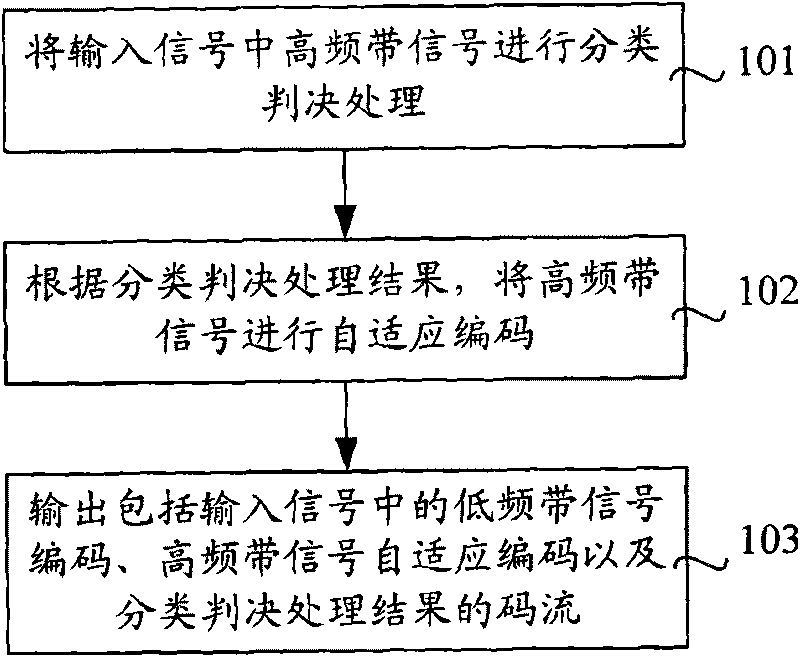
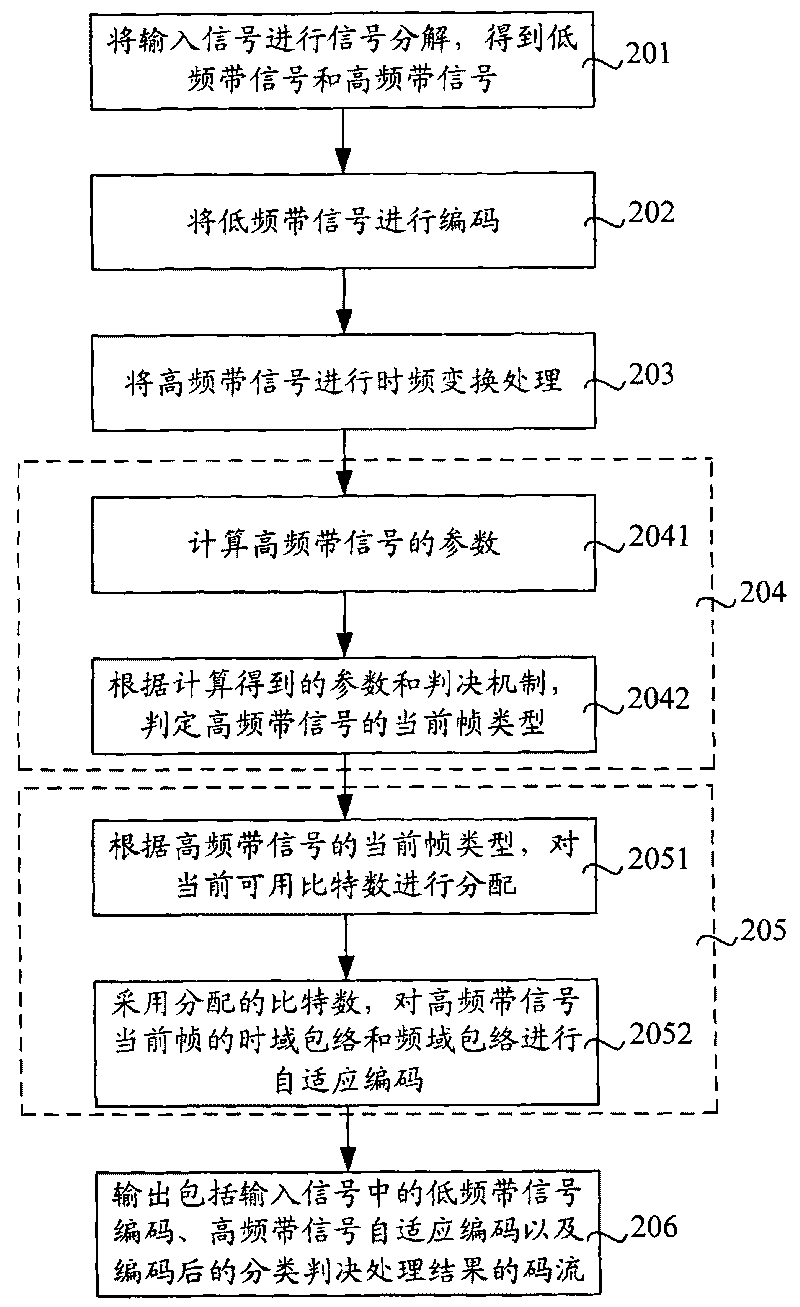
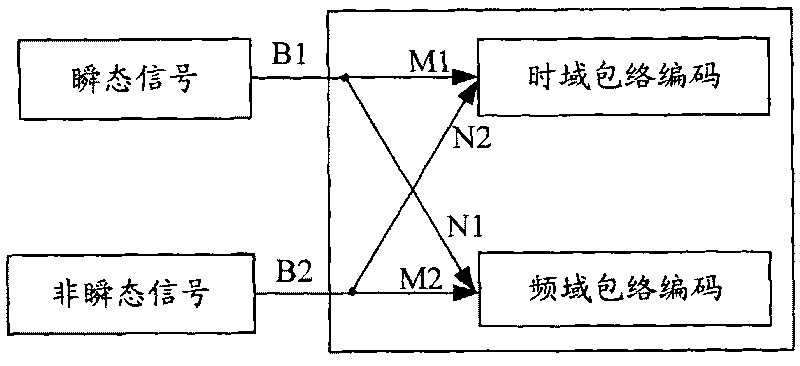
Patents
Literature
555 results about "Signal coding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
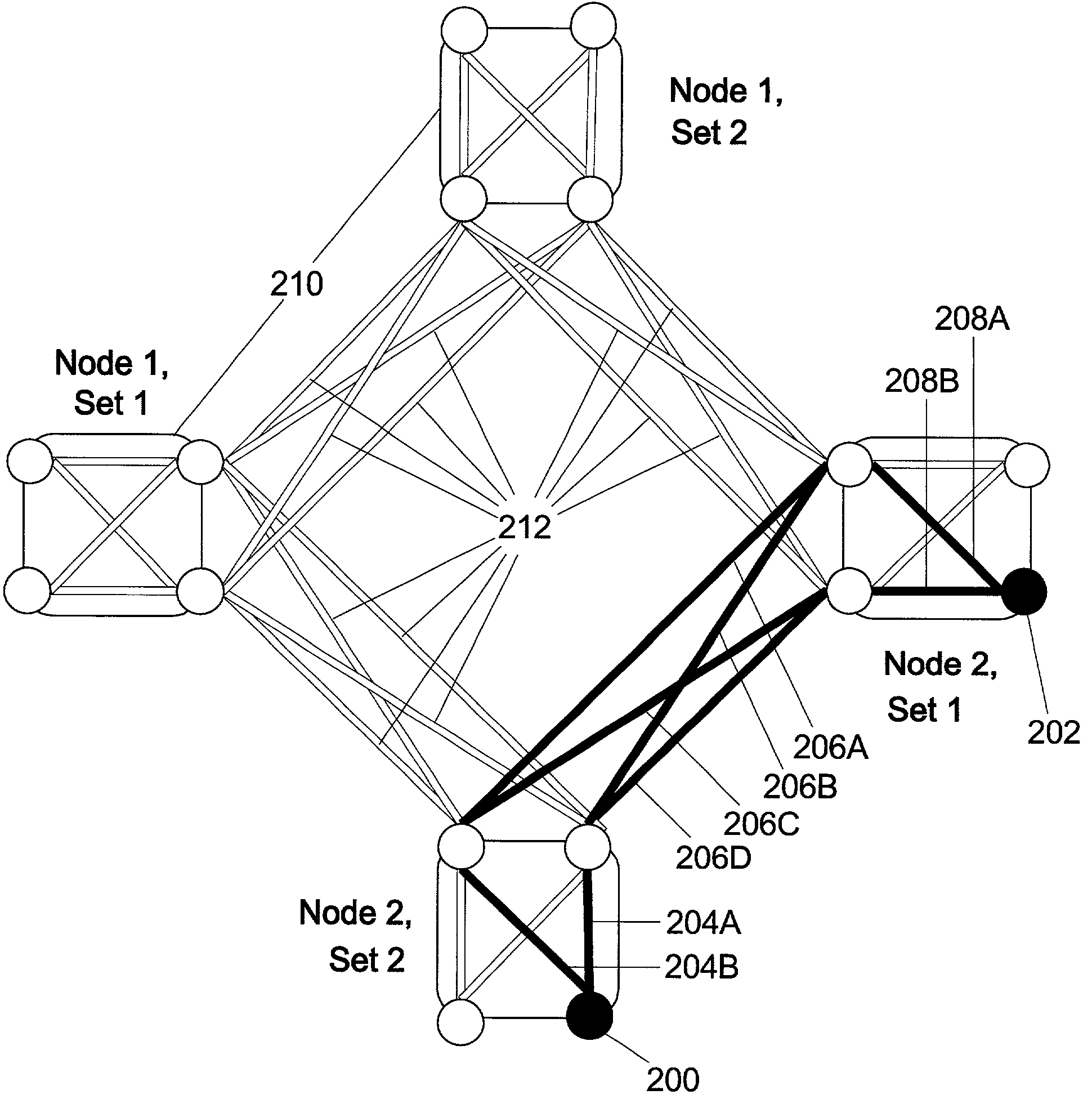
Method and apparatus for optimization of wireless multipoint electromagnetic communication networks
InactiveUS20040095907A1Improve signal qualityReduce interference energyPower managementSpatial transmit diversityGlobal optimizationDiversity scheme
Exploiting the substantive reciprocity of internode channel responses through dynamic, adaptive modification of receive and transmit weights, enables locally enabled global optimization of a multipoint, wireless electromagnetic communications network of communication nodes. Each diversity-channel-capable node uses computationally efficient exploitation of pilot tone data and diversity-adaptive signal processing of the weightings and the signal to further convey optimization and channel information which promote local and thereby network-global efficiency. The preferred embodiment performs complex digital signal manipulation that includes a linear combining and linear distribution of the transmit and receive weights, the generation of piloting signals containing origination and destination node information, as well as interference-avoiding pseudorandom delay timing, and both symbol and multitione encoding, to gain the benefit of substantive orthogonality at the physical level without requiring actual substantive orthogonality at the physical level.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
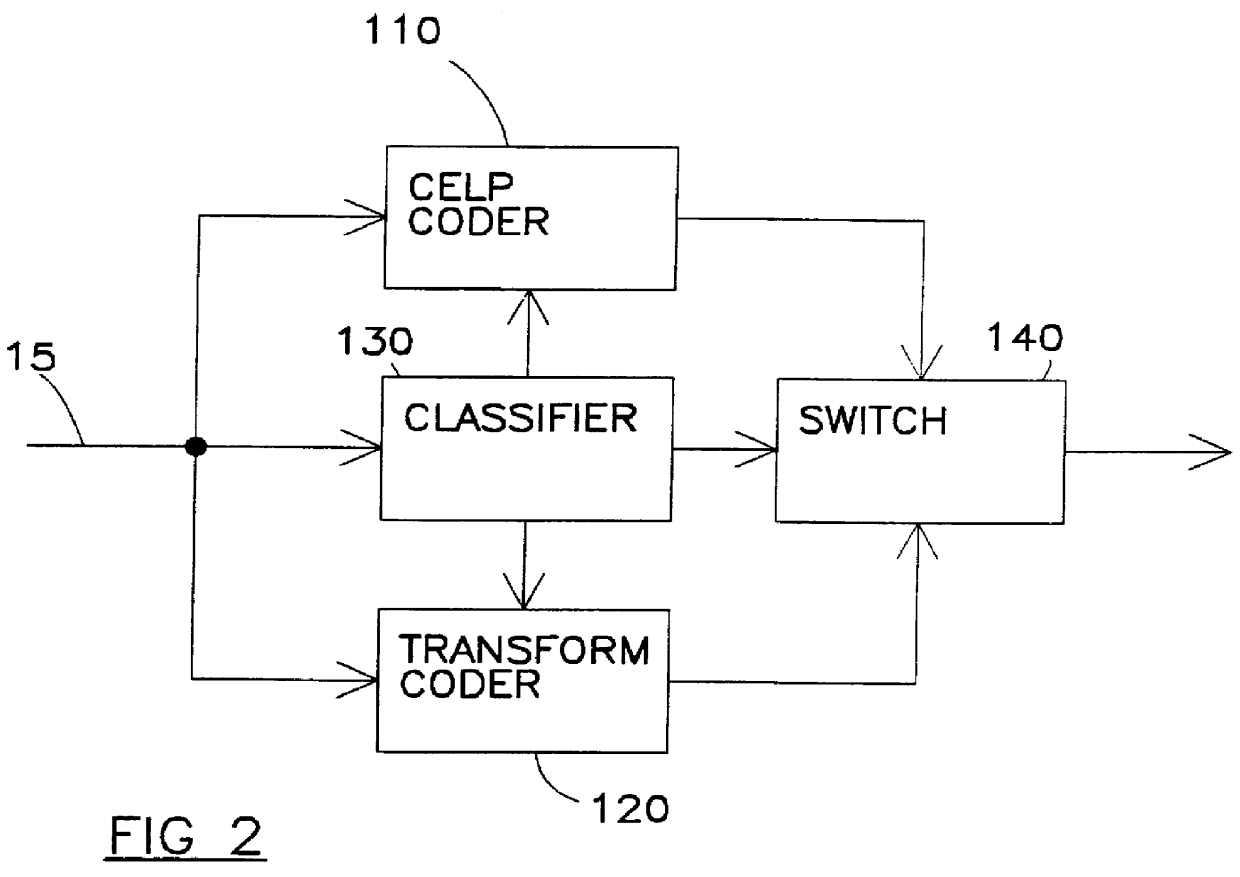
Digital audio signal coding using a CELP coder and a transform coder
Apparatus is described for digitally encoding an input audio signal for storage or transmission. A distinguishing parameter is measure from the input signal. It is determined from the measured distinguishing parameter whether the input signal contains an audio signal of a first type or a second type. First and second coders are provided for digitally encoding the input signal using first and second coding methods respectively and a switching arrangement directs, at any particular time, the generation of an output signal by encoding the input signal using either the first or second coders according to whether the input signal contains an audio signal of the first type or the second type at that time. A method for adaptively switching between transform audio coder and CELP coder, is presented. In a preferred embodiment, the method makes use of the superior performance of CELP coders for speech signal coding, while enjoying the benefits of transform coder for other audio signals. The combined coder is designed to handle both speech and music and achieve an improved quality.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Channel, coding and power management for wireless local area networks
InactiveUS20050003827A1Improve mutual interferenceDecrease network throughputNetwork topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsInternet trafficTrade offs
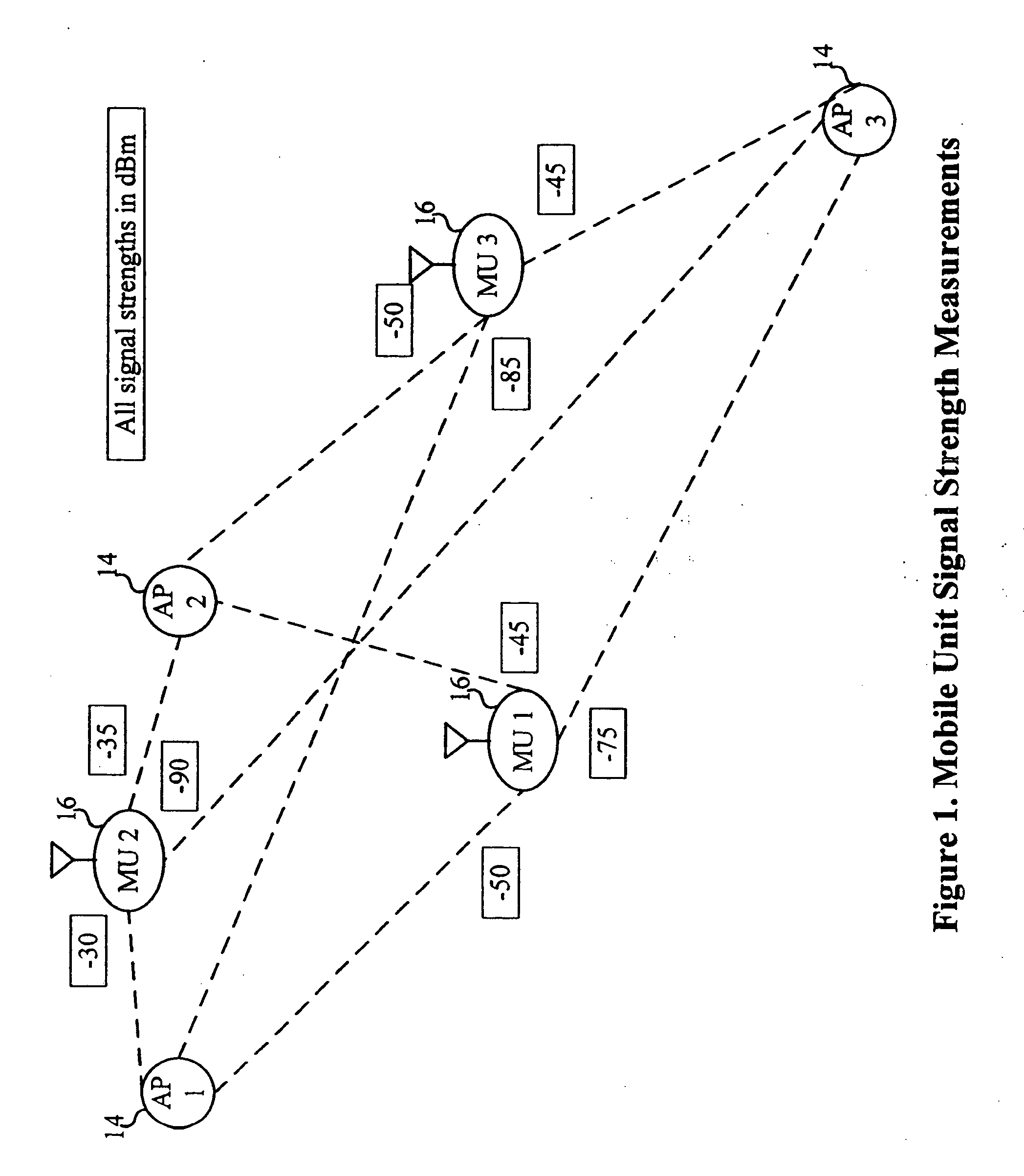
A system and method are disclosed for the management of WLANs in cases where unmanaged access points are present as well as with the addition or removal of access points. The disclosed system and method use signal data and network traffic statistics collected by mobile units to determine optimal configuration settings for the access points. The access point settings so managed can include the operating channel or center frequency, orthogonal signal coding used (optionally including the data rate), if any, and the transmission power. The solutions computed can account for the inherent trade-offs between wireless network coverage area and mutual interference that may arises when two or more access points use the same or overlapping frequency bands or channels and the same or similar signal coding.
Owner:WAVELINK
Apparatus and methods for polychronous encoding and multiplexing in neuronal prosthetic devices
Apparatus and methods for encoding sensory input information into patterns of pulses and message multiplexing. In one implementation, the patterns of pulses are polychronous (time-locked by not necessary synchronous), and a retinal prosthetic encodes the input signal into the polychronous patterns for delivery via stimulating electrodes. Different polychronous patterns simultaneously encode different sensory signals; (such as different features of the image), thus providing for message multiplexing. Increasing data transmission capacity allows for a reduction in the number of electrodes required for data transmission. In one implementation, an adaptive feedback mechanism is employed to facilitate encoder operation. In another aspect, a computer vision system is described.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
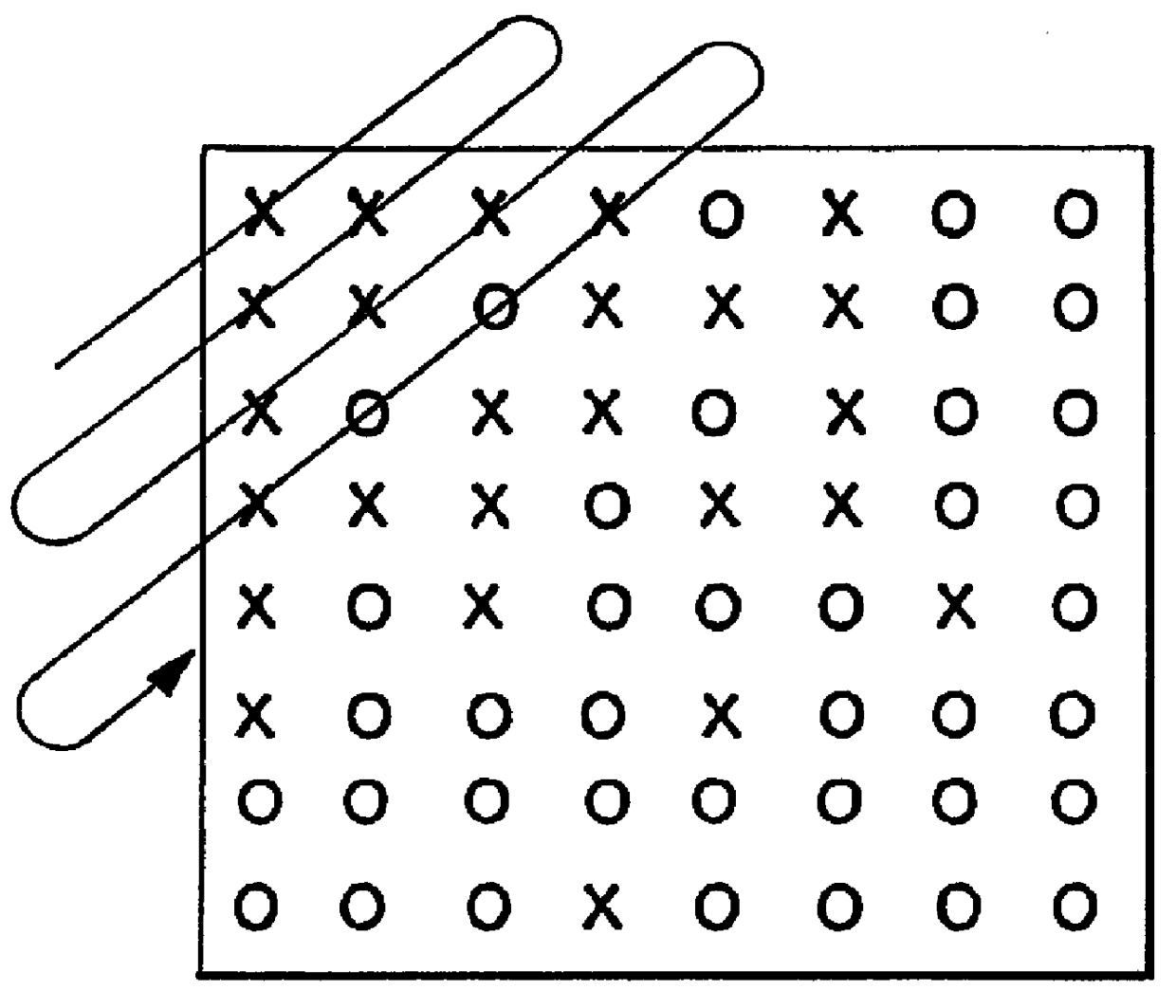
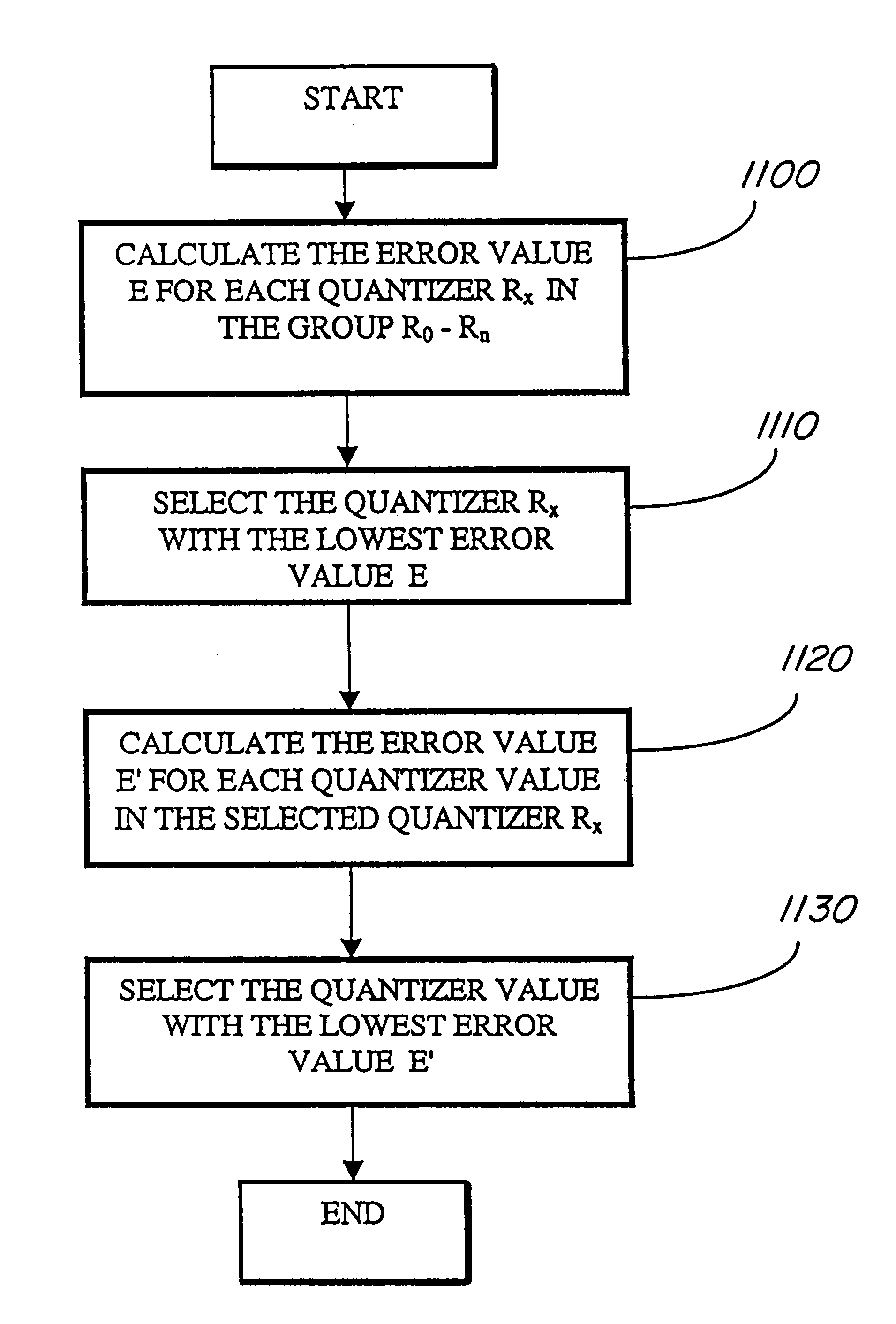
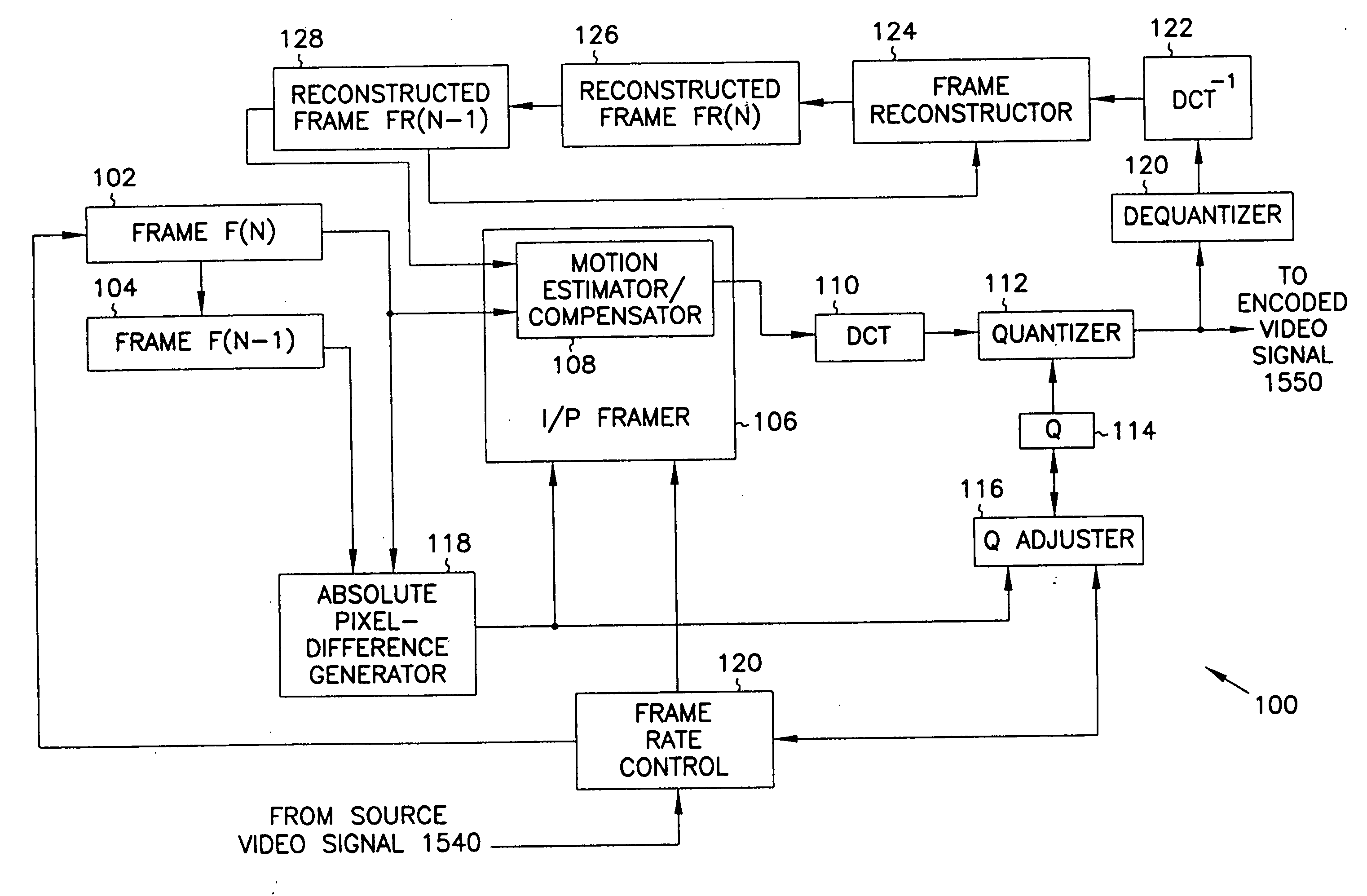
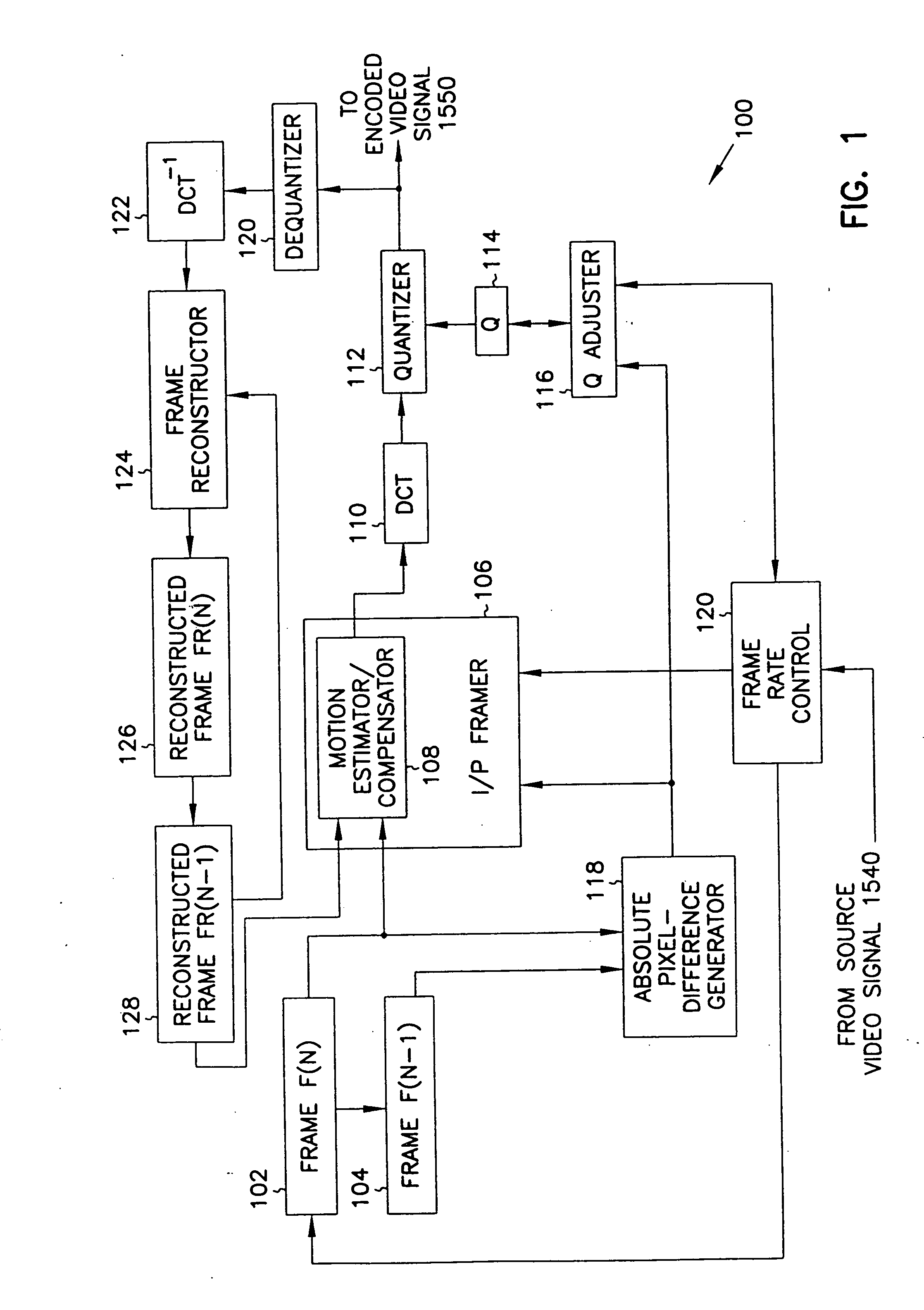
Adaptive entropy coding in adaptive quantization framework for video signal coding systems and processes
InactiveUS6111914AImprove accuracyLess distortionPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesSelf adaptiveComputer science
A compression system and process include adaptive quantization for selection of one quantizer, for each video frame or frame portion, from a group of quantizers, where each quantizer is a set of predefined quantizer values, and coding of the quantized values using a common entropy coding table for all quantizers, or a separate entropy coding table for each quantizer. The entropy coding tables are obtained during a training procedure. The selection of the quantizer is based on a formula which takes into account the distortion and bit rate characteristics of each quantizer. A similar formula, based on the distortion and bit rate characteristics, is used to select the particular quantizer value within the chosen quantizer for each video signal value being coded.
