Patents
Literature
1187 results about "Smart antenna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
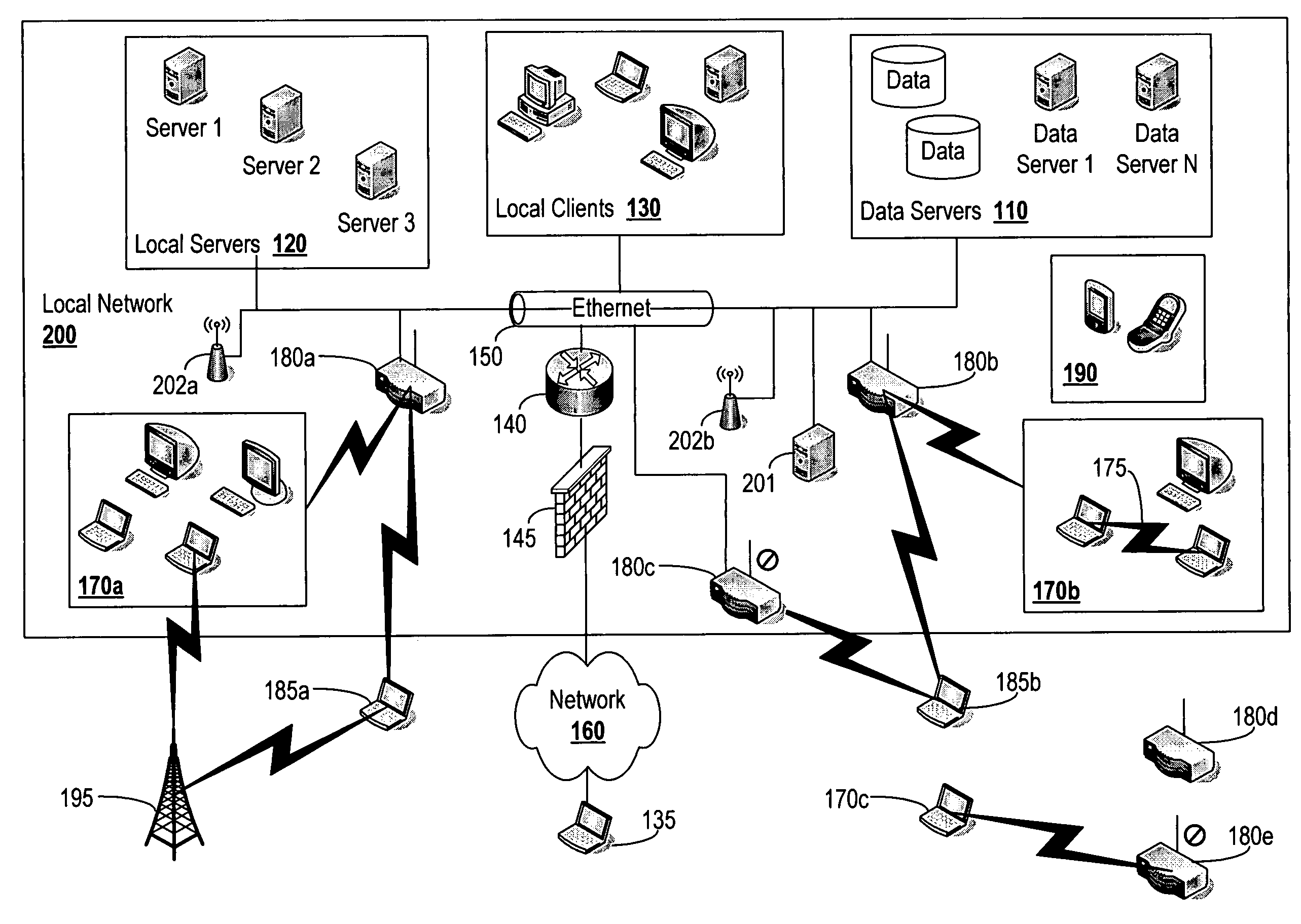
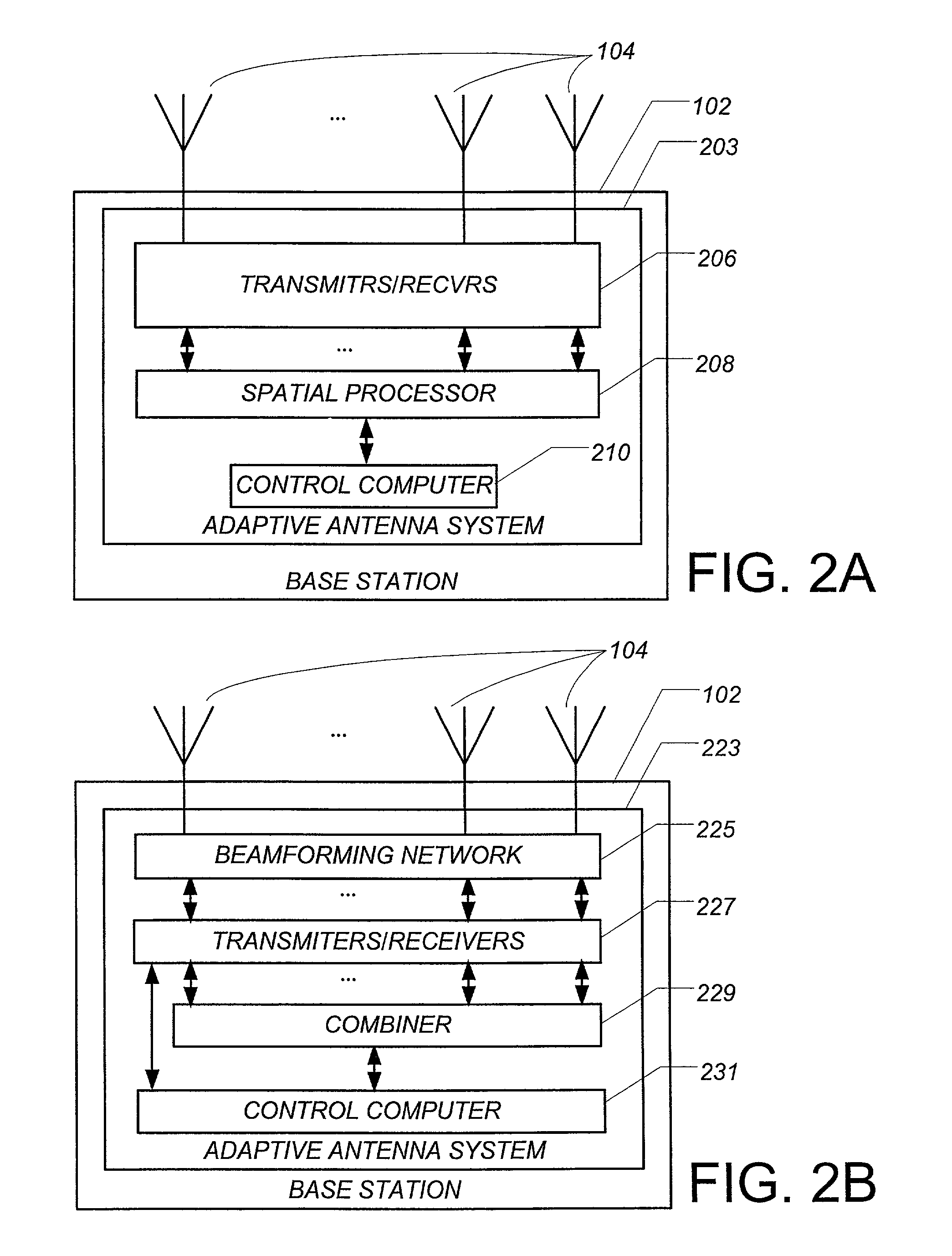
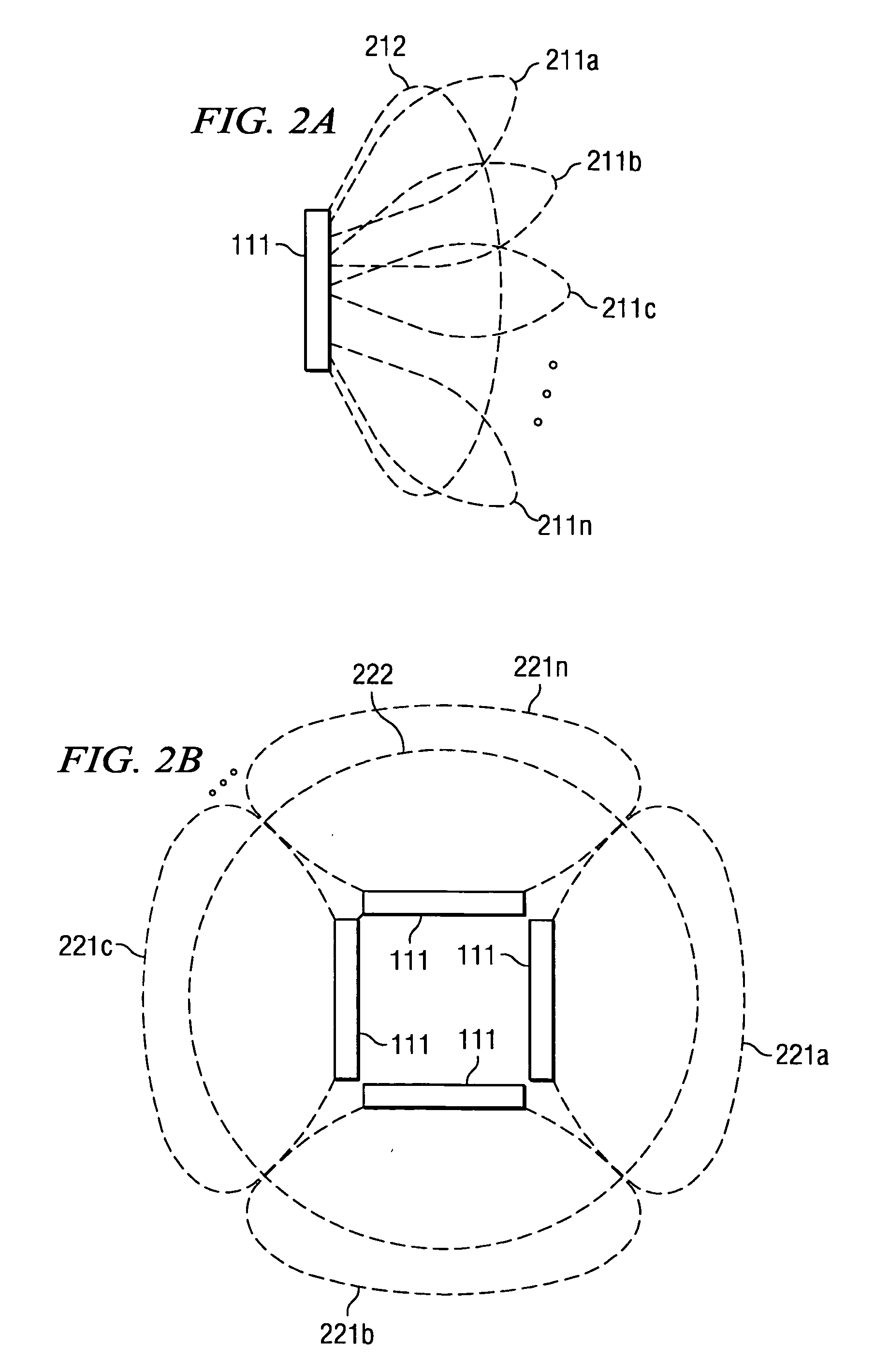
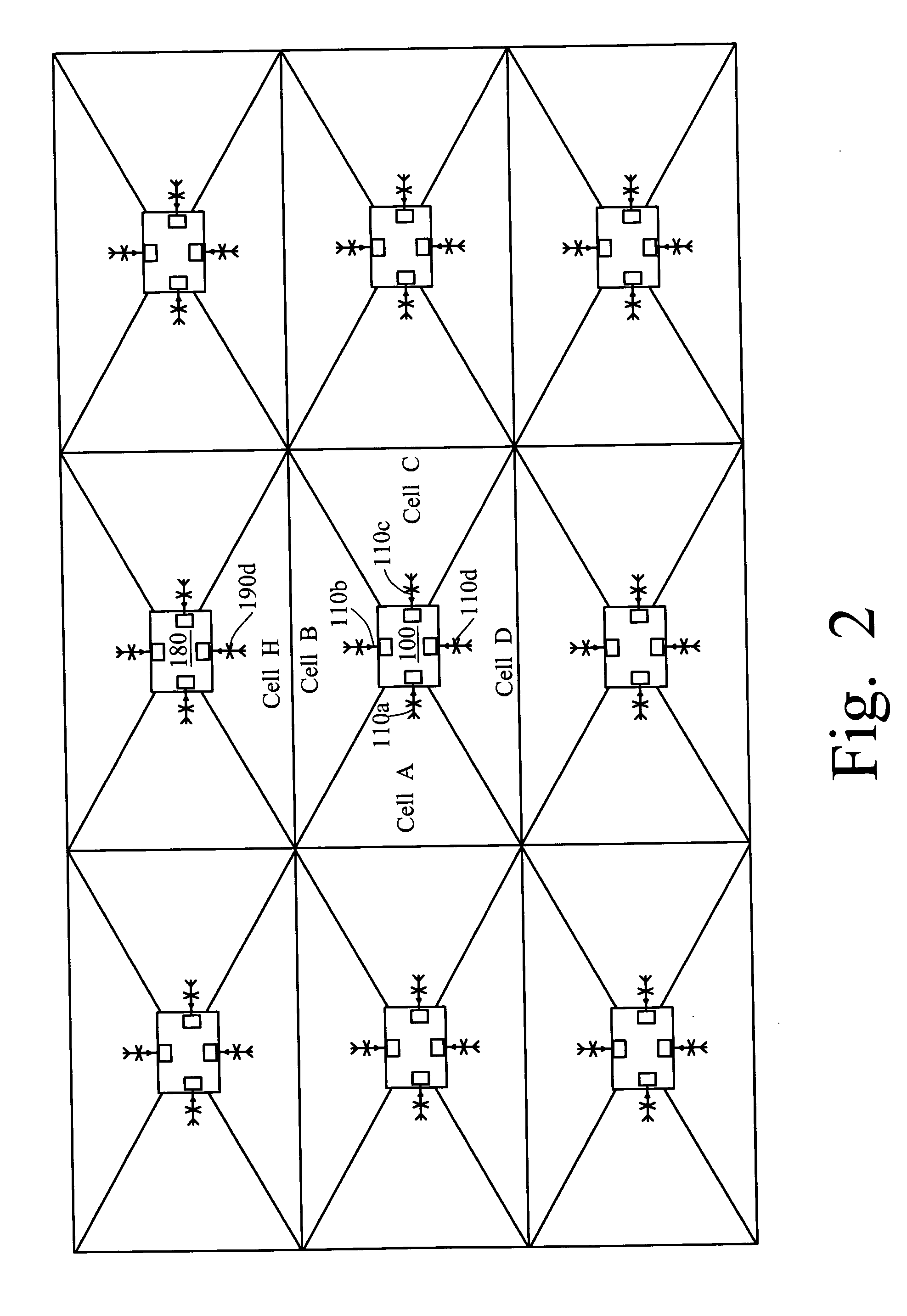
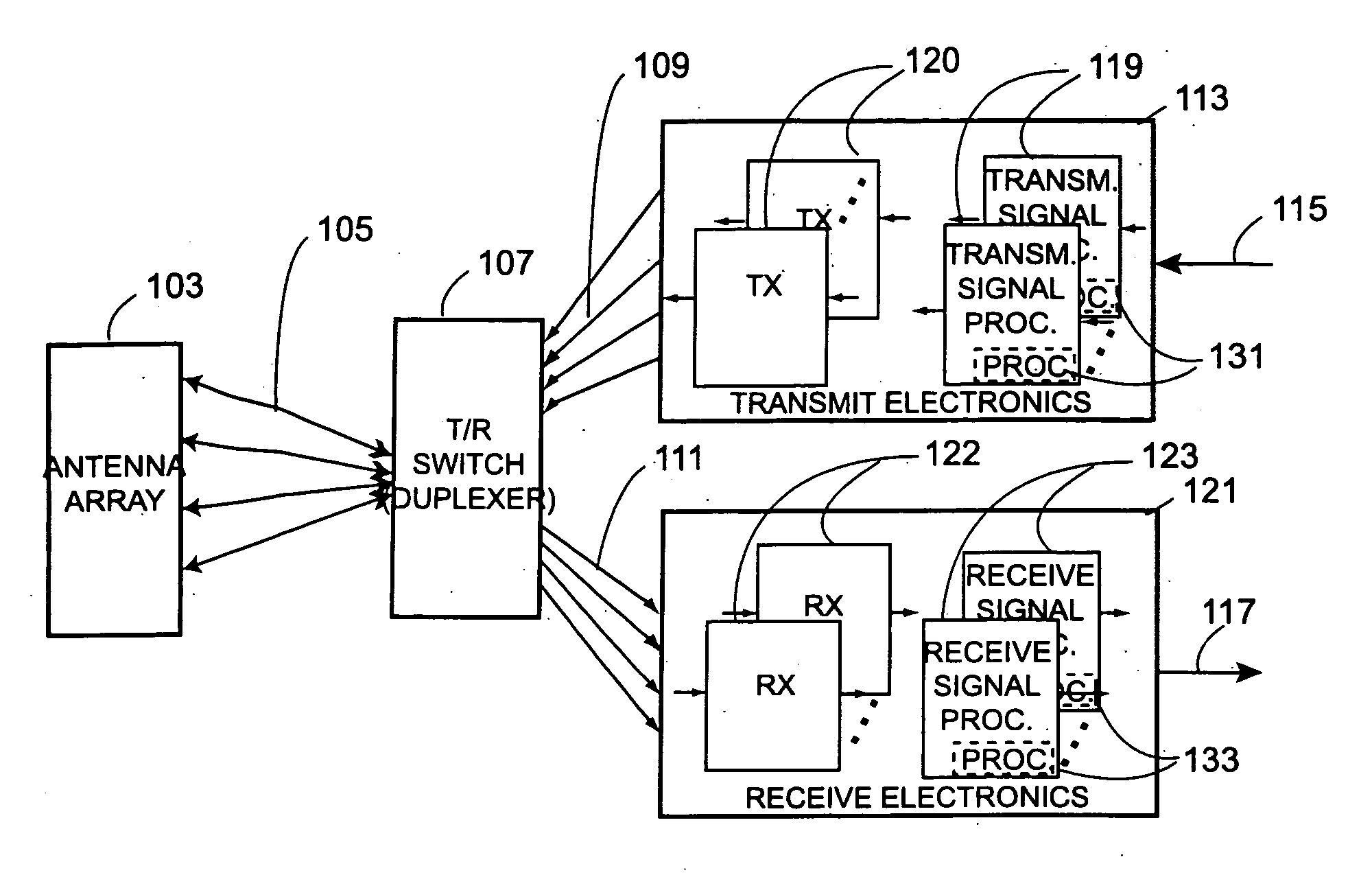
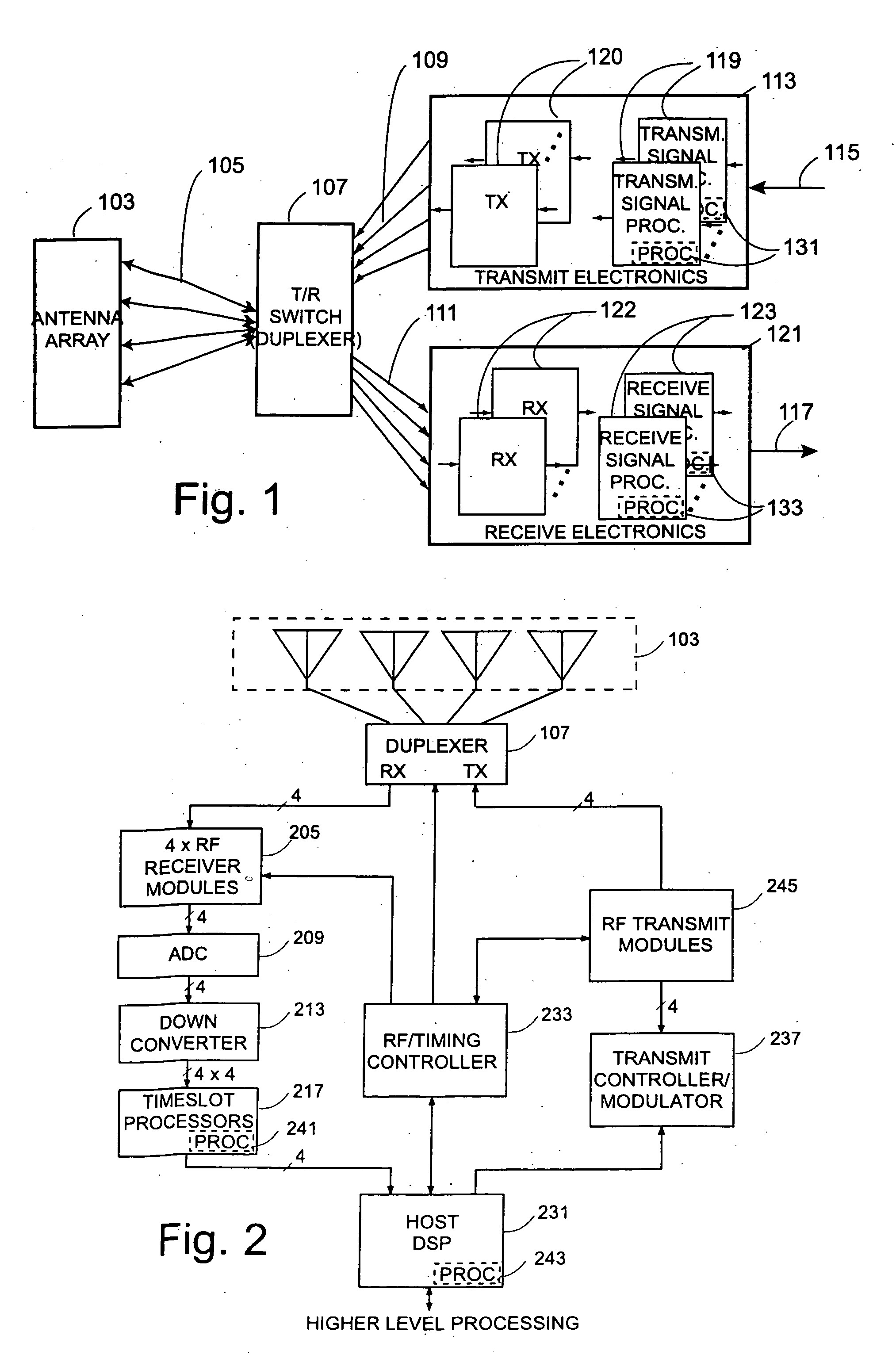
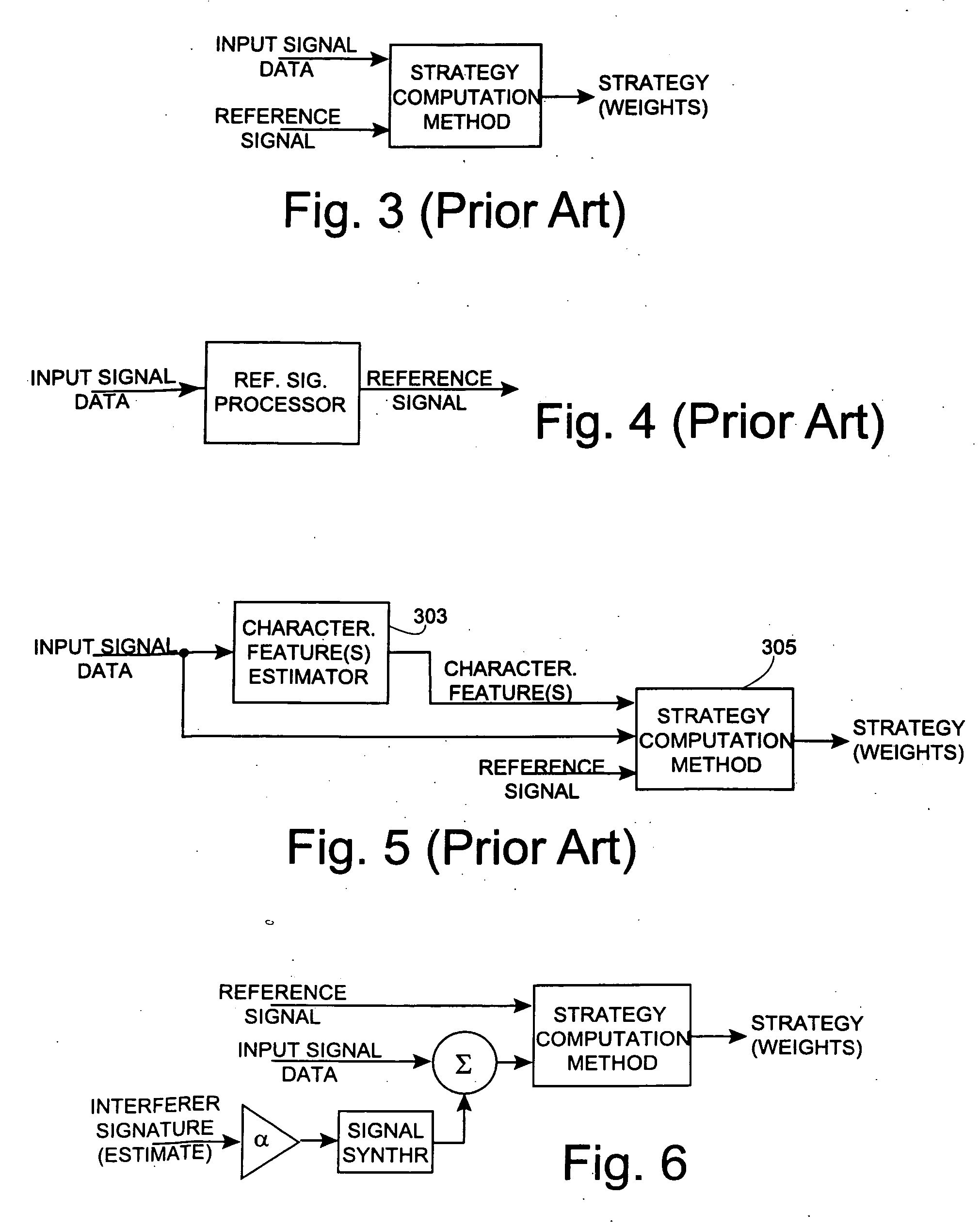
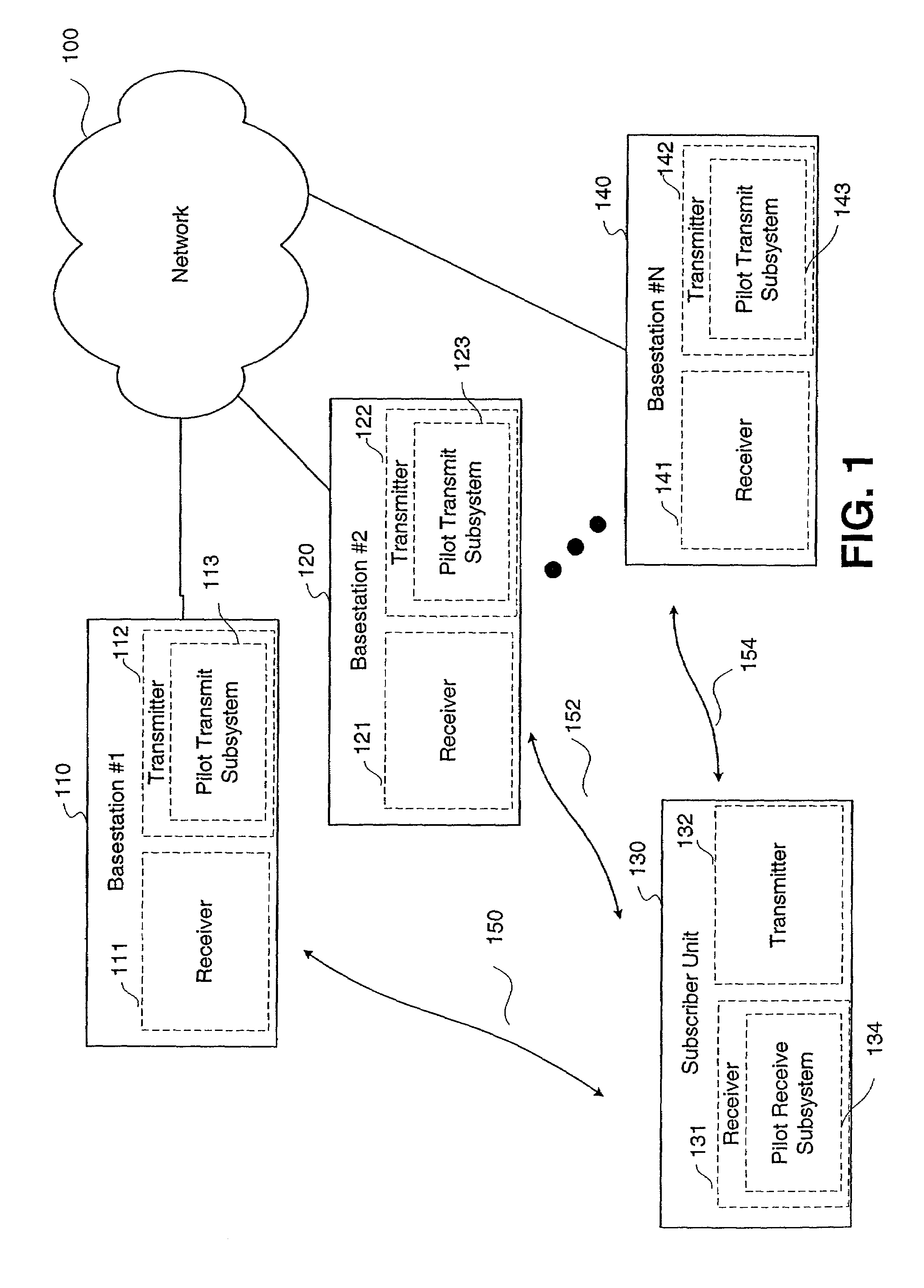
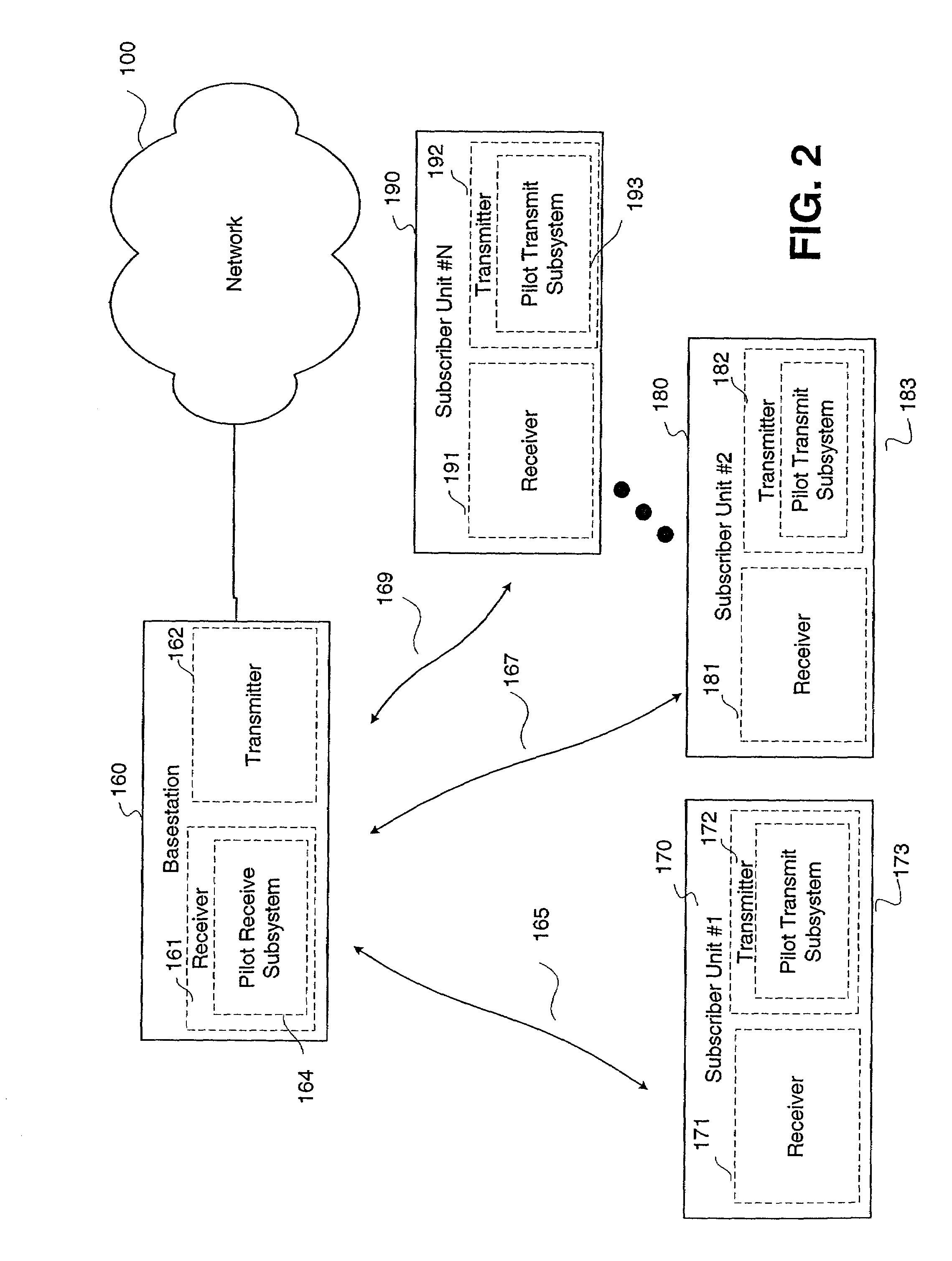
Smart antennas (also known as adaptive array antennas, digital antenna arrays, multiple antennas and, recently, MIMO) are antenna arrays with smart signal processing algorithms used to identify spatial signal signatures such as the direction of arrival (DOA) of the signal, and use them to calculate beamforming vectors which are used to track and locate the antenna beam on the mobile/target. Smart antennas should not be confused with reconfigurable antennas, which have similar capabilities but are single element antennas and not antenna arrays.
