Patents
Literature
320 results about "Power factor control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
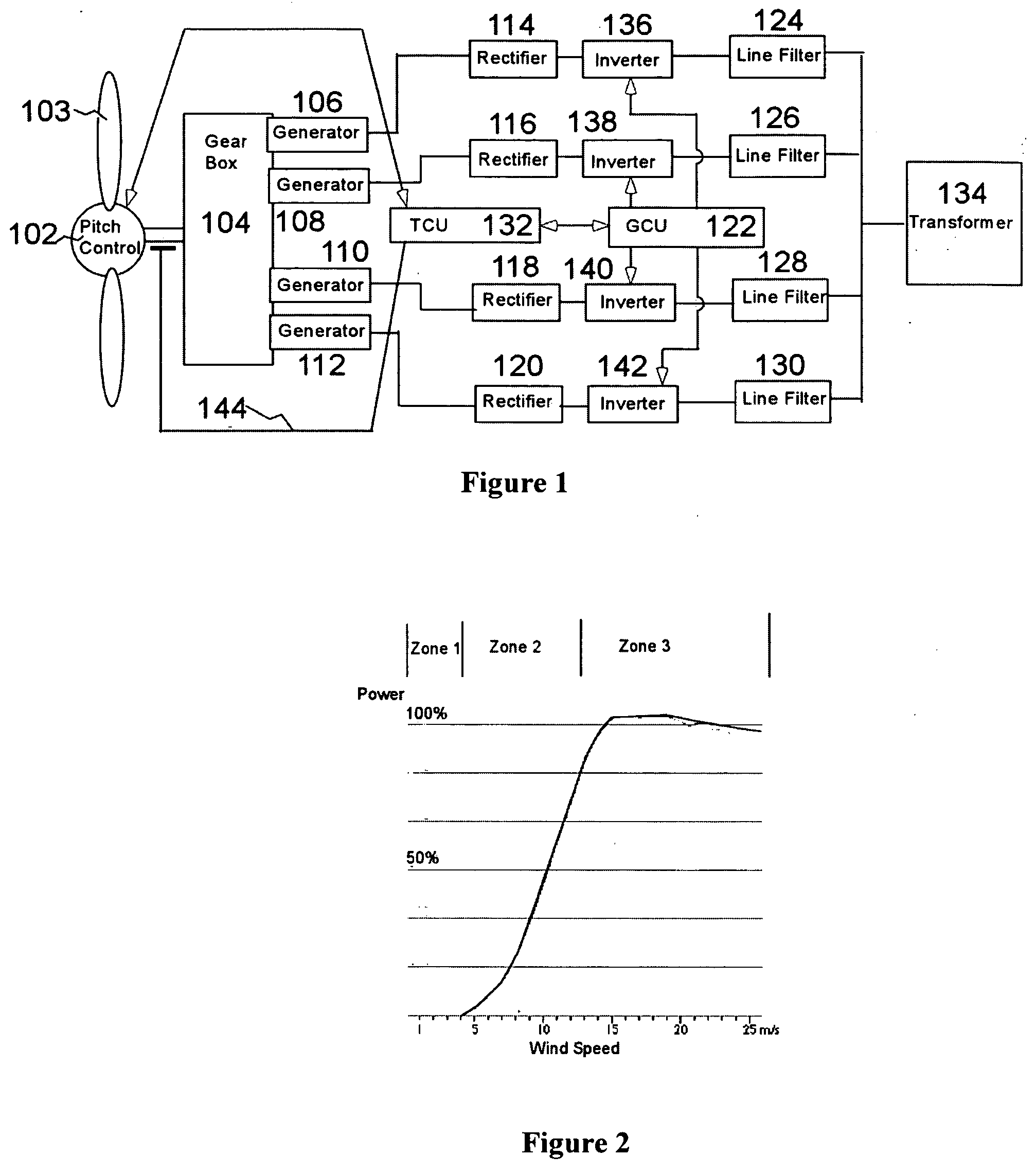
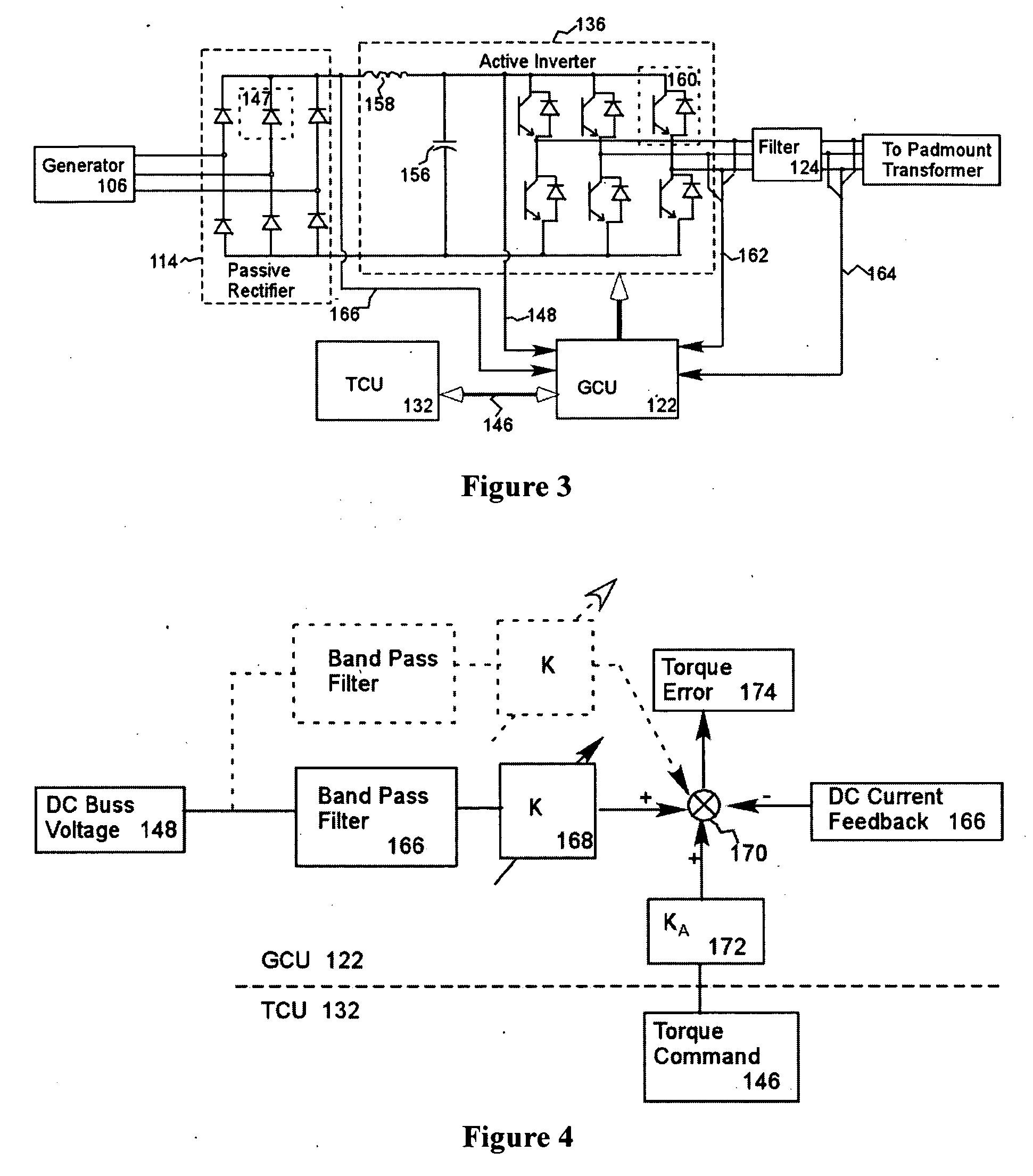
Variable speed distributed drive train wind turbine system
InactiveUS7042110B2Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityWind motor controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPermanent magnet rotorDc current
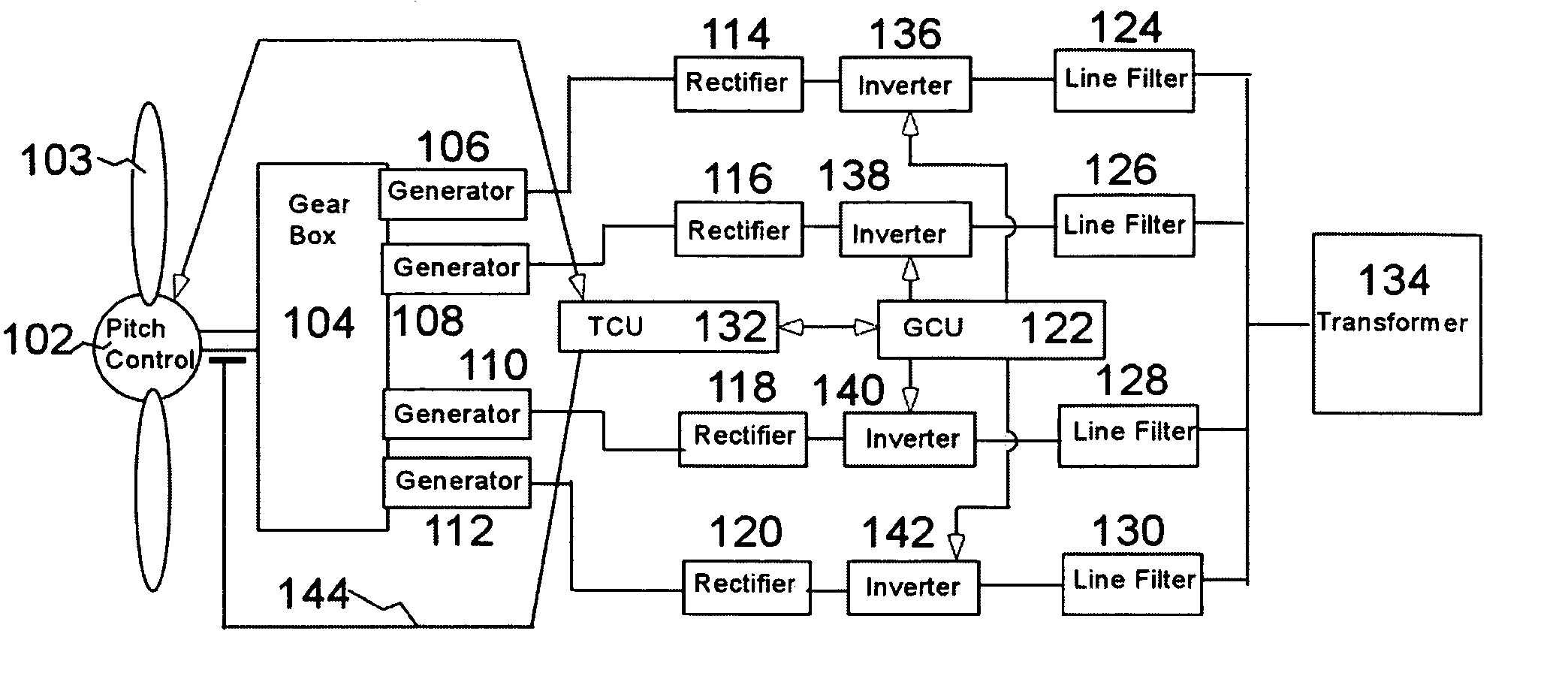
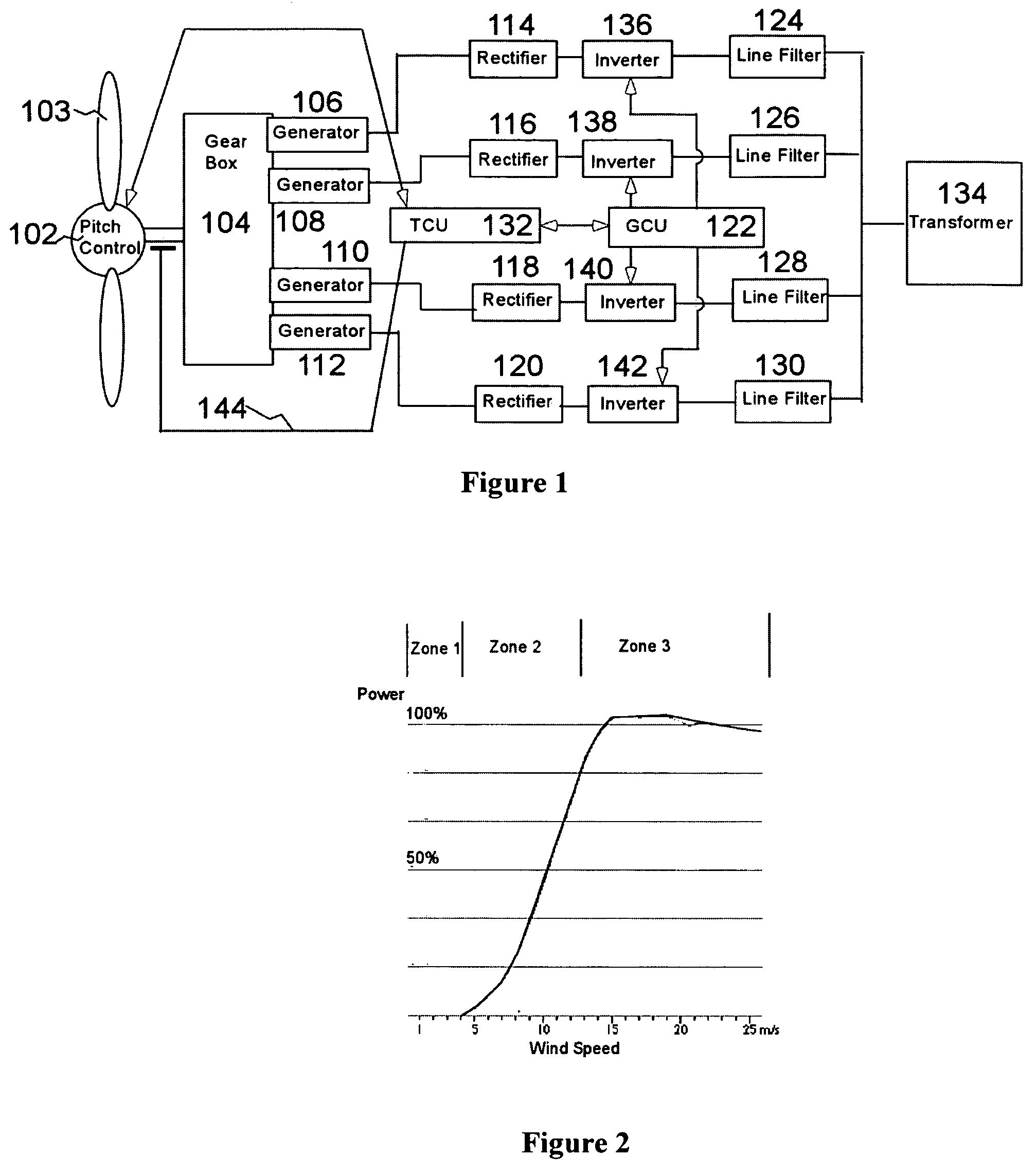
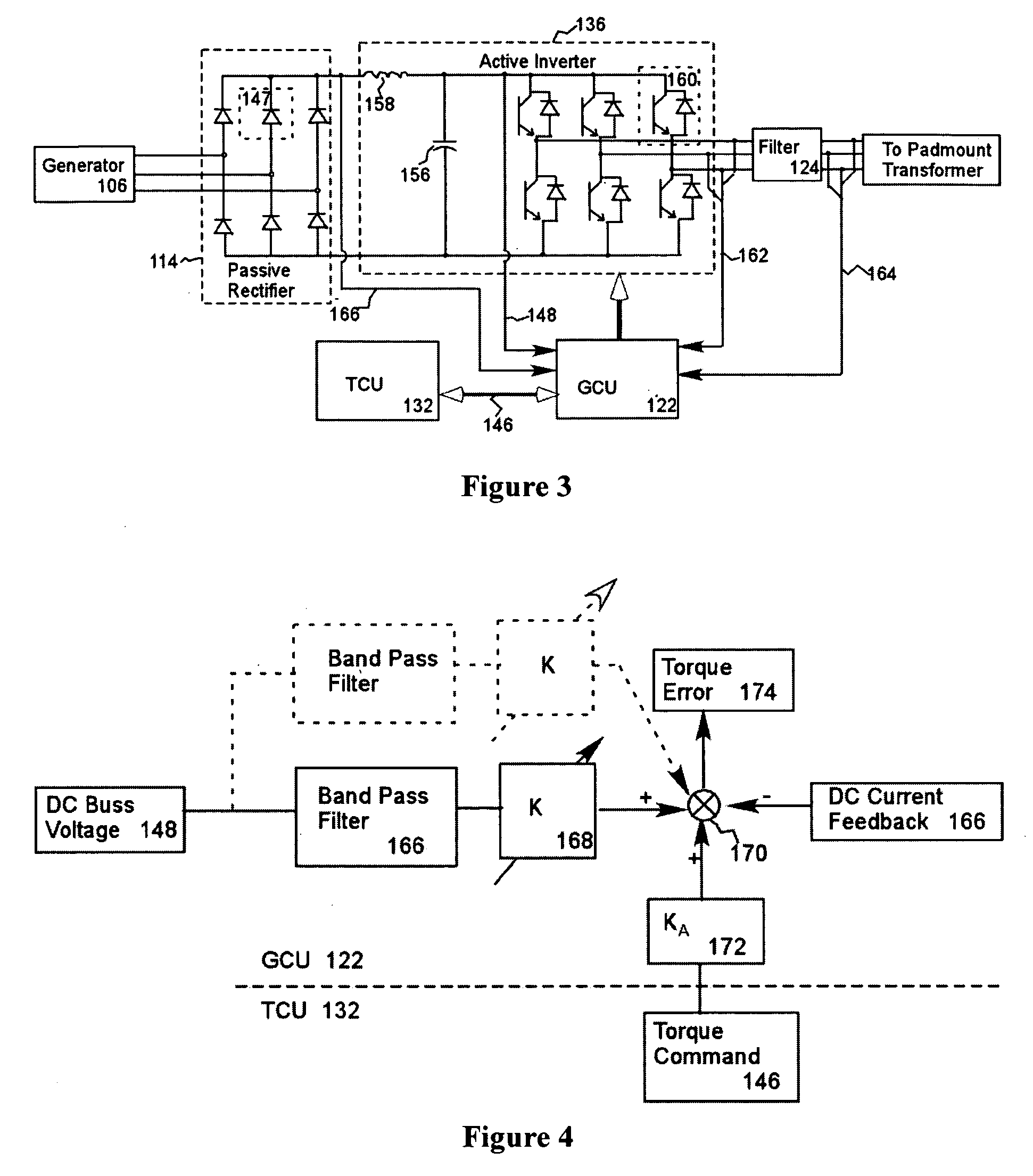
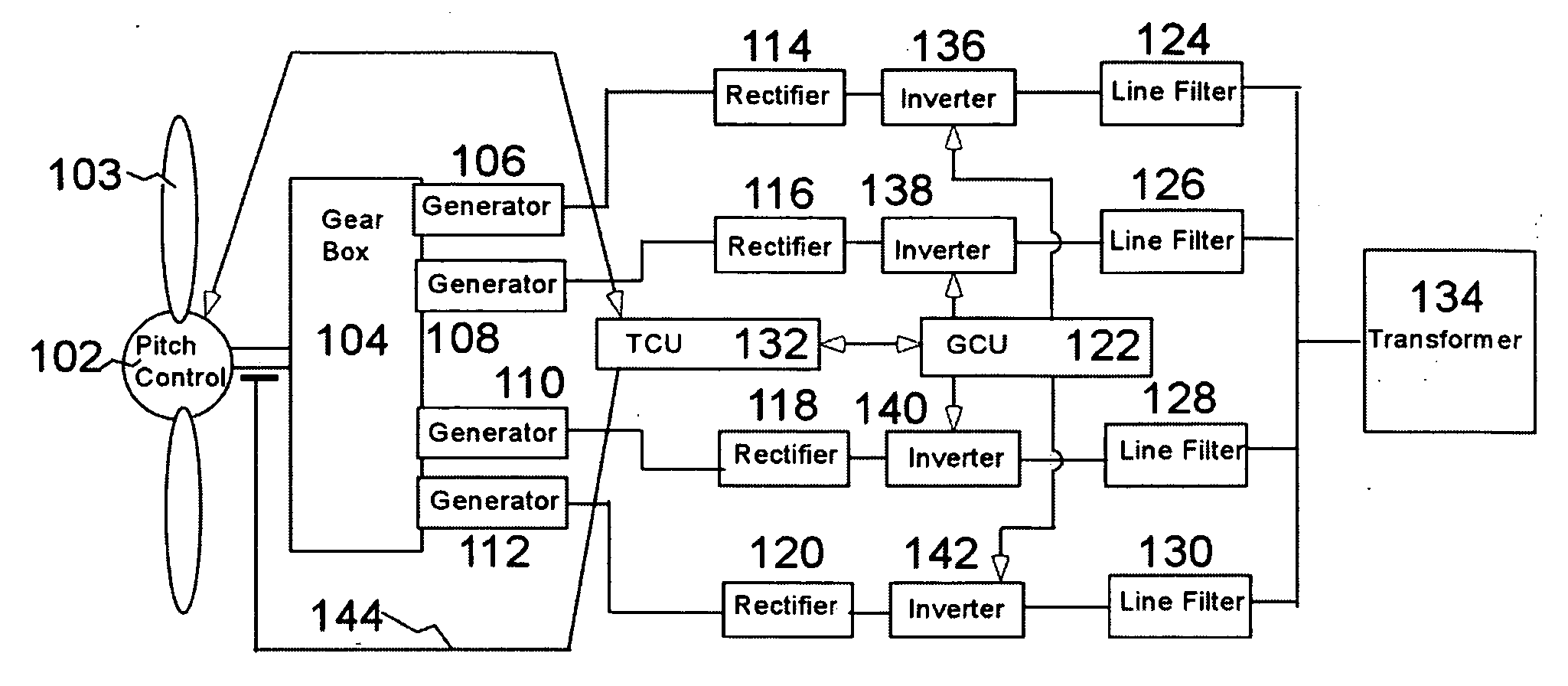
A variable speed wind turbine employing a rotor connected to a multiplicity of synchronous generators with wound field or permanent magnet rotors. A passive rectifier and an inverter are used for power transfer back to the grid. A Turbine Control Unit (TCU) commands a required generator torque based on rotor speed and power output of the turbine inverters. Torque is controlled by regulating the DC current by control of the inverter. A main-shaft-damping filter is provided by measurement of the DC bus voltage. In high winds the turbine remains at a constant average output power through a constant torque command and a varying pitch command to a rotor pitch servo system. A set point is fixed at the inverter output such that output VAR load is minimized running the turbine at very nearly unity power factor. Dynamic VAR and power factor control is provided by a separate VAR apparatus.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Variable speed distributed drive train wind turbine system
InactiveUS20050012339A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityWind motor controlWorking fluid for enginesElectric power transmissionPermanent magnet rotor
A variable speed wind turbine employing a rotor connected to a multiplicity of synchronous generators with wound field or permanent magnet rotors. A passive rectifier and an inverter are used for power transfer back to the grid. A Turbine Control Unit (TCU) commands a required generator torque based on rotor speed and power output of the turbine inverters. Torque is controlled by regulating the DC current by control of the inverter. A main-shaft-damping filter is provided by measurement of the DC bus voltage. In high winds the turbine remains at a constant average output power through a constant torque command and a varying pitch command to a rotor pitch servo system. A set point is fixed at the inverter output such that output VAR load is minimized running the turbine at very nearly unity power factor. Dynamic VAR and power factor control is provided by a separate VAR apparatus.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
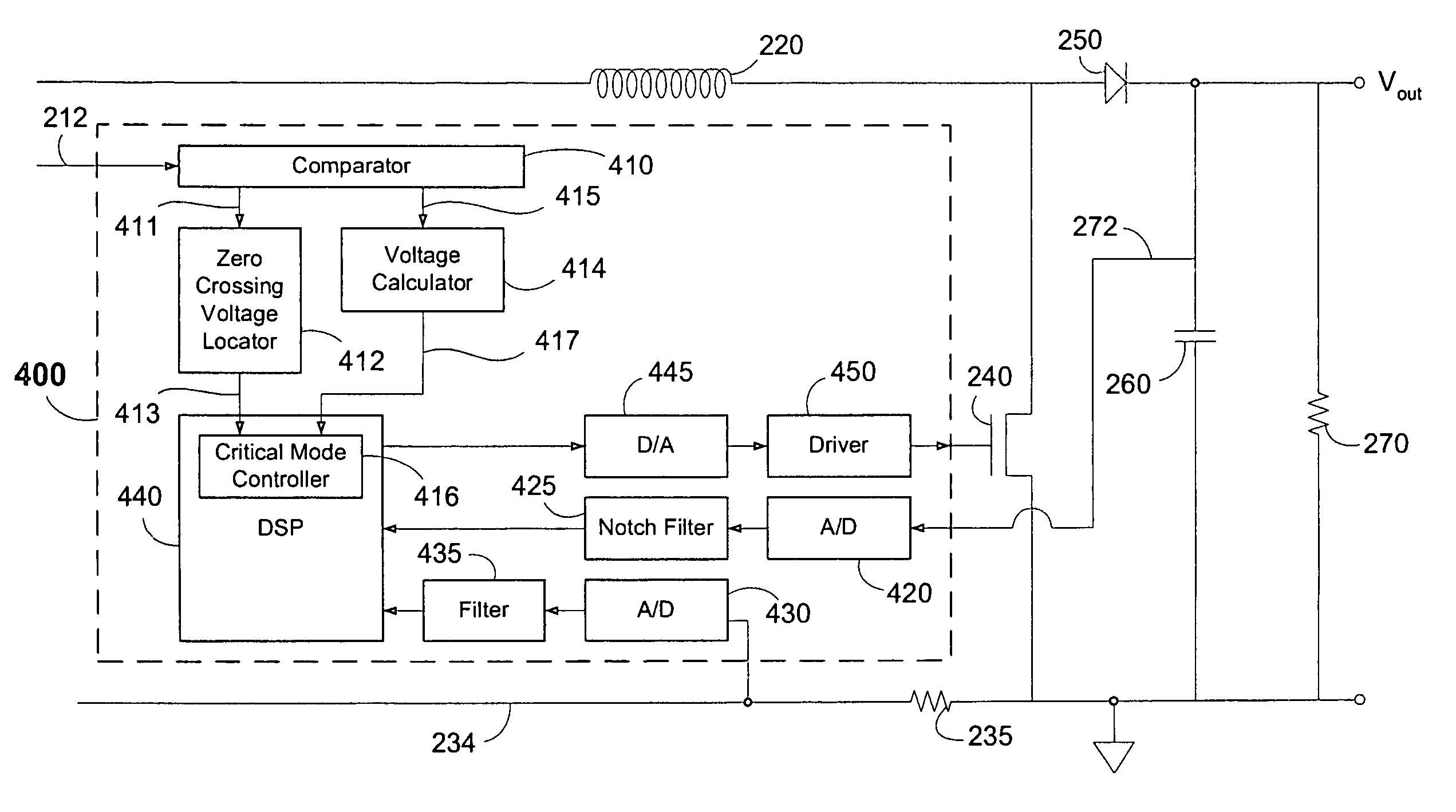
Circuits, systems, methods, and software for power factor correction and/or control
ActiveUS7292013B1Minimize periodMinimize powerAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionImage resolutionPower factor control
Circuits, systems, methods and software for controlling a power conversion and / or correcting and / or controlling a power factor in such conversion(s). The present invention generally takes a computational approach to reducing or minimizing zero current periods in the critical mode of power converter operation, and advantageously reduces zero current periods in the critical mode of power converter operation, thereby maximizing the power factor of the power converter in the critical mode and reducing noise that may be injected back into AC power lines. The present power factor controller allows for greater design flexibility, reduced design complexity, and reduced resolution and greater tolerance for error in certain parameter measurements useful in power factor correction and / or control.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Electric arc welder for variable AC input
