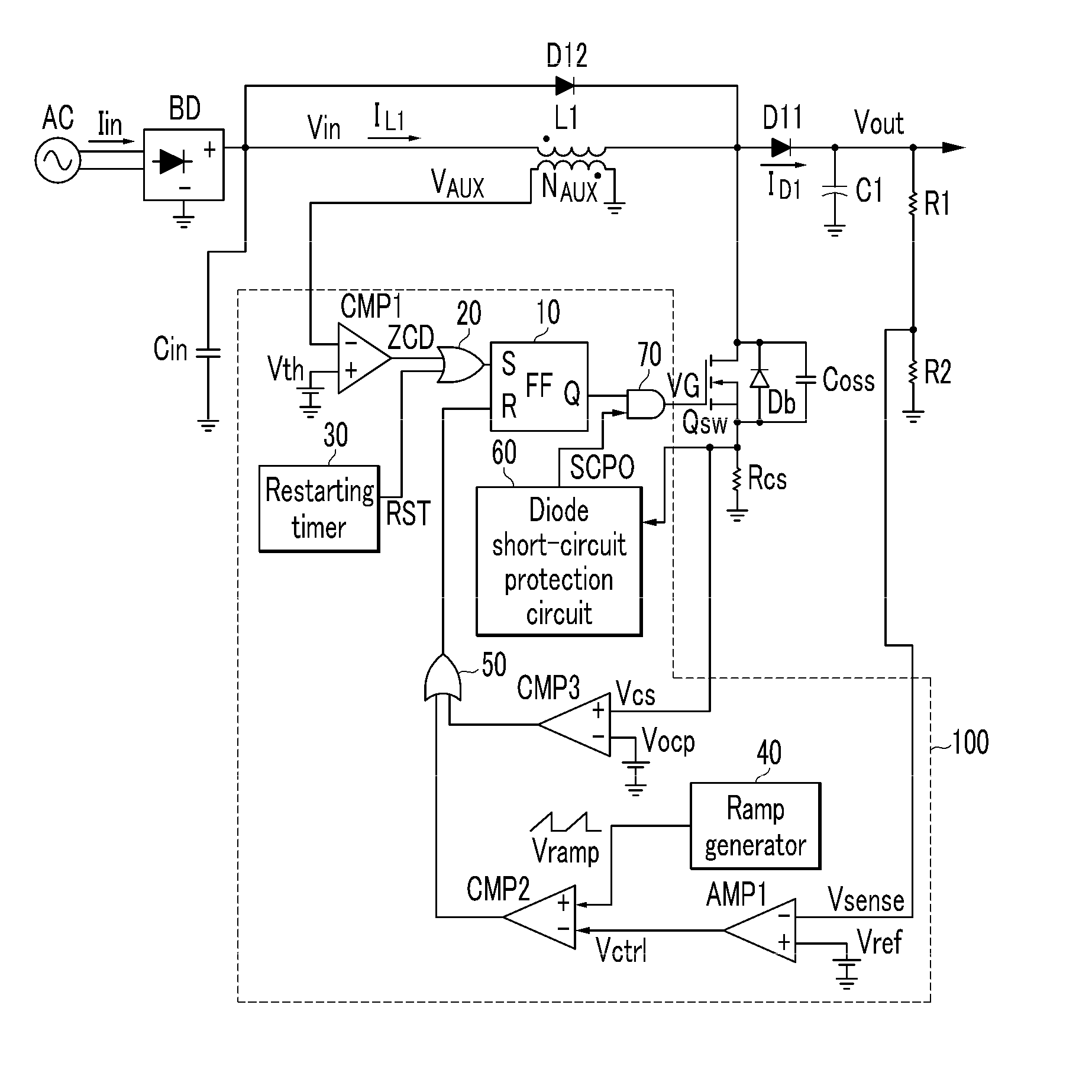
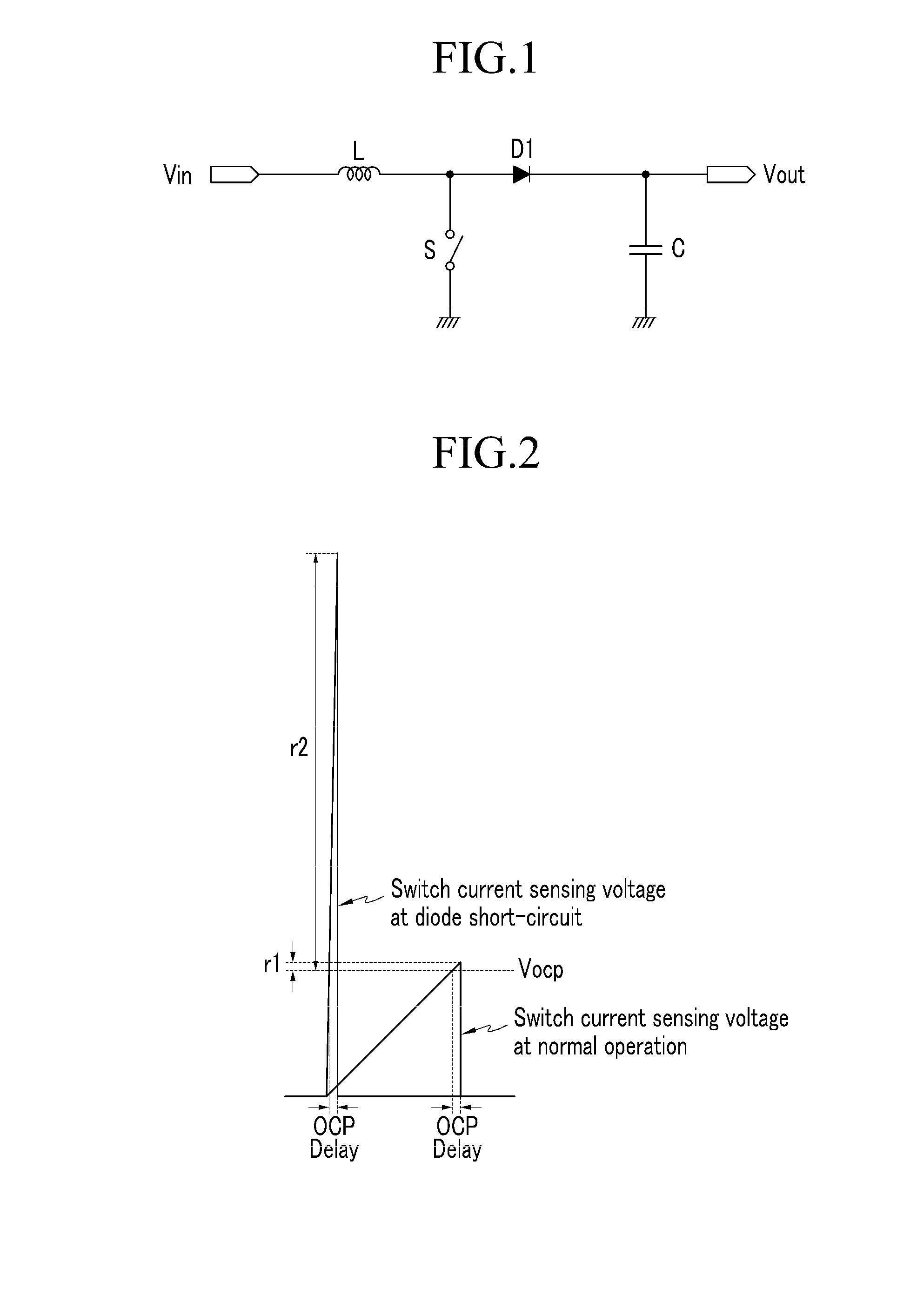
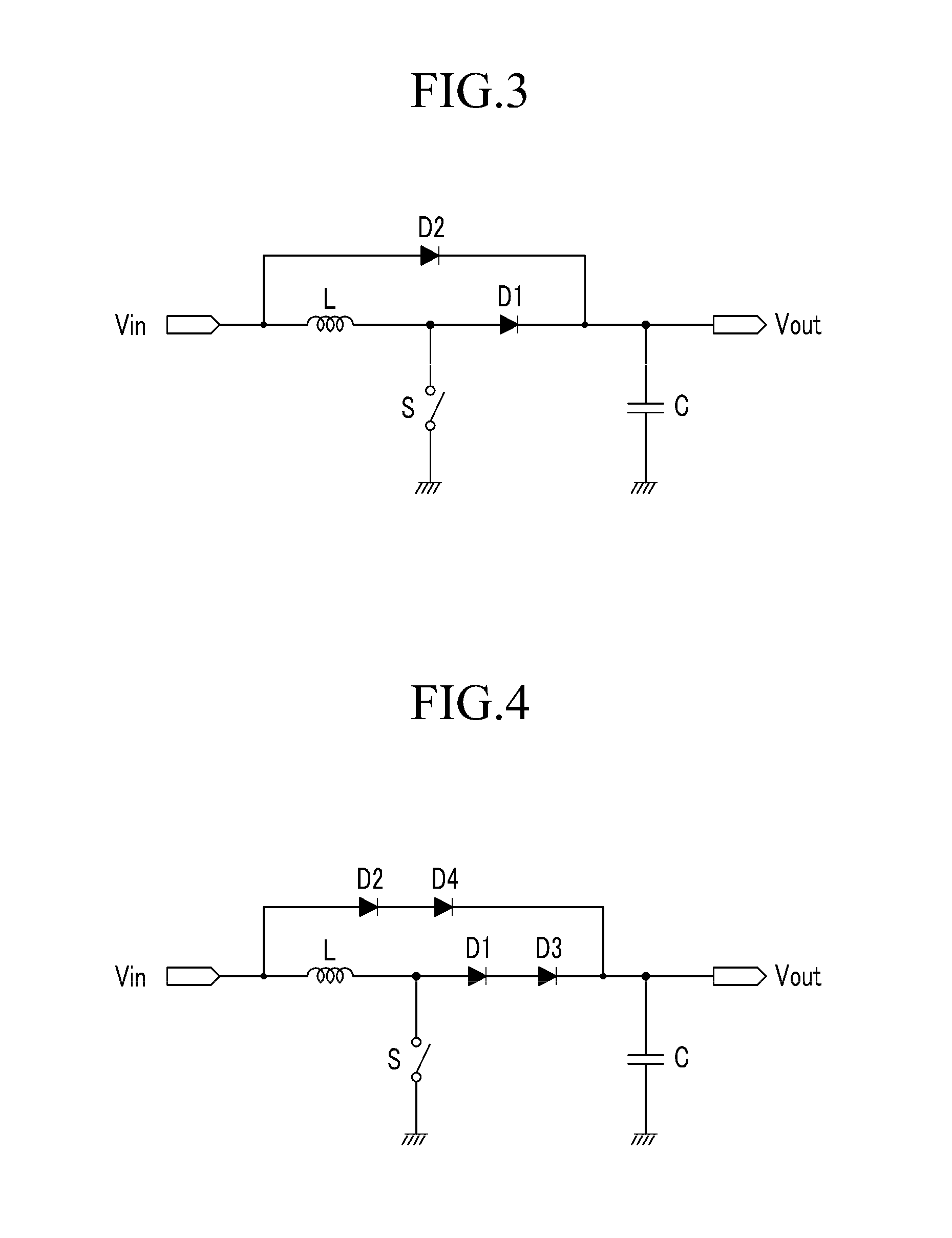
The present invention relates to a set protection circuit for when a diode short-circuit defect occurs in a power factor correction circuit of a critical conduction mode. In a conventional power factor correction circuit, an excessive amount of current flows to a switch if a diode is short-circuited so that the switch is damaged. In order to prevent damage to the switch, the present invention provides a method for stopping turn-on of the switch when a switch current is excessive.
