Patents
Literature
421 results about "Direct digital synthesizer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
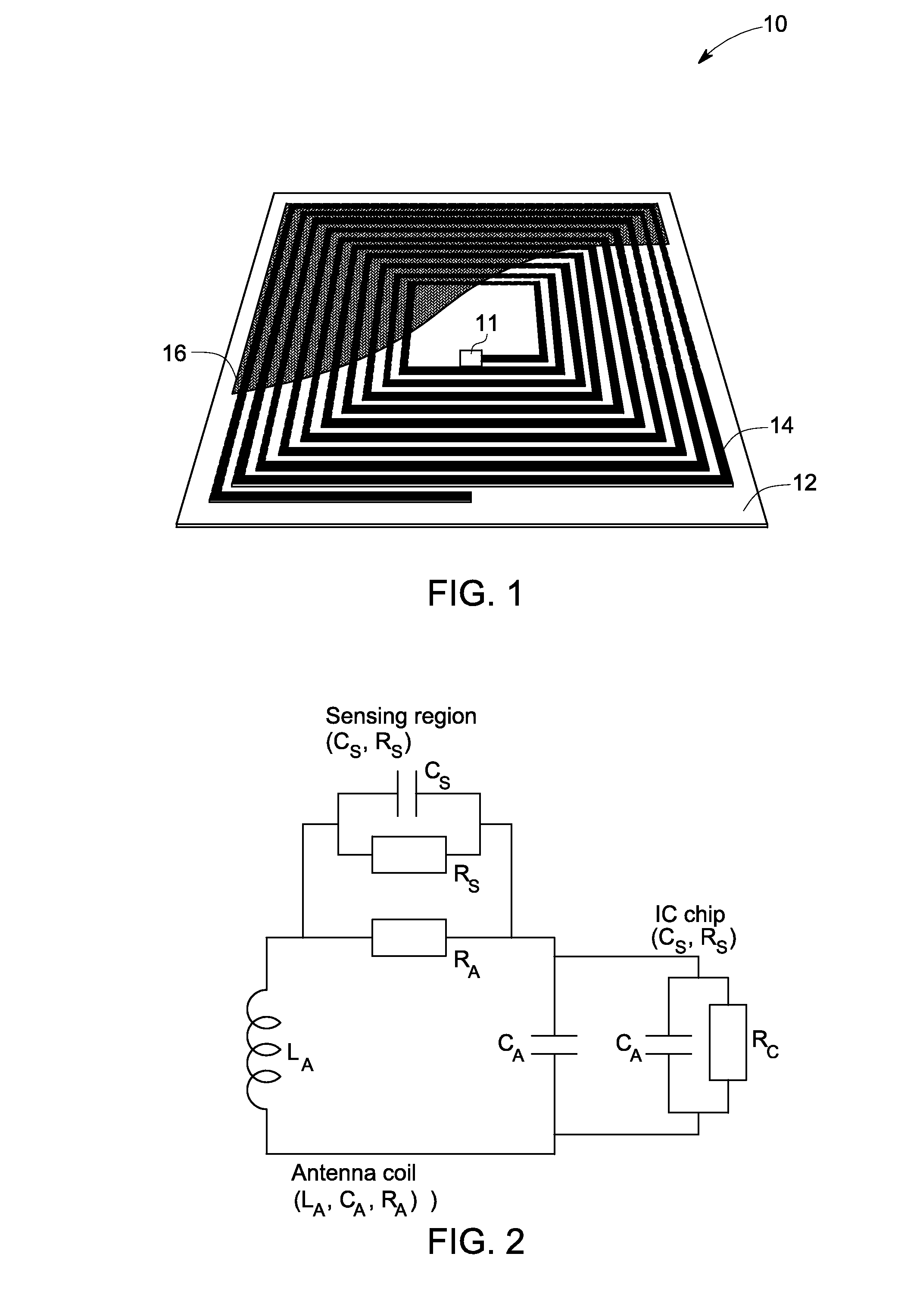
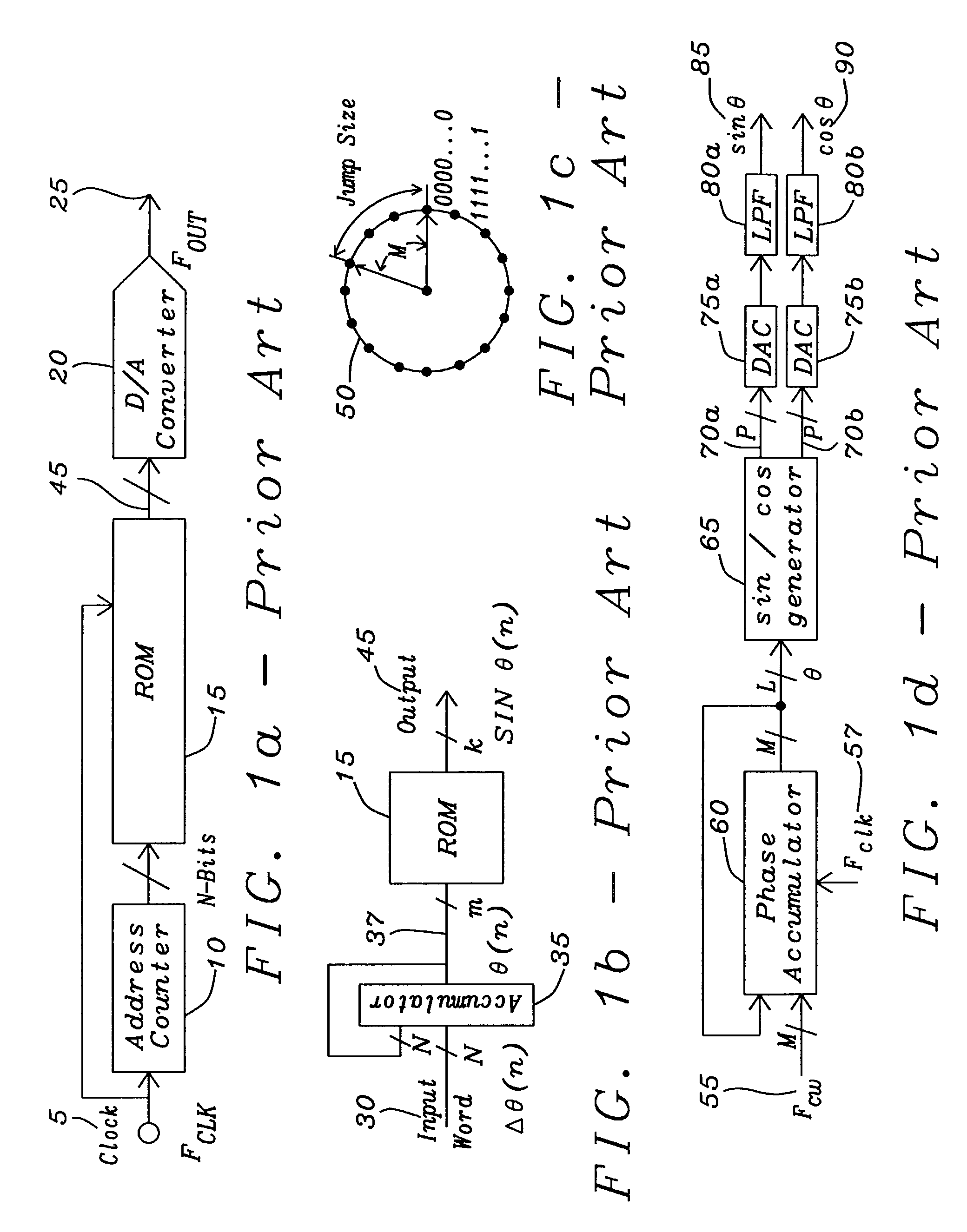
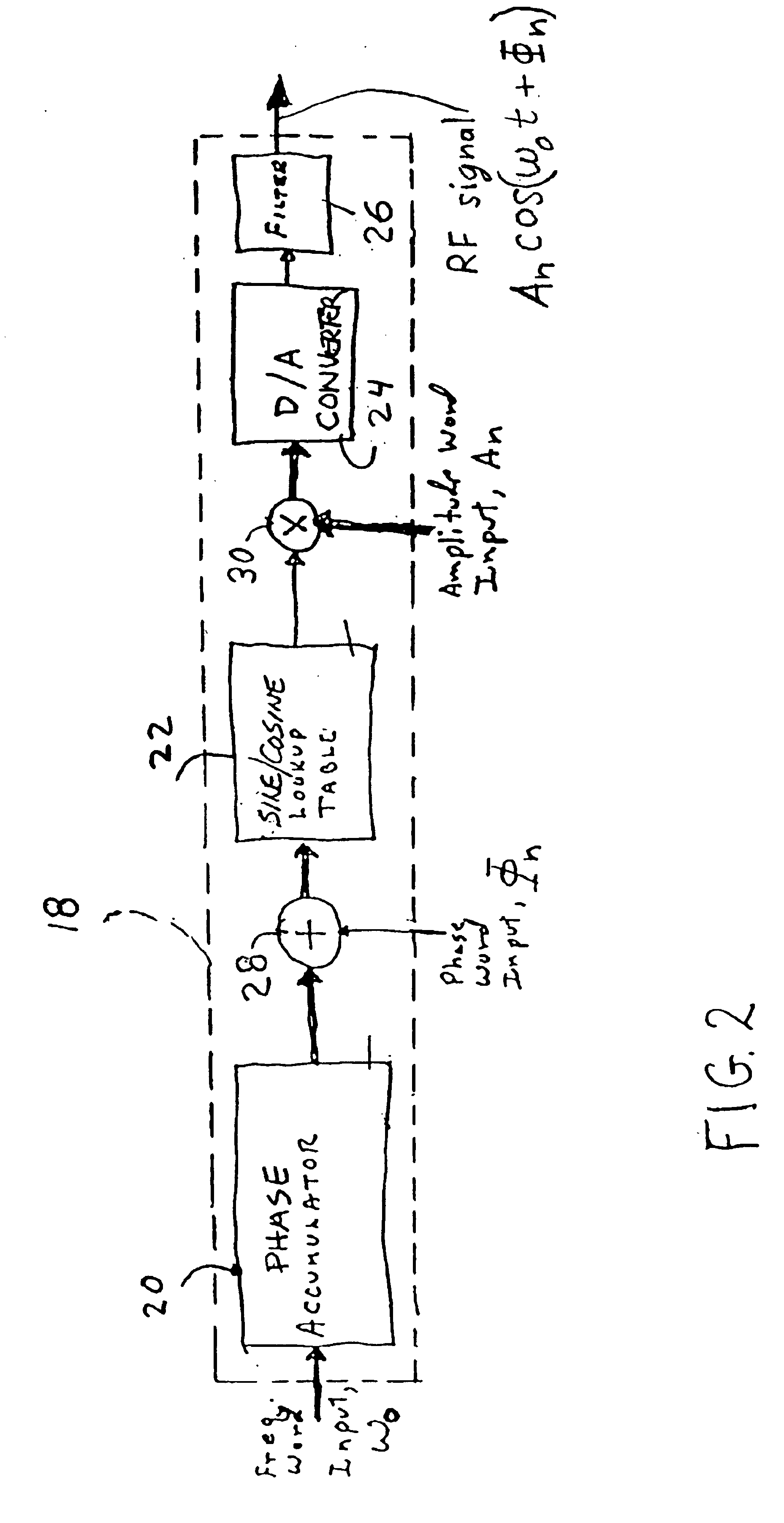
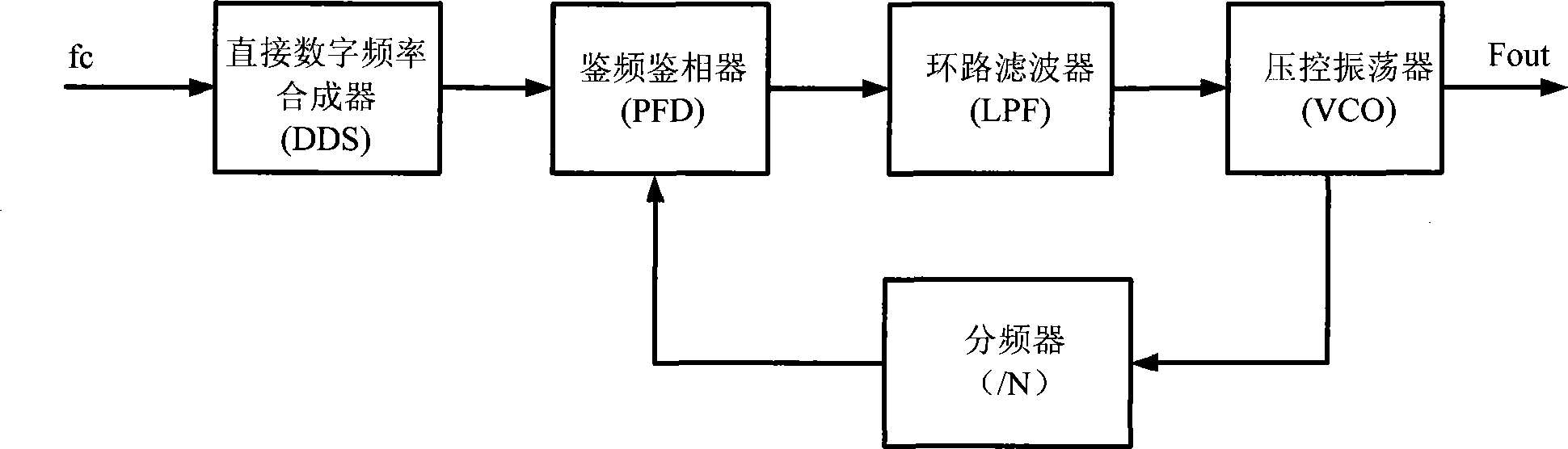
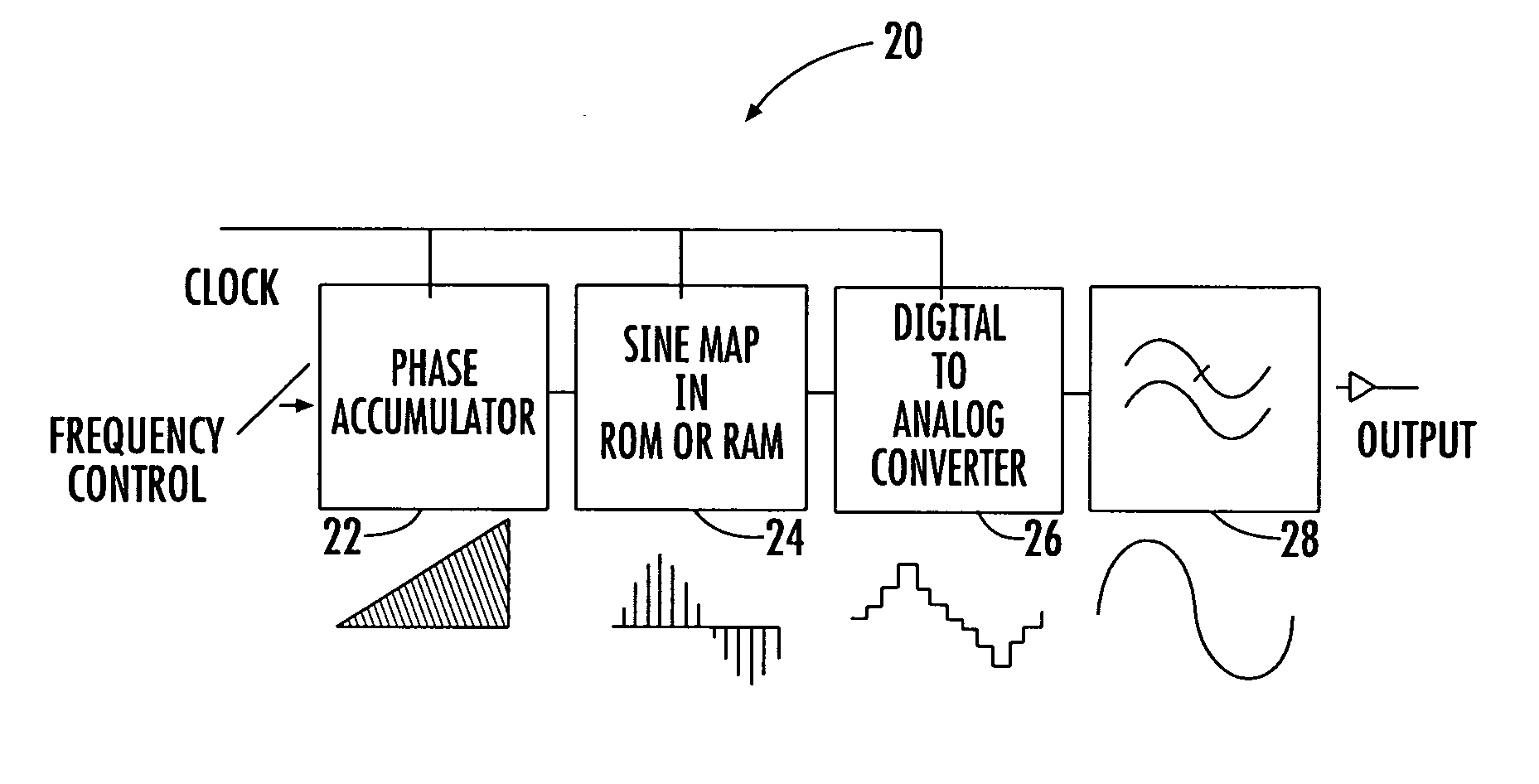
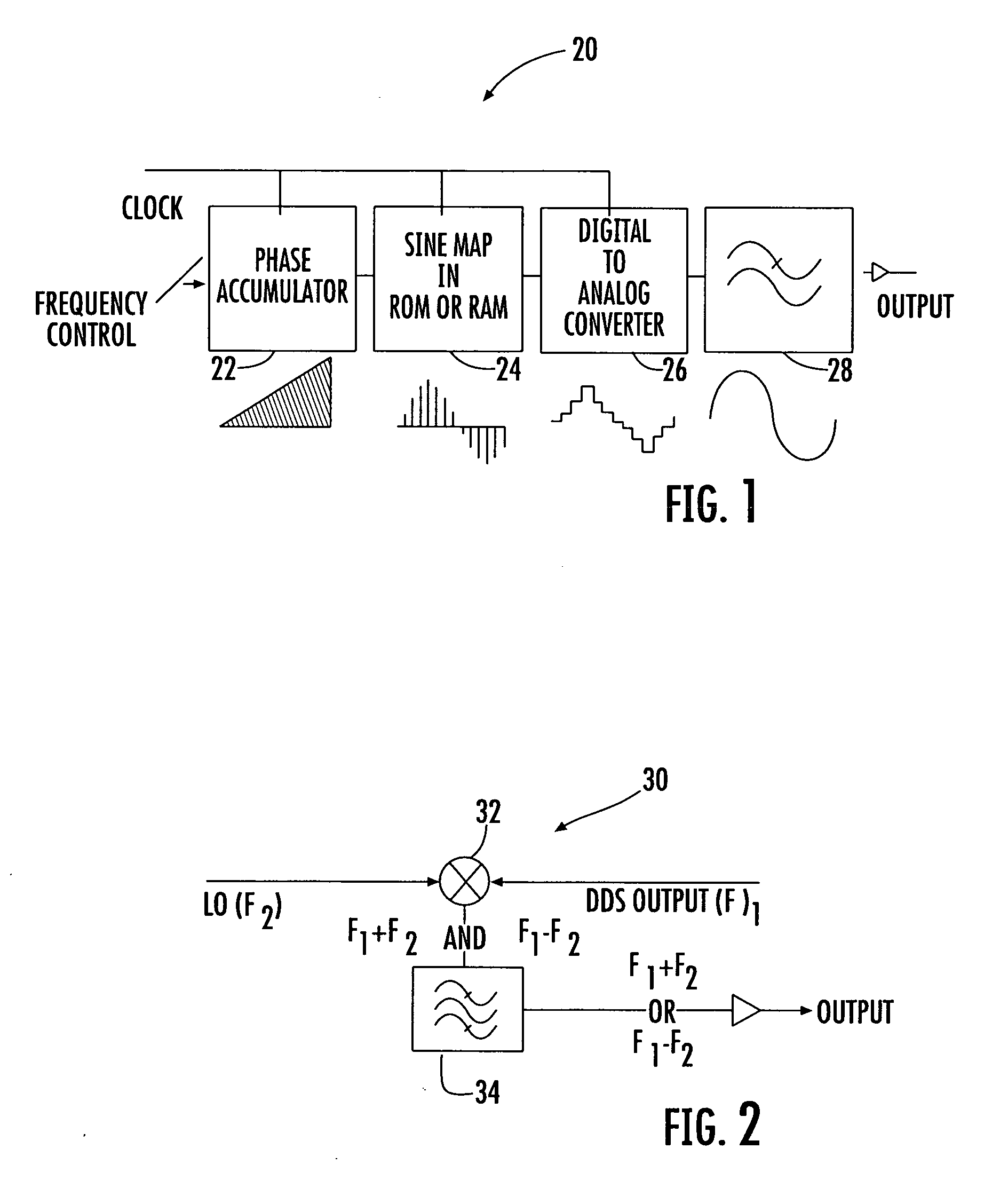
Direct digital synthesis (DDS) is a method employed by frequency synthesizers used for creating arbitrary waveforms from a single, fixed-frequency reference clock. DDS is used in applications such as signal generation, local oscillators in communication systems, function generators, mixers, modulators, sound synthesizers and as part of a digital phase-locked loop.
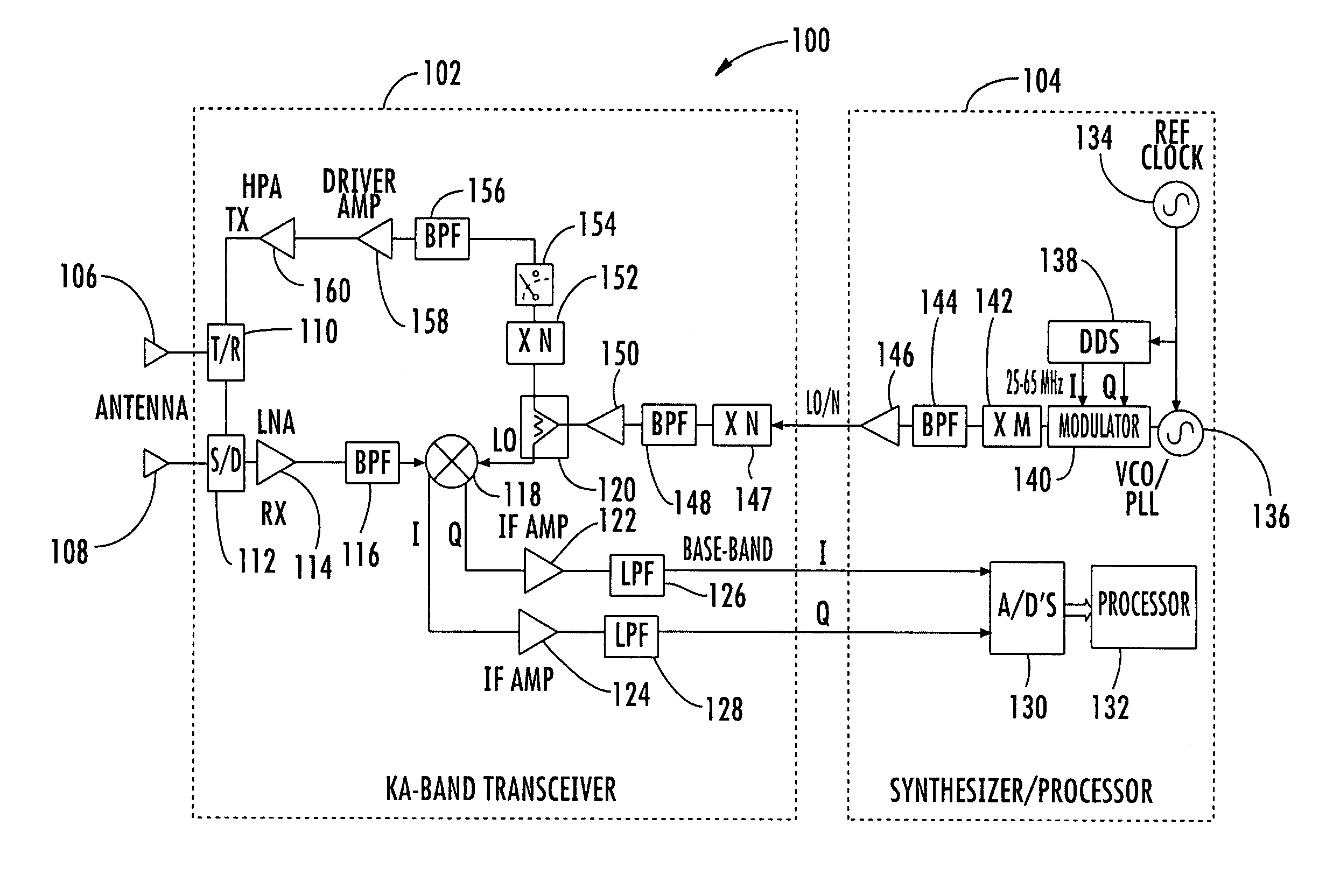
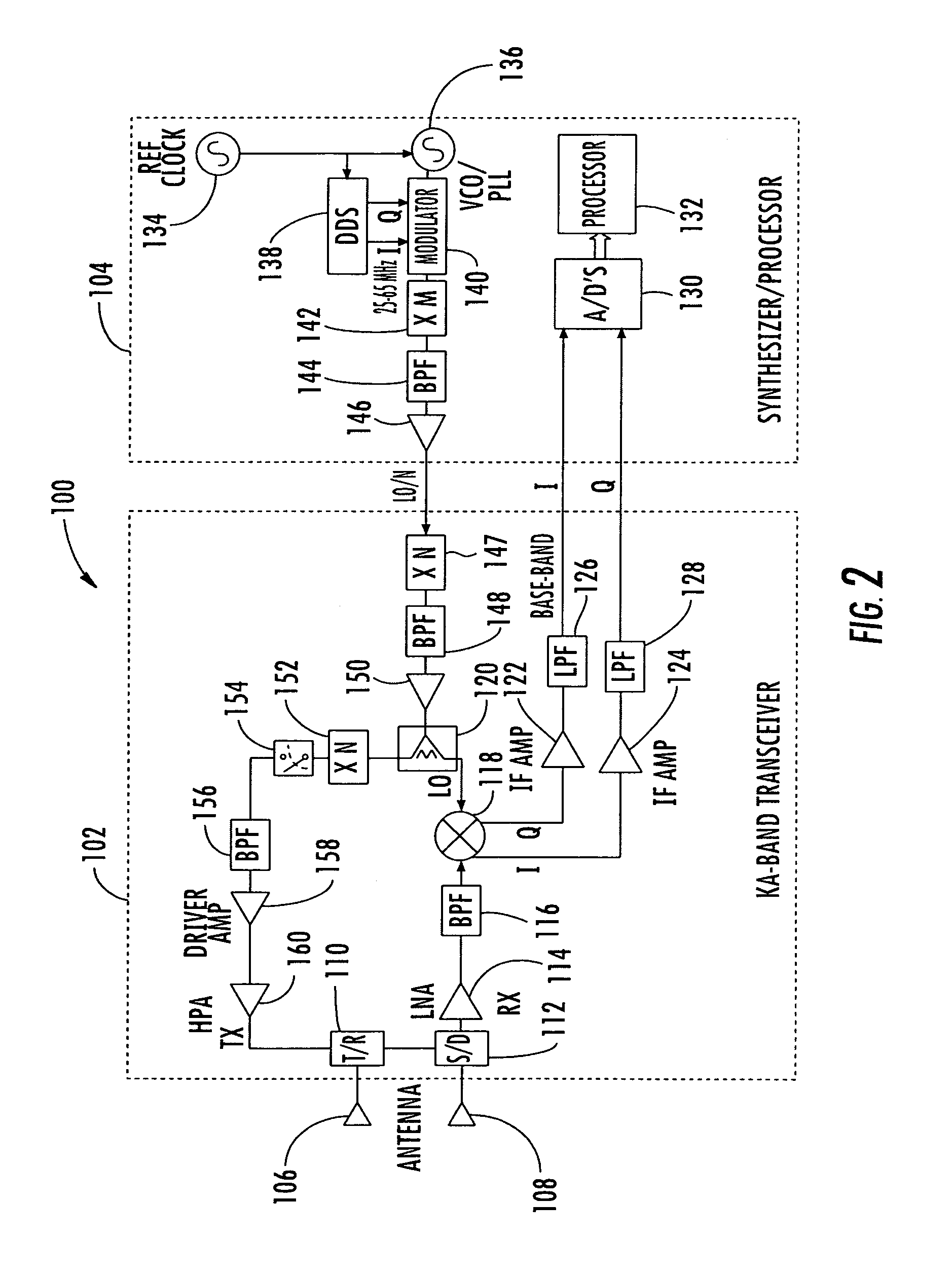
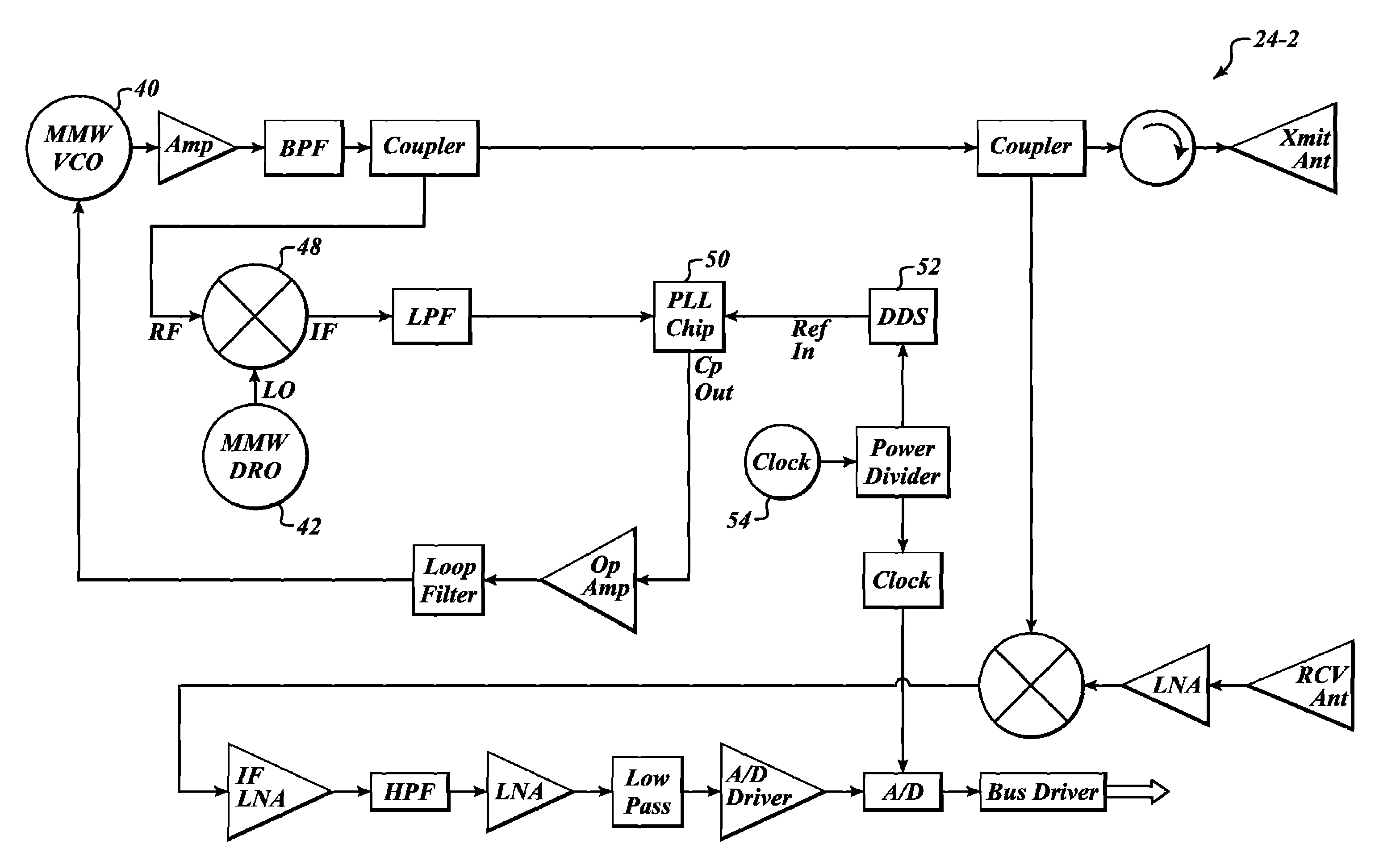
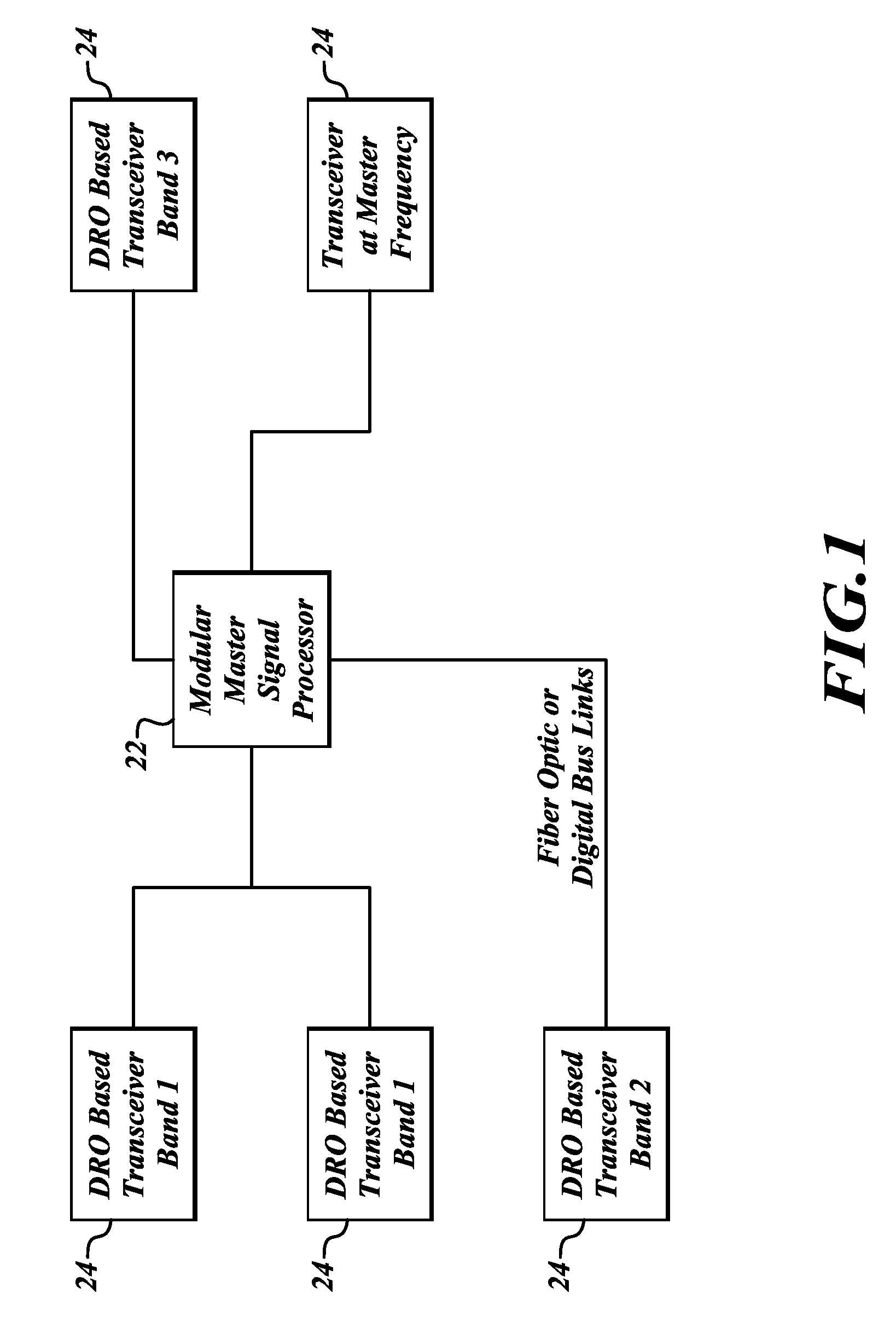
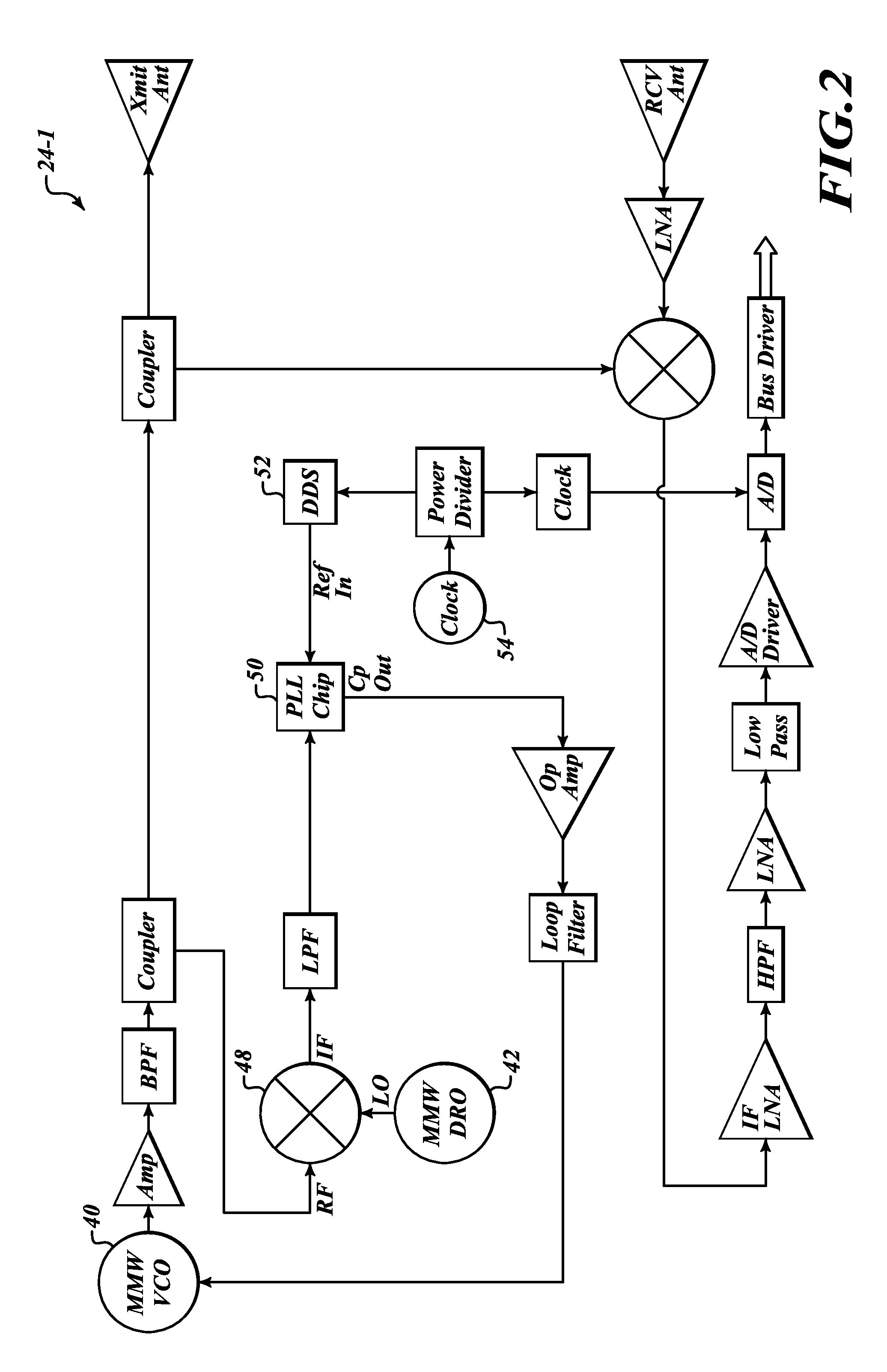
Millimeter wave pulsed radar system
InactiveUS7002511B1Improve efficiencySimplified frequency synthesizer designRadio wave reradiation/reflectionQuadrature modulatorLocal oscillator signal
A millimeter wave pulsed radar system includes a radar synthesizer having a voltage controlled oscillator / phase locked loop (VCO / PLL) circuit, direct digital synthesizer (DDS) circuit and quadrature modulator circuit that are operative to generate an intermediate frequency local oscillator signal (IF / LO signal). A radar transceiver is operative with the radar synthesizer for receiving the IF / LO signal. A transmitter section has a frequency multiplier that multiplies the IF / LO signal up to a millimeter wave (MMW) radar signal and a receiver section and includes a direct conversion mixer that receives a MMW radar signal and the IF / LO signal to produce I / Q baseband signals that are later digitized and processed.
