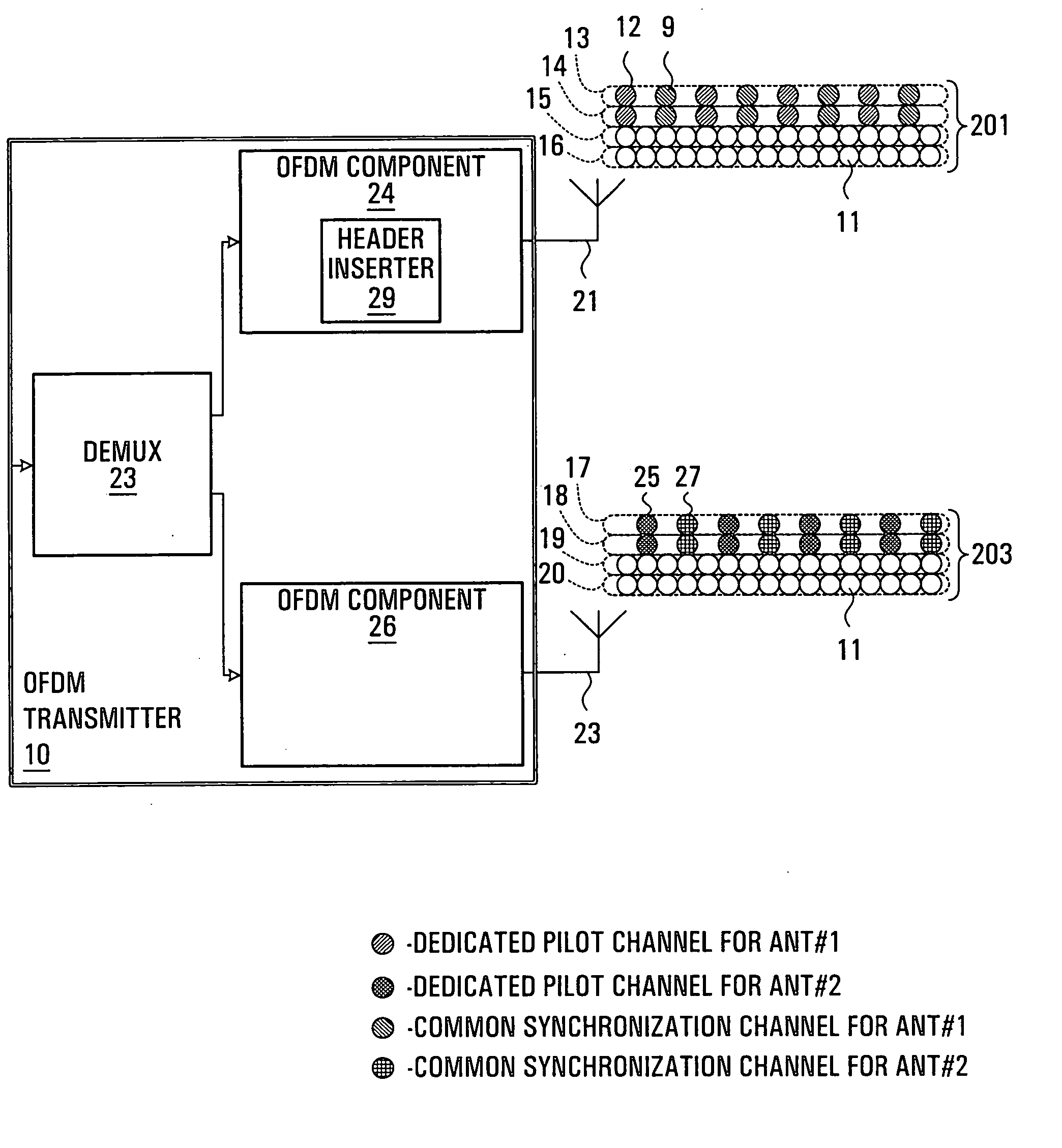
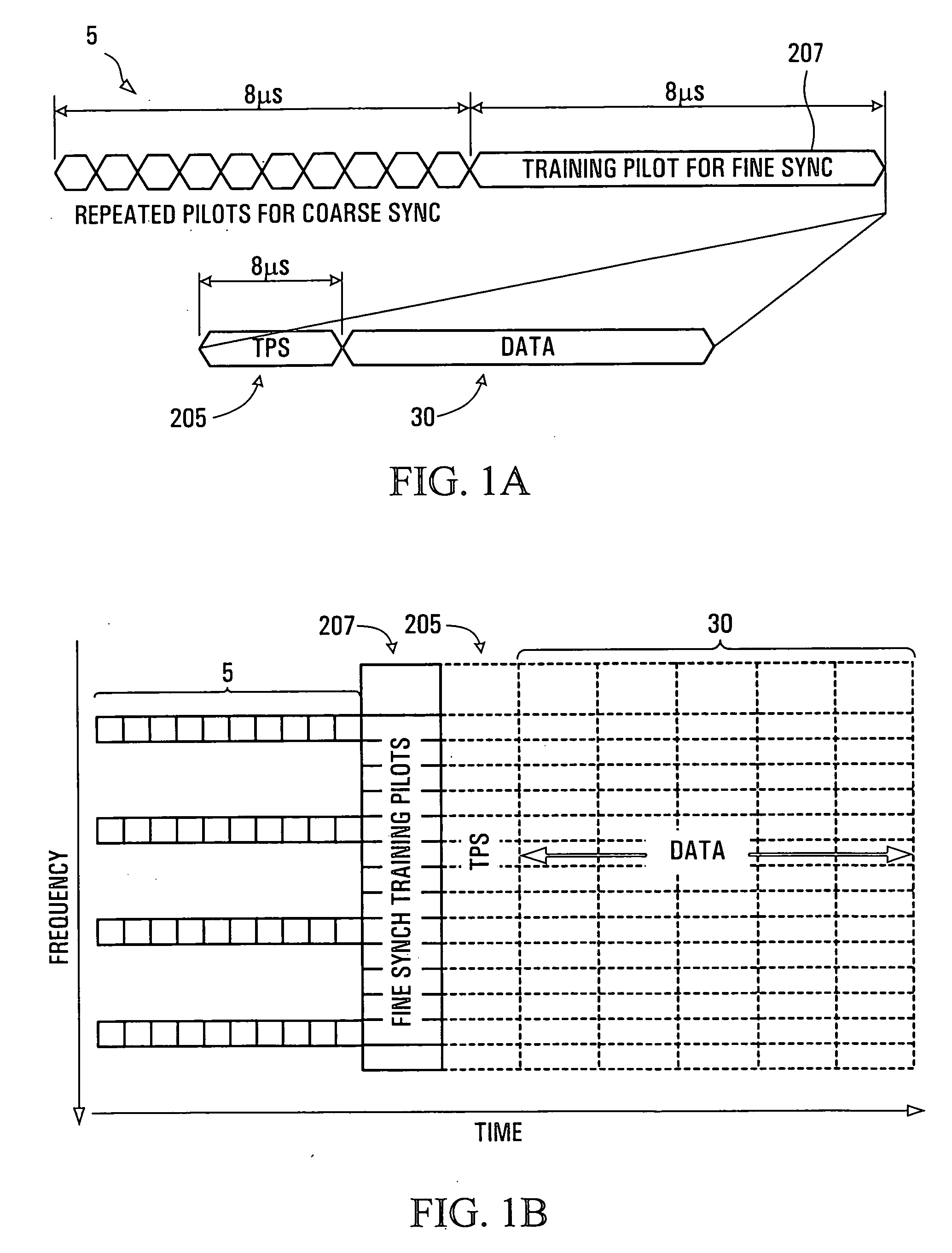
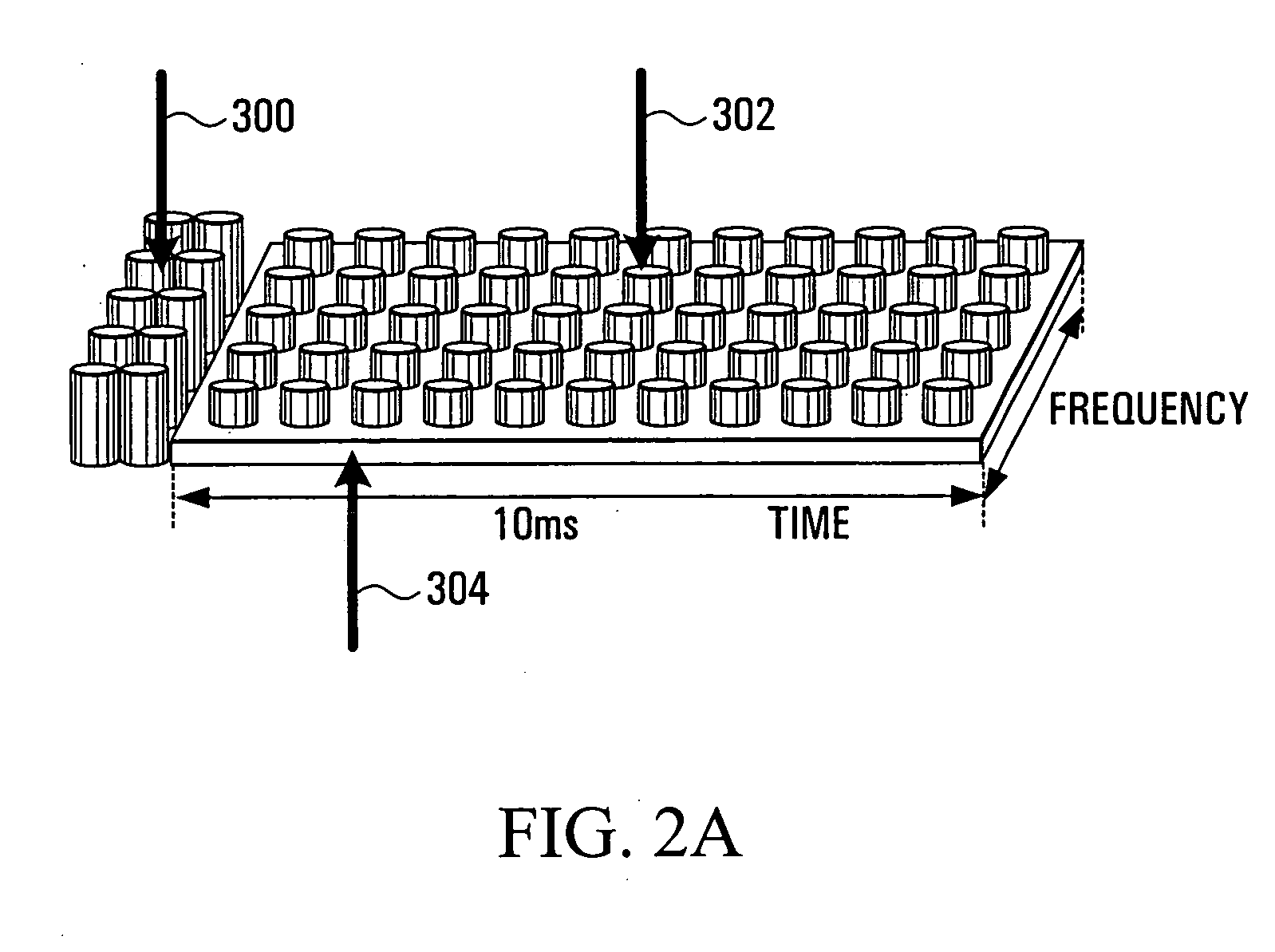
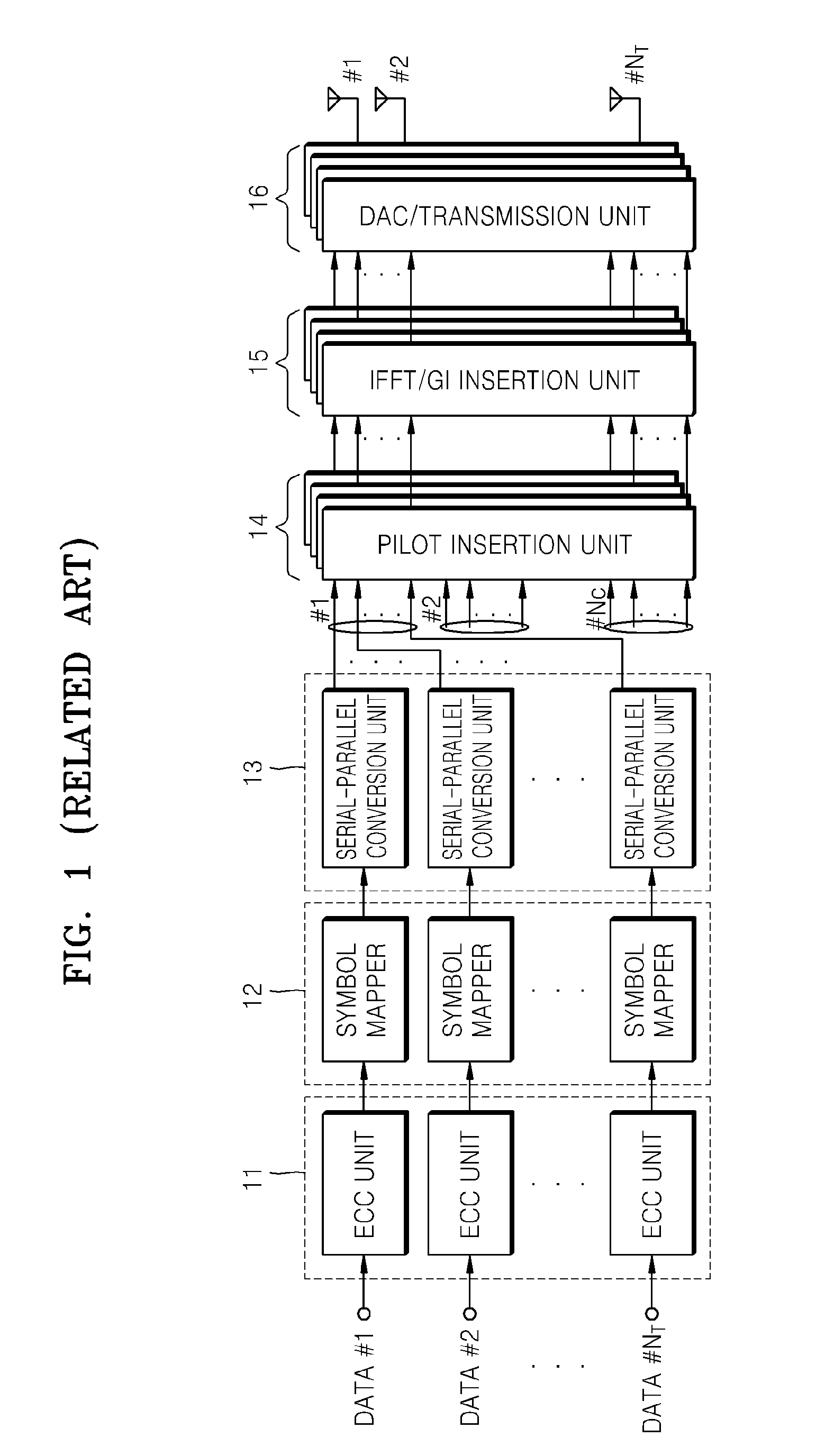
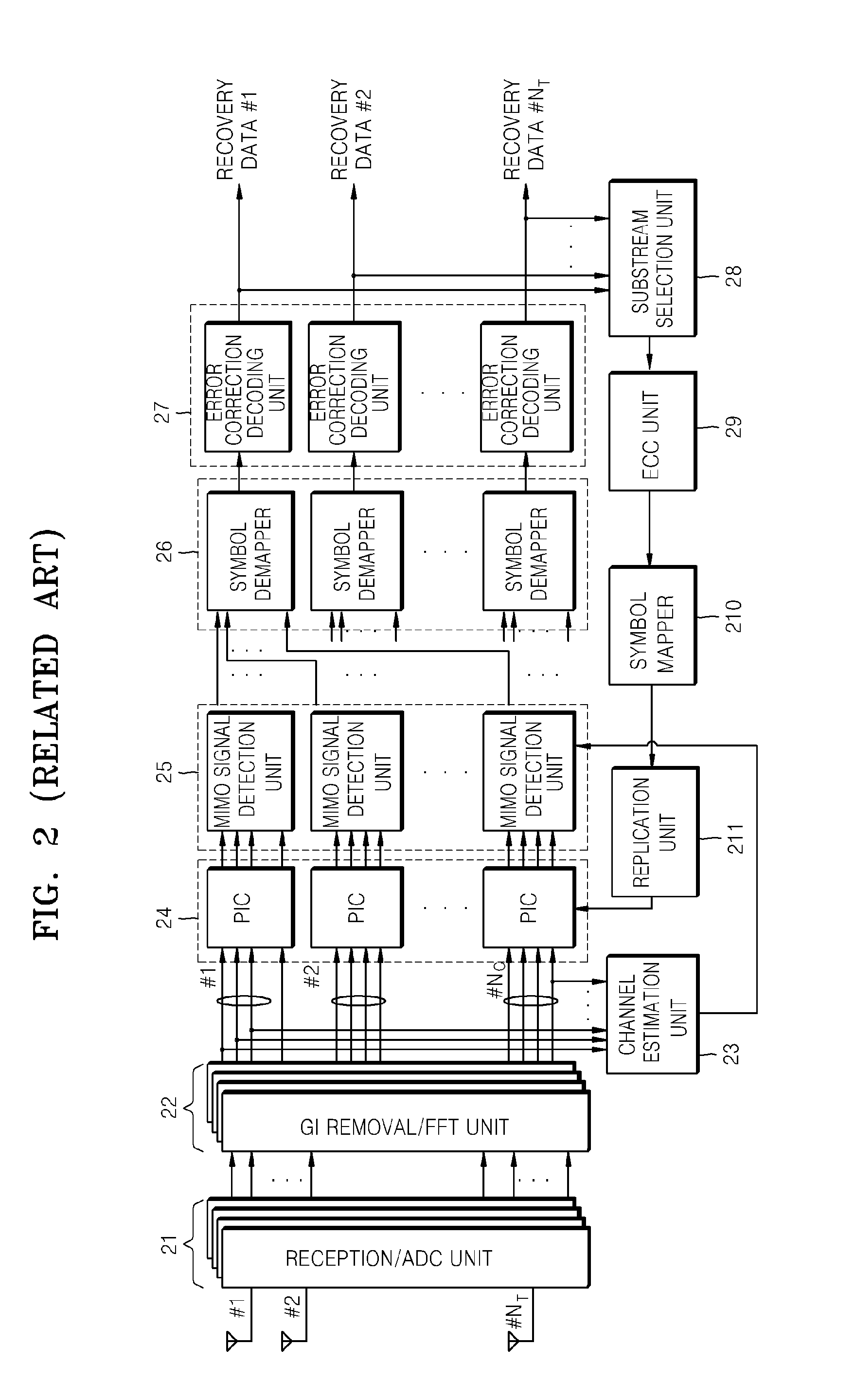
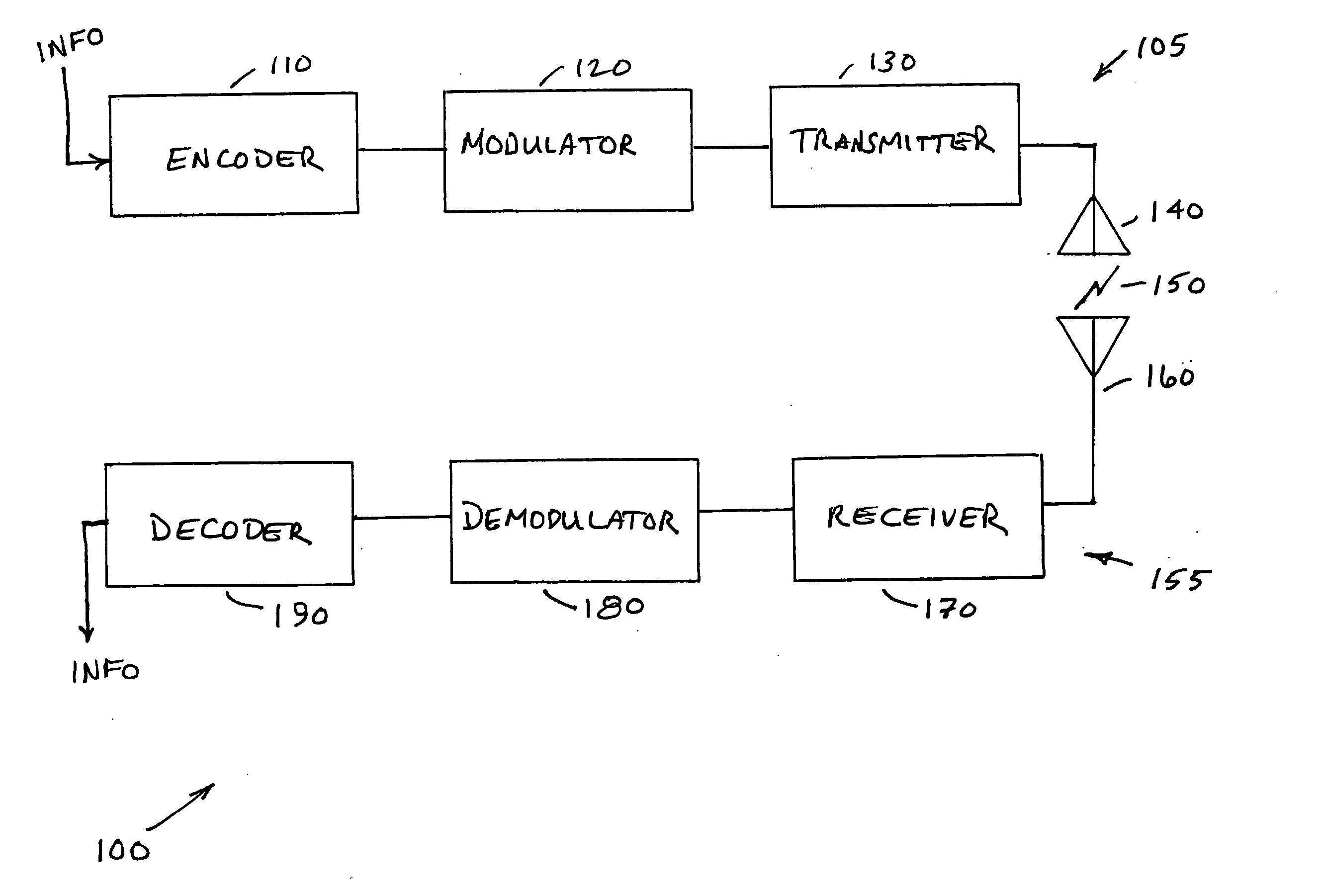
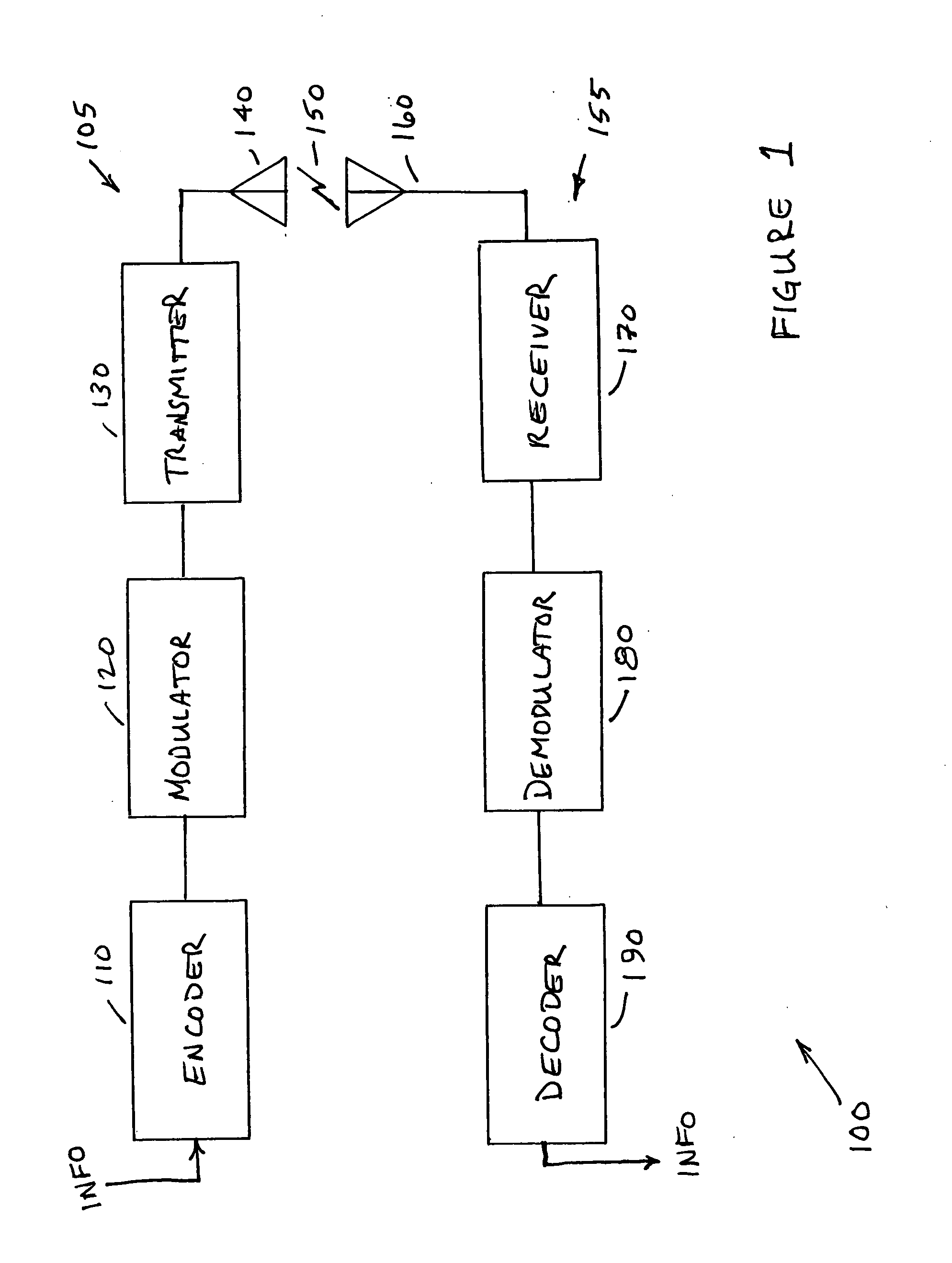
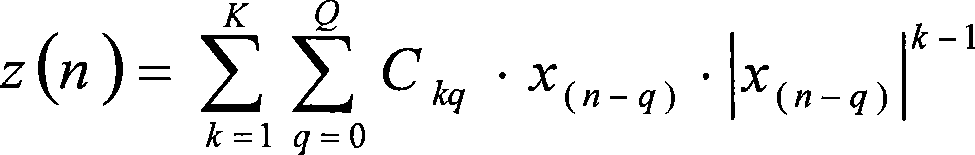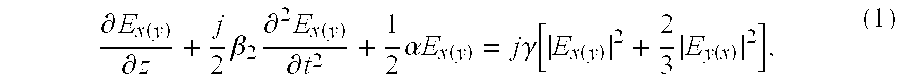Patents
Literature
176 results about "Ofdm transmitter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
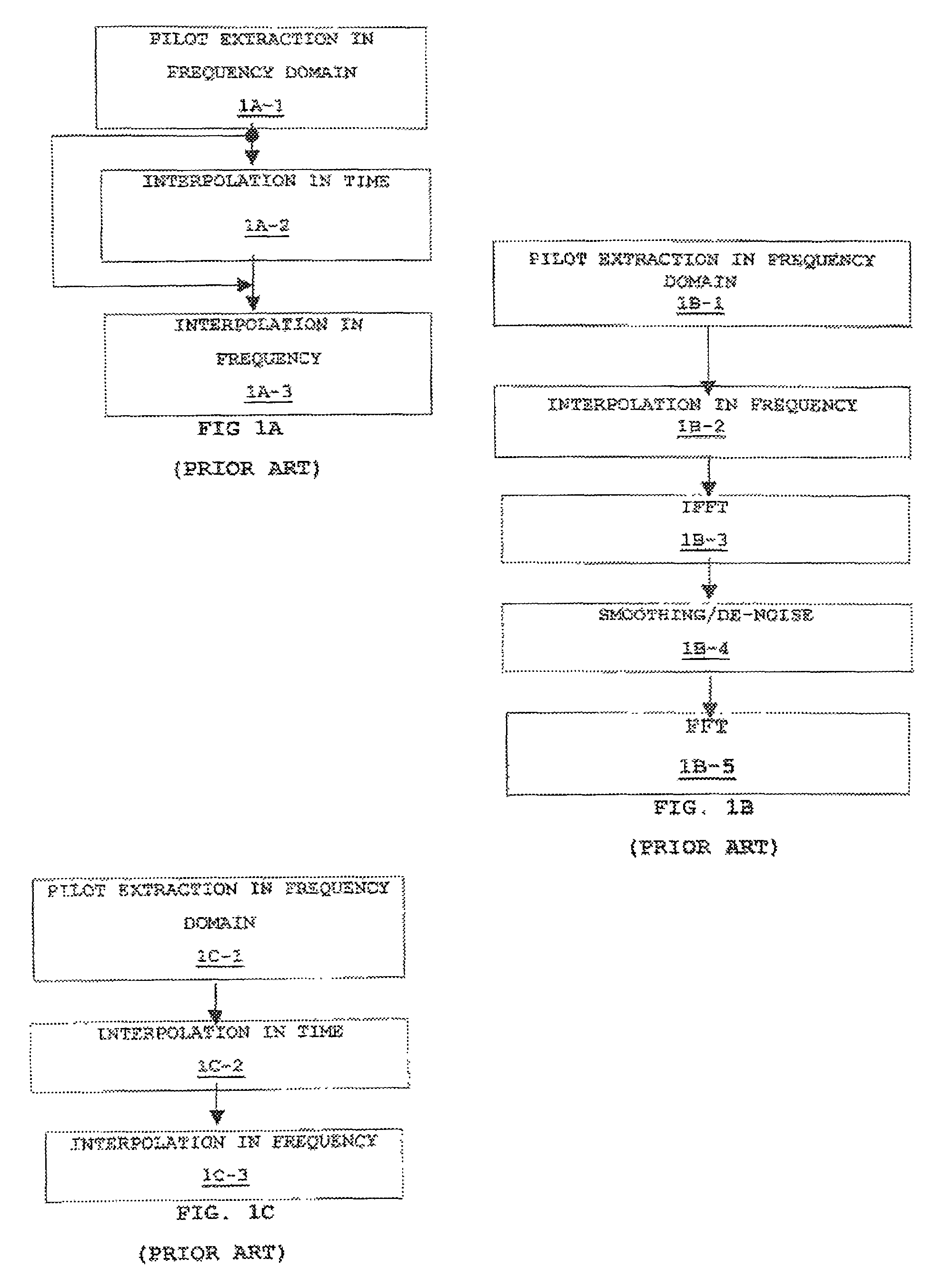
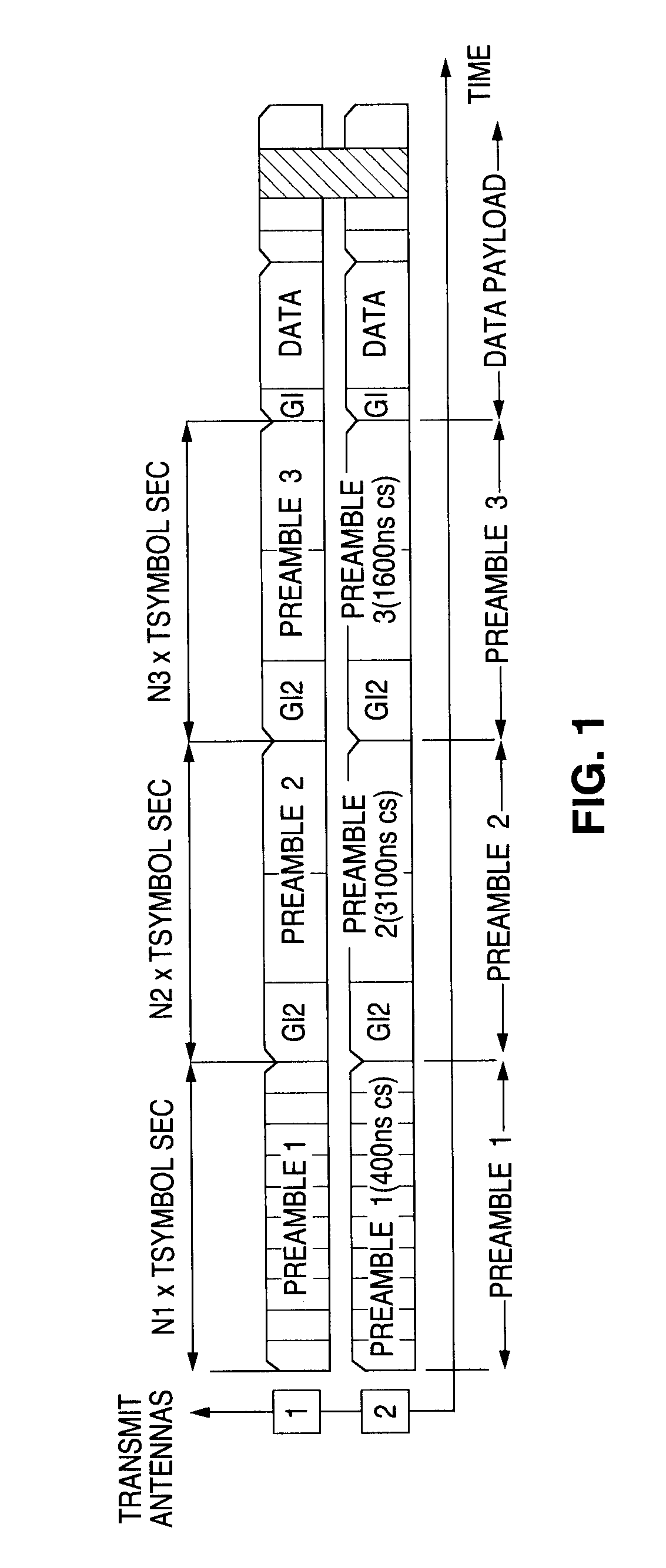
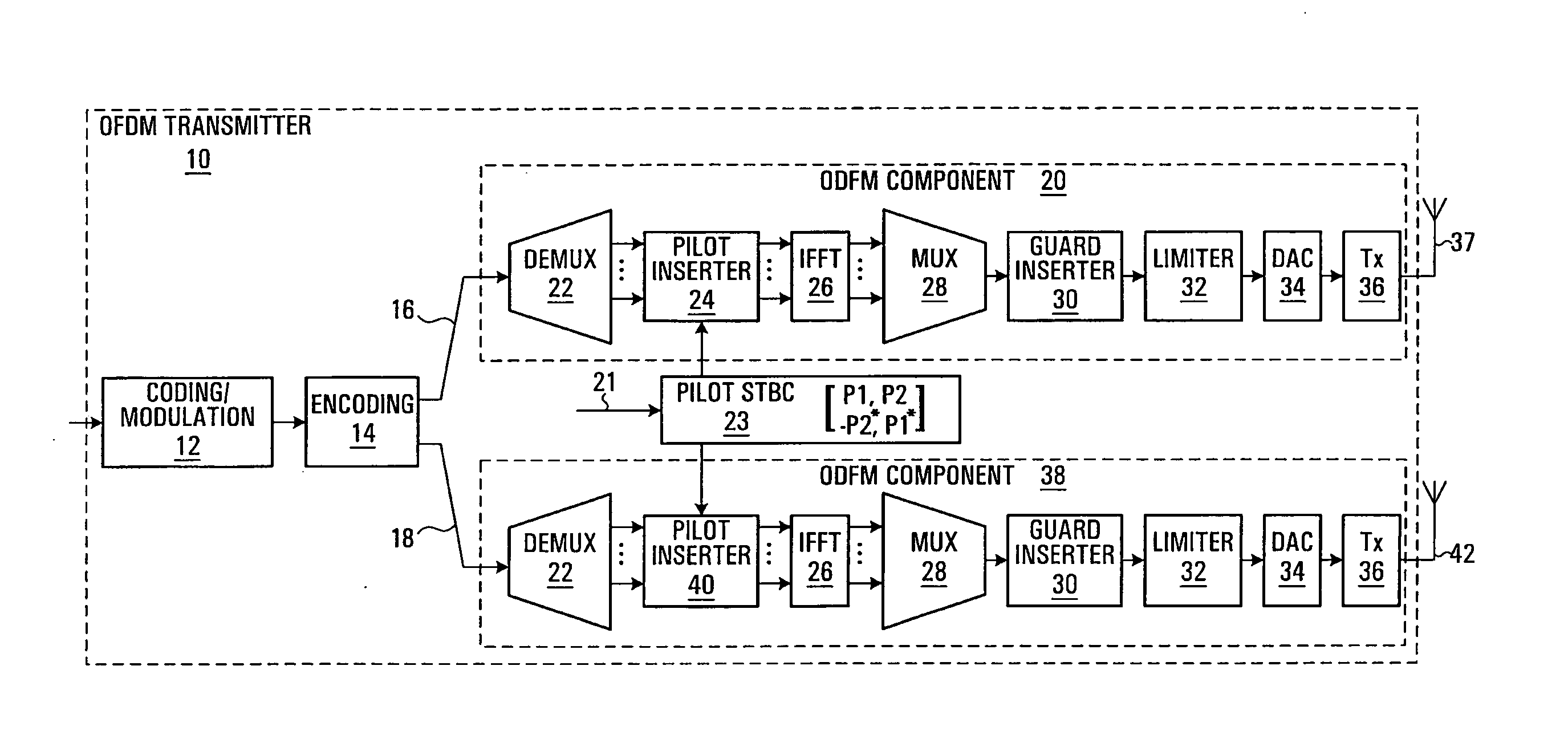
Scattered pilot pattern and channel estimation method for MIMO-OFDM systems
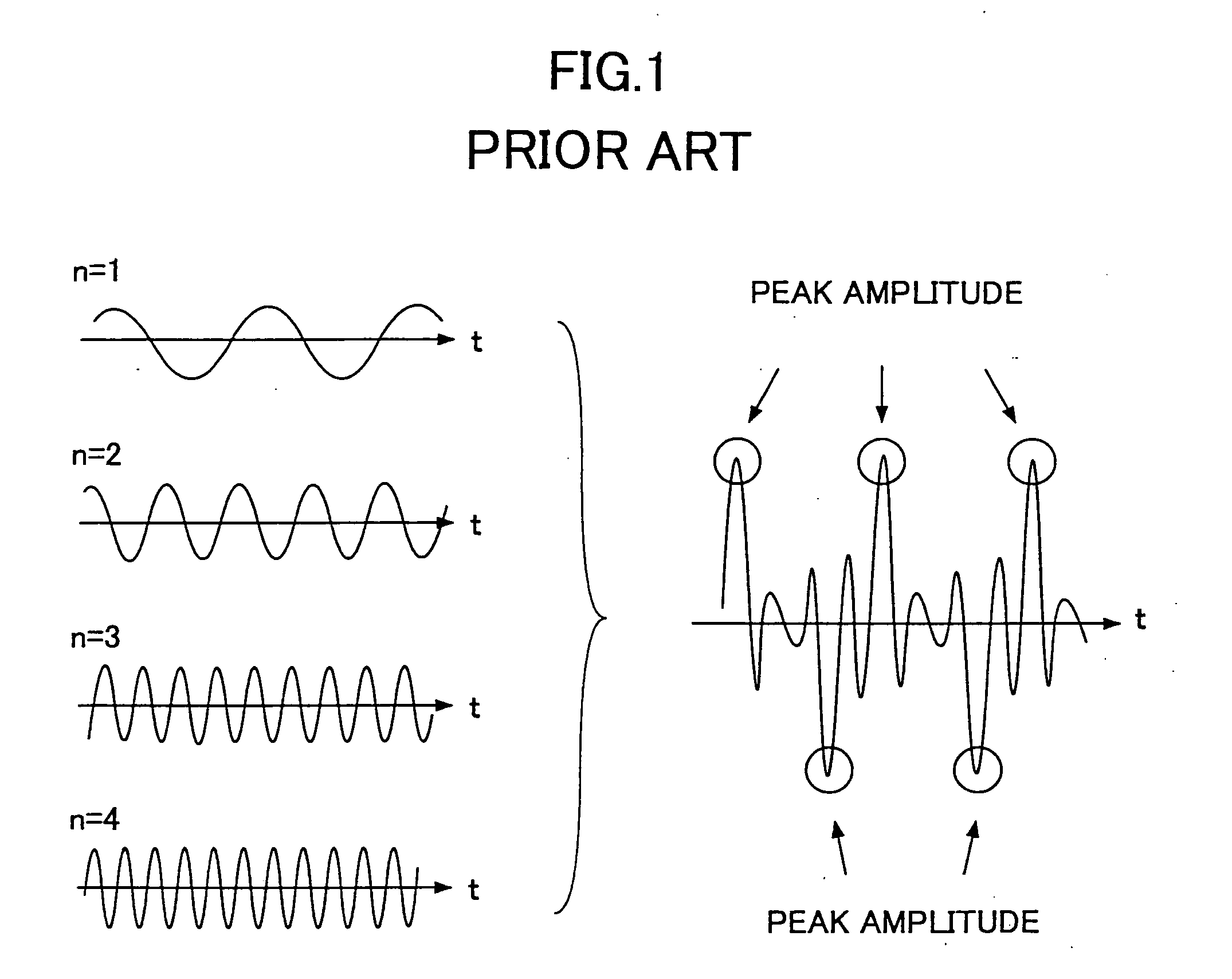
ActiveUS7248559B2Reduced scattered pilot overheadLess computationally complexPower managementSpatial transmit diversityTime domainCommunications system
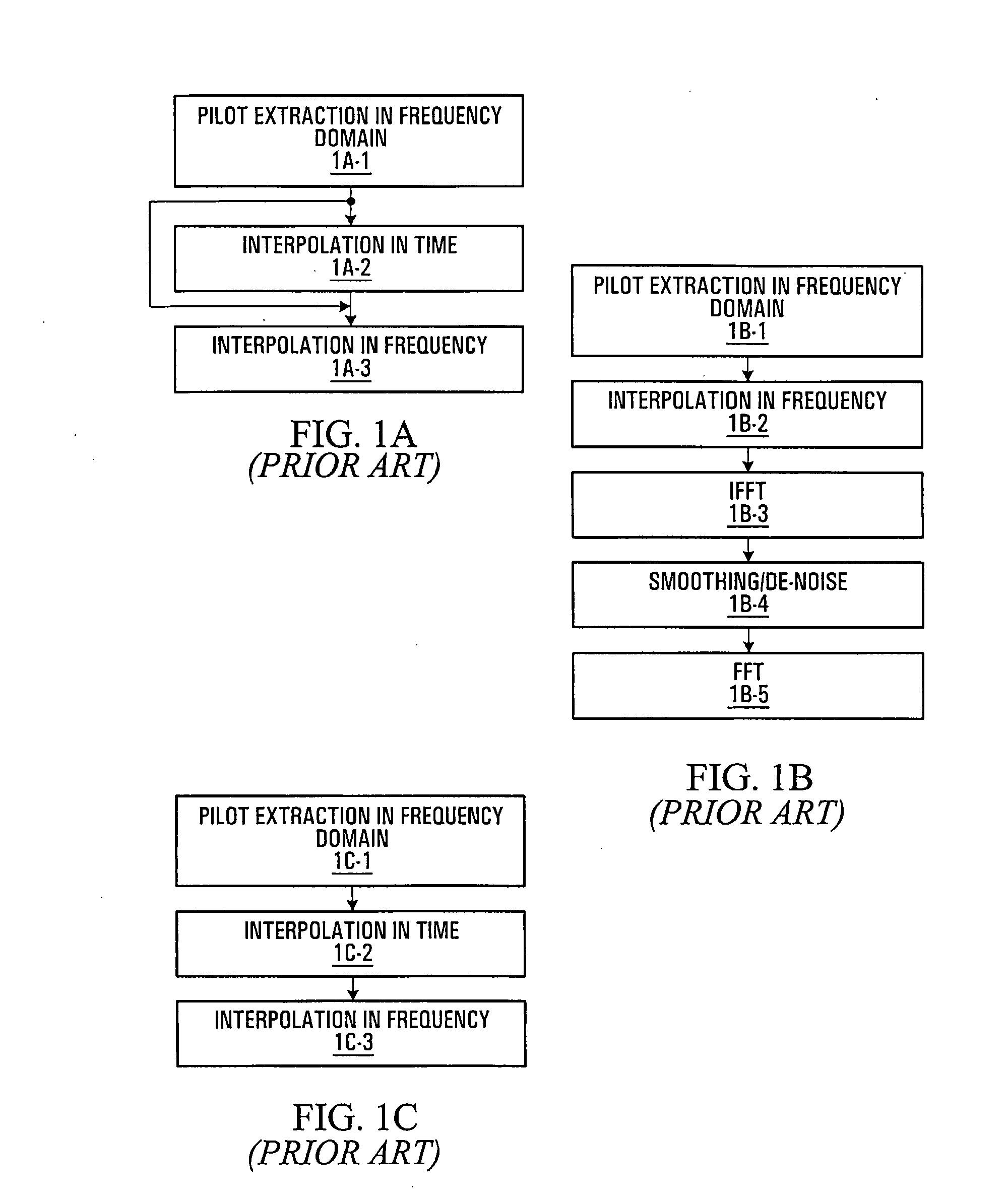
A method and apparatus are provided for reducing the number of pilot symbols within a MIMO-OFDM communication system, and for improving channel estimation within such a system. For each transmitting antenna in an OFDM transmitter, pilot symbols are encoded so as to be unique to the transmitting antenna. The encoded pilot symbols are then inserted into an OFDM frame to form a diamond lattice, the diamond lattices for the different transmitting antennae using the same frequencies but being offset from each other by a single symbol in the time domain. At the OFDM receiver, a channel response is estimated for a symbol central to each diamond of the diamond lattice using a two-dimensional interpolation. The estimated channel responses are smoothed in the frequency domain. The channel responses of remaining symbols are then estimated by interpolation in the frequency domain.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
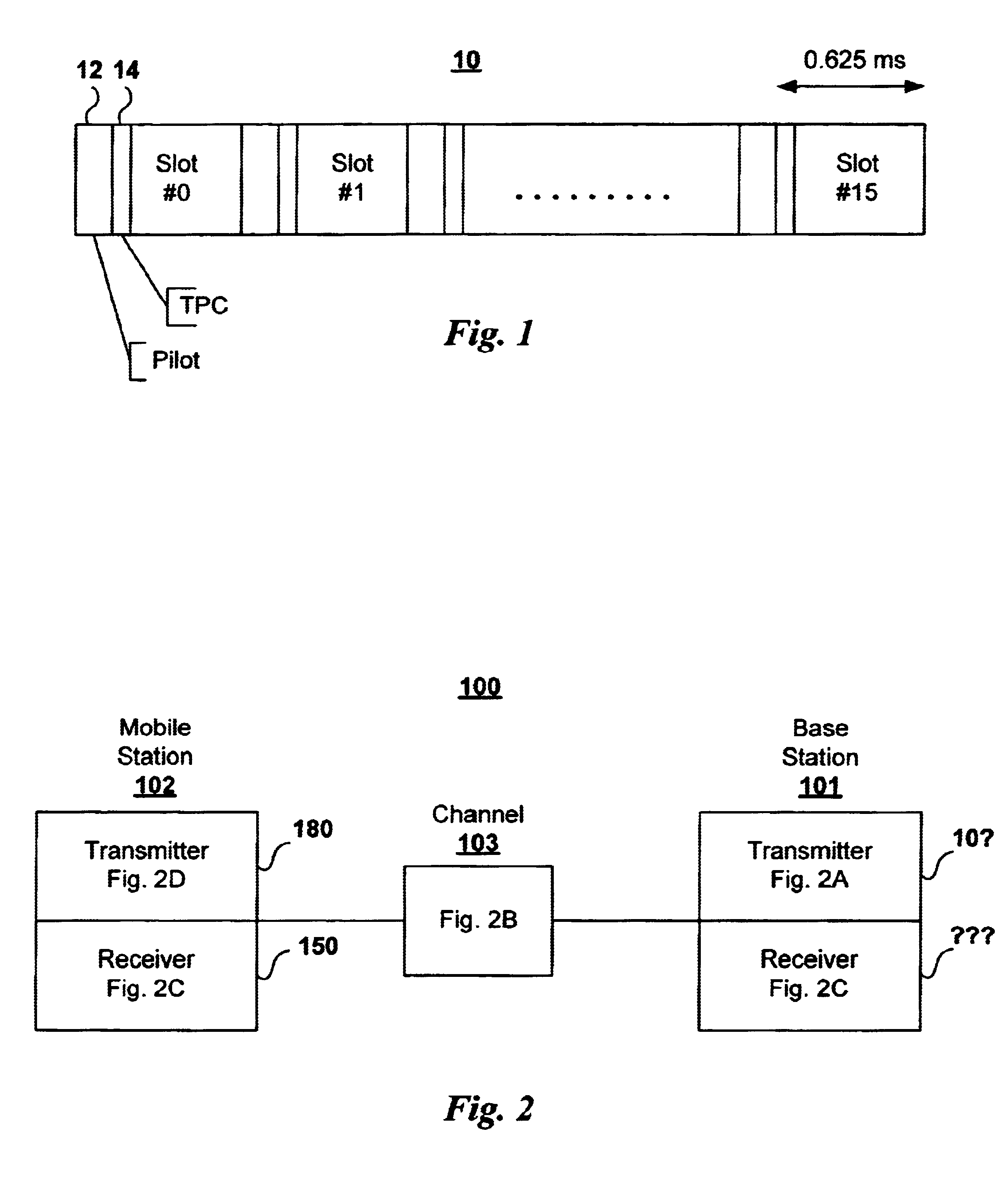
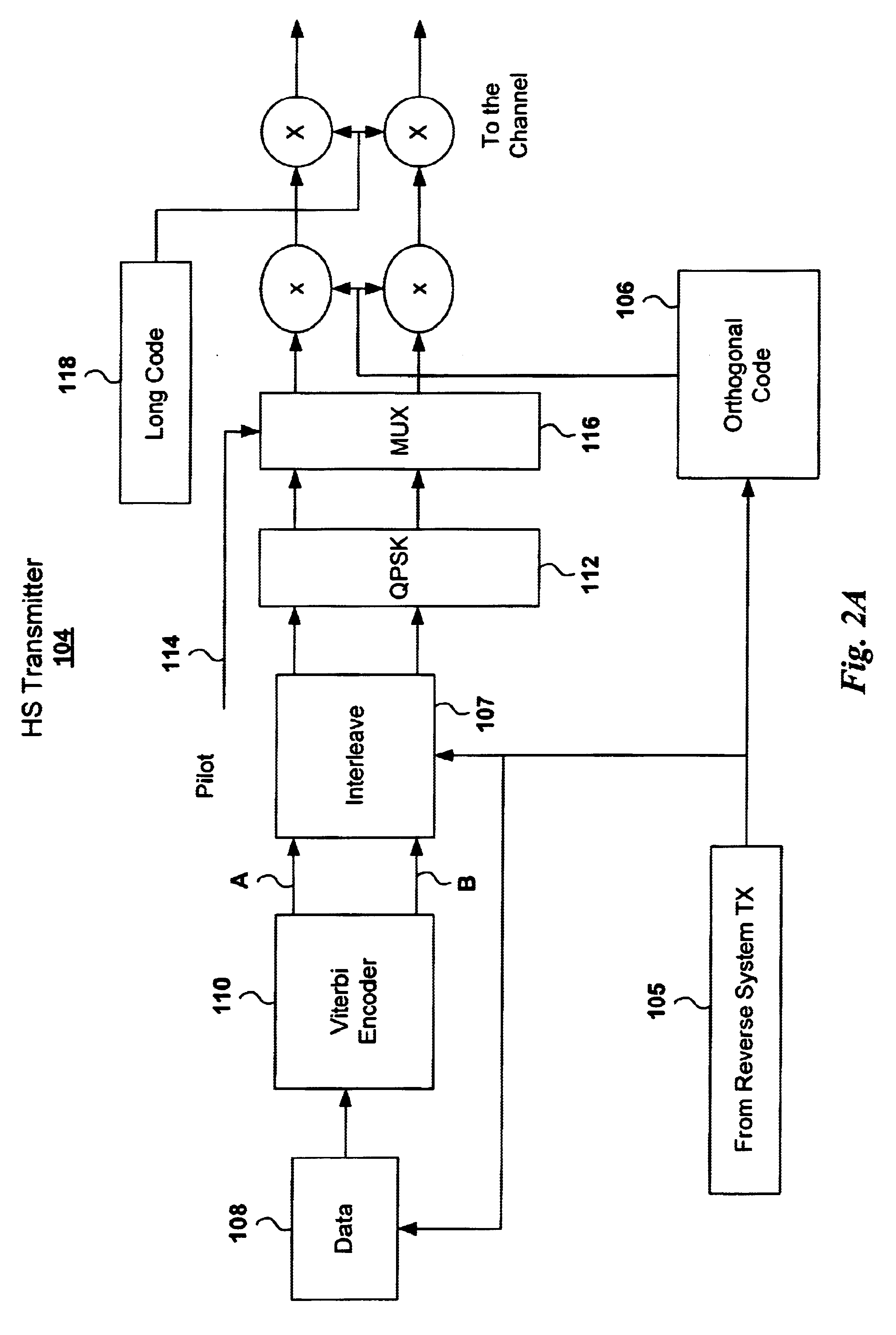
Adaptive power control based on a rake receiver configuration in wideband CDMA cellular systems (WCDMA) and methods of operation
InactiveUS6621808B1Maximizes controlMaximize throughputPower managementTransmission control/equalisingChannel powerOperational system
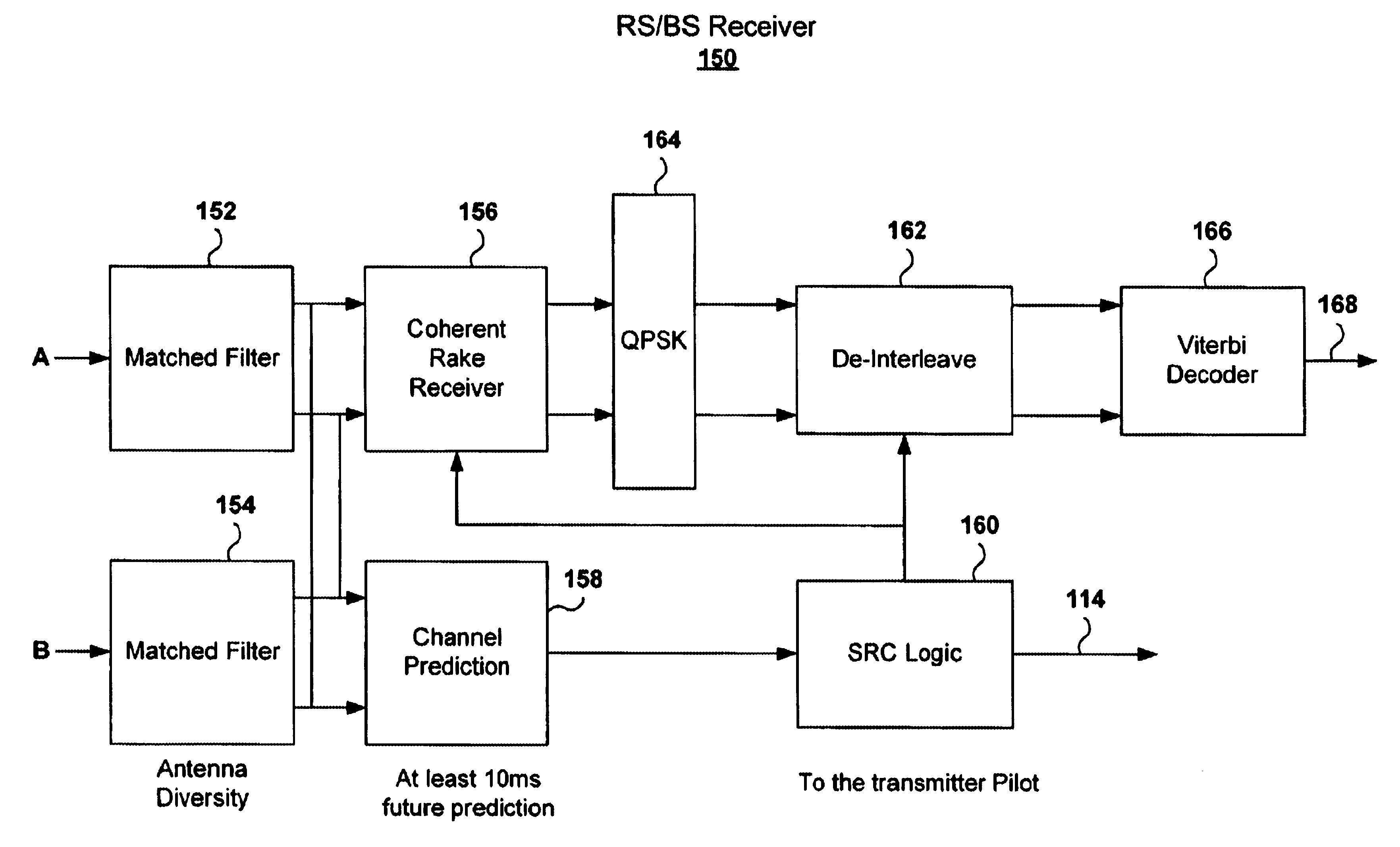
A WCDMA system includes a Base Station (BS) or forward transmitter and a pilot channel that transmits control signals between a Mobile Station (MS) and BS to reconfigure their transmitter / receiver according to the prediction of the channel power and channel power probability density function separated into three distinct equal probable regions. Data signals are encoded using a one-half Viterbi encoder and interleaved. The interleaved data bits are modulated using Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) modulation. The QPSK data is multiplexed with the pilot channel and spread by an appropriate code in an OFDM transmitter modified by a long code. Output of the transmitter may be provided to two diverse antennas for reliable communications to the