InactiveUS6504132B1Increase output powerImprove power factorAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcTransformerPower factor control
An electric arc welder with a variable AC voltage input of up to 600 VAC and a rectifier to provide a DC link, a driven high frequency boost stage with first and second leads connected to the DC link. The boost stage comprises an inductor, a first series output branch with a first primary winding connected to the first lead and a first capacitor connected to the second lead, a second series output branch with a second primary winding connected to the second lead and a second capacitor connected to the first lead and a high frequency operated switch between the leads and having an opened condition charging said capacitors by current through the primary windings in a first direction and discharging the inductor and a closed condition charging the inductor through the primary windings by current in a second direction and discharging the inductor to charge the capacitors. The switch is operated by a power factor control circuit at a frequency greater than about 18 kHz. The boost stage has an AC output stage comprising the secondary winding network of a transformer powered by current flow in the first and second primary windings. An output rectifier converts said AC output to a first DC voltage. At the final portion of the welder an output converter converts the first DC voltage to a second DC voltage connected across the arc of a welding station and having a controlled weld current or voltage.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
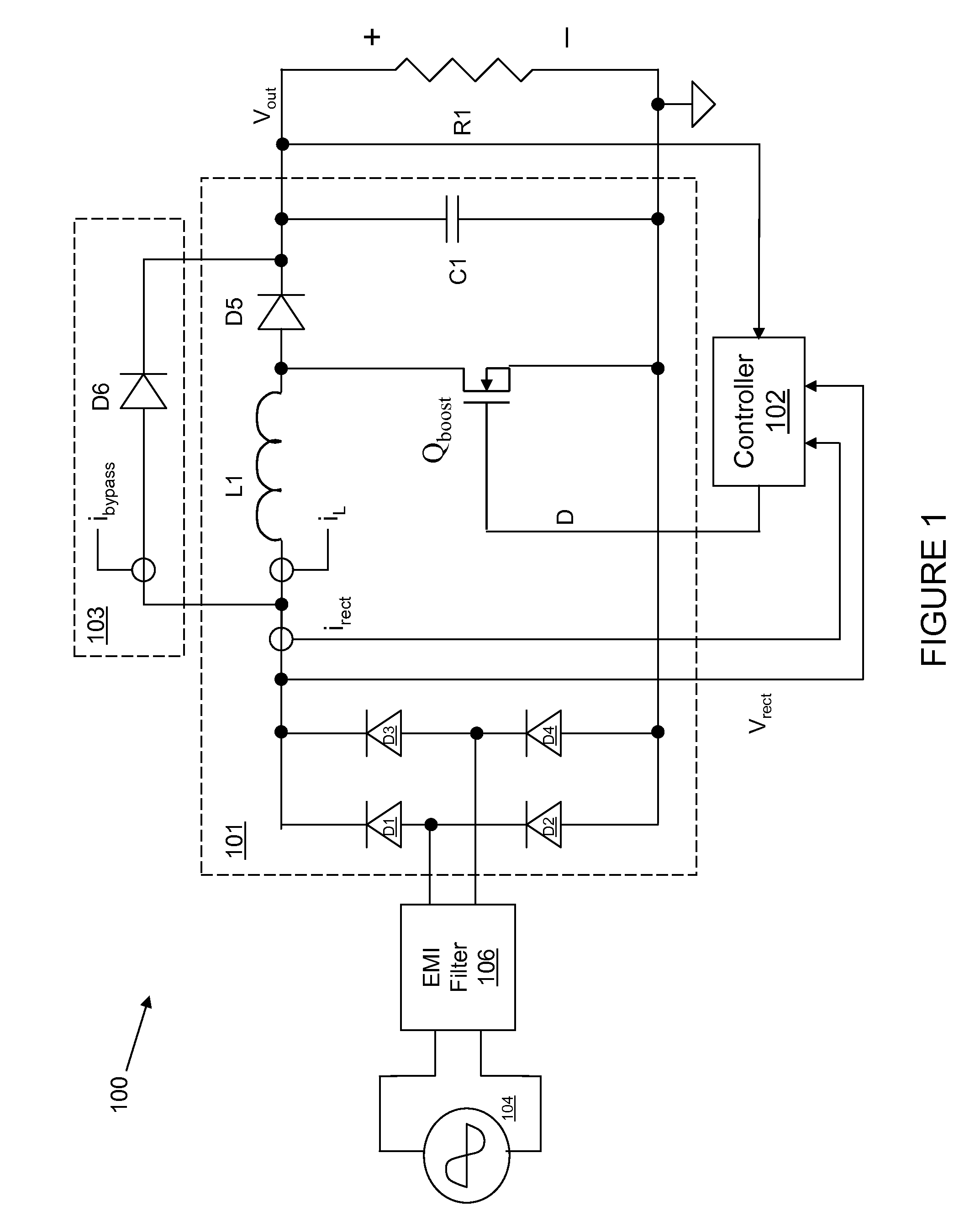
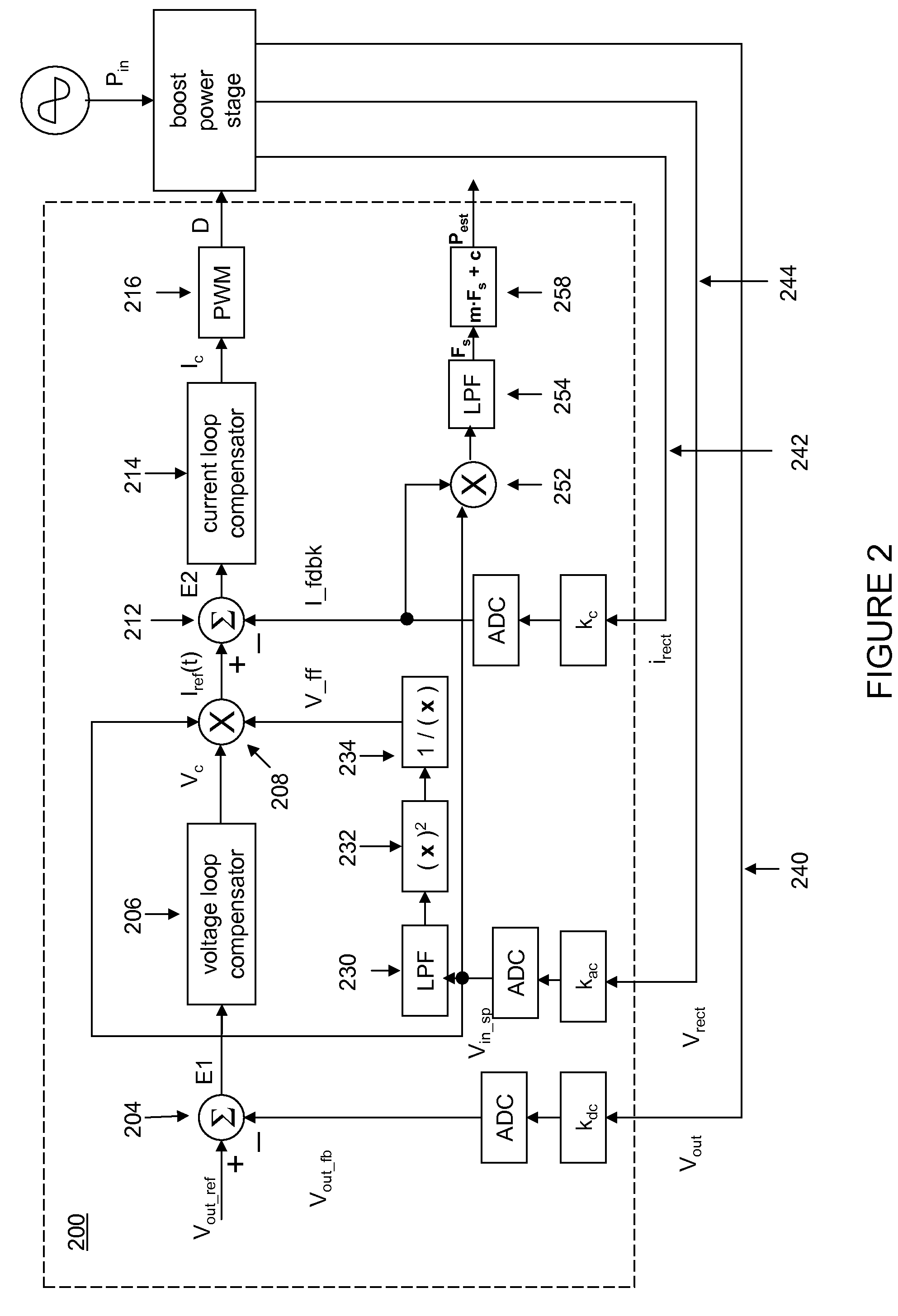
System and method for estimating input power for a power processing circuit
InactiveUS20080316779A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionPower processingLow-pass filter
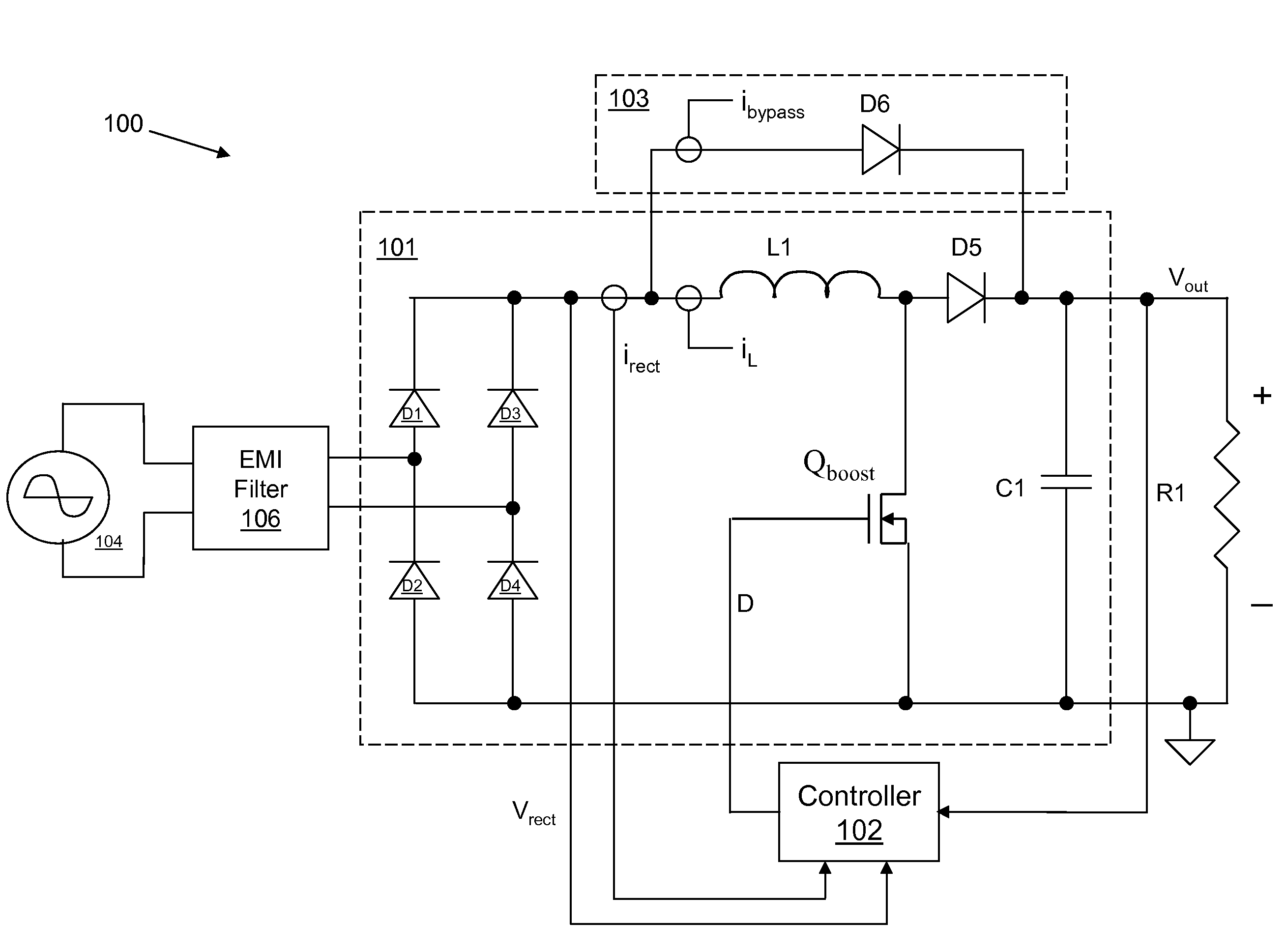
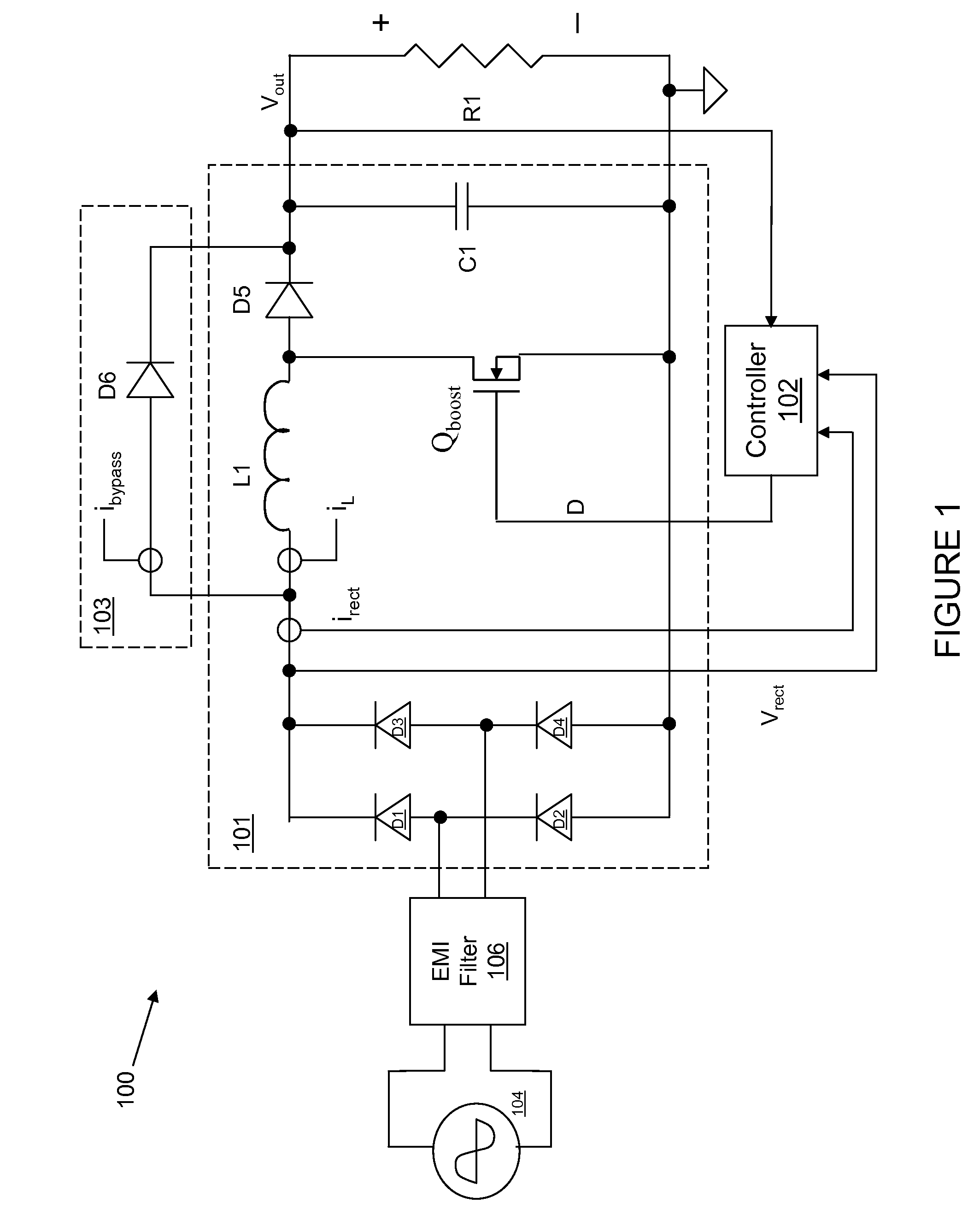
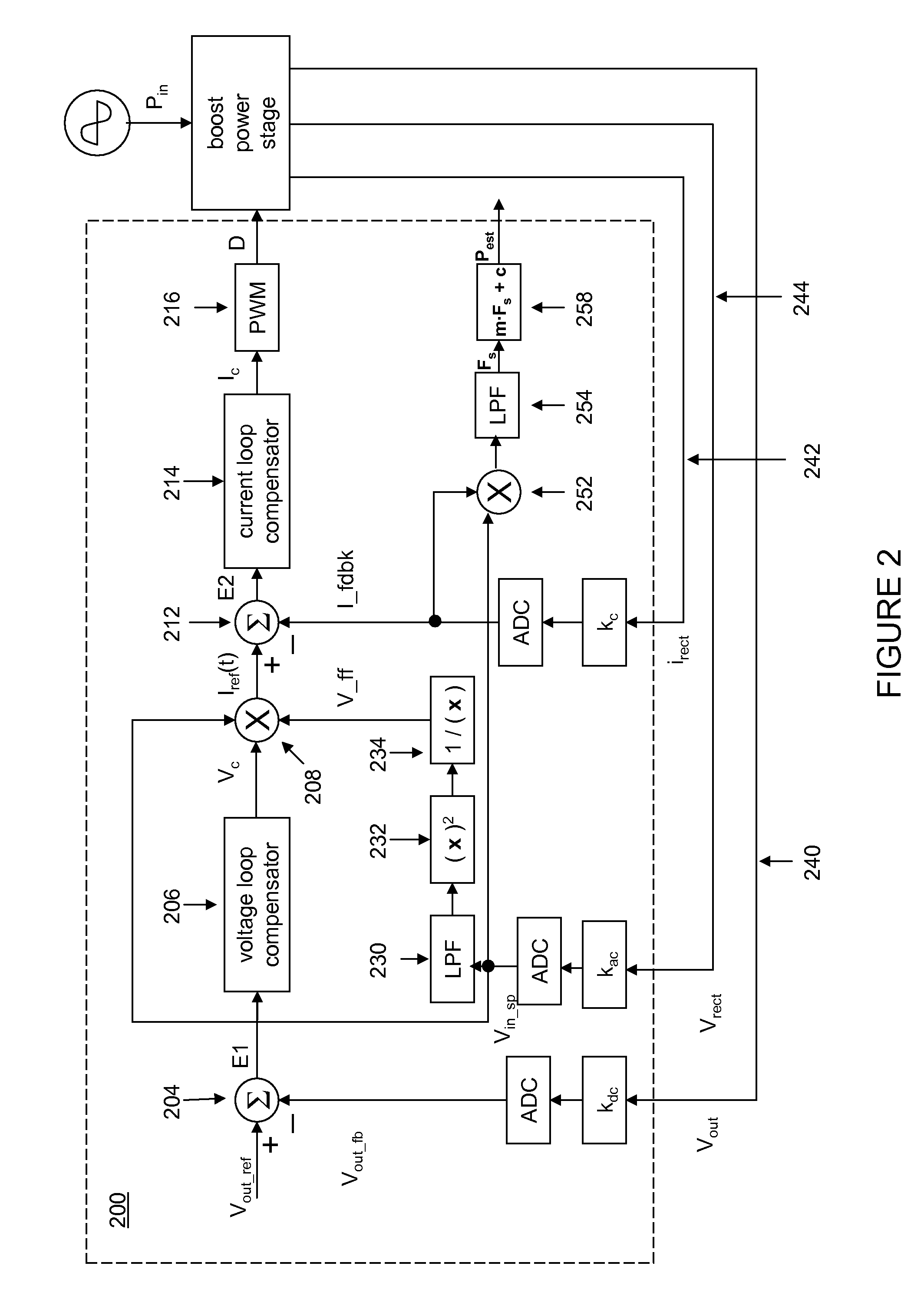
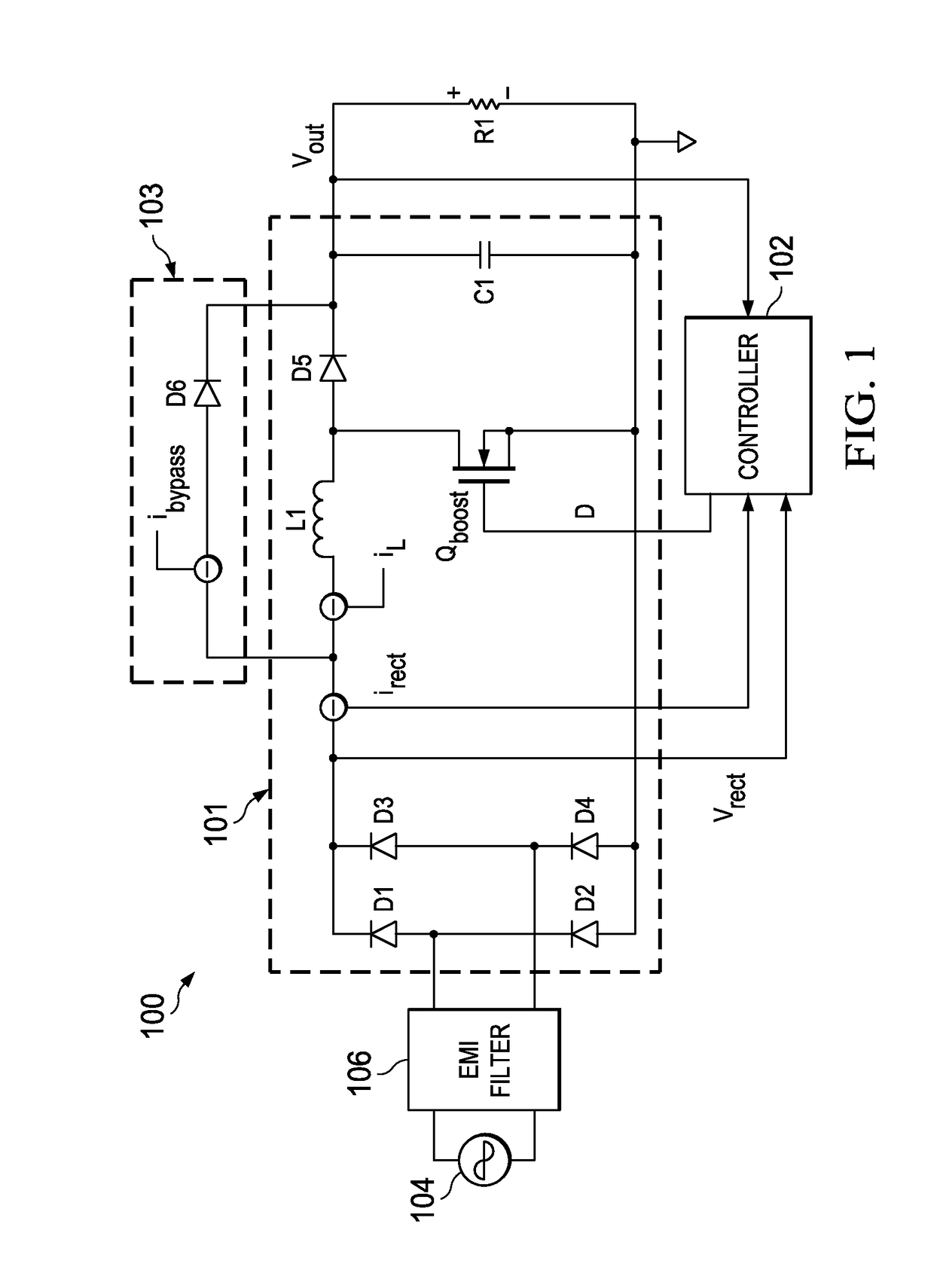
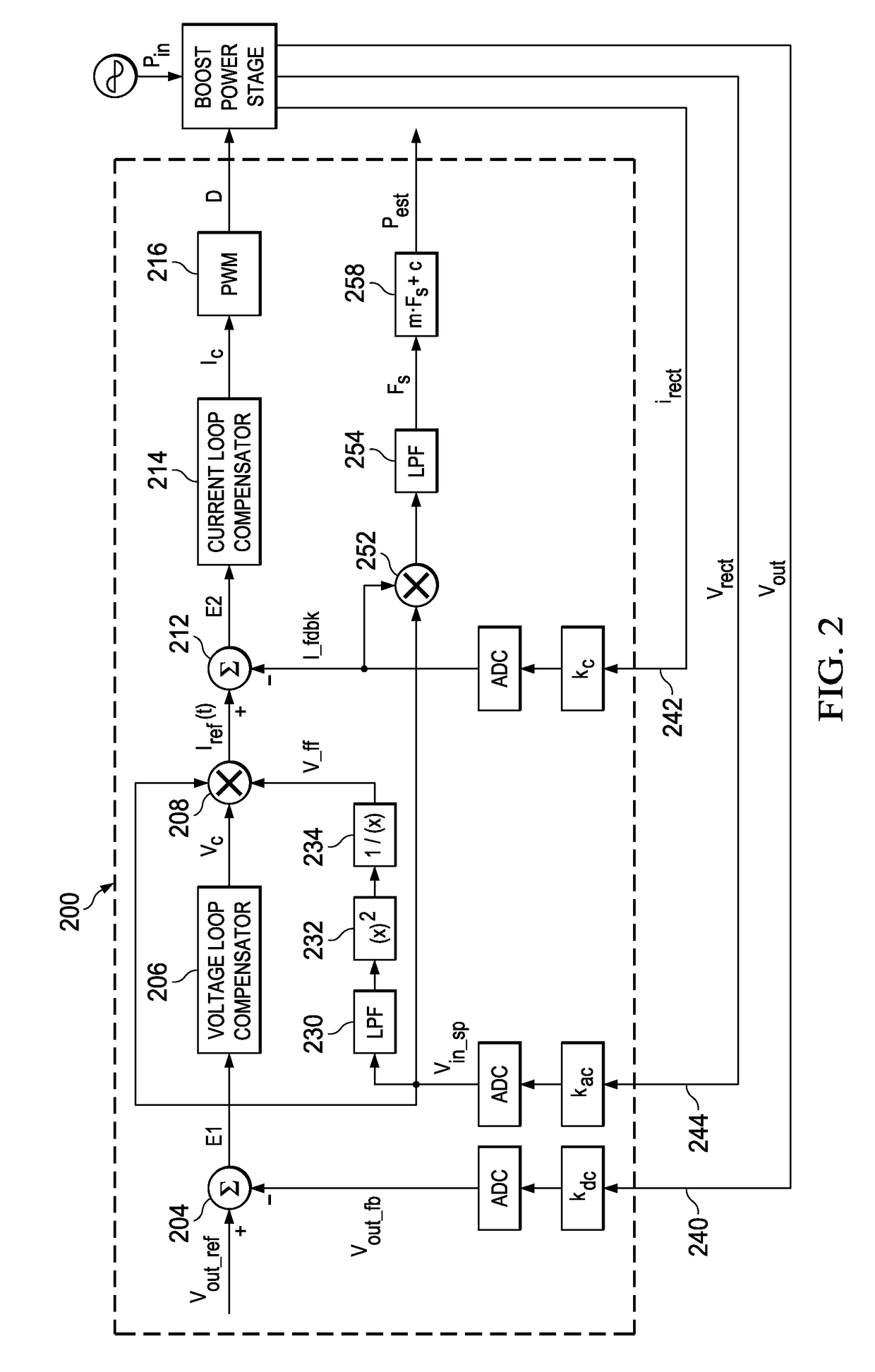
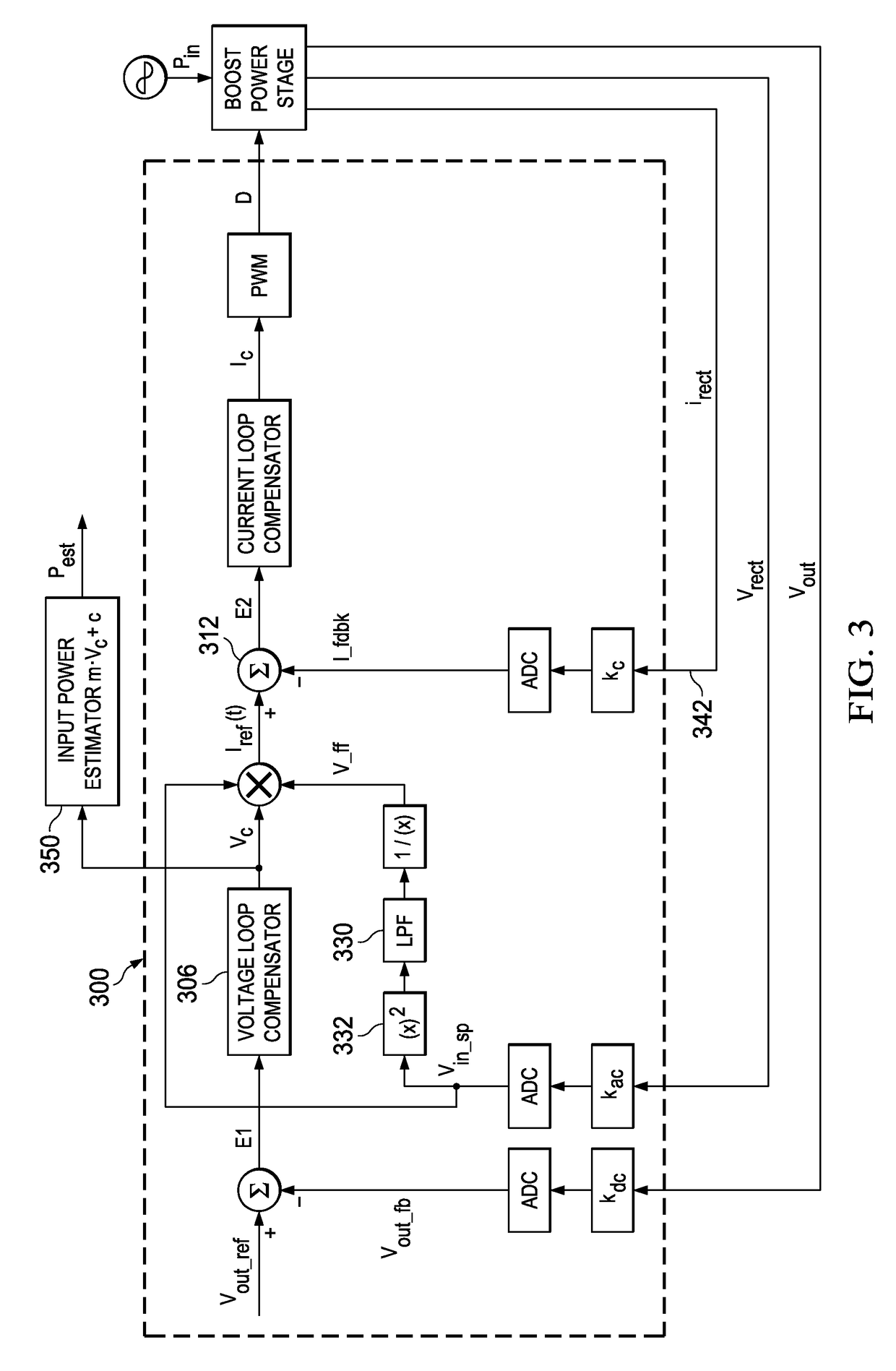
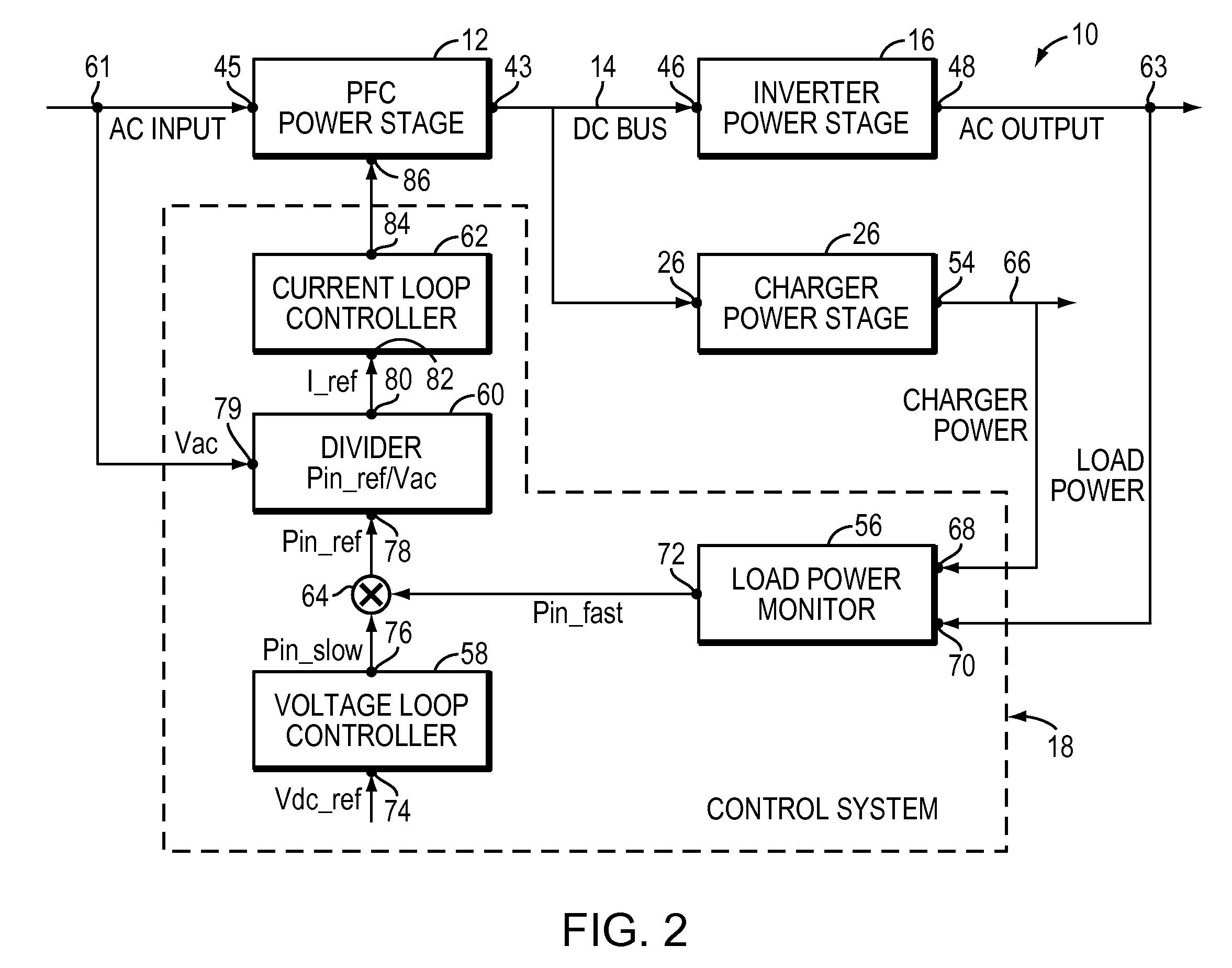
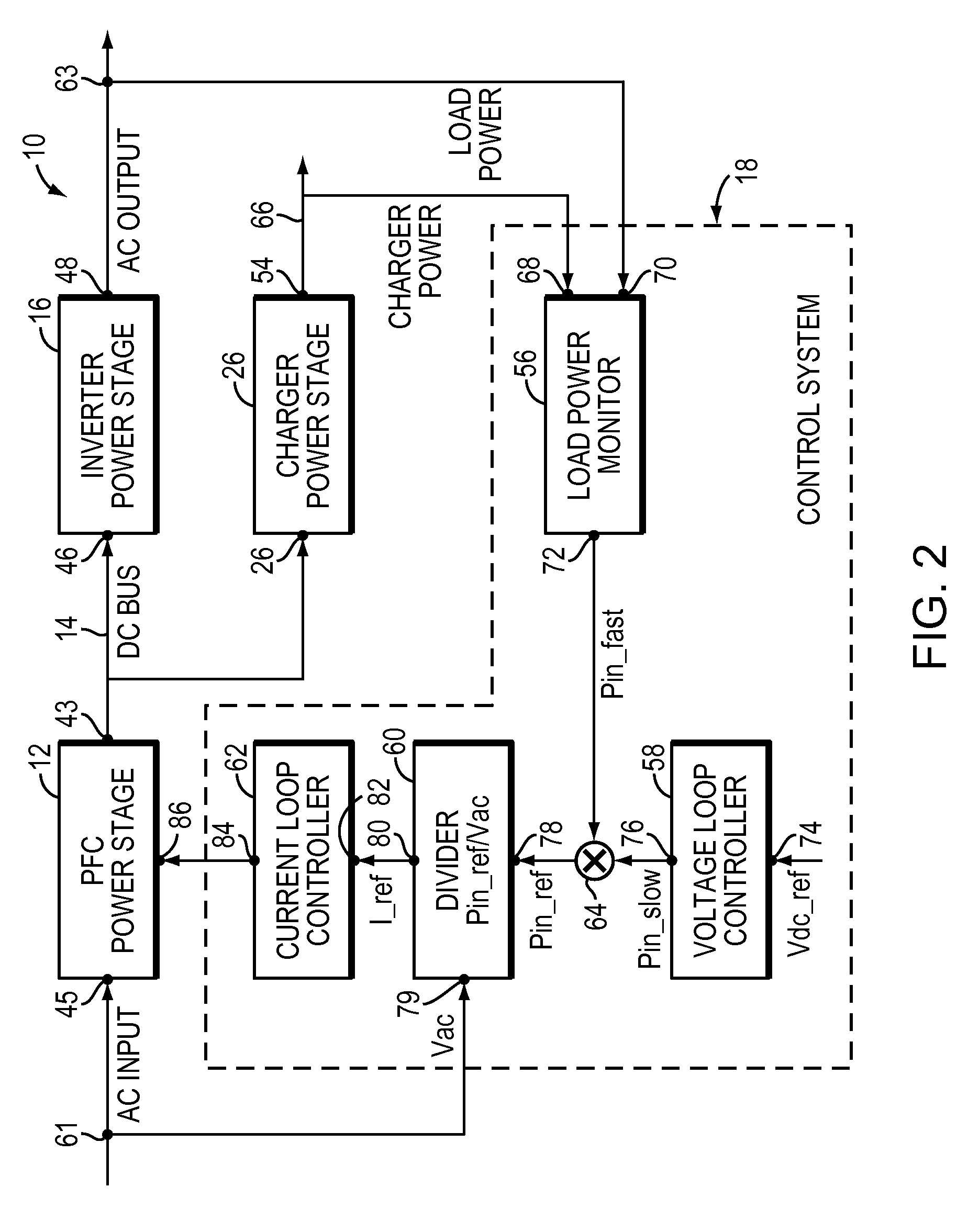
A controller for a power processing circuit and a related method of operating the same. In one embodiment, the controller includes a multiplier configured to produce a product of an input current and an input voltage of the power processing circuit. The controller also includes a low-pass filter configured to produce an input power estimate of an input power to the power processing circuit as a function of the product of the input current and the input voltage. In another embodiment, the controller is a power-factor controller and includes a voltage loop compensator configured to produce a voltage compensation signal as a function of an output voltage of the power processing circuit. The controller also includes an input power estimator configured to produce an input power estimate of an input power to the power processing circuit as a function of the voltage compensation signal.