Owner:REVEAL IMAGING
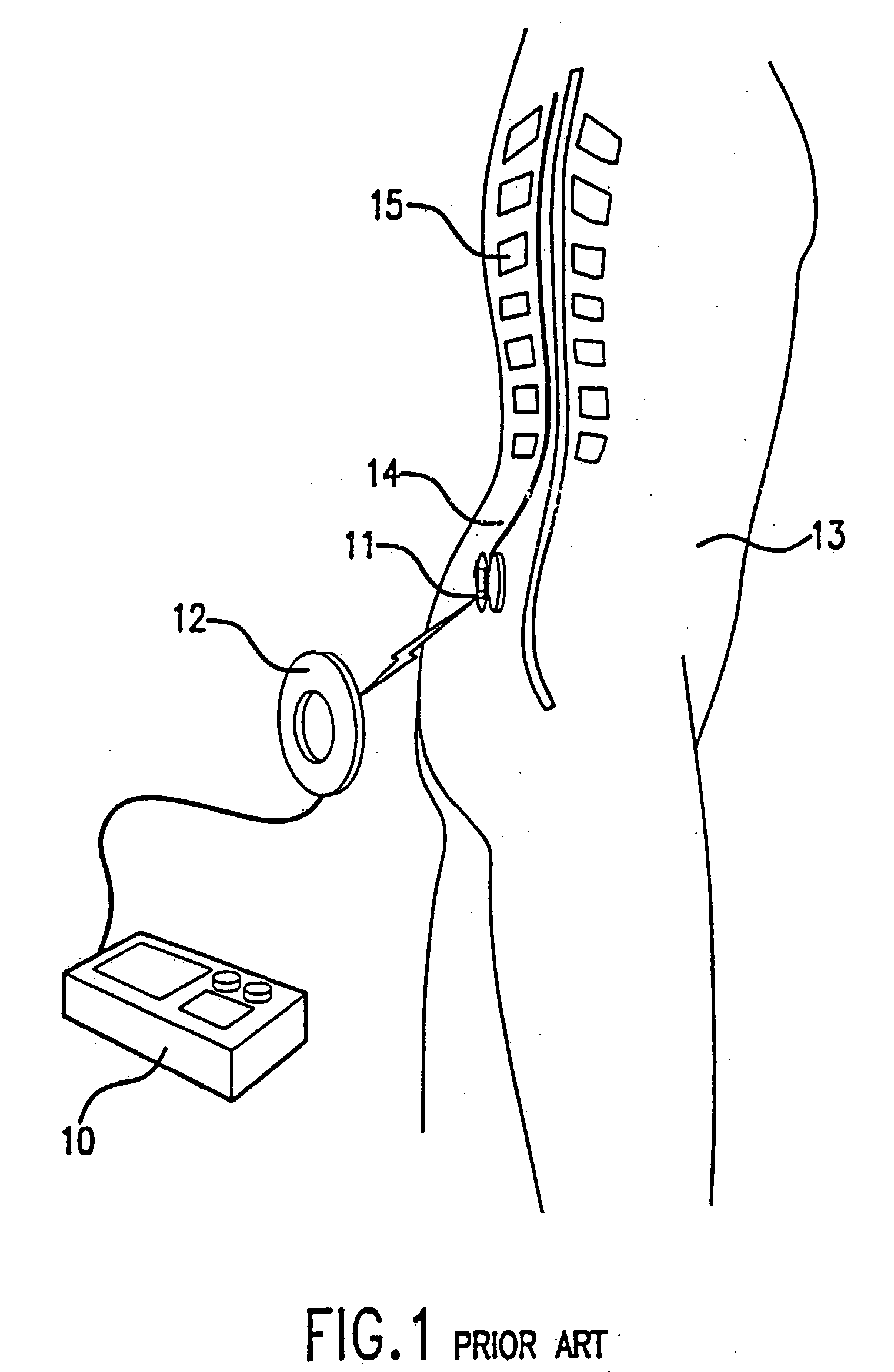
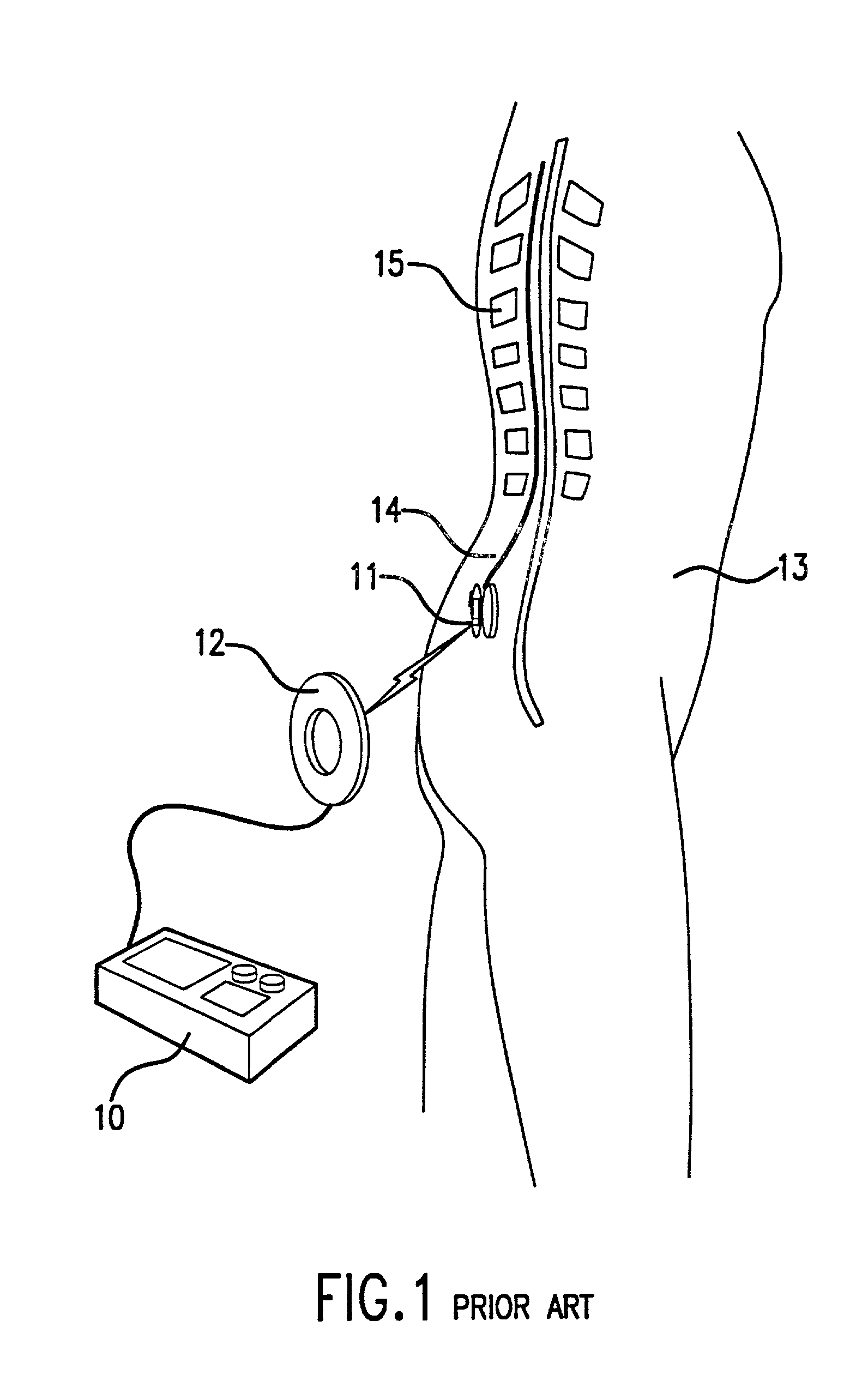
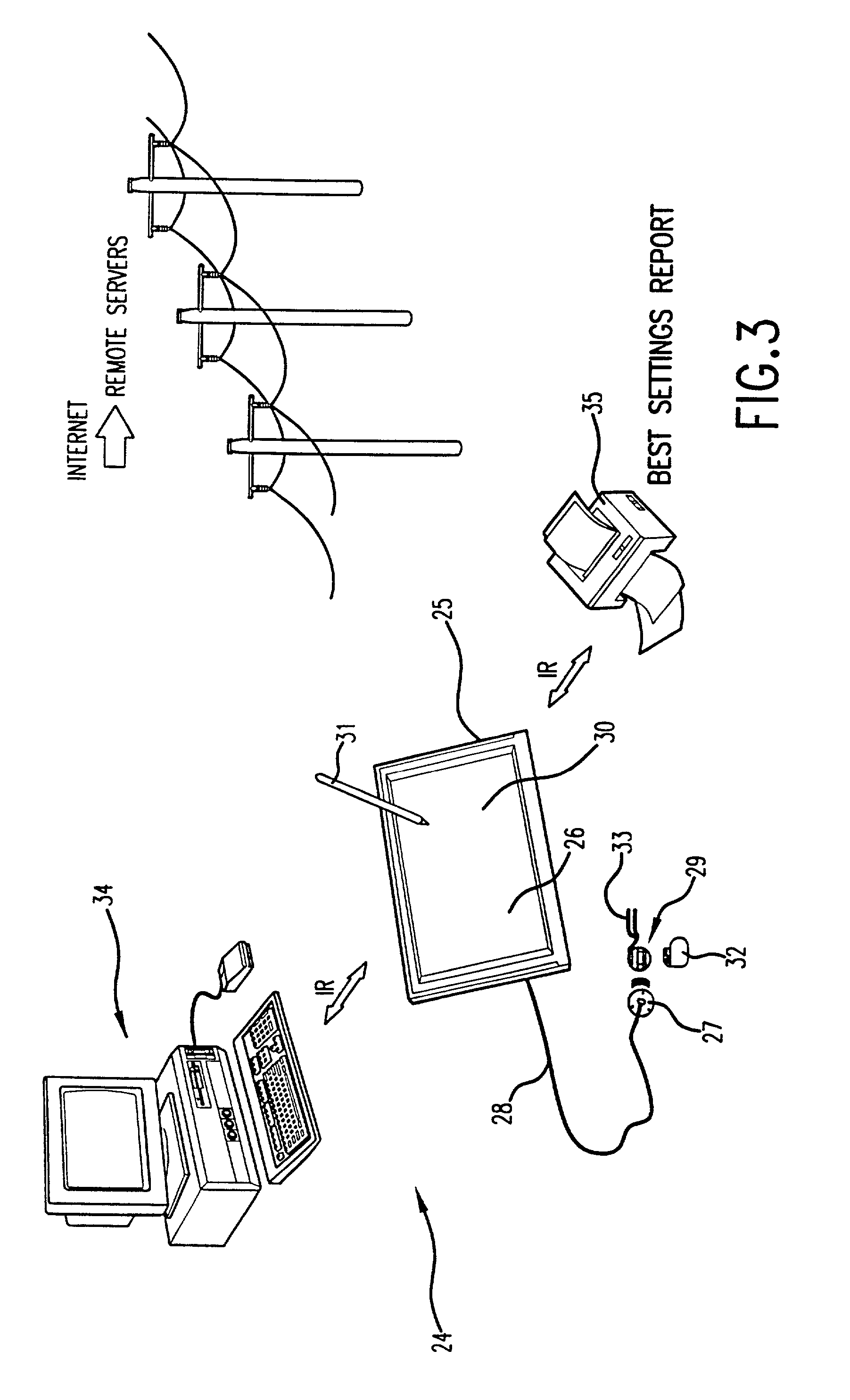
Patient interactive neurostimulation system and method
A fully automated computer controlled system is provided for adjustment of neurostimulation implants used in pain therapy and in treating neurological dysfunction which includes a patient interactive computer, and a universal transmitter interface integrally embedded in the patient interactive computer or built into the antenna which is capable of stimulating any type of implanted neurostimulation devices by imitating programming codes. The patient interacts with the system through the patient interactive computer. The universal transmitter interface includes a direct digital synthesizer, a transistor circuitry driving the antenna in ON-OFF fashion and a gating unit for driving the transistor circuitry under control of the processing means in the patient-interactive computer. Alternatively, the universal transmitting interface includes a balanced modulator for modulation of the carrier signal generated at the direct digital synthesizer.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Patient interactive neurostimulation system and method
A fully automated computer controlled system is provided for adjustment of neurostimulation implants used in pain therapy and in treating neurological dysfunction which includes a patient interactive computer, and a universal transmitter interface integrally embedded in the patient interactive computer or built into the antenna which is capable of stimulating any type of implanted neurostimulation devices by imitating programming codes. The patient interacts with the system through the patient interactive computer. The universal transmitter interface includes a direct digital synthesizer, a transistor circuitry driving the antenna in ON-OFF fashion and a gating unit for driving the transistor circuitry under control of the processing means in the patient-interactive computer. Alternatively, the universal transmitting interface includes a balanced modulator for modulation of the carrier signal generated at the direct digital synthesizer.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Patient interactive neurostimulation system and method
A fully automated computer controlled system is provided for adjustment of neurostimulation implants used in pain therapy and in treating neurological dysfunction which includes a patient interactive computer, and a universal transmitter interface integrally embedded in the patient interactive computer or built into the antenna which is capable of stimulating any type of implanted neurostimulation devices by imitating programming codes. The patient interacts with the system through the patient interactive computer. The universal transmitter interface includes a direct digital synthesizer, a transistor circuitry driving the antenna in ON-OFF fashion and a gating unit for driving the transistor circuitry under control of the processing means in the patient-interactive computer. Alternatively, the universal transmitting interface includes a balanced modulator for modulation of the carrier signal generated at the direct digital synthesizer.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Wideband signal generators, measurement devices, methods of signal generation, and methods of signal analysis
ActiveUS20050003785A1Small sizeReducing or avoiding spurious DDS responsesPulse automatic controlContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationMeasurement deviceSignal analyzer
A wideband signal generator according to one embodiment of the invention includes a variable frequency source and a direct digital synthesizer. Local oscillators, signal analyzers, modulators, demodulators, and other equipment including one or more such generators are also disclosed.
Owner:MERCURY SISTEMS INC
Method and apparatus for synchronizing clock timing between network elements
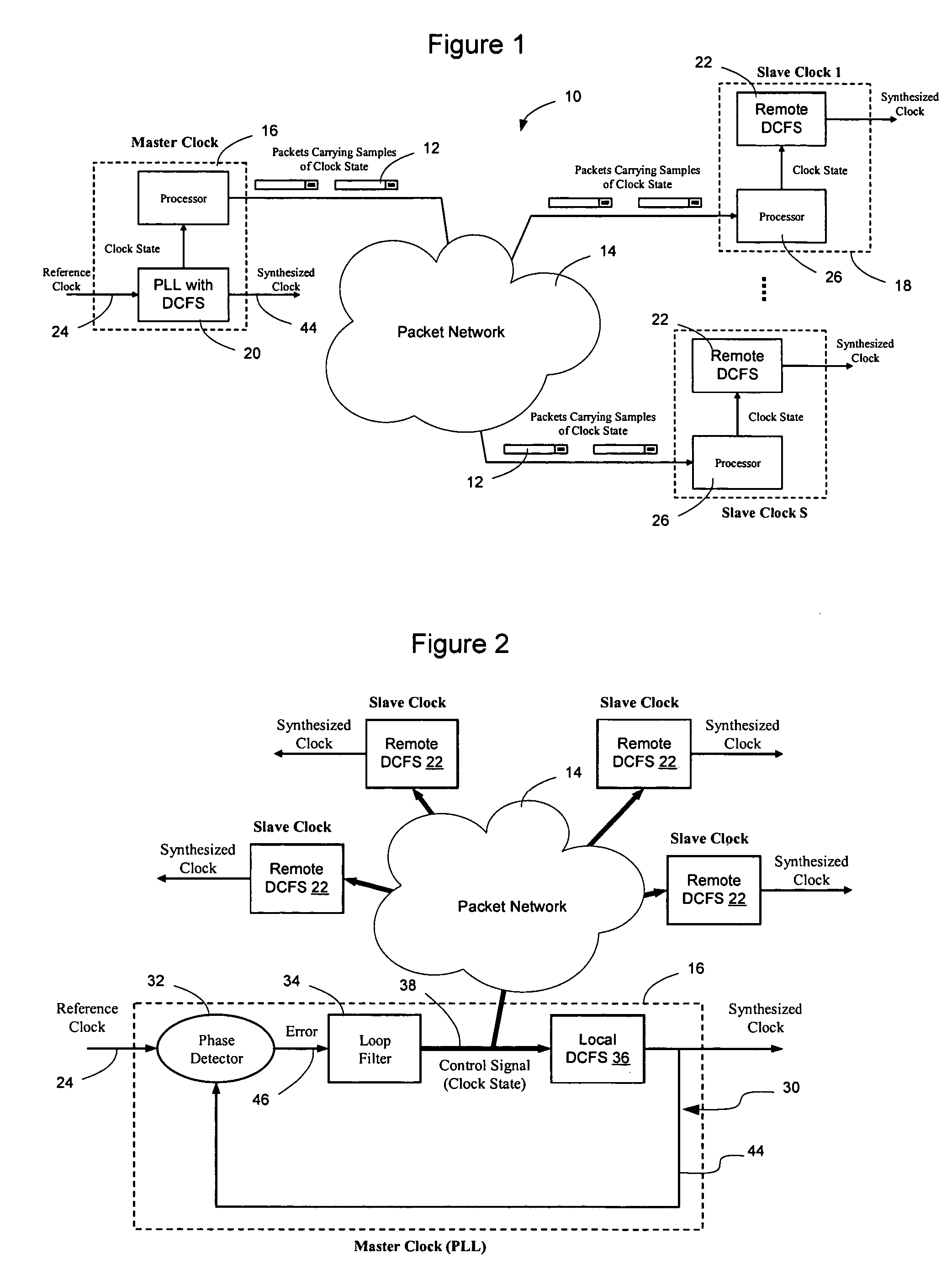
Network elements may be synchronized over an asynchronous network by implementing a master clock as an all digital PLL that includes a Digitally Controlled Frequency Selector (DCFS), the output frequency of which may be directly controlled through the input of a control word. The PLL causes the control word input to the master DCFS to be adjusted to cause the output of the master DCFS to lock onto a reference frequency. Information associated with the control word is transmitted from the master clock to the slave clocks which are also implemented as DCFSs. By using the transmitted information to recreate the master control word, the slaves may be made to assume the same state as the master DCFS without requiring the slaves to be implemented as PLLs. The DCFS may be formed as a digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) or as a Direct Digital Synthesizer (DDS).
Owner:CIENA
Frequency hopping spread spectrum communications system
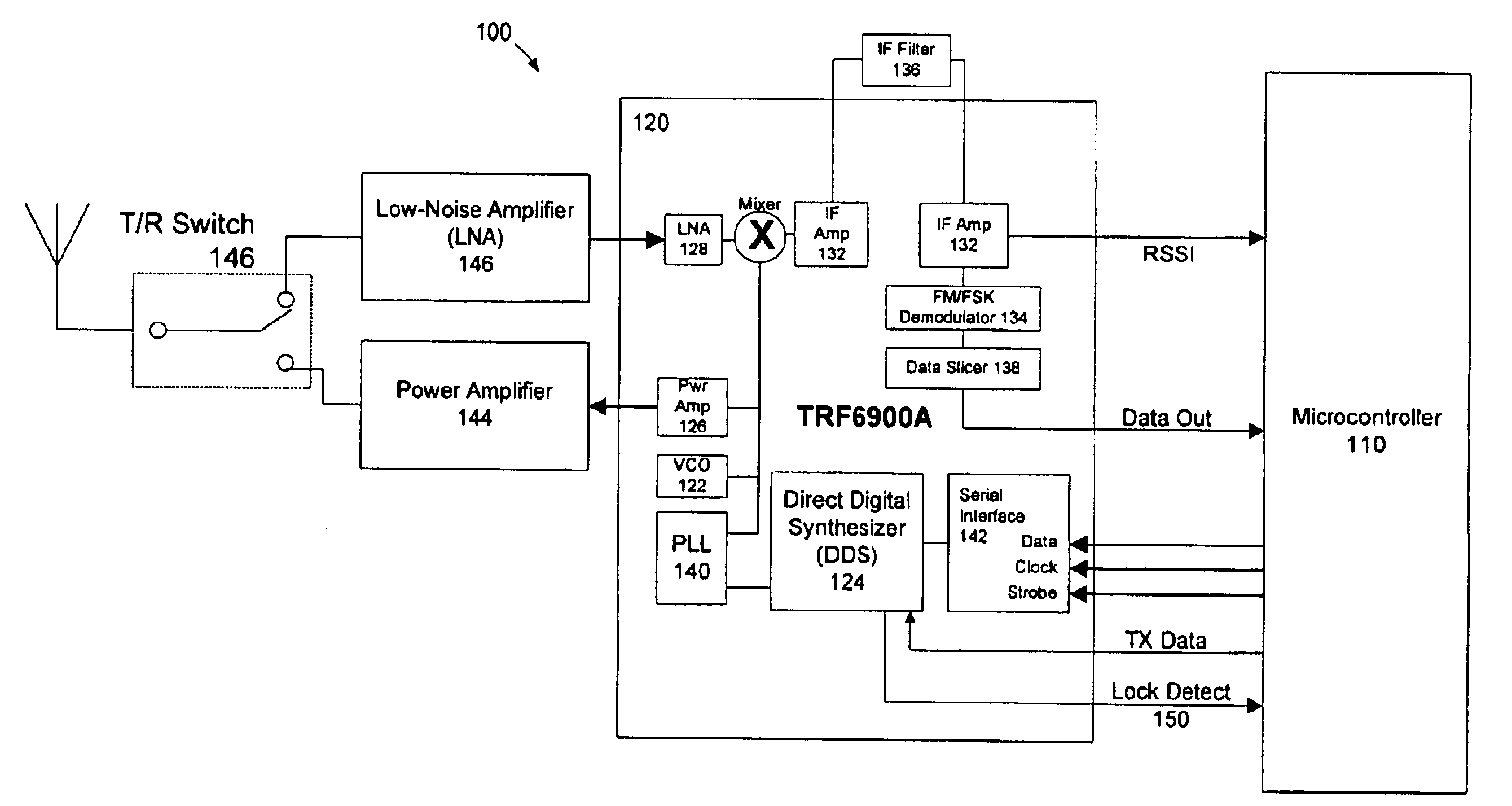
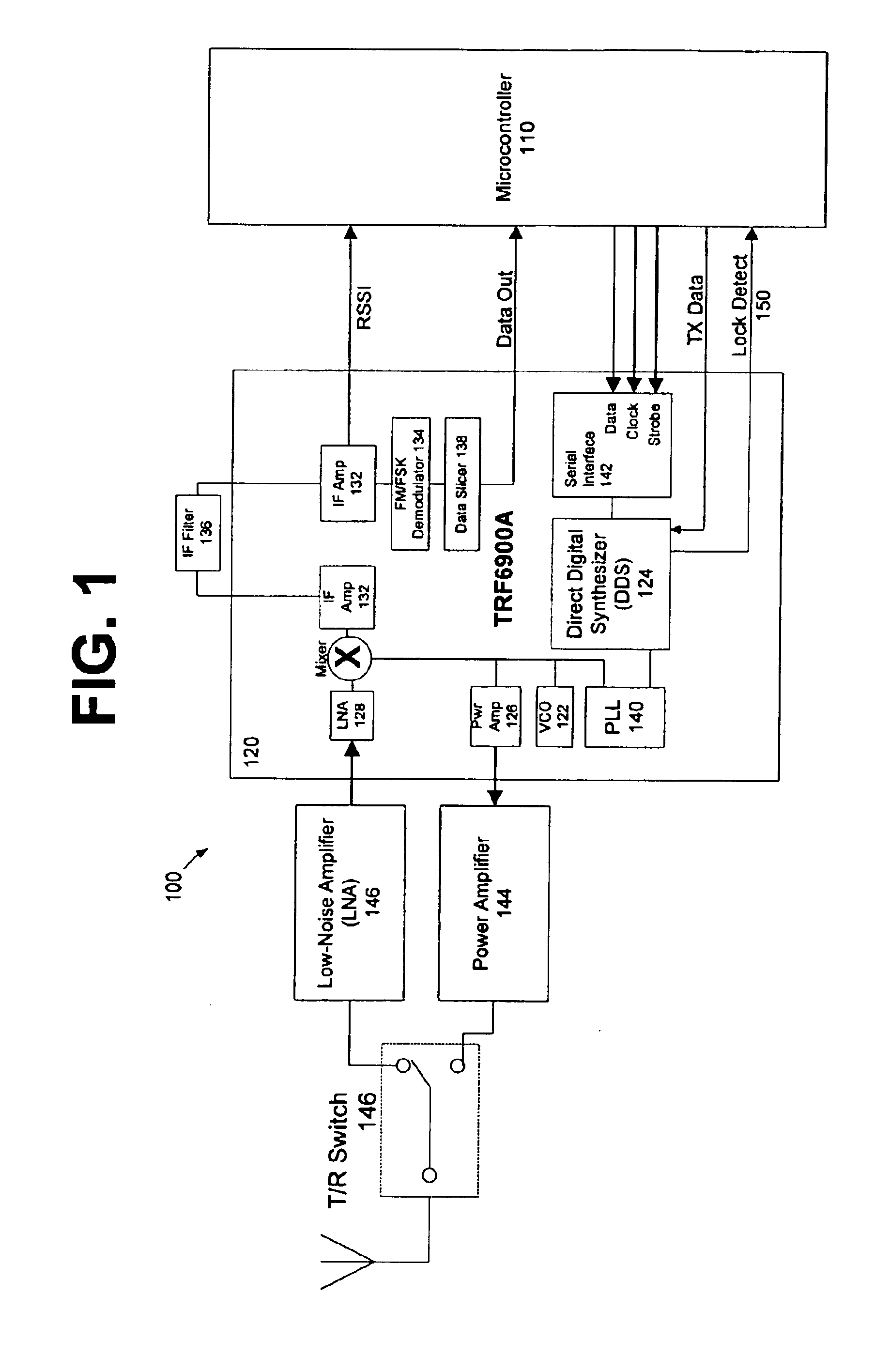
InactiveUS6888876B1Modulated-carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsMicrocontrollerTransceiver
The present invention is directed to a frequency hopping spread spectrum transceiver. The transceiver includes a microcontroller; a transmitter having a voltage controlled oscillator, a direct digital synthesizer, and a power amplifier; and a receiver having an amplifier, a mixer, an IF amplifier, a demodulator, and a data slicer. When transmitting, the transmitter communicates a preamble over a predetermined number of preamble channels, and thereafter communicate groups of data bytes that each comprise a subset of the data message over a predetermined sequence of data channels. When receiving, the receiver investigates the predetermined number of preamble channels to search for the preamble, each of the predetermined number of preamble channels being associated with a predetermined number of data channels in each sequence of data channels. A number of bytes that comprises each group of data bytes is determined in accordance with a number of channels in the sequence of data channels and the predetermined number of times each byte of the data message is to be transmitted.