receiver. Data may be received at two diverse antennas. The outputs are provided to match filters coupled to a coherent rake receiver and a channel prediction system. The future attenuation of the channel coefficients and power are determined by the prediction system for several milliseconds. The power levels of each finger in the Rake receiver can be predicted and the strongest ones used in determining the optimum transmitter power or rate control for operating the system transmitters and receivers based on computing a long range power prediction of each finger of a rake receiver.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
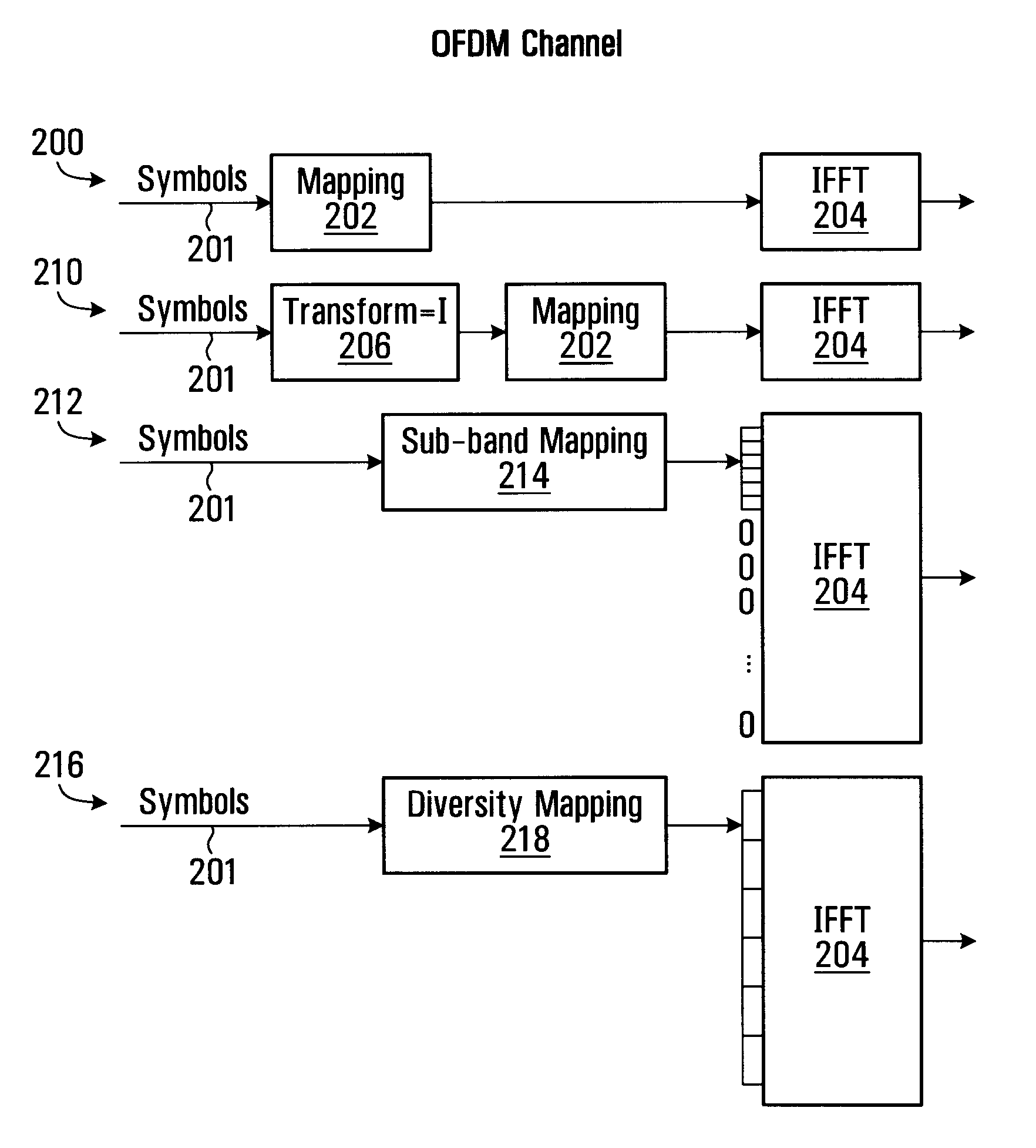
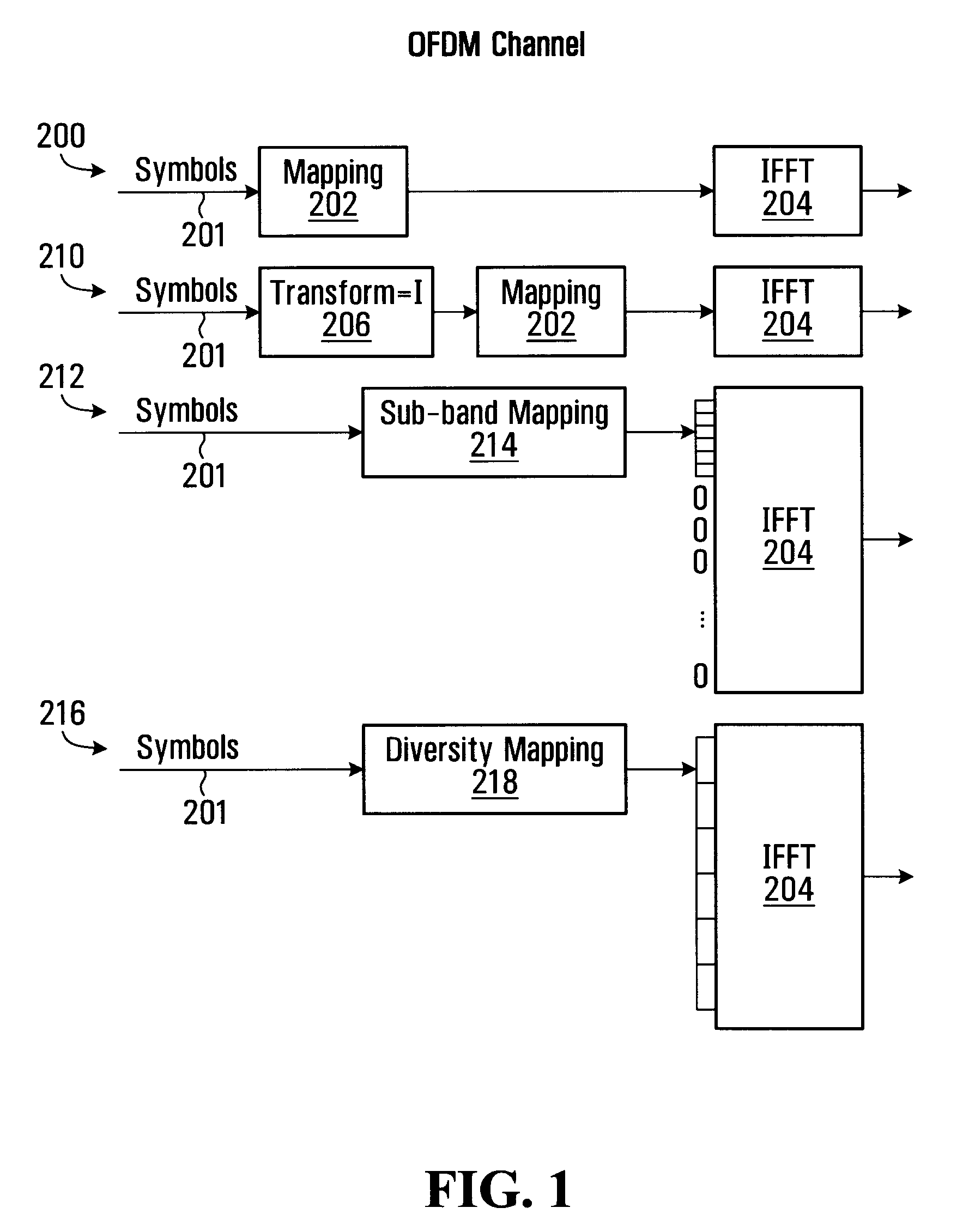
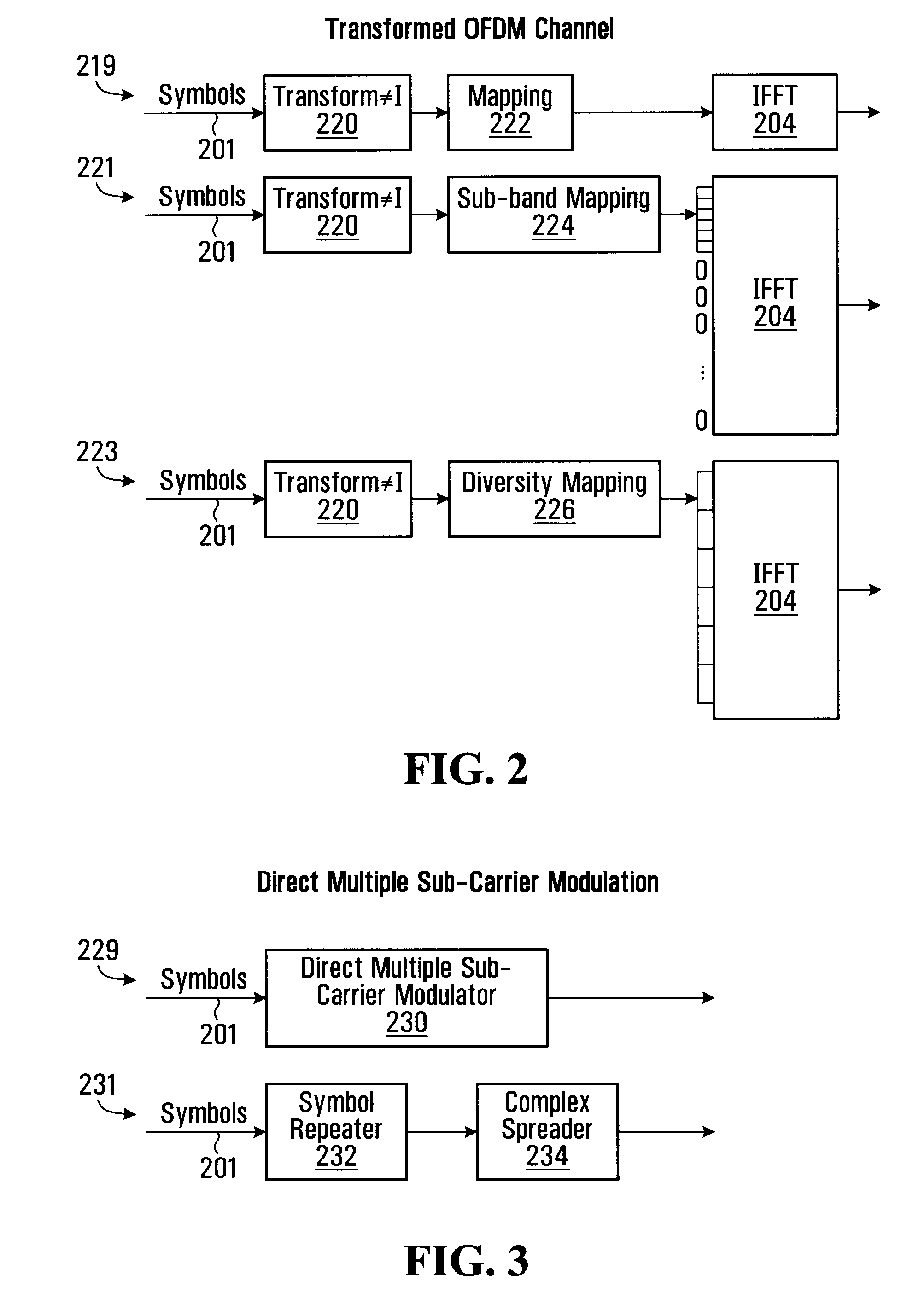
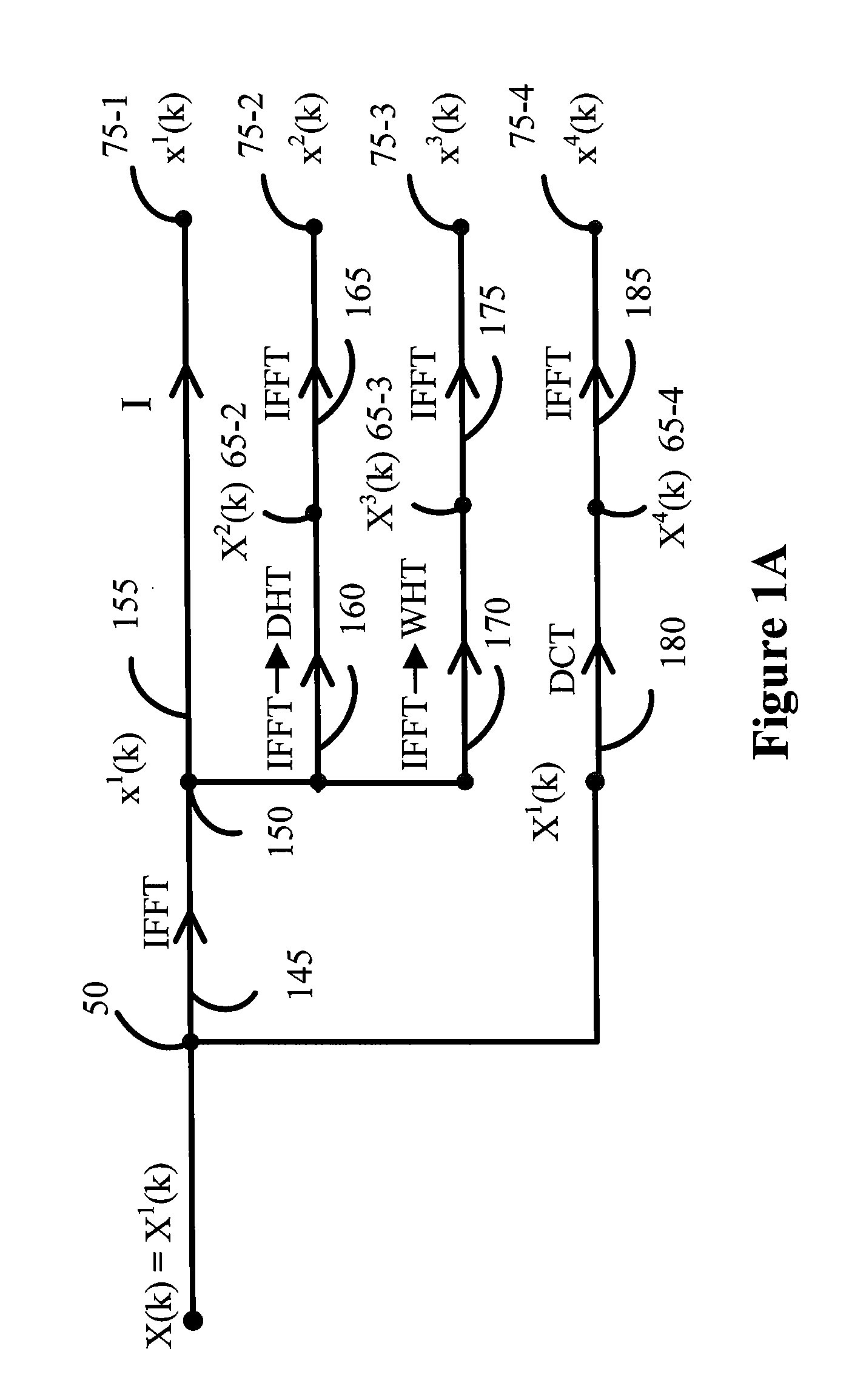
Method and System For Combining Ofdm and Transformed Ofdm
ActiveUS20080186843A1Transmission path divisionFrequency-division multiplexOfdm transmitterTransmitter
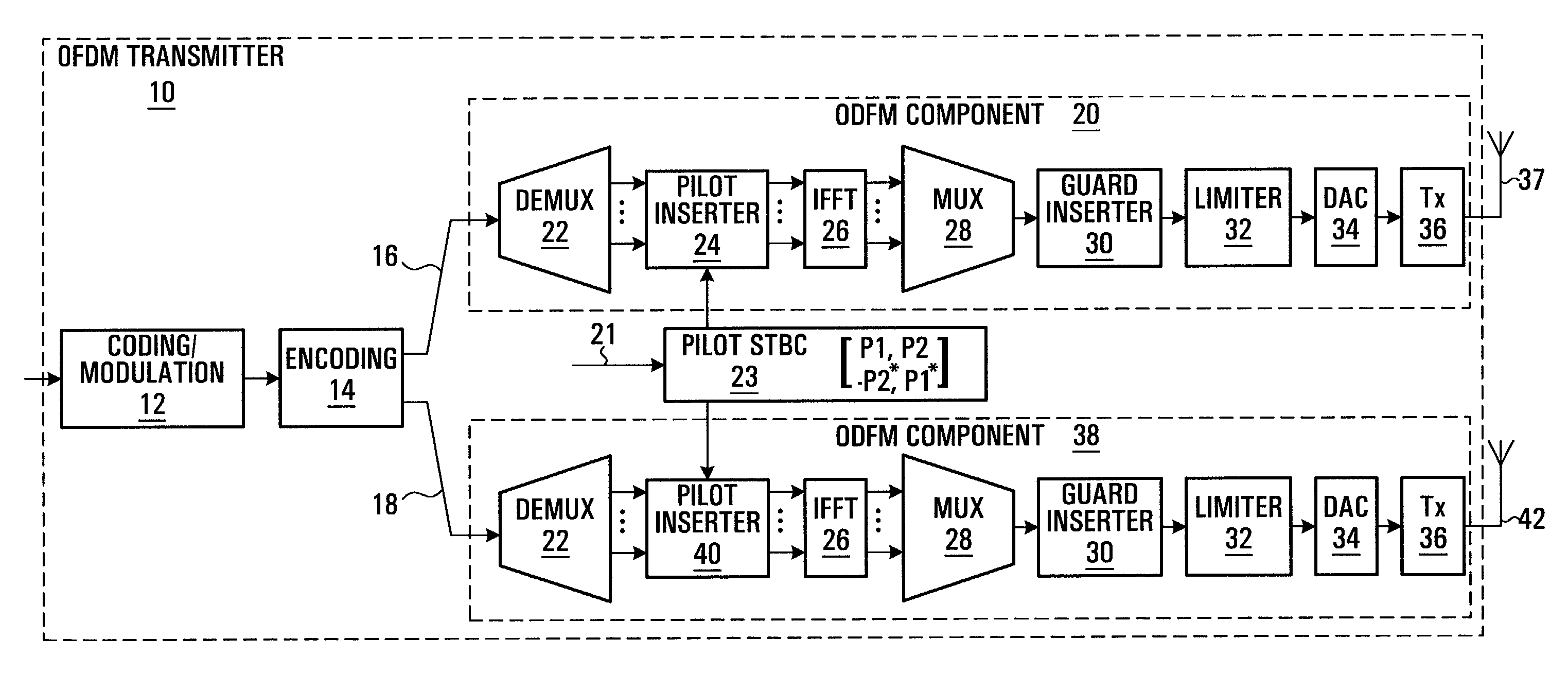
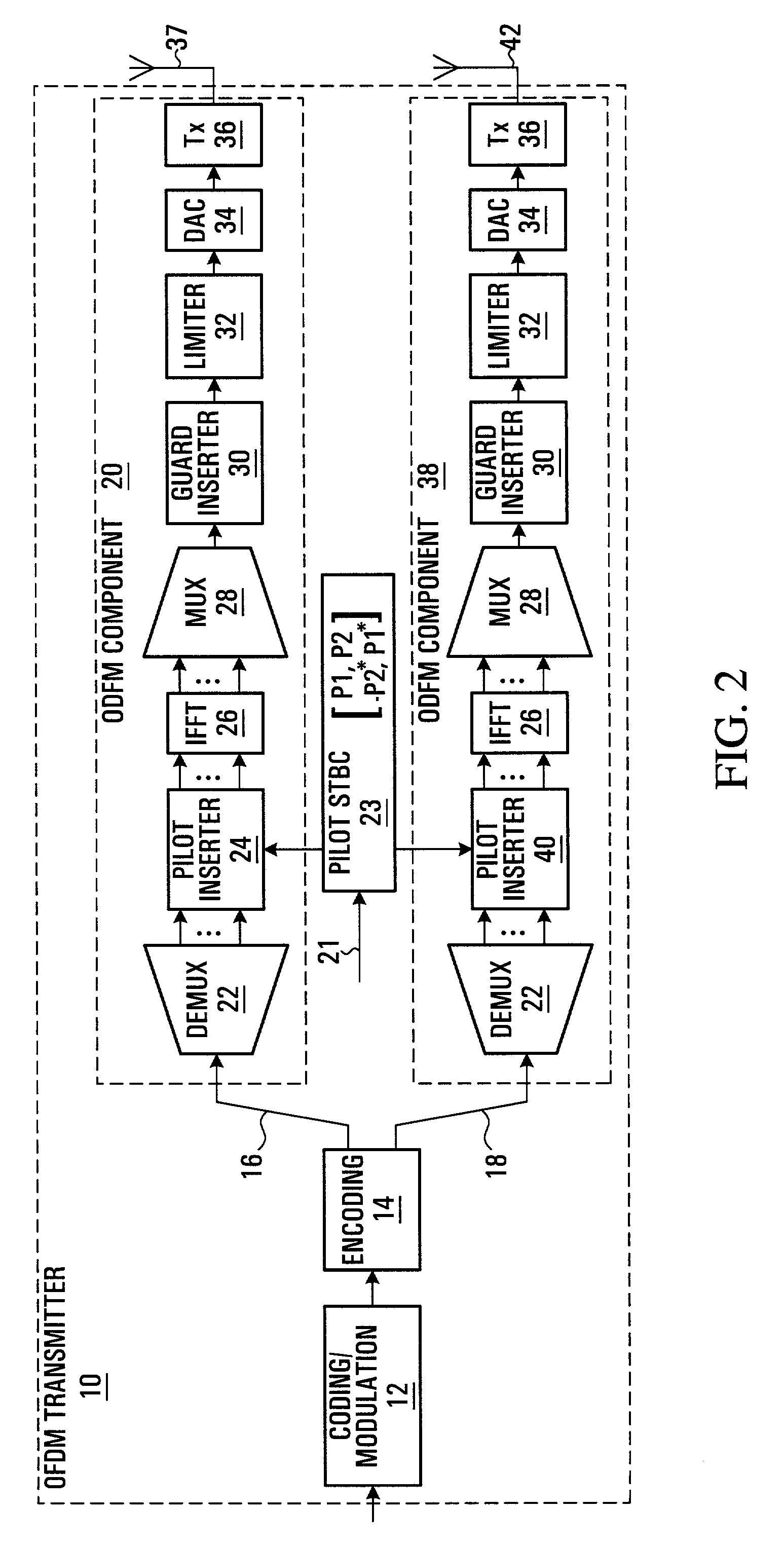
Methods and systems are provided that enable an OFDM transmitter to be used for transmitting conventional OFDM or a form of transformed OFDM. A technique is provided for transforming a coded and modulated sequence of samples prior to an IFFT that enables the transformed sequence of samples to be transmitted using conventional OFDM or transformed OFDM. The selection of a transform function for transforming the coded and modulated sequence of samples may be based on optimizing the transform function for particular operating conditions between the transmitter and receiver. In some embodiments of the invention OFDM and time transformed OFDM are multiplexed in time and / or frequency in a transmission frame. In some embodiments of the invention a pilot pattern is provided in which the pilot are sent using OFDM and data is sent using OFDM and / or transformed OFDM.
Owner:APPLE INC
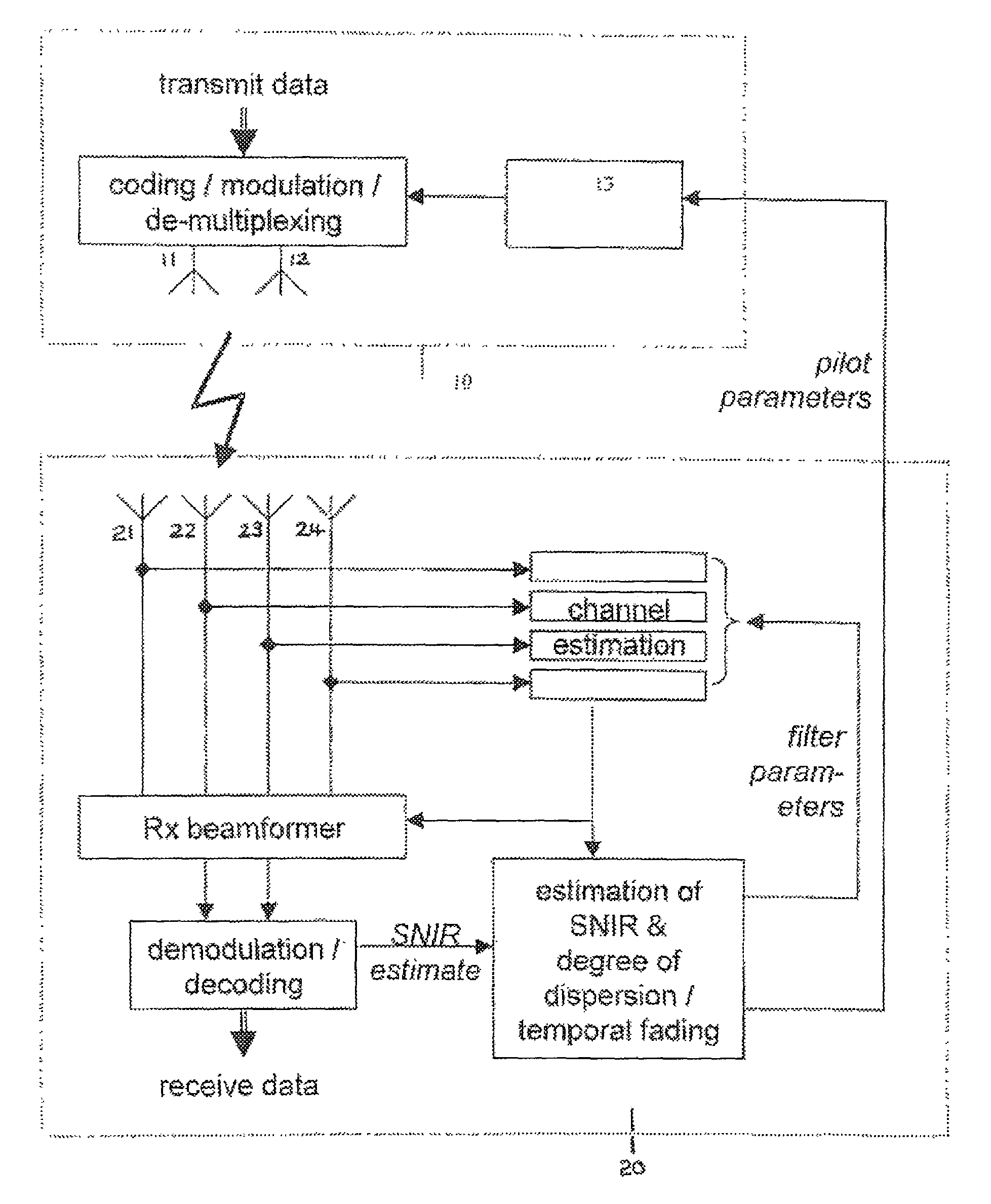
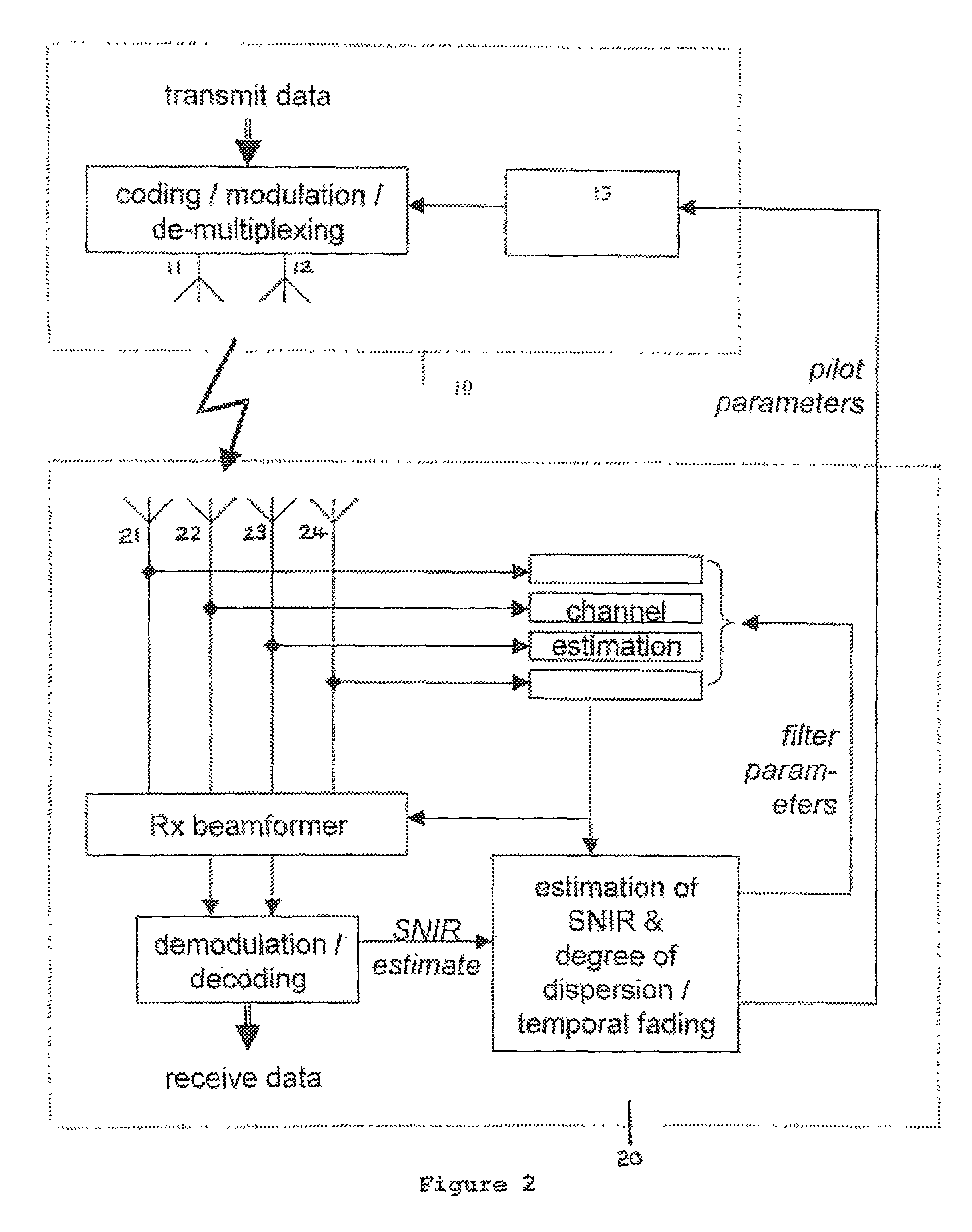
Scattered pilot and filtering for channel estimation
ActiveUS7436757B1Better networkProlong lifeTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationEstimation methodsEngineering
Methods of improving channel estimation are described, in which pilot symbols are inserted into orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) frames at an OFDM transmitter having at least one transmitting antenna, wherein for the or each antenna, historical data regarding channel conditions is obtained so that the scattered pilot symbols are inserted in a scattered pattern dependent upon said historical data. Alternatively, or in addition, an adaptive channel estimation filter is used whose parameters are selected according to analysis of historical data regarding channel conditions.
Owner:APPLE INC
Smart antenna based spectrum multiplexing using existing pilot signals for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) modulations
