Patents
Literature
252 results about "Leaky wave antenna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
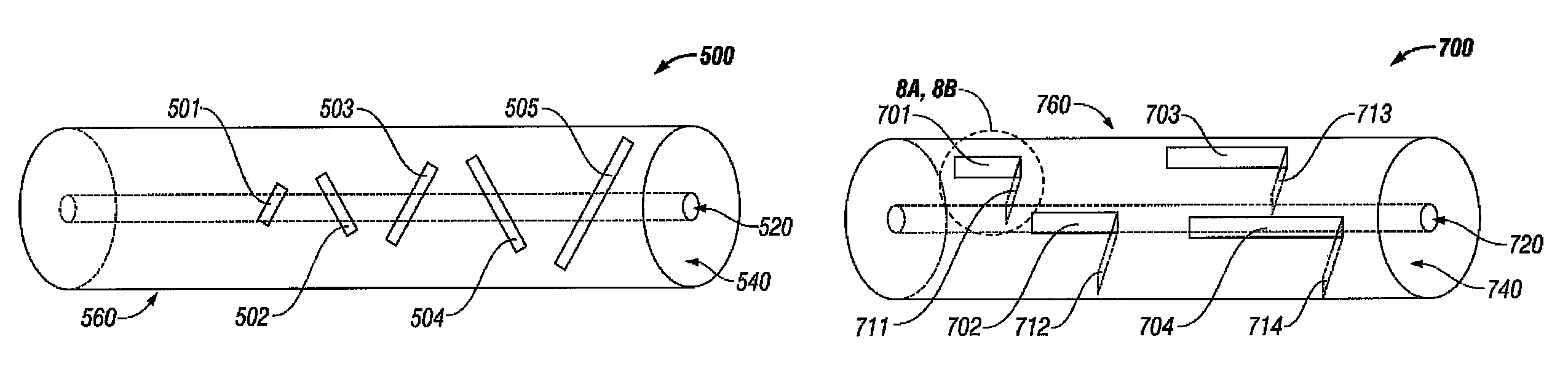
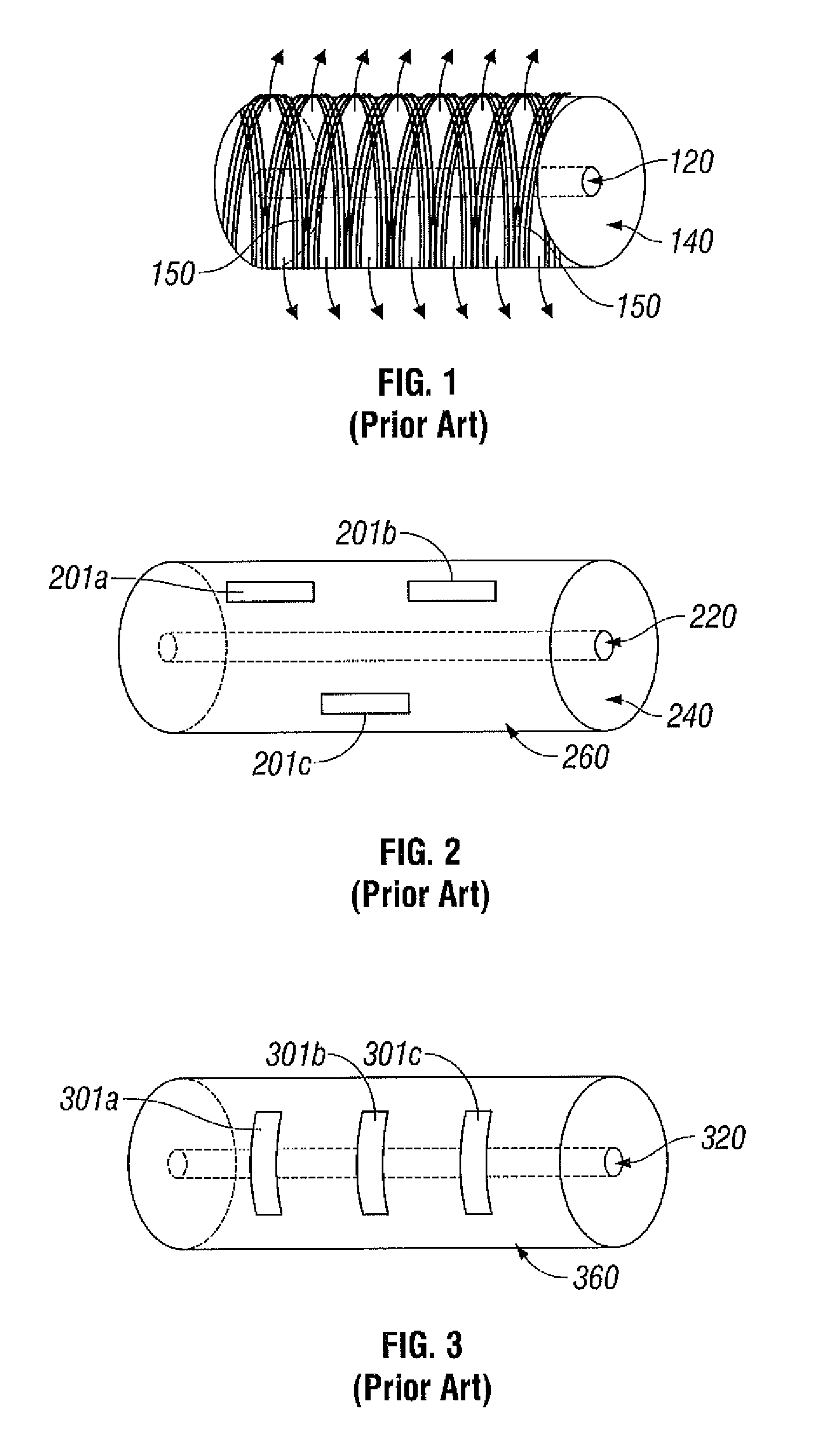
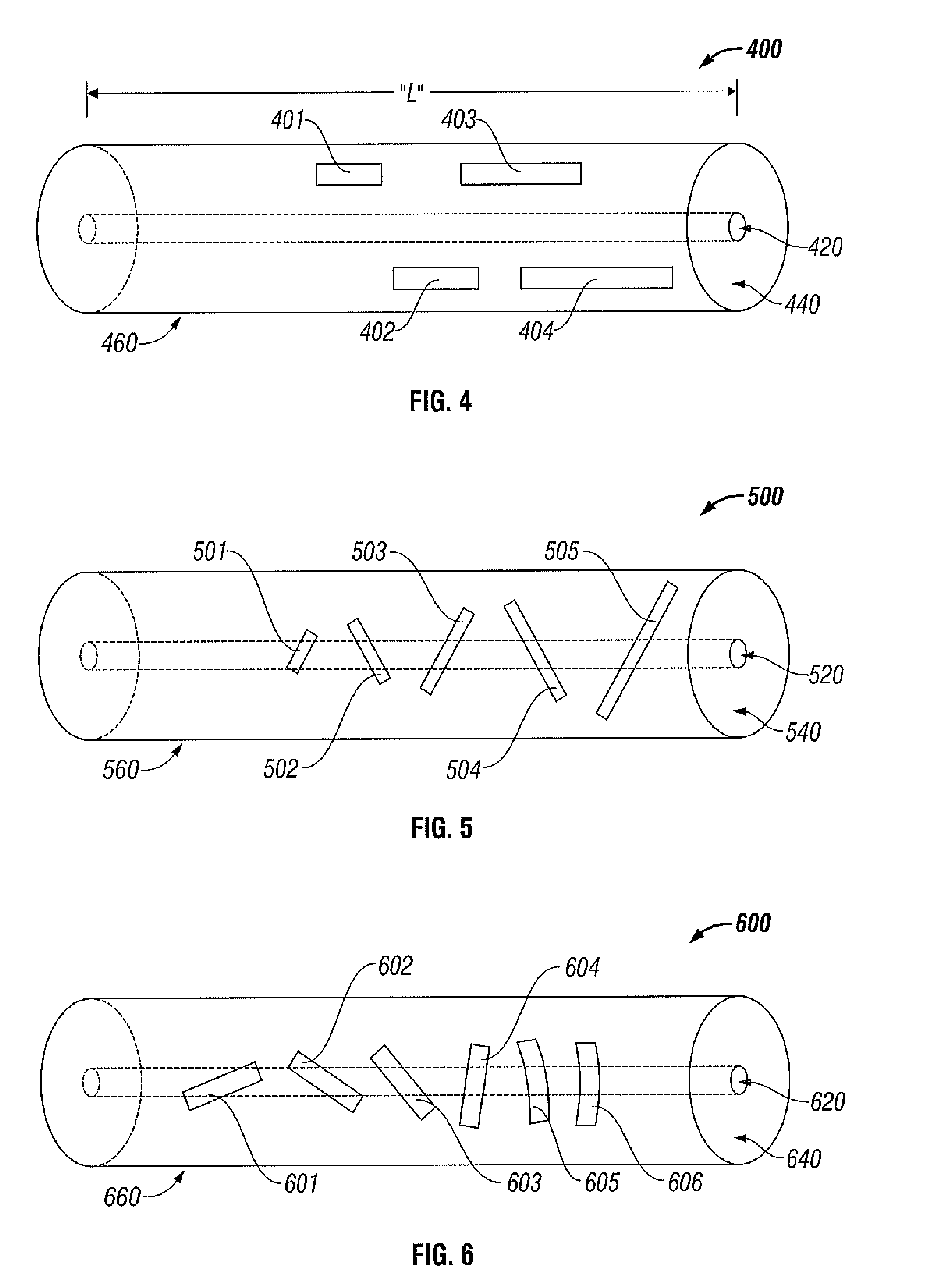
Leaky-Wave Antenna (LWA) belong to the more general class of Traveling wave antenna, that use a traveling wave on a guiding structure as the main radiating mechanism. Traveling-wave antenna fall into two general categories, slow-wave antennas and fast-wave antennas, which are usually referred to as leaky-wave antennas.
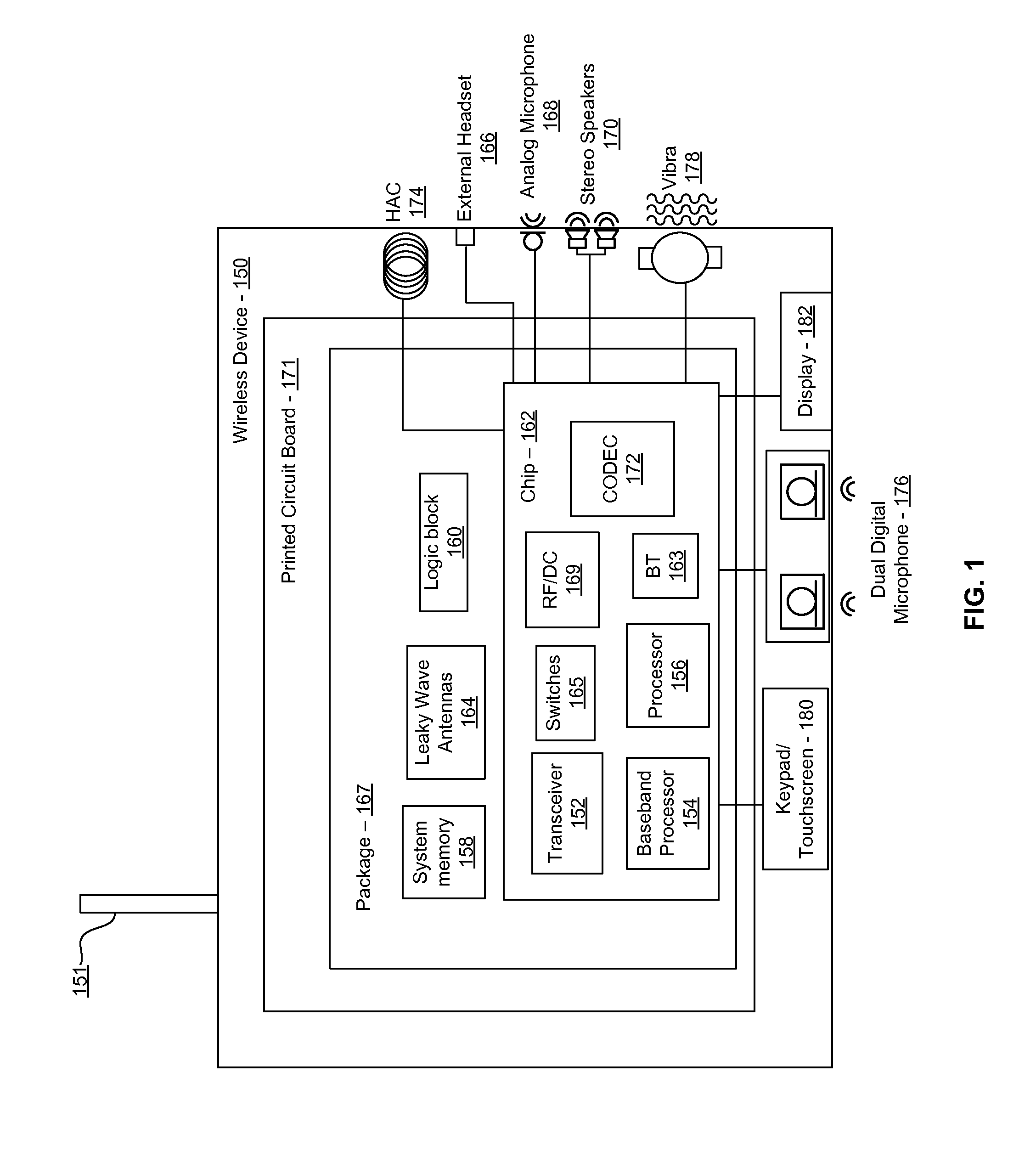
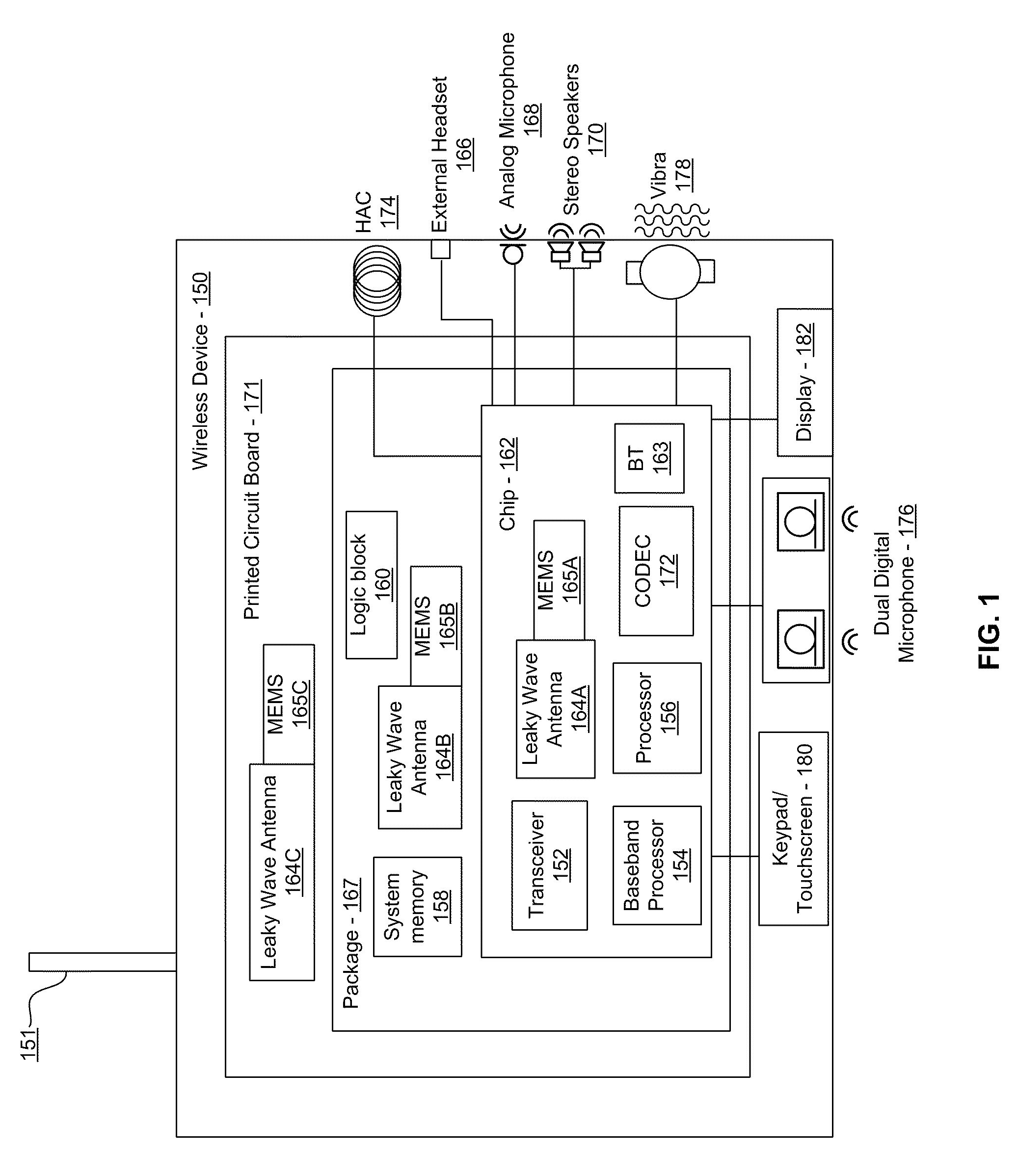
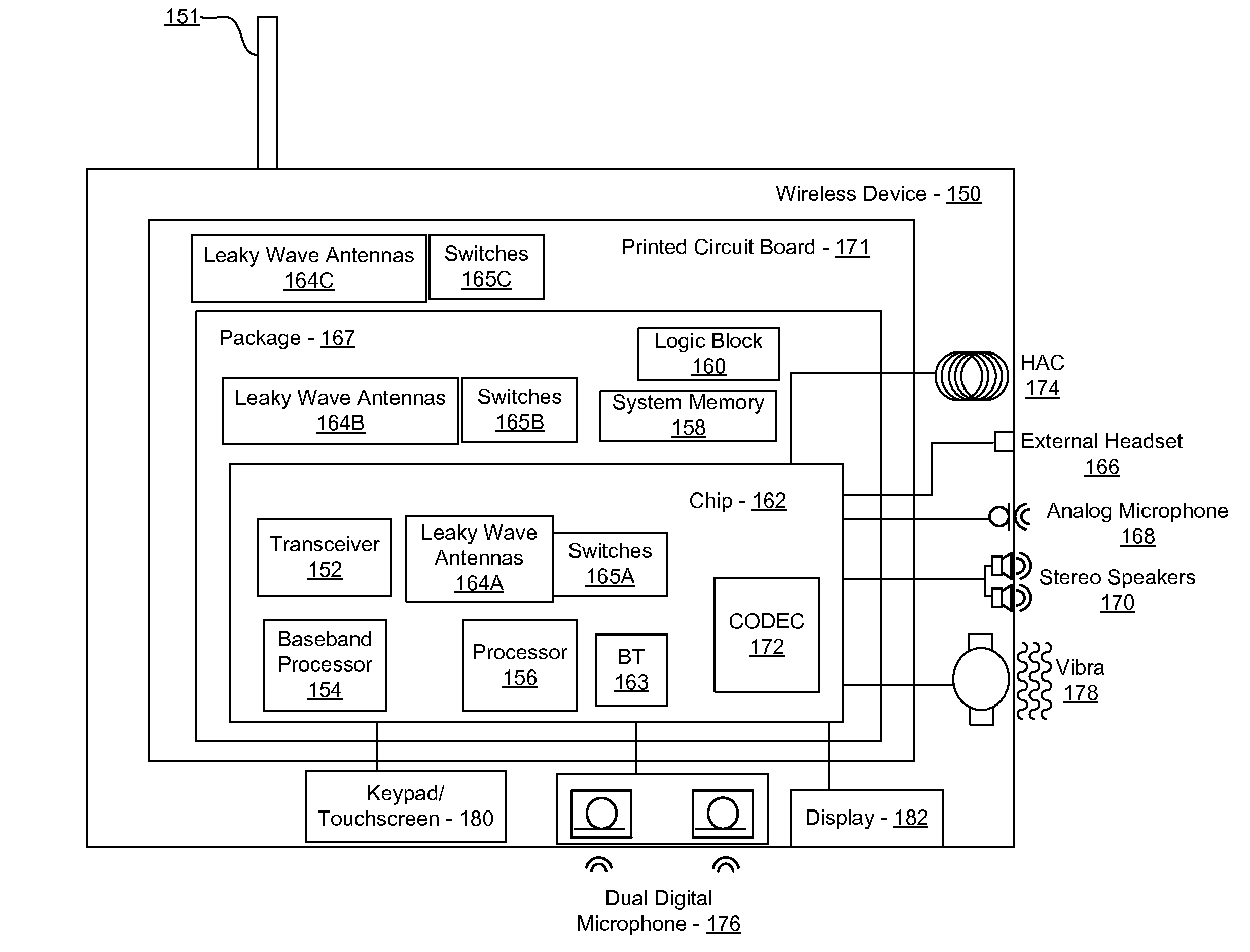
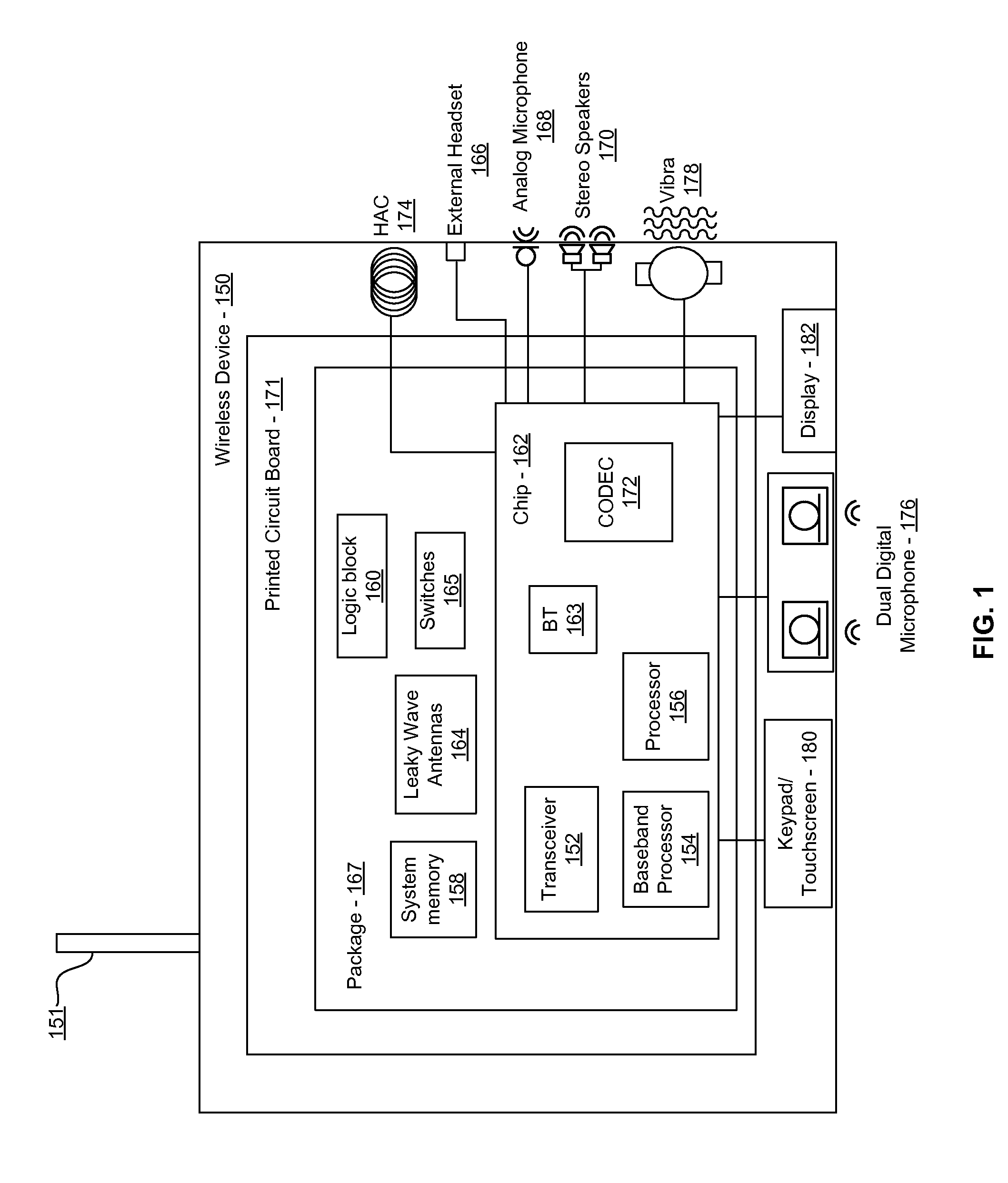
Method and system for a smart antenna utilizing leaky wave antennas
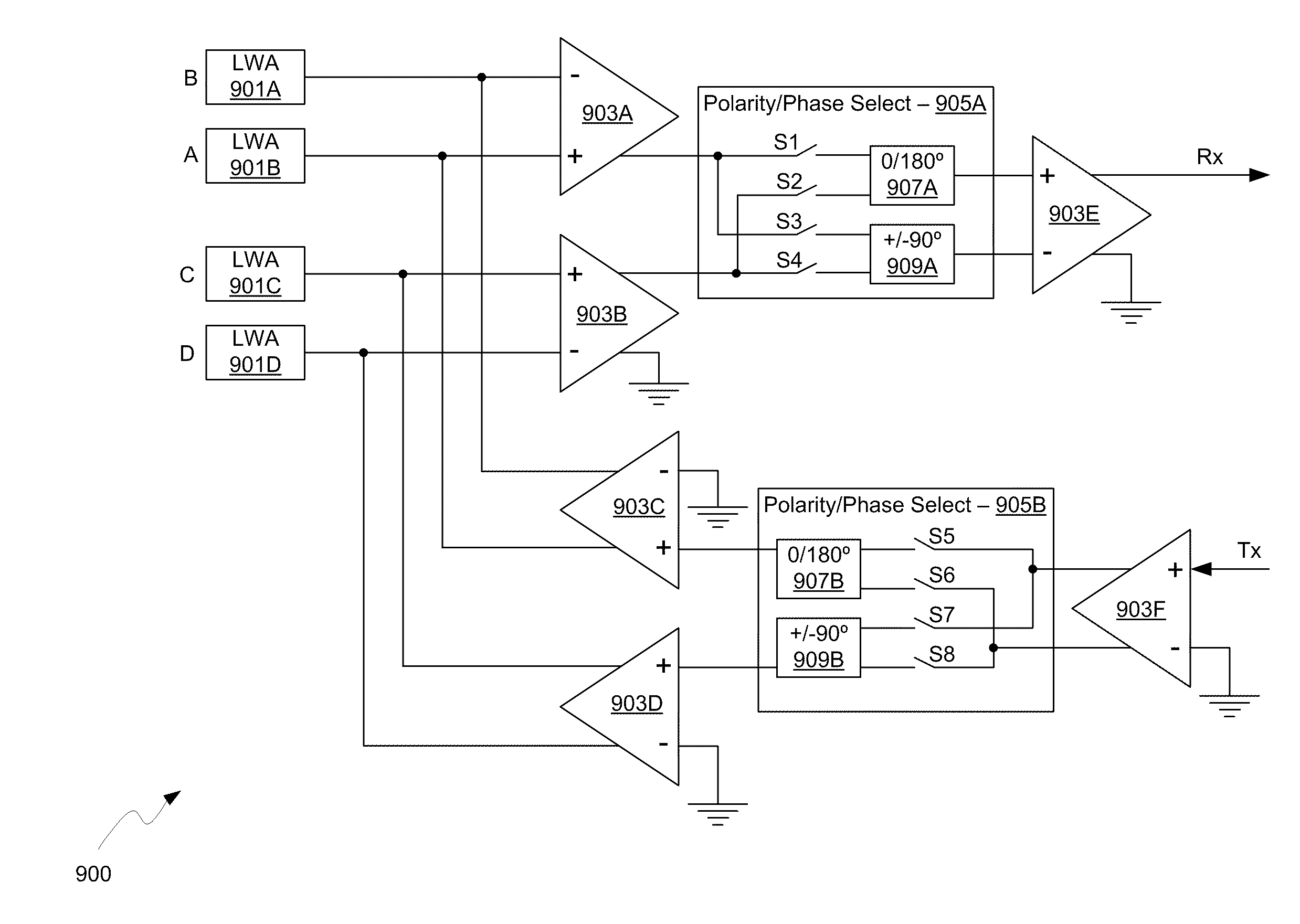
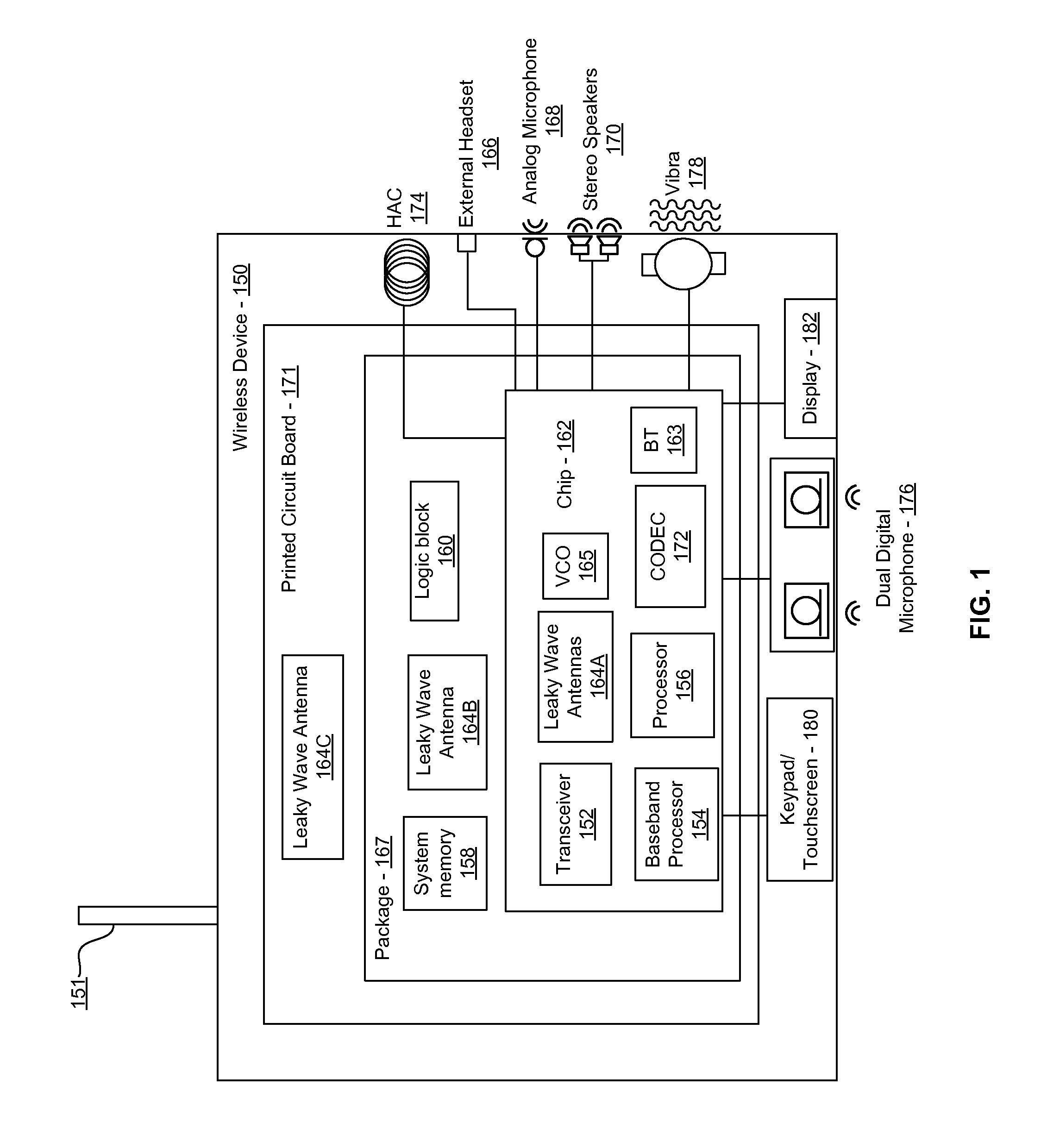
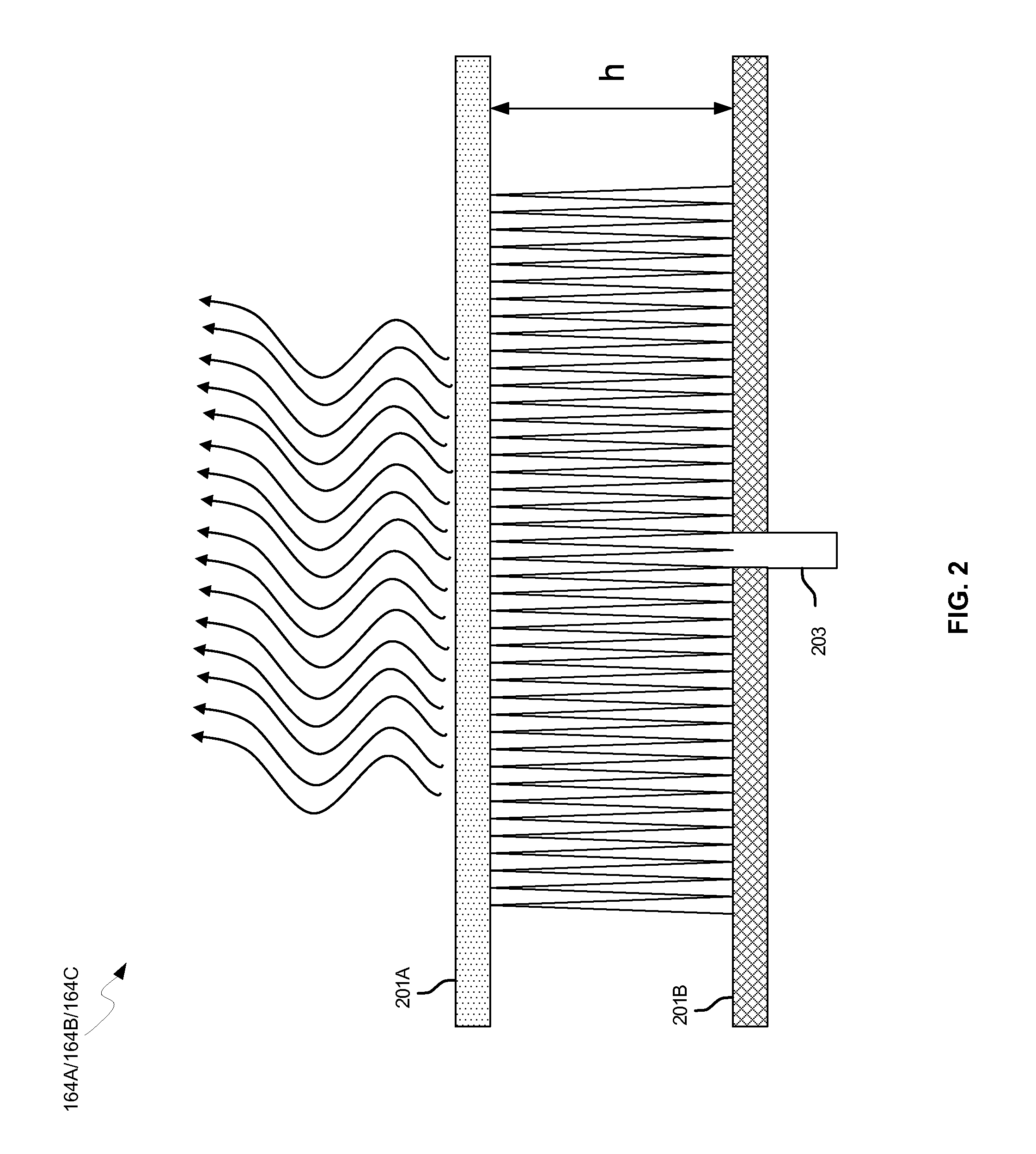
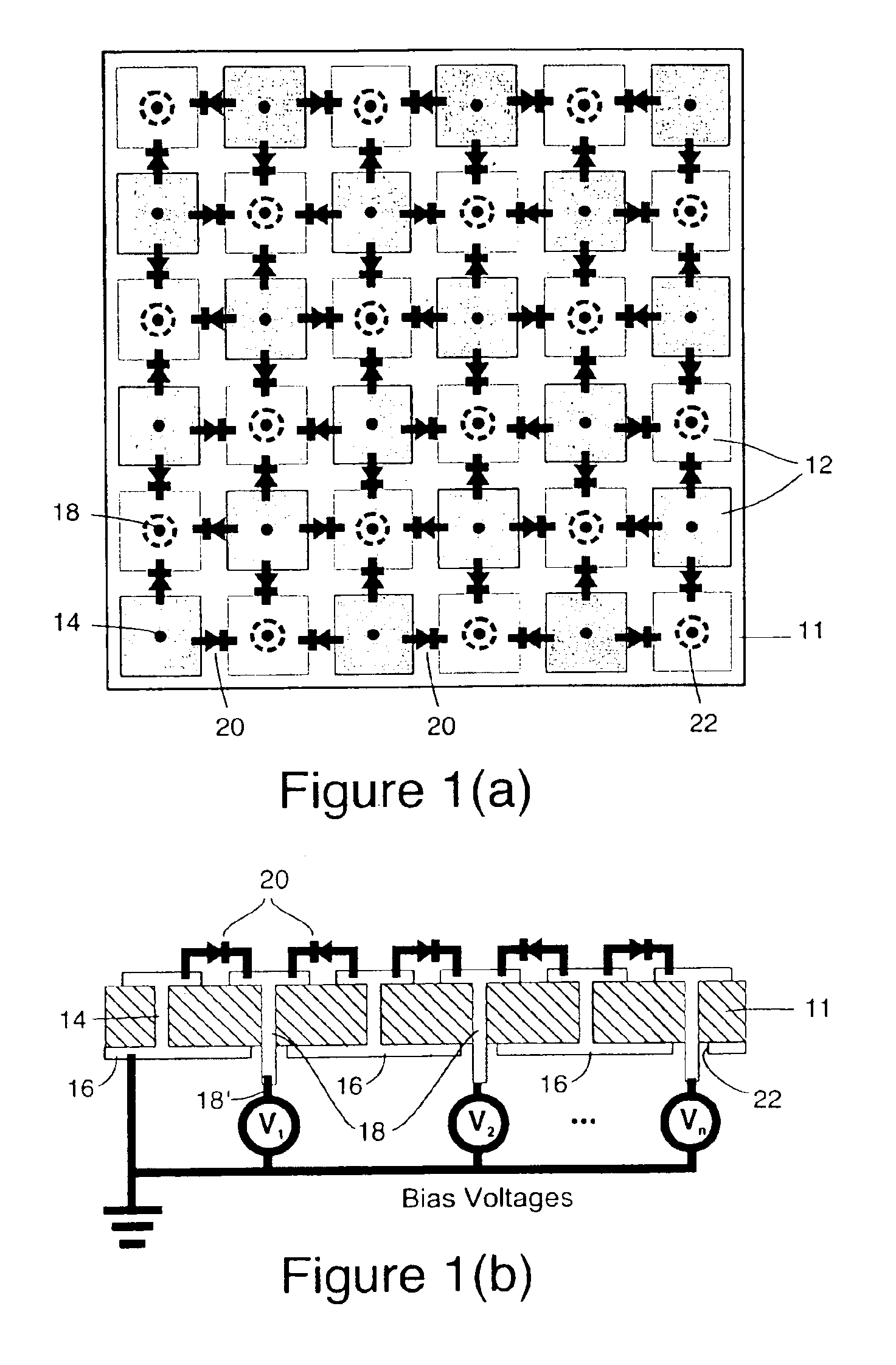
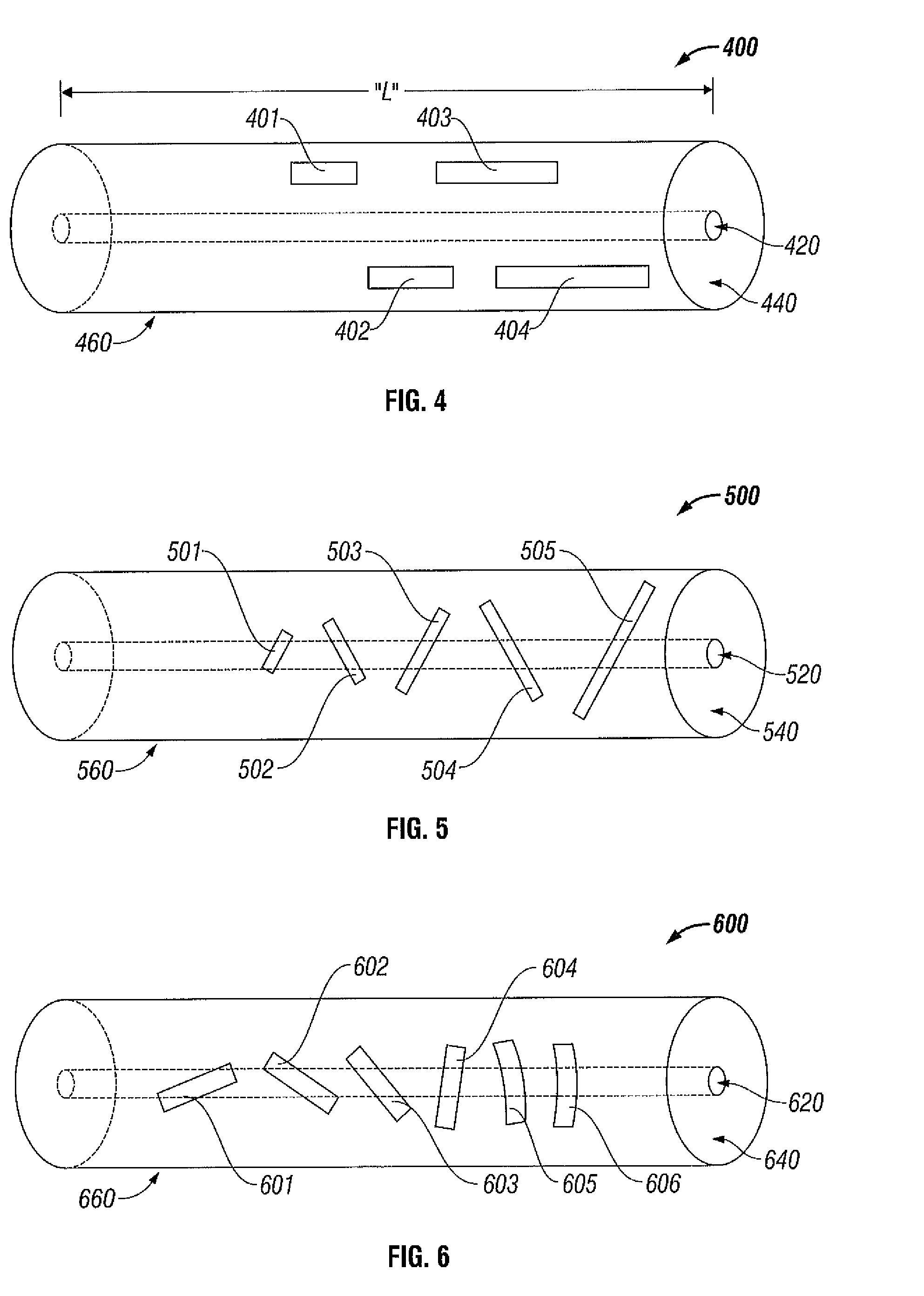
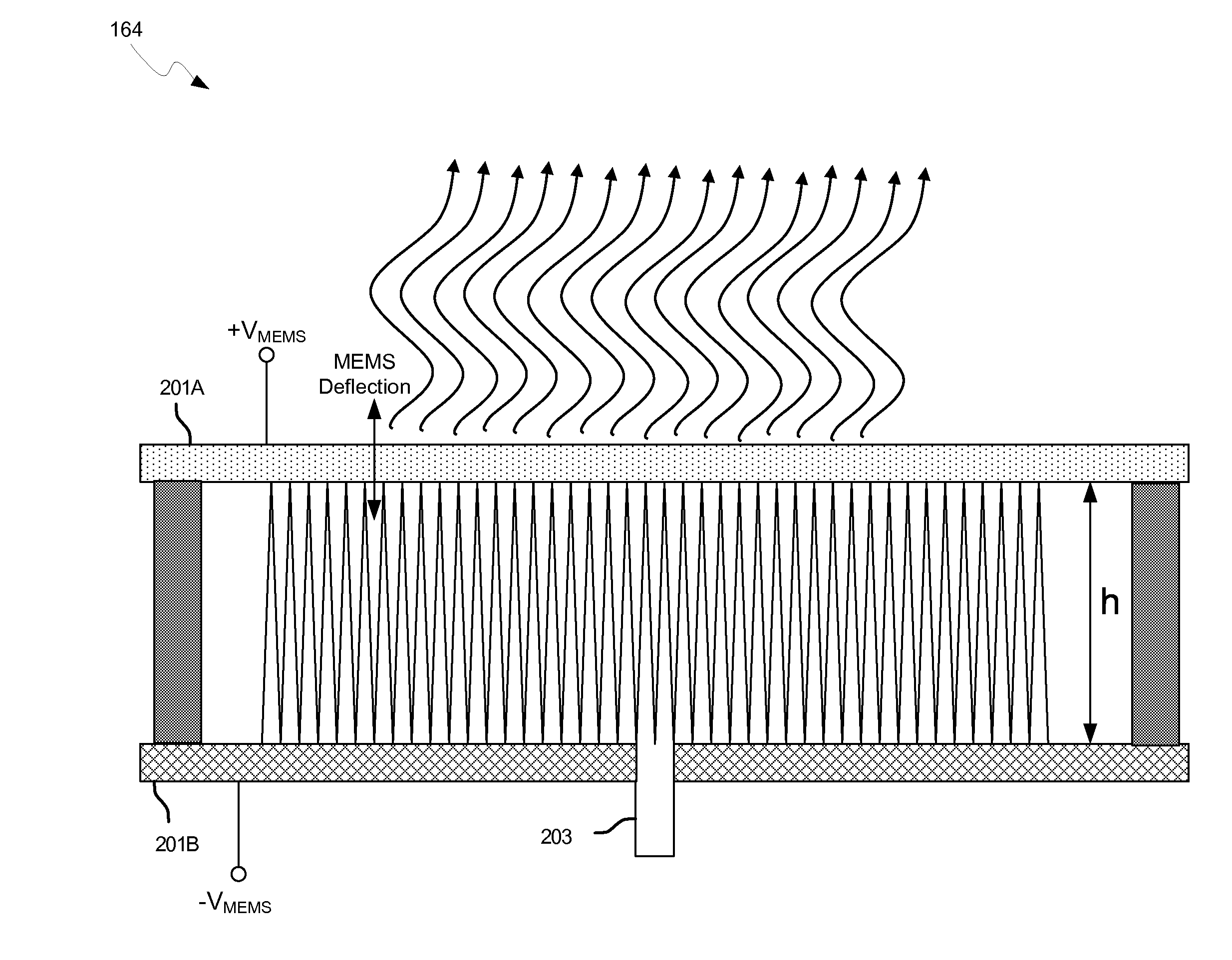
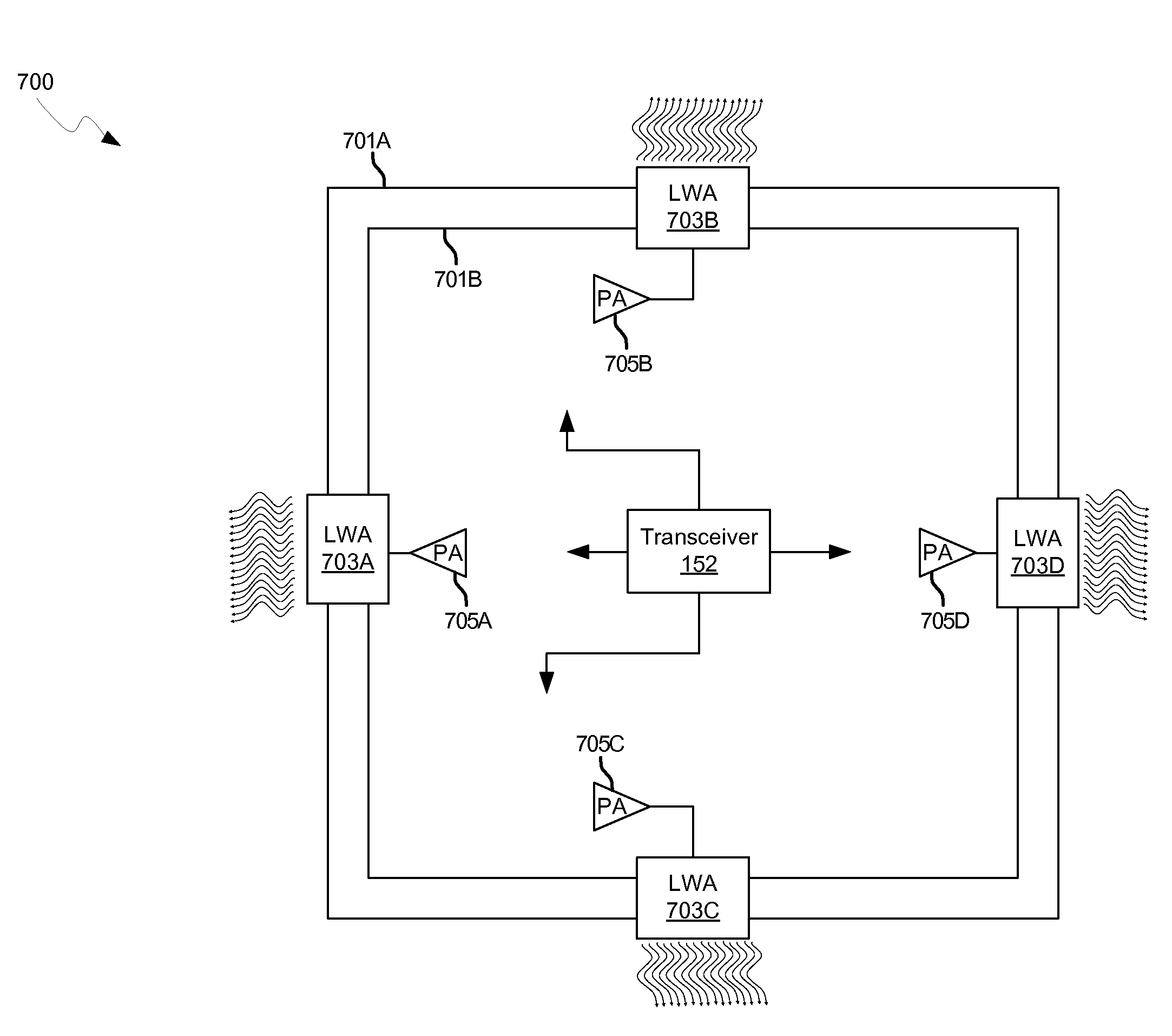
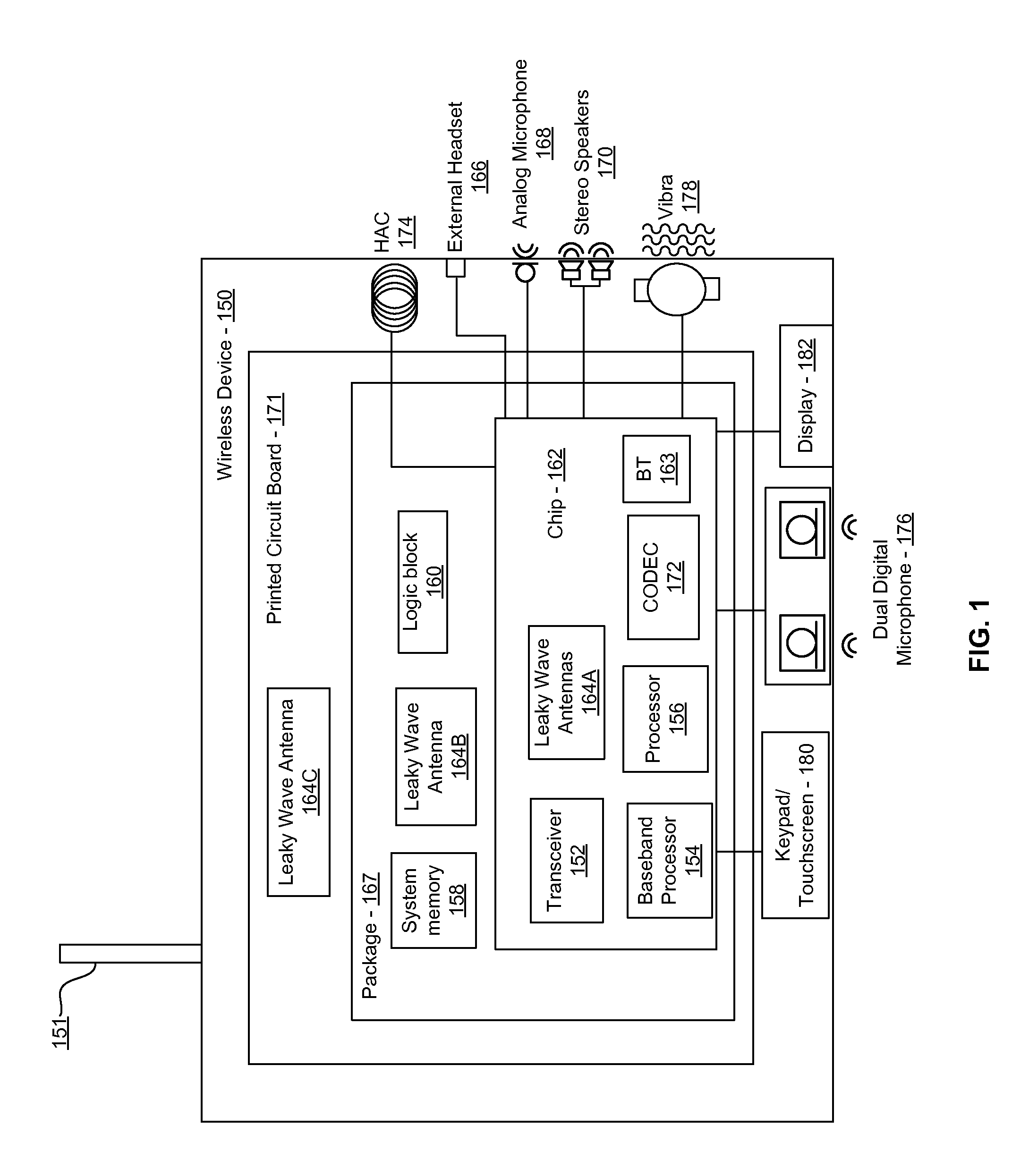
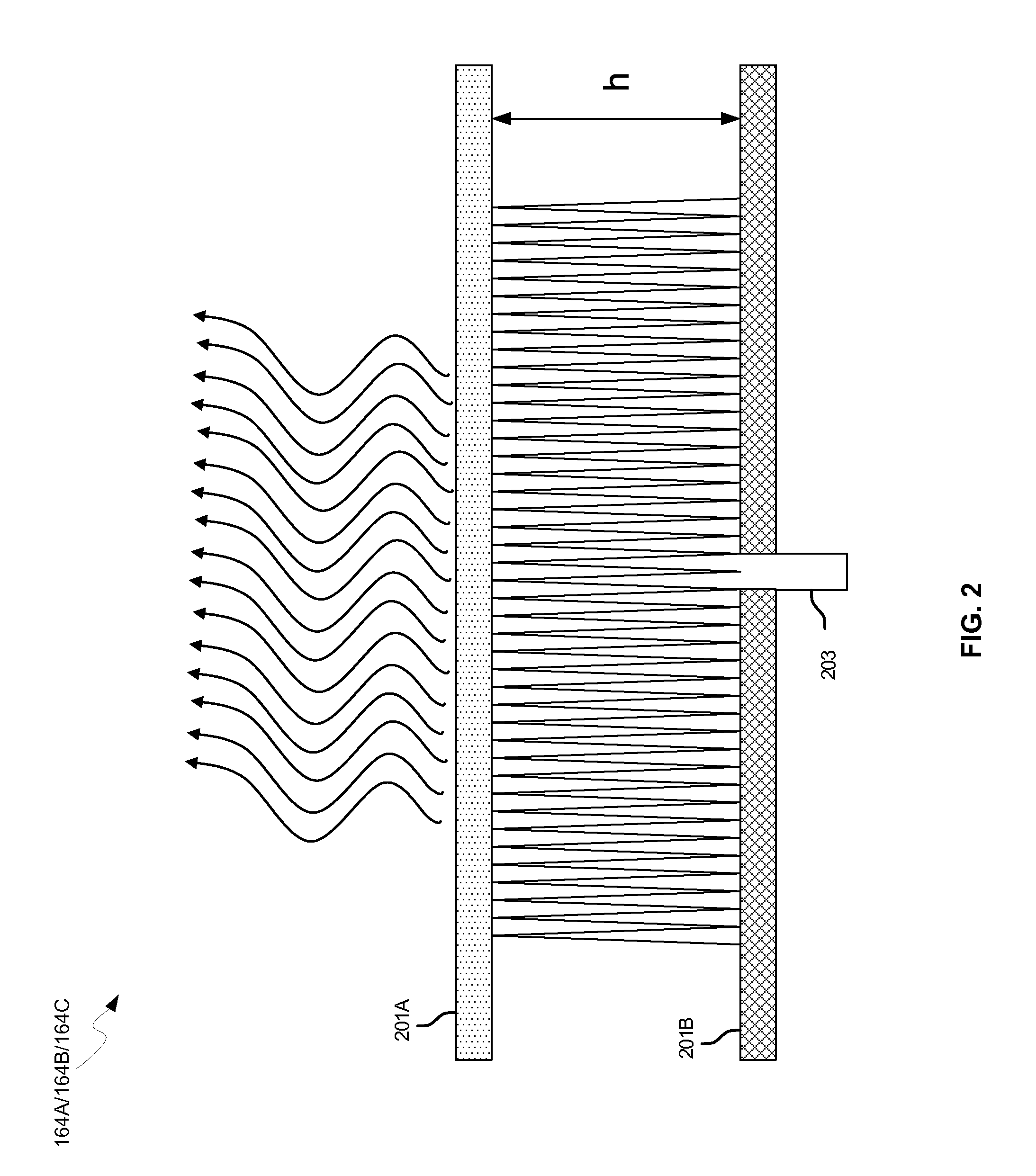
