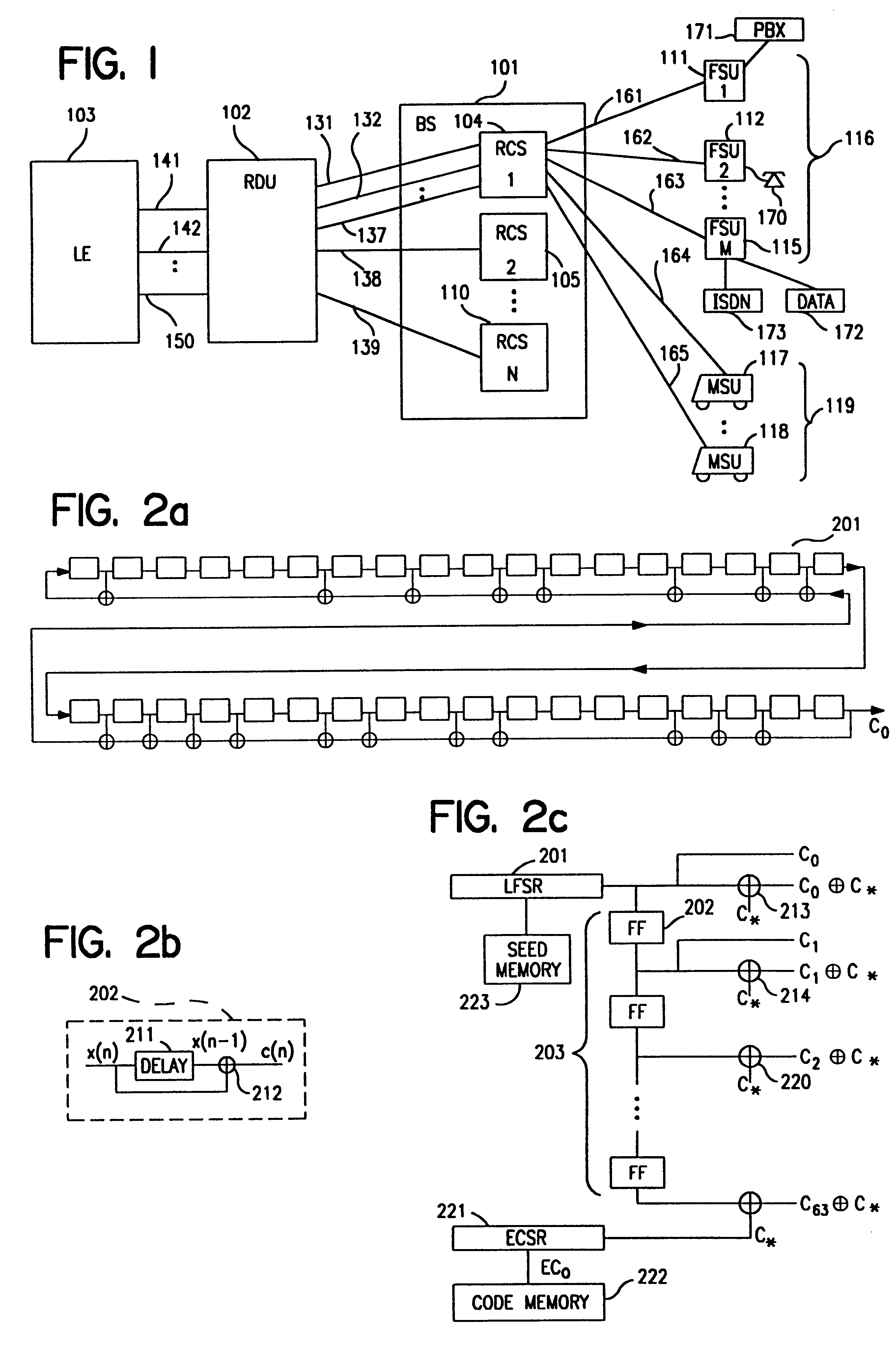
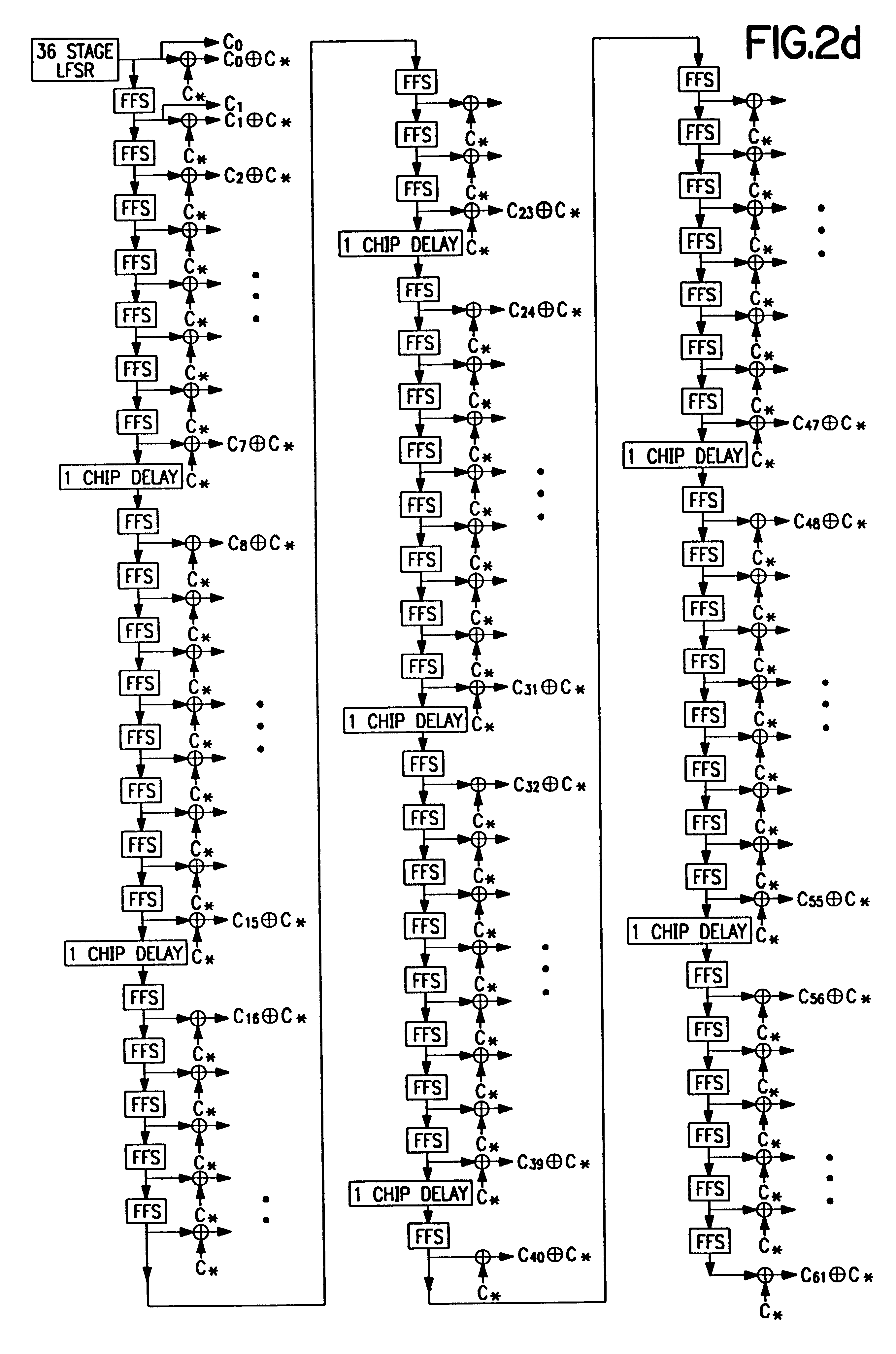
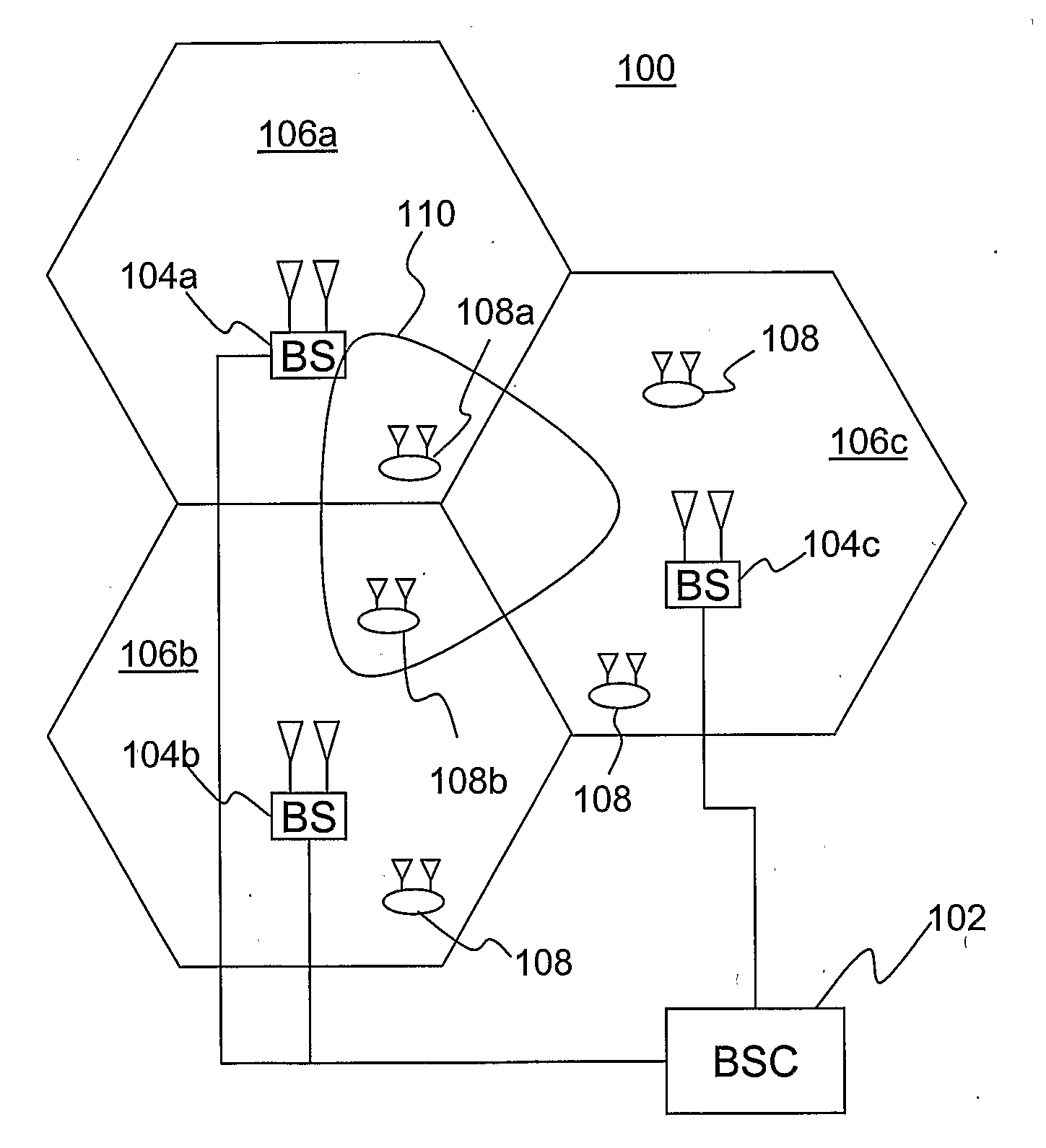
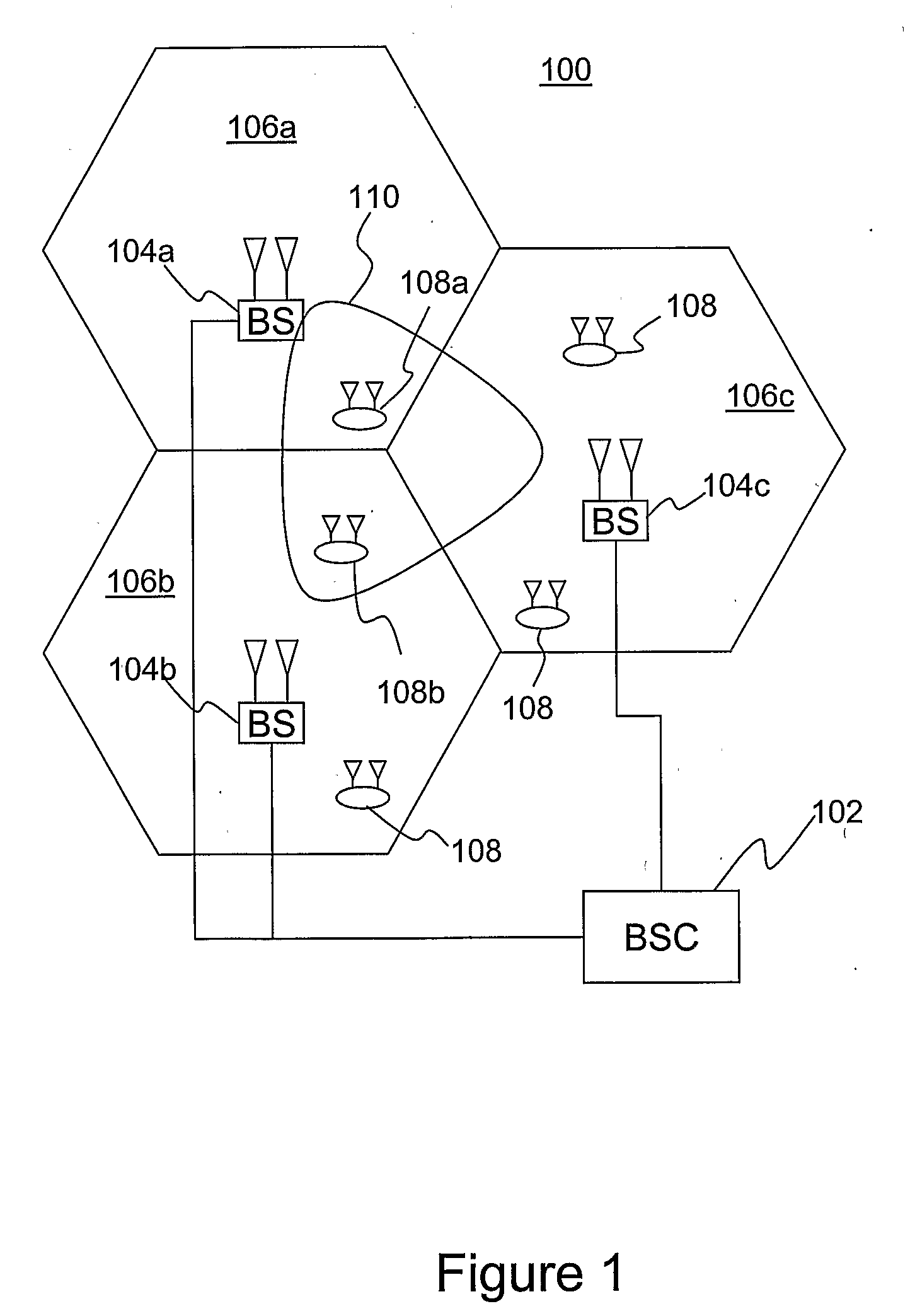
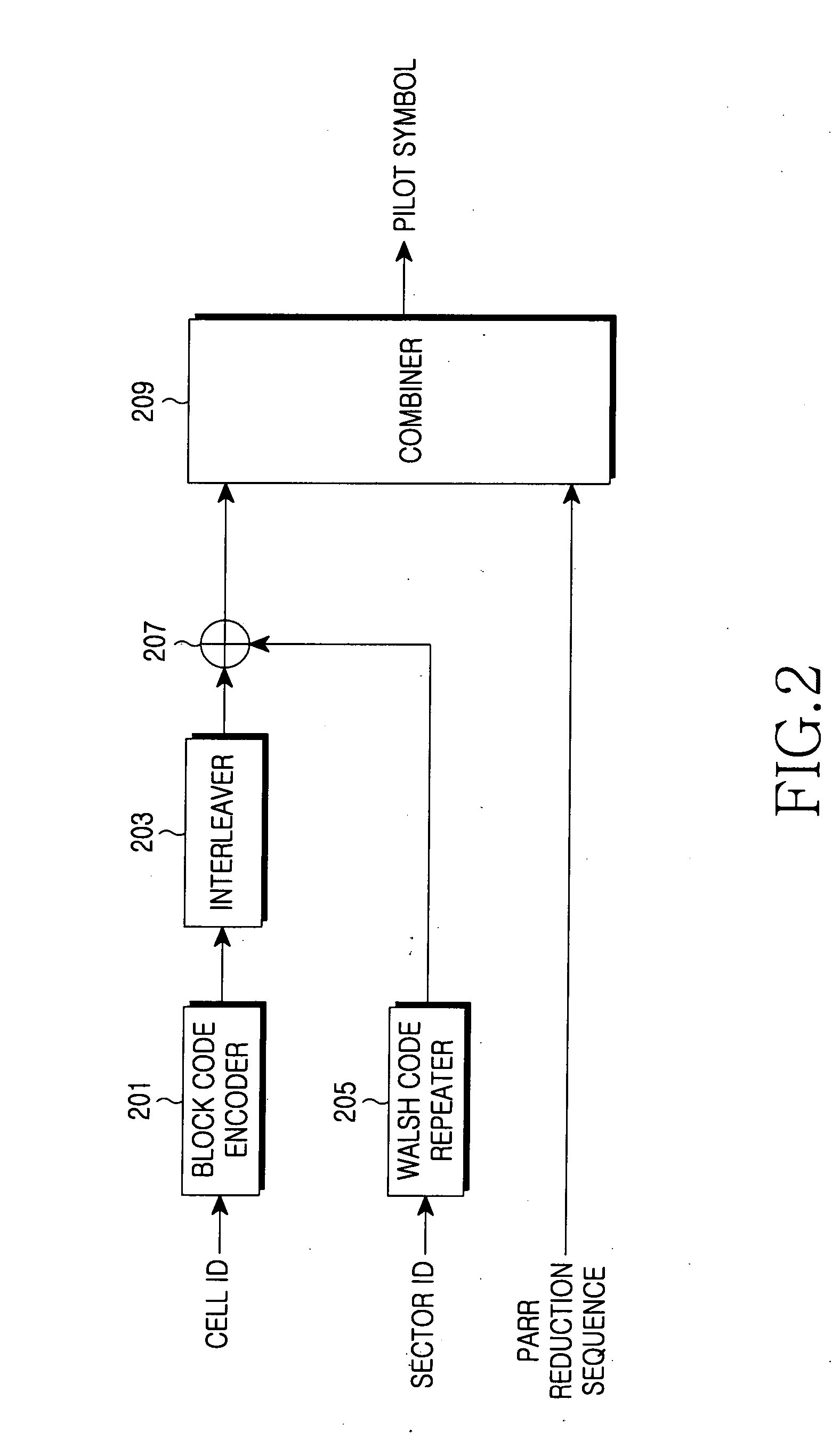
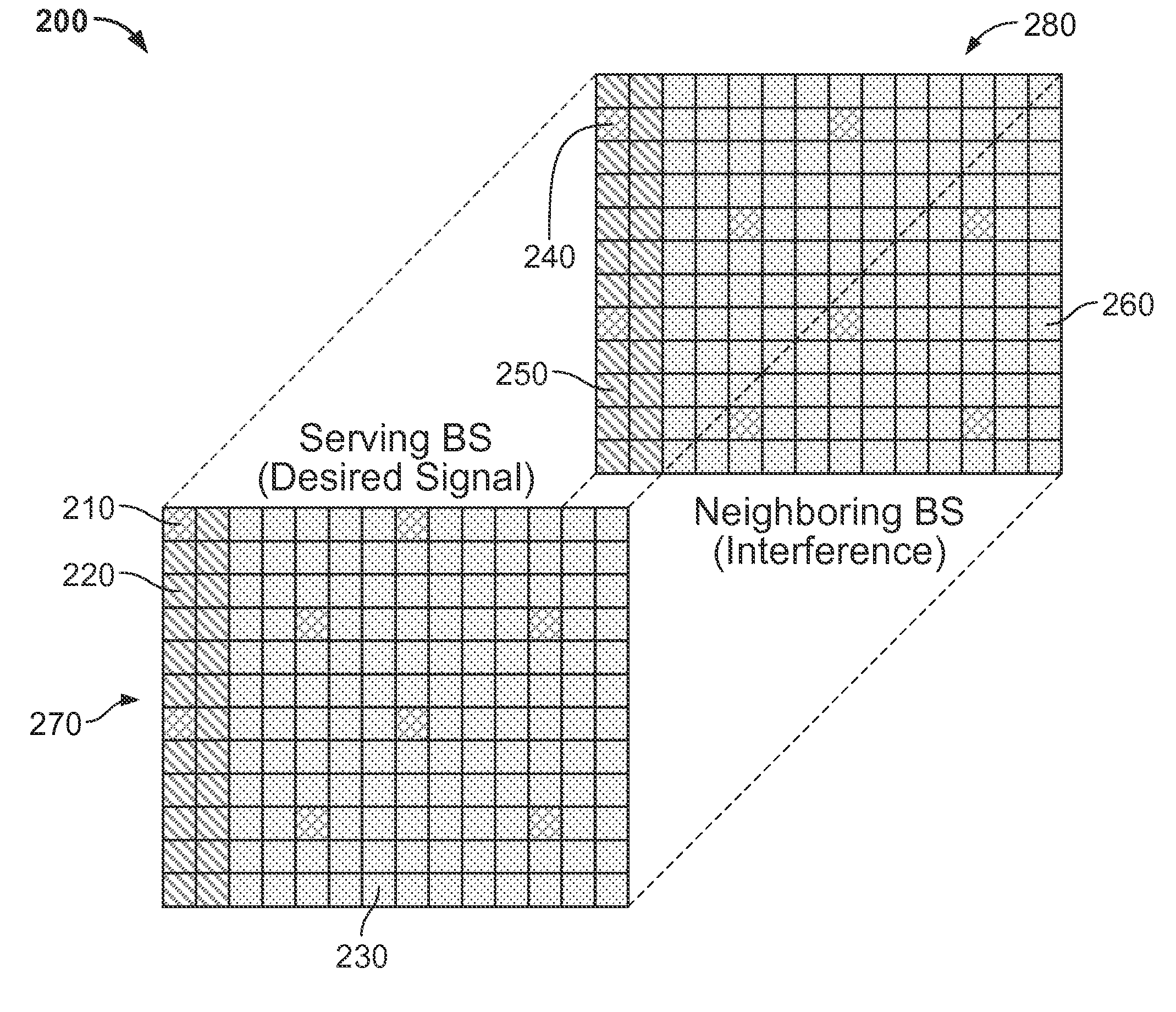
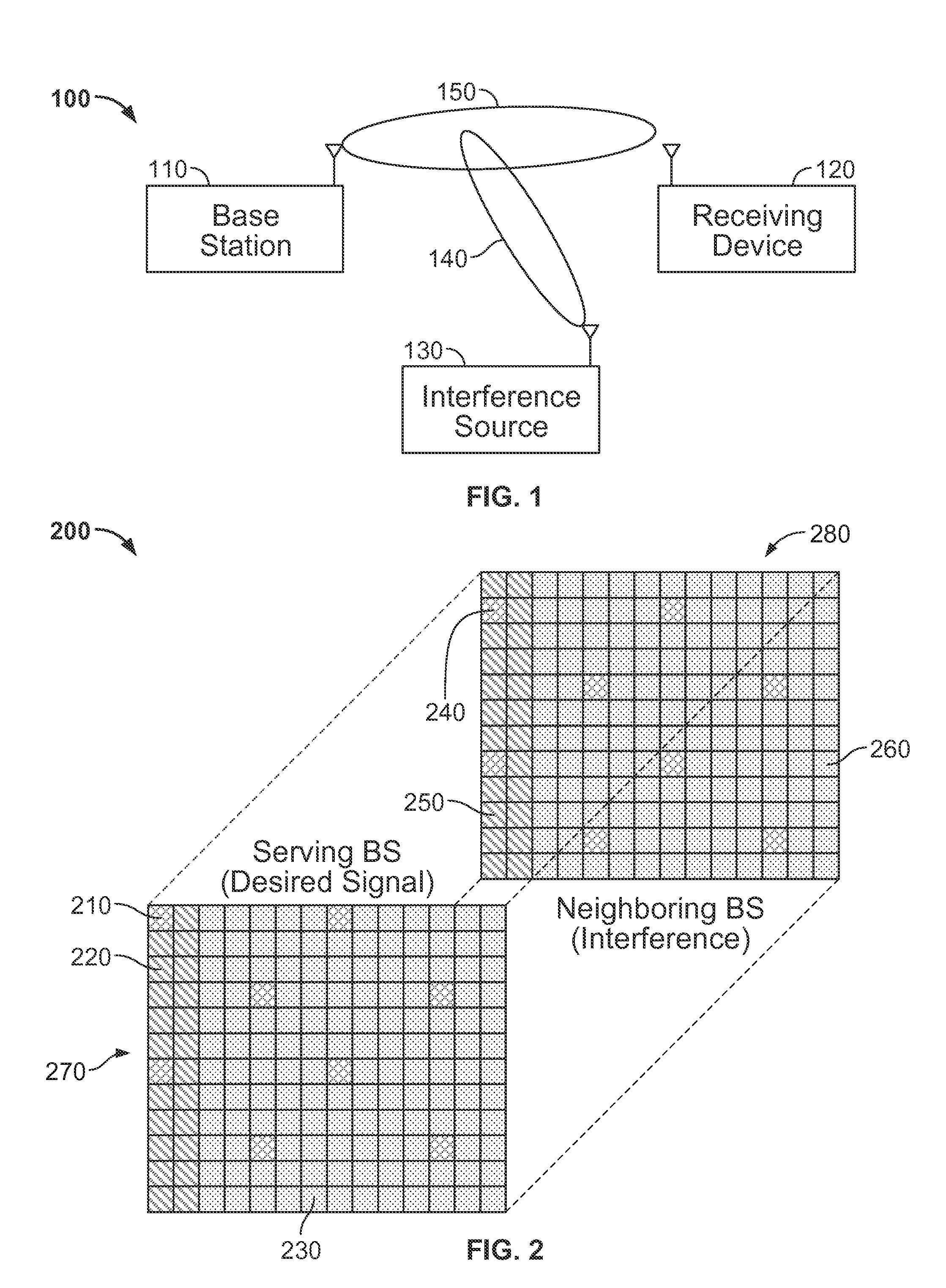
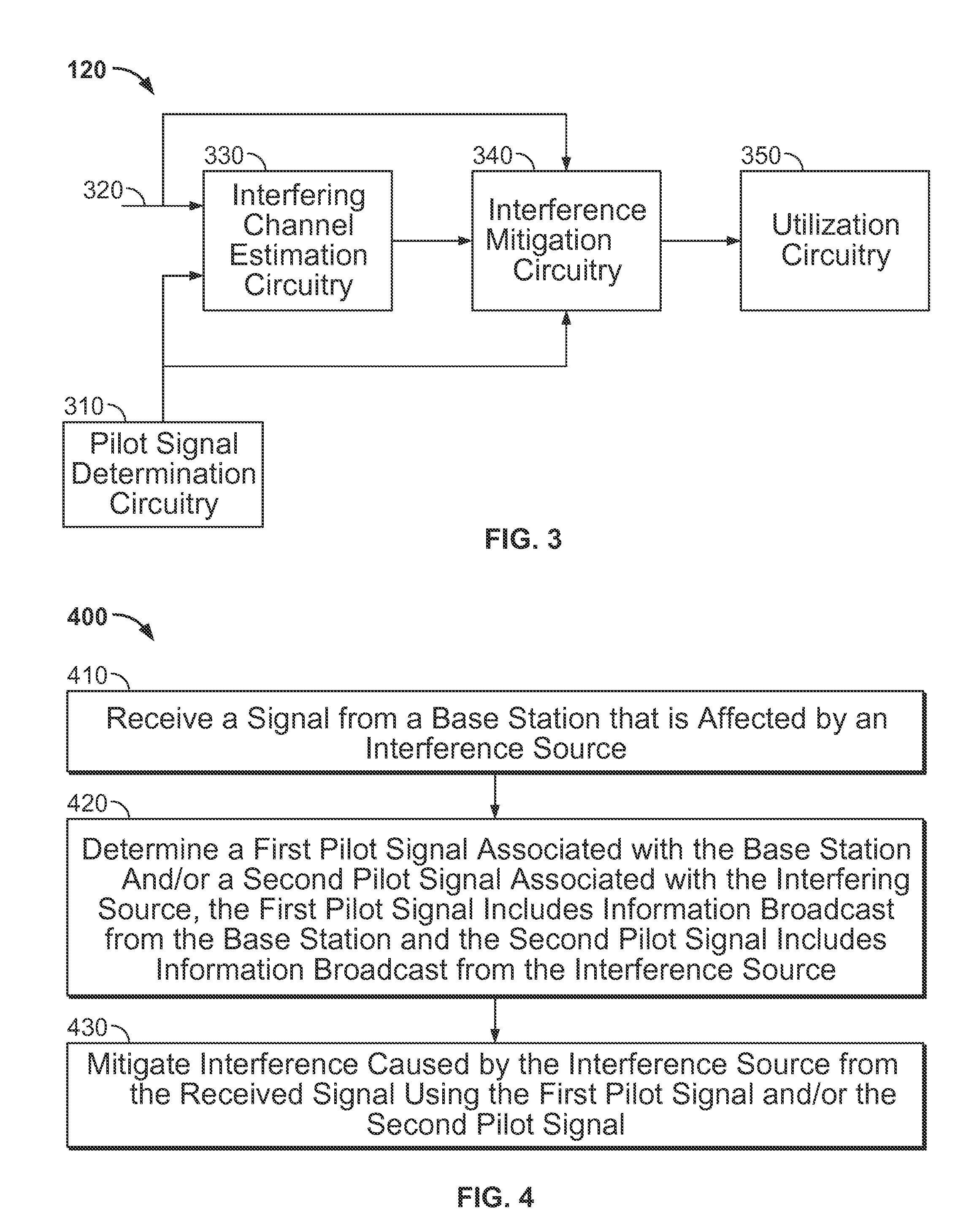
Patents
Literature
4171 results about "Pilot signal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In telecommunications, a pilot signal is a signal, usually a single frequency, transmitted over a communications system for supervisory, control, equalization, continuity, synchronization, or reference purposes.
