Patents
Literature
8942results about "Computation using denominational number representation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
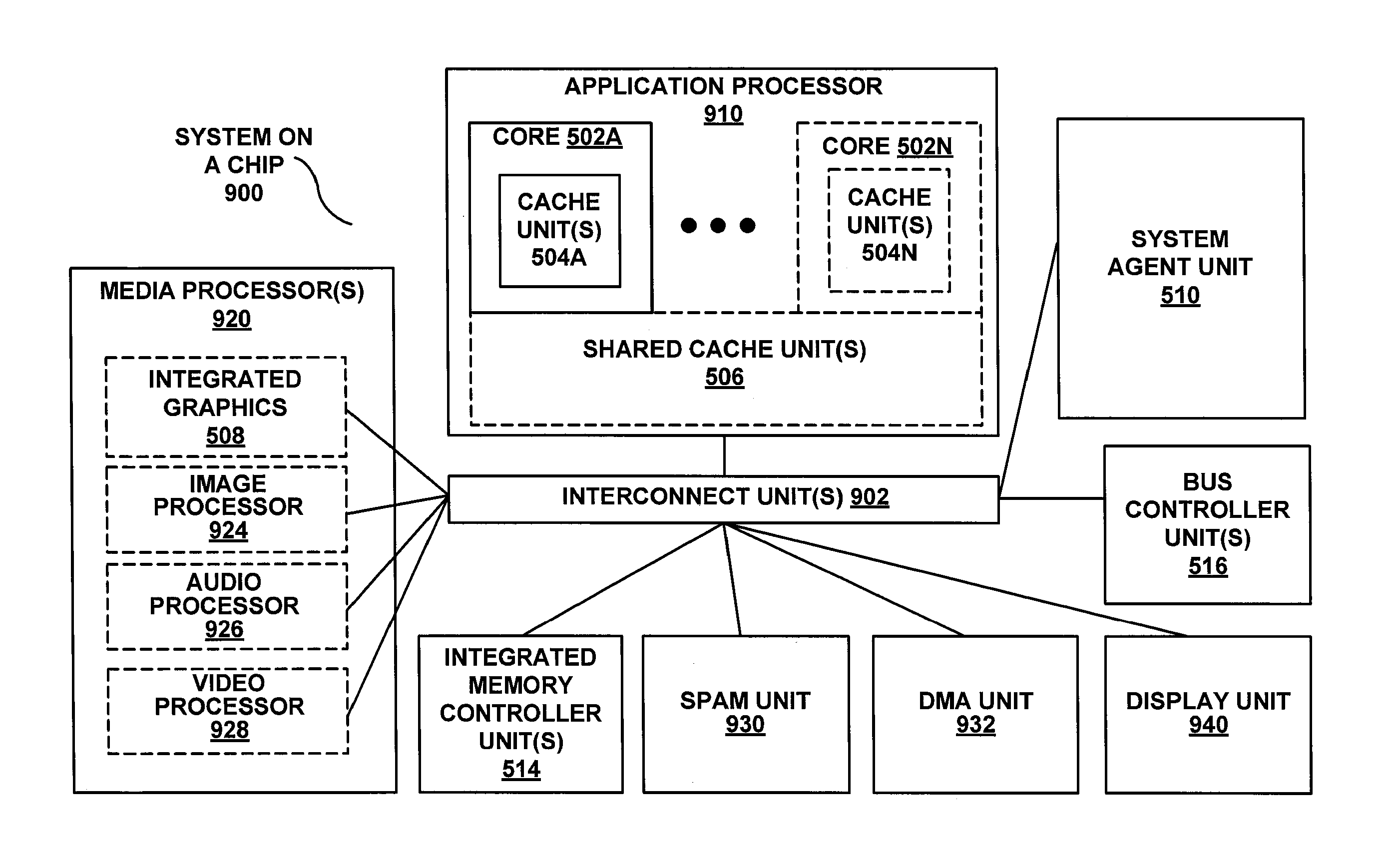
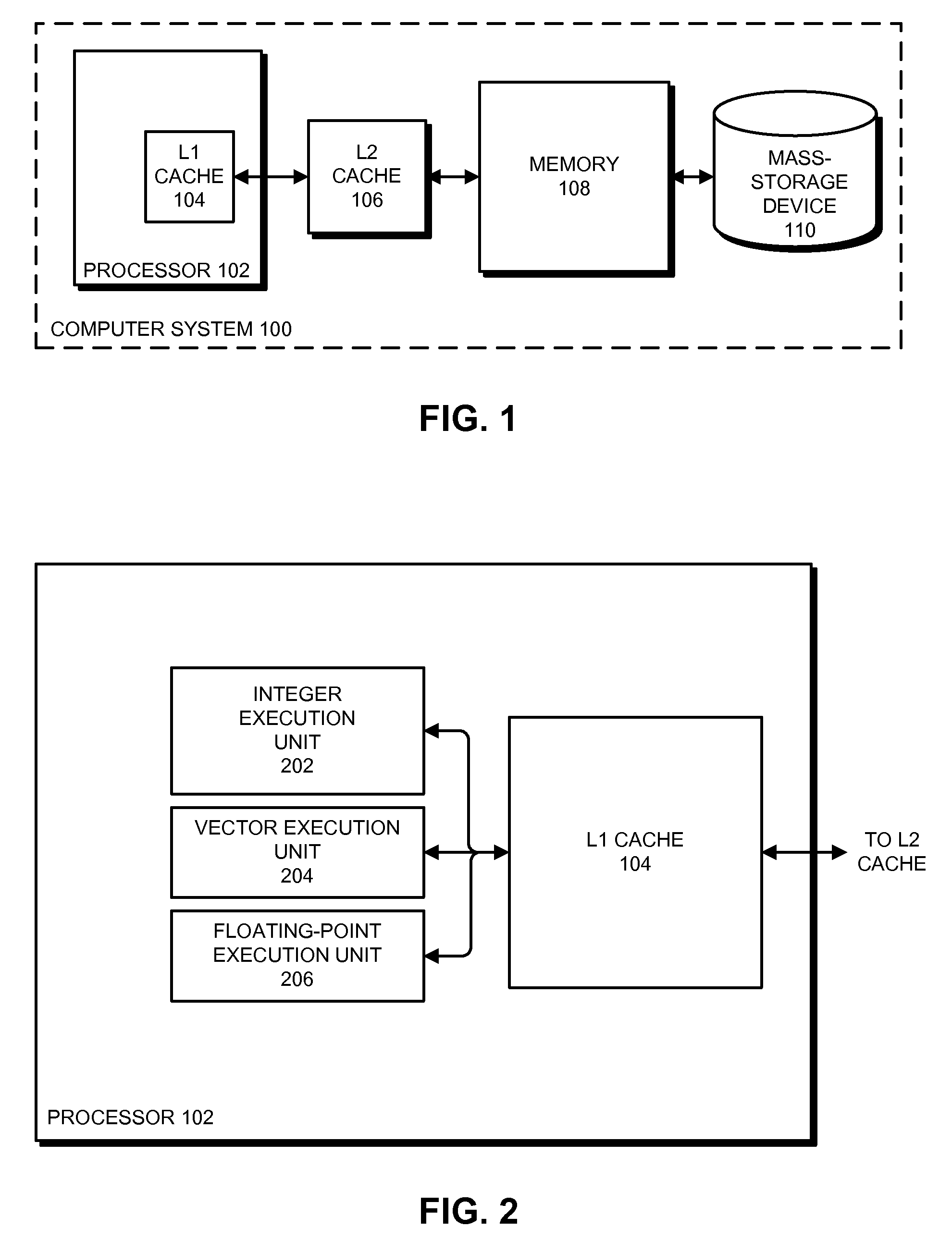
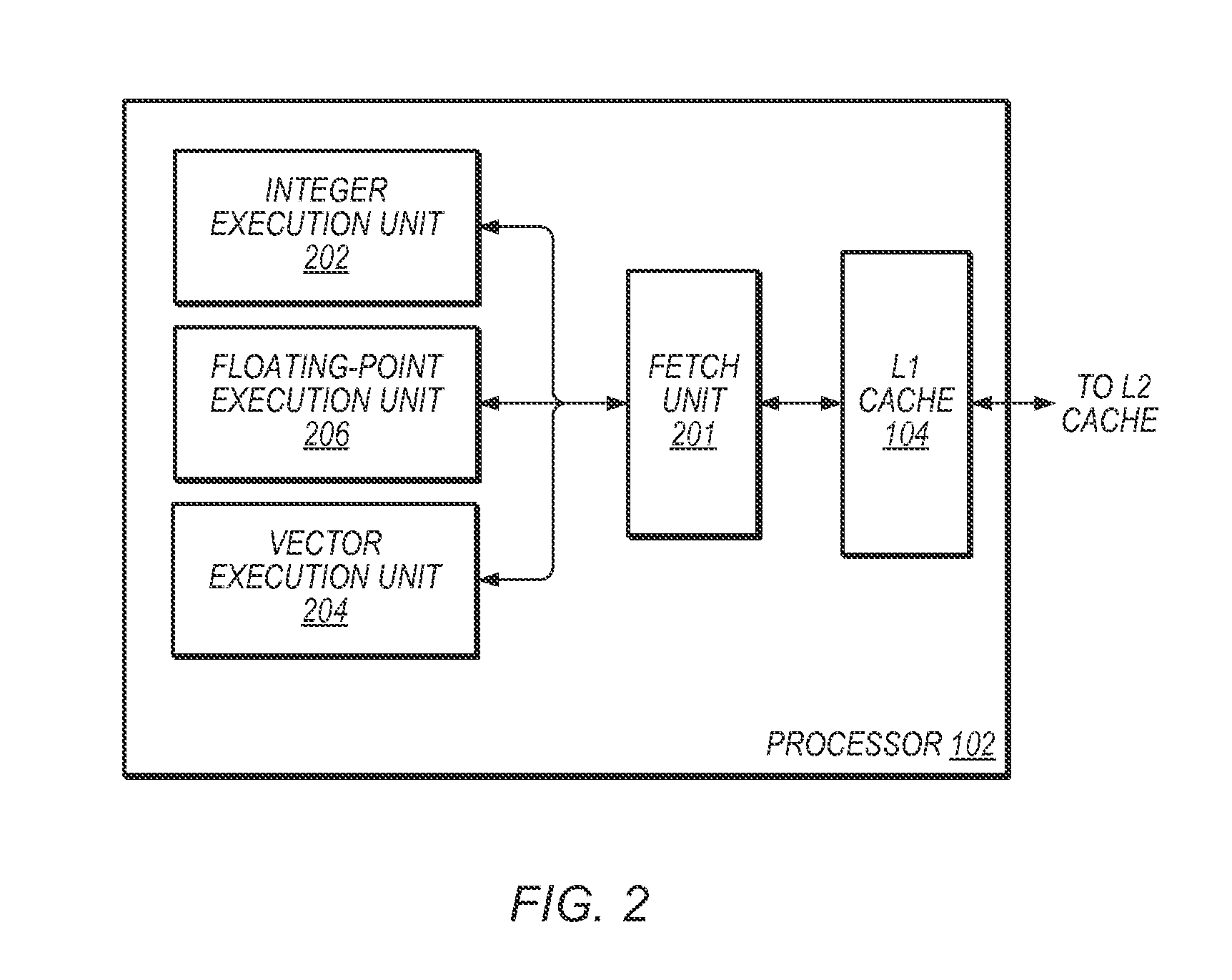
Speed up big-number multiplication using single instruction multiple data (SIMD) architectures
InactiveUS20130332707A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsMatrix multiplicationSIMD
A processing apparatus may be configured to include logic to generate a first set of vectors based on a first integer and a second set of vectors based on a second integer, logic to calculate sub products by multiplying the first set of vectors to the second set of vectors, logic to split each sub product into a first half and a second half and logic to generate a final result by adding together all first and second halves at respective digit positions.
Owner:INTEL CORP
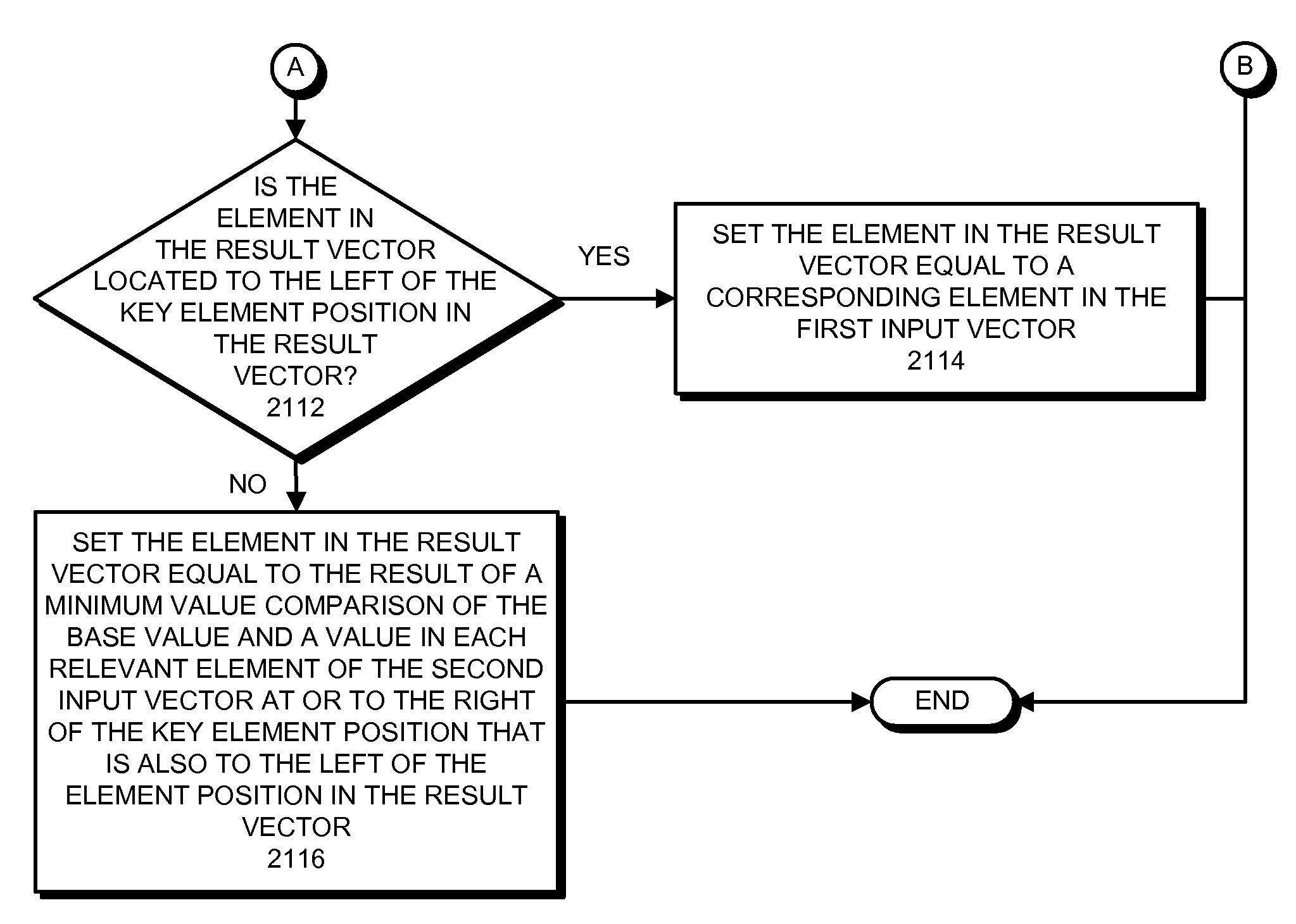
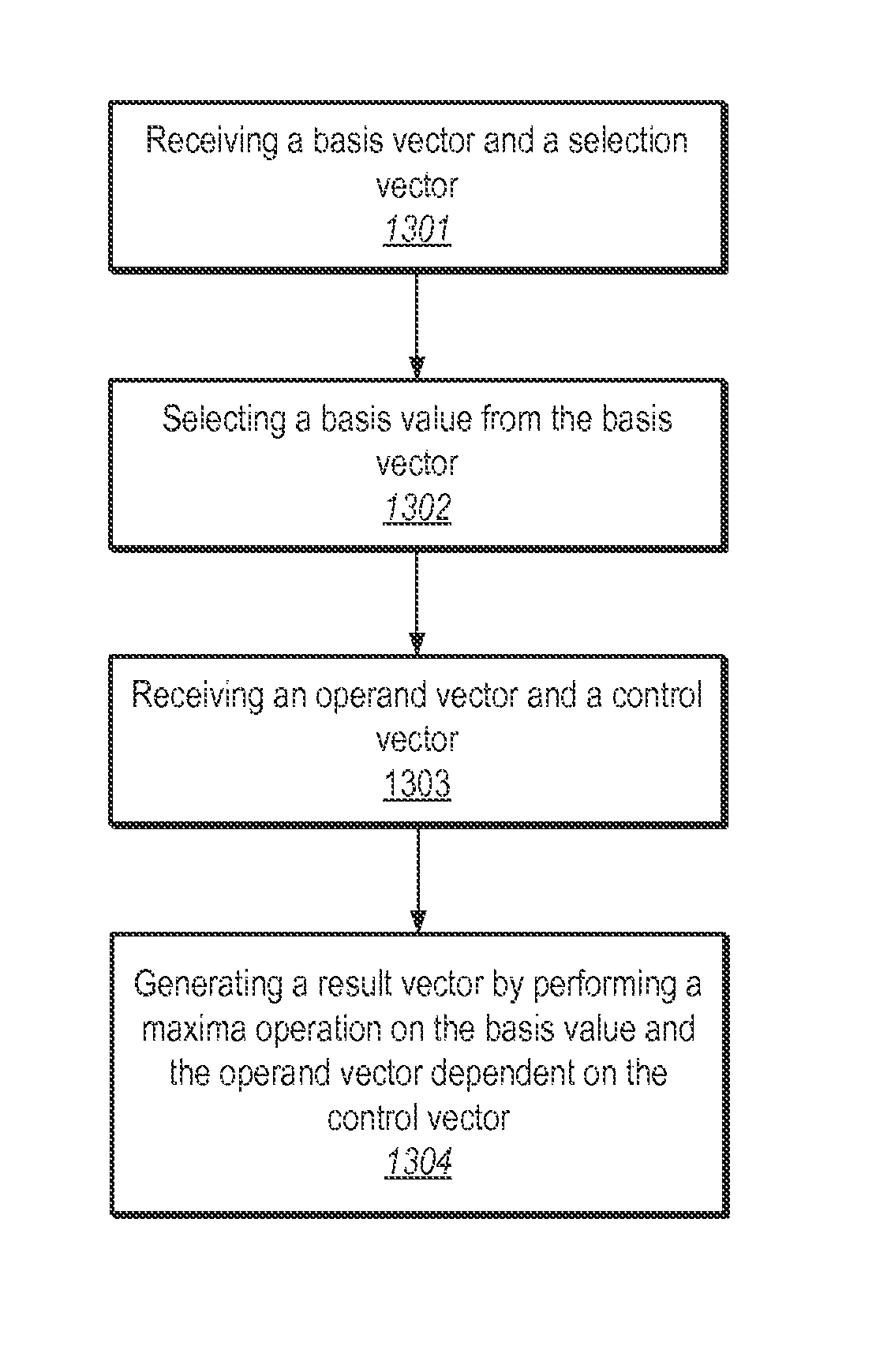
Running-min and running-max instructions for processing vectors using a base value from a key element of an input vector
ActiveUS8417921B2Software engineeringGeneral purpose stored program computerControl vectorTheoretical computer science
The described embodiments provide a processor for generating a result vector that contains results from a comparison operation. During operation, the processor receives a first input vector, a second input vector, and a control vector. When subsequently generating a result vector, the processor first captures a base value from a key element position in the first input vector. For selected elements in the result vector, processor compares the base value and values from relevant elements to the left of a corresponding element in the second input vector, and writes the result into the element in the result vector. In the described embodiments, the key element position and the relevant elements can be defined by the control vector and an optional predicate vector.
Owner:APPLE INC
Processing vectors using wrapping minima and maxima instructions in the macroscalar architecture
ActiveUS8555037B2Software engineeringGeneral purpose stored program computerControl vectorParallel computing
Embodiments of a system and a method in which a processor may execute instructions that cause the processor to receive an input vector and a control vector are disclosed. The executed instructions may also cause the processor to perform a minima or maxima operation on another input vector dependent upon the input vector and the control vector.