MAC extensions for smart antenna support
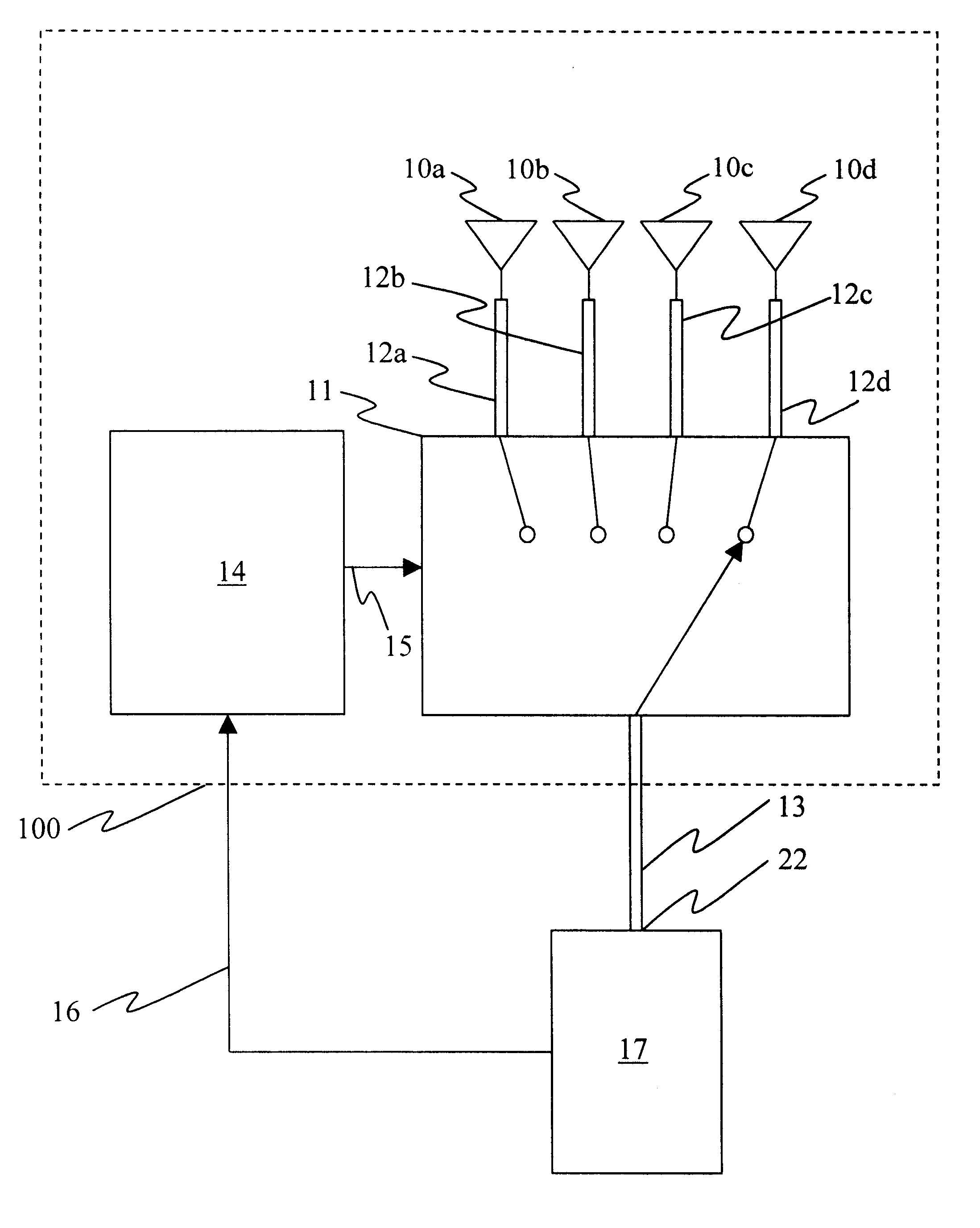
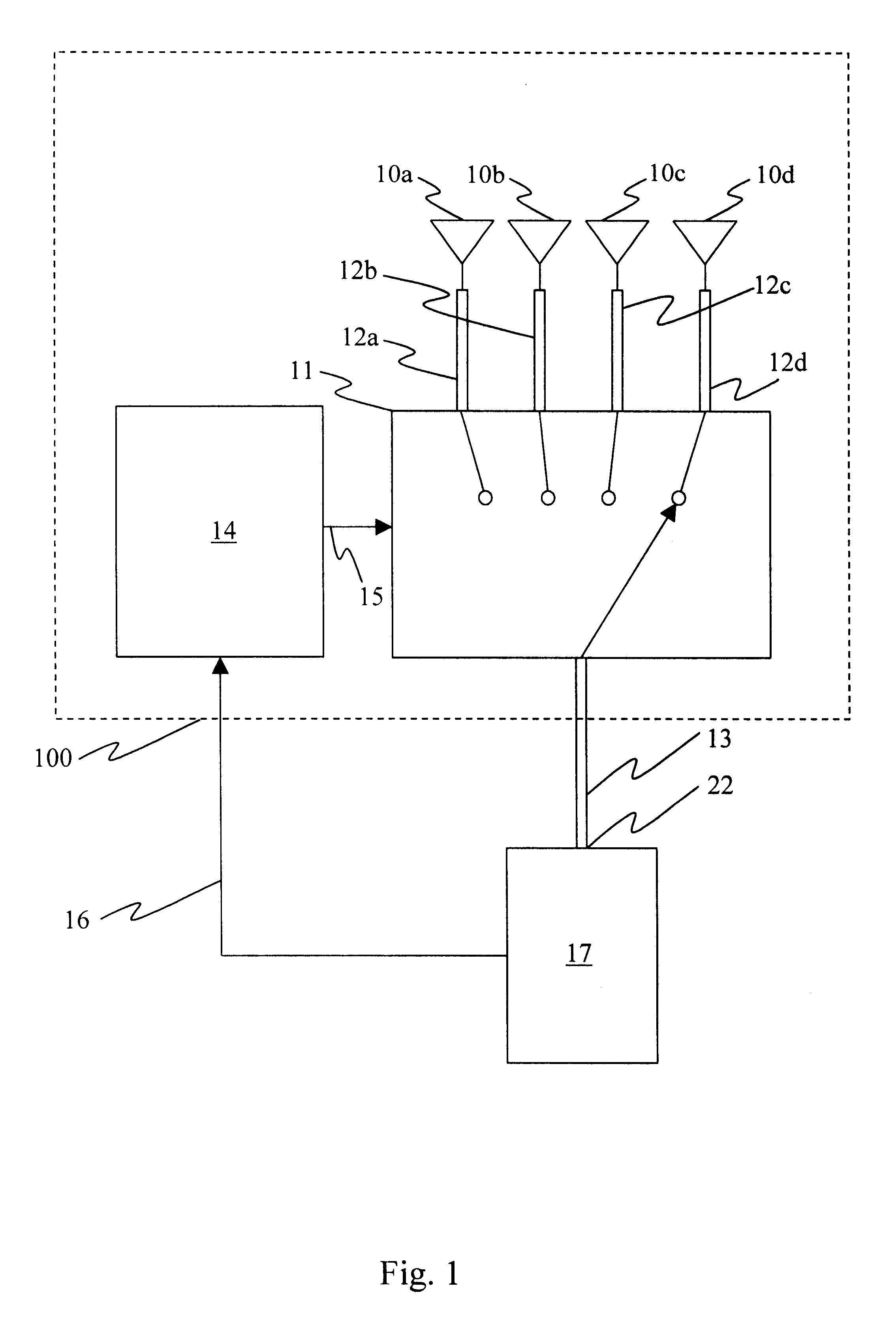
ActiveUS20030169769A1Reduce reception errorsLess bitError prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityTelecommunicationsStation
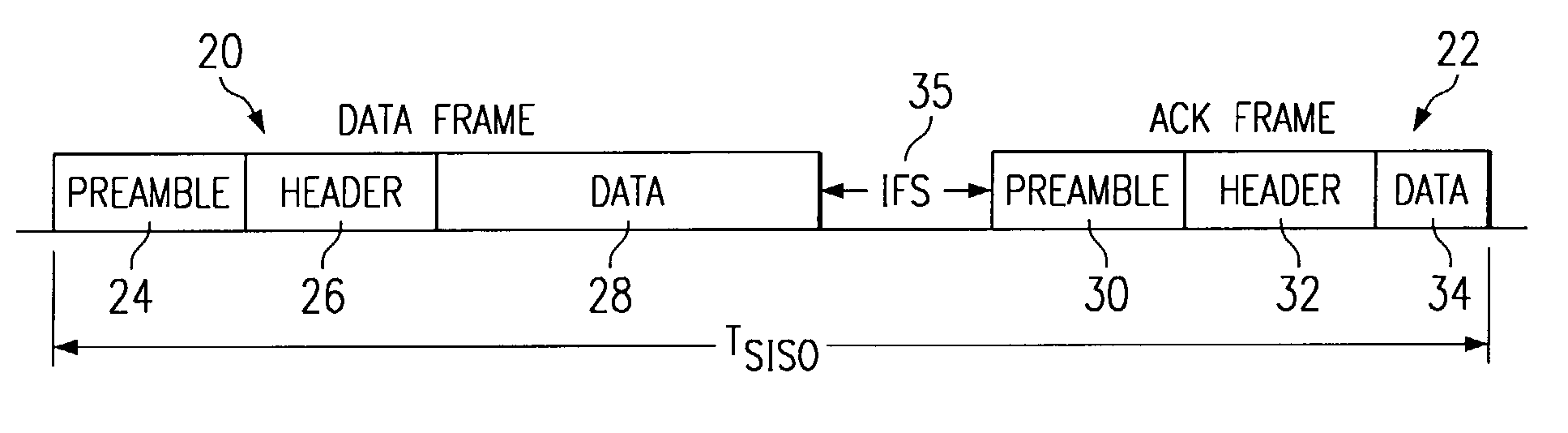
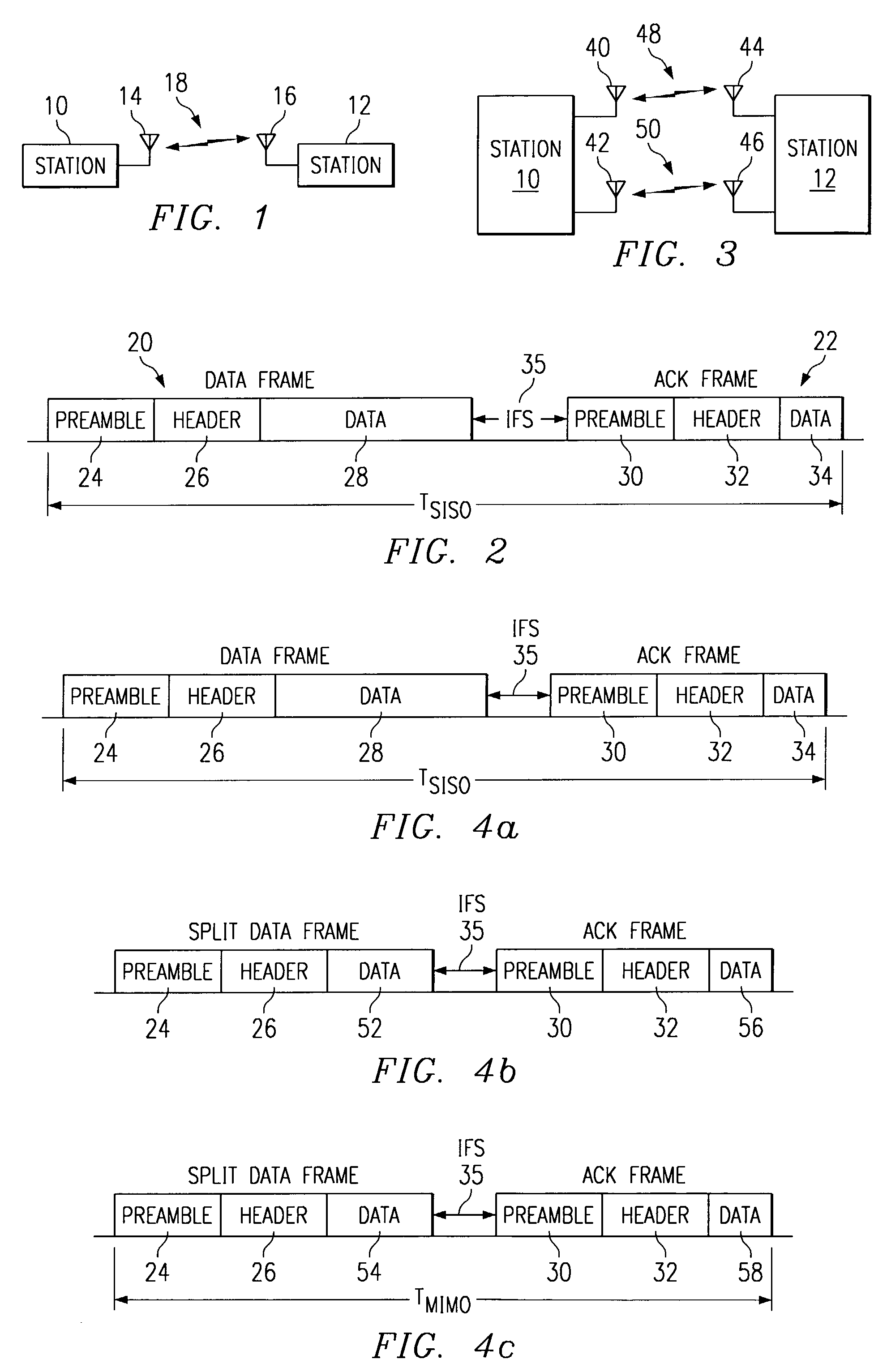
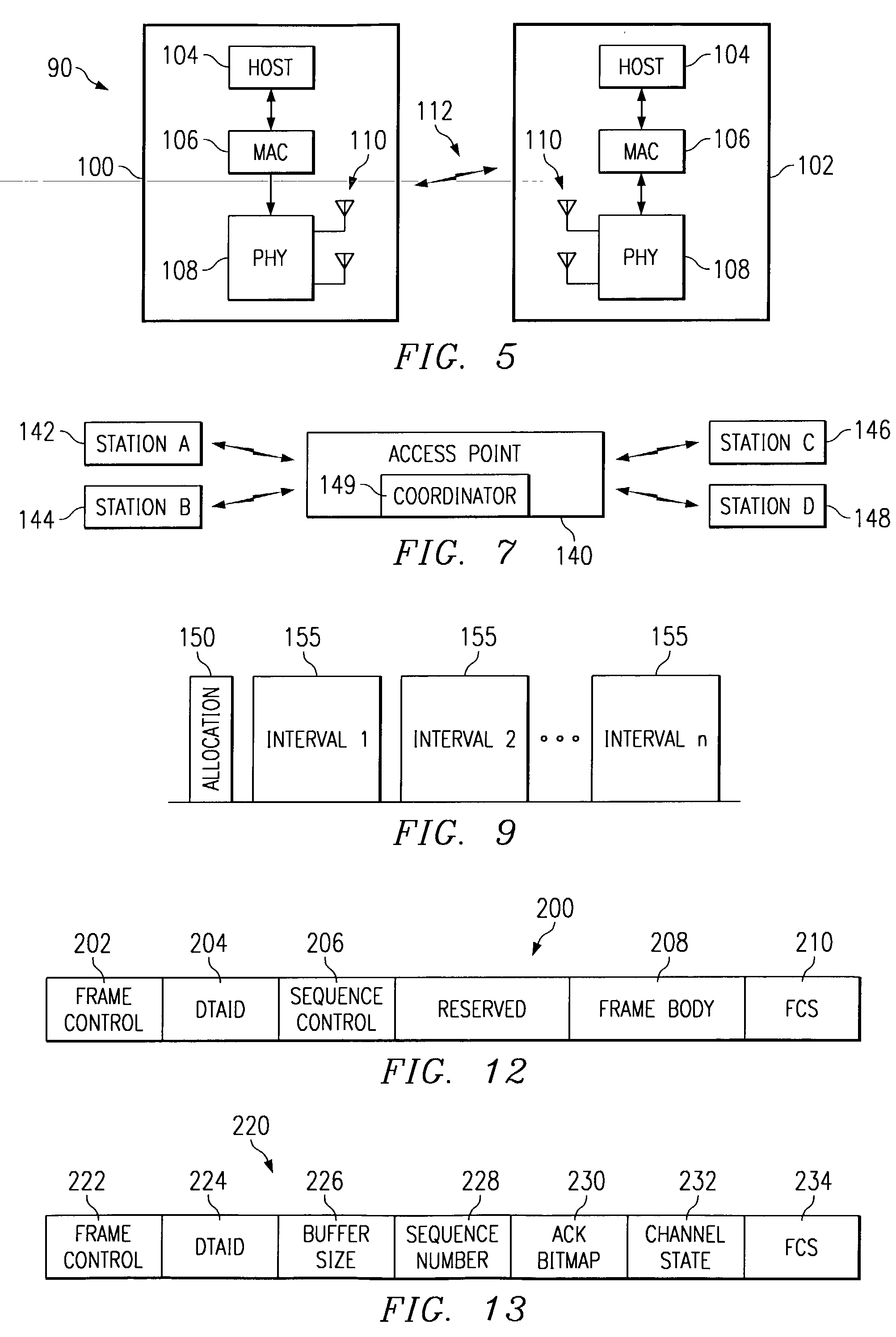
Apparatus and methods implement aggregation frames and allocation frames. The aggregation frames include a plurality of MSDUs or fragments thereof aggregated or otherwise combined together. An aggregation frame makes more efficient use of the wireless communication resources. The allocation frame defines a plurality of time intervals. The allocation frame specifies a pair of stations that are permitted to communicate with each other during each time interval as well as the antenna configuration to be used for the communication. This permits stations to know ahead of time when they are to communicate, with which other stations and the antenna configuration that should be used. A buffered traffic field can also be added to the frames to specify how much data remains to be transmitted following the current frame. This enables network traffic to be scheduled more effectively.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and system for a smart antenna utilizing leaky wave antennas
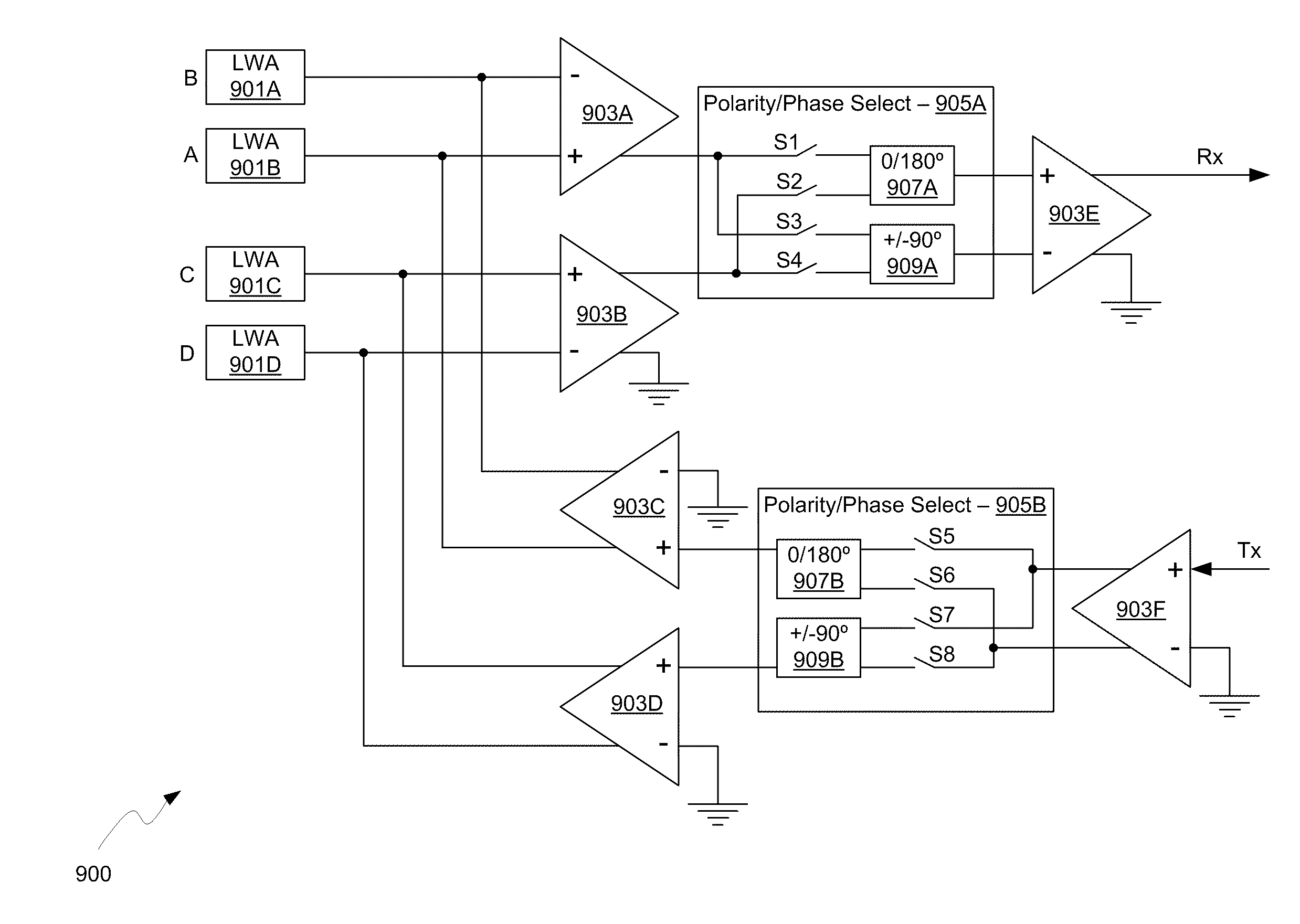
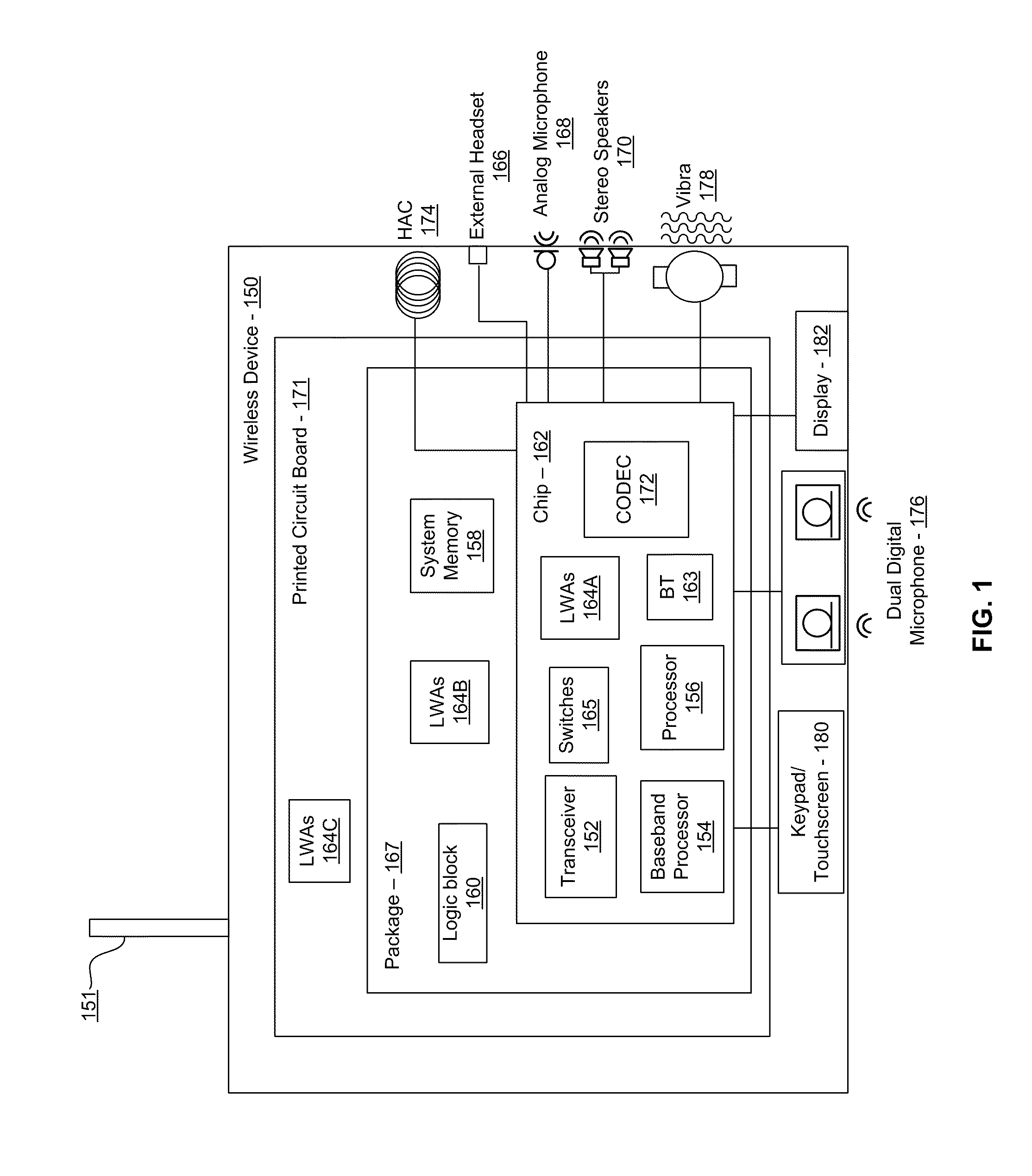
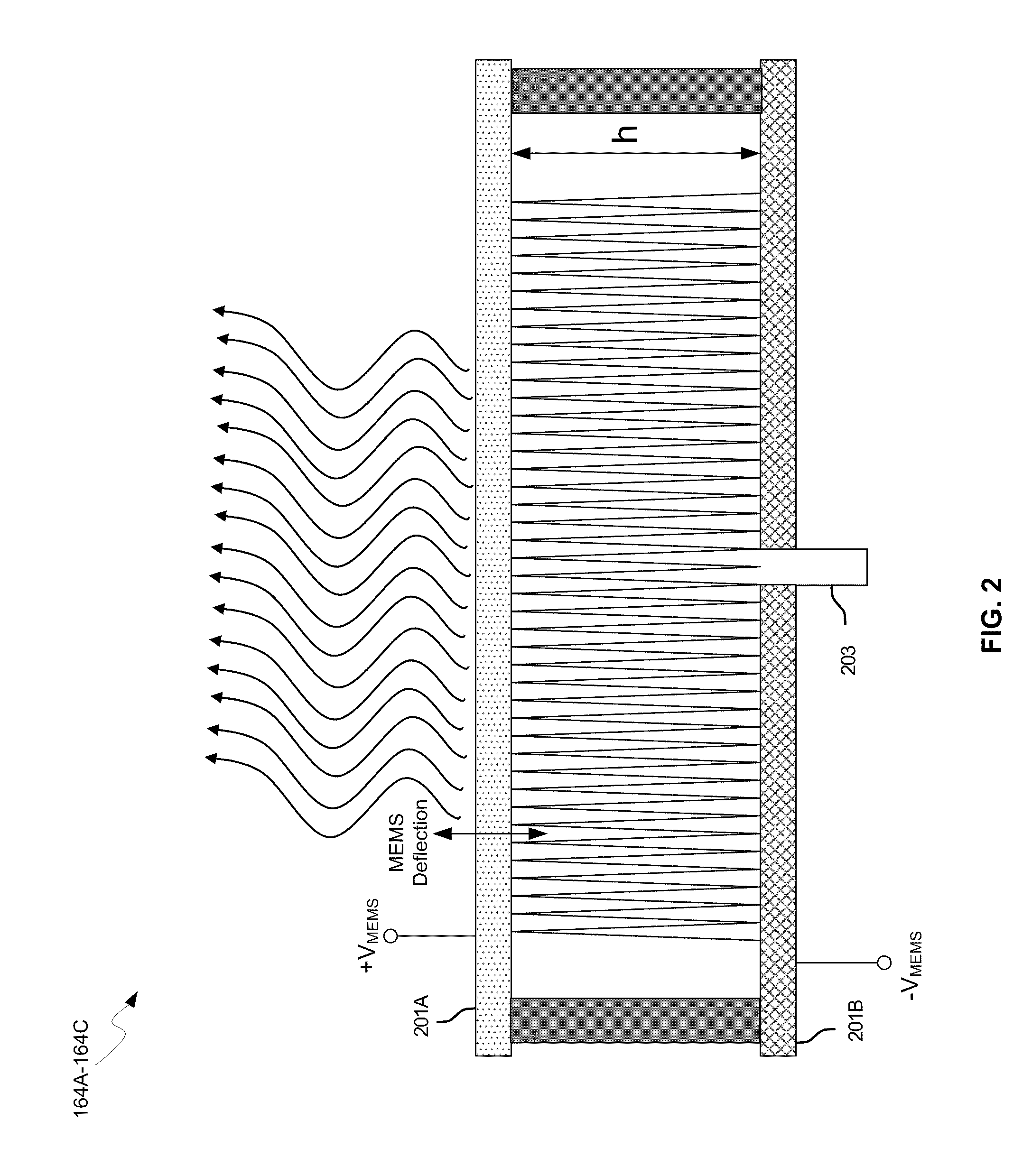
Methods and systems for a smart antenna utilizing leaky wave antennas (LWAs) are disclosed and may include a programmable polarization antenna including one or more pairs of LWAs configured along different axes. One or more pairs of leaky wave antennas may be configured to adjust polarization and / or polarity of one or more RF signals communicated by the programmable polarization antenna. RF signals may be communicated via the configured programmable polarization antenna utilizing the configured one or more pairs of the leaky wave antennas. A resonant frequency of the LWAs may be configured utilizing micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) deflection. The polarization and / or polarity may be configured utilizing switched phase modules. The LWAs may include microstrip or coplanar waveguides, wherein a cavity height of the LWAs is dependent on spacing between conductive lines in the waveguides. The LWAs may be integrated in one or more integrated circuits, packages, and / or printed circuit boards.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
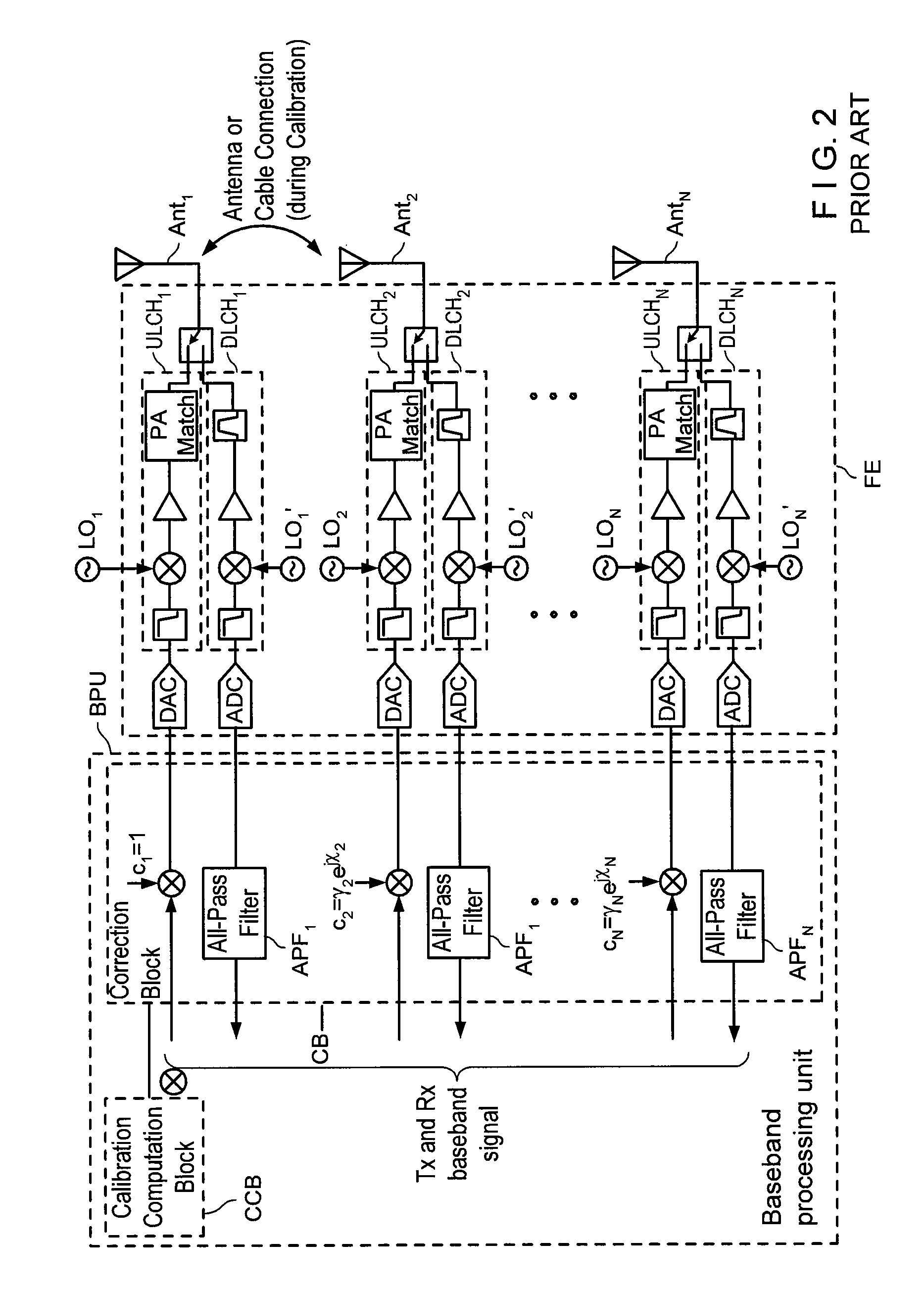
Calibration apparatus for smart antenna and method thereof
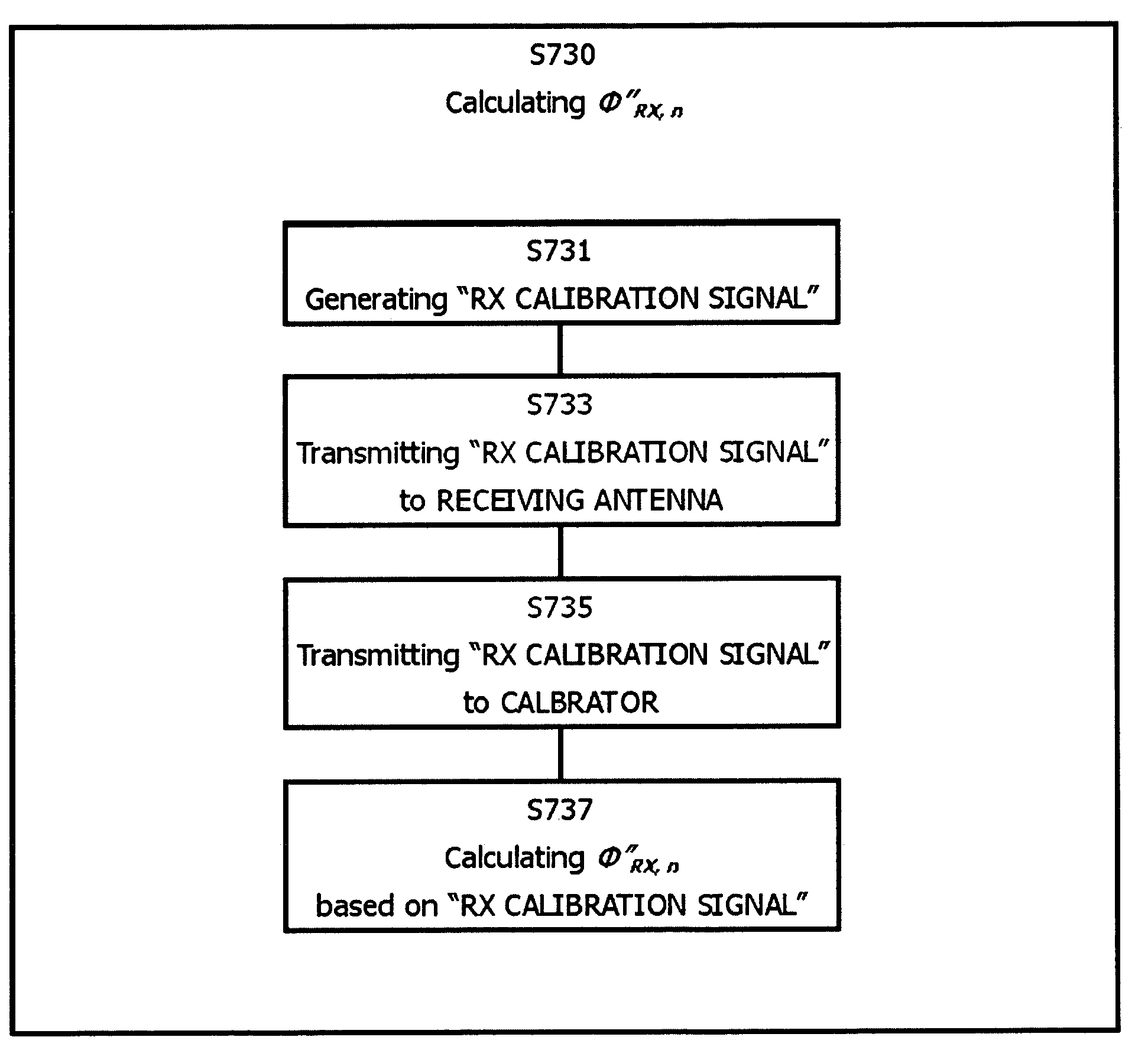
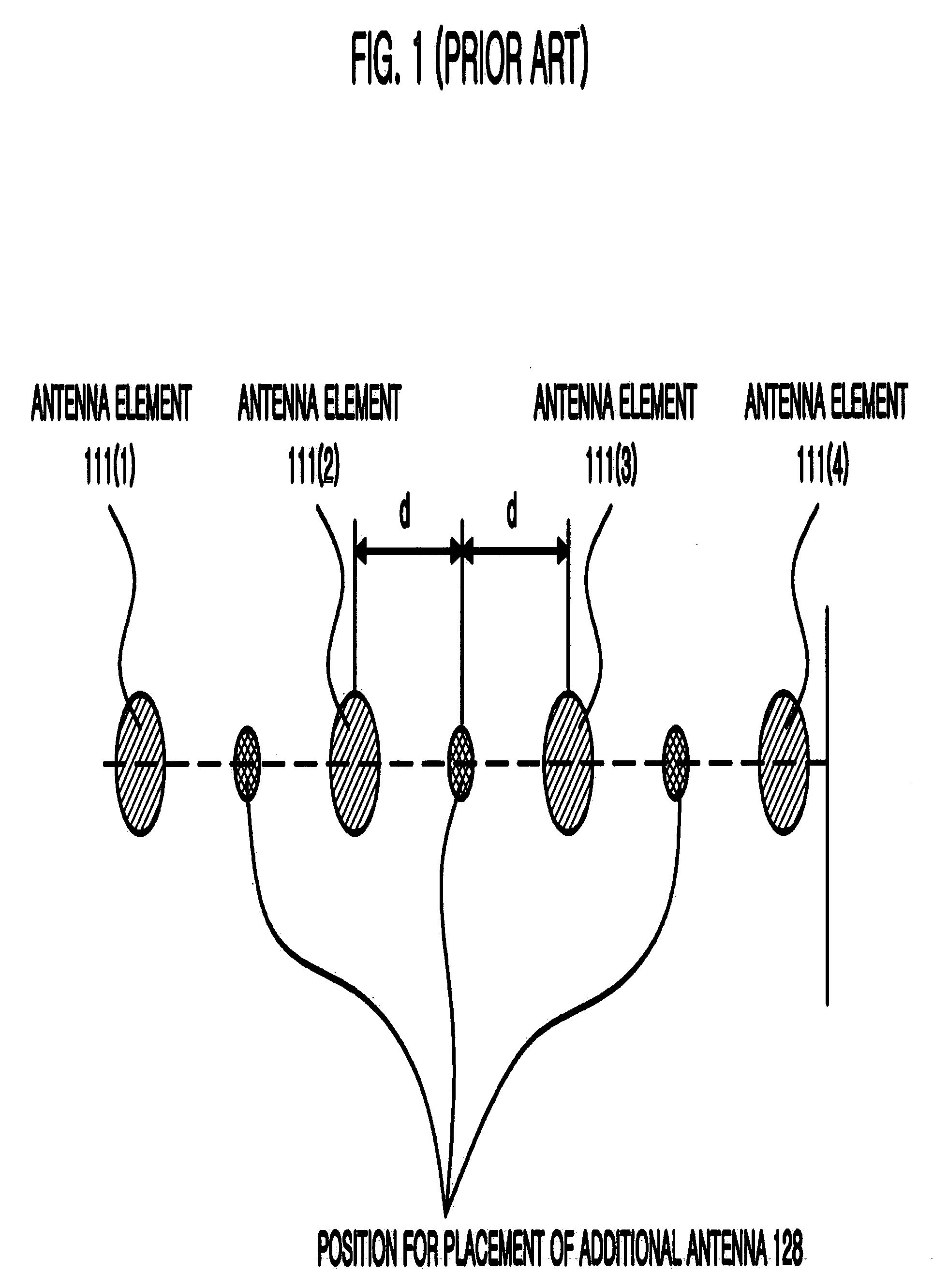
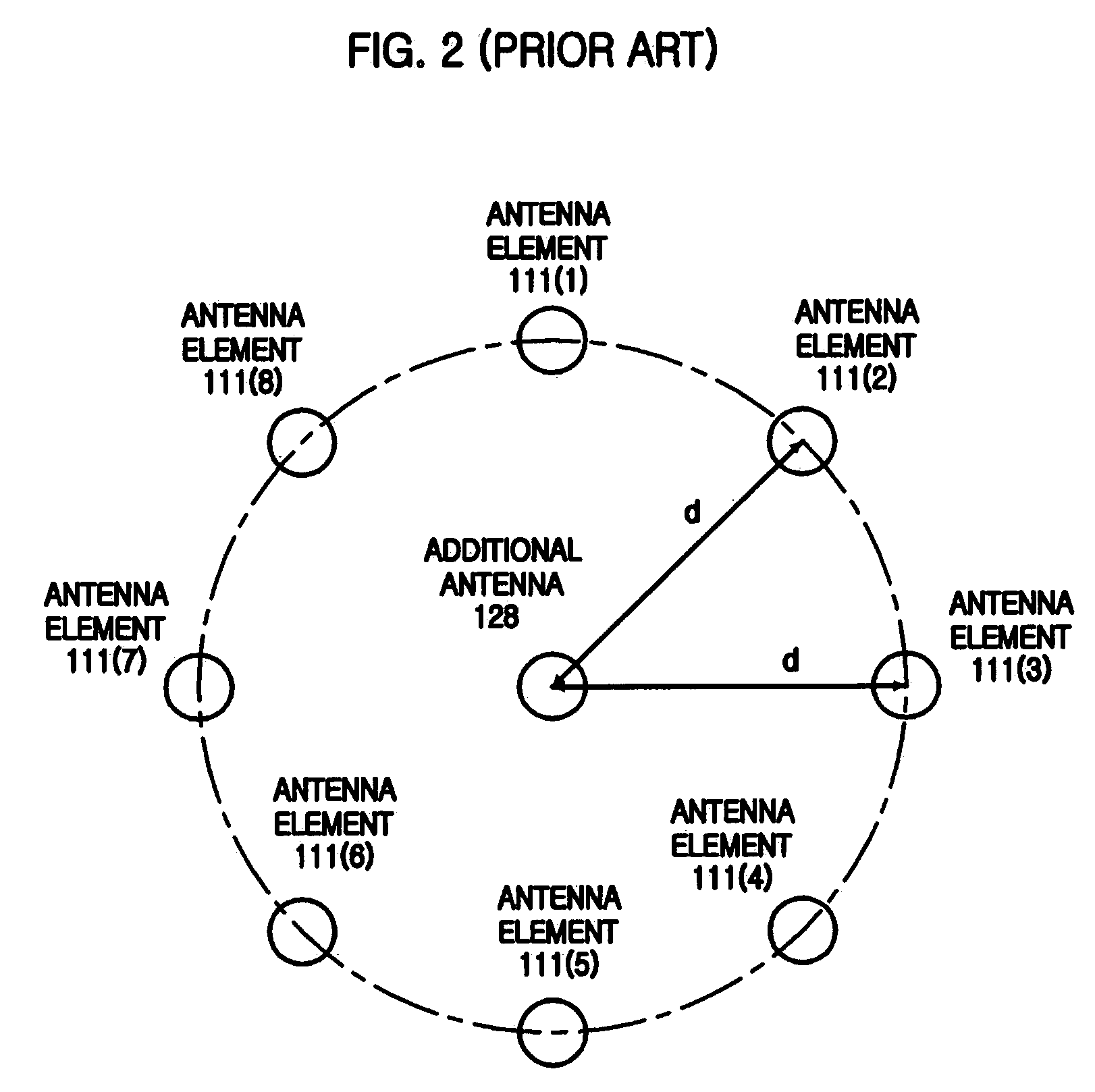
This invention is related to the calibration apparatus and method for compensating the phase characteristics in the receiving and transmitting signal paths of array antenna system, especially adaptive array antenna system operating as the base station system. The objective of this invention is to provide the calibration apparatus and method for the array antenna system to be able to compensate its phase differences or irregularities without any restrictions on the array structure or position of additional antenna or antenna toplogies while the array antenna system is in its operational mode such that the signals used by the subscribers are received or transmitted together with the signals used for the calibration. In this invention the phase delay between the additional antenna element and each of the antenna elements of the array antenna system is measured in advance of the calibration procedure to be used when the phase differences or irregularities are measured during the calibration procedure. The test signals used for the calibration is distinguishable from the signals used by the subscribers. Furthermore, each of the transmitting calibration signals itself is distinguishable from one another when the plural transmitting signal paths are to be calibrated simultaneously.