Owner:INTEL CORP
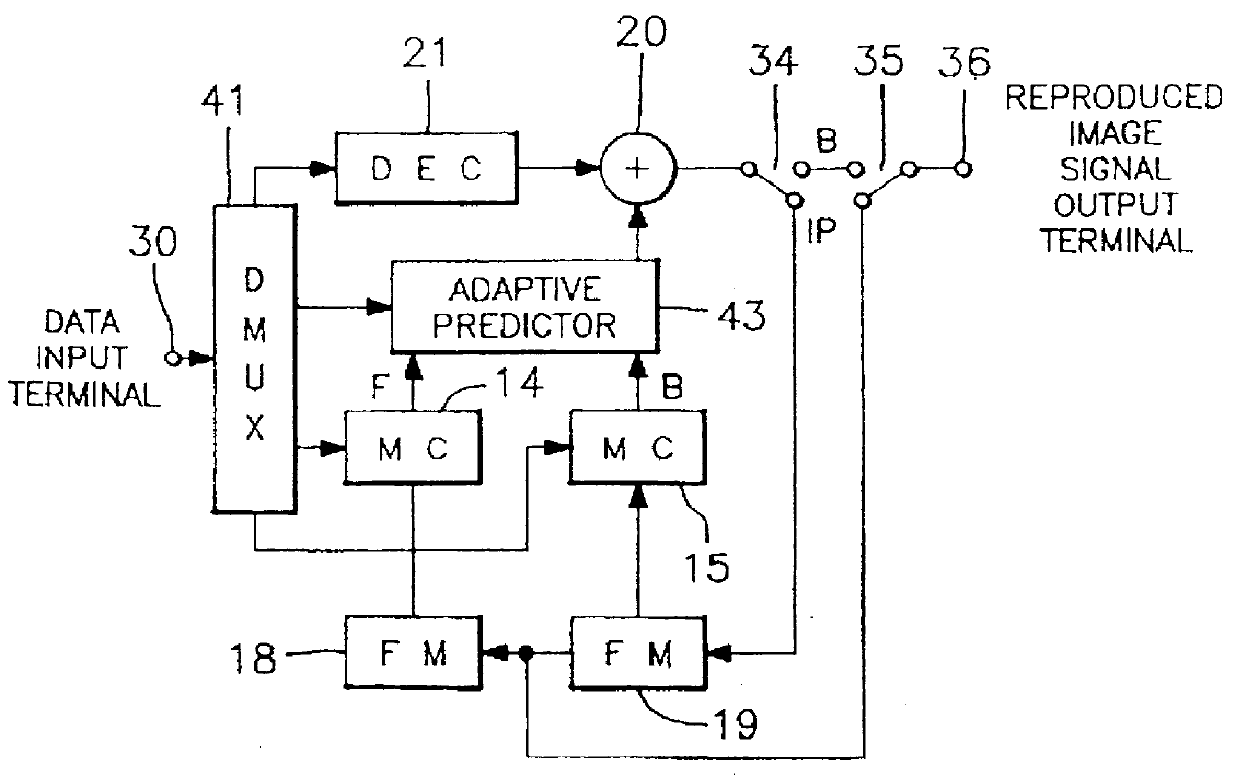
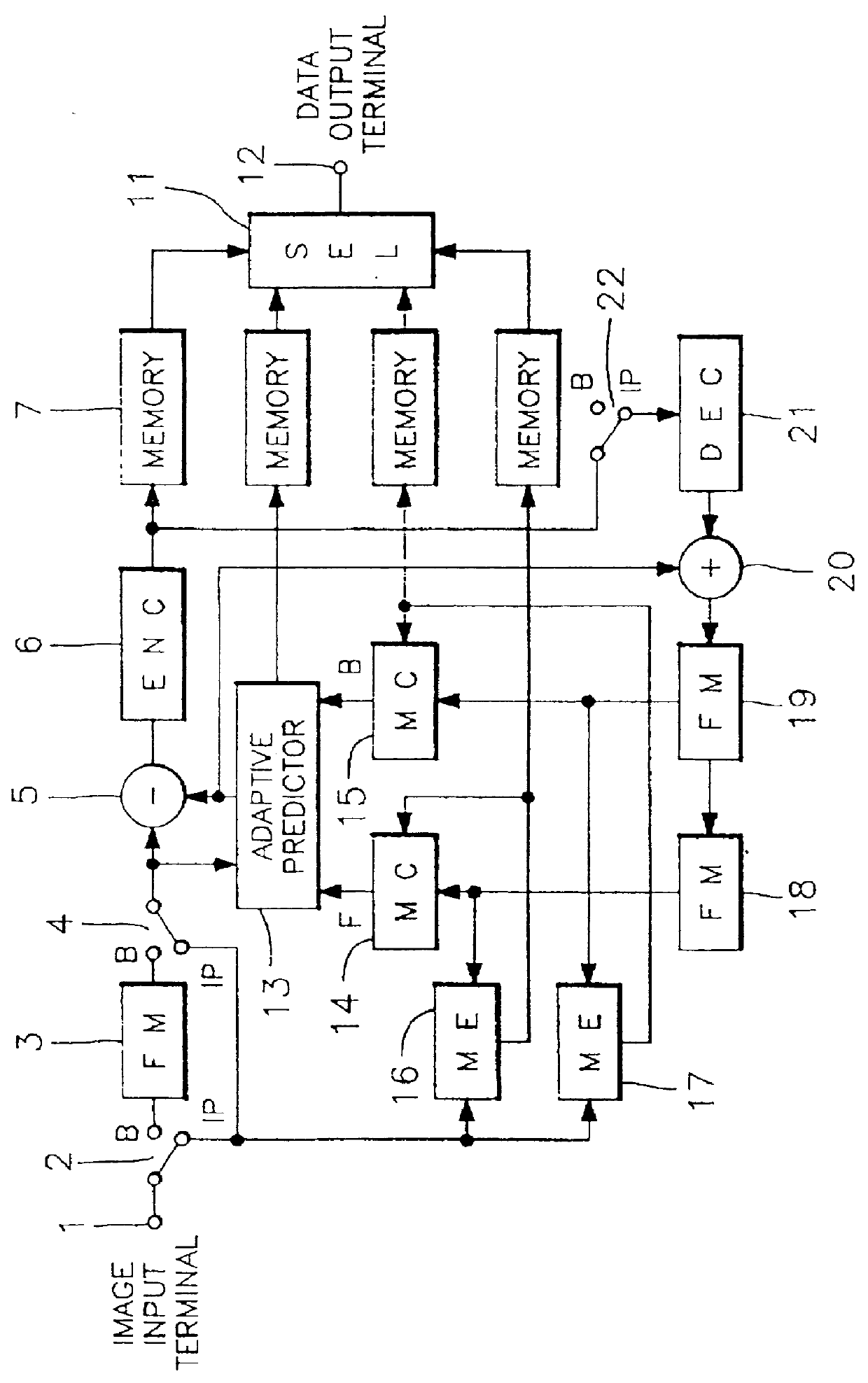
Moving image signal coding apparatus and coded signal decoding apparatus
InactiveUSRE36822E1Good effectColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImaging processingBlock code
A coding apparatus which codes moving image signals into block units, is configured from a signal processing element which performs motion compensation for moving image signals for over a plural number of frames or fields and codes inter-image signals, and a transfer element which recombines coded information for each block coded by said processing element, into macroblock units which are a plural number of block units of each type of coded information, and transfers them. In addition, a decoding apparatus for moving image signals which have been coded in block units is configured from a detector element which detects transfer code errors for each type of coded information, and a processing element which performs motion compensation and inter-image processing of the coded information using only correct frames which do not include transfer code errors, and without using frames which have transfer code errors, by changing a method of inter-frame processing for motion compensation in accordance with the transfer coding errors in the coded information which has been detected for each type.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
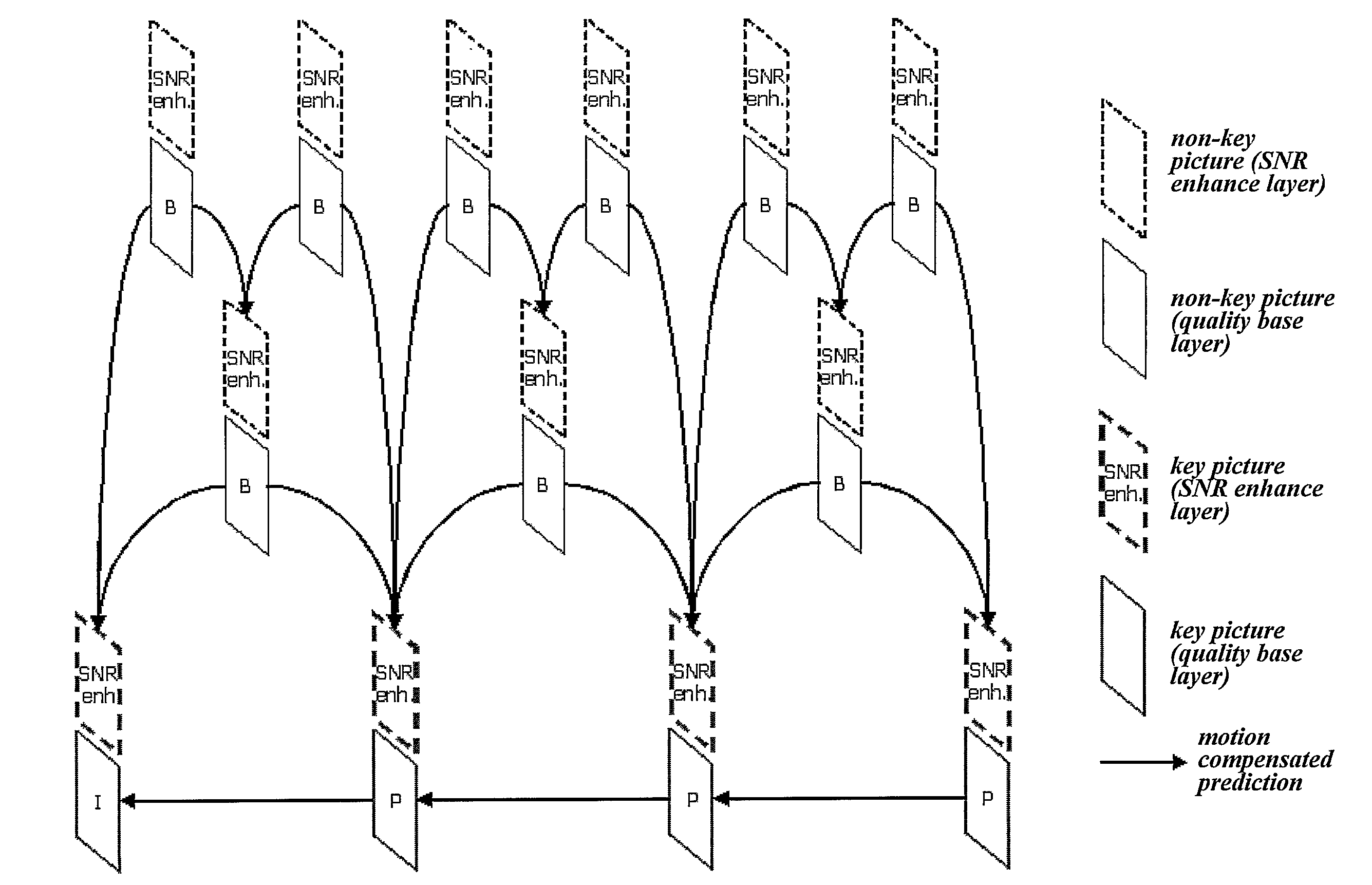
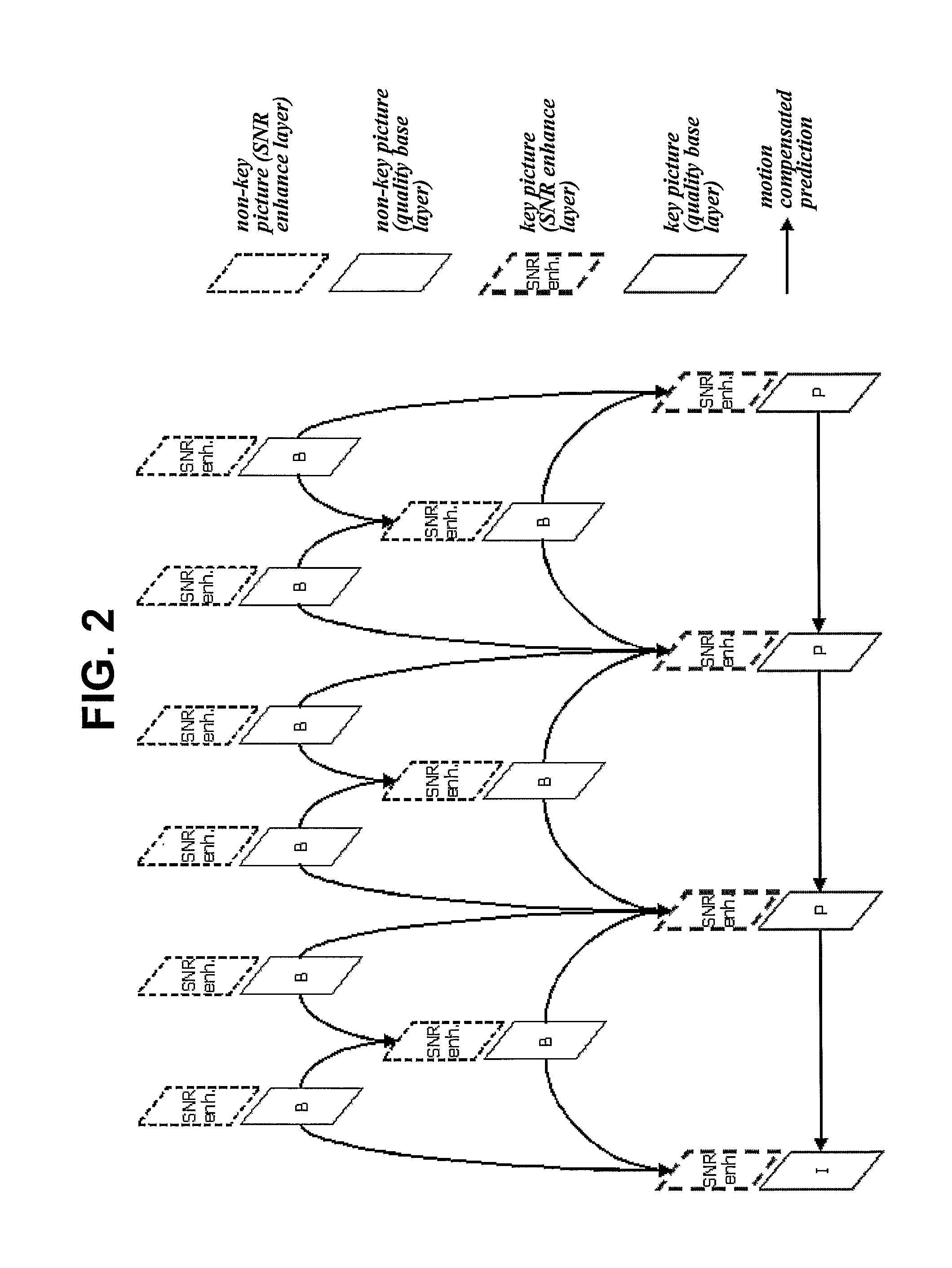
Method of transmitting picture information when encoding video signal and method of using the same when decoding video signal
InactiveUS20090041130A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSignal codingEncoder
A method of transmitting picture information of a video signal from an encoder and a method of using the picture information in a decoder are provided. When a video signal is encoded, the video signal is coded according to a specified scheme while being divided into key and non-key pictures, and a value indicating whether or not coded picture data carried in each NAL unit is key picture data is recorded in a ‘nal_ref_idc’ field in a header of the NAL unit or, alternatively, a value (adaptive_ref_pic_marking_mode_flag=1) indicating that a Memory Management Control Operation (MMCO) is present and a control operation value indicating a key picture are recorded in a header of a picture coded into a key picture.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
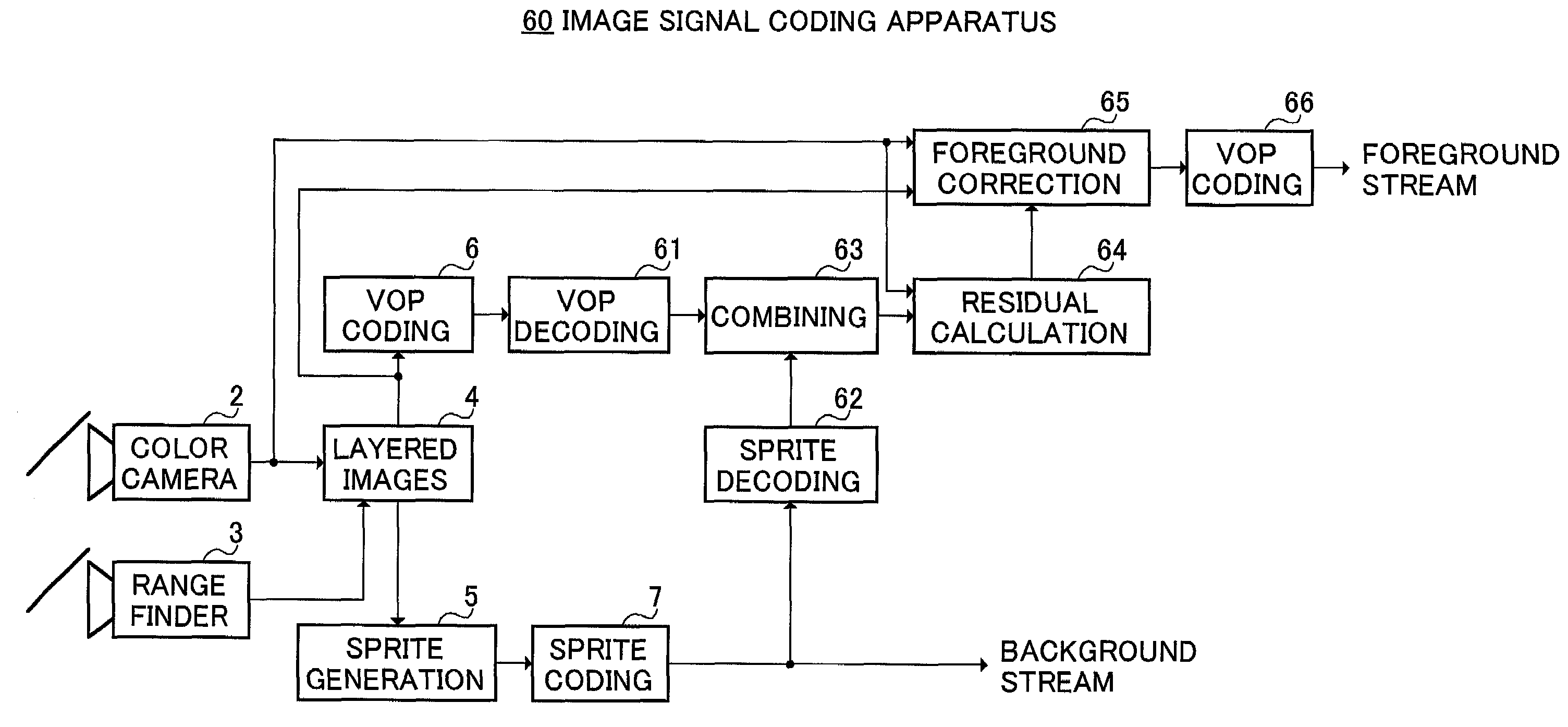
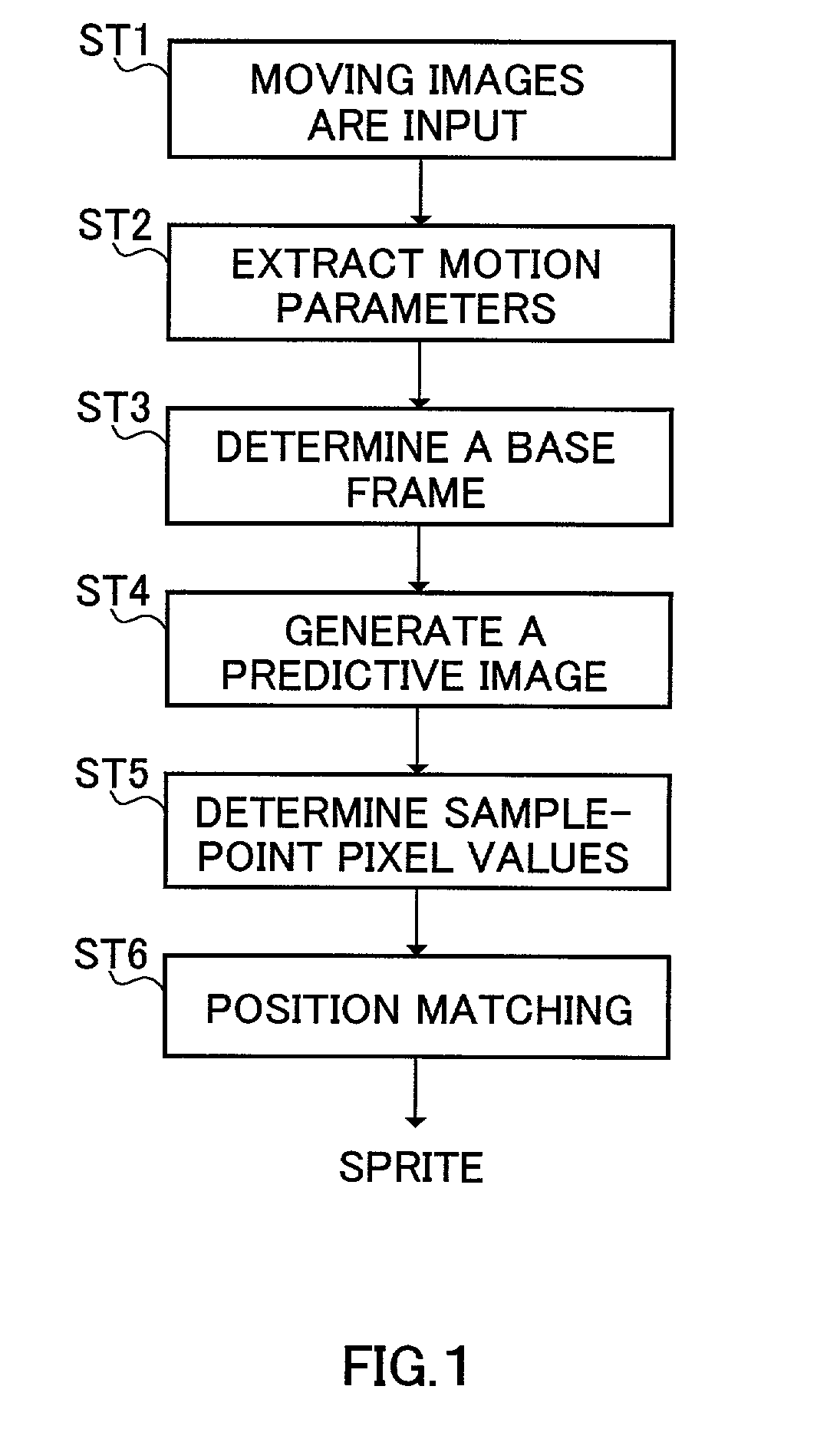
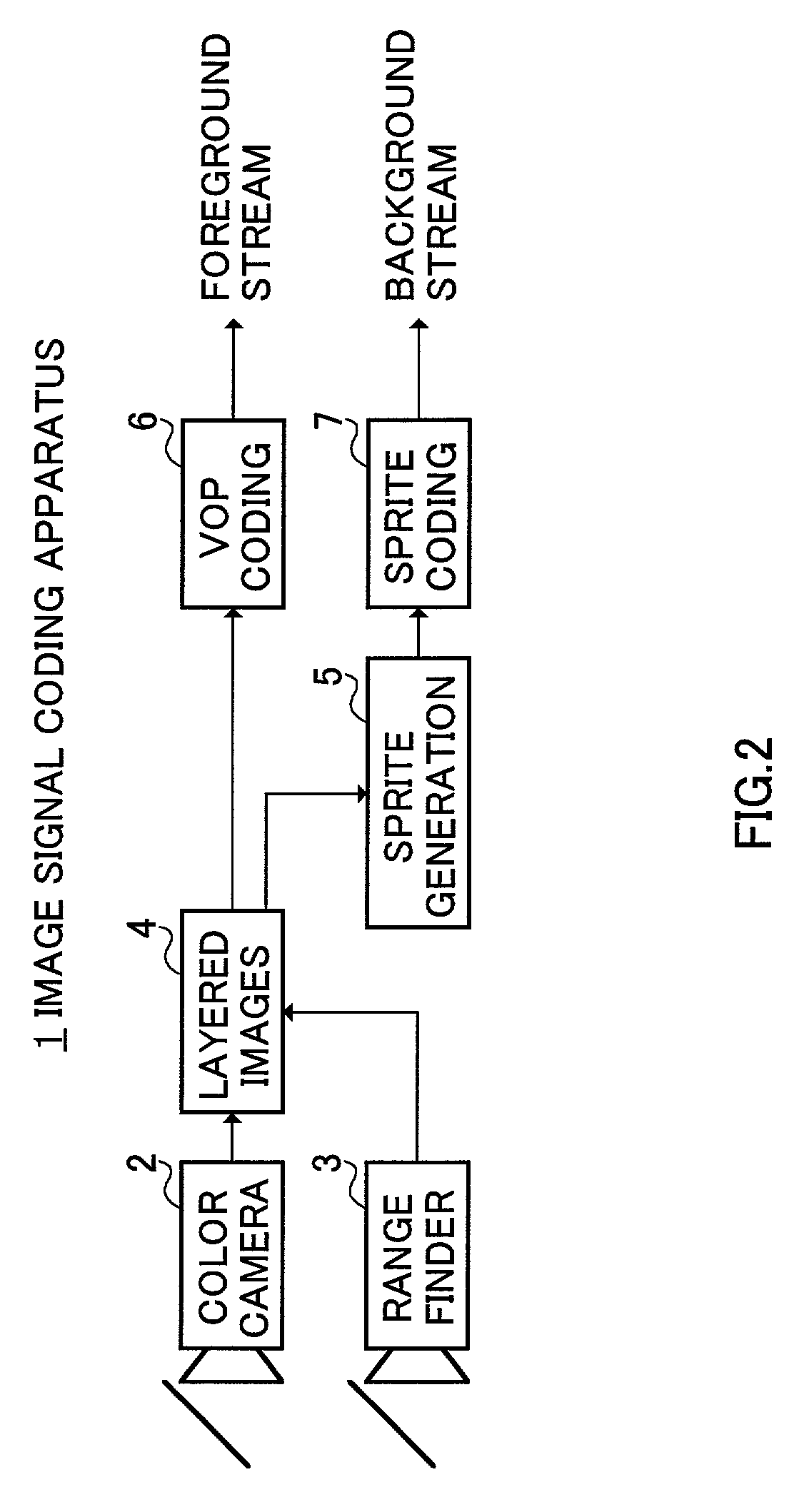
Image signal coding method, image signal coding apparatus and storage medium
Provided are a depth image obtaining section that obtains a depth image from the same viewpoint as in the input image, a layer section that separates the input image into a foreground image and a background image as layered images using depth information of the depth image, a coding section that encodes the foreground image, a background sprite generating section that generates a background sprite image from the background image, and a sprite coding section that encodes the background sprite image. The depth image from the same viewpoint as in the input image is obtained in the depth image obtaining section, the input image is separated into a foreground image and a background image as layered images using the depth information, and based on the separated background image, a background sprite image is generated.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Information processing apparatus and method