Owner:APPLE INC
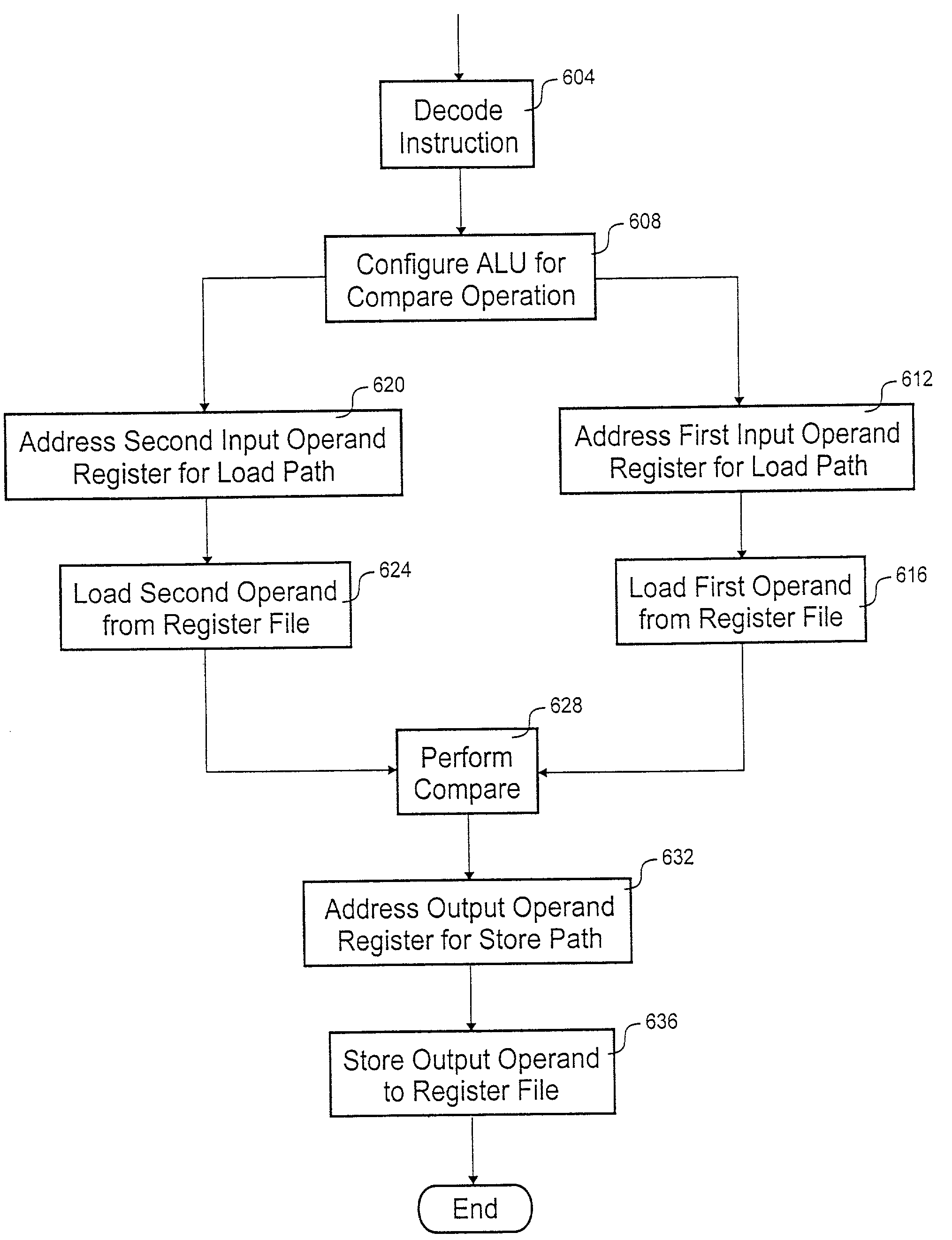
Processing architecture having a compare capability
According to the invention, a processing core that executes a compare instruction is disclosed. The processing core includes a register file, comparison logic, decode logic, and a store path. Included in the register file are a number of general-purpose registers. The general-purpose registers include a first input operand register, a second input operand register and an output operand register. Comparison logic is coupled to the register file. The comparison logic tests for at least two of the following relationships: less than, equal to, greater than and no valid relationship. The decode logic selects the output operand register from the plurality of general-purpose registers. The store path extends between the comparison logic and the selected output operand register.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
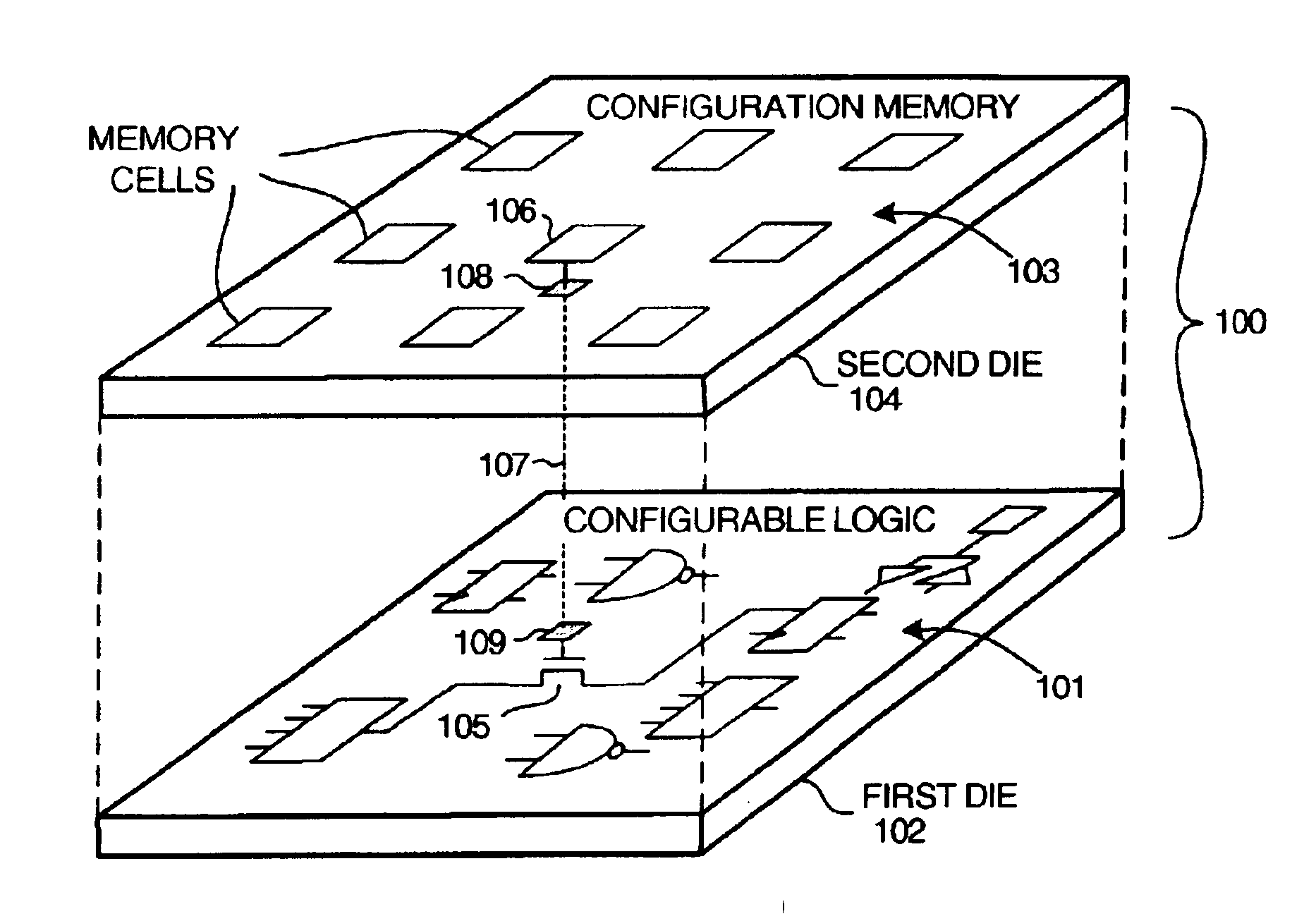
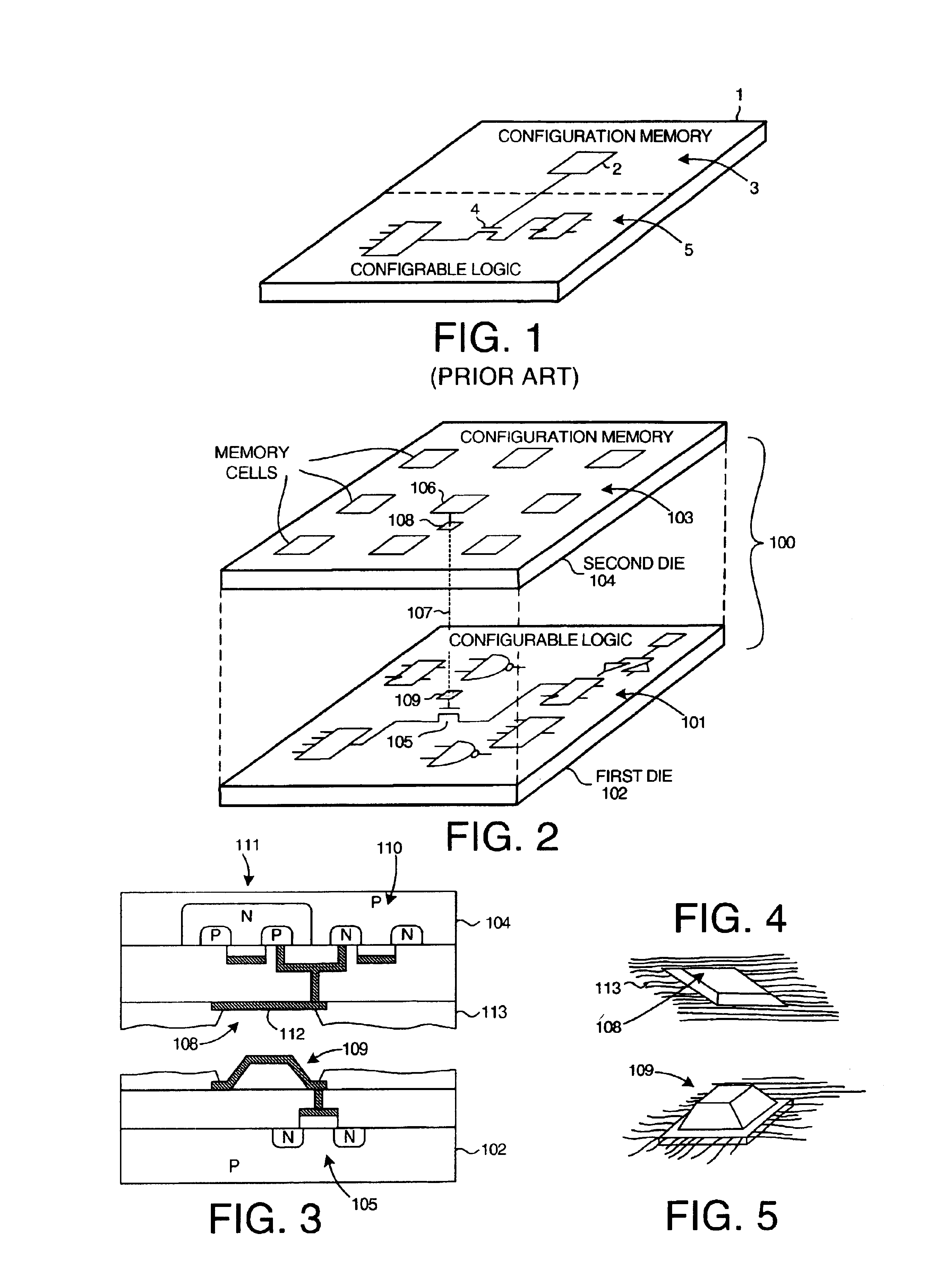
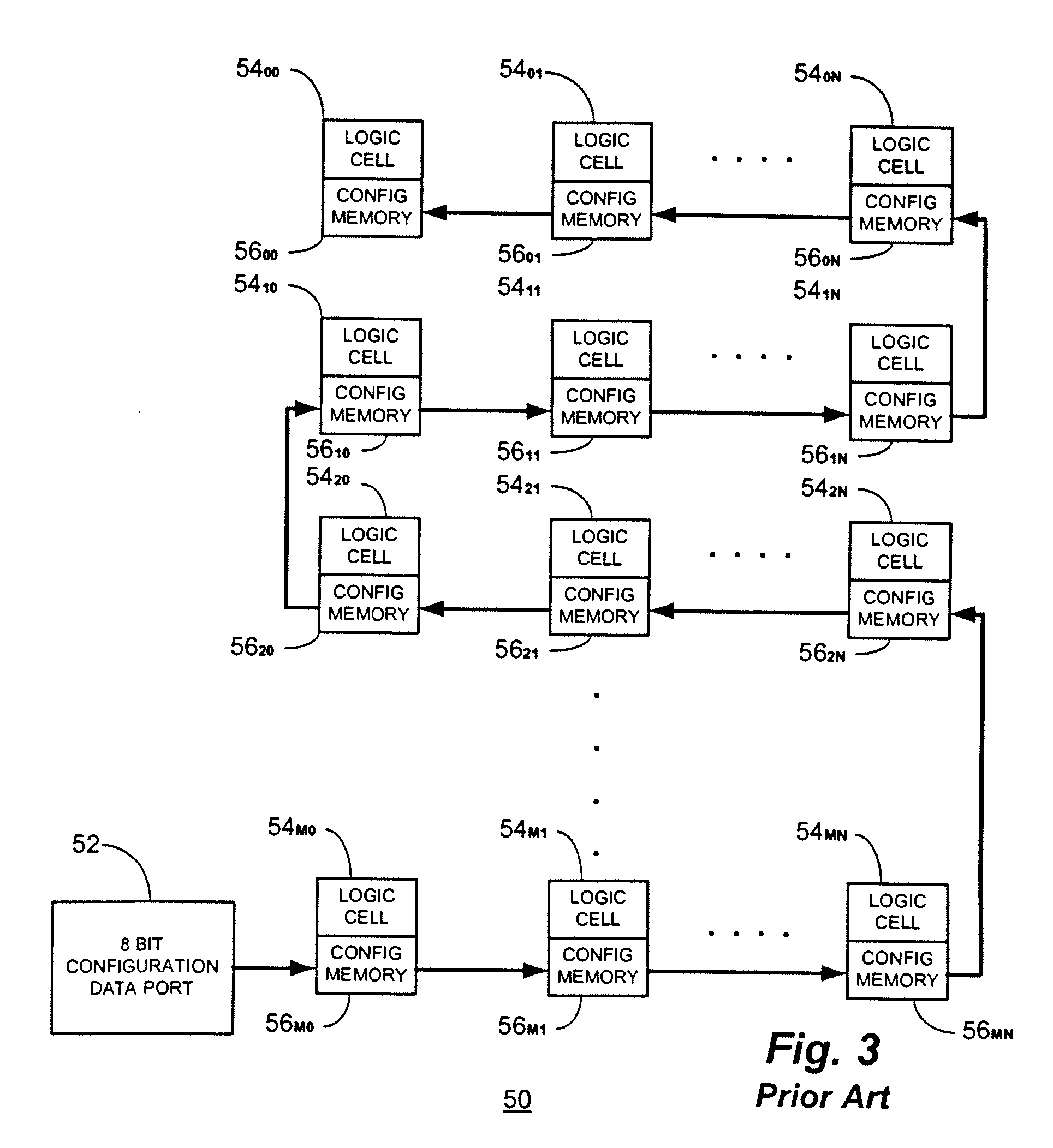
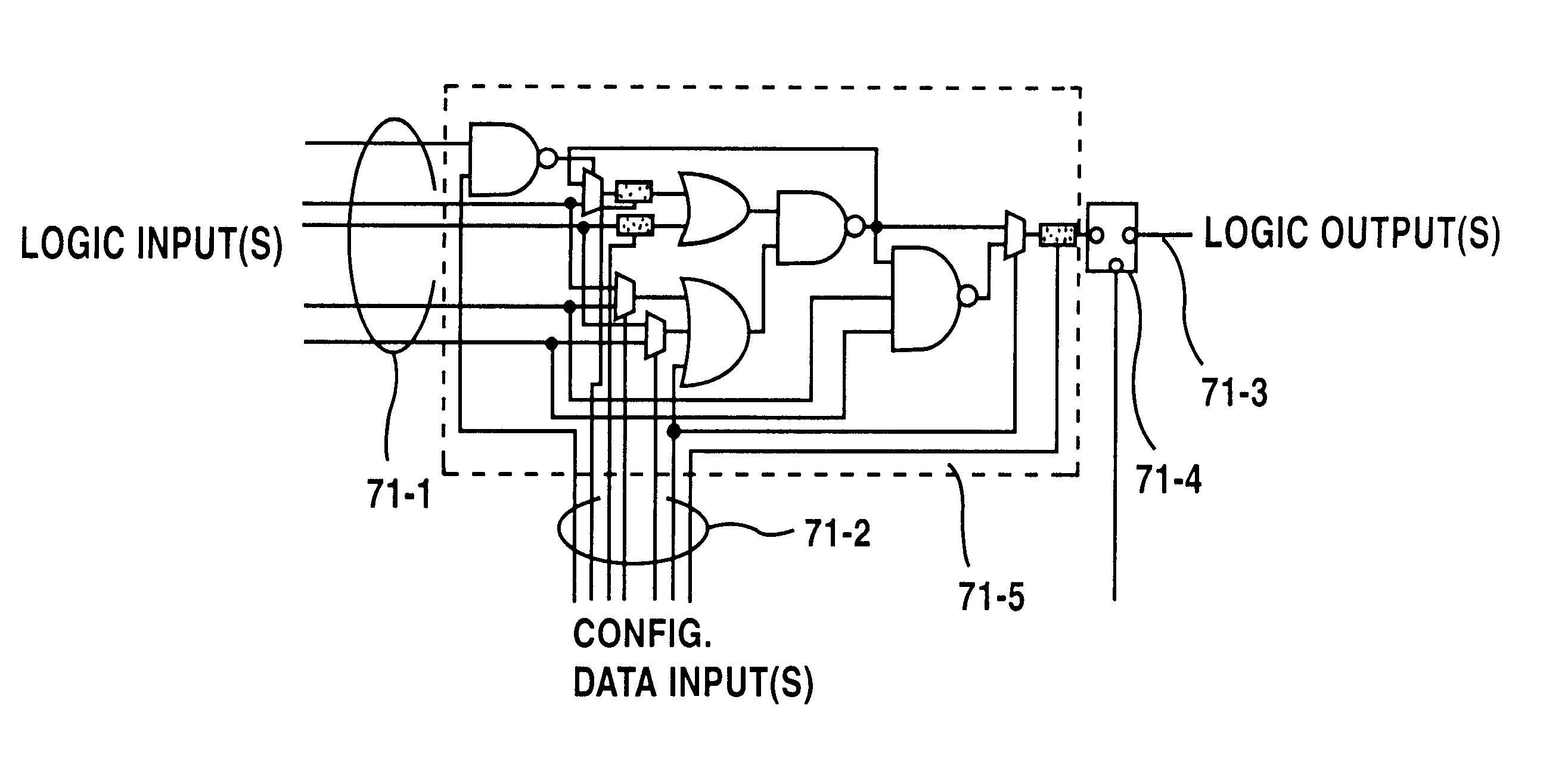
Multi-chip programmable logic device having configurable logic circuitry and configuration data storage on different dice
InactiveUS6917219B2Increase volumeIncrease productionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesProgrammable logic deviceLogical part
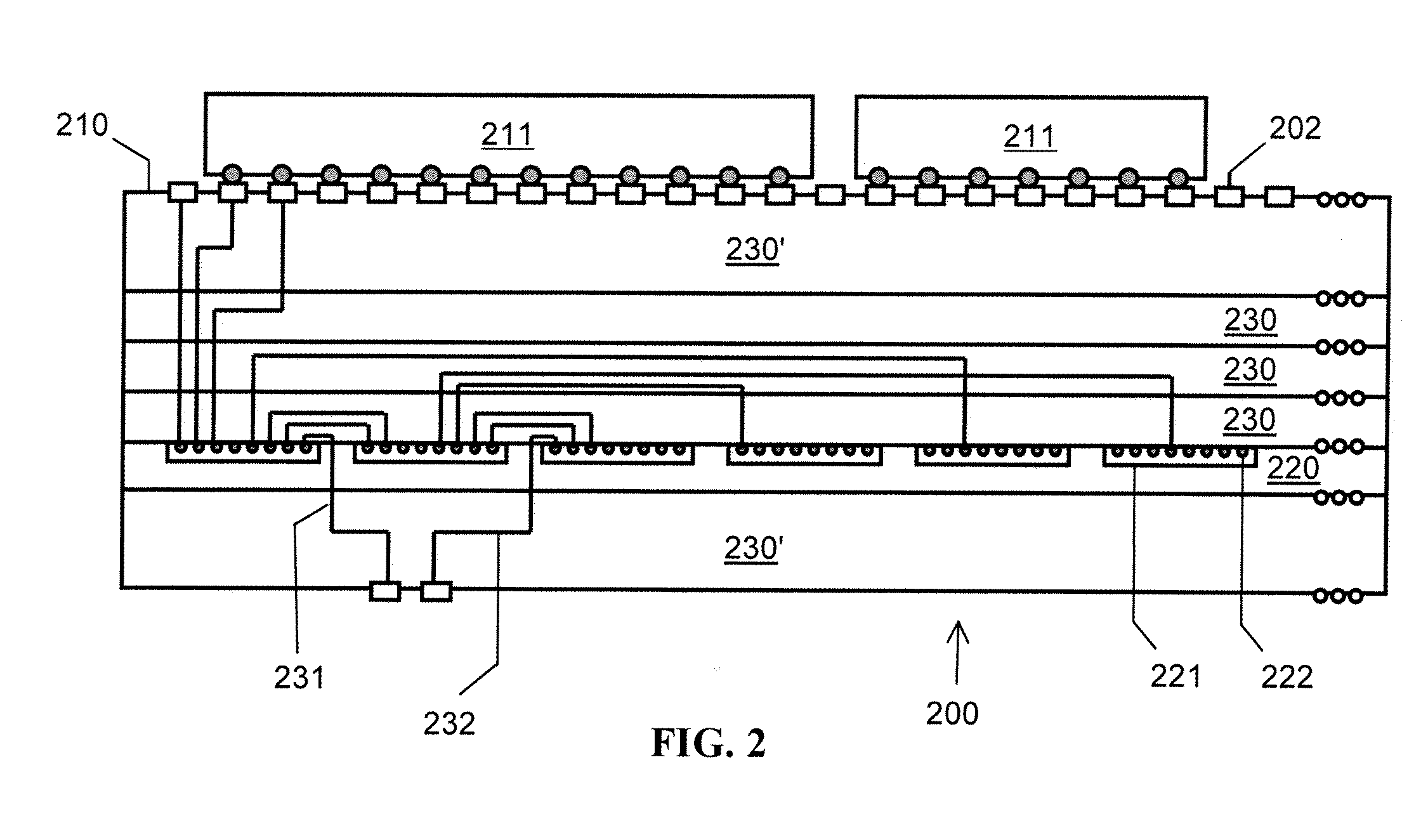
The circuitry of a programmable logic device (for example, an FPGA) includes a configurable logic portion and a configuration memory. The configuration memory stores configuration data that configures the configurable logic portion to realize a user-defined circuit. The configurable logic portion is disposed on a first die whereas the configuration memory is disposed on a second die. The second die is bonded to the first die in stacked relation. Each bit of configuration data passes from the second die to the first die through a pair of micropads. One micropad of the pair is disposed on the first die and the other micropad of the pair is disposed on the second die. When the first die and second die are brought together in face-to-face relation, the two micropads form an electrical connection through which the configuration data bit passes from the second die to the first die.
Owner:XILINX INC
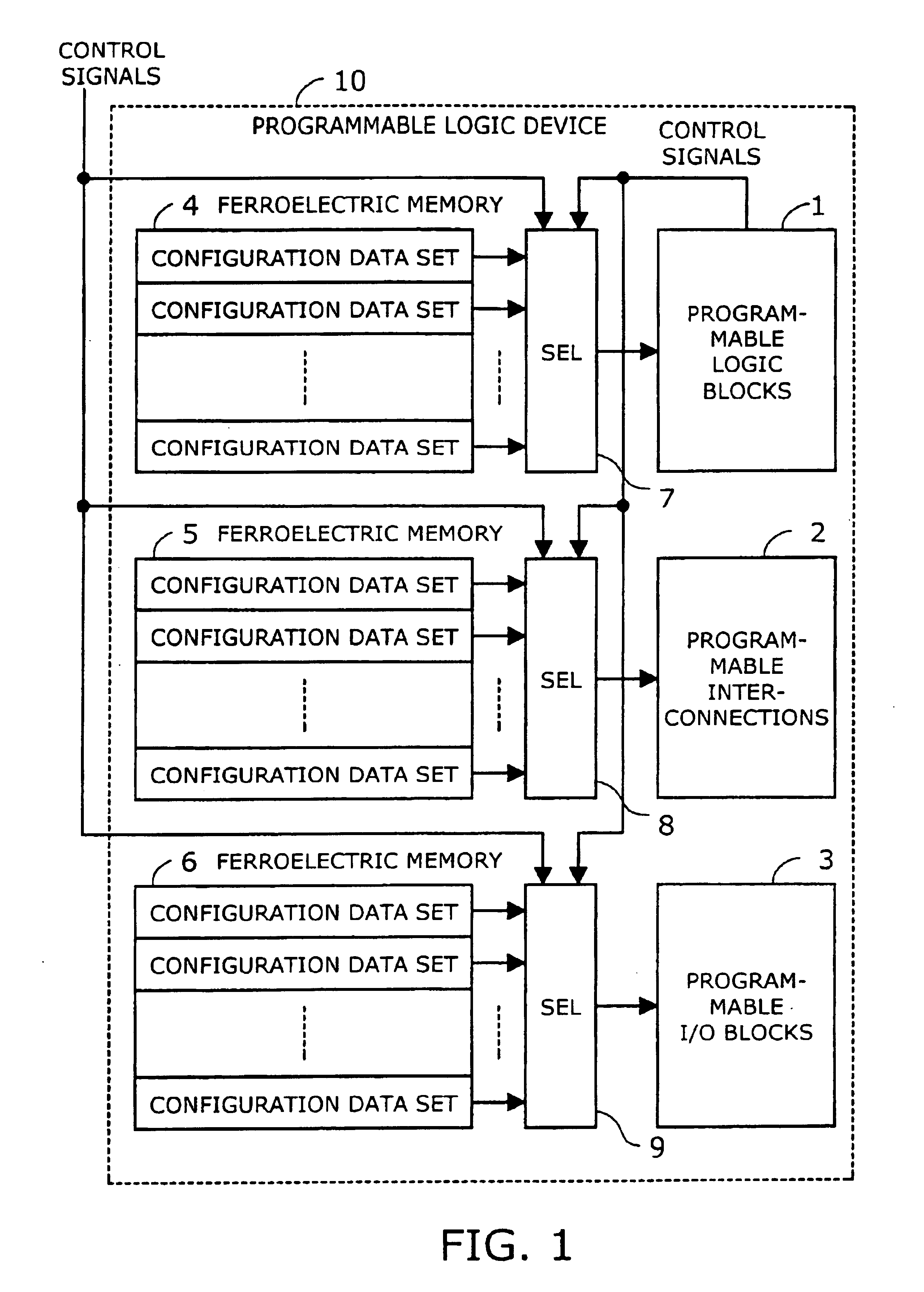
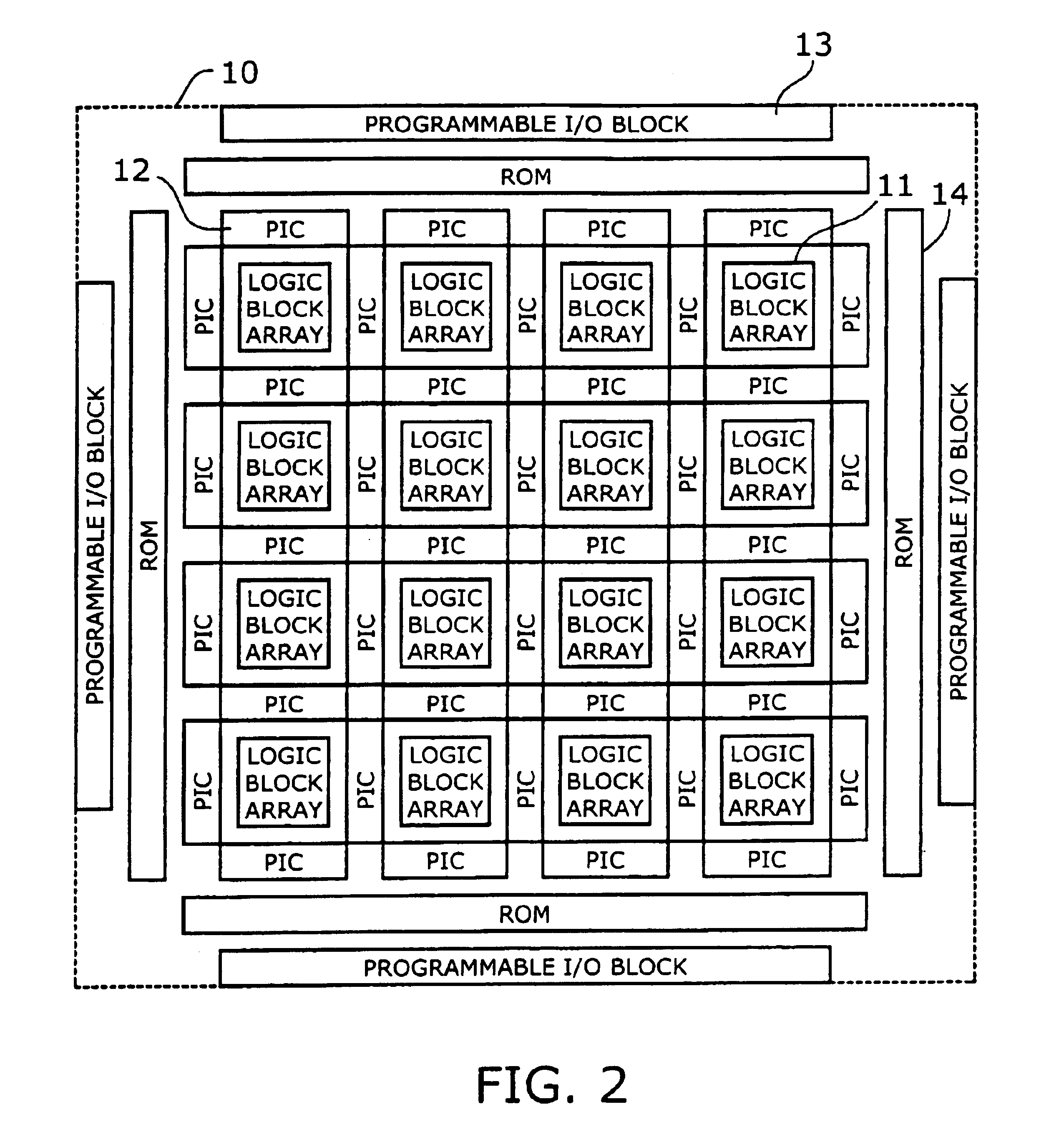
Programmable logic device with ferroelectric configuration memories
InactiveUS6924663B2Increase the effective amountEfficient architectureDigital storageInternal/peripheral component protectionElectricityData stream
A programmable logic device with ferroelectric configuration memories storing multiple configuration data sets. The device has programmable logic blocks, interconnections, and I / O blocks to provide desired logic functions. Those building blocks can be dynamically reconfigured by changing the selection of configuration data stored in the device's integral configuration memories. The configuration memories are divided into groups, so that they can be loaded concurrently with multiple configuration data streams. To protect the content of configuration memories from unauthorized access, the device employs an authentication mechanism that uses security IDs stored in the configuration memories. The device has a memory controller to provide an appropriate power supply sequence for ferroelectric memory cells to ensure the reliable data retention when the device is powered up or shut down.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
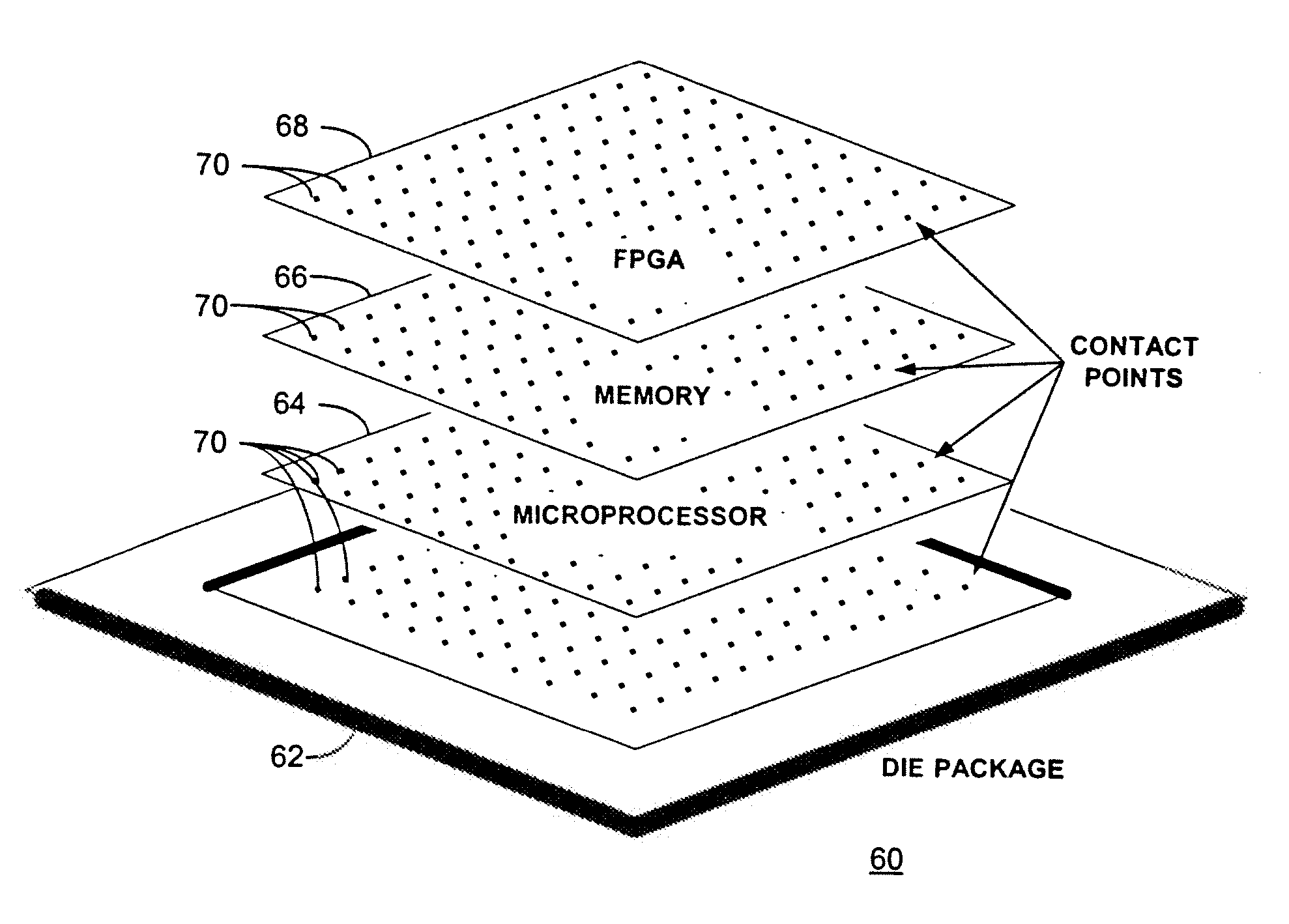
Reconfigurable processor module comprising hybrid stacked integrated circuit die elements
InactiveUS20060195729A1Energy efficient ICTError detection/correctionEngineeringField-programmable gate array
A reconfigurable processor module comprising hybrid stacked integrated circuit (“IC”) die elements. In a particular embodiment disclosed herein, a processor module with reconfigurable capability may be constructed by stacking one or more thinned microprocessor, memory and / or field programmable gate array (“FPGA”) die elements and interconnecting the same utilizing contacts that traverse the thickness of the die. The processor module disclosed allows for a significant acceleration in the sharing of data between the microprocessor and the FPGA element while advantageously increasing final assembly yield and concomitantly reducing final assembly cost.