Owner:MYPAQ HLDG LTD
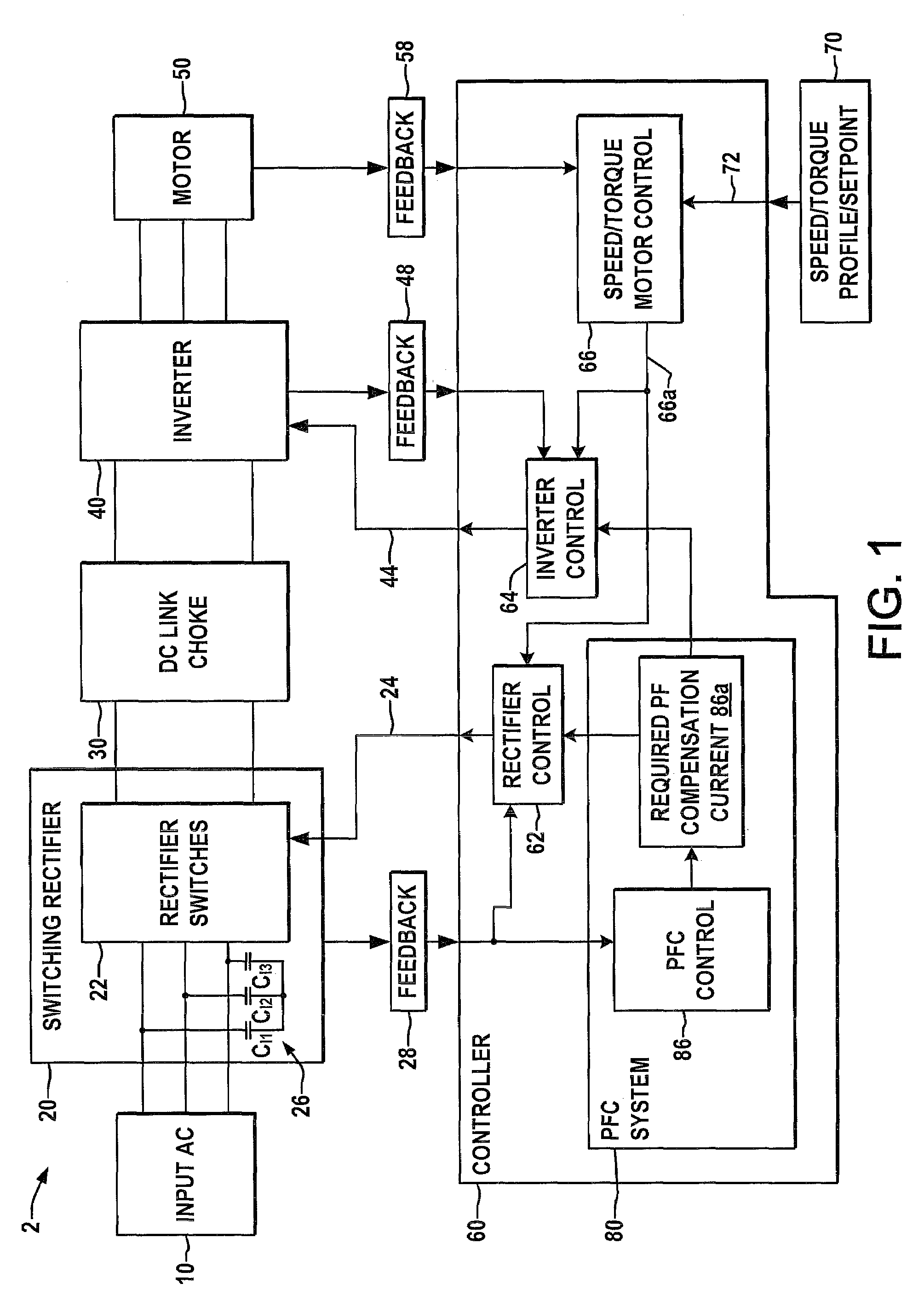
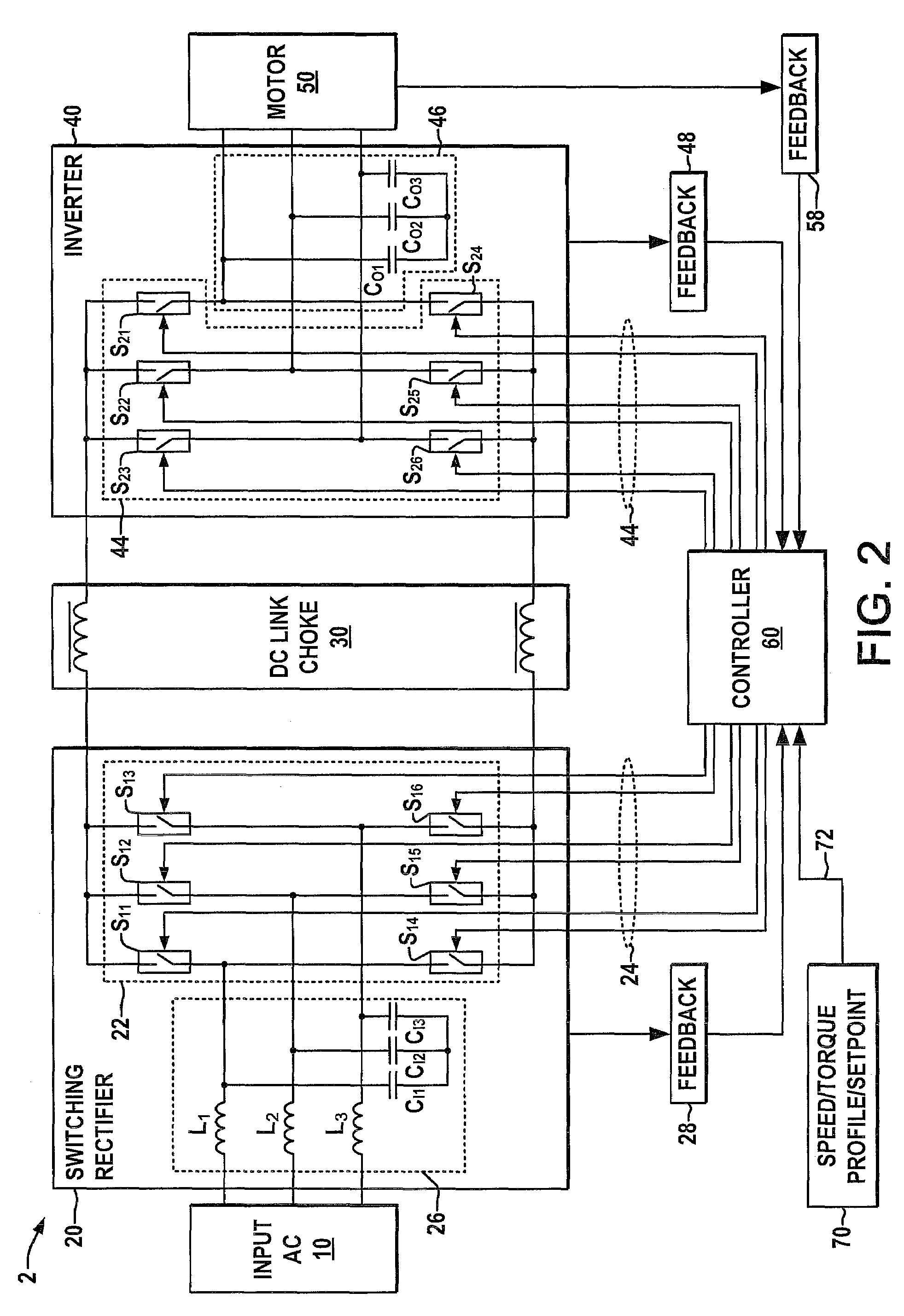
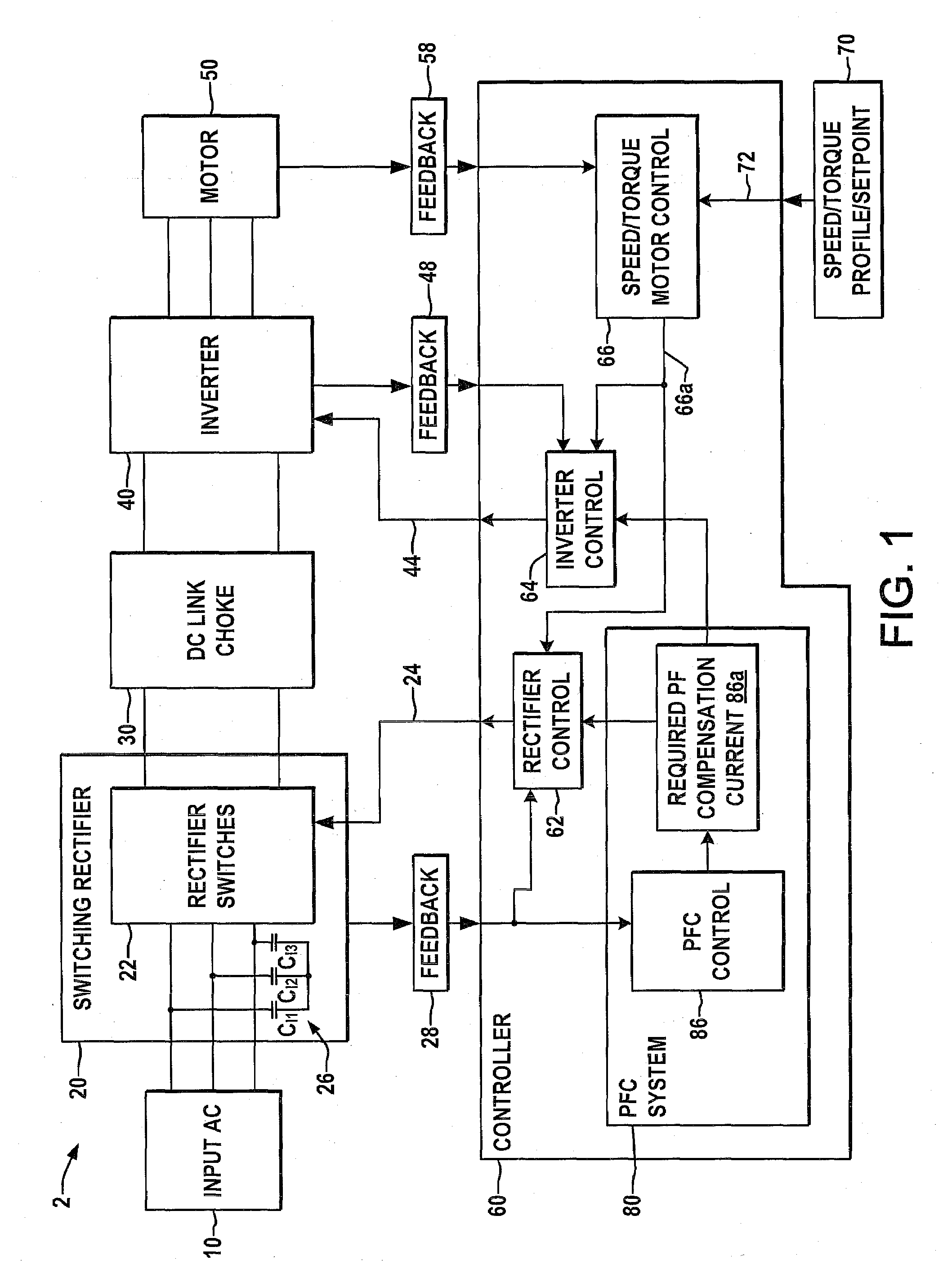
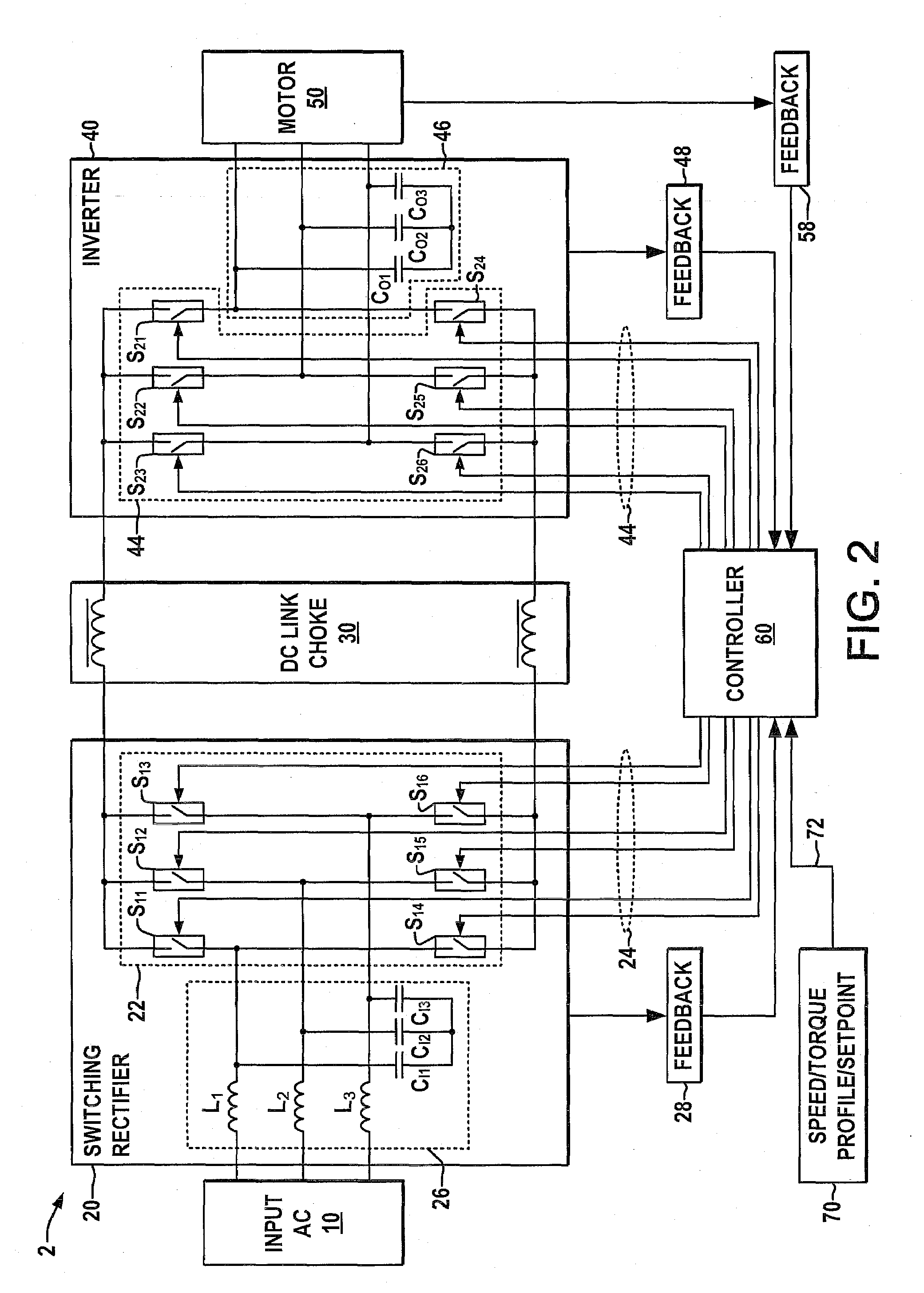
Systems and methods for improved motor drive power factor control
ActiveUS7495410B2Easy to understandReduce adverse effectsSingle-phase induction motor startersAc-dc conversion without reversalPower inverterMotor drive
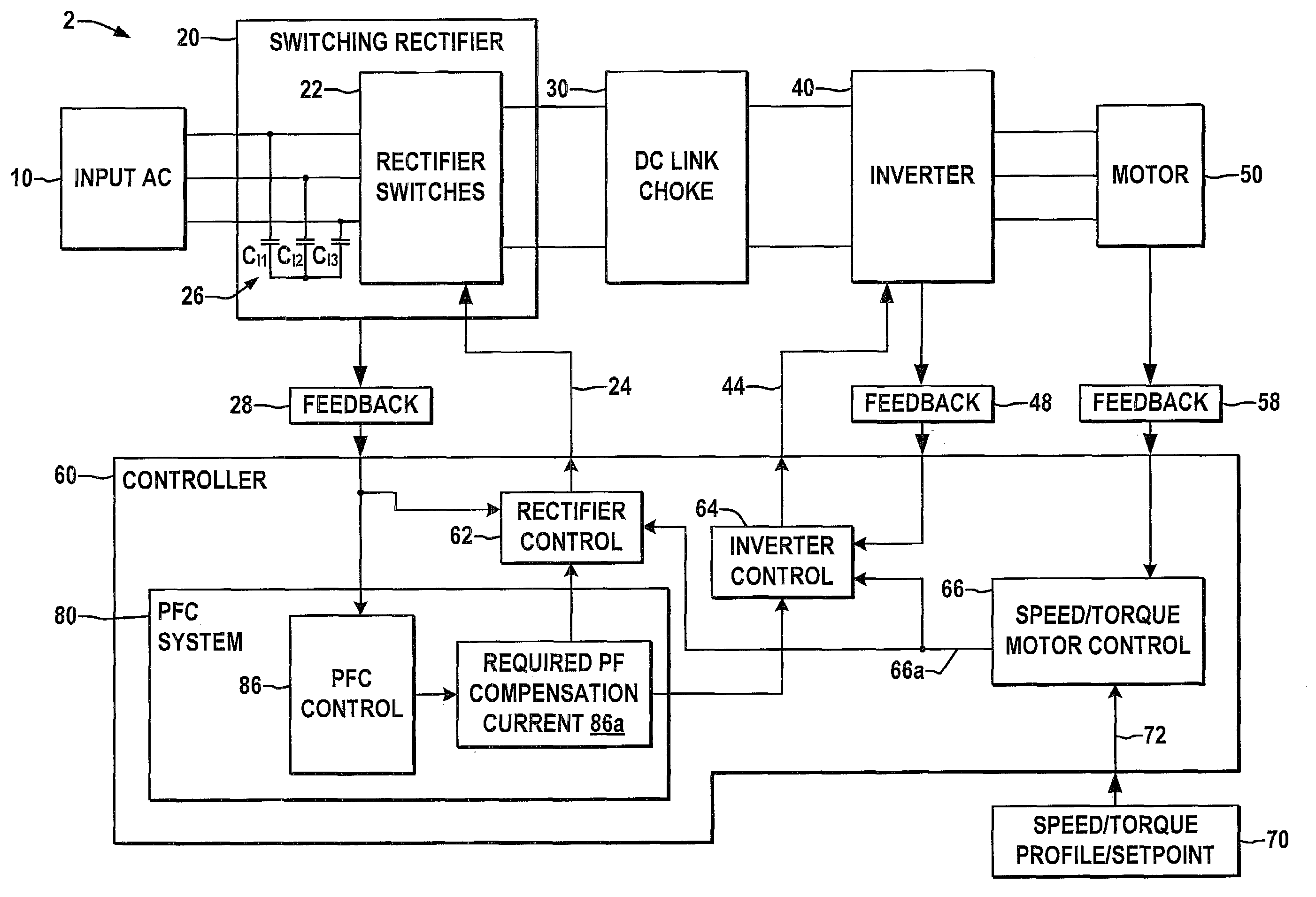
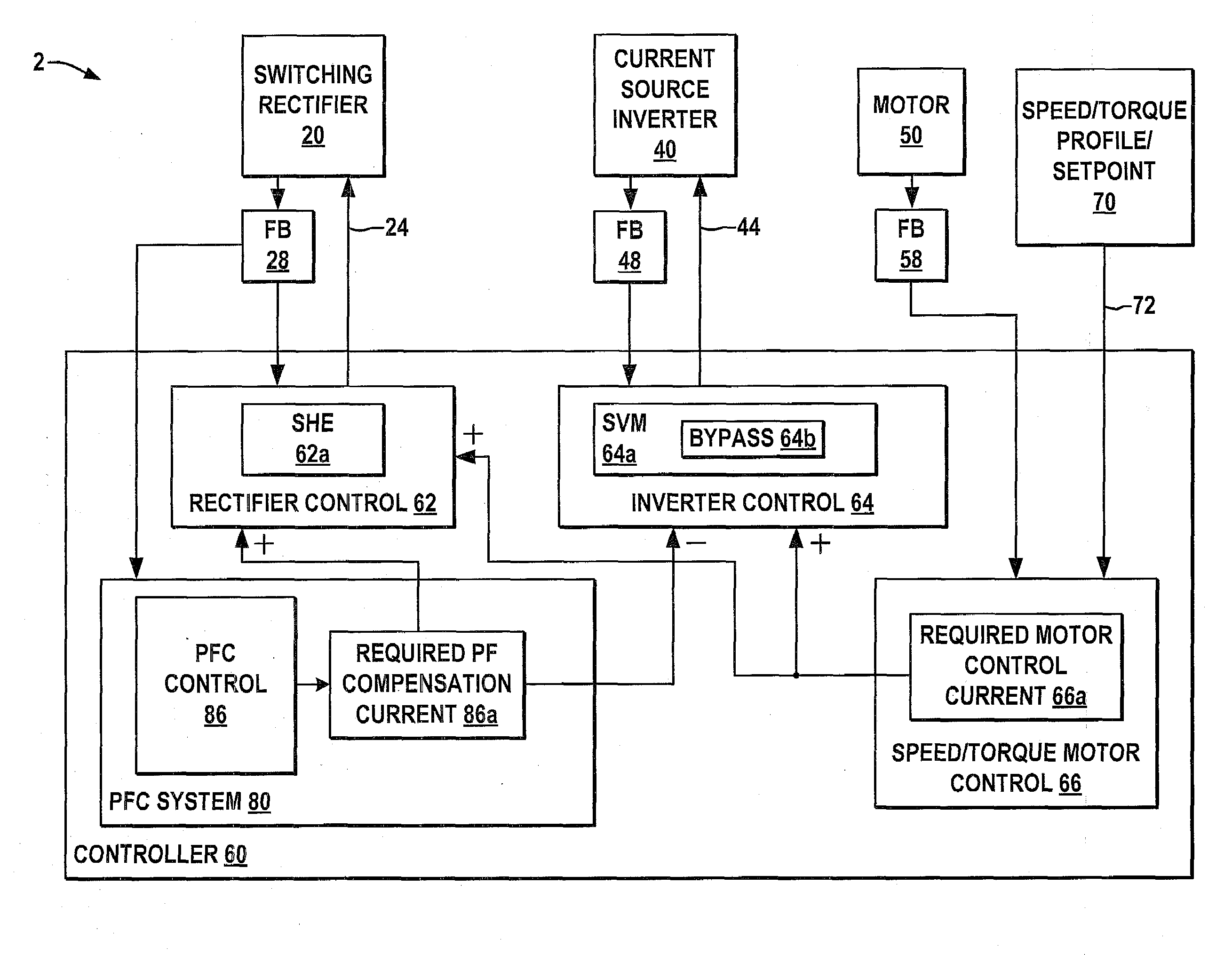
Systems and methods are described for controlling power factor in motor drives having a switching rectifier providing a DC link current to an inverter in which the rectifier gain is increased to provide additional DC link current to correct the drive power factor based on current drawn by capacitors of the AC drive power input, and the inverter gain is decreased by introducing bypass states in the inverter switching control scheme or by reducing the motor flux to accommodate the increased DC link current.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
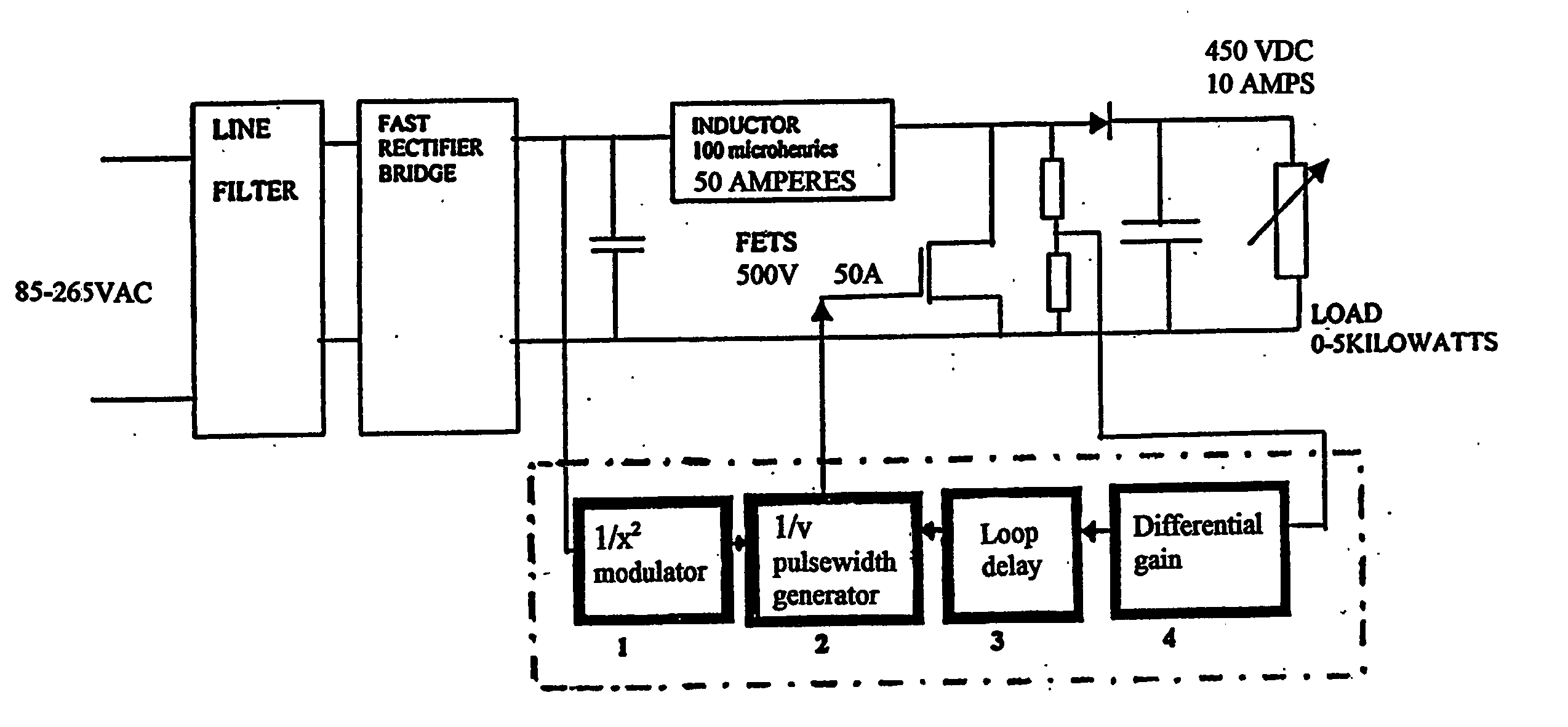
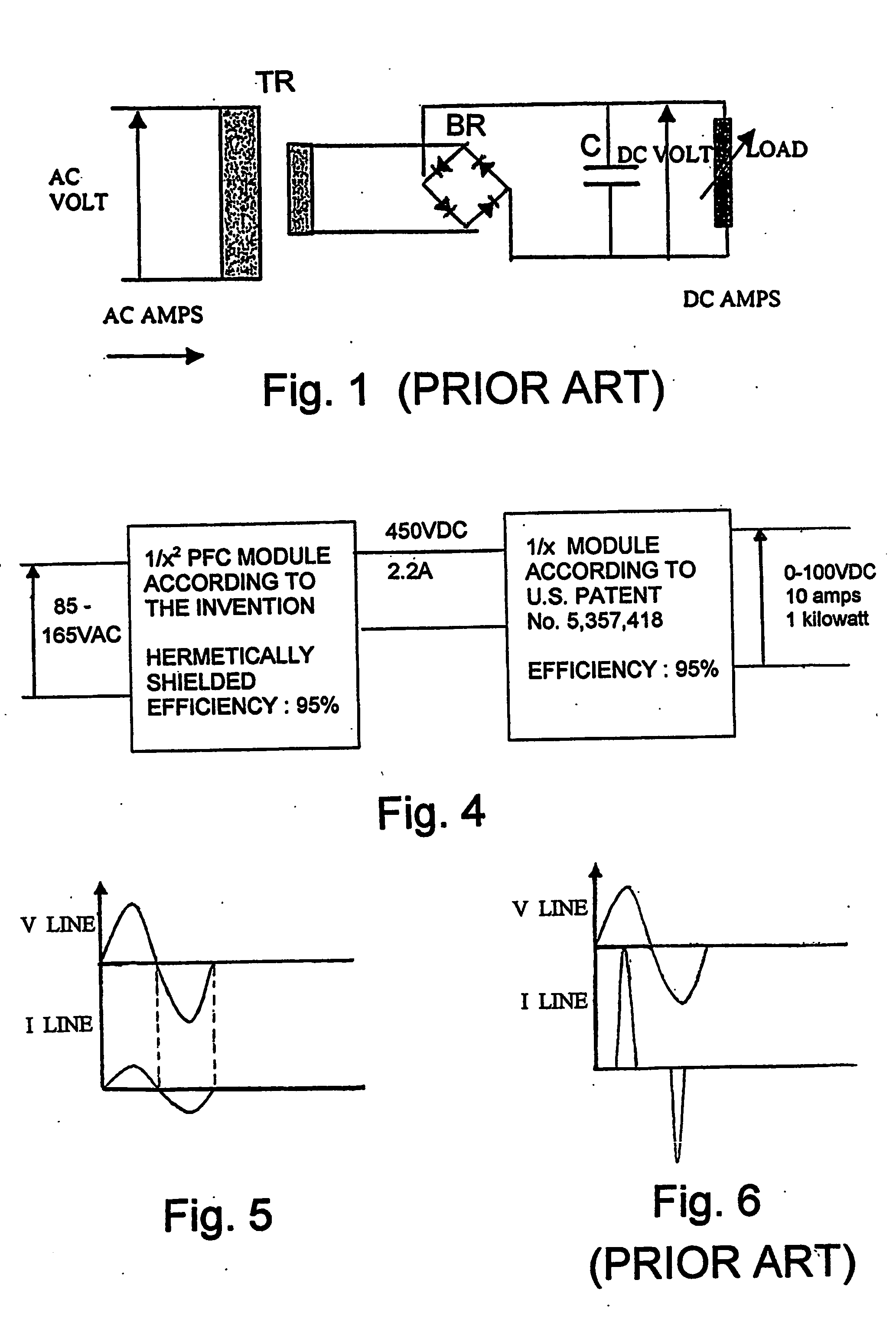
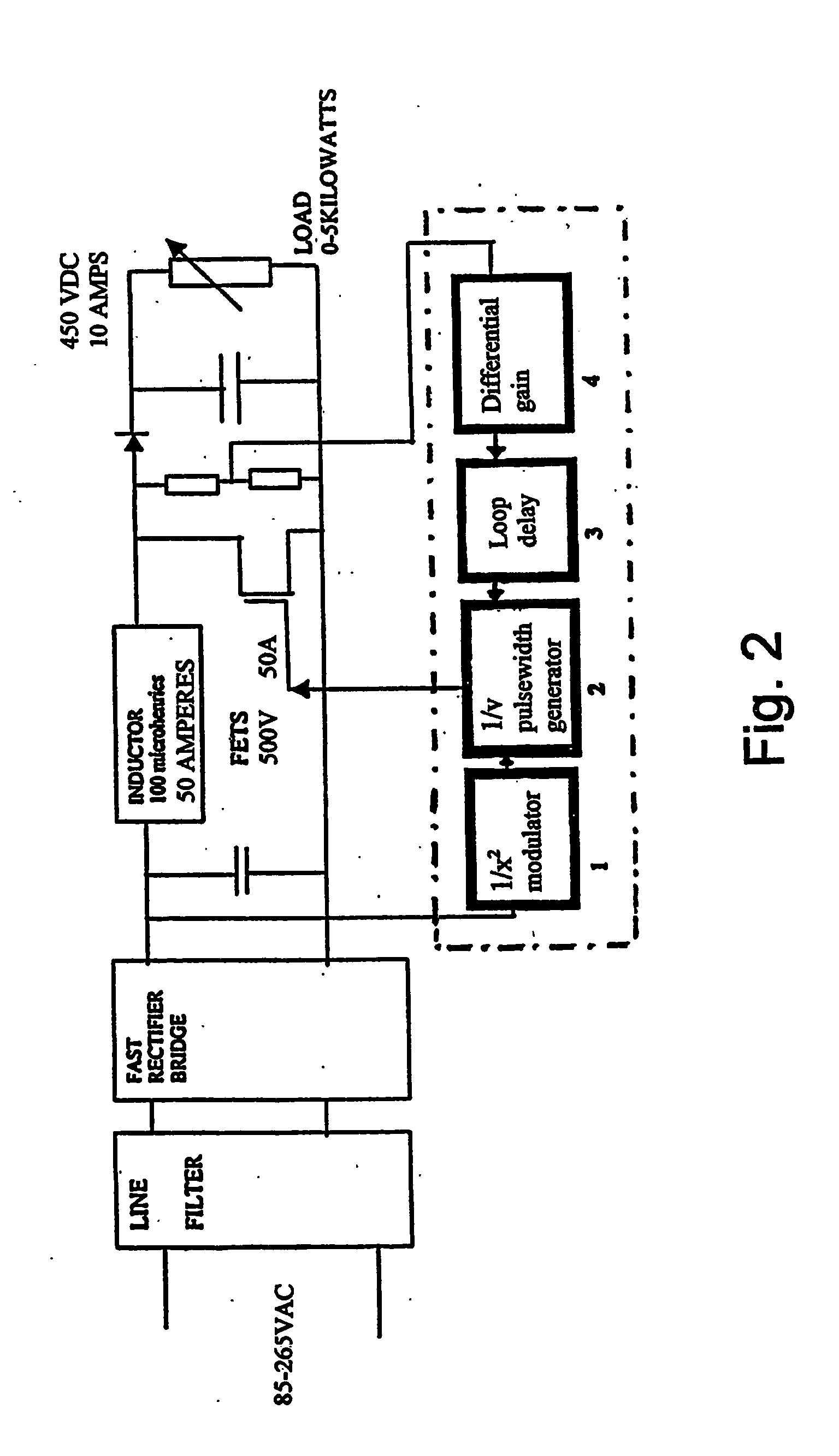
Power factor controller
InactiveUS20050057237A1Improve predictabilitySimple systemAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionPower factor controlSwitching frequency
A power factor controller or corrector is provided in a regulated power supply circuit, in which the load and line regulation circuitry is separate from one another and in which the line regulation is provided with a 1 / x2 modulator in which the switching frequency is inversely proportional to the square of the line voltage.
