Patents
Literature
1049 results about "Inductive load" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An inductive load is a part of an electrical circuit that uses magnetic energy to produce work. Most electrical appliances, motors, and other devices can be classified as either inductive or reductive, and this usually has to do with how they absorb and process energy.
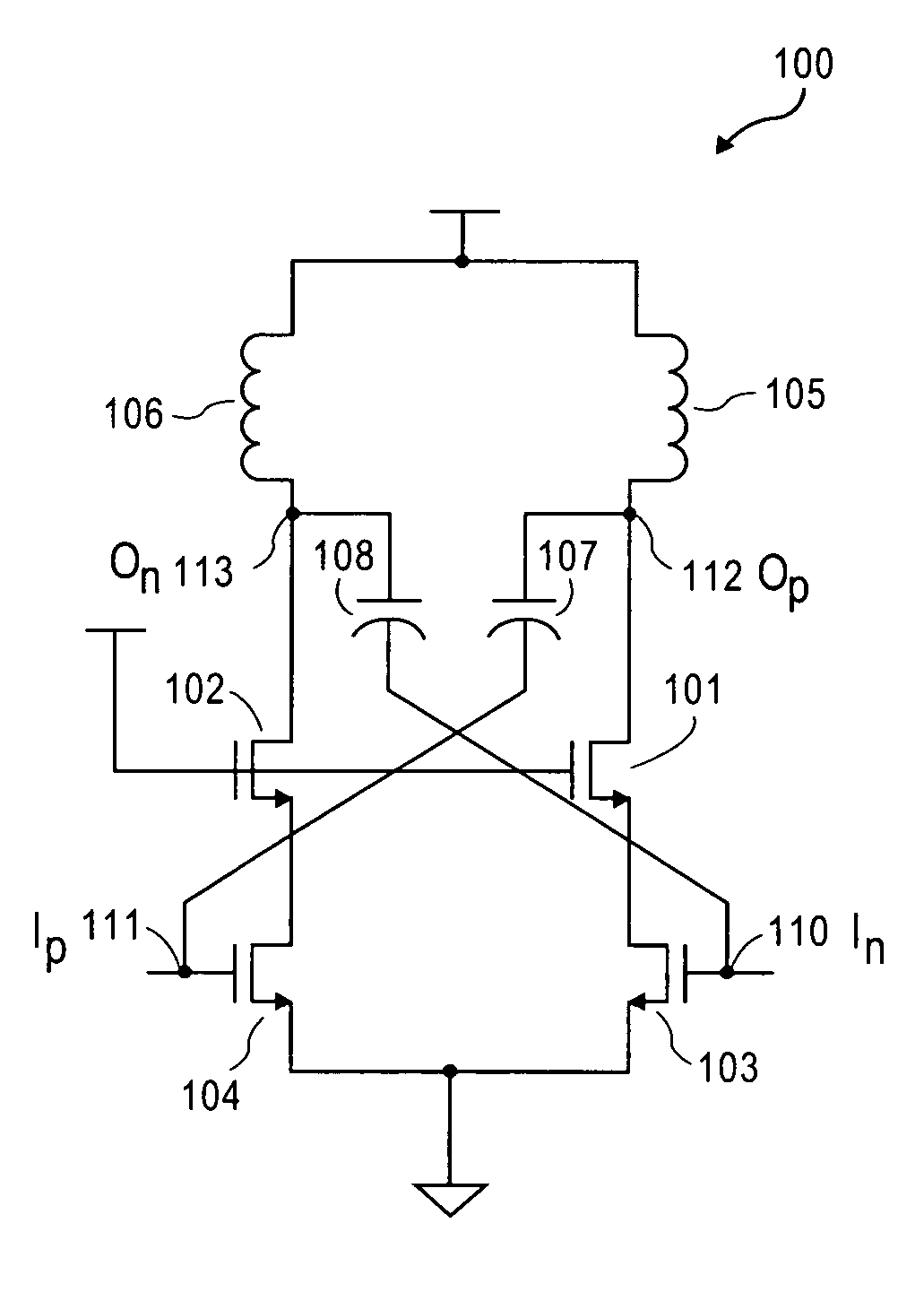
Gain boosting RF gain stage with cross-coupled capacitors
ActiveUS7697915B2Tighter current flow controlHigh gainHigh frequency amplifiersRadio transmissionCapacitanceGain stage
A RF differential gain stage has cross-coupled capacitors between input and output nodes of the amplifier stage to boost gain. The gain boost allows cancellation of the series resistance of an inductive load of the amplifier stage.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Energy savings device and method for a resistive and/or an inductive load and/or a capacitive load
InactiveUS7164238B2Save energyElectrical apparatusElectric ignition installationElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
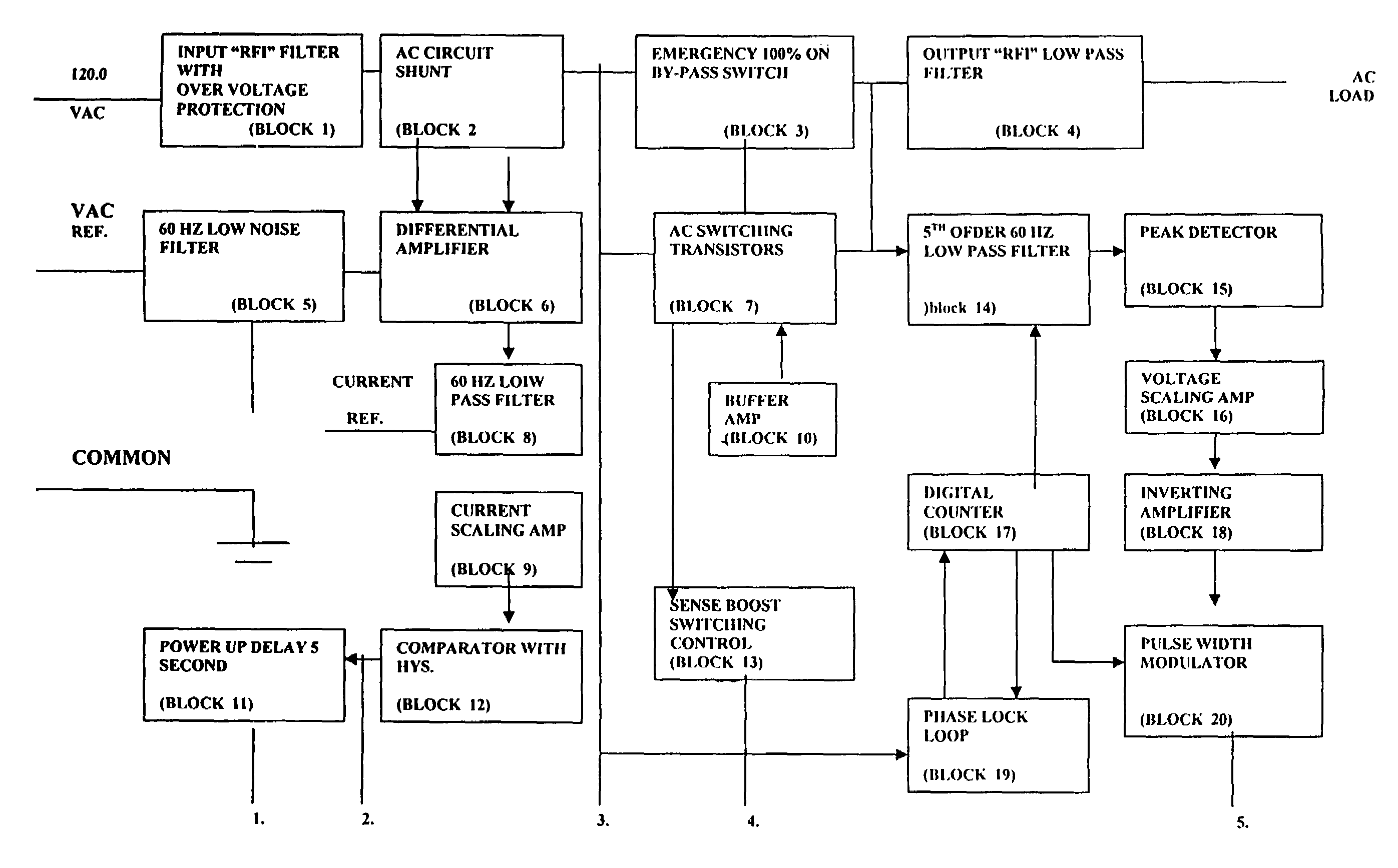
An energy savings device for an inductive, a resistive or a capacitive load, such as a fluorescent light fixture having a magnetic ballast or an electronic ballast, which is powered by an AC voltage waveform. The energy savings device includes a setting unit for setting a desired power operating level for the load. The energy savings device also includes a processor configured to receive a signal from the setting unit indicative of the desired power operating level for the load, to determine a phase delay to be provided to an output AC voltage waveform that is to be provided to the load, and to output a control signal as a result thereof. The energy savings device further includes an active element provided between a line that provides the input AC voltage waveform and the load, the active element receiving the control signal and turning off and on at predetermined times in accordance with the control signal, so as to create the output AC voltage waveform from the AC voltage waveform. The processor includes a synchronization circuit that synchronizes to the Green Safety ground line.
Owner:ASTRAL COMM
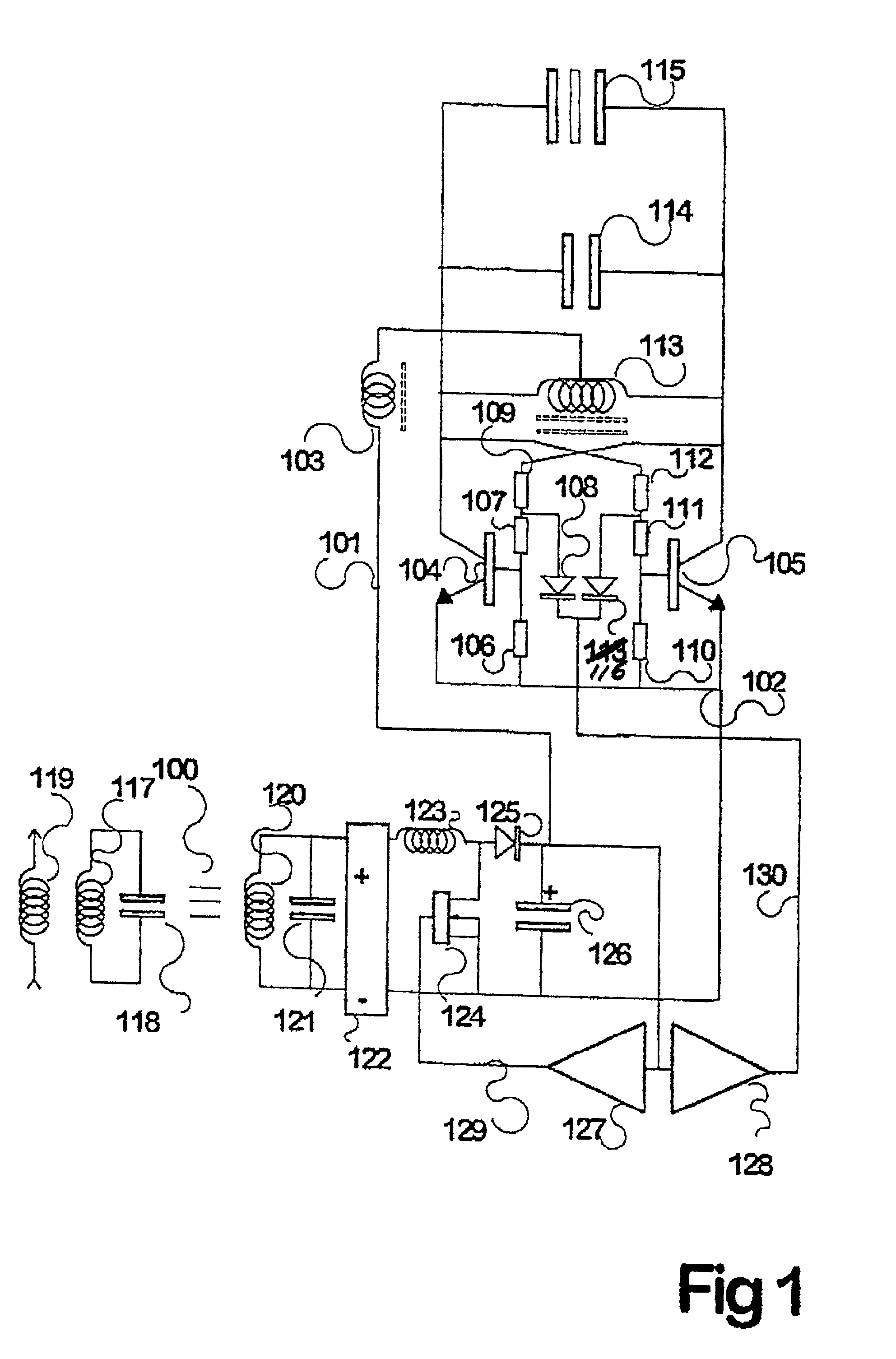
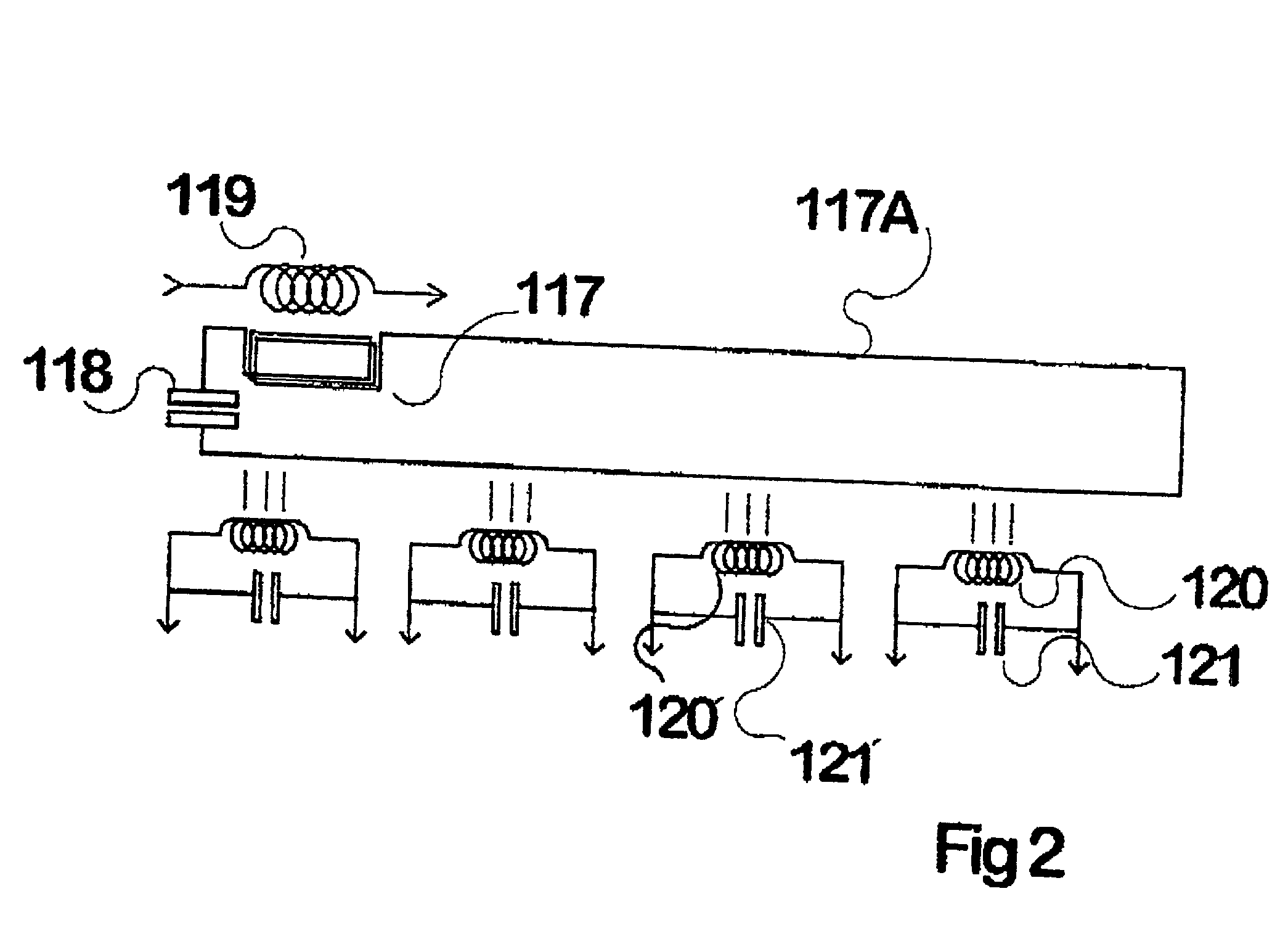
Inductive power distribution system
InactiveUS20010012208A1Spatial width can be increasedEffective distanceRail devicesBatteries circuit arrangementsElectricityElectrical conductor
Inductive power transfer across an extended gap (100) from a primary conductor (119) is provided by means of a resonant intermediate loop comprised of capacitor (118) with inductor (117) carrying a larger resonating current, that can in turn generate an inductive field to be collected by a pickup coil (120). This process and device find application in an electroluminescent advertising panel.
Owner:AUCKLAND UNISERVICES LTD
Lightweight Portable Electric Generator with Integrated Starter/Alternator
ActiveUS20070227470A1Improve torque performanceLow costMagnetic circuit rotating partsAir coolingAlternatorFuel efficiency
A compact and lightweight electric generator for portable power applications employs a new engine design and integration approach for reducing engine, generator, and starter weight. A unique flywheel alternator / starter configuration that generates electrical power, rotates the engine for starting, provides inertia for smooth engine operation, pressurized air for cooling, and inertia for the alternator. An engine cowling provides rotating component protection, a fan shroud mechanism, cooling air ducts, and a cooling mechanism for handling large quantities of heat produced by rectified power conversion. An electrical hook up that allows the generator to provide transient surge capacity for starting inductive loads, or improved load leveling and fuel efficiency.
Owner:MAINSTREAM ENG
Electrical power conservation apparatus and method
InactiveUS7336514B2Process economyEasy to installPower network operation systems integrationCircuit arrangementsEngineeringPower factor control