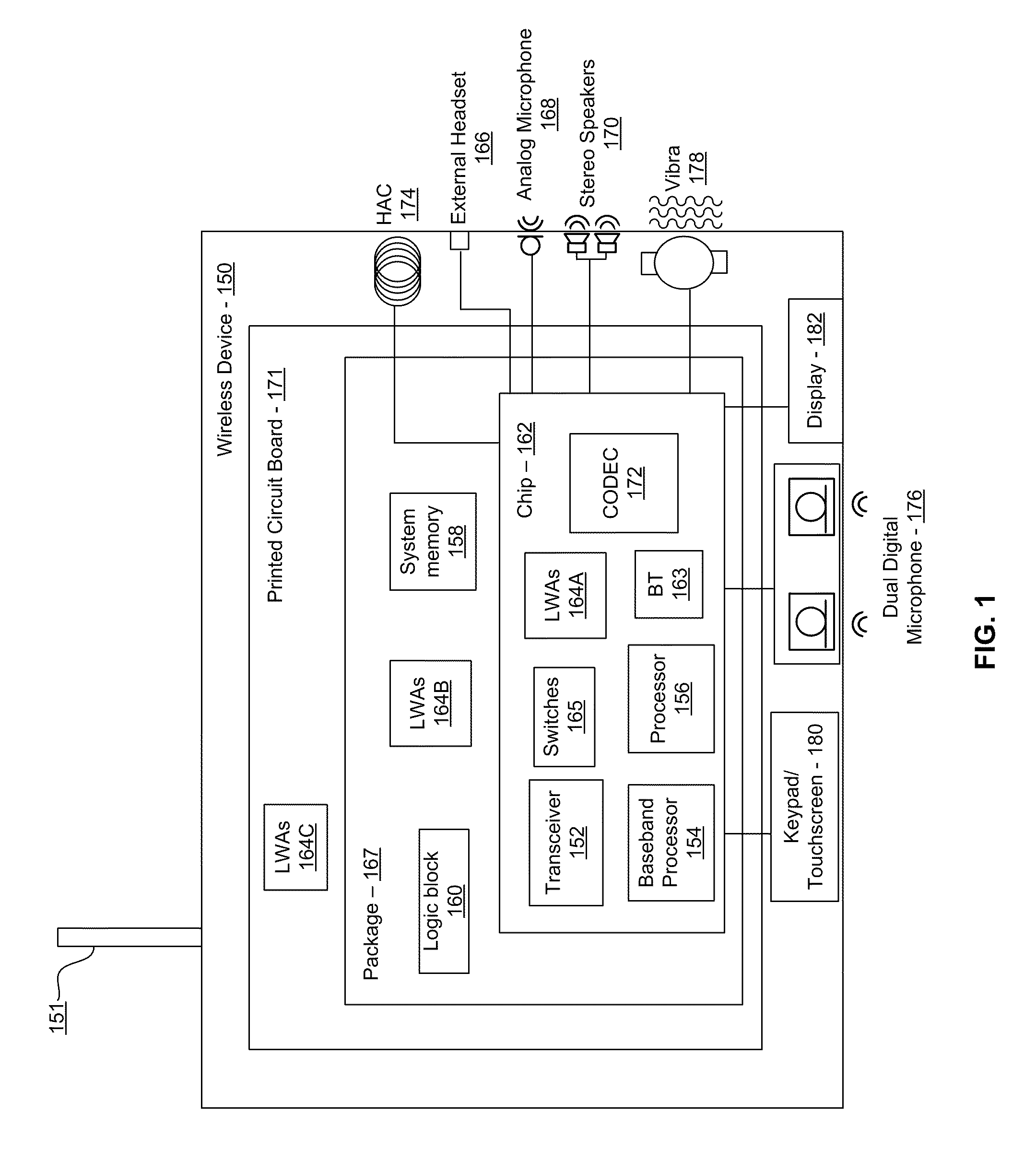
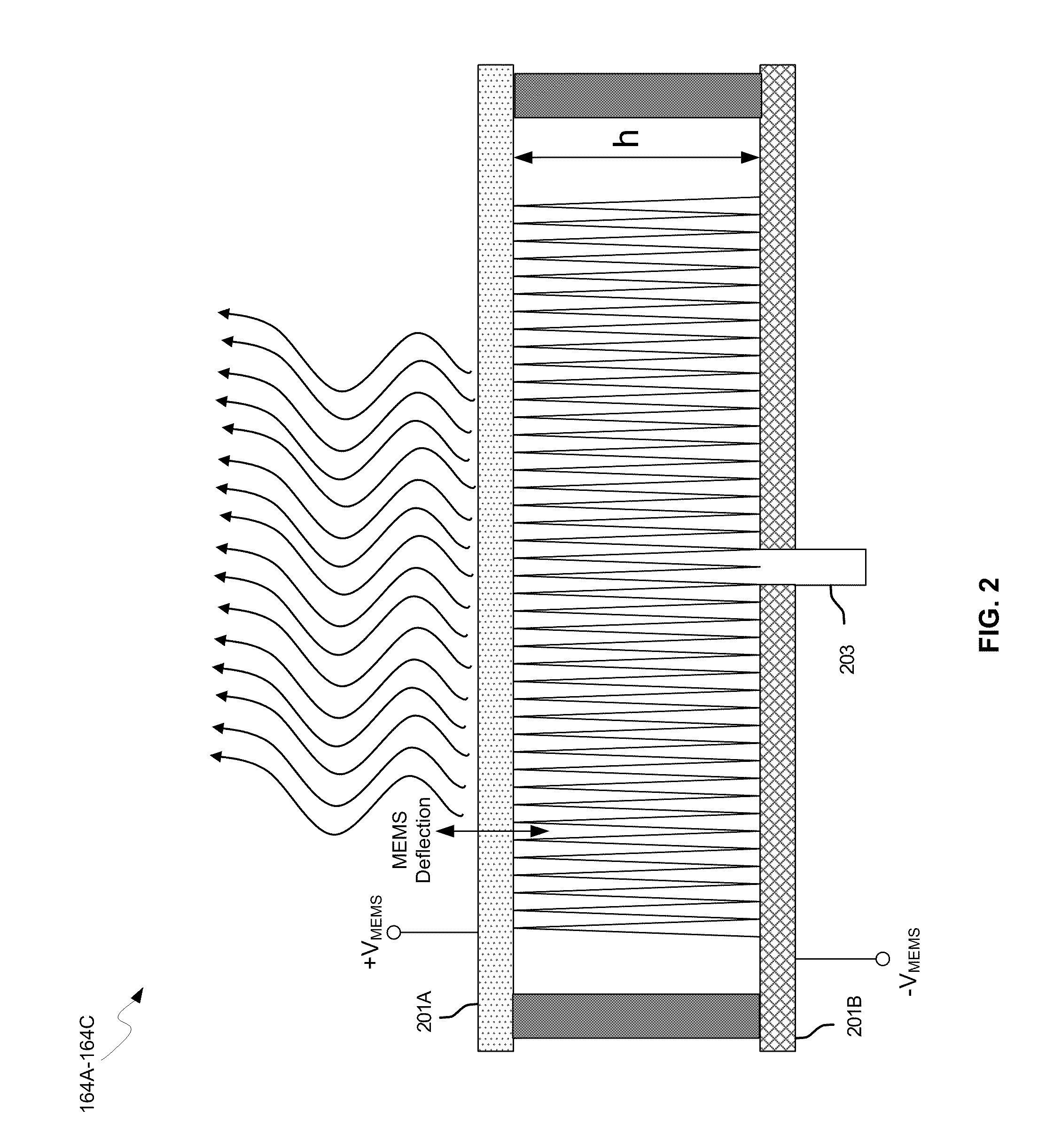
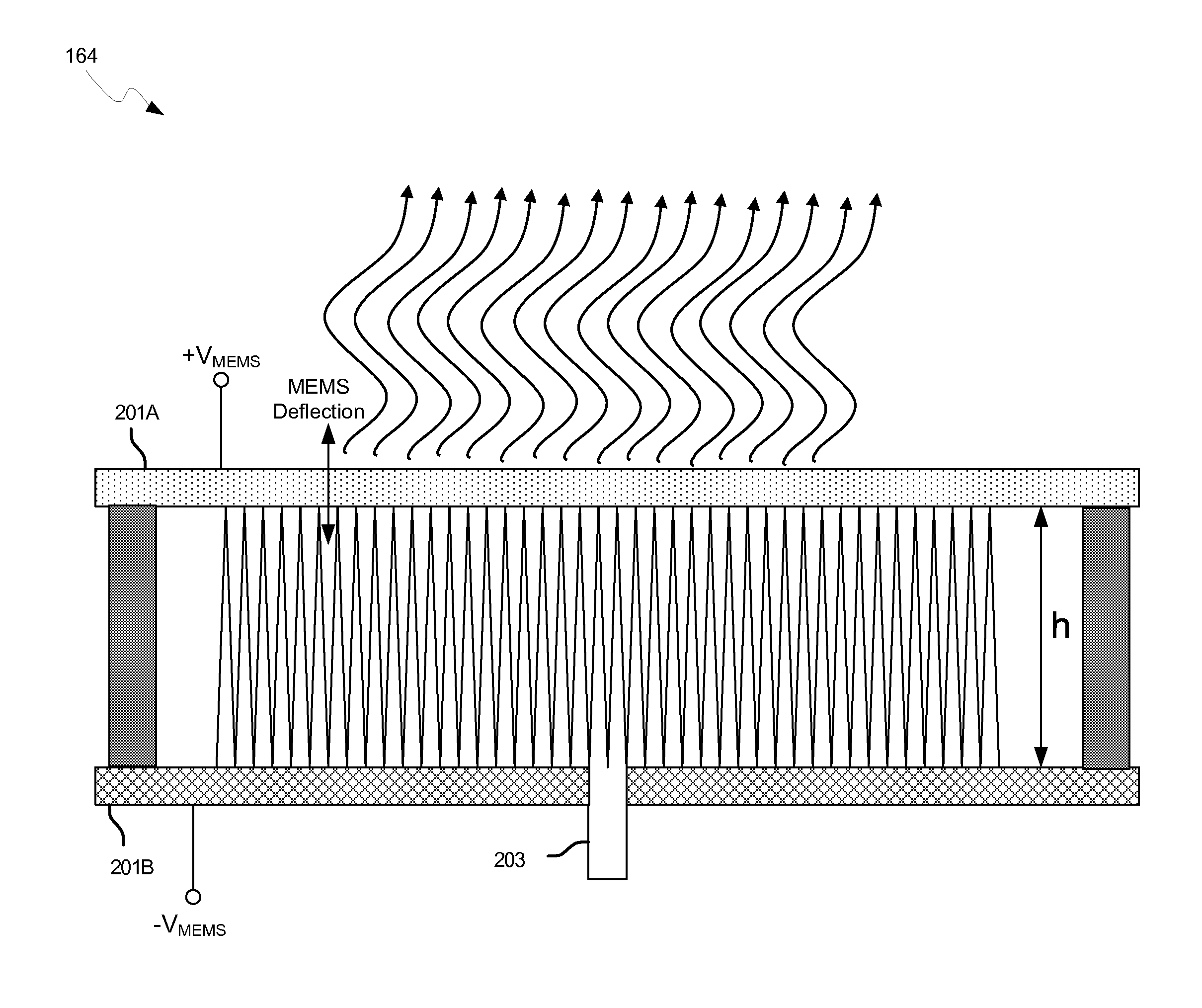
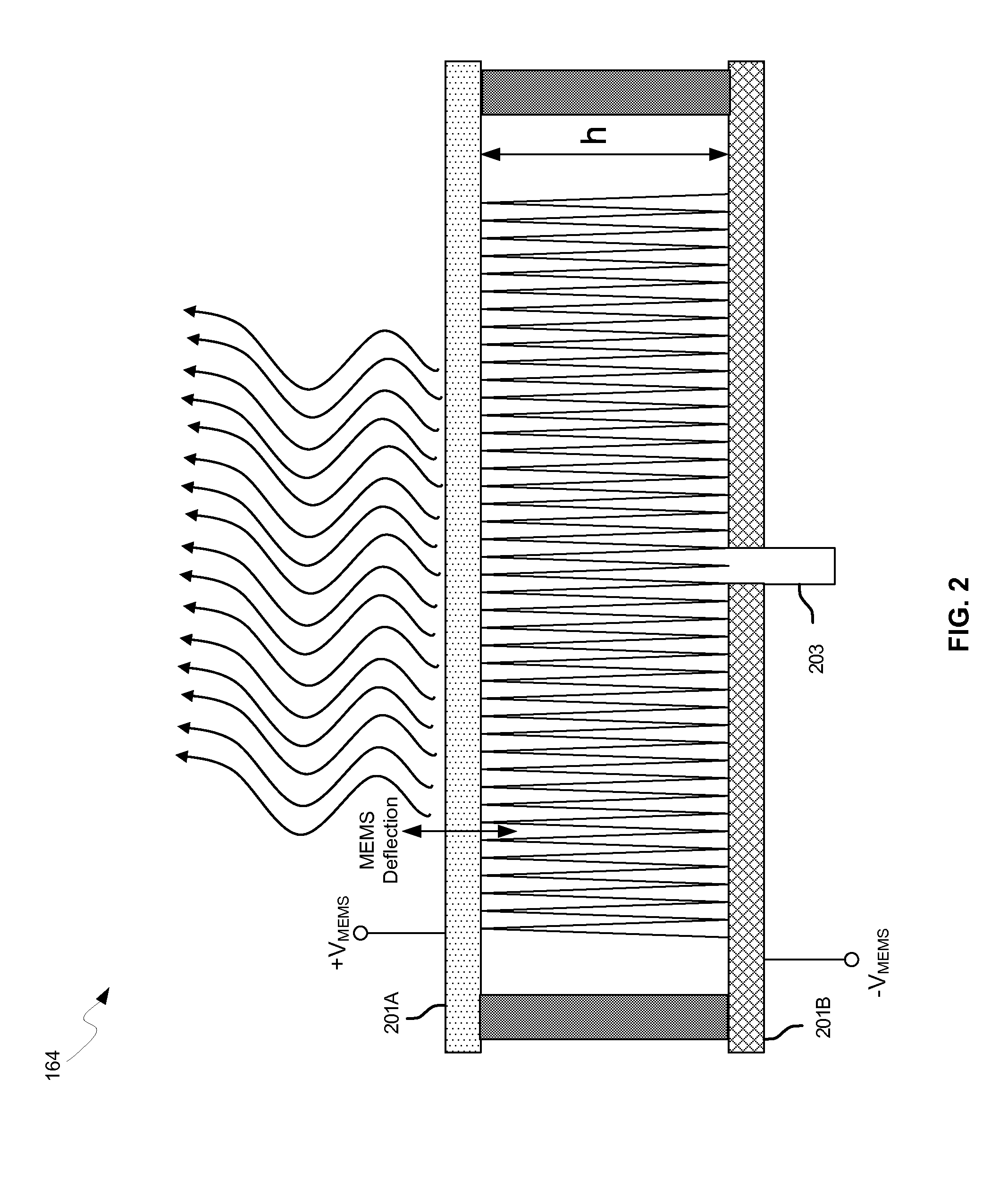
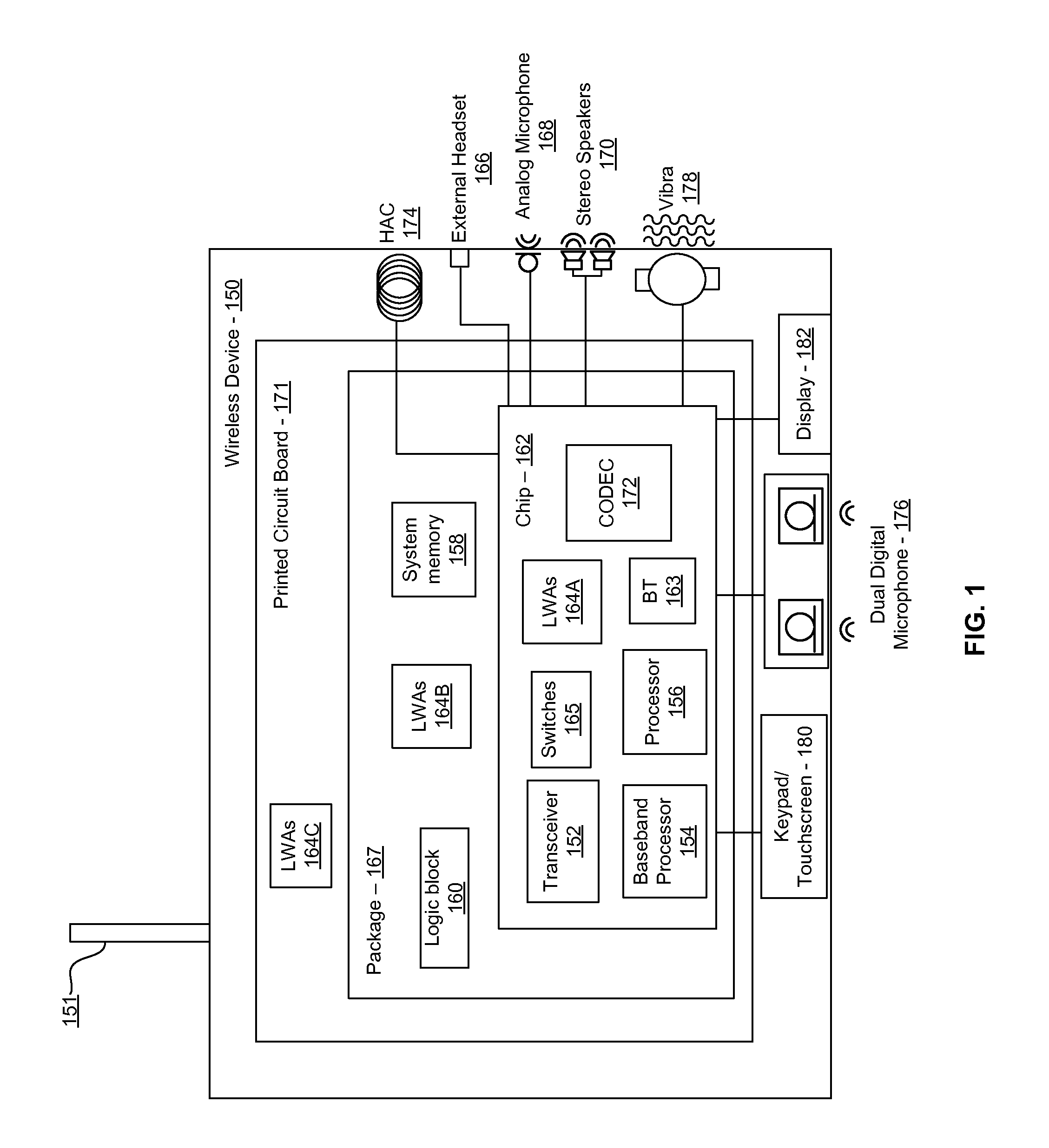
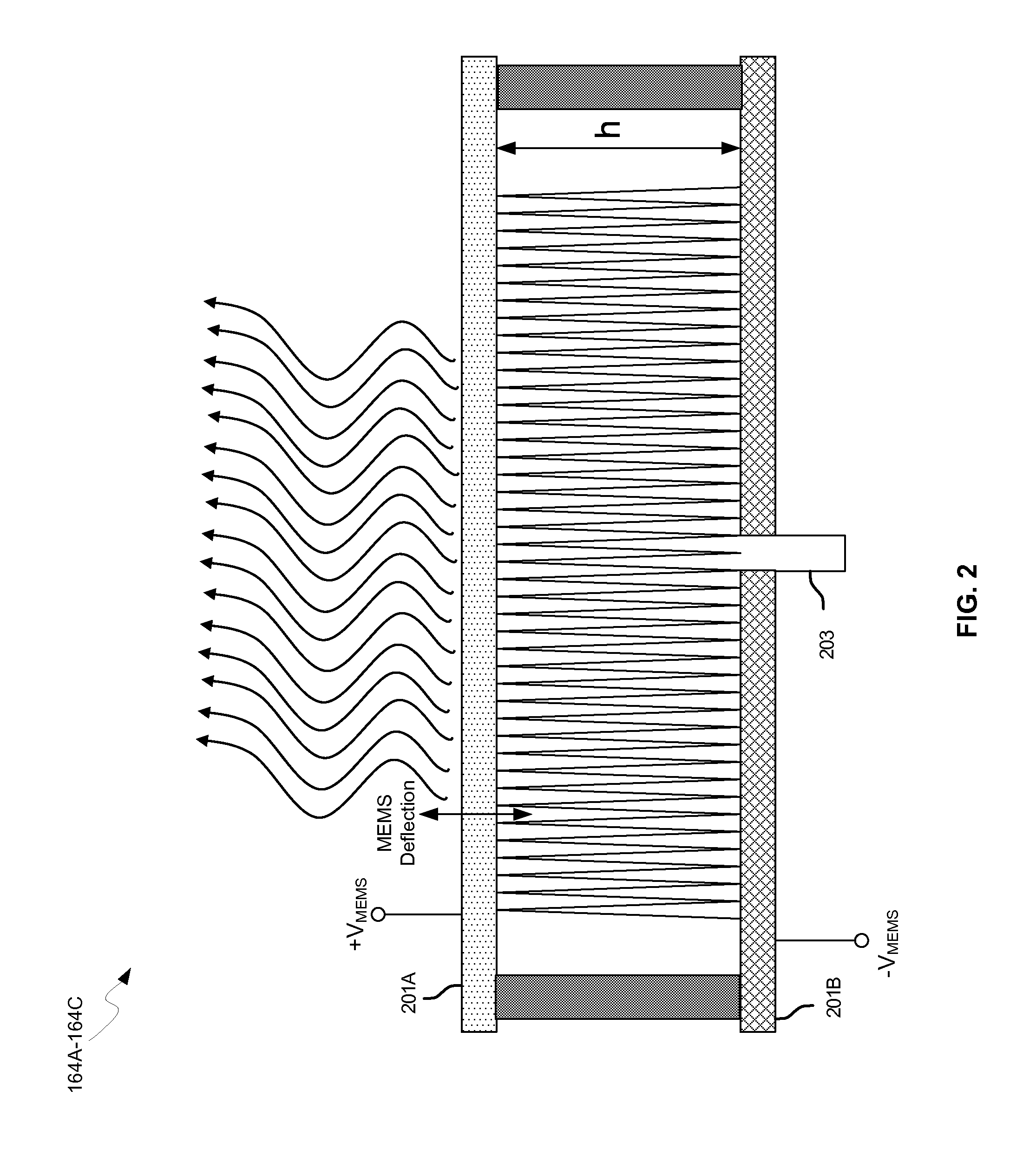
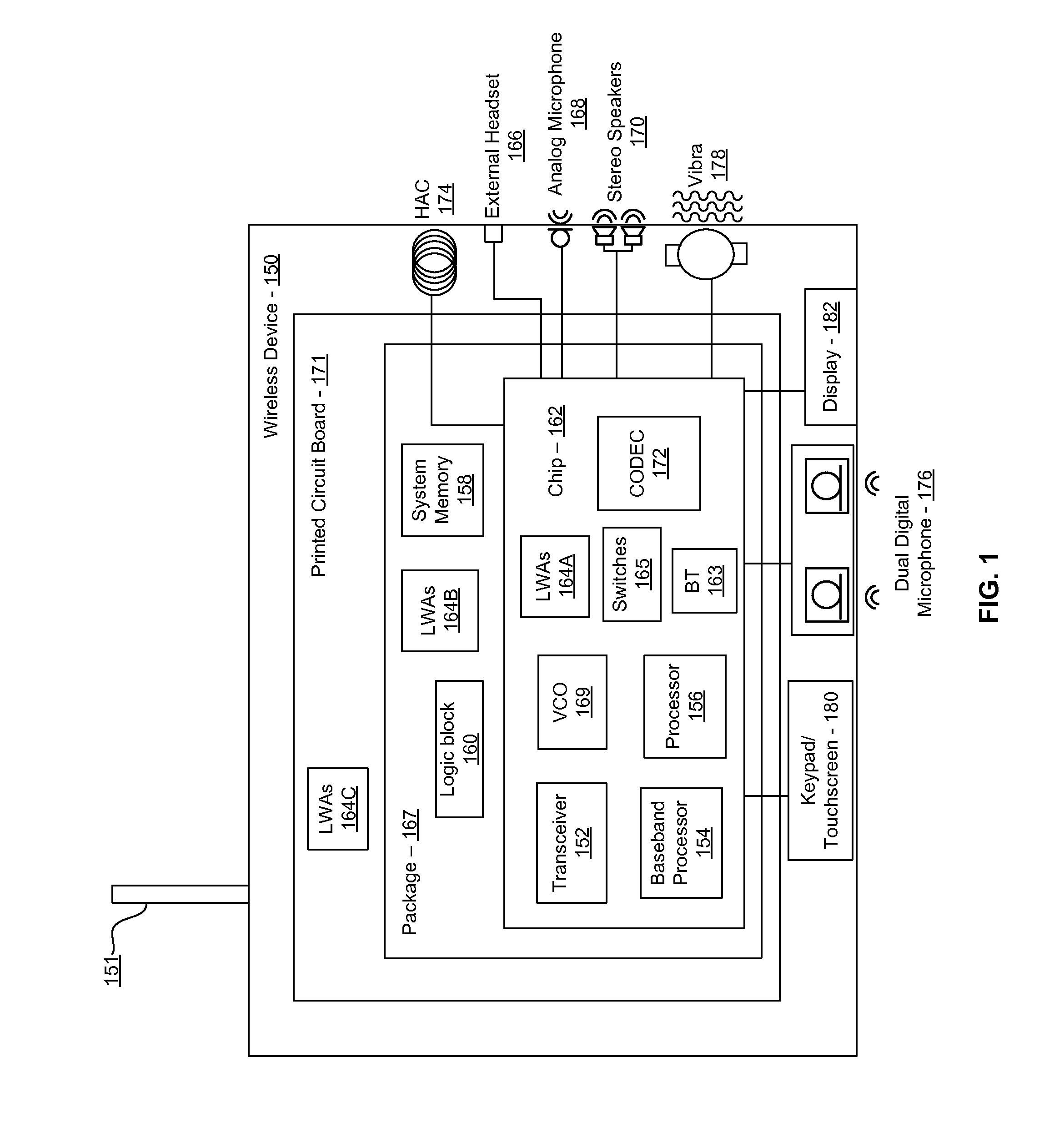
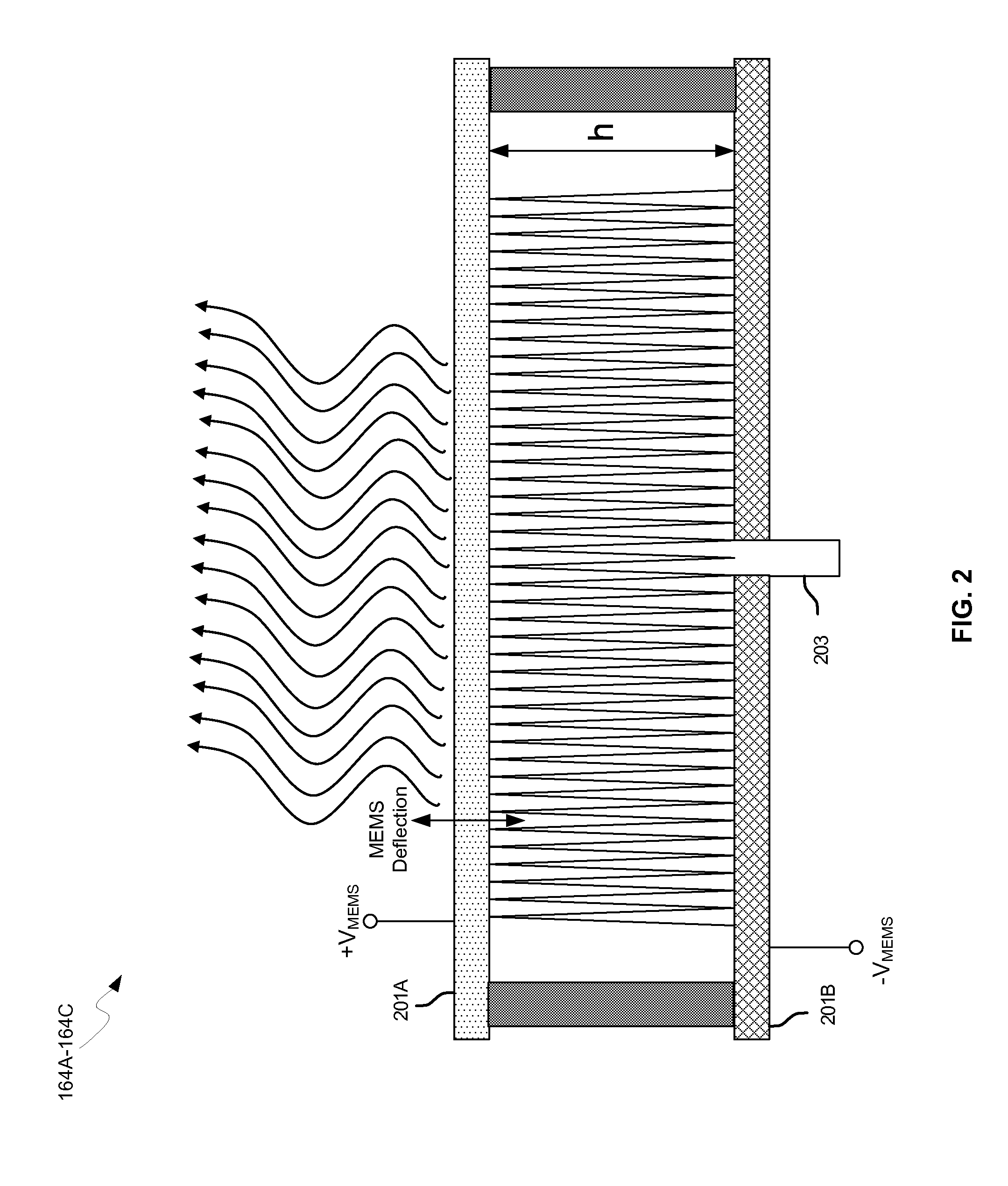
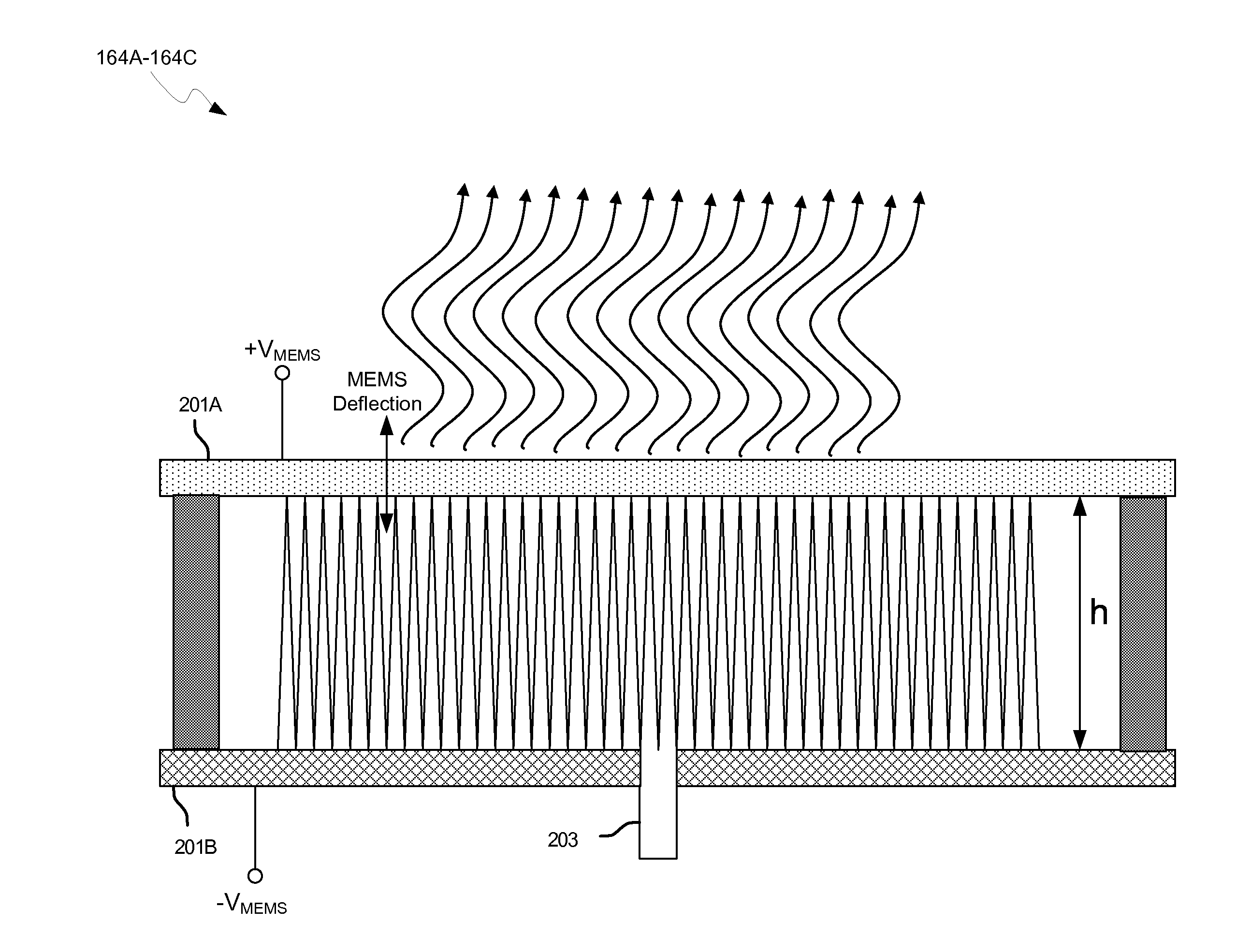
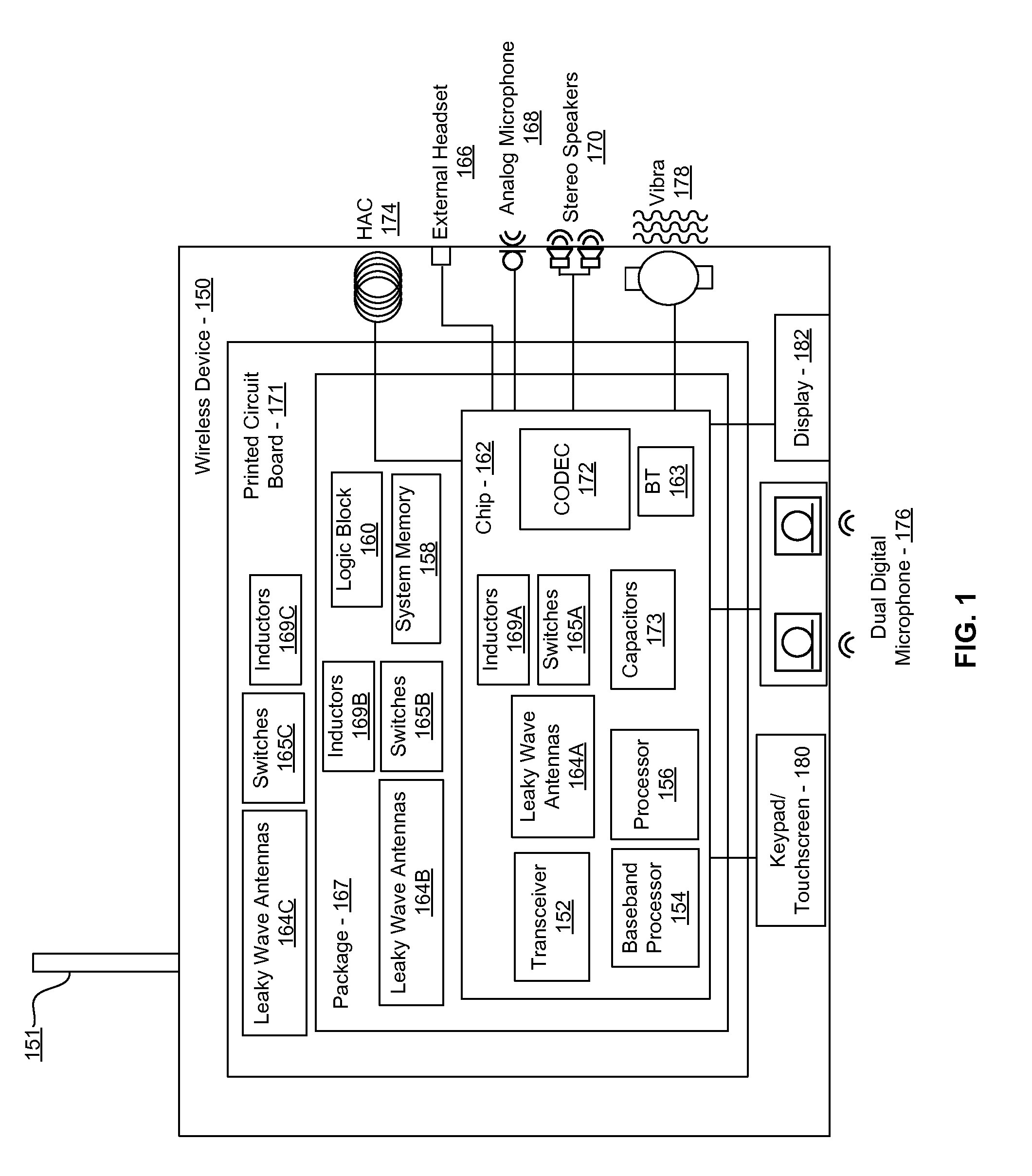
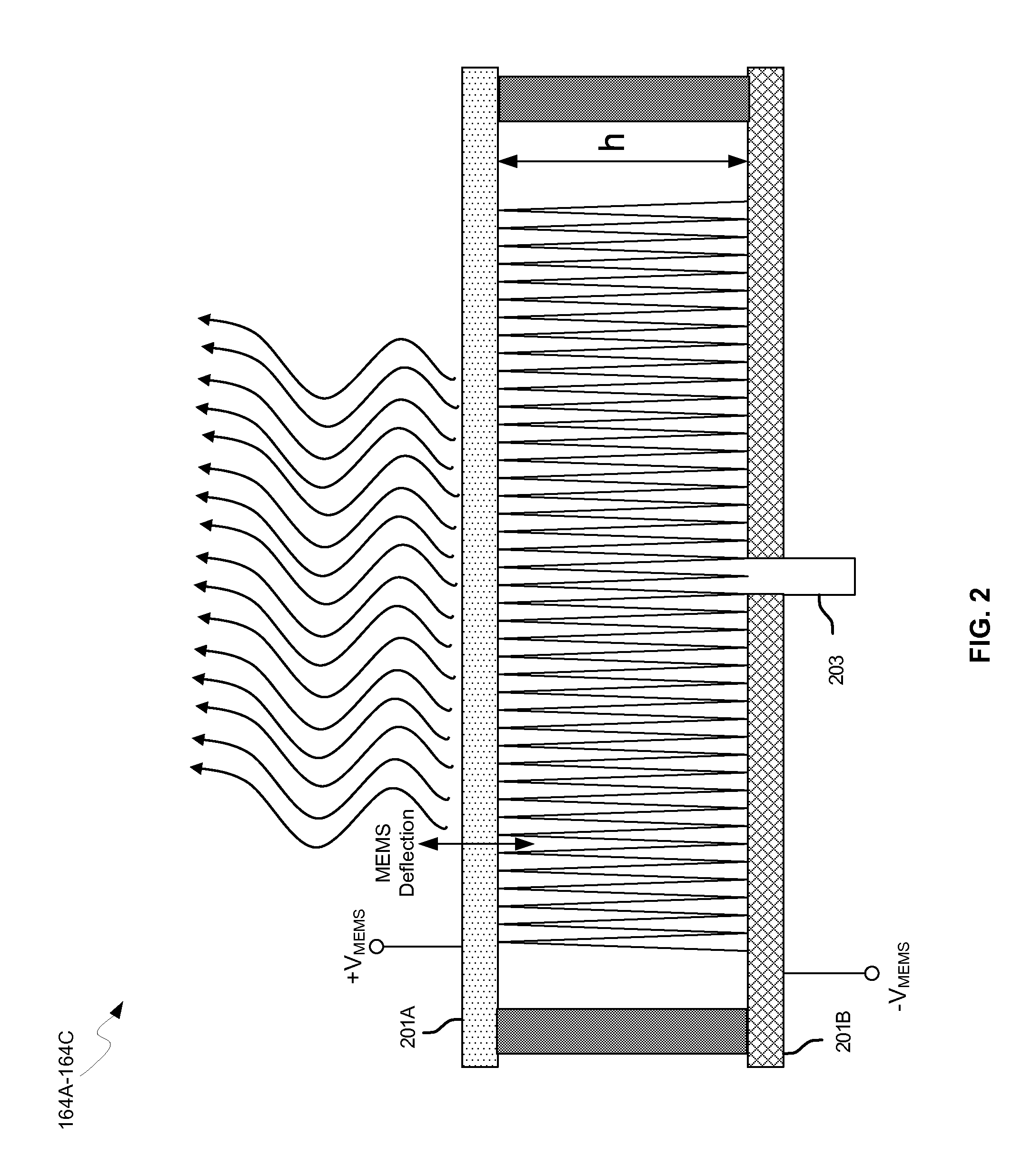
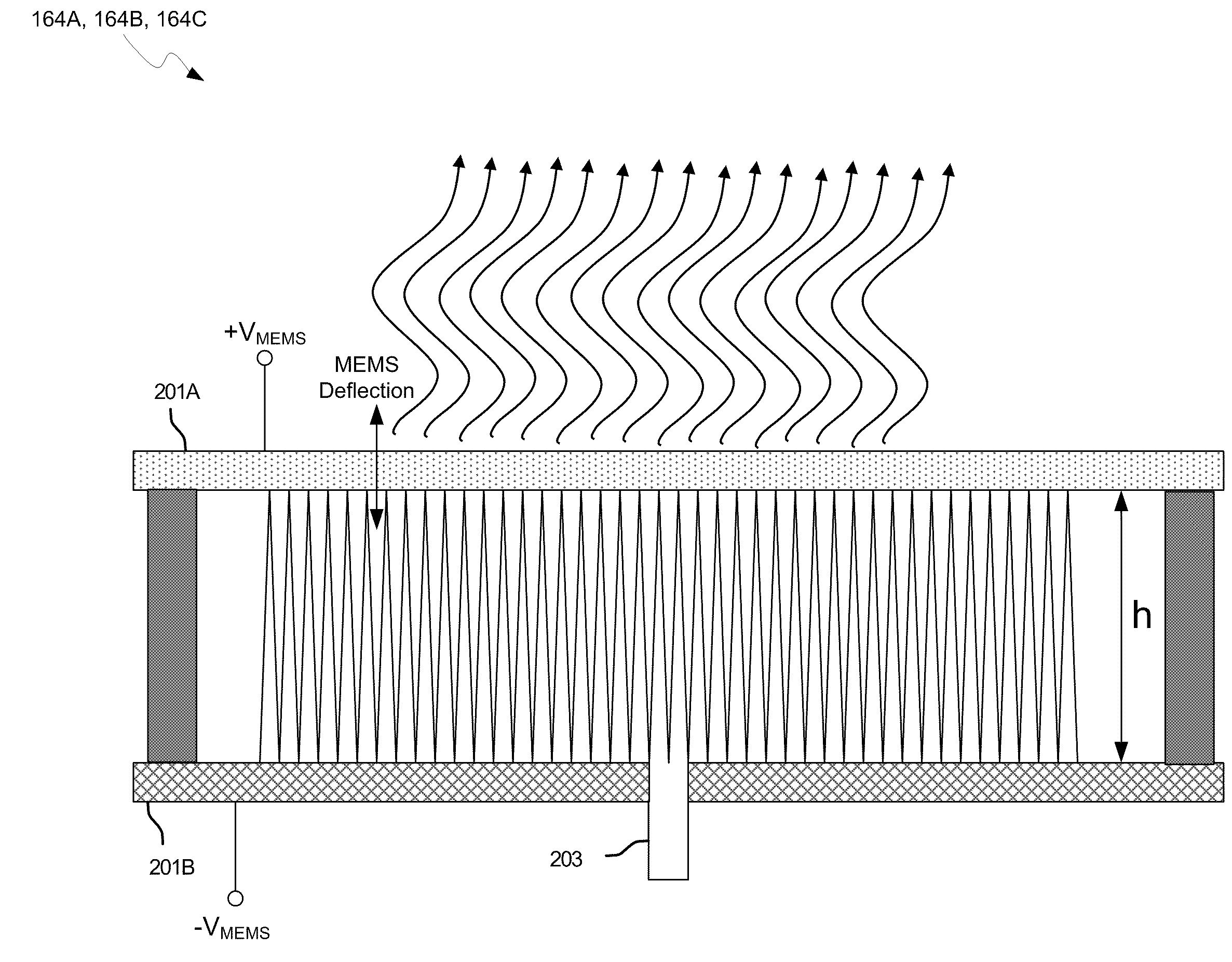
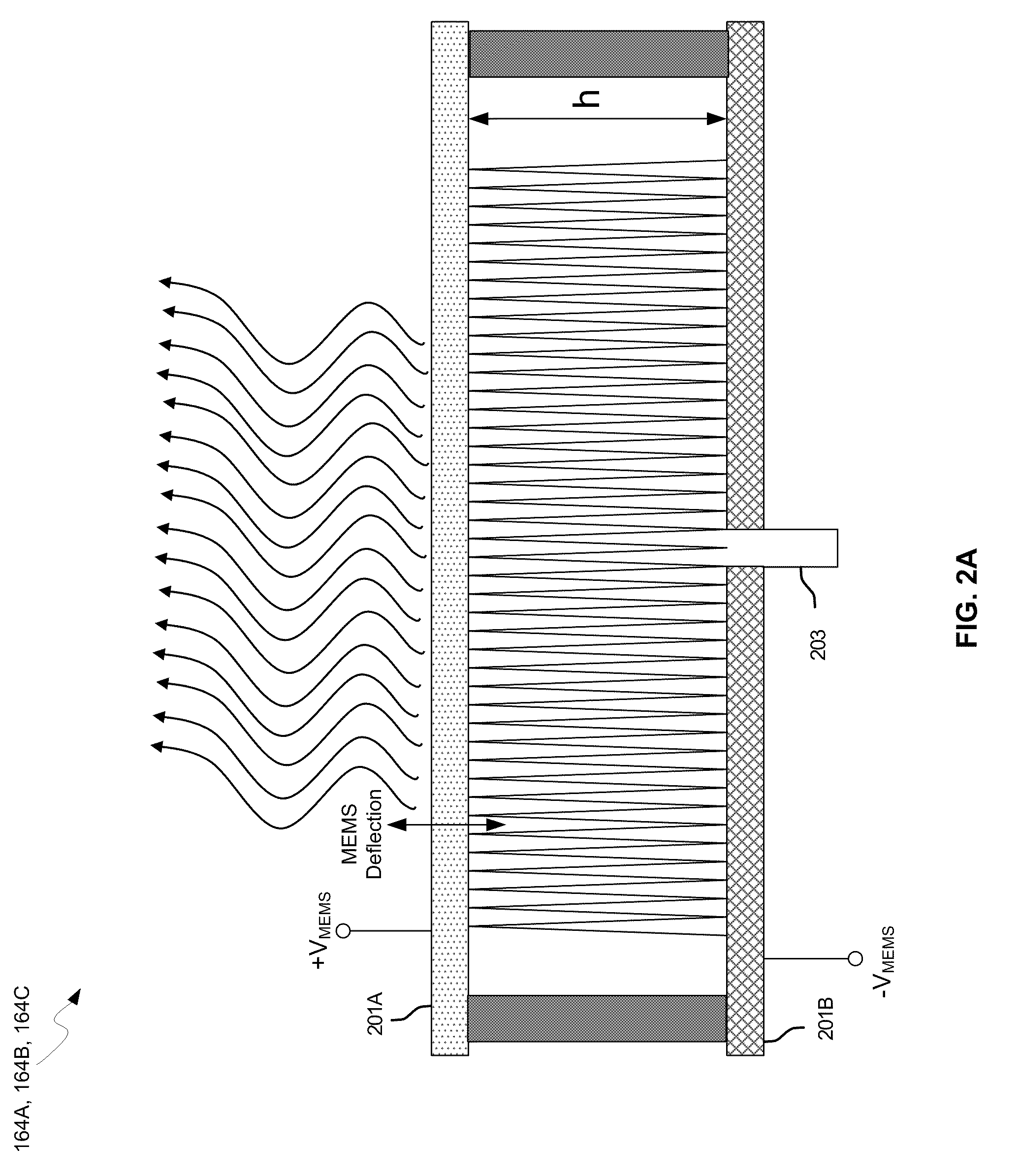
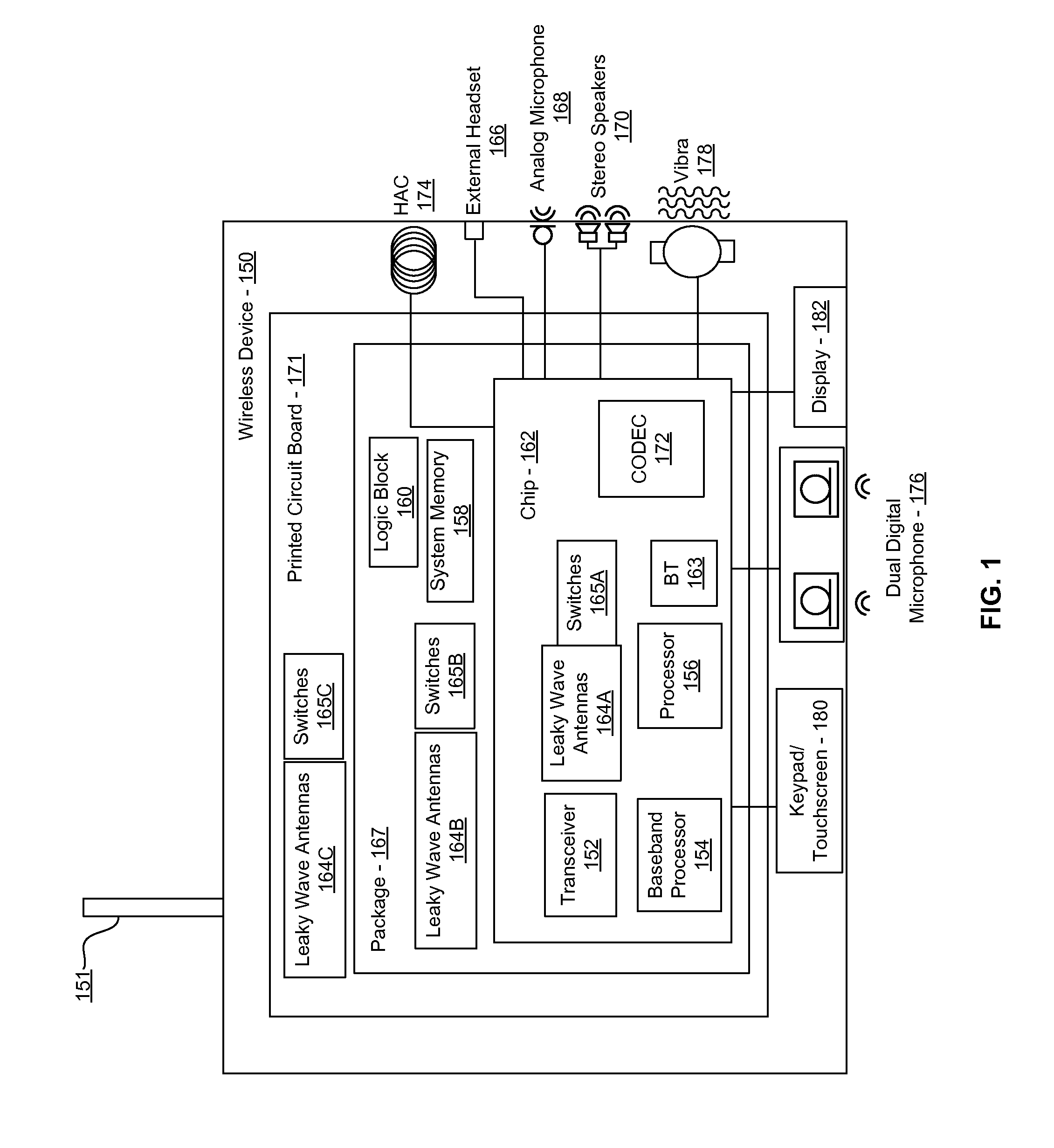
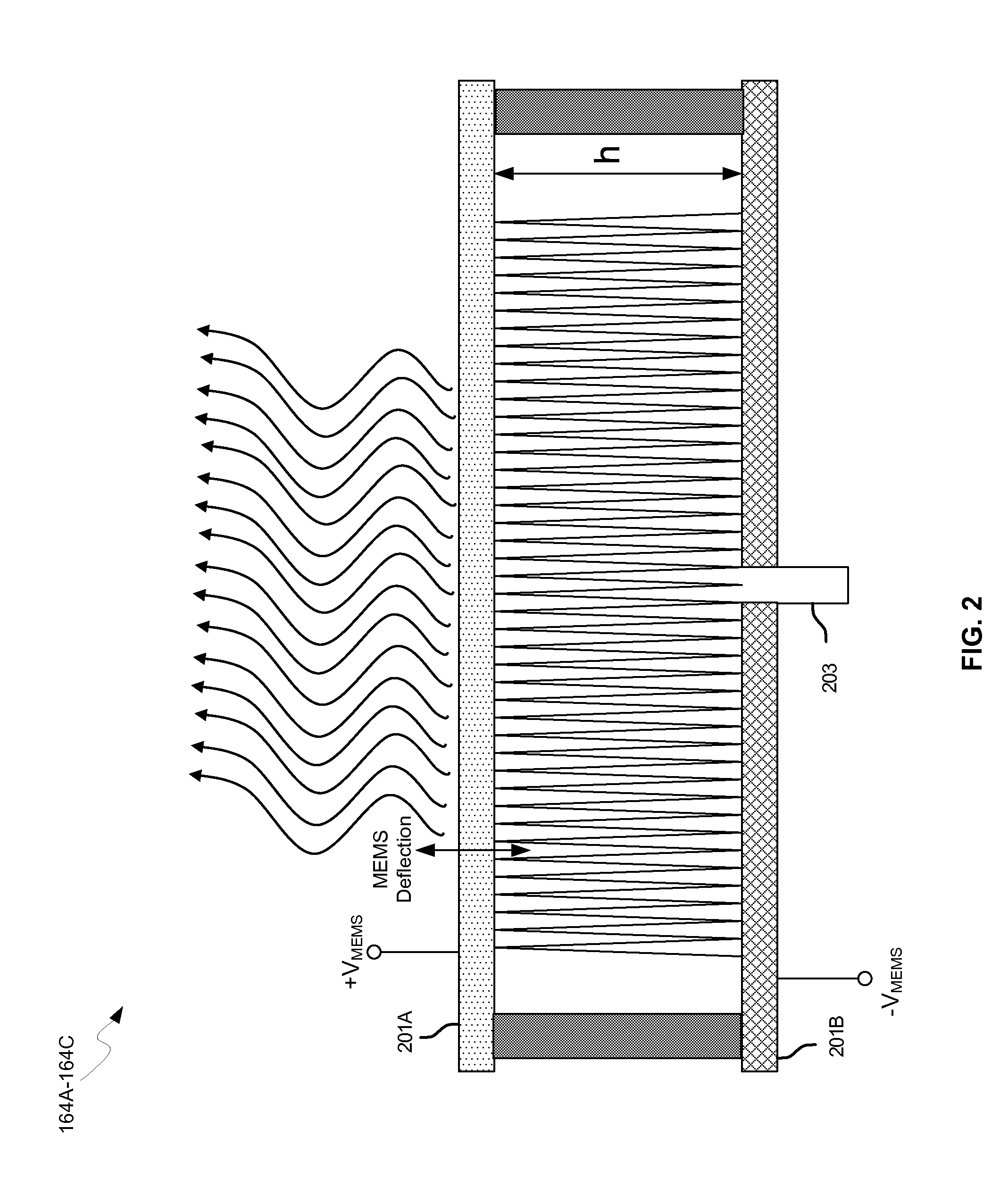
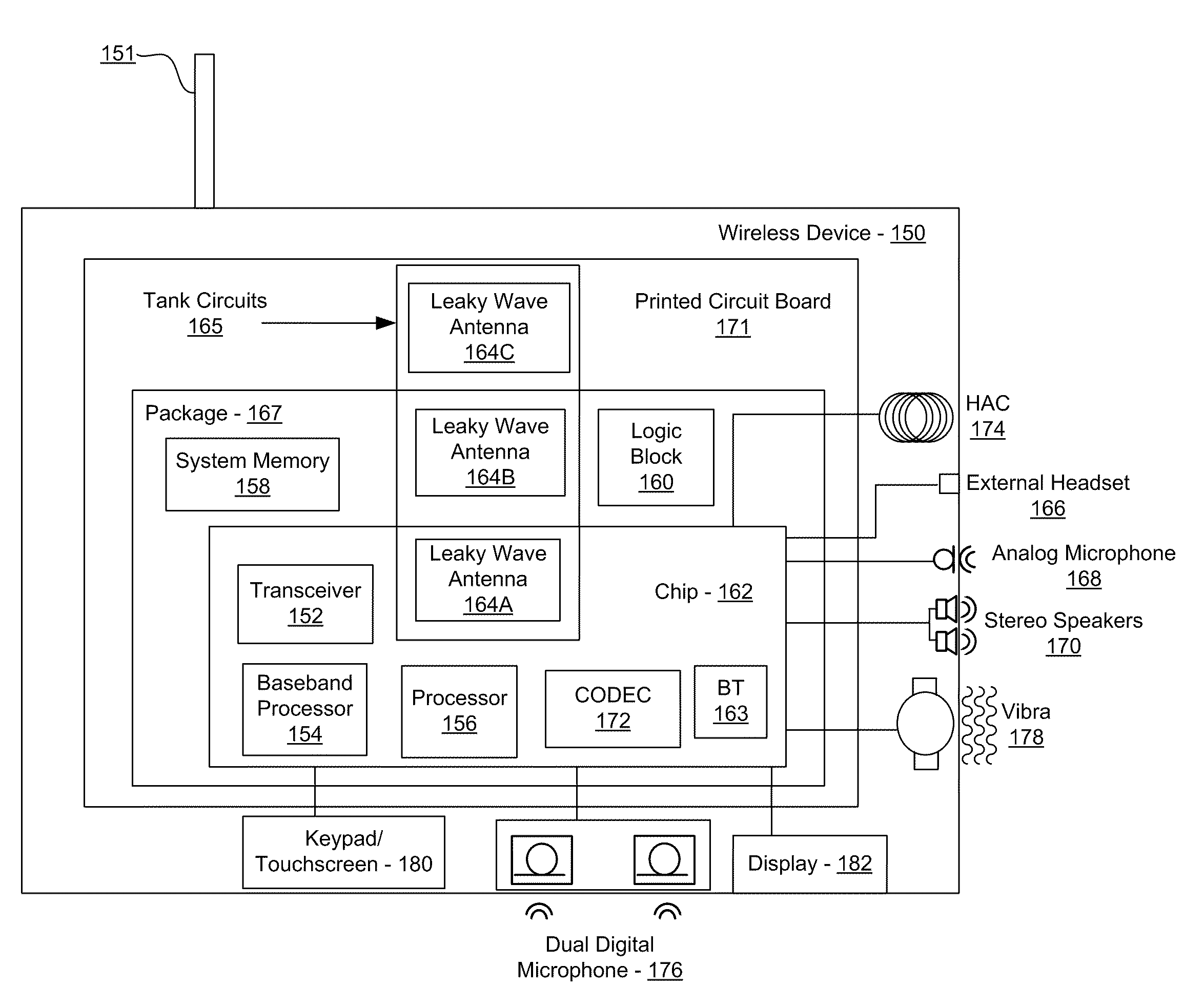
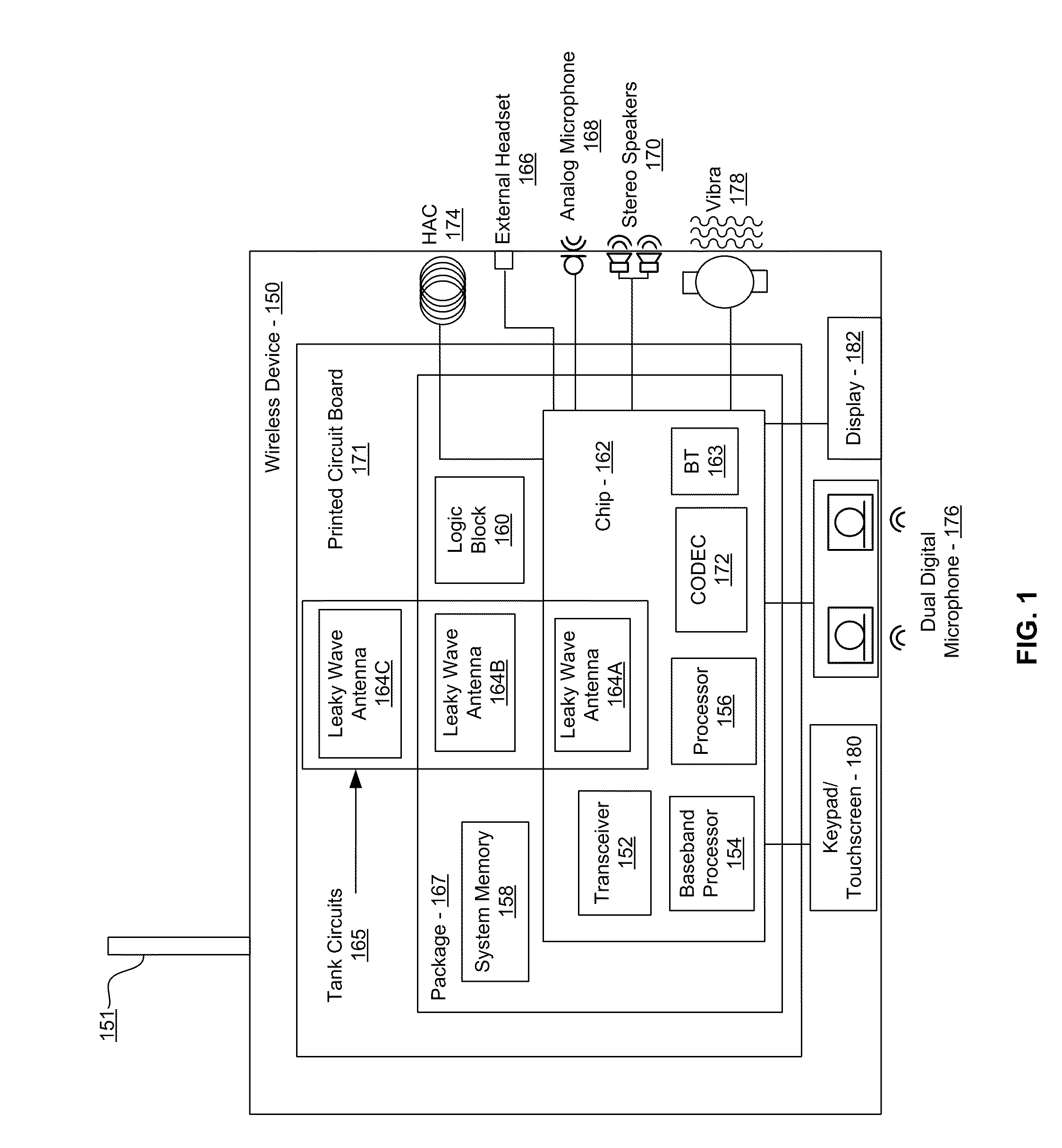
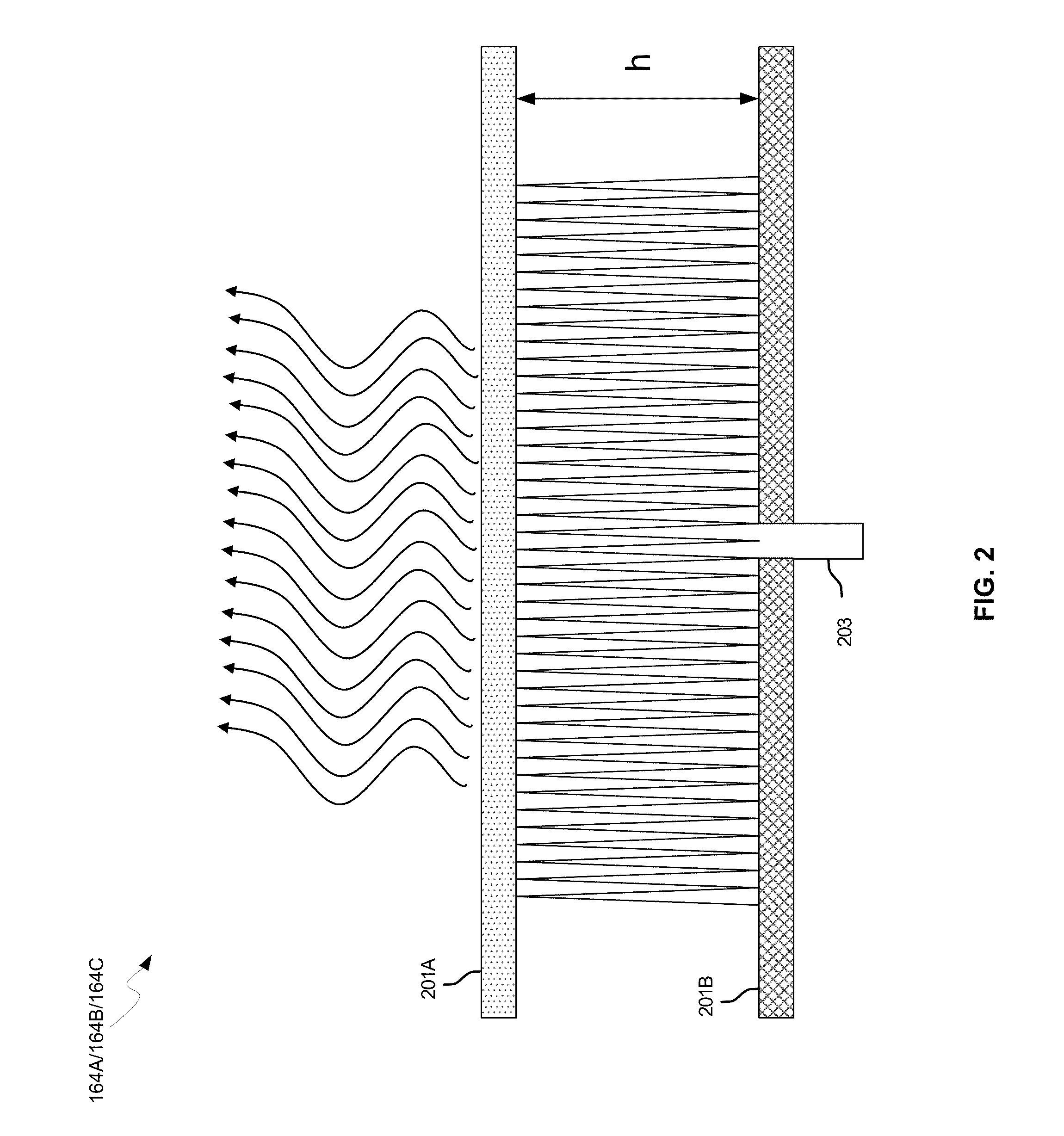
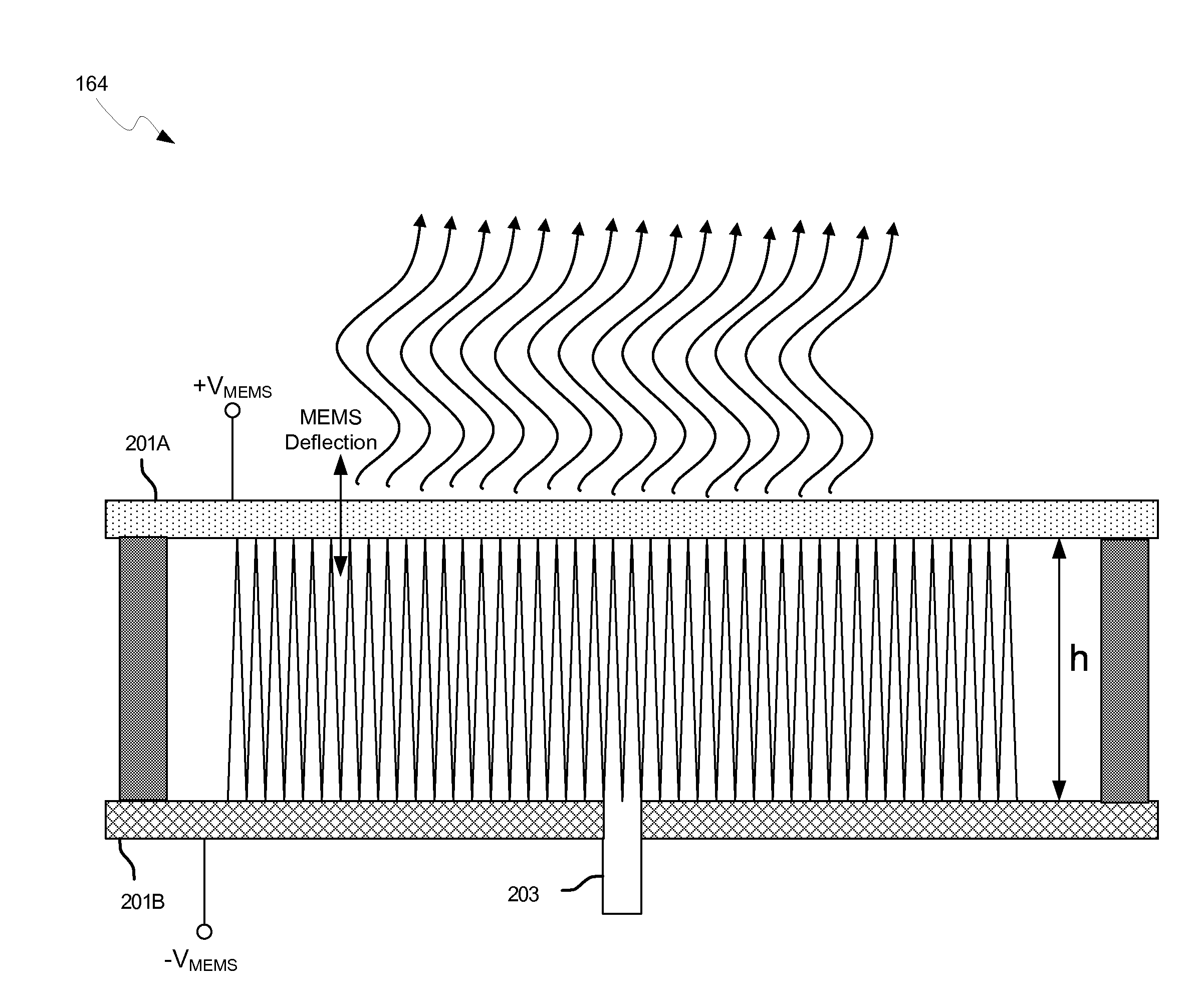
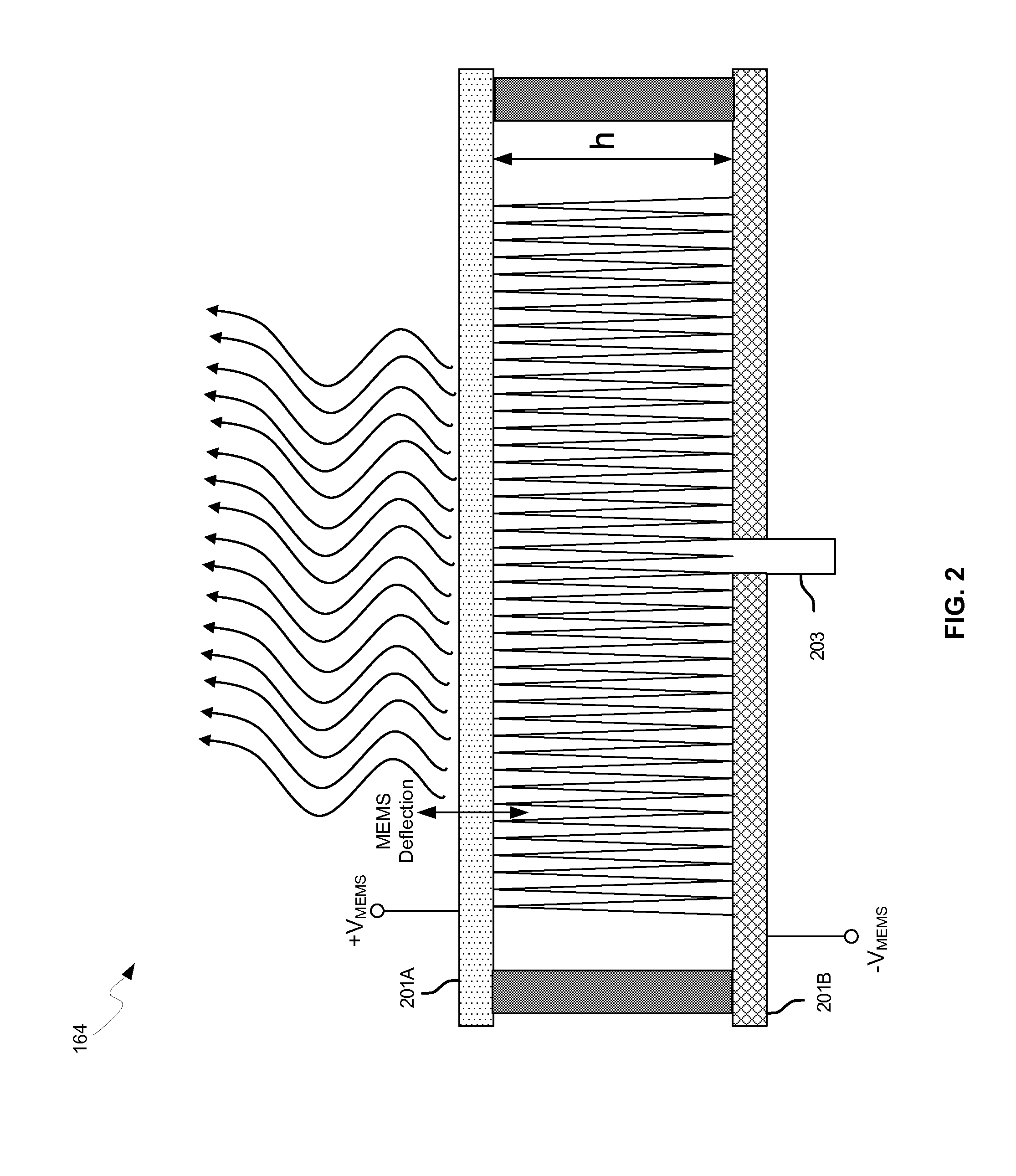
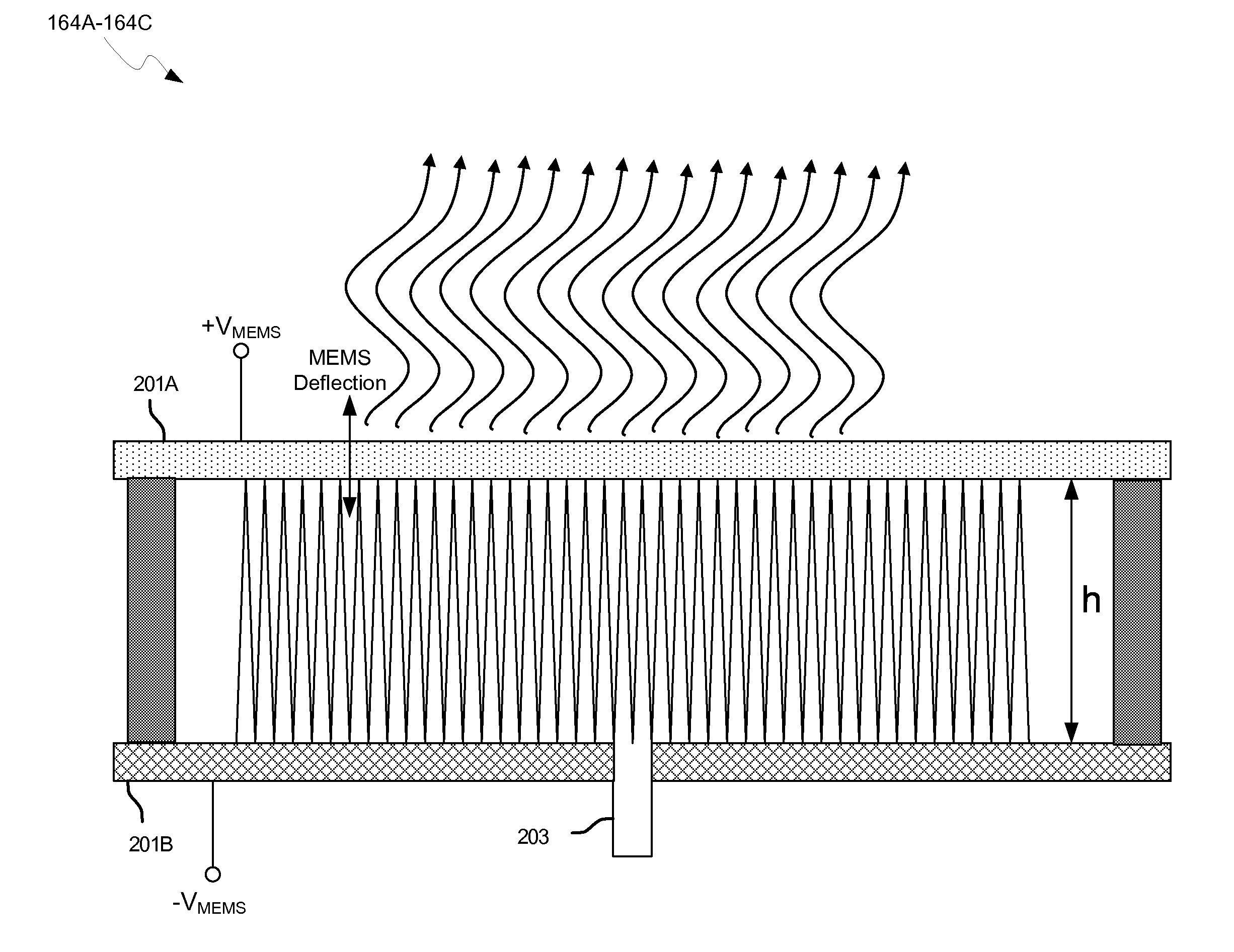
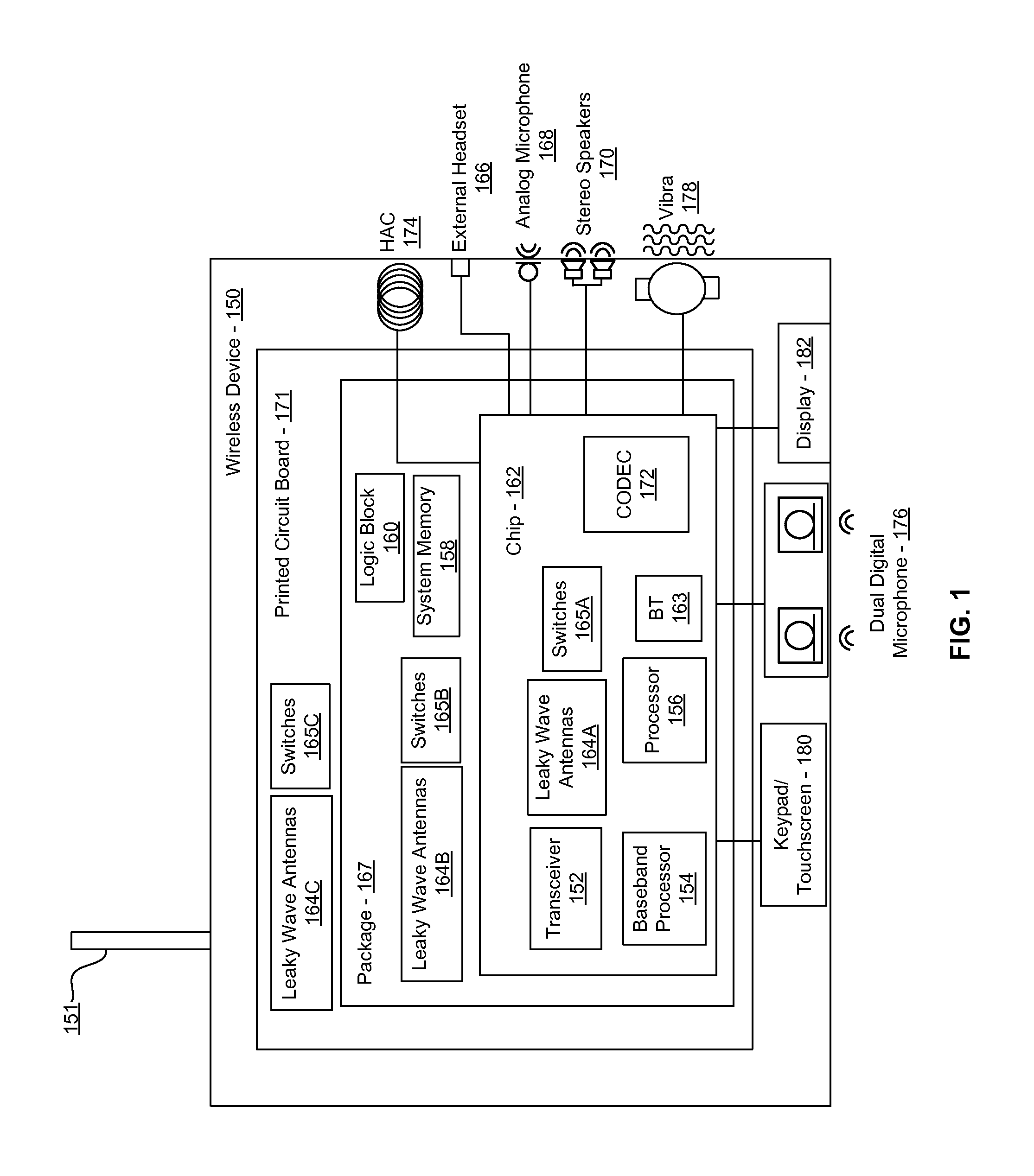
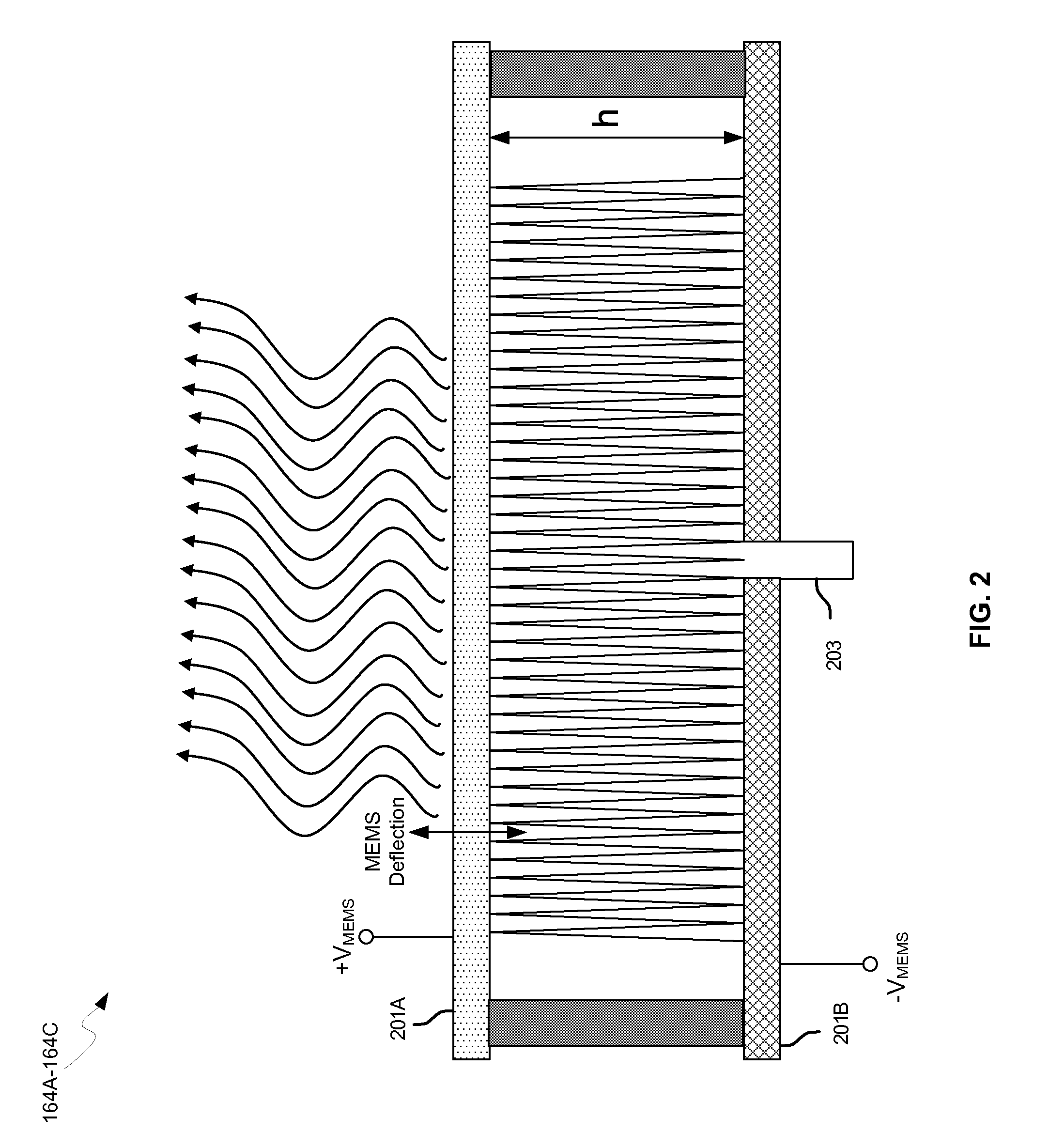
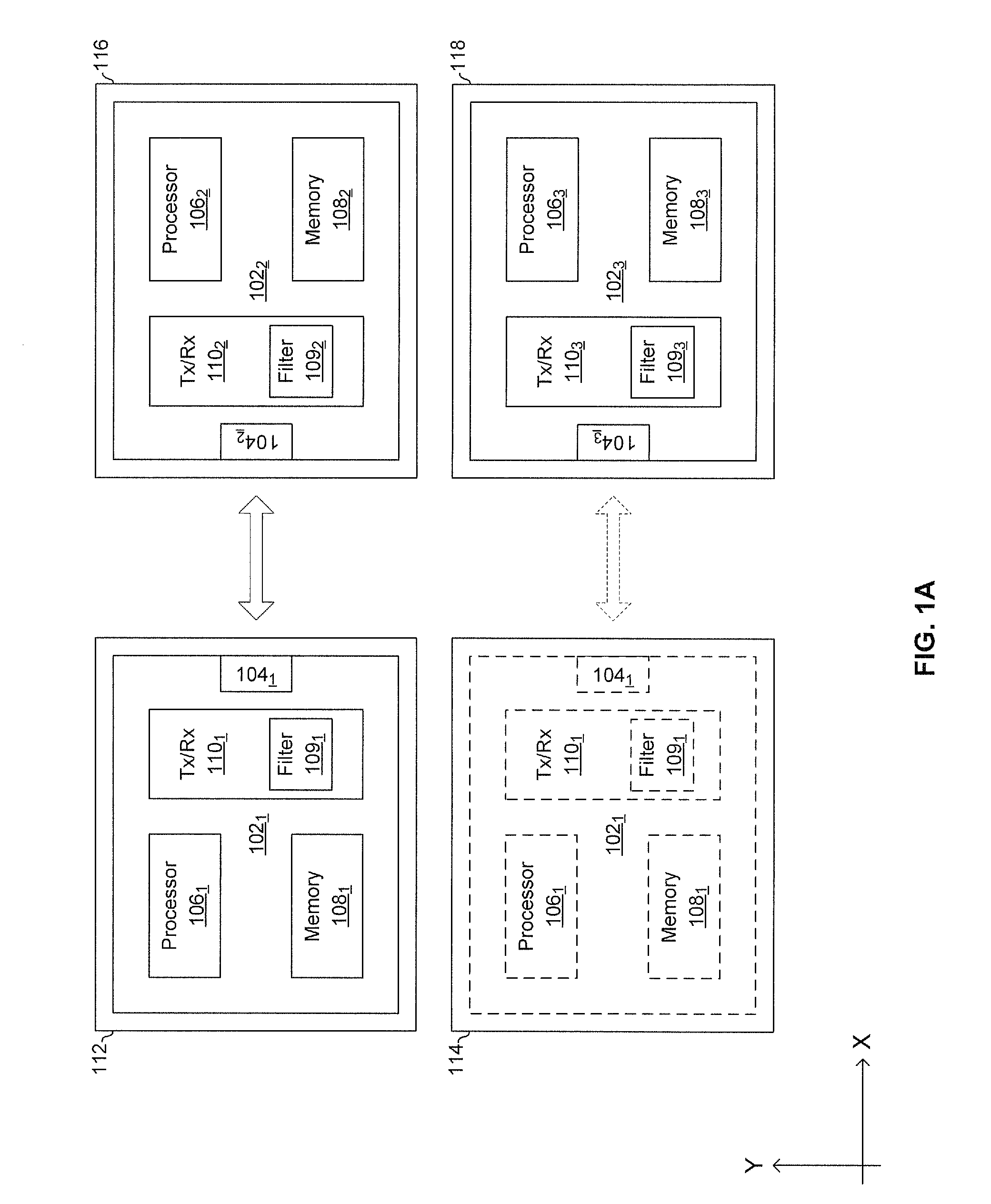
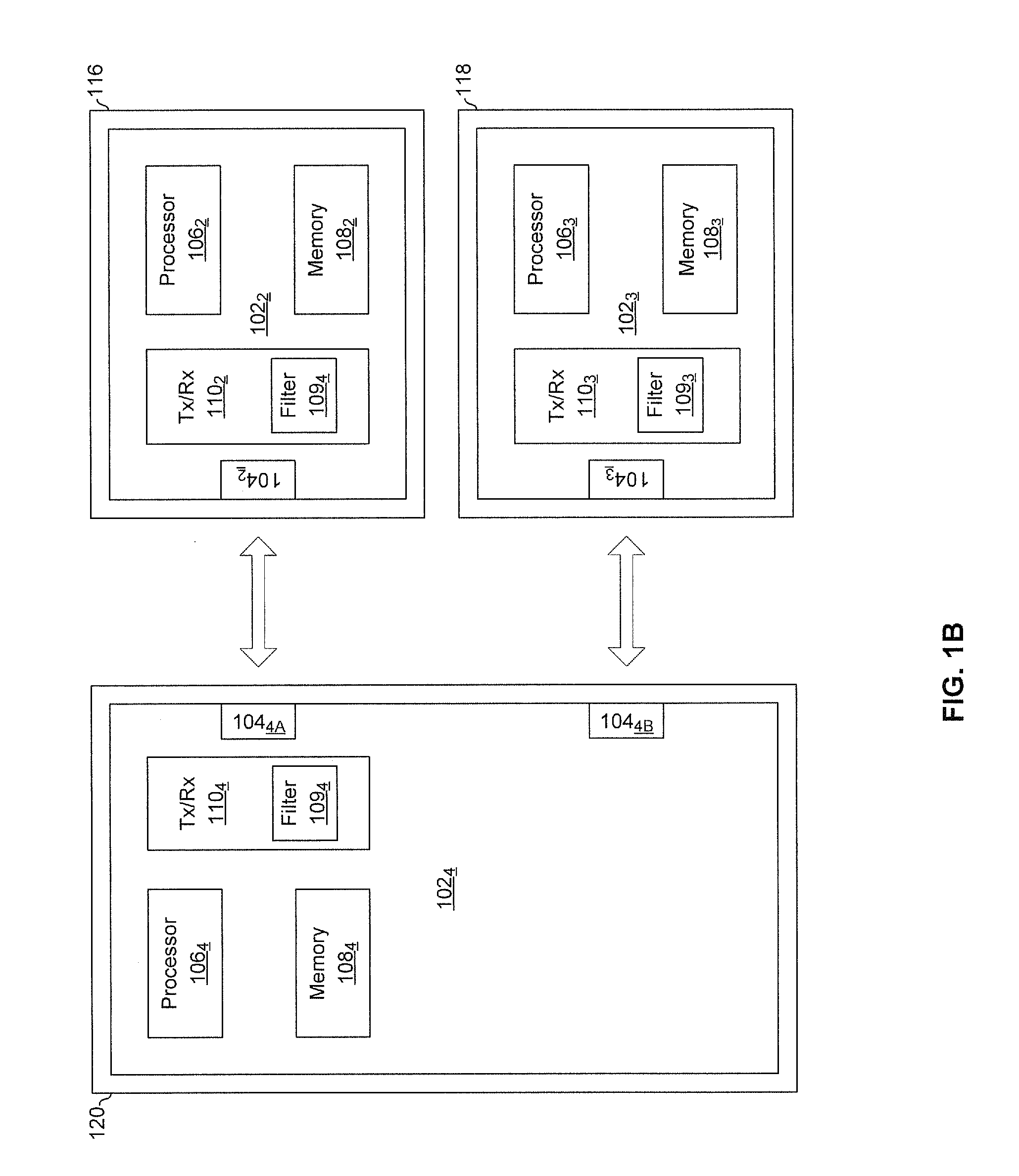
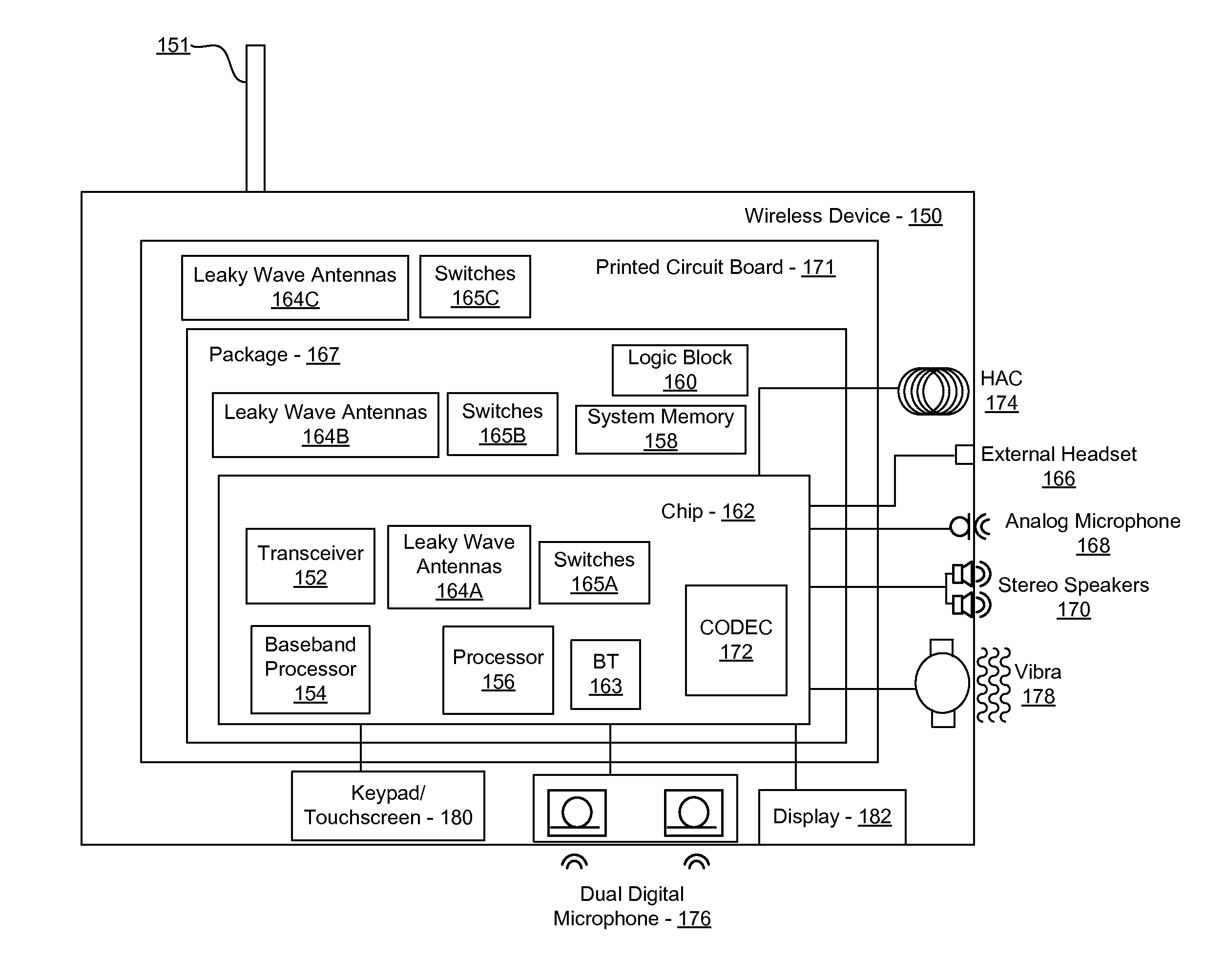
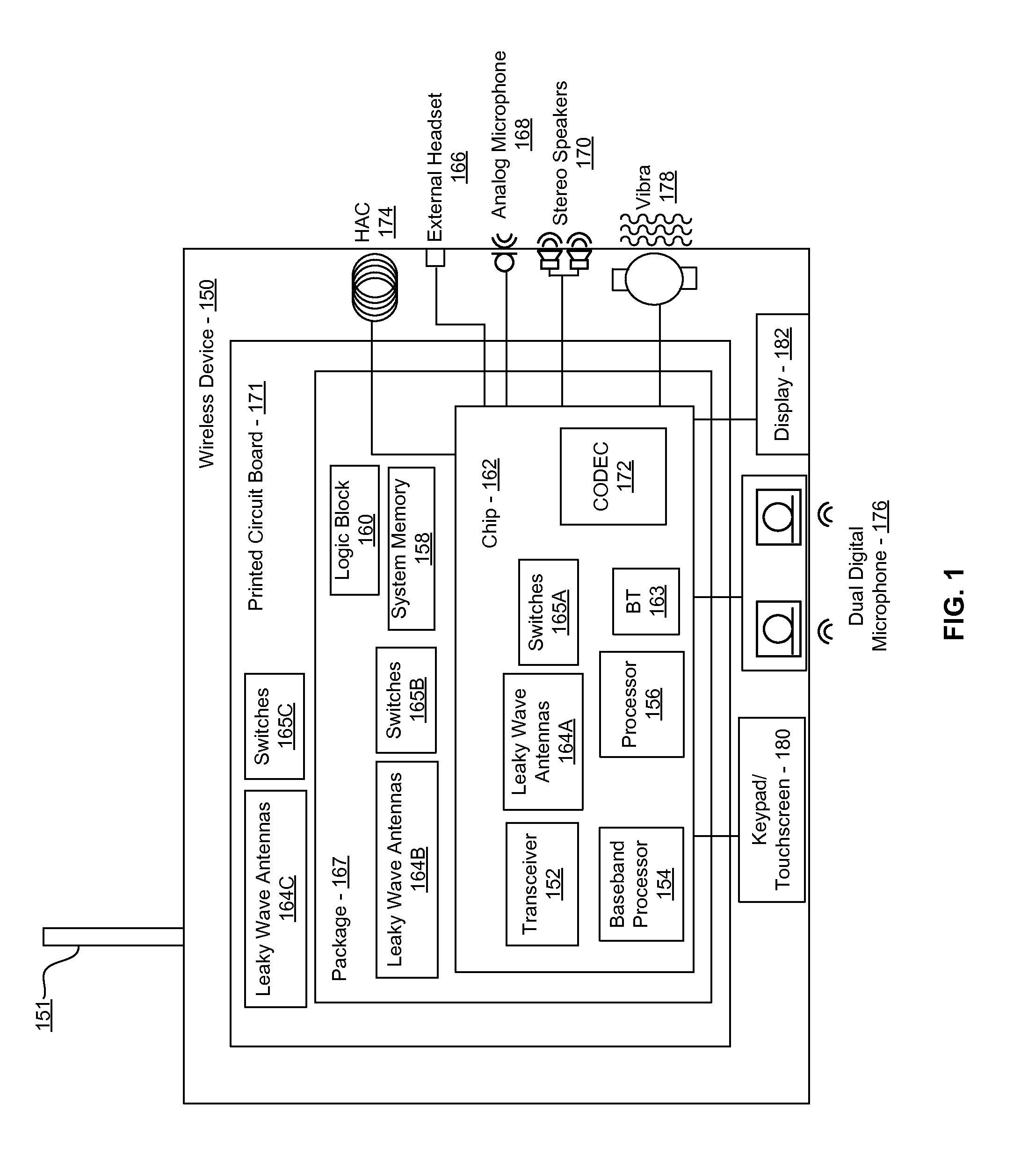
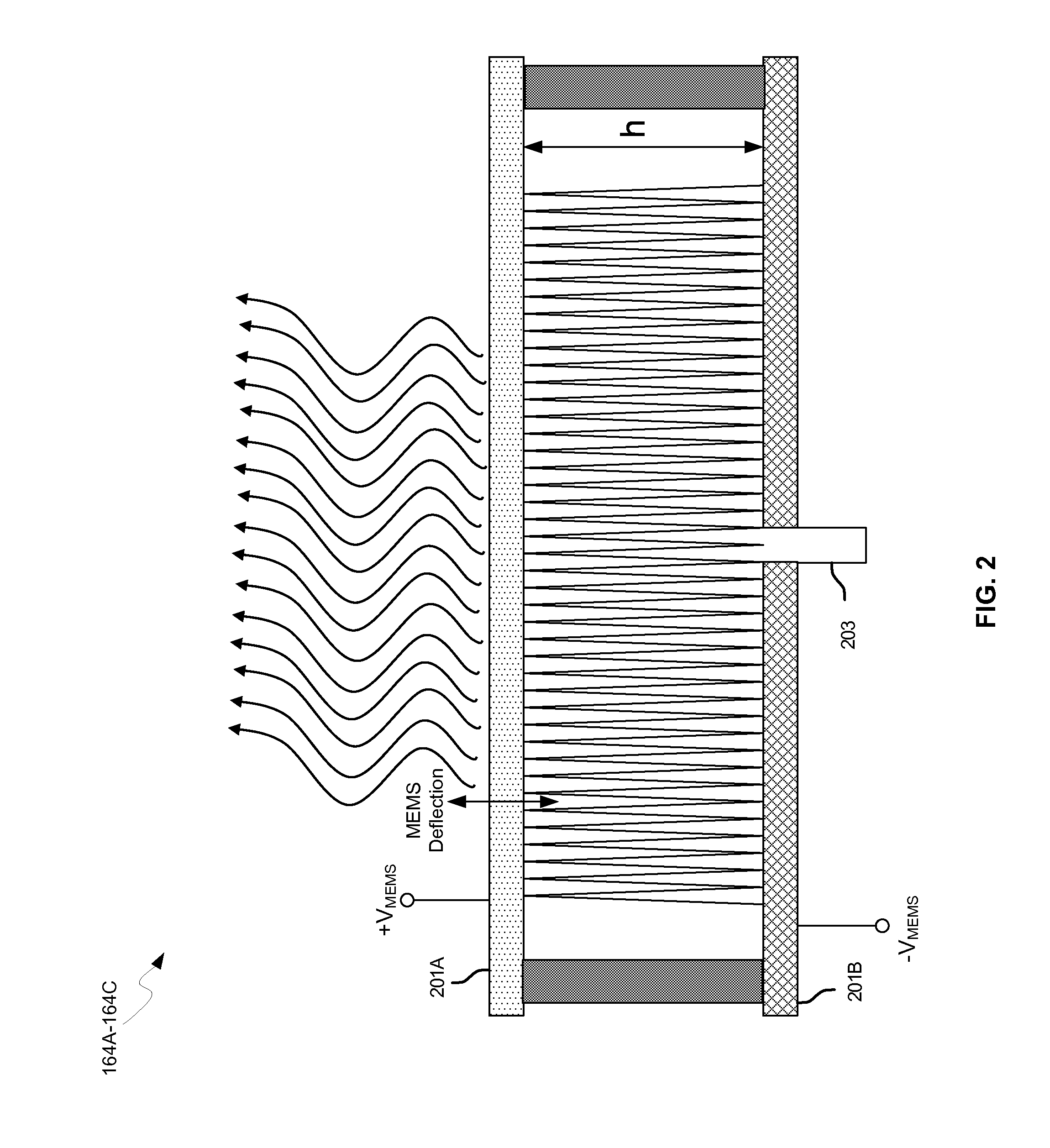
