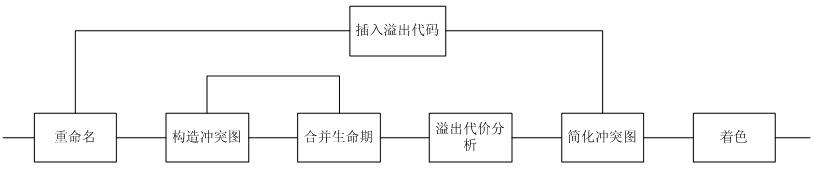
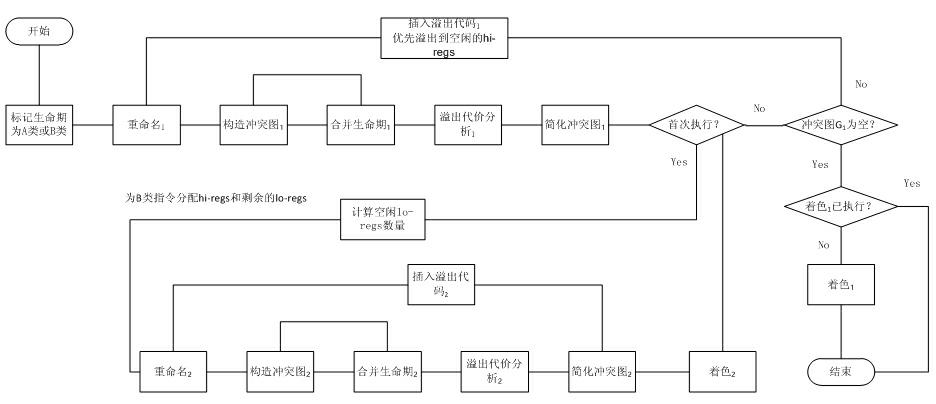
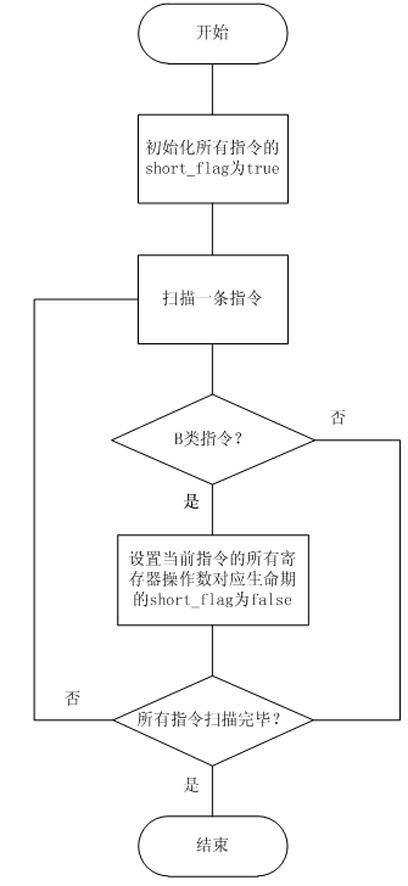
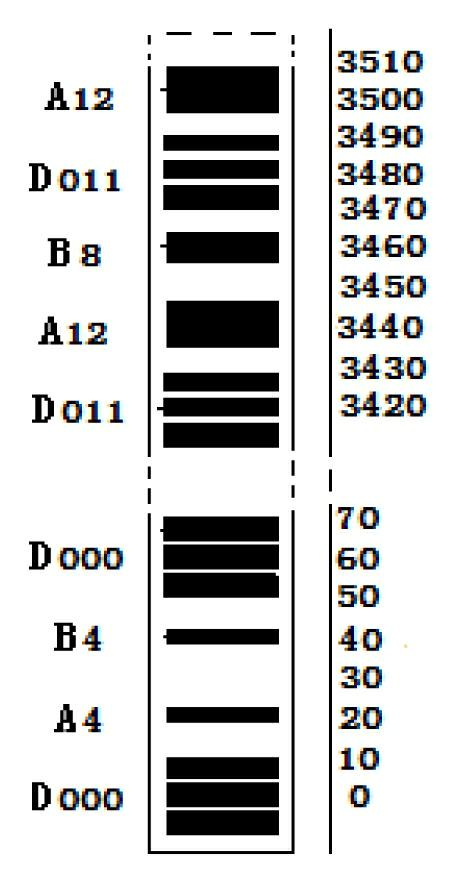
Patents
Literature
55 results about "Code density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
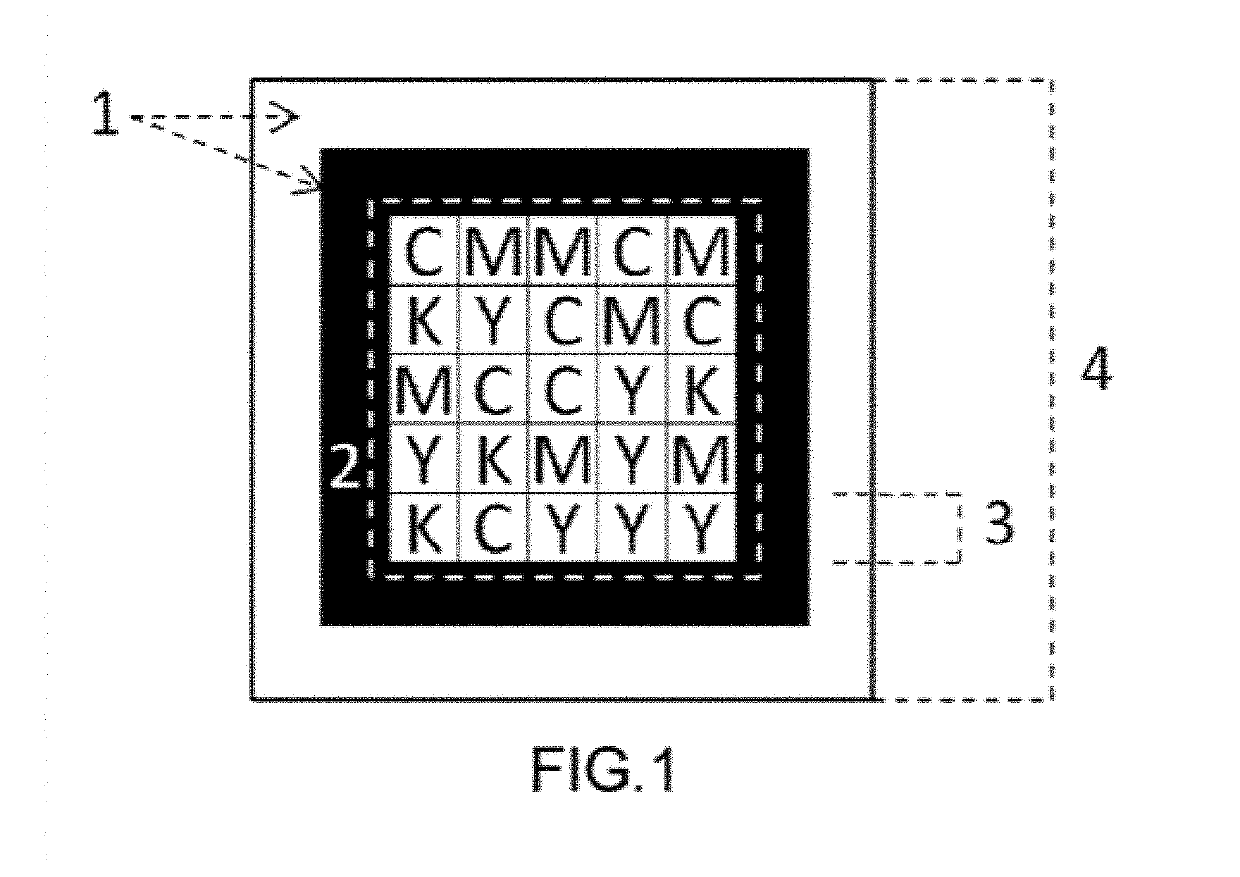
Code density. [′kōd ‚den·səd·ē] (graphic arts) The number of code elements per unit length that can appear on a microfilm. The amount of space that an executable program takes up in memory. Code density is important in mobile devices that contain a limited amount of memory.
Microprocessors
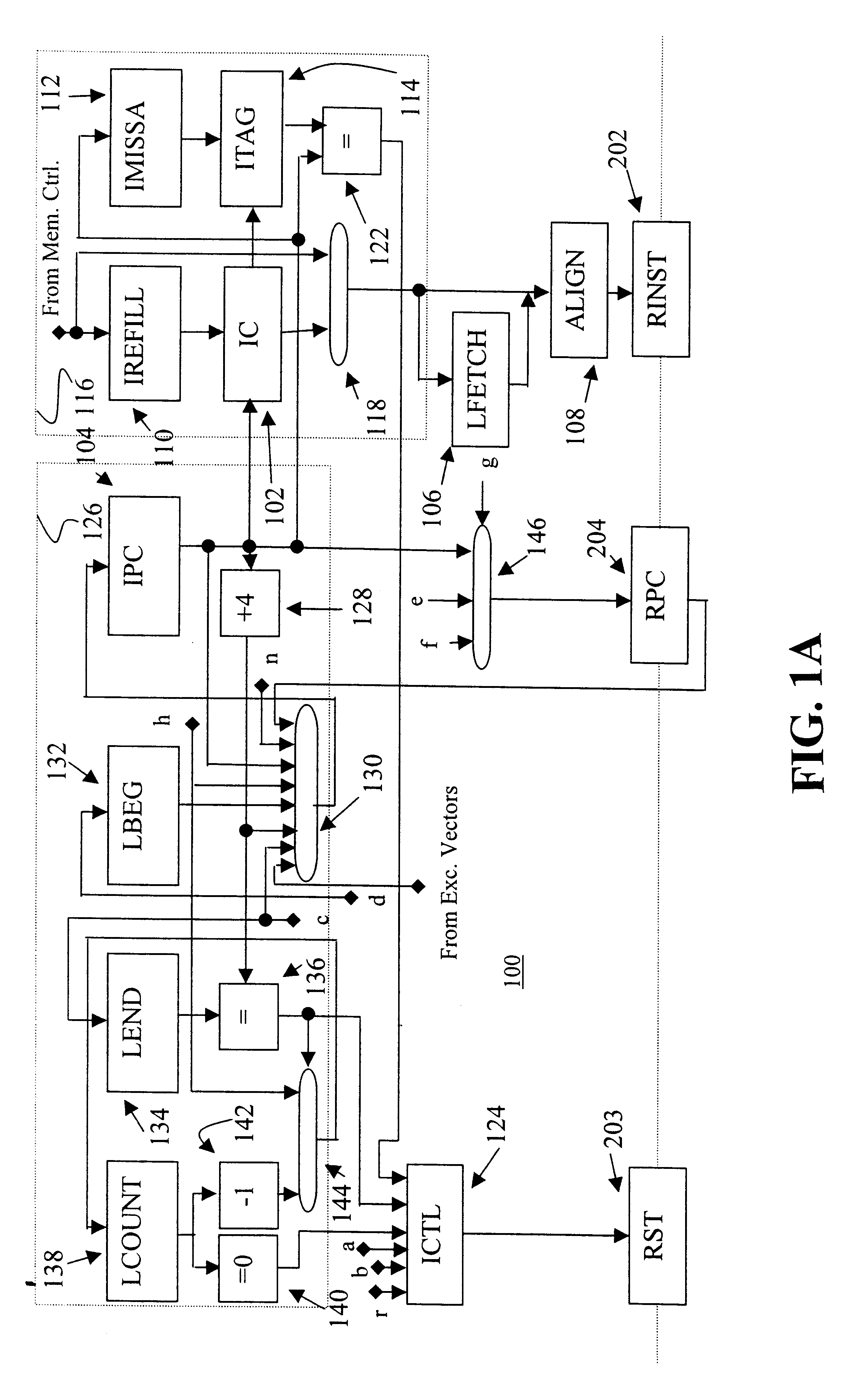
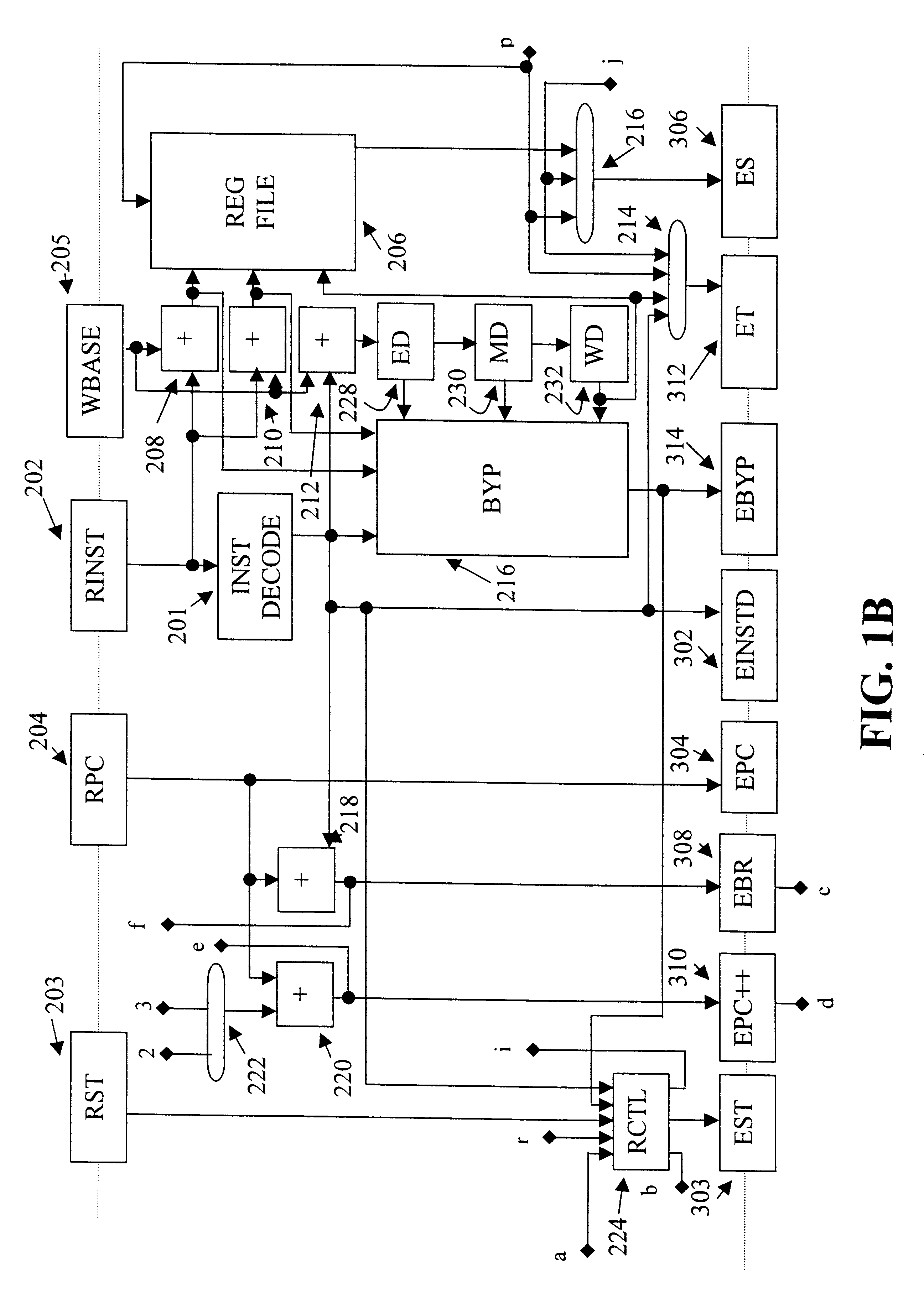
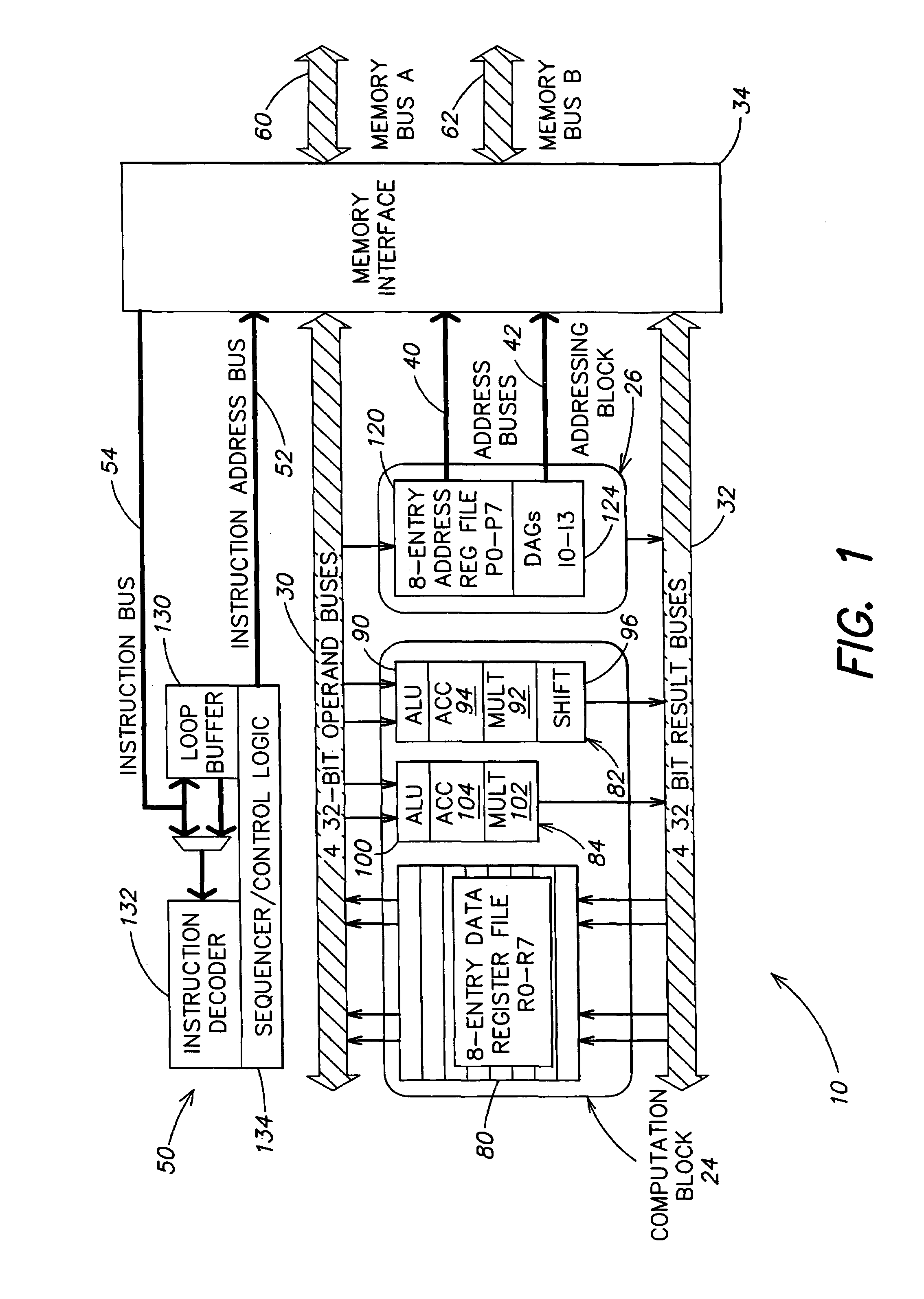
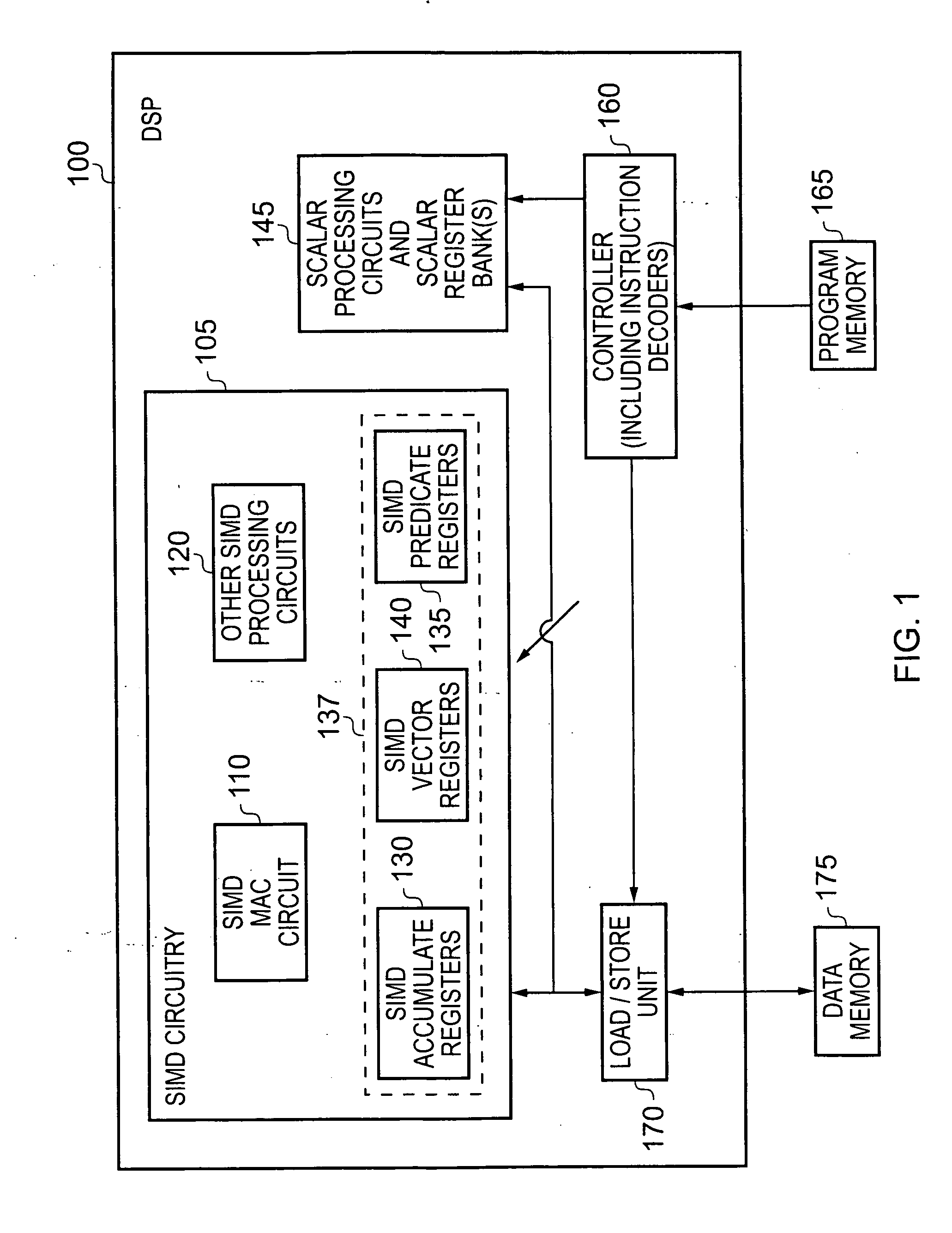
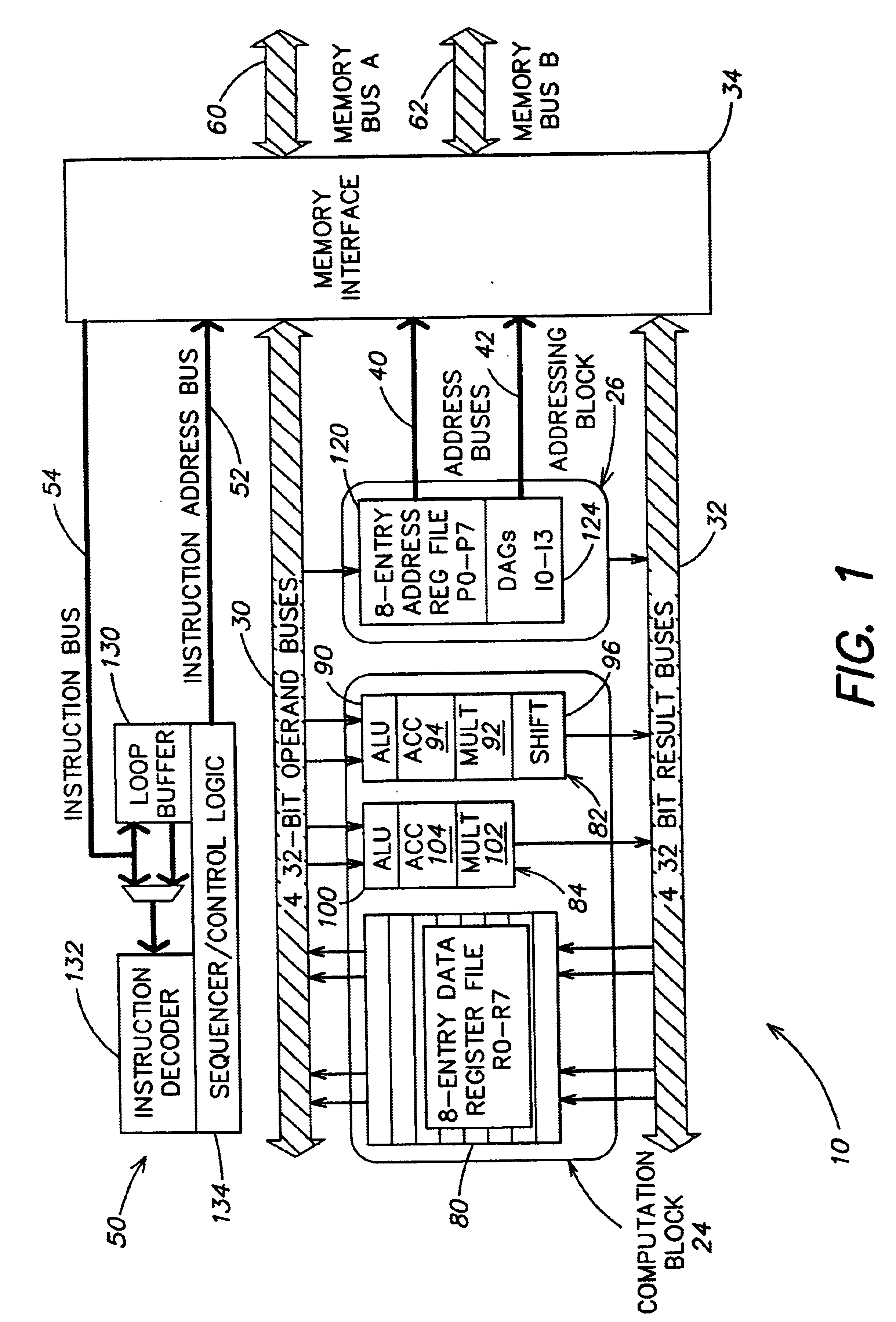
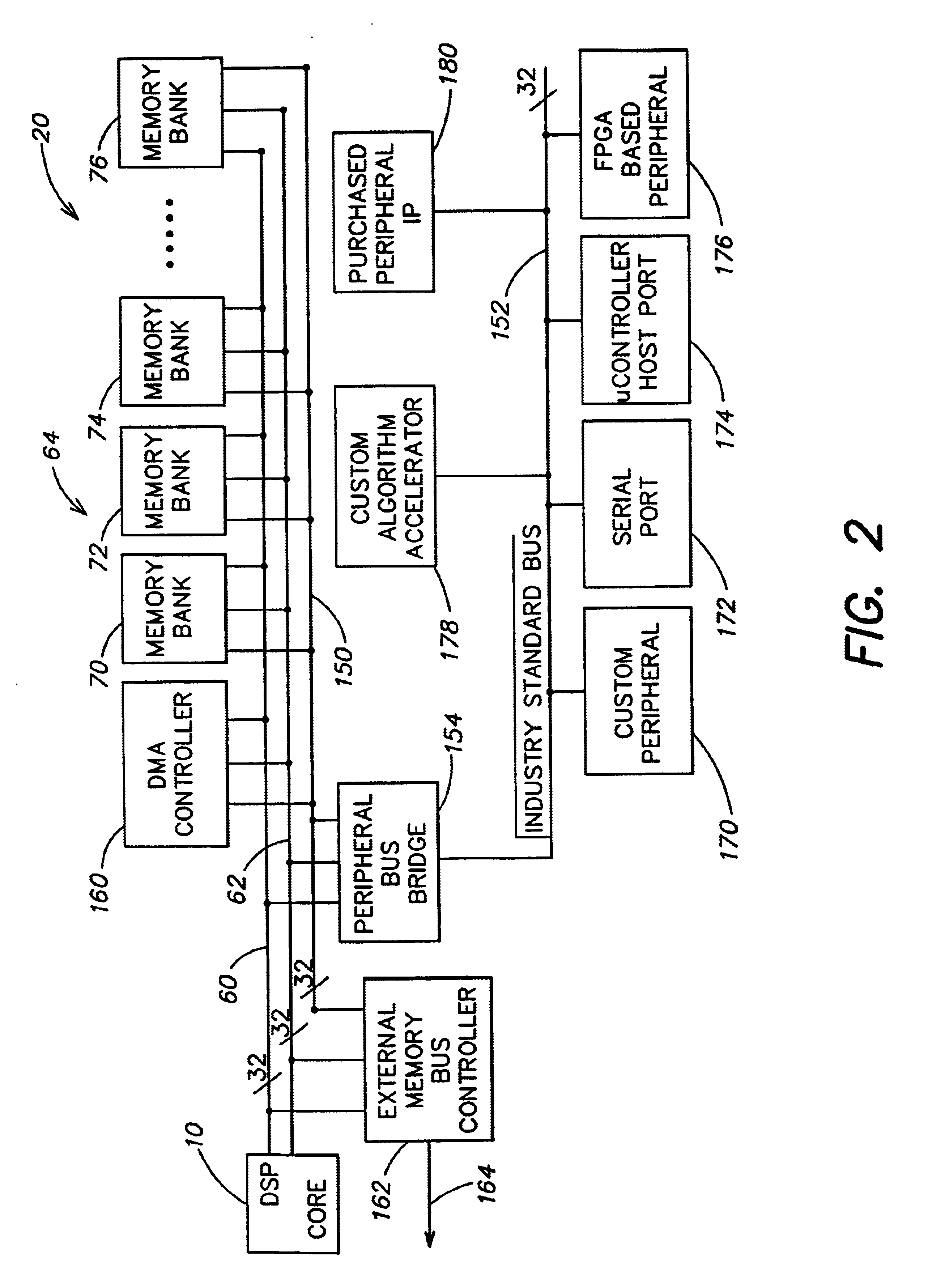
A processor (100) is provided that is a programmable fixed point digital signal processor (DSP) with variable instruction length, offering both high code density and easy programming. Architecture and instruction set are optimized for low power consumption and high efficiency execution of DSP algorithms, such as for wireless telephones, as well as pure control tasks. The processor includes an instruction buffer unit (106), a program flow control unit (108), an address / data flow unit (110), a data computation unit (112), and multiple interconnecting busses. Dual multiply-accumulate blocks improve processing performance. A memory interface unit (104) provides parallel access to data and instruction memories. The instruction buffer is operable to buffer single and compound instructions pending execution thereof. A decode mechanism is configured to decode instructions from the instruction buffer. The use of compound instructions enables effective use of the bandwidth available within the processor. A soft dual memory instruction can be compiled from separate first and second programmed memory instructions. Instructions can be conditionally executed or repeatedly executed. Bit field processing and various addressing modes, such as circular buffer addressing, further support execution of DSP algorithms. The processor includes a multistage execution pipeline with pipeline protection features. Various functional modules can be separately powered down to conserve power. The processor includes emulation and code debugging facilities with support for cache analysis.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
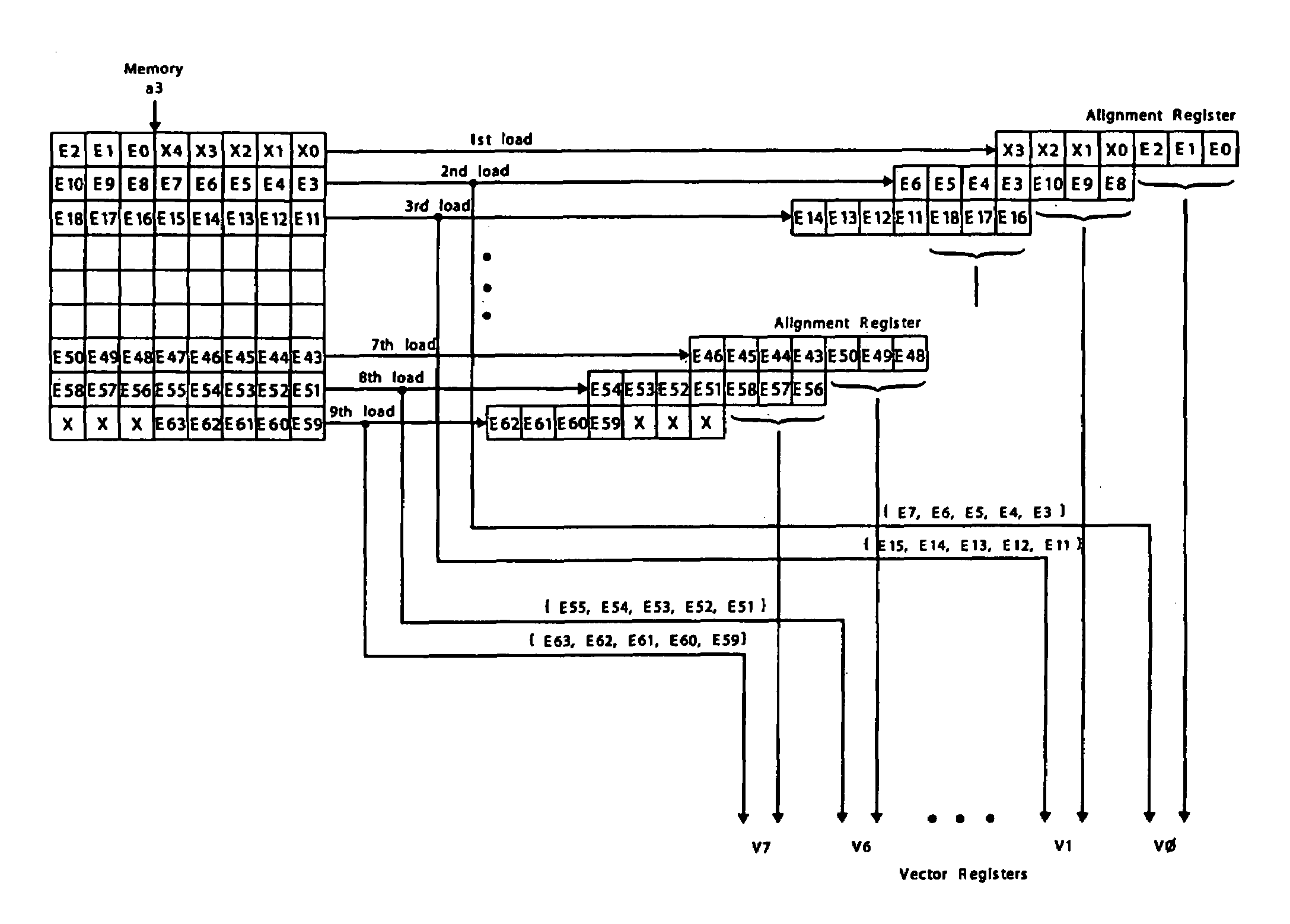
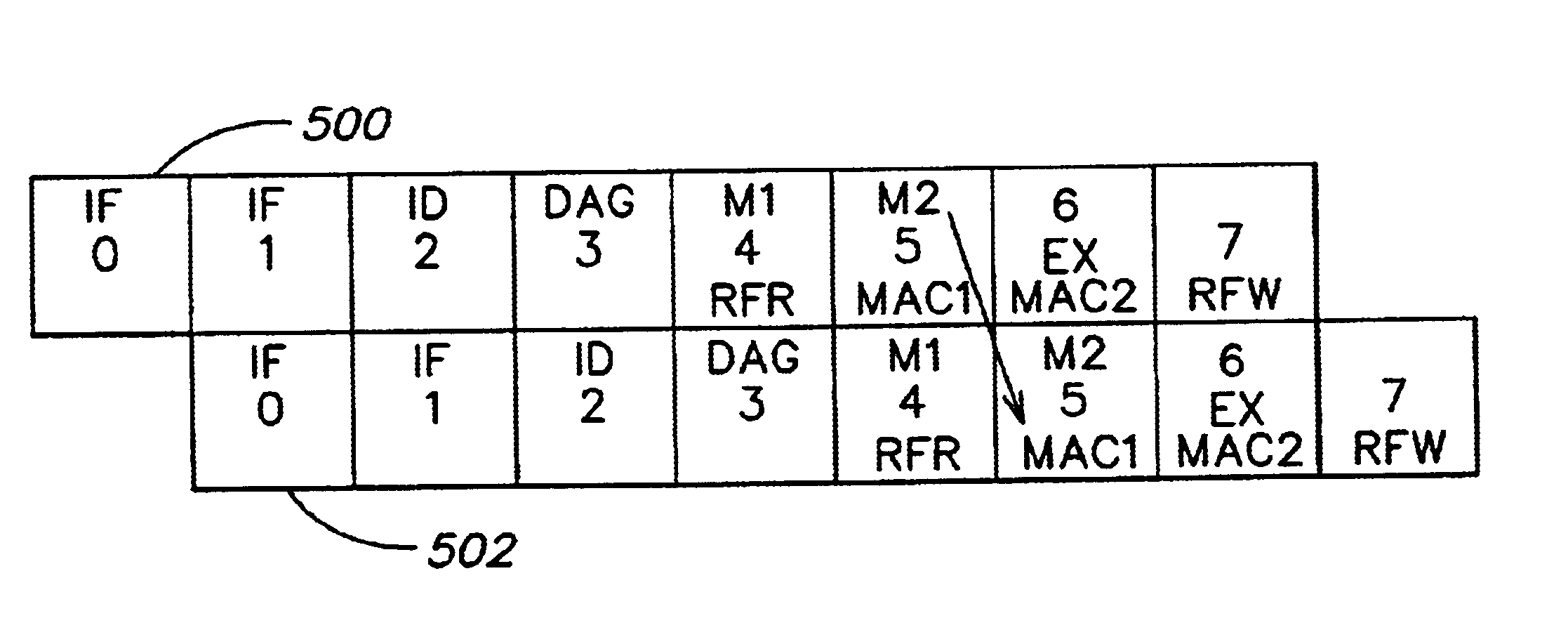
Load/store operation of memory misaligned vector data using alignment register storing realigned data portion for combining with remaining portion
InactiveUS7219212B1High coding densityImprove performanceInstruction analysisGeneral purpose stored program computerDigital signal processingCritical section