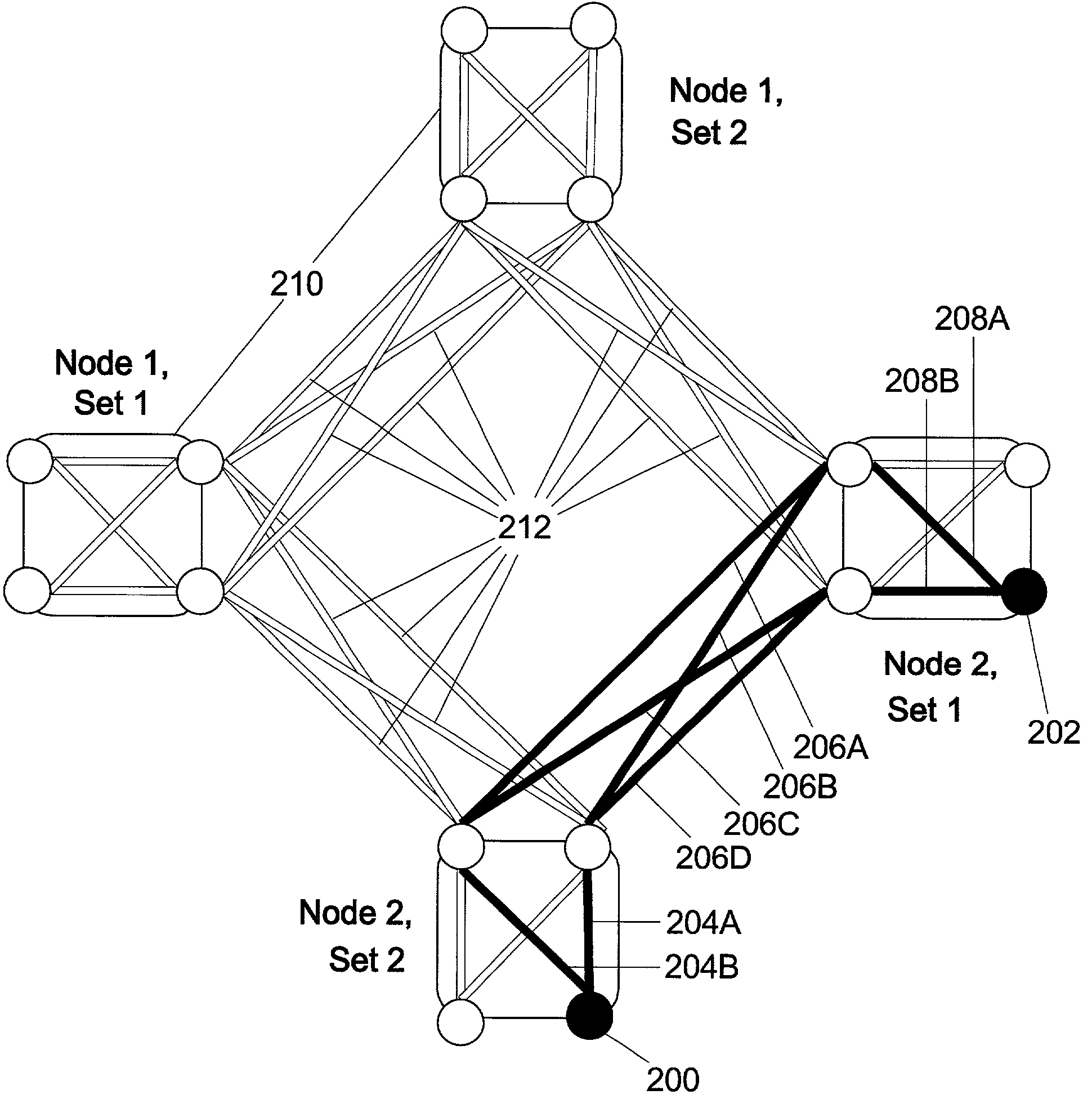
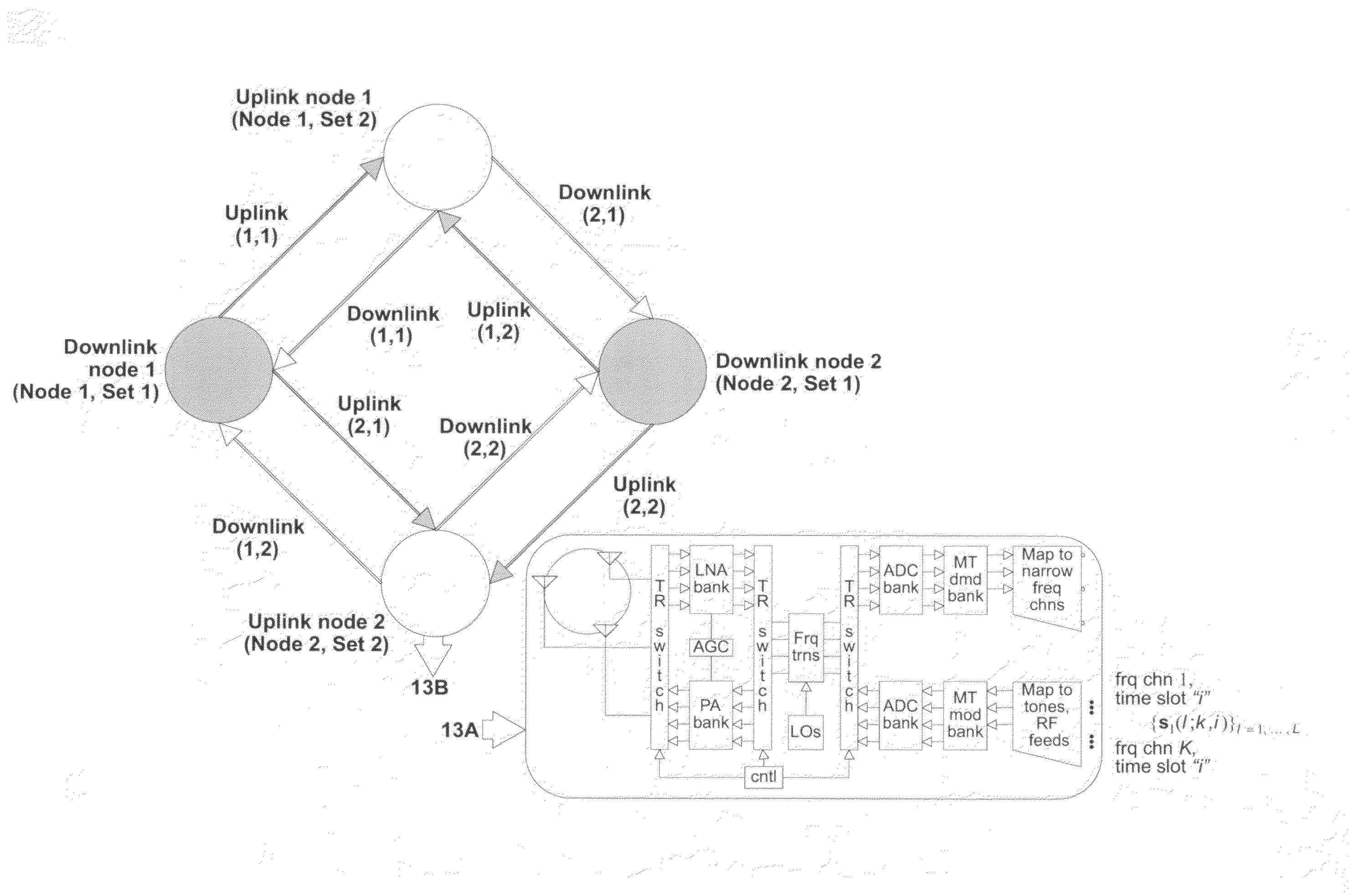
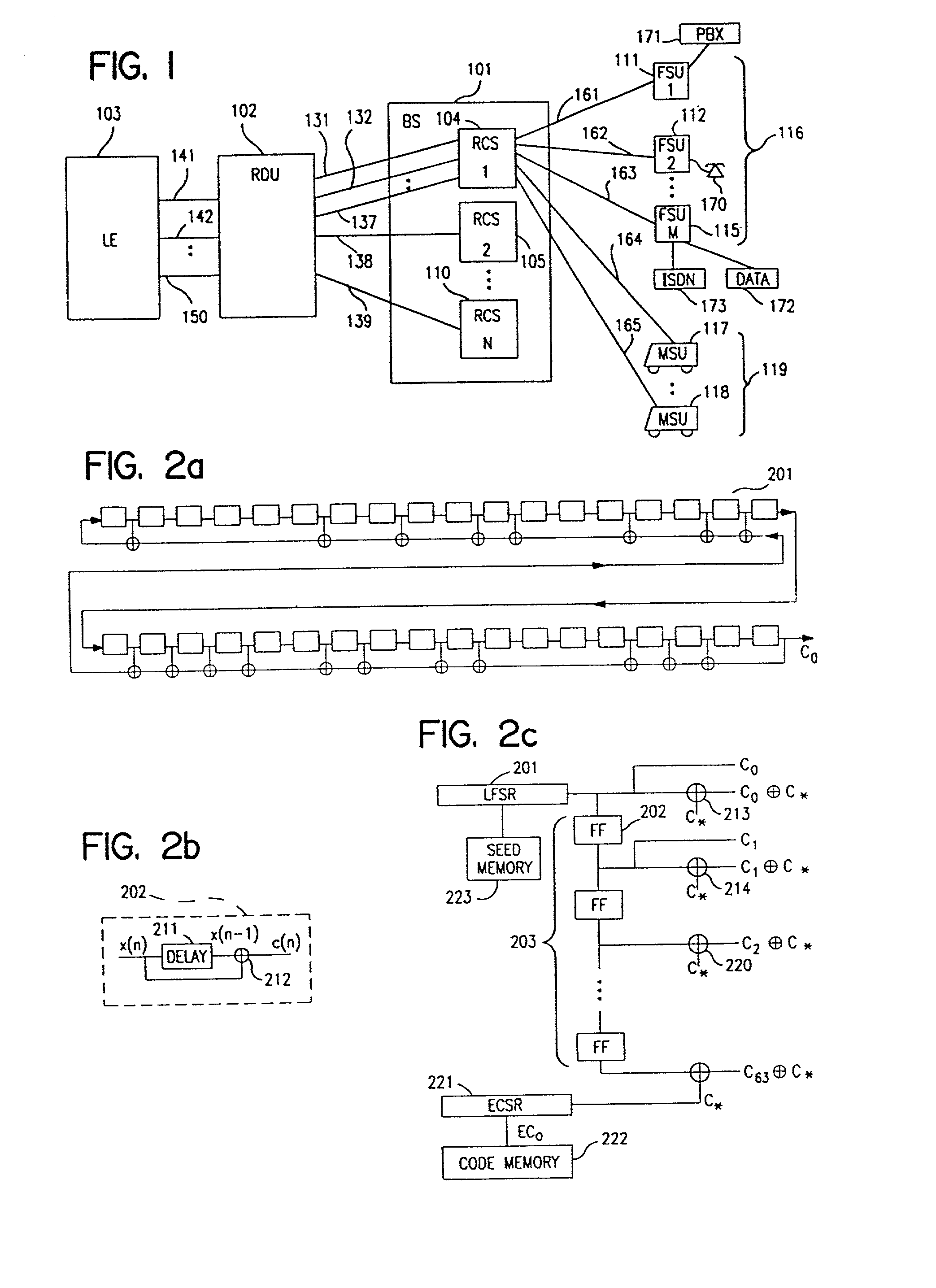
Method and apparatus for optimization of wireless multipoint electromagnetic communication networks
InactiveUS20040095907A1Improve signal qualityReduce interference energyPower managementSpatial transmit diversityGlobal optimizationDiversity scheme
Exploiting the substantive reciprocity of internode channel responses through dynamic, adaptive modification of receive and transmit weights, enables locally enabled global optimization of a multipoint, wireless electromagnetic communications network of communication nodes. Each diversity-channel-capable node uses computationally efficient exploitation of pilot tone data and diversity-adaptive signal processing of the weightings and the signal to further convey optimization and channel information which promote local and thereby network-global efficiency. The preferred embodiment performs complex digital signal manipulation that includes a linear combining and linear distribution of the transmit and receive weights, the generation of piloting signals containing origination and destination node information, as well as interference-avoiding pseudorandom delay timing, and both symbol and multitione encoding, to gain the benefit of substantive orthogonality at the physical level without requiring actual substantive orthogonality at the physical level.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
Method and apparatus for optimization of wireless multipoint electromagnetic communication networks
InactiveUS7248841B2Strong advantageReduced Power RequirementsPower managementSpatial transmit diversityGlobal optimizationRandom delay
Exploiting the substantive reciprocity of internode channel responses through dynamic, adaptive modification of receive and transmit weights, enables locally enabled global optimization of a multipoint, wireless electromagnetic communications network of communication nodes. Each diversity-channel-capable node uses computationally efficient exploitation of pilot tone data and diversity-adaptive signal processing of the weightings and the signal to further convey optimization and channel information which promote local and thereby network-global efficiency. The preferred embodiment performs complex digital signal manipulation that includes a linear combining and linear distribution of the transmit and receive weights, the generation of piloting signals containing origination and destination node information, as well as interference-avoiding pseudorandom delay timing, and both symbol and multitone encoding, to gain the benefit of substantive orthogonality at the physical level without requiring actual substantive orthogonality at the physical level.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
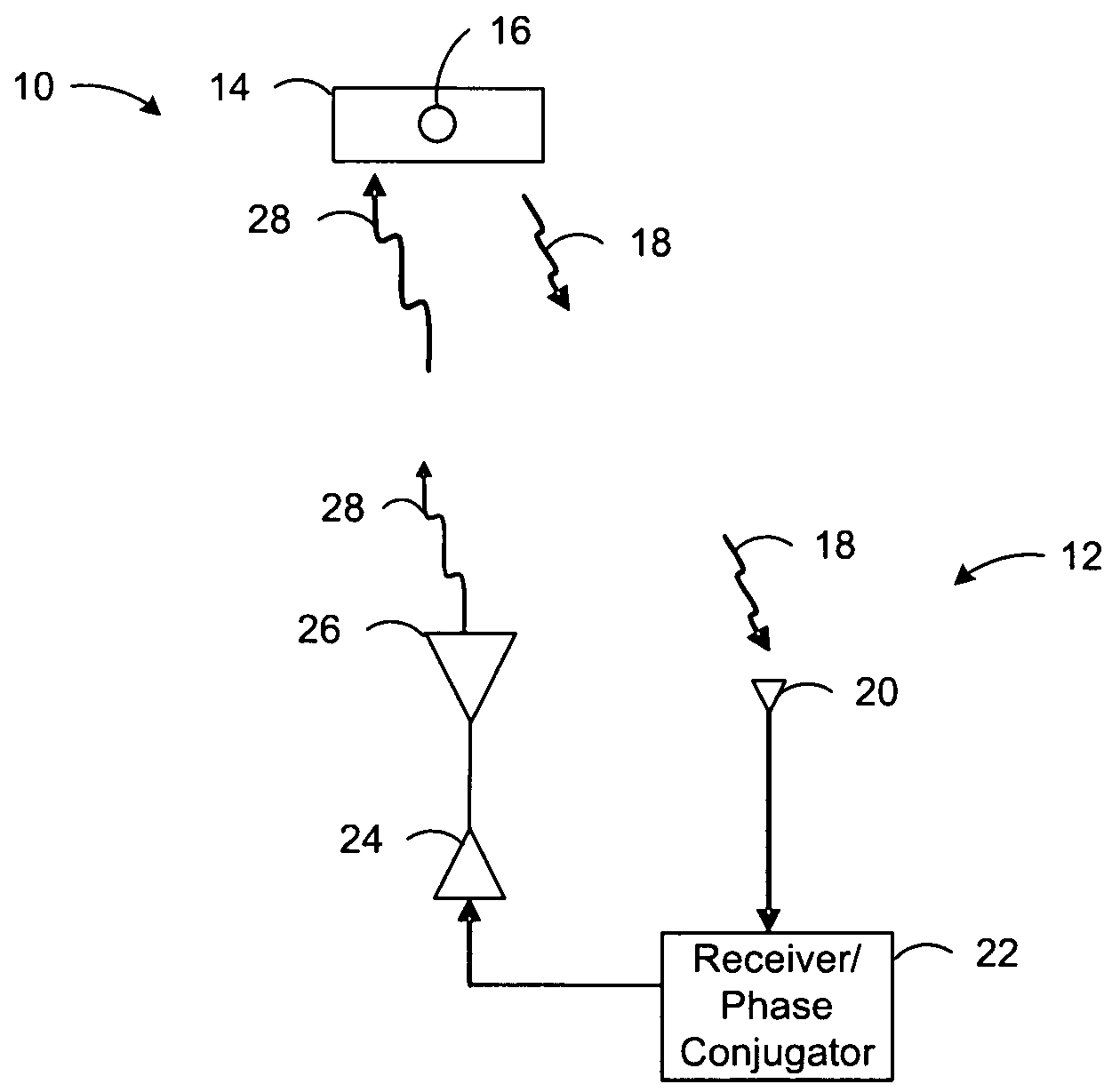
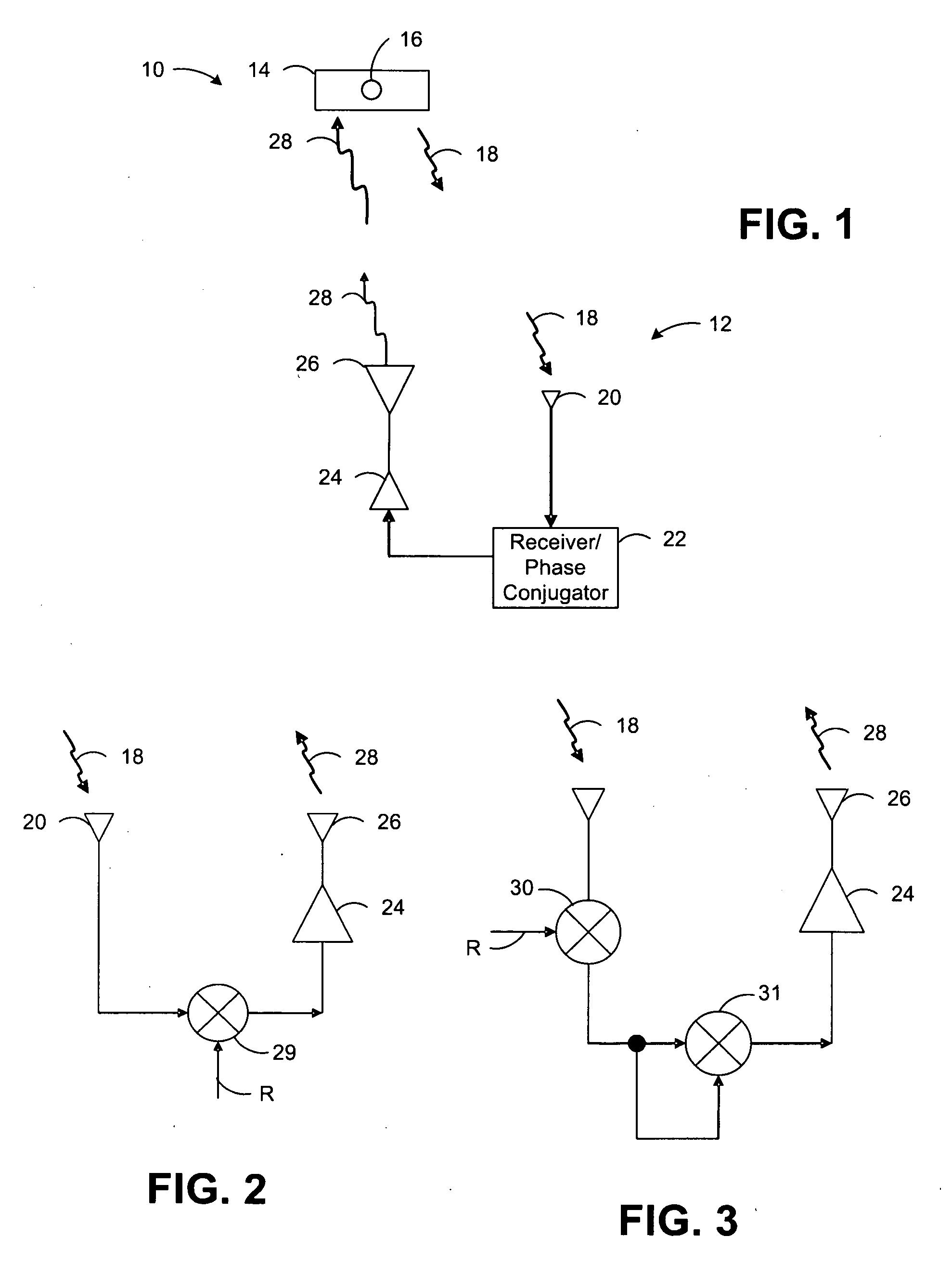
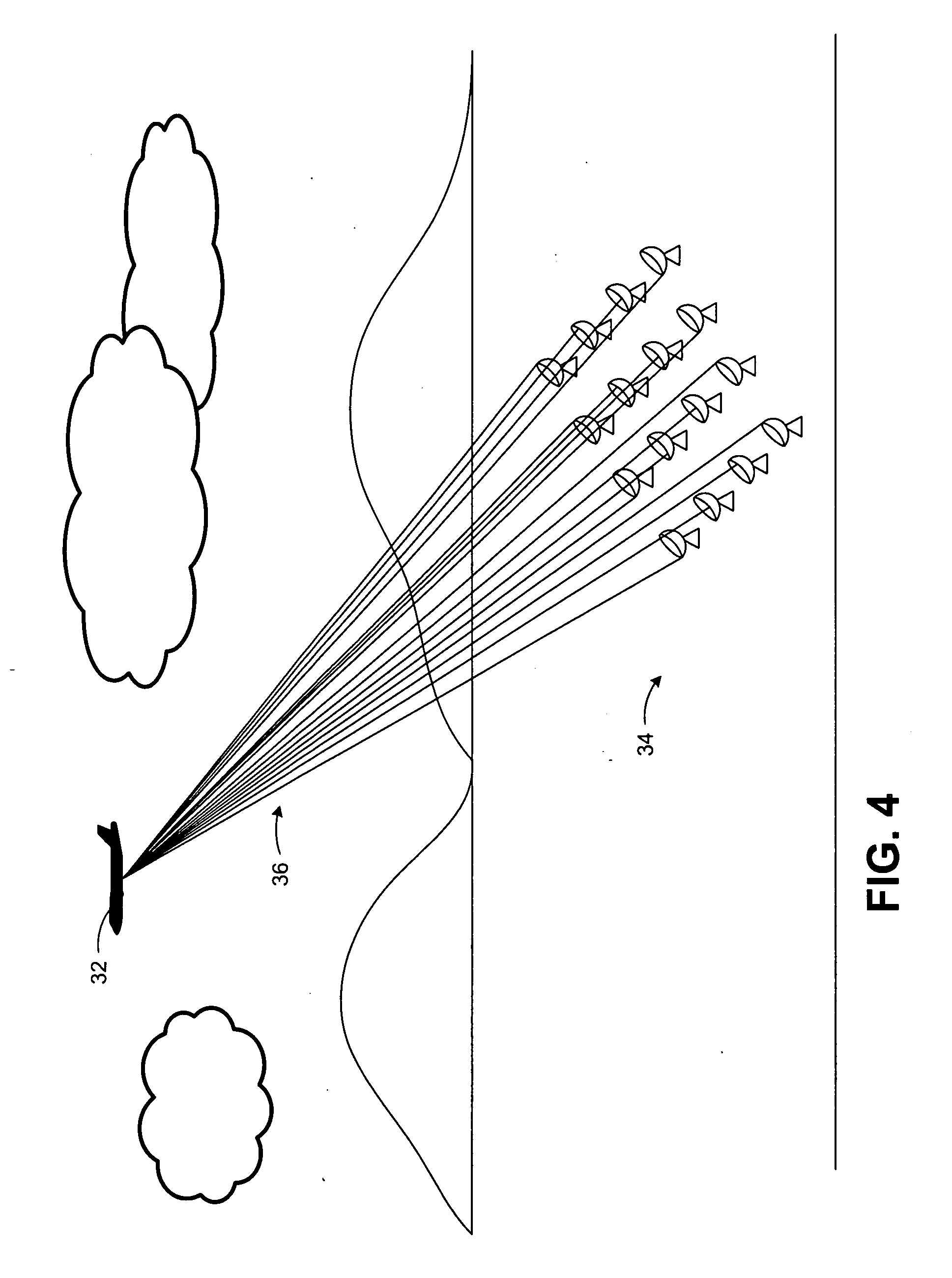
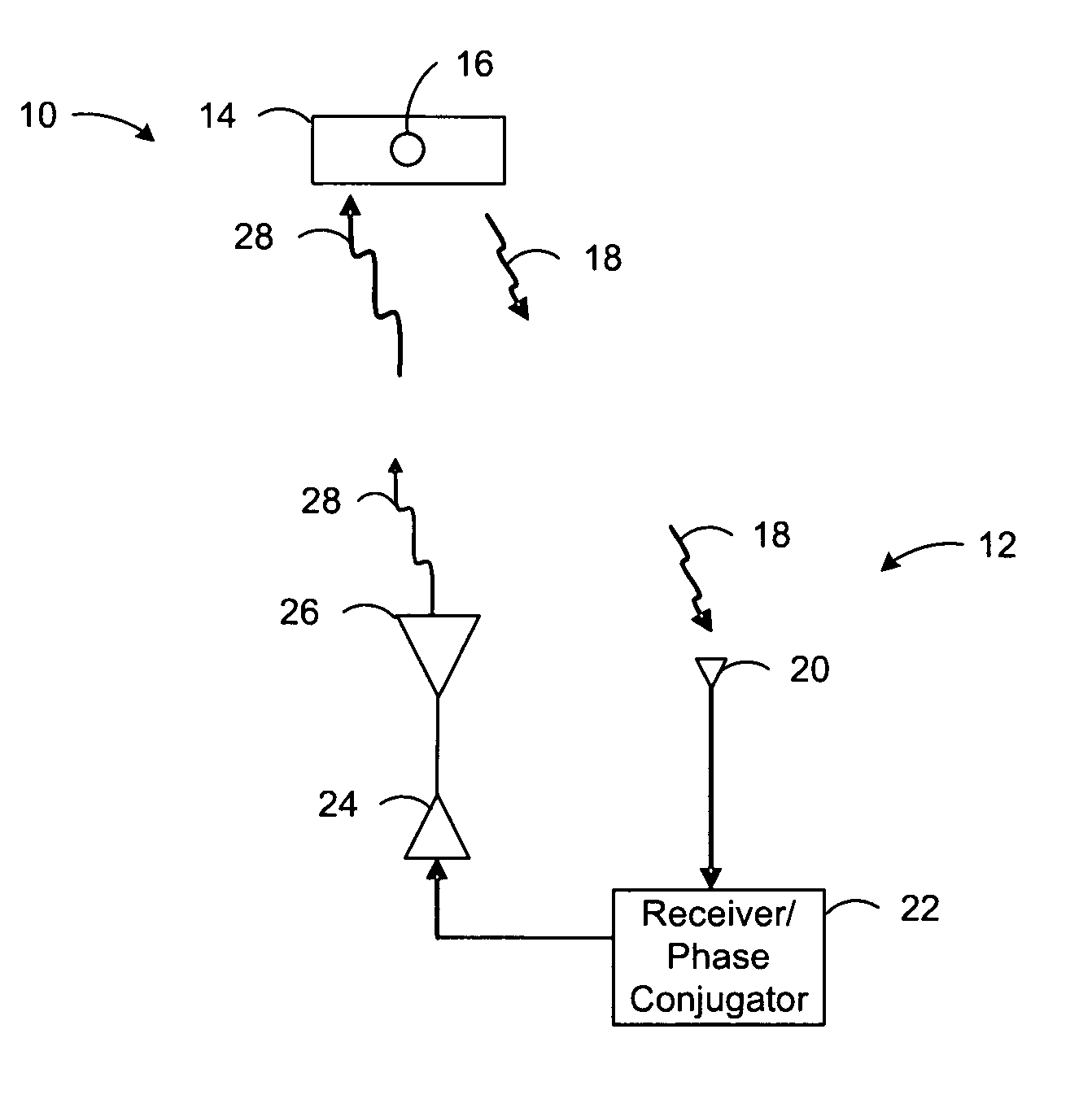
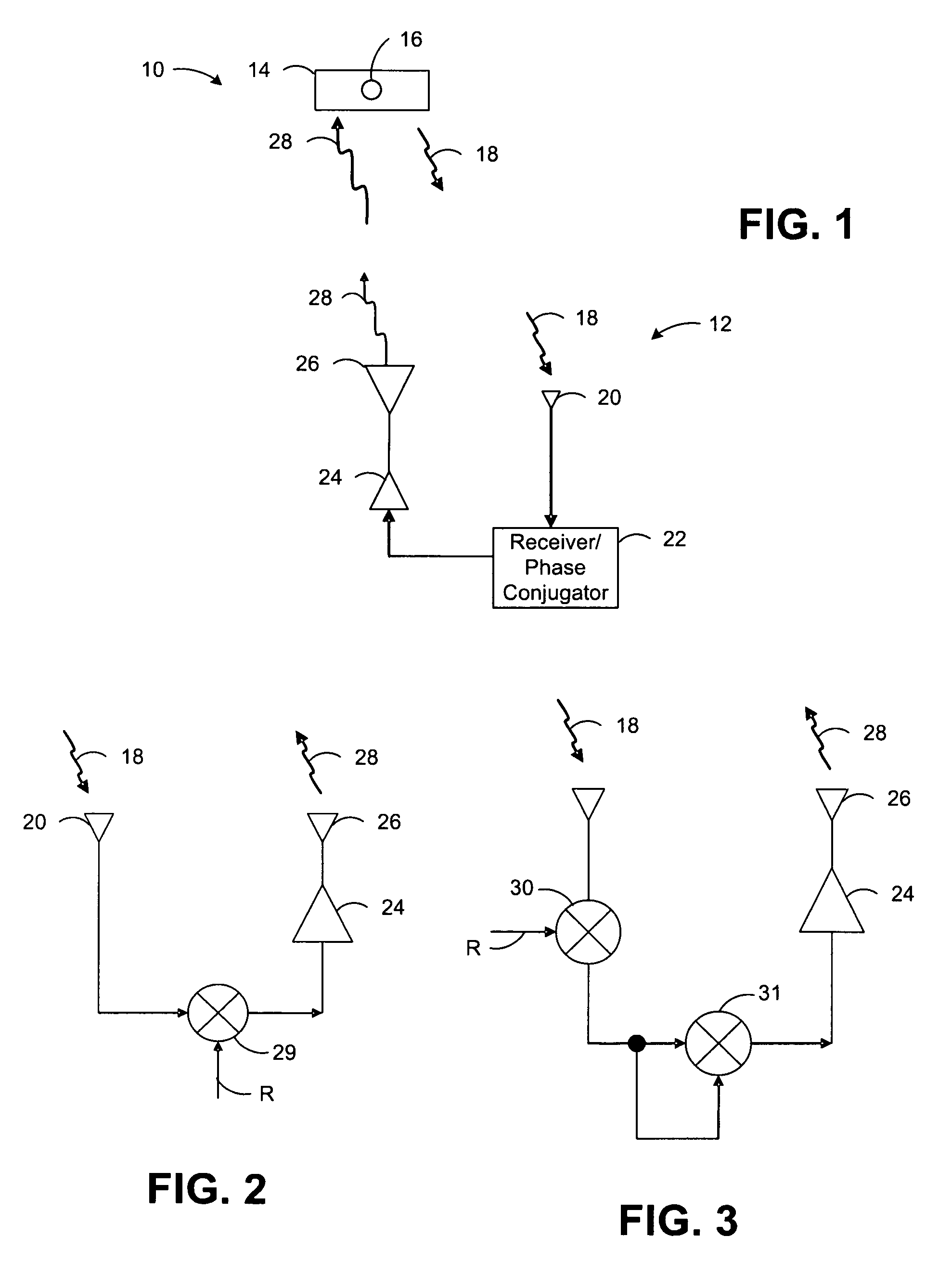
Wireless Power Transmission
ActiveUS20120326660A1Batteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemElectricityElectric power transmission
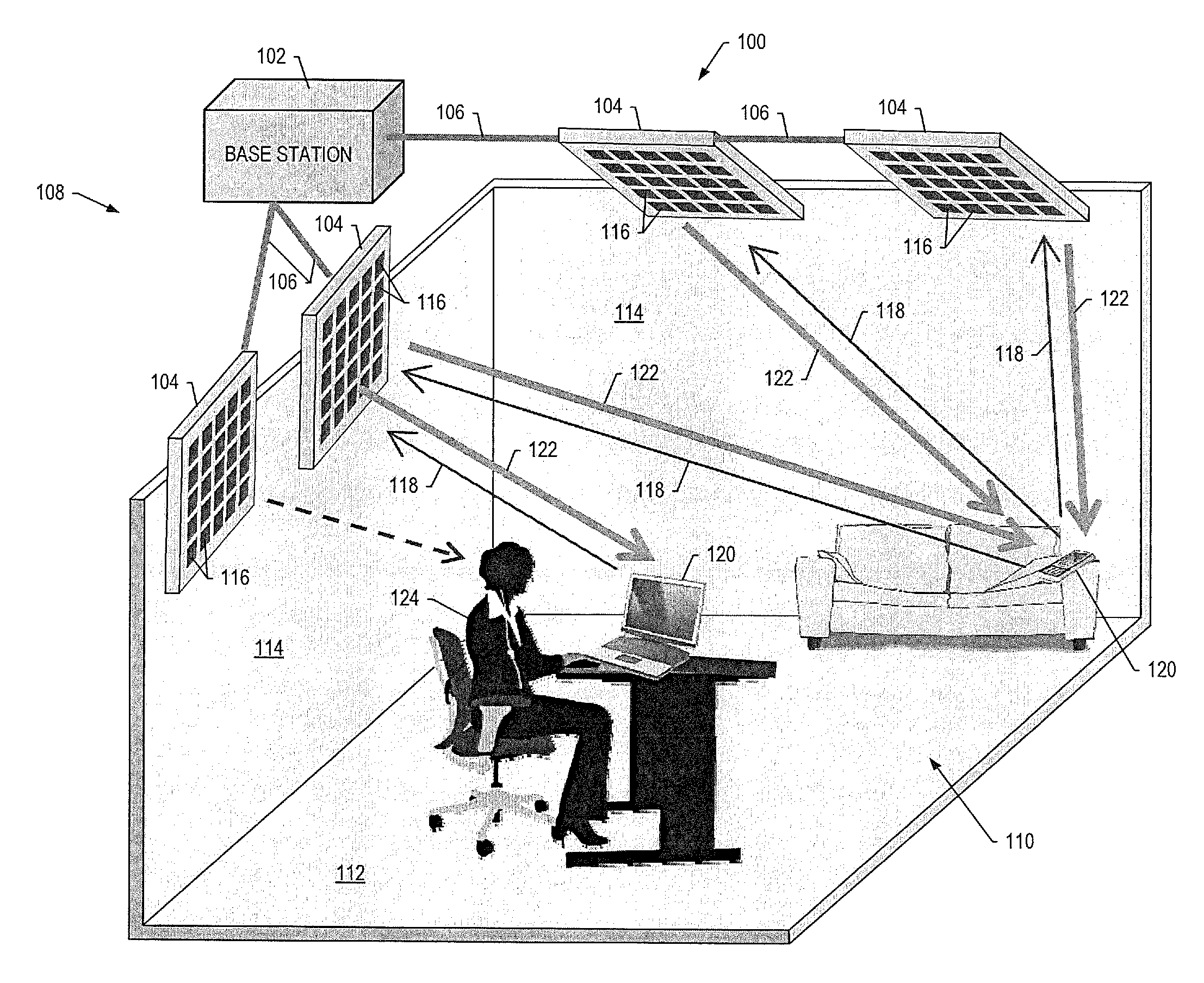
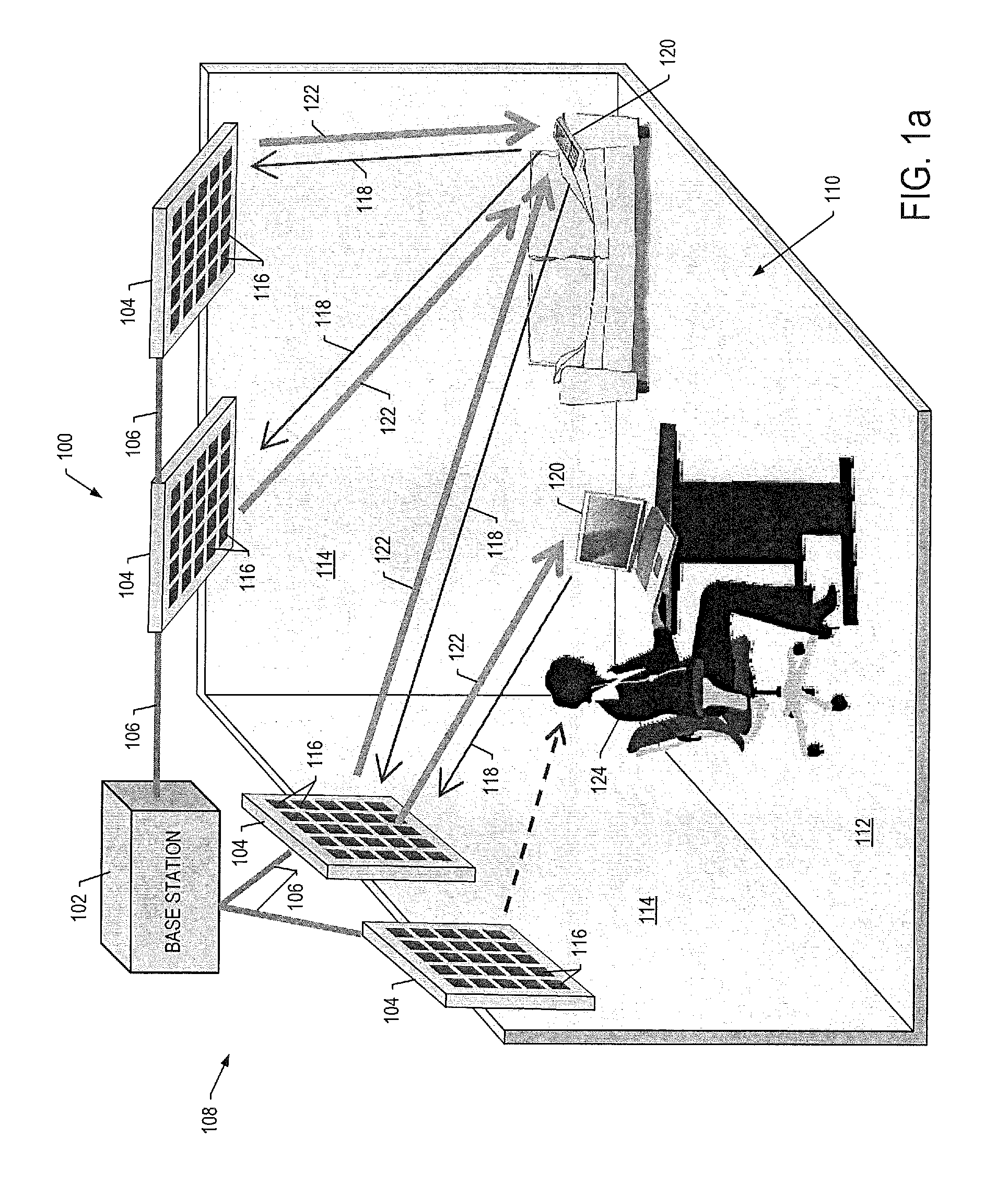
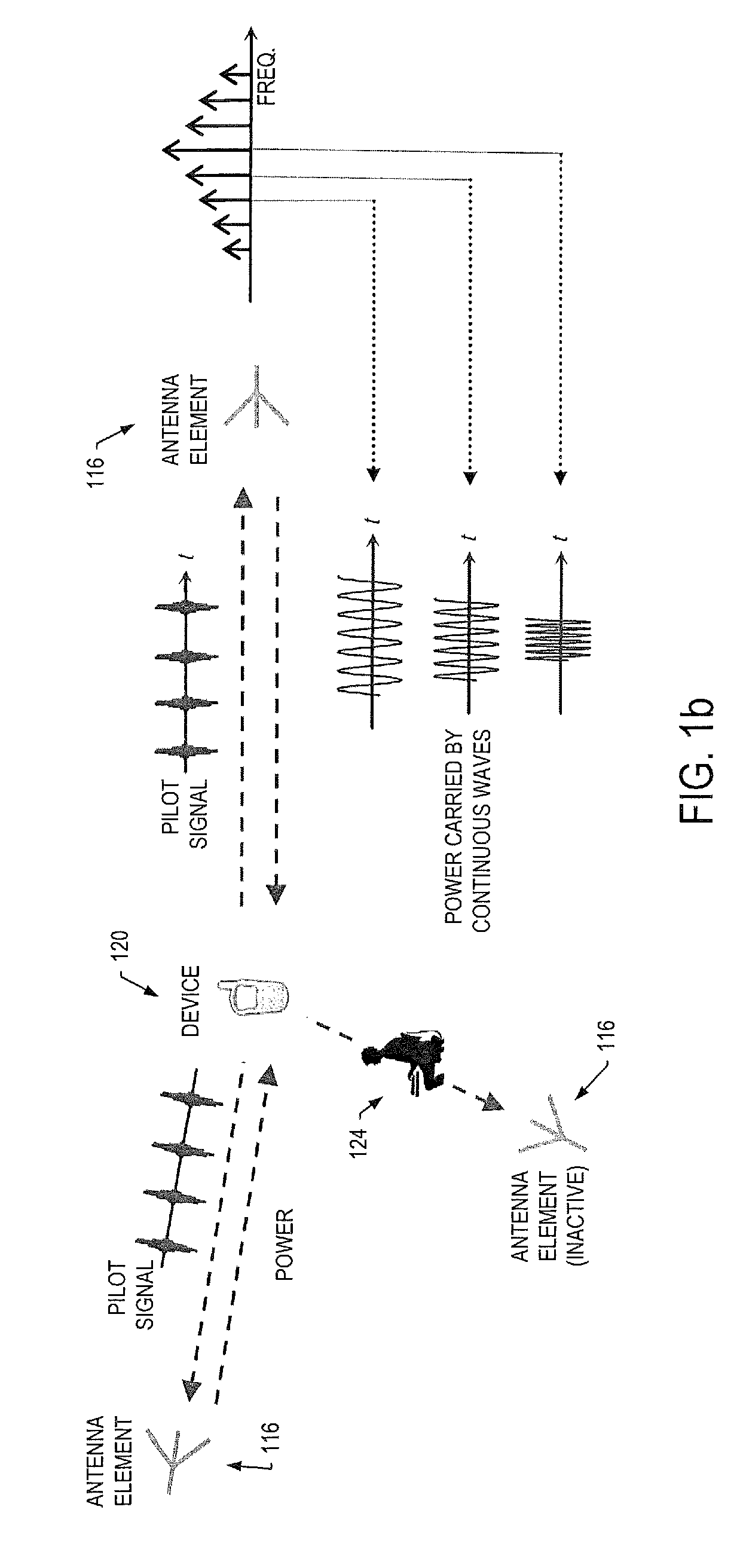
A system for wireless power transmission may include one or more charging panels and one or more powered devices. The charging panel may include a pilot analysis circuitry, processor and power transmitter. The pilot analysis circuitry may be configured to analyze the magnitude and phase of a pilot signal from the powered device, based on which the processor may be configured to determine a complex conjugate of the pilot signal. And the power transmitter may be configured to cause radiation of a focused wireless power beam to the powered device in accordance with the complex conjugate of the pilot signal and via one or more antenna elements. The charging panel may be one of a plurality of spatially-distributed charging panels each of which includes respective antenna elements that may form an array of antenna elements configured to collaboratively radiate wireless power as a distributed, retro-reflective beamformer.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Wireless power transmission system and method
ActiveUS20100259447A1Minimal energyOvercomes drawbackElectromagnetic wave systemCircuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionEngineering
A wireless power transmission system including at least one source of electromagnetic radiation, a plurality of wireless power receivers that receive radiated electromagnetic energy, a beacon collocated with each wireless power receiver, wherein the beacon generates and radiates a pilot signal when the beacon is in an active state, and an array of transmitting antennas connected to the source of electromagnetic radiation that radiates the electromagnetic radiation in the direction of the beacon in the active state. The electromagnetic radiation can be electronically steered from one wireless power receiver to another by activating and deactivating the beacons collocated with each wireless power receiver.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Wireless power transmission system and method