Owner:SILICON MITUS
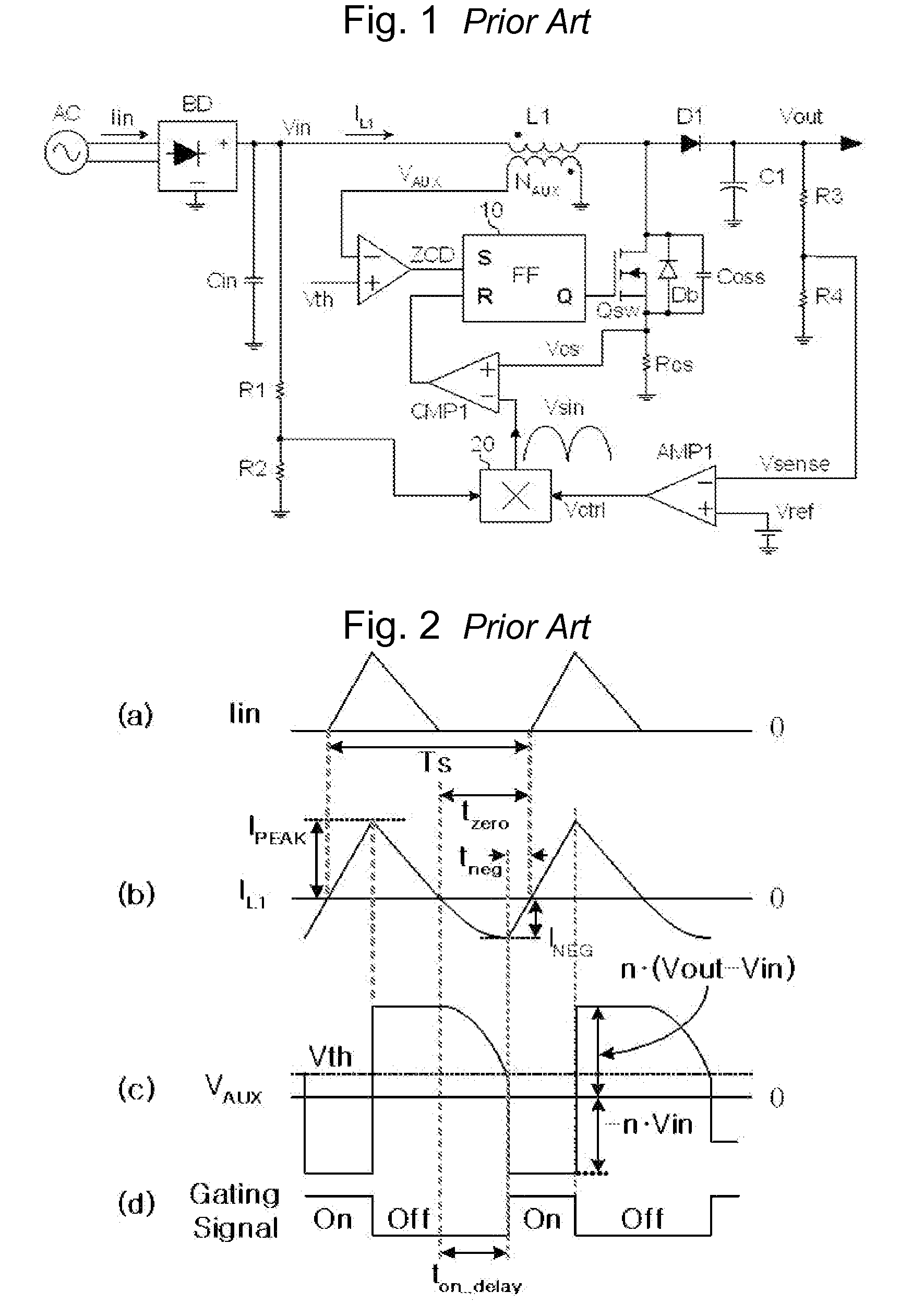
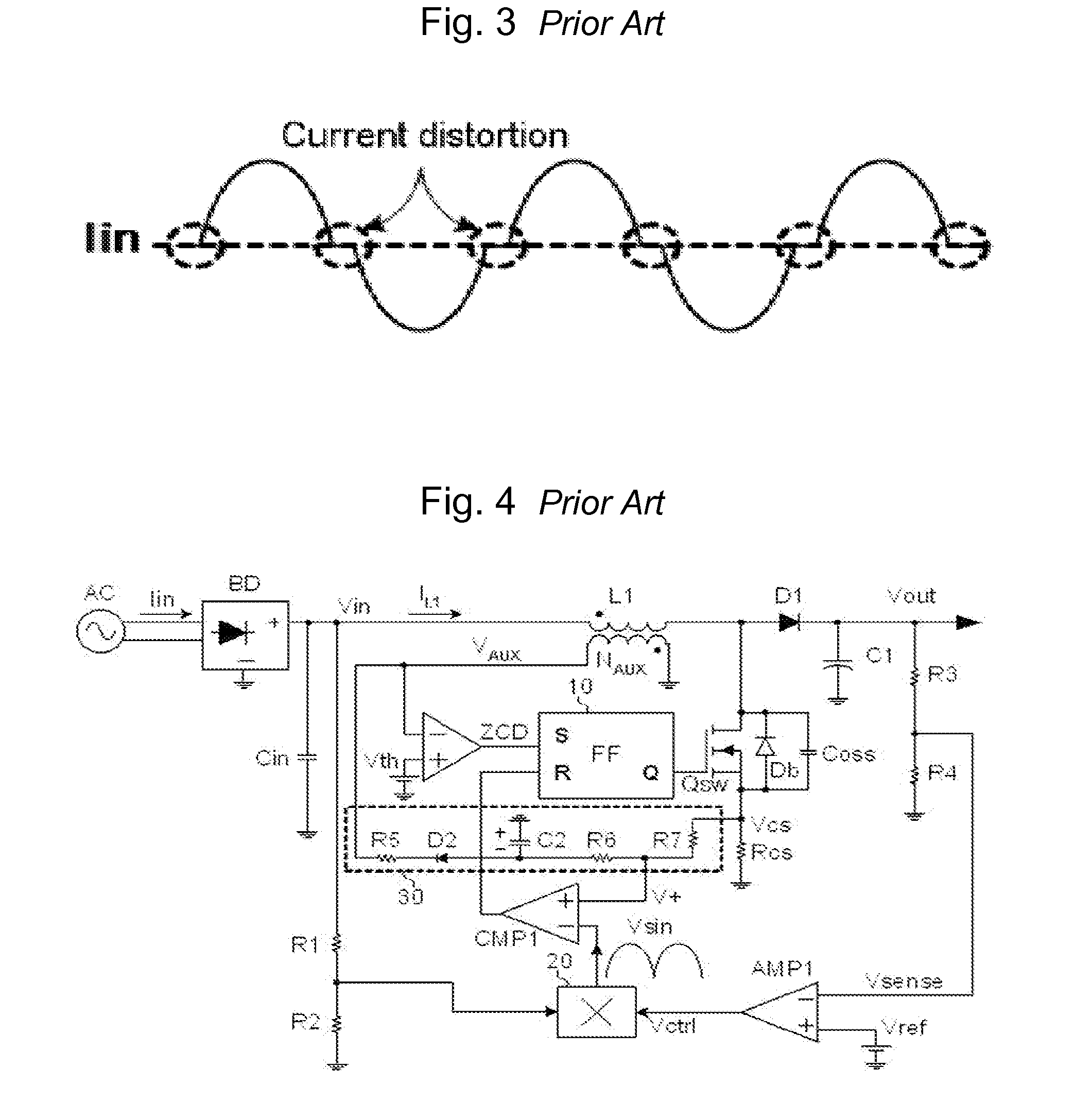
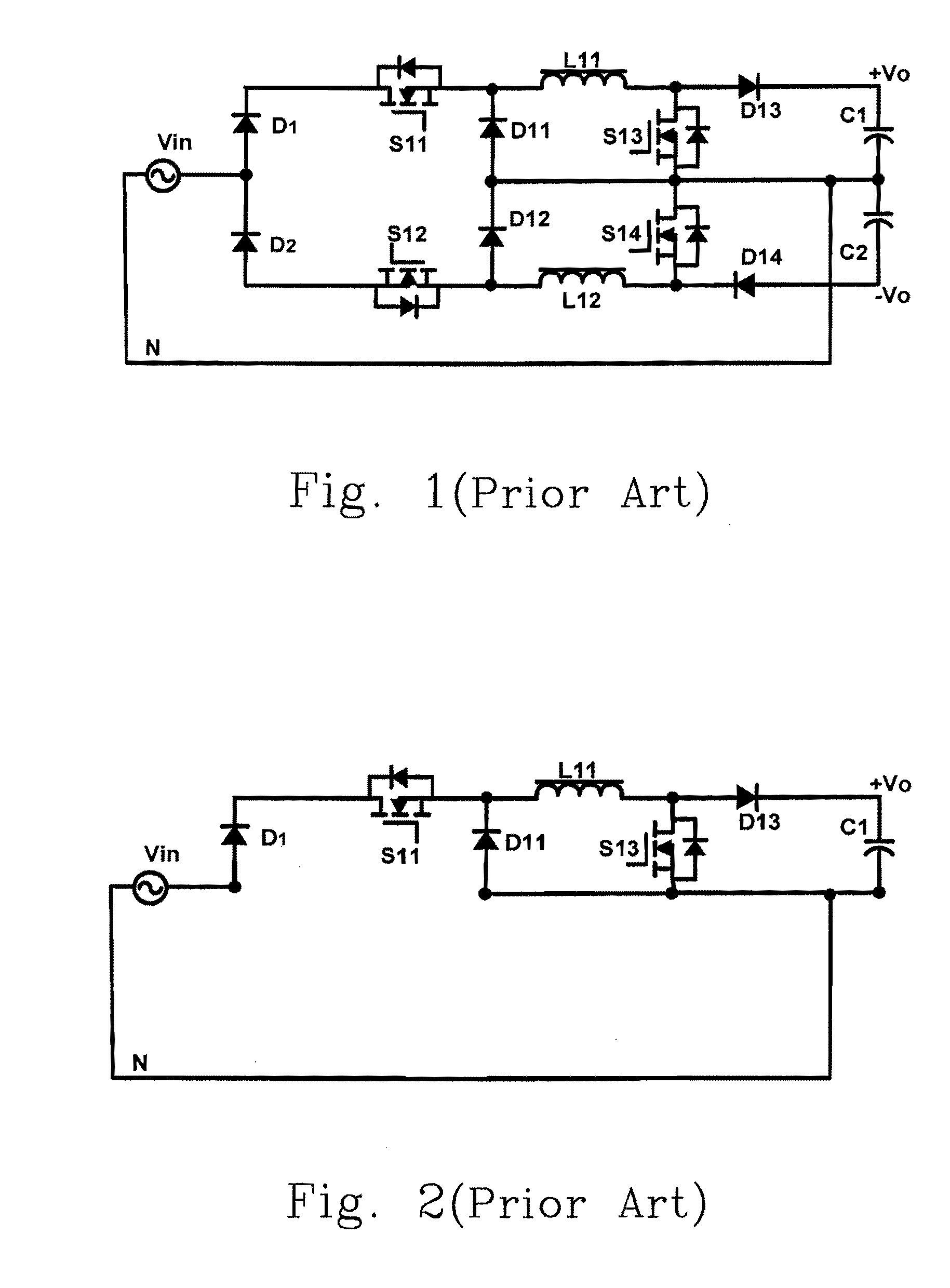
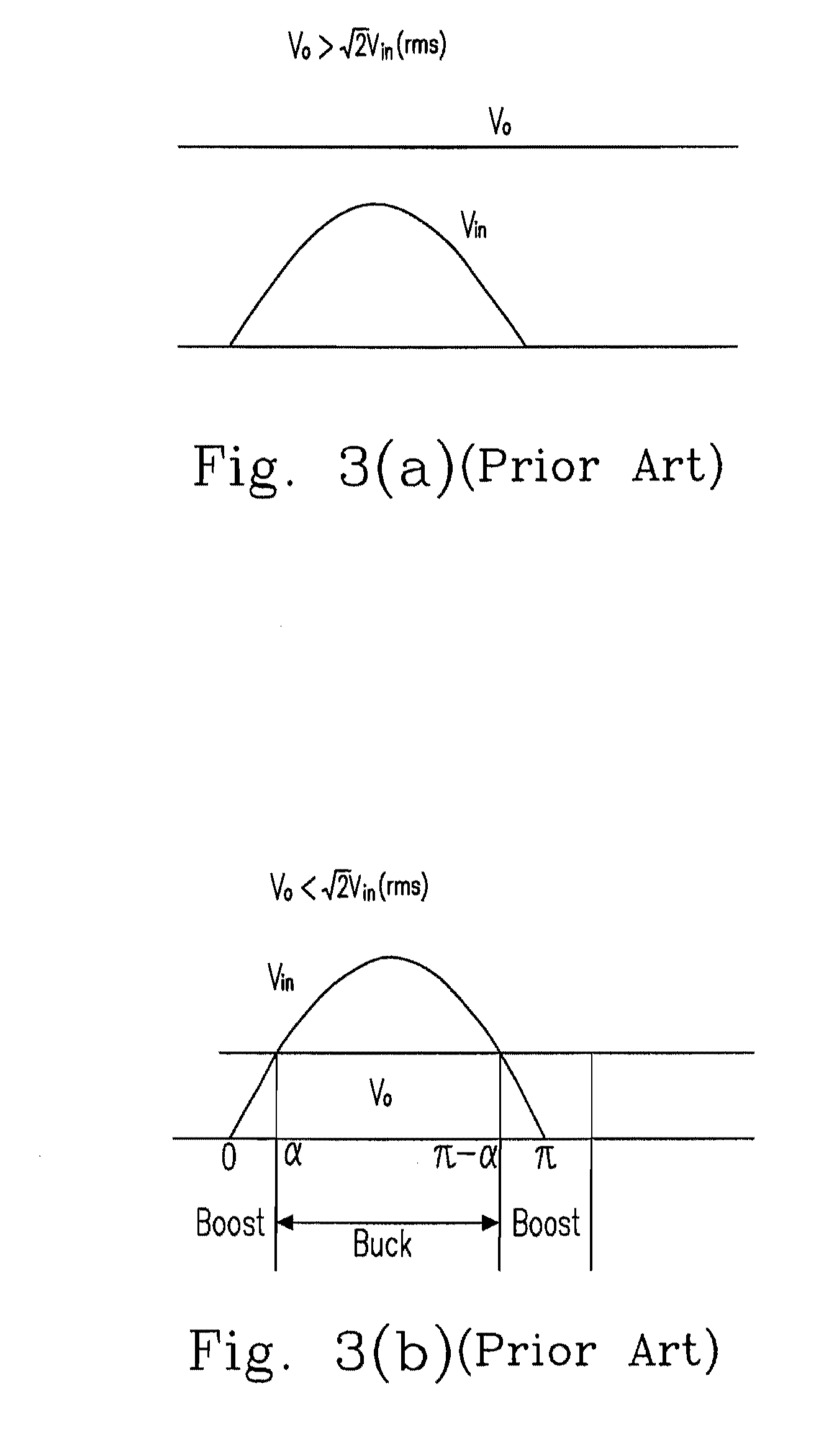
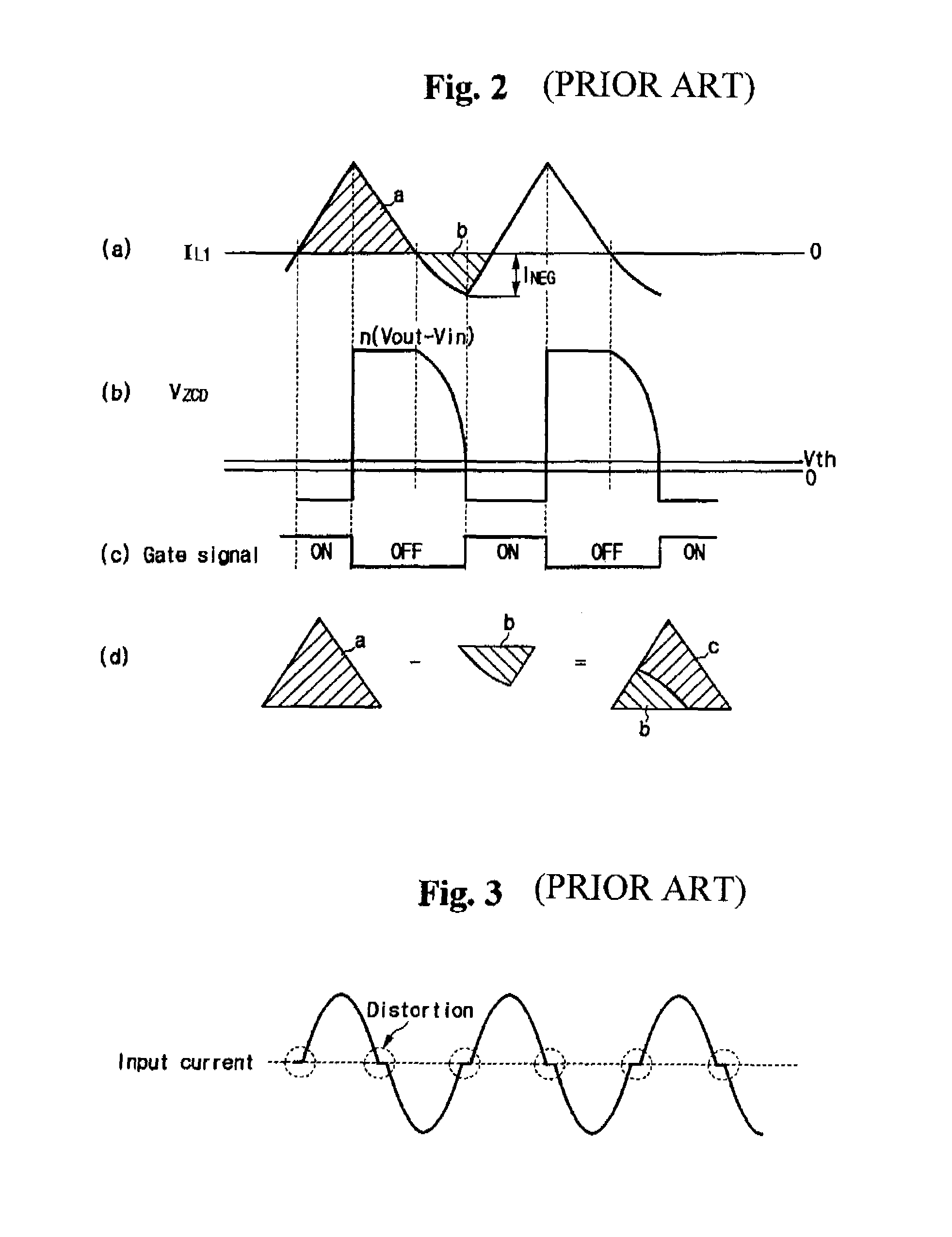
Power factor correction circuits
InactiveUS7279868B2Efficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionPower factor controlEngineering
A bi-directional boost circuit for power factor correction includes a power factor control circuit and a pair of diodes, a pair of inductors, and a pair of switches. A first diode, a second diode, a first inductor, a second inductor, a first switch, and a second switch convert the AC input voltage, rectify the AC input voltage, and output an intermediate DC voltage. The power factor control circuit receives the AC input voltage and receives the intermediate DC voltage. The power factor control circuit regulates the DC output voltage. Based on the AC input voltage and the intermediate DC output voltage, the power factor control circuit controls an inductor current waveform by driving the first switch and the second switch to create a substantially sinusoidal current as seen by the power source that is in phase with the AC input voltage.