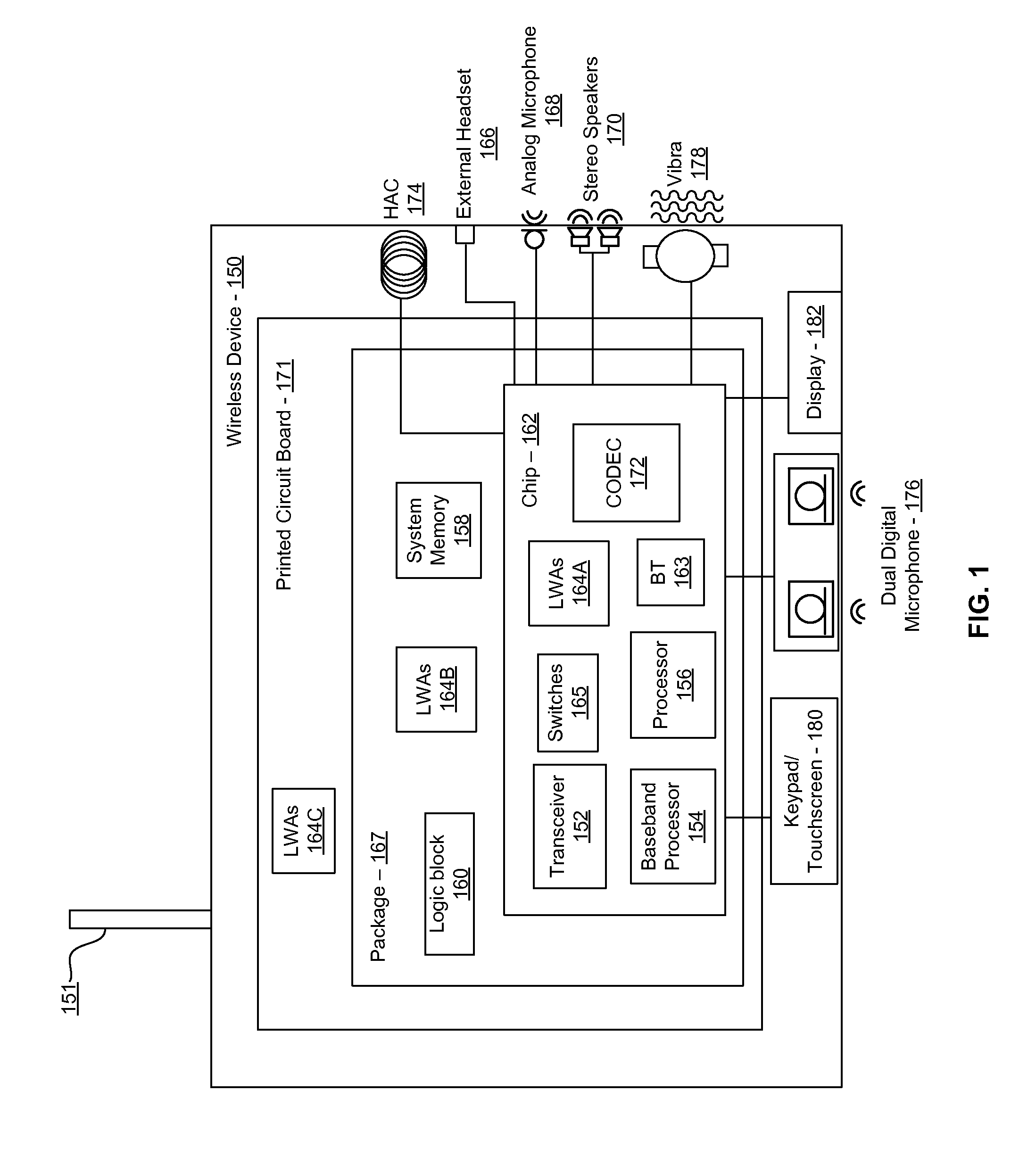
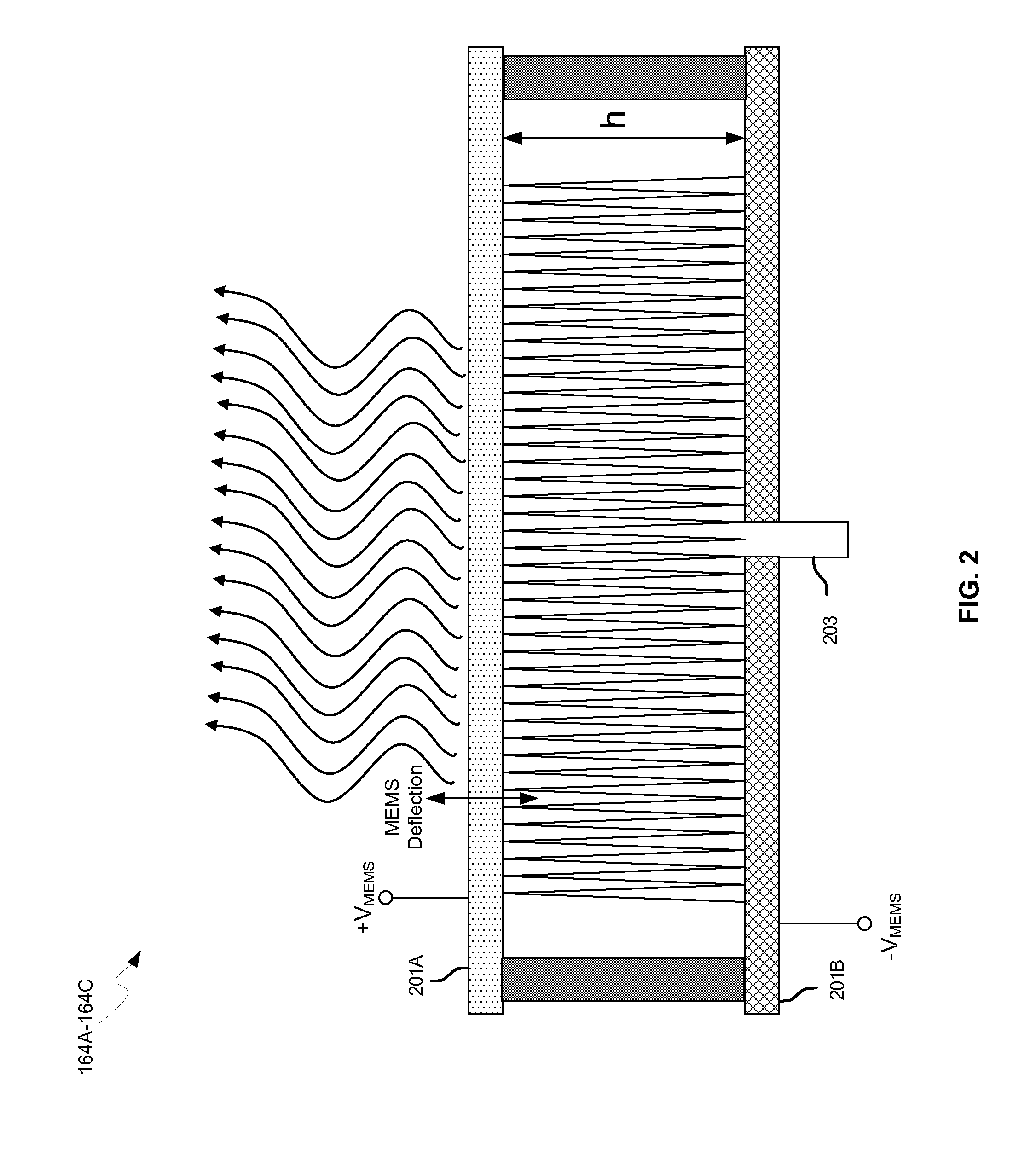
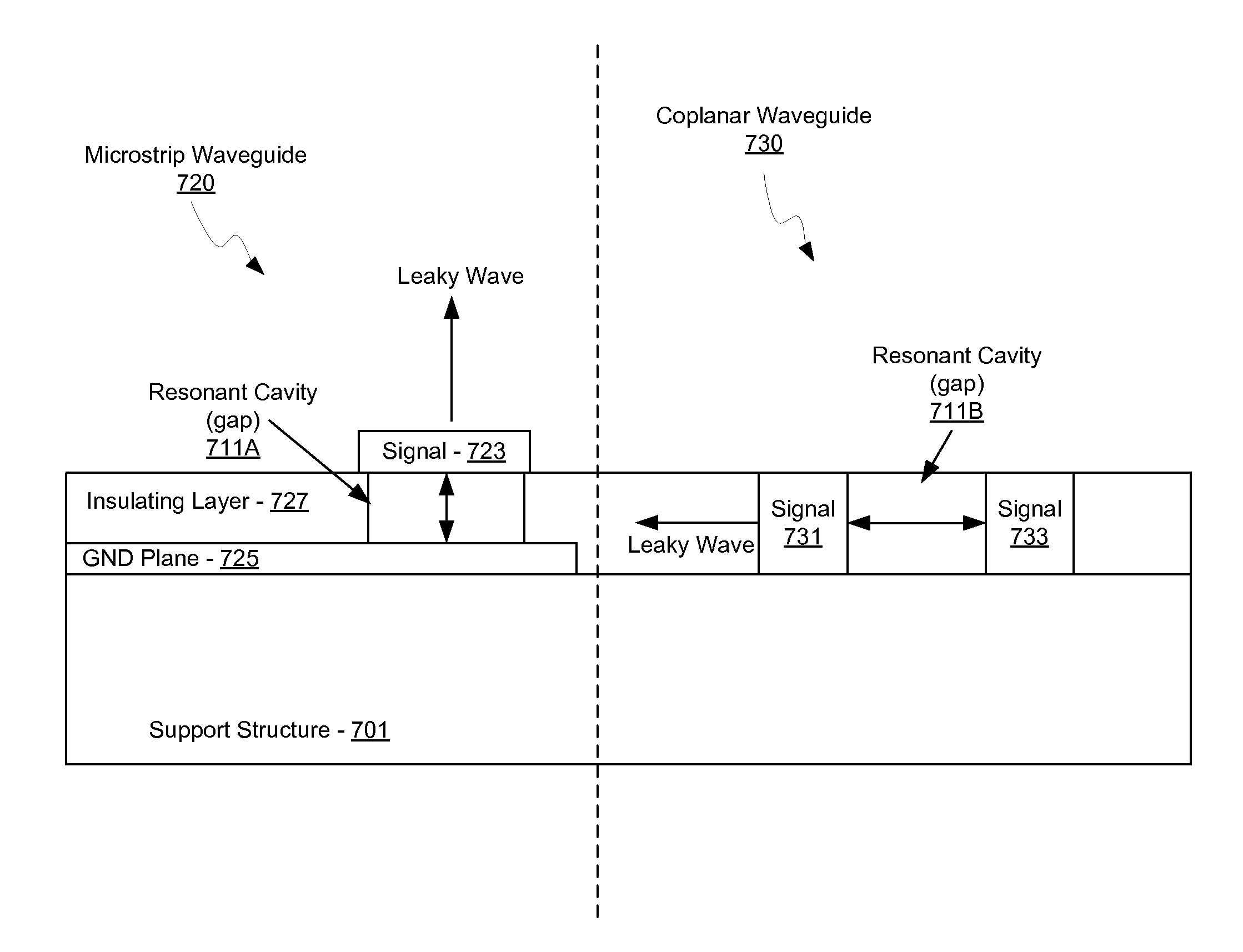
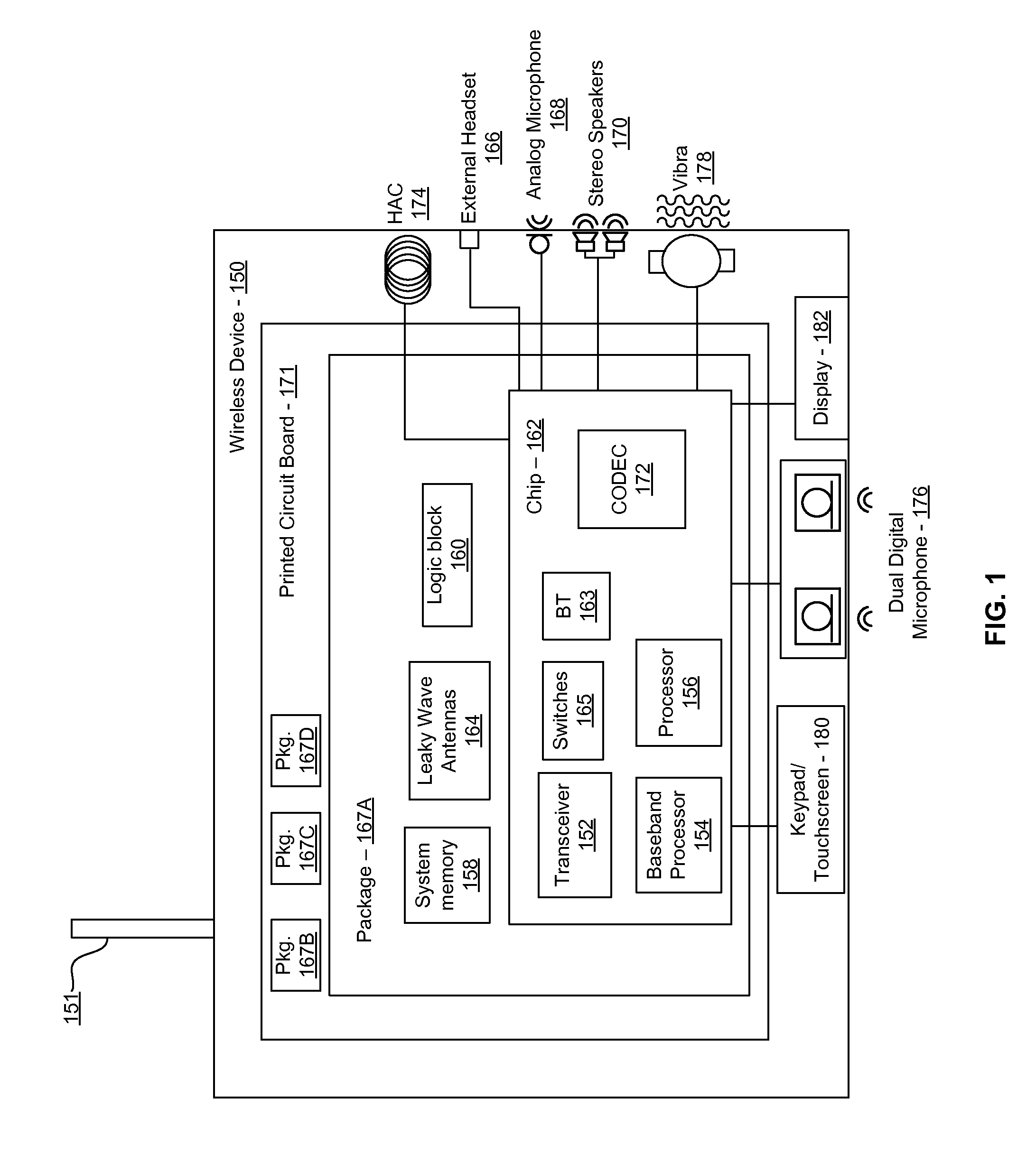
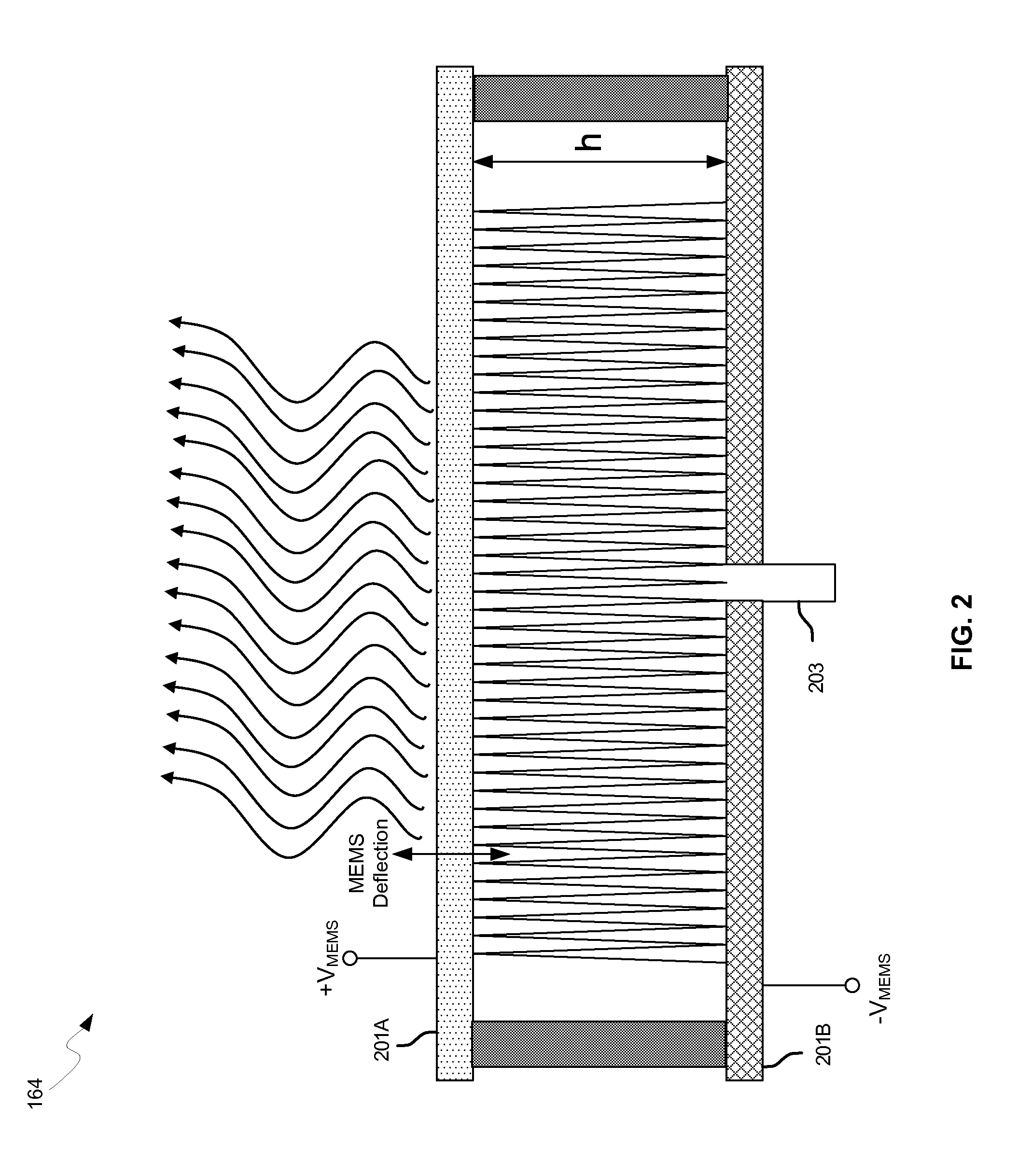
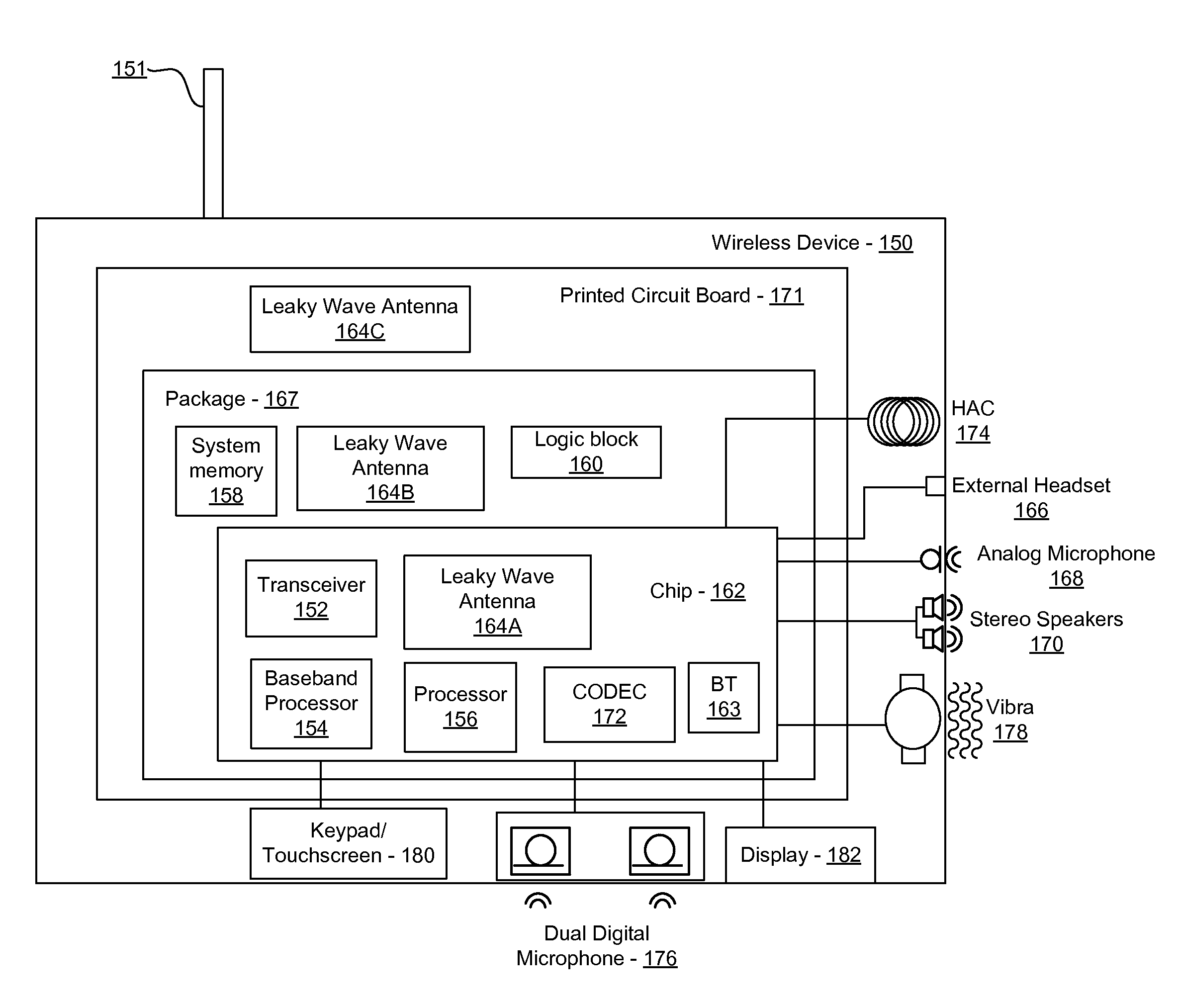
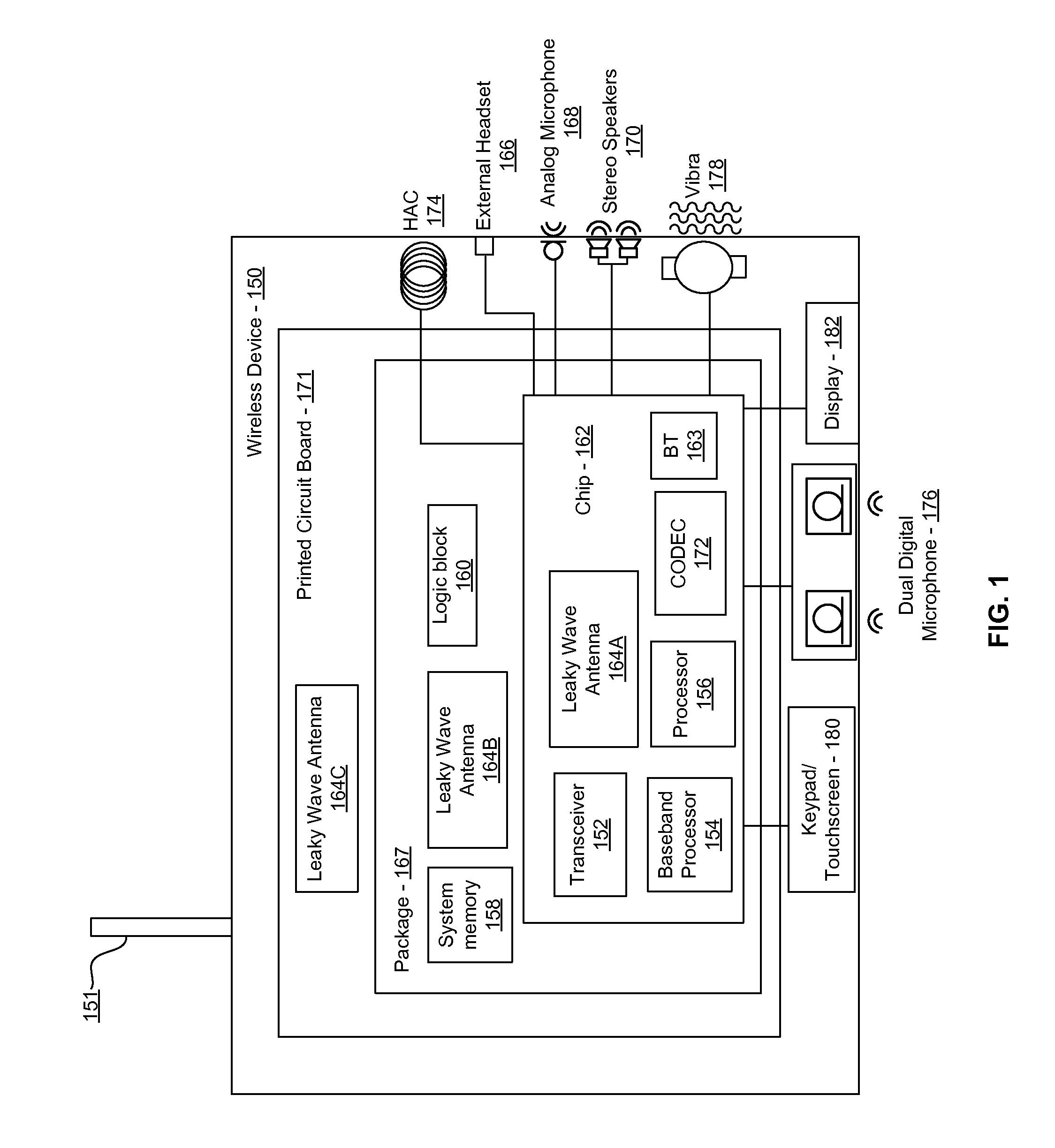
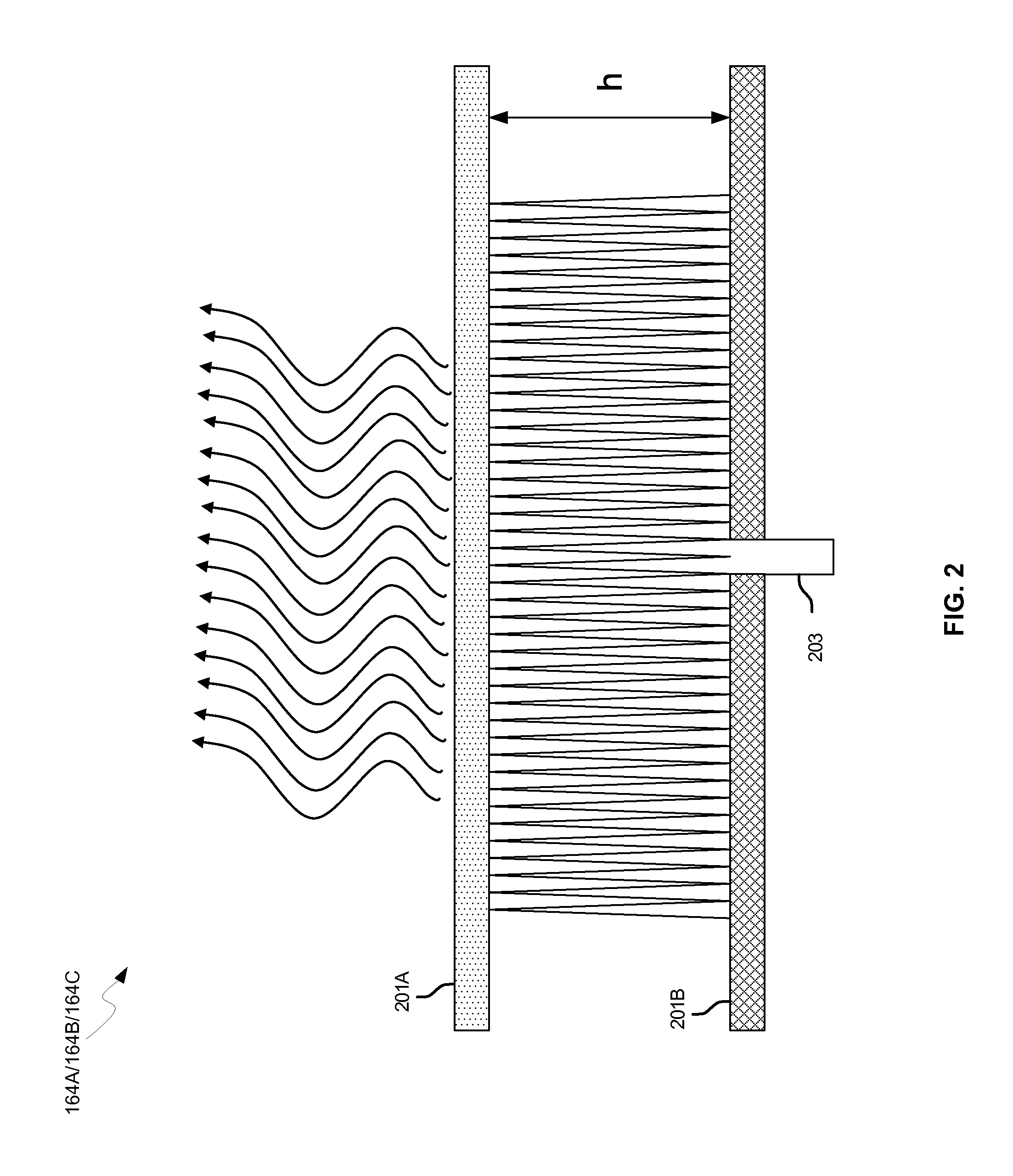
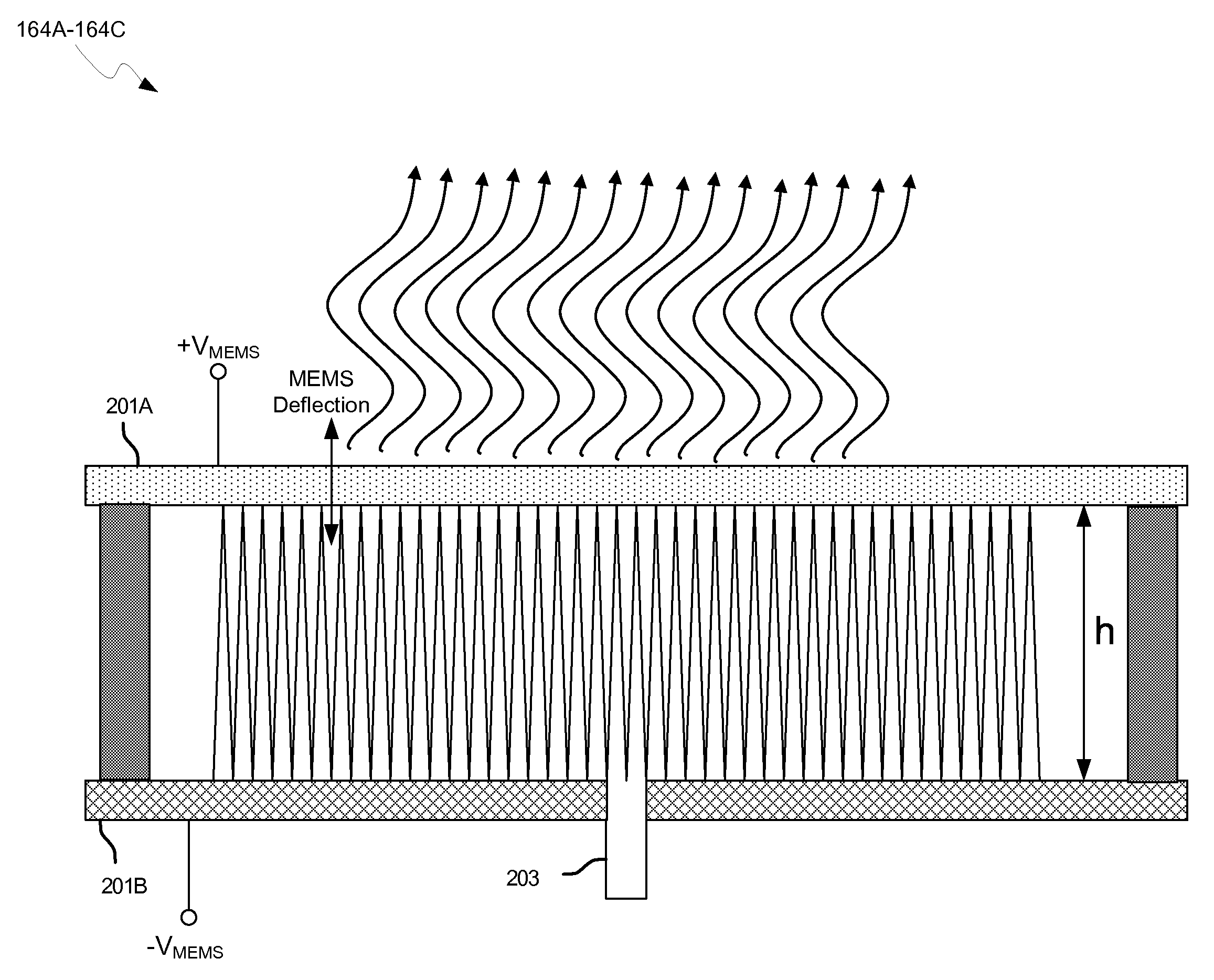
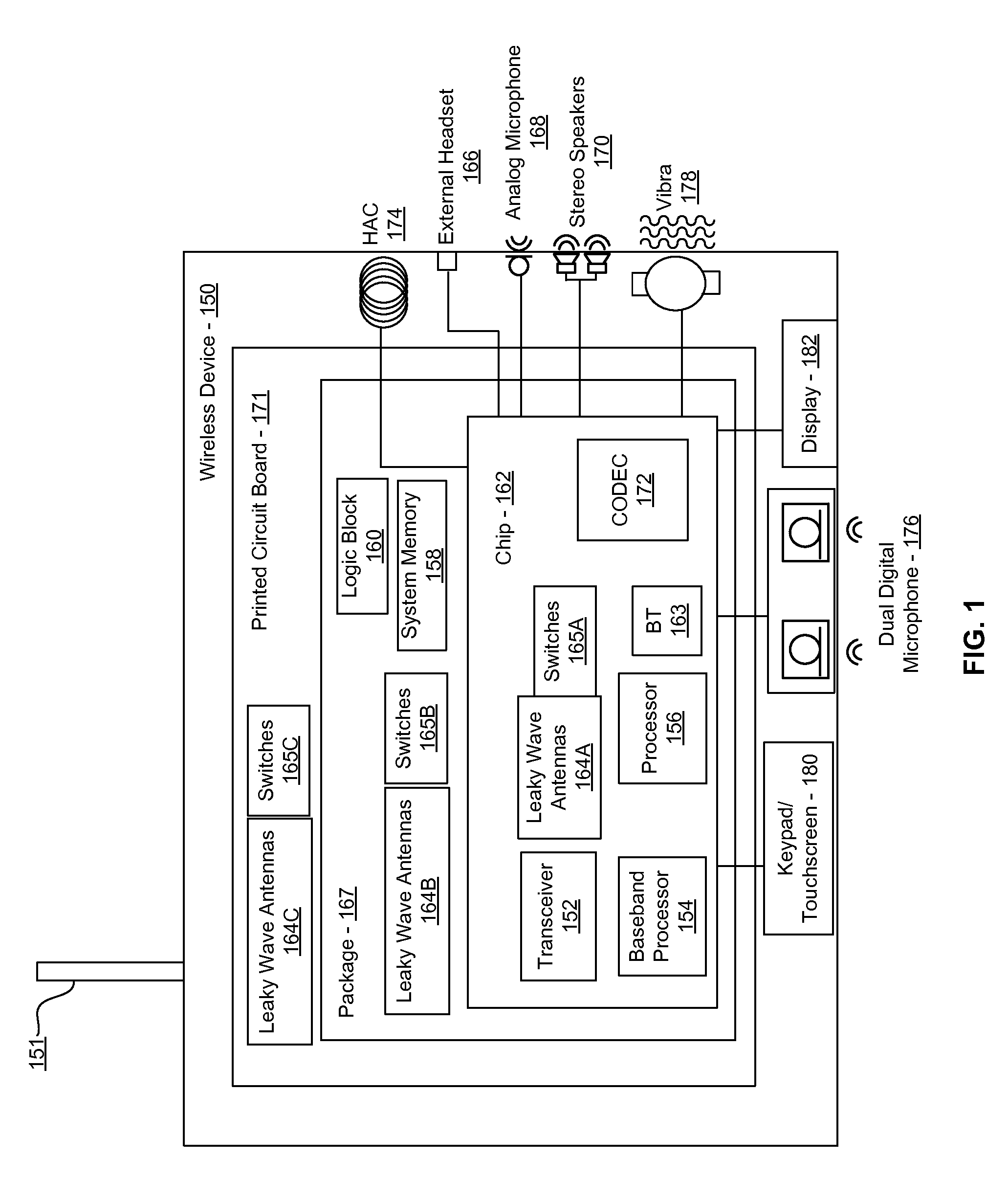
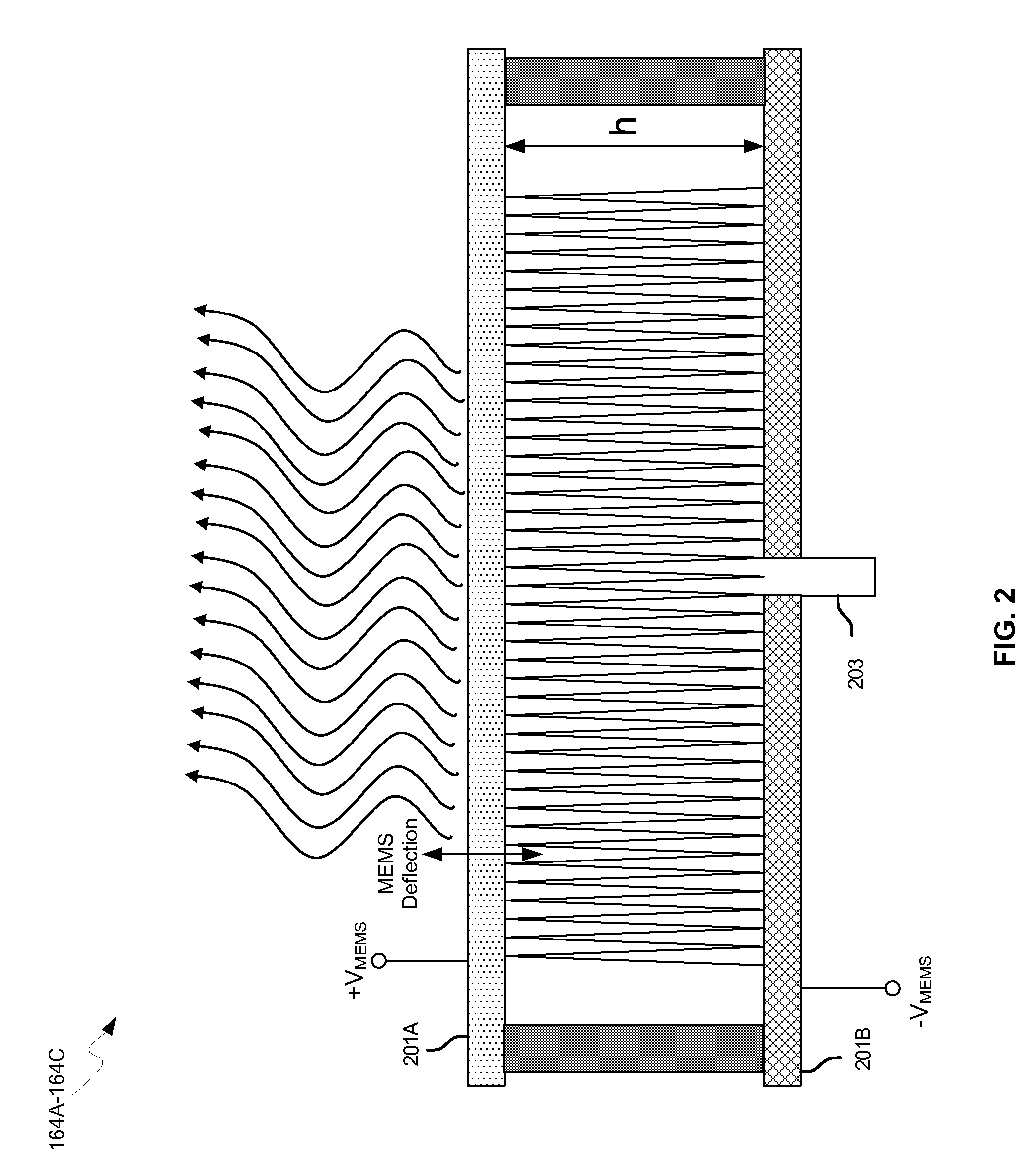
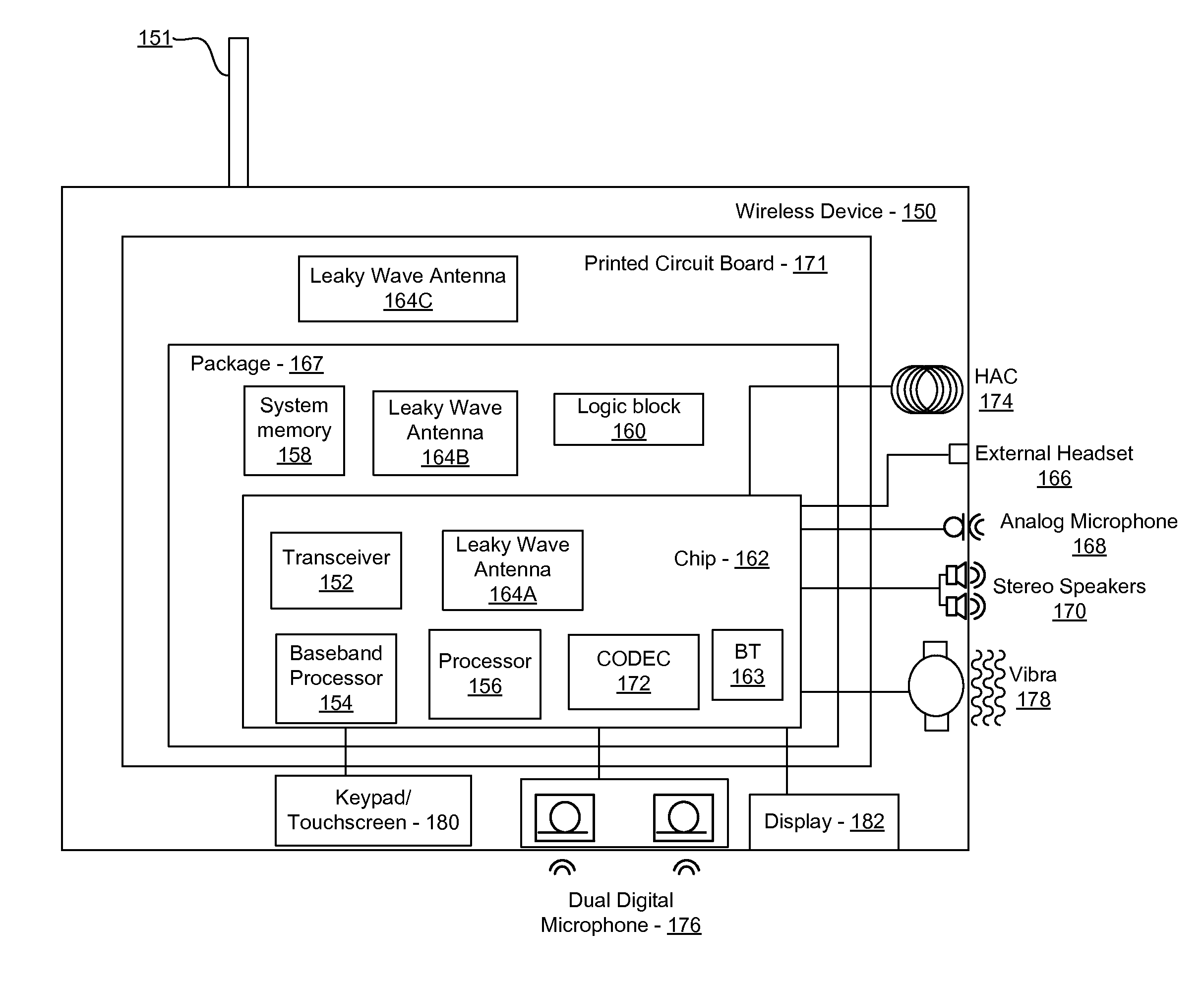
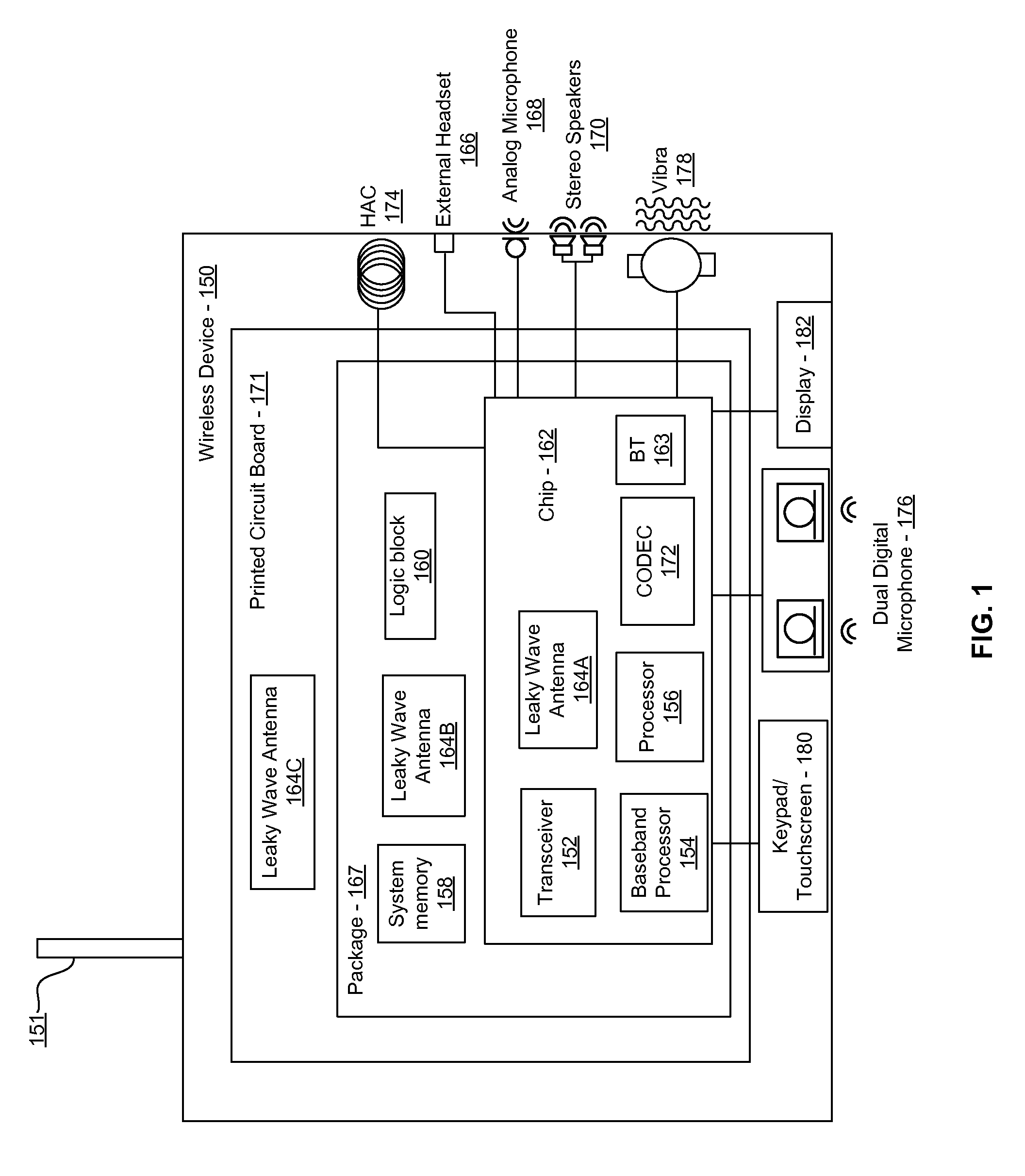
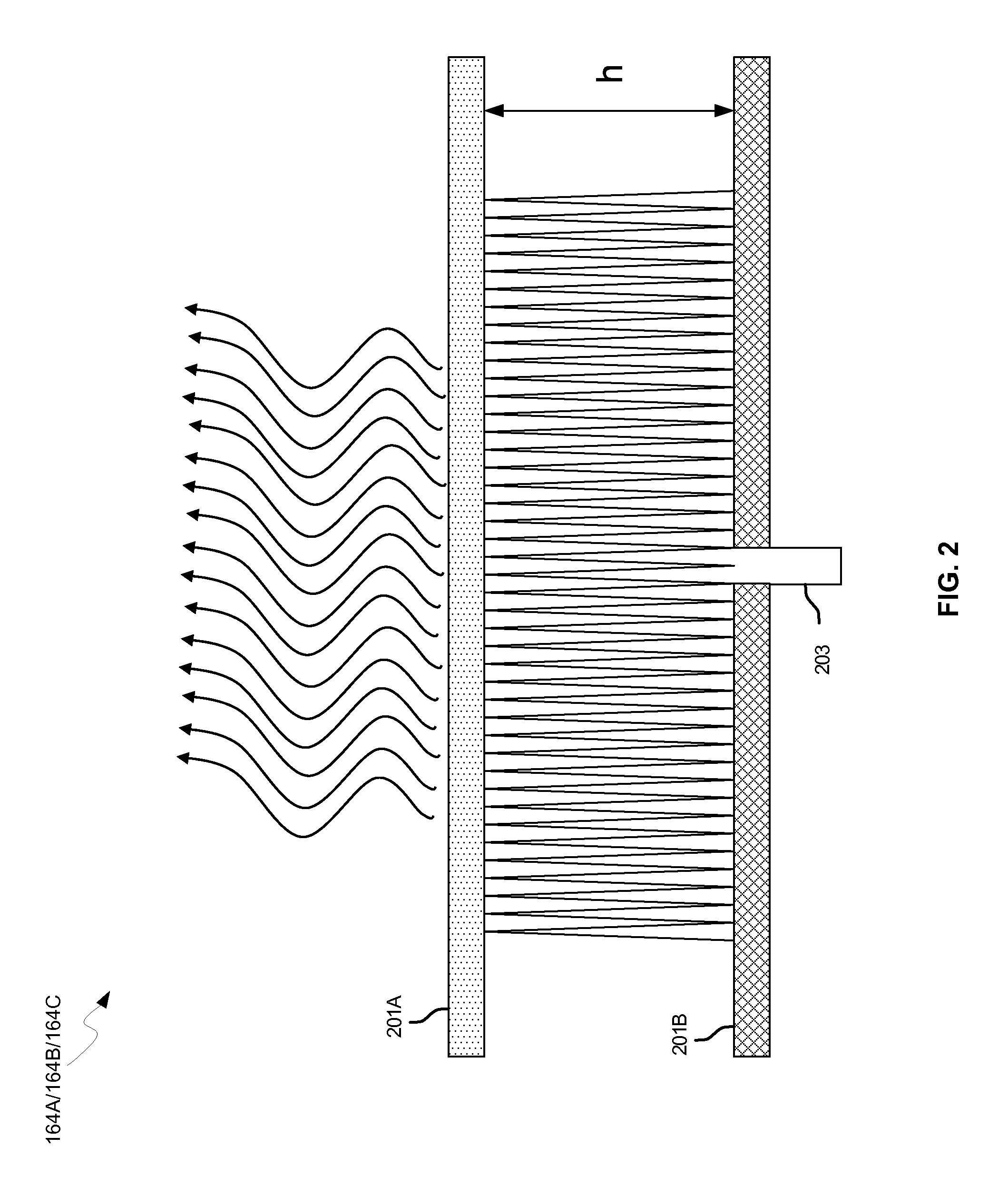
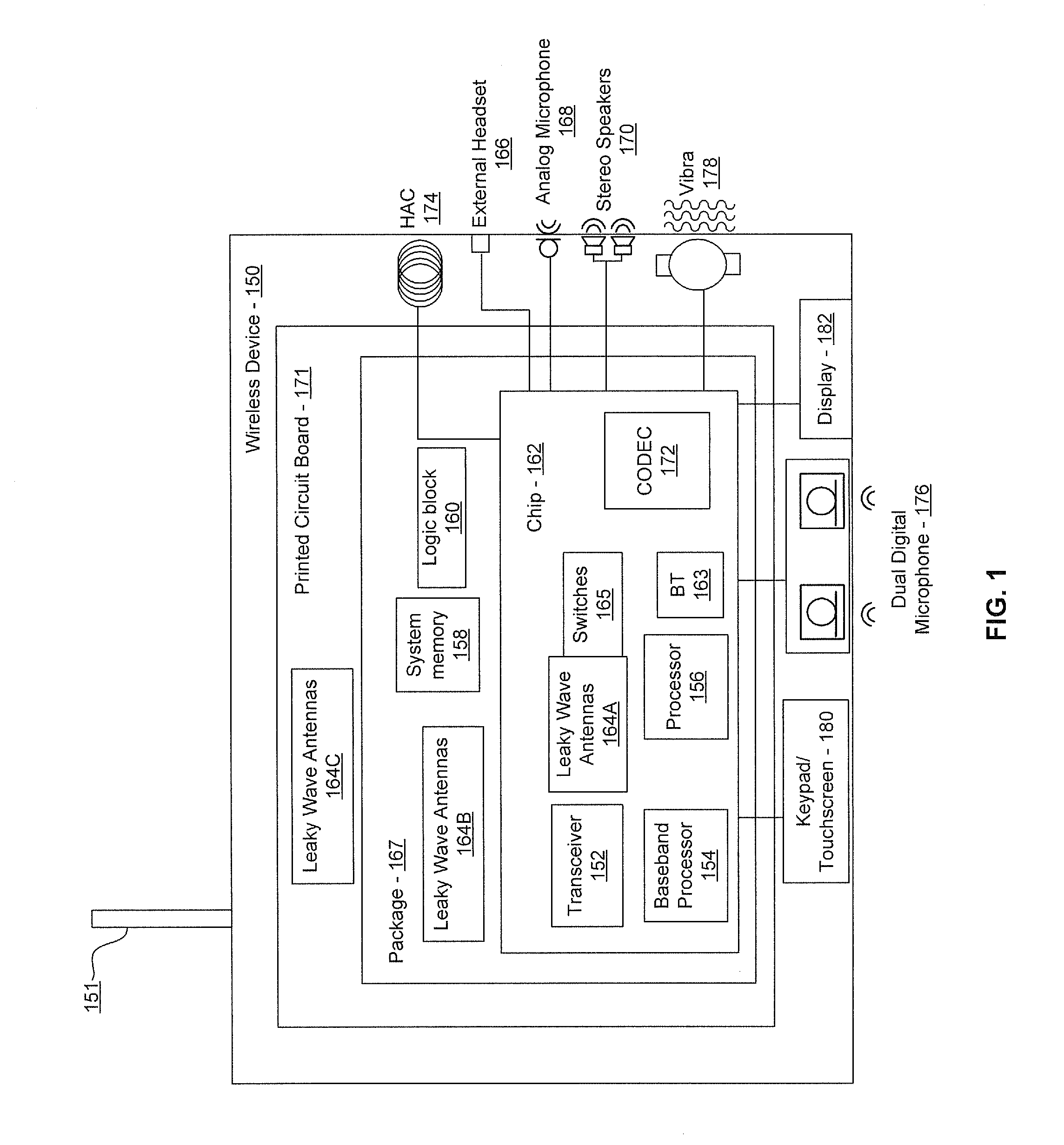
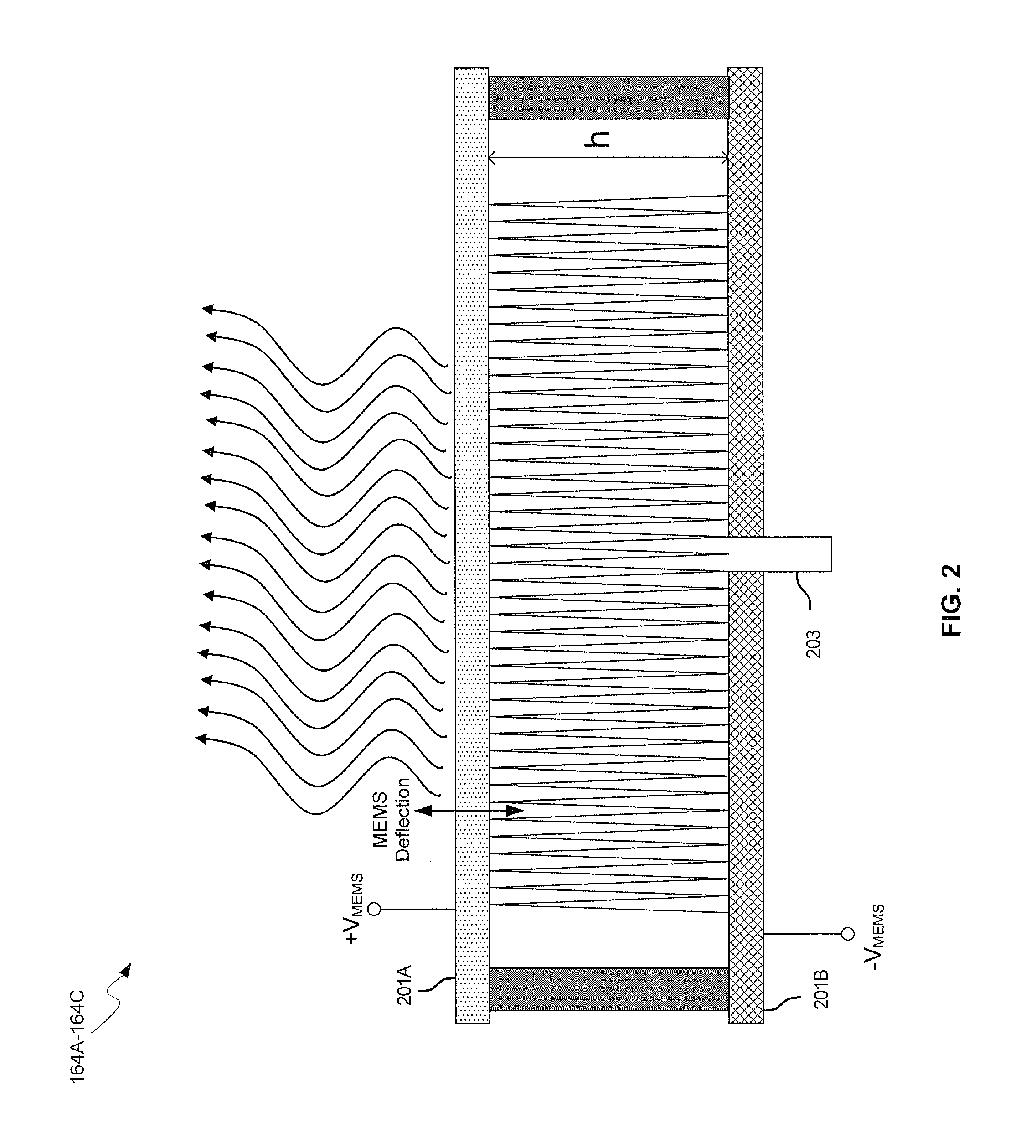
Methods and systems for a smart antenna utilizing leaky wave antennas (LWAs) are disclosed and may include a programmable polarization antenna including one or more pairs of LWAs configured along different axes. One or more pairs of leaky wave antennas may be configured to adjust polarization and / or polarity of one or more RF signals communicated by the programmable polarization antenna. RF signals may be communicated via the configured programmable polarization antenna