InactiveUS7145959B2LevelSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityFrequency spectrumTime segment
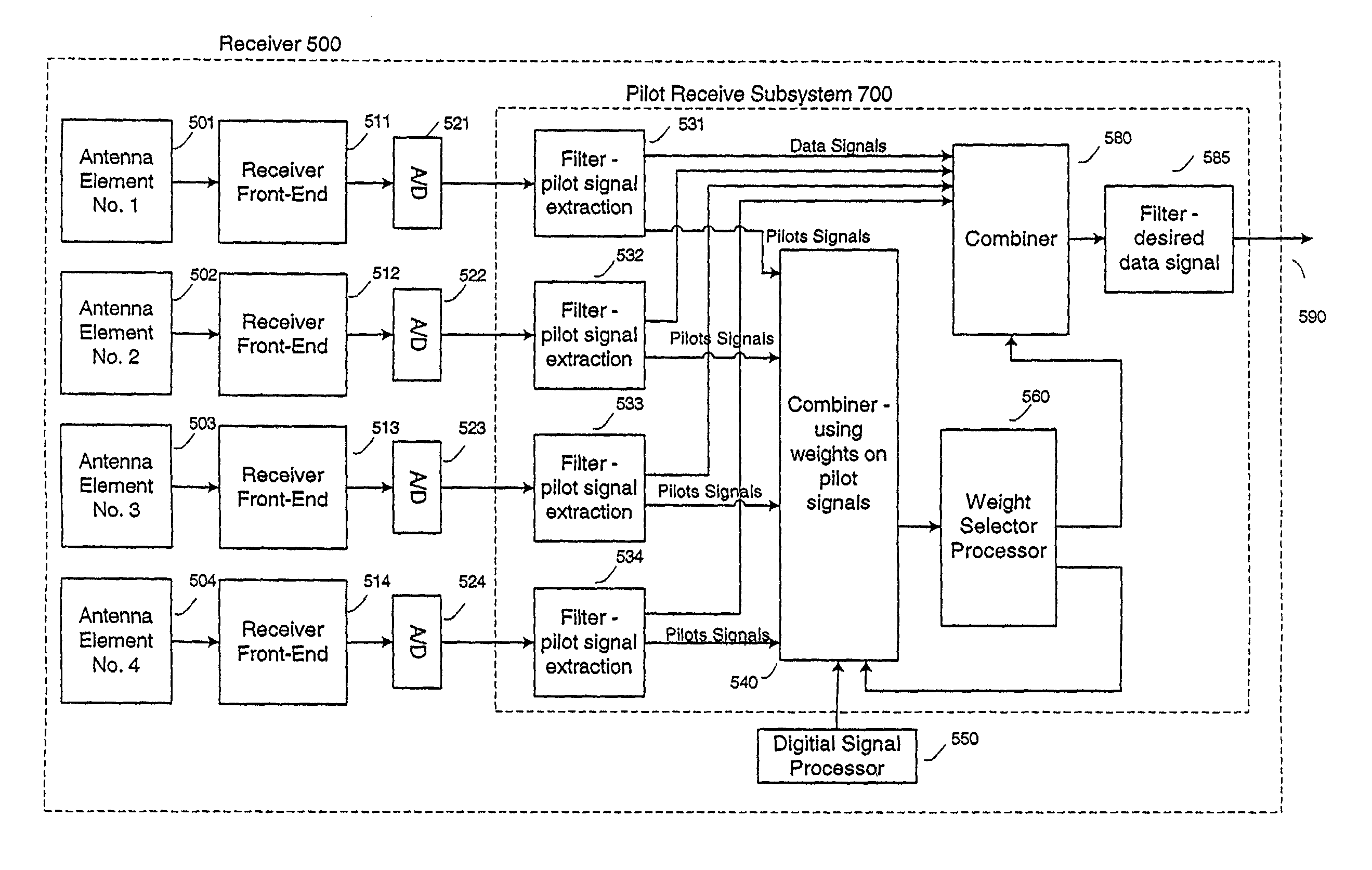
A system and method for using a group of pilot signals to enhance a data signal within an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) multiple-access scheme is described. The OFDM multiple-access scheme has multiple OFDM transmitters using at least overlapping frequency spectrums, during at least overlapping time period, in at least overlapping geographic areas. A set of data signals and a set of pilot signals are received on antenna elements. Each group of data signals from the set of data signals is uniquely associated with a group of pilot signals from the set of pilot signals. Each pilot signal from the set of pilot signals is uniquely associated with its own code from a set of codes. Each code from the set of codes is uniquely associated with an OFDM transmitter from the multiple OFDM transmitters. A group of pilot signals from the set of pilot signals is identified based on its uniquely associated code. A weight value associated with each antenna element from a set of antenna elements is adjusted so that a level of correlation between the group of pilot signals and the code uniquely associated with the group of pilot signals is enhanced while a level of correlation between the remaining groups of pilot signals from the set of pilot signals and the codes uniquely associated with those remaining group of pilot signals are suppressed.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
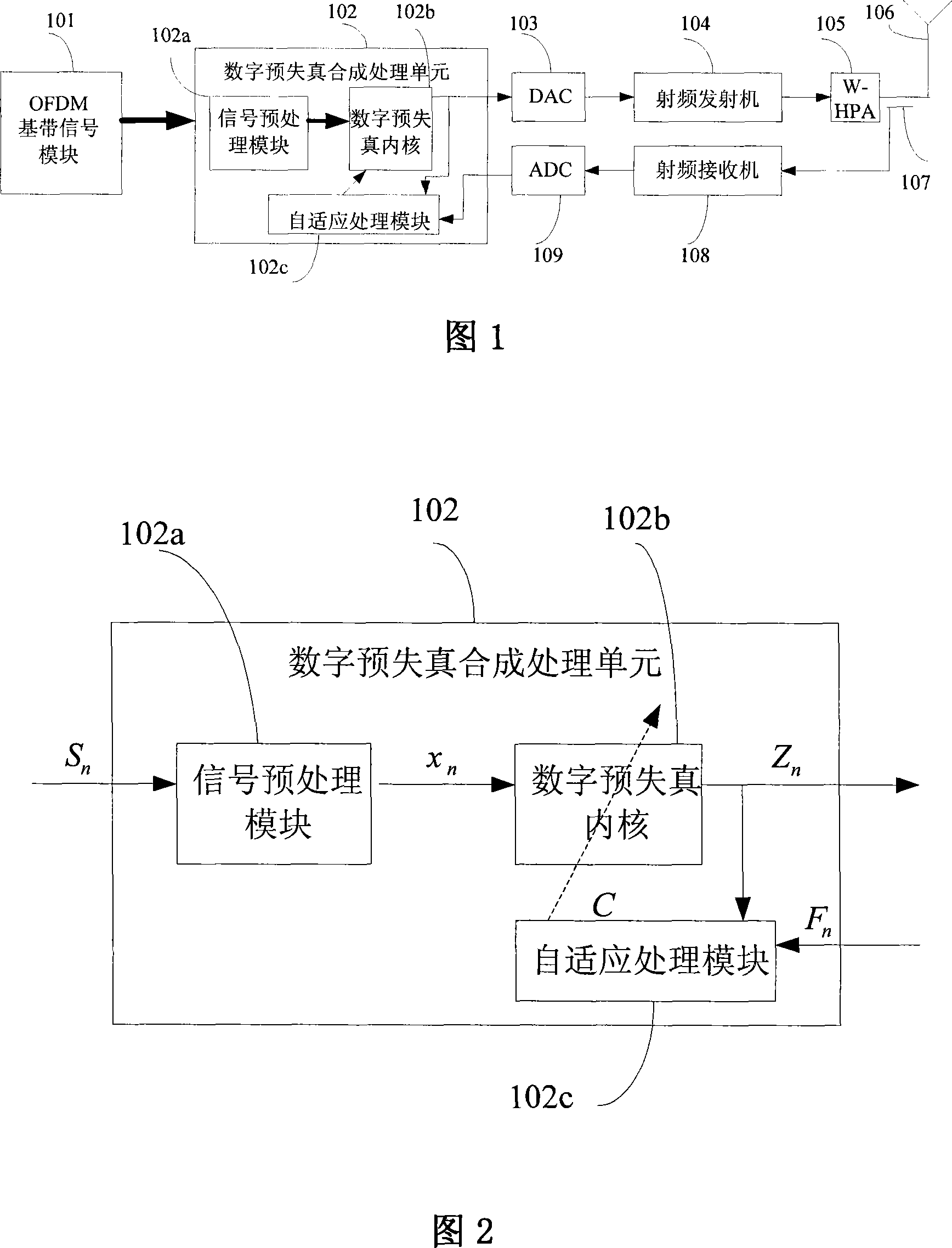
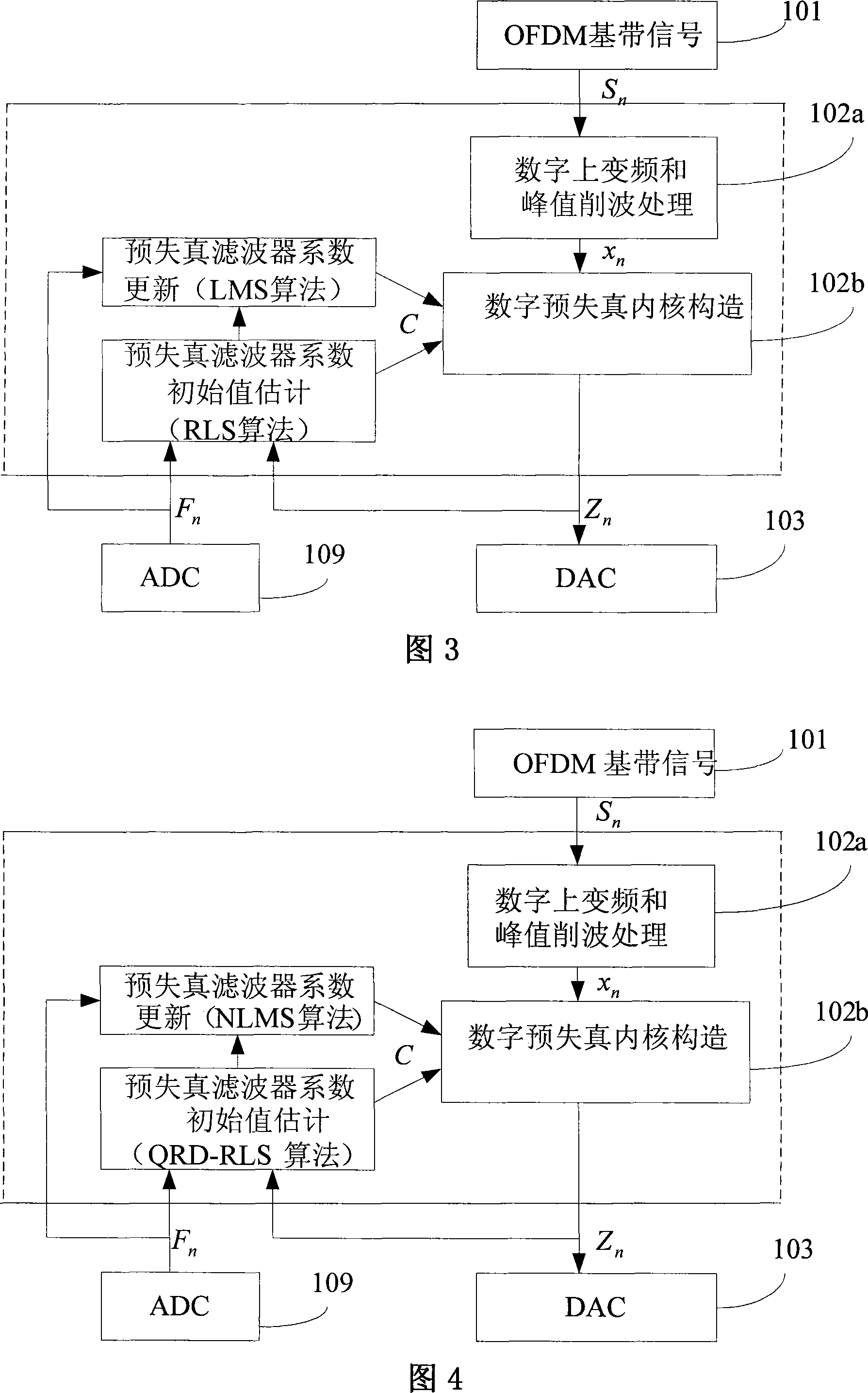
Self-adapting digital predistortion method and apparatus for OFDM transmitter
ActiveCN101175061AImprove linearityImprove efficiencySpatial transmit diversityMulti-frequency code systemsBroadband power amplifierFeedback circuits
The invention provides an adaptive digital pre-distortion technique and device which is suitable for OFDM projector. The device comprises an OFDM baseband signal module for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing technique, a digital pre-distortion synthetic process component, an analog and digital converter DAC, a radio frequency projector, a wideband high power amplifier, i.e., W-HPA, and a feedback circuit. Wherein, a digital pre-distortion internal core, which is structured in polynomial mode, implements pre-distortion process to the digital signals which have undergone signal pre-process; the estimate and uploading to an adaptive digital pre-distortion filter is implemented, based on hybrid algorithm which is the combination of training-sequence-based RLS+LMS algorithm or hybrid algorithm which is the combination of training-sequence-based QRD-RLS+NLMS algorithm. The invention can efficiently reduce the performance degradation of a wideband power amplifier caused by memory effect, improve the projecting performance of a base station system, and improve the linearity and the efficiency of the wideband power amplifier.