Owner:COMARCO WIRELESS TECH
Digital Controller Based Power Factor Correction Circuit
InactiveUS20070036212A1TransistorEfficient power electronics conversionA d converterVoltage reference
A power factor correction circuit utilizes a digital controller string comprised of an analog-to-digital converter, which is input to a digital compensator followed by a pulse width modulation circuit for generating a switching pulse. The loop current in a regulator circuit such as a boost regulator is sensed and input to one side of a differential analog-to-digital converter, the other side thereof providing a digital reference current. This digital reference current is derived from comparing the input AC voltage to the regulator with the DC output voltage and processing these two voltages with a PFC algorithm to provide this reference voltage.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Bridgeless boost converter with pfc circuit
InactiveCN1864319AAvoid restrictionsReduce overload capacity requirementsDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceCycle control
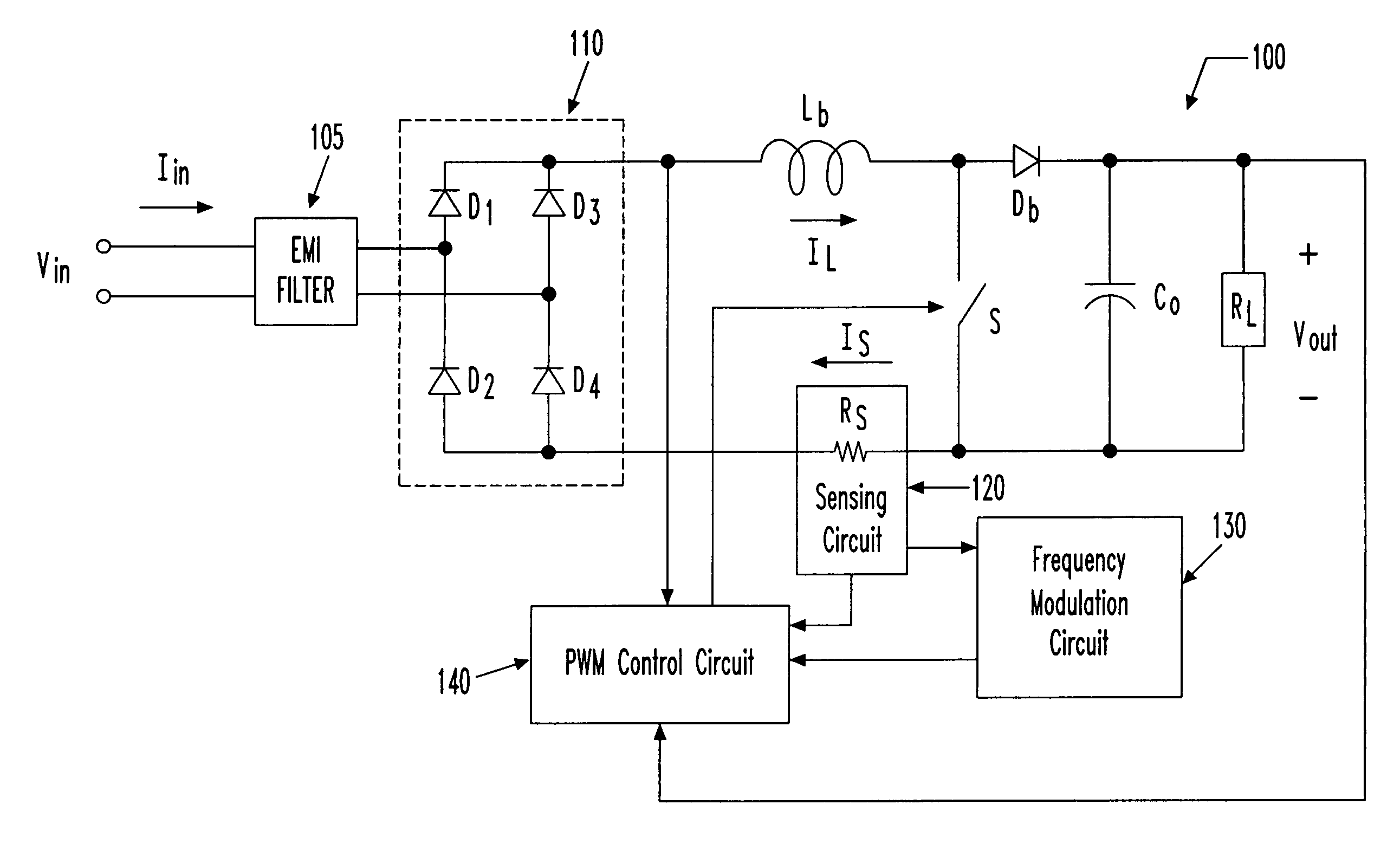
The bridgeless boost topology reduces the power dissipation, cost, and size of prior PFC systems by eliminating the intrinsic loss of the input rectifier bridge. Sensing of the input line voltage by the controller is unnecessary. The use of One Cycle Control (also known as Single Cycle Control) allows the Power Factor Correction function to be performed without complex rectification networks to obtain the AC line voltage reference. The use of bi-directional switches makes it possible to control inrush current (the startup over-current due to the charging of the output bulk capacitor), which allows elimination of over-current limiting devices and reduction of the diode surge capability requirements. Moving the boost inductor to the system input adds an additional filtering function, reducing the cost of input EMI filtering.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL RECTIFIER COEP
Low switching frequency power factor correction circuit
ActiveUS7180273B2Easy to adjustAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionSwitching frequencyVoltage reference
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Controlling inrush current
InactiveUS20060132105A1Efficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentControl signalEngineering
A control circuit and method for controlling a power factor correction circuit comprising: an inductor having an input terminal to receive an input voltage and an output terminal series connected to an anode of a diode; a first capacitor connected between a cathode of said diode and ground; a first switch connected between an anode of said diode and ground; a series arrangement of a second capacitor and a parallel arrangement of a resistor and a second switch series connected with said second capacitor. The control circuit is operable to generate synchronous first and second switch control signals to respectively control said first and second switches, wherein during inrush current conditions when said input voltage drops-in after an interruption, said control circuit is operable to cause said first and second switches to be synchronously switched at increasing duty cycles. The method comprises charging a first capacitor from an input voltage source; isolating the first capacitor from the input voltage source; transferring a portion of charge stored in said first capacitor to a second capacitor while said input voltage source is isolated from said first capacitor and from said second capacitor; and repeatedly said charging, isolating, and transferring until a voltage is formed on said second capacitor that is approximately equal to said input voltage source.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Adaptive on-time control for power factor correction stage light load efficiency
ActiveUS20120014148A1Total current dropImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionHigher order harmonicsSwitching frequency