Owner:PRECISIONH2
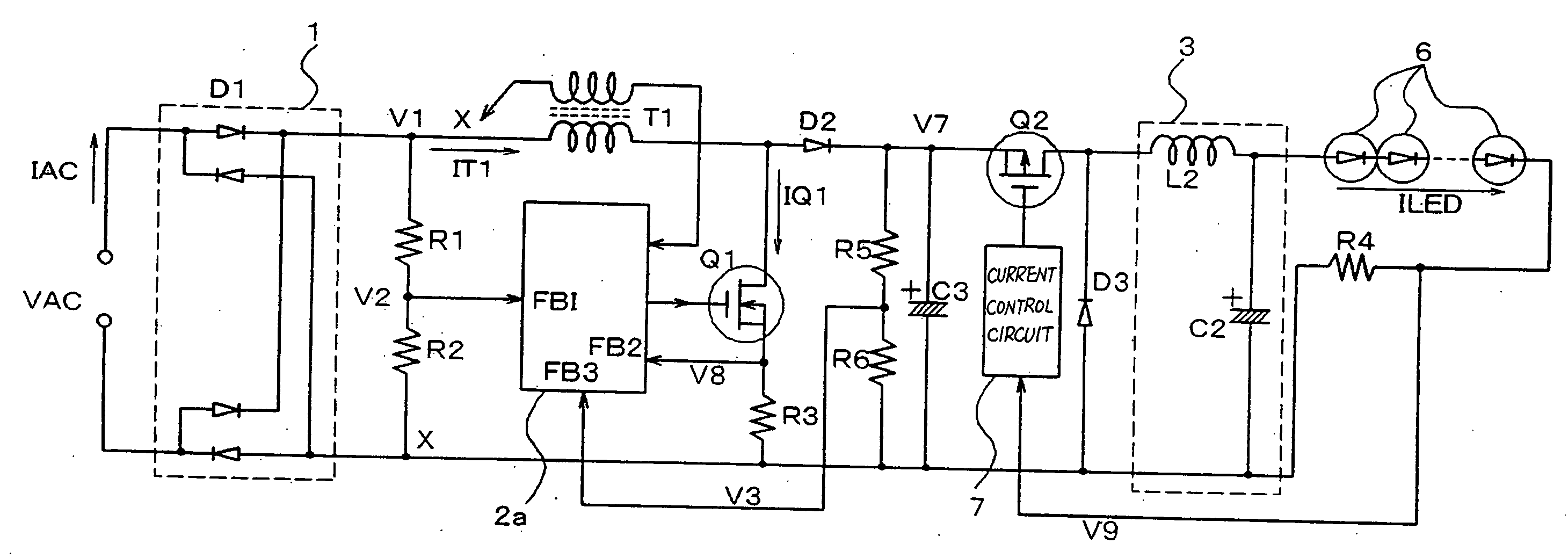
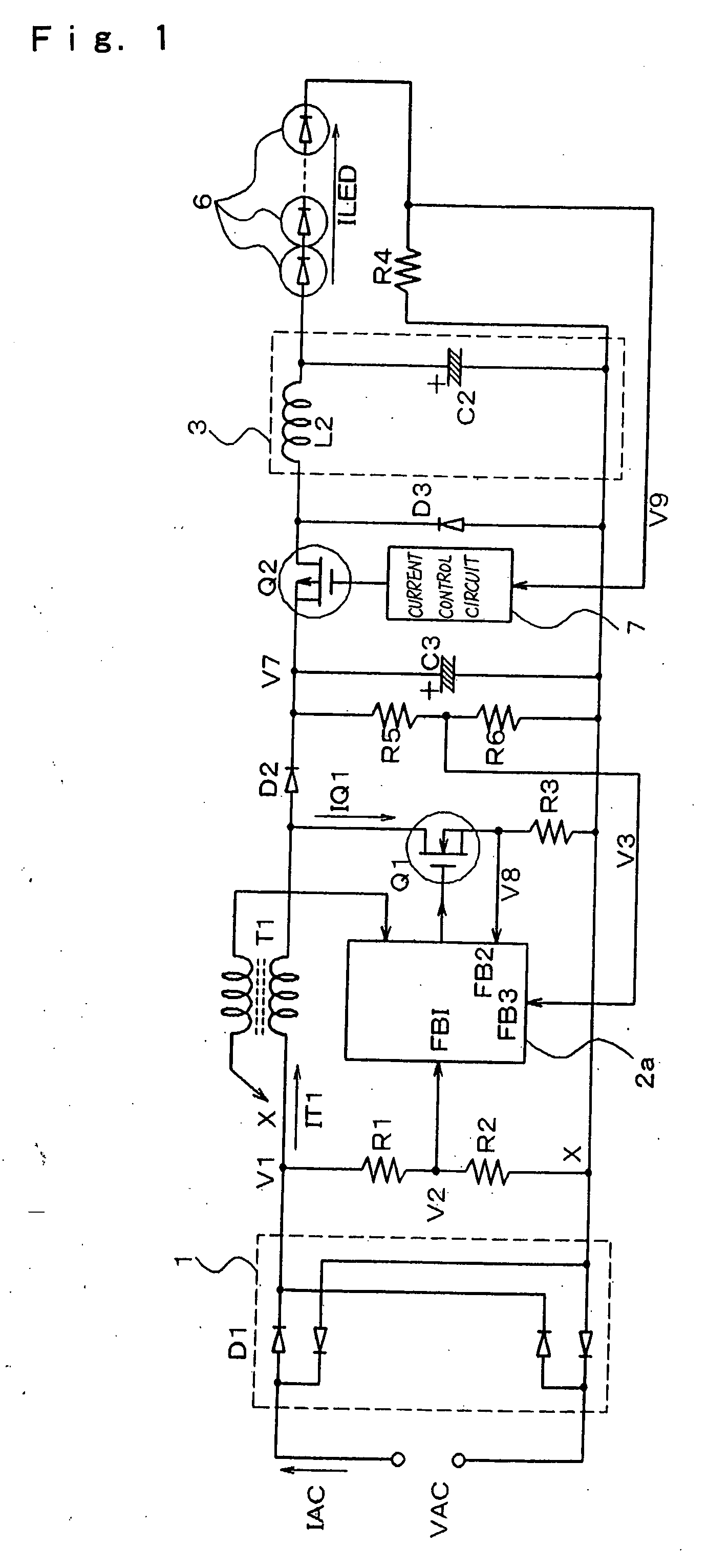
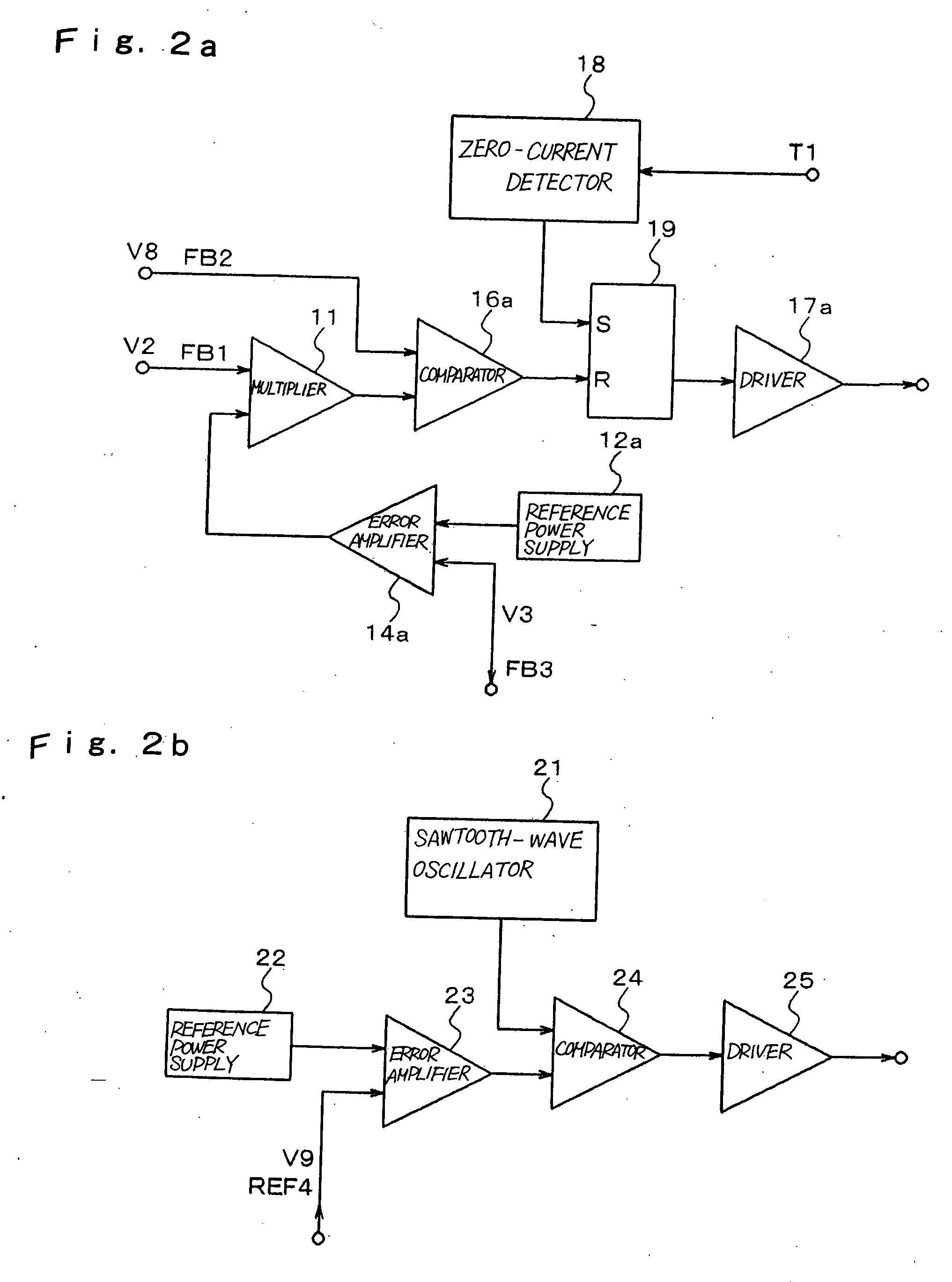
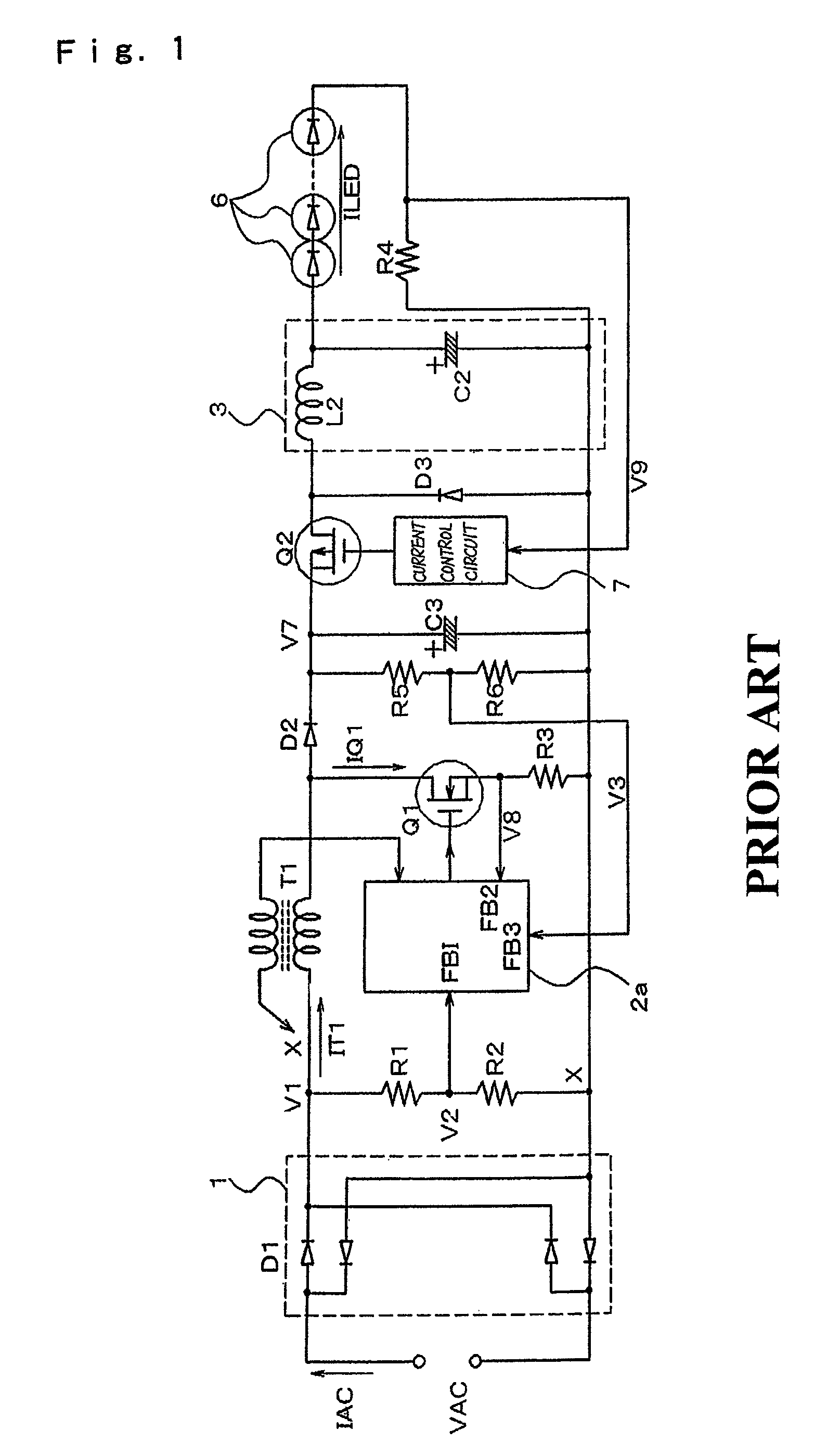
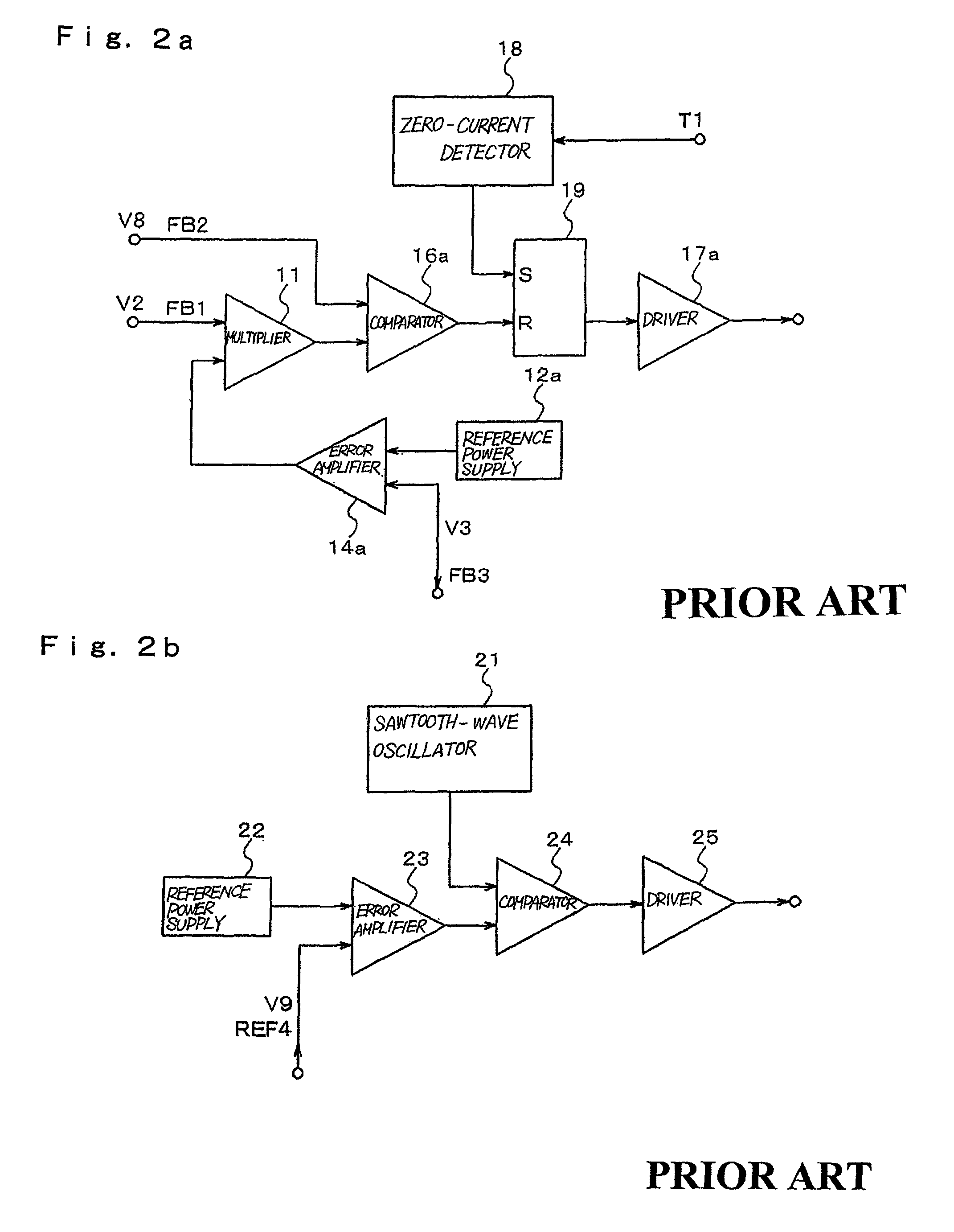
Low-voltage power supply circuit for illumination, illumination device, and low-voltage power supply output method for illumination
ActiveUS20070152604A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalElectroluminescent light sourcesCurrent limitingLow voltage
In a low-voltage power supply circuit for illumination that rectifies an ac power supply by means of a rectifier circuit, that controls this rectified output by means of a power-factor control circuit, and that supplies a low-voltage power supply for illumination, the power-factor control circuit is composed of a step-down circuit and is further provided with a current-limiting capability.
Owner:NEC LIGHTING
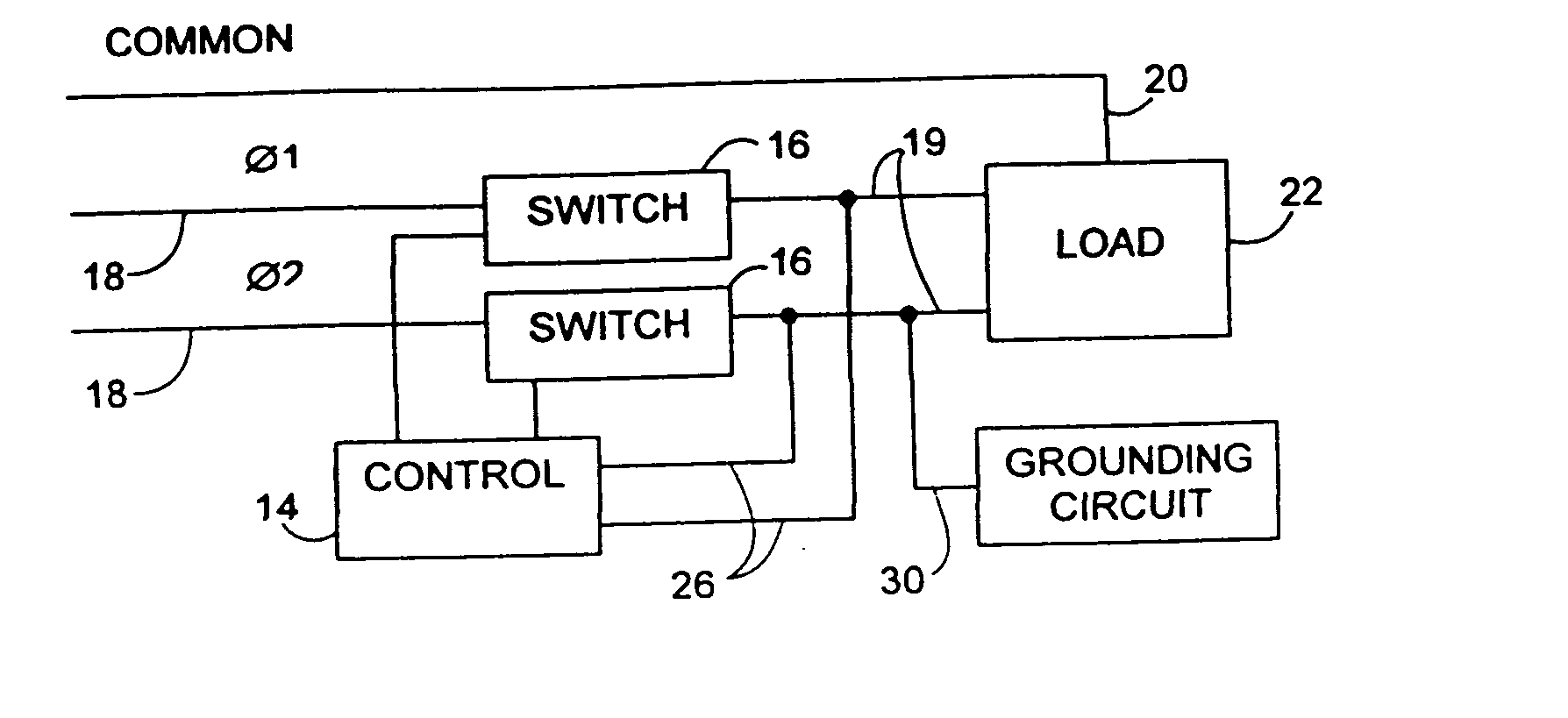
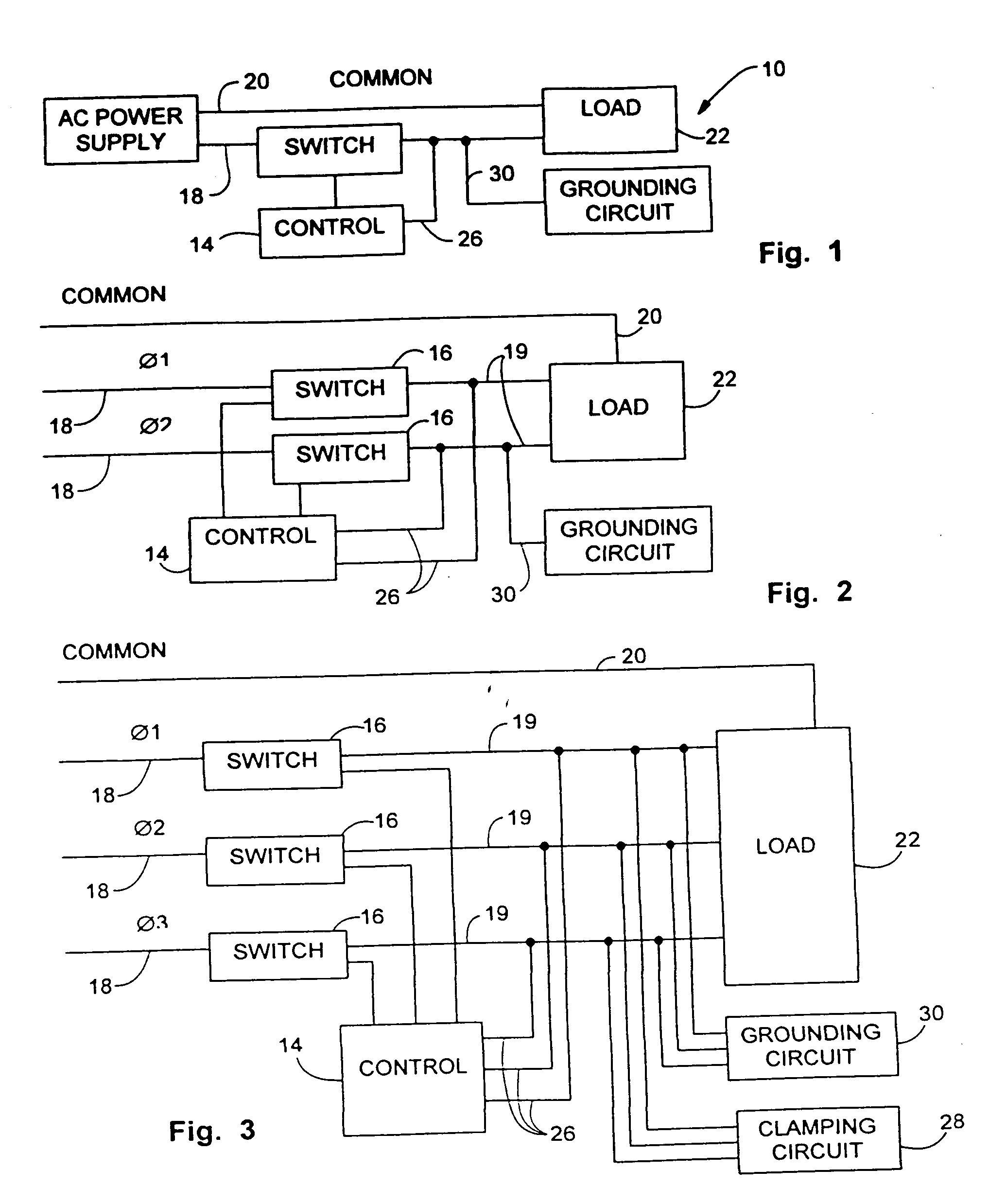
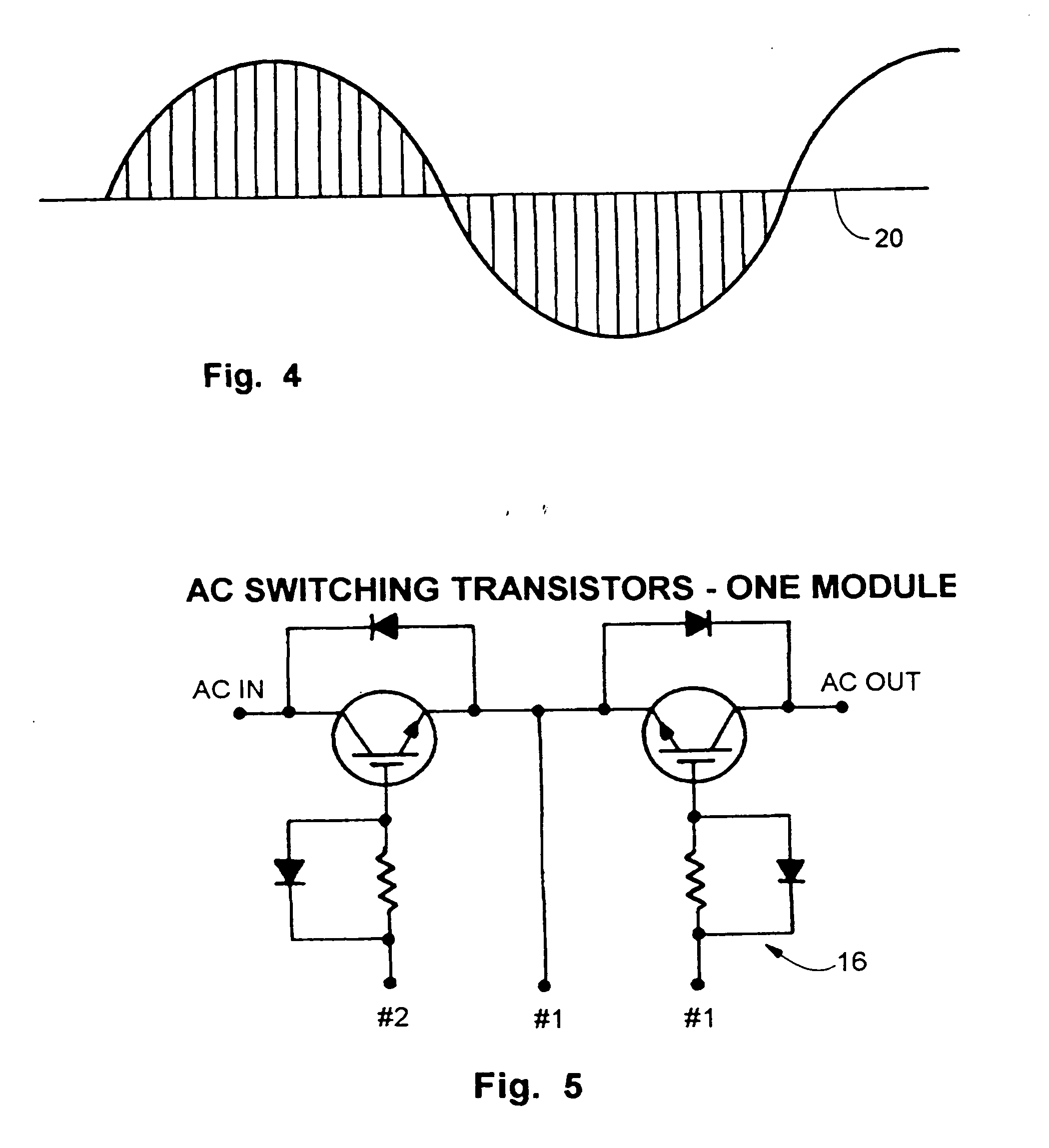
Electrical power conservation apparatus and method
InactiveUS7336514B2Process economyEasy to installPower network operation systems integrationCircuit arrangementsEngineeringPower factor control
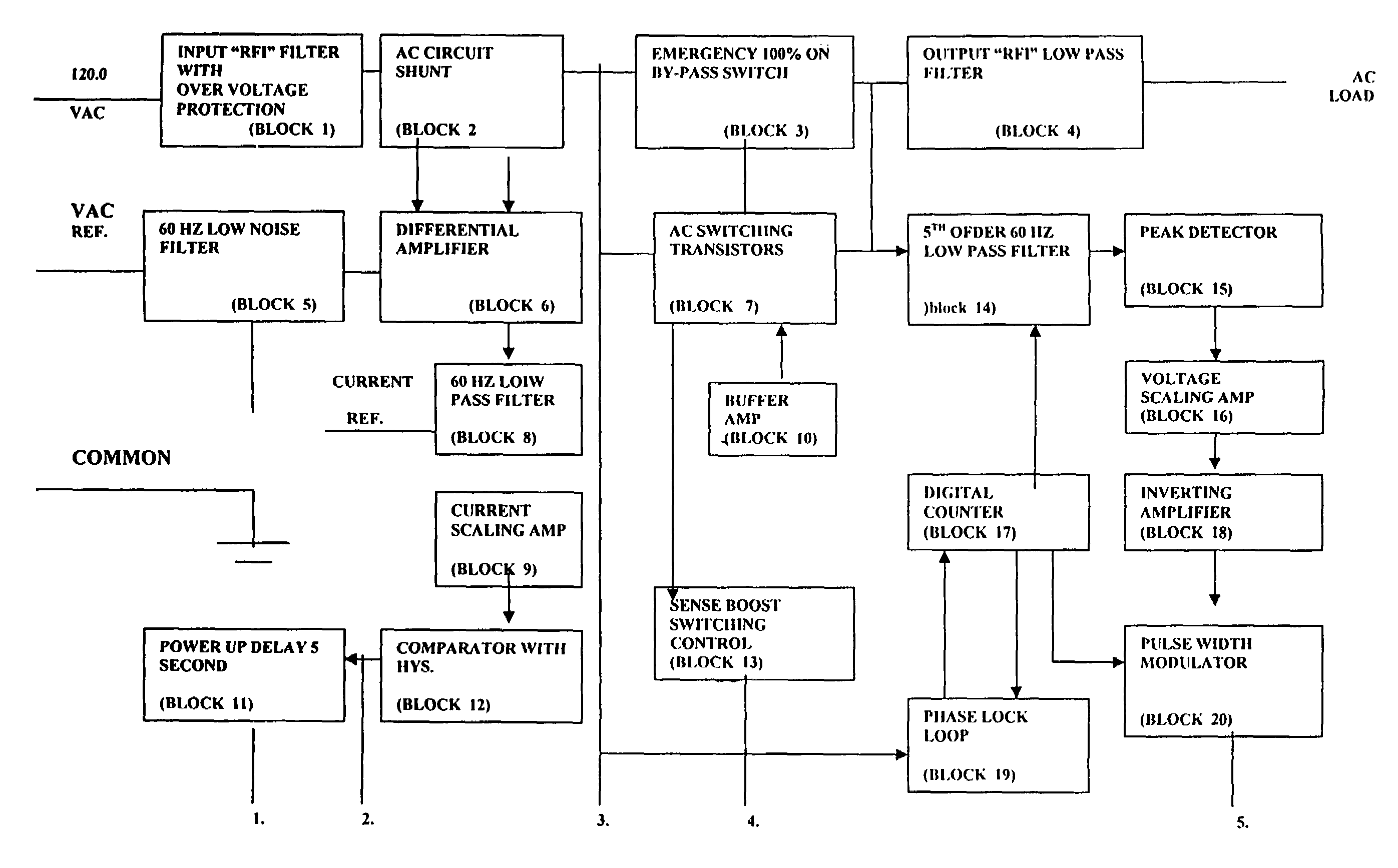
An electrical power control apparatus and method for power factor correction in a conventional 60 hertz or other conventional frequency electrical AC power supply communicated to an inductive load. A plurality of interruptions of current in the line on both sides of an AC current oscillation, are created to control the power factor in a circuit energizing an inductive load. Additional power factor control and correction is provided by grounding of the line during each interruption. A controller controls the length and duration of each interruption based on preprogramming or input regarding current phase read or calculated in the line.
Owner:MICROPULSE TECH
System and Method for Estimating Input Power for a Power Processing Circuit
ActiveUS20080315852A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionVoltage loopLow-pass filter
A controller for a power processing circuit and a related method of operating the same. In one embodiment, the controller includes a multiplier configured to produce a product of an input current and an input voltage of the power processing circuit. The controller also includes a low-pass filter configured to produce an input power estimate of an input power to the power processing circuit as a function of the product of the input current and the input voltage. In another embodiment, the controller is a power-factor controller and includes a voltage loop compensator configured to produce a voltage compensation signal as a function of an output voltage of the power processing circuit. The controller also includes an input power estimator configured to produce an input power estimate of an input power to the power processing circuit as a function of the voltage compensation signal.
Owner:MYPAQ HLDG LTD
Power factor correction circuits
InactiveUS7279868B2Efficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionPower factor controlEngineering
A bi-directional boost circuit for power factor correction includes a power factor control circuit and a pair of diodes, a pair of inductors, and a pair of switches. A first diode, a second diode, a first inductor, a second inductor, a first switch, and a second switch convert the AC input voltage, rectify the AC input voltage, and output an intermediate DC voltage. The power factor control circuit receives the AC input voltage and receives the intermediate DC voltage. The power factor control circuit regulates the DC output voltage. Based on the AC input voltage and the intermediate DC output voltage, the power factor control circuit controls an inductor current waveform by driving the first switch and the second switch to create a substantially sinusoidal current as seen by the power source that is in phase with the AC input voltage.