ActiveUS8072380B2Electromagnetic wave systemCircuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionElectromagnetic radiation
A wireless power transmission system including at least one source of electromagnetic radiation, a plurality of wireless power receivers that receive radiated electromagnetic energy, a beacon collocated with each wireless power receiver, wherein the beacon generates and radiates a pilot signal when the beacon is in an active state, and an array of transmitting antennas connected to the source of electromagnetic radiation that radiates the electromagnetic radiation in the direction of the beacon in the active state. The electromagnetic radiation can be electronically steered from one wireless power receiver to another by activating and deactivating the beacons collocated with each wireless power receiver.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method and apparatus for reducing pilot search times utilizing mobile station location information
InactiveUS6542743B1Time to setValuable searcher resources are not wastedAssess restrictionModulation type identificationTelecommunicationsMultipath effect
A method and apparatus for conducting a pilot signal search in a wireless communications network. The location of a mobile is determined within the network. This location is then used in determining search window sizes and other search parameter information that is used to search all pilot signals identified in a designated pilot signal set. Search window size is also determined based upon the location of the mobile and another component related to multipath effects for a transmitted pilot signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
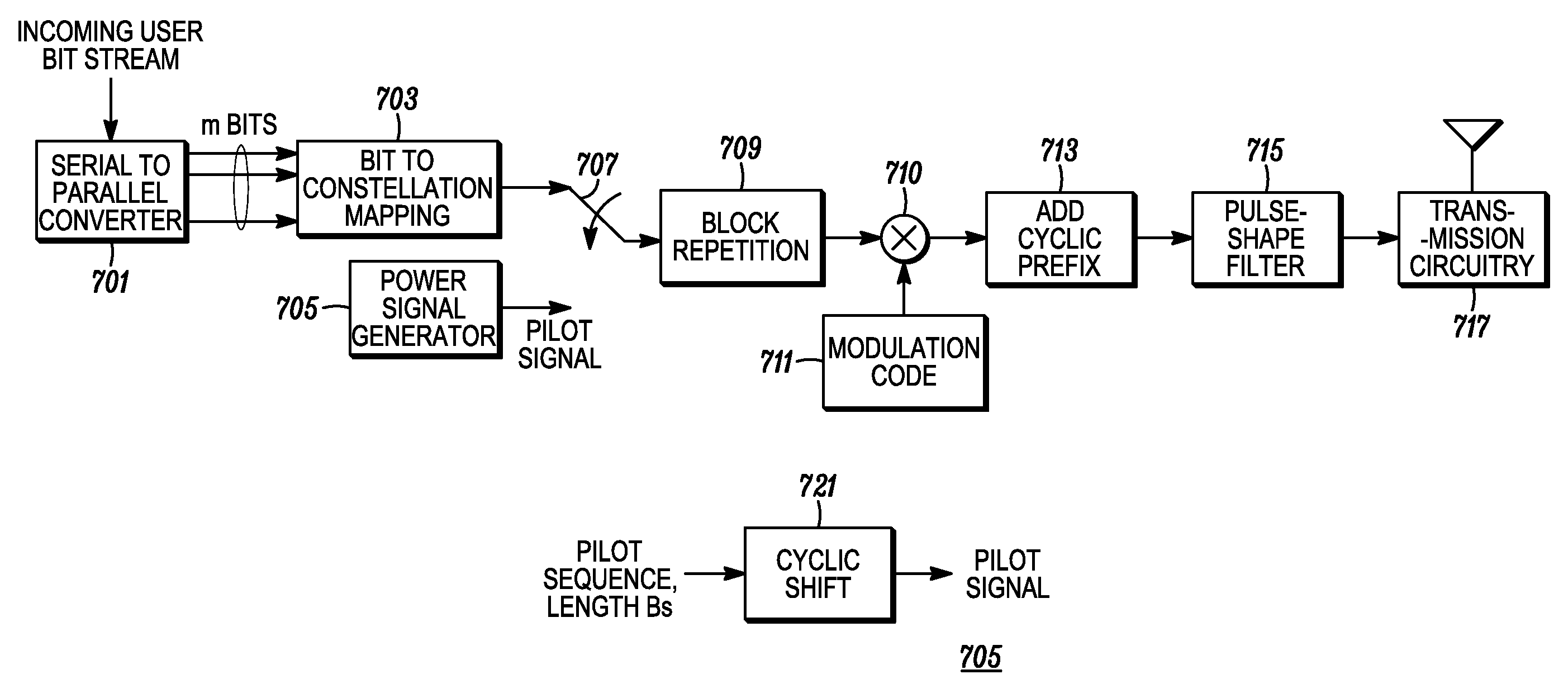
Method and apparatus for pilot signal transmission
A pilot (or reference) transmission scheme is utilized where different transmitters are assigned pilot sequences with possibly different cyclic time shifts. A pilot signal is transmitted concurrently by the transmitters in a plurality of pilot blocks, and a receiver processes the plurality of received pilot blocks to recover a channel estimate for at least one of the transmitters while suppressing the interference due to the pilot signals from the other transmitters.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
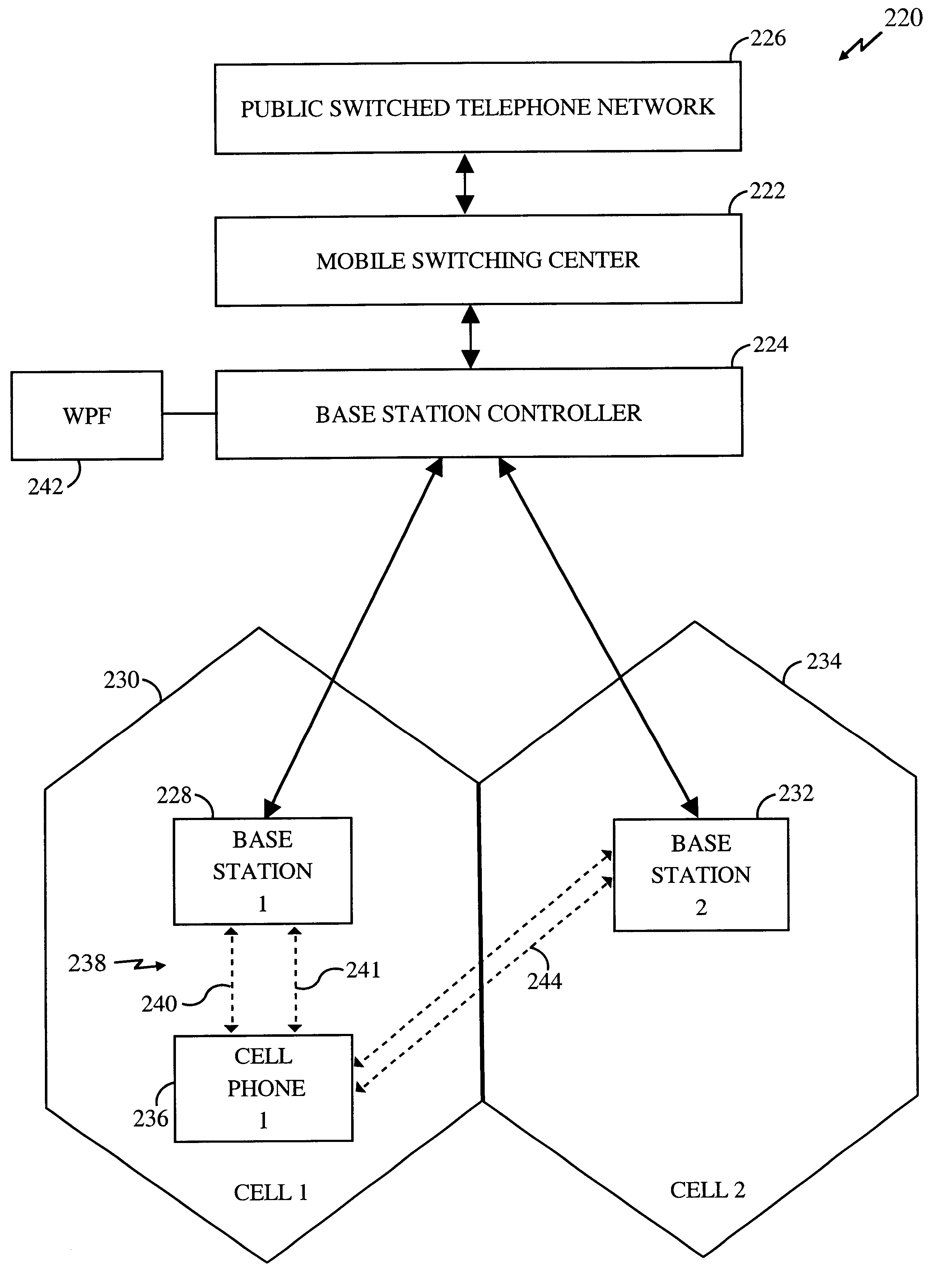
Soft handoff for OFDM
The present invention relates to soft handoffs in an OFDM system. Each mobile terminal measures pilot signal strengths of transmissions from adjacent base stations. If the pilot signal strength for a base station exceeds the defined threshold, that base station is added to an active set list. Each mobile terminal notifies the base stations of their active set lists. By providing the set list to the base station controller and the servicing base station, the mobile terminal identifies the sole servicing base station or triggers a soft handoff mode when multiple base stations appear on the active set list. The soft handoff mode uses a combination of scheduling and space-time coding to affect efficient and reliable handoffs.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
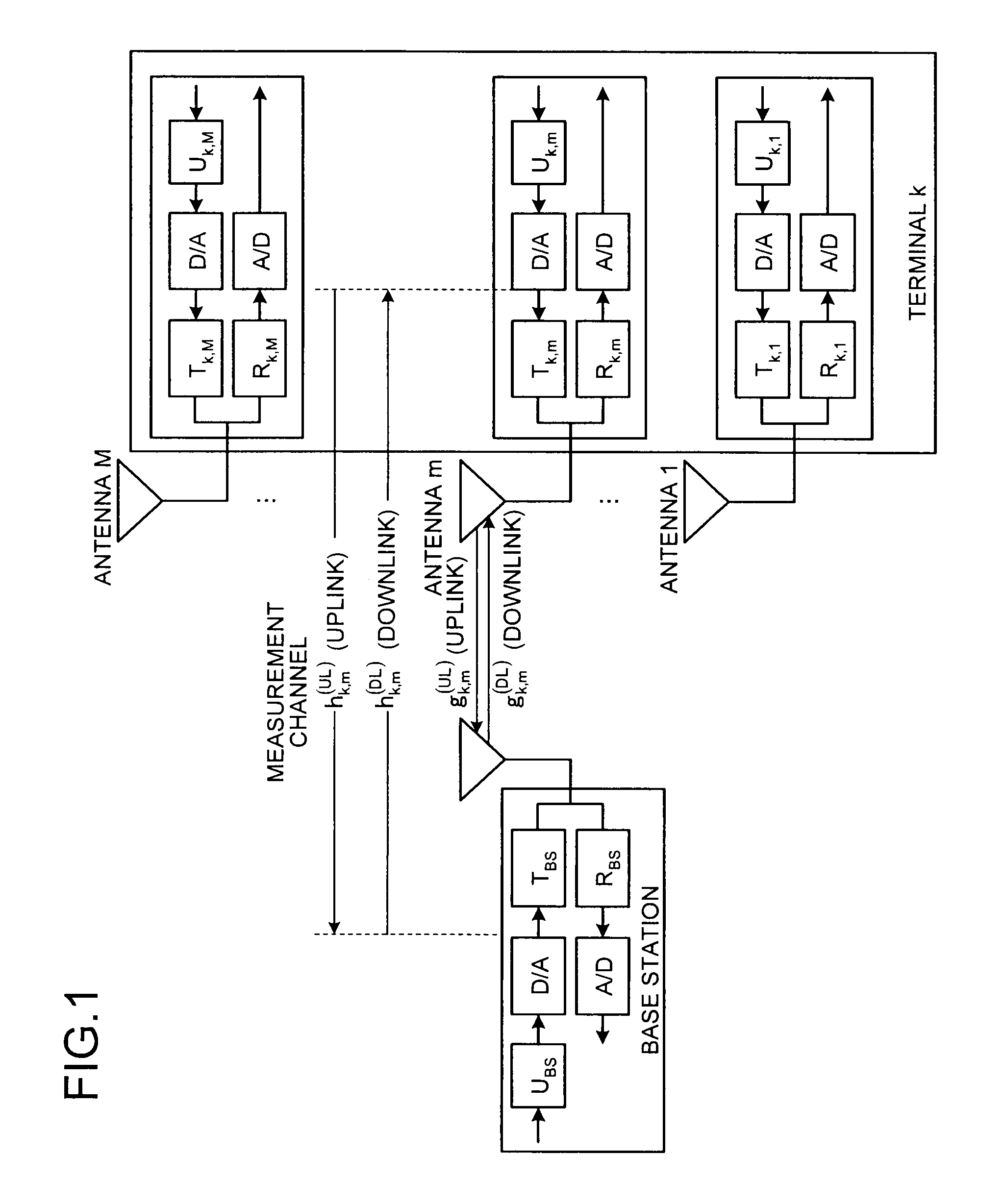
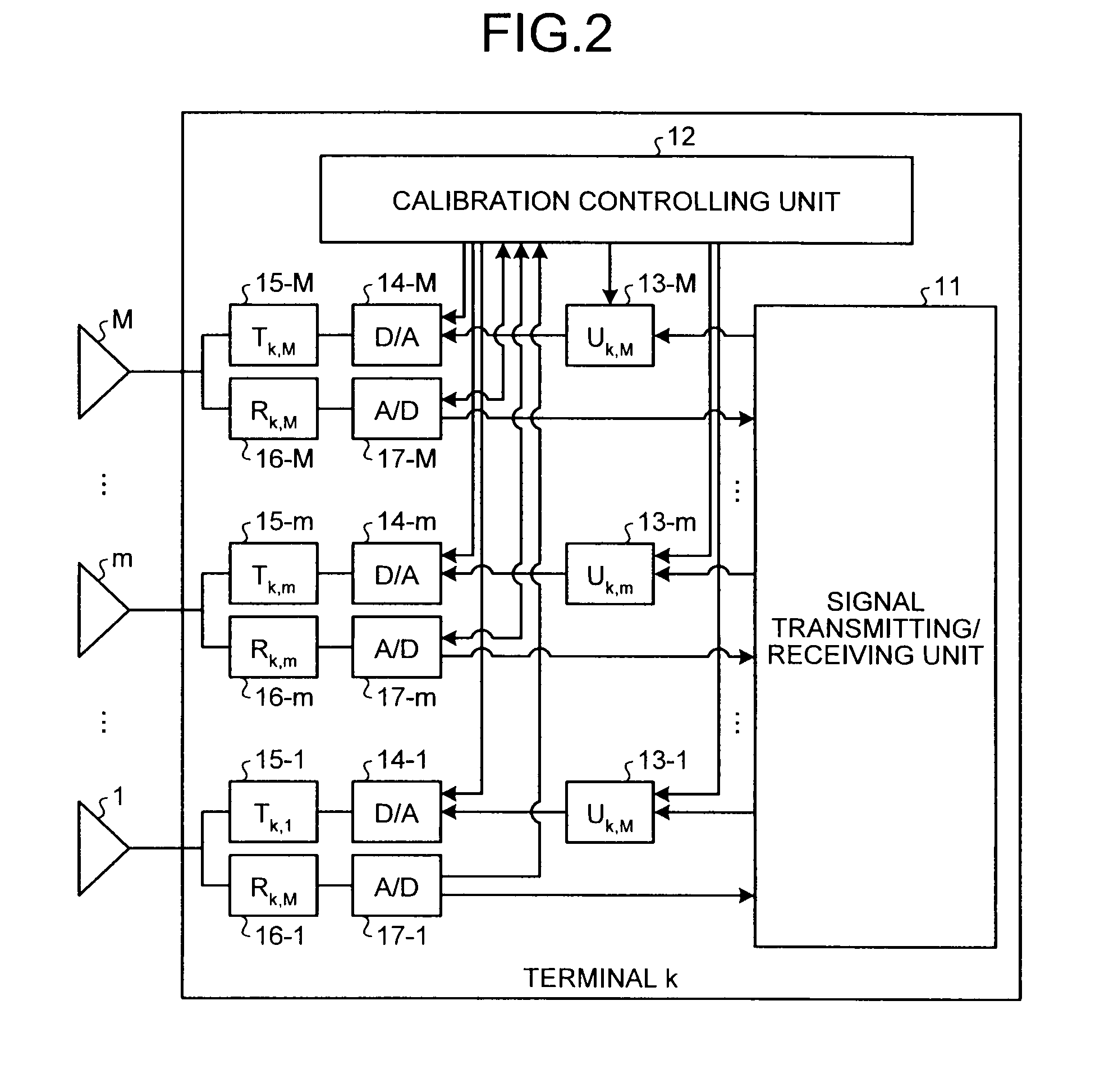
Calibration method, communication system, frequency control method, and communication device
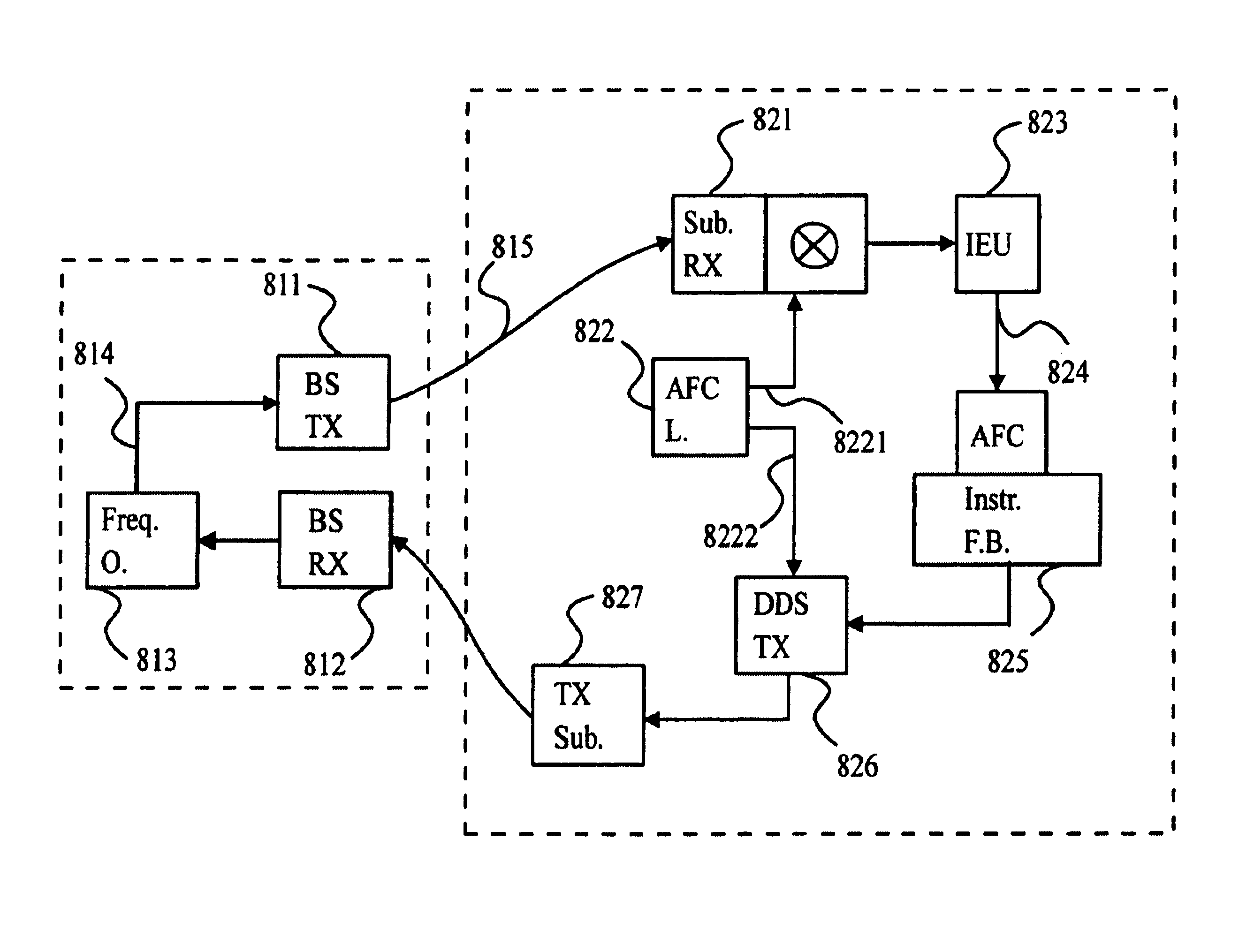
InactiveUS20100150013A1Simple digital processingSimple processTransmitters monitoringPower managementCommunications systemCommunication device
A calibration method according to the present invention includes a step of first channel estimating for transmitting a pilot signal from a first antenna and receiving the pilot signal at a second antenna different from the first antenna to calculate a first channel estimation value; a step of second channel estimating for transmitting a plot signal from the second antenna and receiving the pilot signal at the first antenna to calculate a second channel estimation value; and a step of correction coefficient calculating for calculating, by using the first and second channel estimation values, a correction coefficient.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Adaptive antenna for use in same frequency networks
InactiveUS6404386B1Spatial transmit diversityAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringCellular communication systems