Owner:SASTECH +1
Subscriber based smart antenna
InactiveUS6229486B1Cost effectiveReduce distractionsSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsSystem capacitySignal quality
Owner:KRILE DAVID JAMES
Multi-function wireless apparatus
ActiveUS8385978B2Substation equipmentWireless commuication servicesCommunication interfaceSmart antenna
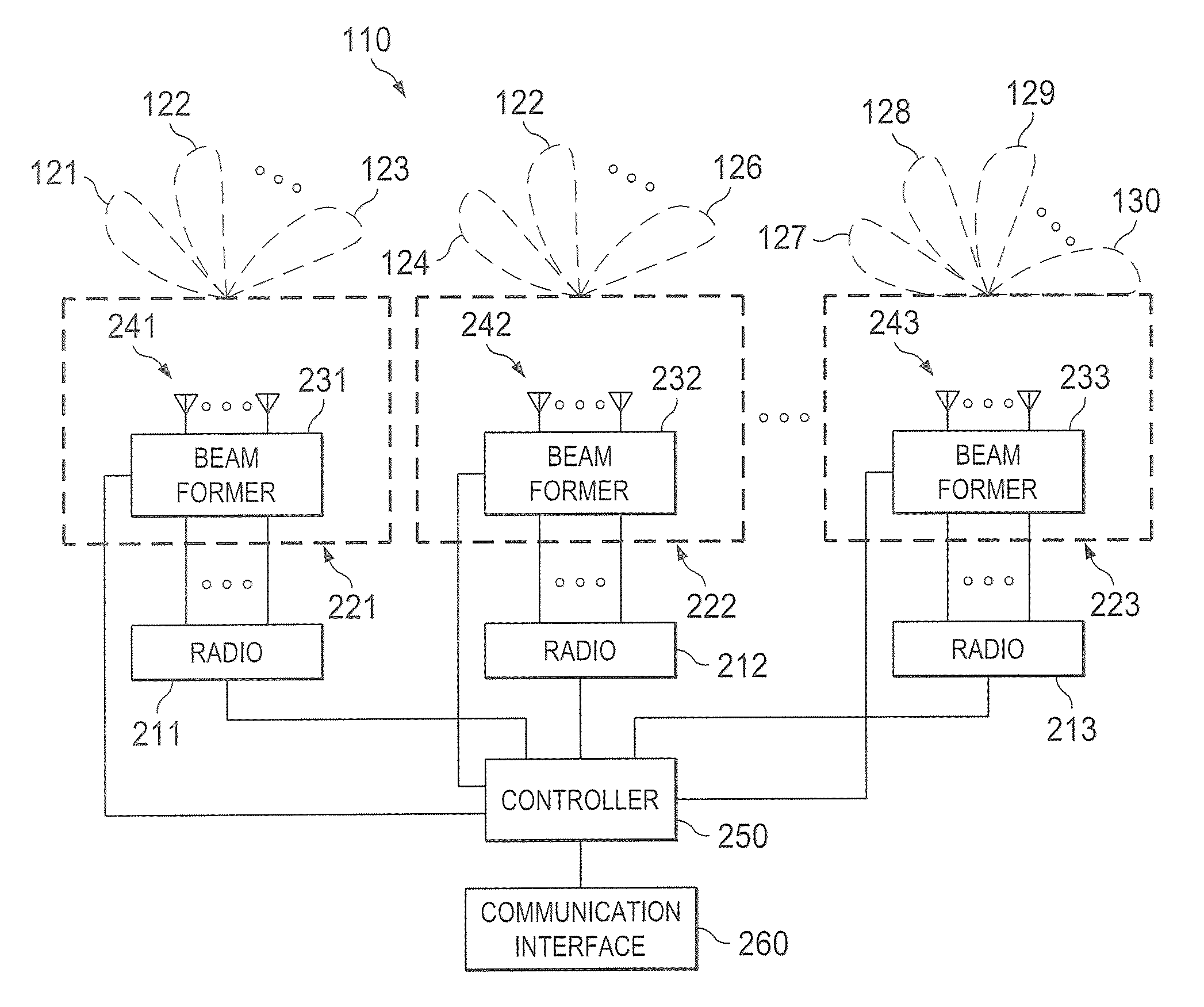
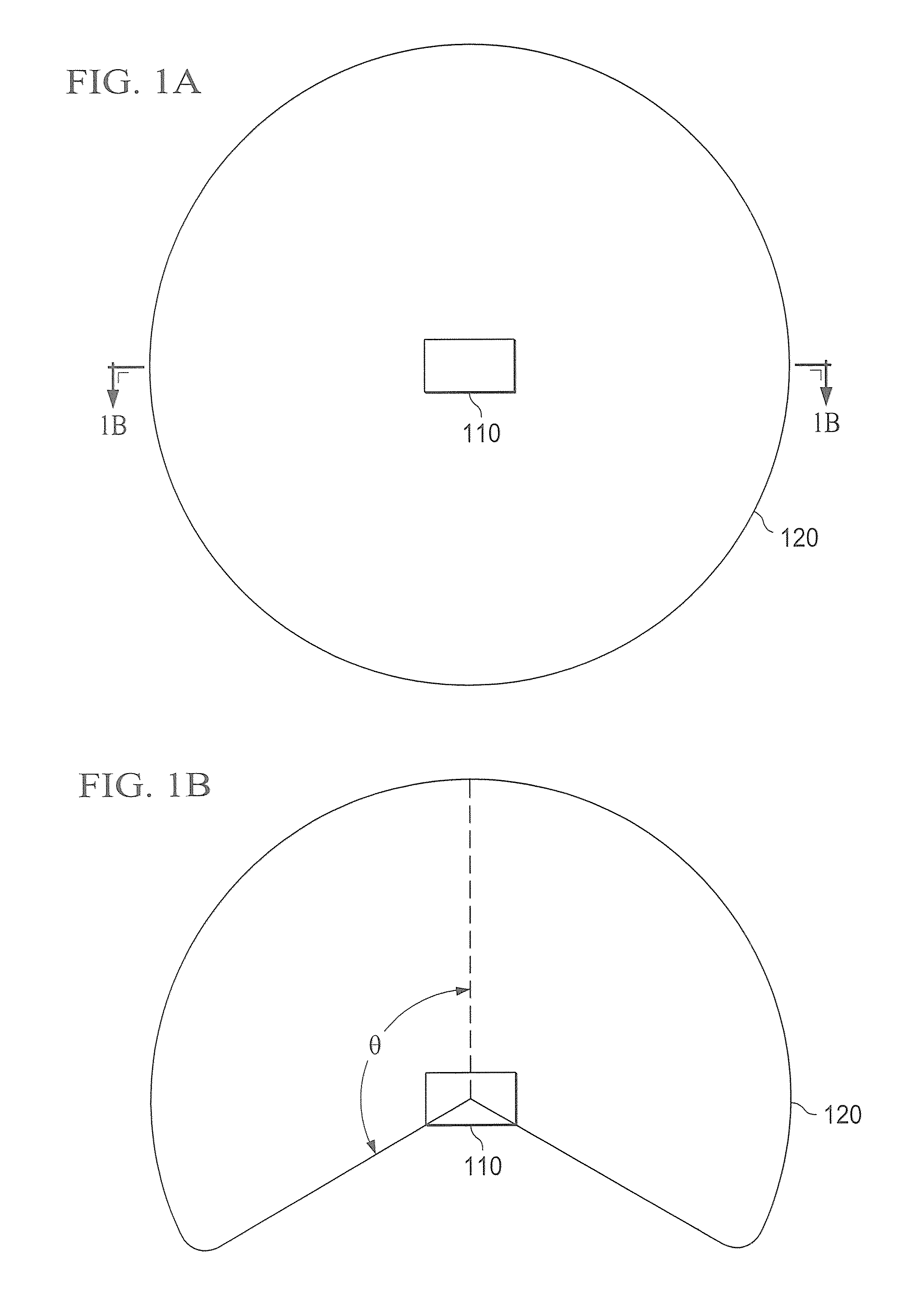
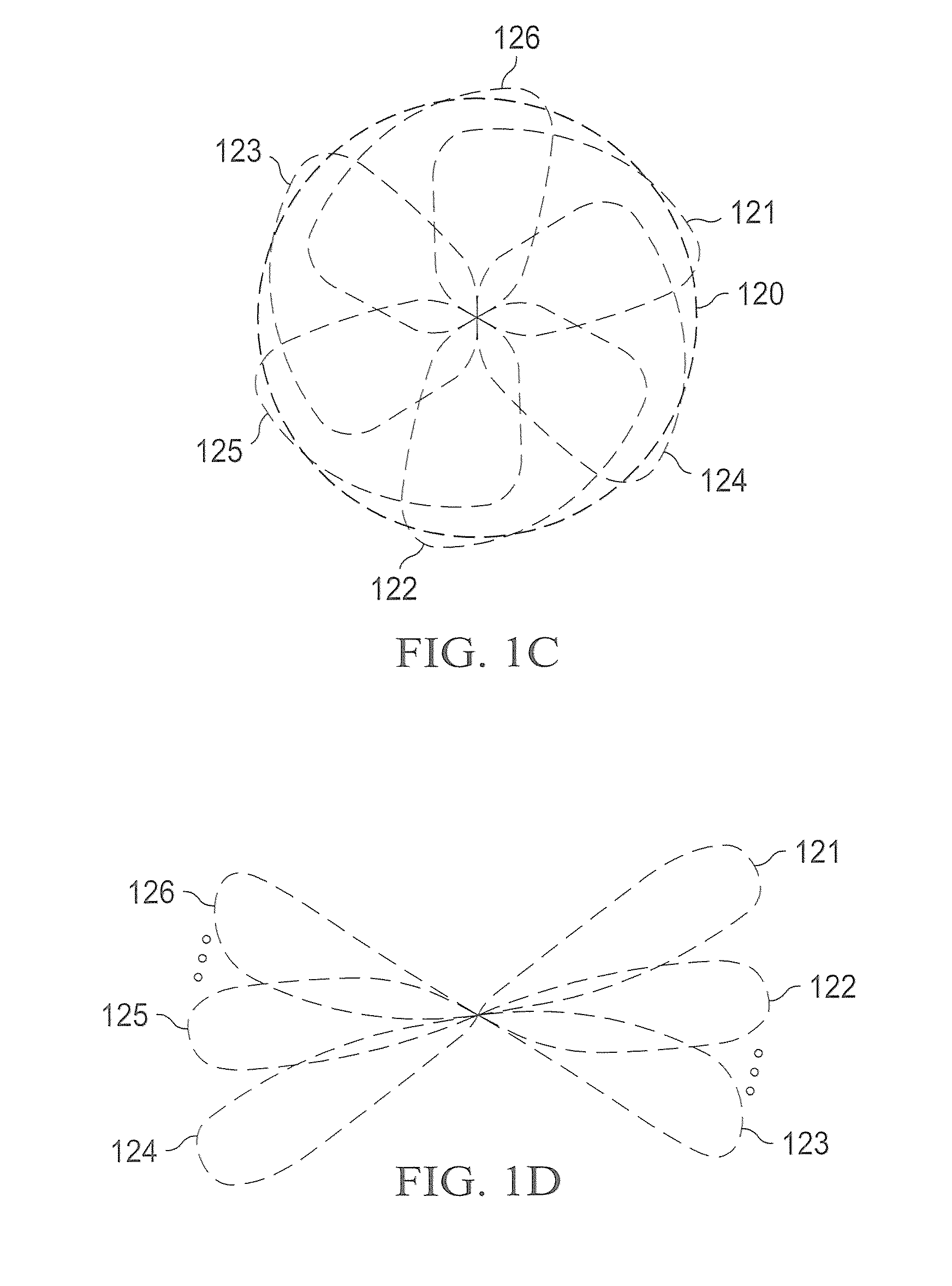
Systems and methods which provide a multi-function wireless node are shown. Multi-function wireless nodes of embodiments provide link completion infrastructure suited for a plurality of situations and environments, such as for repeaters, bridges, gateways, and APs. Embodiments provide a multi-function wireless node comprising a plurality of radios. Multi-function wireless nodes of embodiments further comprise a smart antenna system coupled to radios thereof and providing illumination within a service volume. The service volume of embodiments comprises a semi-spherical volume. Embodiments comprise a controller facilitating proper and / or optimal deployment and commissioning of the multi-function wireless node in each of a plurality of different link completion infrastructure forms. Embodiments further comprise a communication interface providing one or more information communication links in addition to those available through wireless links.
Owner:FIMAX TECH LTD
Tag multiplication
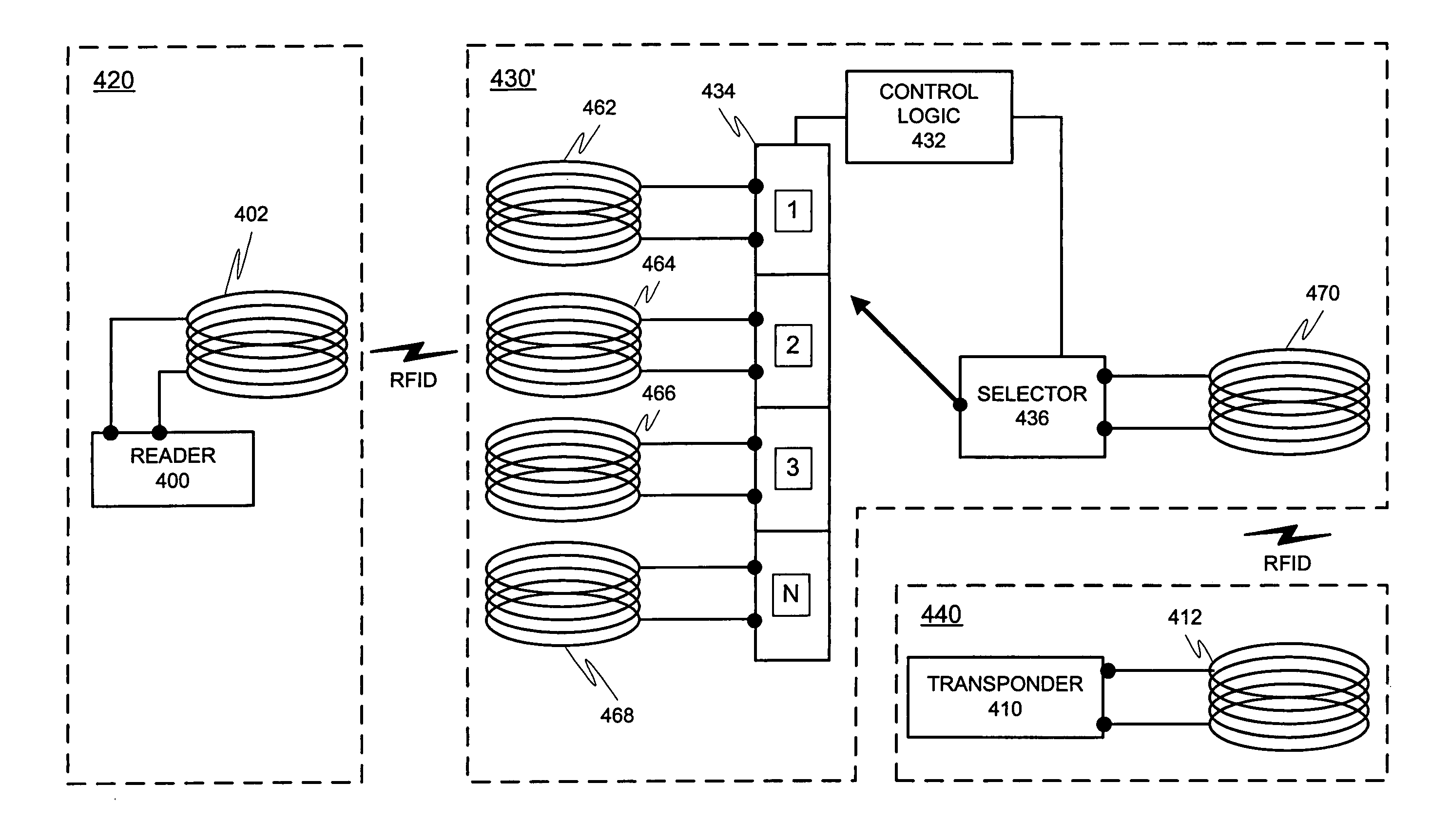
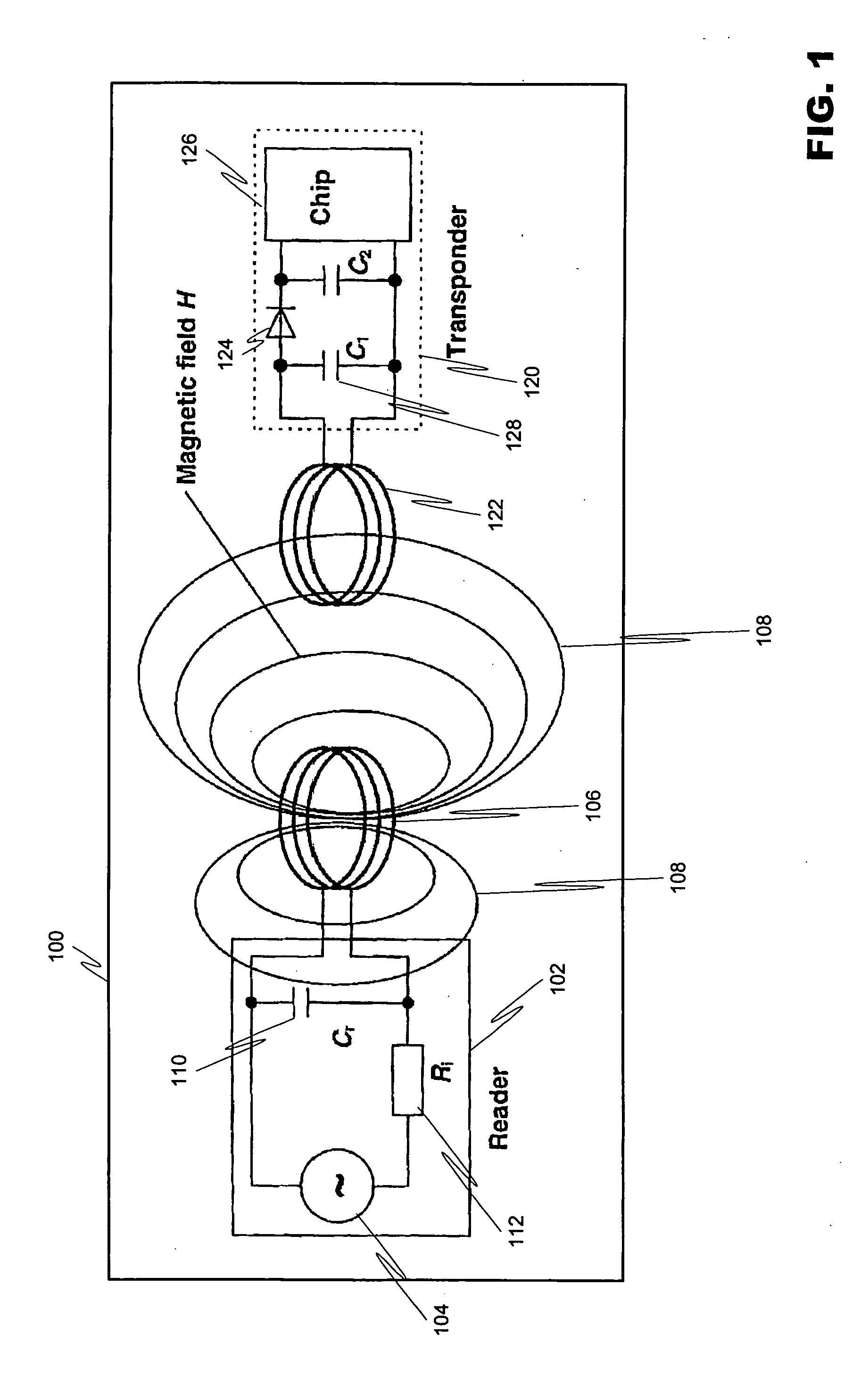
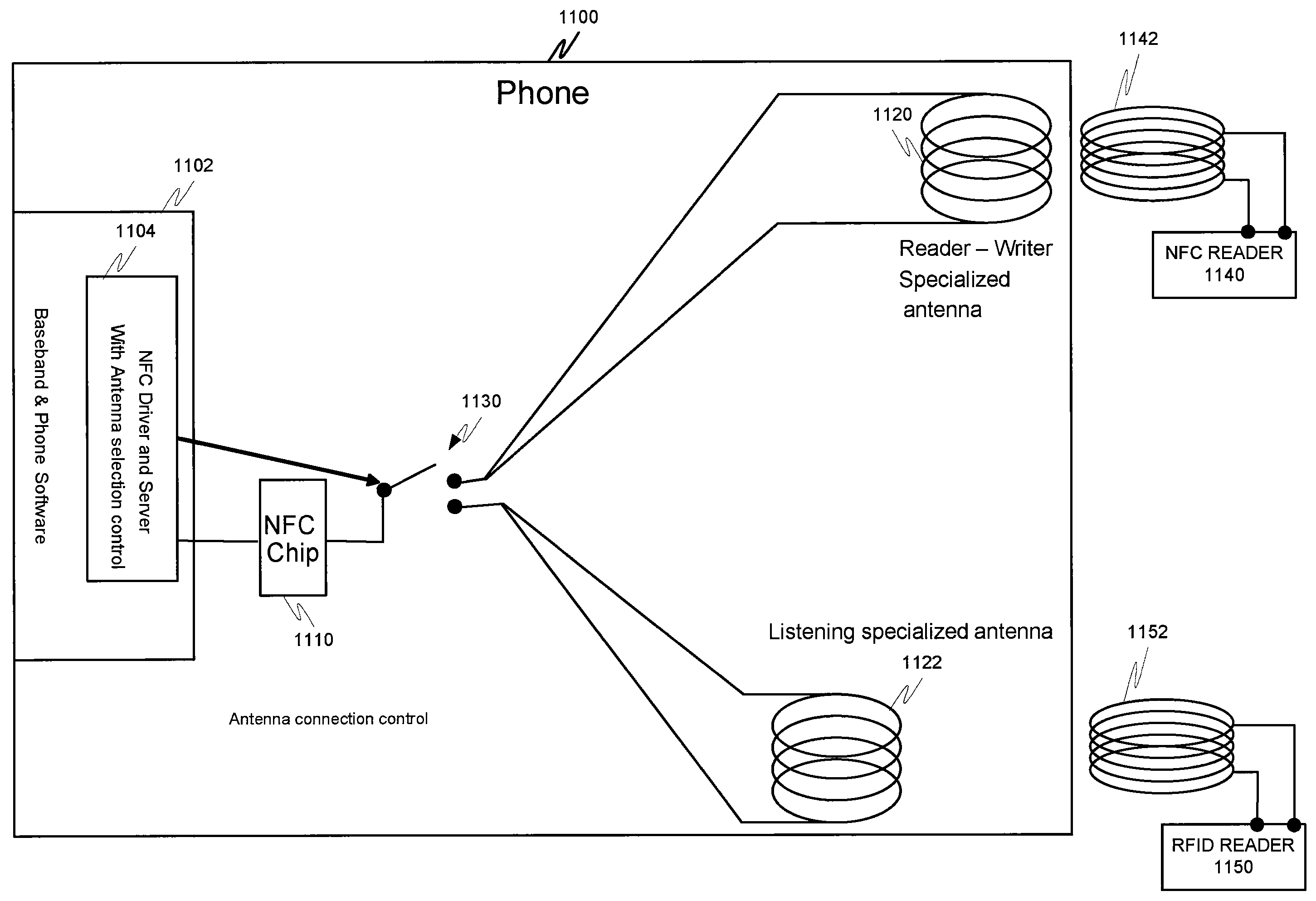
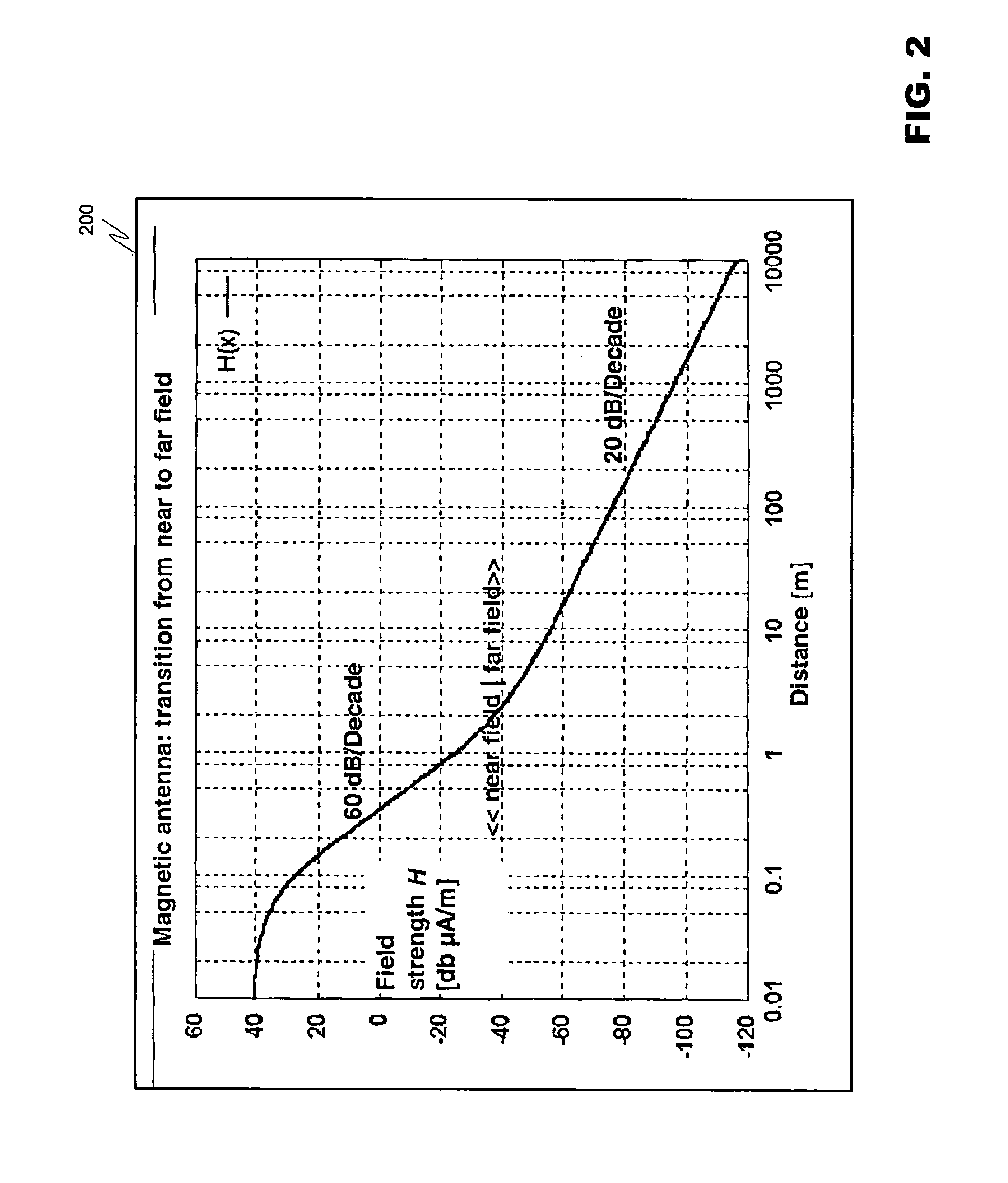
ActiveUS20070008140A1Effective communication rangeFacilitate communicationNear-field transmissionResonant long antennasSmart antennaDisplay device
An intelligent antenna system for extending the effective communication range of a machine-readable passive tag. The system includes intelligence that allows one of a plurality of extension antennas to be active at any given time in order to both facilitate communications and safeguard the system. The machine-readable tag and antenna system may be embedded in a structure. In a further embodiment, the system may include multiple passive tags that are active in correspondence to a display or advertisement currently being exhibited. The system includes means for operatively coupling a designated machine-readable tag to the embedded antenna network previously described. In a further embodiment of the invention, the machine-readable tag includes combined RFID and NFC functionality where both RFID listening functions and NFC read-write functions are to be available in the same NFC communications logic, where different RFID listening applications require different minimum separation distances between the reader and the NFC communications logic. The NFC communications logic chip is selectively connected to at least three antenna coils, the first antenna coil for operating with a first minimum separation distance between the reader and the NFC communications logic, the second antenna coil for operating with a second minimum separation distance between the reader and the NFC communications logic, and the third antenna coil for reading and writing. In a further embodiment of the invention, matching circuits are included with the respective antenna coils to tune the resonant frequency of the RLC oscillator circuit for each antenna coil in the NFC communications logic.