Owner:ARBOR GLOBAL STRATEGIES LLC
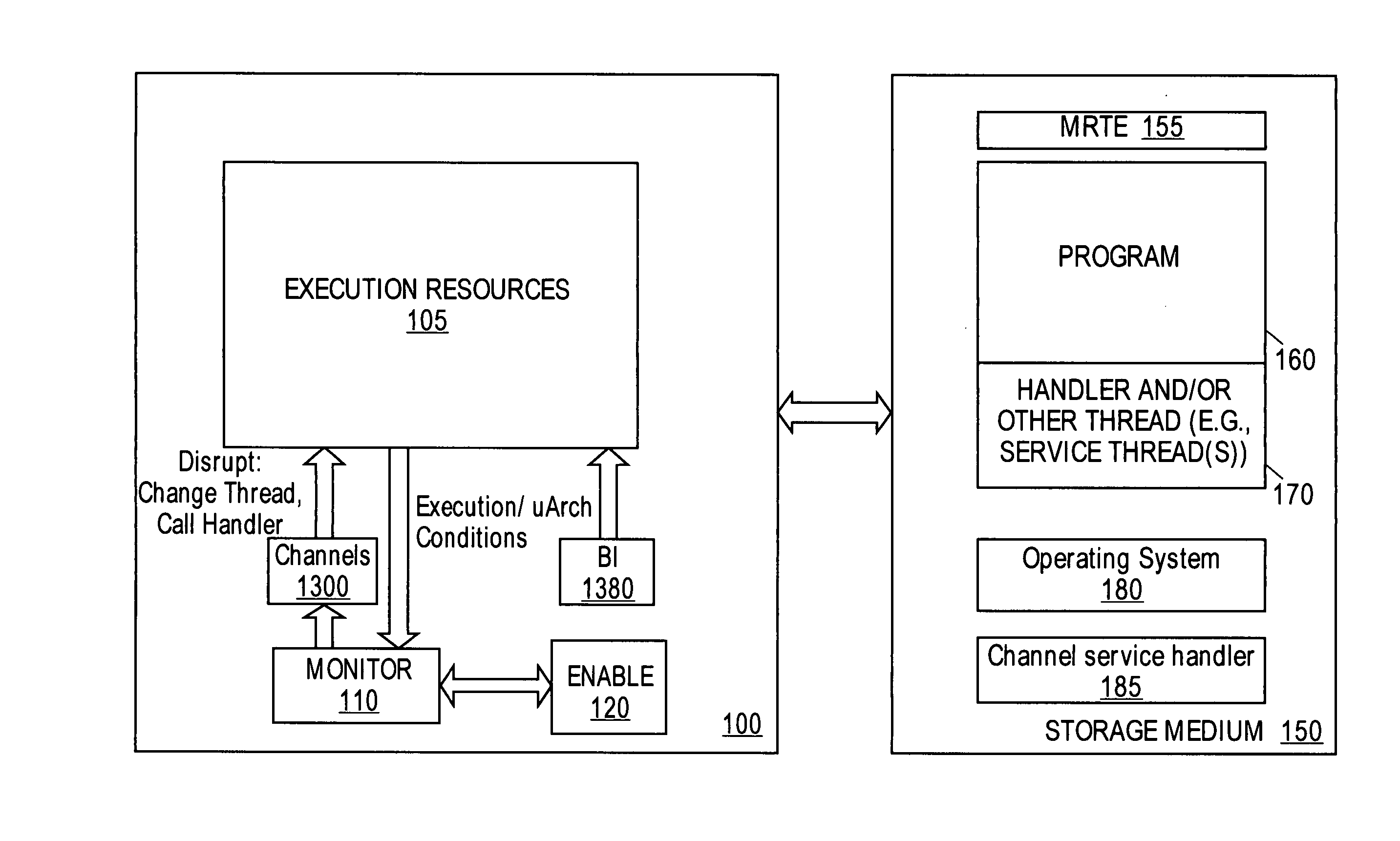
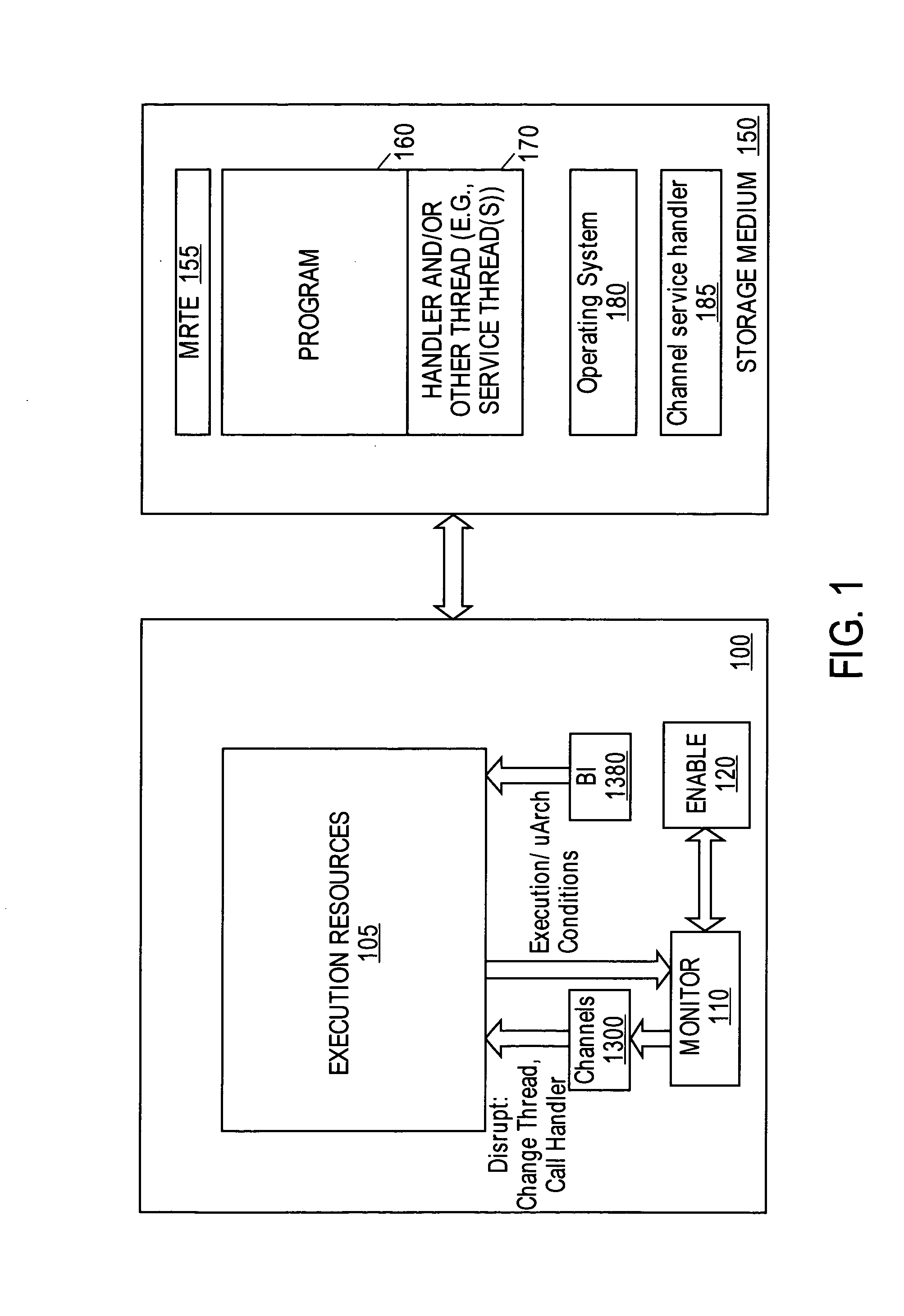
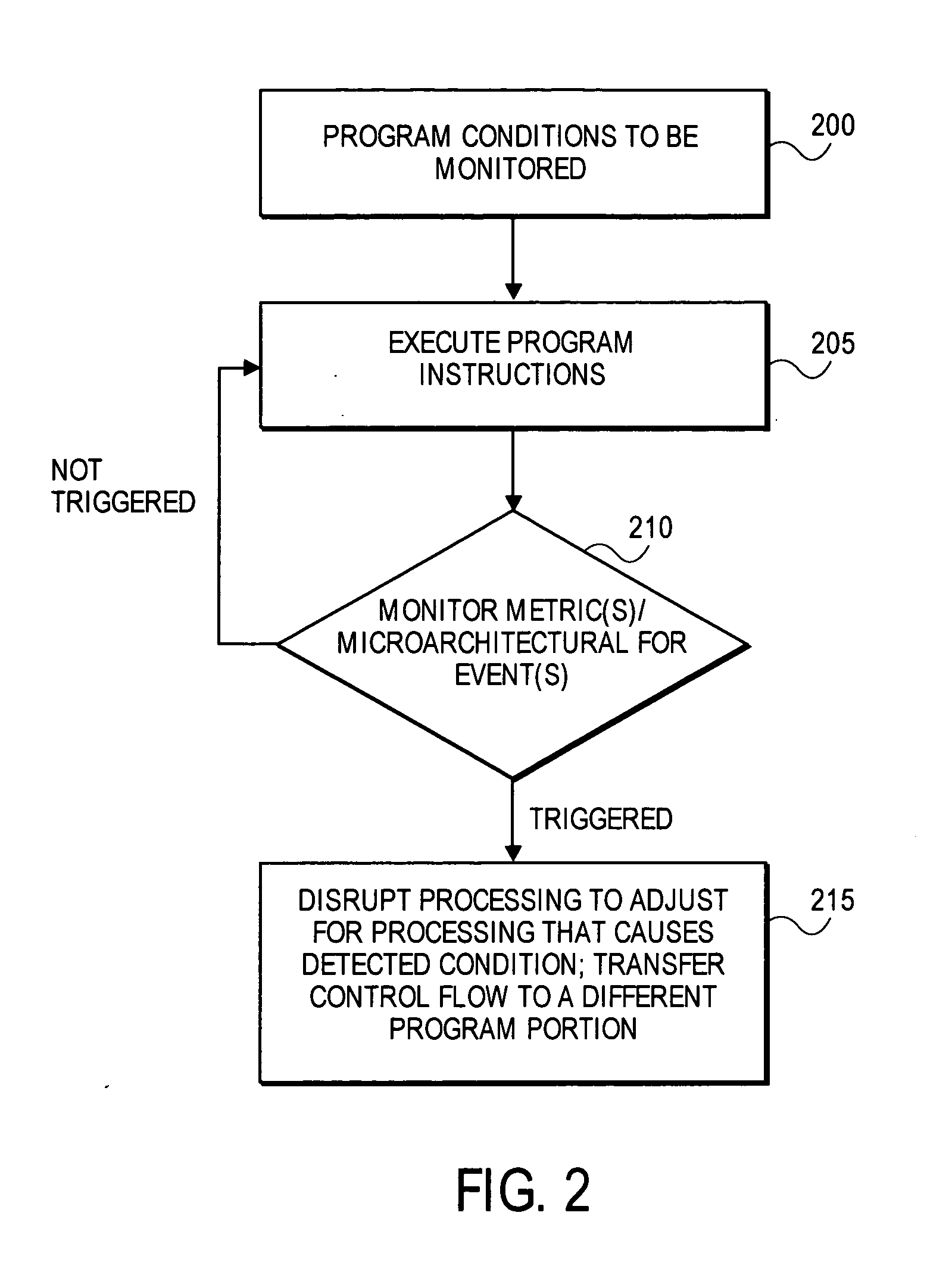
System to profile and optimize user software in a managed run-time environment
InactiveUS20070214342A1Error detection/correctionGeneral purpose stored program computerParallel computingRunning time
Method, apparatus, and system for monitoring performance within a processing resource, which may be used to modify user-level software. Some embodiments of the invention pertain to an architecture to allow a user to improve software running on a processing resources on a per-thread basis in real-time and without incurring significant processing overhead.
Owner:INTEL CORP
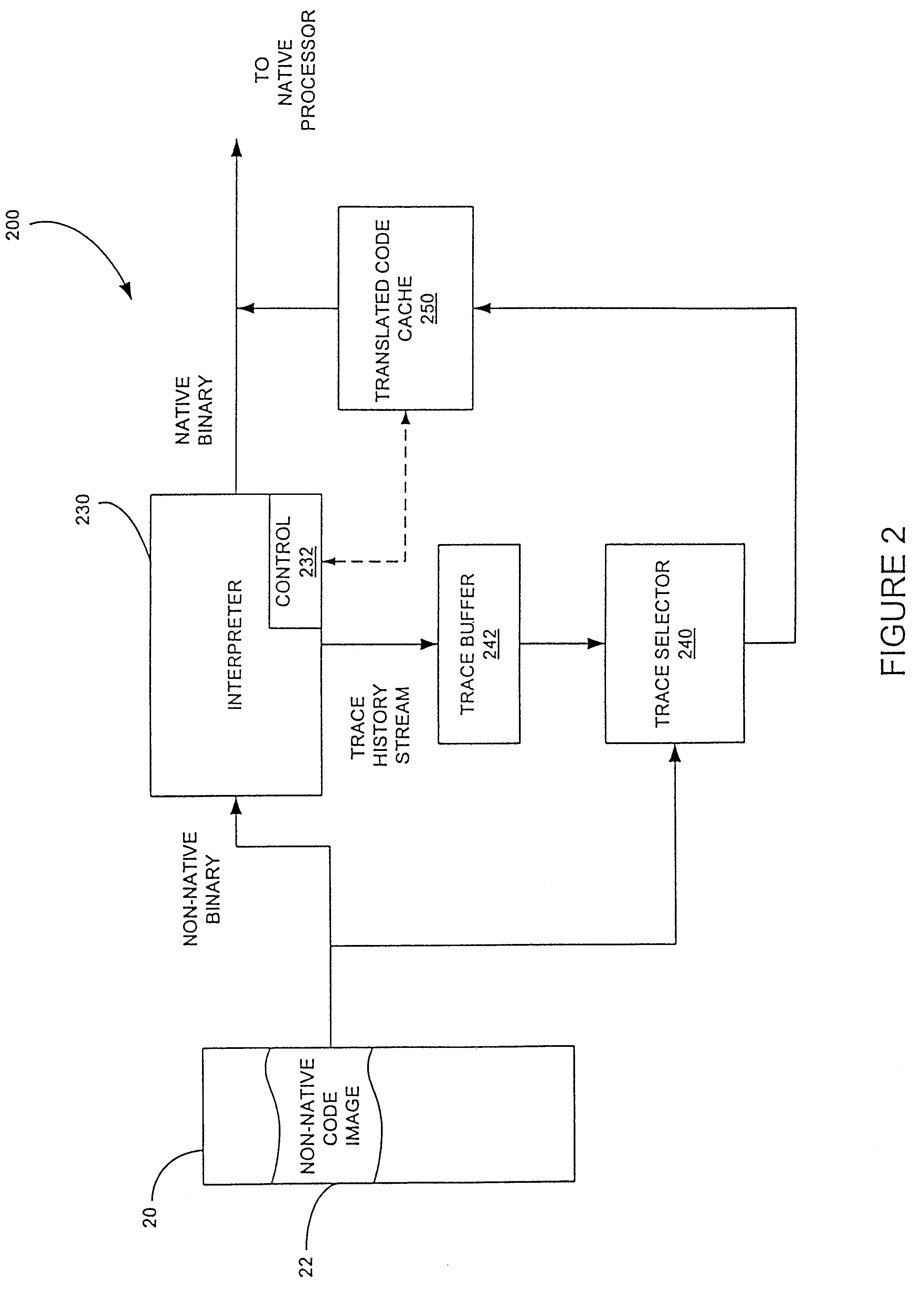
Method for selecting active code traces for translation in a caching dynamic translator
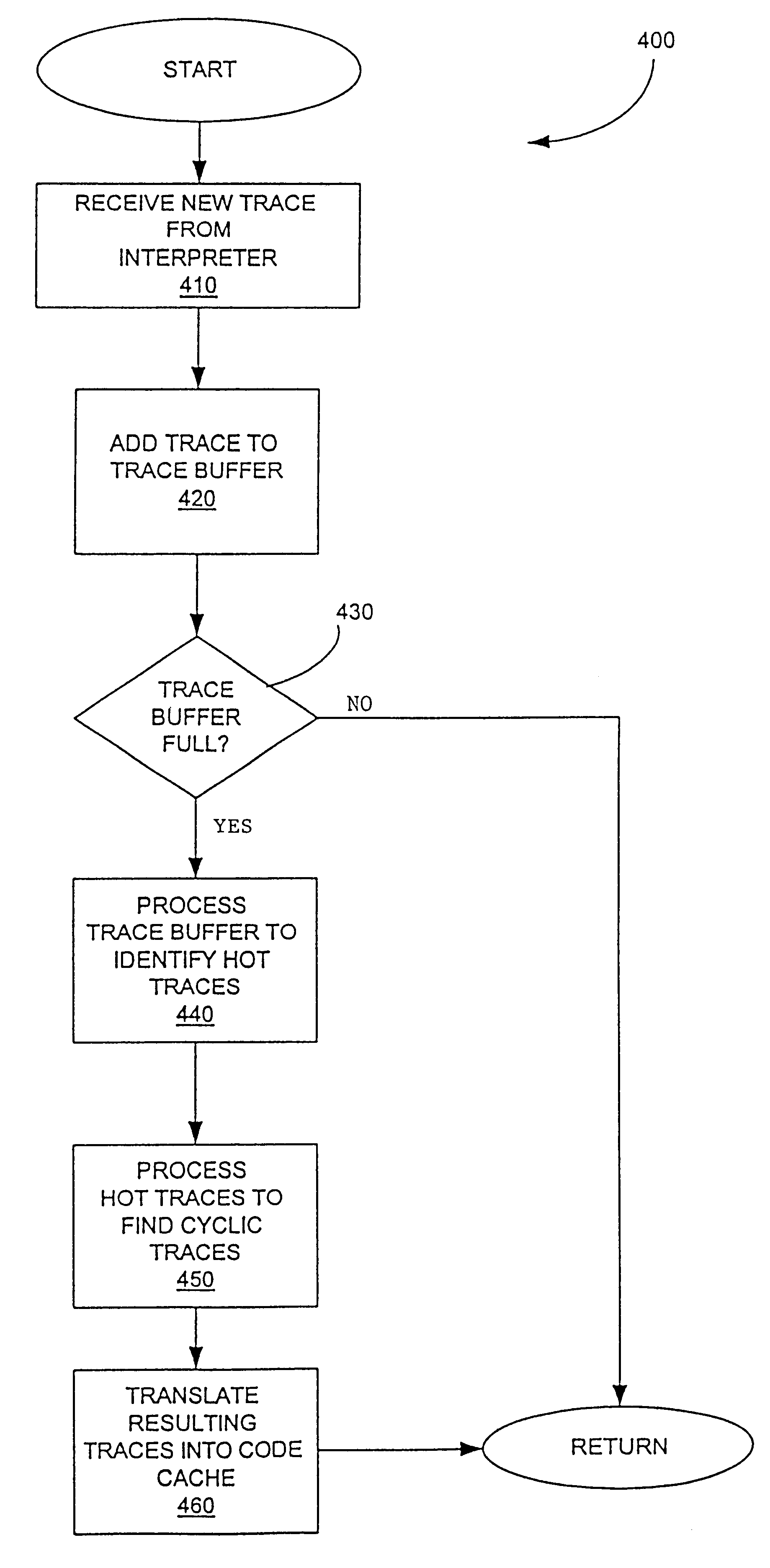
A method is shown for selecting active, or hot, code traces in an executing program for storage in a code cache. A trace is a sequence of dynamic instructions characterized by a start address and a branch history which allows the trace to be dynamically disassembled. Each trace is terminated by execution of a trace terminating condition which is a backward taken branch, an indirect branch, or a branch whose execution causes the branch history for the trace to reach a predetermined limit. As each trace is generated by the executing program, it is loaded into a buffer for processing. When the buffer is full, a counter corresponding to the start address of each trace is incremented. When the count for a start address exceeds a threshold, then the start address is marked as being hot. Each hot trace is then checked to see if the next trace in the buffer shares the same start address, in which case the hot trace is cyclic. If the start address of the next trace is not the same as the hot trace, then the traces in the buffer are checked to see they form a larger cycle of execution. If the traces subsequent to the hot trace are not hot themselves and are followed by a trace having the same start address as the hot trace, then their branch histories are companded with the branch history of the hot trace to form a cyclic trace. The cyclic traces are then disassembled and the instructions executed in the trace are stored in a code cache.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Information routing system and apparatus
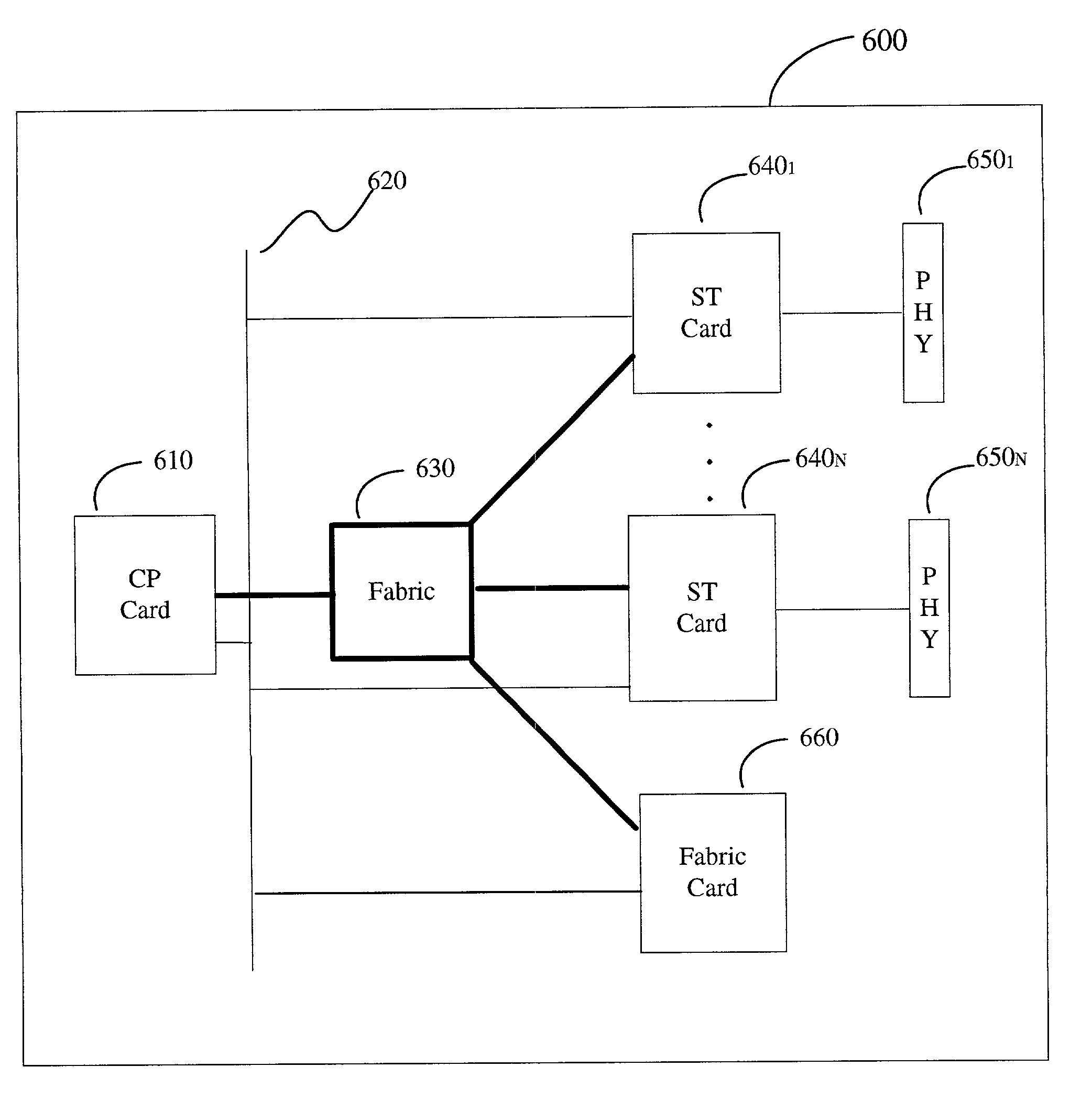
ActiveUS6999454B1Time-division multiplexGeneral purpose stored program computerTraffic capacityRouting table
An information routing system and apparatus includes separate control and forwarding planes. The control plane is split into box management control functions and routing control functions. The box management control functions are isolated to a single processing card, while the routing control functions are distributed across multiple processing cards. The routing table is also distributed across multiple processing cards. The multiple processing cards are interconnected via a high-speed backplane bus for control plane traffic and by a fabric for forwarding plane traffic.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
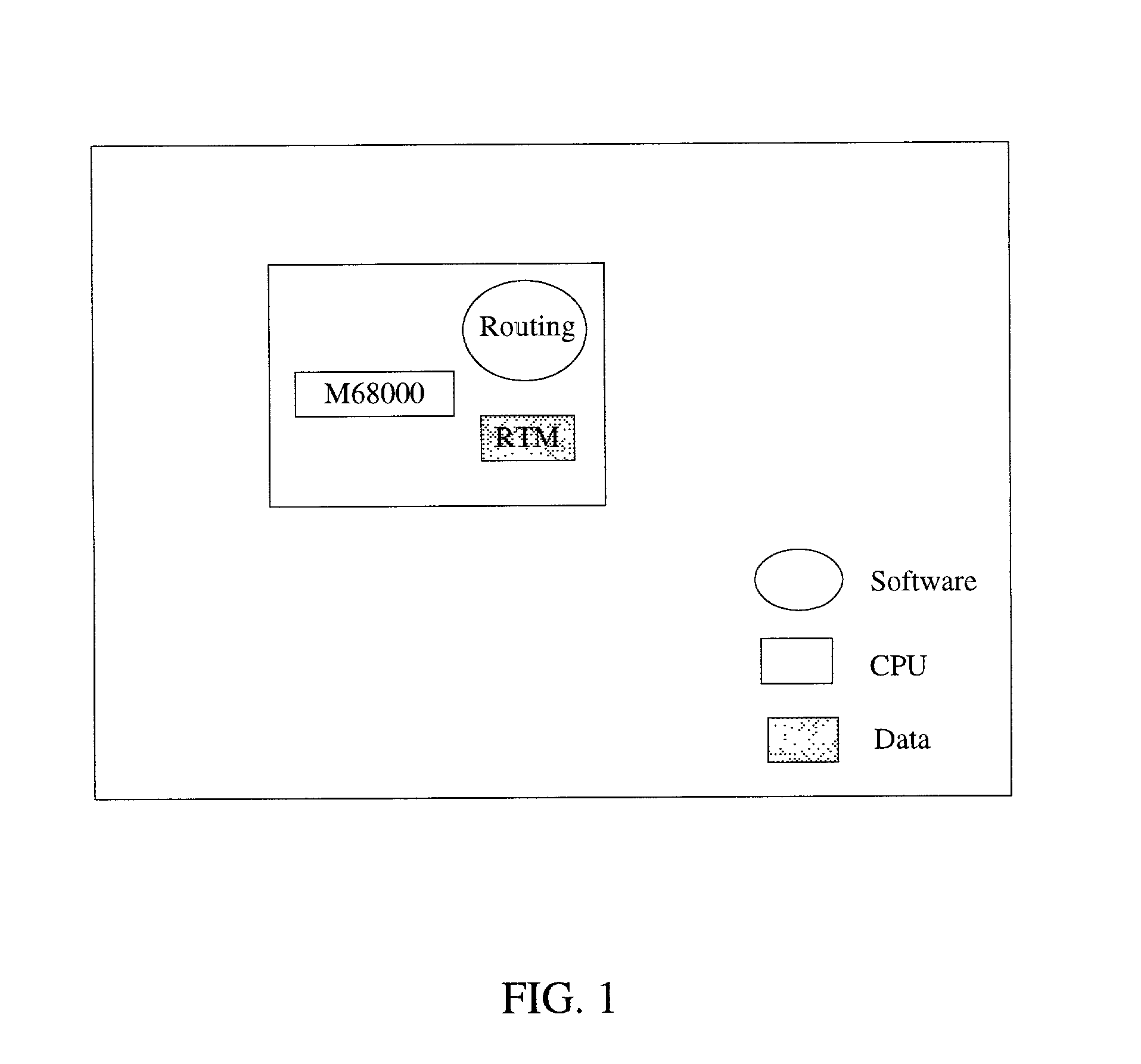
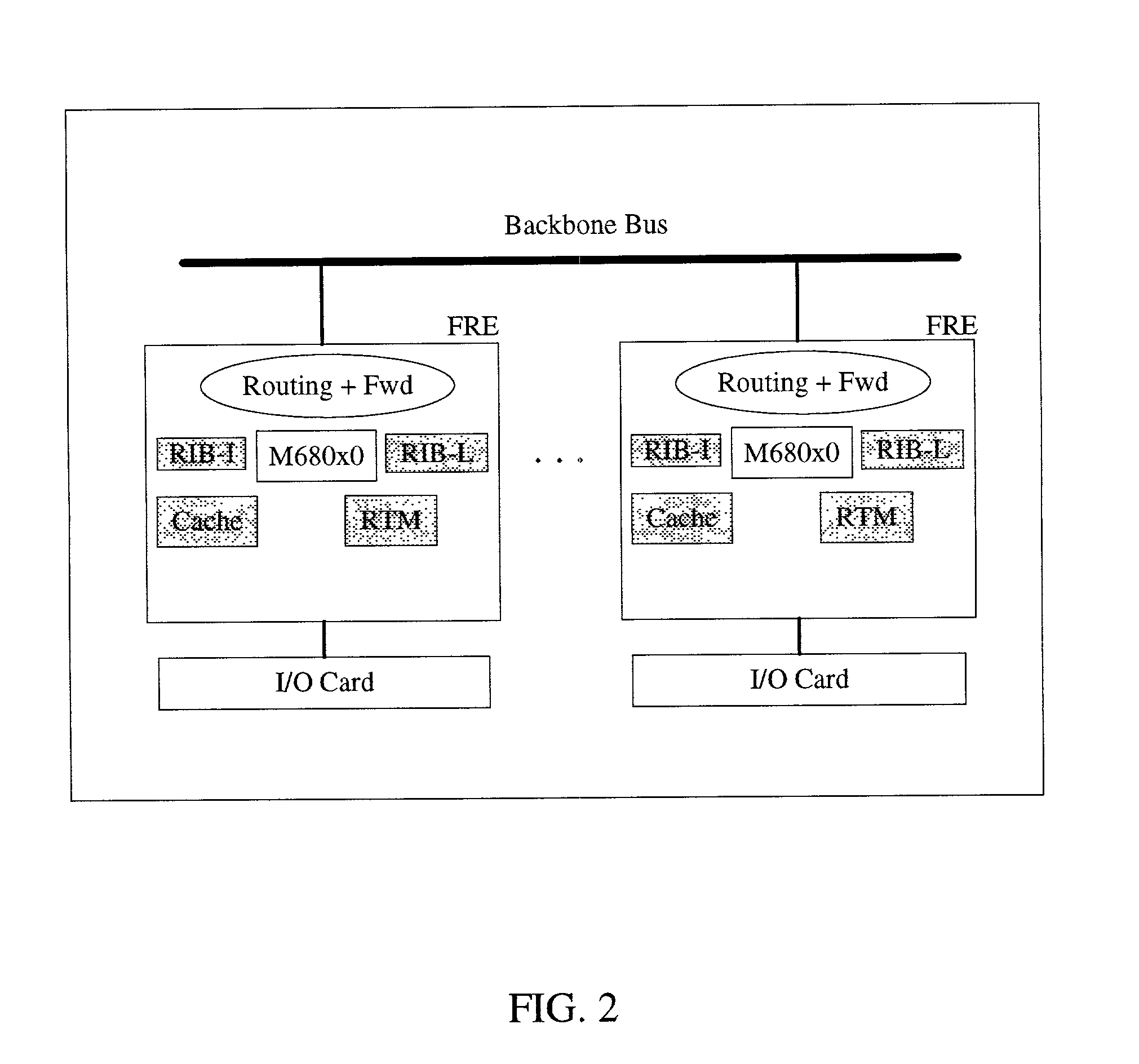
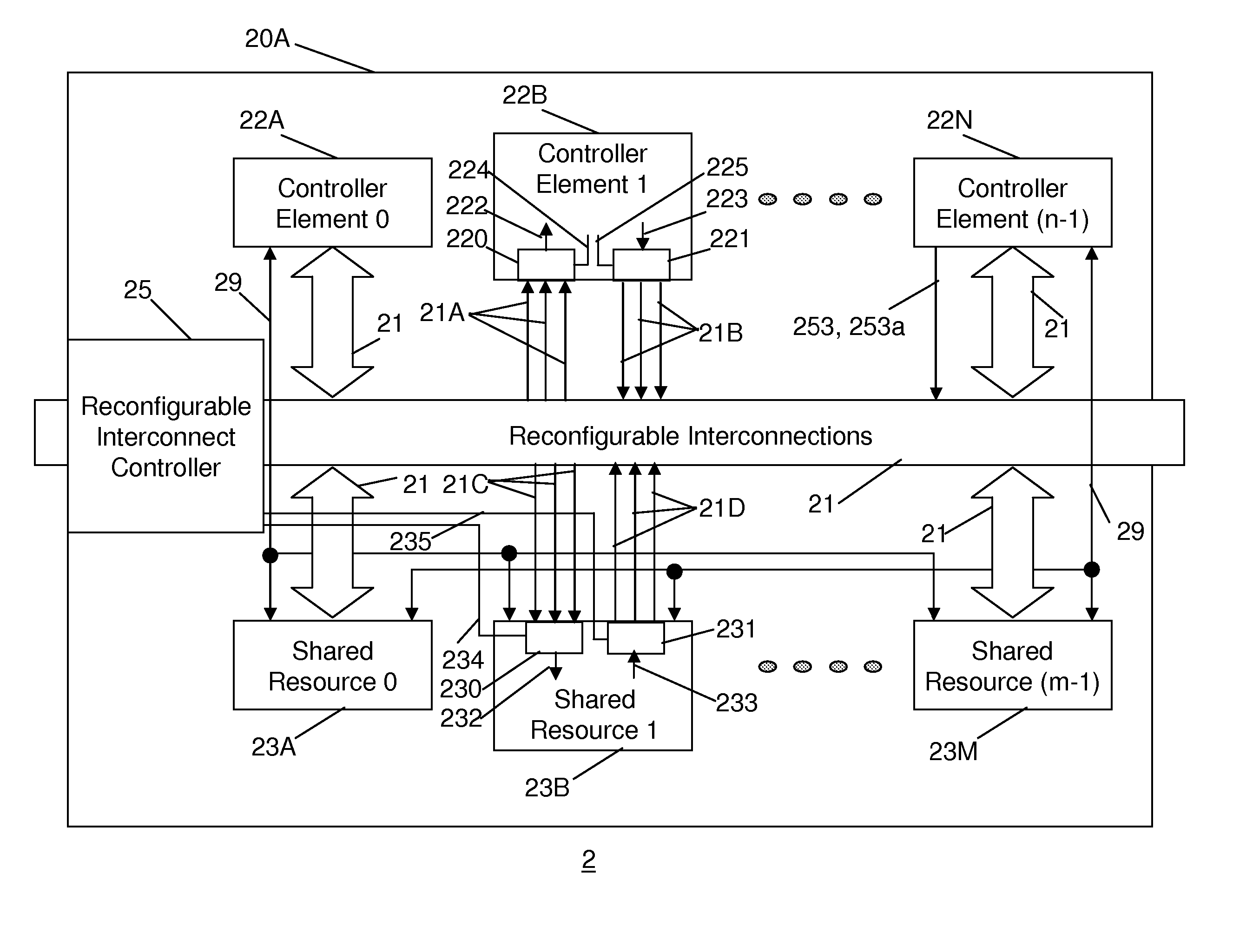
Reconfigurable integrated circuit
InactiveUS20070143577A1Energy efficient ICTArchitecture with single central processing unitNon real timeResource block
A reconfigurable integrated circuit is provided wherein the available hardware resources can be optimised for a particular application. Dynamically reconfiguring (in both real-time and non real-time) the available resources and sharing a plurality of processing elements with a plurality of controller elements achieve this. In a preferred embodiment the integrated circuit includes a plurality of processing blocks, which interface to a reconfigurable interconnection means. A processing block has two forms, namely a shared resource block and a dedicated resource block. Each processing block consists of one or a plurality of controller elements and a plurality of processing elements. The controller element and processing element generally comprise diverse rigid coarse and fine grained circuits and are interconnected through dedicated and reconfigurable interconnect. The processing blocks can be configured as a hierarchy of blocks and or fractal architecture.