Owner:ELSTER ELECTRICTY LLC
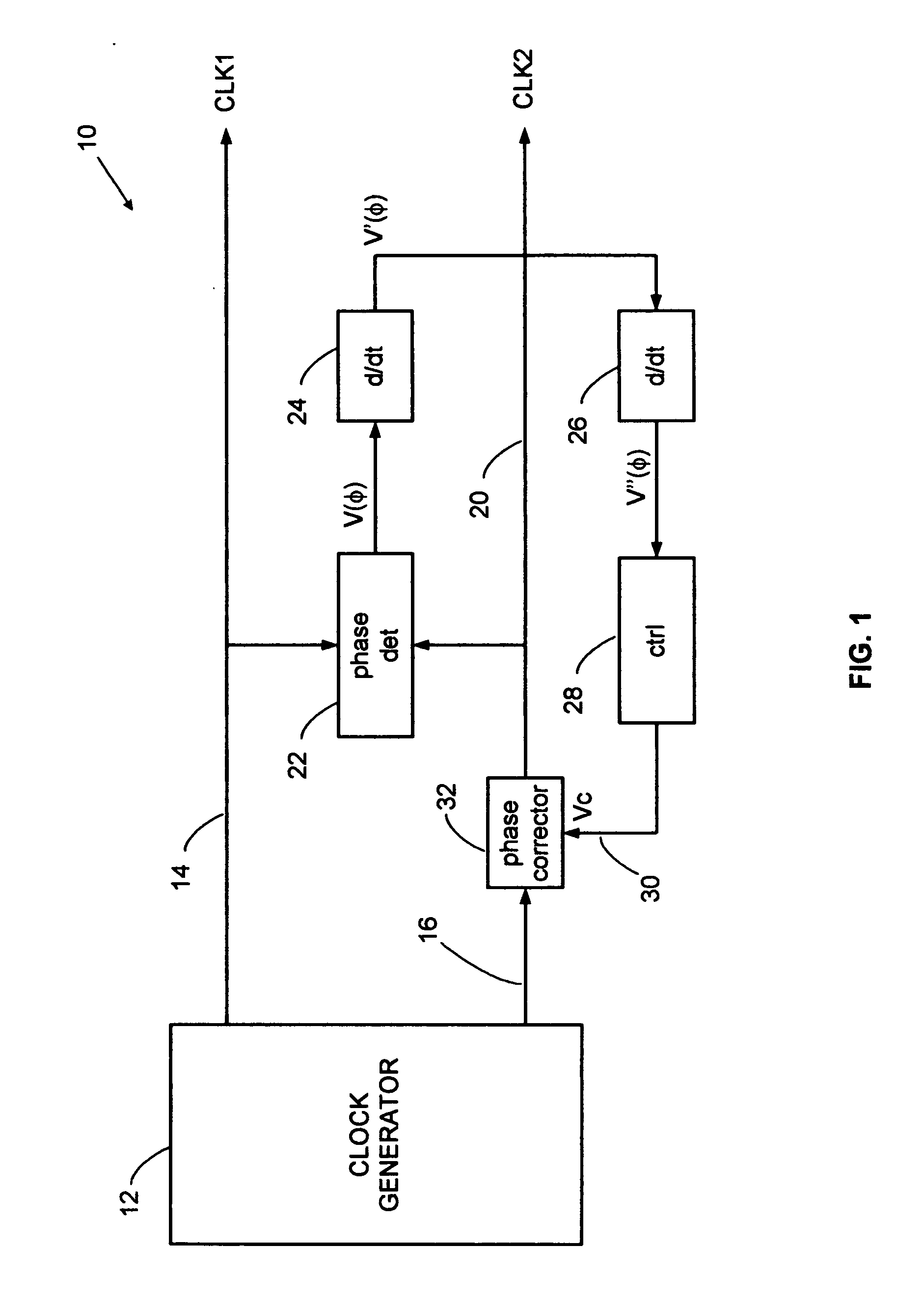
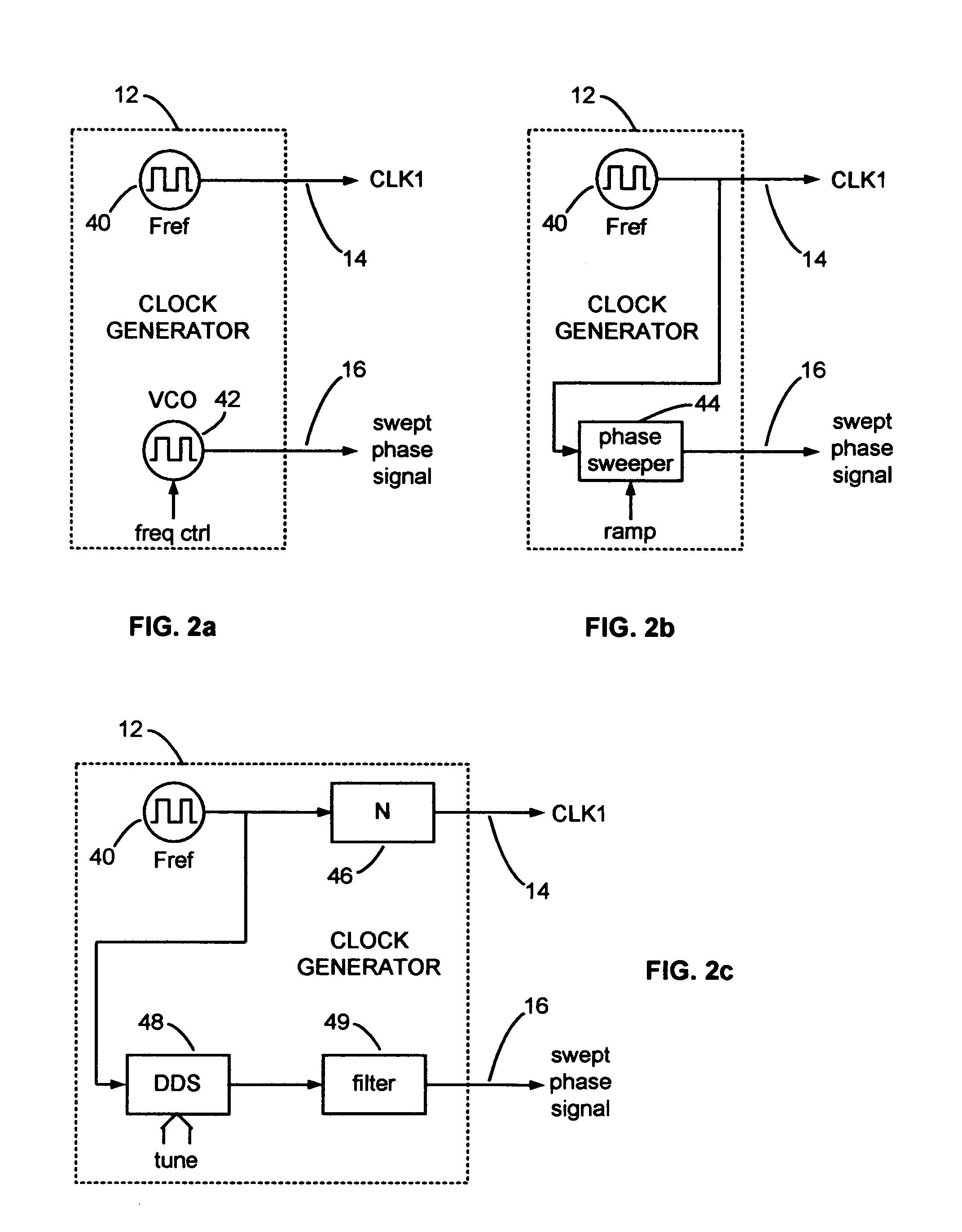
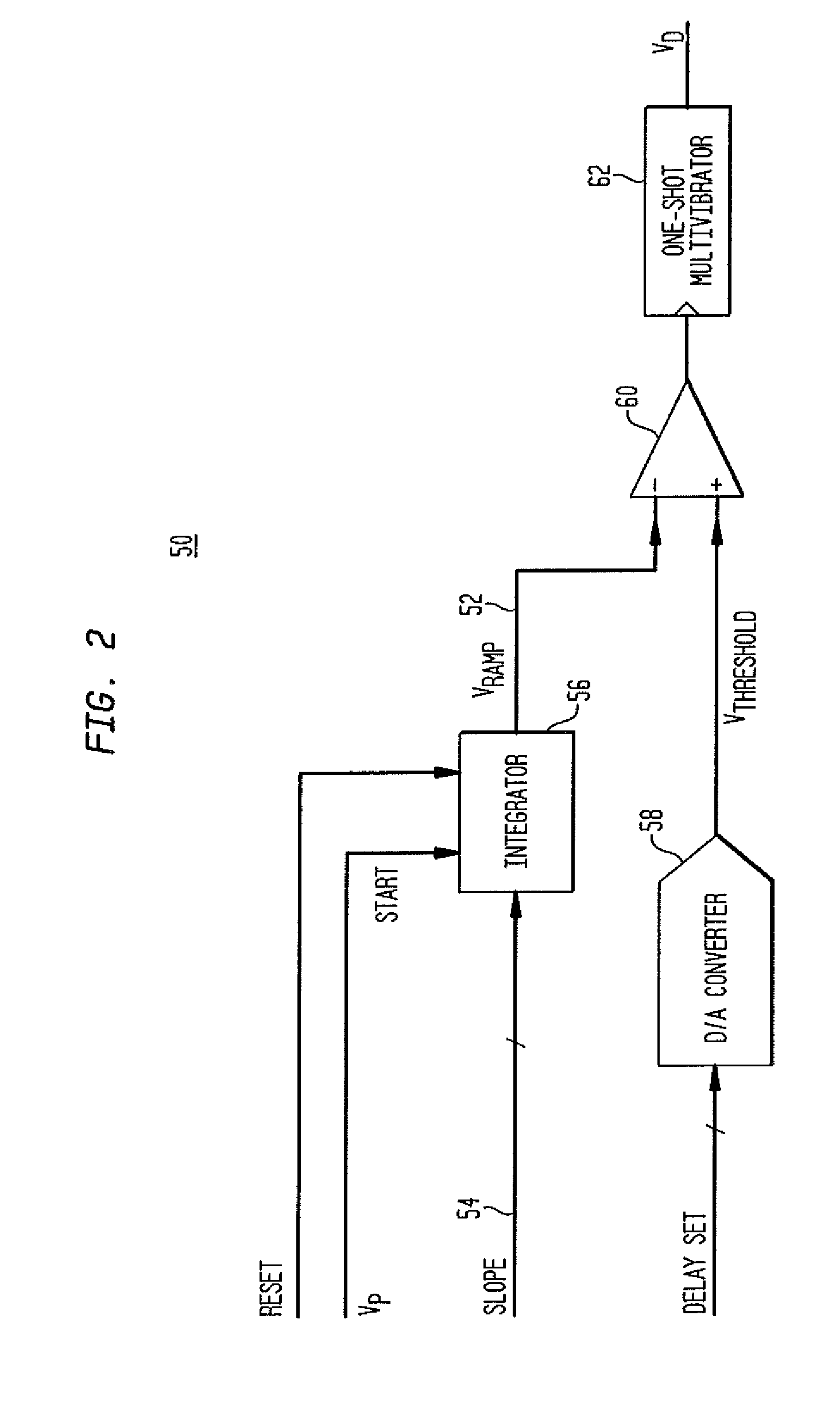
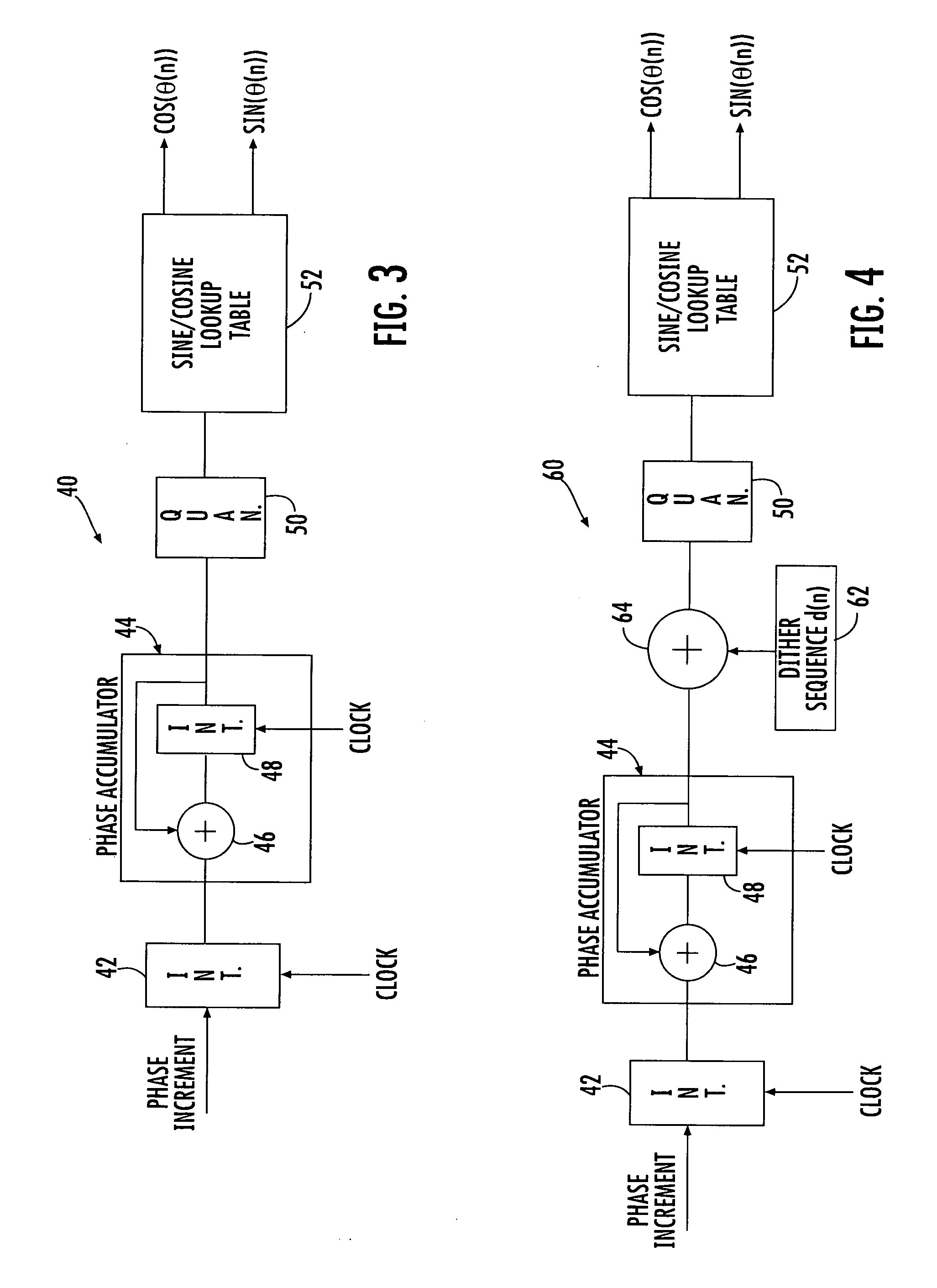
Direct digital synthesizer for reference frequency generation
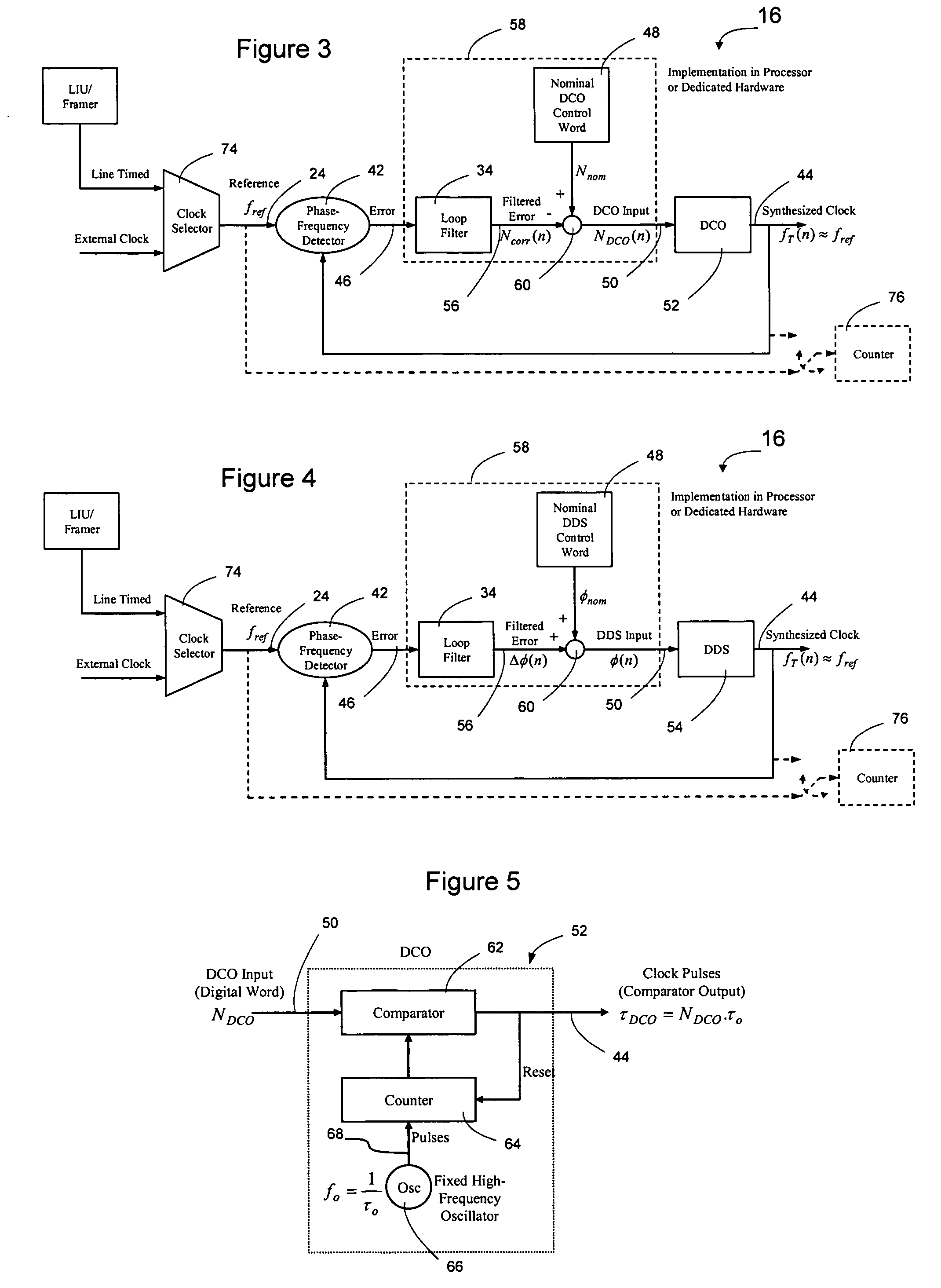
InactiveUS7724097B2Improve noiseImprove performancePulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersFrequency generationDigital controlled oscillator
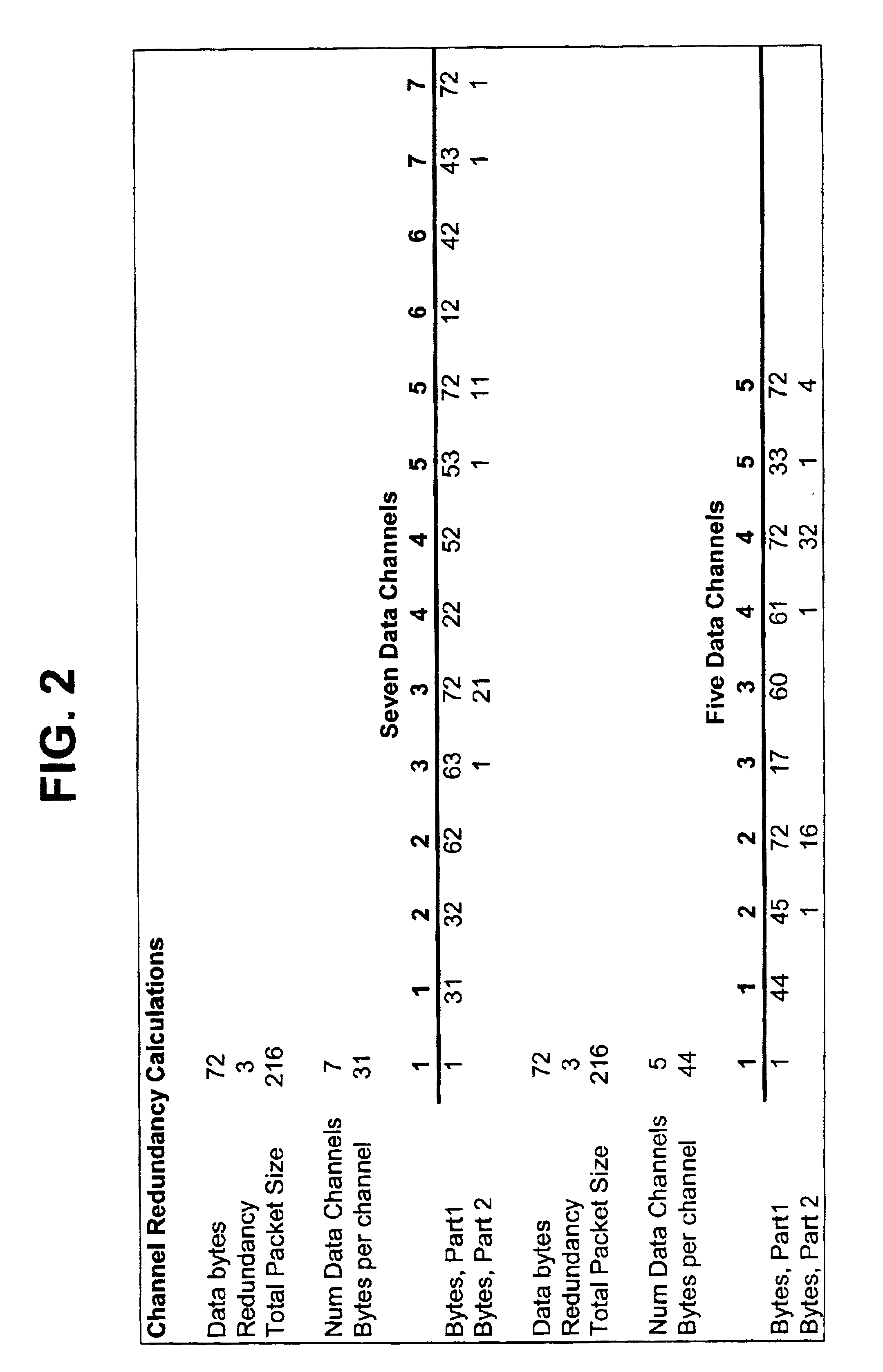
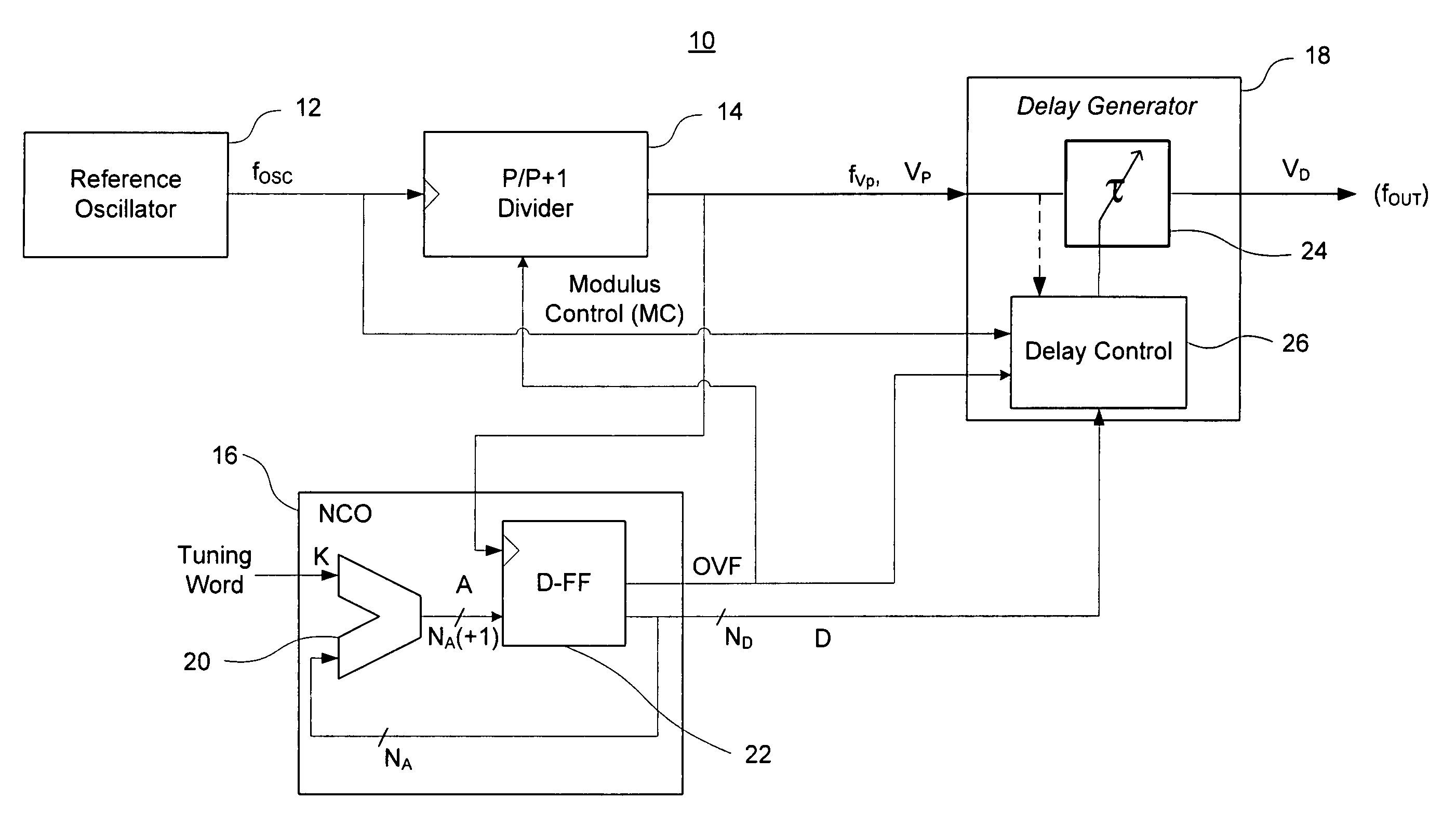
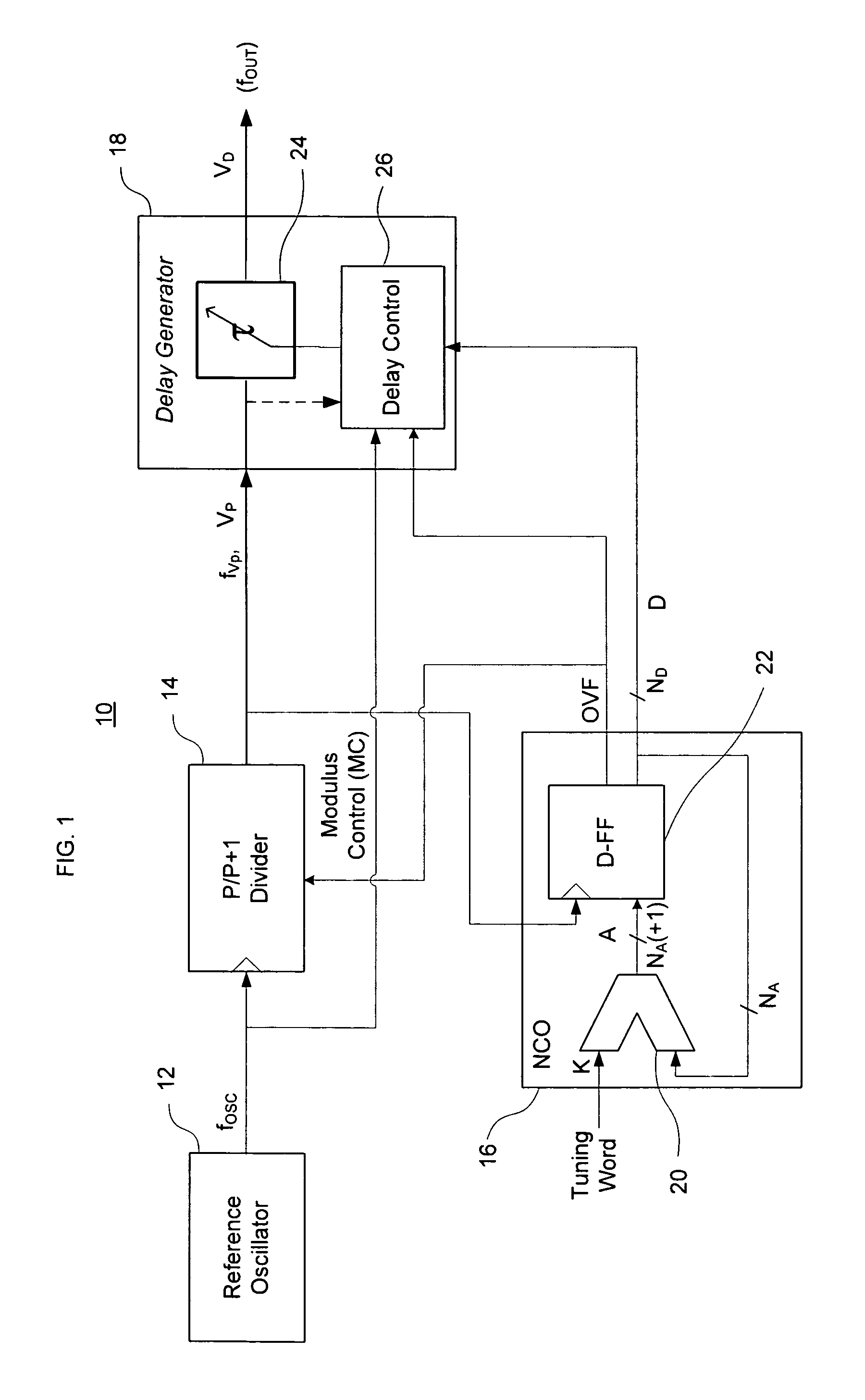
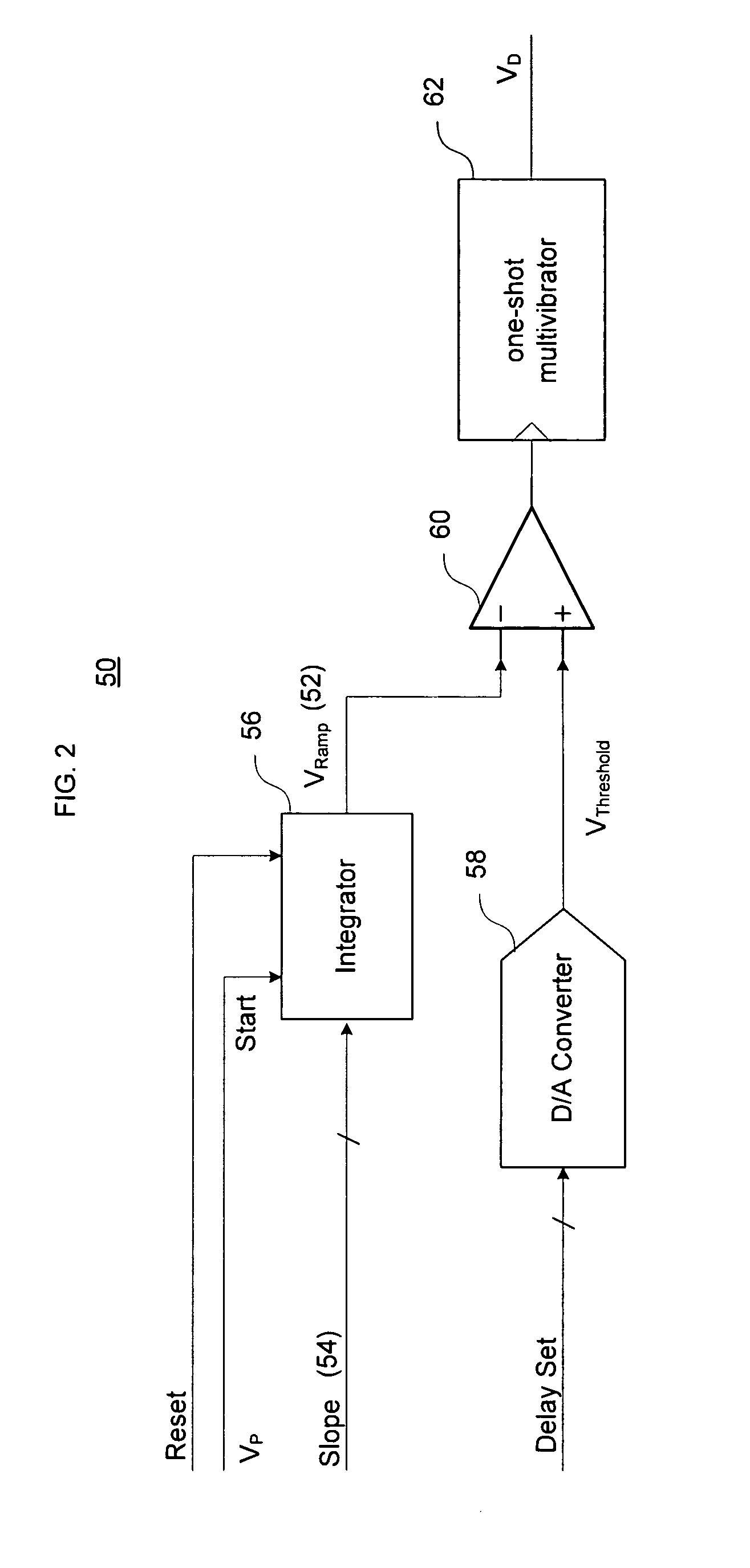
A direct digital frequency synthesizer having a multi-modulus divider, a numerically controlled oscillator and a programmable delay generator. The multi-modulus divider receives an input clock having an input pulse frequency fosc and outputs some integer fraction of those pulses at an instantaneous frequency fVp that is some integer fraction (1 / P) of the input frequency. The multi-modulus divider selects between at least two ratios of P (1 / P or 1 / P+1) in response to a signal from the numerically controlled oscillator. The numerically controlled oscillator receives a value which is the accumulator increment (i.e. the number of divided pulse edges) required before an overflow occurs that causes the multi-modulus divider to change divider ratios in response to receiving an overflow signal. The numerically controlled oscillator also outputs both the overflow signal and a delay signal to the delay generator that further controls the frequency of the multi-modulus divider output signal (Vp) to provide an output signal (VD) with an fout that has improved phase and timing jitter performance over prior art direct digital frequency synthesizer architectures.