An electrical power control apparatus and method for power factor correction in a conventional 60 hertz or other conventional frequency electrical AC power supply communicated to an inductive load. A plurality of interruptions of current in the line on both sides of an AC current oscillation, are created to control the power factor in a circuit energizing an inductive load. Additional power factor control and correction is provided by grounding of the line during each interruption. A controller controls the length and duration of each interruption based on preprogramming or input regarding current phase read or calculated in the line.
Owner:MICROPULSE TECH
Energy savings device and method for a resistive and/or an inductive load and/or a capacitive load
InactiveUS20050104543A1Provide energy savingSave energyElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
An energy savings device for an inductive, a resistive or a capacitive load, such as a fluorescent light fixture having a magnetic ballast or an electronic ballast, which is powered by an AC voltage waveform. The energy savings device includes a setting unit for setting a desired power operating level for the load. The energy savings device also includes a processor configured to receive a signal from the setting unit indicative of the desired power operating level for the load, to determine a phase delay to be provided to an output AC voltage waveform that is to be provided to the load, and to output a control signal as a result thereof. The energy savings device further includes an active element provided between a line that provides the input AC voltage waveform and the load, the active element receiving the control signal and turning off and on at predetermined times in accordance with the control signal, so as to create the output AC voltage waveform from the AC voltage waveform. The processor includes a synchronization circuit that synchronizes to the Green Safety ground line.
Owner:ASTRAL COMM
Soft-switching techniques for power inverter legs
InactiveUS7110269B2Reduce frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionCapacitancePower inverter
This invention relates to new soft-switching techniques for minimizing switching losses and stress in power electronic circuits using inverter legs. By choosing the switching frequency with specific relationships with the resonant frequency of the power electronic circuits, the proposed switching technique enables the power electronic circuits to achieve soft switching under full load and short-circuit conditions at the defined frequencies for both capacitive and inductive loads. This technique can be applied to an electronic circuit with two switches connected in totem pole configuration between two dc voltage rails or commonly known as a power inverter leg or inverter arm. Examples of these circuits are class-D power converter, half-bridge power converters and full-bridge power converters or inverters. The proposed techniques allow inverter circuits with resistive, capacitive and inductive loads to achieve soft switching.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
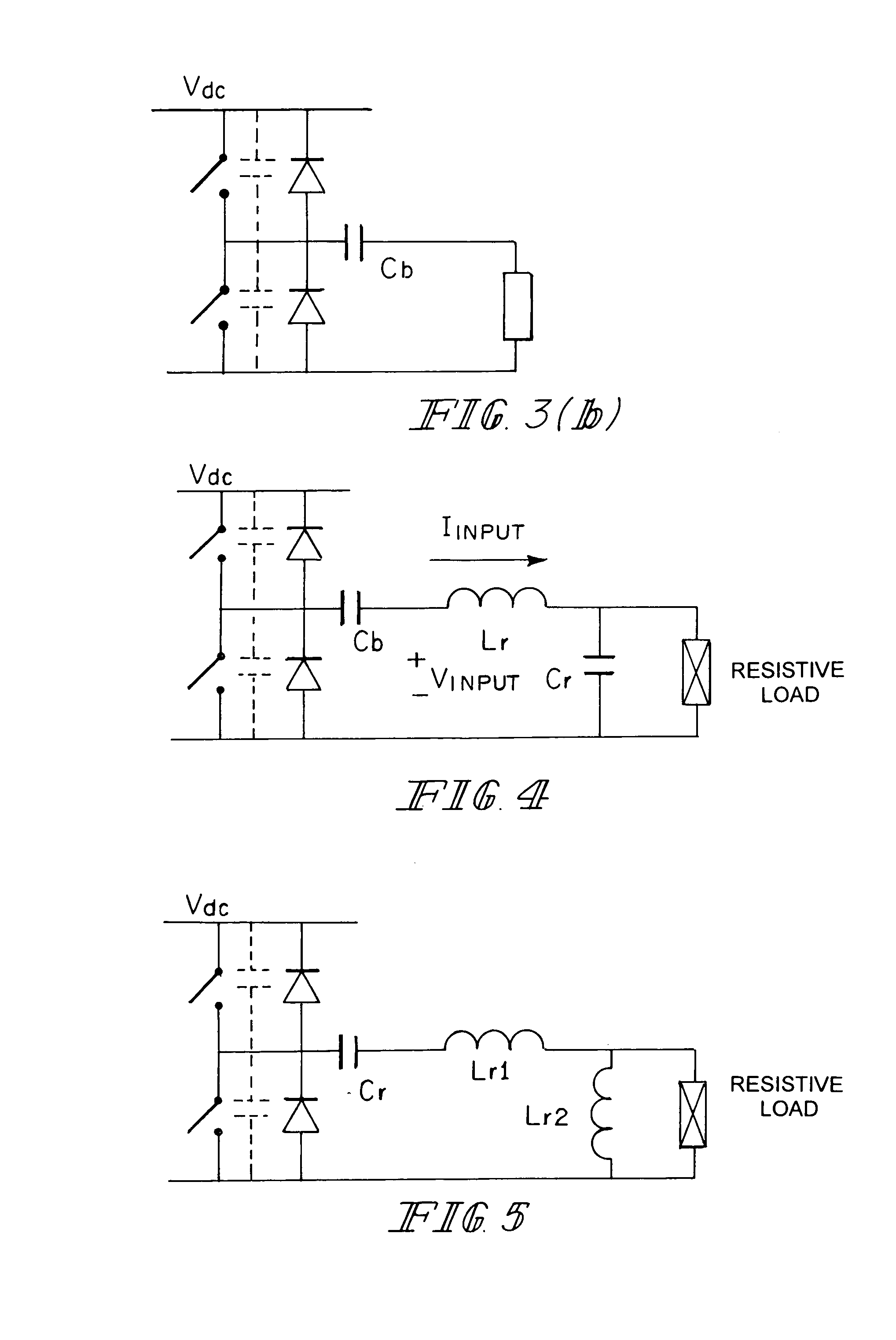
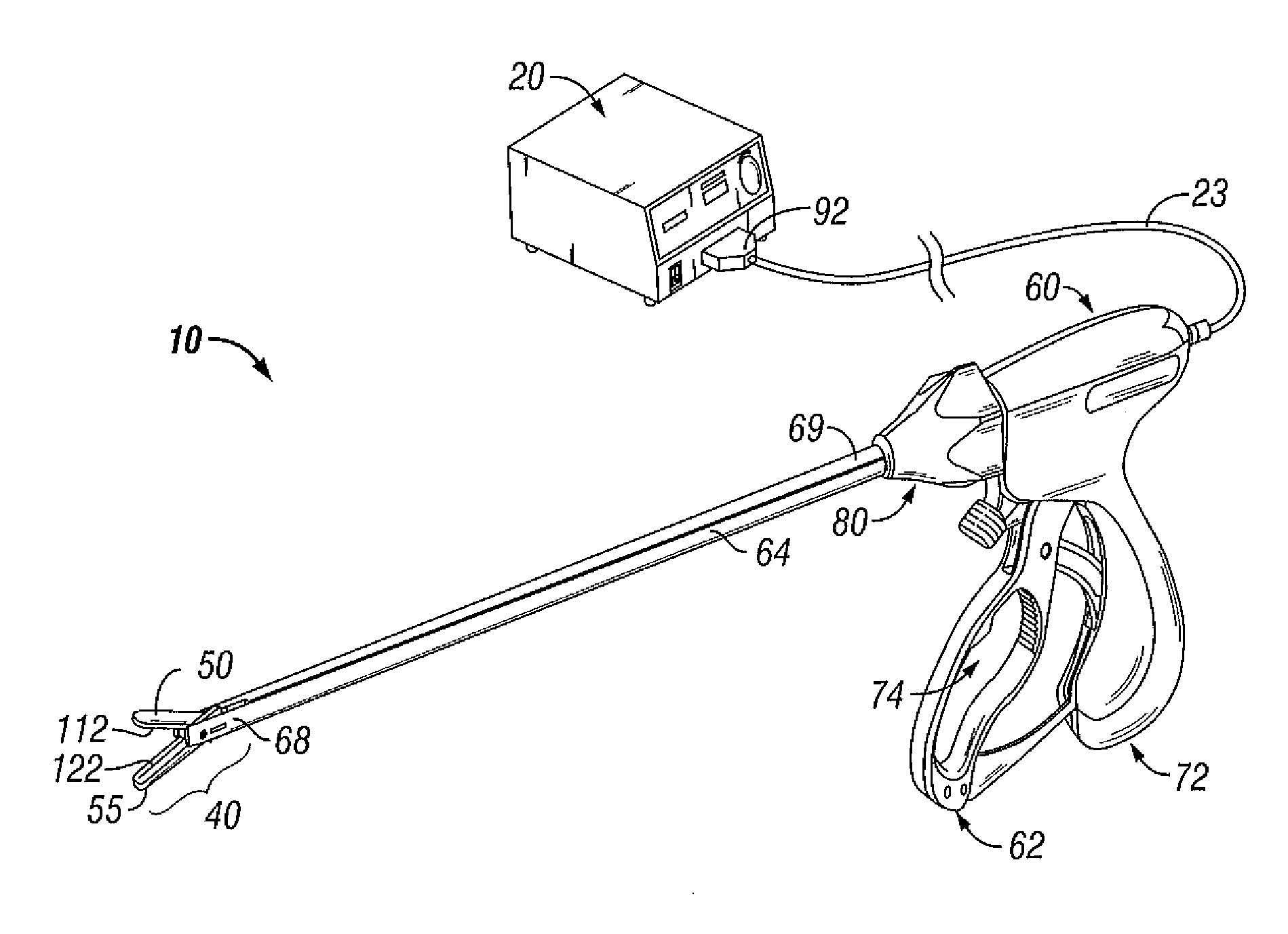
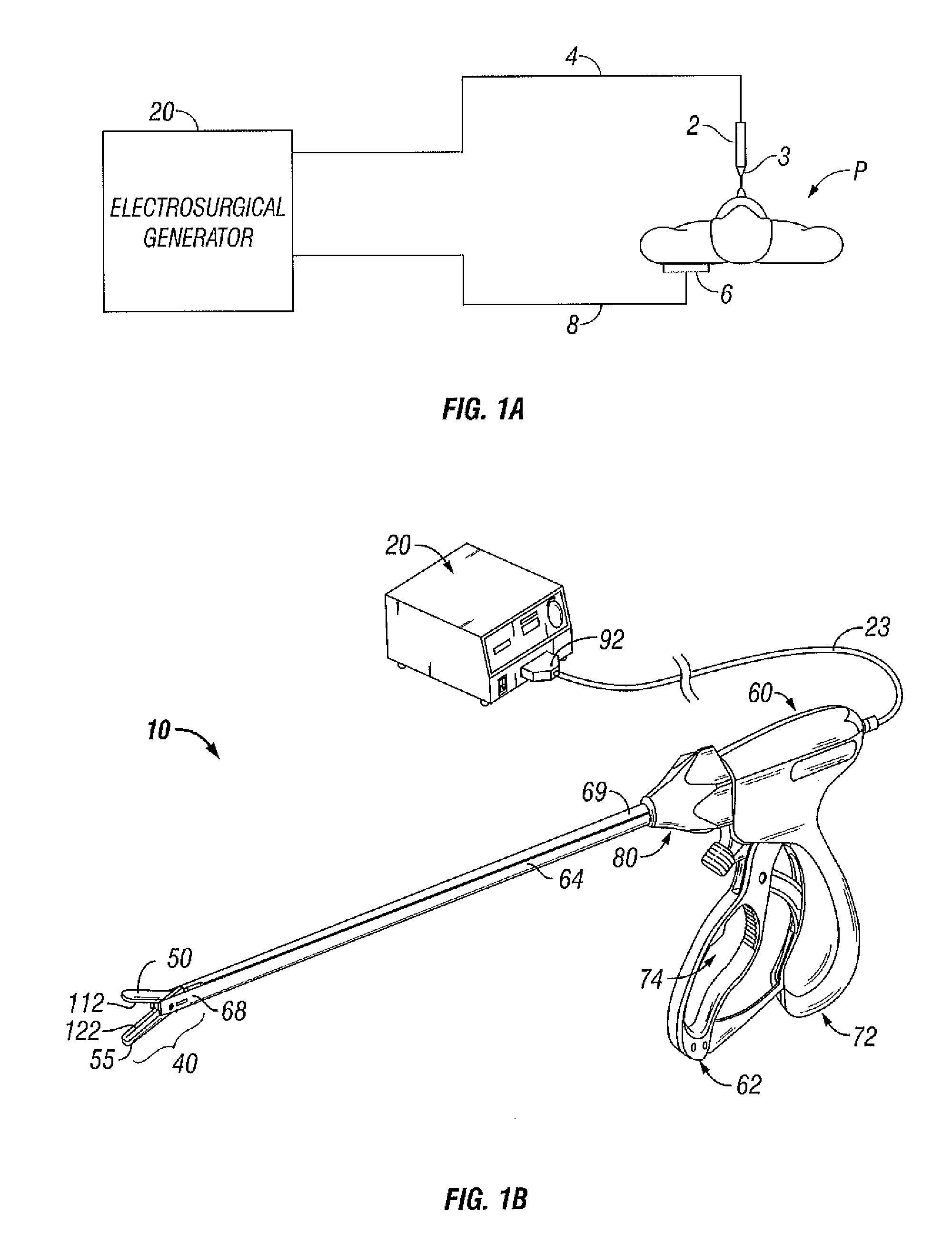
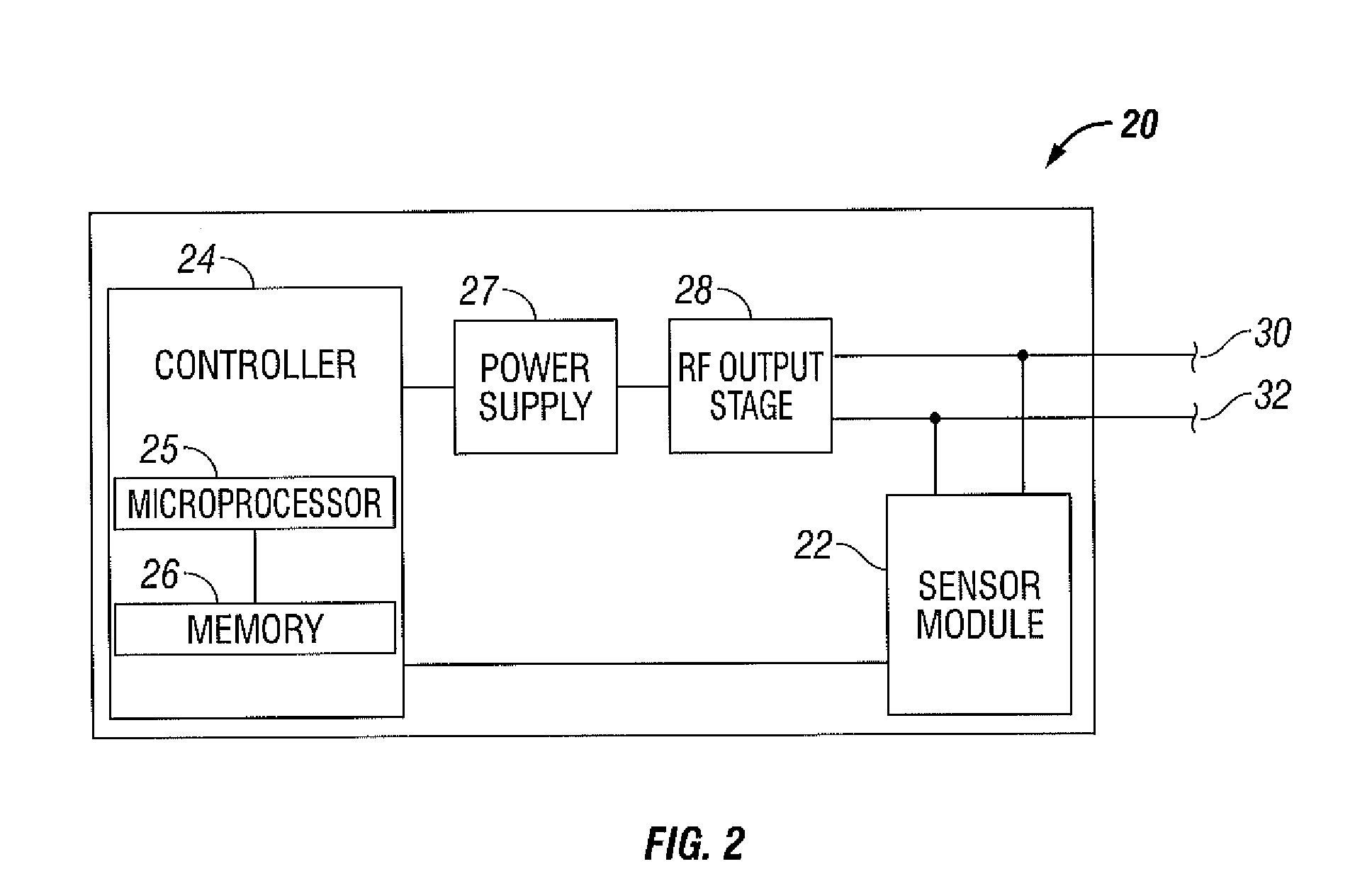
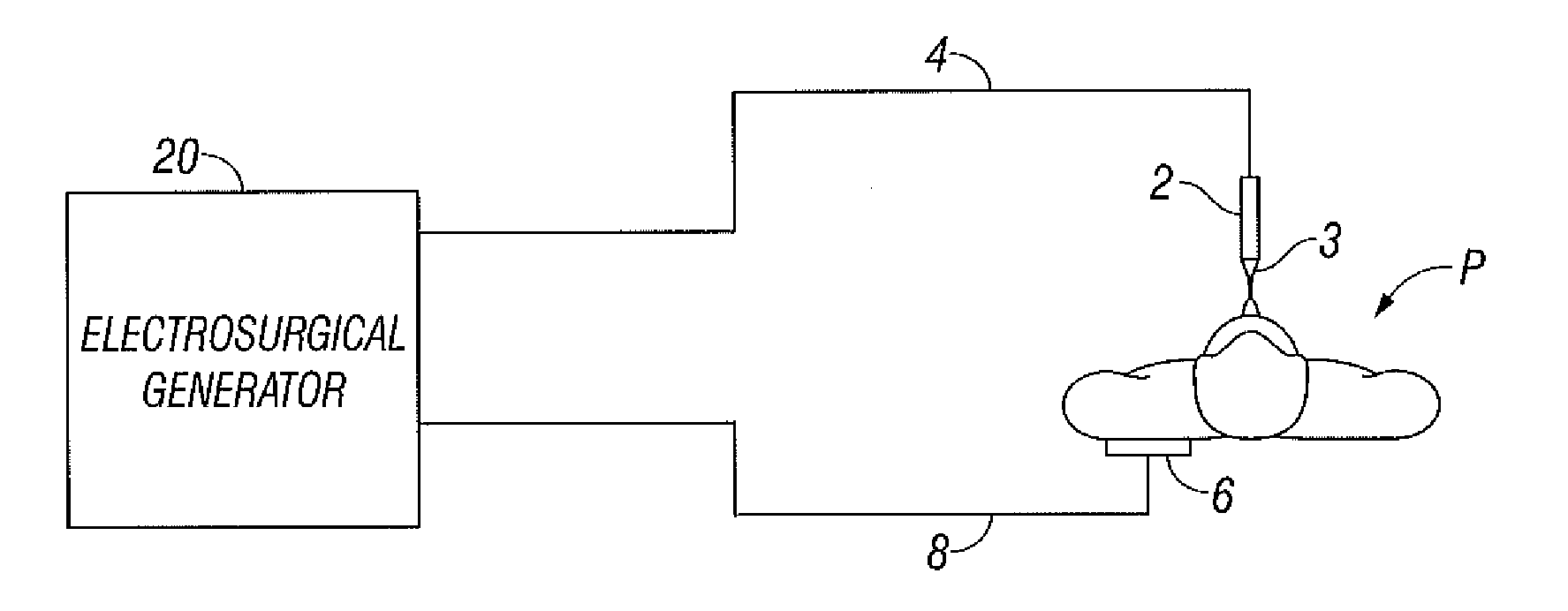
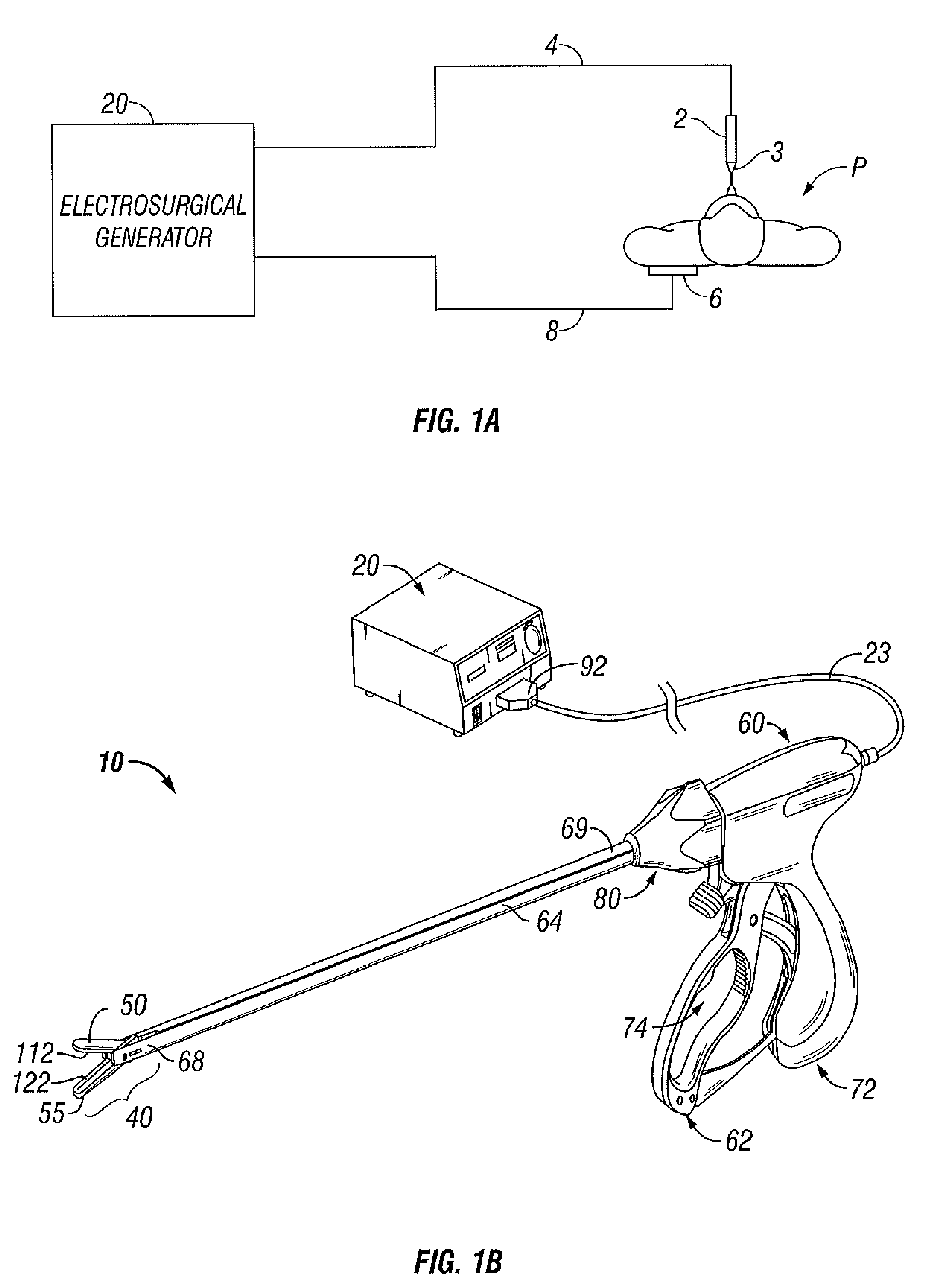
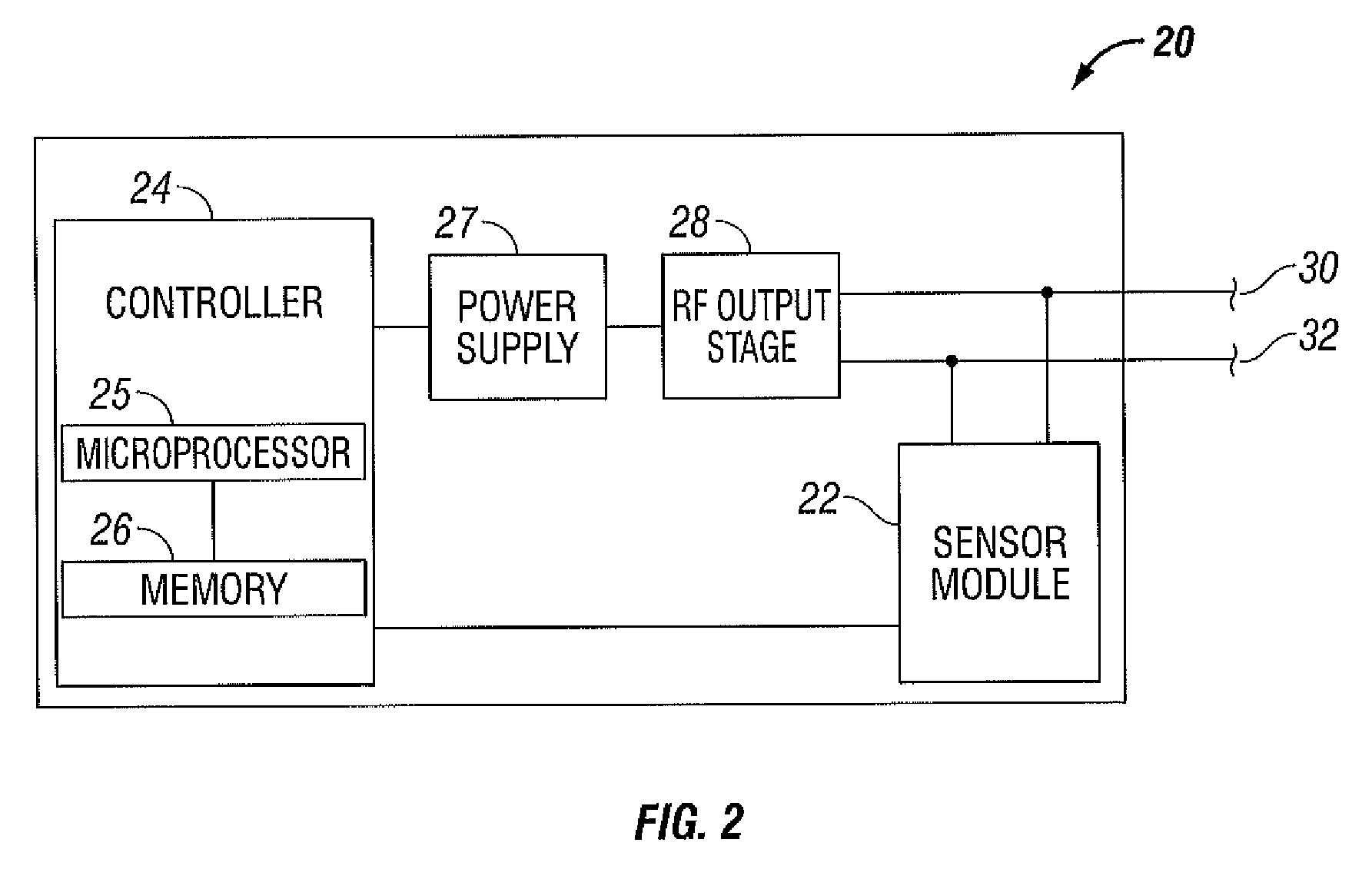
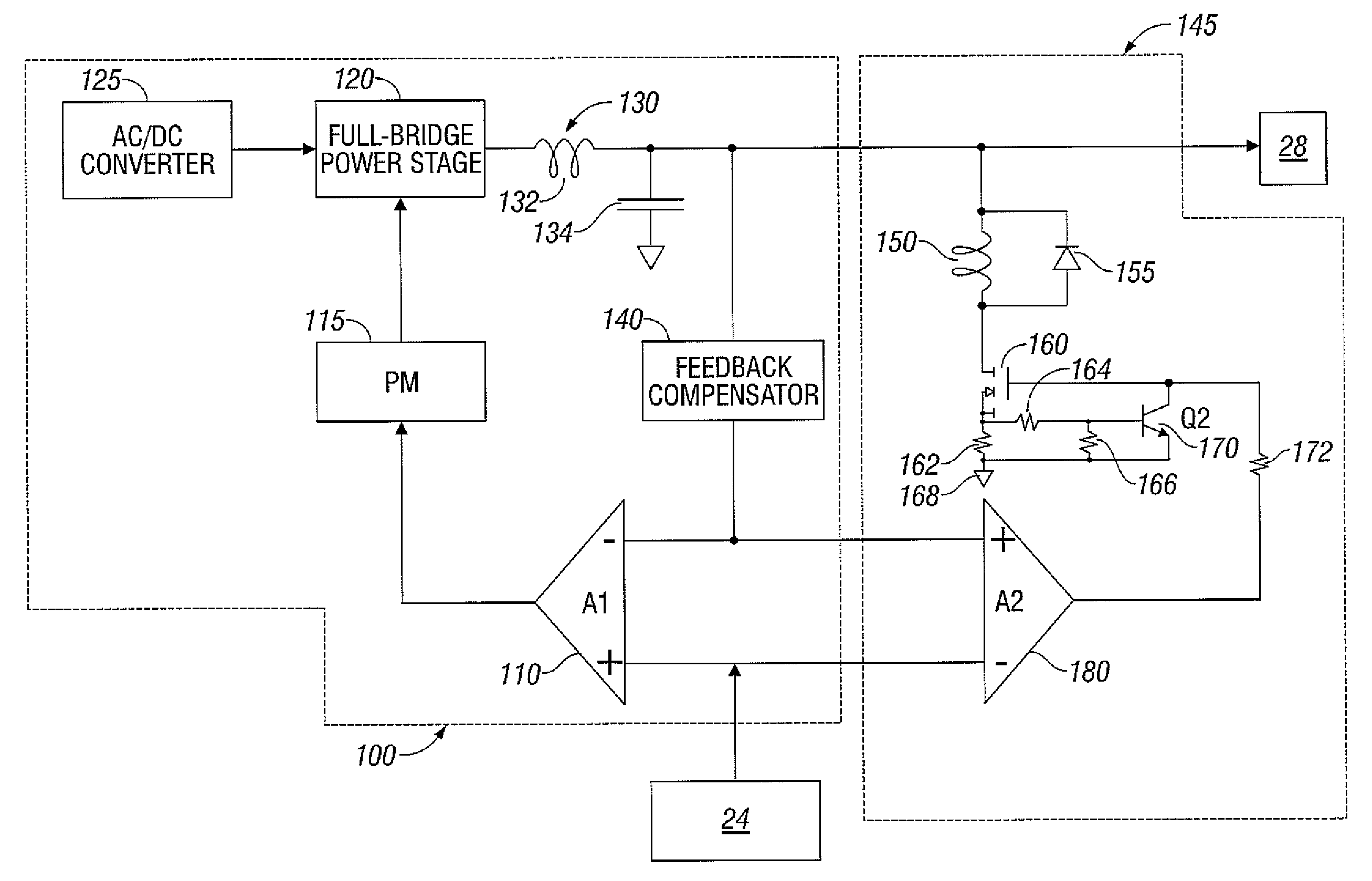
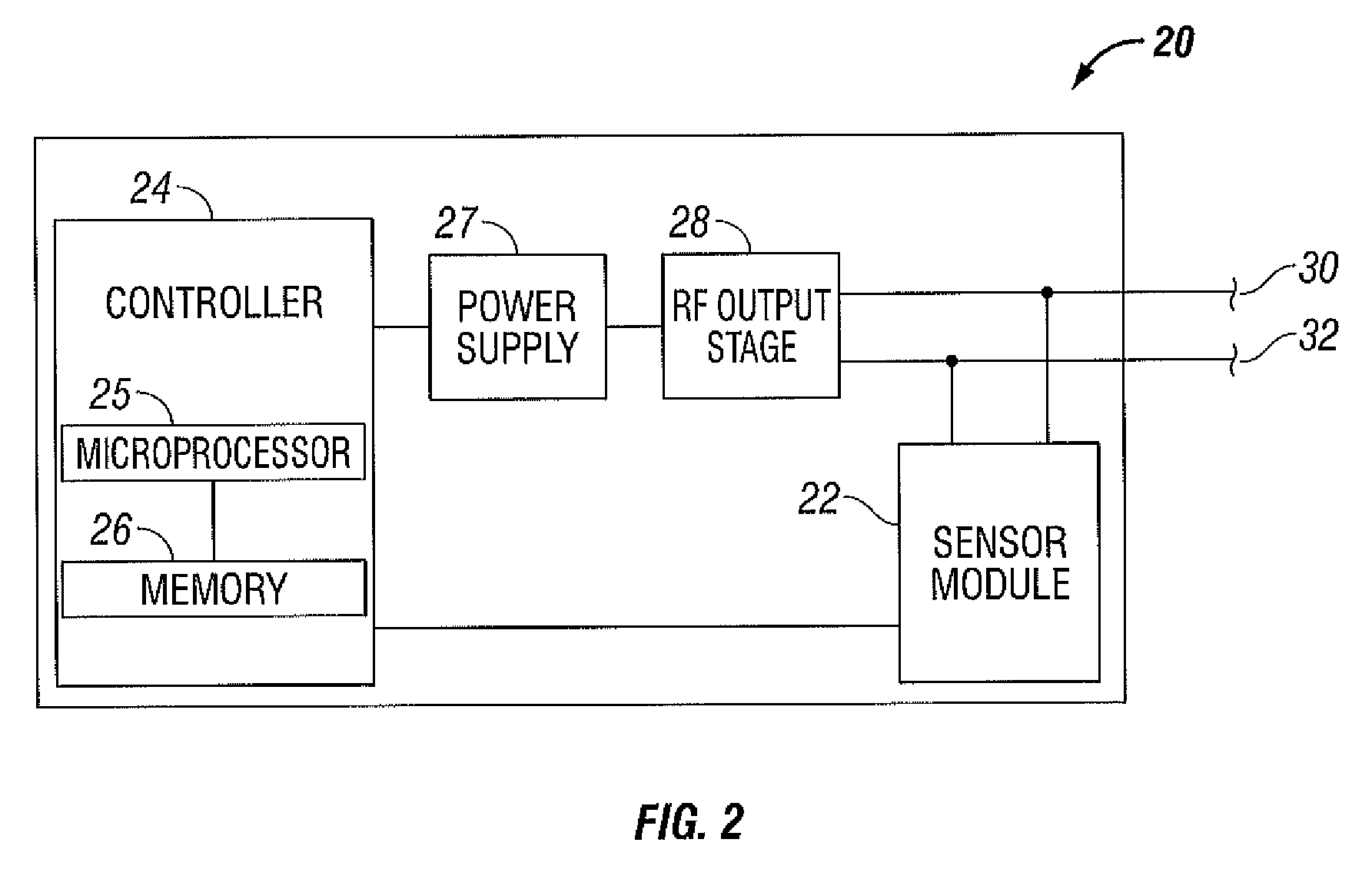
Electrosurgical Apparatus With High Speed Energy Recovery
A circuit for controlling the discharging of stored energy in an electrosurgical generator includes a pulse modulator which controls an output of a power supply. At least one comparator is configured to provide an error signal to the pulse modulator based on a comparison between an output signal generated by the power supply and a feedback signal generated in response to the application of energy to tissue. A discharge circuit is configured to control the discharge of the output of the power supply to an inductive load disposed in parallel with the output of the power supply based on the comparison between the output signal and the feedback signal. The discharge circuit provides a rapid response and time rate control of the delivered electrosurgical energy by controlling the power supply and delivered RF energy in real time, based on a feedback signal generated in response to the application of energy to tissue.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Bipolar transistor drivers