utilizing the configured one or more pairs of the leaky wave antennas. A resonant frequency of the LWAs may be configured utilizing micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) deflection. The polarization and / or polarity may be configured utilizing switched phase modules. The LWAs may include microstrip or coplanar waveguides, wherein a cavity height of the LWAs is dependent on spacing between conductive lines in the waveguides. The LWAs may be integrated in one or more integrated circuits, packages, and / or printed circuit boards.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for an integrated voltage controlled oscillator-based transmitter and on-chip power distribution network
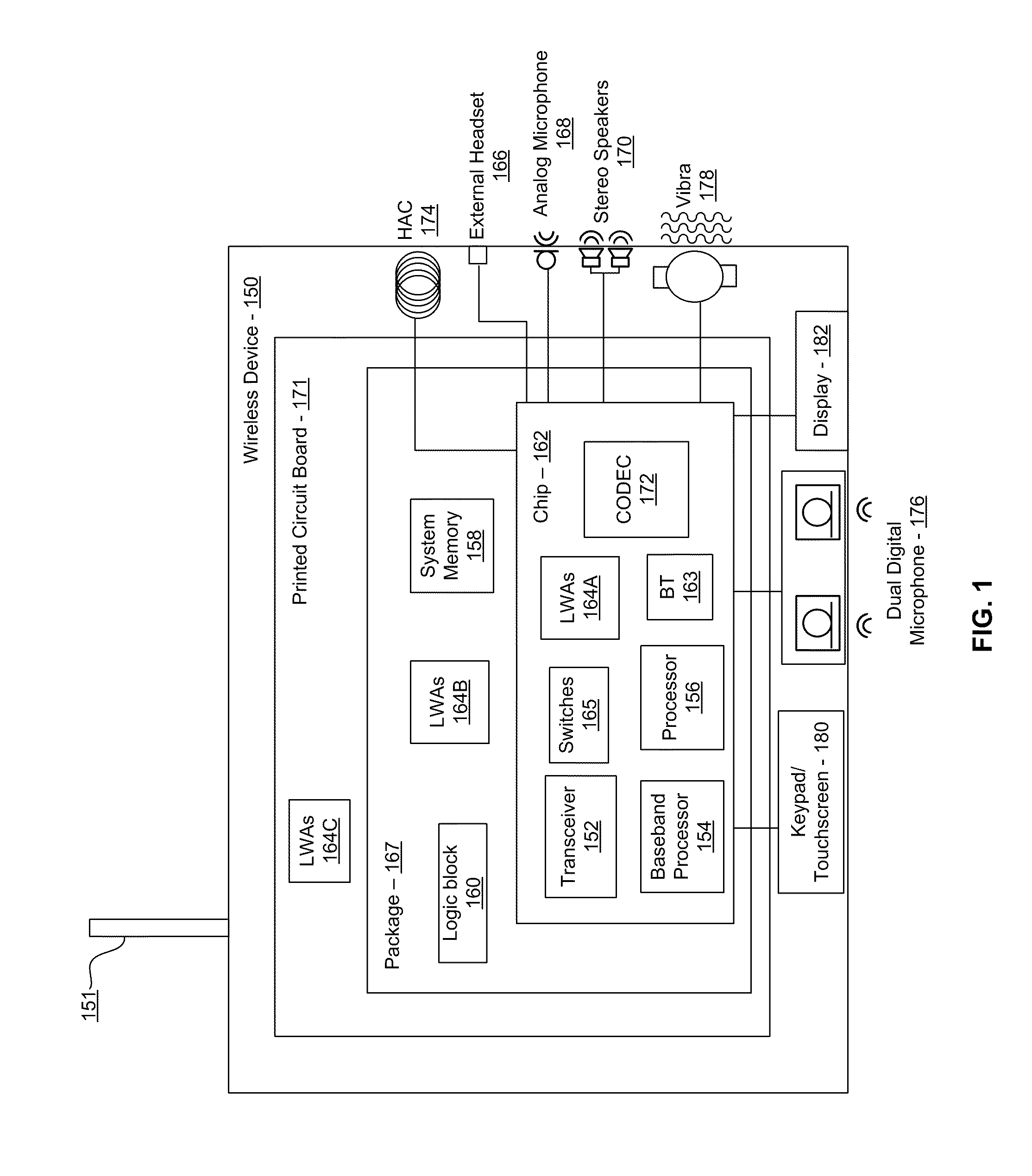
Methods and systems for an integrated voltage controlled oscillator (VCO)-based transmitter and on-chip power distribution network are disclosed and may include supplying bias voltages and / or ground to a chip utilizing conductive lines. One or more VCOs and low-noise amplifiers (LNAs) may each be coupled to a leaky wave antenna (LWA) integrated in the bias voltage and / or ground lines. One