Owner:AKYA HLDG
Method and apparatus for enhanced estimation of an analyte property through multiple region transformation
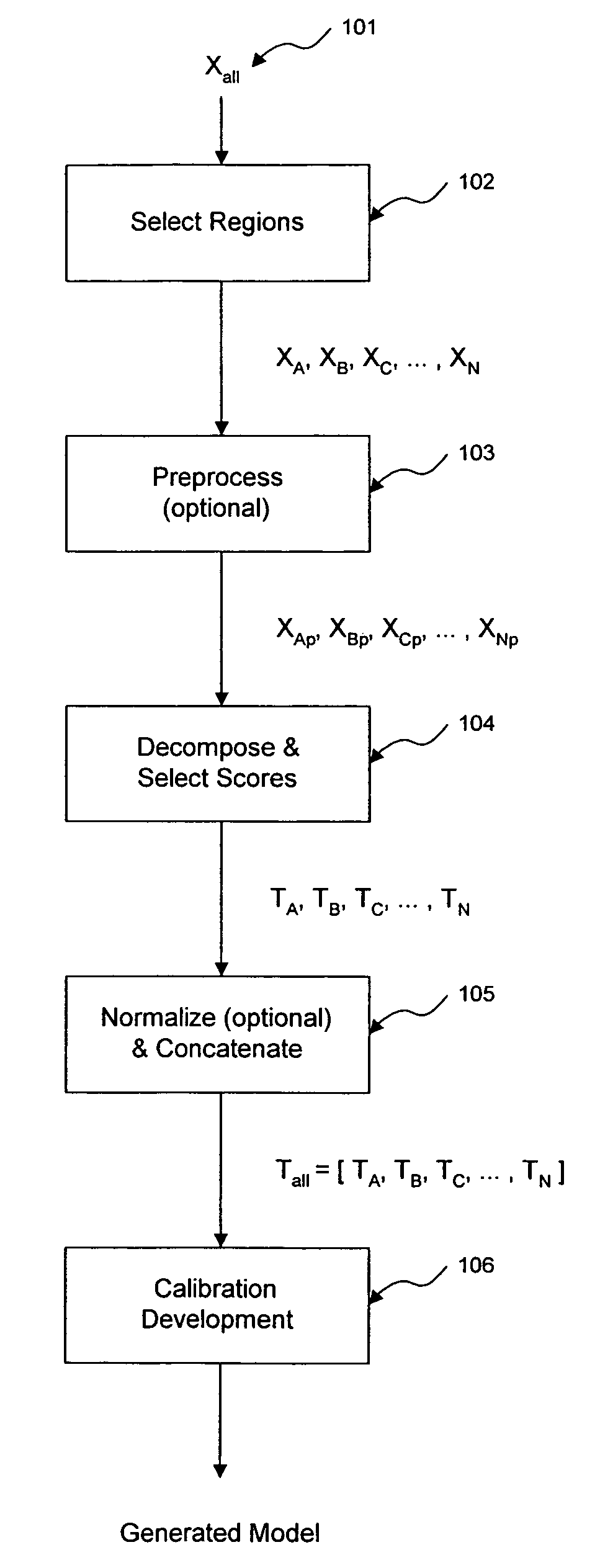
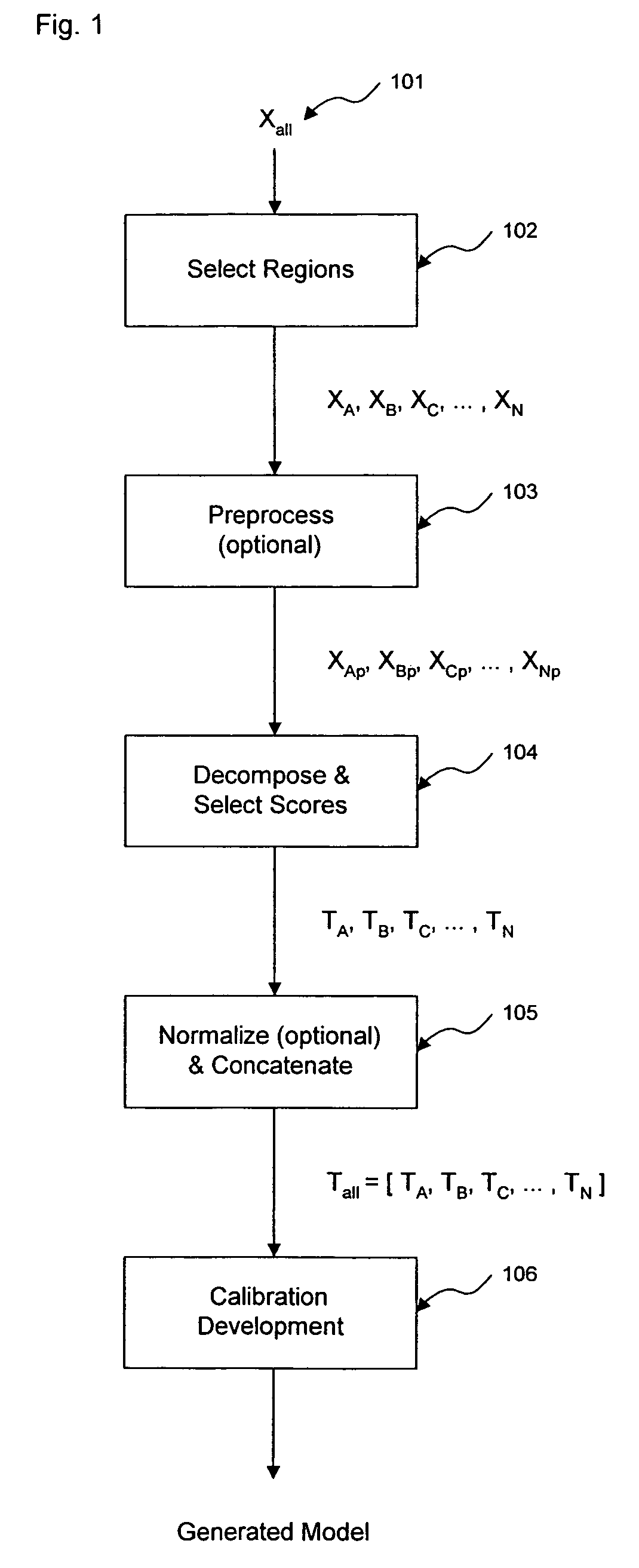
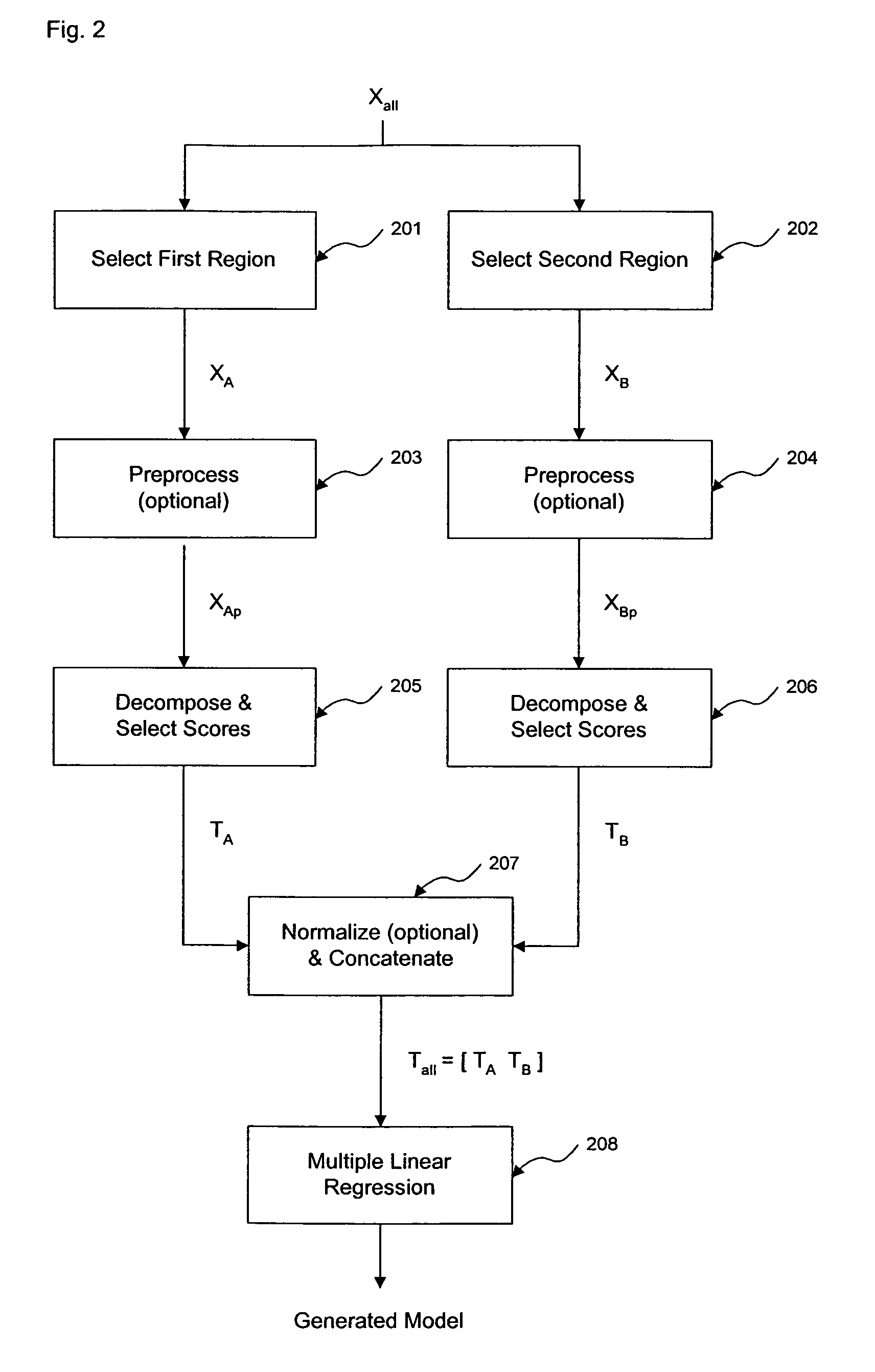
ActiveUS7620674B2Computation using non-denominational number representationDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalyteDecomposition
The invention comprises transformation of a section of a data block independently of the transformation of separate or overlapping data blocks to determine a property related to the original matrix, where each of the separate or overlapping data blocks are derived from an original data matrix. The transformation enhances parameters of a first data block over a given region of an axis of the data matrix, such as signal-to-noise, without affecting analysis of a second data block derived from the data matrix. This allows for enhancement of analysis of an analyte property, such as concentration, represented within the original data matrix. A separate decomposition and factor selection for each selected data matrix is performed with subsequent score matrix concatenization. The combined score matrix is used to generate a model that is subsequently used to estimate a property, such as concentration represented in the original data matrix.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
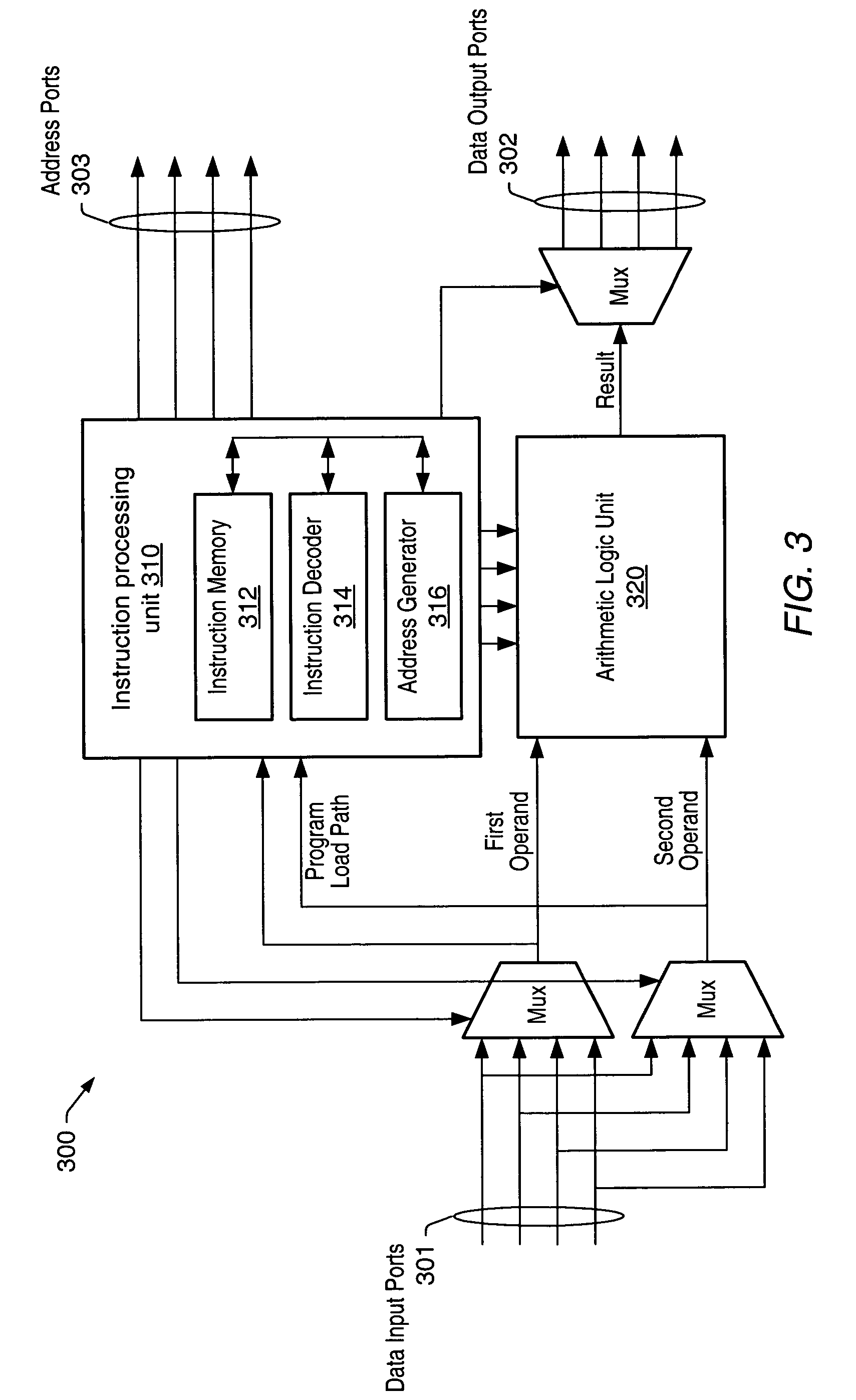
Microprocessors
A processor (100) is provided that is a programmable fixed point digital signal processor (DSP) with variable instruction length, offering both high code density and easy programming. Architecture and instruction set are optimized for low power consumption and high efficiency execution of DSP algorithms, such as for wireless telephones, as well as pure control tasks. The processor includes an instruction buffer unit (106), a program flow control unit (108), an address / data flow unit (110), a data computation unit (112), and multiple interconnecting busses. Dual multiply-accumulate blocks improve processing performance. A memory interface unit (104) provides parallel access to data and instruction memories. The instruction buffer is operable to buffer single and compound instructions pending execution thereof. A decode mechanism is configured to decode instructions from the instruction buffer. The use of compound instructions enables effective use of the bandwidth available within the processor. A soft dual memory instruction can be compiled from separate first and second programmed memory instructions. Instructions can be conditionally executed or repeatedly executed. Bit field processing and various addressing modes, such as circular buffer addressing, further support execution of DSP algorithms. The processor includes a multistage execution pipeline with pipeline protection features. Various functional modules can be separately powered down to conserve power. The processor includes emulation and code debugging facilities with support for cache analysis.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Zero-gap playback using predictive mixing
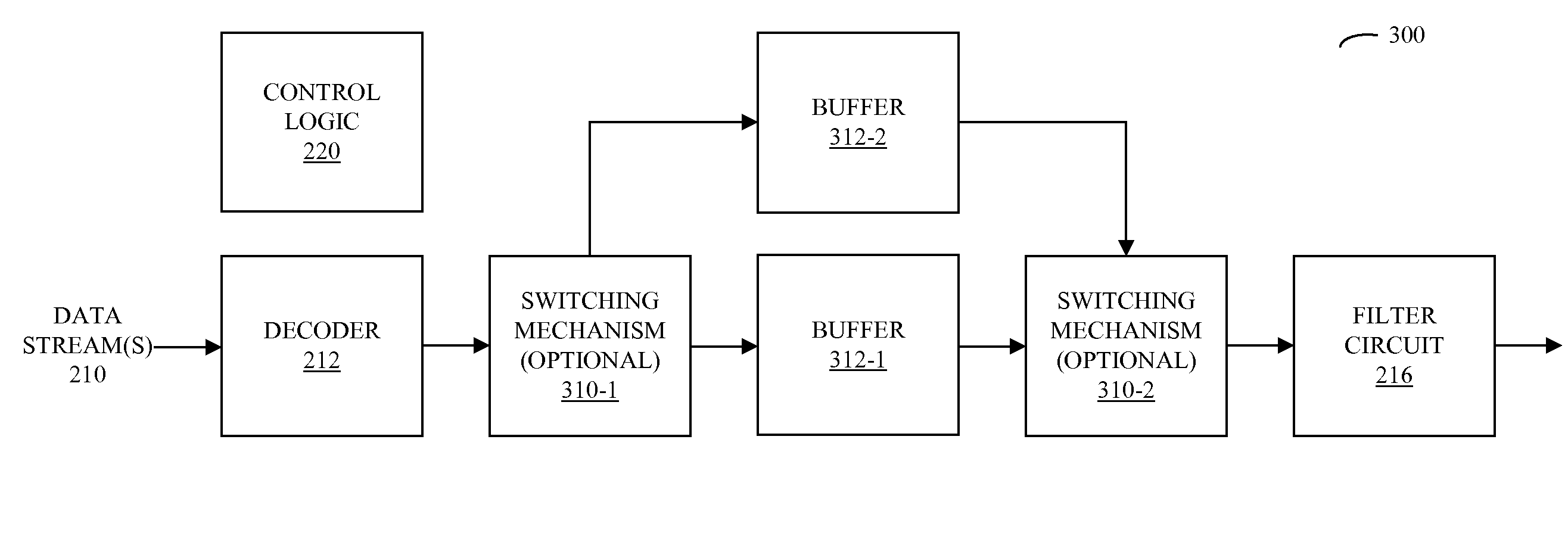
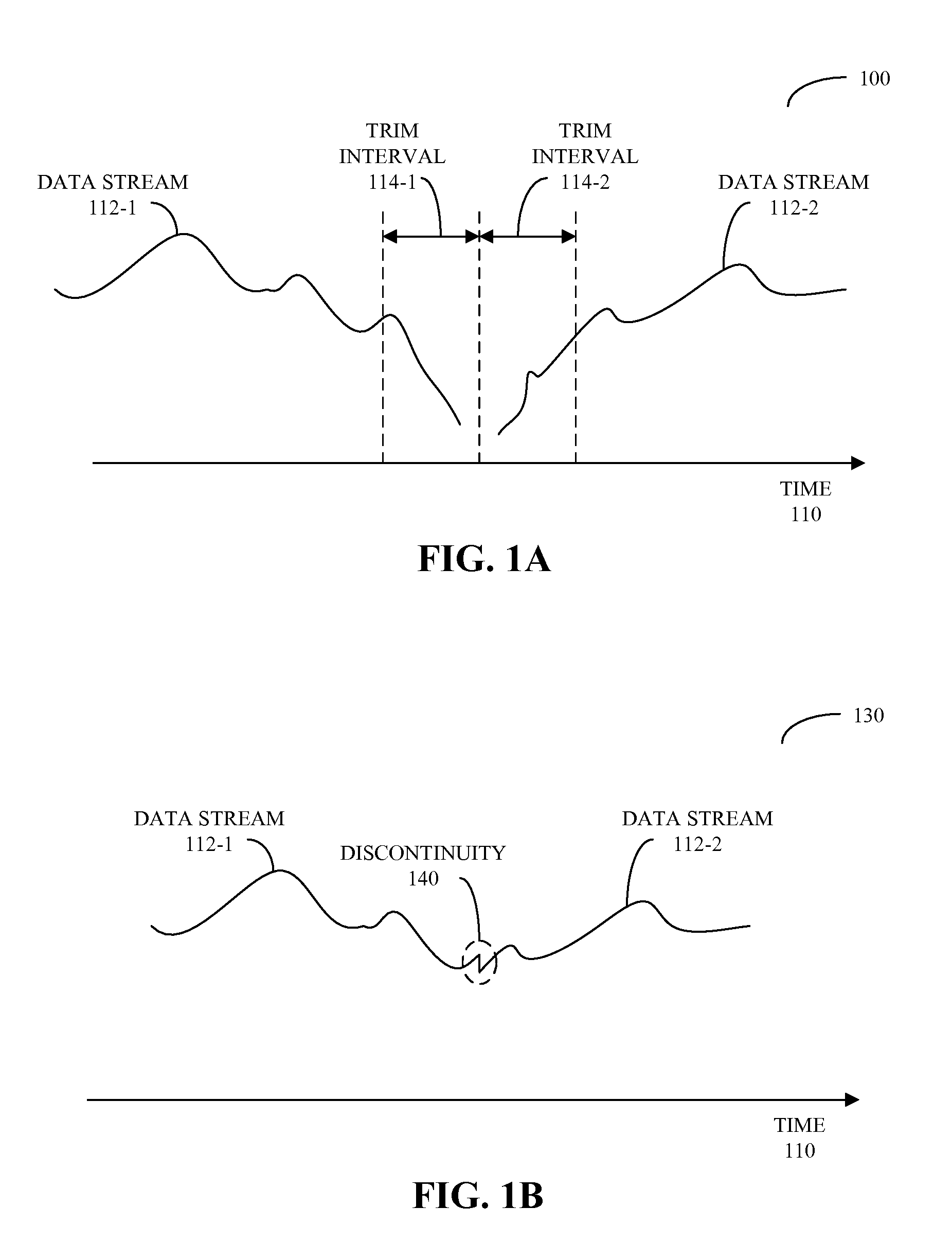
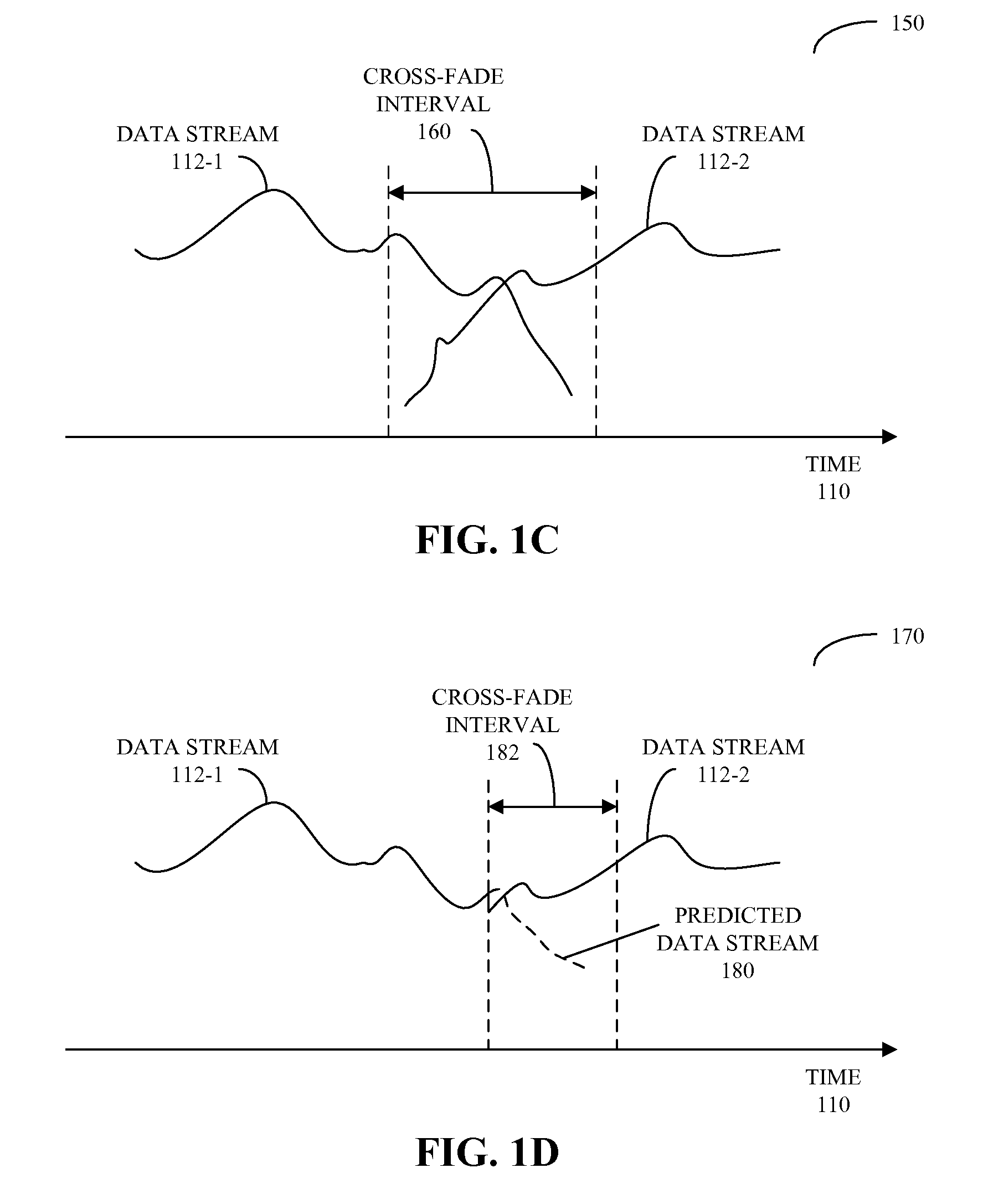
ActiveUS20090083047A1Reducing and eliminating gapReduce discontinuityElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsSpeech analysisElectricityData stream