Owner:WUHAN HONGXIN TELECOMM TECH CO LTD
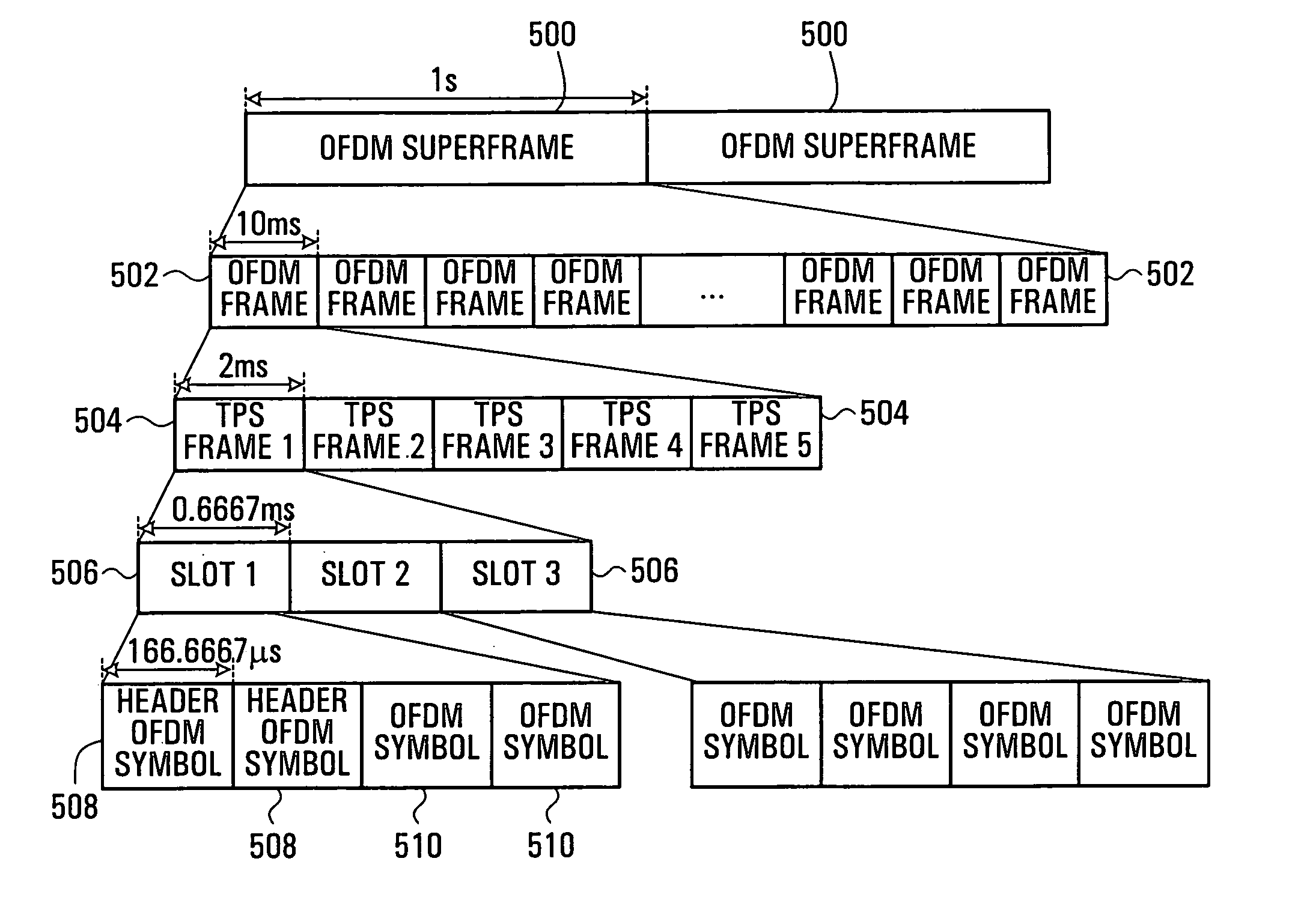
Frame structure, system and method for OFDM communications
ActiveUS20070066362A1Efficient identificationFast and accurate initial acquisitionSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemCell selection
A method and apparatus are provided for performing acquisition, synchronization and cell selection within an MIMO-OFDM communication system. A coarse synchronization is performed to determine a searching window. A fine synchronization is then performed by measuring correlations between subsets of signal samples, whose first signal sample lies within the searching window, and known values. The correlations are performed in the frequency domain of the received signal. In a multiple-output OFDM system, each antenna of the OFDM transmitter has a unique known value. The known value is transmitted as pairs of consecutive pilot symbols, each pair of pilot symbols being transmitted at the same subset of sub-carrier frequencies within the OFDM frame.
Owner:APPLE INC
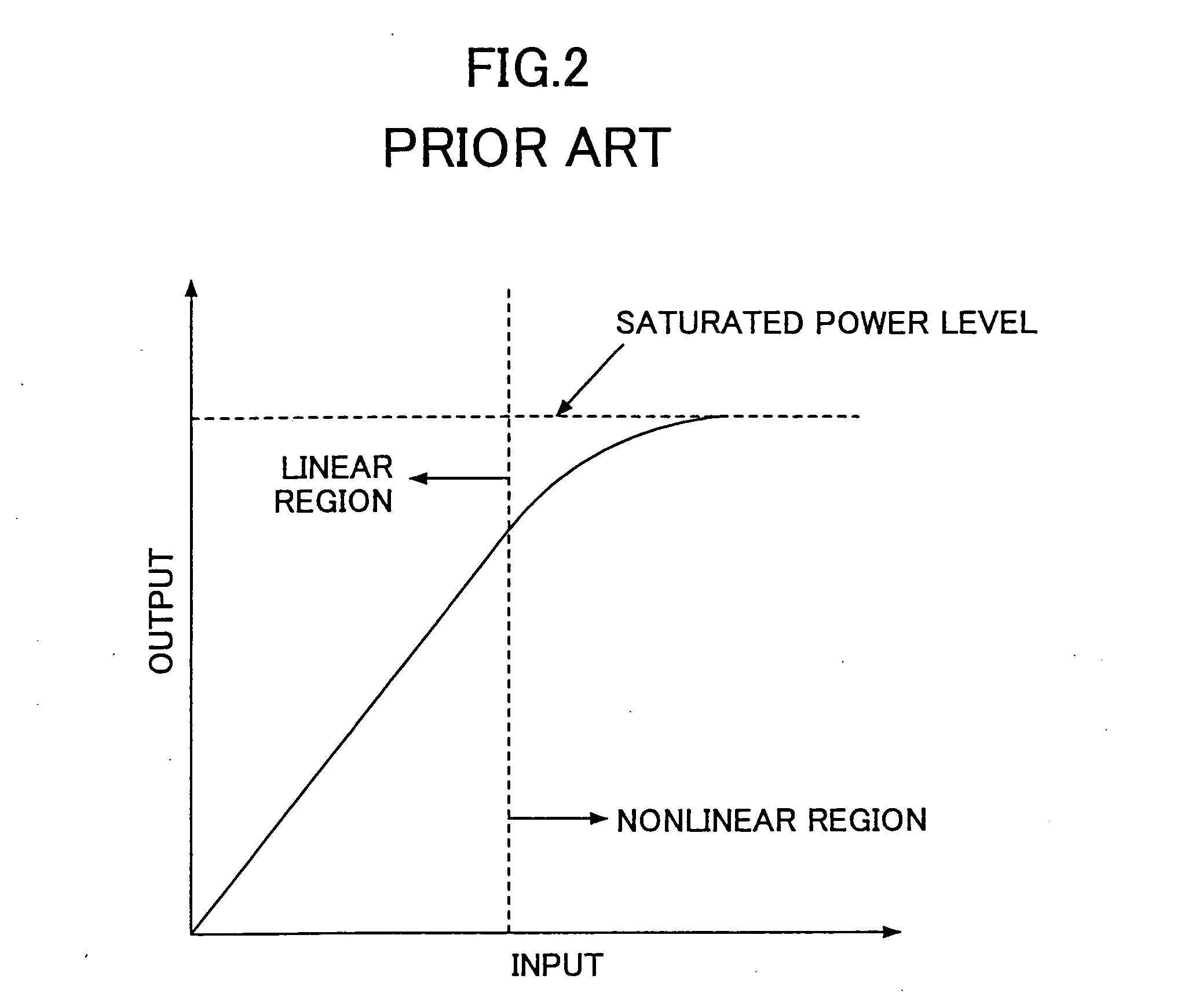
Apparatus for and method of minimizing backoff for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing transmission
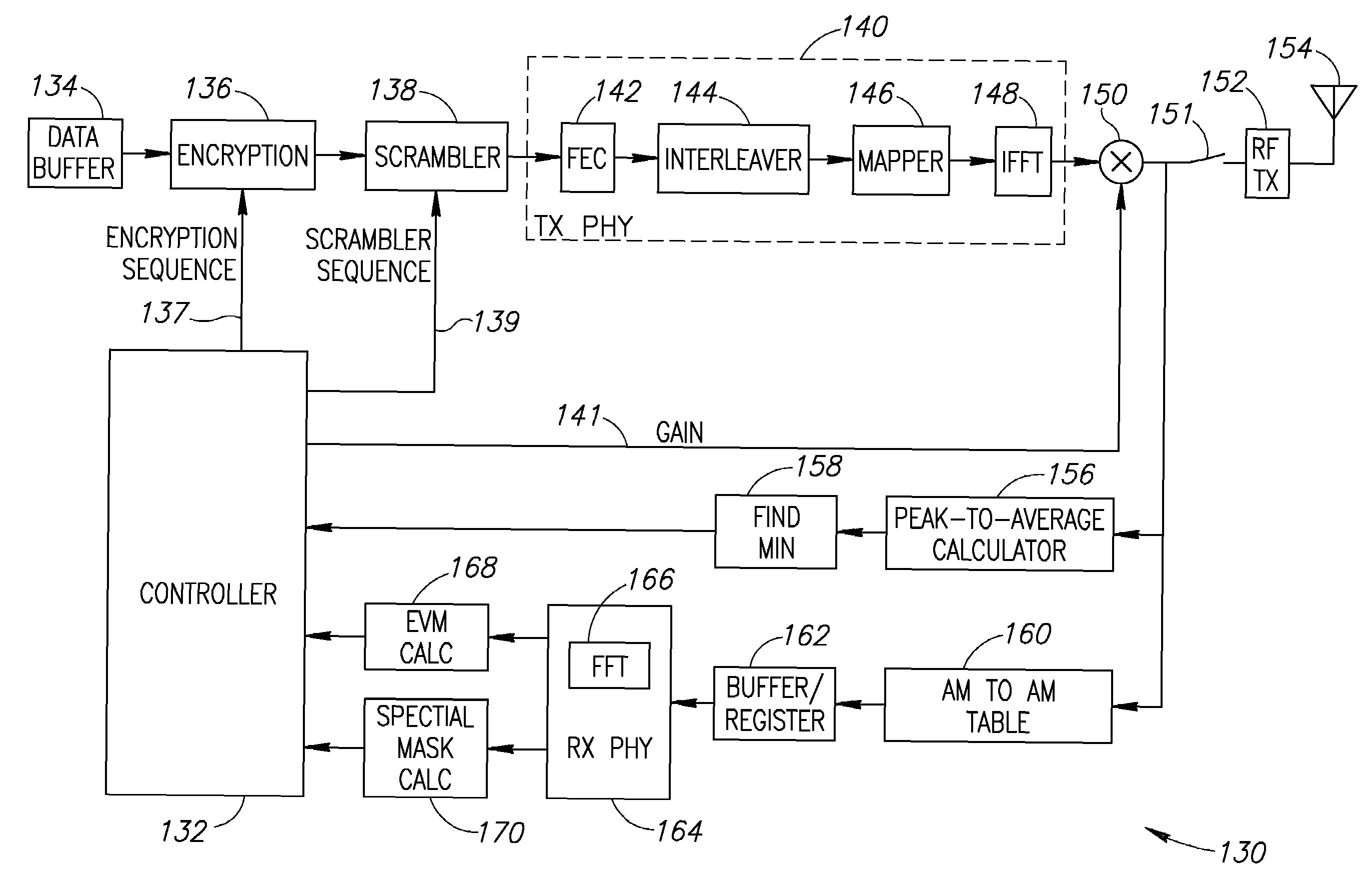
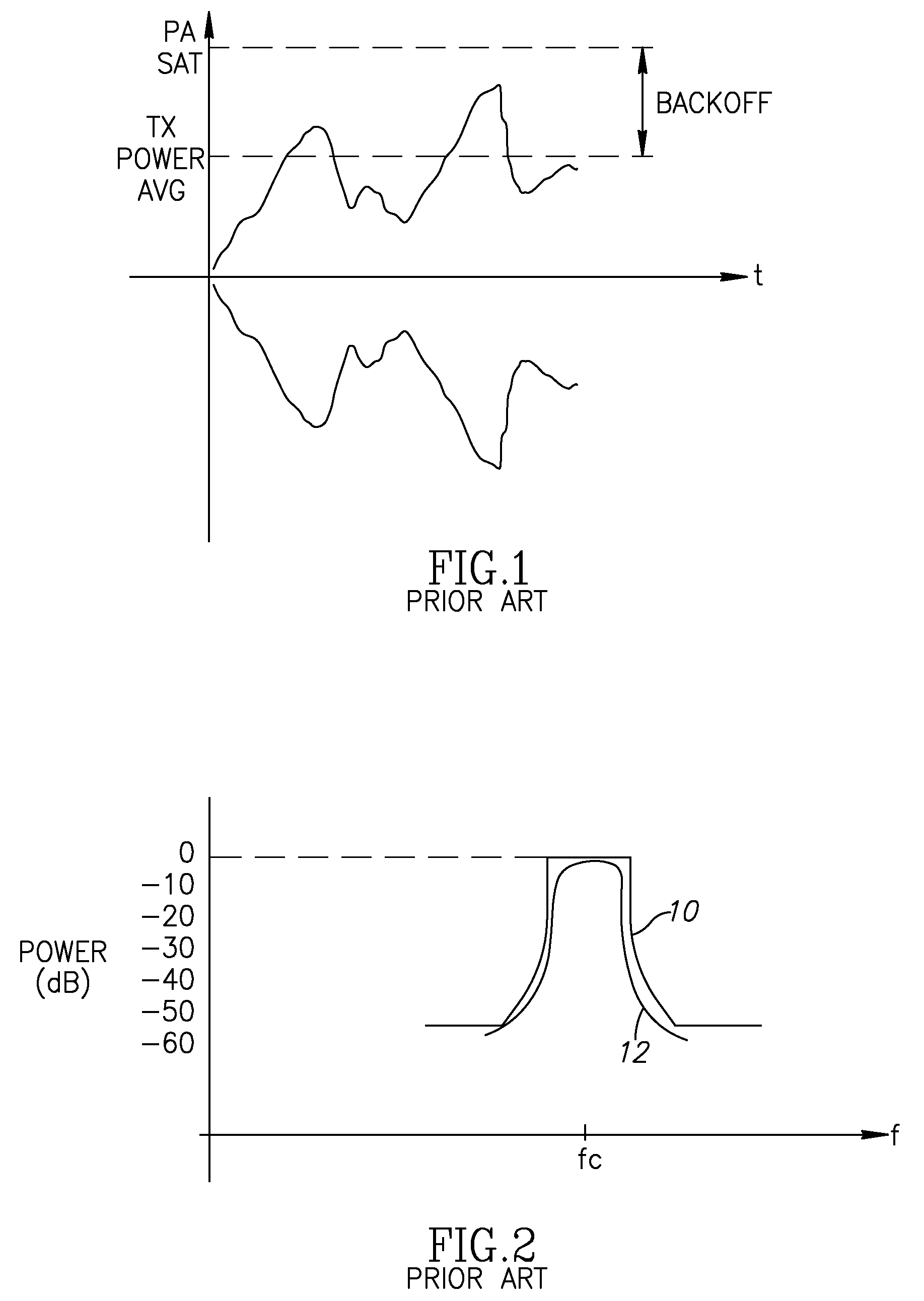
ActiveUS20070223365A1Reducing backoff requiredGood EVMModulated-carrier systemsCode conversionFrequency spectrumHigh probability
A novel and useful mechanism for reducing the required backoff and the peak to average power ratio (PAPR) needed for an OFDM transmitter whiles still meeting spectral mask and EVM specifications. The mechanism searches, for each packet to be transmitted, for several possible scrambler and encryption sequences that would yield the best spectral mask and EVM with lowest PAPR. The search can be performed using the existing transmitter and receiver PHY circuit chain to modulate and demodulate the candidate hypotheses. Once the scrambler sequence and / or encryption sequence is selected, the packet is transmitted using the selected scrambler and encryption sequences. In addition, the invention exploits the fact that even for very low backoff margins, a reduced number of candidate hypotheses may be tested while still yielding a high probability of meet the spectral mask and EVM specifications.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Multi-input multi-output-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing transceiving method and apparatus
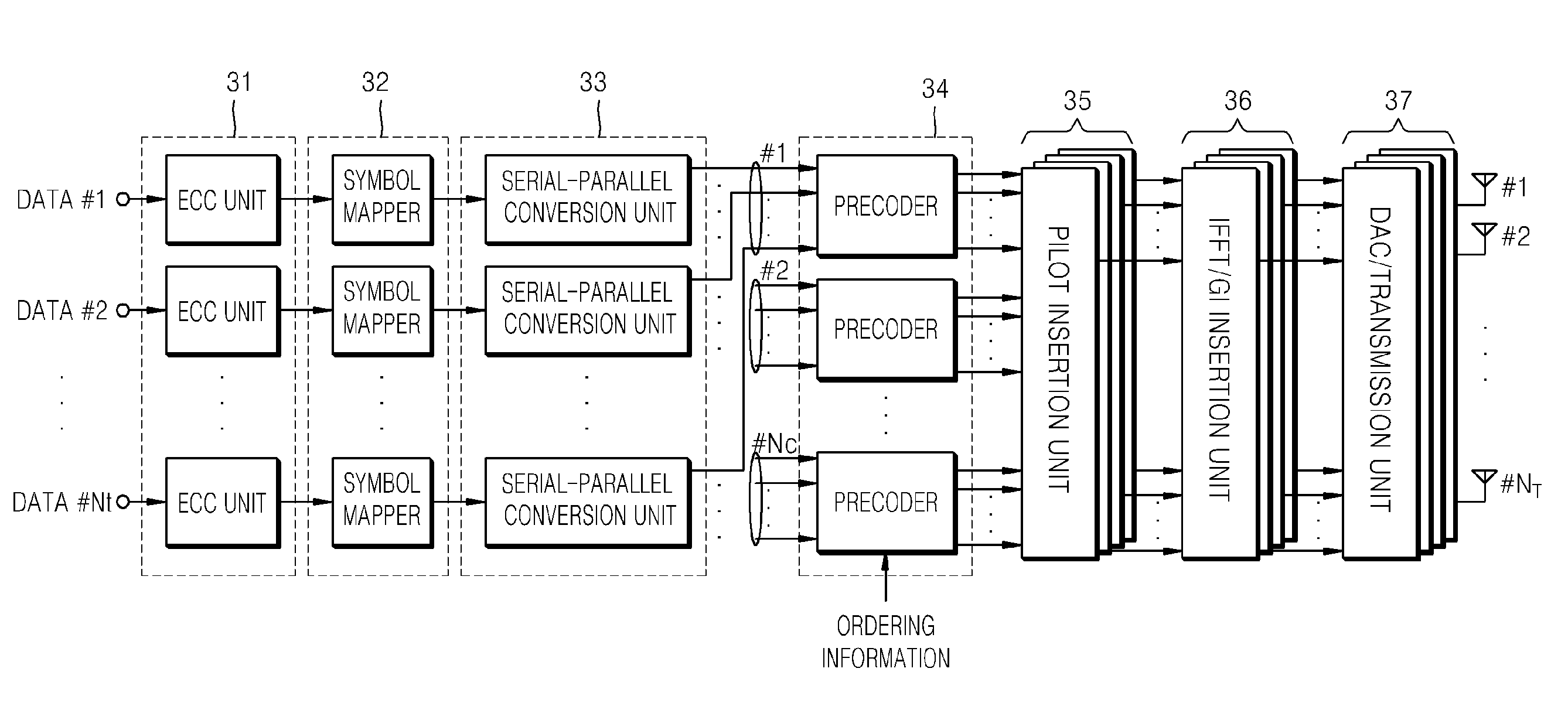
InactiveUS20100027688A1Effectively canceling parallel interferenceAvoid it happening againError preventionMultiplex communicationMulti inputMIMO-OFDM
A multi-input multi-output orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (MIMO-OFDM) transceiving system is provided, in which an MIMO-OFDM receiver feeds back ordering information, such as the order of power intensities of reception signals of a plurality of reception antennas, to an MIMO-OFDM transmitter. The MIMO-OFDM transmitter arranges subcarriers, to which data symbols have been allocated, so that the subcarriers respectively correspond to a plurality of transmission antennas, according to the fed-back information. Thus, a specific substream can be transmitted via a transmission antenna having the greatest channel gain. Consequently, the probability of properly recovering the specific substream is greatly increased.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
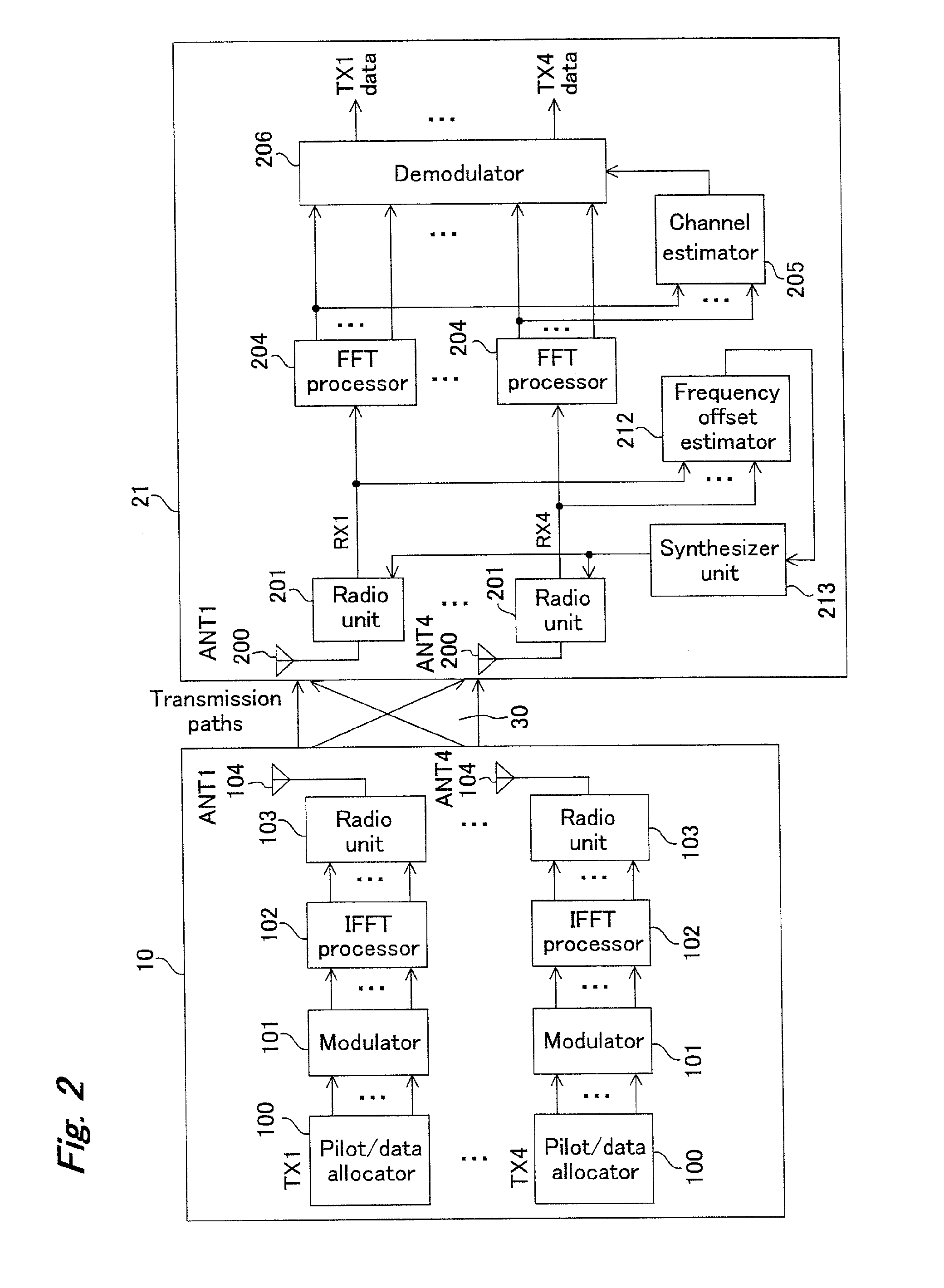
Method and apparatus for frequency synchronization in MIMO-OFDM wireless communication systems
InactiveUS20050041693A1Improve performanceHigh quality estimateSite diversityTime-division multiplexCommunications systemOfdm transmitter
A method and apparatus for synchronizing in the receiver of an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) wireless communication system, and in particular a multiple input multiple output (MIMO) OFDM system. The OFDM transmitter inserts training symbols into the transmission signals, and when the transmission is received a frequency synchronization module develops from them a weighted representation of the received signal from which frequency offset estimates for use in frequency offset compensation may be made.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
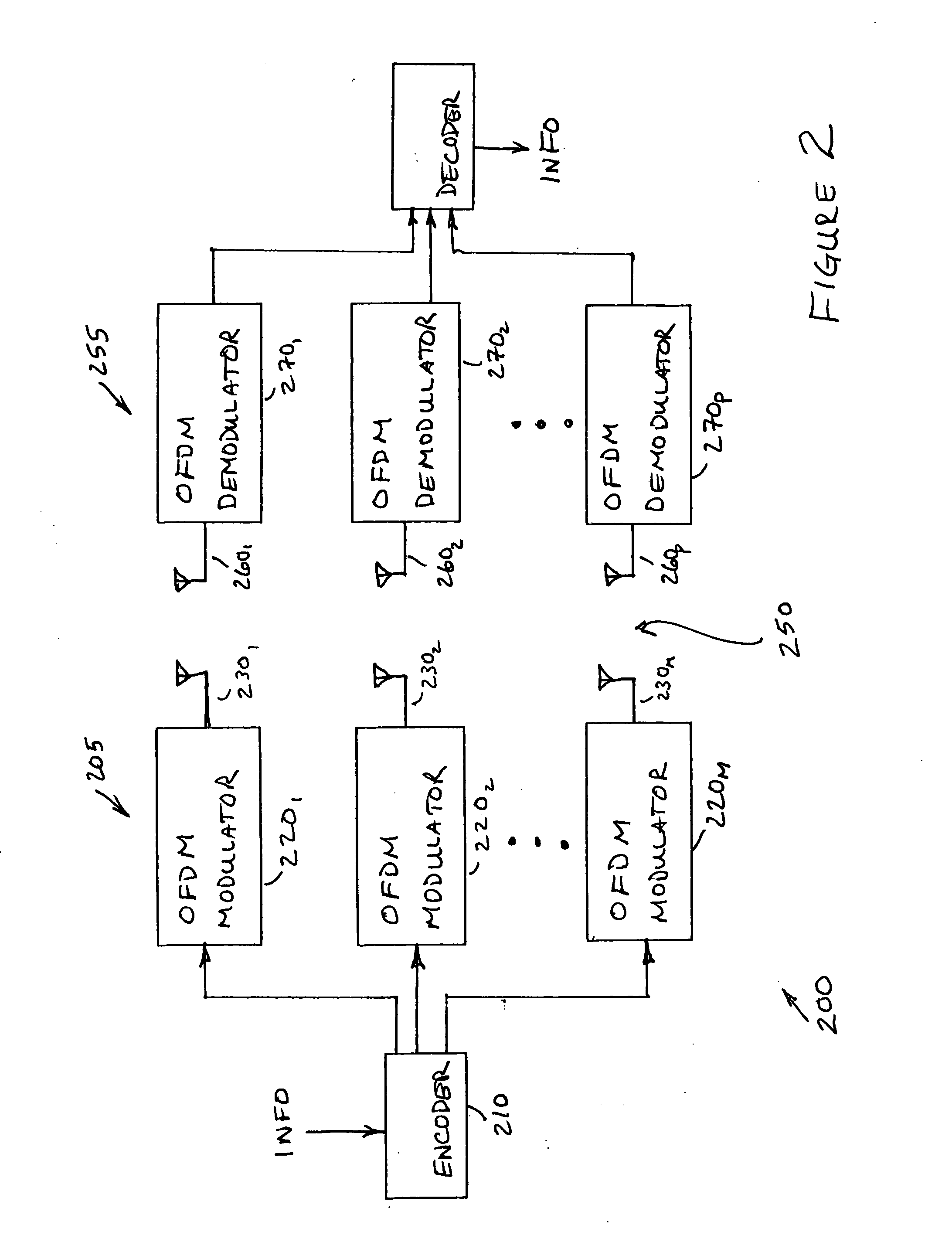
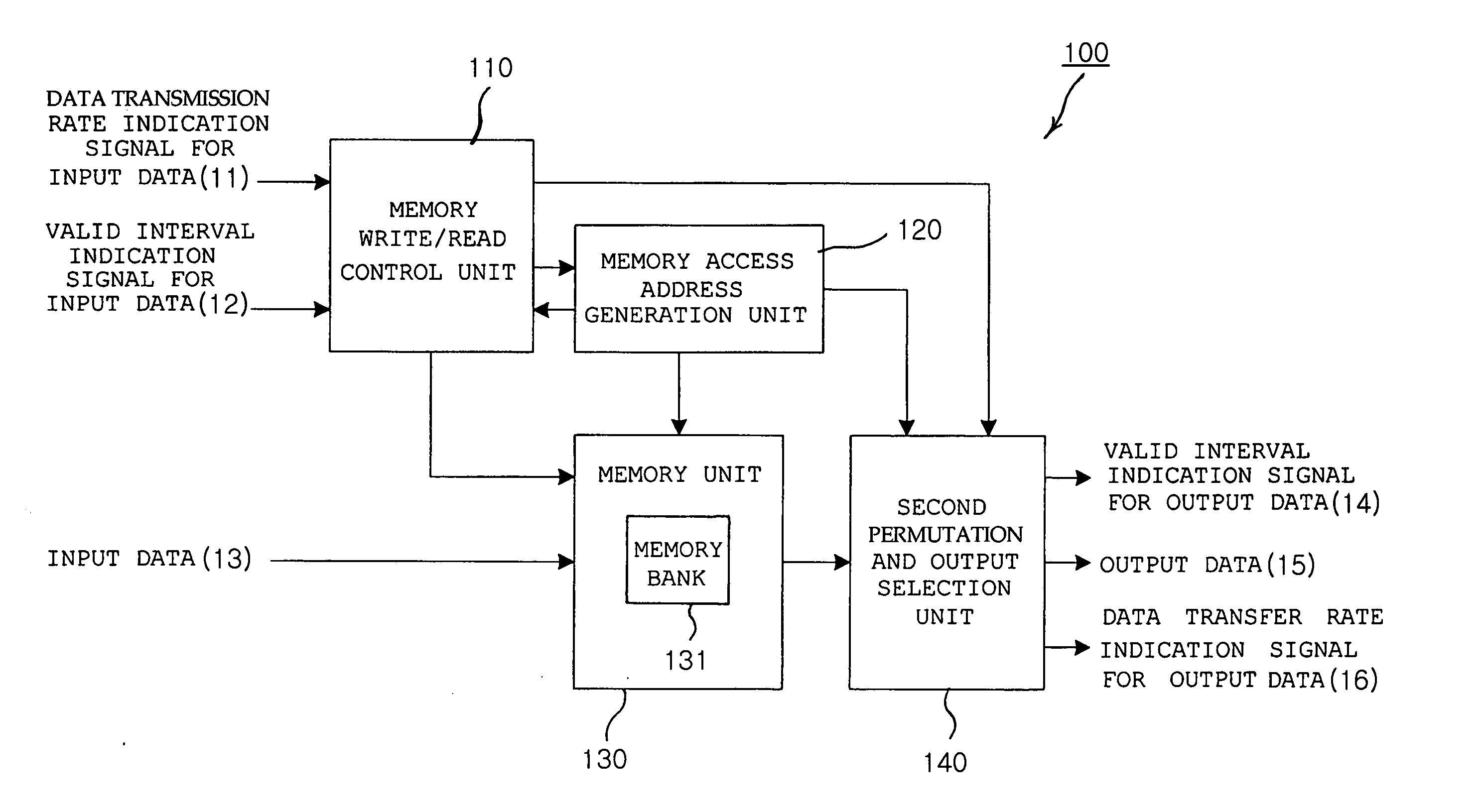
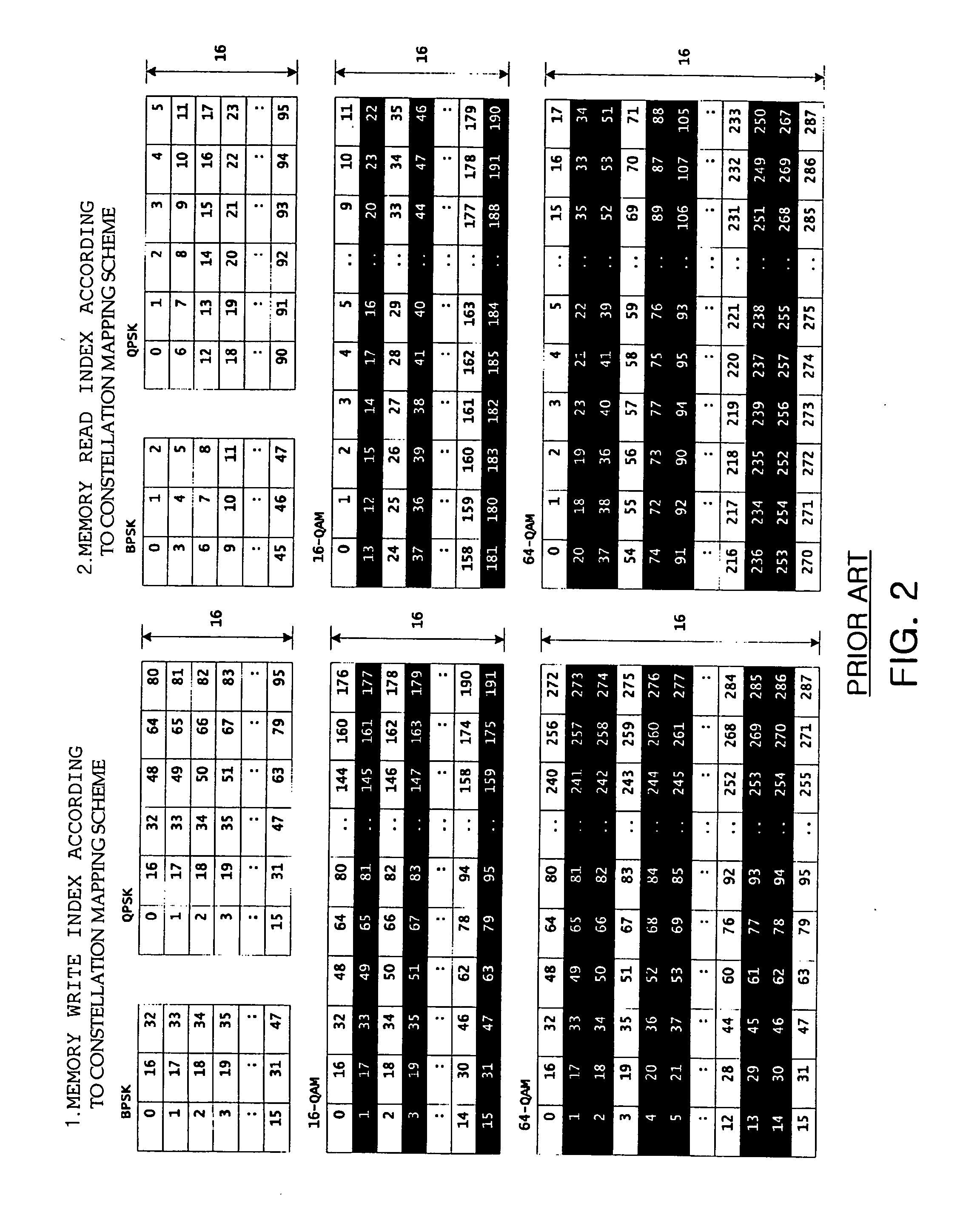