A processor can achieve high code density while allowing higher performance than existing architectures, particularly for Digital Signal Processing (DSP) applications. In accordance with one aspect, the processor supports three possible instruction sizes while maintaining the simplicity of programming and allowing efficient physical implementation. Most of the application code can be encoded using two sets of narrow size instructions to achieve high code density. Adding a third (and larger, i.e. VLIW) instruction size allows the architecture to encode multiple operations per instruction for the performance critical section of the code. Further, each operation of the VLIW format instruction can optionally be a SIMD operation that operates upon vector data. A scheme for the optimal utilization (highest achievable performance for the given amount of hardware) of multiply-accumulate (MAC) hardware is also provided.
Owner:TENSILICA
High data density RISC processor
InactiveUS6282633B1High densityIncrease in CPIInstruction analysisDigital computer detailsProgram instructionProcessor register
A RISC processor implements an instruction set which, in addition to optimizing a relationship between the number of instructions required for execution of a program, clock period and average number of clocks per instruction, also is designed to optimize the equation S=IS * BI, where S is the size of program instructions in bits, IS is the static number of instructions required to represent the program (not the number required by an execution) and BI is the average number of bits per instruction. Compared to conventional RISC architectures, this processor lowers both BI and IS with minimal increases in clock period and average number of clocks per instruction. The processor provides good code density in a fixed-length high-performance encoding based on RISC principles, including a general register with load / store architecture. Further, the processor implements a simple variable-length encoding that maintains high performance.
Owner:TENSILICA
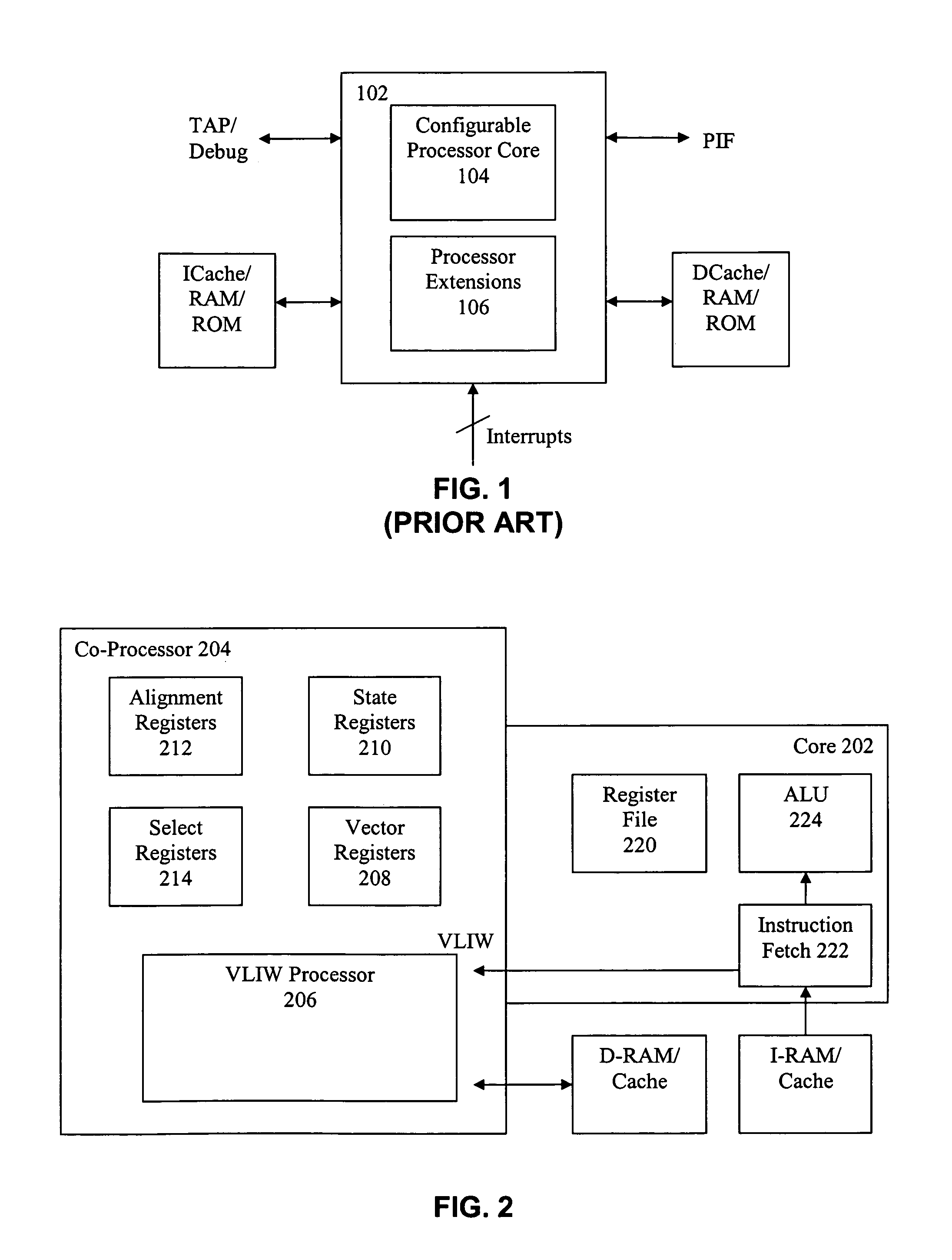
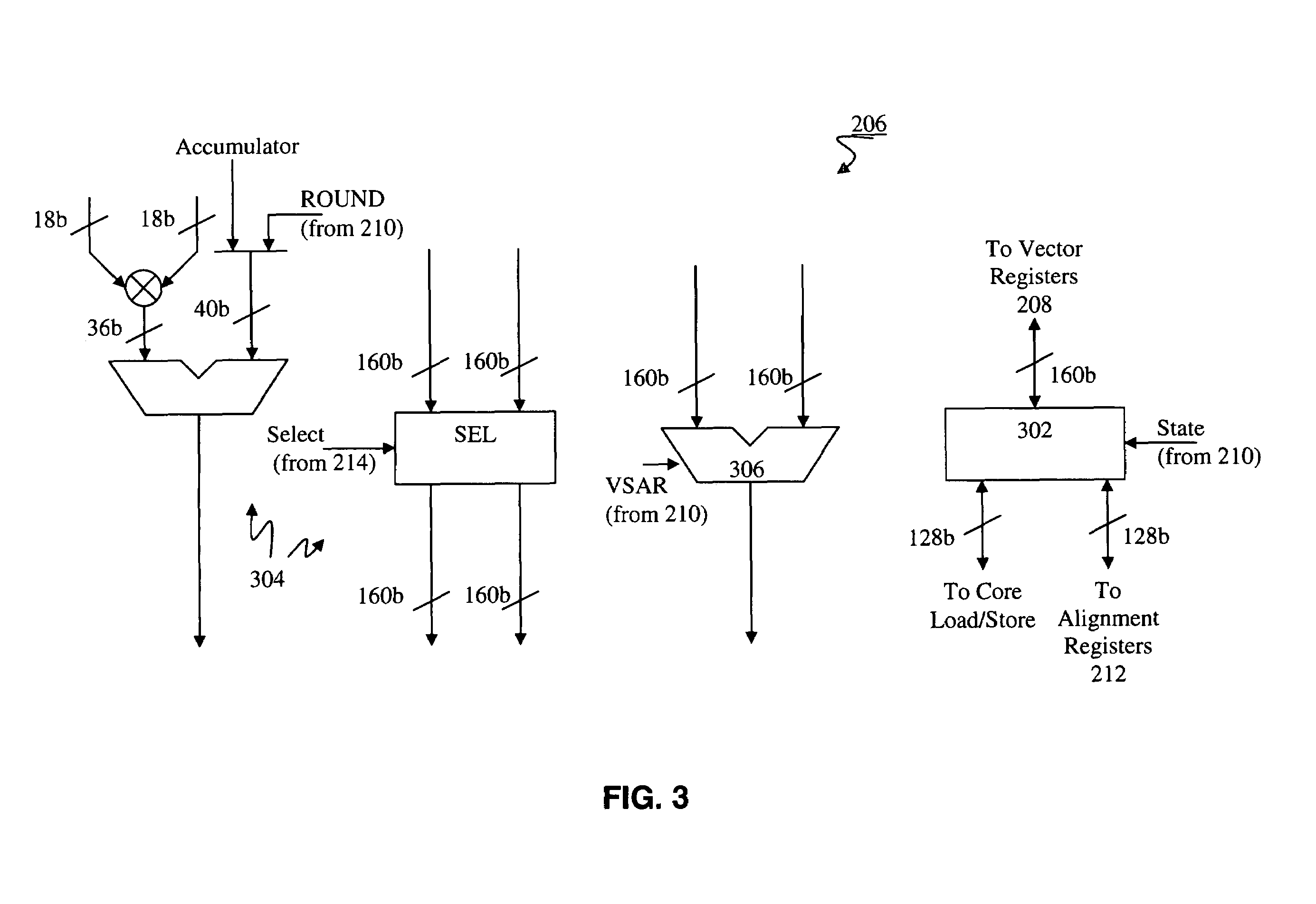
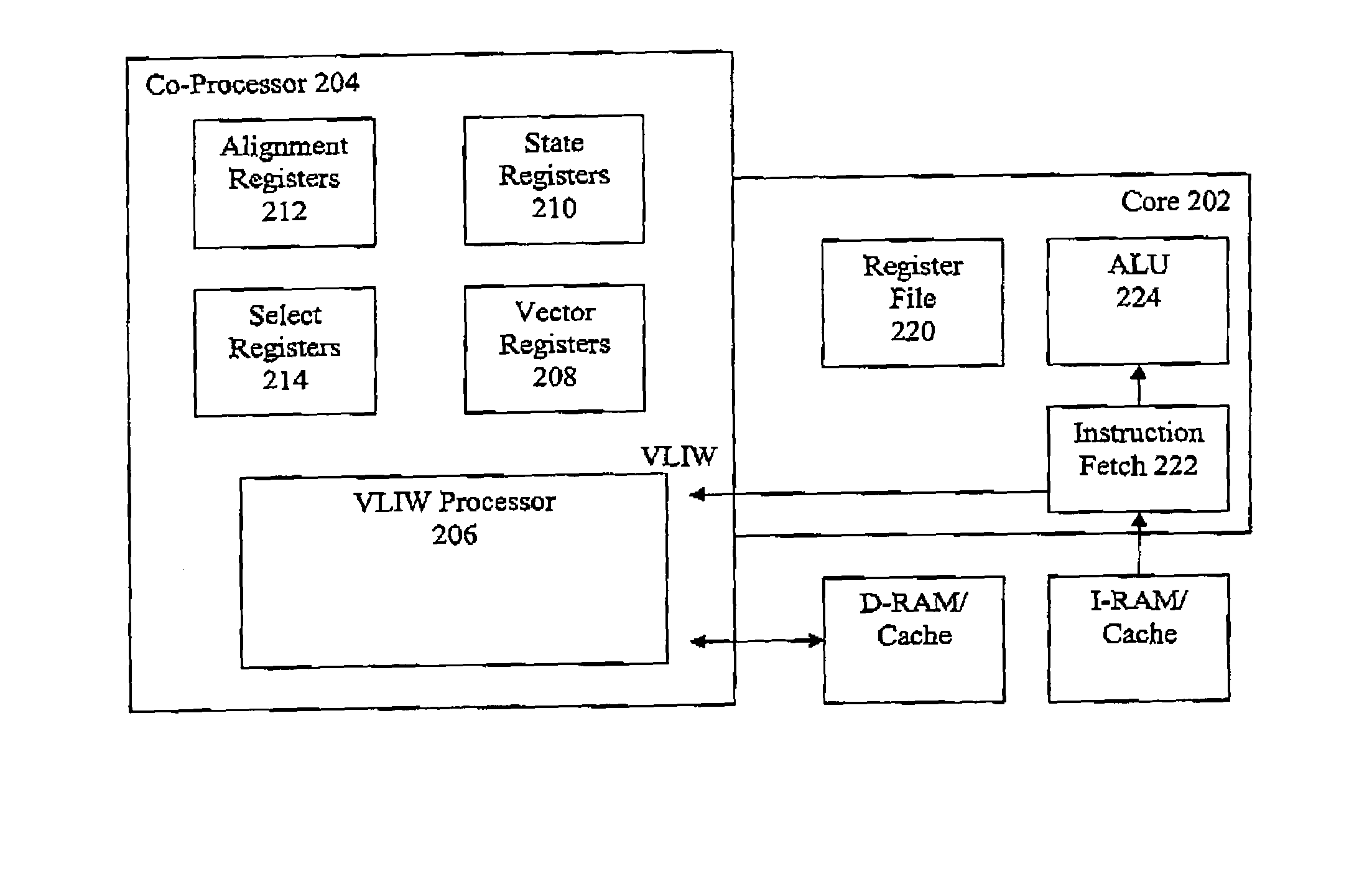
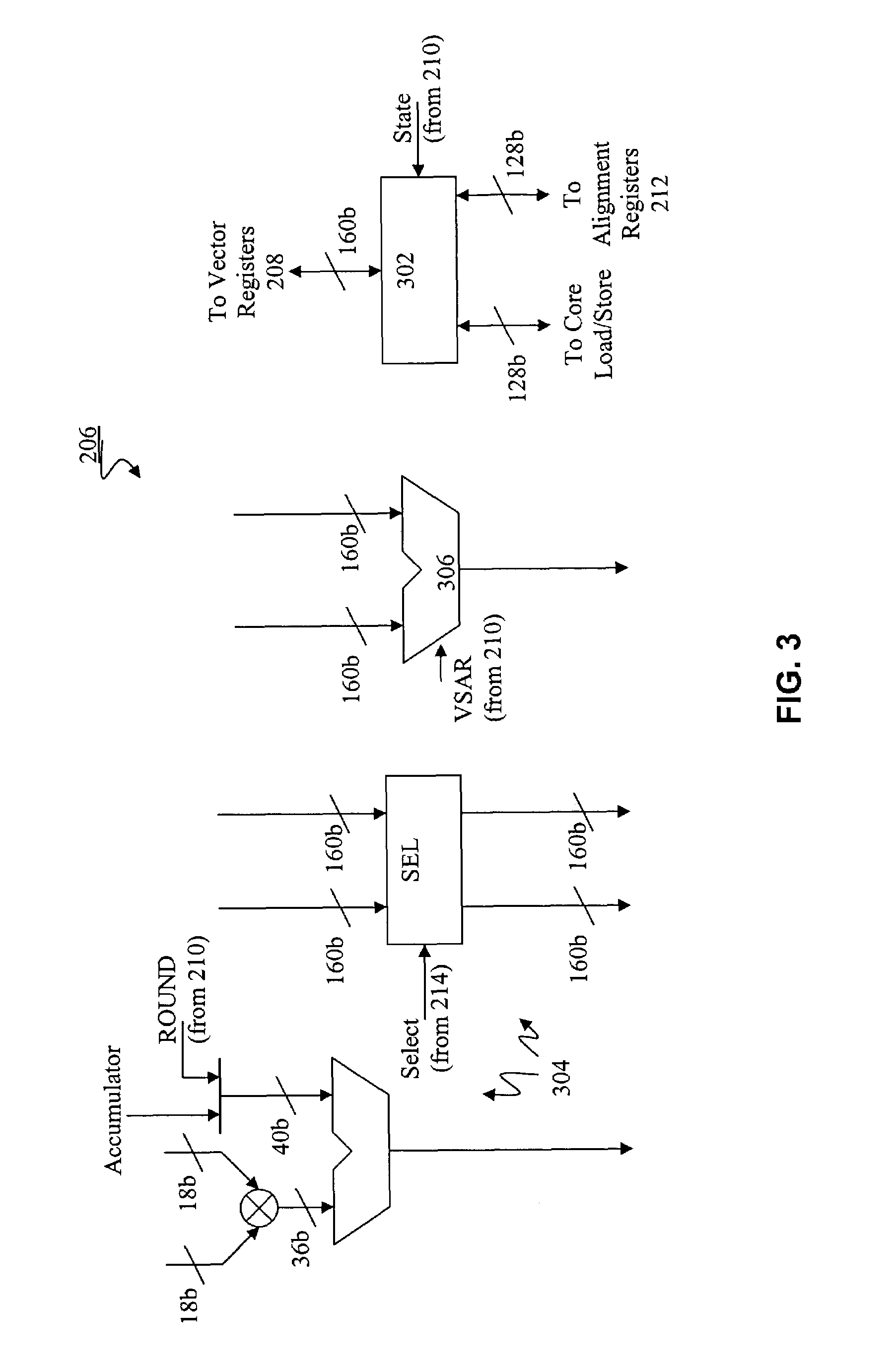
Vector co-processor for configurable and extensible processor architecture
ActiveUS7376812B1High coding densityImprove performanceInstruction analysisGeneral purpose stored program computerDigital signal processingCritical section
A processor can achieve high code density while allowing higher performance than existing architectures, particularly for Digital Signal Processing (DSP) applications. In accordance with one aspect, the processor supports three possible instruction sizes while maintaining the simplicity of programming and allowing efficient physical implementation. Most of the application code can be encoded using two sets of narrow size instructions to achieve high code density. Adding a third (and larger, i.e. VLIW) instruction size allows the architecture to encode multiple operations per instruction for the performance critical section of the code. Further, each operation of the VLIW format instruction can optionally be a SIMD operation that operates upon vector data. A scheme for the optimal utilization (highest achievable performance for the given amount of hardware) of multiply-accumulate (MAC) hardware is also provided.