Owner:III HLDG 3
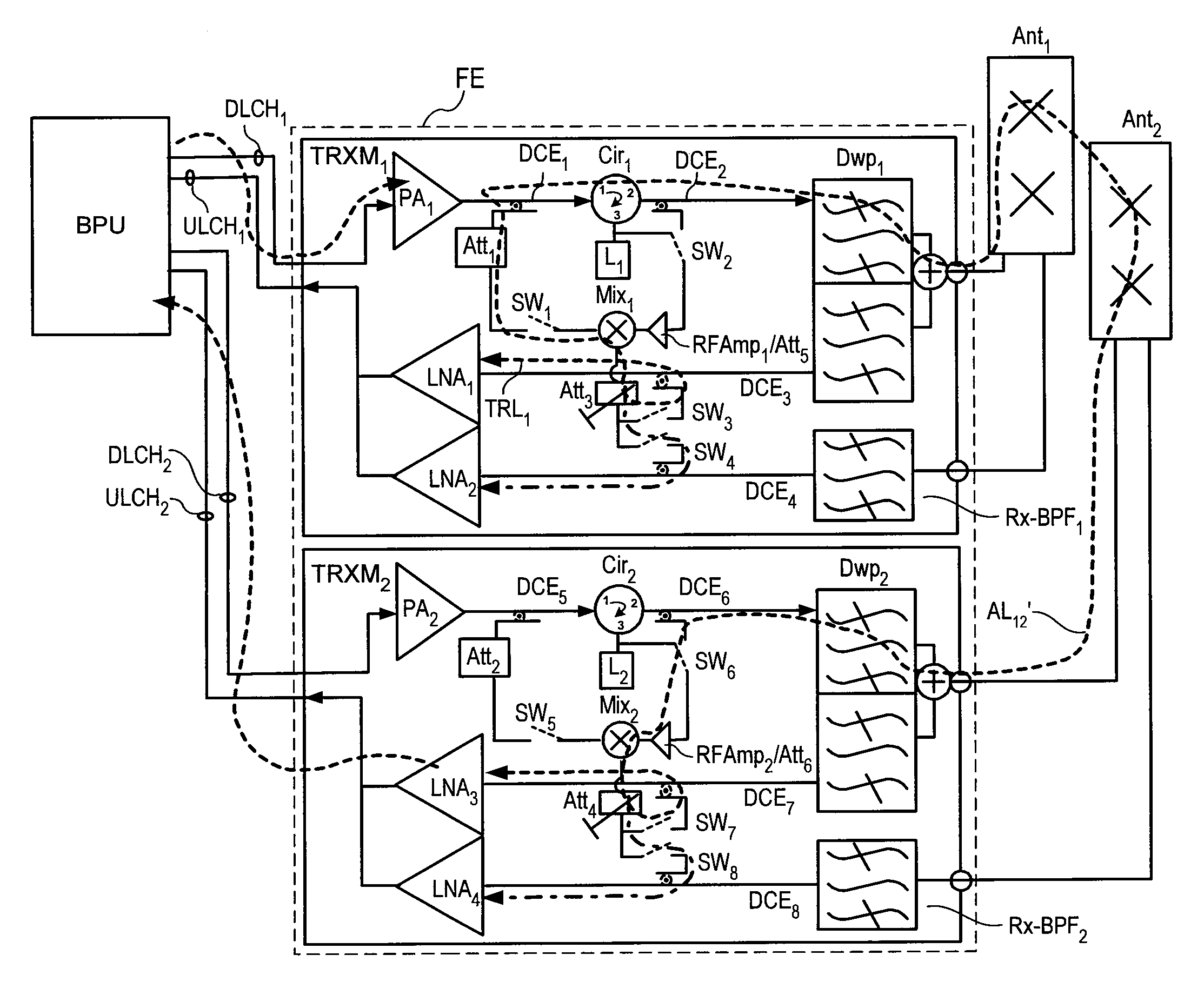
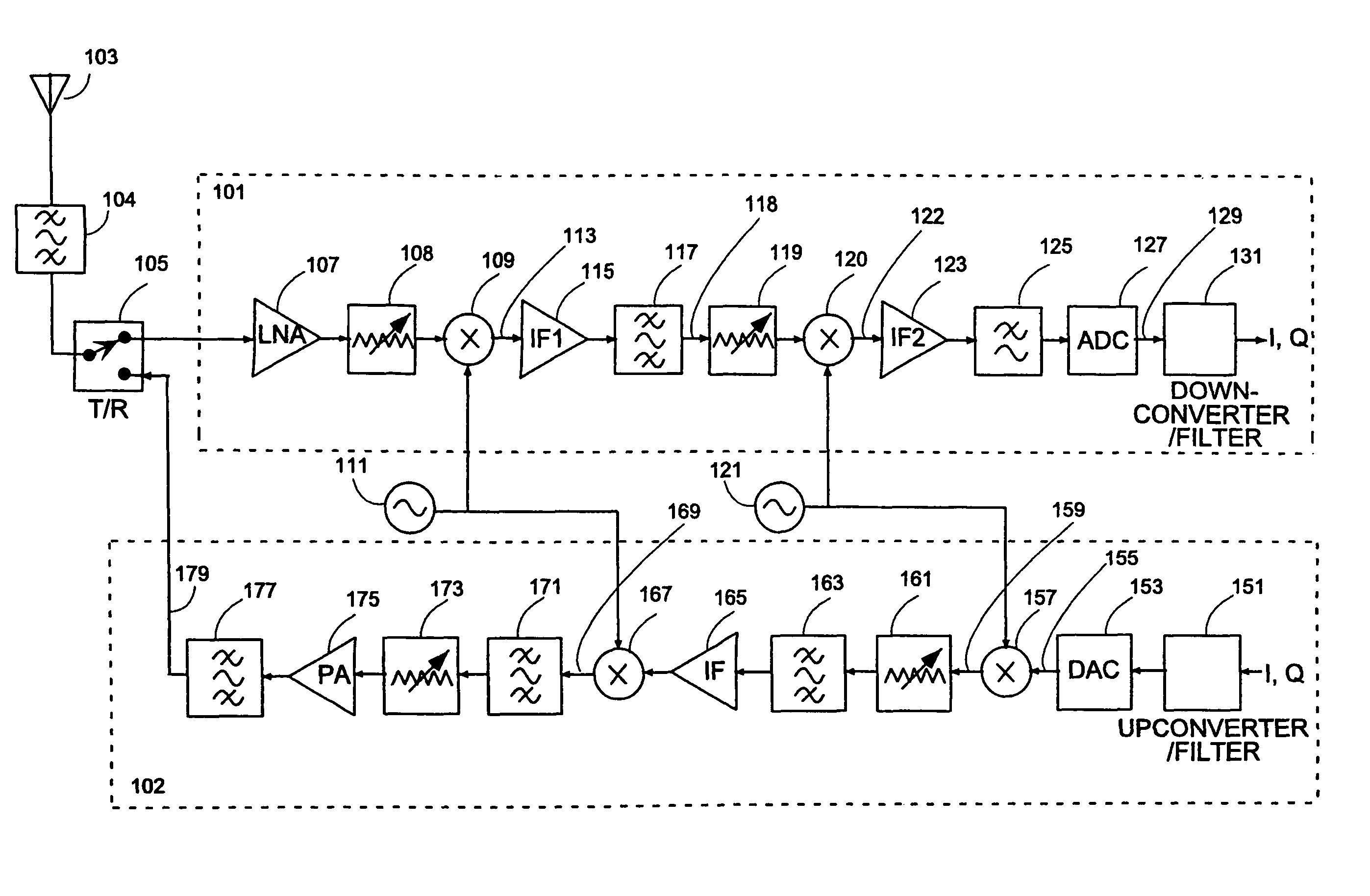
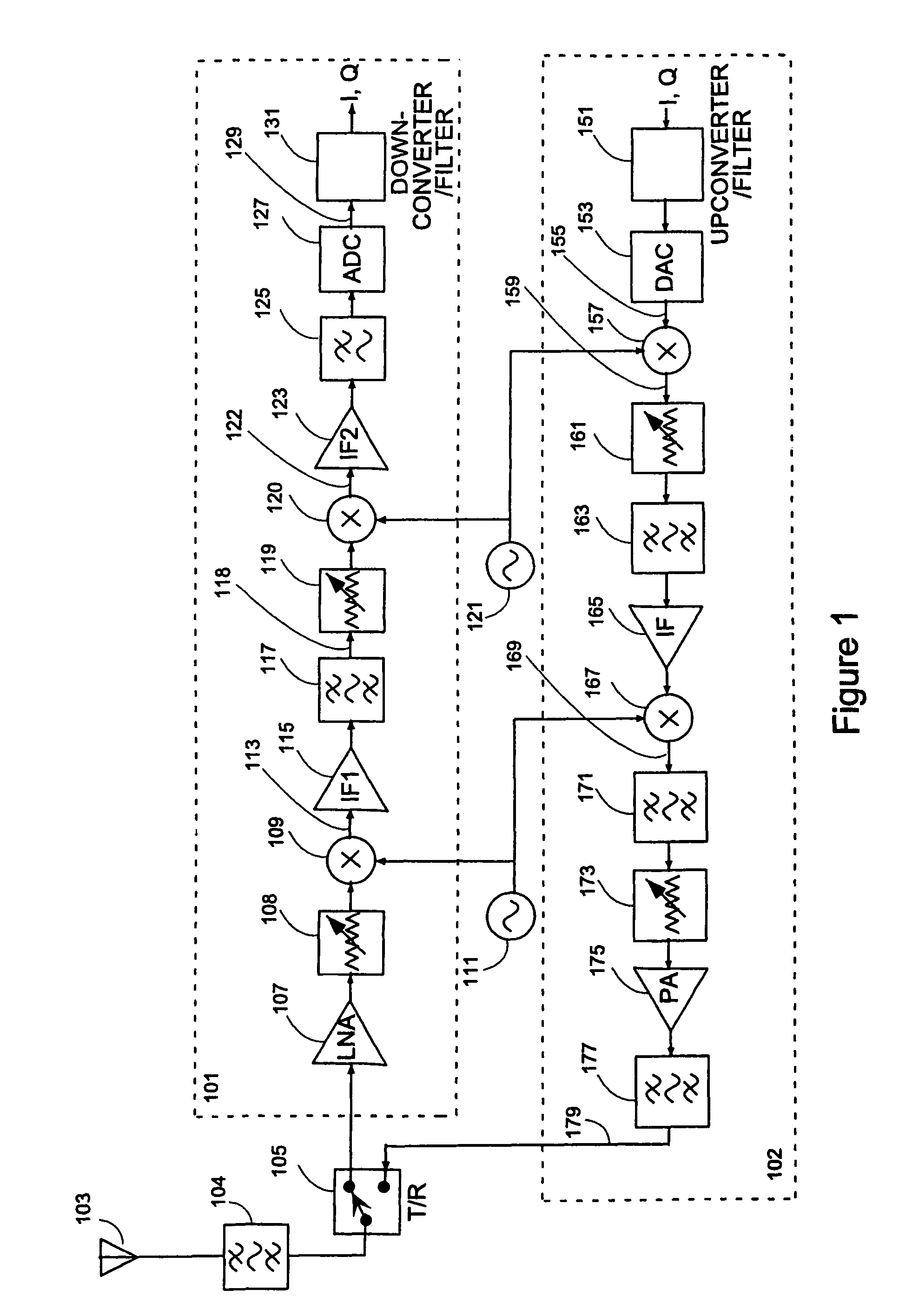
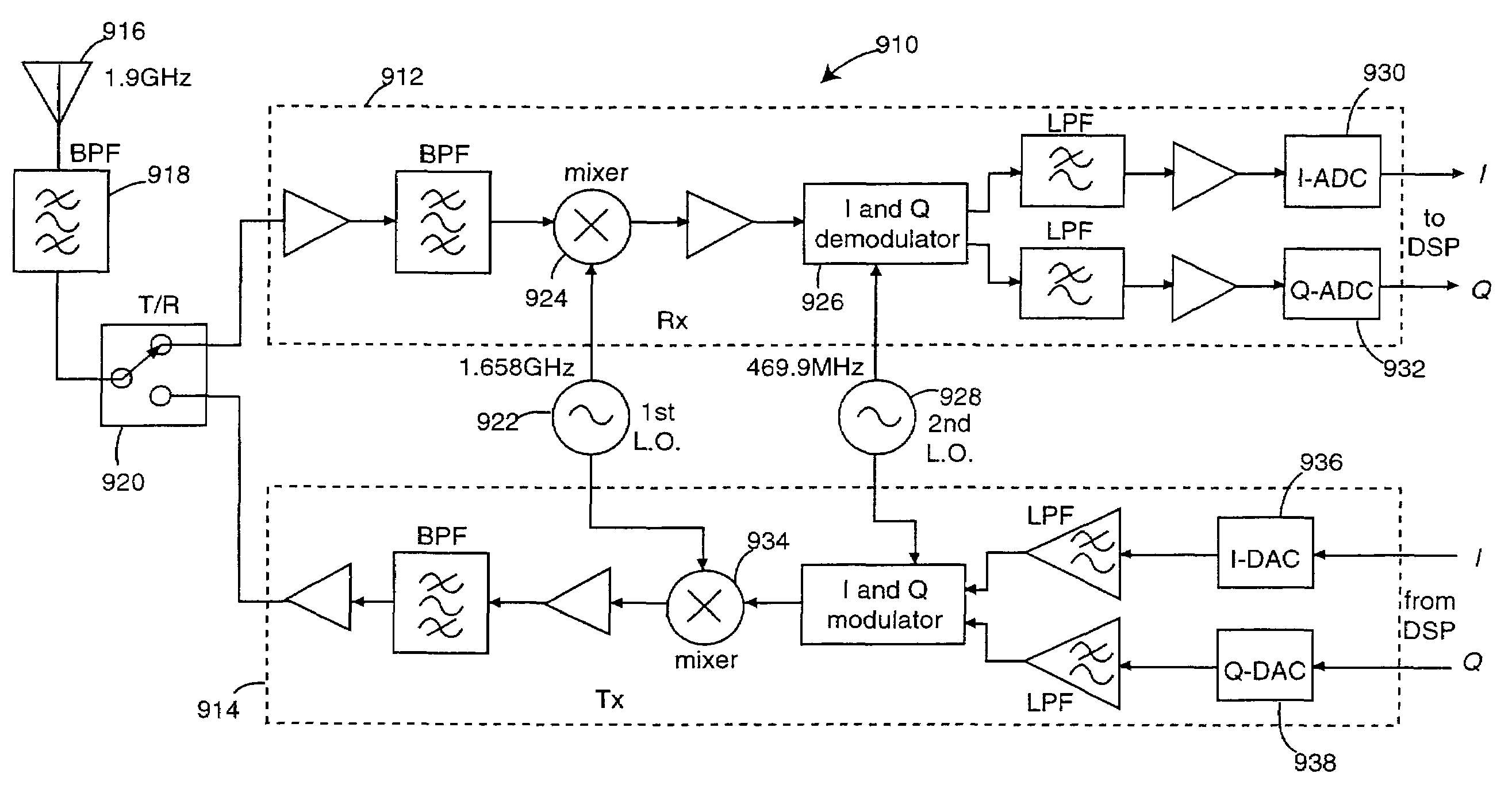
MULTI-TRANSCEIVER ARCHITECTURE FOR ADVANCED Tx ANTENNA MONITORING AND CALIBRATION IN MIMO AND SMART ANTENNA COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
ActiveUS20100093282A1Lower performance requirementsTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringWireless transceiverAir interface
Exemplary embodiments of system and method are provided for measuring signal amplitude, phase and / or delay offsets between multiple transmit signals fed through the transmit signal processing chains and wirelessly transmitted over the transceive antennas of separate transceiver modules, wherein transmit signal coupling between the transmit antennas of said transceiver modules' transmit signal processing chains may be used for synchronizing the transmit signals and calibrating their amplitude, phase and / or delay parameters. The exemplary embodiments further provide a front end arrangement of a wireless transceiver device which can comprise at least two independently controllable transceiver modules, each connected to an associated spatial diversity transceive antenna and comprising at least one associated transmit signal processing chain and at least one associated receive signal processing chain coupled to a common baseband processing unit. The exemplary transceiver architecture can be executed on an antenna loop between the transmit signal processing chain of a first transceiver module and the transmit signal processing chain of a second transceiver over the air interface and relies on an adaptive antenna concept which facilitates a wireless transmission of data via a plurality of wireless communication channels utilizing an array of transceive antennas, receiving feedback information via at least one of said communication channels using such antenna loop and modifying a transmission mode based on the received feedback information.
Owner:RPX CORP
Power control with signal quality estimation for smart antenna communications systems
A method for power control with signal quality estimation for smart antenna communications system is described. The method, for example, starts with a transmit power assignment. Receive weight vector determination is carried out with this assigned transmit power, and the new weights used. An estimate of the resulting received signal quality is obtained and used for another power adjustment.
Owner:INTEL CORP
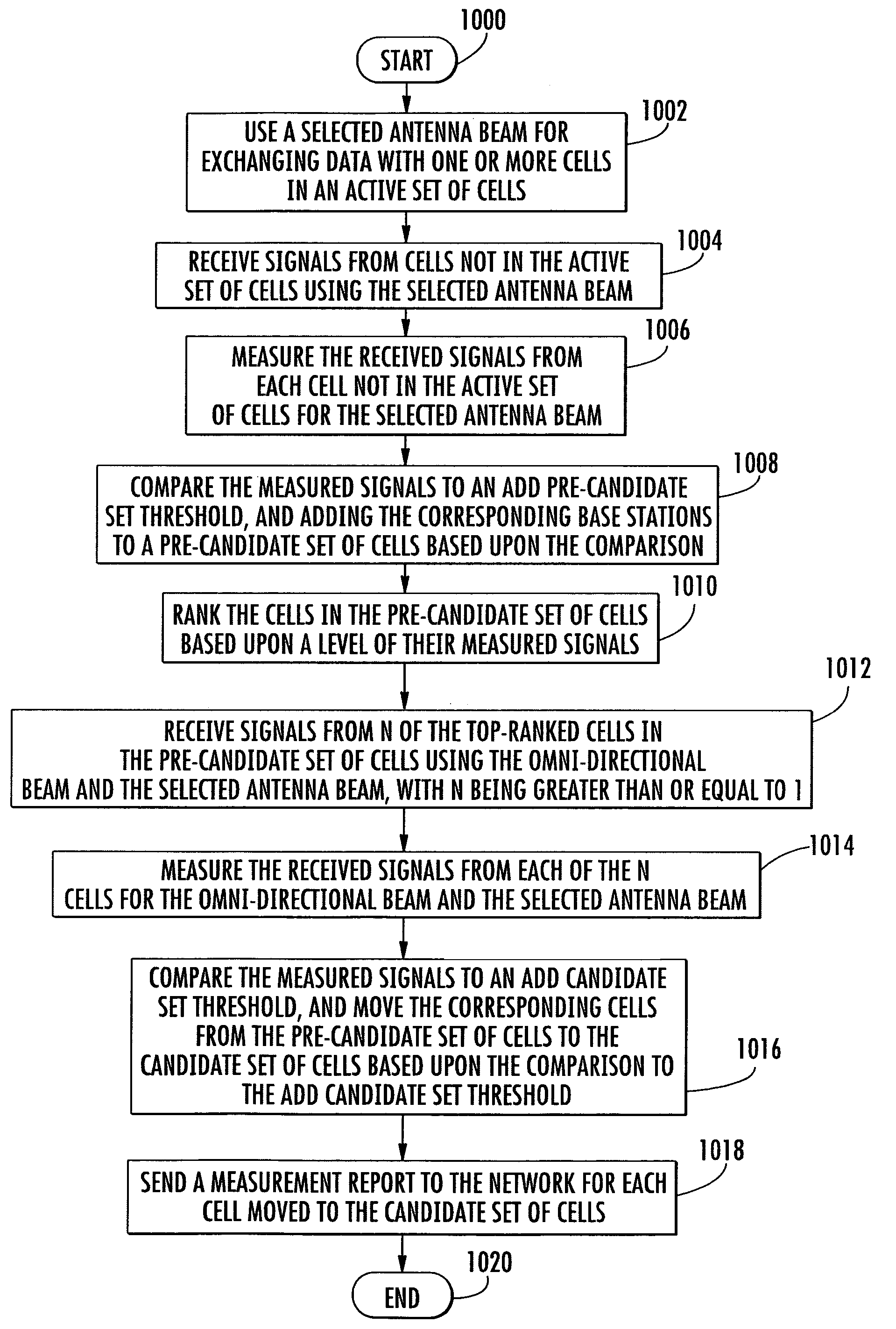
Method for identifying pre-candidate cells for a mobile unit operating with a switched beam antenna in a wireless communication system, and corresponding system
InactiveUS7308264B2Quick identificationStay connectedCode division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemSmart antenna
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
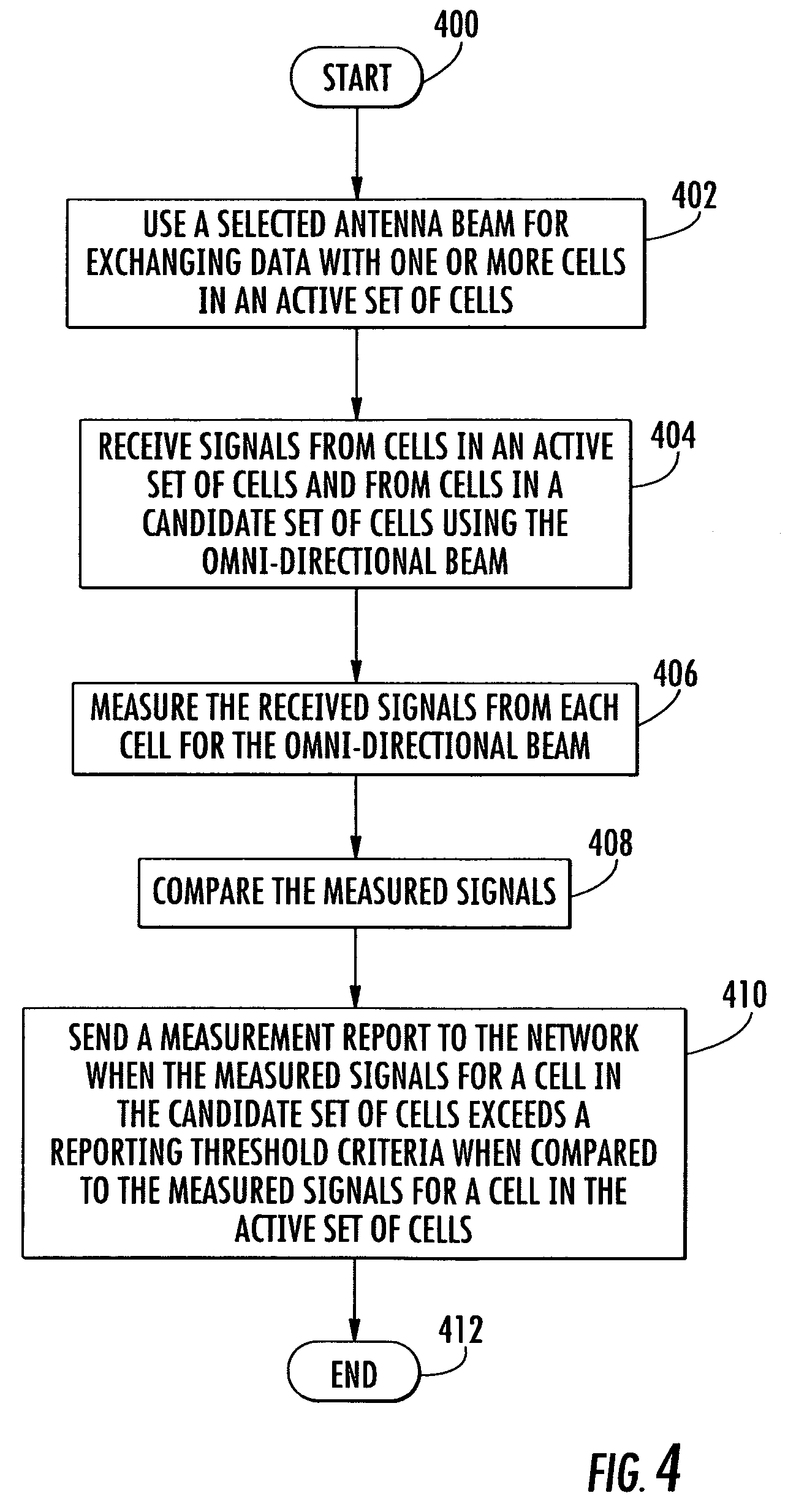
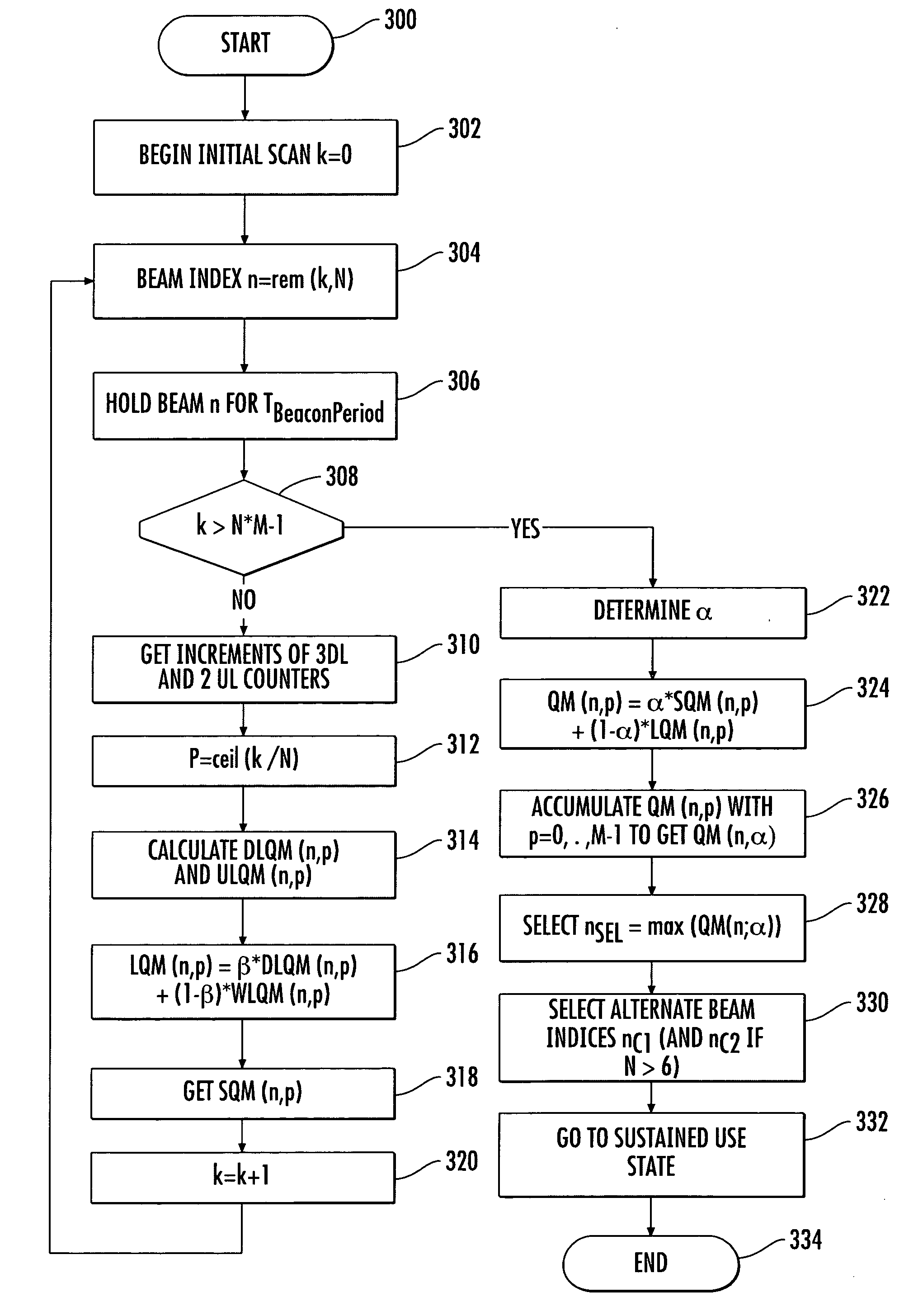
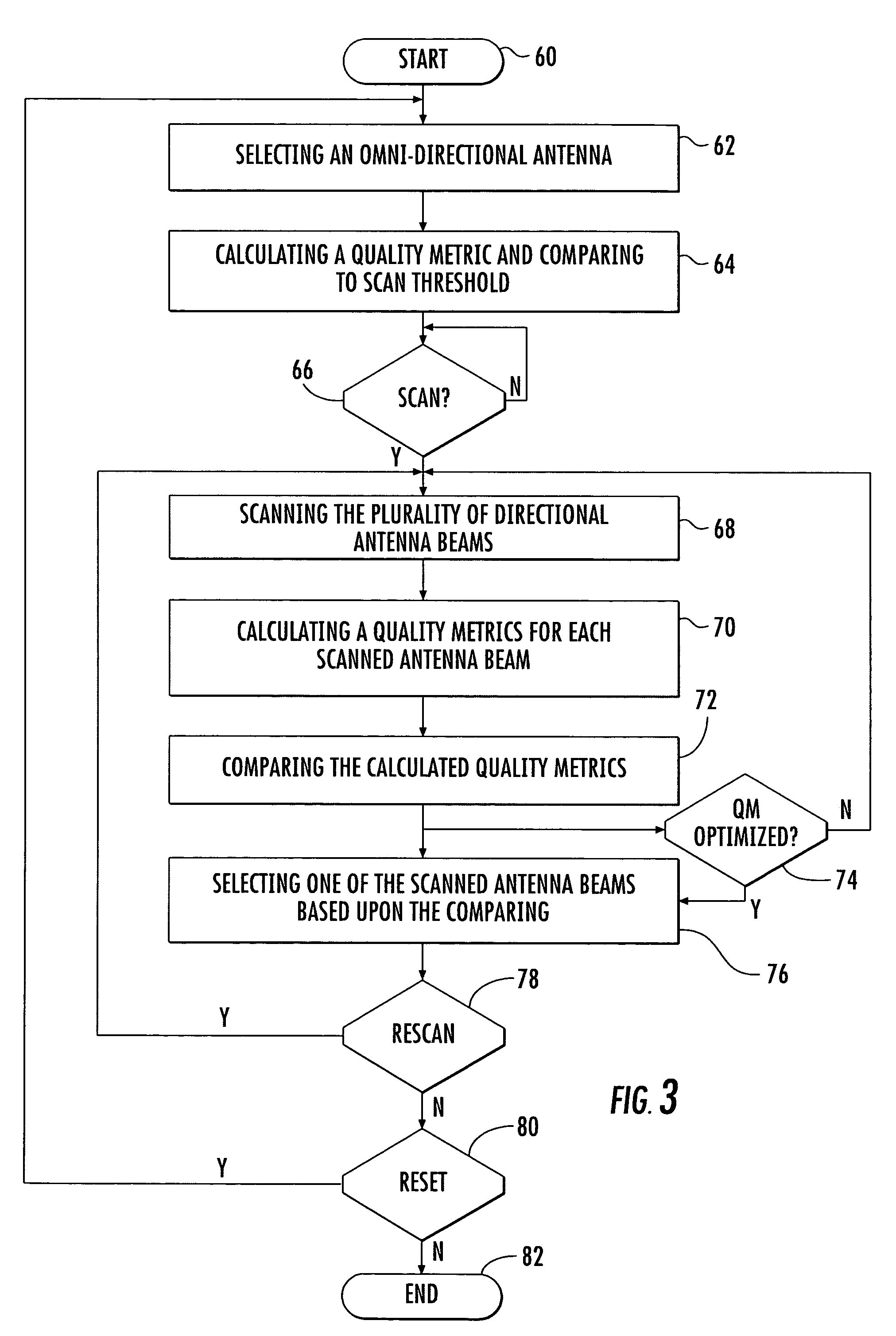
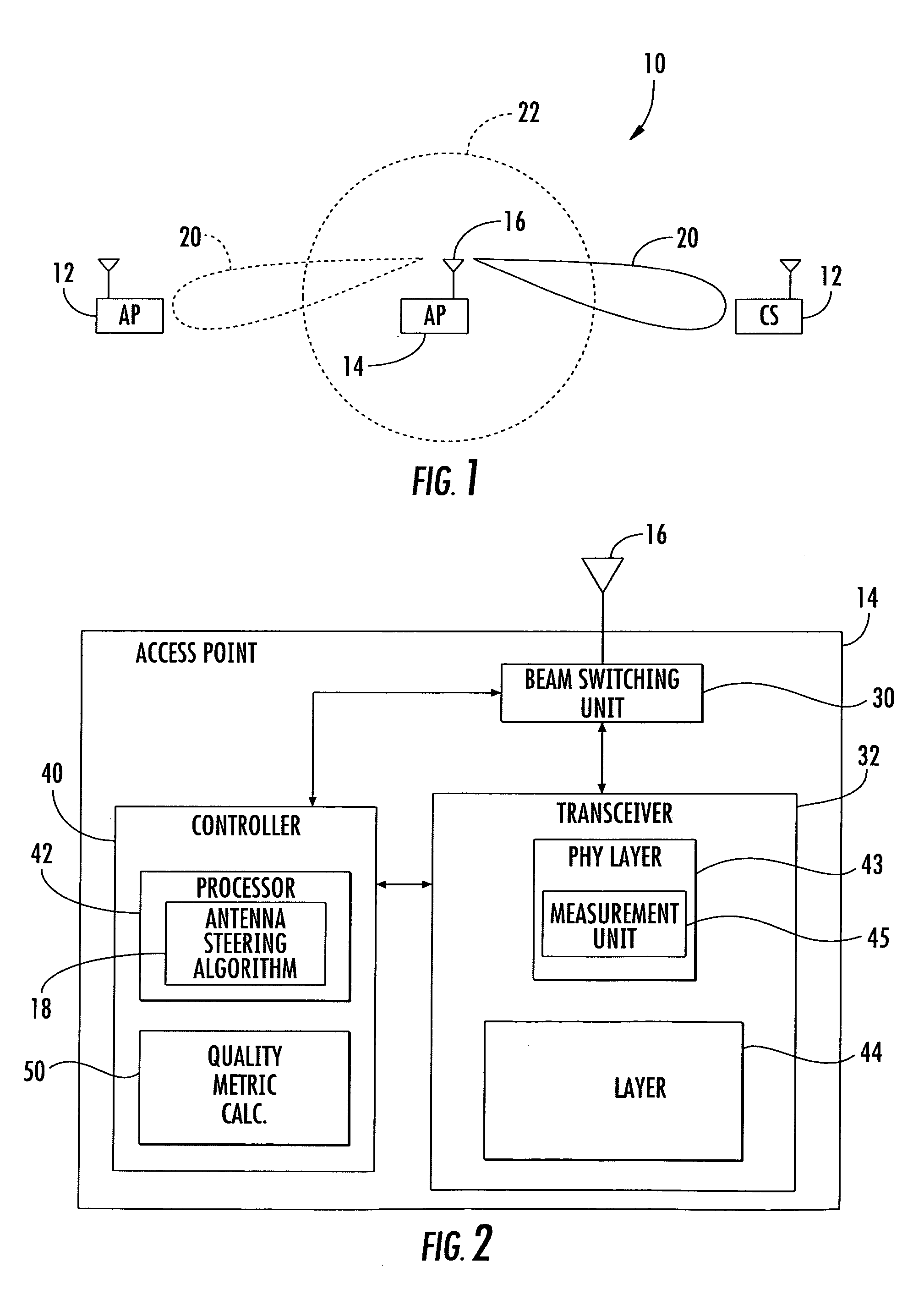
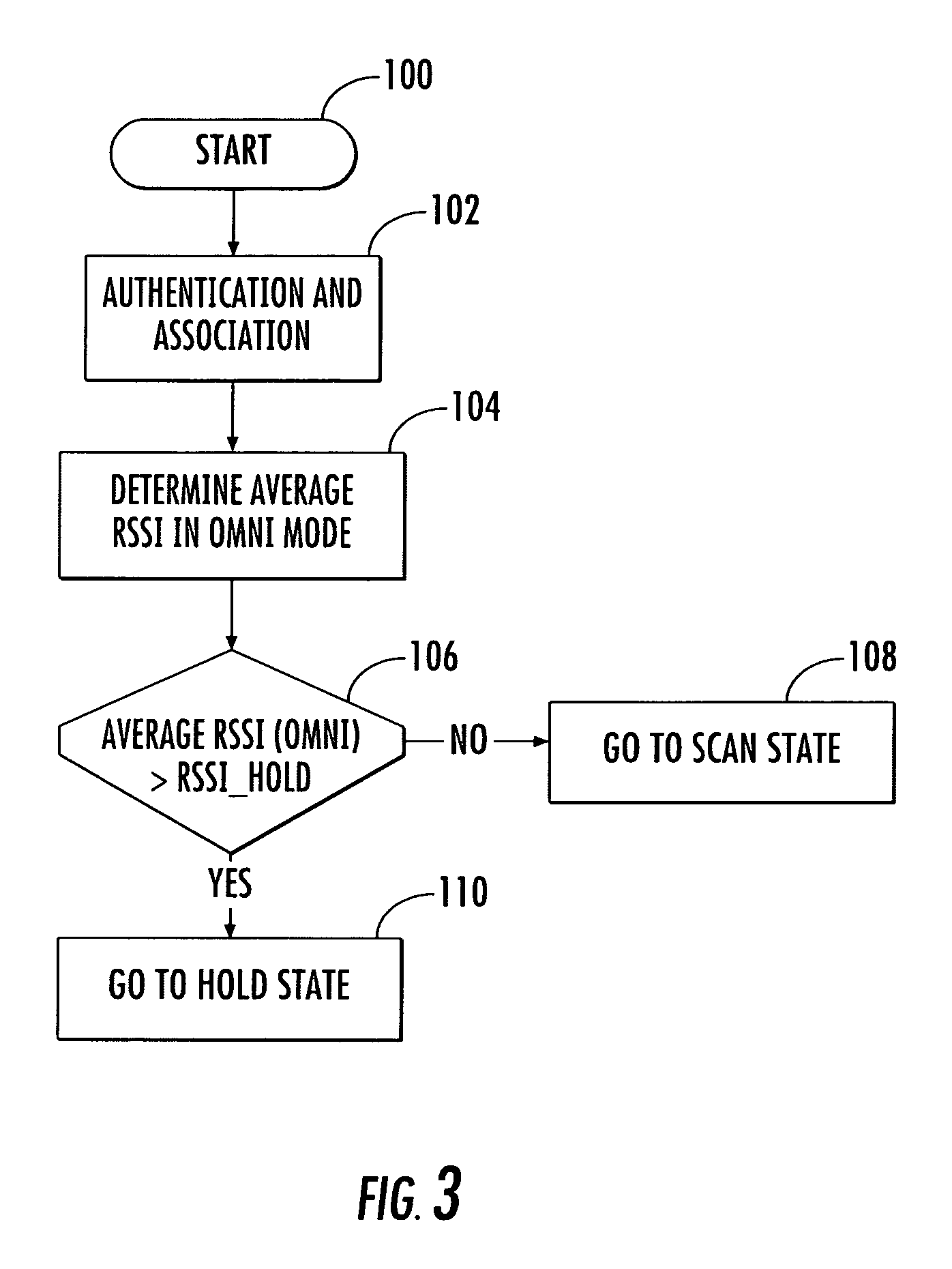
Method for steering a smart antenna for a WLAN using a periodic re-scan
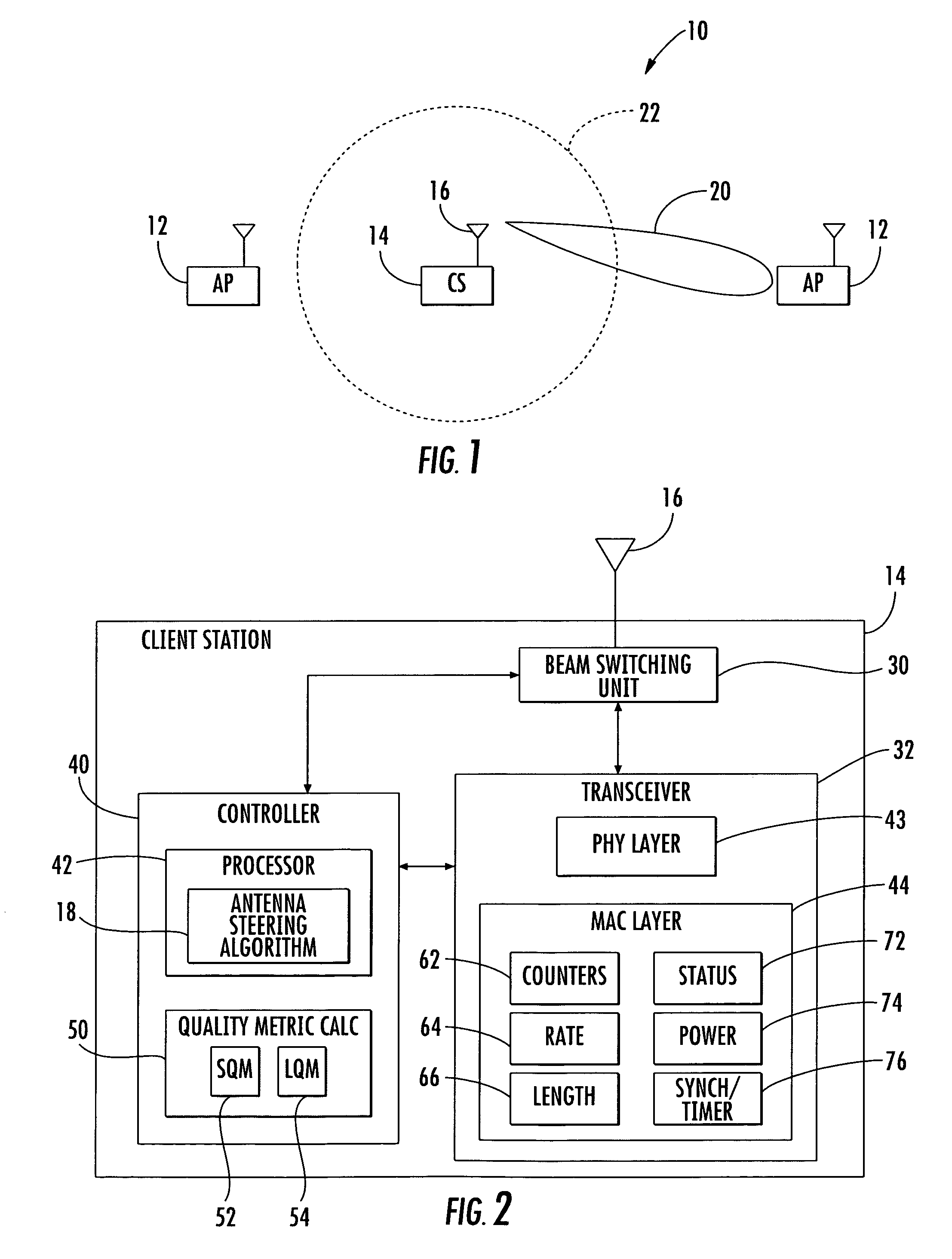
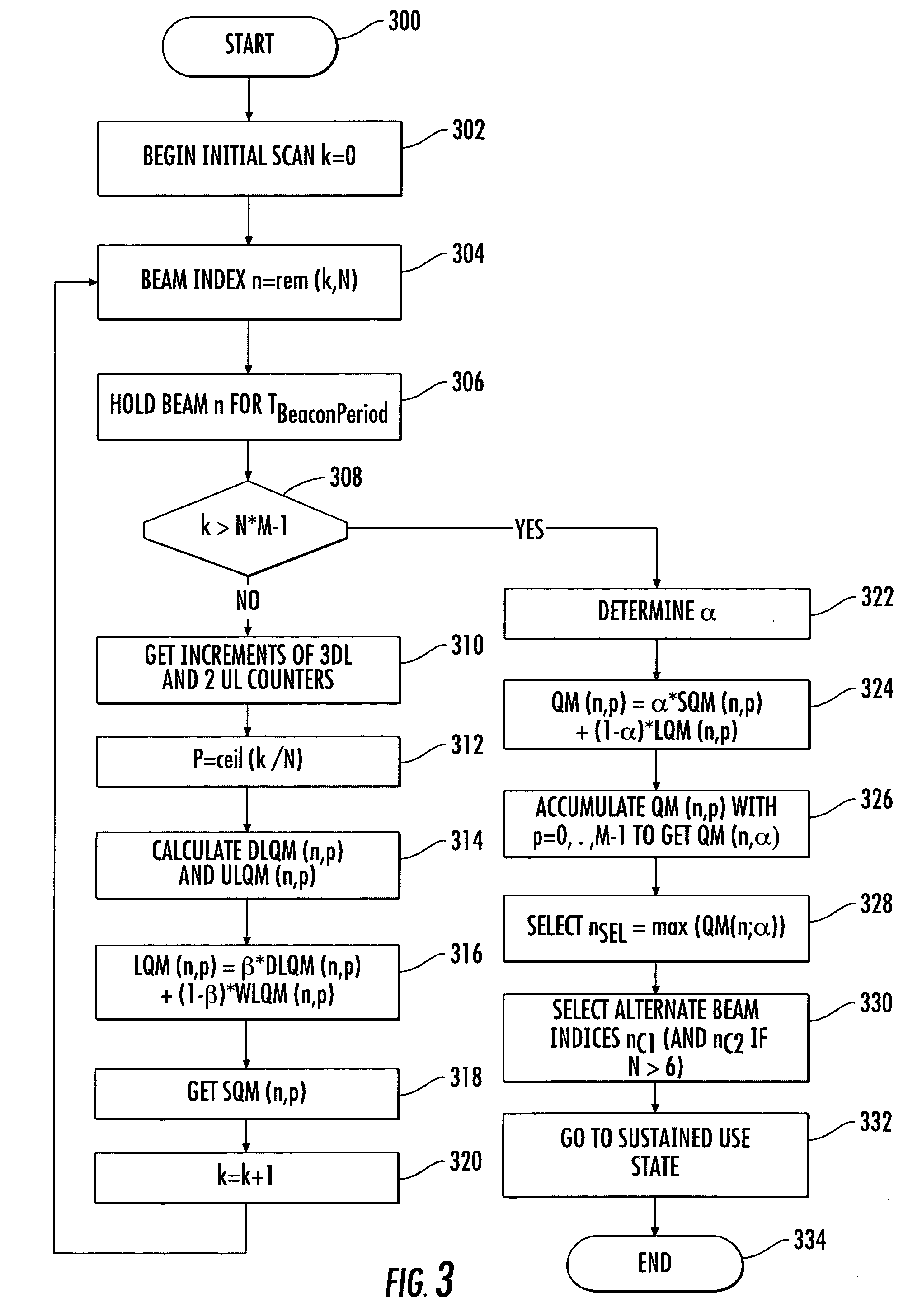
InactiveUS7289828B2Facilitate decision-makingSpatial transmit diversityNetwork topologiesSmart antennaEngineering
A smart antenna steering algorithm performs a periodic re-scan at an end of a sustained use period and before a next sustained use period. During a sustained use period, a re-scan of the other antenna beams is not performed. The periodic re-scan is performed on alternate antenna beams that were selected when the preferred antenna beam was selected. The steering algorithm monitors a quality metric of the alternate antenna beams as well as a quality metric for the preferred antenna beam. If the quality metric of the preferred antenna beam is less than the quality metrics of anyone of the alternate antenna beams, then the alternate antenna beam corresponding to the quality metric having a higher value is selected for the next sustained use period.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
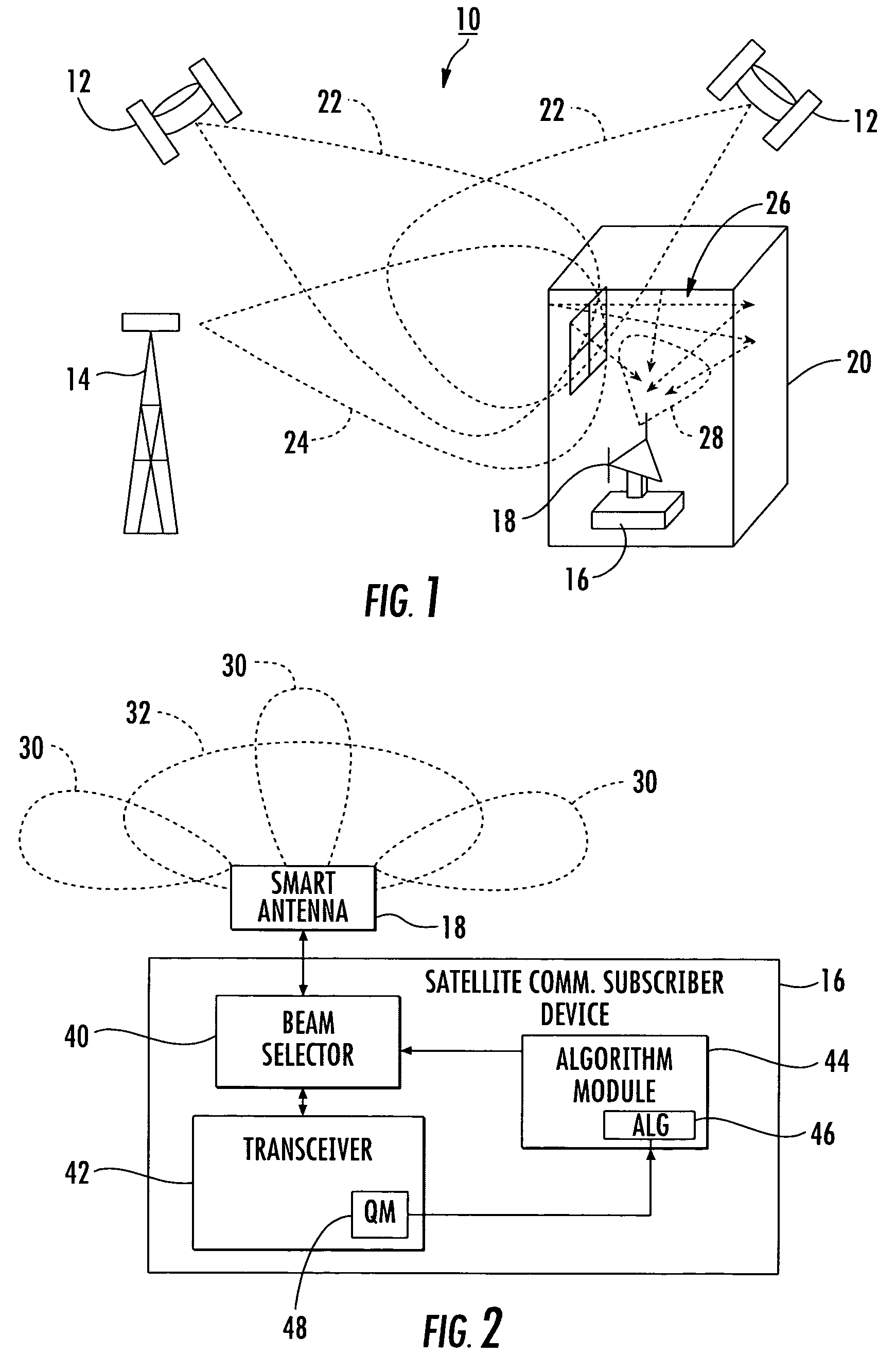
Satellite communication subscriber device with a smart antenna and associated method
InactiveUS7633442B2Easy to receiveSatellite broadcast receivingRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsUser deviceSmart antenna
A satellite communication subscriber device includes a smart antenna for generating antenna beams for receiving signals from at least one satellite, and a receiver. The receiver includes a quality metric module for calculating a quality metric on the signals received by each antenna beam. A beam selector is coupled to the smart antenna for selecting the antenna beams. An antenna steering algorithm module runs an antenna steering algorithm for operating the beam selector for scanning the antenna beams, receiving the calculated quality metrics from the receiver for each scanned antenna beam, and comparing the calculated quality metrics. The algorithm selects one of the scanned antenna beams based upon the comparing for continuing to receive signals from the at least one satellite.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
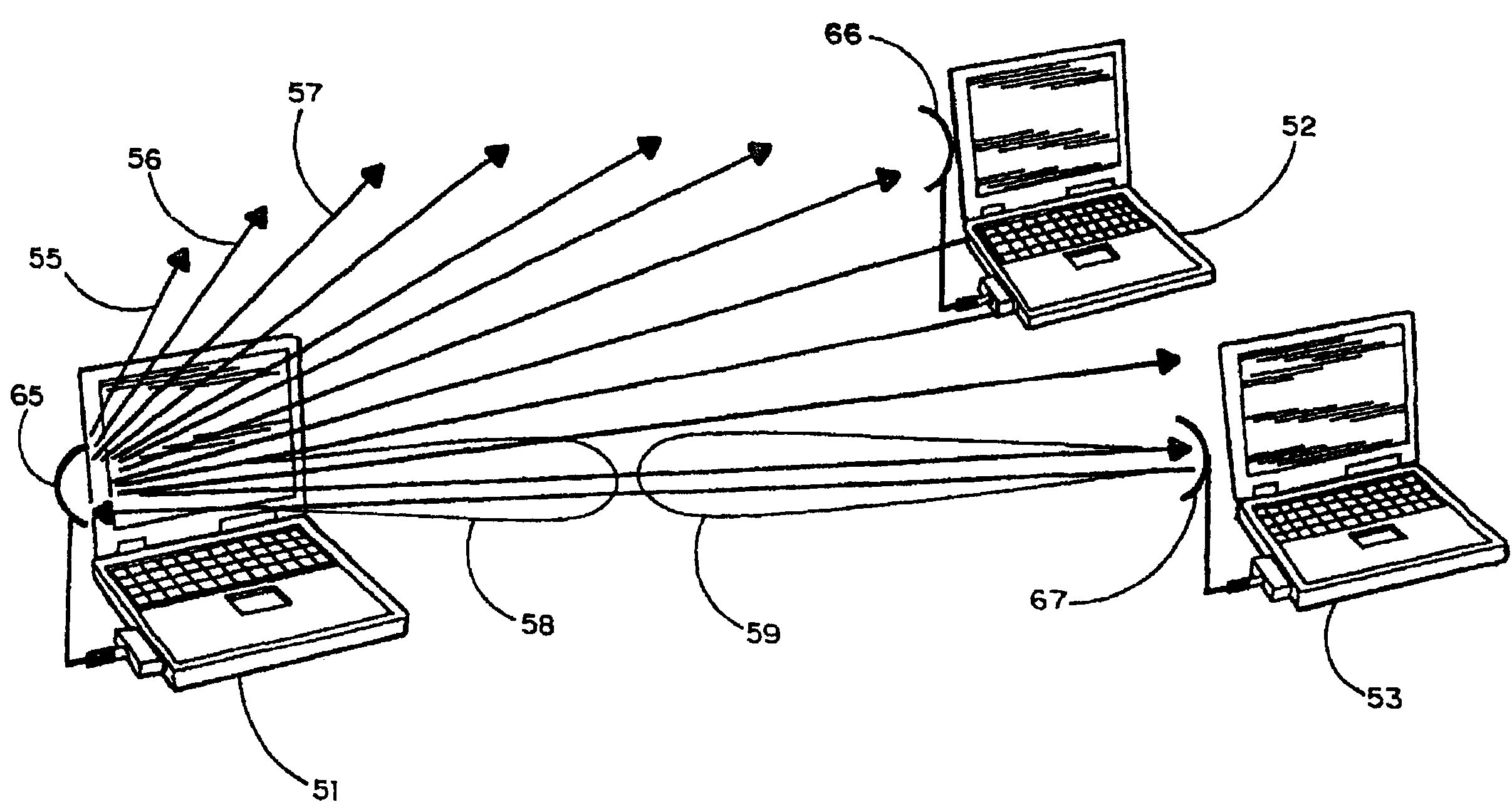
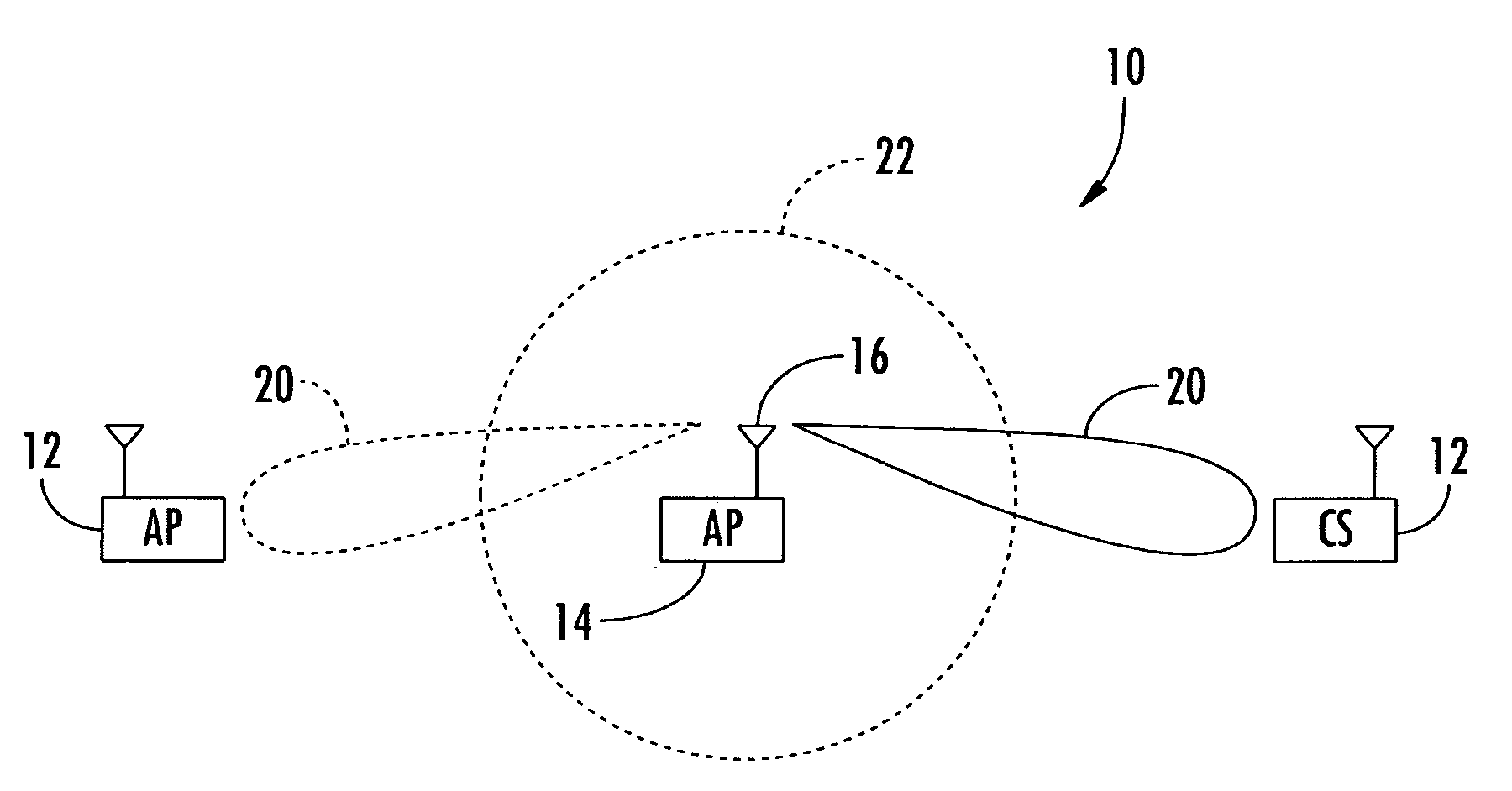
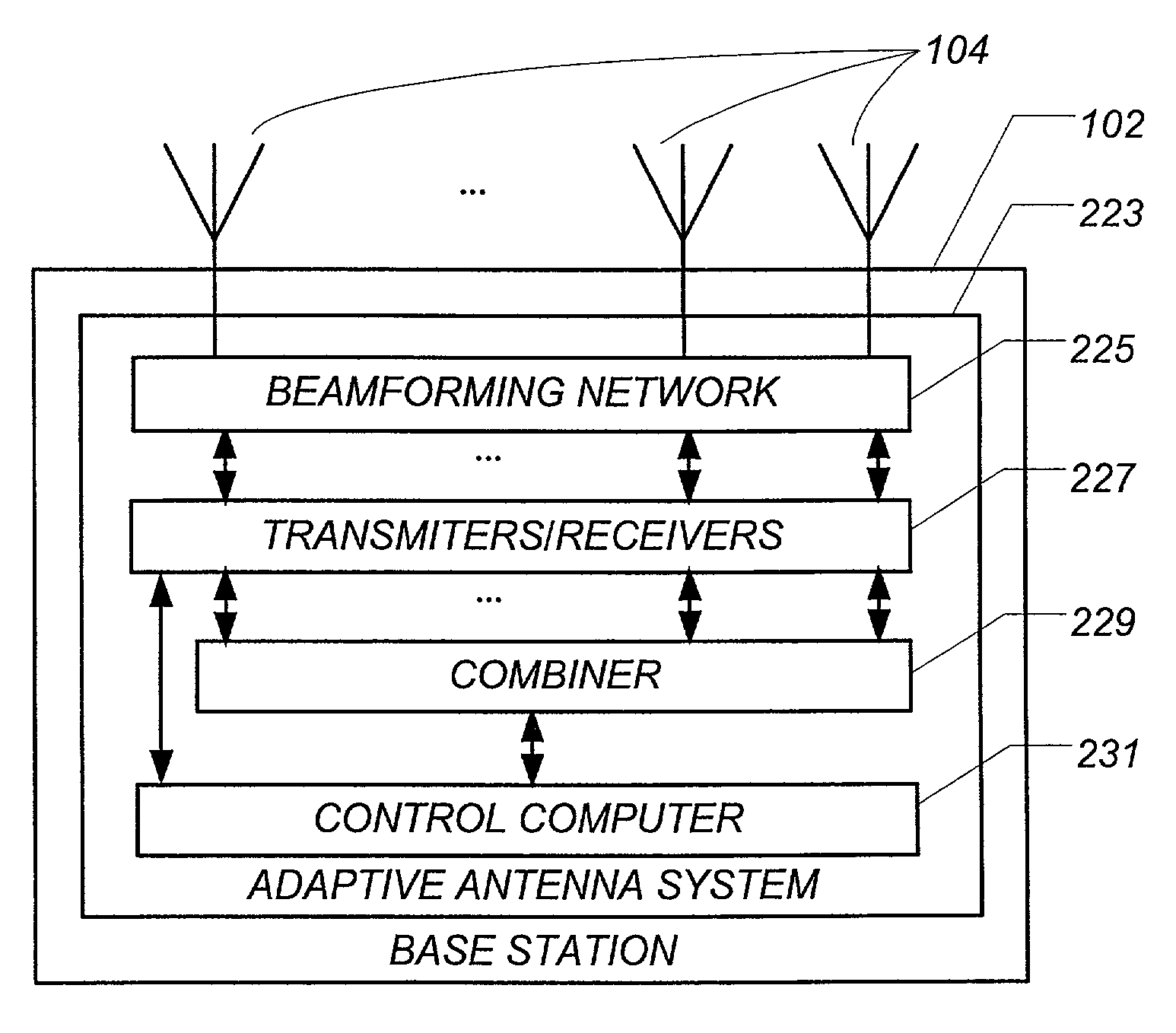
Dynamically optimized smart antenna system