Owner:COMARCO WIRELESS TECH
Single chip ballast control with power factor correction
InactiveUS6956336B2Improve power factorReduce Harmonic DistortionAc-dc conversion without reversalDc-dc conversionManufacturing cost reductionTotal harmonic distortion
An integrated circuit provides a complete electronic ballast control with power factor correction for fluorescent lamps. The integrated circuit contains a simplified power factor correction (PFC) circuit to reduce component count and supply voltage requirements to reduce manufacturing costs while providing a robust control. The PFC circuit has a variable gain for fast response at high gain and optimized power factor control at low gain. An increased on time for the PFC switch when the input line voltage approaches zero dynamically reduces crossover distortion, thereby reducing total harmonic distortion. The integrated circuit incorporates a number of fault protections.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
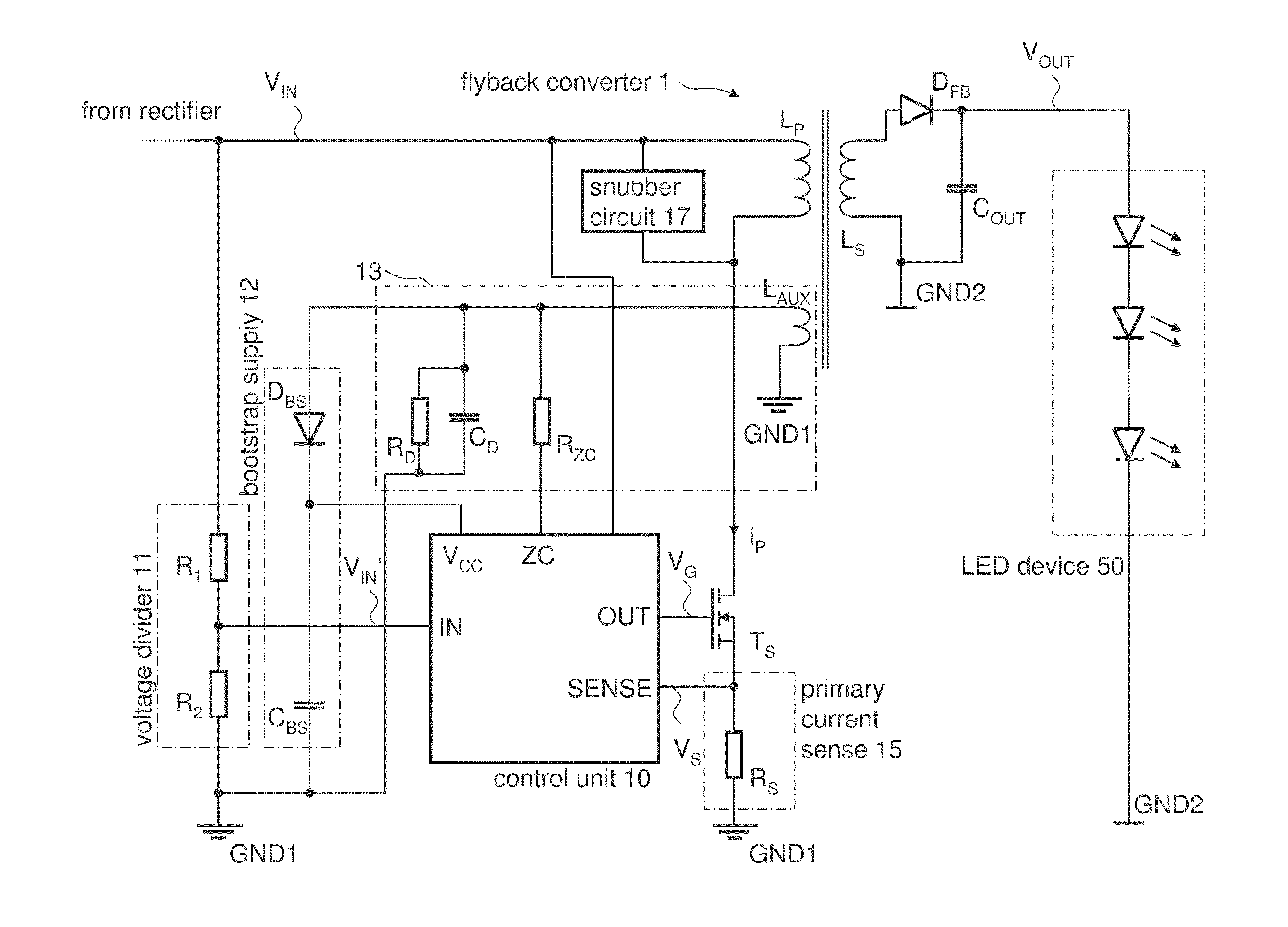
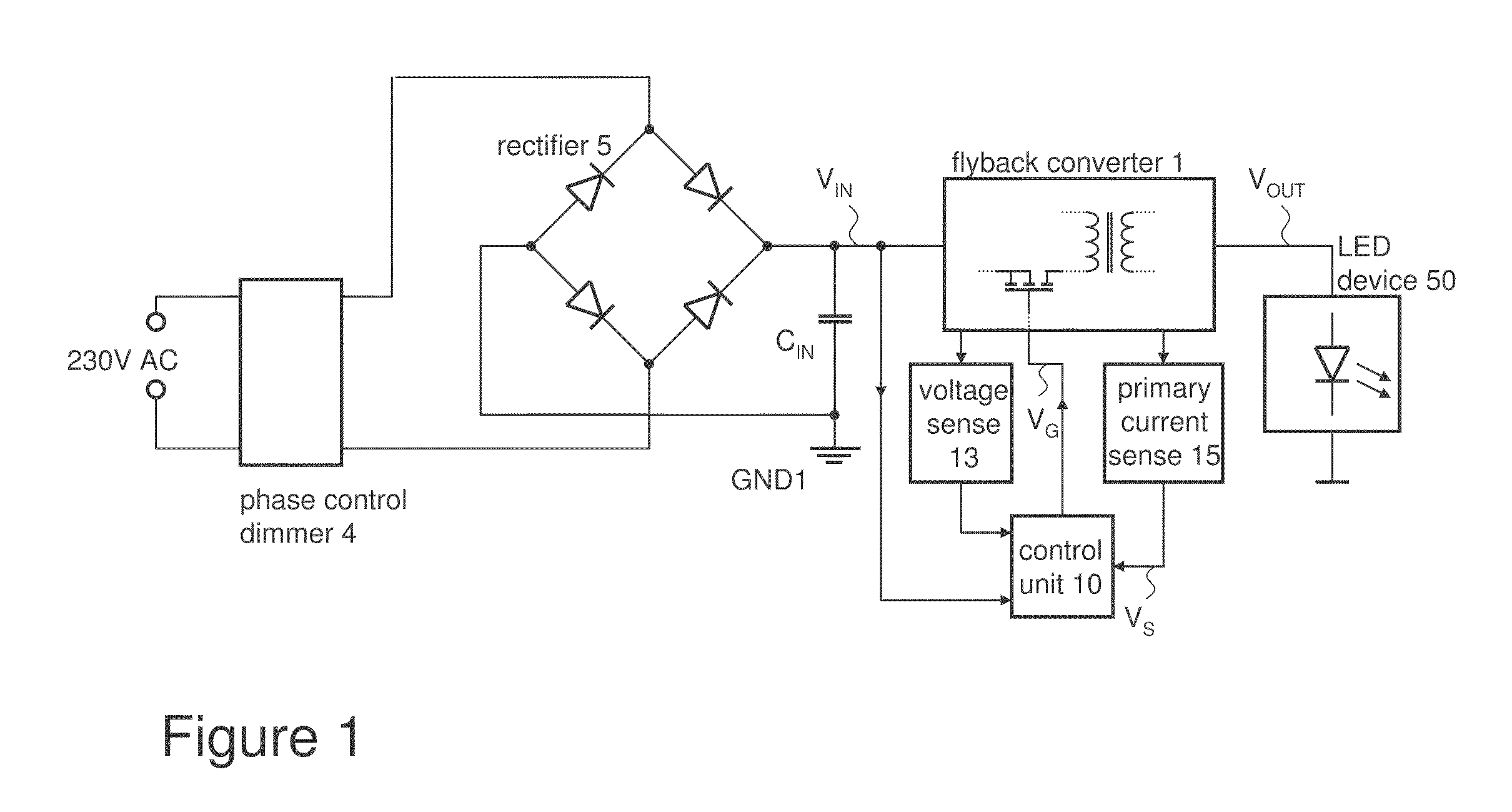
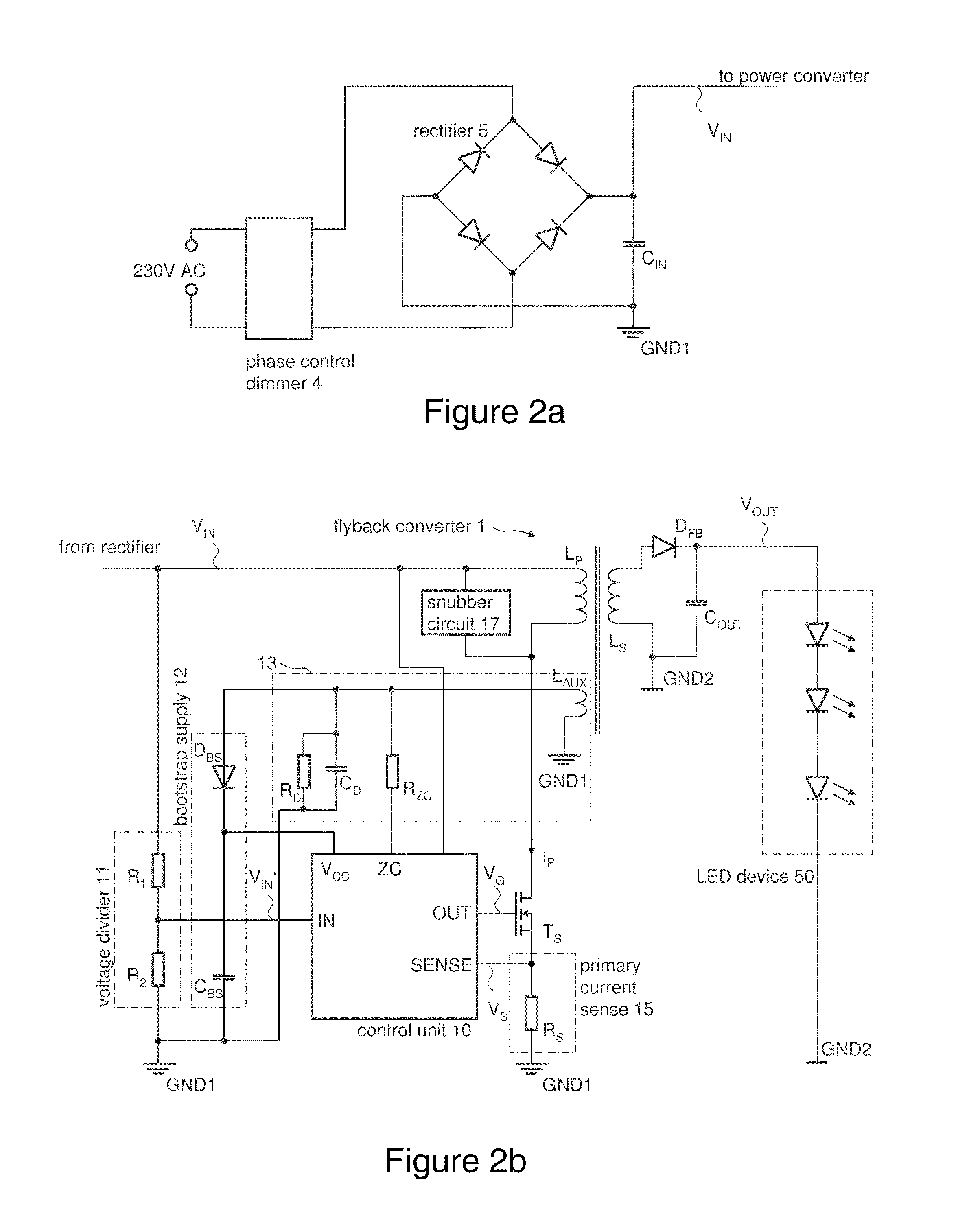
Dimmable LED Power Supply with Power Factor Control
InactiveUS20110266969A1Efficient power electronics conversionElectroluminescent light sourcesBuck converterTransformer
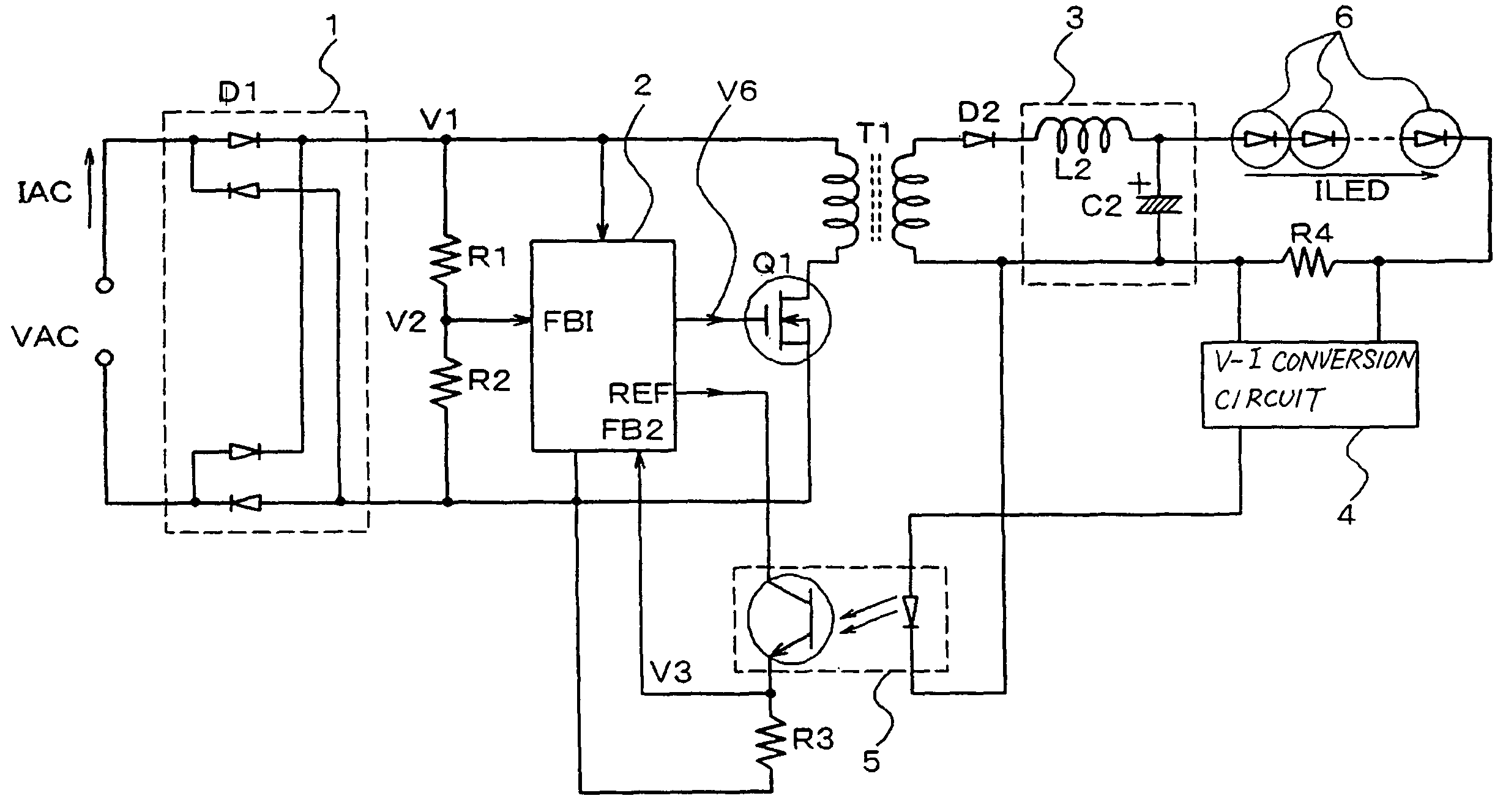
A dimmable LED power supply circuit arrangement is disclosed. The circuit arrangement includes a flyback converter coupled between an input for receiving a rectified alternating line voltage and an output providing power for at least one LED device. The flyback converter includes a transformer and a semiconductor switch for switching a primary current of the transformer. A current sensing unit provides a current sense signal dependent on the primary current. A control unit controls the switching operation of the semiconductor switch dependent on the rectified alternating line voltage and the current sense signal such that the flyback converter operates in a quasi-resonant mode of operation, whereby the current sense signal is compared with a time-varying reference signal representing the rectified alternating line voltage and whereby a switch-off time of the semiconductor switch is determined dependent on the comparison.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
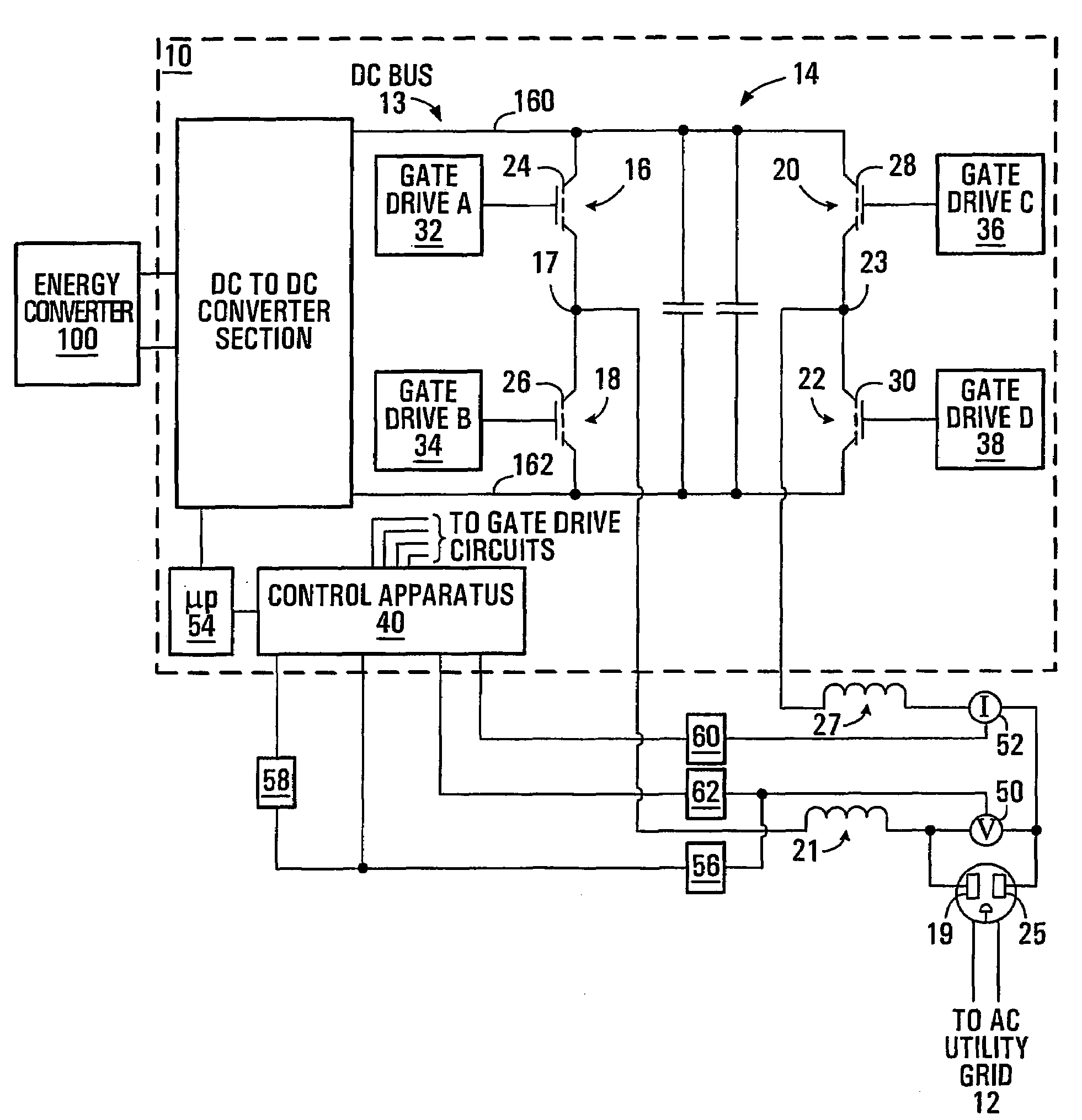
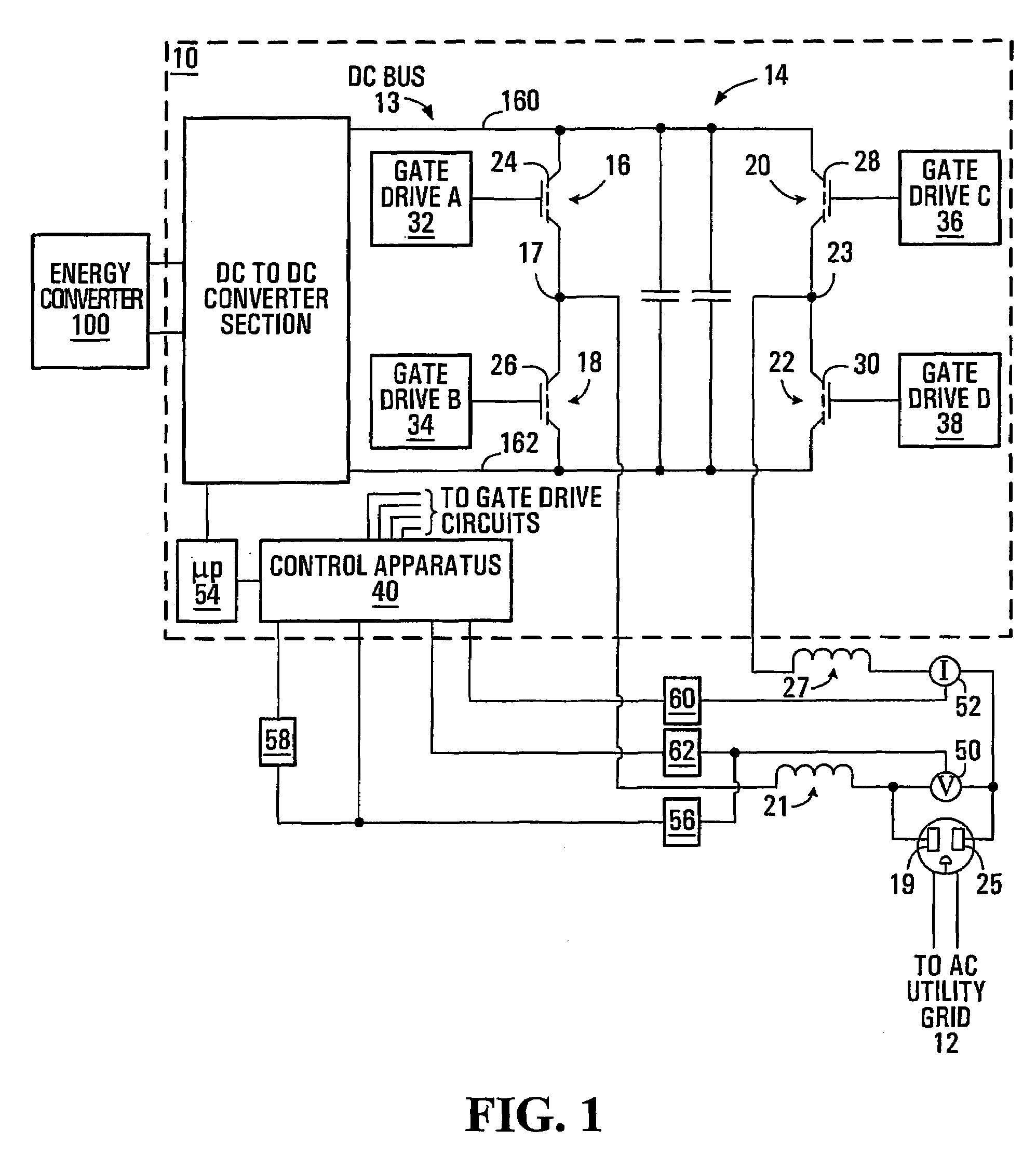
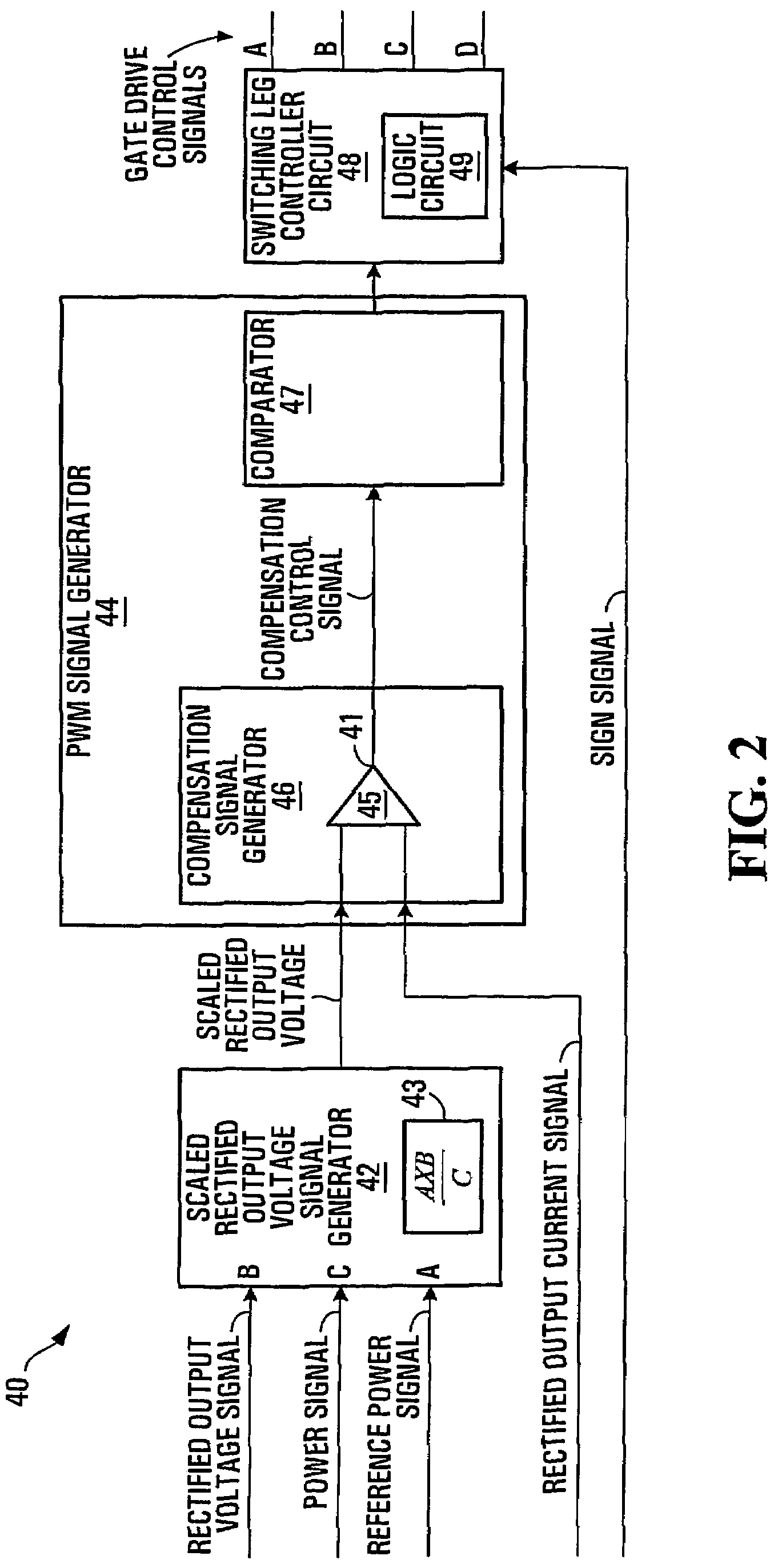
Output power factor control of pulse-width modulated inverter
ActiveUS7660139B2Efficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcFull bridgePower factor control
An inverter operable to supply high power factor electrical power to an AC load including an AC power grid includes a DC bus and a DC to AC converter section of the full bridge type. The inverter further includes a voltage sensor configured to produce an instantaneous output voltage signal representing instantaneous output voltage of the inverter, a rectification circuit configured to produce a rectified output voltage signal, a power signal generator, an output current sensor configured for sensing an output current of the inverter, a rectification circuit configured to produce the rectified output current signal, a sign circuit for producing a signal representing the sign of the output voltage and a control apparatus. The control apparatus includes a scaled rectified voltage signal generator, a pulse width modulation (PWM) signal generator configured to produce a pulse width modulation signal in response to the scaled rectified voltage signal and the rectified output current signal and a switching leg controller circuit configured to control the full bridge switches.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SOLAR INVERTERS USA
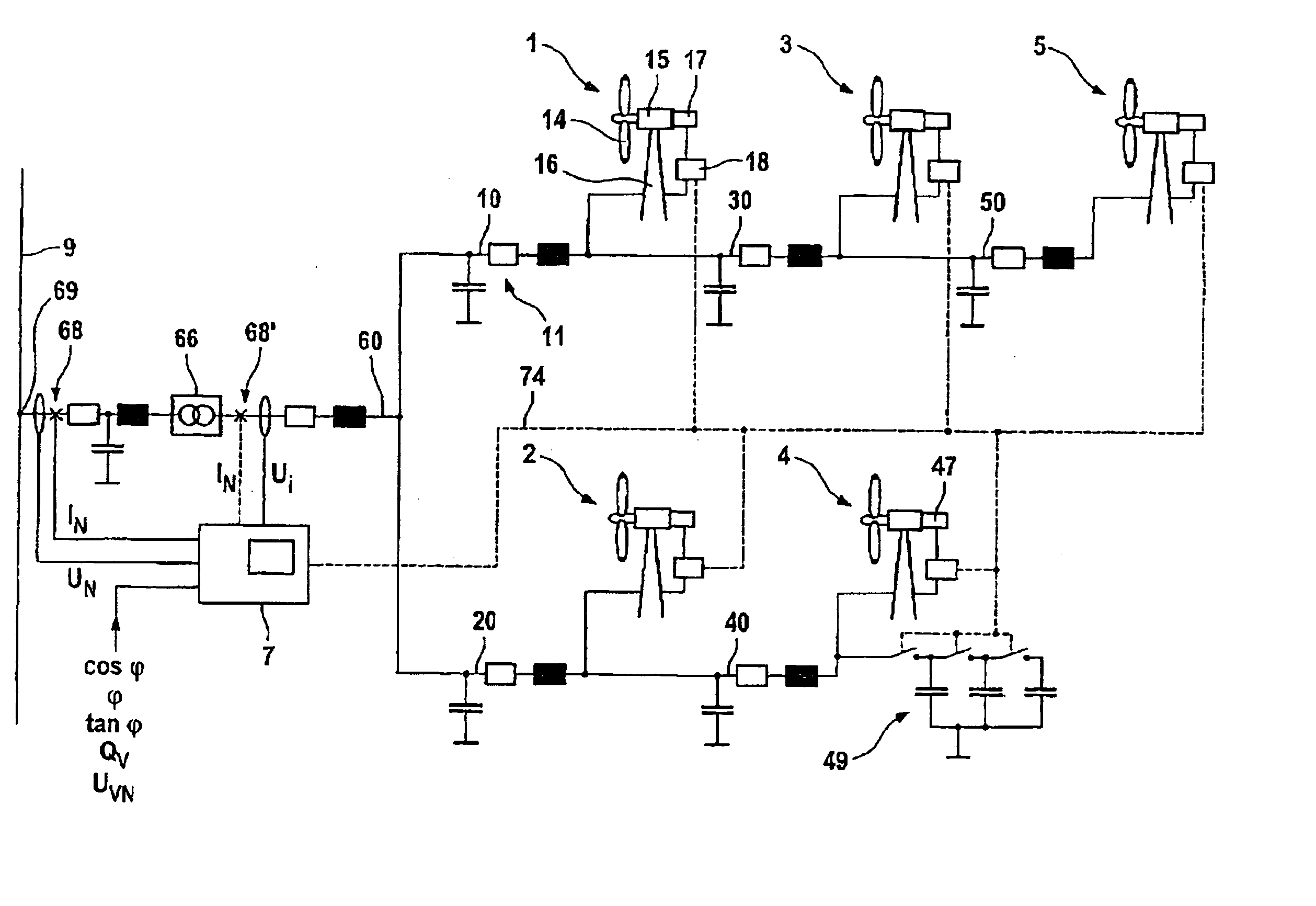
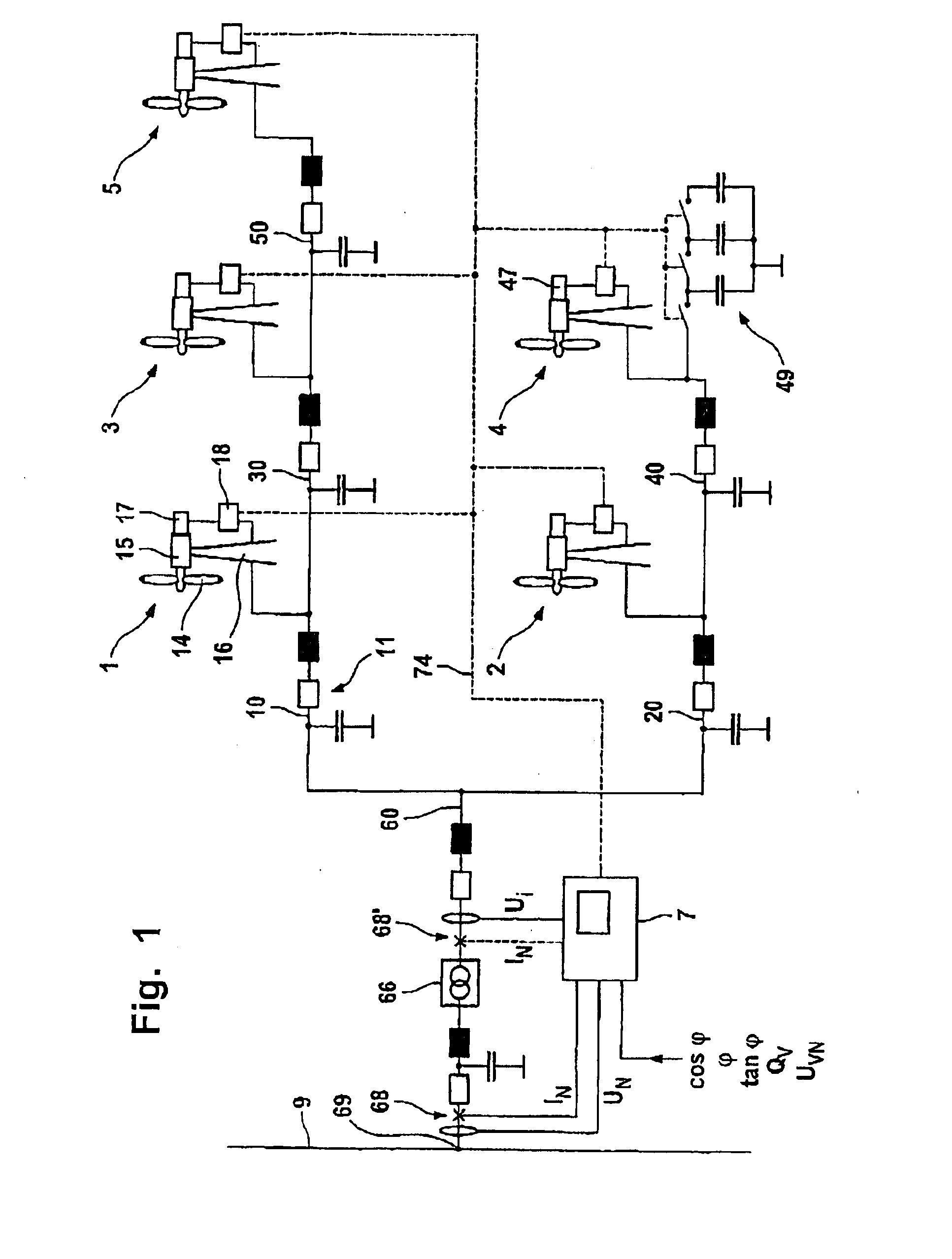
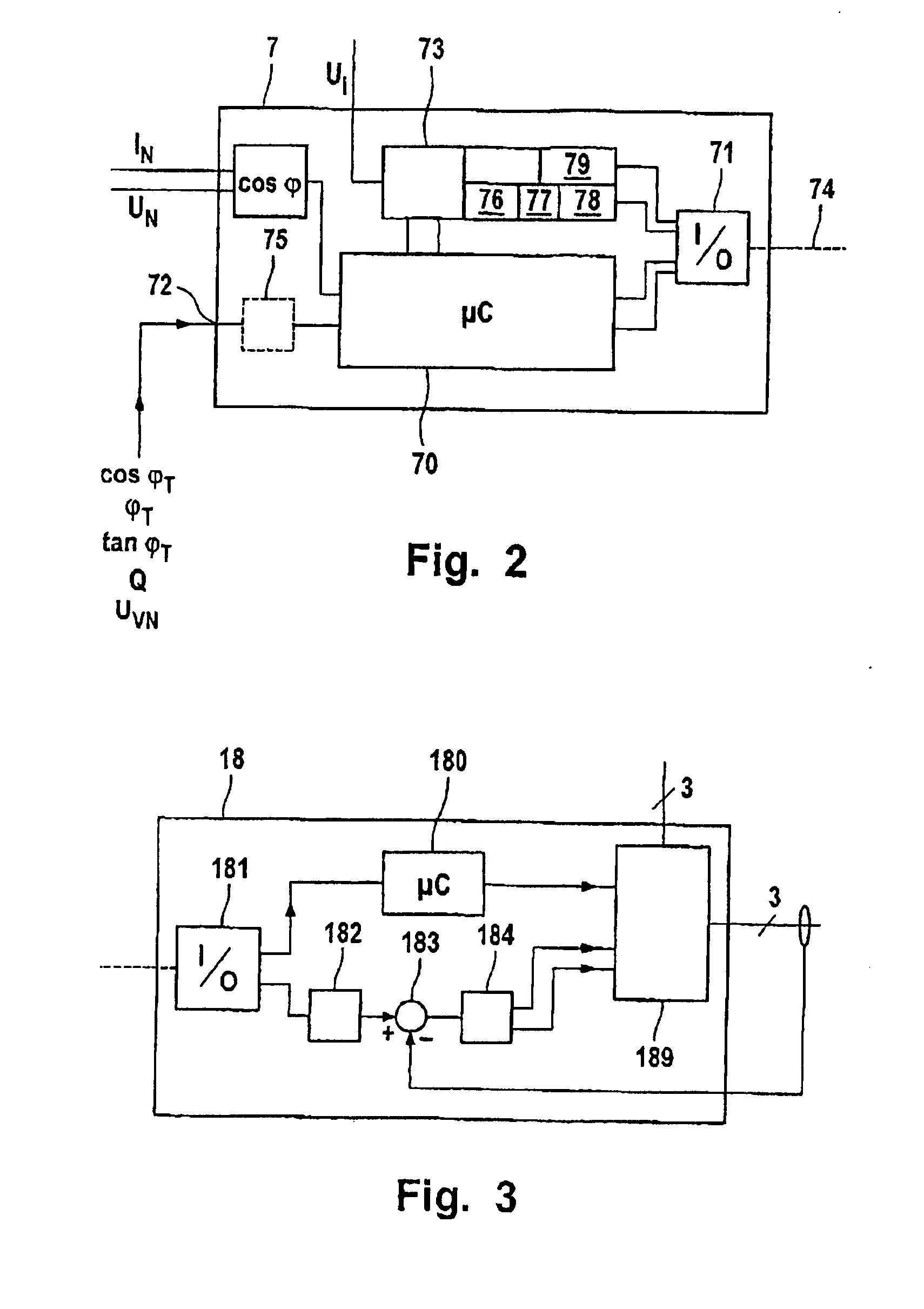
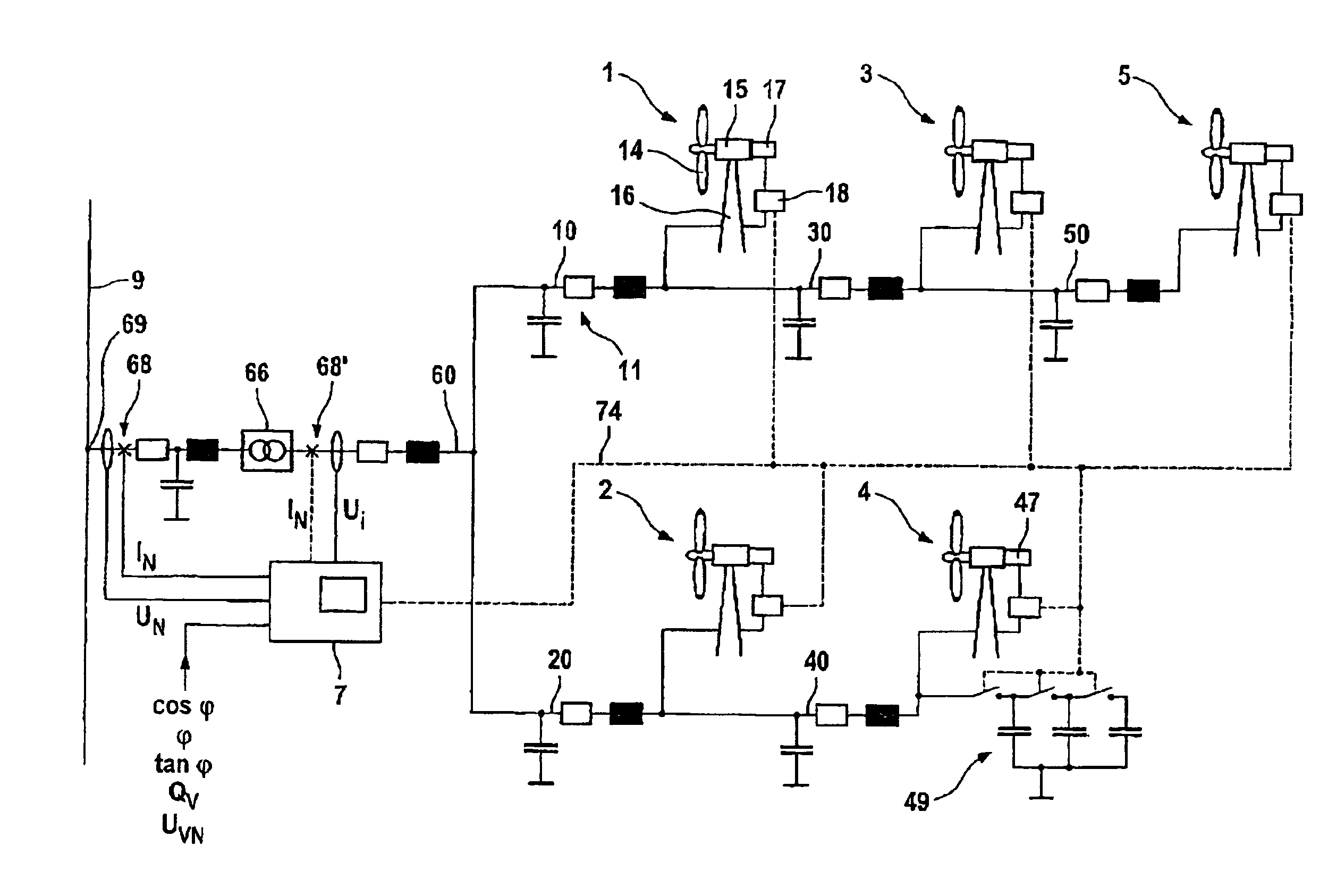
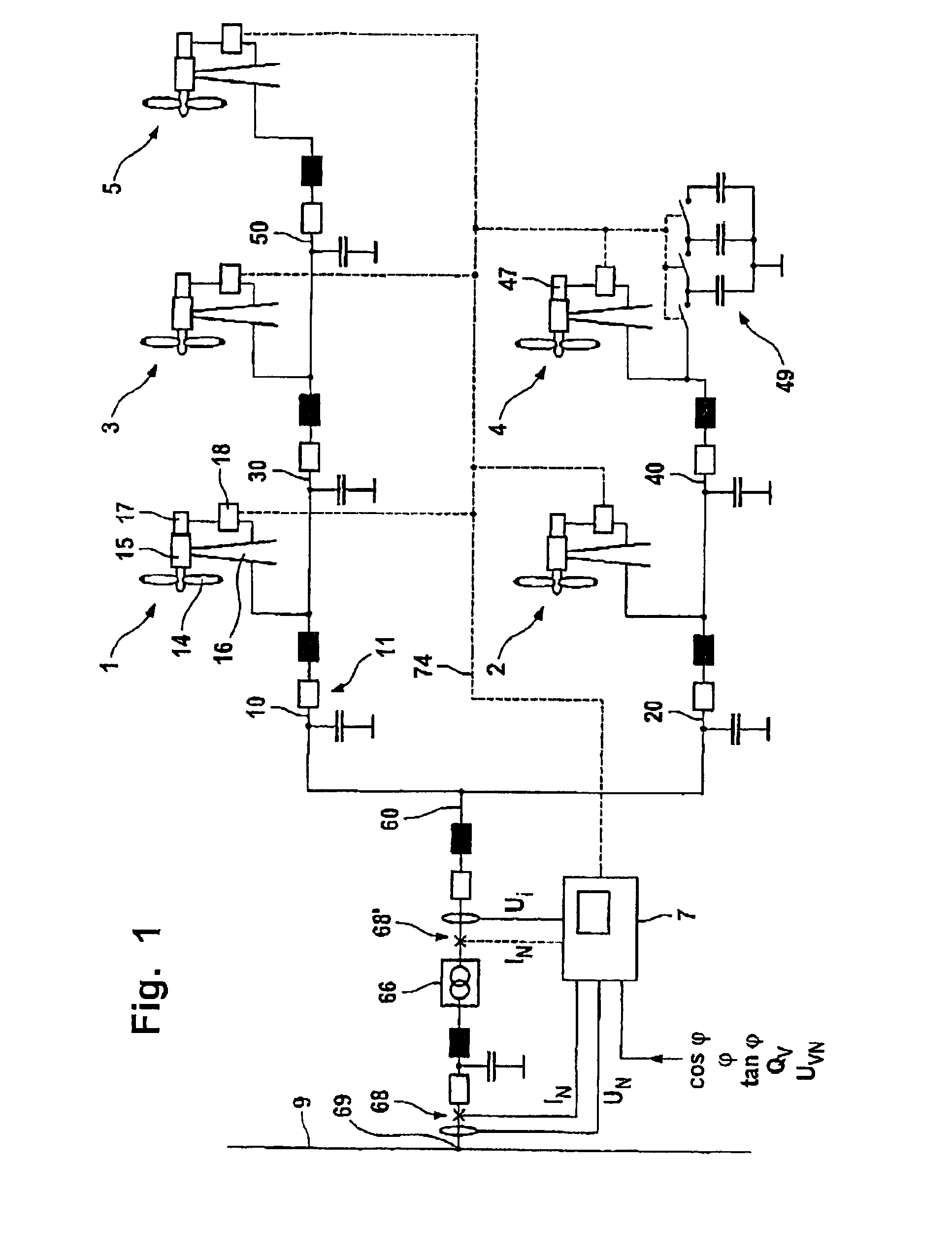
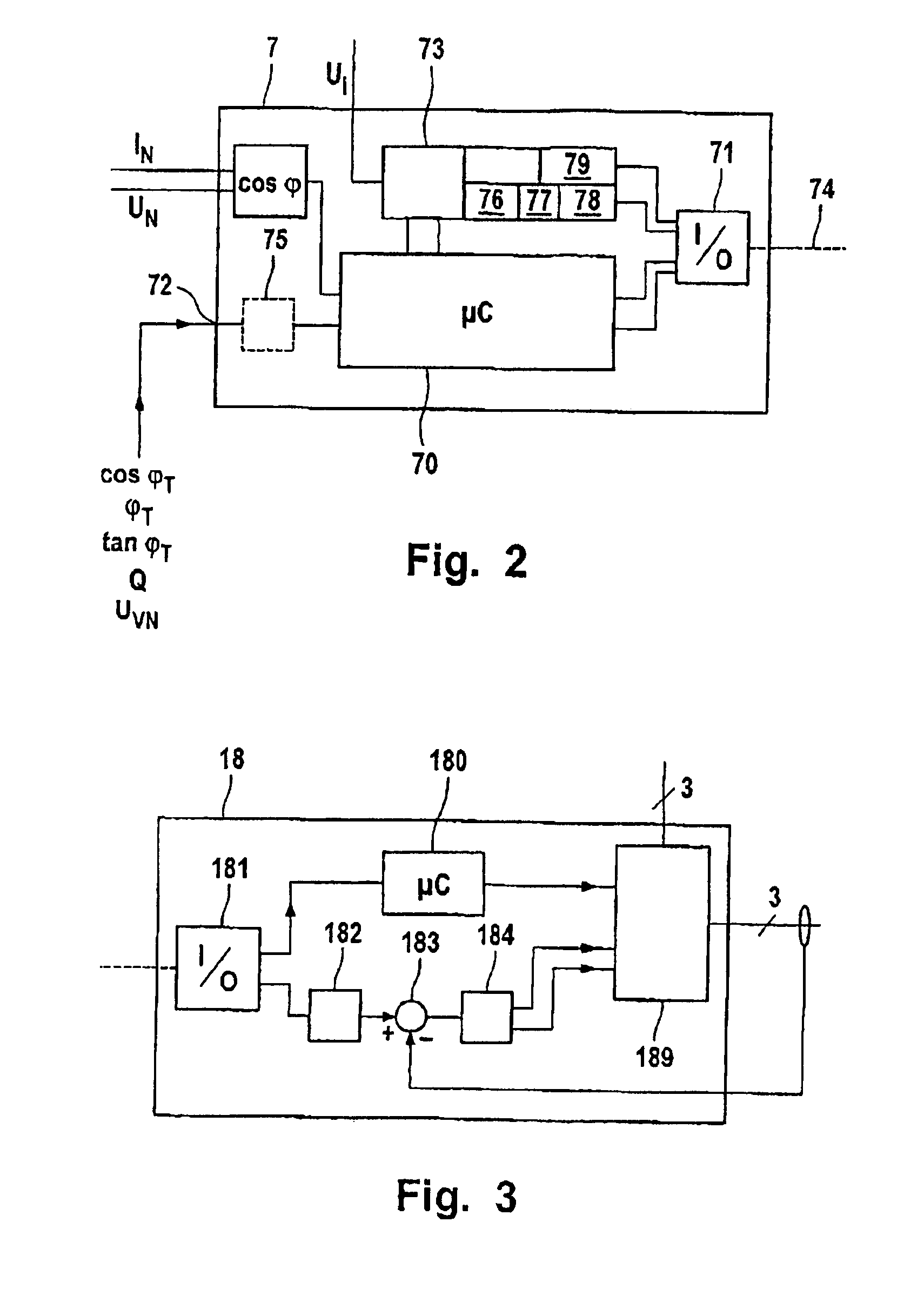
Wind Park with Robust Reactive Power Adjustment System and Method for the Operation Thereof
ActiveUS20080073912A1Robust windpark operational responseRapid responseSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind motor combinationsElectric power transmissionControl signal
A windpark includes at least two wind energy installations, each of which installations comprises a rotor, a generator driven by the rotor and a control device, and which are connected via connecting lines to a main line. The windpark also includes a linking point which connects the main line to a power transmission network, a parkmaster which is configured for power factor control and has communication lines for transmission of control signals to the wind energy installations, and a power-factor control section including a distributed regulator having a higher-level regulator located at the parkmaster which is configured to determine a nominal voltage in order to set a global power coefficient for the power which is emitted to the power transmission network and to emit the global power coefficient as a signal via the communication lines and lower-level regulators at the wind energy installations.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY SERVICE GMBH
Wind park with robust reactive power adjustment system and method for the operation thereof
ActiveUS7606638B2Guaranteed uptimeImprove stabilityMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlElectric power transmissionControl signal