or more clock signals may be generated utilizing the VCOs, which may be transmitted from the LWAs coupled to the VCOs, to the LWAs coupled to the LNAs. RF signals may be transmitted via the LWAs, and may include 60 GHz signals. The LWAs may include microstrip and / or coplanar waveguides, where a cavity length of the LWAs may be dependent on a spacing between conductive lines in the waveguides. The LWAs may be dynamically configured to transmit the clock signals at a desired angle from a surface of the chip.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Fixed-frequency beam-steerable leaky-wave microstrip antenna
InactiveUS7002517B2Continuous changeSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsShunt DeviceBeam steering
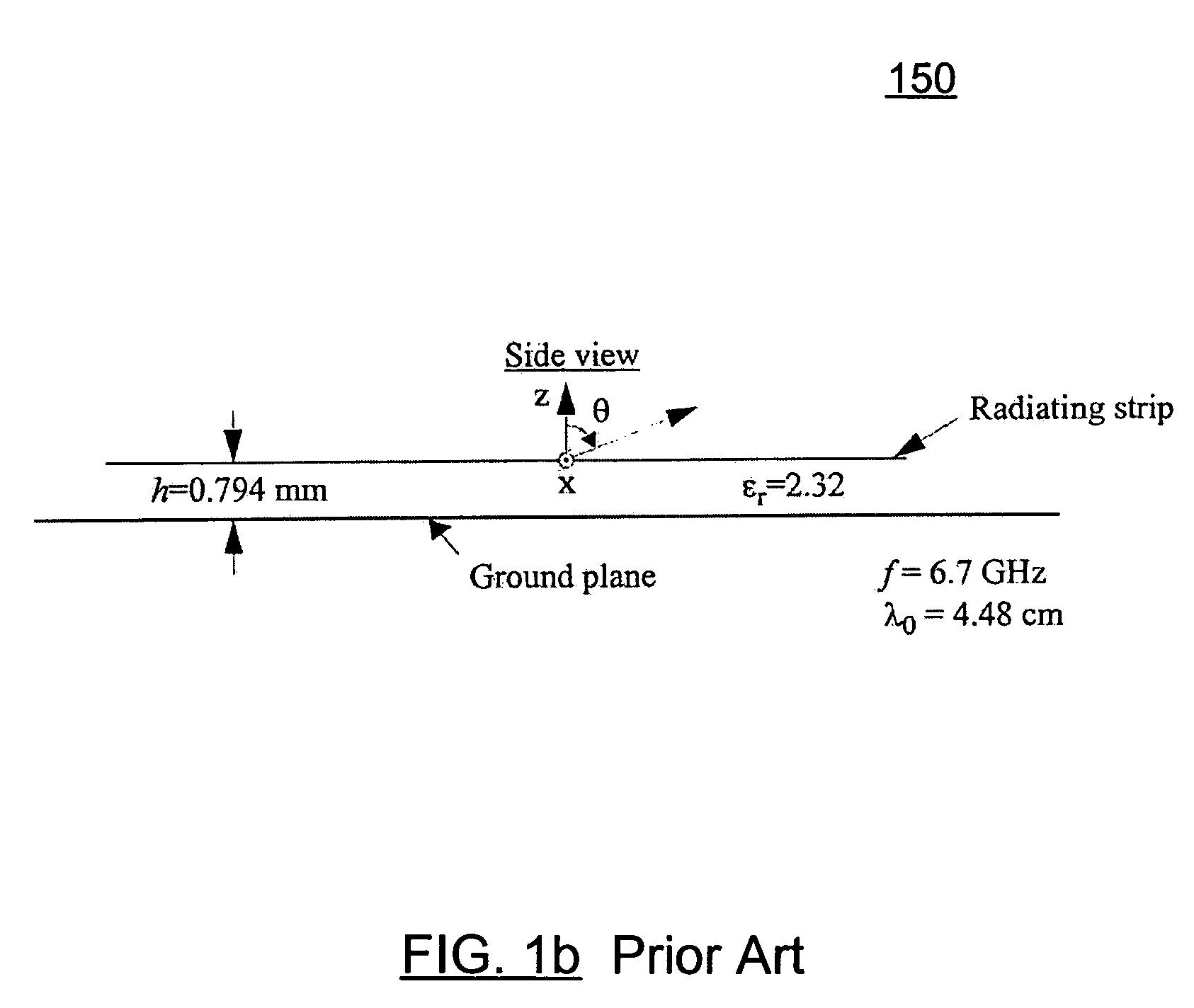
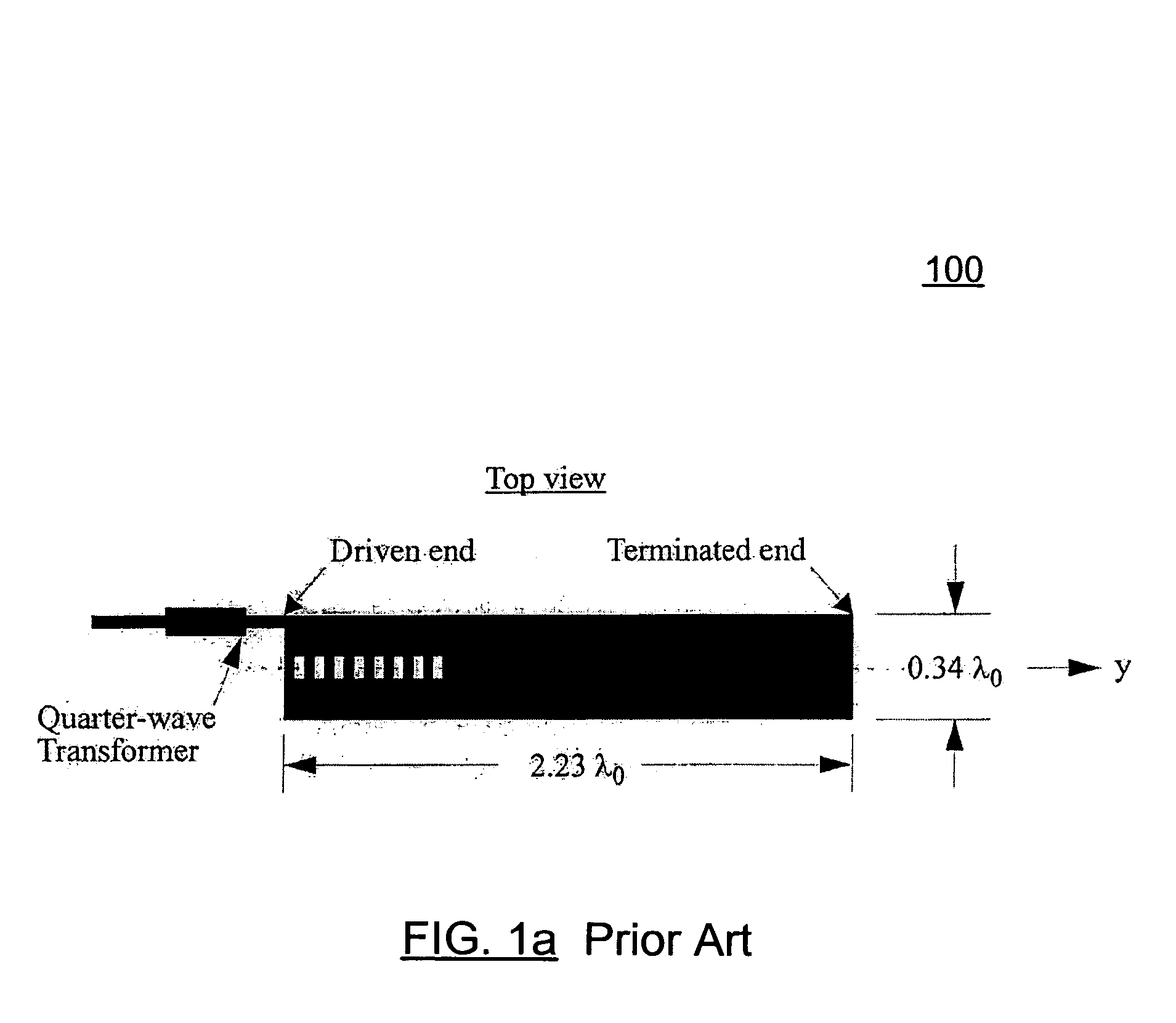
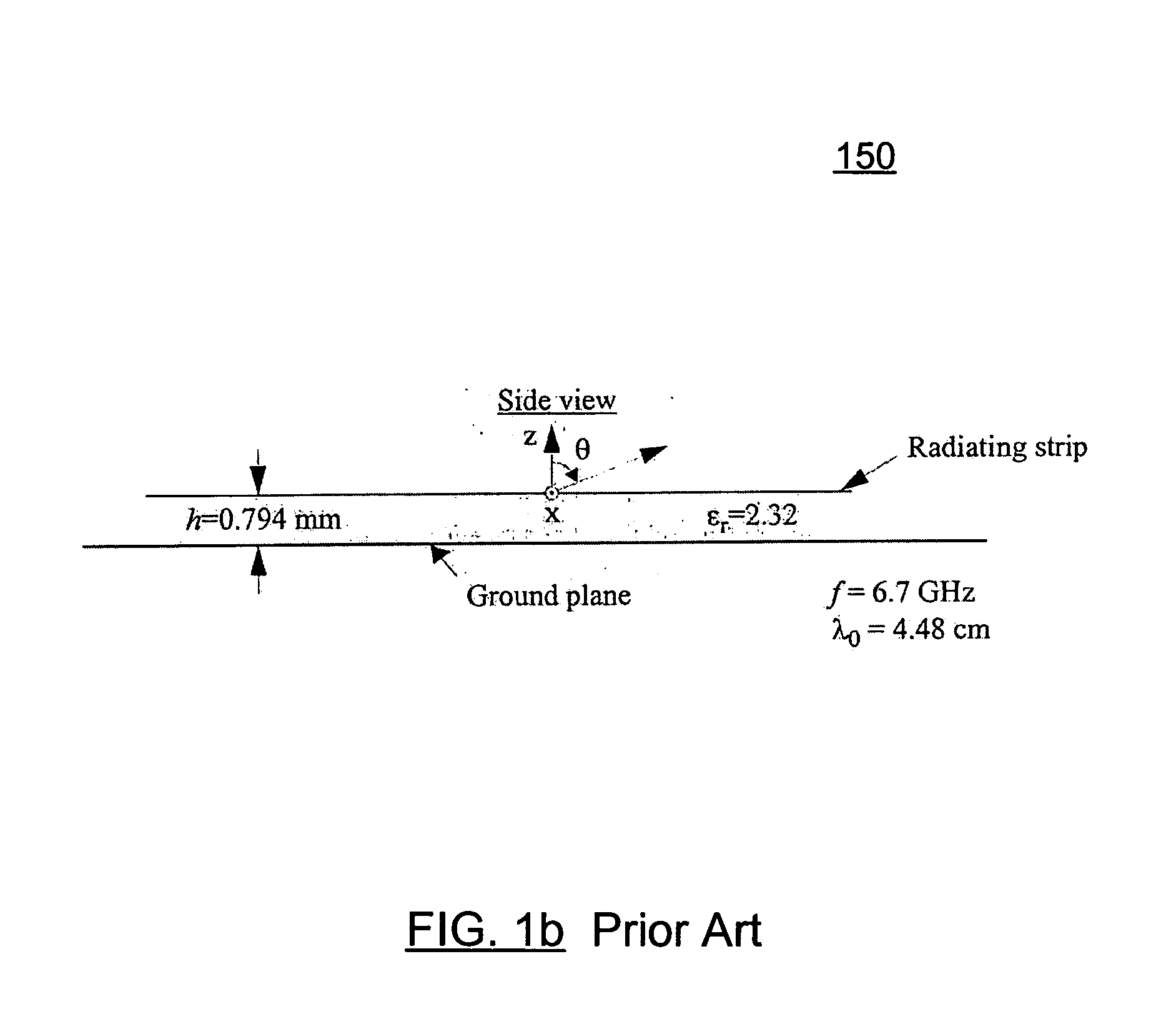
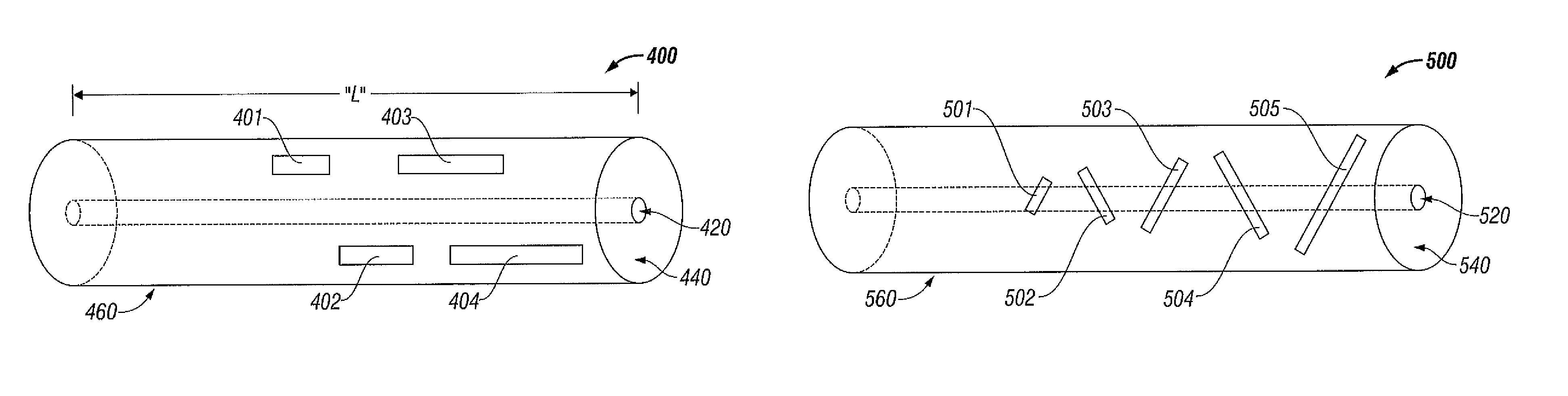
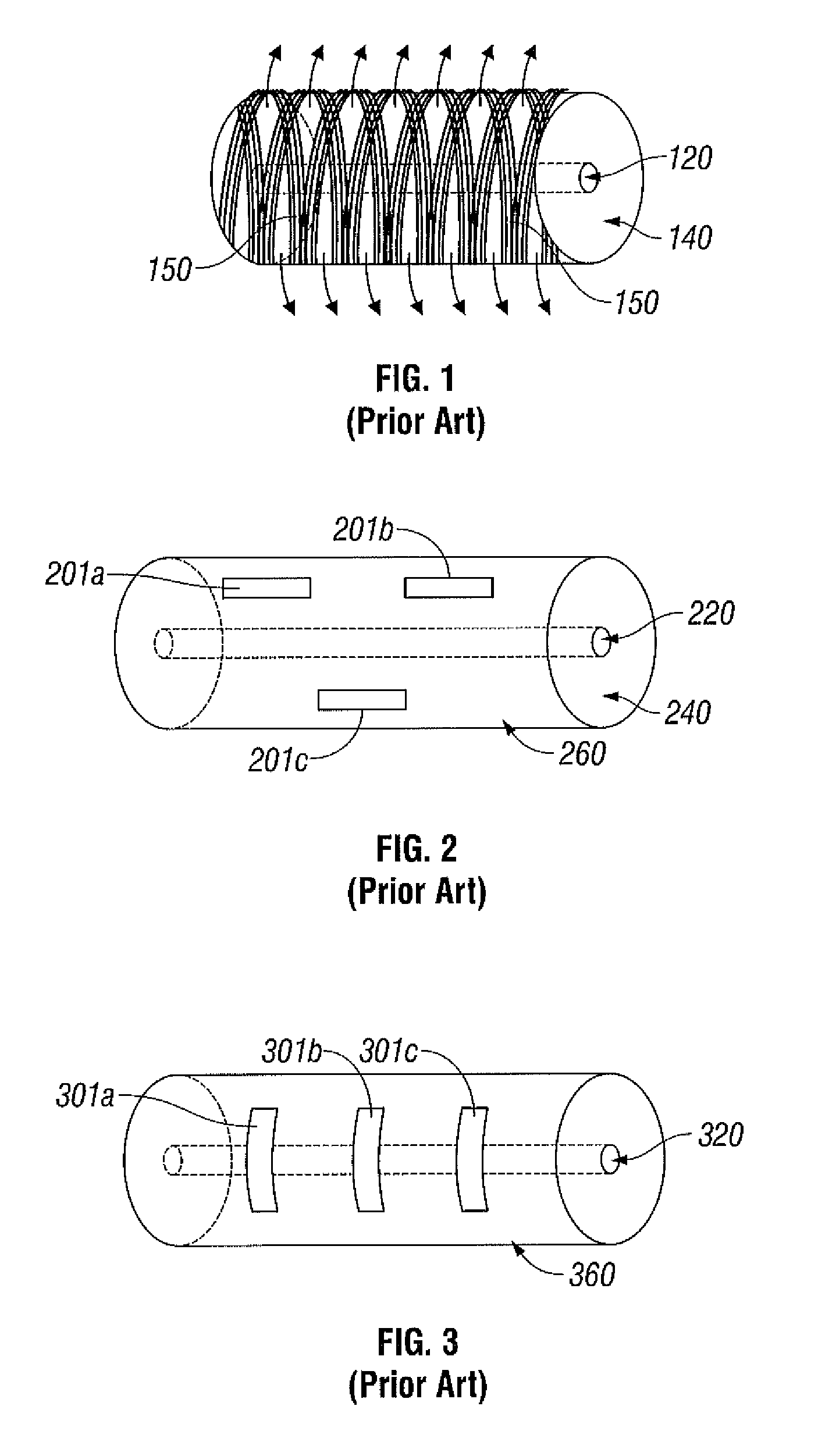
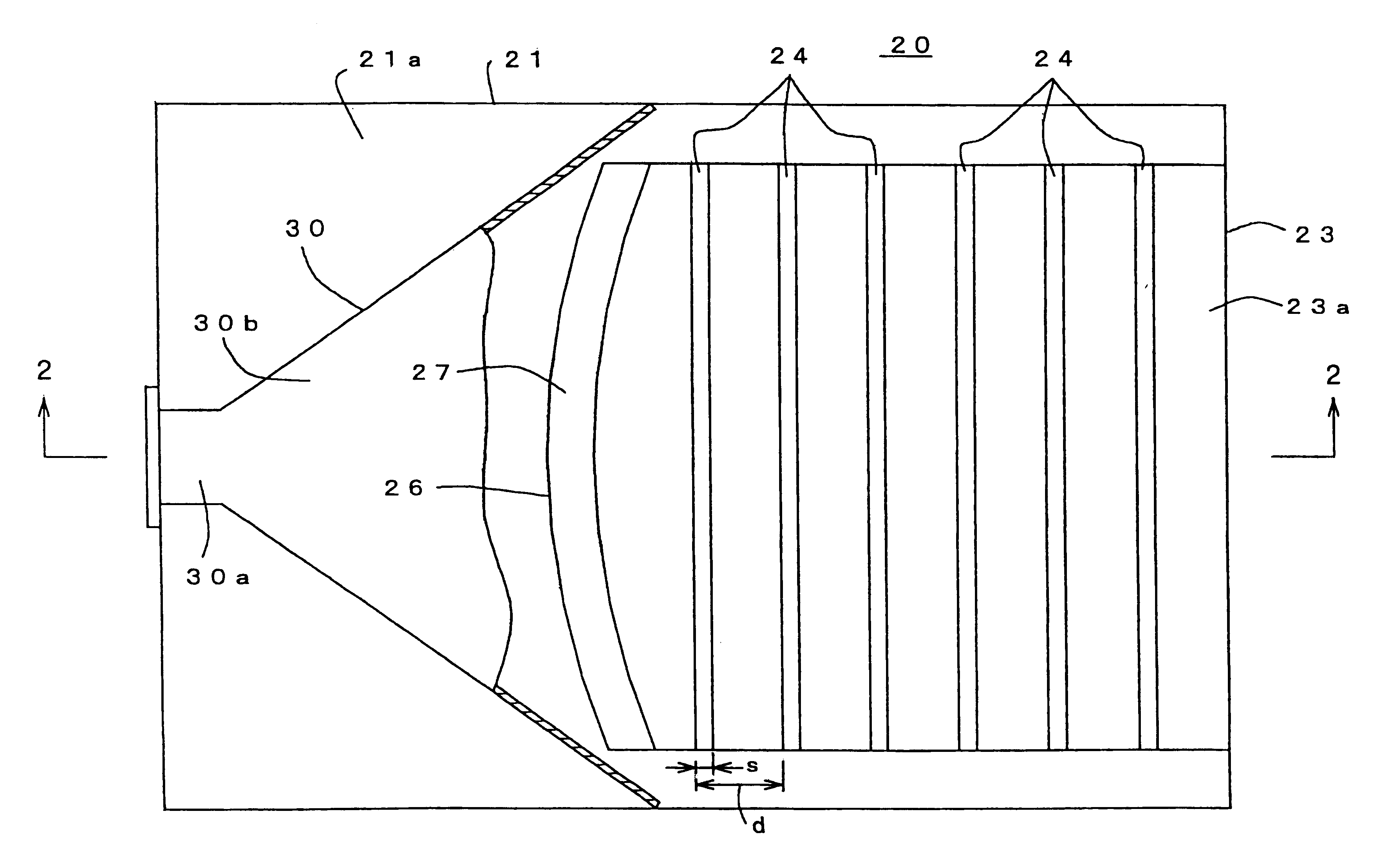
A fixed frequency continuously beam-steerable leaky-wave antenna in microstrip is disclosed. The antenna's radiating strips are loaded with identical shunt-mounted variable-reactance elements, resulting in low reverse-bias-voltage requirements. By varying the reverse-bias voltage across the variable-reactance elements, the main beam of the antenna may be scanned continuously at fixed frequency. The antenna may consist of an array of radiating strips, wherein each strip includes a variable-reactance element. Changing the element's reactance value has a similar effect as changing the length of the radiating strips. This is accompanied by a change in the phase velocity of the electromagnetic wave traveling along the antenna, and results in continuous fixed-frequency main-beam steering. Alternatively, the antenna may consist of two long radiating strips separated by a small gap, wherein identical variable-reactance elements are mounted in shunt across the gap at regular intervals. A continuous change in the reactance value has a similar effect as changing continuously the width of the radiating strips. This results in a continuous change in the phase velocity of the electromagnetic wave traveling along the antenna, thereby achieving continuous fixed-frequency main-beam steering.