InactiveUS20090040796A1Reduce impactEffectively allows the sensed voltage to be scaledTransistorEfficient power electronics conversionControl signalControl system
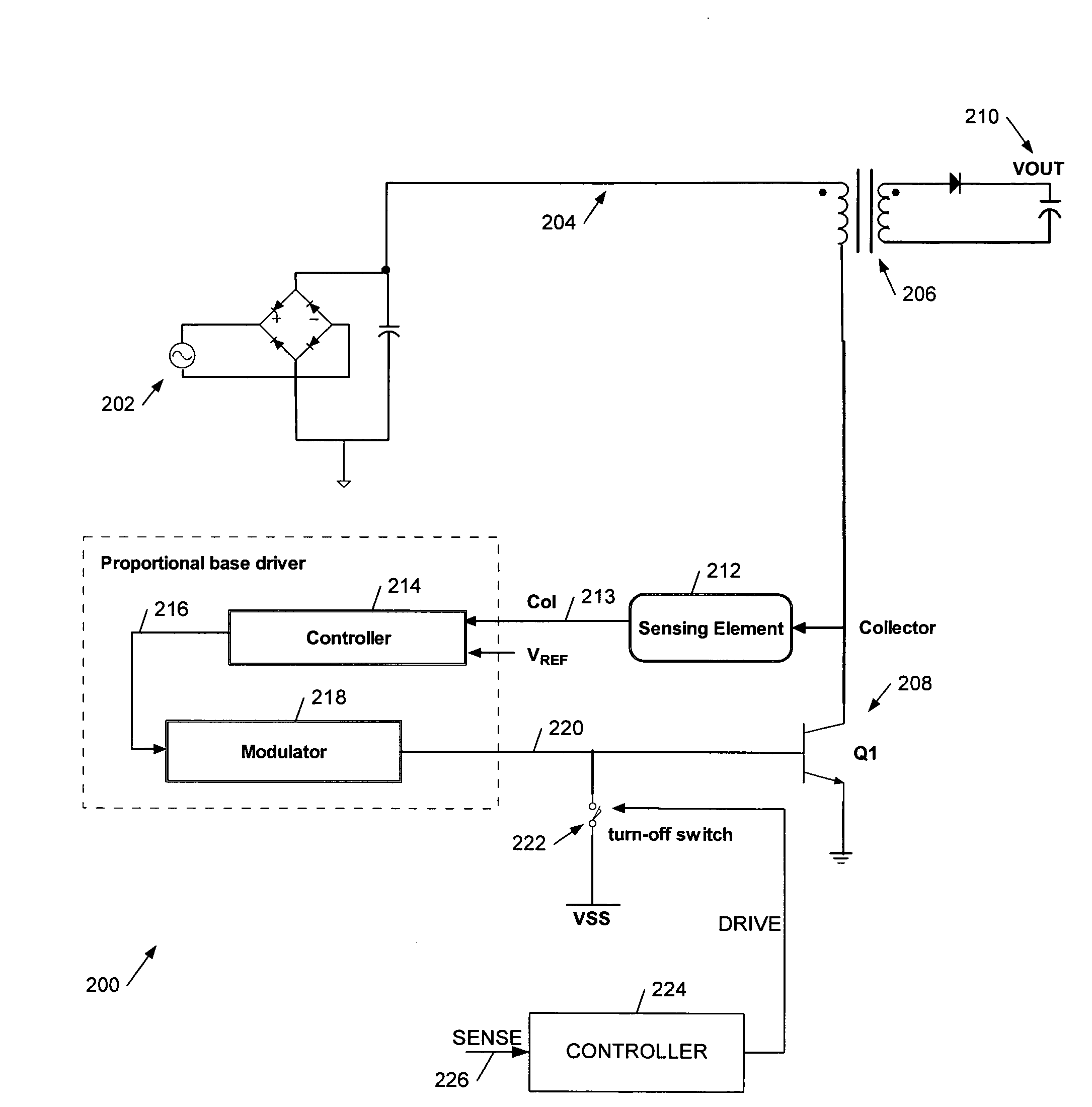
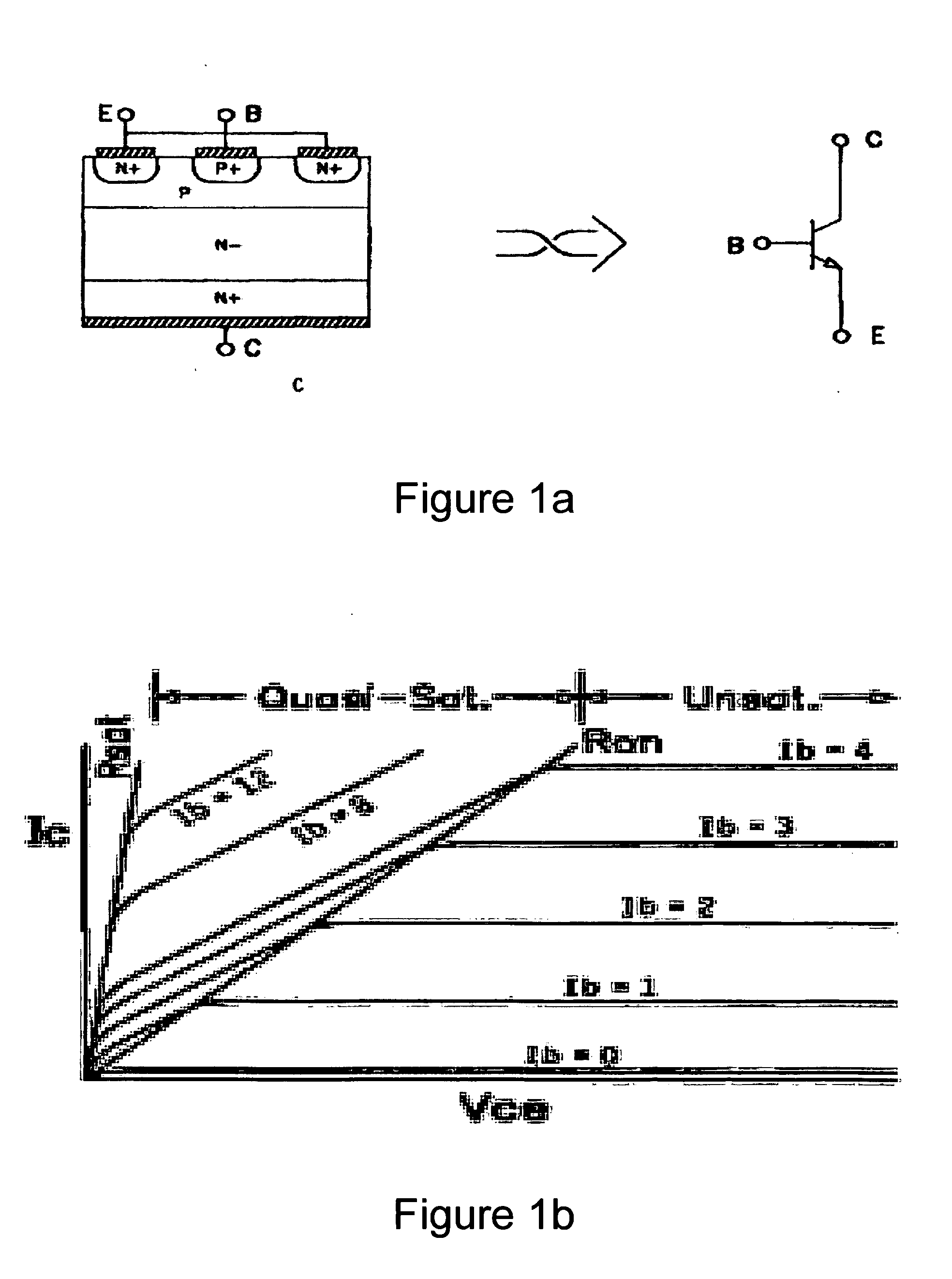
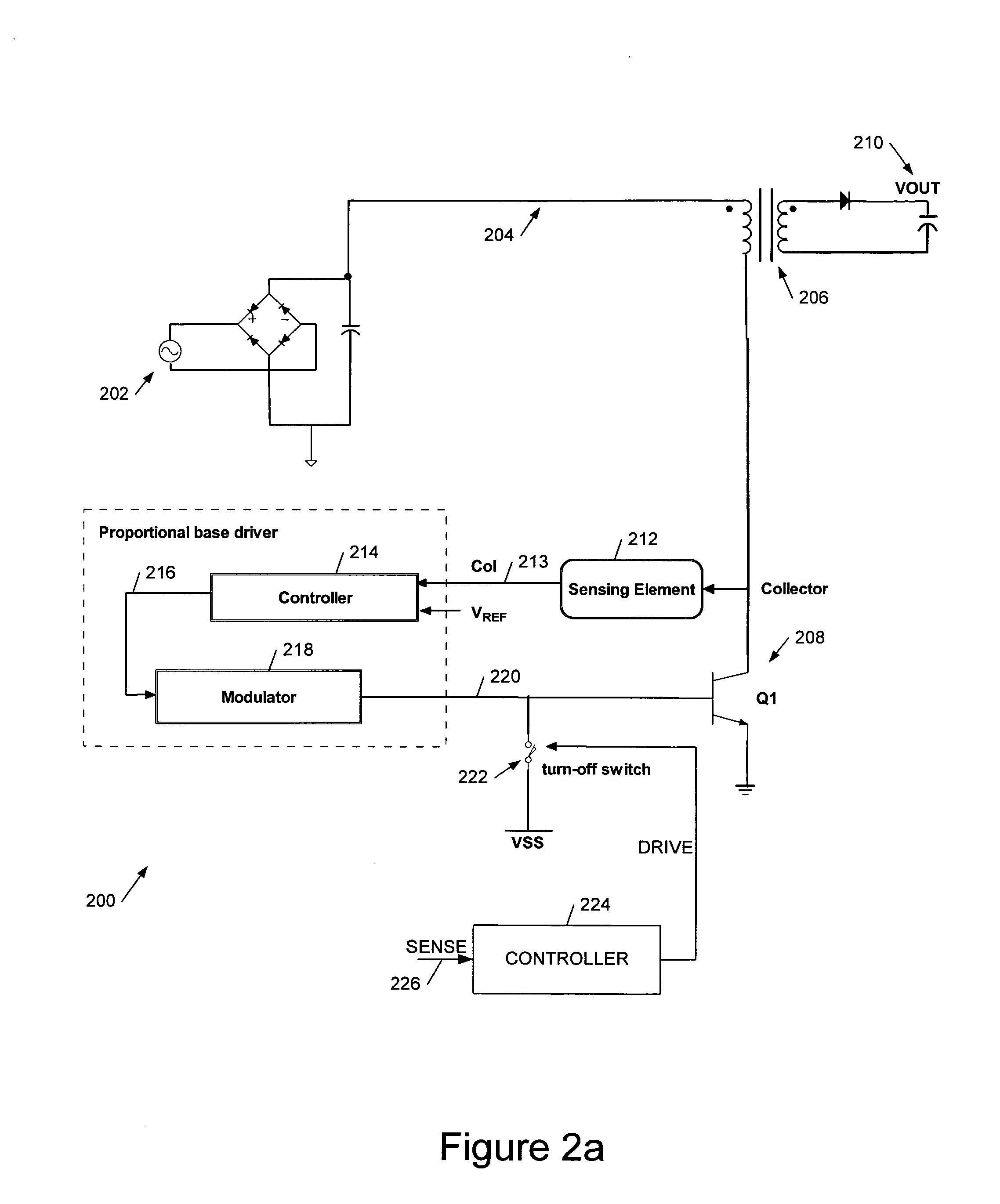
We describe a switching power converter comprising a bipolar switching device (BJT or IGBT) switching an inductive load, and including a closed-loop control system. The control system comprises a voltage sensing system to sense a voltage on a collector terminal of the switching device and provide a voltage sense signal; a controller; and a drive modulation system coupled to an output of the controller for modulating a drive to the control terminal of said bipolar switching device responsive to a controller control signal; wherein said controller is configured to monitor changes in the sensed voltage during a period when said switching device is switched on and to control said drive modulation system to control the degree of saturation of said bipolar switching device when the device is switched on and hence improve turn-off times.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
Method and apparatus using VAR measurements to control power input to a three-phase induction motor circuit
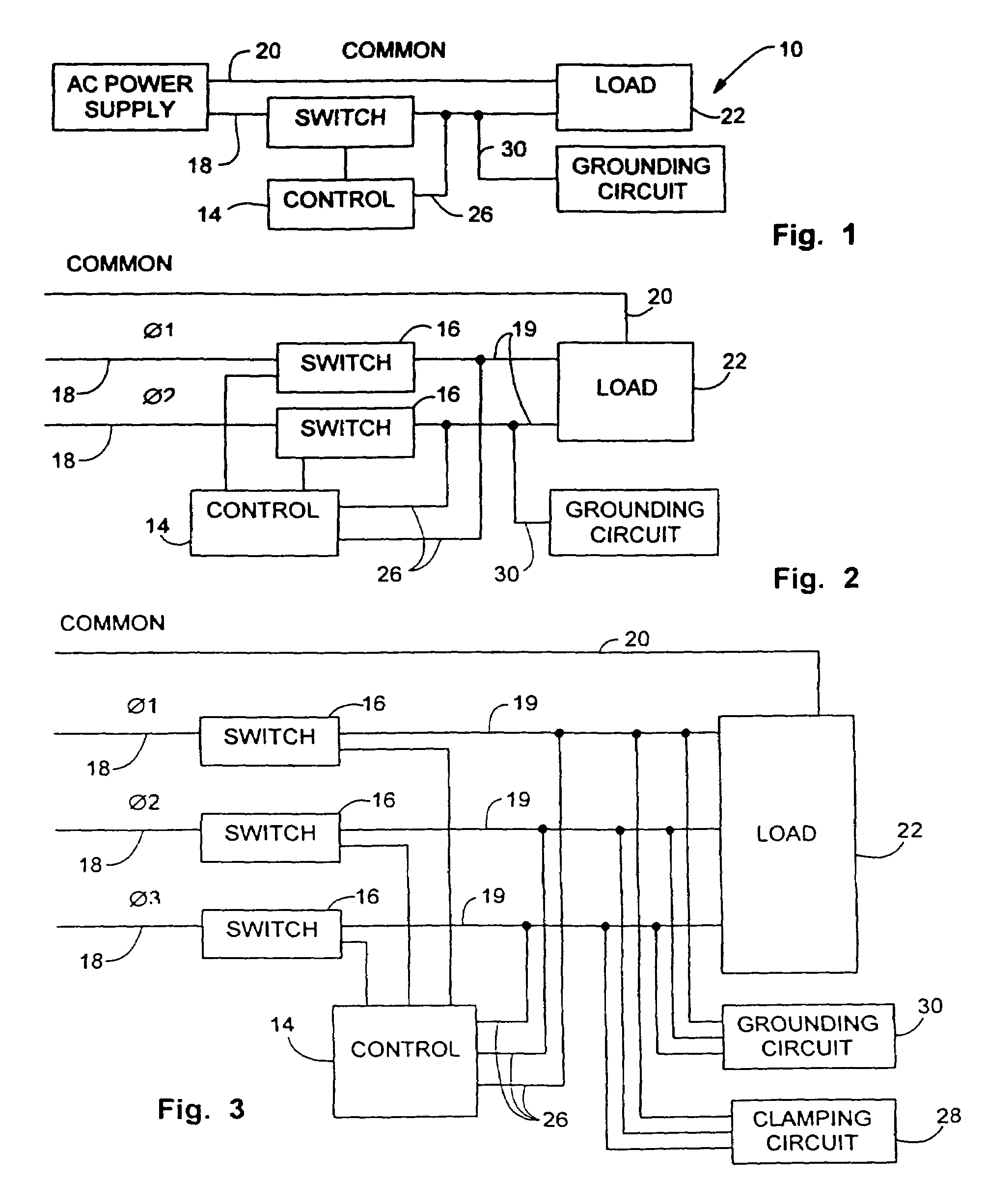
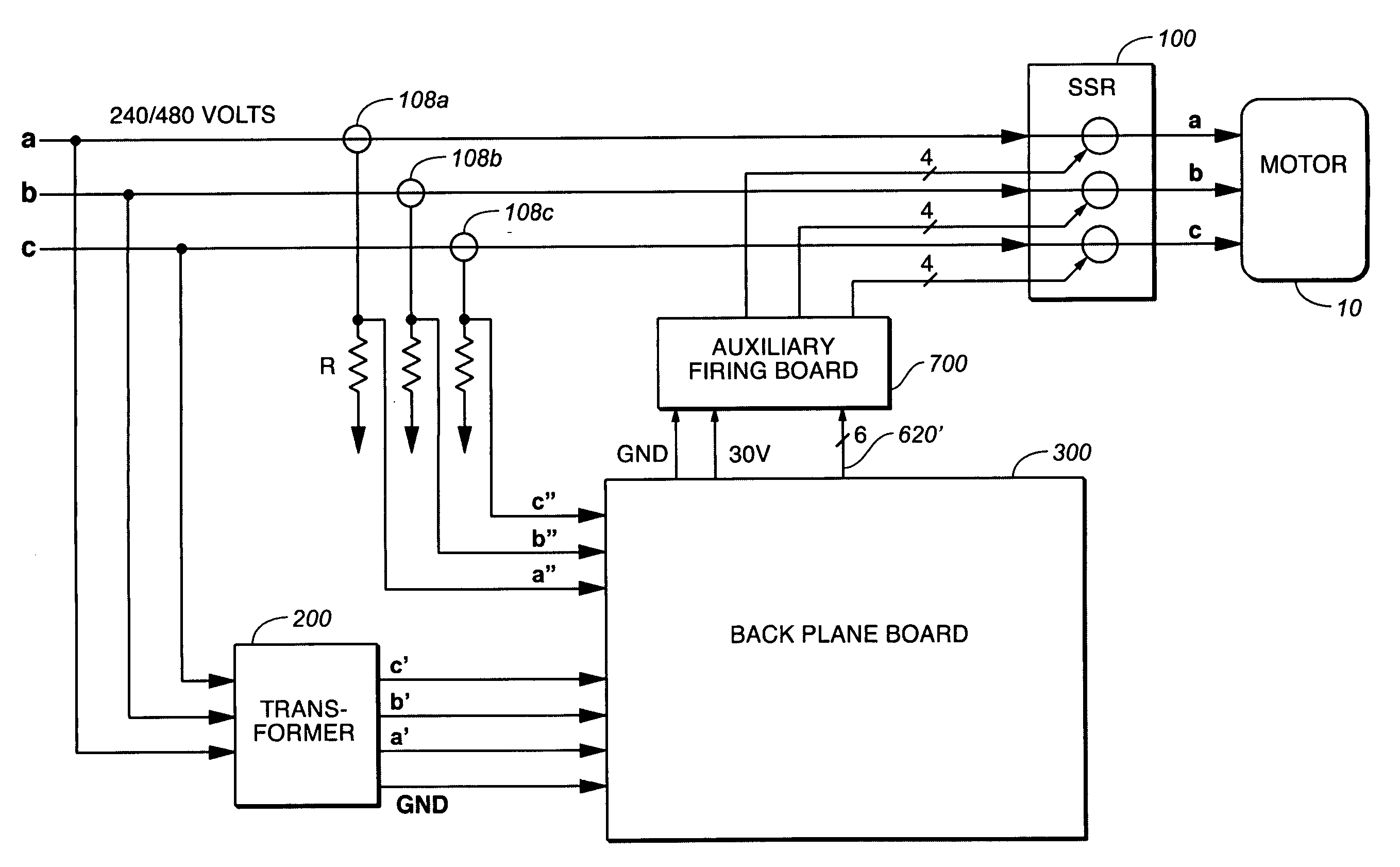
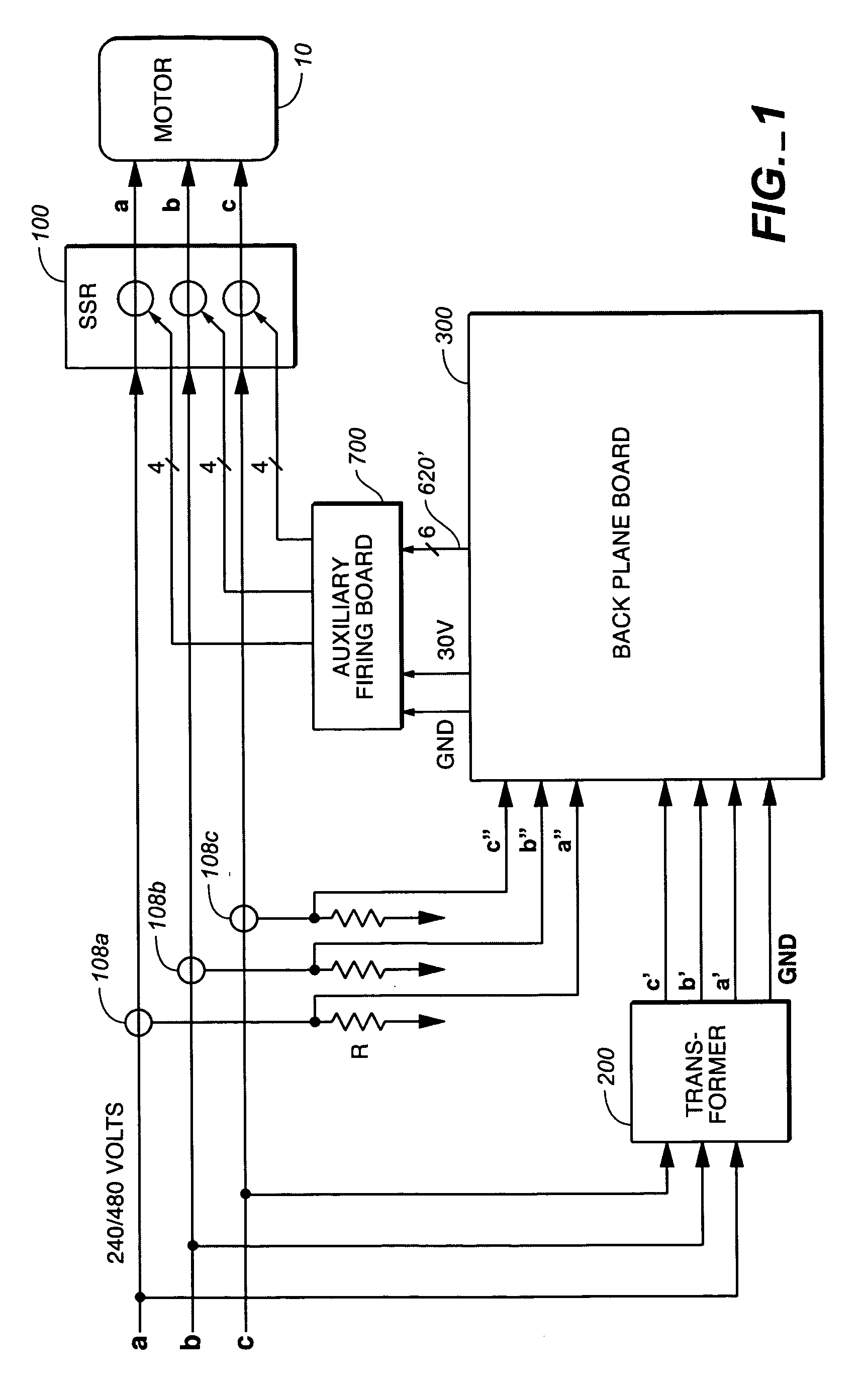
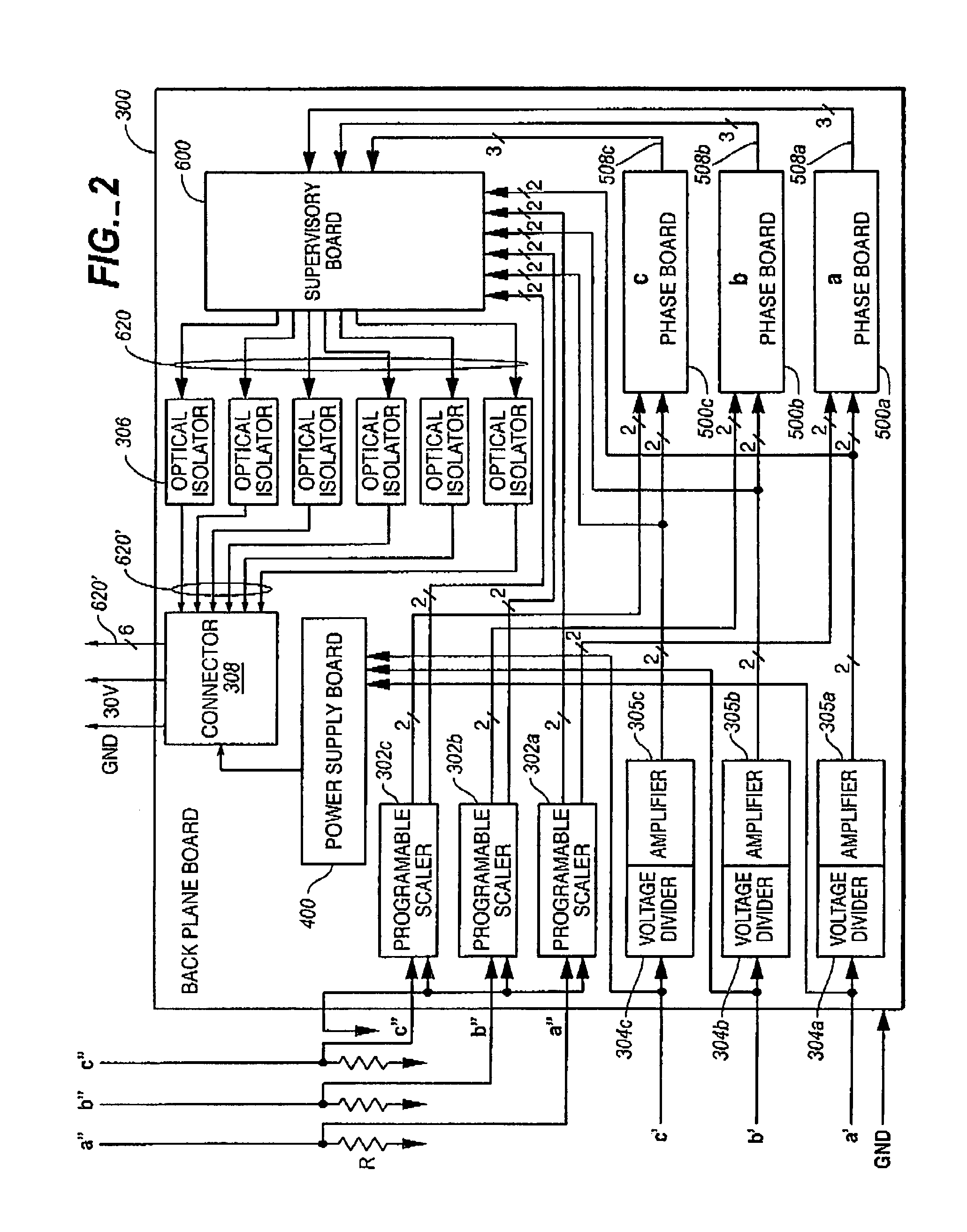
A method and apparatus are described for controlling the flow of power in each input line to a three phase AC inductive load in order to reduce the amount of VAR in the system, and thus increase the operational efficiency of the inductive load. Solid state relays are positioned in series in each of the three inductive load line inputs, and current allowed to flow to the inductive load only during the time during which the SSRs are in a conducting state. The calculation of VAR is achieved by processing data from each of the input lines using a separate controller boards each dedicated to each of the lines. The controller in turn, based on the calculated VAR, increments the time, either increasing or decreasing it from a predetermined value, during which the SSRs in that line remains in the non-conducting state.
Owner:ENVIRO WORLD SYST
Inverter bridge controller implementing short-circuit protection scheme
ActiveUS20050281065A1Statistical likelihood is improvedImprove survivabilityConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionThree-phaseShort circuit protection
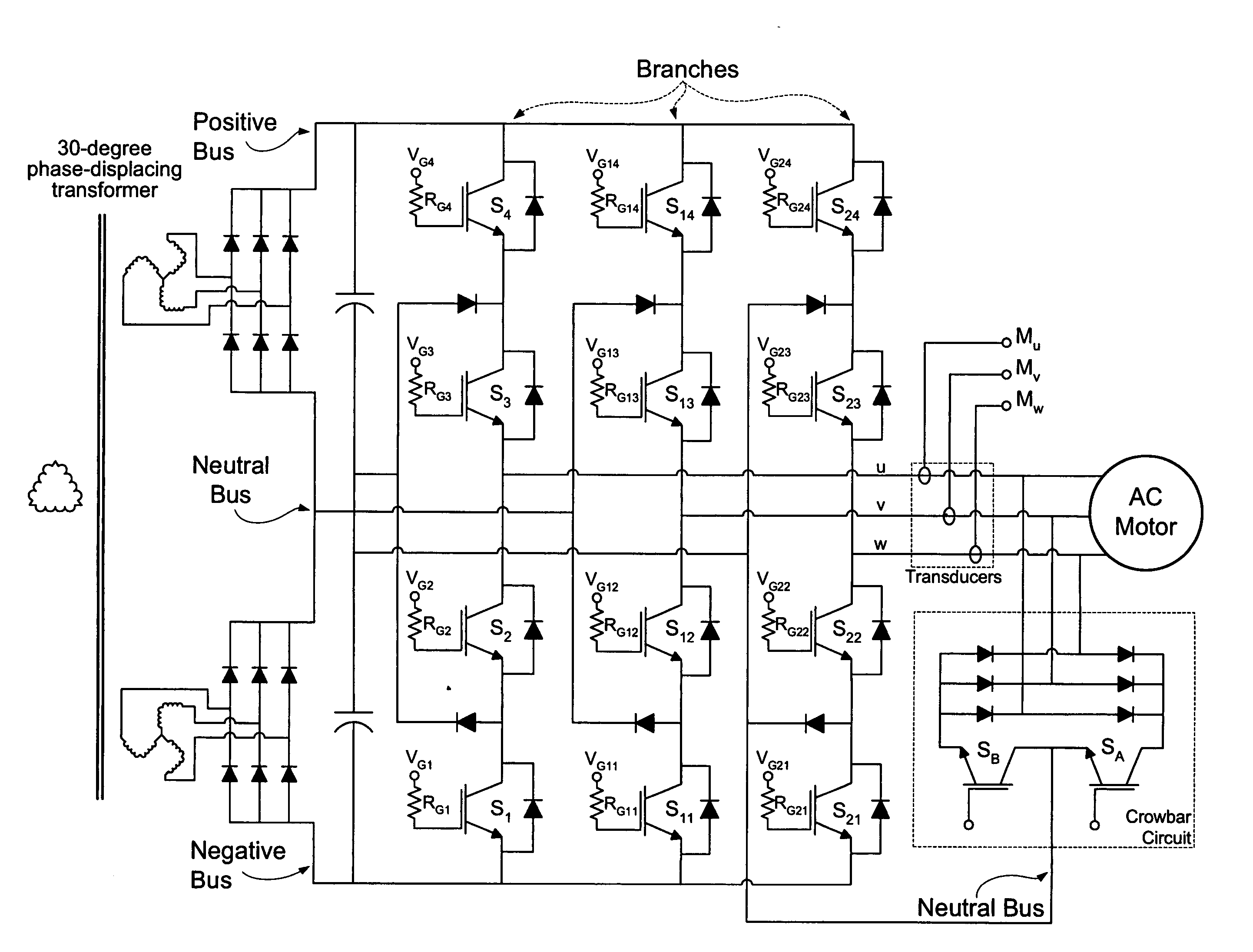
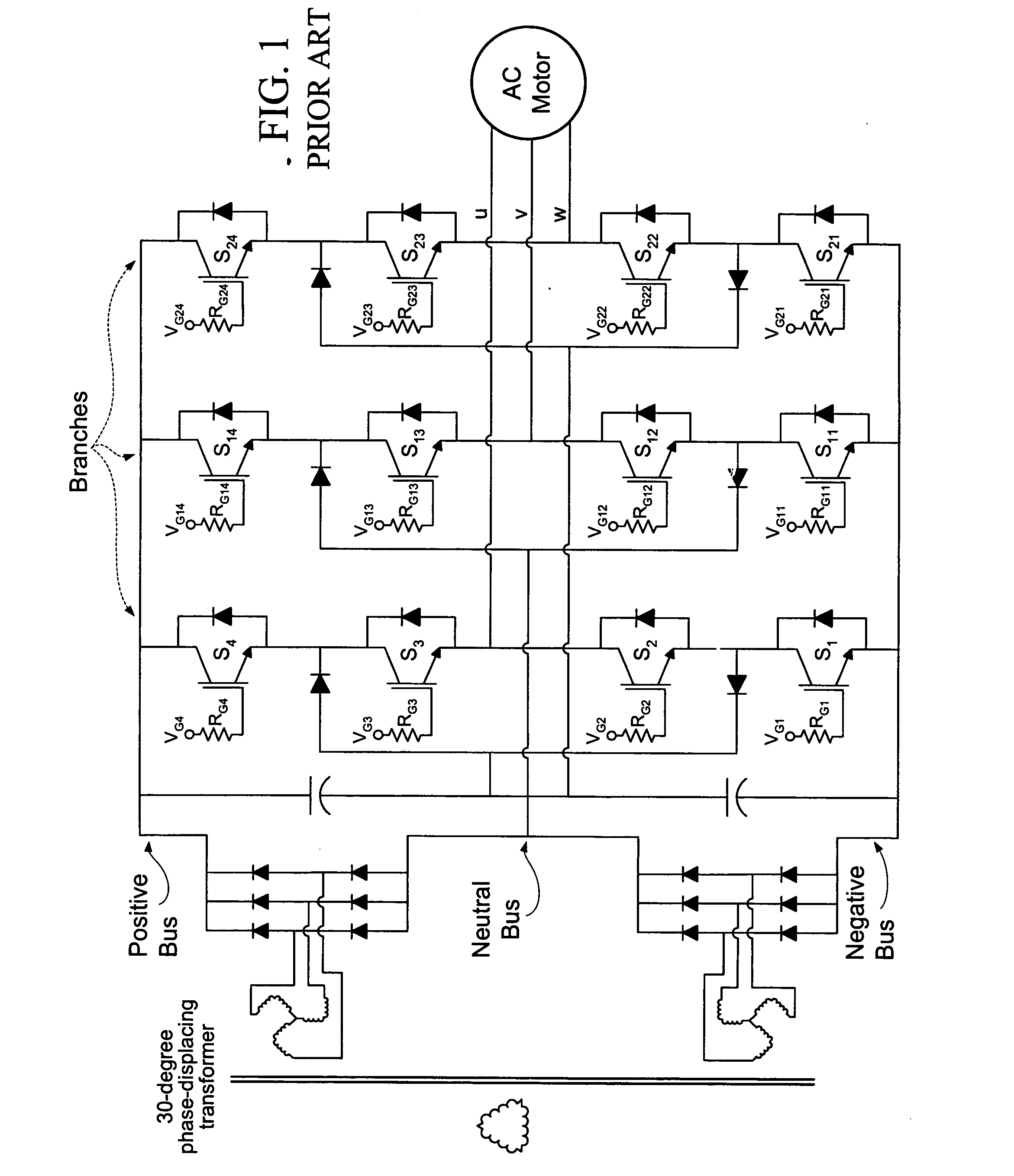
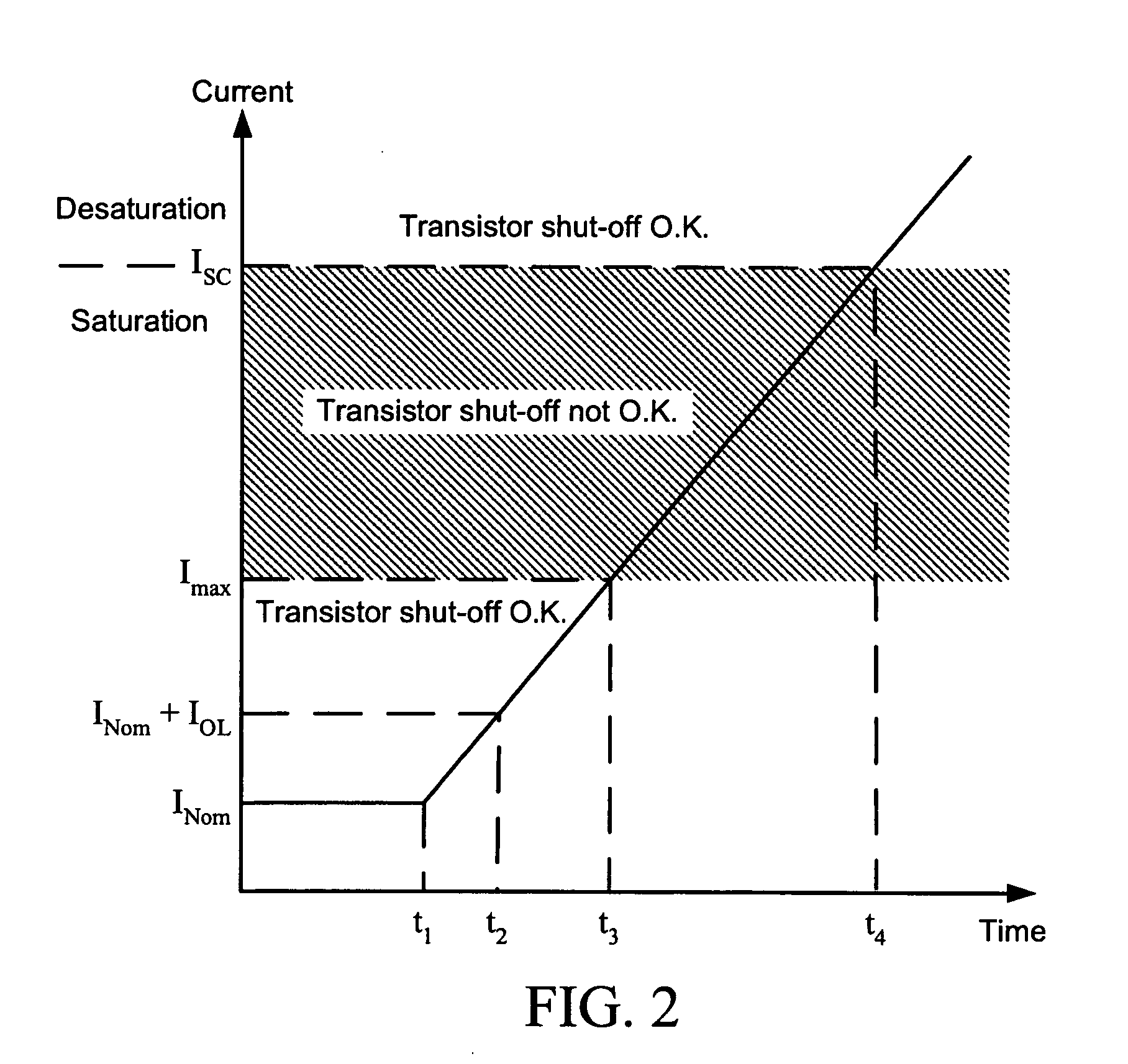
A fault handling system for short circuit recovery in three-phase multiple-level inverter bridges, used to drive inductive loads, which waits for either desaturation of switches or expiration of a delay period based upon an amount of time before saturated switches are damaged before commanding off switches that are saturated, and which artificially creates a dead-short across the three-phase output to force switches conducting a fault current to desaturate. By delaying the switching-off of the inverter bridge during a fault, waiting for desaturation to occur, the statistical likelihood of switch survival is improved.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD +1
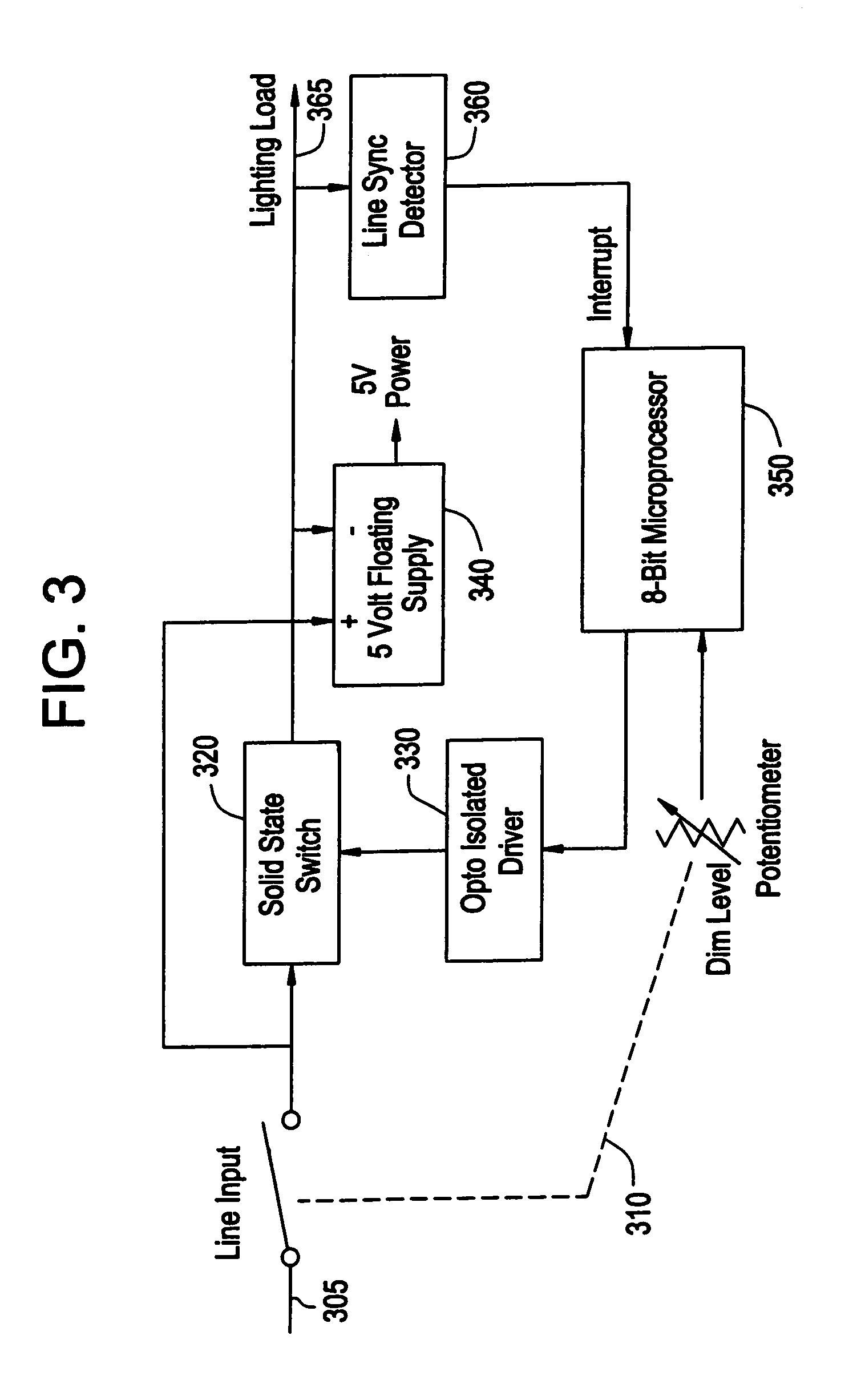
Universal energy regulating controller circuit
InactiveUS20030169014A1Avoid disadvantagesAvoid wastingSingle-phase induction motor startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersMotor speedPower controller
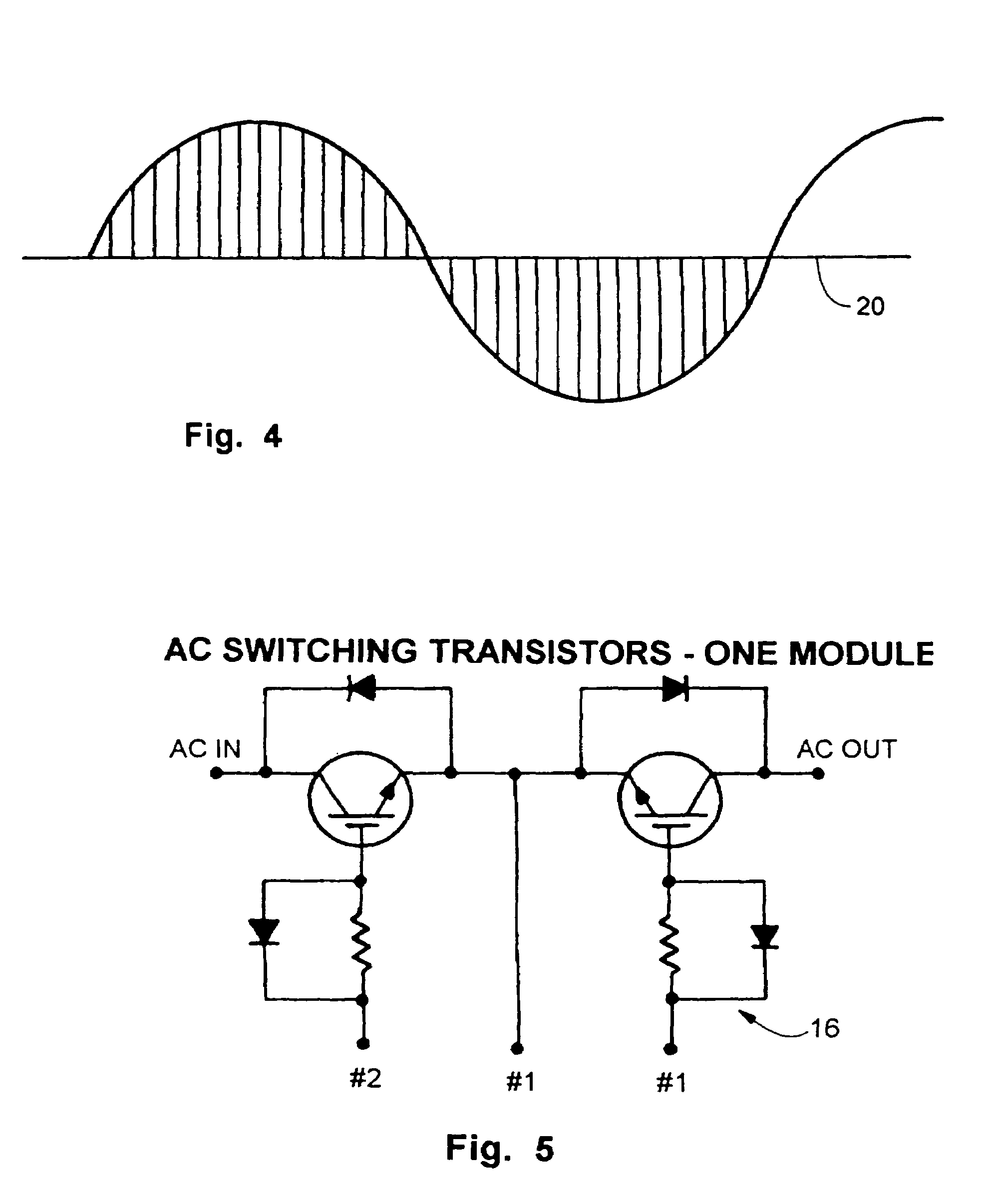
A power controller for applying power to an induction motor or similar AC load has a variable drive circuit for staring and switching a portion of the AC input line power. In one mode, the input line power is fed straight through to the load. In another mode, the AC waveform is reshaped to improve the power factor or to boost its RMS value, e.g., for brownout protection. In a further mode the output power can be provided at a different frequency from the input line power. Vector control increases efficiency through power optimization, with sensing of load requirements. Sensing of regeneration pulses at the commencement of a half cycle can be employed for direct sensing of motor speed or load.