A windpark includes at least two wind energy installations, each of which installations comprises a rotor, a generator driven by the rotor and a control device, and which are connected via connecting lines to a main line. The windpark also includes a linking point which connects the main line to a power transmission network, a parkmaster which is configured for power factor control and has communication lines for transmission of control signals to the wind energy installations, and a power-factor control section including a distributed regulator having a higher-level regulator located at the parkmaster which is configured to determine a nominal voltage in order to set a global power coefficient for the power which is emitted to the power transmission network and to emit the nominal voltage as a signal via the communication lines and lower-level regulators at the wind energy installations.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY SERVICE GMBH
High power-factor control circuit and method for switched mode power supply
ActiveUS20120056551A1Improve power factorLow production costEfficient power electronics conversionElectroluminescent light sourcesTransformerPeak value
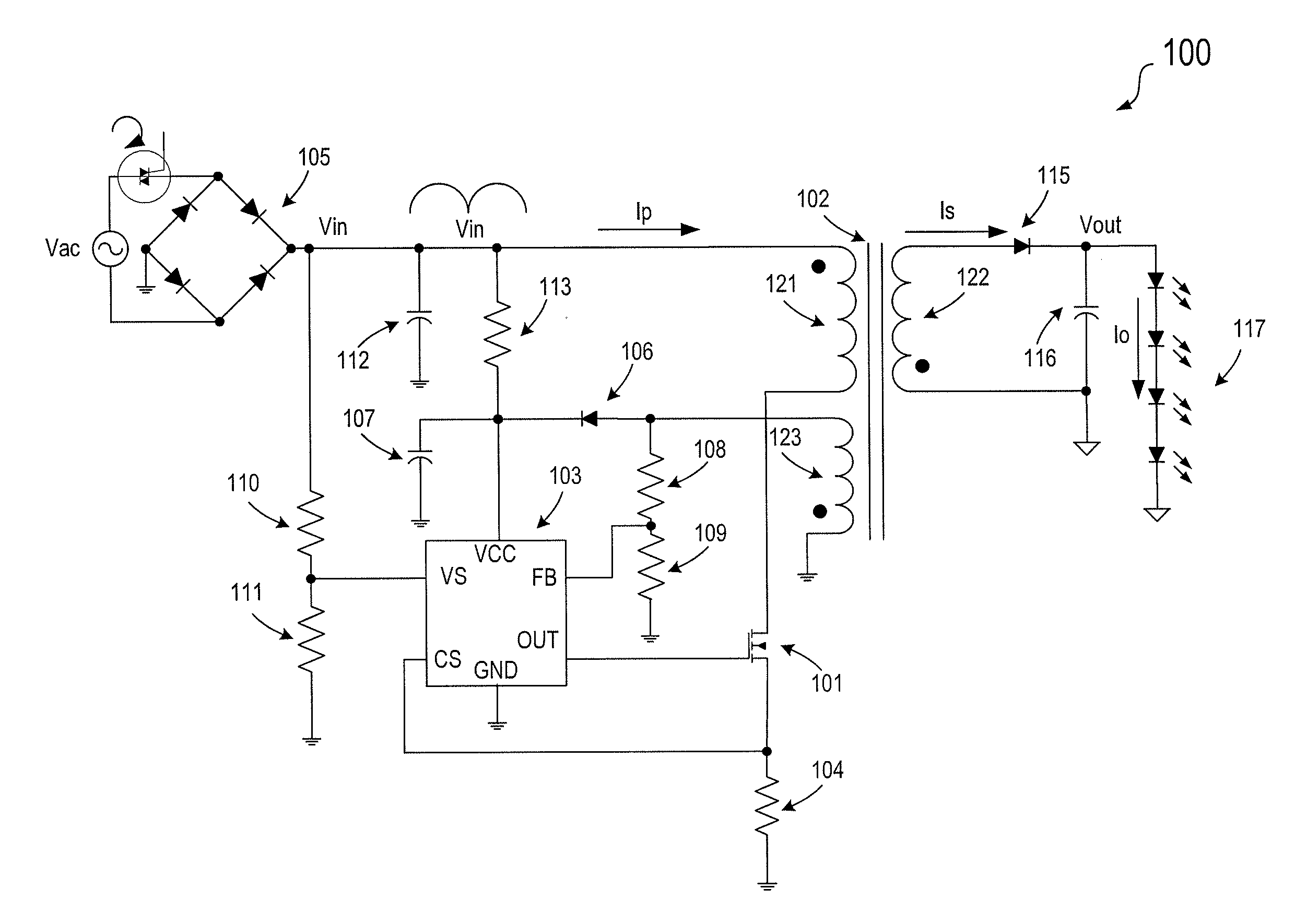
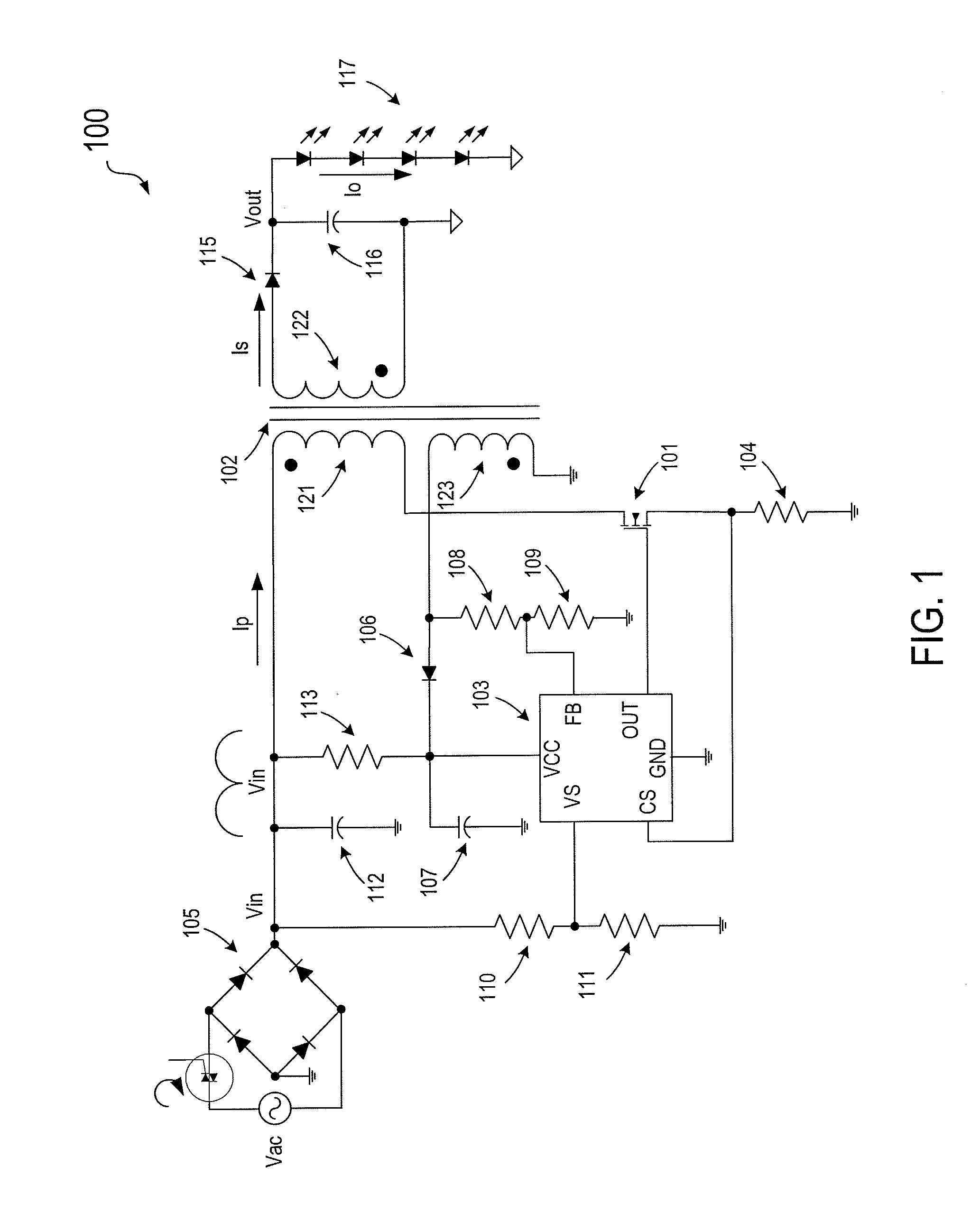
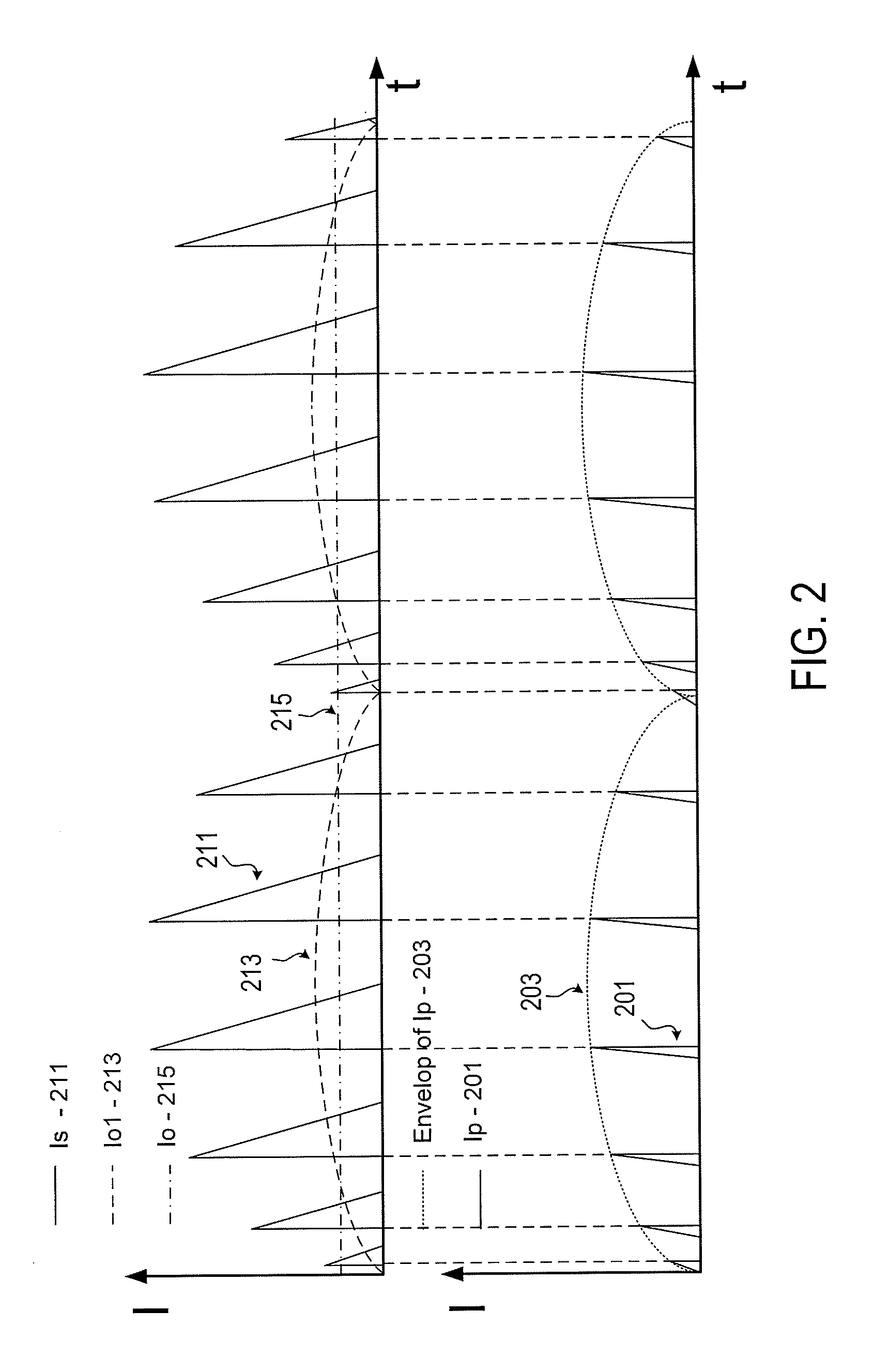
A switch mode power supply (SMPS) system includes a rectifying circuit for coupling to an AC input voltage and a transformer having a primary winding for coupling to the rectifying circuit and a secondary winding coupled to the primary winding. The system also has a power switch coupled to the primary winding and a control circuit coupled to the power switch. The control circuit is configured to control current flow in the primary winding such that an envelop waveform formed by peak points of current pulses are in phase with the magnitude of the AC input voltage. Moreover, the SMPS system is configured to provide a constant average output current.
Owner:BCD SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Systems and methods for improved motor drive power factor control
ActiveUS20080180055A1Reduce adverse effectsHigh gainSingle-phase induction motor startersAc-dc conversion without reversalControl powerMotor drive
Systems and methods are described for controlling power factor in motor drives having a switching rectifier providing a DC link current to an inverter in which the rectifier gain is increased to provide additional DC link current to correct the drive power factor based on current drawn by capacitors of the AC drive power input, and the inverter gain is decreased by introducing bypass states in the inverter switching control scheme or by reducing the motor flux to accommodate the increased DC link current.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
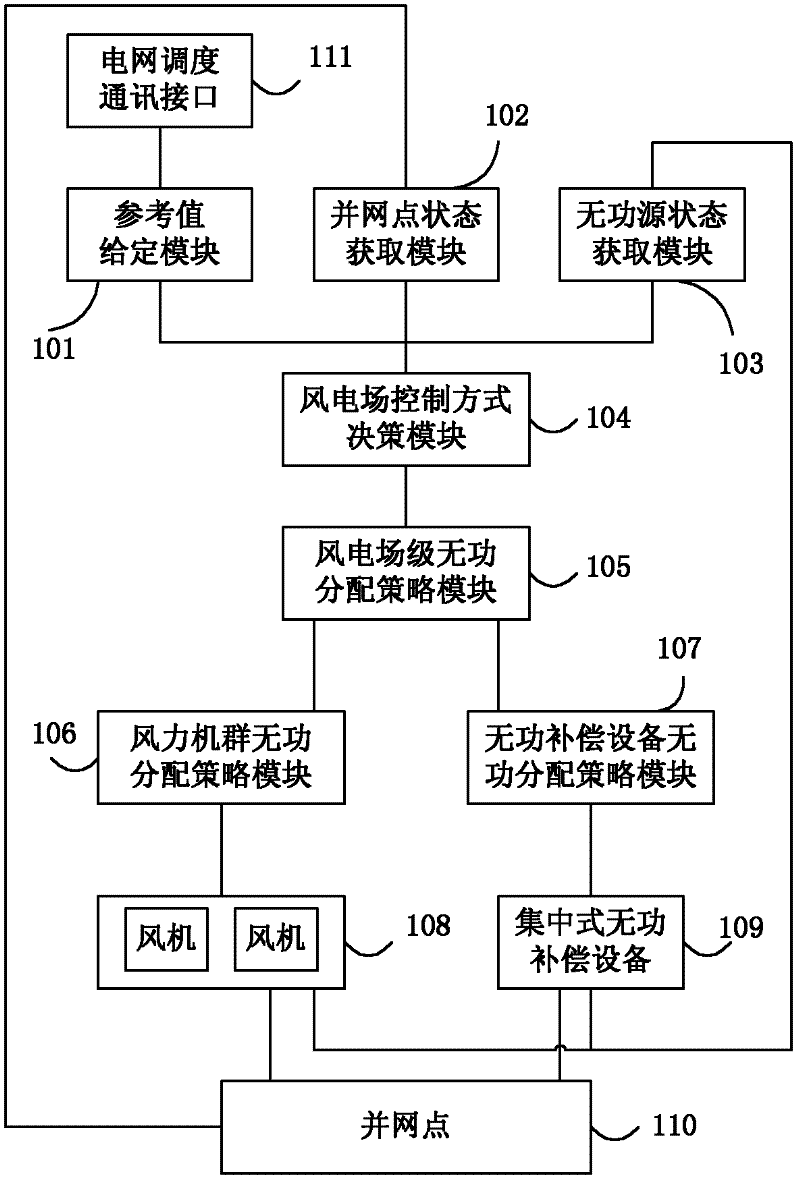
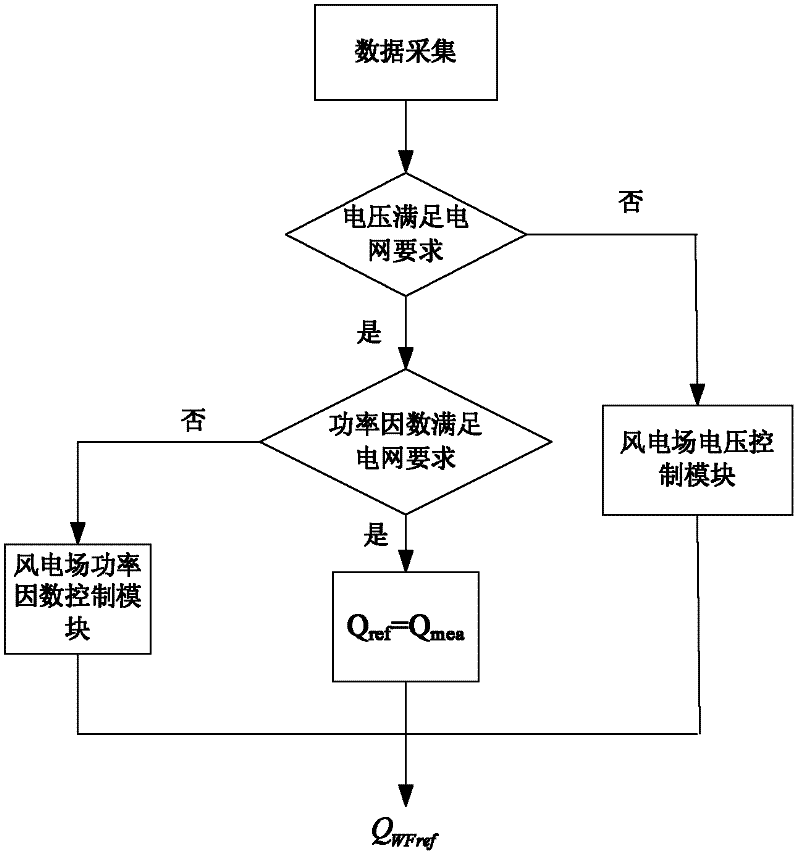
A wind farm reactive power control method and system
ActiveCN102299527ASuppresses voltage fluctuationsGive full play to the reactive power output capabilitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationSystem requirementsEngineering
The invention discloses a wind power station reactive power control method and a system. The wind power station high voltage side bus voltage is used as a control target, the reactive power is used as the regulating quantity, the wind power station voltage control strategy and the power factor control strategy are selected or the system reactive power output is forcibly controlled to be a constant value according to the wind power station voltage fluctuation range and the power factors, and in addition, the reactive power output values of each fan and integrated reactive compensation equipment in the wind power station are determined according to the reactive power reference values required to be output by the wind power station. When the technology of the invention is adopted, the reactive power output of the wind power station networking points meets the system requirements for inhibiting the bus voltage fluctuation and regulating the wind power station power factor, and in addition, the reactive power output of each wind power generator set and integrated reactive compensation equipment in the wind power station can be controlled in a harmonious way.
Owner:GUODIAN UNITED POWER TECH
System and method for estimating input power for a power processing circuit
ActiveUS7906941B2Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionLow-pass filterPower processing
A controller for a power processing circuit and a related method of operating the same. In one embodiment, the controller includes a multiplier configured to produce a product of an input current and an input voltage of the power processing circuit. The controller also includes a low-pass filter configured to produce an input power estimate of an input power to the power processing circuit as a function of the product of the input current and the input voltage. In another embodiment, the controller is a power-factor controller and includes a voltage loop compensator configured to produce a voltage compensation signal as a function of an output voltage of the power processing circuit. The controller also includes an input power estimator configured to produce an input power estimate of an input power to the power processing circuit as a function of the voltage compensation signal.