Owner:CYMATICS LAB CORP
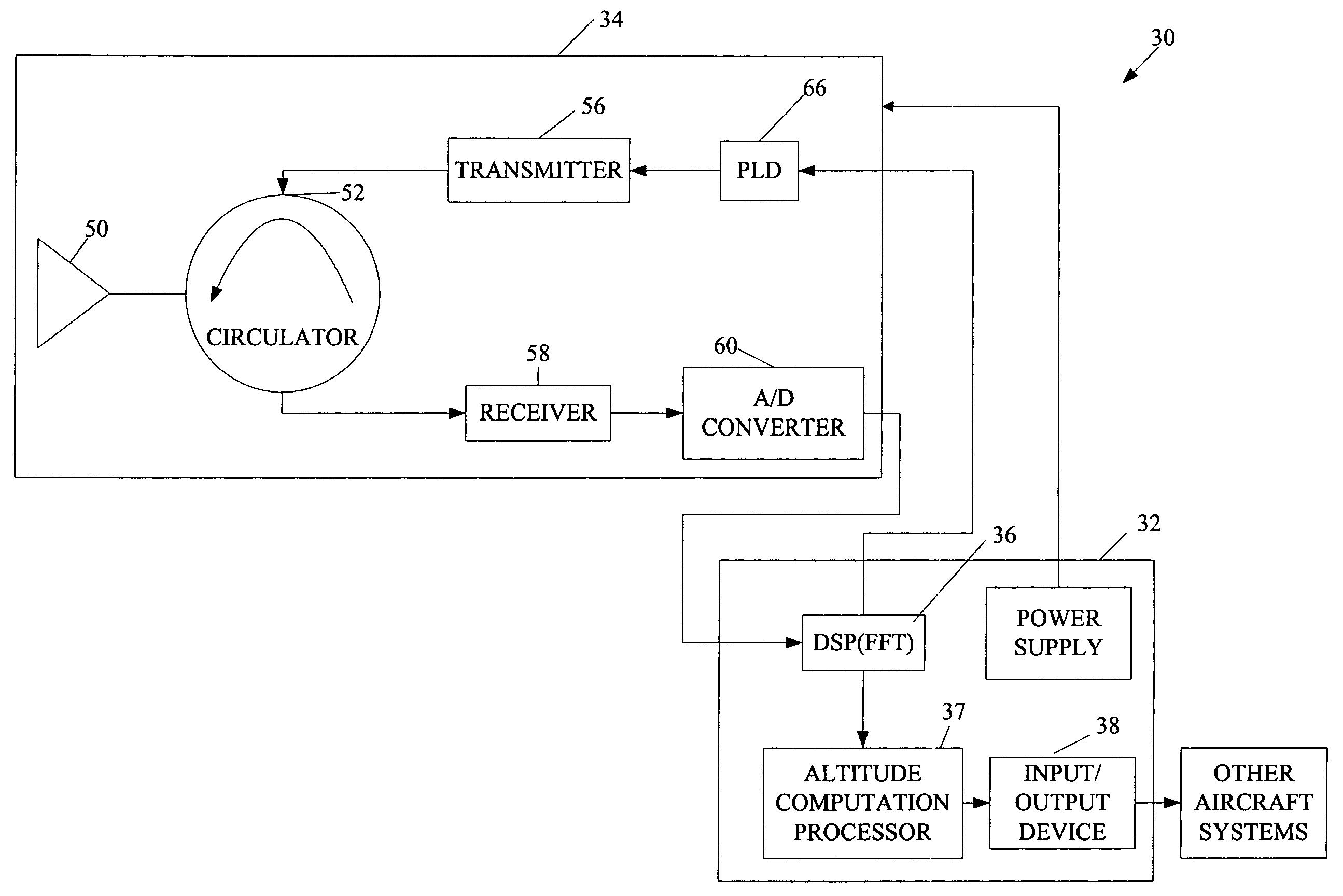
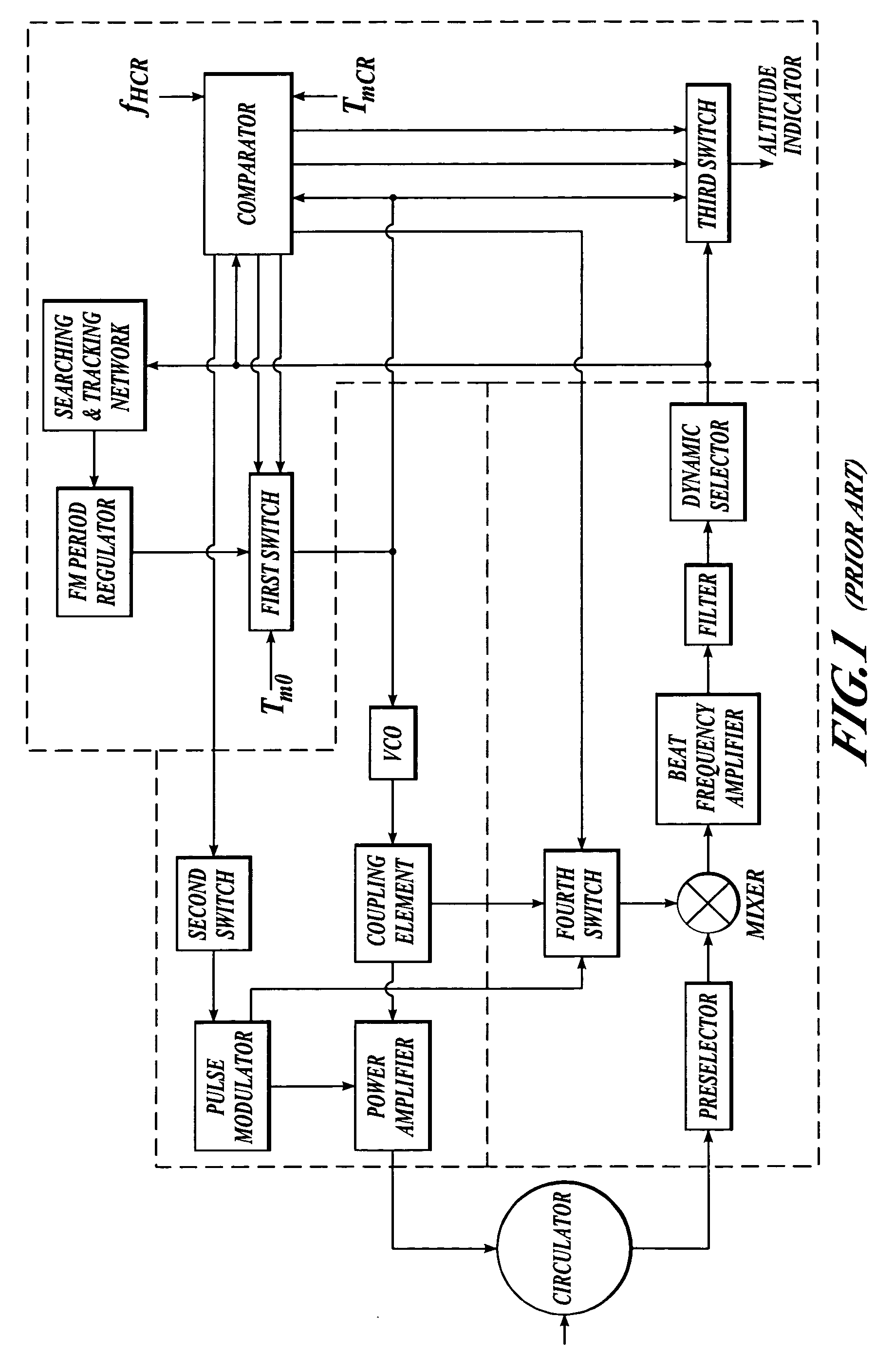
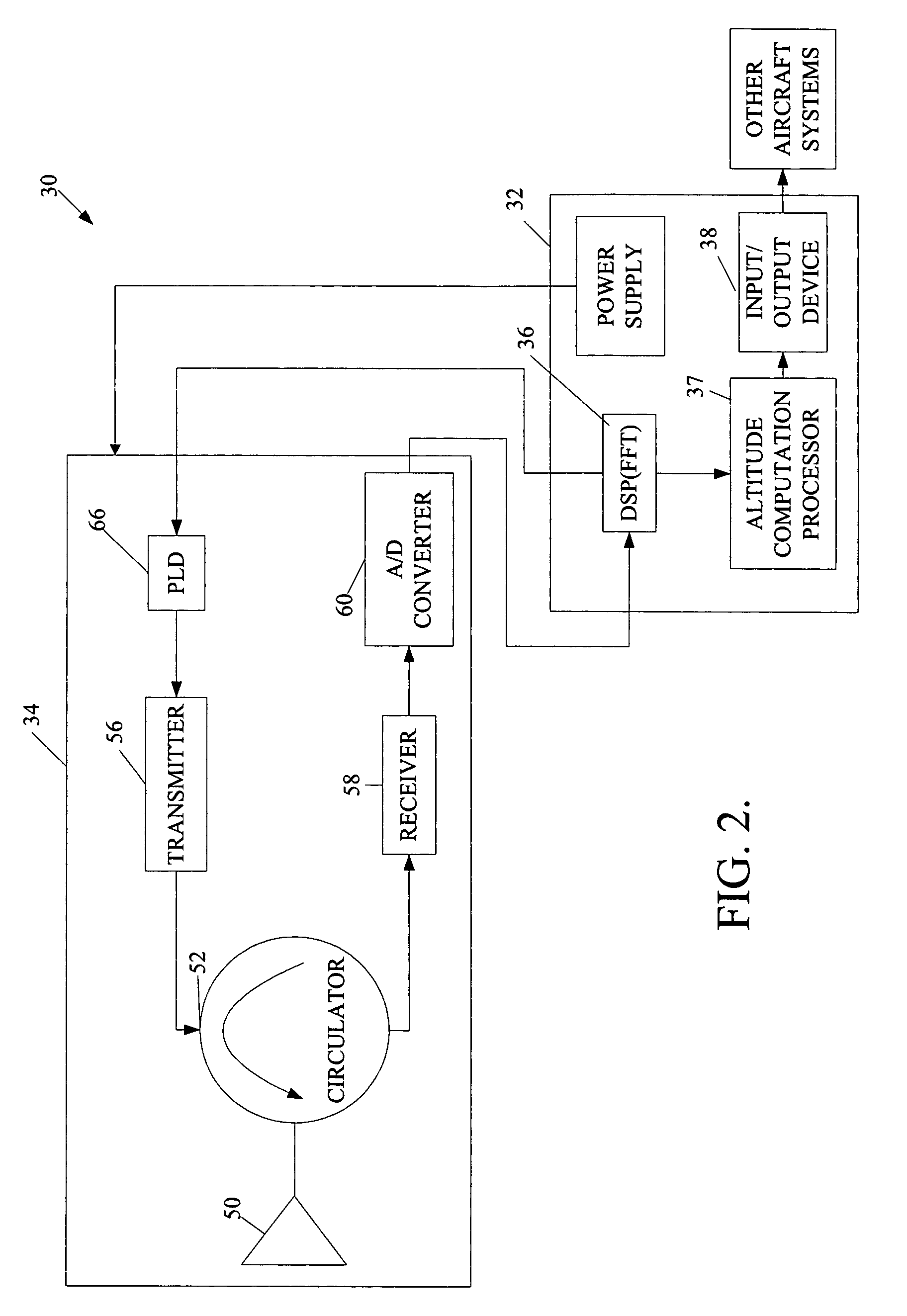
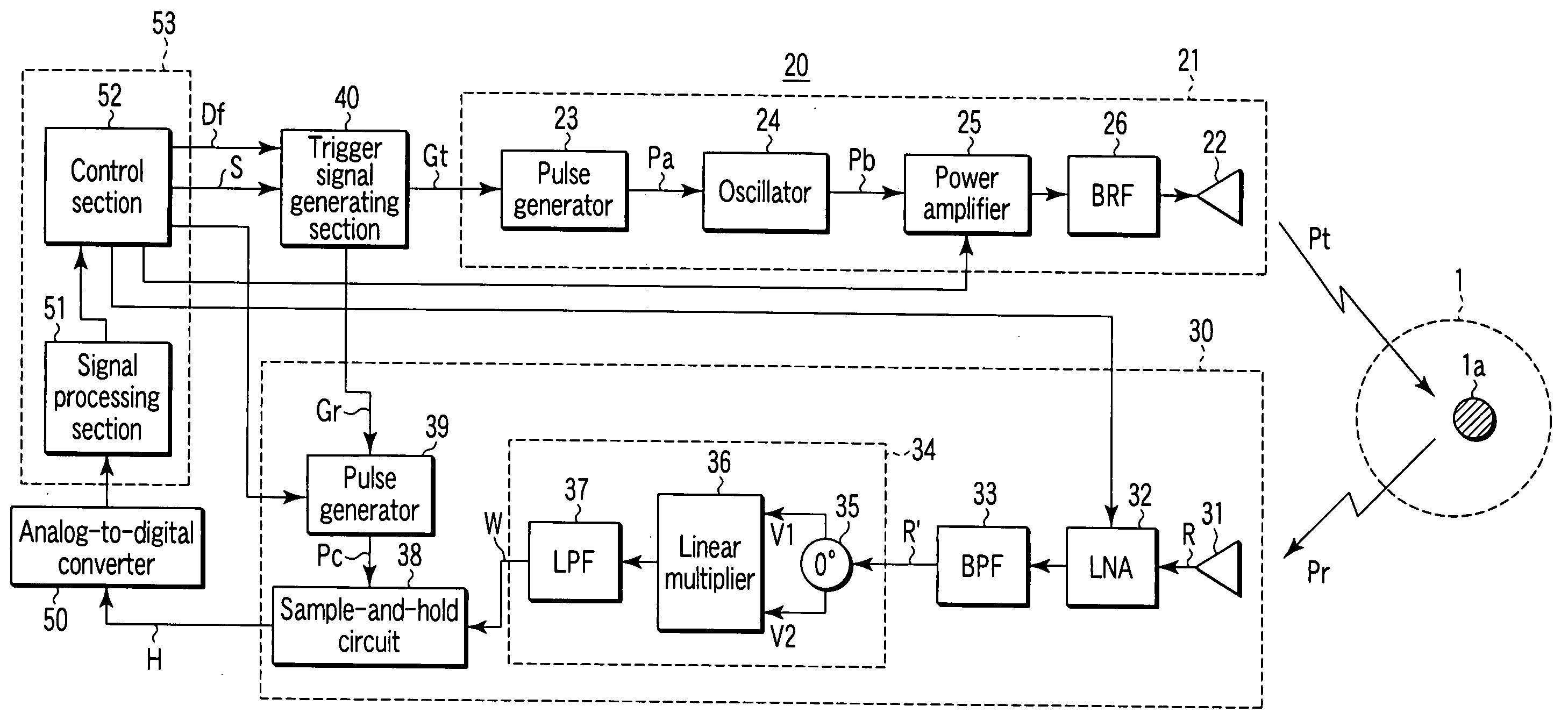
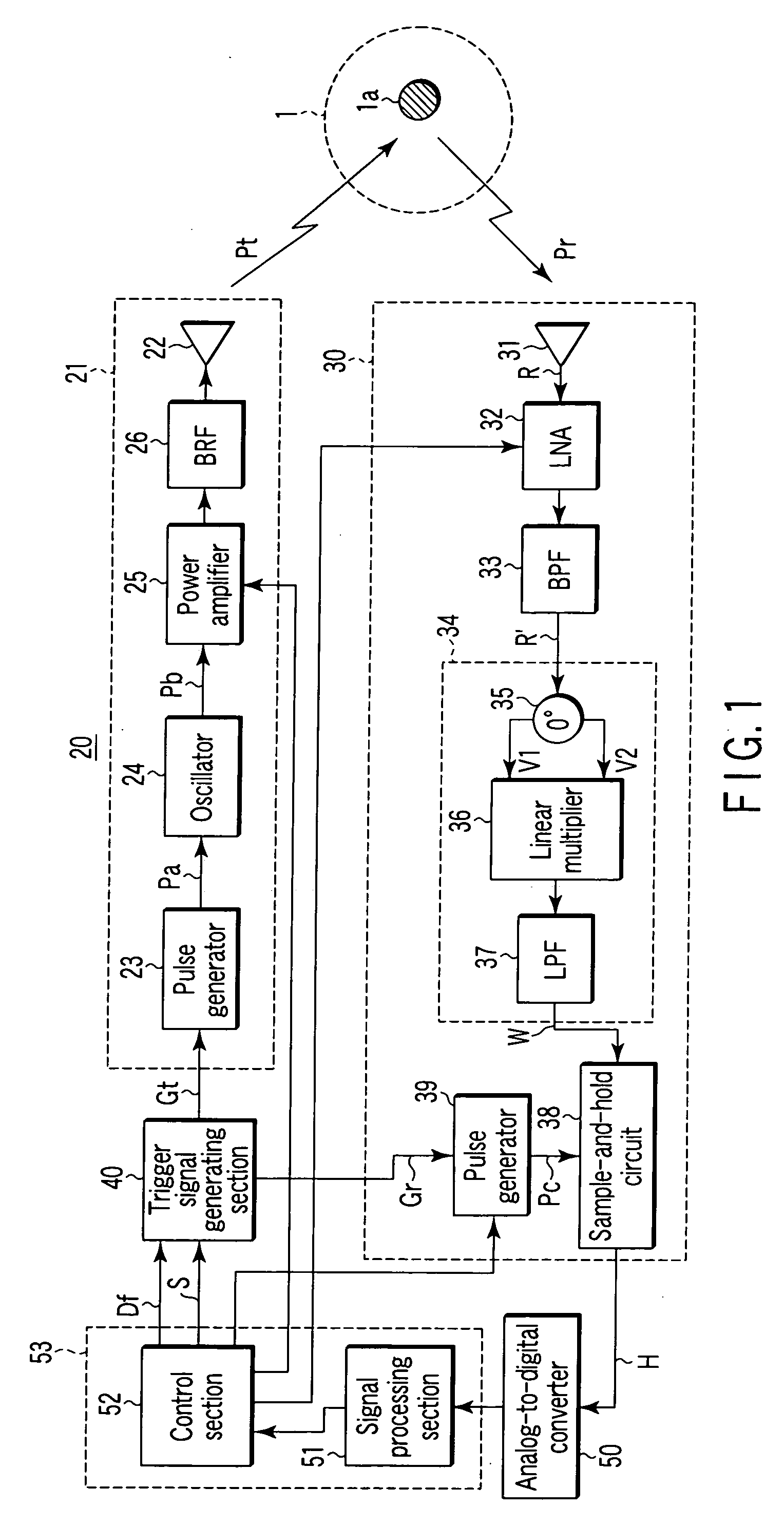
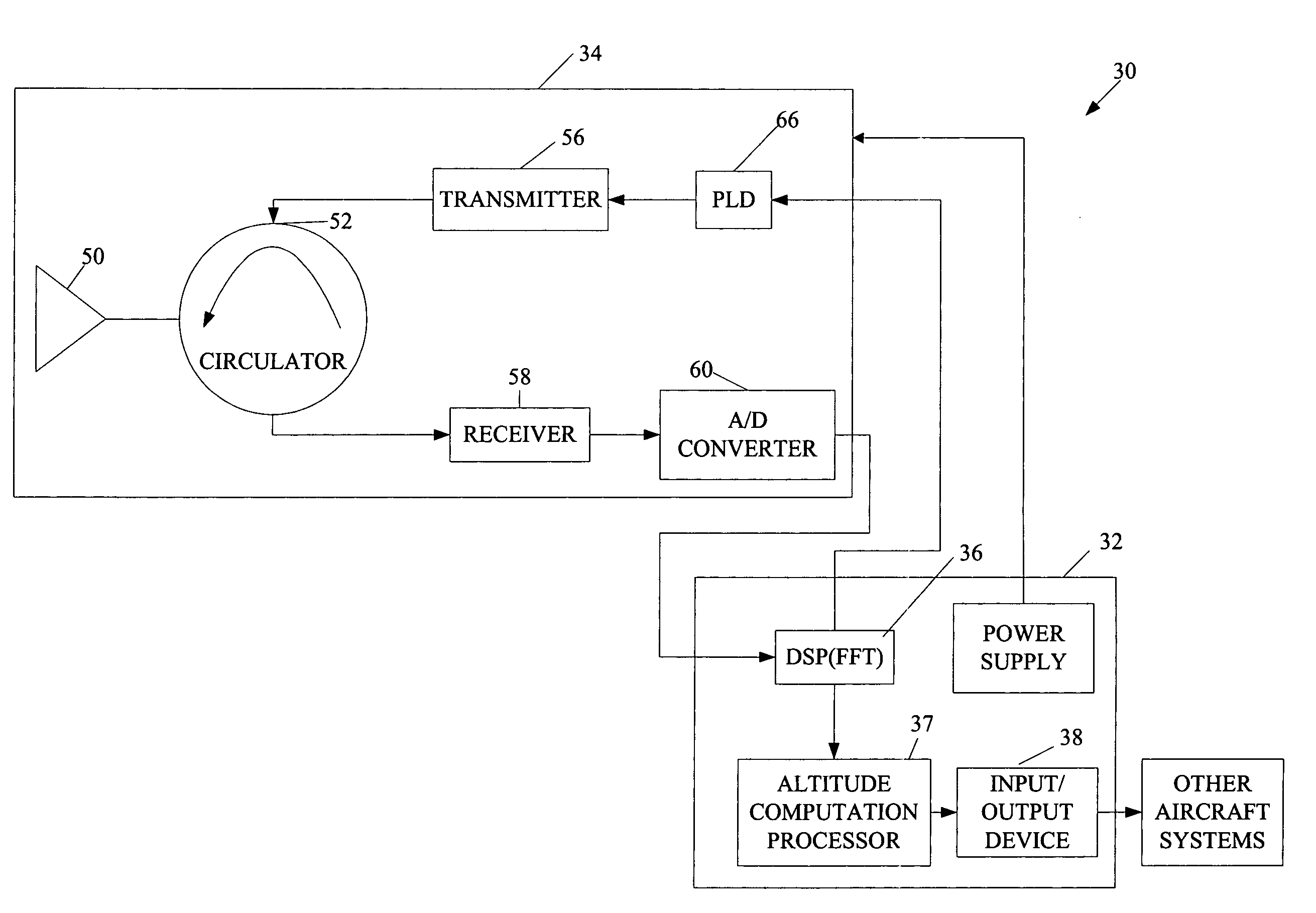
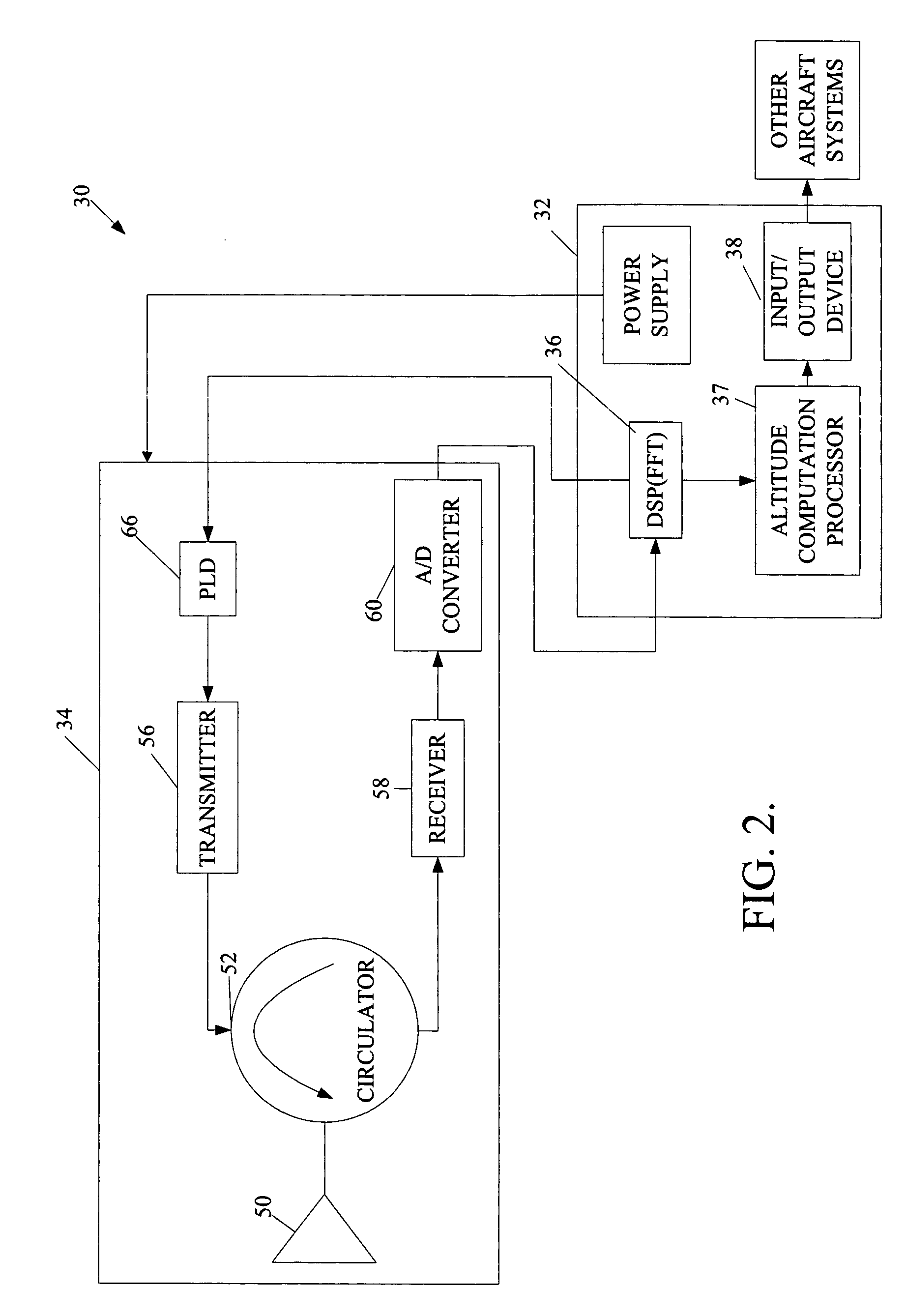
Radar altimeter
ActiveUS7239266B2Constant bandwidthConstant rateRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingPhase locked loop circuit
The present invention provides a radar altimeter system with a closed loop modulation for generating more accurate radar altimeter values. The system includes an antenna, a circulator, a receiver, and a transmitter. The circulator receives or sends a radar signal from / to the antenna. The receiver receives the received radar signal via the circulator. The transmitter generates a radar signal and includes a phase-locked loop circuit for generating the radar signal based on a pre-defined phase signal. The transmitter includes a direct digital synthesizer that generates the phase signal based on a pre-defined clock signal and a control signal. The system includes a digital signal processor and a tail strike warning processor that determine position of a tail of the aircraft relative to ground and present an alert if a warning condition exists based on the determined position of the tail of the aircraft and a predefined threshold.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Systems and methods for monitoring sensors
ActiveUS20140095102A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceDigital computer detailsVoltage converterA d converter
An impedance analyzer is provided. The analyzer includes a signal excitation generator comprising a digital to analog converter, where a transfer function of the digital to analog converter from digital to analog is programmable. The impedance analyzer further includes a receiver comprising a low noise amplifier (LNA) and an analog to digital converter (ADC), where the LNA is a current to voltage converter; where the programmable digital to analog transfer function is implemented by a direct digital synthesizer (DDS) and a voltage mode digital to analog converter, or a digital phase locked loop (PLL), or both. Further, a multivariable sensor node having an impedance analyzer is provided. Furthermore, a multivariable sensor network having a plurality of multivariable sensor nodes is provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
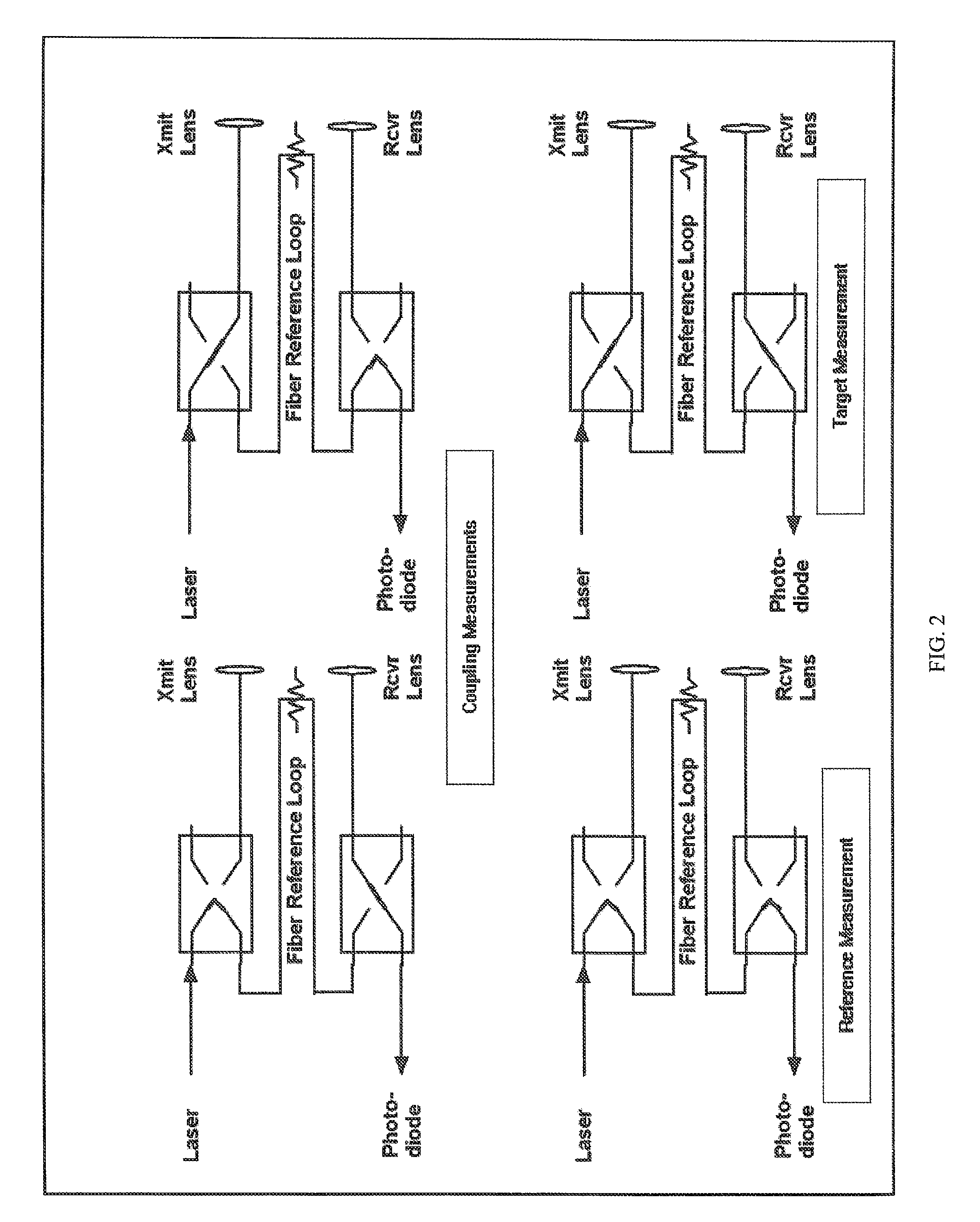
Fiber optically coupled, multiplexed, and chopped laser rangefinder
InactiveUS7586586B2Eliminates phase uncertaintyReduce changesOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationMultiplexingFiber
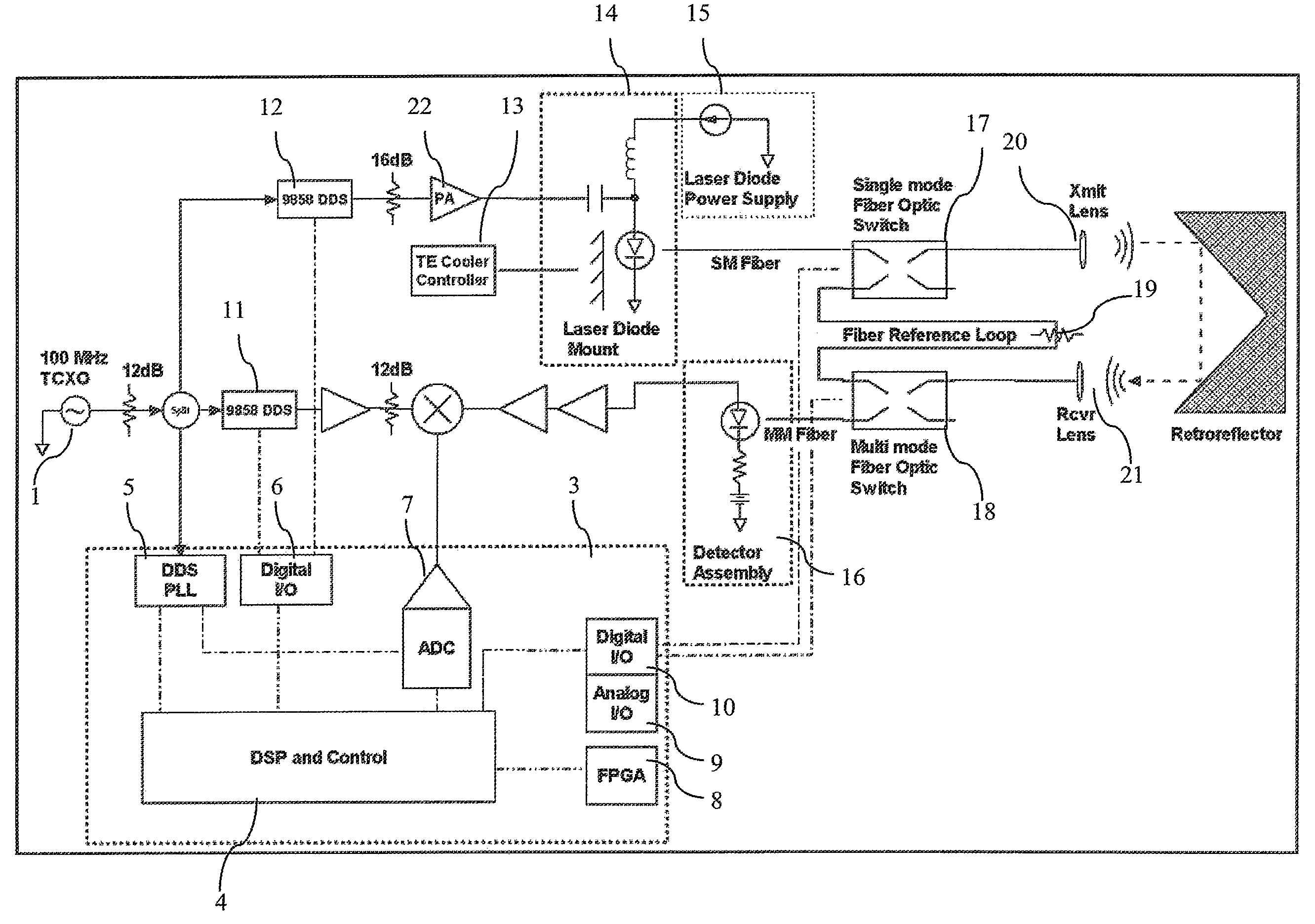
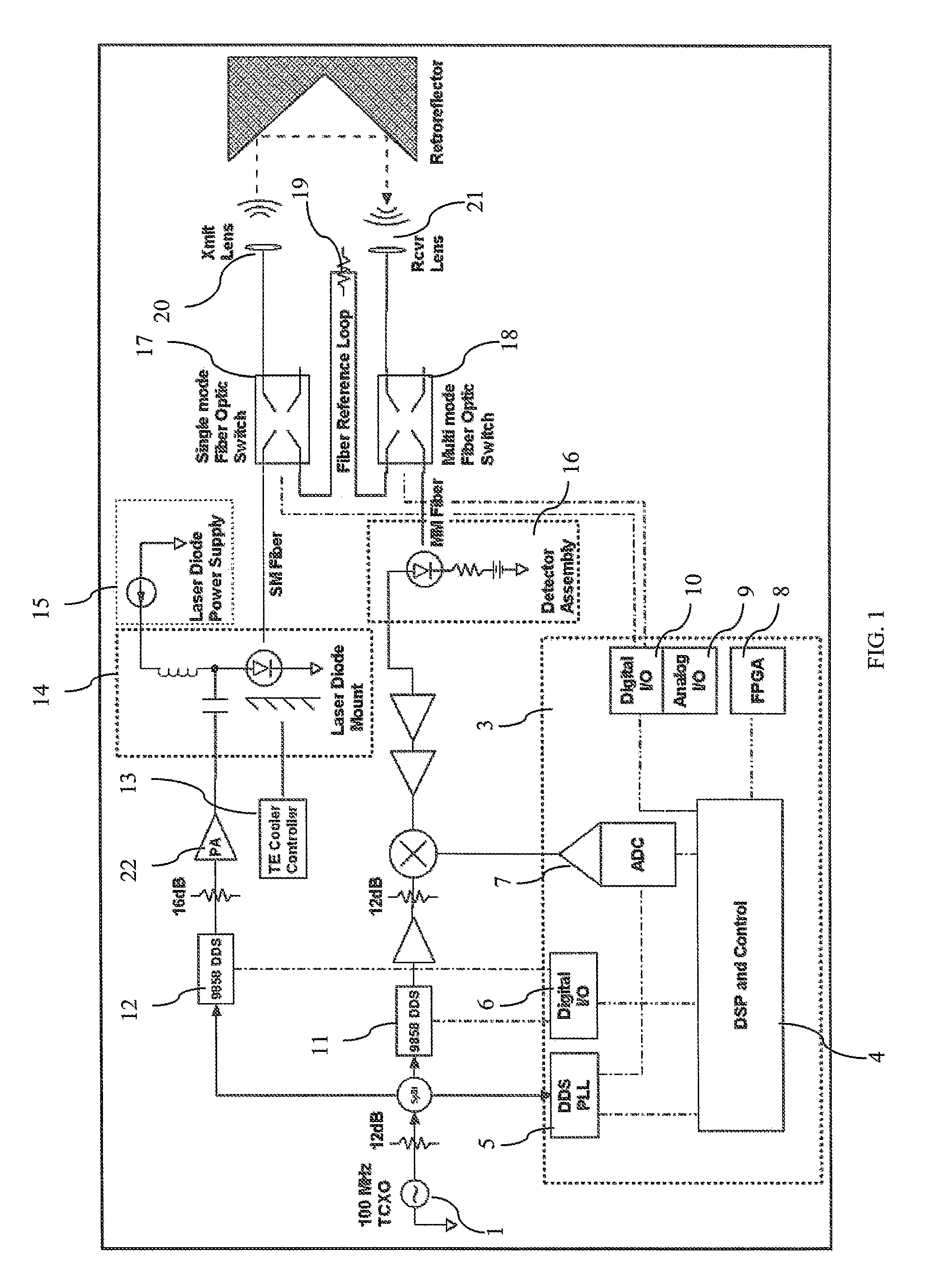
A CW phase-delay distance measuring device is described. The device fiber-optically couples an amplitude modulated laser and a detector though MEMS fiber optic switches to provide chopping and multiplexing capability, and to allow measurement of transmit and receive coupling. Phase continuous direct digital synthesizers are used to generate transmit and local oscillator frequencies in an agile frequency diverse way to disambiguate range. Fiber-optic coupling mitigates systematic errors such as variable detector group delay and provides for multiplexing multiple transmit and receive optics onto a single electro-optical system.