Owner:INT CONTROLS & MEASUREMENT
Capacitive sensing system configured for using heating element as antenna electrode
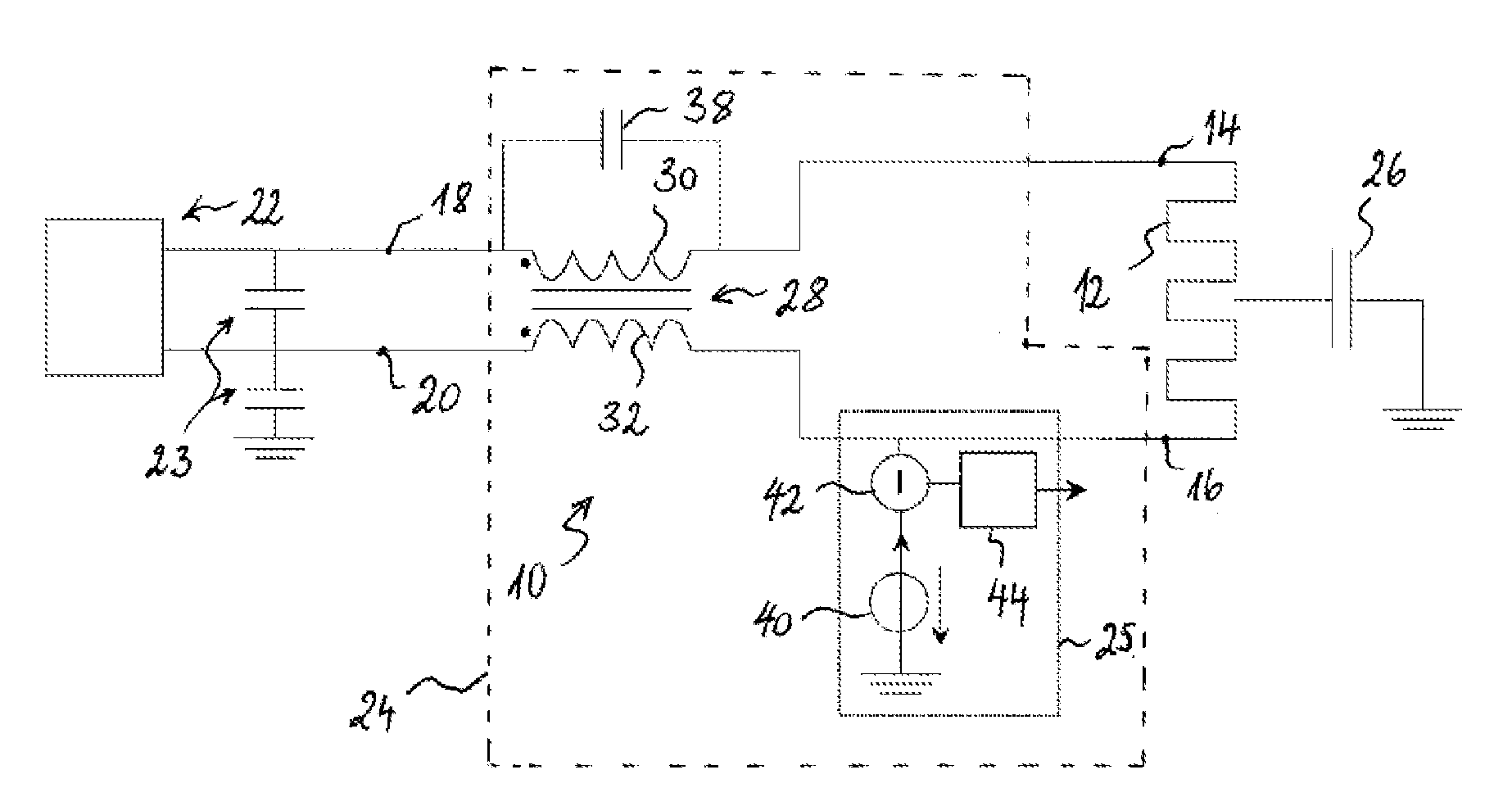
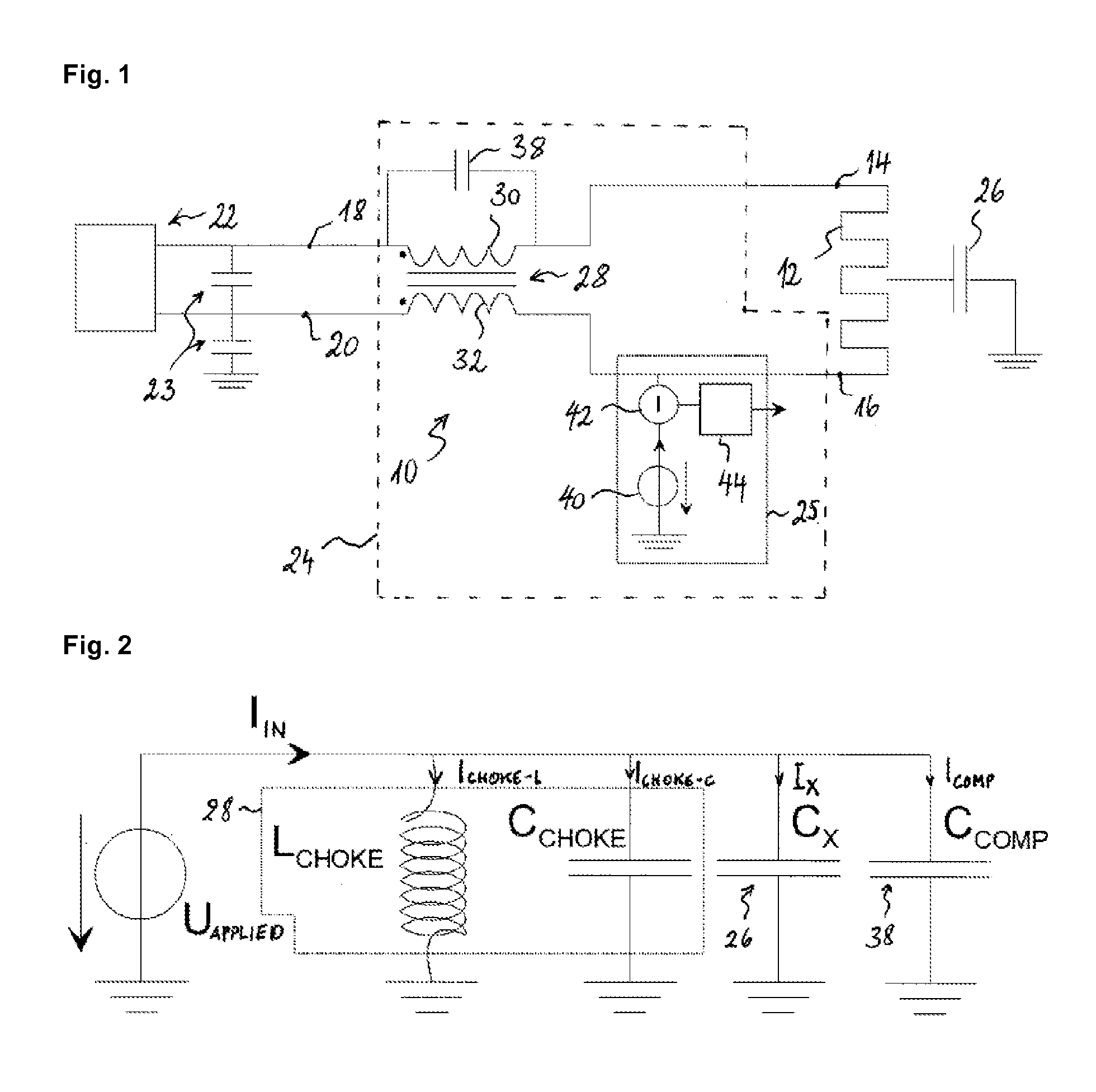
A capacitive sensing system for a heating element comprises a capacitive detector connectable to the heating element and a common mode choke for connecting the heating element with a heating current supply. The detector drives an alternating current into the heating element and produces an output depending on the capacitive load, which the alternating current is subject to. Depending on the object sensed, the load varies in a range between a minimum and a maximum value. The choke represents an inductive load in parallel of the capacitive load. The capacitive load and the inductive load contribute to a complex impedance dominated by the inductive load. A compensation capacitor arranged parallel to the choke represents an additional capacitive load also contributing to the complex impedance. The compensation capacitor is dimensioned such that the sum of additional capacitive load and maximum value amounts to at least 50% of the inductive load.
Owner:IEE INT ELECTRONICS & ENG SA
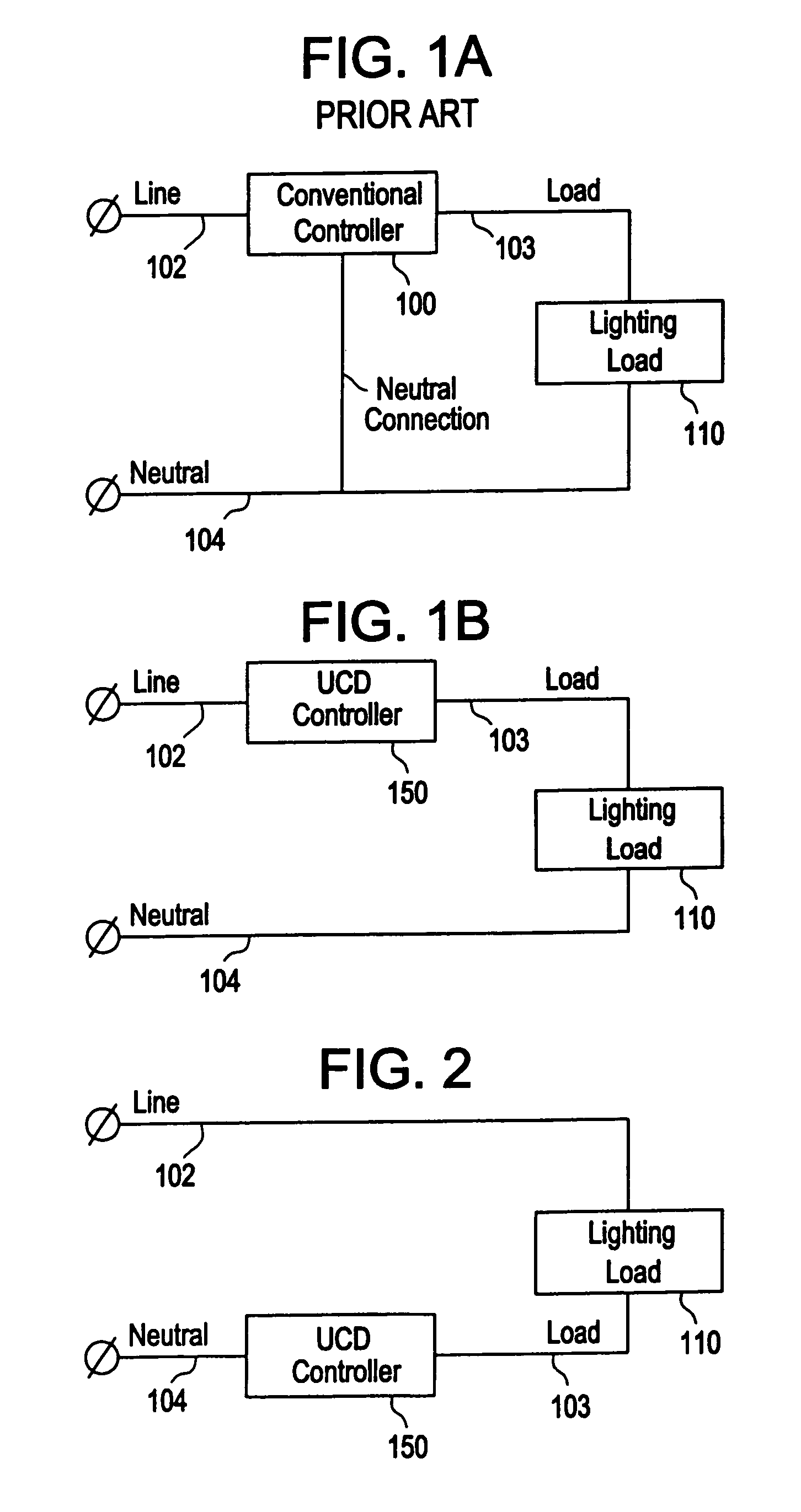
Two-wire dimmer with power supply and load protection circuit in the event of switch failure
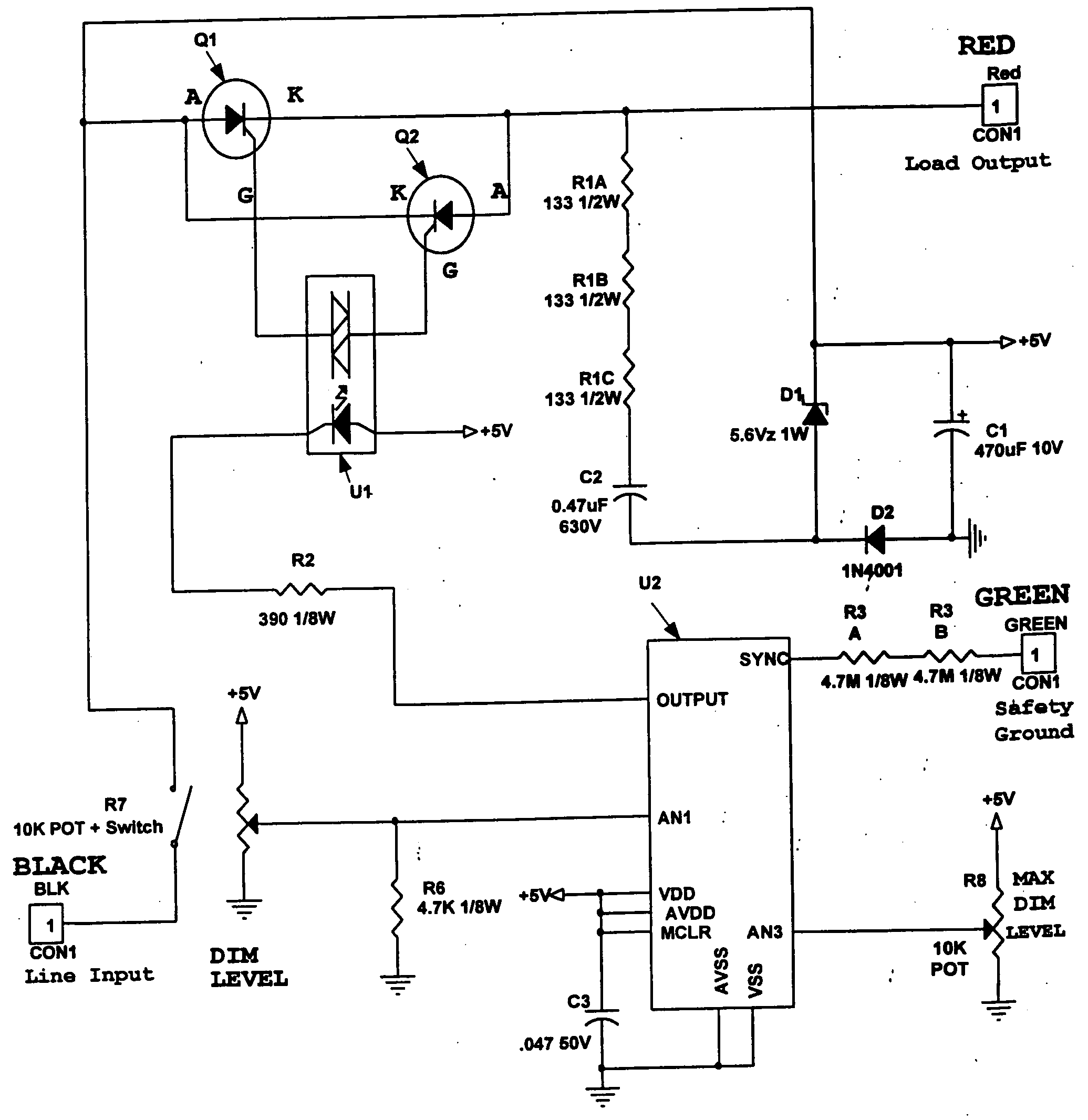
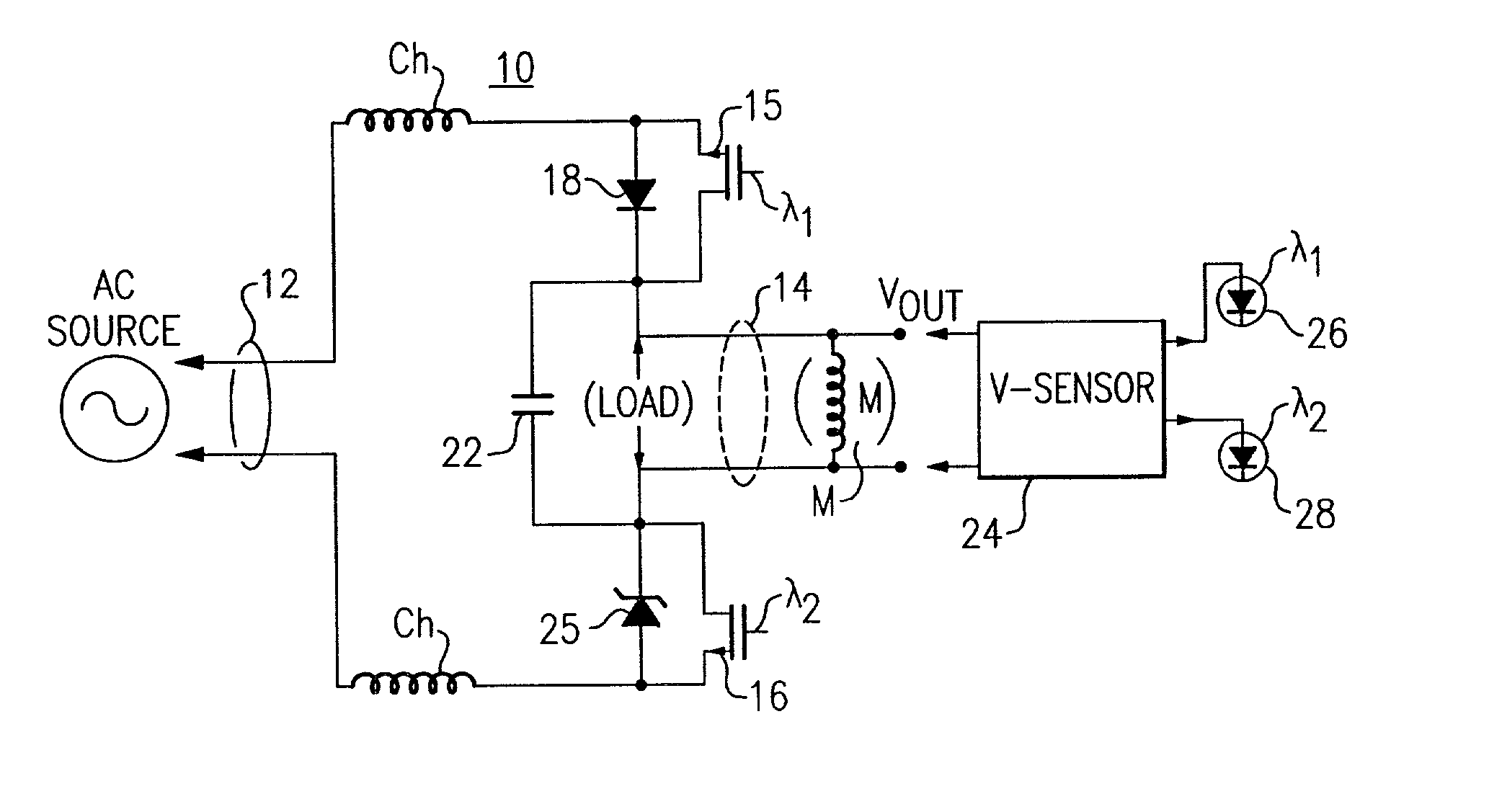
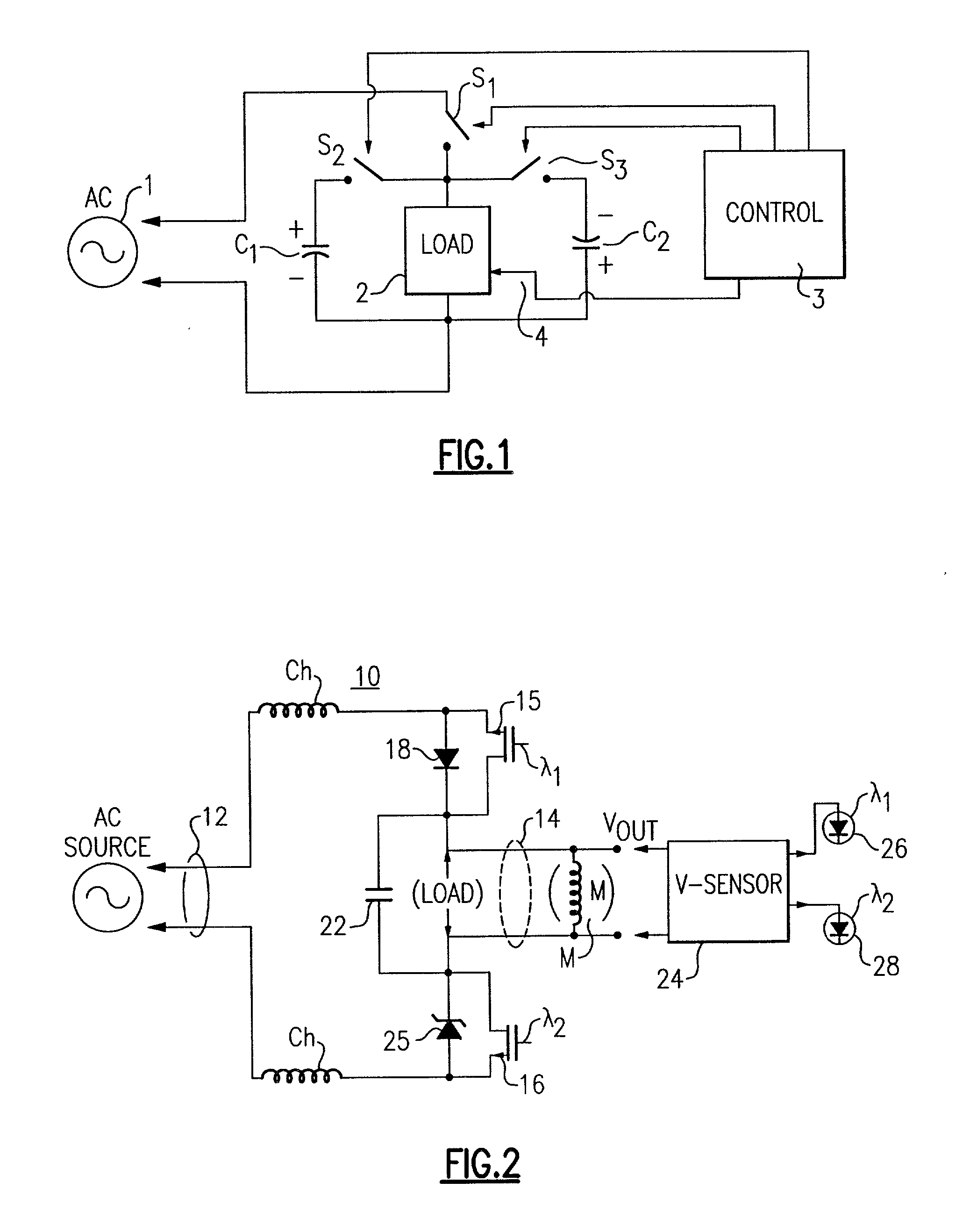
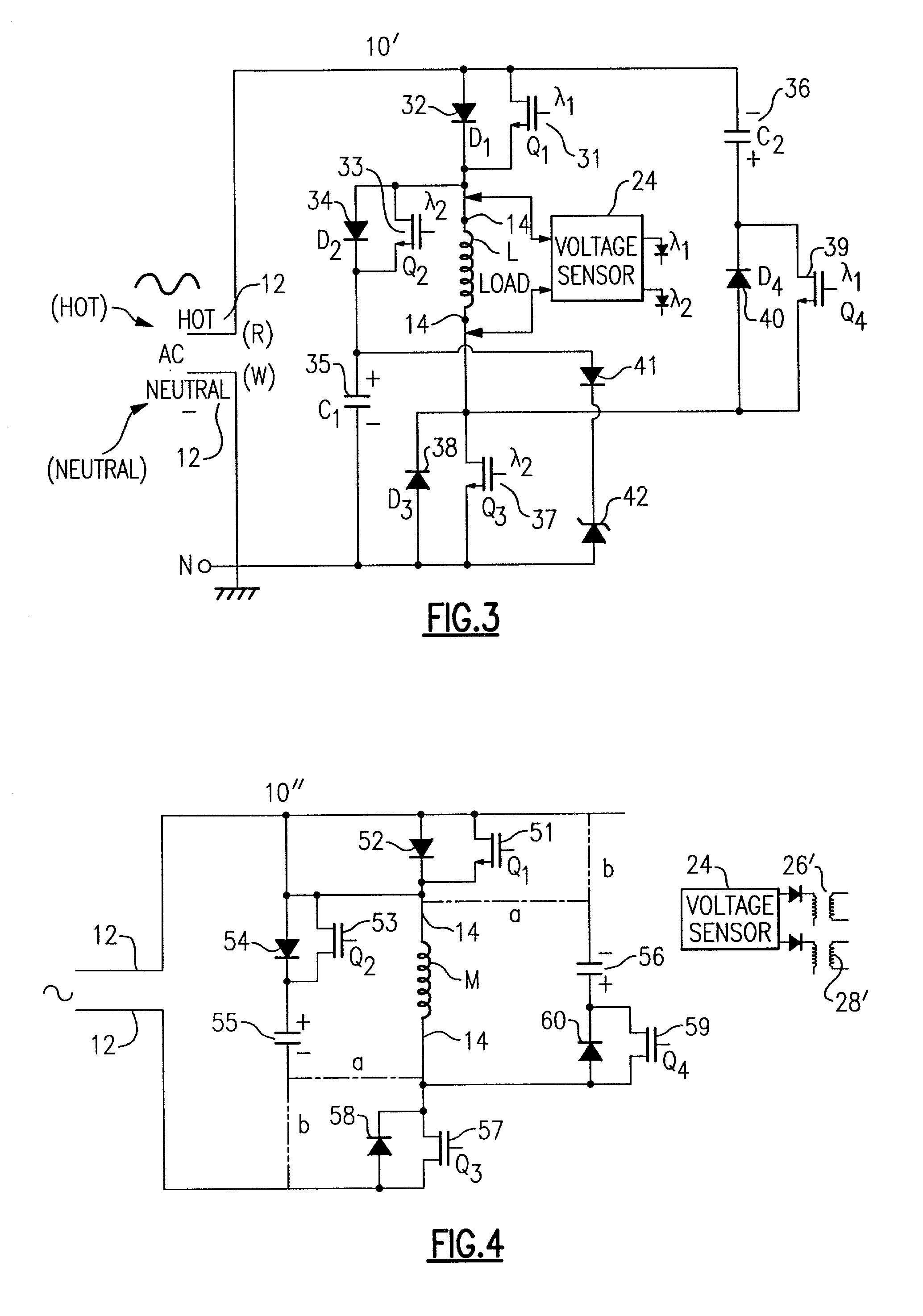
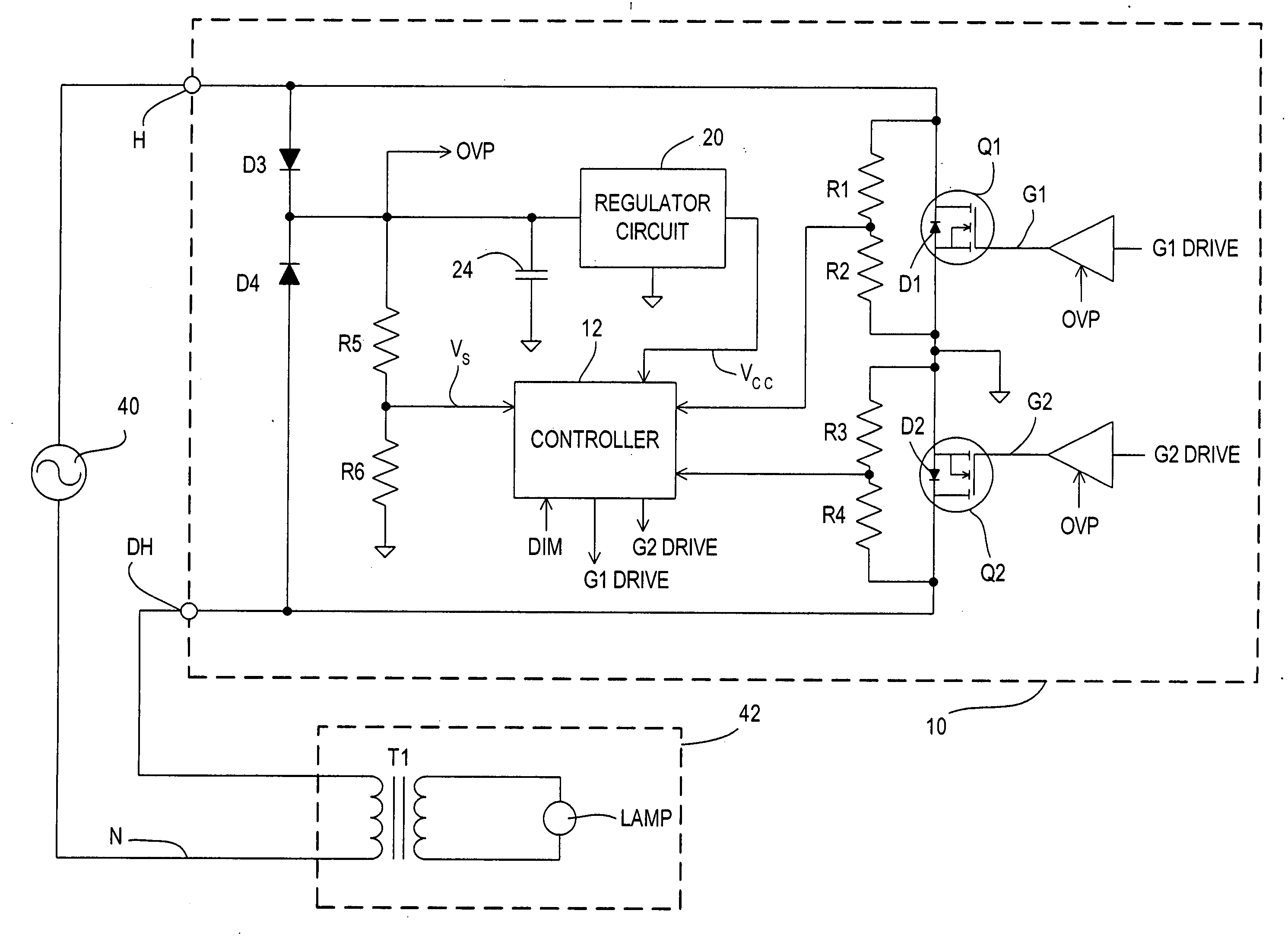
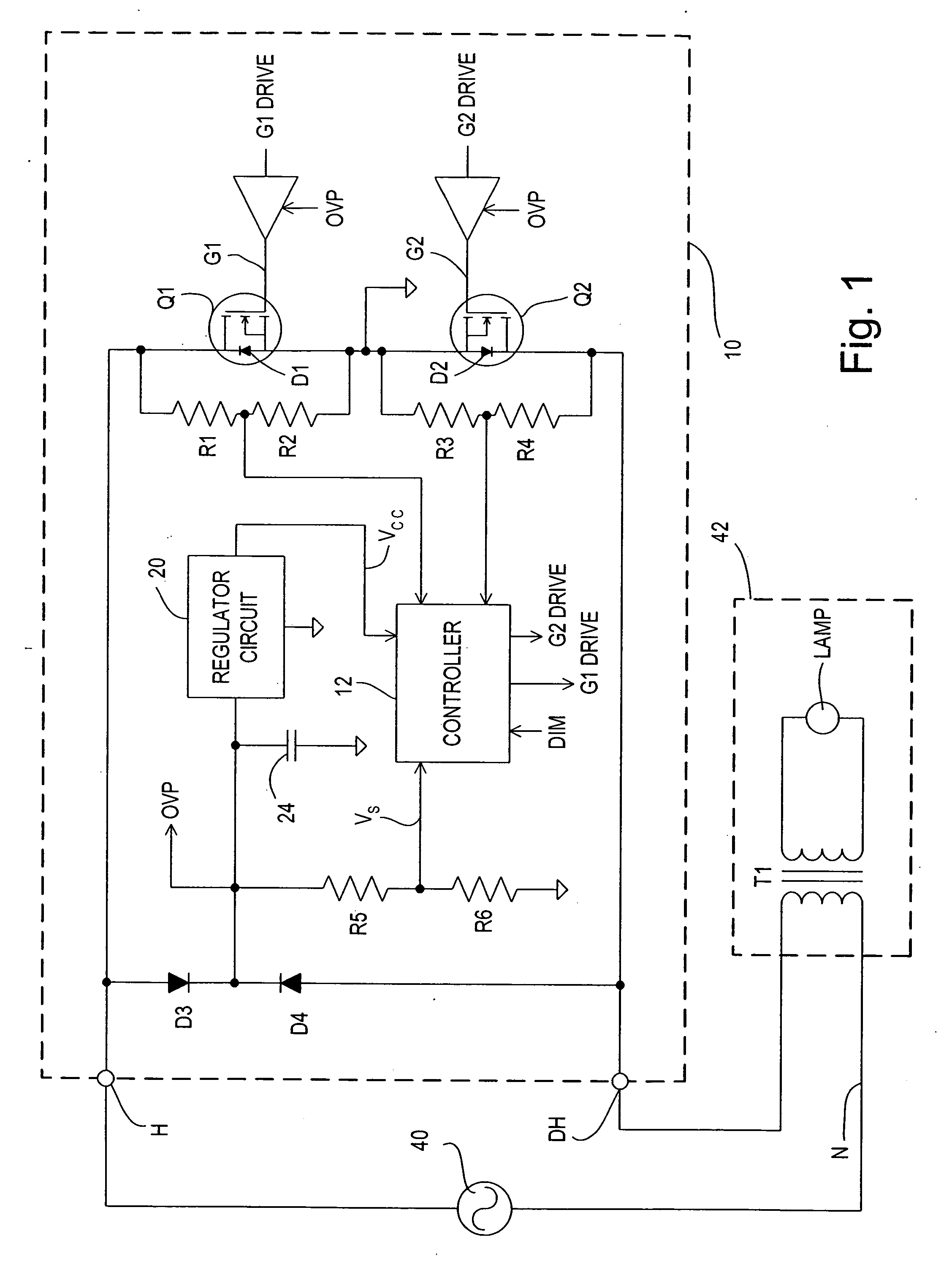
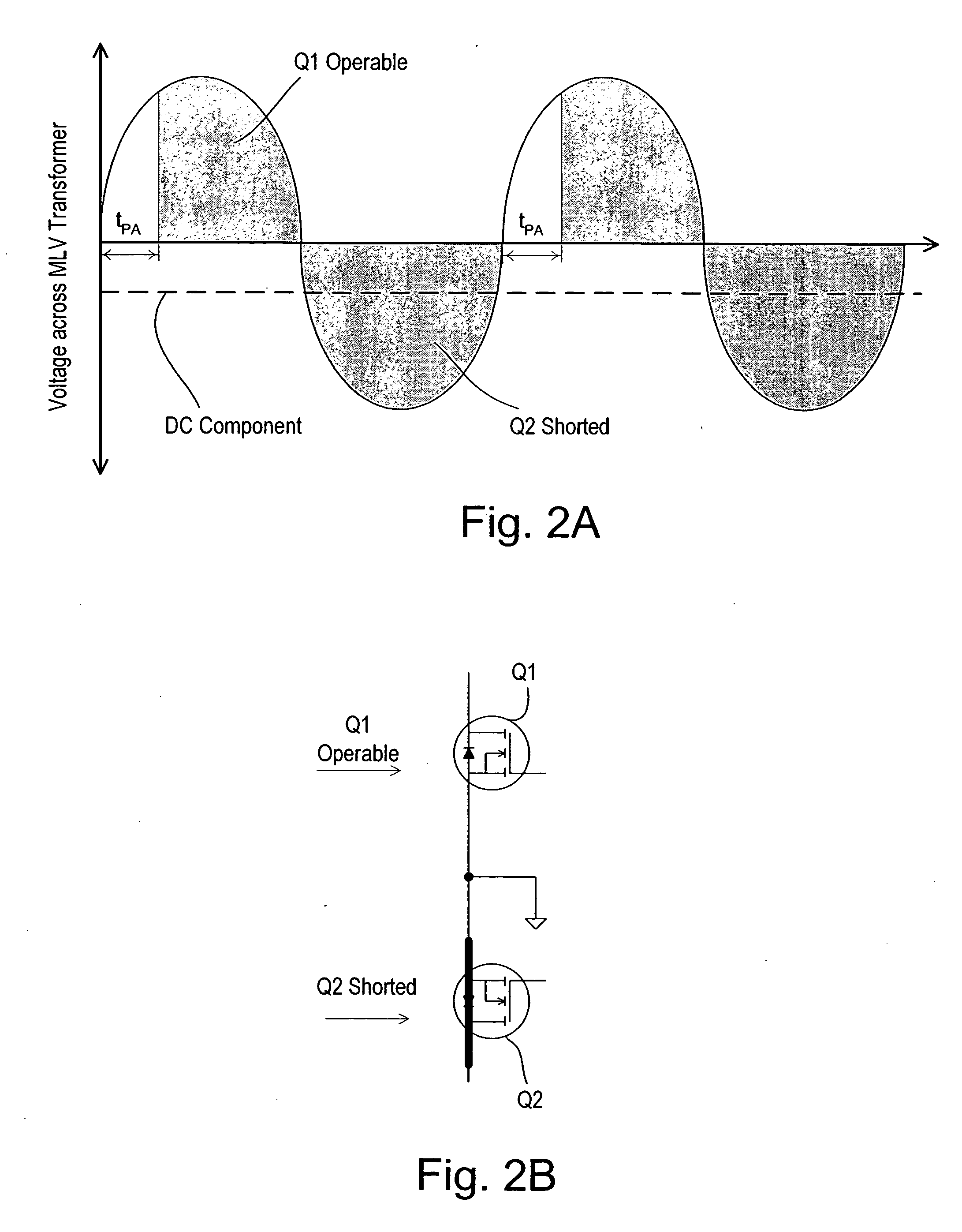
ActiveUS20060255746A1Minimizing over-heatingProtect the loadElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementTransformerControl signal
A dimmer circuit for providing AC power from an AC voltage source to an inductive lighting load disposed in series with the dimmer circuit, comprising: a bidirectional semiconductor switch having at least one control electrode provided with a control signal for controlling the amount of power provided to the load, the switch in normal operation being able to be controlled to block voltage in first and second opposite polarity half-cycles of the AC voltage source but in a failure mode being able to block the AC voltage source in only one polarity half-cycle of the AC voltage source and not being able to block the AC voltage source in the second opposite polarity half-cycle; a controller for the switch for determining if said failure mode of the switch occurs which can cause an asymmetry between the half-cycles delivered to the load and thus a DC voltage component to be delivered to the load; a power supply for supplying power to the controller and provided with power across the dimmer circuit; the controller controlling the switch if such failure mode occurs so as to: drive the switch into substantially full conduction during most of the half-cycle which the switch is able to control; and drive the switch into non-conduction for a brief duration of time during that same half-cycle so as to prevent a DC voltage component supplied to the load from exceeding a predetermined level below which excessive transformer heating does not occur, thereby minimizing overheating of the inductive load and enabling the power supply for the controller to be provided with sufficient voltage from the AC voltage source to enable the controller to continue to operate.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Drive circuit for reducing inductive kickback voltage
InactiveUS7639064B2Reduce voltageReduce chip sizeTransistorElectronic switchingTime segmentEngineering
In one embodiment a drive circuit includes two comparators which are adapted to sense kickback voltage generated in an inductive load and conduct two field-effect transistors connected to ground in a very short period of time so as to quickly reduce the kickback voltage to a minimum value. In another embodiment only one comparator is provided.