Circuits and methods for providing zero-gap playback of consecutive data streams in portable electronic devices, such as media players, are described. In some embodiments, a circuit includes a decoder circuit configured to receive encoded audio data and to output decoded audio data including data streams associated with a data file and a subsequent data file. Moreover, a predictive circuit, which is electrically coupled to the decoder circuit, is configured to selectively generate additional samples based on samples in the data file, where the additional samples correspond to times after the end of a data stream associated with the data file. Additionally, a filter circuit, which is electrically coupled to the decoder circuit and selectively electrically coupled to the predictive circuit, is configured to selectively combine or blend samples at a beginning of the subsequent data file with the additional samples. Note that the circuit may be included in an integrated circuit.
Owner:APPLE INC
Internal bus system for DFPS and units with two- or multi-dimensional programmable cell architectures, for managing large volumes of data with a high interconnection complexity
InactiveUS7010667B2Multiple digital computer combinationsArchitecture with single central processing unitNetwork packetInterconnection
An internal bus system for DFPs and units with two- or multi-dimensional programmable cell architectures, for managing large volumes of data with a high interconnection complexity. The bus system can transmit data between a plurality of function blocks, where multiple data packets can be on the bus at the same time. The bus system automatically recognizes the correct connection for various types of data or data transmitters and sets it up.
Owner:PACT XPP TECH
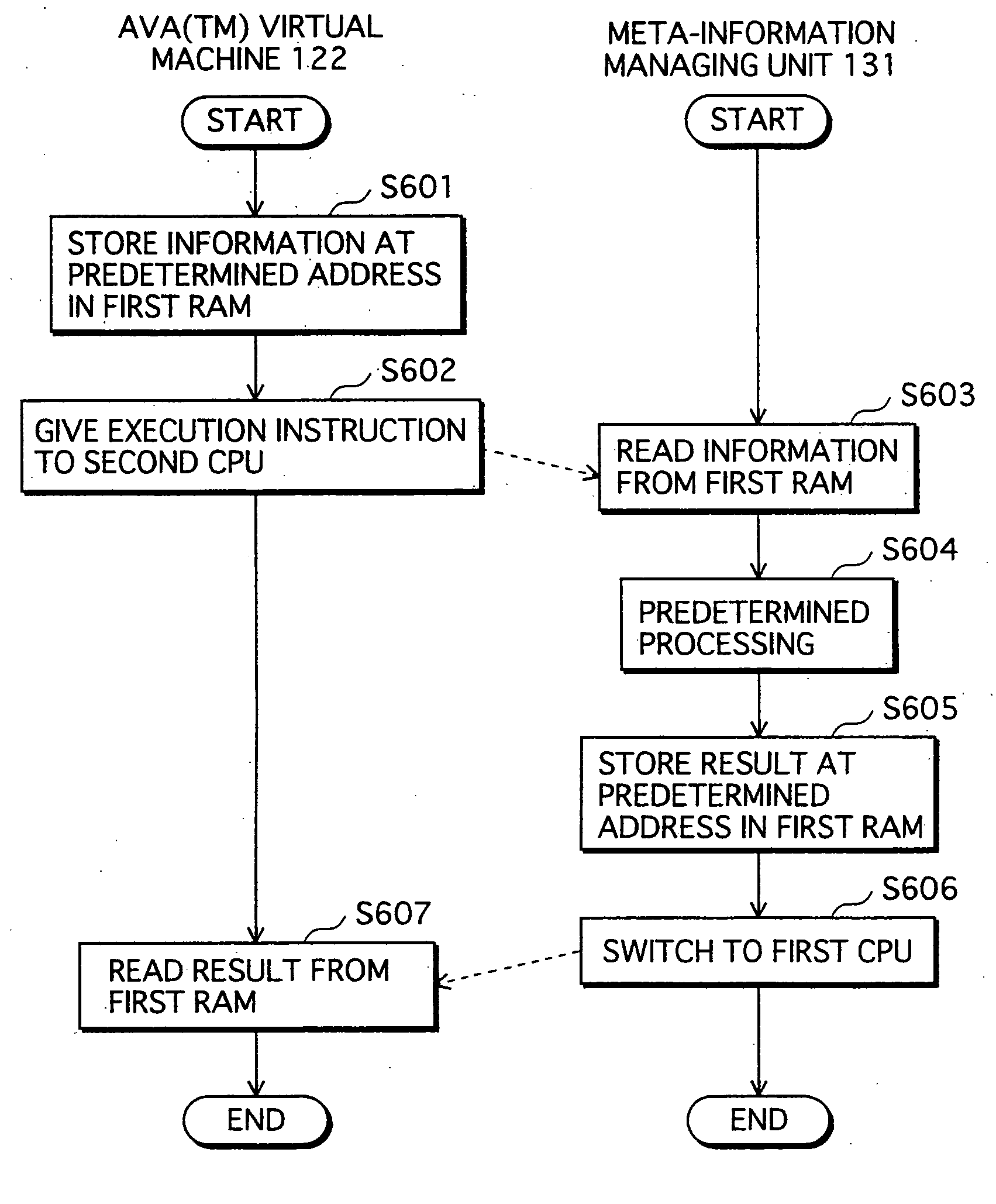
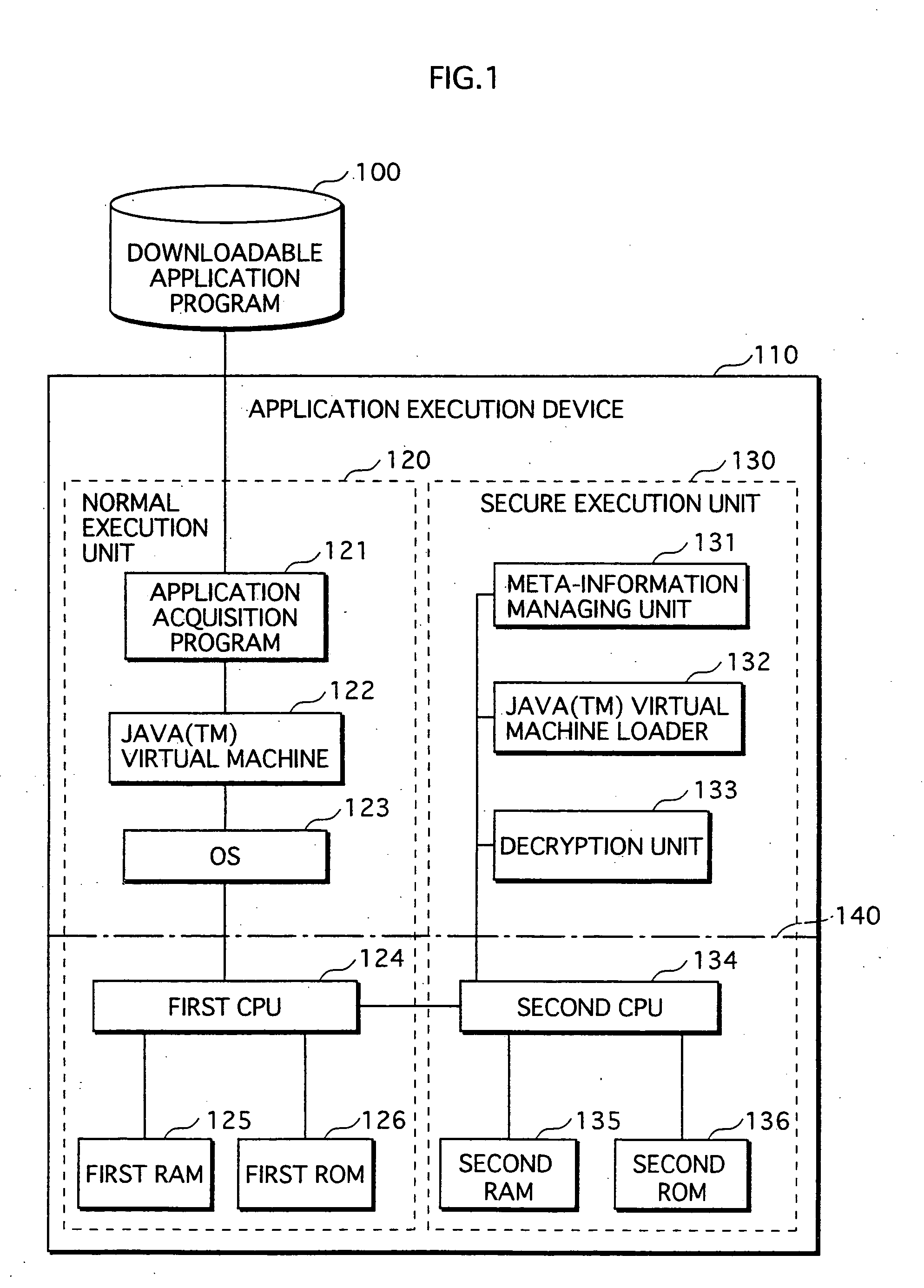
Application Execution Device and Application Execution Device Application Execution Method
InactiveUS20070271446A1High protection levelDigital computer detailsPlatform integrity maintainanceExecution unitOperating system
The conventional application protection technique complicates an application to make it difficult to analyze the application. However, with such a complication method, the complicate program can be analyzed sooner or later by taking a lot of time no matter how the degree of the complication is high. Also, it is impossible to protect the application from unauthorized copying. The meta-information managing unit that is to be executed in the secure execution unit stores the meta-information of the application in an area that can not be accessed by a debugger. When the meta-information is required by the normal execution unit to execute the application, a result of predetermined calculation using the meta-information is notified to the normal execution unit. In this way, the meta-information of the application can be kept secret.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Remote data copy using a prospective suspend command
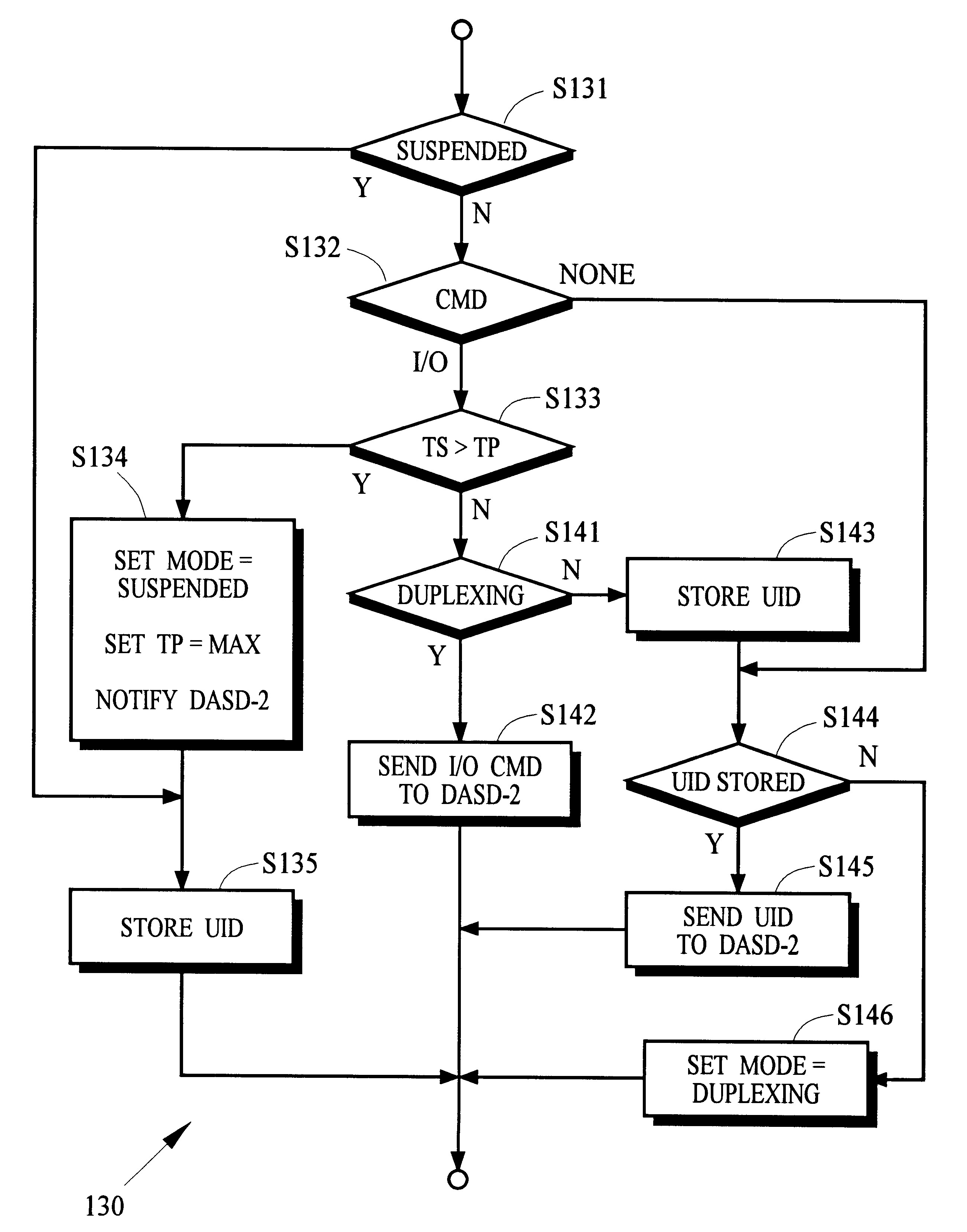
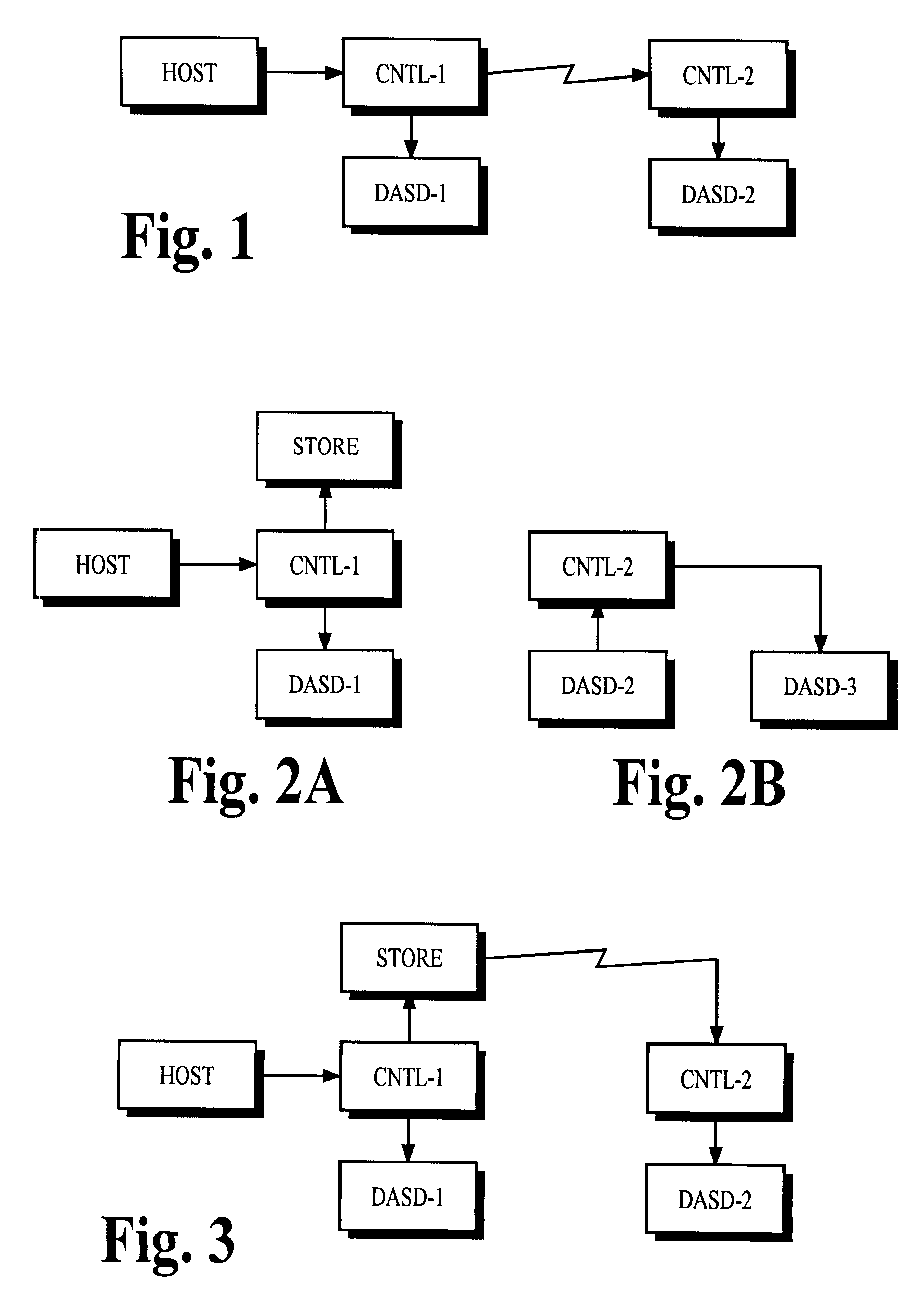
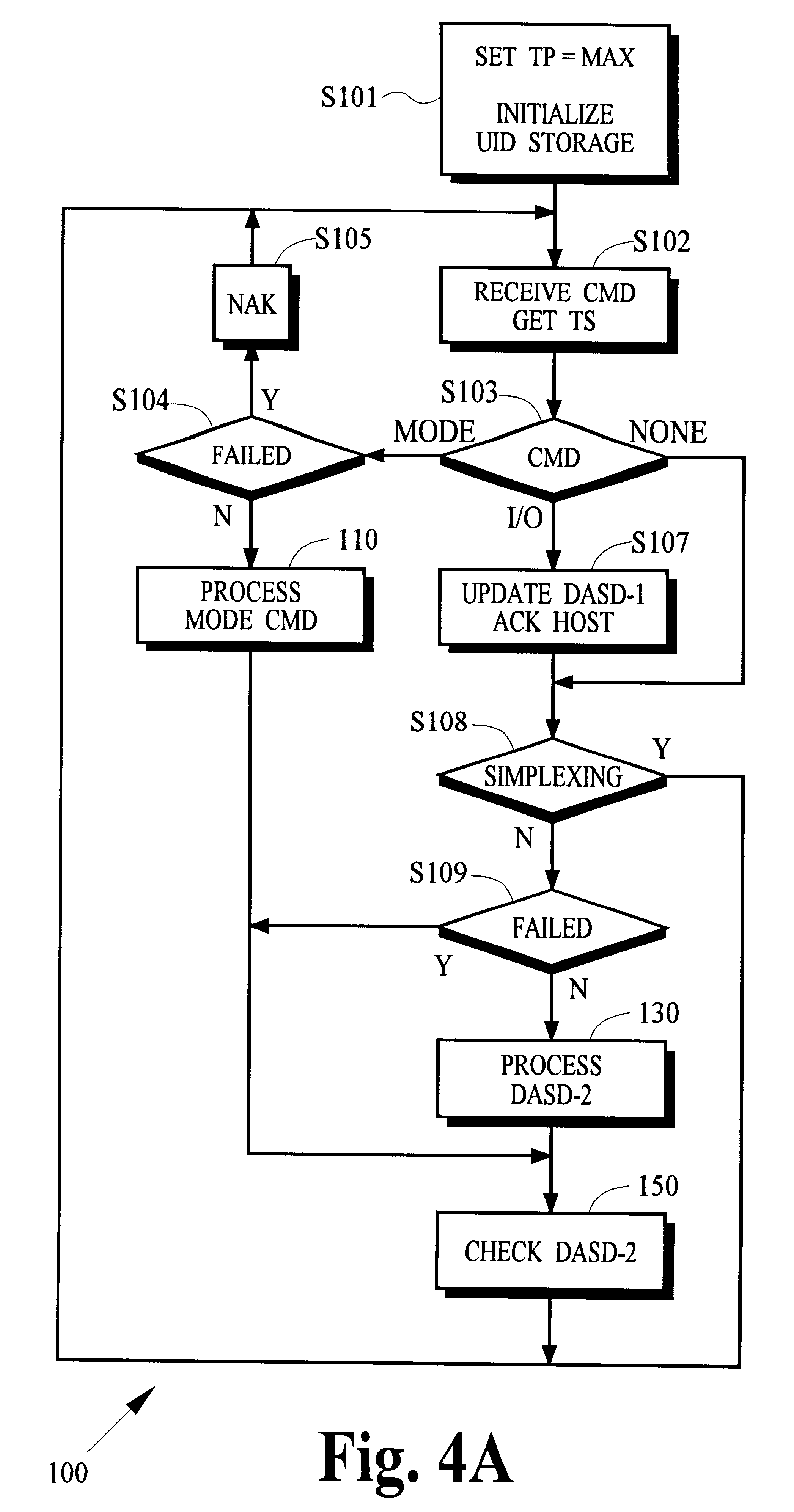
InactiveUS6539462B1Improve usabilityReducing resourceData processing applicationsInput/output to record carriersComputerized systemOperation mode
In a computer system, the controller of one or more primary data recording devices sends update information to the controller of one or more secondary data recording devices to maintain a remote copy of data stored on the primary data recording devices. The primary controller receives a command from a computer that specifies a prospective suspend time after which remote copy operation is to be suspended. After the suspend time passes, the primary controller stops sending the update information to the secondary controller and begins storing indicators of the updated information in cache memory. The primary controller may resume remote copy operation in response to a command received from the computer by first entering into a pending mode of operation in which cached indicators are used to identify update information that must be sent to the secondary controller to resynchronize the remote copy. When the information for all cached indicators has been sent, normal remote copy operation may be resumed.