Owner:TENSILICA
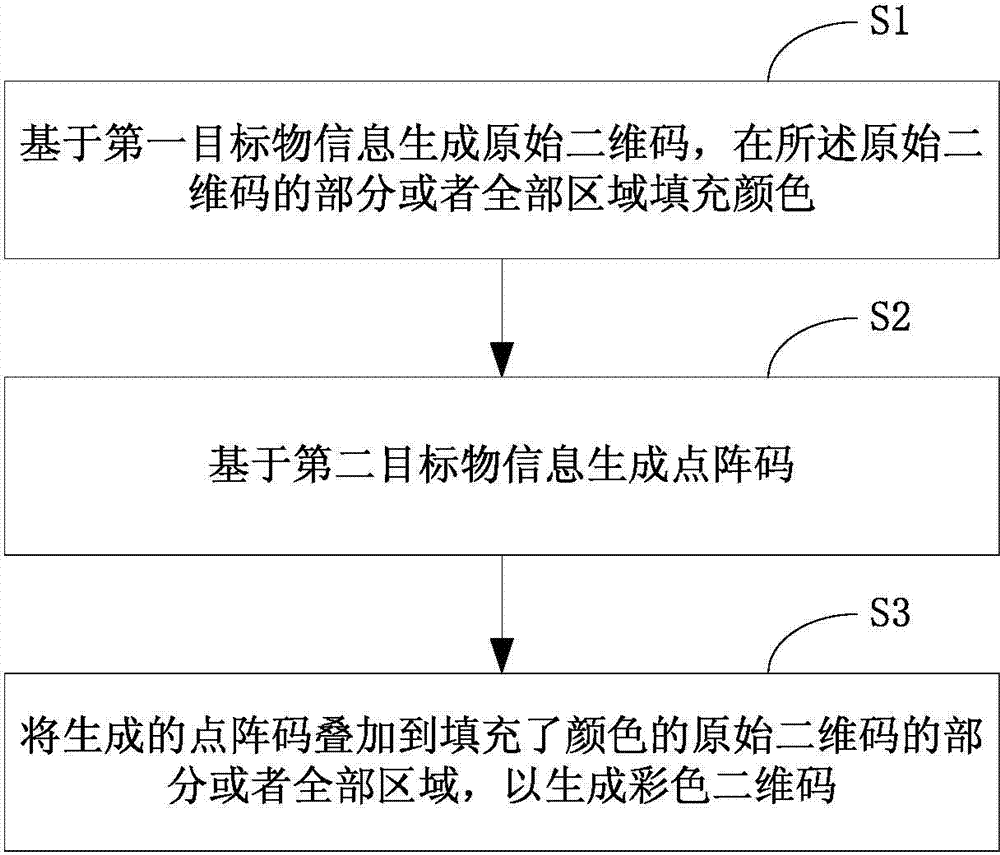
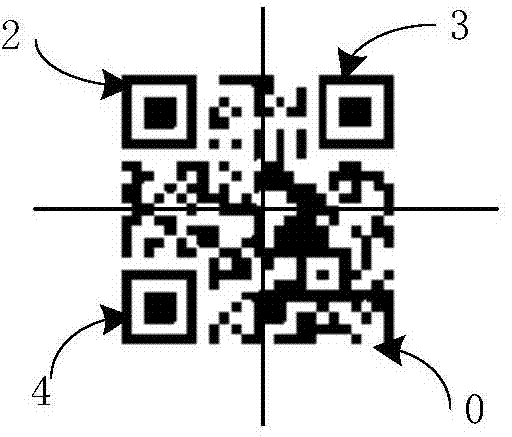
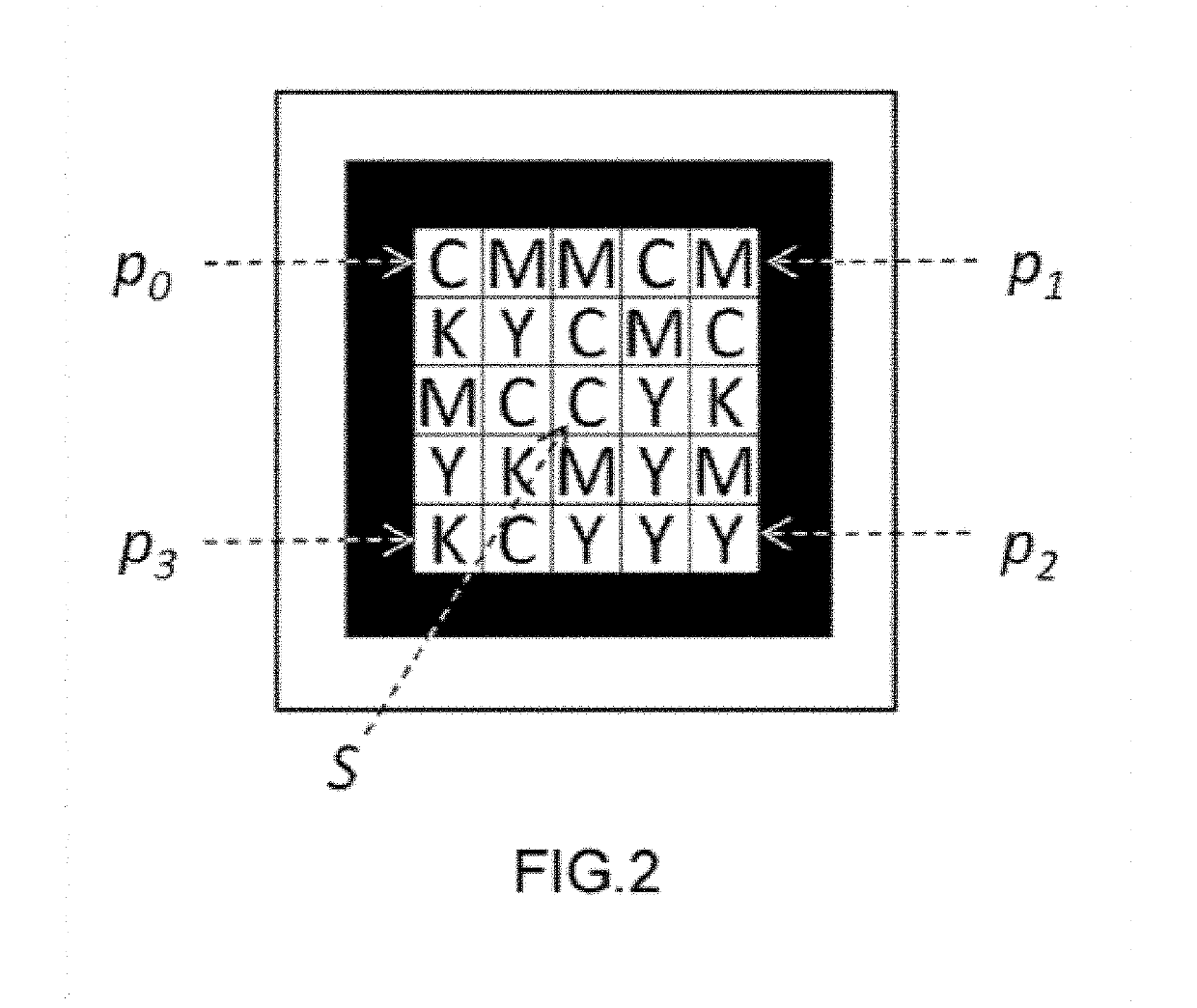
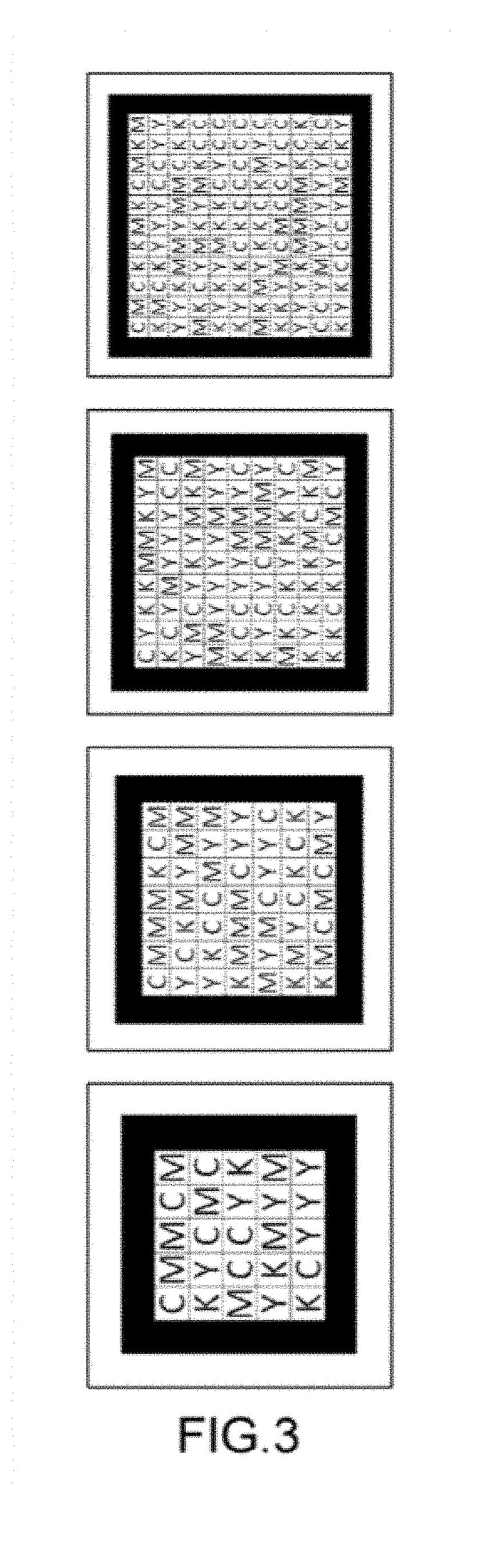
Colorful two-dimension code, generating method and generating system thereof and printed article
ActiveCN103489026AHigh coding densityEasy to crackRecord carriers used with machinesDot matrixTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a colorful two-dimension code, a generating method and generating system thereof and a printed article. The colorful two-dimension code is printed on the printed article, and the system comprises an original two-dimension code generating module, a dot matrix code generating module and an overlaying module. The method comprises the steps that S1, an original two-dimension code is generated on the basis of first target article information, and part of or all areas of the original two-dimension code are filled with colors; S2, a dot matrix code is generated on the basis of second target article information; S3, the dot matrix code is overlaid to the part or all the areas of the original two-dimension code, filled with the colors, so that the colorful two-dimension code is generated. The generated colorful two-dimension code is large in coding density, and high in decoding difficulty and imitation difficulty.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINACHOICE SCI & TECH CO LTD
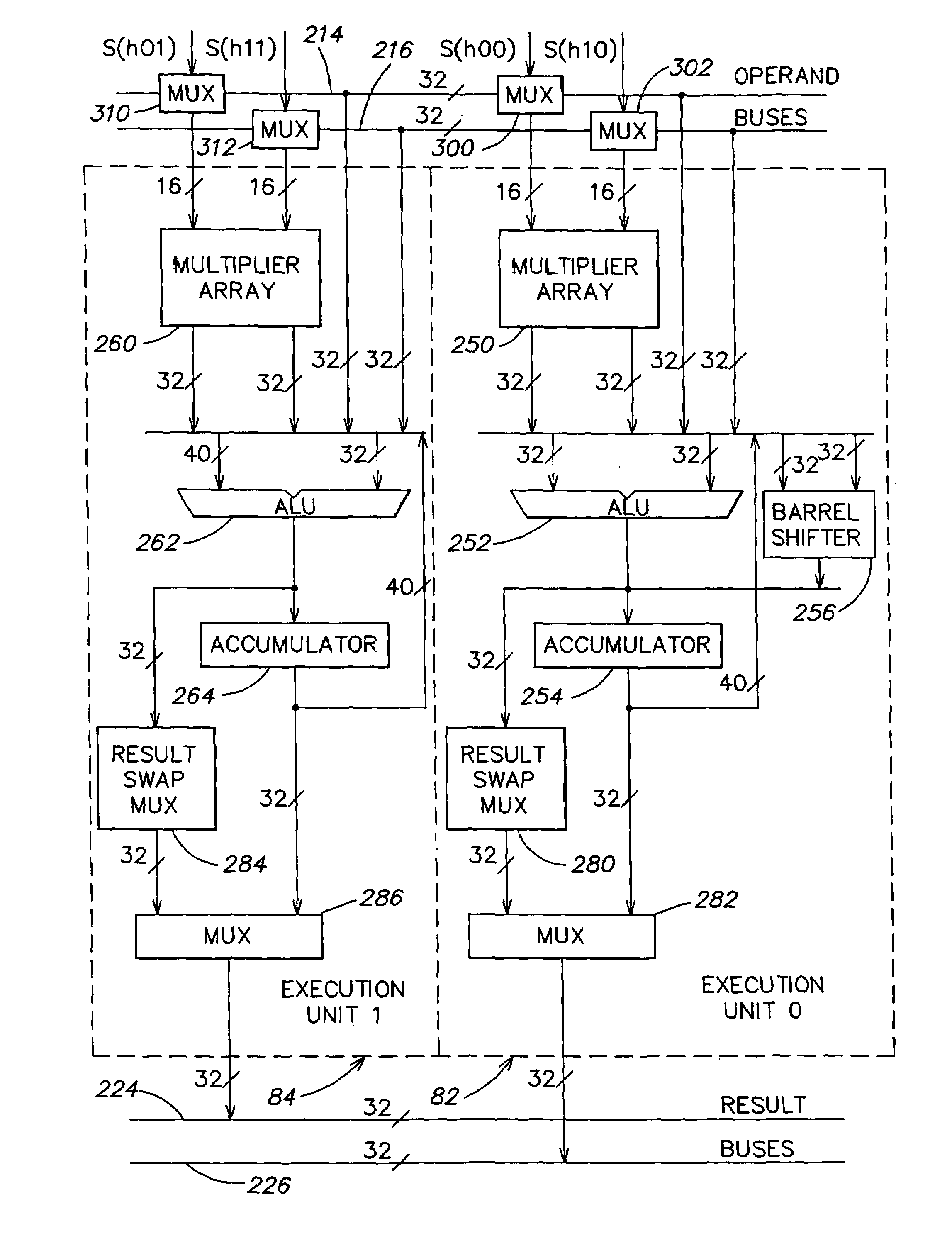
Digital signal processor computation core with input operand selection from operand bus for dual operations
InactiveUS7111155B1High code storage densityEfficient digital signalRegister arrangementsInstruction analysisMemory interfaceCode density
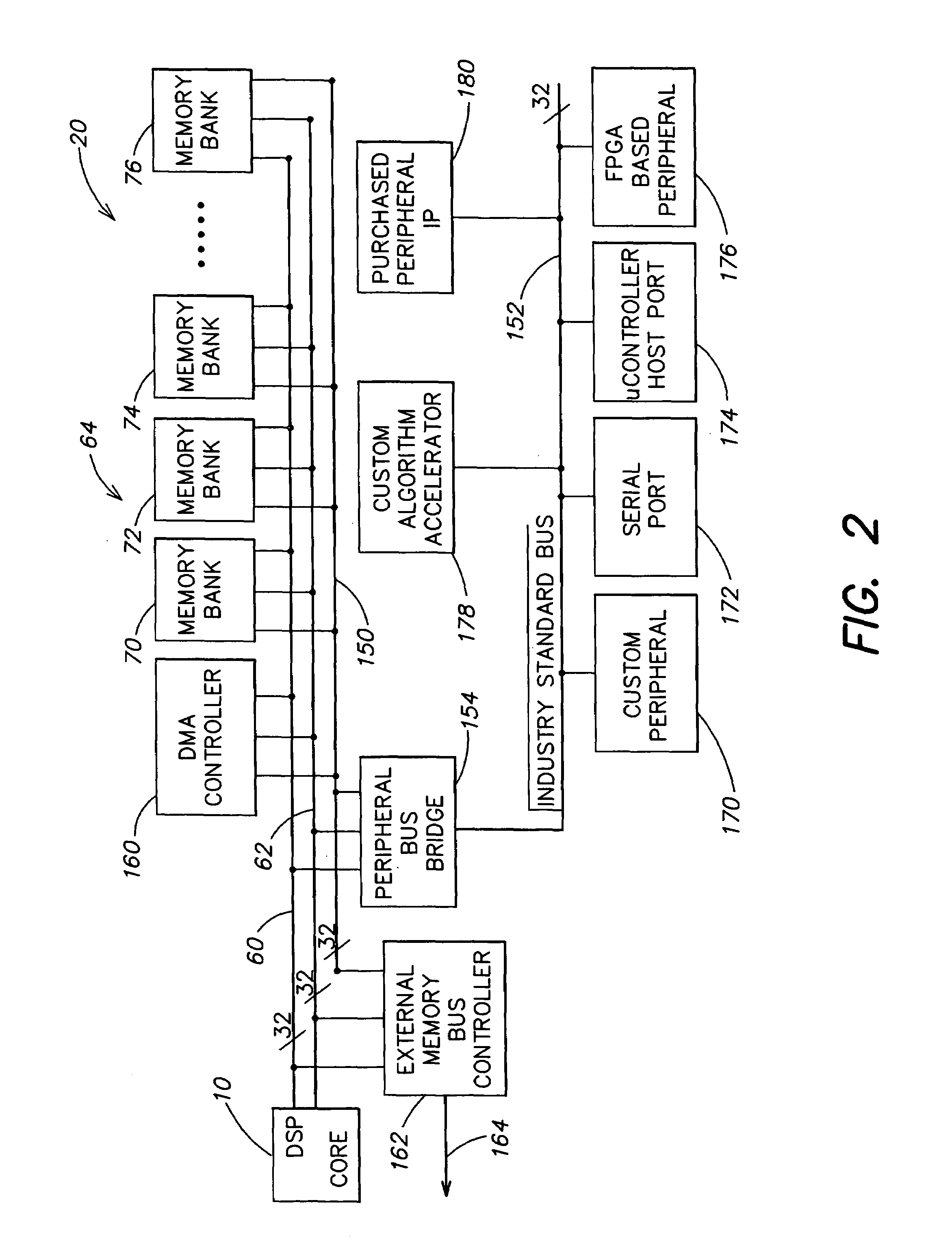
A computation core includes a computation block, an addressing block and an instruction sequencer, which are coupled to a memory through a memory interface. The computation block includes a register file and dual execution units. The execution units include features for enhanced performance in executing digital signal computations. The computation core is configured for executing digital signal processor instructions and microcontroller instructions, while achieving efficient digital signal processor computation and high code density. A finite impulse response filter algorithm achieves high performance on the dual execution units.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Structured light coding method and related device
ActiveCN103983213AIncrease varietyNo increase in difficultyUsing optical meansPattern recognitionGraphics
The invention discloses a structured light coding method and a related device. The structured light coding method includes the first step of generating a first coding pattern through a pseudo-random code, wherein coding elements in the first coding pattern are distinguished through at least color graphs in four colors and at least one geometric graph, the second step of projecting the first coding pattern onto the surface of a measured object, the third step of obtaining a second coding pattern formed after the first coding pattern and the surface of the measured object are overlapped, the fourth step of determining a feature point set on the second coding pattern, the fifth step of determining the corresponding position of each feature point in the feature point set in the first coding pattern, and the sixth step of calculating the depth of each feature point in the feature point set in the second coding pattern according to the position of each feature point in the feature point set in the first coding pattern and finally determining three-dimensional contour information of the measured object. Through the technical scheme of the method, on the premise that the coding density is ensured, the success rate of decoding is effectively increased.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Apparatus and method for performing multiply-accumulate operations
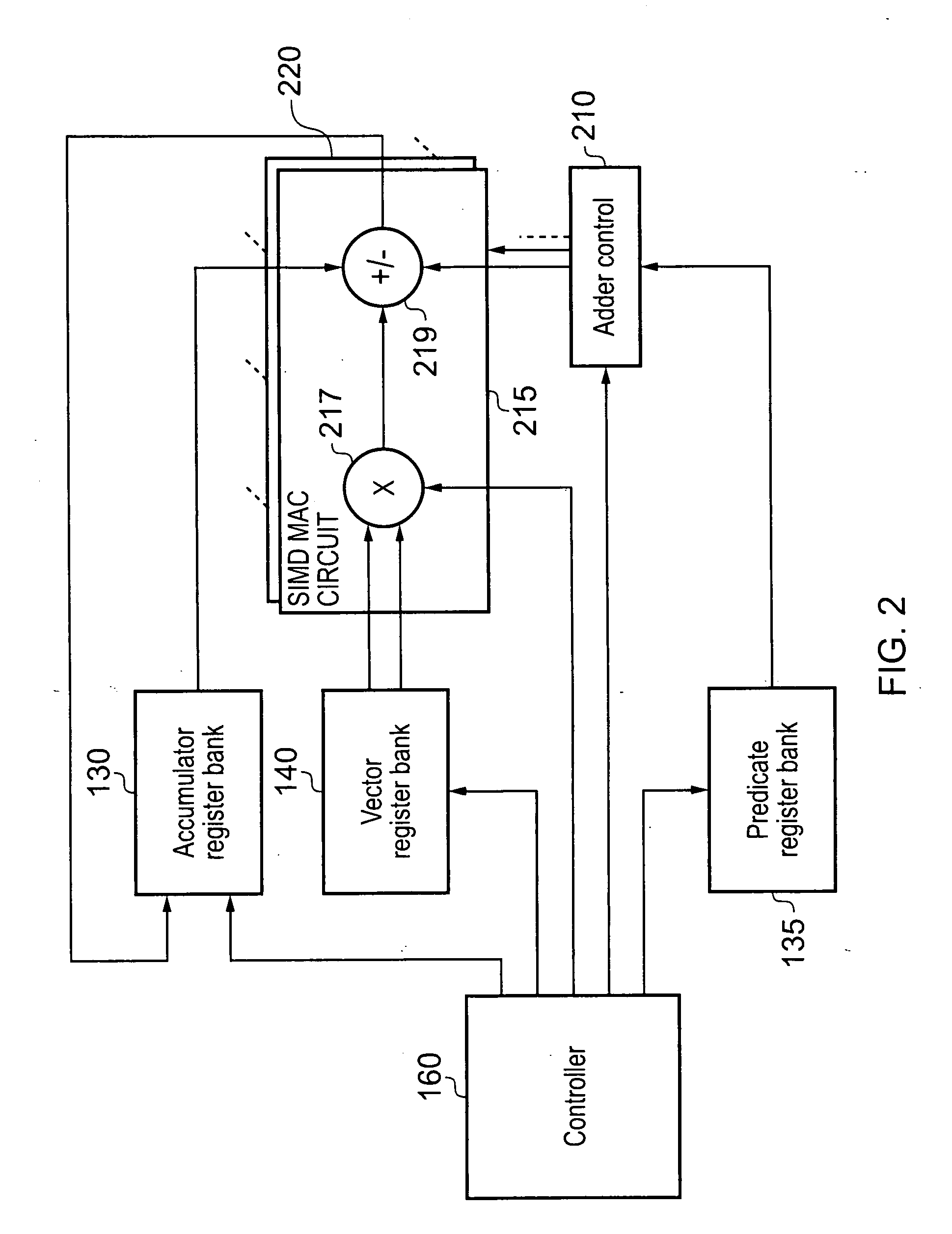
ActiveUS8595280B2Reduce the amount requiredEasy to useDigital computer detailsProgram controlControl signalMultiply–accumulate operation
Owner:ARM LTD
Apparatus and method for performing multiply-accumulate operations
ActiveUS20110106871A1Reduce the amount requiredEasy to useComputation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsControl signalMultiply–accumulate operation
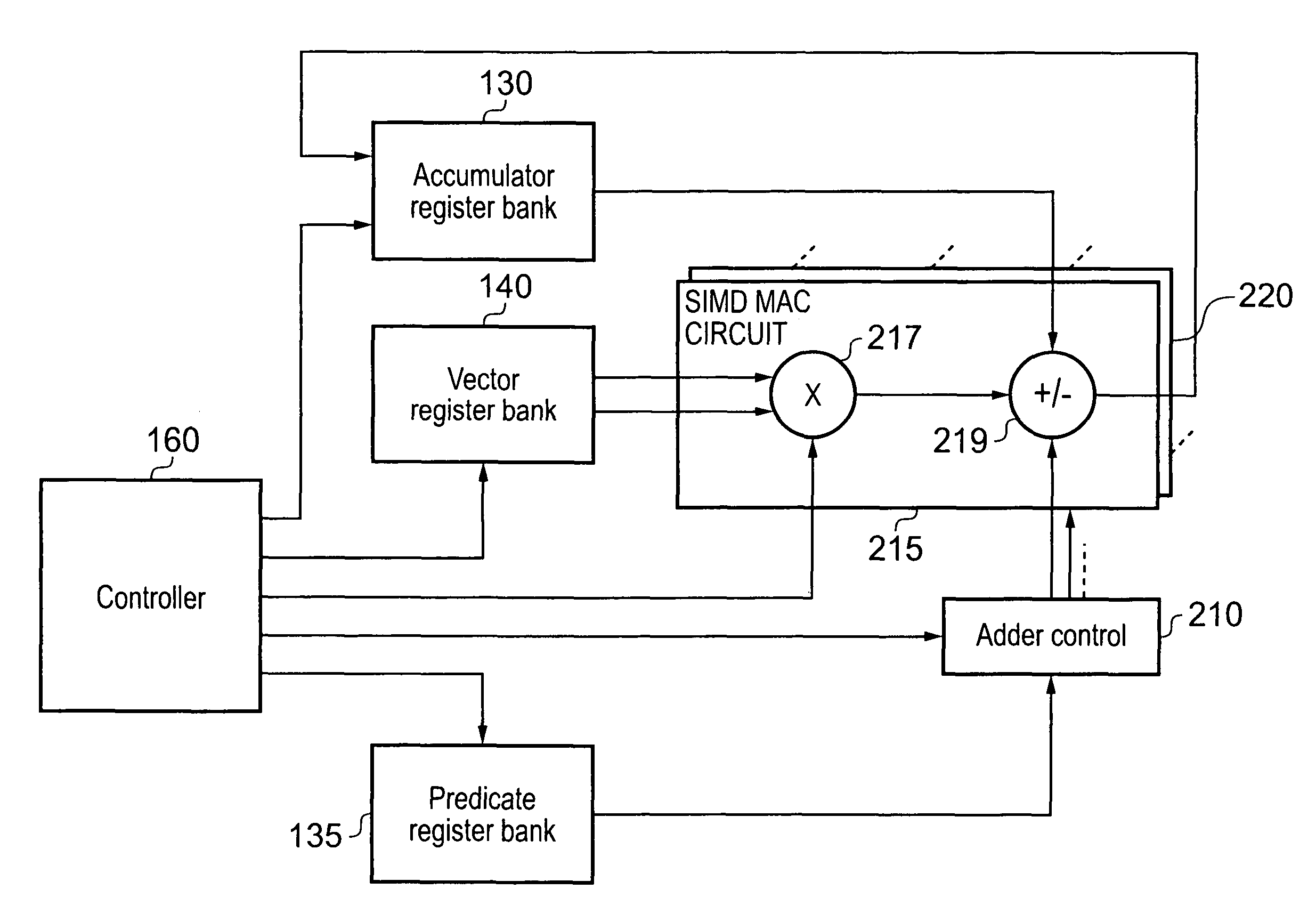
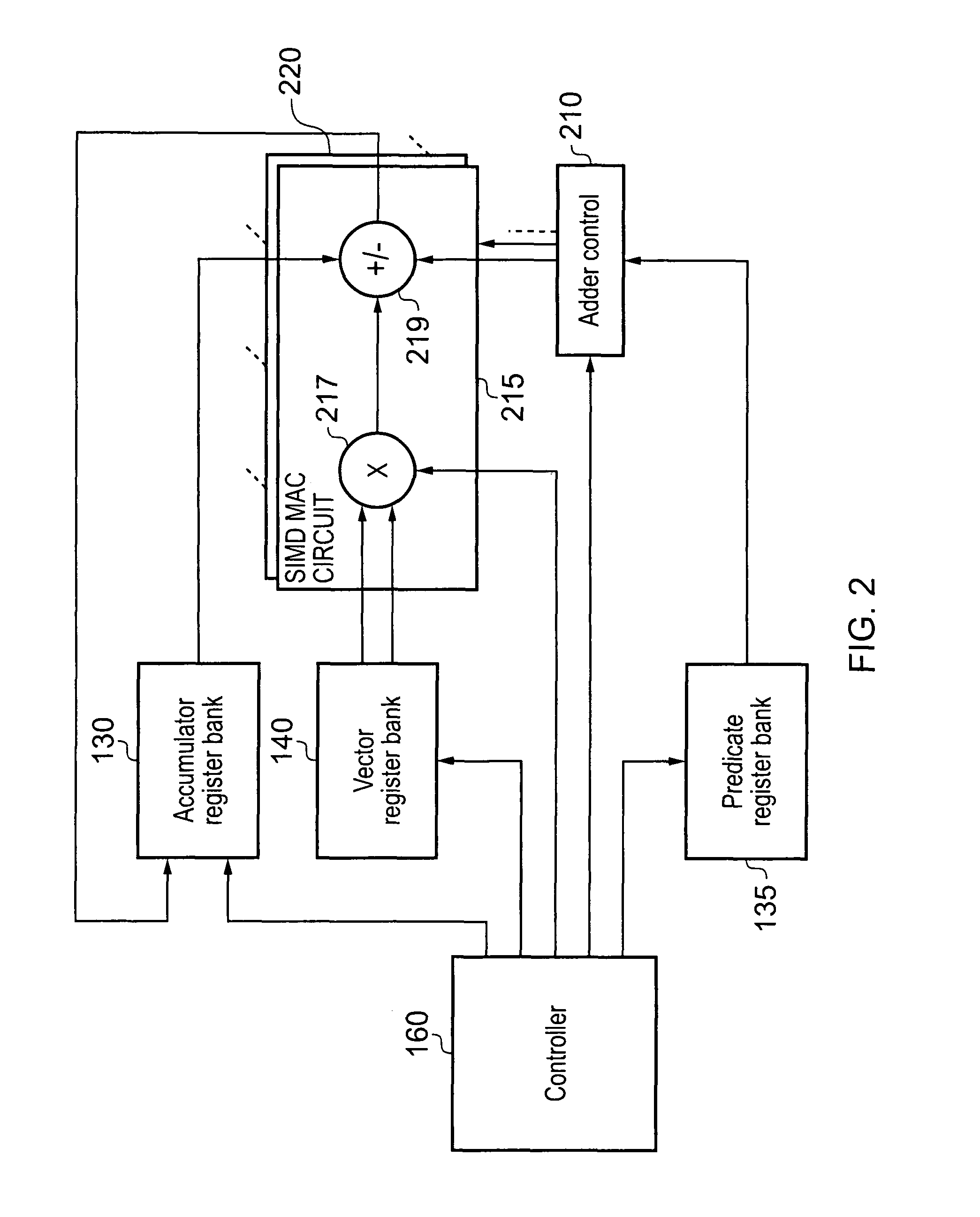
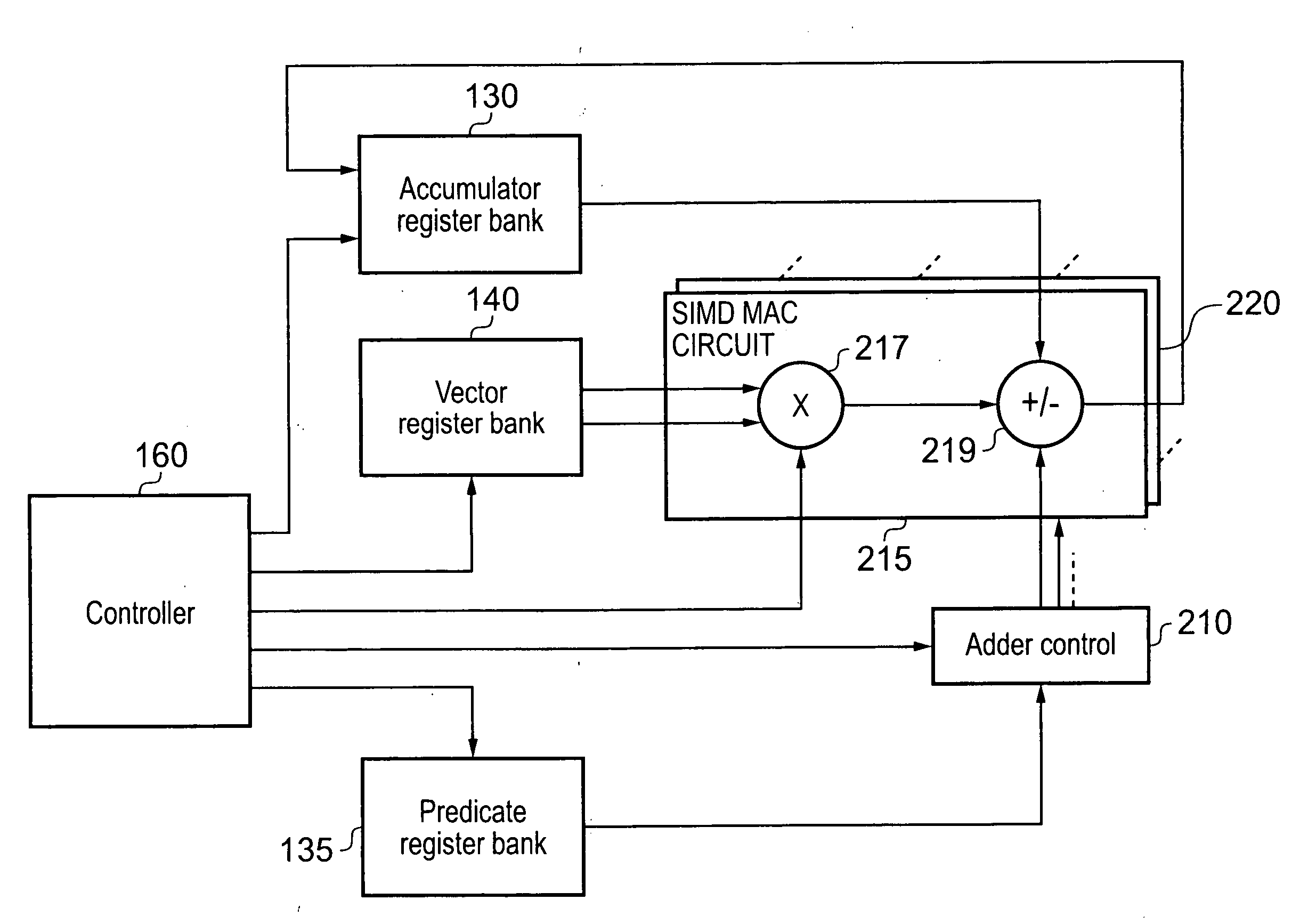
A data processing apparatus and method for performing multiply-accumulate operations is provided. The data processing apparatus includes data processing circuitry responsive to control signals to perform data processing operations on at least one input data element. Instruction decoder circuitry is responsive to a predicated multiply-accumulate instruction specifying as input operands a first input data element, a second input data element, and a predicate value, to generate control signals to control the data processing circuitry to perform a multiply-accumulate operation by: multiplying said first input data element and said second input data element to produce a multiplication data element; if the predicate value has a first value, producing a result accumulate data element by adding the multiplication data element to an initial accumulate data element; and if the predicate value has a second value, producing the result accumulate data element by subtracting the multiplication data element from the initial accumulate data element. Such an approach provides a particularly efficient mechanism for performing complex sequences of multiply-add and multiply-subtract operations, facilitating improvements in performance, energy consumption and code density when compared with known prior art techniques.