A wireless communications network includes a plurality of wireless devices equipped with direction-agile antenna systems to allow the wireless devices to establish and maintain wireless data links with each other.
Owner:AIRGAIN INC
Systems and methods for proactively enforcing a wireless free zone
ActiveUS20080119130A1Minimize signal bleedMinimize signalingNetwork topologiesCommunication jammingWireless intrusion prevention systemFree zone
The present disclosure is directed to systems and methods for proactively enforcing a wireless free zone over an enterprise's airspace using Open Systems Interconnect (OSI) layer one, two, and three based techniques. The systems and methods prevent wireless communications over IEEE 802.11 (WiFi), IEEE 802.16 (WiMax), and IEEE 802.15.1 (Bluetooth) networks to enable an enterprise to enforce compliance to a no-wireless policy. Smart antennas and coverage planning are included to avoid disrupting a neighbor's wireless communications. Further, the disclosed systems and methods can be combined into existing Wireless Intrusion Prevention Systems (WIPS) or in a stand-alone sensor and server configuration to offer proactive no-wireless zones.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
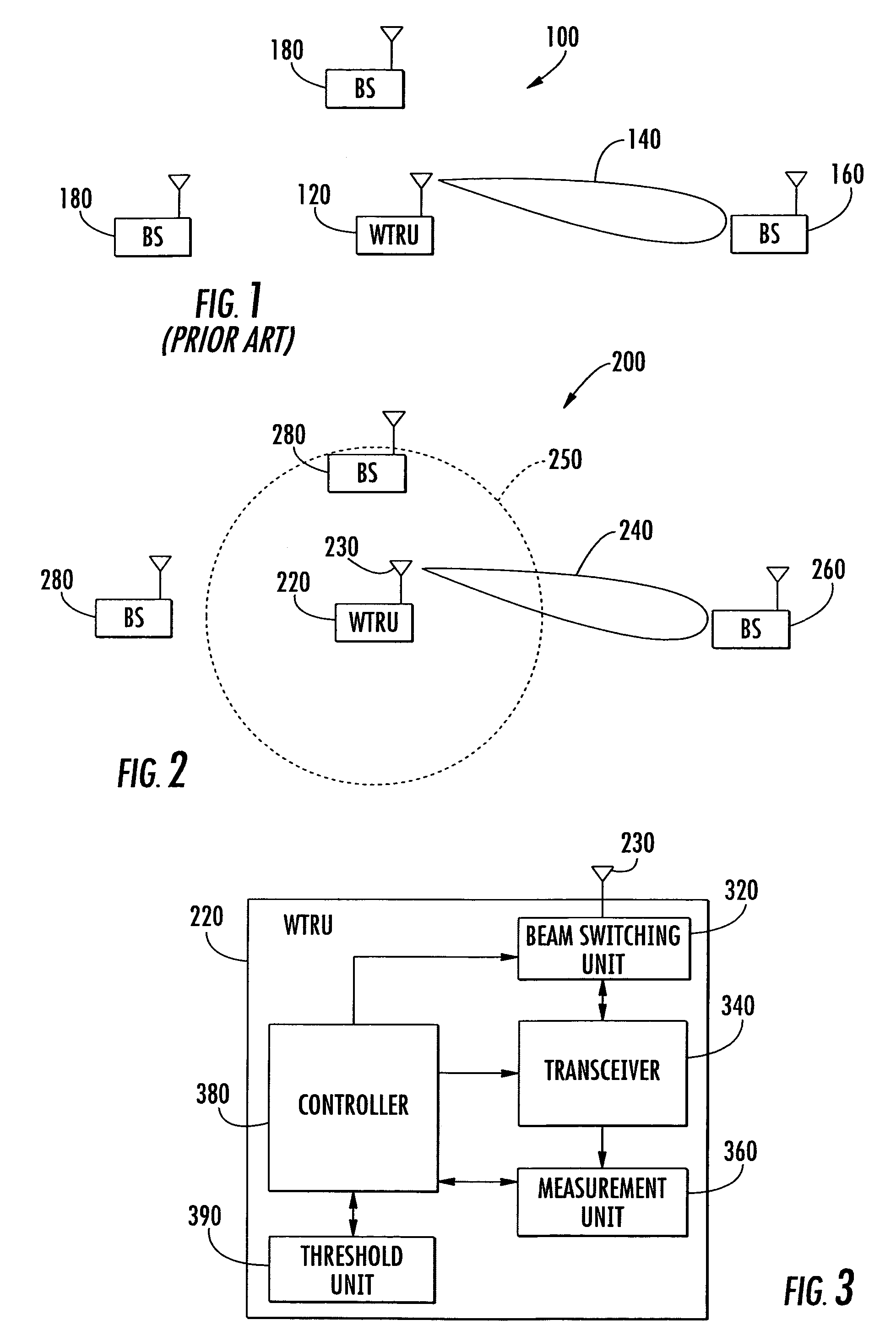
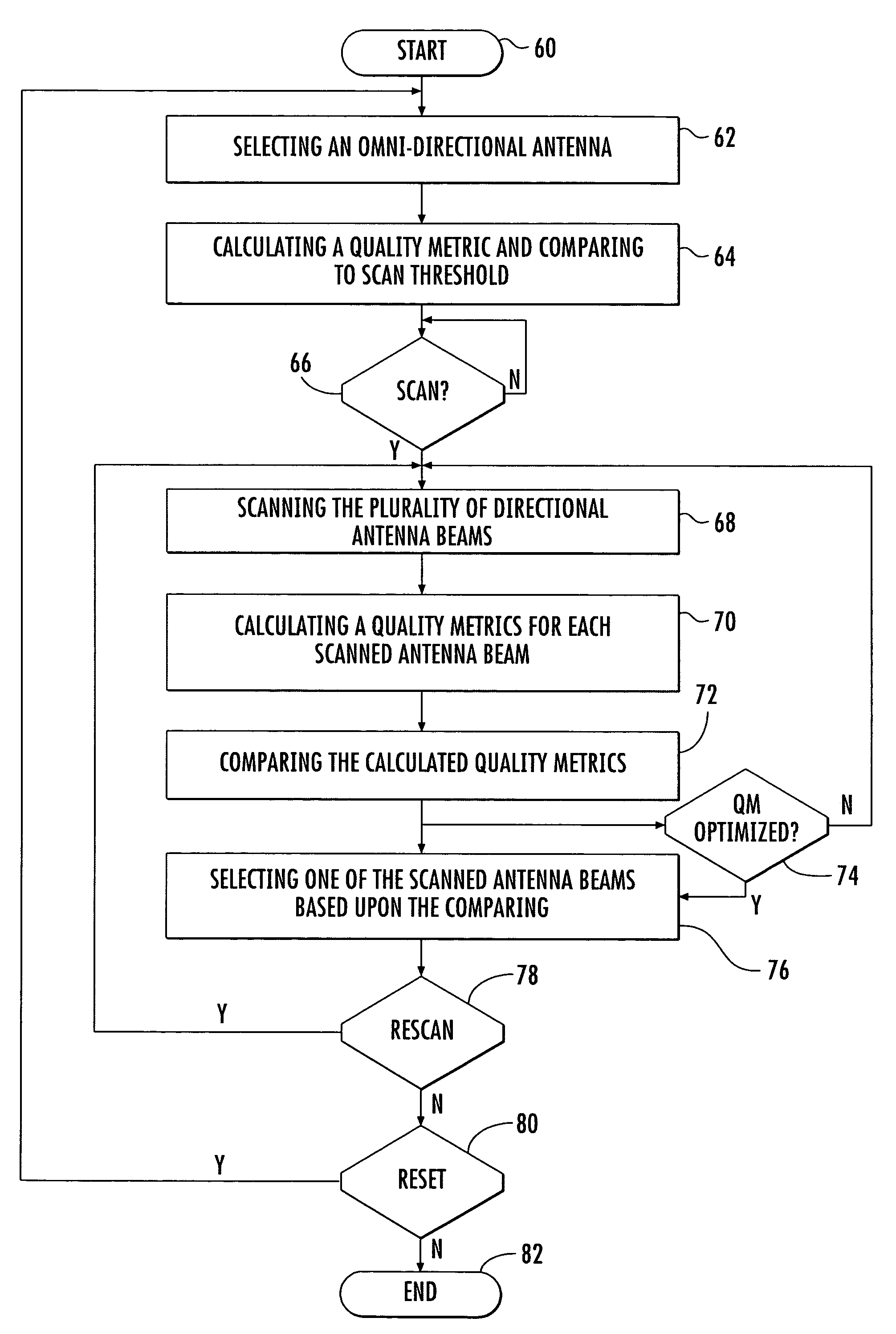
Access point operating with a smart antenna in a WLAN and associated methods
InactiveUS20050285803A1Increase rangeImprove network throughputAntenna supports/mountingsSubstation equipmentOmnidirectional antennaSmart antenna
An access point operates in an 802.11 wireless communication network communicating with a client station, and includes a smart antenna for generating directional antenna beams and an omni-directional antenna beam. An antenna steering algorithm scans the directional antenna beams and the omni-directional antenna beam for receiving signals from the client station. The signals received via each scanned antenna beam are measured, and one of the antenna beams is selected based upon the measuring for communicating with the client station. The selected antenna beam is preferably a directional antenna beam. Once the directional antenna beam has been selected, there are several usage rules for exchanging data with the client station. The usage rules are directed to an active state of the access point, which includes a data transmission mode and a data reception mode.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Non-directional transmitting from a wireless data base station having a smart antenna system
InactiveUS6982968B1Reduce distractionsSubstation equipmentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsInterference (communication)Communications system
A method, communication apparatus, and machine-readable medium to transmit a downlink signal in a substantially non directional manner from a first communication station of a communication system on a first downlink conventional channel. The first communication station includes a smart antenna system having a plurality of antenna elements. The method includes providing a first set of sequential time intervals for the communication device for communication with its remote communication devices. One or more remote communication devices of the communication system known to the first communication station to be undesired remote communication devices transmit a signal on a first uplink conventional channel. The signals transmitted are received. In one version, they are received at the first communication station, and in another version, by another communication station of the communication system. The signal received are used to configure the smart antenna system for transmitting a downlink signal in a non-directional manner that includes mitigating interference towards the undesired remote communication devices on the first downlink conventional channel.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Power control with signal quality estimation for smart antenna communication systems
A method for ongoing power control for a communication station with a multiple antenna array, the power control using a method for signal quality estimation applicable for angle modulated signals. One aspect of the ongoing power control method is applicable for the uplink and includes separating the joint determination of a receive weight vector and ongoing power control into a receive weight vector determining part and a separate transmit power adjustment part. In one embodiment, the ongoing power control method for the downlink includes separating the joint determination of a receive weight vector and ongoing power control into a receive weight vector determining part and a separate transmit power adjustment part. The method starts with one part, for example transmit power assignment. Receive weight vector determination is carried out with this assigned transmit power, and the new weights used. An estimate of the resulting received signal quality is obtained and used for new ongoing power adjustment. Another aspect is applicable for the downlink and includes one aspect of the ongoing power control method is applicable for the uplink and includes separating the determination of a complete transmit weight vector including the vector of relative transmit weights and the scaling to use with the relative transmit weights into a part for determining a set of relative transmit weights and a separate transmit power adjustment part that determines the scaling factor.