An antenna apparatus which can increase capacity in a cellular communication system. The antenna operates in conjunction with a mobile subscriber unit and provides a plurality of antenna elements, each coupled to a respective signal control component such as a switch. The switch position of each antenna element is programmed for optimum reception during, for example, an idle mode which receives a pilot signal. The antenna array creates a beamformer for signals to be transmitted from the mobile subscriber unit, and a directional receiving array to more optimally detect and receive signals transmitted from the base station. By directionally receiving and transmitting signals, multipath fading is greatly reduced as well as intercell interference. Various techniques for determining the proper arrangement of signal control components for each antenna element are accommodated.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
Presence-aware cellular communication system and method
InactiveUS20100056184A1Increase capacityReduce consumptionPower managementAssess restrictionAir interfaceCellular communication systems
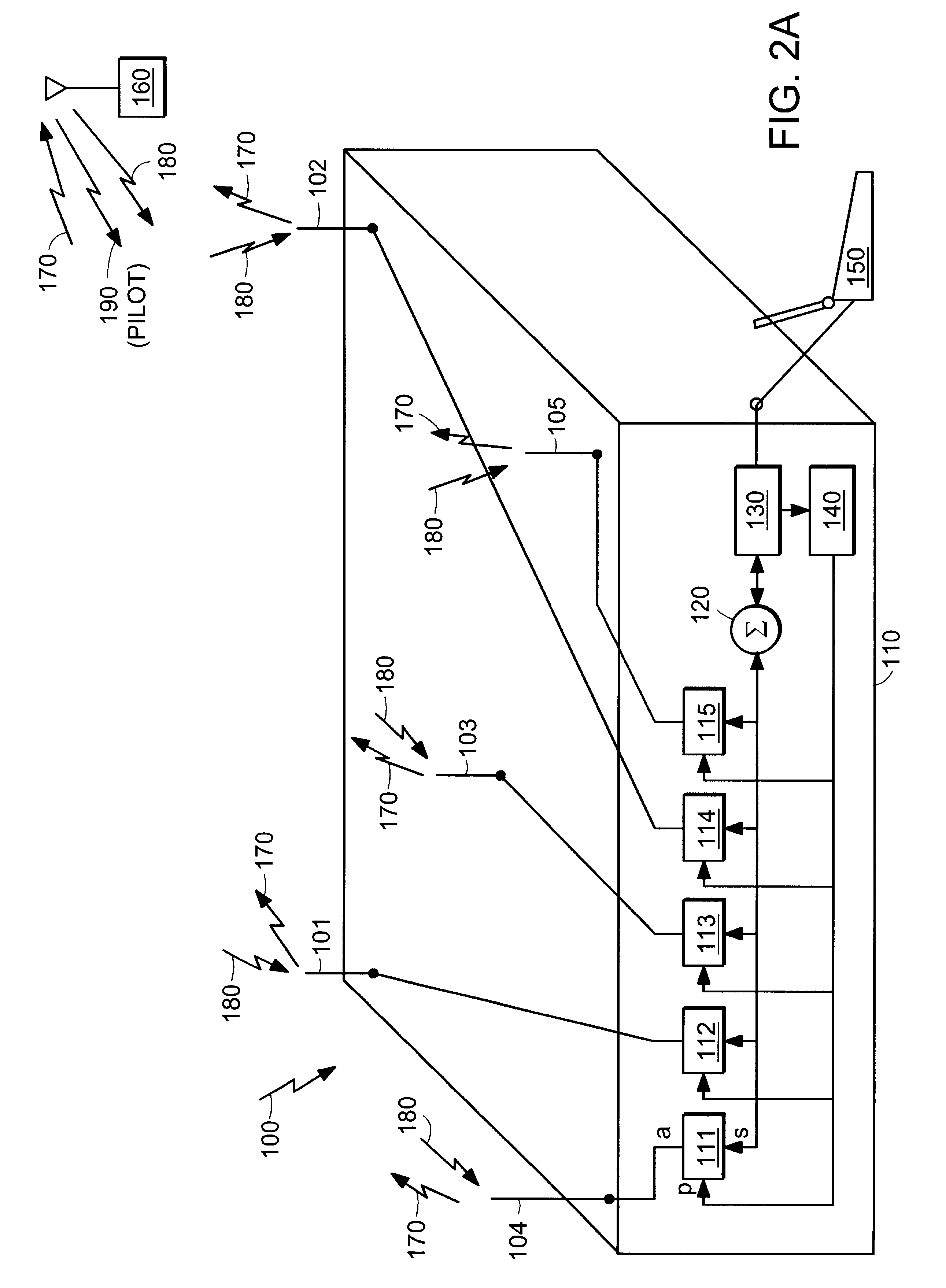
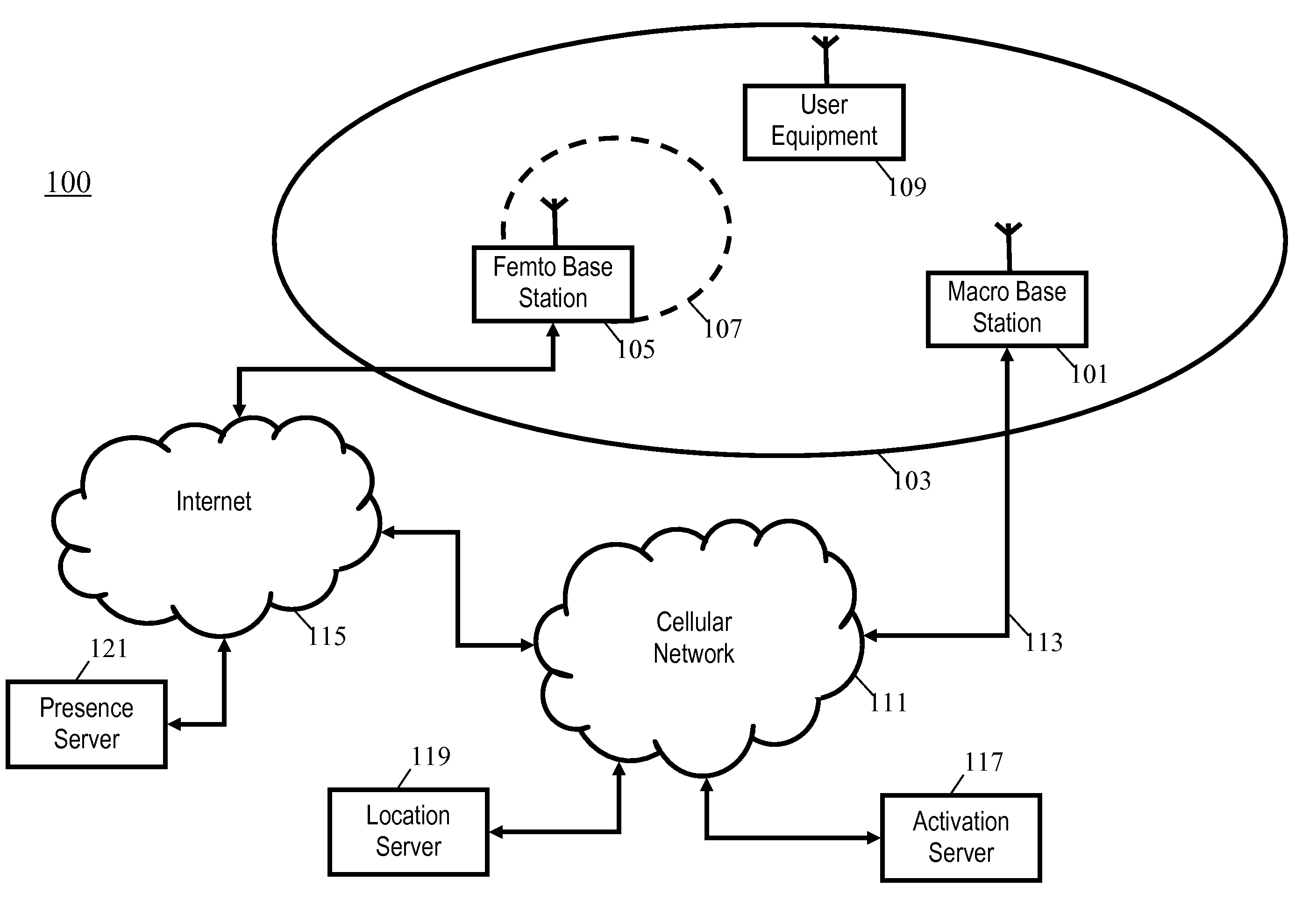
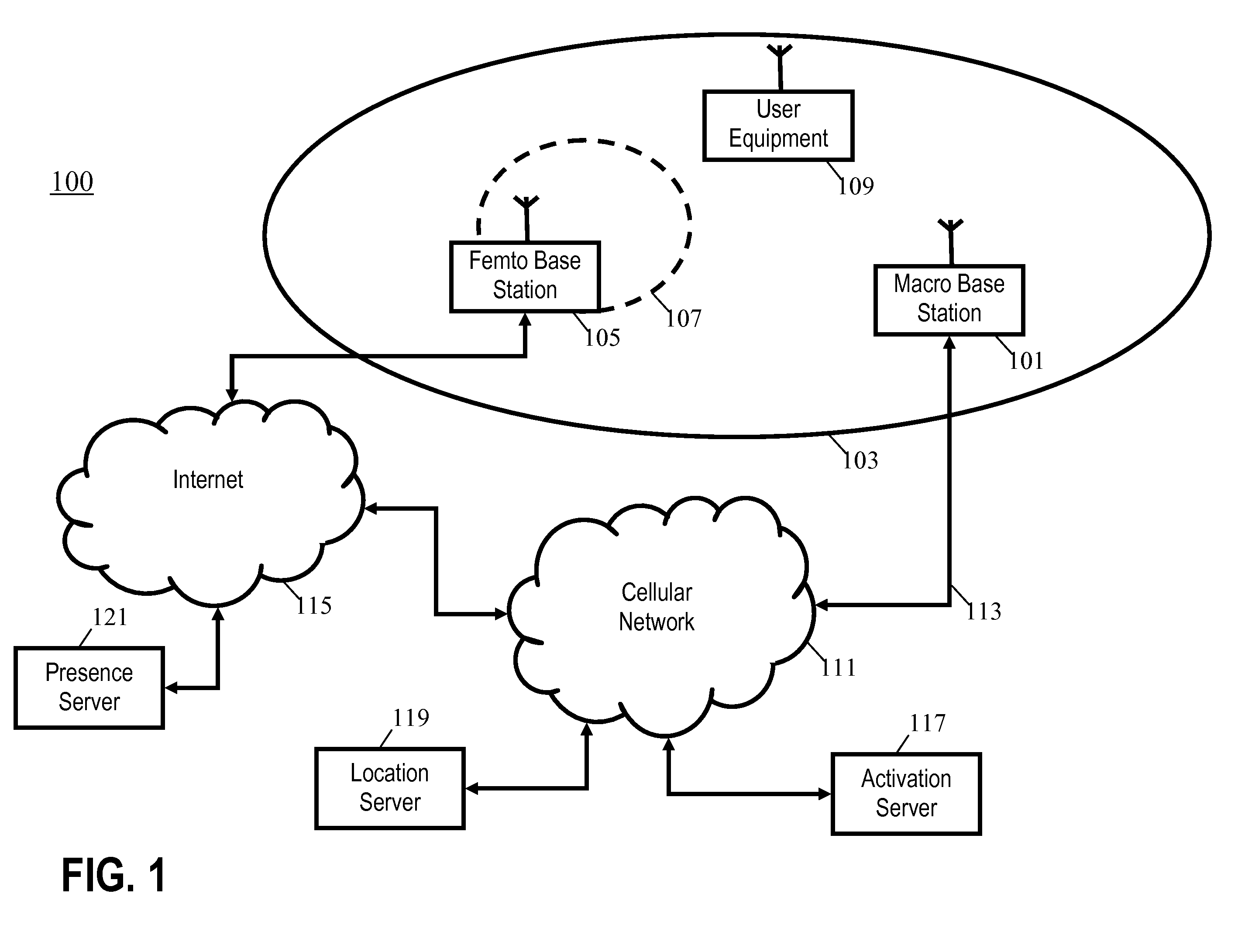
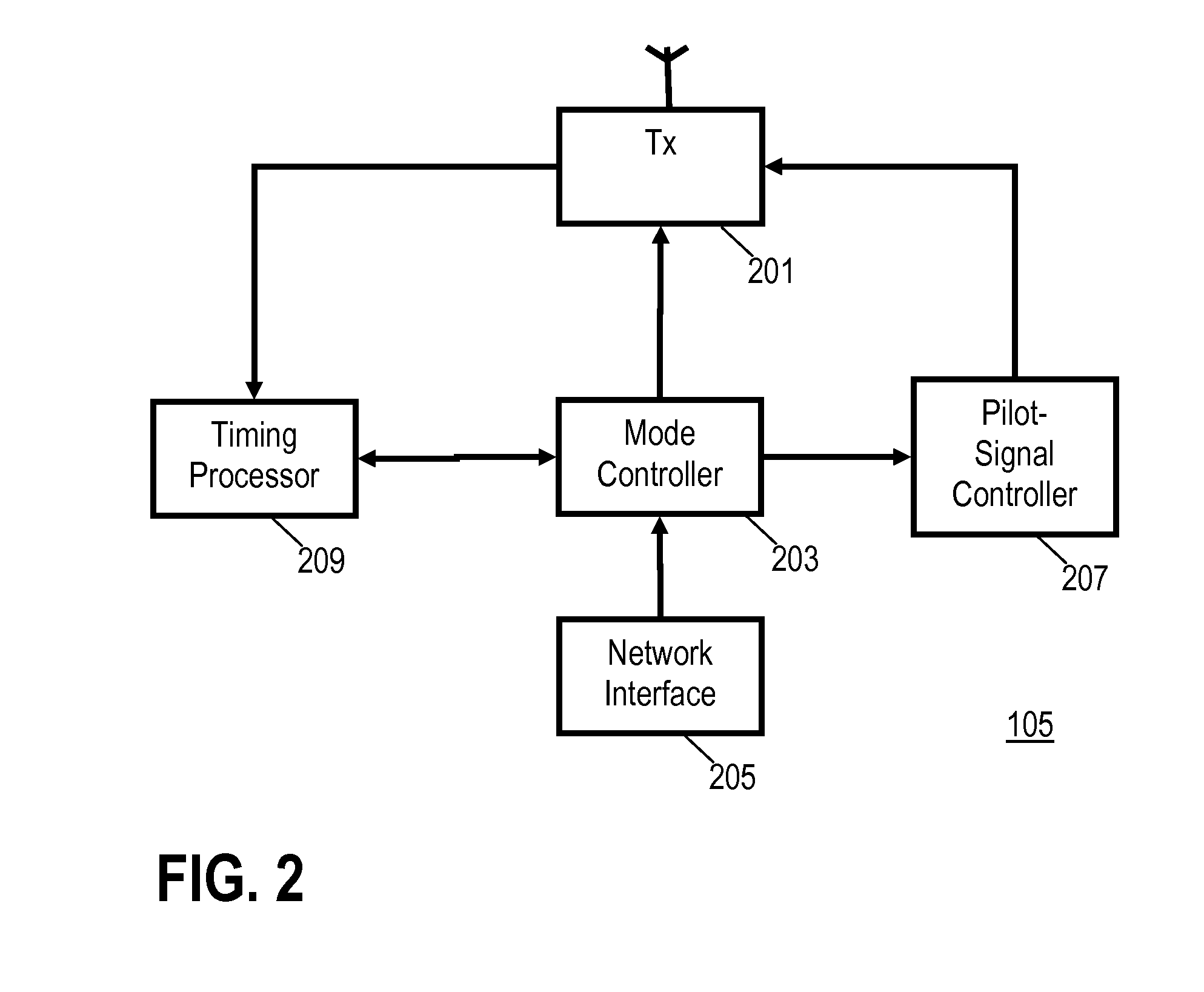
A cellular communication system comprises a network supporting user equipment over an air interface, the network having a hierarchical cell arrangement with overlay cells and underlay cells. An underlay base station is associated with a subset of registered user equipment. An activation server switches the underlay base station between an inactive mode and an active mode in response to detecting that registered user equipment meets a location criterion. The underlay base station only supports user equipment when in the active mode, e.g., it may only transmit a pilot signal in this mode. Interference and power consumption may be substantially reduced by sending the base station into the inactive mode thereby resulting in increased capacity of the cellular communication system as a whole.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
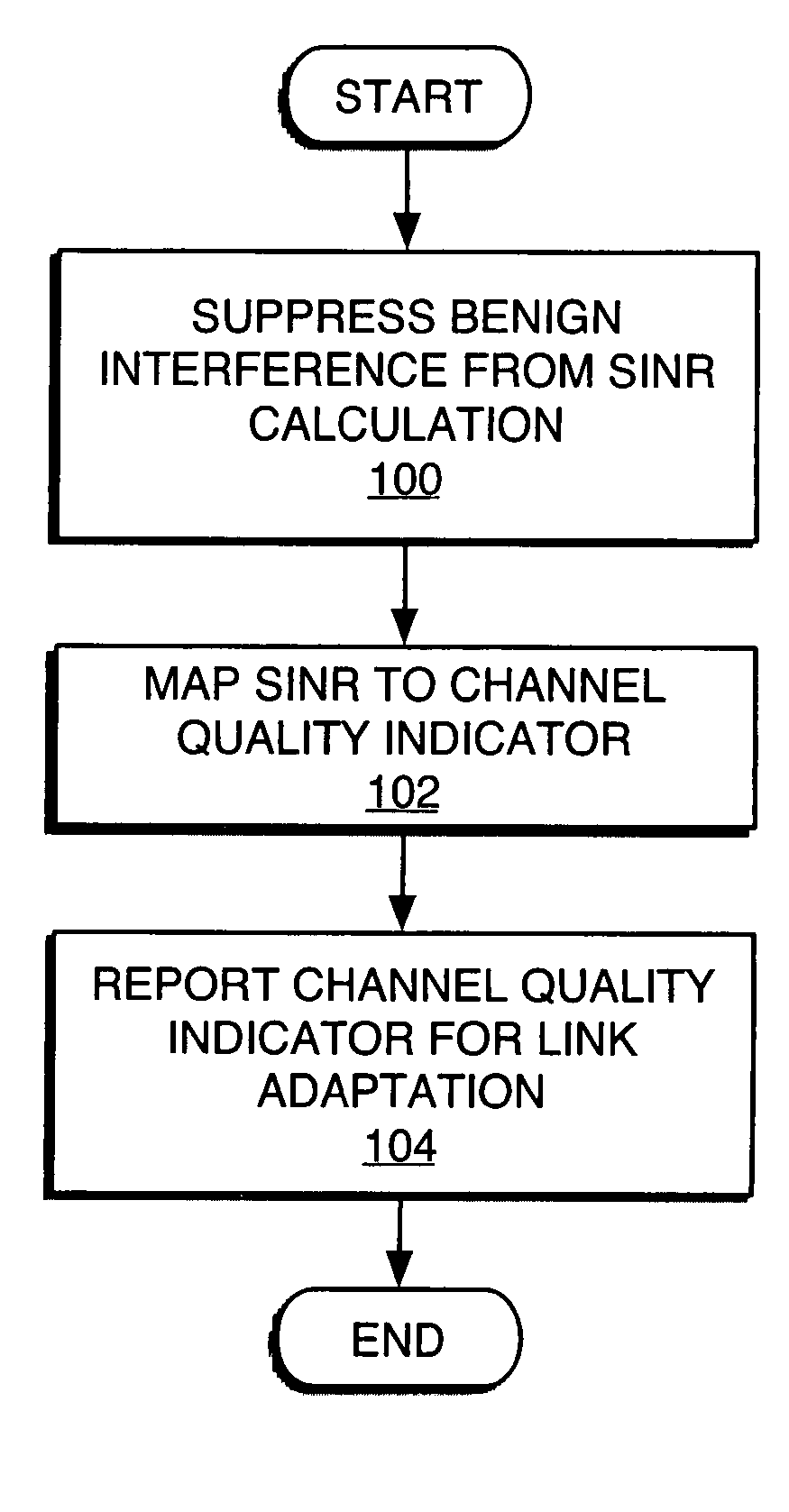
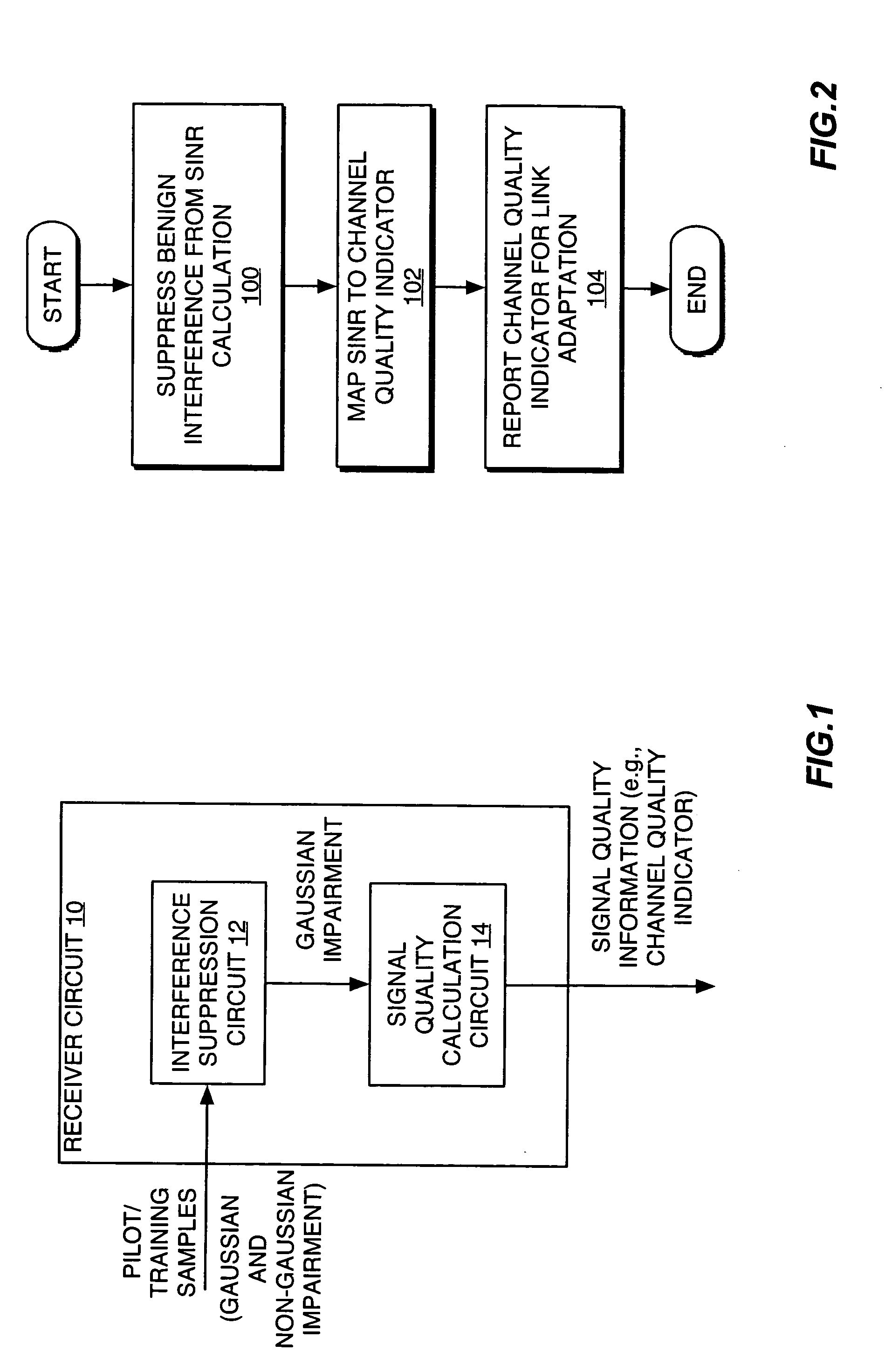
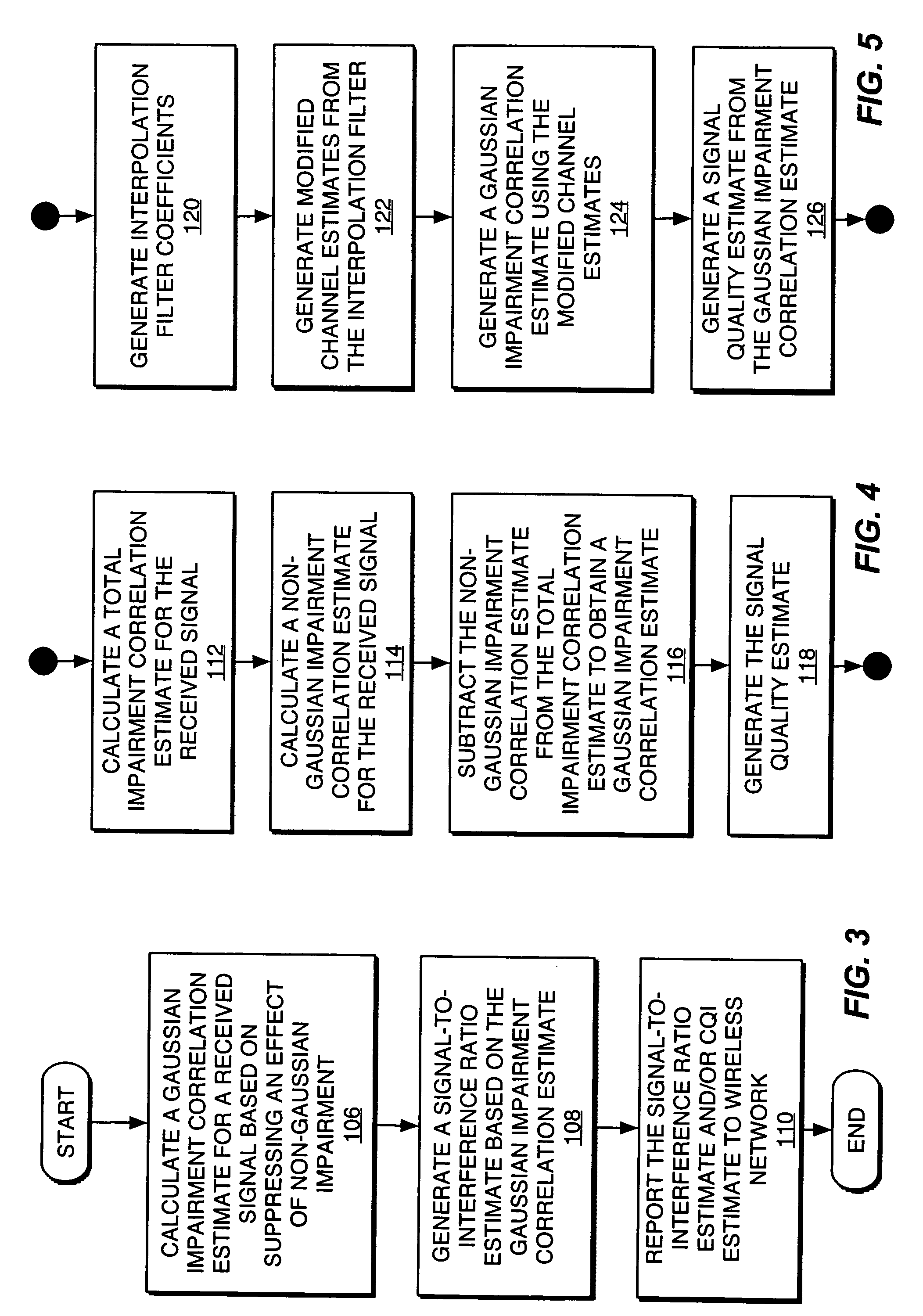
Benign interference suppression for received signal quality estimation
InactiveUS20050282500A1Good estimateReduce impactError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission control/equalisingSelf interferenceSignal quality
A receiver circuit suppresses effects of “benign” impairment from the calculation of received signal quality estimates, such that the estimate depends primarily on the effects of non-benign impairment. For example, a received signal may be subject to same-cell and other-cell interference plus noise, which is generally modeled using a Gaussian distribution, and also may be due to certain forms of self-interference, such as quadrature phase interference arising from imperfect derotation of the pilot samples used to generate channel estimates for the received signal. Such interference generally takes on a distribution defined by the pilot signal modulation, e.g., a binomial distribution for binary phase shift keying modulation. Interference arising from such sources is relatively “benign” as compared to Gaussian interference and thus should be suppressed or otherwise discounted in signal quality calculations. Suppression may be based on subtracting benign impairment correlation estimates from total impairment correlation estimates, or on filtering the benign impairment in channel estimation.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Multi-path mitigation in rangefinding and tracking objects using reduced attenuation RF technology
ActiveUS20110111751A1Small incremental costImprove accuracyMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesDigital computer detailsDigital signal processingSignal element
A method and system for identification, tracking and locating in wireless communications and wireless networks. The method and system use reference and / or pilot signals that are present in wireless communications and wireless networks. The method and system might also use RTT, TOA and time-stamping measurements / techniques to determine one or more reference signals traveling time between the Base Station (eNB) or its functional equivalent and mobile device (UE) and or network device. Other wireless networks that do not use reference and / or pilot signals may employ one or more of the following types of alternate embodiments of present invention: 1) where a portion of frame is dedicated to the ranging signal / ranging signal elements; 2) where the ranging signal elements are embedded into (spread across) transmit / receive signals frame(s); and 3) where the ranging signal elements are embedded with the data. The method and system includes multi-path mitigations processor and multi-path mitigations techniques and algorithms which improve the track-locate accuracy. The method and system allow achieving increased accuracy by using multi-path mitigations processor and multi-path mitigations techniques and algorithms. The techniques of Digital Signal Processing and Software-Defined Radio are used.