Owner:ARM LTD
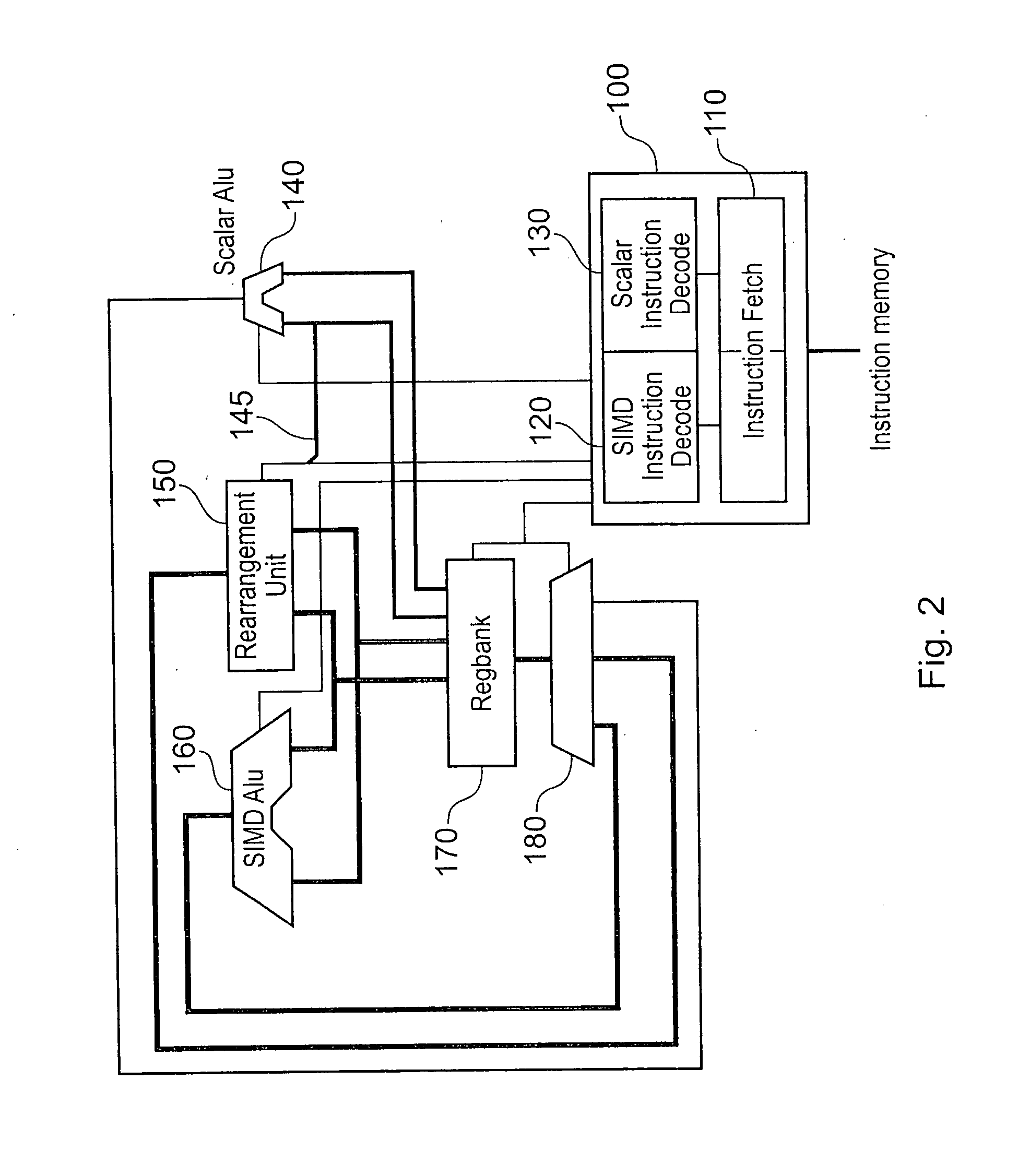
Apparatus and method for performing re-arrangement operations on data
ActiveUS20080141004A1Reduce needHigh densityRegister arrangementsSpecific program execution arrangementsProcessor registerParallel computing
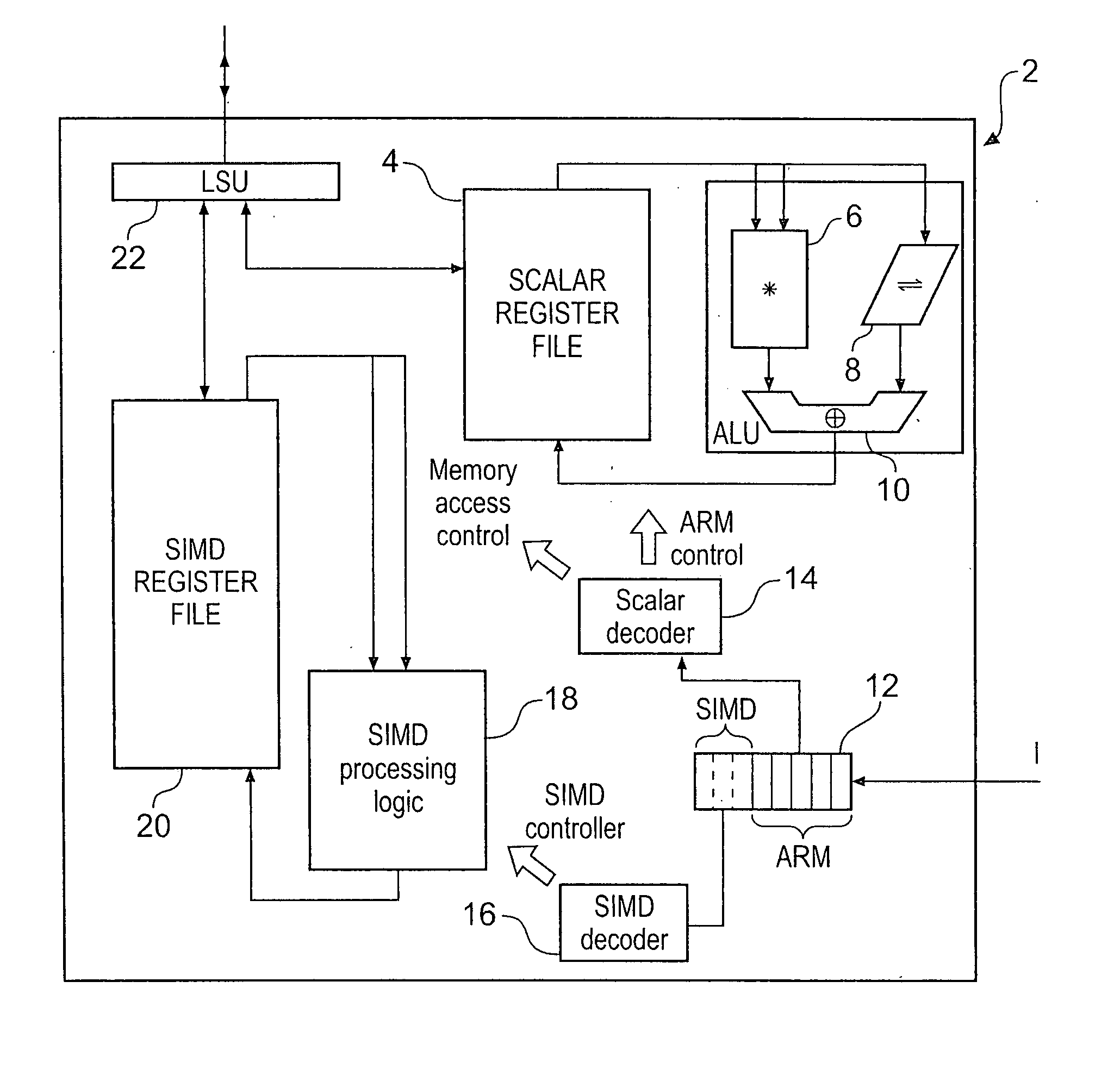
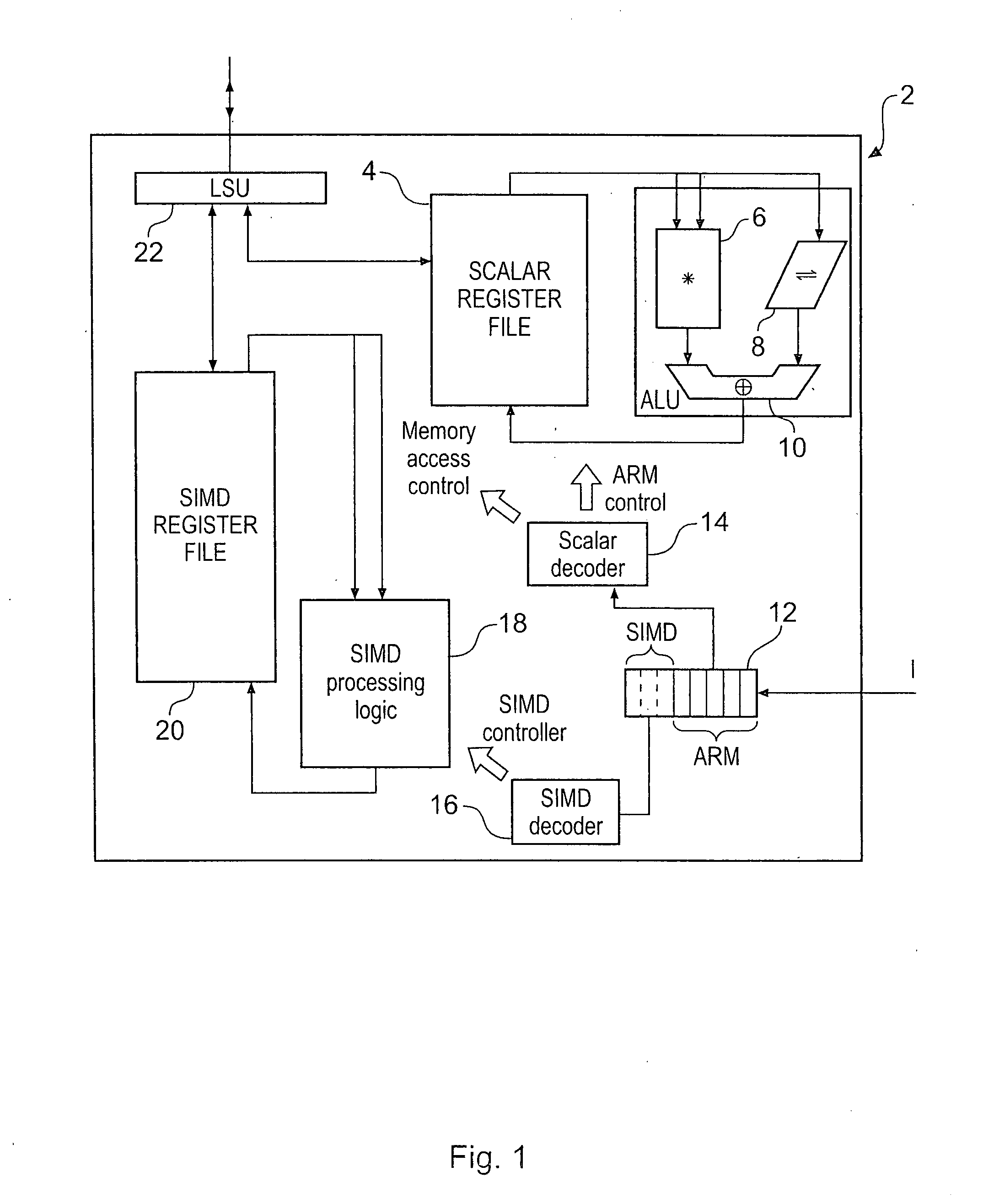
An apparatus and method are provided for performing re-arrangement operations on data. The data processing apparatus has a register data store with a plurality of registers for storing data, and processing logic for performing a sequence of operations on data including at least one re-arrangement operation. The processing logic has scalar processing logic for performing scalar operations and SIMD processing logic for performing SIMD operations. The SIMD processing logic is responsive to a re-arrangement instruction specifying a family of re-arrangement operations to perform a selected re-arrangement operation from that family on a plurality of data elements constituted by data in one or more registers identified by the re-arrangement instruction. The selected re-arrangement operation is dependent on at least one parameter provided by the scalar processing logic, that parameter identifying a data element width for the data elements on which the selected re-arrangement operation is performed. By such an approach, significant code density improvements can be made in respect of the code executed by the SIMD processing logic.
Owner:ARM LTD
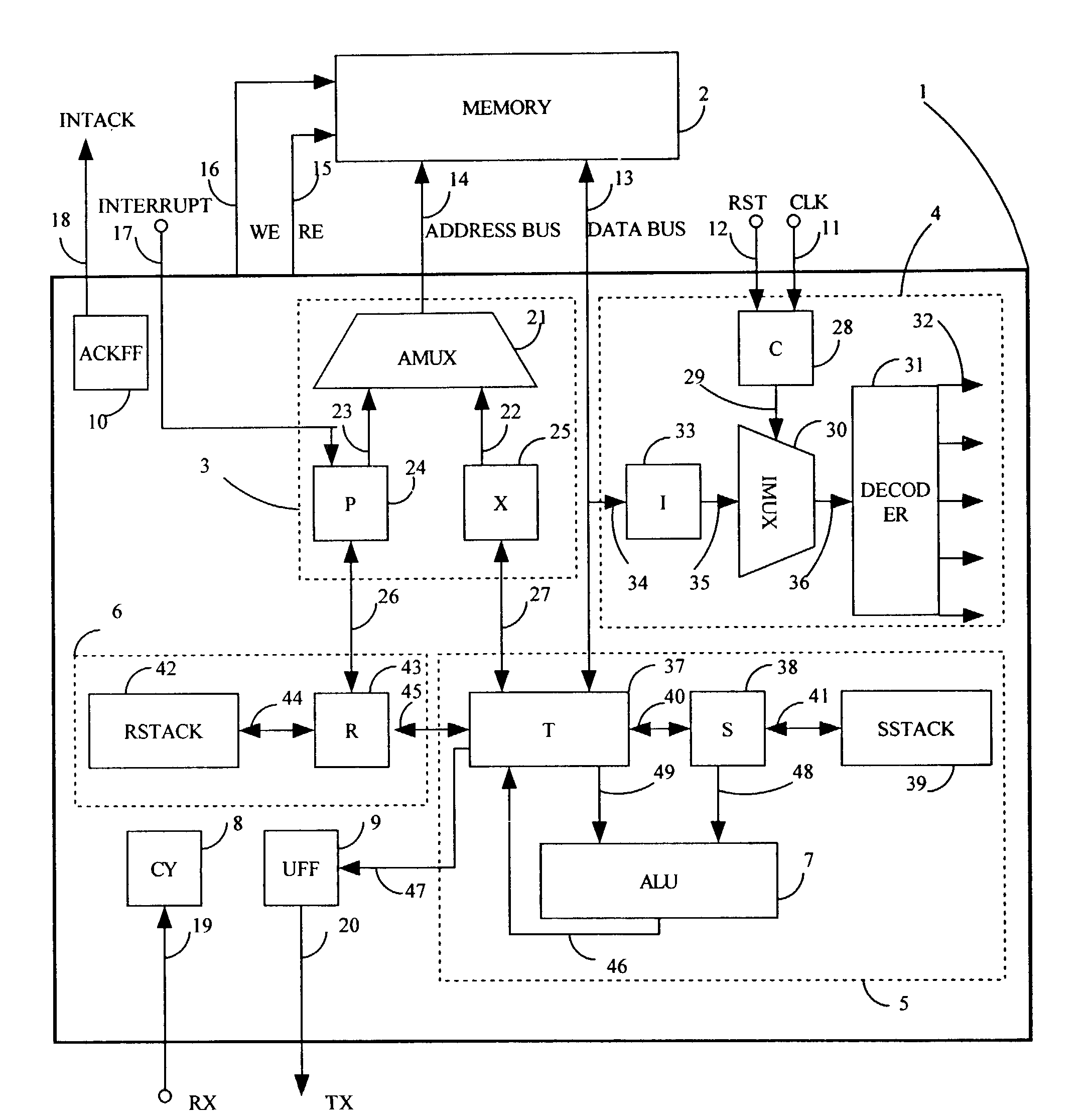
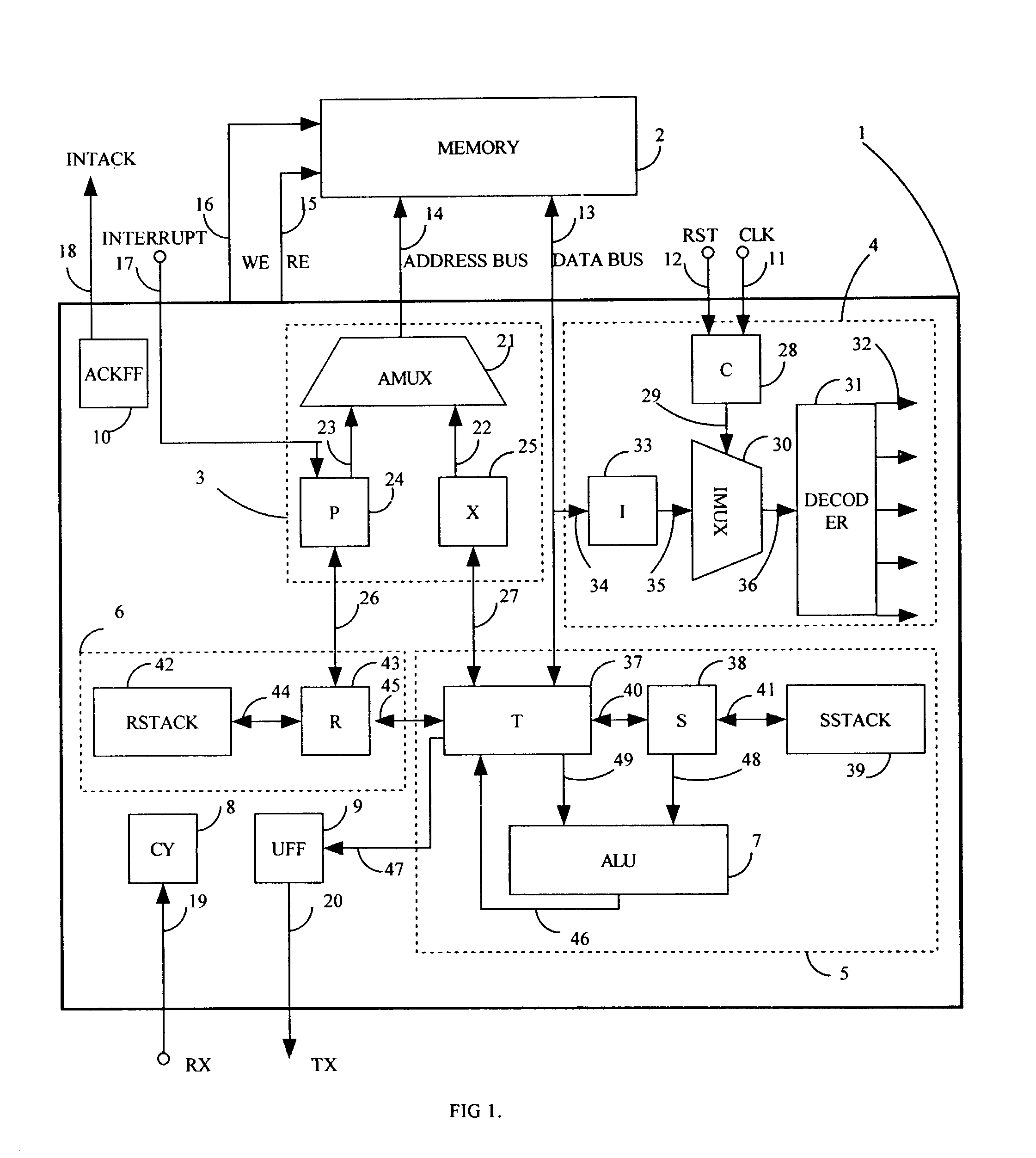
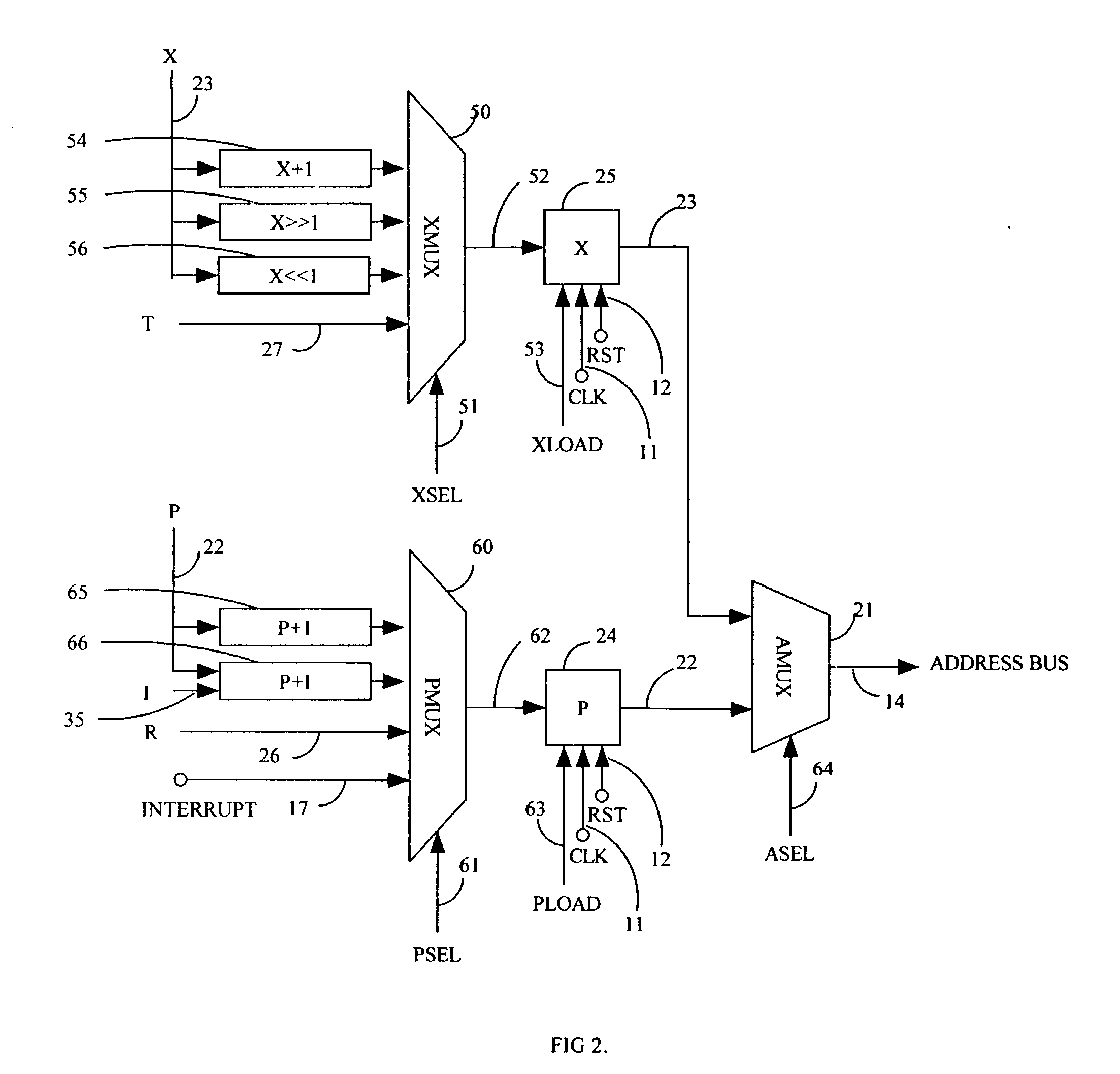
Scaleable microprocessor architecture
InactiveUS20030212878A1Executed quickly and reliablyGeneral purpose stored program computerNext instruction address formationArray data structureCode density
A scaleable microprocessor architecture has an efficient and orthogonal instruction set of 20 basic instructions, and a scaleable program word size from 15 bits up, including but not limited to 16, 24, 32, and 64 bits. As many instructions are packed into a single program word as allowed by the size of a program word. An integral return stack is used for nested subroutine calls and returns. An integral data stack is also used to pass parameters among nested subroutines. The simplified instruction set and the dual stack architecture make it possible to execute all instructions in a single clock cycle from a single phase master clock. Additional instructions can be added to facilitate accessing arrays in memory, for multiplication and division of integers, for real time interrupts, and to support an UART I / O device. This scaleable microprocessor architecture greatly increases code density and processing speed while decreasing significantly silicon area and power consumption. It is most suitable to serve as microprocessor cores in System-on-a-Chip (SOC) integrated circuits.