Owner:INTEL CORP
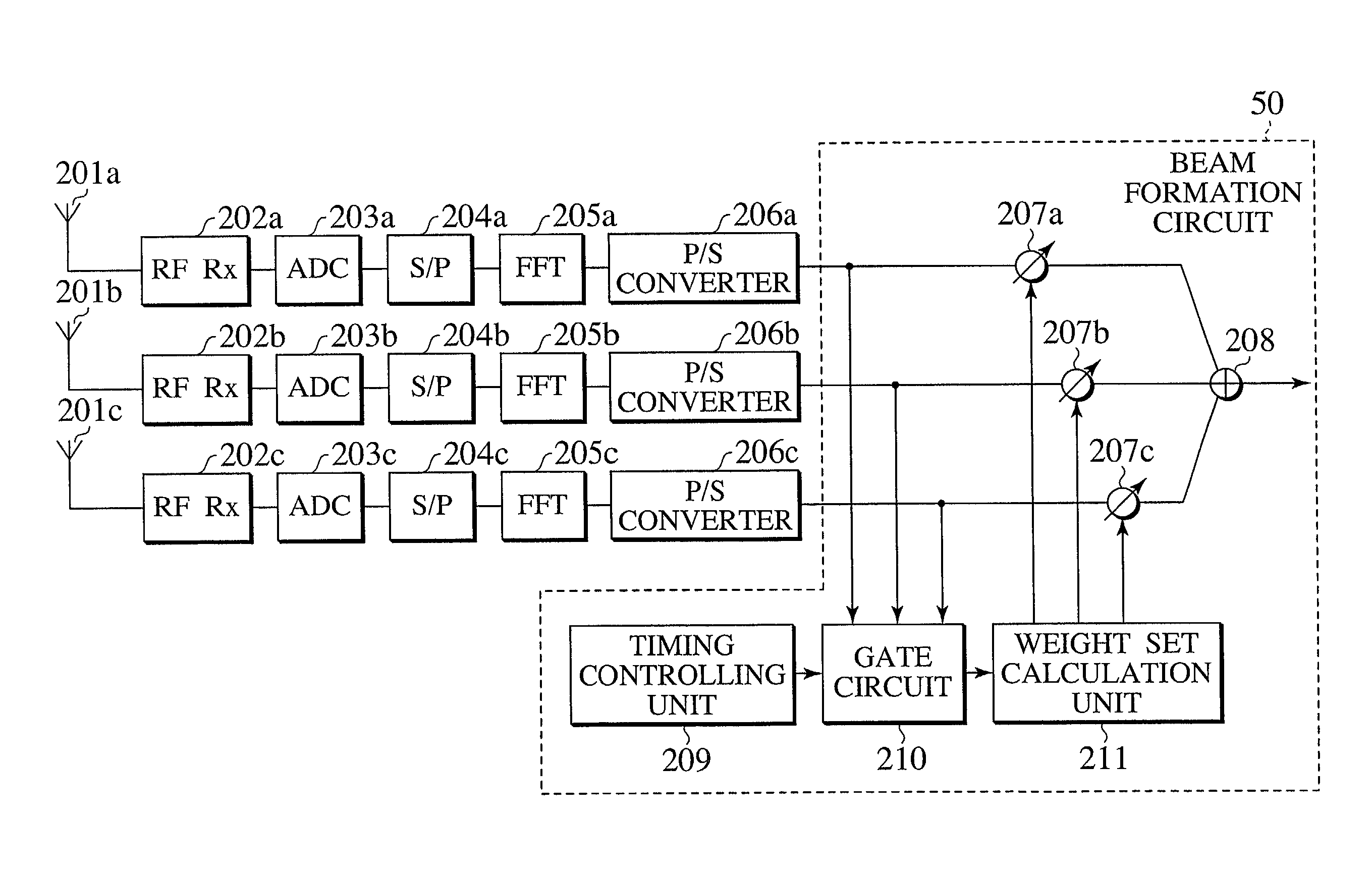
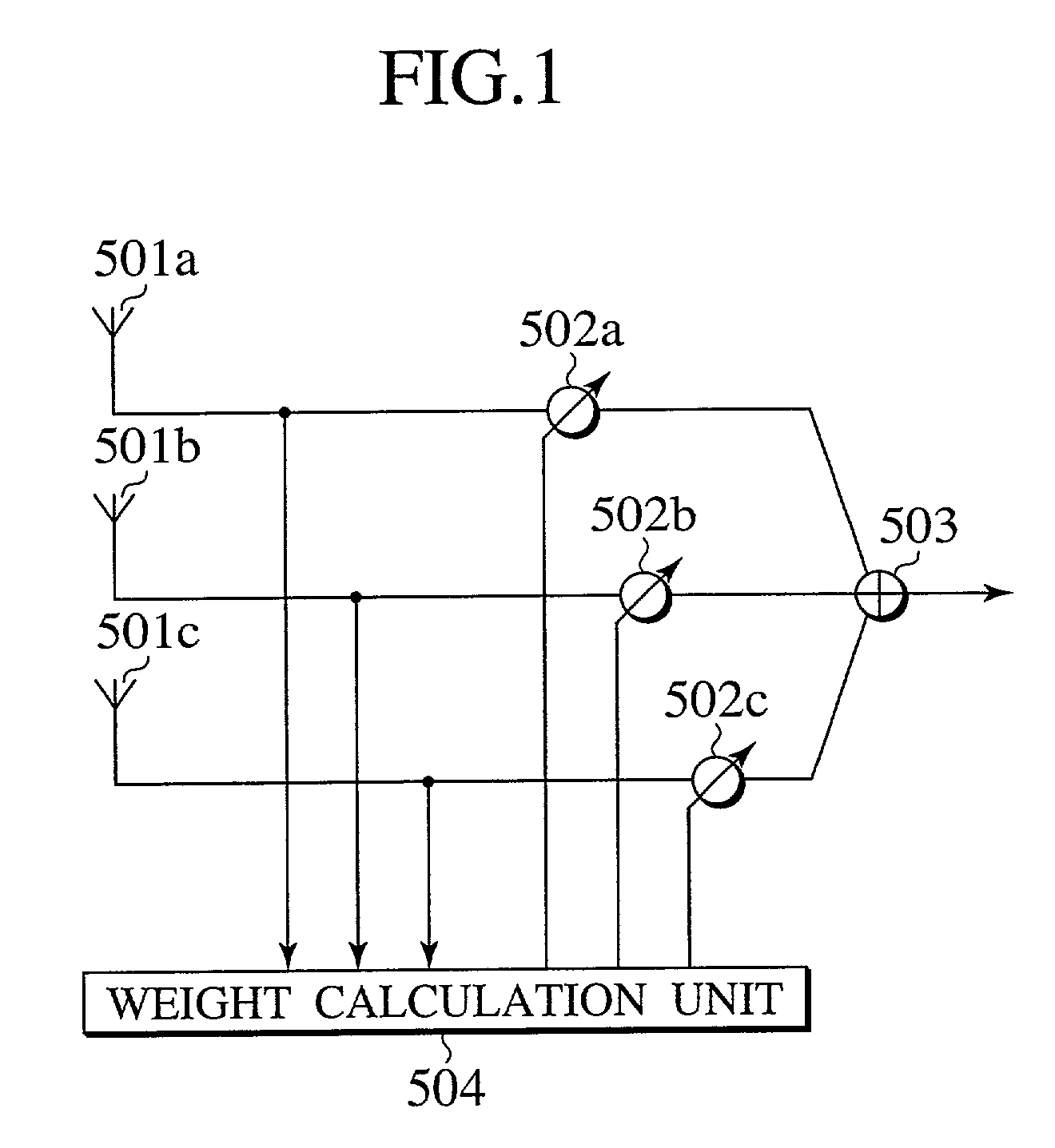
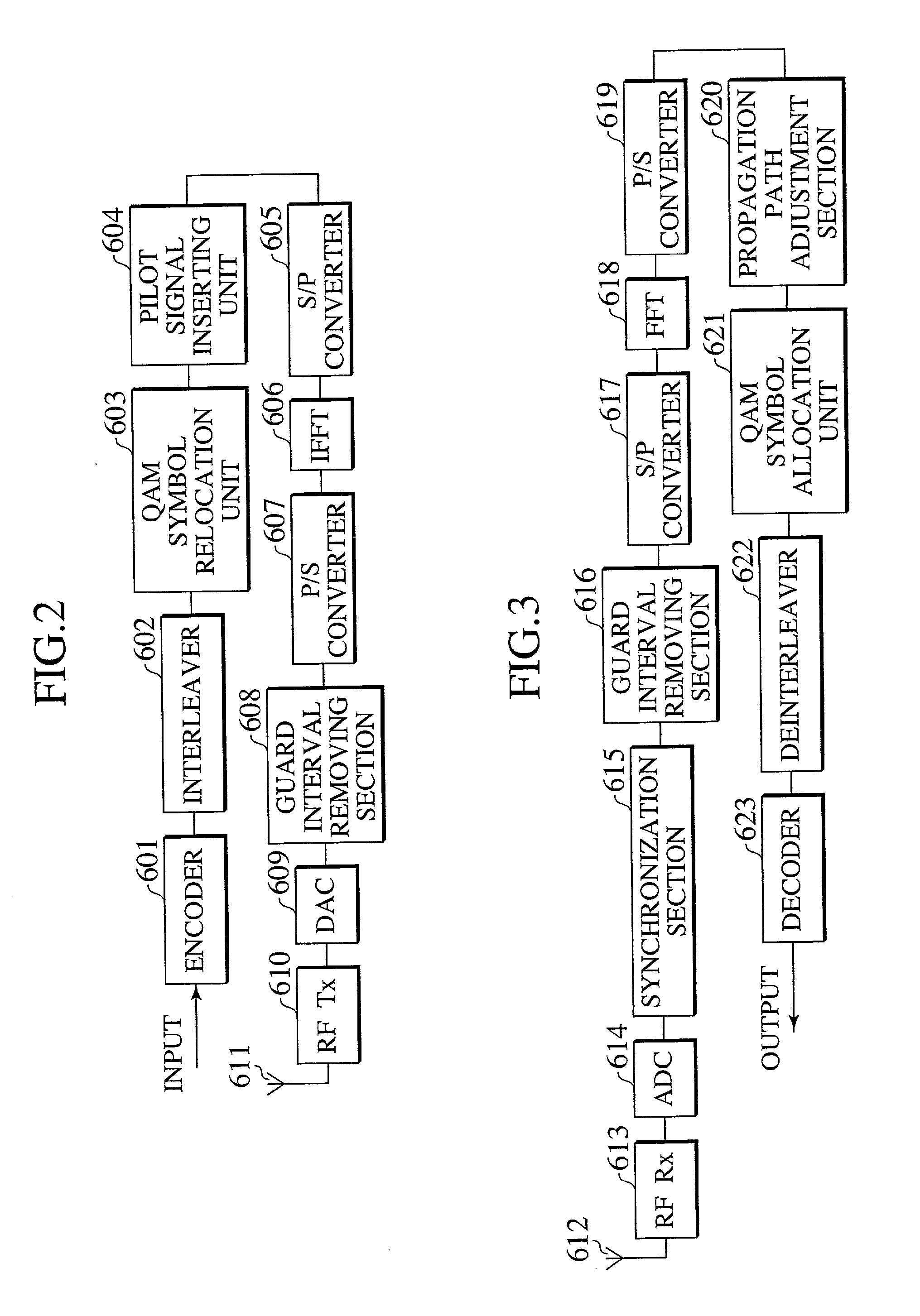
Use of smart antenna in beam formation circuit
InactiveUS7103119B2Spatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversitySmart antennaRadio frequency signal
A beam formation circuit and an apparatus and a method of receiving radio frequency signals making use of a smart antenna are described in which the amount of computation tasks required for the weight calculation is significantly reduced. In realizing the directivity of the smart antenna, the output signals corresponding to a plurality of sub-carriers are weighted with a common antenna weight for each of the antenna elements.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Smart antenna array over fiber
InactiveUS20080007453A1Improve performanceQuality improvementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsModular arraysFiberSmart antenna
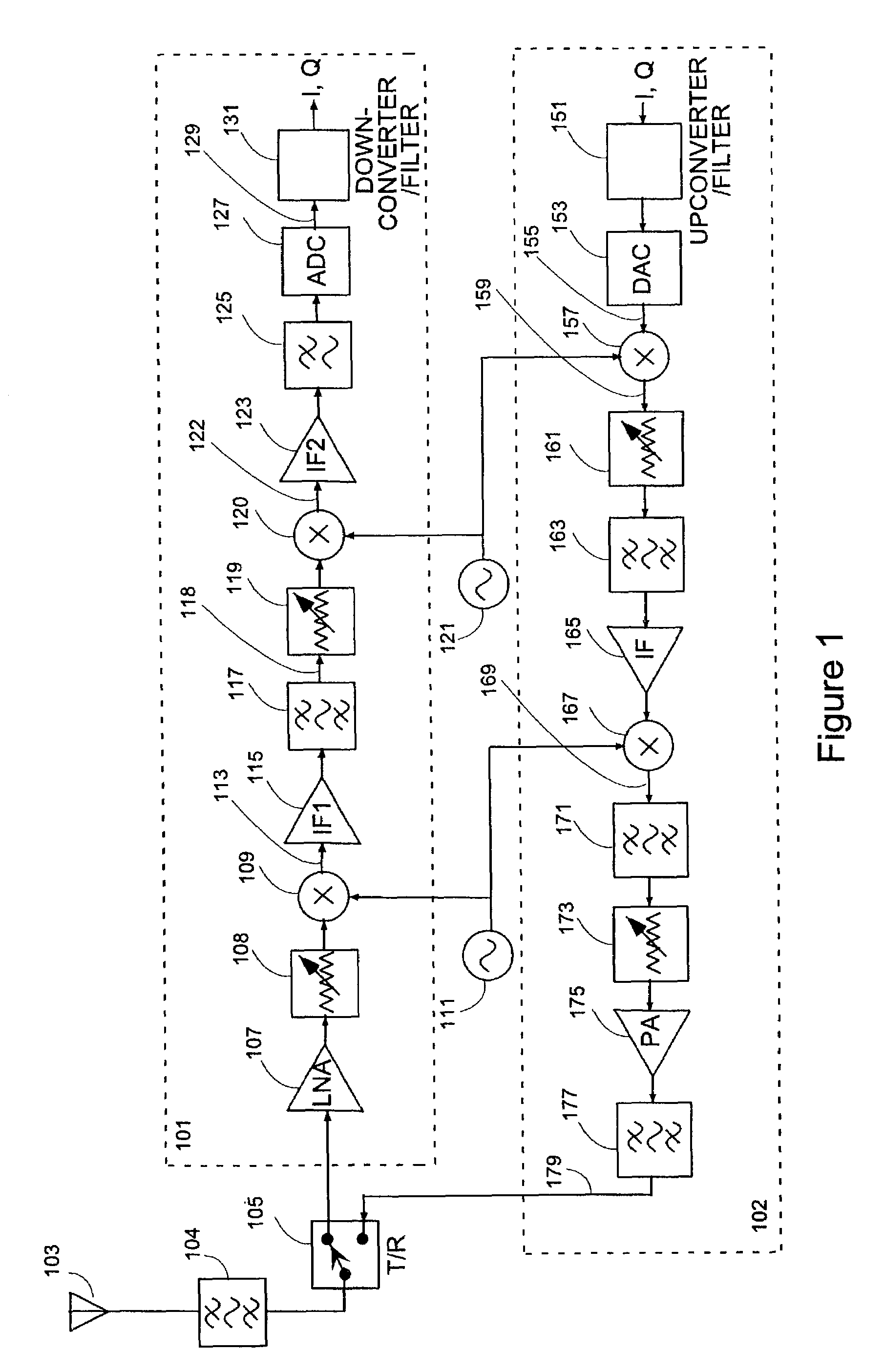
A smart antenna system includes a plurality of antennas, a plurality of Transmit—Receive Modules (TRMs) coupled respectively to the plurality of antennas, and a beam steering module coupled to the plurality of TRMs and providing radiation beam steering for the plurality of TRMs. The beam steering module includes a pilot generator for generating a pilot signal and providing it to the TRMs to calibrate a receive (RX) reference plane. The pilot signal is injected at a first location before the receiver section into the RX path, and the pilot signal is sampled at a second location after the receiver section. The TRMs and the beam steering module can also be used to calibrate a transmit (TX) reference plane by sampling output signals from the TRMs. The output signals have a pilot signal component, and are sampled at the first location in the TX path after the transmitter section.
Owner:POWERWAVE TECH INC
WLAN access point with extended coverage area
ActiveUS20060025178A1Reduce bitrateImprove link qualityNetwork topologiesSubstation equipmentExtended coverageHigh bandwidth
Disclosed are systems and methods which provide high bandwidth data communication with respect to a large coverage area using smart antenna and / or directional antenna (referred to herein as multi-beam antenna) technology. Circuitry may be provided at a WLAN AP to provide selection of particular antenna beams used in the downlink and / or uplink, control of multicast transmission, control of unicast transmission, and to provide antenna pattern shaping techniques. Embodiments implement multi-beam antenna technology with little or no hardware modifications to AP circuitry. Other embodiments implement multi-beam technology using radio front-end and / or radio hardware modifications to AP circuitry. Various diversity techniques may be implemented, such as selection diversity, maximum ratio combining, and equal gain combing. To provide desired antenna pattern shaping, phase offsets with respect to a signal as transmitted in each antenna beam may be employed.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
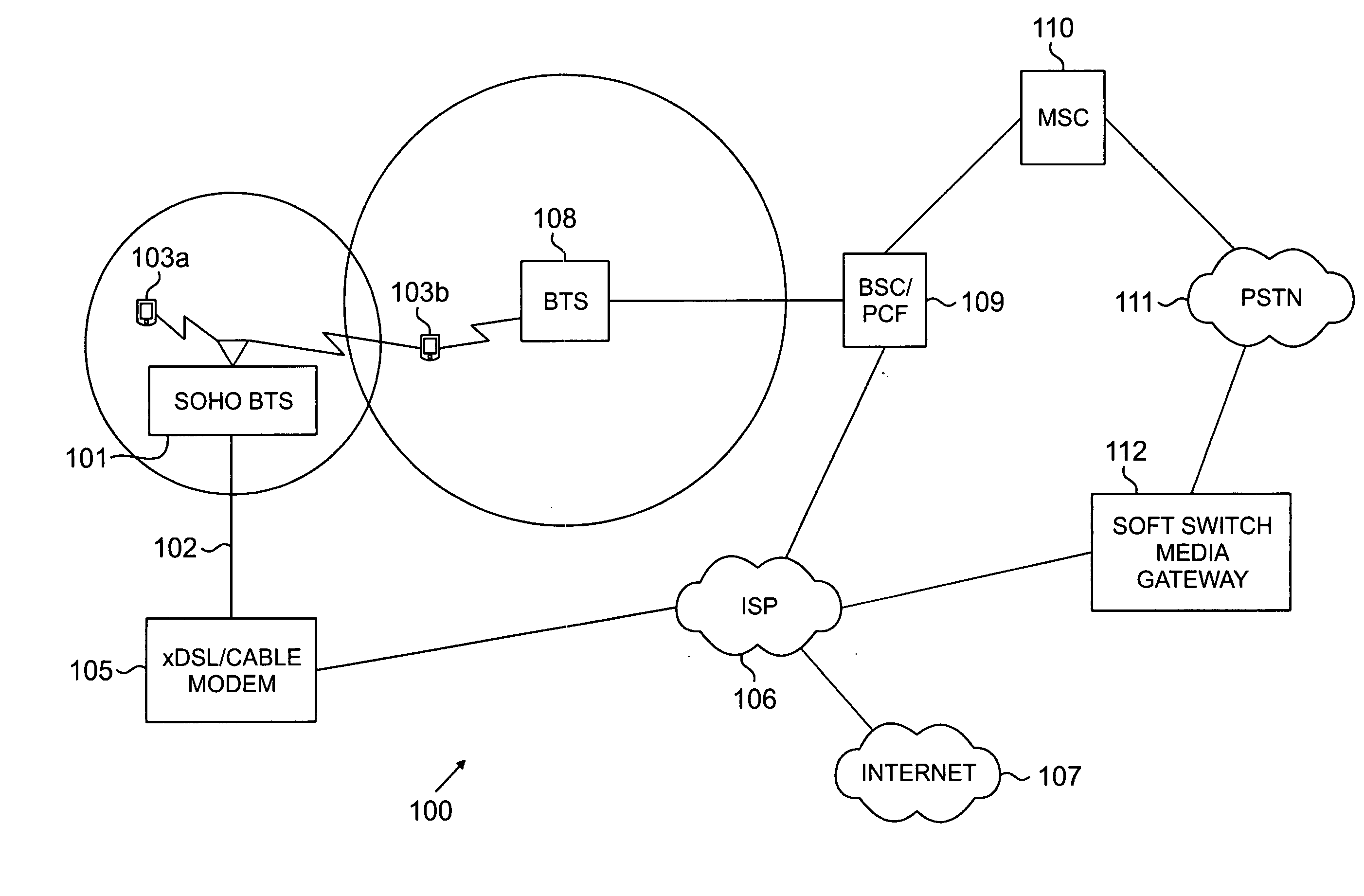
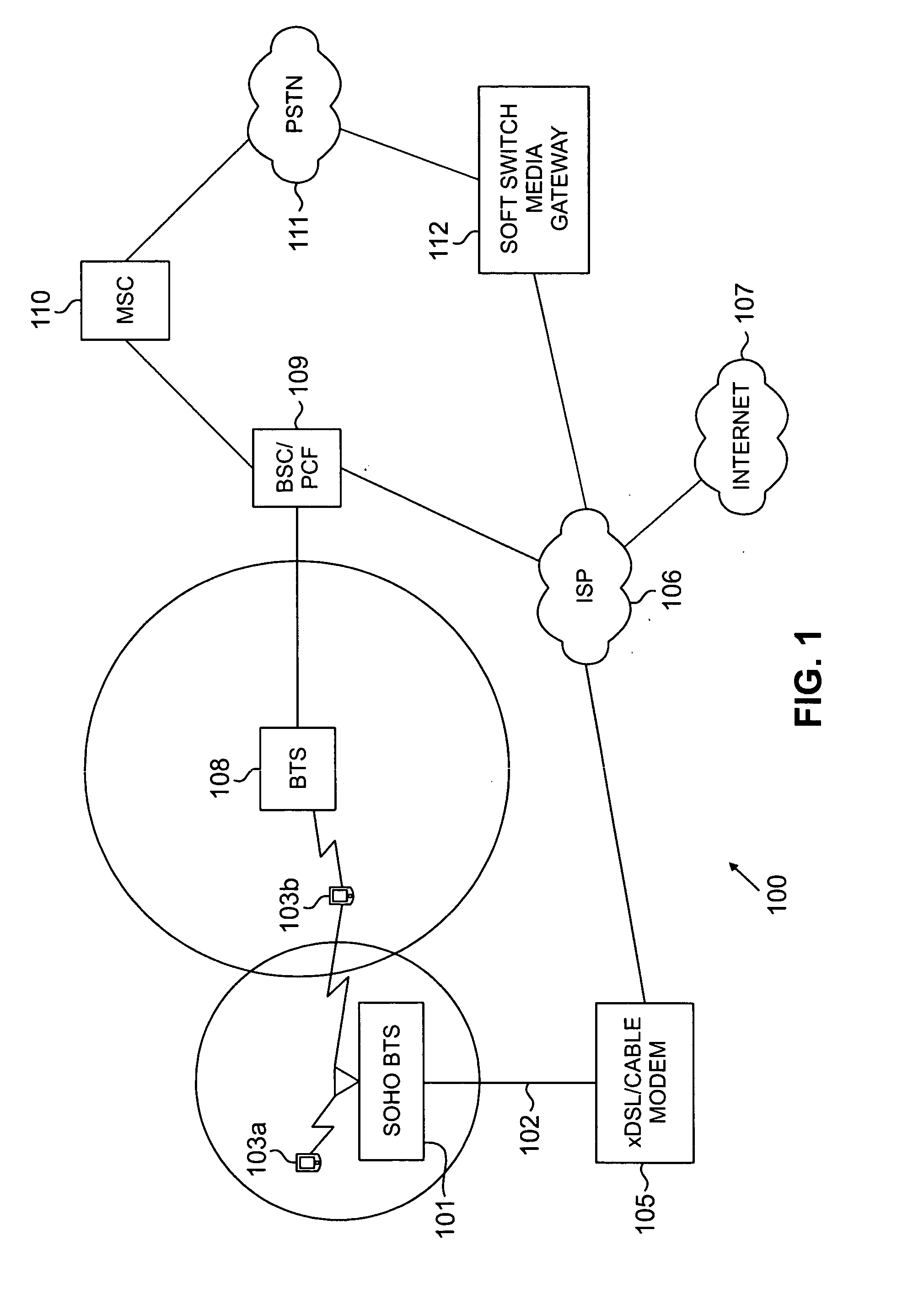
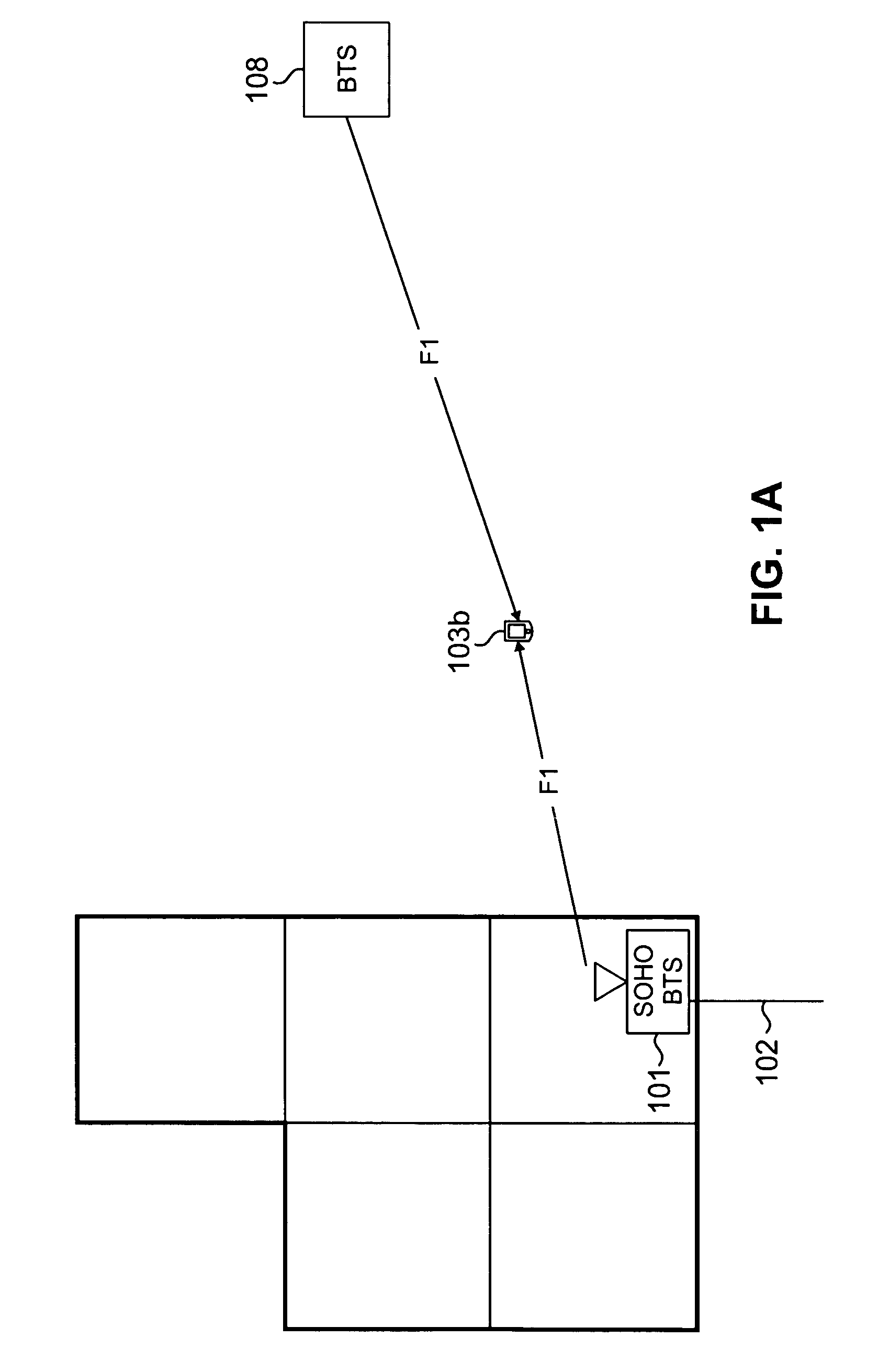
System and method for providing SOHO BTS coverage based on angle of arrival of mobile station signals
InactiveUS20080026763A1Optimizes RF coverageControl interferenceEnergy efficient ICTRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsFrequency spectrumTransmitted power
Beamforming techniques to limit radiated power where there is the potential for interference with macro-cellular coverage or with adjacent mobile stations. Smart antenna beamforming techniques (including the use of angle of arrival information) are combined with access probe information to determine the direction for radiated power and the level of the needed transmitted power as well for the small office or home (SOHO) environment. The placement of RF power in the SOHO specific to where it is needed, minimizes radiating power in directions where it will cause interference with macrocell coverage. In addition, the beamforming techniques provide a base transceiver station with an economical method to quickly solve coverage issues internal to a SOHO, without introducing interference external to this coverage environment. In addition, there specific placement of the RF power where it is needed provides an increase in spectral efficiency of a deployed network.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