Owner:NATIONAL UNITED UNIVERSITY
Small-sized low-power dissipation short-range radar that can arbitrarily change delay time between transmission and reception with high time resolution and method of controlling the same
InactiveUS20070132633A1Improve time resolutionSimple configurationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImage resolutionEngineering
In a configuration according to a short-range radar of the present invention and a method of controlling the same, the timing at which a variable-period pulse output from a variable-period pulse generator including a direct digital synthesizer (DDS) has shifted in level first since reception of a search instruction is used as a reference timing, so that a signal that shifts in level at the reference timing or a fixed lapse of time later than the reference timing is generated and output as a transmission trigger signal, and a signal that shifts in level at a timing delayed by half a period of the variable-period pulse or its integral multiple from the timing at which the transmission trigger signal is output is generated and output as a reception trigger signal. With this, by varying beforehand frequency data of the DDS based on the relationship between the frequency data and delay time between transmission and reception stored in a memory, it is possible to vary delay time between the transmission trigger signal and the reception trigger signal. It is thus possible to arbitrarily vary the delay time between transmission and reception at a high time resolution by using a simple configuration and low power dissipation.
Owner:ANRITSU CORP +1
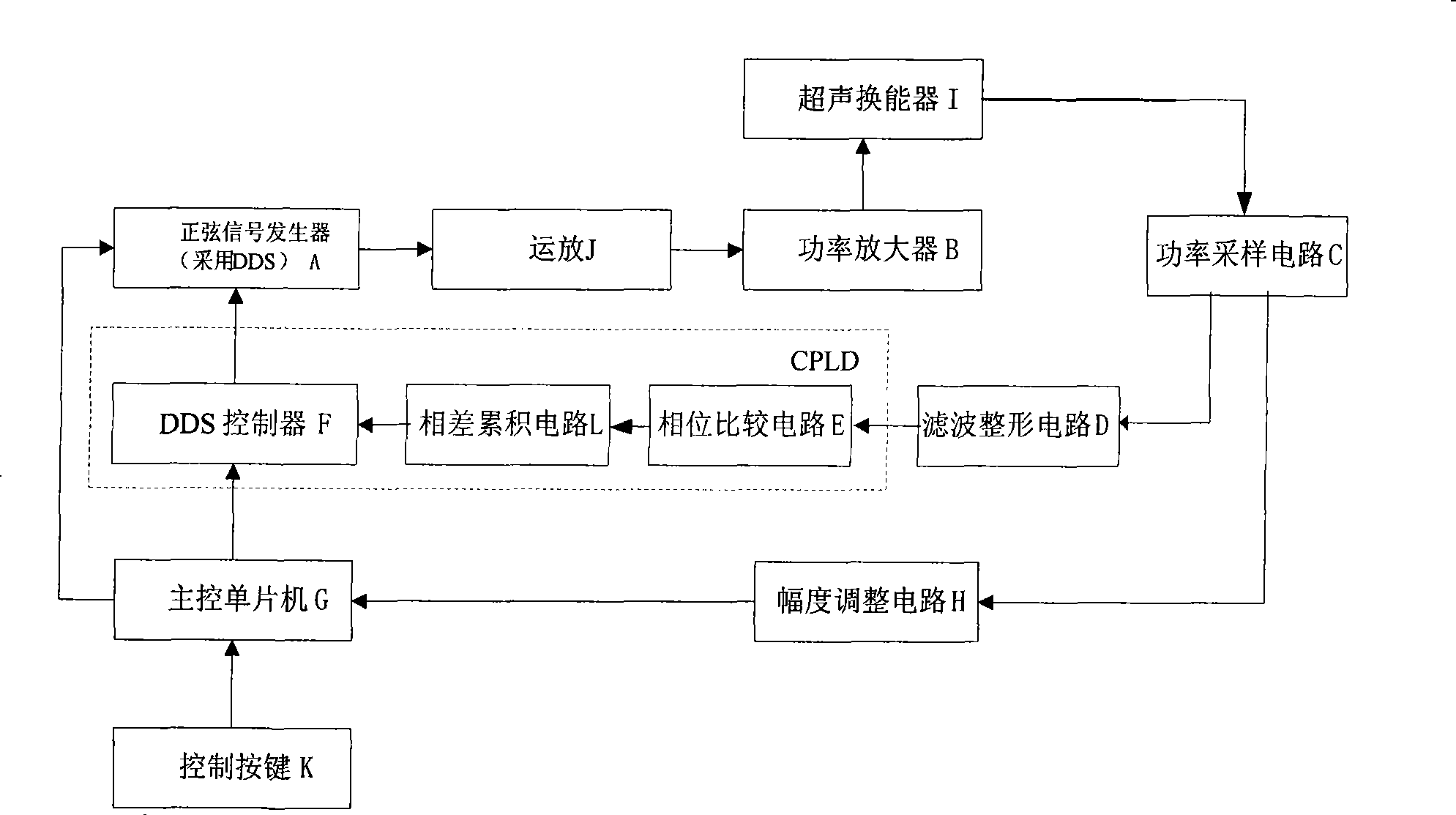
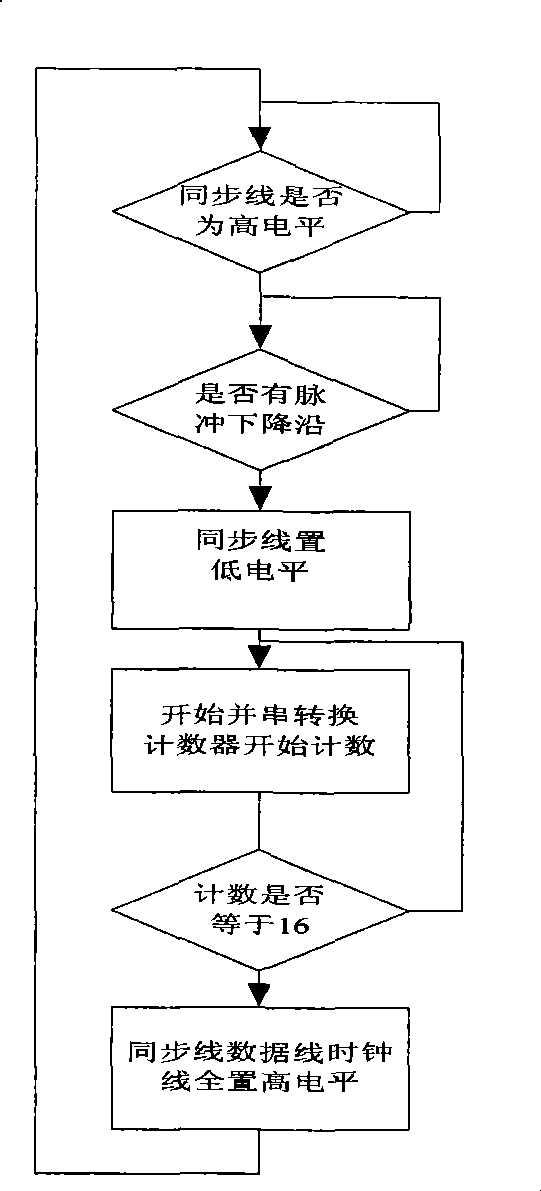
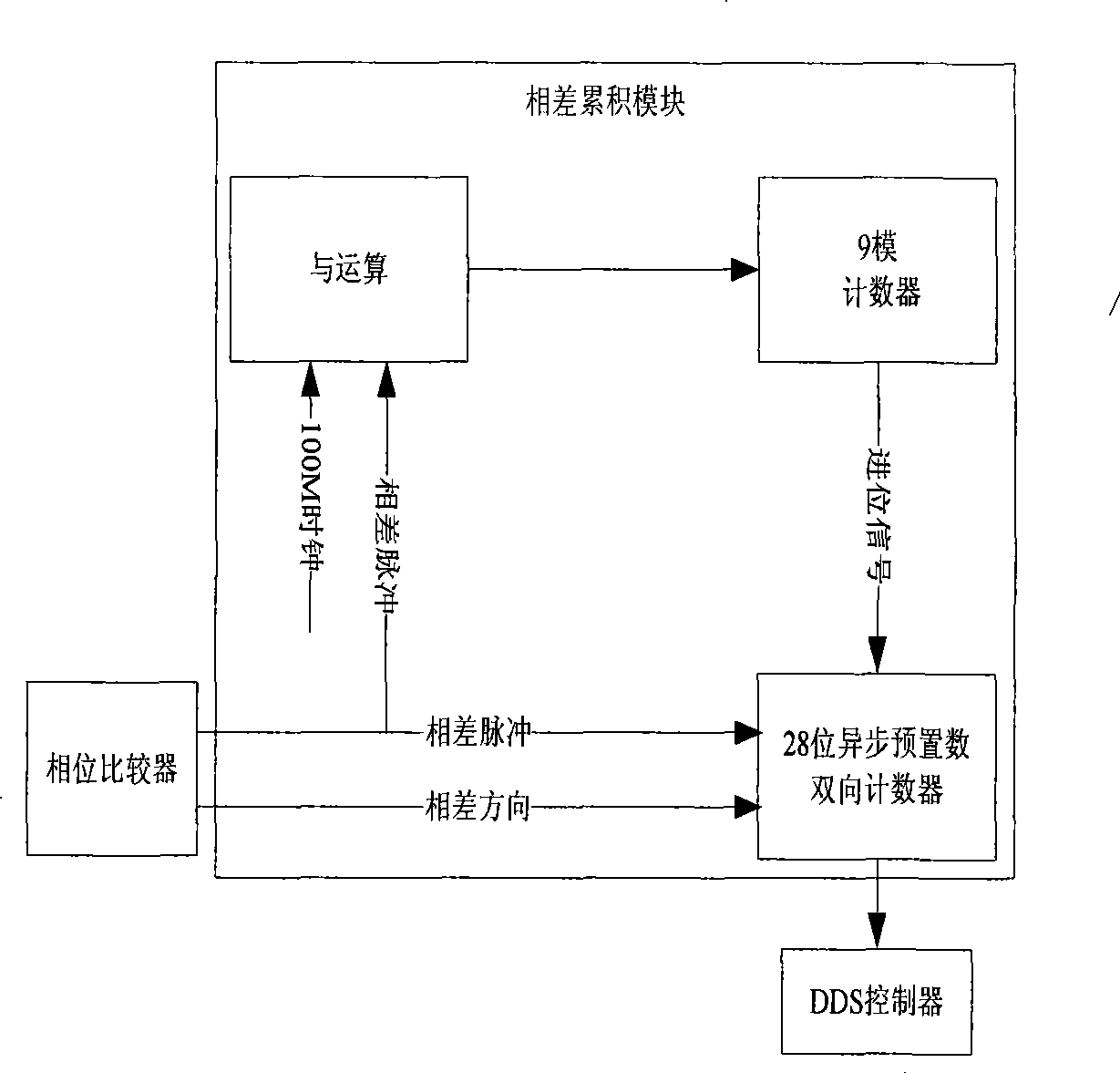
Automatic frequency tracking method of supersonic transducer and system thereof
ActiveCN101468347ARealize digital controlWork reliablyMechanical vibrations separationLogical elementUltrasonic sensor
The invention relates to an automatic frequency tracking method and a system for an ultrasonic transducer. A direct digital frequency synthesizer is used as a signal source, wherein the direct digital frequency synthesizer can be an independent integrated chip and also be achieved by the method that a digital part of a DDS is integrated in a site programmable logical element FPGA and then a digital-analog converter is additionally added. The design of the invention adopts a frequency sweeping and tracking policy, and an automatic frequency controller achieved by the programmable element controls the output frequency of the DDS according to a feedback signal sampled from the self transducer end so as to achieve the full digitization automatic frequency tracking and ensure that the ultrasonic transducer work near a resonance point all the time to obtain the optimal efficiency. A phase comparator utilizes a trigger to give out the arriving time difference of two riser edge signals of two input signals I ph and V ph aiming to the sensitive characteristics of the riser edge signals, and the sequence of the riser edge signals of the two input signals I ph and V ph is given out by a Dirrect pin.
Owner:BEIJING ANHEJIALIER TECH CO LTD
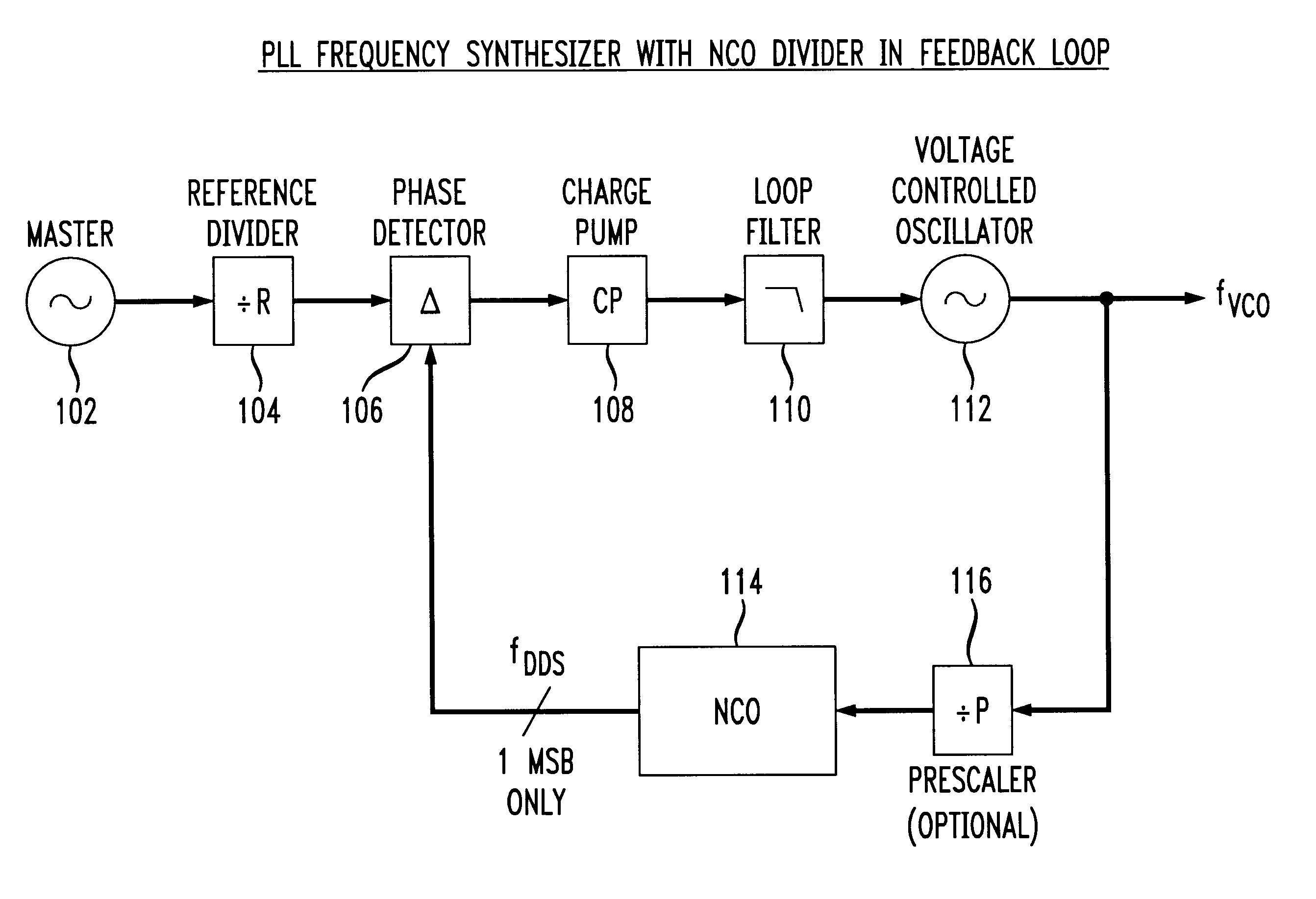
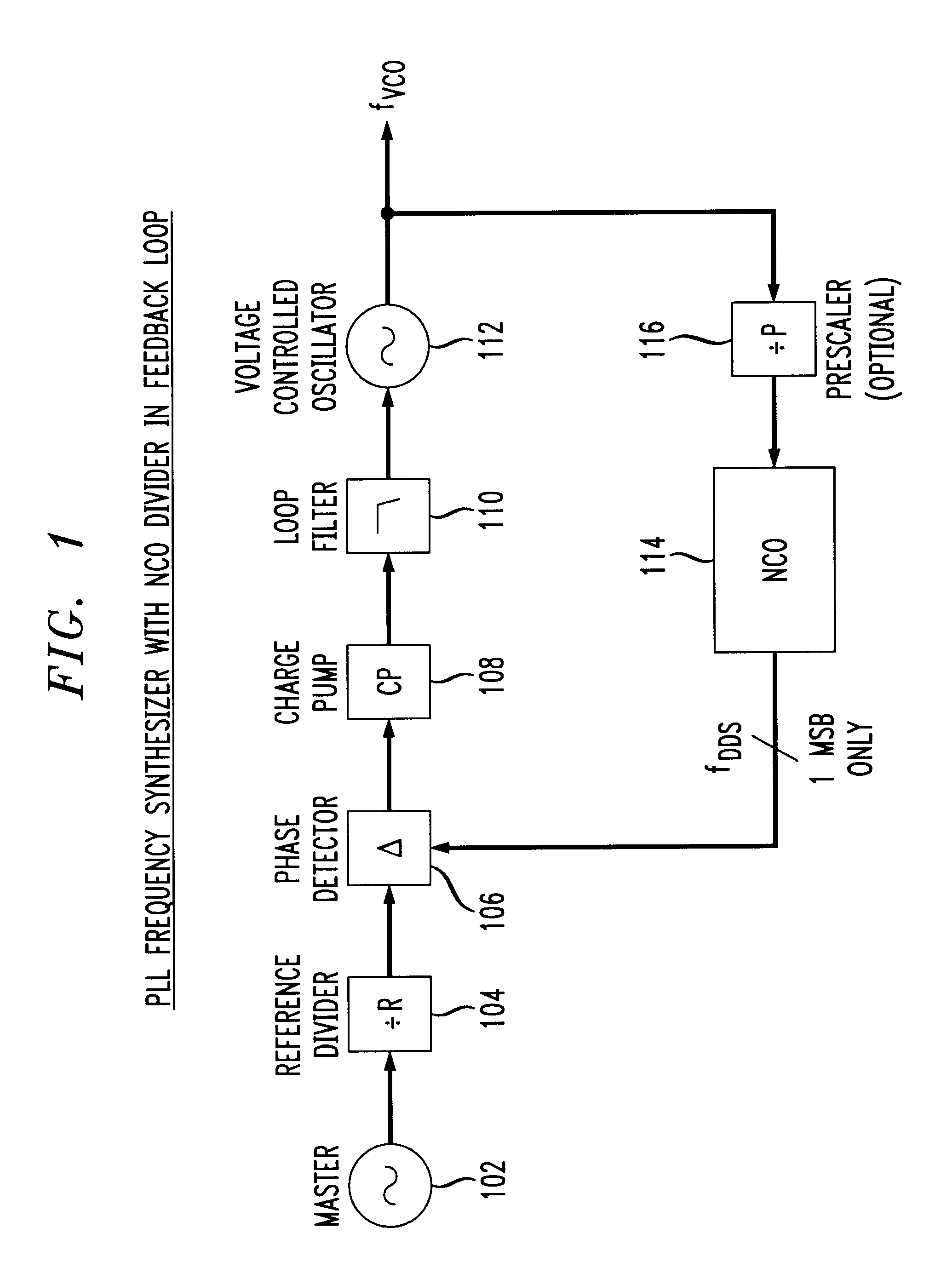
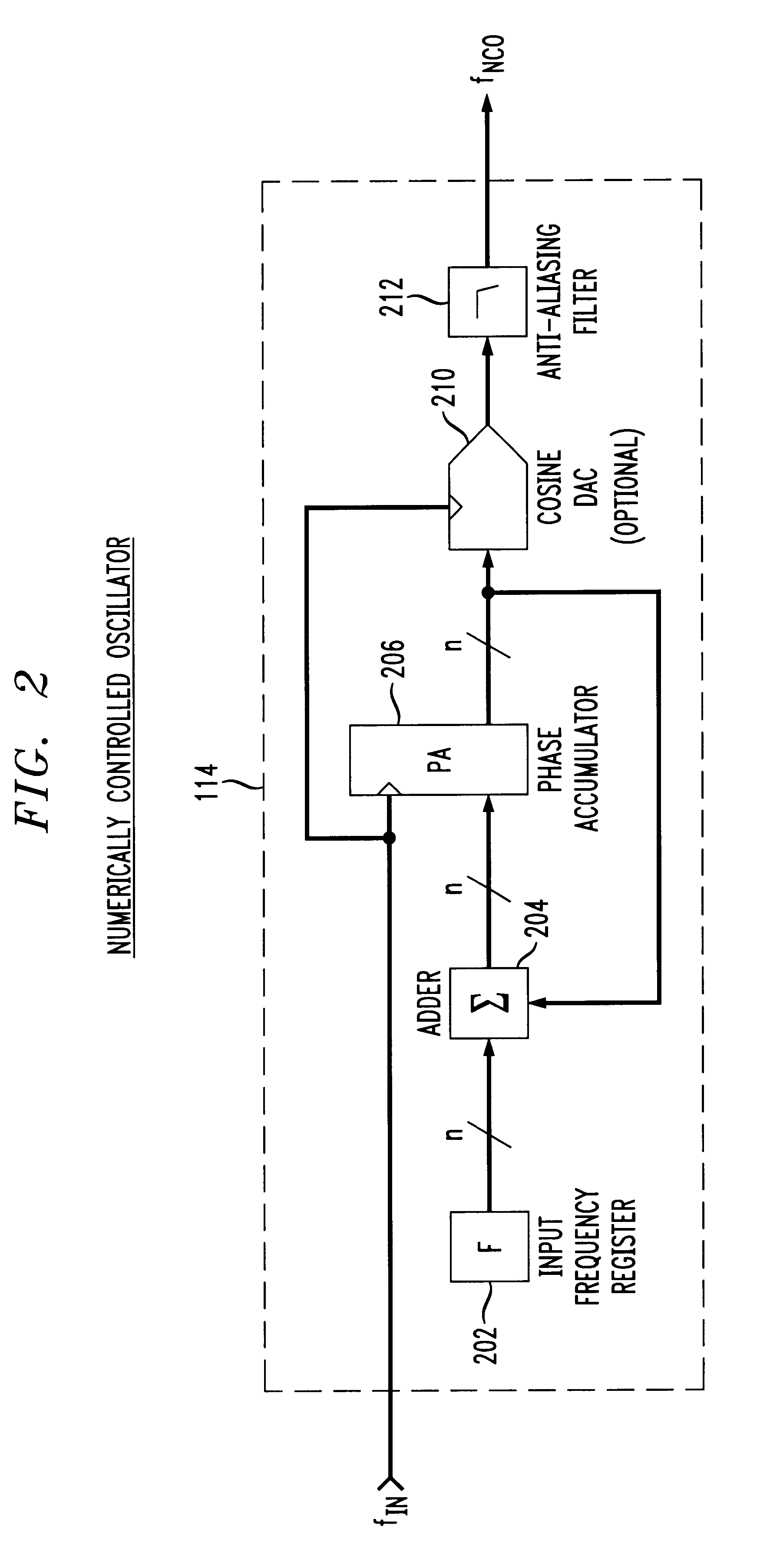
Phase locked loop with numerically controlled oscillator divider in feedback loop
A digital phase locked loop (PLL) frequency synthesizer includes a 1-bit numerically controlled oscillator (NCO) to negate the requirement that a VCO frequency be an integer multiple of its reference frequency. Thus, in accordance with the principles of the present invention, a direct digital synthesizer (DDS) or numerically controlled oscillator (NCO) is used to form a frequency divider in a feedback path of a PLL. Thus, a synthesizer with fine frequency control and very fast settling time is disclosed. The conventional integer-ratio relationship between the reference frequency fREF and the synthesized output frequency signal fVCO is overcome by replacement of a conventional VCO divider in a feedback path of a digital PLL with a 1-bit NCO. This allows the reference frequency fREF to be greater than the channel spacing, i.e., the channel spacing can be smaller than the reference frequency fREF. Thus, a much quicker settling time and improved VCO phase noise are provided, either of which results in a significant improvement in the performance of virtually any communications system.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE +1
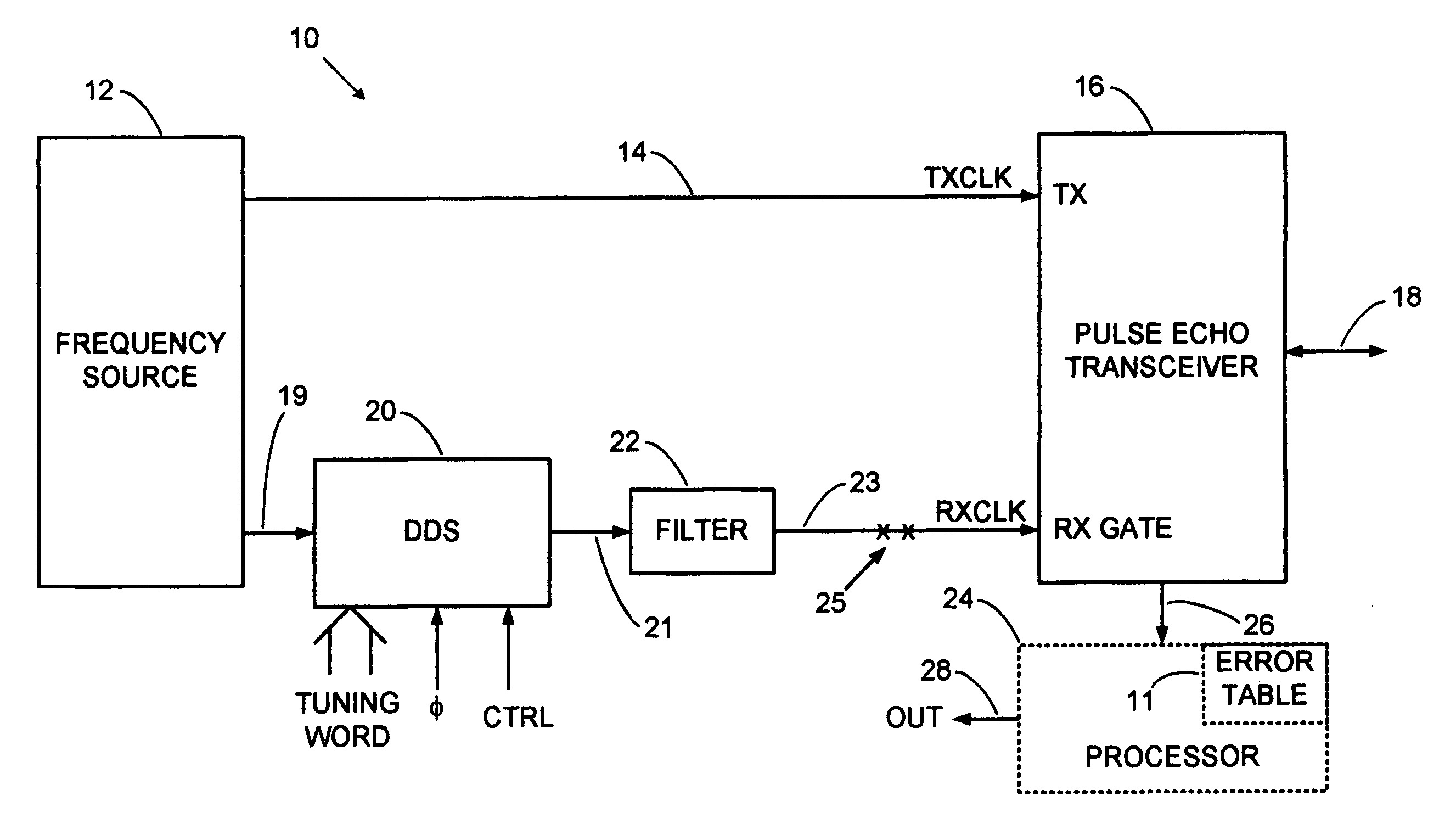
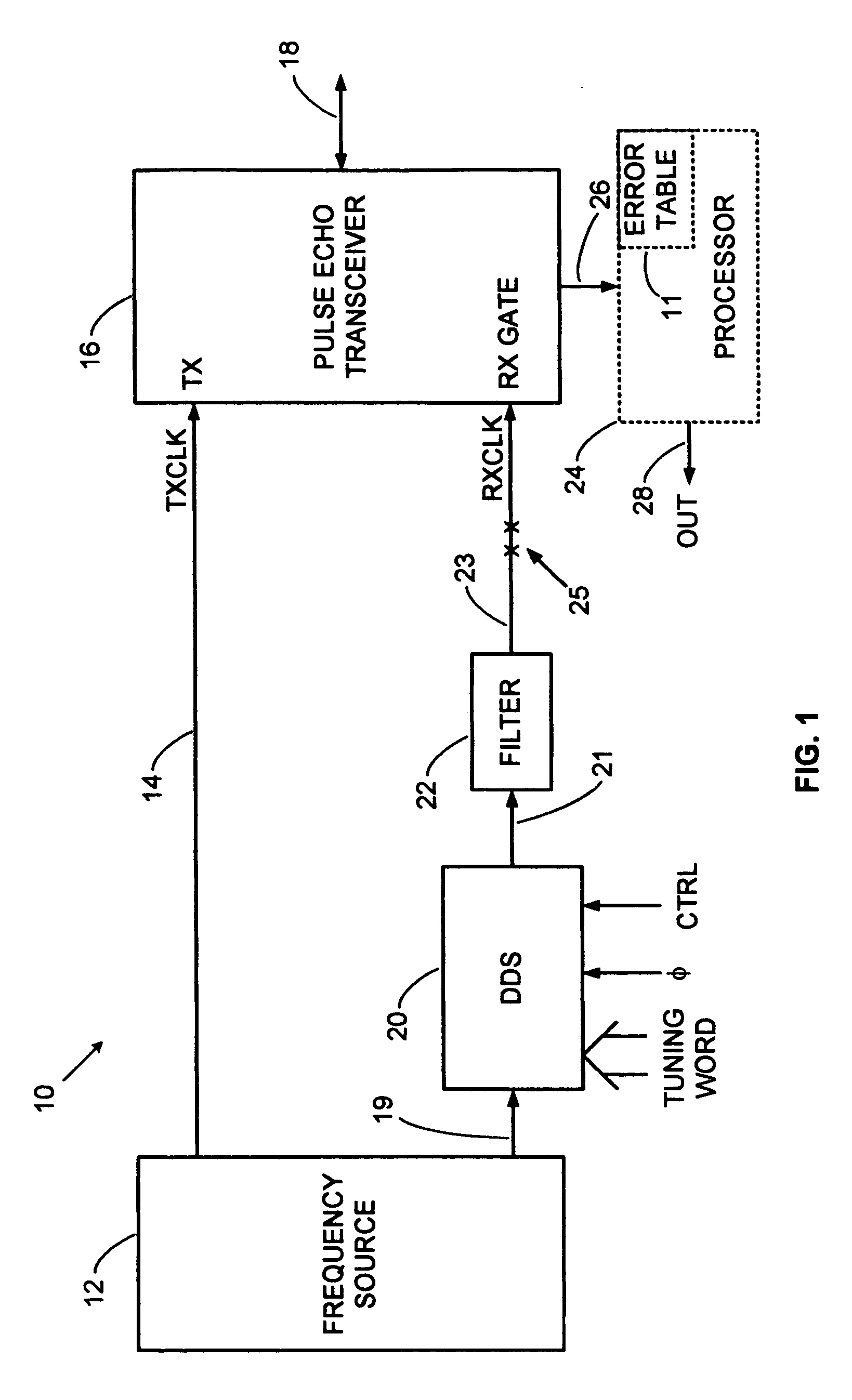
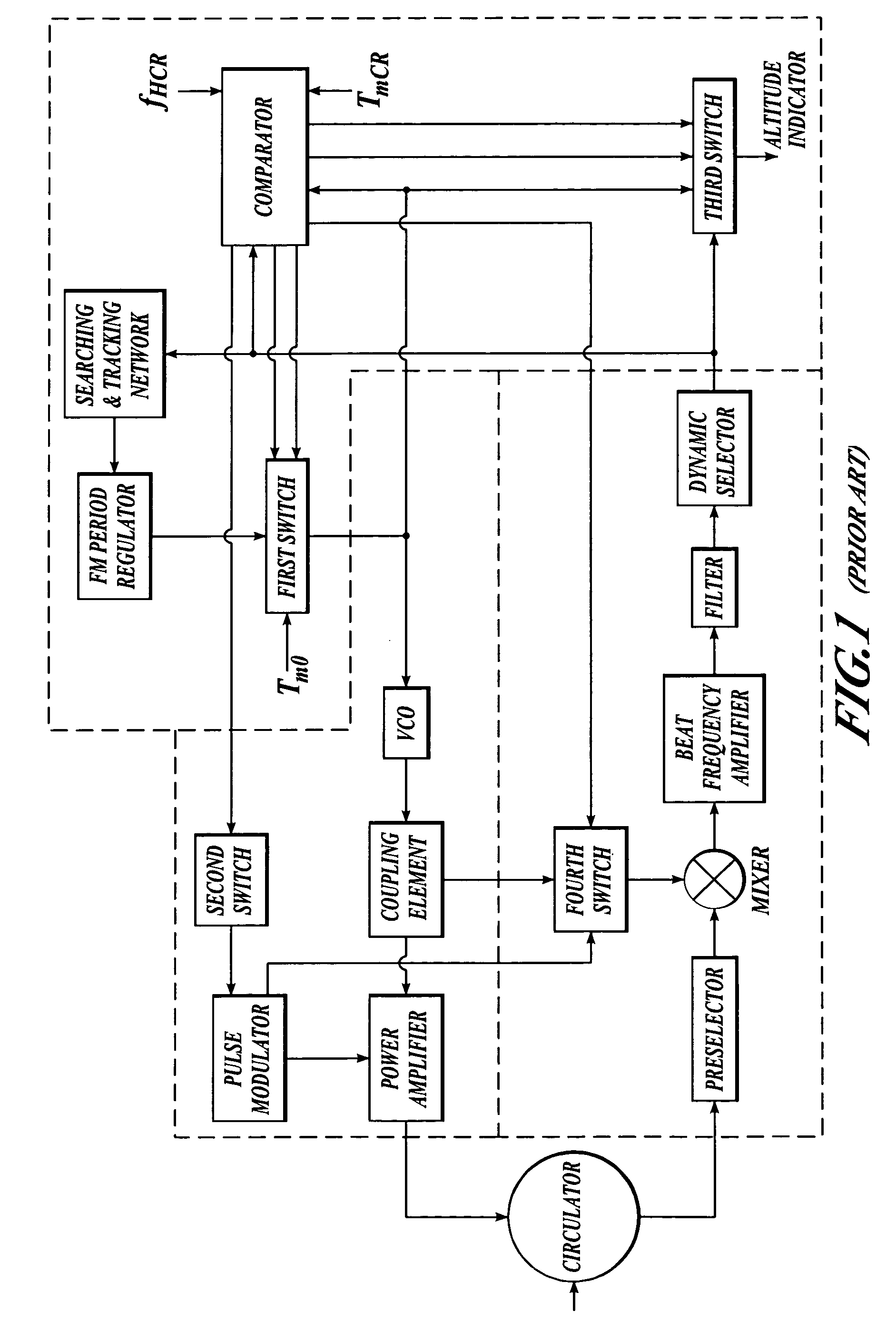
Direct digital synthesis radar timing system
InactiveUS20070192391A1Reducing timing system errorImprove stabilityWave based measurement systemsDigital function generatorsAccuracy improvementRadar
A direct digital synthesizer (DDS) drives a receive sampling gate at a frequency that is offset from a transmit pulse frequency to produce an expanded time sampled echo signal. The frequency offset generates a smoothly slipping phase between realtime received echoes and the sampling gate that stroboscopically expands the apparent time of the sampled echoes with an exemplary factor of 1-million and a range accuracy of 1-centimeter. The flexibility and repeatability of the digitally synthesized timing system is a quantum leap over analog prior art. The rock solid stability of the DDS allows further accuracy improvement via an error correction table.