Owner:EUTECH MICROELECTRONICS
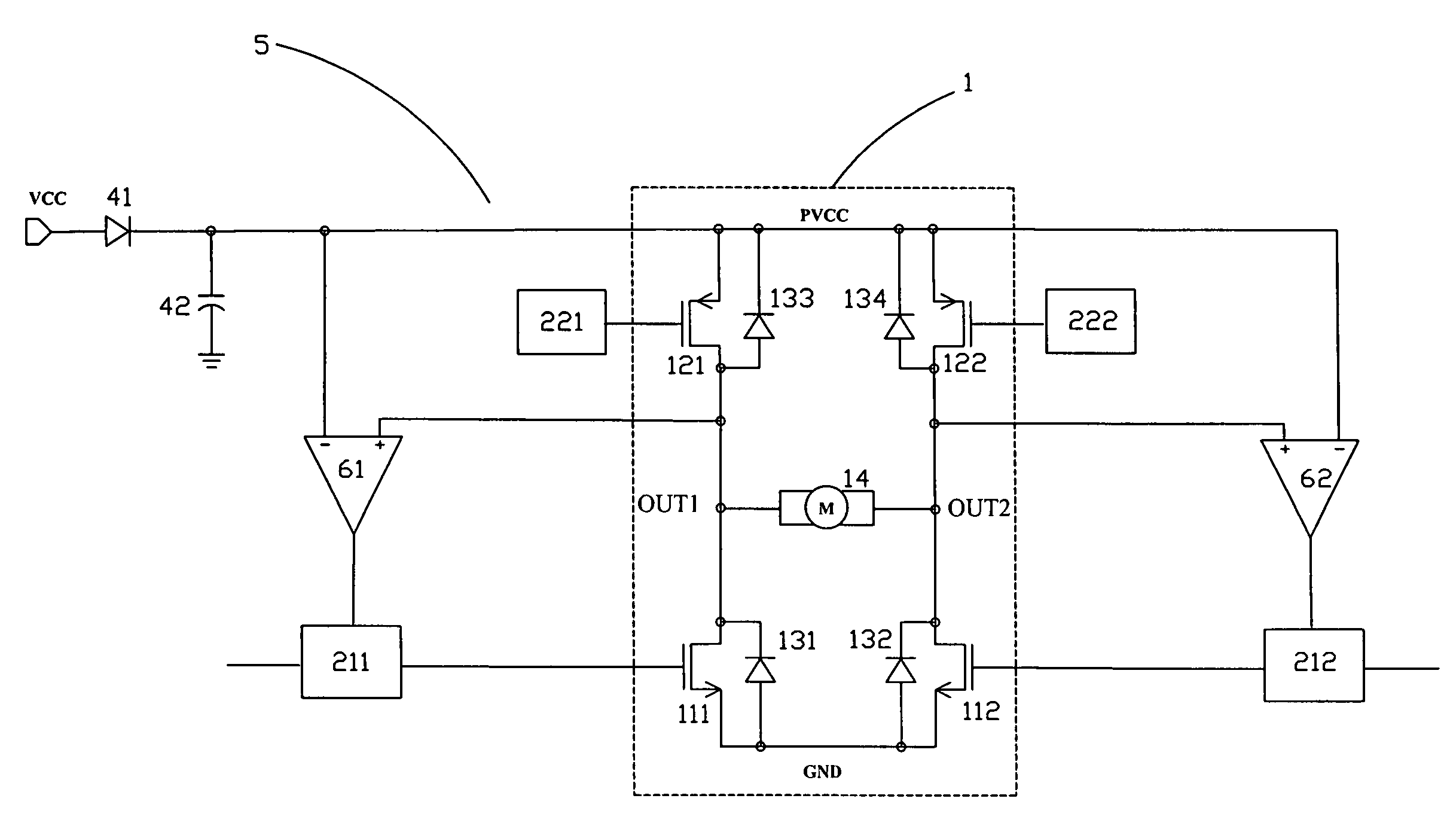
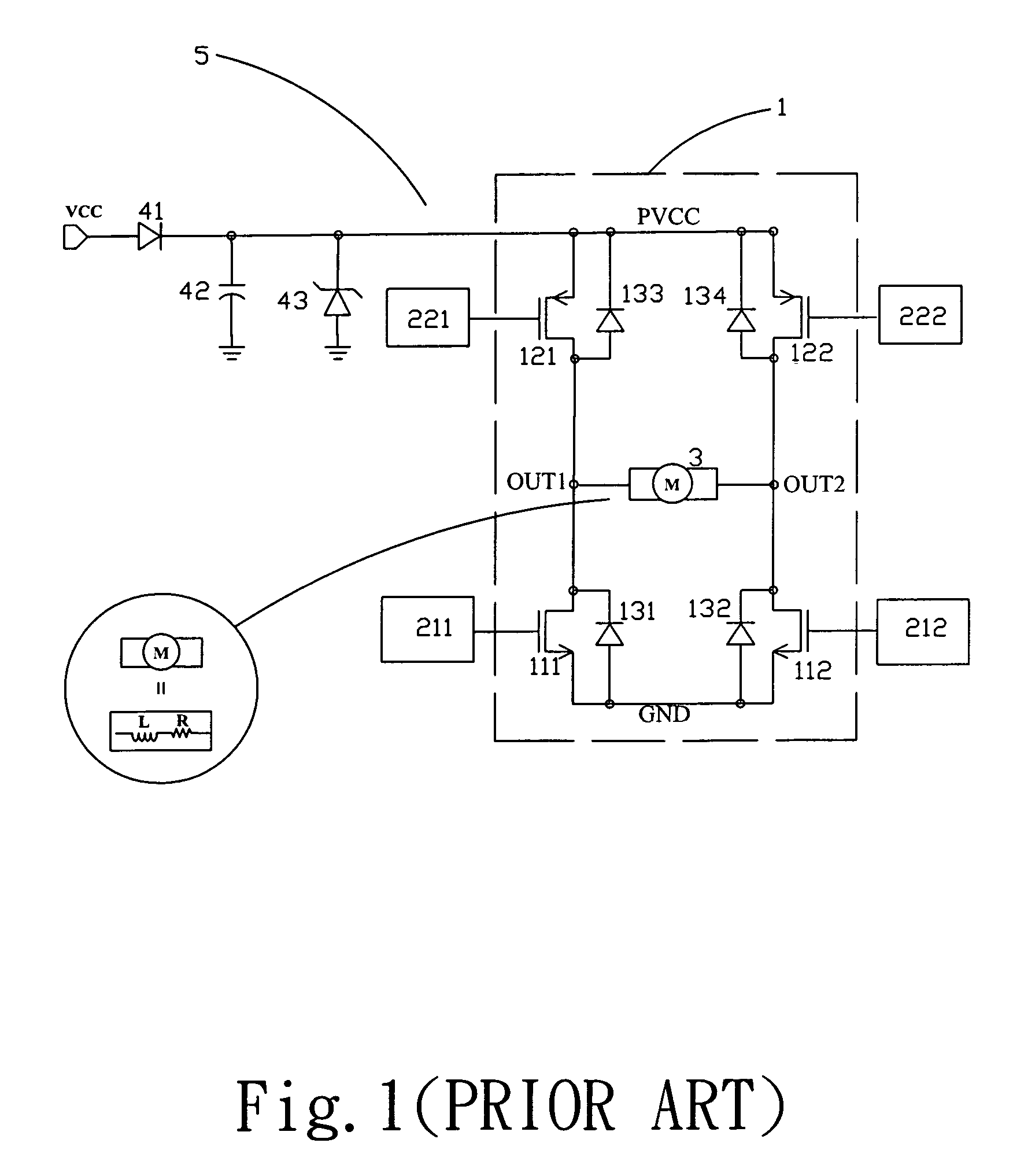
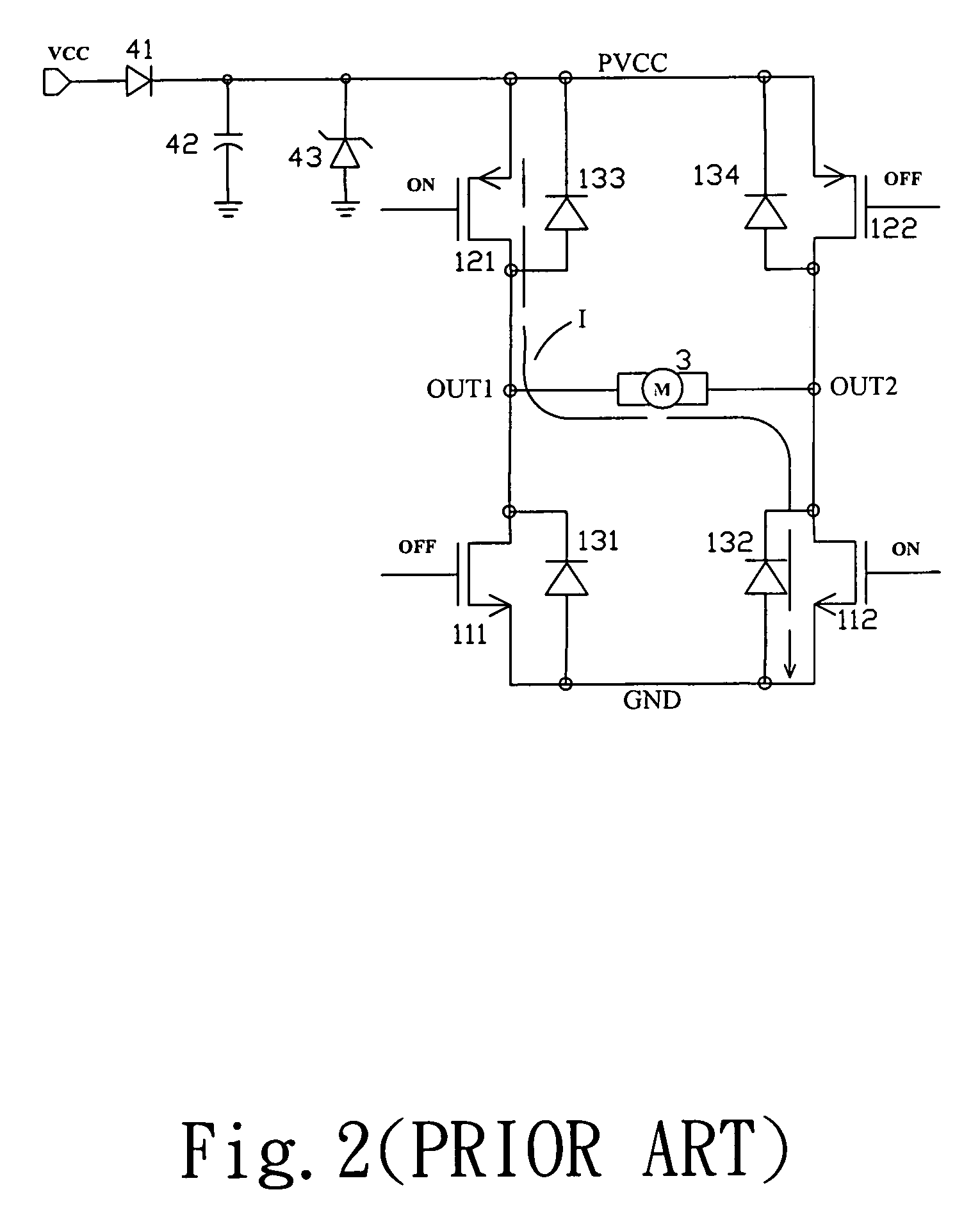
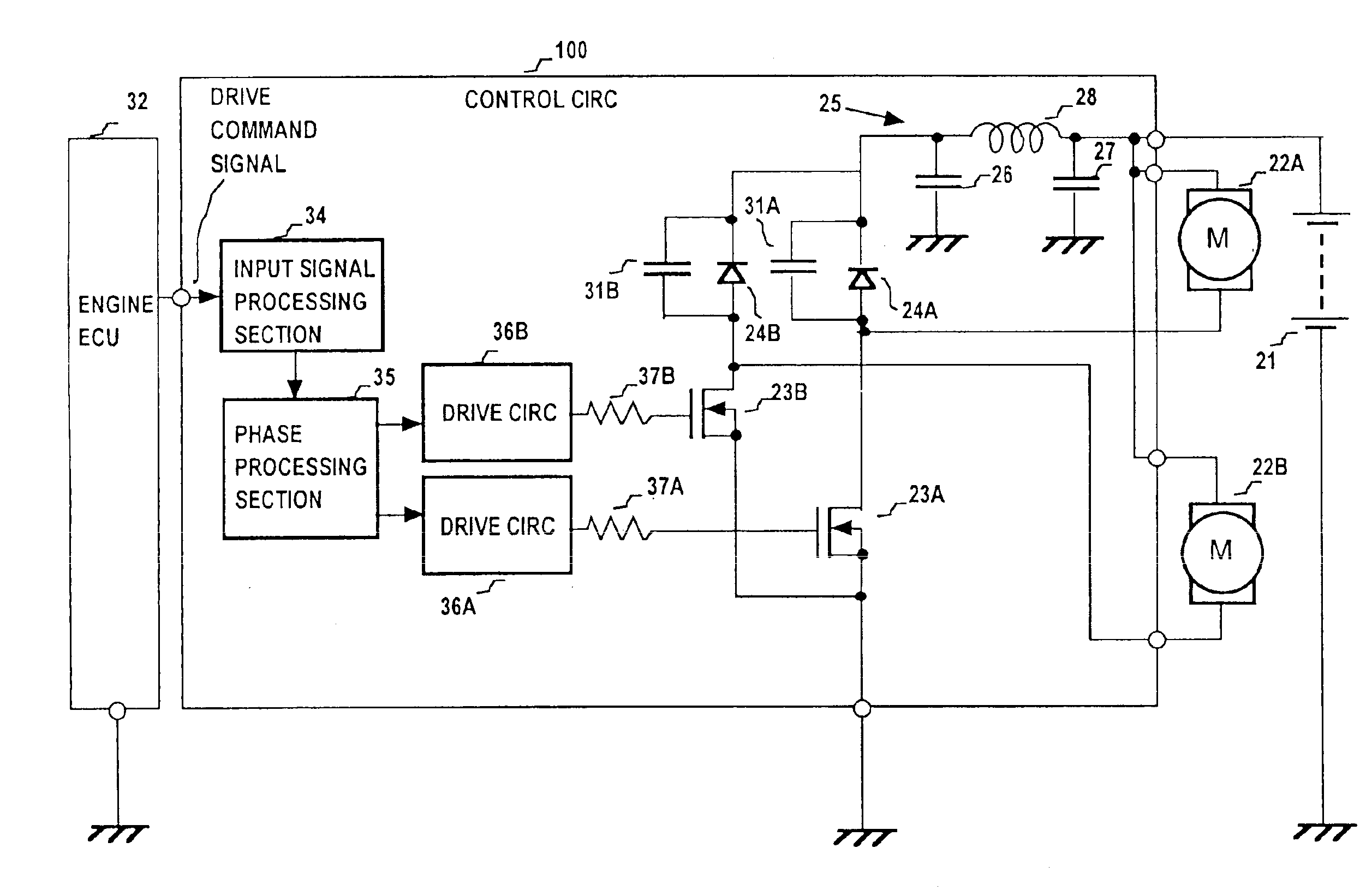
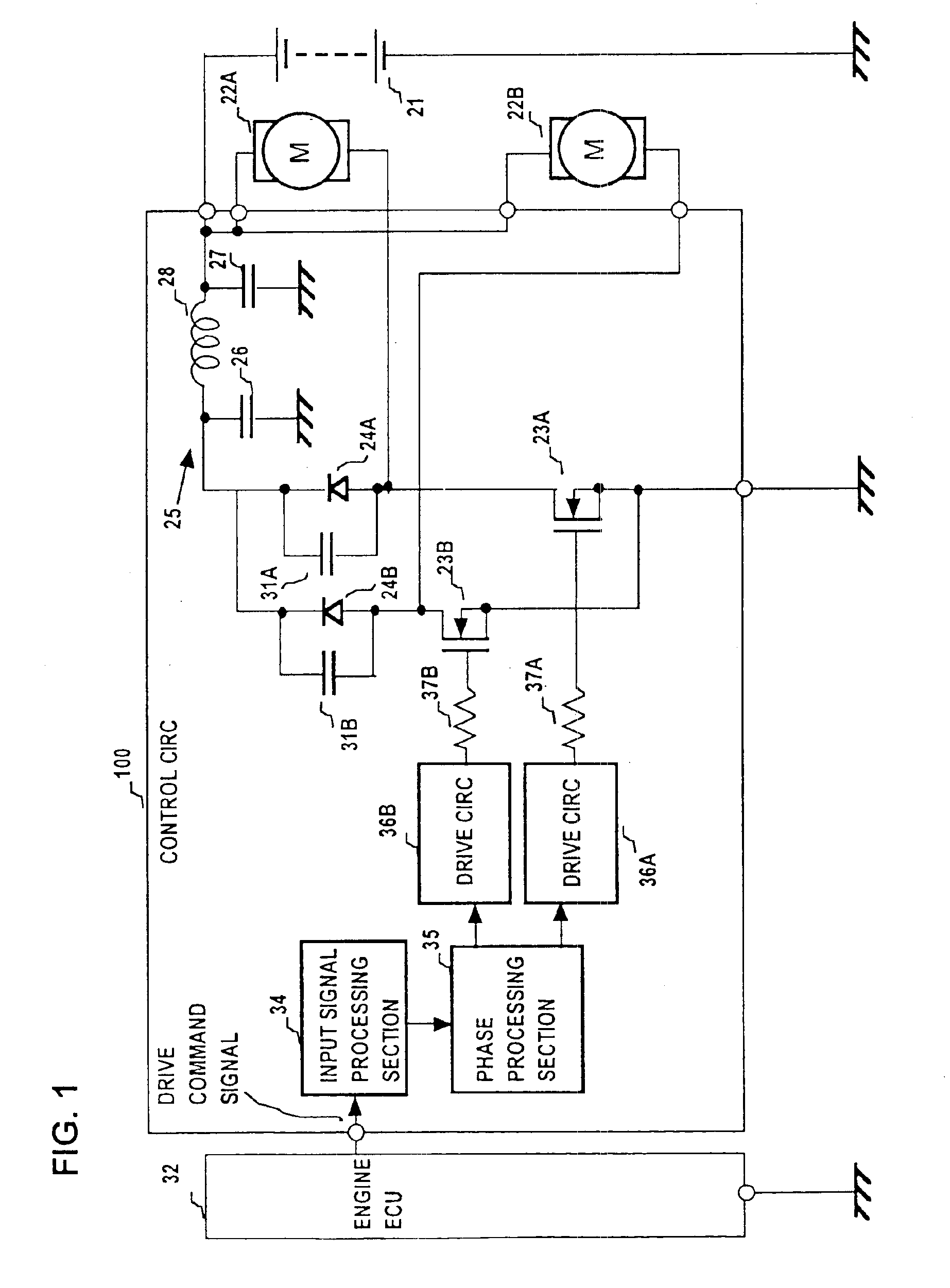
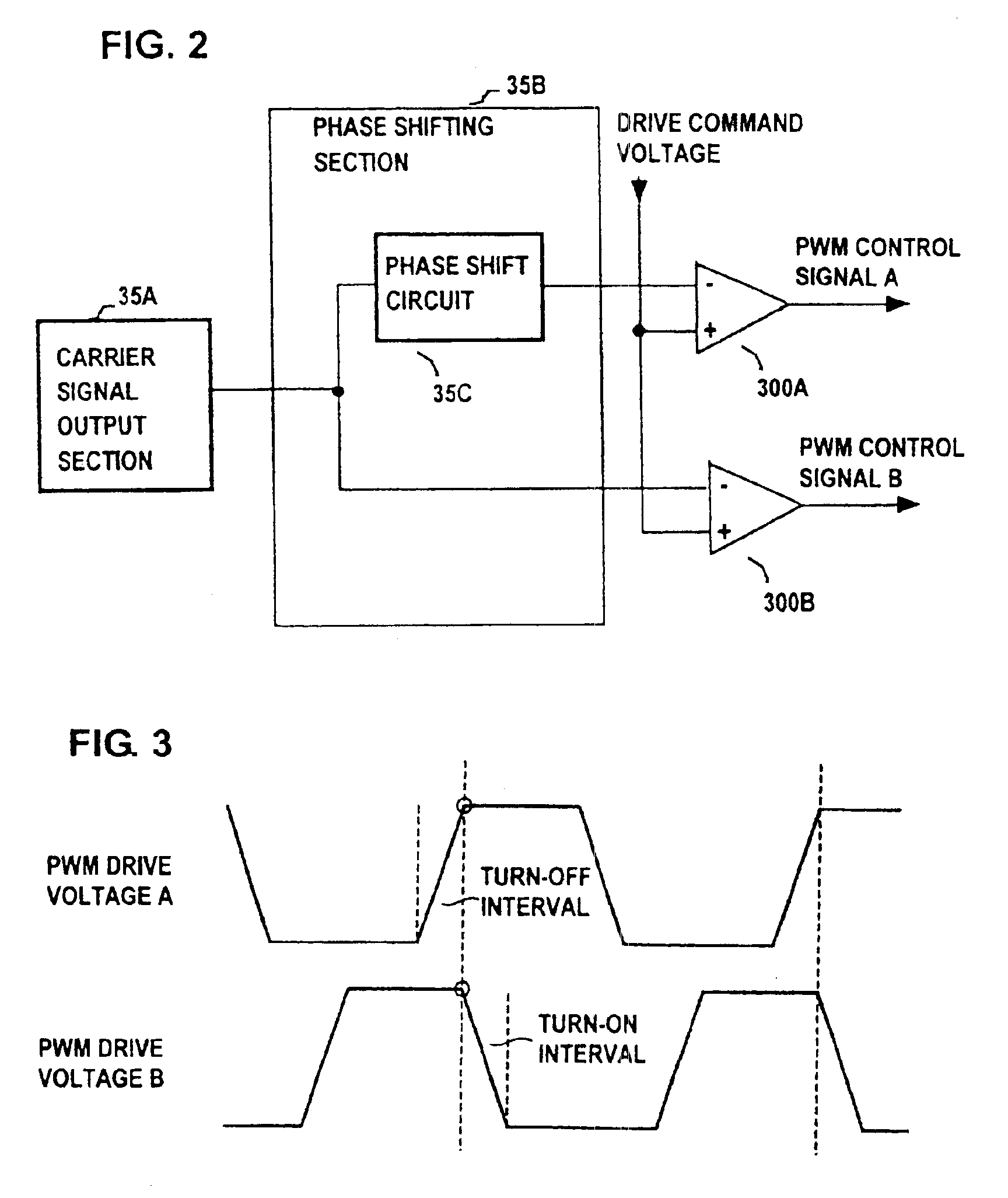
Drive apparatus for PWM control of two inductive loads with reduced generation of electrical noise
InactiveUS6891342B2Lower levelReduce generationAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlControl signalInductive load
A drive apparatus for driving two motors by PWM control of respective switching elements connected to the motors, whereby respective control signals are applied to the switching elements such that each commencement of a transition of one of the switching elements from the non-conducting to the conducting state coincides with the termination of a transition of the other switching element from the conducting to the non-conducting state, thereby reducing generated electrical noise, and for supplying equivalent values of drive voltage to two motors of different power ratings which rotate respective cooling fans, to obtain equalized levels of air flow rate.