Owner:TING CHEN HANSON
Digital signal processor computation core with pipeline having memory access stages and multiply accumulate stages positioned for efficient operation
InactiveUS6859872B1High code storage densityEfficient digital signalRegister arrangementsDigital computer detailsMicrocontrollerFinite impulse response
A computation core includes a computation block, an addressing block and an instruction sequencer, which are coupled to a memory through a memory interface. The computation block includes a register file and dual execution units. The execution units include features for enhanced performance in executing digital signal computations. The computation core is configured for executing digital signal processor instructions and microcontroller instructions, while achieving efficient digital signal processor computation and high code density. A finite impulse response filter algorithm achieves high performance on the dual execution units.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Time interpolation flash adc having automatic feedback calibration
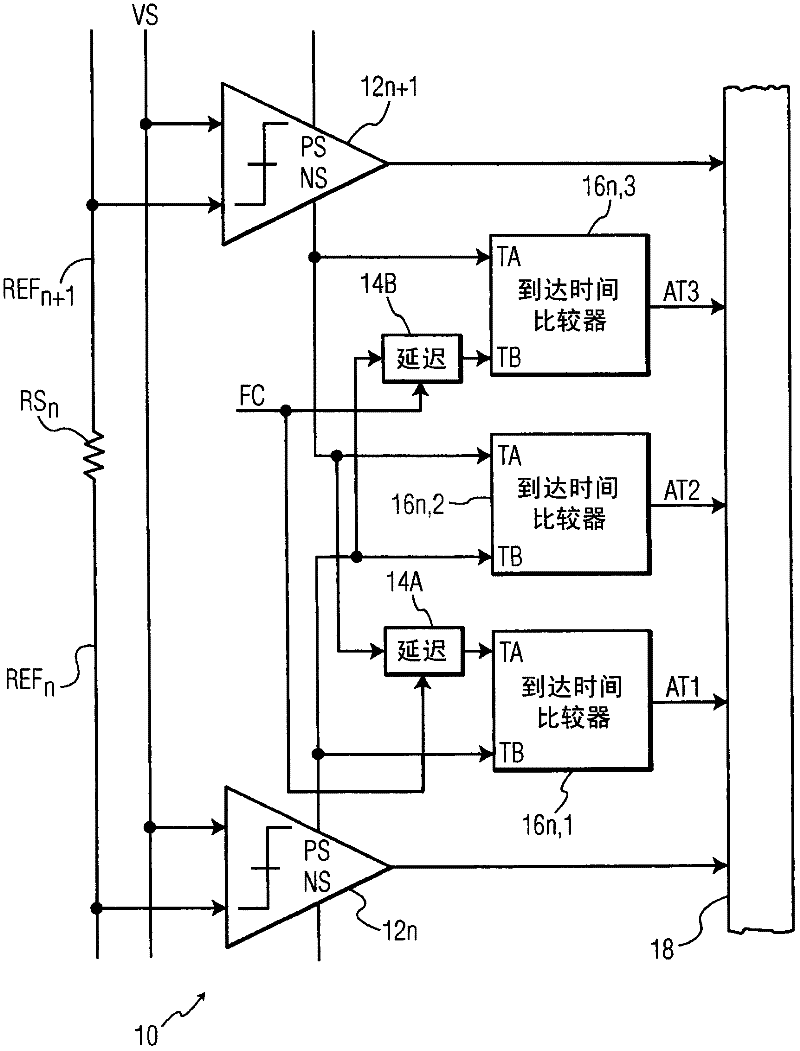
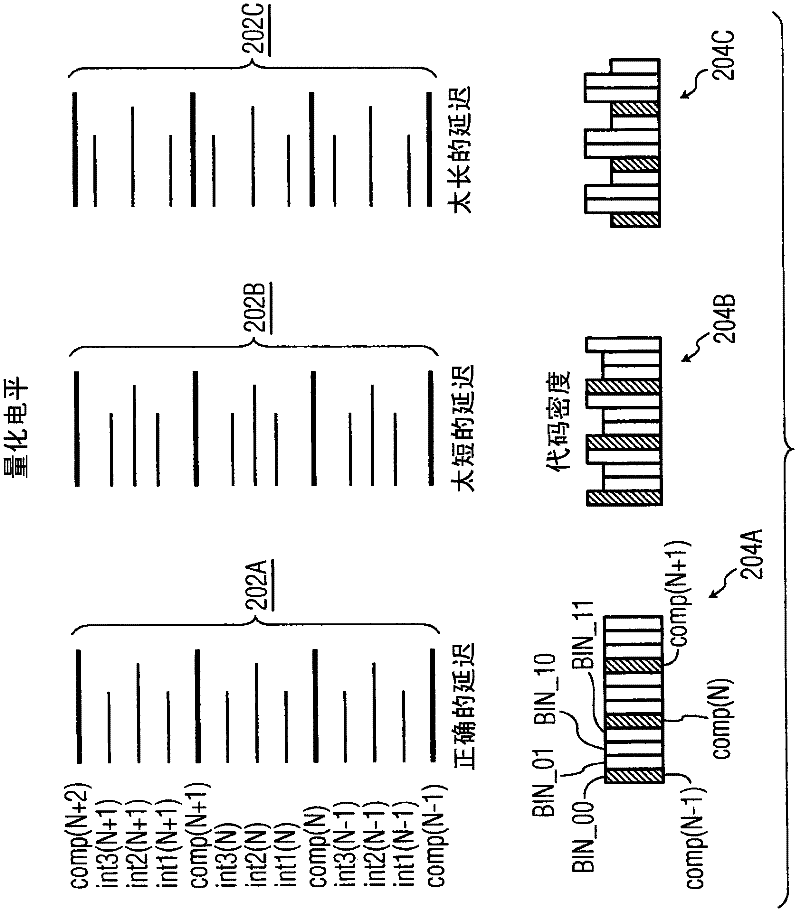
InactiveCN102210104AHigh resolution bitsAchieve resolutionAnalogue-digital convertersLeast significant bitArrival time
An input signal is compared to 2N - 1 reference voltages to generate 2N - 1 corresponding binary valued comparison signals, delaying at least one of the comparison signals by a variable delay and detecting a difference in arrival time between the delayed signal and another comparison signal. A time interpolation signal encoding a plurality of bins within a least significant bit quantization level is generated, based on the detected difference in arrival time. An M-bit output data is generated based on the comparison signals and the time interpolation signal. A non-uniformity of a code density of the M-bit output data is detected, and based on the detecting the delaying is varied.
Owner:NXP BV
Image coding/decoding method, image coding apparatus and image decoding apparatus for obtaining decoded images having small distortion in DCT based standard coding/decoding
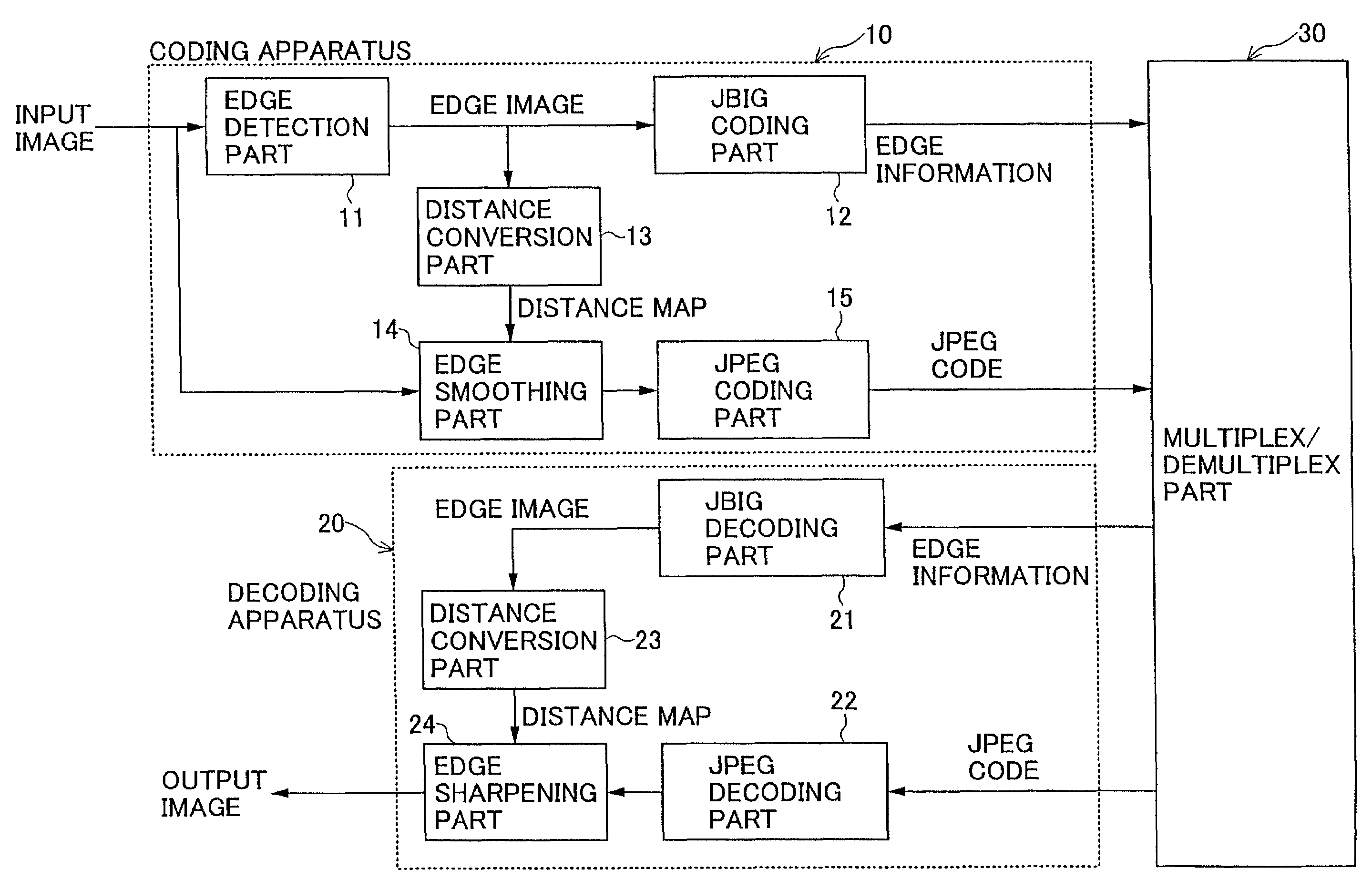
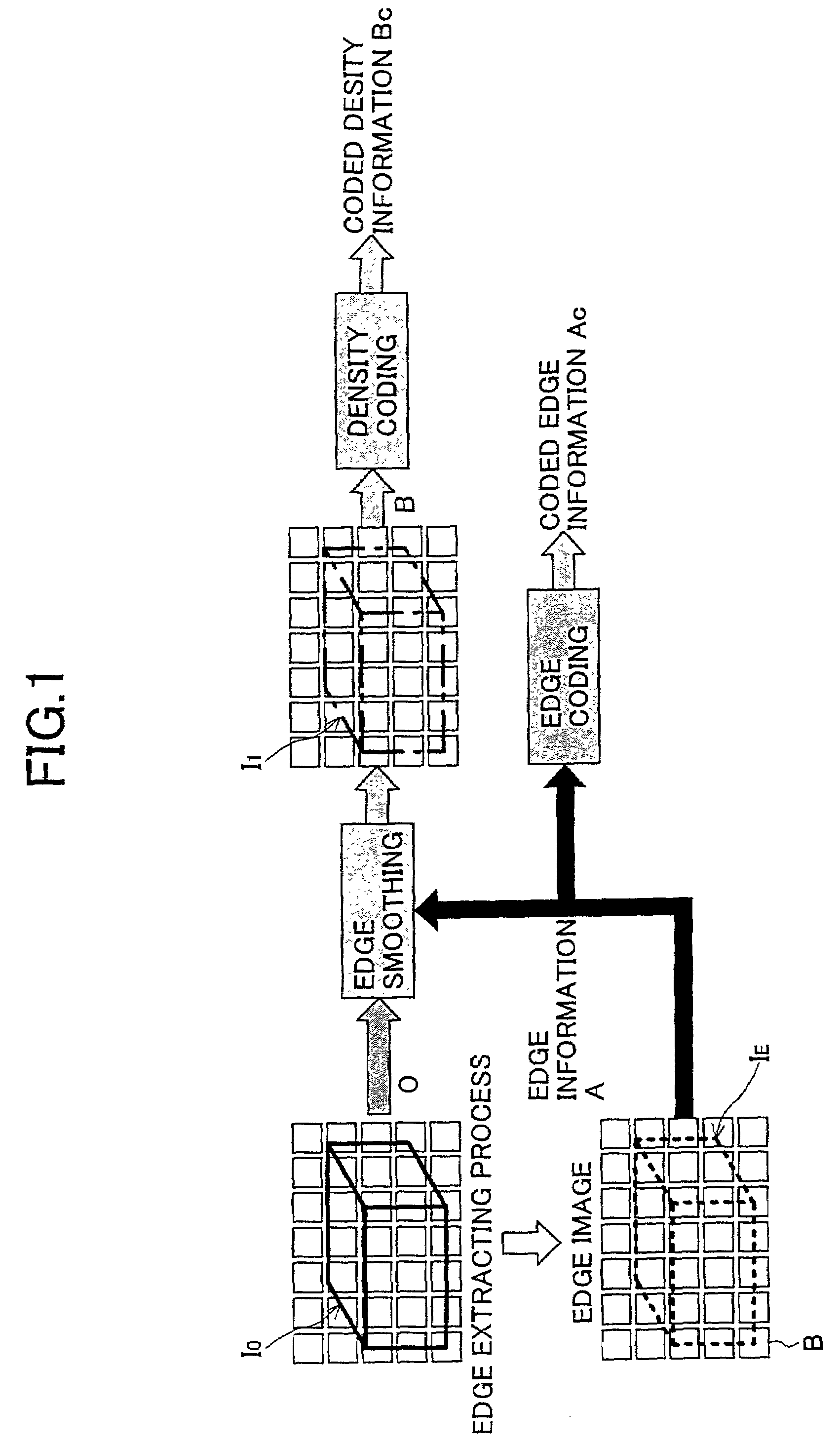
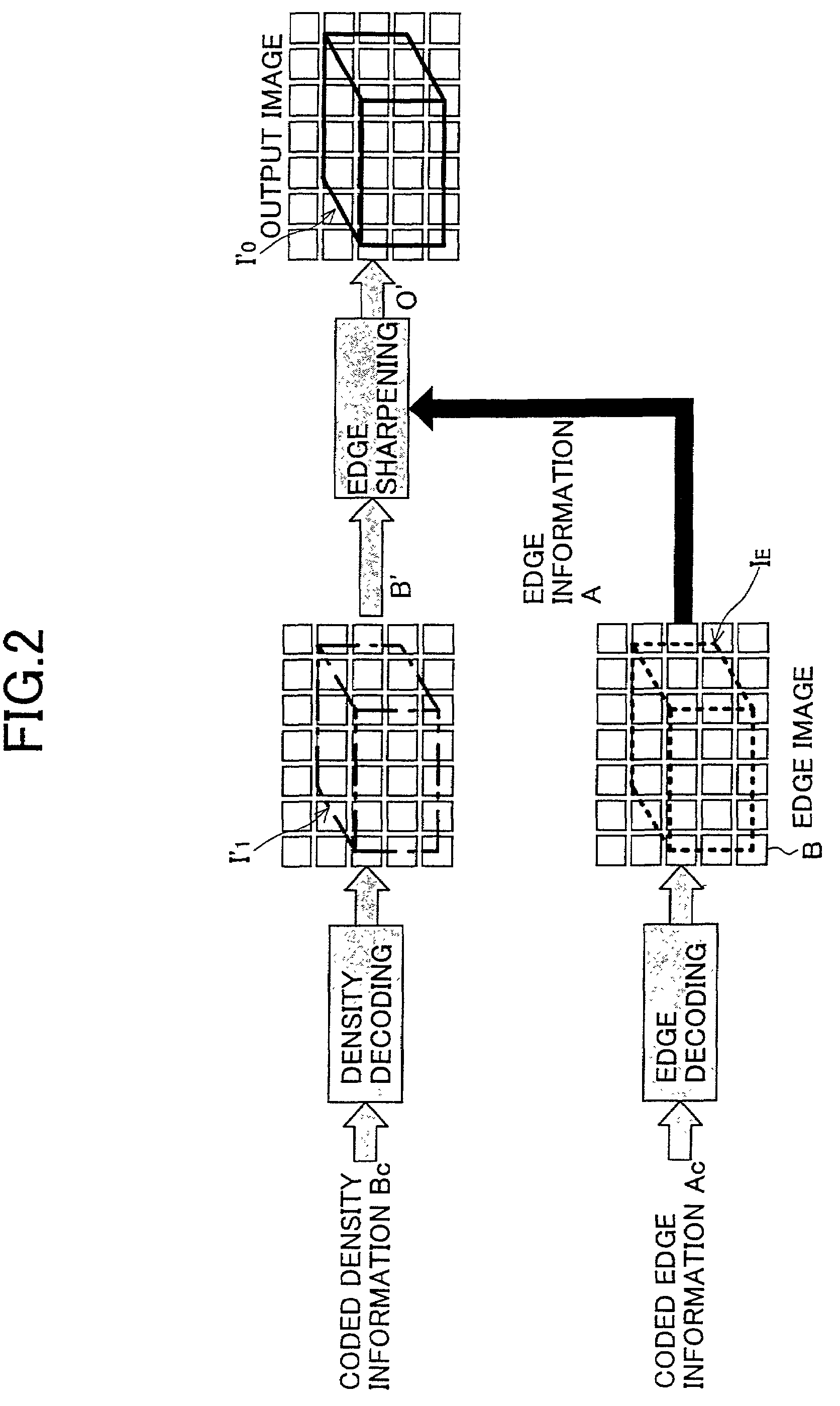
InactiveUS7532762B2Small distortionImage enhancementImage analysisDecoding methodsEncoding algorithm
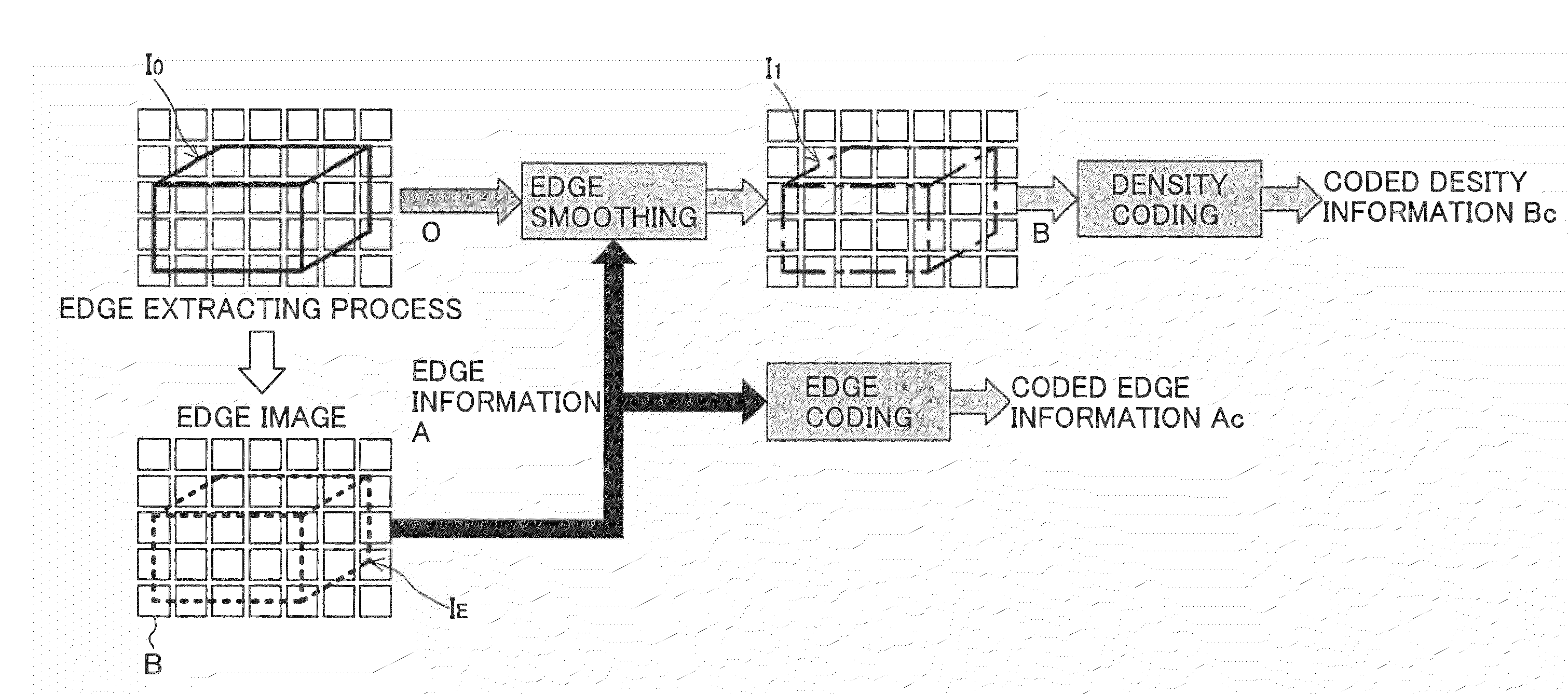
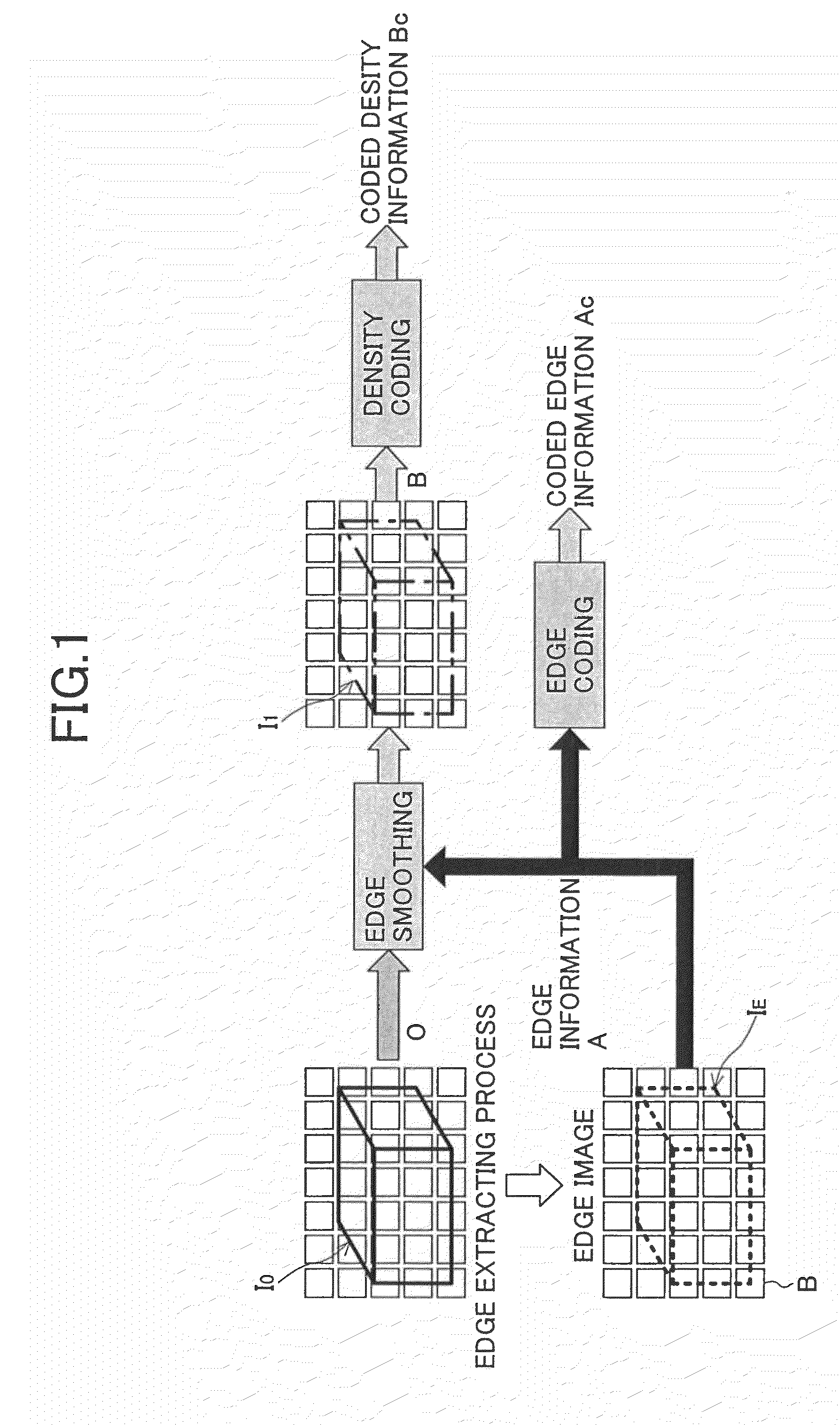
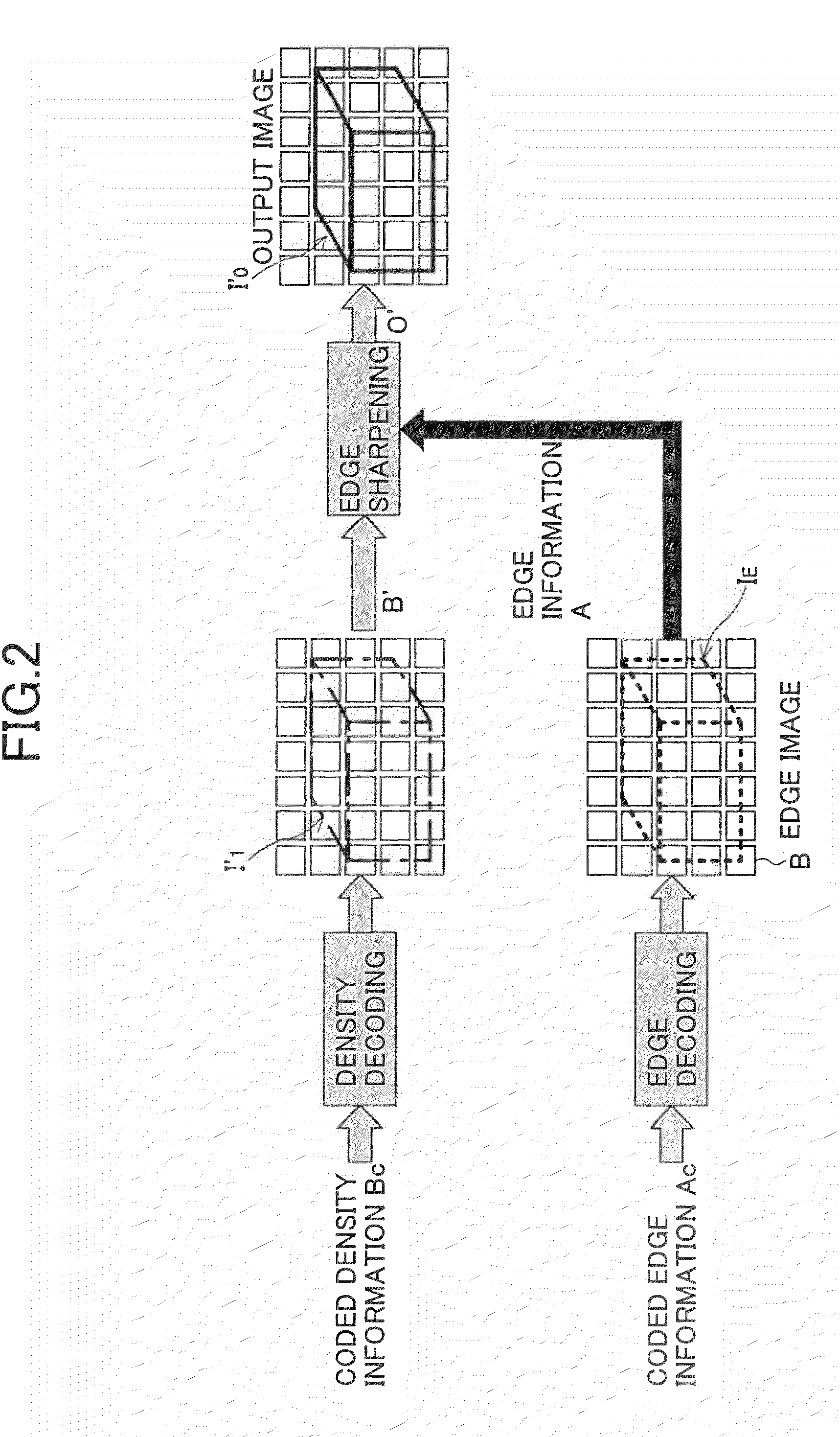
An image coding method is provided, in which the method includes the steps of: extracting edge information which represents an edge part of an original image; obtaining density information of an edge smoothed image from the original image by smoothing the edge part; obtaining coded edge information by coding the edge information according to a first coding algorithm; obtaining coded density information by coding the density information of the edge smoothed image according to a second coding algorithm; and sending the coded edge information and the coded density information as coded information to an image decoding apparatus.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Method and system for efficient range and stride checking
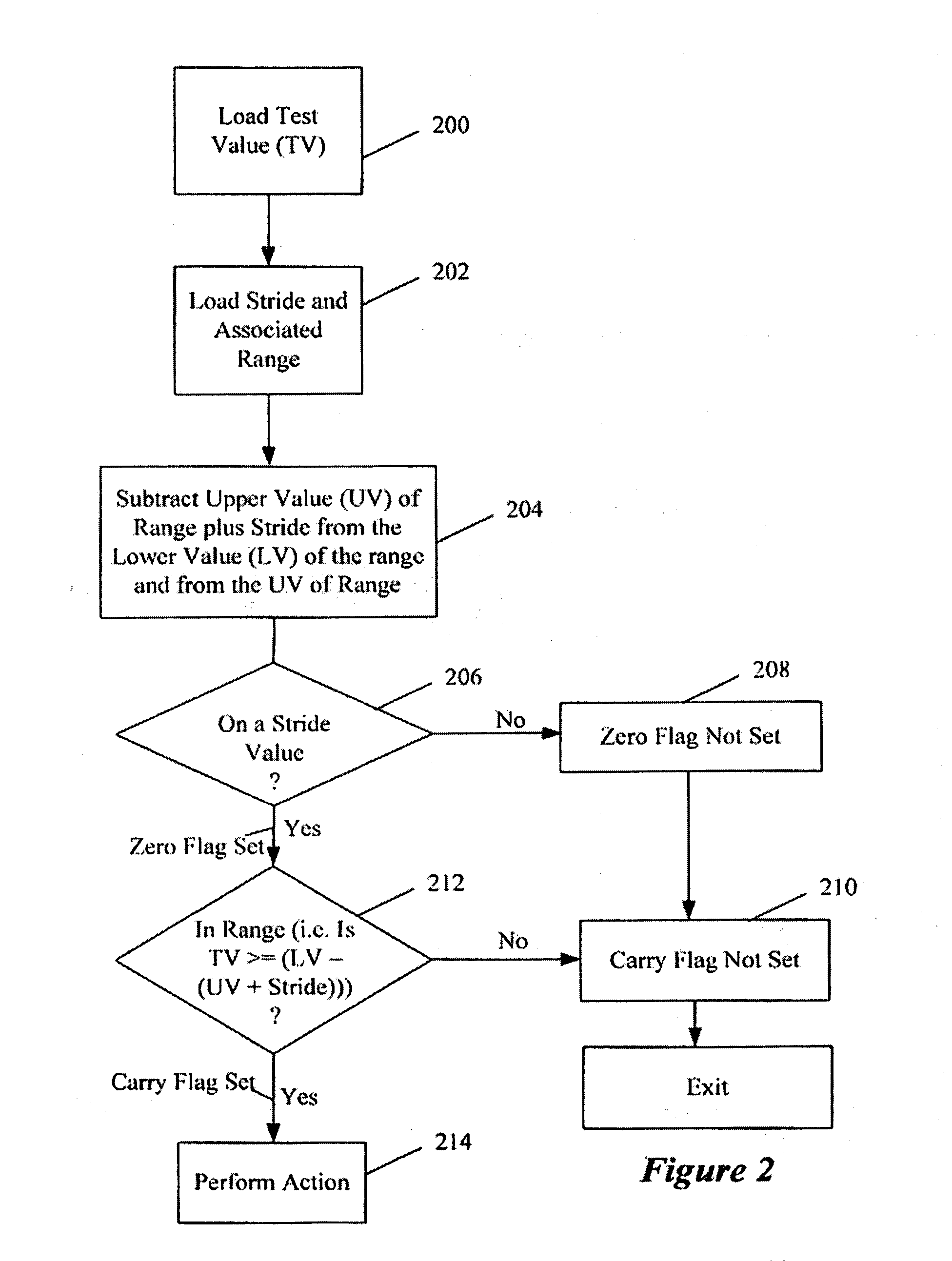
Embodiments of a method and system for compiling code, such as program-generated code, are disclosed herein. The method and system efficiently encode combined range and stride checks. For example, the method and system are operable to encode combined range and stride checks as they occur in a translation of switch statements. The method and system can generate code to perform the range and stride check, and to branch to the case body, if the range and stride checks are successful. The various embodiments may operate to provide an efficient code transformation, better code density, and processing performance. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method for allocating registers for mixed length instruction set
ActiveCN102360280AIncrease instruction densityStrong reliabilityMemory systemsMachine execution arrangementsRegister allocationProcessor register
The invention discloses a method for allocating registers for a mixed length instruction set. By less revising the conventional graph coloring register allocation method, namely fully utilizing the characteristics of a mixed coding instruction set, codes with higher code density are generated. The method has the characteristics of simplicity, practicability and high in reliability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Bar gauge by grading coding