Owner:ANRITSU CO
Fixed-frequency beam-steerable leaky-wave microstrip antenna
InactiveUS20050012667A1Continuous changeSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsShunt DeviceBeam steering
A fixed frequency continuously beam-steerable leaky-wave antenna in microstrip is disclosed. The antenna's radiating strips are loaded with identical shunt-mounted variable-reactance elements, resulting in low reverse-bias-voltage requirements. By varying the reverse-bias voltage across the variable-reactance elements, the main beam of the antenna may be scanned continuously at fixed frequency. The antenna may consist of an array of radiating strips, wherein each strip includes a variable-reactance element. Changing the element's reactance value has a similar effect as changing the length of the radiating strips. This is accompanied by a change in the phase velocity of the electromagnetic wave traveling along the antenna, and results in continuous fixed-frequency main-beam steering. Alternatively, the antenna may consist of two long radiating strips separated by a small gap, wherein identical variable-reactance elements are mounted in shunt across the gap at regular intervals. A continuous change in the reactance value has a similar effect as changing continuously the width of the radiating strips. This results in a continuous change in the phase velocity of the electromagnetic wave traveling along the antenna, thereby achieving continuous fixed-frequency main-beam steering.
Owner:ANRITSU CO
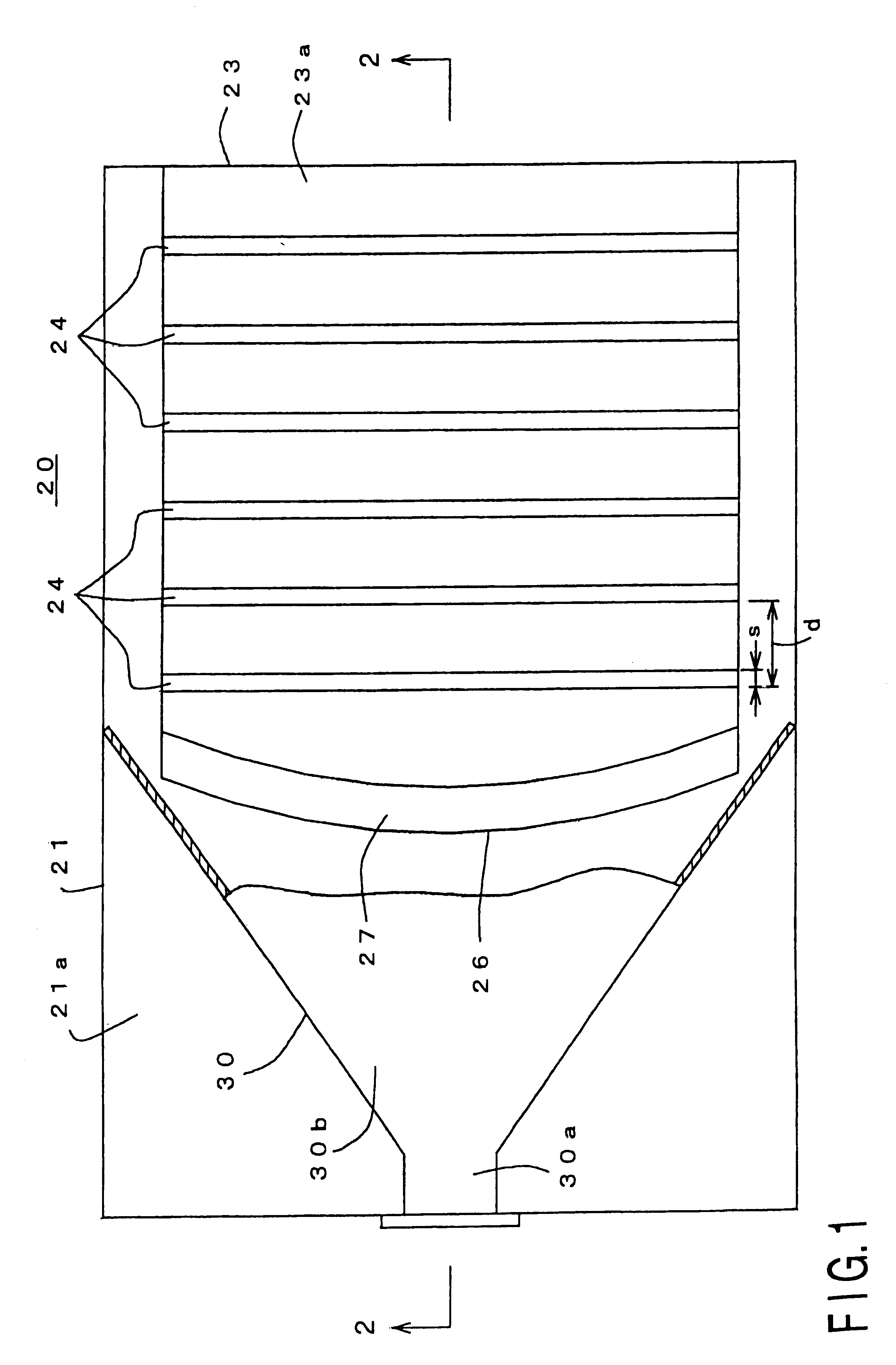
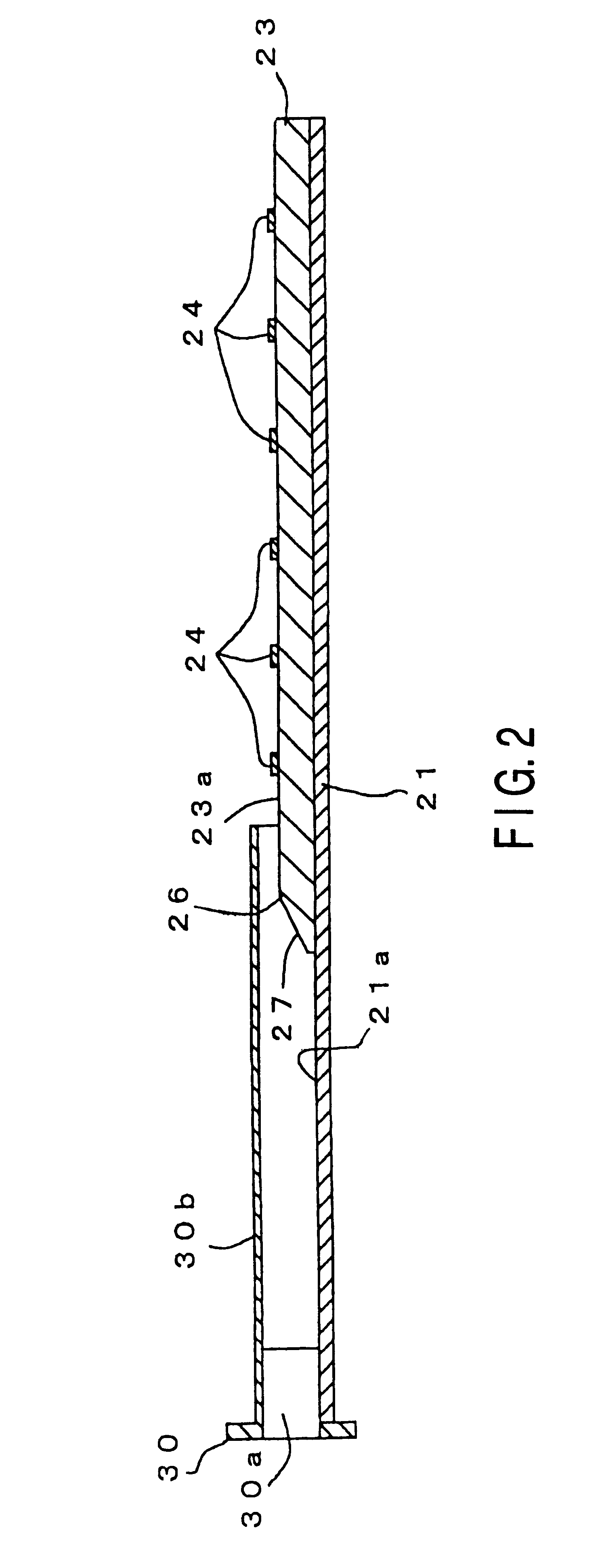
Leaky-wave antennas for medical applications
InactiveUS8197473B2Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments using microwavesElectrical conductorDistal portion
A device for directing energy to a target volume of tissue includes an inner conductor having a length and an outer conductor coaxially surrounding the inner conductor along the length. The outer conductor has a proximal portion and a distal portion. The distal portion of the outer conductor is provided with a number of apertures N defined therein for radiating energy, where N is an integer greater than 1, each aperture having a size and extending at an angle relative to a longitudinal axis of the outer conductor. At least one of the size and the angle of each aperture is varied in relation to the other apertures N−1 such that the energy radiated along the distal portion is substantially uniform.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Steerable leaky wave antenna capable of both forward and backward radiation
ActiveUS7071888B2Individually energised antenna arraysElectrically short antennasHorizonBeam steering
Leaky wave antenna beam steering that is capable of steering in a backward direction, as well as further down toward the horizon in the forward direction than was previously possible, and also directly toward zenith. The disclosed antenna and method involve applying a non-uniform impedance function across a tunable impedance surface in order to obtain such leaky wave beam steering.
Owner:HRL LAB
Leaky-wave antennas for medical applications
ActiveUS8202270B2Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments using microwavesElectrical conductorDistal portion
A device for directing energy to a target volume of tissue includes a proximal portion including a first antenna subassembly extending therethrough, and a distal portion including a second antenna subassembly. The first antenna subassembly includes a leaky-wave antenna assembly having an outer conductor and an inner conductor disposed within the outer conductor. The distal portion of the device is attached to the inner conductor. The outer conductor includes a plurality of radiating apertures defined in a distal portion thereof and is configured for radiating energy substantially uniformly along a longitudinal axis of the proximal portion.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Method and system for converting RF power to DC power utilizing a leaky wave antenna
Methods and systems for converting RF power to DC power utilizing a leaky wave antenna (LWA) are disclosed and may include receiving RF wireless signals utilizing one or more LWAs in a wireless device, and generating one or more DC voltages from the received RF signals utilizing cascaded rectifier cells. A resonant frequency of the LWAs may be configured utilizing micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) deflection. The LWAs may be configured to receive the RF signals from a desired direction. The LWAs may comprise microstrip or coplanar waveguides, wherein a cavity height of the LWAs is dependent on a spacing between conductive lines in the waveguides. The LWAs may be integrated in one or more integrated circuits, integrated circuit packages, and / or printed circuit boards. The packages may be affixed to one or more printed circuit boards and the integrated circuits may be flip-chip-bonded to the packages.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for an integrated leaky wave antenna-based transmitter and on-chip power distribution
InactiveUS8285231B2Near-field transmissionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierDistribution method
Methods and systems for an integrated leaky wave antenna-based transmitter and on-chip power distribution are disclosed, and may include supplying one or more bias voltages and ground for a chip including a plurality of power amplifiers (PAs) utilizing bias voltage and ground lines. One or more leaky wave antennas (LWAs) may be communicatively coupled to the power amplifiers. Wireless signals may be transmitted utilizing the LWAs integrated in the lines in the chip. Radio frequency (RF) signals may be transmitted via the plurality of LWAs. The RF signals may include 60 GHz signals and the LWAs may include microstrip and / or coplanar waveguides. A cavity length of the LWAs may be configured by a spacing between conductive lines in the microstrip and / or coplanar waveguides. The LWAs may be configured to transmit the wireless signals at a desired angle from a surface of the chip.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Dielectric leaky wave antenna having mono-layer structure
InactiveUS6597323B2Improve efficiencyIndividually energised antenna arraysWaveguide type devicesElectromagnetic wave transmissionGround plane
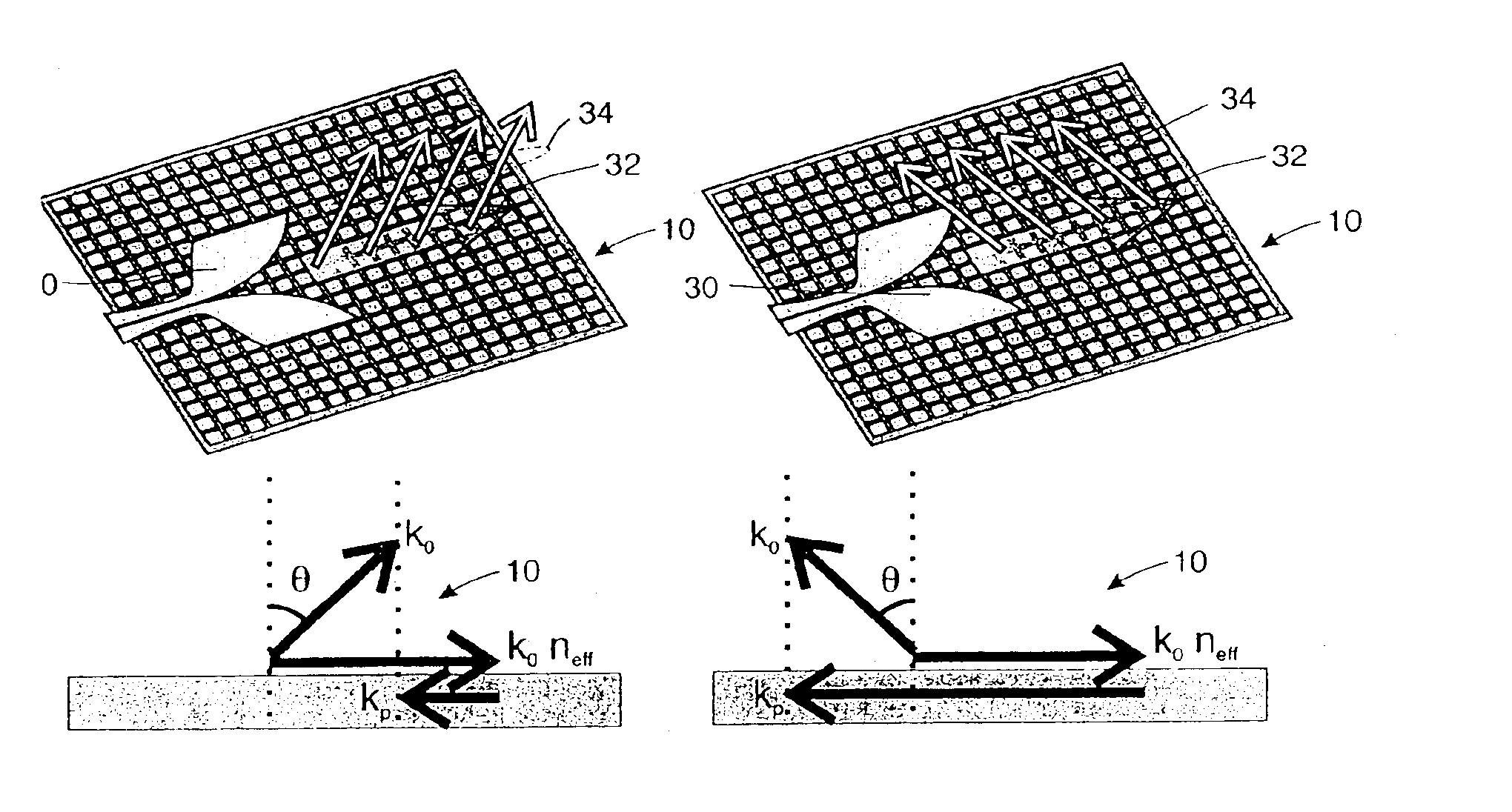
The present invention provides a dielectric leaky-wave antenna having a single-layer structure which is effective for realizing a highly efficient low-cost antenna in a quasi-millimeter wave zone in particular. This dielectric leaky-wave antenna includes a ground plane, a dielectric slab which is laid on one surface of the ground plane and forms a transmission guide for transmitting an electromagnetic wave from one end side to the other end side between itself and the ground plane along the surface, perturbations which are loaded on the surface of the dielectric slab along the electromagnetic wave transmission direction of the transmission guide at predetermined intervals and leak the electromagnetic wave from the surface of the dielectric slab, and a feed which supplies the electromagnetic wave to one end side of the transmission guide.
Owner:ANRITSU CORP
Method and system for power transfer utilizing leaky wave antennas
ActiveUS20100308668A1Near-field transmissionElectromagnetic wave systemCoplanar waveguideEngineering
Methods and systems for power transfer utilizing leaky wave antennas (LWAs) are disclosed and may include configuring one or more LWAs in a communication device to receive RF signals that are communicated from one or more other LWAs that are external to the communication device. The communication device may be powered utilizing the RF signals that are received via the configured LWAs. A resonant frequency of the LWAs may be configured utilizing micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) deflection. The LWAs may be configured to receive the RF signals from a desired direction. The LWAs may comprise microstrip or coplanar waveguides, wherein a cavity height of the LWAs is dependent on spacing between conductive lines in the waveguides. The LWAs may be integrated in integrated circuits, integrated circuit packages, and / or printed circuit boards. The packages may be affixed to printed circuit boards and the integrated circuits may be flip-chip-bonded to the packages.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
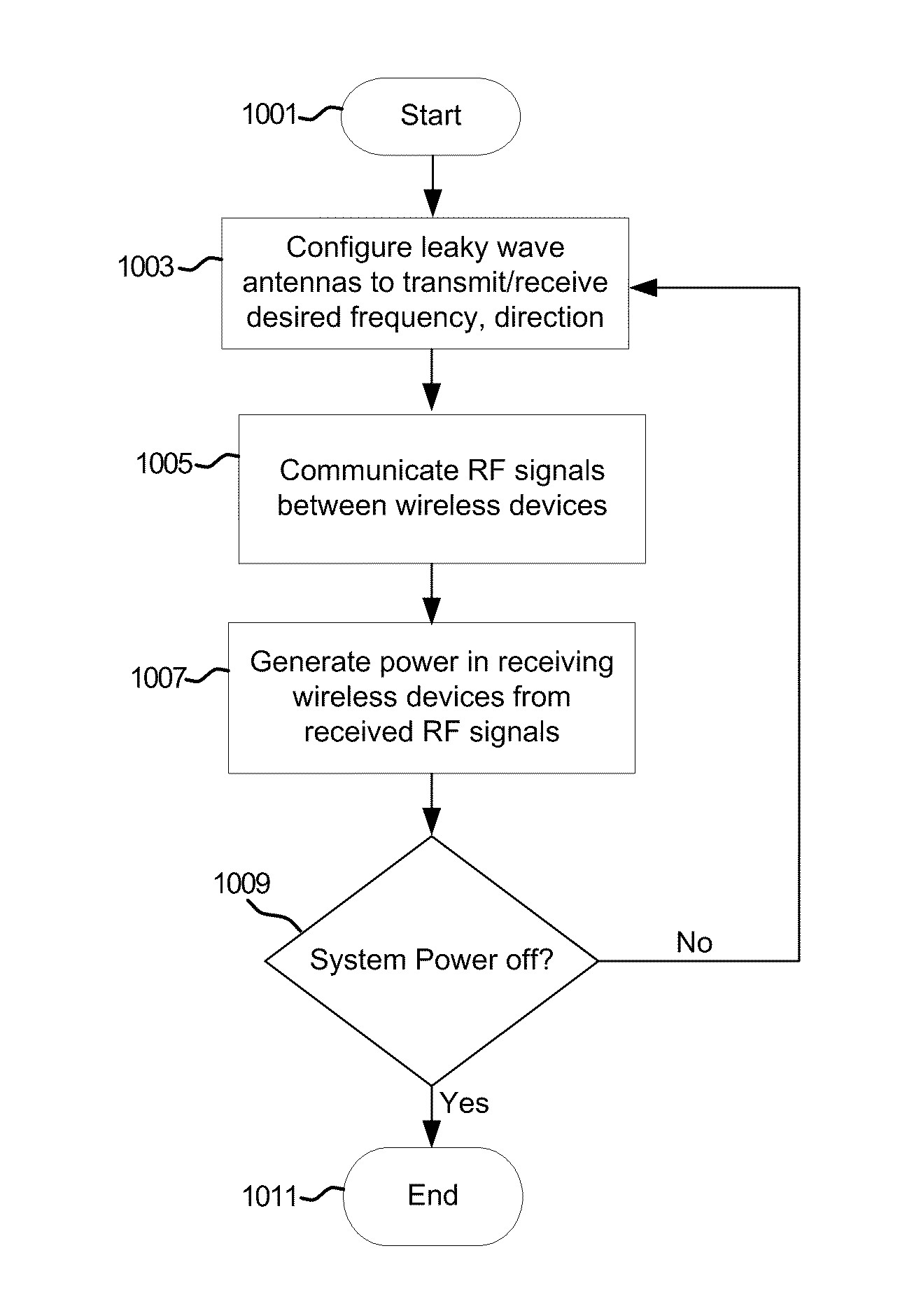
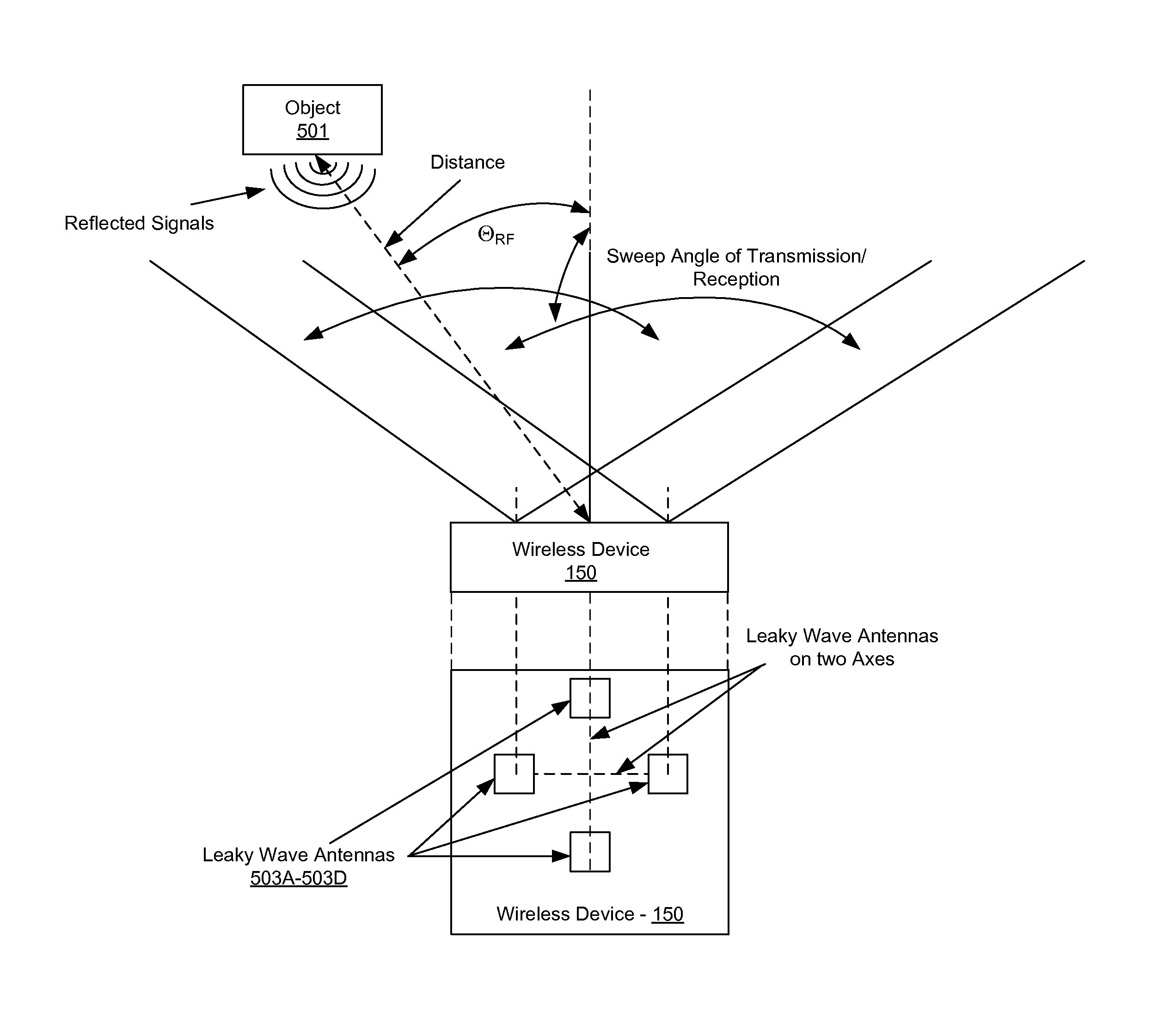
Method and system for dynamic tracking utilizing leaky wave antennas
InactiveUS8242957B2Near-field transmissionBeacon systems using radio wavesCoplanar waveguideEngineering
Methods and systems for dynamic tracking utilizing leaky wave antennas (LWAs) are disclosed and may include configuring a transmitting angle of a plurality of leaky wave antennas in a wireless device at a desired starting angle. A RF signal strength may be measured at the sweeping transmitting angles for each of the leaky wave antennas, and a location of one or more objects may be tracked from the measured RF signal strength and a corresponding angle of reception of the LWAs. A resonant frequency of the LWAs may be configured utilizing micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) deflection. The LWAs may be situated along a plurality of axes in the wireless device. The LWAs may comprise microstrip or coplanar waveguides, where a cavity height of the LWAs is dependent on spacing between conductive lines in the waveguides. The LWAs may be integrated in integrated circuits, integrated circuit packages, and / or printed circuit boards.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method and system for dynamic range detection and positioning utilizing leaky wave antennas
InactiveUS20100309040A1Near-field transmissionResonant long antennasCoplanar waveguideLeaky wave antenna
Methods and systems for dynamic range detection and positioning utilizing leaky wave antennas (LWAs) are disclosed and may include configuring one or more LWAs to enable communication of signals in a particular direction. RF signals that are reflected from an object may be received via the LWAs, and a location of the object may be determined based on the received reflected RF signals. The velocity of the object may be determined based on a Doppler shift associated with the received reflected RF signals. A frequency chirped signal may be transmitted by the LWAs to determine a location of the object. A resonant frequency of the LWAs may be configured utilizing micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) deflection. LWAs may be situated along a plurality of axes in the wireless device. The LWAs may include microstrip or coplanar waveguides, where a cavity height is dependent on spacing between conductive lines in the waveguides.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
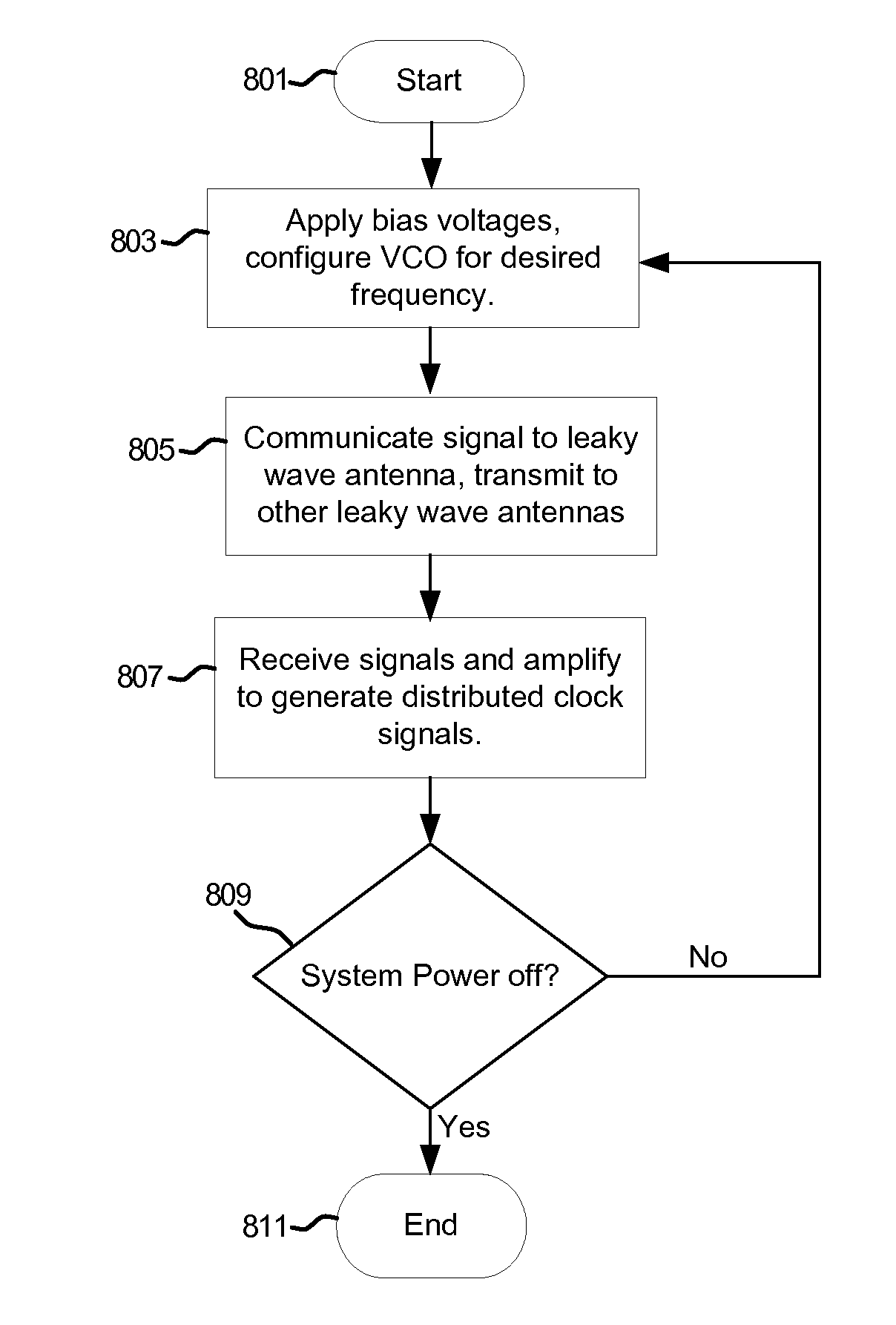
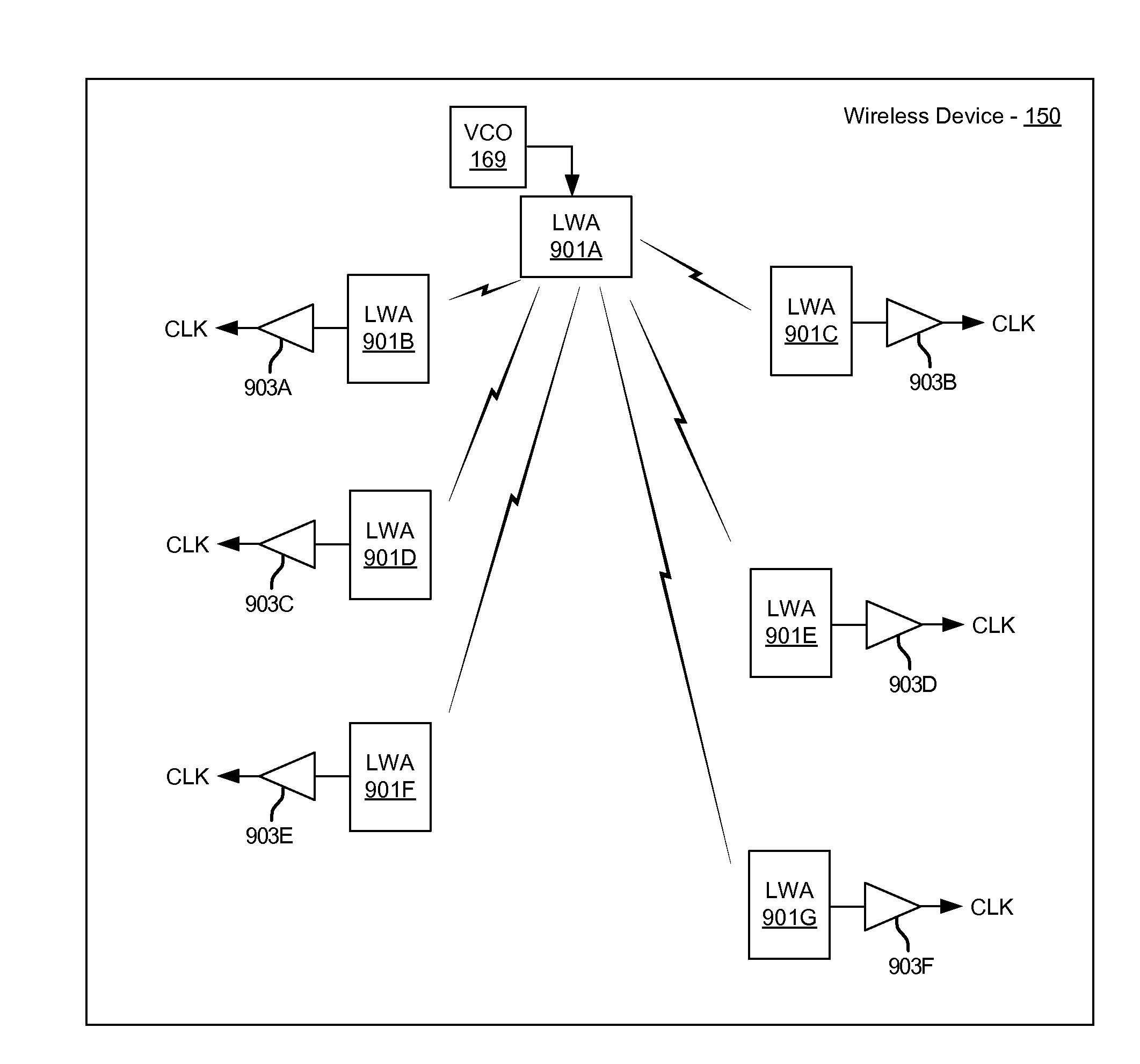
Method and system for clock distribution utilizing leaky wave antennas
Methods and systems for clock distribution utilizing leaky wave antennas (LWAs) in a wireless device are disclosed and may include configuring voltage-controlled oscillators (VCO) to generate one or more clock signals at desired clock frequencies and configuring LWAs at a resonant frequency corresponding to the clock frequencies, which may be generated at the desired clock frequencies utilizing the VCO. The clock signals may be communicated via LWAs in the wireless device and may be amplified utilizing one or more low-noise amplifiers. A resonant frequency of the LWAs may be configured utilizing micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) deflection. LWAs may be configured to enable beamforming. One or more of the LWAs may comprise microstrip or coplanar waveguides, wherein a cavity height of the LWAs is dependent on spacing between conductive lines in the waveguides. The LWAs may be integrated in one or more integrated circuits, integrated circuit packages, and / or printed circuit boards.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Traveling wave antenna
InactiveUS6016127ASimultaneous aerial operationsNon-resonant long antennasTraveling-wave antennaGround plane
A flat strip-like radiator is angled along the width of the strip to form radiating arms of predetermined length and angles to radiate a design radiation patter. The flat strip is secured to a ground plane such that the flat strip is perpendicular to the ground plane.