Owner:MYPAQ HLDG LTD
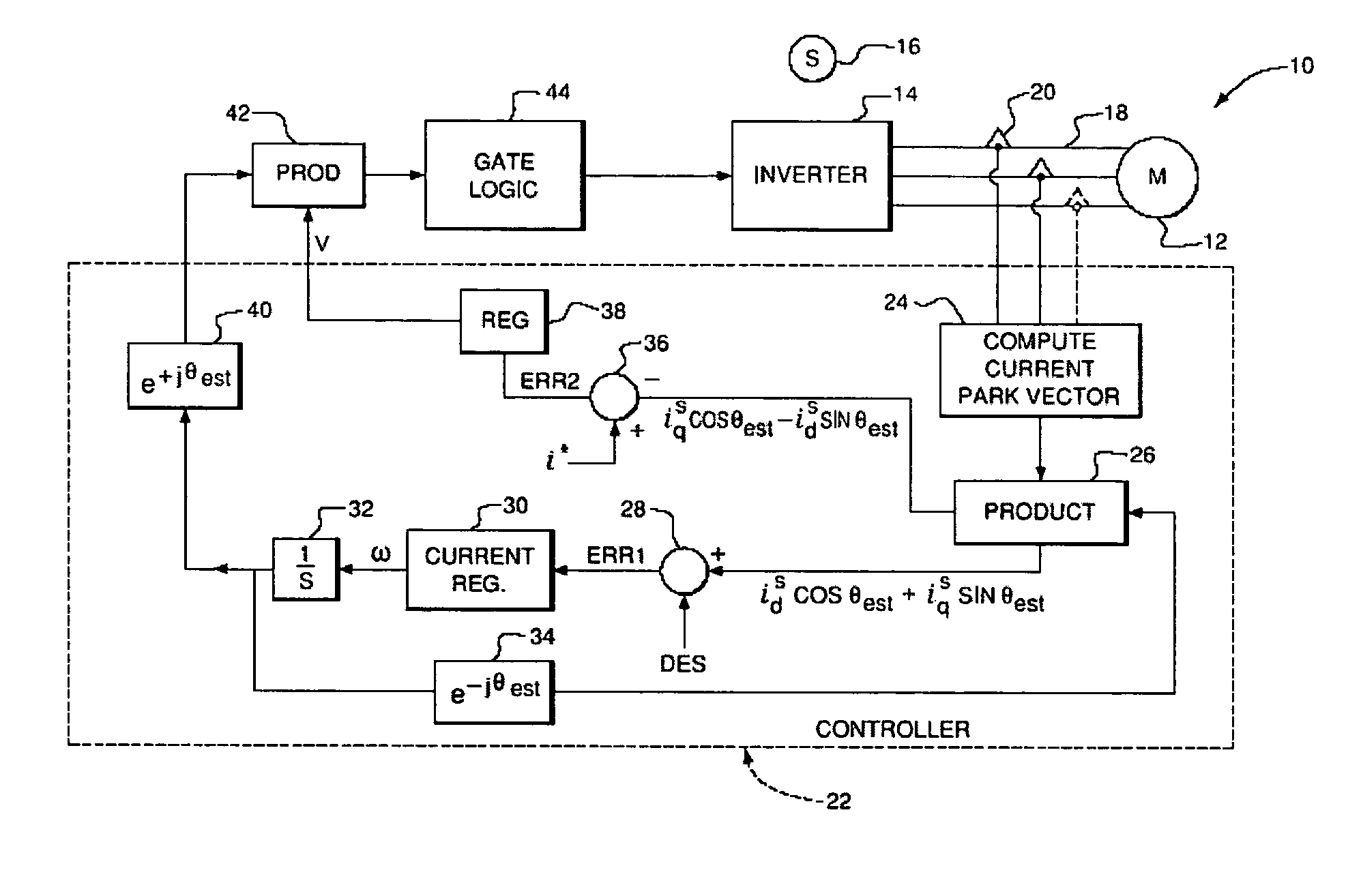
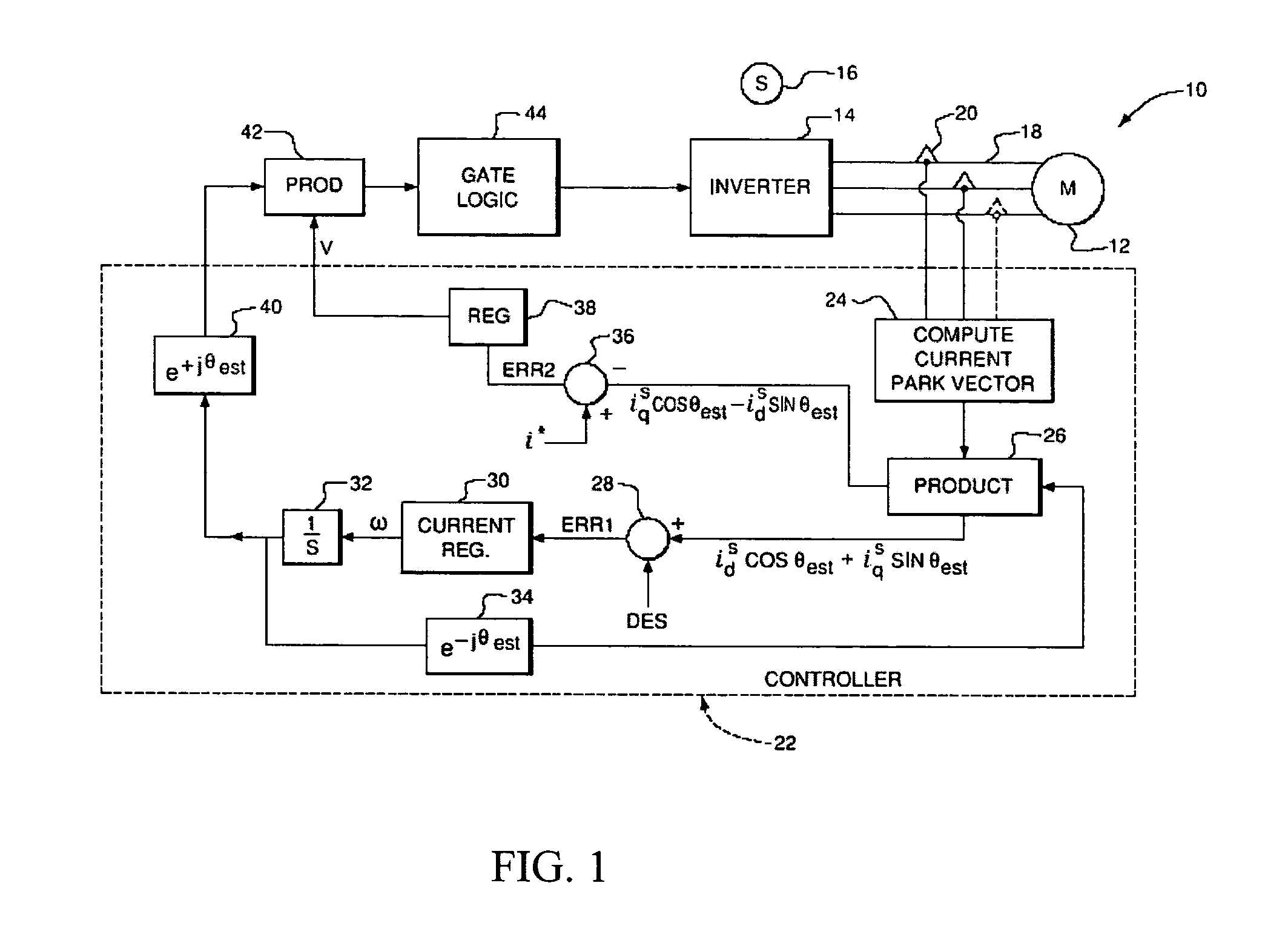
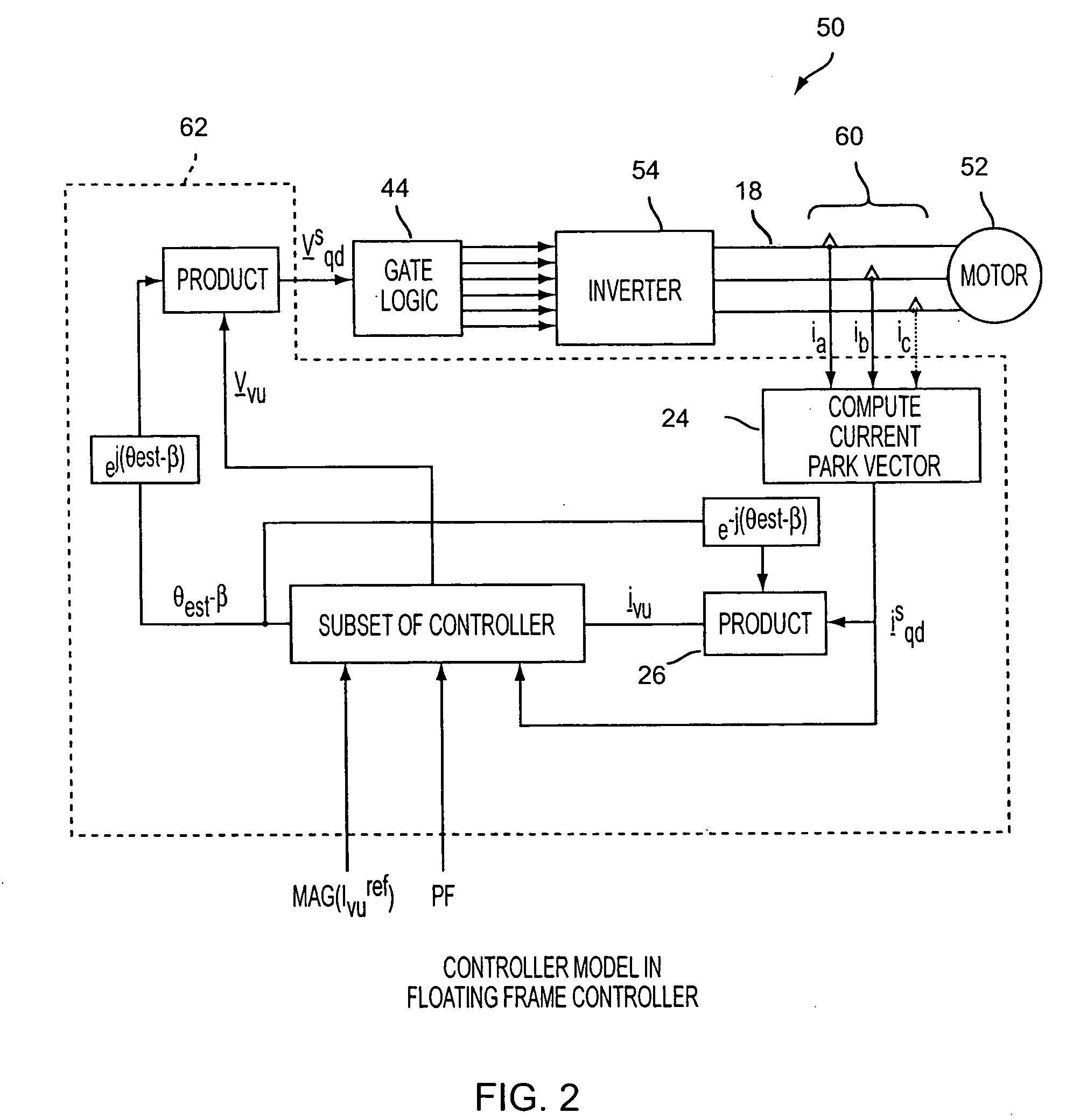
Power factor control for floating frame controller for sensorless control of synchronous machines
ActiveUS20070040524A1Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersPhase currentsControl system
A system and method of controlling the power factor for providing either unity, leading or lagging results for the sensorless control of synchronous machines. The system and method provides an estimated angle of the phase current Park vector and uses a floating synchronous reference frame that is shifted from the estimated angle of the phase current Park vector by an angle β to allow the active control and change of the power factor during operation for applications such as producing reluctance torque of a salient pole synchronous machine during Main Engine Start (MES), and field weakening for Environmental Control Systems (ECS) and MES applications.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Systems for and methods of controlling operation of a ups
ActiveUS20090160254A1Reduce voltage “ excursion ”Effective approachBatteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionPower factor controlEngineering
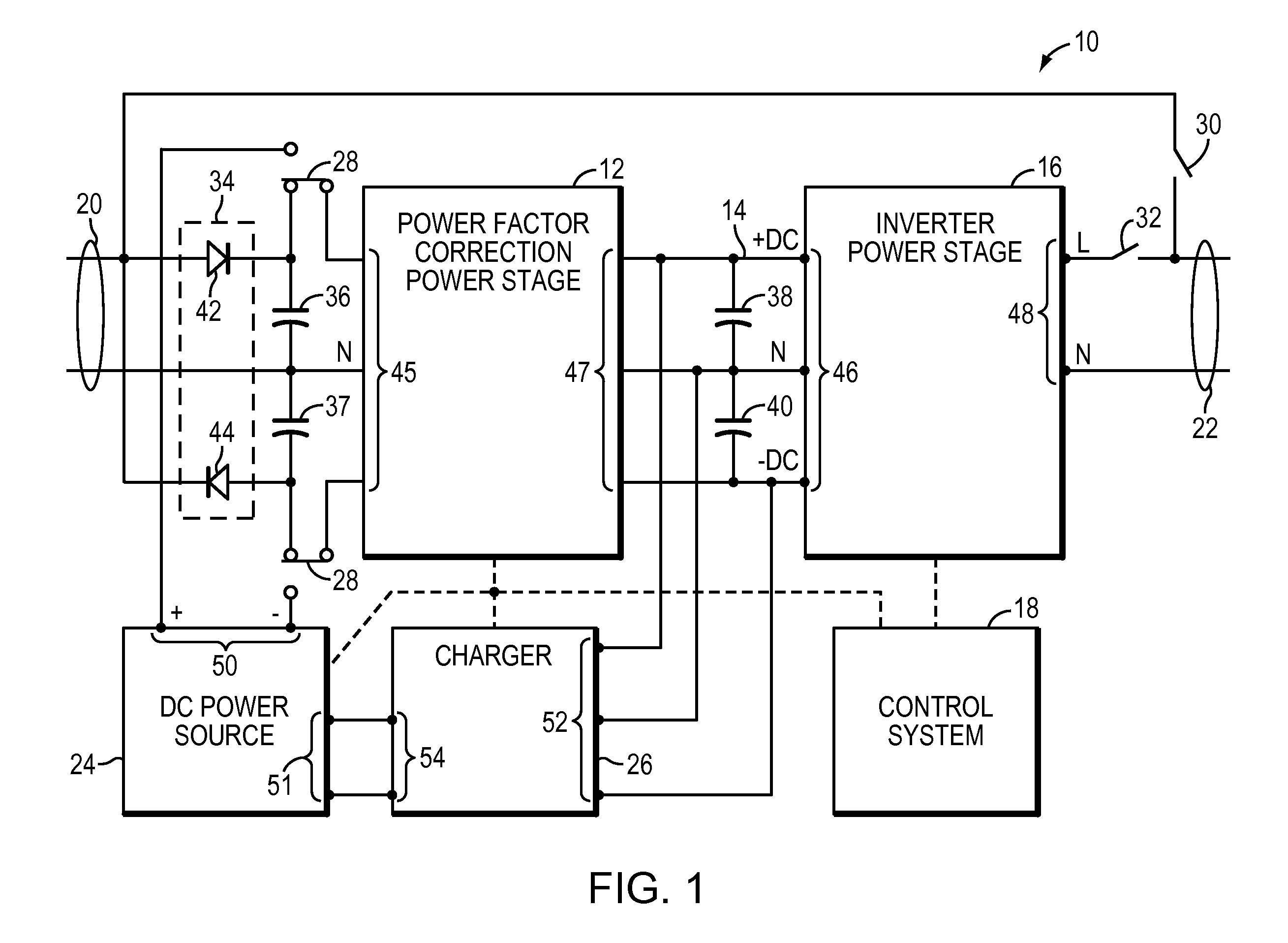
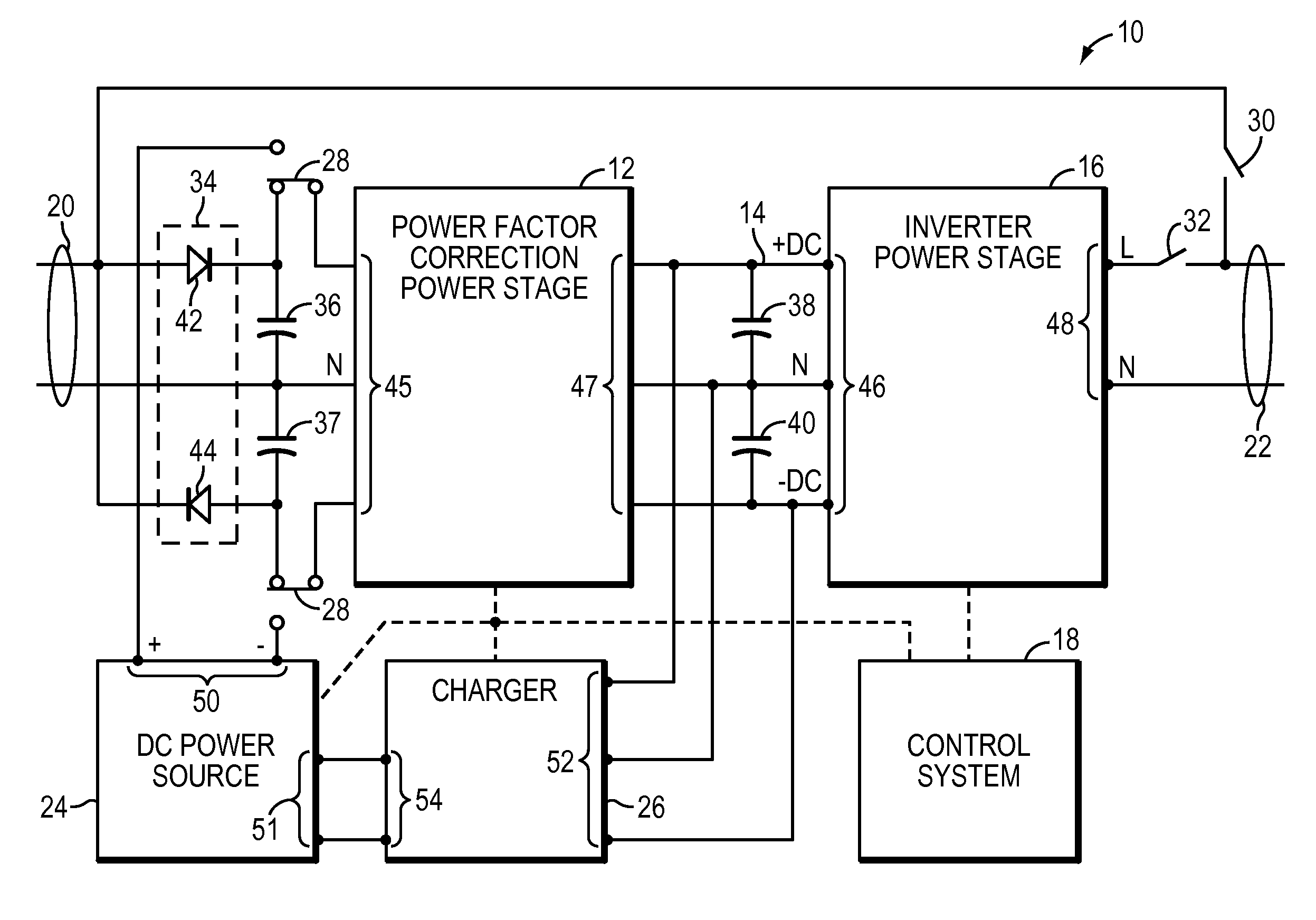
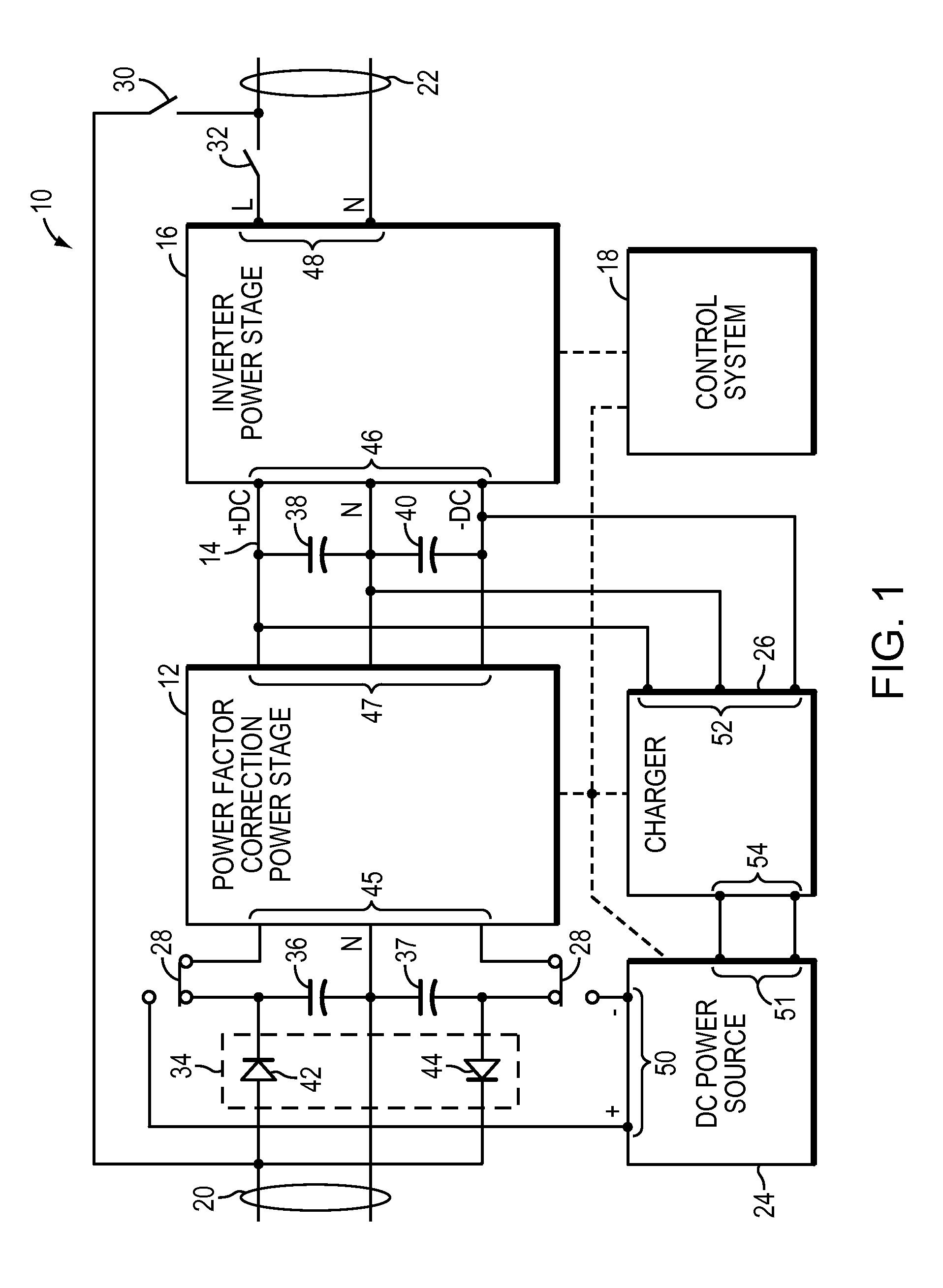
A UPS includes an AC output, power factor control circuitry; and a DC bus coupled to the power factor control circuitry where the power factor control circuitry is configured to determine a difference in instantaneous power supplied to the AC output and to adjust a voltage of the DC bus based, at least partly, on the difference. In one embodiment, the UPS includes a single phase AC input. In another embodiment, the power factor control circuitry is configured to determine a cumulative difference in instantaneous power supplied to the AC output.
Owner:AMERICA POWER CONVERSION CORP
Switching power supply circuit and power factor controller
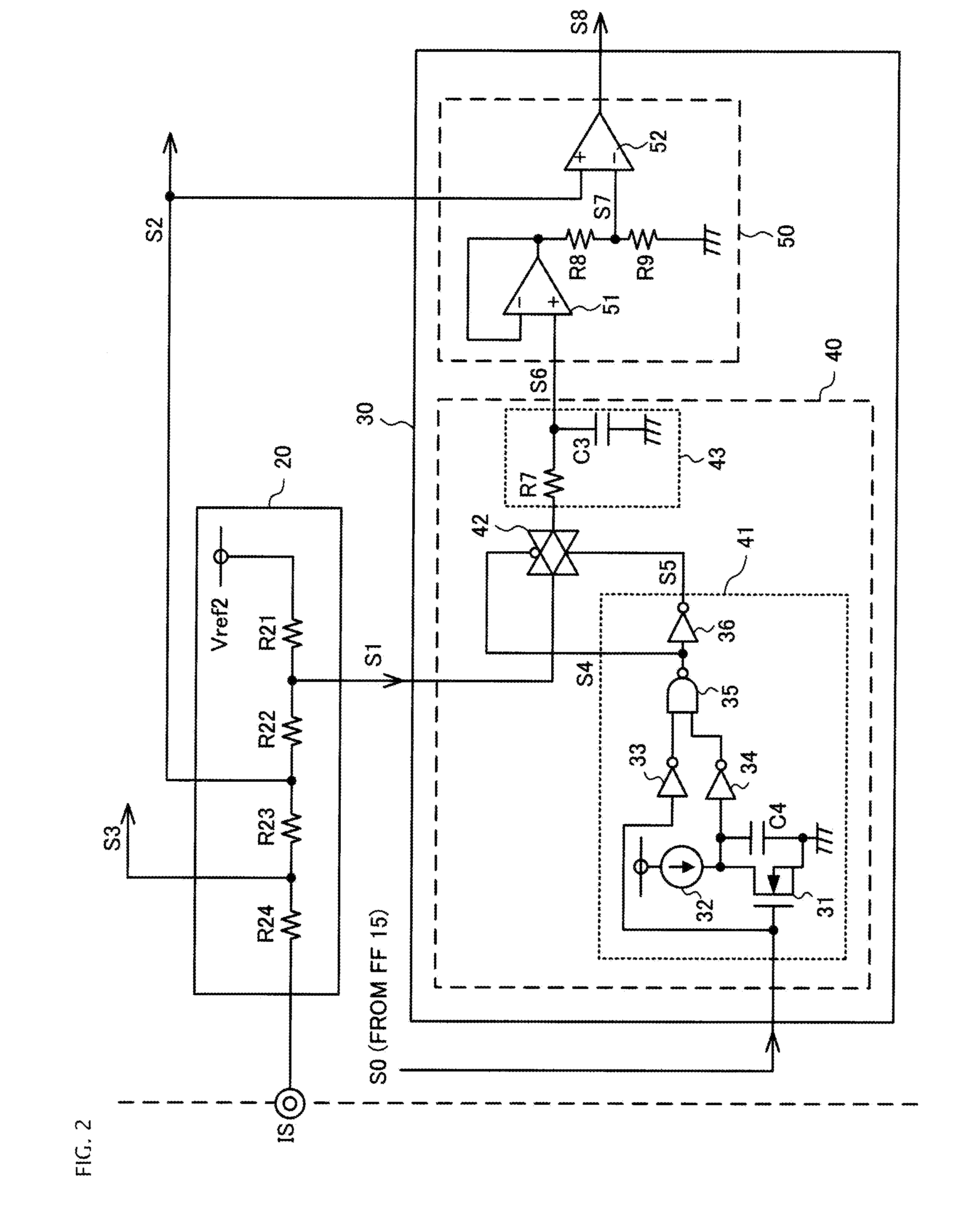
ActiveUS20120201063A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionControl setFull wave
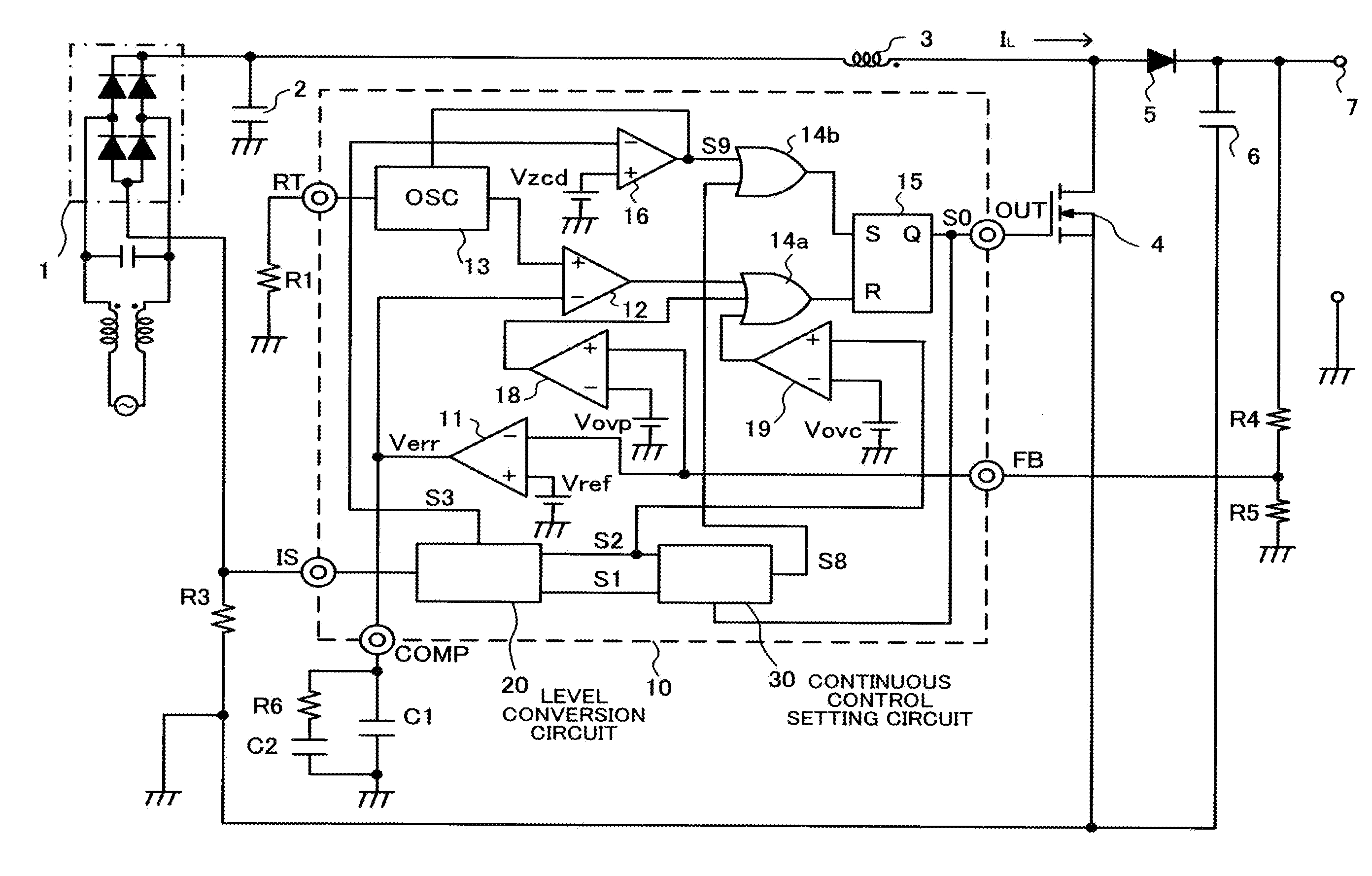
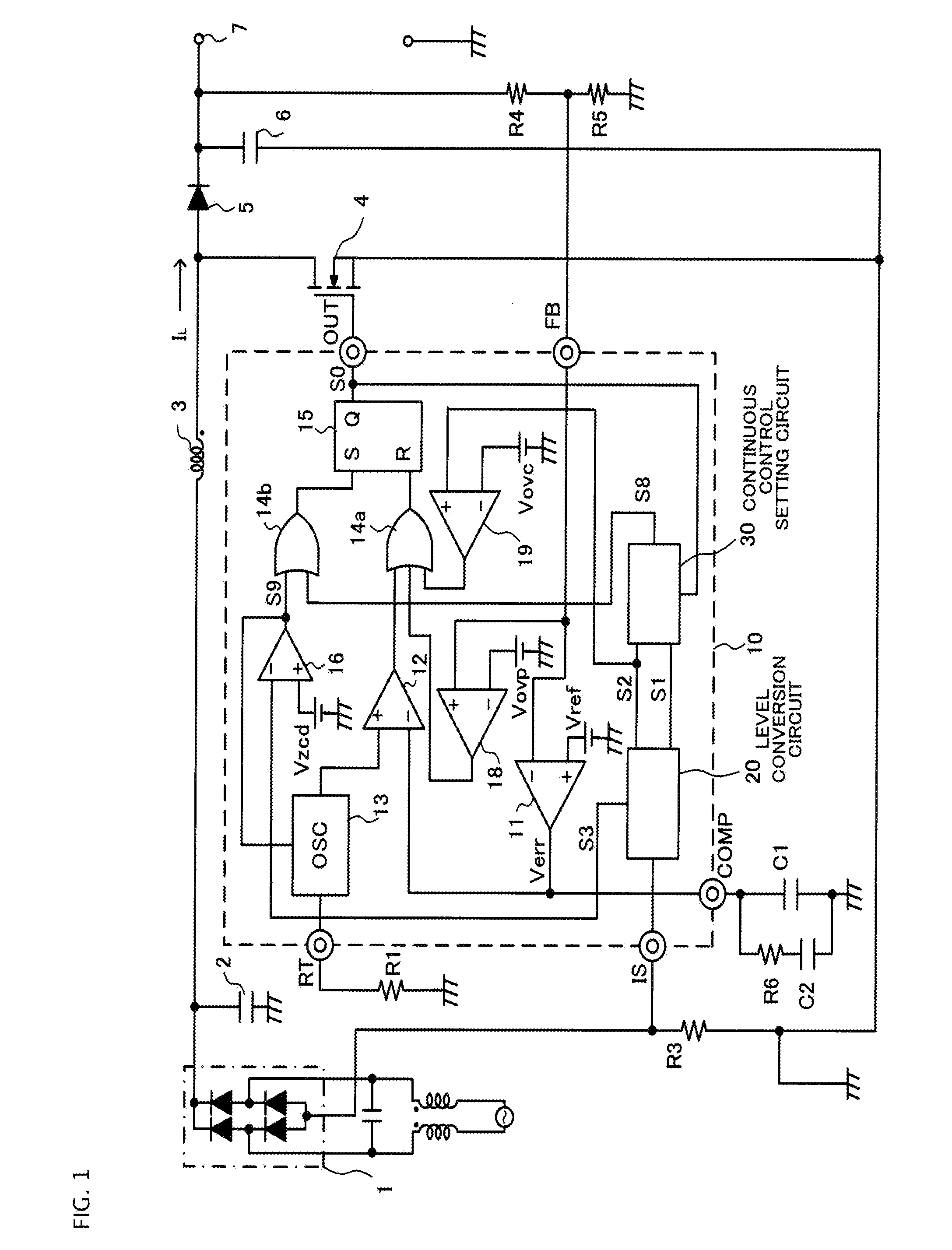
The switching power supply circuit includes a full-wave rectifier (1) which full-wave rectifies alternating power-supply voltage to output a pulsating current, and an inductor (3) connected to the full-wave rectifier (1). A level conversion circuit (20) includes a plurality of resistors connected in series, and converts inductor current detection voltage to a first current level signal and a second current level signal (S1 and S2) which are different in voltage level and which are proportional to inductor current. A continuous control setting circuit (30) generates a reference potential signal a phase of which is approximately the same as a phase of alternating input voltage from the first current level signal (S1) and compares a voltage level of the reference potential signal with a voltage level of the second current level signal (S2) to output a second set pulse (S8) that specifies timing at which a switching element (4) turns on.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Electrical power conservation apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050099131A1Save energySave componentPower network operation systems integrationCircuit arrangementsElectric forceEngineering
An electrical power control apparatus and method for power factor correction in a conventional 60 hertz or other conventional frequency electrical AC power supply communicated to an inductive load. A plurality of interruptions of current in the line on both sides of an AC current oscillation, are created to control the power factor in a circuit energizing an inductive load. Additional power factor control and correction is provided by grounding of the line during each interruption. A controller controls the length and duration of each interruption based on preprogramming or input regarding current phase read or calculated in the line.
Owner:MICROPULSE TECH
Method of and apparatus for power factor correction in a power supply
ActiveUS8493754B1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionControl signalPower factor control
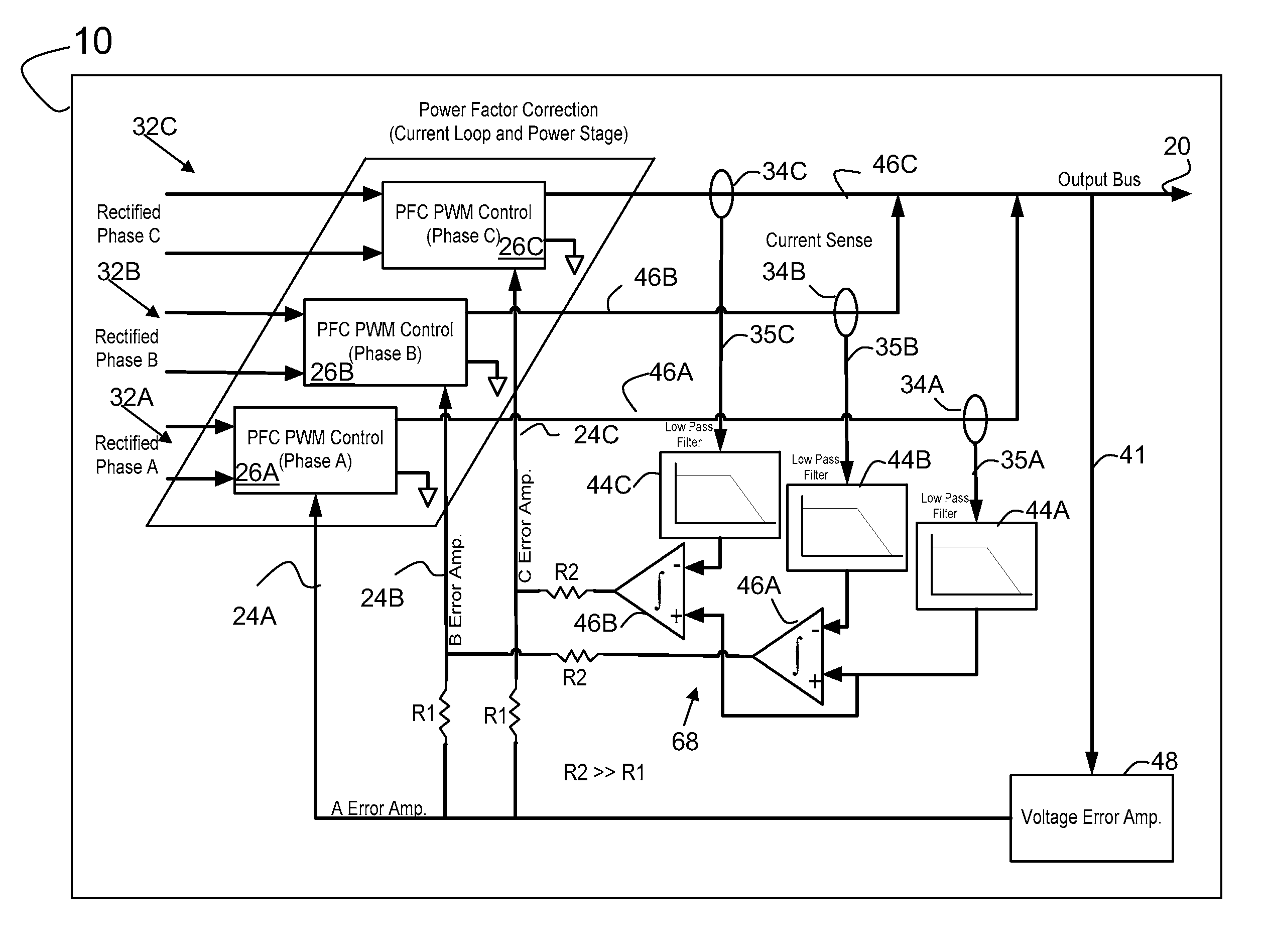
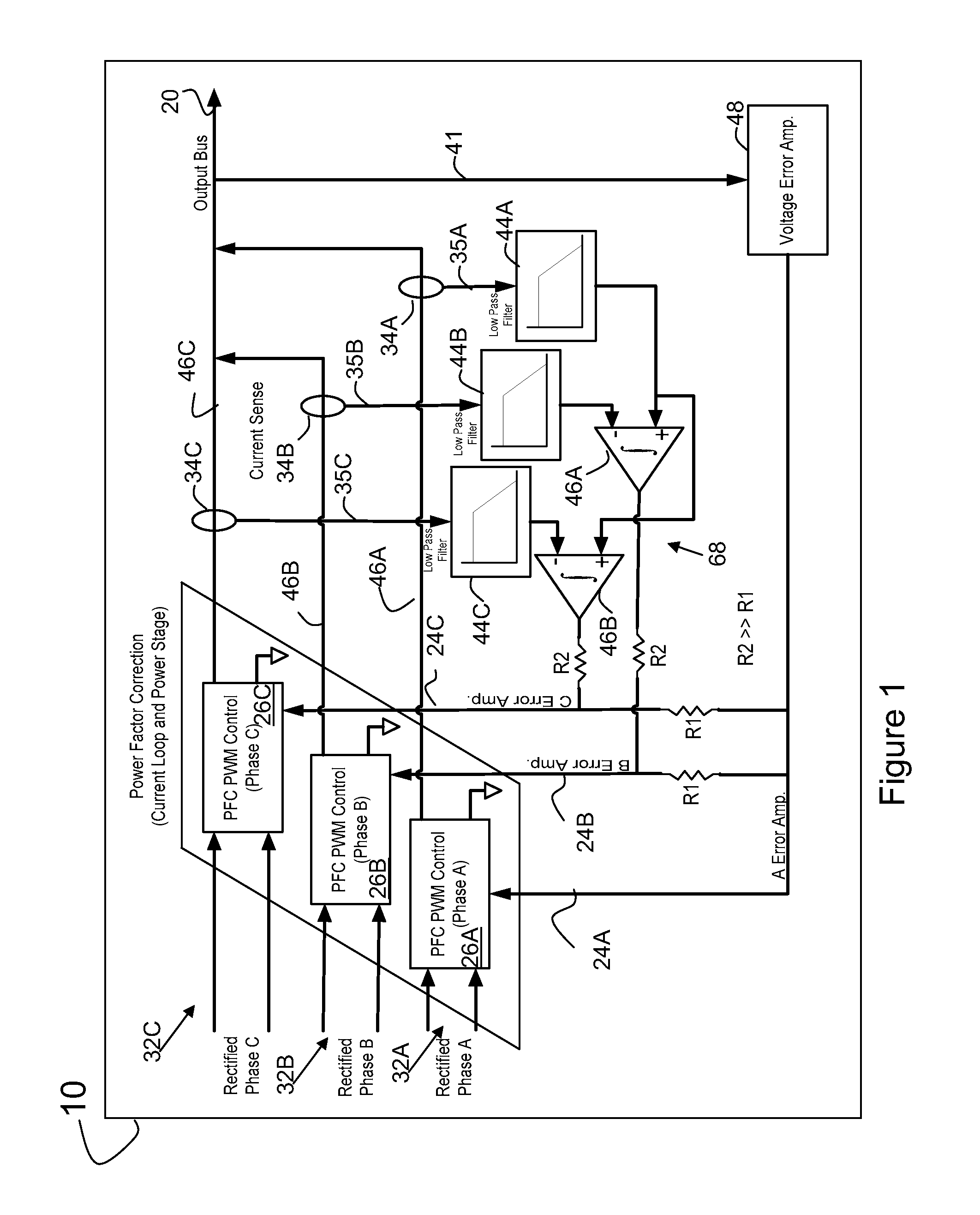
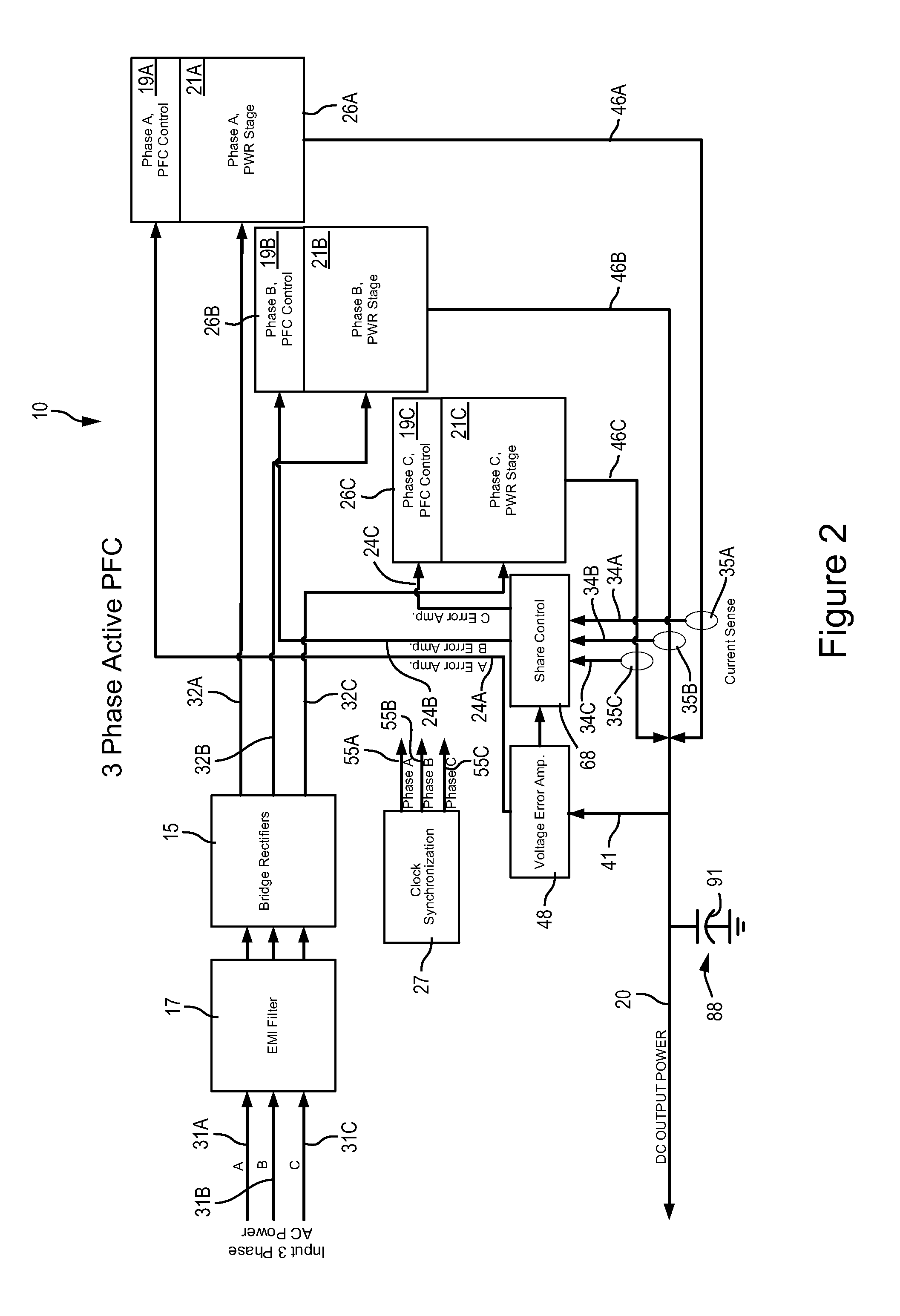
A converter can include at least two power stages. Each power stage can include a power factor control circuit. An active shared control circuit for a three power stage system receives at least three sense signals. Each of the sense signals is associated with a parameter of the respective one of the power stages. The control circuit provides at least three control signals. Each of the control signals being associated with the respective power factor control circuit of the power stages. The active share control circuit balances the current supplied by the power stages via the control signals.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Single phase AC-DC converter having a power factor control function
InactiveUS6388905B2Improve efficiencySmall sizeEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcPower factor controlEngineering
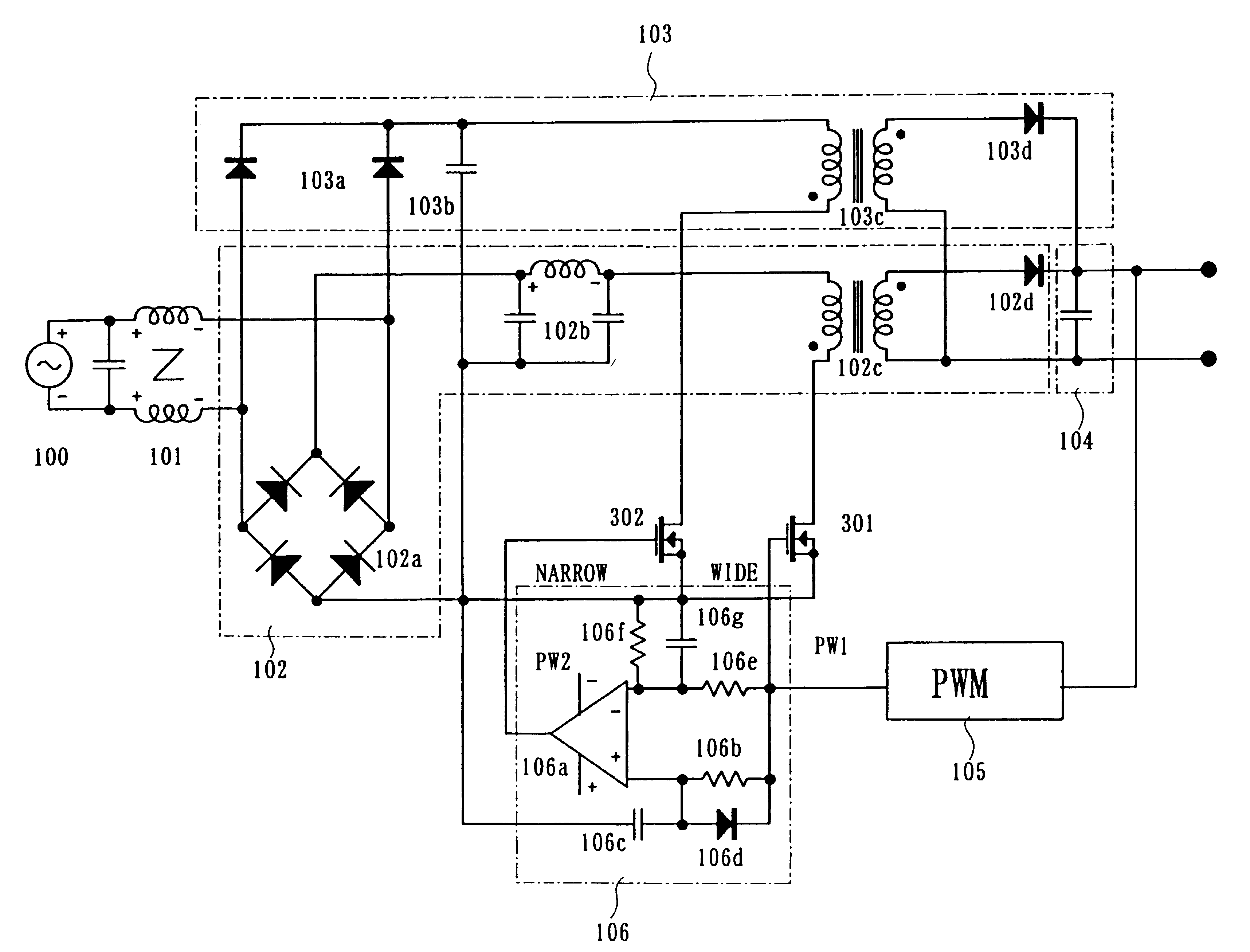
The single-phase AC-DC converter includes a PFC power supply section, where a rectified current obtained by rectifying an electric current from an AC supply is switched; a DC-DC power supply section, where a direct current obtained by rectifying and smoothing an electric current from an AC supply is switched; a first switching element for conducting a switching operation in the PFC power supply section; a second switching element for conducting a switching operation in the DC-DC power supply section; a drive pulse generating circuit for generating first drive pulses for driving said first switching element and second drive pulses for driving said second switching element; and a servo loop for controlling the drive pulse generating circuit. The servo loop is constituted of only one serve loop; and the duty ratio of the drive pulses for driving the first switching element is different from the duty ratio of the drive pulses for driving the second switching element from each other in a linked manner.