Owner:HITACHI DATA SYST CORP
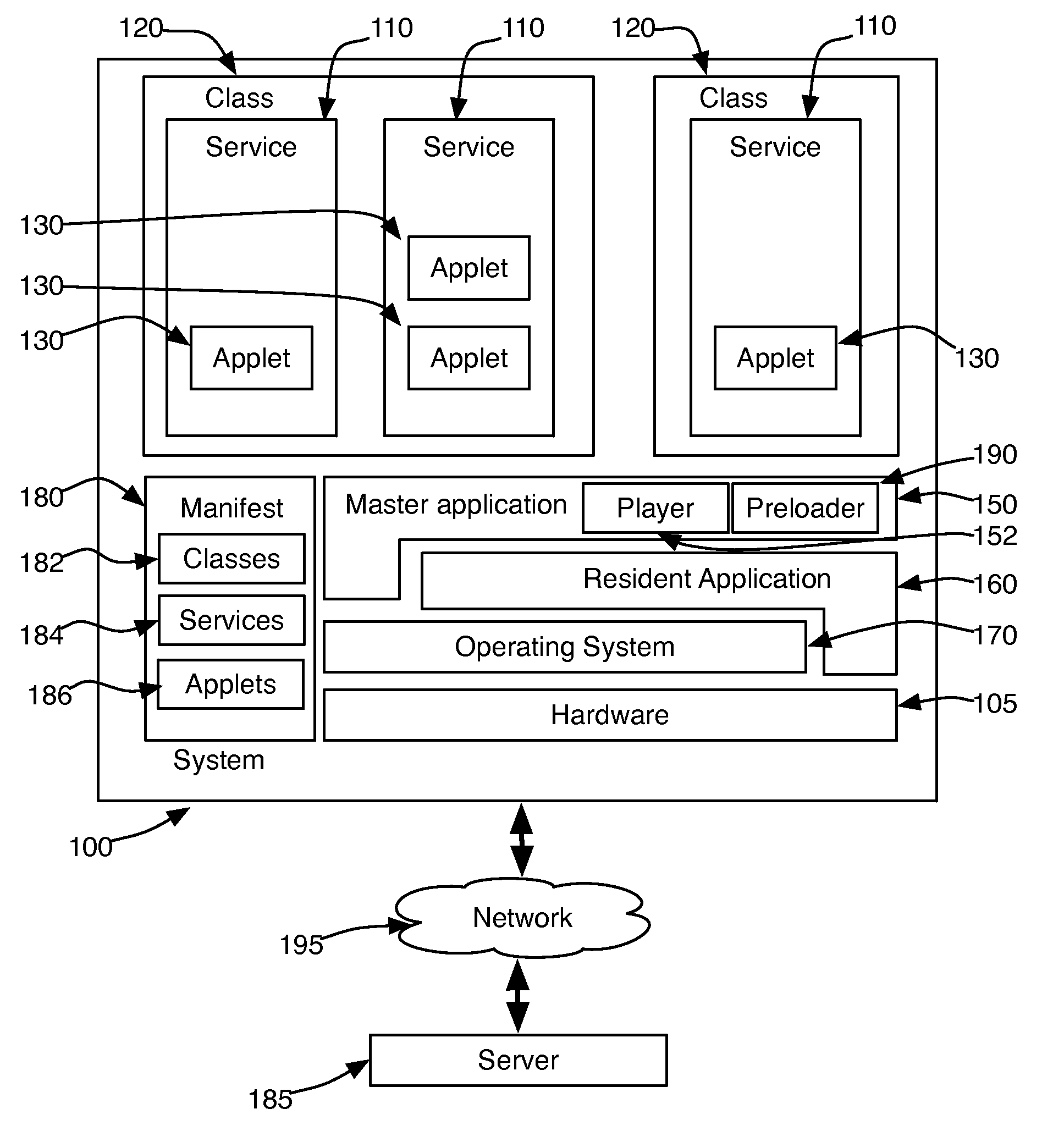
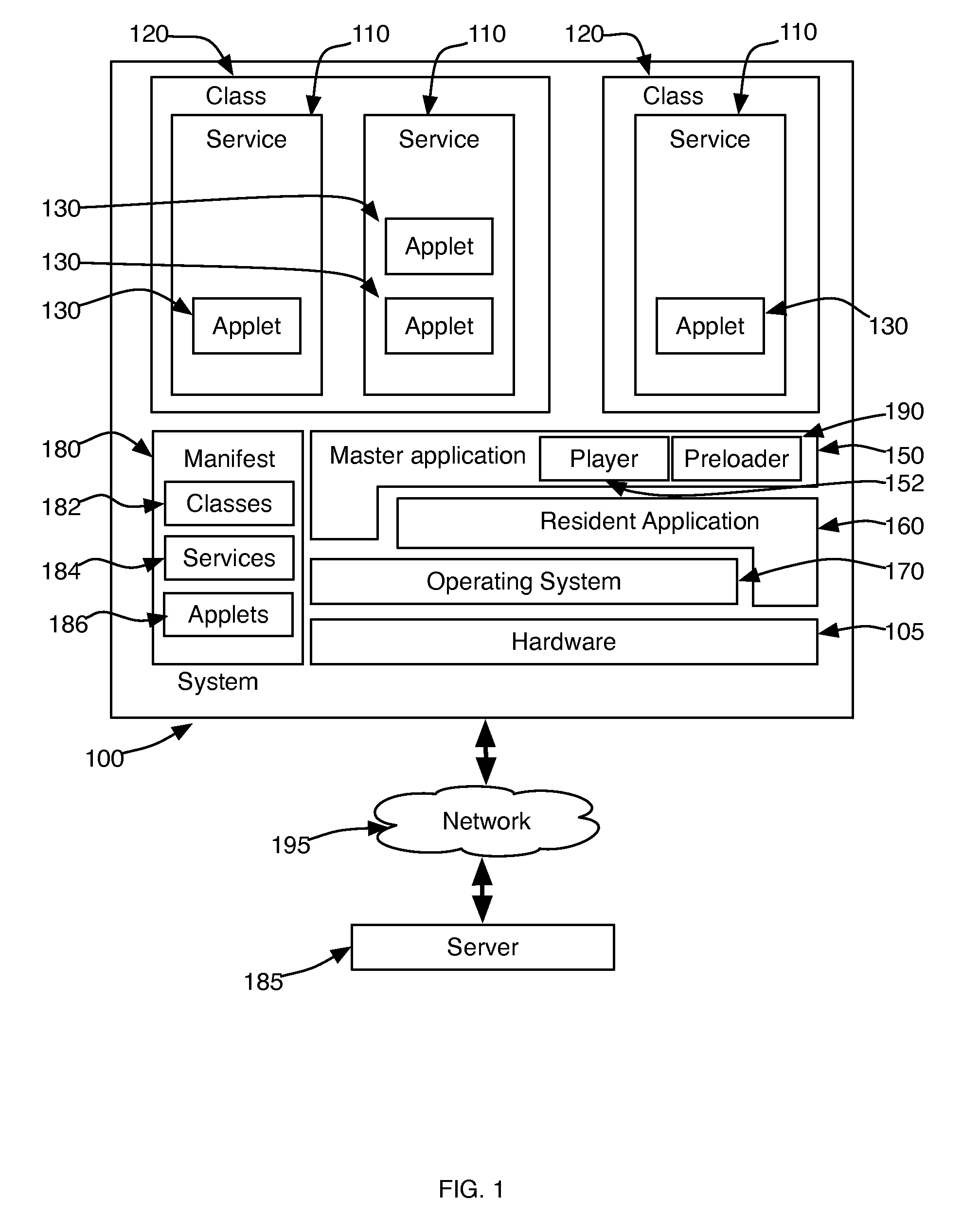
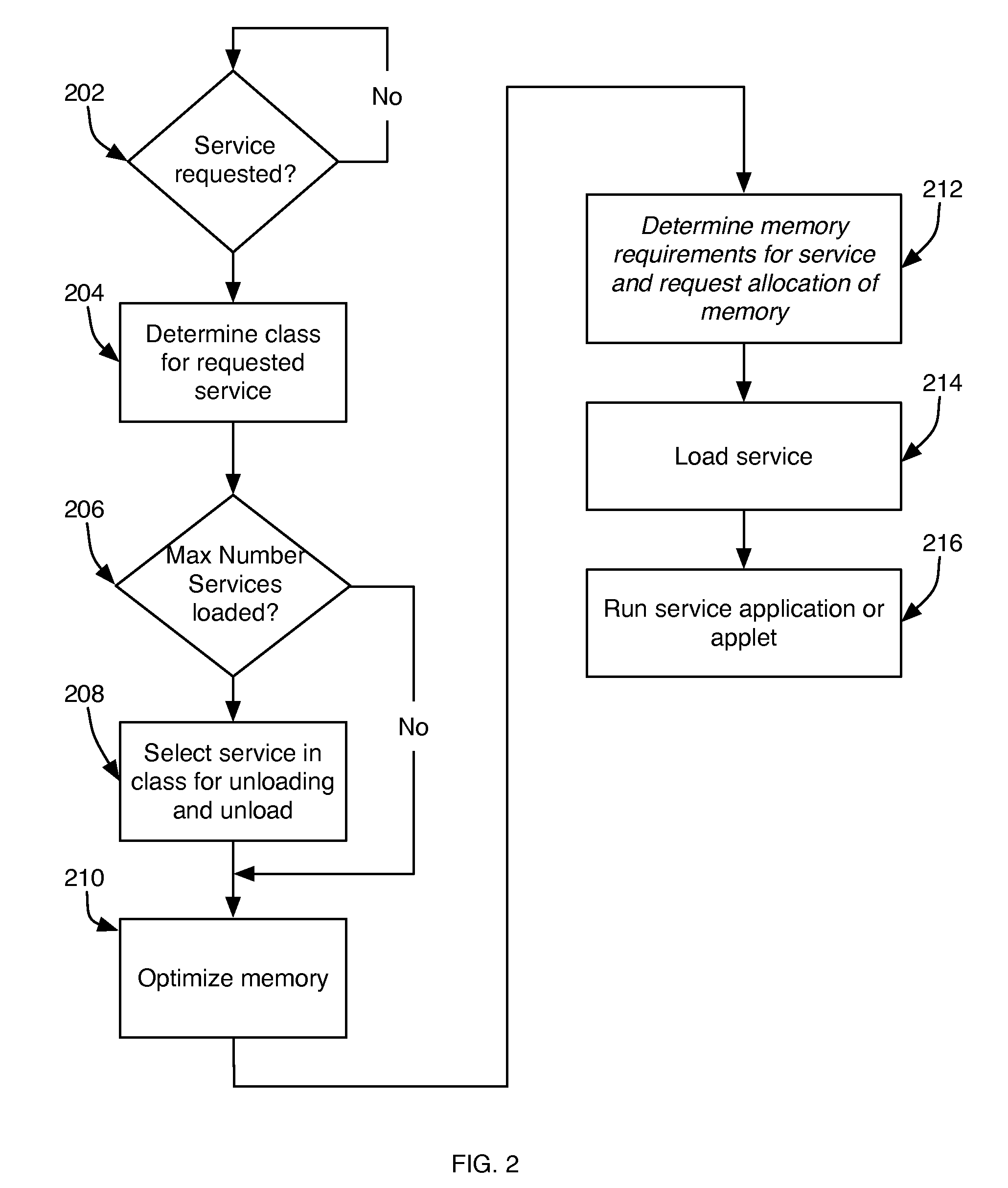
Management of Software Implemented Services in Processor-Based Devices
InactiveUS20090013157A1Reduce memory fragmentationShorten activation timeDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsSatellite televisionApplication software
A service management system for devices with embedded processor systems manages use of memory by programs implementing the services by assigning services to classes and limiting the number of services per class that can be loaded into memory. Classes enable achieving predictable and stable system behavior, defining the services and service classes in a manifest that is downloaded to embedded devices operating on a network, such as a cable or satellite television network, telephone or computer network, and permit a system operator, administrator, or manager to manage the operation of the embedded devices while deploying new services implemented with applications downloaded from the network when the service is requested by a user.
Owner:BLUESTREAK TECH INC
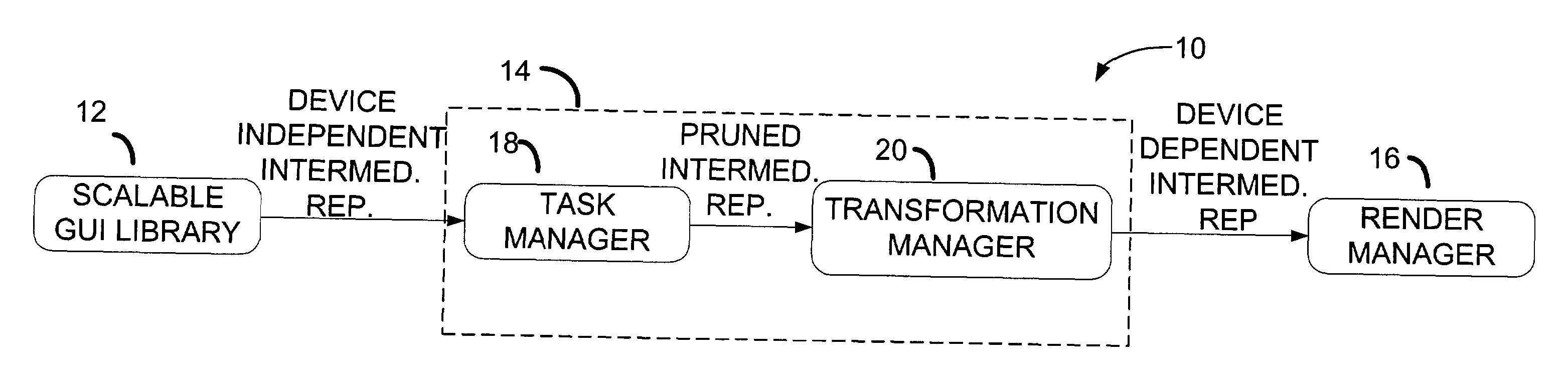
Transformation of platform specific graphical user interface widgets migrated between heterogeneous device platforms
ActiveUS20030070061A1Avoid complex processSoftware engineeringDigital computer detailsGraphical user interfaceEngineering
A scalable graphical user interface system may dynamically transform platform specific graphical user interface widgets migrated within an application graphical user interface between any of a plurality of heterogeneous device platforms. The scalable graphical user interface system includes a platform independent presentation model that is mapped to platform specific graphical user interface widgets. The platform independent presentation model includes platform independent graphical user interface widgets. The platform independent graphical user interface widgets may be selectively transformed with transformation rules to generate a platform specific presentation for use by the application graphical user interface on one of the heterogeneous device platforms. Applicable transformation rules may be prioritized for each selected platform independent graphical user interface widget. A highest priority transformation rule may be applied to transform the selected platform independent graphical user interface widget.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Reprogrammable circuit board with alignment-insensitive support for multiple component contact types
InactiveUS20080143379A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementWave amplification devicesSignal conditioningContact type
The present invention is directed to a system that programmably interconnects integrated circuit chips and other components at near-intra-chip density. The system's contact structure allows it to adapt to components with a wide variety of contact spacings and interconnection requirements, the use of releasable attachment means allows component placement to be modified as needed, the system identifies the contacts and the components to facilitate specifying the inter-component connections, and the system provides signal conditioning and retiming to minimize issues with signal integrity and signal skew.
Owner:NORMAN RICHARD
Integrated circuit with interface tile for coupling to a stacked-die second integrated circuit
ActiveUS7068072B2Designing can be facilitatedPromote formationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGeneral purposeProgrammable logic device
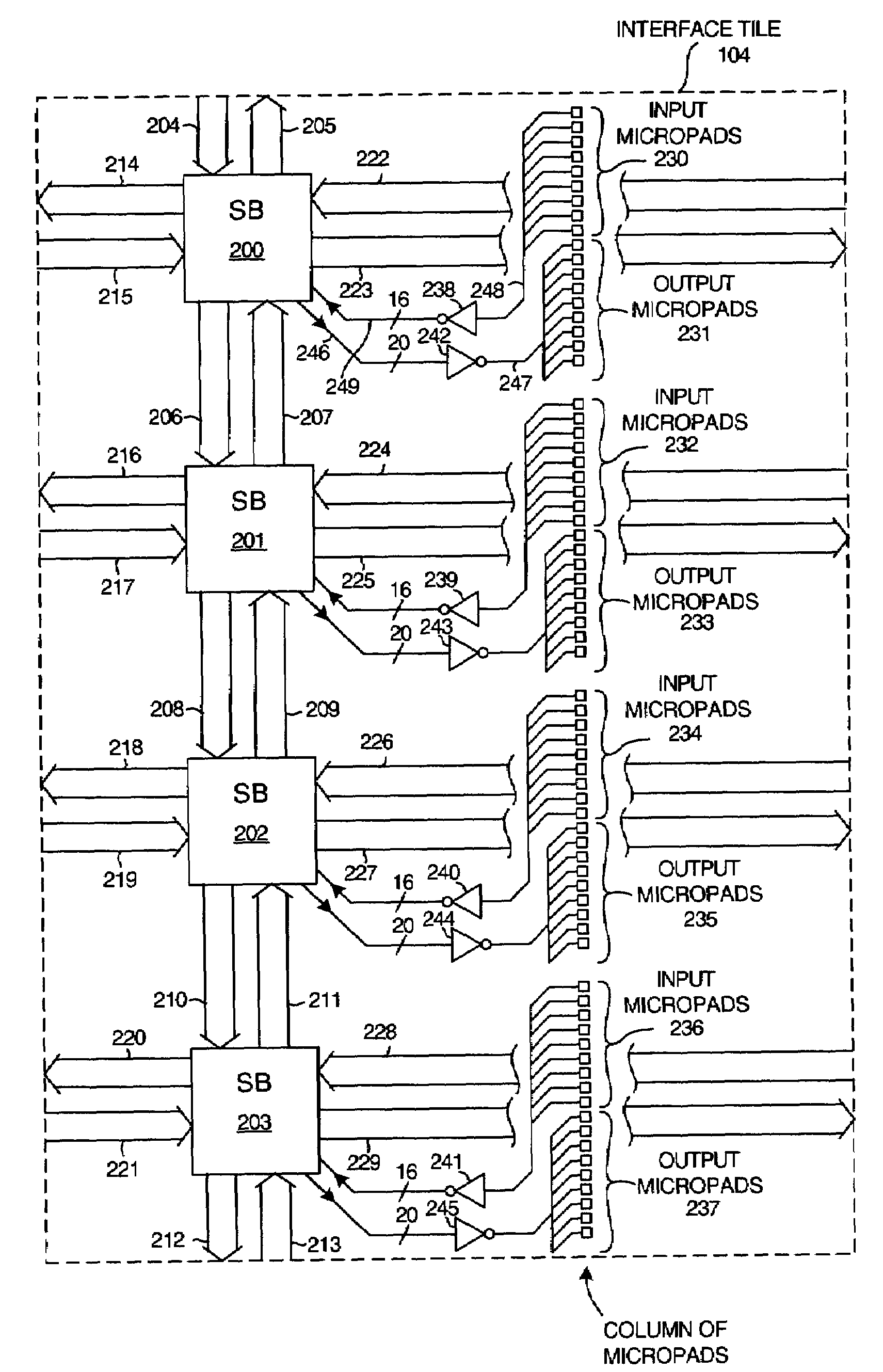
A general purpose interface tile of a first integrated circuit includes a plurality of micropads. A second integrated circuit may be stacked on the first integrated circuit such that signals from the second integrated circuit are communicated through the micropads and the interface tile to other circuitry on the first integrated circuit. Similarly, signals from the first integrated circuit are communicated through the interface tile and the micropads to the second integrated circuit. In the event that the first integrated circuit is a programmable logic device having a programmable interconnect structure, the interface tile is part of and hooks into the programmable interconnect structure and provides a general purpose mechanism for coupling signals from the second integrated circuit to the programmable interconnect structure and / or for coupling signals from the programmable interconnect structure to the second integrated circuit.