InactiveUS20080056383A1Maintain continuityTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesInformation processingComputer science
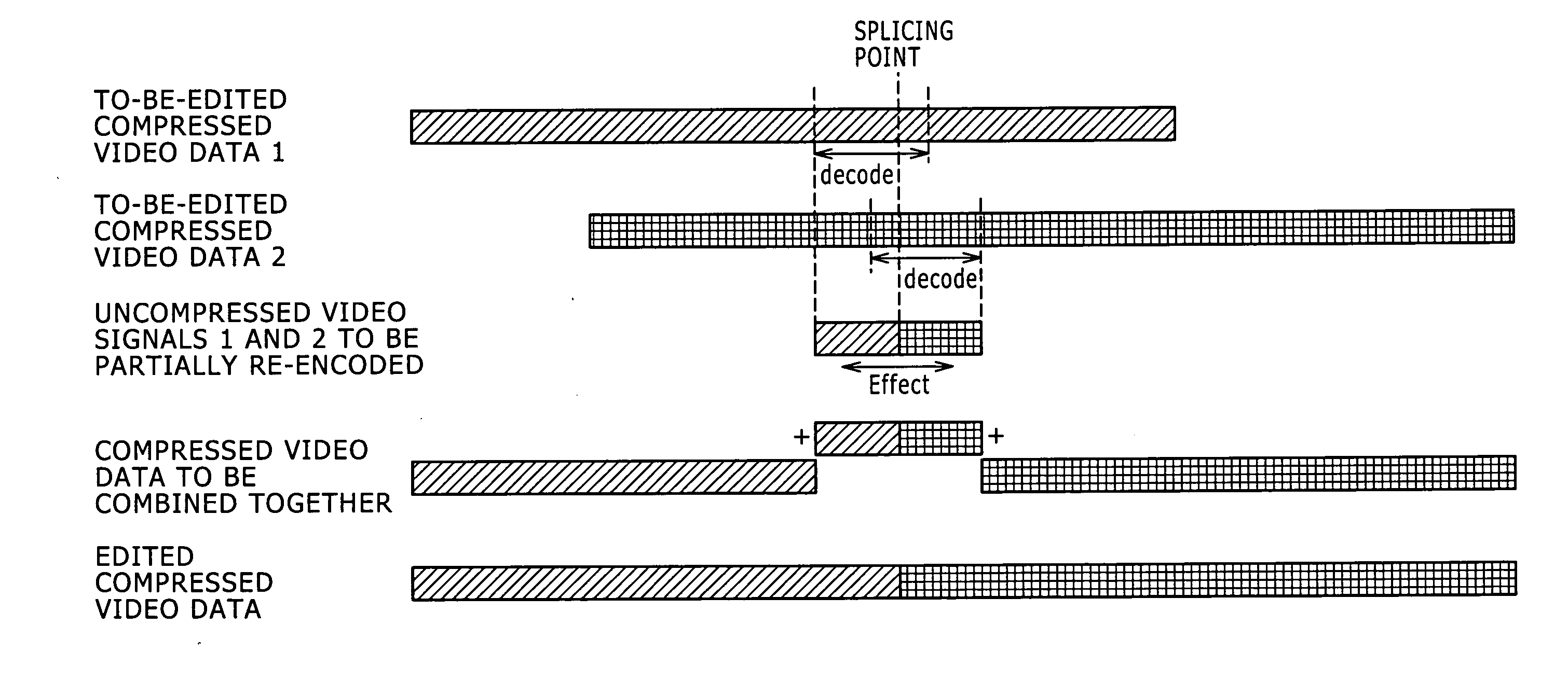
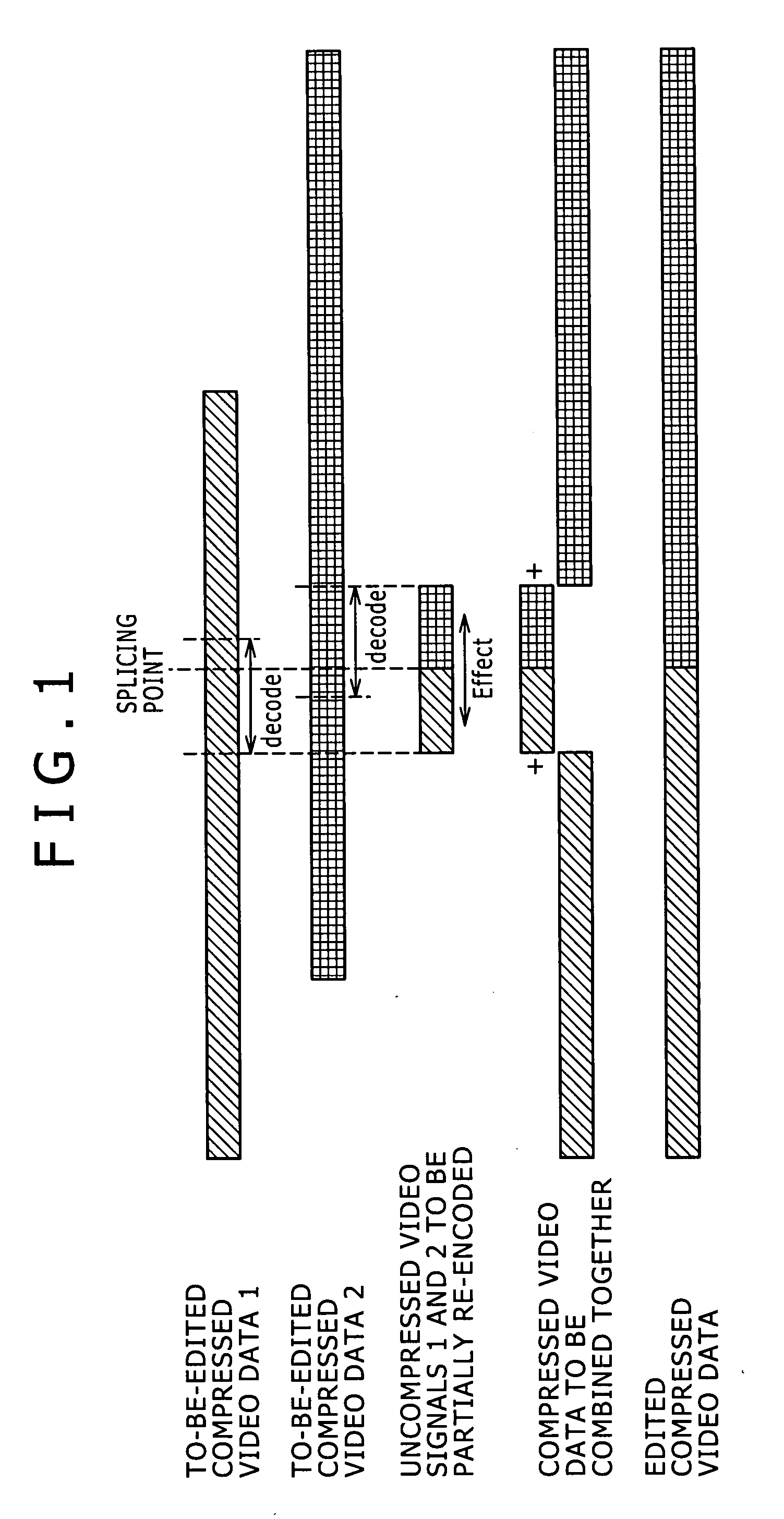
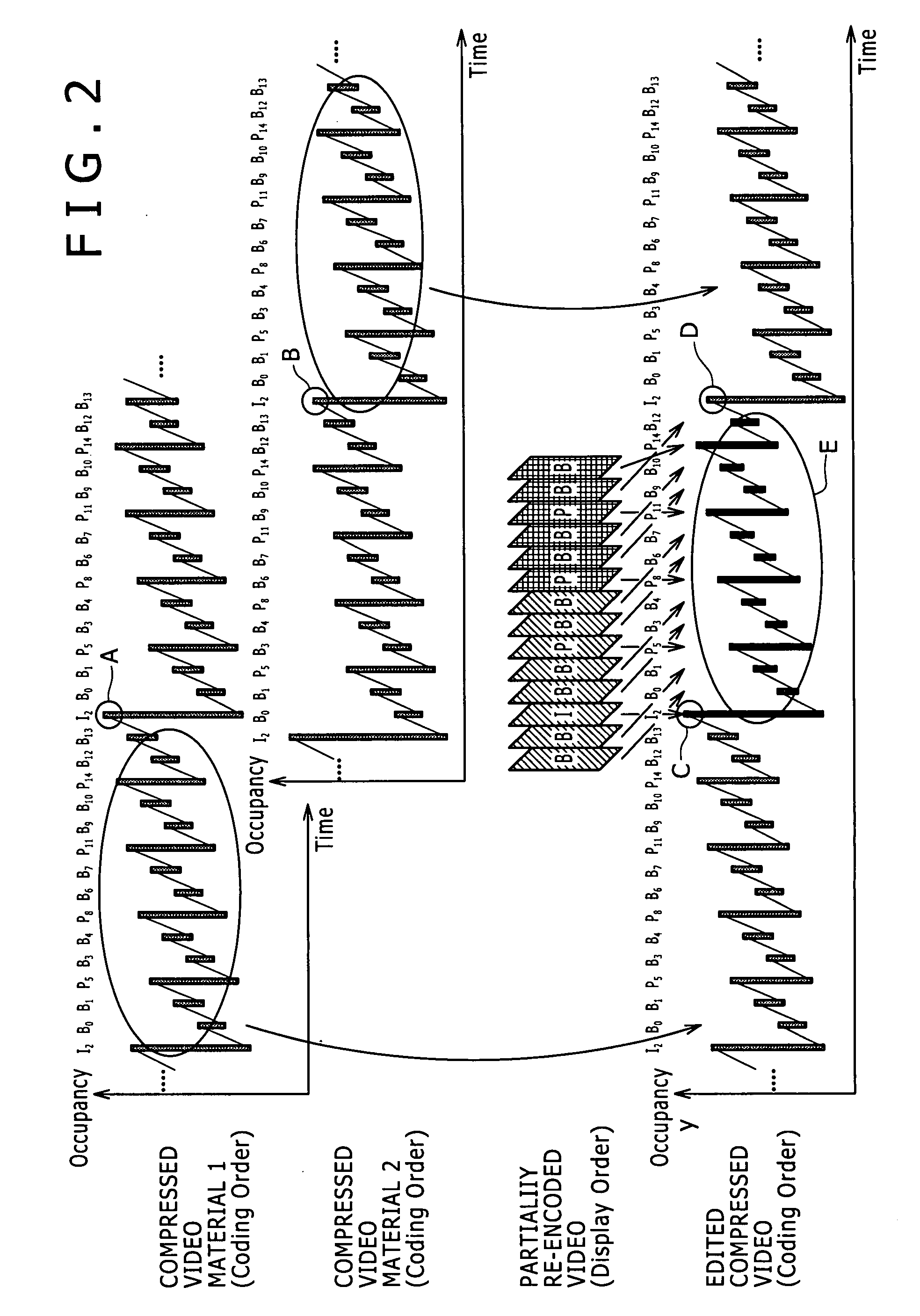
Disclosed herein is an information processing apparatus that performs a process of splicing encoded streams together at a splicing point, the apparatus including: control means for determining a section to be subjected to re-encoding in the encoded streams; decoding means for decoding the encoded streams to generate baseband signals; and encoding means for encoding an edited baseband signal generated by splicing the baseband signals generated by the decoding means together at the splicing point to generate an edited encoded stream. The control means provisionally determines a first section to be subjected to re-encoding in first and second encoded streams to be spliced together at a first splicing point. When a second splicing point exists in the first section or a predetermined section that follows the first section, the control means determines a second section to be subjected to re-encoding based on the second splicing point.
Owner:SONY CORP
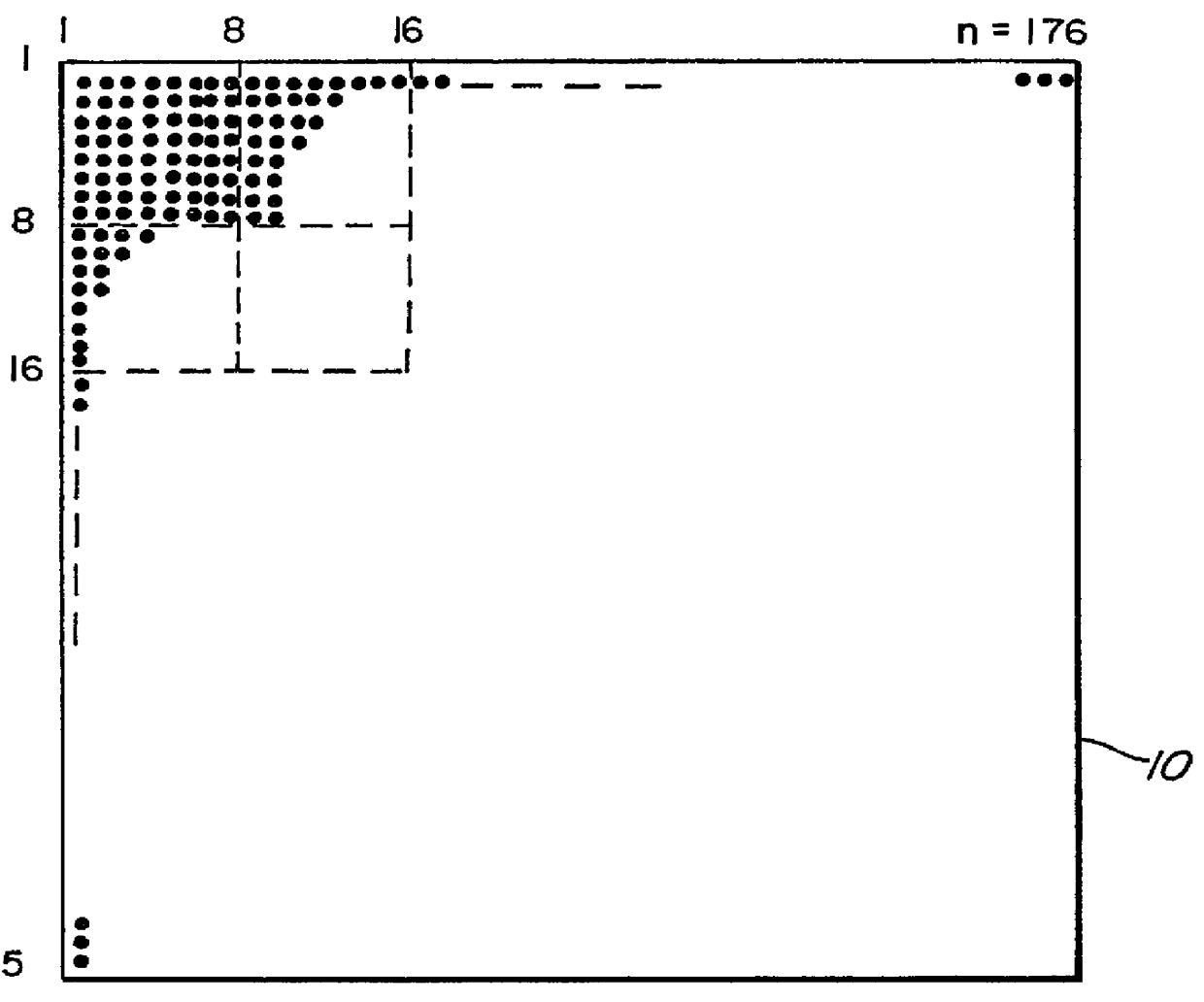
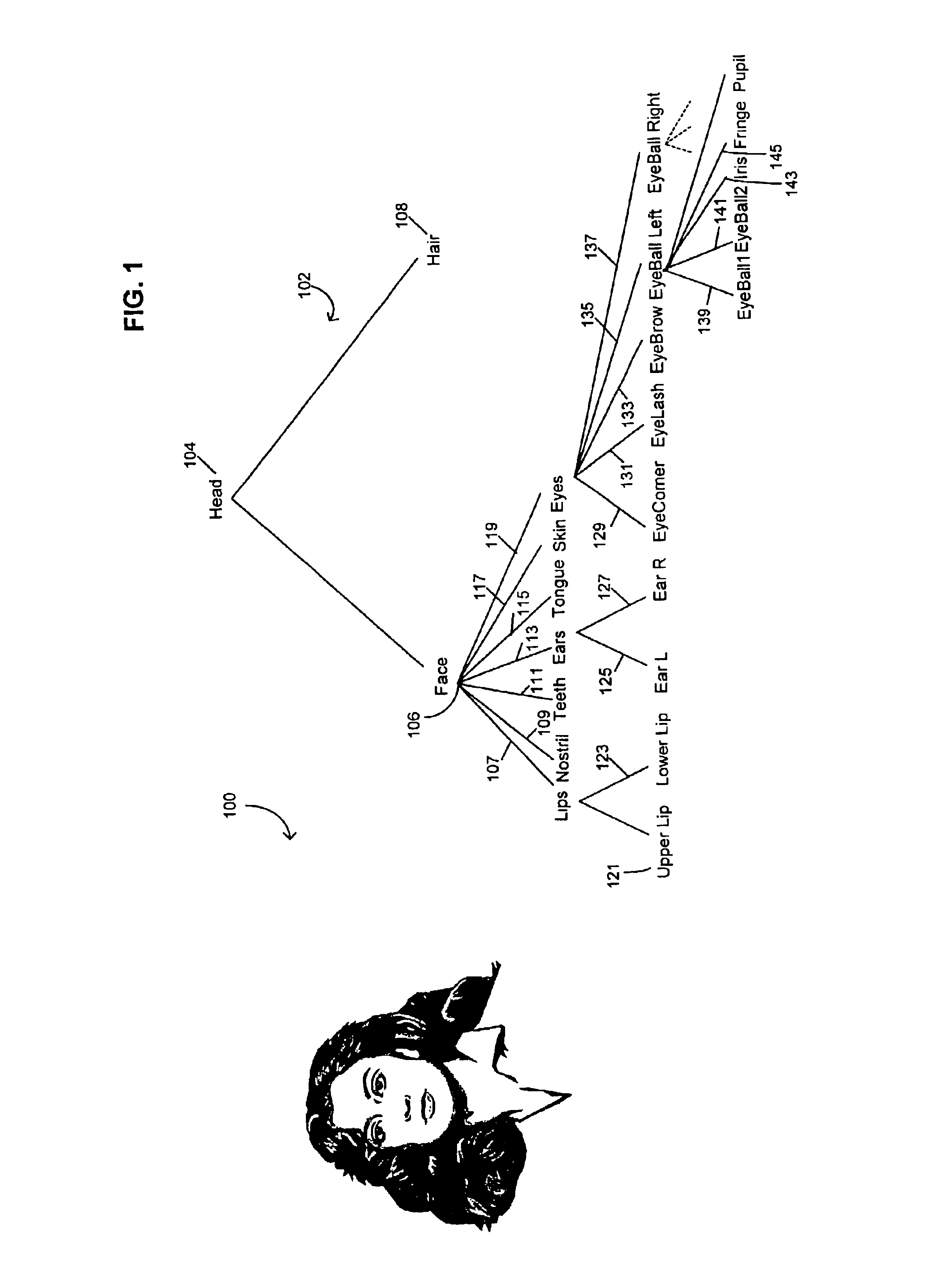
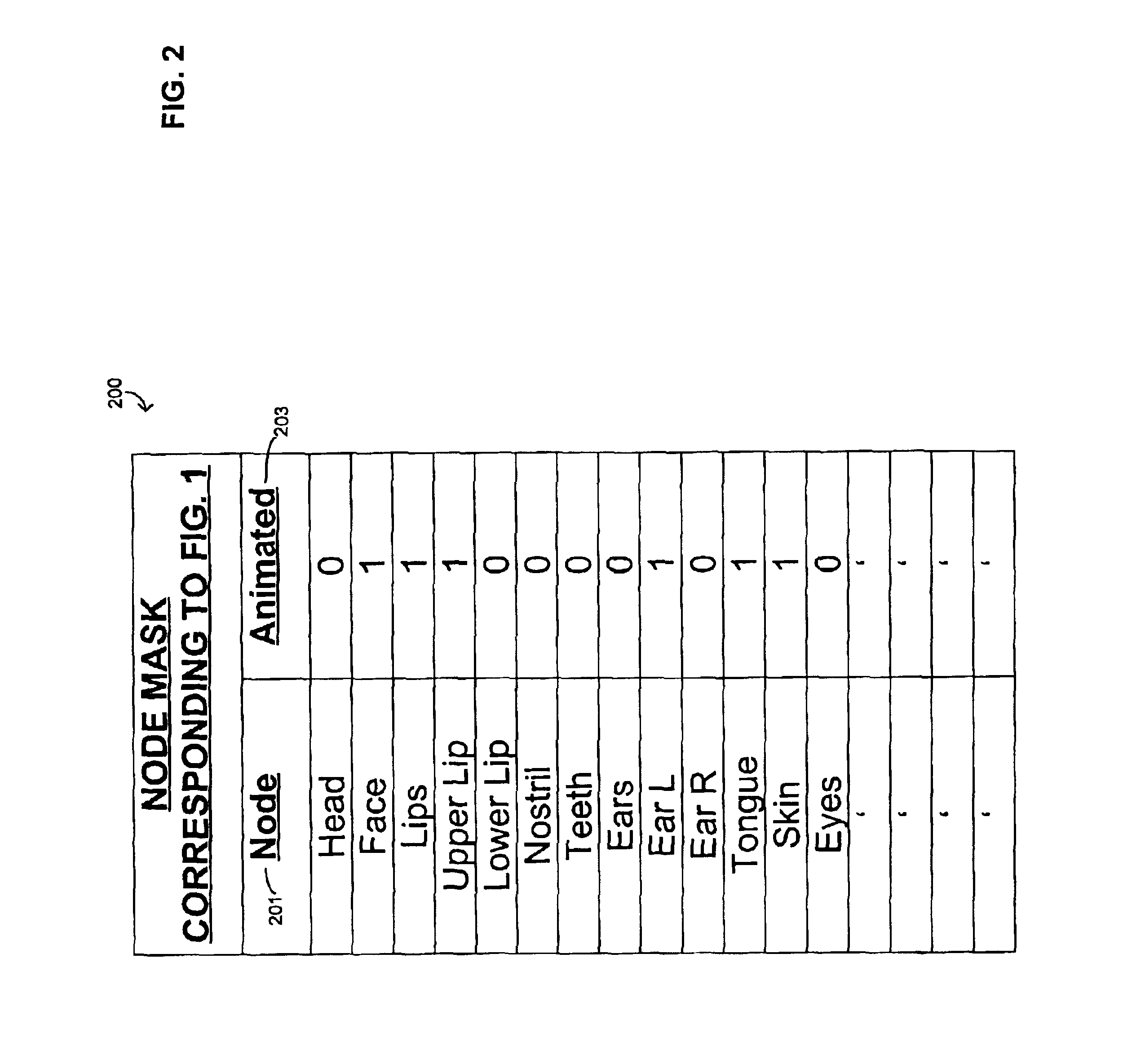
Coding of animated 3-D wireframe models for internet streaming applications: methods, systems and program products
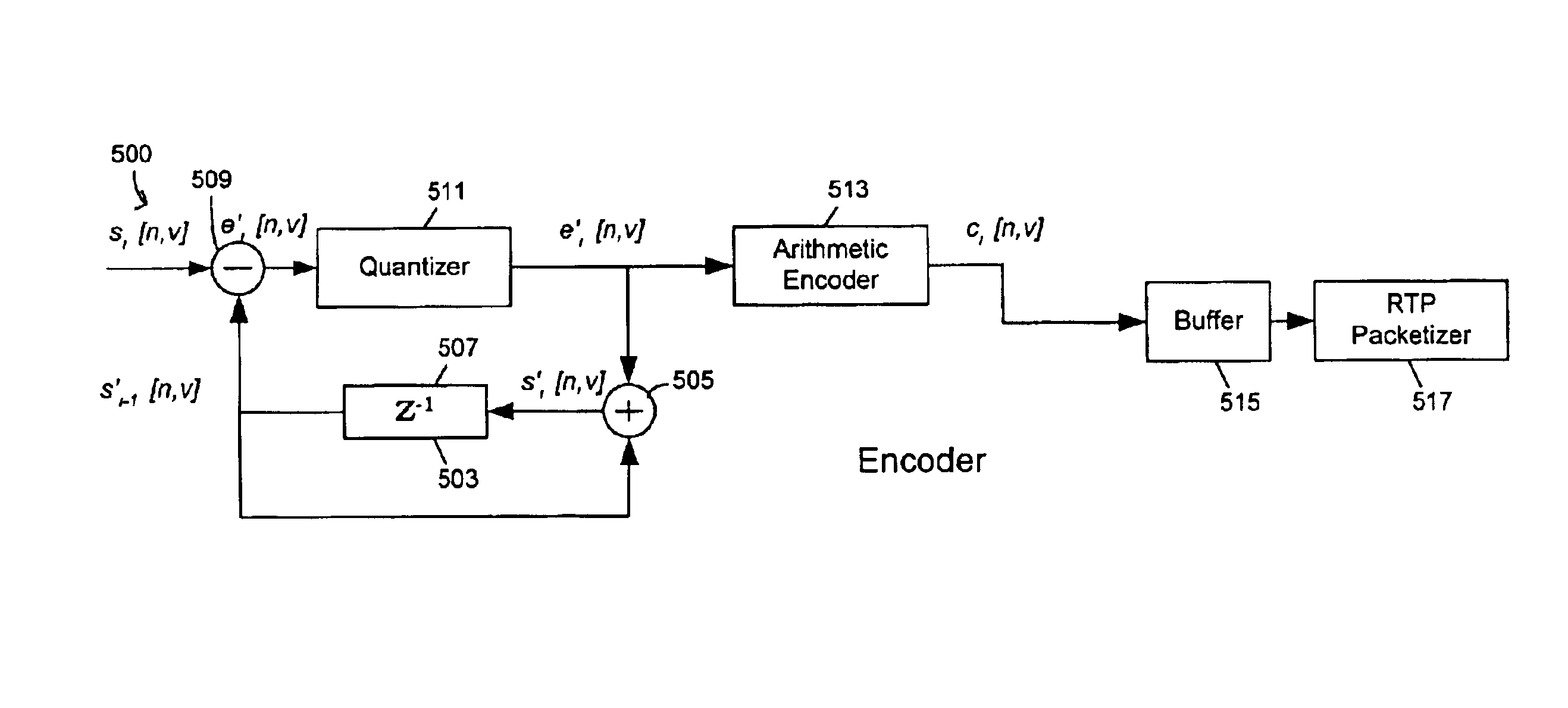
A 3-D wireframe model expressed in terms of nodes and vertices receives a 3-D video or like signal representative of a scene expressed in terms of a reference model, I frames and P frames. A DPCM coder takes advantage of the temporal correlation of the displacement of each vertex along every axis in the 3-D space. The 3-D signal is a set of non-zero displacements of all vertices and all nodes (sl[n, v]) at time tl. The decoded set (animation frame) of the previous instance is used as the predicted value (si-l[n, v]). The prediction error el[n, v], i.e. the difference between the current displacement set and the predicted one, is computed and quantised (el[n, v]). Finally, the quantised samples are entropy coded (ci[n, v]) using an adaptive arithmetic coding algorithm to handle the unknown data statistics. The predictive scheme described above prevents quantization error accumulation. A DPCM decoder first decodes arithmetically the received samples (‘e’ [n, v]) and computers the decoded samples (si′ [n, v]).
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Adaptive entropy coding in adaptive quantization framework for video signal coding systems and processes
InactiveUS6249546B1Improve accuracyLess distortionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSelf adaptiveSignal coding
A compression system and process include adaptive quantization for selection of one quantizer, for each video frame or frame portion, from a group of quantizers, where each quantizer is a set of predefined quantizer values, and coding of the quantized values using a common entropy coding table for all quantizers, or a separate entropy coding table for each quantizer. The entropy coding tables are obtained during a training procedure. The selection of the quantizer is based on a formula which takes into account the distortion and bit rate characteristics of each quantizer. A similar formula, based on the distortion and bit rate characteristics, is used to select the particular quantizer value within the chosen quantizer for each video signal value being coded.