Owner:MCEWAN TECH
System and method for fast data encryption/decryption using time slot numbering
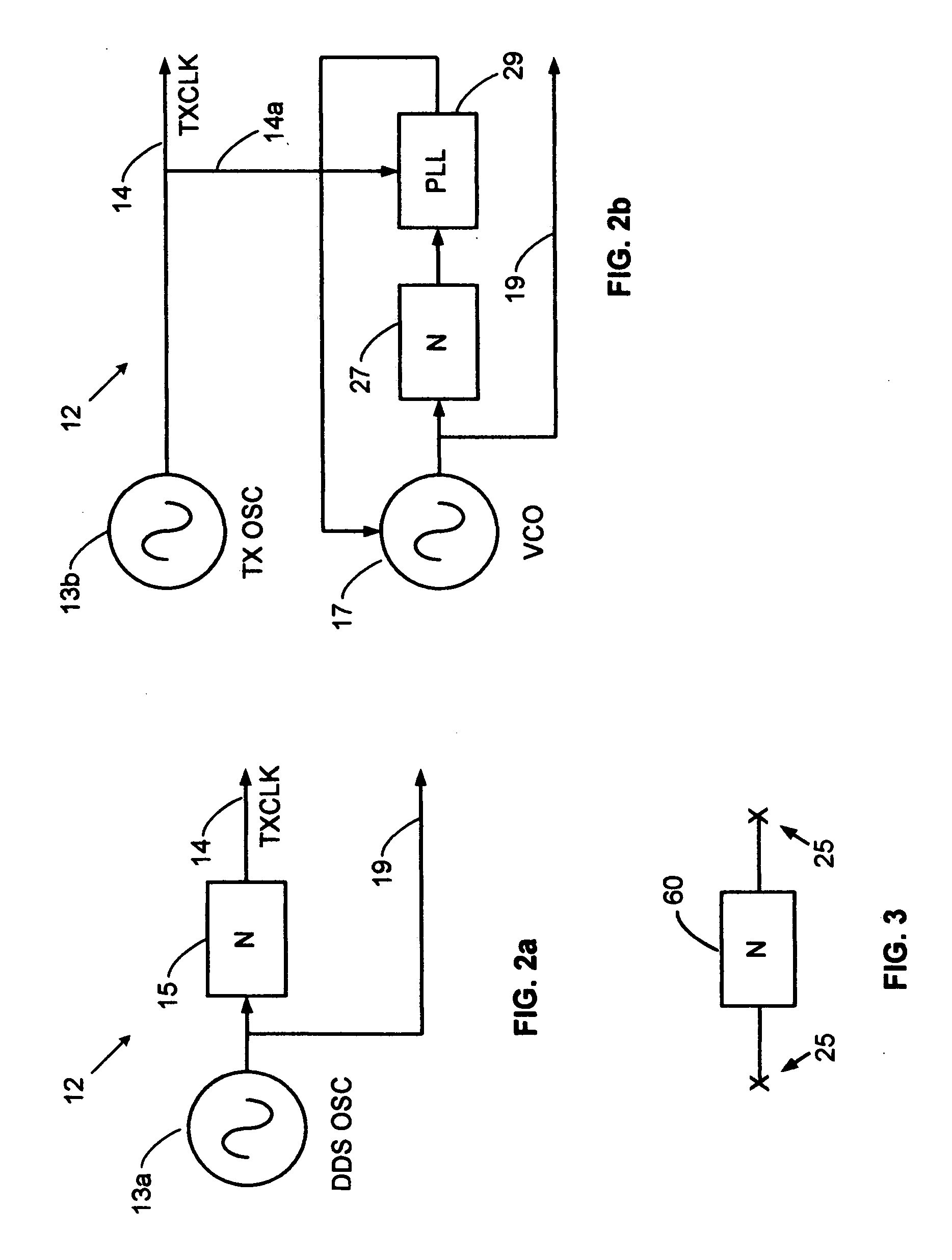
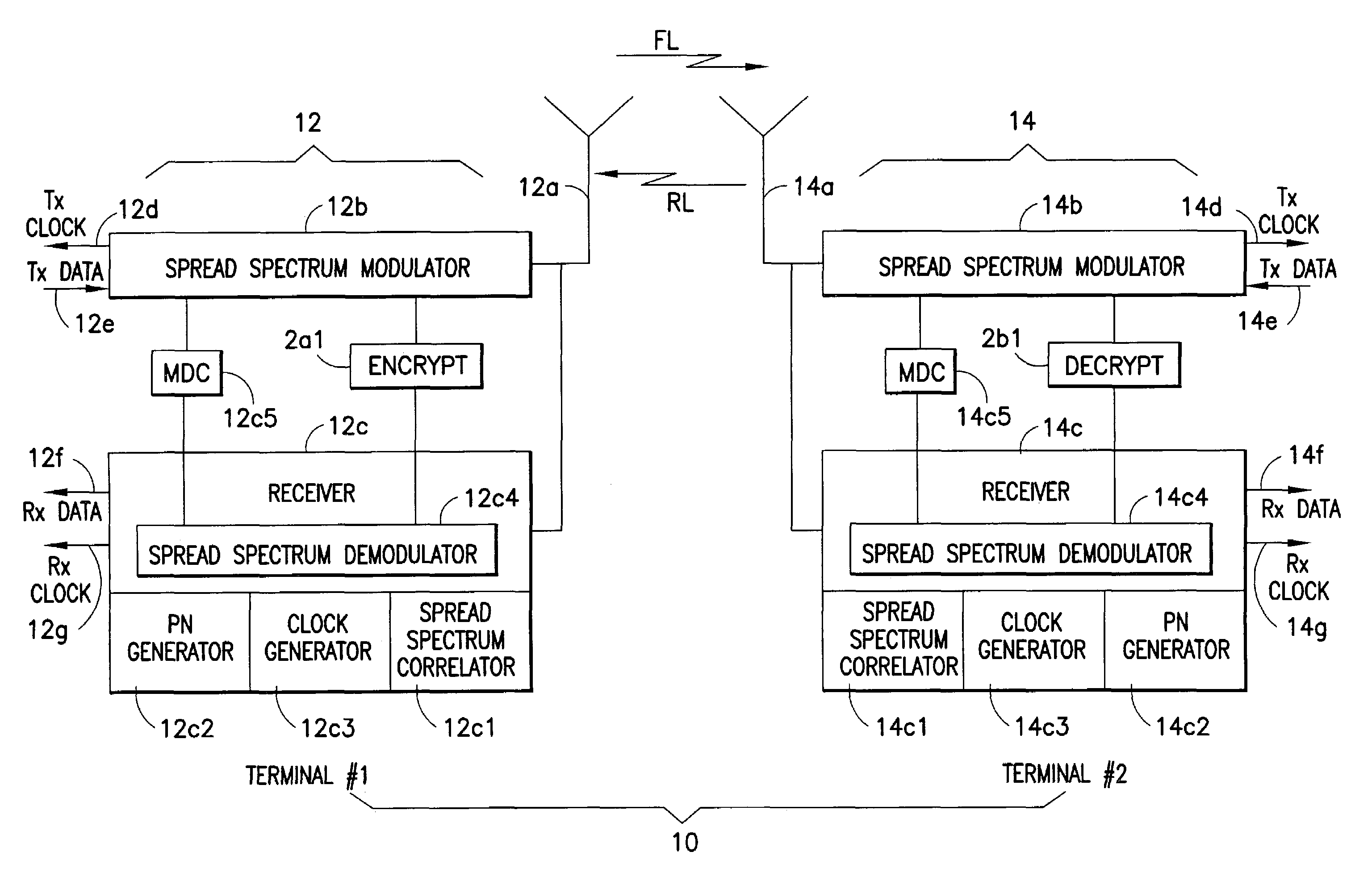
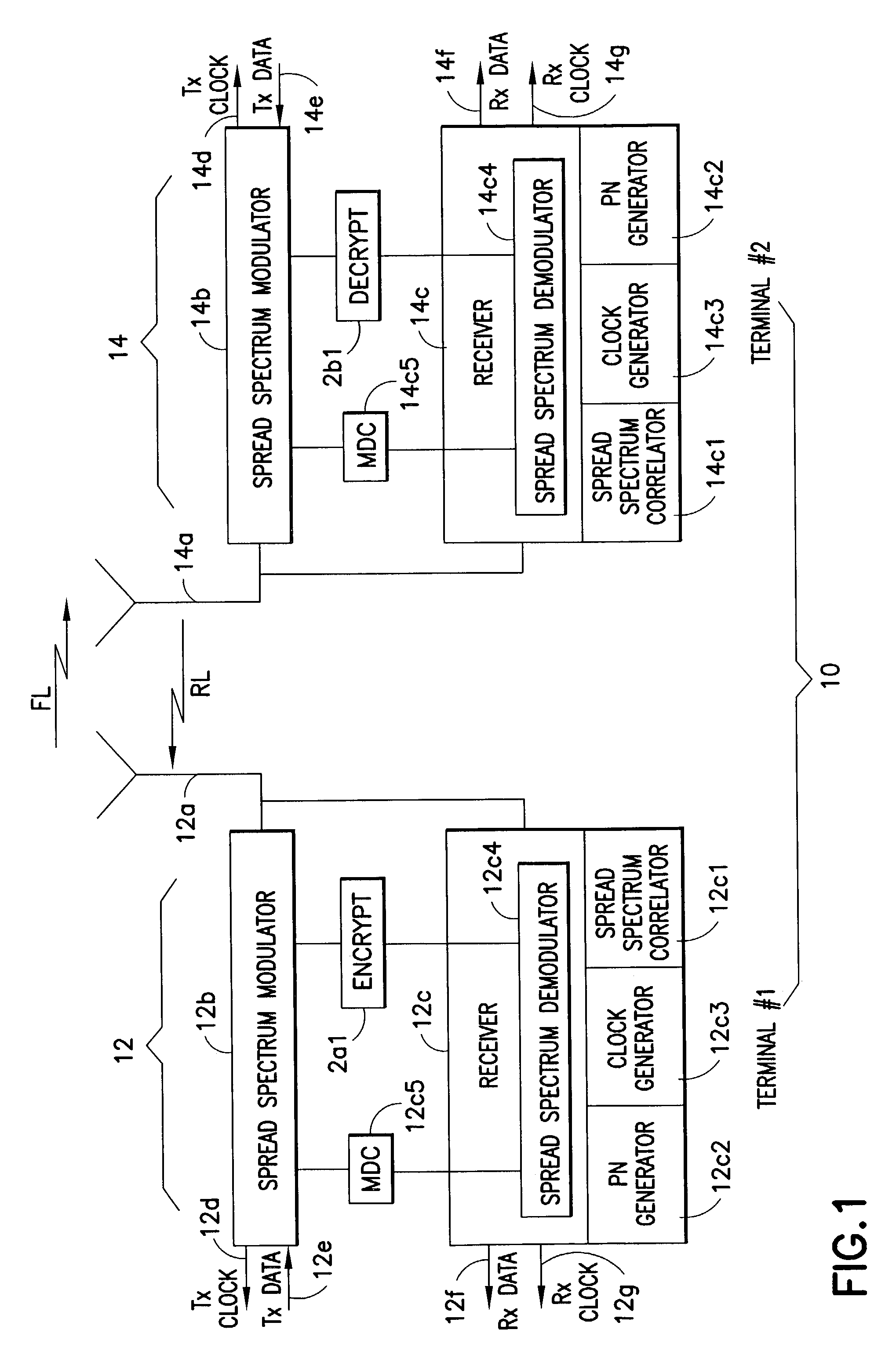
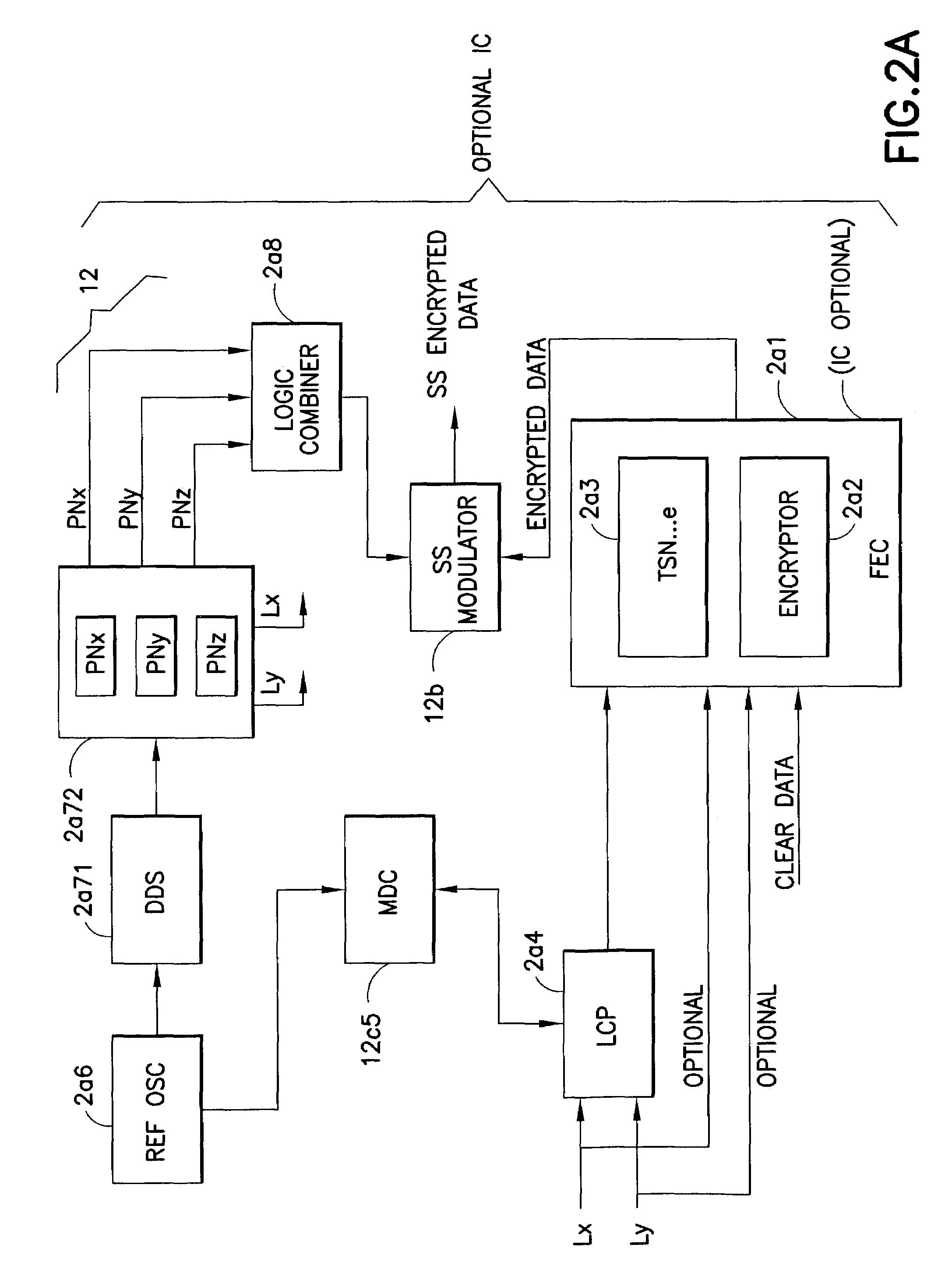
ActiveUS7200233B1Fast decryptionSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesUnauthorized memory use protectionDirect digital synthesizerComputer science
A system for fast data encryption / decryption is provided. The system includes a transmitter system having a transmitter direct digital synthesizer (DDS). The DDS includes at least three transmitter pseudo-noise (PN) component code generators PNx, PNy, PNz, where each transmitter PN component code generator is adapted to generate relatively prime transmitter PN component codes when compared with each of the other transmitter PN component code generators. The transmitter also includes a first processor coupled to the transmitter DDS, where the first processor is adapted to determine a time slot number (TSN) relative to at least two of the relatively prime transmitter PN component codes. Also included in the transmitter is an encryptor for encrypting clear data in accordance with the TSN. The system includes a receiver system having a second processor adapted to determine the TSN; and a decryptor coupled to the second processor. The decryptor is adapted to decrypting the encrypted clear data in accordance with the TSN.
Owner:L3 TECH INC
Digital IF demodulator with carrier recovery
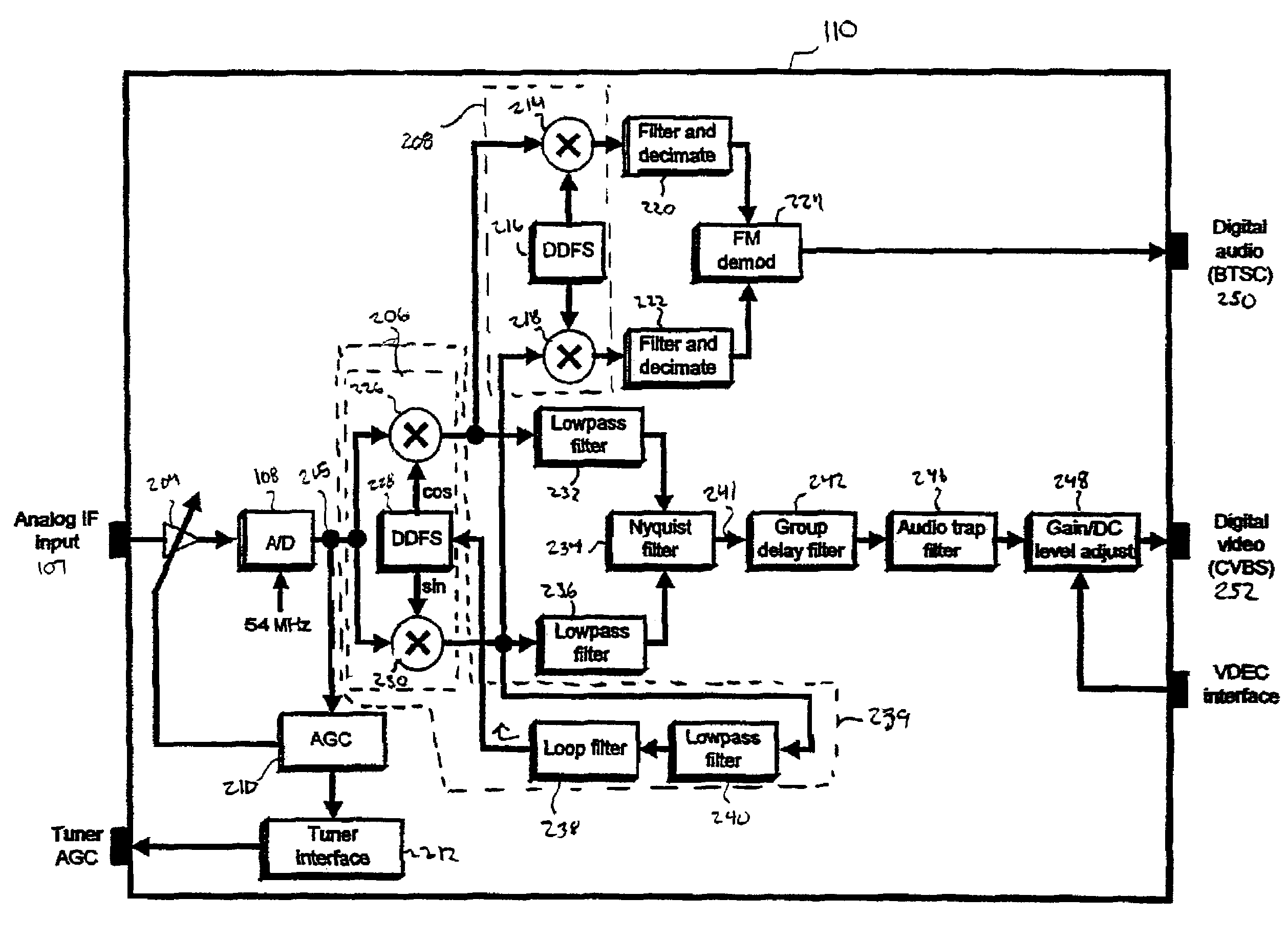
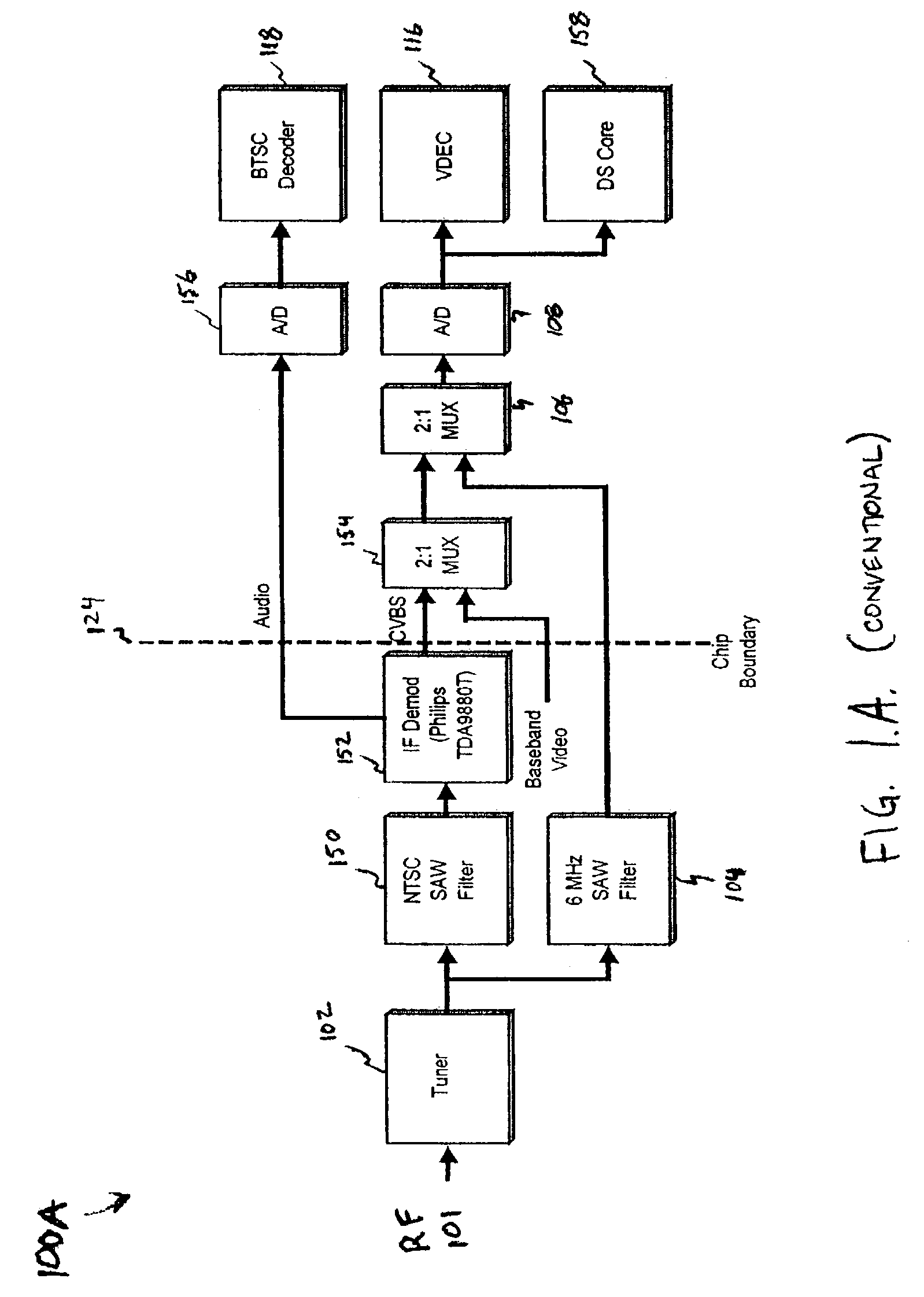
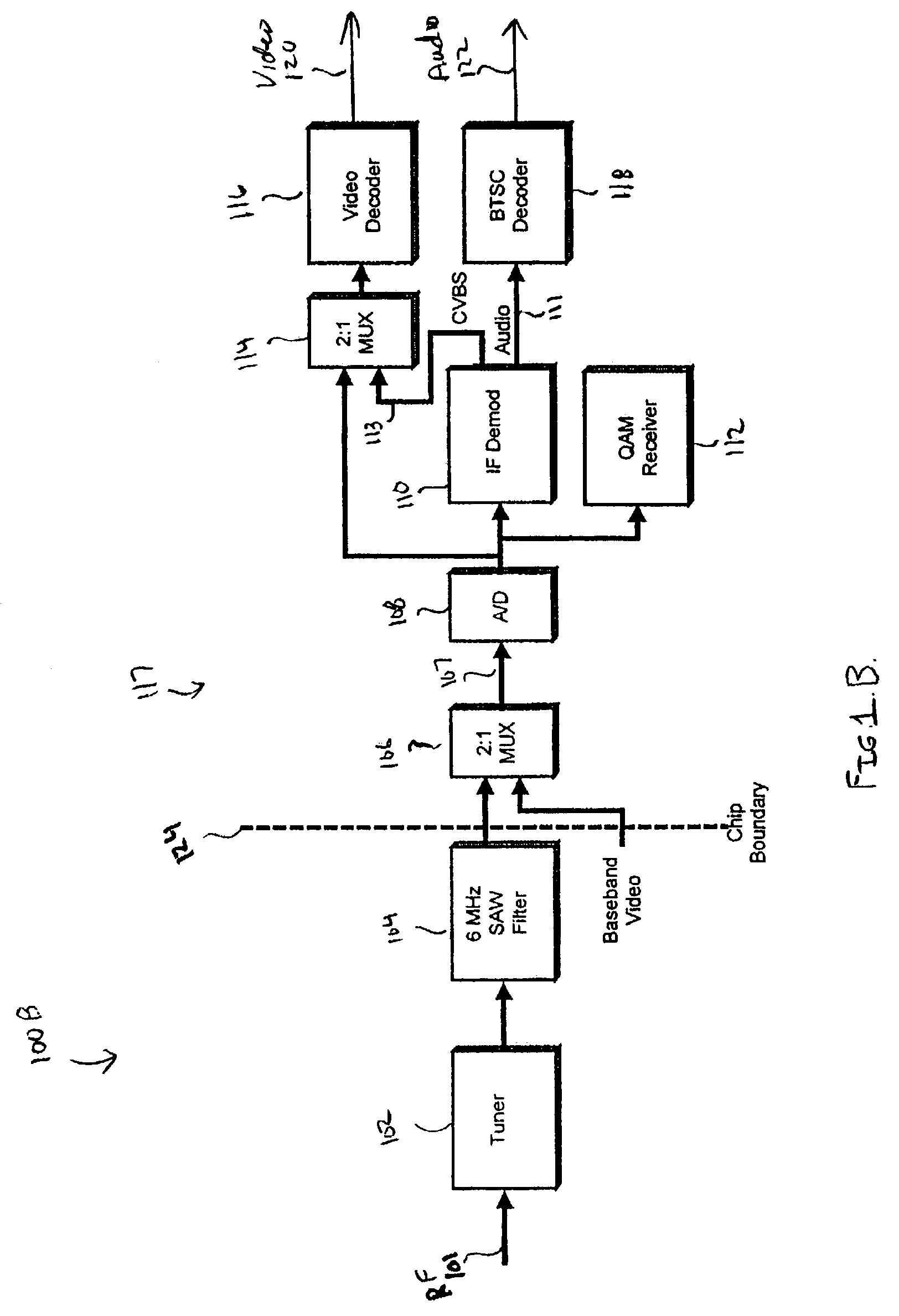
A digital IF demodulator receives and demodulates an analog IF input signal to produce a digital audio signal and a digital video signal. The digital IF demodulator includes an A / D converter, a first digital complex mixer, a second digital complex mixer, and various digital filters. The first digital complex mixer receives the output of the A / D converter and down-converts the output of the A / D converter to baseband. Additionally, the picture carrier is recovered from the output of the first digital complex mixer, and fed back to a direct digital synthesizer to control the tuning accuracy of the first digital complex mixer. More specifically, a feedback loop is formed to so that the picture carrier is down-converted to DC so as to control the tuning accuracy of the first digital complex mixer. The complex output of the first complex mixer is further processed using Nyquist filtering and other filtering to recover the digital video signal. The digital audio signal is recovered by further processing the output of the first digital complex mixer. With the picture carrier located at DC, the audio signal is shifted off DC by approximately 4.5 Mhz. A second complex mixer down-converts the output of the first digital complex mixer so that the audio signal at 4.5 MHz is down-converted to baseband. After filtering and demodulation, the digital audio signal is recovered.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
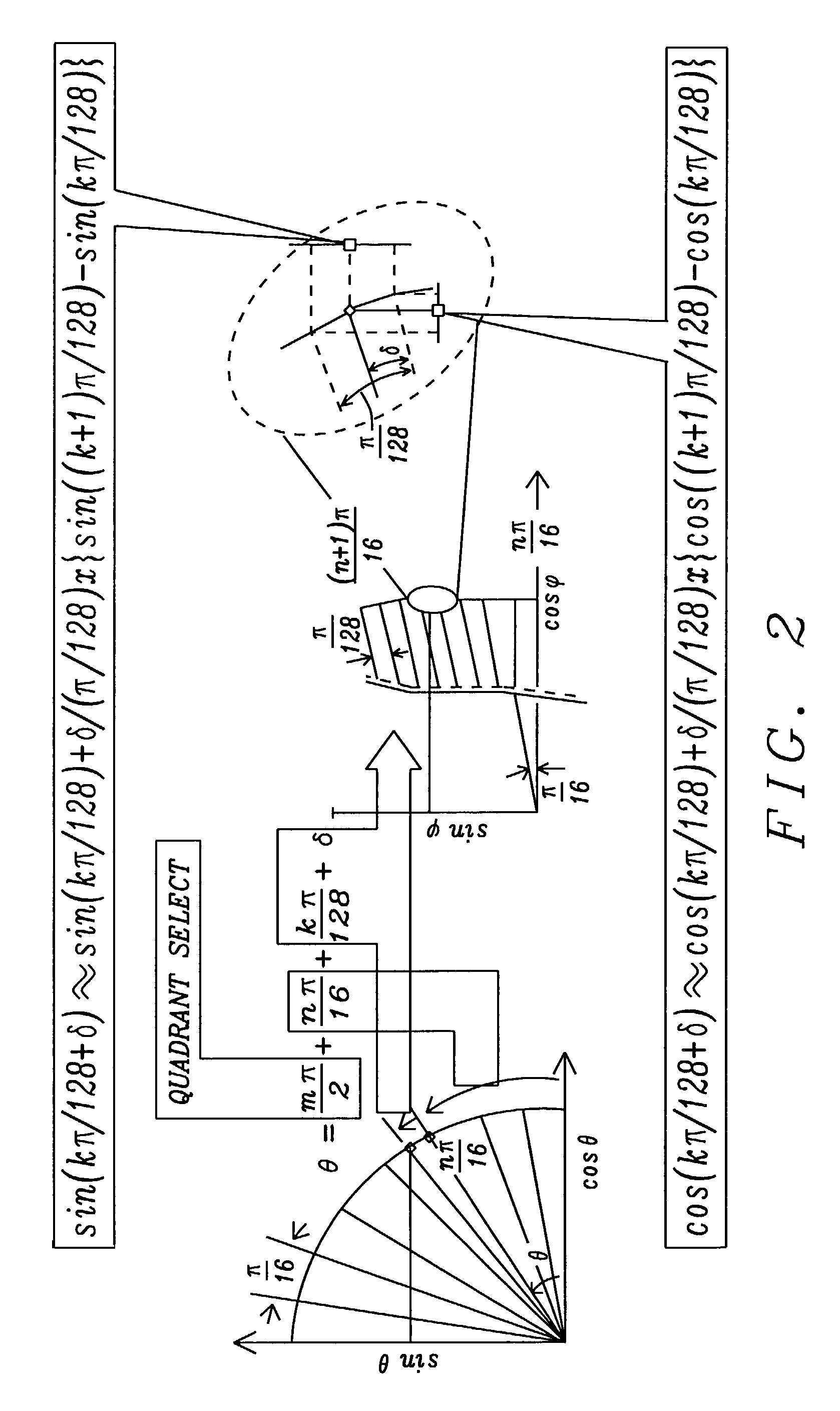
16 bit quadrature direct digital frequency synthesizer using interpolative angle rotation
ActiveUS7440987B1Digital function generatorsComputation using denominational number representation16-bitFunction generator
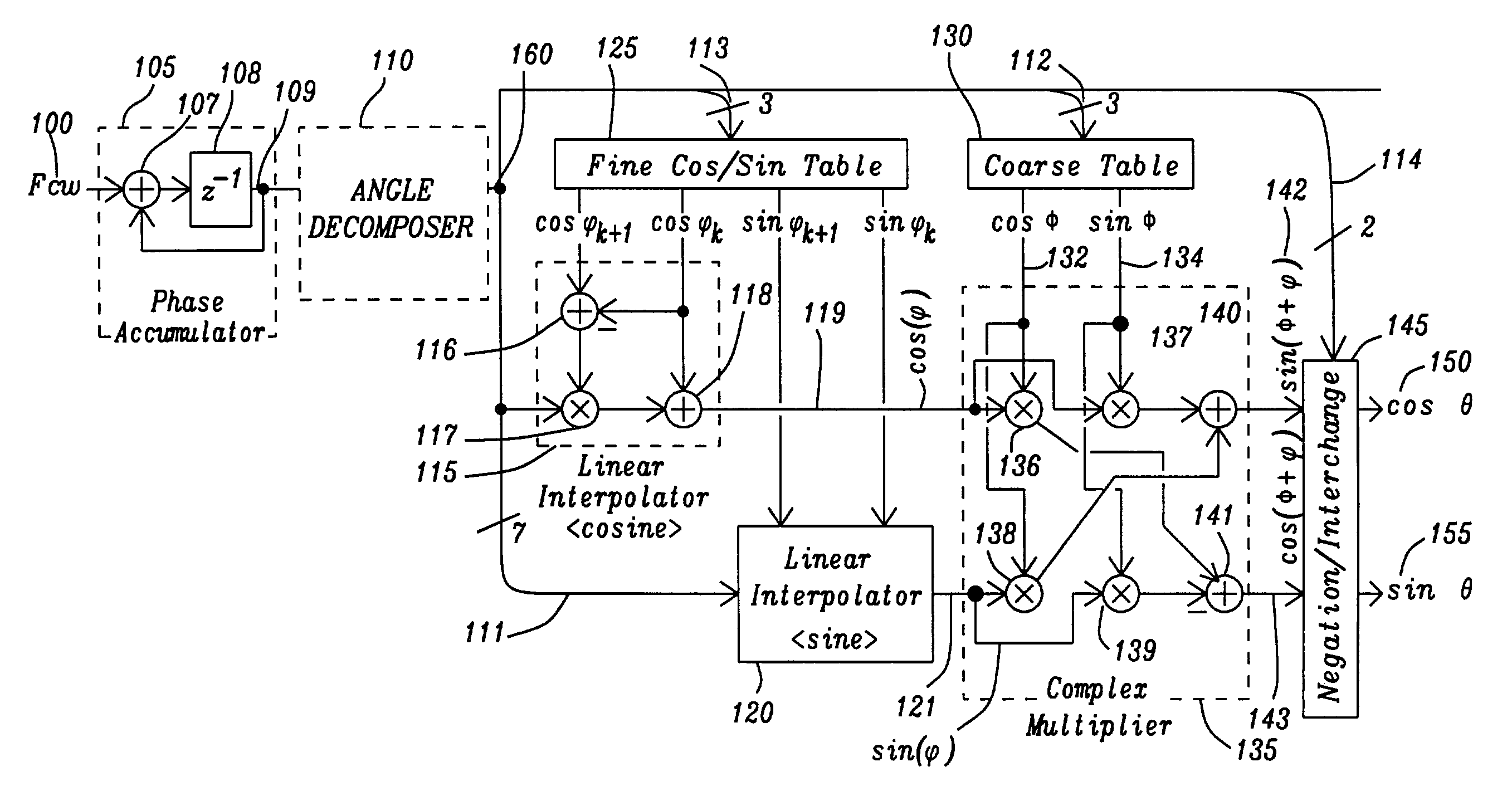
A direct digital synthesizer employs a trigonometric function generator utilizing decomposition of a larger angle into smaller sub-angles, interpolation of a desired sub-angle between two known angles and calculating the trigonometric function using complex arithmetic. The direct digital synthesizer has a phase accumulator to generate an angular increment signal of the output signal. A trigonometric function generator in communication with the phase accumulator receives the angle signal and from the angle signal creates the trigonometric function signal. An angle decomposing circuit is connected to receive the angle signal to separate the angle signal into sub-angles of the angular increment, a sum of the sub-angles equaling the angular increment. An interpolation circuit receives the smallest of the sub-angles to generate the trigonometric function for the smallest of the sub-angles by interpolating between the trigonometric function of two known angles. The direct digital synthesizer has a first angle trigonometric retaining for retaining the trigonometric functions of the known angles. At least one second angle trigonometric retaining circuit retains the trigonometric functions of for the remaining sub-angles. A complex arithmetic unit combines the interpolated trigonometric function and the second trigonometric function from each of the second angle trigonometric retaining circuits to create the trigonometric function.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Radar altimeter
ActiveUS20060044182A1Eliminate needAmplitude variationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionControl signalPhase locked loop circuit
The present invention provides a radar altimeter system with a closed loop modulation for generating more accurate radar altimeter values. The system includes an antenna, a circulator, a receiver, and a transmitter. The circulator receives or sends a radar signal from / to the antenna. The receiver receives the received radar signal via the circulator. The transmitter generates a radar signal and includes a phase-locked loop circuit for generating the radar signal based on a pre-defined phase signal. The transmitter includes a direct digital synthesizer that generates the phase signal based on a pre-defined clock signal and a control signal. The system includes a digital signal processor and a tail strike warning processor that determine position of a tail of the aircraft relative to ground and present an alert if a warning condition exists based on the determined position of the tail of the aircraft and a predefined threshold.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
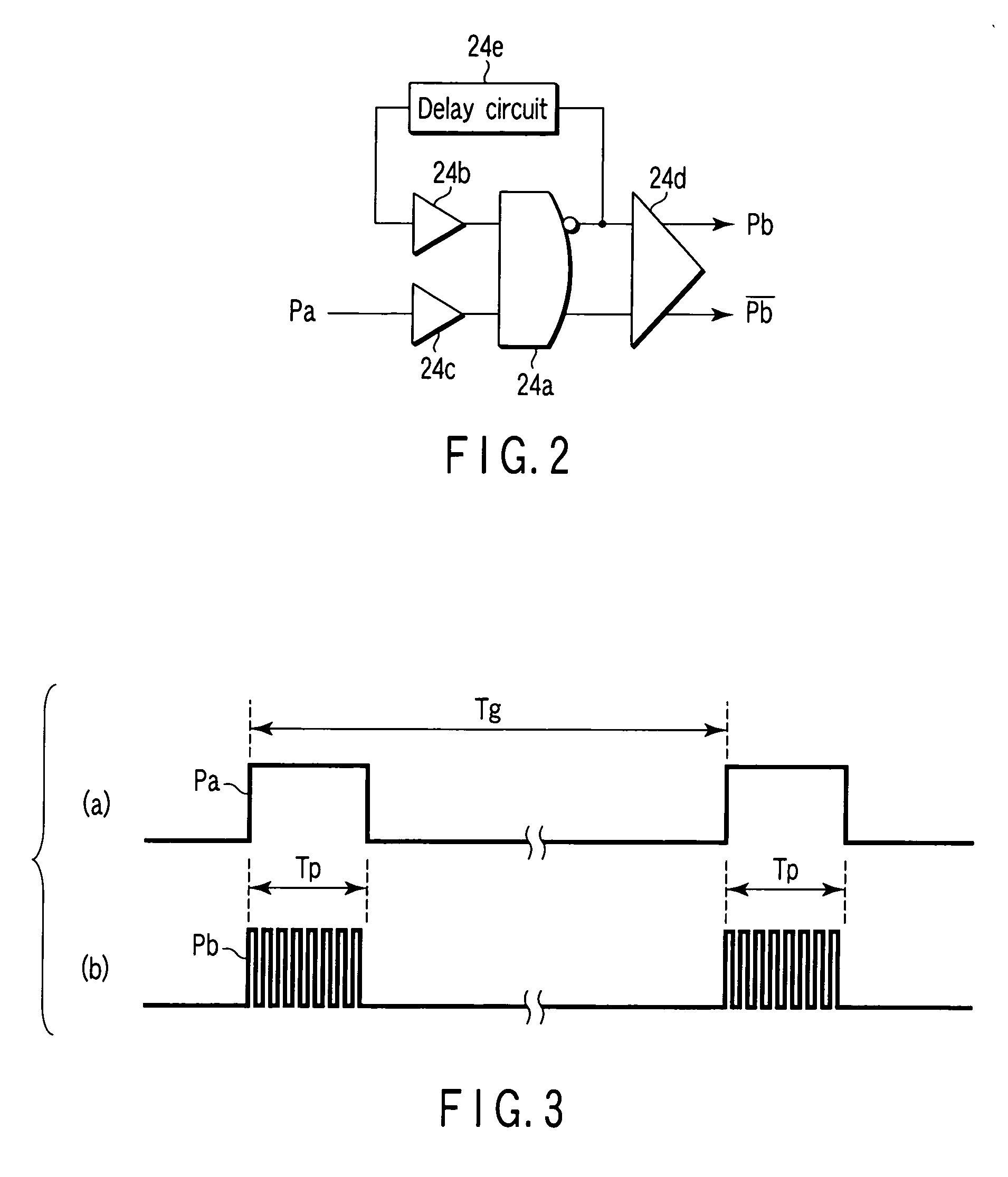