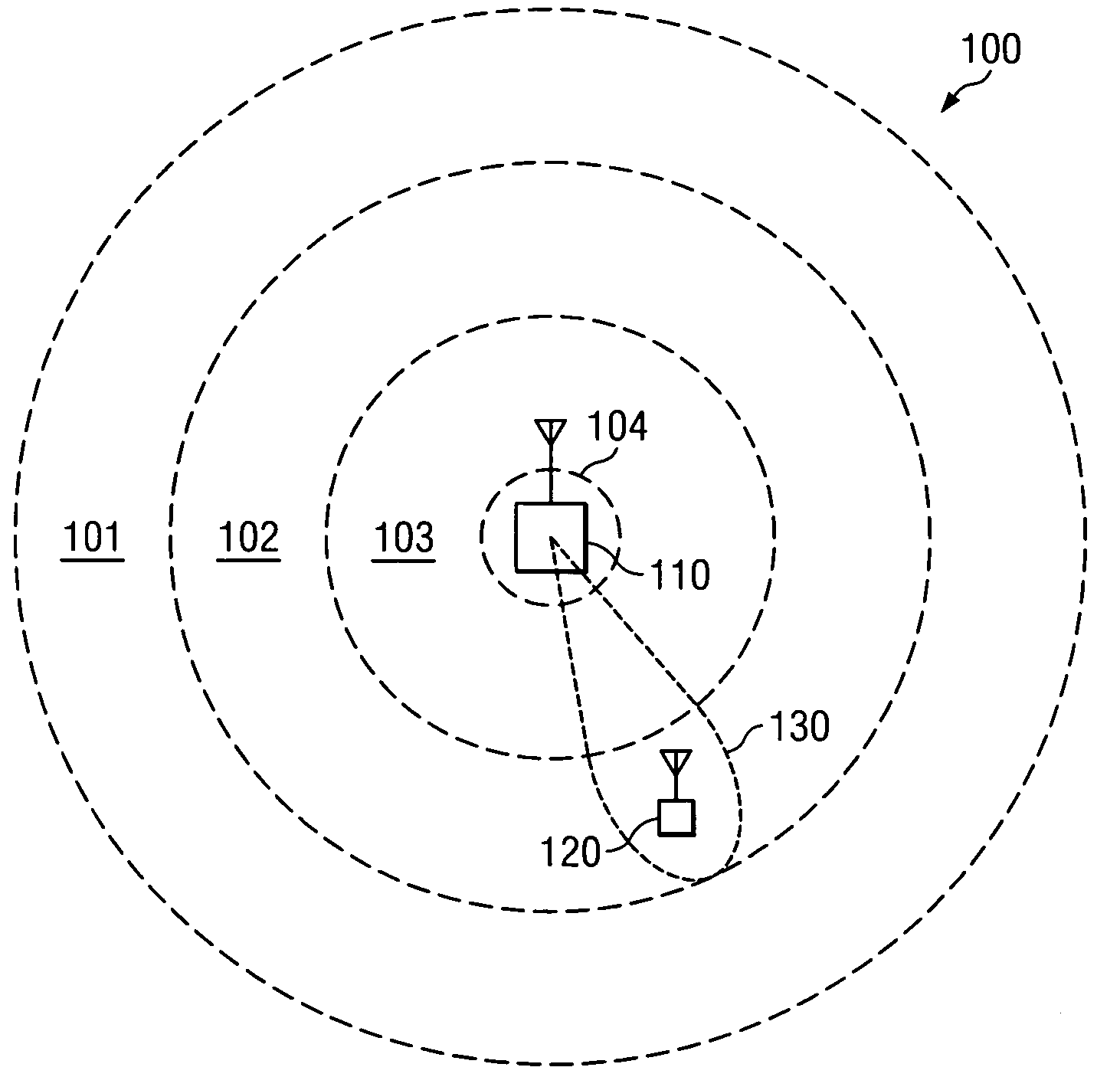
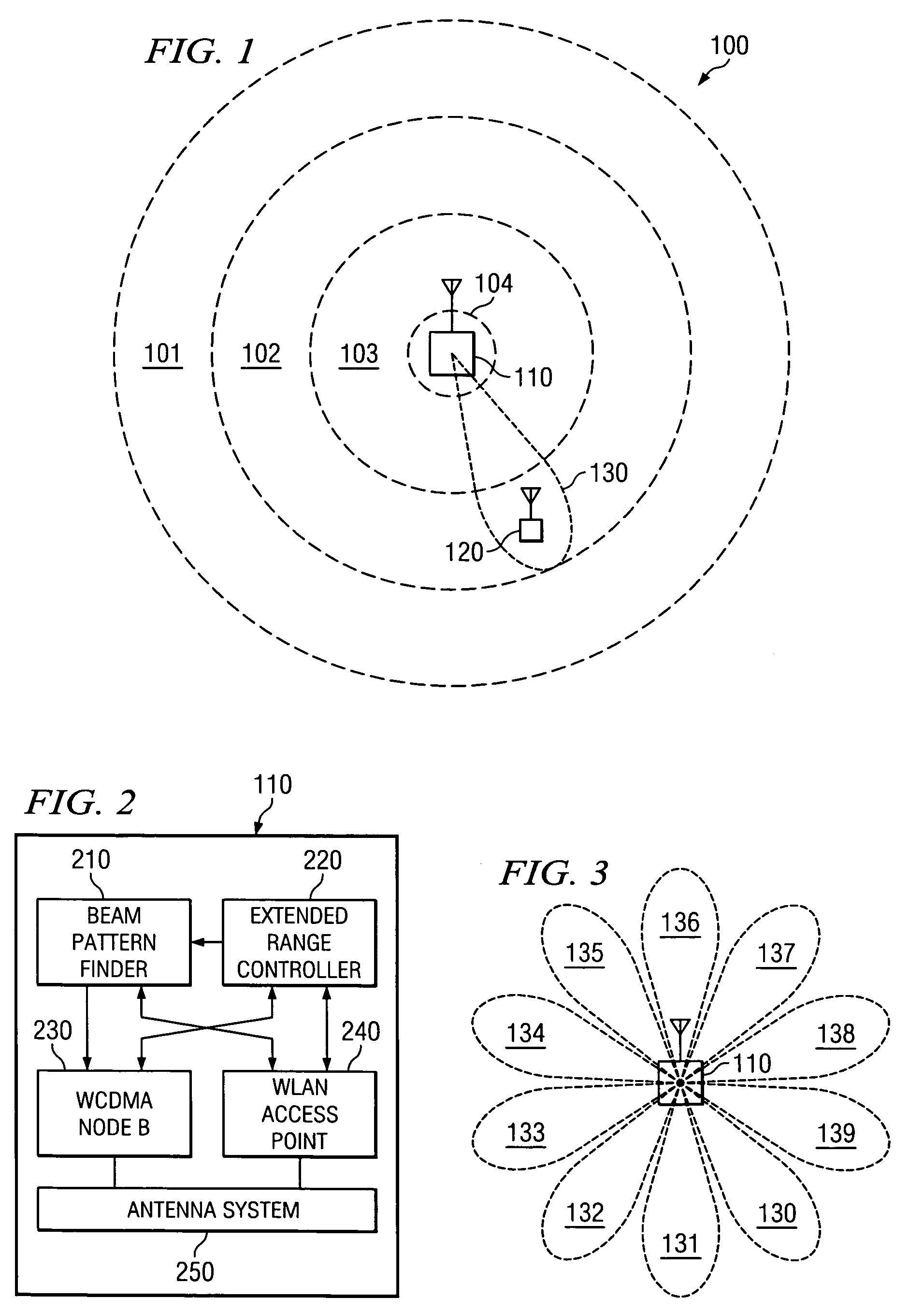
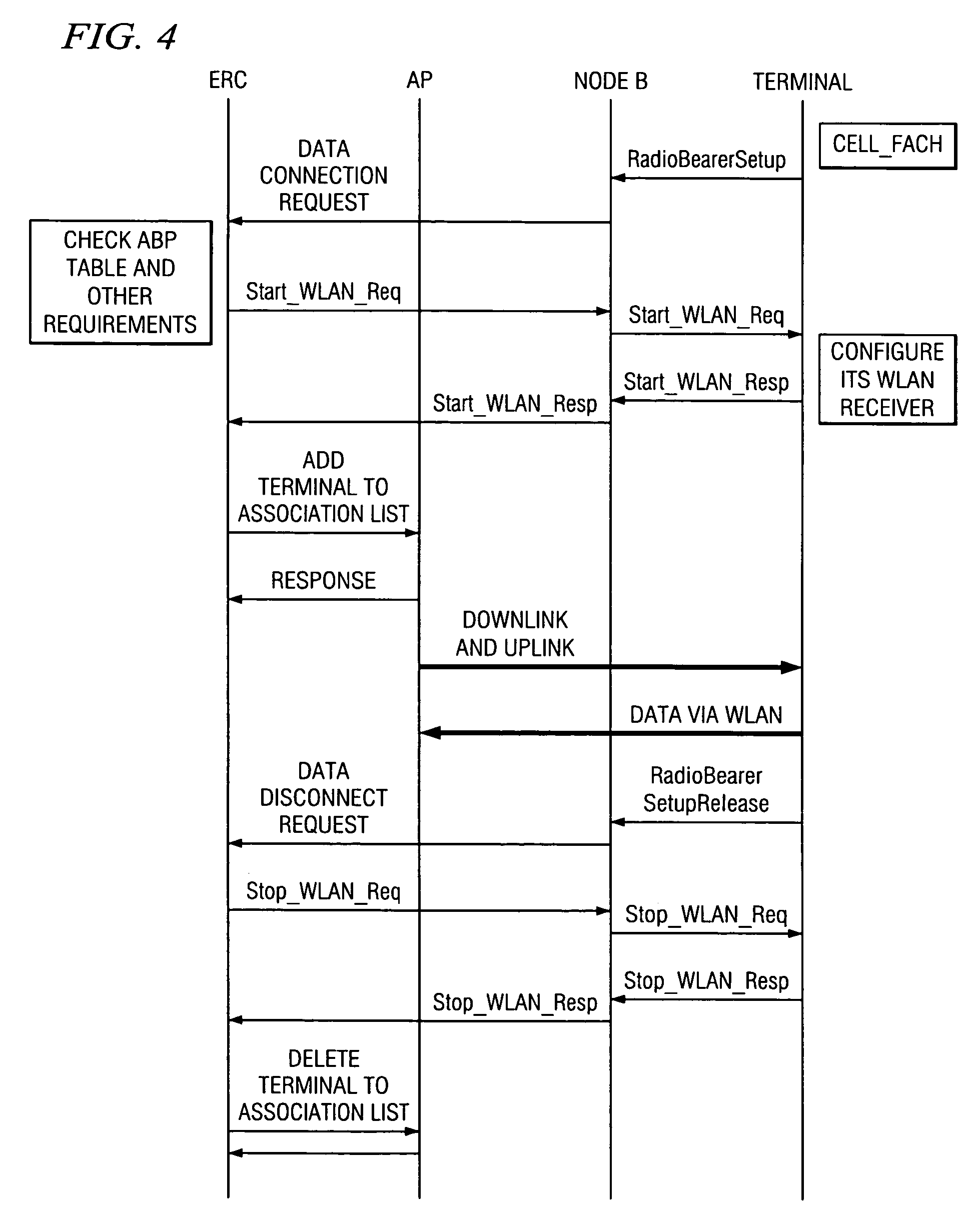
Systems and methods for wireless network range extension
ActiveUS20050255892A1High bandwidth data communicationHigh bandwidth communicationSubstation equipmentRadio transmission for post communicationTelecommunicationsHigh bandwidth
Disclosed are systems and methods which provide high bandwidth data communication with respect to a large coverage area using smart antenna and / or directional antenna techniques. Embodiments provide extended wireless local area network (WLAN) coverage areas using a directional antenna, with the cooperation of a cellular system or proprietary WLAN infrastructure to perform best antenna beam pattern estimation and signaling. Stations disposed beyond a WLAN coverage area may establish contact and exchange signaling information with an access point through a secondary control channel. Such a secondary control channel signaling may be relatively low bandwidth and may be utilized to identify the need to communicate data, to identify a “best” directional antenna beam through which to communicate data, etcetera. Payload data may then be transmitted at a high bit rate through one or more smart antenna beams targeted at the appropriate stations.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
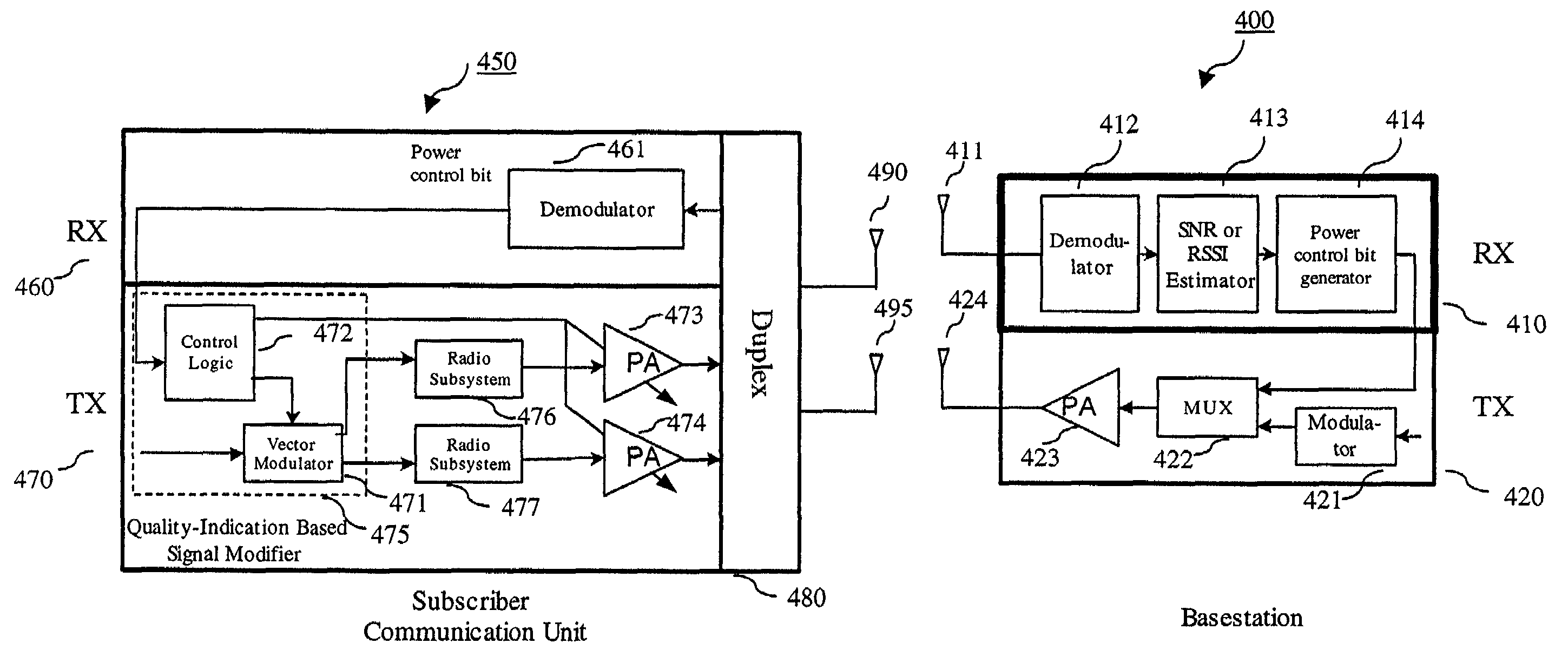
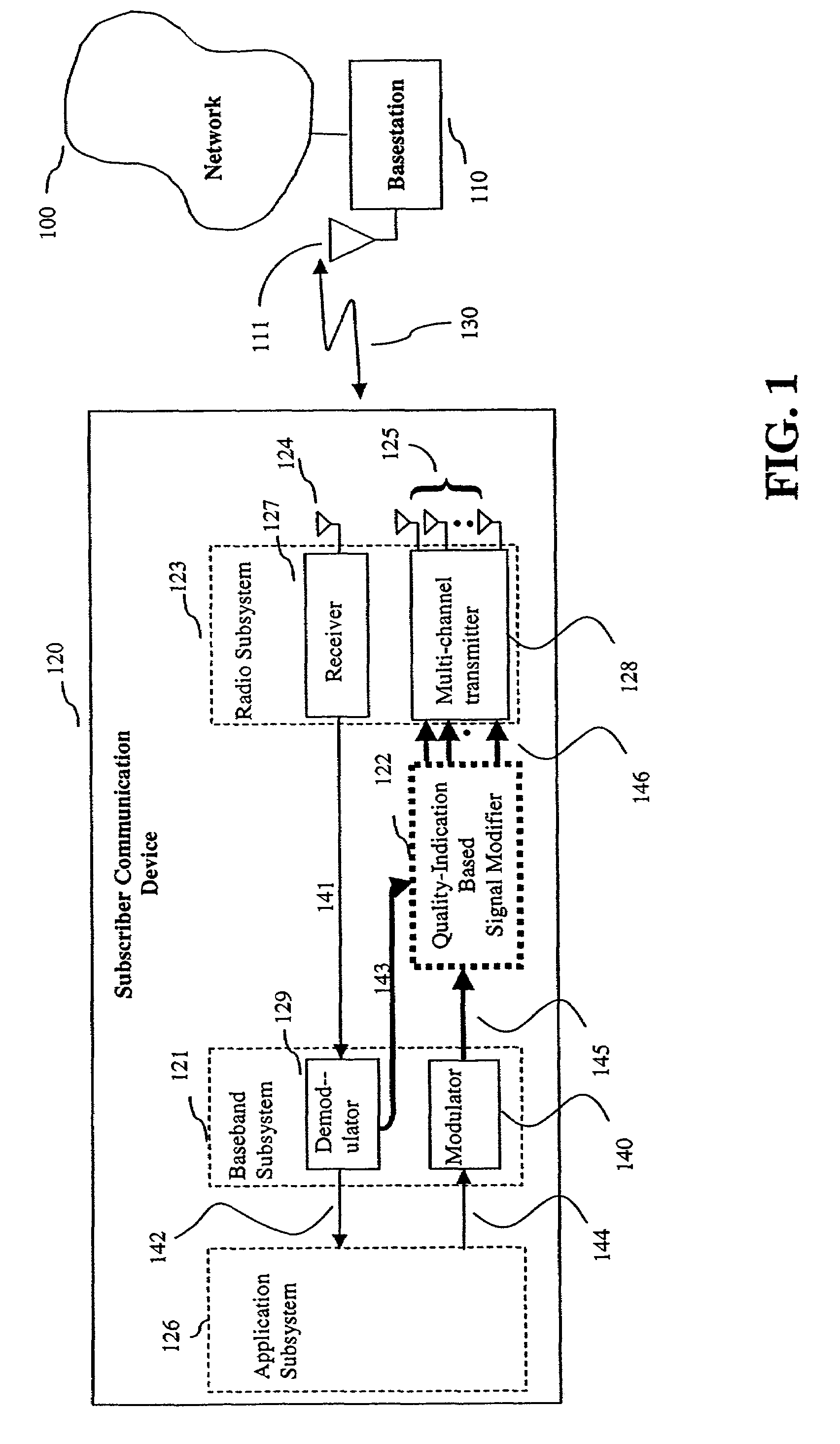
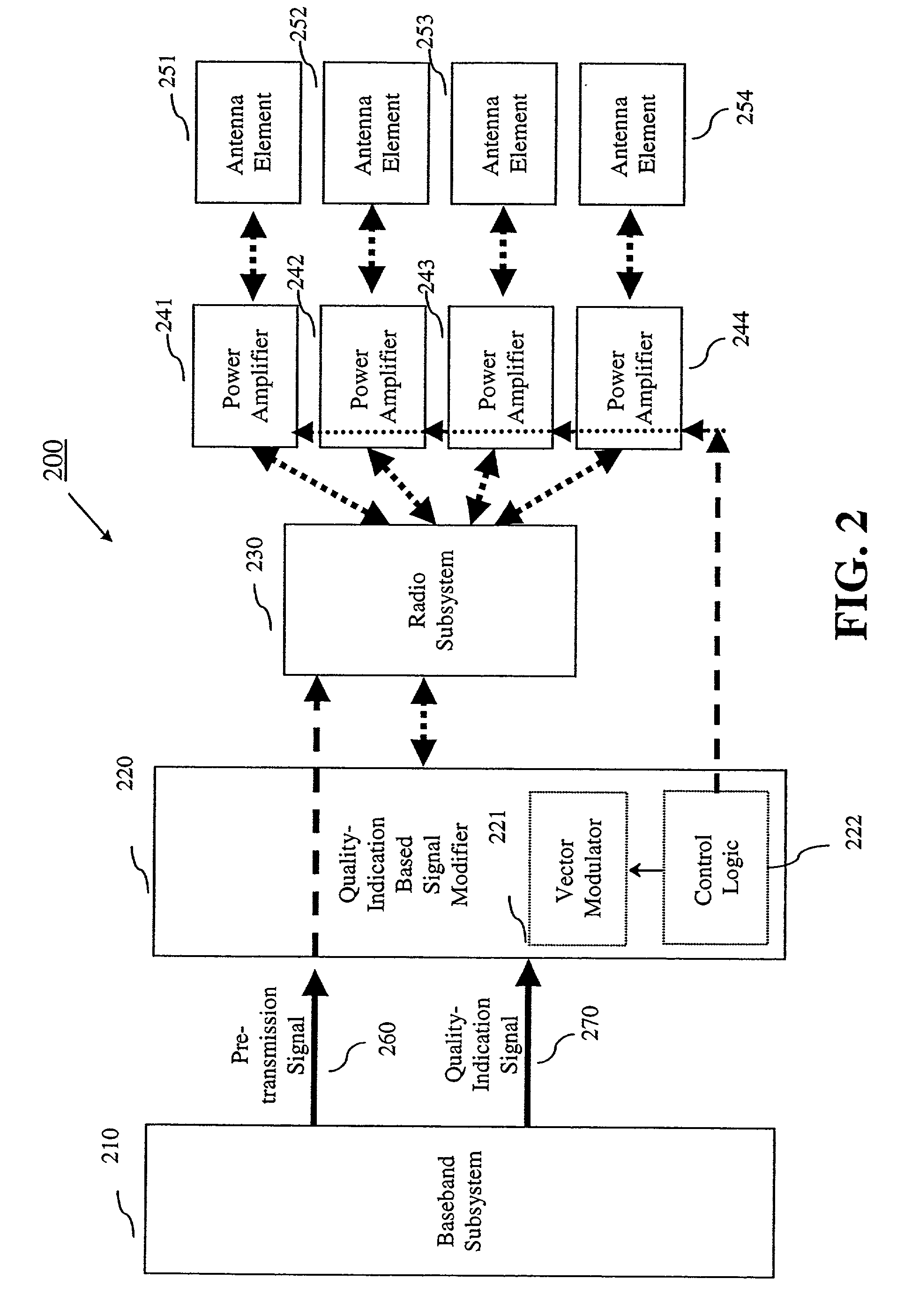
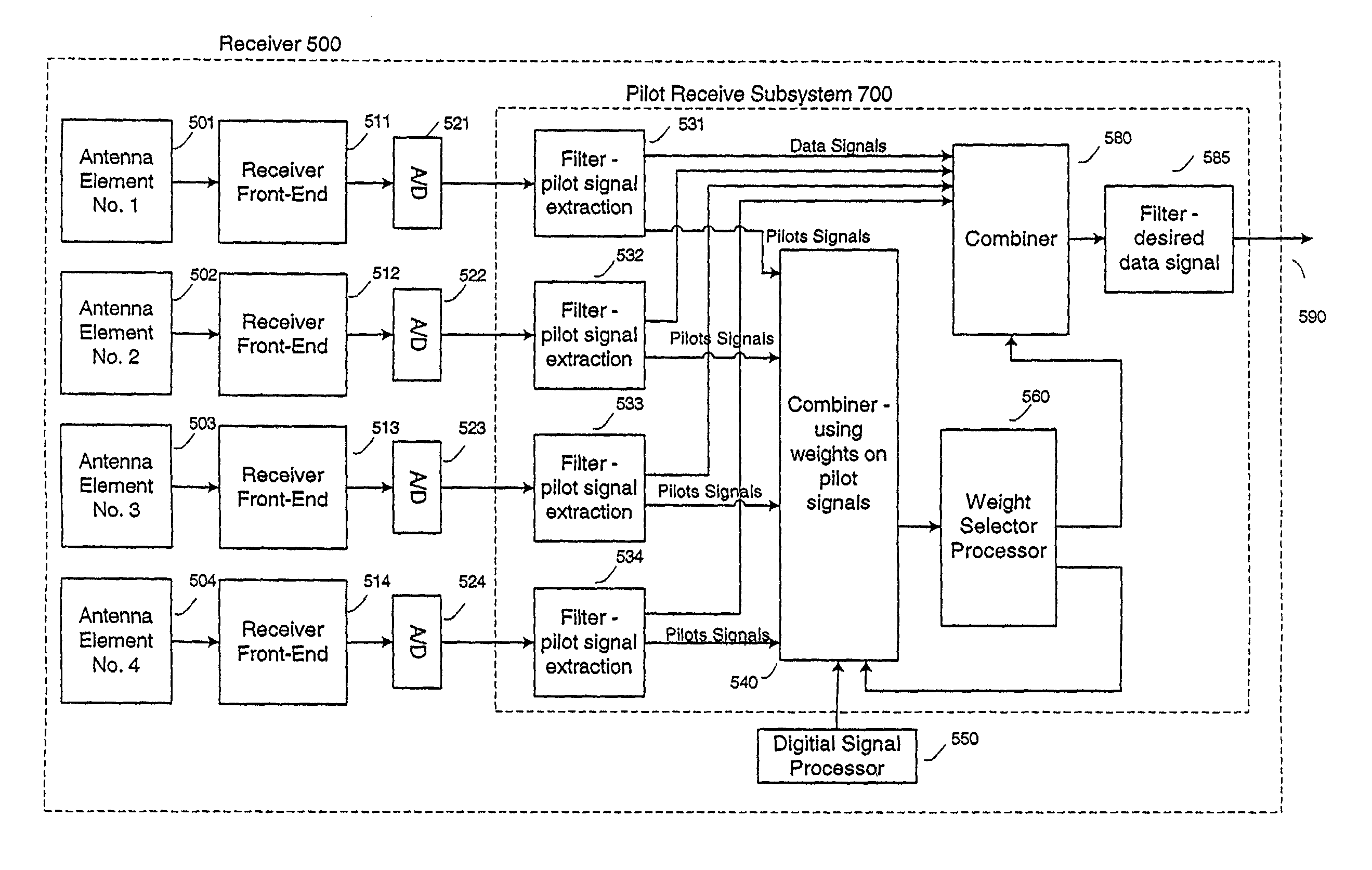
Communication device with smart antenna using a quality-indication signal
Communication is performed for a first communication device having a set of antenna elements. A quality-indication signal is received from a second communication device. A complex weighting is calculated based on the quality-indication signal. A pre-transmission signal is modified based on the complex weighting to produce a set of modified-pre-transmission signals. Each modified pre-transmission signal from the set of modified-pre-transmission signals is uniquely associated with an antenna element from the set of antenna elements. The set of modified-pre-transmission signals is sent from the set of antenna elements to produce a transmitted signal.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Smart antenna beamforming device in communication system and method thereof
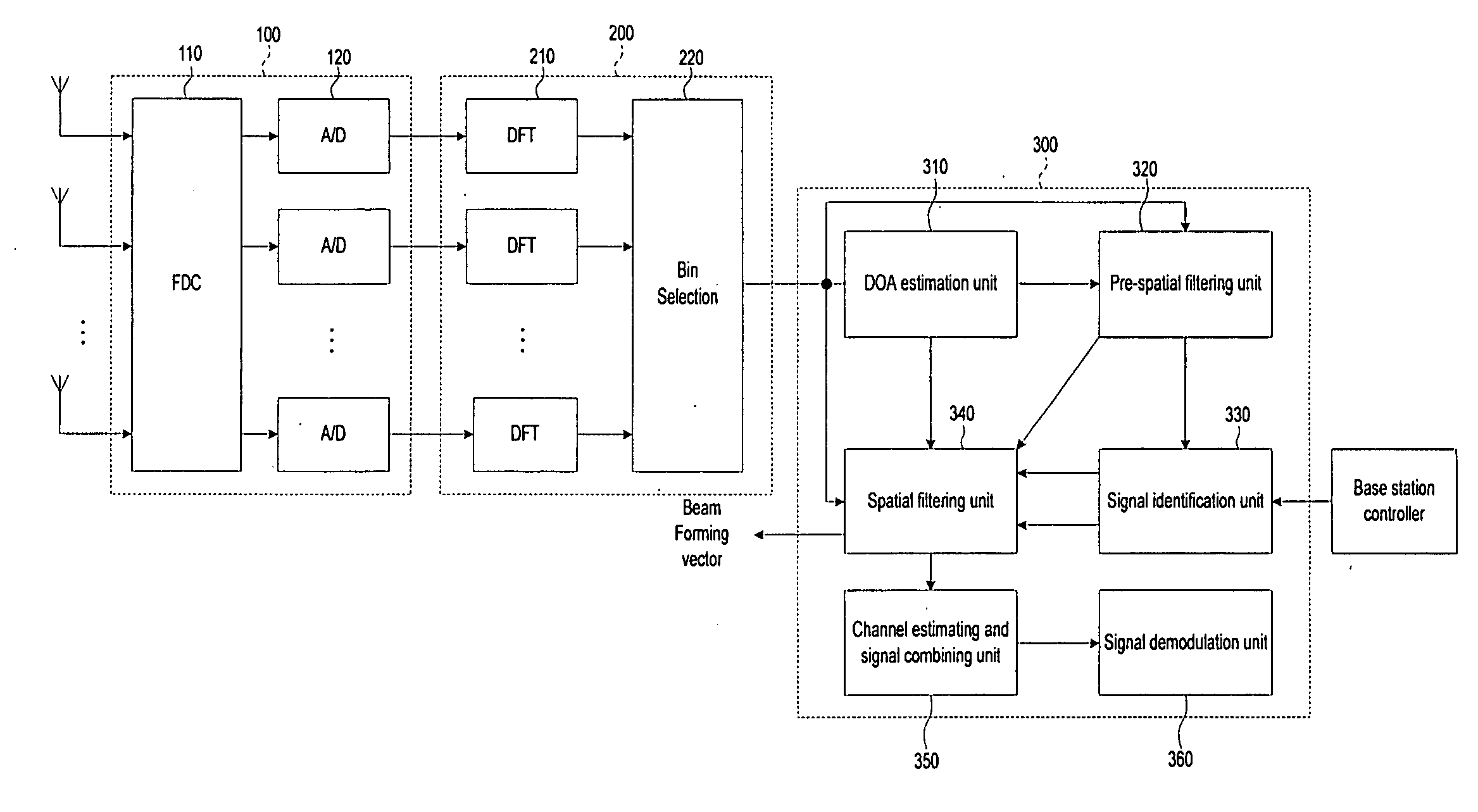
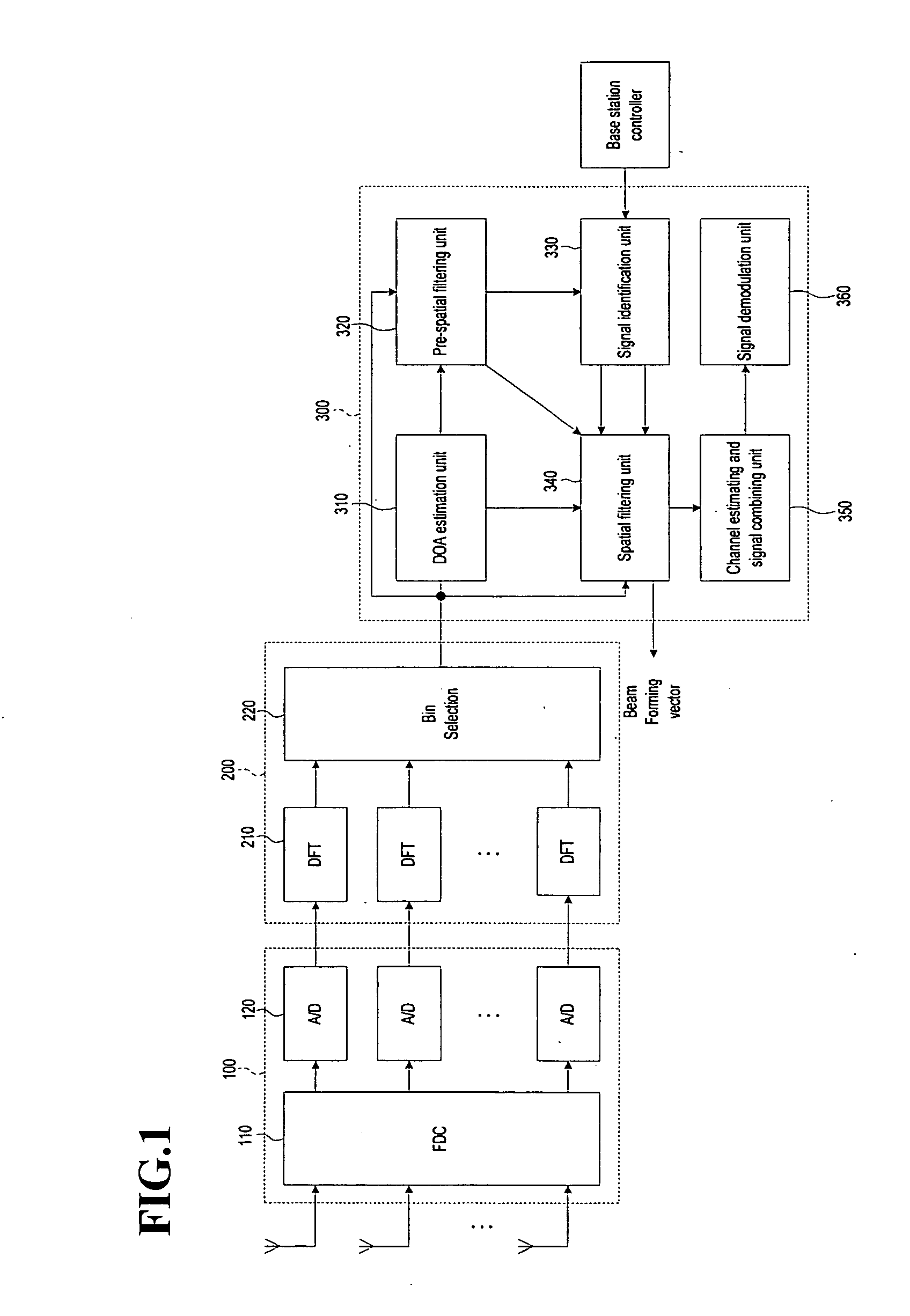
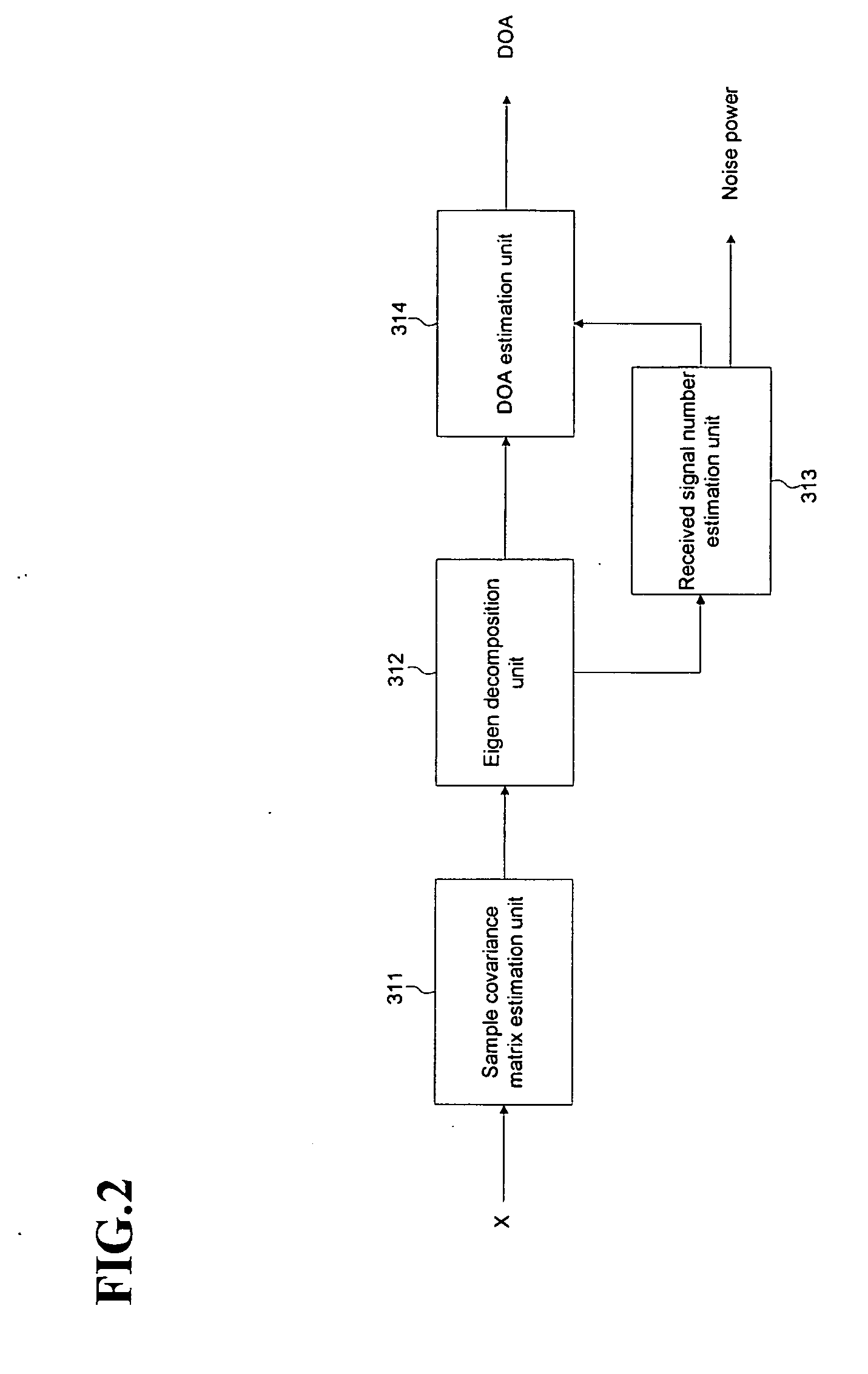
ActiveUS20070164902A1Maximizing signal to interferenceRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemSmart antenna
A beamforming device includes a Direction Of Arrival (DOA) estimation unit for estimating DOAs of the received signals based on a data subcarrier matrix; a pre-spatial filtering unit for using the estimated DOA, performing a filtering operation for the data subcarrier matrix, and generating filtering matrixes; a signal identification unit for using a data sequence, identifying original and interference signals, and generating the DOAs of the original and interference signals; a spatial filtering unit for generating an interference-plus-noise covariance matrix by using the DOA of the interference signal, eliminating the interference signal by using the covariance matrix and the DOA of the original signal, and forming final beams for the original signal; and a channel estimating and signal combining unit for performing a maximal ratio combining operation so that the final beams are combined as one combined final beam.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +4
Apparatus and method for controlling diverse short-range antennas of a near field communications circuit
An intelligent antenna system for extending the effective communication range of a machine-readable passive tag. The system may include intelligence that allows one of a plurality of extension antennas in an antenna network to be active at any given time. The machine-readable tag and antenna network may further be embedded in a structure. For example, the system may include multiple passive tags that are active in correspondence to a display or advertisement currently being exhibited. The system may include means for operatively coupling the corresponding machine-readable tag to the embedded antenna network.