Owner:XILINX INC
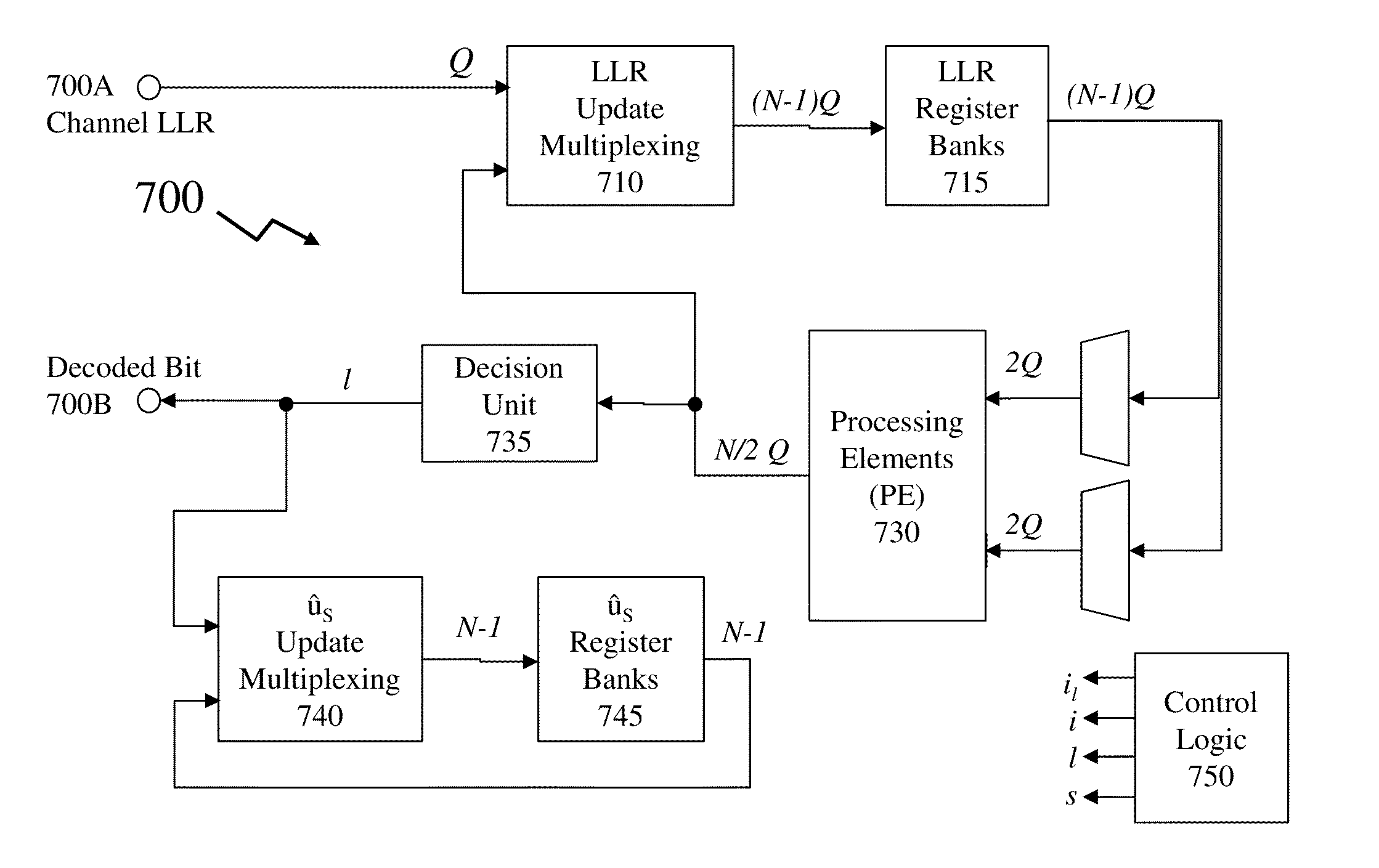
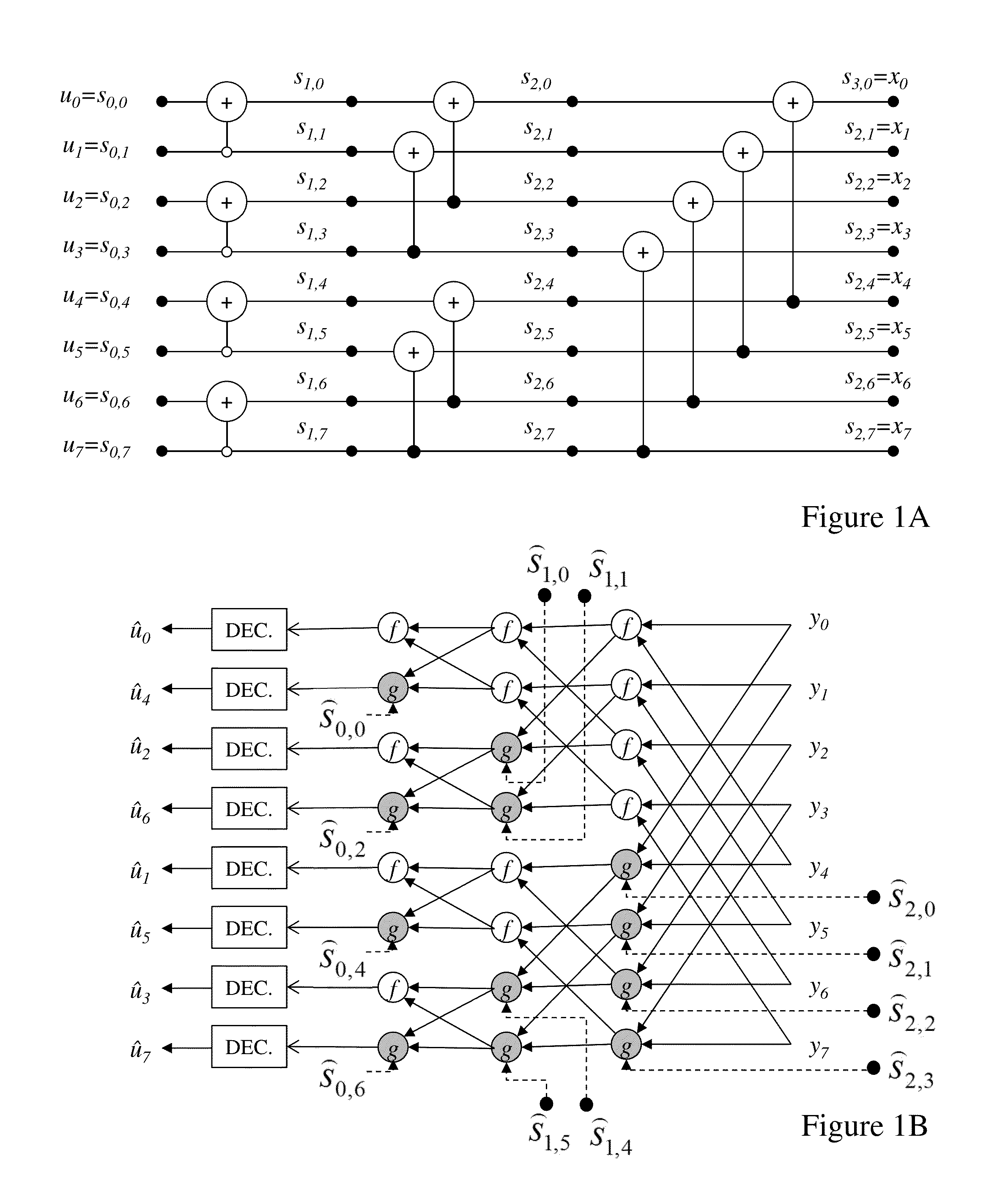
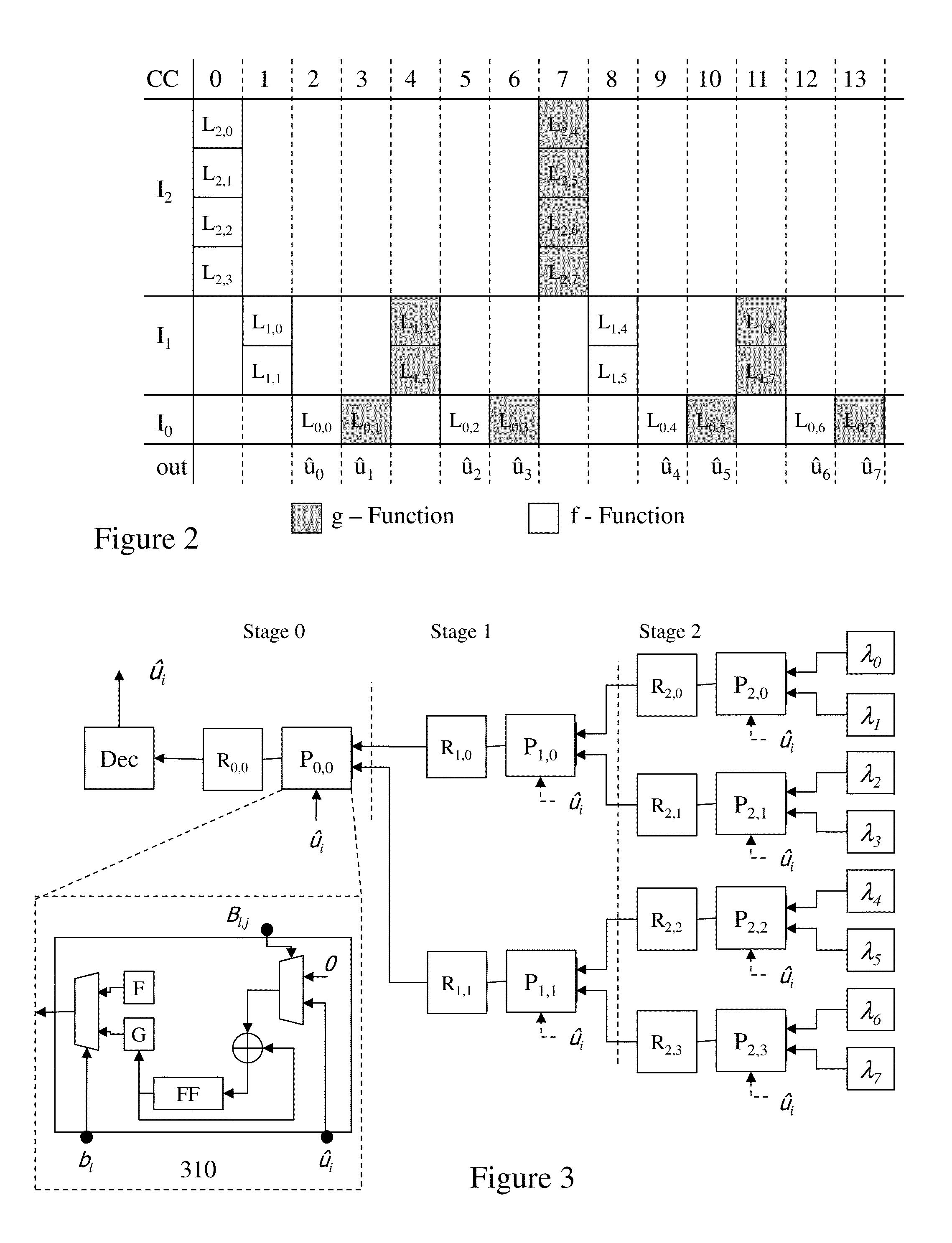
Methods and Systems for Decoding Polar Codes
ActiveUS20130117344A1Improve performanceMitigate such drawbackCode conversionError correction/detection using linear codesProcessing elementHardware implementations
Coding within noisy communications channels is essential but a theoretical maximum rate defines the rate at which information can be reliably transmitted on this noisy channel. Capacity-achieving codes with an explicit construction eluded researchers until polar codes were proposed. However, whilst asymptotically reaching channel capacity these require increasing code lengths, and hence increasingly complex hardware implementations. It would be beneficial to address architectures and decoding processes to reduce polar code decoder complexity both in terms of the number of processing elements required, but also the number of memory elements and the number of steps required to decode a codeword. Beneficially architectures and design methodologies established by the inventors address such issues whilst reducing overall complexity as well as providing methodologies for adjusting decoder design based upon requirements including, but not limited to, cost (e.g. through die area) and speed (e.g. through latency, number of cycles, number of elements etc).
Owner:THE ROYAL INSTITUTION FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF TECH MCGILL UNIV +1
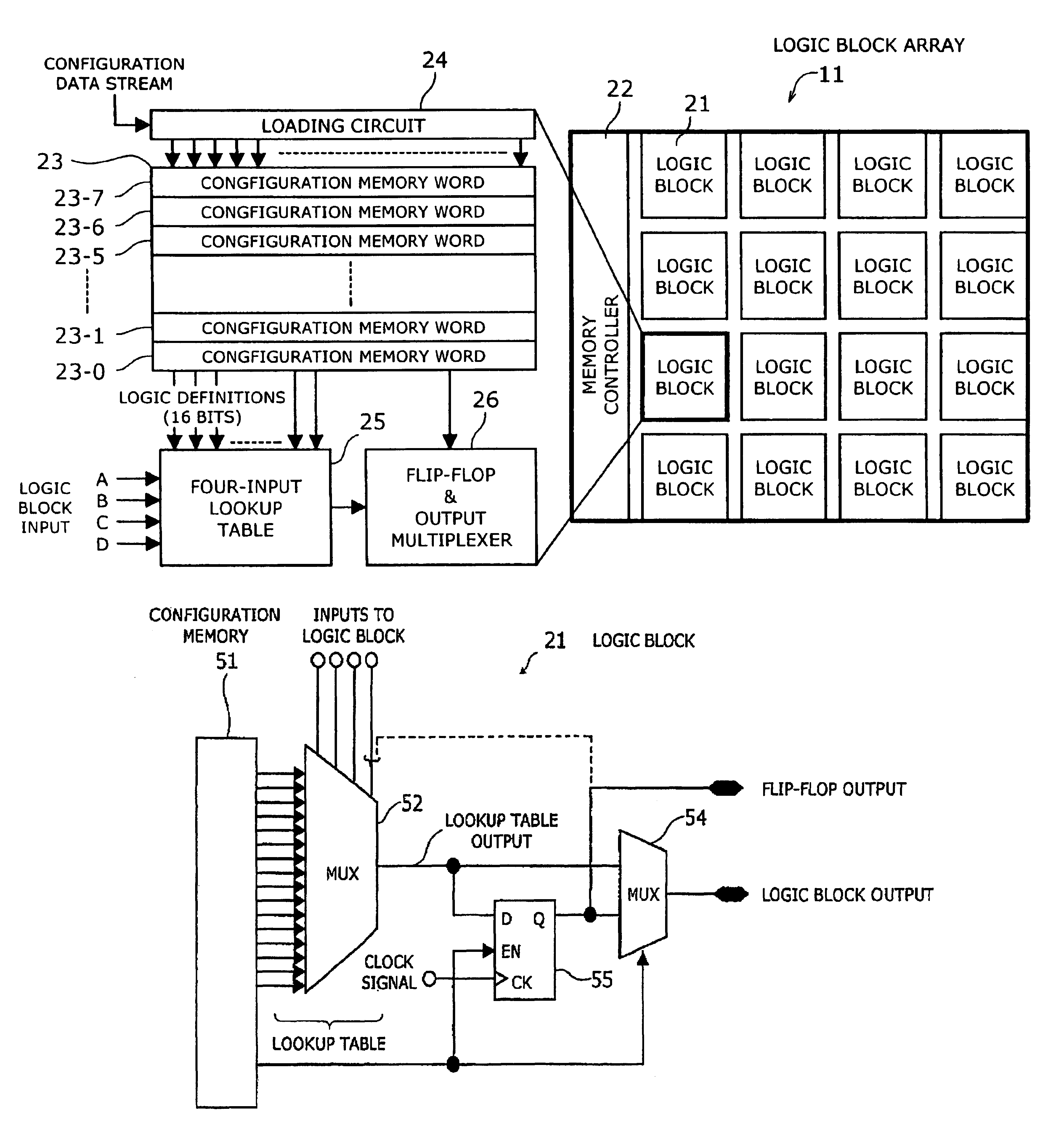
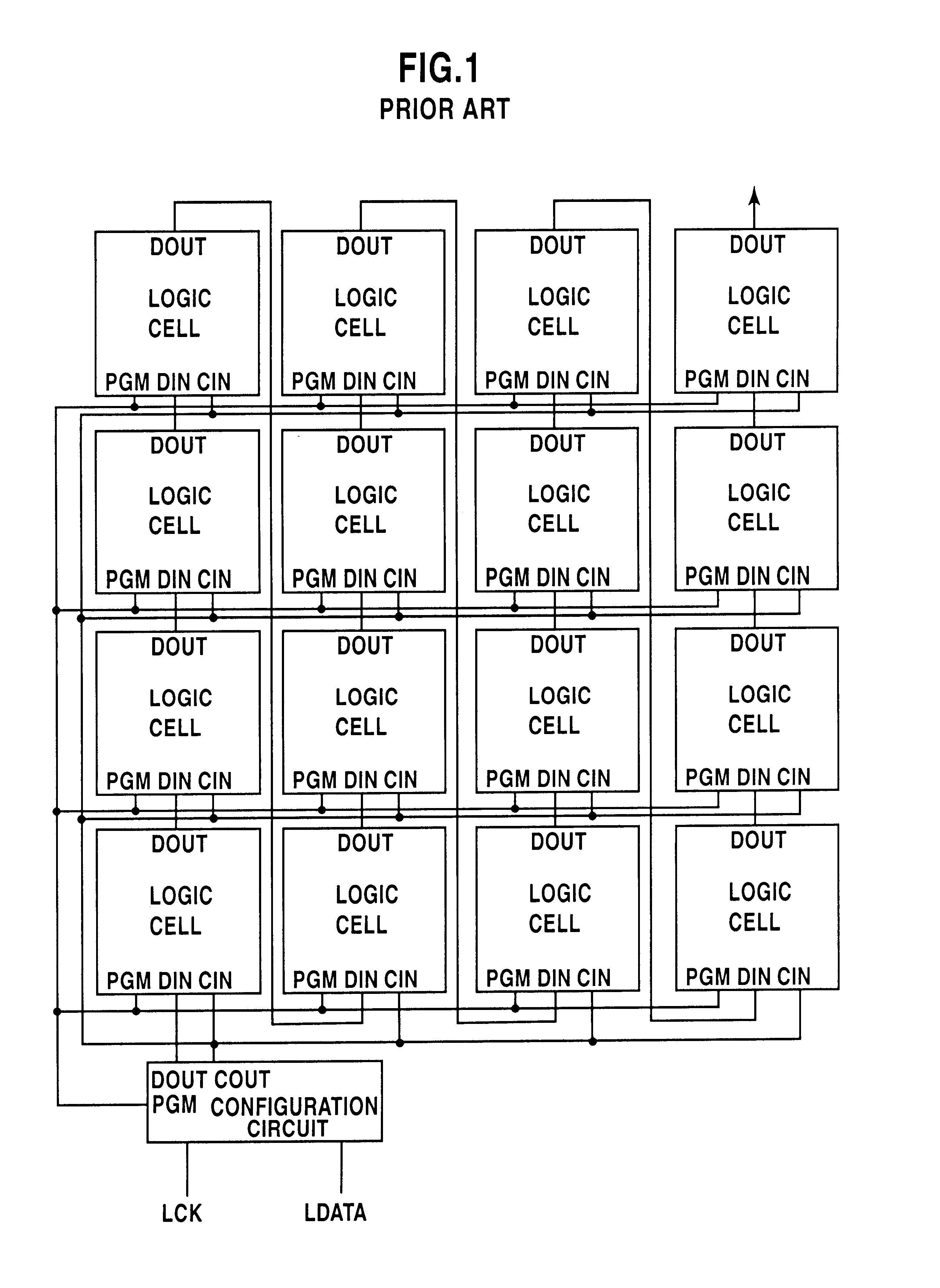
Chain-connected shift register and programmable logic circuit whose logic function is changeable in real time
A shift register having a plurality of circuit cells successively connected in a chain formation is proposed. Each of the circuit cells includes a first inversion gate, a first transmission gate, connected to an output of the first inversion gate, being switched by a clock, and a second inversion gate connected to an output of the first transmission gate. The circuit cell further includes a first P-channel transistor, connected between an output of the second inversion gate and an input of the first inversion gate, being switched by the clock, a second transmission gate, connected to the output of the second inversion gate, being switched by an inversion clock, and a second P-channel transistor, connected to the output of the first transmission gate, being switched by the inversion clock. In the shift register, the plurality of circuit cells are successively connected such that the input of the first inversion gate of the circuit cell is connected to an output of a second transmission gate of a former-stage circuit cell, and the output of the first inversion gate of the circuit cell is connected to an output of a second P-channel transistor of the former-stage circuit cell.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Nanostructures and methods for manufacturing the same
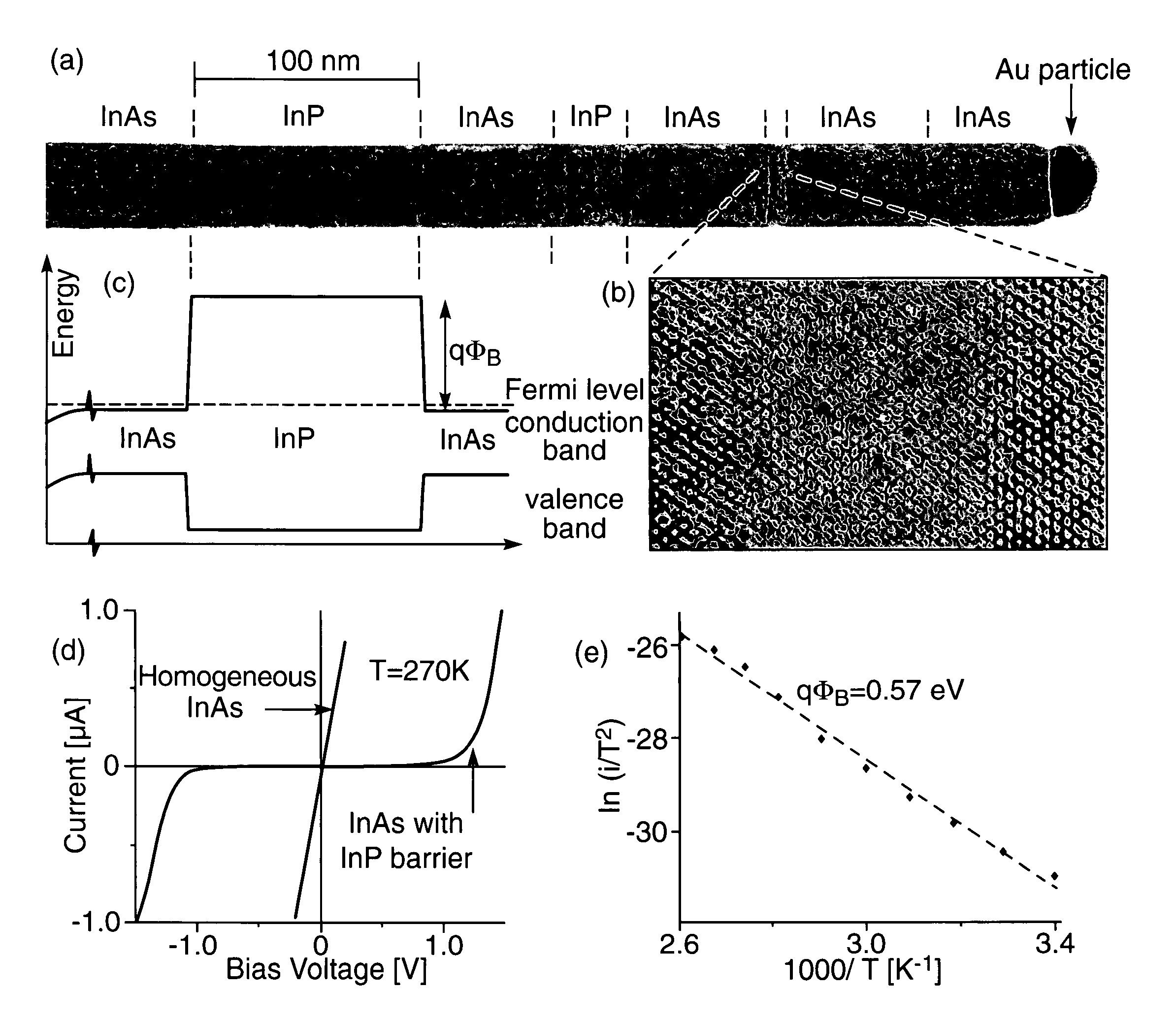
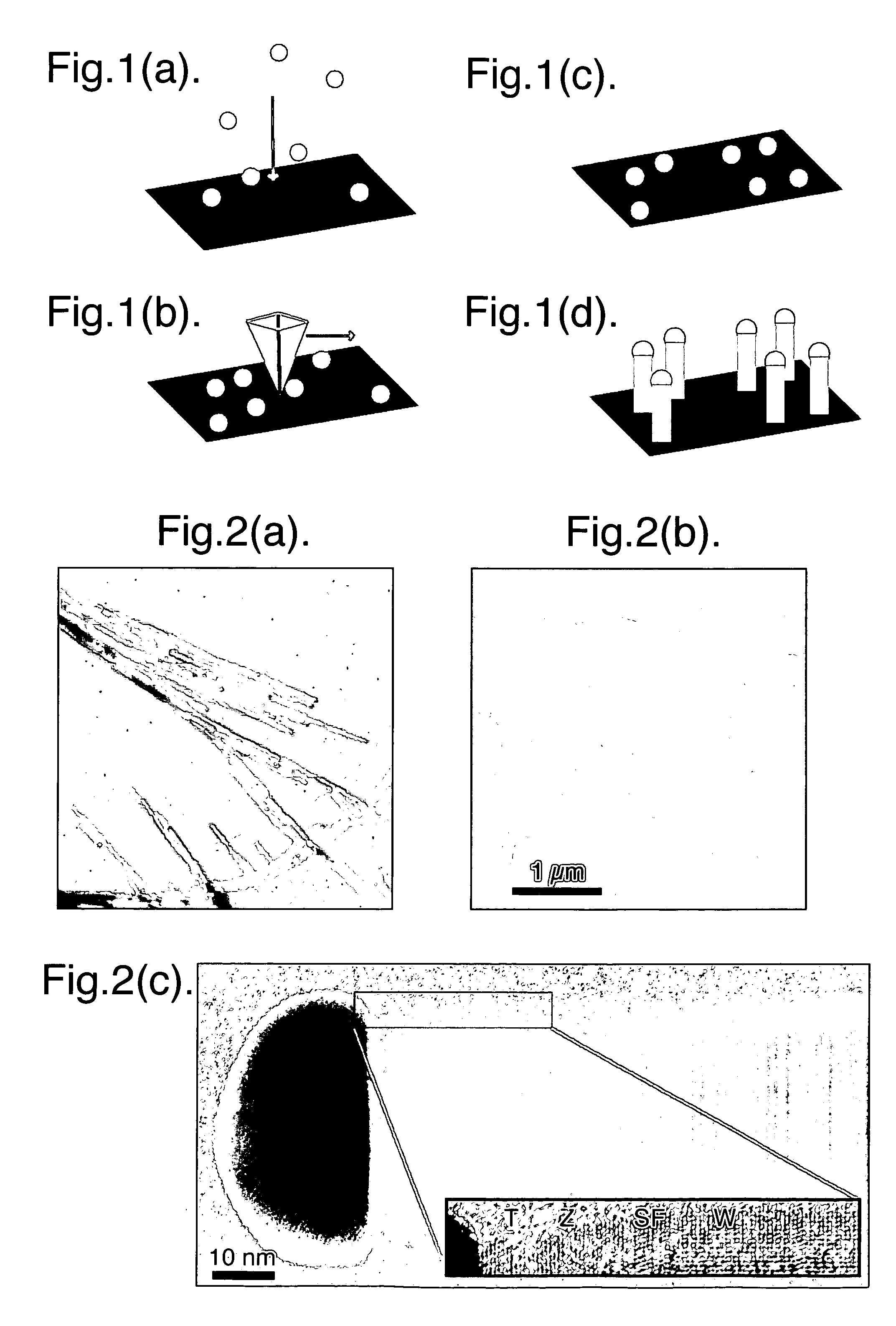
InactiveUS7335908B2Accurate weighingEnhances width controlPolycrystalline material growthIndividual molecule manipulationPhotonicsWhiskers
A resonant tunneling diode, and other one dimensional electronic, photonic structures, and electromechanical MEMS devices, are formed as a heterostructure in a nanowhisker by forming length segments of the whisker with different materials having different band gaps.