Owner:DENSO CORP
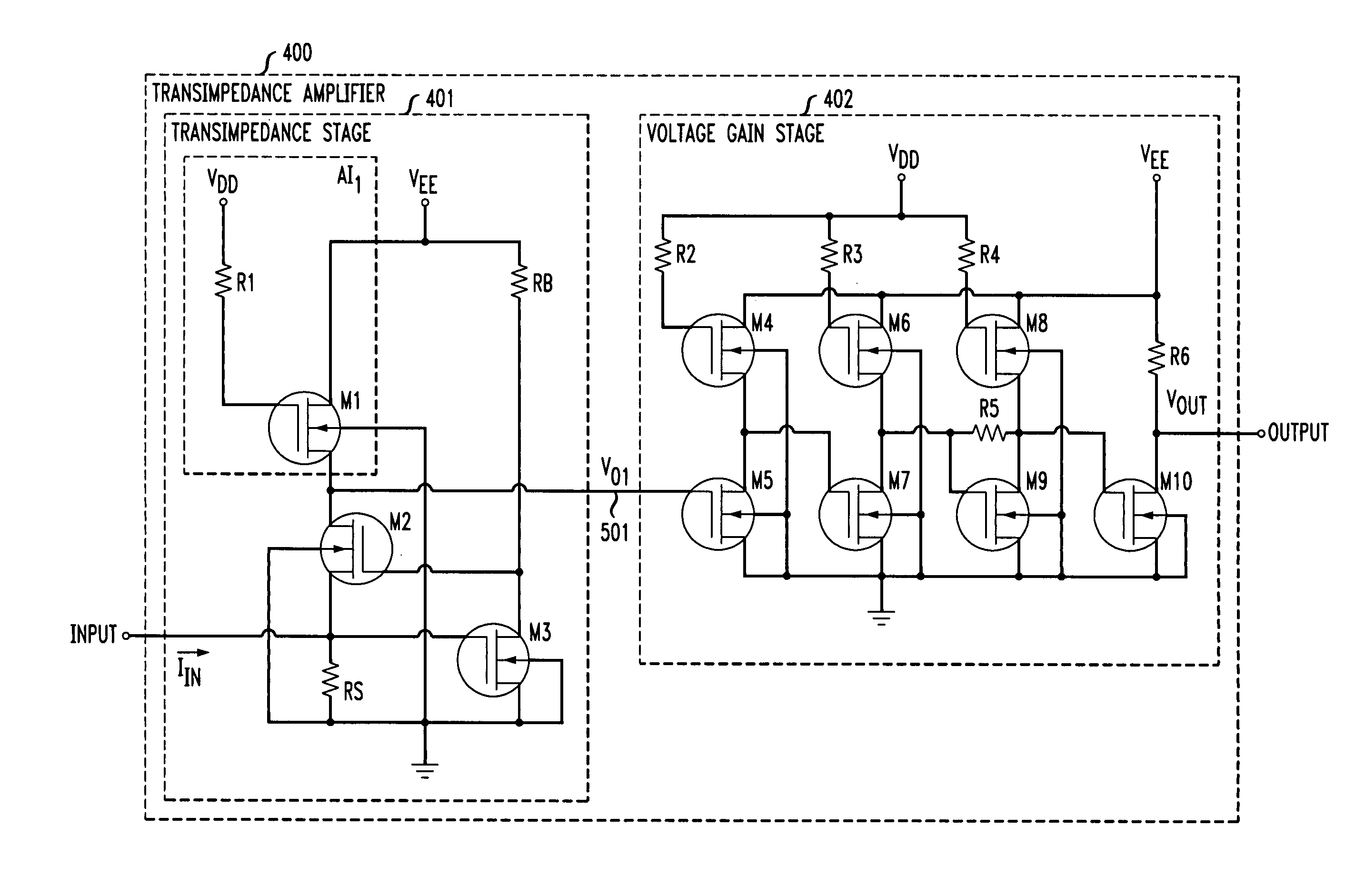
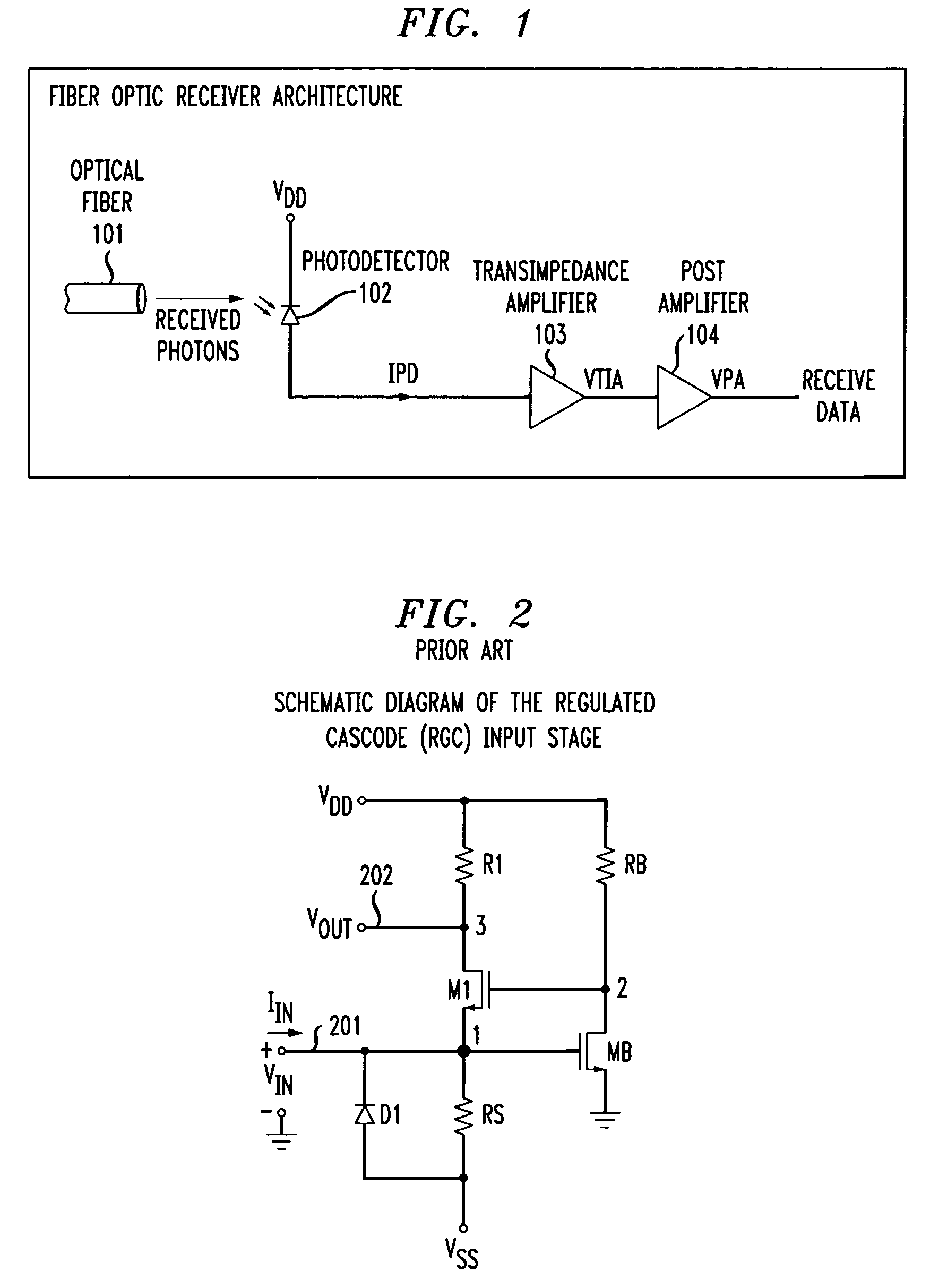
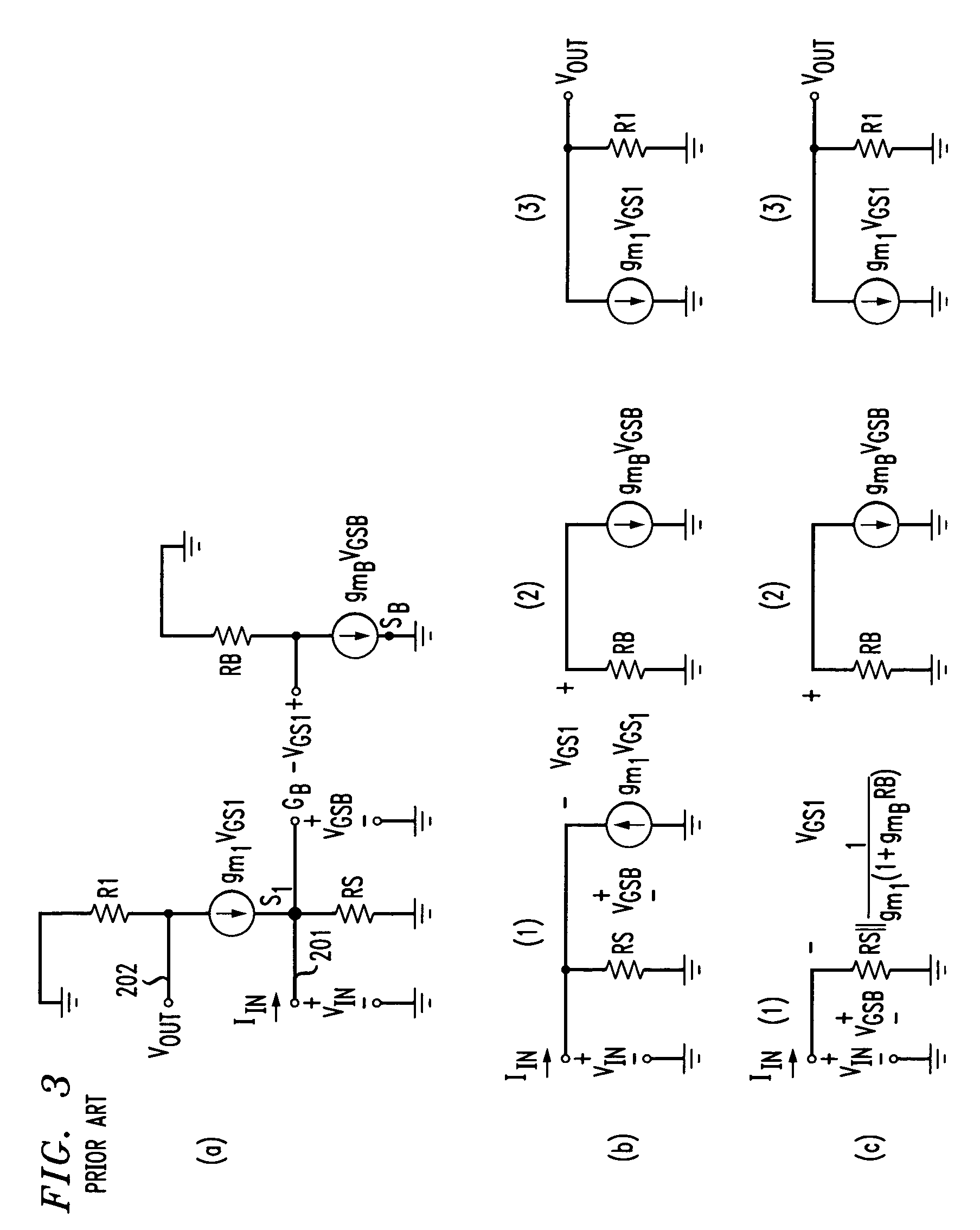
Transimpedance amplifier
InactiveUS7135932B2Minimise currentWide bandwidthAmplifier combinationsAmplifiers controlled by lightAudio power amplifierEngineering
A transimpedance amplifier, which is useful as an optical fiber preamplifier, is disclosed. The illustrative embodiment exhibits four characteristics. First, it minimizes the equivalent input noise current. Second, it has a wide bandwidth. Third, it has a reasonably large output voltage, and fourth, it is stable over wide temperature and voltage ranges. The illustrative embodiment comprises a transimpedance stage and a gain stage. Both stages employ a pure NMOS design which contributes to the above four advantages. Bandwidth is further increased over the prior art by the use of inductive loads. The inductive loads of the illustrative embodiment are not physical inductors, but transistor-based “active” inductors: the combination of a resistor connected in series with the gate of an NMOS transistor.
Owner:SIRES LABS
Electrosurgical Apparatus With High Speed Energy Recovery
A circuit for controlling the discharging of stored energy in an electrosurgical generator includes a pulse modulator which controls an output of a power supply. At least one comparator is configured to provide an error signal to the pulse modulator based on a comparison between an output signal generated by the power supply and a feedback signal generated in response to the application of energy to tissue. A discharge circuit is configured to control the discharge of the output of the power supply to an inductive load disposed in parallel with the output of the power supply based on the comparison between the output signal and the feedback signal. The discharge circuit provides a rapid response and time rate control of the delivered electrosurgical energy by controlling the power supply and delivered RF energy in real time, based on a feedback signal generated in response to the application of energy to tissue.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
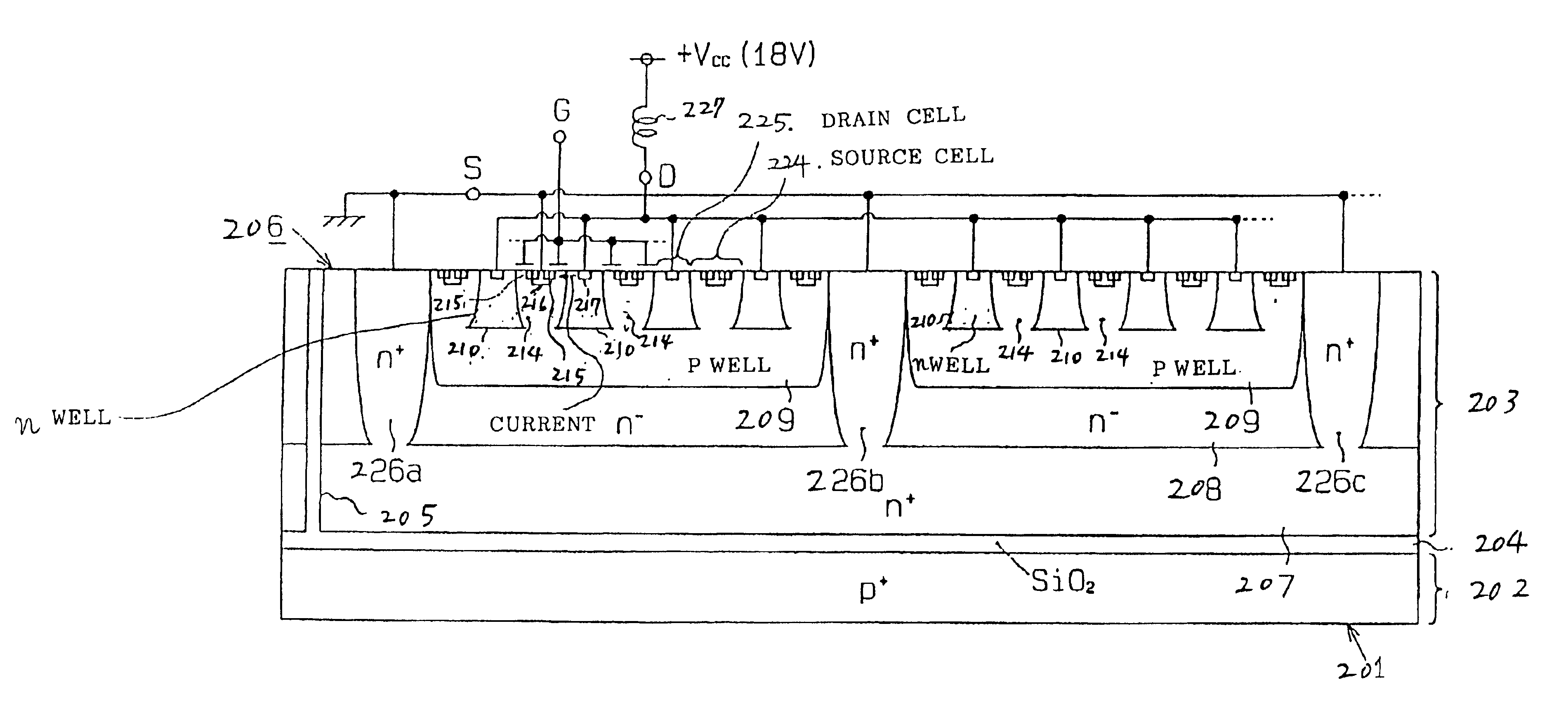
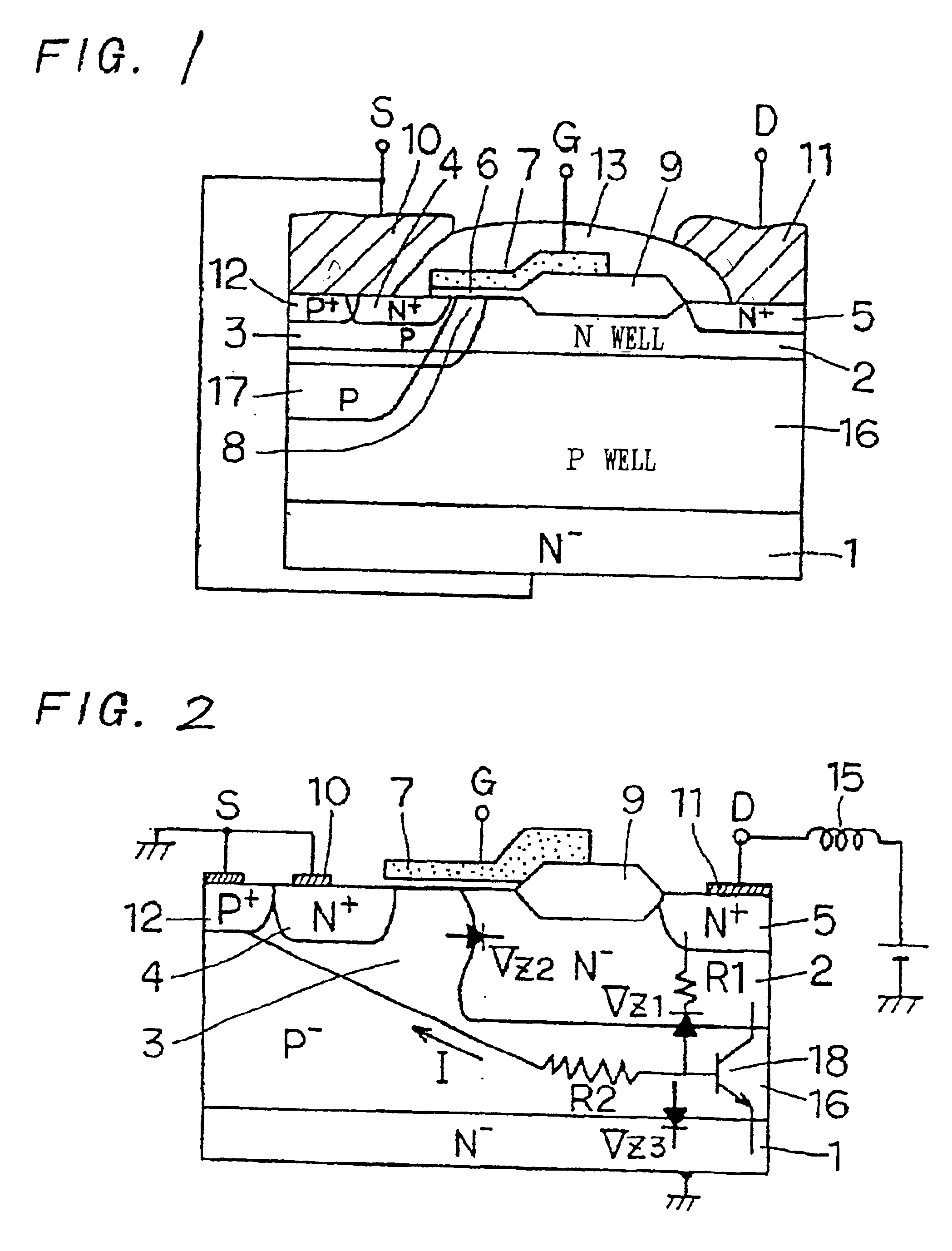
Power MOS transistor for absorbing surge current
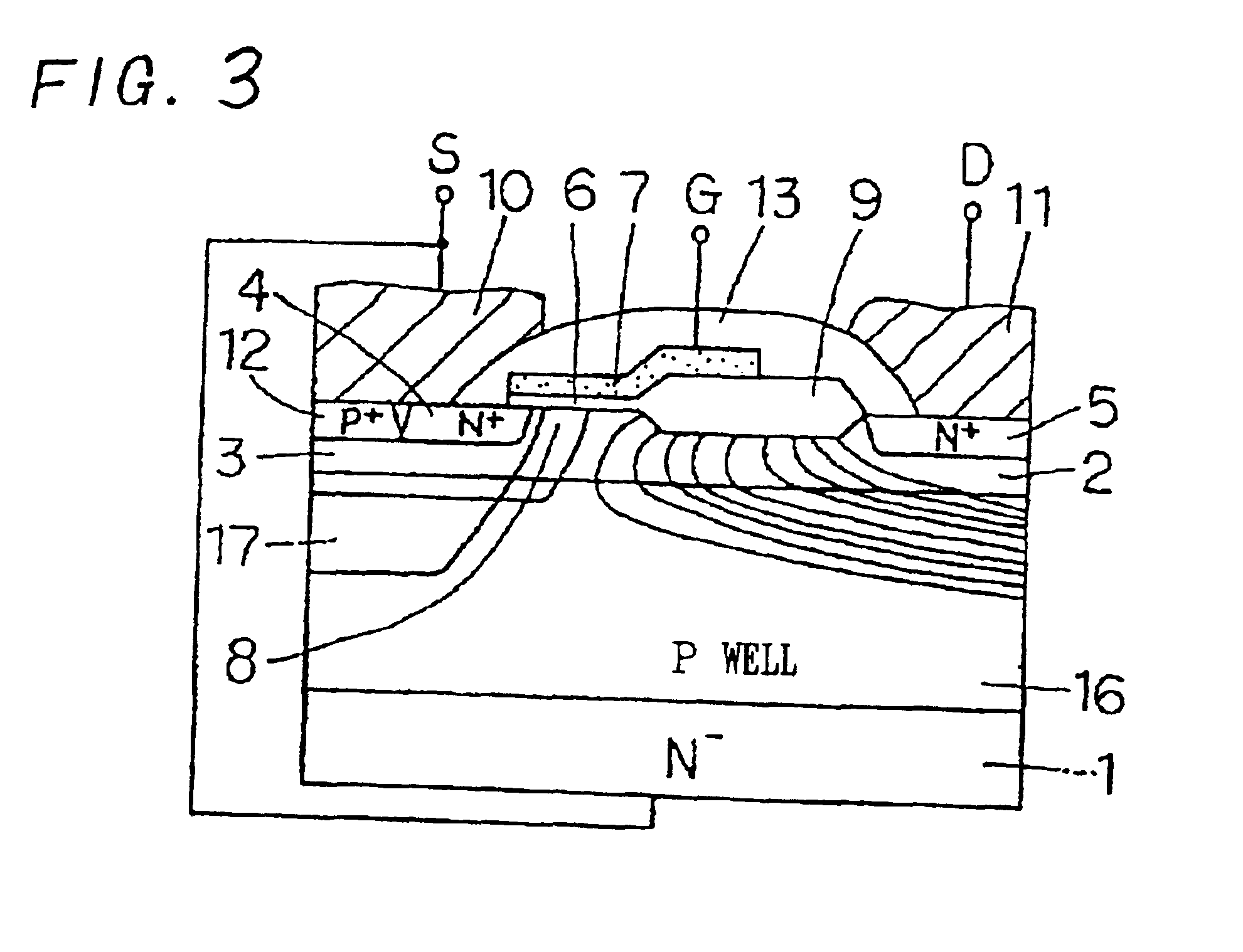
A semiconductor device is provided having a power transistor structure. The power transistor structure includes a plurality of first wells disposed independently at a surface portion of a semiconductor layer; a deep region having a portion disposed in the semiconductor layer between the first wells; a drain electrode connected to respective drain regions in the first wells; a source electrode connected to respective source regions and channel well regions in the first wells, such that either the drain electrode or the source electrode is connected to an inductive load; and a connecting member for supplying the deep region with a source potential, where the connecting member is configurable to connect to the drain electrode when the drain electrode is connected to the inductive load and to connect to the source electrode when the source electrode is connected to said inductive load.
Owner:DENSO CORP
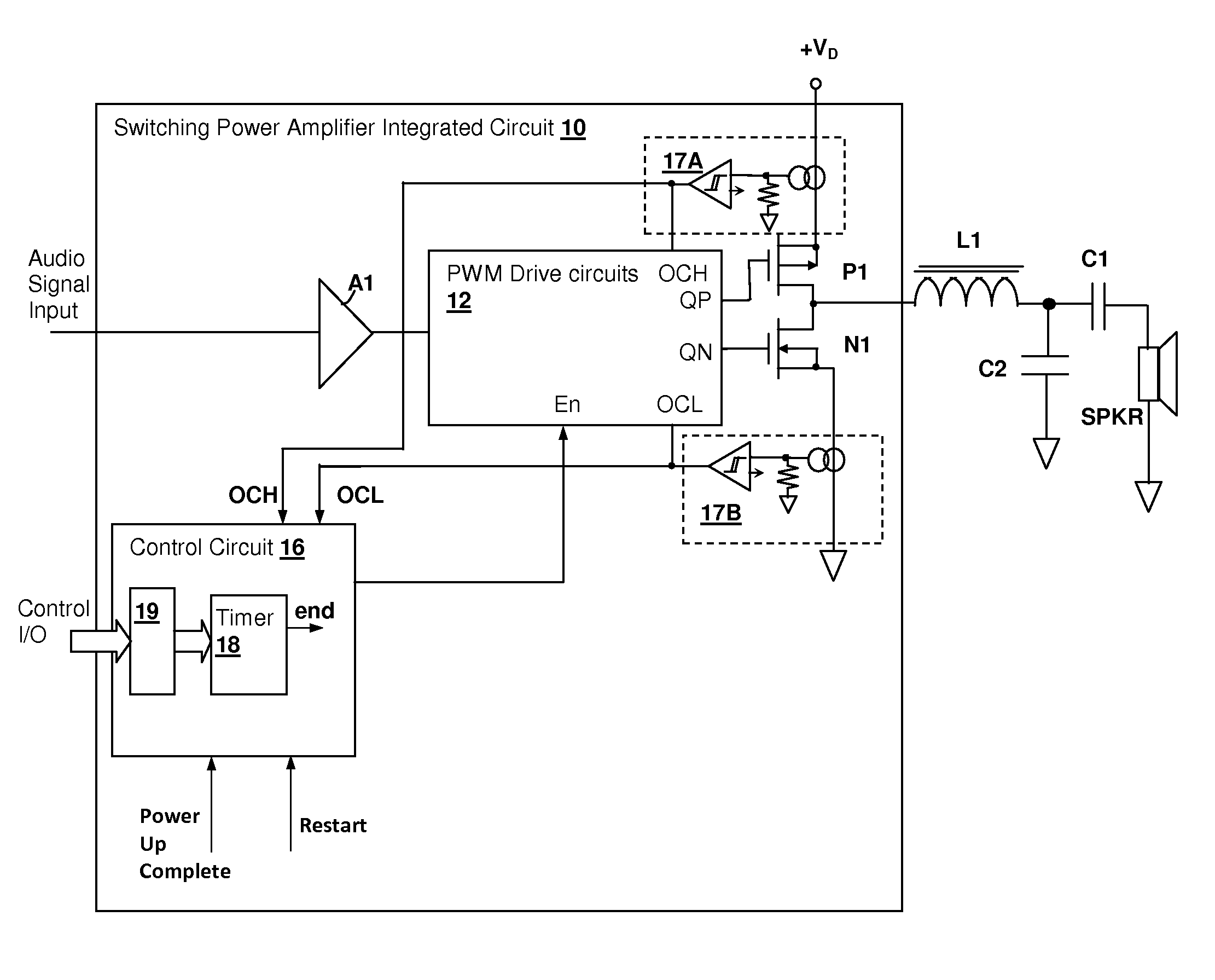
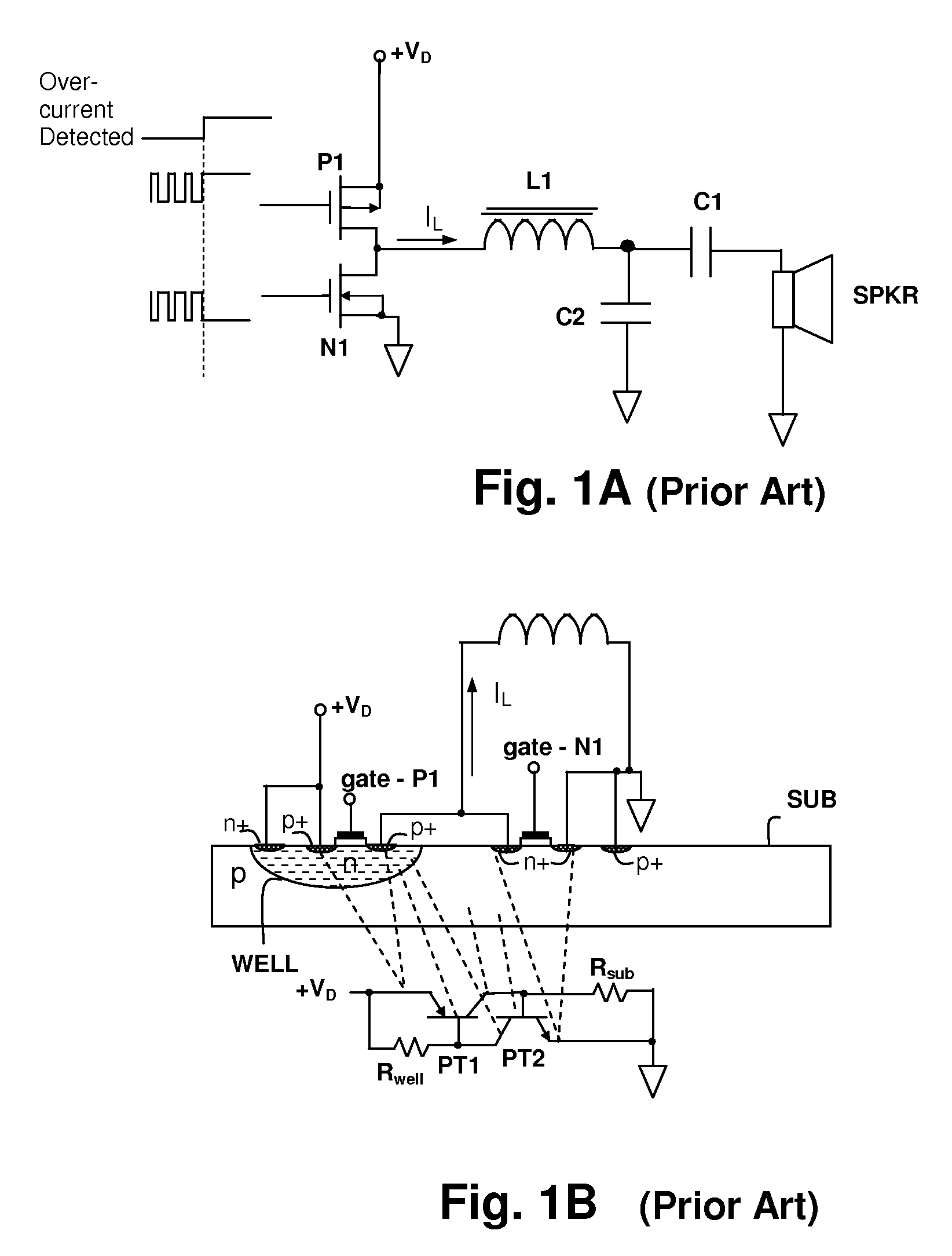
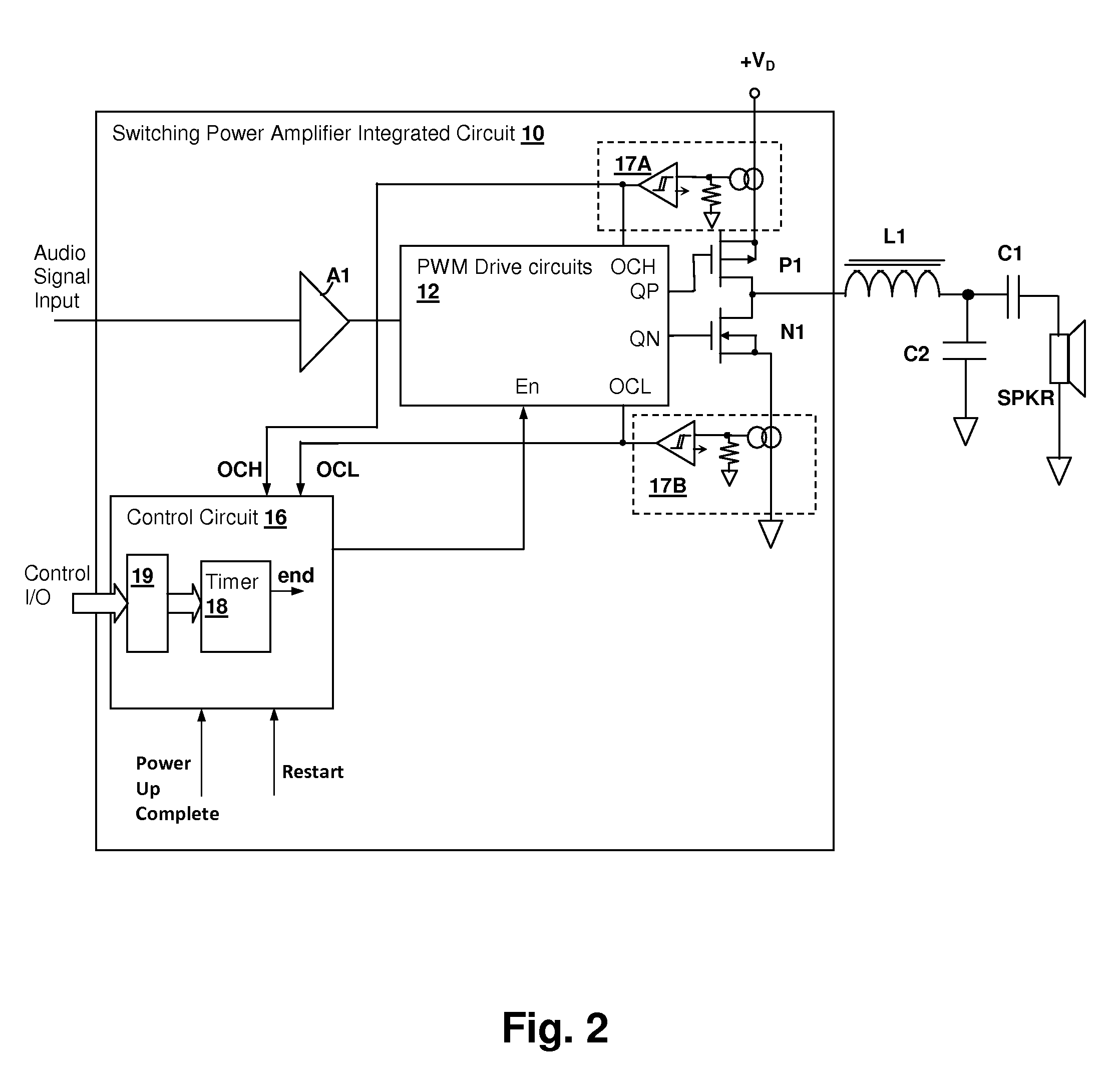
Over-current protection circuit and method for protecting switching power amplifier circuits
ActiveUS7554409B1Decreasing total stored energyWeaken energyEmergency protective circuit arrangementsLow frequency amplifiersInductive loadCircuit protection
An over-current protection circuit protection circuit and method for protecting switching power amplifier circuits provides protection against latch-up and other failures due to energy returned from an inductive load when one or more transistors in the amplifier output are disabled in response to an over-current condition. Upon detection of an over-current condition, the transistor corresponding to the over-current conduction direction is disabled. At the same time, the transistor corresponding to the conduction direction opposite the over-current direction is enabled for a predetermined time period, or until the magnitude of the load current has dropped, so that energy stored in inductance of the load is reduced, preventing back-currents that would otherwise cause latch-up and consequent destruction of the output stage when the switching power output stage is disabled. After the predetermined time period has elapsed or the load current has dropped below a threshold, the entire output stage is disabled.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
DC solid-state power switch circuit
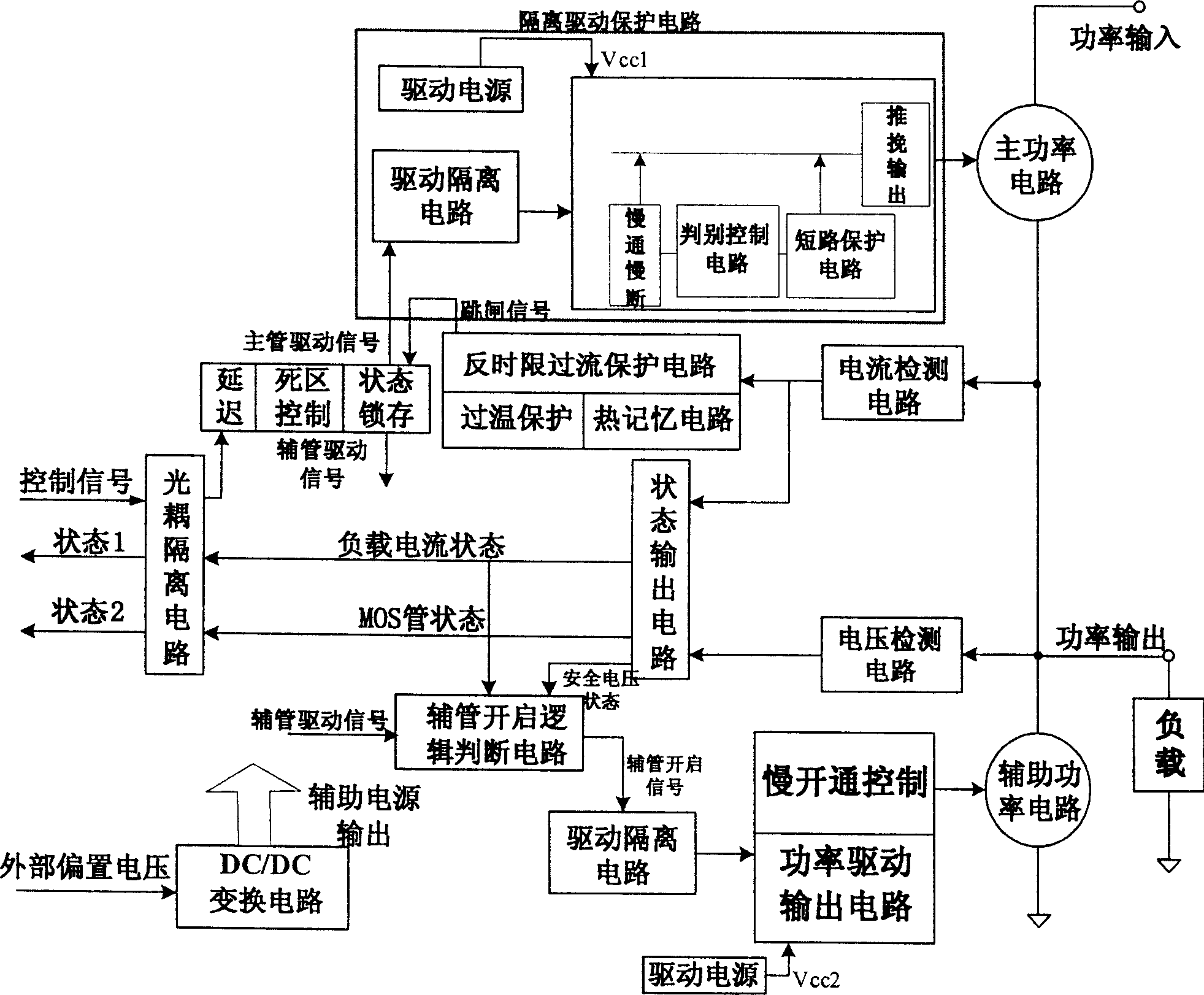
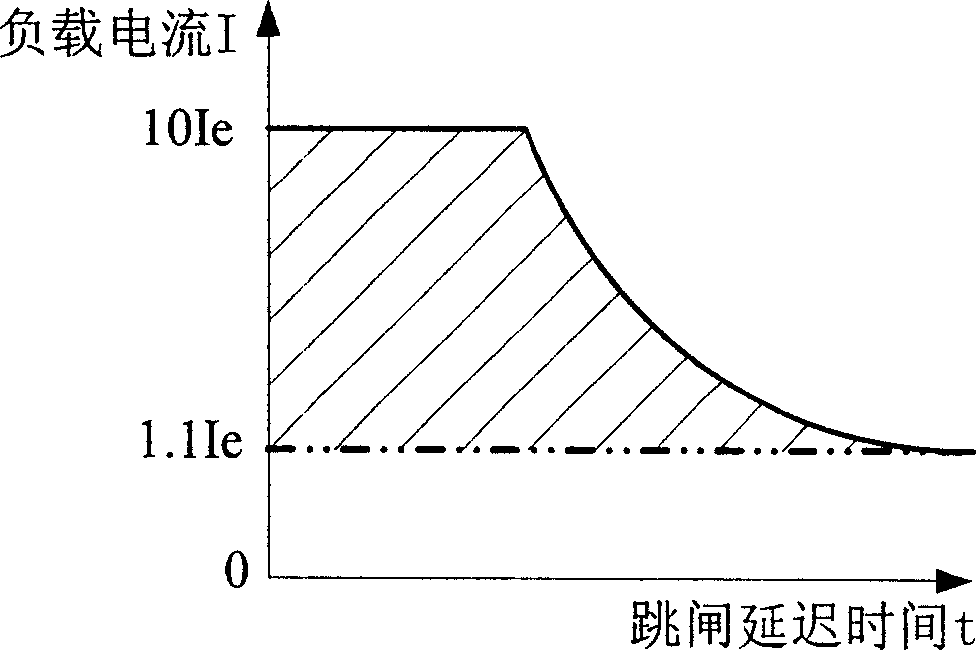
ActiveCN1667951APrecise inverse time overcurrent protection functionLimit current surgeElectronic switchingDriver circuitPush and pull
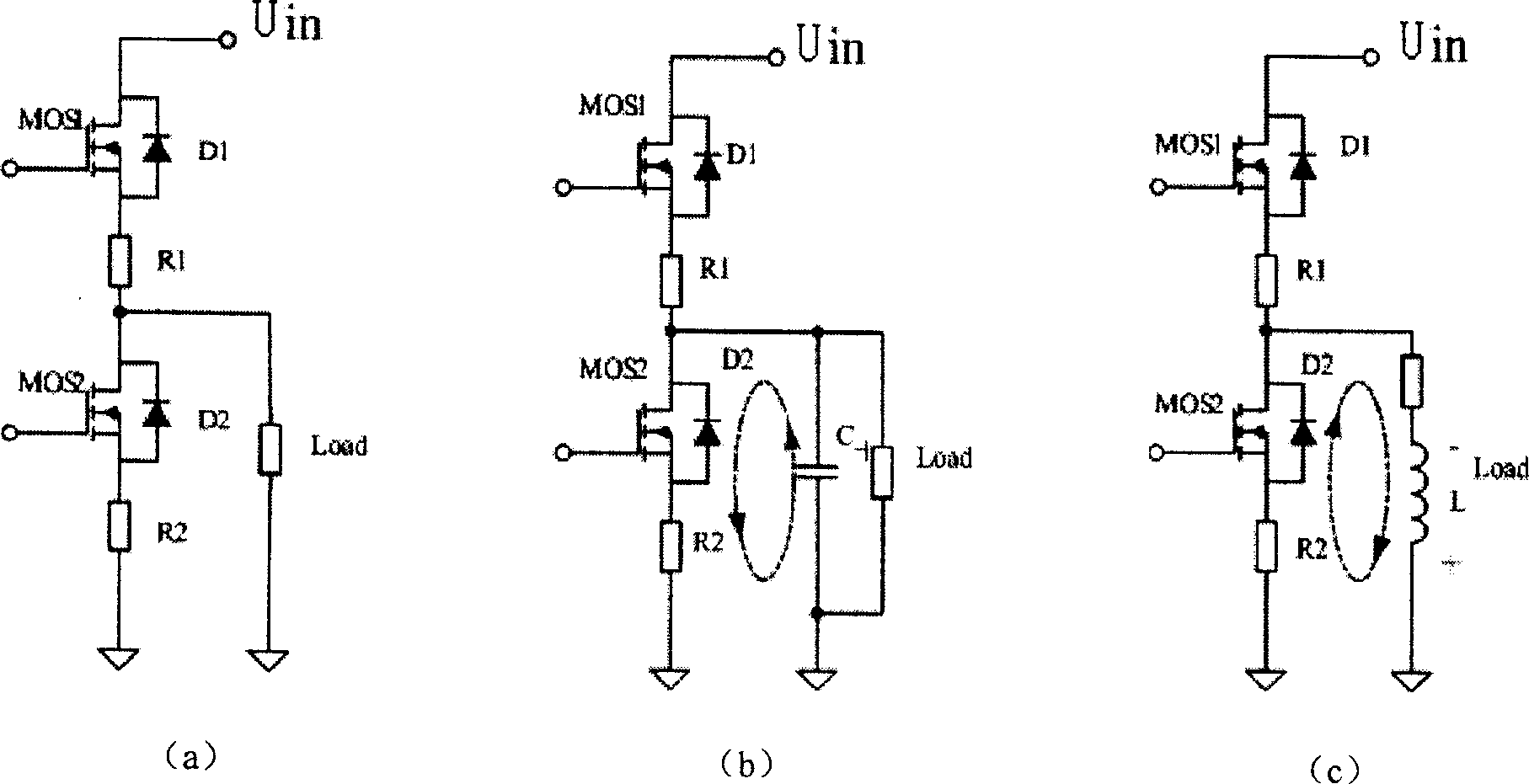
A DC solid power switch circuit includes a main power circuit, a subsidiary power circuit parallel to the load, an isolated drive protection circuit composed of a drive supply, a drive isolation circuit, a slow turned-on-off control circuit, a discriminating control circuit, a short circuit protection circuit and a push and pull output circuit, a current detection circuit, a voltage detection circuit, a main power valve drive circuit, a light-coupled isolating circuit, an assistant power valve switch-on logic circuit and a power drive output circuit, which can limit the current impulse in the period of switching on capacitive load, and suppress the peak voltage in turning off the inductive load.