Owner:INTEL CORP
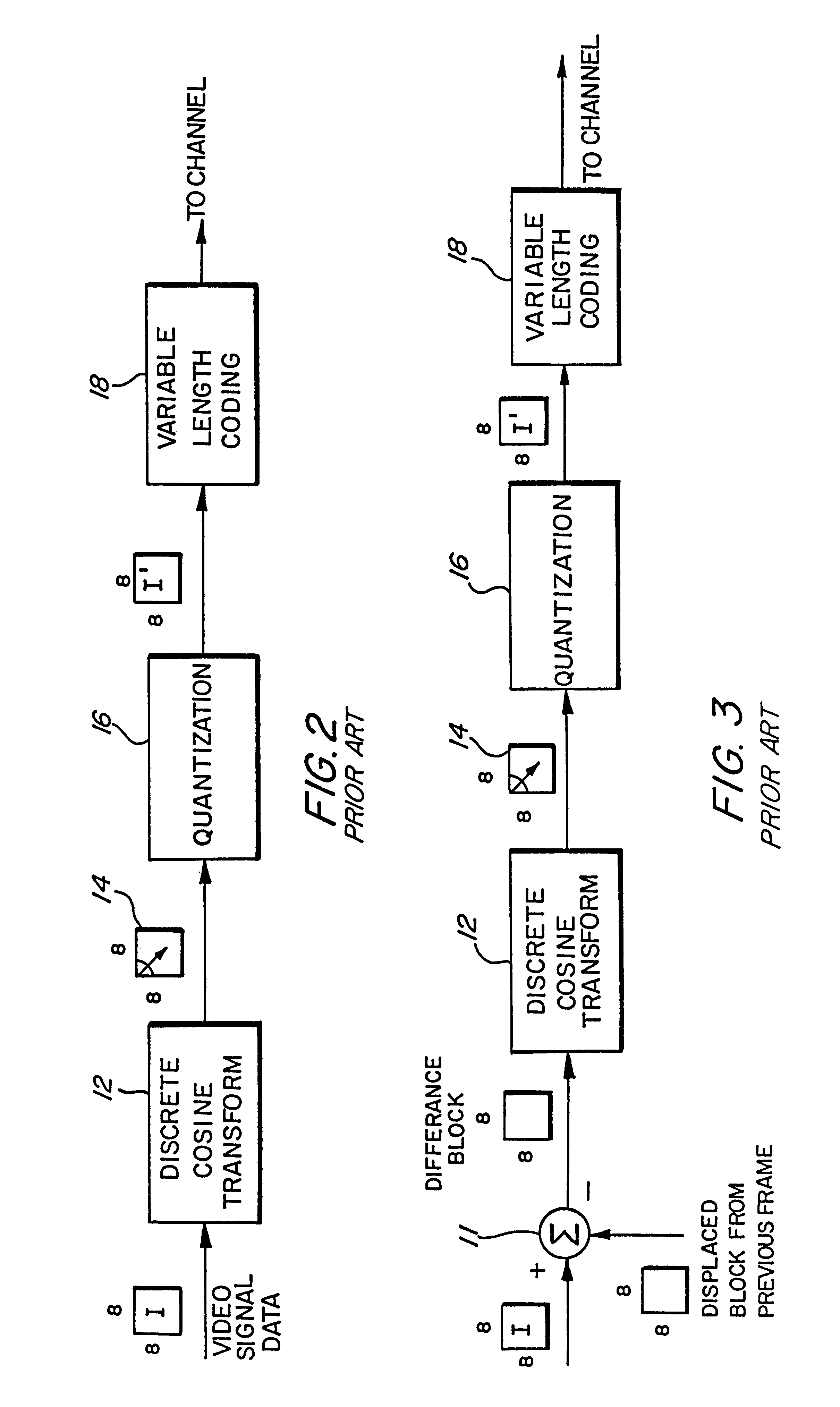
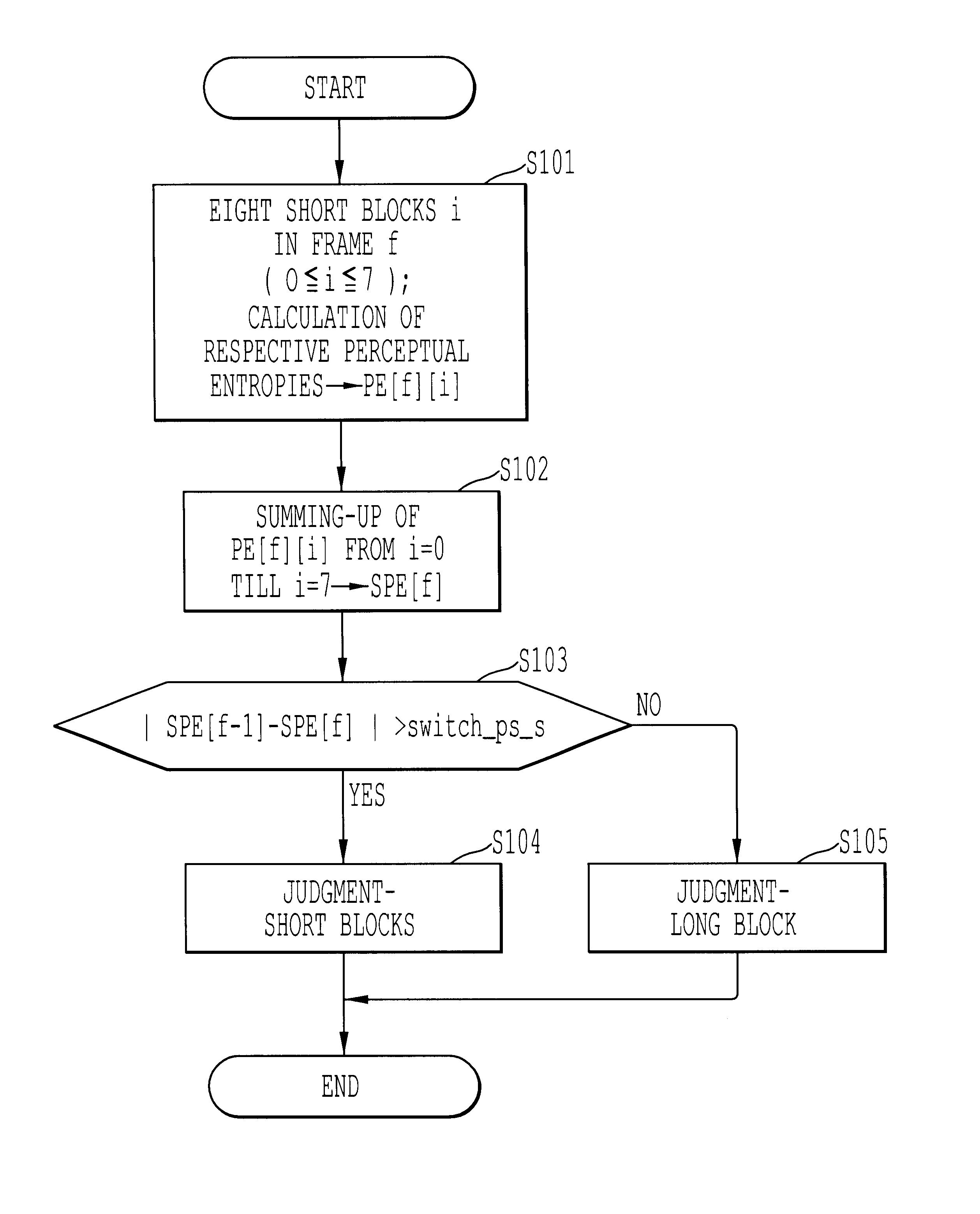
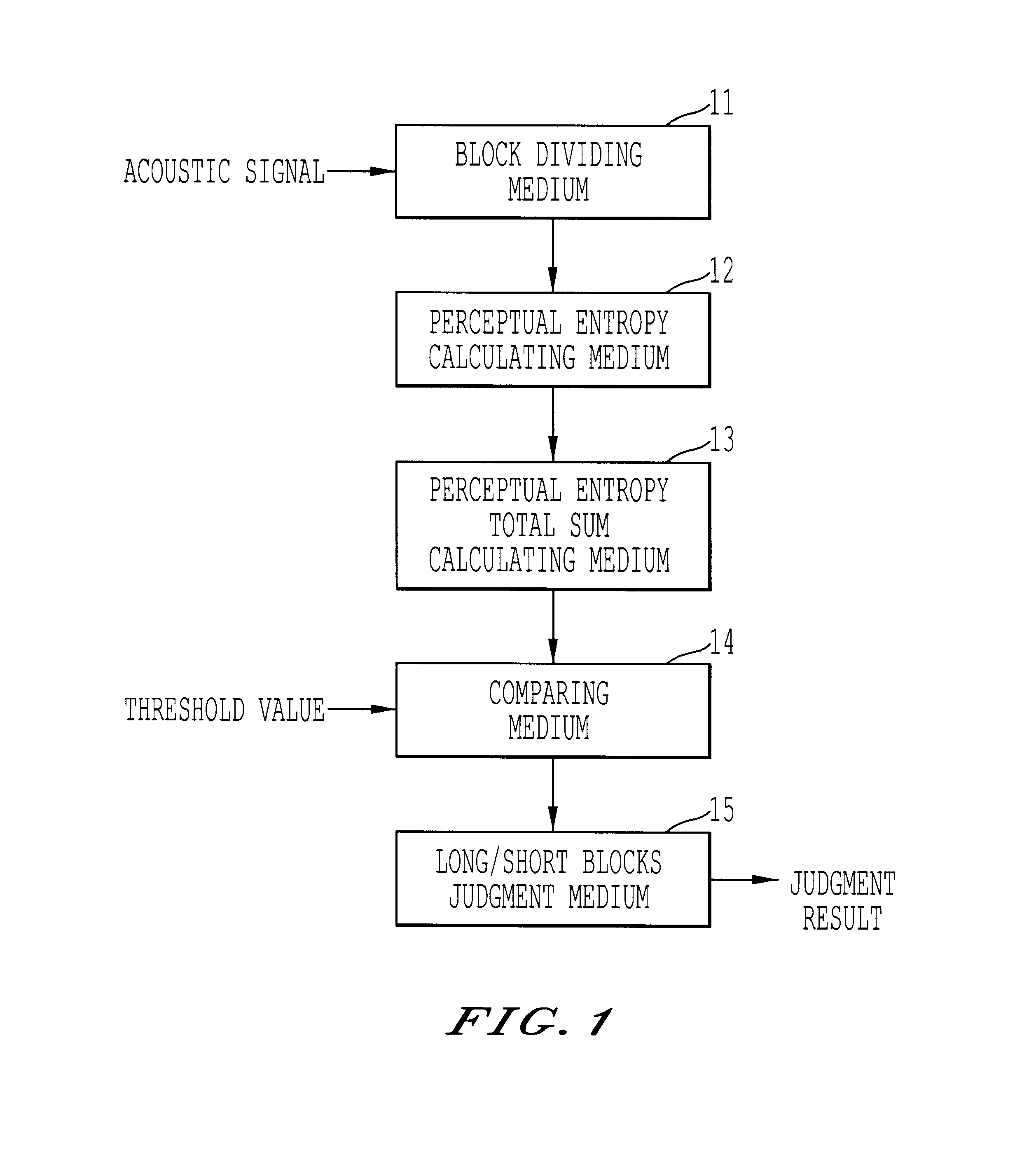
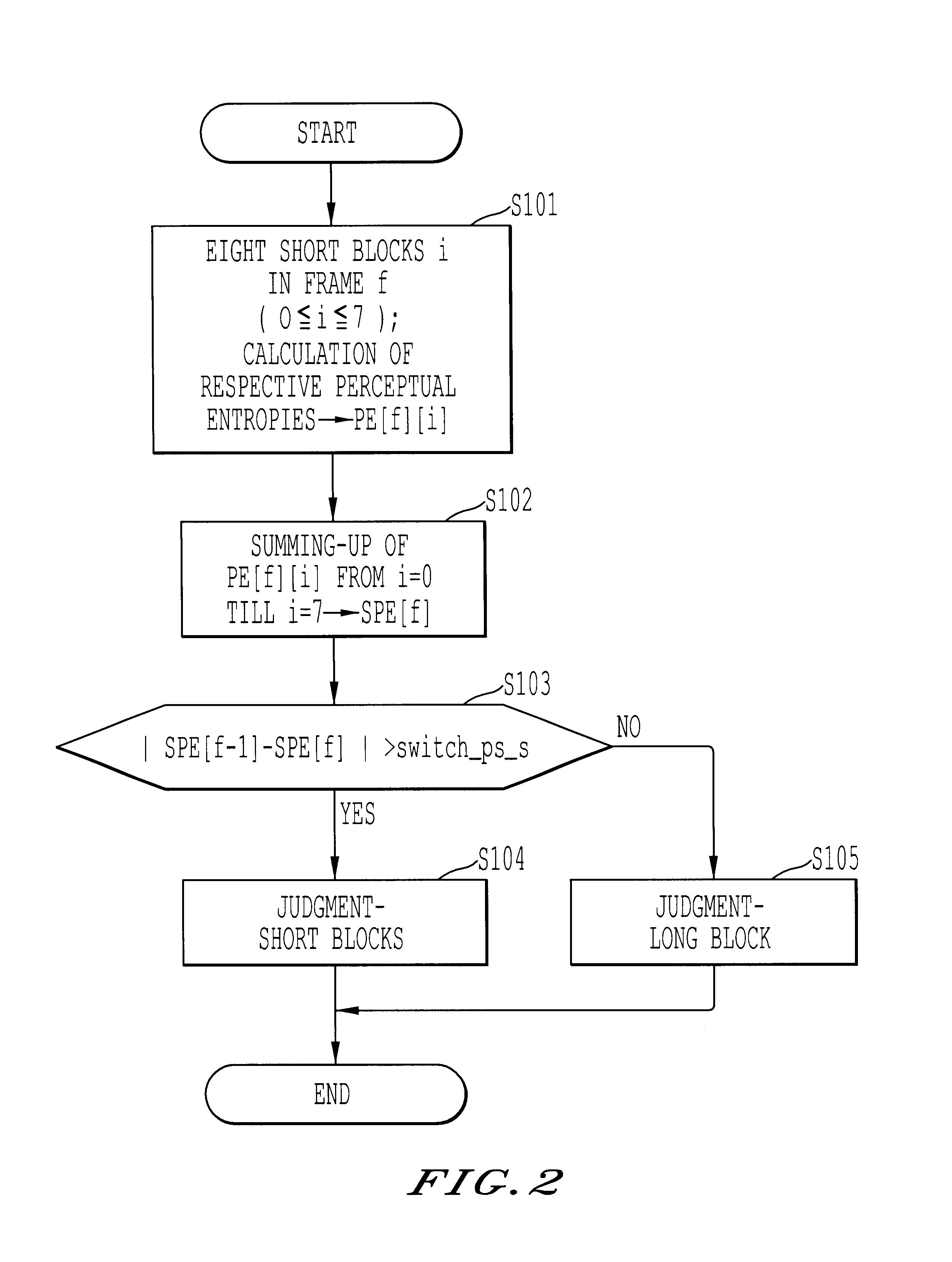
Method, apparatus, and medium of digital acoustic signal coding long/short blocks judgement by frame difference of perceptual entropy
A digital acoustic signal coding apparatus, a method of coding the digital acoustic signal, and a recording medium for recording a program of coding the digital acoustic signal are respectively realized. It is possible to provide the digital acoustic signal coding method and apparatus, in which, corresponding to the difference between the sampling frequencies of the input acoustic signal, short blocks can be suitably classified into groups without deteriorating sound quality and the suitability of using either long / short blocks can be judged. The coding apparatus is composed of a calculation medium for calculating the sensation entropy of an input acoustic signal per each of the respective short sensation blocks; a sensation entropy sum total calculation medium for obtaining a total sum in a frame of the sensation entropy; a comparison medium for comparing an absolute value of the difference between the respective total sums of the sensation entropy of successive two frames with a previously determined threshold value; and a long / short block judgment medium for judging whether a long block or short blocks should be used to convert a block of the input acoustic signal on the basis of the comparison result.
Owner:RICOH KK
Wireless LAN with enhanced carrier sensing
ActiveUS20030026198A1Improve data throughputBetter networkError preventionTransmission systemsCarrier signalData signal
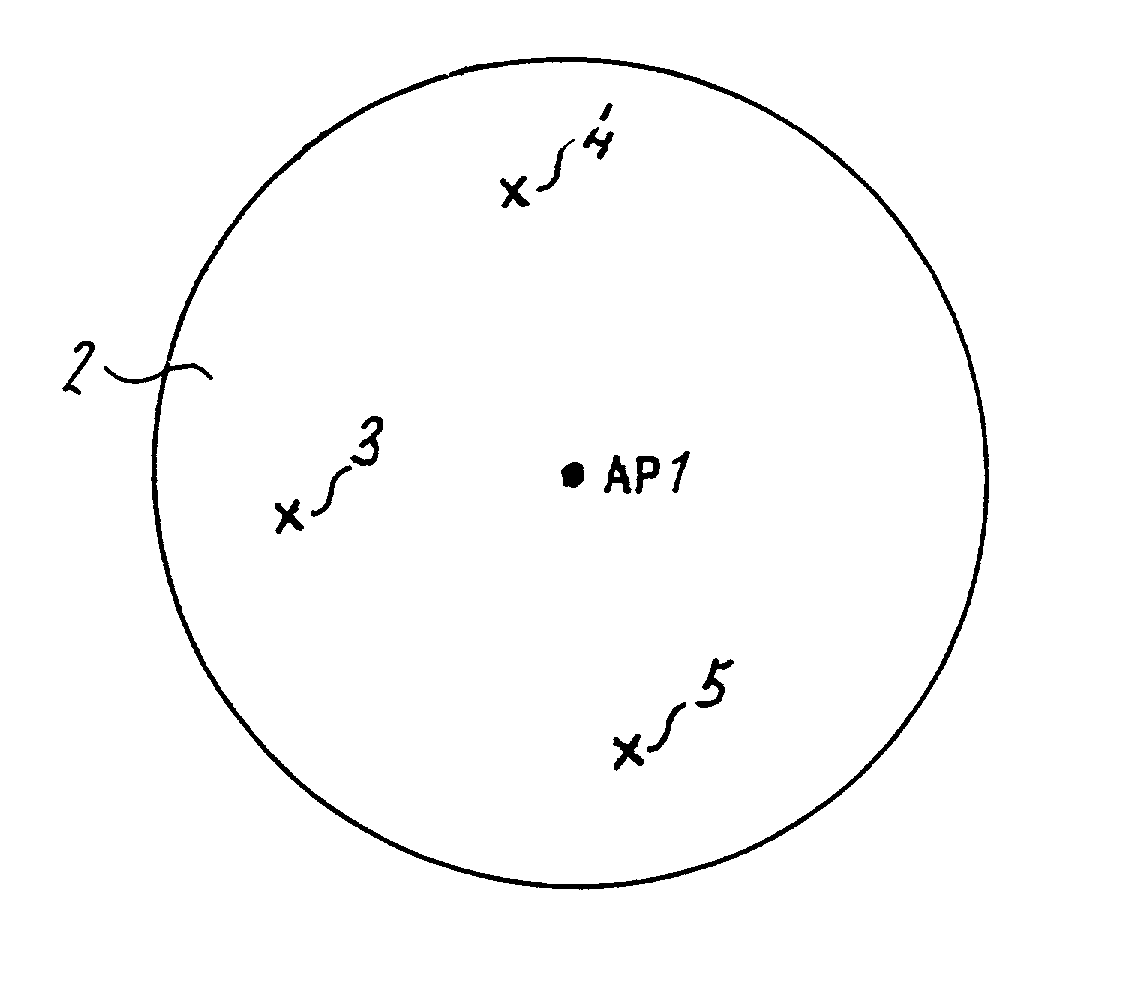
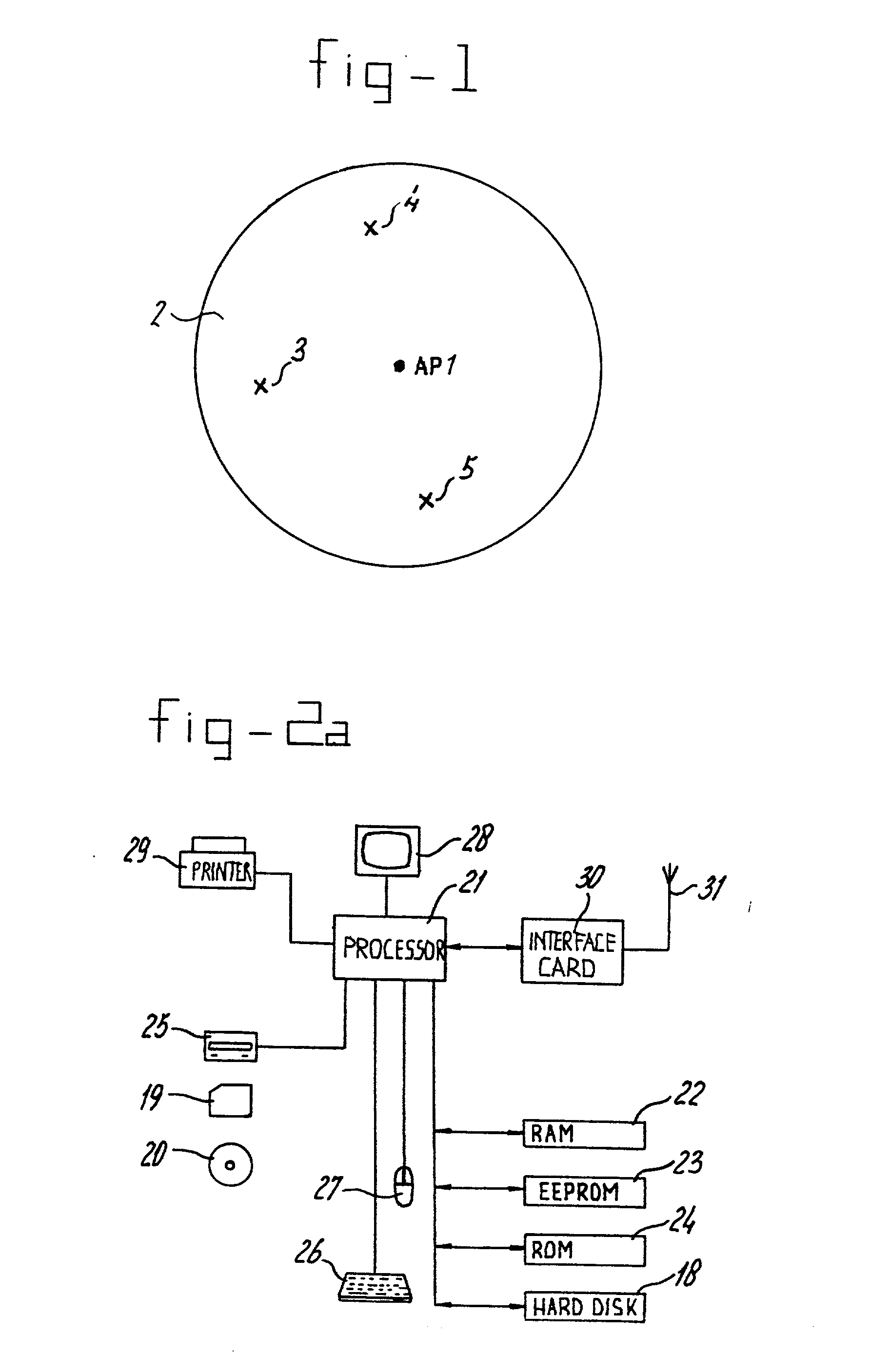
Medium access control device (301) for a mobile network station (3, 4, 5) or an access point (AP1) in a wireless local area network (1), having controlling means (302), processing means (303) and transmitting and receiving means (304); the controlling means (302) being arranged to control transmission and reception of radio frequency data signals containing data symbols; the transmitting and receiving means (304) being arranged for transmission and reception of electromagnetic data signals; the processing means (303) being arranged for detecting a first signal portion and a second signal portion in the received data signal, the second signal portion following the first signal portion and having a signal coding differing from a signal coding of the first signal portion.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Process, method and mobile phone utilizing mobile phone sharing television screen to control television
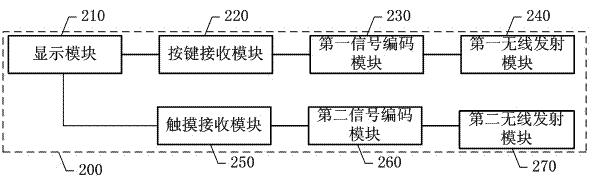
ActiveCN102395012AAdd TV remote control functionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCode moduleKey pressing
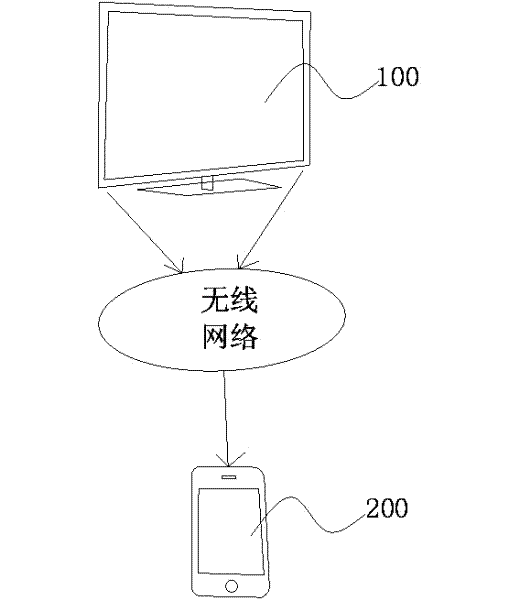
The invention discloses a process, a method and a mobile phone utilizing a mobile phone sharing television screen to control a television. The method comprises the following steps: the mobile phone with the screen sharing program is connected with the television through a wireless network; the current screen picture of the television is sent to the mobile phone end and scaled down for being displayed on the mobile phone screen through the wireless network; when the mobile phone end triggers a keystroke, ID coding information and keystroke coding information are generated through the signal coding module at the mobile phone end; and after the information is sent to the television for decoding, an corresponding keystroke event is triggered at the television end. The invention adopts the mobile phone sharing television screen and utilizes the mobile phone touch screen and the keystrokes to control the television, a corresponding position on the mobile phone screen is touched, the corresponding position touch event on the television screen can be correspondingly triggered, and the mobile phone keystrokes can also be used to trigger corresponding television keystroke event; and the mobile phone can also be used for performing menu selection and character input on the television so as to realize the purpose of utilizing the mobile phone to operate the television. Therefore, the television remote control function is added to the mobile phone.
Owner:KONKA GROUP
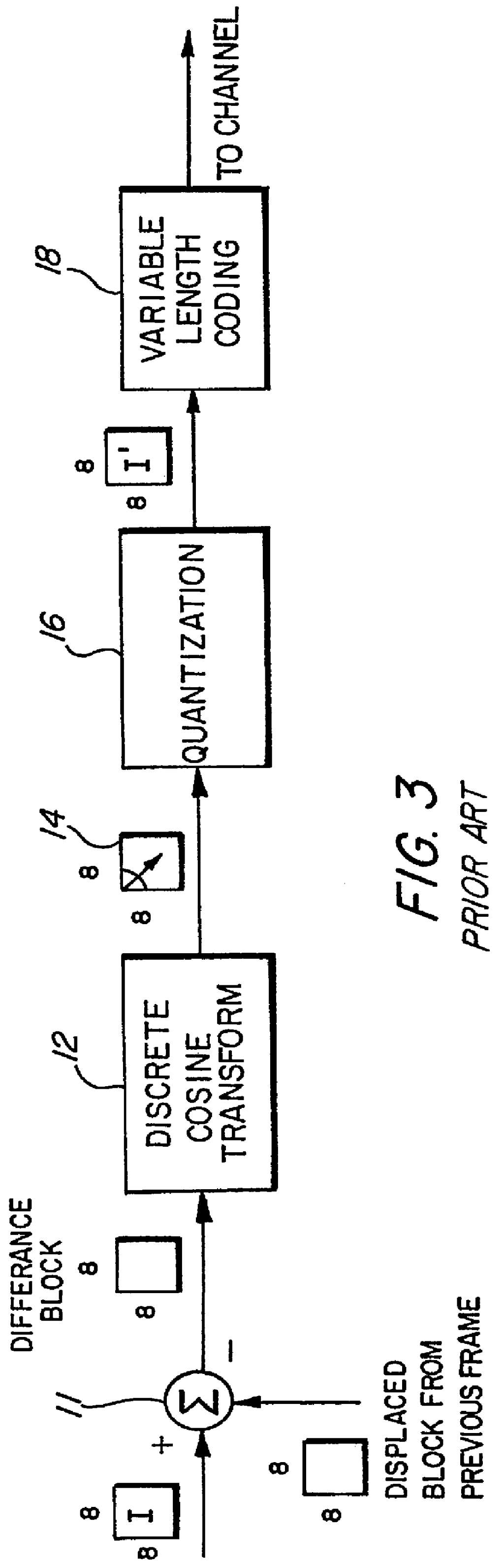
Digital video signal encoder and encoding method
InactiveUS20050220188A1Less bandwidthImprove image qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionDigital video
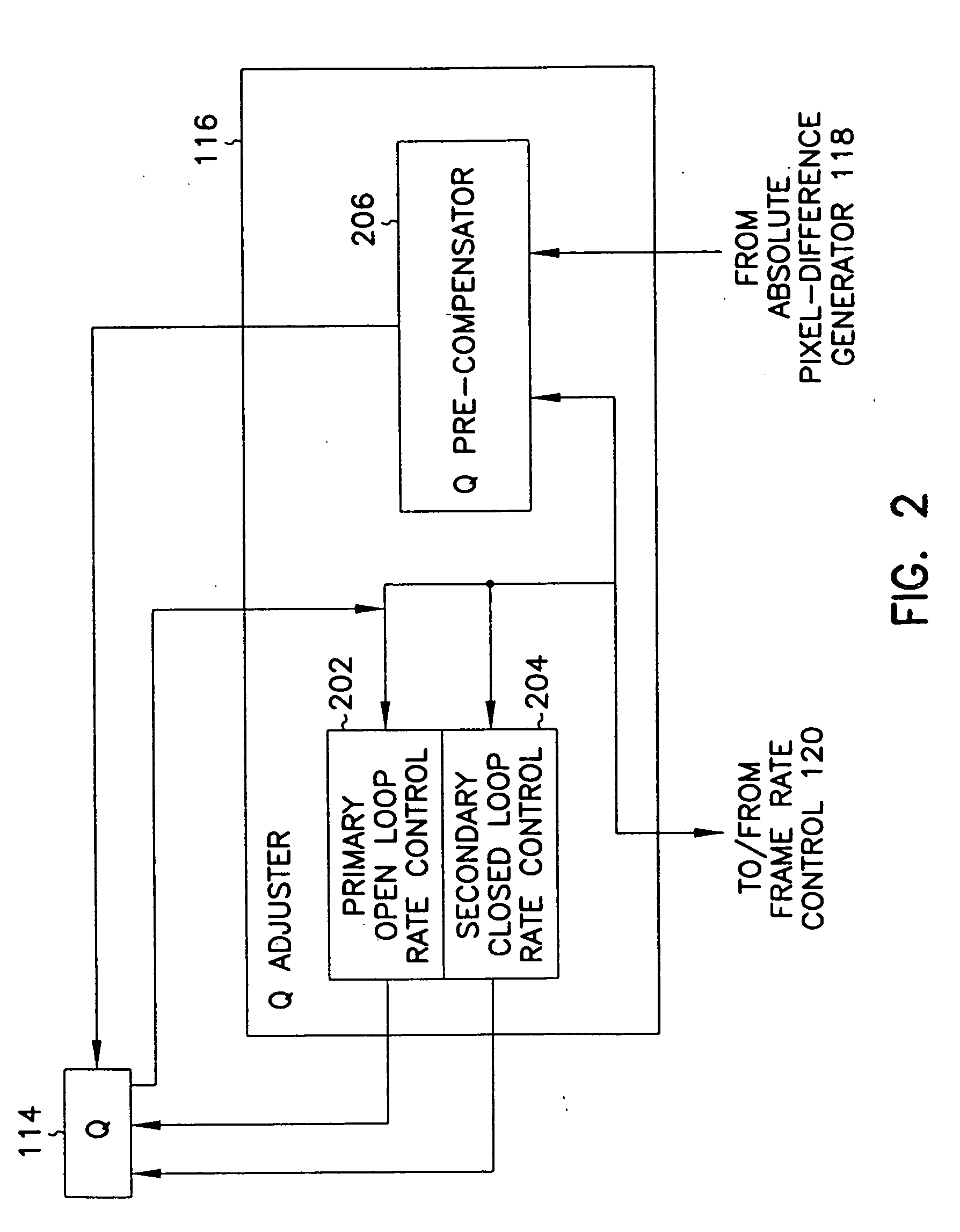
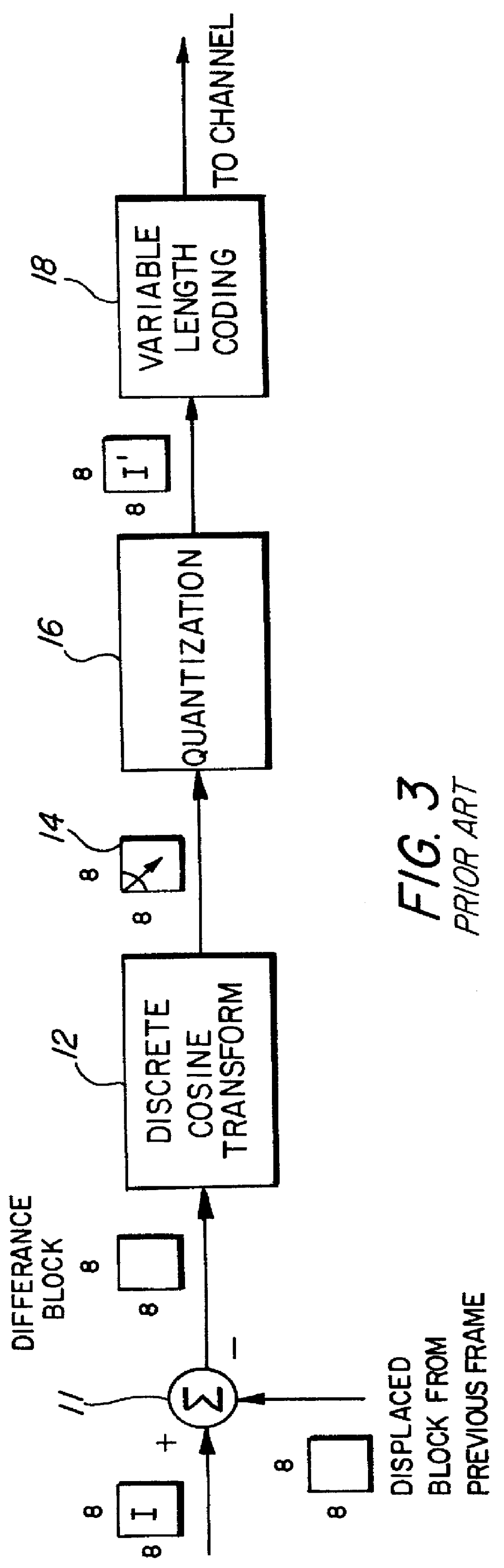