Light load efficiency of a power factor correction circuit is improved by adaptive on-time control and providing for selection between a continuous conduction mode and a discontinuous conduction mode wherein the discontinuous conduction mode increases time between switching pulses controlling connection of a cyclically varying voltage to a filter / inductor that delivers a desired DC voltage and thus can greatly reduce the switching frequency at light loads where switching frequency related losses dominate efficiency. The mode for controlling switching is preferably selected for each switching pulse within a half cycle of the cyclically varying input voltage. A multi-phase embodiment allows cancellation of EMI noise at harmonics of the switching frequency and adaptive change of phase angle allows for cancellation of dominant higher order harmonics as switching frequency is reduced.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Power transfer system with reduced component ratings
InactiveUS7164590B2Ripple voltage can be minimizedMinimize the differenceAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcElectric power transmissionPower inverter
A power inverter control adjusts input power to track with output power to reduce energy handling requirements for an inverter DC bus. Input power to the power inverter circuit is measured and compared with a measurement of inverter output power. The comparison result is applied to a power factor correction circuit to adjust input power to track with output power, while obtaining a good power factor for the power inverter circuit. The energy requirements and ripple voltages or ripple currents on the DC bus are reduced, leading to a reduction in rating specifications for passive energy storage elements on the DC bus.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
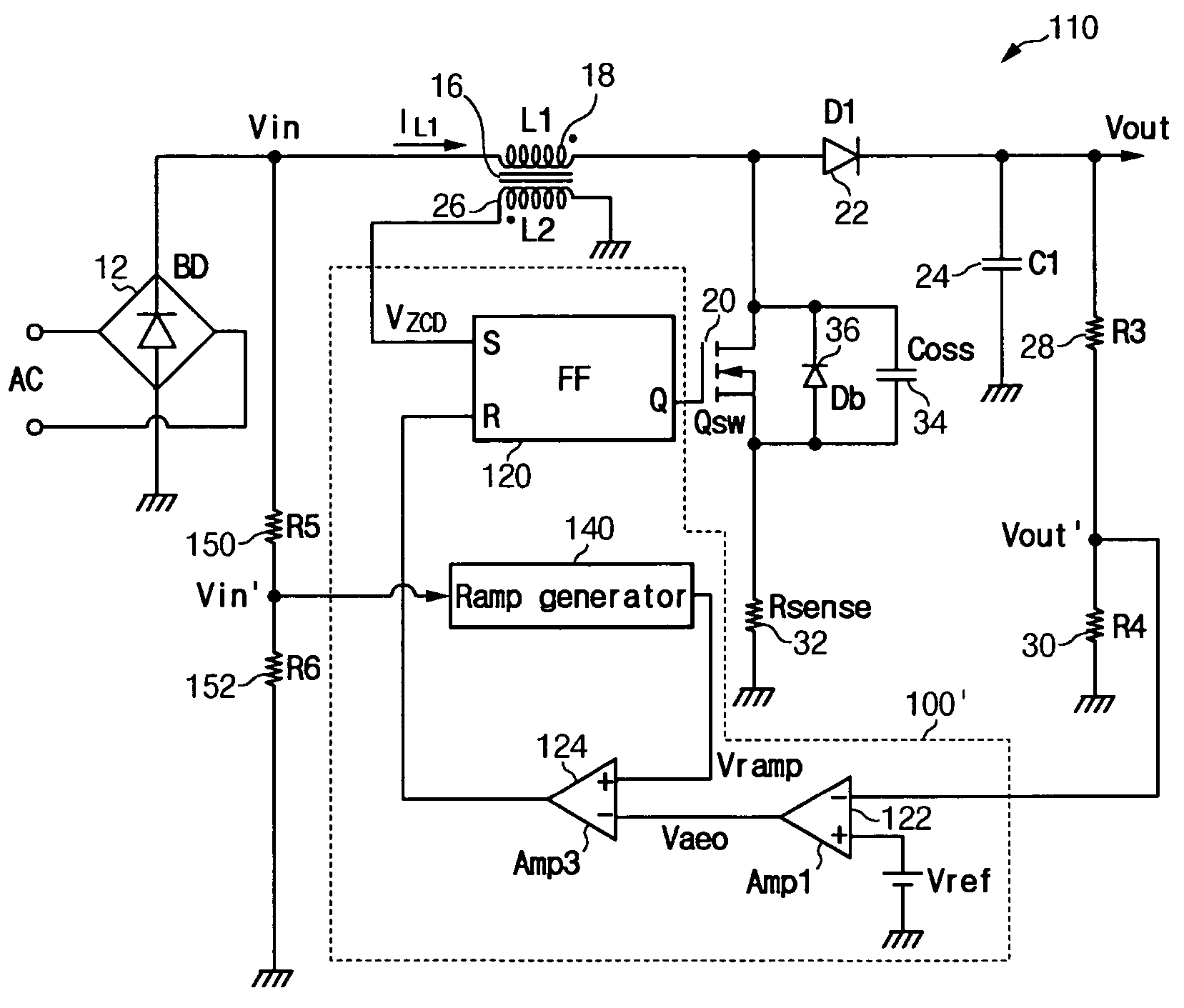
Power factor correction circuit
ActiveUS20110110127A1Improve power factorAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcElectricityPower factor correction circuits
The present invention relates to a power factor correction circuit that can reduce distortion of input current in a switching mode power supply. The power factor correction circuit provided in the present invention basically comprises a first inductor which is electrically connected at a first end thereof to an input terminal, a second coil that is coupled to the first inductor to form an induced voltage, a switch electrically connected to the a second terminal of the first inductor, and a switching control unit for controlling turn-on and turn-off of the switch. In such a power factor correction circuit of the present invention, the switching control unit is configured to differently set a turn-on period of the switch depending on the input voltage by generating a signal for controlling the turn-off of the switch using a second coil voltage induced at the secondary coil of the inductor by input voltage or a directly sensed input voltage. Accordingly, distortion of input current can be effectively corrected.
Owner:SILICON MITUS
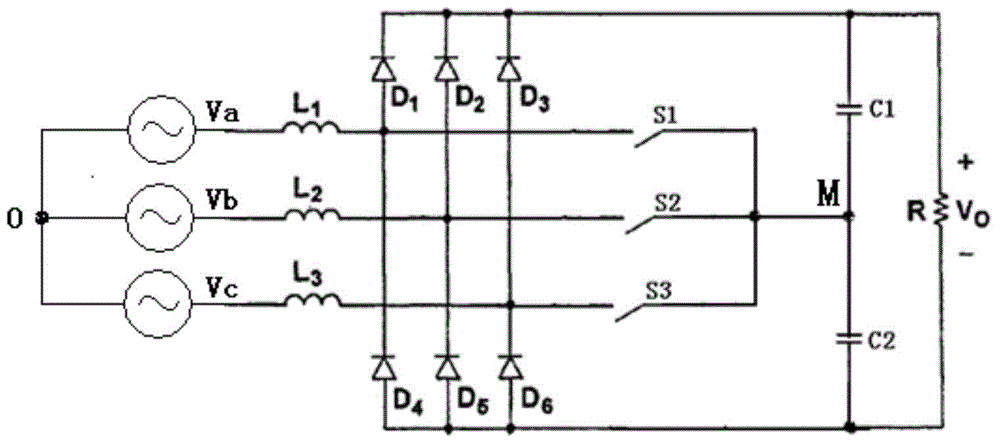
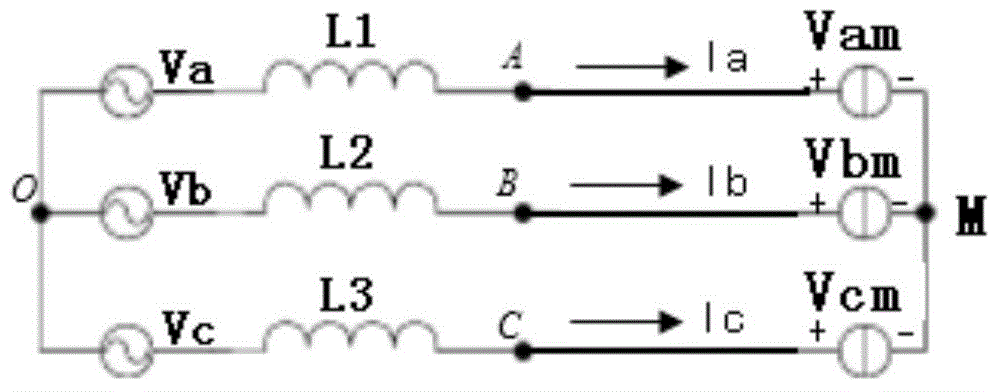
Novel three-phase PFC (power factor correction) rectifier
InactiveCN104811061AMeeting the Needs of High Power DensityImprove efficiencyAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionCapacitanceActive power factor correction
The invention provides a novel three-phase PFC (power factor correction) rectifier. The novel three-phase PFC rectifier is characterized in that three-phase input currents are respectively rectified by a full-wave rectifier circuit in a full-bridge mode after input voltages of three-phase alternating-current input ends are transmitted through respective boost inductors, switch circuits are respectively arranged between the boost inductors and middle points M of output voltages of output ends in a connected manner, voltages of output capacitors C1 and C2 of the output ends are boosted and stabilized by the switch circuits by means of PWM (Pulse width modulation) required by corresponding phases, and accordingly constant voltages V<o> can be outputted even under the condition of variation of loads R of the output ends in design ranges; magnet excitation and demagnetization circuits which comprise capacitors are formed between the middle points M of the output voltages of the output ends and nodes of the input voltages of the three-phase alternating-current input ends, so that the boost inductors can be decoupled under working conditions and can work in critical current modes. The novel three-phase PFC rectifier has the advantages that the novel three-phase PFC rectifier can work in the critical current modes (CRM) and also can work in CCM (continuous current mode) or DCM (discontinuous current mode) states according to requirements, and accordingly requirements on high power density and high efficiency can be met.