Owner:QUNANO
High-performance hybrid processor with configurable execution units
InactiveUS20050166038A1High bandwidthFlexibilityInstruction analysisConcurrent instruction executionHigh bandwidthLatency (engineering)
A new general method for building hybrid processors achieves higher performance in applications by allowing more powerful, tightly-coupled instruction set extensions to be implemented in reconfigurable logic. New instructions set configurations can be discovered and designed by automatic and semi-automatic methods. Improved reconfigurable execution units support deep pipelining, addition of additional registers and register files, compound instructions with many source and destination registers and wide data paths. New interface methods allow lower latency, higher bandwidth connections between hybrid processors and other logic.
Owner:TENSILICA
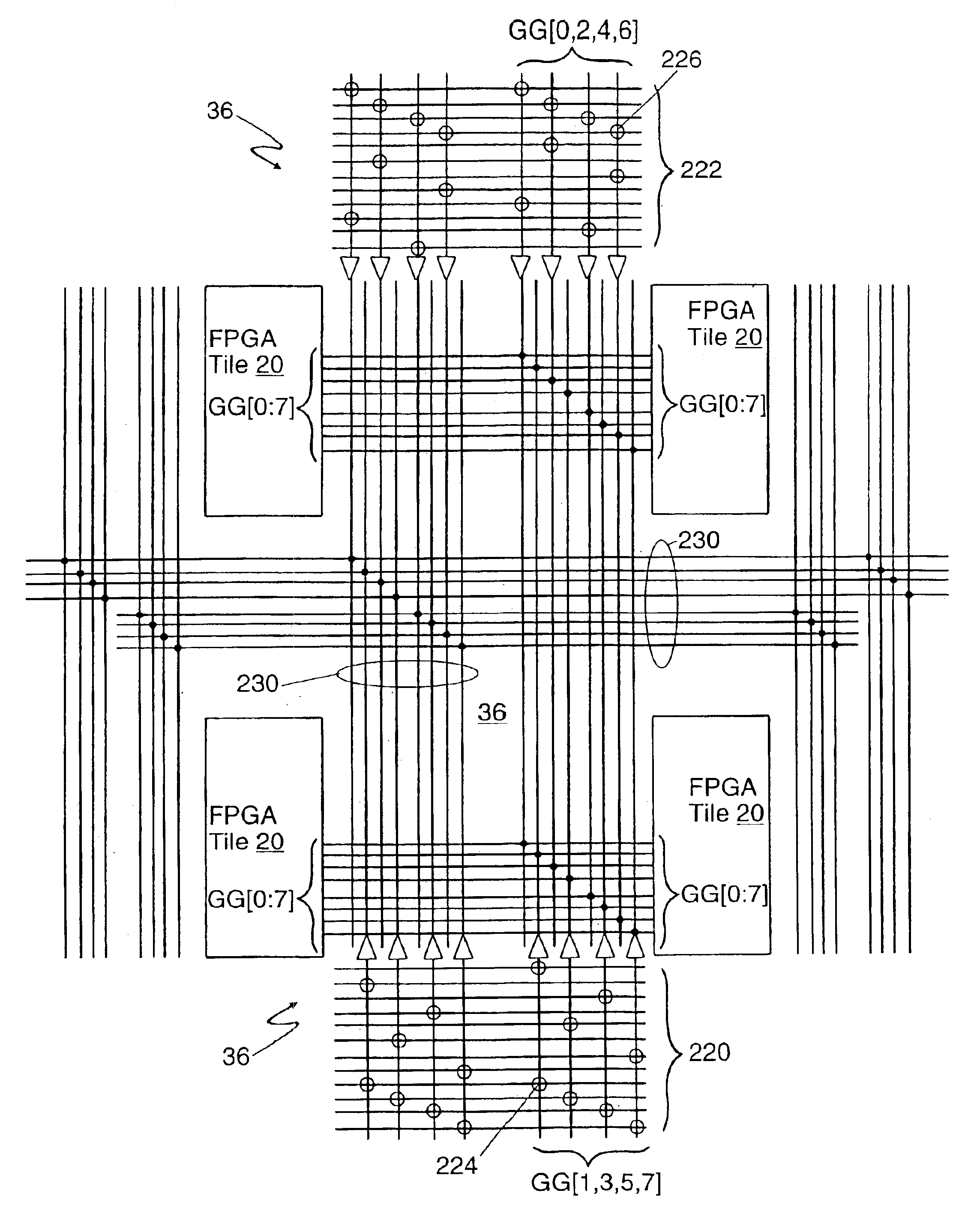
Tileable field-programmable gate array architecture
InactiveUS6888375B2Solid-state devicesCAD circuit designElectrical conductorField-programmable gate array
An apparatus includes a field-programmable gate array (FPGA). The FPGA includes a first FPGA tile, and the first FPGA tile includes a plurality of functional groups (FGs), a third set of routing conductors, in addition to a first set of routing conductors and a second set of routing conductors and a plurality of interface groups (IGs). The plurality of FGs are arranged in rows and columns with each of the FGs being configured to receive tertiary input signals as well as regular input signals, perform a logic operation, and generate regular output signals. The third set of routing conductors is coupled to the first set of output ports of the FGs and configured to receive signals, route signals within the first FPGA tile, and provide input signals to the third set of input ports of the FGs. The plurality of IGs surround the plurality of FGs such that one IG is positioned at each end of each row and column. Each of the IGs is coupled to the third set of routing conductors and configured to transfer signals from the third set of routing conductors to outside of the first FPGA tile.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
Reconfigurable circuit, processor having reconfigurable circuit, method of determining functions of logic circuits in reconfigurable circuit, method of generating circuit, and circuit
InactiveUS20050134308A1Reduce in quantityReduce switchingEnergy efficient ICTSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLogical circuit
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
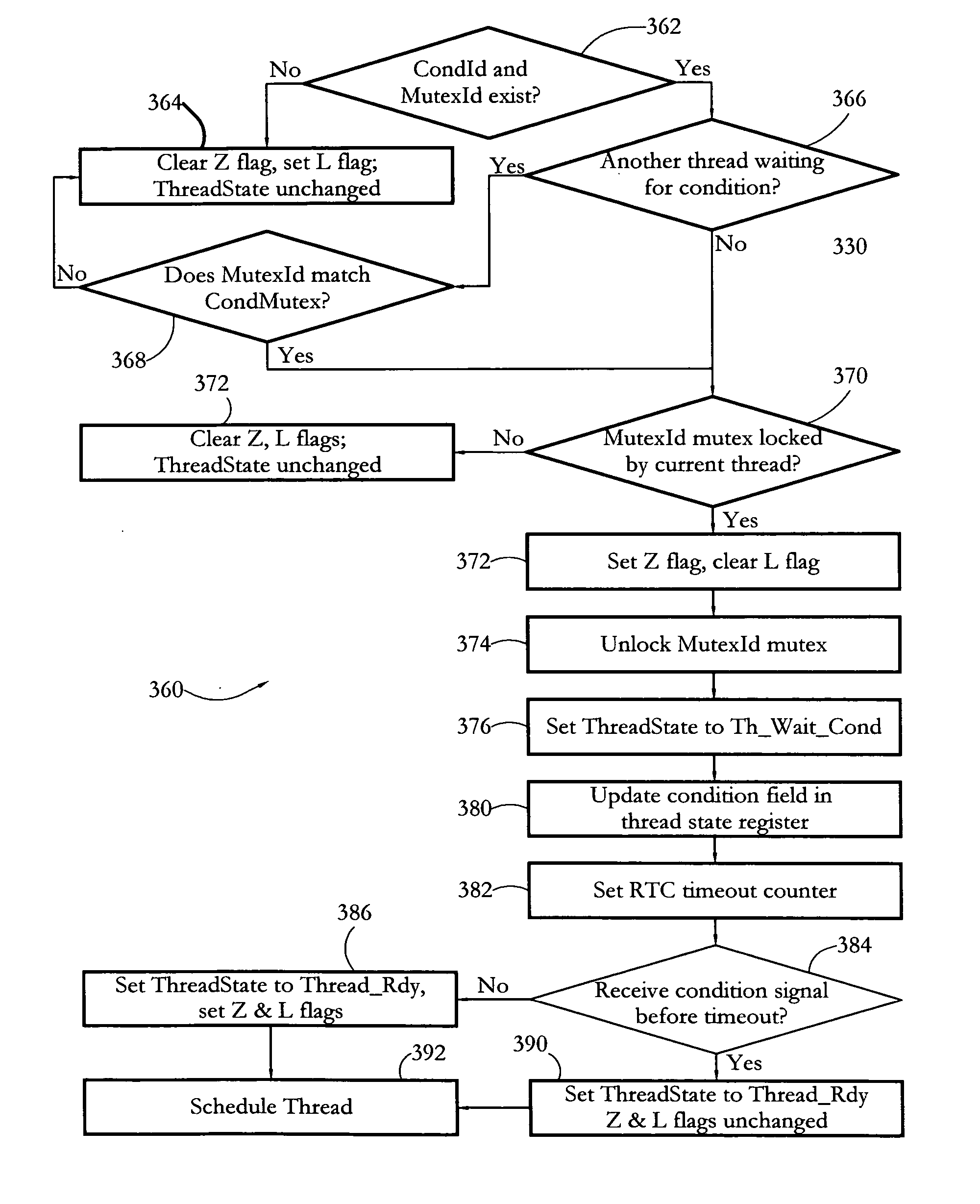
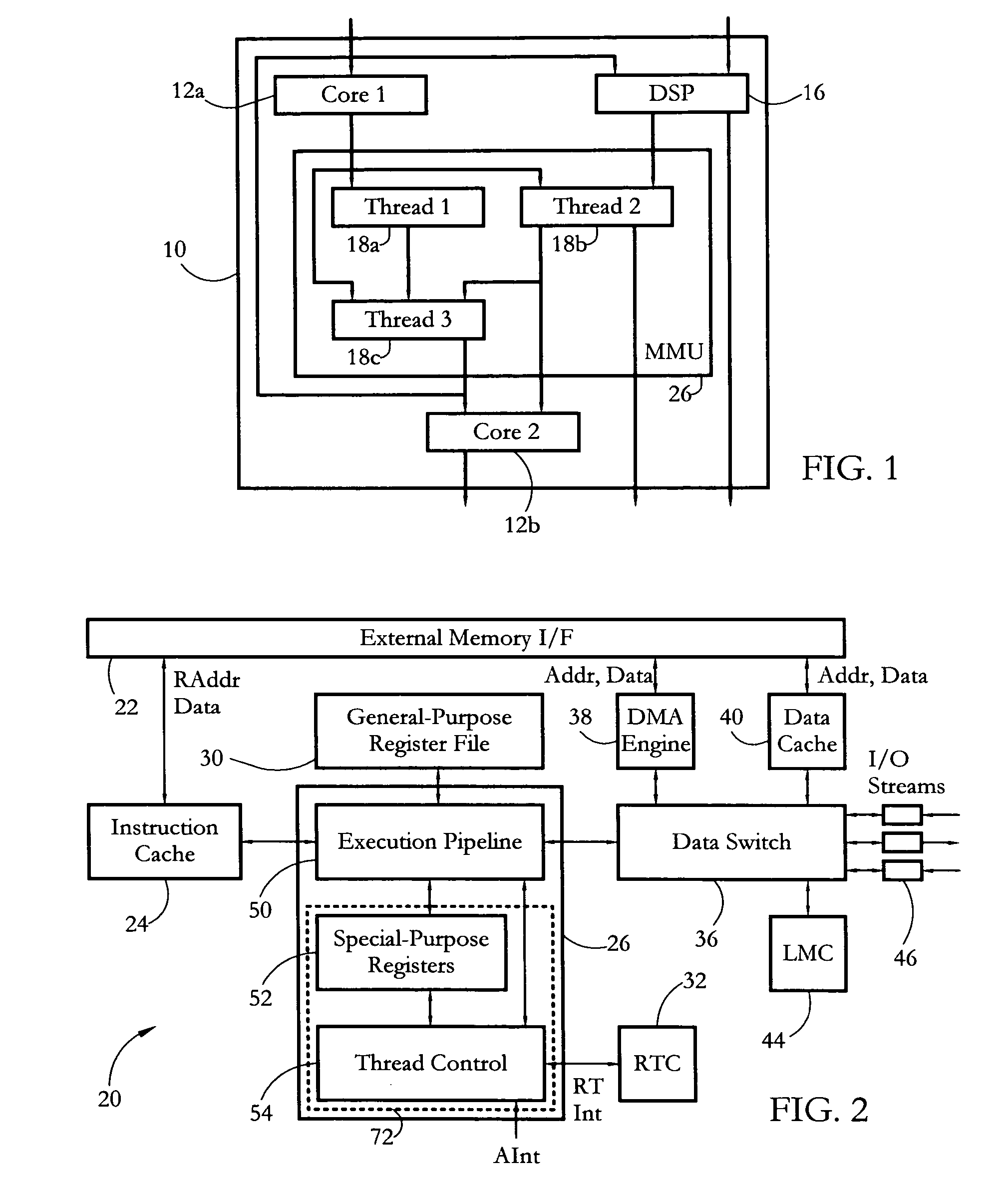
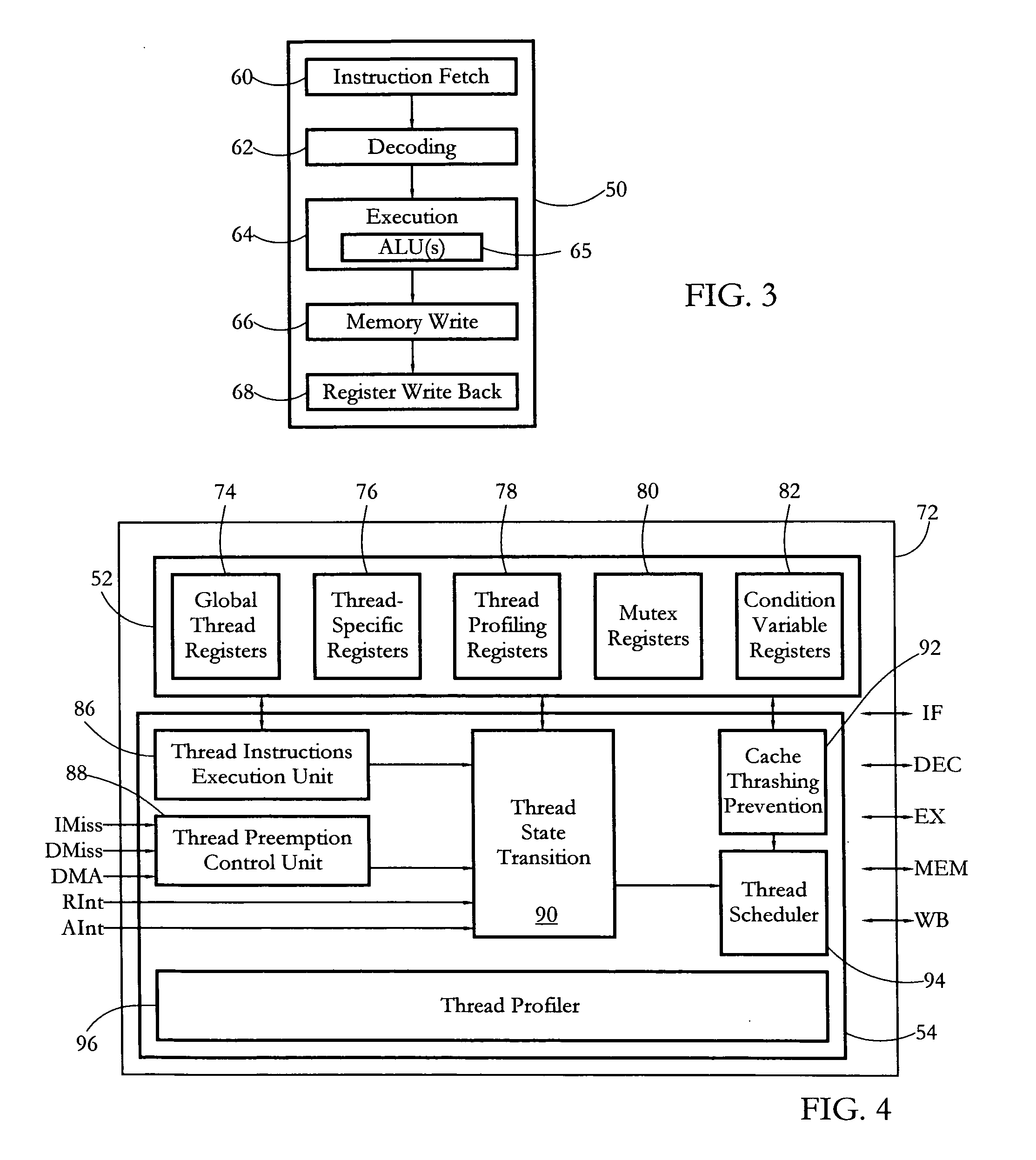
Hardware multithreading systems and methods
According to some embodiments, a multithreaded microcontroller includes a thread control unit comprising thread control hardware (logic) configured to perform a number of multithreading system calls essentially in real time, e.g. in one or a few clock cycles. System calls can include mutex lock, wait condition, and signal instructions. The thread controller includes a number of thread state, mutex, and condition variable registers used for executing the multithreading system calls. Threads can transition between several states including free, run, ready and wait. The wait state includes interrupt, condition, mutex, I-cache, and memory substates. A thread state transition controller controls thread states, while a thread instructions execution unit executes multithreading system calls and manages thread priorities to avoid priority inversion. A thread scheduler schedules threads according to their priorities. A hardware thread profiler including global, run and wait profiler registers is used to monitor thread performance to facilitate software development.
Owner:GEO SEMICONDUCTOR INC
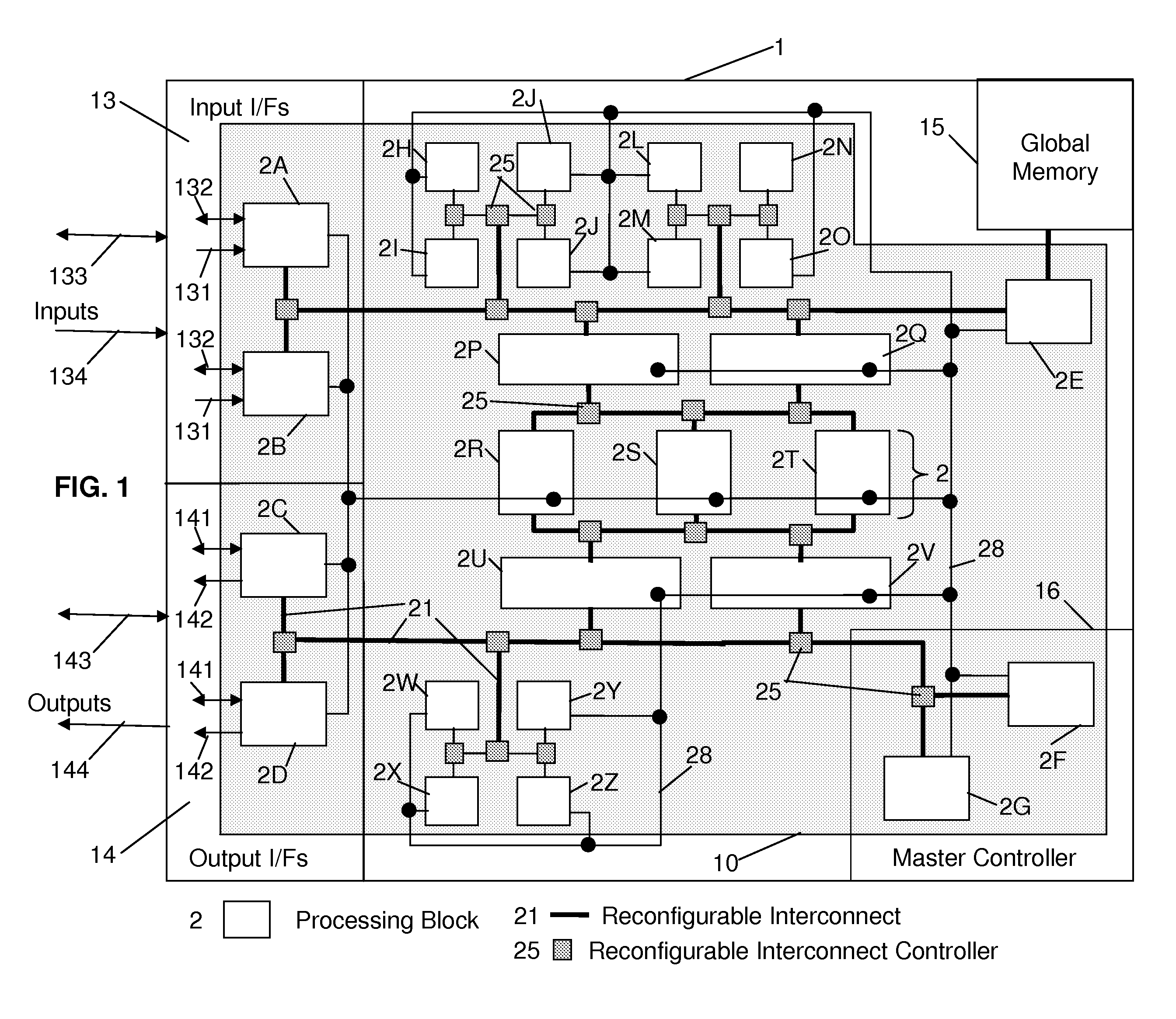
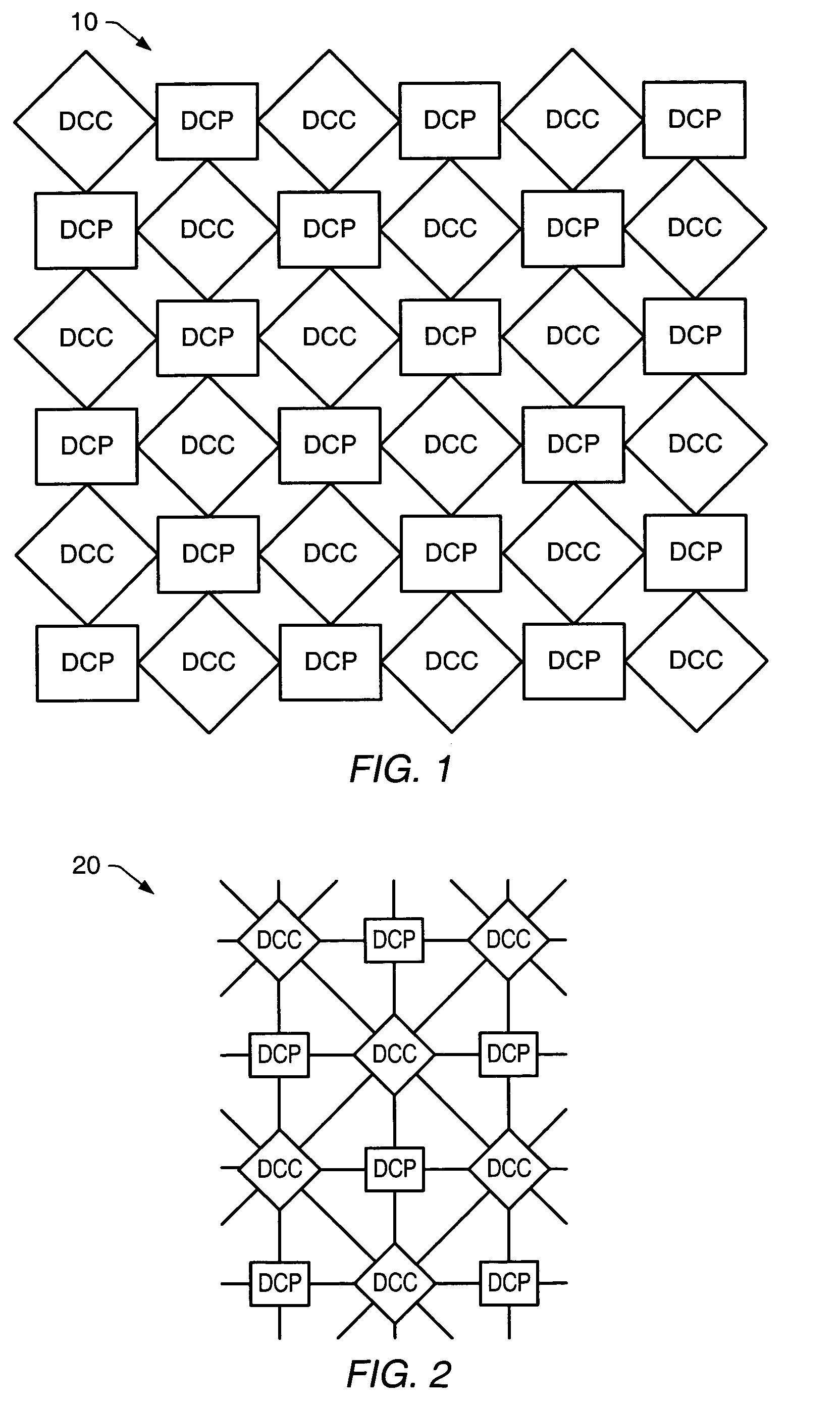
Processing system with interspersed stall propagating processors and communication elements
ActiveUS7415594B2Energy efficient ICTSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsArithmetic logic unitInstruction processing unit
A processing system comprising processors and the dynamically configurable communication elements coupled together in an interspersed arrangement. The processors each comprise at least one arithmetic logic unit, an instruction processing unit, and a plurality of processor ports. The dynamically configurable communication elements each comprise a plurality of communication ports, a first memory, and a routing engine. For each of the processors, the plurality of processor ports is configured for coupling to a first subset of the plurality of dynamically configurable communication elements. For each of the dynamically configurable communication elements, the plurality of communication ports comprises a first subset of communication ports configured for coupling to a subset of the plurality of processors and a second subset of communication ports configured for coupling to a second subset of the plurality of dynamically configurable communication elements.
Owner:COHERENT LOGIX
Structured integrated circuit device
InactiveUS7514959B2Solid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsLogic cellMetal
A configurable logic array may include: a multiplicity of logic cells, containing look-up tables; customizable metal and via connection layers overlying the multiplicity of logic cells; a multiplicity of device customizable I / O cells; a multiplicity of configuration customizable RAM blocks; a ROM block with customizable contents; and a microprocessor with customizable I / O for configuring and testing the array, where the customizations are all done on a single via layer.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Popular searches
Memory systems Computation using denominational number representation Comparison of digital values Semiconductor devices Energy efficient computing Machine execution arrangements Software simulation/interpretation/emulation Data switching by path configuration Electric digital data processing Color/spectral properties measurements
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com