Interleaving apparatus and method for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing transmitter
ActiveUS20060123323A1Digital storageMulti-frequency code systemsAddress generation unitControl signal
An interleaving apparatus and method for an OFDM transmitter are provided. The interleaving apparatus comprises a memory unit, a memory write / read control unit, a memory access address generation unit, and a second permutation and output selection unit. The memory unit includes a plurality of memory banks, which are capable of being independently controlled so that data can be written or read in / from the memory banks, each having memory cells arranged in an NxM matrix structure. The memory write / read control unit generates control signals to write / read data in / from the memory unit. The memory access address generation unit generates a memory access address used to write / read data in / from the memory unit in response to the memory write / read control signals. The second permutation and output selection unit rearranges the positions of data bits output from the memory unit and outputs the position-rearranged data bits.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
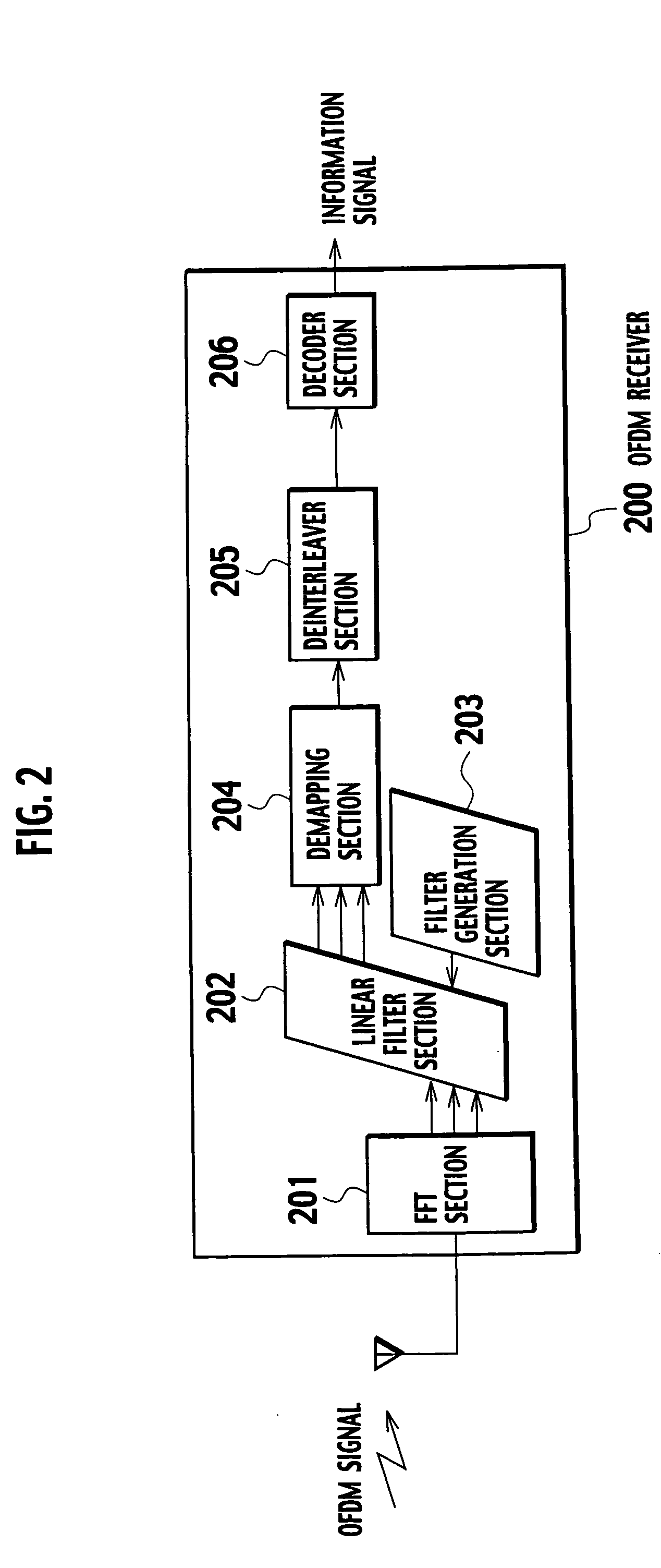
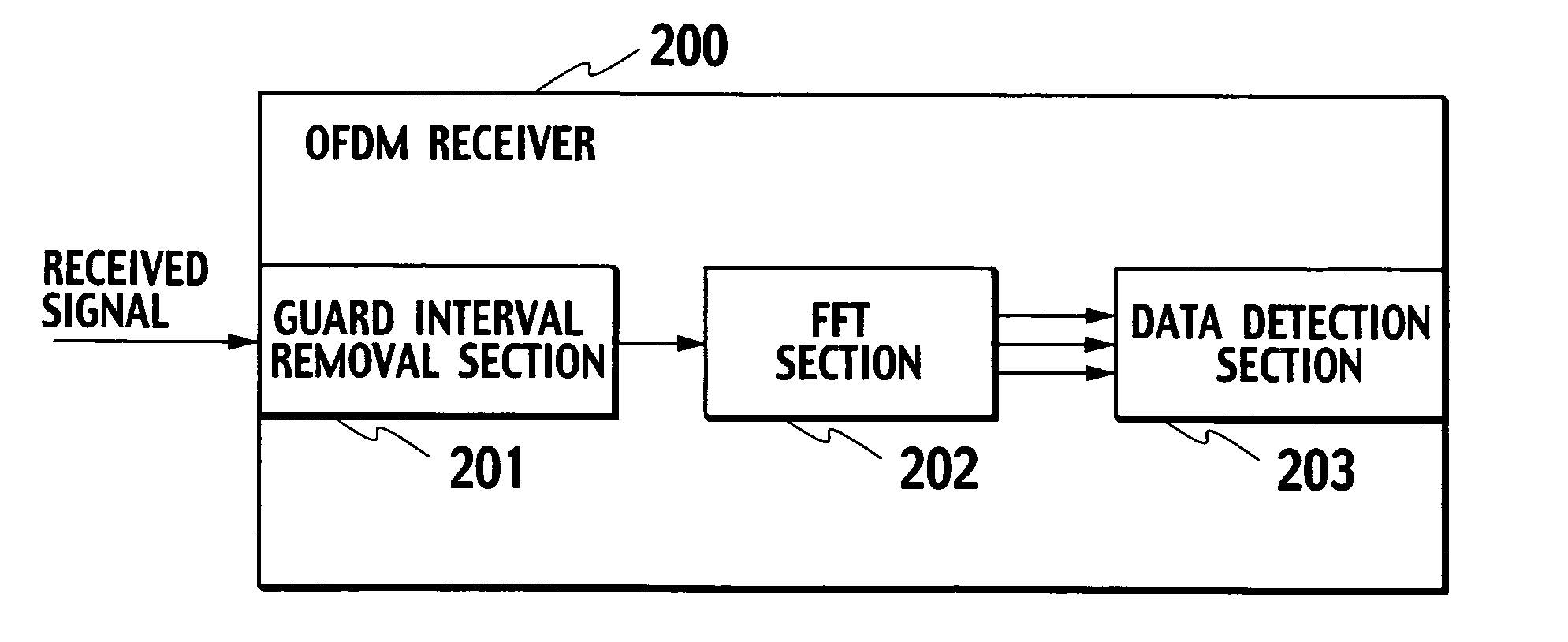
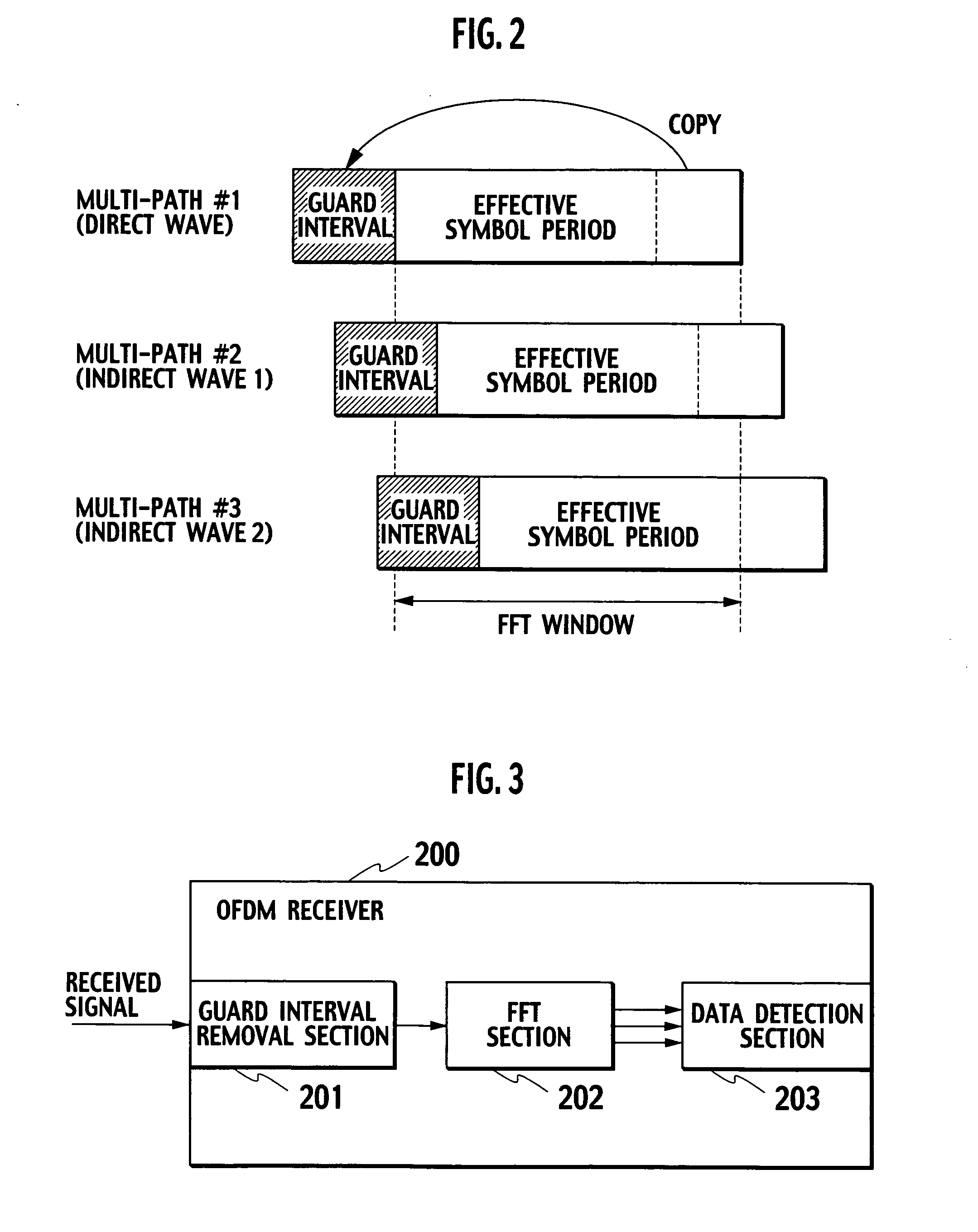
OFDM receiver
InactiveUS20050129136A1Reduce the amount of processingSpatial transmit diversityLine-faulsts/interference reductionOfdm transmitterMulti path
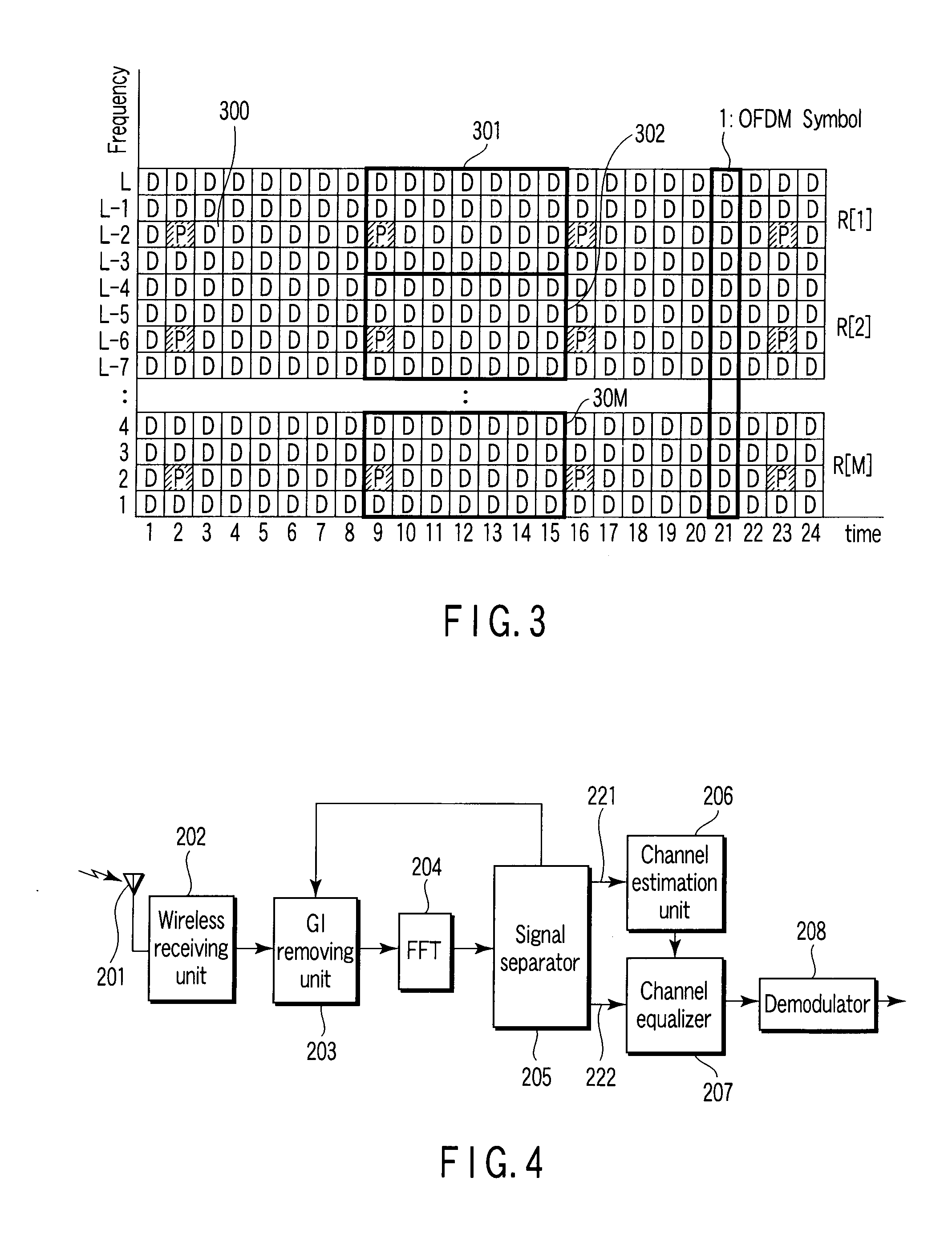
An OFDM receiver receives an OFDM signal transmitted from an OFDM transmitter by using a sub-carrier. The OFDM receiver includes a channel estimator configured to obtain a channel estimated value of each multi-path based on OFDM signals received through a plurality of multi-paths; a transmission signal estimated value calculator configured to calculate a transmission signal estimated value as an estimated value of the OFDM signal; and an inter-carrier interference compensator configured to extract a multi-path not becoming a form to contain a signal component only of a target symbol in an FFT window based on the transmission signal estimated value and the channel estimated value of each multi-path, and to compensate for inter-carrier interference in the OFDM signal based on signal components corresponding to all sub-carriers of the multi-paths.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
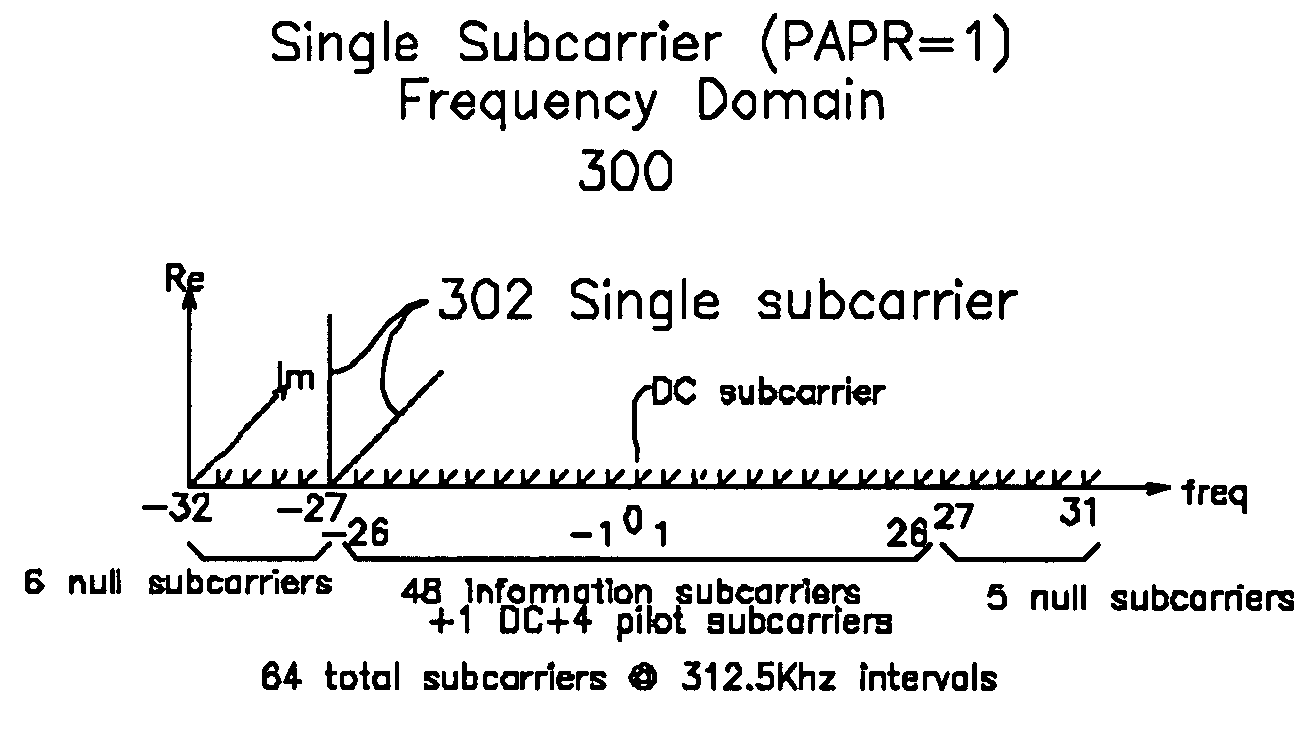
Peak to Average Power Ratio Reduction Apparatus and Method for a Wireless OFDM transmitter
ActiveUS20090103639A1Minimizing PAPRDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationCarrier signalOfdm transmitter
An OFDM symbol comprises information subcarriers which carry the information to be transmitted, accompanied by edge subcarriers, which are selected to minimize the PAPR of the transmitted signal. The selection of edge subcarriers which minimizes PAPR enables either higher power transmission for the same information content, or lower power consumption for the same transmitted symbol power.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
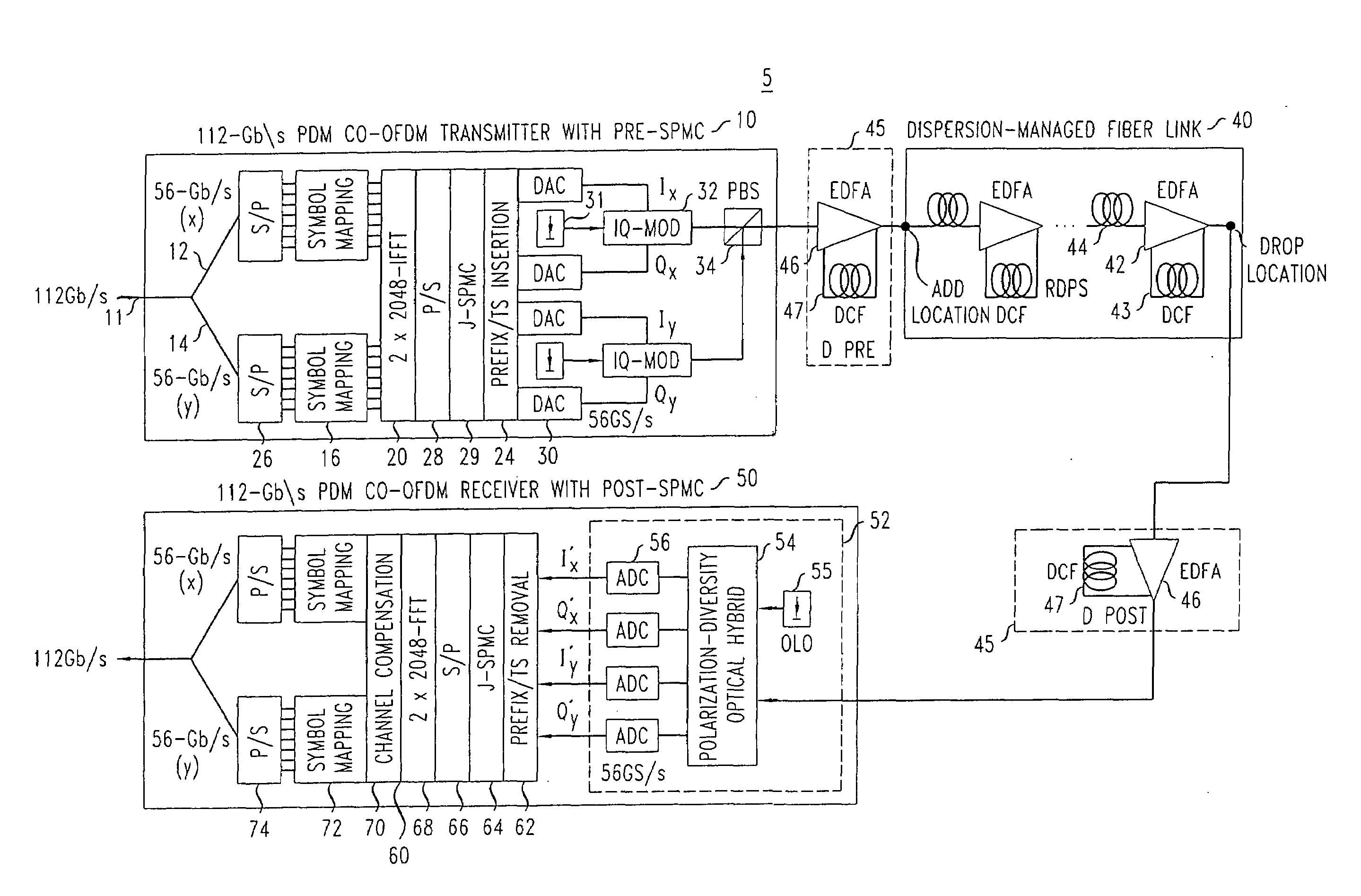
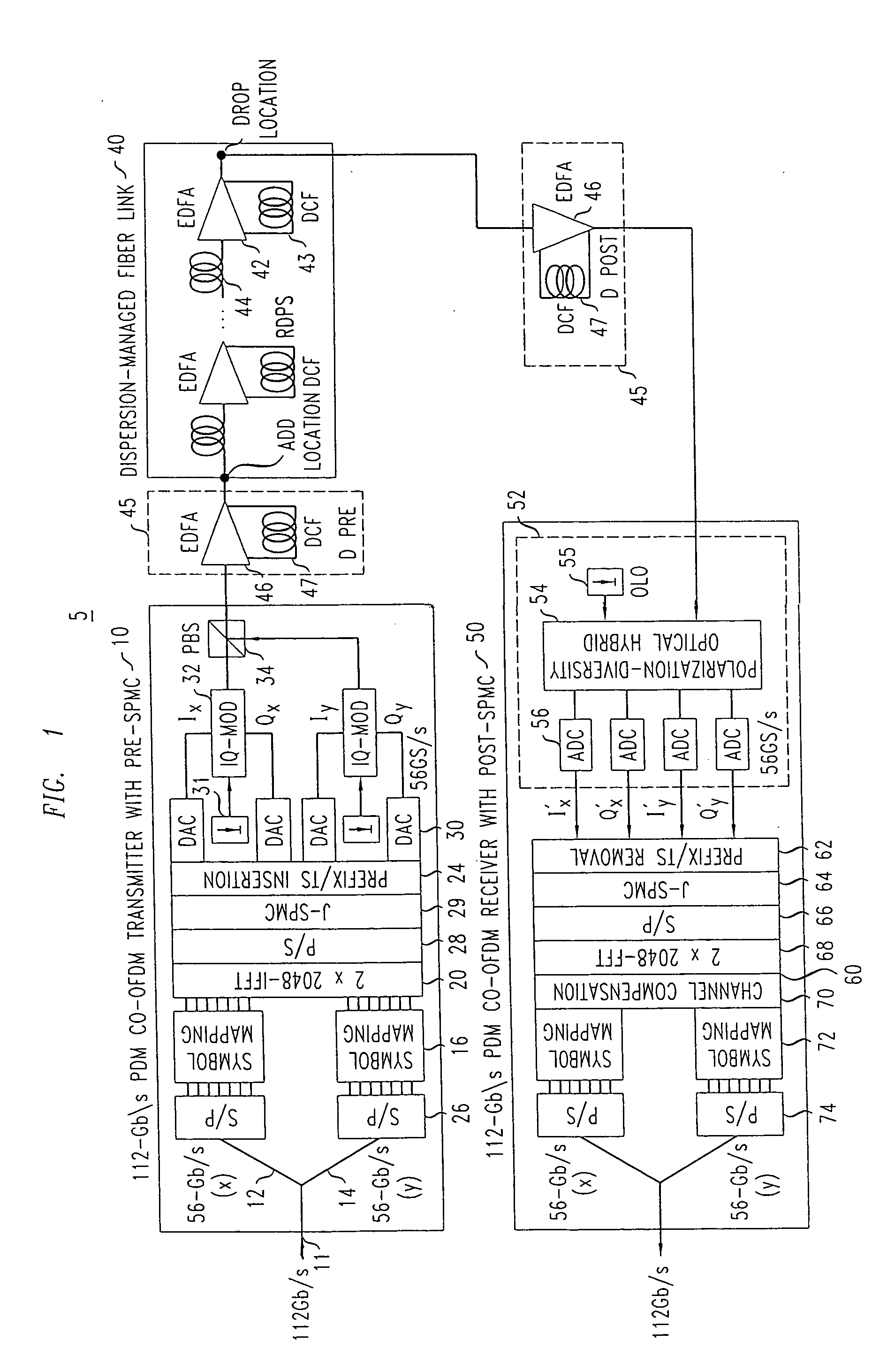
System, method and apparatus for joint self phase modulation compensation for coherent optical polarization-division-multiplexed orthogonal-frequency division-multiplexing systems
ActiveUS20100104284A1Polarisation multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationMultiplexingWave shape
System, apparatus and method of optical communication are provided for performing digital compensation of the self-phase modulation (SPM) effect experienced by a polarization-division multiplexed (PDM) orthogonal frequency-division multiplexed (OFDM) signal in fiber transmission by compensating a complex digital waveform representing one orthogonal polarization component of the optical PDM-OFDM signal based on both digital waveforms representing two orthogonal polarization components of the PDM-OFDM signal. The compensation of the digital waveform may be further based on an anticipated mean total nonlinear phase shift experienced by the signal during fiber transmission due to SPM. The compensation may be divided into pre-compensation at the PDM-OFDM transmitter and post-compensation at the PDM-OFDM receiver. The fiber transmission link preferably includes a pre-dispersion compensation module, distributed inline dispersion compensation modules, and a post-dispersion compensation module arranged in a judiciously chosen manner.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