Owner:ANHUI DYNAMIC POWER
Integrated circuit of vehicle-mounted charger and DCDC
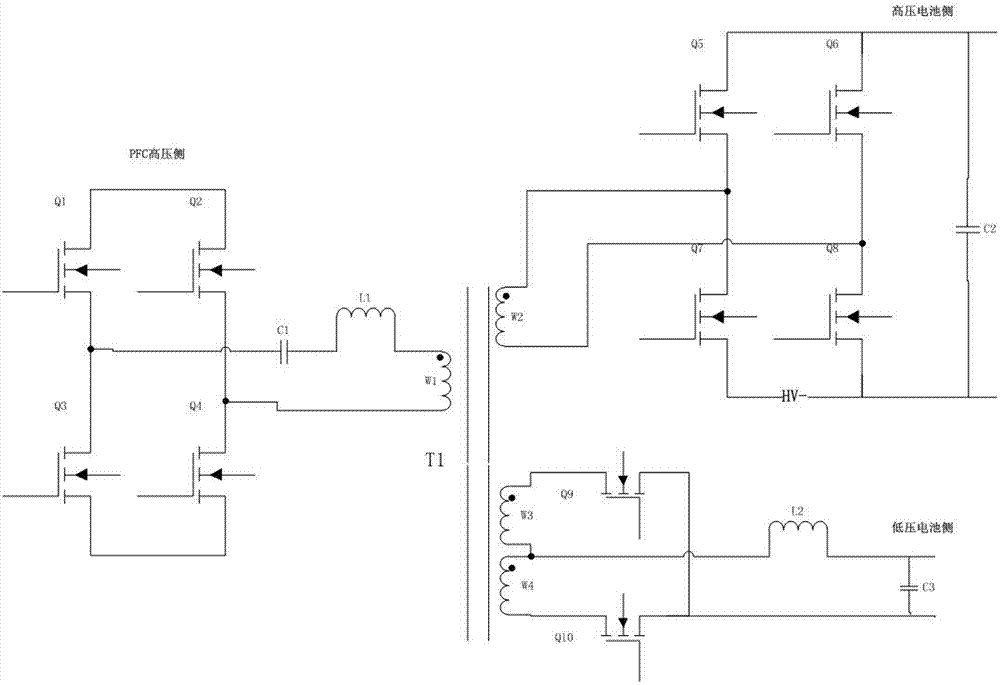
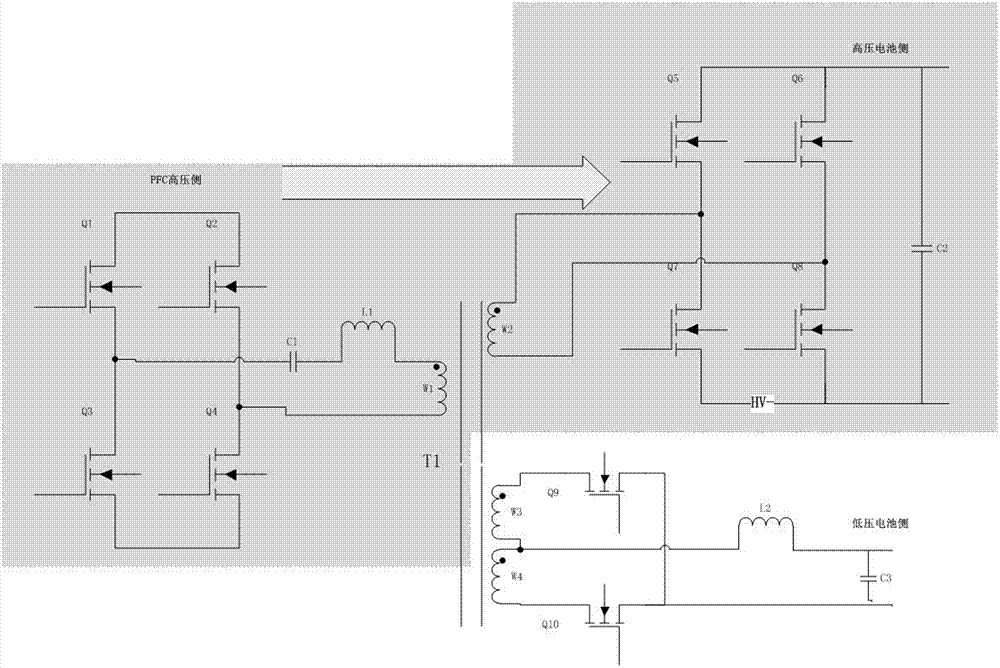
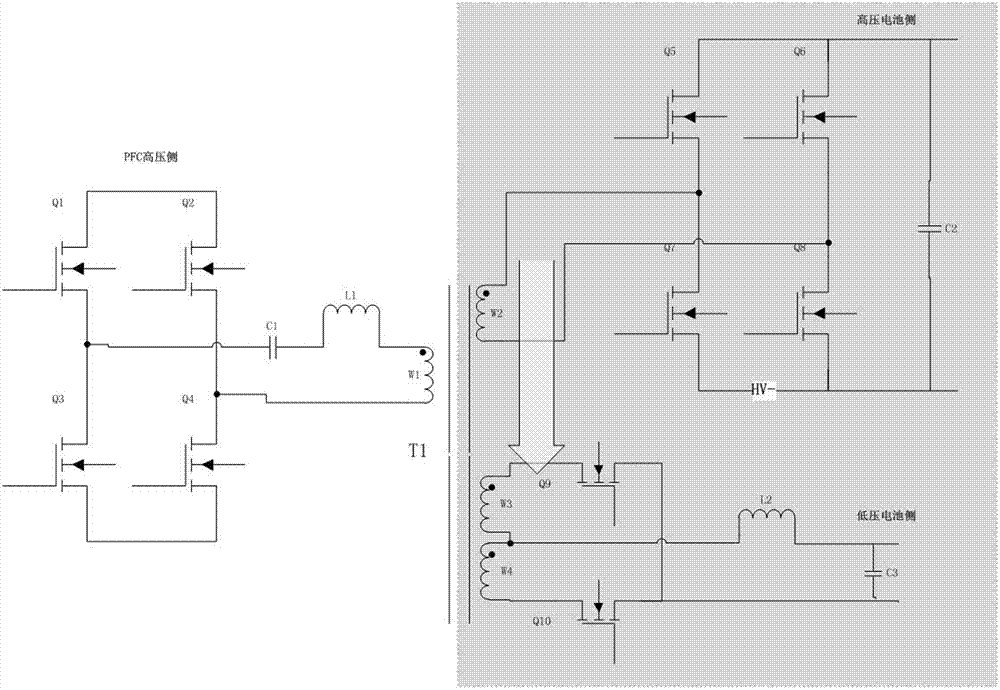
InactiveCN106936184AIngenious designReduce volumeCharging stationsElectric powerElectrical batteryLow voltage
The invention discloses an integrated circuit of a vehicle-mounted charger and a DCDC. The integrated circuit comprises a power factor correction side circuit connected with a power factor correction circuit, a high-voltage battery side circuit connected with a high-voltage battery circuit, a low-voltage battery side circuit connected with a low-voltage battery circuit, and a transformer T1 coupled with the three circuits. The integrated circuit integrates the vehicle-mounted charger and a high-power DCDC module which are independent, shares a power switching tube and a control circuit, shares a magnetic core for energy delivery, can flexibly realize control and switching of a charger mode, a DCDC mode and an inversion mode, and is concise and ingenious in design, small in size, light in weight and low in cost.
Owner:SHENZHEN VMAX POWER
Power factor correction by measurement and removal of overtones
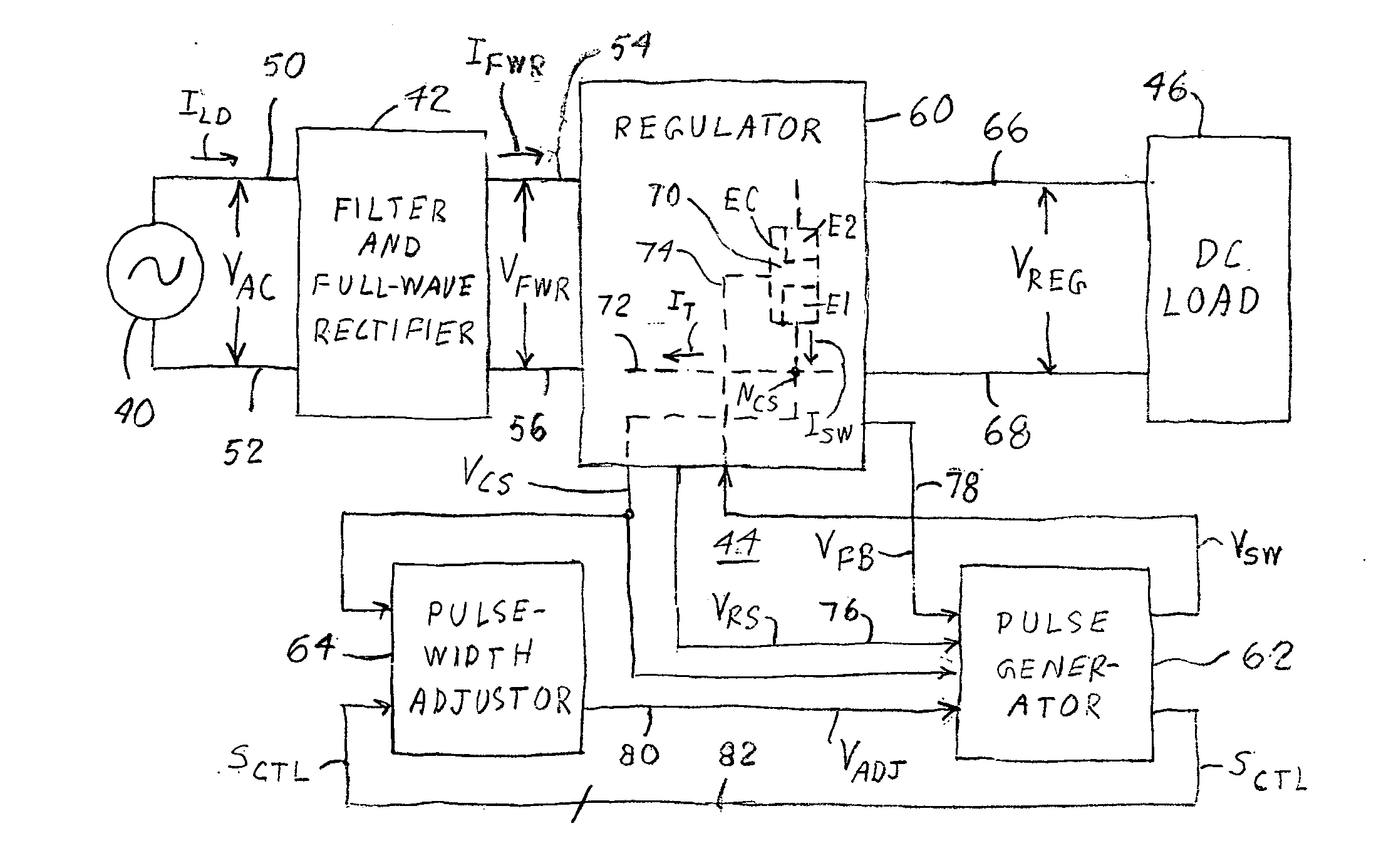
InactiveUS20080246445A1Increase flexibilityReduce sensitivitySpectral/fourier analysisPulse automatic controlEngineeringPower factor correction circuits
A power factor correction circuit (42 / 44) responsive to an input power supply signal at an input supply voltage (VAC) that varies largely sinusoidally with time at a fundamental supply frequency contains regulator / control circuitry (60, 62, and 64) for measuring and removing overtones (ILDm or IFWRm) in the input supply current (ILD) or in a rectified form (IFWR) of the input supply current. Each overtone is expressible as the product of an amplitude component (Im) and a sinusoidal function (Im sin [(m+1)ωACt]) that varies with time at an integer multiple of the fundamental supply frequency. The regulator / control circuitry measures an overtone by determining the overtone's amplitude component. After generating an adjustment factor (SADJ) largely as the product of that overtone's amplitude component and an associated sinusoidal function, the regulator / control circuitry adjusts the input supply current or its rectified form by an amount corresponding to the adjustment factor for each measured overtone.