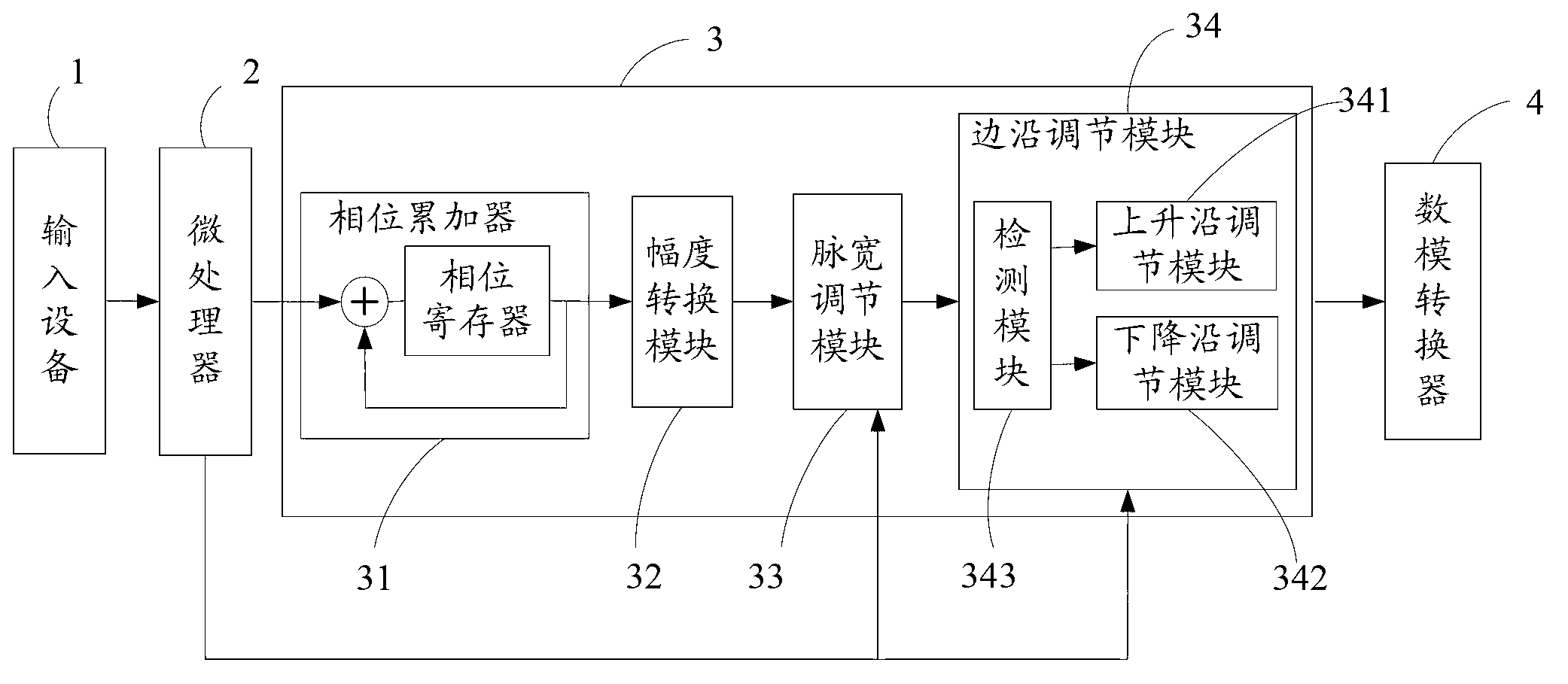
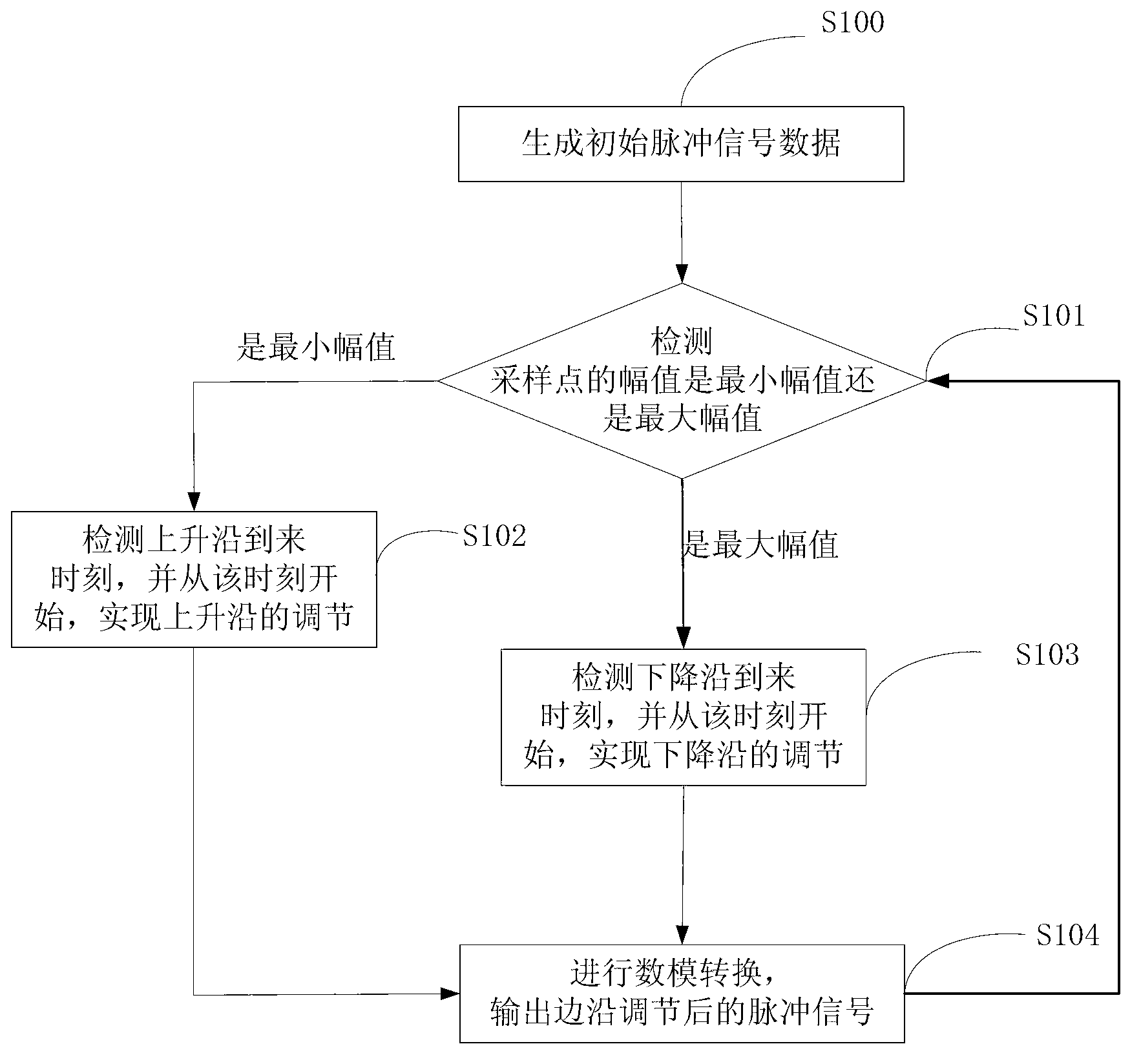
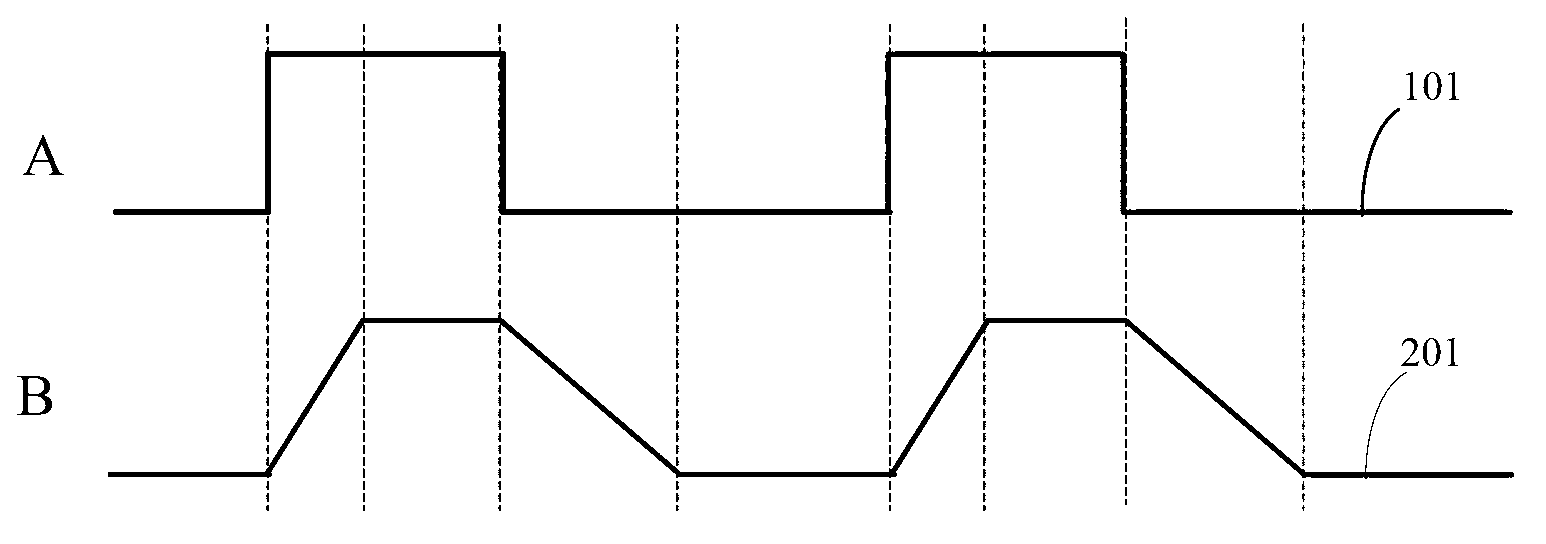
Method and module for DDS (direct digital synthesizer) pulse edge adjusting and pulse signal generator
ActiveCN103178809AEasy to adjustGrow fastElectric pulse generator circuitsPulse manipulationDigital analog converterArrival time
The invention discloses a method and a system for DDS (direct digital synthesizer) pulse edge adjusting and a pulse signal generator. The pulse signal generator comprises input equipment, a microprocessor, a DDS module and a digital-analog converter in sequential connection, the DDS module comprises a phase accumulator, an amplitude converting module, a pulse-width adjusting module and an edge adjusting module, the edge adjusting module comprises a detection module, a rising edge adjusting module and a falling edge adjusting module, the detection module is used for detecting arrival time of a rising edge and arrival time of a falling edge of initial pulse signal data, the rising edge adjusting module is used for realizing rising edge adjusting of the initial pulse signal data according to an upper stepping value, and the falling edge adjusting module is used for realizing falling edge adjusting of the initial pulse signal data according to a lower stepping value. Compared with the prior art, by the technical scheme, quick rising and falling of pulse signal edges can be realized when frequency is low, the duty ratio is extremely low, and large-scale accurate pulse signal edge adjusting can also be realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN CITY SIGLENT TECH
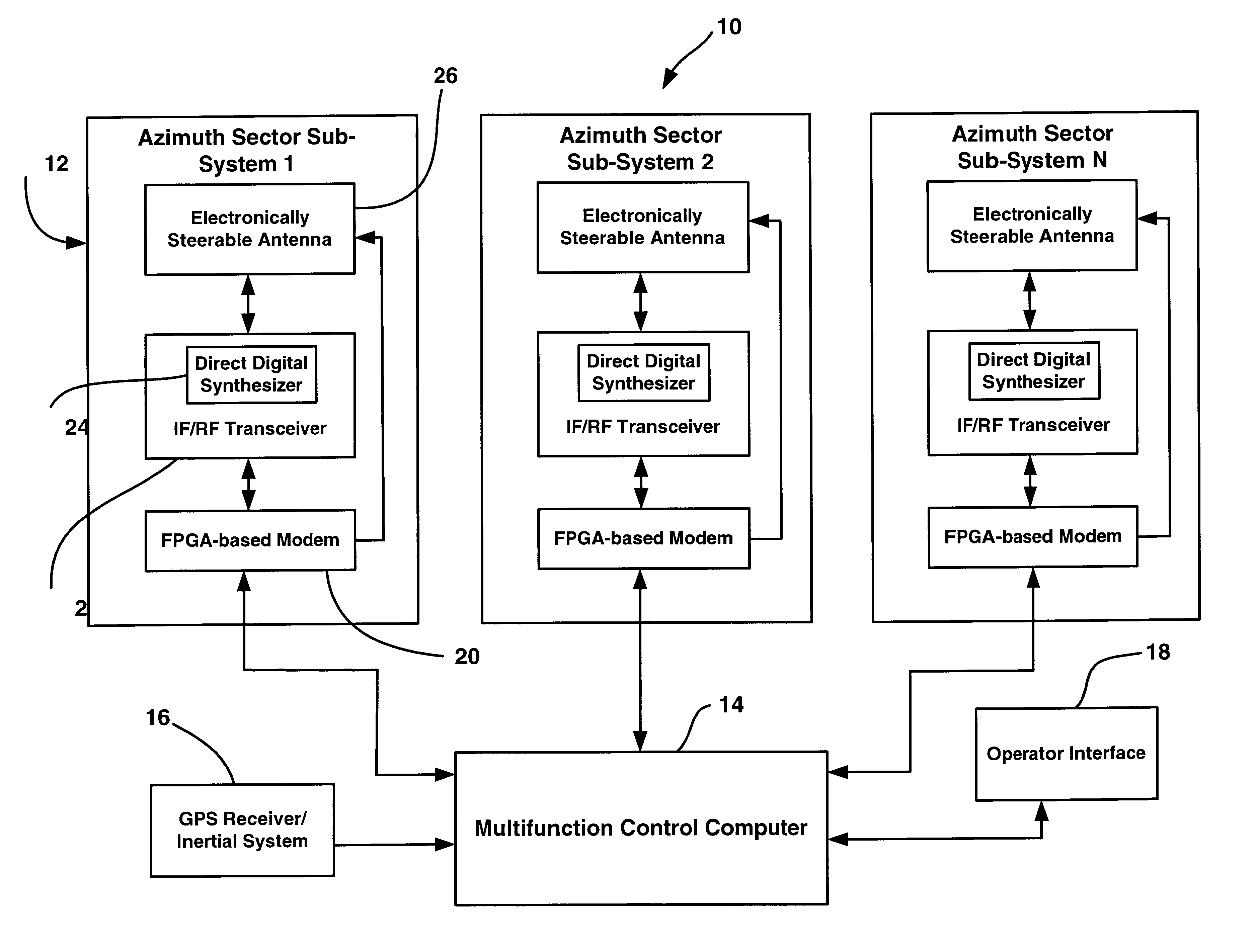
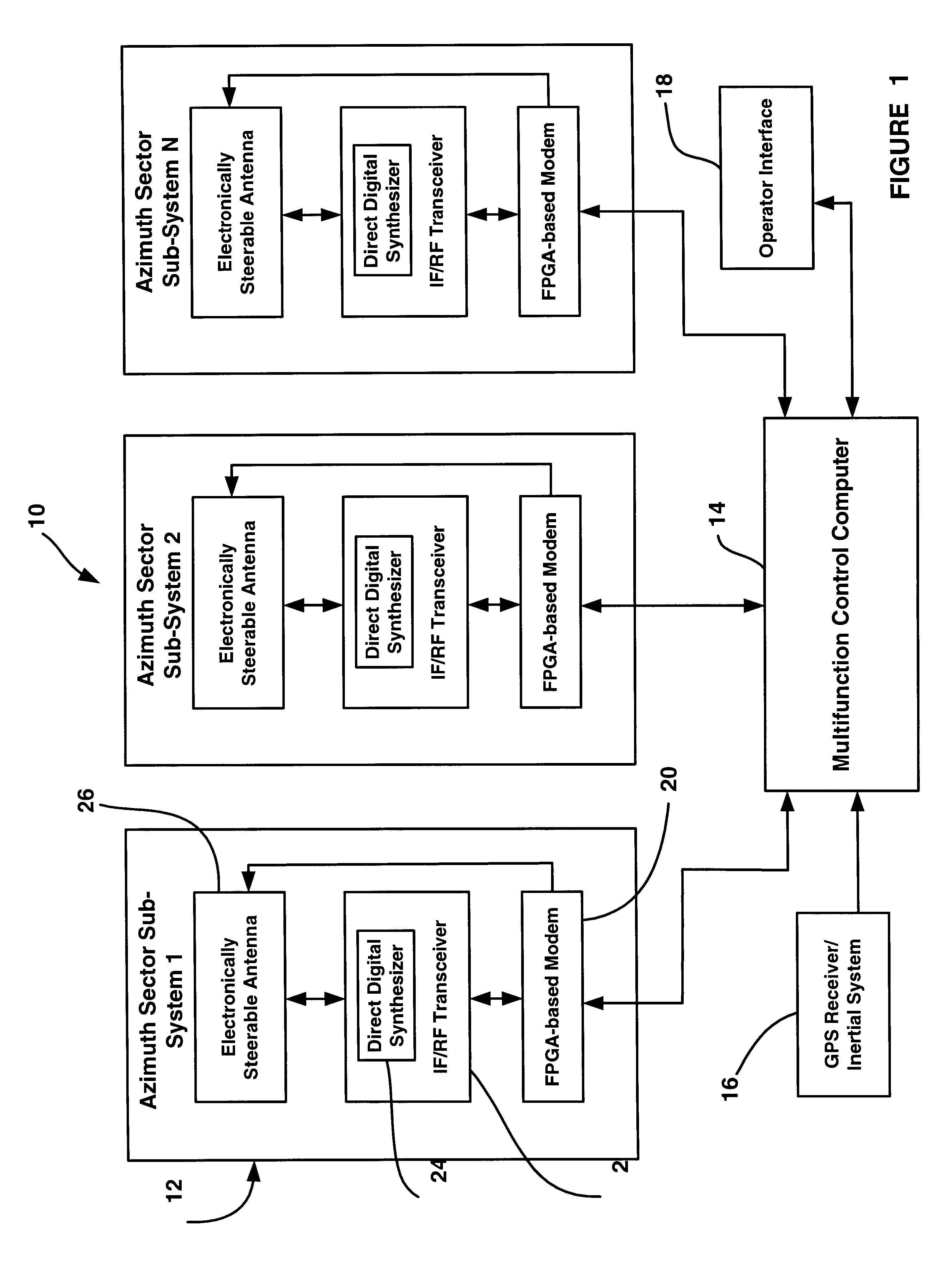
Multifunction millimeter-wave system for radar, communications, IFF and surveillance
InactiveUS6693580B1Communication jammingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingDigital data
A multifunction millimeter-wave system (10) that provides simultaneous and prioritized active radar protection and surveillance, high digital data rate communications, interceptor missile guidance, passive surveillance and IFF interrogation for a military vehicle. The system (10) includes a multi-function control computer (14) that provides high level control functions. The system (10) also includes a plurality of azimuth sector sub-systems (12), each including a steerable antenna (26) that directs a millimeter-wave beam to a particular location within the area covered by the sector sub-system (12). Each sector sub-system (12) also includes an FPGA-based modem (20) that performs digital signal processing for the various system operations, such as signal modulation and demodulation. Each sector sub-system (12) also includes an IF / RF transceiver (22), including a direct digital synthesizer (24), for providing signal tuning and frequency up-conversion and down-conversion.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
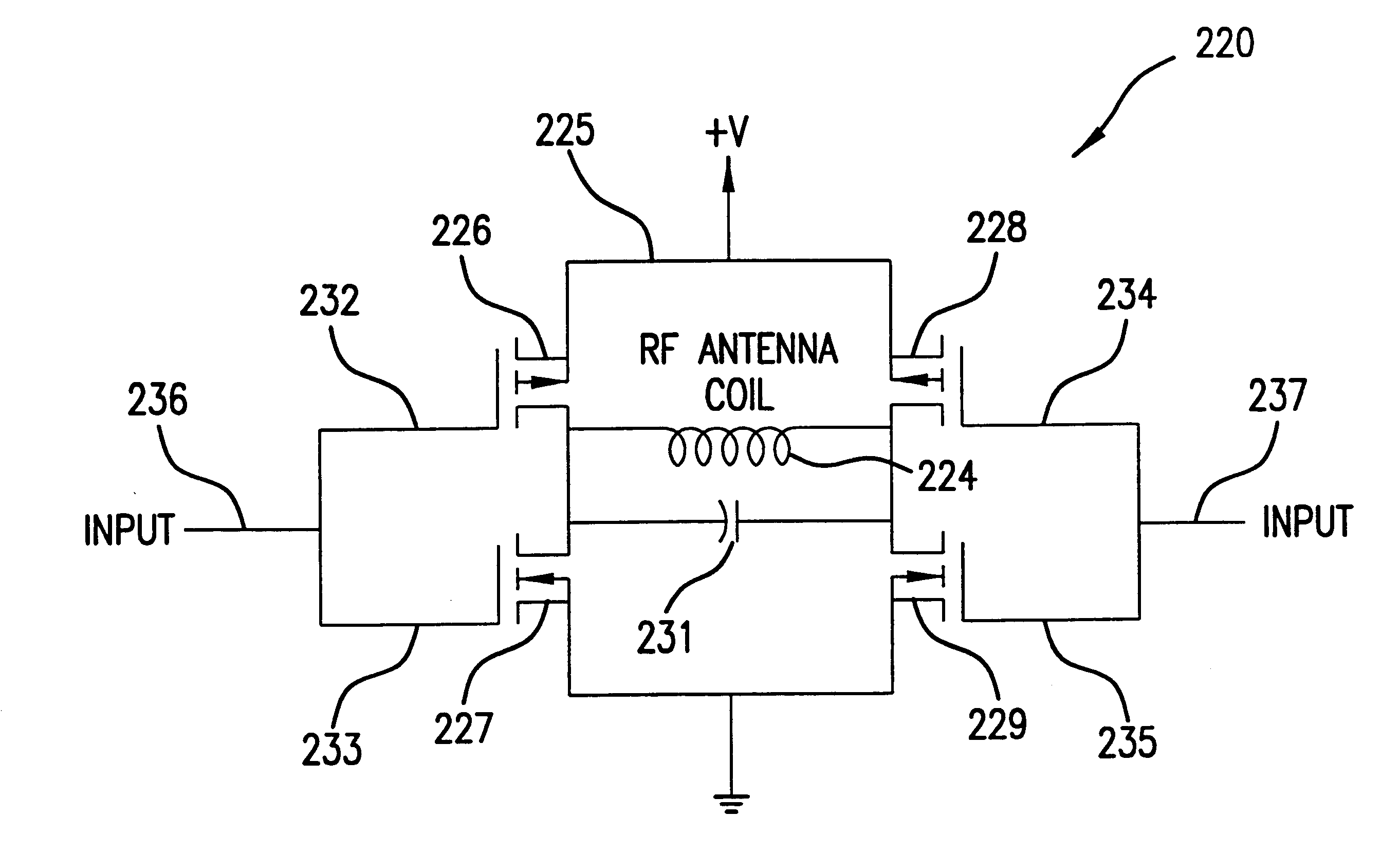
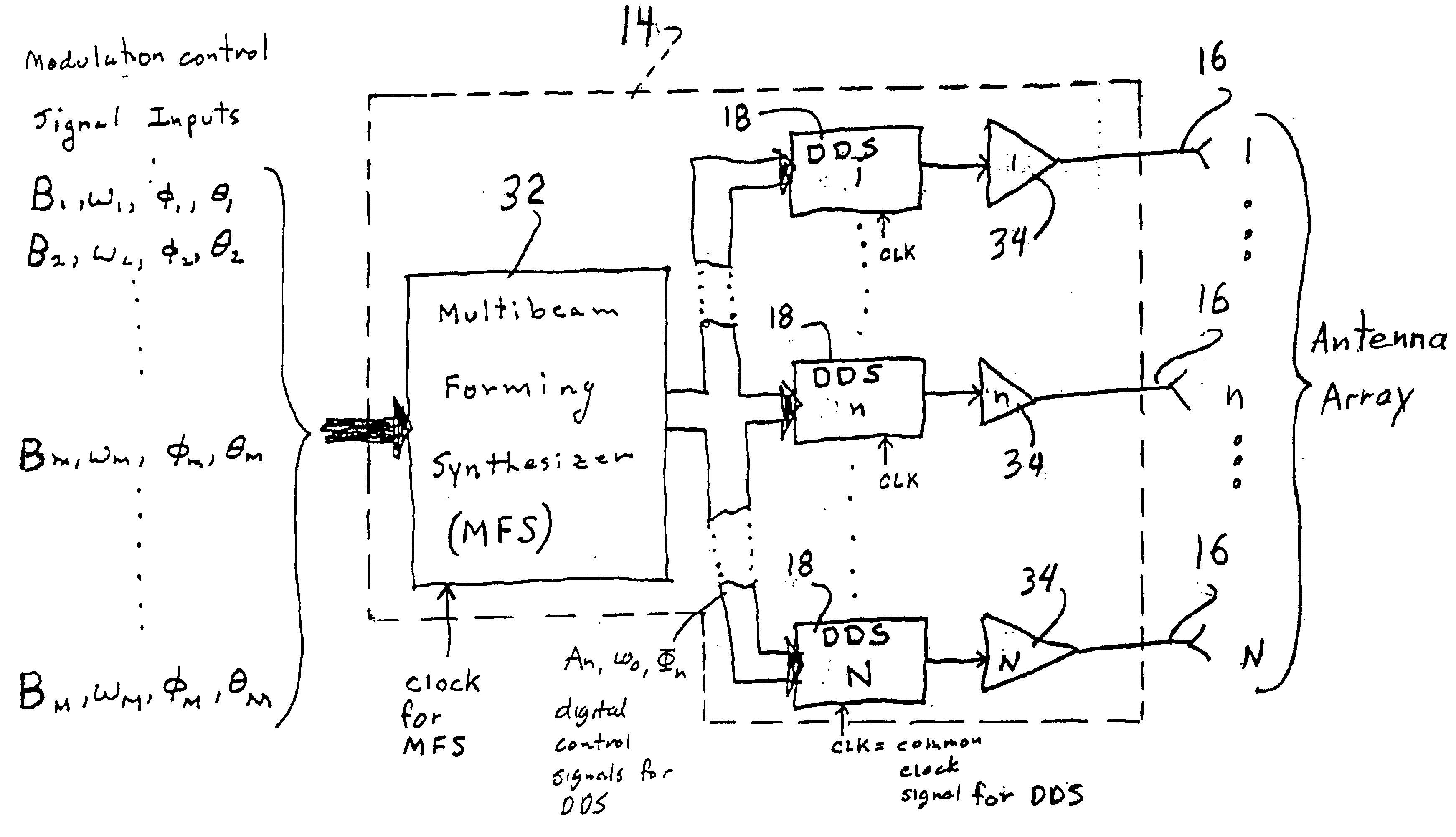
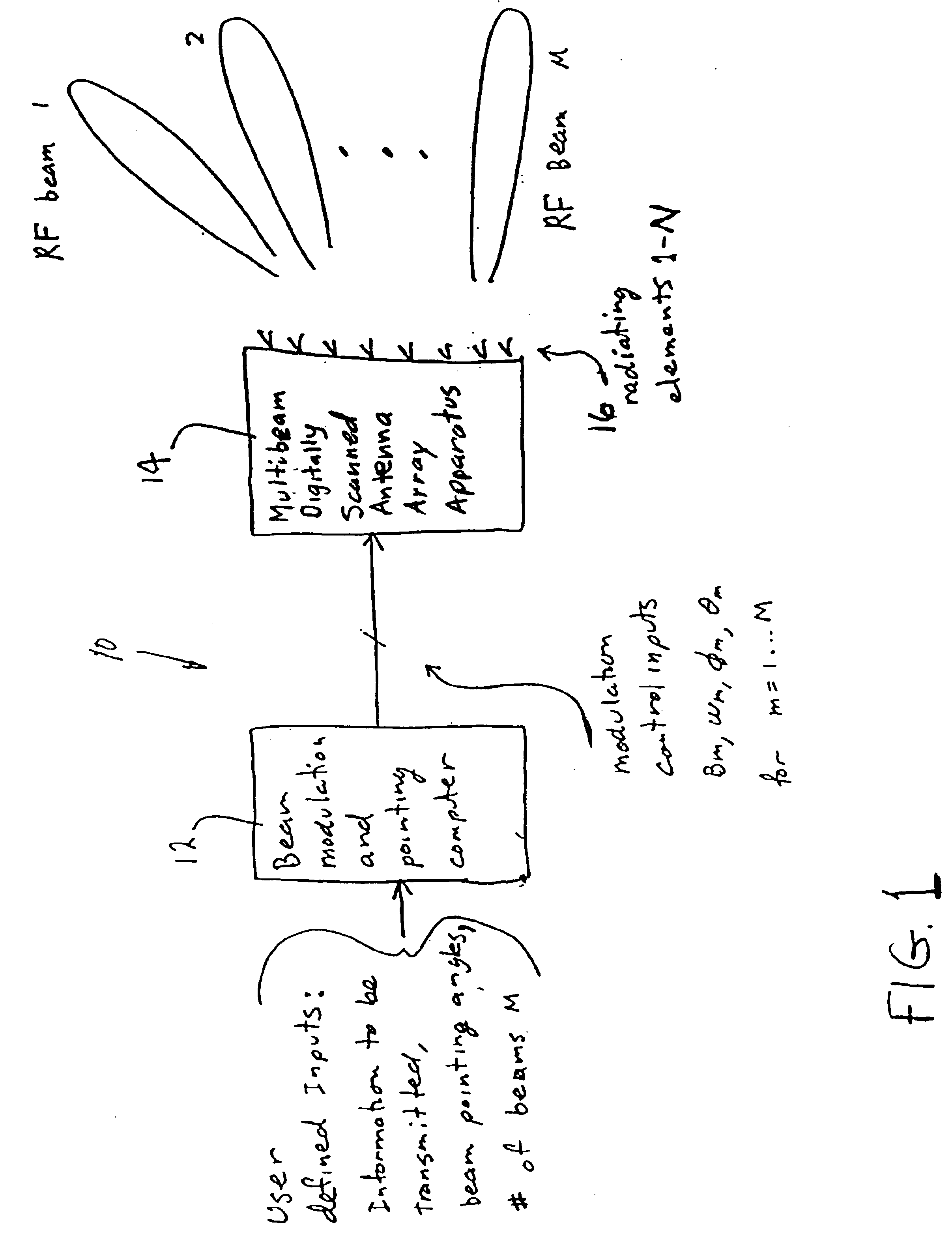
Apparatus for and method of forming multiple simultaneous electronically scanned beams using direct digital synthesis
InactiveUS6778138B2Simple definitionReduce in quantityDirection findersAntennasAudio power amplifierLight beam
The apparatus / method according to the present invention accomplishes a reduction in the total number of direct digital synthesizers (DDSs) needed for use in electronically scanned antenna array to generate multiple simultaneous radio frequency (RF) beams. The apparatus includes, inter alia, a multi-beam forming synthesizer, a plurality of DDSs, a corresponding plurality of amplifiers all operatively connected to a plurality of radiating elements of the antenna array. This arrangement uses a single DDS per radiating element. Each DDS uses a composite amplitude, phase and frequency information computed by the multi-beam forming synthesizer to create the proper waveform for driving the antenna array, and accordingly, generating the desired multiple simultaneous RF beams, i.e. 1-M (e.g. 1 through M) RF beams each of which can have a different frequency and separate modulation.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
Multi-channel nuclear magnetic resonance radio frequency signal transmitter
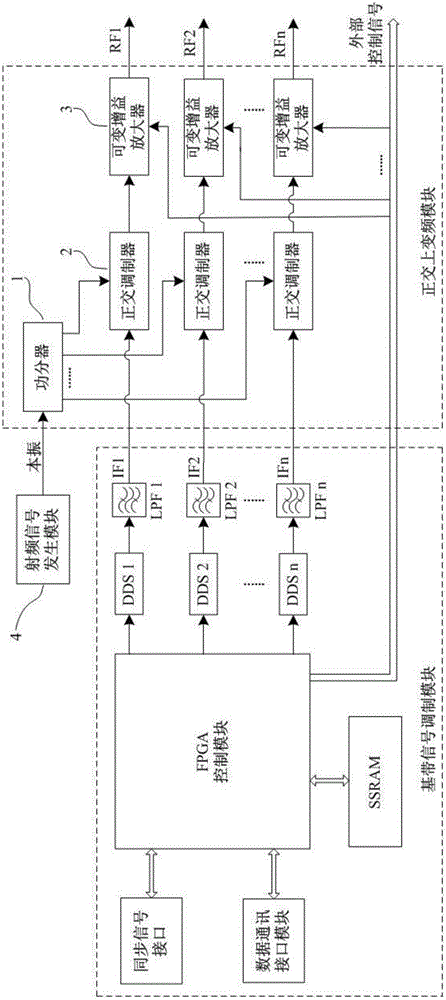
ActiveCN102724162AImplement parallel launchIndividually control the modulation methodMultiple carrier systemsMeasurements using magnetic resonanceQuadrature modulatorModulation function
The invention discloses a multi-channel nuclear magnetic resonance radio frequency signal transmitter which comprises a baseband signal modulation module, an orthometric up-conversion module and a radio frequency signal generation module, wherein the baseband signal modulation module comprises a field programmable gate array control module and a direct digital signal synthesizer; the orthometric up-conversion module comprises a power splitter, an orthometric modulator, a variable gain amplifier and the like; the radio frequency signal generation module supplies a local oscillation signal to the orthometric up-conversion module; and at least one baseband signal modulation module is arranged, and the orthometric up-conversion module is connected with the baseband signal modulation module and in the same number with the baseband signal modulation module. According to the multi-channel nuclear magnetic resonance radio frequency signal transmitter, the sole control and the parallel transmission of a plurality of paths of radio frequency signals are realized; all modulation functions are realized in a single-chip direct digital synthesizer (DDS), so that the integrated level of a system is improved; the radio frequency transmission of broadband can be carried out, and the full-range coverage of the signals is realized; and an orthogonal modulation system is adopted in the generation of the radio frequency signals, so that the mirror image frequency band is effectively suppressed, and the radio frequency power utilization rate is improved.