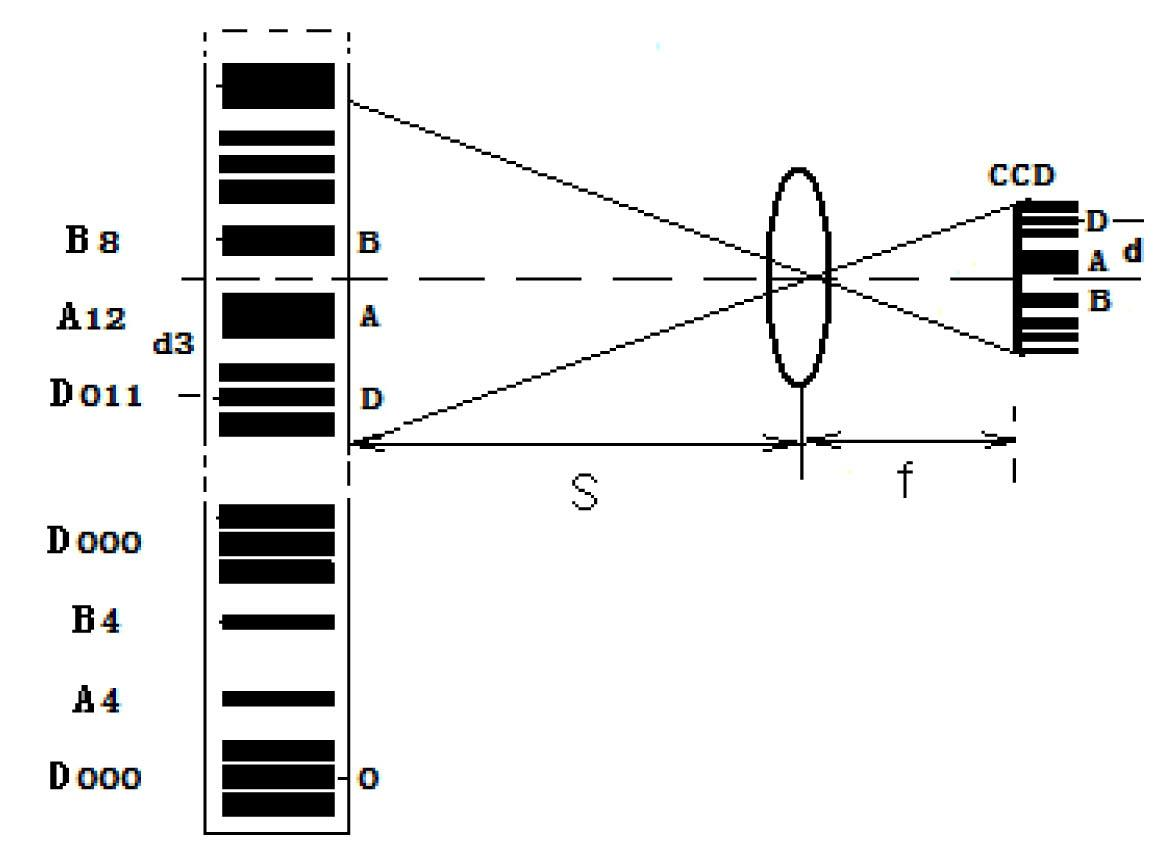
InactiveCN102494669AReduce the difficulty of identificationLow barcode densityHeight/levelling measurementMeasuring instrumentBarcode
A bar gauge by grading coding relates to the technical field of measuring instrument. According to the invention, the technical problem of high difficulty of present bar gauge identification is solved. Scale of the bar gauge provided by the invention is equally divided into a plurality of code segments. Each code segment is divided into a plurality of code words. Each code word is equally dividedinto D code element, A code element and B code element. The distances between centers of adjacent code elements are consistent. The D code element has a plurality of code bars, which are centrosymmetrically distributed to form a code segment counter. There is only one code bar at the center of the A code element and the B code element. The A code element and the B code element form a code word counter. The center line of the D code element is the start point of code words as well as the stop point of the front code word. There are a plurality of code bars in the D code element. Code segment counter values in the same code segment are consistent and convenient to identify. The bar gauge provided by the invention is characterized by few combinations of code elements and low bar code density. Wide-range levelling can be realized by using few combinations of code elements. Good conditions are created for long-distance measurement of barcode positioning, and measurement reliability is raised.
Owner:谢佑坤 +3
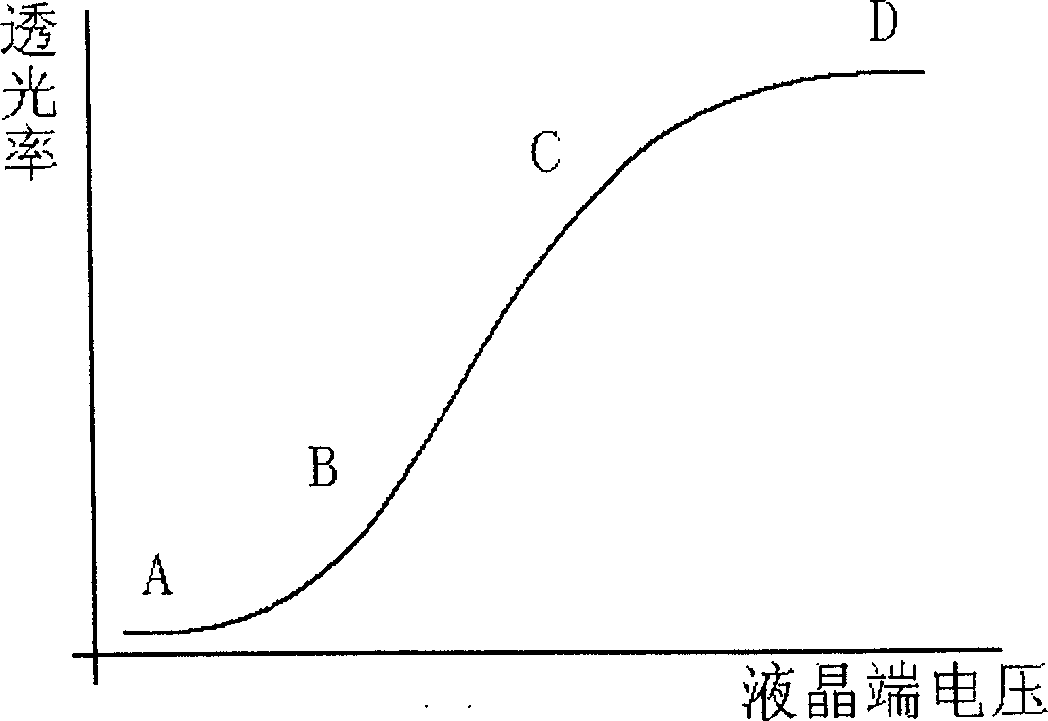
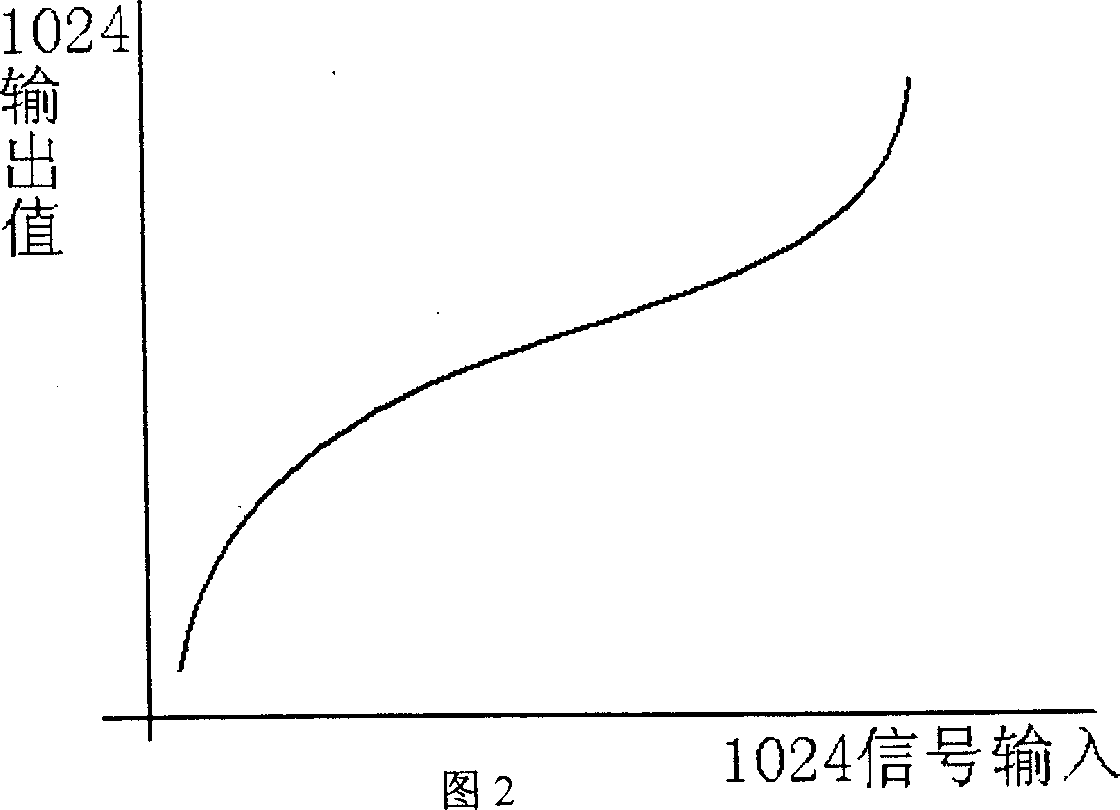
Method for decreasing LCD display distortion
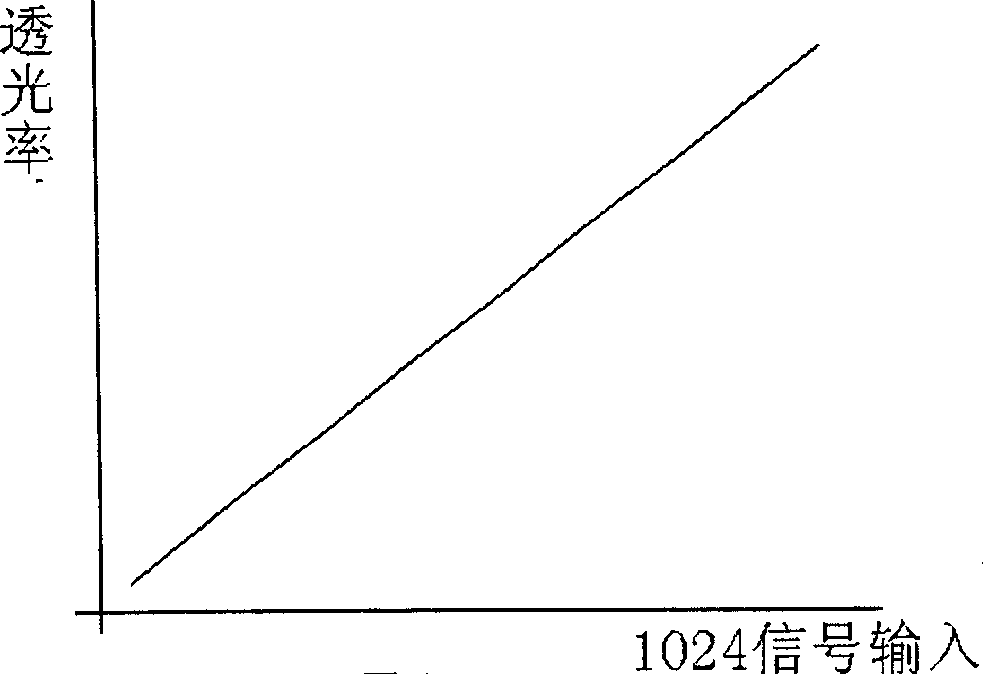
This invention relates to a method for decreasing LCD display distortion. Wherein, changing the forced voltage on liquid crystal ends to control the LCD; taking gamma conversion to the image signal by the front circuit to provide control voltage, controlling the conversion to set lower / higher code density on slow / serious varying interval respectively, and expressing the bit length from n into n+2; applying one DA circuit of n+2 bit on back of the gamma conversion. This invention saves much cost with almost same display effect.
Owner:PANDA ELECTRONICS GROUP +1
Image coding/decoding method, image coding apparatus and image decoding apparatus
An image coding method is provided, in which the method includes the steps of: extracting edge information which represents an edge part of an original image; obtaining density information of an edge smoothed image from the original image by smoothing the edge part; obtaining coded edge information by coding the edge information according to a first coding algorithm; obtaining coded density information by coding the density information of the edge smoothed image according to a second coding algorithm; and sending the coded edge information and the coded density information as coded information to an image decoding apparatus.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Binary translation stack operation accelerated processing method and processor thereof
ActiveCN104461676AImprove performanceIncrease flexibilitySoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationLoad instructionProcessor register
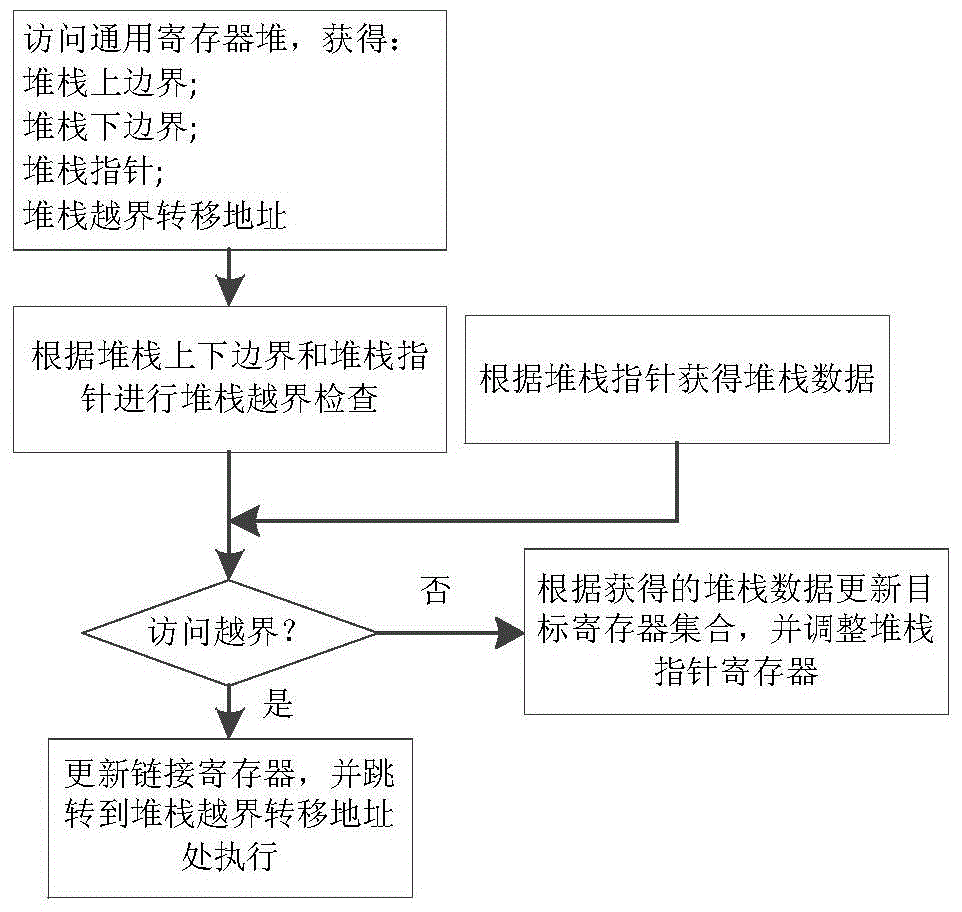
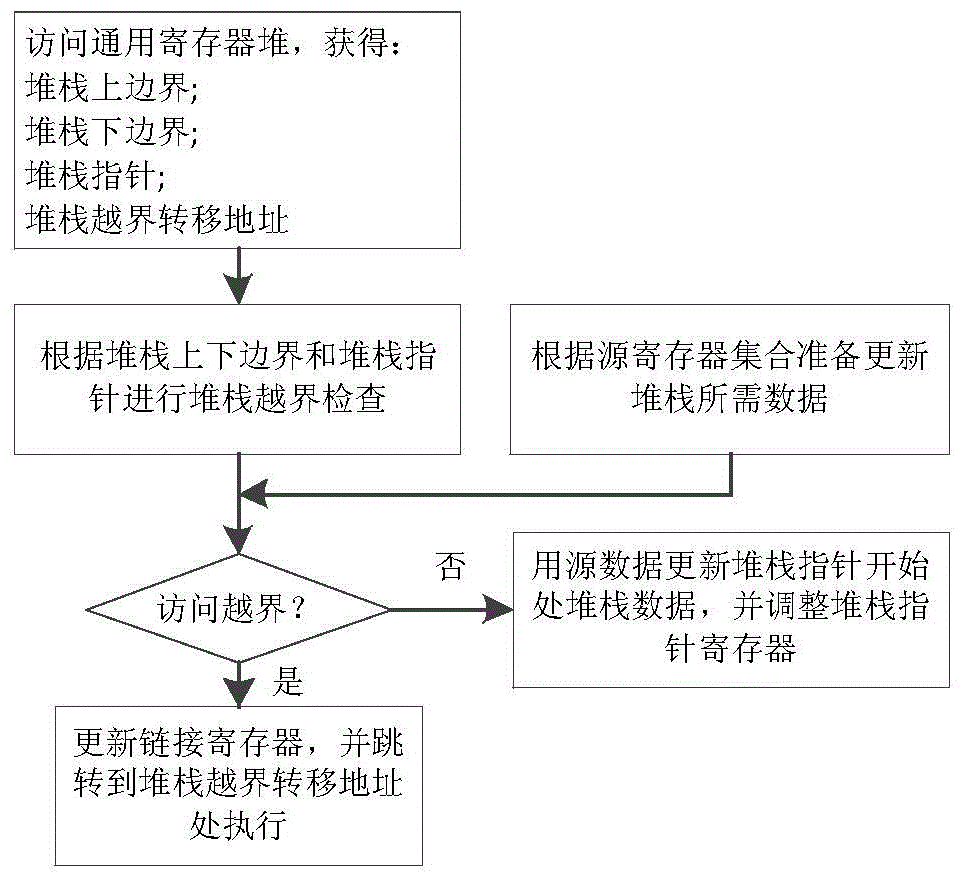
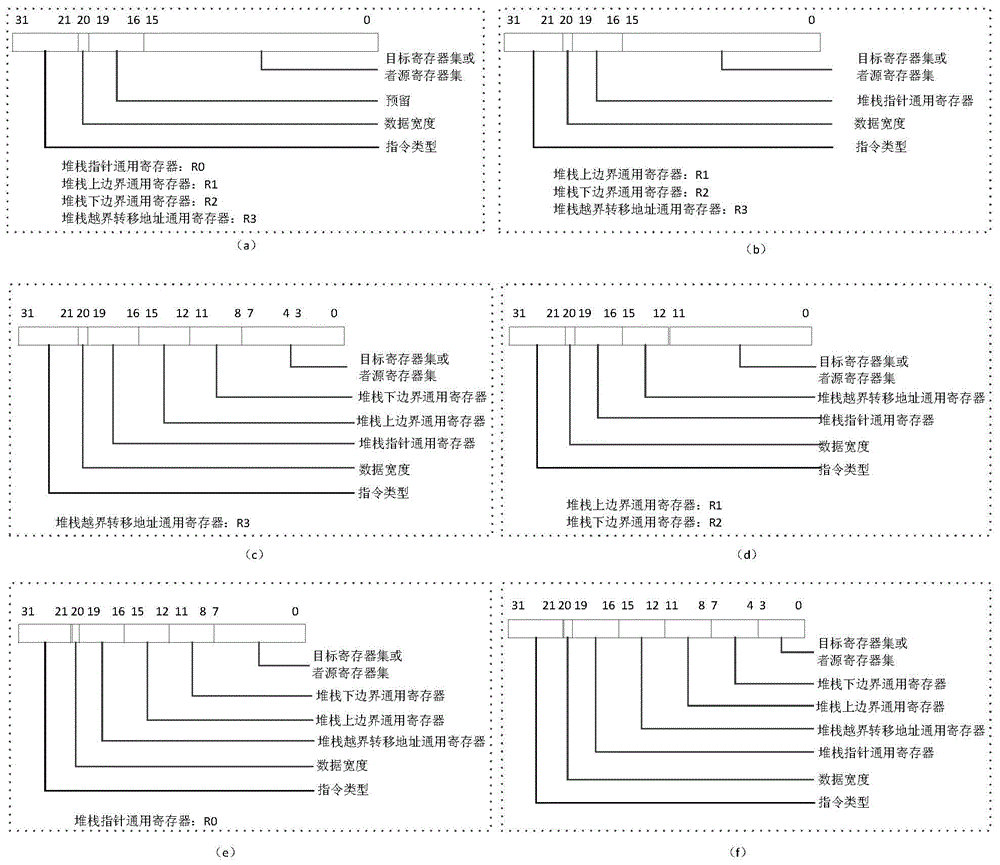
A binary translation stack operation accelerated processing method includes a stack data loading instruction and a stack data storage instruction, the two instructions finish reading, writing, modification of a stack pointer, inspection of stack boarder crossing and processing of stack boarder crossing on the basis of a stack boarder universal register, a stack pointer universal register, a stack boarder crossing transfer address universal register, a source universal register set and a target universal register set, and finish updating of the state of a processor according to whether stack access crosses the boarder or not. The invention provides the binary translation stack operation accelerated processor. On the situation that it is guaranteed that hardware resources are unchanged, binary translation system performance and code density are greatly improved.