Owner:QUALCOMM TECHNOLOGIES INC
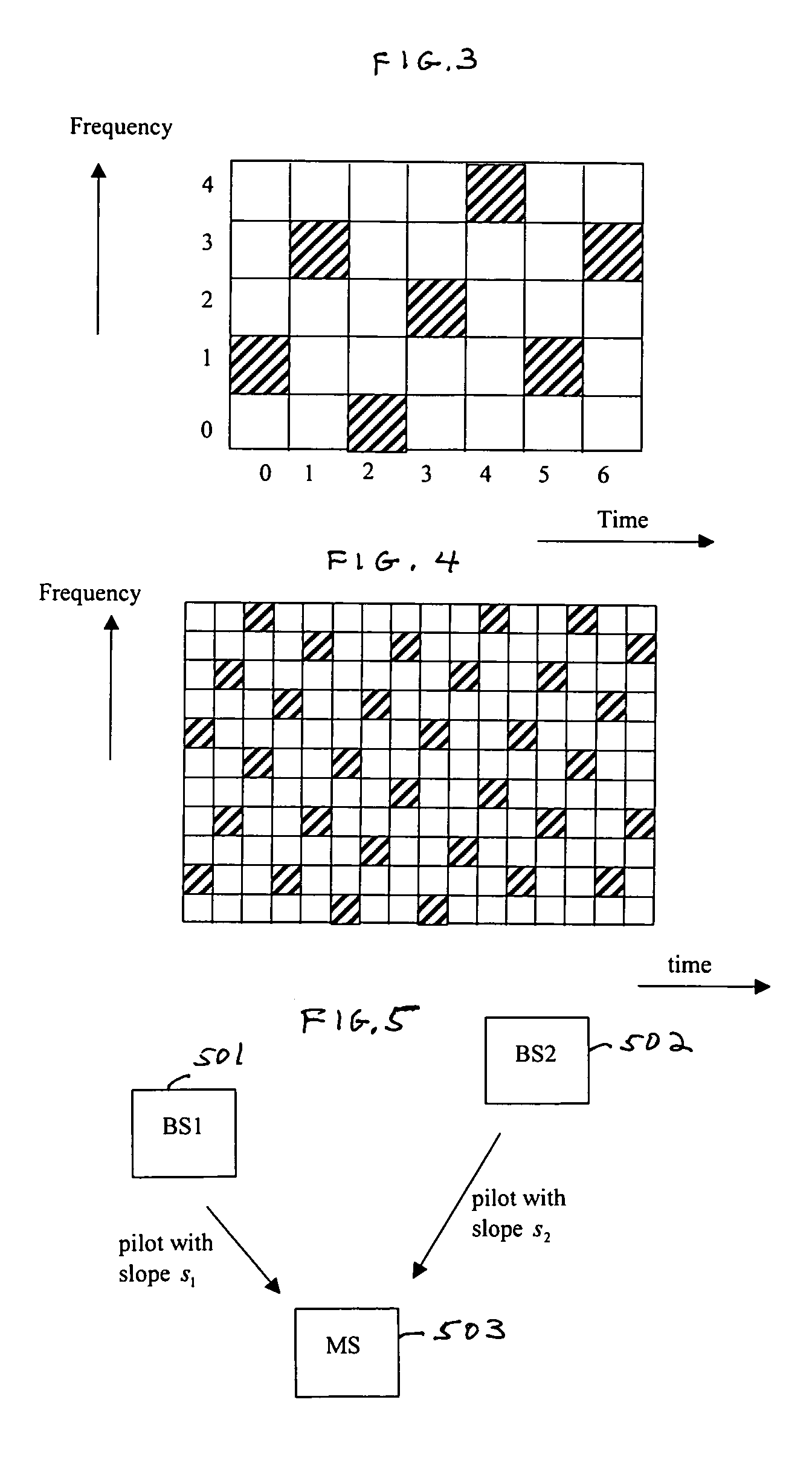
Base station identification in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing based spread spectrum multiple access systems
InactiveUS6961364B1Radio transmission for post communicationMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency shiftSpread spectrum
A base station having the strongest downlink signal is identified by utilizing a unique slope of a pilot tone hopping sequence being transmitted by a base station. Specifically, base station identification is realized by determining the slope of the strongest received pilot signal, i.e., the received pilot signal having the maximum energy. In an embodiment of the invention, the pilot tone hopping sequence is based on a Latin Squares sequence. With a Latin Squares based pilot tone hopping sequence, all a mobile user unit needs is to locate the frequency of the pilot tones at one time because the pilot tone locations at subsequent times can be determined from the slope of the Latin Squares pilot tone hopping sequence. The slope and initial frequency shift of the pilot tone hopping sequence with the strongest received power is determined by employing a unique maximum energy detector.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
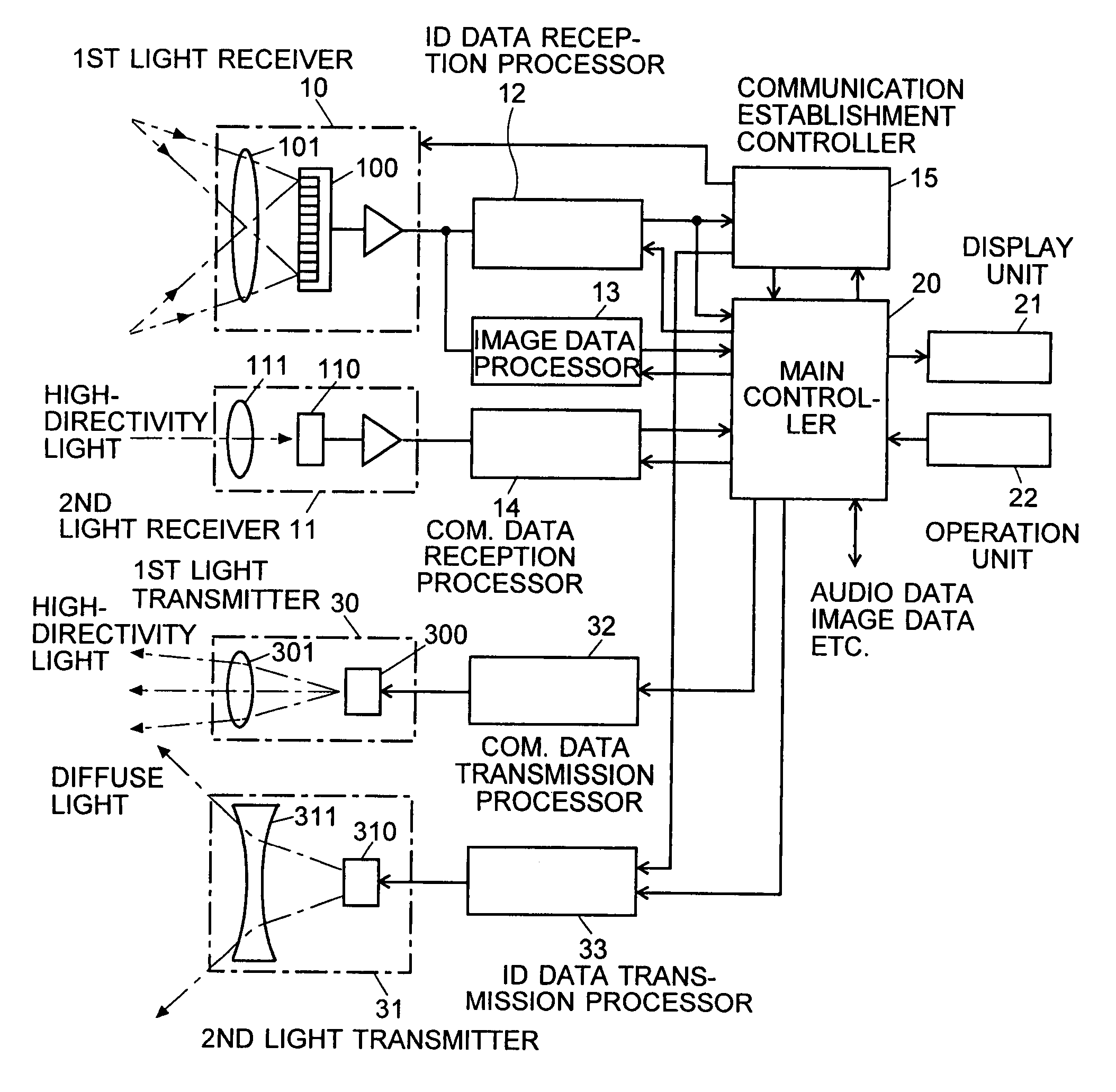
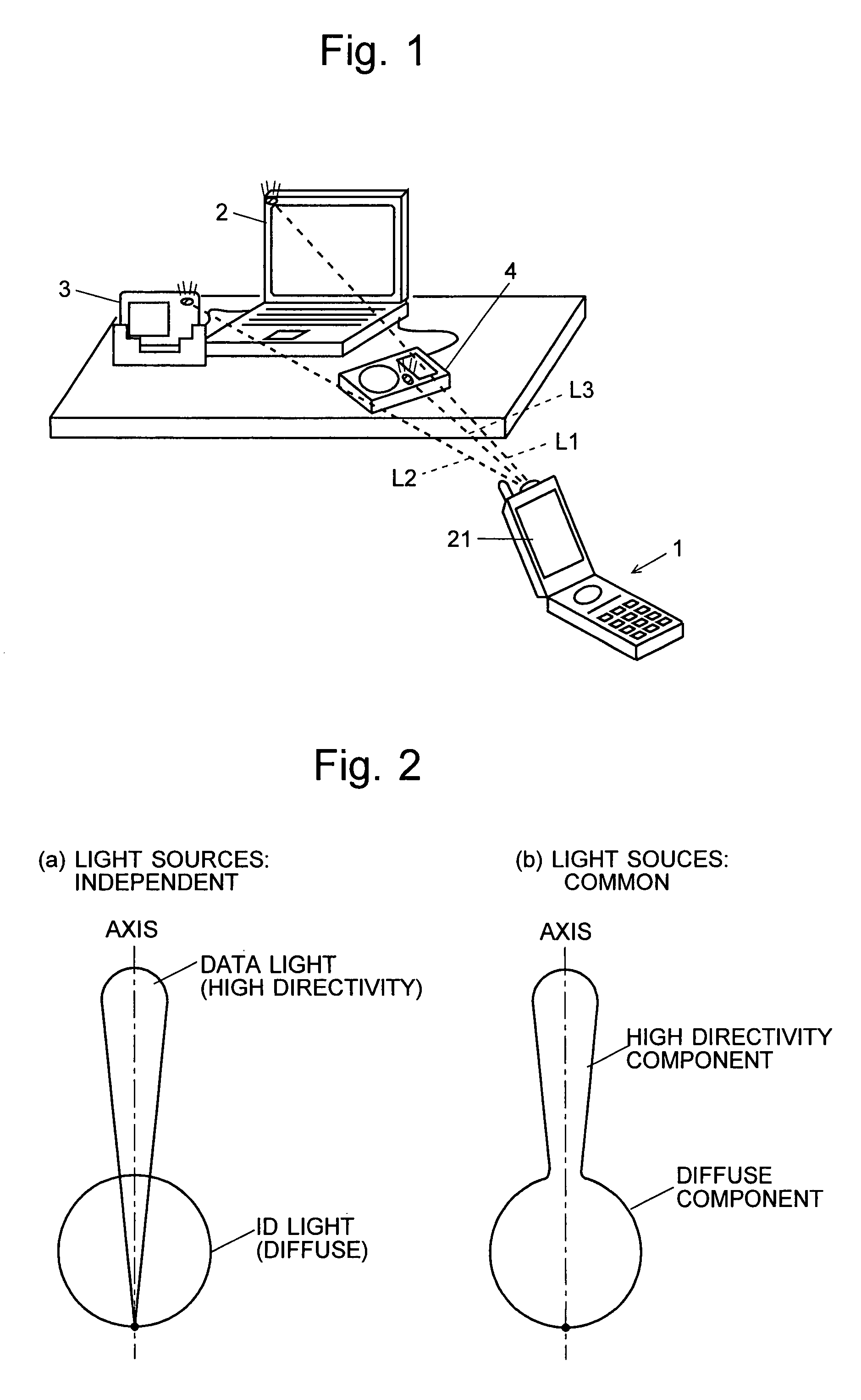
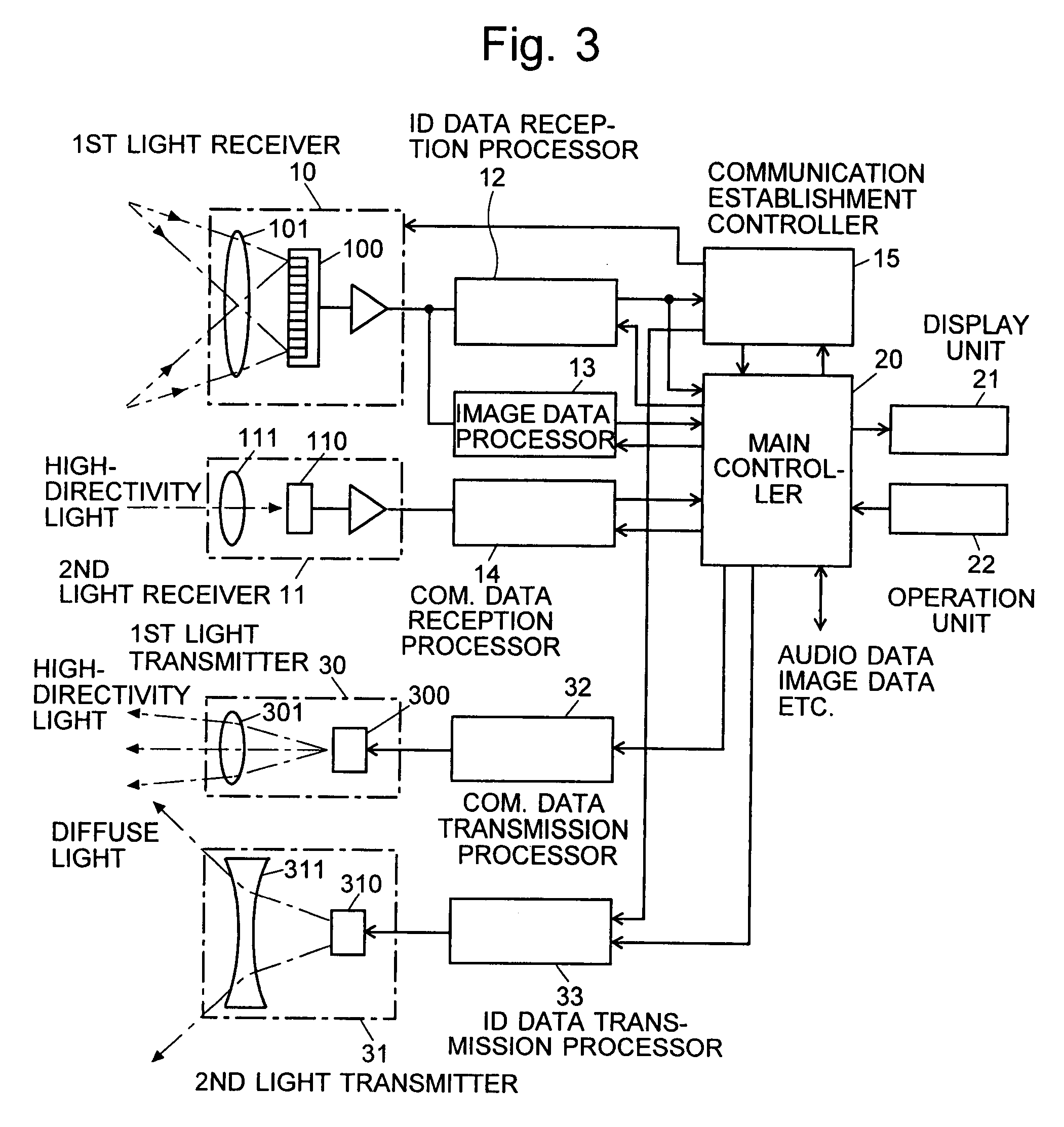
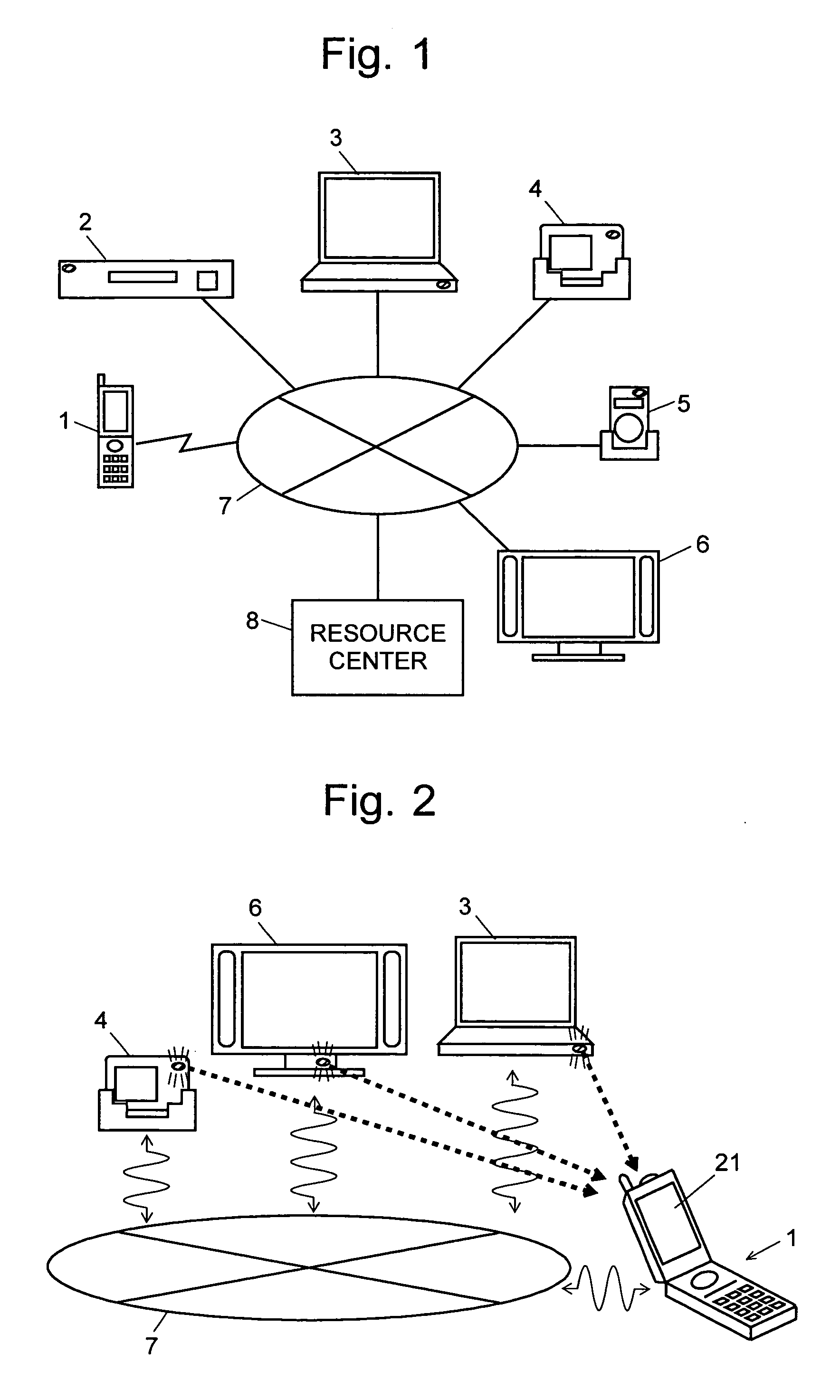
Information-processing system using free-space optical communication and free-space optical communication system
InactiveUS7715723B2Suppress power consumptionSmall sizeNetwork topologiesConnection managementInformation processingImaging data
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
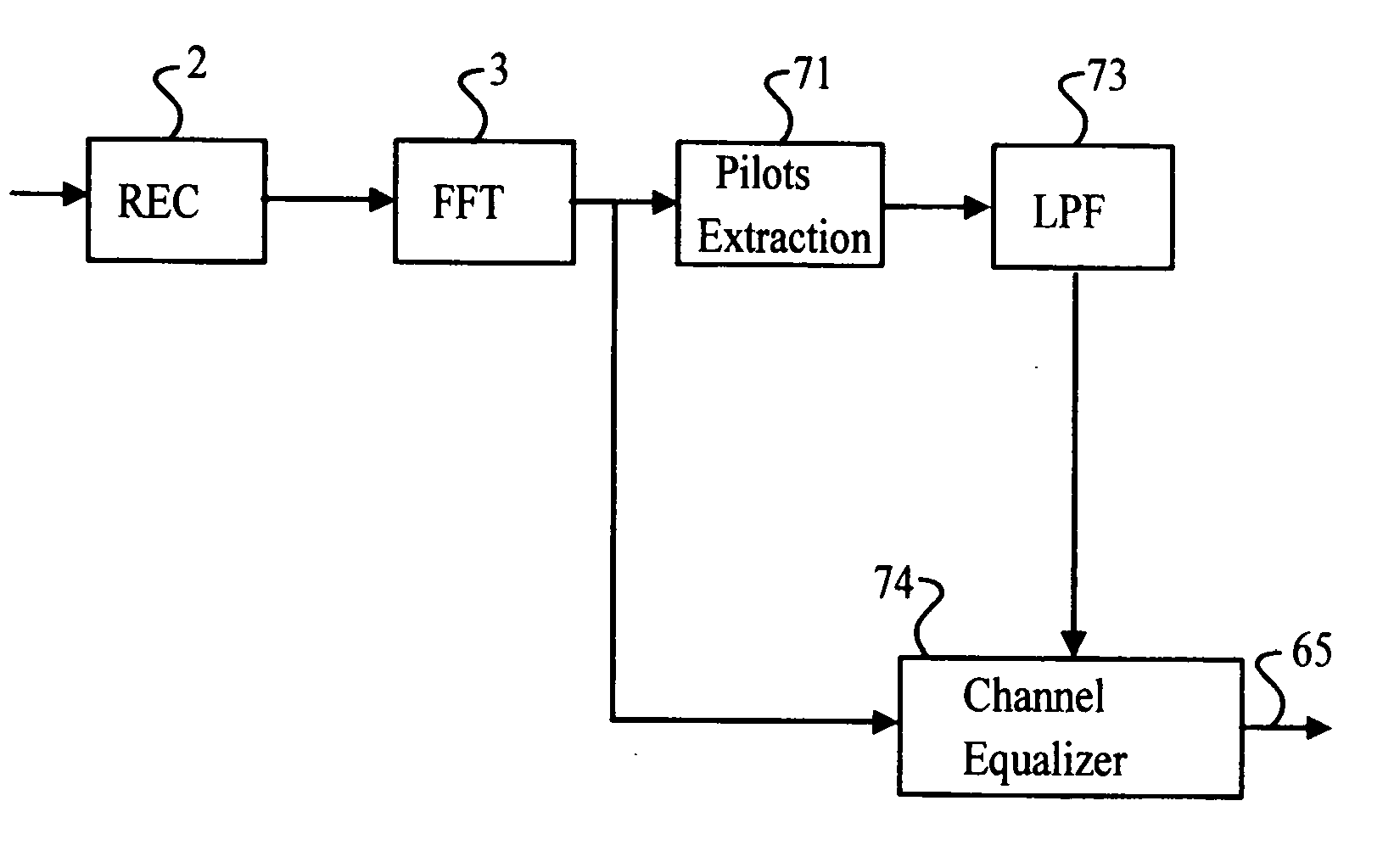
OFDM communication channel
InactiveUS20050207334A1Improve performanceFacilitate communicationTime-division multiplexChannel estimationComputer scienceDistortion
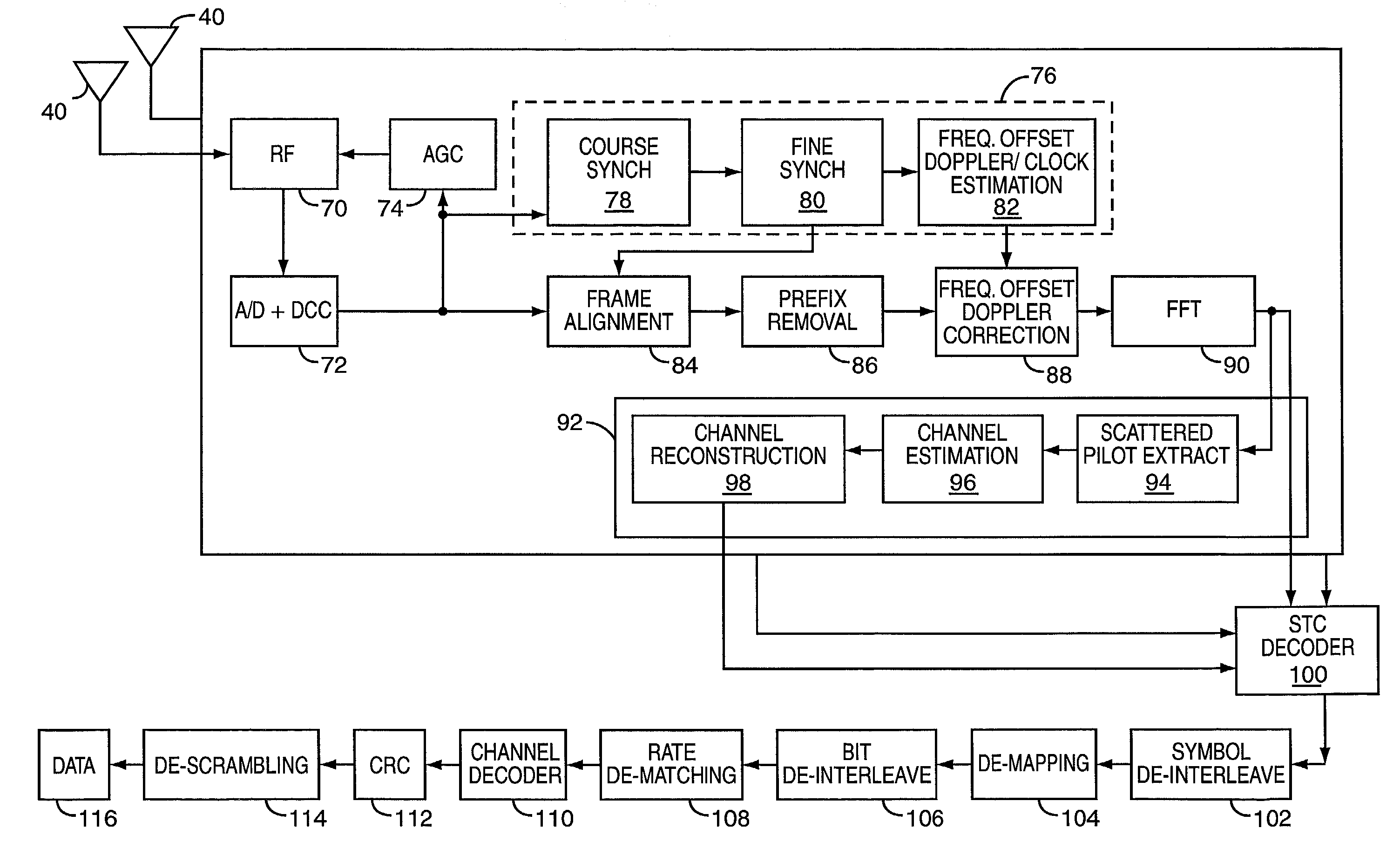
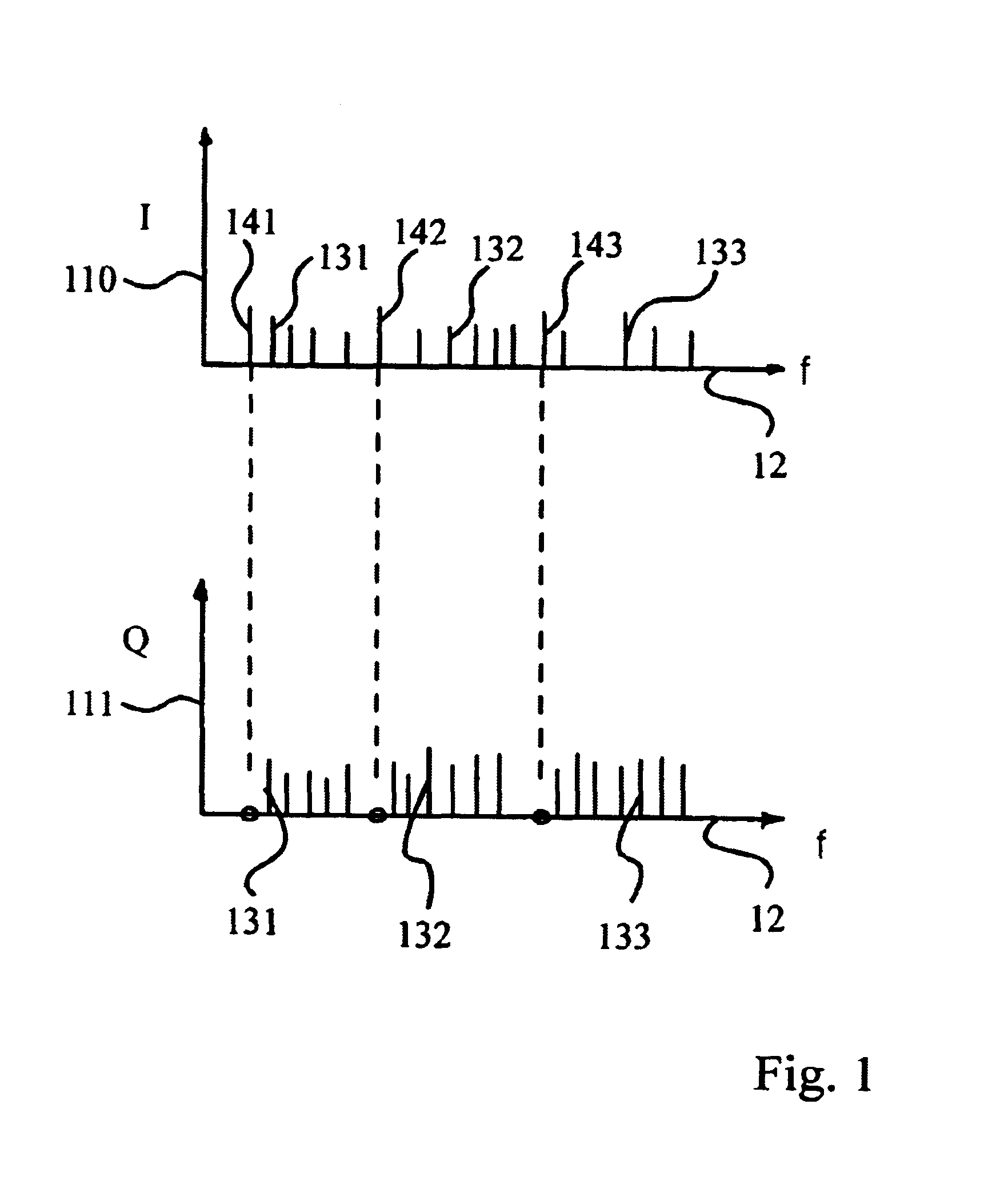
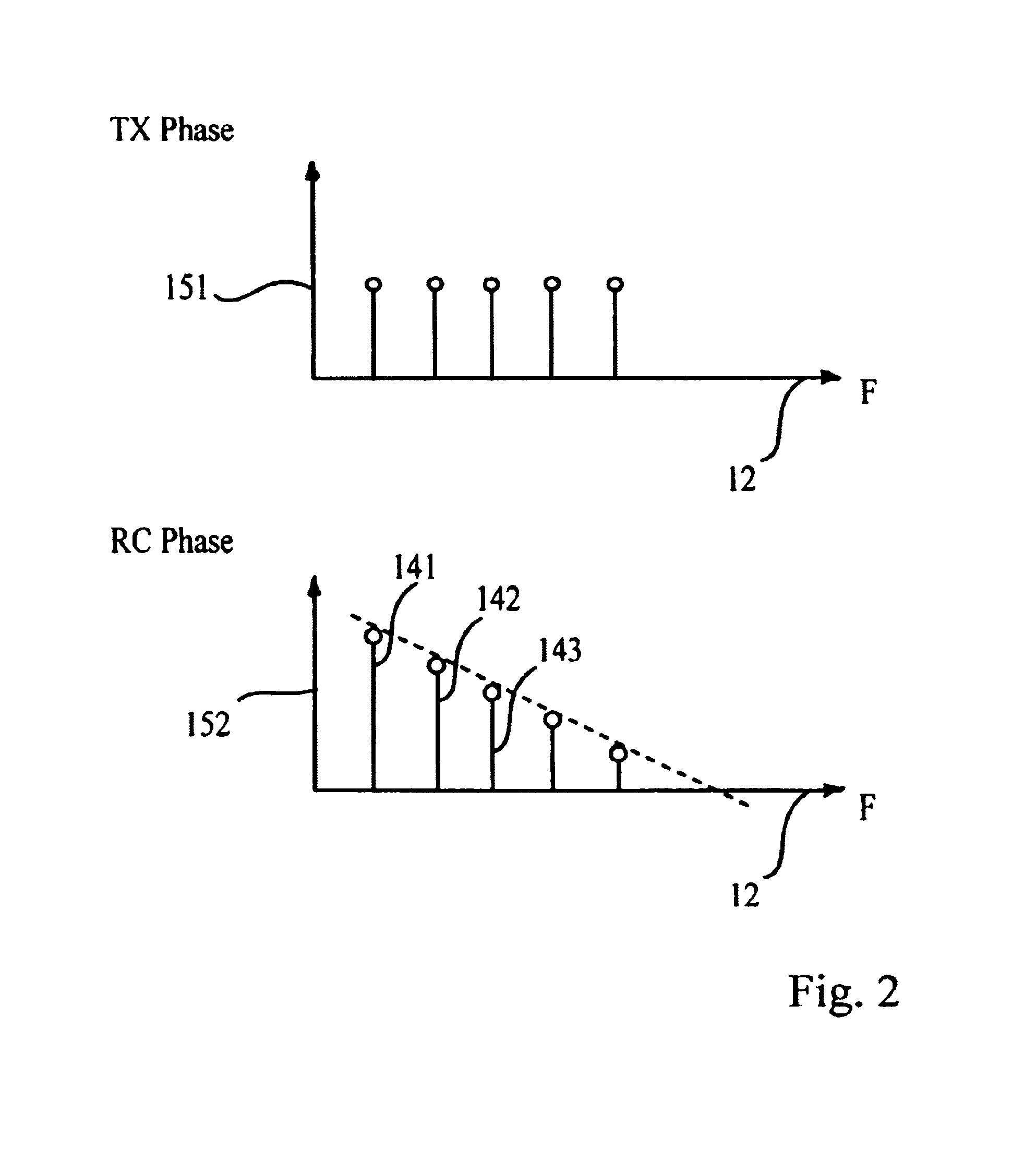
In an OFDM-based receiver, means for achieving time synchronization comprising: A. means for extracting pilot signals contained in the OFDM received signal; B. means for analyzing the pilot signals in the frequency domain and for issuing a signal indicative of a synchronization error in the received signal; C. means for correcting the synchronization error responsive to the signal indicative of the synchronization error. In an OFDM-based receiver, automatic frequency correction means in a subscriber unit comprising: A. an inner frequency correction loop for generating a LO frequency related to a frequency of a received signal; B. an outer frequency correction loop for correcting the LO frequency according to instructions received from a base station. In an OFDM-based receiver, a channel sounder comprising: A. means for extracting pilot signals contained in the OFDM received signal; B. means for analyzing the pilot signals in the frequency domain and for issuing signals indicative of a distortion in each pilot signal, wherein each of said pilot distortion signals comprises both an amplitude and a phase component; C. means for analyzing the signals indicative of a distortion in each pilot signal and for computing therefrom corrective signals for correcting distortions in the received signal.