A motion video signal encoder maximizes image quality without exceeding transmission bandwidth available to carry the encoded motion video signal by comparing encoded frames of the motion video signal to a desired size of frame. If the size of encoded frames differ from the desired size, quantization is adjusted to produce encoded frames closer in size to the desired size. In addition, a cumulative bandwidth balance records an accumulated amount of available bandwidth. The cumulative bandwidth balance is adjusted as time elapses to add to the available bandwidth and as each frame is encoded to thereby consume bandwidth. If the cumulative bandwidth balance deviates from a predetermined range, quantization is adjusted as needed to either improve image quality to more completely consume available bandwidth or to reduce image quality to thereby consume less bandwidth. Rapid changes in the amount of change or motion in the motion video signal are detected by comparing the amount of change between two consecutive frames and the amount of change between the next two consecutive frames. Quantization is precompensated according to the measured rapid change. Conditional replenishment is improved by dividing macroblocks into quadrants and measuring differences between corresponding quadrants of macroblocks. As a result, sensitivity to changes along edges and corners of macroblocks is increased. In addition, sensitivity to changes in a particular macroblock is increased when an adjacent macroblock contains sufficient change to be encoded and therefore not a candidate for conditional replenishment.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Adaptive entropy coding in adaptive quantization framework for video signal coding systems and processes
InactiveUS6118822AImprove accuracyLess distortionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSelf adaptiveSignal coding
A compression system and process include adaptive quantization for selection of one quantizer, for each video frame or frame portion, from a group of quantizers, where each quantizer is a set of predefined quantizer values, and coding of the quantized values using a common entropy coding table for all quantizers, or a separate entropy coding table for each quantizer. The entropy coding tables are obtained during a training procedure. The selection of the quantizer is based on a formula which takes into account the distortion and bit rate characteristics of each quantizer. A similar formula, based on the distortion and bit rate characteristics, is used to select the particular quantizer value within the chosen quantizer for each video signal value being coded.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Energy based split vector quantizer employing signal representation in multiple transform domains
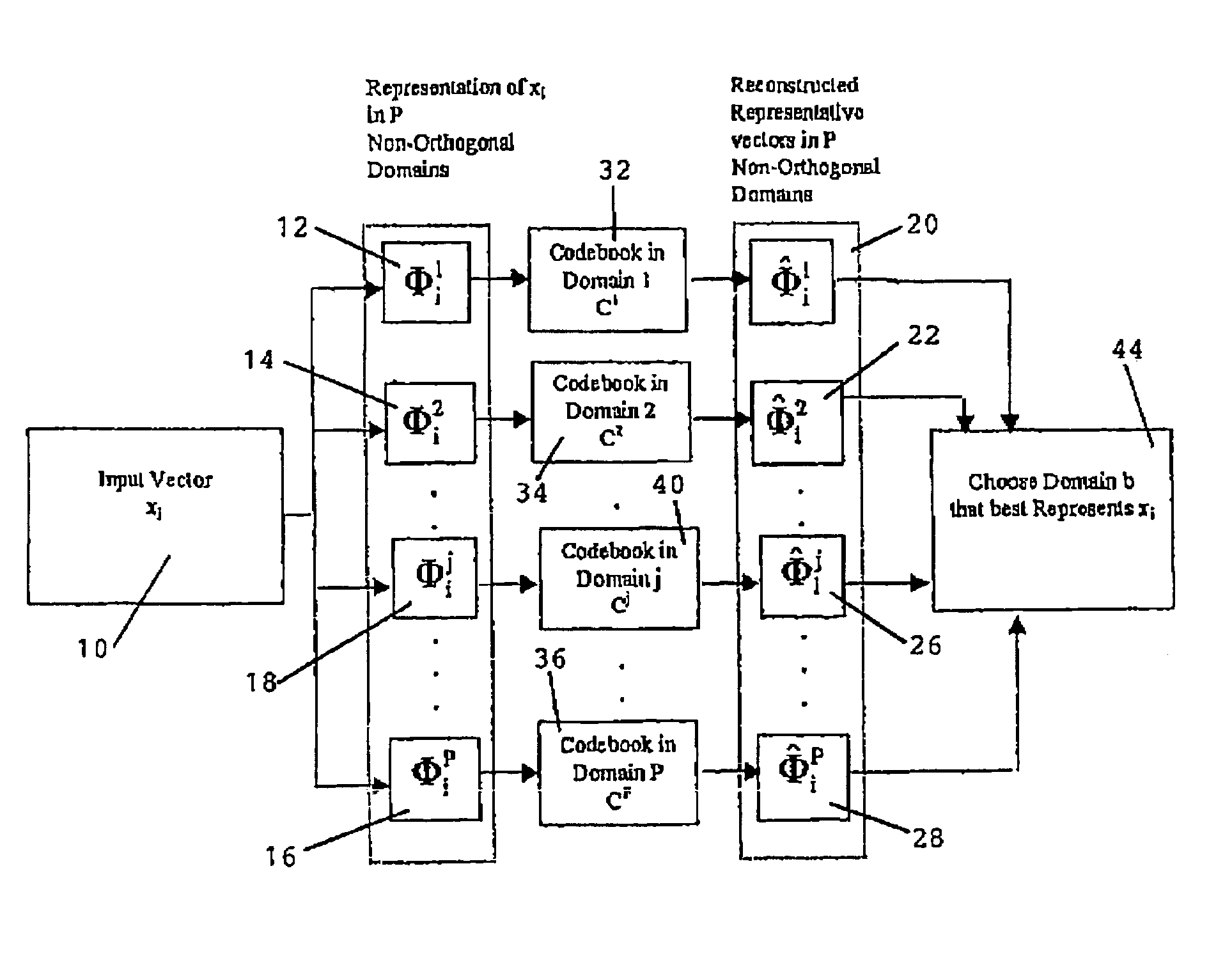
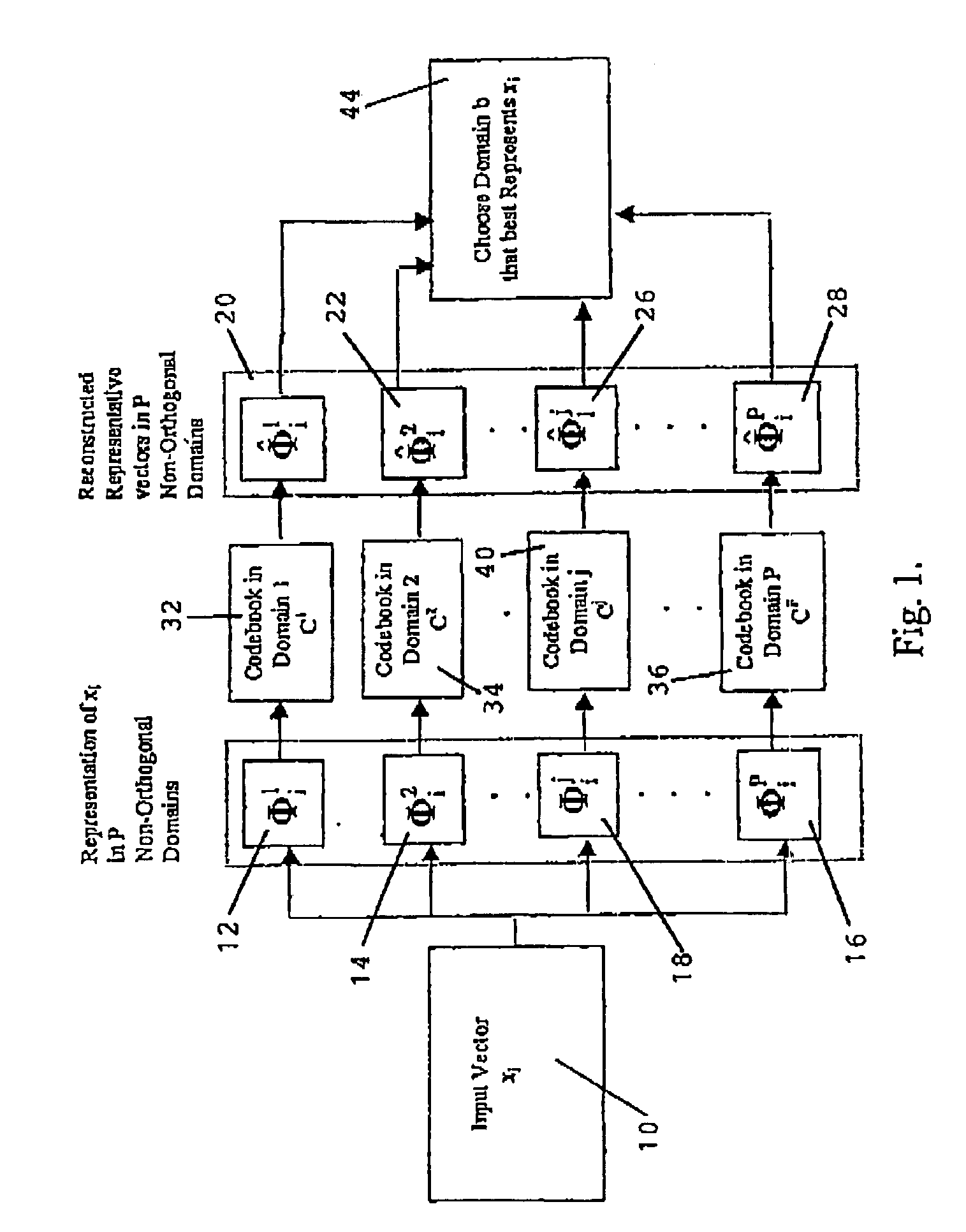
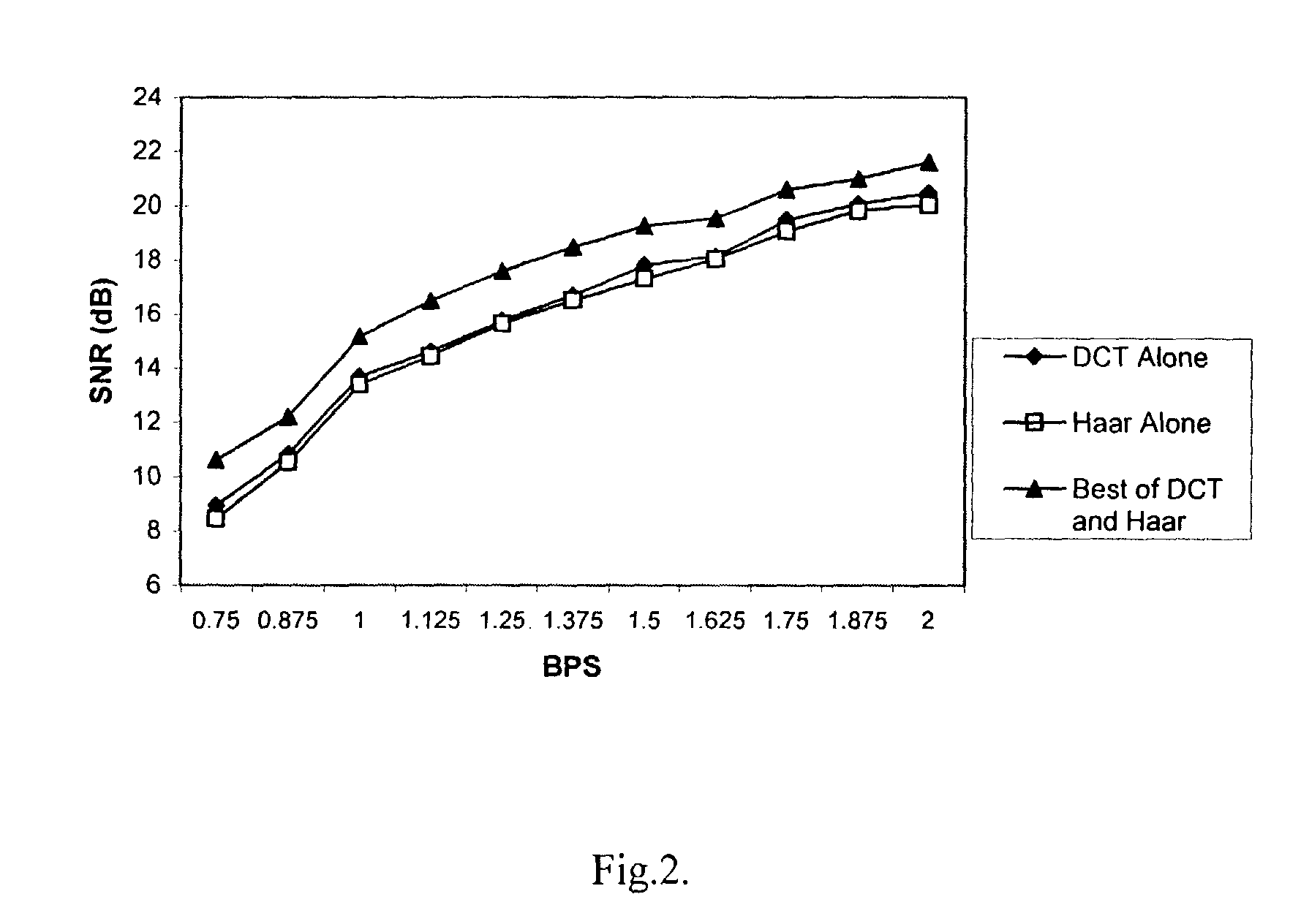
The invention relates to representation of one and multidimensional signal vectors in multiple nonorthogonal domains and design of Vector Quantizers that can be chosen among these representations. There is presented a Vector Quantization technique in multiple nonorthogonal domains for both waveform and model based signal characterization. An iterative codebook accuracy enhancement algorithm, applicable to both waveform and model based Vector Quantization in multiple nonorthogonal domains, which yields further improvement in signal coding performance, is disclosed. Further, Vector Quantization in multiple nonorthogonal domains is applied to speech and exhibits clear performance improvements of reconstruction quality for the same bit rate compared to existing single domain Vector Quantization techniques. The technique disclosed herein can be easily extended to several other one and multidimensional signal classes.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
System and method for generating many ones codes with hamming distance after precoding
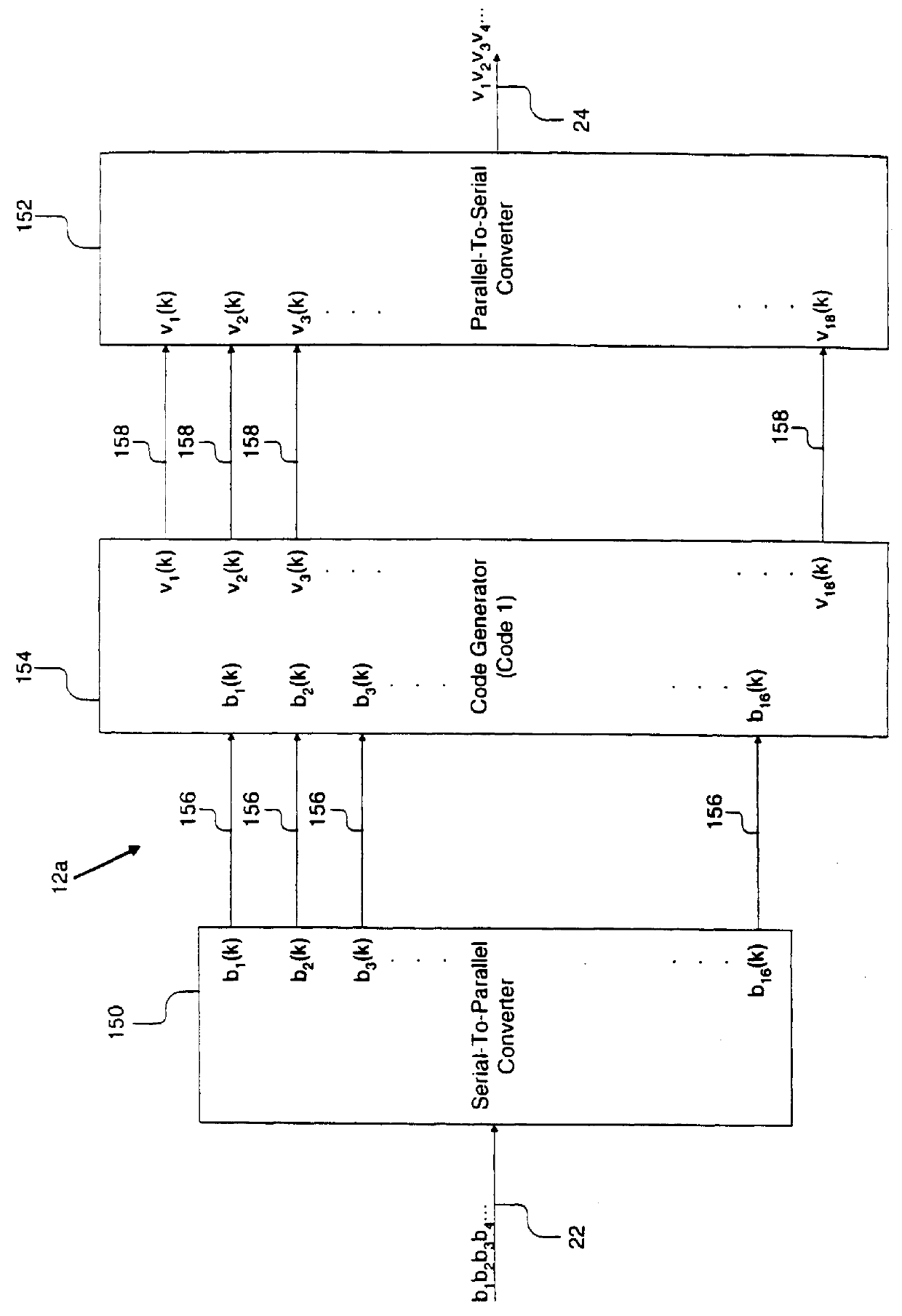
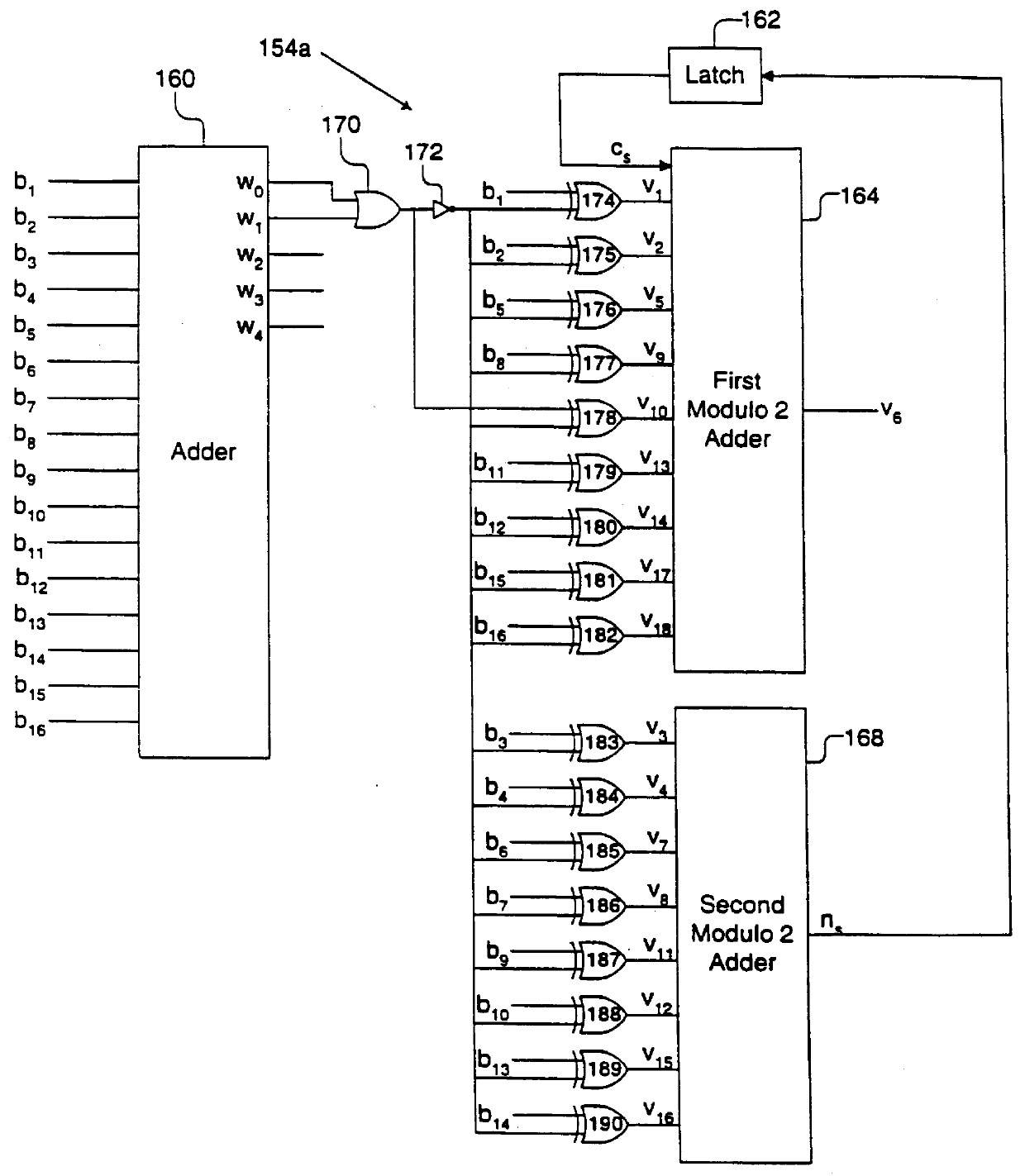
InactiveUS6084535AModification of read/write signalsRecord information storagePrecodingComputer hardware
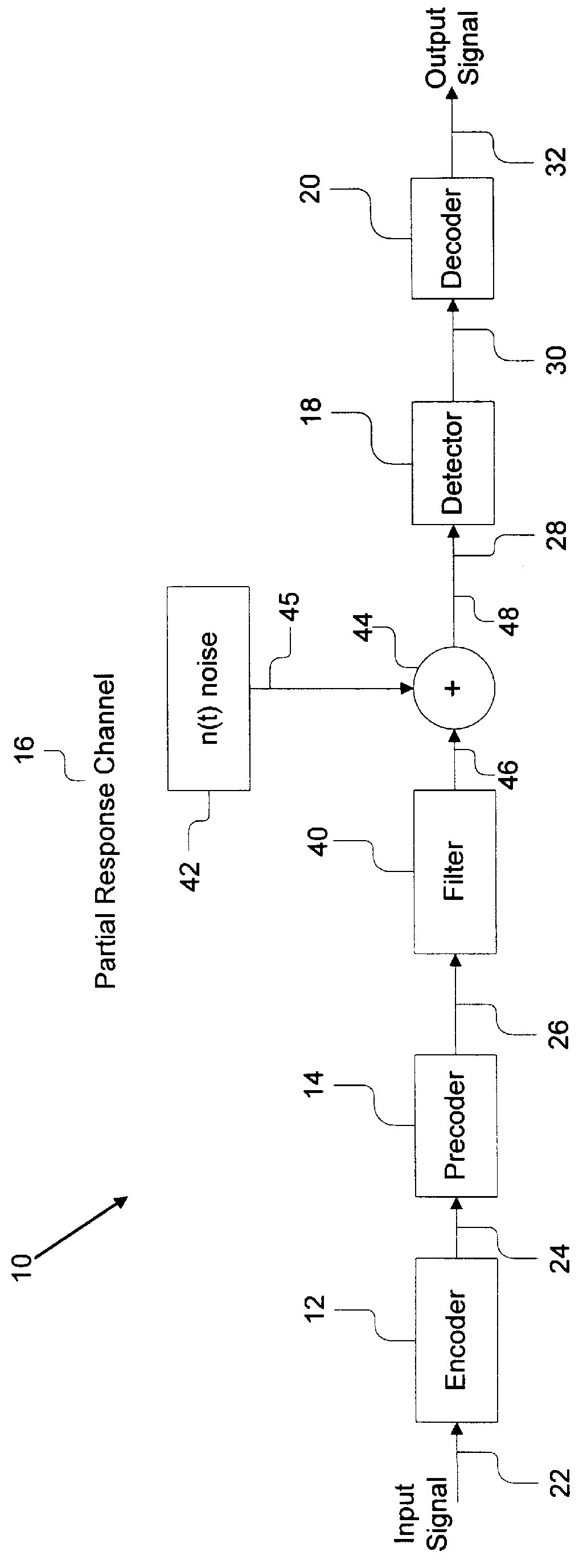
A system comprises an encoder, a precoder, a PRML channel, a detector, and a decoder. An input signal is received by the encoder. The encoder generates a code string by adding one or more bits and outputs the code string to the precoder. The encoder applies encoding such that the code string after passing through the precoder has a Hamming distance greater than one to eliminate error events with a small distance at the output of the PRML channel. The present invention also provides codes that after precoding have Hamming distance of 2 and 0 mod 3 number of ones. These codes when used over a PRML channel in an interleaved manner preclude + / -( . . . 010-10 . . . ) error events and error events + / -( . . . 