Owner:FIDELIX
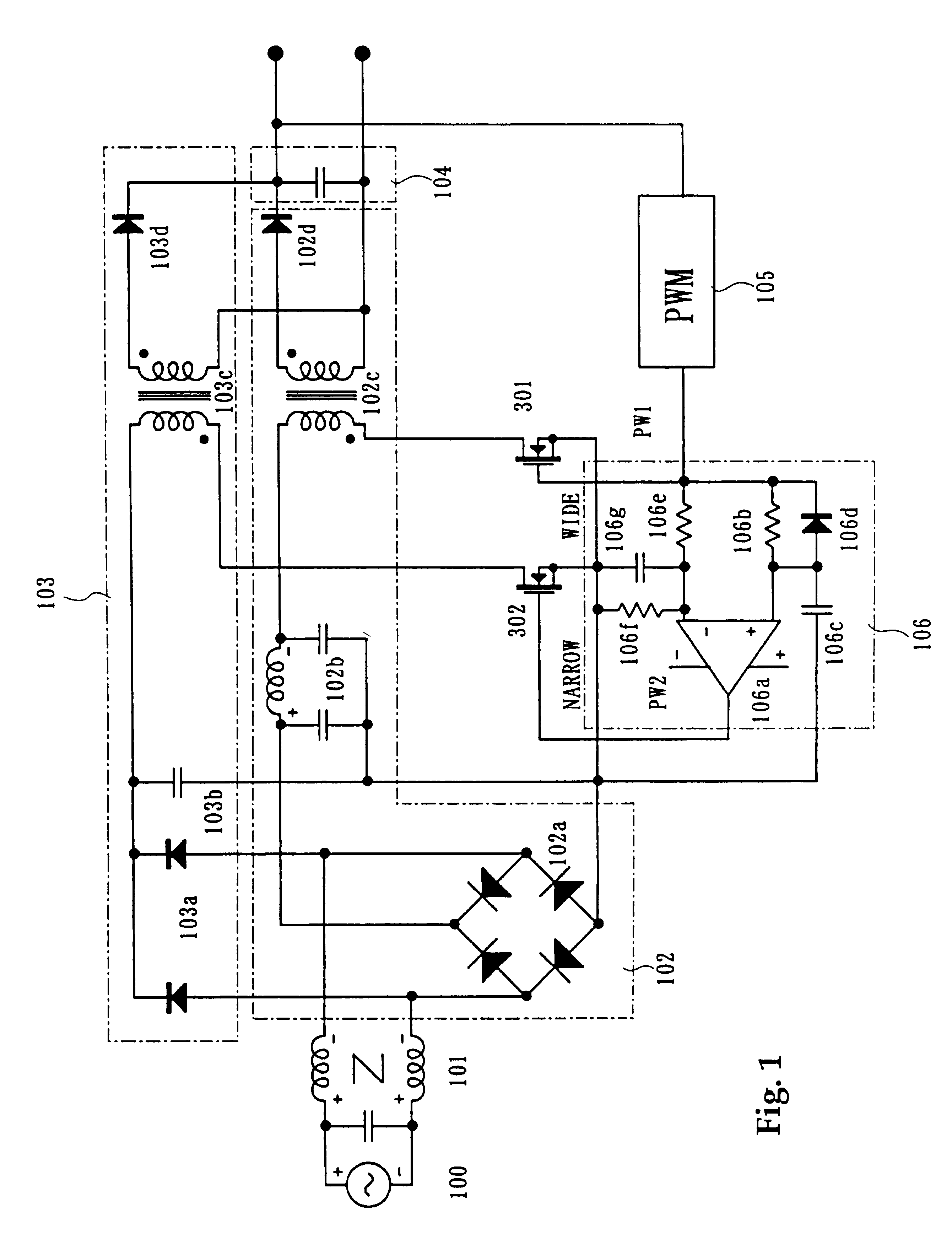
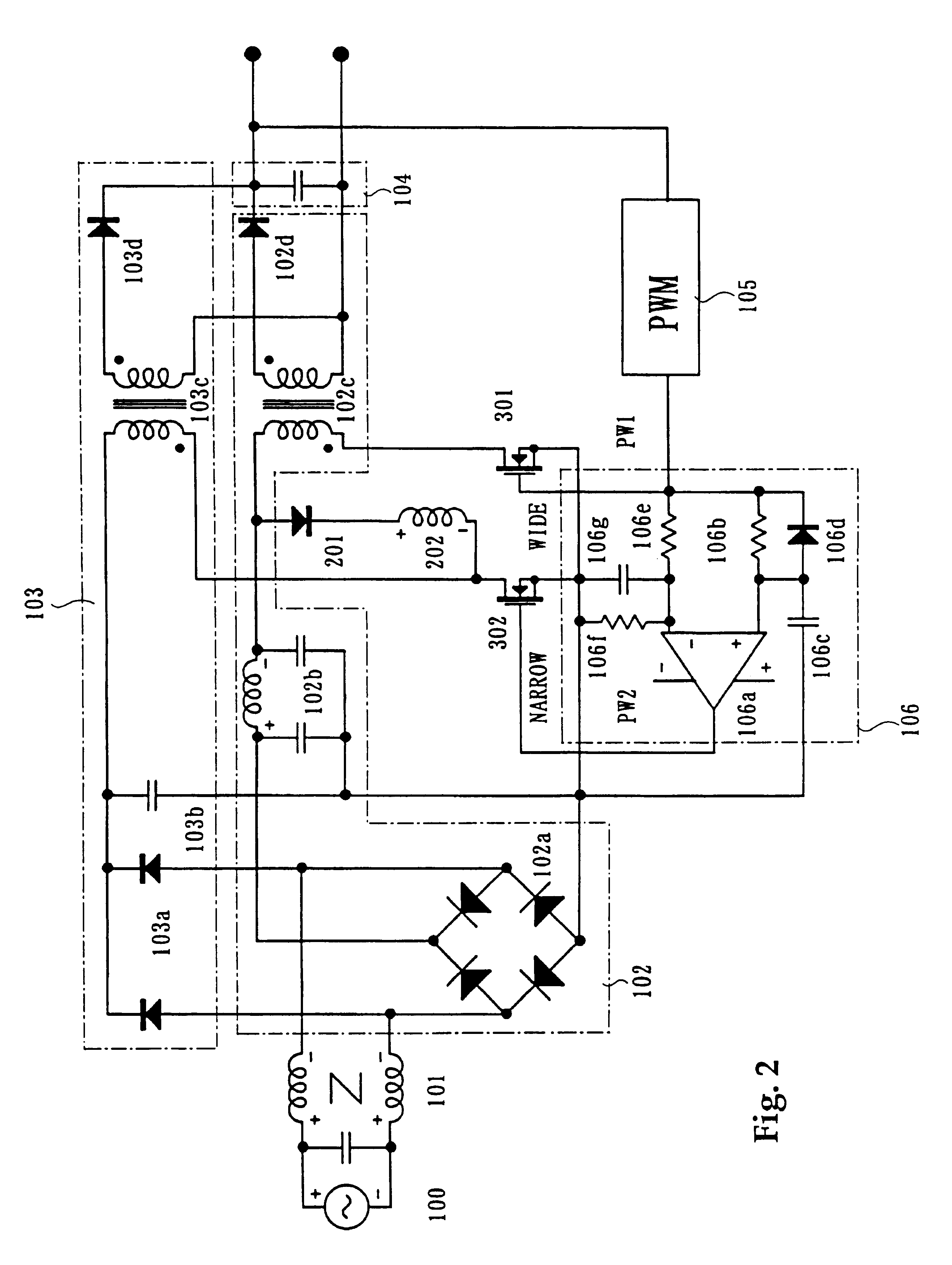
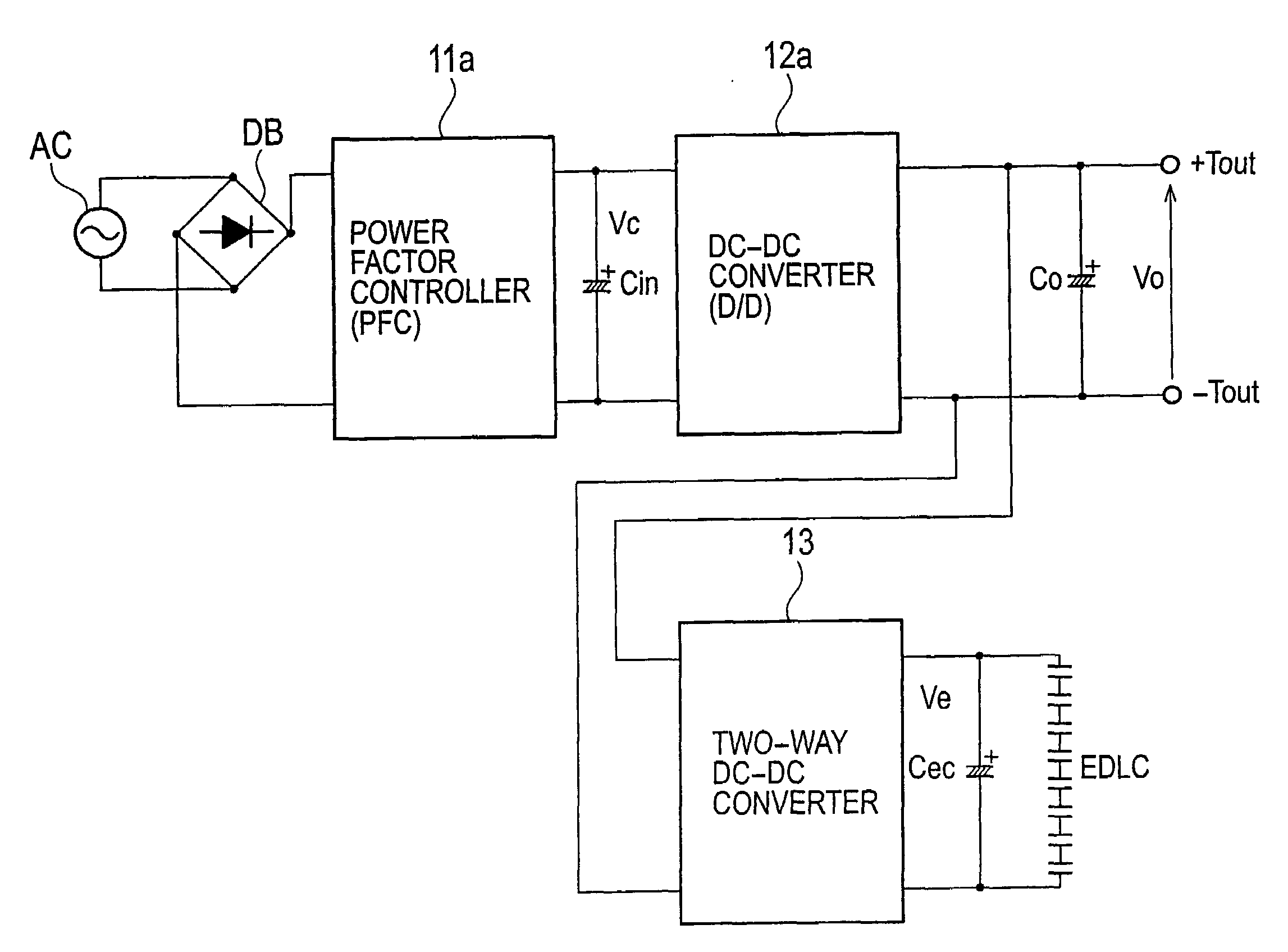
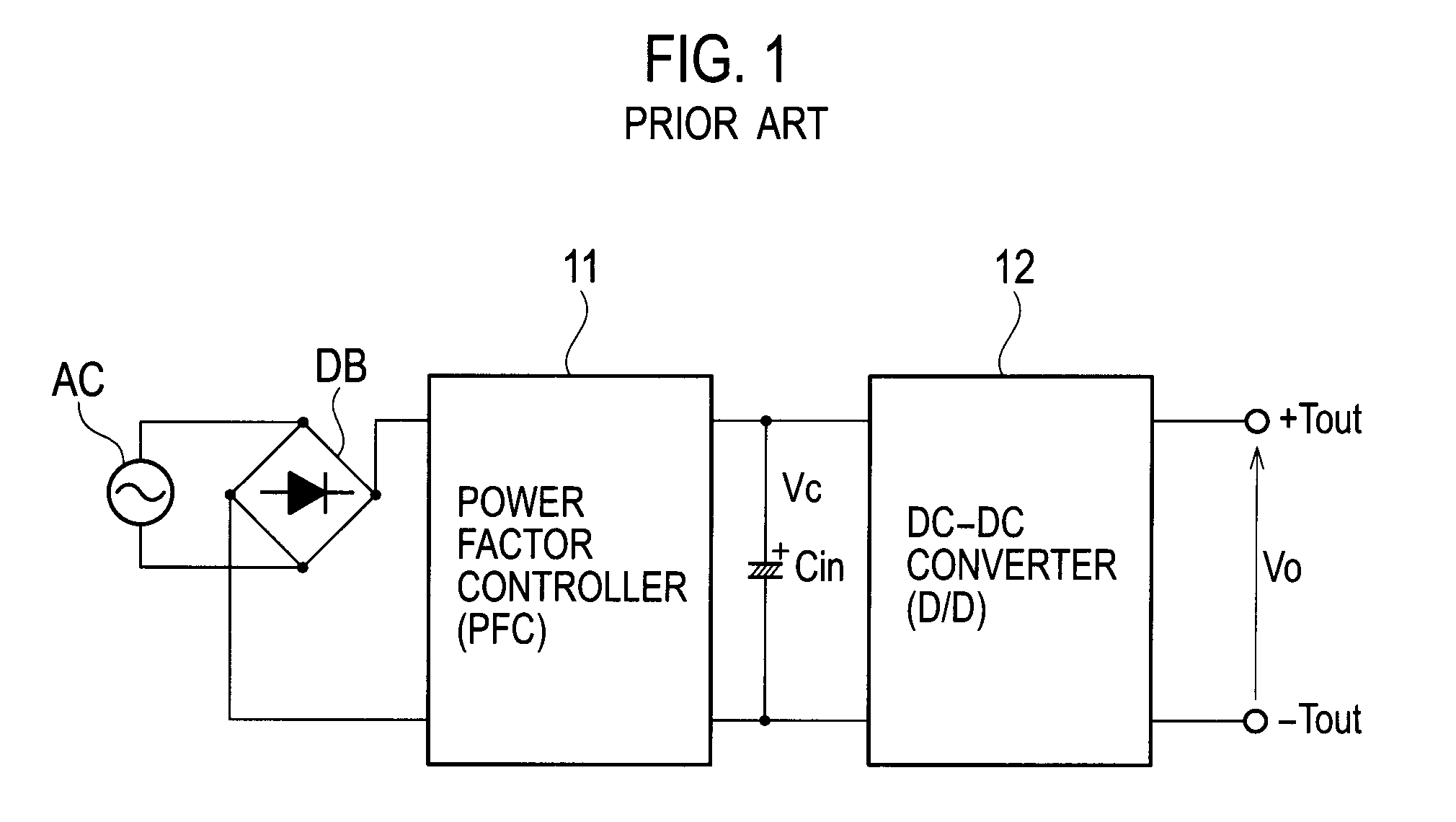
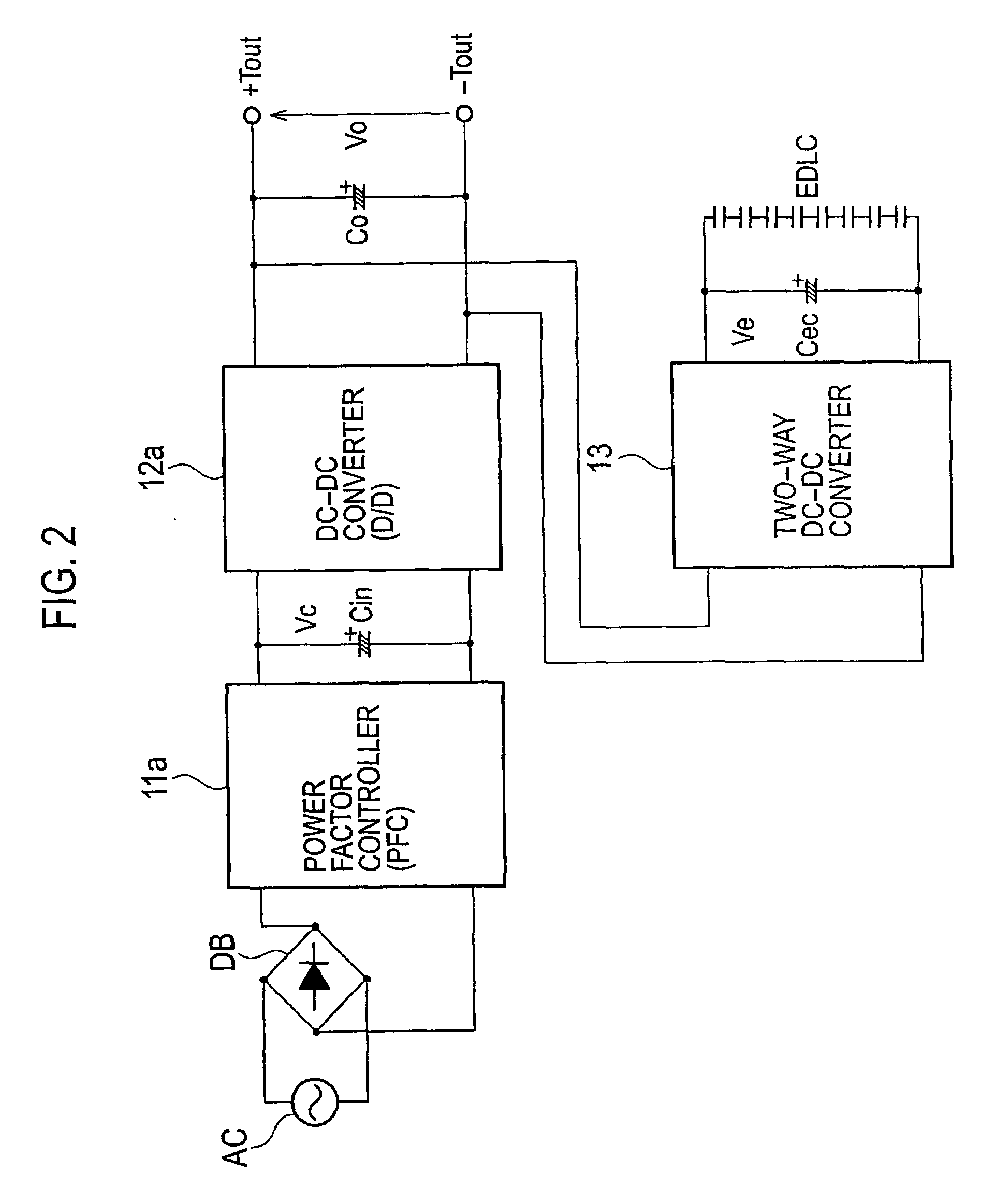
Ac-dc converter
InactiveUS20090027930A1High peak powerAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionDc dc converterPower factor control
An AC-DC converter includes a rectifier DB for rectifying an alternating current supplied from an alternating power source AC, a power factor controller 11 connected to an output side of the rectifier DB to improve a power factor, a DC-DC converter 12 that converts a voltage outputted from the power factor controller 11 to another voltage and also outputs either a power or a current limited to a predetermined value, a capacitor for storing an energy and a two-way converter 13 having one input / output terminals connected to output terminals of the DC-DC converter 12 and the other input / output terminals connected to the capacitor to carry out a two-way power conversion.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
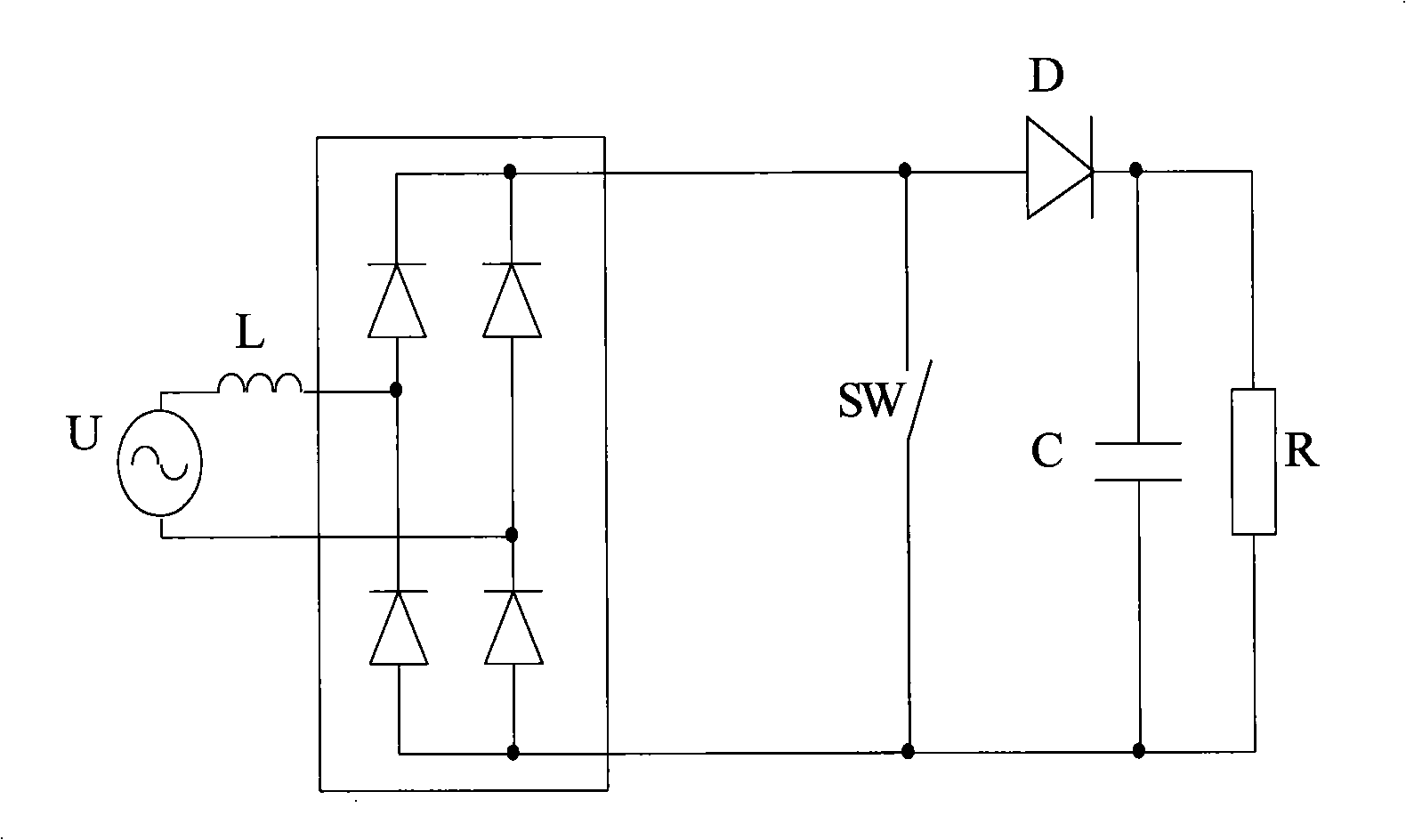
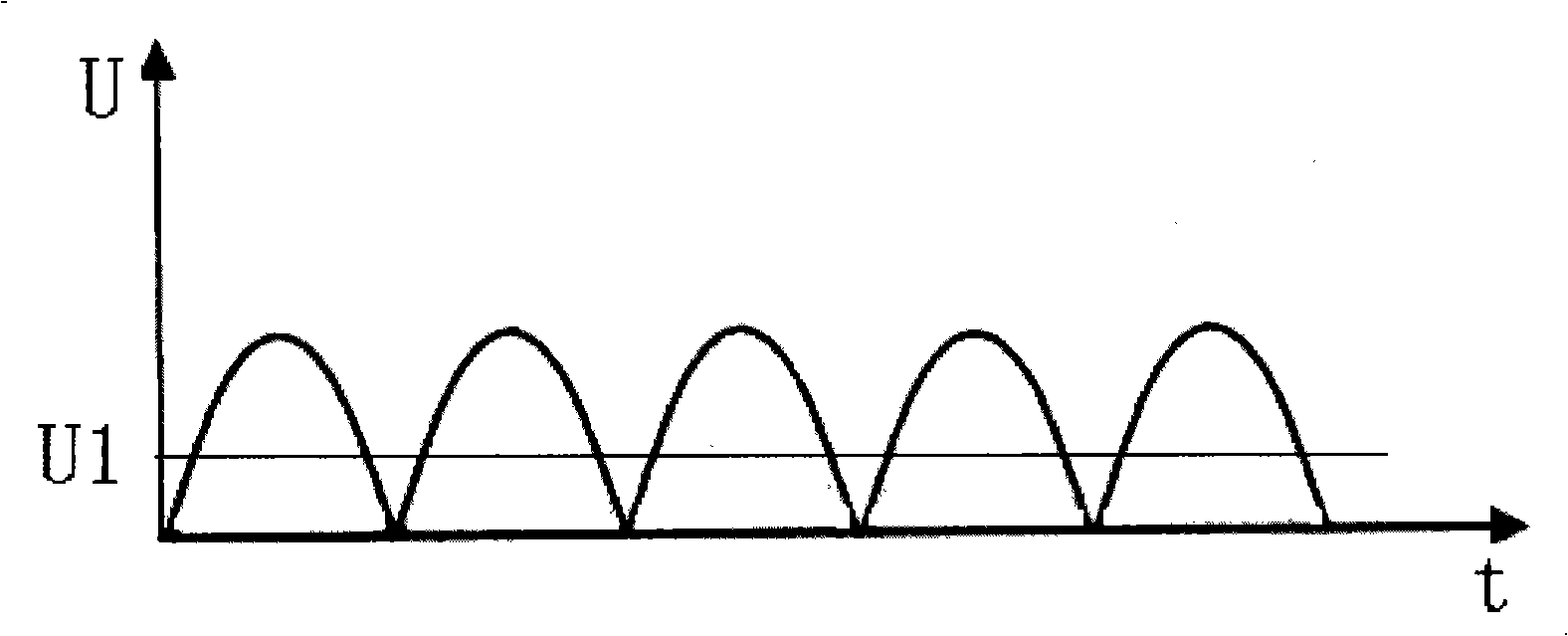
Circuit for correcting part active power factor
ActiveCN101325367AConsistent current waveformConsistent desired current waveformEfficient power electronics conversionPower conversion systemsWave shapeTime changes
The invention discloses a partial active power factor correcting circuit, comprising a current detecting circuit, for real-time detecting the output current of a rectifying circuit; a power factor control unit, for obtaining the actual current waveform which reflects the real-time change of the current before the correction according to the current realtime value detected by the current detecting unit before the power factor correcting circuit starts working, and working out the continuous sine waveform as the expected current waveform with the same waveform, the same frequency and the continuous sine waveform according to the waveform; after obtaining the current waveform, the power factor control unit computes the difference between the expected current waveform and the real-time detected current actual measurement waveform, and controls the on / off of the controlled switch always in the ascending stage of the waveform and the moment with the largest difference, and controls the on / off of the controlled switch after delaying some time. The partial active power factor correcting circuit of the invention causes the actual current waveform consistent with the expected current waveform, which realizes the optimum correcting effect.
Owner:HAIER GRP CORP +1
Systems for and methods of controlling operation of a UPS
ActiveUS7615891B2Reduce offsetEffective approachBatteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionPower factor controlEngineering
A UPS includes an AC output, power factor control circuitry; and a DC bus coupled to the power factor control circuitry where the power factor control circuitry is configured to determine a difference in instantaneous power supplied to the AC output and to adjust a voltage of the DC bus based, at least partly, on the difference. In one embodiment, the UPS includes a single phase AC input. In another embodiment, the power factor control circuitry is configured to determine a cumulative difference in instantaneous power supplied to the AC output.
Owner:AMERICA POWER CONVERSION CORP
Low-voltage power supply circuit for illumination, illumination device, and low-voltage power supply output method for illumination
ActiveUS7781982B2Ac-dc conversion without reversalElectroluminescent light sourcesCurrent limitingLow voltage
In a low-voltage power supply circuit for illumination that rectifies an ac power supply by means of a rectifier circuit, that controls this rectified output by means of a power-factor control circuit, and that supplies a low-voltage power supply for illumination, the power-factor control circuit is composed of a step-down circuit and is further provided with a current-limiting capability.
Owner:NEC LIGHTING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com