Owner:HADAD ZION
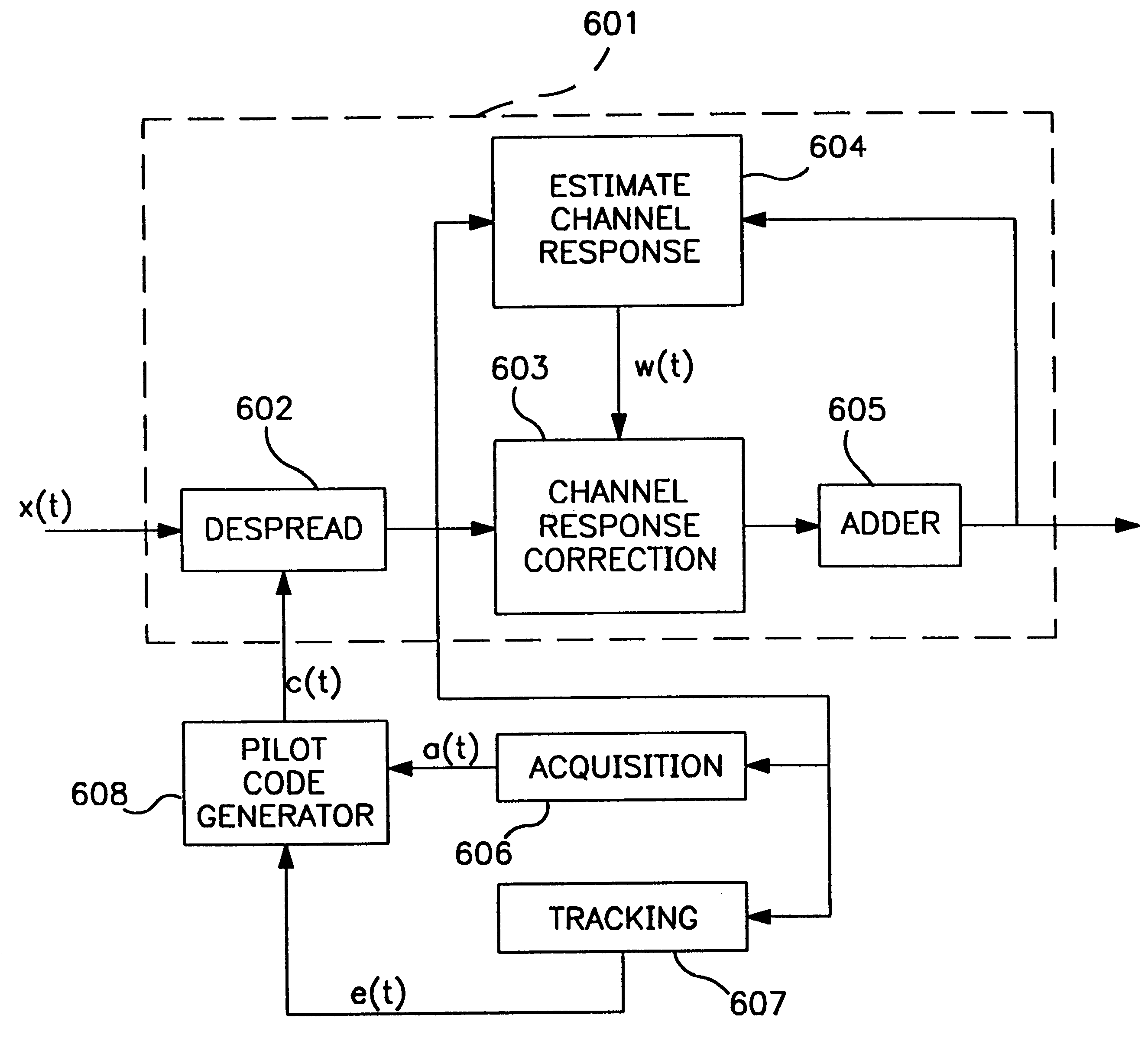
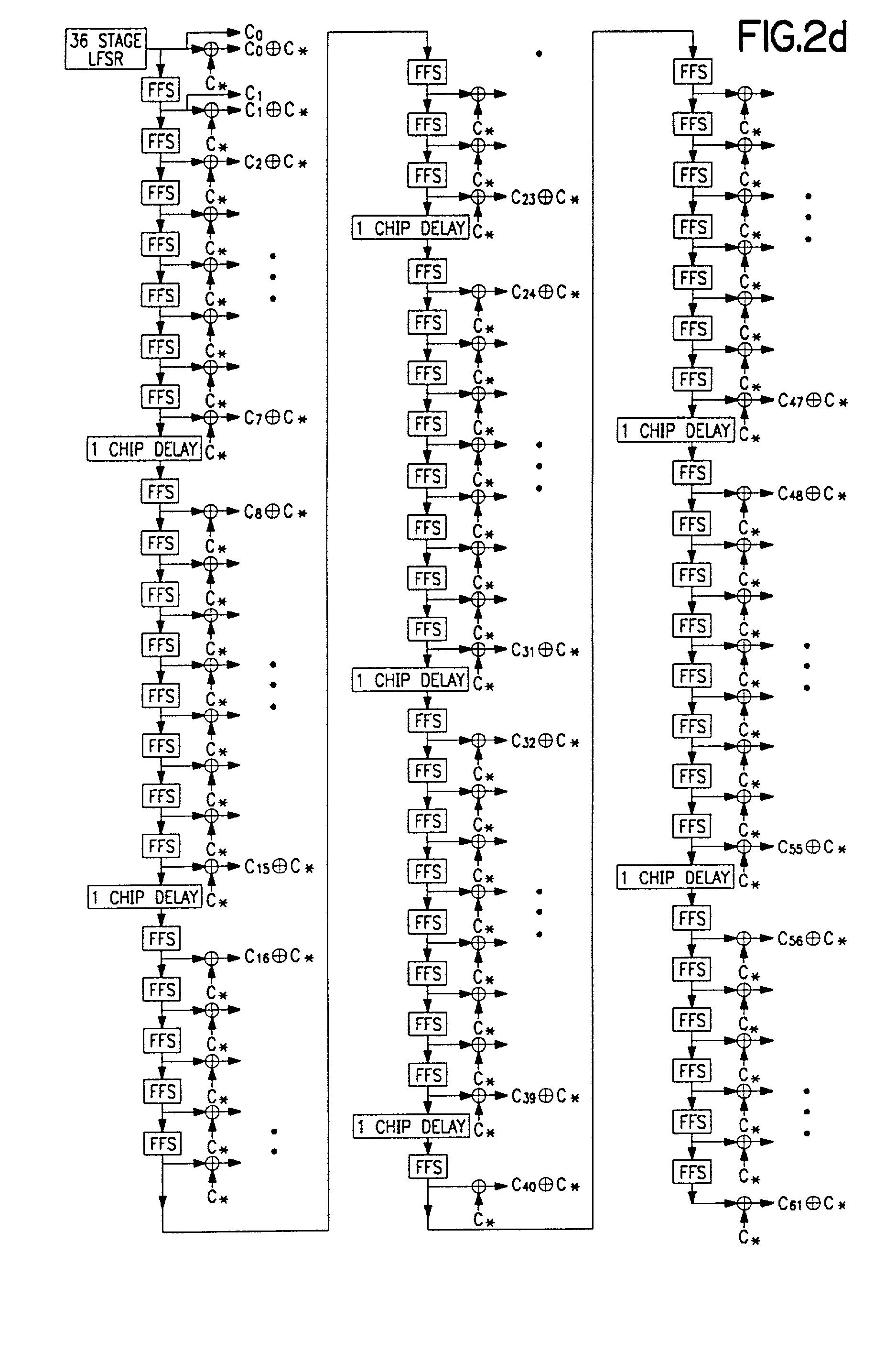
Code sequence generator in a CDMA modem
A CDMA modem includes a modem transmitter having: a code generator which provides an associated pilot code signal and which generates a plurality of message code signals: a spreading circuit which produces a spread-spectrum message signal by combining each of the information signals with a respective one of the message code signals; and a global pilot code generator that provides a global pilot code signal to which the message code signals are synchronized. The CDMA modem also includes a modem receiver having an associated pilot code generator and a group of associated pilot code correlators for correlating code-phase delayed versions of the associated pilot signal with a receive CDM signal to produce a despread associated pilot signal. The code phase of the associated pilot signal is changed responsive to an acquisition signal value until a pilot signal is received. The associated pilot code tracking logic adjusts the associated pilot code signal in phase responsive to the acquisition signal so that the signal power level of the despread associated pilot code signal is maximized. Finally, the CDMA modem receiver includes a group of message signal acquisition circuits, each including a plurality of receive message signal correlators which correlate respective local received message code signal to the CDM signal to produce a respective despread received message signal.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Soft handoff in Ofdma system
ActiveUS20090129334A1Increase frequency diversityBroaden the use of channelsSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityCarrier signalSoft handover
The soft handoff in an OFDMA system. If the pilot signal strength for a base station exceeds the defined threshold, the base station is added to an active set list. Subcarriers in a plurality of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) symbols are divided and allocated into subchannels. The OFDM symbols are divided and multiplexed. A soft handoff zone with a first dimension of the subchannels and a second dimension of the divided and multiplexed OFDM symbols is defined. The soft handoff zone have subcarriers with a subchannel definition, for example, an identical permutation.
Owner:APPLE INC
Active antenna array configuration and control for cellular communication systems
InactiveUS20030073463A1Spatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityBeam patternCellular communication systems
Various antenna arrangements are provided with active transmit and receive antenna elements for transmitting and receiving signals within a cellular communication system. Also presented are specific base station antenna systems and methods, and portions thereof, which improve and control specific characteristics and features of antenna systems including antenna beam patterns. In addition, method for the optimization of a cellular communications network is provided which exploits reverse-link, forward-link, and pilot signal information to optimize network operations.
Owner:CELLETRA
OFDM communication channel
InactiveUS6985432B1Facilitate communicationImprove performanceFrequency-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsComputer scienceTime synchronization
In an OFDM-based receiver, a time synchronization unit comprising: A. a device for extracting pilot signals contained in the OFDM received signal; B. a device for analyzing pilot signals in the frequency domain and for issuing a signal indicative of a synchronization error in the received signal; C. a device for correcting the synchronization error, responsive to the signal indicative of the synchronization error. In an OFDM-based receiver, an automatic frequency correction device in a subscriber unit comprising: A. an inner frequency correction loop for generating a LO frequency related to a frequency of a received signal; B. an outer frequency correction loop for correcting the LO frequency according to instructions received from a base station.
Owner:ZION HADAD COMM
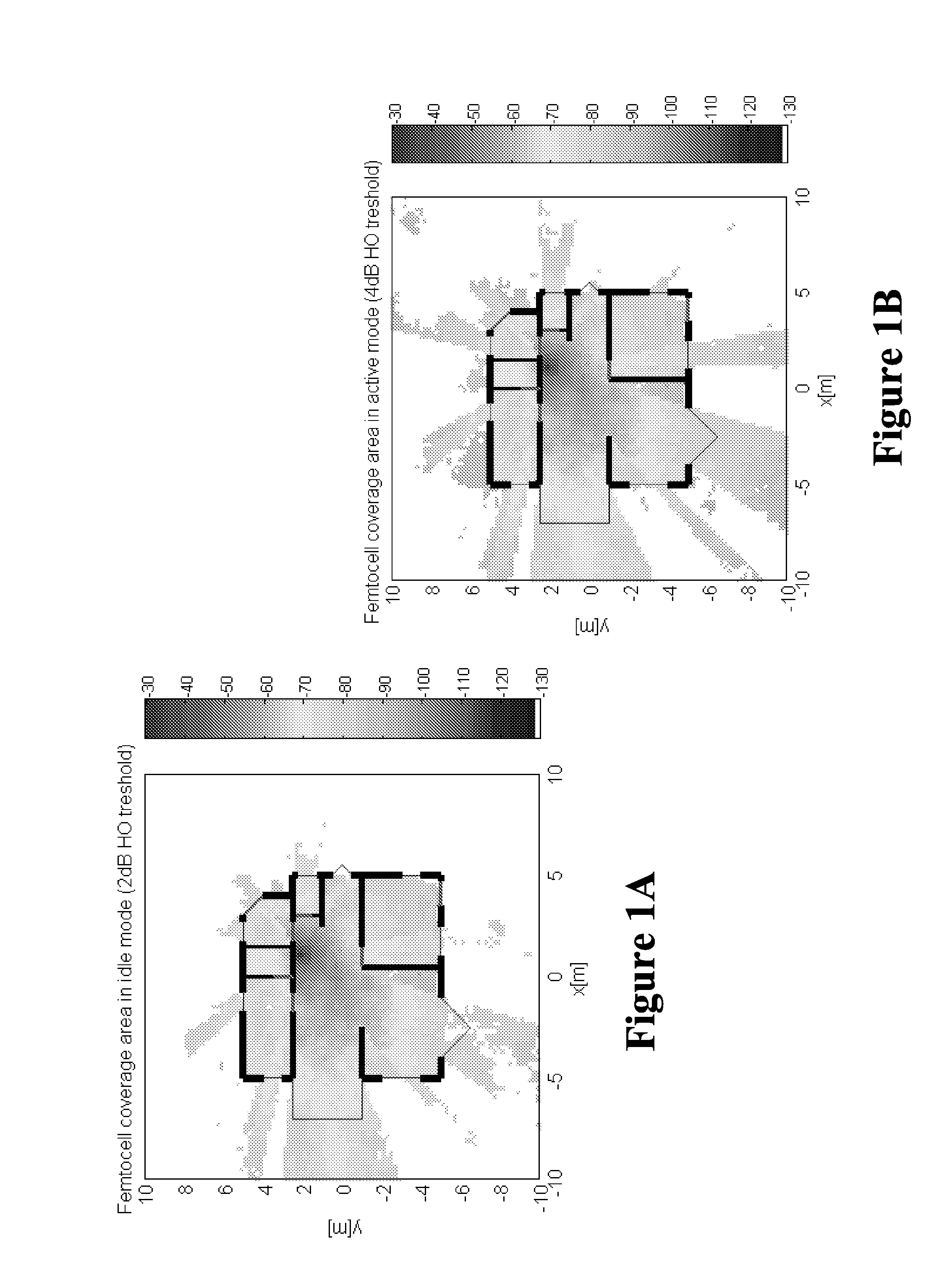
Method of modifying pilot power for a home base station router based on user demand
The present invention provides a method implemented in a base station router. One embodiment of the method includes determining a transmission power for a pilot signal transmitted by the base station router. The transmission power being determined based upon a number of mobile units that are camped on the base station router. Another embodiment of the method includes deploying the first base station router in a physical structure and estimating the dimensions of the physical structure based on a statistical representation of at least one handover attempt associated with the first base station router. Estimation of the dimensions of the physical structure occurs in response to deployment of the first base station router in the physical structure.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