Owner:WRATHALL ROBERT S
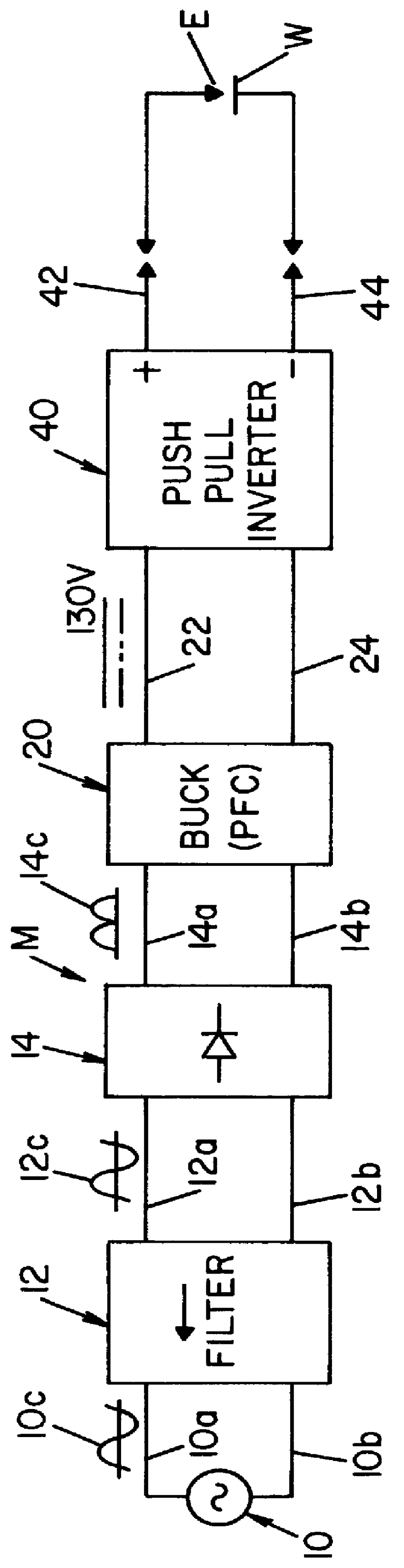
Transmitting Device for Free-Space Optical Transmission
InactiveUS20080063404A1Promote resultsElectric lighting sourcesClose-range type systemsLow voltagePower filter
Transmitting device for free-space optical transmission. The invention relates to a transmitting device for transmission through space, using electromagnetic waves of the infrared and / or visible and / or ultraviolet bands produced by one or several discharge lamps. The device is connected by its input terminals (1) to an a.c. energy distribution system. A mains filter (2) reduces the conducted electromagnetic disturbances produced by the power circuits comprising a rectifier (3), a power-factor-correction circuit (4), a low-voltage power supply (5) and an inverter (8). The inverter (8) is connected to a series inductor (9) connected in series with a hot-cathode fluorescent lamp (10) and a capacitor (12), a parallel capacitor (11) allowing an optimal start of the lamp. A receiving set for transmission via power distribution lines (6) delivers “demodulated signals” applied to the control circuitry (7) which controls the state of the switches of the inverter (8). The light produced is modulated as a function of the “demodulated signals”.
Owner:ZXTALK ASSETAB
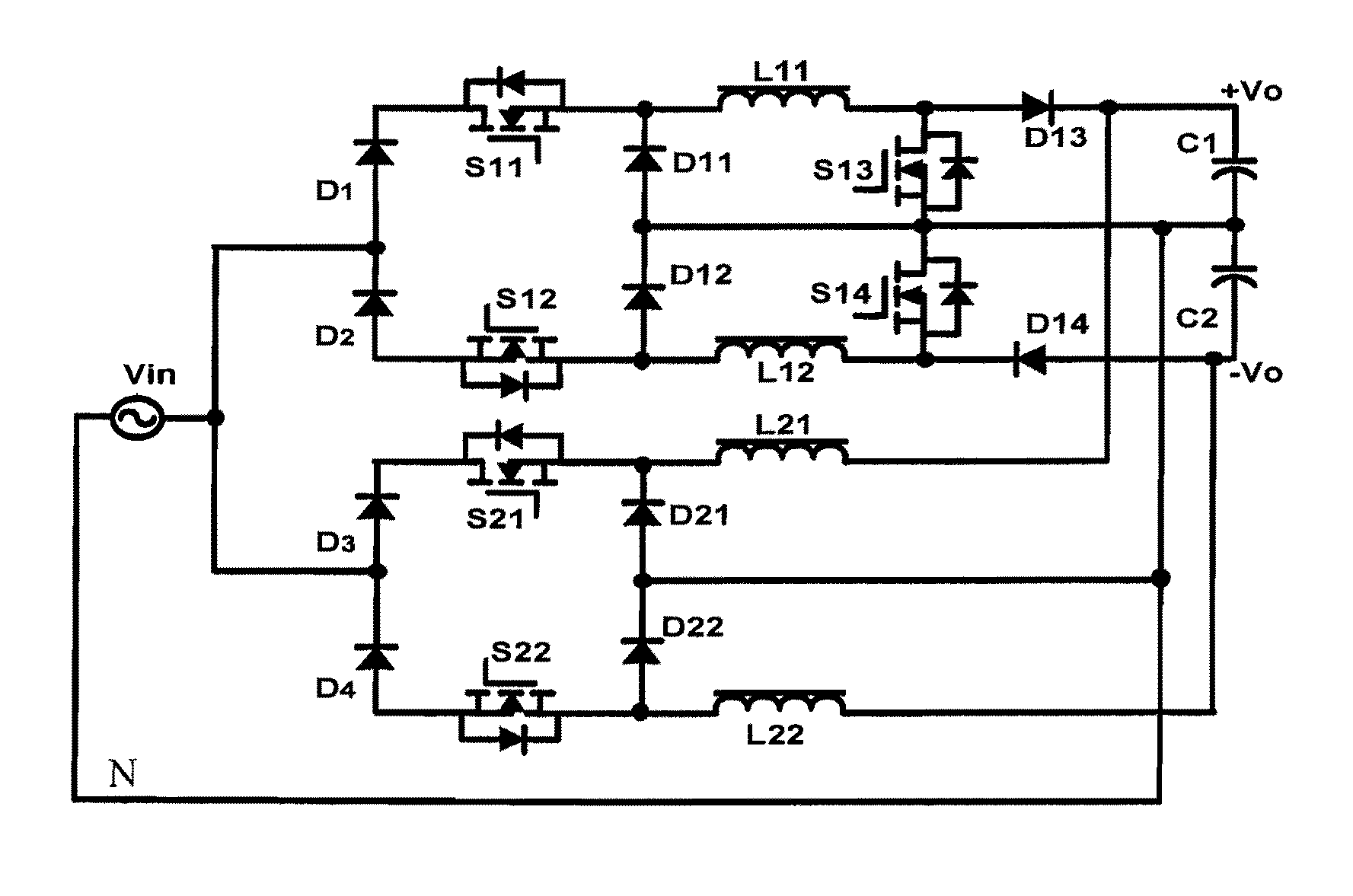
Three-phase buck-boost power factor correction circuit and controlling method thereof
ActiveUS20090268496A1Improve efficiencyReduce in quantityAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionThree-phaseNeutral line
The configurations of a three-phase buck-boost power factor correction (PFC) circuit and a controlling method thereof are provided in the present invention. The proposed circuit includes a first single-phase buck-boost PFC circuit receiving a first phase voltage and having a first and a second output terminals and a neutral-point for outputting a first and a second output voltages, a second single-phase buck-boost PFC circuit receiving a second phase voltage and coupled to the first and the second output terminals and the neutral-point, a third single-phase buck-boost PFC circuit receiving a third phase voltage and coupled to the first and the second output terminals and the neutral-point, a first and a second output capacitors coupled to the first and the second output terminals respectively, and to the neutral-point also and a neutral line coupled to the neutral-point.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Power Factor Correction Circuit And Method Of Driving The Same
ActiveUS20100109615A1Reduce power consumptionSimple configurationAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionEngineeringPower factor correction circuits
The present invention relates to a power factor correction circuit and a method of driving the power factor correction circuit. The power factor correction circuit according to the present invention includes a power transfer element configured to receive an input voltage, an input current corresponding to the input voltage flowing through the power transfer element, and a switch connected to the power transfer element and configured to control an output voltage generated by the current flowing through the power transfer element. The power factor correction circuit is configured to detect a zero voltage edge timing of the input voltage by detecting the input voltage, generate a reference clock signal having a frequency that varies according to the detected edge timing, generate a reference signal using the reference clock signal, generate an error amplification signal based on a difference between the output voltage and a predetermined error reference signal, generate the amplification reference signal by multiplying the reference signal by the error amplification signal, and control a switching operation of the switch using the amplification reference signal and a detection signal corresponding to a current flowing through the switch.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Power factor correction circuit
ActiveUS20090290395A1Increase in circuit sizeReduce riskAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionVoltage referencePower factor correction circuits
A power factor correction circuit includes a first rectifier to rectify an AC voltage, a series circuit connected to an output of the first rectifier and including a step-up reactor and a switching element, a rectifying-smoothing circuit connected to both ends of the switching element and including a second rectifier and a smoothing capacitor, an input voltage detector to detect an output voltage of the first rectifier, an output voltage detector to detect a voltage across the smoothing capacitor, an error amplifier to amplify an error between the output voltage signal and a reference voltage, and a controller to determine an ON / OFF duty ratio of the switching element according to the amplified error signal and a result of a calculation carried out on the input voltage signal and output voltage signal.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Adaptive control method of power factor
InactiveCN102857087AReduce harmonic contentIncrease profitEfficient power electronics conversionPower conversion systemsEngineeringVoltage reference
The invention discloses an adaptive control method of a power factor. The adaptive control method comprises the following steps of: generating three voltage reference values by calculating, multiplying the three voltage reference values, taking a product of the three voltage reference values as a current reference value, comparing the current reference value with a direct current bus current, and outputting a calculation result after carrying out current error compensation processing; determining a duty ratio by virtue of the calculation result to form a pulse signal, controlling the make-break operation of a chopper to carry out chopping processing on a direct current voltage rectified and output by a rectifier bridge, generating a smooth direct current bus current and an alternating current input current in a same phase with an alternating current input voltage, improving the power factor, and reducing the current harmonic distortion ratio. A power factor correction method, provided by the invention, can be used for realizing the adaptive control on alternating current power supplies in different frequencies. The adaptive control method of the power factor is applied into variable frequency air conditioner products, and can be suitable for air conditioners based on inputs of 50-Hz and 60-Hz alternating current power supplies; and according to the adaptive control method of the power factor, a design purpose that a development is suitable for multiple types of machines is really achieved, the development period is shortened, and the research and development costs are lowered.