Owner:ウーハン ジョンケ ニウジン マグネティック レゾナンス テクノロジー カンパニー リミテッド
All-digital satellite signal simulated source
InactiveCN102710316AIntegrity guaranteedFlexible configurationRadio transmissionSymbol rateHigh-Speed Serial Interface
The invention provides an all-digital satellite signal simulated source. The all-digital satellite signal simulated source comprises a double-port storage, the double-port storage is a FPGA which provides interfaces for various rate conversions between coding and modulation, is connected with a digital to analog converter through a high-speed serial interface to form a core hardware framework of the satellite signal simulated source, and is connected with a broadband filter directly through a simulation output end to produce multimode high and moderate frequency broadband satellite signal simulated signals with code rates which can vary continuously, a digital signal processor serves as a main control device of the simulated source and performs analysis of various parameters issued by a monitor and parameter configuration of the FPGA, a 32-channel parallel modulation system is arranged inside the FPGA, for example, a 32-channel direct digital synthesizer (DDS) performs parallel output and composition of the central frequency, the FPGA determines the overturn of the carrier phase according to a symbol rate and a main frequency of parallel calculation, IQ two-channel signals, signal coding, code conversion and quadrature modulation are produced through a logical algorithm, a Q channel uniformization coefficient is calculated according to an IQ unbalanced parameter, Q channel uniformization coefficient and the Q channel signal amplitude are subjected to multiply-add arithmetic to calculate the Q channel amplitude, IQ is added, and a unbalanced quadrature phase shift keying (UQPSK) modulation method is simulated.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Error corrector for radar timing systems
InactiveUS20070210955A1Reduce biasOvercome limitationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase correctionRadar
A feedback loop corrects timing errors by reducing deviations from a constant radar sweep rate. Errors are detected and fed back to a phase corrector in a high gain feedback system. A precision radar rangefinder can be implemented with a direct digital synthesizer (DDS) that includes feedback error correction for reducing range errors by, for example, 100 times, or to 0.1 mm. An error-corrected DDS swept timing system can enable a new generation of highly flexible, repeatable and accurate radar, laser and guided wave rangefinders.
Owner:MCEWAN TECH
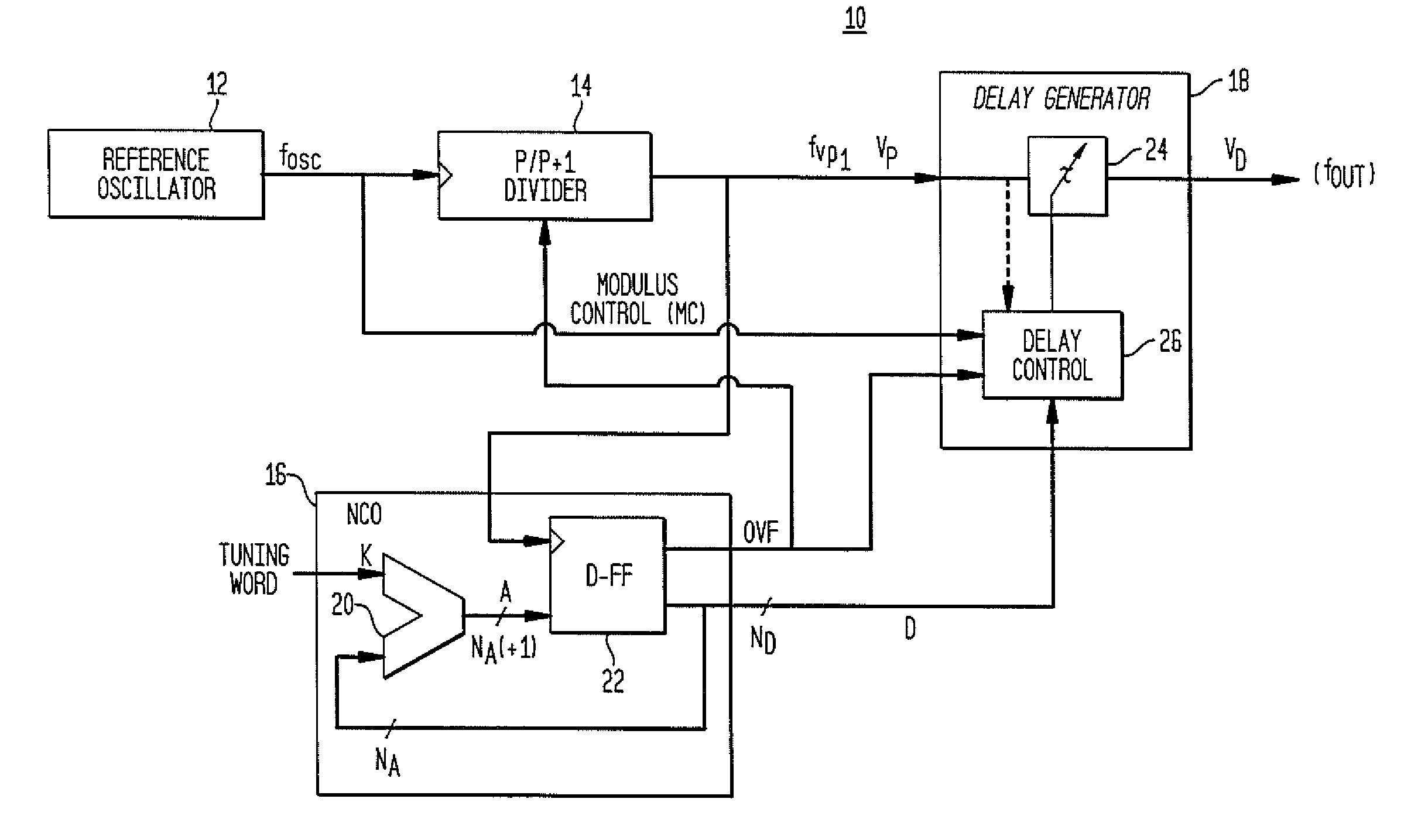
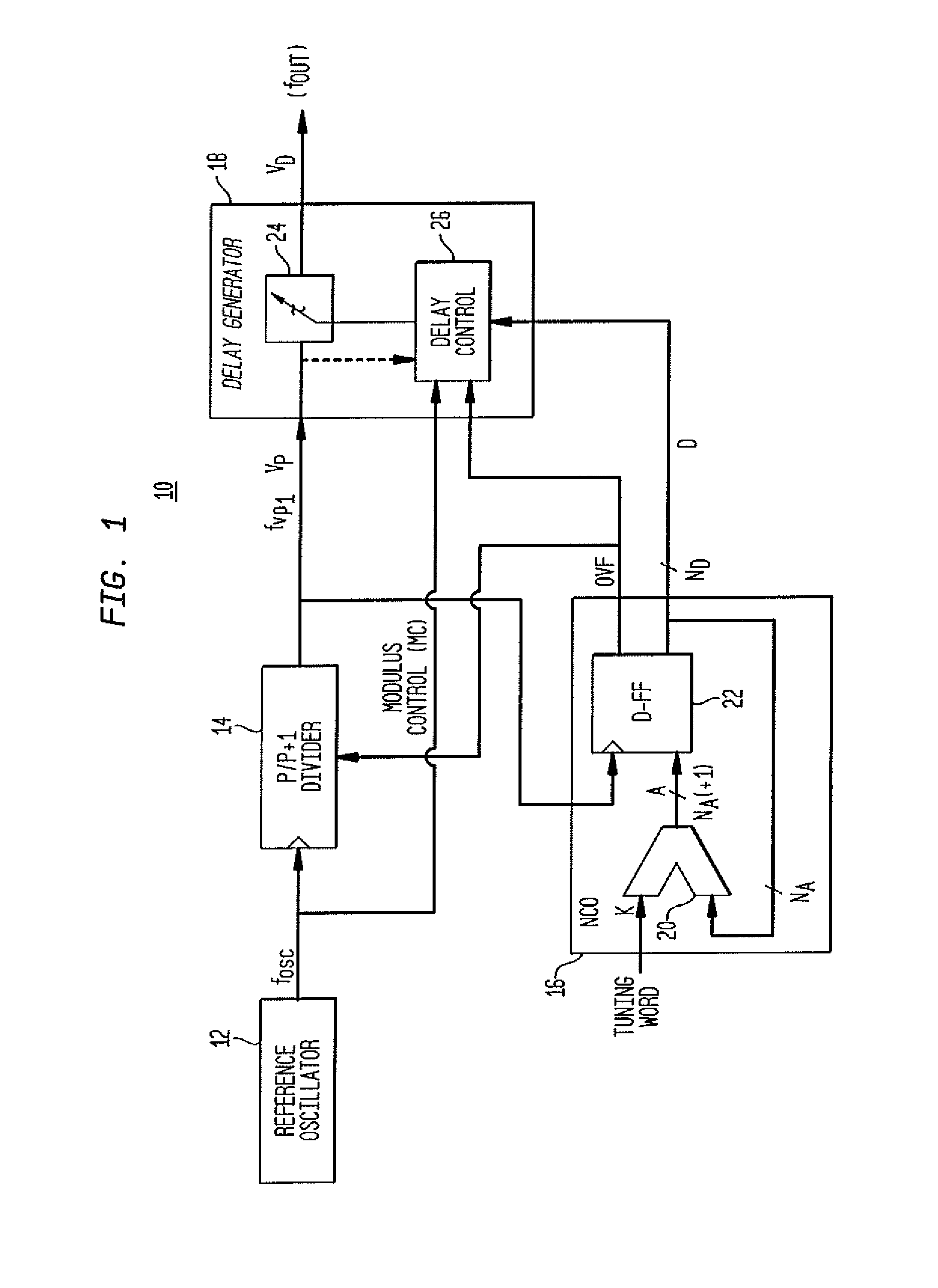
Direct digital synthesizer for reference frequency generation
InactiveUS20110095830A1Reduce power consumptionLow frequency signalPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersFrequency generationRandom noise
A direct digital frequency synthesizer having a multi-modulus divider, a numerically controlled oscillator and a programmable delay generator. The multi-modulus divider receives an input clock having an input pulse frequency fosc and outputs some integer fraction of those pulses at an instantaneous frequency fVp that is some integer fraction (1 / P) of the input frequency. The multi-modulus divider selects between at least two ratios of P (1 / P or 1 / P+1) in response to a signal from the numerically controlled oscillator. The numerically controlled oscillator receives a value which is the accumulator increment (i.e. the number of divided pulse edges) required before an overflow occurs that causes the multi-modulus divider to change divider ratios in response to receiving an overflow signal. The numerically controlled oscillator also outputs both the overflow signal and a delay signal to the delay generator. The delay signal contains phase-dithering noise that is induced by input into the accumulator of an increment generated from a pseudo-random noise generator. The delay signal further controls the frequency of the multi-modulus divider output signal (Vp) to provide an output signal (VD) with an fOUT that has improved phase and timing jitter performance over prior art direct digital frequency synthesizer architectures.
Owner:CYMATICS LAB CORP
Microwave and millimeterwave radar sensors
A radar sensor system and method for vehicles. An example radar system includes a processor, a plurality of transceivers having antenna(e). The antenna of the transceivers are located at various points around the vehicle. The transceivers include receive and transmit electronics that are in signal communication with the corresponding antenna. The transmit electronics output radar signals via the antenna. The transmit electronics include a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO), a dielectric resonator oscillator (DRO), a phase locked loop (PLL) component and a direct digital synthesizer (DDS). The receive electronics receive from the antenna any radar reflections corresponding to the outputted radar signals and send signals associated with the radar reflections to the processor. The processor generates output signals based on the signals received from the plurality of transceivers.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Low-rate spread spectrum communication transmission base band system
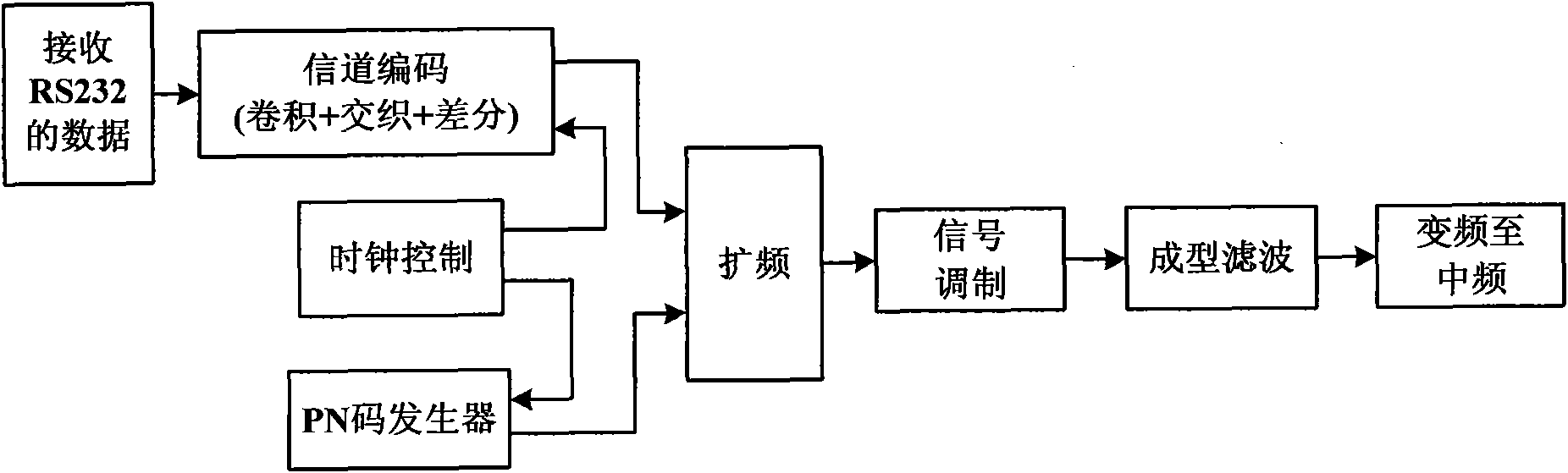
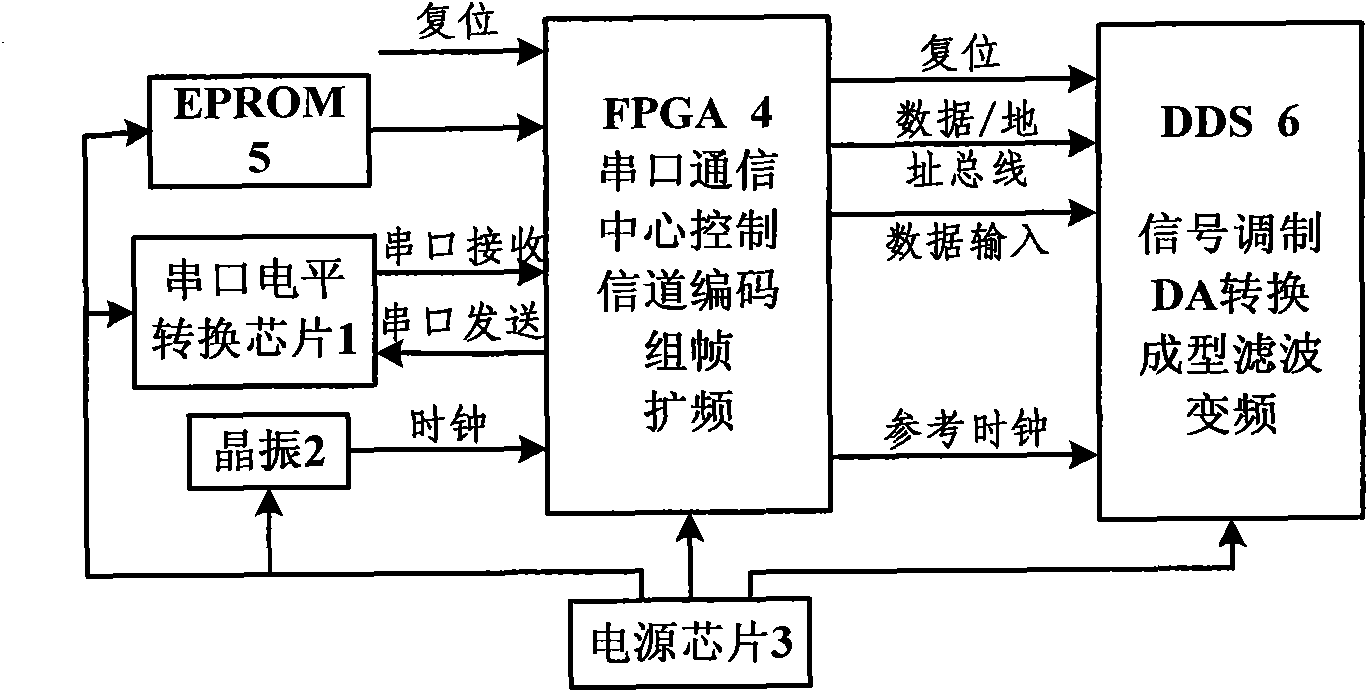
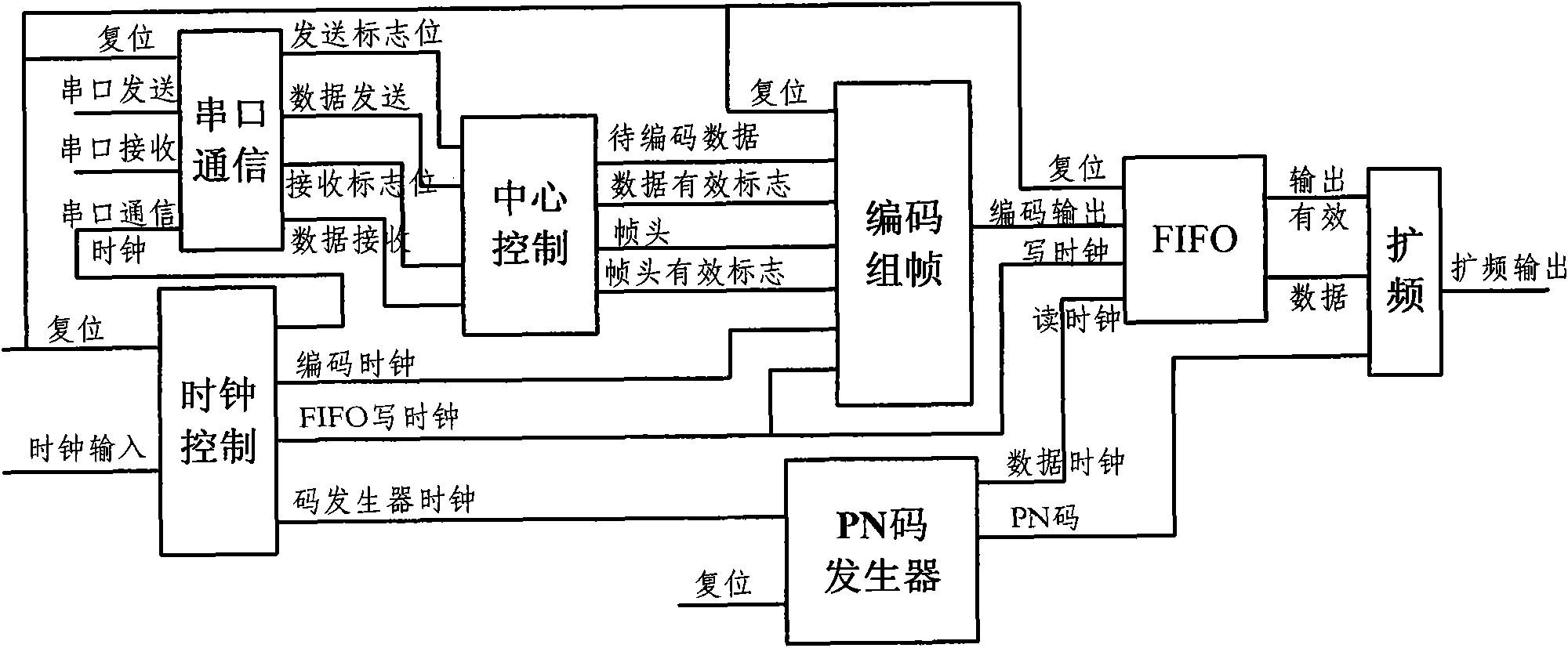
ActiveCN102104394AUnrestrictedRun fastError preventionBaseband system detailsControl signalRead-only memory
The invention relates to a low-rate spread spectrum communication transmission base band system. The system is characterized by using an FPGA (field-programmable gate array) and a DDS (direct digital synthesizer) to realize the low-rate spread spectrum transmission base band system with settable parameters. The system specifically comprises an FPGA chip, a DDS chip and a peripheral module, wherein the FPGA chip comprises a clock signal generating module, an RS (recommended standard)-232 serial communication module, a central control module, a framing module, a channel coding module, a PN (pseudo noise) code generator module, a digital shaping filter module and a DDS working condition controller; the DDS chip comprises a phase accumulator module, a waveform ROM (read only memory) module, aD / A conversion module and a lowpass filtering module and is used for D / A conversion and signal modulation; the input / output port of the FPGA chip is connected with the input port of the DDS chip; andthe FPGA chip inputs the data to be modulated and the condition control signal to the DDS chip and controls the working mode of the DDS chip.
Owner:ZHONGKE KAIPU TIANJIN SATELLITE NAVIGATION COMM TECH CO LTD
A frequency mixer and frequency mixing method
InactiveCN101242181ALarge spurLow spurs generated by large-step phase-locked loopPulse automatic controlTransmissionLow noiseFrequency mixer
The invention discloses a frequency synthesizer and a frequency synthesis method. The frequency synthesizer comprises: a large-stepping phase lock loop and a direct digital frequency synthesizer, an orthogonal mixer and a tracking phase lock loop. The orthogonal mixer is connected with the large-stepping phase lock loop and the digital frequency synthesizer respectively for mixing the frequency generated by the large-stepping phase lock loop and the low frequency generated by the direct digital frequency synthesizer to generate a single-sideband single tone; the tracking phase lock loop is connected with the orthogonal mixer for receiving the single-sideband single tone output by the orthogonal mixer and filtering the sideband leakage and oscillation leakage of the signal. The invention provides a frequency synthesizer with wide band width, small stepping, low stray and low noise and a frequency synthesis method. The invention has simple hardware structure and is easy to accomplish.
Owner:INNOFIDEI TECHNOLOGIES INC
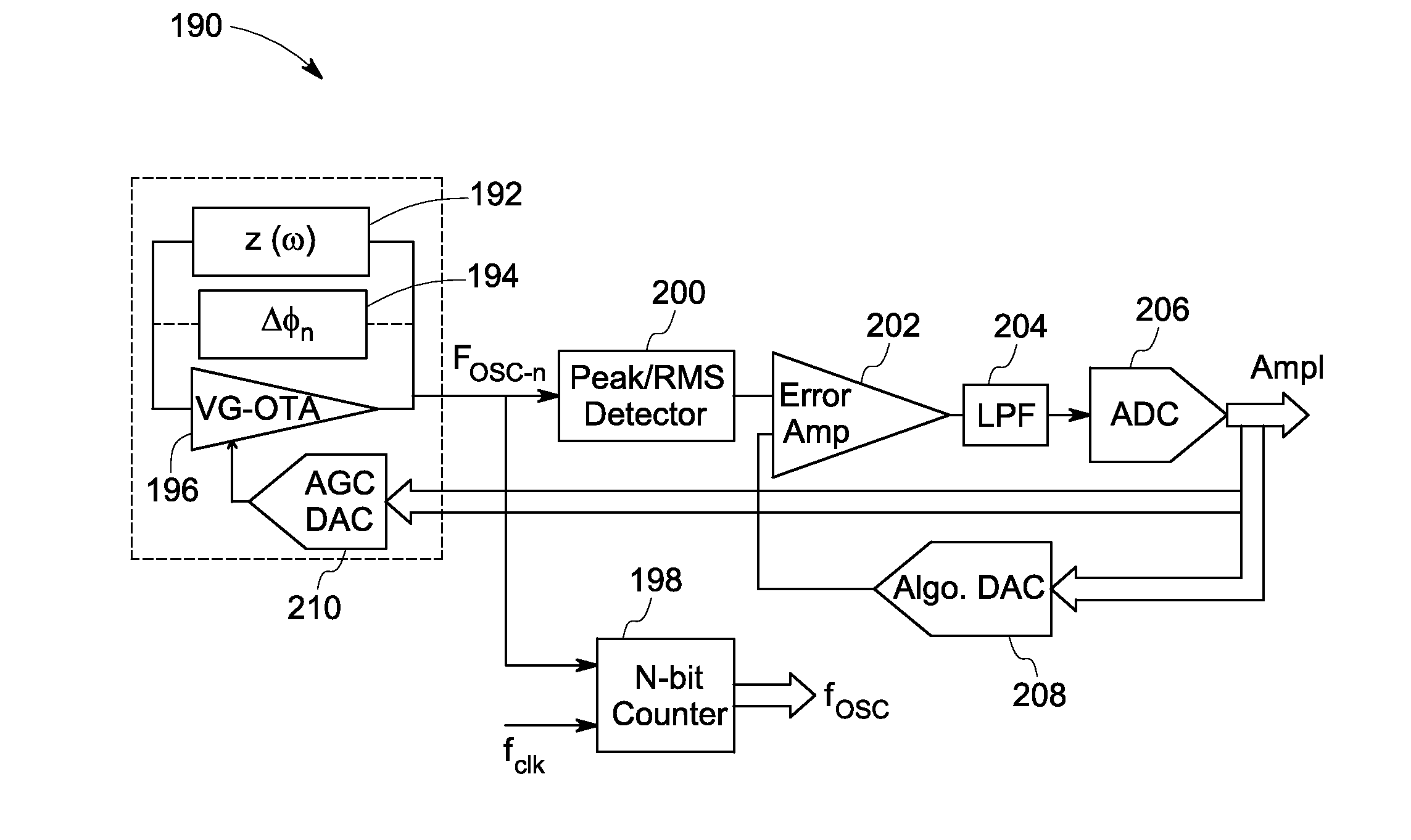
Direct digital synthesizer system and related methods
InactiveUS20070040615A1Avoid stimulationPulse automatic controlDigital function generatorsDirect digital synthesizerFixed frequency
A direct digital synthesizer (DDS) has reduced spurious signals and includes a DDS core that produces a digital representation of a signal to be synthesized. A plurality of DDS circuits are operatively connected to the DDS core, each having a digital-to-analog converter connected to the DDS core for receiving the digital representation and converting it into a signal. A modulator is operatively connected to an oscillator circuit and digital-to-analog converter for receiving signals from the digital-to-analog converter and producing a modulated output signal. The individual frequencies of the respective DDS circuits are randomly and continuously changed from each other. A mixer receives and mixes the modulated output signals from the plurality of DDS circuits to create a mixed output signal at a selected and fixed frequency.
Owner:REVEAL IMAGING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com