01000-10 . . . ). The code string also has a predetermined minimum number of ones at the output of the PRML channel to help derive a clock from the input signal. The encoder provides a "systematic" encoding scheme in which for many code strings the encoded bits are the same as the input bits used to generate the encoded bits. This systematic approach of the present invention provides an encoder that is easy to implement because a majority of the bits directly "feed through" and non-trivial logic circuits are only needed to generate the control bits. The systematic encoding also dictates a decoder that is likewise easy to construct and can be implemented in a circuit that simply discards the control bit. The encoder preferably comprises a serial-to-parallel converter, a code generator, and a parallel-to-serial converter. The code generator produces a rate 16 / 18 or 16 / 17 code. The present invention also includes a method that is directed to encoding bit strings and comprises the steps of: 1) converting the input strings to input bits, and 2) adding at least one bit to produce an encoded string with many ones and a Hamming distance greater than one after precoding.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Transcoder and imaging apparatus for converting an encoding system of video signal
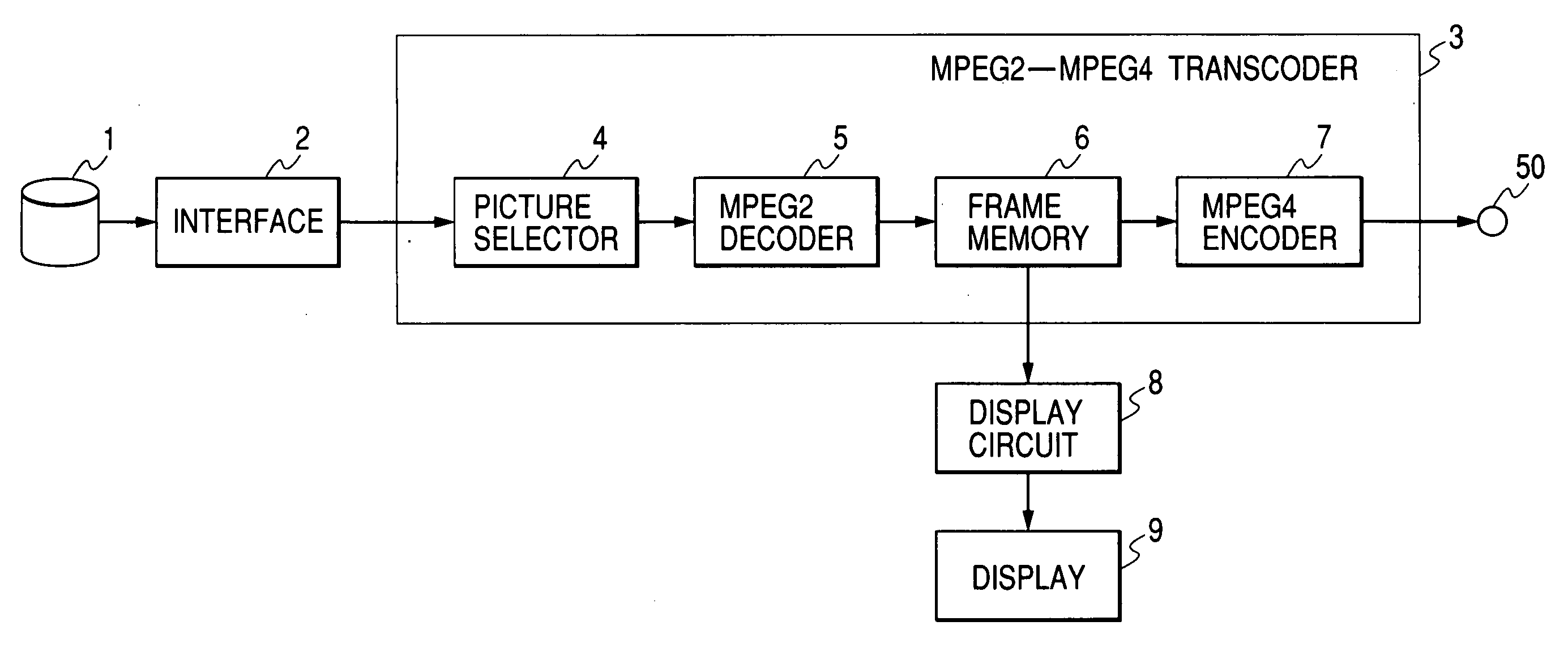
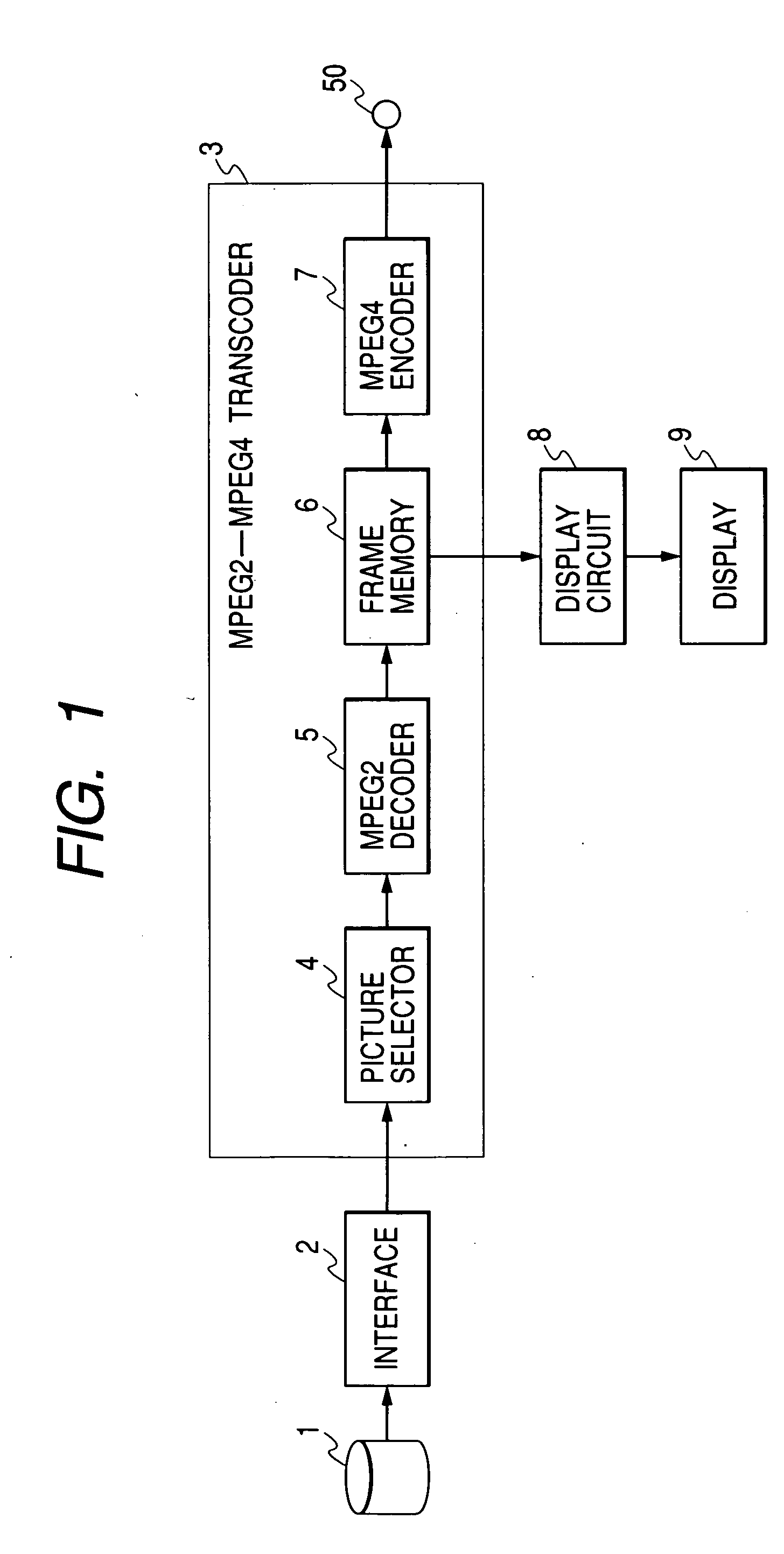
InactiveUS20050047501A1Shorten transcoding timeShorten the timeTelevision system detailsCode conversionEffective lengthImaging equipment
The time required to transcode an encoded image signal to an image signal encoded by a different encoding method is reduced. Disclosed herein is a transcoder comprising: a picture selector 4 which extracts specific types of pictures (I- and P- pictures) from a first image signal (MPEG2 stream) and generates a subset of the first image signal; a first decoder 5 which decodes the subset image signal; and a first encoder 7 which encodes the decoded image signal to a second image signal (MPEG4 stream). The picture selector 4 uses the extracted pictures to generate the subset image signal with a reduced effective length.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
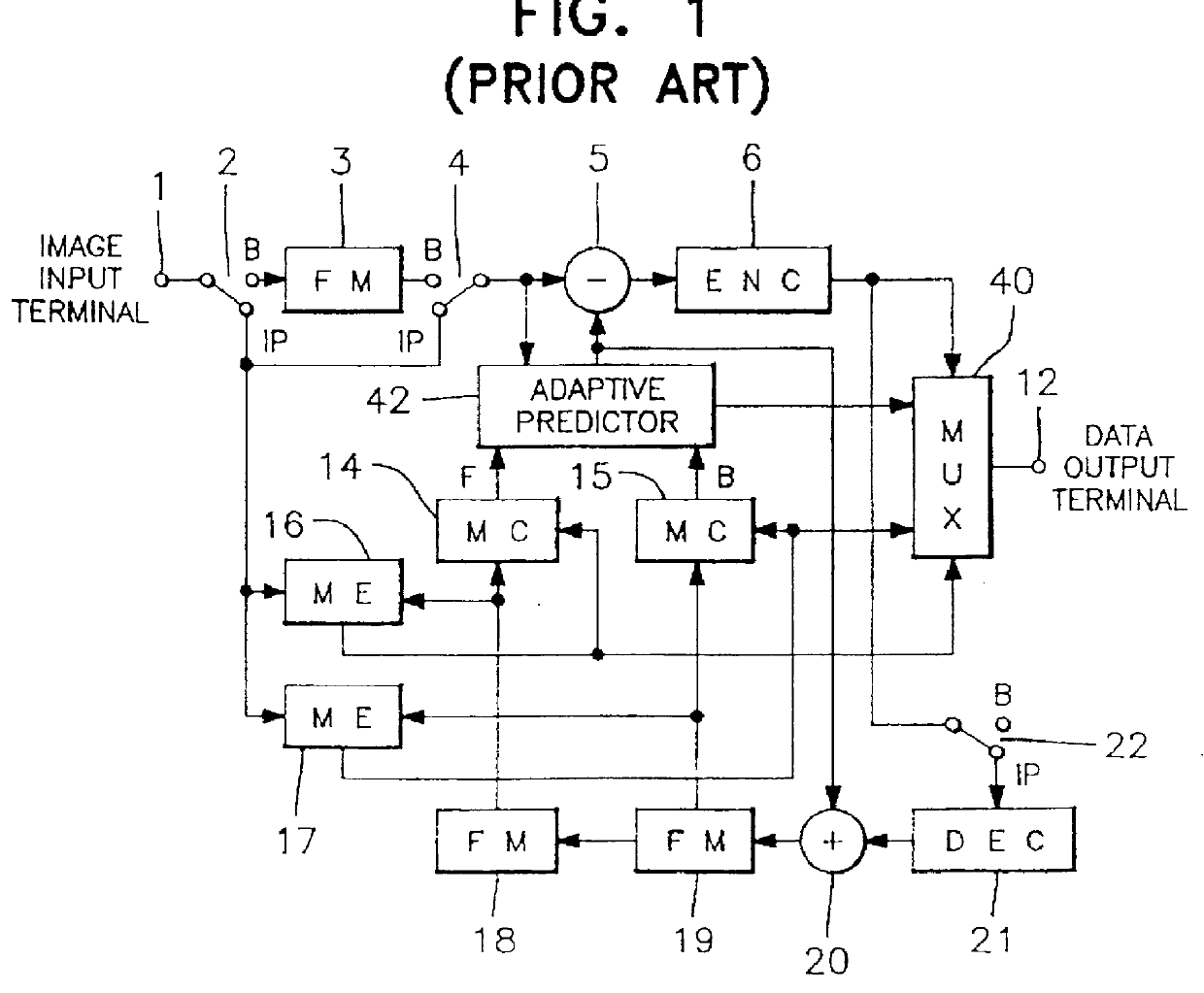
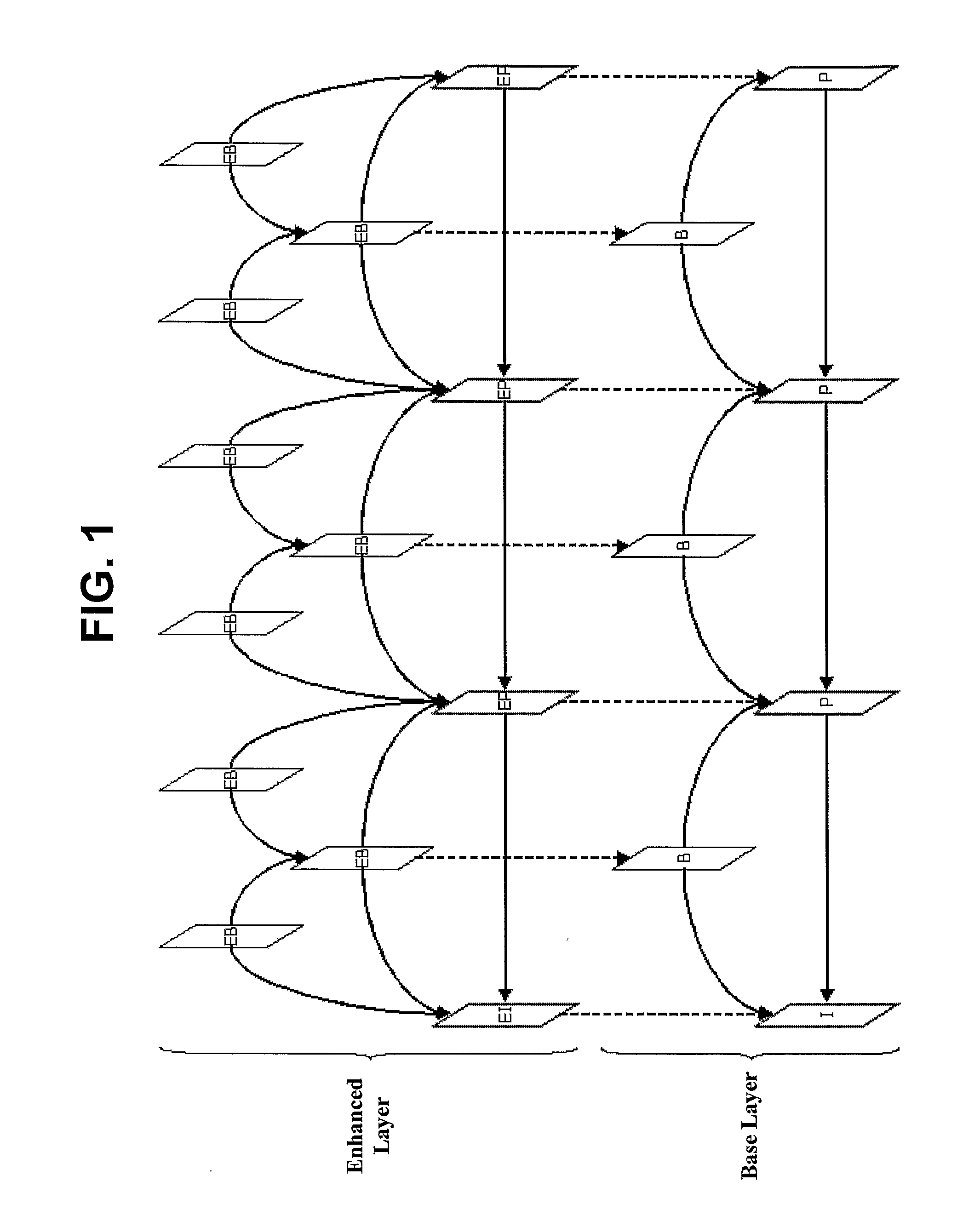
Method and Apparatus for Scalably Encoding/Decoding Video Signal
InactiveUS20090168880A1Reduce screen sizeColor television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionMotion vectorComputer science
The present invention relates to a method that uses a motion vector of a predictive video frame of a sub-layer to encode a video signal and decode encoded video data. The method encodes a video signal using a preset method to a bit stream of a base layer while encoding the video signal using a scalable MCTF method to a bit stream of an enhanced layer. When an arbitrary frame of the video signal is encoded, information, enabling at least one vector, derived from a first motion vector of a first block included in the bit stream of the base layer in the same direction as the first motion vector, to be used as a motion vector of an image block in the arbitrary frame, is recorded in the bit stream of the enhanced layer. The first motion vector is directed in the same direction as a temporal direction from the arbitrary frame to the first block.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
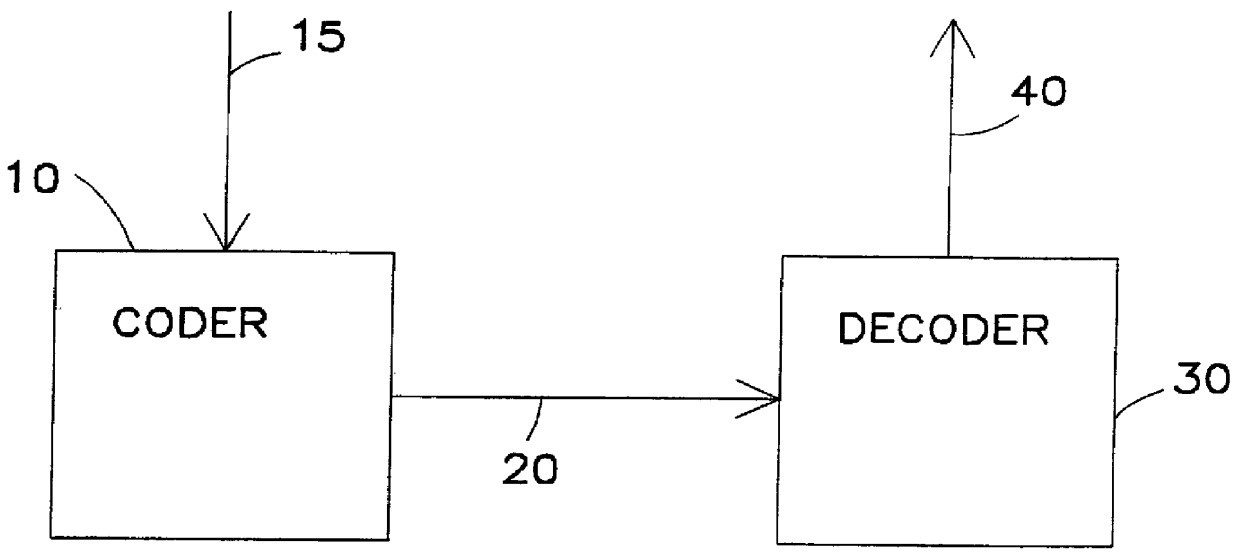
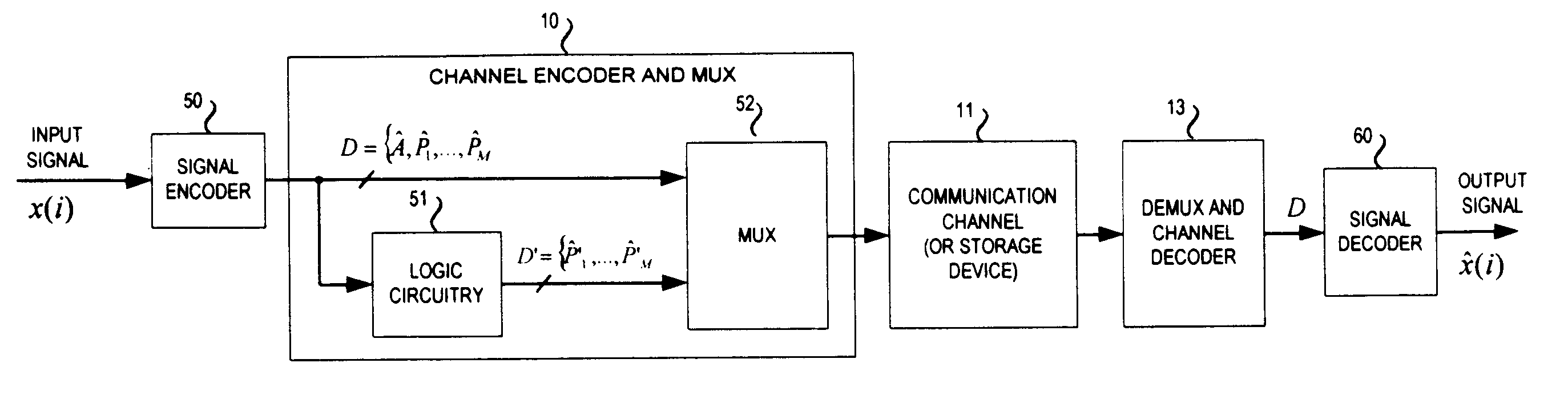
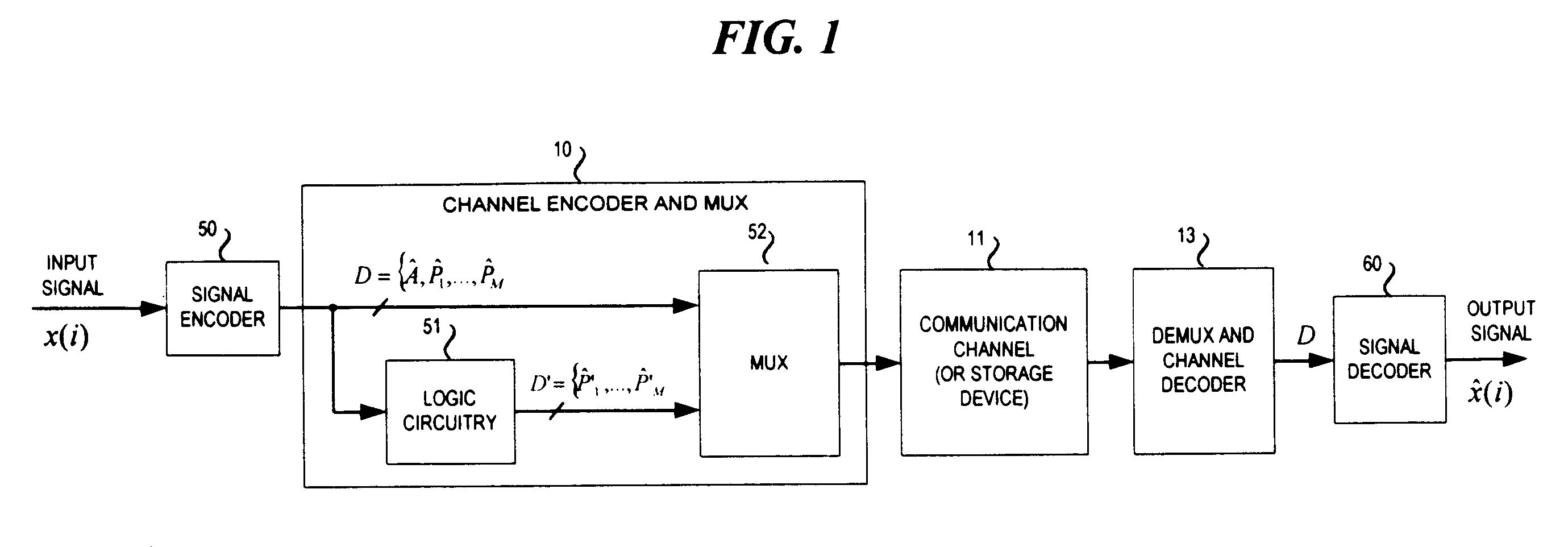
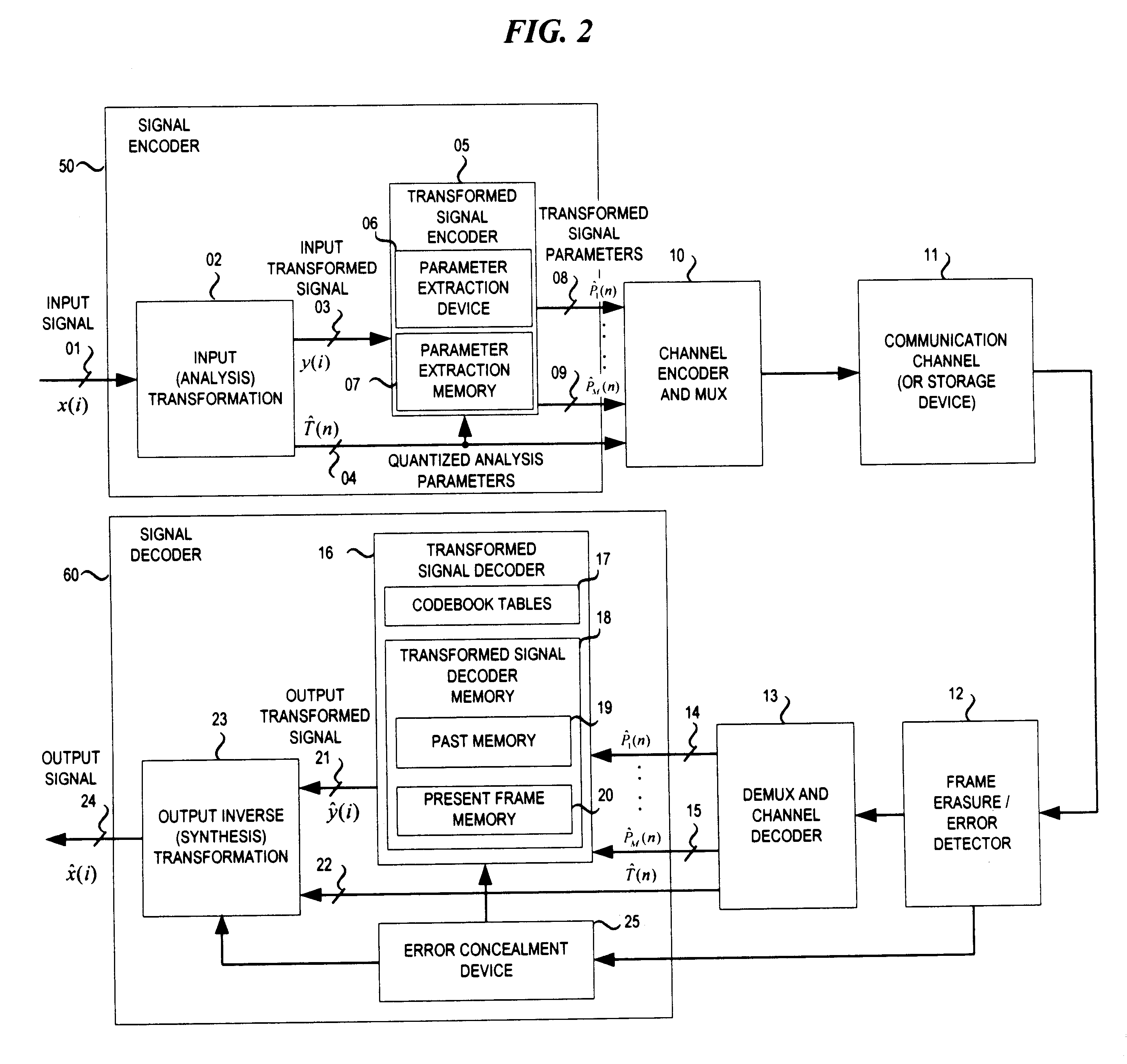
Signal coding and decoding method and device, and coding and decoding system
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
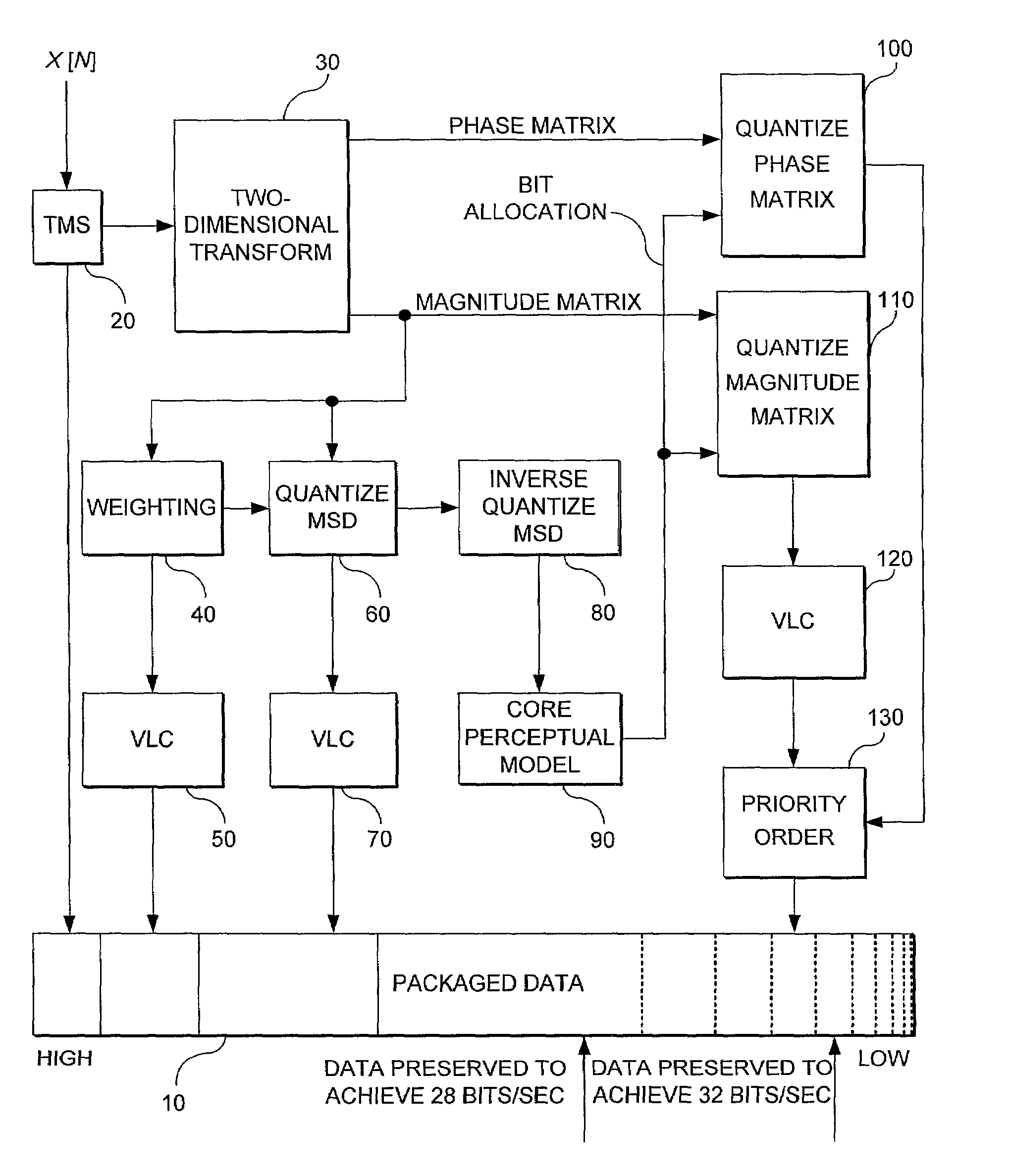
Scalable and perceptually ranked signal coding and decoding
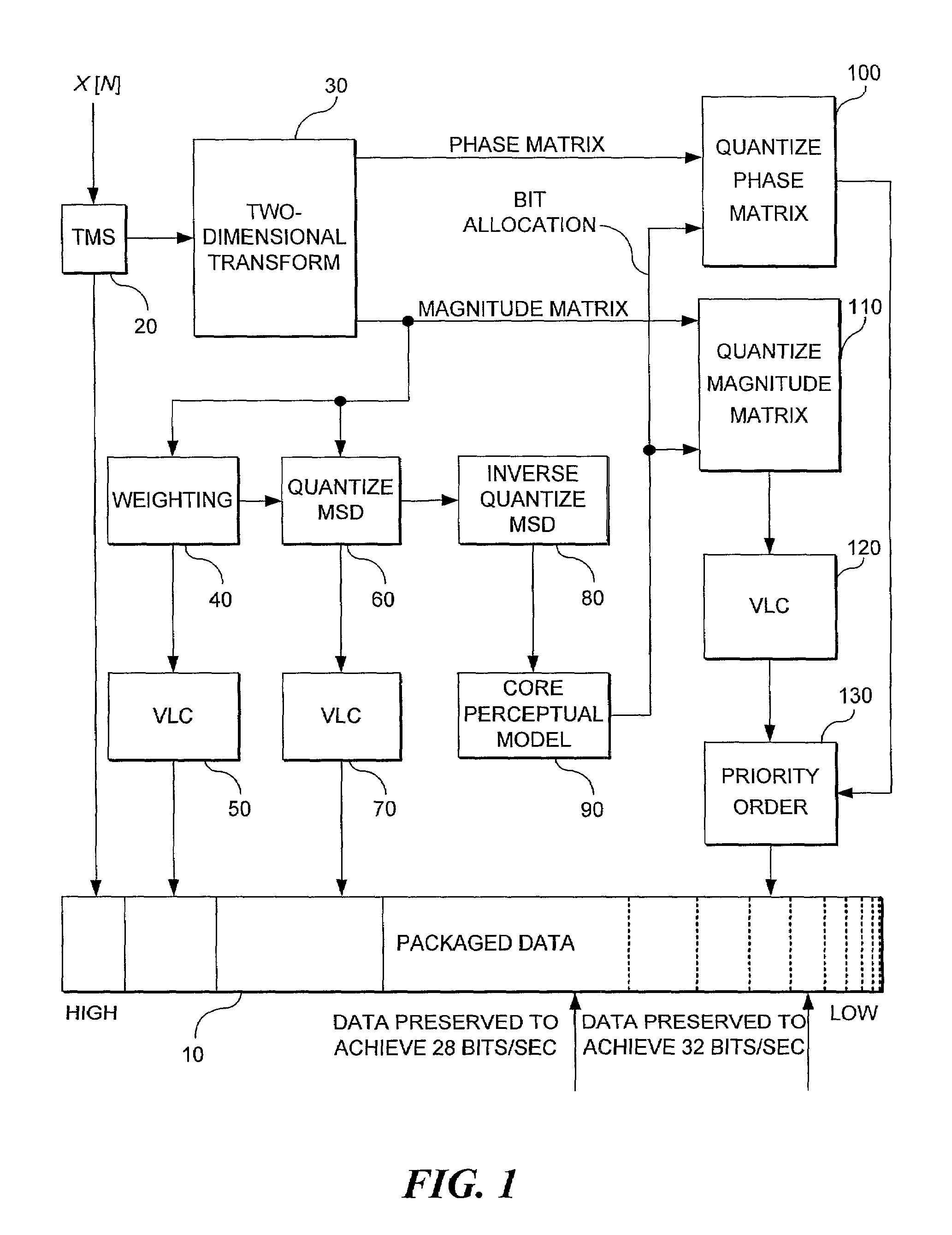
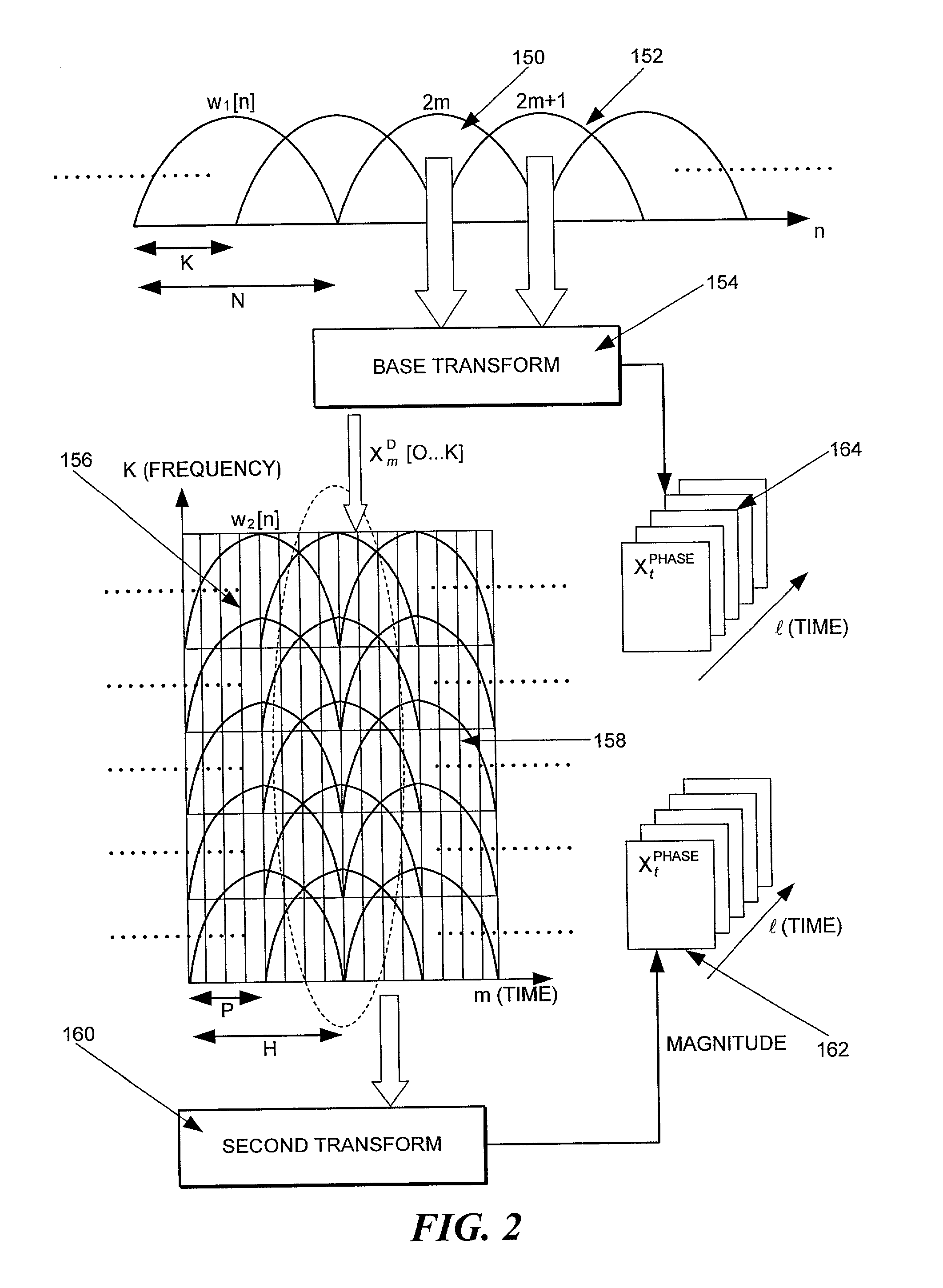
A method and system for encoding and decoding an input signal in relation to the most perceptually relevant aspects of the input signal. A two-dimensional (2D) transform is applied to the input signal to produce a magnitude matrix and a phase matrix that can be inverse quantized by a decoder. A first column of coefficients of the magnitude matrix represents a mean spectral density (MSD) function of the input signal. Relevant aspects of the MSD function are encoded at a beginning of a data packet. The MSD function is also processed through a core perception model to determine bit allocation. The matrices are then quantized and priority ordered into a data packet, with the least perceptually relevant information at the end of the packet so that it may be ignored or truncated for scalability to the channel data rate capacity.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
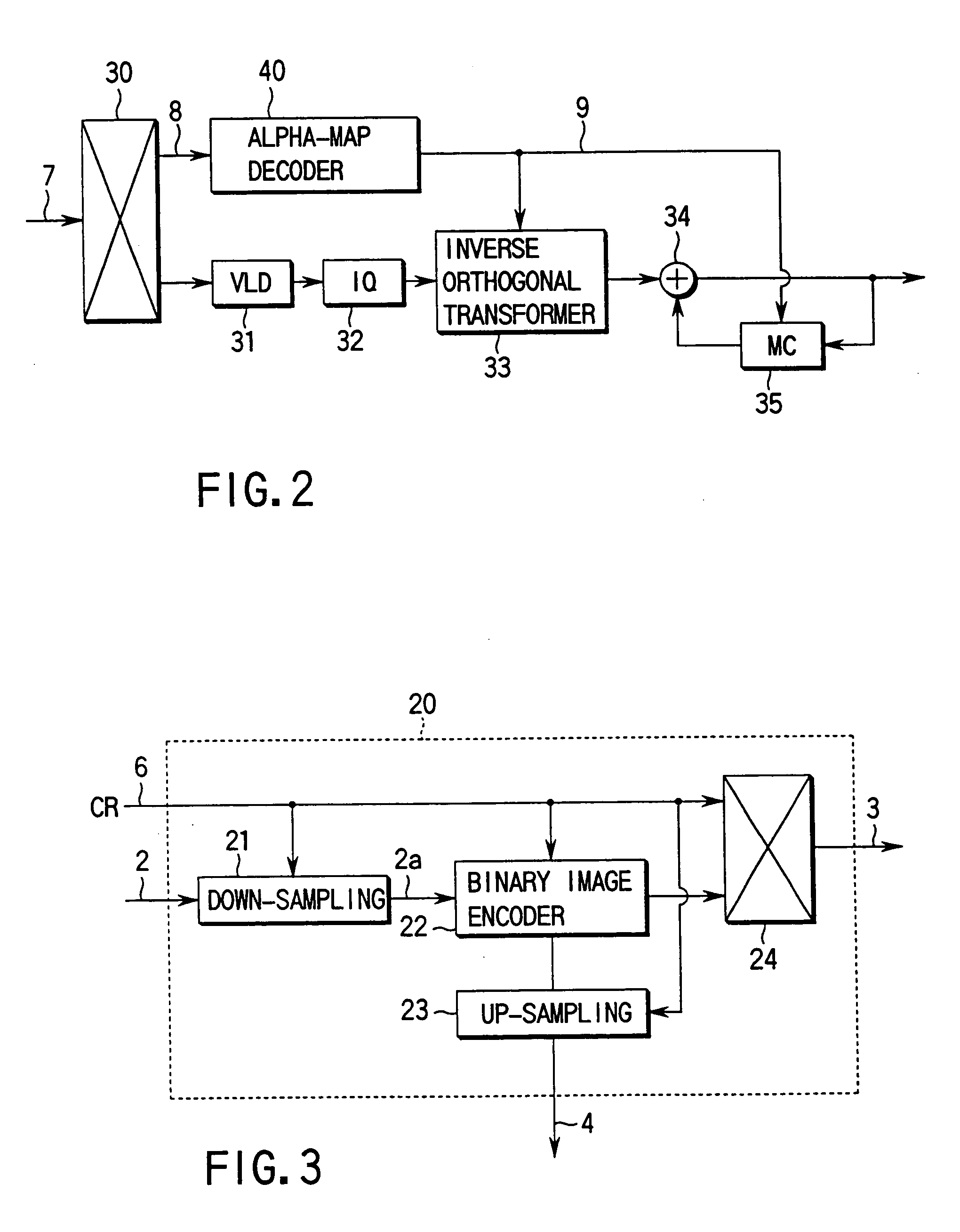
Video encoding apparatus and video decoding apparatus