Owner:III HLDG 3
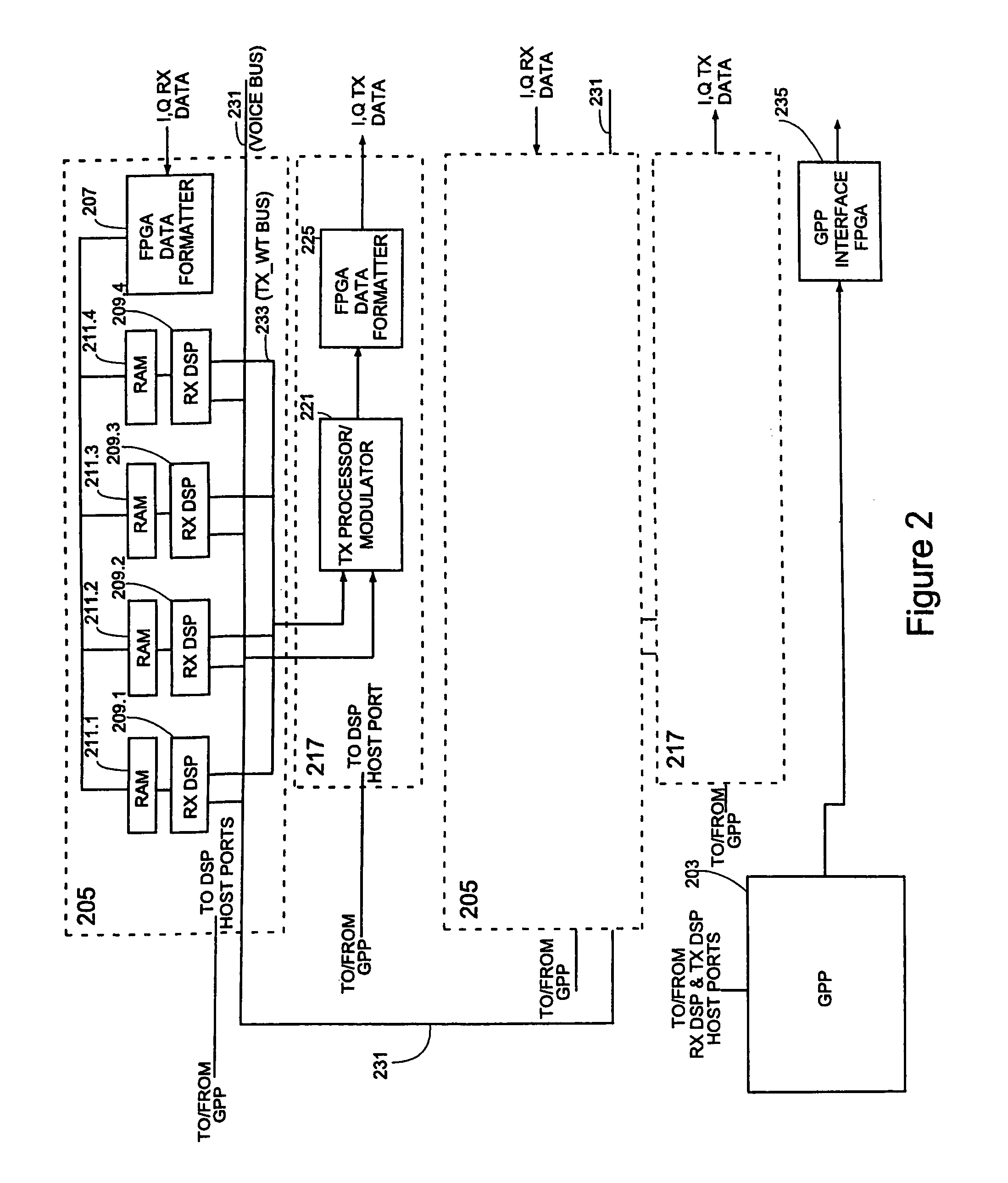
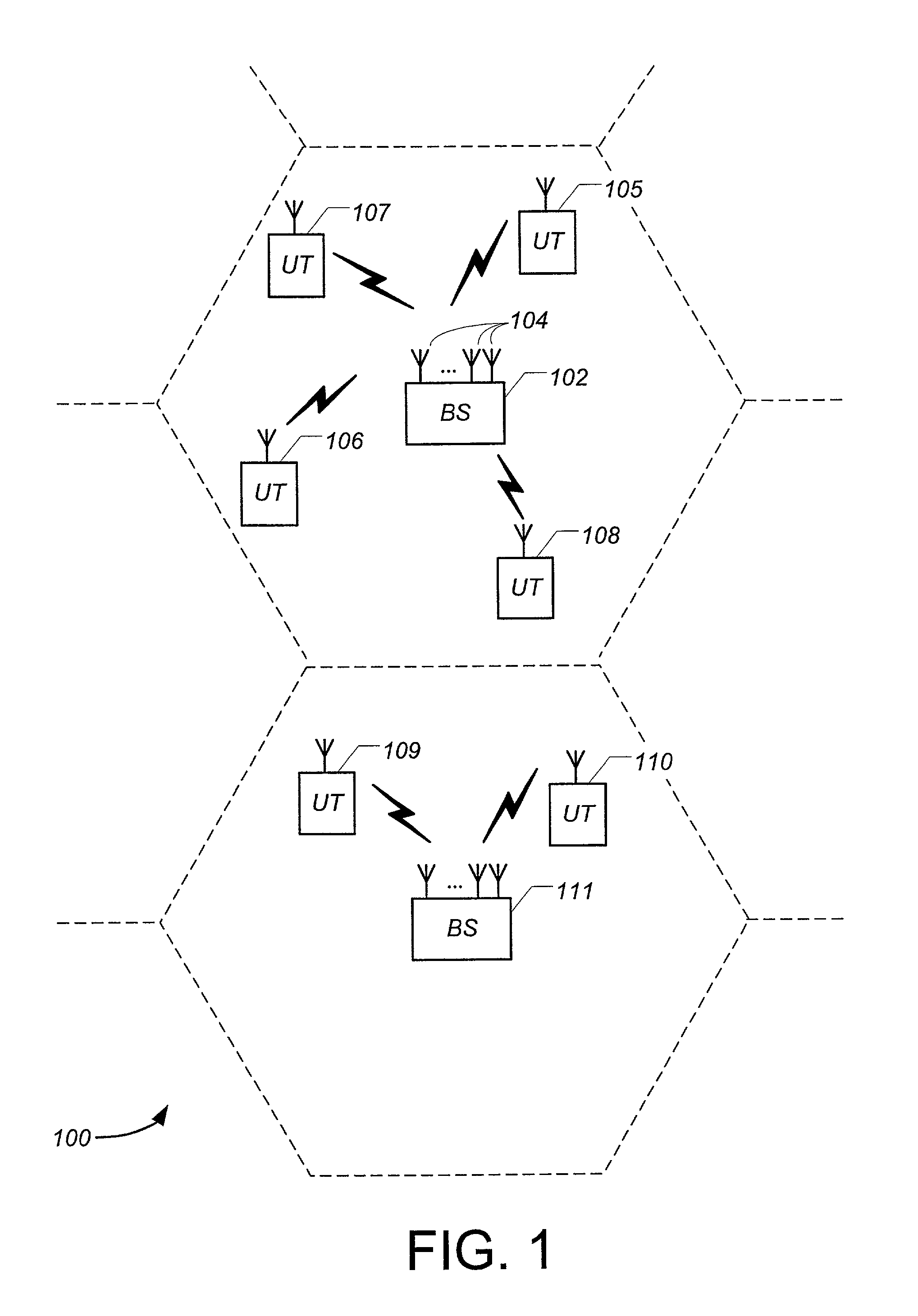
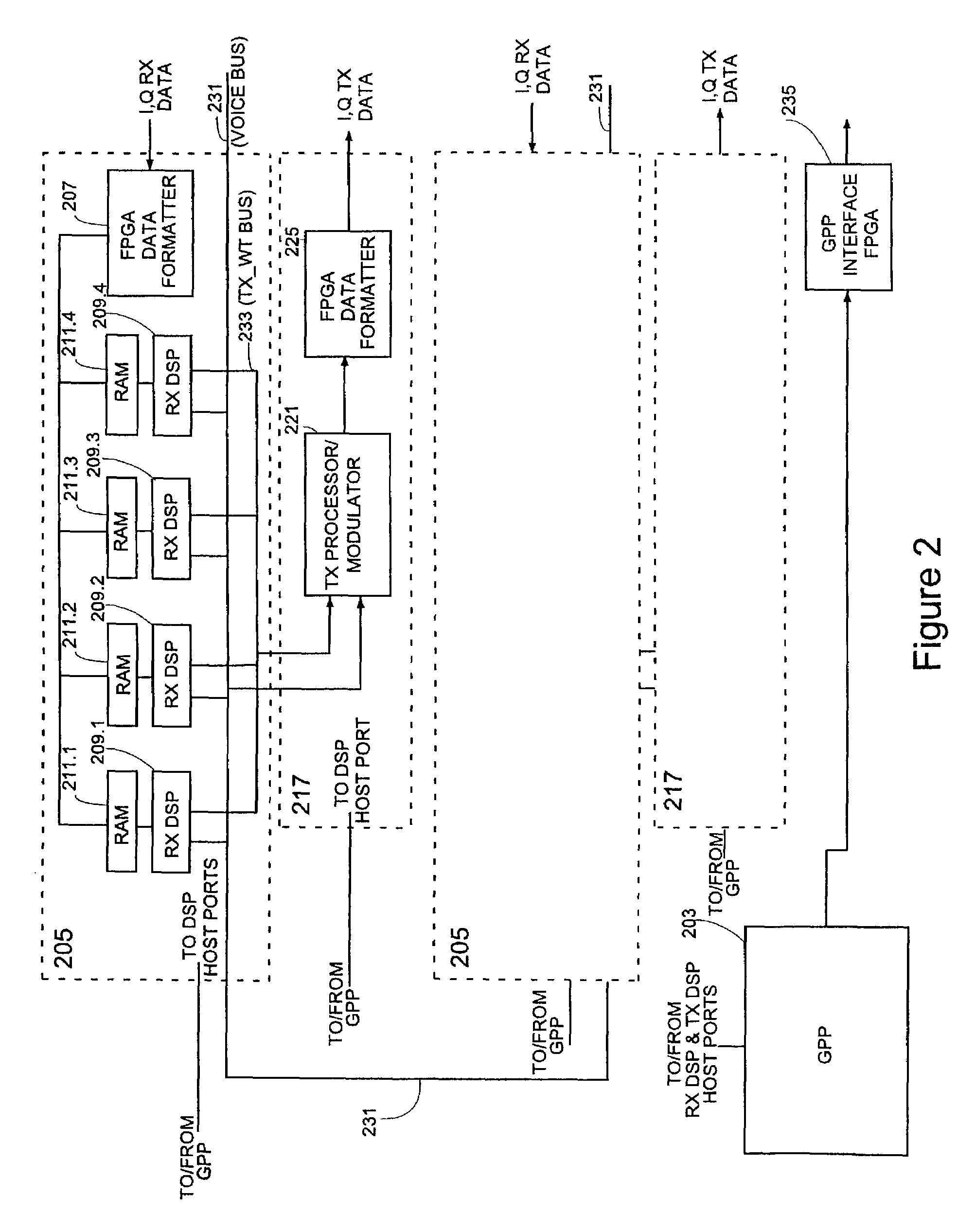
Framing for an adaptive modulation communication system
ActiveUS7197022B2Synchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexTime division multiple accessCommunications system
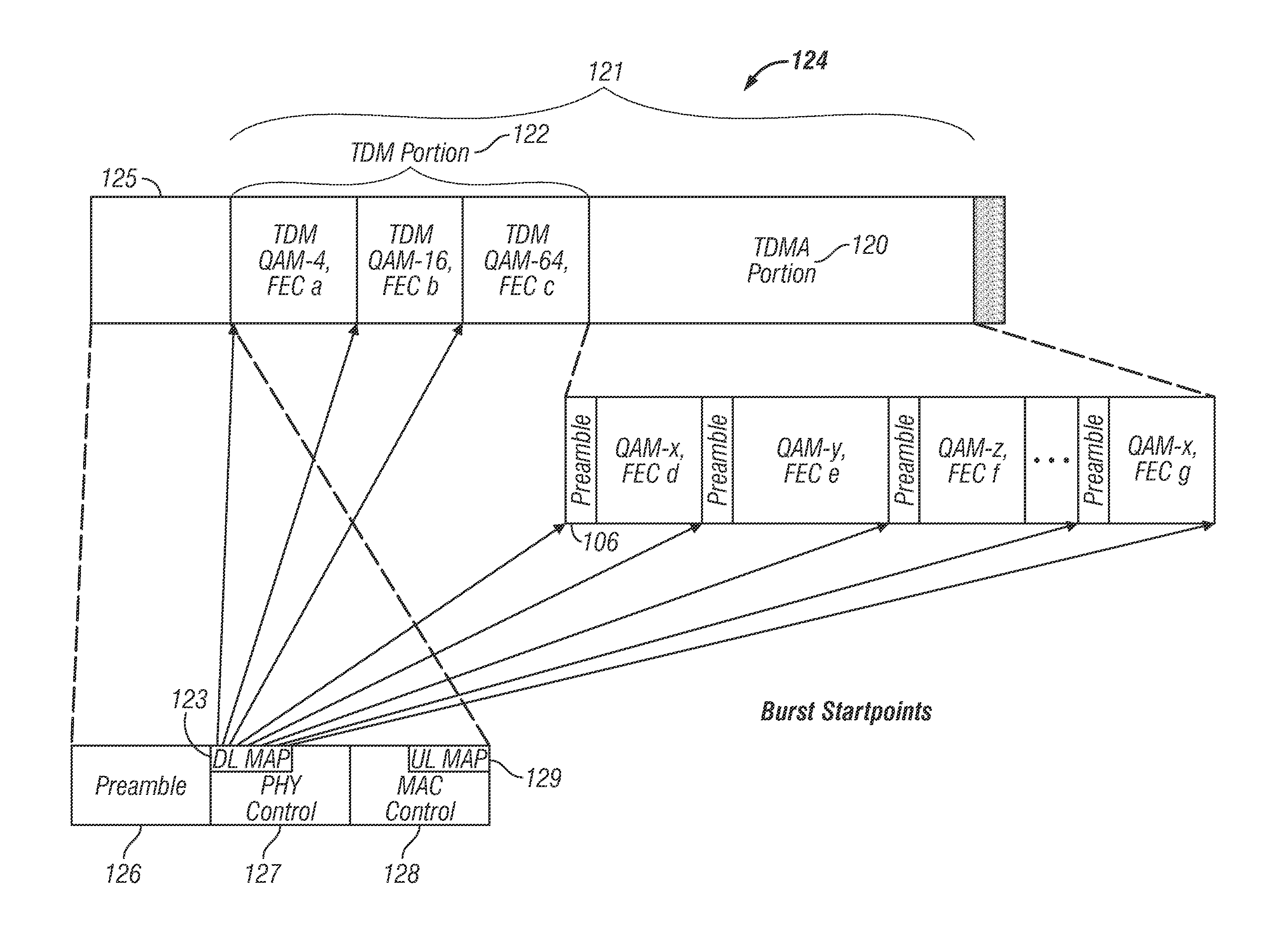
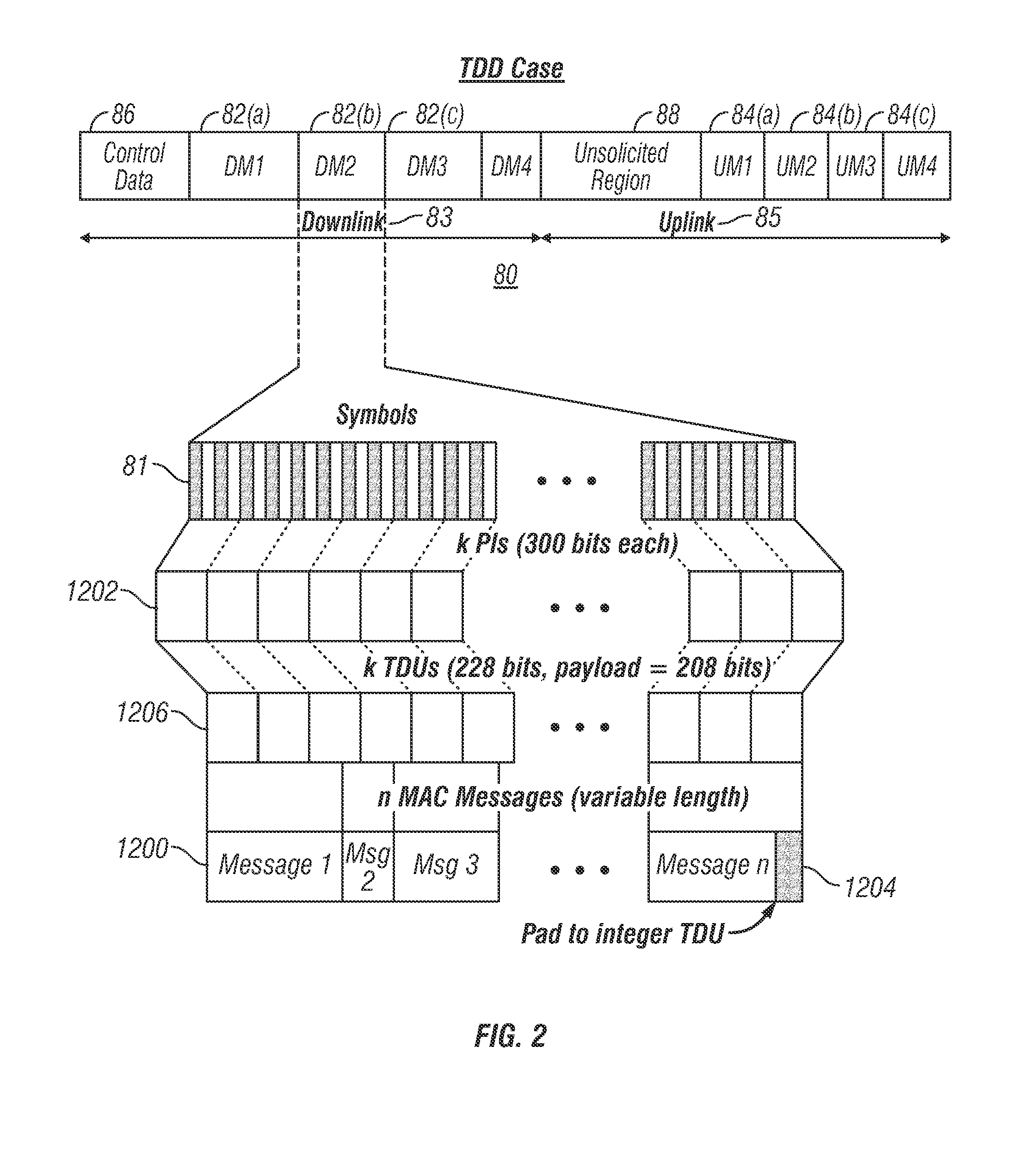
A system and method for mapping a combined frequency division duplexing (FDD) Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) / Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) downlink subframe for use with half-duplex and full-duplex terminals in a communication system. Embodiments of the downlink subframe vary Forward Error Correction (FEC) types for a given modulation scheme as well as support the implementation of a smart antennae at a base station in the communication system. Embodiments of the system are also used in a TDD communication system to support the implementation of smart antennae. A scheduling algorithm allows TDM and TDMA portions of a downlink to efficiently co-exist in the same downlink subframe and simultaneously support full and half-duplex terminals. The algorithm further allows the TDM of multiple terminals in a TDMA burst to minimize the number of map entries in a downlink map. The algorithm limits the number of downlink map entries to not exceed 2n+1, where n is the number of DL PHY modes (modulation / FEC combinations) employed by the communication system.
Owner:WI LAN INC +1
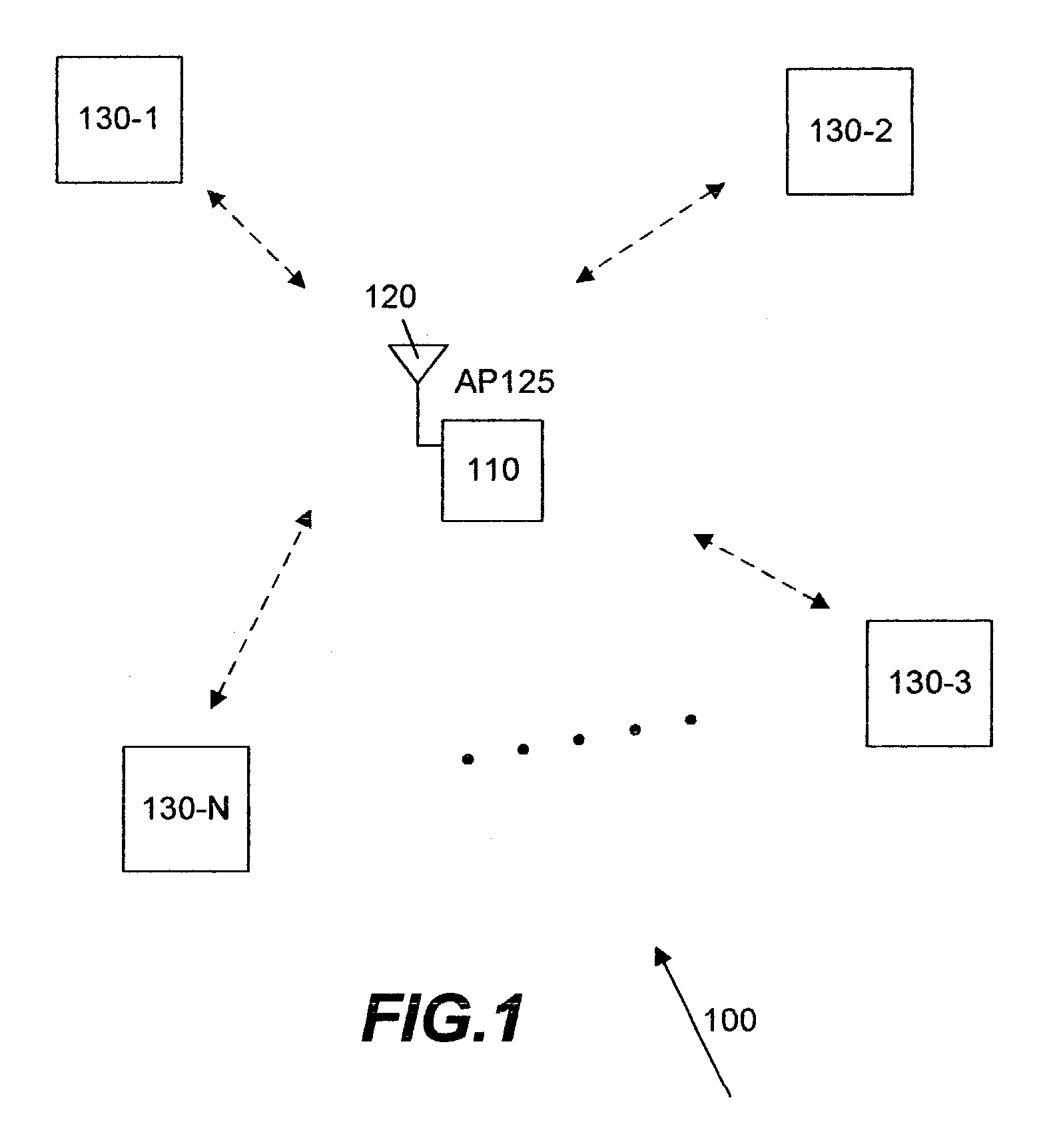
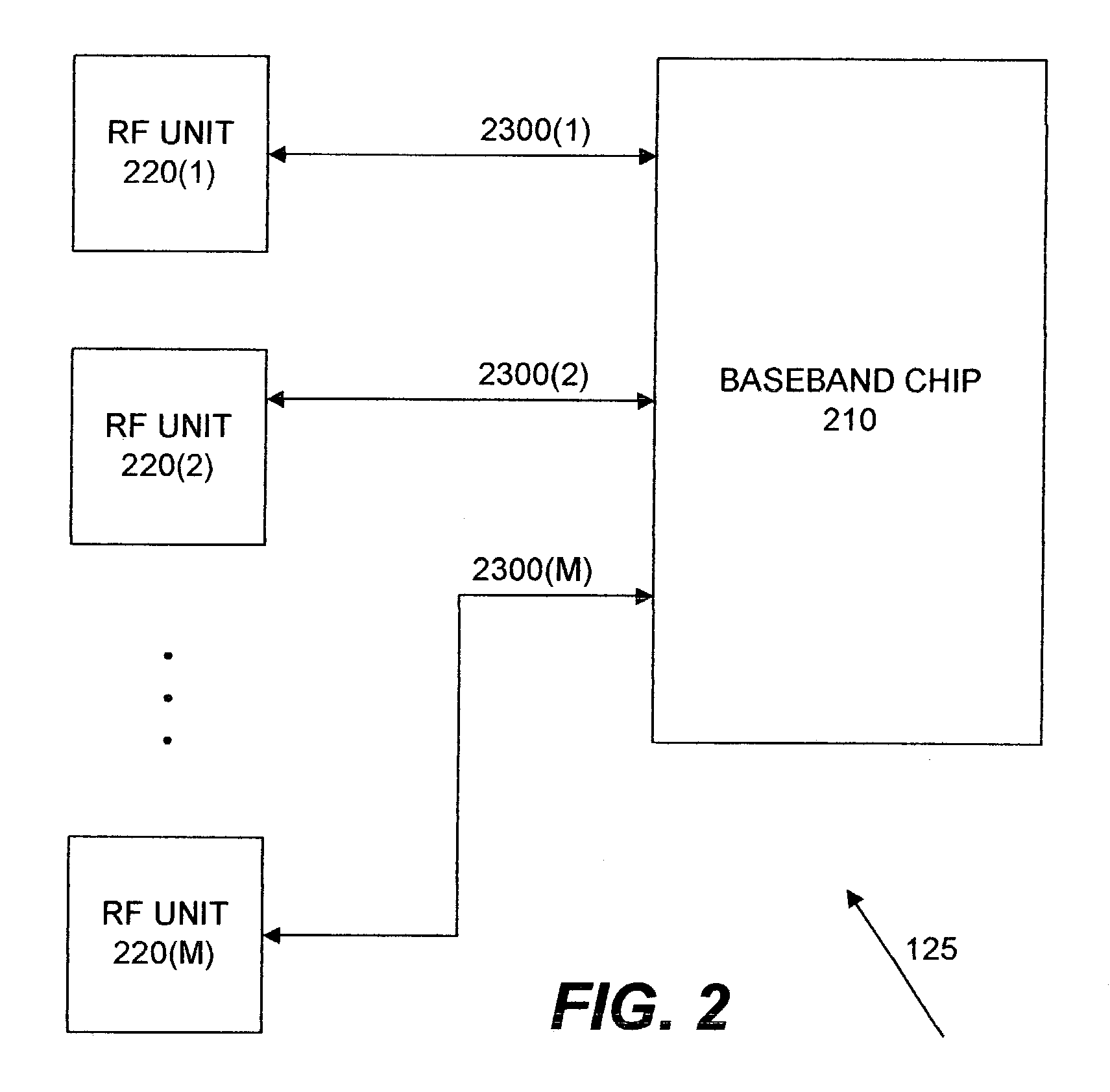
Selecting a set of antennas for use in a wireless communication system
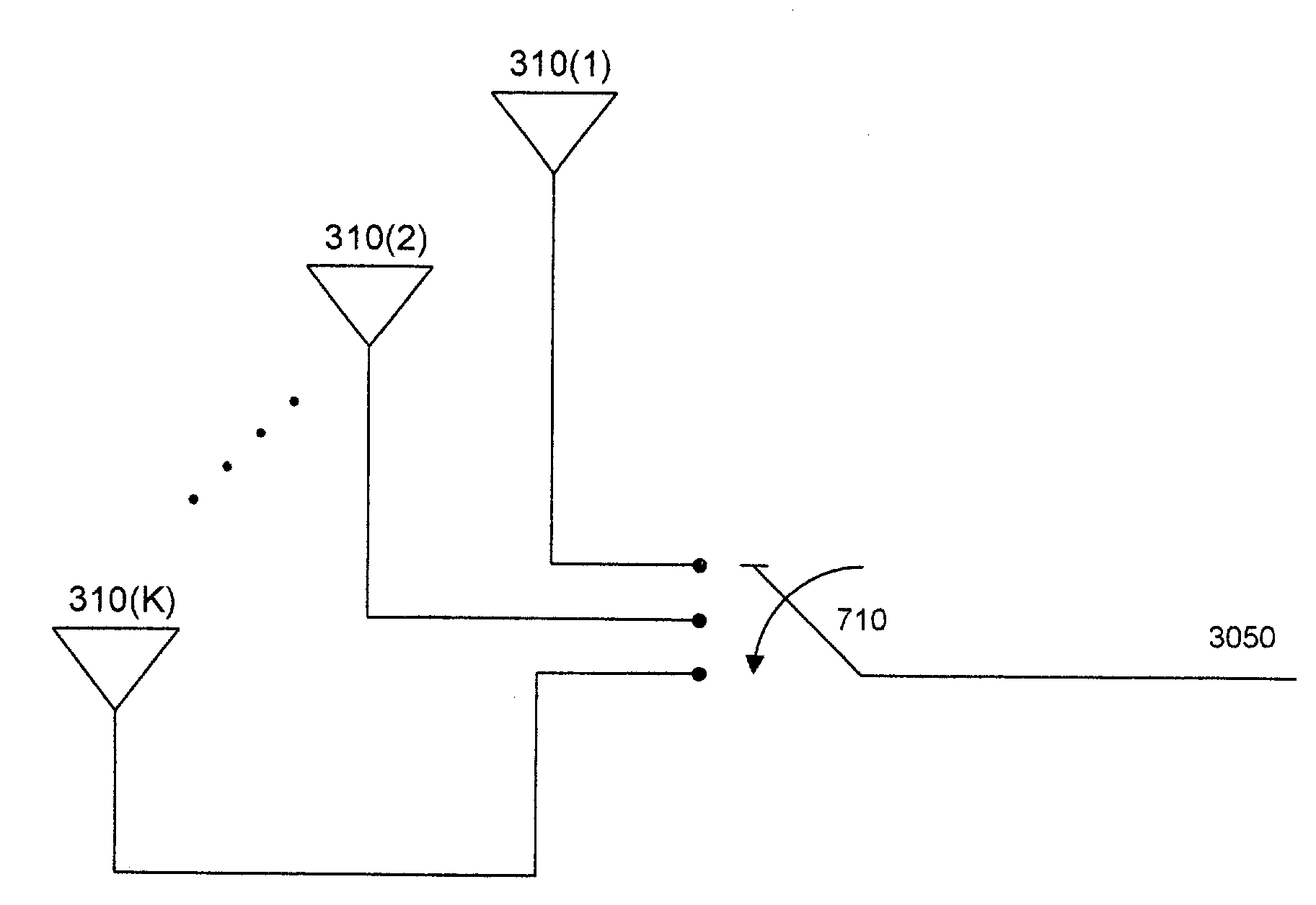
ActiveUS7039356B2Spatial transmit diversityData switching by path configurationCommunications systemSmart antenna
Mechanisms for selecting a set of antennas for use in a wireless communication system are disclosed. The selected set of antennas is for use in communicating data in a wireless local area network (WLAN) comprising an access point and a plurality of mobile stations. The access point includes a baseband chip capable of adapting various radio frequency (RF) units. Each RF unit in turns includes a plurality of RF sub units, each of which connects to a plurality of antennas. The access point thus includes a number of antennas that, together with the RF units and the baseband chip, form a smart antenna. To identify the selected set of antennas to communicate with a particular mobile station, the access point initially uses a first set of antennas each in a RF sub unit. From this first set of antennas, the access point identifies a first set of winner antennas and a first set of non-winner antennas. From the first set of winner antennas, the access point identifies a first set of winner RF sub units each connecting to a winner antenna in the first set of winner antennas. From each winner RF sub unit, the access point identifies a final winner. The access point then uses the final winner antenna in the selected set of antennas. The access point also uses the first set of non-winner antennas in the selected set of antennas.
Owner:V SILICON SEMICON (HANGZHOU) CO LTD
WLAN device having smart antenna system
InactiveUS20050058111A1Increase the number ofHigh gainNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationOmnidirectional antennaTransceiver
A WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) device having a smart antenna system is disclosed for increasing the number of user under a limited bandwidth and a confined environment. The WLAN device having the smart antenna system comprises: a plurality of WLAN transceiver module; and a plurality of directional antennas or array antennas installed on the WLAN transceiver modules by the way of one-to-one, wherein each of the array antennas is composed of a plurality of omni-directional antenna, such as dipole antennas.
Owner:ACCTON TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Null deepening for an adaptive antenna based communication station
InactiveUS20070015545A1Reduce transmit powerReduce sensitivitySpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentSmart antennaAntenna element
A method and apparatus is described for modifying a smart antenna processing strategy determined from a set of signals received at an array of antenna elements of a wireless station, such as a set of weights for processing received antenna signals or forming a set of antenna signals for transmission. The method and apparatus uses the signatures of one or more interferers to produce a modified processing strategy that improves the nulling to the one or more interferers in that, when the modified strategy is applied on the downlink, the transmit signal strength in the direction of the one or more interferers is decreased, and, when the modified strategy is applied on the uplink, the sensitivity to signals from the direction of the one or more interferers is decreased.
Owner:INTEL CORP
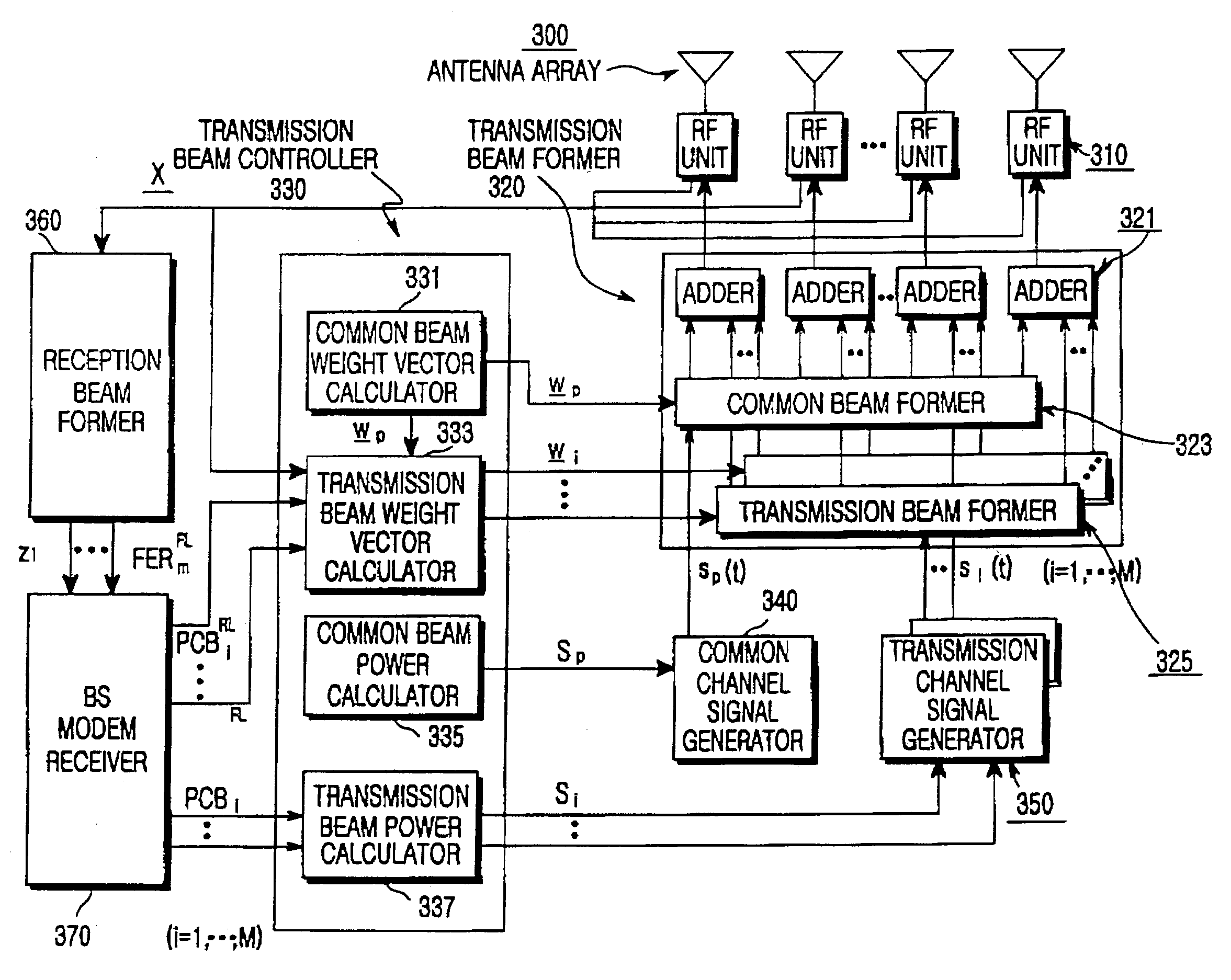
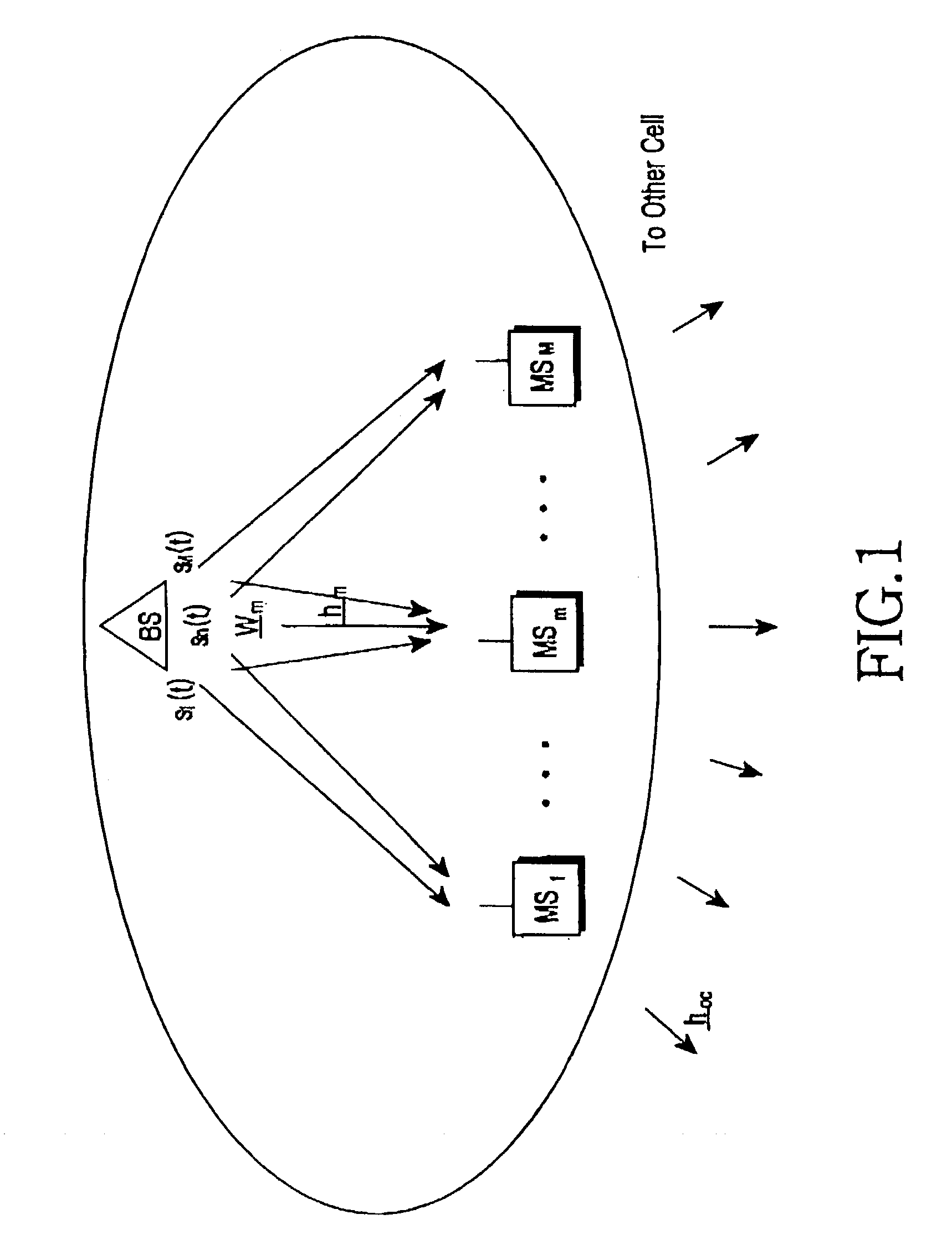
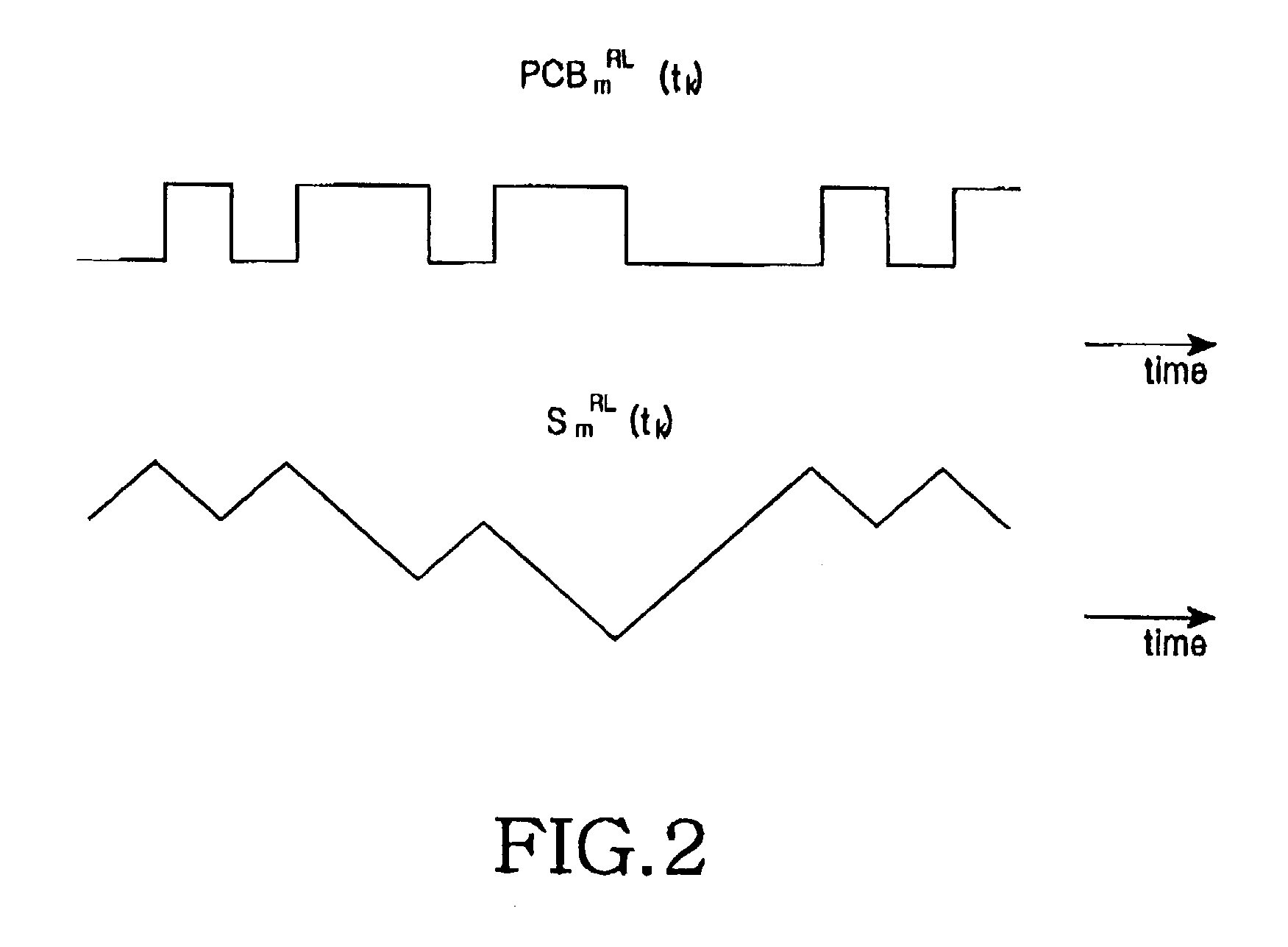
Apparatus and method for forming a forward link transmission beam of a smart antenna in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS7103384B2Power maximizationMinimize sumRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsSpatial transmit diversitySmart antennaTransmission channel
A method and apparatus for a base station including an antenna array calculates a direction of a weight vector of a transmission beam to maximize in-phase component power for a common channel signal in a transmission channel signal for transmission to a mobile station and to minimize a sum of quadrature-phase power component and interference power for other mobile stations inside and outside a cell due to a transmission channel signal for the mobile station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Smart antenna based spectrum multiplexing using existing pilot signals for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) modulations
InactiveUS7145959B2LevelSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityFrequency spectrumTime segment
A system and method for using a group of pilot signals to enhance a data signal within an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) multiple-access scheme is described. The OFDM multiple-access scheme has multiple OFDM transmitters using at least overlapping frequency spectrums, during at least overlapping time period, in at least overlapping geographic areas. A set of data signals and a set of pilot signals are received on antenna elements. Each group of data signals from the set of data signals is uniquely associated with a group of pilot signals from the set of pilot signals. Each pilot signal from the set of pilot signals is uniquely associated with its own code from a set of codes. Each code from the set of codes is uniquely associated with an OFDM transmitter from the multiple OFDM transmitters. A group of pilot signals from the set of pilot signals is identified based on its uniquely associated code. A weight value associated with each antenna element from a set of antenna elements is adjusted so that a level of correlation between the group of pilot signals and the code uniquely associated with the group of pilot signals is enhanced while a level of correlation between the remaining groups of pilot signals from the set of pilot signals and the codes uniquely associated with those remaining group of pilot signals are suppressed.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com