Owner:HISENSE (SHANDONG) AIR CONDITIONING CO LTD
Bridgeless power factor circuit correcting circuit system used for critical conduction mode and control method thereof
ActiveCN101552546AEfficient power electronics conversionEnergy industryPower factor correction circuitsConductor Coil
The invention discloses a bridgeless power factor circuit correcting circuit system used for critical conduction mode and a control method thereof. The bridgeless power factor circuit correcting circuit system comprises a bridgeless power factor correcting circuit, a first auxiliary winding and a second auxiliary winding, wherein the bridgeless power factor correcting circuit comprises a first switch, a first inductance and a second inductance; the first auxiliary winding is coupled to the first inductance and produces a first sensing signal; the second auxiliary winding is coupled to the second inductance and produces a second sensing signal, the first sensing signal and the second sensing signal are used for producing an inductance current detection signal; meanwhile, when the value of the inductance current detection signal is zero, the first switch is connected.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC +1
High efficiency power drive device enabling serial connection of light emitting diode lamps thereto
InactiveUS20110279044A1Extended service lifeEliminate needElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLED lampPower factor correction circuits
A high efficiency power drive device enabling serial connection of LED lamps thereto, which includes a power source filter circuit, an AC to DC rectifier, a power factor correction circuit and an LED constant current drive circuit. The power factor correction circuit is utilized using the so-called transition mode technique to obtain voltage required by the LED lamps when serially connected, and current control is used to achieve a state whereby the current and voltage are in the same phase. A current control IC and an externally set resistor are further used to eliminate the need to adopt any CPU (central processing unit) while accurately directly controlling the output pulse width of PWM (Pulse Width Modulation).
Owner:MAIW FU HWA
Single-phase and three-phase dual buck-boost/buck power factor correction circuits and controlling method thereof
ActiveUS20100253295A1High conduction lossImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionEnergy industryThree levelCapacitance
The configurations of a single-phase dual buck-boost / buck power factor correction (PFC) circuit and a controlling method thereof are provided in the present invention. The proposed circuit includes a single-phase three-level buck-boost PFC circuit receiving an input voltage and having a first output terminal, a neutral-point and a second output terminal for outputting a first and a second output voltages, a single-phase three-level buck PFC circuit receiving the input voltage and coupled to the first output terminal, the neutral-point and the second output terminal, a first output capacitor coupled to the first output terminal and the neutral-point, a second output capacitor coupled to the neutral-point and the second output terminal, and a neutral line coupled to the neutral-point.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
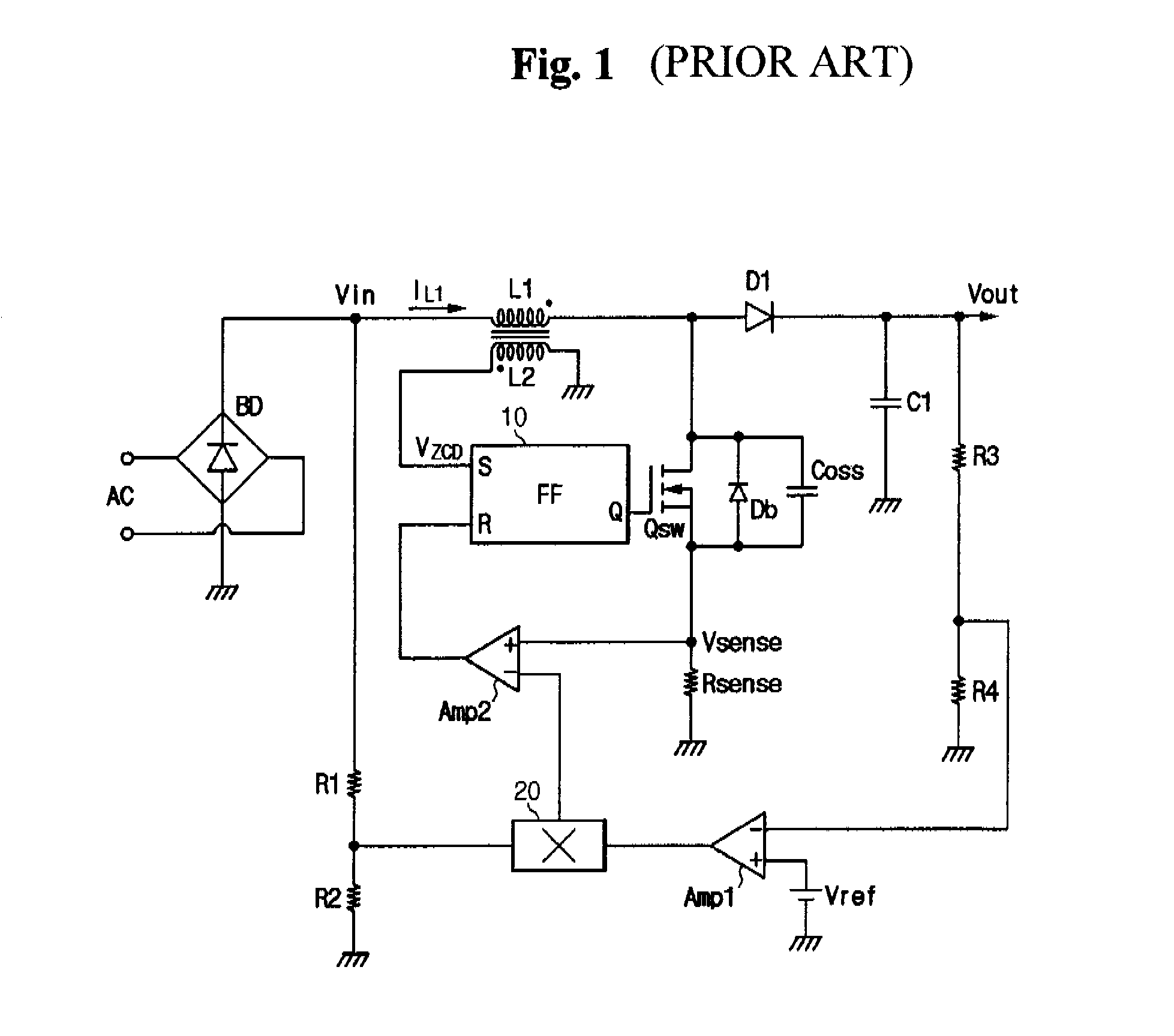
Power factor correction circuit
ActiveUS7538525B2Reduce distortion problemsAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionEngineeringConductor Coil
The present invention relates to a power factor correction circuit for compensating distortion of an input current. According to the exemplary embodiment of the present invention, a turn-on interval length of a switch is controlled according to a voltage induced in a secondary winding wire of an inductor since the voltage induced in the secondary winding wire has information on an input voltage when the switch is turned on. The turn-on interval length of the switch is reduced when the input voltage is great and is increased when the input voltage is low. Therefore, distortion of the input current may be compensated by controlling the turn-on interval of the switch according to the voltage induced in the secondary winding wire without using an additional circuit for sensing the input voltage.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com