InactiveUS20040091049A1Reduce in quantityReduce the numberGeometric image transformationPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMotion vectorSignal on
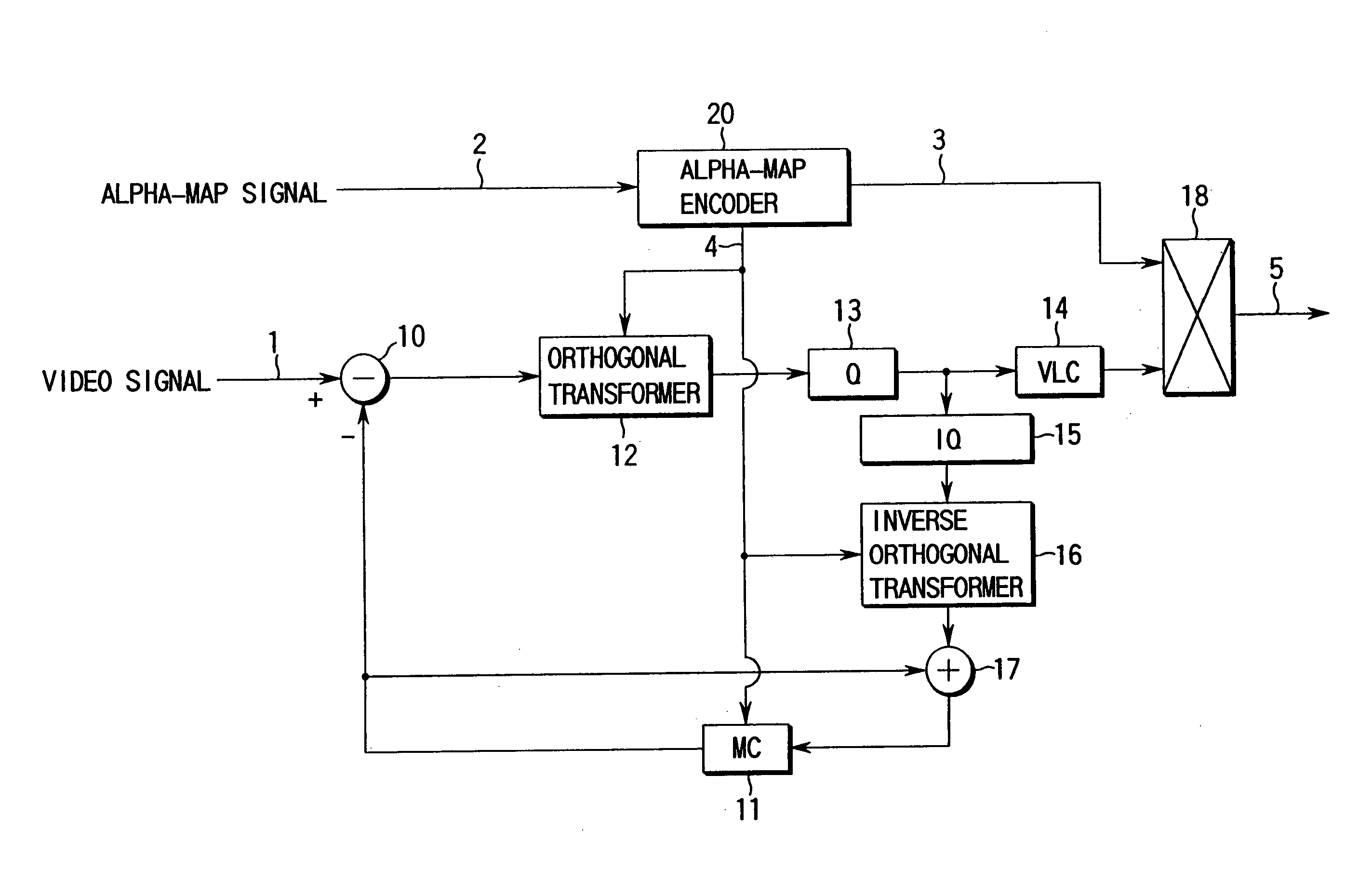
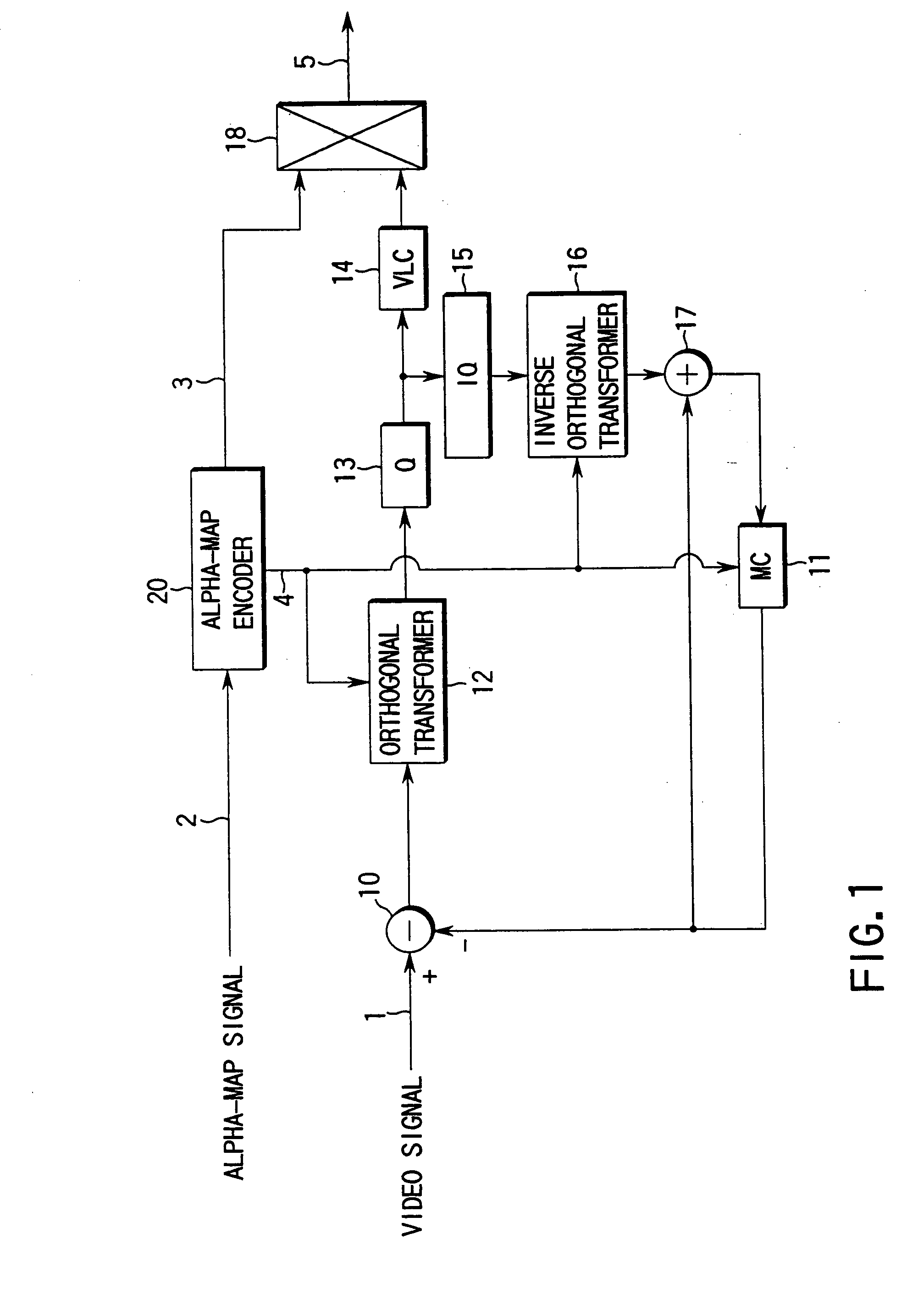
An alpha-map encoding apparatus includes a first down-sampling circuit (21) for down-sampling an alpha-map signal which represents the shape of an object and the position in the frame of the object at a down-sampling ratio based on size conversion ratio information, an up-sampling circuit (23) for up-sampling the alpha-map signal at an up-sampling ratio based on size conversion ratio information given to restore the down-sampled alpha-map signal to an original size, and outputting a local decoded alpha-map signal, a motion estimation / compensation circuit (25) for generating a motion estimation / compensation signal on the basis of the previous decoded video signal and a motion vector signal, a second down-sampling circuit (26) for down-sampling the motion estimation / compensation signal at the down-sampling ratio, a binary image encoder for encoding the alpha-map signal down-sampled by the first down-sampling circuit to a binary image in accordance with the motion estimation / compensation signal down-sampled by the second down-sampling circuit, and outputting an encoded binary image signal, and a multiplexer for multiplexing and outputting the encoded binary image signal and the up-sampling ratio information.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Redundant compression techniques for transmitting data over degraded communication links and/or storing data on media subject to degradation
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Video signal coding apparatus and video signal coding method
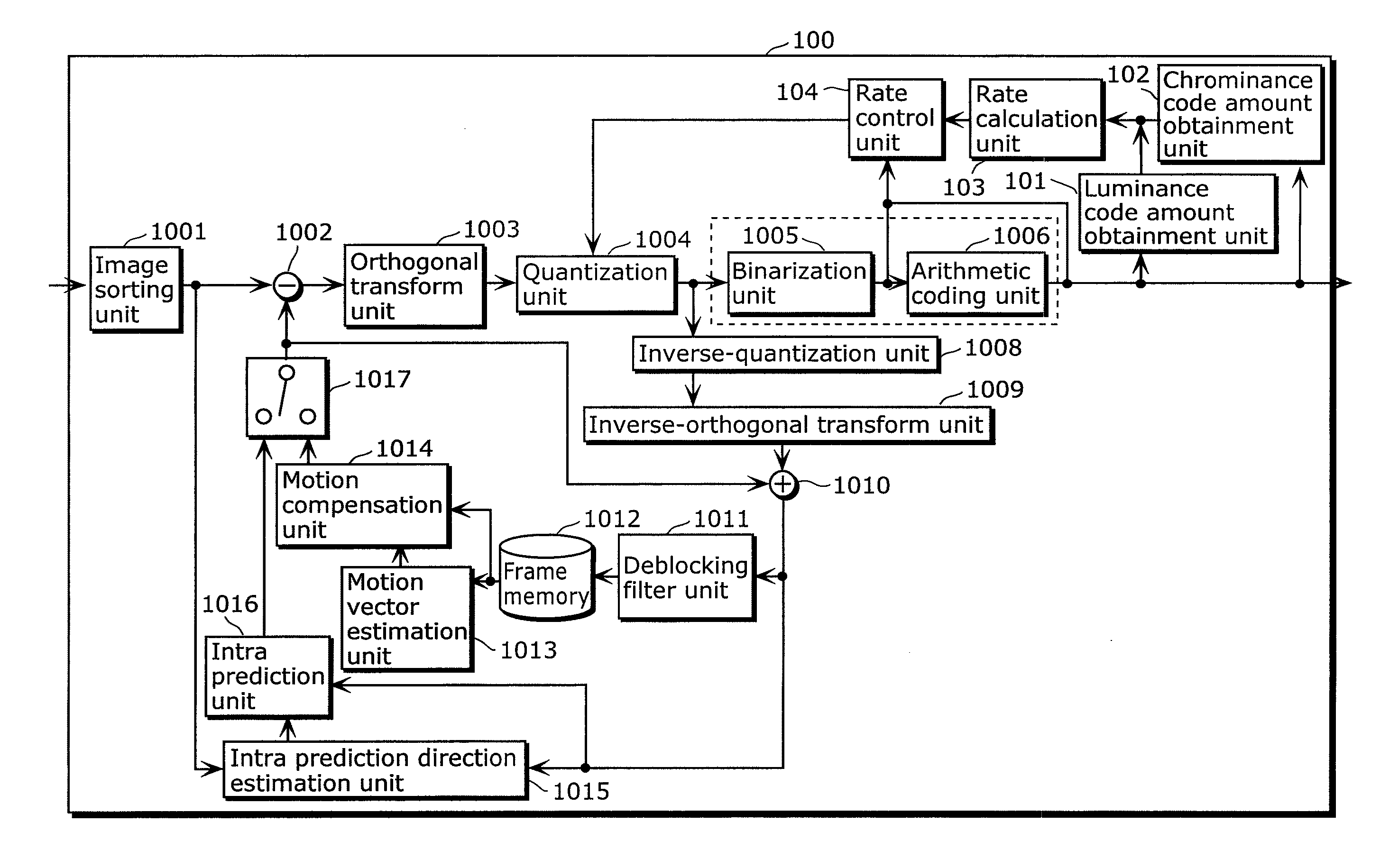
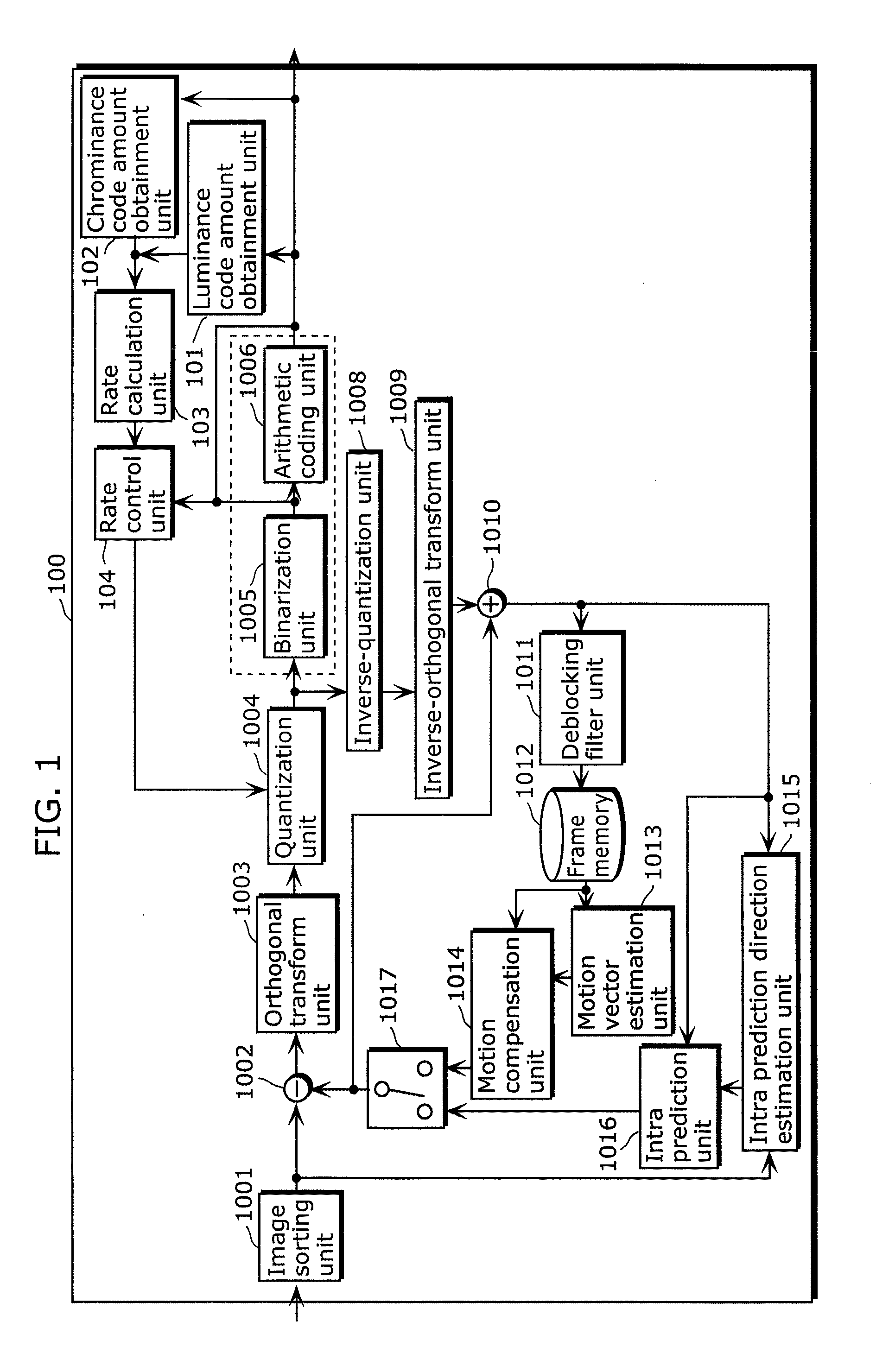
ActiveUS20100202513A1Improve image qualityAmount of codeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionParallel computingQuantization matrix
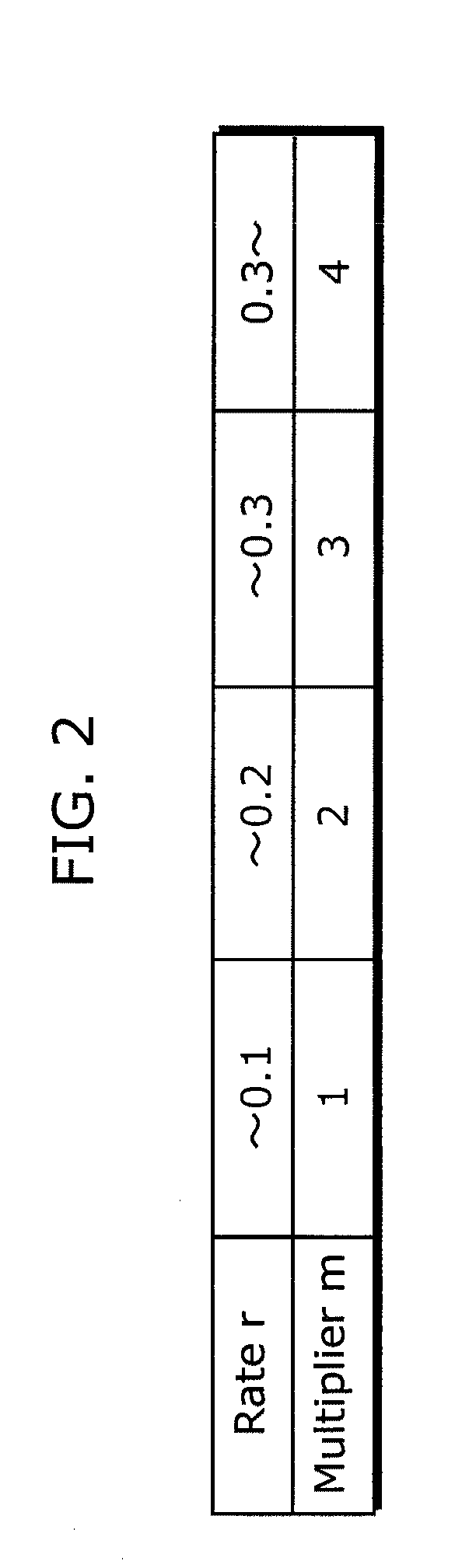
Video signal coding apparatus includes: a quantization unit which quantizes, using coefficient values in a first quantization matrix, a luminance signal of each of a first picture and a second picture coded after the first picture, and quantizes, using coefficient values in a second quantization matrix, a chrominance signal of each of the first picture and the second picture; a code amount obtainment unit which obtains a luminance code amount and a chrominance code amount of each of the first picture and the second picture; a rate calculation unit which calculates a rate of the chrominance code amount with respect to the luminance code amount for each of the first picture and the second picture, obtained by the code amount obtainment unit; and a rate control unit which changes a coefficient value of at least one of the first matrix and the second matrix used in quantizing the second picture, before the quantization unit quantizes the second picture, so that the rate for the second picture becomes smaller than the rate for the first picture.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
All-digital satellite signal simulated source
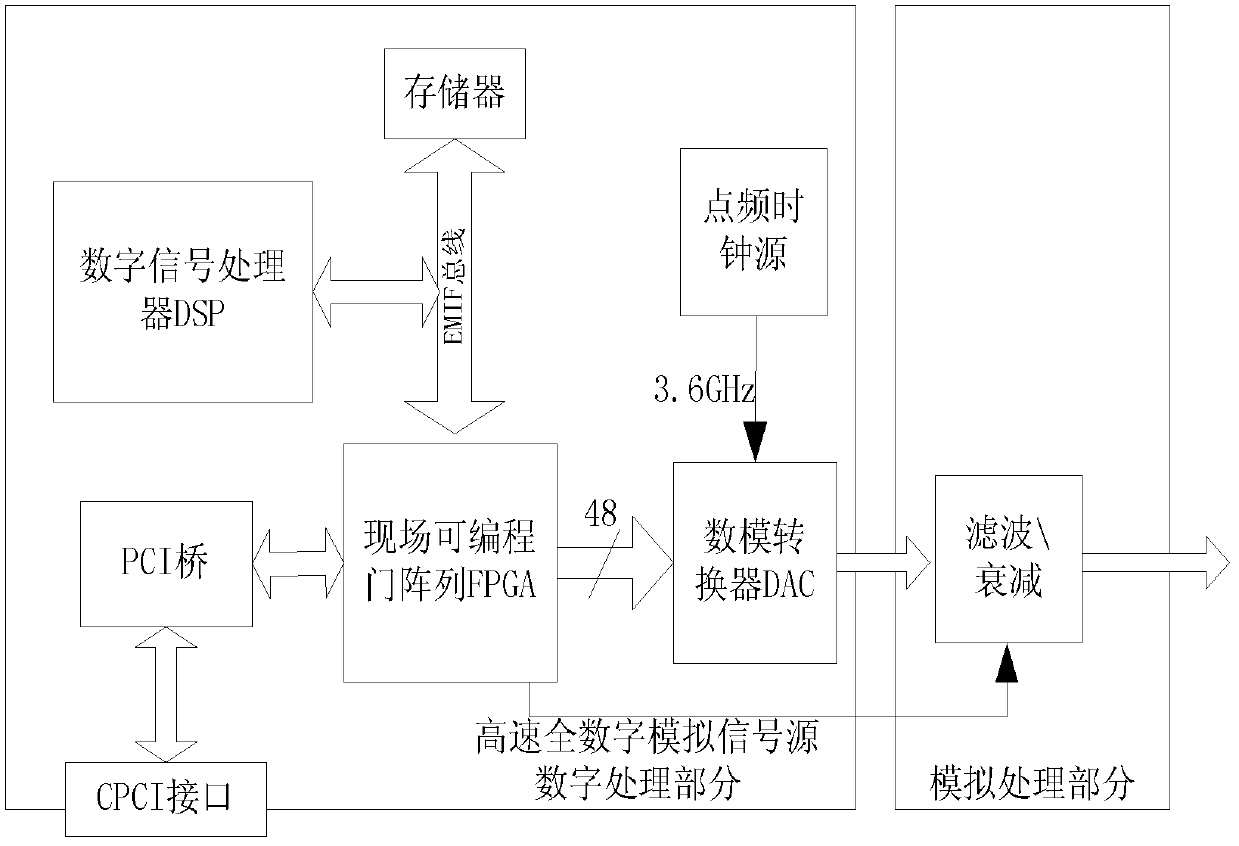
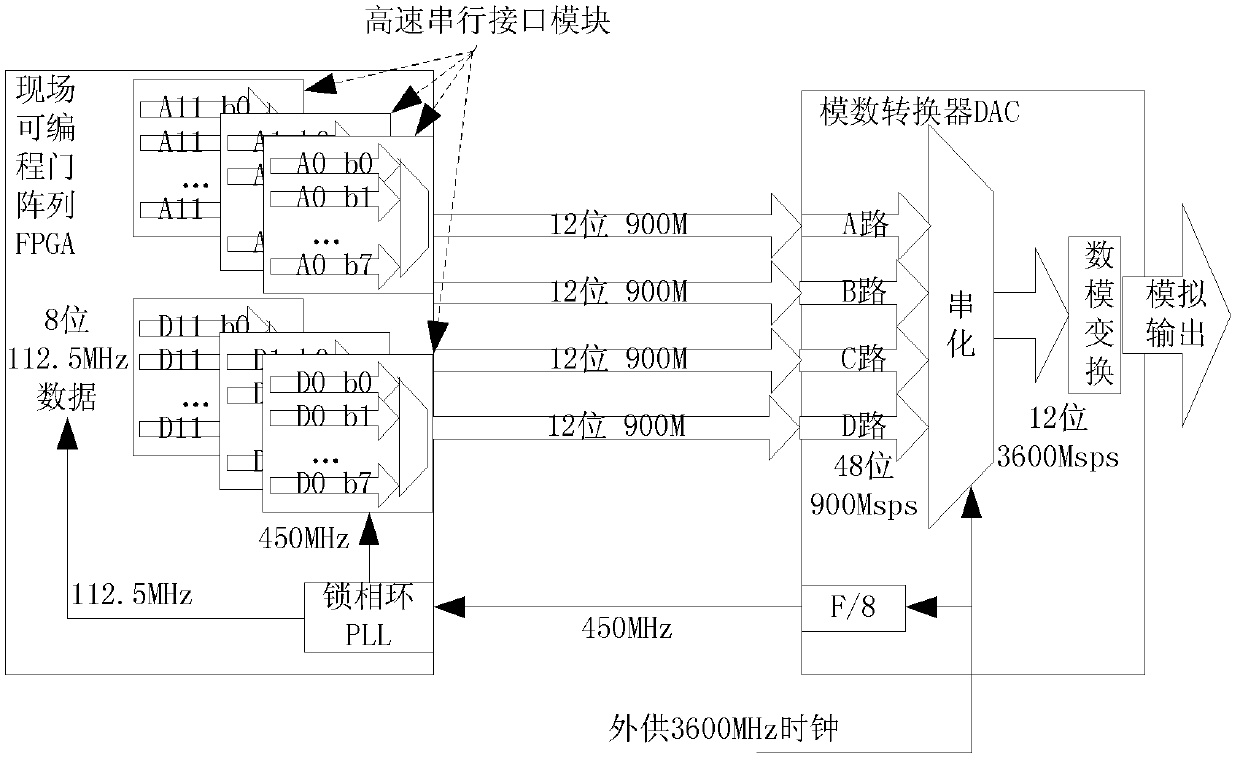
InactiveCN102710316AIntegrity guaranteedFlexible configurationRadio transmissionSymbol rateHigh-Speed Serial Interface
The invention provides an all-digital satellite signal simulated source. The all-digital satellite signal simulated source comprises a double-port storage, the double-port storage is a FPGA which provides interfaces for various rate conversions between coding and modulation, is connected with a digital to analog converter through a high-speed serial interface to form a core hardware framework of the satellite signal simulated source, and is connected with a broadband filter directly through a simulation output end to produce multimode high and moderate frequency broadband satellite signal simulated signals with code rates which can vary continuously, a digital signal processor serves as a main control device of the simulated source and performs analysis of various parameters issued by a monitor and parameter configuration of the FPGA, a 32-channel parallel modulation system is arranged inside the FPGA, for example, a 32-channel direct digital synthesizer (DDS) performs parallel output and composition of the central frequency, the FPGA determines the overturn of the carrier phase according to a symbol rate and a main frequency of parallel calculation, IQ two-channel signals, signal coding, code conversion and quadrature modulation are produced through a logical algorithm, a Q channel uniformization coefficient is calculated according to an IQ unbalanced parameter, Q channel uniformization coefficient and the Q channel signal amplitude are subjected to multiply-add arithmetic to calculate the Q channel amplitude, IQ is added, and a unbalanced quadrature phase shift keying (UQPSK) modulation method is simulated.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