Owner:SHANGHAI AVIATION ELECTRIC
Electrical power conservation apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050099131A1Save energySave componentPower network operation systems integrationCircuit arrangementsElectric forceEngineering
An electrical power control apparatus and method for power factor correction in a conventional 60 hertz or other conventional frequency electrical AC power supply communicated to an inductive load. A plurality of interruptions of current in the line on both sides of an AC current oscillation, are created to control the power factor in a circuit energizing an inductive load. Additional power factor control and correction is provided by grounding of the line during each interruption. A controller controls the length and duration of each interruption based on preprogramming or input regarding current phase read or calculated in the line.
Owner:MICROPULSE TECH
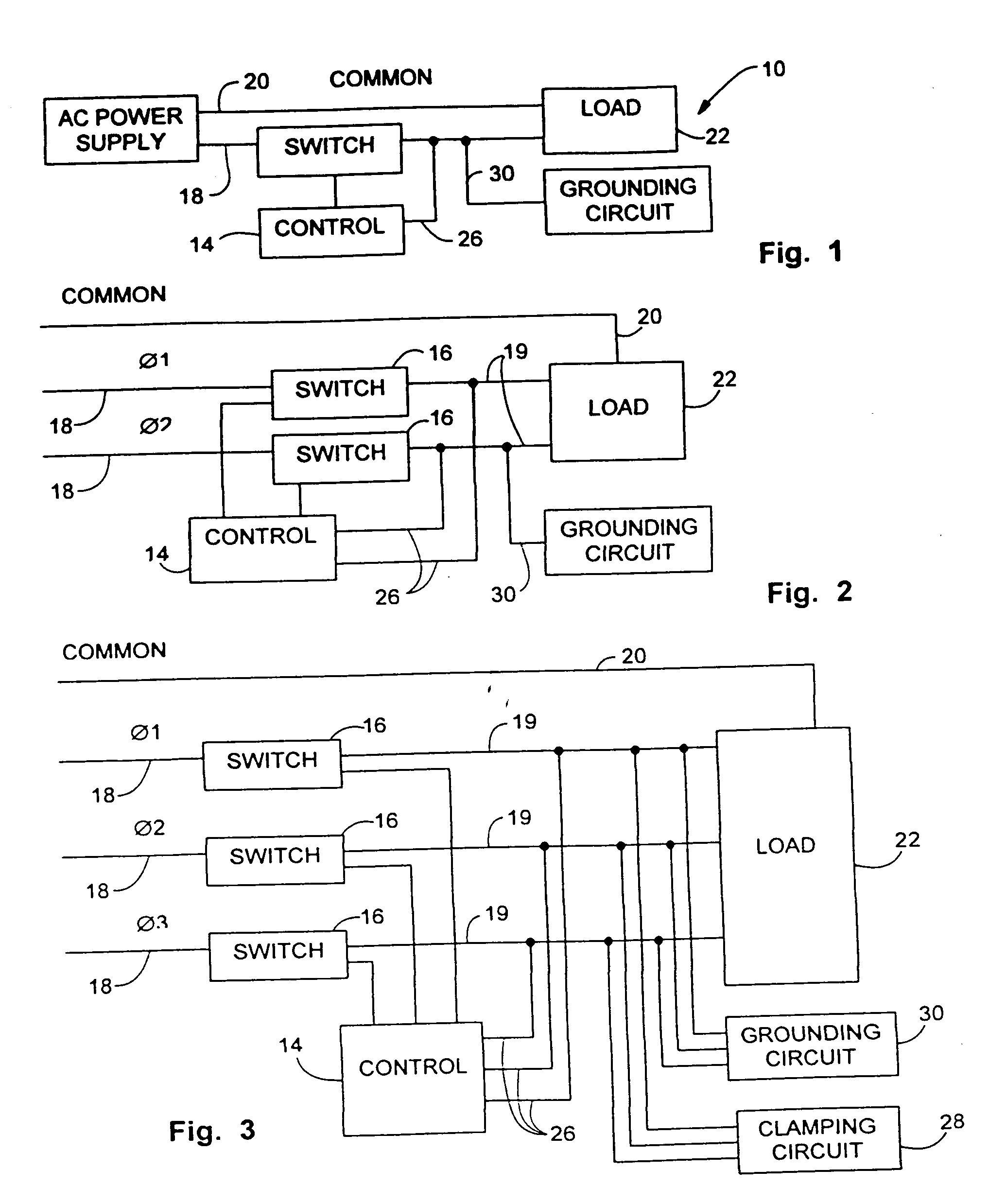
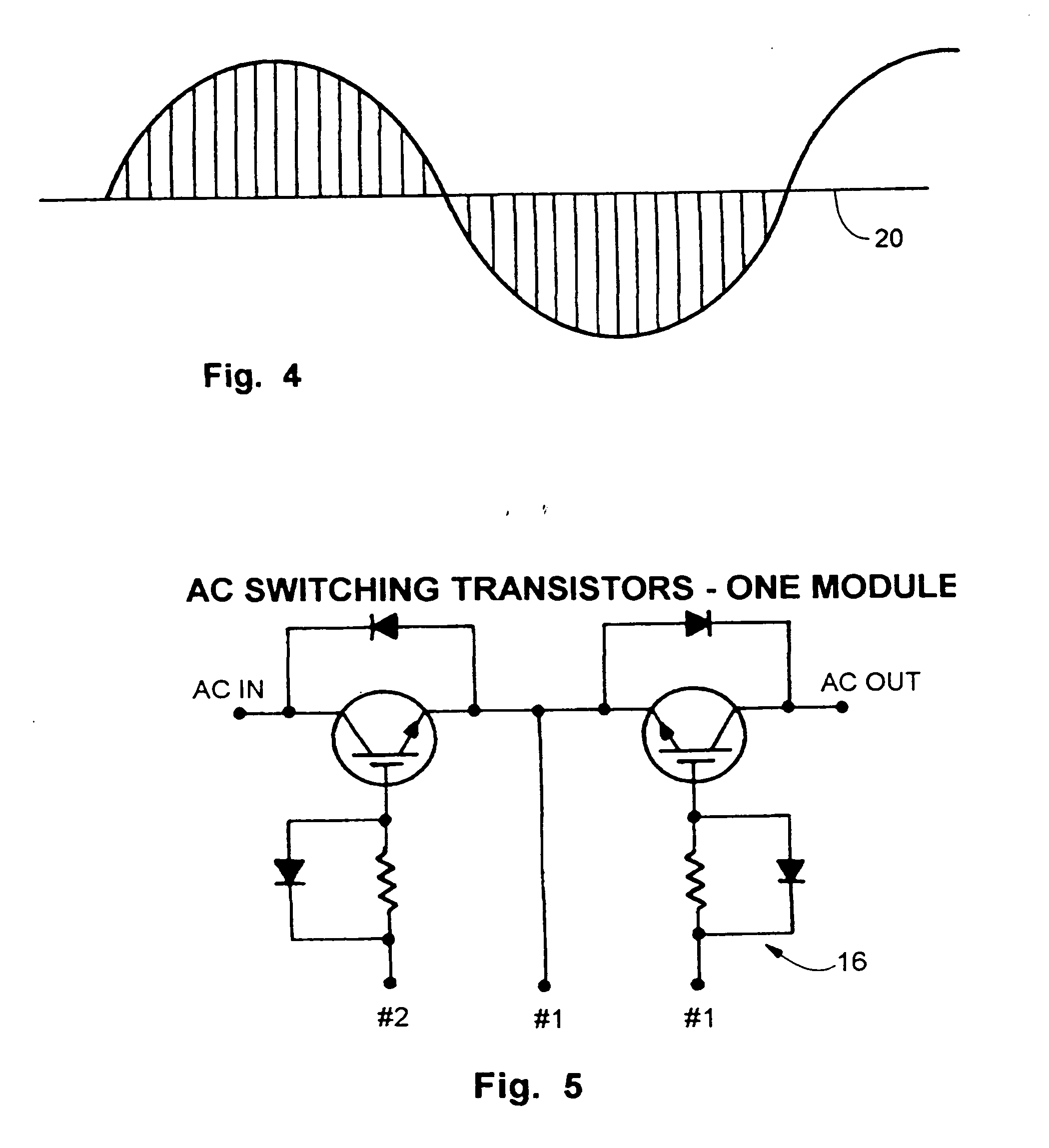
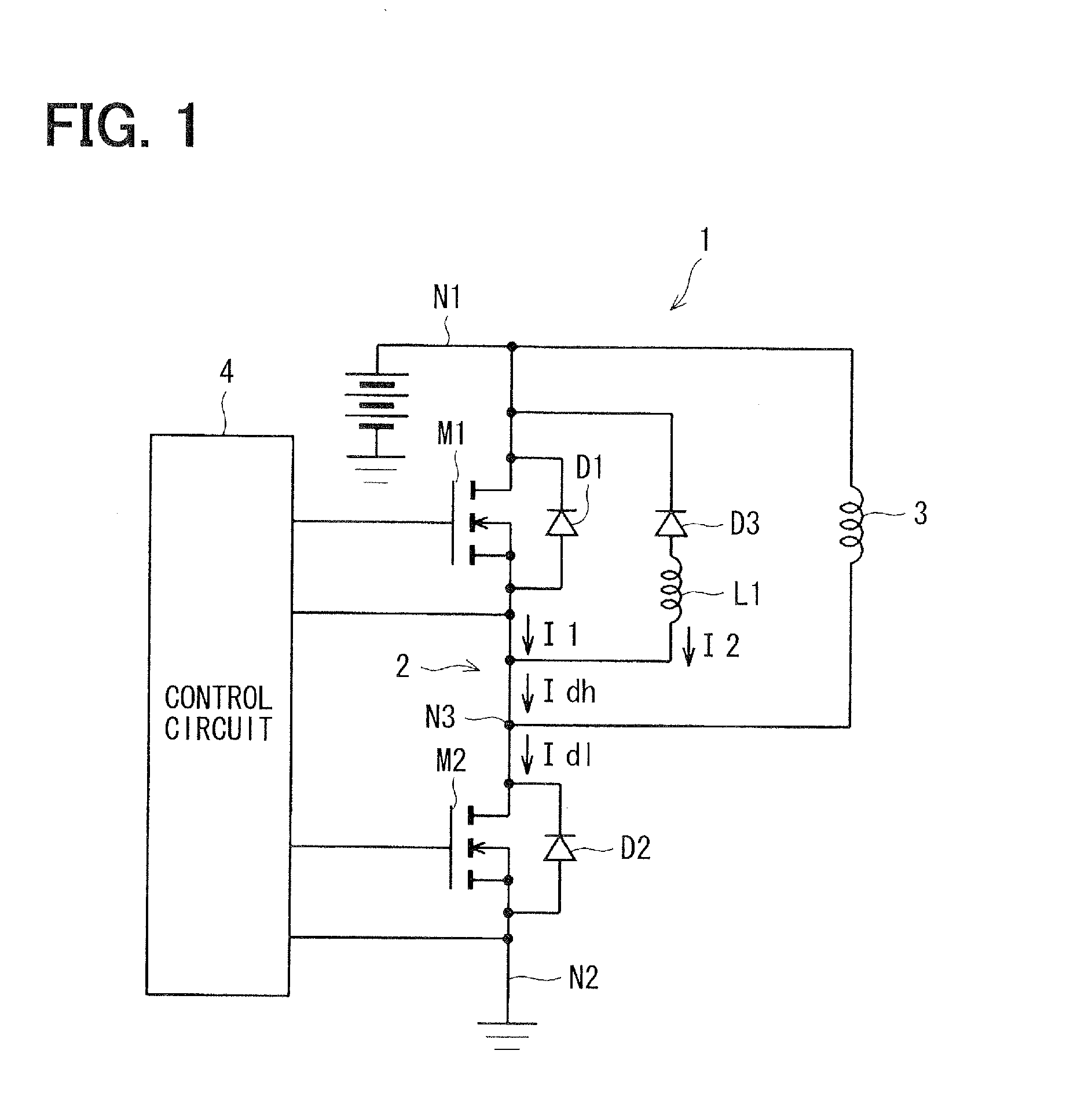
Inductive load power switching circuits
Power switching circuits including an inductive load and a switching device are described. The switches devices can be either low-side or high-side switches. Some of the switches are transistors that are able to block voltages or prevent substantial current from flowing through the transistor when voltage is applied across the transistor.
Owner:TRANSPHORM INC
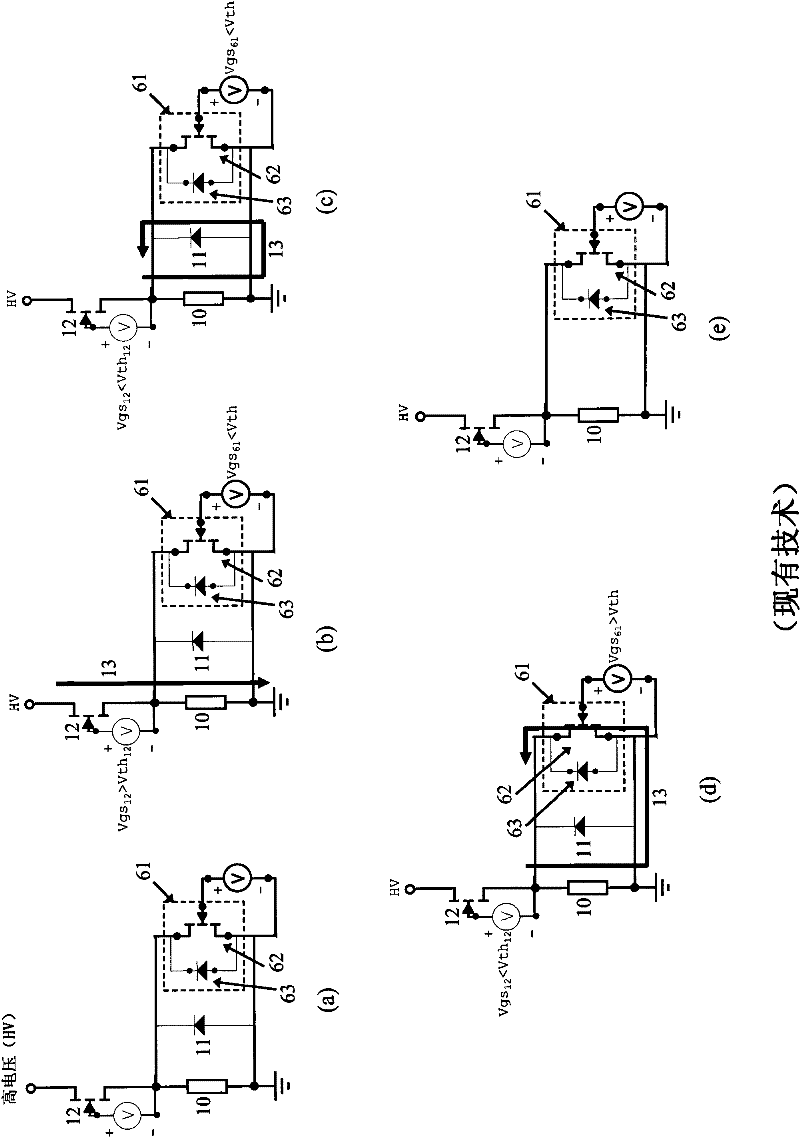
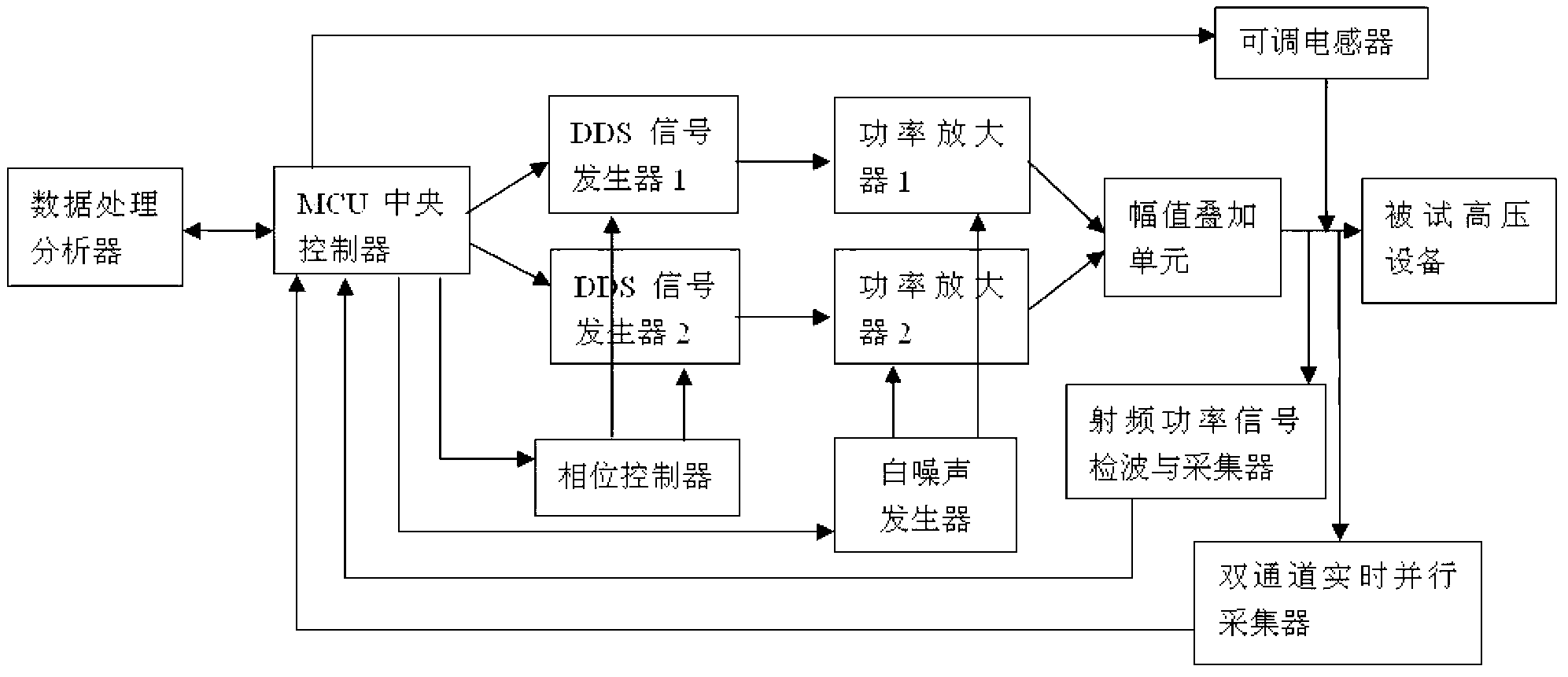
Capacitive high-voltage equipment insulation aging diagnostic test system and working method thereof
ActiveCN103323718ACause insulation damageGood test resultsTesting dielectric strengthInformation processingNoise control
The invention discloses a capacitive high-voltage equipment insulation aging diagnostic test system and a working method thereof. Double-frequency time-varying signals are used in the system for carrying out an overlaying impact test, two independent DDS signal generators, a power amplifier with white noise control, an amplitude overlaying unit and a controllable inductive load which is in output connection with the amplitude overlaying unit in series or in parallel form a composite aliasing waveform output loop, a set of information processing analysis method is combined, and insulation aging of tested high-voltage equipment is subjected to test diagnosis. Compared with the prior art, the insulation aging diagnosis test can be completed by exerting a test signal which is lower than a nominal voltage on the tested high-voltage equipment, insulation damage cannot be caused on the high-voltage equipment, the test can be carried out at any time, on-site testing is convenient, testing efficiency is high, compared with an existing diagnosis test signal which is single in waveform, the overlaying impact test signals can obtain abundant testing parameters, and potential fault of the high-voltage equipment can be easily found.