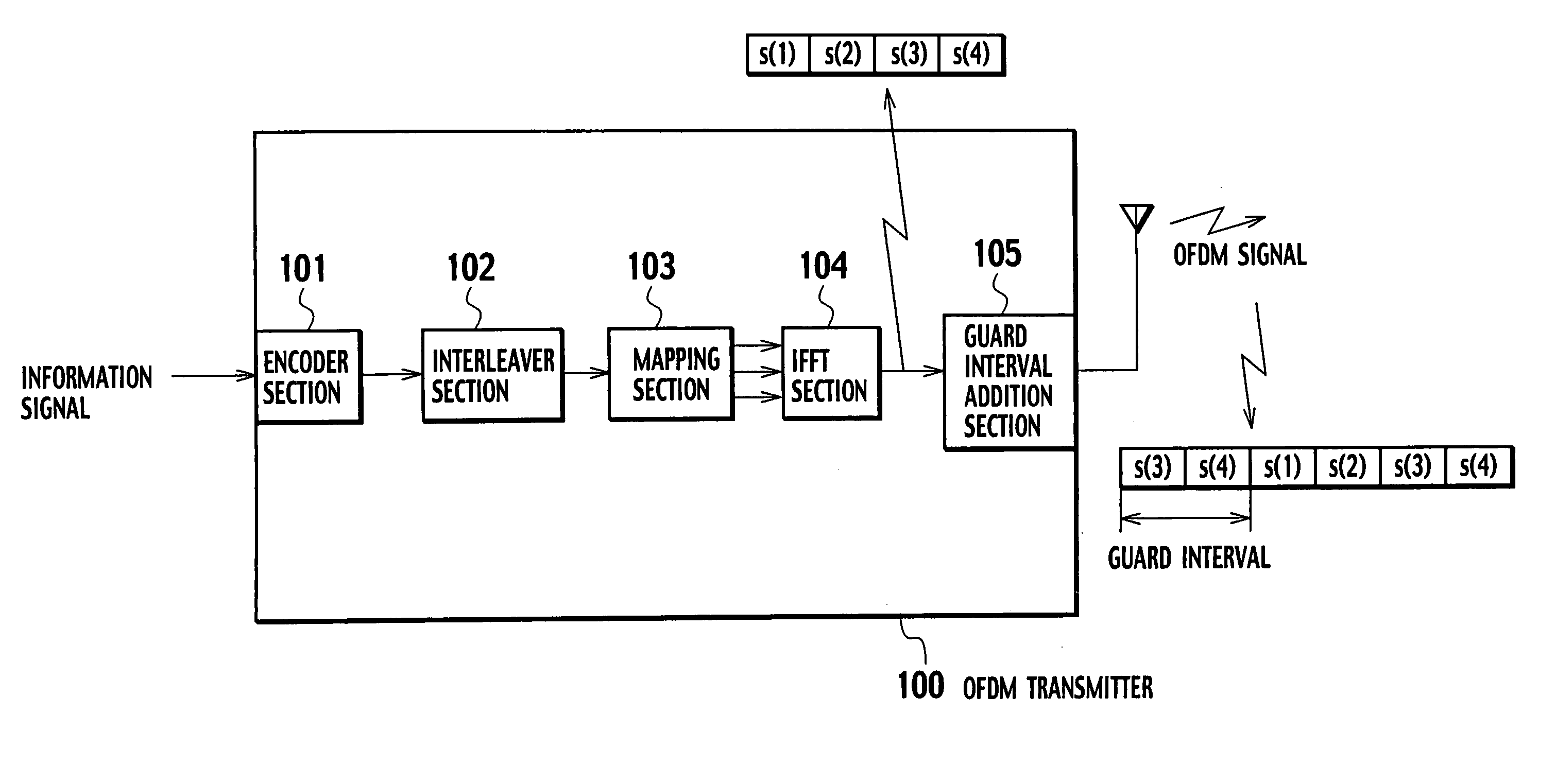
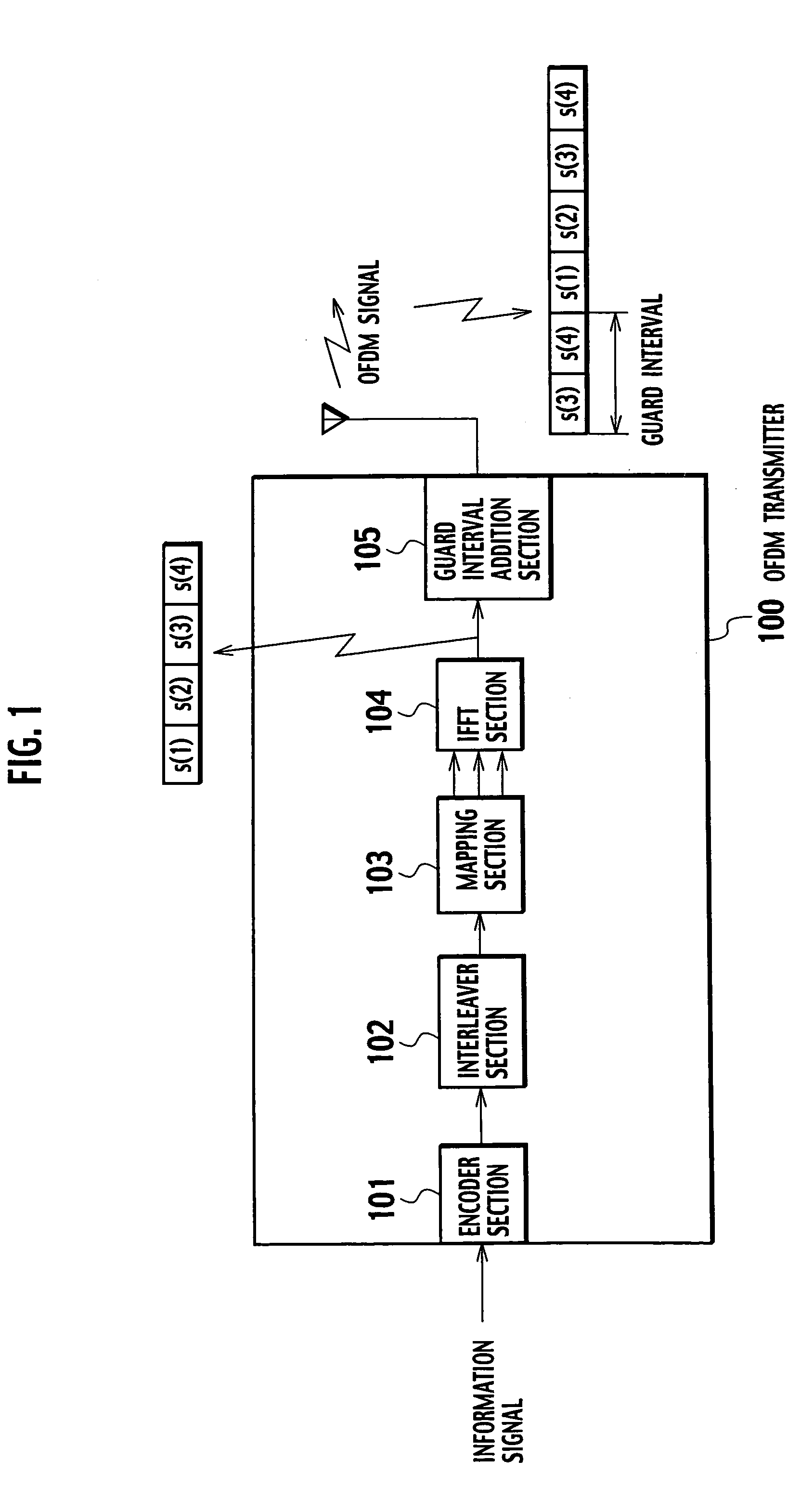
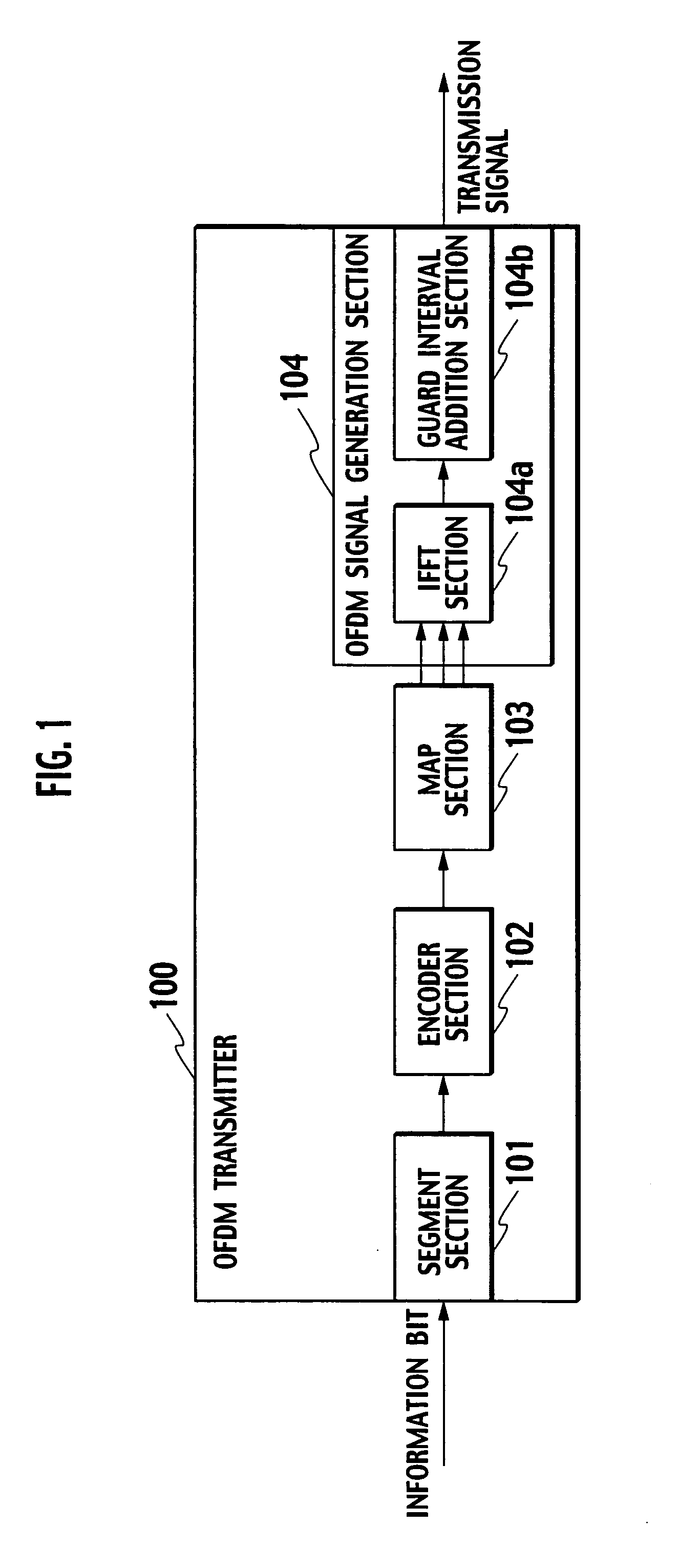
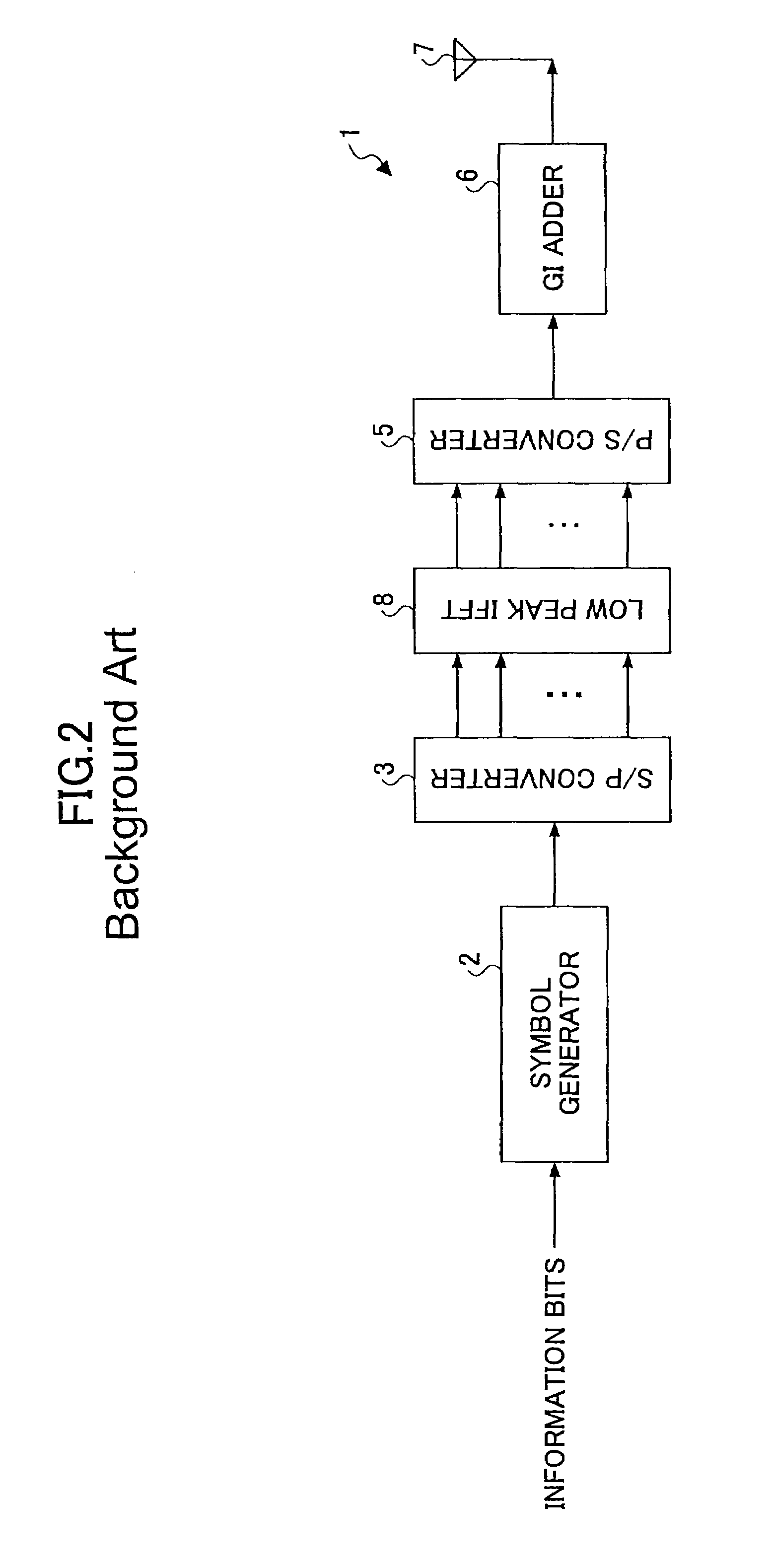
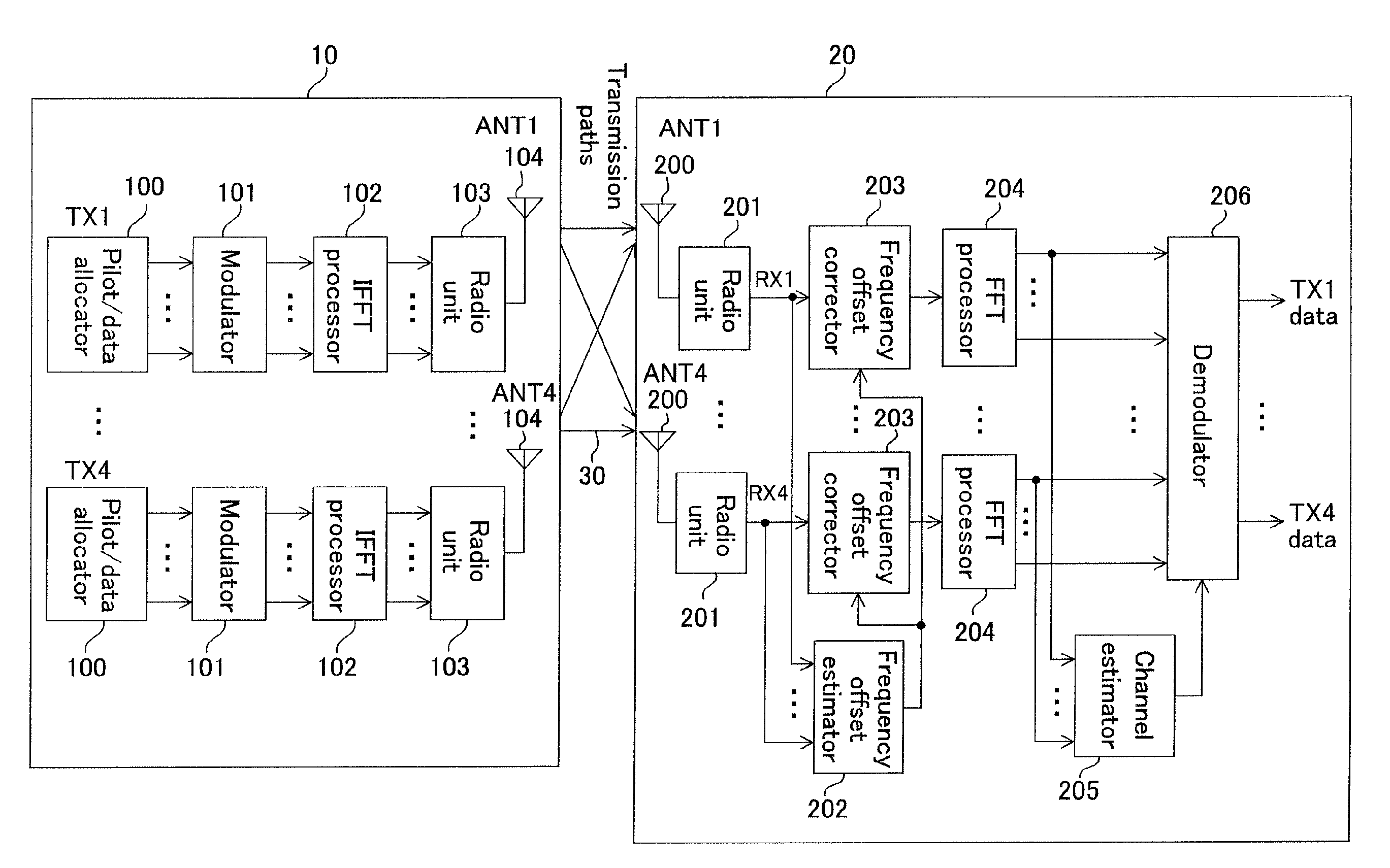
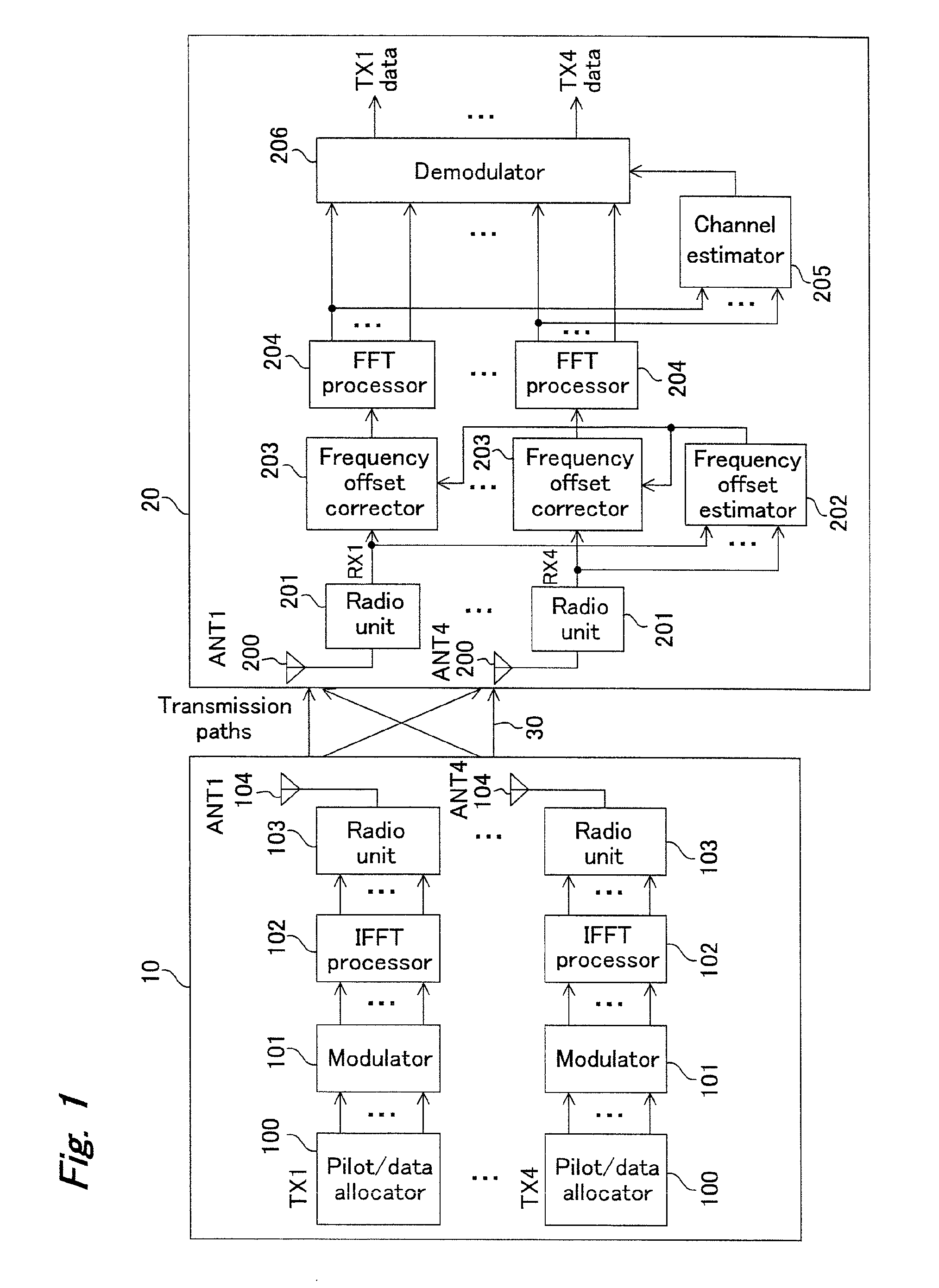
OFDM transmitter and OFDM receiver
ActiveUS20050099936A1Improve reception characteristicsLine-faulsts/interference reductionAmplitude demodulation detailsGuard intervalOfdm transmitter
An OFDM transmitter transmits an OFDM signal by a frame having a plurality of transmission symbol periods constituted of an effective symbol period for transmitting an information bit and a guard interval. The OFDM transmitter includes a guard interval length decider configured to decide a guard interval length in accordance with a feedback signal from an OFDM receiver; and a guard interval length changer configured to change a guard interval length in each transmission symbol period, in accordance with a decided guard interval length without changing a frame length.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Method and system for performing cell selection for OFDM communications
ActiveUS20070064586A1Efficient identificationFast and accurate initial acquisitionSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemCell selection
A method and apparatus are provided for performing acquisition, synchronization and cell selection within an MIMO-OFDM communication system. A coarse synchronization is performed to determine a searching window. A fine synchronization is then performed by measuring correlations between subsets of signal samples, whose first signal sample lies within the searching window, and known values. The correlations are performed in the frequency domain of the received signal. In a multiple-output OFDM system, each antenna of the OFDM transmitter has a unique known value. The known value is transmitted as pairs of consecutive pilot symbols, each pair of pilot symbols being transmitted at the same subset of sub-carrier frequencies within the OFDM frame.
Owner:APPLE INC
Scattered pilot pattern and channel estimation method for MIMO-OFDM systems
InactiveUS20070253324A1Reduced scattered pilot overheadLess computationally complexPower managementSpatial transmit diversityTime domainCommunications system
A method and apparatus are provided for reducing the number of pilot symbols within a MIMO-OFDM communication system, and for improving channel estimation within such a system. For each transmitting antenna in an OFDM transmitter, pilot symbols are encoded so as to be unique to the transmitting antenna. The encoded pilot symbols are then inserted into an OFDM frame to form a diamond lattice, the diamond lattices for the different transmitting antennae using the same frequencies but being offset from each other by a single symbol in the time domain. At the OFDM receiver, a channel response is estimated for a symbol central to each diamond of the diamond lattice using a two-dimensional interpolation. The estimated channel responses are smoothed in the frequency domain. The channel responses of remaining symbols are then estimated by interpolation in the frequency domain.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Method and apparatus providing adaptive learning in an orthogonal frequency division multiplex communication system
InactiveUS20050025040A1Wide applicabilityImprove performanceTime-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexMultiplexingCommunications system
Disclosed is a method to operate an orthogonal frequency duplex multiplexing (OFDM) communications system, and an OFDM system that operates in accordance with the method. The method includes, when transmitting data over a plurality of OFDM sub-channels from an OFDM transmitter (12A) to an OFDM receiver (12B) through a channel (24), operating an adaptive learning automaton (50) to adjust values of modulation coding scheme (MCS) switching thresholds so as to maximize at least one selected performance criterion; based on the values of the switching thresholds, selecting a MCS and modulating data with the selected MCS and transmitting the modulated data over at least some of the sub-channels. The method further includes receiving the data at the OFDM receiver and demodulating the received data using a demodulator that corresponds to the selected MCS.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method and system for performing synchronization in OFDM systems