Owner:HOWELL LAB
Method and system for dynamic control of output power of a leaky wave antenna
ActiveUS20100309069A1Near-field transmissionSolid-state devicesAudio power amplifierCoplanar waveguide
Methods and systems for dynamic control of output power of a leaky wave antenna (LWA) are disclosed and may include configuring one or more LWAs in a wireless device to transmit RF signals at a desired frequency. The LWAs may be integrated in support structures, including an integrated circuit, an integrated circuit package, and / or a printed circuit board. Impedances that are coupled to the LWAs and to a power amplifier enabled to amplify the RF signals may be dynamically configured. A resonant frequency of the LWAs may be tuned, which may be configured to transmit the RF signals at a desired angle from a surface of the support structure. The LWAs may include microstrip or coplanar waveguides where a cavity height of the LWAs may be configured by controlling spacing between conductive lines in the waveguides. The impedances may include capacitor arrays and / or inductors in the support structures.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
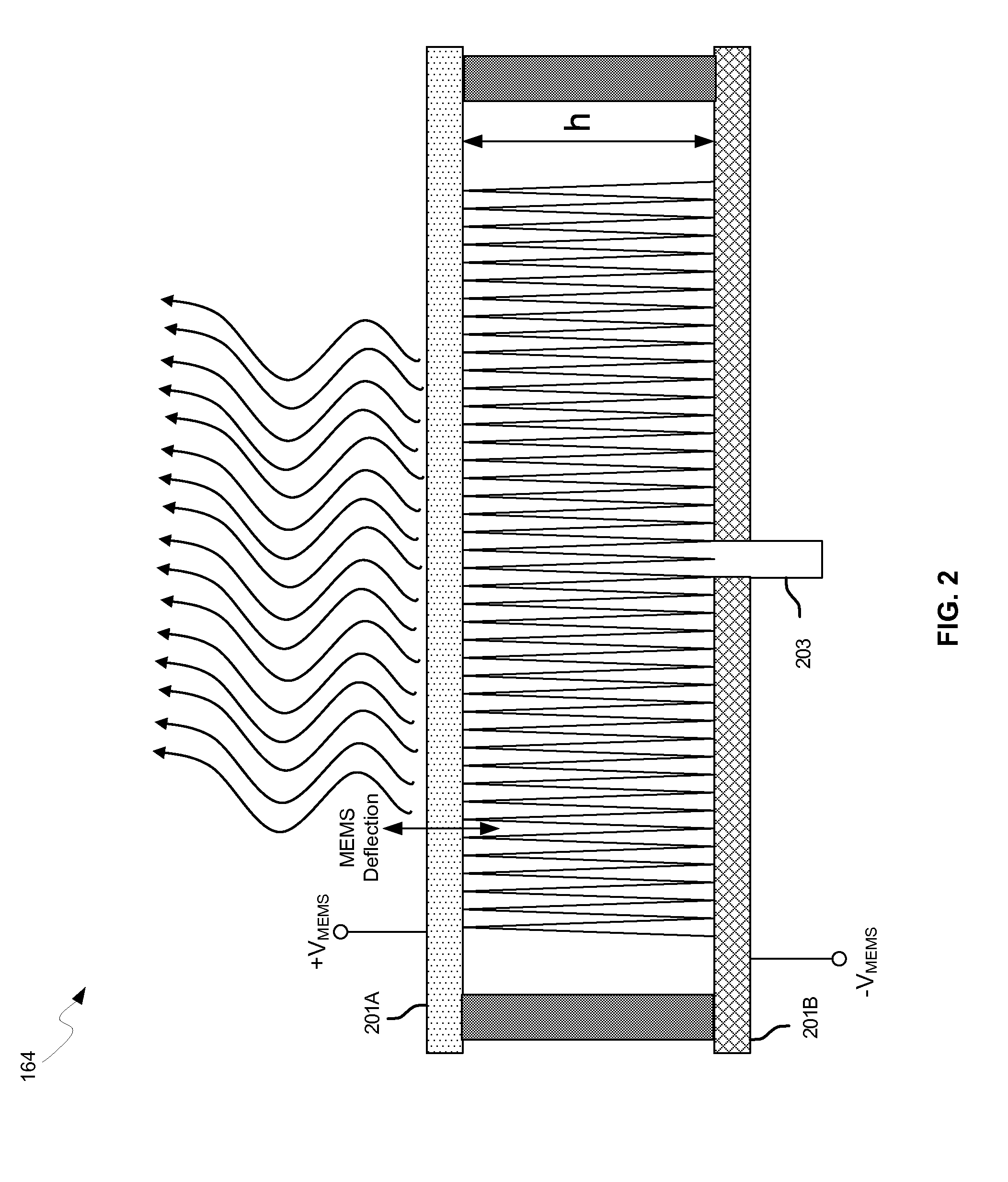
Method and system for configuring a leaky wave antenna utilizing micro-electro mechanical systems
InactiveUS20100309072A1Near-field transmissionSolid-state devicesPrinted circuit boardLeaky wave antenna
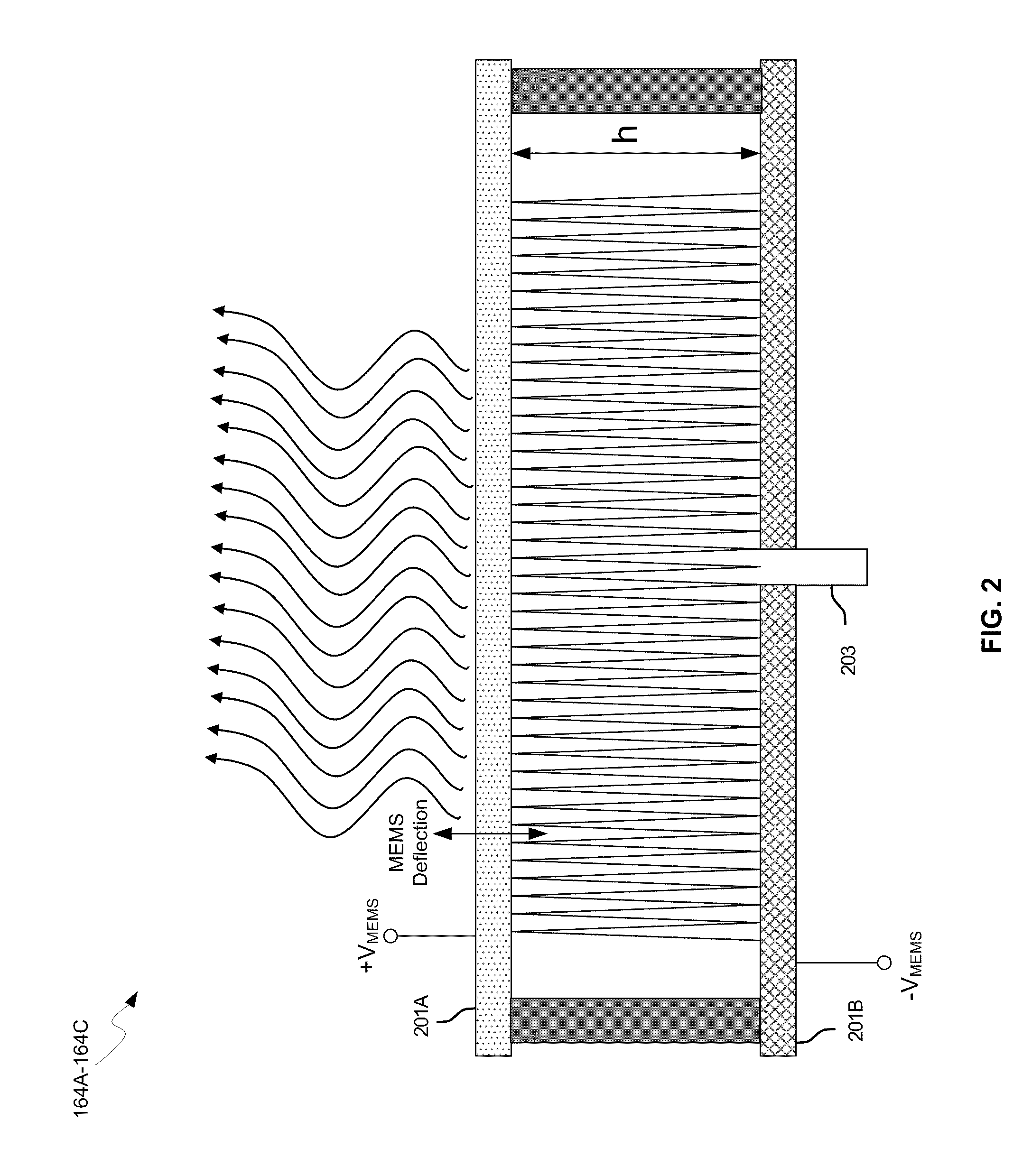
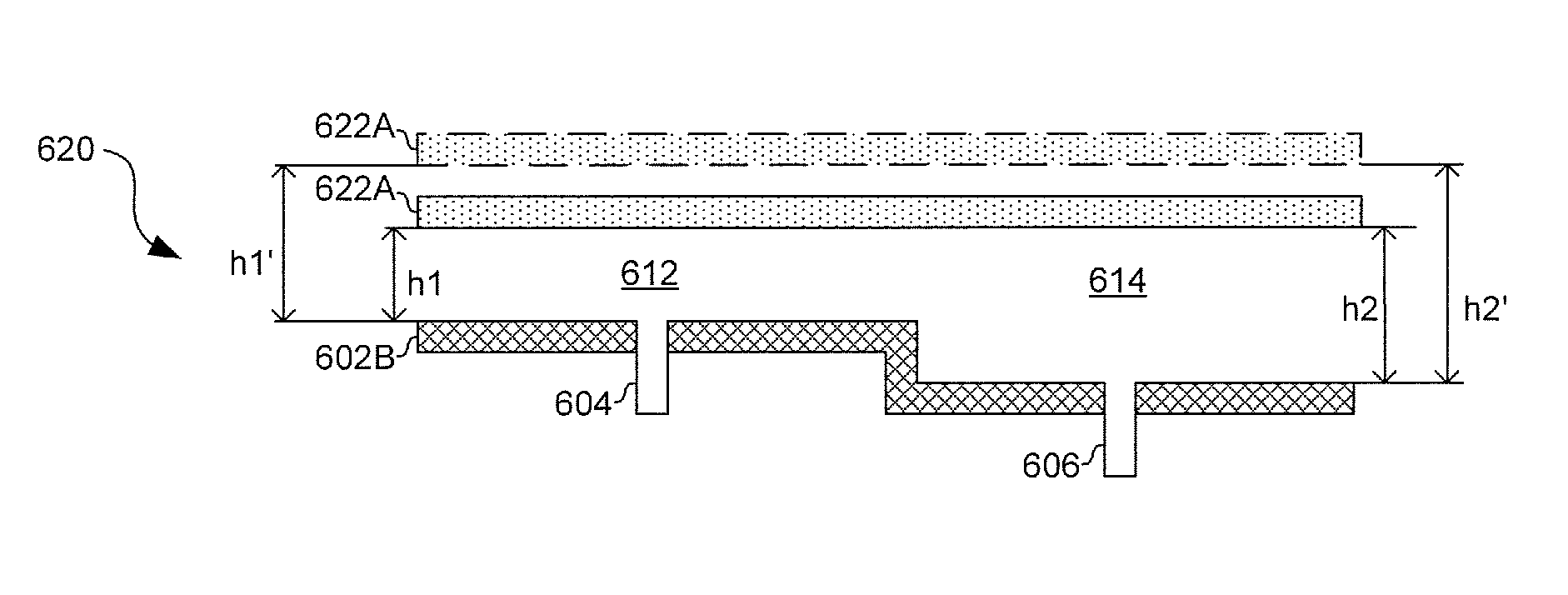
Methods and systems for configuring a leaky wave antenna (LWA) utilizing micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) are disclosed and may include configuring a resonant frequency of one or more LWAs in a wireless device utilizing MEMS actuation. RF signals may be communicated using the LWAs. The LWAs may be integrated in metal layers in a chip, an integrated circuit package, and / or a printed circuit board in the wireless device. The LWAs may include microstrip waveguides where a cavity height of the LWAs may be dependent on a spacing between conductive lines in the microstrip waveguides. The LWAs may be configured to transmit the wireless signals at a desired angle. The integrated circuit package may be affixed to a printed circuit board and an integrated circuit may be flip-chip-bonded to the integrated circuit package. An air gap may be integrated adjacent to one or more of the metal layers for the MEMS actuation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for communicating via leaky wave antennas within a flip-chip bonded structure
Methods and systems for communicating via leaky wave antennas (LWAs) within a flip-chip bonded structure are disclosed and may include communicating RF signals in a wireless device including one or more LWAs between a plurality of support structures, the structures being coupled via flip-chip bonding. Low-frequency signals may be communicated via flip-chip bonding contacts. The RF signals may be communicated perpendicular to a surface and / or at a desired angle from the surface of the structures, which may include at least one of: an integrated circuit, an integrated circuit package, and a printed circuit board. The LWAs may include microstrip and / or coplanar waveguides where a cavity height of the LWAs may be configured by controlling spacing between conductive lines in the waveguides. The low-frequency signals may include DC bias voltages. The RF signals may be communicated from a single LWA to a plurality of LWAs.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method and System for a Voltage-Controlled Oscillator with a Leaky Wave Antenna
Methods and systems for a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) with a leaky wave antenna are disclosed and may include transmitting wireless signals via one or more leaky wave antennas in one or more tank circuits coupled to one or more VCOs. The VCOs may be two-point modulated. Two modulating signals may be communicated to the one or more VCOs via varactors coupled to tank circuits on the one or more VCOs. The varactors may include CMOS transistors with source and drain terminals shorted together. The one or more leaky wave antennas may be integrated on the chip, on a package to which the chip is affixed, or on a printed circuit board to which the chip is affixed. The VCOs may be integrated in a phase-locked loop and an output of the one or more VCOs in the phase-locked loop may be fed back via a multi-modulus detector.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for a leaky wave antenna on an integrated circuit package
InactiveUS20100309074A1Near-field transmissionSolid-state devicesCoplanar waveguidePrinted circuit board
Methods and systems for a leaky wave antenna LWA on an integrated circuit (IC) package are disclosed and may include communicating RF signals using one or more LWAs in a wireless device. The LWAs may be integrated in metal layers in an IC package, and a resonant frequency of the LWAs may be dependent on cavity heights associated with the metal layers. The cavity heights may be configured utilizing micro-electro-mechanical systems deflection. The RF signals may include 60 GHz signals. The LWAs may include microstrip and / or coplanar waveguides where a cavity height of the LWAs may be dependent on a spacing between conductive lines in the waveguides. The LWAs may be configured to transmit the wireless signals at a desired angle from a surface of the IC package. The IC package may be affixed to a printed circuit board, and an IC may be flip-chip-bonded to the IC package.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method and system for communicating via leaky wave antennas on high resistivity substrates
Methods and systems for communicating via leaky wave antennas (LWAs) on high resistivity substrates are disclosed and may include communicating RF signals using one or more LWAs that may be integrated in an integrated circuit (chip) comprising a high resistivity substrate, which may include a silicon-on-sapphire substrate. The LWAs integrated in the chip may be configured to transmit the RF signals at a desired angle from the surface of the chip. The RF signals may be communicated between regions within the chip. The LWAs may include microstrip or coplanar waveguides where the cavity height of the one or more of the LWAs may be configured by controlling spacing between conductive lines in the waveguides. The RF signals may be communicated from the LWAs integrated in the chip to LWAs in a package to which the chip is bonded or in a printed circuit board to which the package is bonded.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method and system for point-to-point wireless communications utilizing leaky wave antennas
A method and system for point-to-point wireless communications utilizing leaky wave antennas is provided. In this regard, a first device may transmit a RF signal via a leaky wave antenna, and may determine an angle between the leaky wave antenna of the first device and a leaky wave antenna of a second device by adjusting a frequency of the RF signal until a response is received from the second device. The first device may be configured based on the determined angle. A wireless connection may be established between the leaky wave antenna of the first device and the leaky wave antenna of the second device based on the configuration. The first device may generate a notification when the angle is beyond a threshold. The wireless connection may adhere to wireless USB protocols and / or Bluetooth protocols, for example. The second device may generate the response after receiving sufficient energy from the RF signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for a distributed leaky wave antenna
InactiveUS20100311363A1Resonant long antennasNear-field transmissionPartially reflective surfaceCoplanar waveguide
Methods and systems for a distributed leaky wave antenna (LWA) are disclosed and may include communicating RF signals at one or more frequencies via distributed LWAs in a wireless communication device. The distributed LWAs may be integrated in one or more multi-layer support structures. The RF signals may be communicated at the one or more frequencies via a plurality of cavity heights in the distributed LWAs or via a plurality of sections of the distributed LWAs with different partially reflective surfaces. The distributed LWAs may be configured to transmit the RF signals at a desired angle from a surface of the multi-layer support structures. The distributed LWAs may include microstrip or coplanar waveguides where the plurality of cavity heights of the one or more distributed LWAs may be configured based on distances between conductive lines in the waveguides.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for a mesh network utilizing leaky wave antennas
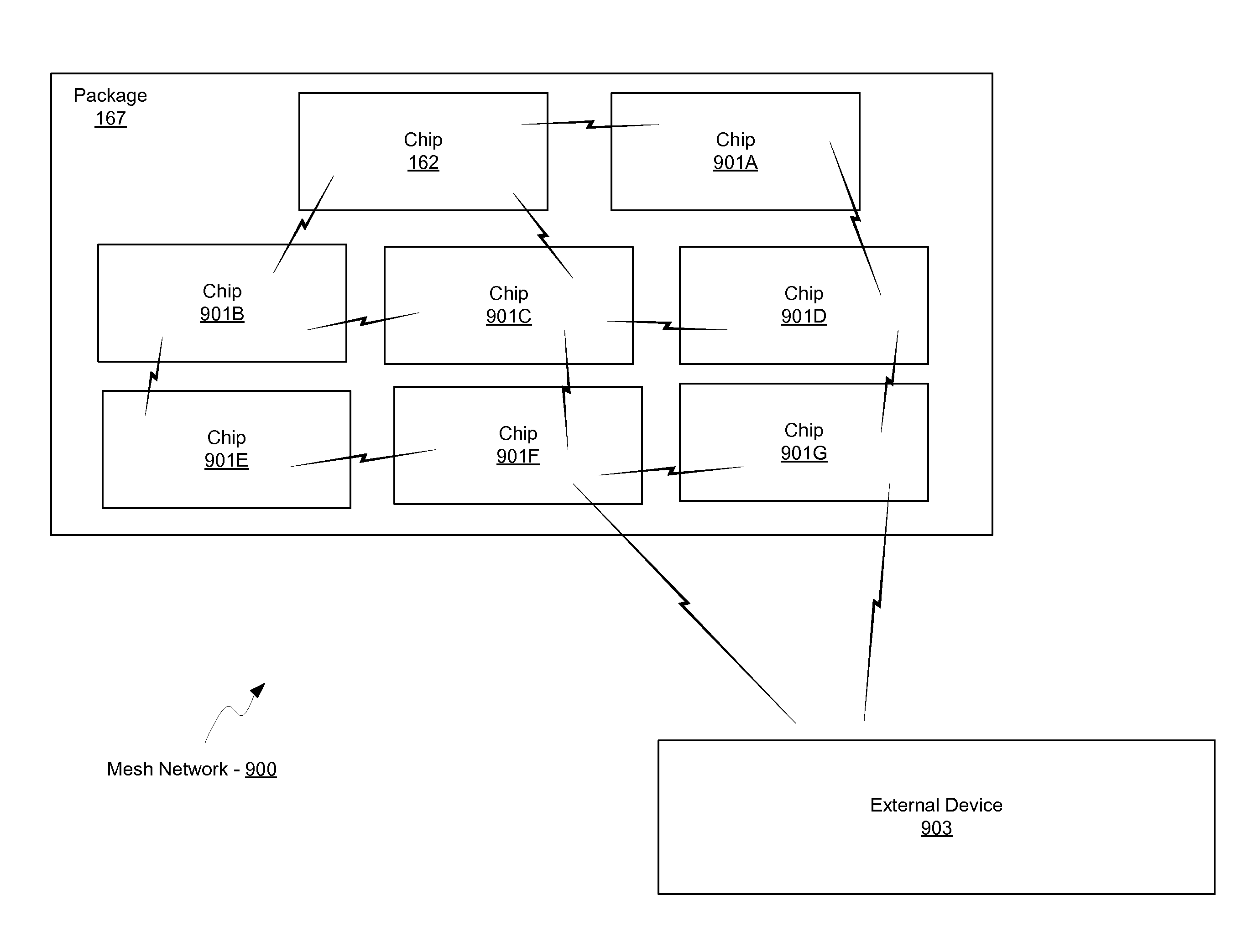
Methods and systems for a mesh network utilizing leaky wave antennas (LWAs) are disclosed and may include configuring one or more devices as a mesh network in a wireless device coupled to a plurality of LWAs, and communicating data between said devices via the configured mesh network. A resonant frequency of the LWAs may be configured utilizing micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) deflection. A plurality of the LWAs may be configured to enable beamforming. The LWAs may comprise microstrip or coplanar waveguides, wherein a cavity height of the LWAs is dependent on spacing between conductive lines in the waveguides. The plurality of LWAs may be integrated in one or more of: integrated circuits, integrated circuit packages, and printed circuit boards. The devices may be internal to the wireless device. The data may be communicated via the mesh network to devices external to the wireless device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for wireless communication utilizing on-package leaky wave antennas
Methods and systems for wireless communication utilizing on-package leaky wave antennas (LWAs) are disclosed and may include communicating wireless signals via an RF digital bus between integrated circuit packages in a wireless device utilizing LWAs integrated in metal layers in the plurality of packages. A resonant frequency of the LWAs may be configured utilizing micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) deflection. A plurality of the LWAs may be configured to enable beam-forming. The LWAs may include microstrip or coplanar waveguides wherein a cavity height of the LWAs is dependent on spacing between conductive lines in the waveguides. The LWAs may be configured to transmit the wireless signals at a desired angle from a surface of the packages. The packages may be affixed to one or more printed circuit boards. An integrated circuit may be flip-chip-bonded to one or more of the packages.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method and System for a Low Noise Amplifier Utilizing a Leaky Wave Antenna
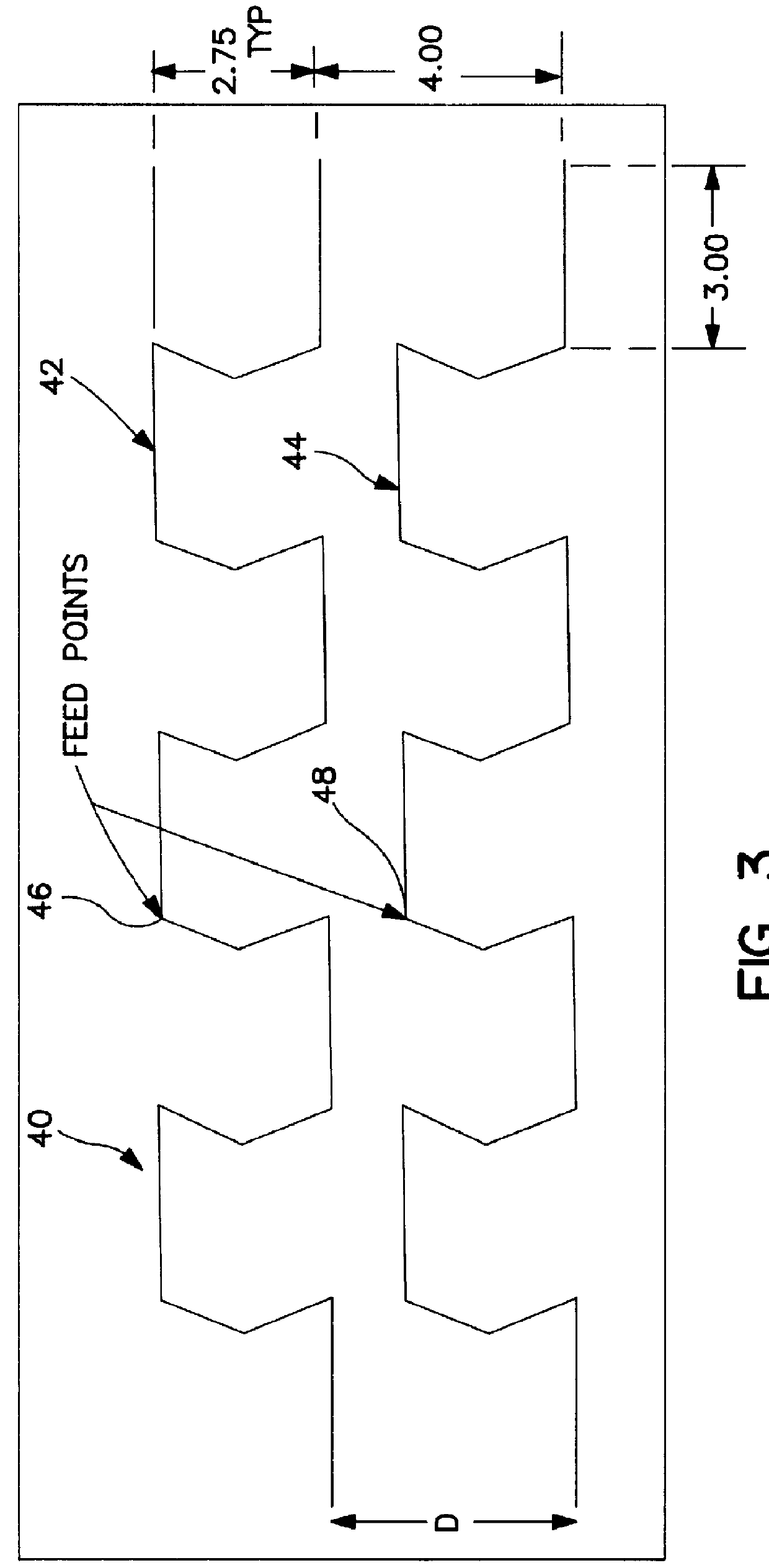
Methods and systems for a low noise amplifier utilizing a leaky wave antenna are disclosed and may include one or more low-noise amplifiers (LNAs) coupled to one or more leaky wave antennas (LWAs) in a wireless device. RF signals may be received via one or more LNAs coupled to one or more feed points on a LWA. The one or more LNAs may be coupled to the feed points based on an impedance of the feed points and an input impedance of the one or more LNAs. The impedance of the feed points may be configured by locating them along a vertical axis in a resonant cavity of the LWA. The LWAs may be integrated on a chip, and / or on a package or printed circuit board to which the chip is affixed. The RF signals may be amplified by the LNAs and may be down-converted to baseband signals.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
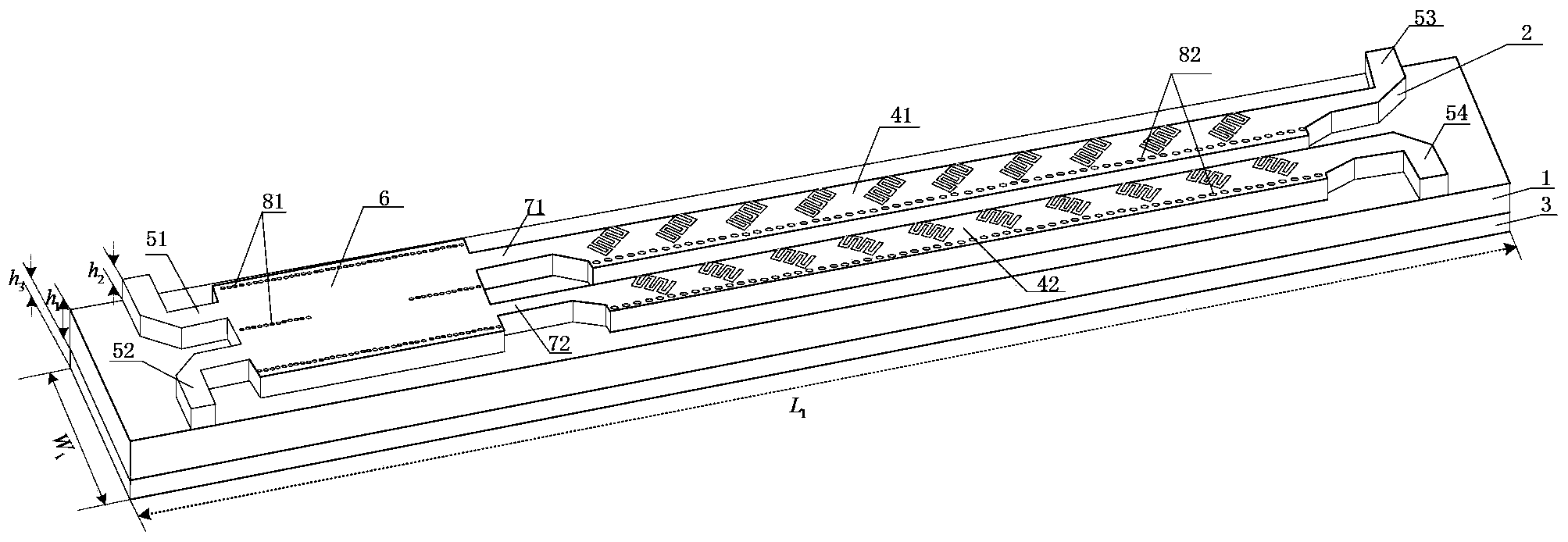
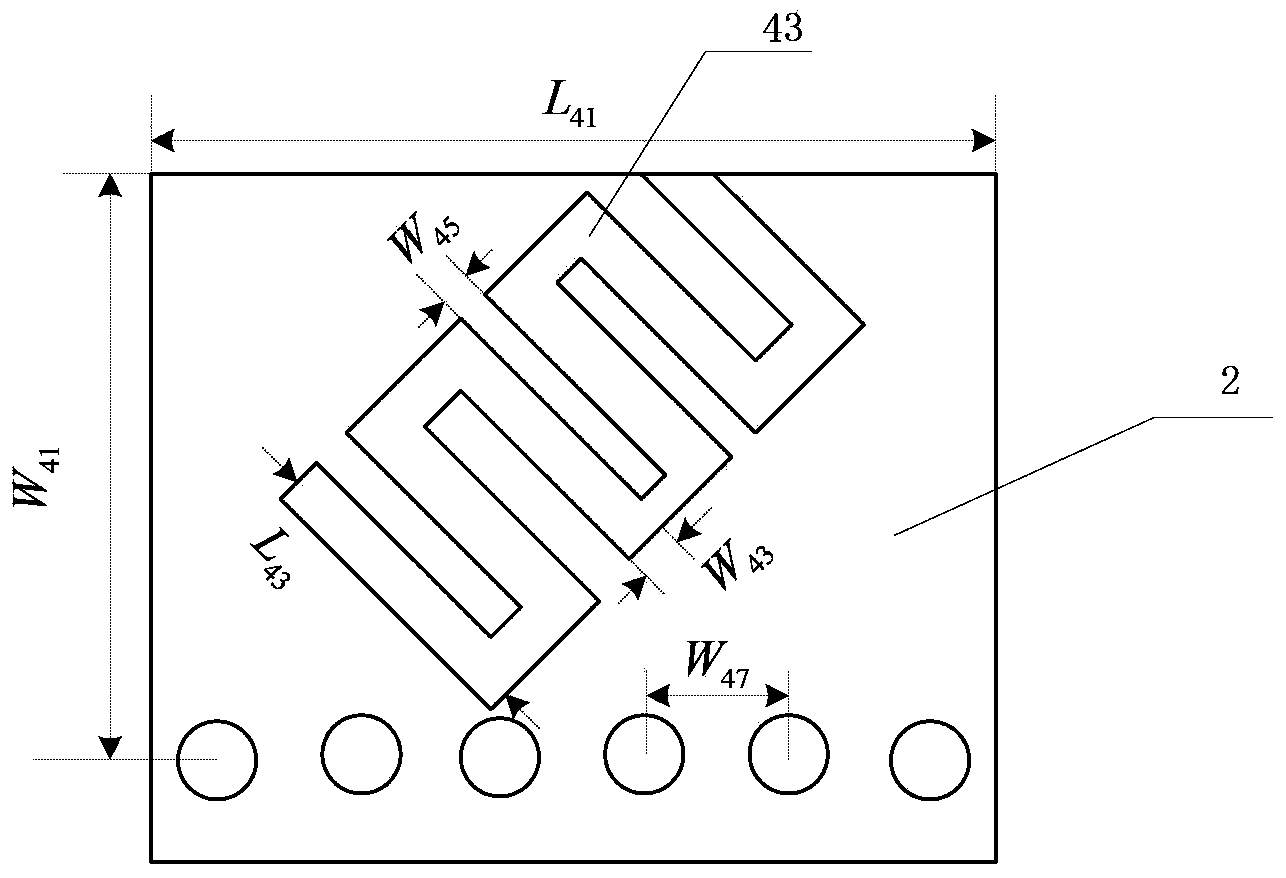
Half-mode substrate integrated waveguide leaky-wave antenna for variable polarization and frequency scanning
ActiveCN103441340AReduce lossLow and low loss characteristicsRadiating elements structural formsPolarised antenna unit combinationsBeam scanningFeed line
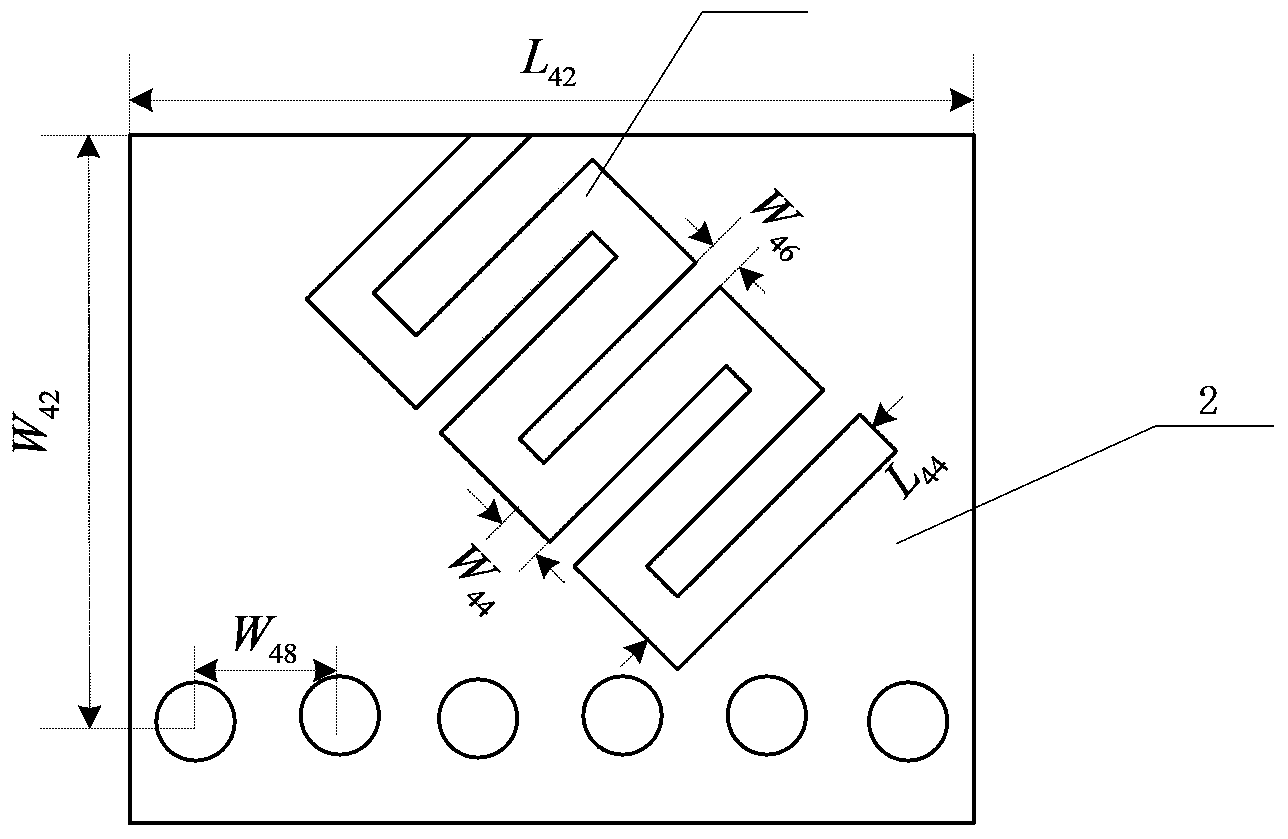
The invention discloses a half-mode substrate integrated waveguide leaky-wave antenna for variable polarization and frequency scanning, and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The antenna comprises a medium substrate with metal patches arranged on two faces, a half-mode substrate integrated waveguide antenna array A, a half-mode substrate integrated waveguide antenna array B, four micro-strip feeder lines, a 3dB directional coupler and two micro-strip connecting lines are arranged on one metal patch, an interdigital groove inclined by -45 degrees and a metal through hole A are etched in the half-mode substrate integrated waveguide antenna array A, and an interdigital groove inclined by 45 degrees and a metal through hole A are etched in the half-mode substrate integrated waveguide antenna array B. Compared with the prior art, the half-mode substrate integrated waveguide leaky-wave antenna is low in loss, low in cost, small in size and capable of achieving multiple kinds of polarization simply and effectively and achieving beam scanning economically and practically.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and system for wireless communication utilizing leaky wave antennas on a printed circuit board
Methods and systems for wireless communication utilizing leaky wave antennas (LWAs) on a printed circuit board are disclosed and may include communicating RF signals via LWAs in an integrated circuit (chip) and / or package in a wireless device to LWAs in a printed circuit board in the wireless device. RF signals may then be communicated via the LWAs in the printed circuit board to external devices, and may communicated vertically or at a desired angle from the surface. The RF signals may be communicated between regions within the printed circuit board. The LWAs may include microstrip or coplanar waveguides where a cavity height of the LWAs may be configured by controlling spacing between conductive lines in the waveguides. The chip may be flip-chip-bonded to an package which may be affixed to a printed circuit board. A pair of the plurality of LWAs may be stacked to communicate signals in opposite directions.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method and System for a Sub-Harmonic Transmitter Utilizing a Leaky Wave Antenna
Methods and systems for a sub-harmonic transmitter utilizing a leaky wave antenna are disclosed and may include transmitting wireless signals at a harmonic frequency of a source signal utilizing one or more leaky wave antennas (LWAs) in a wireless device including one or more transceivers on a chip. The LWAs may be configured with a resonant frequency at the harmonic frequency. The source signal may be communicated to the LWAs utilizing a power amplifier, which may be operated in switching mode thereby generating a square wave from the source signal. The LWAs may be integrated on the chip, on a package to which the chip is affixed and / or on a printed circuit board to which the chip is affixed. The harmonic frequency may be three times a frequency of the source signal. The transmitted wireless signal may be amplitude modulated utilizing a bias voltage applied to the LWAs.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for a duplexing leaky wave antenna
Methods and systems for a duplexing leaky wave antenna (LWA) are disclosed. In this regard, RF signals may be concurrently transmitted and received via a leaky wave antenna, wherein a height of a first portion of a resonant cavity of the leaky wave antenna is different than a height of a second portion of the resonant cavity. RF signals transmitted may be at or near a first frequency and RF signals received be at or near a second frequency. The height of the first portion of the resonant cavity and / or the height of the second portion of the resonant cavity may be controlled by applying one or more voltages which causes one or both reflective surface of the leaky wave antenna to deflect. The leaky wave antenna may be integrated on and / or within an integrated circuit, an integrated circuit package, a printed circuit board, or a combination thereof.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com