Owner:GAUSS ELECTRONICS TECH
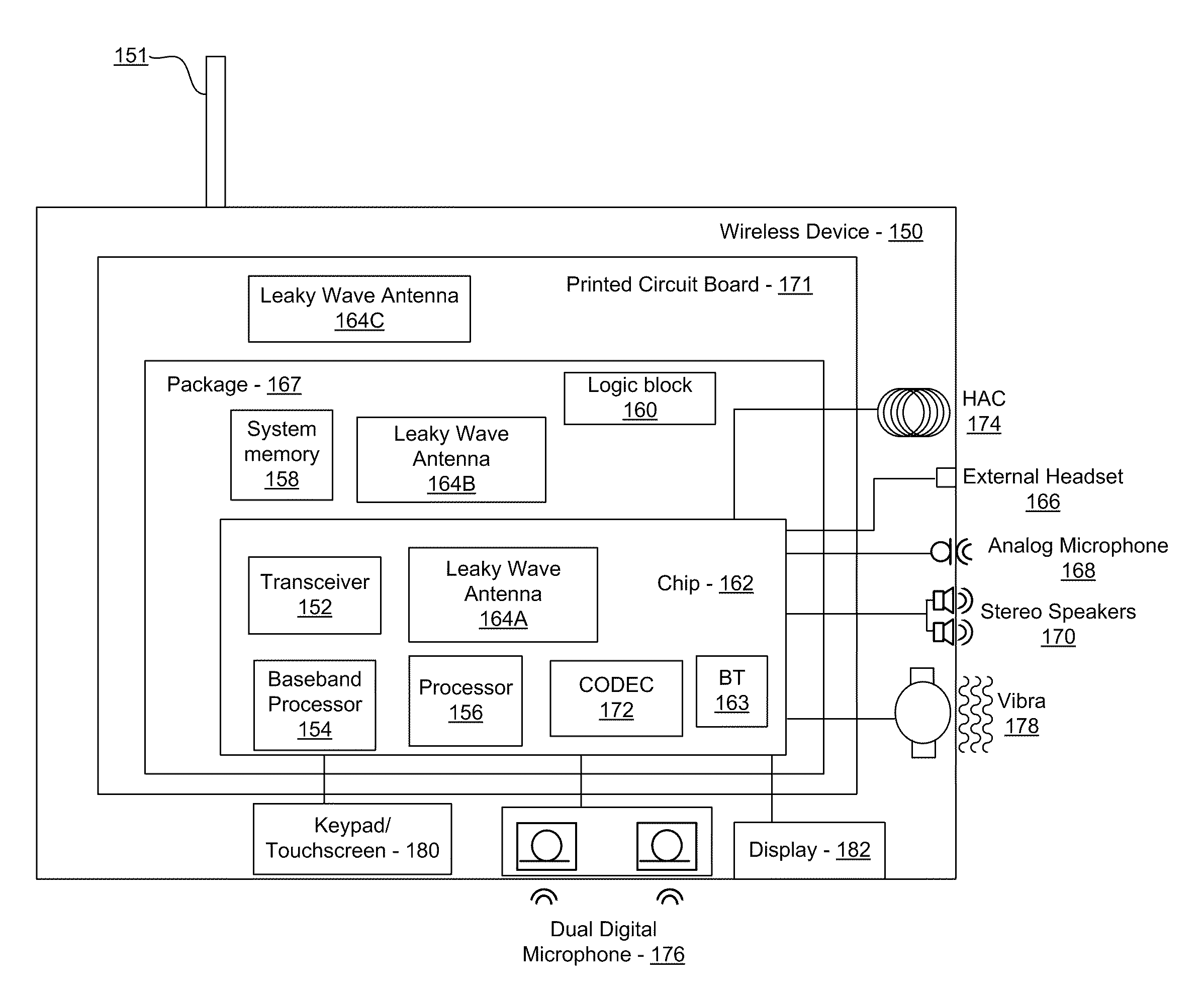
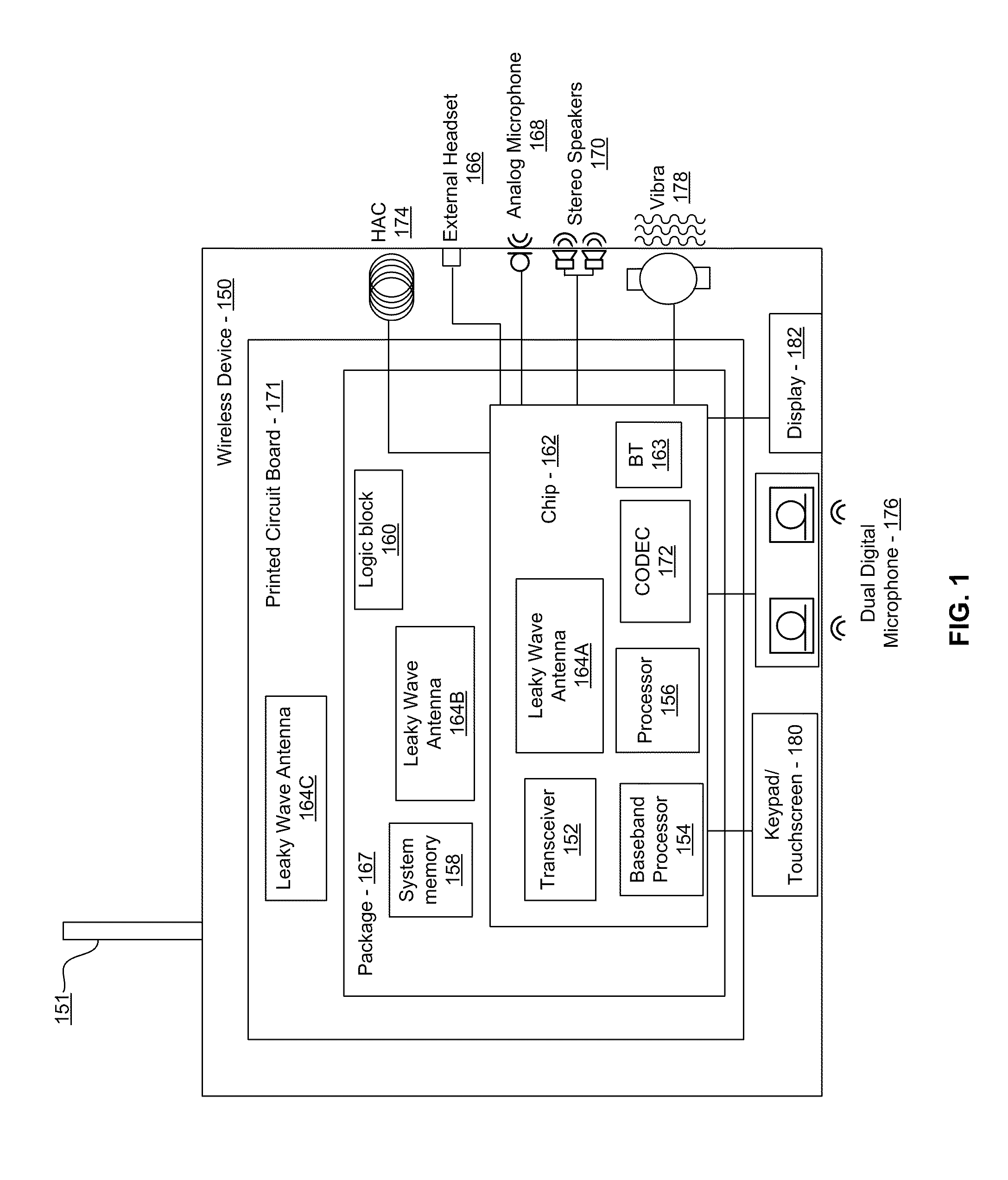
Method and System for a Leaky Wave Antenna as a Load on a Power Amplifier
ActiveUS20100311368A1Resonant long antennasSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsAudio power amplifierEngineering
Methods and systems for utilizing a leaky wave antenna as a load on a power amplifier are disclosed and may include configuring one or more leaky wave antennas as a load for one or more power amplifiers (PAs) in a wireless device. RF signals may be transmitted via the leaky wave antennas which may be integrated on the chip, a package to which the chip is affixed, or on a printed circuit board to which the chip is affixed. The antennas may include an inductive load and / or a balun for the one or more PAs. The leaky wave antennas may be impedance matched to the PAs. The PAs may amplify a signal to be transmitted, and an output power of the PAs may be configured by controlling a bias voltage for the PAs.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Dimmer circuit with improved inductive load imbalance protection
InactiveUS20050168896A1Reduce the possibilityEliminate needAc-dc conversion without reversalElectric heatingDimmerEngineering
A protection circuit for protecting a dimmer circuit controlling an inductive load including an imbalance detector for detecting an asymetrical operation in the load and circuit control means for causing the dimmer circuit to reduce a DC component in the load upon detection of the asymetrical operation. A load imbalance detector is also disclosed having a load DC component detector, a comparator and a signal generating means for generating means for generating a circuit shut down signal if the DC component exceeds a pre-set DC threshold.
Owner:CLIPSAL INTEGRATED SYST
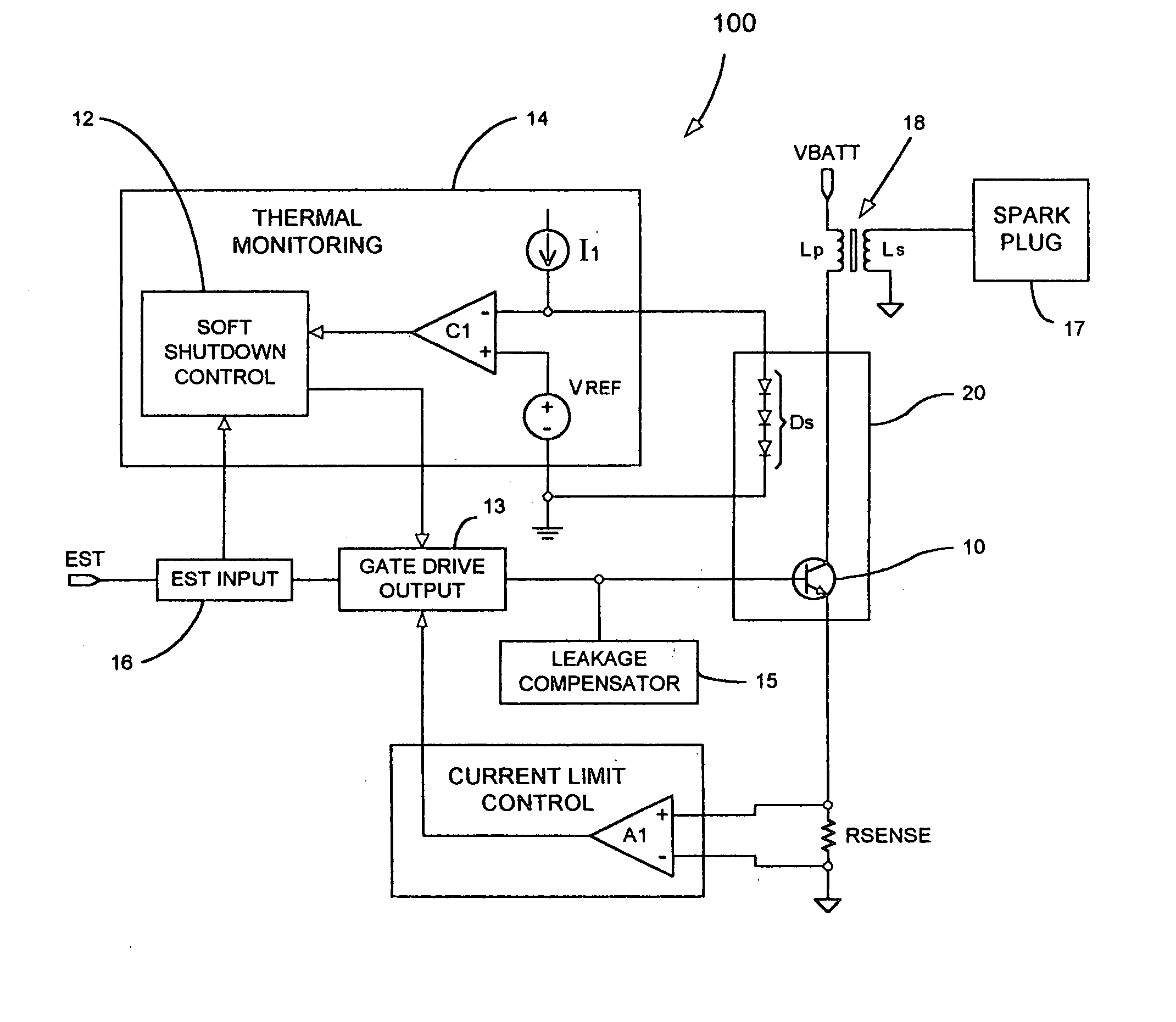
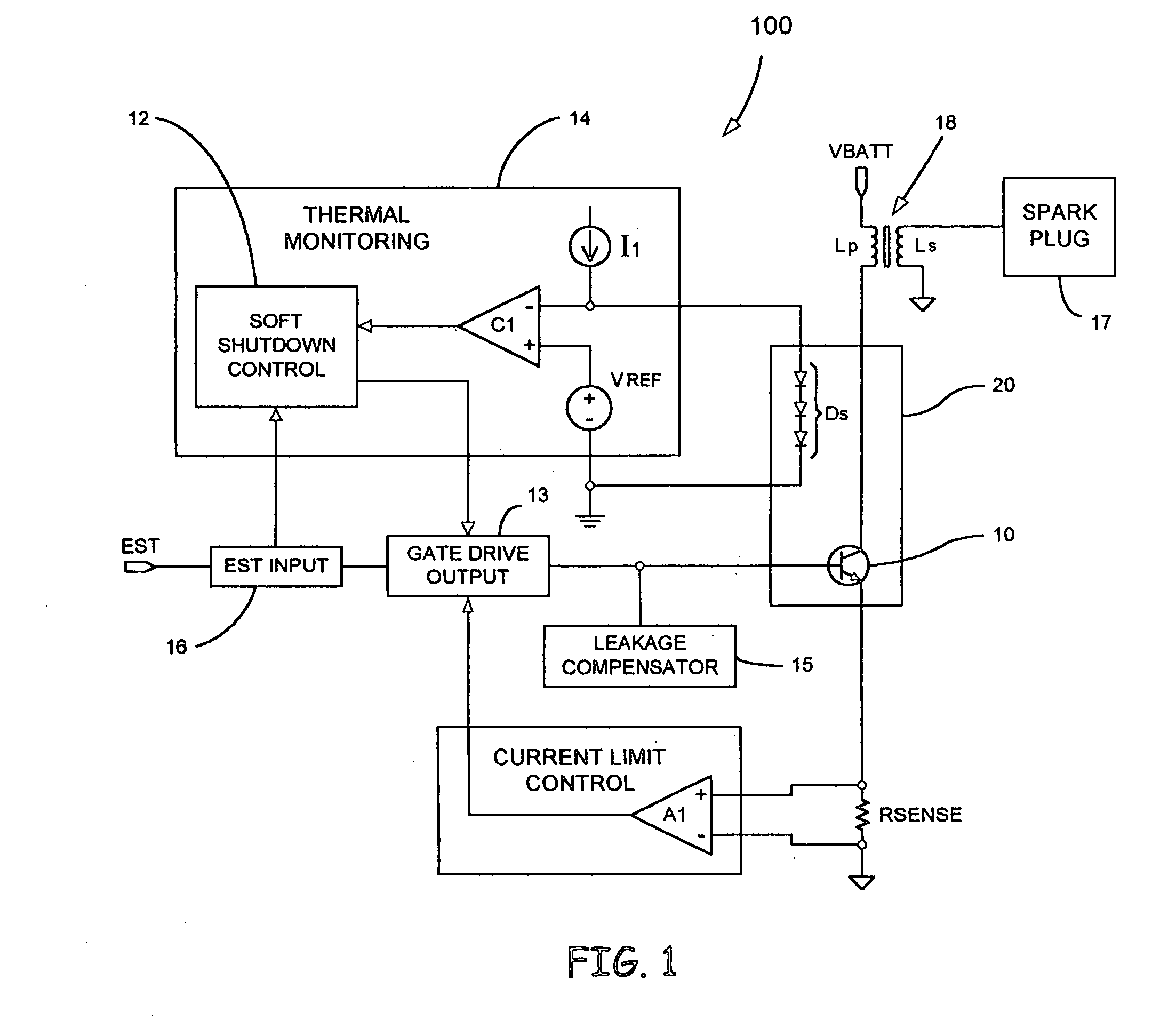
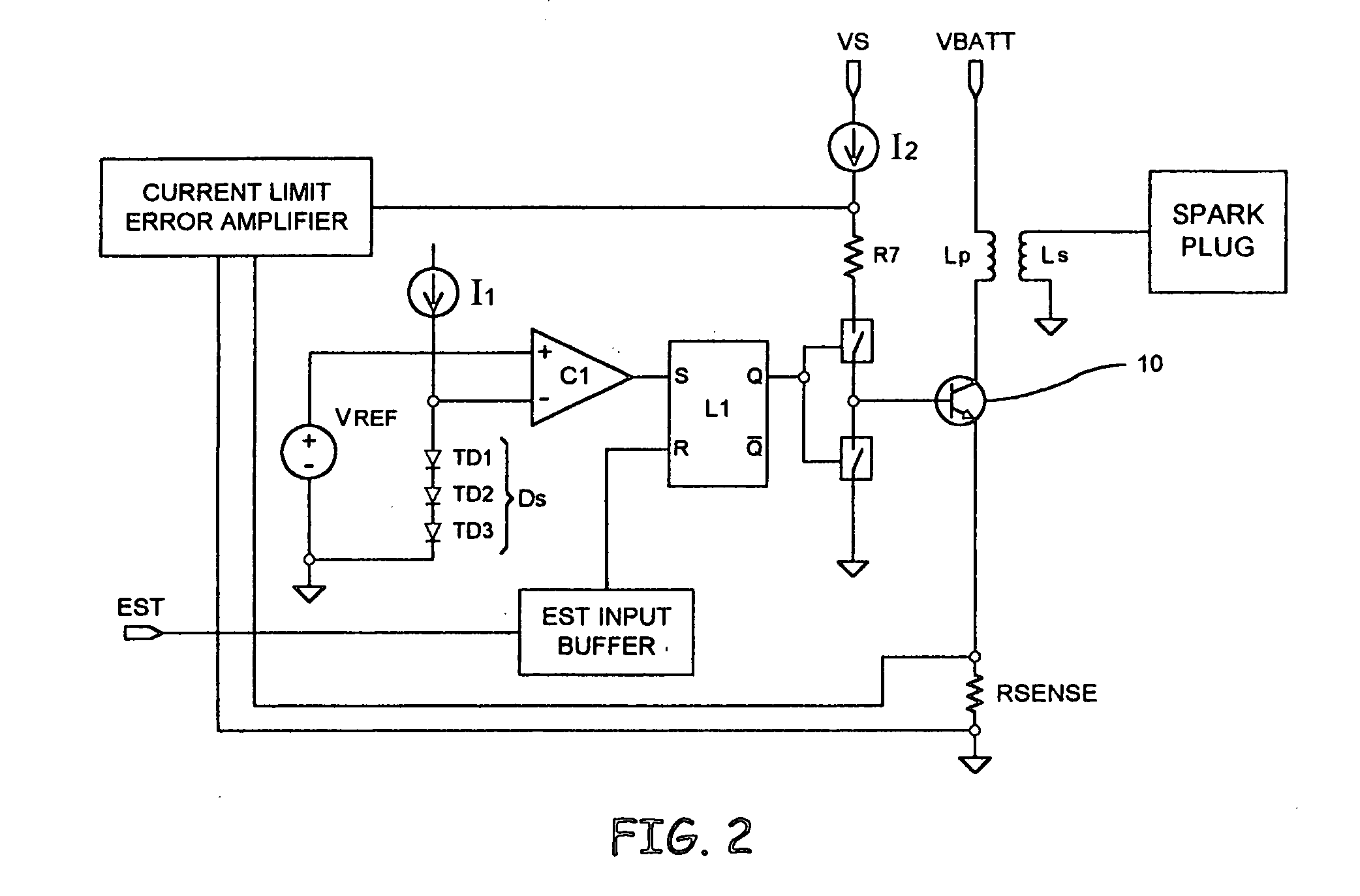
Automotive ignition system with sparkless thermal overload protection
ActiveUS20050178372A1Electrical controlThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsThermal monitoringDriving current
An interface for providing thermal overload protection includes a switching device, a temperature indicating device, a drive circuit and a thermal monitoring circuit. The thermal monitoring circuit is coupled across the temperature indicating device and provides a shutdown signal to the drive circuit when the temperature of the switching device is above a predetermined temperature level as indicated by a temperature signal provided by the temperature indicating device. The drive circuit responds to the shutdown signal by removing current sources and current sinks from a control terminal of the switching device at which point leakage currents cause the switching device to reduce a drive current to an inductive load.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
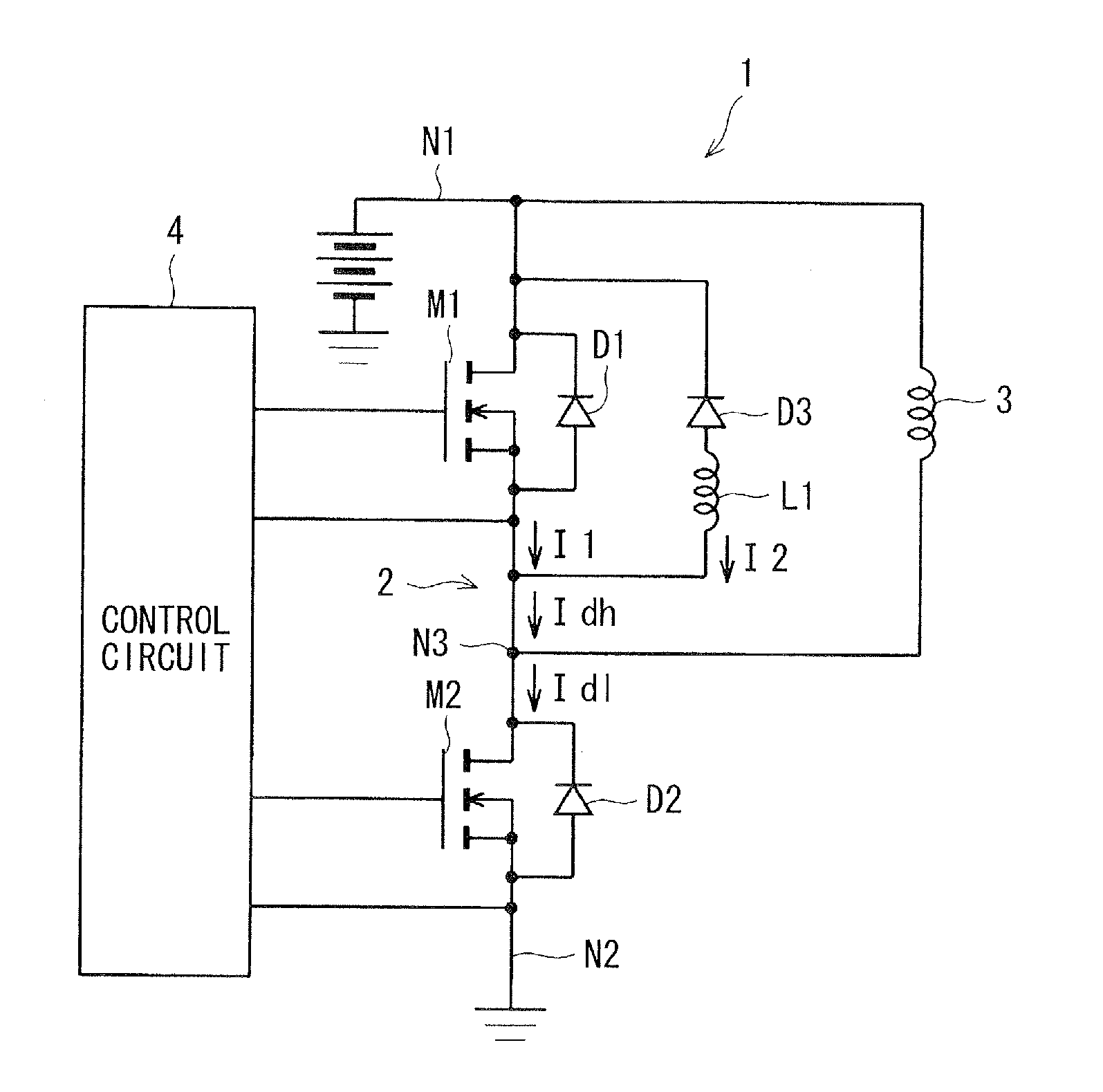
Drive controller
A drive controller for driving an inductive load connected to a node between first and second switches connected in series with a direct current voltage source includes a first diode, a series circuit of a second diode and an inductor, and a control circuit. The first diode is a parasitic diode of the first switch and connected in antiparallel with the first switch. The series circuit is connected in parallel with the first diode. The control circuit drives the inductor load by applying a control voltage to the first switch before applying a first ON-voltage to the second switch. The first ON-voltage turns ON the second switch. The control voltage is greater than zero and less than a second ON-voltage. The second ON-voltage turns ON the first switch. The control voltage causes the first switch to operate in weak inversion.
Owner:DENSO CORP
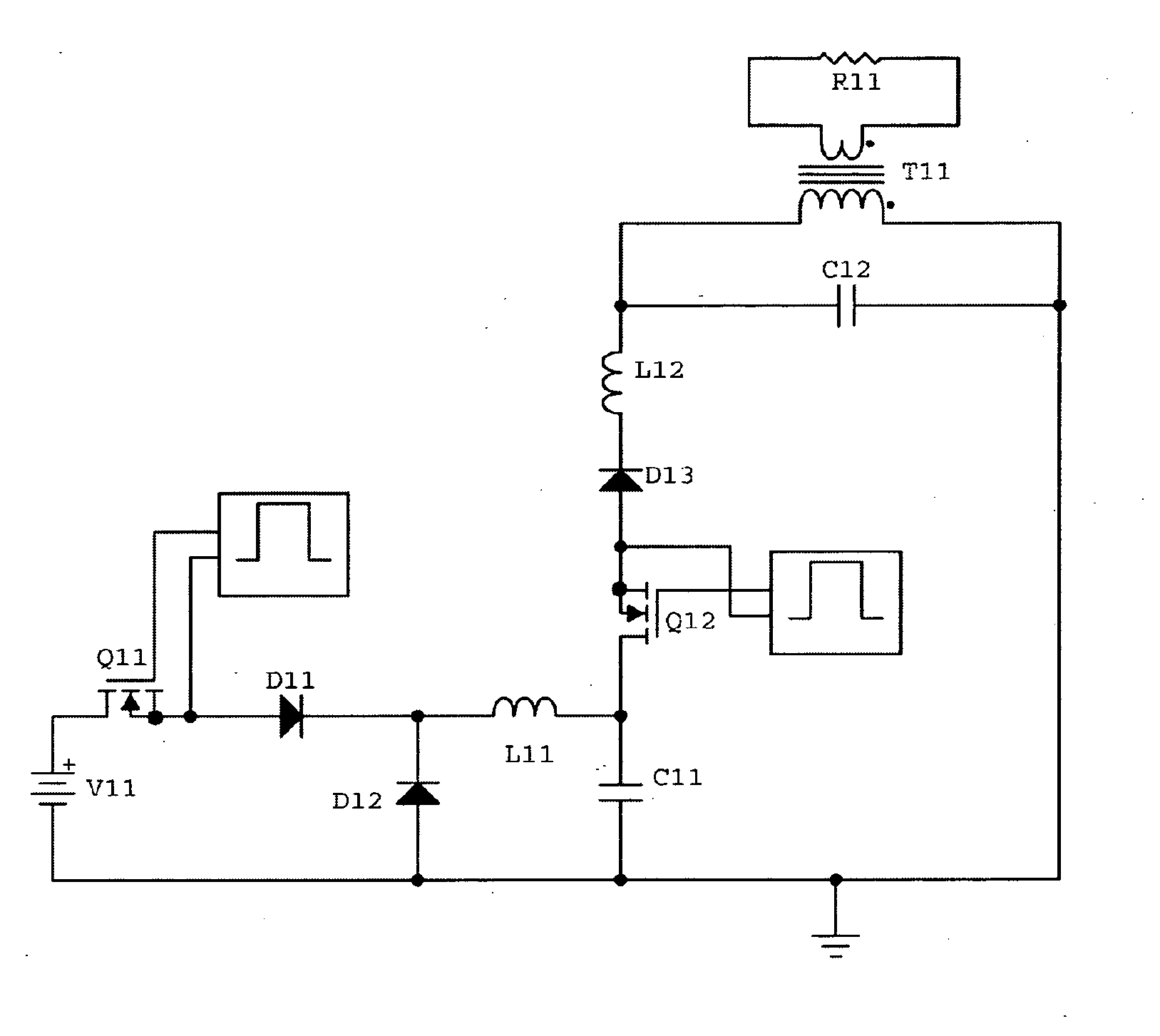
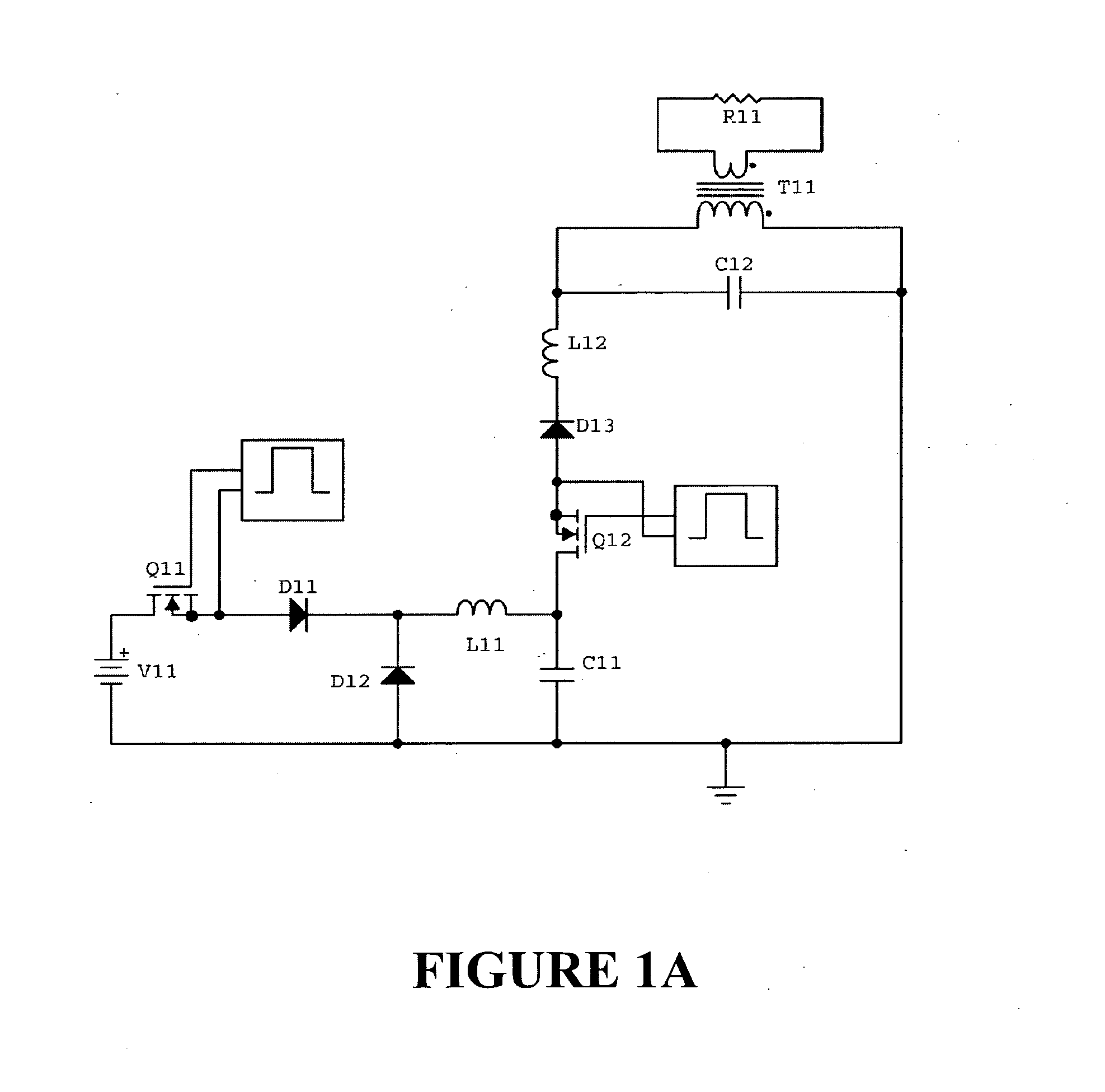
Circuit and method for coupling electrical energy to a resonated inductive load
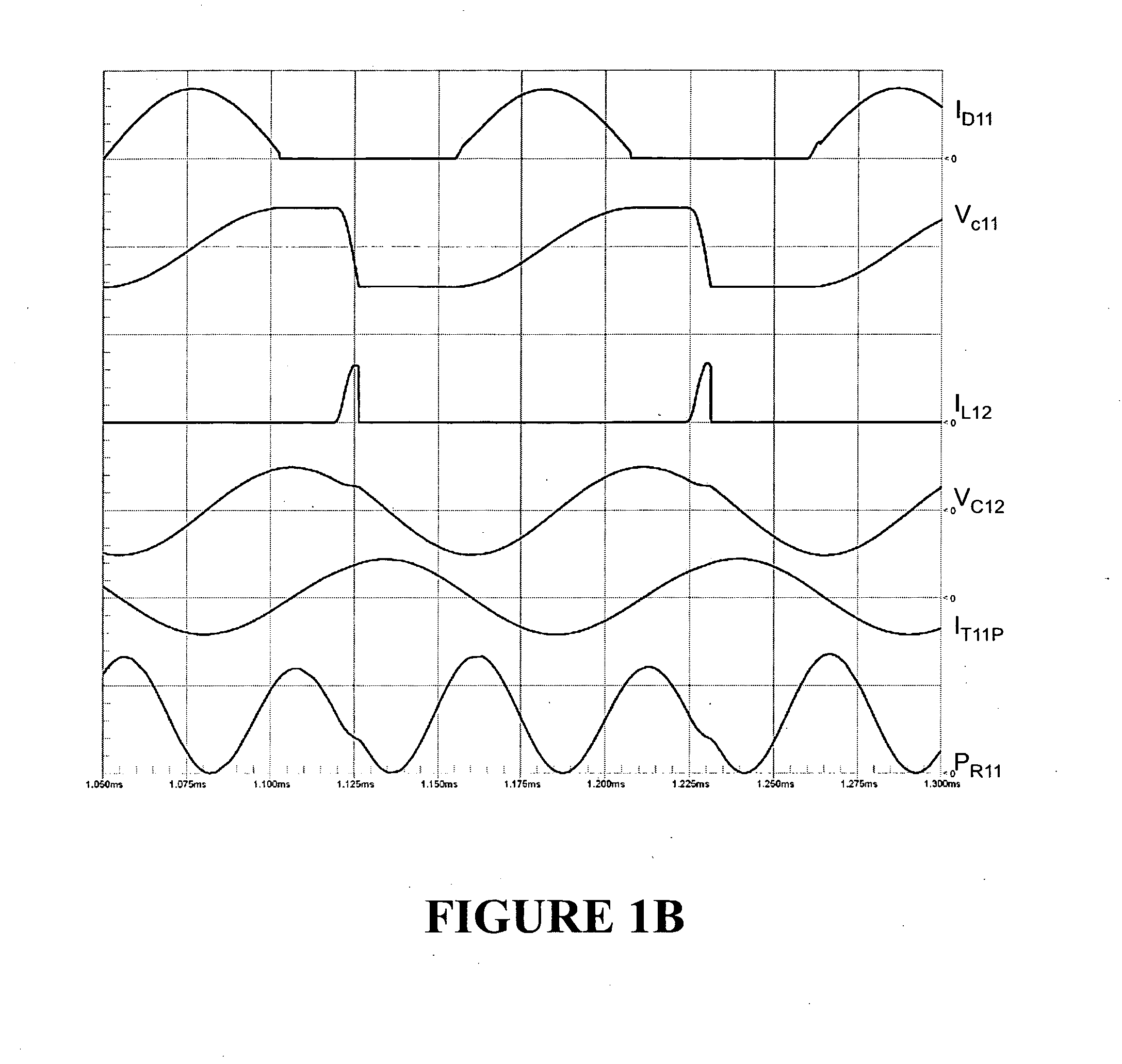
InactiveUS20110242868A1Active connectionEfficient transferEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionElectric power transmissionCapacitance
A switching circuit (Q11, Q12, D11, D12, D13, L11, L12) is repetitively configured to charge an energy transfer capacitance (C11) from an electrical supply (V11) and then inject a discrete pulse of energy into a resonated load circuit by dis charging the capacitance. The load circuit is formed by a resonating capacitance (C12) and an inductive load device (T11, R11), eg motor, or induction heating or power transfer device. Energy circulates in the load circuit at or near to its natural resonant frequency. There is no injection of energy into the load circuit while energy for charging the transfer capacitance is being delivered from the supply to the switching circuit. During injection, the two capacitances and the inductive load device may be connected together in parallel or in series, or the transfer capacitance may be connected in series with the inductive load device but not the resonating capacitor.
Owner:RES LIMITED
Electrosurgical apparatus with high speed energy recovery
A circuit for controlling the discharging of stored energy in an electrosurgical generator includes a pulse modulator which controls an output of a power supply. At least one comparator is configured to provide an error signal to the pulse modulator based on a comparison between an output signal generated by the power supply and a feedback signal generated in response to the application of energy to tissue. A discharge circuit is configured to control the discharge of the output of the power supply to an inductive load disposed in parallel with the output of the power supply based on the comparison between the output signal and the feedback signal.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com