Owner:C SKY MICROSYST CO LTD
Device and method for generating floating point constant
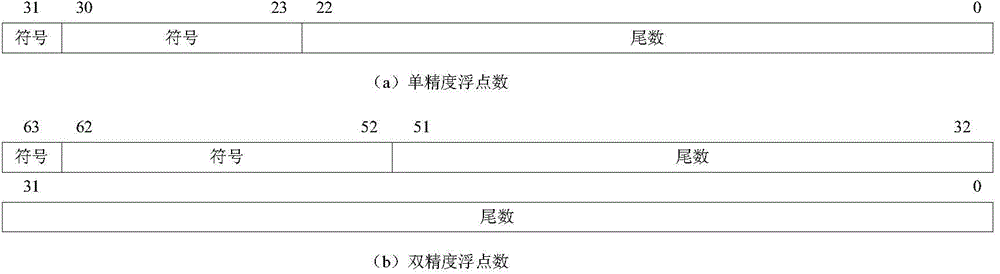
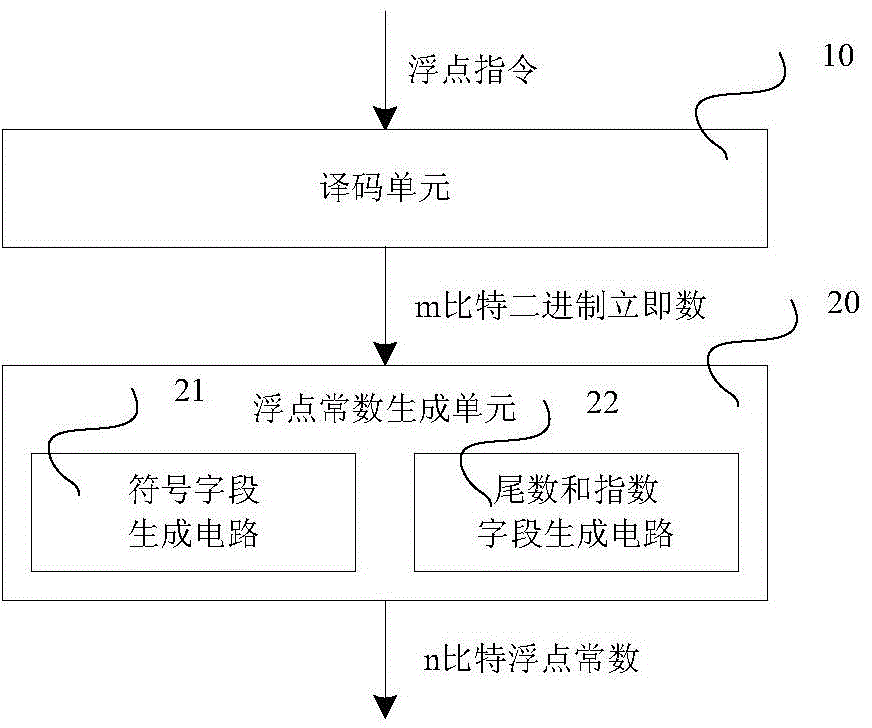
InactiveCN104572018ACapable of generatingImprove execution efficiencyMachine execution arrangementsParallel computingCode density
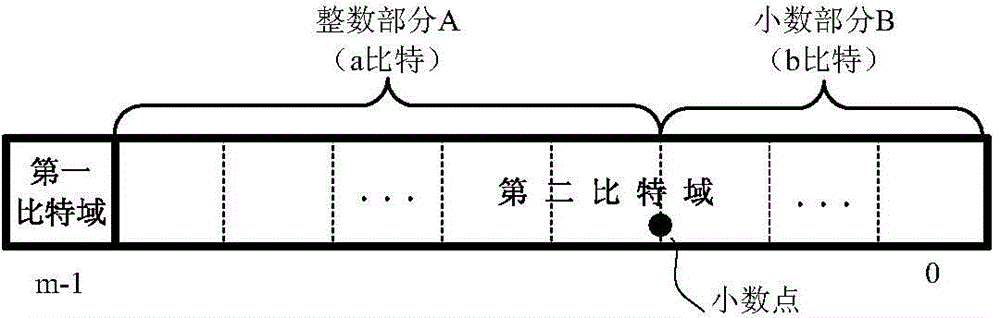
A device for generating a floating point constant comprises a decoding unit and a floating point constant generating unit. The decoding unit is used for decoding a floating point instruction to generate an instruction indication symbol and an m-bit binary immediate value. The floating point constant generating unit is used for receiving information of the decoding unit to perform logic operation on the m-bit binary immediate value, wherein the m-bit binary immediate value comprises two domains, namely a 1-bit first bit domain and a (m-1)-bit second bit domain, the first bit domain in the m-bit binary immediate value is extracted to generate a symbol field of the floating point constant, the second bit domain in the m-bit binary immediate value is extracted and serves as a fixed-point number with a fixed scaling position to be processed to generate a mantissa field and an index field of the floating point constant, the symbol field, the index field and the mantissa field are packaged into the n-bit floating point constant jointly, and the n is an integer. The invention further discloses a method for generating the floating point constant. By the device and the method, execution efficiency is improved effectively, and code density is reduced.
Owner:C SKY MICROSYST CO LTD
No-chip tag structure
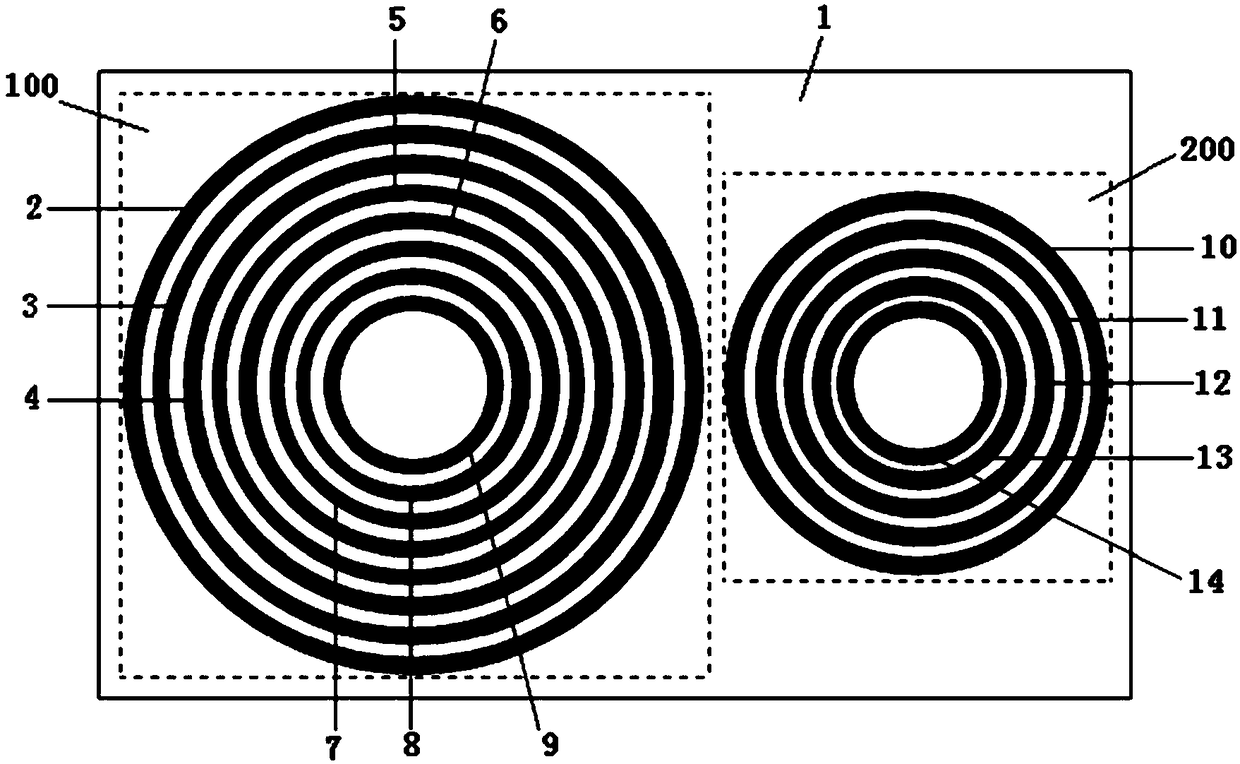
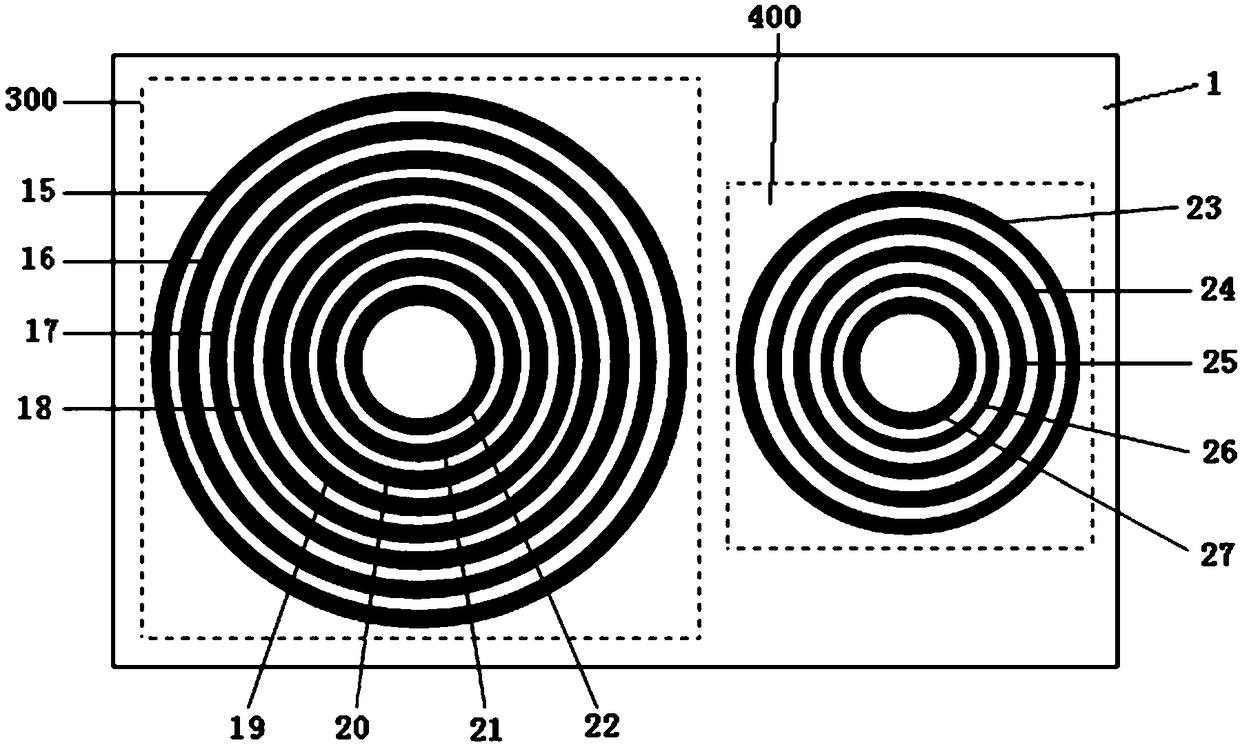
InactiveCN108629398ALow costLarge encoding capacityRecord carriers used with machinesDielectric plateMiniaturization
The invention discloses a no-chip tag structure, and the structure comprises a dielectric plate, wherein the surface of the dielectric plate is provided with at least one multi-ring nested paster unit. The multi-ring nested paster unit comprises a plurality of concentric annular pasters with different internal diameters and different external diameters. The structure provided by the invention aimsat the problems existing in the prior art, and the surface of the dielectric plate is flexibly provided with the multi-ring nested paster unit. The structure is small in size, is low in cost, is large in code capacity, and is high in code density.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Methods and apparatus for indirect compound VLIW execution using operand address mapping techniques
InactiveUS7272700B1Easy to handleDelay minimizationInstruction analysisRuntime instruction translationAddress mappingCode density
An VLIW instruction mechanism is described which accesses multiple slot instructions for execution to achieve high levels of selectable parallelism and to make improvements to code density. To this end, the VLIW instruction mechanism includes a short instruction word (SIW) register for holding an SIW. The SIW includes an indication of a slot instruction to execute and a dynamic slot instruction operand which is used by the slot instruction to execute. Further, the VLIW instruction mechanism includes a register for holding slot instructions which are retrieved from VLIW memory. The retrieved slot instructions include a stored operand which is used when executing the retrieved slot instruction. The VLIW instruction mechanism further includes a controller and an execution unit. The controller selects which of the operands are utilized with the retrieved slot instructions. The execution unit executes the retrieved slot instruction with the selected operand.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Method for detecting and recognizing long-range high-density visual markers
ActiveUS20190294936A1Prevents effect of degradationSolve the real problemGeometric image transformationTexturing/coloringBase codeHigh density
The proposal relates to a complete system of long-range, high-density visual markers (marker design and detection method). In the design, a conventional location system for the long-range markers is used. The proposal therefore focuses on a system for coding information, which in this case is a colour-based code having four states, duplicating the code density with respect to conventional black-and-white systems. Moreover, the detection method requires very few computational resources, making it very efficient and especially suitable for mobile devices. To a great extent, the success of the technique lies in the methods proposed for the treatment of the colour.
Owner:UNIV DE ALICANTE
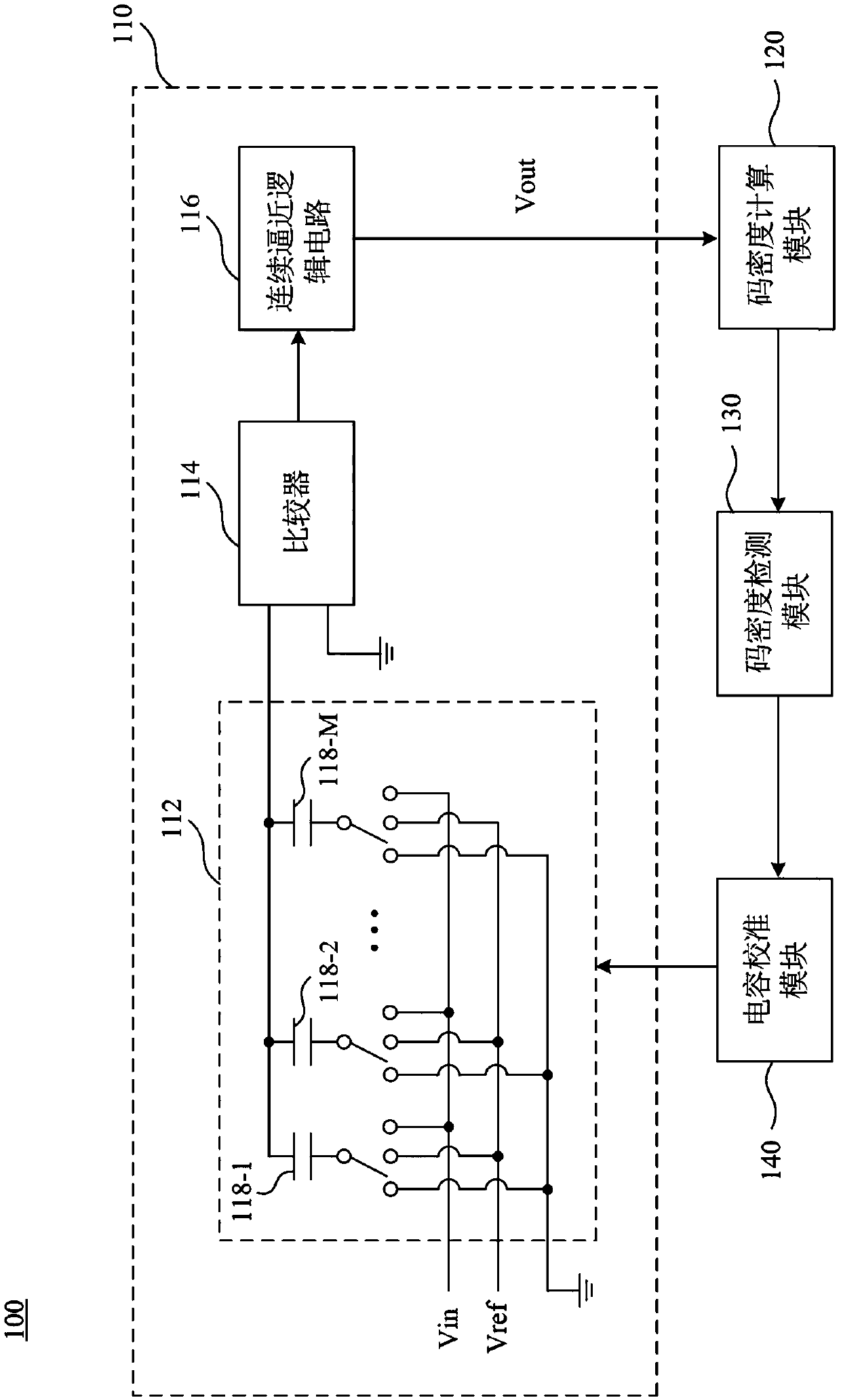
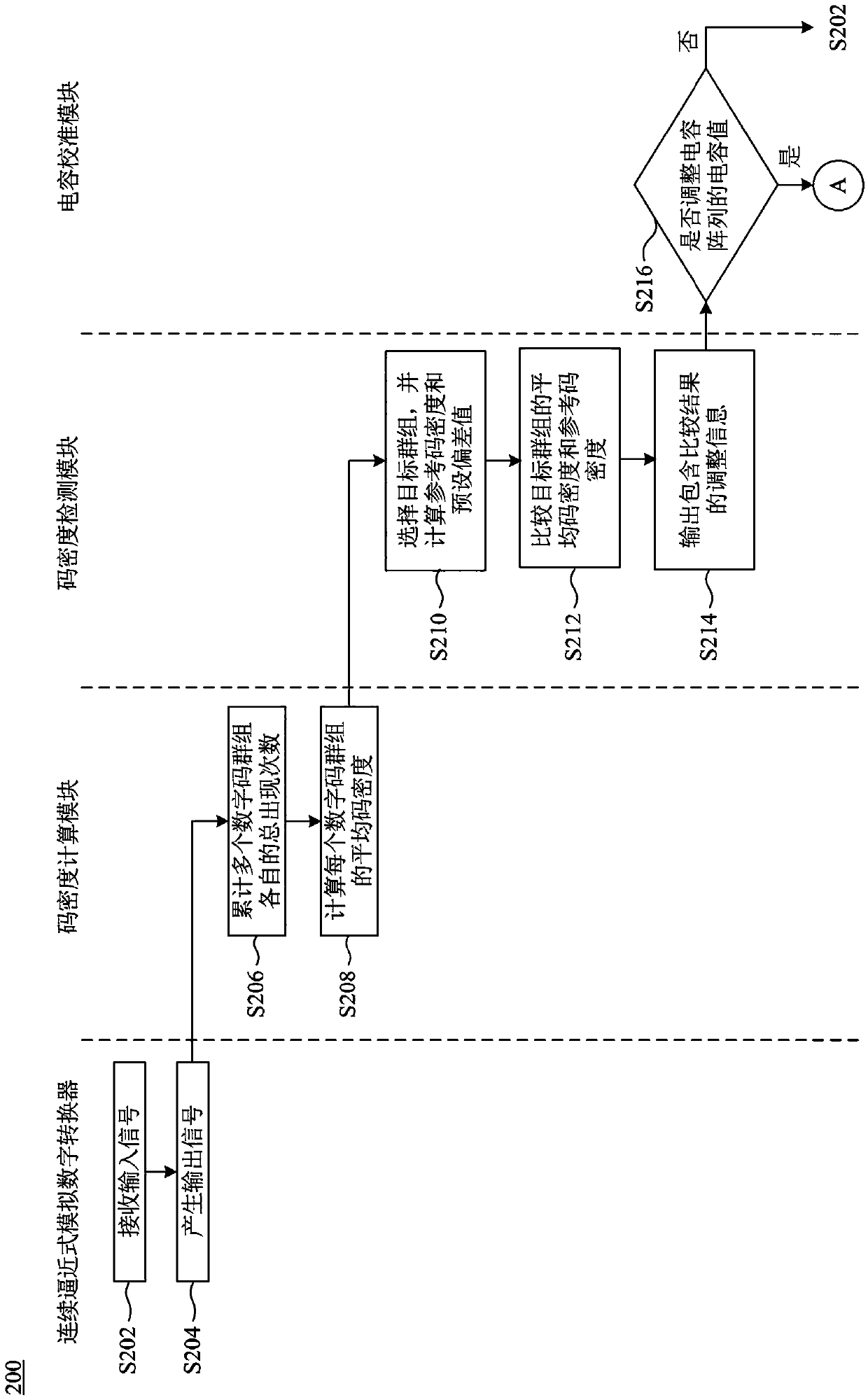
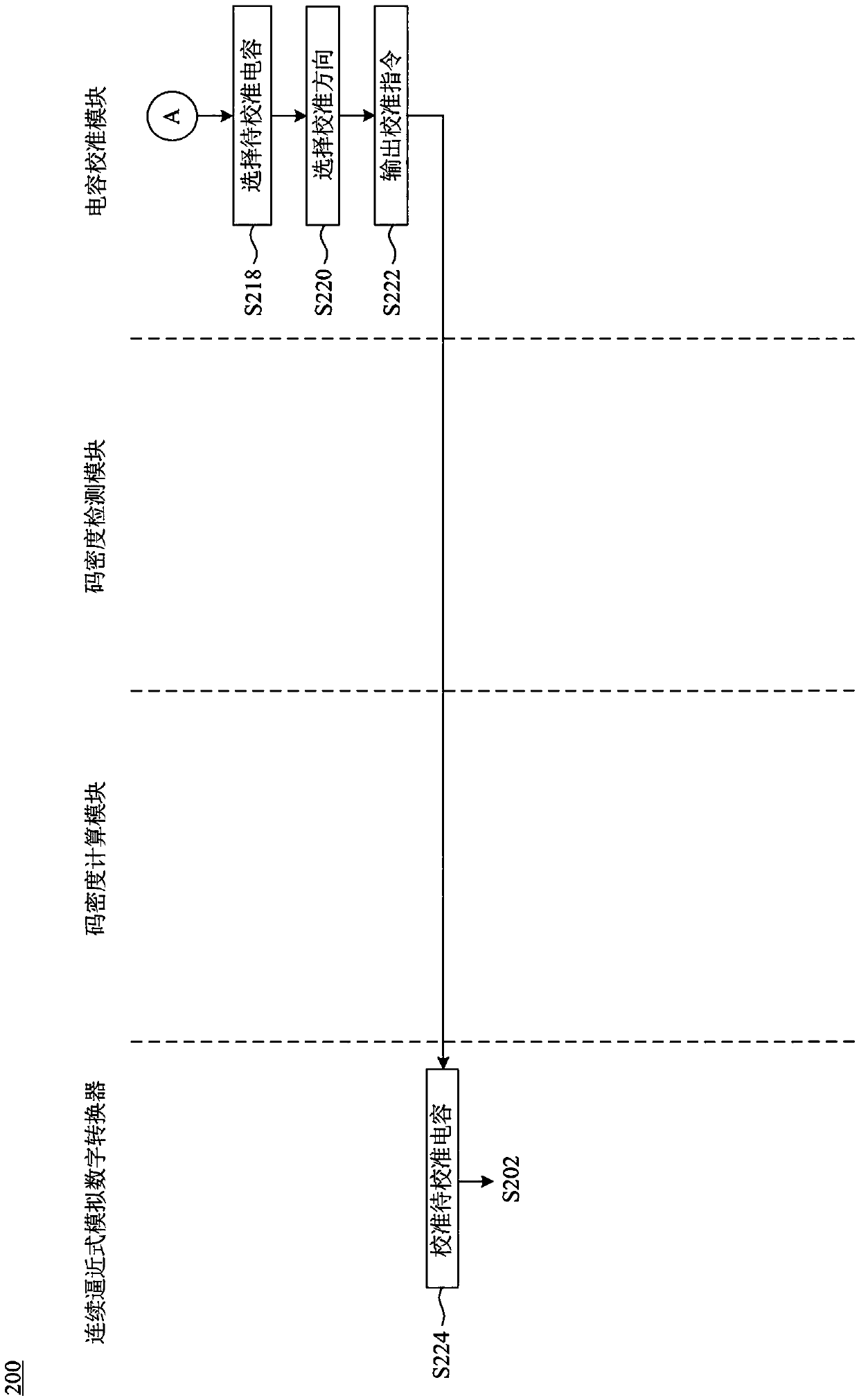
Calibration method and calibration system
ActiveCN111064468AReal-time calibrationElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingCapacitanceConverters
The invention relates to a calibration method and a calibration system. The calibration method is suitable for a successive approximation analog-digital converter, and the successive approximation analog-digital converter comprises a capacitor array. The calibration method comprises the following steps: inputting an input signal into the analog-digital converter, wherein the analog-digital converter generates an output signal according to the input signal, and the output signal comprises a plurality of specific digital codes; calculating respective average code densities of a plurality of digital code groups in the plurality of specific digital codes, wherein each digital code group comprises one or more specific digital codes in the plurality of specific digital codes; comparing the average code density of a first target group in the plurality of digital code groups with a first reference code density to generate a first comparison result; and calibrating the capacitance value of a first capacitor unit to be calibrated of the capacitor array according to the first comparison result. The calibration method can be used for calibrating the successive approximation analog-digital converter in real time.
Owner:GLOBAL UNICHIP CORPORATION +1
Instruction processing method and processor
PendingCN112269596ADoes not affect flexibilityDoes not affect efficiencyRegister arrangementsEnergy efficient computingMemory addressComputer architecture
The invention relates to an instruction processing method and a processor, and the method comprises the steps of dividing 16 universal registers equally into two groups, defining one group as an address register, and defining the other group as an integer register, wherein the address register is used for storing a memory address, and the integer register is used for storing integer data; when a specific instruction is parsed, respectively using 3bit operands for pointing to the address register or the integer register which is used as a source register or a target register. According to the present invention, on the basis of hardly influencing the flexibility and high efficiency of an instruction set, the bit number used by the instruction set can be reduced, so that the 16bits compressedinstruction set can accommodate more functions, the effect of using less 32-bit instructions or not using 32-bit instructions in a mixed manner is achieved, and the code density and the execution efficiency are further improved.