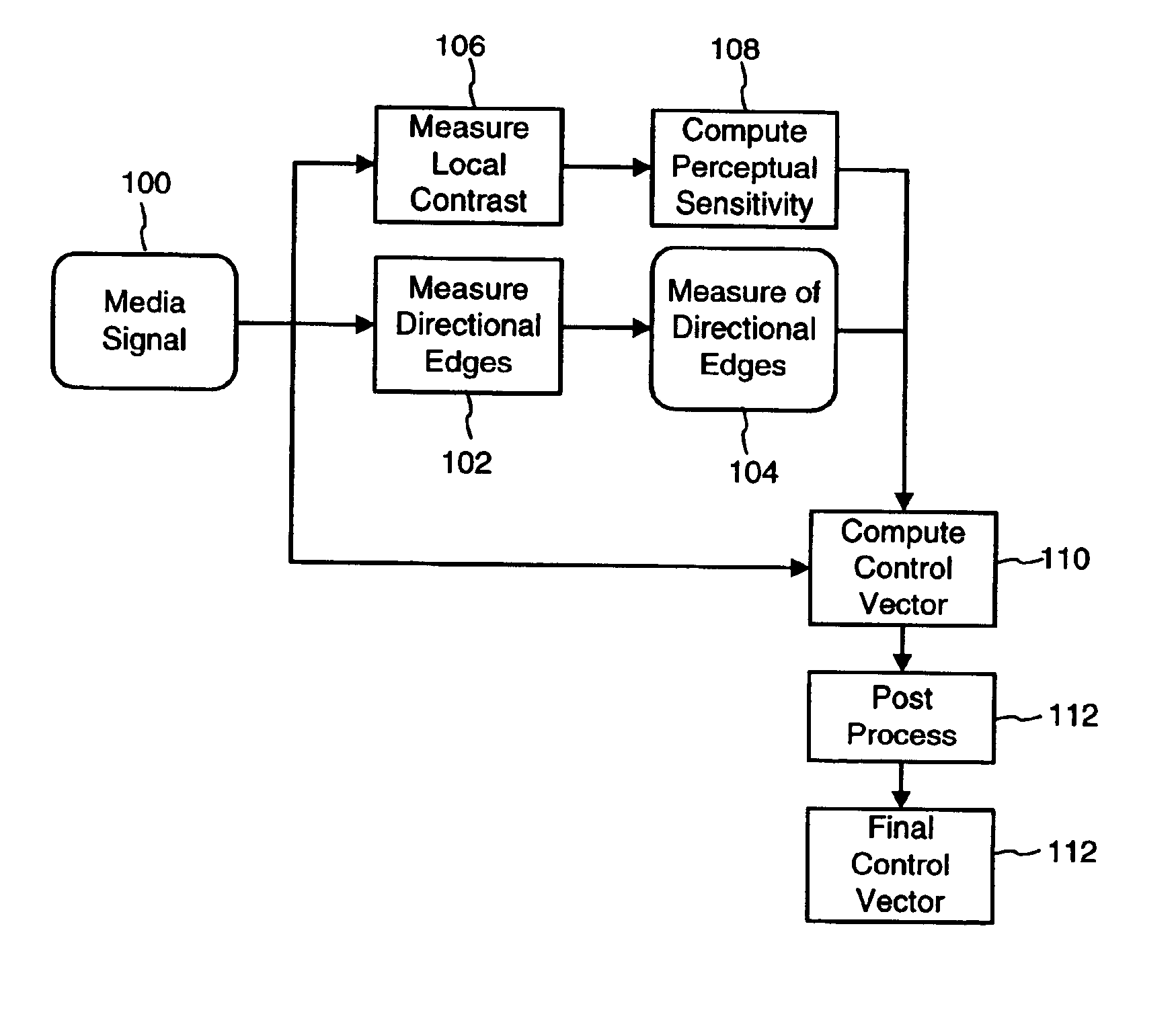
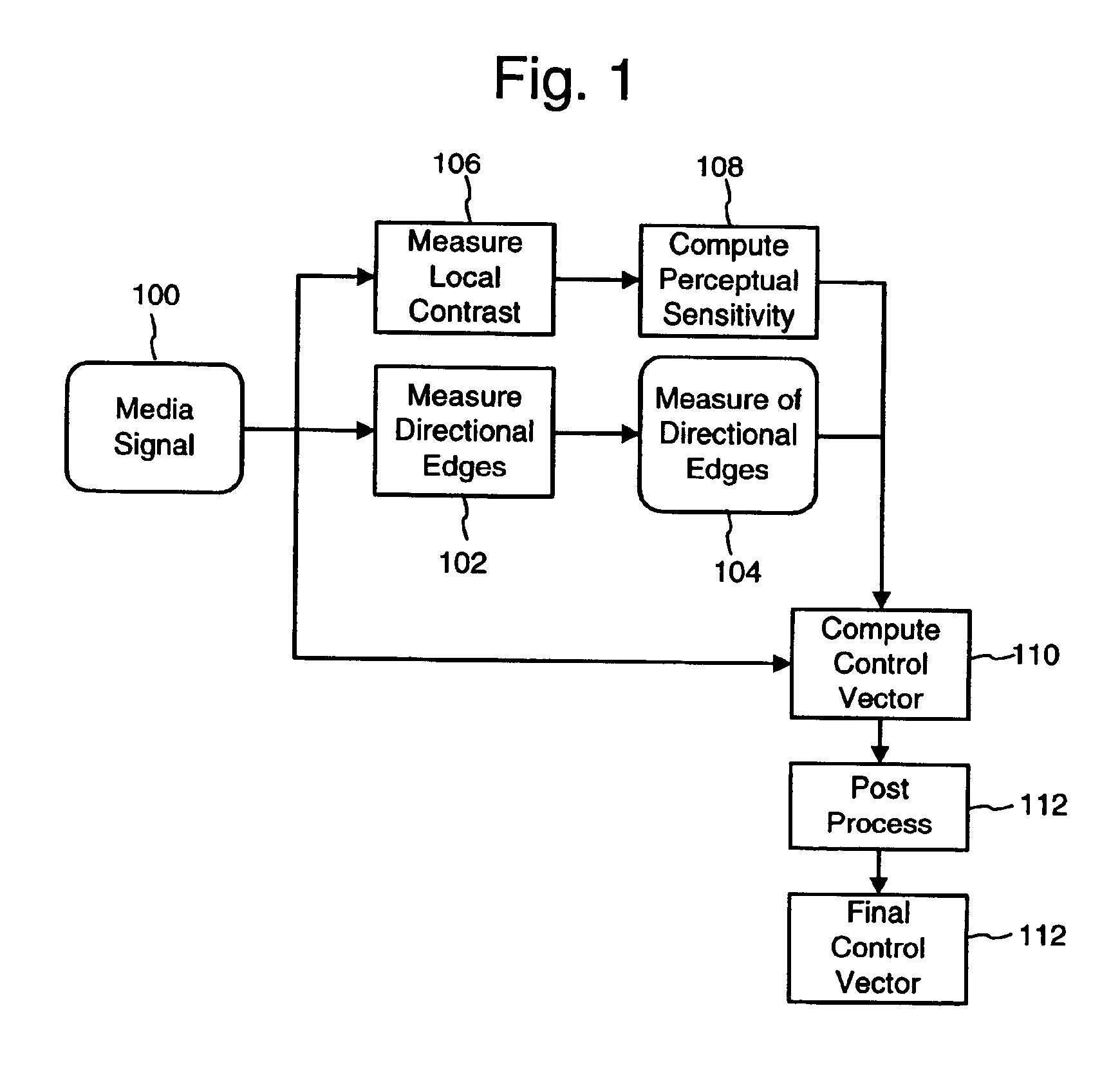
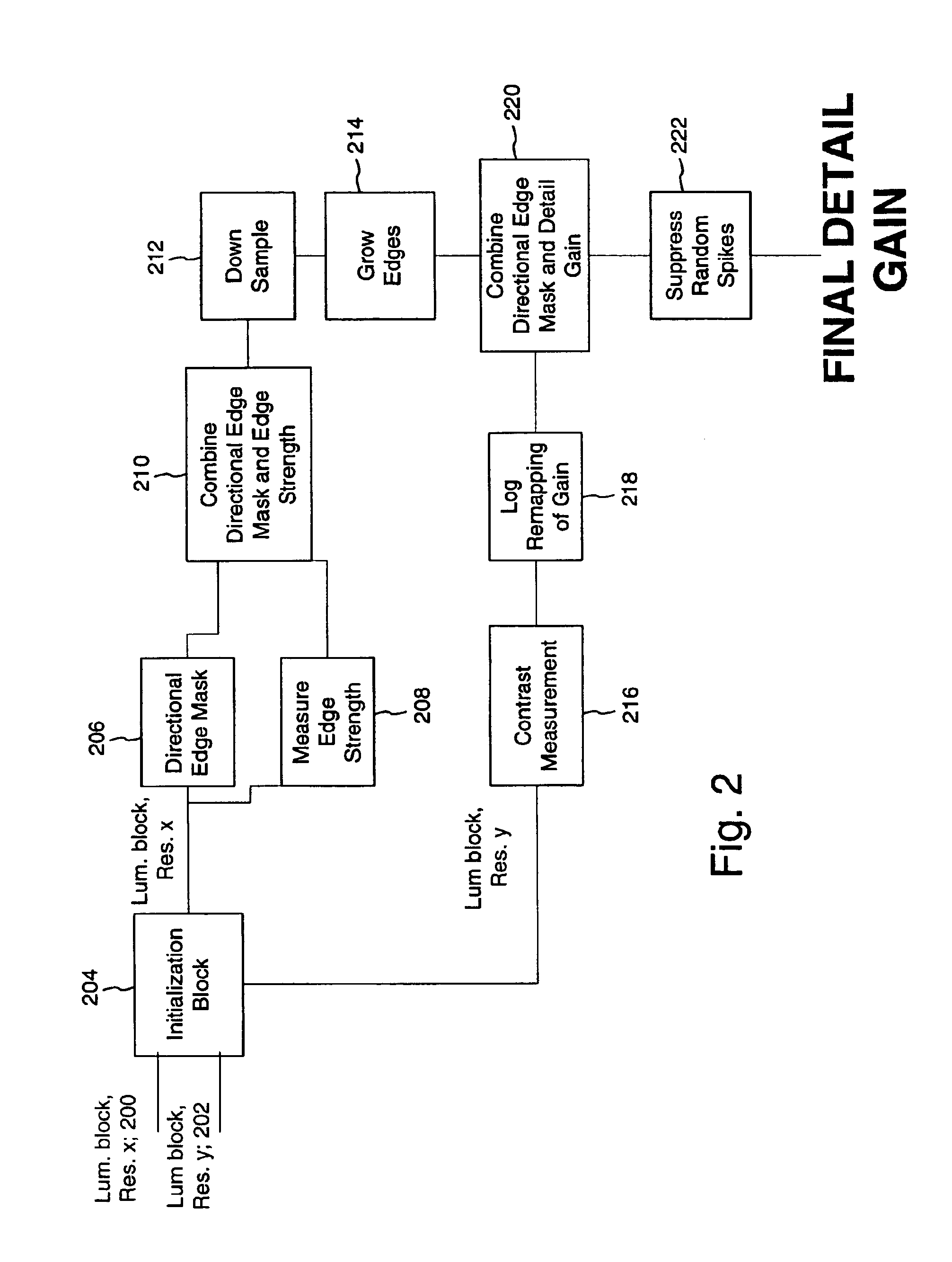
Perceptual modeling of media signals based on local contrast and directional edges
InactiveUS7088844B2Reduce memoryAttenuation bandwidthUser identity/authority verificationCharacter and pattern recognitionData compressionMediaFLO
A perceptual model performs an analysis of a media signal, such as an image or audio signal. The model may be used in media signal processing applications such as digital watermarking and data compression to reduce perceptibility of changes made to code the signal. In one implementation, a method of reducing human perceptibility of visible artifacts attributable to embedding a digital watermark in a media signal is provided. The method determines a contrast measurement for local areas of the media signal; adjusts a contrast measurement for a local area if the contrast measurement is above a predetermined level; and embeds the digital watermark in the local areas in a manner determined at least in part by their respective contrast measurement.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
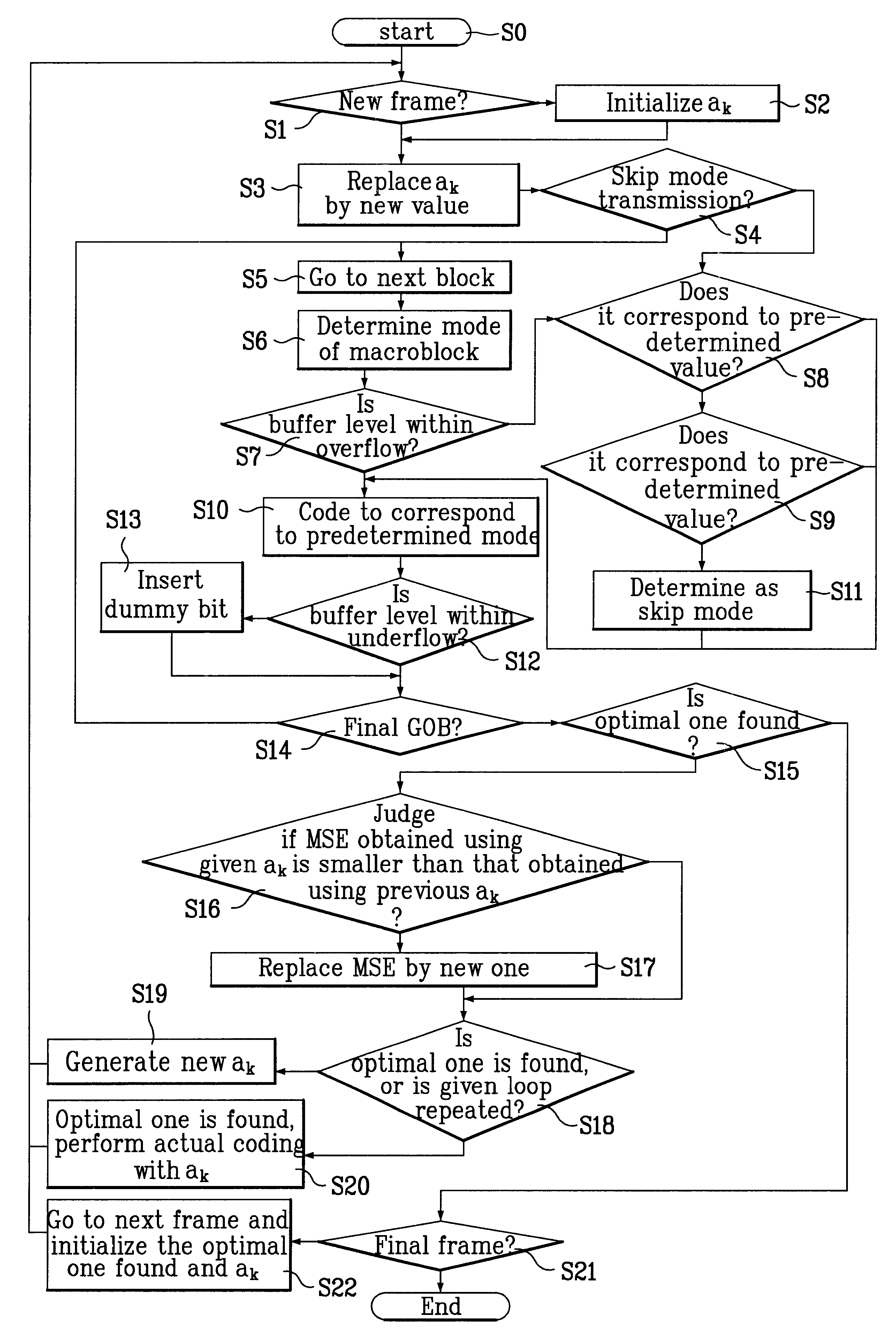
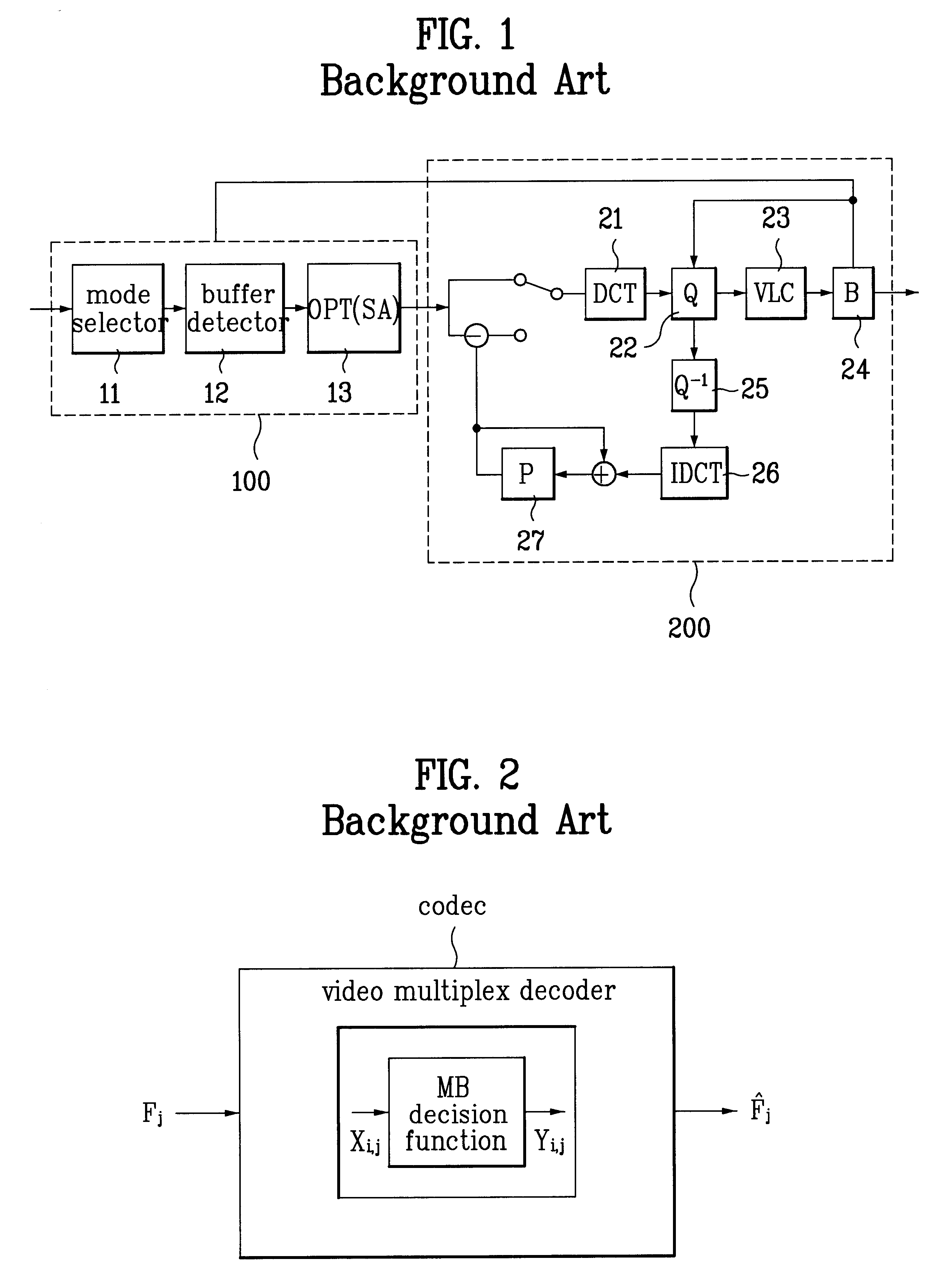
Video signal coding method
InactiveUS6507616B1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionInterframe codingAlgorithm
A video signal coding method is provided which finds proper decision curves according to characteristics of input frames and encodes the optimal macroblock by using the decision curves instead of a fixed motion / no-motion compensation curve and intra / inter coding curve. The optimal mode is selected for each macroblock of input frame and it is determined through a step of judging whether the input frame is intra mode using a given function, a step of judging whether the input frame is inter mode when it is not intra mode using a given function, a step of controlling quantizer using a predetermined critical value when it is not inter mode, and step of performing skip when the quantizer controlling step is not carried out.
Owner:LG ERICSSON
Audio coding apparatus, audio decoding apparatus, audio coding and decoding apparatus, and teleconferencing system
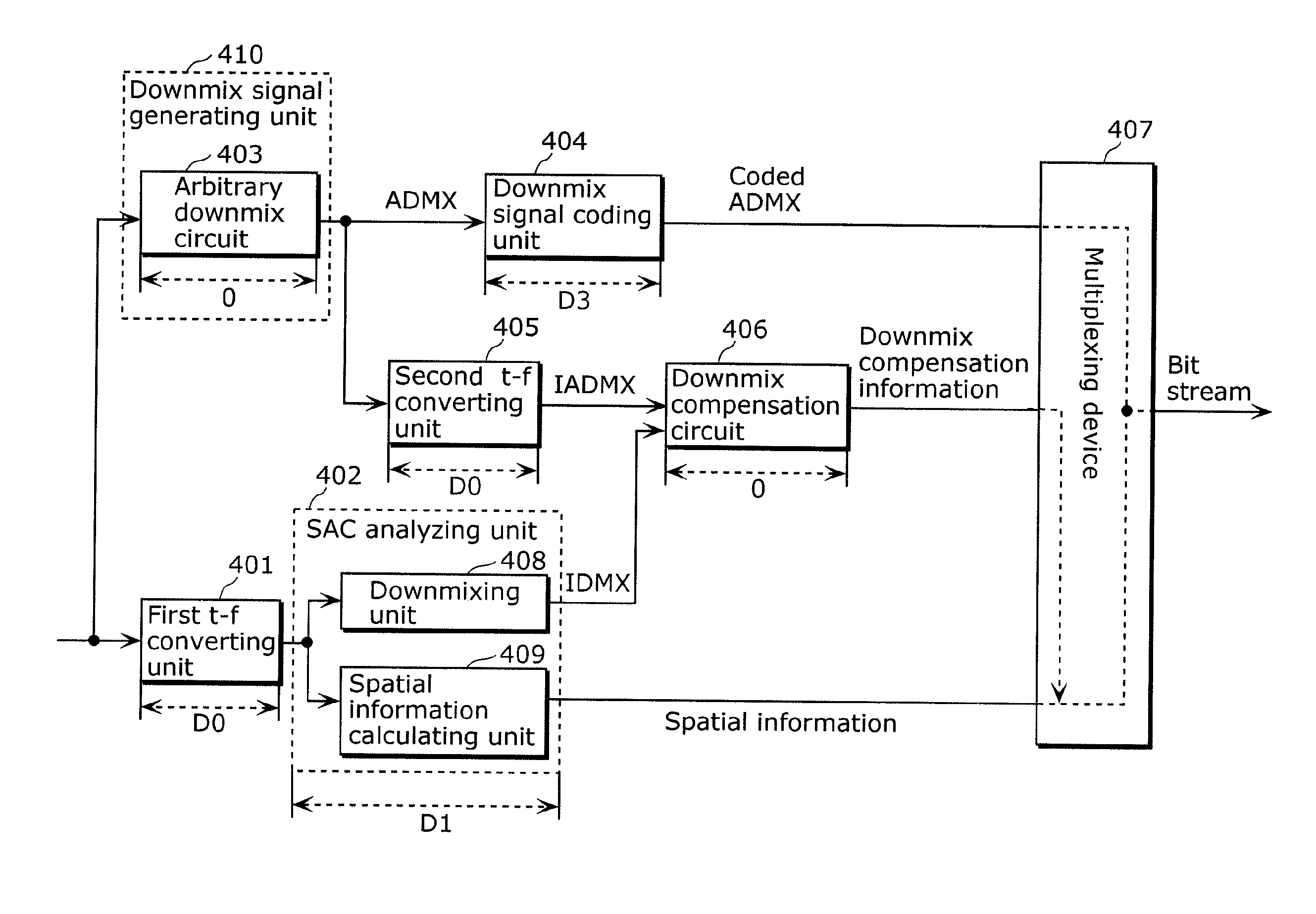
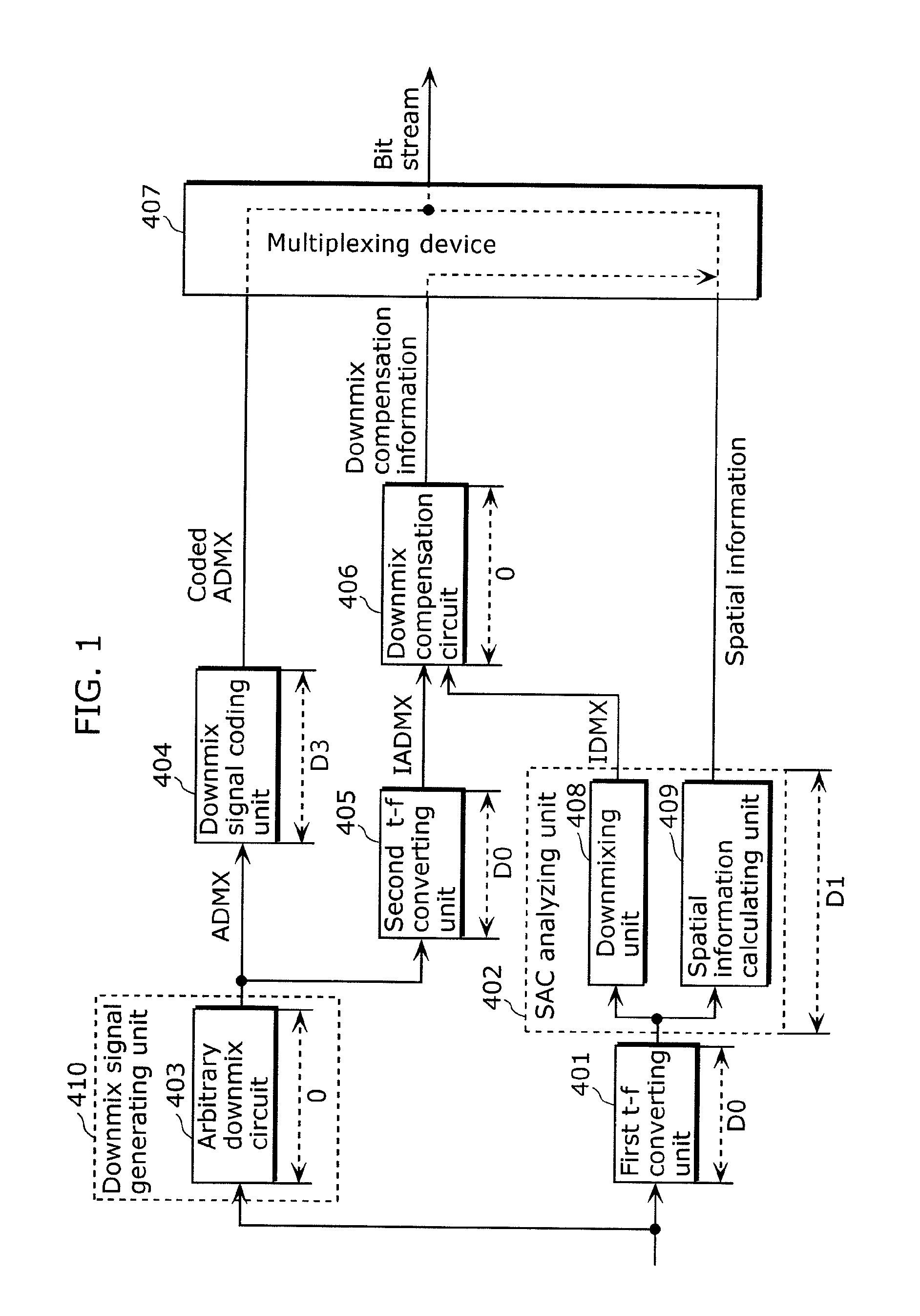
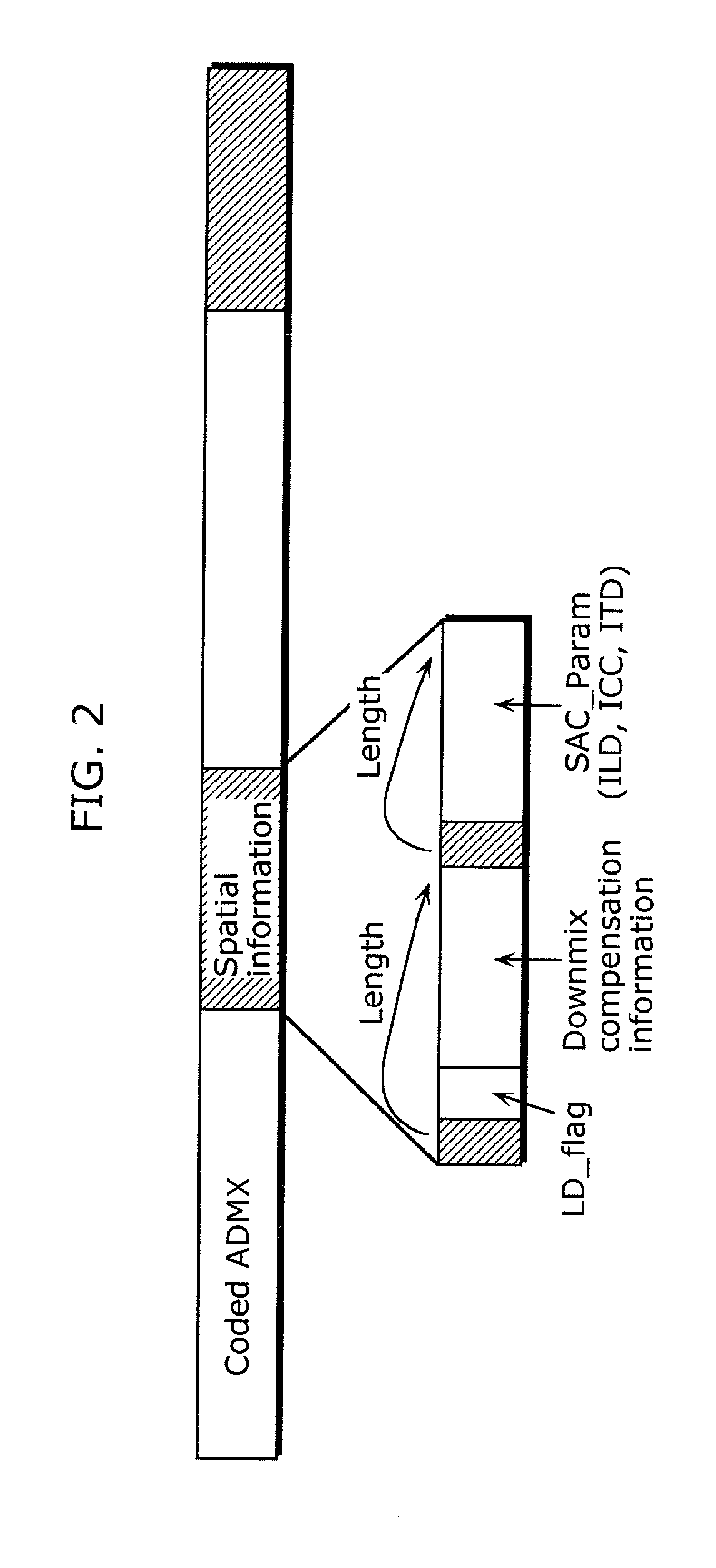
The delay in a multi-channel audio coding apparatus and a multi-channel audio decoding apparatus is reduced. The audio coding apparatus includes: a downmix signal generating unit (410) that generates, in a time domain, a first downmix signal that is one of a 1-channel audio signal and a 2-channel audio signal from an input multi-channel audio signal; a downmix signal coding unit (404) that codes the first downmix signal; a first t-f converting unit (401) that converts the input multi-channel audio signal into a multi-channel audio signal in a frequency domain; and a spatial information calculating unit (409) that generates spatial information for generating a multi-channel audio signal from a downmix signal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Synchronizer and synchronization method for quantum key distribution
ActiveCN101800636AReduce the impactHigh precision and wide rangeKey distribution for secure communicationError preventionFault toleranceControl signal
The invention relates to a synchronizer and a synchronization method for quantum key distribution. The synchronizer is characterized in that the signal output end of a synchronous signal coding module is connected with the signal input end of a synchronous laser transmitting module the signal output end of which is connected with the signal input end of a comparator circuit module through optical fibers; and the signal output ends of an optical detector and the comparator circuit module are respectively connected with the signal input ends of an adjustable time delay circuit which is used to generate door control signals and has adjustable time delay and a synchronous detection and coding module which counts by using one frame counter and codes the synchronous signals. The invention further provides a high-performance quantum key distribution system which uses single optical fiber to transmit signal light and synchronous light in a system with frequency of dozens of megahertz, realizes accurate synchronization of both systems, can realize synchronization again in the case of loss of the synchronization and improves the fault tolerance of the systems.
Owner:QUANTUMCTEK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com