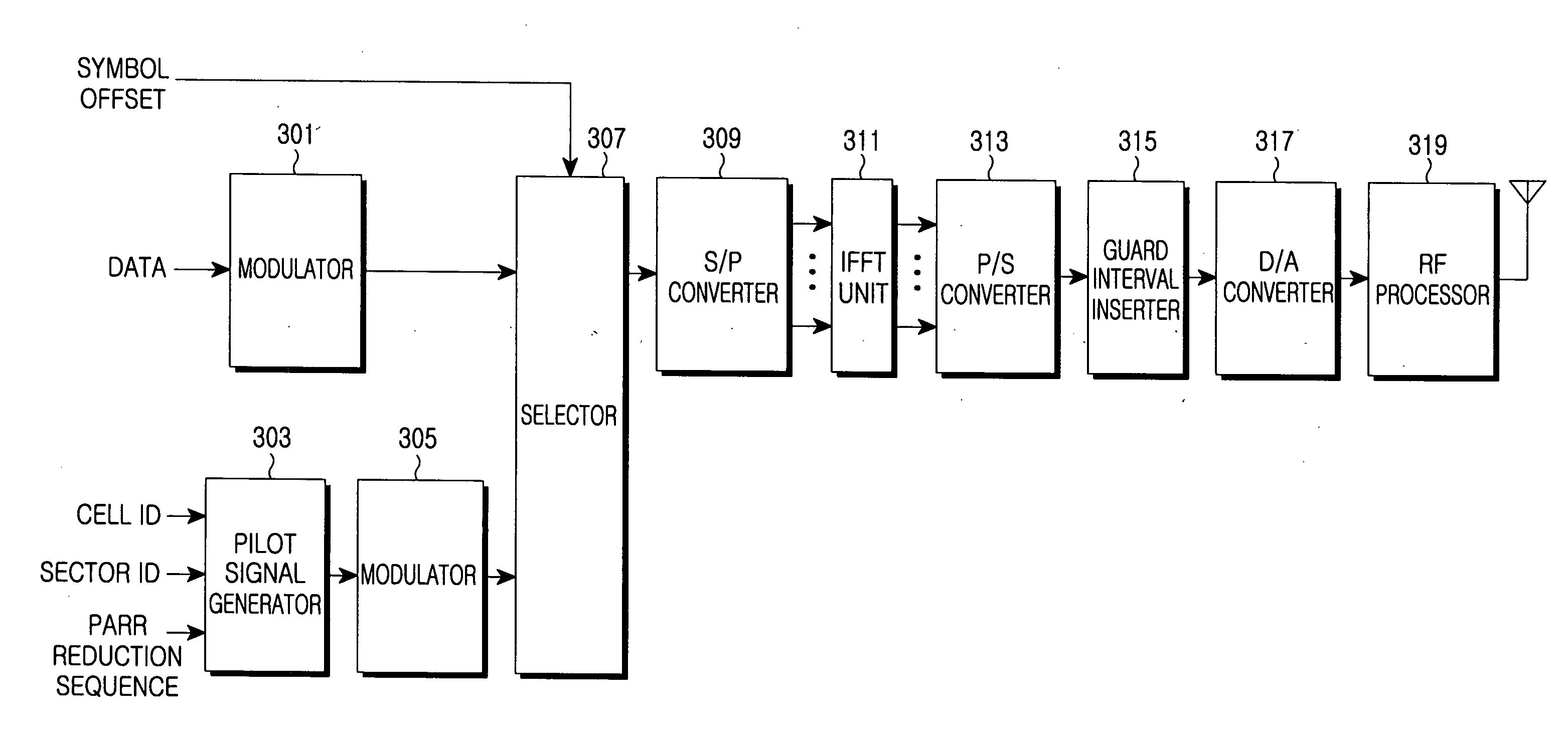
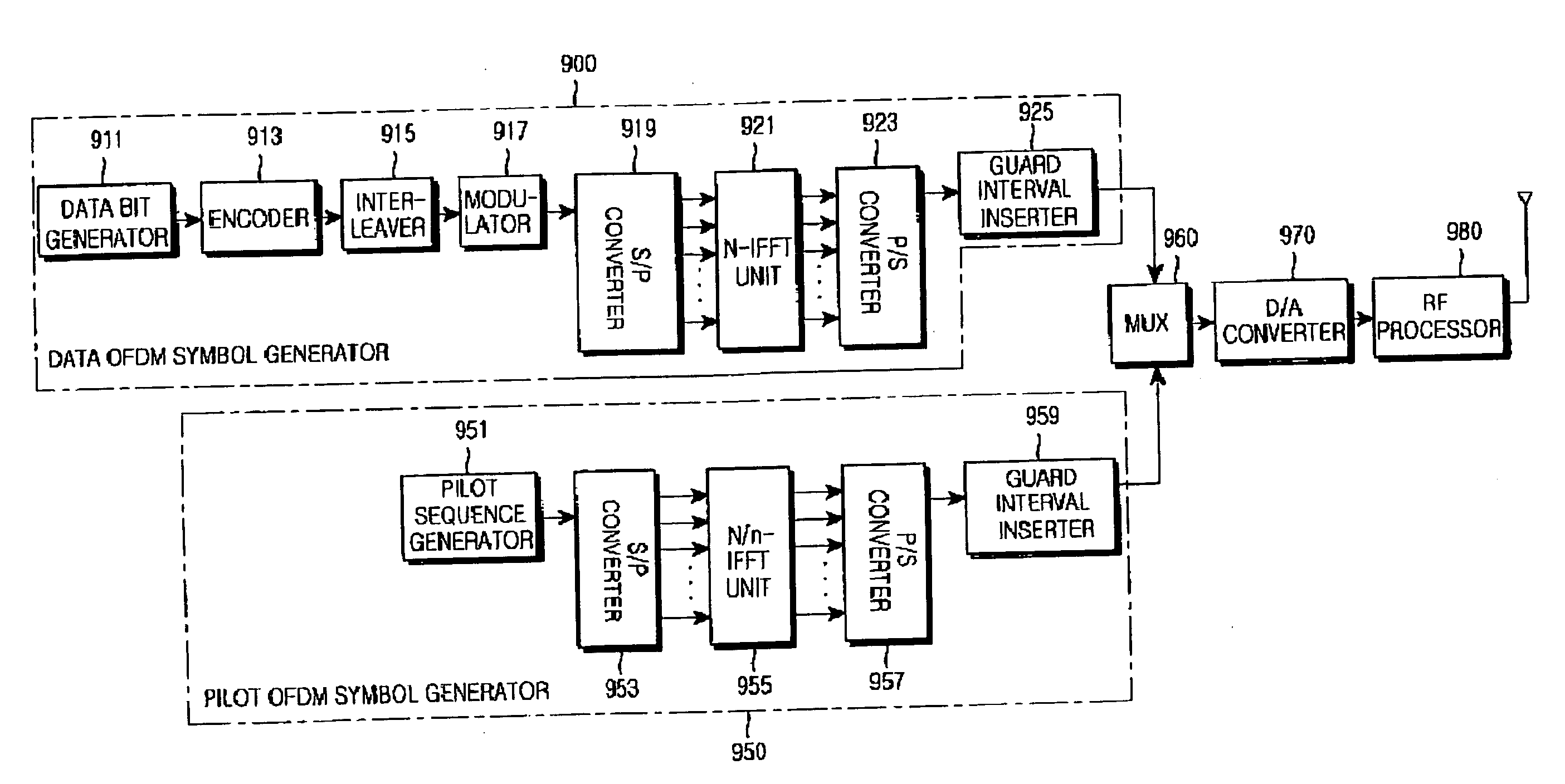
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving pilot signal in communication system using OFDM scheme
ActiveUS20060028976A1Interference minimizationMinimize interferenceModulated-carrier systemsRadio transmissionComputer hardwareFast Fourier transform
Disclosed is a method for transmitting a reference signal for identification of each cell in a communication system including a plurality of cells each of which is identified by a cell identifier. The method includes receiving a cell identifier, and generating a block code corresponding to the cell identifier using a predetermined block code generator matrix, and generating a first part sequence using the block code; selecting a second part sequence in accordance with the cell identifier; generating a reference signal of a frequency domain using the first part sequence and the second part sequence; converting the reference signal of the frequency domain to a reference signal of a time domain through an Inverse Fast Fourier Transform operation and transmitting the reference signal of the time domain in a predetermined reference signal transmission interval.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Methods and apparatus for mitigating known interference
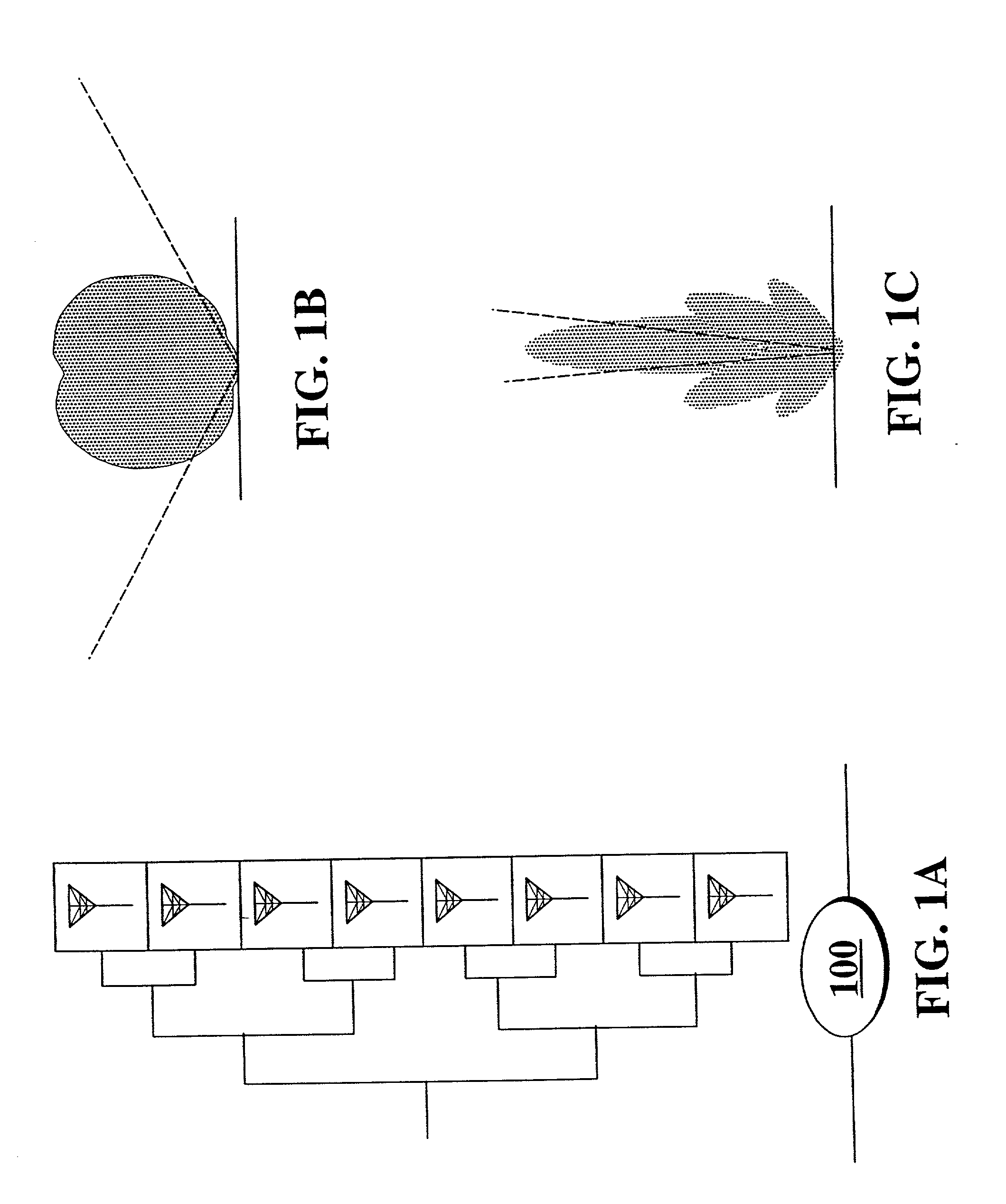
ActiveUS20130115988A1Reduce distractionsSynchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsPilot signalSystems engineering
Systems and methods for mitigating known interference at a receiving device are provided. A signal from a transmission source is received by a receiving device that is affected by an interference source. At least one of a first pilot signal associated with the transmission source and a second pilot signal associated with the interfering source is determined. The first pilot signal includes information broadcast from the transmission source and the second pilot signal includes information broadcast from the interference source. Interference caused by the interference source is mitigated from the received signal using at least one of the first pilot signal and the second pilot signal.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Communication method and system
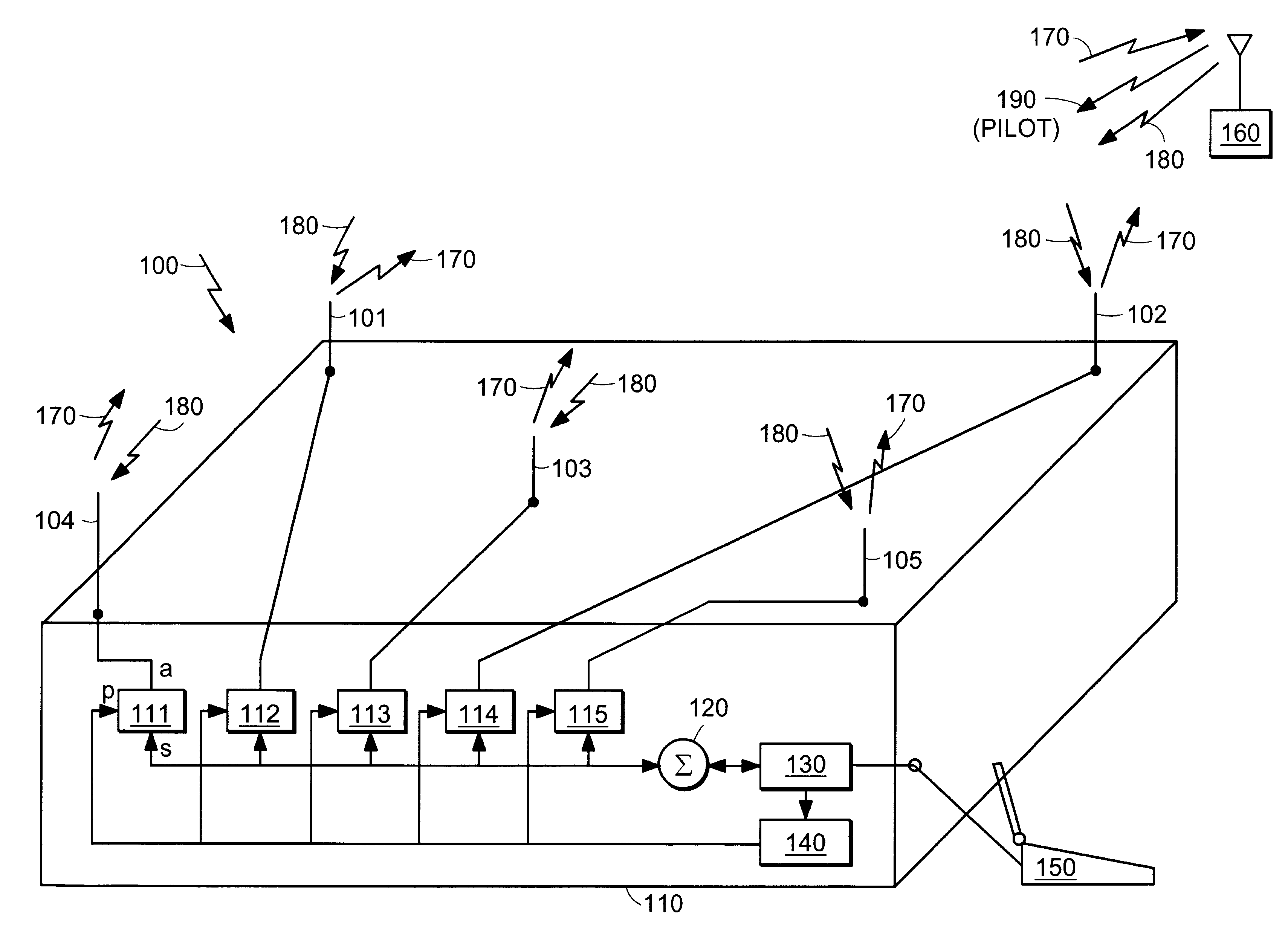
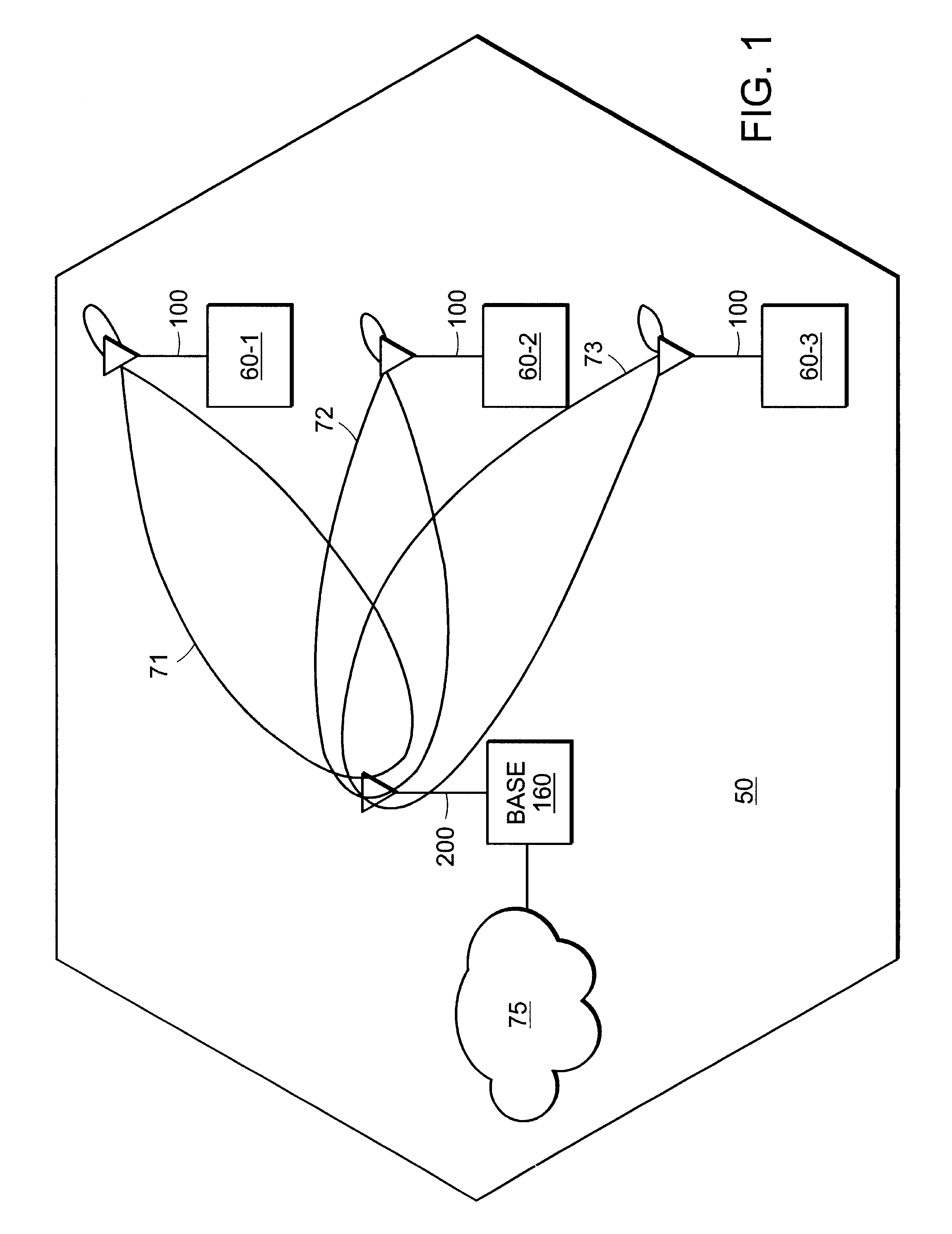
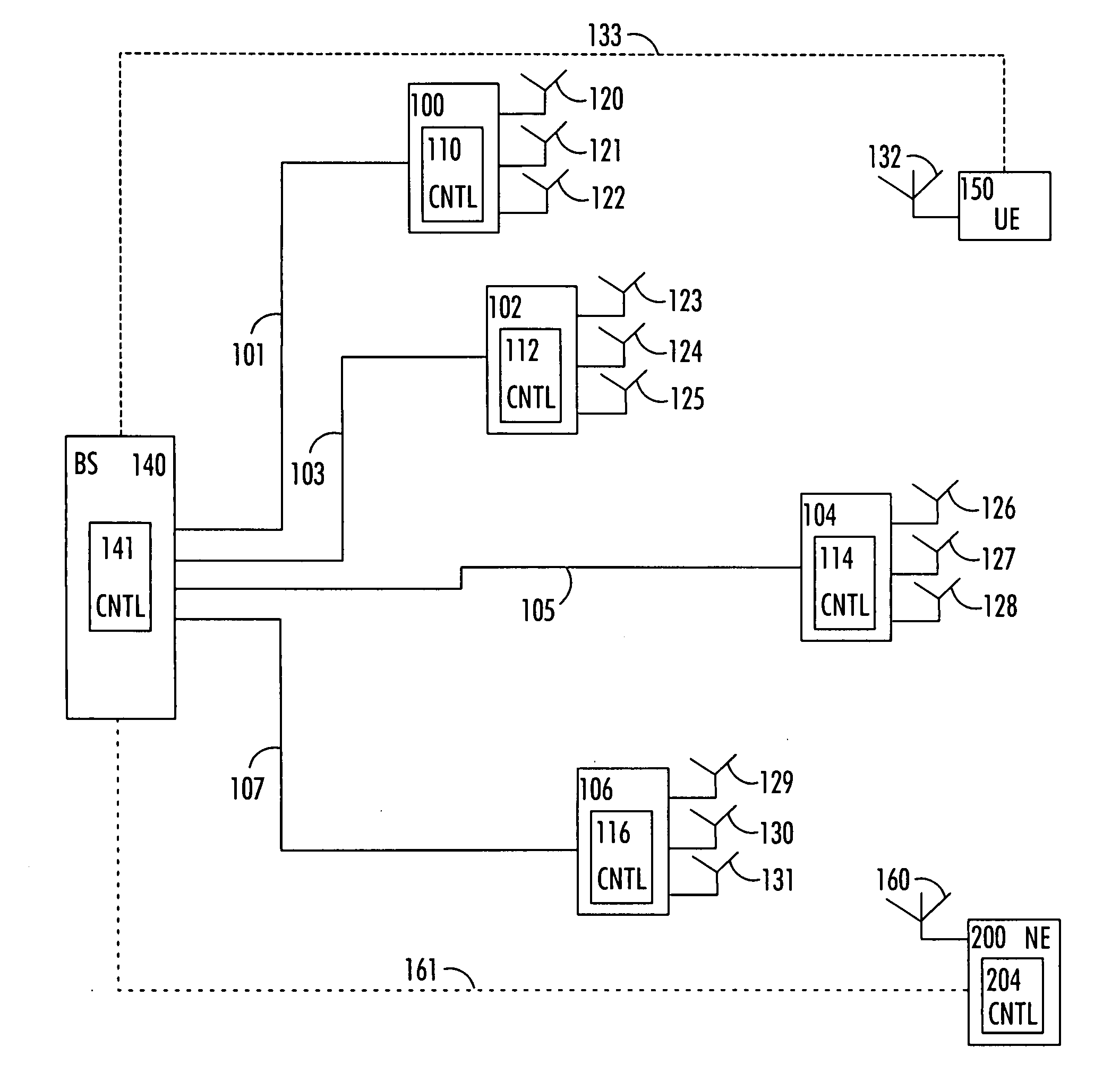
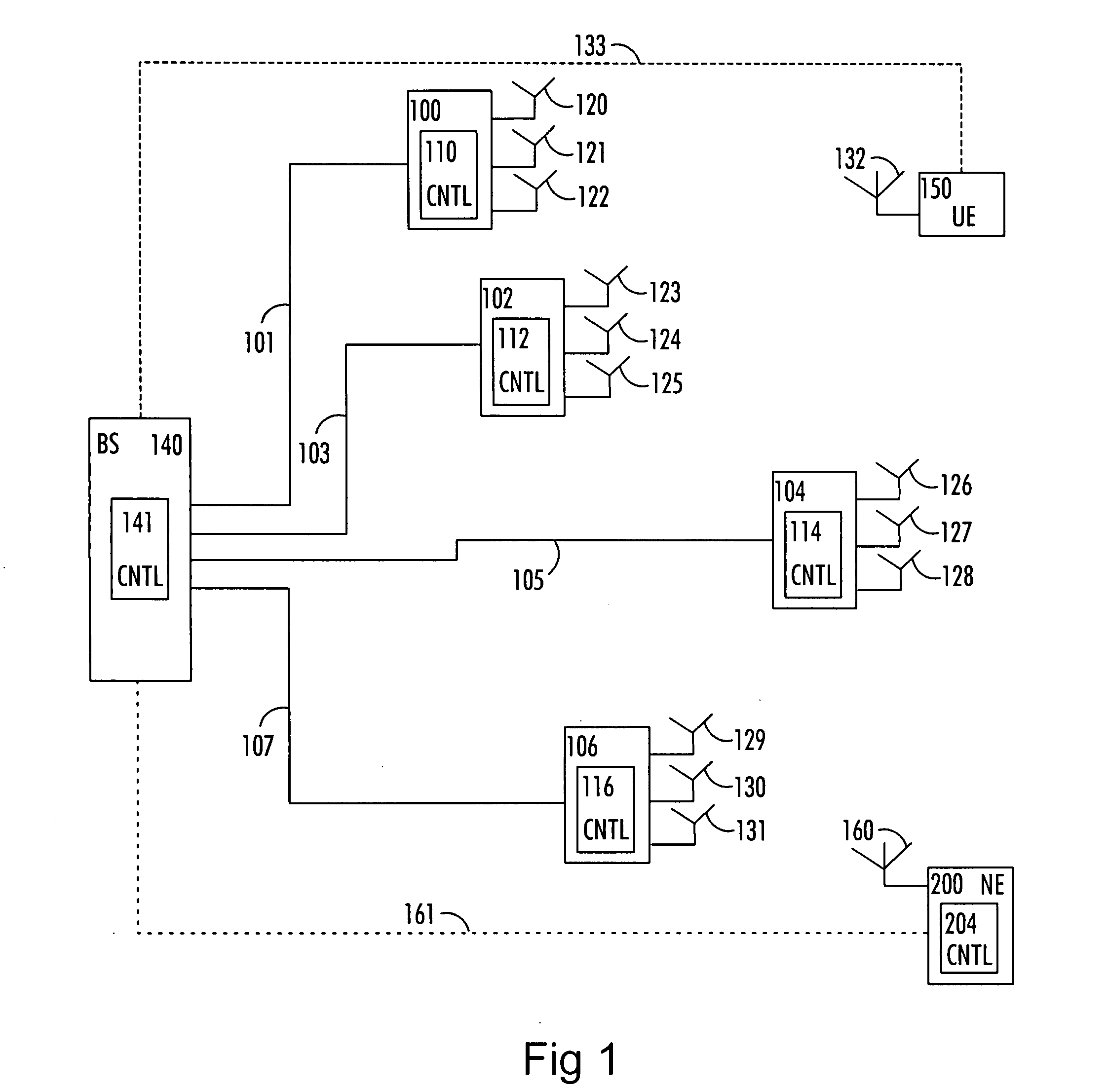
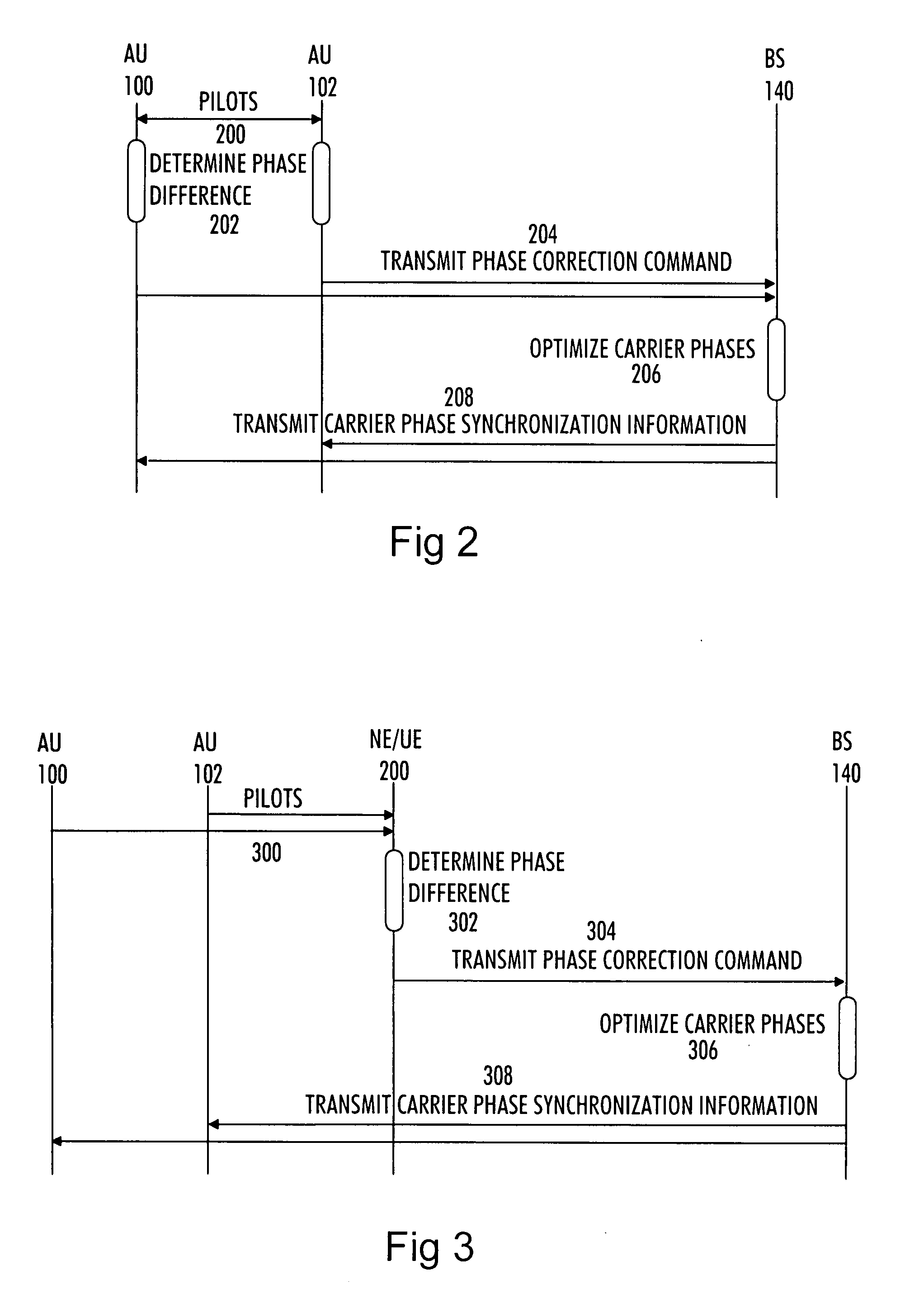
ActiveUS20080150514A1Increase network capacityCooperate fullySite diversityReceivers monitoringPhase correctionCommon base
There is provided a method comprising: determining a phase difference between at least two antenna units of a distributed antenna system on the basis of at least one pilot signal received from at least one of a plurality of antenna units; and transmitting phase correction commands to a common base station of the plurality of antenna units on the basis of the determined phase difference in order to synchronize carrier phases between at least two antenna units of the distributed antenna system.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
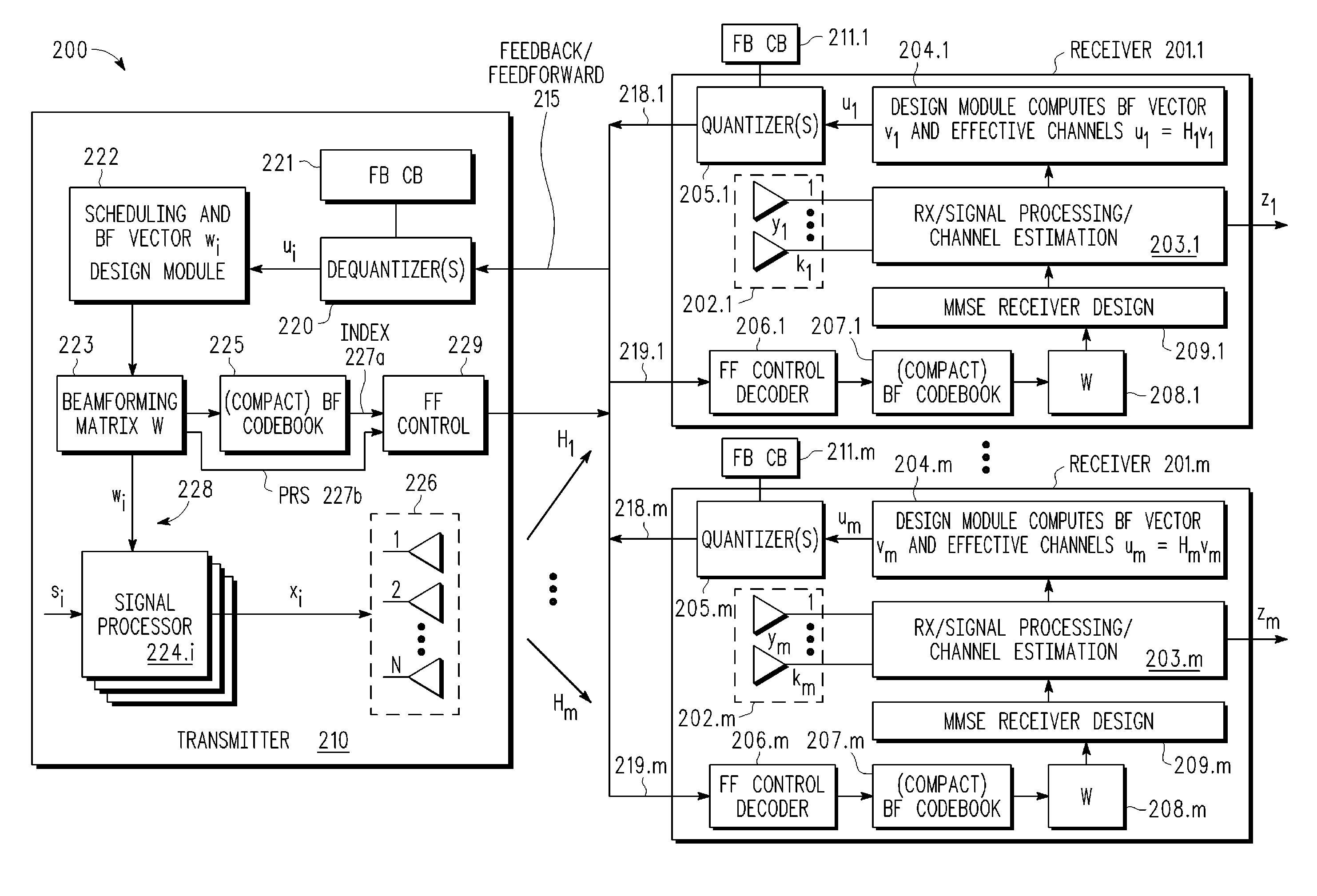
Reference signaling scheme using compressed feedforward codebooks for MU-MIMO systems
InactiveUS20080227495A1Spatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsDownlink beamformingTransmission matrix
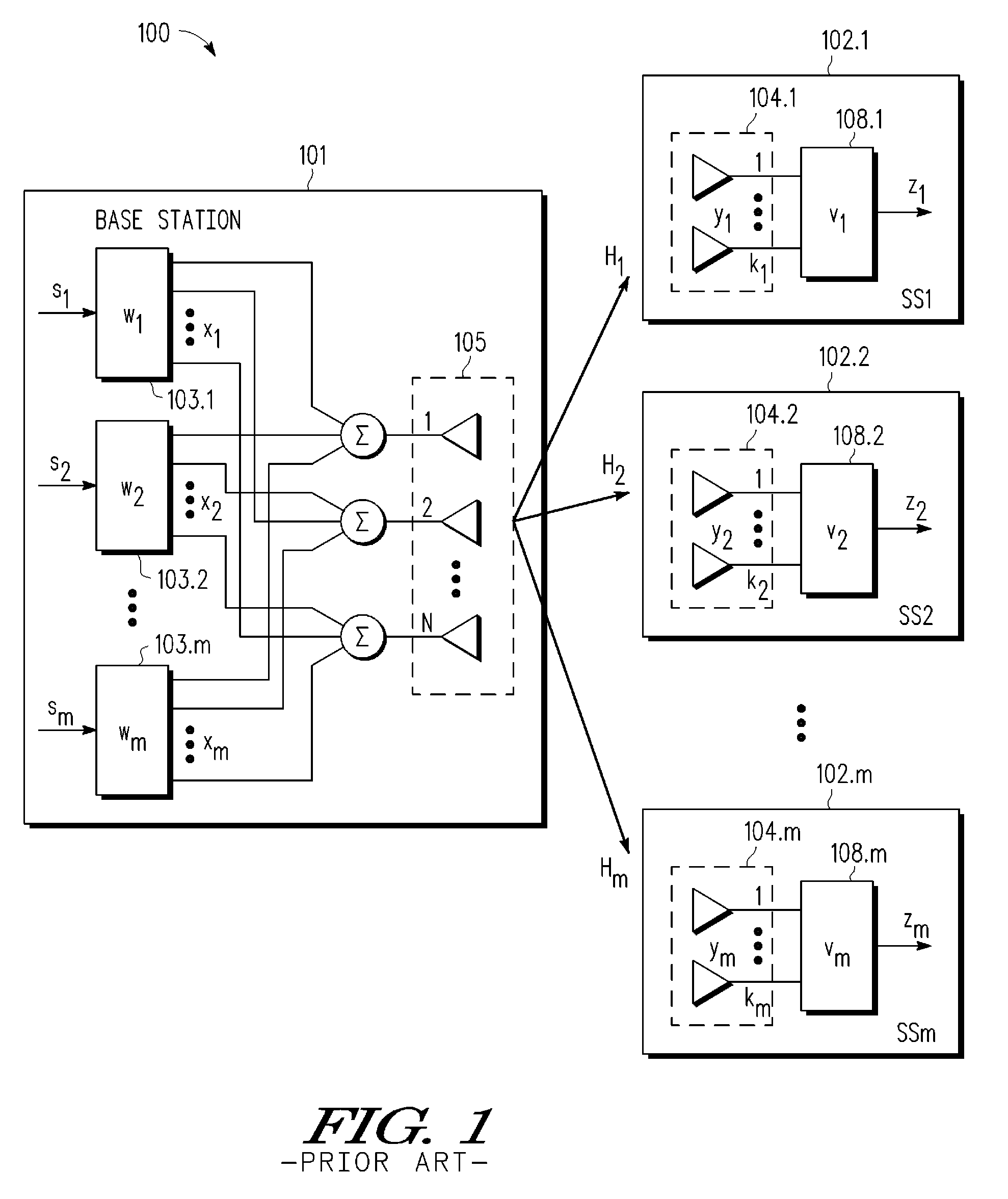
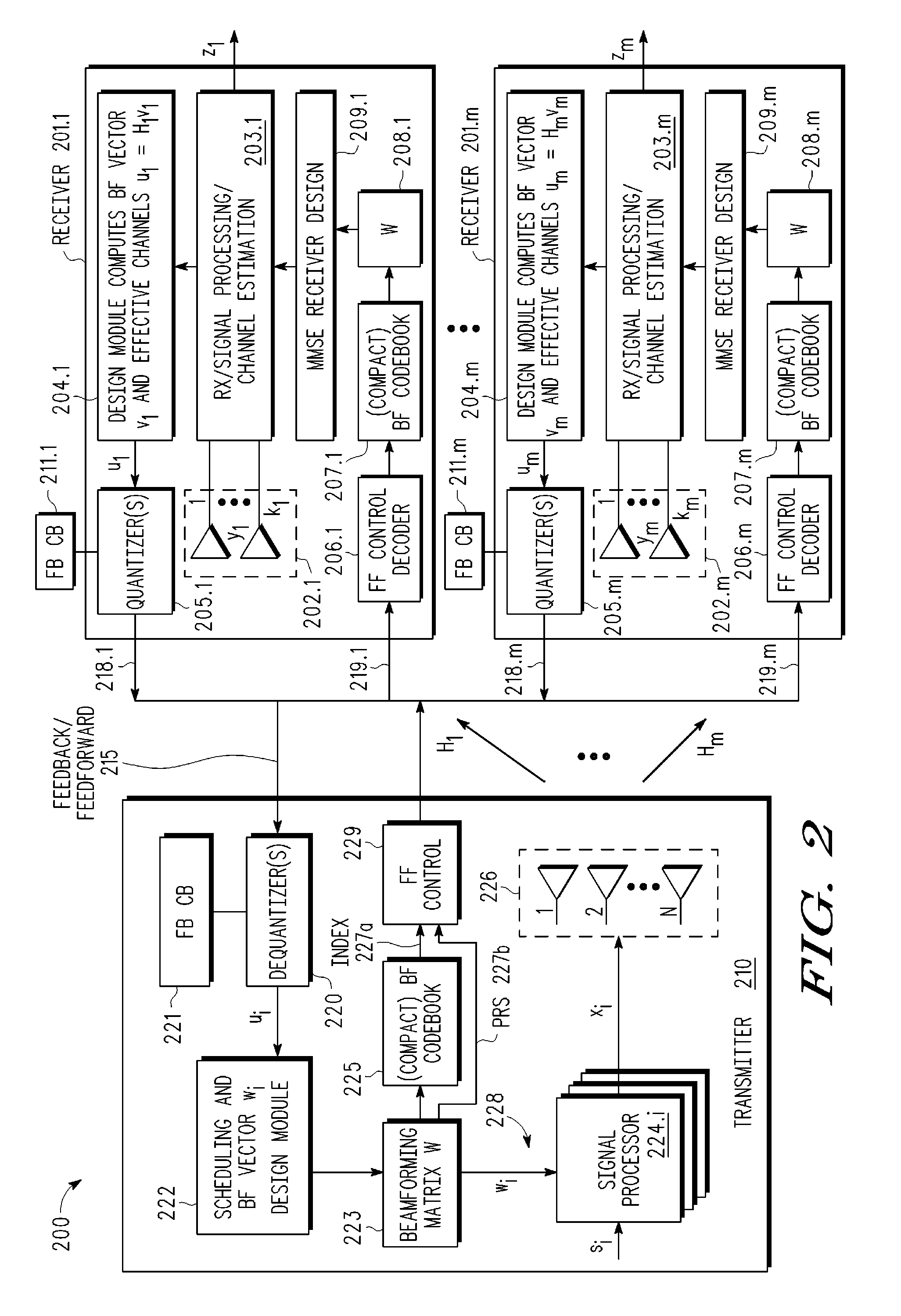
A multi-user MIMO downlink beamforming system with limited feed forward (200) is provided to enable preceding matrix information to be efficiently provided to a subset of user equipment devices (201.i), where zero-forcing transmit beamformers (wi) are computed at the base station (210) and assembled into a precoding matrix (W). The precoding matrix is encoded using a compact reference signal codebook (225, 207.i) for forward link signaling, either by sending bits indicating the index of the transmission matrix used, or by transmitting one or more precoded pilots or reference signals wherein the pilot signals are precoded using vectors uniquely representative of the transmission matrix used which includes candidate reference signal matrices which meet a predetermined condition number requirement, such as a condition number threshold. The preceding matrix information (227) is extracted at the user equipment devices (201.i) using the compact reference signal codebook (207.i) and used by the MMSE receiver (209.i) to generate receive beamformers (vi).