ActiveUS20070025236A1Efficient identificationFast and accurate initial acquisitionSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemCell selection
A method and apparatus are provided for performing acquisition, synchronization and cell selection within an MIMO-OFDM communication system. A coarse synchronization is performed to determine a searching window. A fine synchronization is then performed by measuring correlations between subsets of signal samples, whose first signal sample lies within the searching window, and known values. The correlations are performed in the frequency domain of the received signal. In a multiple-output OFDM system, each antenna of the OFDM transmitter has a unique known value. The known value is transmitted as pairs of consecutive pilot symbols, each pair of pilot symbols being transmitted at the same subset of sub-carrier frequencies within the OFDM frame.
Owner:APPLE INC
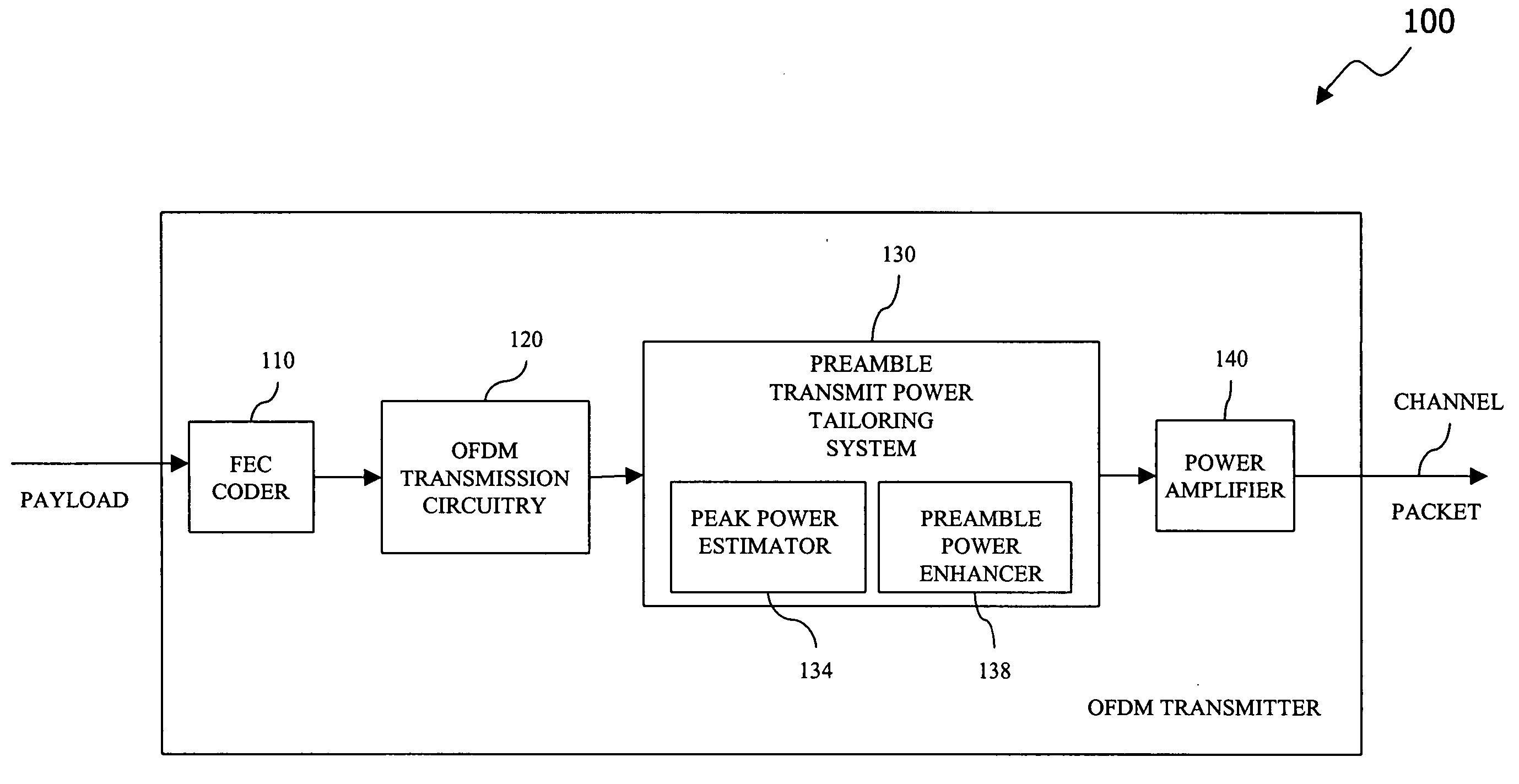
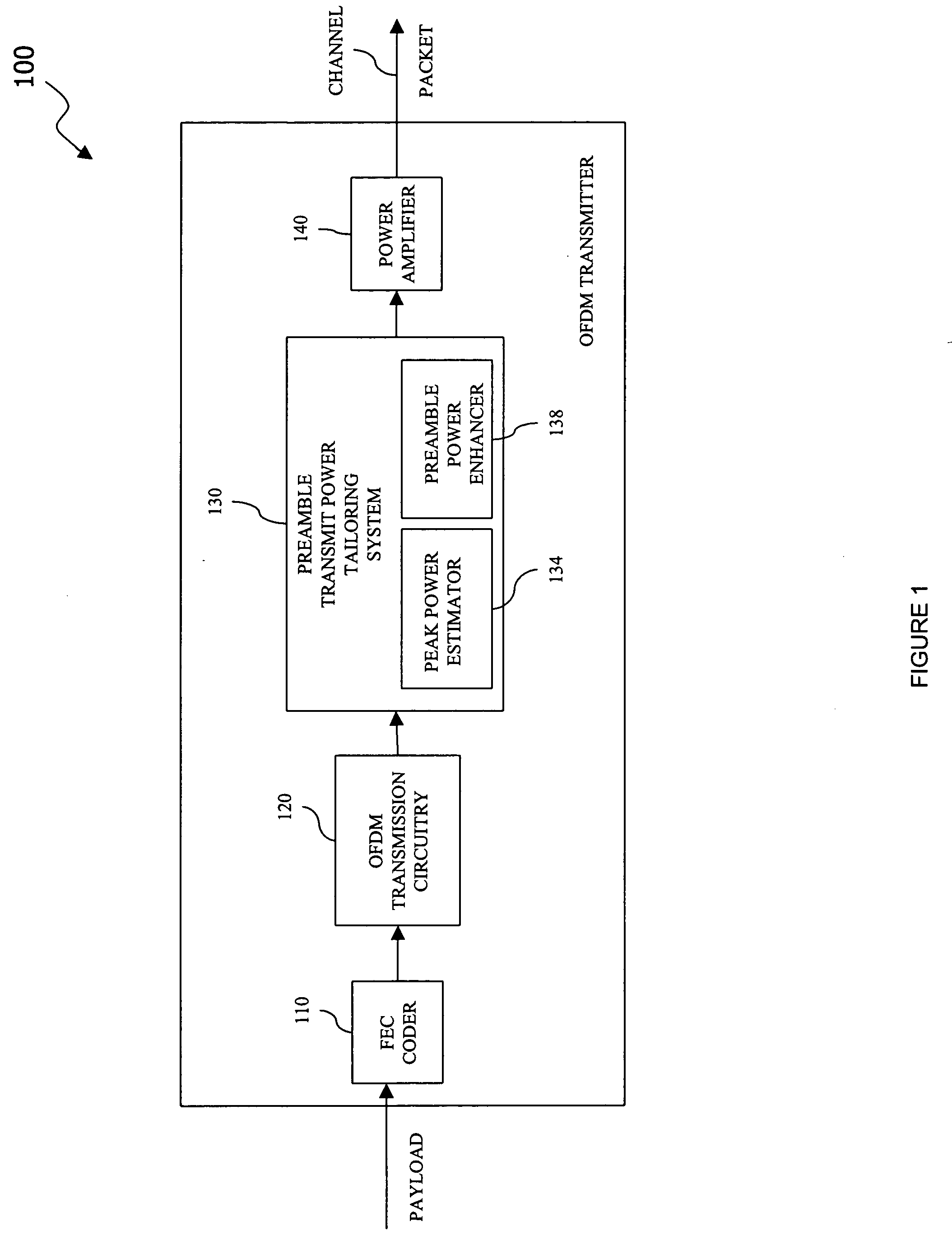
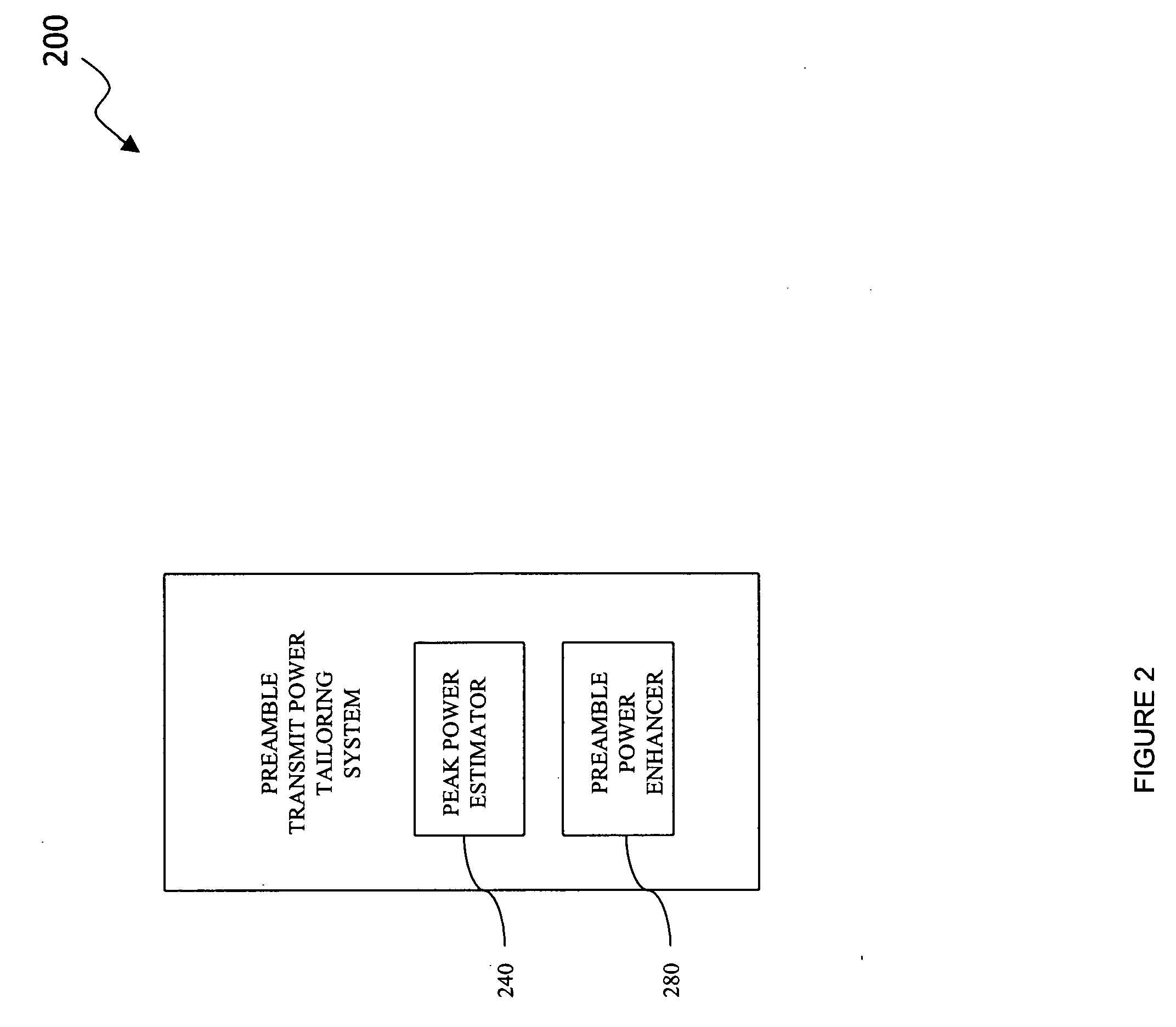
Preamble transmit power tailoring system, a method of tailoring preamble transmit power and an OFDM transmitter employing the same
InactiveUS20050147022A1Increase transmit powerIncrease powerPower managementTransmission control/equalisingTransmitted powerOfdm transmitter
A preamble transmit power tailoring system for use with an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) transmitter, a method of tailoring preamble transmit power, and an OFDM transmitter. In one embodiment, the preamble transmit power tailoring system includes (1) a peak power estimator configured to calculate, based on a payload to be transmitted by the OFDM transmitter and an associated transmit power limitation value, an available power headroom and (2) a preamble power enhancer, associated with the peak power estimator, configured to increase transmit power of at least a portion of a preamble for the payload subject to the available power headroom.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
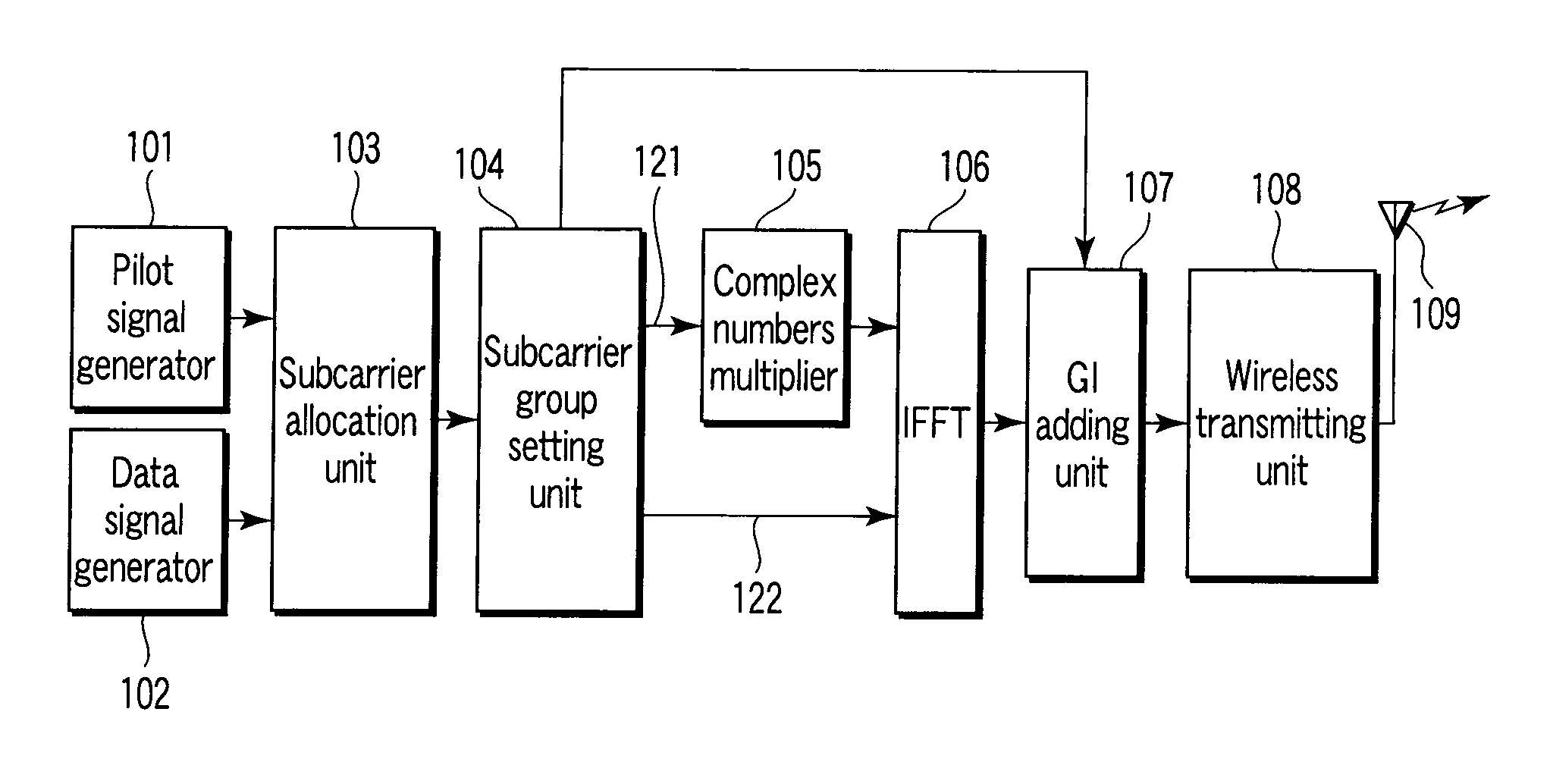
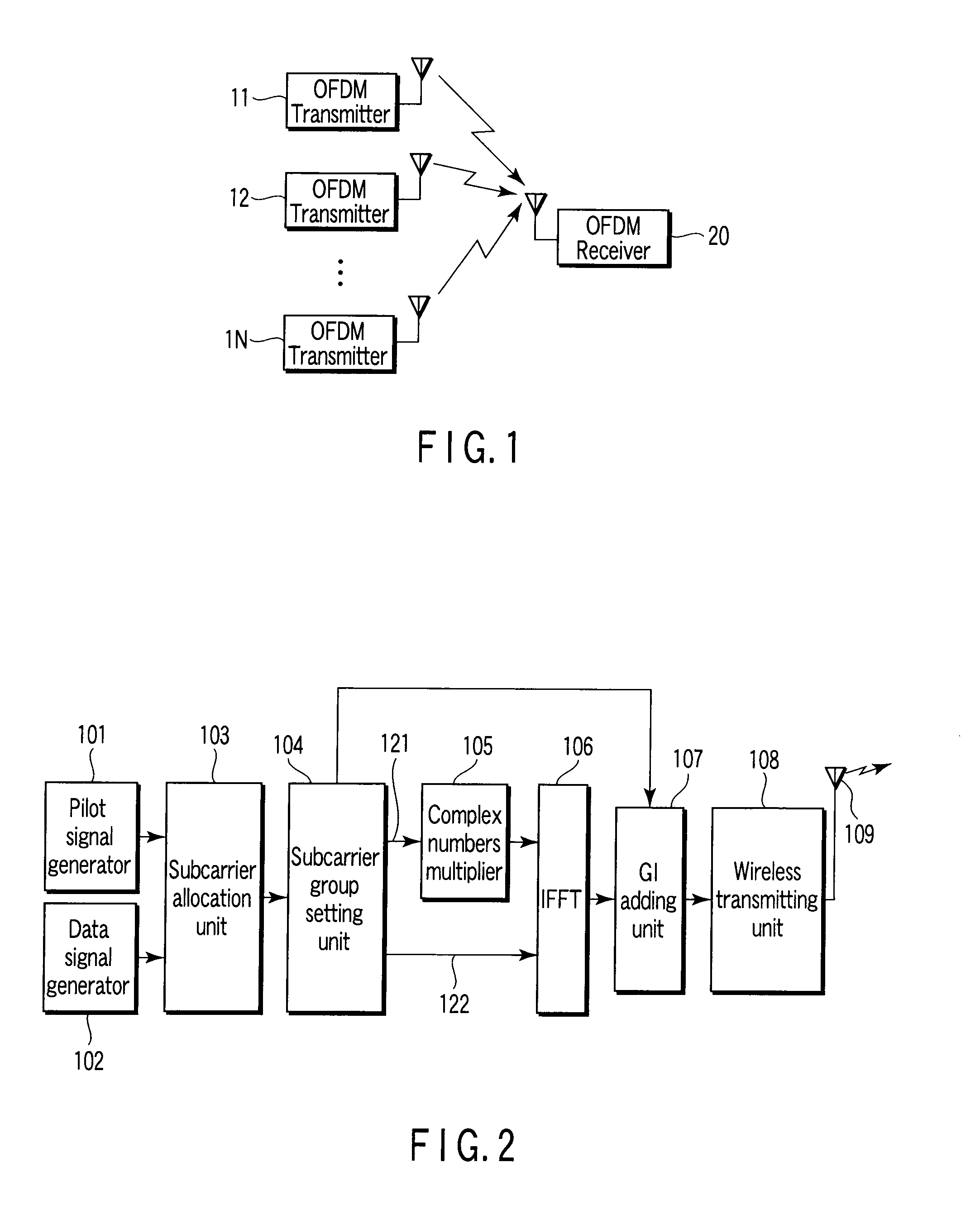
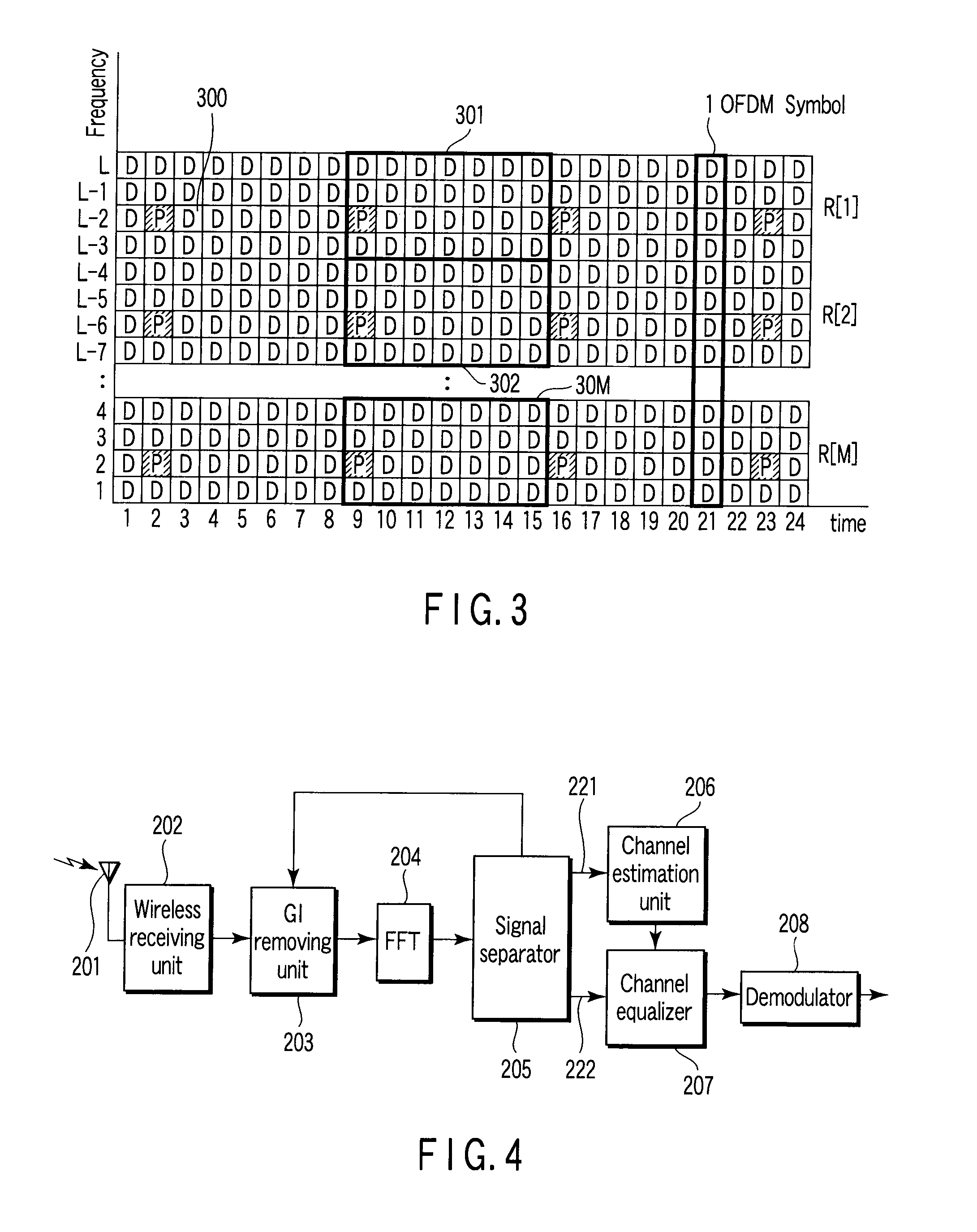
Method of transmitting OFDM signal and transmitter and receiver thereof
ActiveUS20070253321A1Small amount of calculationLess deteriorationSite diversityTransmission control/equlisationData signalCarrier signal
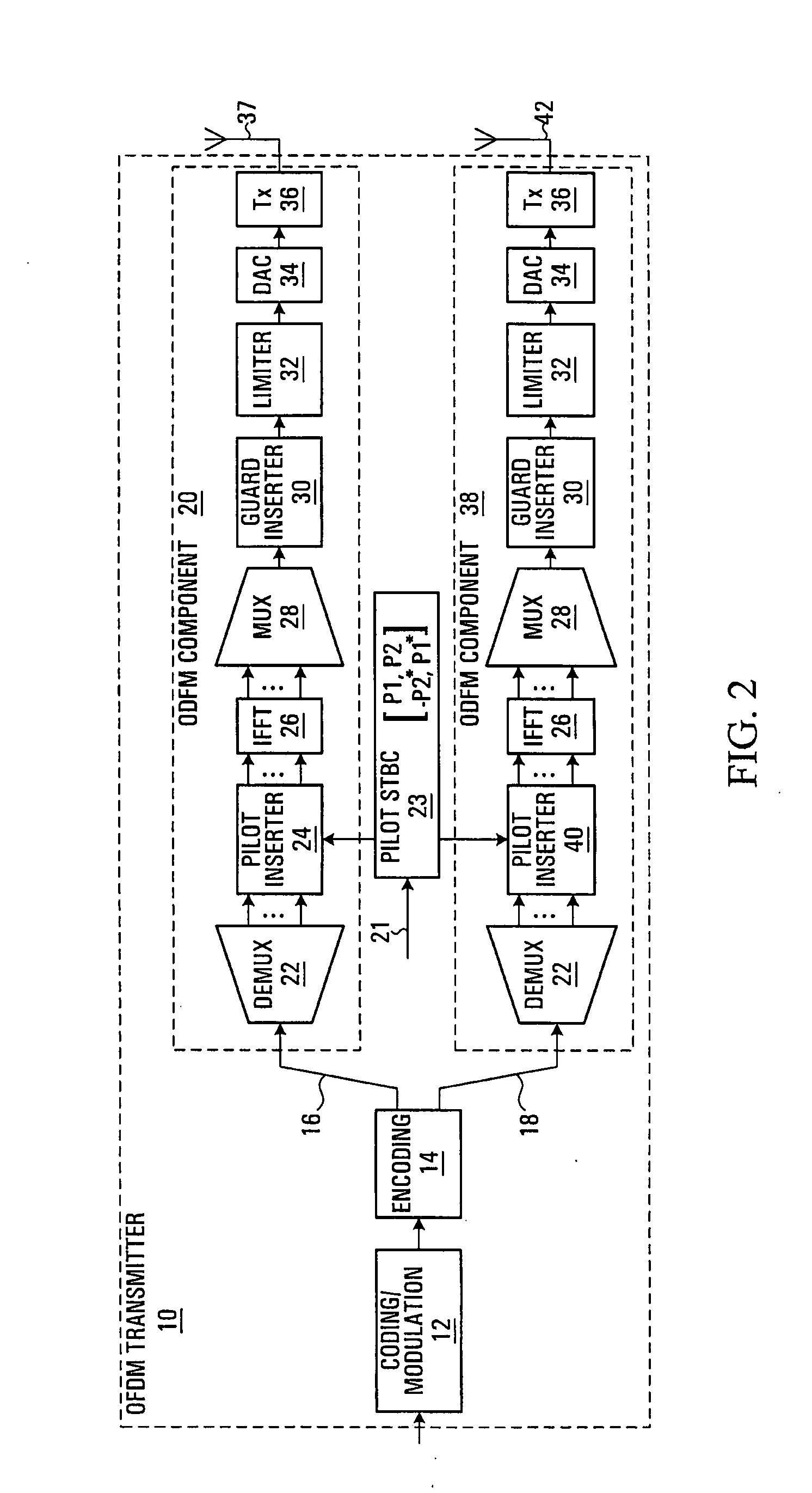
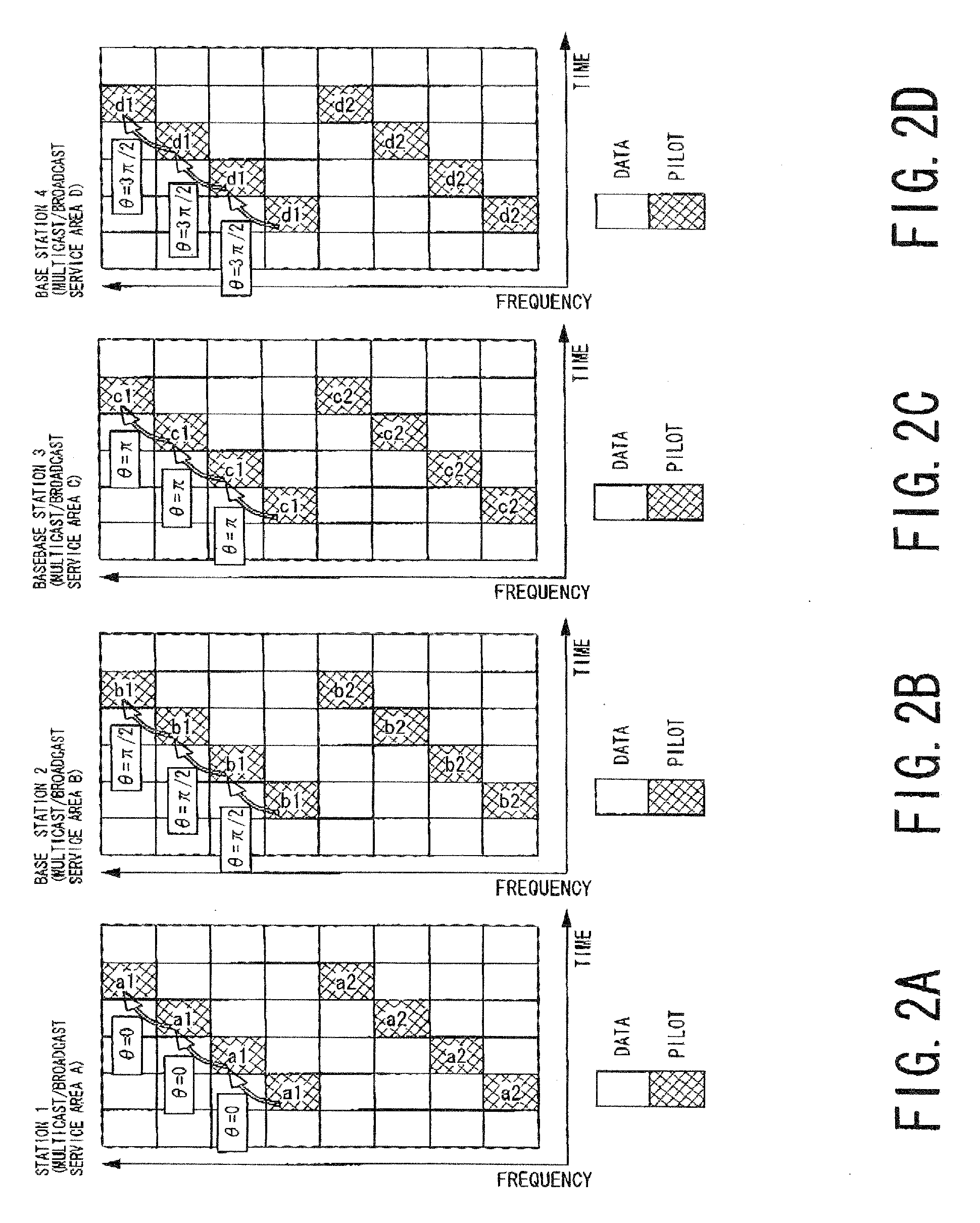
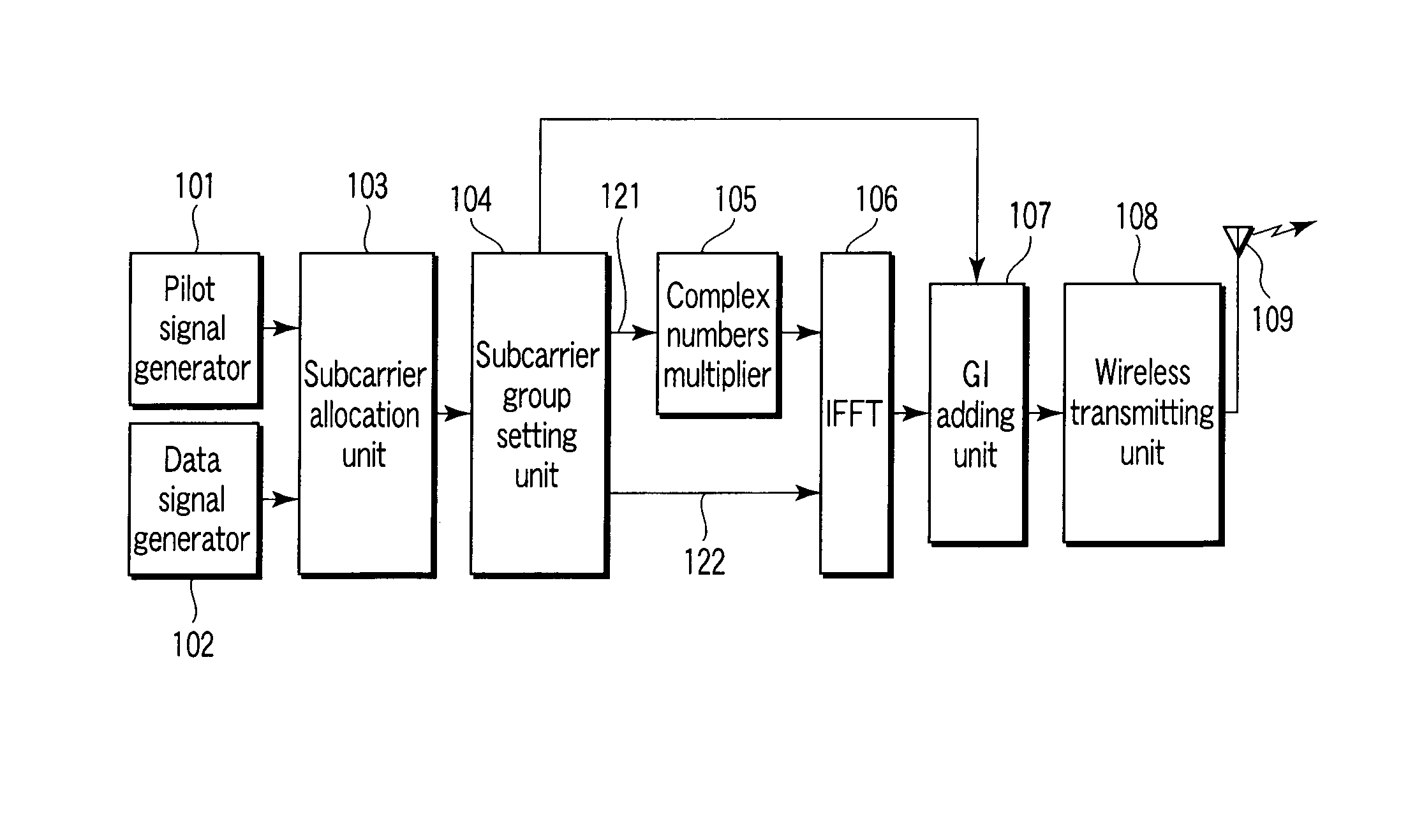
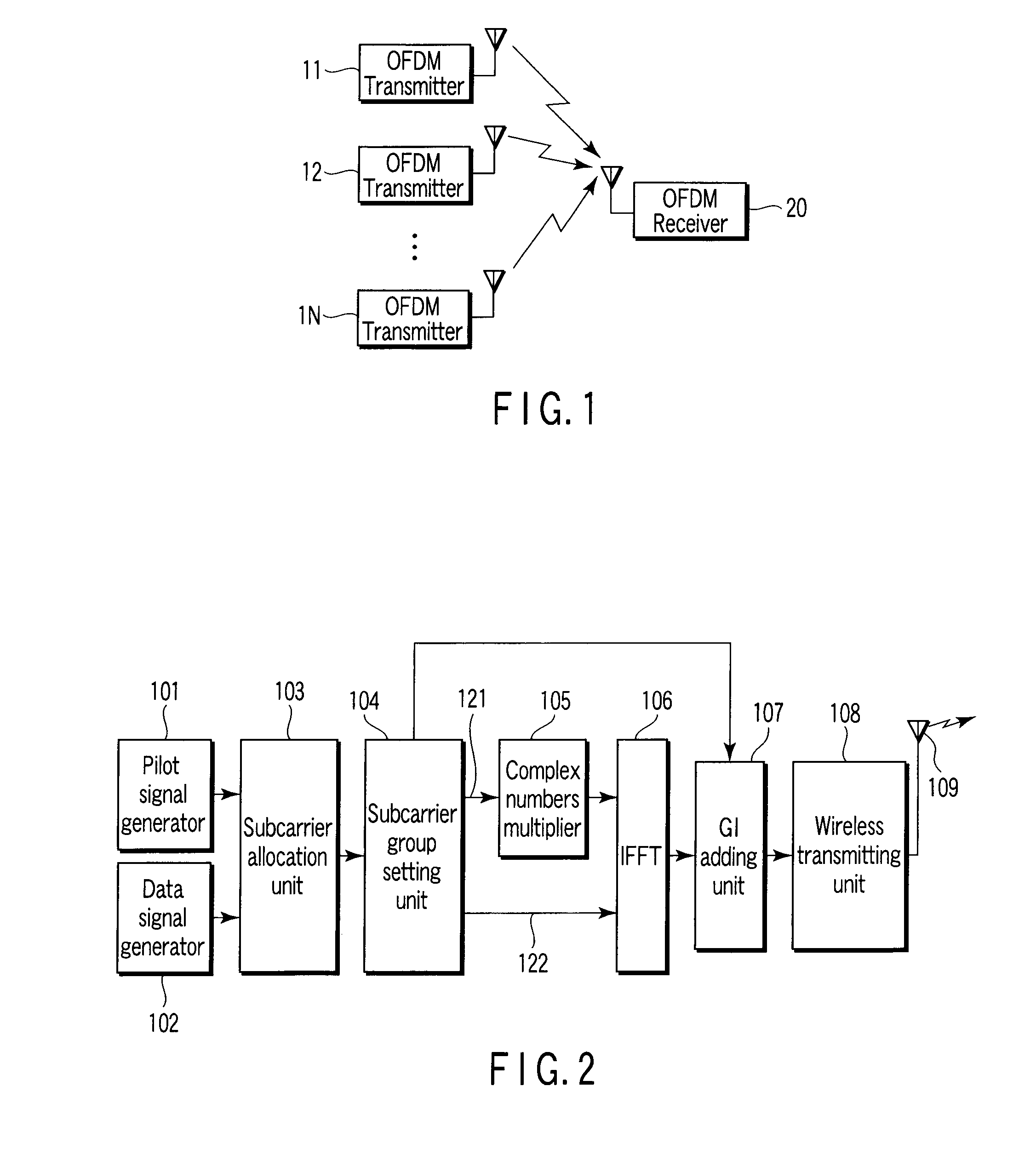
An OFDM transmitter includes, a data signal generator which generates a data signal by modulating a bit string obtained by channel coding, a pilot signal generator which generates a pilot signal, an allocation unit which allocates the pilot signal and data signal to a pilot subcarrier and a data subcarrier, a multiplier which multiples the first pilot signal and the first data signal by complex numbers for subcarrier group formed of specific pilot subcarrier of the pilot subcarriers and specific data subcarrier of the data subcarriers, a modulator which performs OFDM modulation on the second pilot signal and the second data signal to generate an OFDM signal, and a transmitting unit which transmits the OFDM signal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
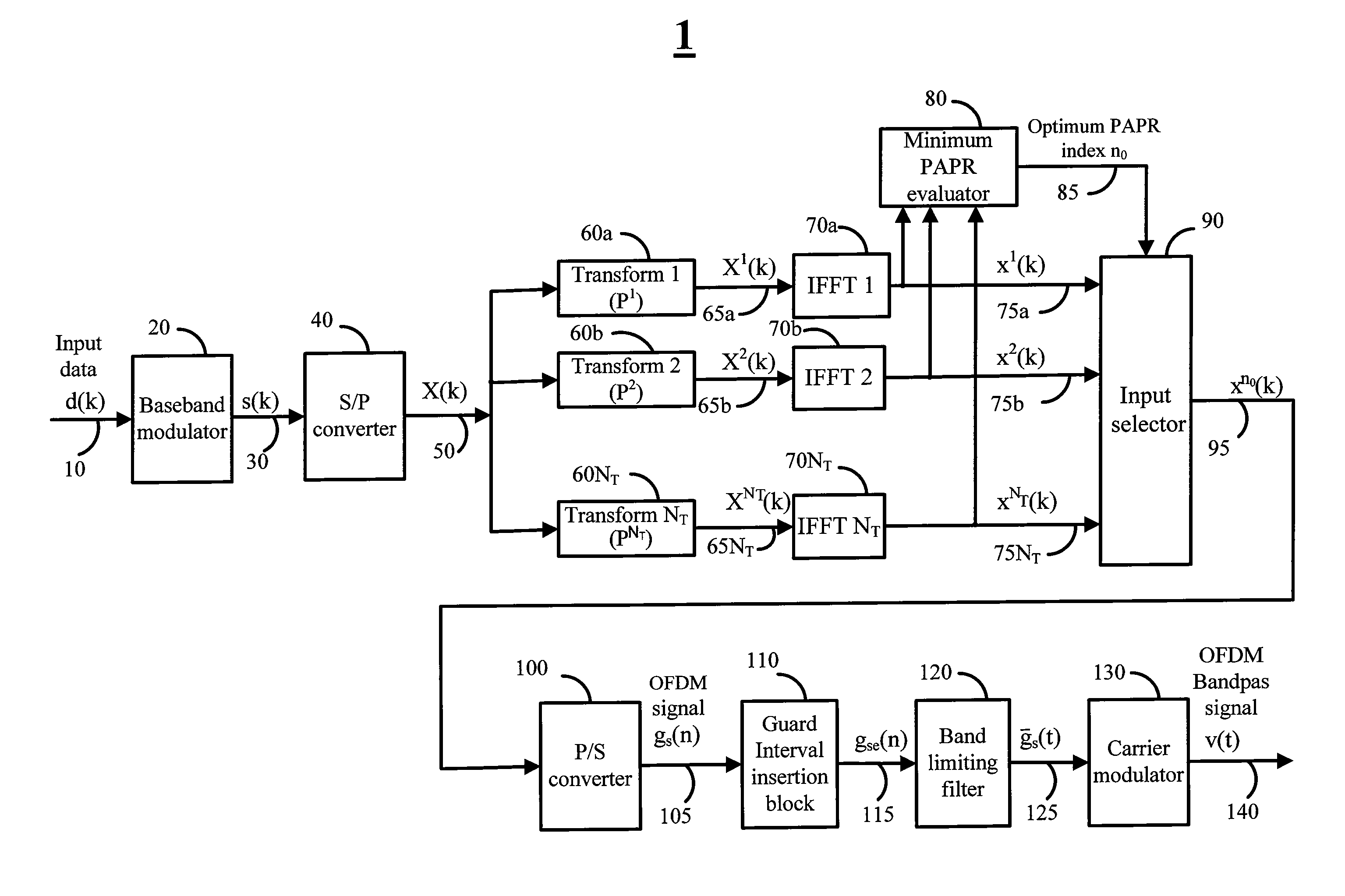
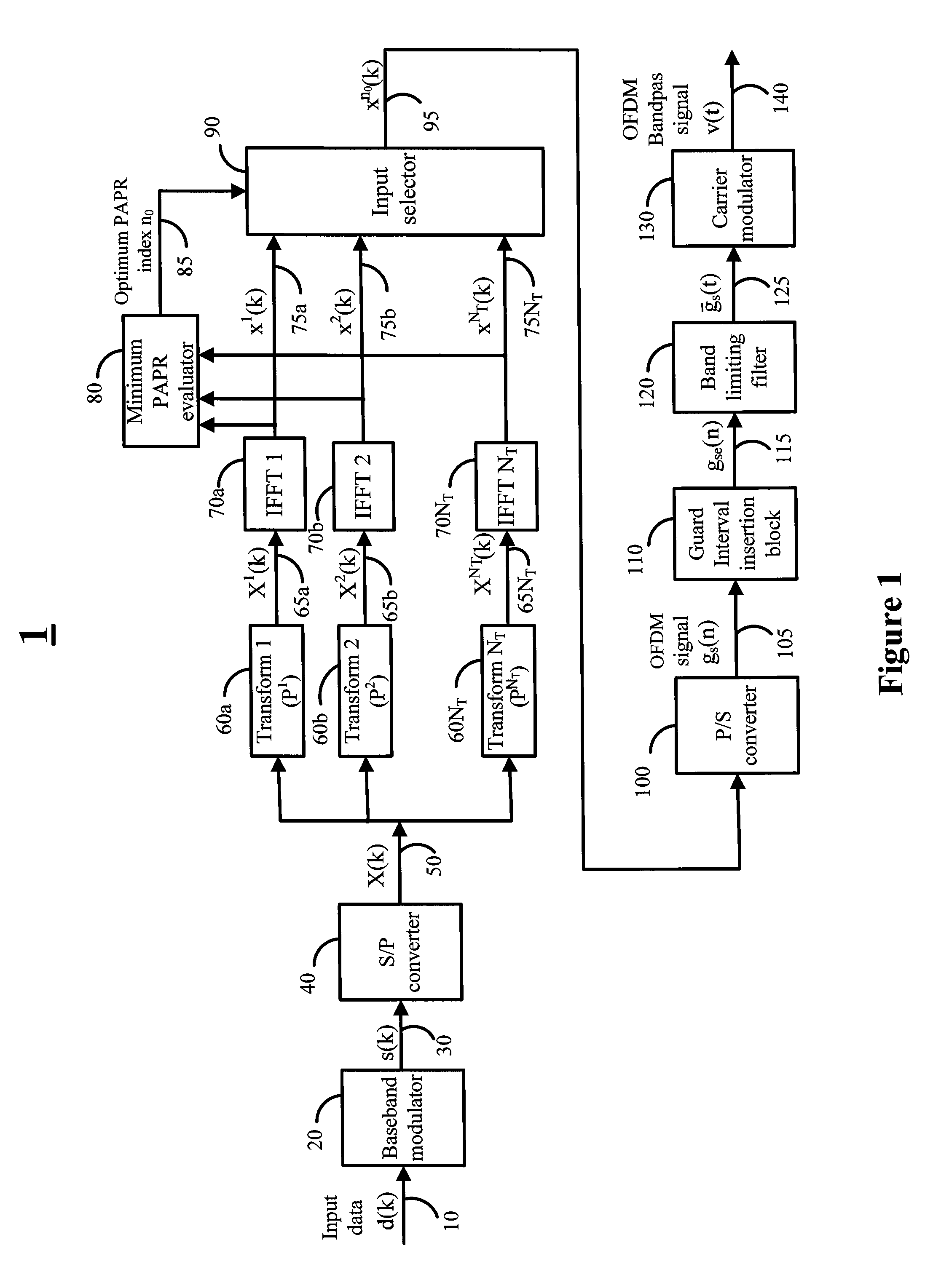
Multi transform OFDM systems and methods with low peak to average power ratio signals
InactiveUS20140362934A1Low peak to average power ratioImprove bandwidth efficiencyAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationHigh bandwidthOfdm transmitter
Various embodiments of the invention are directed to methods and systems for multi transform OFDM transmitter and receivers with low peak to average power ratio (PAPR) signals, that have high bandwidth efficiency and are computational efficient. For example, various embodiments of the transmitter may utilize an architecture comprised of a baseband modulator, a serial to parallel converter, a bank of multiplicity NT orthonormal transforms unit, a bank of multiplicity NT inverse Fourier transforms unit, a dummy symbols generator, and a minimum PAPR evaluation unit for finding the optimum transform index n0. Various embodiments of the receiver may comprise of a transform index detection unit for the detection of the transform index imbedded in the OFDM signal.