Owner:童先娥
Memory and memorizing method thereof
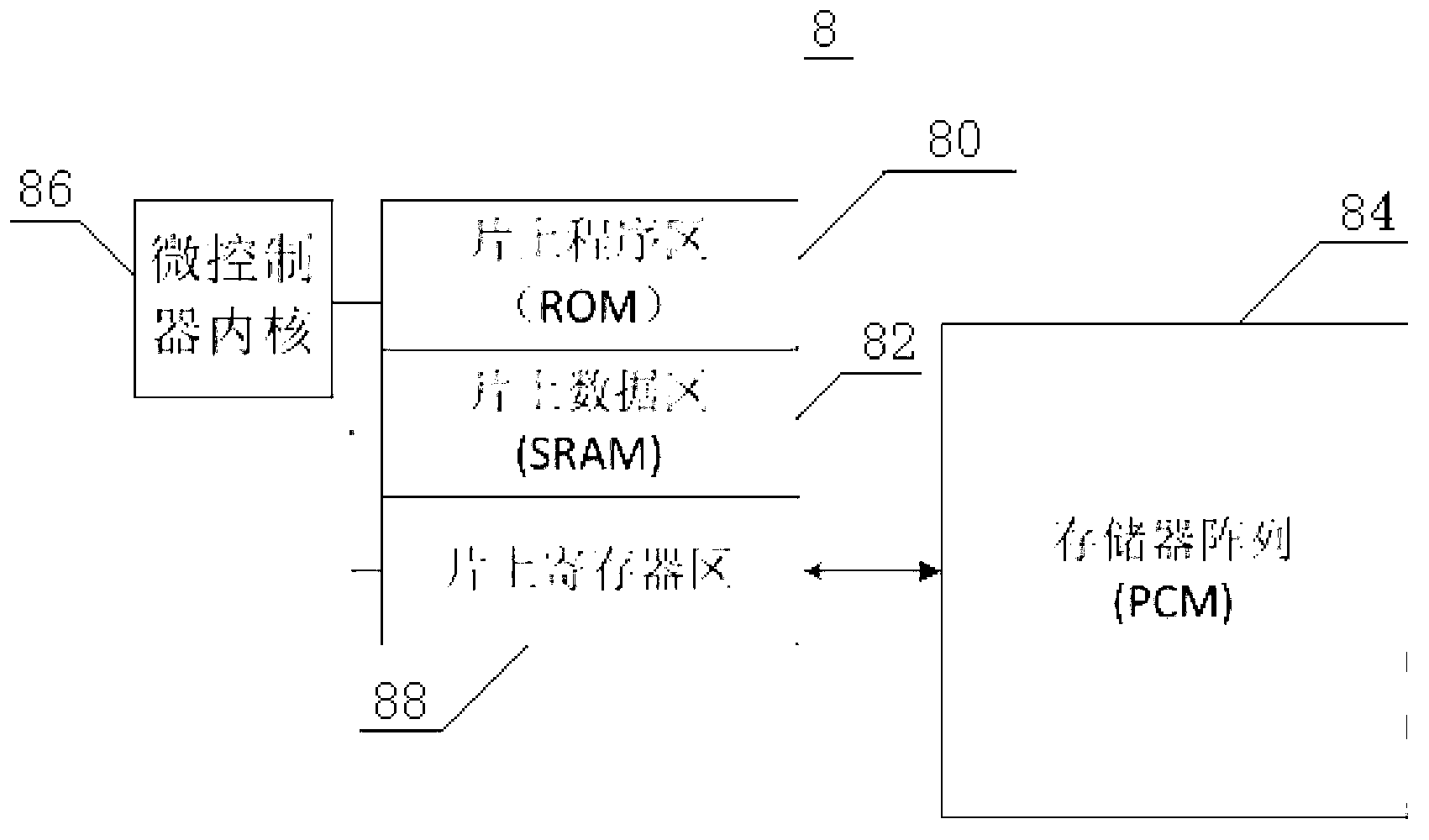
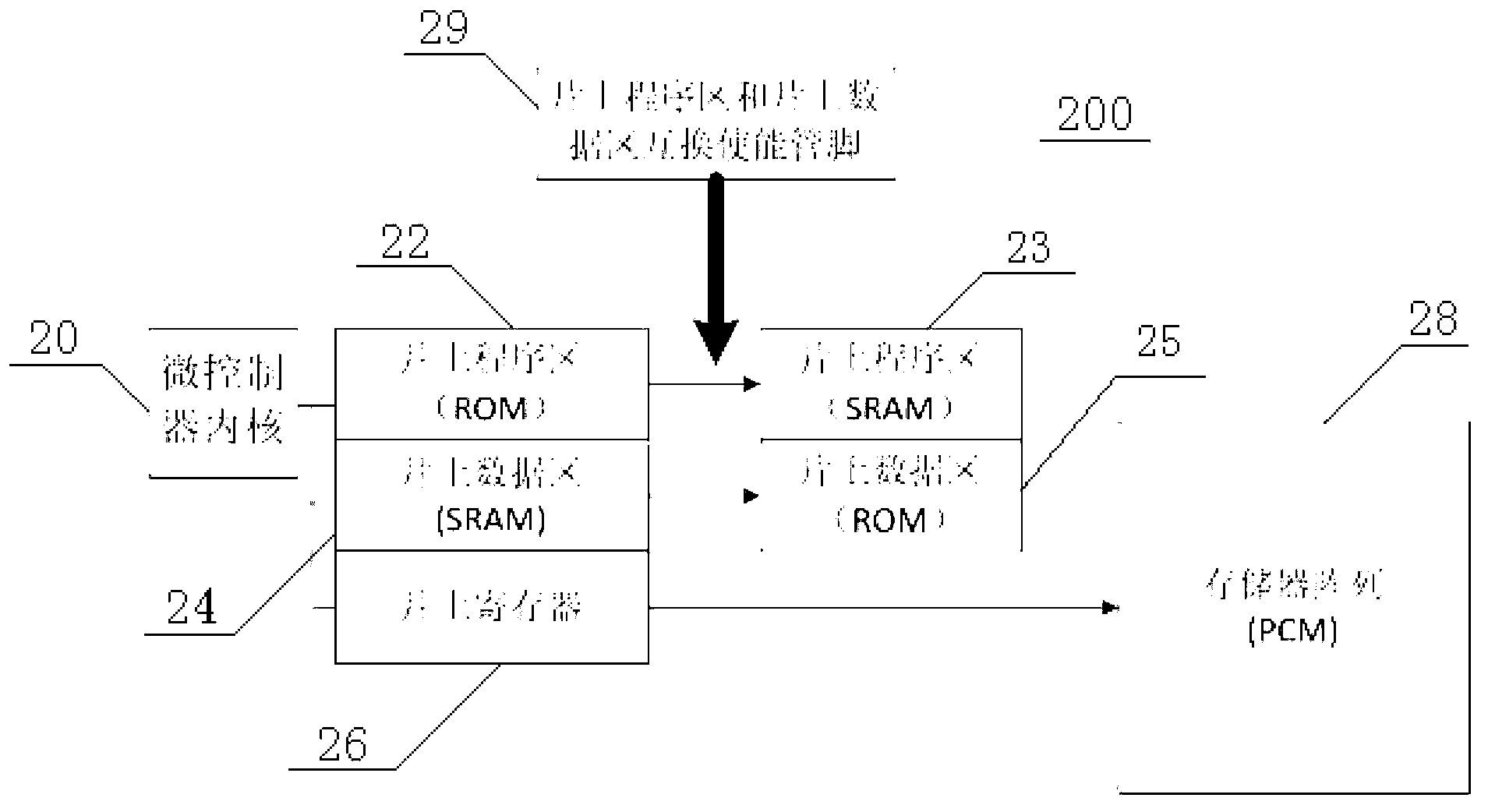
ActiveCN103021471AAvoid using effectsAvoiding the disadvantages of PCMStatic storageComputer moduleCode density
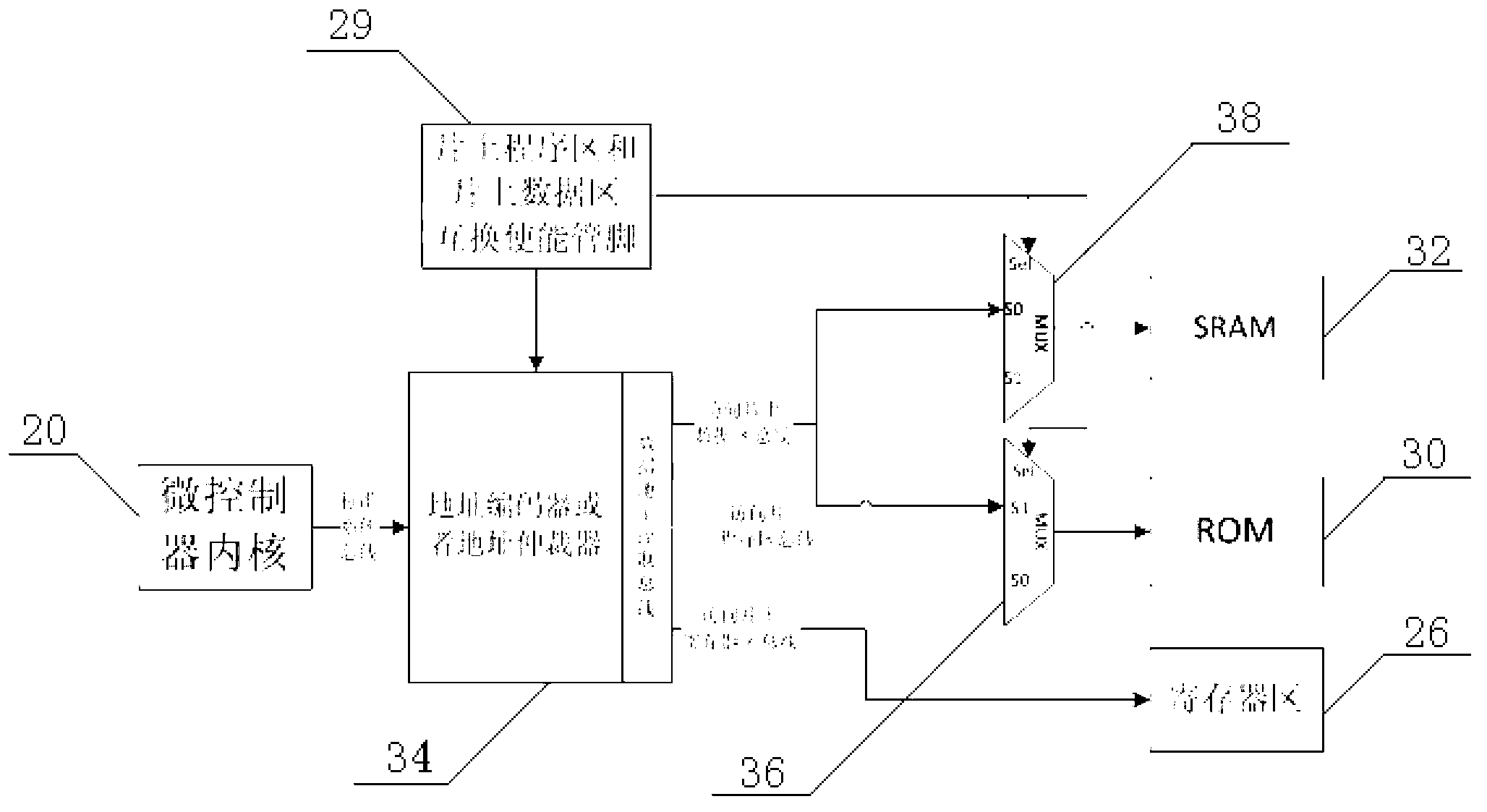
The invention discloses a memory which comprises an on-chip program area and an on-chip data area that are arranged for a normal working mode, an on-chip program area and on-chip data area exchange enable pin, an on-chip address encoder or an address arbiter module, a first selector, and a second selector, wherein the on-chip program area and on-chip data area exchange enable pin provides an enable signal for exchanging the on-chip program area and the on-chip data area; the on-chip address encoder or the address arbiter module receives the enable signal, and outputs a program area bus accessing to the on-chip program area, and a data area bus accessing to the on-chip data area; the first selector is provided with a selection end for receiving the enable signal, an input end for receiving the program area bus, an input end for receiving the data area bus, and an output end connected with the on-chip program area; and the second selector is provided with a selection end for receiving the enable signal, an input end for receiving the program area bus, an input end for receiving the data area bus, and an output end connected with the on-chip data area. The memory has the advantages of flexible testing, high client code density, and the like. The invention further discloses a memorizing method of the memory.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINCHU INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
Calibration method for inherent errors of TDC time interval measurement
ActiveCN108594933AHigh measurement accuracyReduce mistakesRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsReconfigurabilityTest sample
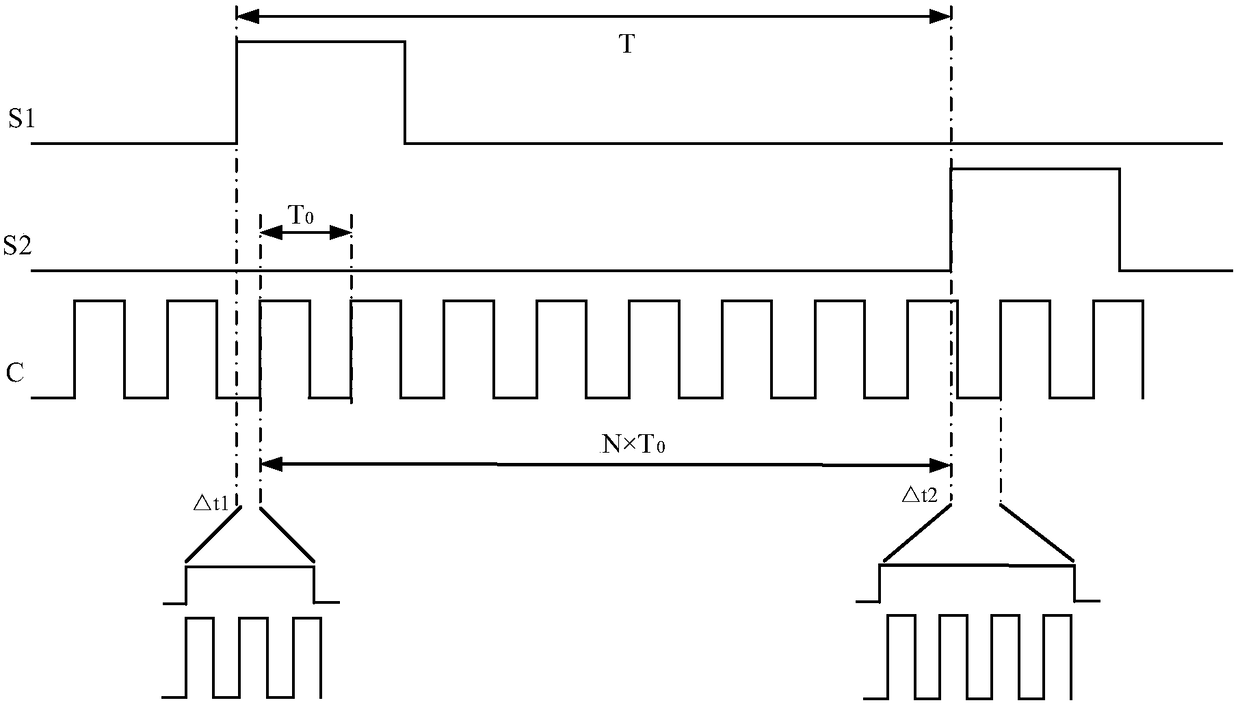
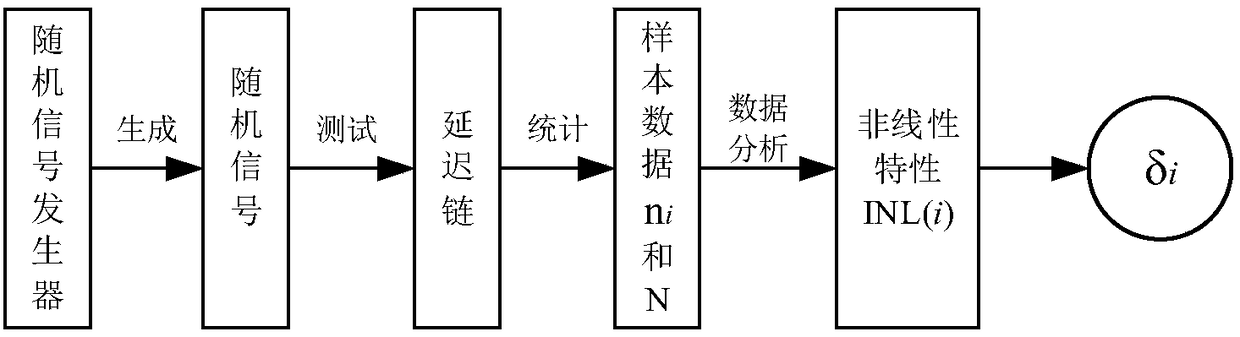
The invention discloses a calibration method for inherent errors of TDC time interval measurement. An existing calibration method for the inherent errors of time interval measurement may increase thecomplexity of the whole measurement system structure and is poor in reconfigurability. The method disclosed by the invention includes the following steps: designing a random signal required for code density calibration according to the source of TDC inherent errors, wherein the random signal is composed of signals with different pulse widths and is used to simulate a time interval signal to be measured with a random width in actual measurement; and testing a delay chain by using the random signal to obtain a test sample, analyzing sample data to obtain a delay chain unit bit width error, and calibrating the delay chain unit bit width error. According to the scheme of the invention, a cyclic sequence of a random sequence can be ensured on the premise of preventing deadlock, and an originalcyclic sequence can be remained unchanged on the premise of adding an all-zero state.
Owner:米银(杭州)信息科技有限公司
An image capture control device and method
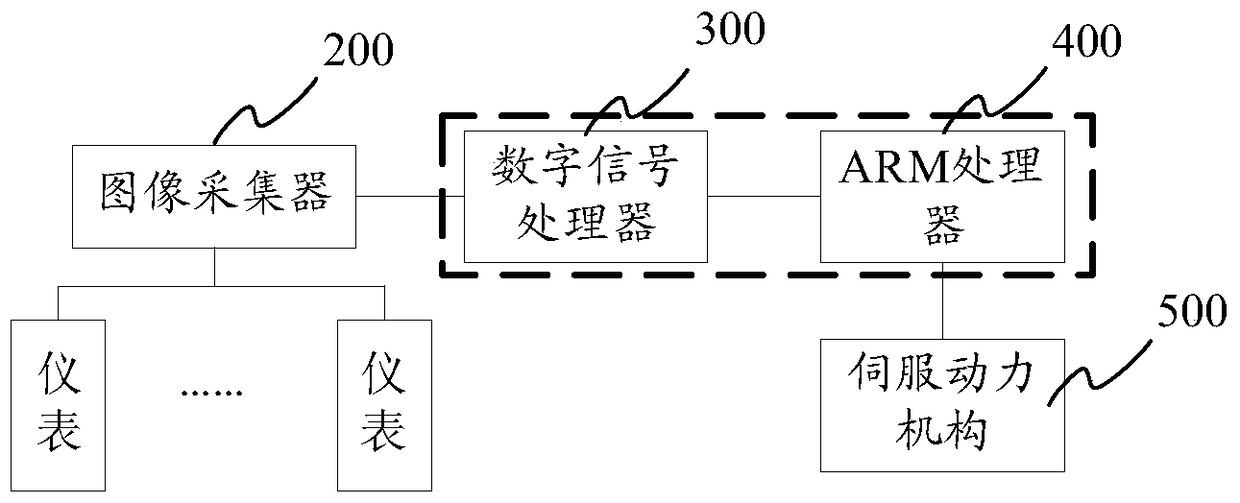
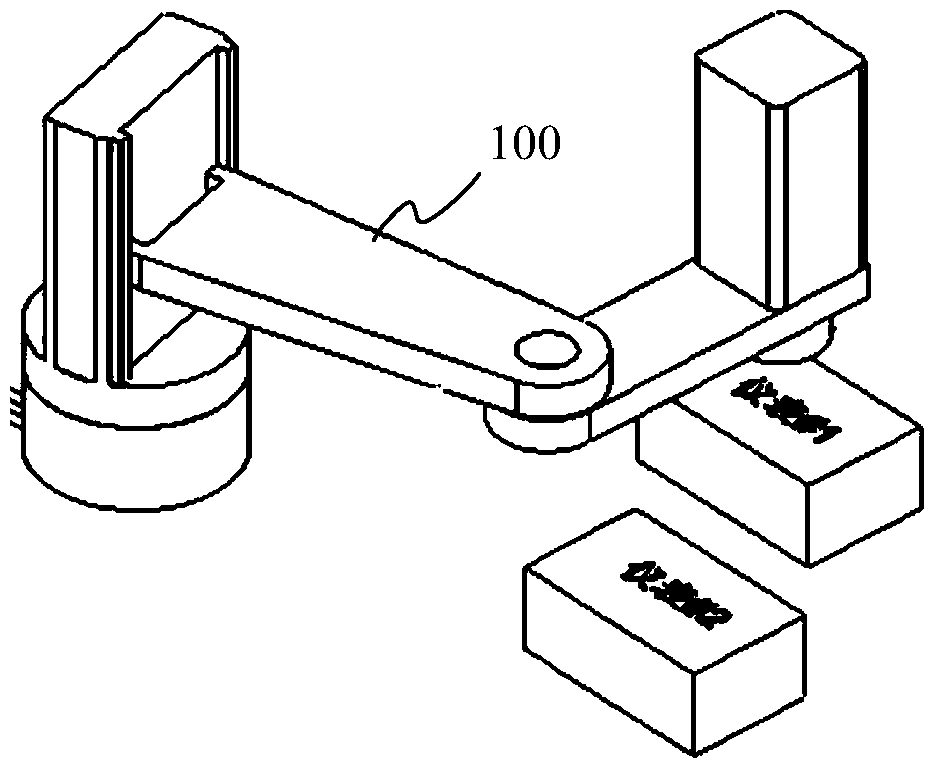
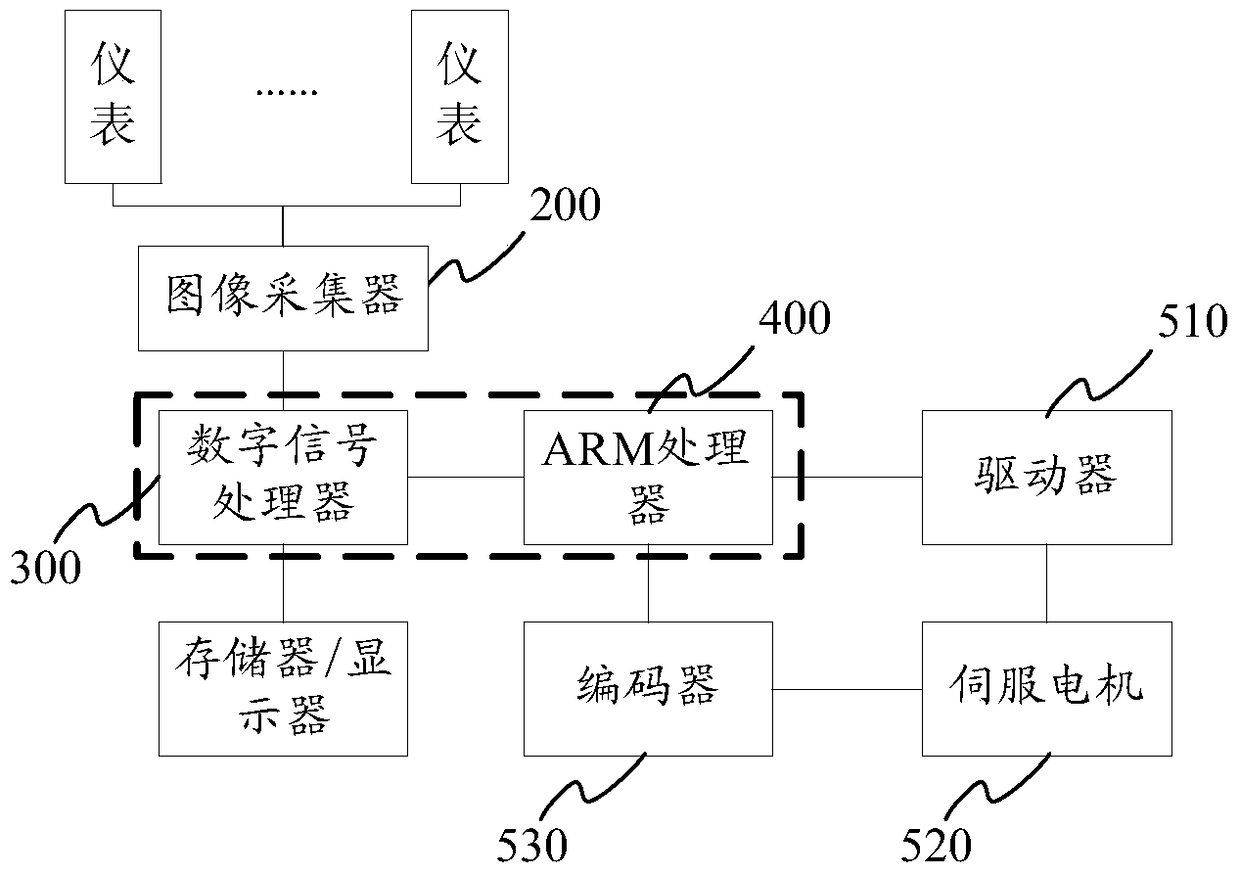
ActiveCN104469166BReduce collection costsHigh densityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCode densityHuman–computer interaction
The invention provides an image collecting control device and method. In practical instrument image collecting, the device drives an image collector located at the tail end of the device to change a collecting position by controlling a fixing support to move, and therefore instrument images of multiple instruments can be collected in sequence through one image collector, and the image collecting cost is lowered. A DSP is used for controlling the image collector to conduct image collecting, an ARM processor is used for achieving man-machine interaction, a servo power mechanism is controlled to adjust the moving track of the fixing support, and therefore the collecting position of the image collector is adjusted. It is clear that the control mode with the ARM and the DSP is adopted so that the image collecting control device can meet the practical requirements for the high code density, the high storage device utilization rate, the high control capability and the like.
Owner:STATE GRID CHONGQING ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
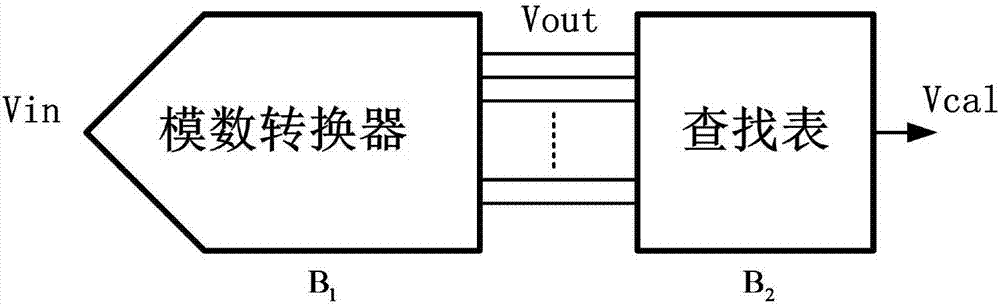
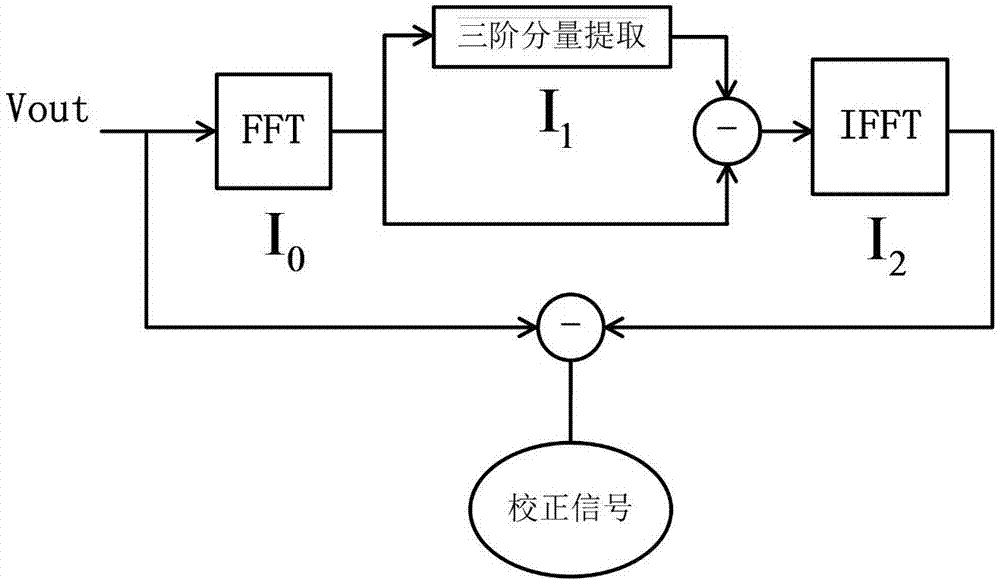
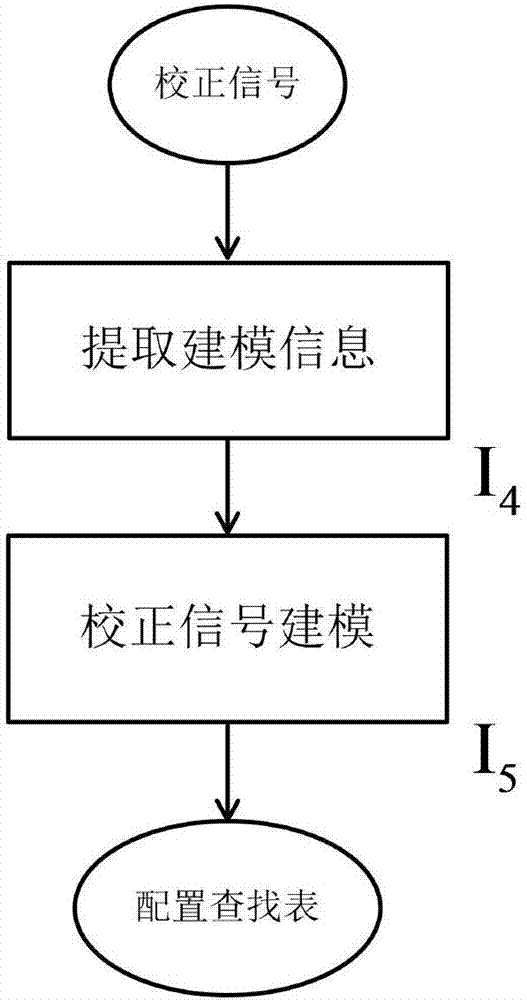
Code density high-order harmonic calibration system based on FFT extraction
ActiveCN106936434AAchieve correctionAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingHigher order harmonicsCode density
The invention discloses a code density high-order harmonic calibration system based on FFT extraction. The system comprises an analog to digital converter, an operation unit for extracting high-order harmonic distortion information, modeling unit for extracting and modeling code density information of a calibration signal, and a lookup table. The analog to digital converter is used for converting an input analog signal into a digital signal. The operation unit is used for obtaining a time domain signal required for calibration of three-order distortion. The modeling unit is used for modeling the code density information of the calibration signal, thereby obtaining code density calibration configuration information. The code density calibration configuration information is stored in the lookup table. The lookup table is used for carrying out data calibration processing on the digital signal according to the code density calibration configuration information stored in the lookup table. According to the code density high-order harmonic calibration system based on FFT extraction, corresponding high-order harmonic can be effectively suppressed in a high bandwidth, so the frequency response of a whole information system can be improved.
Owner:NO 24 RES INST OF CETC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com