Owner:APPLE INC
Wireless communication method
ActiveUS20070243878A1Prevent throughput degradationReduce the amount requiredSite diversityCode division multiplexData rateBeam direction
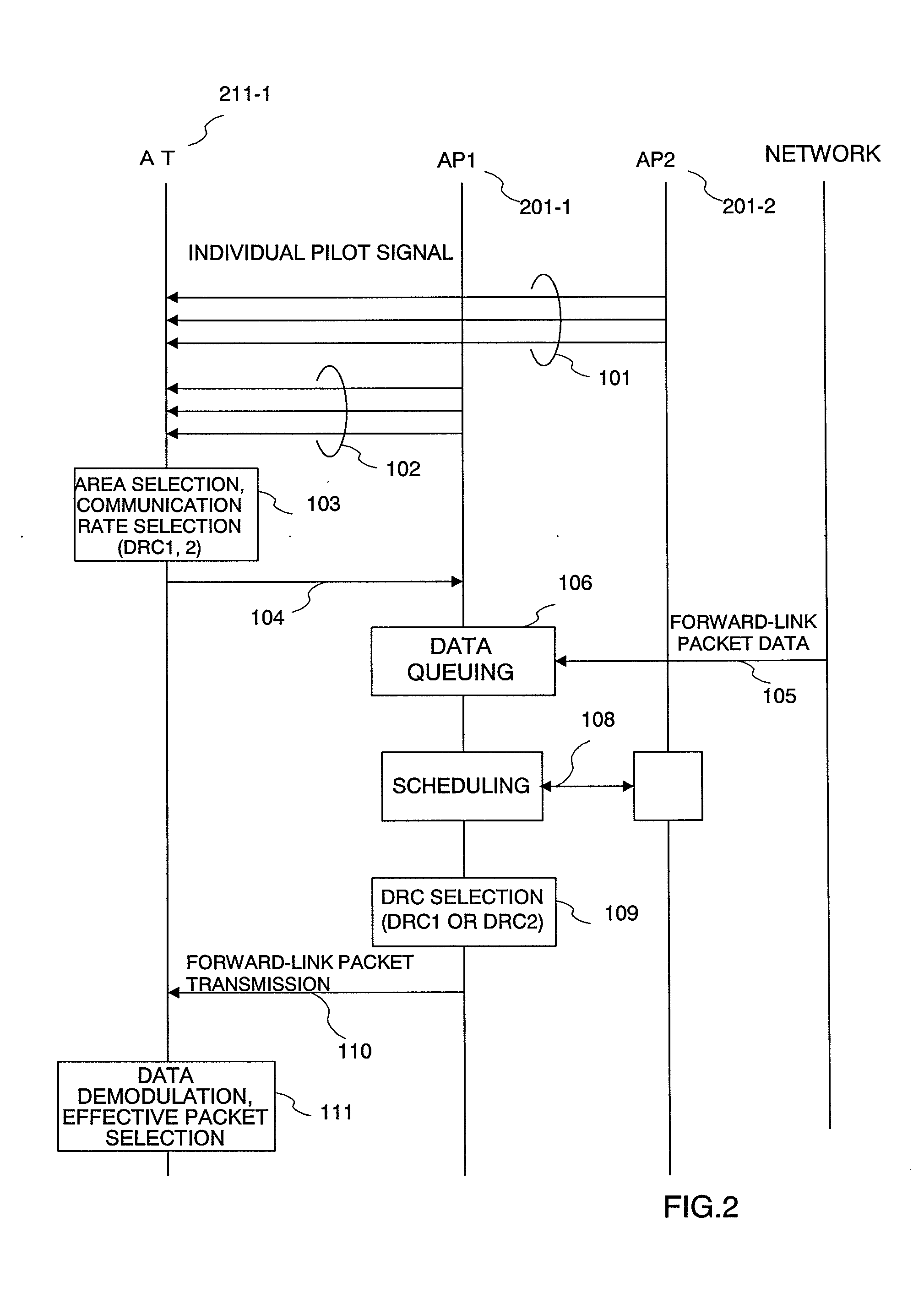
A terminal 211 measures pilot signals transmitted in directional (beam) patterns from an adjacent cell and an own cell, and estimates reception qualities with the presence (high) / absence (low) of the interference from the adjacent cell. The terminal 211 requests data rate request values (DRC1, DRC2) corresponding to the reception qualities with the presence / absence of the interference to the base station 201. The base station 201 shares beam direction schedule with an adjacent cell base station, and confirms the presence / absence of interference to the terminal 211 for each slot. In accordance with the presence / absence of the interference, the base station 201 selects a suitable one of the two values of the data rates requested from the terminal 211, and modulates the data and transmits it.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
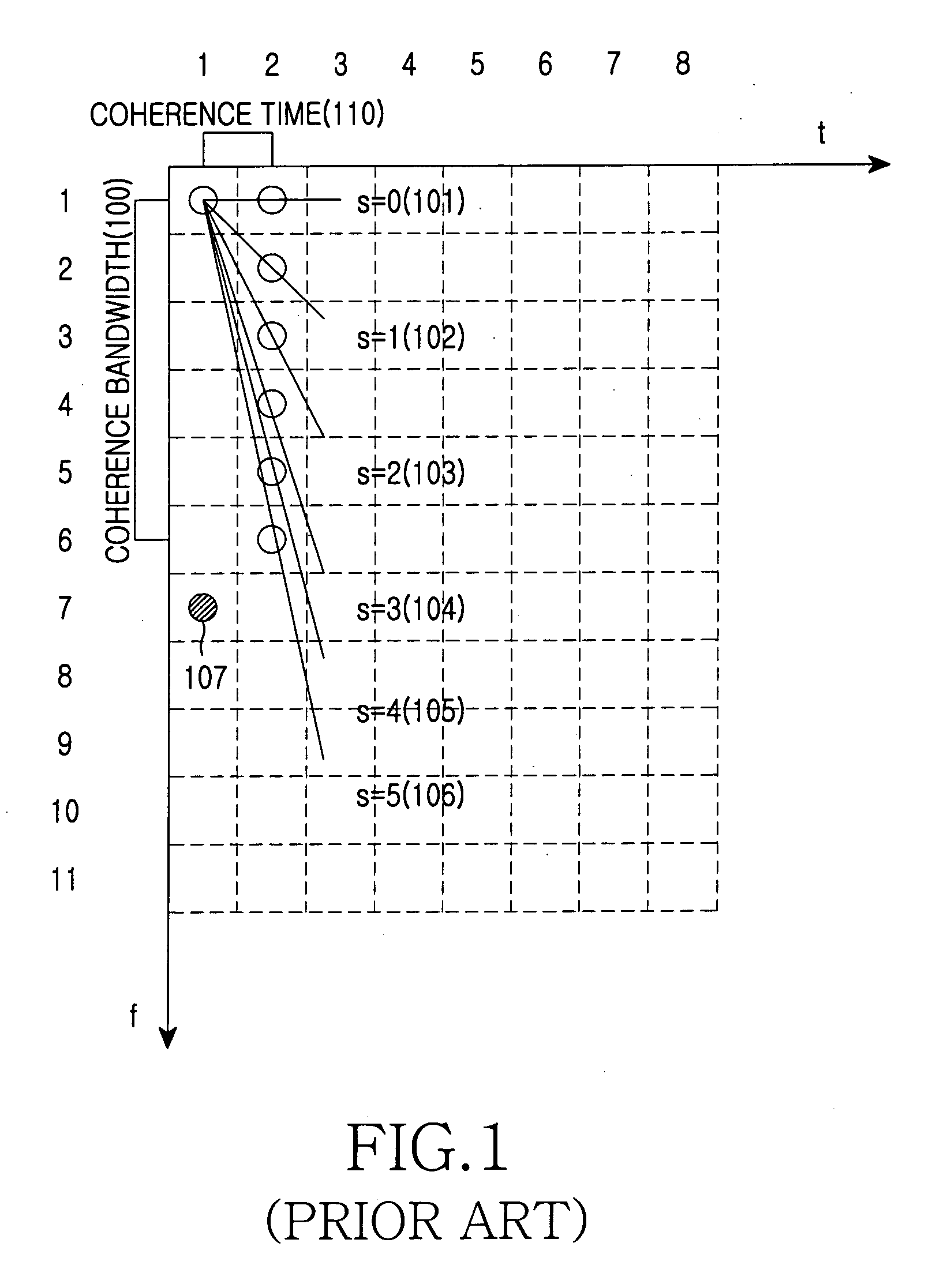
Pilot signals for synchronization and/or channel estimation
InactiveUS6987746B1Optimal autocorrelation resultEliminate and prevent sidelobesSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexCode division multiple accessCorrelation function
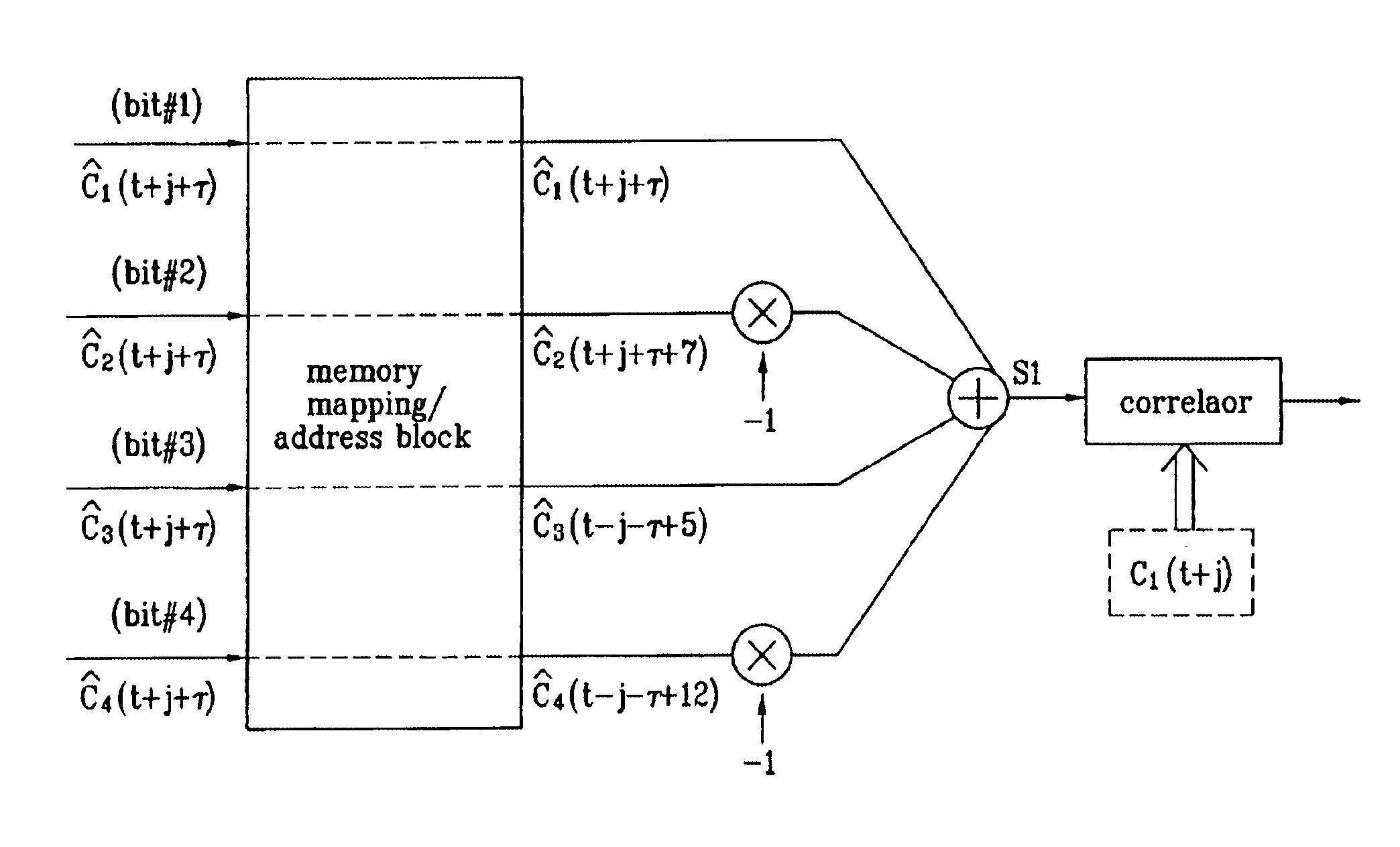
The frame words of the preferred embodiment are especially suitable for frame synchronization and / or channel estimation. By adding the autocorrelation and cross-correlation functions of frame words, double maximum values equal in magnitude and opposite polarity at zero and middle shifts are obtained. This property can be used to slot-by-slot, double-check frame synchronization timing, single frame synchronization and / or channel estimation and allows reduction of the synchronization search time. Further, the present invention allows a simpler construction of a correlator circuit for a receiver. A frame synchronization apparatus and method using an optimal pilot pattern is used in a wide band code division multiple Access (W-CDMA) next generation mobile communication system. This method includes the steps of storing column sequences demodulated and inputted by slots, in a frame unit, in detecting frame synchronization for upward and downward link channels; converting the stored column sequences according to a pattern characteristic related to each sequence by using the pattern characteristic obtained from the relation between the column sequences; adding the converted column sequences by slots; and performing a correlation process of the added result to a previously designated code column.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving pilot signals in an OFDM communication system
InactiveUS20050094550A1Maximizing a carrier to interference noise ratioMinimize overheadTransmission path divisionMulti-frequency code systemsFast Fourier transformCommunications system
A radio communication system divides an entire frequency band into a plurality of subcarrier bands, forms a symbol with signals on the subcarrier bands, forms a frame with a plurality of symbols, transmits a pilot signal within symbols in a predetermined position of the frame, and transmits a data signal within symbols other than the symbols for transmitting the pilot signal. A transmitter allocates subcarriers through which the reference signal is transmitted, wherein the subcarriers are allocated to have an exclusive relation with subcarriers through which reference signals of other transmitters are transmitted, generates the pilot signal, performs an inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) on the pilot signal by applying an IFFT size which is less than or equal to an IFFT size applied to the data signal, and transmits the IFFT-processed reference signal to a receiver.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for using rapid acquisition spreading codes for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS20020051434A1Easy to liftReduce capacityRadio transmission for post communicationSystem capacityModem device
A multiple access, spread-spectrum communication system processes a plurality of information signals received by a radio carrier station over telecommunication lines for simultaneous transmission over a radio frequency channel as a code-division-multiplexed signal to a group of subscriber units. The radio carrier station receives a call request signal that corresponds to a telecommunication line information signal, and a user identification signal that identifies a user to receive the call. The radio carrier station includes a plurality of CDMA modems, one of which provides a global pilot code signal. The modems provide message code signals synchronized to the global pilot signal. Each modem combines an information signal with a message code signal to provide a code division multiplexed signal. The RCS includes a system channel controller is coupled to receive a remote call. A radio frequency transmitter is connected to all of the modems to combine the code division multiplexed processed signals with the global pilot code signal to generate a code division multiplexed signal. The transmitter also modulates a carrier signal with the code division multiplexed signal and transmits the modulated carrier signal through a radio frequency communication channel to the subscriber units. Each subscriber unit includes a CDMA modem which is also synchronized to the global pilot signal. The CDMA modem despreads the code division multiplexed signal and provides a despread information signal to the user. The system includes a closed loop power control system for maintaining a minimum system transmit power level for the radio carrier station and the subscriber units, and system capacity management for maintaining a maximum number of active subscriber units for improved system performance.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
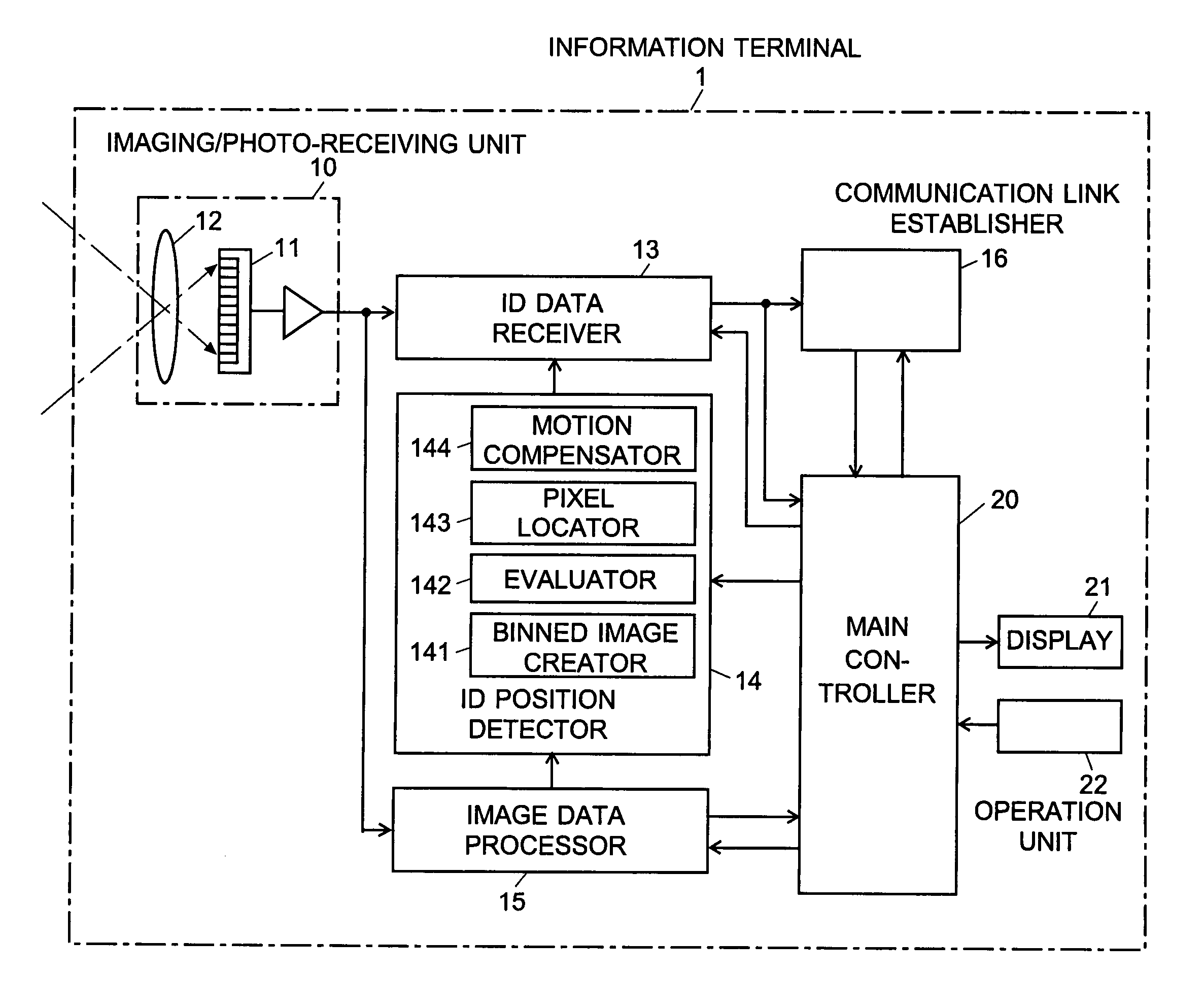
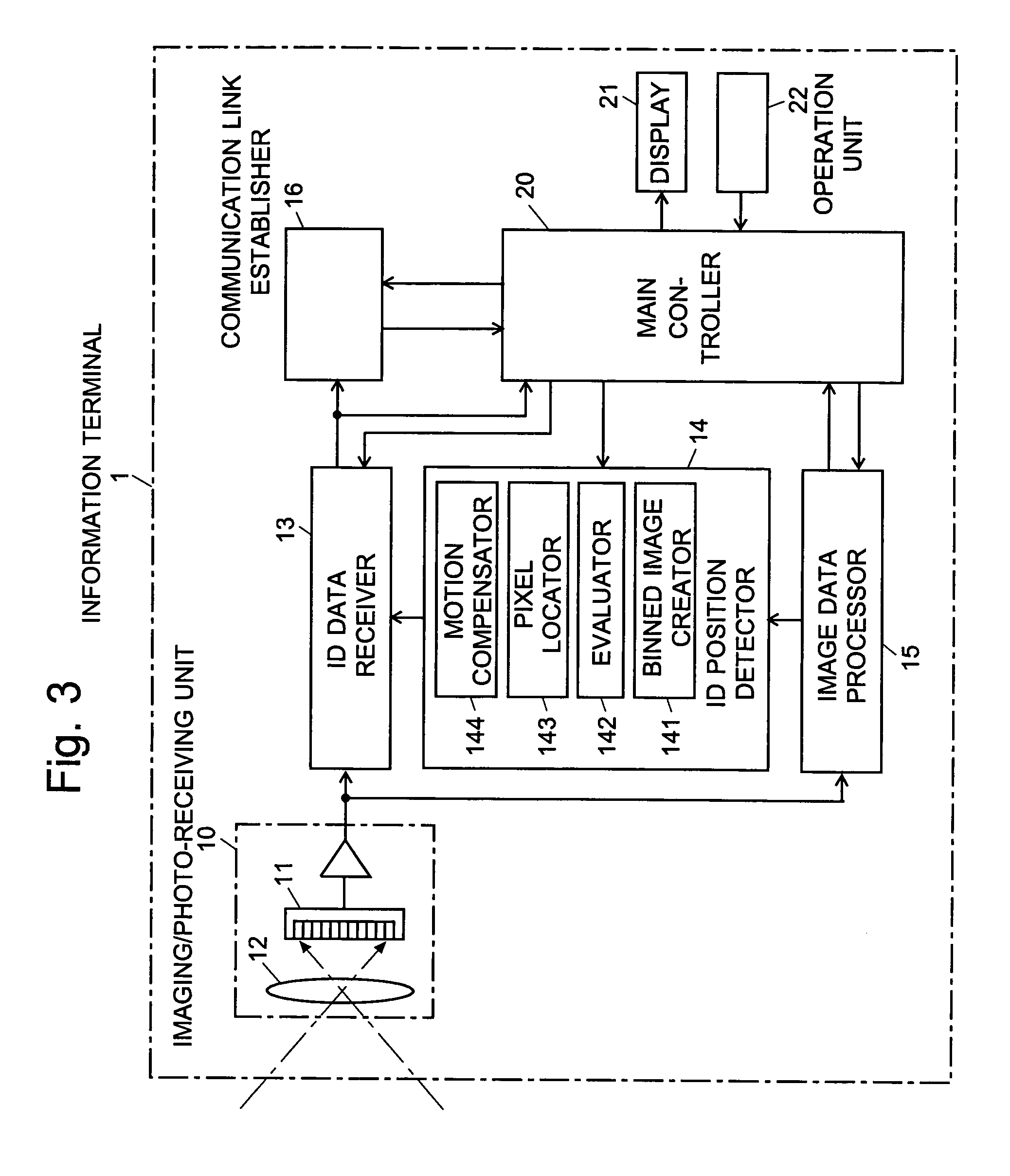
Information-processing device and information-processing system
InactiveUS20070070060A1Reduce in quantityReduce the number of timesTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsInformation processingFourier transform on finite groups
For an information terminal to be operated by users for collecting predetermined pieces of information from remote information devices by free-space optical communication, the present invention provides a technique for suppressing the power consumption of the information terminal by minimizing the amount of calculation performed to collect the aforementioned information. According to the present invention, each information device emits ID light on which a low-frequency pilot signal is superimposed. The information terminal captures a series of frames of images including the ID light and locates the ID light within the images by the following steps: (1) creating multiple levels of binned images having different resolutions for each frame of the image; (2) calculating an evaluation index for each pixel within a target range of the binned images at each level, from the lowest to the highest resolution, where the target range is narrowed every time the process switches over to a lower level. In (2), the evaluation index is calculated by an evaluation function including fast Fourier transformation performed throughout the series of frames of images. The evaluation index thus calculated is compared with a threshold to determine whether the pixel concerned is receiving ID light. The present technique significantly reduces the number of pixel to be analyzed and evaluated, thereby decreasing the total number of arithmetic operations to be performed using the evaluation function. Thus, the power consumption is suppressed.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com