Owner:KUMAR RAJENDRA
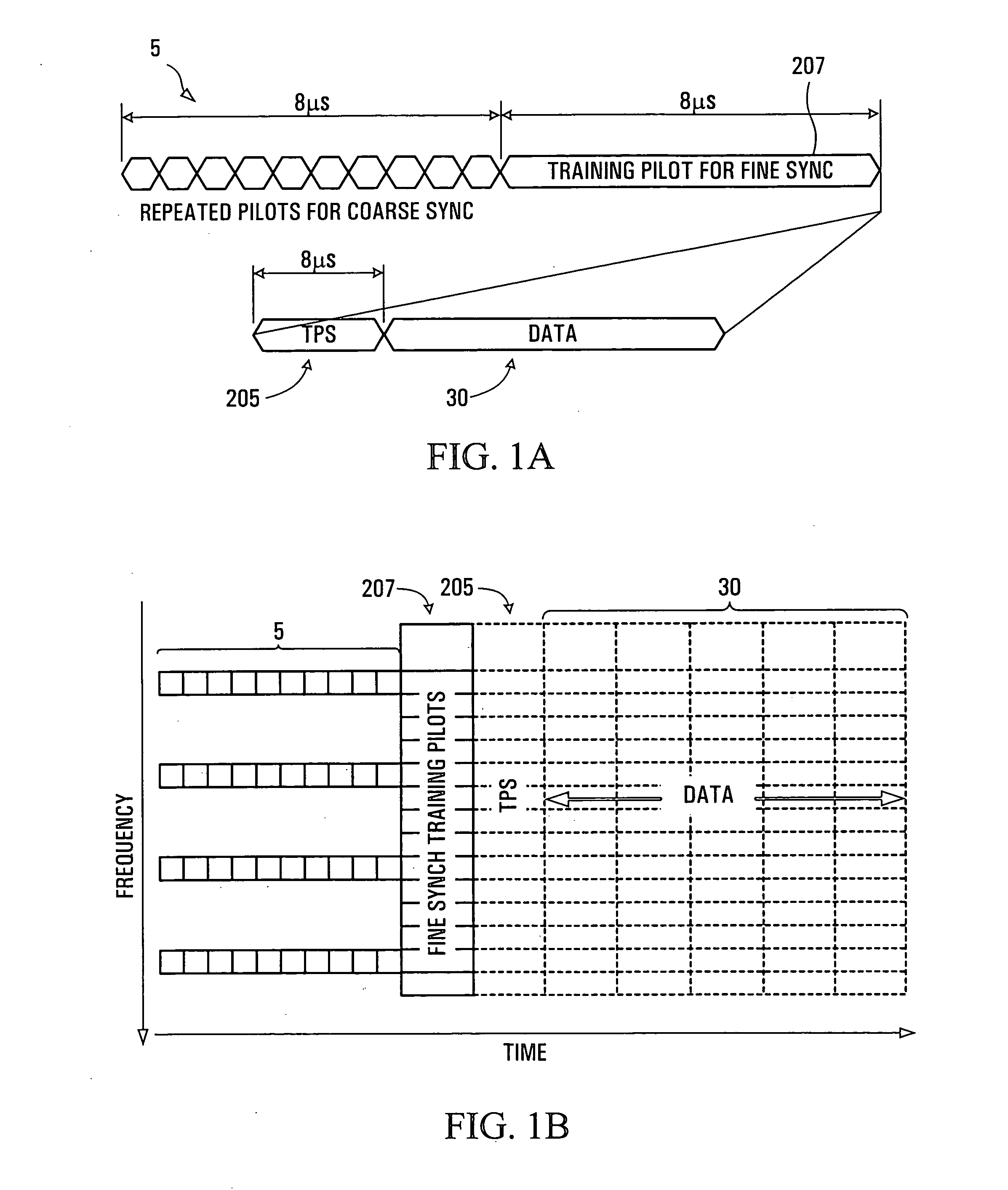
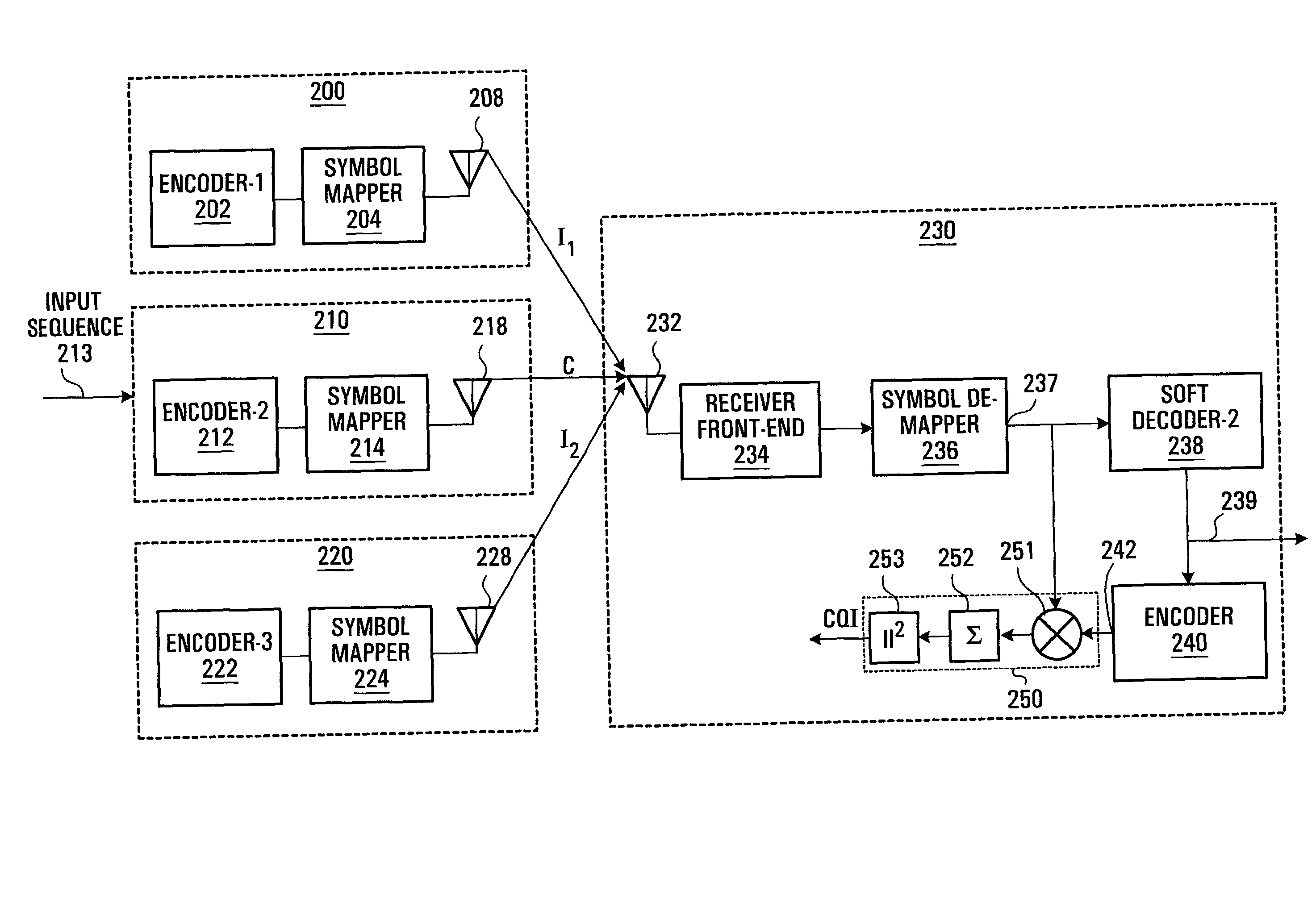
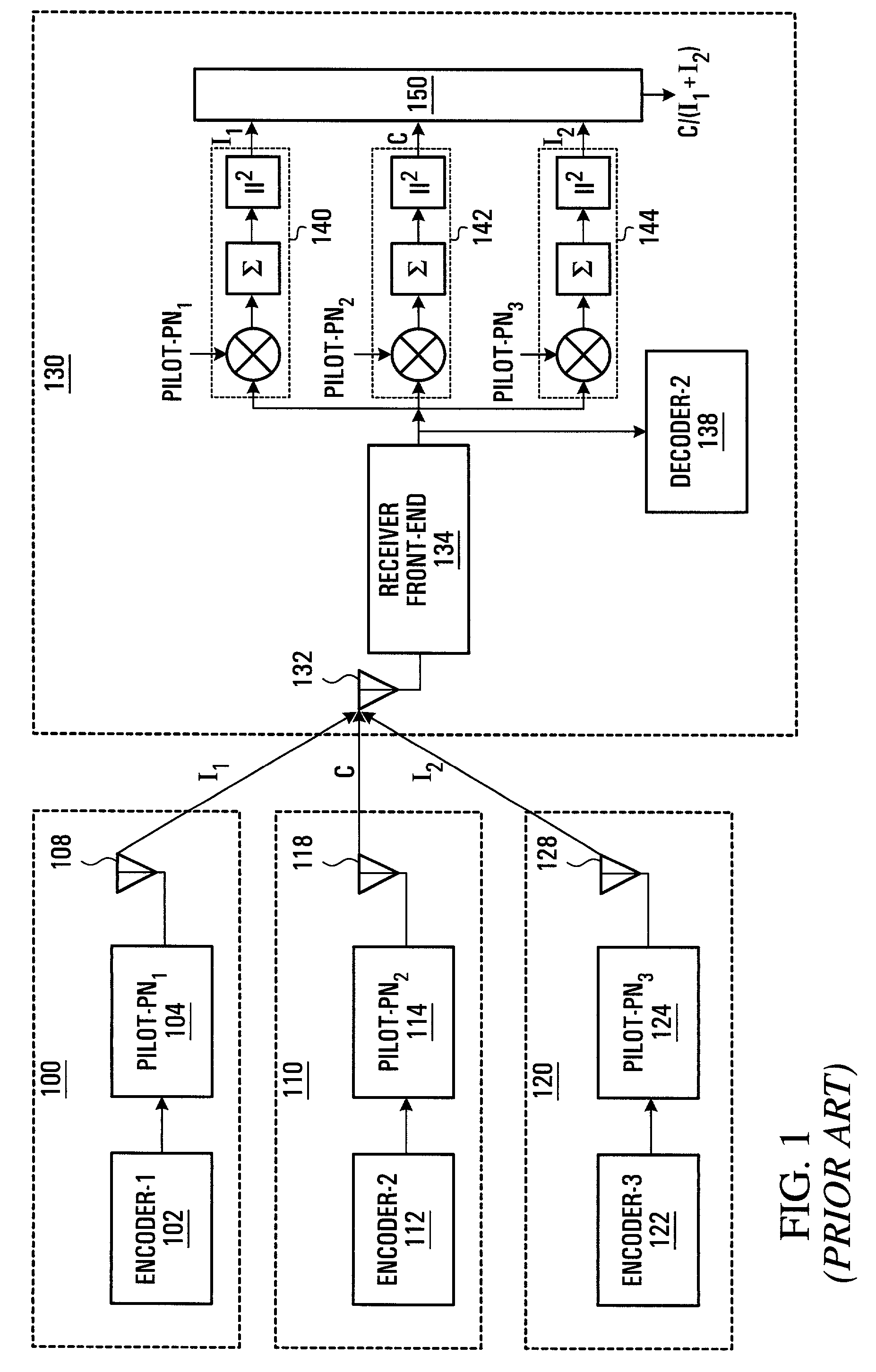
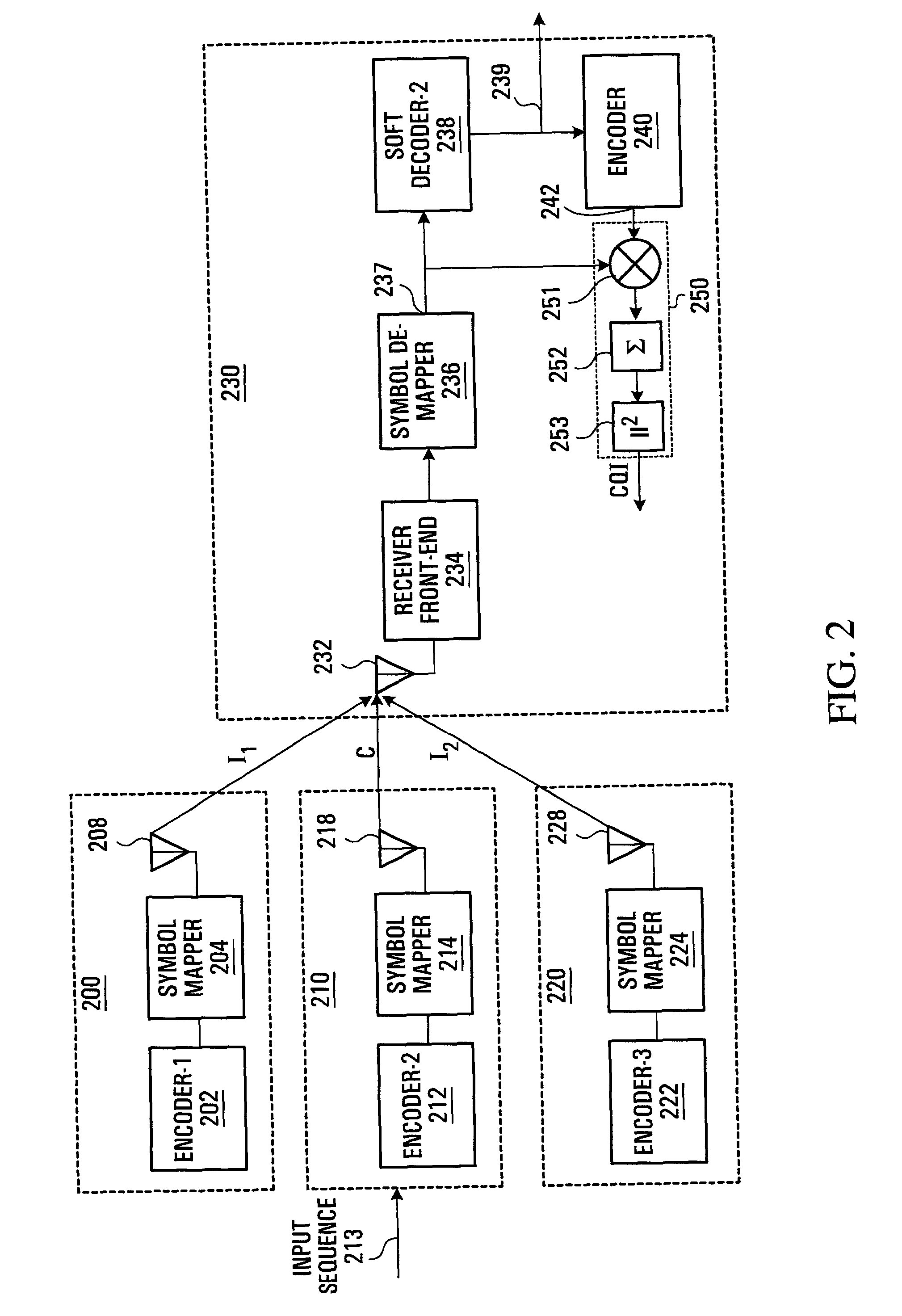
Method and apparatus for channel quality measurements
ActiveUS7773699B2Simple accurate and robust channel quality measurementAvoids Walsh Code Coherent LossError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionDifferential space timeOfdm transmitter
A method and apparatus are provided for combining pilot symbols and Transmit Parameter Signalling (TPS) channels within an OFDM frame. The method uses Differential Space-Time Block Coding to encode a fast signalling message at an OFDM transmitter. At an OFDM receiver, the encoded fast signalling message can be decoded using differential feedback to recover information about the channel responses that would normally be carried by pilot symbols. In wireless data transmission employing adaptive modulation and coding, an instantaneous channel quality measurement, independent of the origin of interference for example, neighboring-cell interference, white thermal noise, or residual Doppler shift is provided. Using the correlation between a signal which has been symbol de-mapped, and one which has also been soft decoded and re-encoded, a channel quality indicator is produced. Another embodiment uses TPS data as pilot symbols by decoding TPS and then re-encoding.
Owner:APPLE INC
6mhz bandwidth OFDM transmitter with the same guard interval as 8mhz dvb-t2
ActiveUS20160006593A1Easy to useMulti-frequency code systemsPilot signal allocationTime domainCarrier signal
A transmitter transmits data to a receiver using OFDM symbols including plural sub-carrier symbols, some carrying data symbols and some carrying pilot symbols. A data formatter can form the data for transmission into sets of data symbols for each OFDM symbol, and an OFDM symbol builder can receive each set of data symbols from the data formatter and combine the data symbols with pilot symbols. A modulator can map the data symbols and the pilot symbols onto modulation symbols and modulate the plural sub-carriers to form the OFDM symbols. An inverse Fourier transform can convert the OFDM symbols from the frequency domain to the time domain, and a guard interval inserter can add a guard interval to each of the OFDM symbols by copying a part of the OFDM symbols and appending the copied part sequentially in the time domain to the OFDM symbols.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Communication processing system, OFDM signal transmitting method, OFDM transmitter, OFDM receiver, and control station
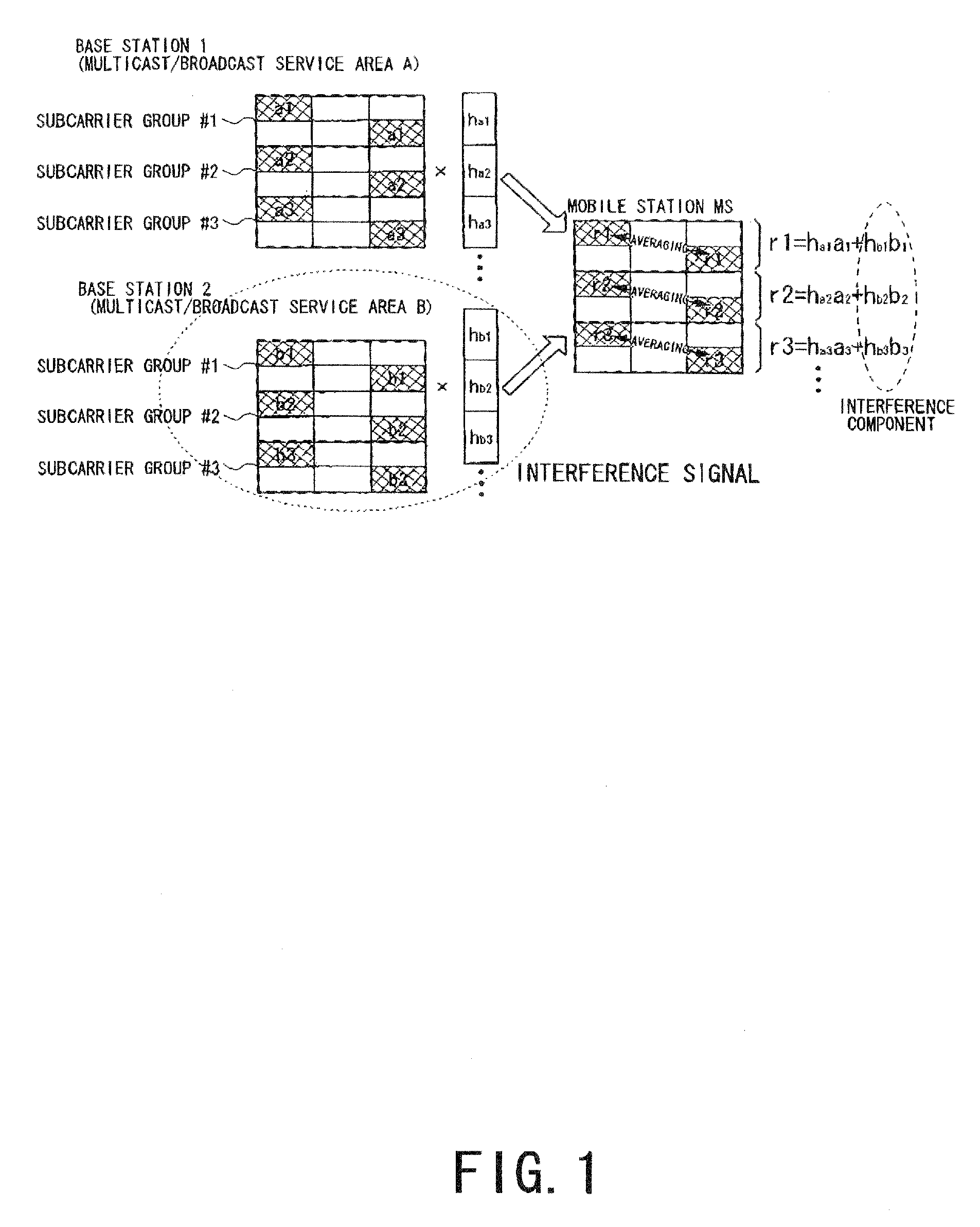
ActiveUS20100119003A1Suppress interferenceImprove accuracySite diversityElectric signal transmission systemsTelecommunicationsOfdm transmitter
In an OFDM transmitter included in a first service area, an orthogonal-code-pattern multiplication unit multiplies pilot channel signals belonging to any subcarrier group by an orthogonal code which is different from that for one or a plurality of OFDM transmitters adjacent to the OFDM transmitter included in the first service area, or a subcarrier assignment unit assigns pilot channel signals to pilot subcarriers which are common to a plurality of OFDM transmitters and based on a pilot arrangement notified in advance by a control station to all OFDM transmitters included in the first service area.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Transmitter and transmission controlling method
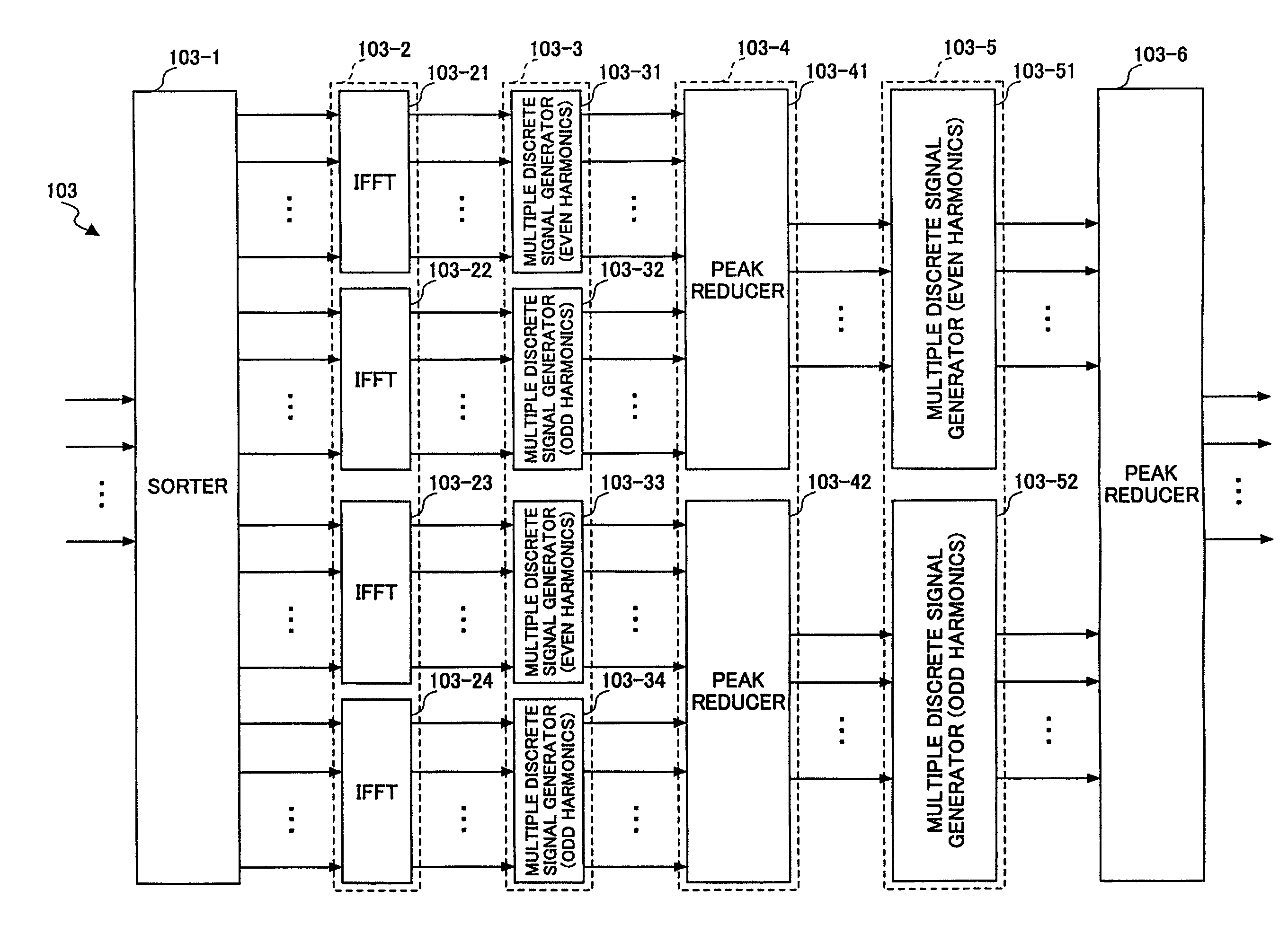
InactiveUS7499496B2Efficiently perform inverse Fourier transform and peak reductionDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationFourier transform on finite groupsOfdm transmitter
An OFDM transmitter (100) is disclosed. The OFDM transmitter comprises: a sorter (103-1) for sorting plural input complex signals and partitioning them into plural groups; plural IFFTs (103-2) for performing inverse Fourier transform on the input complex signals in groups; a peak reducer (103-4) for performing peak reduction, based on outputs from at least one of the IFFTs; and a multiple discrete signal generator (103-5) for generating a designated number of discrete signals from outputs of the peak reducer.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Method of transmitting OFDM signal and transmitter and receiver thereof
InactiveUS20070258357A1Small amount of calculationLess deteriorationSite diversityTransmission control/equlisationData signalCarrier signal
A method of transmitting OFDM signals including, allocating a first pilot signal and a first data signal which are both common among OFDM transmitters respectively to at least one first pilot subcarrier and first data subcarriers within a specific time-frequency domain that is common among the OFDM transmitters and different among wireless transmitting units, allocating a second pilot signal and a second data signal respectively to second pilot subcarrier and second data subcarriers outside the time-frequency domain, multiplying the first pilot signal and the first data signal by a complex number set for the time-frequency domain, generating an OFDM signal by performing OFDM modulation on the first pilot signal and the first data signal multiplied by the complex number and the second pilot signal and the second data signal, and transmitting the OFDM signal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
OFDM transmittter and OFDM receiver
InactiveUS20090323515A1Reduce errorsImprove accuracyModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionFrequency compensationTransmission latency
In an environment with large transmission delays, use of an OFDM transmitter which includes: a pilot / data allocator for allocating pilot / data symbols on OFDM symbols and an OFDM receiver which includes: an antenna for receiving the OFDM signals sent out from the antenna of this OFDM transmitter; a ratio unit for frequency transforming the OFDM signals received as RF signals to baseband signals; a frequency offset estimate for estimating an offset value; and a frequency offset corrector for performing frequency compensation by the amount of the frequency offset, improves data transmission efficiency while reducing interference of data between sub-carriers to prevent degradation of reception characteristics by performing appropriate frequency offset correction.
Owner:SHARP KK
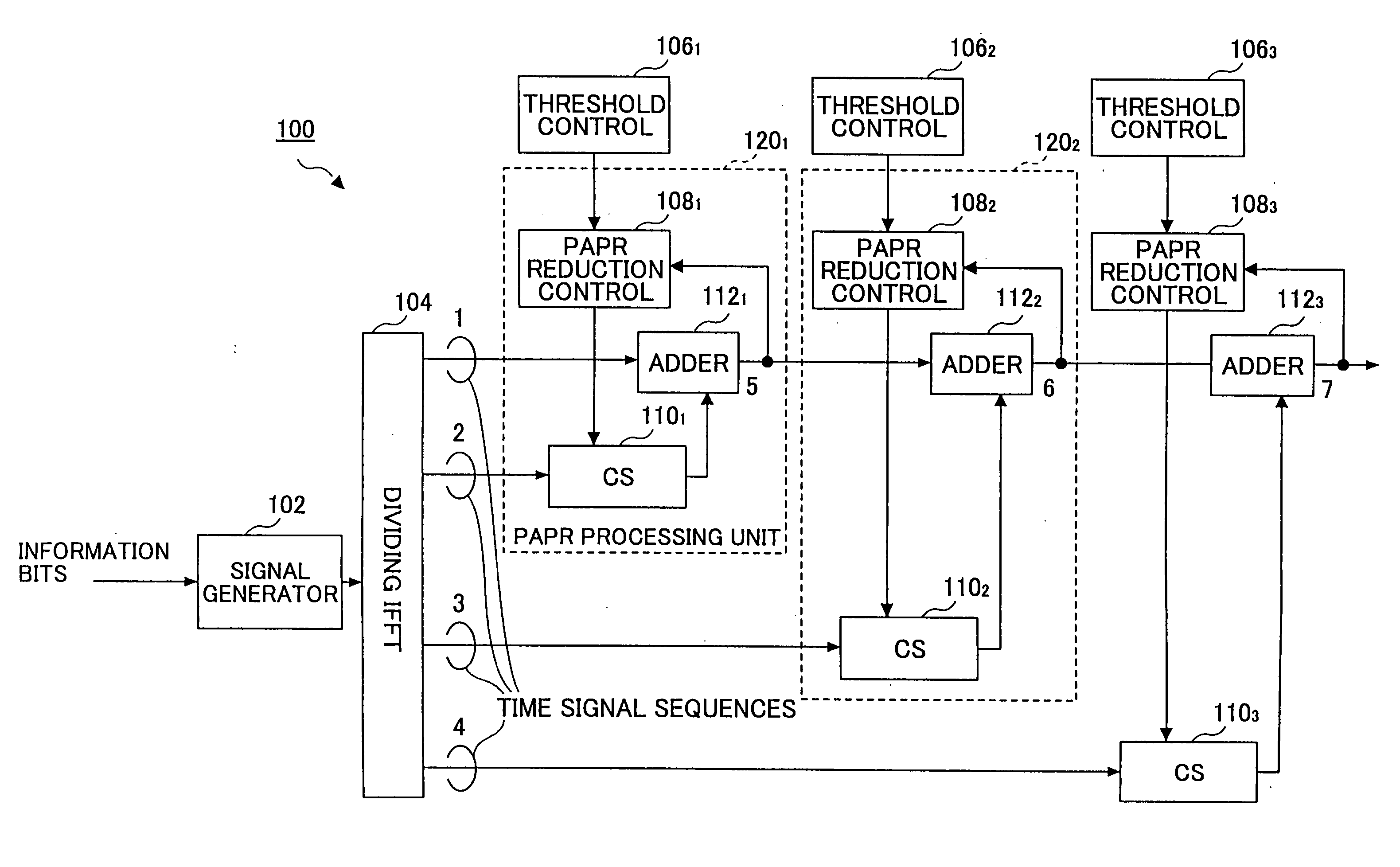
OFDM transmitter
InactiveUS20060193393A1Sufficient PAPR reducing effectReduce ratio of average powerSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsFast Fourier transformEngineering
An OFDM transmitter is configured to perform a peak reduction process on a signal sequence to be transmitted in a stepwise manner to transmit a peak processed transmission signal. The OFDM transmitter includes a dividing inverse fast Fourier transform unit (104) configured to divide the signal sequence to be transmitted into N signal sequences (N>2) and perform inverse fast Fourier transform on each of the divided signal sequences to output N time signal sequences; a threshold control unit (106) configured to determine at least two threshold values (Cth) used in the stepwise peak reduction process; and a first peak reduction processing unit (1201) configured to determine a first cyclic shift to be applied to one of the time signal sequences based on a first one of the threshold values, produce a first cyclically shifted signal sequence according to the first cyclic shift, and output a first peak processed signal sequence based on the first cyclically shifted signal sequence. The first cyclic shift is determined such that an exceeding power level over the first threshold value in the first peak processed signal sequence becomes the minimum.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com